Patents
Literature
4136 results about "Sound field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
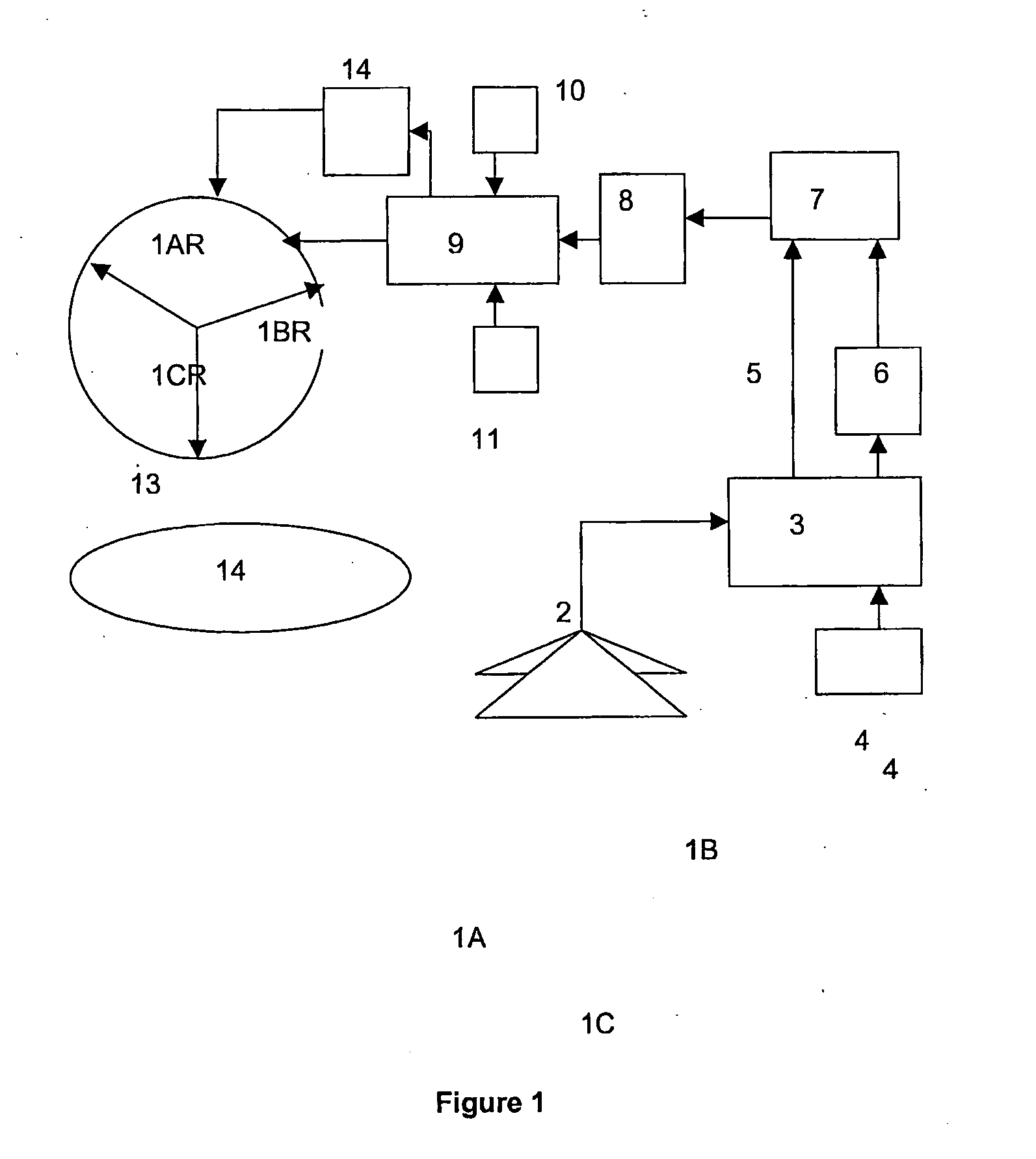
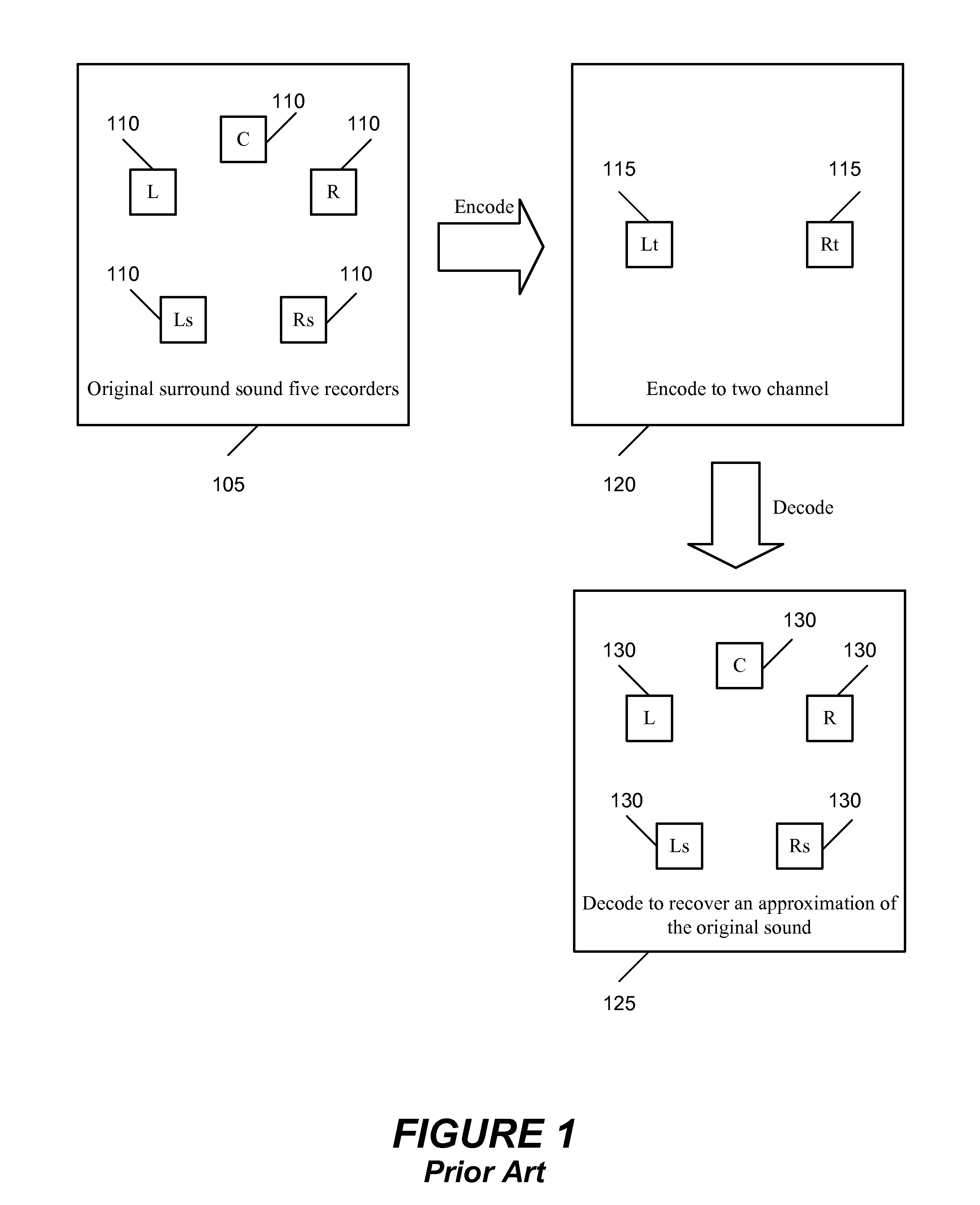
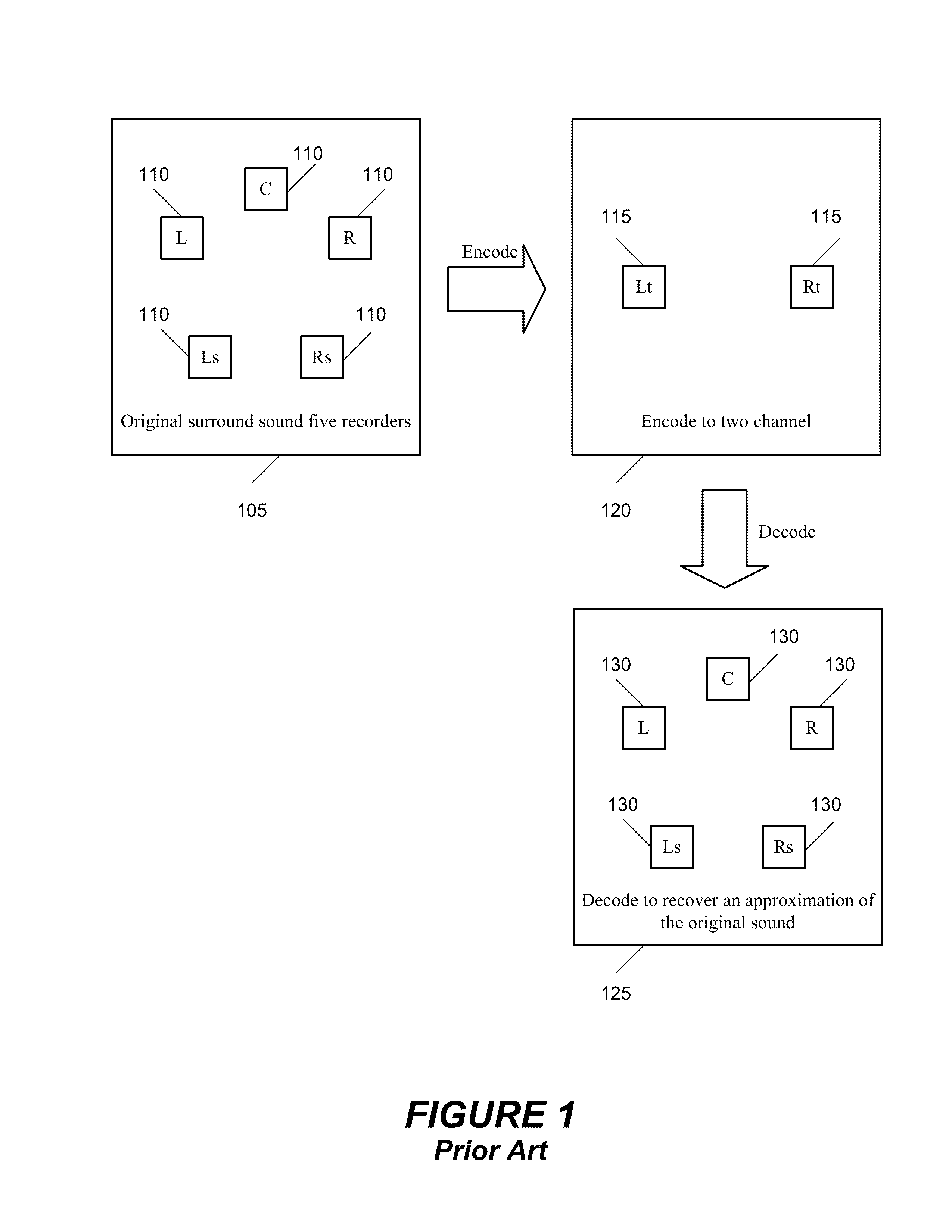
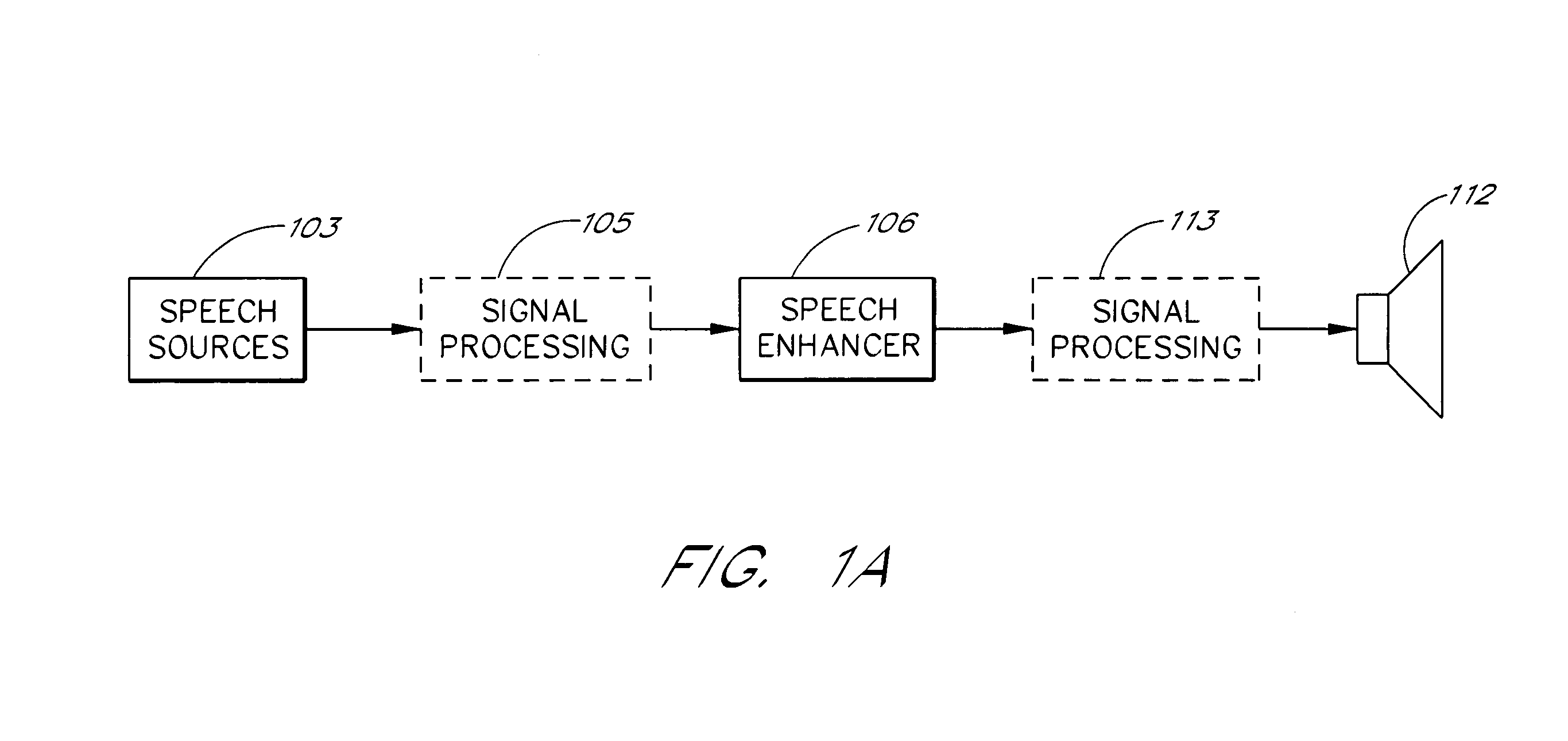
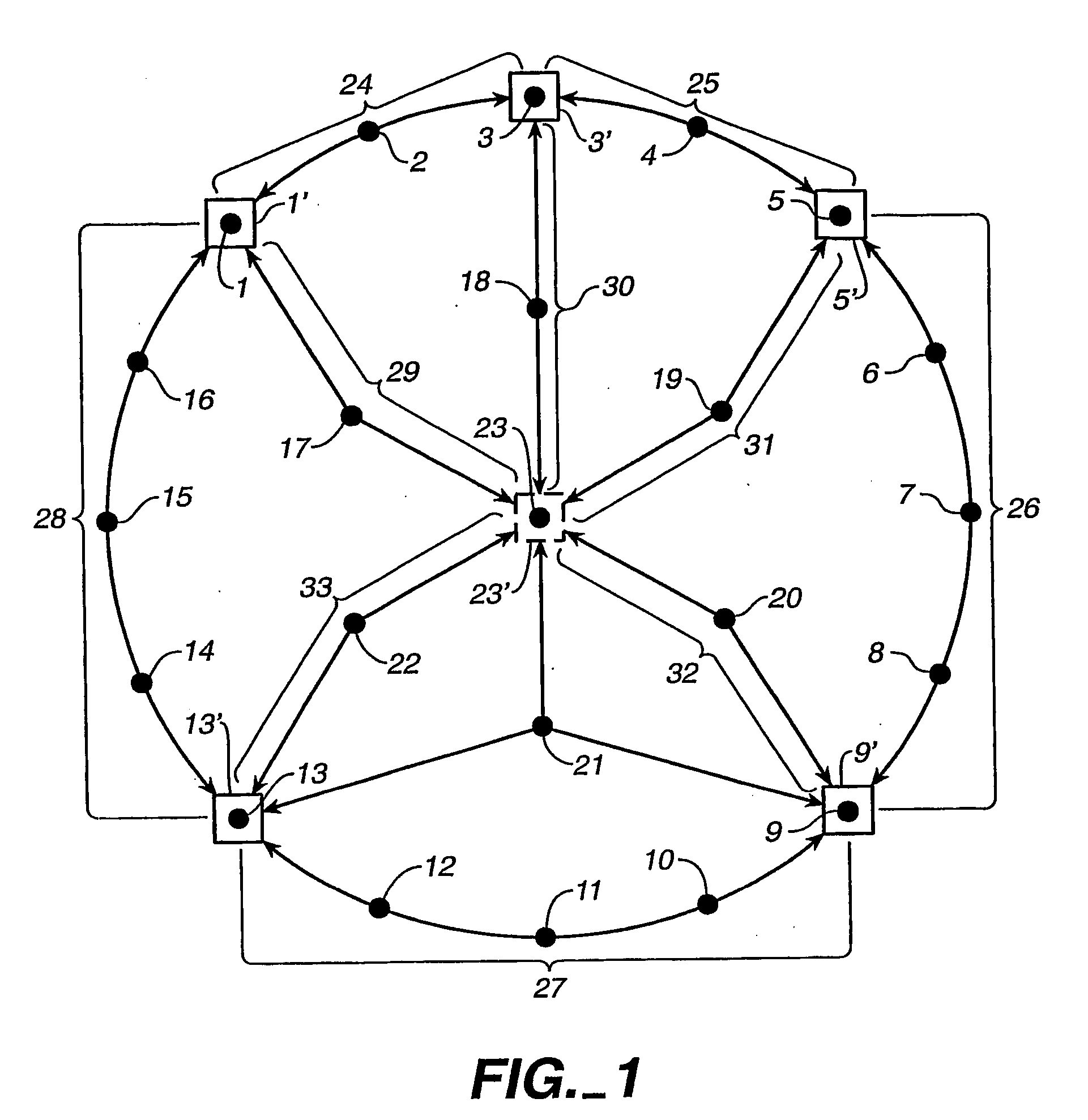
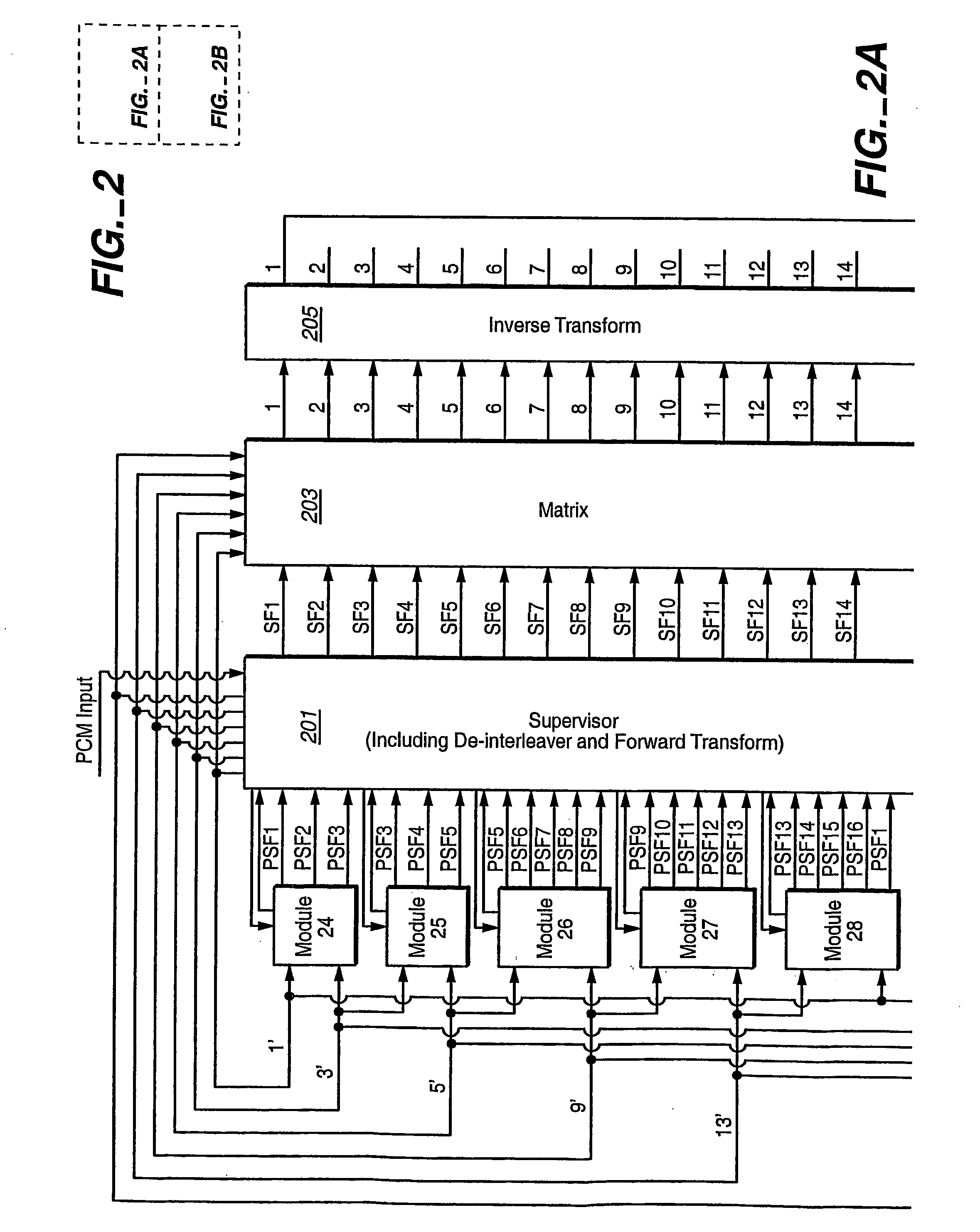
Coding method and apparatus for multiple channels of audio information representing three-dimensional sound fields
InactiveUS6021386AConserve substantial bandwidthConveniently implementedBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumBit allocation
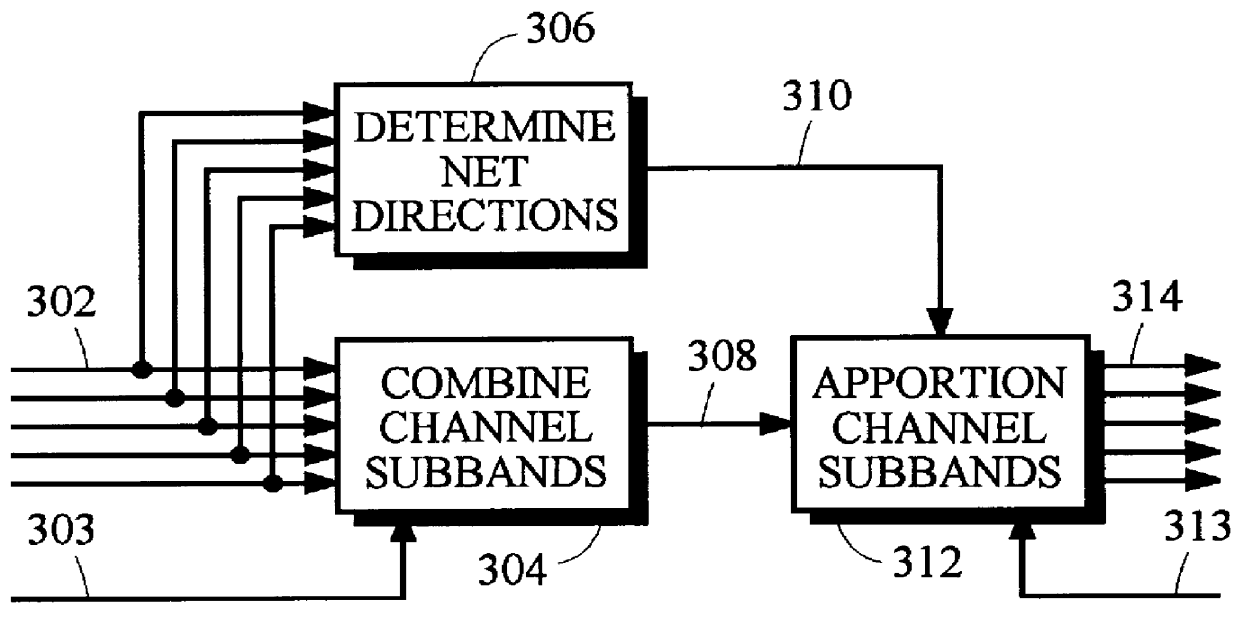
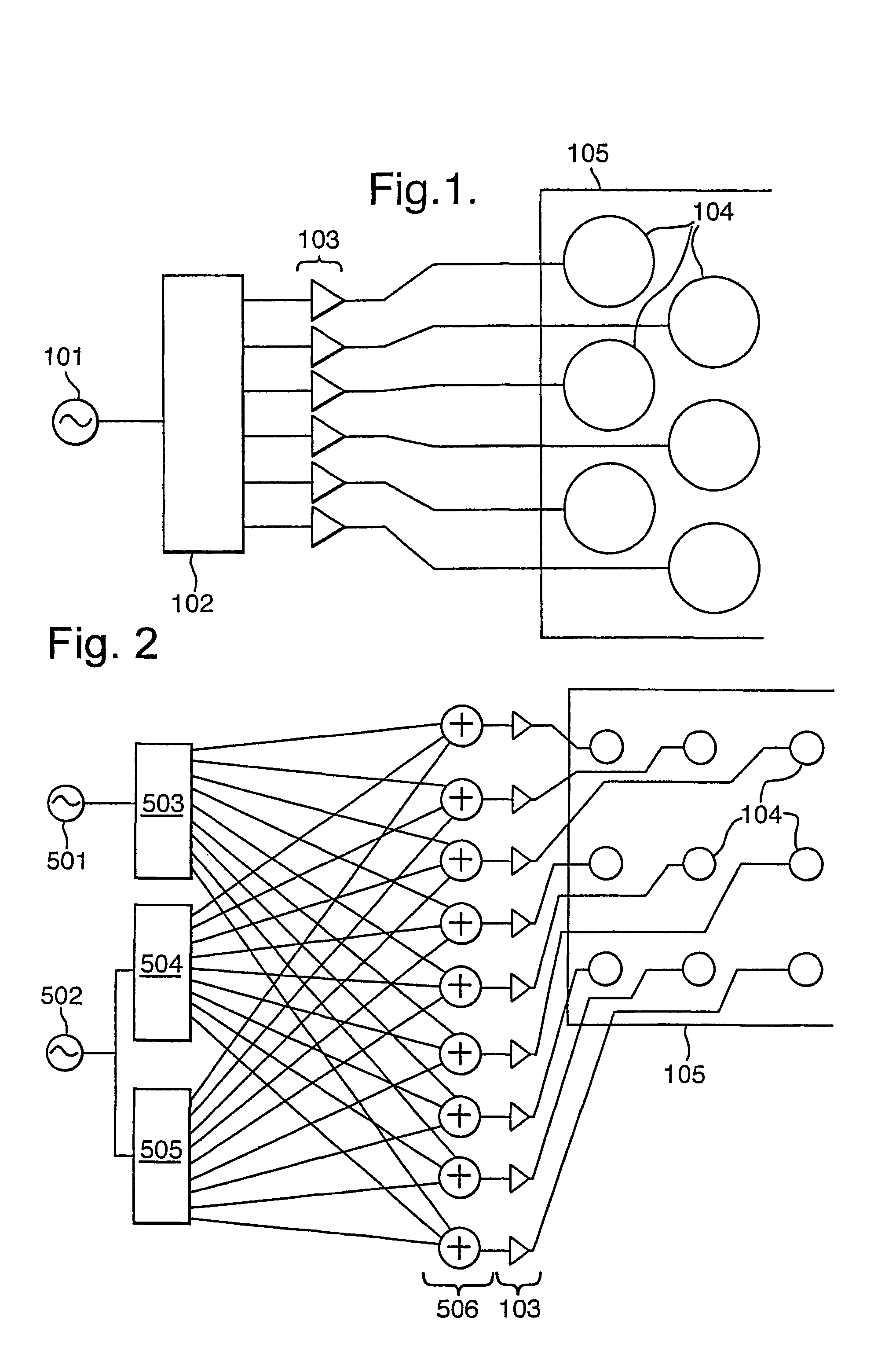
In an encoder, multiple channels of audio information representing multidimensional sound fields are split into subband signals and the subband signals in one or more subbands are combined to form composite signals. The composite signals, the subband signals not combined into a composite signal and information describing the spectral levels of subband signals combined into composite signals are assembled into an encoded output signal. The spectral level information conveys either the amplitude or power of the combined subband signals or the apparent direction of the sound field represented by the combined subband signals. In digital implementations, adaptive bit allocation may be used to reduce the informational requirements of the encoded signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Audio Apparatus And Method
InactiveUS20080144864A1Suitable sealMicrophones signal combinationFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsSound sourcesHeightened perception
The invention enables the capture of sound fields with coding and efficient distribution of electrical signals representing the sound fields for subsequent reproduction in a listening environment utilising pairs of non-equidistant apparatus in various defined configurations such that the acoustic distance as well as direction of sound sources is consistently presented with regard to in front of, behind, beside or below from a listening point anywhere in the listening environment and for any listener orientation, thus making the whole listening area a sweet spot and enabling true shared audio experiences, without the need for worn apparatus. New apparatus and methods for capture, distribution and reproduction or render are also disclosed that enable enhanced perception of captured and reproduced sound for shared experiences with both common and individual capture and reproduction apparatus and new communications and control methods and apparatus for multiple users including heightened perception capability and also improved security aspects are also disclosed.
Owner:HUONLABS
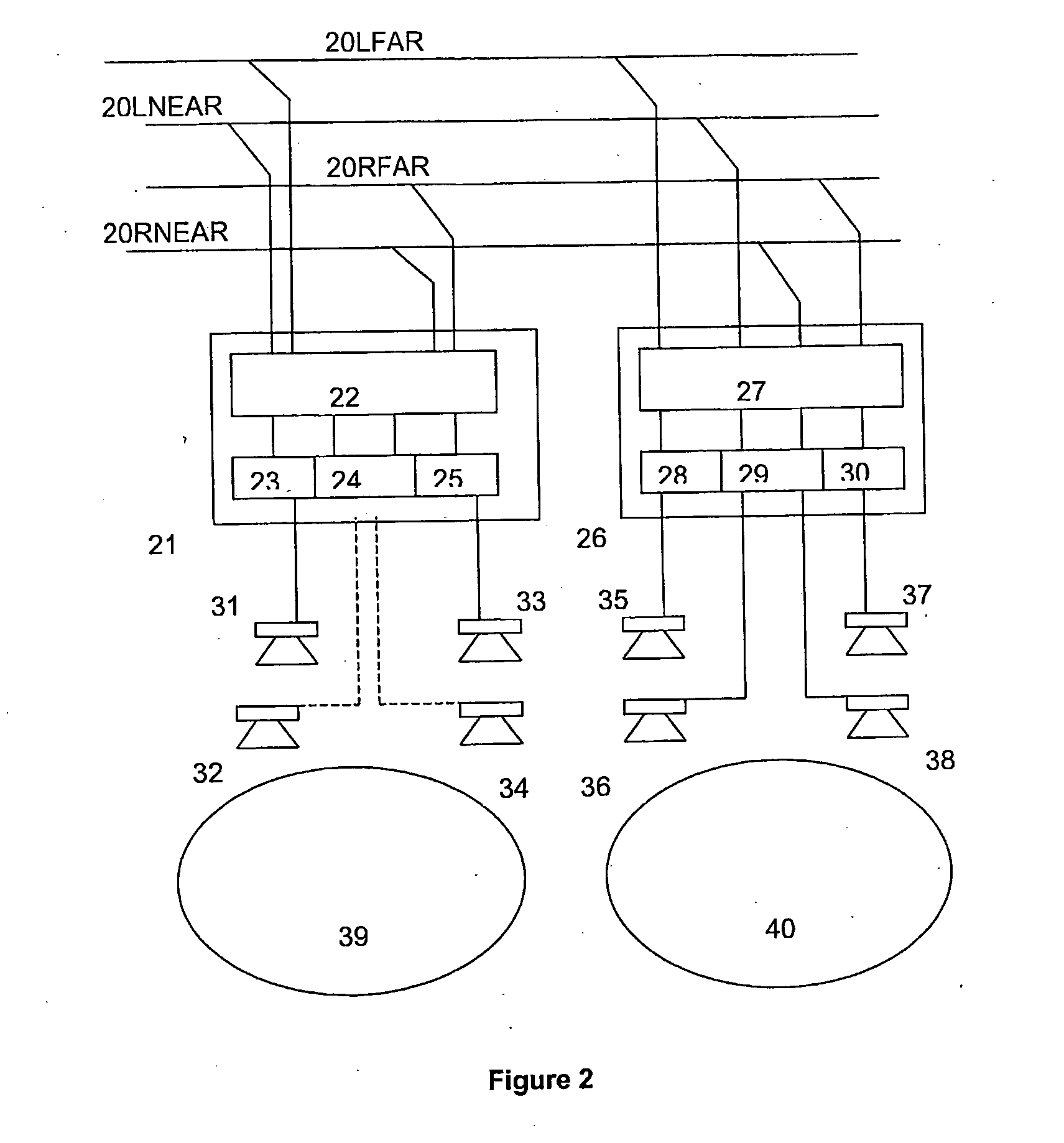
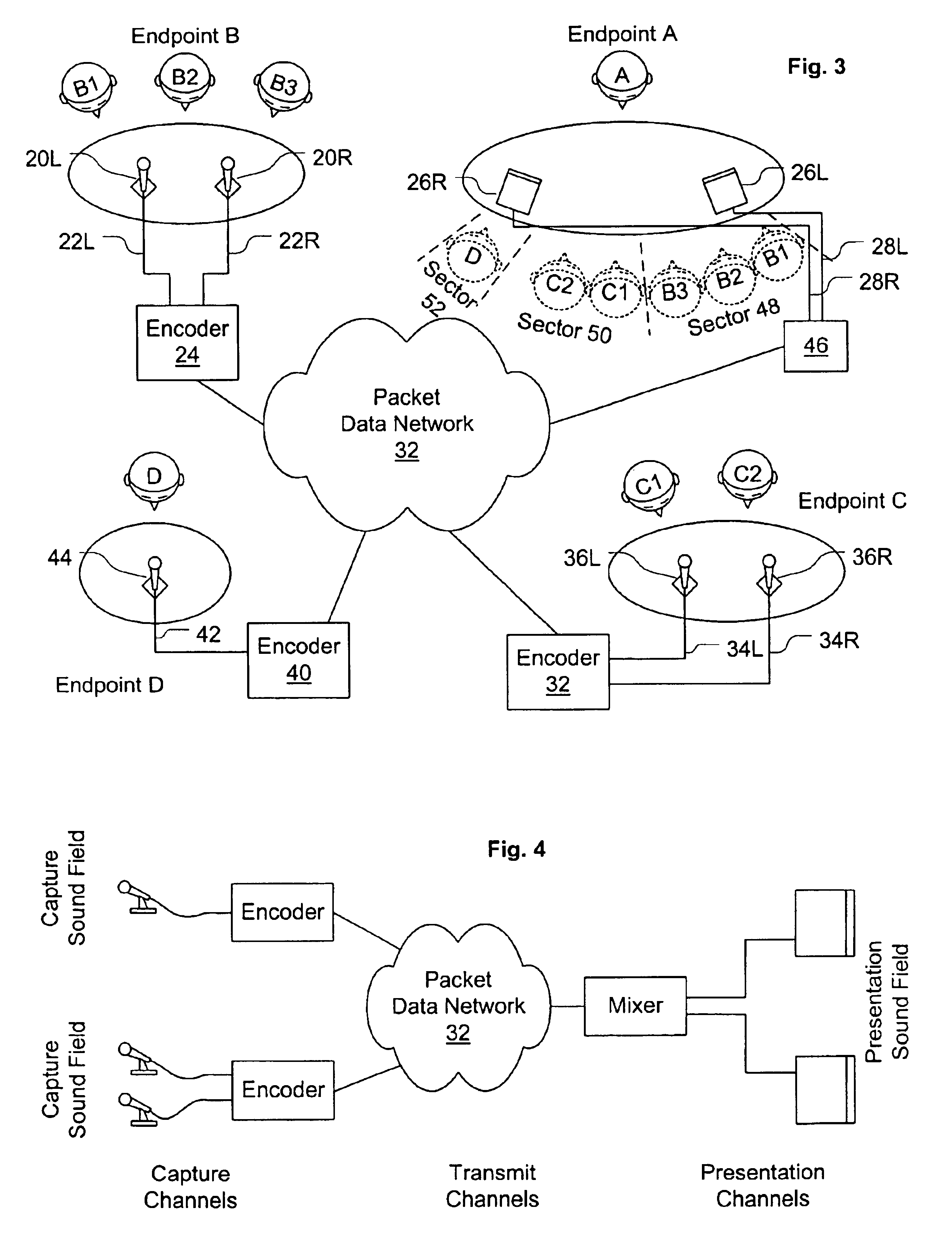
Virtual conference room for voice conferencing
InactiveUS6850496B1Increase voice comprehensionEasy to identifySpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsConfusionVirtual conference
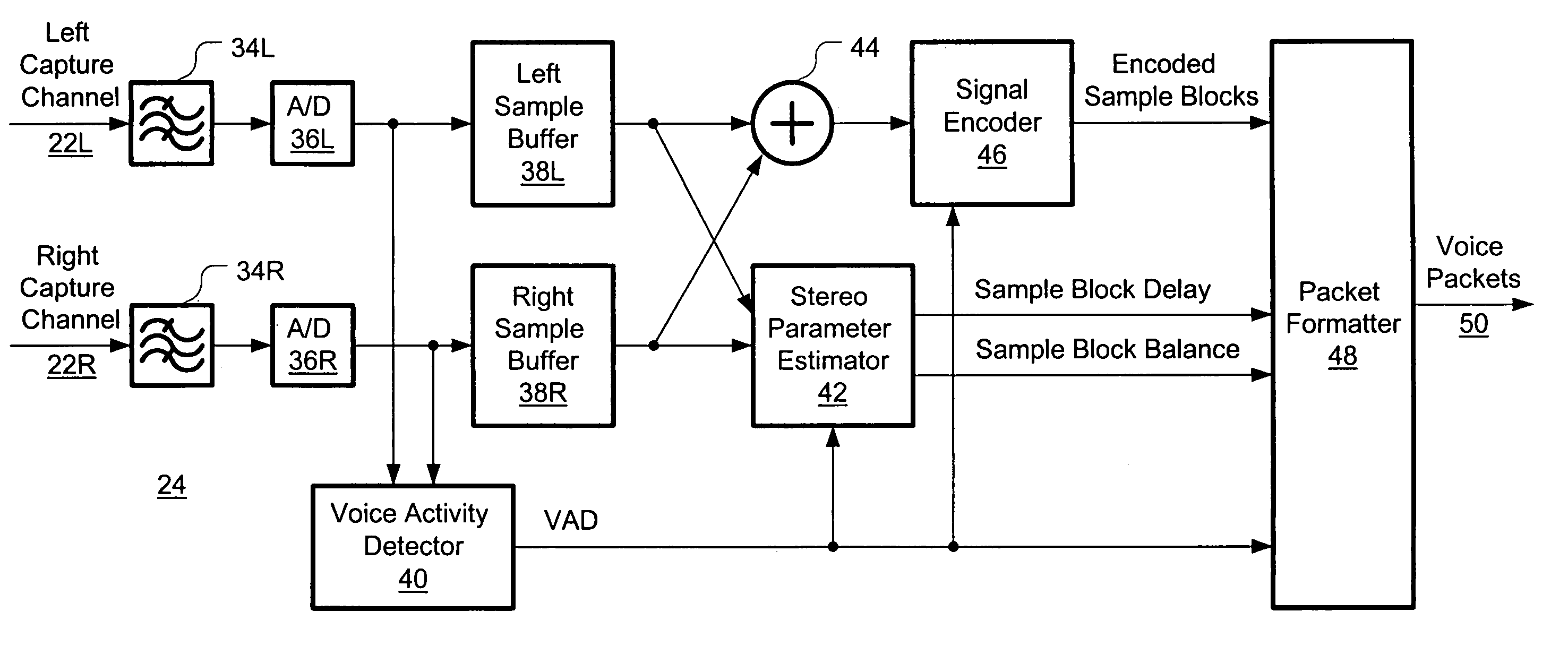
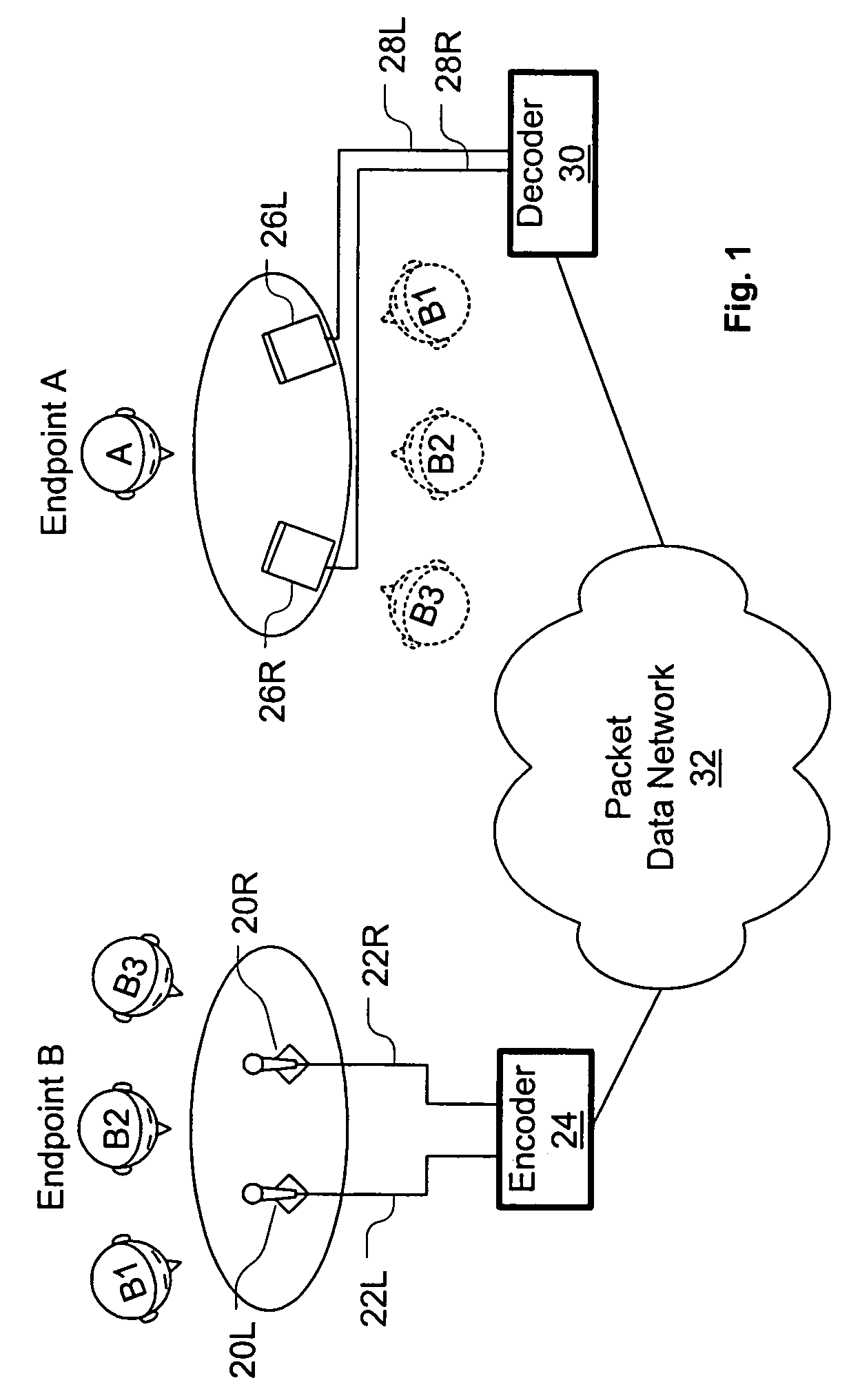
A system and method are disclosed for packet voice conferencing. The system and method divide a conferencing presentation sound field into sectors, and allocate one or more sectors to each conferencing endpoint. At some point between capture and playout, the voice data from each endpoint is mapped into its designated sector or sectors. Thereafter, when the voice data from a plurality of participants from multiple endpoints is combined, a listener can identify a unique apparent location within the presentation sound field for each participant. The system allows a conference participant to increase their comprehension when multiple participants speak simultaneously, as well as alleviate confusion as to who is speaking at any given time.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
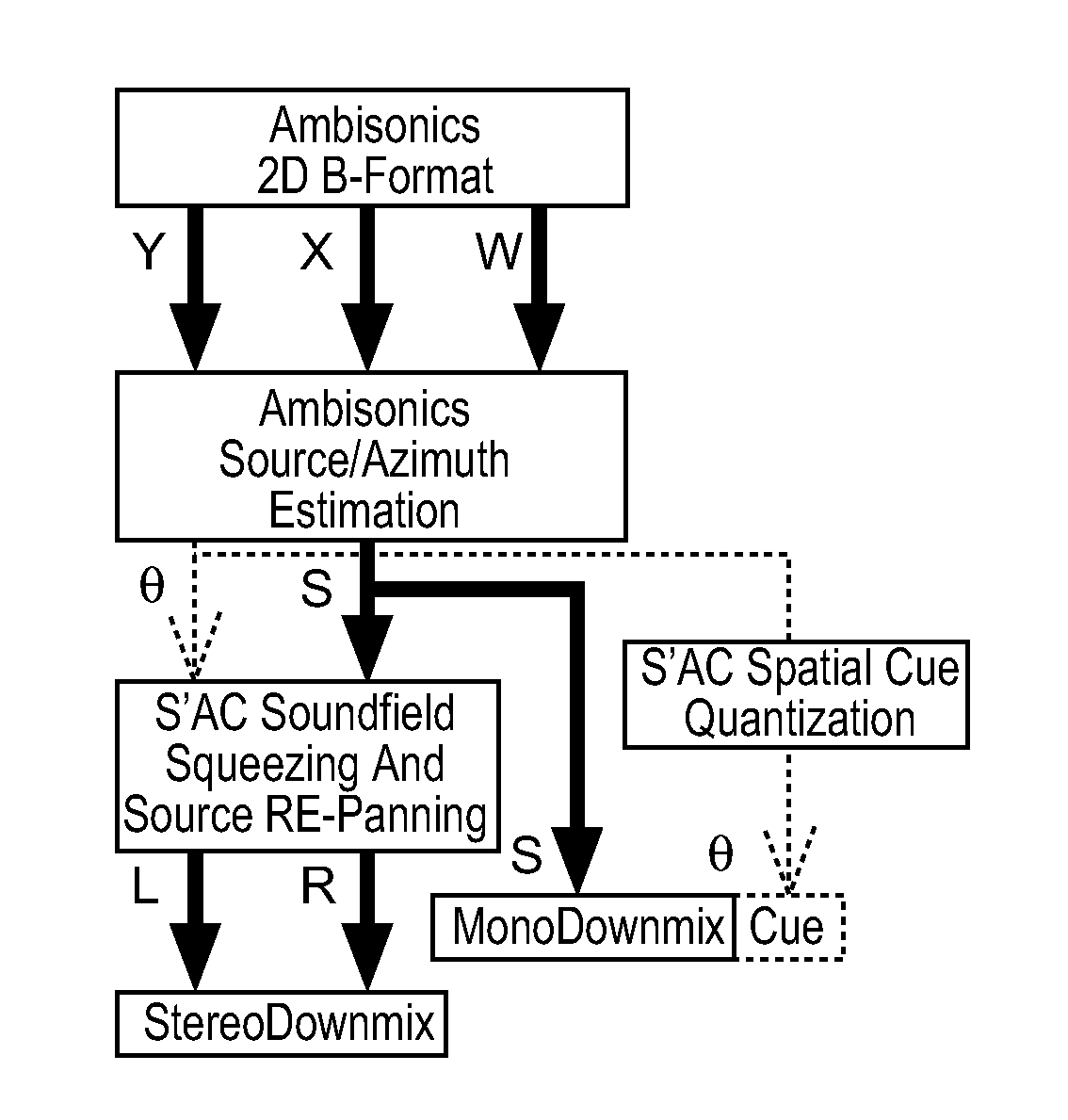
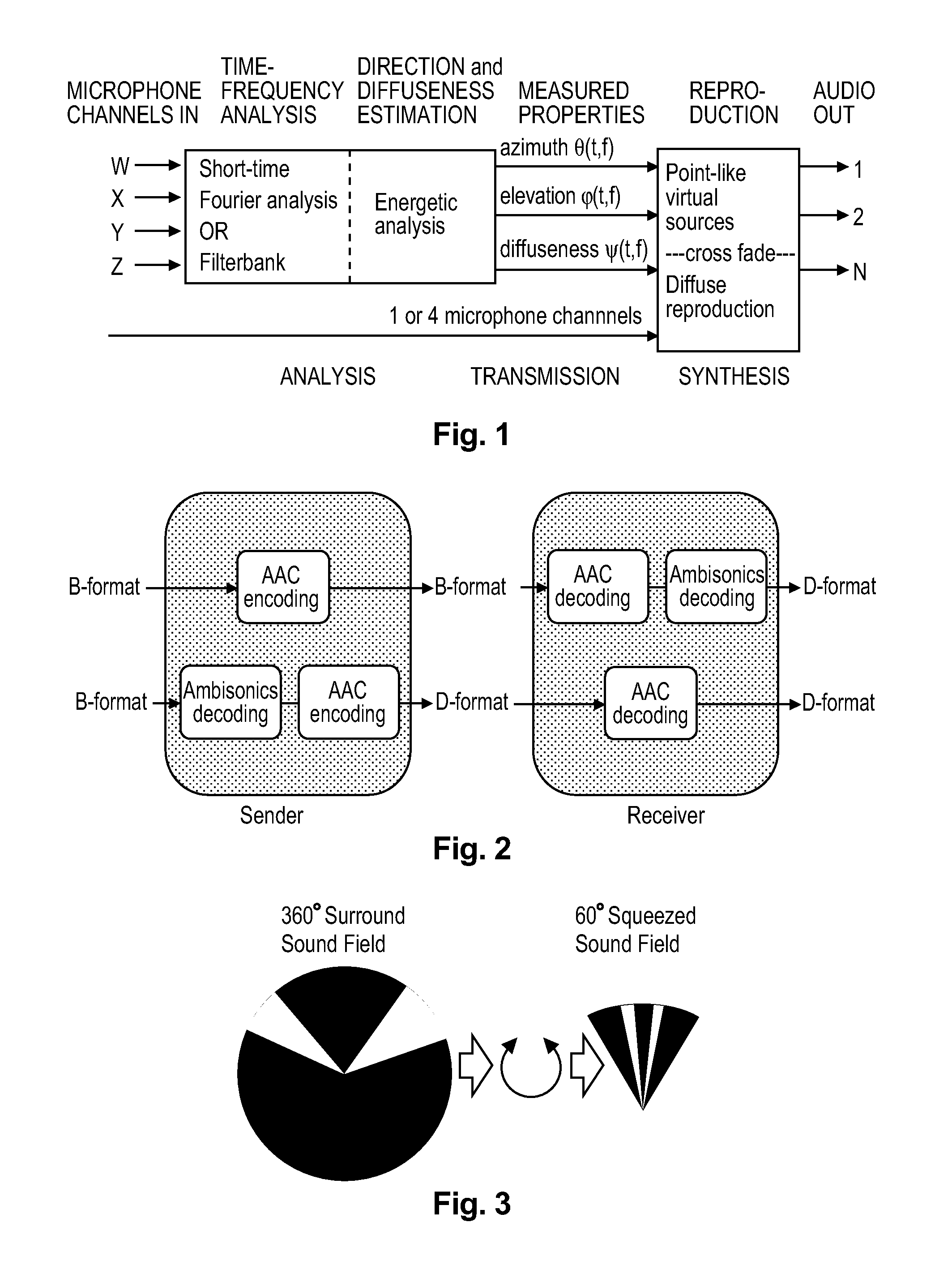
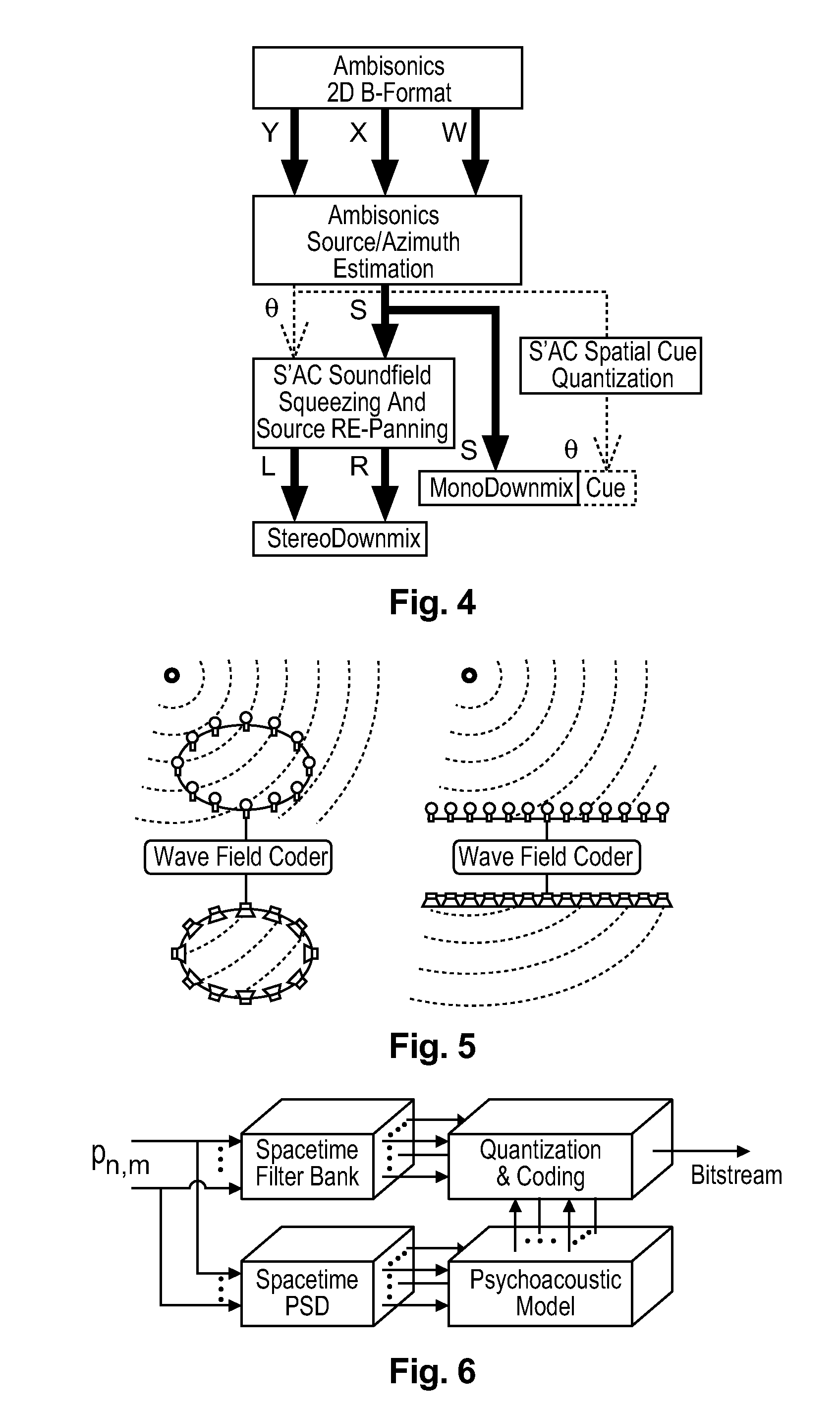
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding successive frames of an ambisonics representation of a 2- or 3-dimensional sound field
ActiveUS20120155653A1Easy accessThe result is reasonableBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisTime domainData rate
Representations of spatial audio scenes using higher-order Ambisonics HOA technology typically require a large number of coefficients per time instant. This data rate is too high for most practical applications that require real-time transmission of audio signals. According to the invention, the compression is carried out in spatial domain instead of HOA domain. The (N+1)2 input HOA coefficients are transformed into (N+1)2 equivalent signals in spatial domain, and the resulting (N+1)2 time-domain signals are input to a bank of parallel perceptual codecs. At decoder side, the individual spatial-domain signals are decoded, and the spatial-domain coefficients are transformed back into HOA domain in order to recover the original HOA representation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Noise protection verification device
InactiveUS6567524B1Hearing protectionFacilitate communicationVibration measurement in fluidIntra aural earpiecesVocal tractEngineering
Ear protecting device with a sealing section for acoustically sealing the meatus of a human, includes a sound generator with a sound outlet for being directed toward the user meatus; an inner microphone with a sound inlet from the meatus, arranged for measuring the resulting sound field in the meatus; connected to an electronics unit including a sound analyser coupled to the inner microphone, for analyzing sound characteristics of the resulting sound field in the meatus, producing analyzed sound characteristics; storing part in the electronics unit for storing measured predetermined sound characteristics of a properly functioning ear protecting device; a comparing part in the electronics unit for comparing the inner microphone analyzed sound characteristics with the stored measured predetermined sound characteristics; indicating part coupled to the comparing part for being activated if the analyzed sound characteristics differ significantly from the predetermined sound characteristics.
Owner:HONEYWELL HEARING TECH
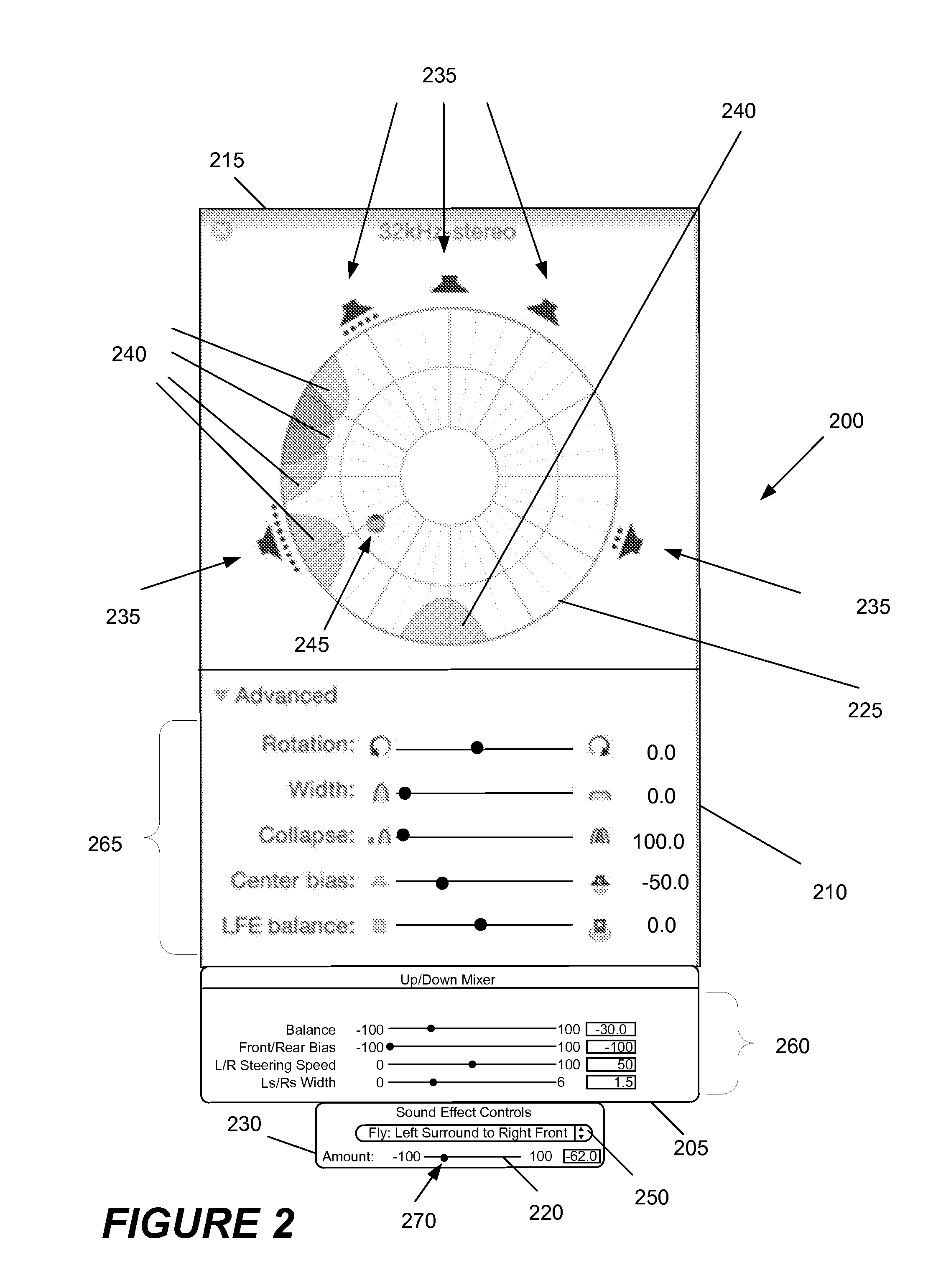
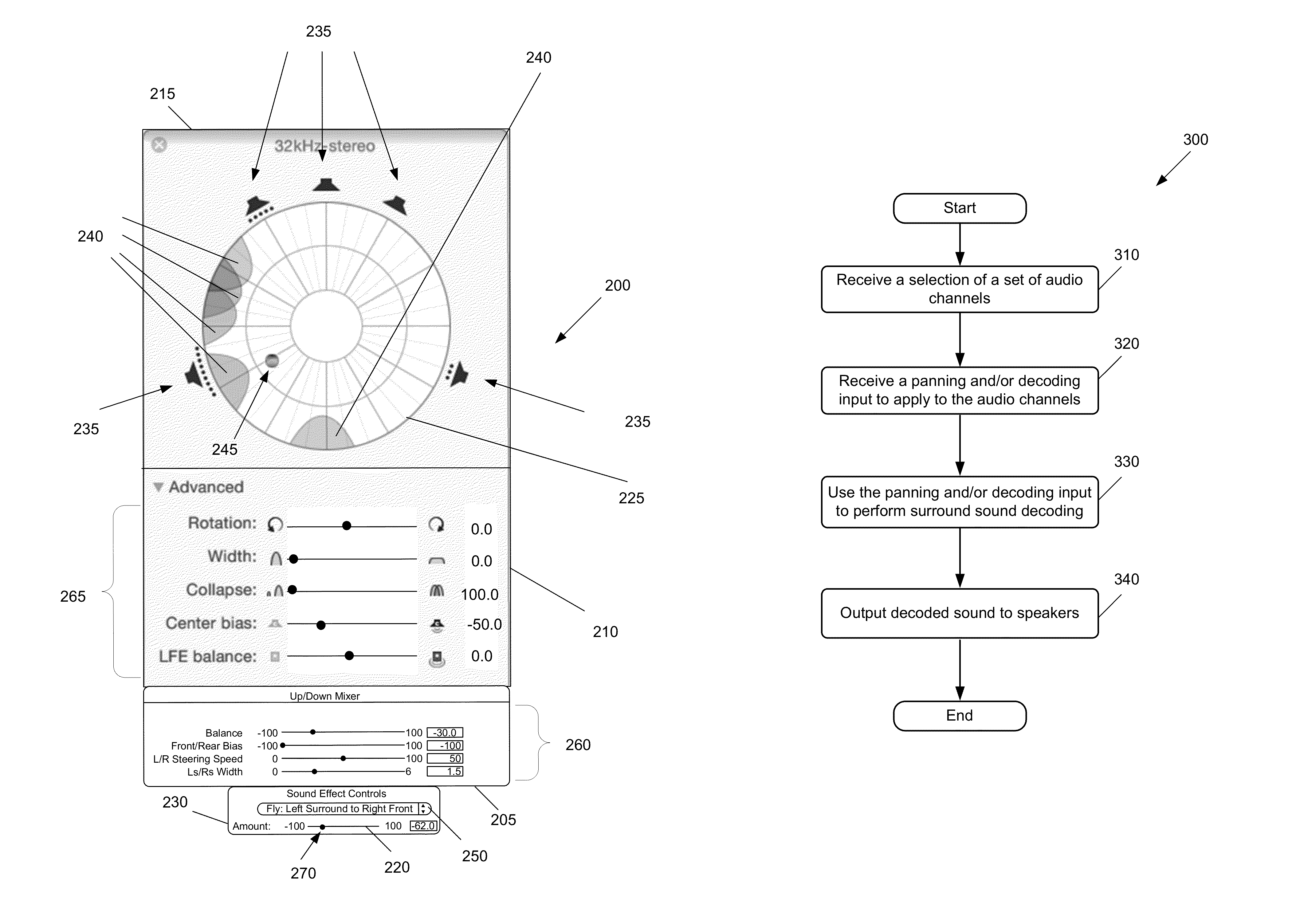
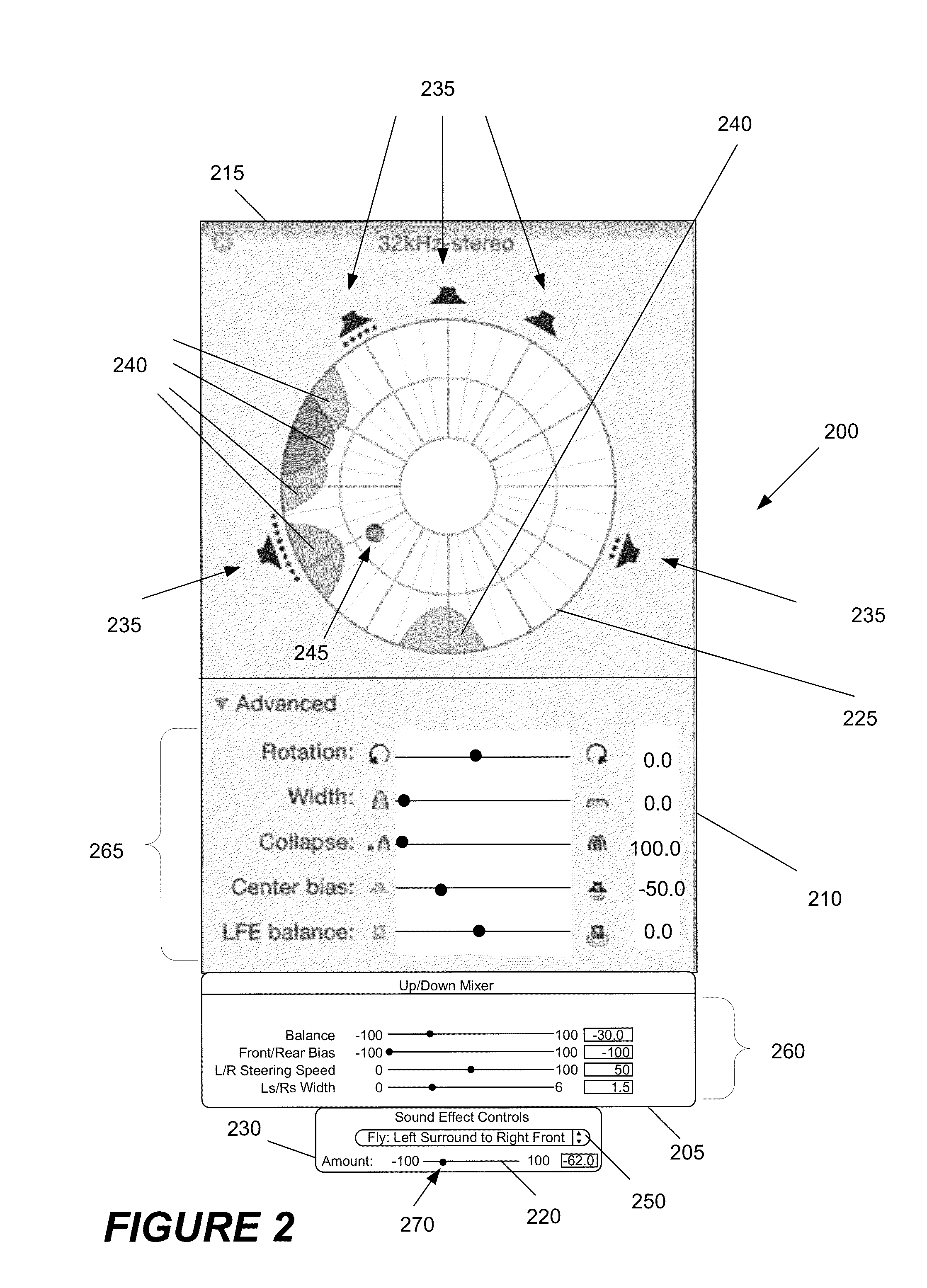
Audio Panning with Multi-Channel Surround Sound Decoding
ActiveUS20120210223A1Easy to separateKeep uniqueTwo-channel systemsInput/output processes for data processingVocal tractComputer science
A panner is provided that incorporates a surround sound decoder. The panner takes as input the desired panning effect that a user requests, separates sounds using surround sound decoding, and places the separated sounds in the desired places in an output sound field.
Owner:APPLE INC
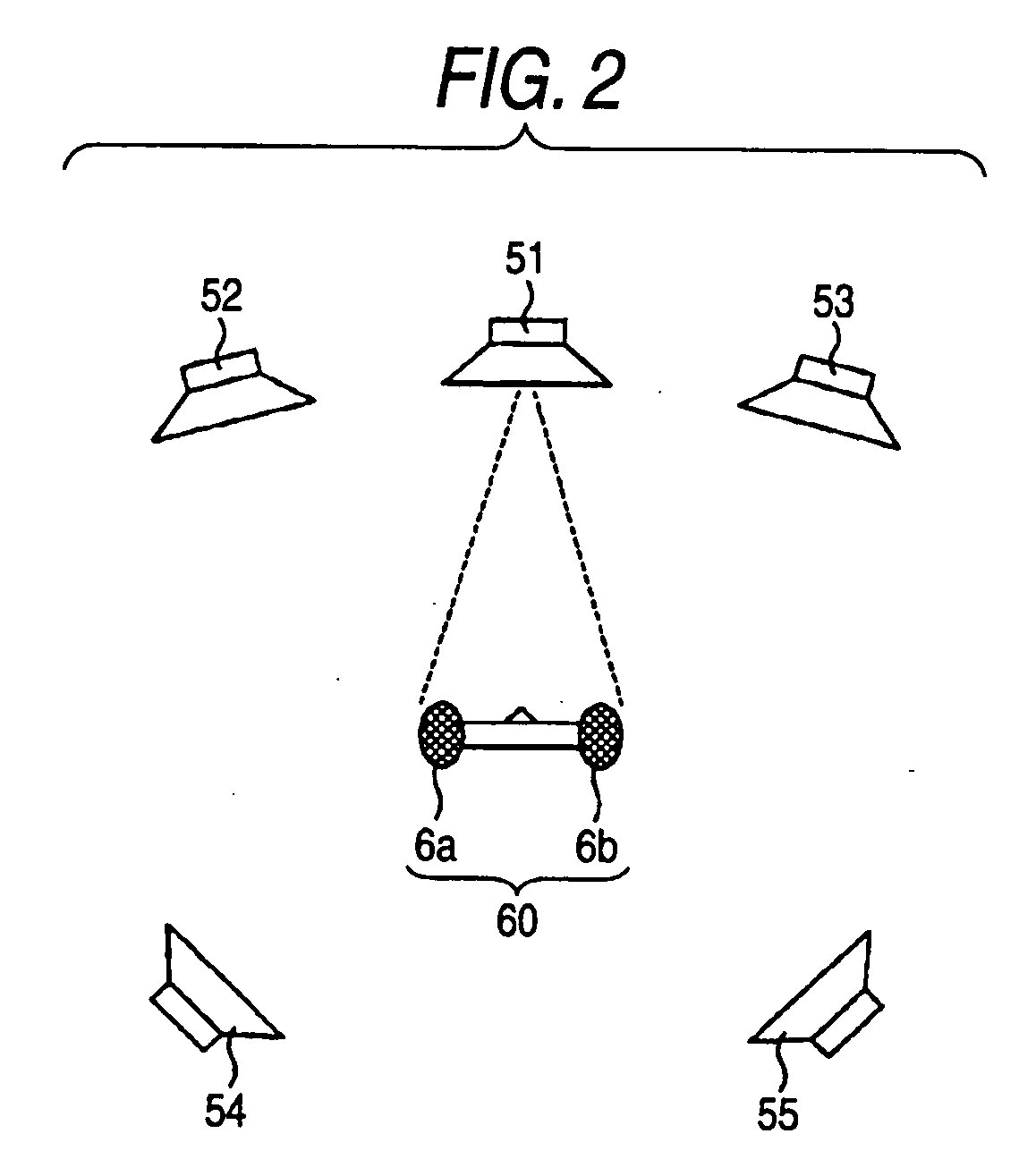
Sound field measuring apparatus and sound field measuring method
InactiveUS20070019815A1Flexible handlingLoudspeaker enclosure positioningLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsLoudspeakerAudio frequency
A sound field measuring apparatus includes a microphone set having a first and second microphones arranged at a prescribed interval, which collects audio signals outputted from a first and second speakers, a measuring unit measuring distances between the first and second speakers, and the first and second microphones based on audio signals collected by the first and second microphones, and a position calculating unit calculating a position of the first and second microphones and a position of the second speaker when the first speaker is taken as a standard position based on the respective measured distances.
Owner:SONY CORP
Audio panning with multi-channel surround sound decoding
ActiveUS8767970B2Easy to separateKeep uniqueTwo-channel systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsVocal tractComputer science
A panner is provided that incorporates a surround sound decoder. The panner takes as input the desired panning effect that a user requests, separates sounds using surround sound decoding, and places the separated sounds in the desired places in an output sound field.
Owner:APPLE INC
Audio system and method
InactiveUS6990211B2Easy to controlImprove distributionTransducers for sound channels pluralityHeadphones for stereophonic communicationLoudspeakerComputer science
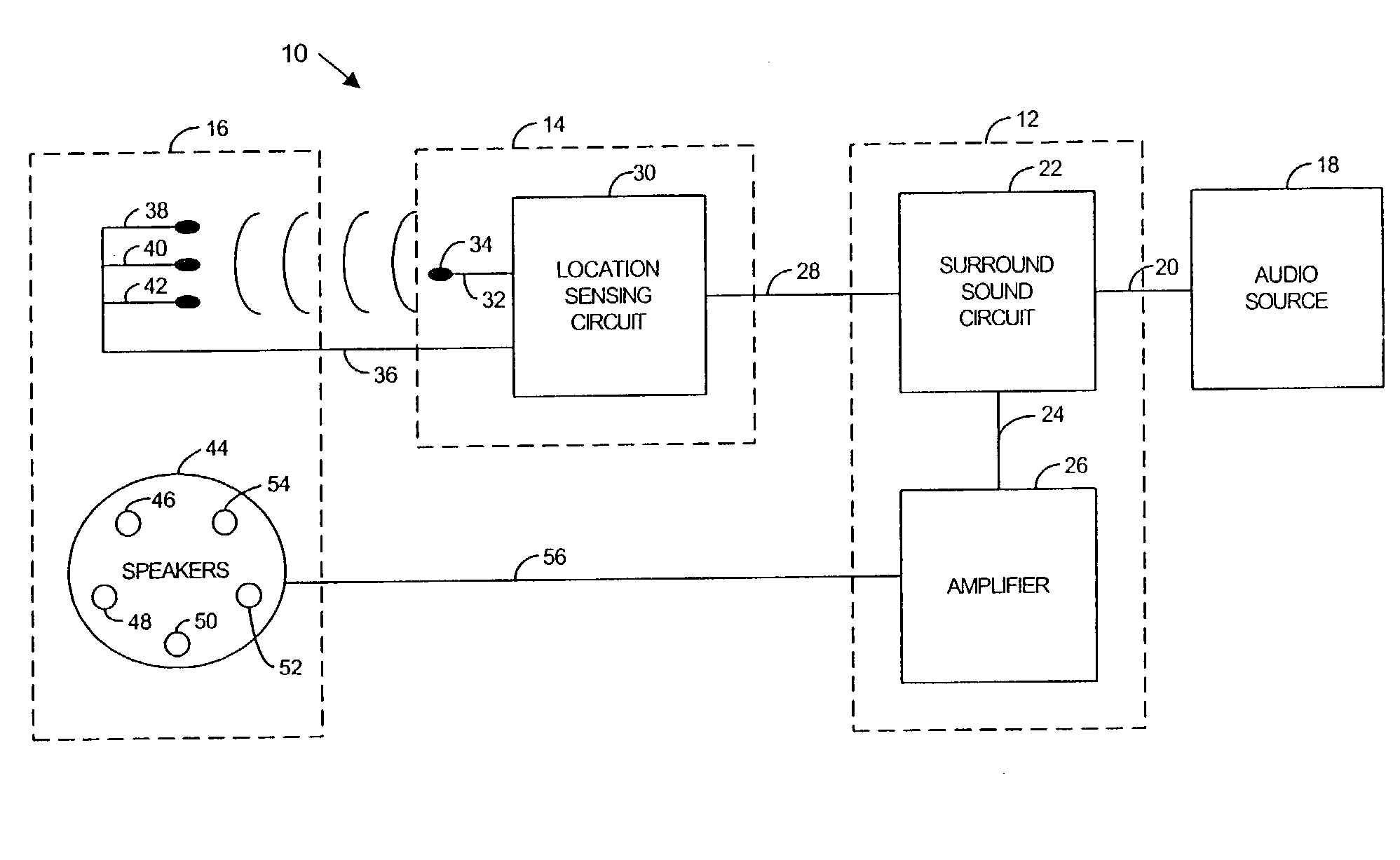
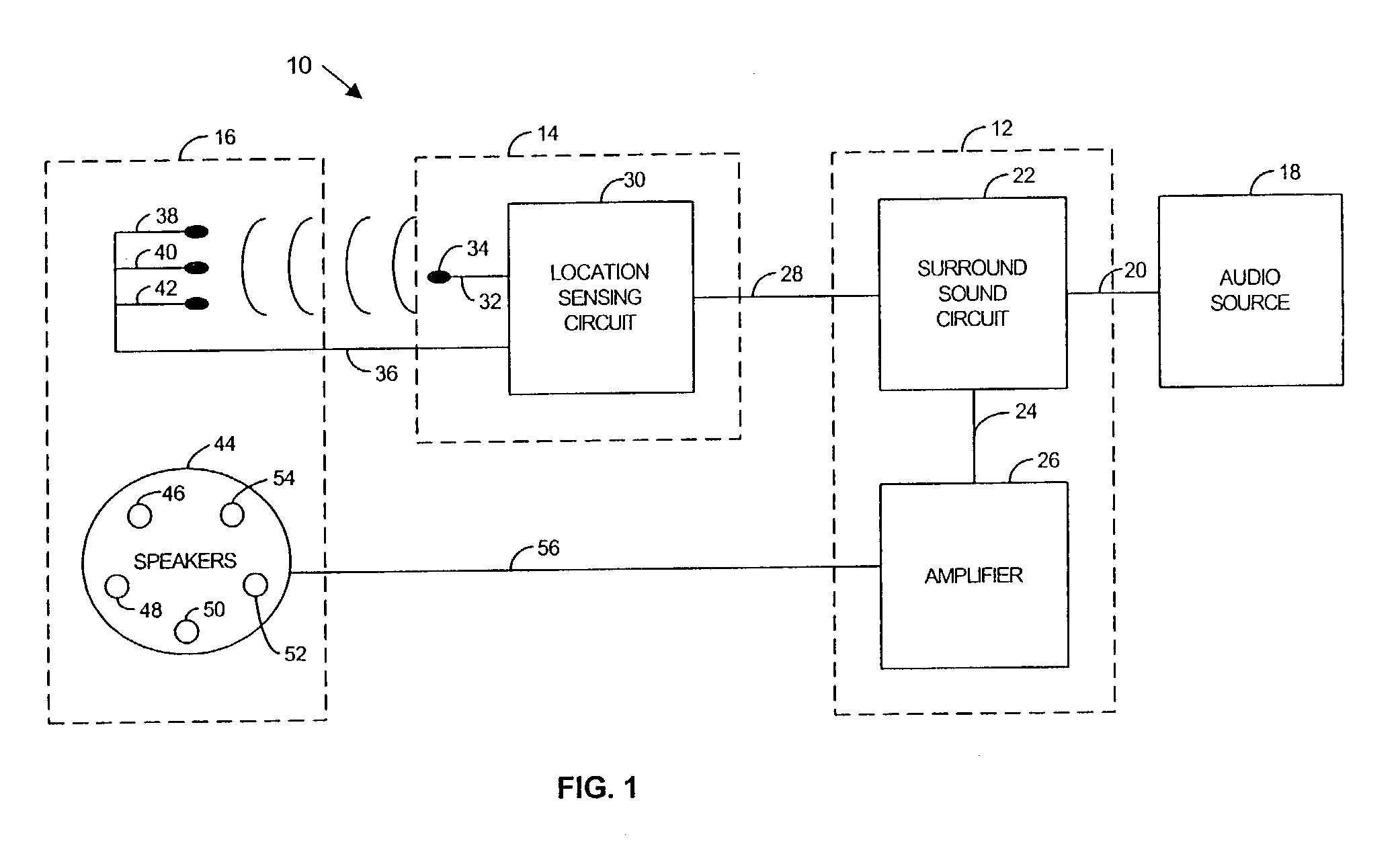
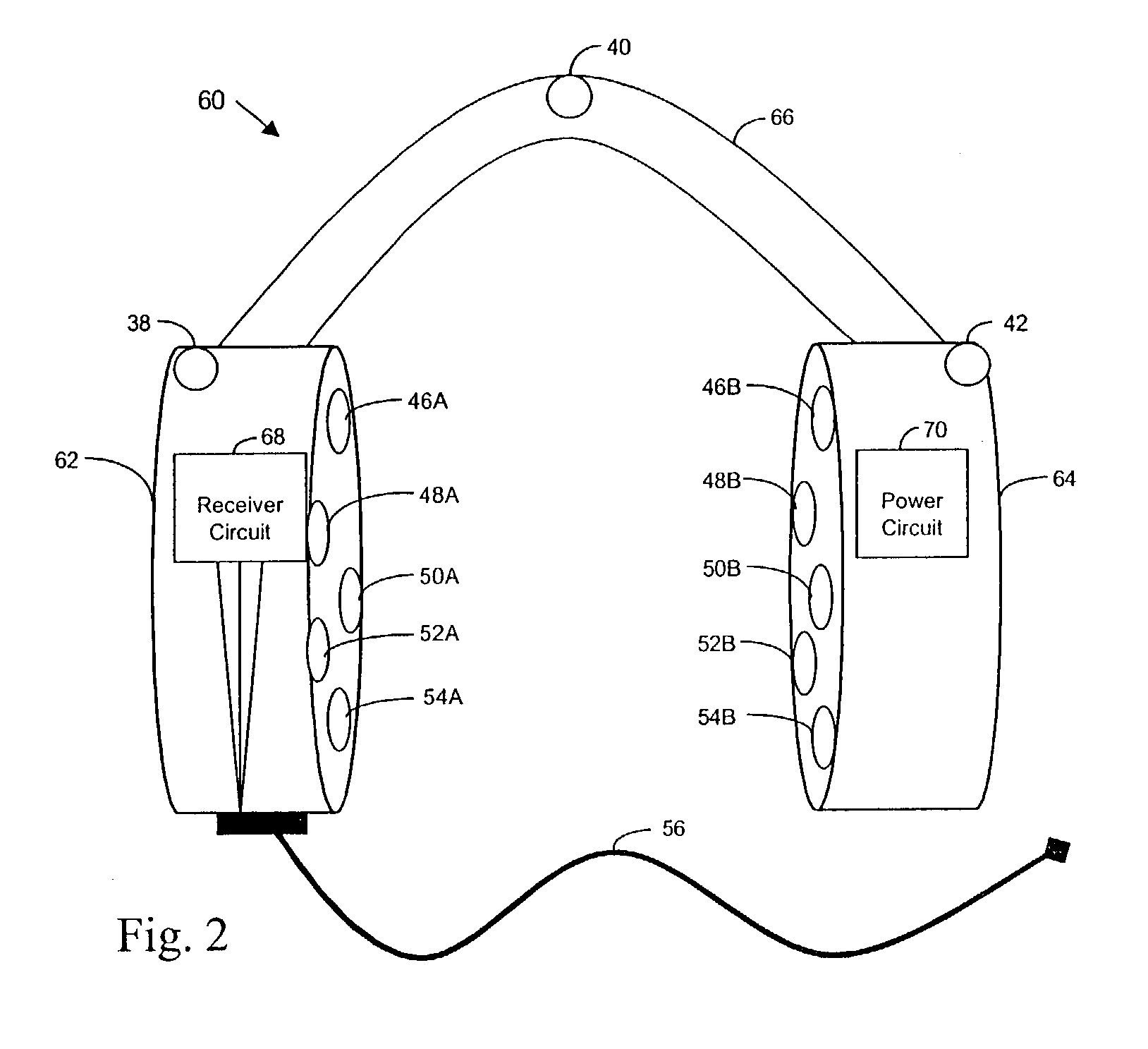
The disclosed embodiments relates to orienting a sound field in relation to a user and a generated set of images. For instance, a system may include a sound subsystem, a location subsystem, and a speaker subsystem. The speaker subsystem may include a plurality of sensors and a plurality of speakers. The sound subsystem may include a surround sound circuit that may be connected to a signal source and the speaker subsystem. The location subsystem may receive position information reflective of the orientation of a user and provide a signal that may be used by the sound circuit to adjust the audio signal based on the orientation of the user.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP +1
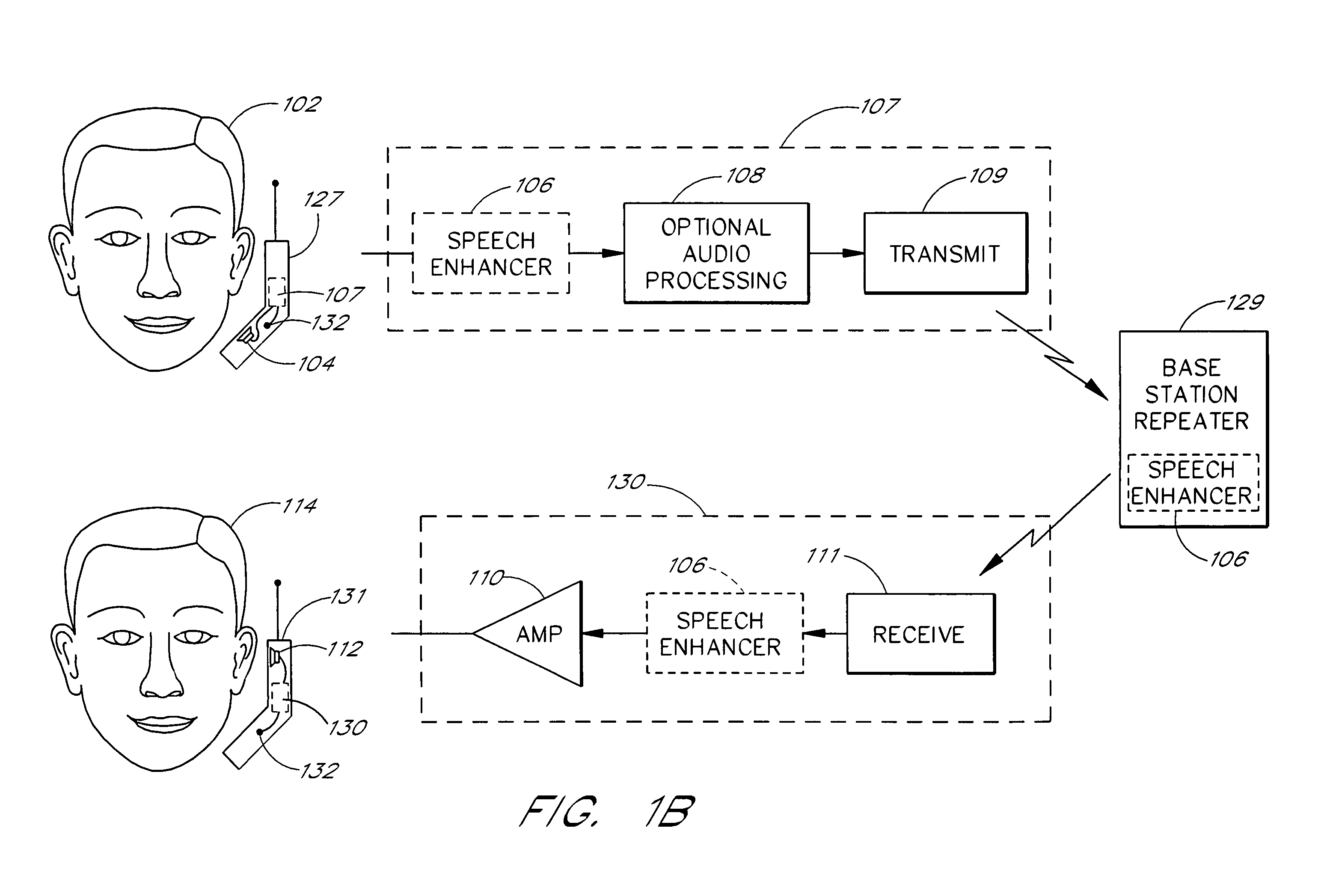
Voice intelligibility enhancement system
InactiveUS6993480B1Improve intelligibilityImprove speech clarityPublic address systemsSpeech analysisEnvironmental noiseHearing acuity
Intelligibility of a human voice projected by a loudspeaker in an environment of high ambient noise is enhanced by processing a voice signal in accordance with the frequency response characteristics of the human hearing system. Intelligibility of the human voice is derived largely from the pattern of frequency distribution of voice sounds, such as formants, as perceived by the human hearing system. Intelligibility of speech in a voice signal is enhanced by filtering and expanding the voice signal with a transfer function that approximates an inverse of equal loudness contours for tones in a frontal sound field for humans of average hearing acuity.
Owner:DTS
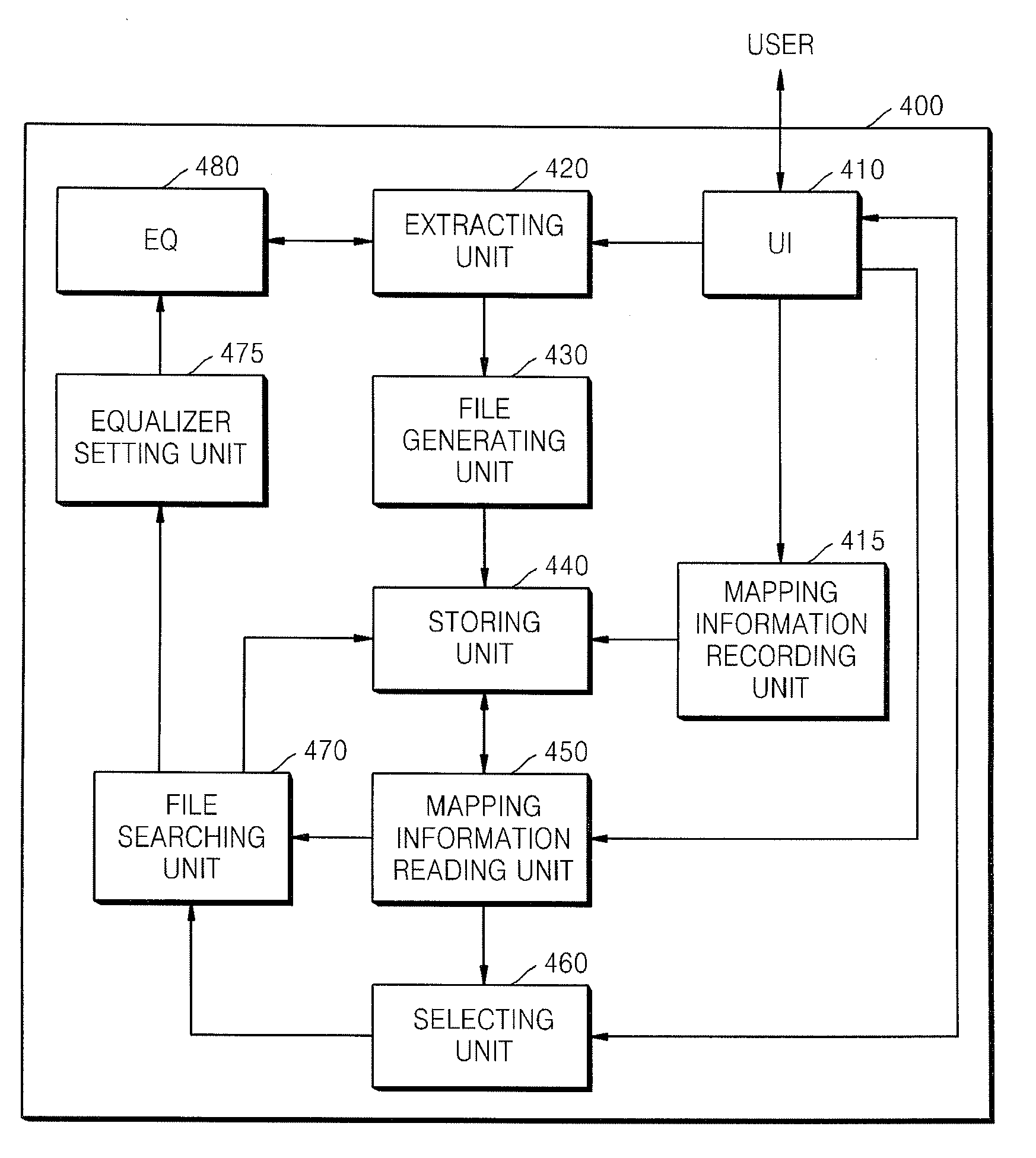
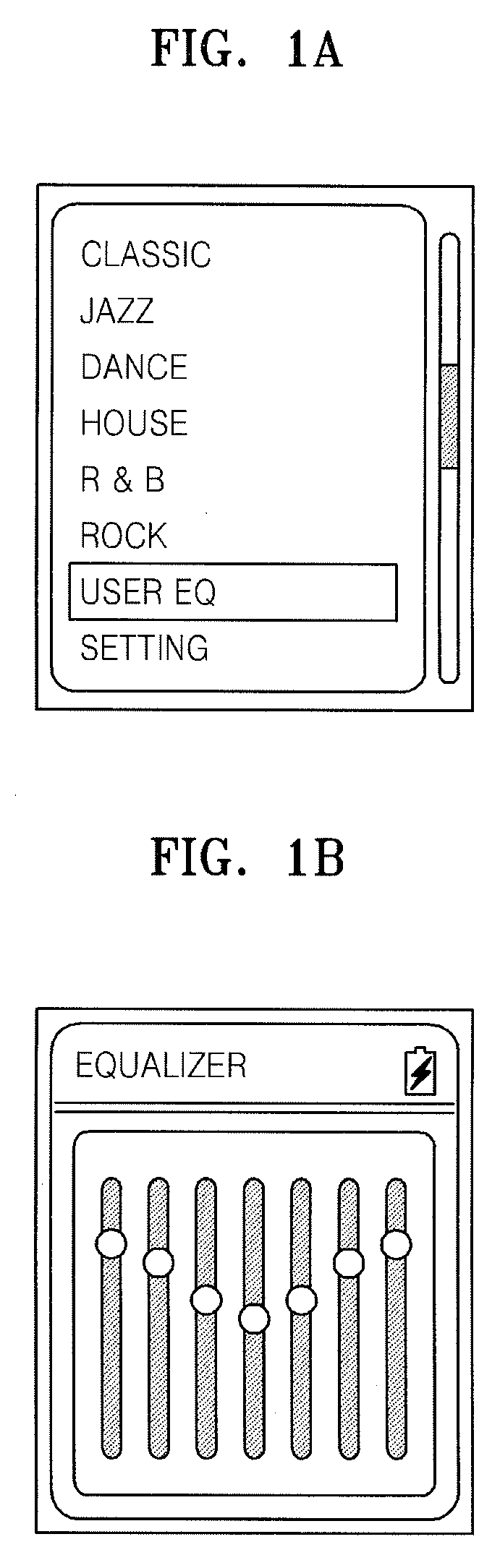
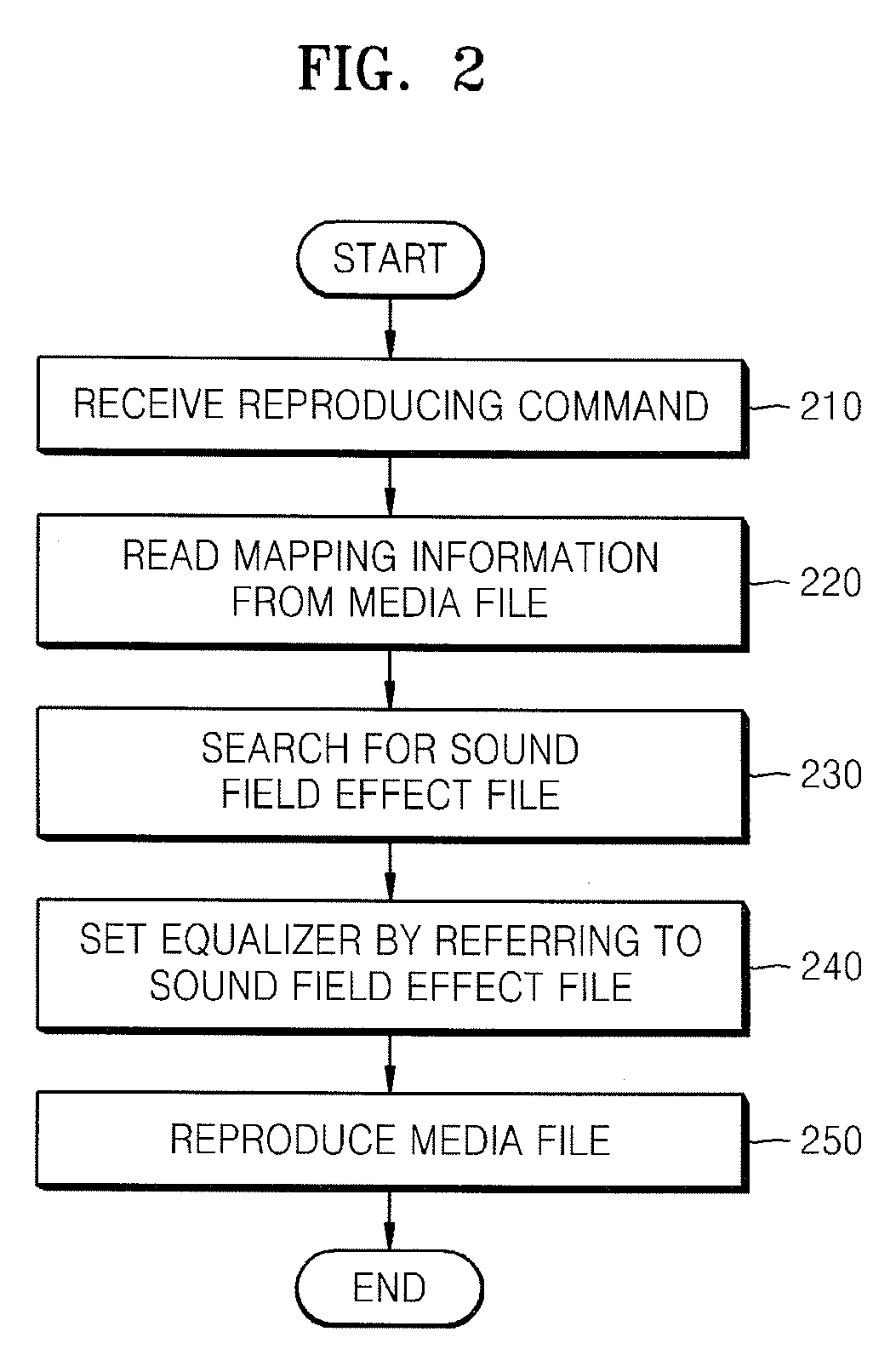
Method of setting an equalizer in an apparatus to reproduce a media file and apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20090024662A1Electronic editing digitised analogue information signalsUsing non-detectable carrier informationComputer hardwareInformation searching
A method and apparatus to reproduce a media file including reading mapping information from a predetermined position of the media file, searching for a sound field effect file of the media file by referring to the mapping information, and setting an equalizer of the audio data on the basis of the sound field effect file. A user can reproduce a media file by using an optimized equalizer of each media file even though the user himself does not set the equalizer. Also, since an equalizer setting of the reproducing apparatus can be applied to another reproducing apparatus, a user can enjoy listening to a media file in the other reproducing apparatus under the same reproducing conditions as those of the reproducing apparatus.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
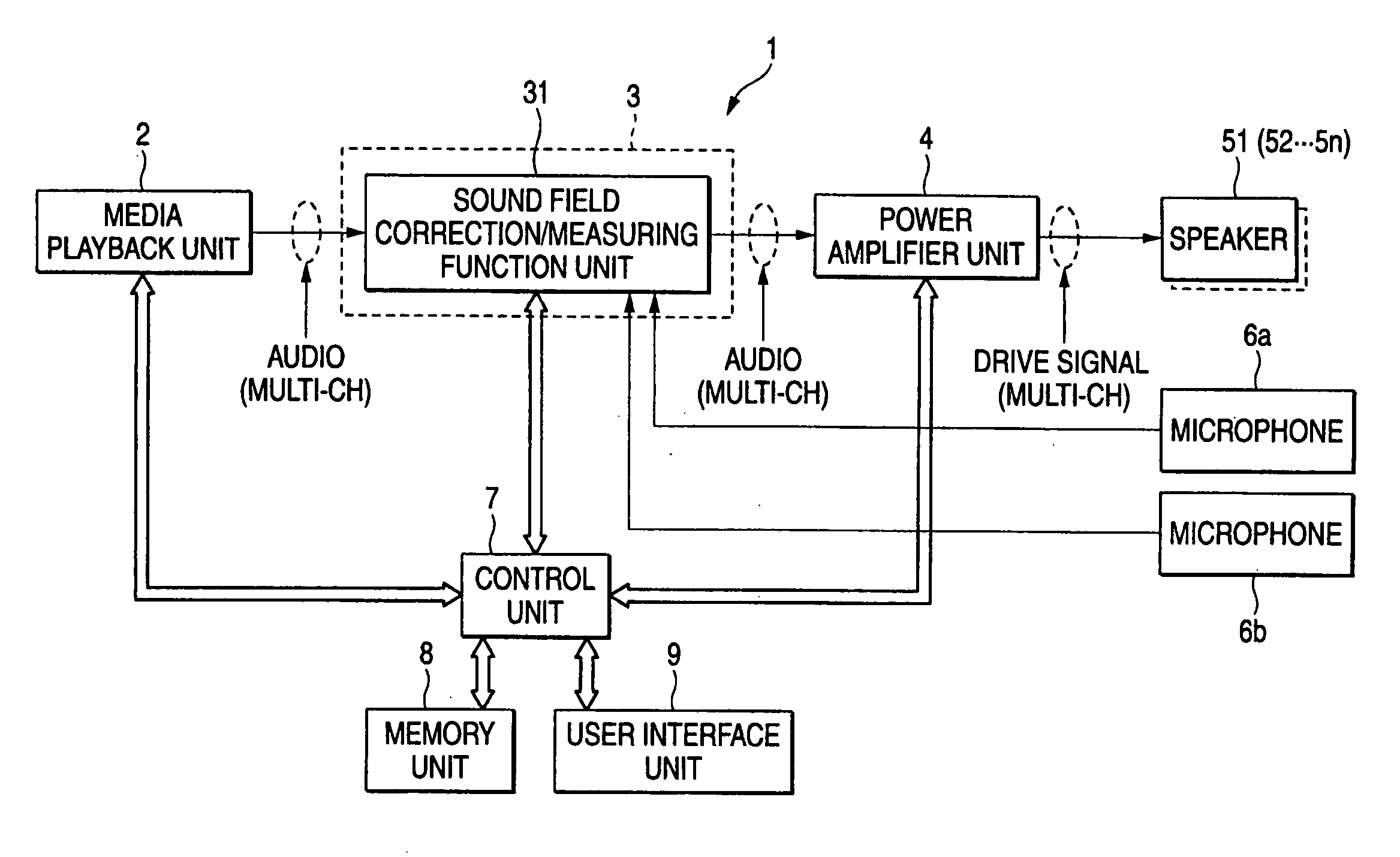
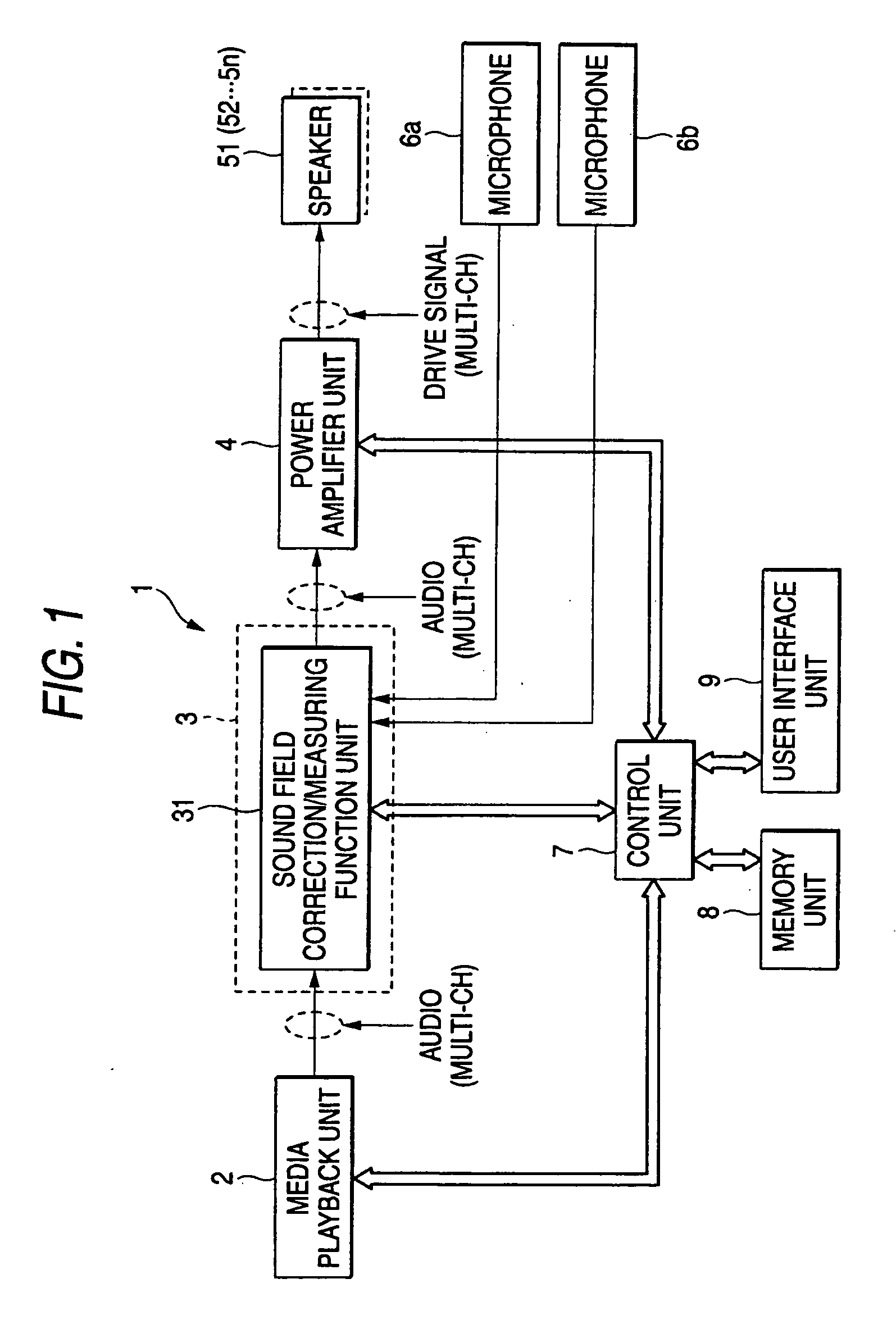
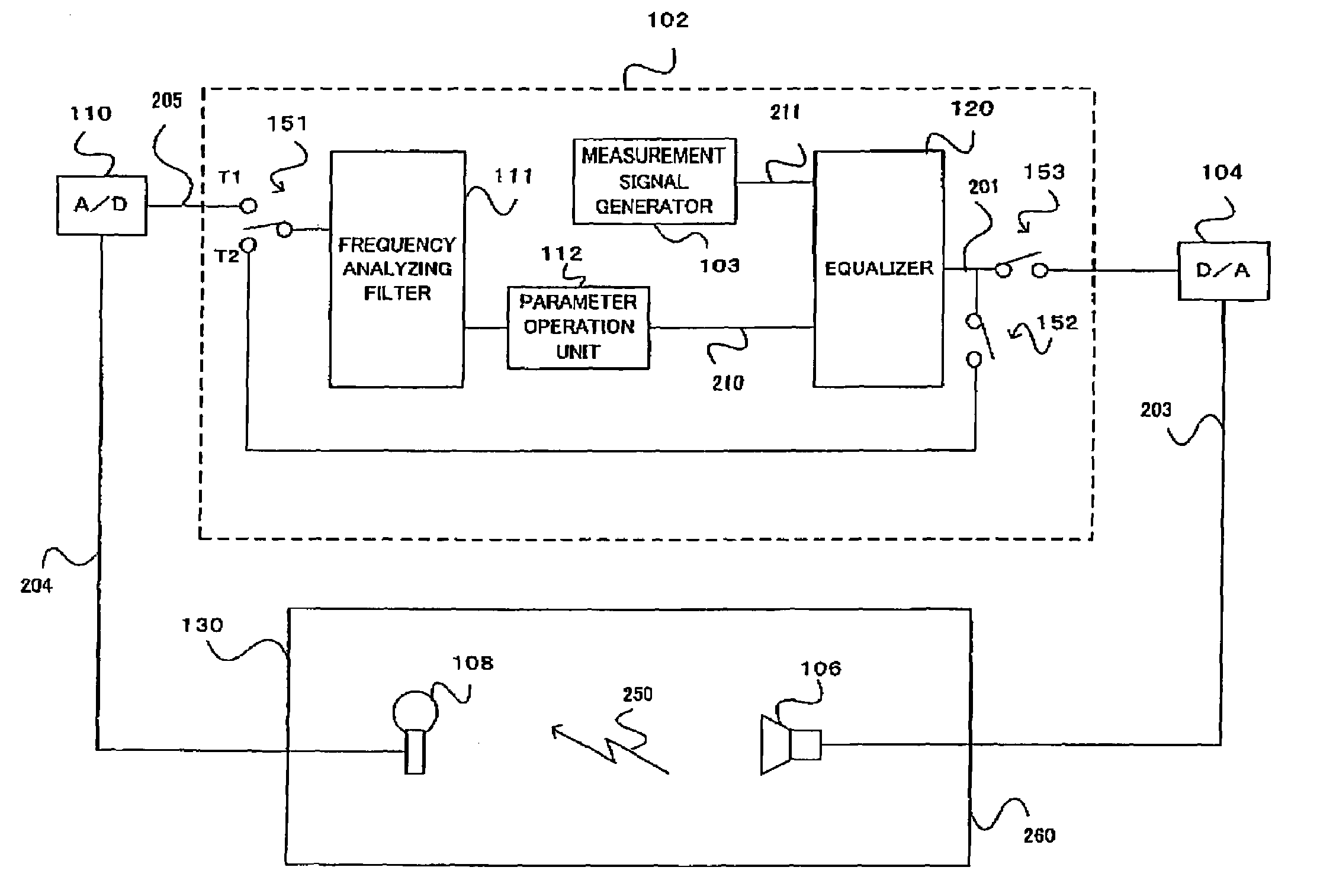
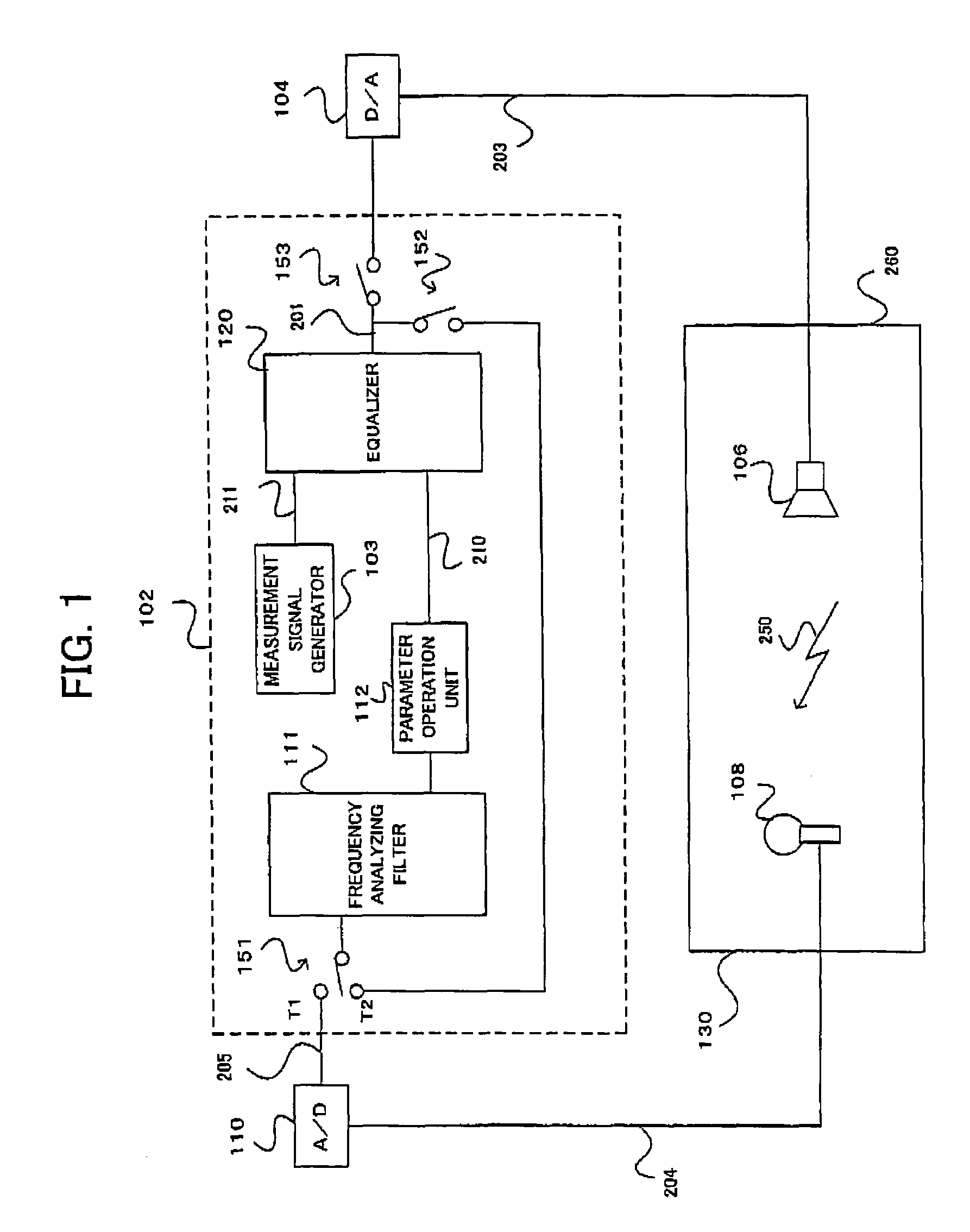
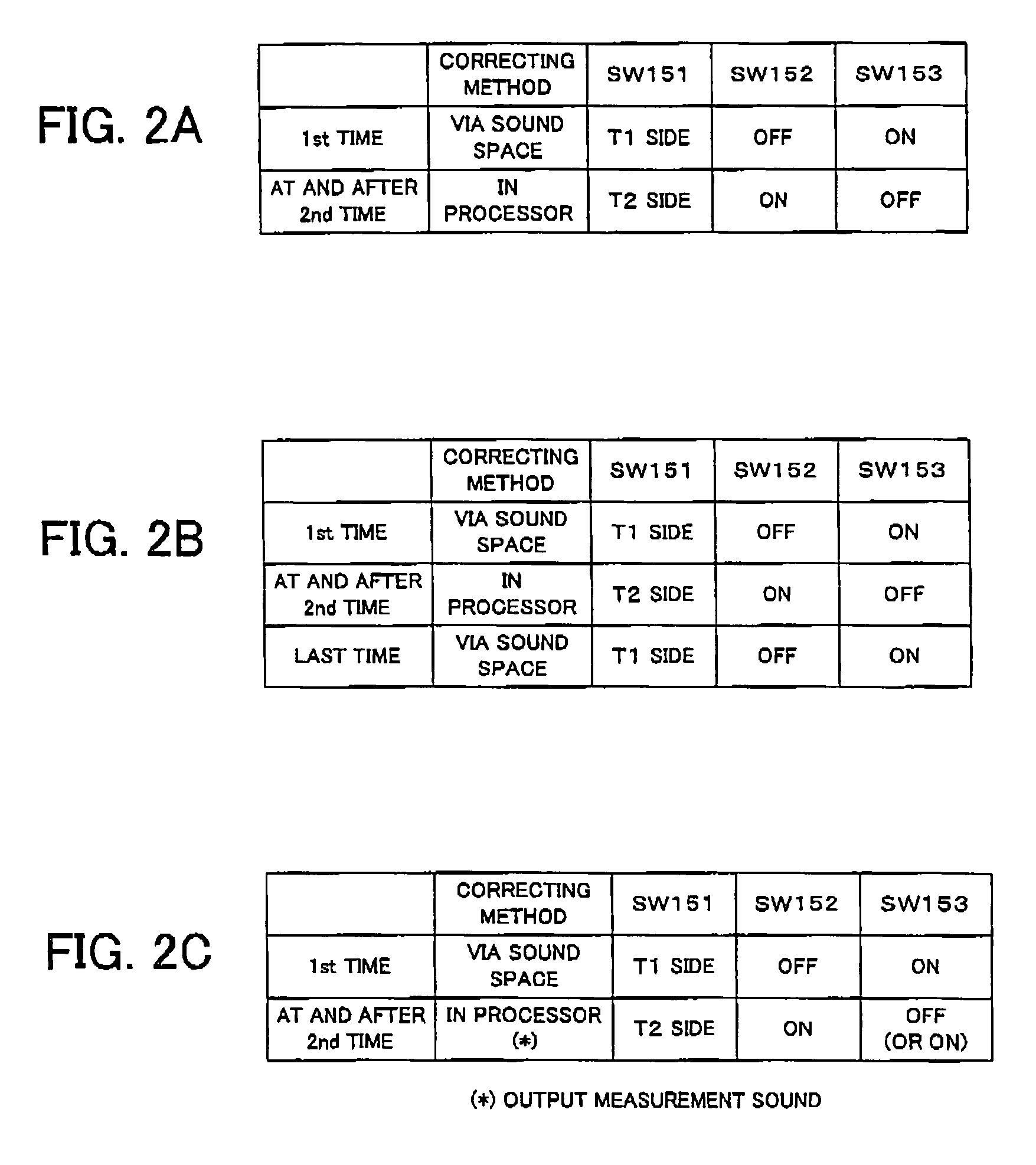
Automatic sound field correcting device and computer program therefor
InactiveUS7489784B2Performed quicklyReduce processing timePseudo-stereo systemsFrequency response correctionSignal processing circuitsLoudspeaker
An automatic sound field correcting device executes a signal process to the plurality of audio signals on respective correspondent signal transmission paths, and outputs them to a plurality of correspondent speakers to correct sound characteristics on the respective signal transmission paths. Namely, a measurement signal is supplied to each signal transmission path, and a measurement sound corresponding to it is outputted from the speaker to a sound space. The outputted measurement sound is detected as a detecting signal. The frequency characteristic of the audio signal on each signal transmission path is corrected by an equalizer, and a gain value of the equalizer is determined by a correction amount determining unit. A frequency characteristics correction is performed predetermined times. At a first correction, the correction amount determining unit determines the correction amount by performing a frequency analysis, based on the detecting signal, i.e. base on the detecting signal corresponding to the measurement sound actually outputted to the sound space. On the contrary, at and after a second correction, the correction amount determining unit determines the correction amount based on the detecting signal or an output signal of the equalizer. Namely, at and after the second correction, the output signal of the equalizer is supplied to the correction amount determining unit in a signal processing circuit as the need arises, and the frequency characteristics correction is performed without actually outputting the measurement sound to the sound space.
Owner:ONKYO KK D B A ONKYO CORP
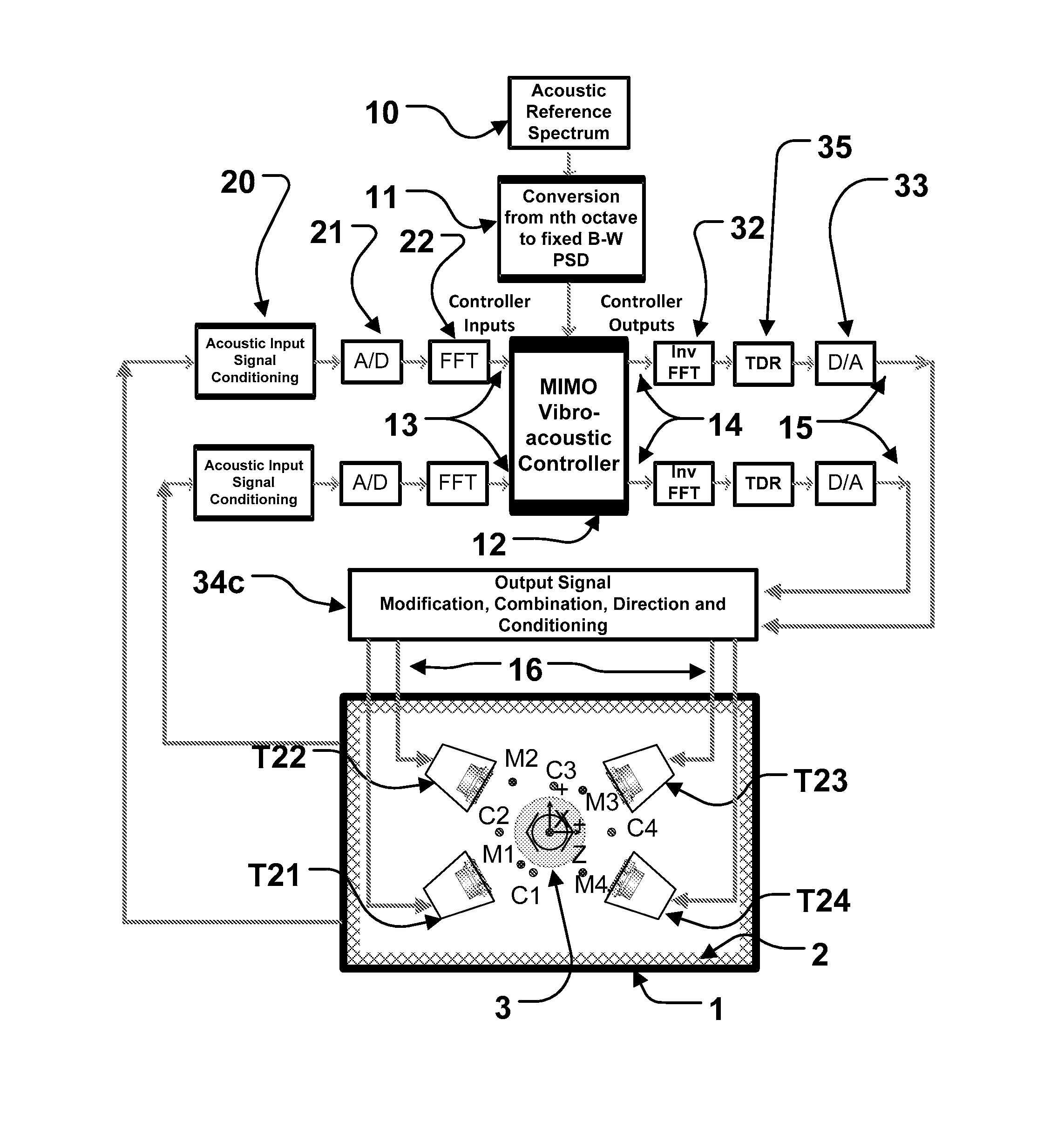
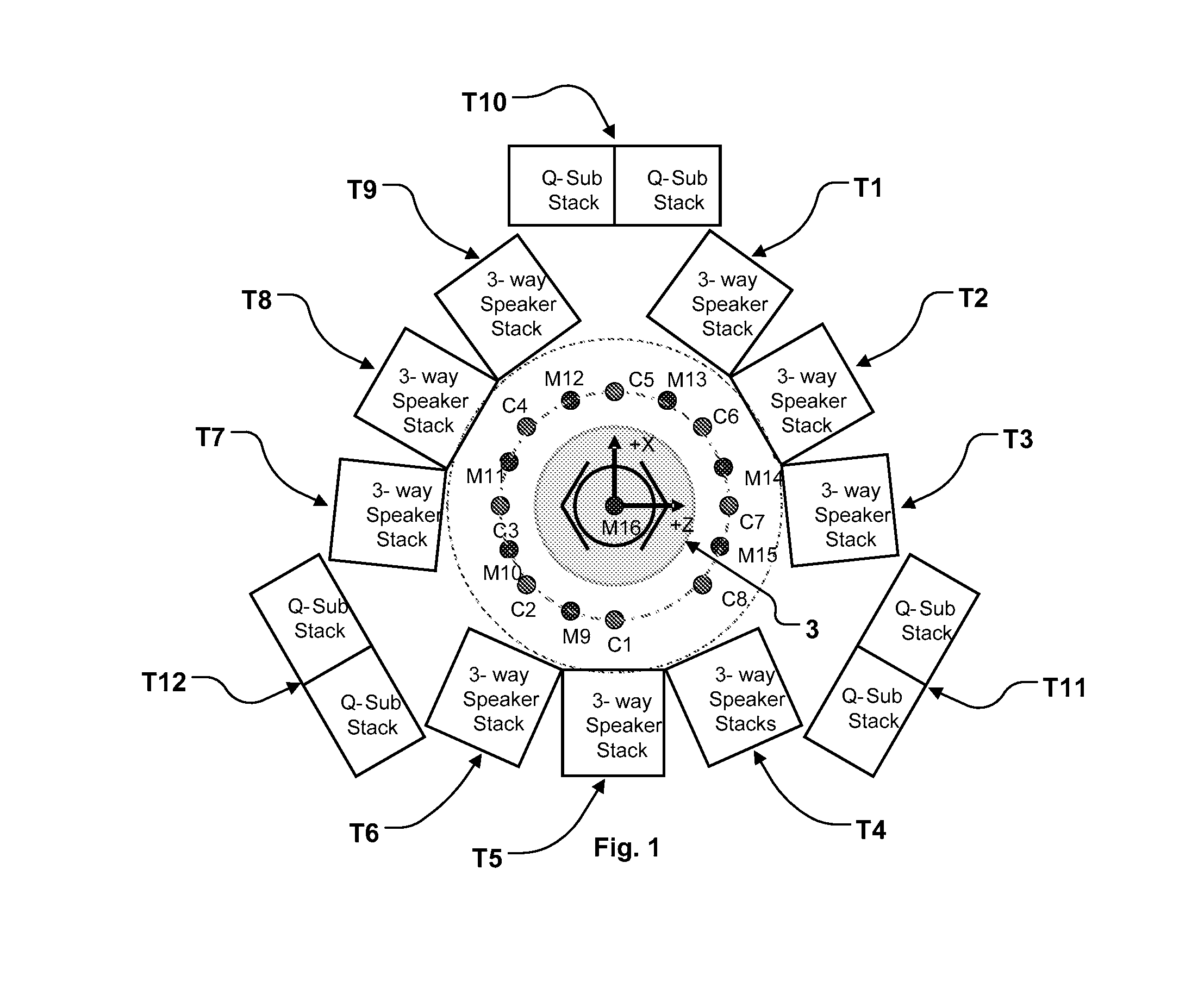
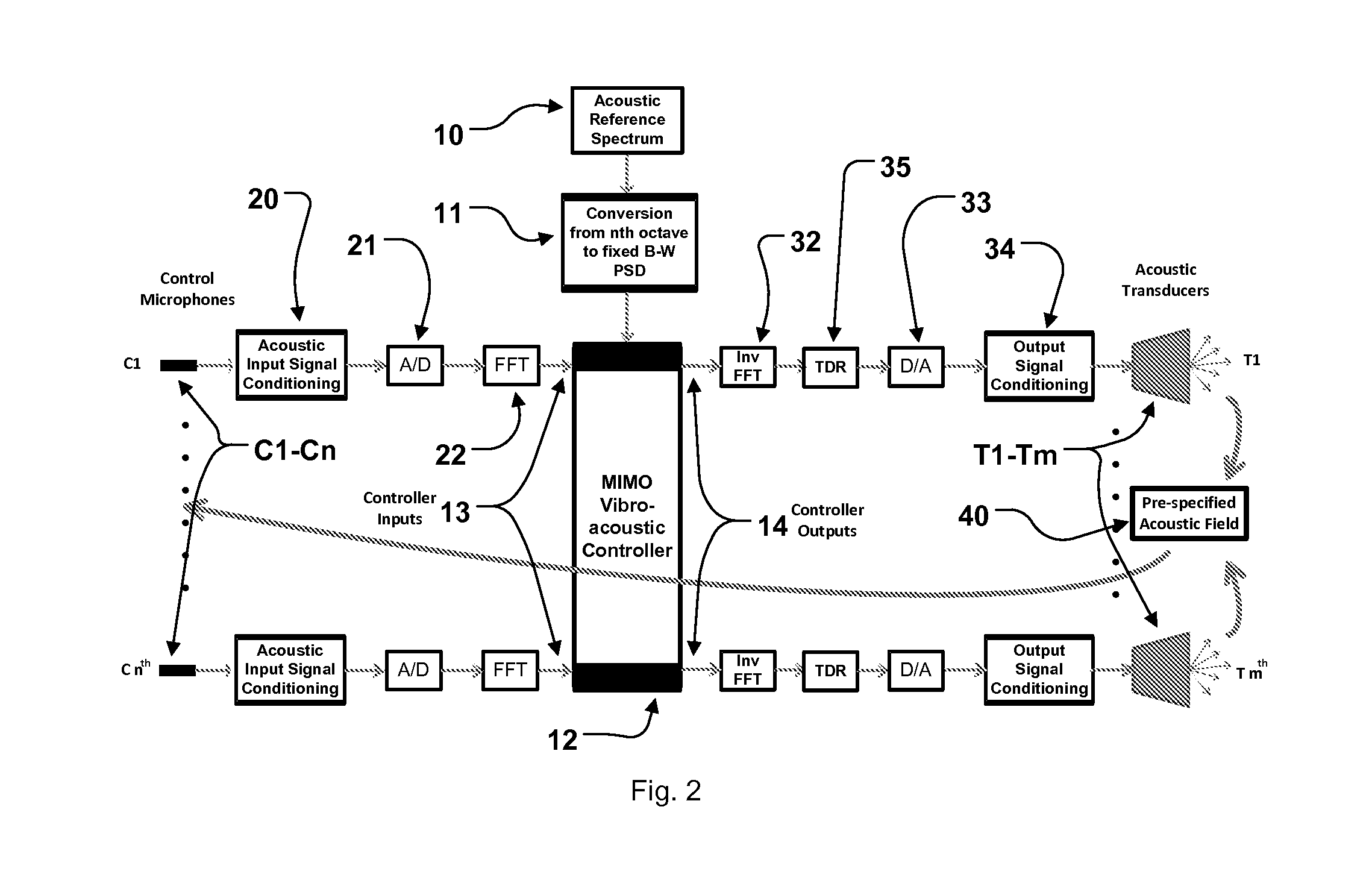
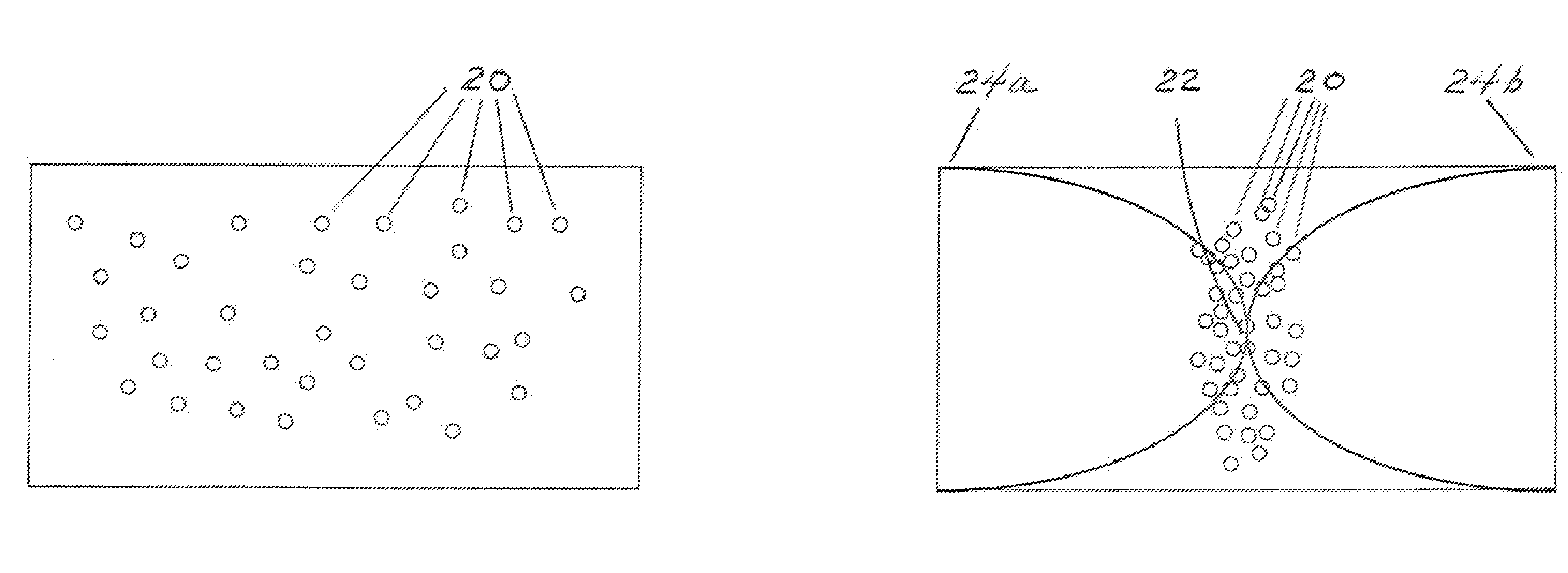
Direct field acoustic testing in a semi-reverberant enclosure
ActiveUS20150253292A1Evenly spacedAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalControl systemTransducer
An acoustic testing system includes at least four control microphones, at least four acoustic transducers, an acoustic enclosure with pre-determined reverberant characteristics which contains the at least four control microphones and the at least four acoustic transducers, a control system configured to produce a predetermined acoustic field as measured by the at least one control microphone. A unit under test is also disposed within the acoustic enclosure. Using an acoustic enclosure with pre-determined reverberant characteristics results of the increased proportion of reflected sounds in the area proximate to the unit under test such that less power is required to achieve a given acoustic test level than in a purely direct field acoustic test.
Owner:MSI DFAT
Apparatus and method for separation of particles suspended in a liquid from the liquid in which they are suspended
InactiveUS20100078384A1Improve concentrationAvoid turbulenceSemi-permeable membranesLiquid separation by electricityUltrasonic sensorCompressibility
A method for separating, or removing, particulate material, e.g., blood cells, from a sample of fluid, e.g., whole blood of a patient, in which the particulate material is suspended. In the case of separating blood cells from blood plasma or blood serum, the resulting samples of blood plasma or blood serum can be used for in vitro diagnostic applications. In normal practice, a whole blood sample of a patient are provided and then introduced into an apparatus that contains a flow channel. An acoustic field, which contains acoustic standing waves from external ultrasonic transducers, is located within the flow channel. Laminar flow is maintained in the flow channel. Blood cells and platelets are separated from blood plasma or blood serum at the end of the flow channel and collected. The method described herein allows fluid components to differentially migrate to areas of preferred acoustic interaction. The parameters that affect separation of particles are size, density, compressibility of the particles, and the fluid surrounding the particles.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
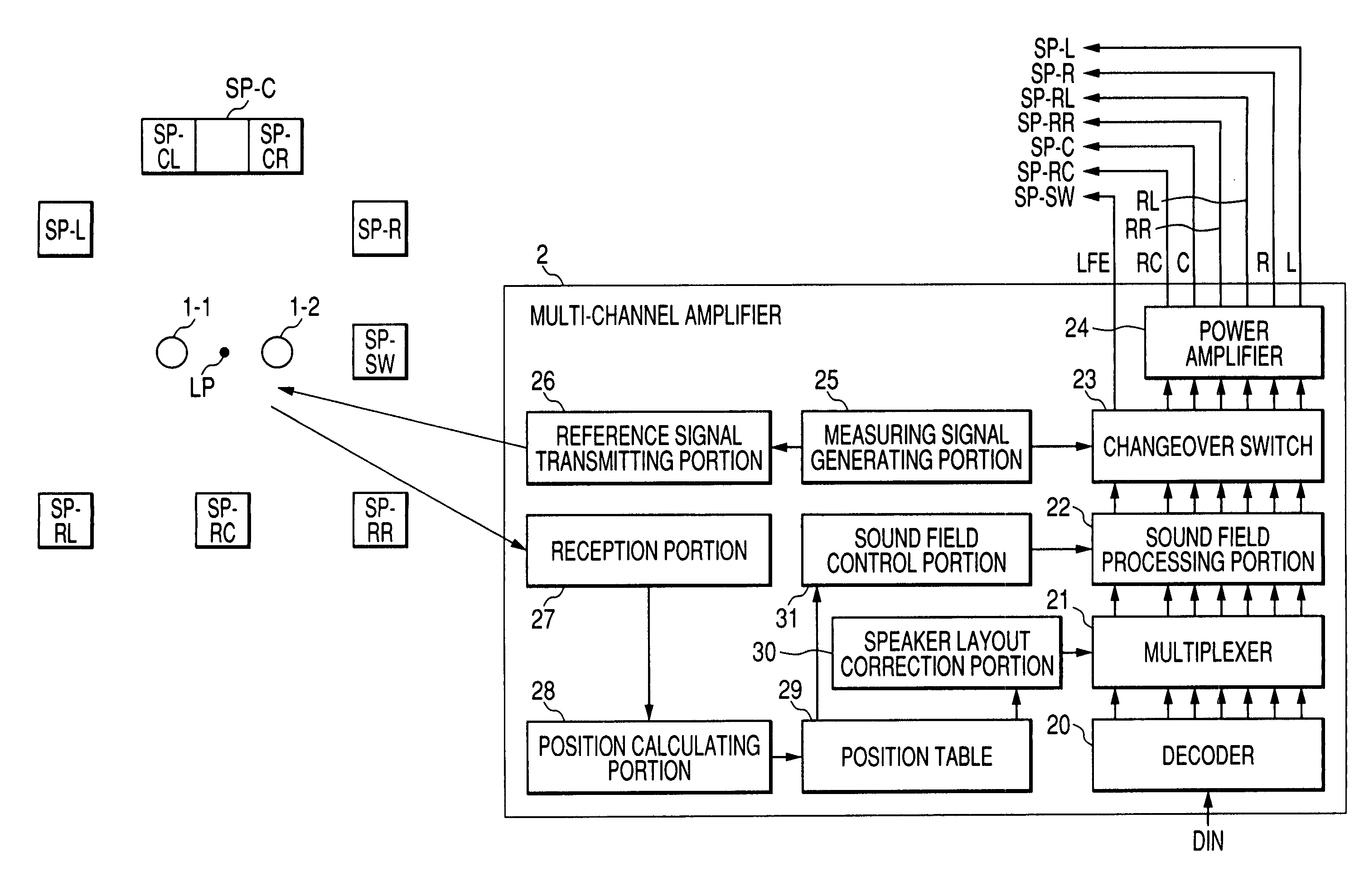
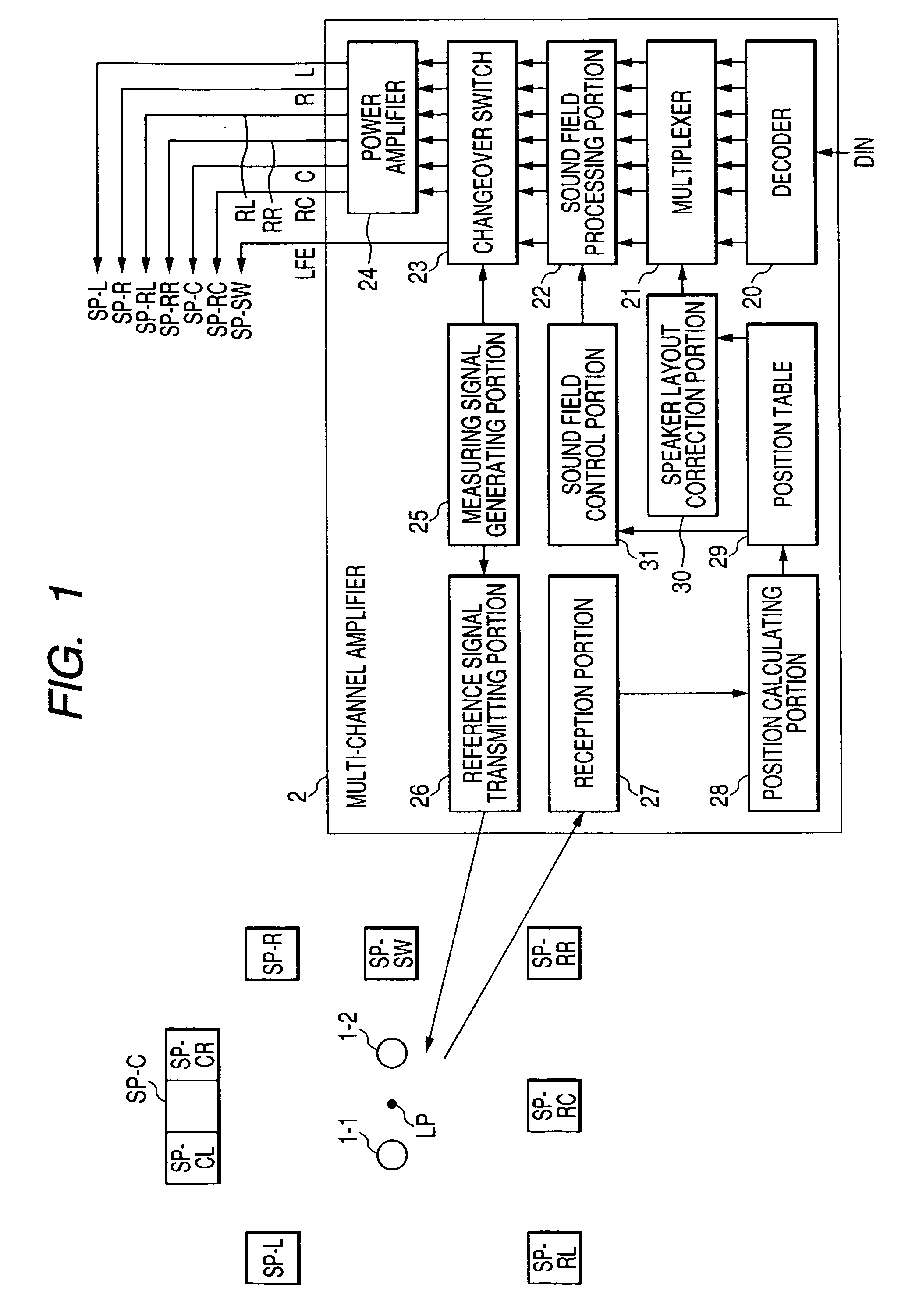
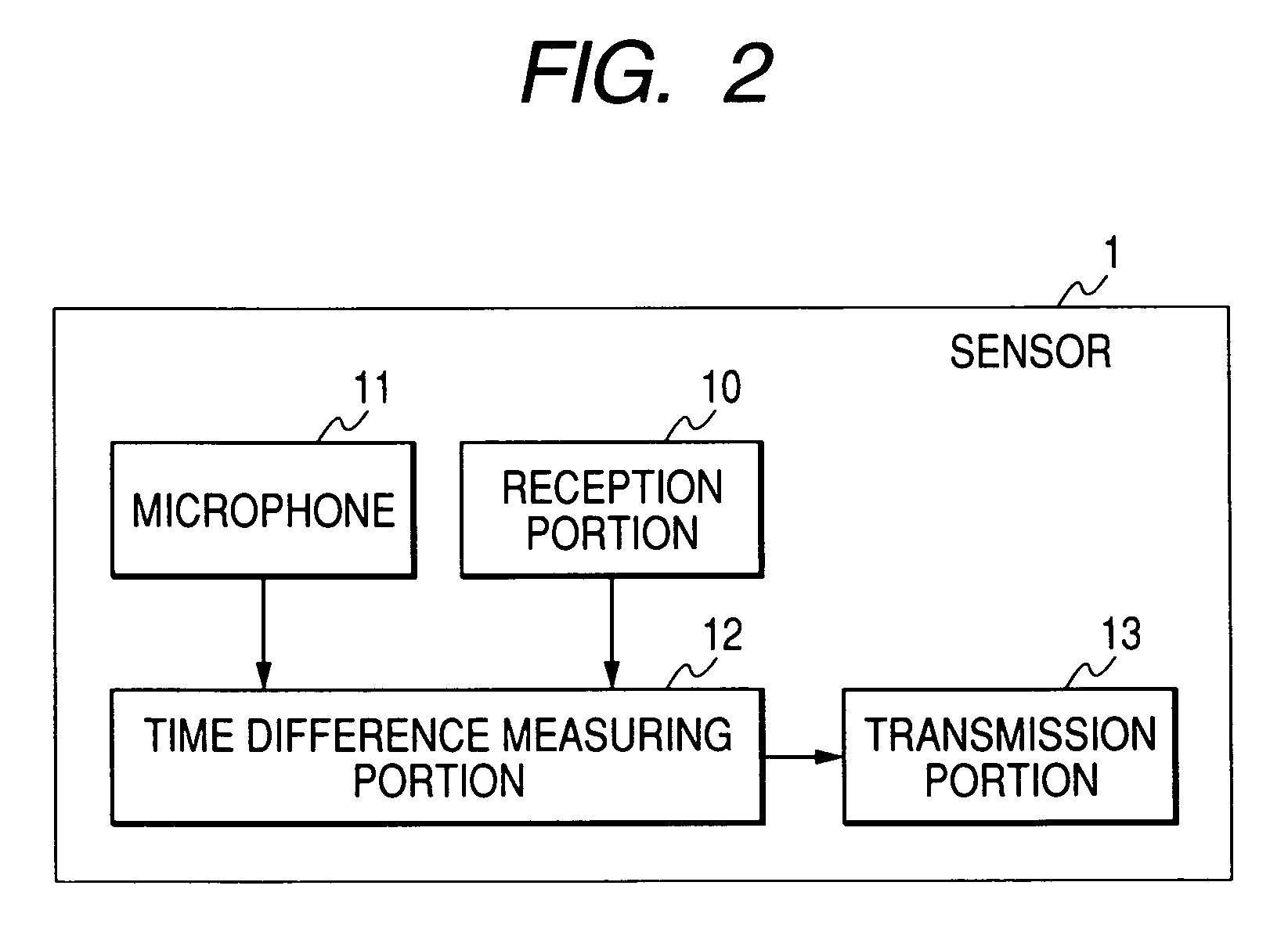
Sound reproducing apparatus and method of identifying positions of speakers
A position of a speaker is detected two-dimensionally or three-dimensionally, and a sound field is corrected. A sound reproducing apparatus includes a measuring signal generating portion for generating a first measuring signal, a transmission portion for transmitting a second measuring signal as soon as the first measuring signal is generated, sensors disposed in a listening position and for measuring a time difference between a time instant when the second measuring signal was received and a time instant when a measuring sound wave radiated from a to-be-detected speaker in accordance with the first measuring signal was received, and a position calculating portion for calculating a distance, as to each of n sensors, between each of the n sensors and the to-be-detected speaker based on the measured time difference, and calculating the position of the to-be-detected speaker based on distances among the n sensors and the calculated distance.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Media delivery platform
InactiveUS7548875B2The process is convenient and fastEasy accessModulated-carrier systemsPayment architectureCorrection algorithmComputer hardware
A improved method for delivery and play back of sound and image files is provided, including the use of the files as alerts for various electronic devices or for playing on a handheld device. Algorithms are provided for the delivery, storage, and playback of sound files, including a delivery method algorithm, a parametric optimization and compression algorithm, and an error correction algorithm. The files may be selected from and downloaded to the electronic device with or without the use of a worldwide network connection.
Owner:SKKY
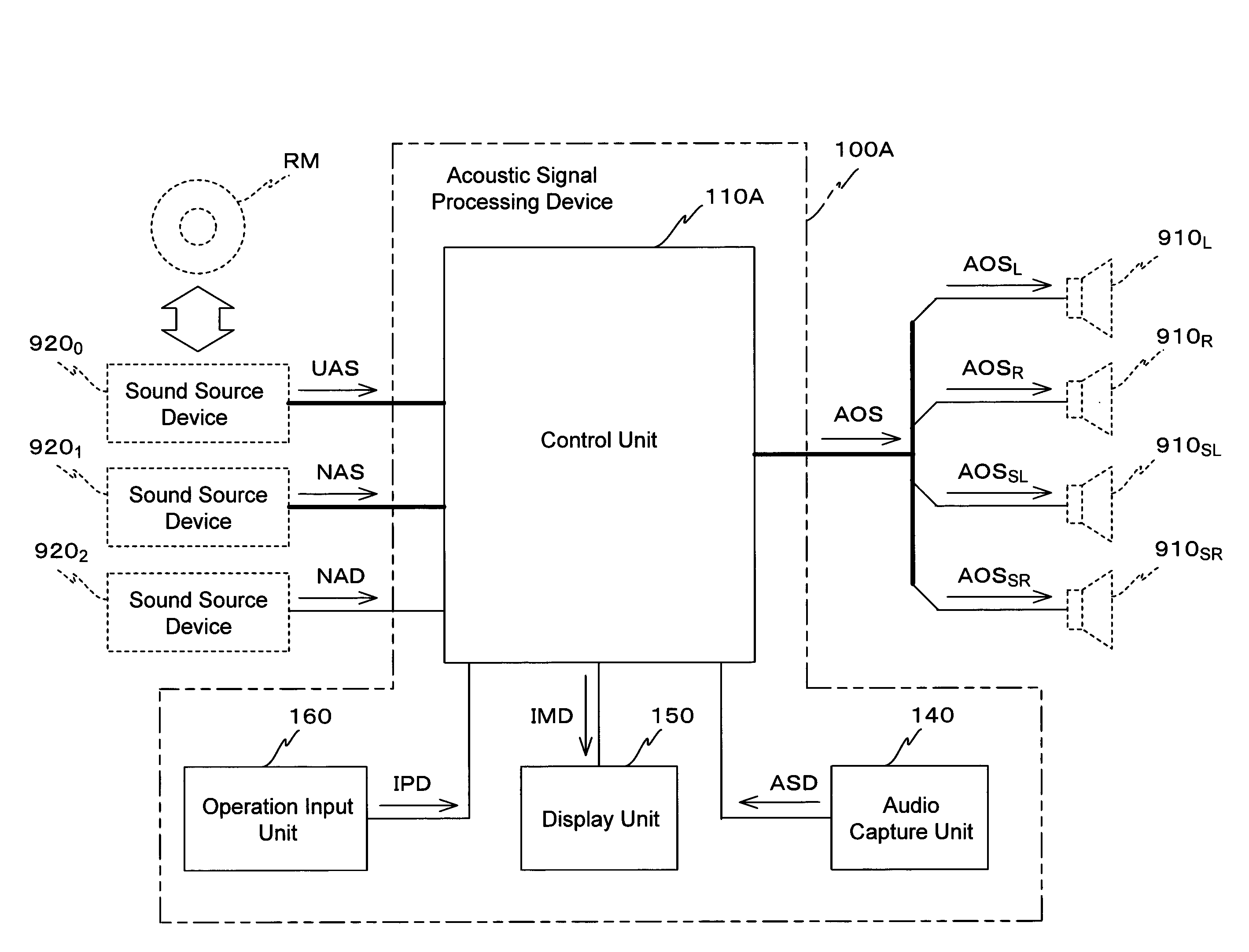
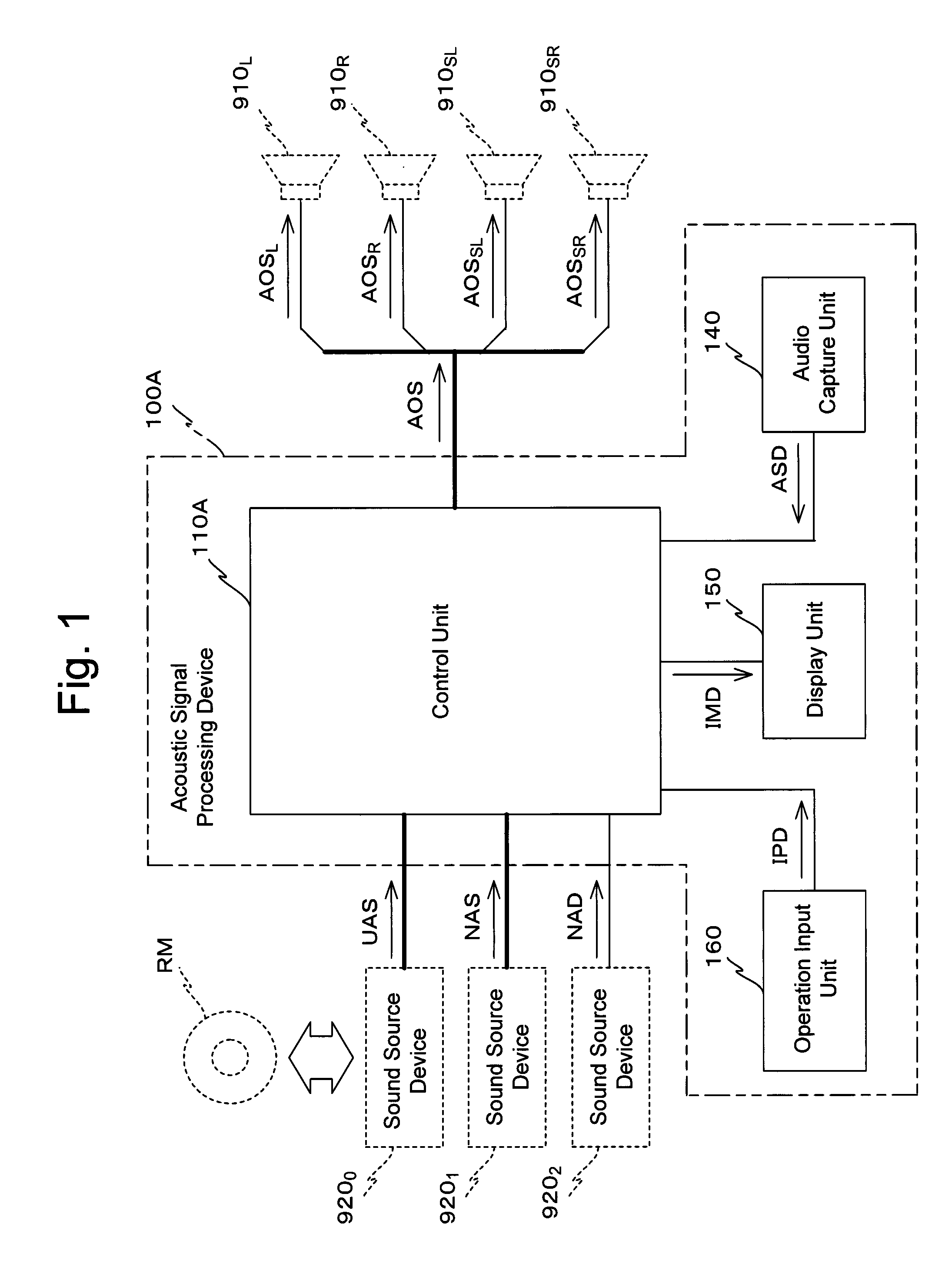
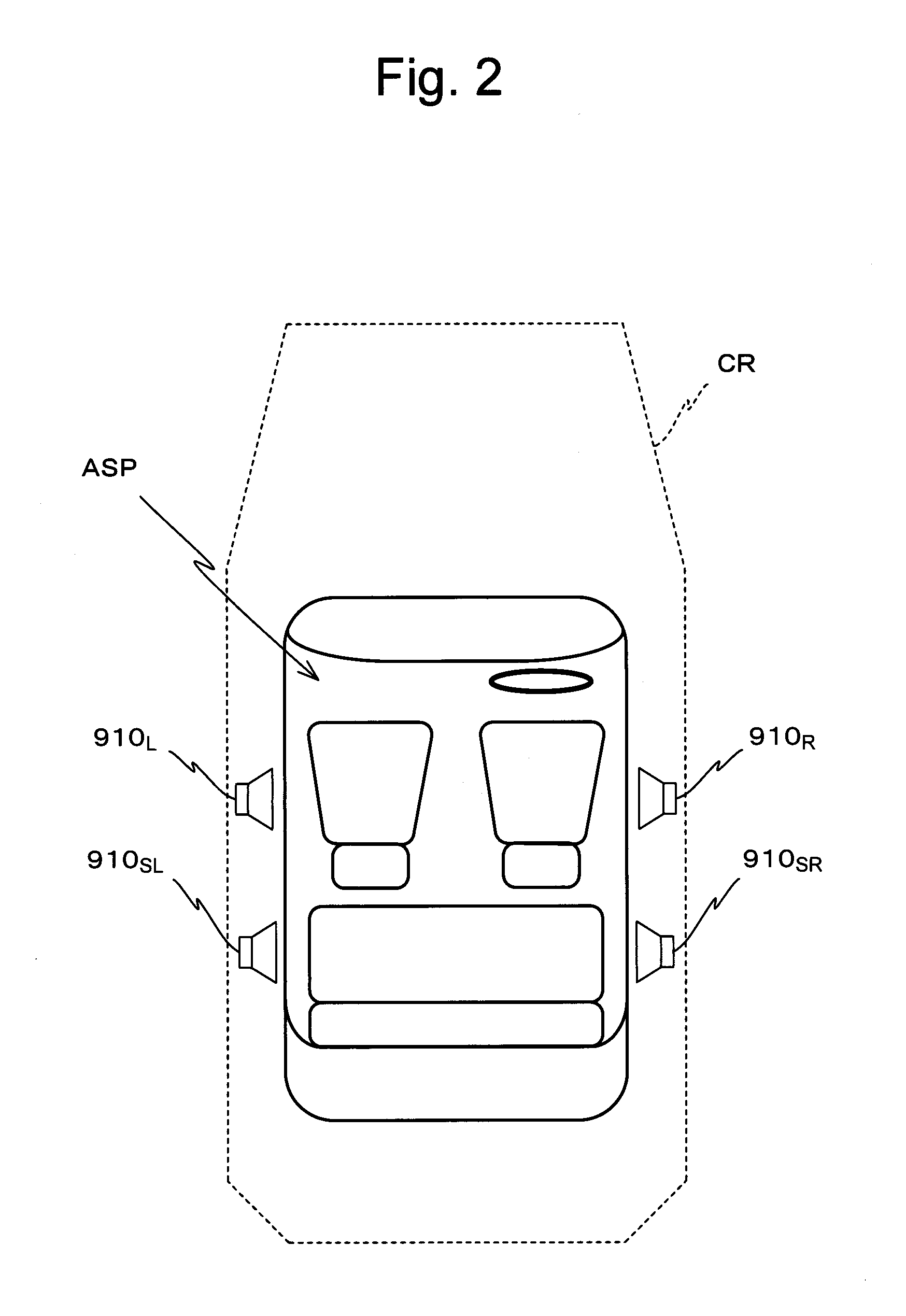
Acoustic signal processing device and acoustic signal processing method
InactiveUS20110007904A1InhibitionStereophonic systemsStereophonic arrangmentsLoudspeakerComputer science
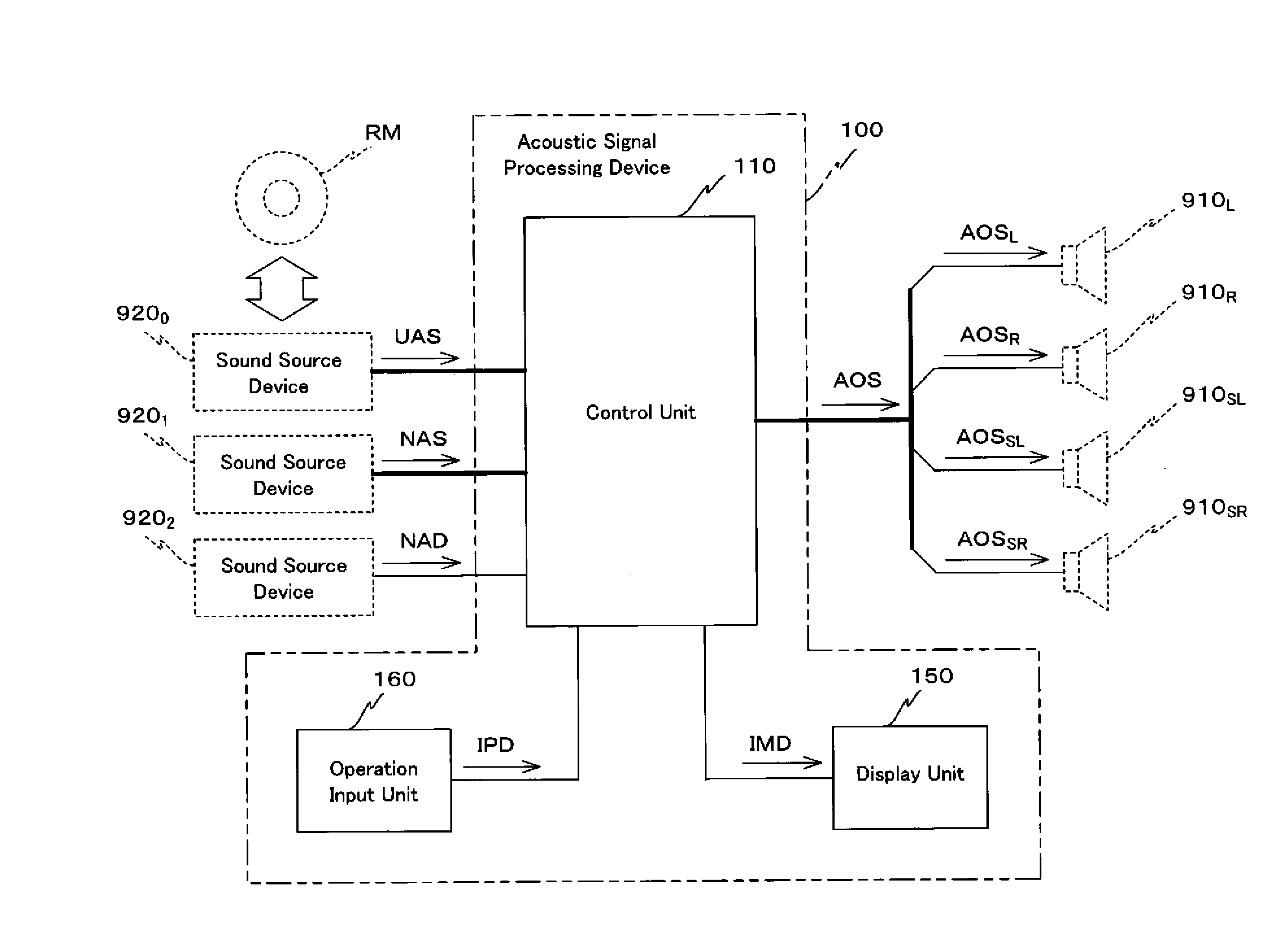
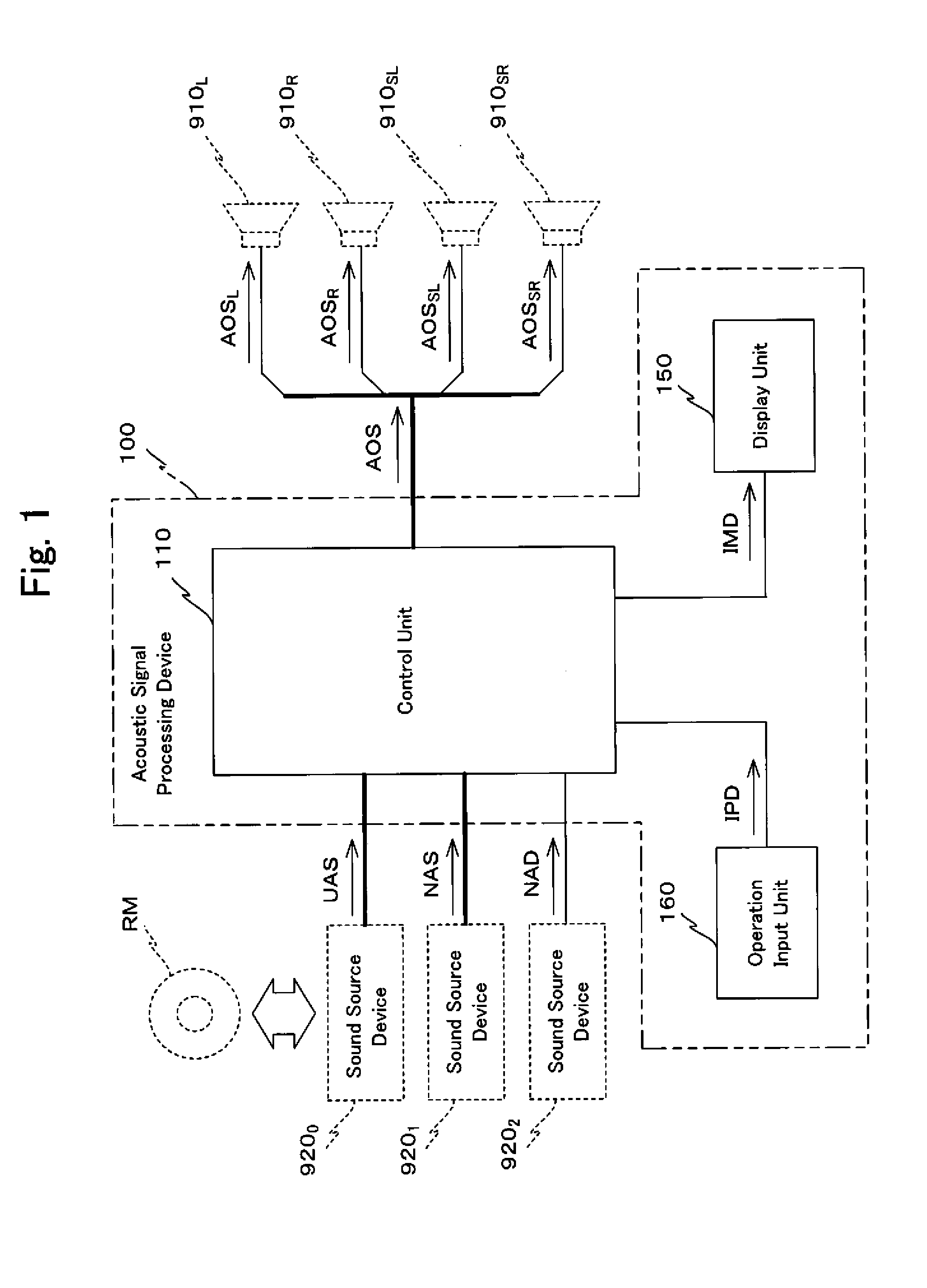
A corrective measurement part of a processing control part 119A measures an aspect of specific sound field correction processing performed on an acoustic signal received from a specific external device. Based on this measurement result, settings for cancellation of specific sound field correction processing performed on that acoustic signal are made for a correction cancellation part 310. Furthermore, an aspect of appropriate sound field processing corresponding to the actual sound field space is acquired by an appropriate correction acquisition part of the processing control part 119A. Based on the result acquired in this manner, settings for performing appropriate sound field correction processing upon a signal SND are made for a correction processing part 330. Thus, whichever one of acoustic signals received by a reception processing part 111 is selected, an output acoustic signal can be supplied to speaker units in after appropriate sound field correction processing.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Method and apparatus to create a sound field
ActiveUS7515719B2Eliminate the effects ofReduce calculationTelevision system detailsGain controlTransducerVocal tract
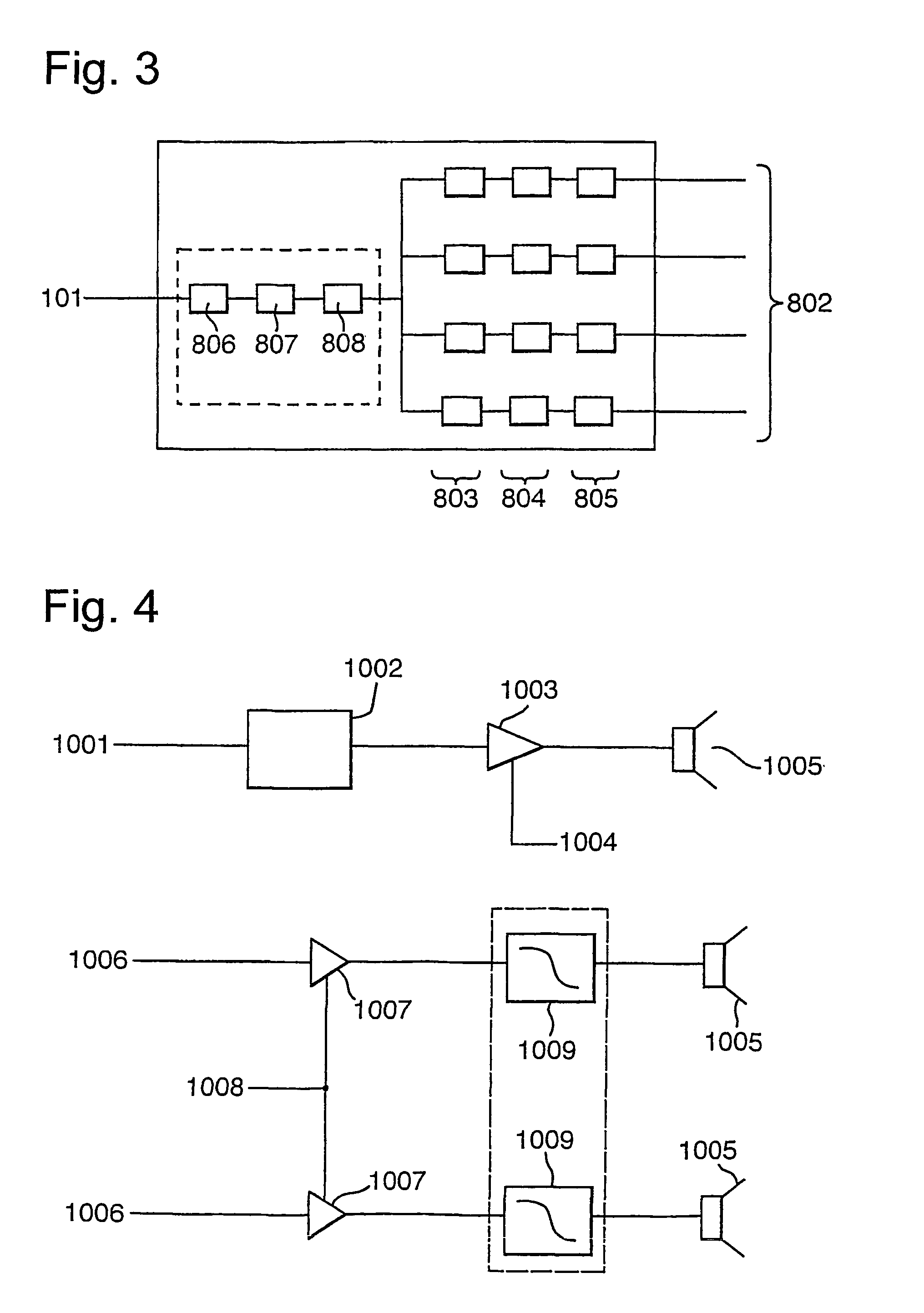
The invention generally relates to a method and apparatus for taking an input signal, replicating it a number of times and modifying each of the replicas before routing them to respective output transducers such that a desired sound field is created. This sound field may comprise a directed beam, focussed beam or a simulated origin. In a first aspect, delays are added to sound channels to remove the effects of different travelling distances. In a second aspect, a delay is added to a video signal to account for the delays added to the sound channels. In a third aspect, different window functions are applied to each channel to give improved flexibility of use. In a fourth aspect, a smaller extent of transducers is used top output high frequencies than are used to output low frequencies. An array having a larger density of transducers near the centre is also provided. In a fifth aspect, a line of elongate transducers is provided to give good directivity in a plane. In a sixth aspect, sound beams are focussed in front or behind surfaces to give different beam widths and simulated origins. In a seventh aspect, a camera is used to indicate where sound is directed.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Acoustic signal processing device and acoustic signal processing method
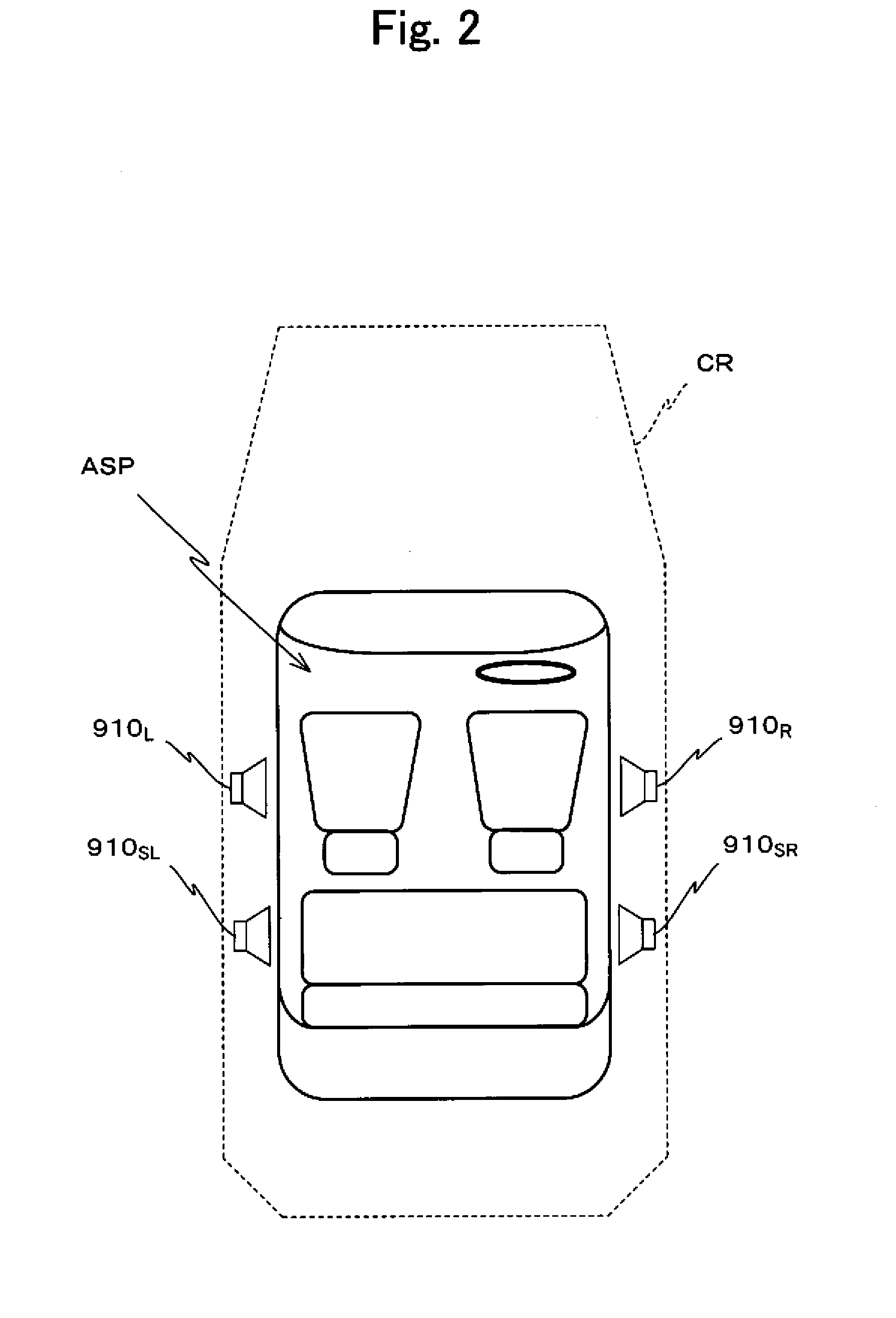
In a processing control unit 119, a correction measurement unit measures an aspect of sound field correction processing executed upon an acoustic signal UAS received from a sound source device 9200, that is a particular external device. And if an acoustic signal NAS or an acoustic signal NAD other than the acoustic signal UAS is selected as an acoustic signal to be supplied to speaker units 910L, through 910SR, then a sound field correction unit 113 generates an acoustic signal APD by executing sound field correction processing for the aforementioned measured aspect upon the selected acoustic signal. Due to this, whichever of the plurality of acoustic signals UAS, NAS, and NAD is selected, it is possible to supply that signal to the speaker units 910L, through 910SR in a state in which uniform sound field correction processing has been executed thereupon.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
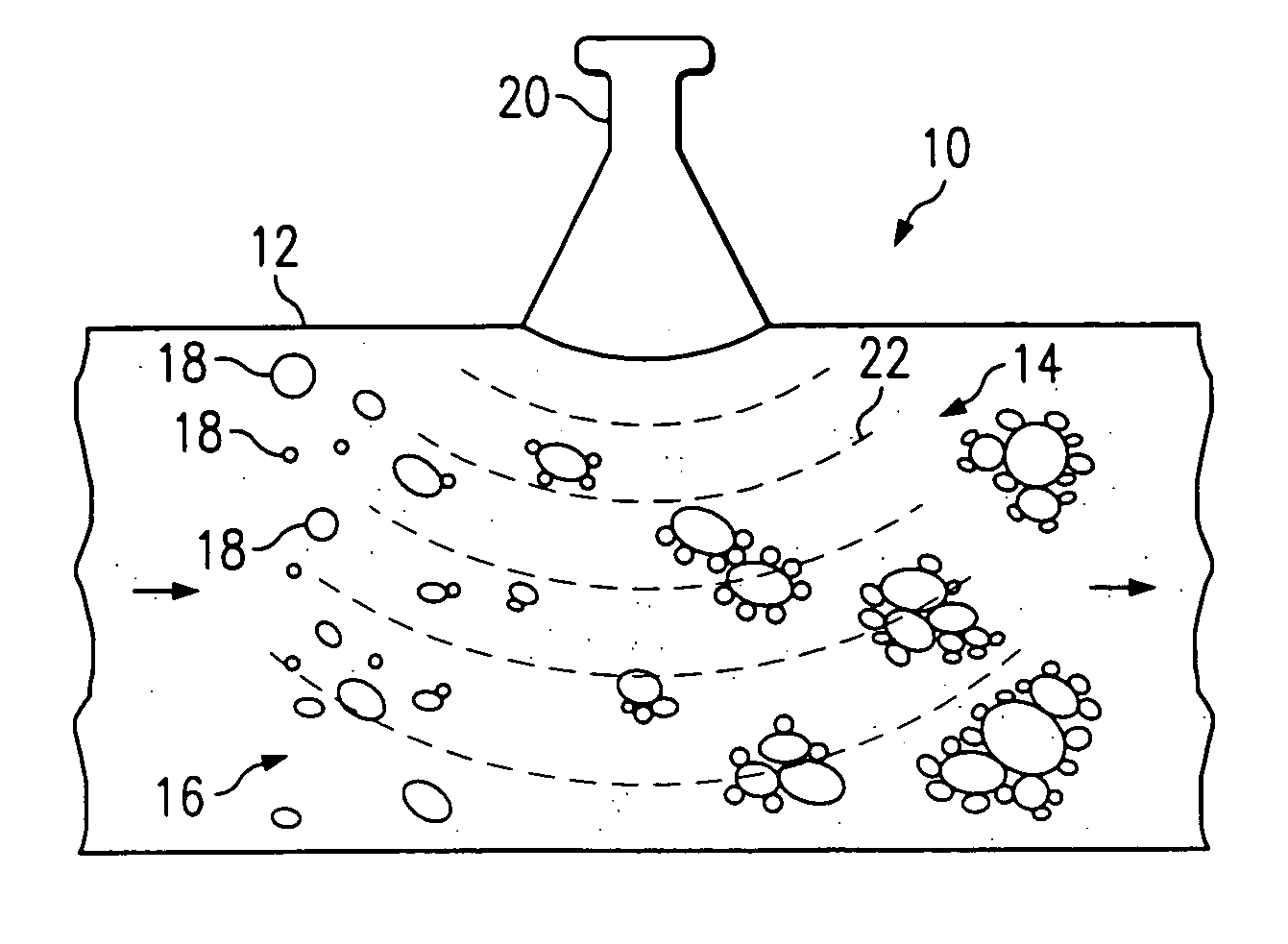
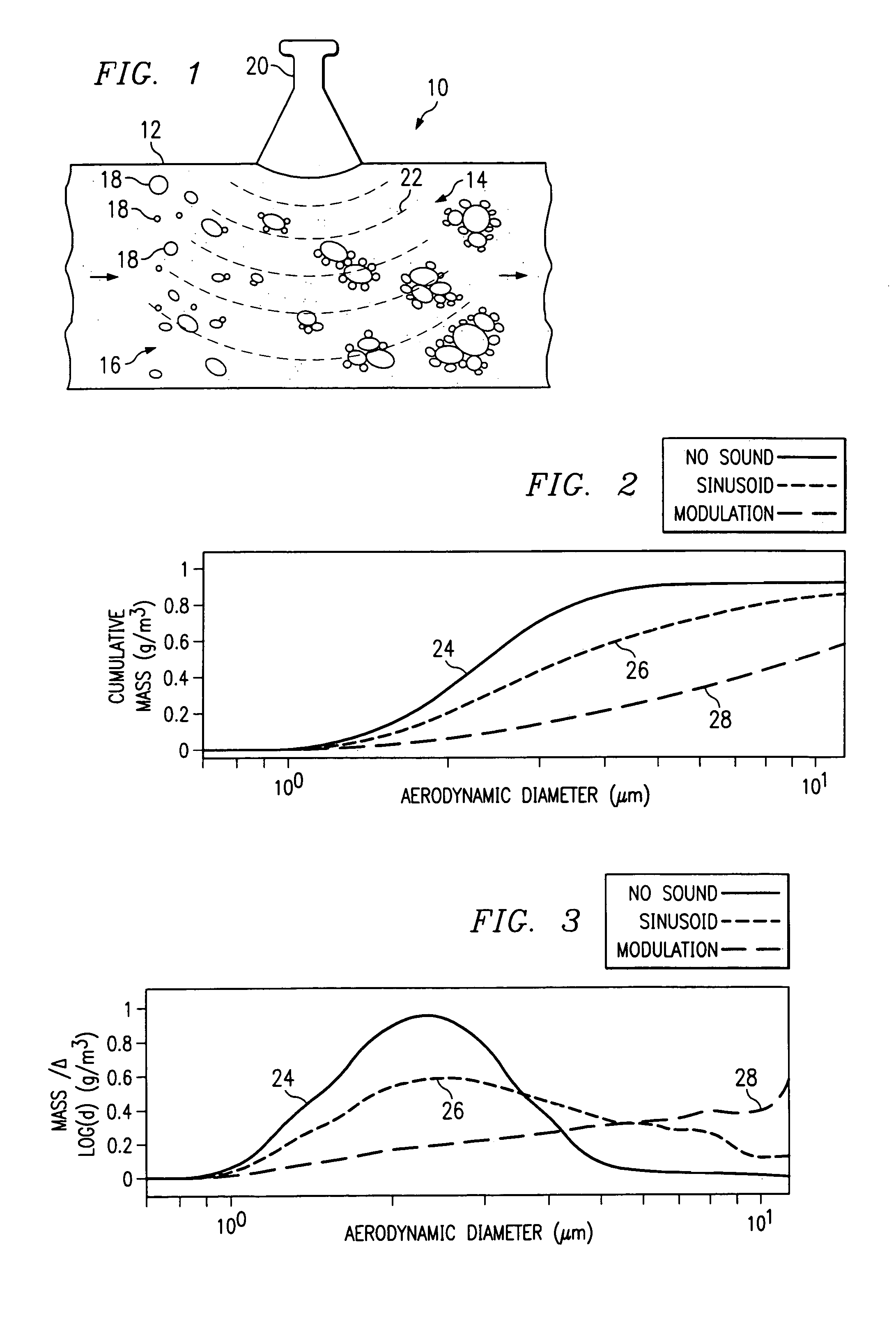
Modulated acoustic agglomeration system and method
InactiveUS7150779B2Improve agglomerationCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentFrequency modulationSound field
An acoustic agglomerator for agglomerating constituents in a fluid is provided. The acoustic agglomerator includes an area containing a fluid having constituents and an acoustic generator operable to generate a modulated acoustic field to enhance agglomeration of the constituents in the fluid. In one aspect the acoustic field is frequency modulated and in other aspects the acoustic field is amplitude modulated, while yet in other aspects the acoustic field is both frequency and amplitude modulated. A method for agglomerating constituents in a fluid is also provided. The method includes providing a fluid with a constituent and applying an acoustic field to the fluid. The method provides for modulating the acoustic field to cause the constituent to agglomerate.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Implantable wireless accoustic stimulators with high energy conversion efficiencies
ActiveUS8588926B2Efficient HarvestingImprove isotropyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityAcoustic energy
Receiver-stimulator with folded or rolled up assembly of piezoelectric components, causing the receiver-stimulator to operate with a high degree of isotropy are disclosed. The receiver-stimulator comprises piezoelectric components, rectifier circuitry, and at least two stimulation electrodes. Isotropy allows the receiver-stimulator to be implanted with less concern regarding the orientation relative the transmitted acoustic field from an acoustic energy source.
Owner:EBR SYST
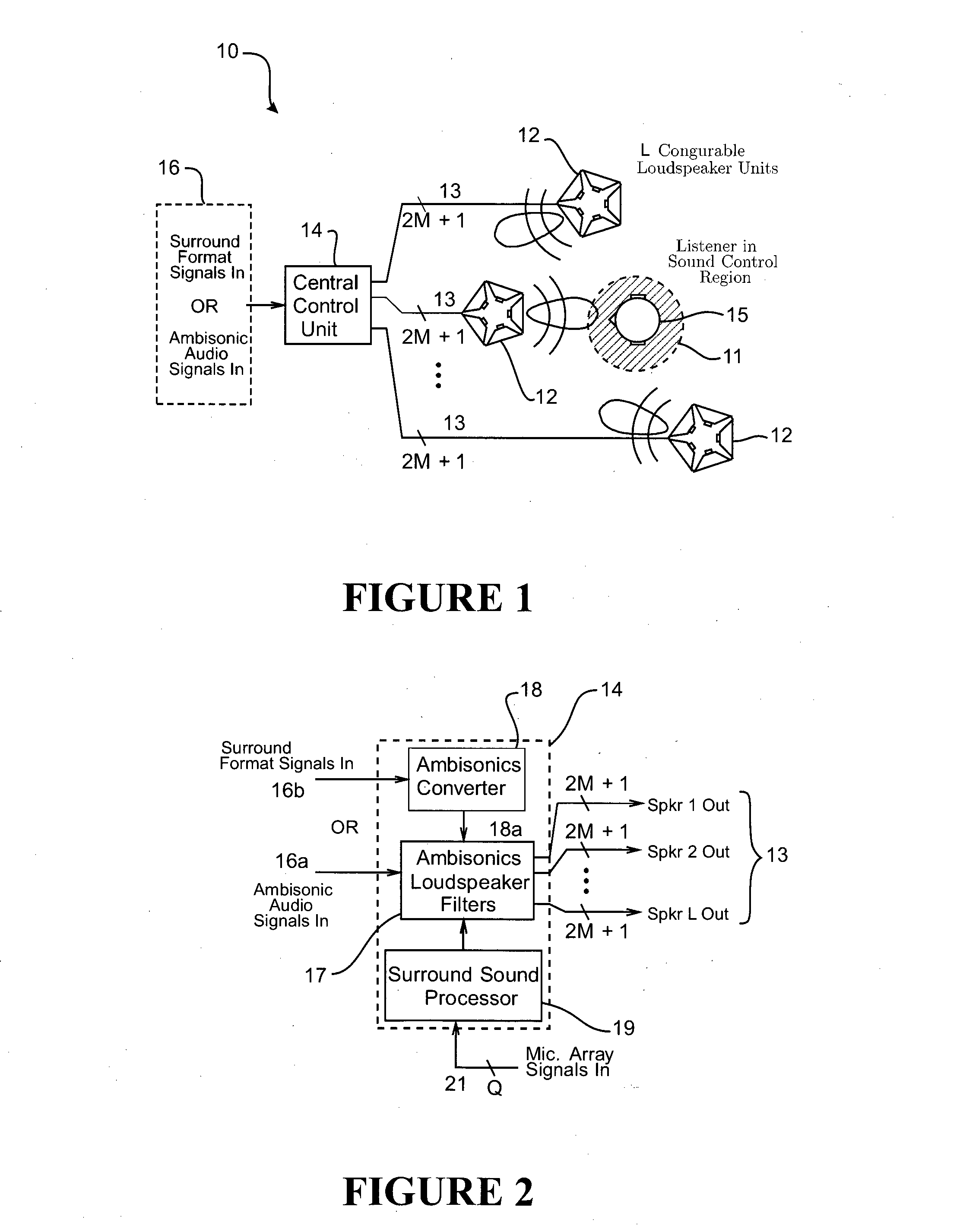
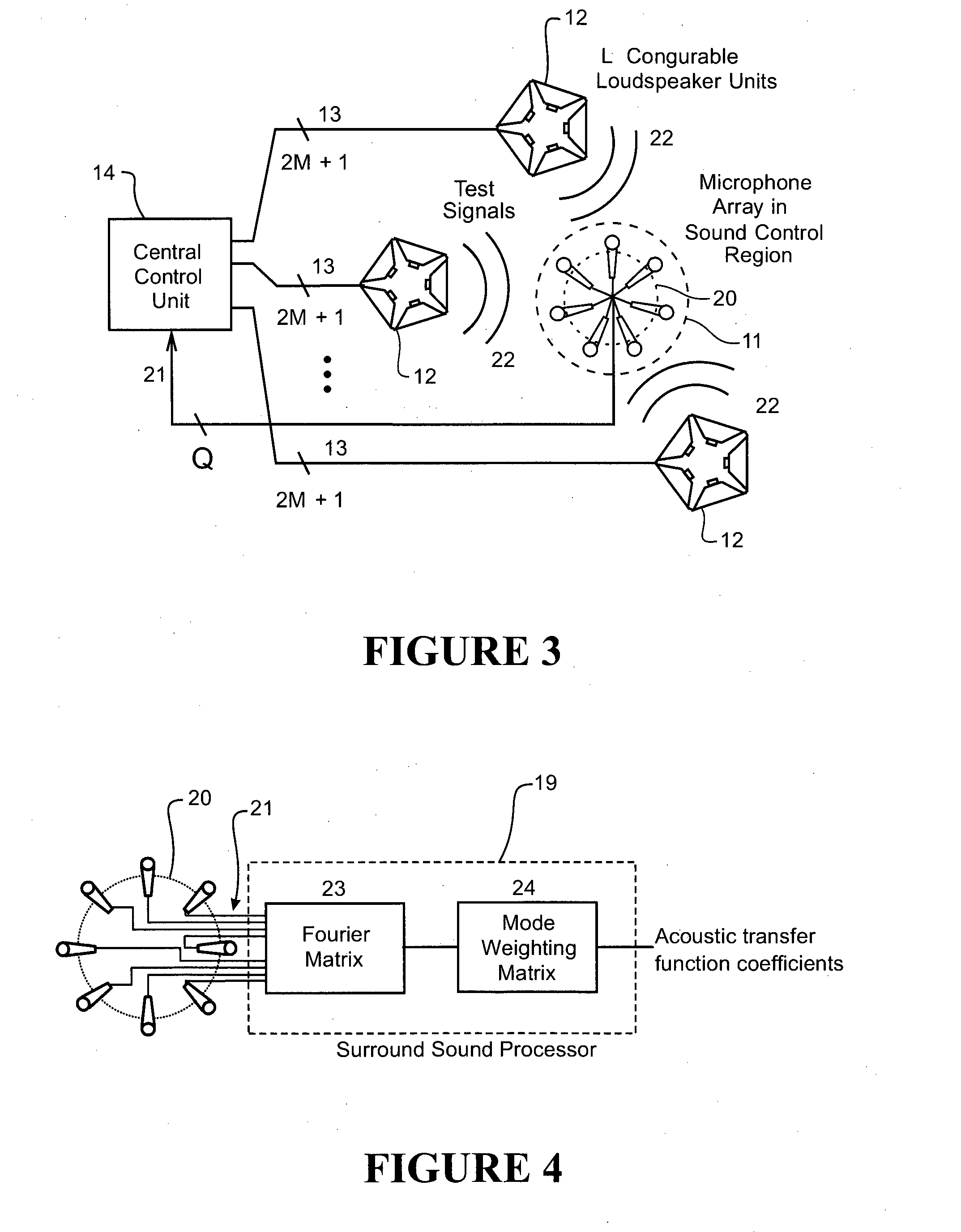
Surround Sound System
ActiveUS20130223658A1Constant controlSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsAcoustic transfer functionVocal tract
A surround sound system for reproducing a spatial sound field in a sound control region within a room having at least one sound reflective surface. The system uses multiple steerable loudspeakers located about the sound control region, each loudspeaker having a plurality of different individual directional response channels being controlled by respective speaker input signals to generate sound waves emanating from the loudspeaker with a desired overall directional response. A control unit connected drives each of the loudspeakers and has pre-configured filters based on measured acoustic transfer functions for the room for filtering the input spatial audio signals to generate the speaker input signals for all the loudspeakers to generate sound waves with co-ordinated overall directional responses that combine together at the sound control region in the form of either direct sound or reflected sound from the reflective surface(s) of the room to reproduce the spatial sound field.
Owner:CALLAGHAN INNOVATION
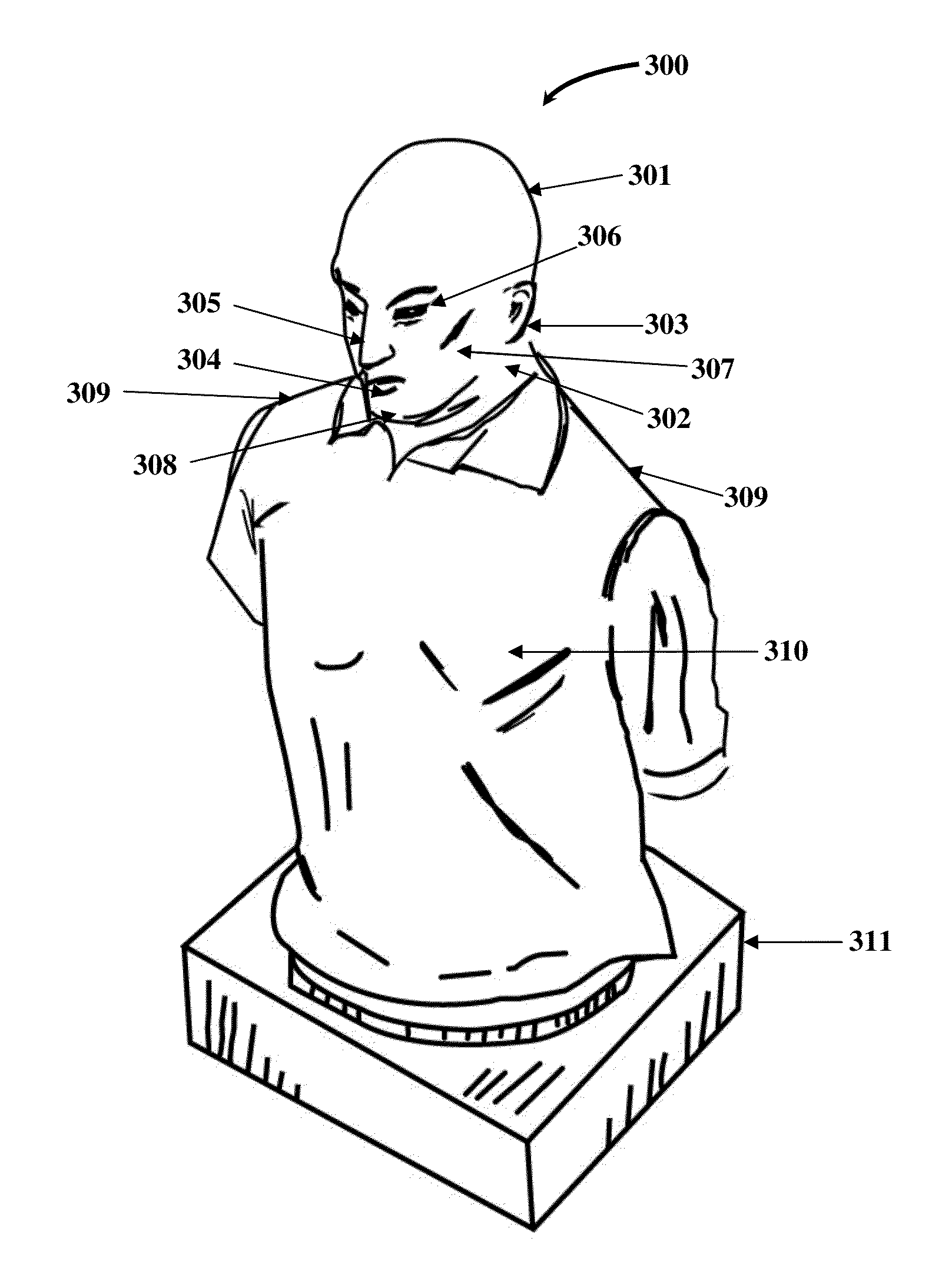
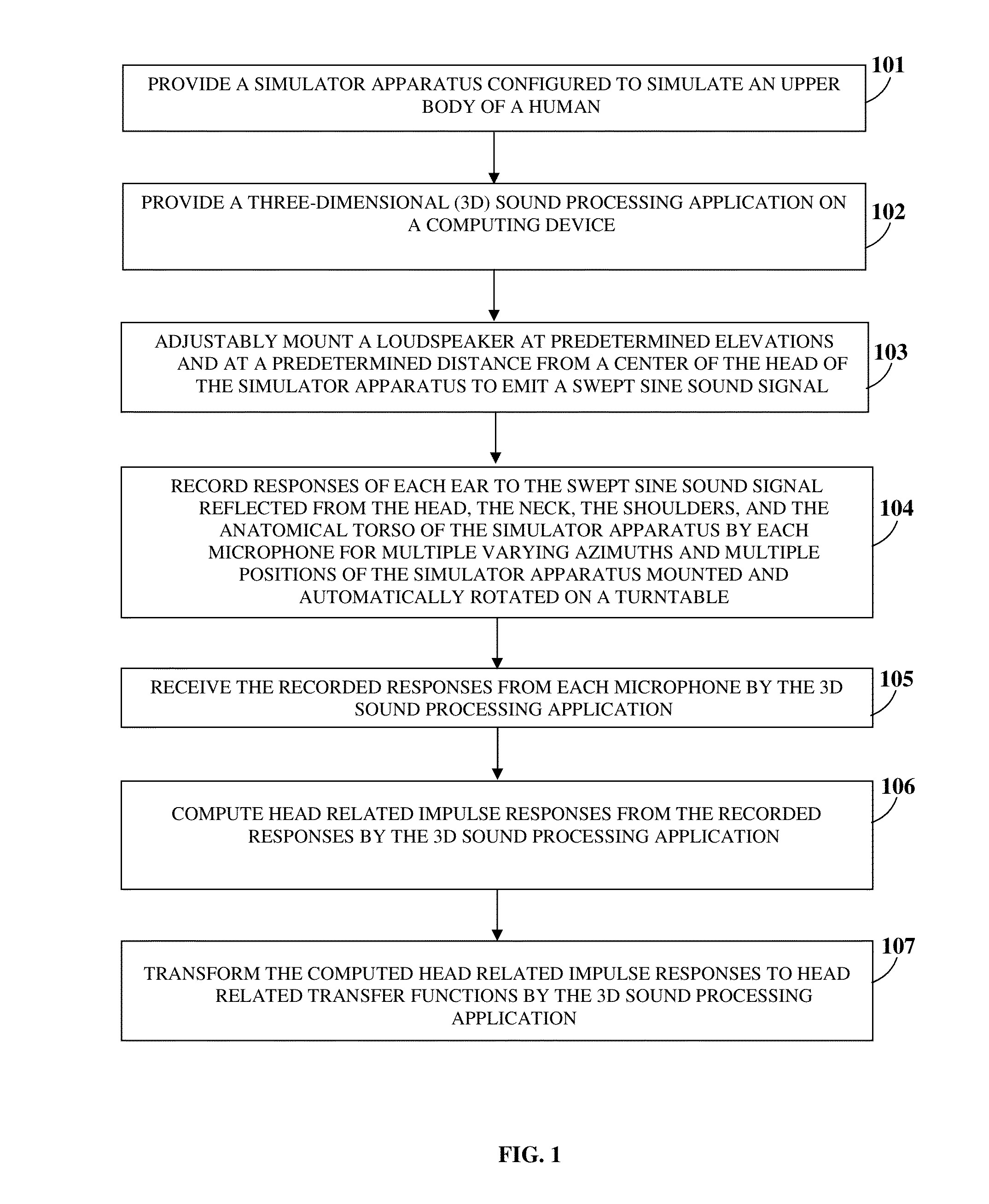
Configurable Three-dimensional Sound System
ActiveUS20140198918A1Improve audio performanceImprove experienceMicrophonesLoudspeakersSound sourcesAudio electronics
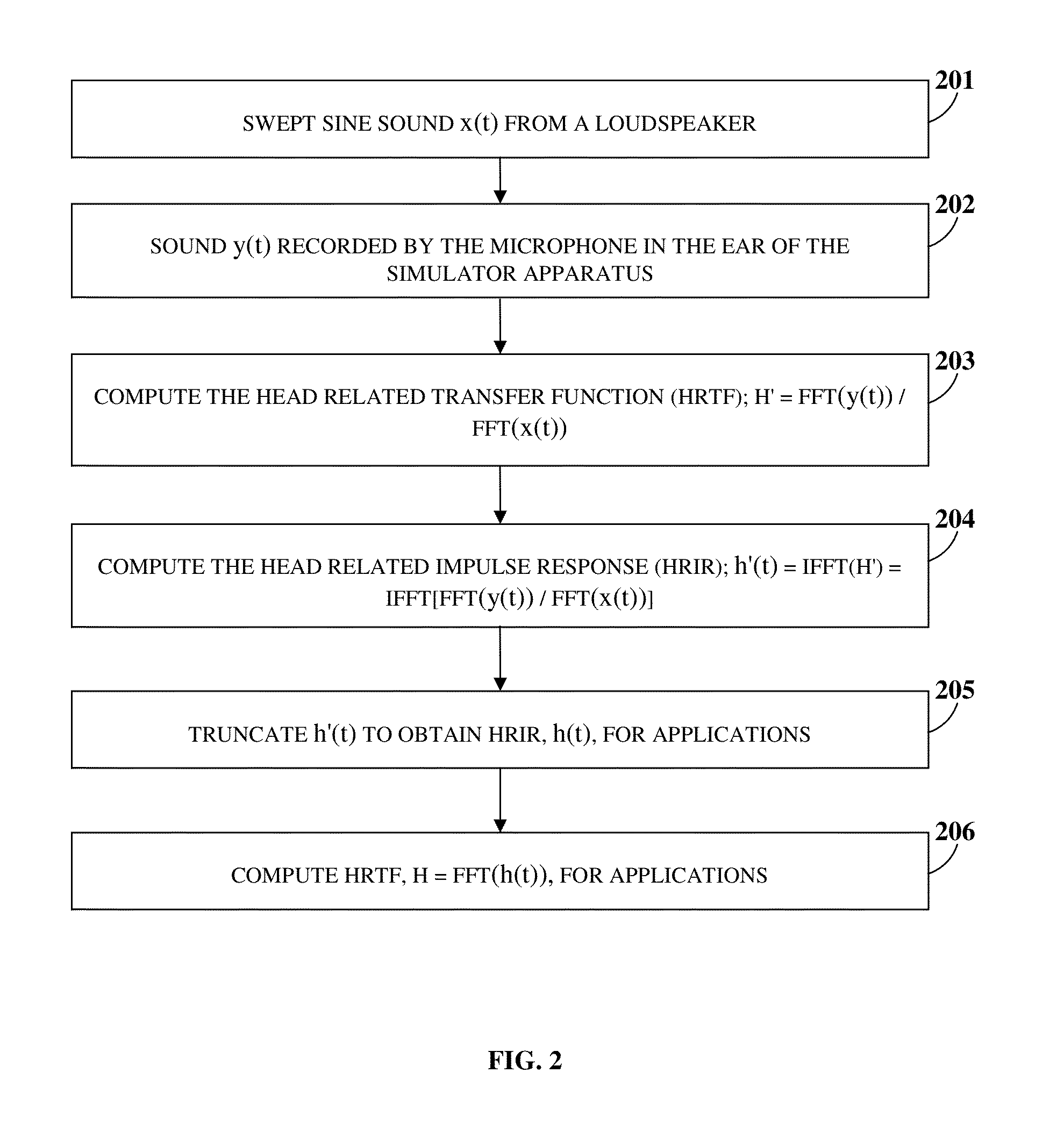
A method and a system for simultaneously generating configurable three-dimensional (3D) sounds are provided. A 3D sound processing application (3DSPA) in operative communication with a microphone array system (MAS) is provided on a computing device. The MAS forms acoustic beam patterns and records sound tracks from the acoustic beam patterns. The 3DSPA generates a configurable sound field on a graphical user interface using recorded or pre-recorded sound tracks. The 3DSPA acquires user selections of configurable parameters associated with sound sources from the configurable sound field. The 3DSPA dynamically processes the sound tracks using the user selections to generate a configurable 3D binaural sound, surround sound, and / or stereo sound. The 3DSPA measures head related transfer functions (HRTFs) in communication with a simulator apparatus that simulates a human's upper body. The 3DSPA generates the binaural sound by processing the sound tracks with the HRTFs based on the user selections.
Owner:LI CREATIVE TECH
Apparatus for separating particles utilizing engineered acoustic contrast capture particles
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Device and method for converting spatial audio signal
ActiveUS20100329466A1Promote reproductionPromote conversionSignal processingLoudspeaker signals distributionSound sourcesHeadphones
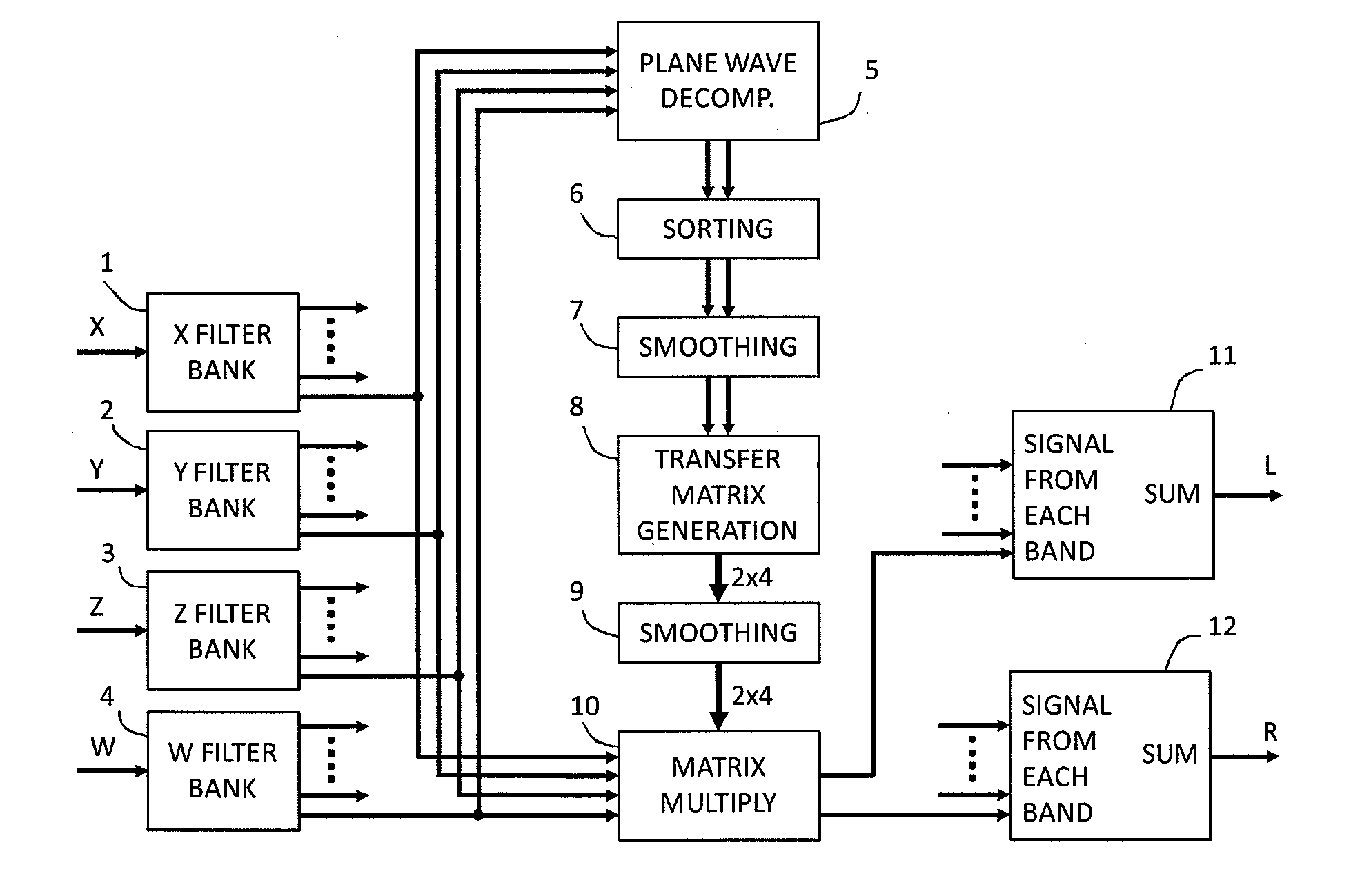
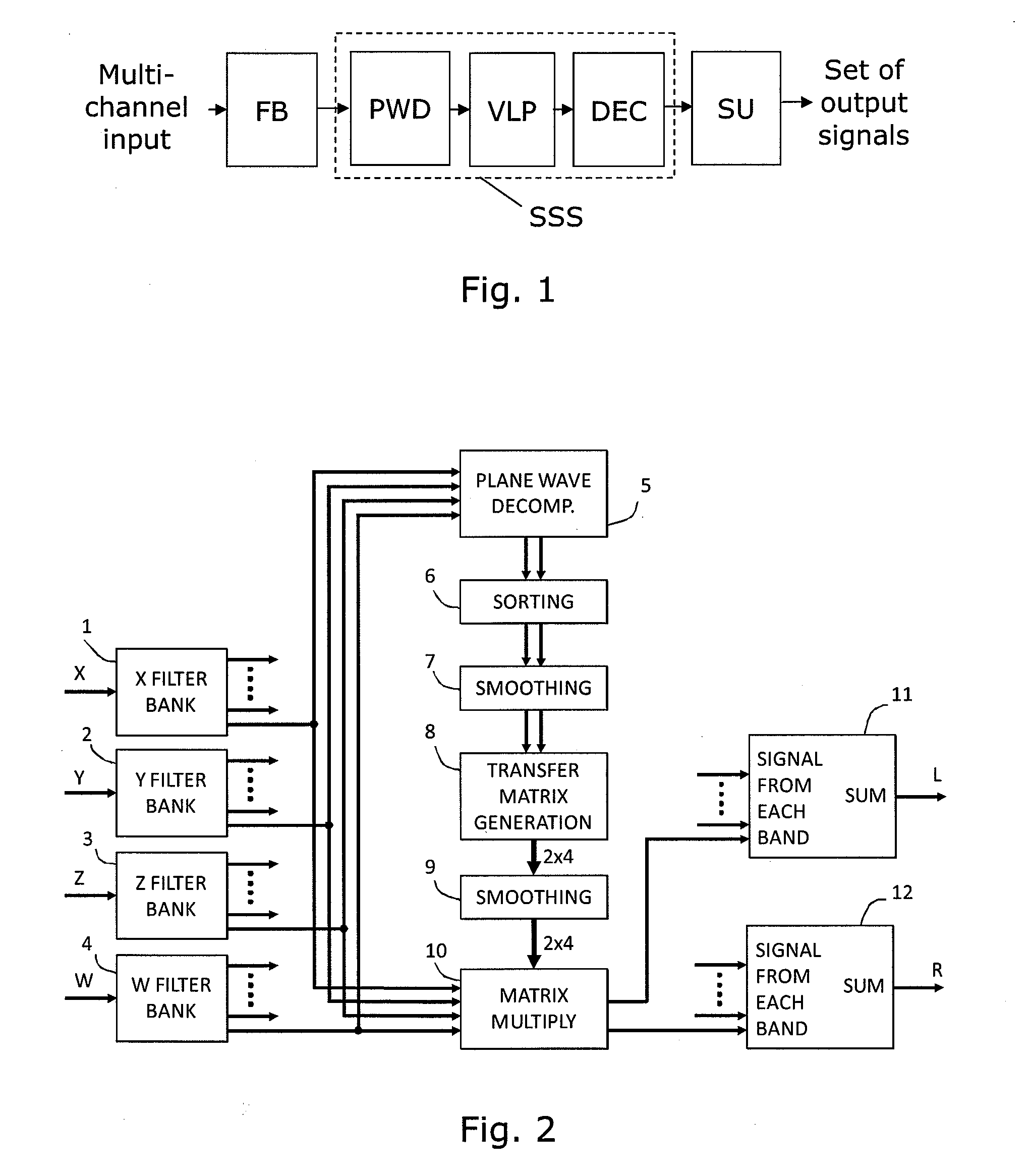
An audio processor for converting a multi-channel audio input signal, such as a B-format sound field signal, into a set of audio output signals, such as a set of two or more audio output signals arranged for headphone reproduction or for playback over an array of loudspeakers. A filter bank splits each of the input channels into frequency bands. The input signal is decomposed into plane waves to determine one or two dominant sound source directions. The(se) are used to determine a set of virtual loudspeaker positions selected such that the dominant direction(s) coincide(s) with virtual loudspeaker positions. The input signal is decoded into virtual loudspeaker signals corresponding to each of the virtual loudspeaker positions, and the virtual loudspeaker signals are processed with transfer functions suitable to create the illusion of sound emanating from the directions of the virtual loudspeakers. A high spatial fidelity is obtained due to the coincidence of virtual loudspeaker positions and the determined dominant sound source direction(s). Improved performance can be obtained in the case where Head-Related Transfer Functions are used by differentiating the phase of a high frequency part of the HRTFs with respect to frequency, followed by a corresponding integration of this part with respect to frequency after combining the components of HRTFs from different directions.
Owner:HARPEX LTD
Implantable wireless accoustic stimulators with high energy conversion efficiencies
ActiveUS20130197609A1Improve isotropyEfficient of acoustic powerPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityAcoustic energy
Receiver-stimulator with folded or rolled up assembly of piezoelectric components, causing the receiver-stimulator to operate with a high degree of isotropy are disclosed. The receiver-stimulator comprises piezoelectric components, rectifier circuitry, and at least two stimulation electrodes. Isotropy allows the receiver-stimulator to be implanted with less concern regarding the orientation relative the transmitted acoustic field from an acoustic energy source.
Owner:EBR SYST
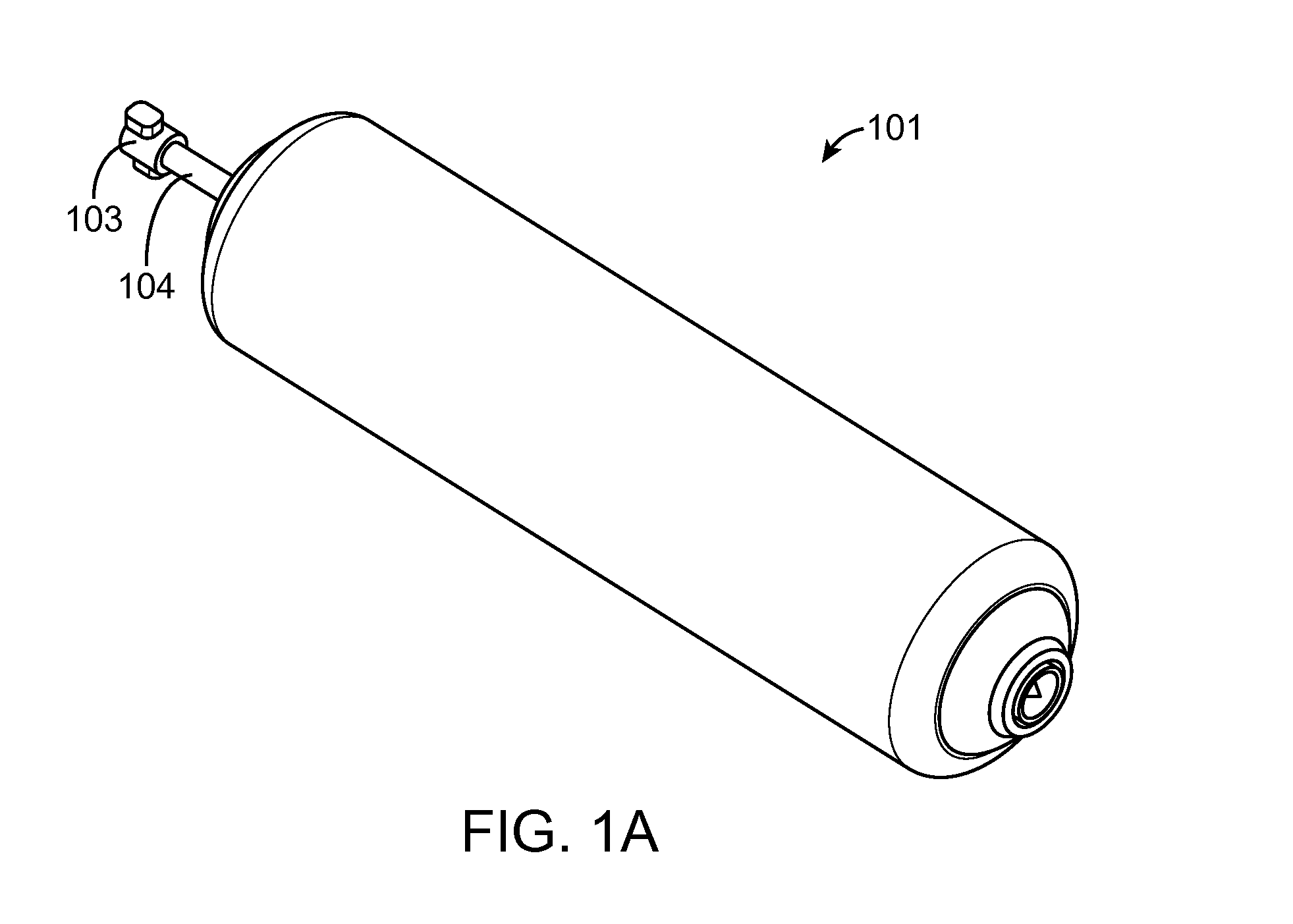
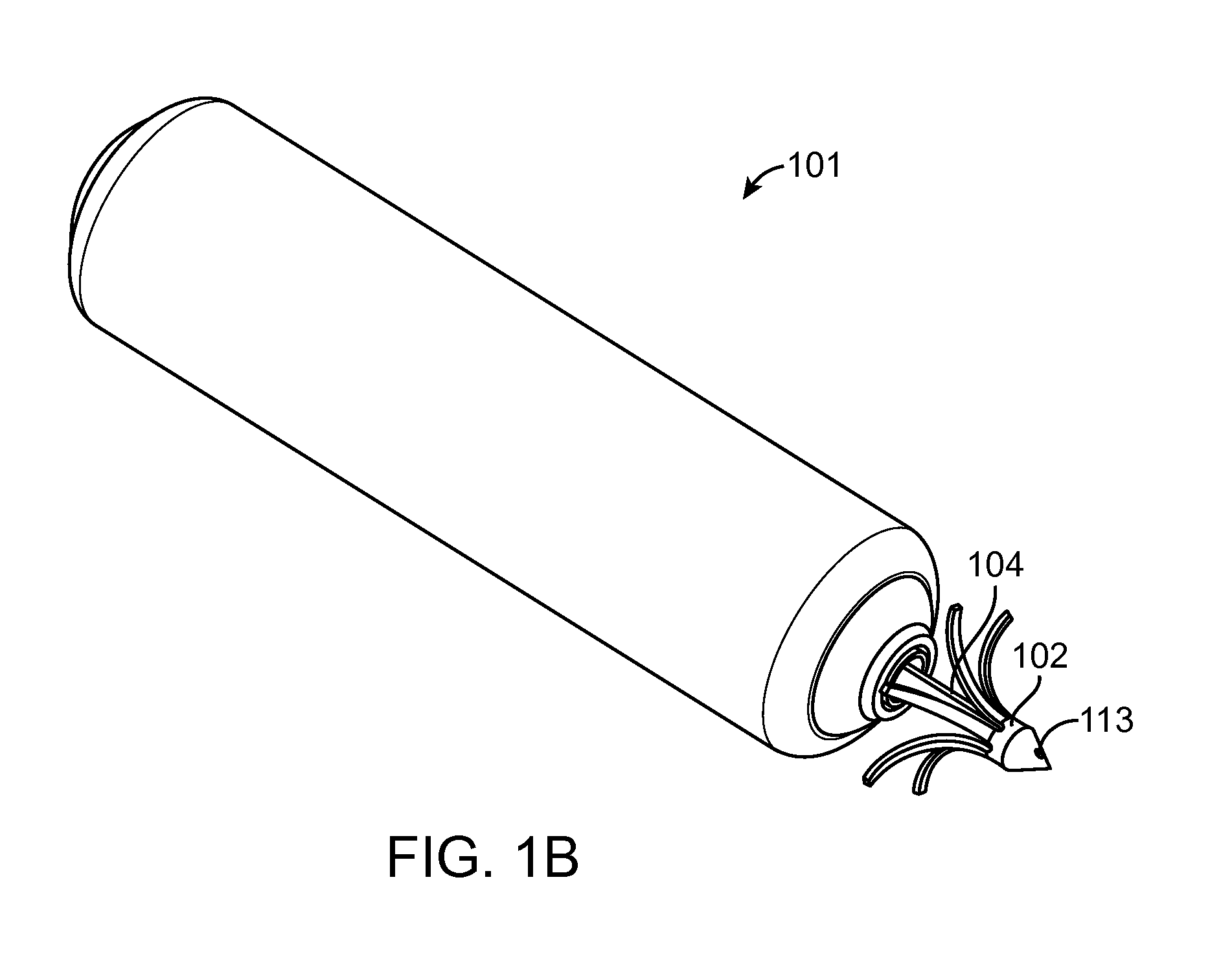
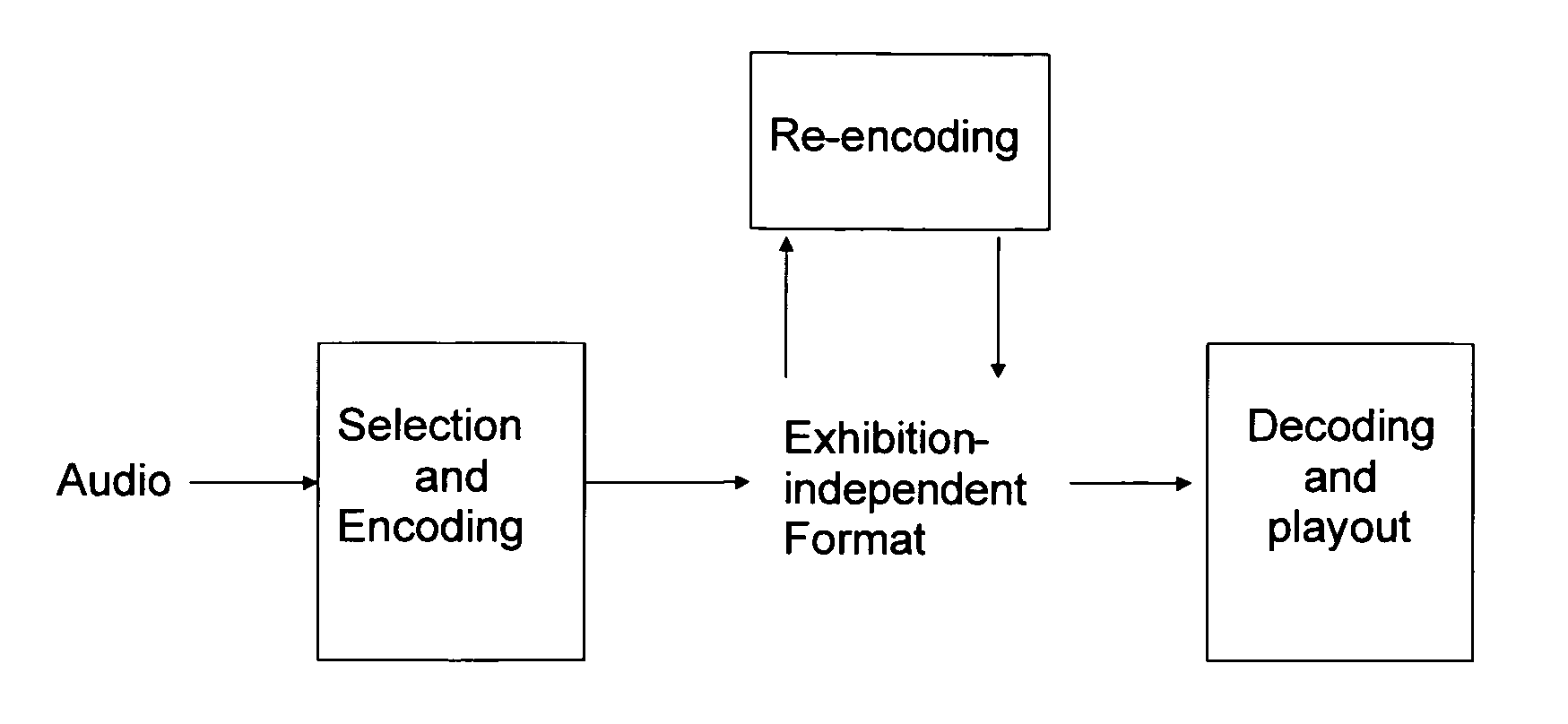
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional acoustic field encoding and optimal reconstruction
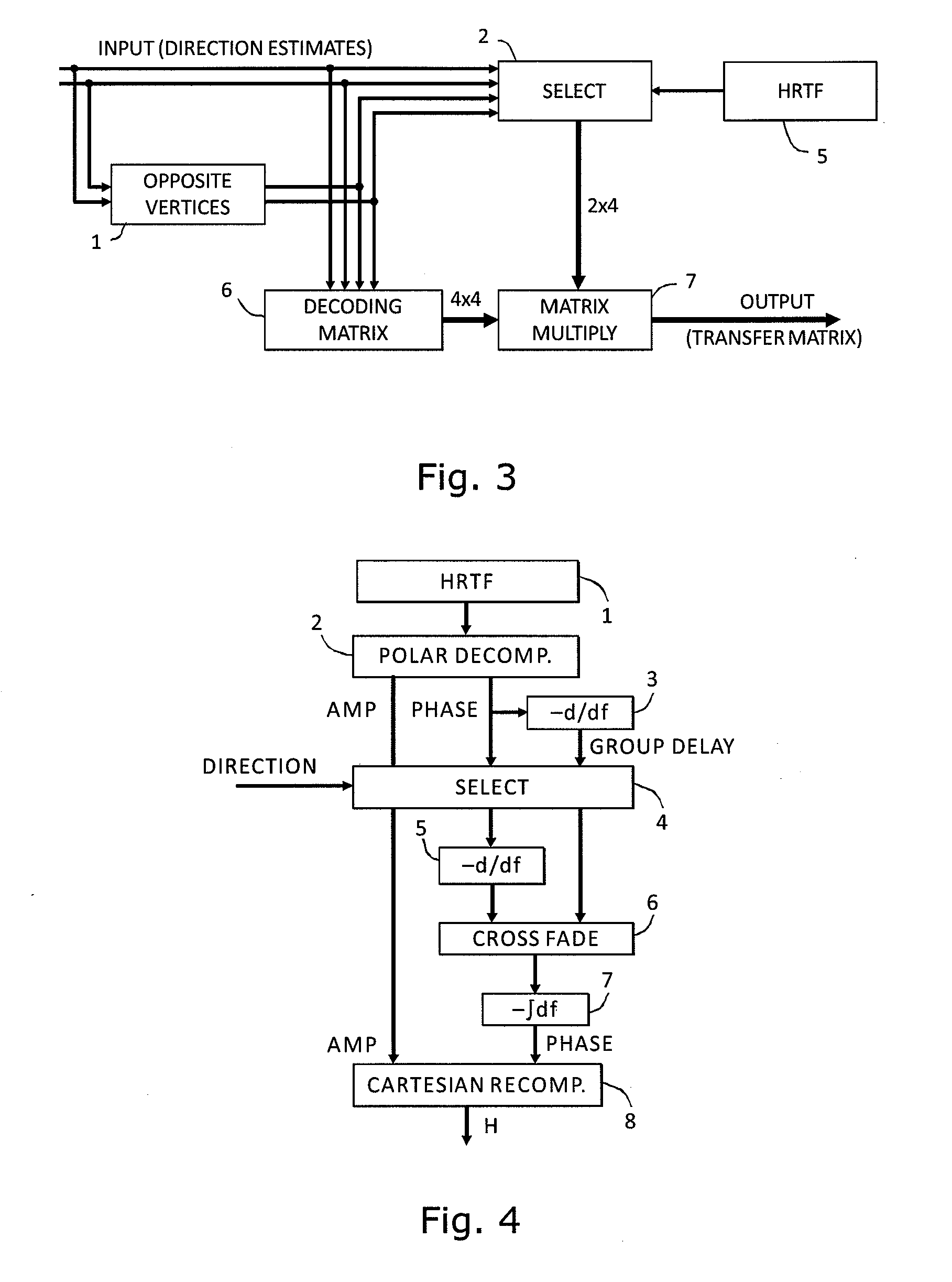
ActiveUS20110305344A1Exact reproductionIncrease the areaSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsDecoding methodsVocal tract
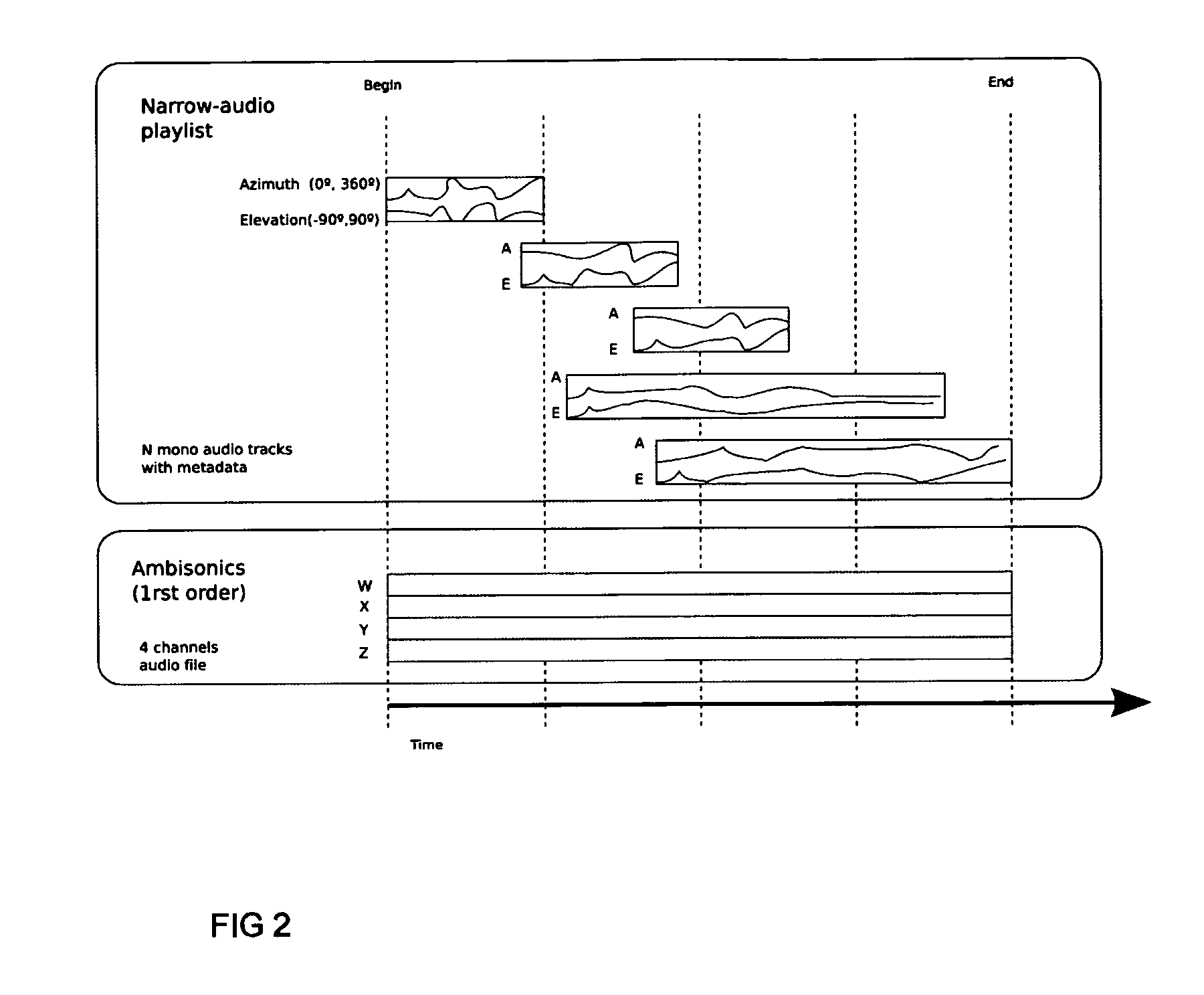
A method and apparatus to encode audio with spatial information in a manner that does not depend on the exhibition setup, and to decode and play out optimally for any given exhibition setup, maximizing the sweet-spot area, and including setups with loudspeakers at different heights, and headphones. The part of the audio that requires very precise localization is encoded into a set of mono tracks with associated directional parameters, whereas the remaining audio is encoded into a set of Ambisonics tracks of a chosen order and mixture. Upon specification of a given exhibition system, the exhibition-independent format is decoded adapting to the specified system, by using different decoding methods for each assigned group.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
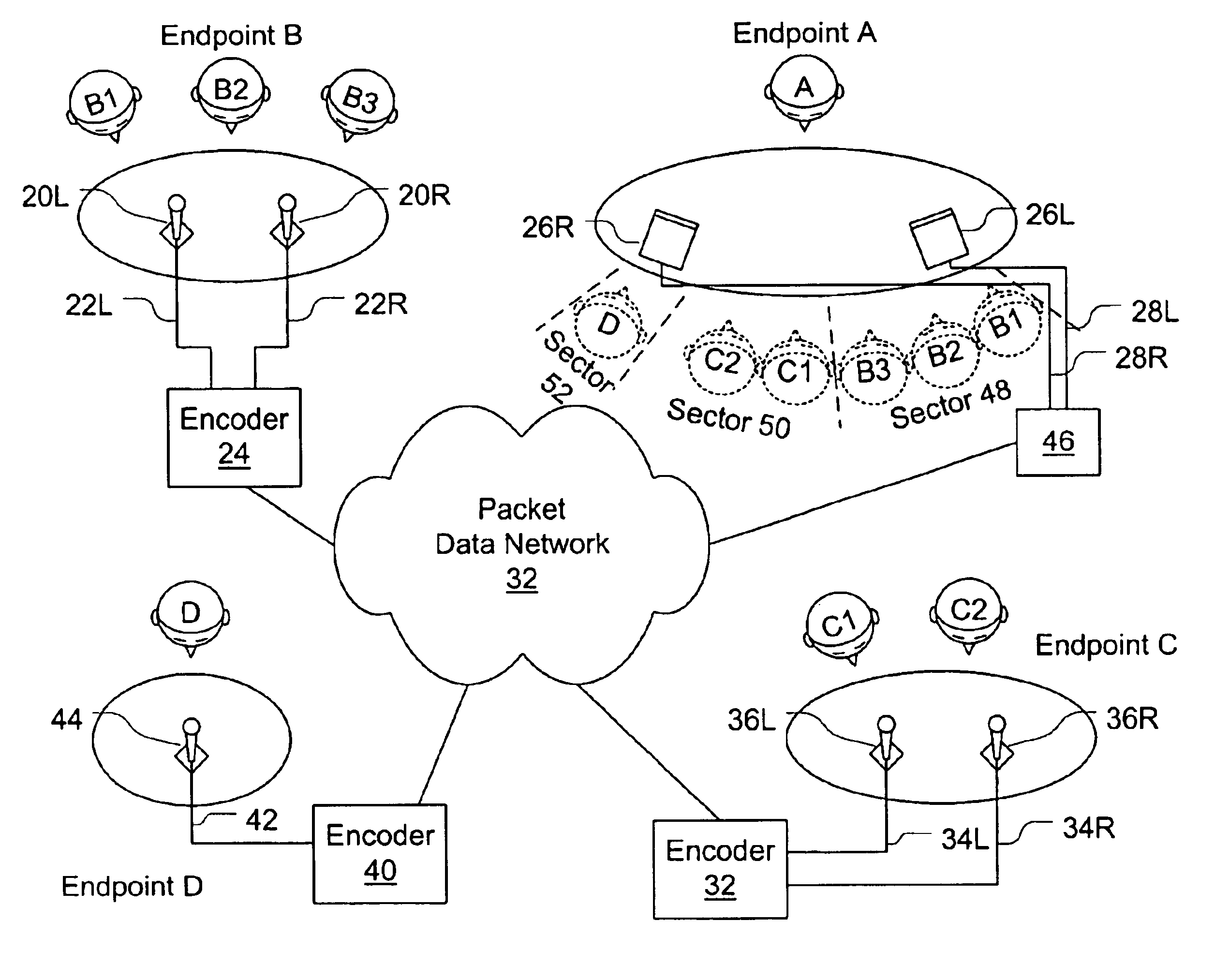
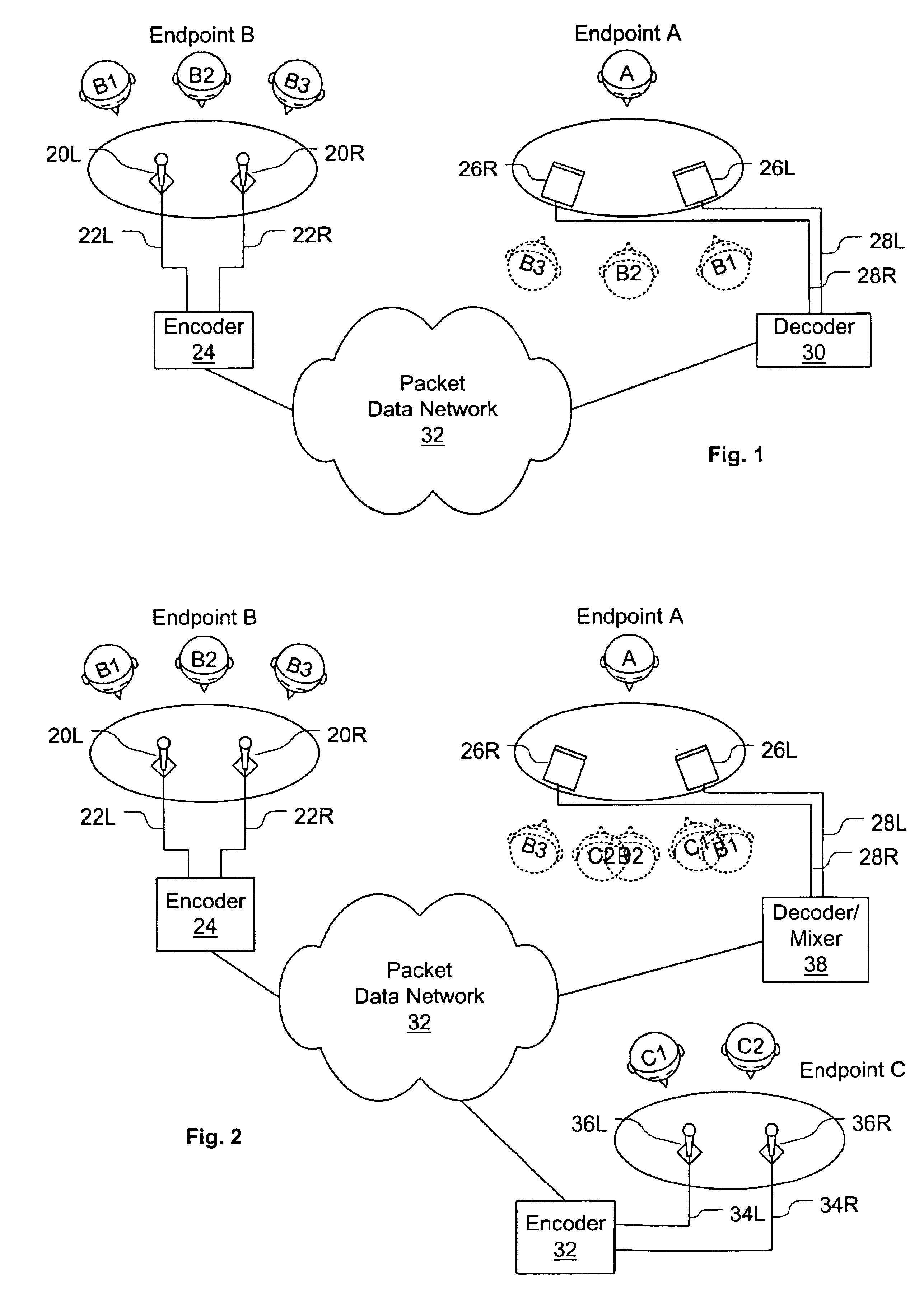
System and method for stereo conferencing over low-bandwidth links
InactiveUS6973184B1Satisfactory sound qualityTangible benefitTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsPublic address systemsVocal tractSpeech sound
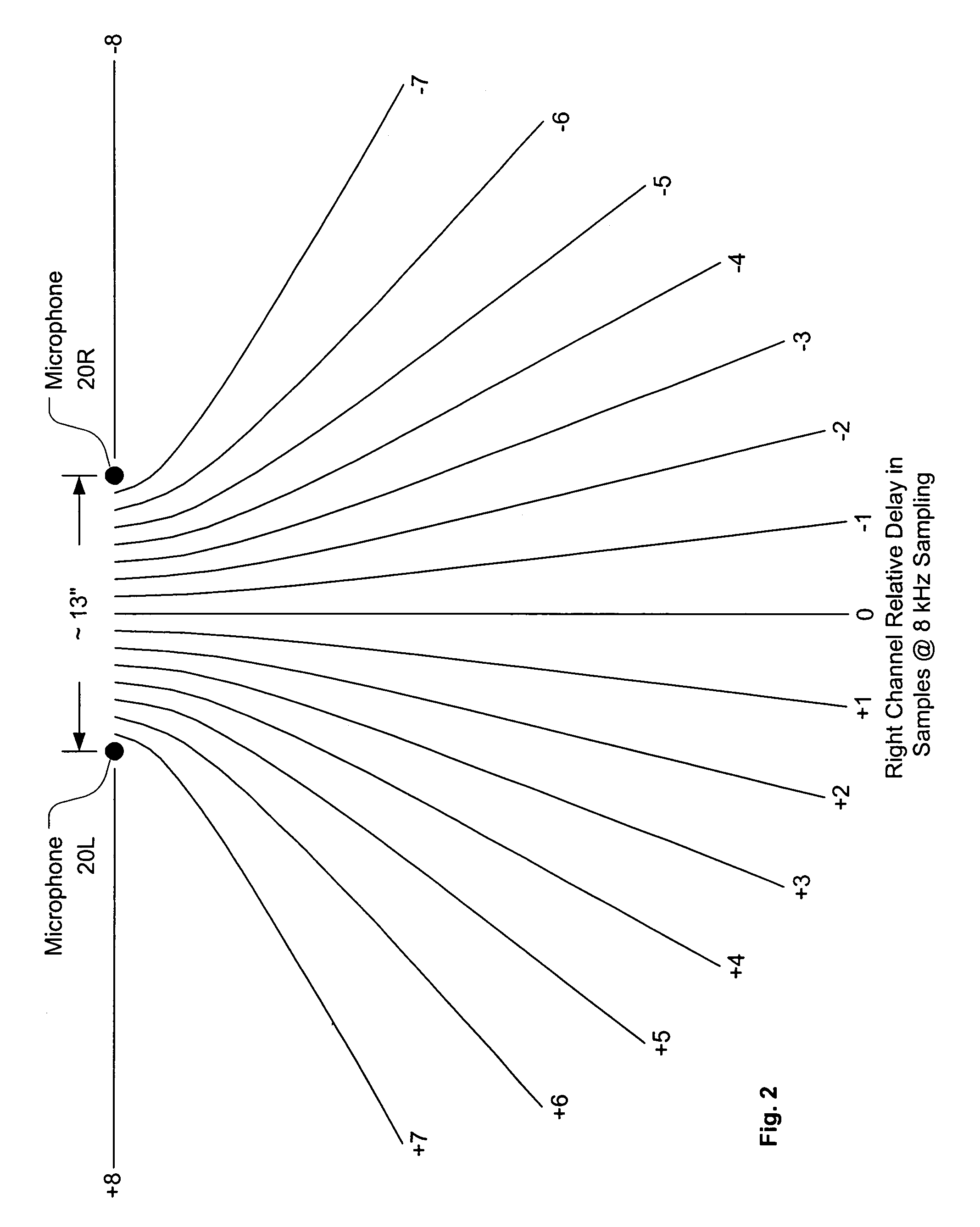
Systems and methods are disclosed for packet voice conferencing. An encoding system accepts two sound field signals, representing the same sound field sampled at two spatially-separated points. The relative delay between the two sound field signals is detected over a given time interval. The sound field signals are combined and then encoded as a single audio signal, e.g., by a method suitable for monophonic VoIP. The encoded audio payload and the relative delay are placed in one or more packets and sent to a decoding device via the packet network. The decoding device uses the relative delay to drive a playout splitter—once the encoded audio payload has been decoded, the playout splitter creates multiple presentation channels by inserting the transmitted relative delay in the decoded signal for one (or more) of the presentation channels. The listener thus perceives a speaker's voice as originating from a location related to the speaker's physical position at the other end of the conference. An advantage of these embodiments is that a pseudo-stereo conference can be conducted with virtually the same bandwidth as a monophonic conference.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and device for enhanced sound field reproduction of spatially encoded audio input signals
ActiveUS20130148812A1Stereophonic circuit arrangementsStereophonic systemsSpatial analysisSpatial encoding
A method for sound field reproduction into a listening area of spatially encoded first audio input signals according to sound field description data using an ensemble of physical loudspeakers. The method includes computing reproduction subspace description data from loudspeaker positioning data describing the subspace in which virtual sources can be reproduced with the physically available setup. Then, second and third audio input signals with associated sound field description data, in which second audio input signals include spatial components of the first audio input signals located within the reproducible subspace and third audio input signals include spatial components of the first audio input signals located outside of the reproducible subspace. A spatial analysis is performed on second audio input signals to extract fourth audio input signals corresponding to localizable sources within the reproducible subspace with associated source positioning data. Components of second audio input signals after spatial analysis are merged with third audio input signals into fifth audio input signals with associated sound field description data for reproduction within the reproducible subspace. Loudspeaker alimentation signals are computed from fourth and fifth audio input signals.
Owner:SENNHEISER ELECTRONICS GMBH & CO KG
Audio channel spatial translation
ActiveUS20050276420A1Reduce the impactLower performance requirementsPseudo-stereo systemsStereophonic arrangmentsSound imageSignal correlation
Using an M:N variable matrix, M audio input signals, each associated with a direction, are translated to N audio output signals, each associated with a direction, wherein N is larger than M, M is two or more and N is a positive integer equal to three or more. The variable matrix is controlled in response to measures of: (1) the relative levels of the input signals, and (2) the cross-correlation of the input signals so that a soundfield generated by the output signals has a compact sound image in the nominal ongoing primary direction of the input signals when the input signals are highly correlated, the image spreading from compact to broad as the correlation decreases and progressively splitting into multiple compact sound images, each in a direction associated with an input signal, as the correlation continues to decrease to highly uncorrelated.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com