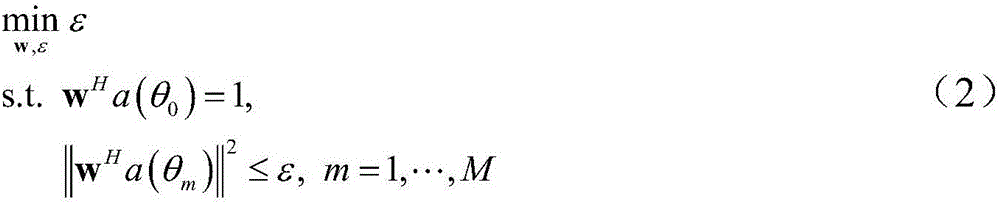Patents
Literature
220results about How to "Reduce sidelobe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
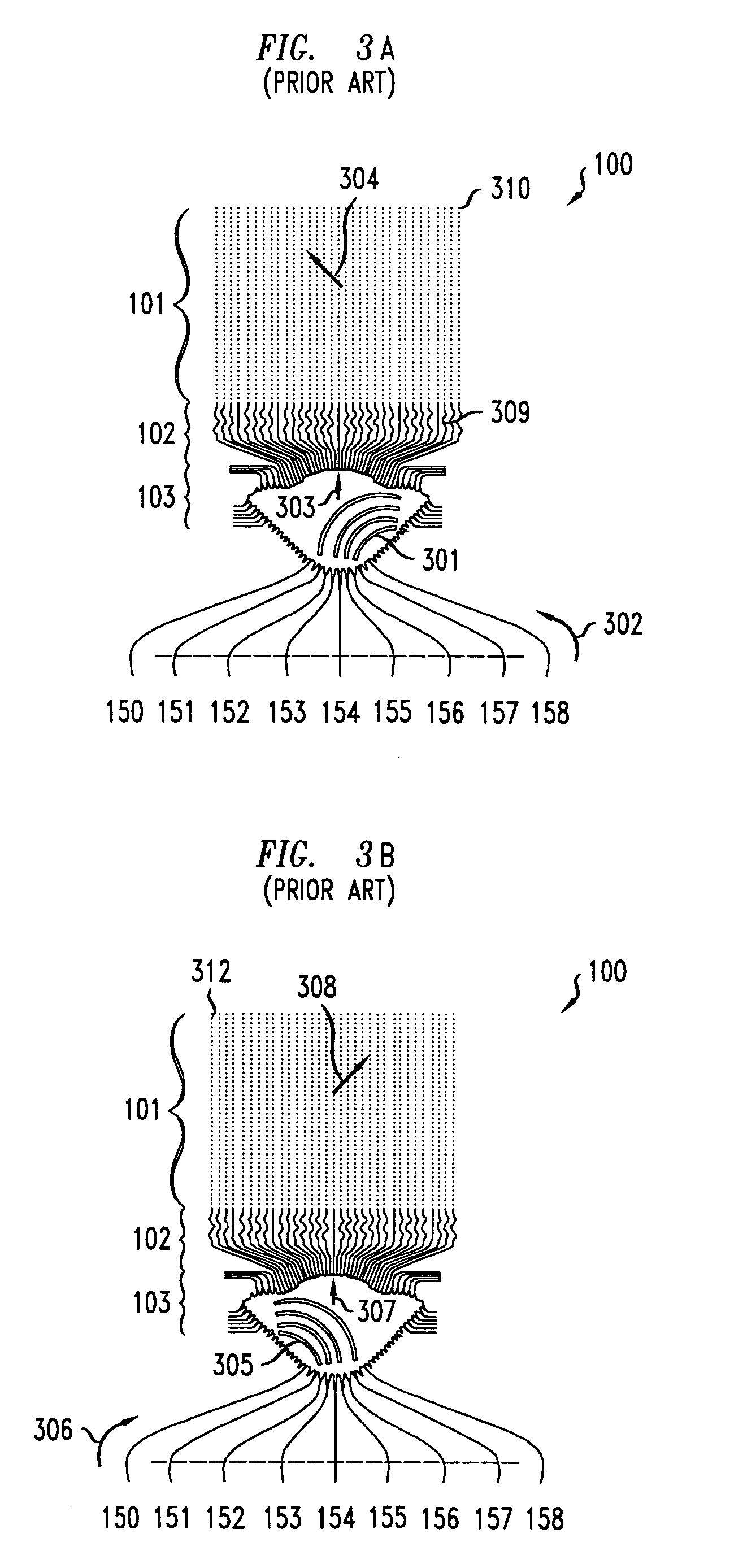
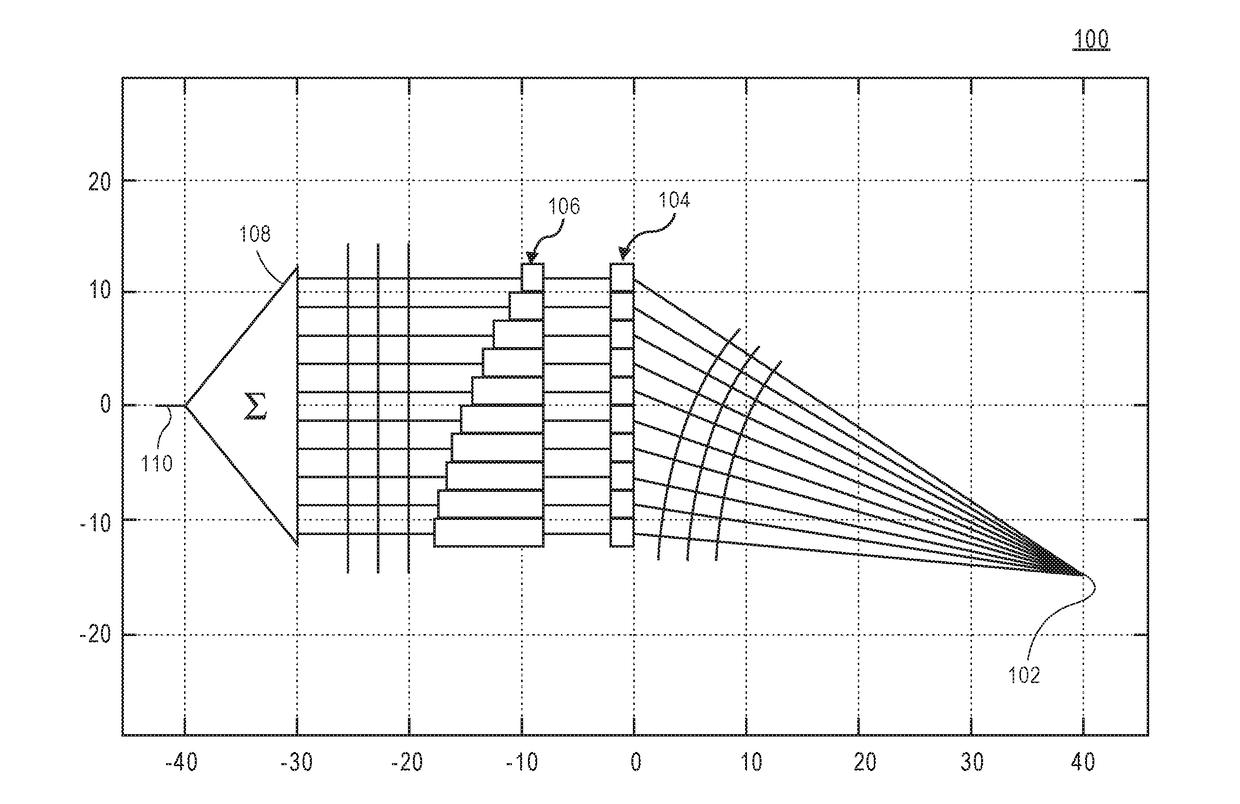
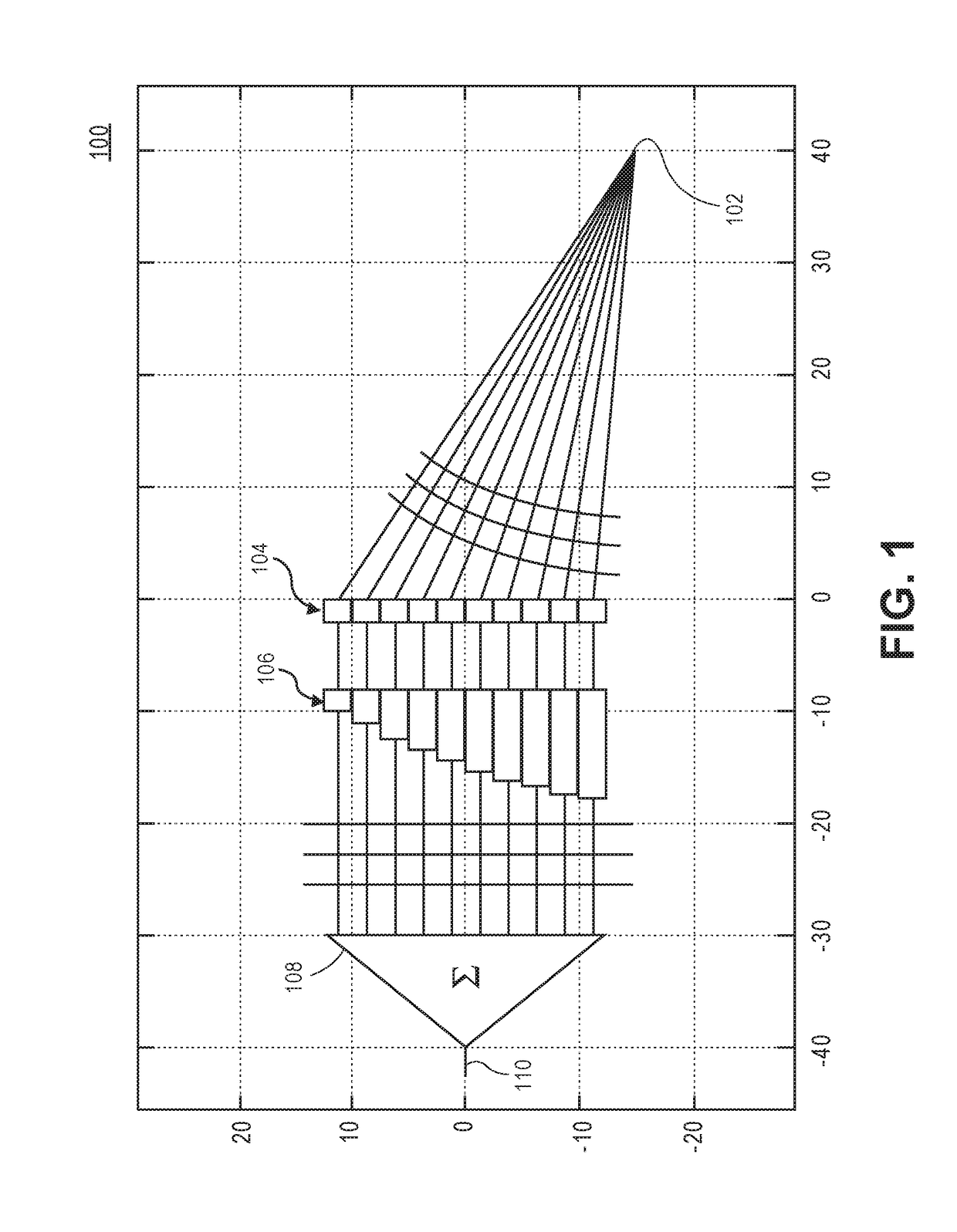
Phased array metamaterial antenna system
ActiveUS6958729B1Reduce sidelobeIncrease amplitude performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsSolid substratePhased array
An efficient, low-loss, low sidelobe, high dynamic range phased-array radar antenna system is disclosed that uses metamaterials, which are manmade composite materials having a negative index of refraction, to create a biconcave lens architecture (instead of the aforementioned biconvex lens) for focusing the microwaves transmitted by the antenna. Accordingly, the sidelobes of the antenna are reduced. Attenuation across microstrip transmission lines may be reduced by using low loss transmission lines that are suspended above a ground plane a predetermined distance in a way such they are not in contact with a solid substrate. By suspending the microstrip transmission lines in this manner, dielectric signal loss is reduced significantly, thus resulting in a less-attenuated signal at its destination.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Antenna system
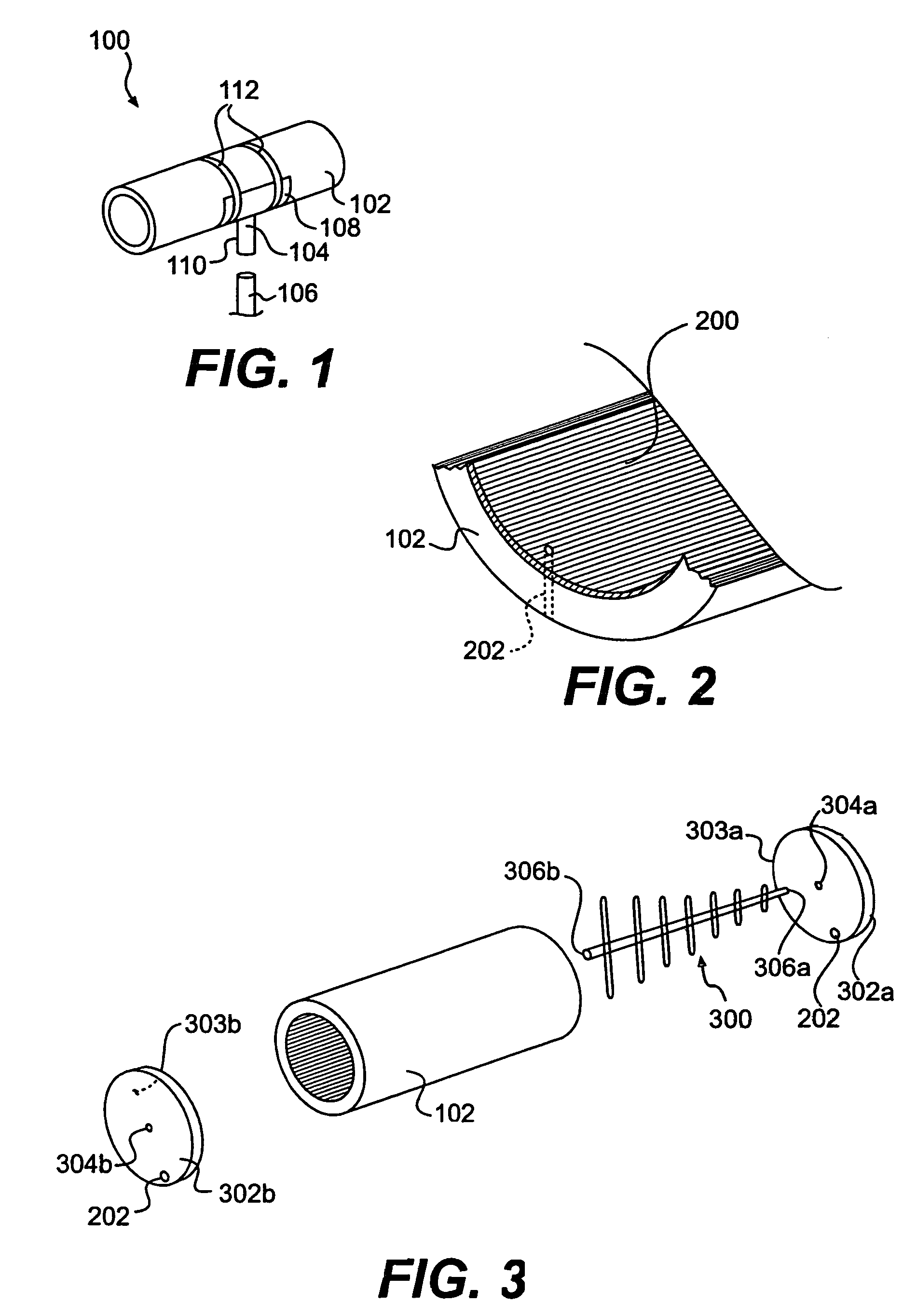
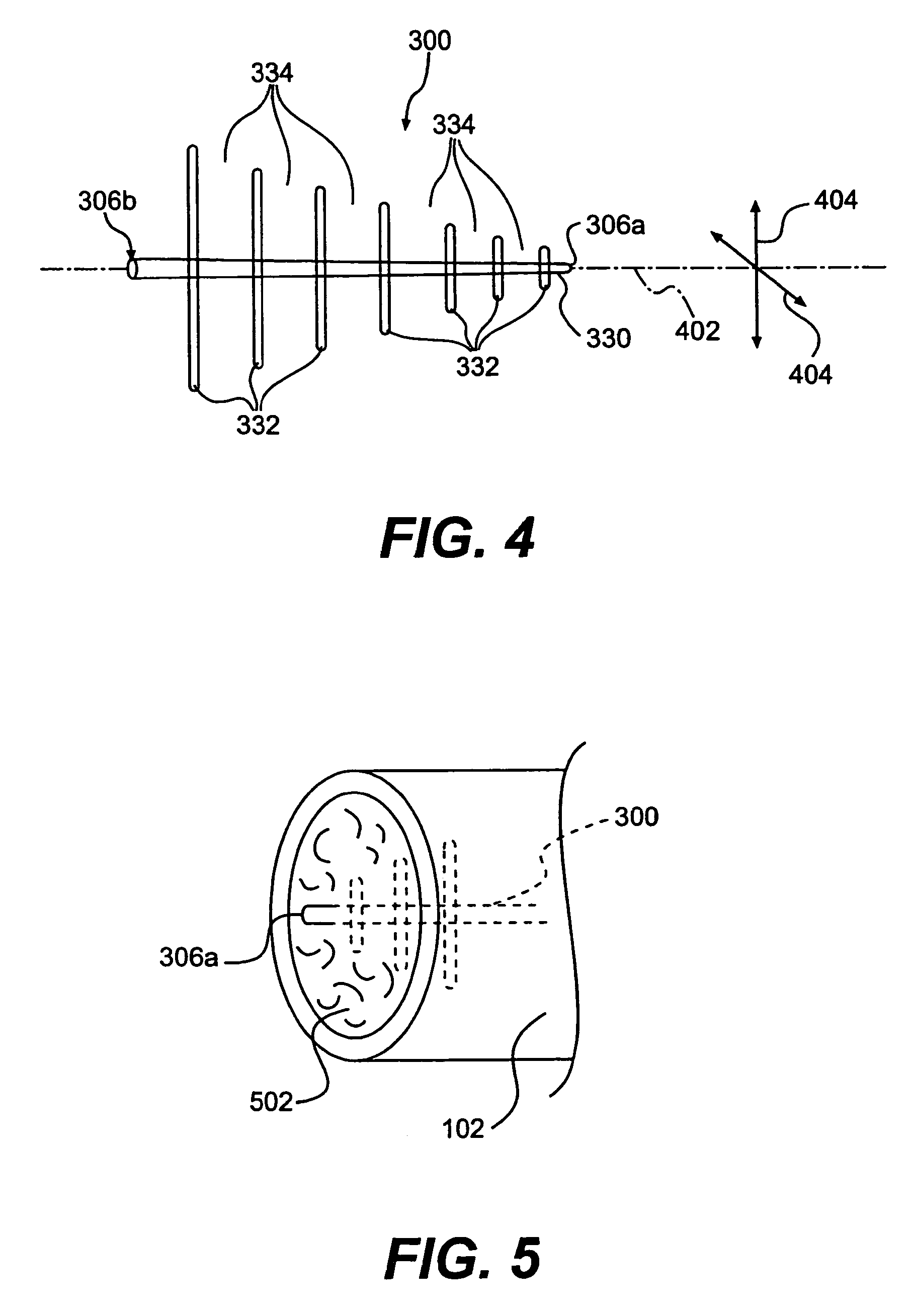
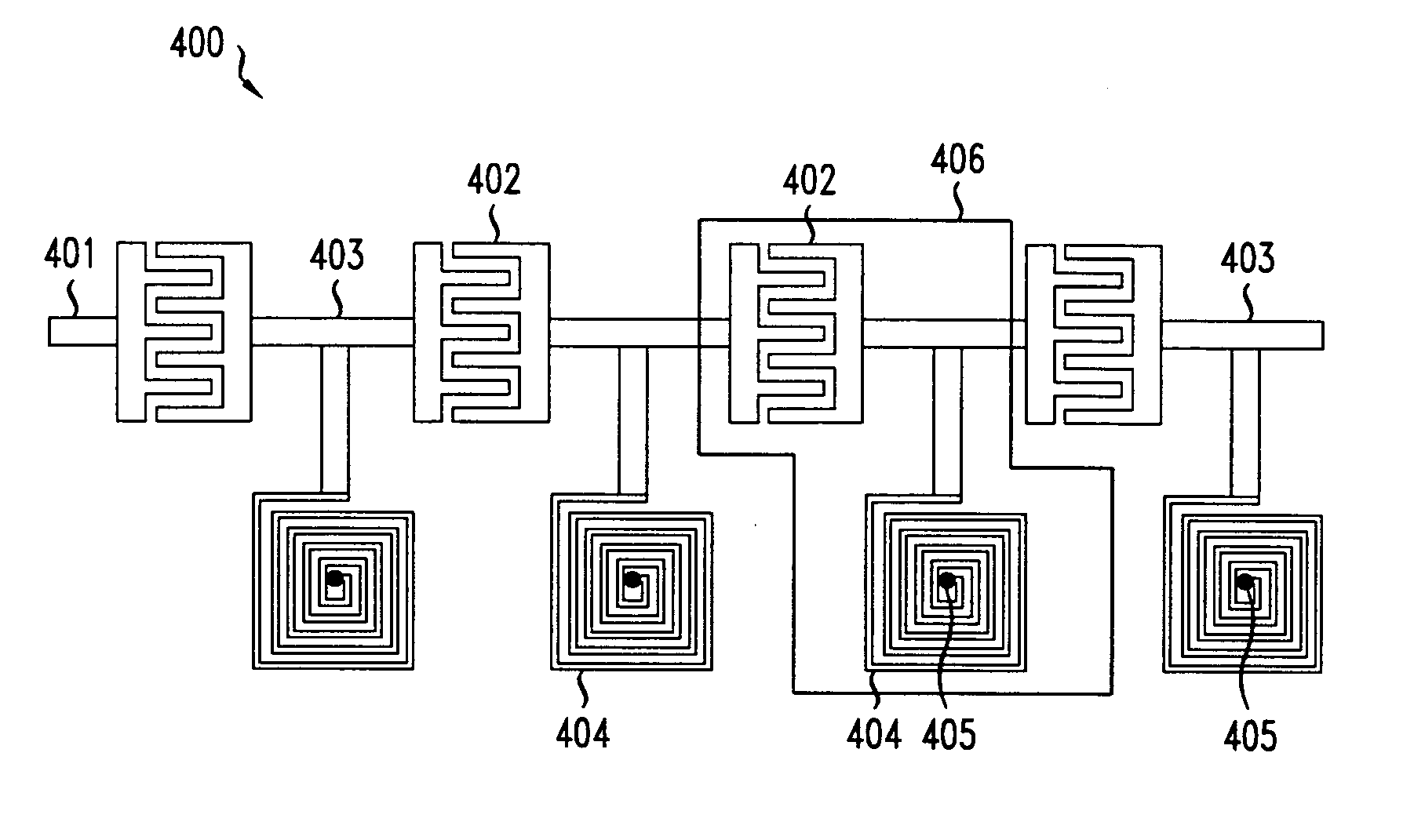
InactiveUS7023400B2Reduce decreaseMinimizing signal looping effectLogperiodic antennasAntenna supports/mountingsDirectional antennaSide lobe
An antenna system that includes a directional antenna designed to reduce the occurrence of side lobes, thus reducing the possibility of interference with other radio frequencies is disclosed. The directional antenna includes an antenna member and a reflecting tube. The reflective tube is sleeved over the antenna member. The reflective serves to block unwanted radial side lobes. The directional antenna can also include provisions that assist in suspending the antenna member within the reflective tube.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Phased array metamaterial antenna system
ActiveUS20050225492A1Low Sidelobe PerformanceReduce sidelobeRadiating elements structural formsWaveguidesSolid substratePhased array
An efficient, low-loss, low sidelobe, high dynamic range phased-array radar antenna system is disclosed that uses metamaterials, which are manmade composite materials having a negative index of refraction, to create a biconcave lens architecture (instead of the aforementioned biconvex lens) for focusing the microwaves transmitted by the antenna. Accordingly, the sidelobes of the antenna are reduced. Attenuation across microstrip transmission lines may be reduced by using low loss transmission lines that are suspended above a ground plane a predetermined distance in a way such they are not in contact with a solid substrate. By suspending the microstrip transmission lines in this manner, dielectric signal loss is reduced significantly, thus resulting in a less-attenuated signal at its destination.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
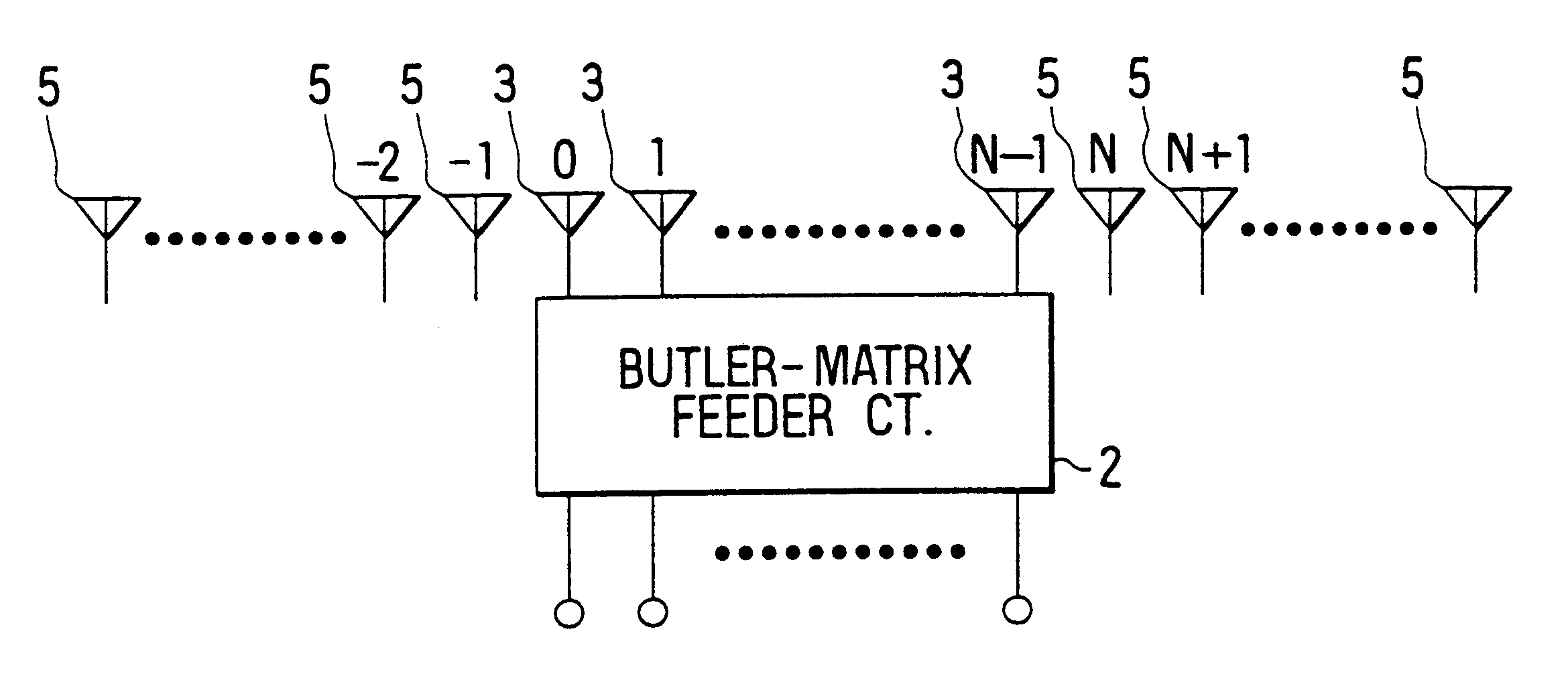
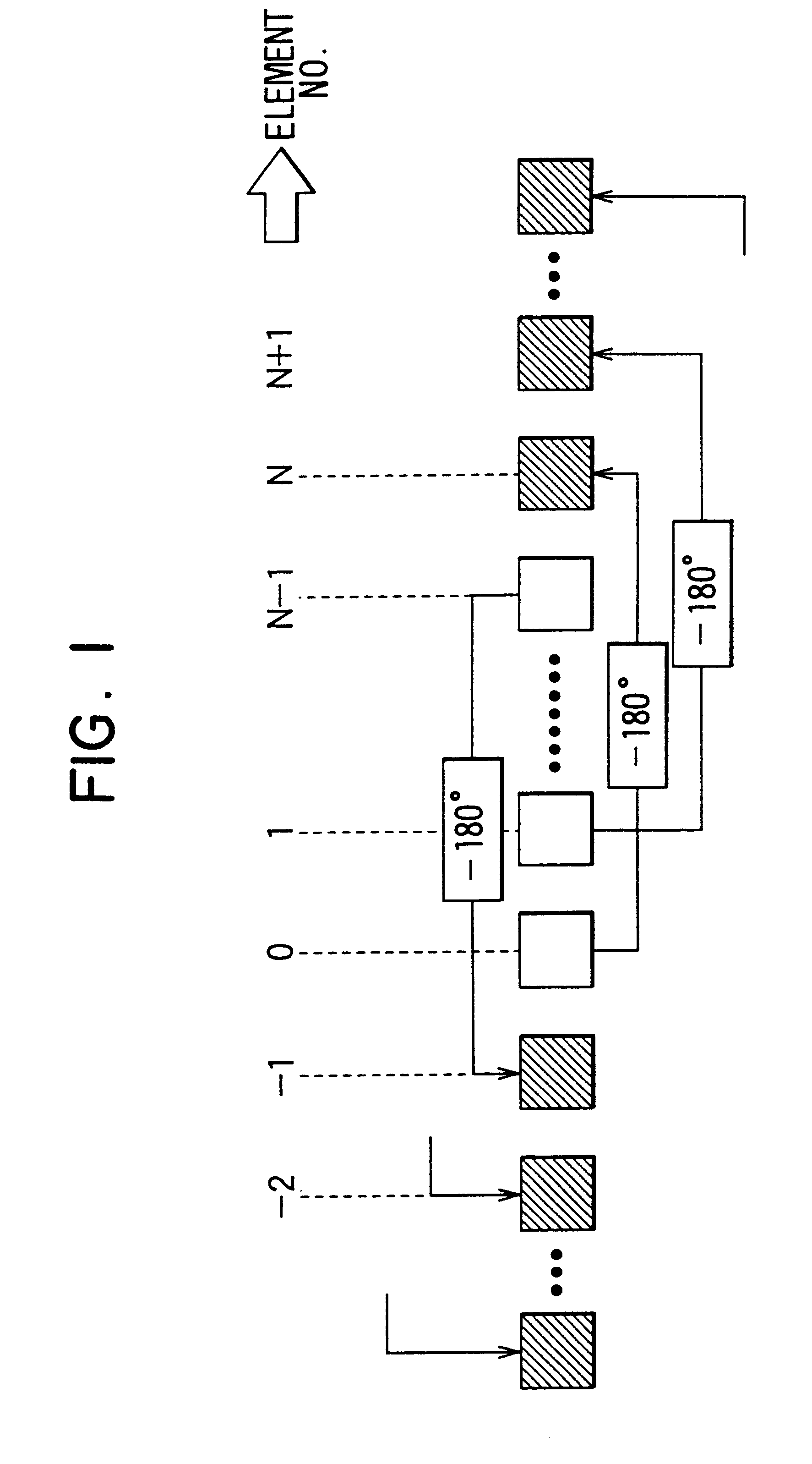
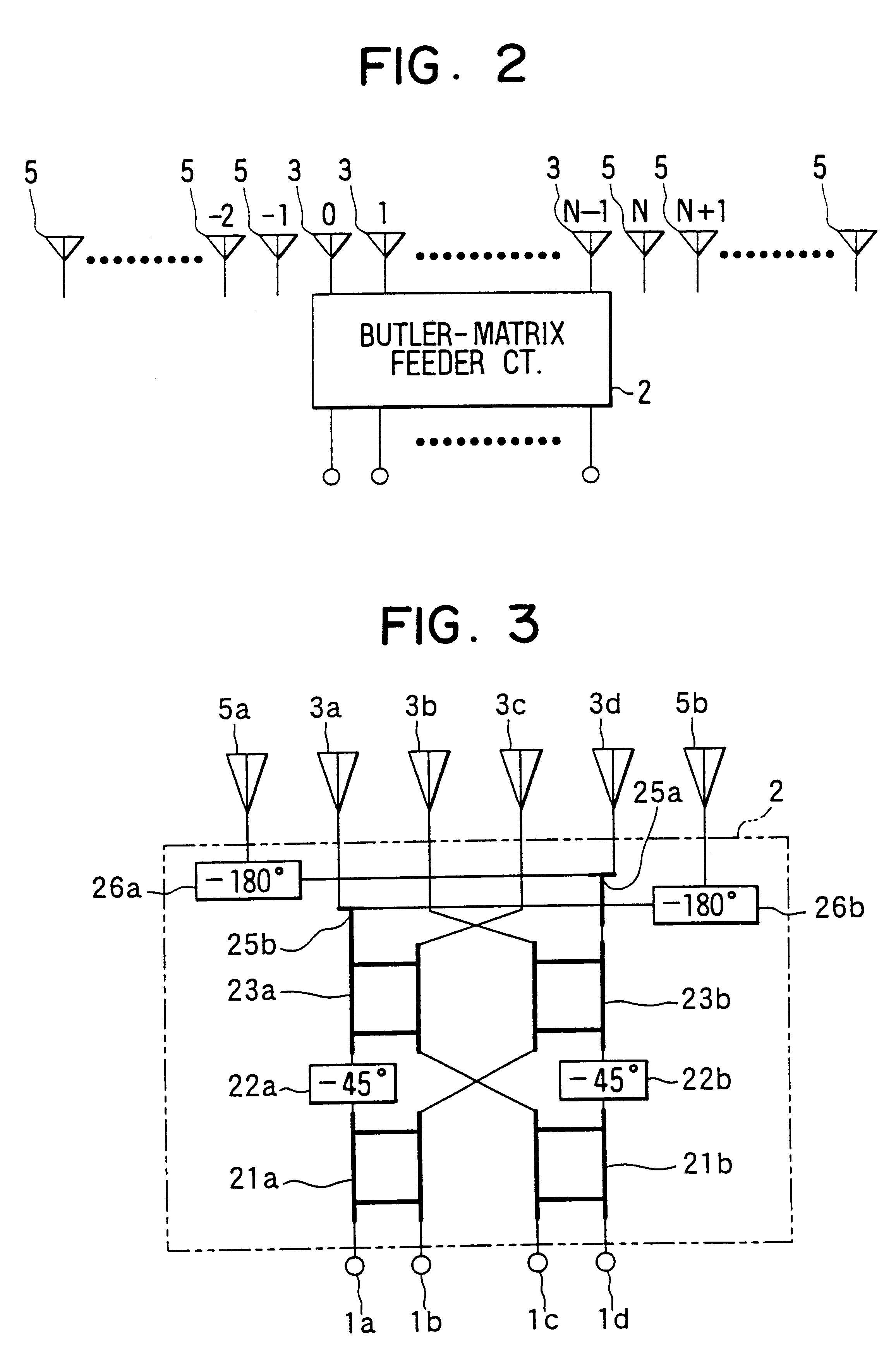
Multibeam antenna having auxiliary antenna elements
InactiveUS6252560B1Improve directivityReduce sidelobeAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysPhase shiftedEngineering
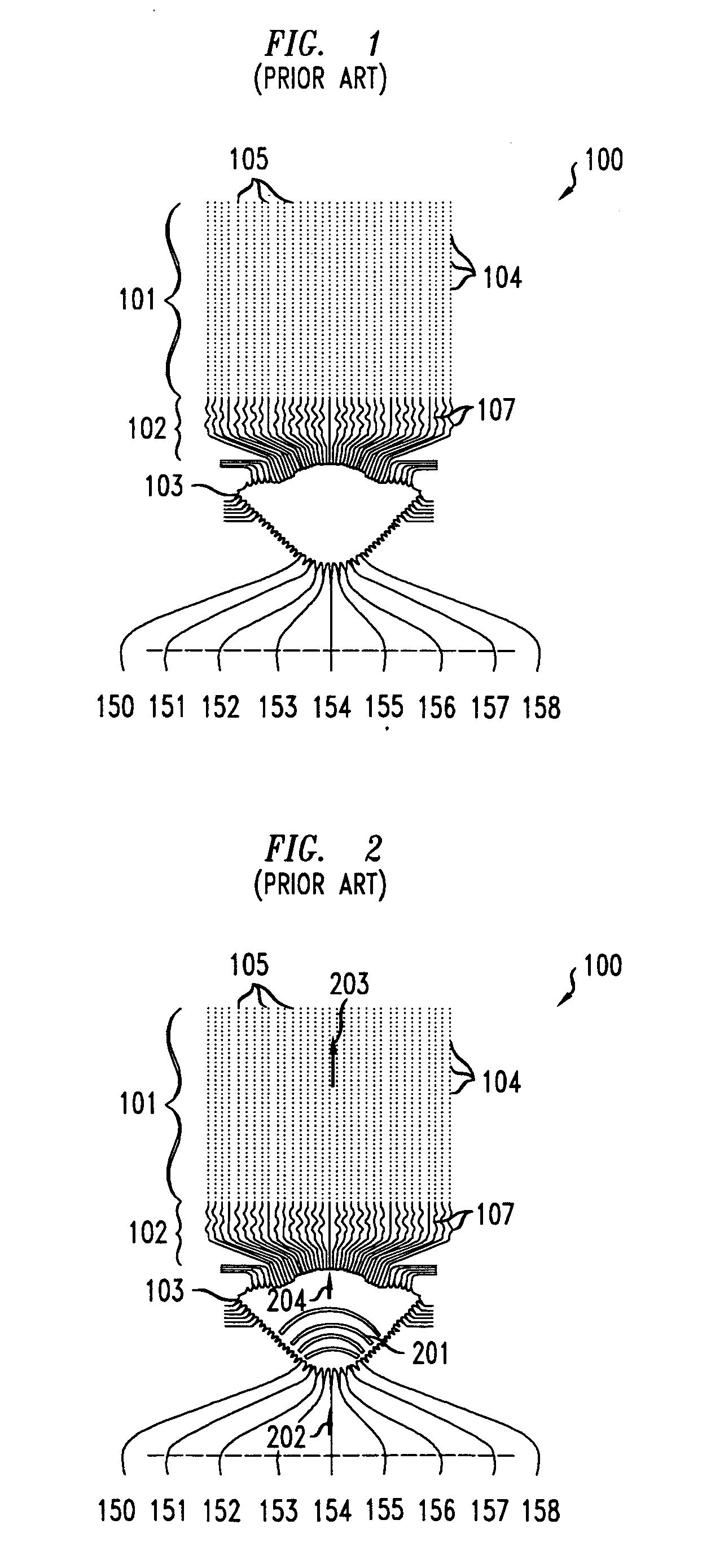
A multibeam antenna for forming multiple beams includes an antenna array and a Butler-matrix feeder circuit. The antenna array is composed of 2.sup.n main antenna elements and a group of 2.sup.n or less auxiliary antenna elements placed at either one or both sides of the main antenna elements. Antenna power is supplied to the antenna array from the Butler-matrix feeder circuit and is distributed to all the antenna elements with higher power to the elements located in the middle of the array and lower power to the elements located at sides of the array. Phase of the power supplied to the main antenna elements is shifted by 180-degree, and the phase-shifted power is distributed to predetermined auxiliary antenna elements. Thus, sidelobes associated with antenna beams are reduced and the beam directivity is improved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
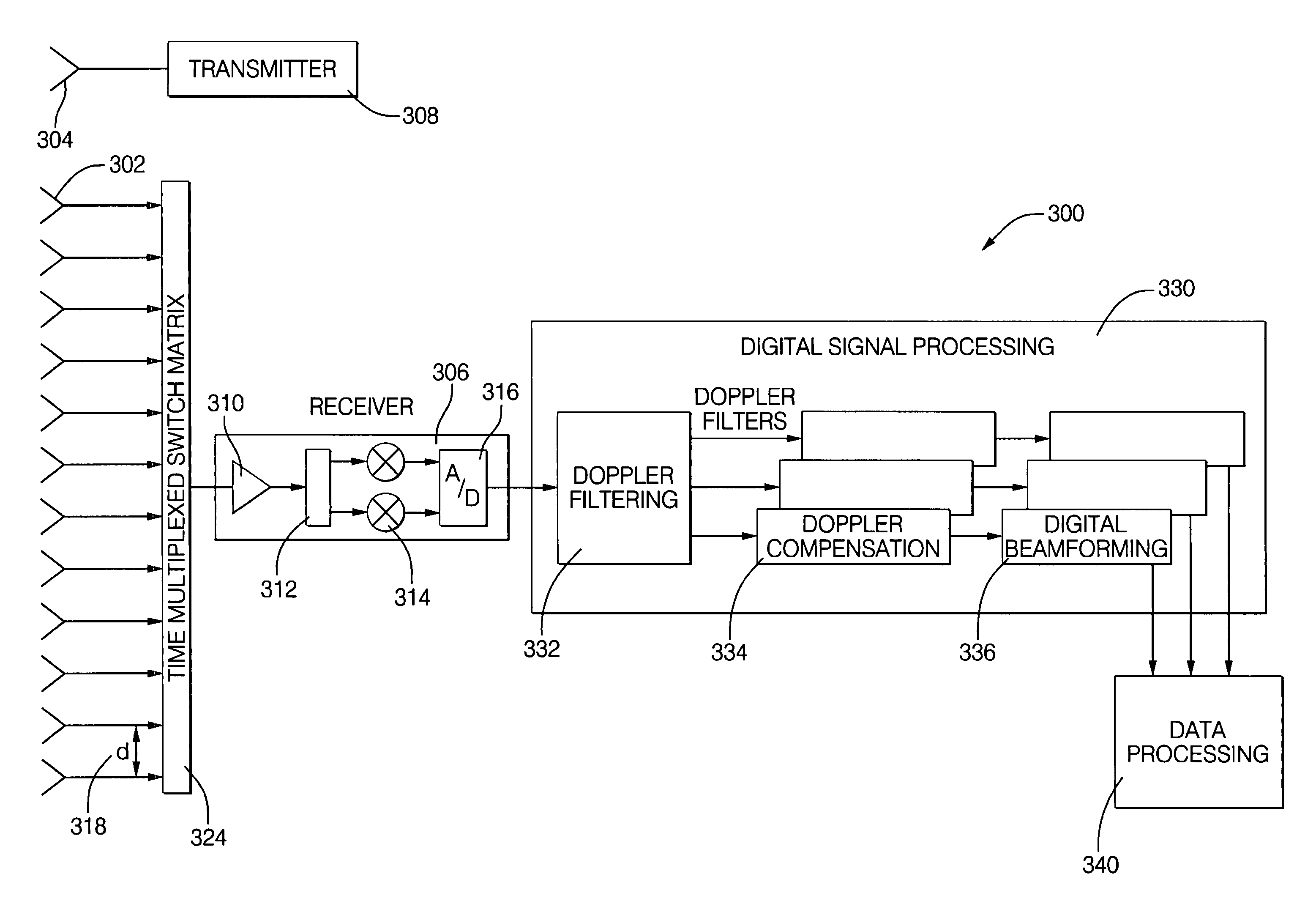
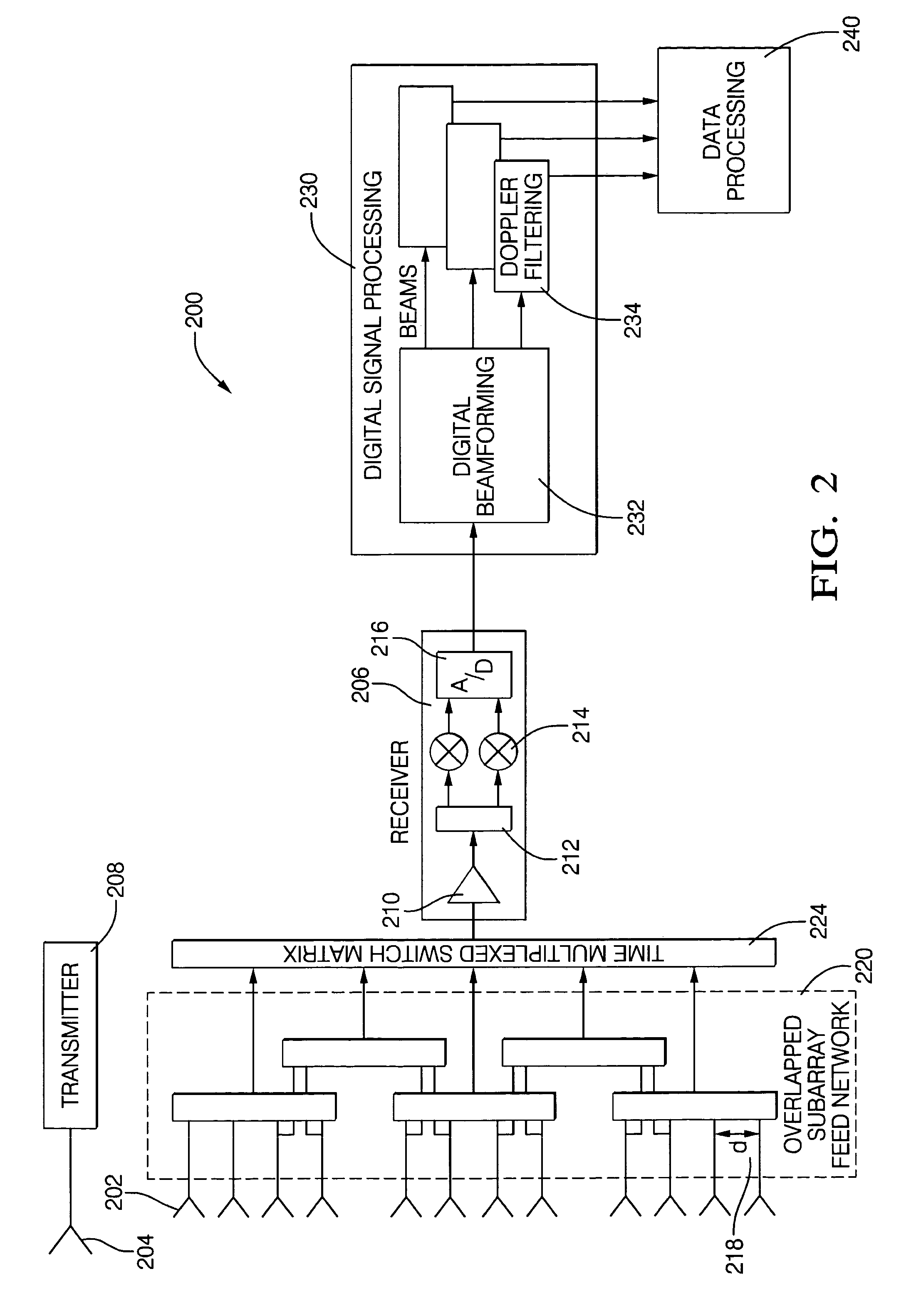
Digital beamforming for an electronically scanned radar system
ActiveUS7474262B2Improve performanceLow costParticular array feeding systemsRadio transmissionRadar systemsEngineering
Digital beamforming is provided for use with electronically scanned radar. In an aspect, the present invention provides enhanced sensitivity, wide angle or field of view (FOV) coverage with narrow beams, minimized number of receivers, reduced sidelobes, eliminated grating lobes and beam compensation for target motion. In an aspect, the present invention employs a uniform overlapped subarray feed network, a time multiplexed switch matrix, and a restructured digital signal processor. Antenna channels share a receiver, rather than maintain a dedicated receiver for each antenna element, as in conventional systems. In an aspect, Doppler / frequency filtering is performed on each antenna element or subarray output prior to digital beamforming. Further, Doppler compensation is employed following Doppler / frequency filtering, followed by digital beamforming.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
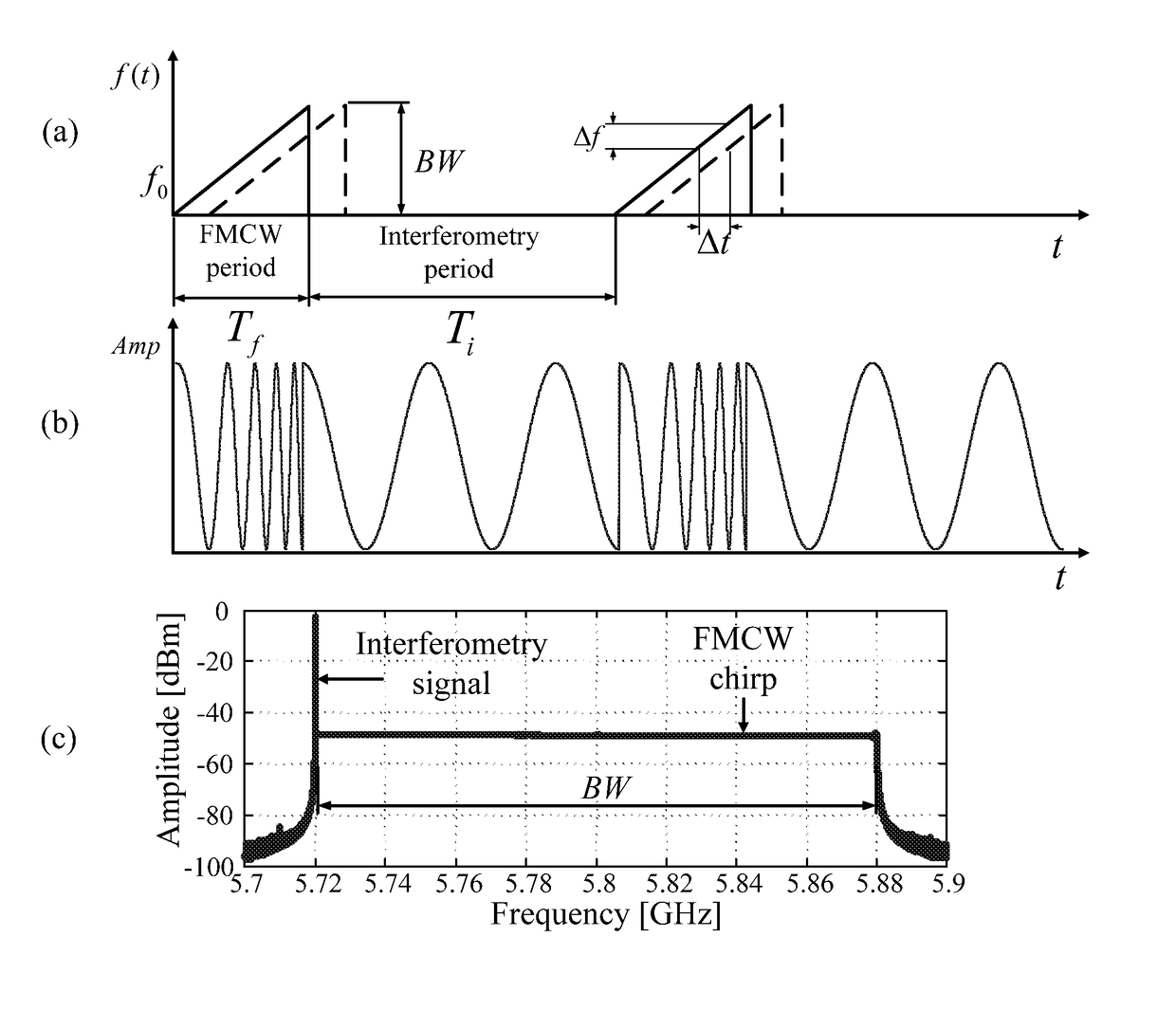
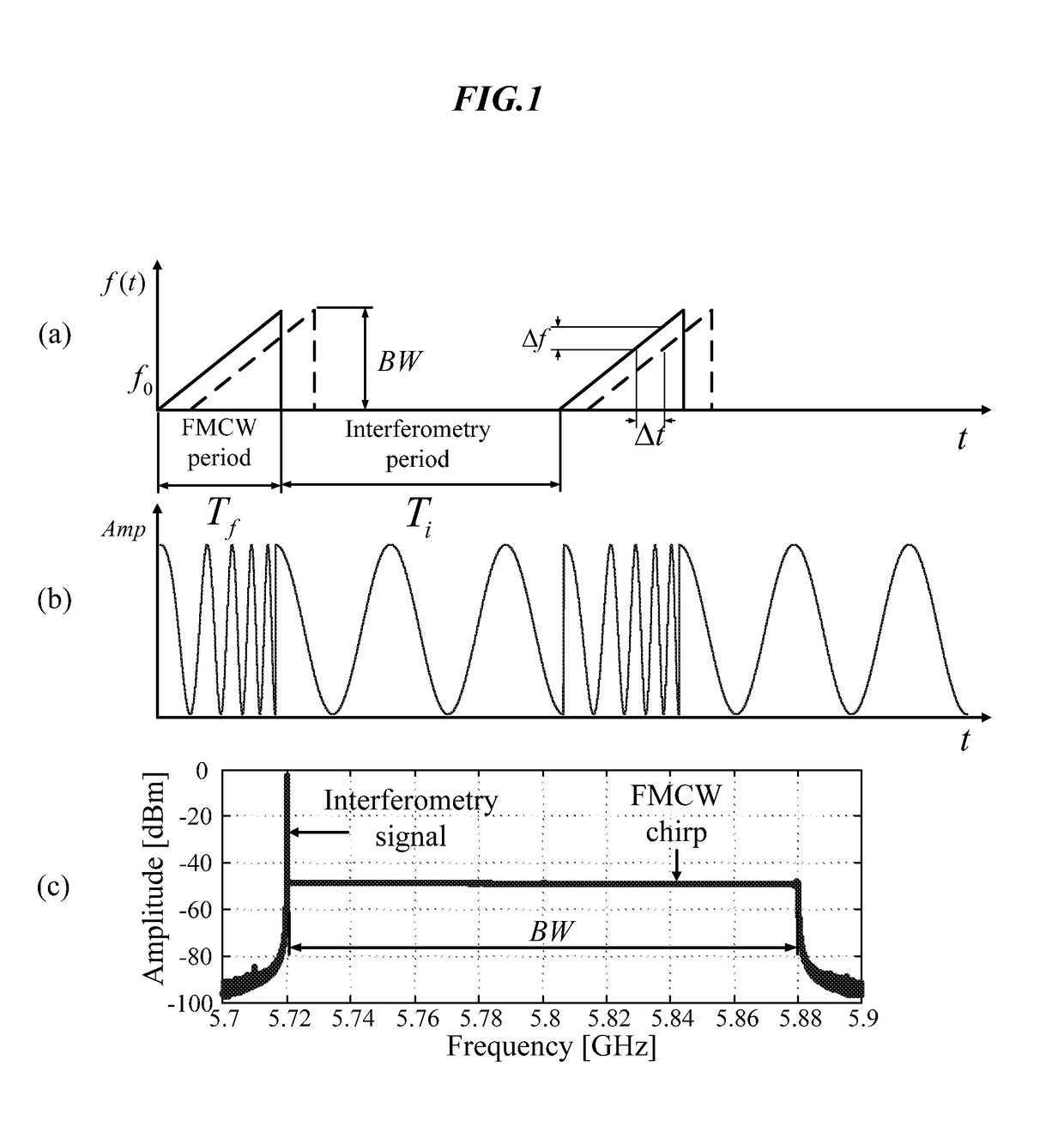
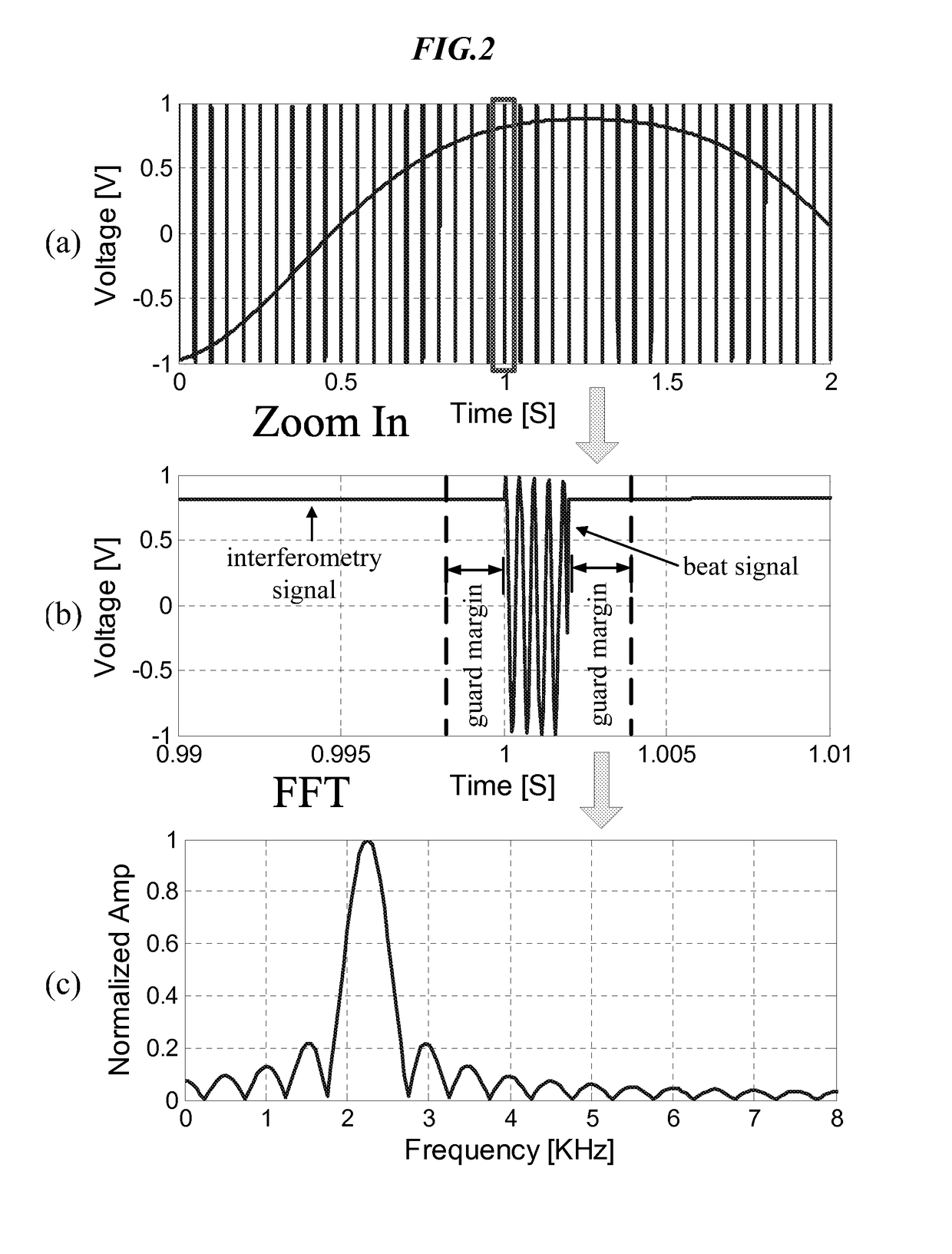
Hybrid fmcw-intererometry radar for positioning and monitoring and methods of using same
ActiveUS20170102457A1Reduce sidelobeImprove isolationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsPhysiological movement
Disclosed is a system and method for a hybrid radar system that integrates frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) mode and interferometry mode. The radar works as a time division system that continuously switches between the FMCW mode and interferometry mode. The FMCW mode is responsible for absolute range detection and the interferometry mode takes cares of the weak physiological movement monitoring. The respective accuracies in range detection and displacement measurement complements the advantages of the two radar modes, providing versatile performance. By steering the antenna beam, the proposed radar system becomes an ideal solution for indoor health care, human localization, and human-computer interaction. Objects or human targets with or without stationary clutters can be precisely located. At the same time, the targets' vital signs and gestures can be monitored.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST
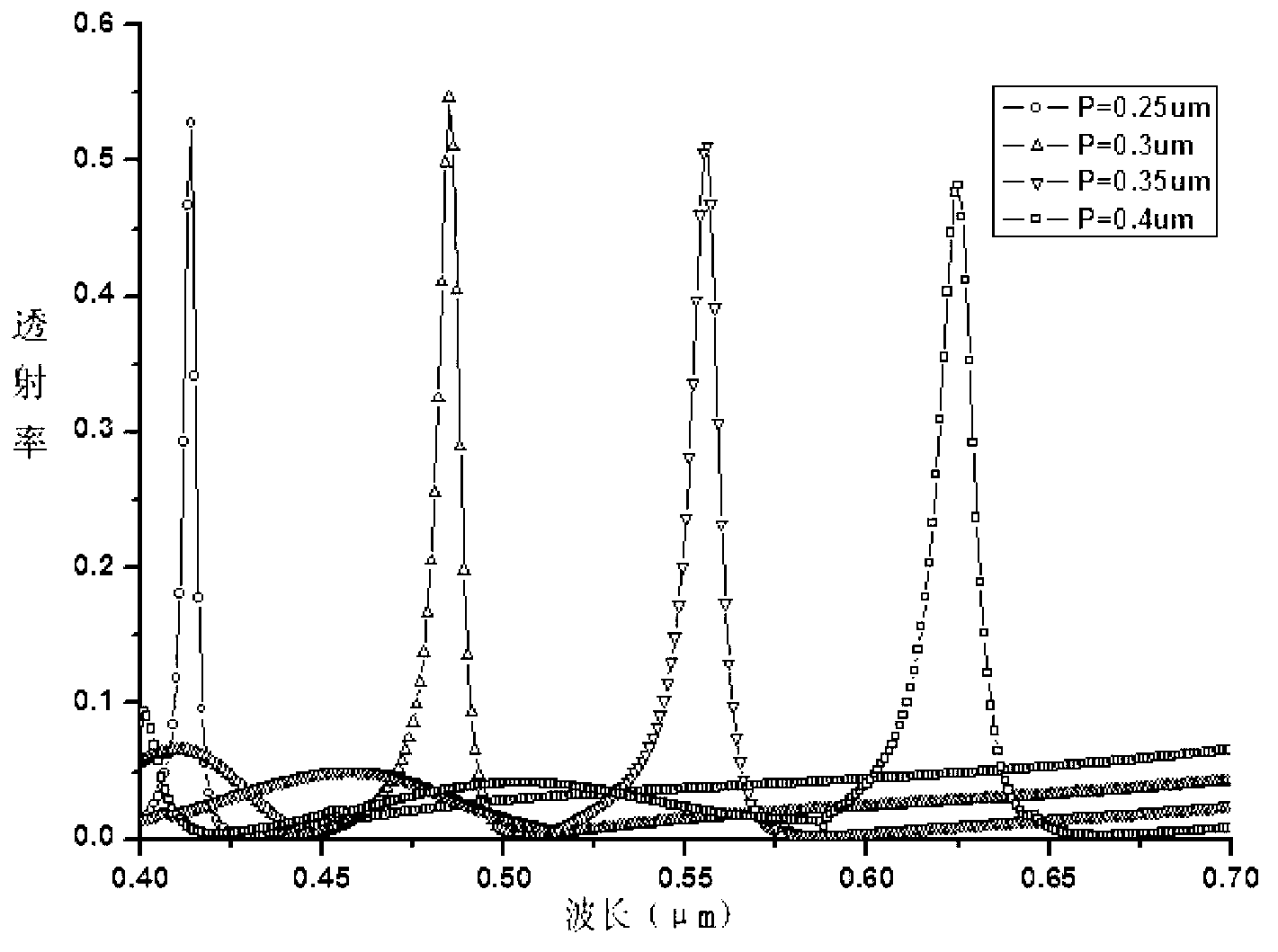
Array multispectral optical filter and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to an array multispectral optical filter and a manufacturing method thereof, belongs to the field of a micro-nano optical filter and solves the problem of integration of multichannel array detection in an existing nanofluidic chip. The optical filter only comprises the following four layers of structures: a two-dimensional metal grating layer, a buffer layer, a waveguide layer and a substrate. The invention also provides the manufacturing method of the optical filter, which utilizes a guided mode resonance principle of a two-dimensional metal grating and implements selection of different wavelengths by regulating the period of the grating. By the thickness of the buffer layer, the half-wave bandwidth of the cut-off wavelength also can be regulated. By regulating a suitable duty cycle of the two-dimensional metal grating layer, side lobes can be reduced. Therefore, relative to other turnable optical filters, the array multispectral optical filter manufactured by the method disclosed by the invention has the outstanding advantages of simple structure, low side lobes, adjustability of the half-wave bandwidth, high transmittance, no relation with polarization and the like. After the optical fiber disclosed by the invention is adopted, the integration of the nanofluidic chip can be implemented.
Owner:广东长光中科生物科技有限公司
Low profile antenna assembly for use in cellular communications
InactiveUS6025803ALow visual profile site capabilityReduce sidelobeSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsRadarMicrostrip array
The low profile antenna assembly comprises a generally rectangular frame member housing a planar antenna. A radar absorbing material is attached to the front side of the housing with a radome covering the front side of the planar antenna and attached to the frame member. The planar antenna is a microstrip array fed by a beam forming network that uses either delay lines or phase shifters to electronically steer the antenna pattern horizontally and vertically. The antenna assembly is weatherproofed, painted and flush mounted against a building surface for camouflaging the antenna assembly from observers at a distance.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
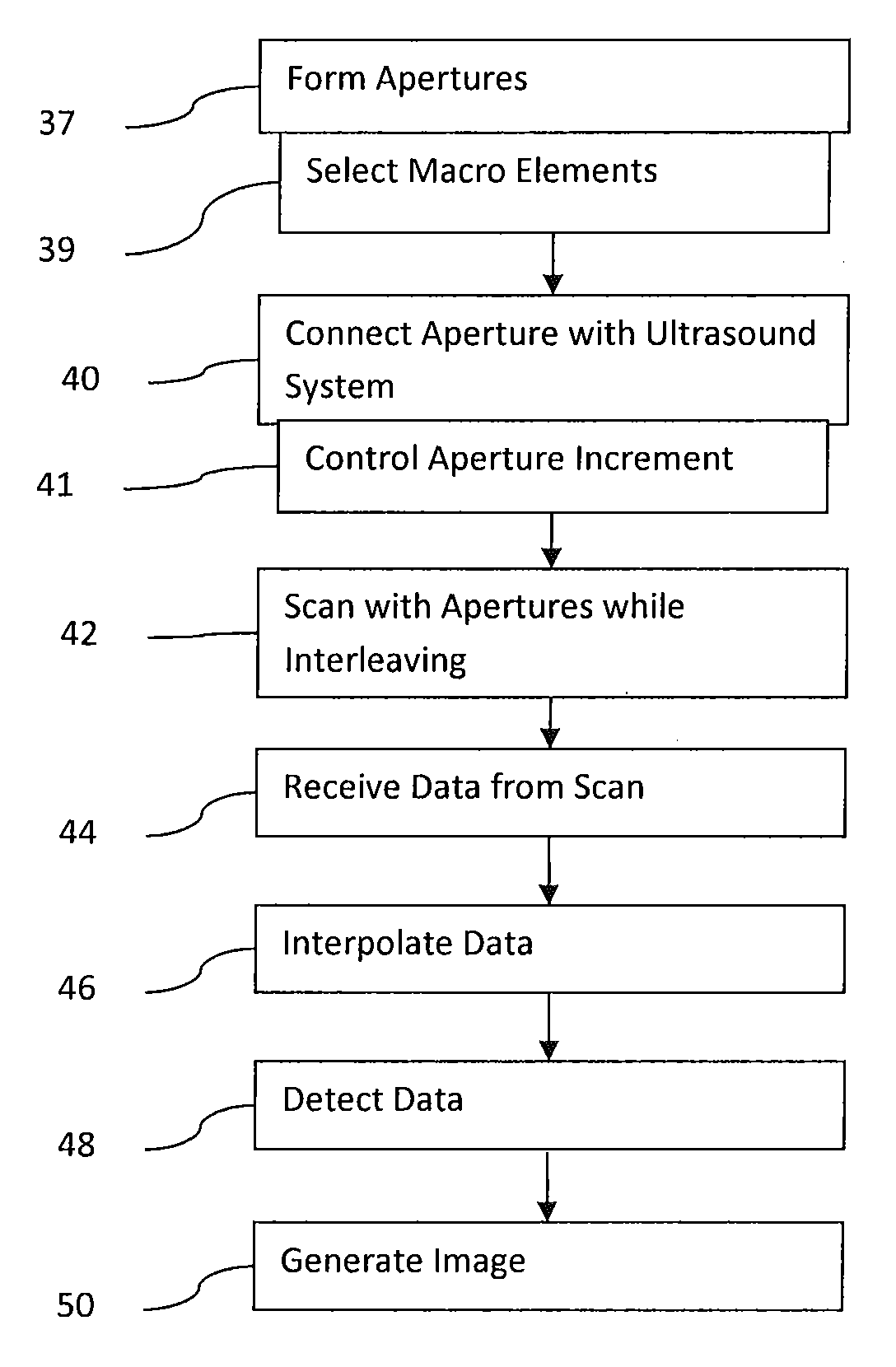
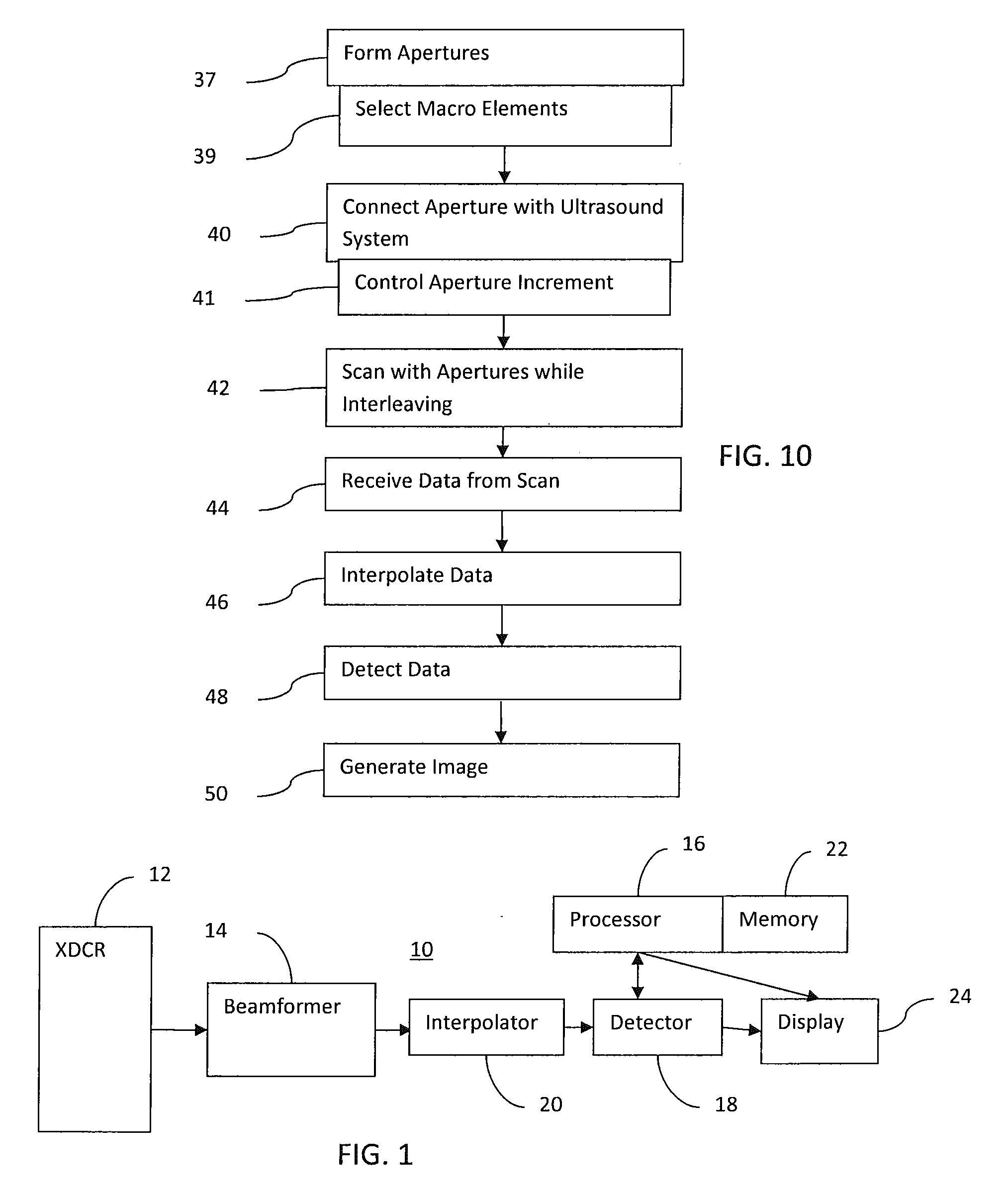
Redistribution Layer in an Ultrasound Diagnostic Imaging Transducer
ActiveUS20110021923A1Good energyReduce peakMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingRedistribution layer
Medical diagnostic ultrasound imaging is performed with a multi-dimensional transducer array and an imaging system for planar scanning. The elements of the array may be distributed on a periodic grid with aperiodic shifts in position. When a one-dimensional array is formed on the array, the aperiodic shifts better distribute acoustic energies, reducing peaks in side lobes. Using a layered structure of switches underneath the acoustic elements, side lobes may be further reduced. The switches are used for interconnecting elements to form macro elements of the one-dimensional aperture on the multi-dimensional array. The switches are distributed on a grid corresponding to the desired imaging frequency. The acoustic elements are distributed with a finer pitch. The finer pitch allows formation of the macro elements for the one-dimensional aperture where the edges of the macro elements have fewer or no periodic patterns.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
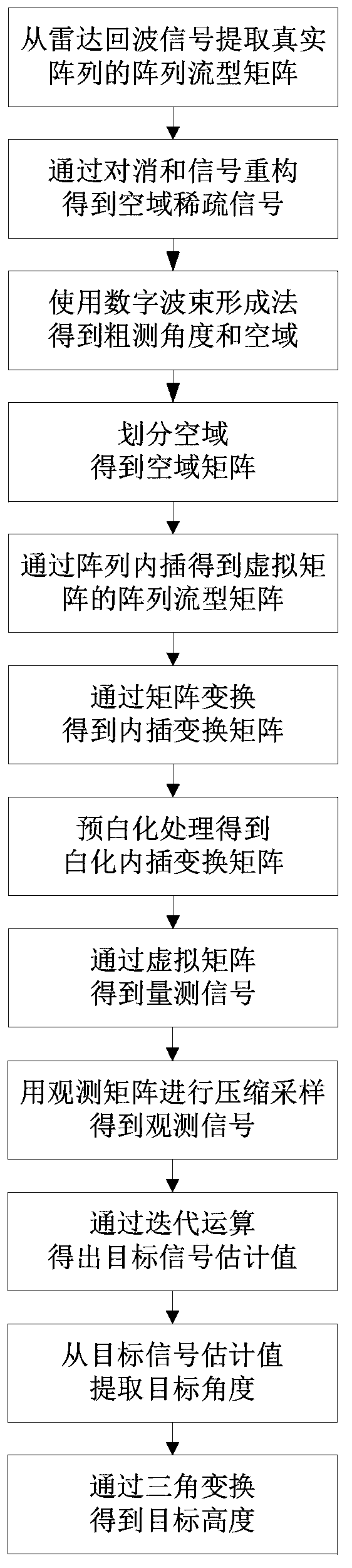
Meter wave radar height measurement method based on array interpolation compression perception
ActiveCN103353595AReduce sidelobeImprove performanceWave based measurement systemsTarget signalRadar
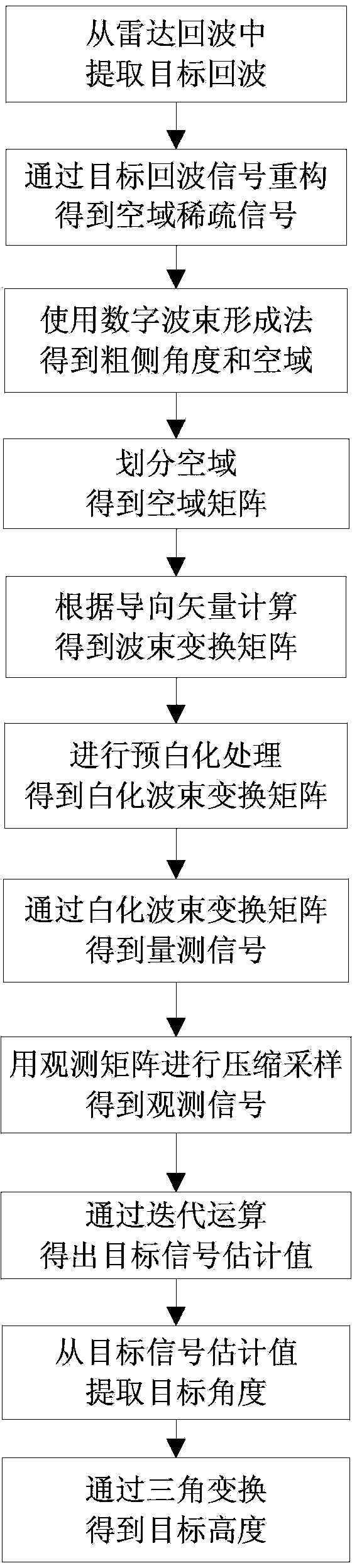
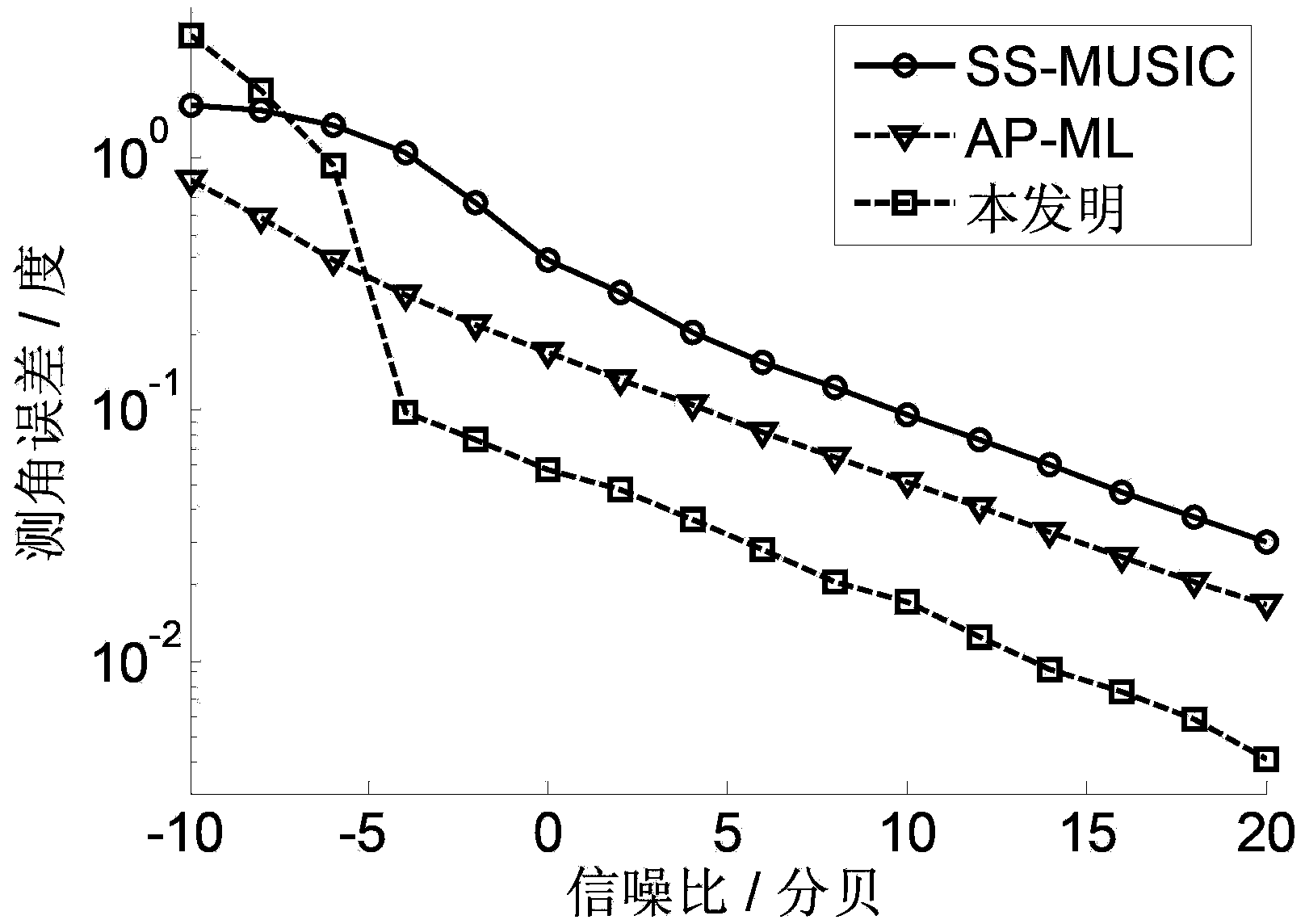
The invention discloses a height measurement method based on an array interpolation compression perception. The height measurement method mainly aims at solving a low elevation height measurement problem under a multipath environment, and especially under low signal to noise ratio and less snapshot environments. The method comprises the following steps of extracting a target signal from a radar echo; acquiring a spatial-domain sparse signal through cancellation and signal reconstruction; using a wave beam formation method to obtain a rough measurement target angle; according to the rough measurement angle, acquiring the spatial domain and dividing the spatial domain; using the array interpolation to acquire a virtual array; according to a matrix transformation relation, acquiring an interpolation transformation matrix and carrying out prewhitening processing on the interpolation transformation matrix; using a whitening interpolation transformation matrix and an observation matrix to acquire an observation signal; using a whitening interpolation transformation matrix and observation signal iteration operation to acquire a target signal estimation value; extracting a target angle from the target signal estimation value so as to acquire a target height. By using the method of the invention, sampling points of the target signal and computation intensity are obviously reduced; sidelobes of a signal power spectrum and a space spectrum are effectively reduced; the method can be used in target tracking.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Wave beam space domain meter wave radar height measurement method based on compressed sensing
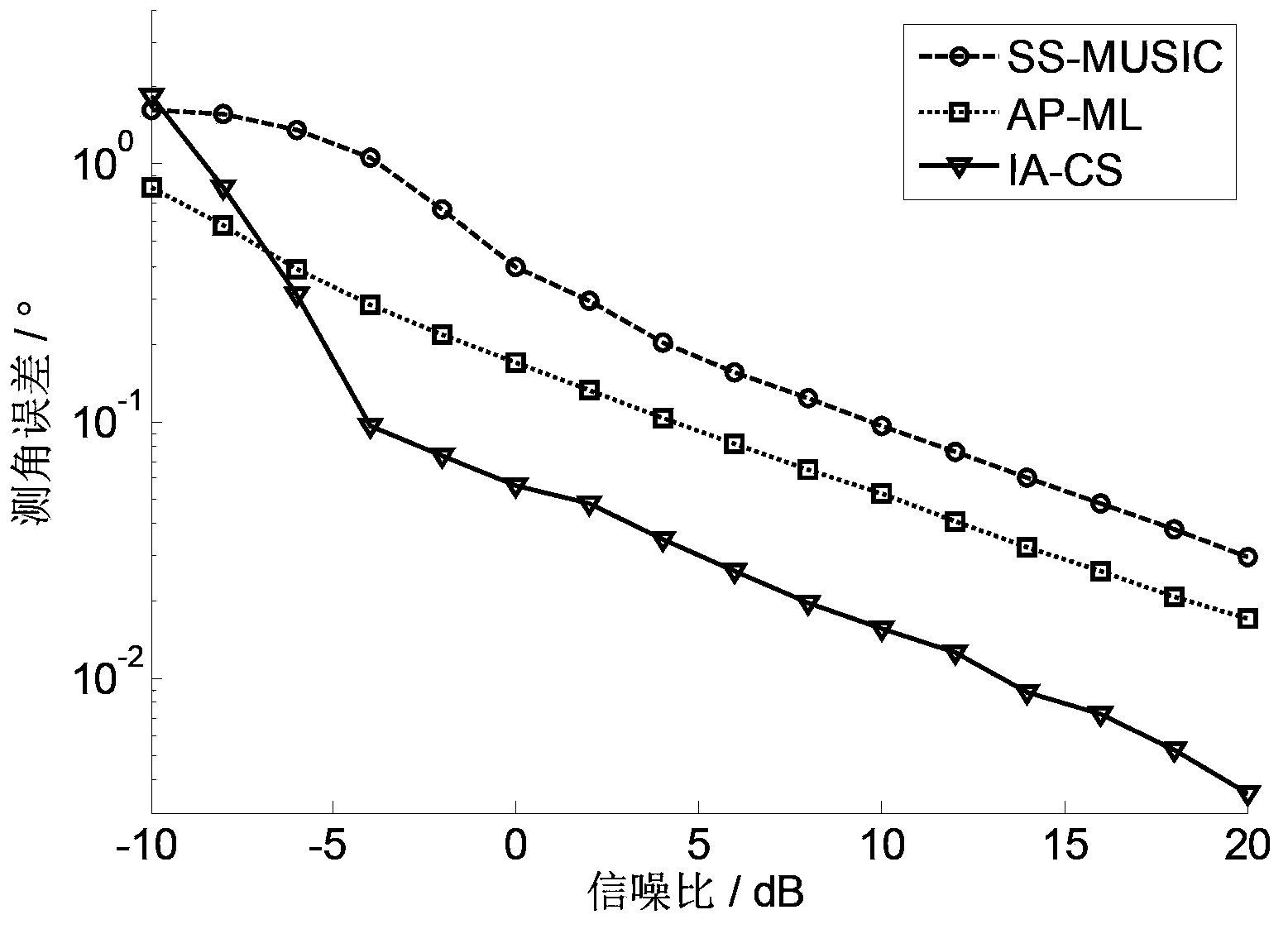
ActiveCN103353596AReduce sidelobeImprove angle measurement accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Target signal
The invention discloses a wave beam space domain meter wave radar height measurement method based on compressed sensing and relates to low elevation height measurement under the condition that a signal to noise ratio is low and snapshots are less. A realization process is characterized in that a target signal is extracted from a radar echo and rough measurement of the elevation is performed so that the space domain theta where a target signal elevation is located is obtained; the space domain theta is divided into P parts, wave beam formation is performed in the space domain theta so as to obtain a wave beam transformation matrix B and prewhitening is performed on the wave beam transformation matrix B so as to obtain a whitening wave beam transformation matrix T; receiving data is projected to the whitening wave beam transformation matrix so as to obtain a wave beam domain measurement signal z and an observation matrix phi carries out compression sampling on the z so as to obtain an observation signal y; iterative operation of the whitening wave beam transformation matrix T and the observation signal y is used to obtain a target signal estimation value; a target angle is extracted from the target signal estimation value so as to obtain the target height. By using the method of the invention, sampling points of the target signal and operands are reduced; sidelobes of a signal power spectrum and a space spectrum are effectively reduced; height measurement precision under the low signal to noise ratio is increased; the method can be used in target positioning.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
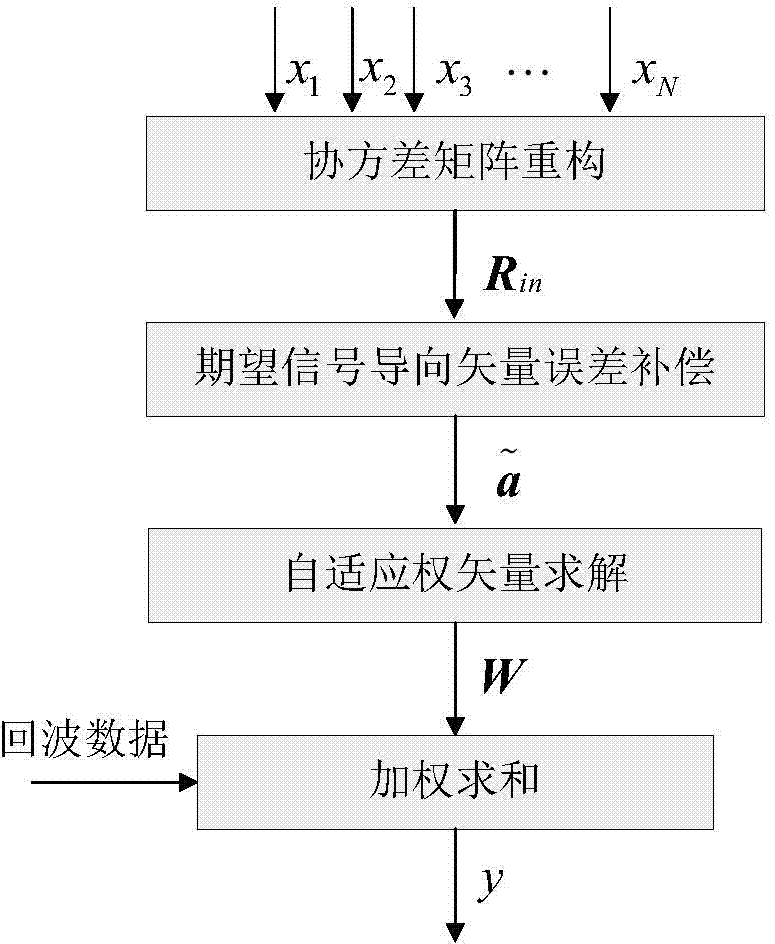
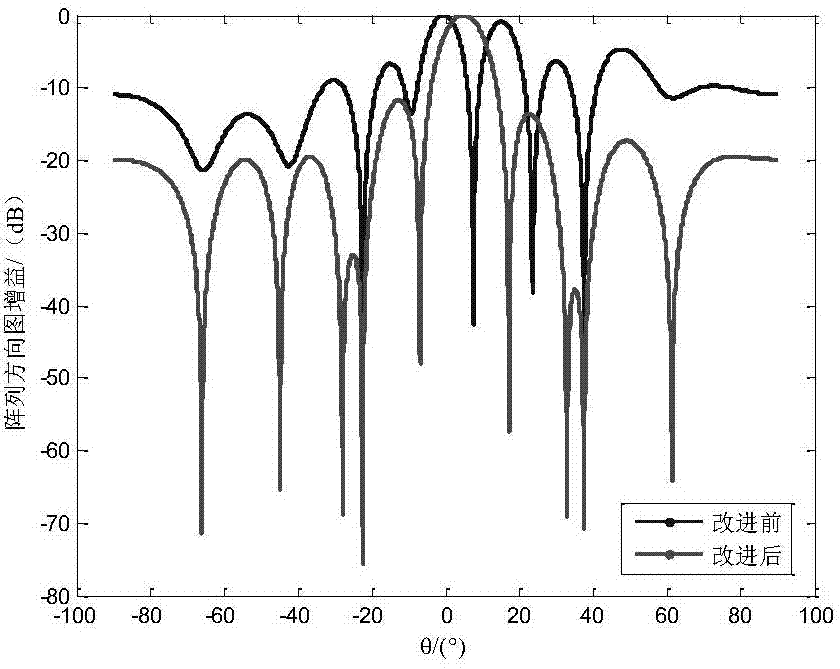
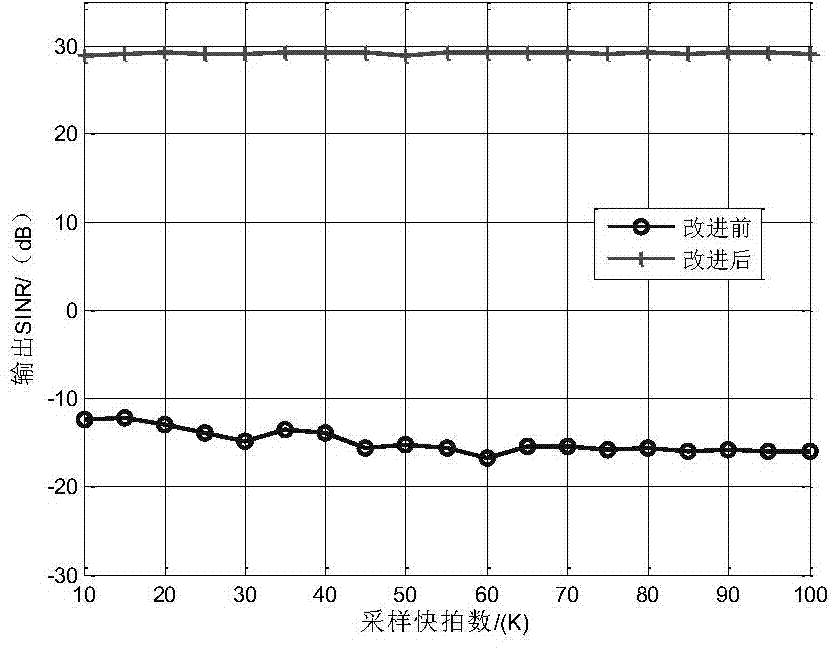
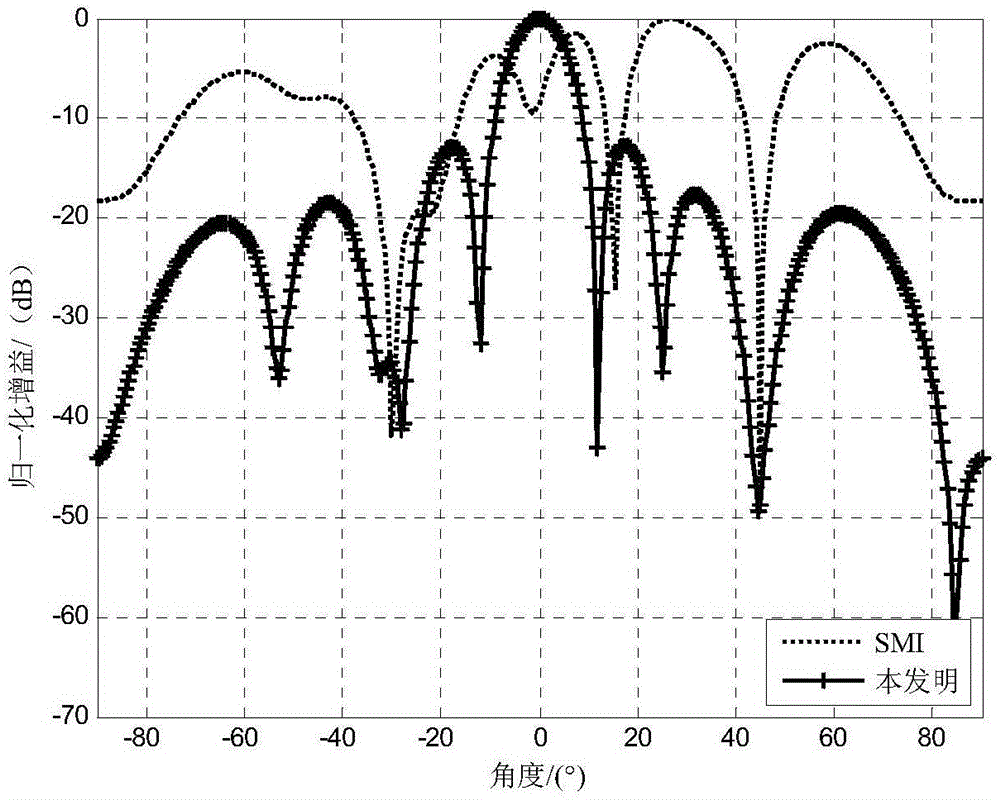
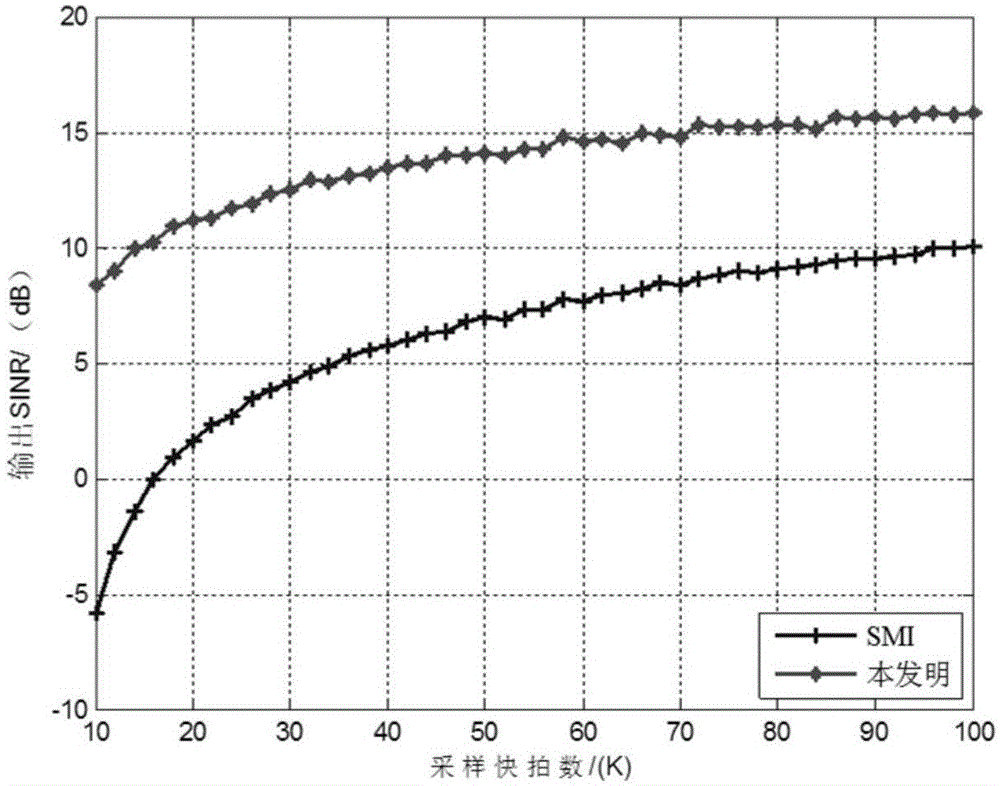
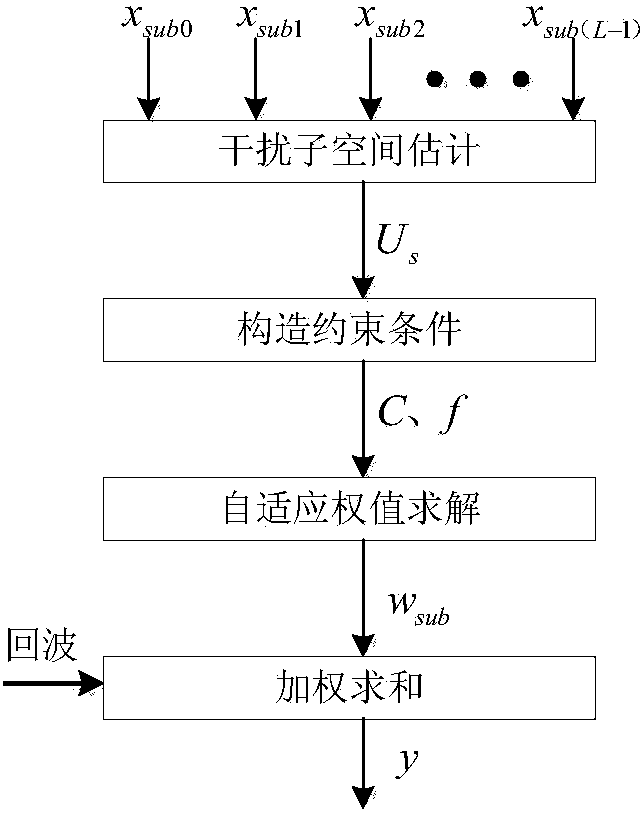
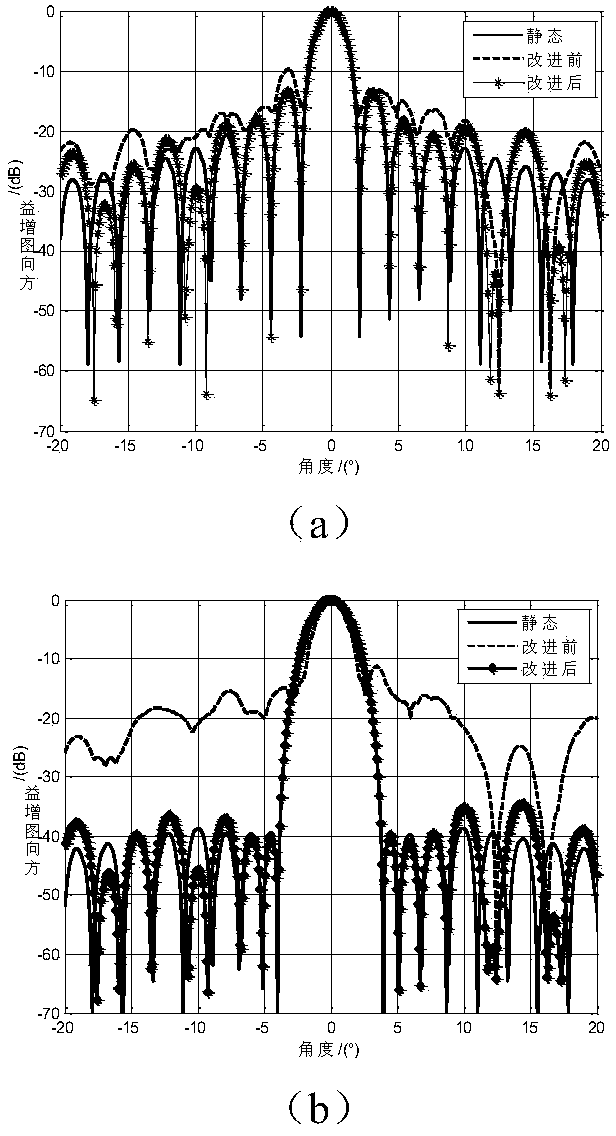
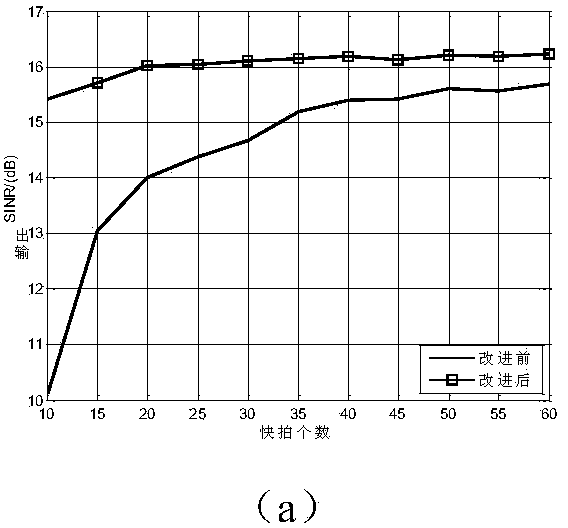
Self-adaptive beam forming method based on covariance reconstruction and guide vector compensation
InactiveCN104270179AAdaptive Beamforming EffectiveSuppress interferenceSpatial transmit diversityDecompositionAlgorithm
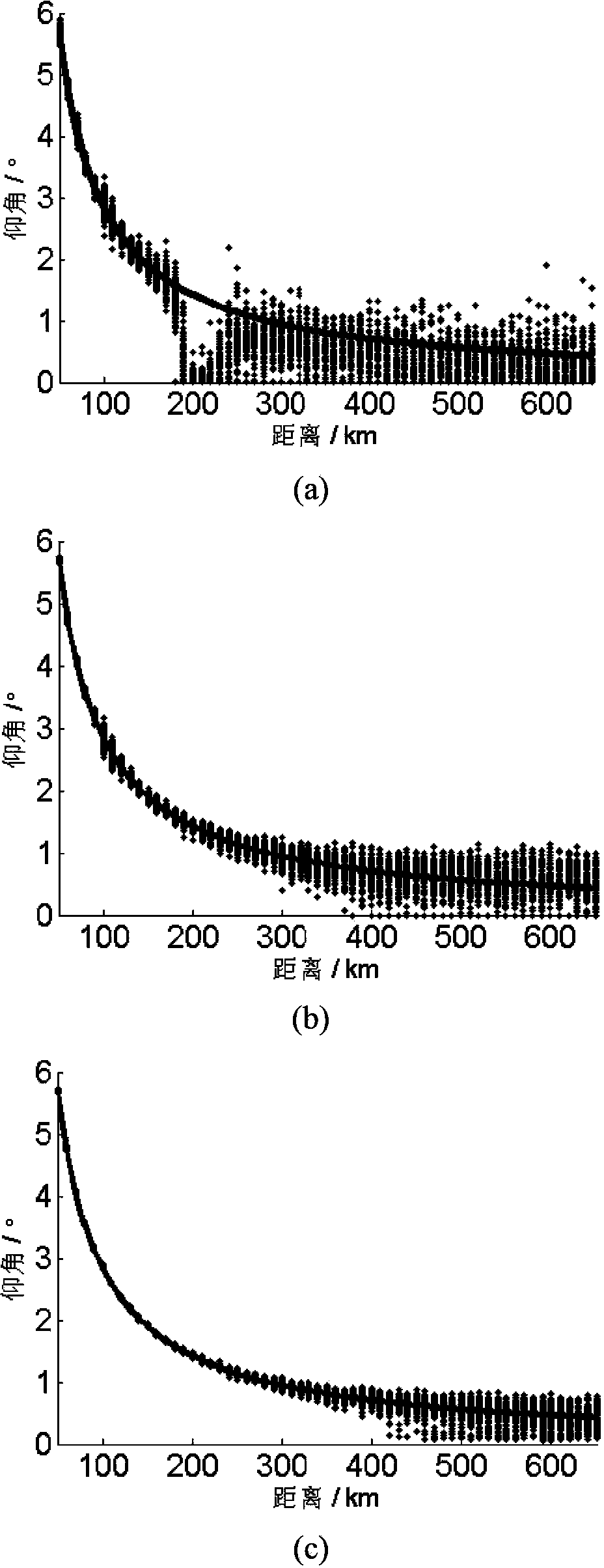
The invention discloses a self-adaptive beam forming method based on covariance reconstruction and guide vector compensation. According to the method, in the situation that desired signals exist in sampling snapshot and signal guide vectors are mismatched, interference can be effectively inhibited, main lobe shape preservation and side lobes of a self-adaptive directional diagram can be reduced, and high output SINR and quick convergence speed can be obtained. According to the method, eigenvalue decomposition is carried out on a sampling covariance matrix, noise sub space is estimated by means of an MDL criterion, the incident angle of a signal source is estimated in a Root-MUSIC method, the incident angle of the desired signals is judged, and then a new interference and noise covariance matrix is reconstructed; mismatching of the guide vectors of the desired signals is compensated by solving a quadratic programming problem with quadratic constraints; ultimately, a self-adaptive weight vector is solved by means of the reconstructed new interference and noise covariance matrix and the corrected guide vectors, a null is formed in the interference direction in a self-adaptive mode, and interference is effectively inhibited.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Acoustic vector array DOA estimation method
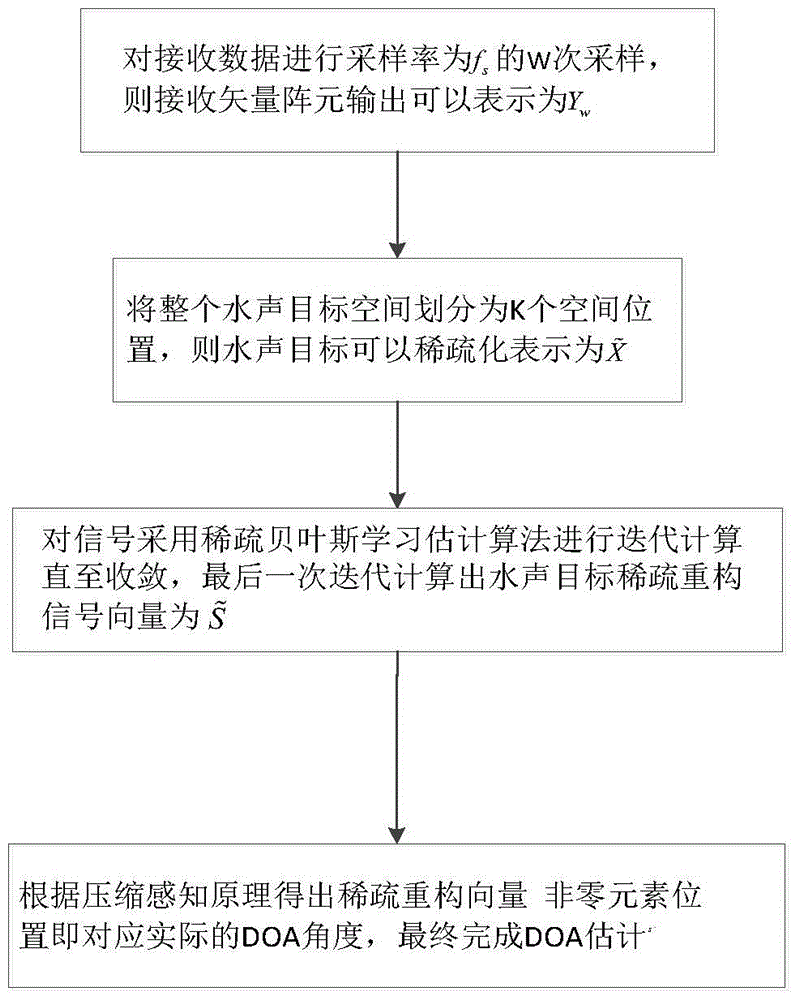
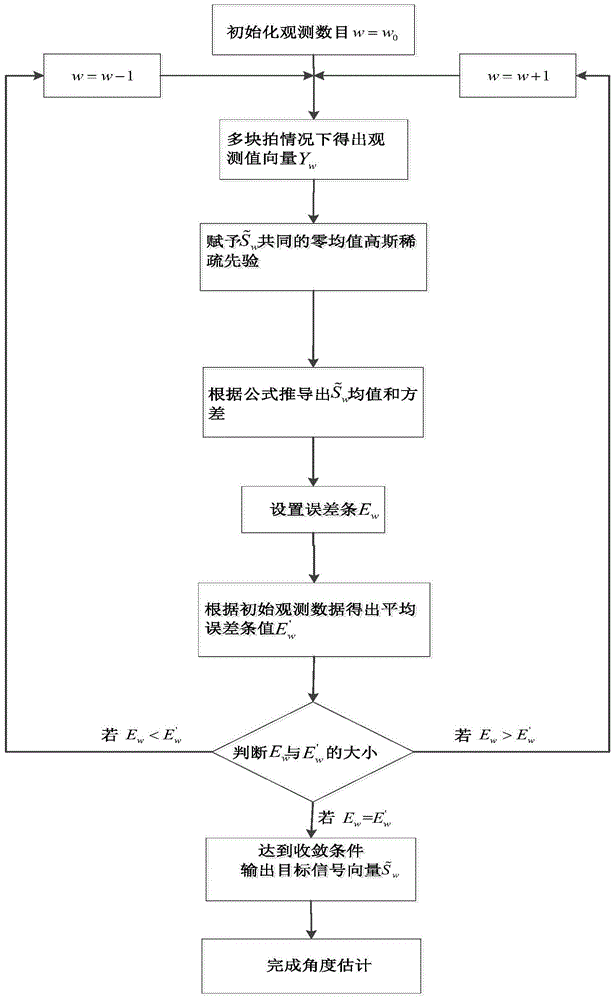
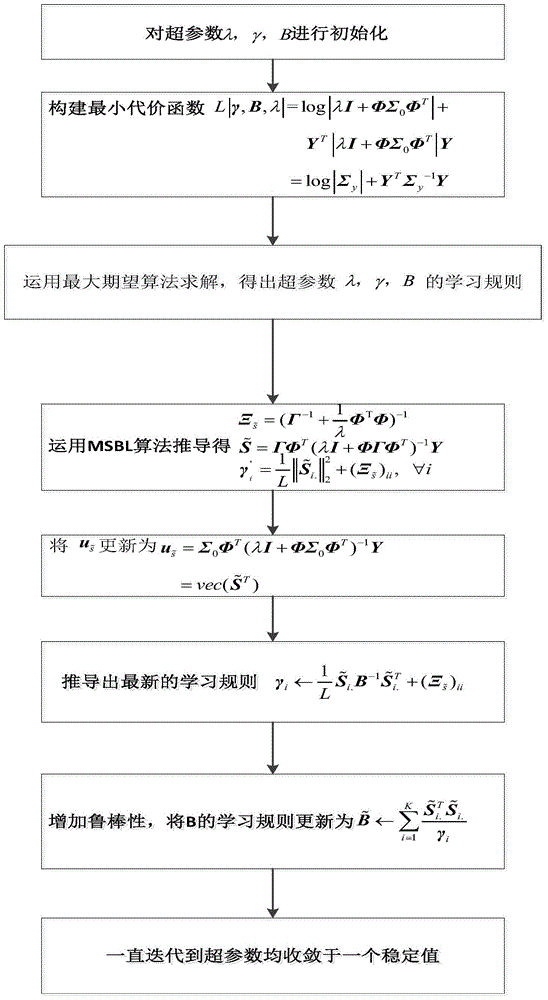
ActiveCN105676168AReduce sidelobeHigh precisionDirection/deviation determination systemsMaximum a posteriori estimationArray element
The invention discloses an acoustic vector array DOA estimation method, which comprises the steps that: signals sent by L remote underwater acoustic targets are narrowband signals at frequency f, a receiving signal array is a uniform linear array comprising M vector sensor array elements, and an array element distance is half wavelength of the transmitted signals; an entire underwater acoustic target space is divided into K spatial positions, and each spatial position corresponds to one directional angle; a sparse bayesian learning DOA estimation algorithm is adopted for the signal Sw<~>, a maximum posterior probability of a signal source is obtained to achieve azimuth angle estimation of the targets through solving a value of a hyper-parameter, the hyper-parameter is subjected to iterative calculation till convergence, and an underwater acoustic target sparse reconstructed signal vector is calculated to be Si<~> through the final iterative calculation; a position of a S<~> non-zero row is determined, a non-zero element position of the sparse reconstructed vector S<~> corresponds to an actual DOA angle, and the DOA estimation is completed finally. The acoustic vector array DOA estimation method can improve DOA estimation accuracy, obtains more incisive directional beams and lower side lobes, and achieves omnibearing DOA estimation.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Self-adaptive beam-forming method based on related calculation and clutter covariance matrix reconstruction
ActiveCN105302936ASolve the cancellation problemFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmSignal subspace
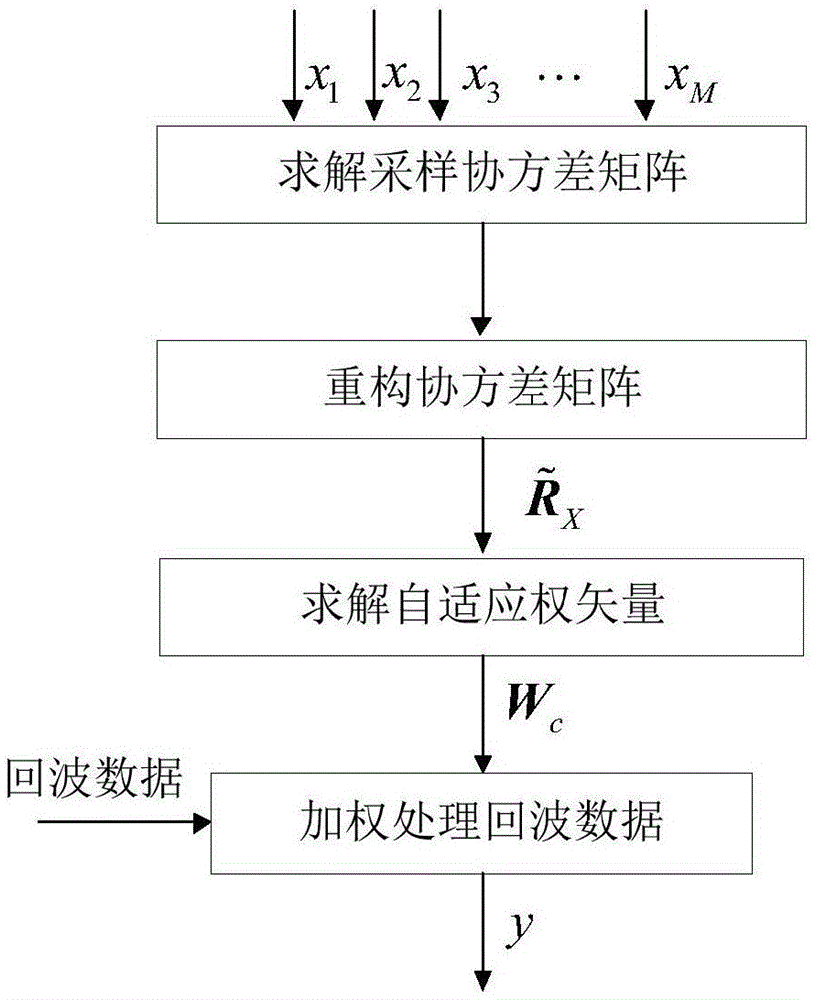
The invention relates to a self-adaptive beam-forming method based on related calculation and clutter covariance matrix reconstruction. The self-adaptive beam-forming method comprises following steps: solving an array sampling covariance matrix by limited sampling snapshot data; decomposing eigenvalue of the array sampling covariance matrix and estimating signal subspace; making related calculations between eigenvector corresponding to a signal and an assumed steering vector of a desired signal and solving eigenvector corresponding to the desired signal; resetting eigenvalue corresponding to the desired signal in order to reconstruct a new covariance matrix; solving self-adaptive weight vector based on the minimum variance orthoscopic principle by the reconstructed covariance matrix; and utilizing self-adaptive weight vector to performing weighting operation on echoed data.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
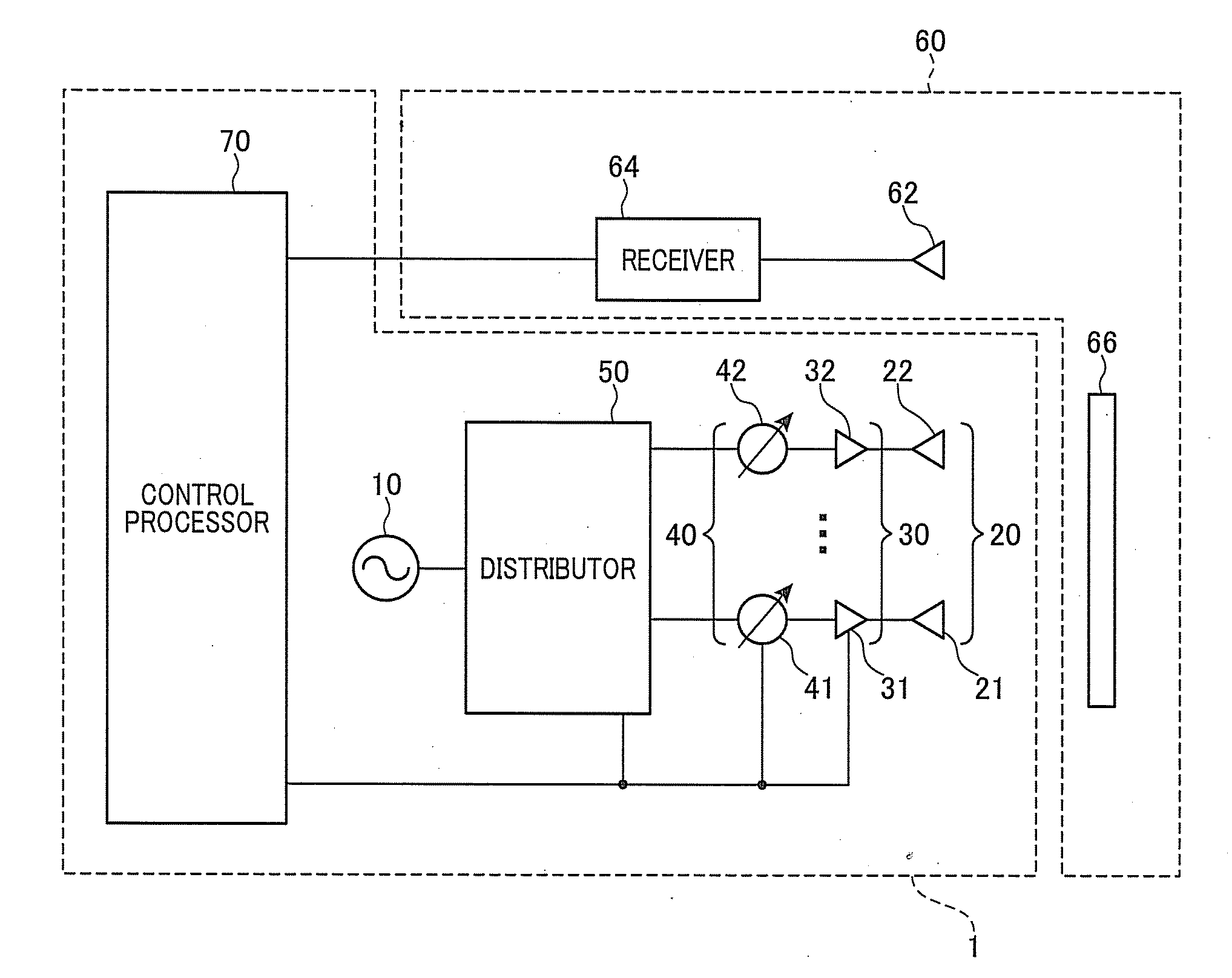
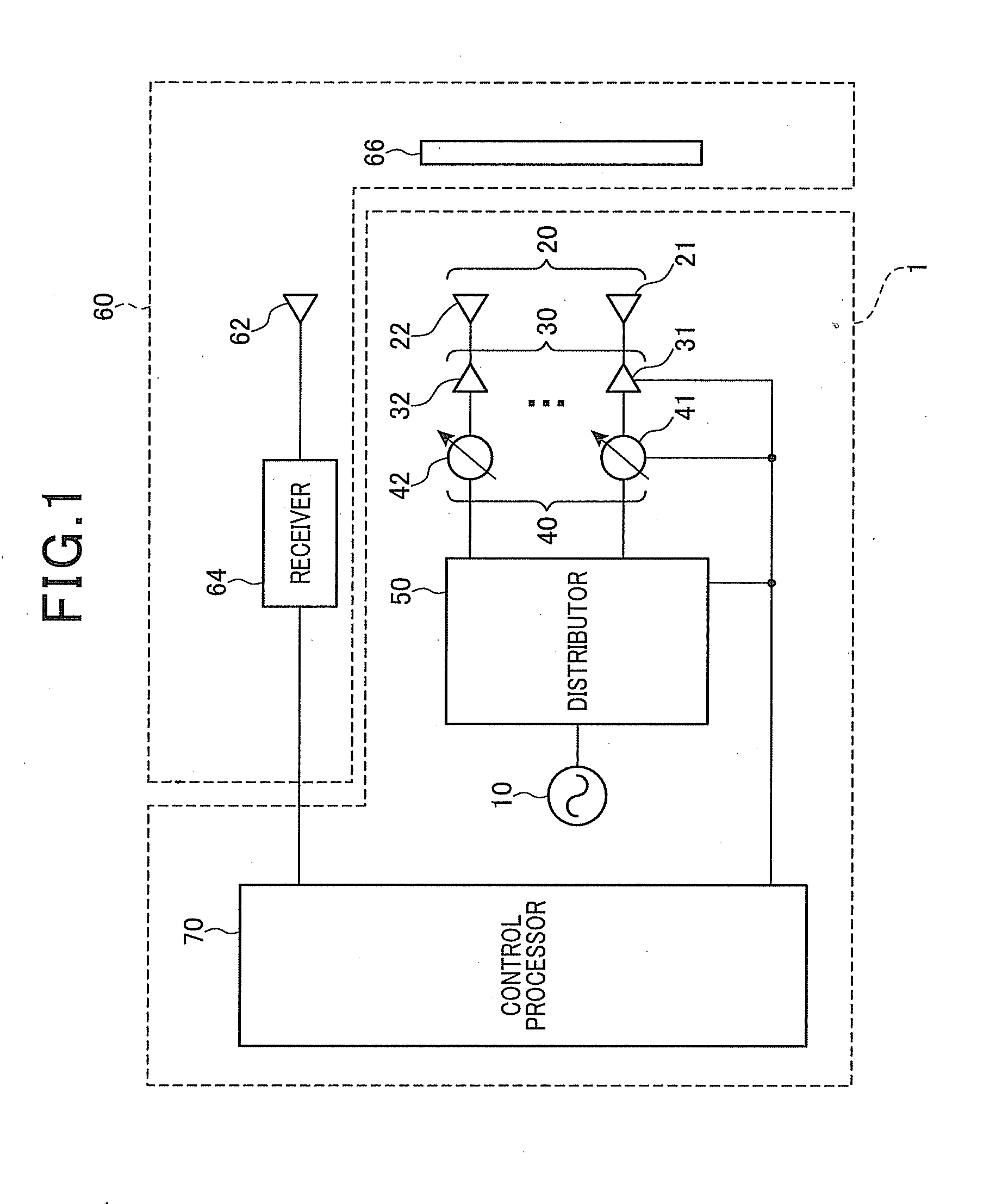
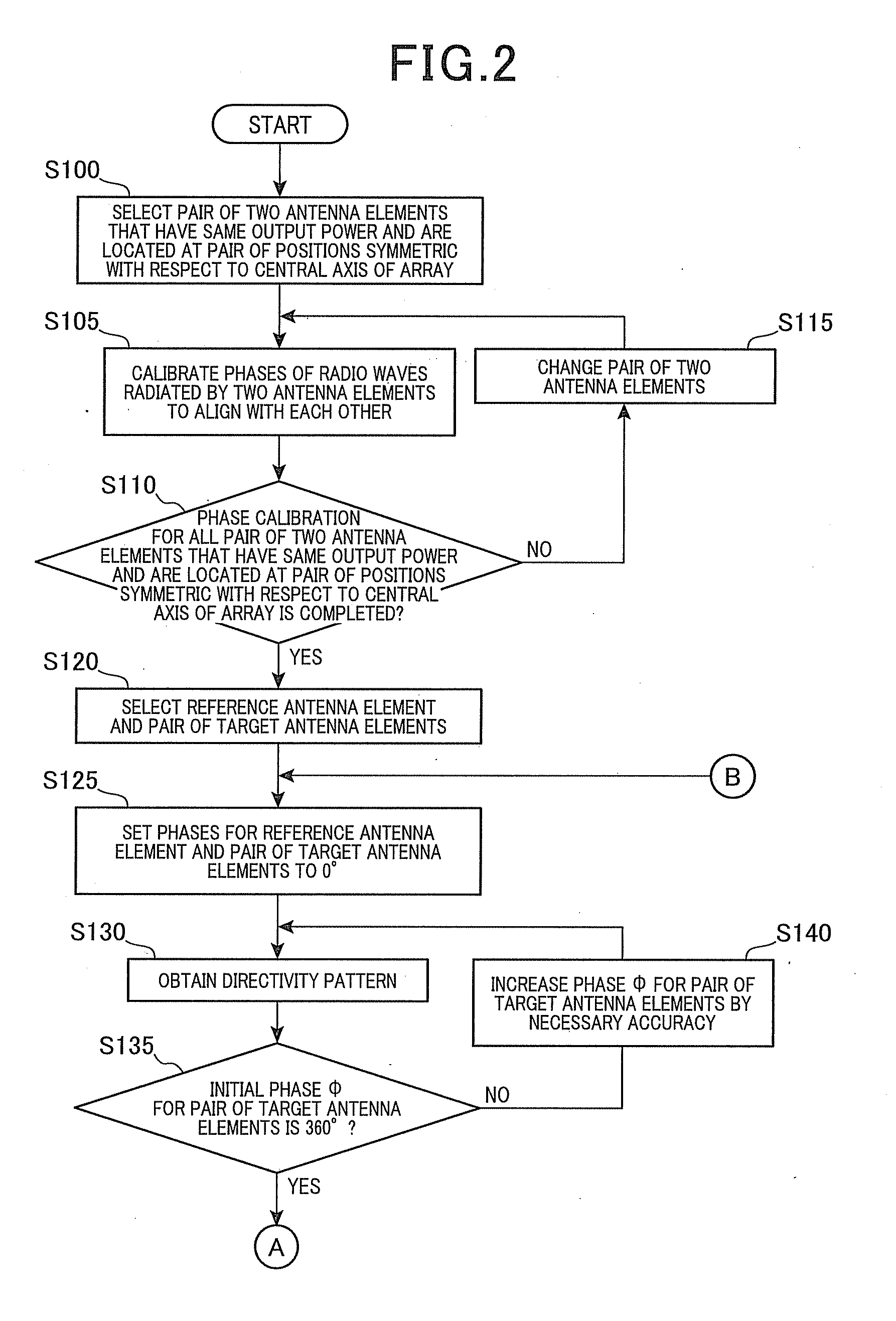
Phased array antenna and its phase calibration method
ActiveUS20120146841A1Easily and accurately calibratingReduce sidelobeWave based measurement systemsAntennasPhysicsReference antenna
A phased array antenna includes an oscillator, a plurality of antenna elements, a phase shifter, a distributor, a receiver, and a control processor. The control processor performs a first calibration process to calibrate a phase of the phase shifter connected to a pair of antenna elements that is selected from the antenna elements and are located at a pair of positions symmetric with respect to a central axis of an array formed by the phased array antenna, and a second calibration process to calibrate a phase of the phase shifter connected to a pair of target antenna elements with respect to a phase of the phase shifter connected to a reference antenna elements located at a central portion of the array. The pair of target antenna elements are located at a pair of positions that are symmetric with respect to the central axis of the array.
Owner:DENSO CORP
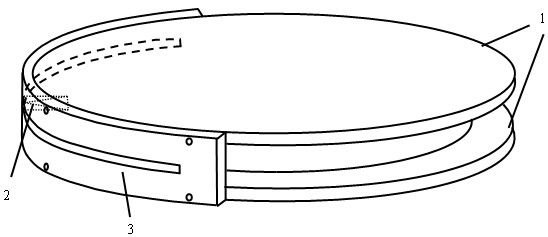
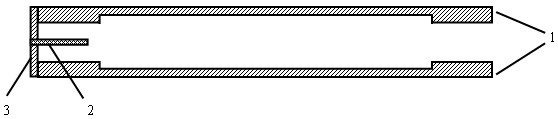
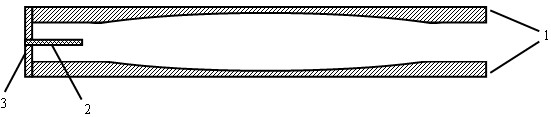
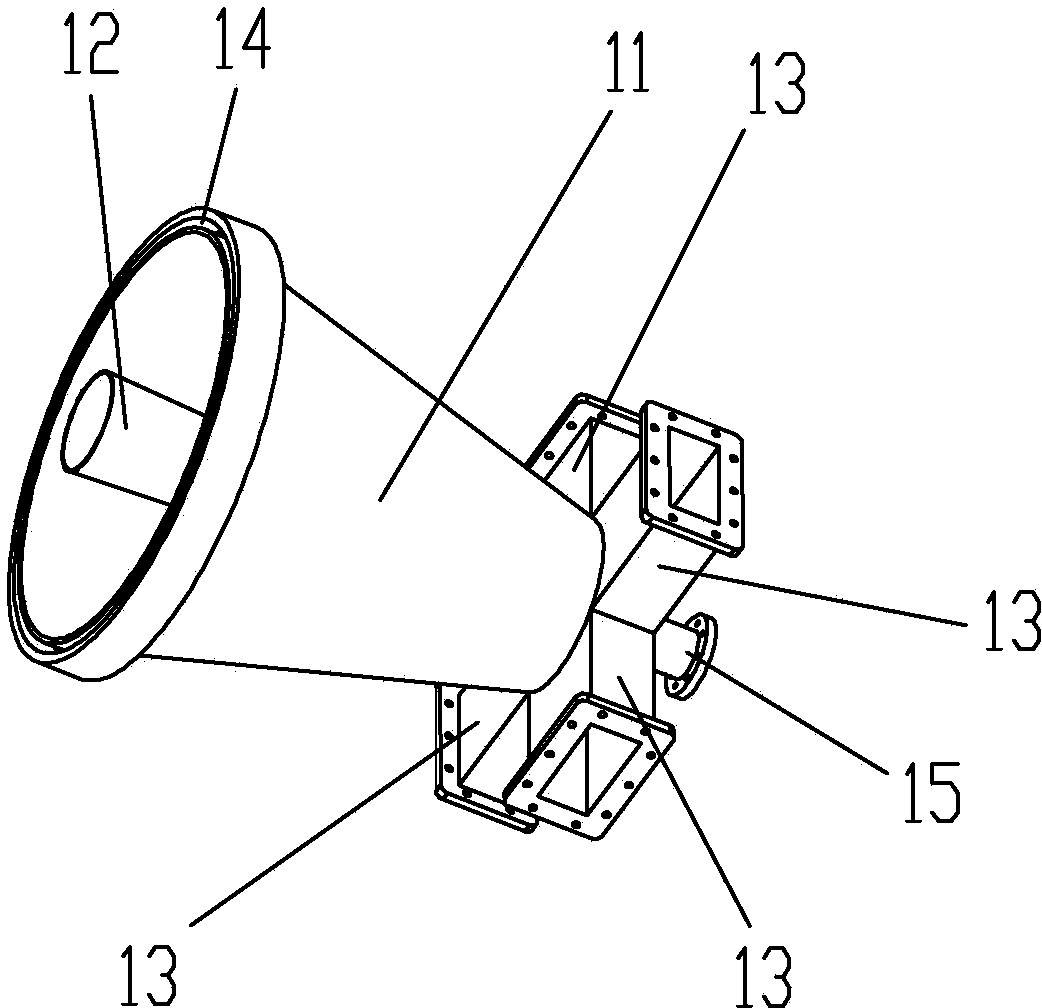
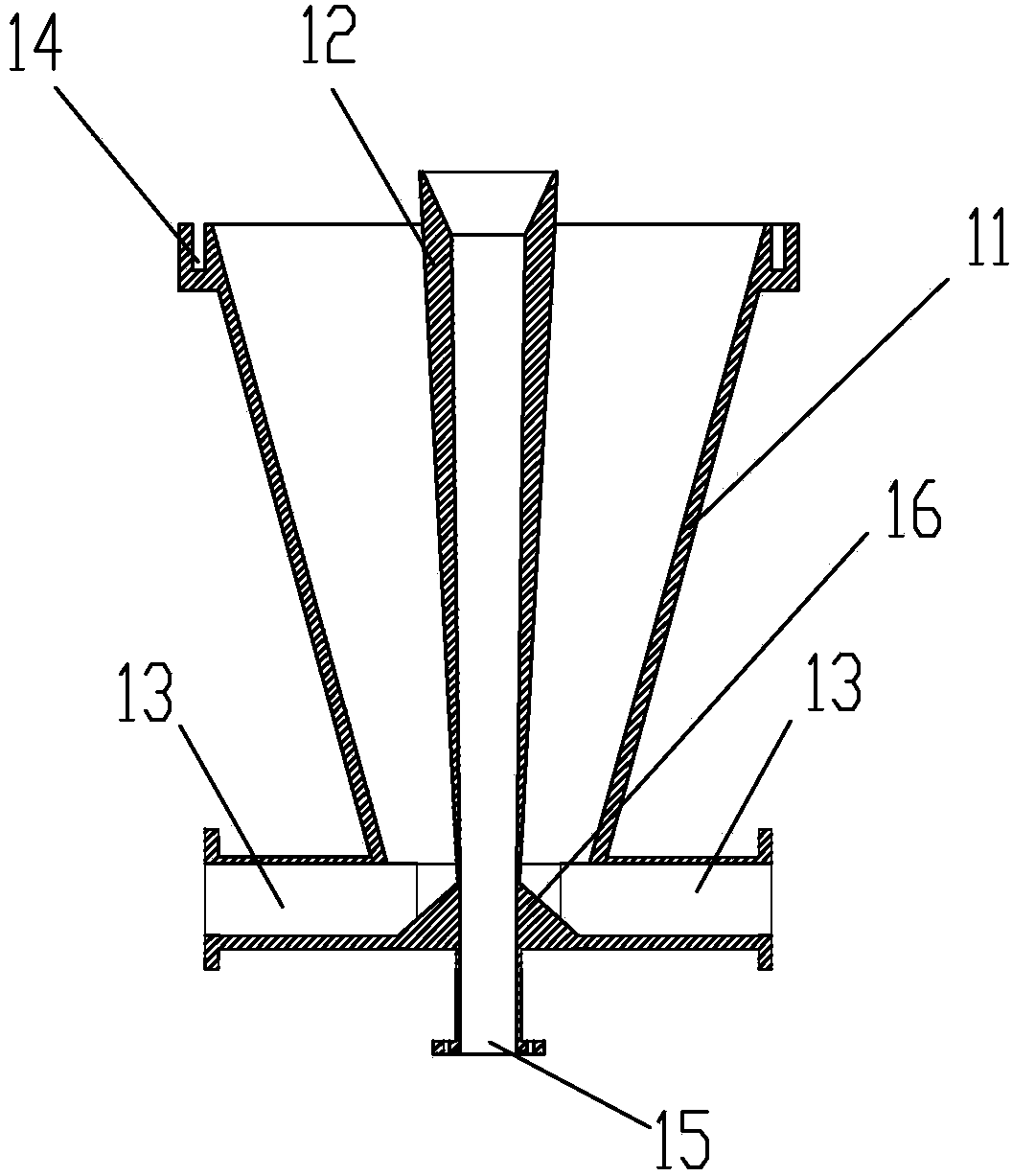
Air dielectric cylindrical lens antenna
The invention discloses an air dielectric cylindrical lens antenna. The air dielectric cylindrical lens antenna comprises a metal disc-shaped parallel plate waveguide, a feed source antenna and arc-shaped metal support plates, wherein the metal disc-shaped parallel plate waveguide comprises an upper metal disc and a lower metal disc, the upper and the lower inner surfaces of the metal disc-shaped parallel plate waveguide are planes or arc-shaped surfaces, a central cavity of the metal disc-shaped parallel plate waveguide forms an air dielectric cylindrical lens, an annular boss is arranged below the edge of the upper disc of the metal disc-shaped parallel plate waveguide, the annular boss is arranged above the edge of the lower disc of the metal disc-shaped parallel plate waveguide, the feed source antenna is arranged between the two annular bosses, the feed source antenna is embedded in an arc-shaped groove between the arc-shaped metal support plates on the edges of the two metal discs, and the arc-shaped metal support plates are connected with the two metal discs through screws. The feed source antenna is a horizontal polarization gradient groove antenna or a horizontal polarization gradient groove antenna array.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Waveguide slotted array antenna
ActiveUS20180358709A1Reduce size of antennaLower complexityRadiating elements structural formsIndividually energised antenna arraysRadiationWideband
A waveguide slotted array antenna comprises a feed layer and a radiation layer, wherein the feed layer is located below the radiation layer, and the radiation layer comprises a first radiation unit, a second radiation unit, a third radiation unit and a fourth radiation unit which are stacked from bottom to top; the first radiation unit comprises a first flat metal plate and a first radiation array arranged on the first flat metal plate, the second radiation unit comprises a second flat metal plate and a second radiation array arranged on the second flat metal plate, the third radiation unit comprises a third flat metal plate and a third radiation array arranged on the third flat metal plate, and the fourth radiation unit comprises a fourth flat metal plate and a fourth radiation array arranged on the fourth flat metal plate. The waveguide slotted array antenna has the advantages of low sidelobes and low cost while ensuring broad bands and high gains, and can be made small.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
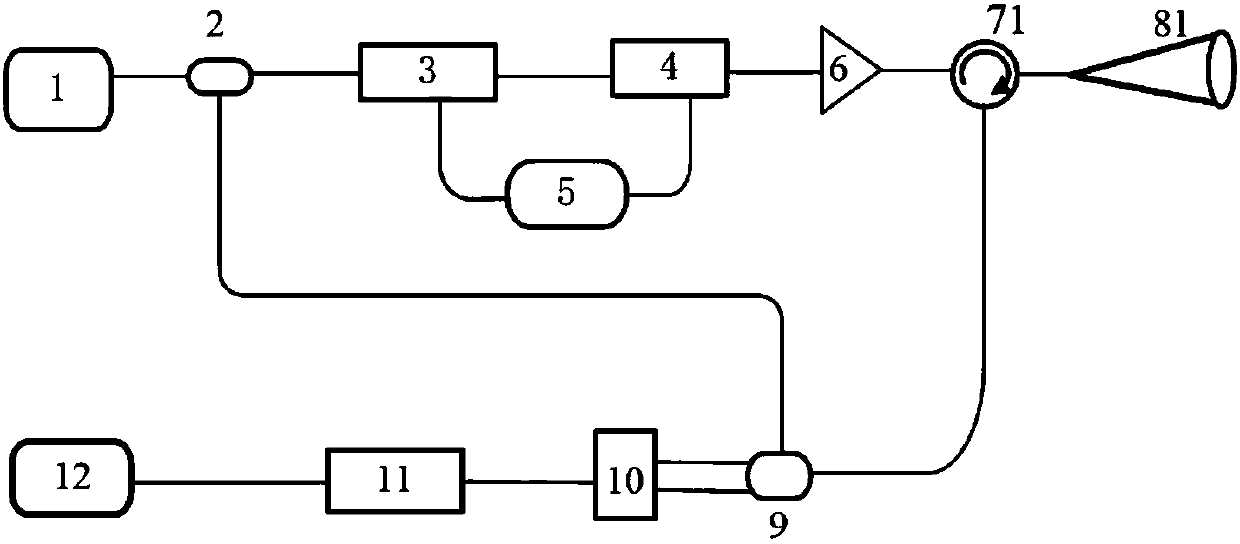
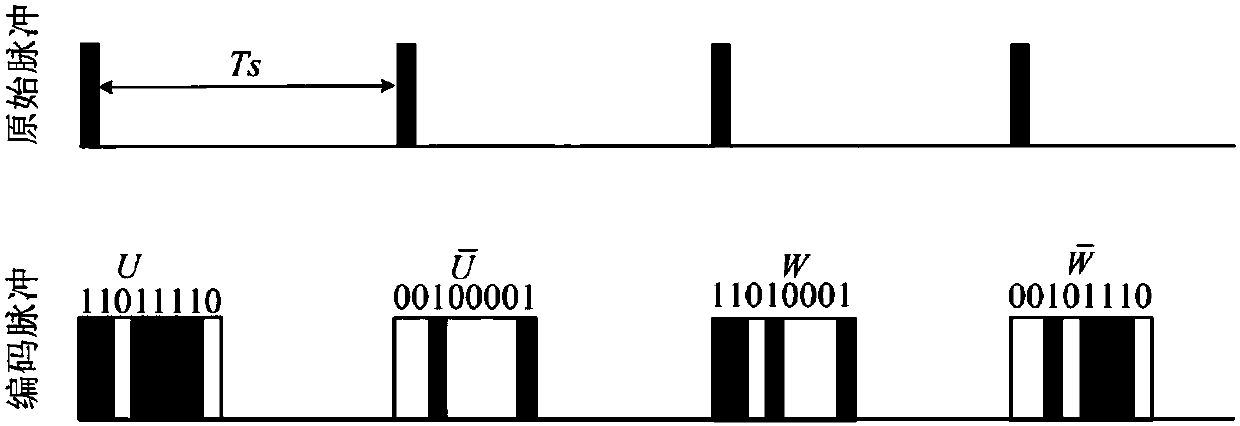
Coherent laser radar based on pulse coding technology
ActiveCN108594256AReduce time-domain cross-correlationReduce sidelobeFluid speed measurementElectromagnetic wave reradiationGolay complementary sequencesSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a coherent laser radar based on pulse coding technology. The invention aims at low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of echo signals of coherent laser radars, and proposes a method for improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the system and increasing the dynamic range of the system by using the pulse coding technology. The invention outputs the pulse coding sequence codes by an electro-optic modulator, reduces the time-domain cross-correlation between the respective transmit waveforms, reduces auto-correlated side lobes by using the complementary properties of the Golay complementary sequence, and reduces side lobes after the waveform pulse compression. In addition, the present invention performs decoding according to the decoding rule, solves the problem that the pulse peak power of the fiber laser is limited, significantly improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the coherent laser radar, effectively improves the detection range, and does not require pulse accumulationtime, without sacrificing detection time and distance resolution.
Owner:夏和娣
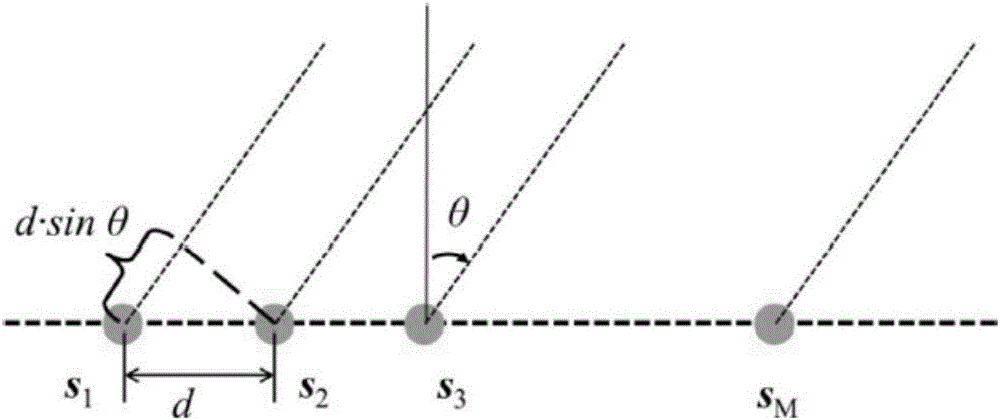
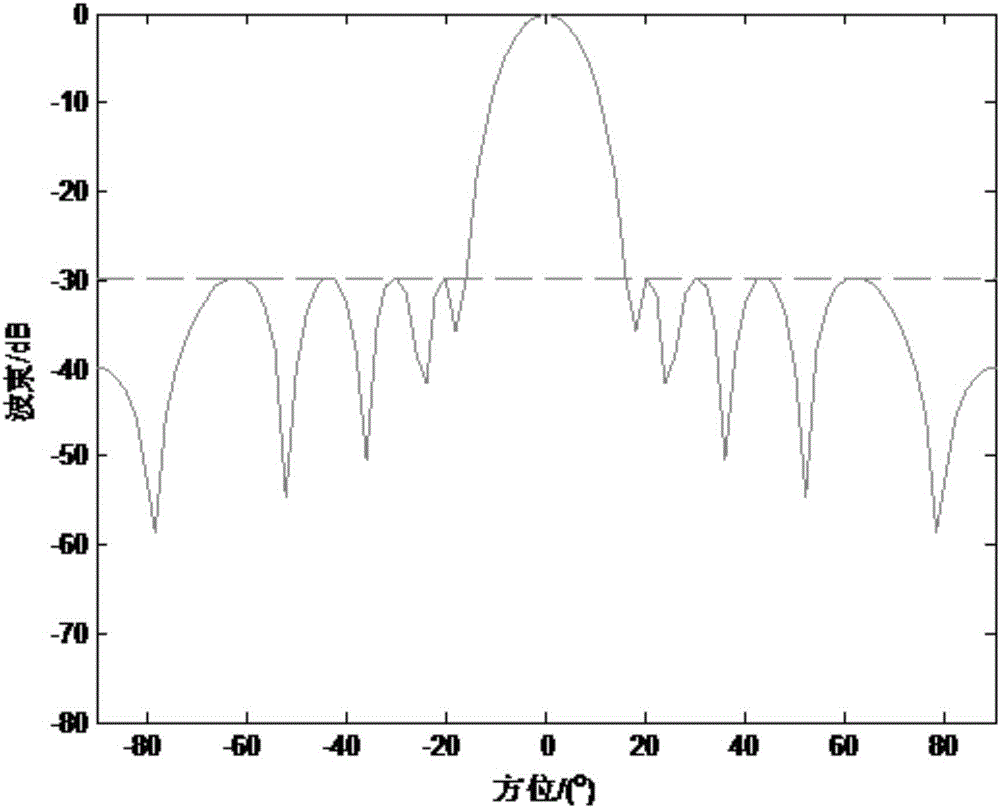
Low-side-lobe beam pattern integrated design method based on convex optimization
ActiveCN106682405AImprove robustnessReduce sidelobeSpecial data processing applicationsSide effectBeam pattern
The invention discloses a low-side-lobe beam pattern integrated design method based on convex optimization. Auxiliary variables are introduced to achieve variable separation by adopting an alternative direction multiplier method (ADMM), a large amount of original inequality constraint limits are converted into solvable problems, iteration solution is performed by applying an ADMM thought, and accordingly parameters are determined to obtain an ideal wave beam, namely side-lobe values are reduced. The robustness of a wave beam forming device is good in the process by optimizing wave beam side lobes, the side effect of the side lobes on array gains is low, the obtained side lobe values are low, and the low-side-lobe beam pattern integrated design method is simple and simple in operation and has a very good practical value.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
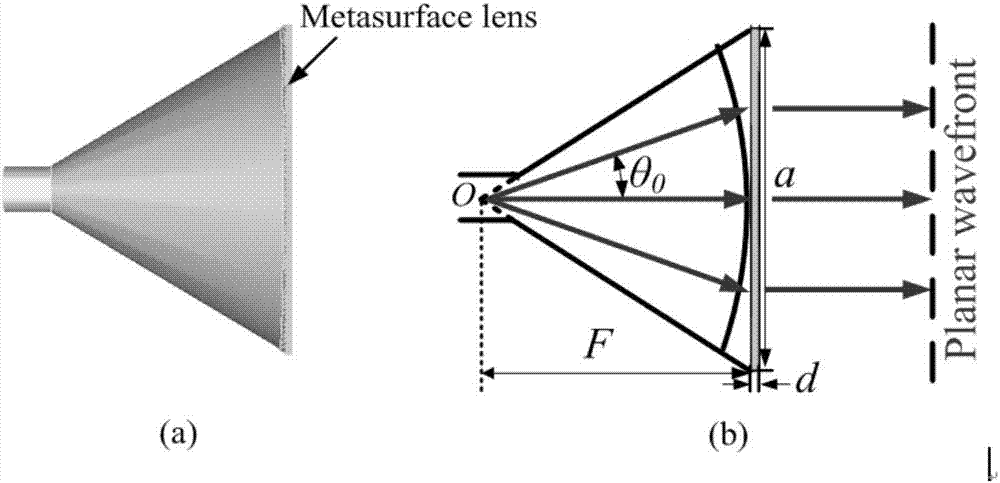
Super-surface lens antenna
The invention discloses a super-surface lens antenna, and belongs to the technical field of antennas. The antenna consists of a conical-horn antenna and a wave beam focusing super-surface with the sub-wavelength thickness. The wave beam focusing super-surface is formed by a transmission-type linear polarization unit structure array with the parabolic-type cross polarization phase space distribution. The transmission-type linear polarization unit structure sequentially comprises a metal grid, a dielectric substrate, a metal elliptical opening resonant ring, a dielectric substrate and a metal grid from the bottom to the top. The size and period of the transmission-type linear polarization unit structure can change the working frequency band, bandwidth and the focusing efficiency of the wave beam focusing super-surface. According to the invention, the core component, the wave beam focusing super-surface, of the super-surface lens antenna is manufactured through the printed circuit board technology. The super-surface lens antenna is low in construction cost, employs a plane structure, has the sub-wavelength thickness, is light in weight, is small in size, is small in standing-wave ratio, is narrow in beam, is high in gain, and can be designed and implemented at any band.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Submatrix level linear constraint self-adaptive beam forming method based on feature subspaces
ActiveCN103837861AReduce sidelobeGood output SINR performanceWave based measurement systemsDecompositionSide lobe
The invention discloses a submatrix level linear constraint self-adaptive beam forming method based on feature subspaces, and belongs to the technical field of array signal processing. The method includes the steps that eigenvalue decomposition is conducted on a sampling covariance matrix, so that the needed interference subspaces are estimated, then, interference signals are restrained in a self-adaptive mode by the way that interference subspace constraint beam response is zero, a self-adaptive directional diagram is constrained by introducing a penalty function, so that a main lobe achieves shape preserving, and a side lobe is lowered. According to the method, self-adaptive interference restraint is carried out, meanwhile main lobe shape preserving and side lobe lowering of the self-adaptive directional diagram obtained in a submatrix are achieved, and good output SINR performance can be obtained. The method is suitable for submatrix level linear constraint self-adaptive beam forming.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
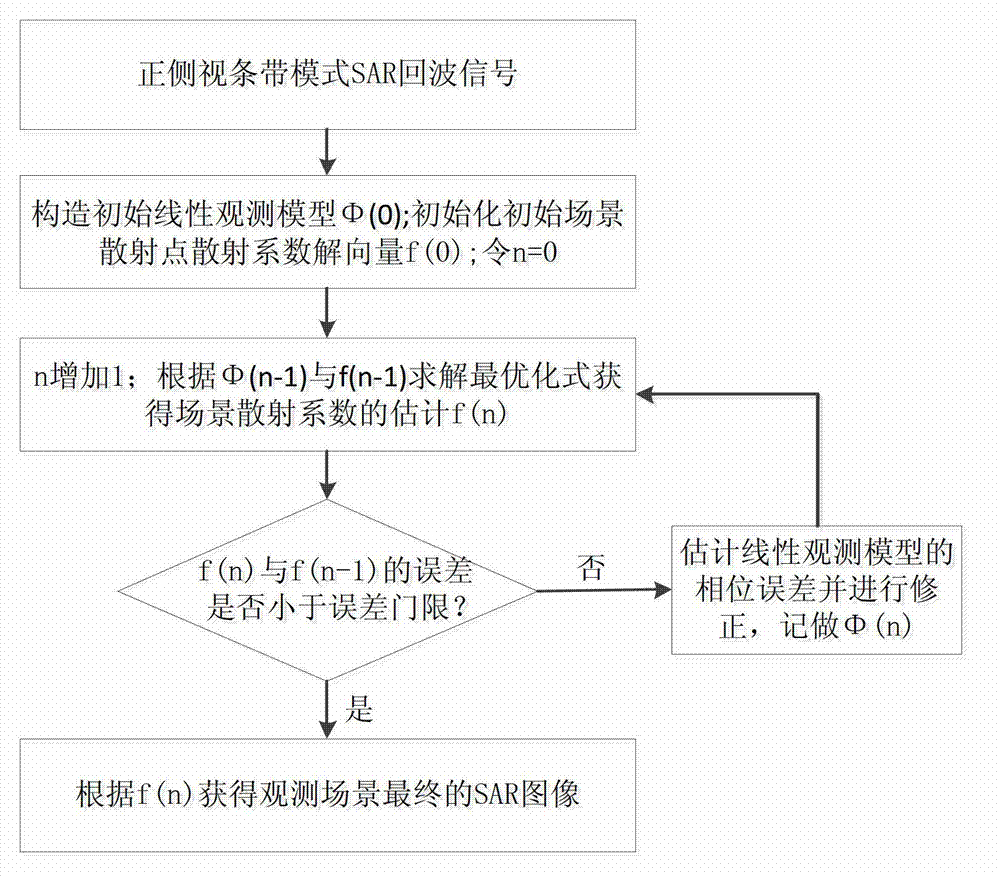
Weighting sparse-driven self-focusing SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) imaging method
InactiveCN102854505AFocusReduce sidelobeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarRadar
The invention discloses a weighting sparse-driven self-focusing SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) imaging method. The method comprises the steps as follows: establishing a linear observing model of echo data and an observing scene to construct the optimized target function; adopting the weighted L1 norm; and then carrying out an L1 norm approximating method to approximate the L1 norm in the target function; iterating and solving the optimized target function; and estimating the phase error of the linear observing model, and modifying the linear observing model to obtain a more accurate observing model, thus achieving the focusing of the synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image. Compared with the synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image reconstructed via a traditional focusing method (such as PGA (Programmable Gain Amplifier) and a sparse-driven auto-focusing (SDA), the synthetic aperture radar image obtained via the method provided by the invention is lower in sidelobe, and has a better effect on focusing.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Double-slot double-frequeny-range sheared corrugated horn feed
InactiveCN1438733AOvercoming the inability to achieve LGet over workWaveguide hornsSimultaneous aerial operationsReflection lossSide lobe
The feed source of the corrugated horn comprises a harmful harmonic mode suppresser, the corrugation groove mode converter with double-groove structure, the frequency change and angle change transition section with double-groove deep corrugation structure and the radiation section with double-groove deep corrugation structure. The corrugation groove mode converter combines the harmful harmonic suppresser and the annular loading groove as well as the straight groove so as to reach the purpose of restraining excitation of the harmful harmonic mode, lowering reflectino loss and dual-band joint use. The invention possesses the features of rotation symmetry of the radiation pattern in two discrete frequency ranges, low electrical level of the side lobe and cross polarization, low reflection loss and high gain.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
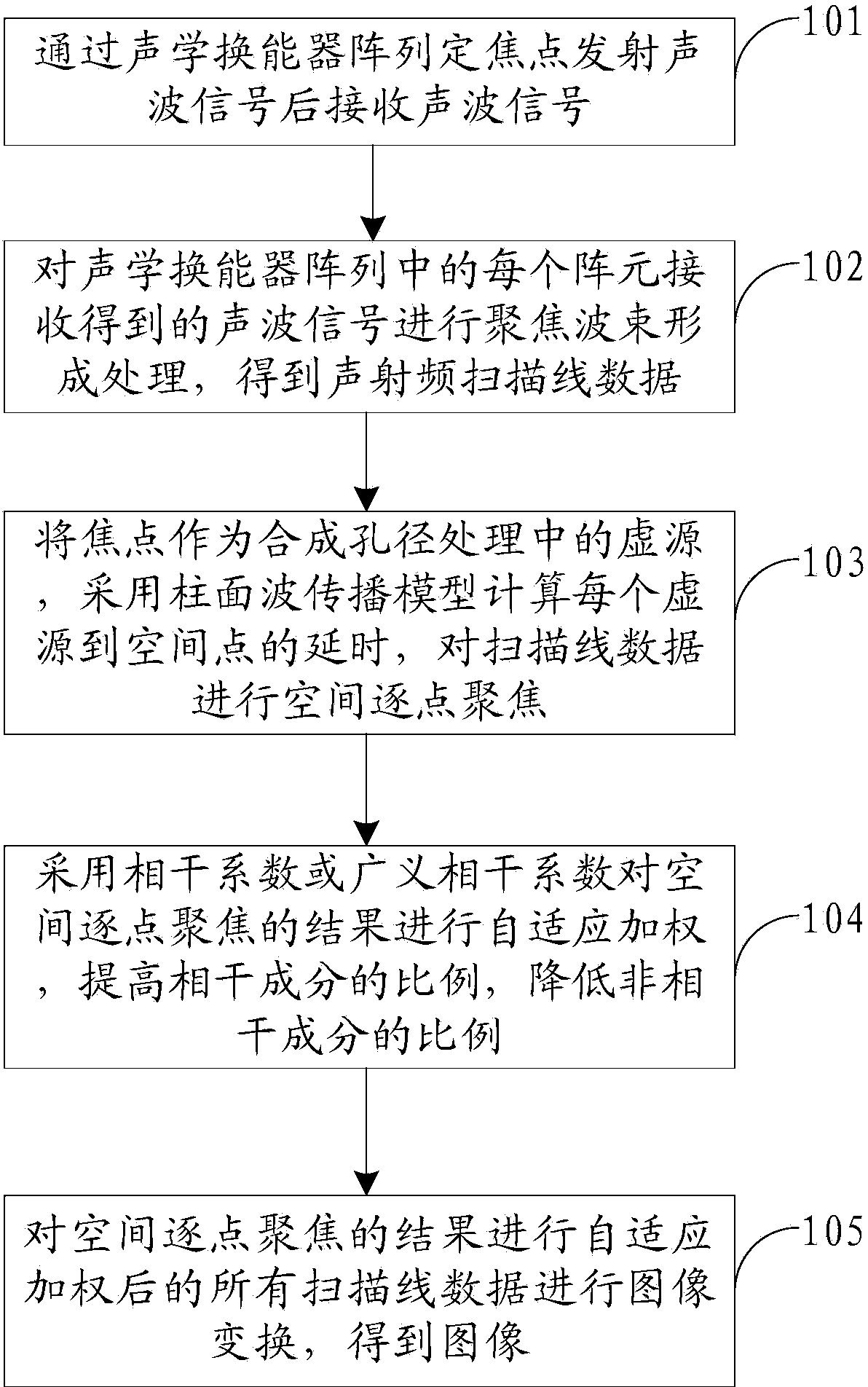
Self-adaptive acoustic imaging method
InactiveCN103969651AReduce sidelobeImprove Acoustic Imaging QualityAcoustic wave reradiationImaging qualityArray element
The invention relates to a self-adaptive acoustic imaging method. The method includes the steps that acoustic wave signals are received after being transmitted at fixed focuses through an acoustic transducer array; focusing beamforming processing is carried out on the acoustic wave signals received by each array element in the acoustic transducer array to obtain acoustic radio frequency scanning line data; the focuses are used as virtual sources in synthetic aperture processing, tine delay from each virtual source to the spatial point is calculated by means of a cylindrical wave propagation model, and spatial point-by-point focusing is carried out on the scanning line data; self-adaptive weighting is conducted on the result of the spatial point-by-point focusing by the adoption of correlation coefficients or generalized correlation coefficients, the proportion of coherent components is increased, and the proportion of incoherent component is reduced; image transformation is carried out on all the scanning line data after self-adaptive weighting conducted on the result of the spatial point-by-point focusing to obtain images. According to the method, the lateral resolution and contrast ratio which are identical in depth are achieved, the number of sidelobes is effectively reduced, and therefore all-round improvement in acoustic imaging quality is achieved.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
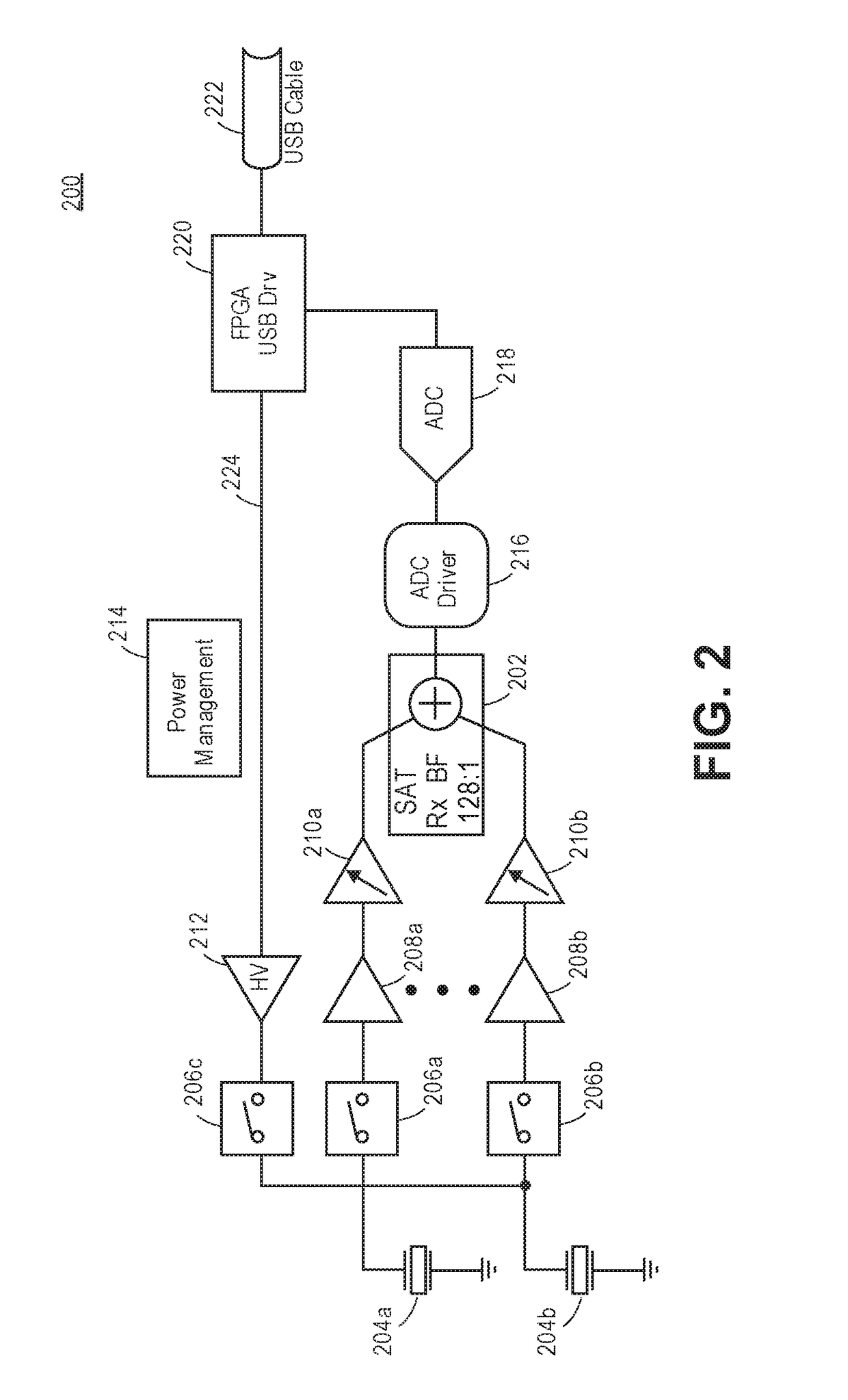
Analog ultrasound beamformer
ActiveUS20170146643A1Reduces power usageMinimize number of componentBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionVIT signalsEngineering
A sampled analog beamformer for ultrasound beamforming includes an array of transducers for transmitting analog signals and receiving reflected analog signals, and a sampled analog filter for filtering the received reflected analog. The sampled analog filter includes a delay line for adding a delay to each of the received reflected analog signals. Using a sampled analog filter in an ultrasound beamforming system reduces the power usage of the system and decreases the number of components in the system.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Coaxial S/X dual-frequency sharing feed source network
ActiveCN103872460AAchieving rotational symmetrySolve the problems of large radiation loss and low irradiation efficiencyWaveguide hornsAntennas earthing switches associationSignal waveDual frequency
The invention discloses a coaxial S / X dual-frequency sharing feed source network. The coaxial S / X dual-frequency sharing feed source network comprises a coaxial horn feed source, wherein the coaxial horn feed source is composed of an S-frequency-band horn and an X-frequency-band horn, the S-frequency-band horn is externally connected with an S-frequency-band feed network, and the X-frequency-band horn is externally connected with an X-frequency-band feed network, arranged in the S-frequency-band horn in a sleeved mode and coaxial with the S-frequency-band horn. Four transmission arms distributed in the form of a cross and used for achieving S-frequency-band signal wave separating are arranged at the bottom of the S-frequency-band horn, and inner cavities of the four transmission arms are communicated with the inner cavity of the S-frequency-band horn. The coaxial S / X dual-frequency sharing feed source network achieves S-frequency-band single-pulse tracking and circular polarization signal receiving and sending and X-frequency-band single-pulse tracking and circular polarization signal receiving, has the advantages of being wide in working band, small in standing wave, large in power capacity, small in consumption, low in sidelobe, good in directional diagram equalization, small in axial ratio and the like and is suitable for a double-reflection-face multi-frequency multi-tracking-satellite communication and control antenna with the length larger than 7.3 m.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Omni-directional side lobe suppression method for synthetic aperture radar imaging processing
InactiveCN102721965ANo lossThere is no special requirement for scattering intensityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging processingSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses an omni-directional side lobe suppression method for synthetic aperture radar imaging processing. The method comprises the following steps of: arranging two-dimensional echo signals obtained by synthetic aperture radar into one-dimensional data; determining an imaging plane region position; constructing into a measuring matrix corresponding to an imaging plane; and finally, processing the one-dimensional echo data by using a linear least square method in combination with a measuring matrix, thereby realizing omni-directional side lobe suppression of a synthetic aperture radar imaging result and obviously reducing the energy leakage. Thus, the energy leakage of the imaging result of the processed satellite-borne echo data is the minimum, and further, the aim of suppressing side lobe is fulfilled. The omni-directional side lobe suppression method has no special requirement on target scattering intensity, can be used for imaging processing of any scene target and has a wide application range.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Planar compact slot antenna array based on substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity
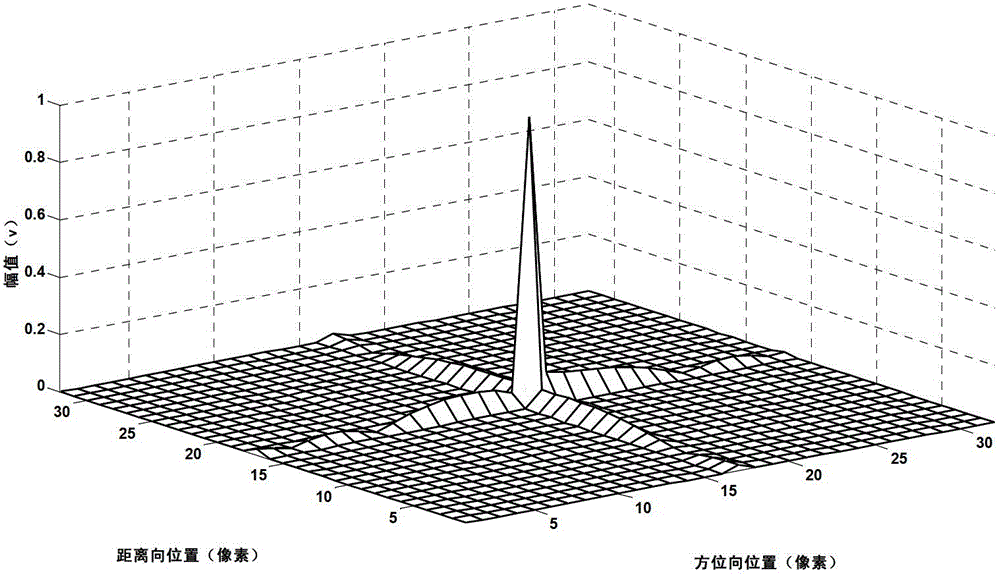
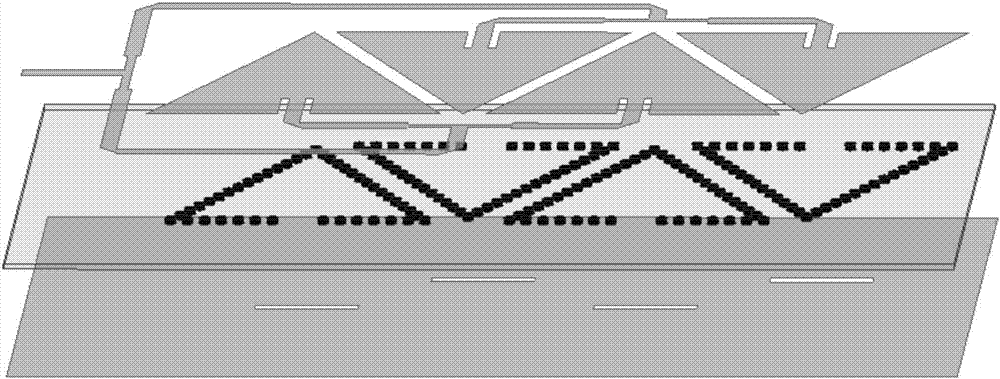
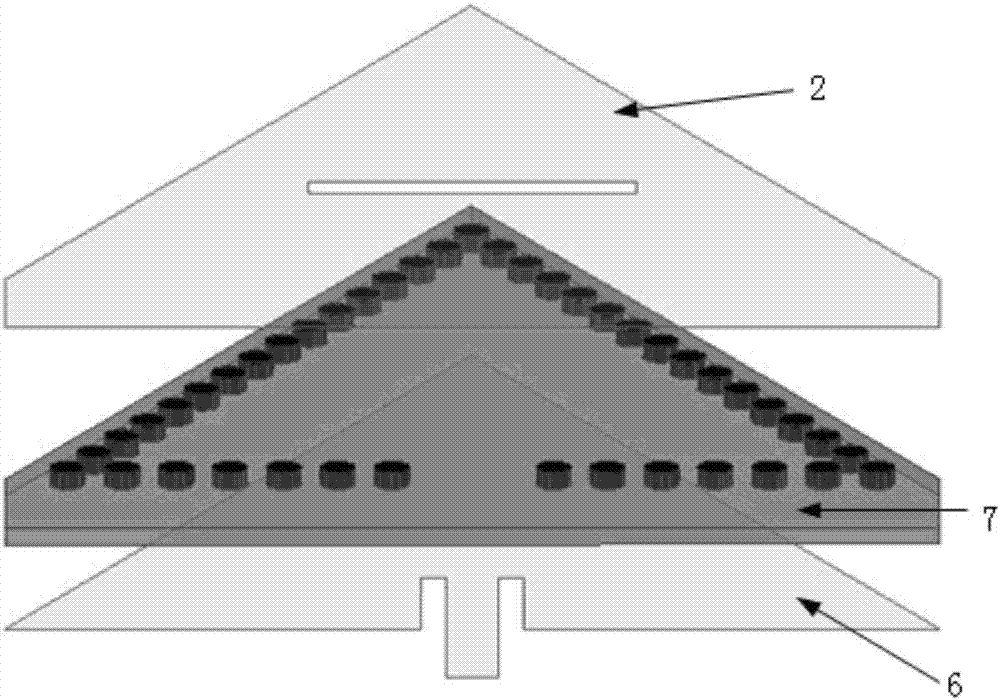
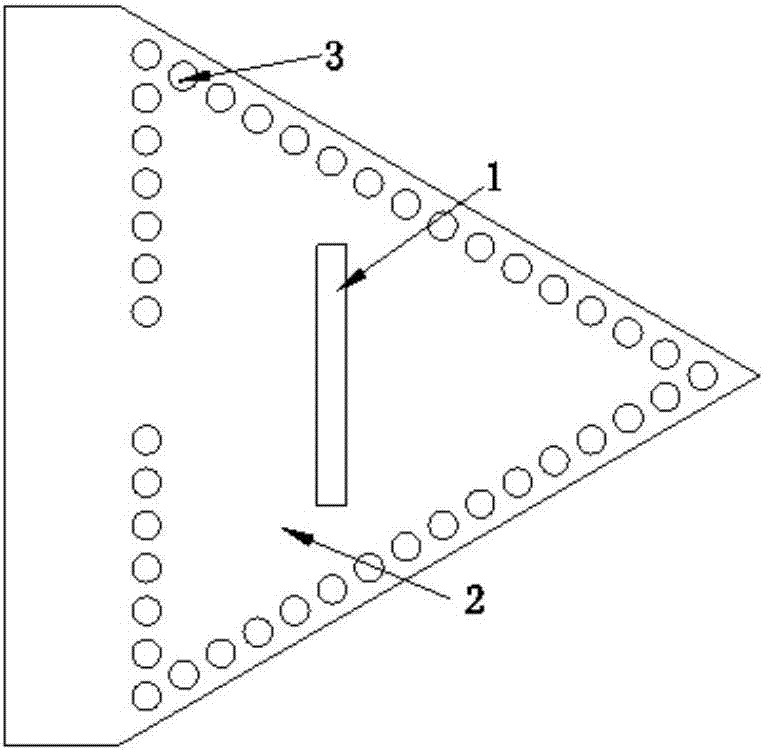
ActiveCN107134653AImprove Radiation PerformanceImprove radiation efficiencyIndividually energised antenna arraysSlot antennasResonant cavityIsoetes triquetra
The invention discloses a planar compact slot antenna array based on a substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity. The planar compact slot antenna array is composed of four equilaterally triangular back cavity unit antennas. As for the equilaterally triangular back cavity unit antennas, the central area of the upper surface of an equilaterally triangular substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity is slotted, and feeding is performed by the grounded coplanar waveguide on the lower surface of a dielectric plate. The triangular substrate integrated waveguide resonant cavity is realized in a way that three rows of metal through holes which are connected in an end-to-end way are punched on the medium of which the upper and lower surfaces are metallic. When the working mode of the resonant cavity is TE<120>, the most dramatically changed area of the electric field is the center of the cavity so that the rectangular slots are punched at the center of the triangular cavity, displacement current is generated on the slots and electromagnetic waves are enabled to be radiated out. Compared with the rectangular or circular resonant cavity, the equilaterally triangular resonant cavity has the advantages of convenient layout and compact structure and has higher radiation efficiency under the condition of the same area and working mode.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
GIS equipment mechanical fault detection system and method based on acoustic imaging
ActiveCN113267330AReduce sidelobeImprove anti-interference abilityMachine part testingPosition fixationSound sourcesEngineering
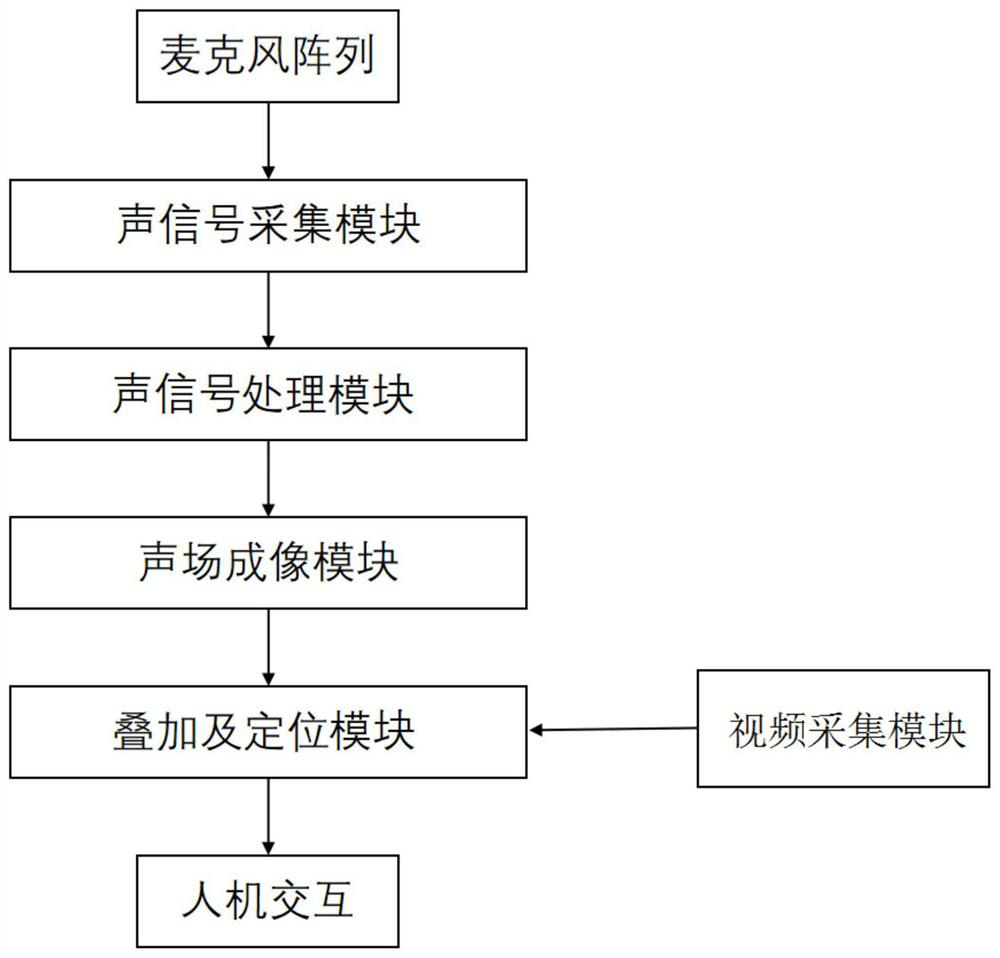
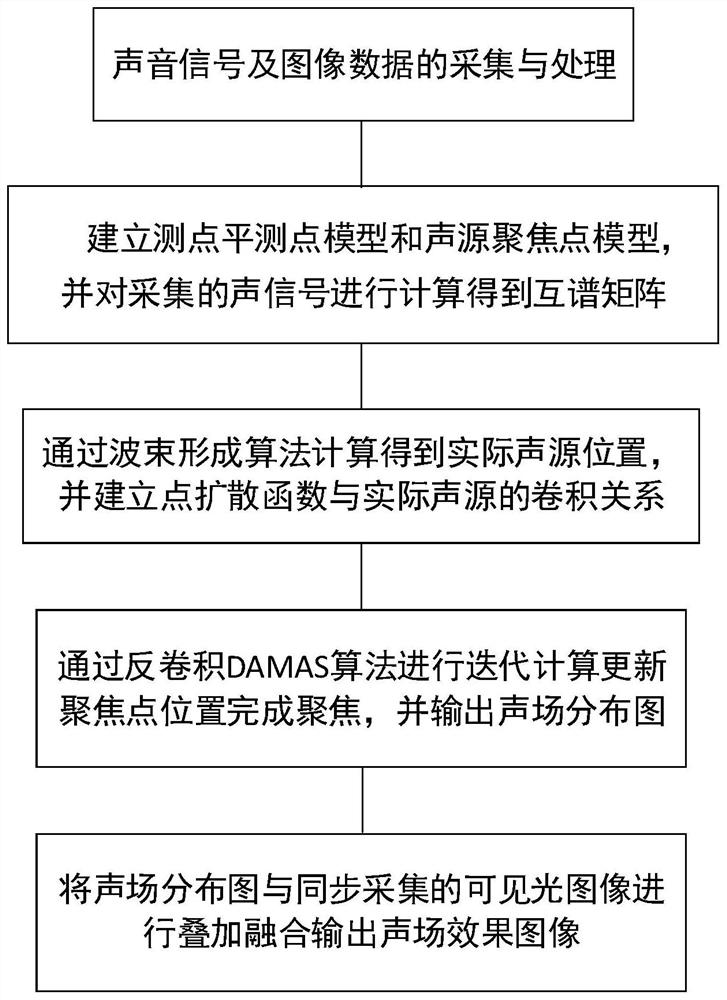
The invention provides a GIS equipment mechanical fault detection system and method based on acoustic imaging, and the system comprises an acoustic signal collection module, an acoustic signal processing module, a sound field imaging module, a video collection module, a superposition positioning output module, and a man-machine interaction terminal. The sound signal acquisition module comprises a microphone array with a non-uniform spiral arrangement structure and an analog-to-digital conversion module, and is used for acquiring multichannel sound signals. According to the detection method, collected sound signals are processed through spectral subtraction, sound field models including a measuring point plane measuring point model and a sound source focus point model are constructed based on an array, then an intermediate structure is obtained through calculation of a beam forming algorithm, iterative calculation is carried out in combination with a deconvolution DAMAS algorithm, a sound field cloud distribution diagram is output, the image data synchronously acquired with the sound signal are overlapped and fused, and a sound field effect picture is output.
Owner:STATE GRID CHONGQING ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
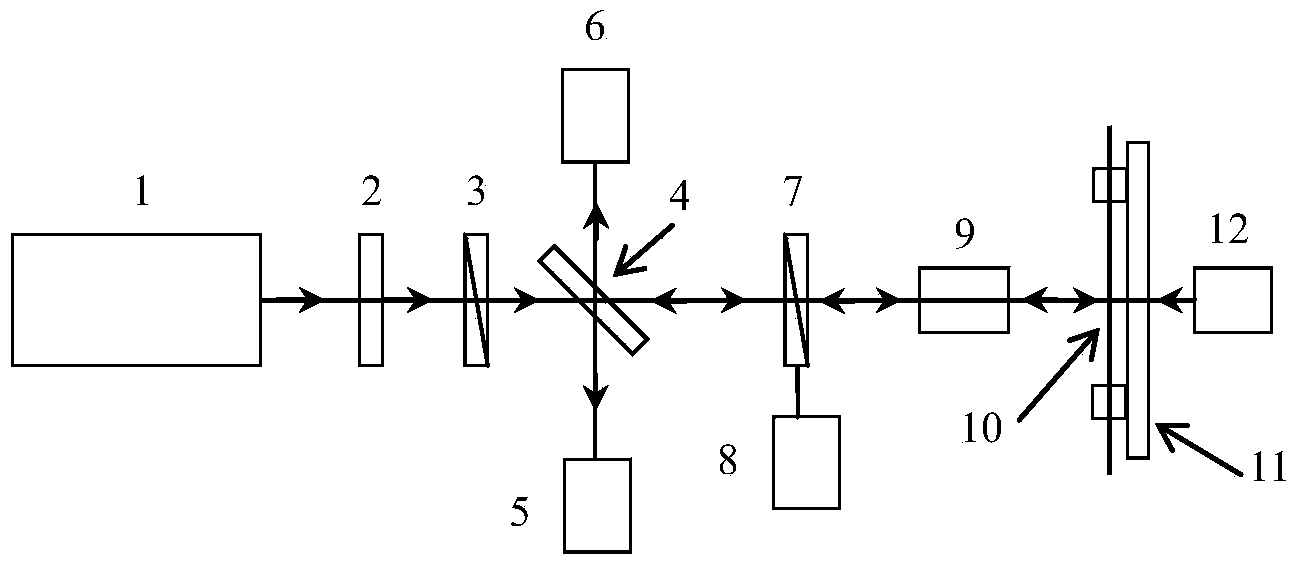
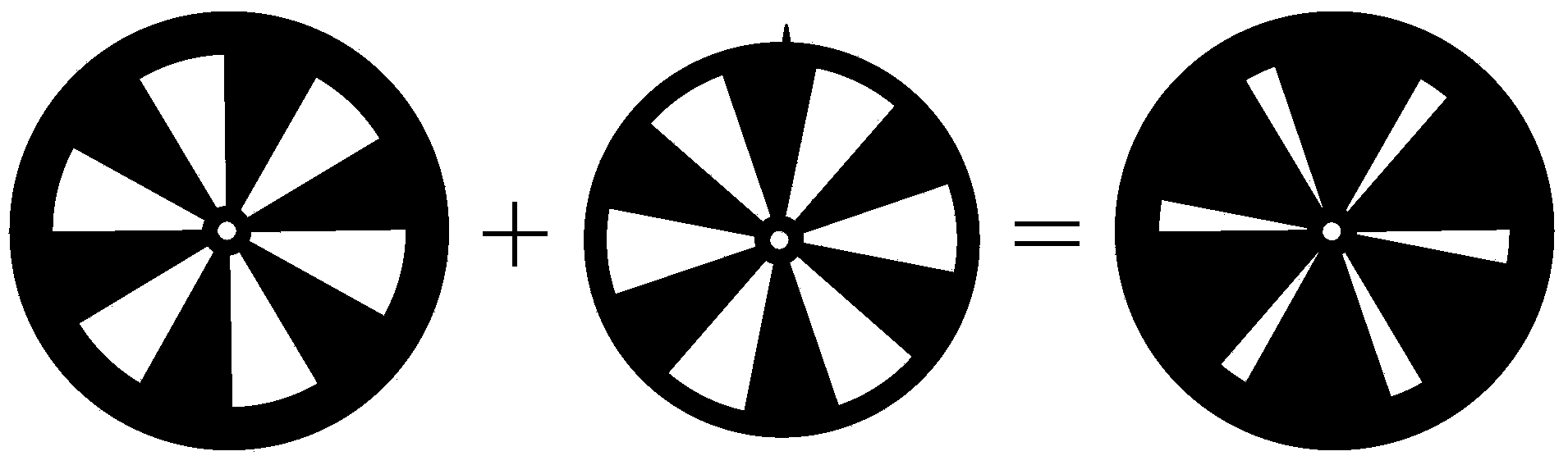
Femtosecond laser manufacturing device and method of SFBG
InactiveCN104076435AAchieving apodizationEasy to operateCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideUltimate tensile strengthLaser beams
The invention relates to a femtosecond laser manufacturing device and method of an SFBG. Two optical chopper blades with different diameters and same parameters are overlapped, the relative positions of the two blades can be continuously adjusted, the strength of a femtosecond laser is modulated, the modulated femtosecond laser is focused and then irradiates a fiber core of an optical fiber, the optical fiber is fixed to a high-precision micro displacement platform and moves at the constant speed in the direction perpendicular to a laser beam, and the SFBG with the sampling period and duty ratio continuously adjusted is manufactured by changing the moving speed of the micro displacement platform and the modulation frequency and the duty ratio of an optical chopper. The method and device have the advantages of being convenient to operate, high in manufacturing efficiency and the like, are suitable for manufacturing the SFBG of the complex structure and can be widely applied to a multi-wavelength optical fiber filter and an optical fiber laser system.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com