Patents
Literature
8630results about How to "Lower performance requirements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
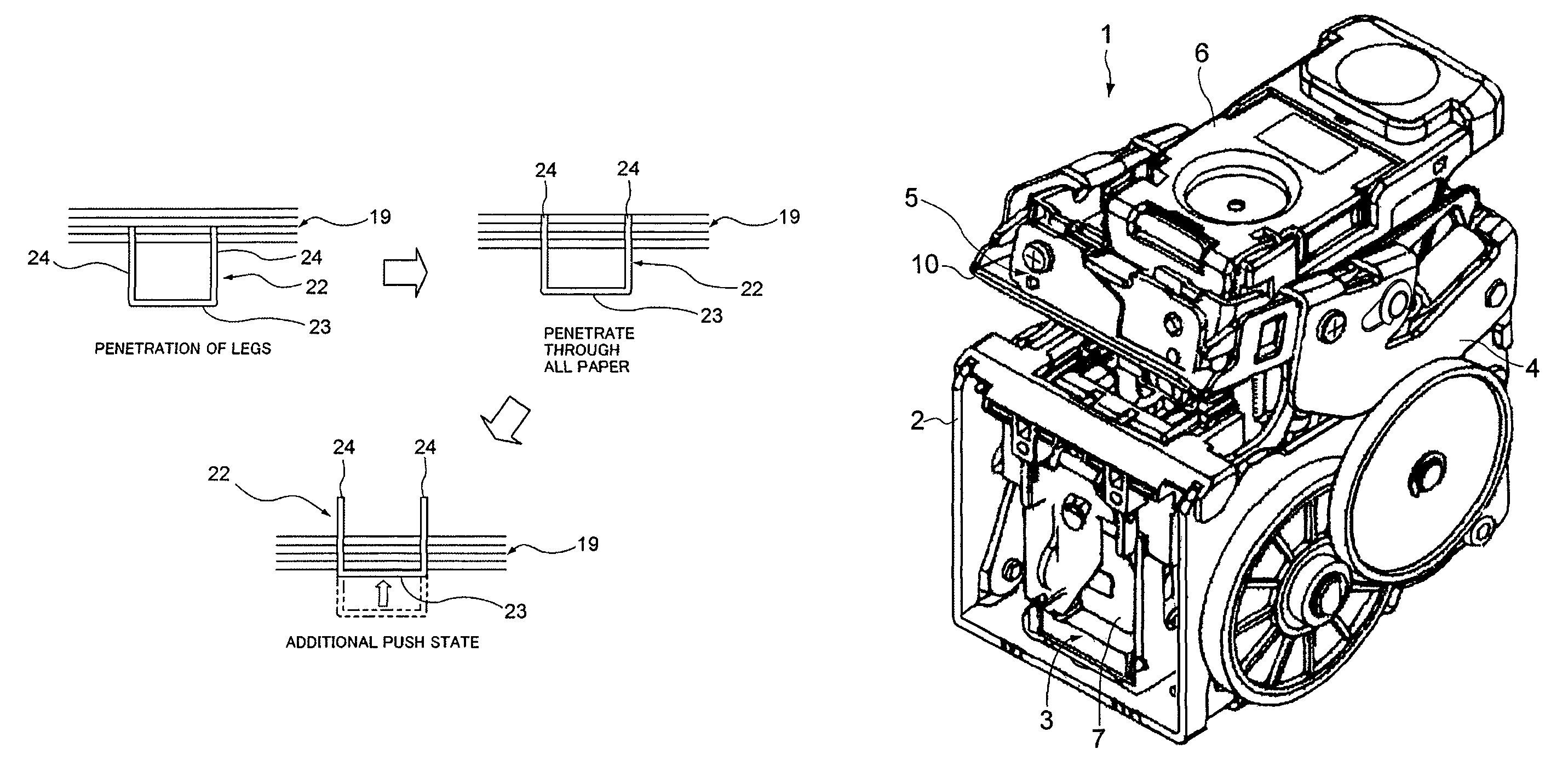
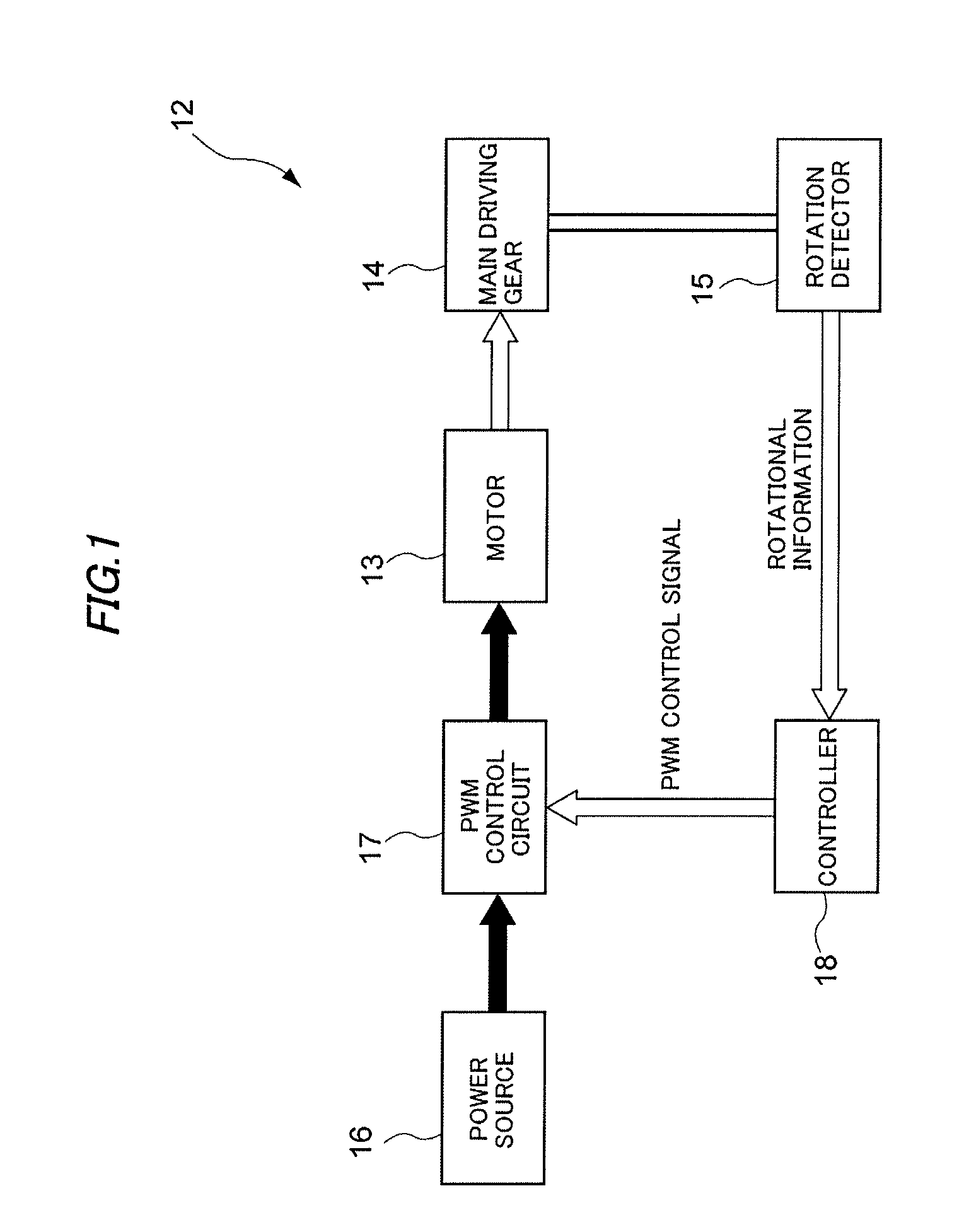
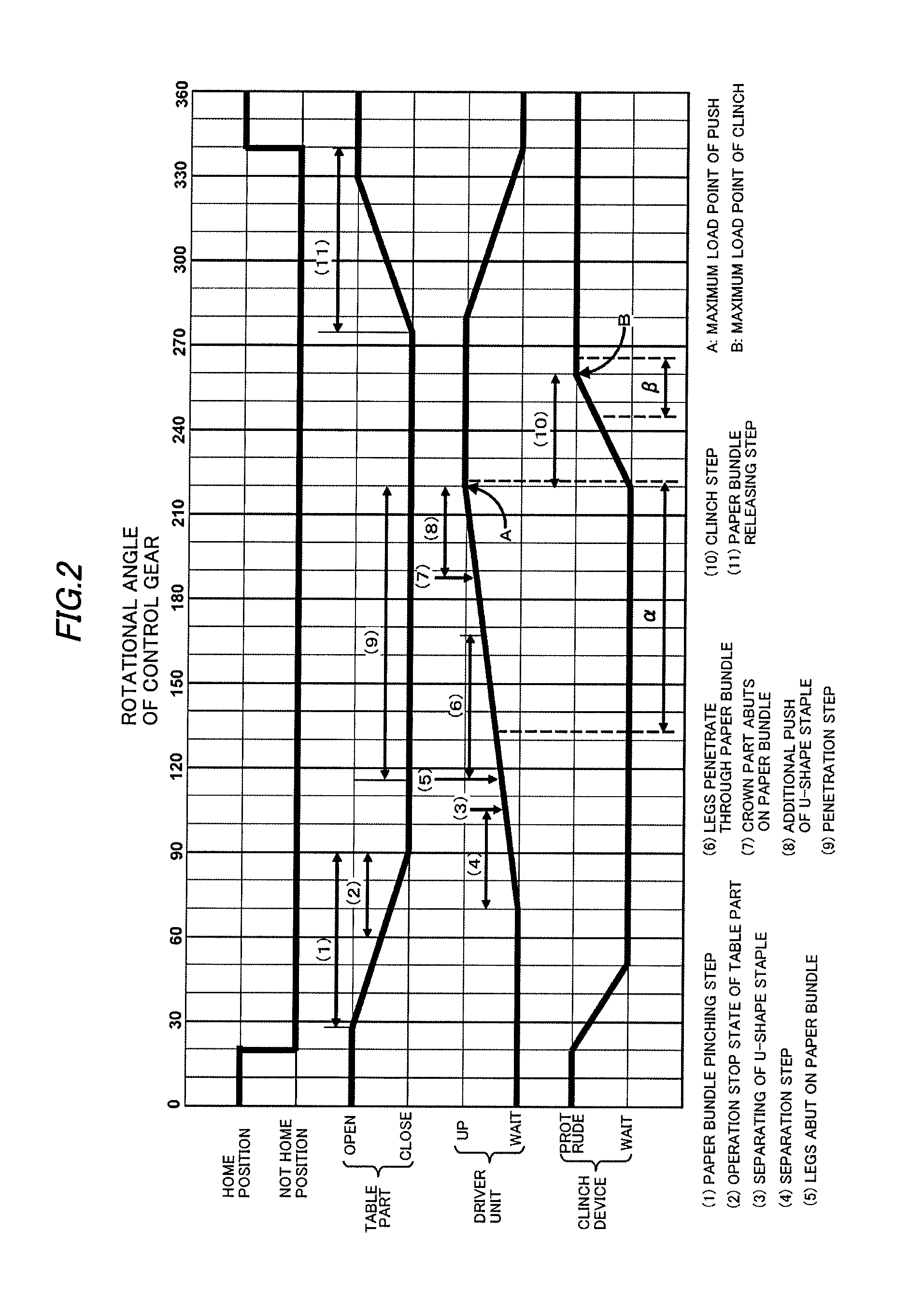
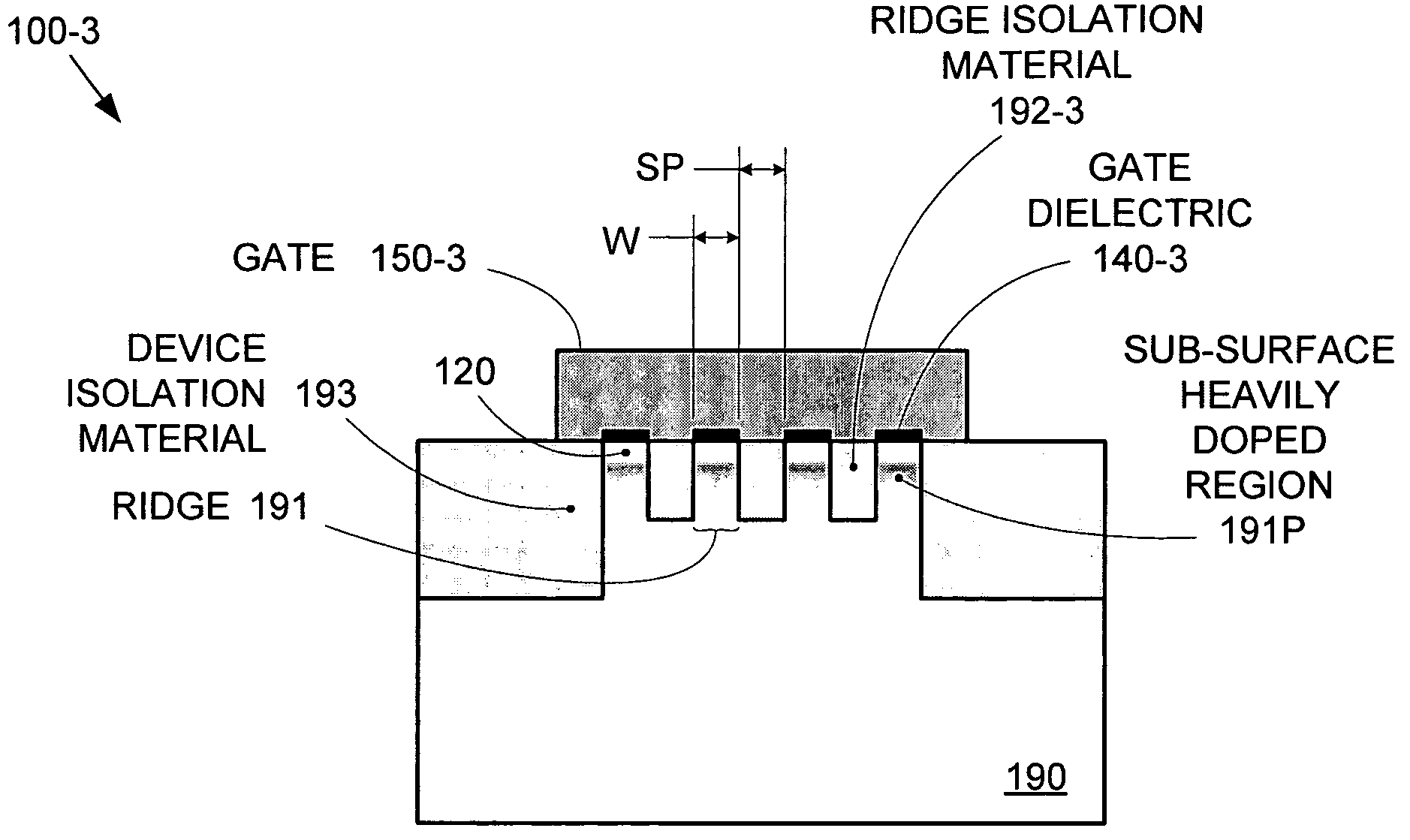
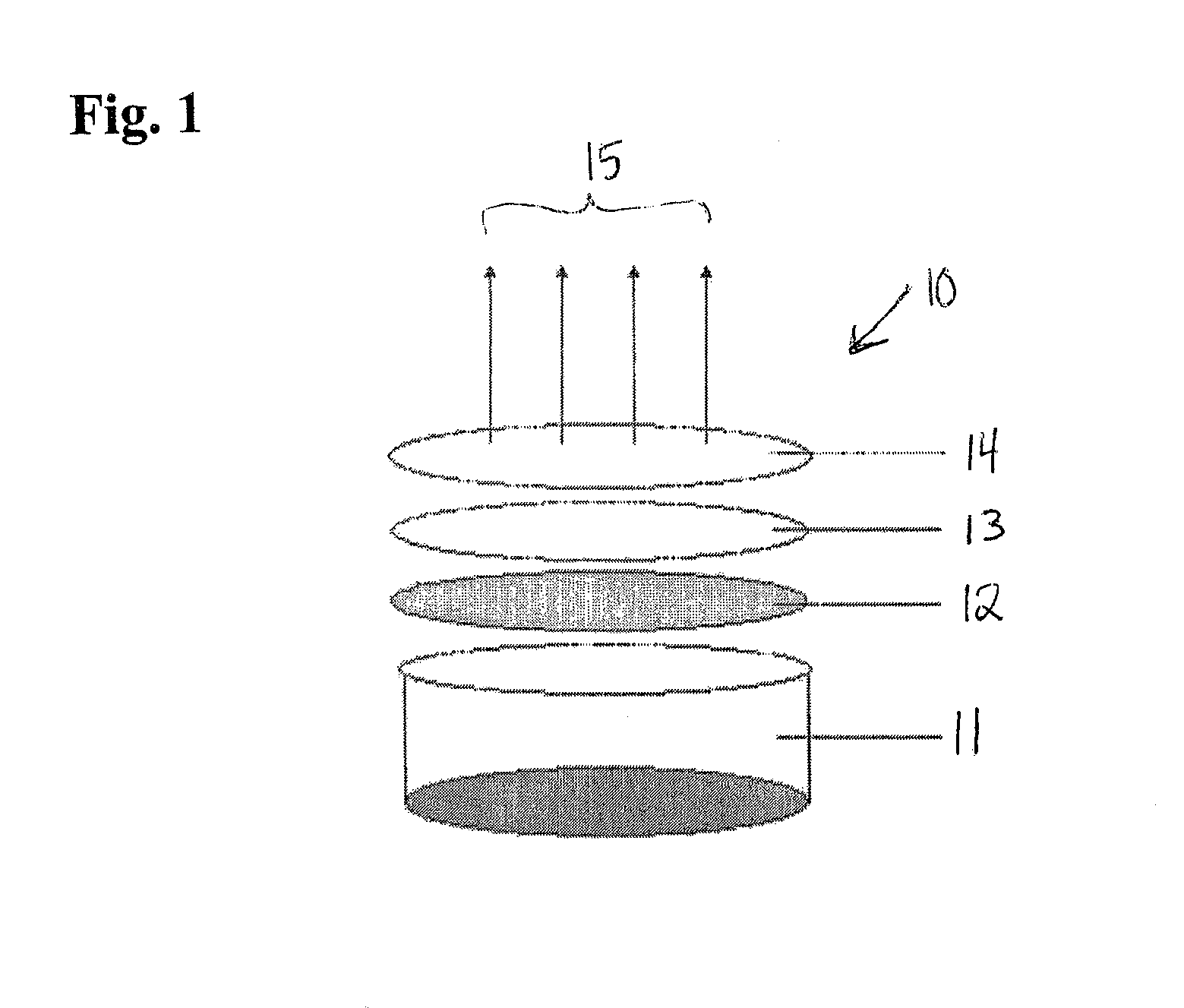
Electric stapler and operation method of electric stapler
ActiveUS8371393B2Reduce running noiseIncrease the number ofStapling toolsDispensing apparatusEngineeringElectric motor
Owner:MAX CO LTD
Process for producing a hydrocarbon component of biological origin
ActiveUS20040230085A1Improve performanceLow densityLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbonsIsomerizationHydrocarbon
The invention relates to a process for producing a hydrocarbon component of biological origin. The process comprises at least two steps, the first one of which is a HDO step and the second one is an isomerization step operated using the counter-current flow principle. A biological raw material containing fatty acids and / or fatty acid esters serves as the feed stock.
Owner:OYJ NESTE OIL +1
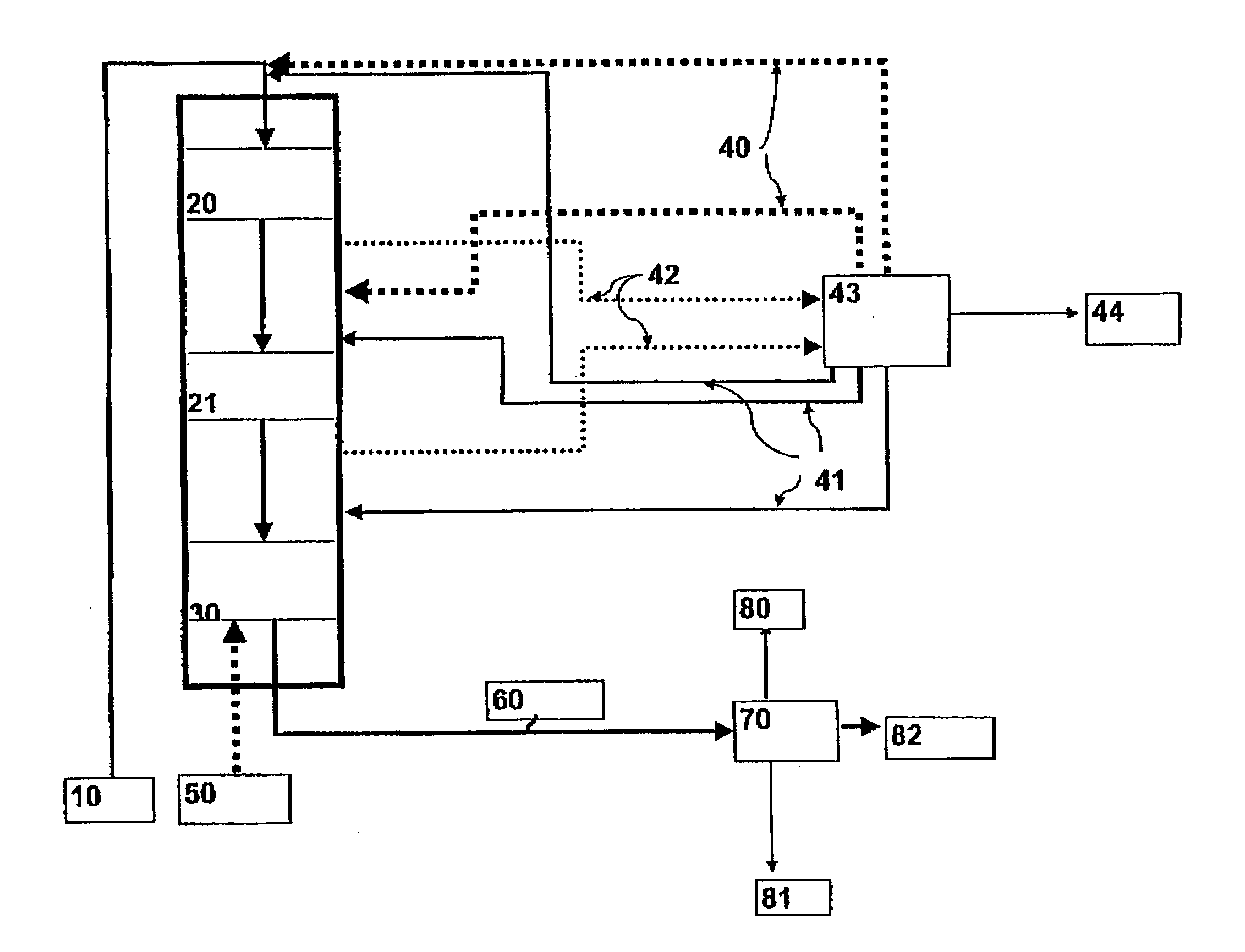
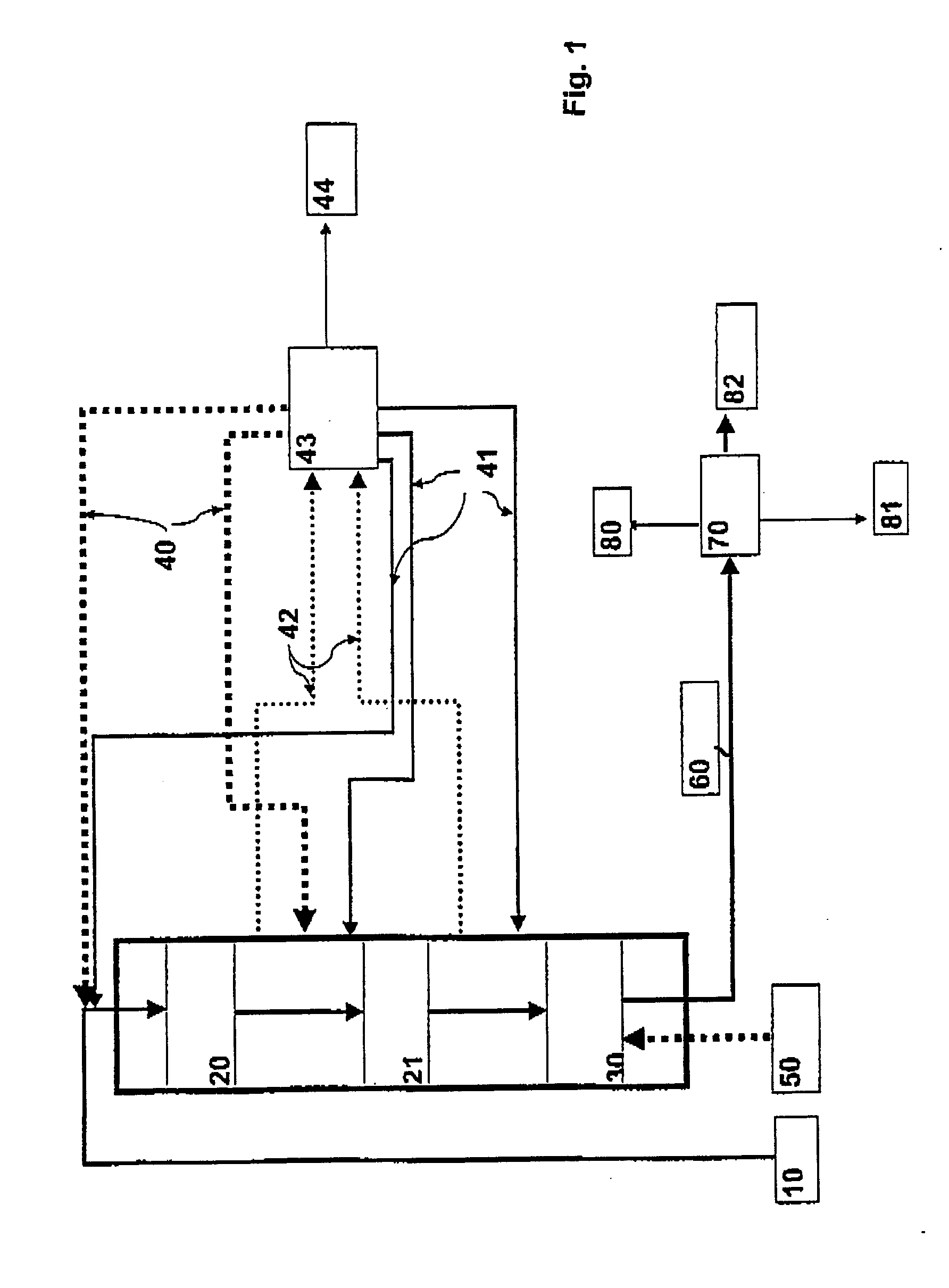
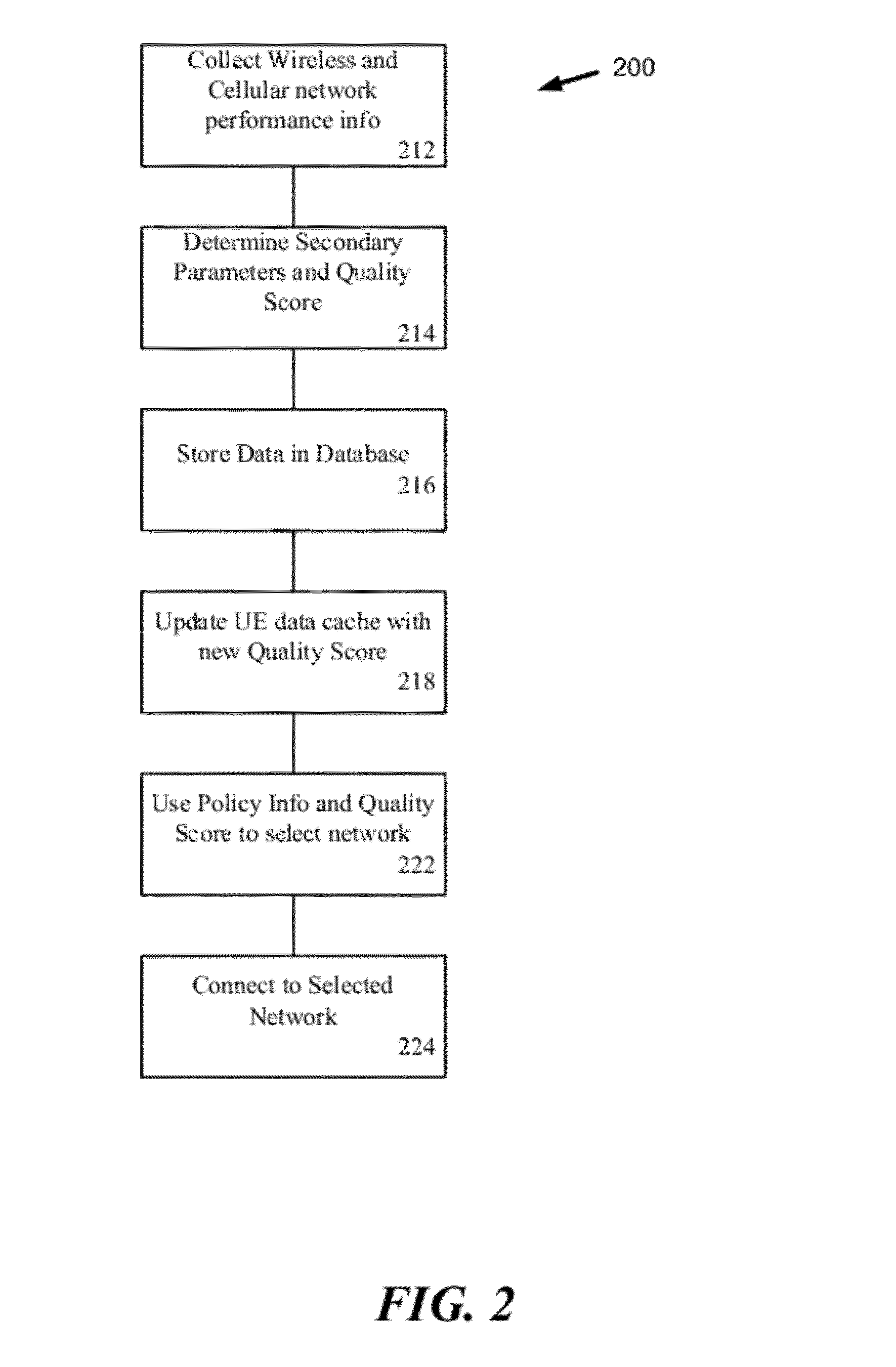
Dynamic Network Connection System and Method
ActiveUS20120196644A1Reduce error rateReduce noiseAssess restrictionRadio transmissionNetwork connectionChoice making
A method and system for selecting a network to establish a connection to from a set of available network includes a network database providing historical information about each of the networks and sends the database information to end user terminals. The end user terminals monitor real-time performance information about each of the available networks and can send this information to the network database. The end user terminals also include network connection policy information which can be used to make the selection decision. The end user terminal determines a network quality score for each available network as a function of the historical information from the network database, the real-time performance information about each available network and the network connection policy information. The end user terminal can select the available network as a function of the network quality score, for example, selecting the available network with the highest network quality score.
Owner:WEFI
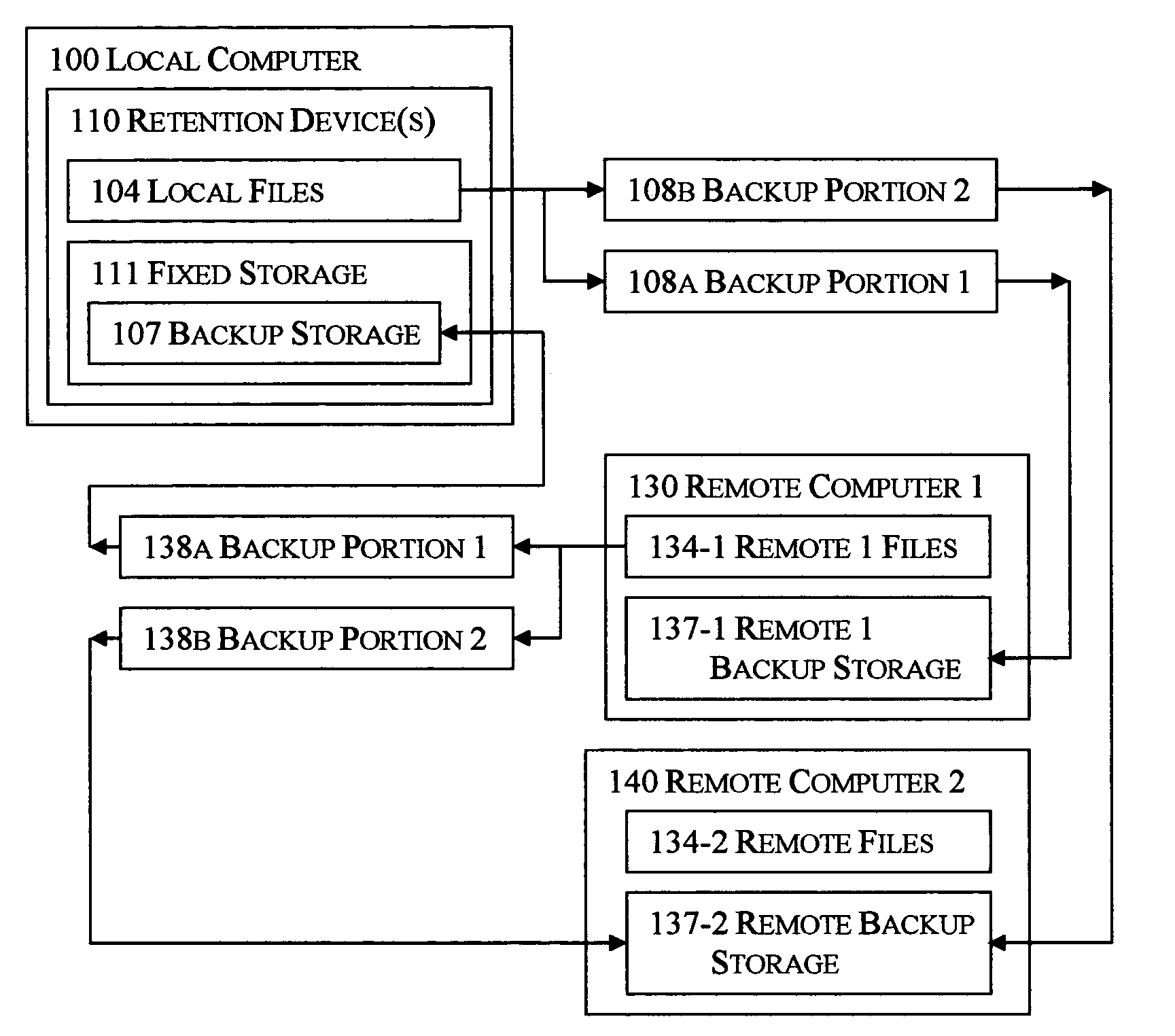
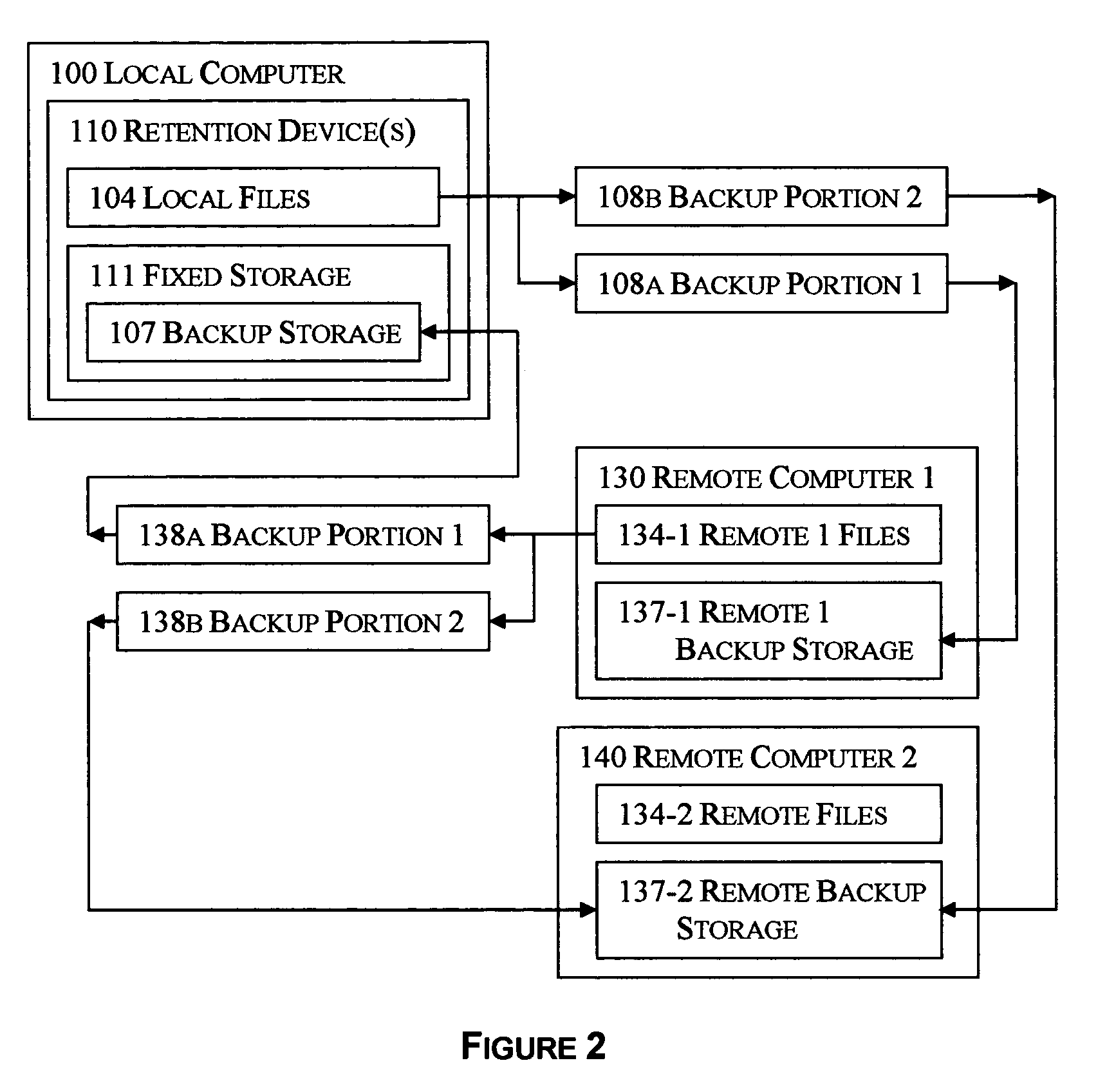
Selective reciprocal backup
InactiveUS7330997B1Risk minimizationIncrease probabilityError detection/correctionMemory systemsNetwork connectionApplication software
The disclosed technology applies the principle of anonymous reciprocity to facilitate remote backups. A local computer stores other computer's backup files, while storing backup copies of local files on other computers connected through a network. Each computer may securely maintain and manage storage for other computers' files. Application may be constrained to a local area network, or work on the Internet. The disclosed technology works in a peer-to-peer environment; no central server is required. The same disclosed technology may also apply to file sharing.
Owner:ODOM GARY
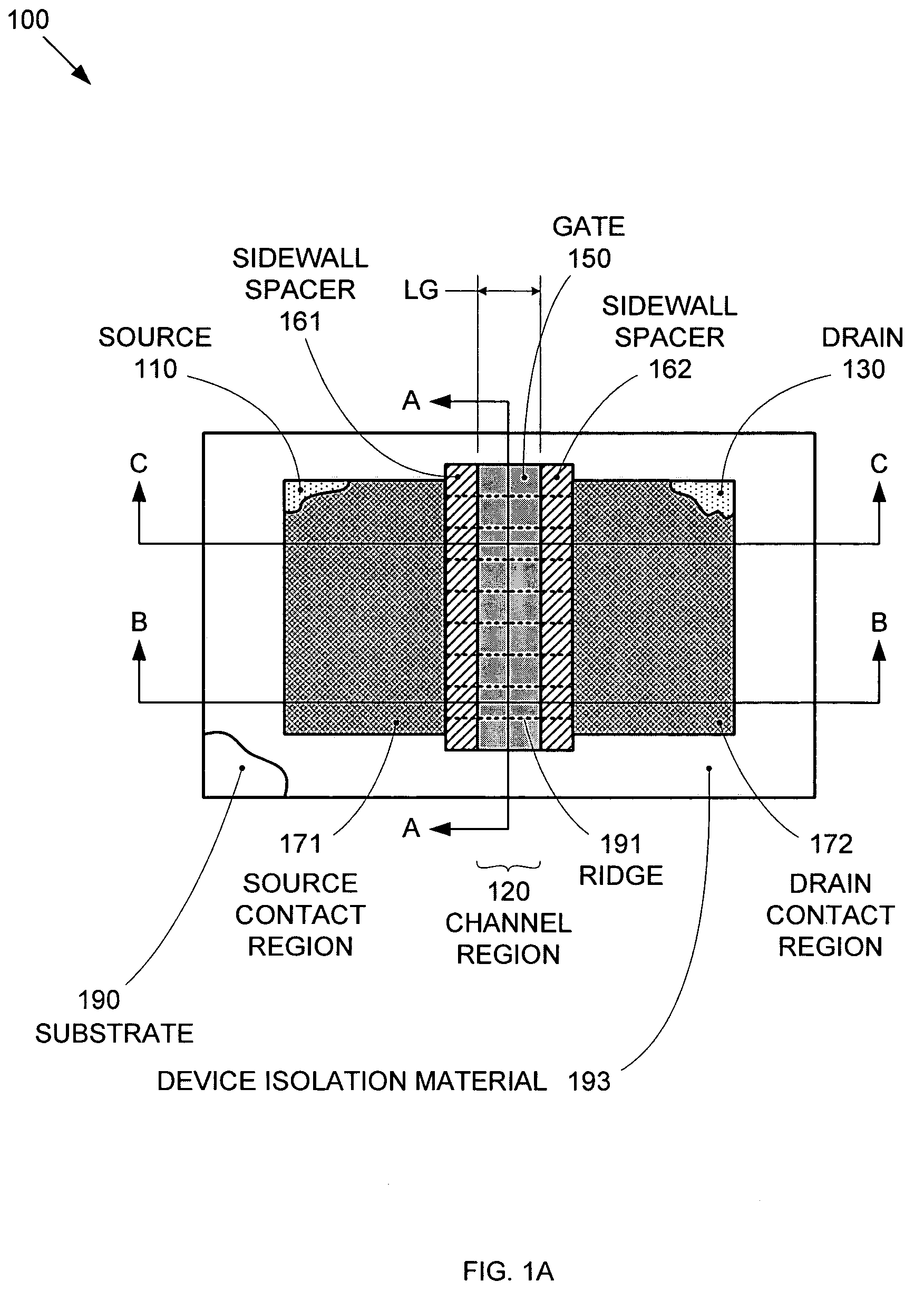
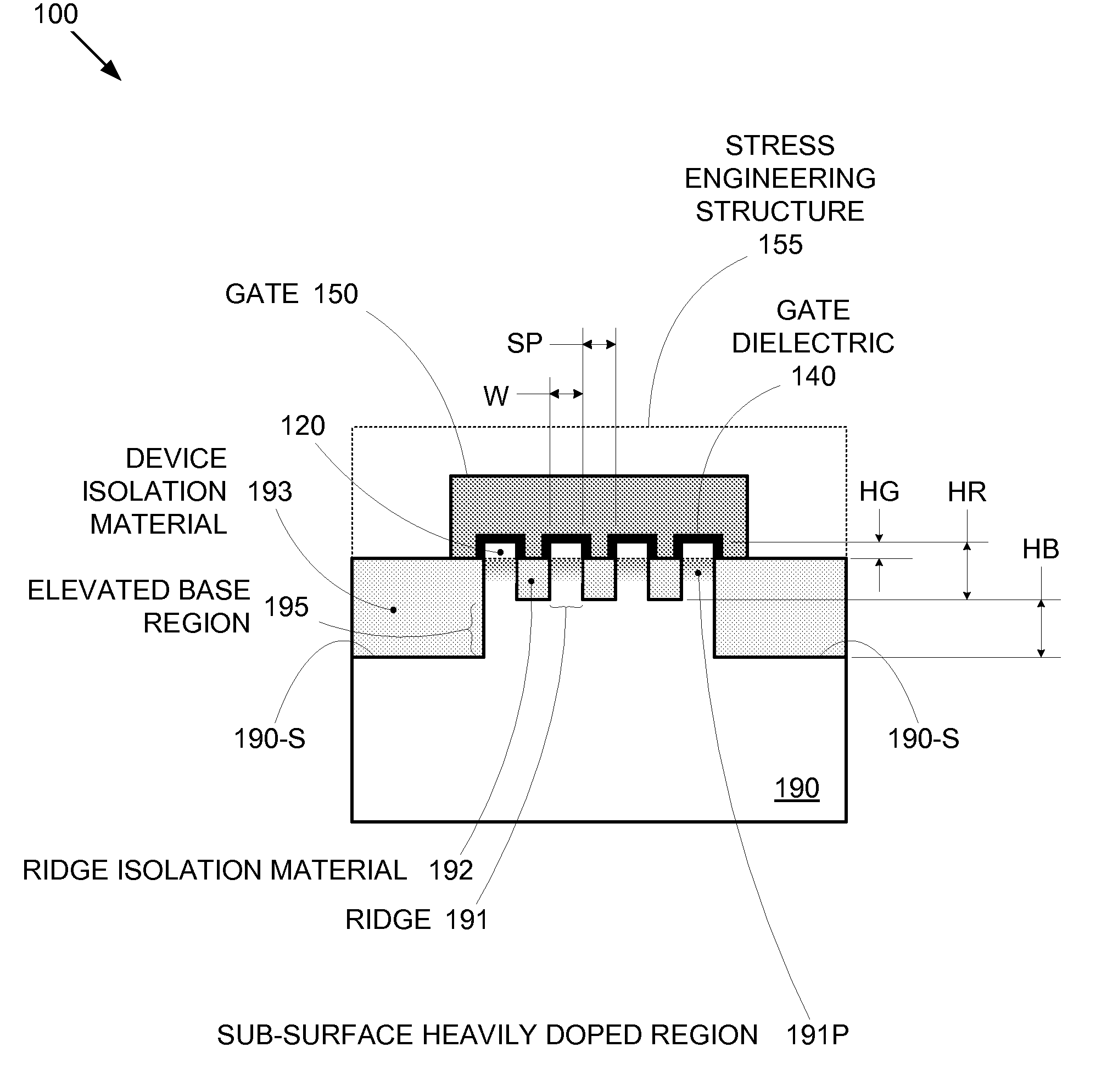
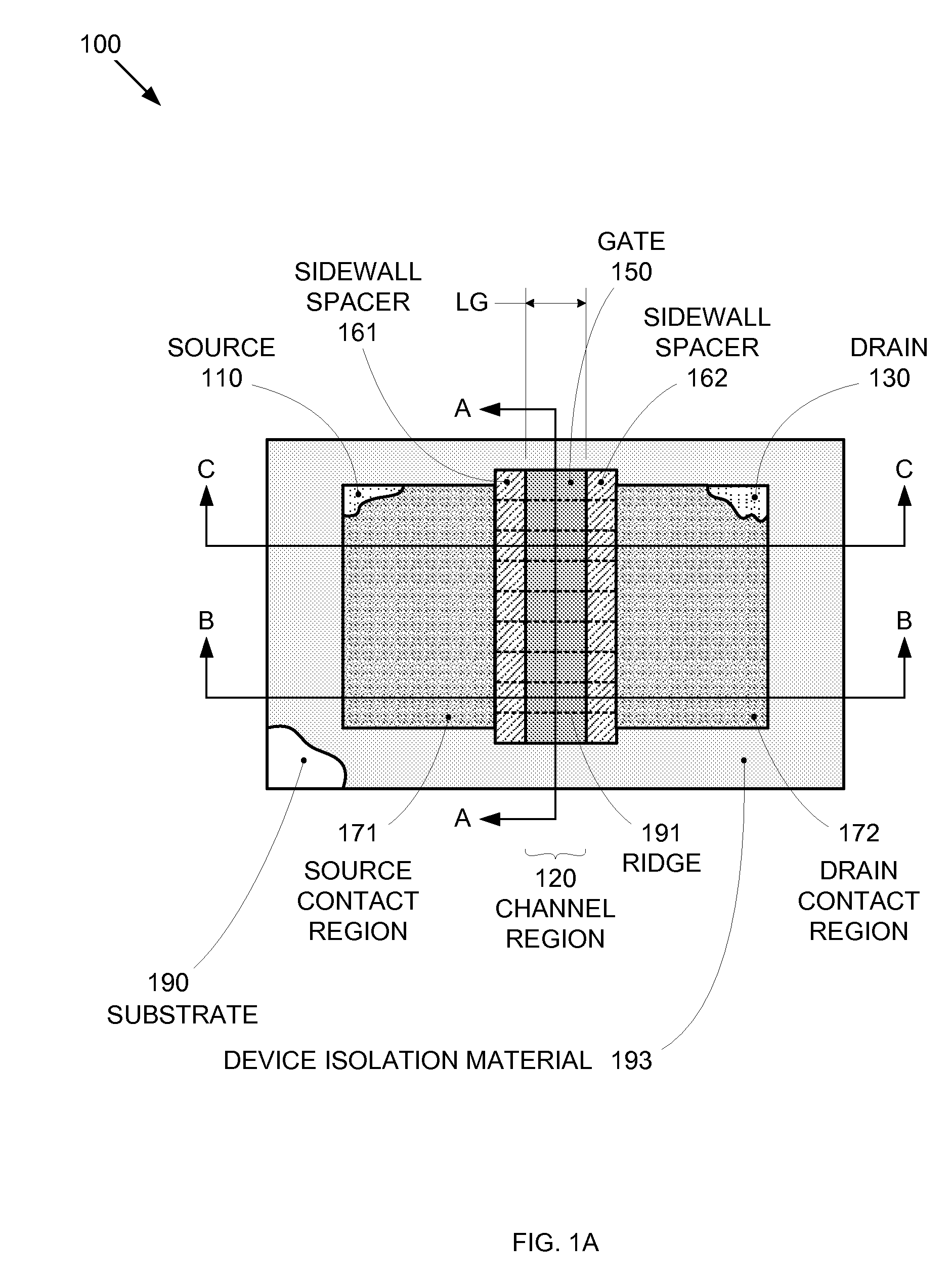
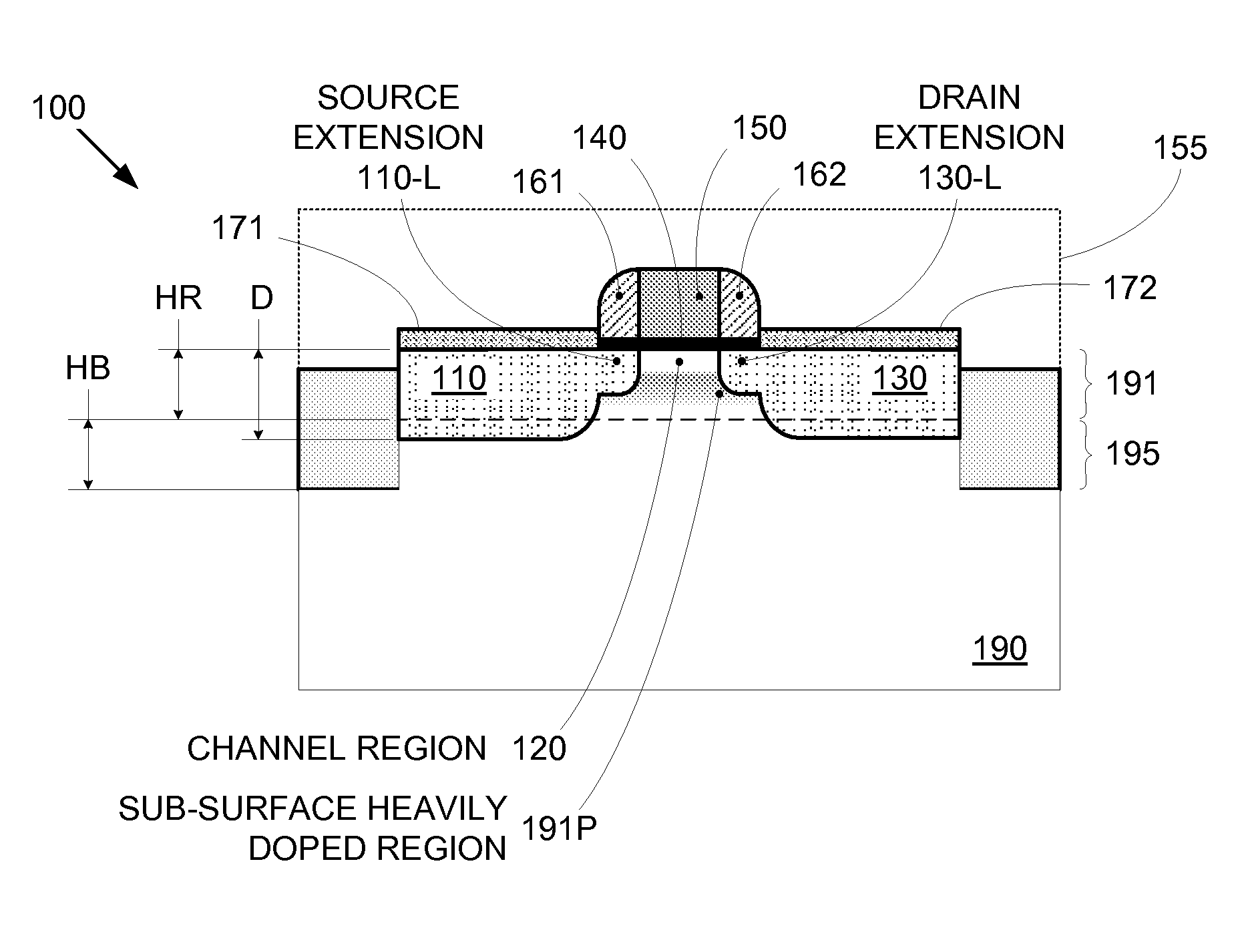
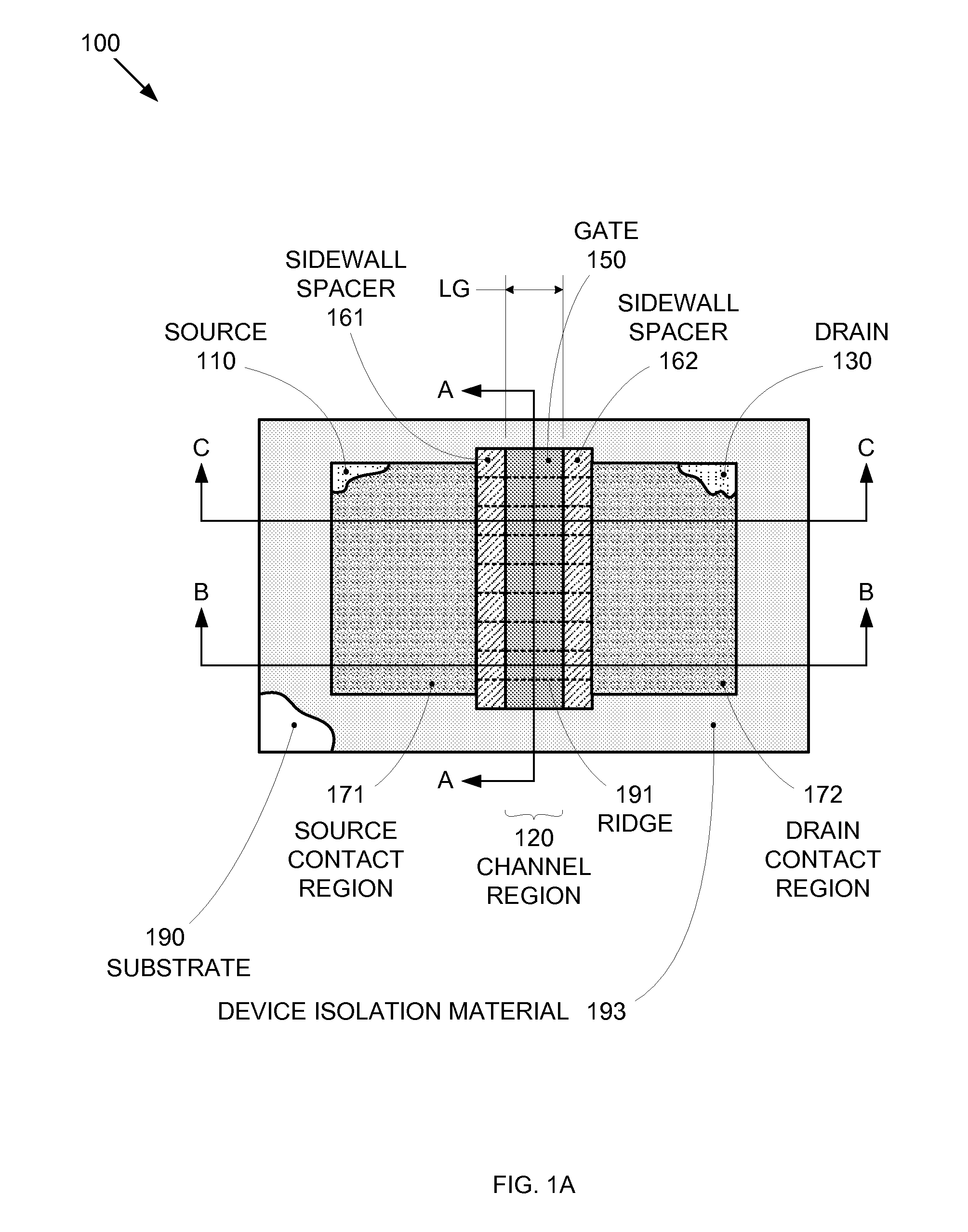
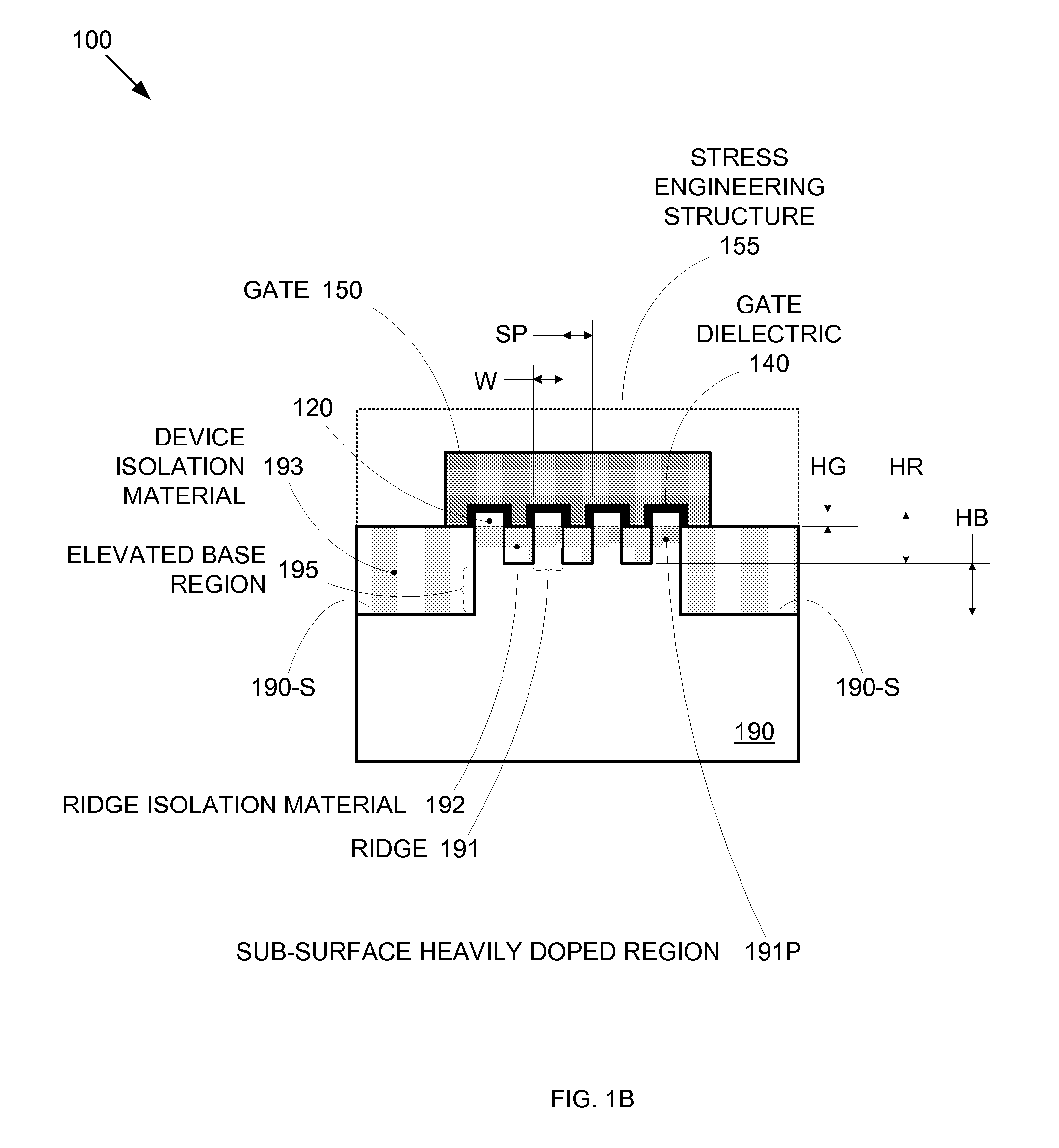
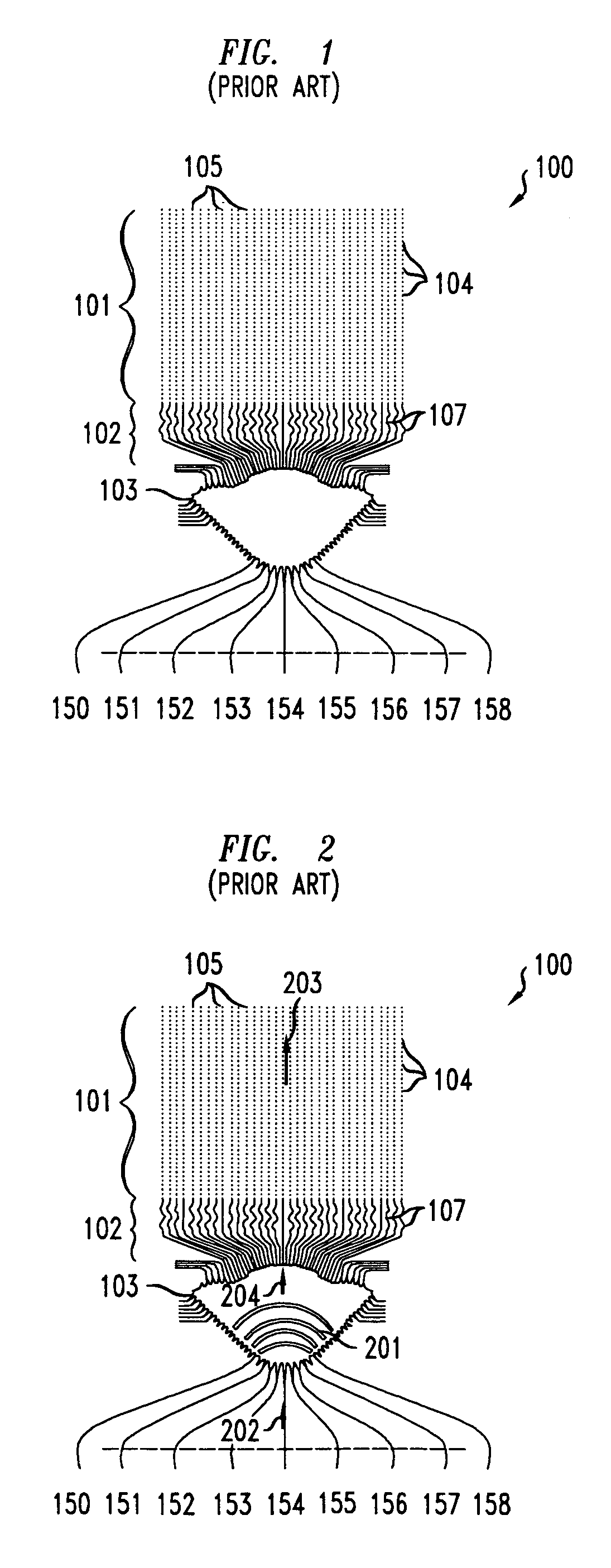
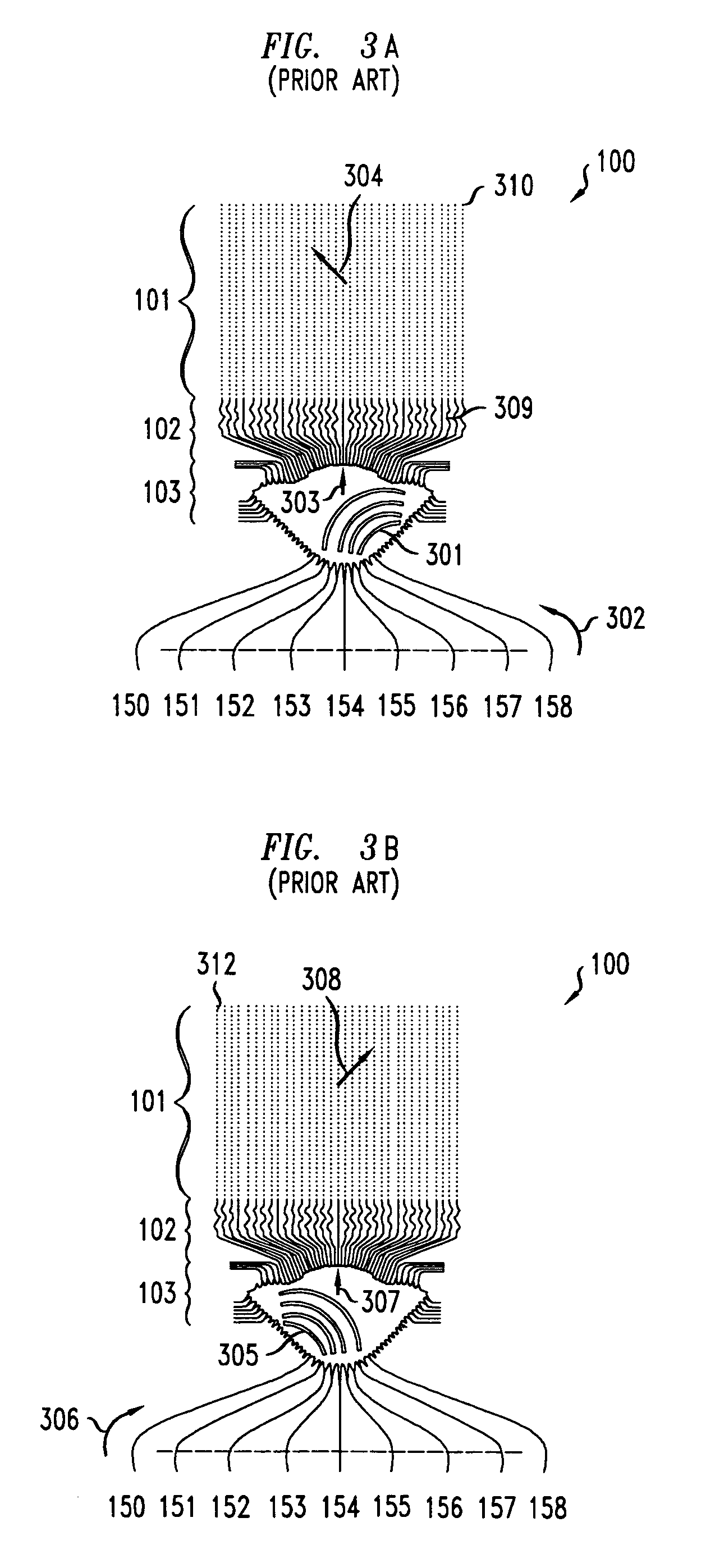
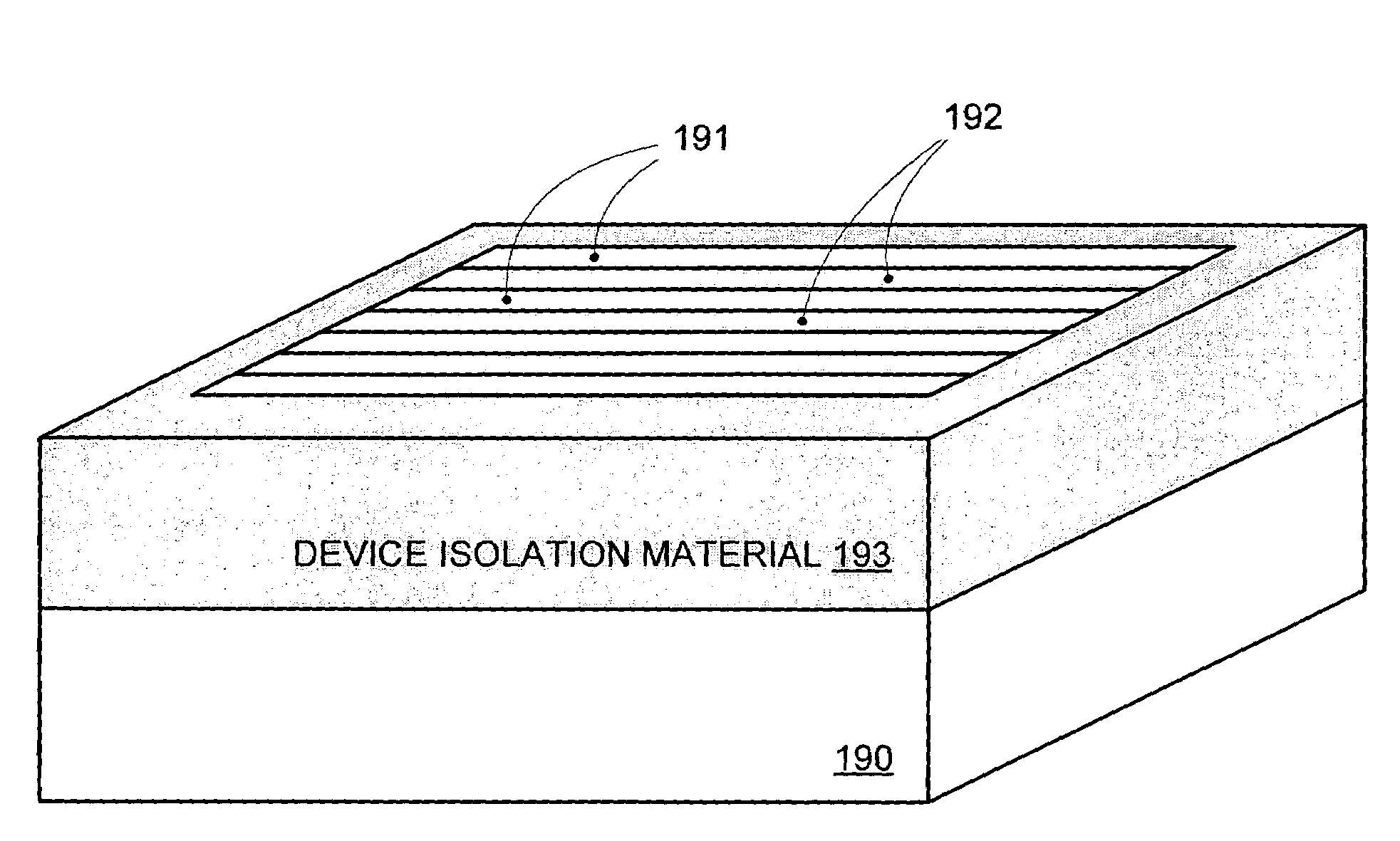
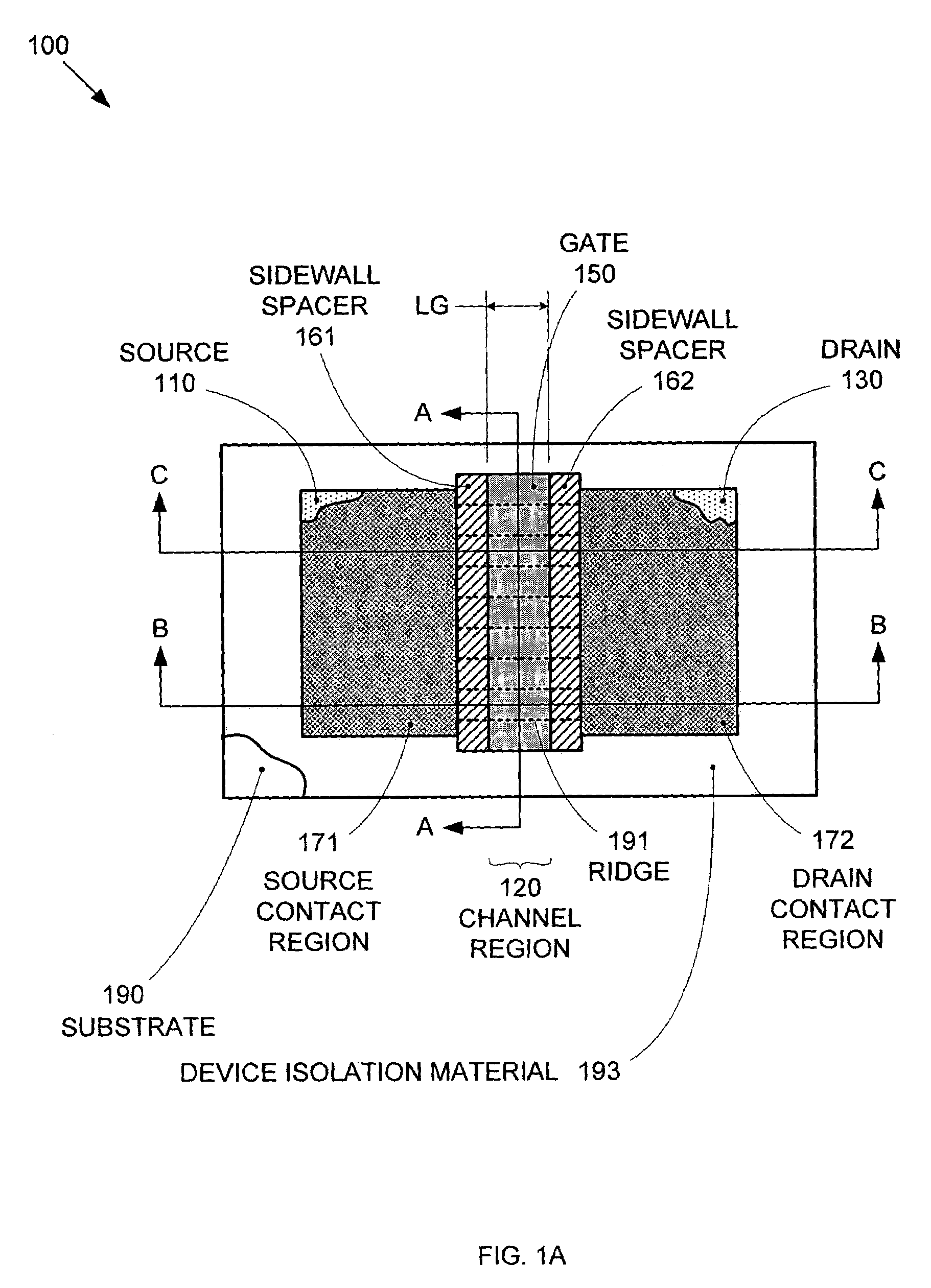
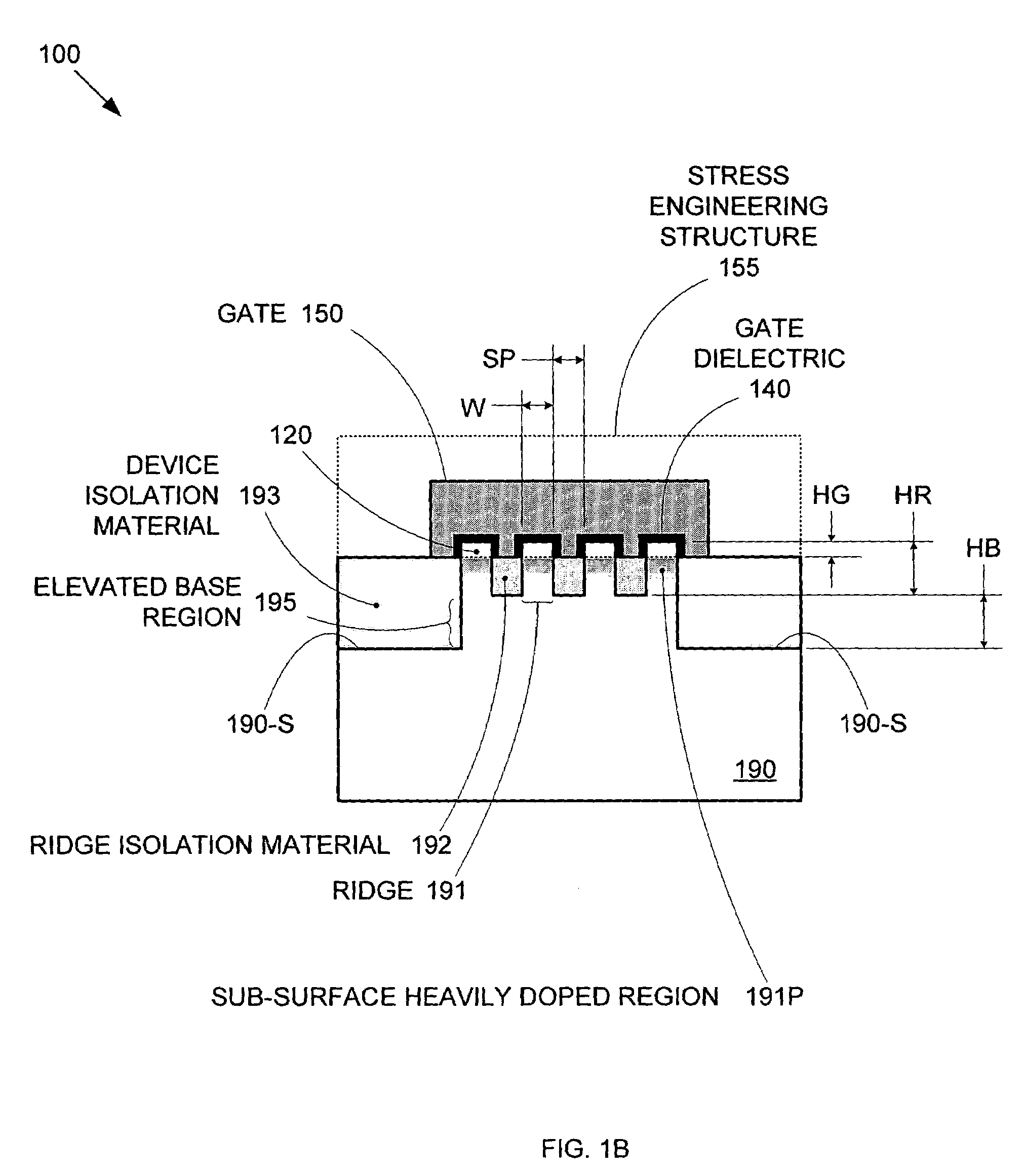
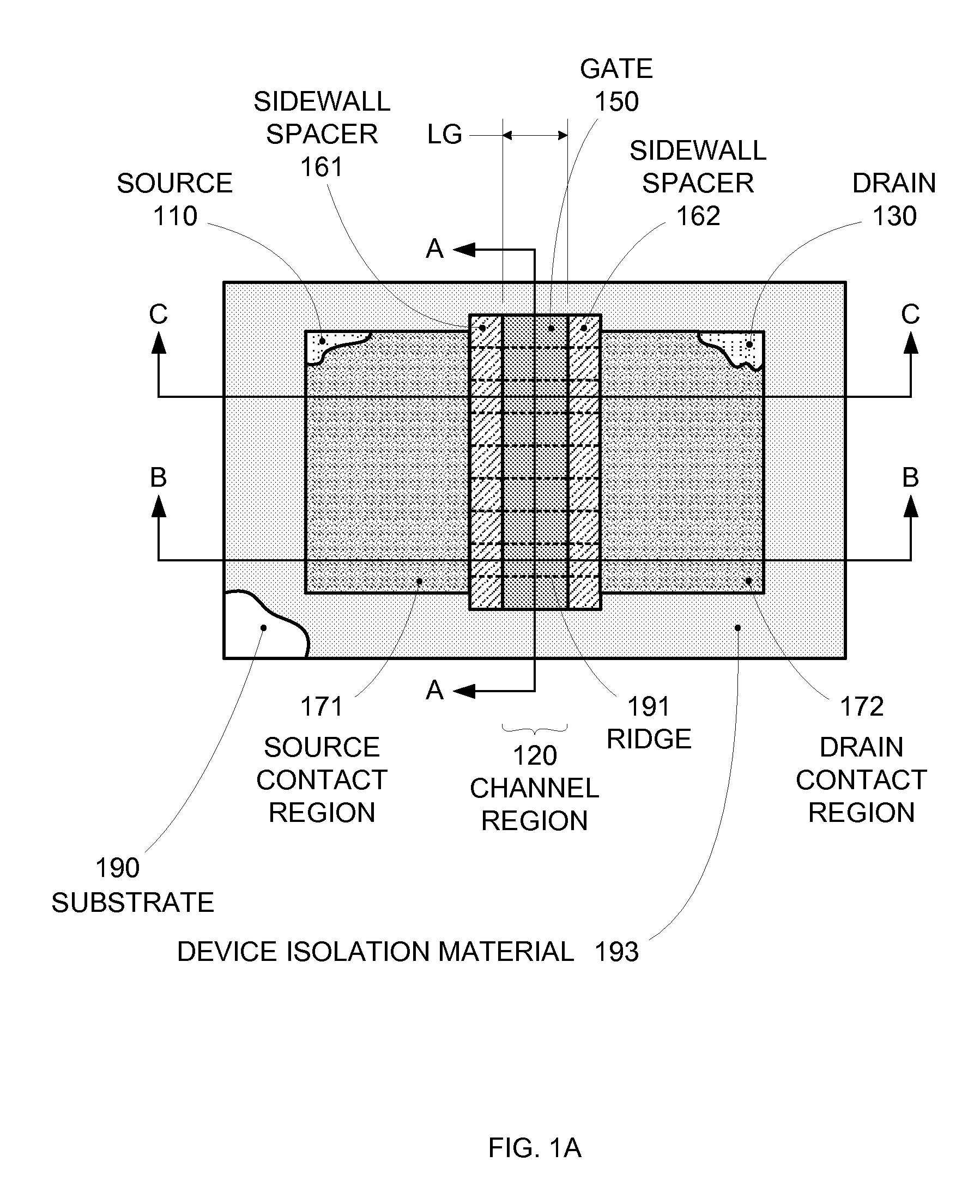
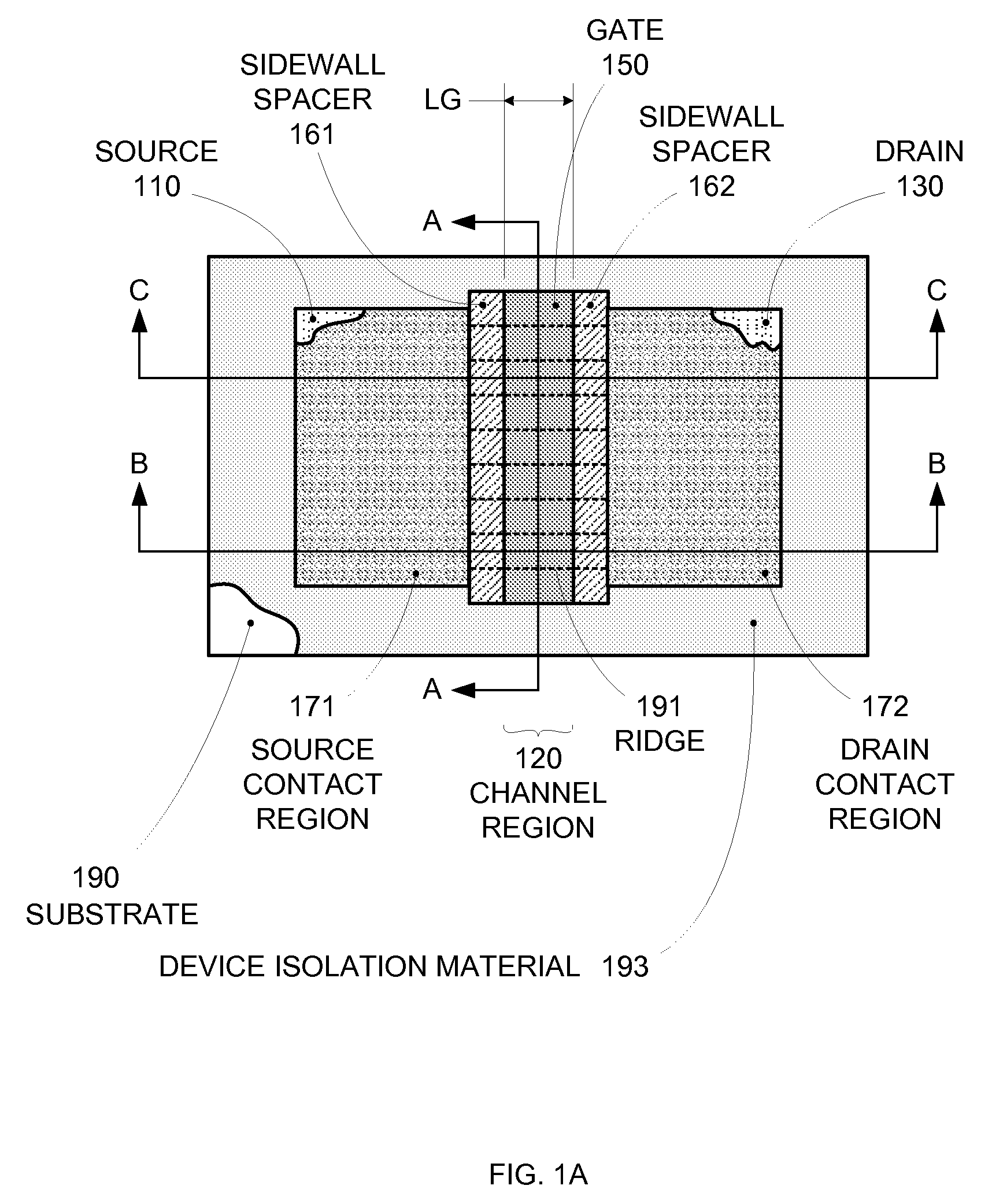
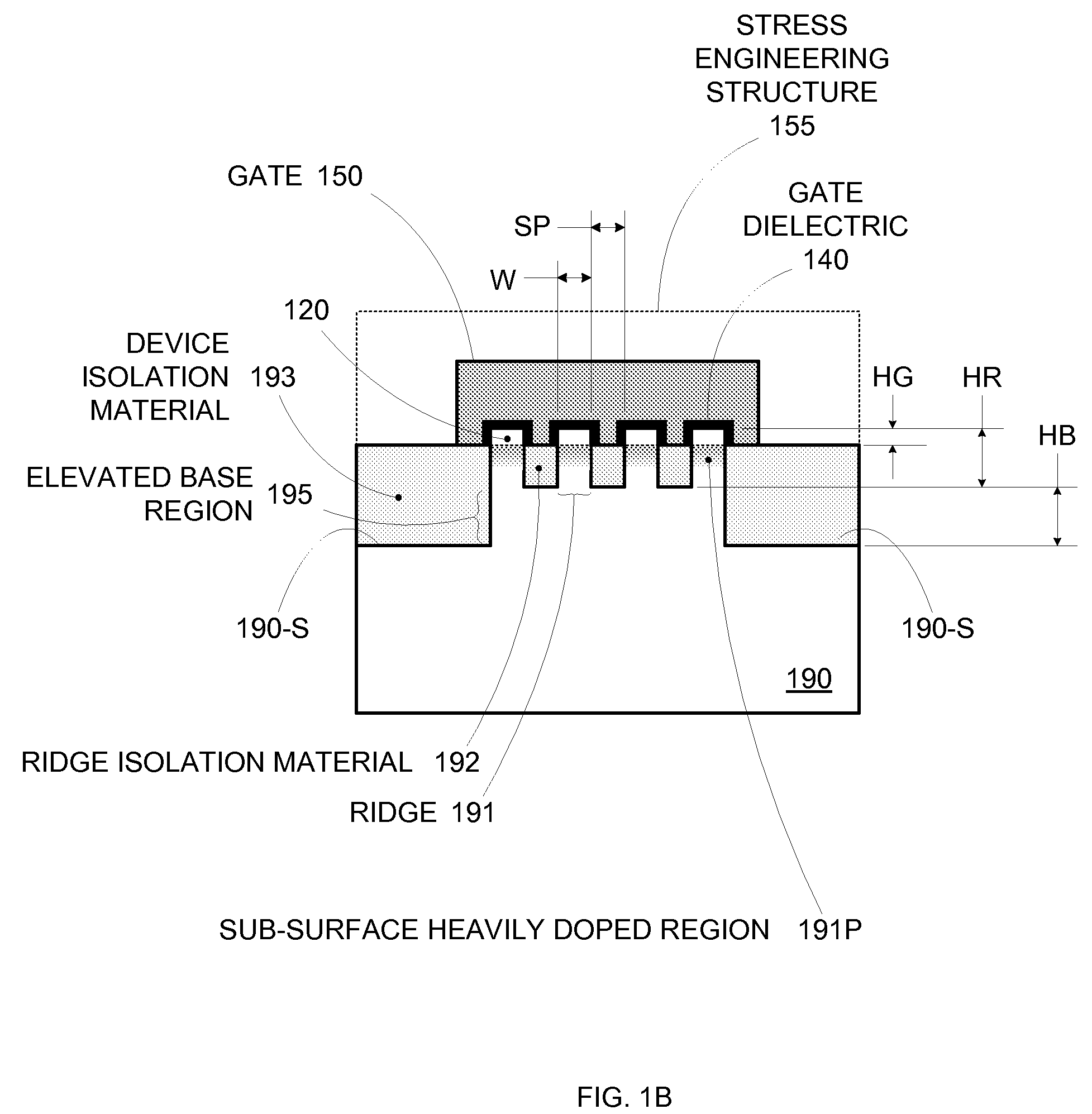
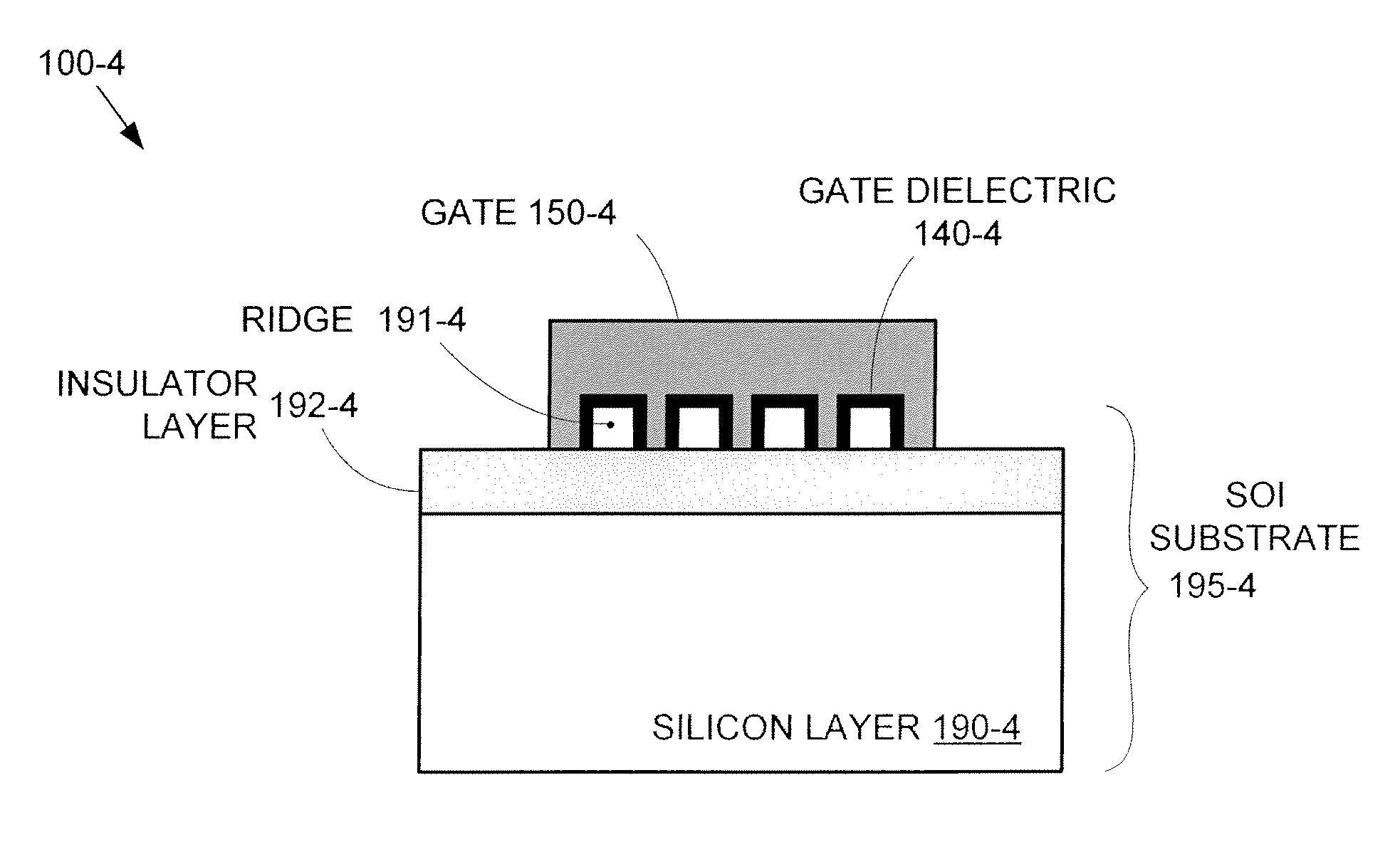
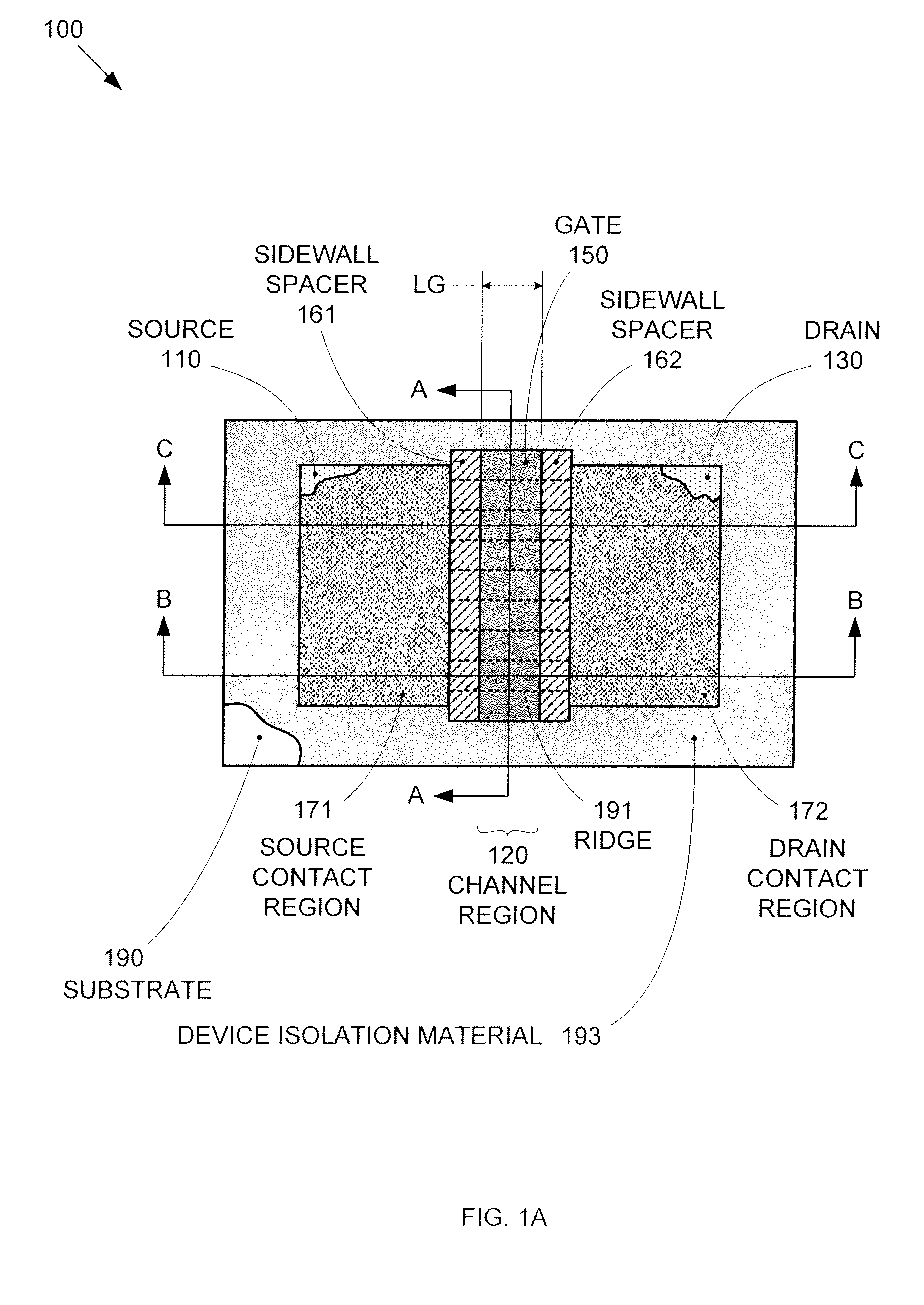
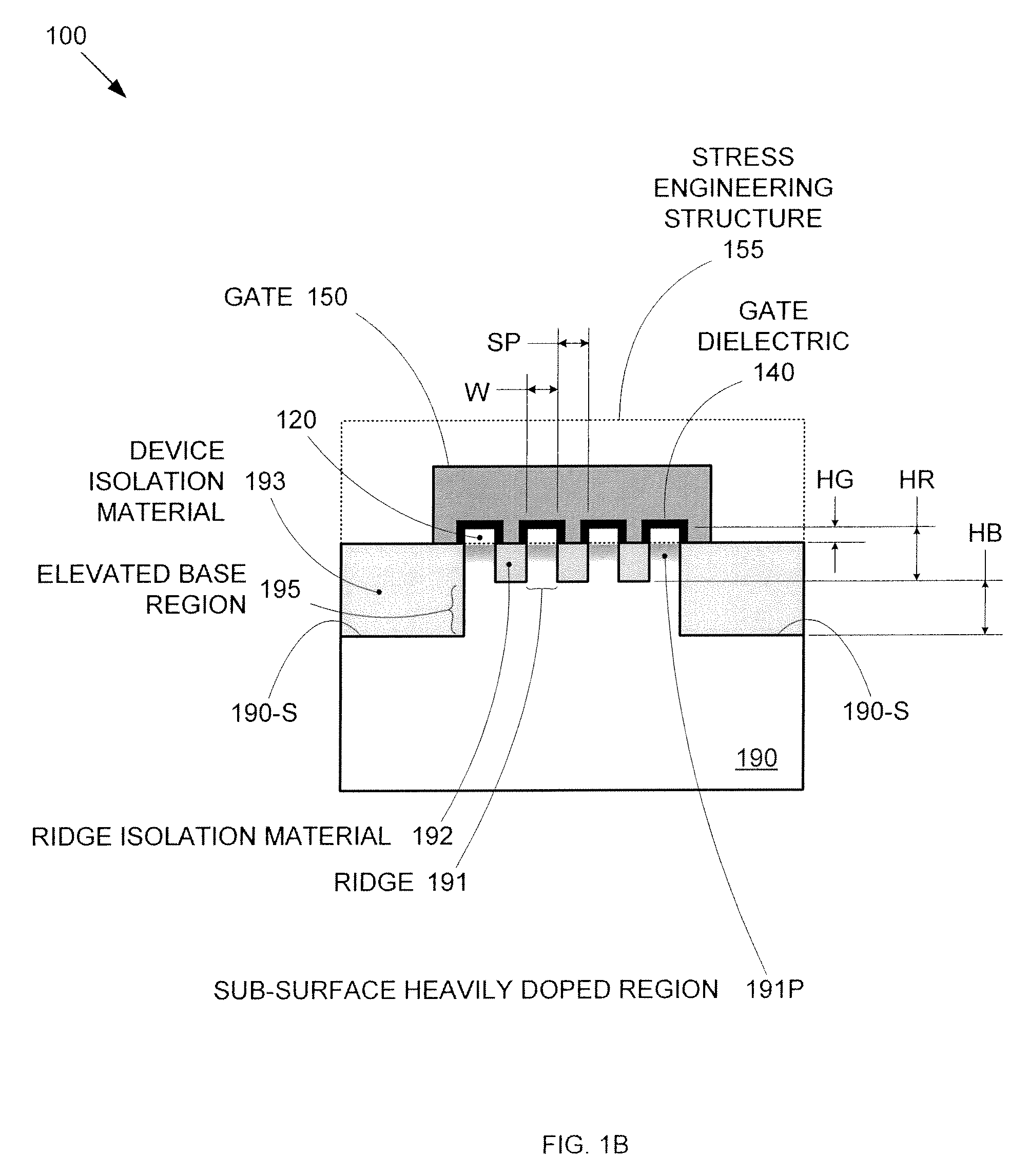
Segmented channel MOS transistor
ActiveUS7247887B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETLithographic artist
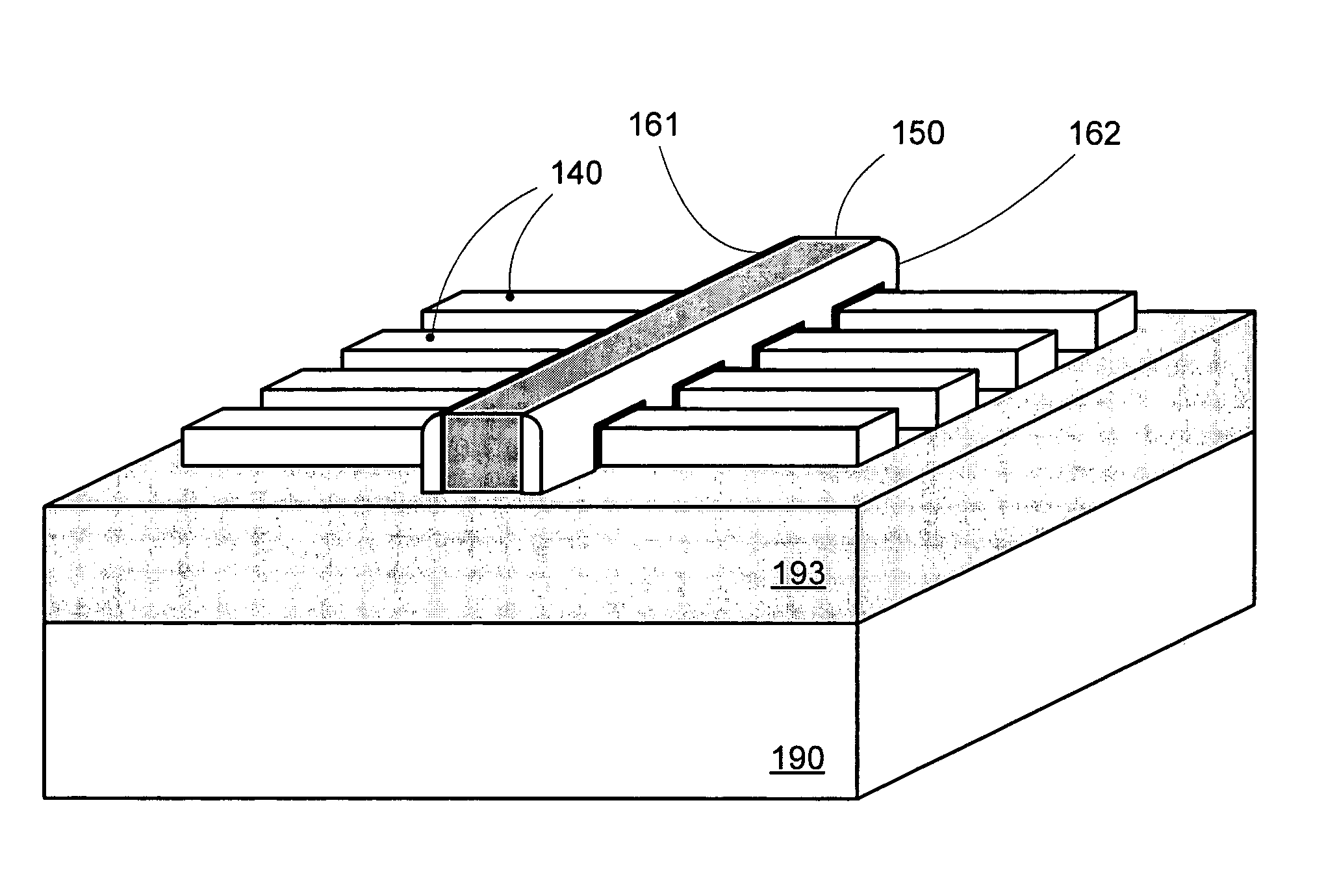
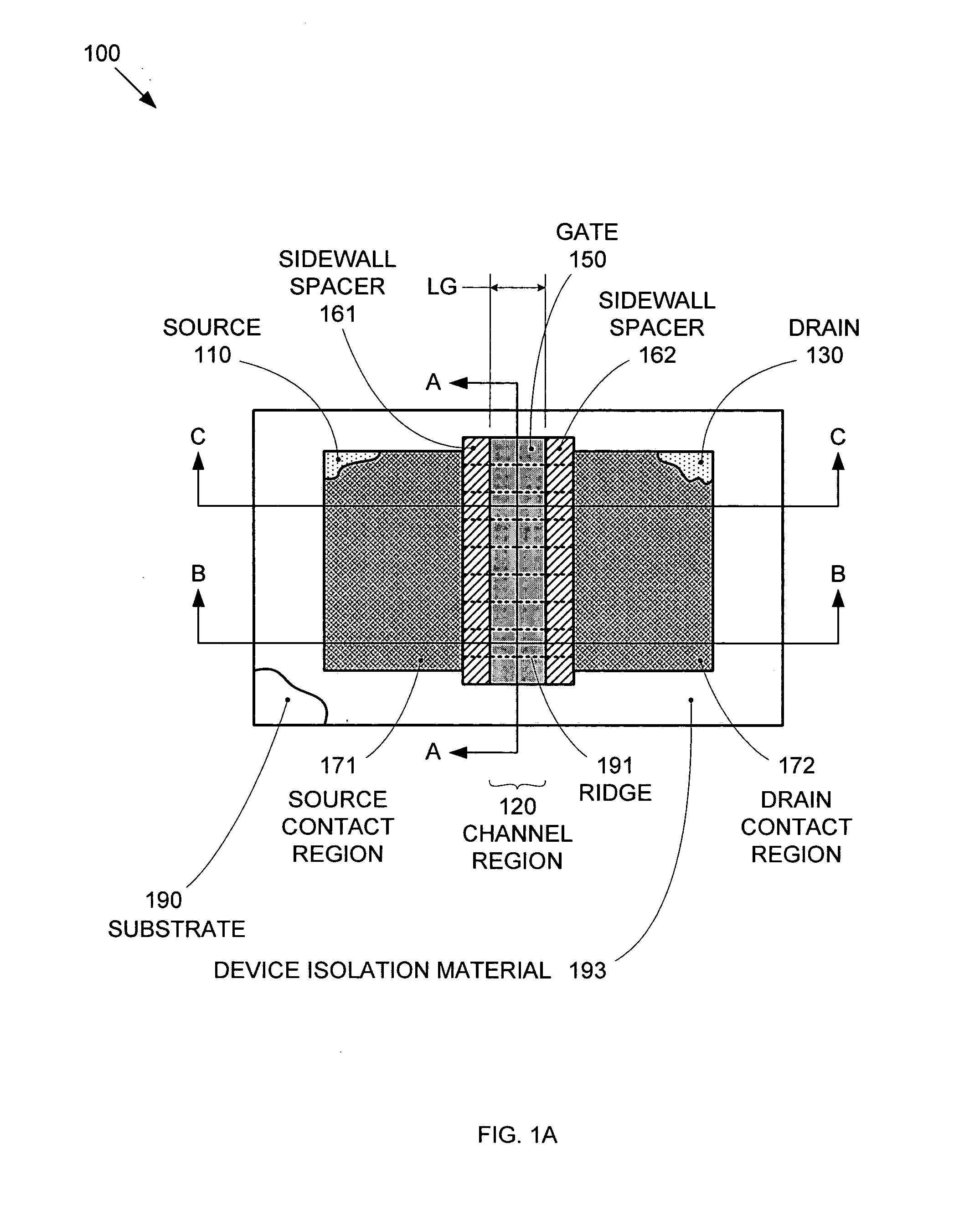
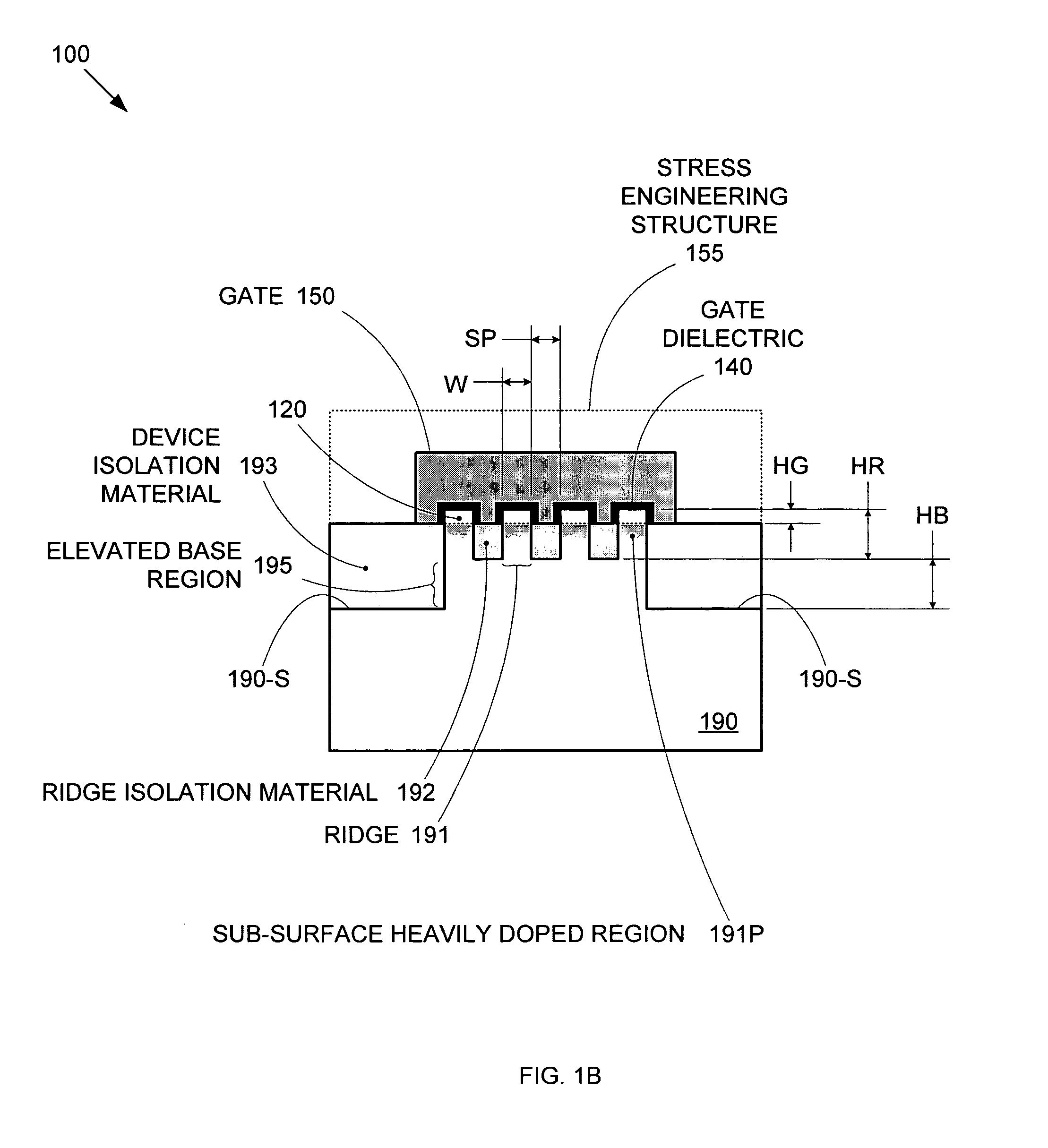
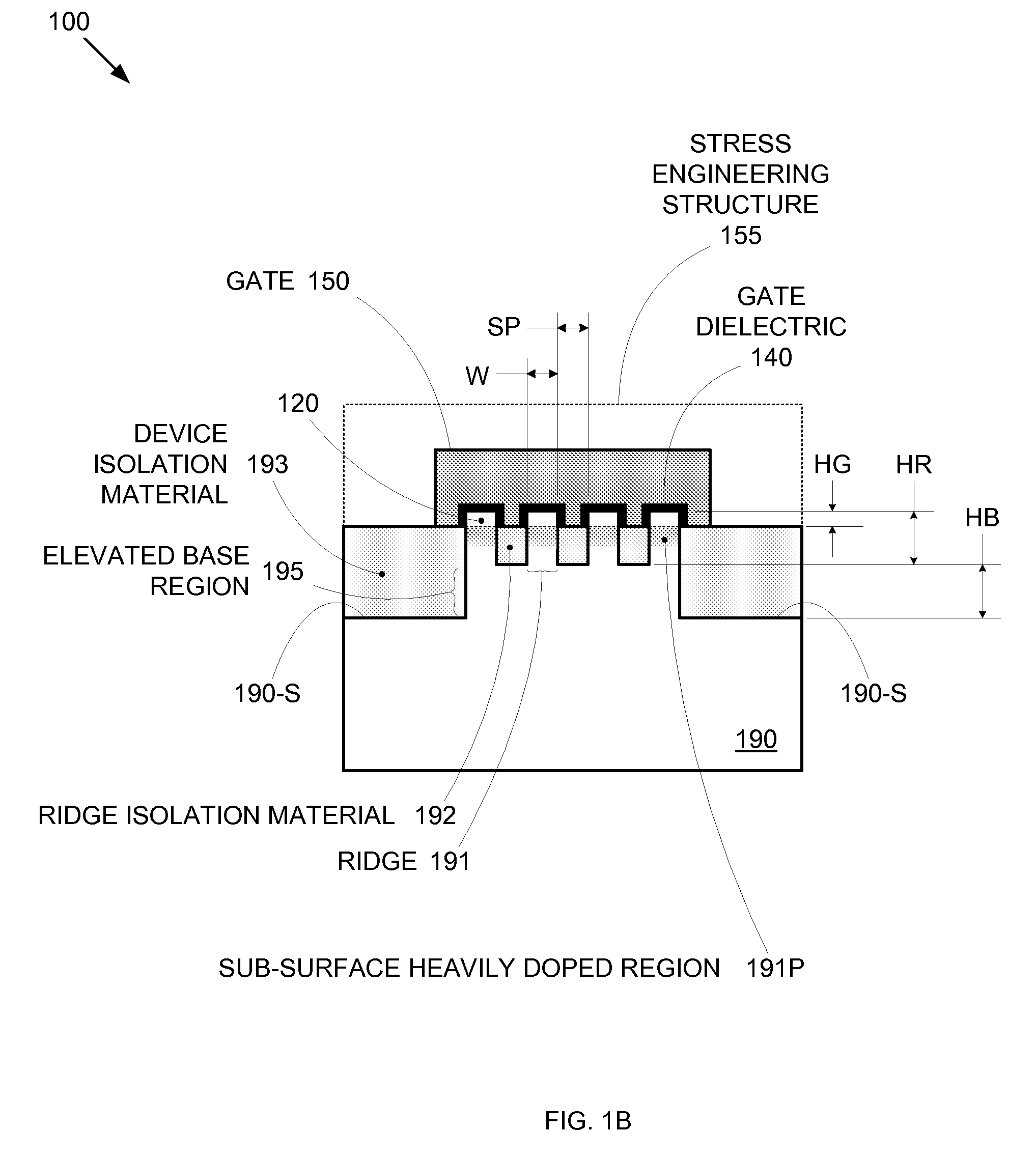
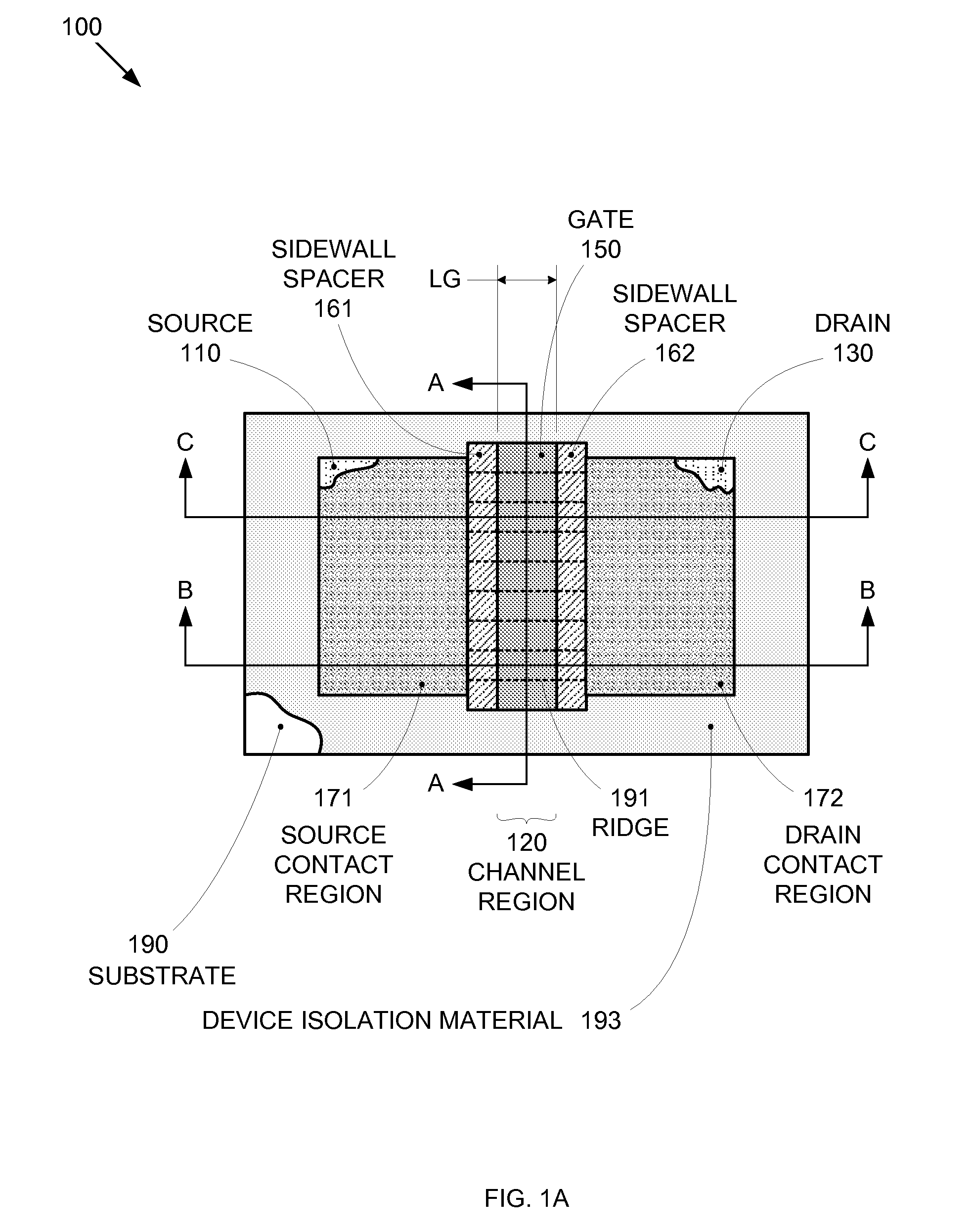
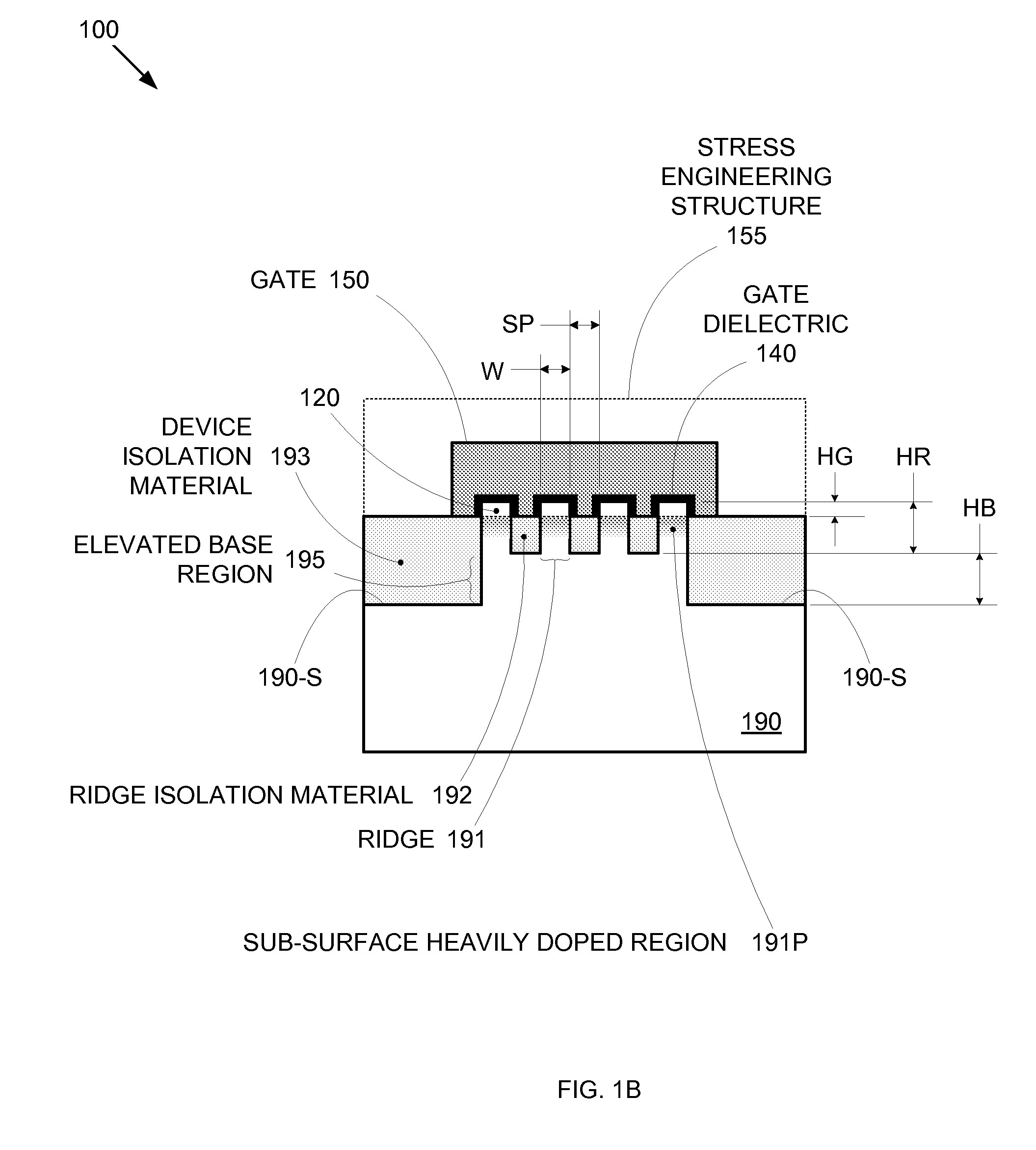
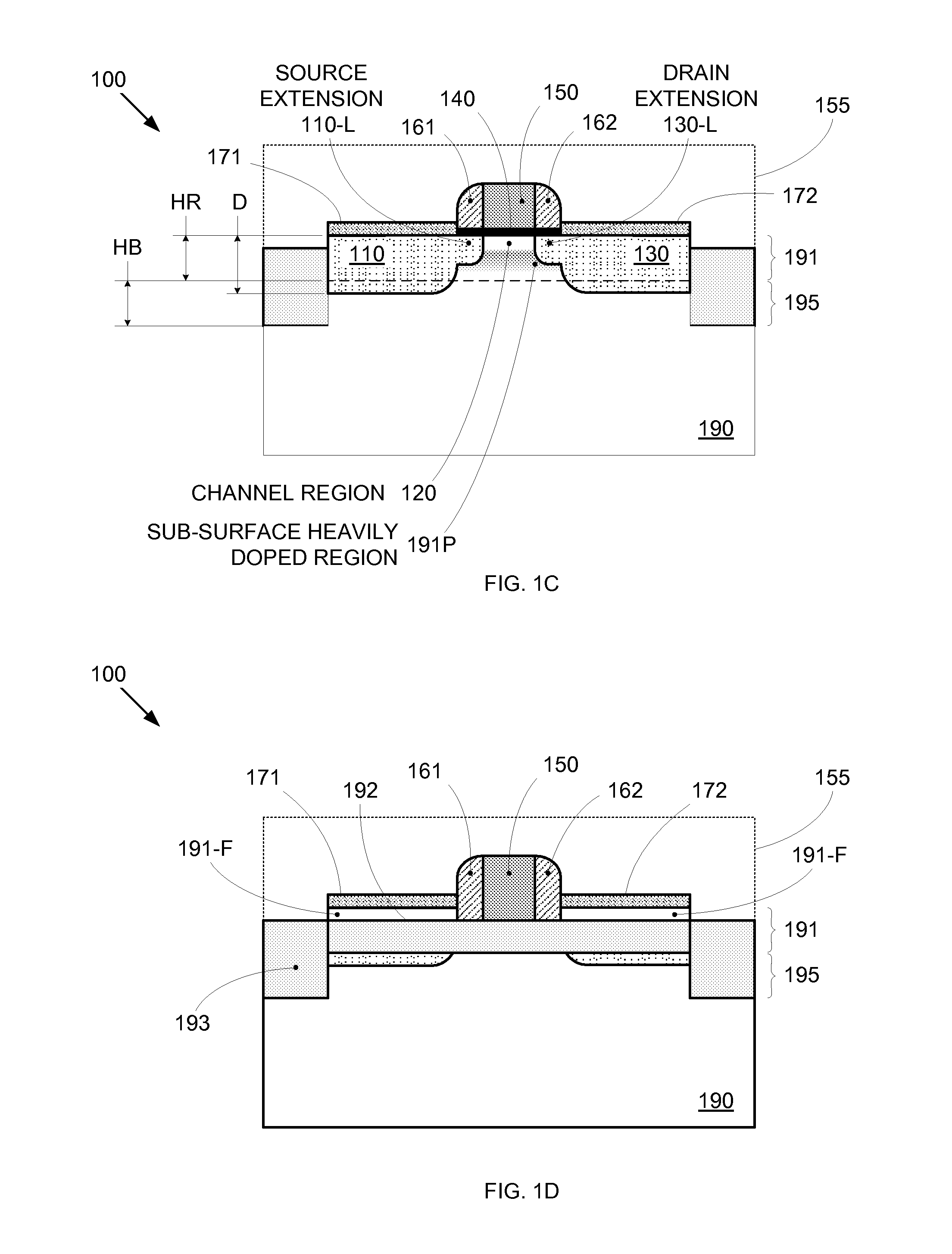
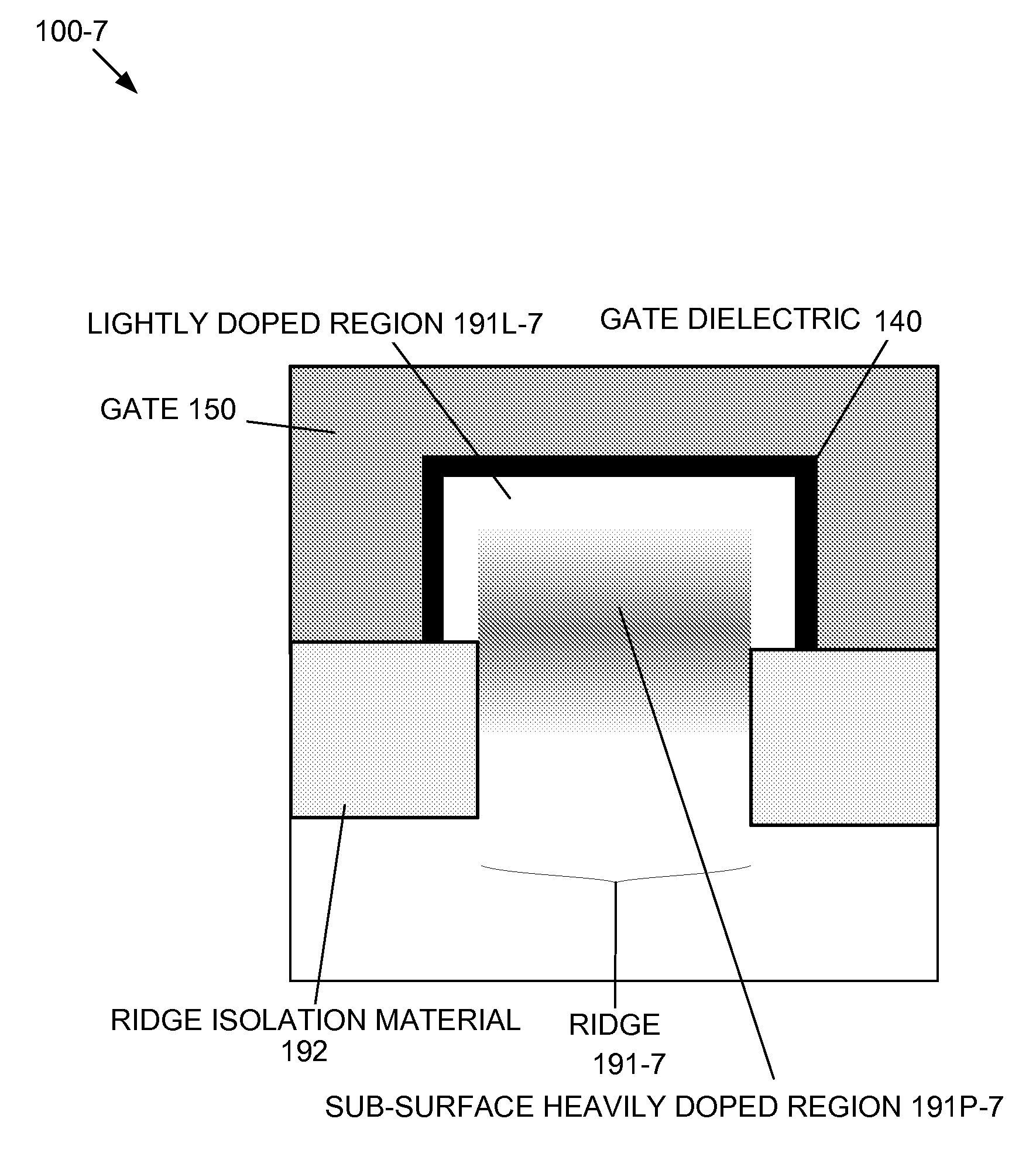
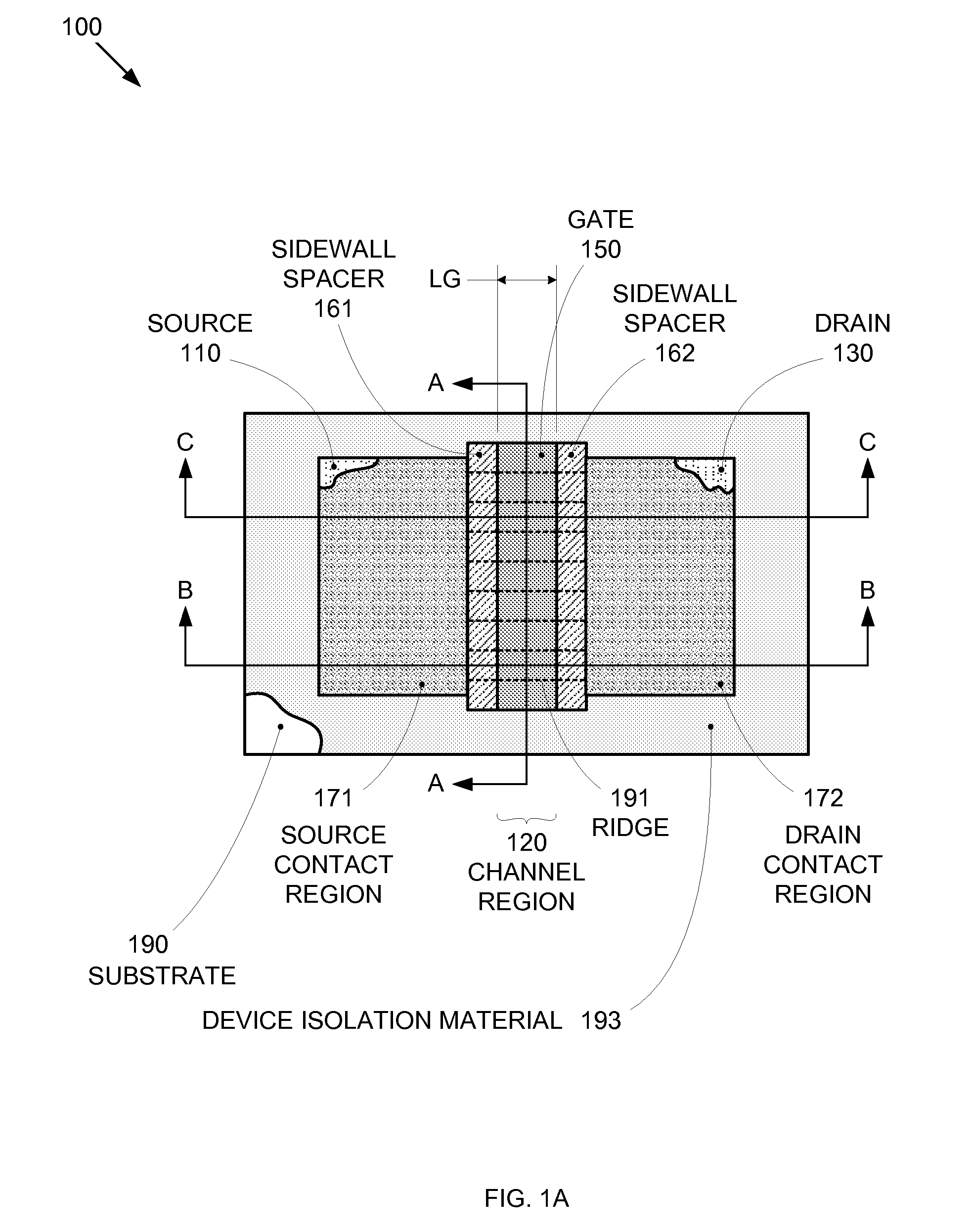
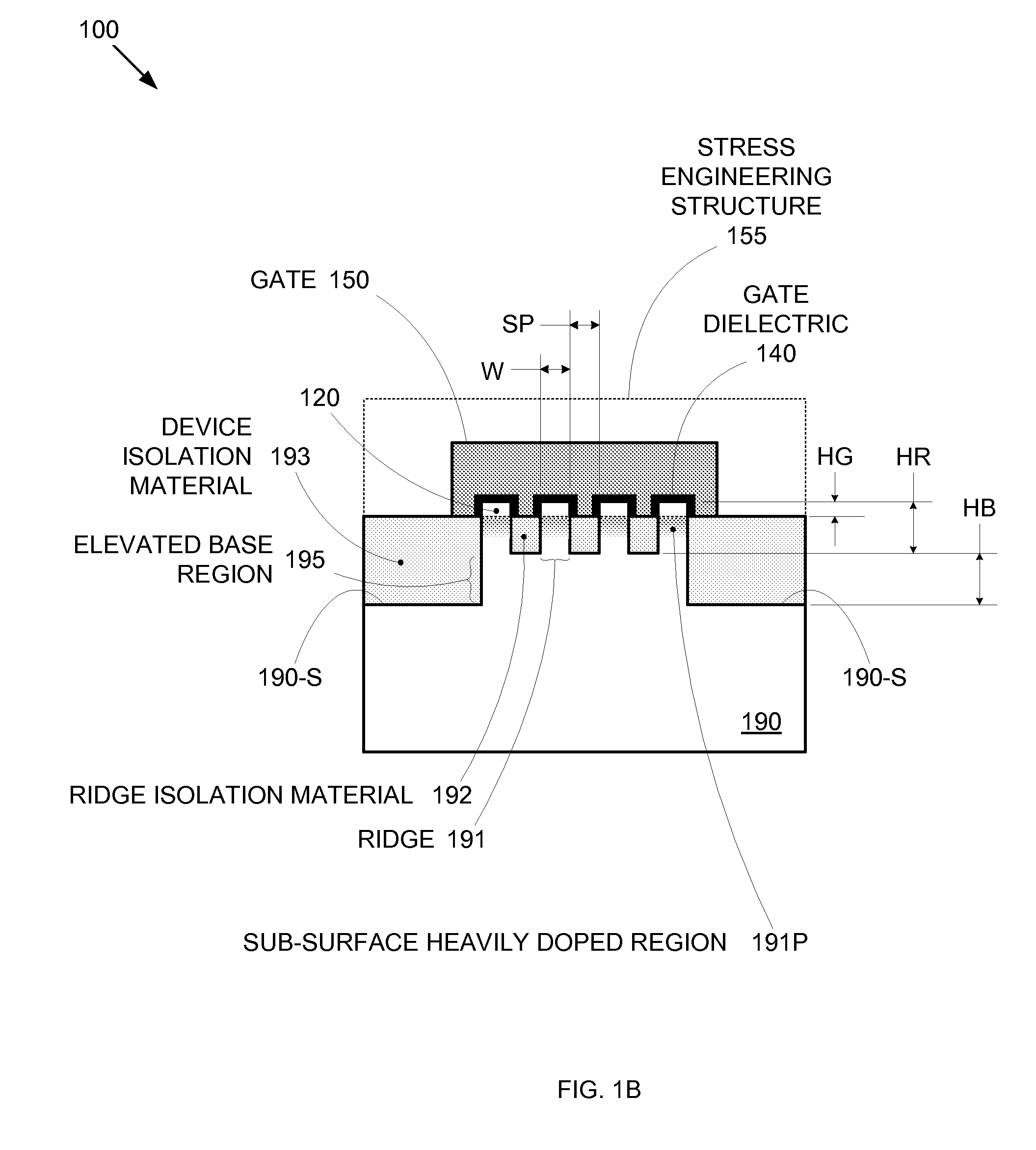
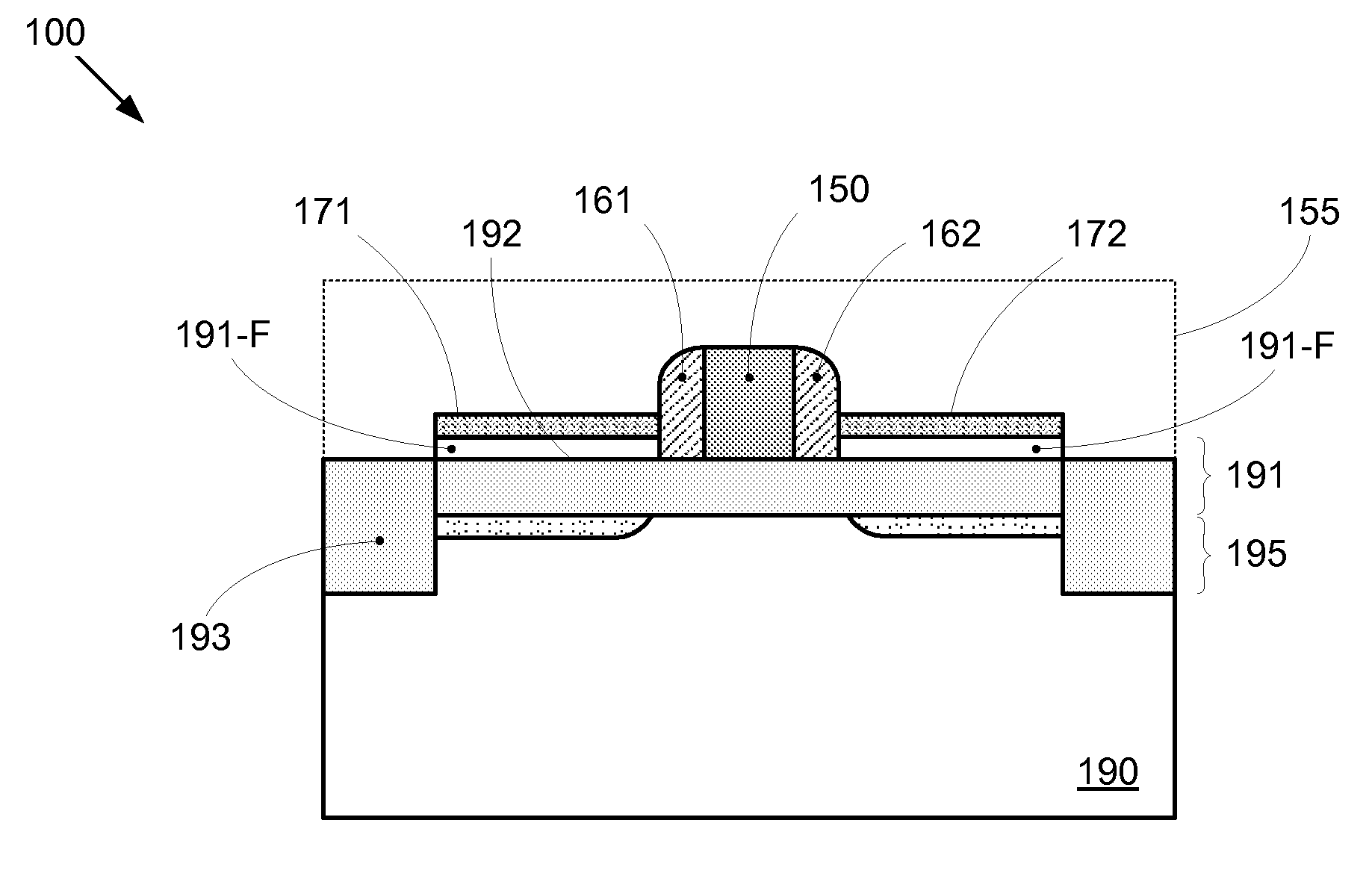
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
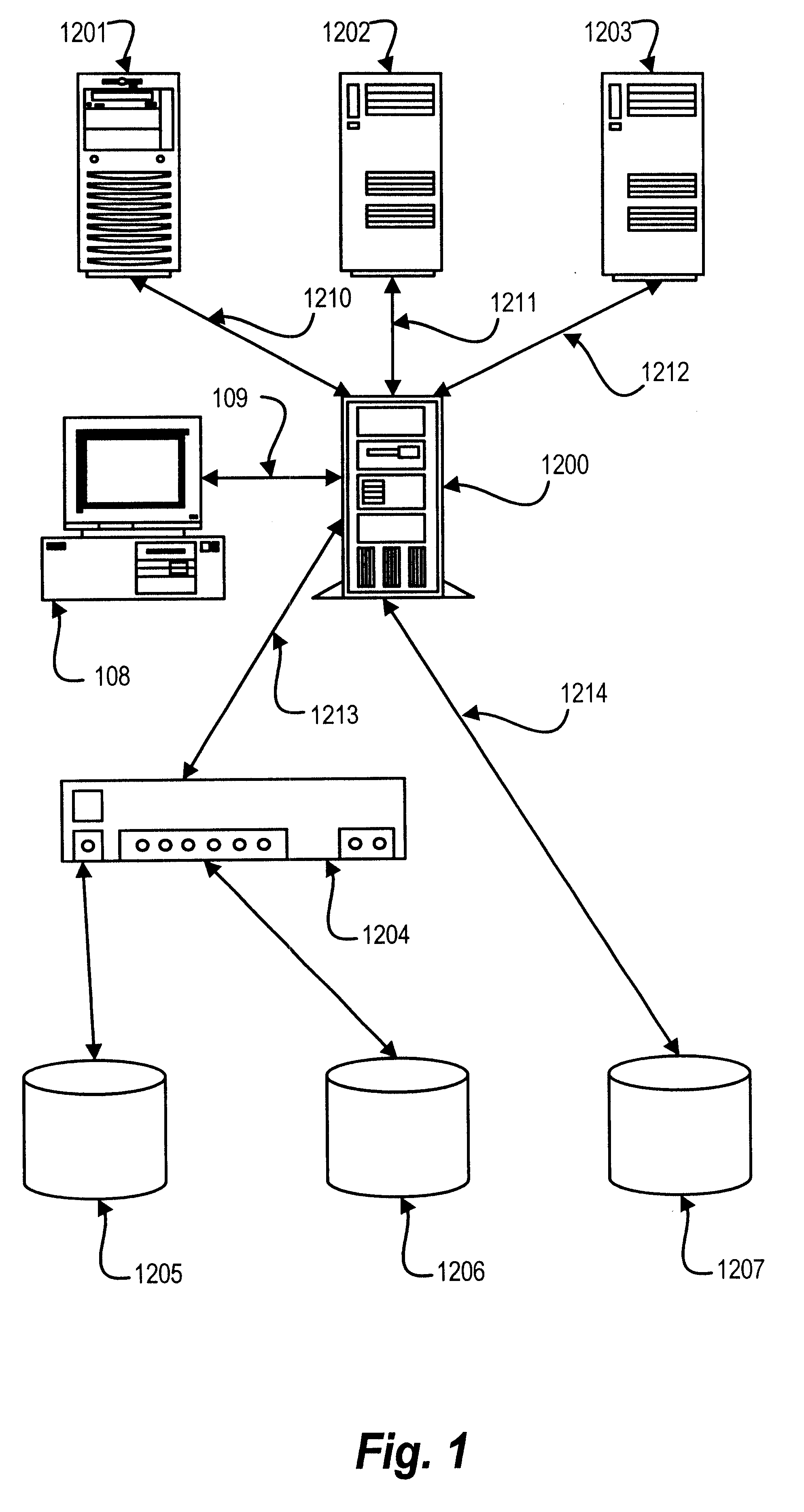
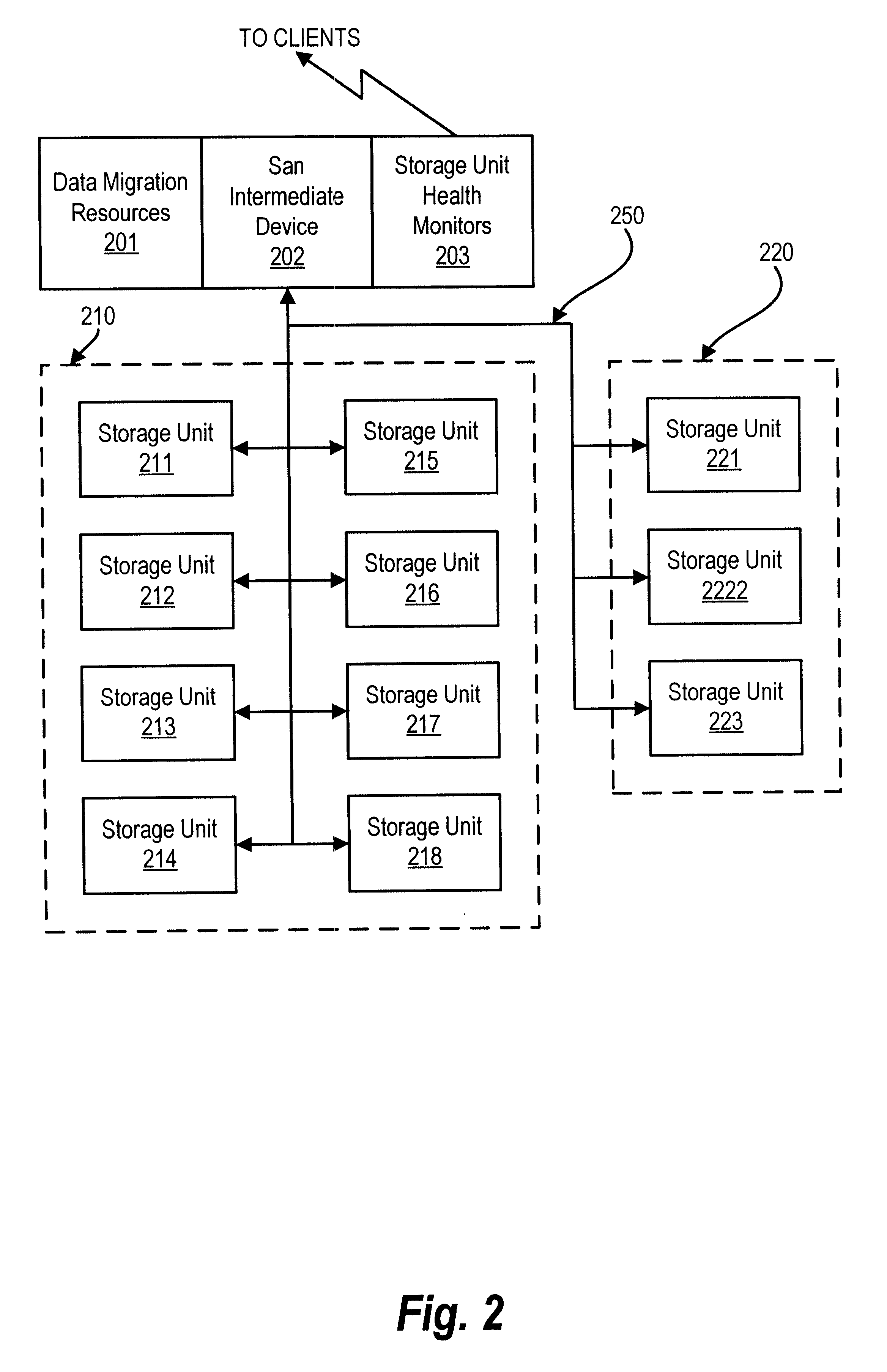
Method and apparatus for storage unit replacement in non-redundant array
InactiveUS6598174B1Lower performance requirementsMaintaining accessMemory loss protectionReliability/availability analysisRAIDData storing
A method and apparatus used in a storage network facilitates the protection of data in, and replacement of, storage devices about to fail before the failure happens. In a network that includes a set of storage devices organized as a non-redundant (for example RAID 0) array, a storage device about to fail in the non-redundant array can be replaced by another storage device, typically from a pool of spares. The method includes detecting a condition of a first particular storage device in the non-redundant array. Conditions which are detected according to various embodiments indicate that the first particular storage device is suffering events indicating that it is likely to fail, or otherwise suffering from reduced performance. The conditions are detected for example, by the receipt of a signal from the storage device itself, or by the monitoring of statistics concerning the performance of the storage device. The method further provides for selecting a particular spare storage device, which can be used in place of the first particular storage device. In response to detecting the condition, data stored in the first particular storage device is migrated to the second particular storage device, and the second particular storage takes the place of the first particular storage device in the non-redundant array. The first particular storage device can then be gracefully removed from the network without loss of service to the clients computers.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
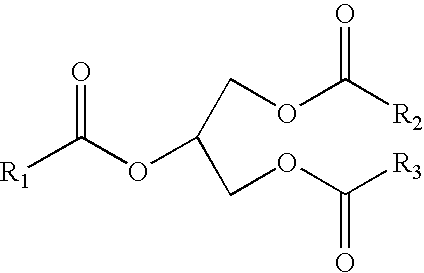
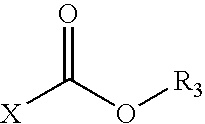
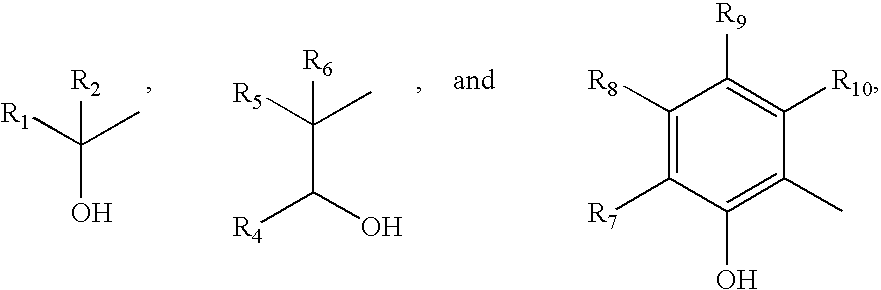
Lubricant and fuel compositions containing hydroxy carboxylic acid and hydroxy polycarboxylic acid esters
InactiveUS20050198894A1Reduce the amount requiredWithout diminishing anti-wear performanceOrganic chemistryLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCarboxylic acidMedicinal chemistry
Disclosed herein is a composition comprising: (A) a lubricant or a hydrocarbon fuel; (B) at least one hydroxy carboxylic acid ester or hydroxy polycarboxylic acid ester having the generic formula defined herein; and (C) at least one phosphorus-containing additive.
Owner:CHEMTURA CORP
Integrated circuit on corrugated substrate
ActiveUS7190050B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
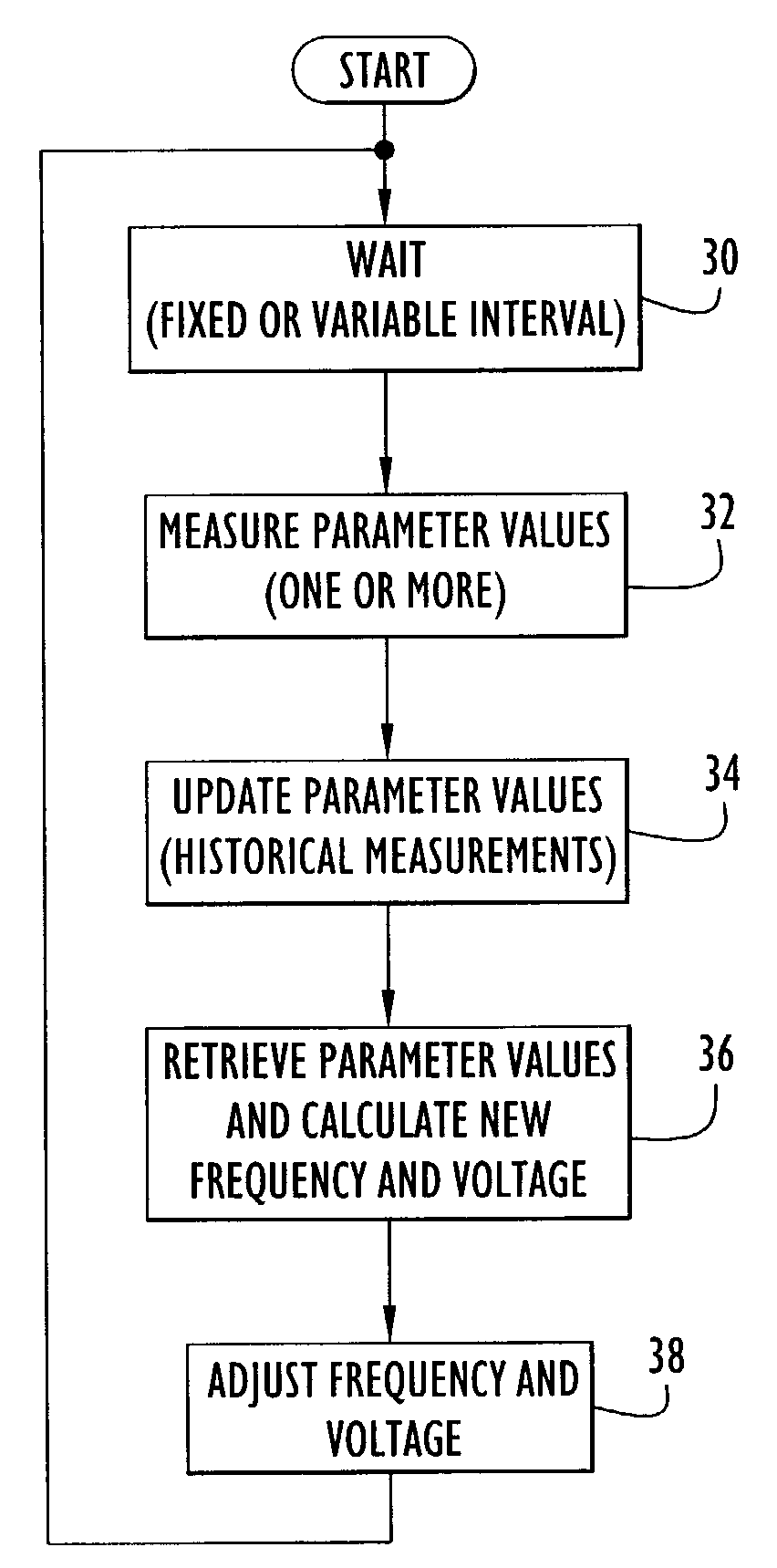
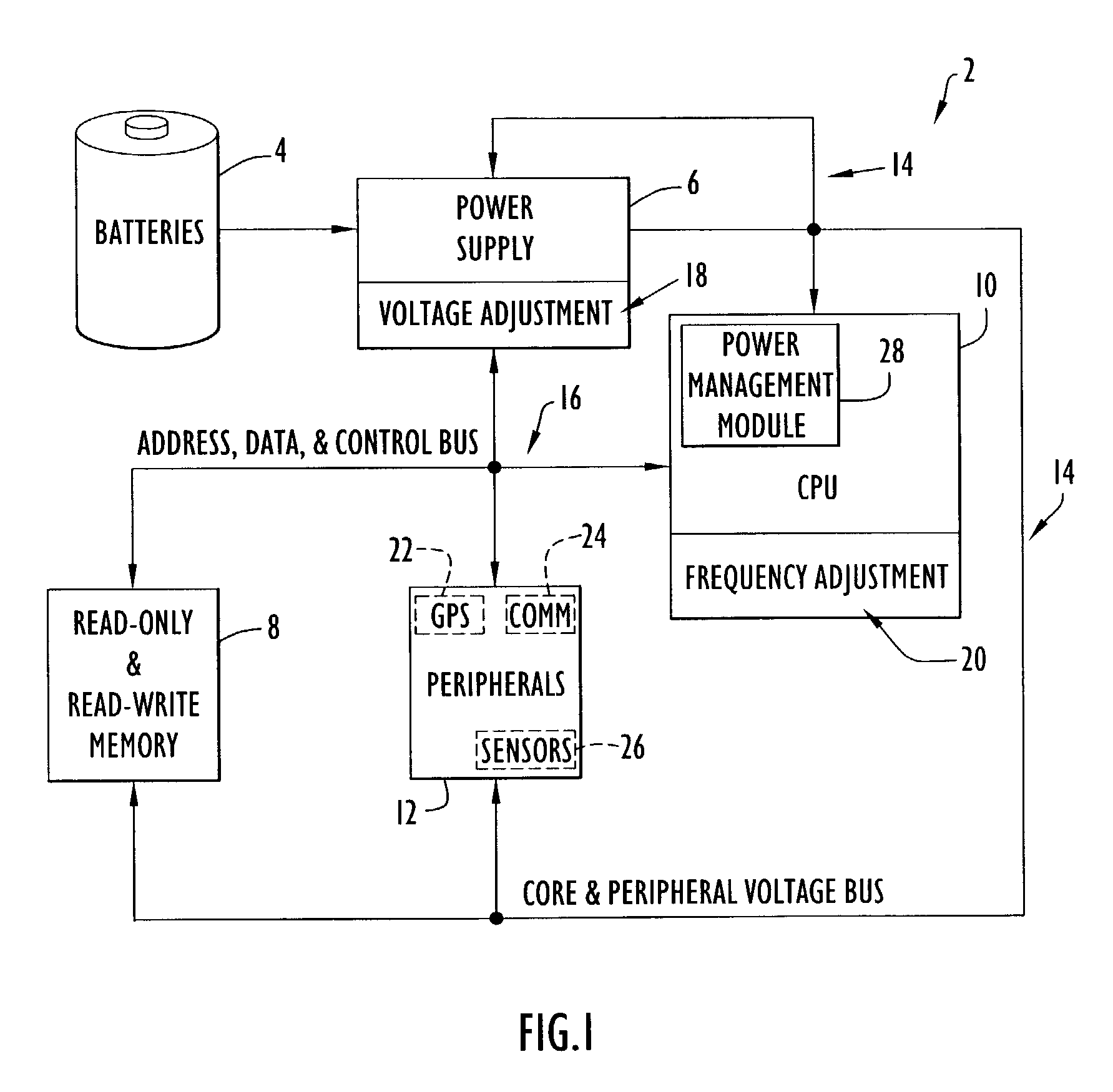
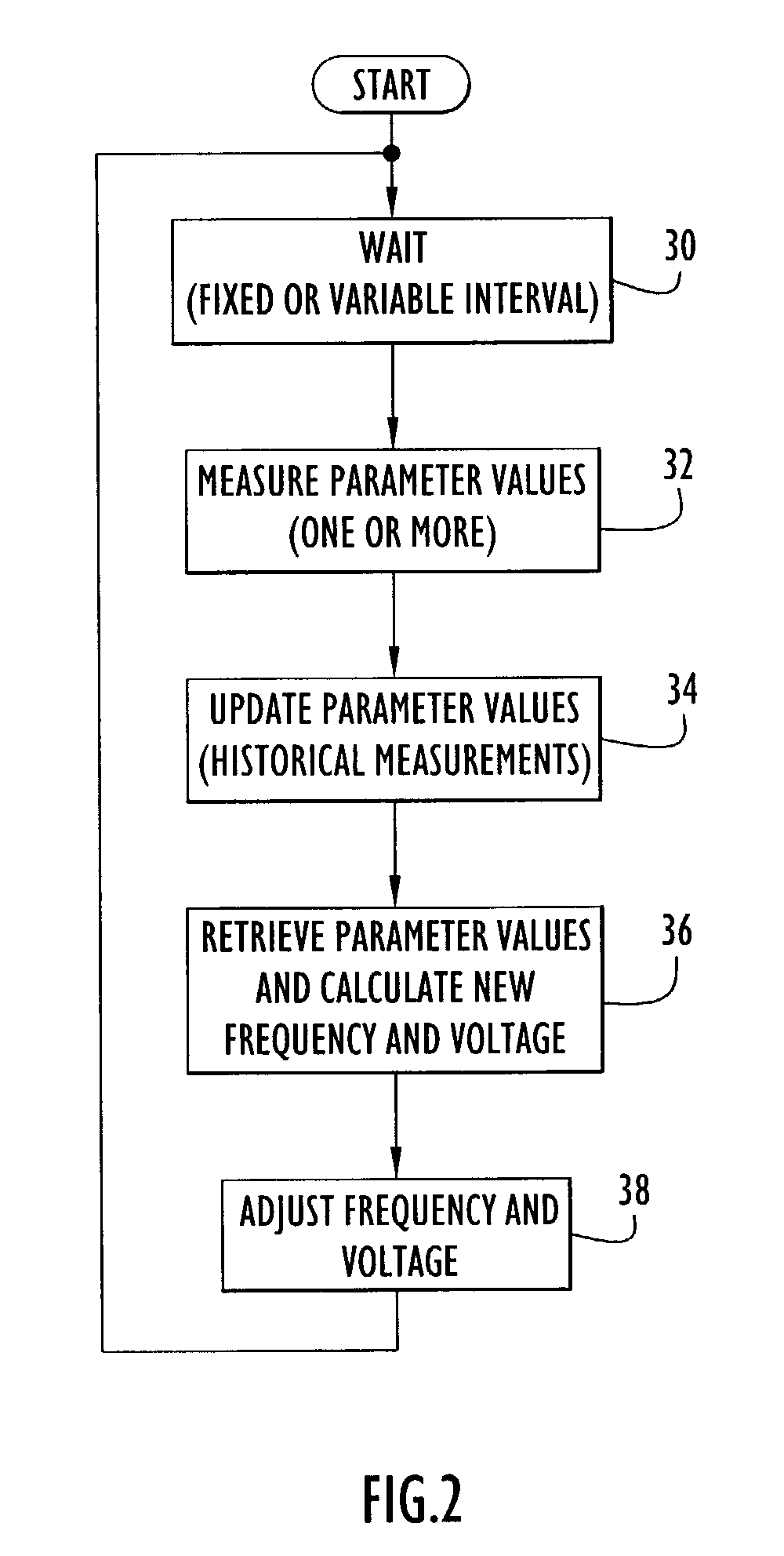
Method and apparatus for optimizing performance and battery life of electronic devices based on system and application parameters
InactiveUS7111179B1Reduce power consumptionExtending device operating lifeEnergy efficient ICTBatteries circuit arrangementsOperational systemElectrical battery
An electronic device (e.g., computer system, etc.) employing dynamic power management of the present invention adjusts power consumption in accordance with an analysis of parameters and events occurring over one or more time-periods. Preferably, the electronic device monitors microprocessor, operating system, peripheral and / or device-level events and adjusts run-time parameters, such as microprocessor clock frequency and voltage, to reduce power consumption with minimal perceived degradation in performance.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
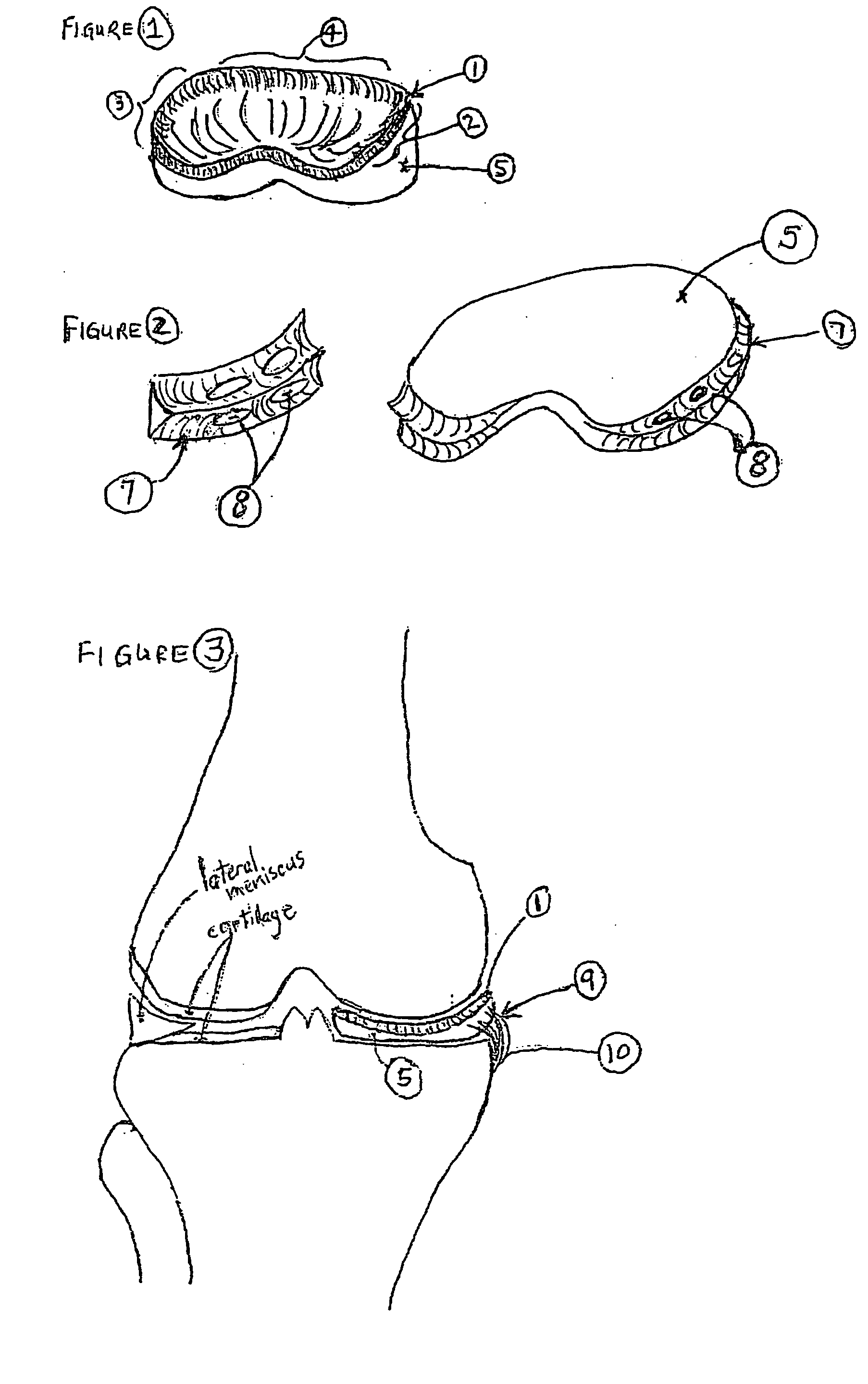
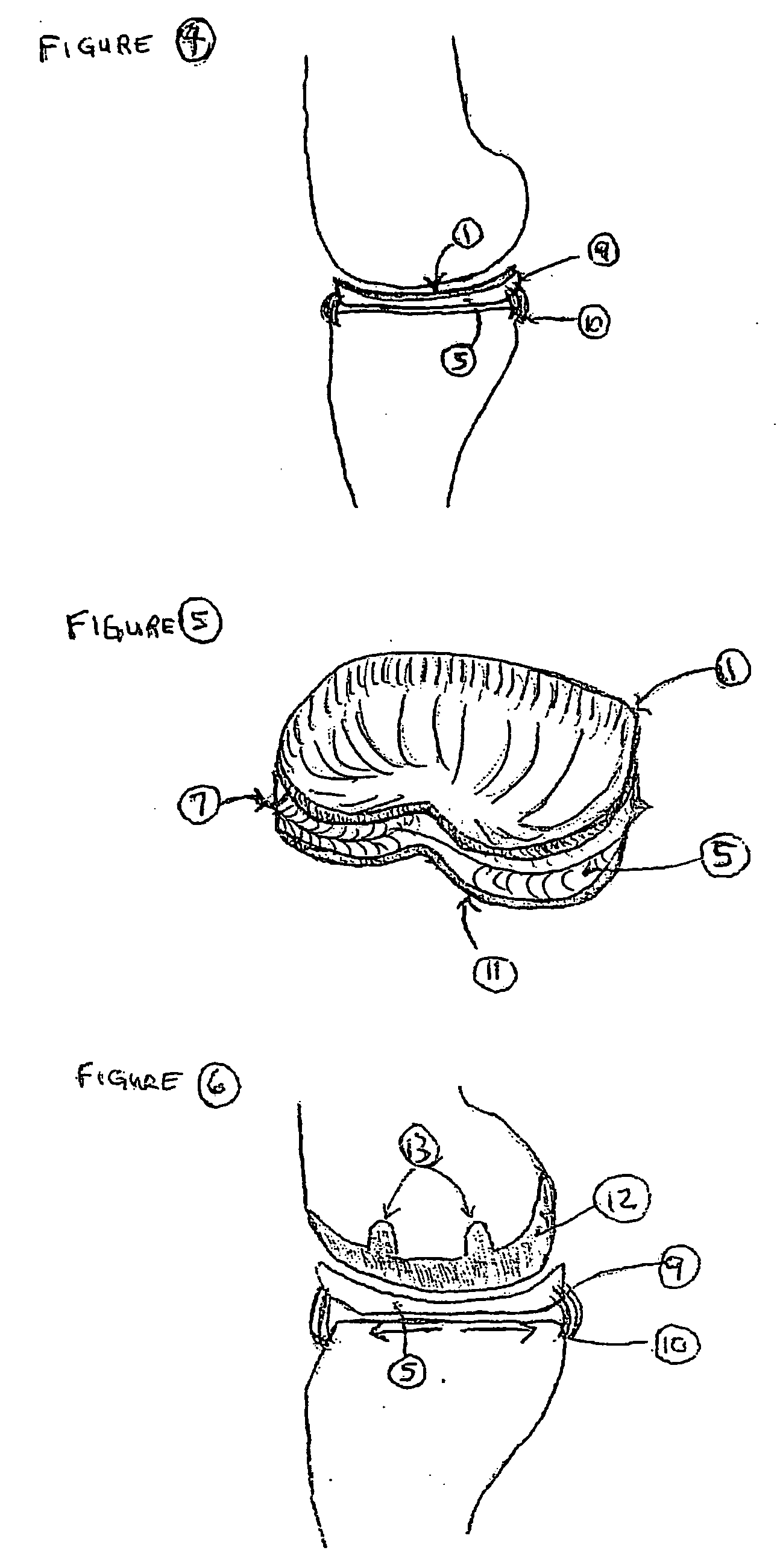
Unicondylar knee implant
InactiveUS20050171604A1Reduce frictionMinimal incisionSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesFiberSide effect
A knee prosthesis, methods of implanting the prosthesis, method of treating arthritis of the knee, and a kit therefore are provided. The prosthesis answers many of the limitations of current knee prosthetic devices by providing a two-component (or alternatively, an optional three-component) device, as either a single structure, or as separate pieces. One of the components is constructed of low friction material, while the second is composed of a weight-dissipating cushioning material; the optional third component is constructed of low friction material. The prosthesis is initially attached to surrounding soft tissue in the knee by biodegradable sutures; it is held permanently in place by fibrous ingrowth into a porous collagen rim in the cushioning component. Major improvements provided by the present invention over currently available prostheses include minimal incisions, minimal or no bone cuts, minimal overall dissection (these improvements lead to shorter hospital stays and rapid rehabilitation and fewer potential for side effects), less prosthetic wear, greater longevity, fewer activity restrictions, able to be used on young, large, active patients, ease of revision, ease of conversion into a total knee arthroplasty if needed.
Owner:MICHALOW ALEXANDER
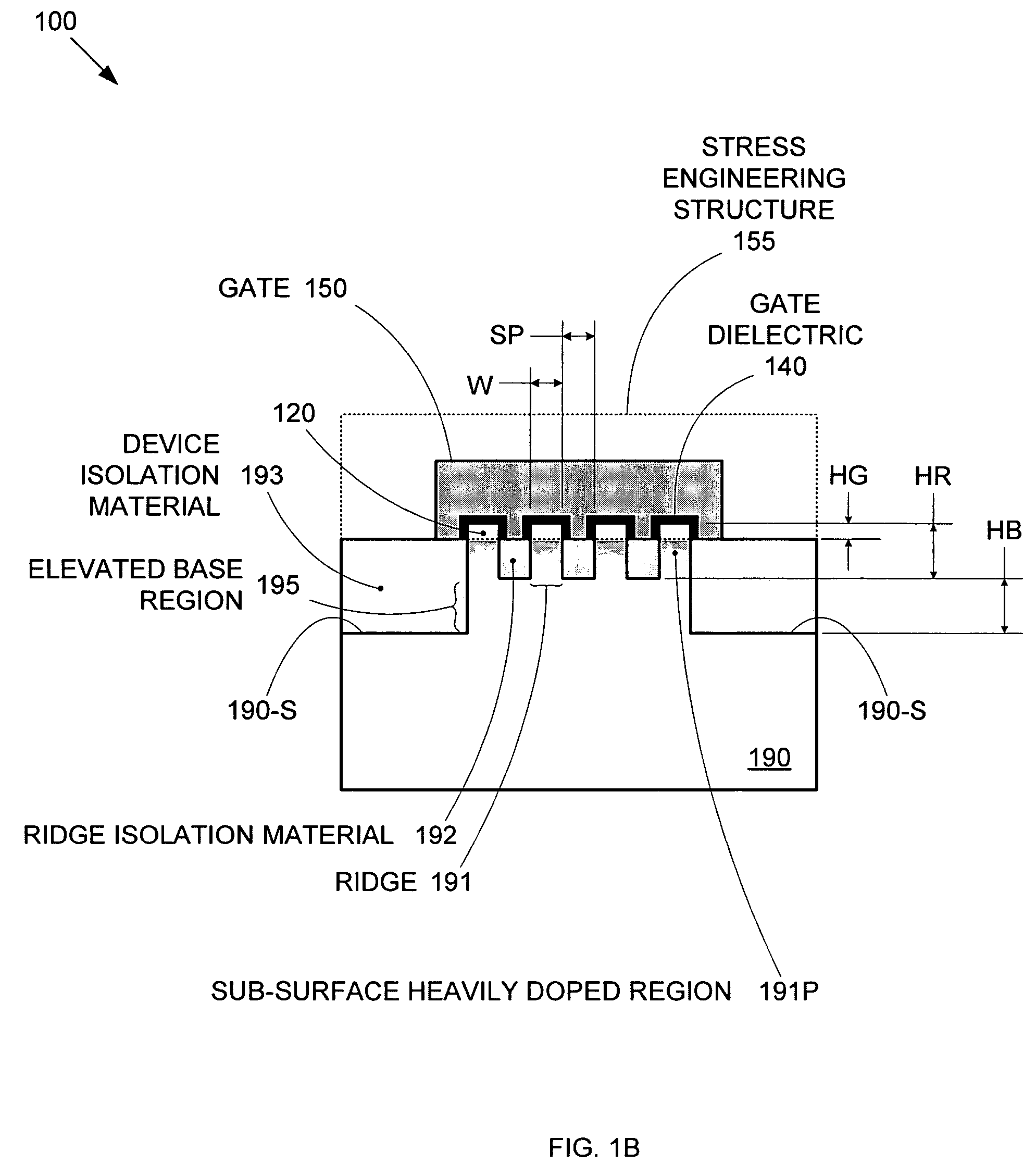
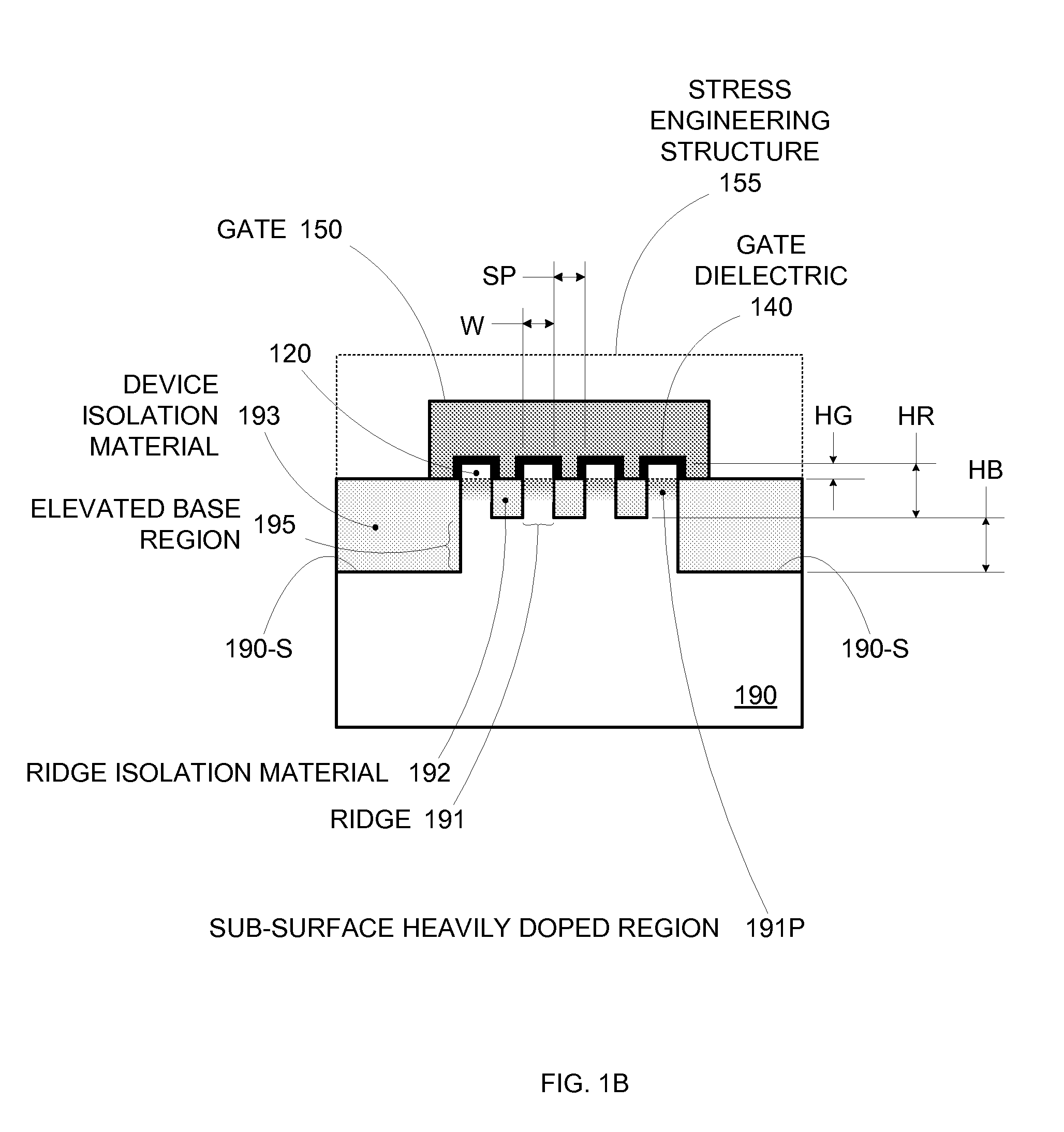
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with Multi Layer Regions
ActiveUS20070120156A1Increase costImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with Narrowed Base Regions
ActiveUS20070128782A1Increase costImprove performanceThyristorSolid-state devicesPre-existingImage resolution
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Sequential Selective Epitaxial Growth
ActiveUS20070122954A1Increase costImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETCMOS
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. A multi step epitaxial process can be used to extend the ridges with different dopant types, high mobility semiconductor, and or advanced multi-layer strutures. For CMOS integrated circuits a capping layer is formed over the a first region. Epitaxial layers are formed in a second region. Then the capping layer is removed from the first region and a capping layer is formed over the second region. Epitaxial layers can than be formed in the first region.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Phased array metamaterial antenna system
ActiveUS6958729B1Reduce sidelobeIncrease amplitude performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsSolid substratePhased array
An efficient, low-loss, low sidelobe, high dynamic range phased-array radar antenna system is disclosed that uses metamaterials, which are manmade composite materials having a negative index of refraction, to create a biconcave lens architecture (instead of the aforementioned biconvex lens) for focusing the microwaves transmitted by the antenna. Accordingly, the sidelobes of the antenna are reduced. Attenuation across microstrip transmission lines may be reduced by using low loss transmission lines that are suspended above a ground plane a predetermined distance in a way such they are not in contact with a solid substrate. By suspending the microstrip transmission lines in this manner, dielectric signal loss is reduced significantly, thus resulting in a less-attenuated signal at its destination.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method of IC production using corrugated substrate
ActiveUS7265008B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceLaser detailsSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
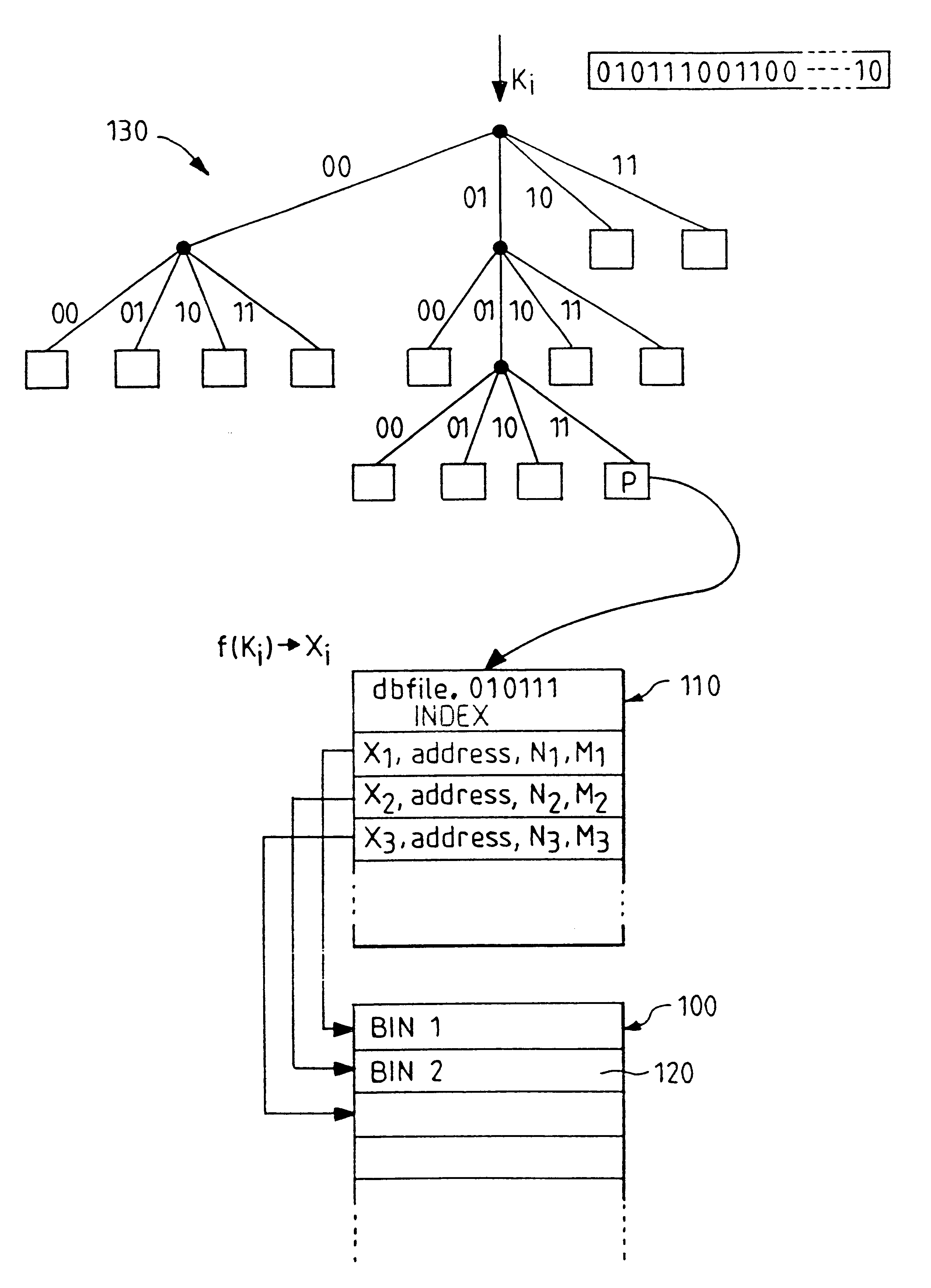
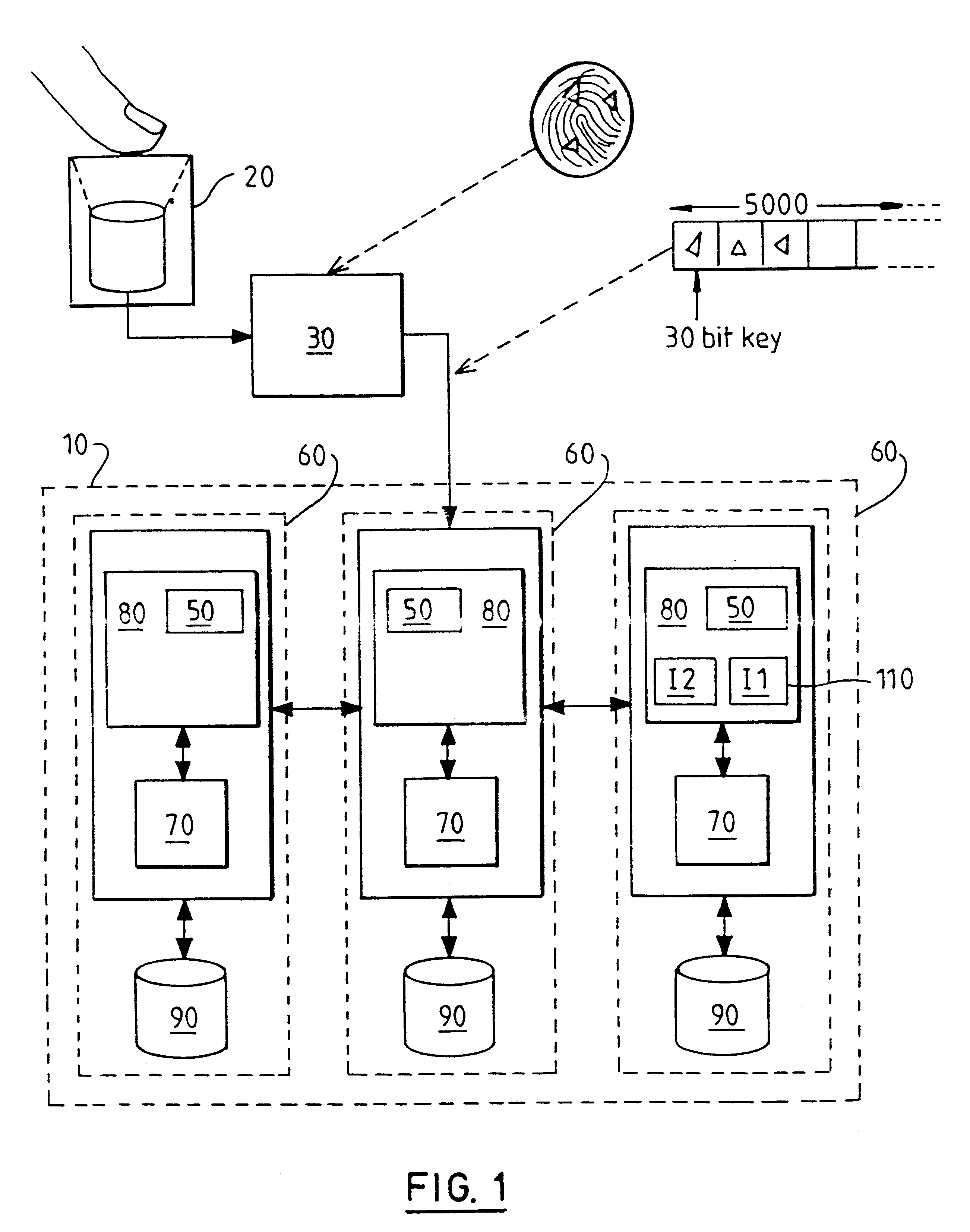
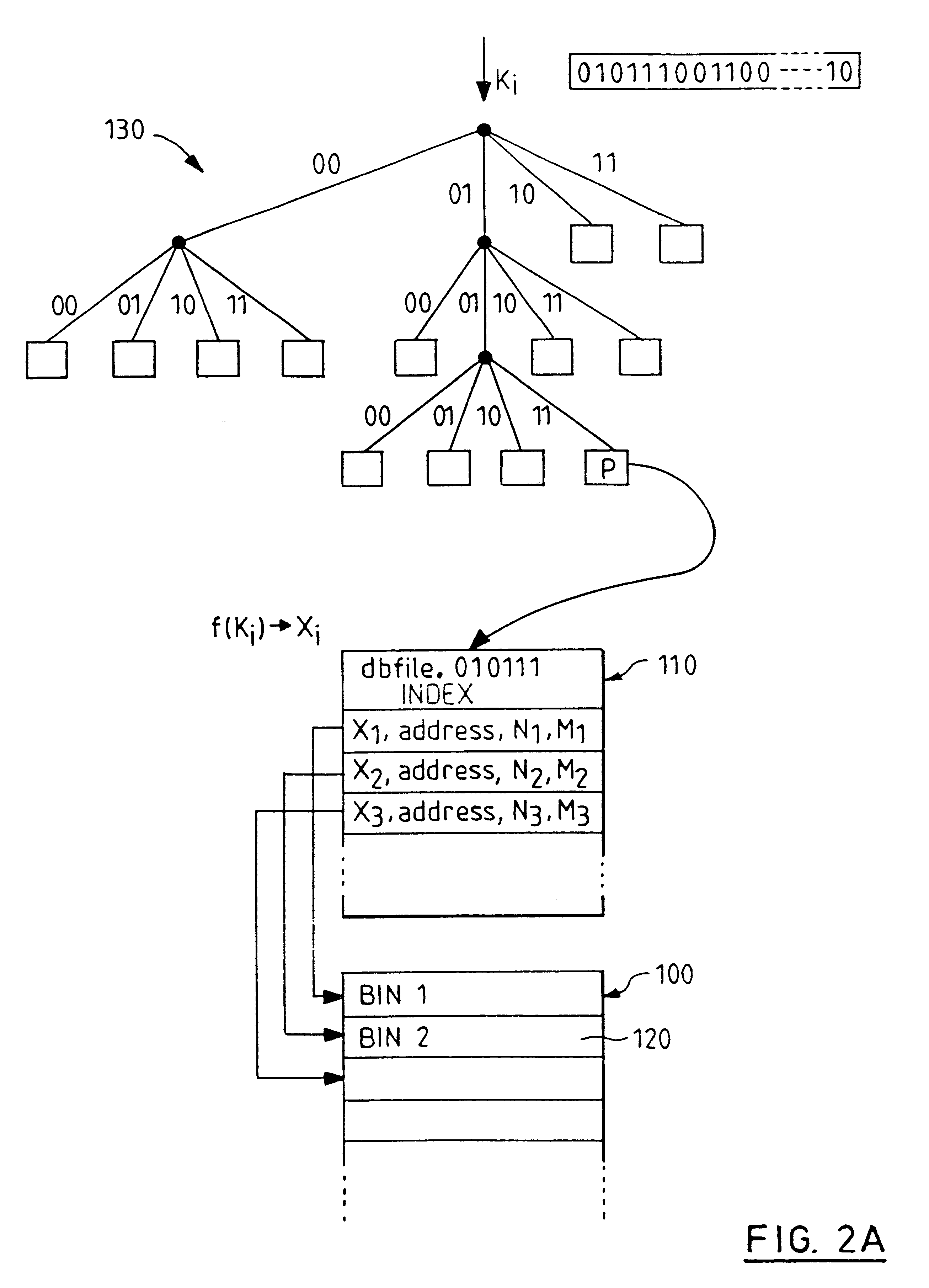
Indexed file system and a method and a mechanism for accessing data records from such a system
InactiveUS6292795B1Efficient access to dataWastefulData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExtensibilityCollision detection
A computer filing system includes a data access and allocation mechanism including a directory and a plurality of indexed data files or hash tables. The directory is preferably a radix tree including directory entries which contain pointers to respective ones of the hash tables. Using a plurality of hash tables avoids the whole database ever having to be re-hashed all at once. If a hash table exceeds a preset maximum size as data is added, it is replaced by two hash tables and the directory is updated to include two separate directory entries each containing a pointer to one of the new hash tables. The directory is locally extensible such that new levels are added to the directory only where necessary to distinguish between the hash tables. Local extensibility prevents unnecessary expansion of the size of the directory while also allowing the size of the hash tables to be controlled. This allows optimisation of the data access mechanism such that an optimal combination of directory-look-up and hashing processes is used. Additionally, if the number of keys mapped to an indexed data file is less than a threshold number (corresponding to the number of entries which can be held in a reasonable index), the index for the data file is built with a one-to-one relationship between keys and index entries such that each index entry identifies a data block holding data for only one key. This avoids the overhead of the collision detection of hashing when it ceases to be useful.
Owner:IBM CORP
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with narrowed base regions
ActiveUS7508031B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably produced. Ridges on the corrugated substrate can be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials, high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
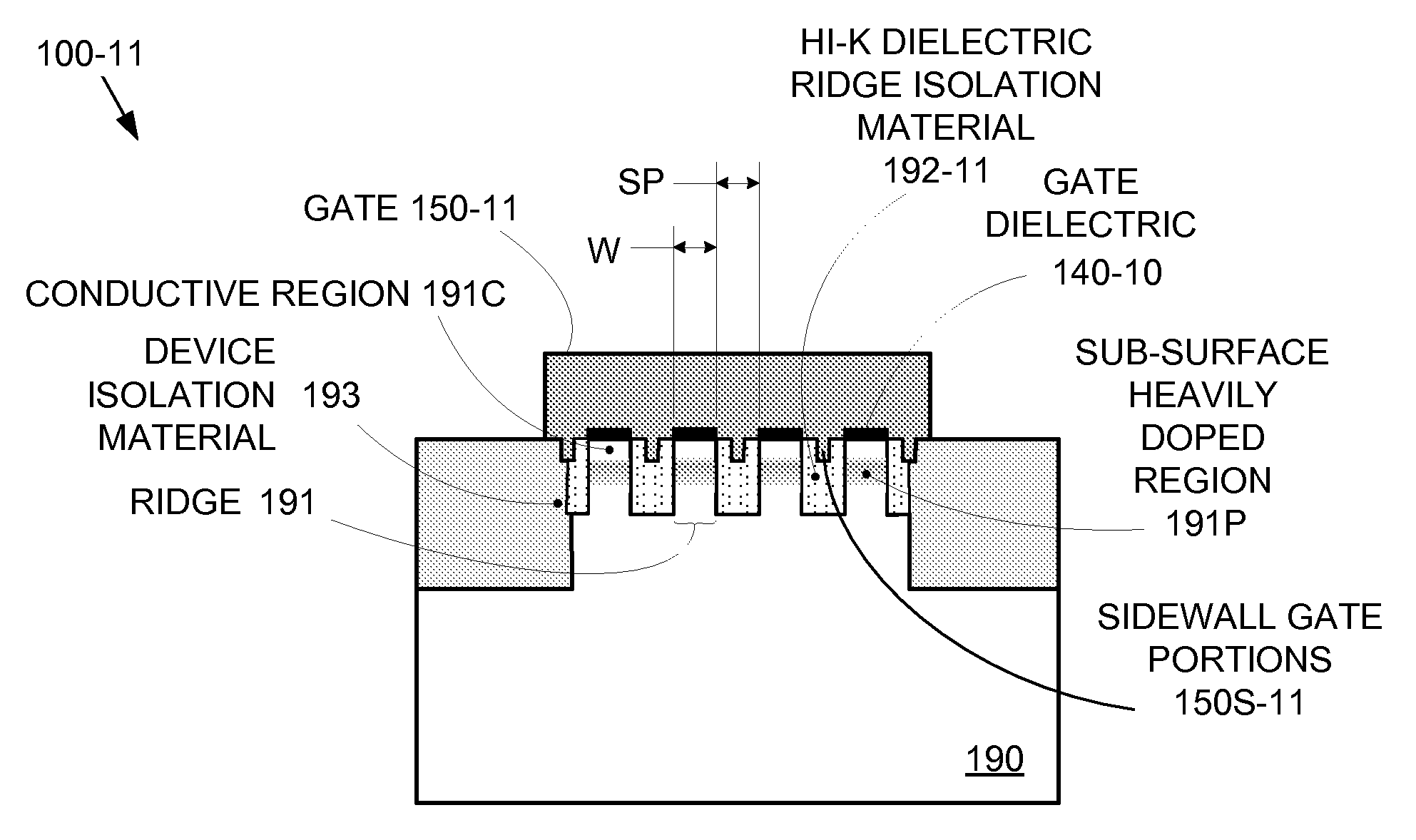
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with High-Permittivity Dielectric Isolation Material
ActiveUS20070122953A1Increase costImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with high-permittivity dielectric isolation material
ActiveUS7605449B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Integrated Circuit On Corrugated Substrate
ActiveUS20070132053A1Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETSemiconductor materials
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Lighting device
ActiveUS7614759B2Maximizing light extractionReduce probabilityPoint-like light sourceLighting elementsElement spaceEffect light
A lighting device comprising at least one solid state light emitter and at least one luminescent element spaced from the light emitter, a surface of the luminescent element being at least twice as large as the illumination surface of the light emitter. Also, a lighting device comprising at least one solid state light emitter and at least one luminescent element spaced from the light emitter, a surface of the luminescent element surface being at least twice as large as and substantially parallel to the illumination surface of the light emitter. Also, a lighting device comprising at least one solid state light emitter and at least one luminescent element spaced from the light emitter, a surface area of a projection of the luminescent element being at least twice as large as a surface area of a projection of the light emitter.
Owner:CREELED INC
Display apparatus having image scanning function
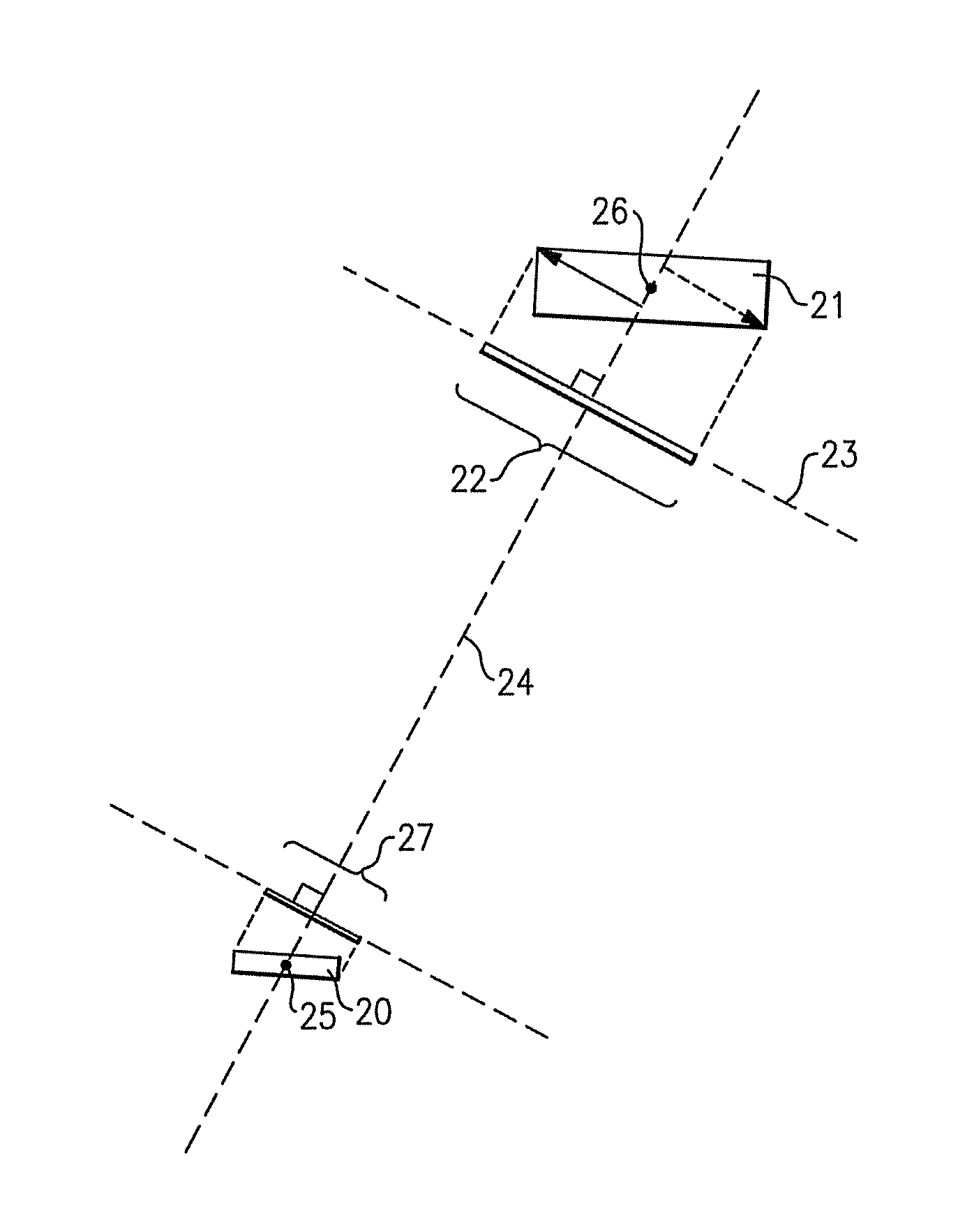
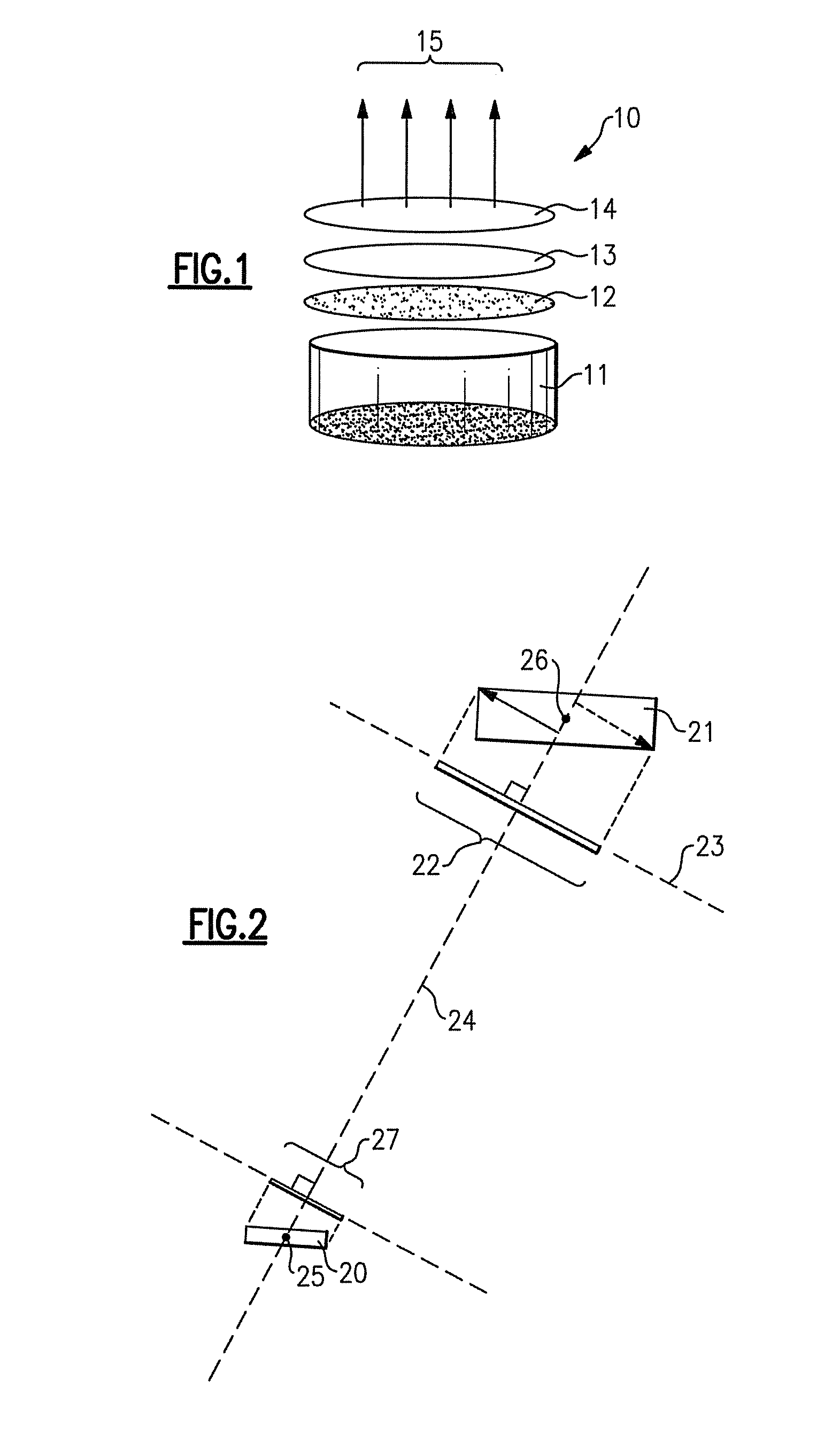
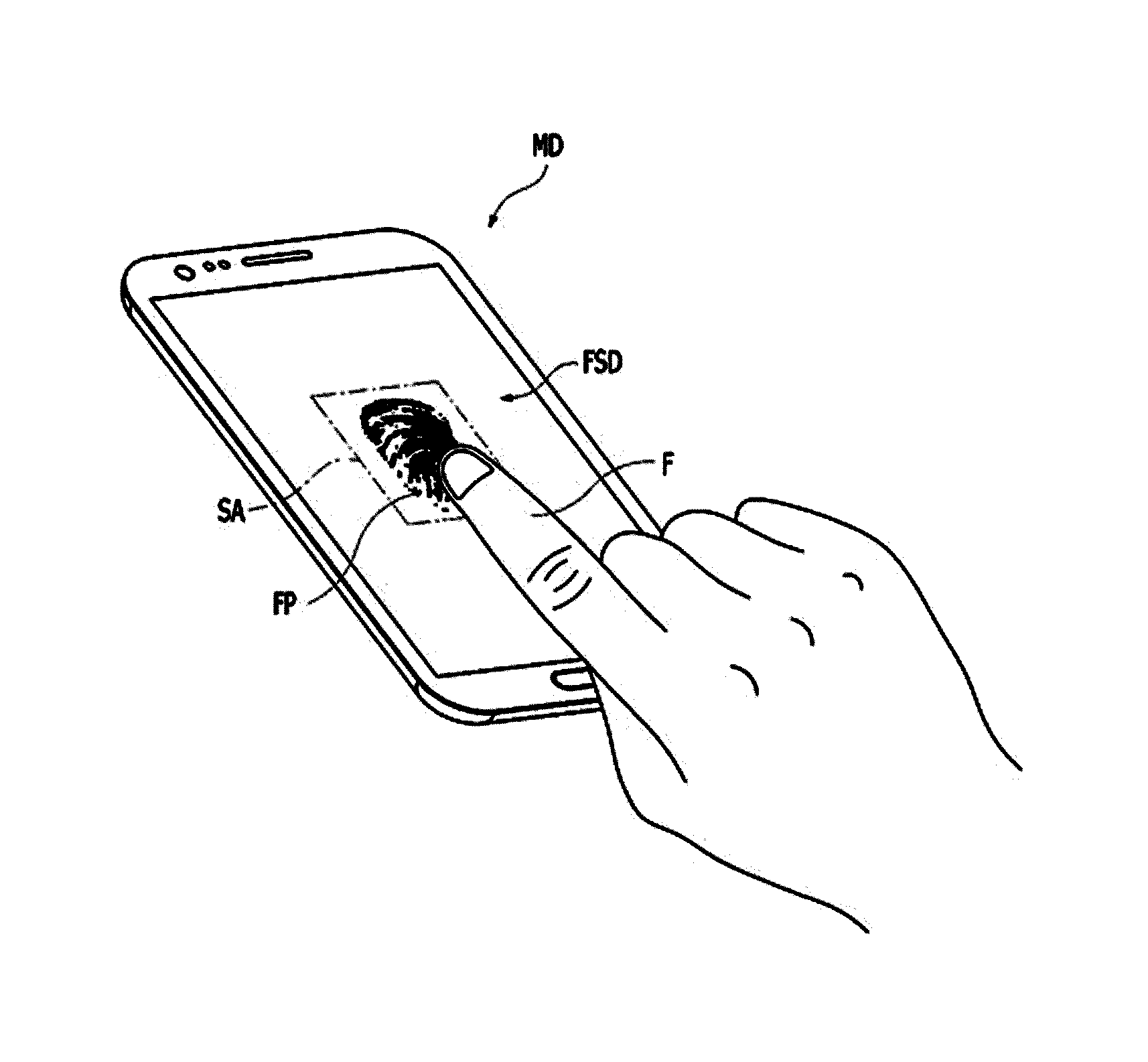
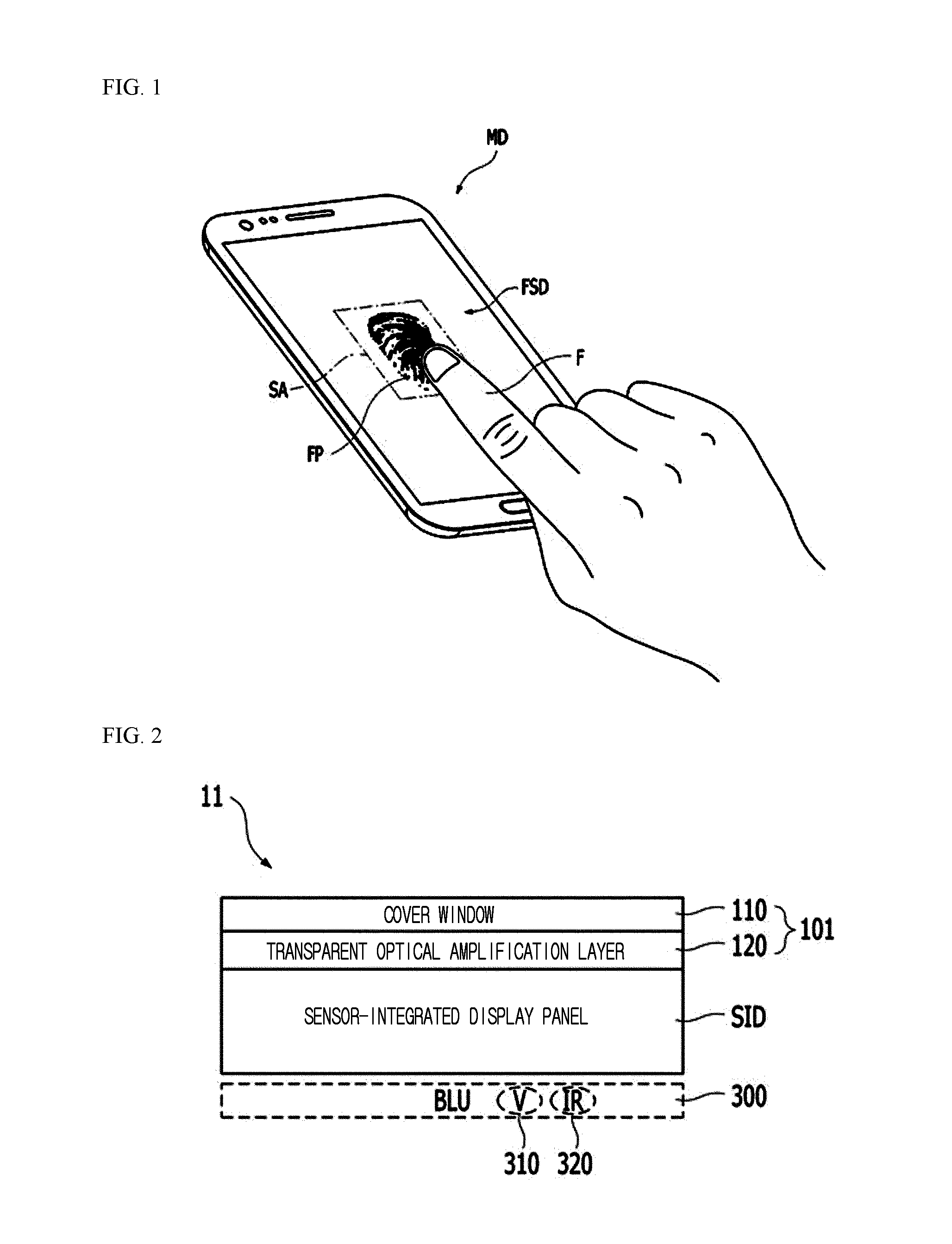
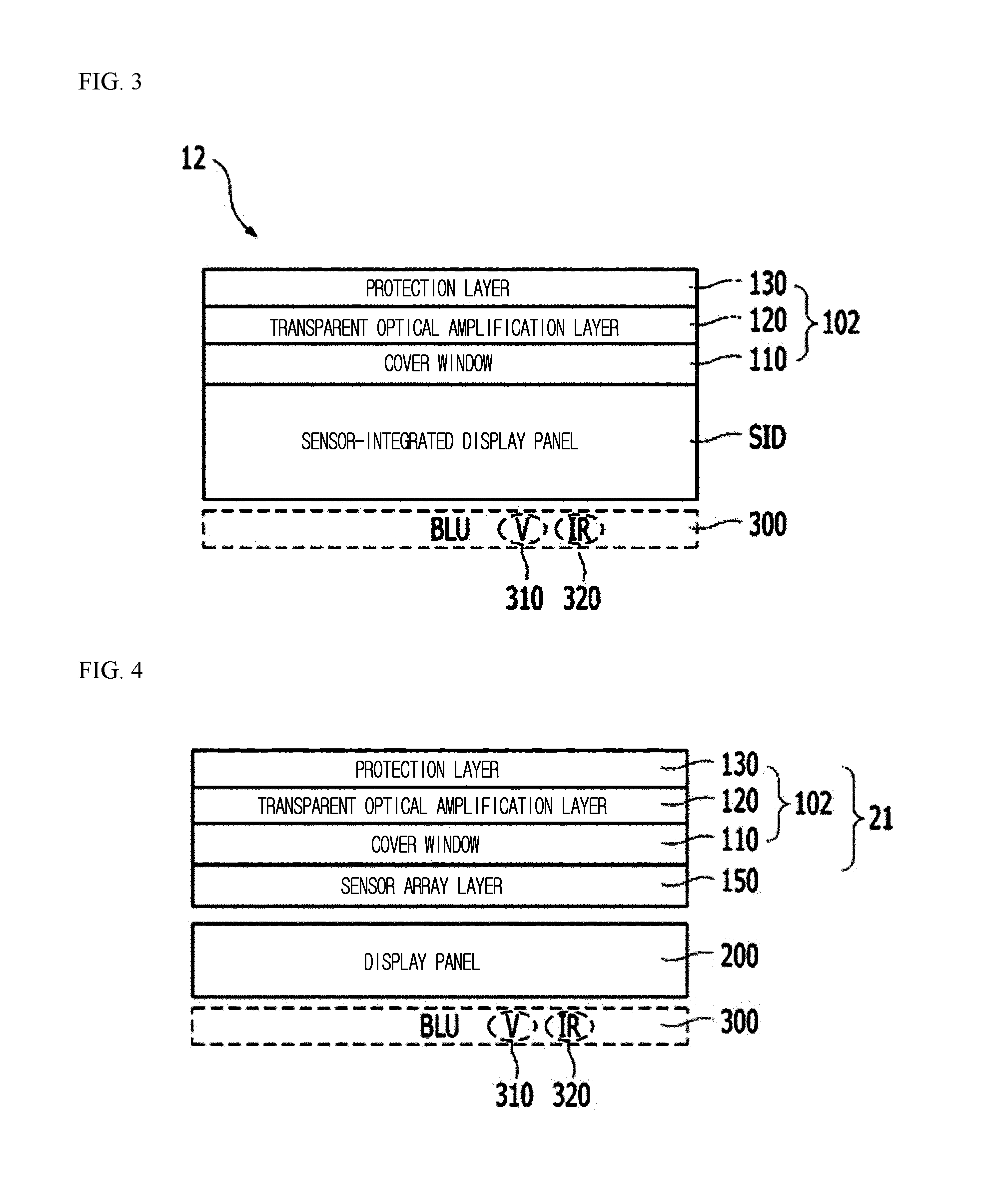
InactiveUS20160266695A1No degradation in display performanceSufficient sensor sensitivityStatic indicating devicesDigital data processing detailsFingerprintSensor array
Disclosed is a fingerprint-sensing display capable of sensing a fingerprint on a display screen. The display apparatus having an image scanning function includes an optical amplification cover, one side of which forms a display surface, including a transparent optical amplification layer configured to amplify an optical pattern generated by a fingerprint of a user in contact with the display surface and a cover window for reinforcement, a thin film transistor (TFT) array configured to drive a plurality of pixels forming an image, and an optical sensor array disposed between the optical amplification cover and the TFT array and configured to sense the optical pattern amplified by the optical amplification cover.
Owner:CRUCIALTEC
Augmented reality for testing and training of human performance
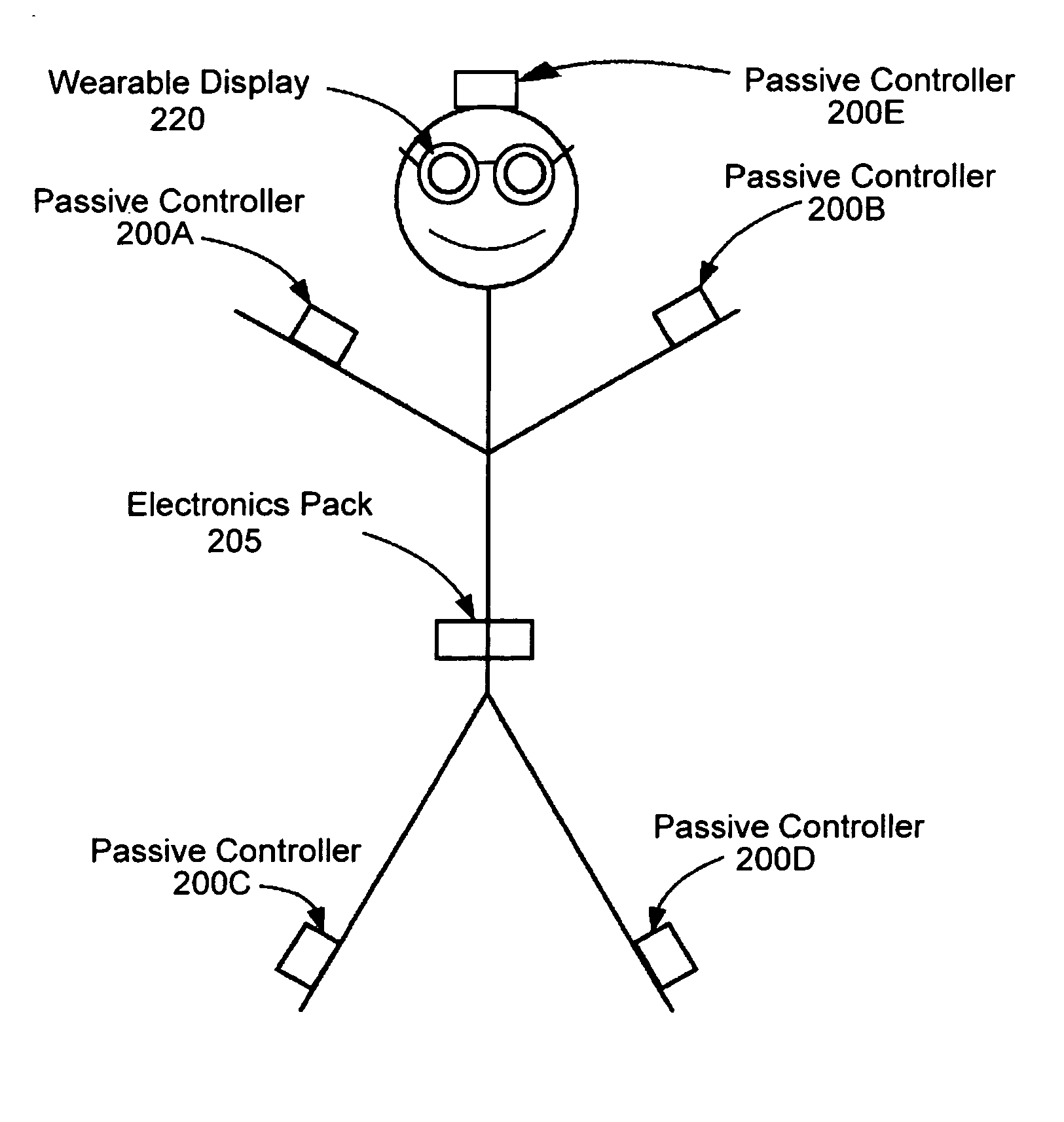
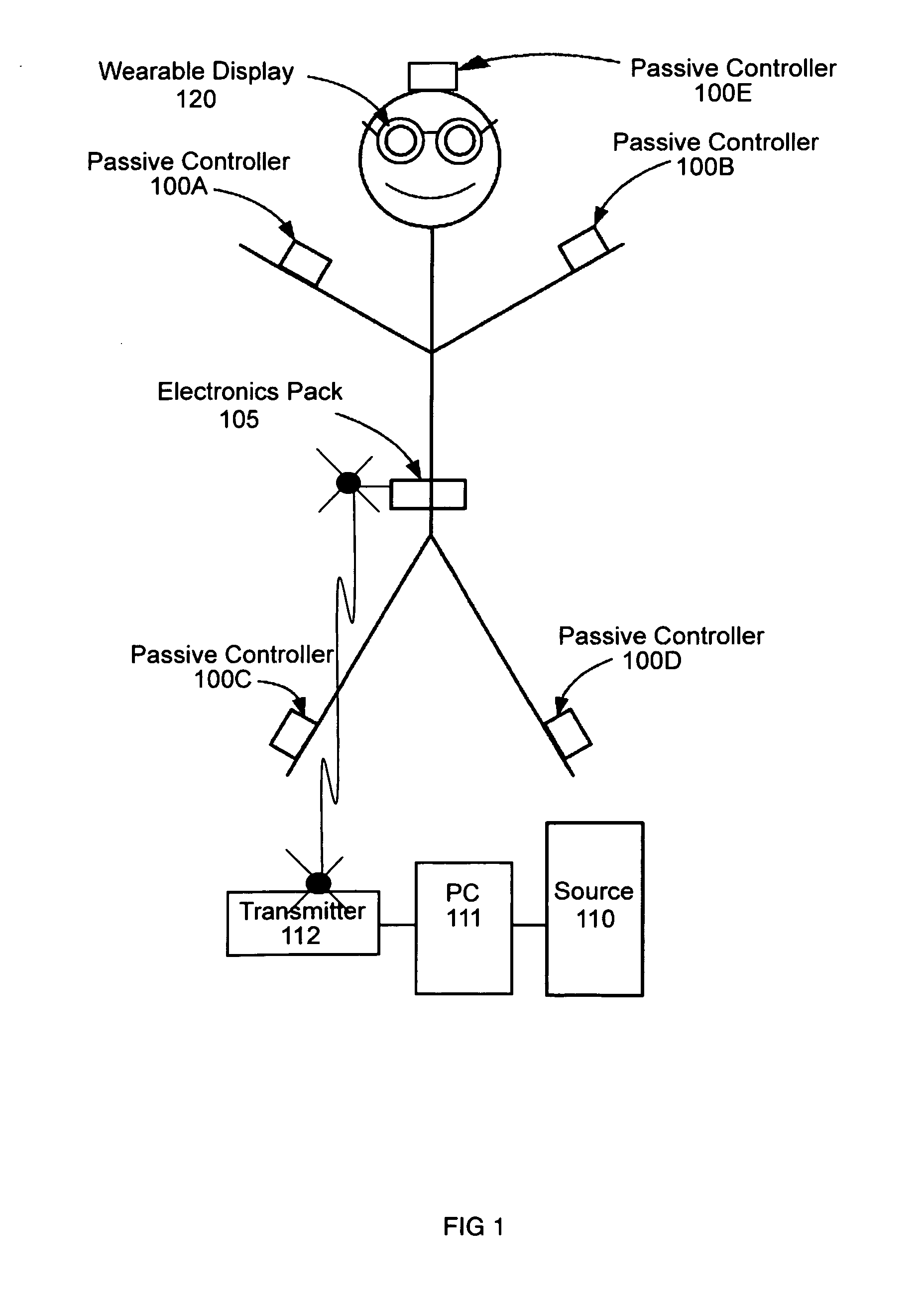
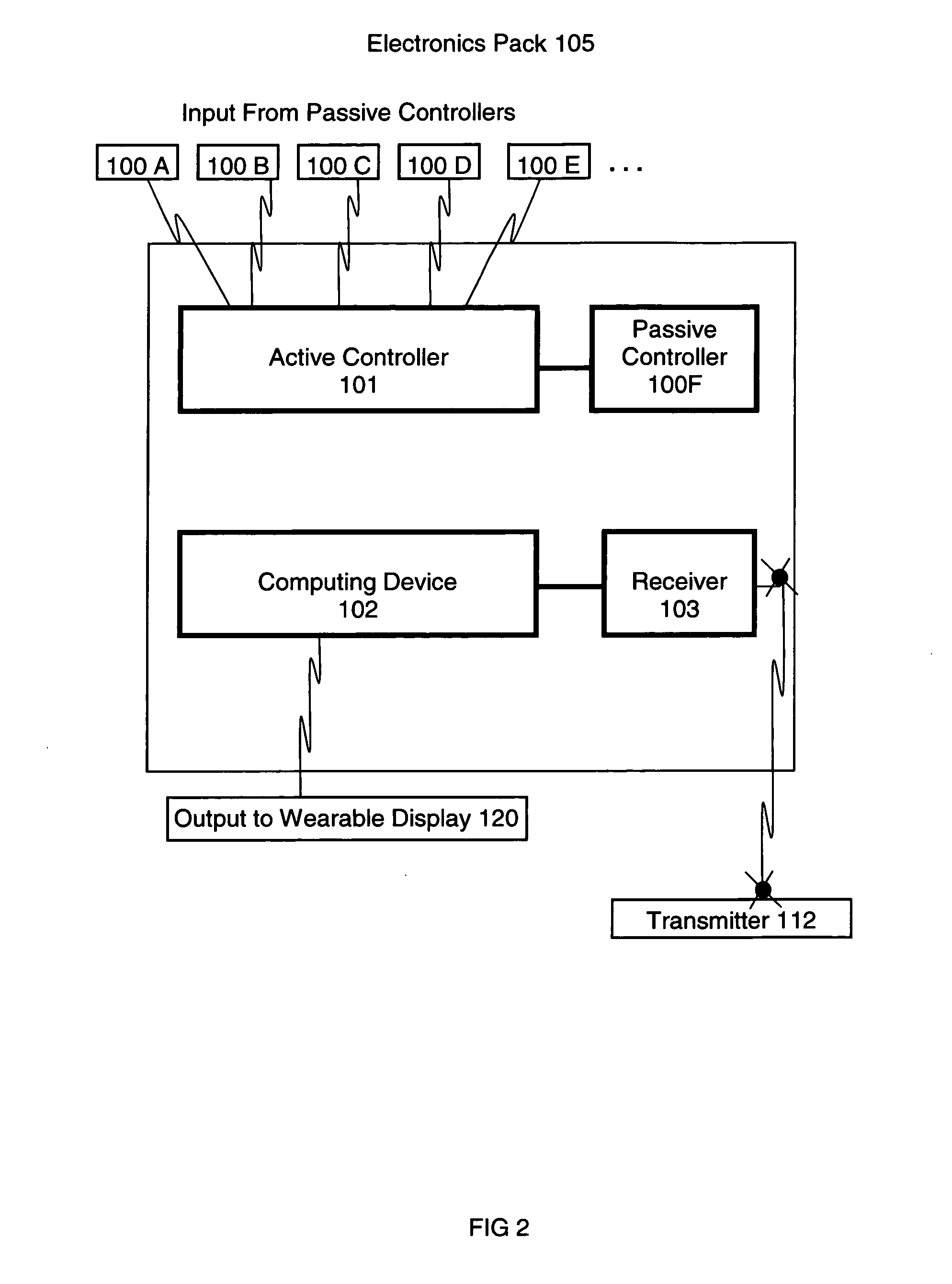
InactiveUS20110270135A1Facilitate communicationImprove injuryPhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationEyewearCause injury
A system for continuously monitoring a user's motion and for continuously providing realtime visual physical performance information to the user while the user is moving to enable the user to detect physical performance constructs that expose the user to increased risk of injury or that reduce the user's physical performance. The system includes multiple passive controllers 100A-F for measuring the user's motion, a computing device 102 for communicating with wearable display glasses 120 and the passive controllers 100A-F to provide realtime physical performance feedback to the user. The computing device 102 also transmits physical performance constructs to the wearable display glasses 120 to enable the user to determine if his or her movement can cause injury or reduce physical performance.
Owner:FRENCH BARRY JAMES
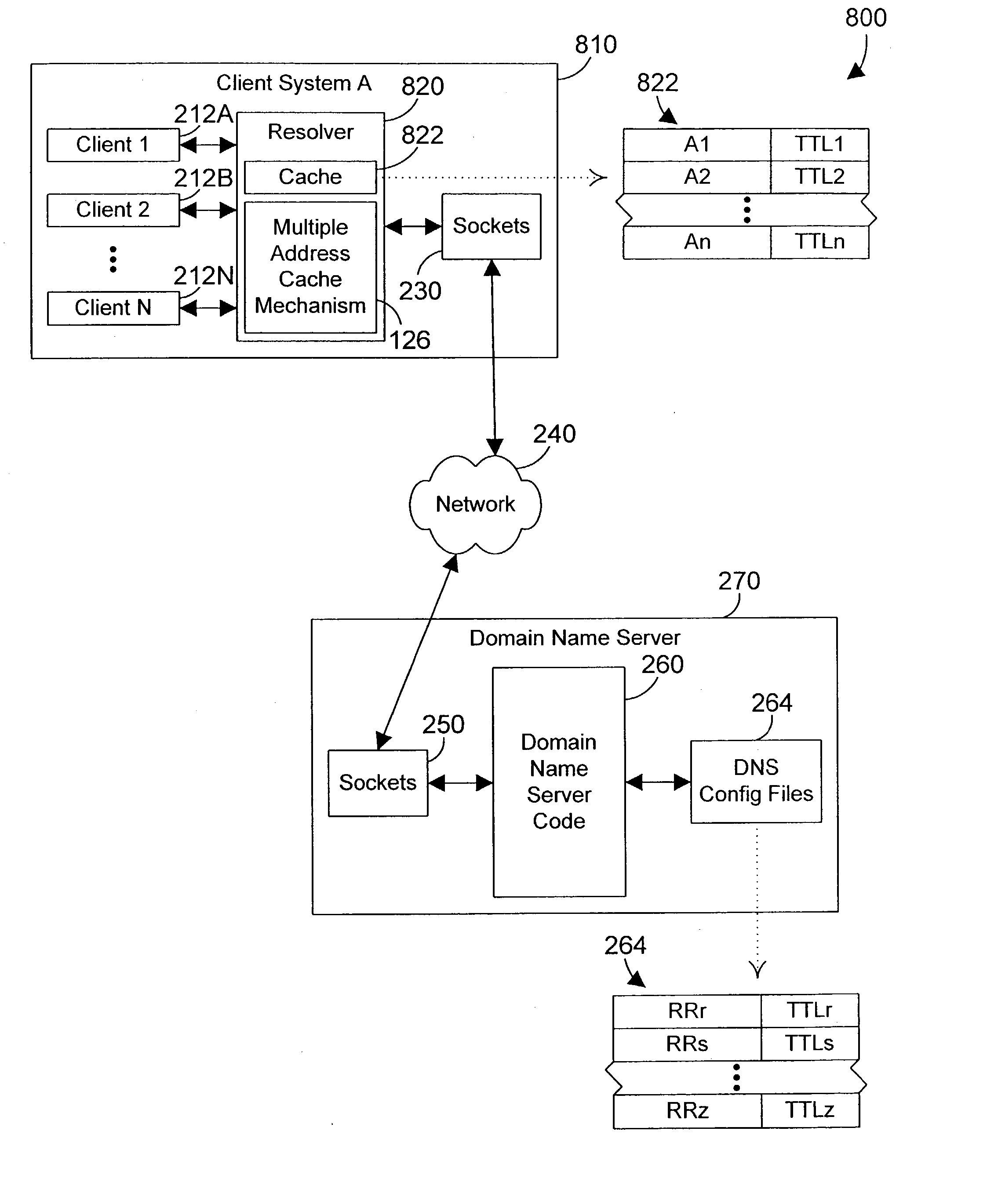
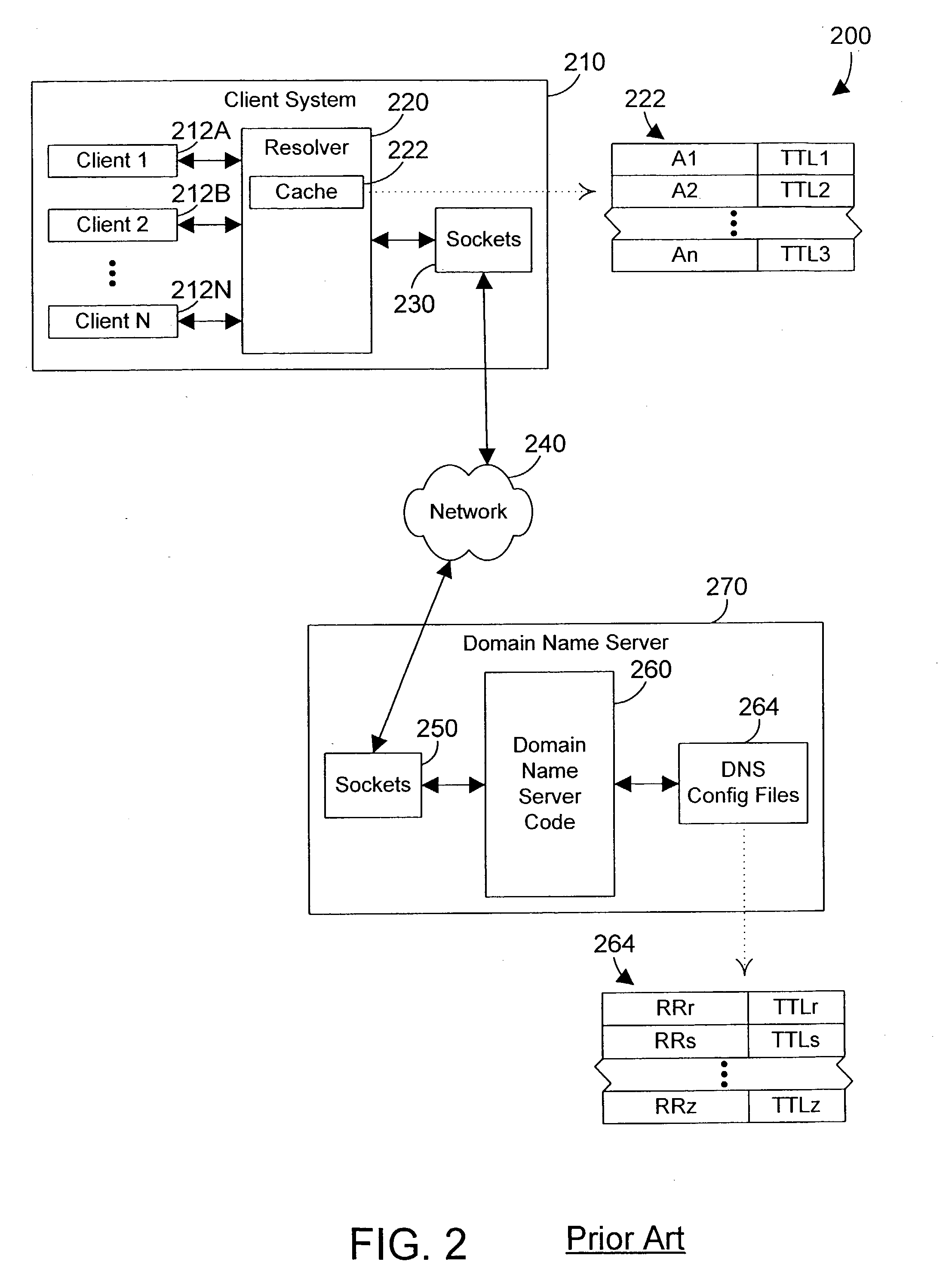
Network address cache apparatus and method
InactiveUS20040078487A1Improve query performanceLower performance requirementsDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork addressClient-side
Cached information that includes multiple network addresses is delivered in a manner that changes the order of the network addresses each time the cached information is delivered to a client, thereby achieving load balancing in a manner that reduces network traffic and improves system performance. In the preferred embodiments, the user defines a minimum time to live (TTL) and one or more order change criteria. When a query is made to a DNS, the DNS returns an answer that includes a time to live (TTL). This answer may be stored in a cache, and may include multiple network addresses. If the TTL for the answer received from a DNS is less that the minimum TTL, the TTL for the answer is set to the minimum TTL before storing the answer in the cache. When a query may be satisfied by a cached answer that includes multiple network addresses, a cache mechanism delivers the multiple cached network addresses in an order determined by the one or more order change criteria if the TTL for the cached results is a positive number. In this manner load balancing can be achieved while still benefitting from the performance enhancements of caching DNS query results.
Owner:IBM CORP
Process for producing a hydrocarbon component of biological origin
ActiveUS7232935B2Improve performanceLow densityHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionIsomerizationHydrocarbon
The invention relates to a process for producing a hydrocarbon component of biological origin. The process comprises at least two steps, the first one of which is a HDO step and the second one is an isomerization step operated using the counter-current flow principle. A biological raw material containing fatty acids and / or fatty acid esters serves as the feed stock.
Owner:OYJ NESTE OIL +1
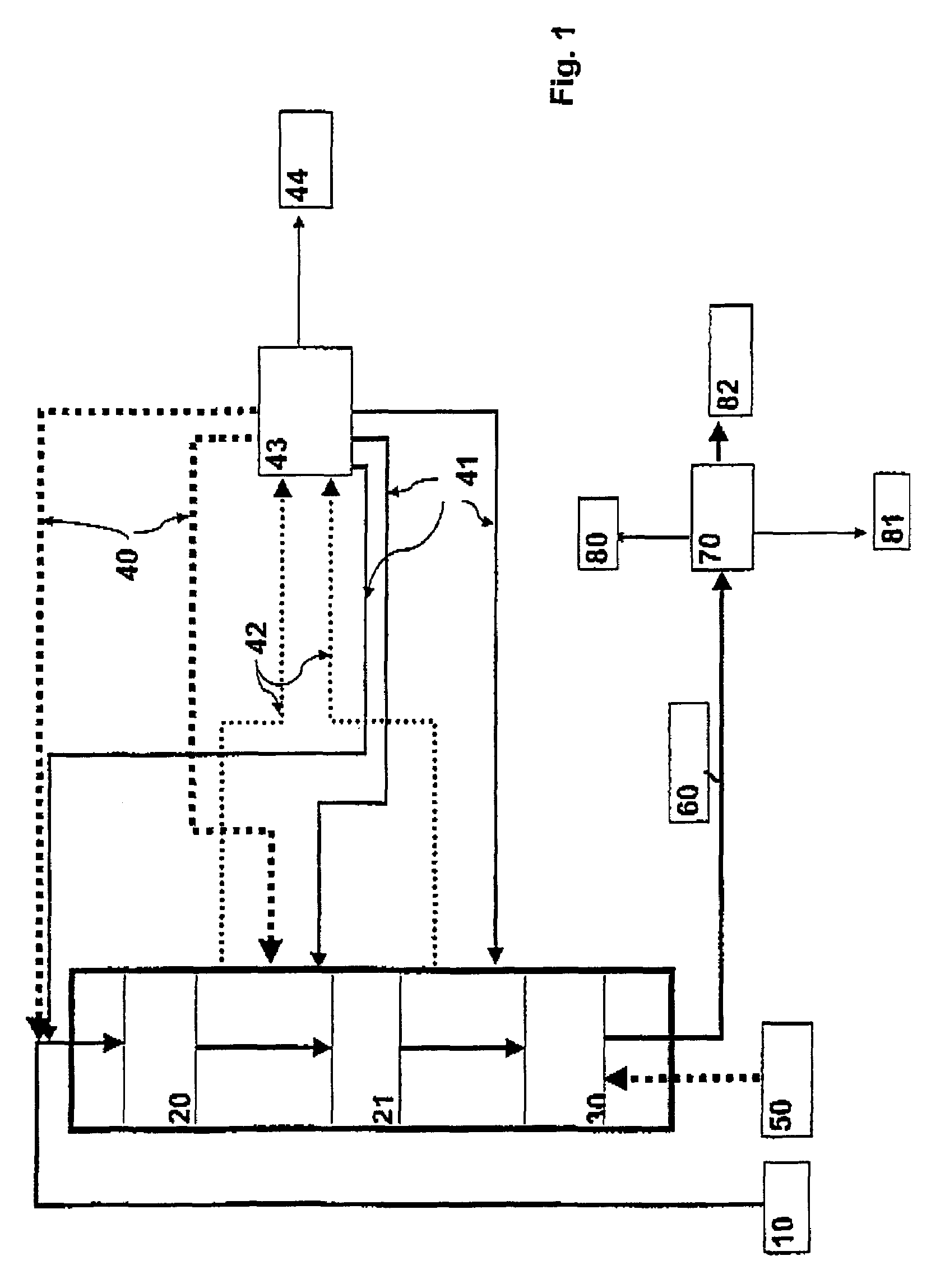
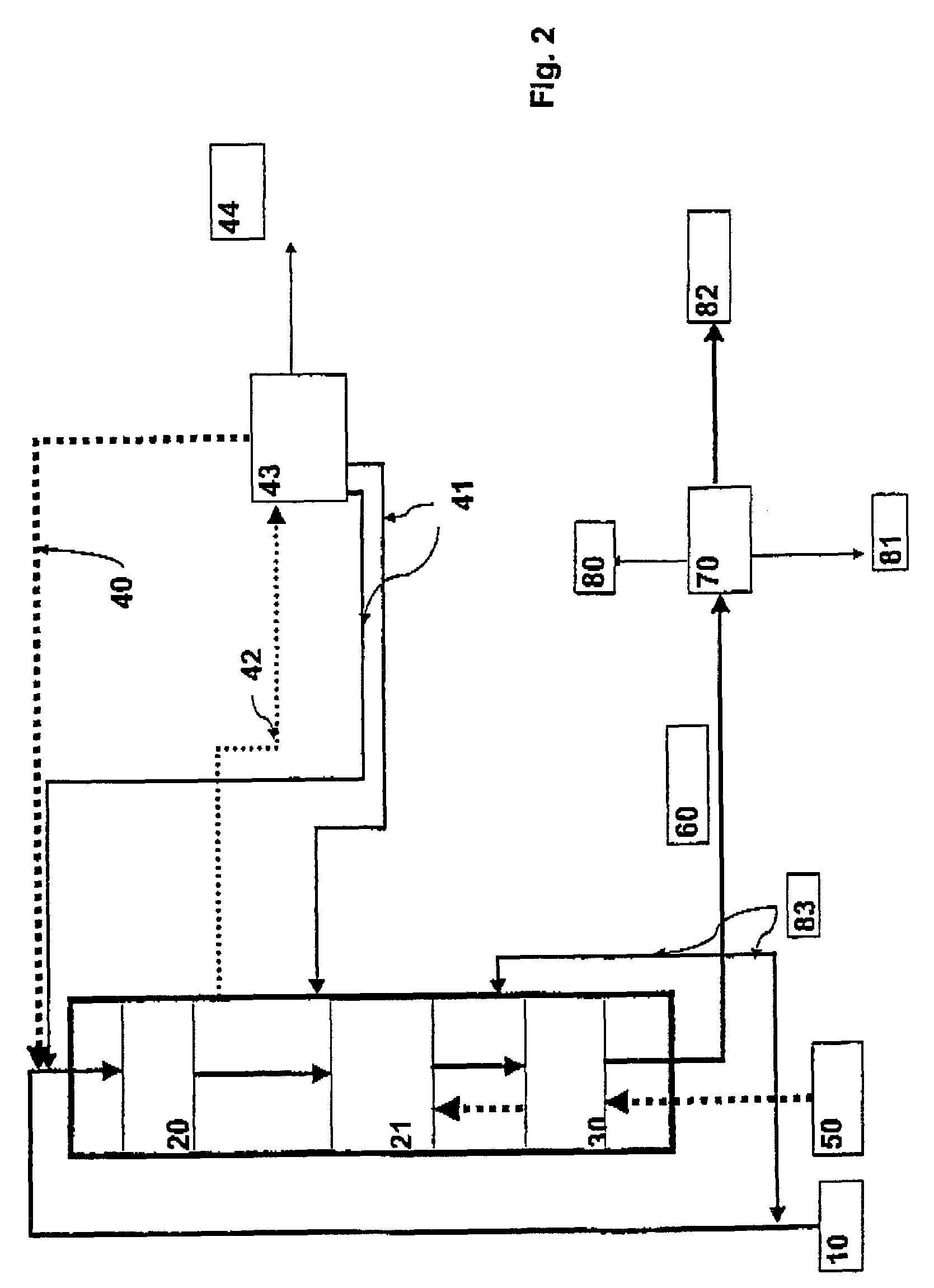
Method for adjusting battery power limits in a hybrid electric vehicle to provide consistent launch characteristics
ActiveUS6868318B1Lower performance requirementsOvercome deficienciesHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical energy storageAutomotive engineering
A method is disclosed for improving the performance of an energy storage system that incorporates a high density electrical energy storage device, such a battery or ultracapacitor. The method may be implemented in an energy storage system of a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) as a computer control algorithm for controlling the discharge power limits of an energy storage device, such as a battery. The method allows the discharge power limits of the battery to be temporarily expanded under vehicle launch conditions where the power demands are high, thereby making additional stored energy available for use under such conditions by improving battery utilization and providing more consistent vehicle launch characteristics than would otherwise be available.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Lighting device and method of making same
ActiveUS20080089053A1Simple materialReducing performance (intensity)Solid-state devicesVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureEffect lightEngineering
A lighting device comprising a light emitter chip, a reflective cup and a lumiphor positioned between the chip and the cup. Also, a lighting device comprising a light emitter chip, a wire bonded to a first surface of the chip and a lumiphor which faces a second surface of the chip. Also, a lighting device comprising a light emitter chip, and a lumiphor, a first surface of the chip facing a first region of the lumiphor, a second surface of the chip facing a second region of the lumiphor. Also, a lighting device comprising a light emitter chip and first and second lumiphors, a first surface of the chip facing the second lumiphor, a second surface of the chip facing the first lumiphor. Also, methods of making lighting devices.
Owner:CREELED INC
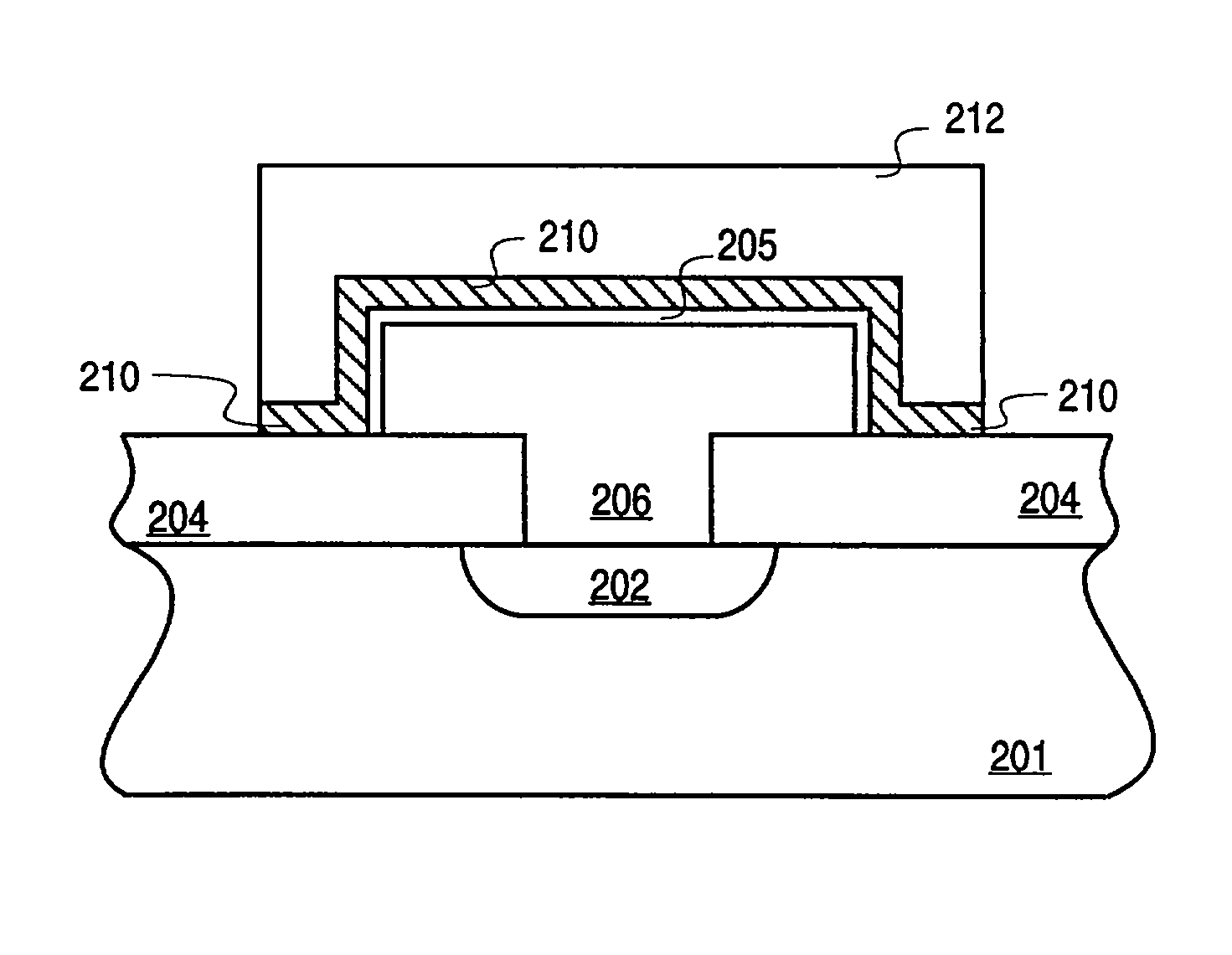
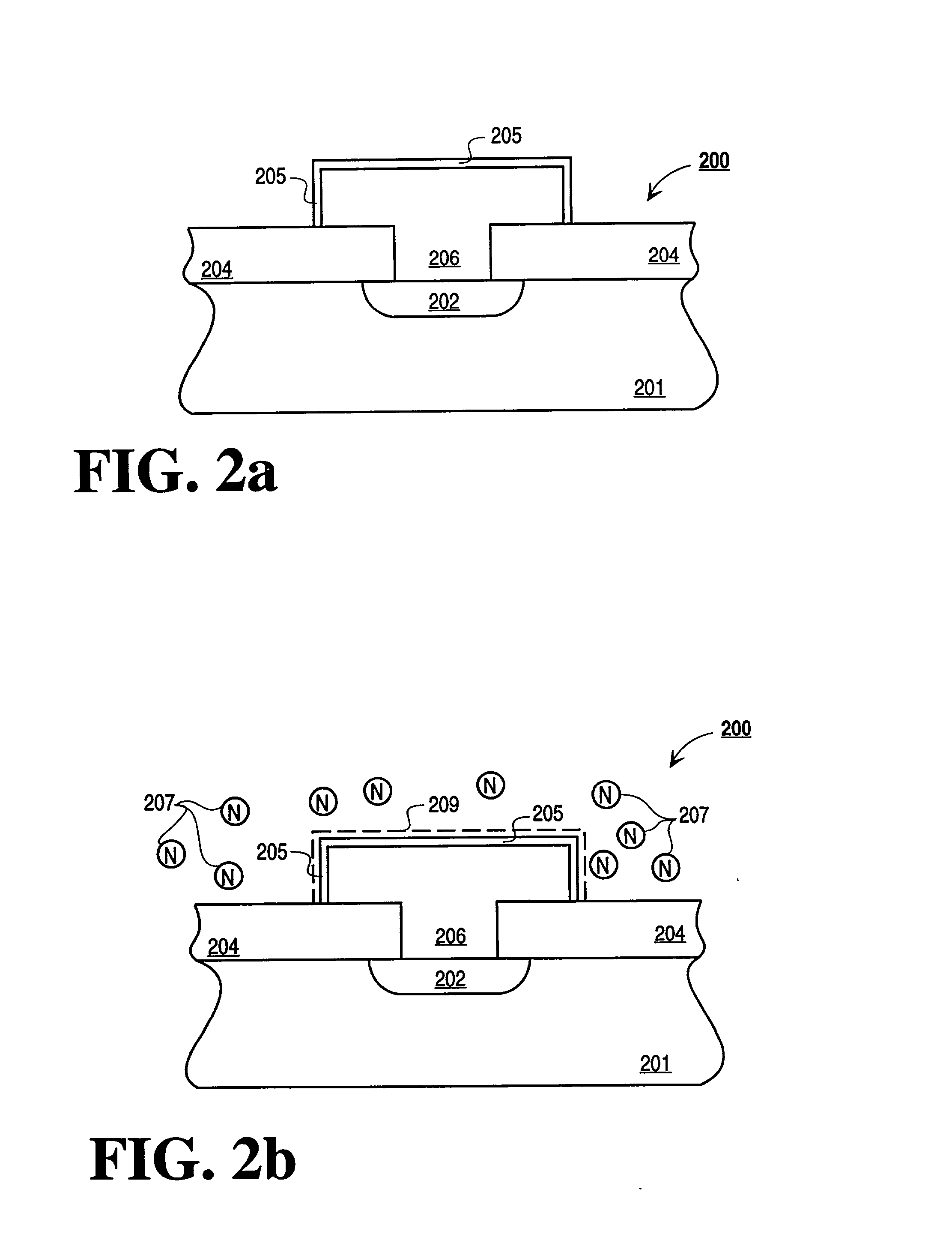
Method and apparatus for the formation of dielectric layers
InactiveUS20020009861A1Simple interfaceImprove performanceTransistorVacuum evaporation coatingAtomic speciesDielectric layer
A method and apparatus for forming and annealing a dielectric layer. According to the present invention an active atomic species is generated in a first chamber. A dielectric layer formed on a substrate is then exposed to the active atomic species in a second chamber, wherein the second chamber is remote from the first chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Lighting device
ActiveUS20070236911A1Improve extraction efficiencyReduce probabilityPoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsElement spaceEffect light
A lighting device comprising at least one solid state light emitter and at least one luminescent element spaced from the light emitter, a surface of the luminescent element being at least twice as large as the illumination surface of the light emitter. Also, a lighting device comprising at least one solid state light emitter and at least one luminescent element spaced from the light emitter, a surface of the luminescent element surface being at least twice as large as and substantially parallel to the illumination surface of the light emitter. Also, a lighting device comprising at least one solid state light emitter and at least one luminescent element spaced from the light emitter, a surface area of a projection of the luminescent element being at least twice as large as a surface area of a projection of the light emitter.
Owner:CREELED INC
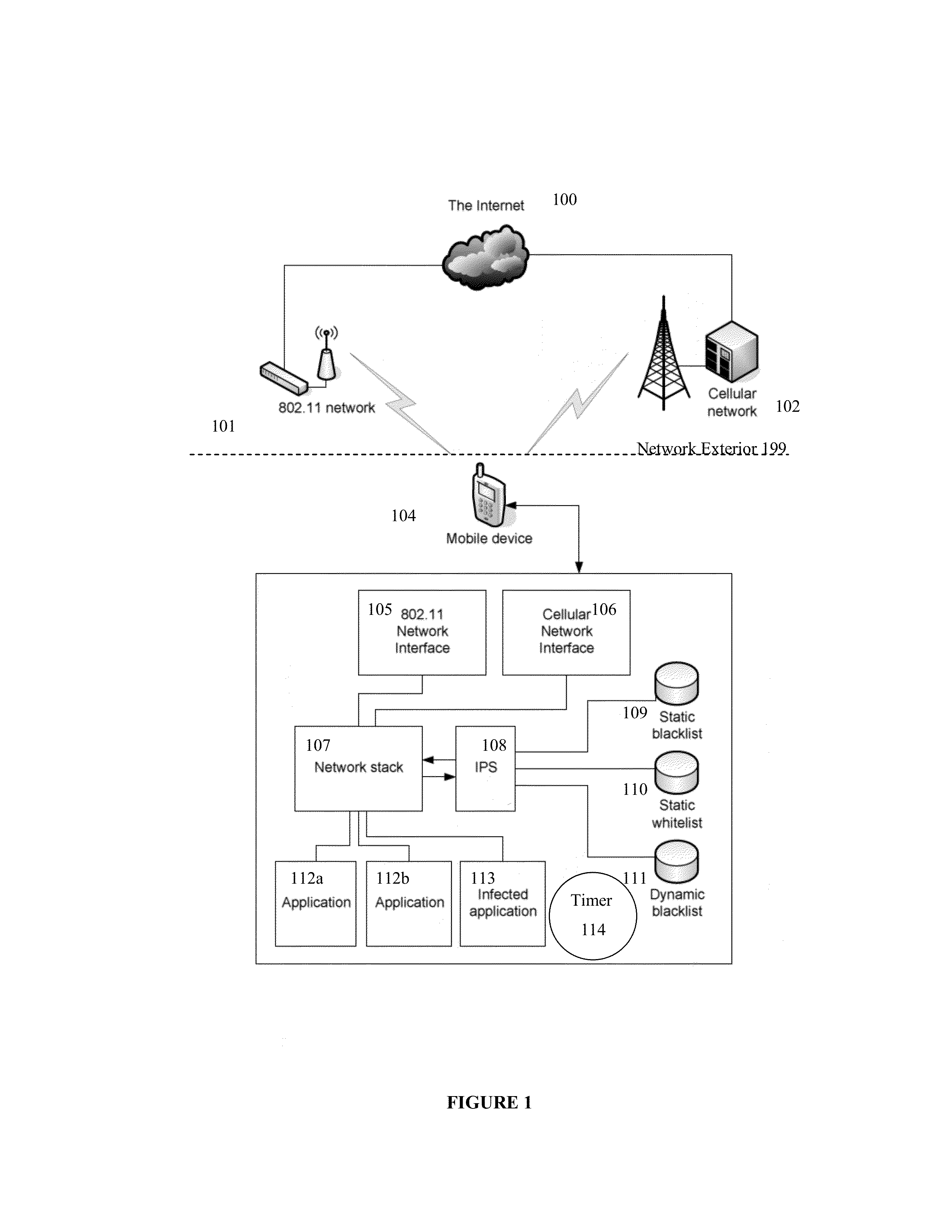
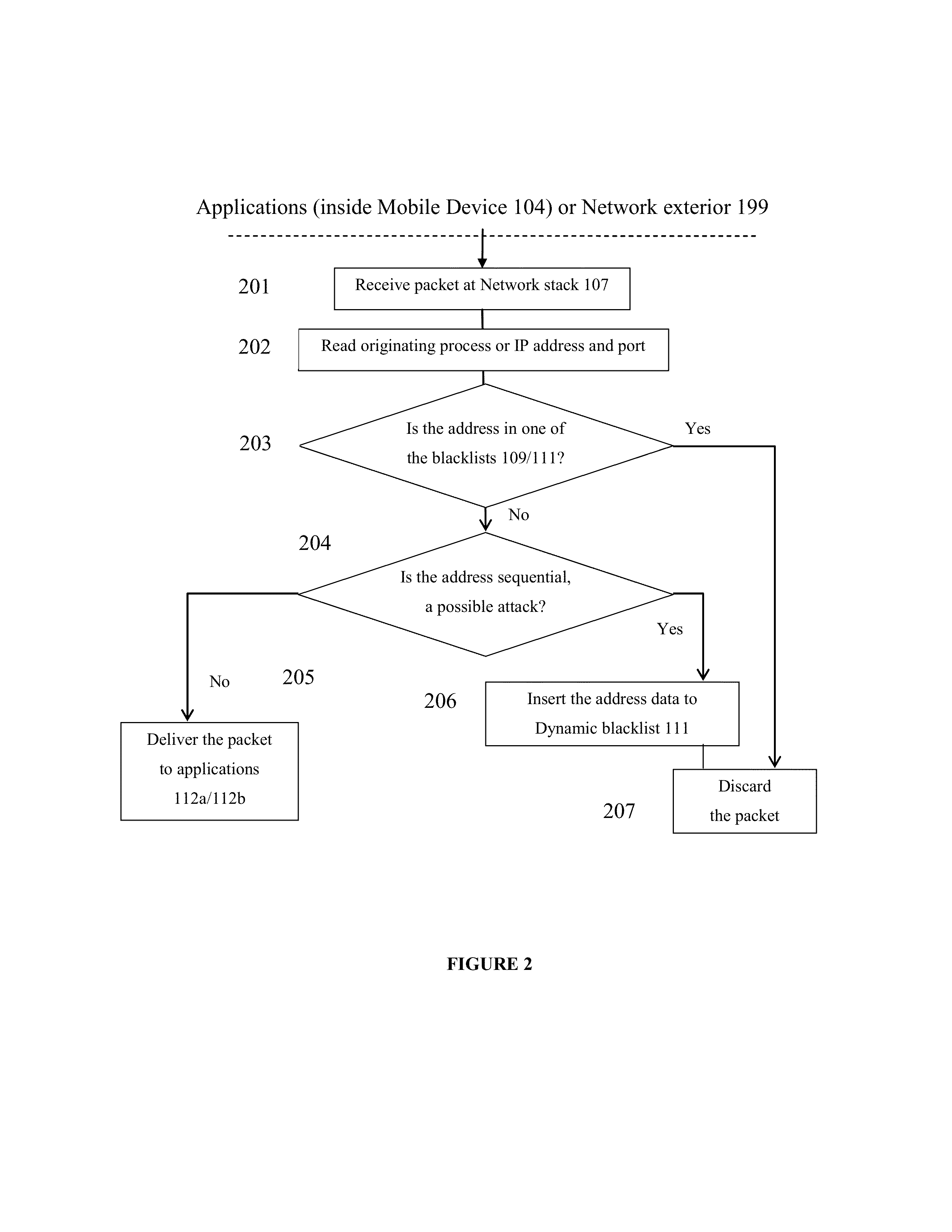
Methods and systems for providing network protection by progressive degradation of service
InactiveUS20130185795A1Reduce performance of data communicationLower performance requirementsMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionCountermeasureNetwork service
Systems and methods are provided for protecting a defense with a self defending intrusion system. Data packets may be monitored to detect a pattern of activity indicating a potential attack. Upon detection of a threat, a countermeasure or progressive degradation of network services may be initiated on a selected basis so controllable reduce performance of data communication of the device.
Owner:ARXCEO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com