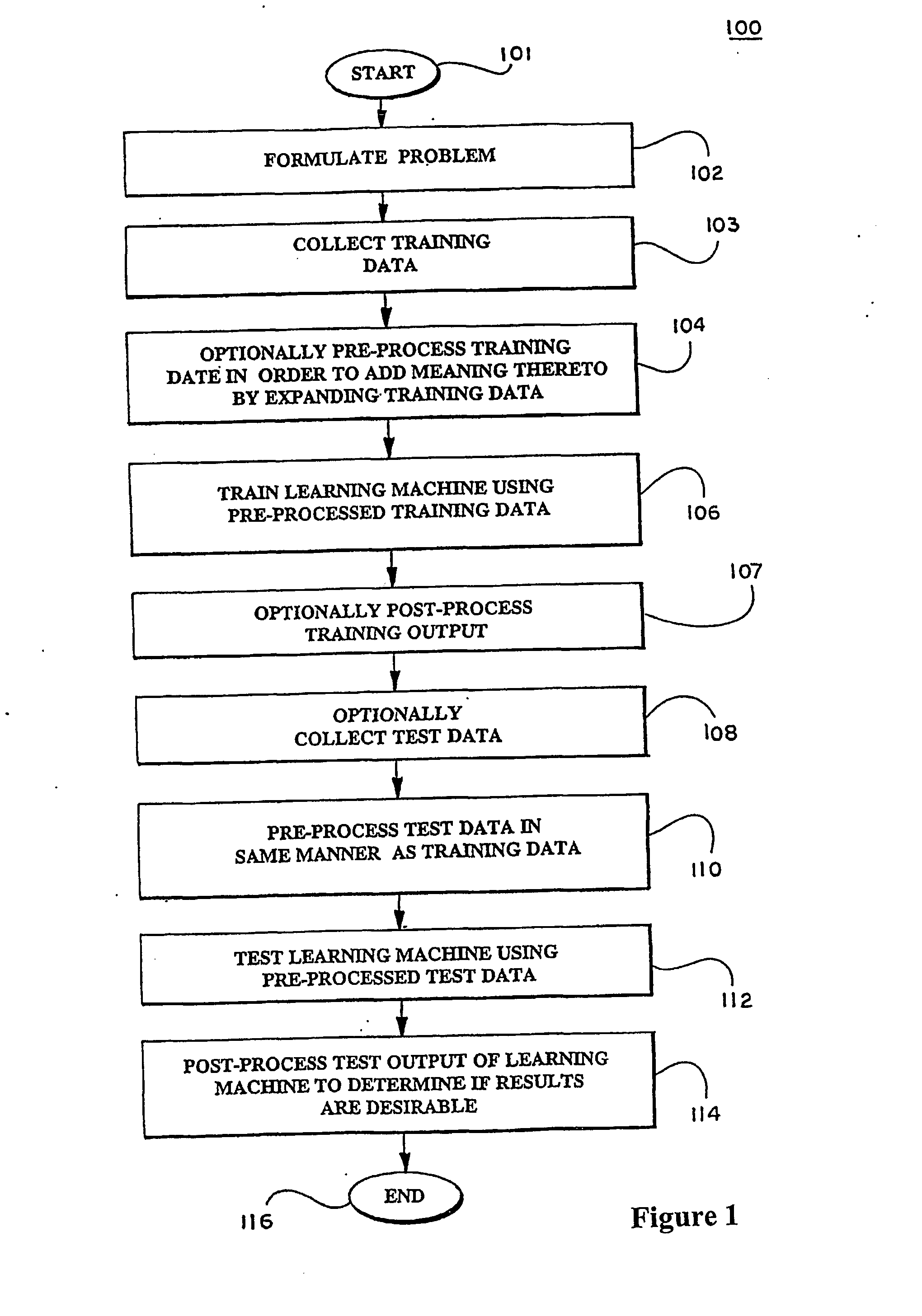
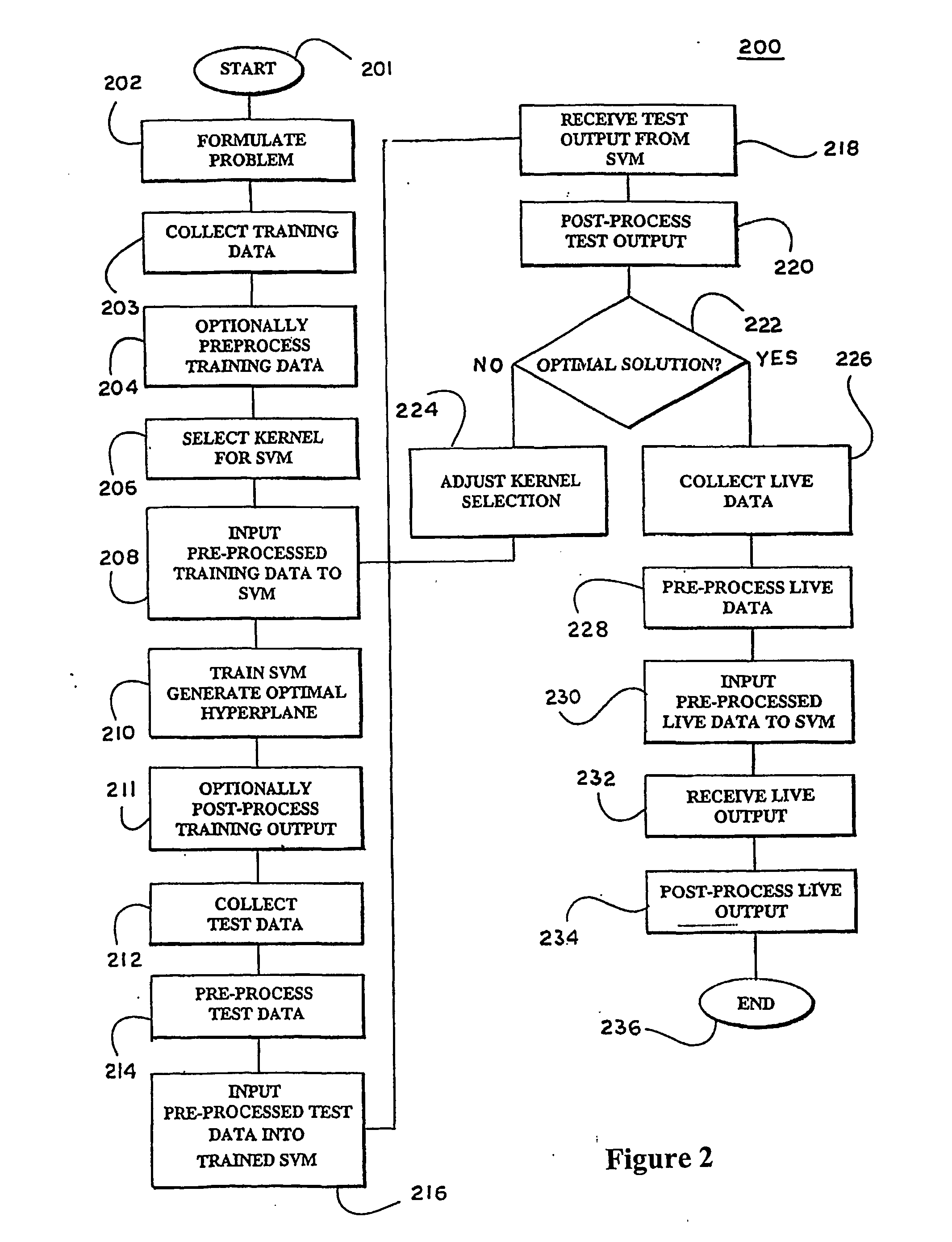
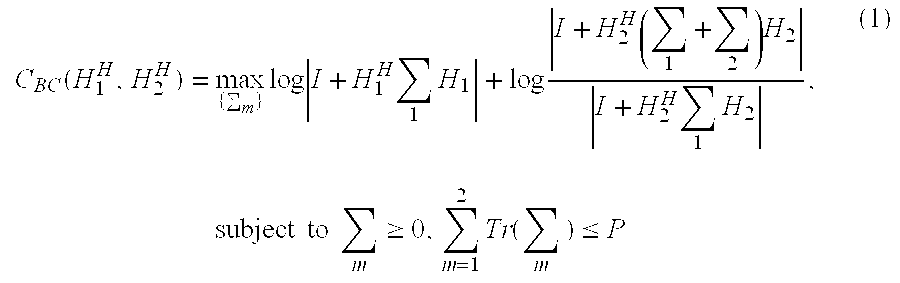Patents
Literature
4160 results about "Covariance matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In probability theory and statistics, a covariance matrix, also known as auto-covariance matrix, dispersion matrix, variance matrix, or variance–covariance matrix, is a matrix whose element in the i, j position is the covariance between the i-th and j-th elements of a random vector. A random vector is a random variable with multiple dimensions. Each element of the vector is a scalar random variable.
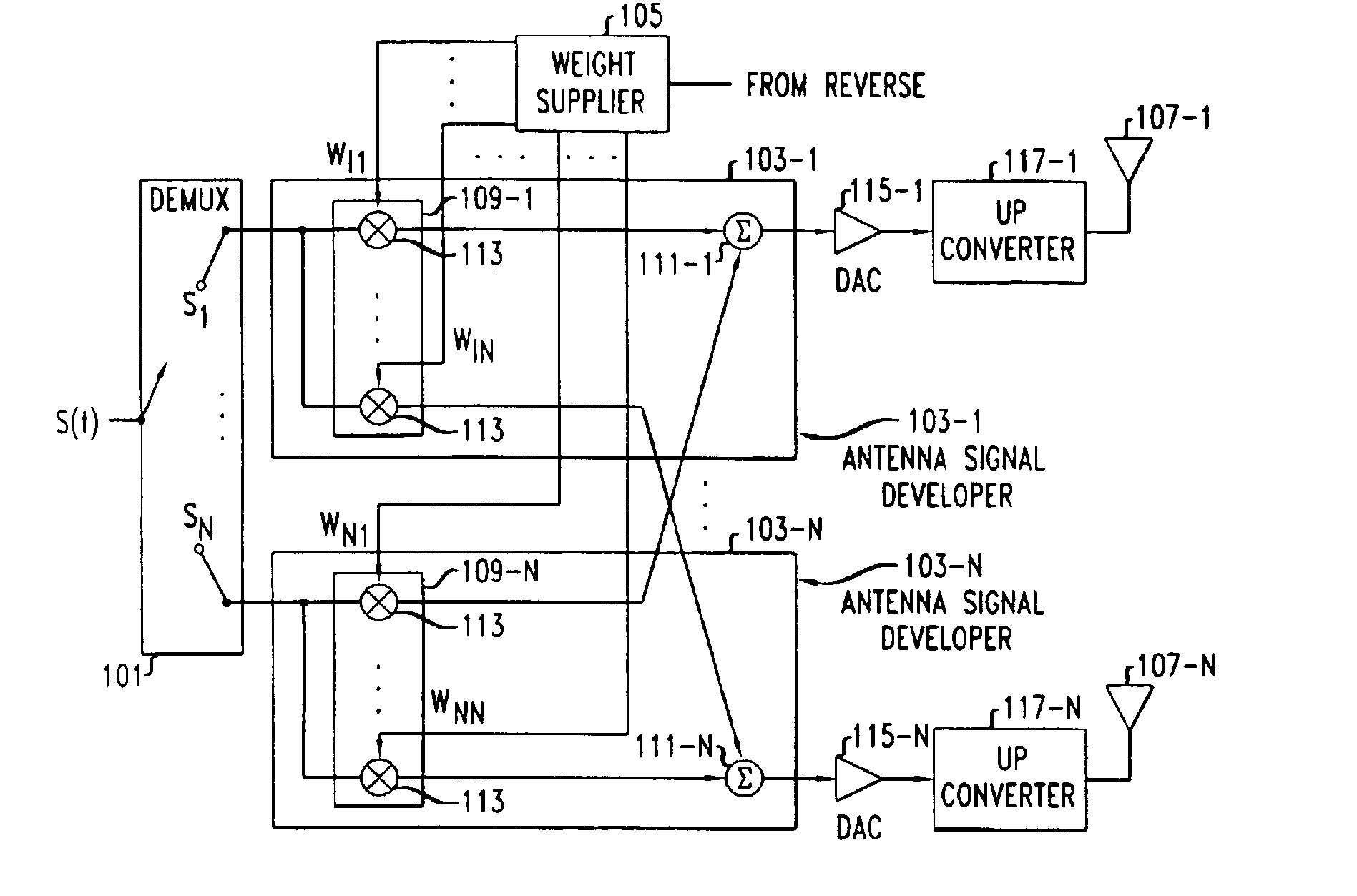
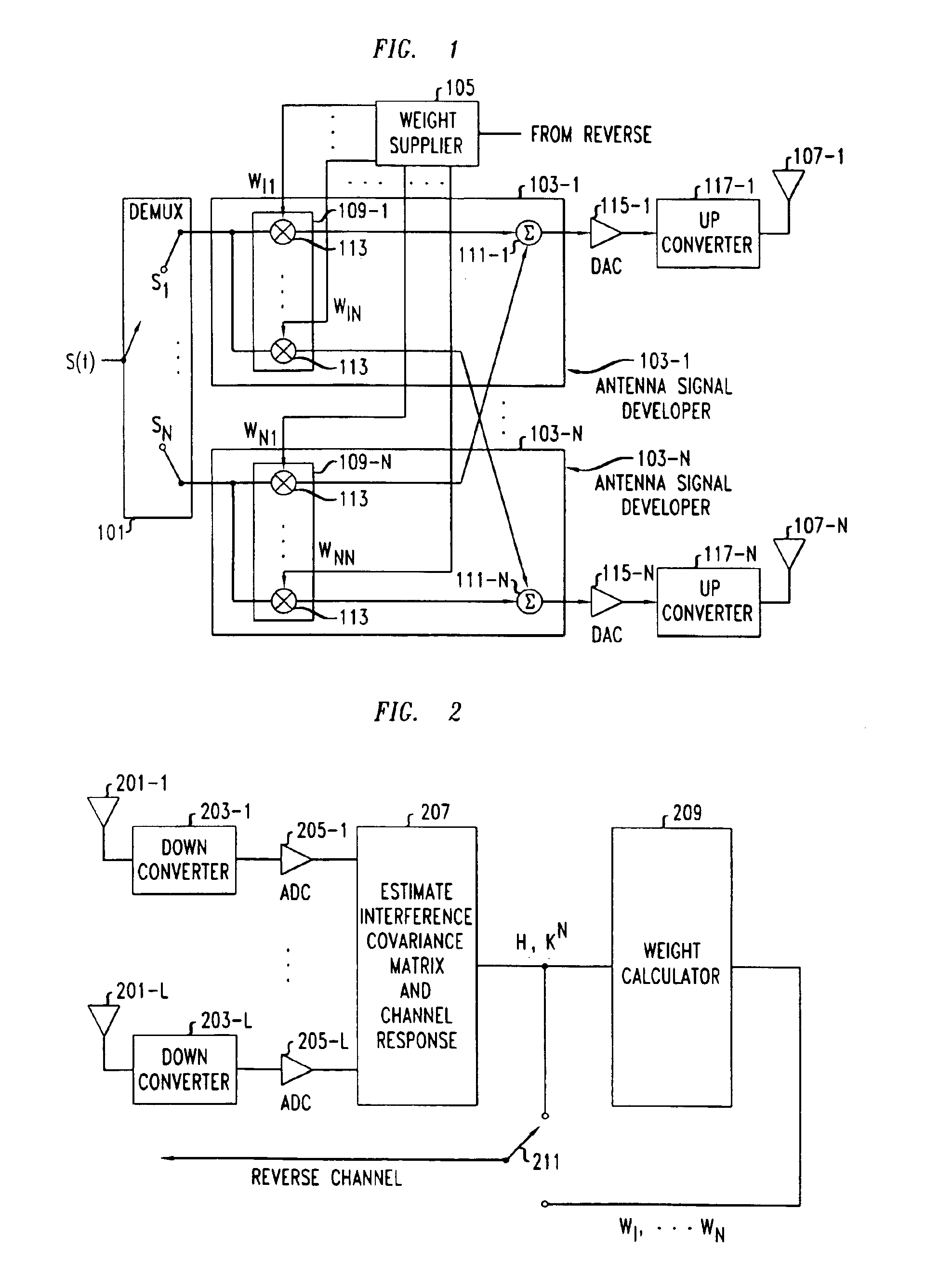
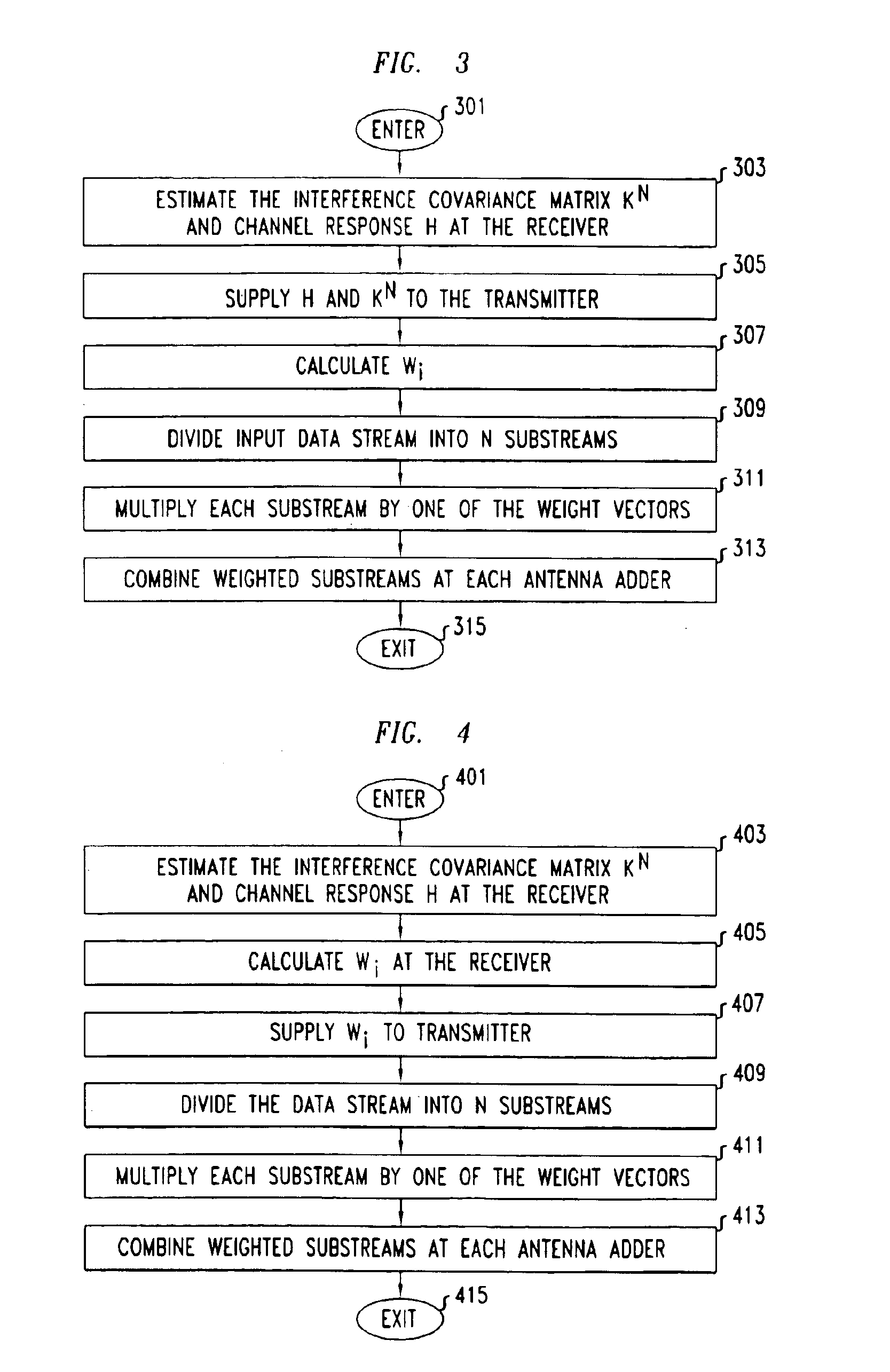
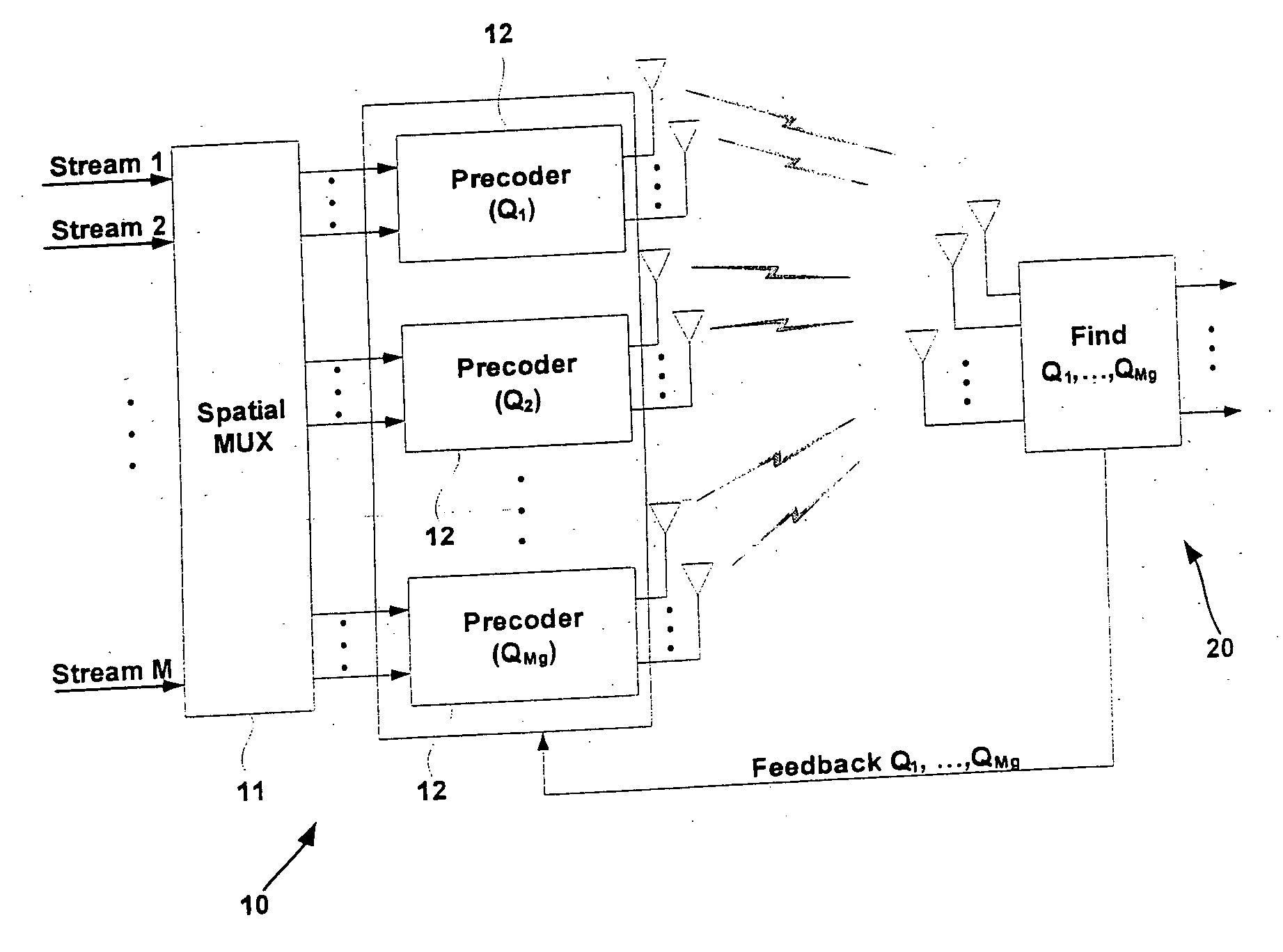
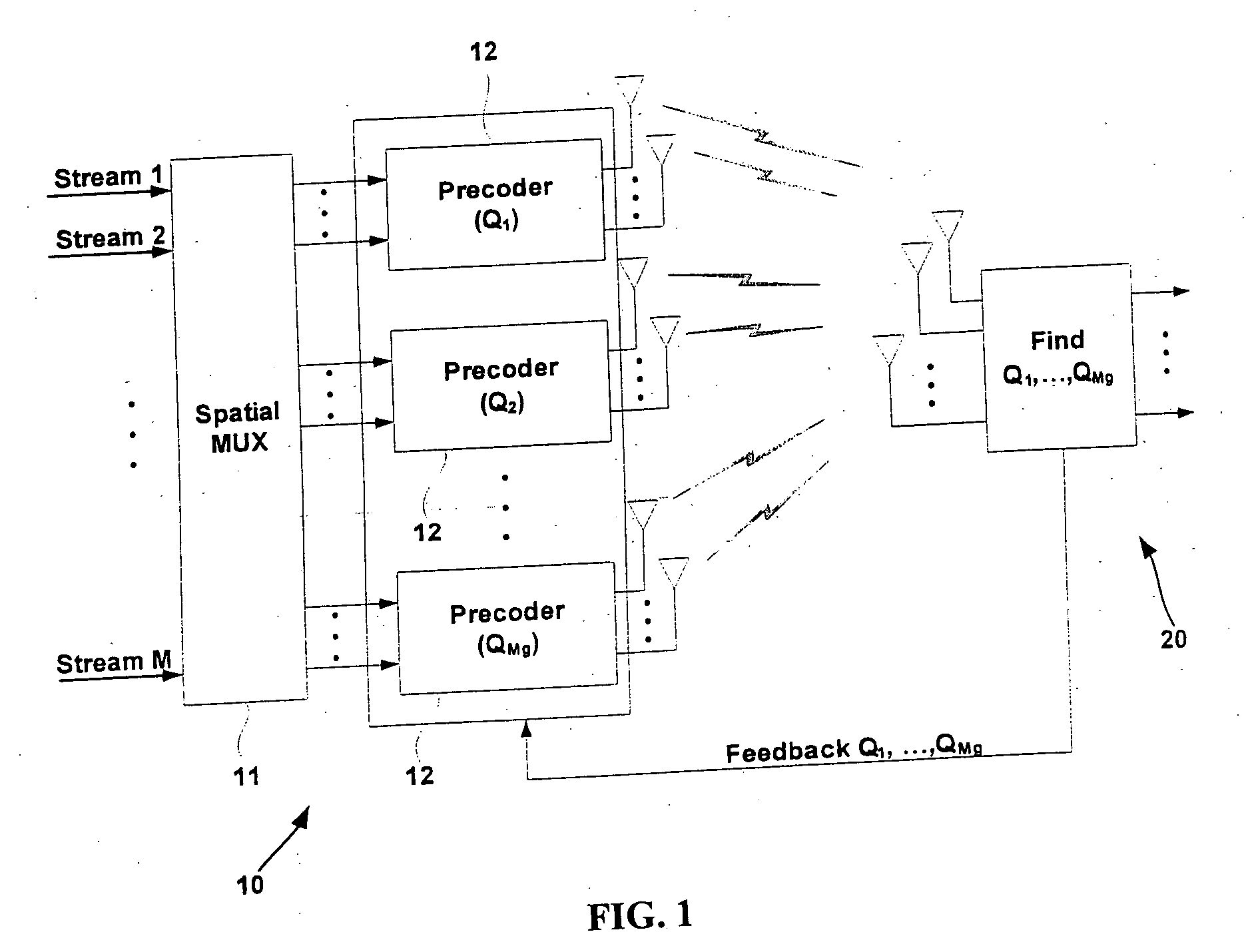
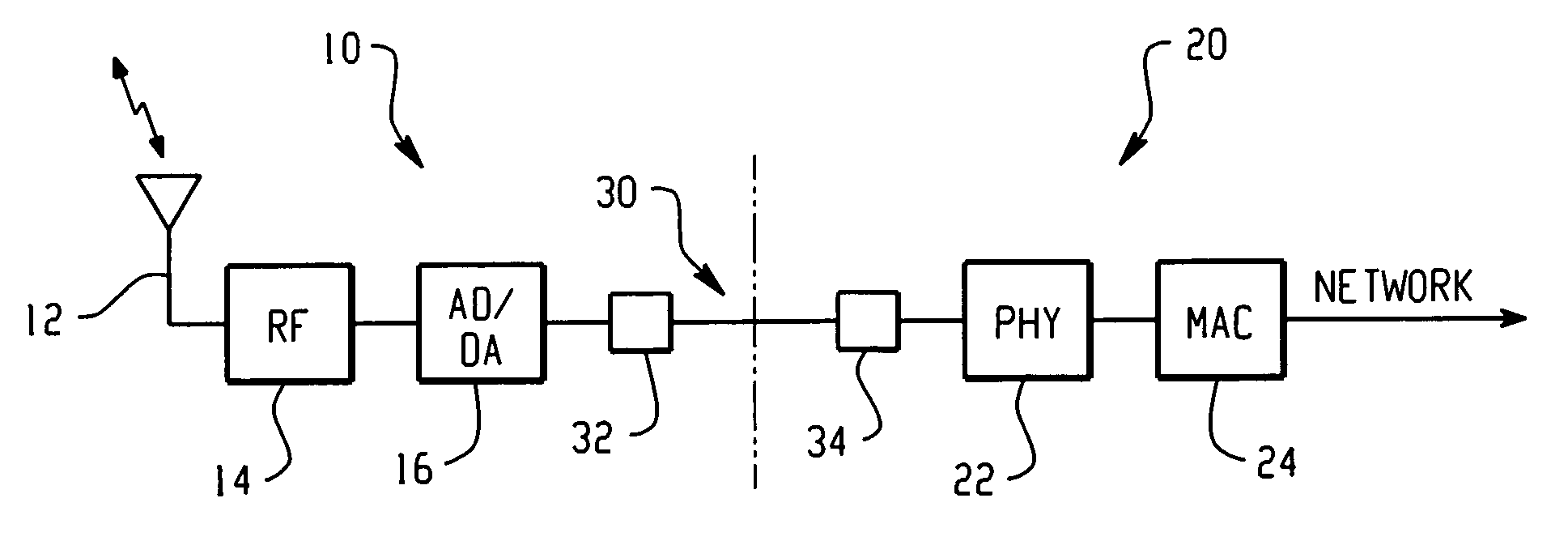
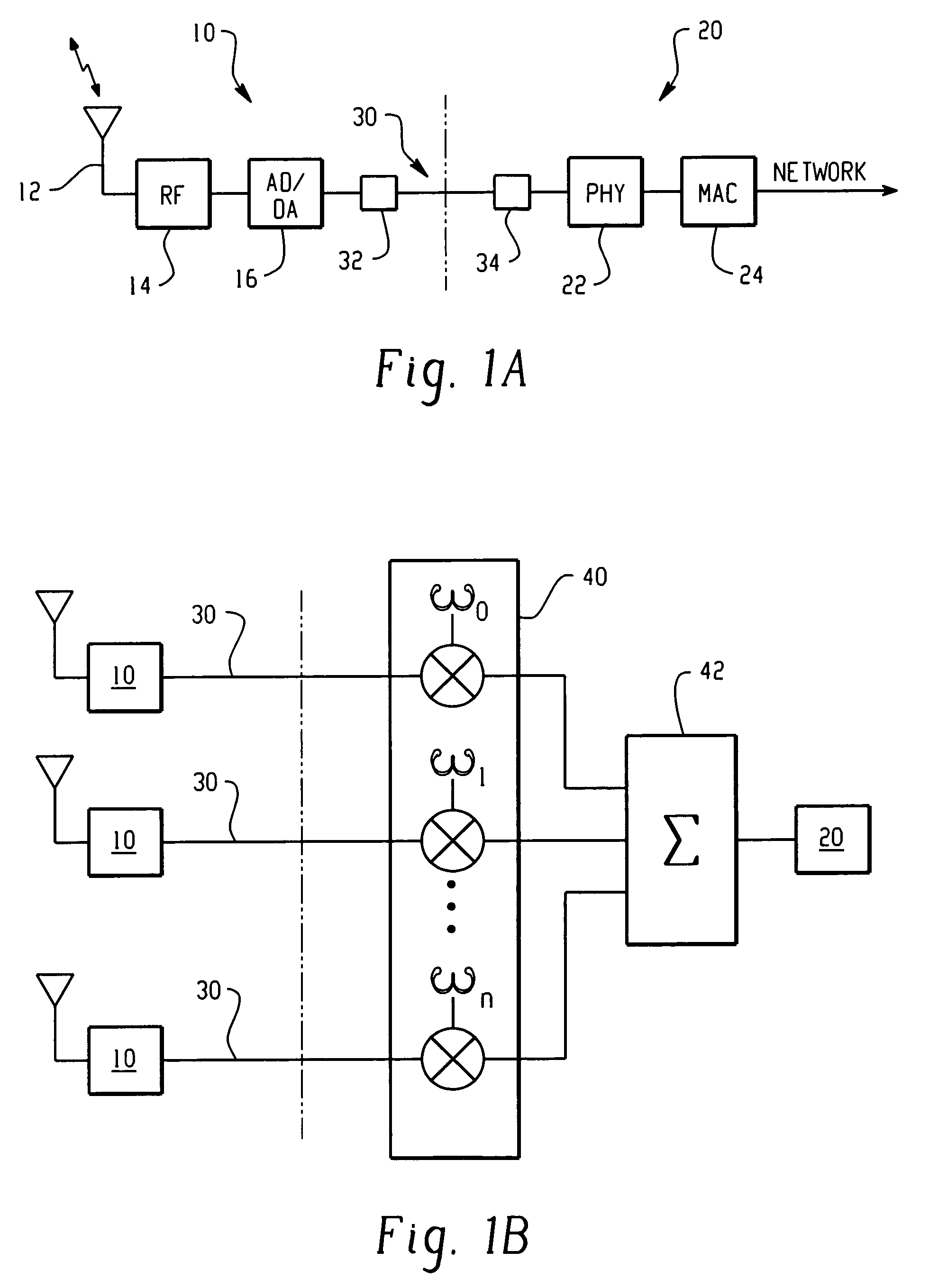
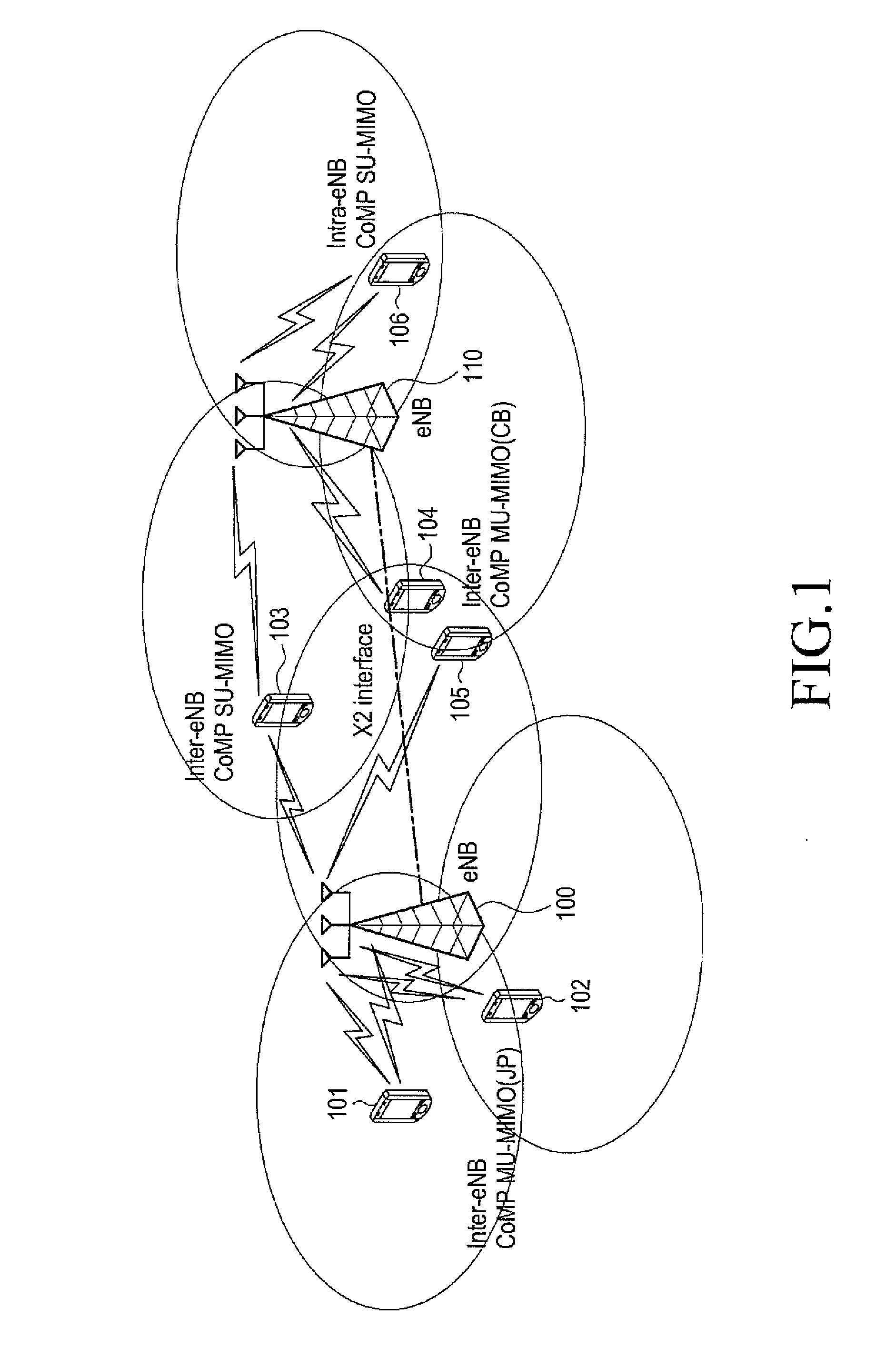
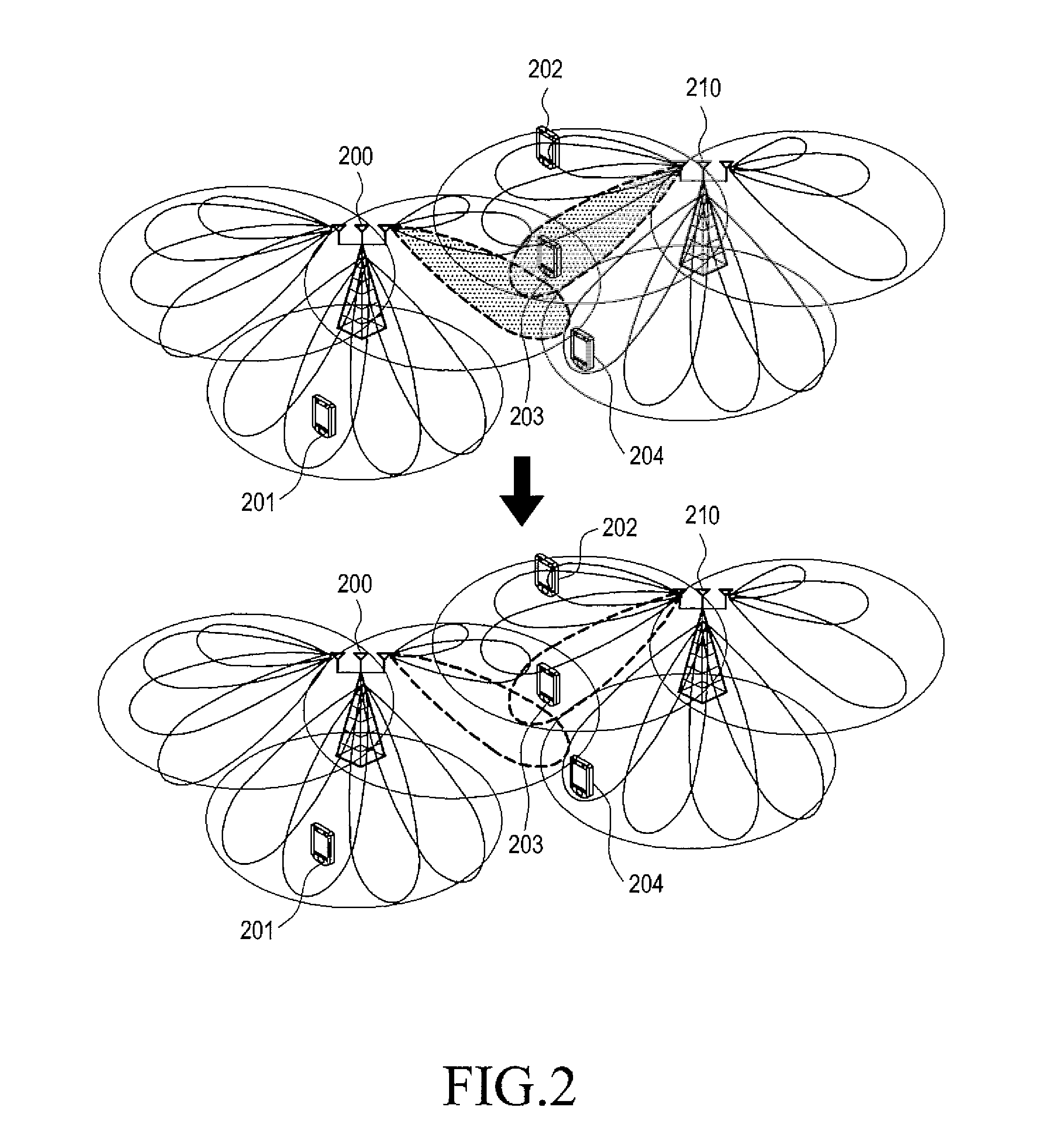
Space-time processing for multiple-input, multiple-output, wireless systems
InactiveUS6888809B1Most capacityMost performanceSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityMultiple inputCovariance matrix
In a MIMO system the signals transmitted from the various antennas are processed so as to improve the ability of the receiver to extract them from the received signal even in the face of some correlation. More specifically the number of bit streams that is transmitted simultaneously is adjusted, e.g., reduced, depending on the level of correlation, while multiple versions of each bit stream, variously weighted, are transmitted simultaneously. The variously weighted versions are combined to produced one combined weighted signal. The receiver processes the received signals in the same manner as it would have had all the signals reaching the receive antennas been uncorrelated. The weight vectors may be determined by the forward channel transmitter using the channel properties of the forward link which are made known to the transmitter of the forward link by being transmitted from the receiver of the forward link by the transmitter of the reverse link or the weight vectors may be determined by the forward channel transmitter using the channel properties of the forward link and the determined weight vectors are made known to the transmitter of the forward link by being transmitted from the receiver of the forward link by the transmitter of the reverse link. The channel properties used to determine the weight vectors may include the channel response from the transmitter to the receiver and the covariance matrix of noise and interference measured at the receiver.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
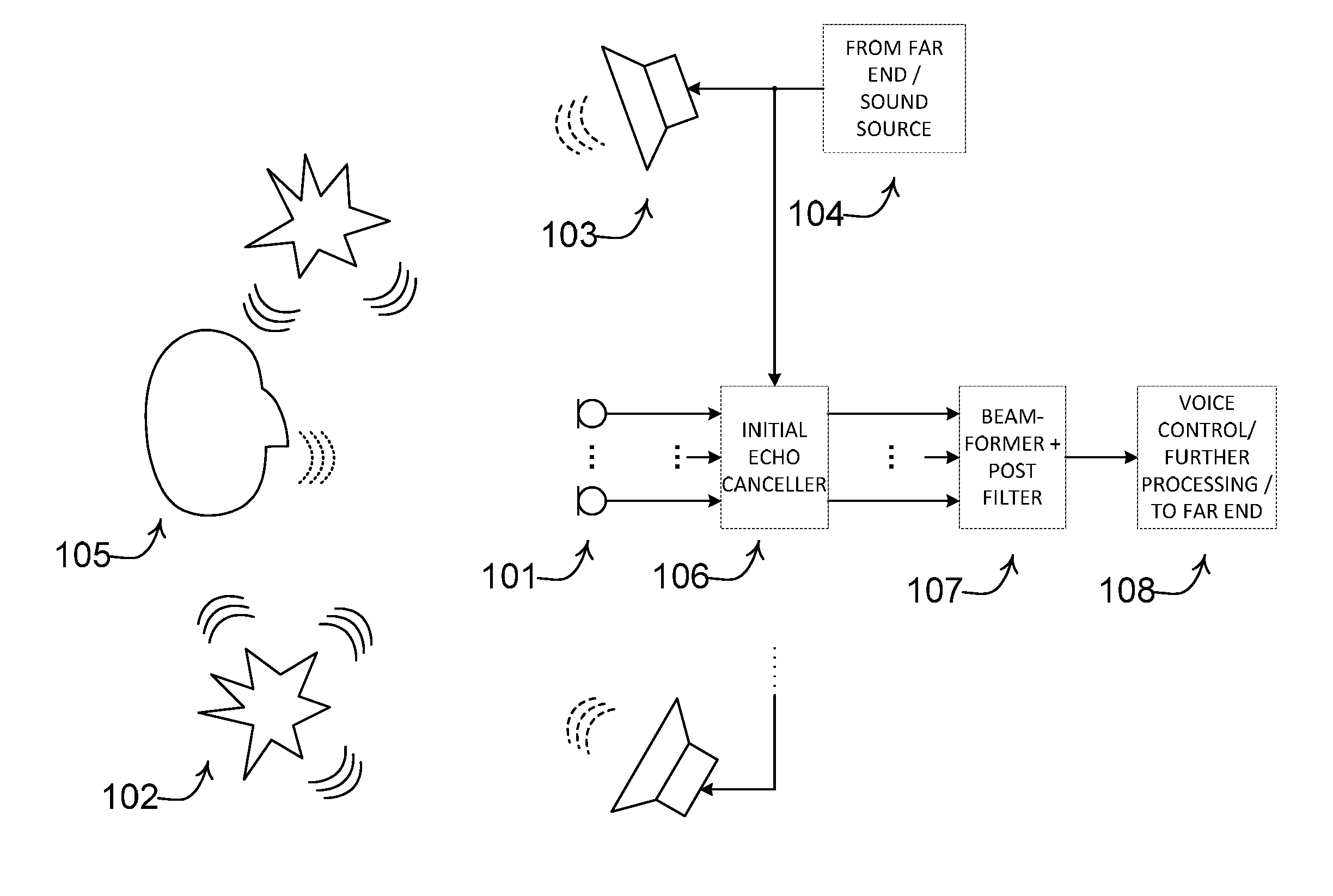
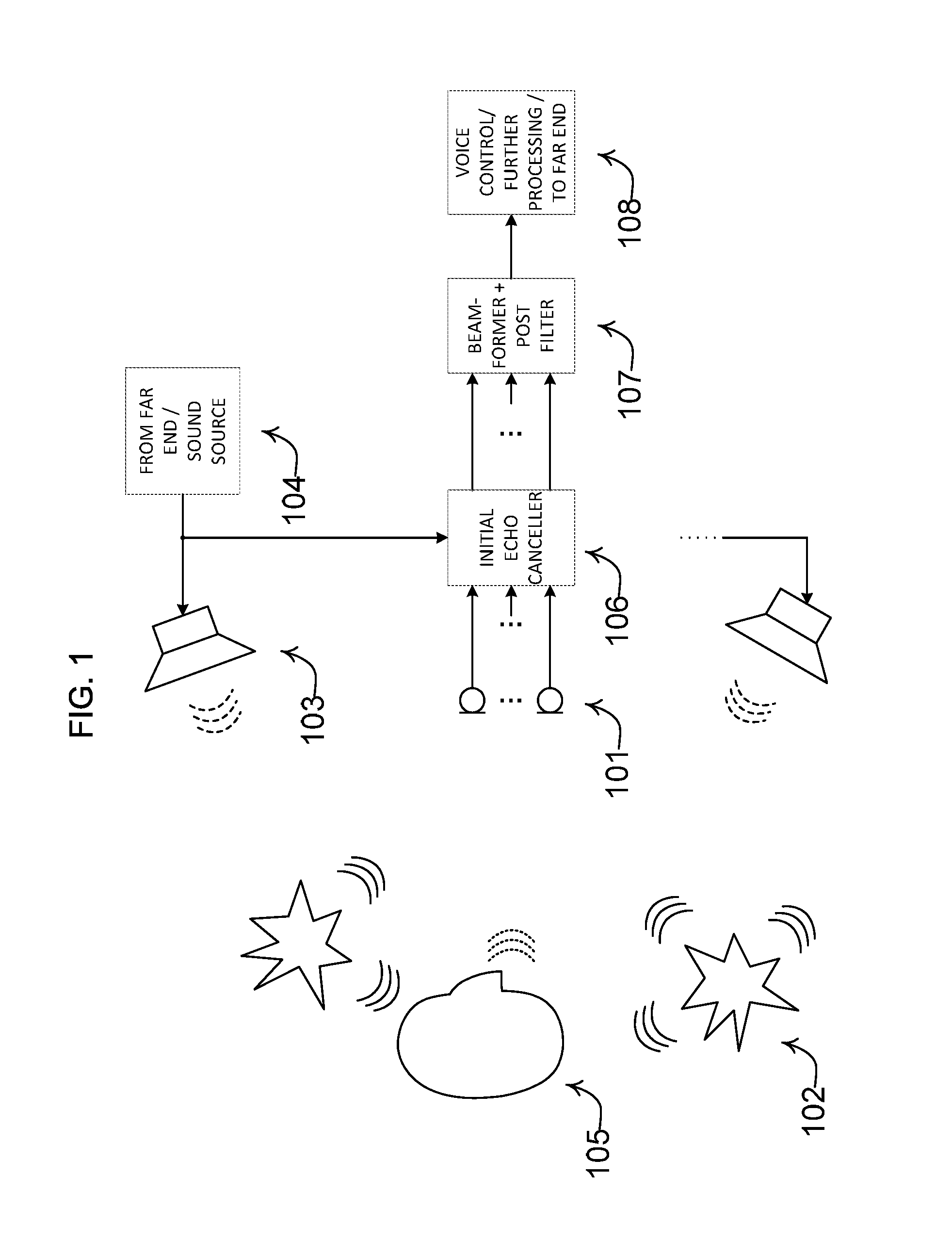
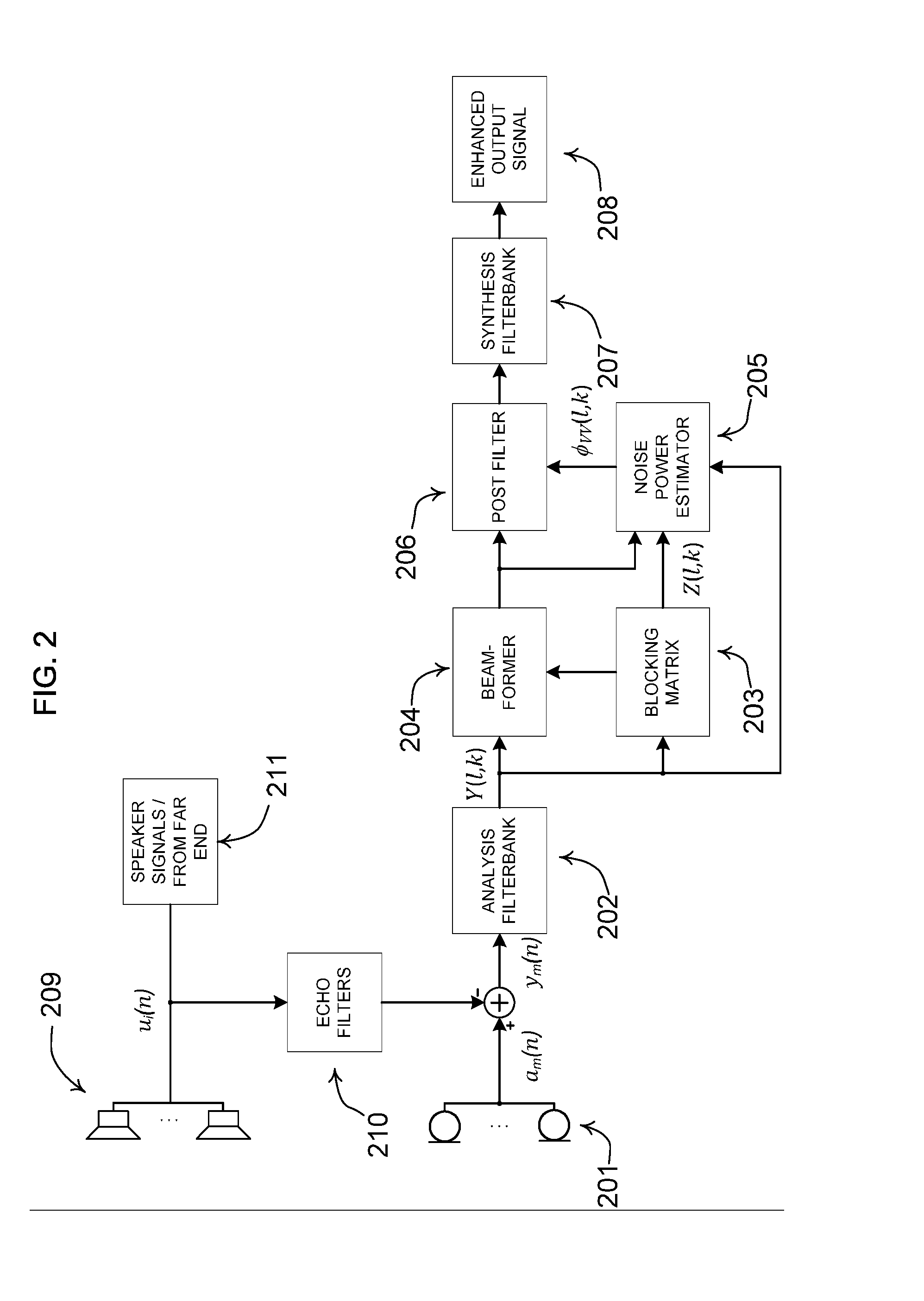
Noise estimation for use with noise reduction and echo cancellation in personal communication
ActiveUS20140056435A1Improve recognition rateImprove sound qualityInterconnection arrangementsEar treatmentNoise correctionEngineering
A method comprises processing M subband communication signals and N target-cancelled signals in each subband with a set of beamformer coefficients to obtain an inverse target-cancelled covariance matrix of order N in each band; using a target absence signal to obtain an initial estimate of the noise power in a beamformer output signal averaged over recent frames with target absence in each subband; multiplying the initial noise estimate with a noise correction factor to obtain a refined estimate of the power of the beamformer output noise signal component in each subband; processing the refined estimate with the magnitude of the beamformer output to obtain a postfilter gain value in each subband; processing the beamformer output signal with the postfilter gain value to obtain a postfilter output signal in each subband; and processing the postfilter output subband signals to obtain an enhanced beamformed output signal.
Owner:OTICON
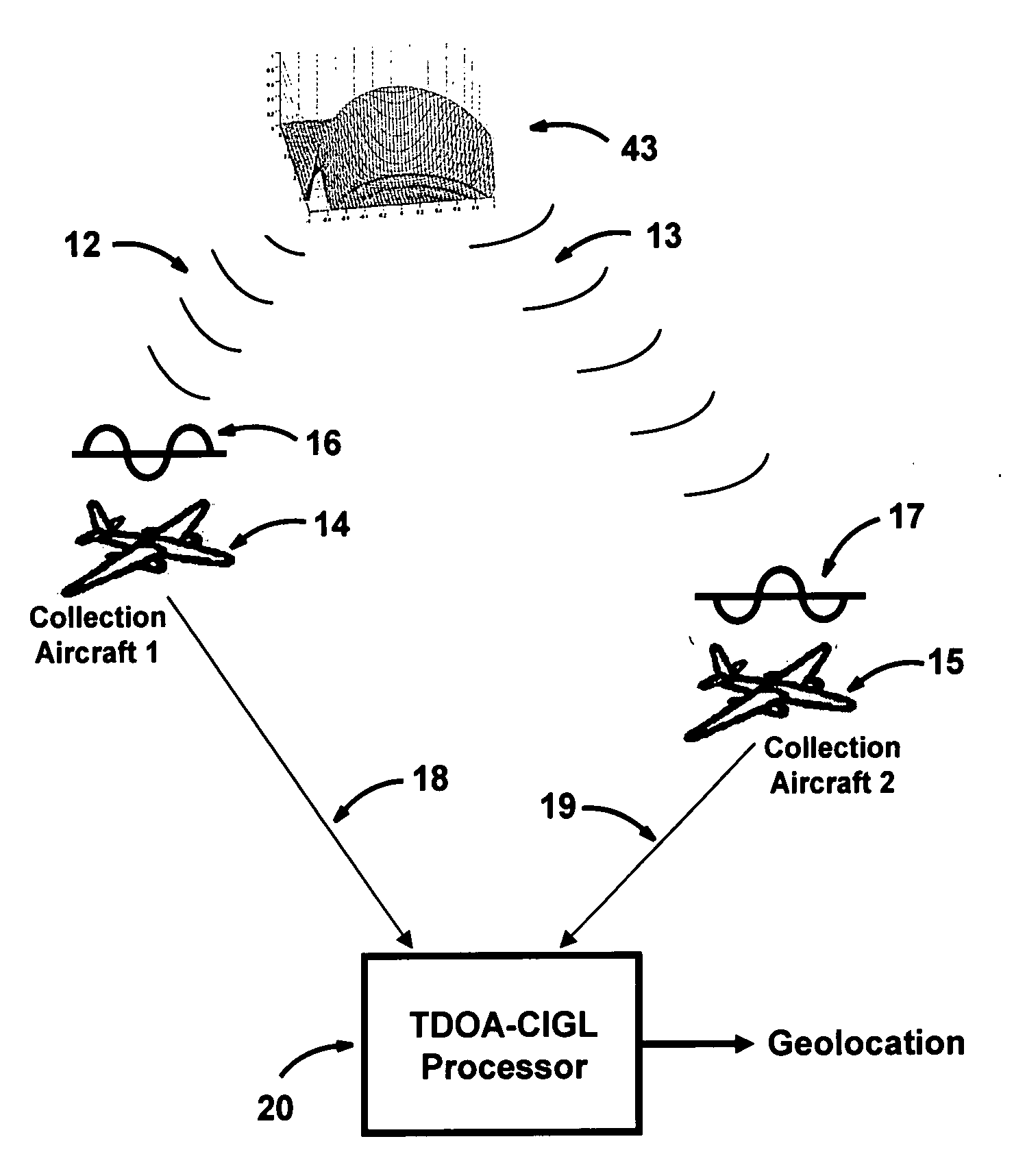
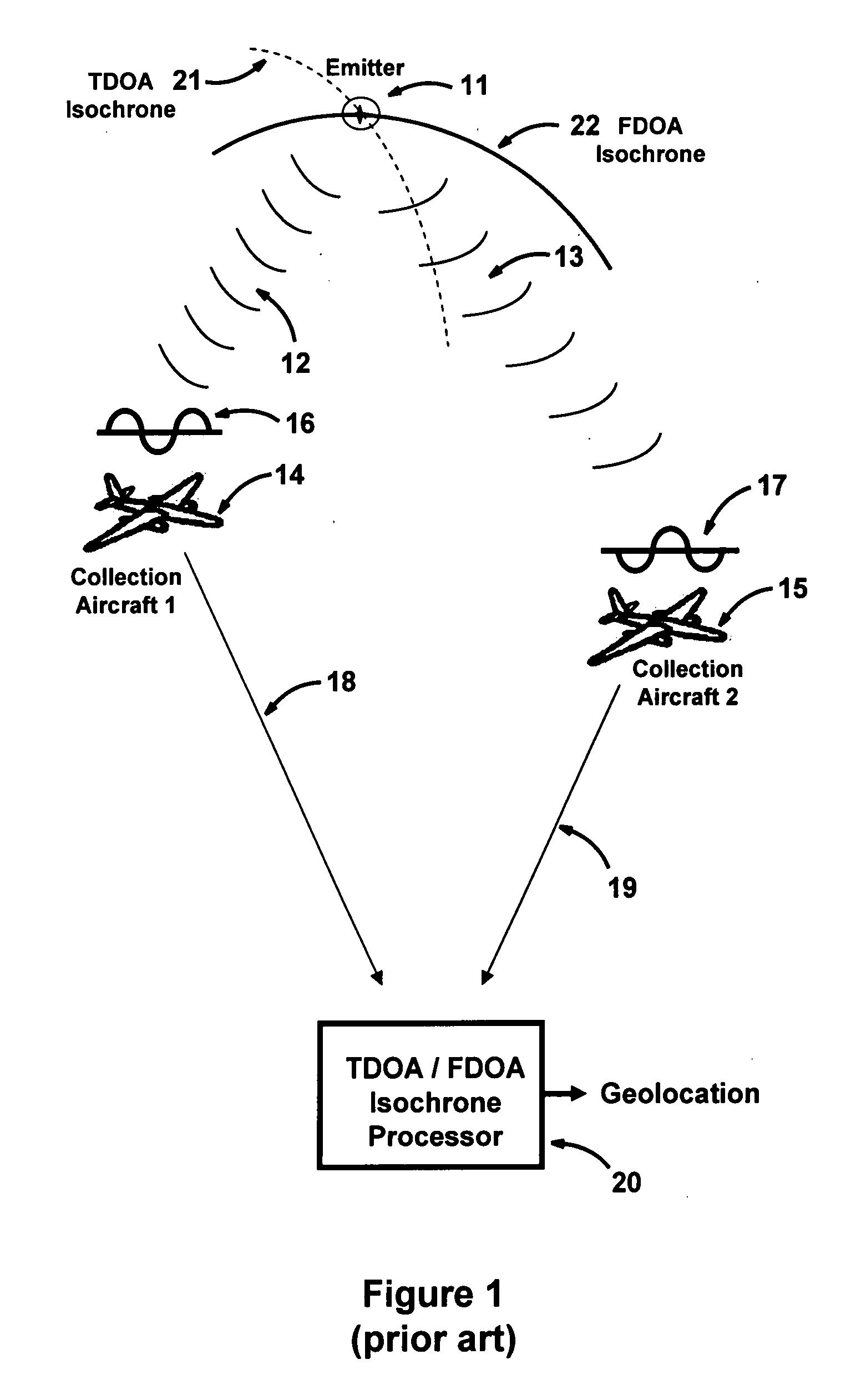
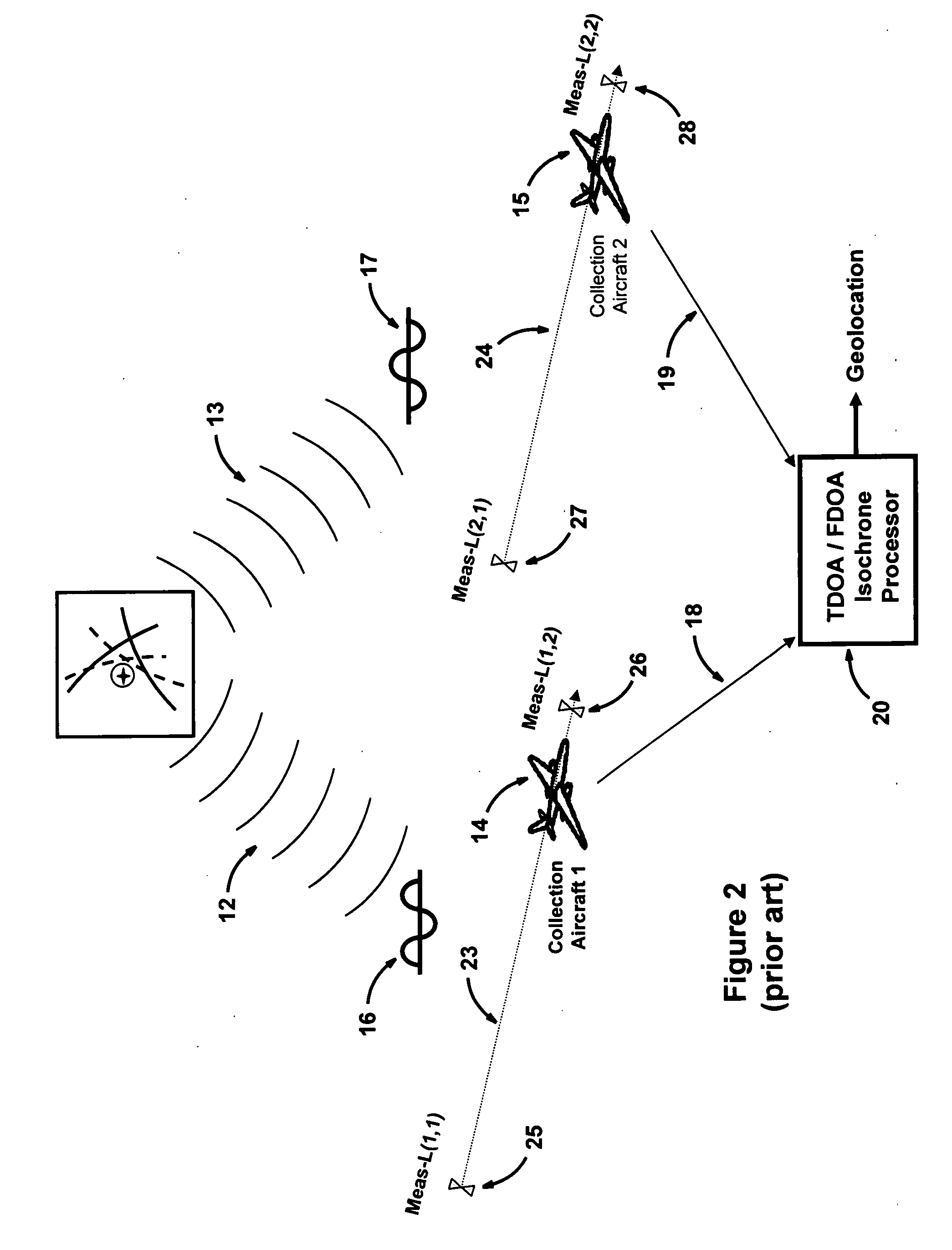
Multiplatform TDOA correlation interferometer geolocation
ActiveUS20080186235A1Improve geolocation accuracyGeographical information is accurateDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationData setGeolocation
A radio geolocation system is described in which a plurality of moving platforms such as aircraft concurrently receive a signal from a remote transmitter and the geolocation of the transmitter is determined. At each platform every thirty seconds a plurality of samples of the received signal are taken over a one second period. The samples are digitized and a time and GPS location stamp are added to each sample. The digitized samples with time and location stamps from all platforms are transmitted to a central location and stored in covariance matrices, one matrix per one second sample period. The signal samples in each matrix are processed utilizing a unique algorithm to generate a data set which defines a correlation surface. The data from a plurality of data sets are summed together on a point by point basis and normalized to yield a summation data set which defines a summation correlation surface. The summation correlation surface has a well defined peak that defines the geolocation of the remote transmitter.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Beam and power allocation method for MIMO communication system
InactiveUS20060098754A1Maximizing rate capabilityReduce the amount requiredPower managementDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCommunications systemData stream
A beam and power allocation method for a MIMO system transmitting multiple data streams from a transmitter having a plurality of transmit antennas to a receiver having at least two receive antennas, the transmit antennas being grouped based on feedback information from the receiver, includes obtaining covariance matrices for respective transmit antenna group, and allocating beam and power to the transmit antenna groups according to the covariance matrices of the respective antenna groups. The power allocation method can be adapted to various partial beamforming techniques by generalizing the optimization problem as a function of transmit covariance matrices.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
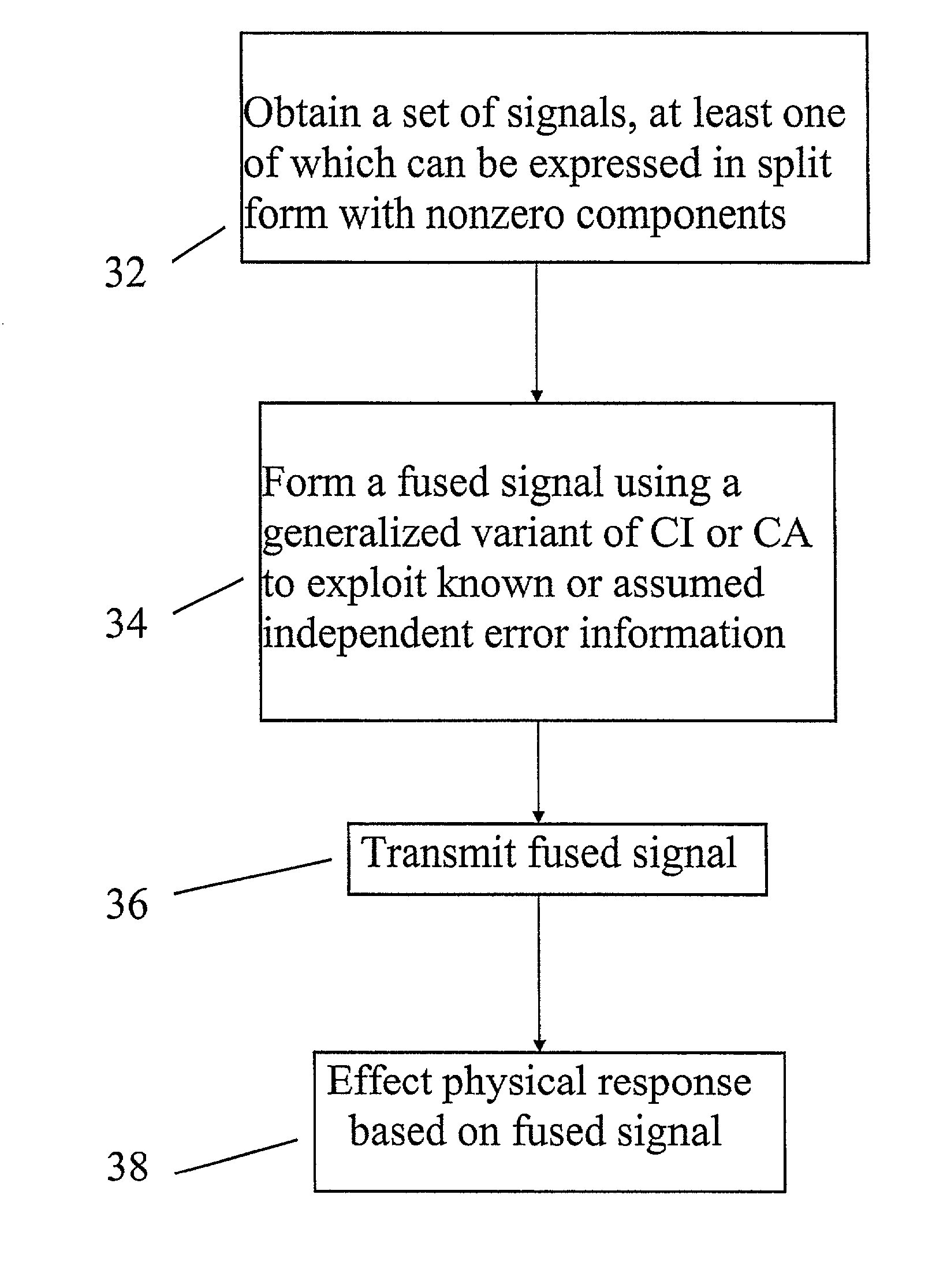
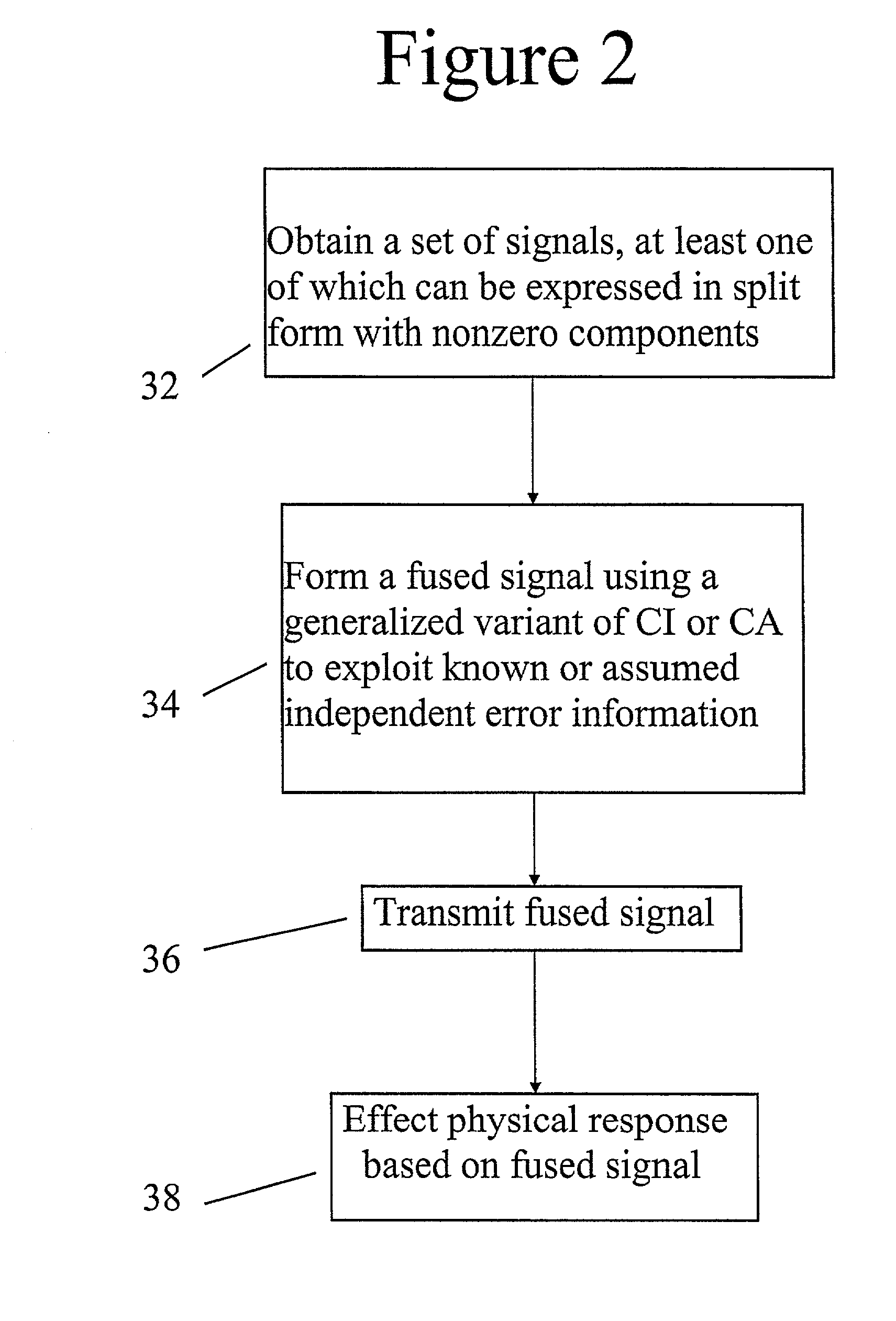
Wireless LAN with distributed access points for space management
A directional antenna system is disclosed in which a plurality of RF nodes are provided for cooperatively forming a directional antenna array for transmitting and receiving wireless signals between a wireless client at a predetermined position in space. One or more network interface assemblies are provided for exchanging signals between the plurality of RF nodes and a network. Preferably, the plurality of RF nodes are distributed in space with respect to each other and the network interface assembly. The network interface includes a beamformer for applying a plurality of antenna weighting factors to the respective RF nodes, for introducing phase differences in the respective transmitted and received wireless signals that produce a directional steering vector for the wireless signals. In one embodiment of the invention, a processing arrangement is provided for deriving an array manifold, which includes a respective plurality of antenna weighting factors corresponding respectively to distances between each of the plurality of RF nodes, for producing the directional steering vector for the wireless signals. In another embodiment of the invention, a subspace beamforming arrangement is provided for building a covariance matrix from sampled values of a wireless client signal at each RF node, and deriving dominant eigenvectors corresponding to each RF node. The dominant eigenvectors are used as the respective antenna weighting factors for producing the directional steering vectors for the wireless signals.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
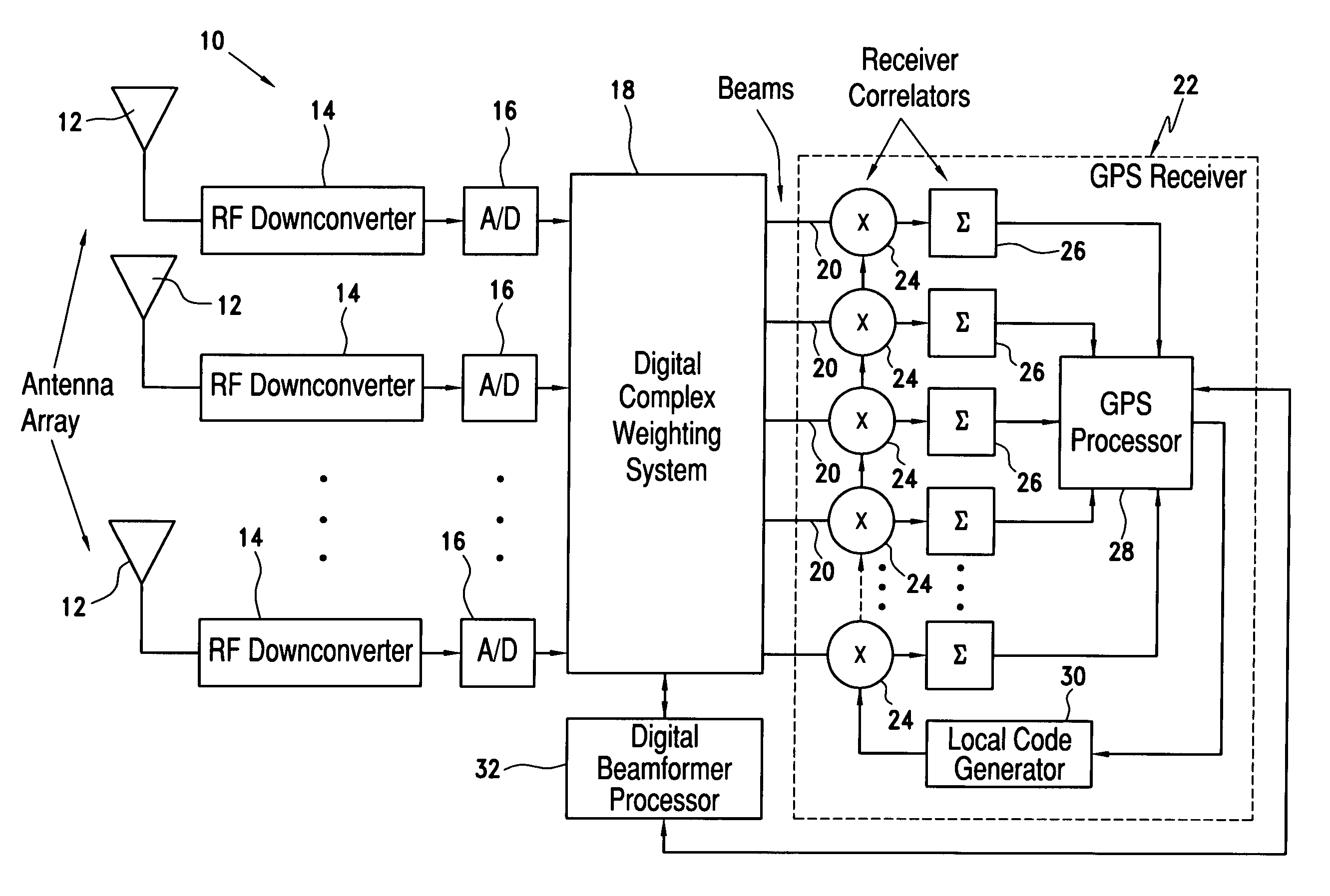
GPS spoofer and repeater mitigation system using digital spatial nulling
ActiveUS7250903B1Mitigate repeater threatMitigate GPS spoofer and repeater threatsPosition fixationRadio transmissionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Gps receiver
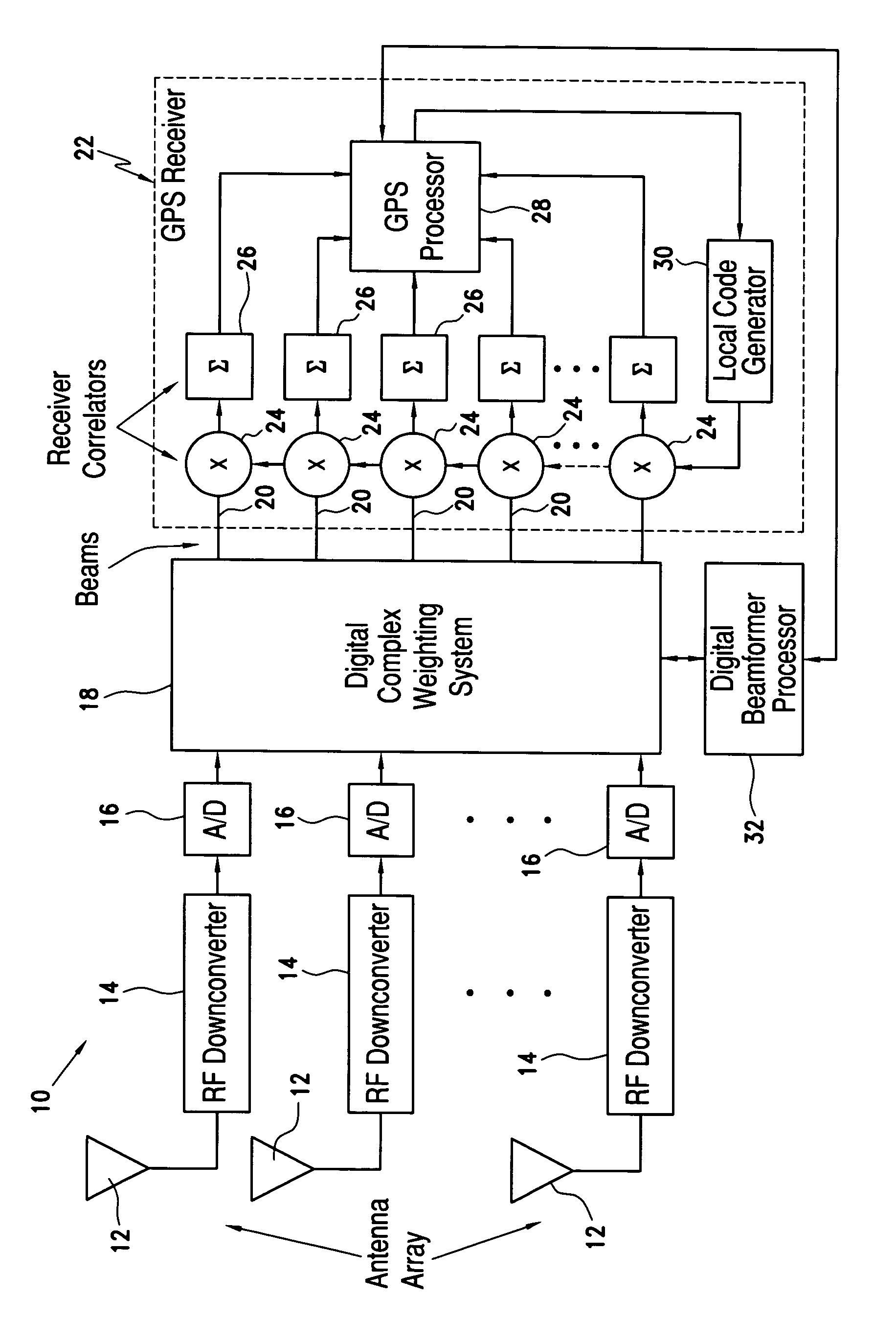
A system and method using a multi-element digital beamformer for detection and mitigation of spoofer and repeater threats to GPS that would not be addressed by baseline signal-to-noise (SNR) maximization algorithms is disclosed. GPS correlators and processing are applied to multiple beam outputs to detect and locate spoofer and repeater threats. In the beamformer processing, detected threats can be spatially nulled, even in the presence of traditional high power jamming, by modifying the normal sample covariance matrix to introduce synthetic nulls. A digital complex weighting system multiples each input channel by a complex (gain / phase) weight and adds the weighted channels together to form beams that the GPS receiver can use to reacquire the satellites in use without knowledge of platform attitude or the antenna manifold.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Efficient space-time adaptive processing (STAP) filter for global positioning system (GPS) receivers
InactiveUS6952460B1Easy to trackEfficiently null a relatively large number of jammersBeacon systems using radio wavesCommunication jammingComputation complexityFourier transform on finite groups
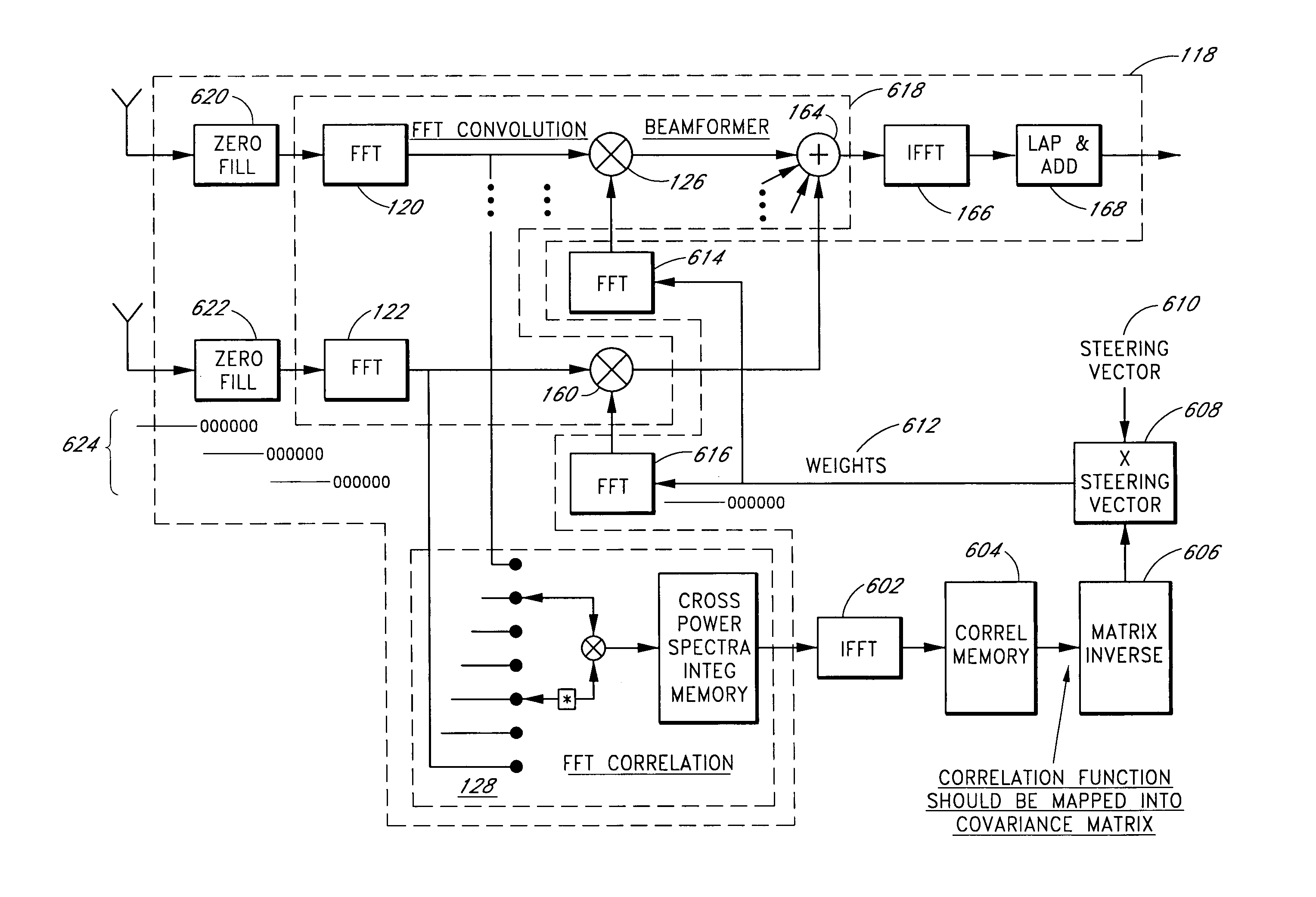
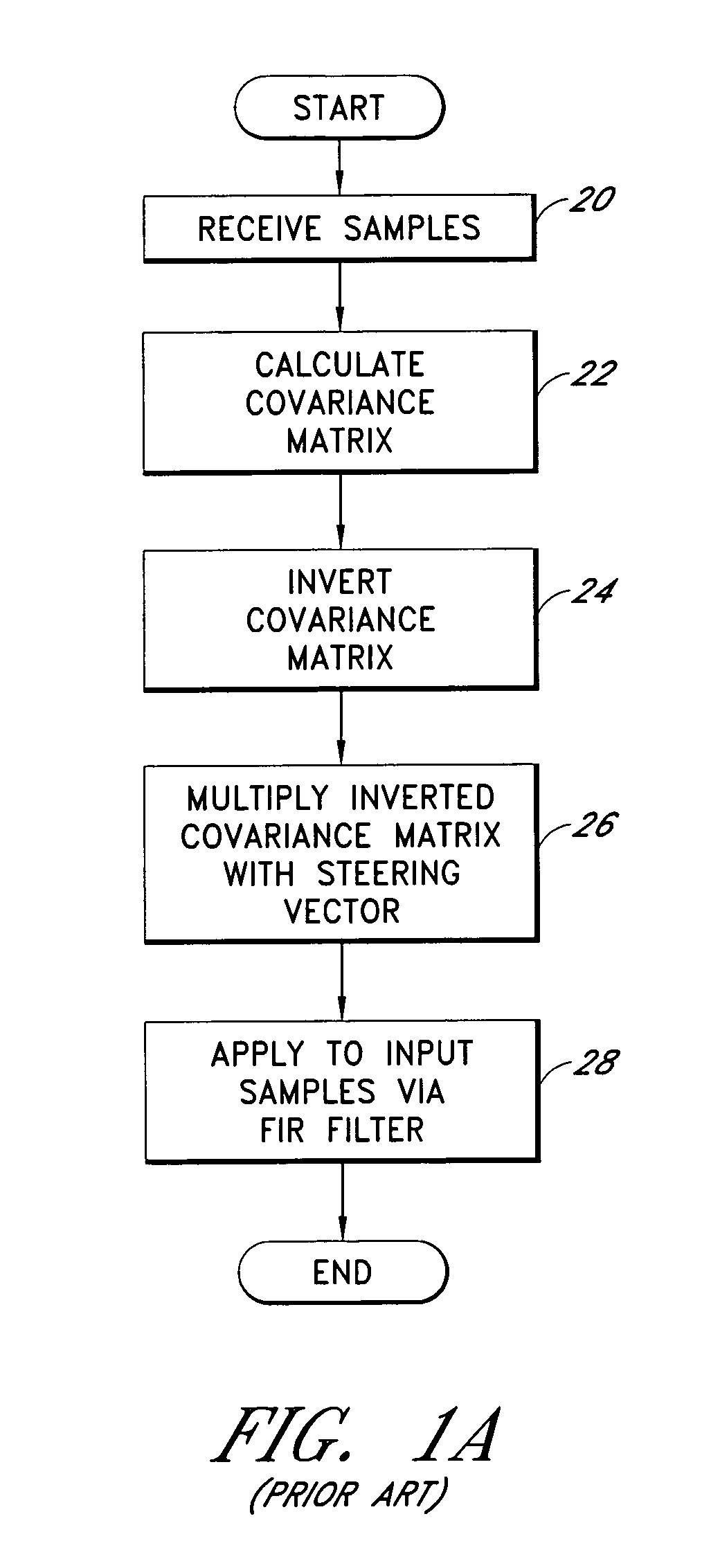
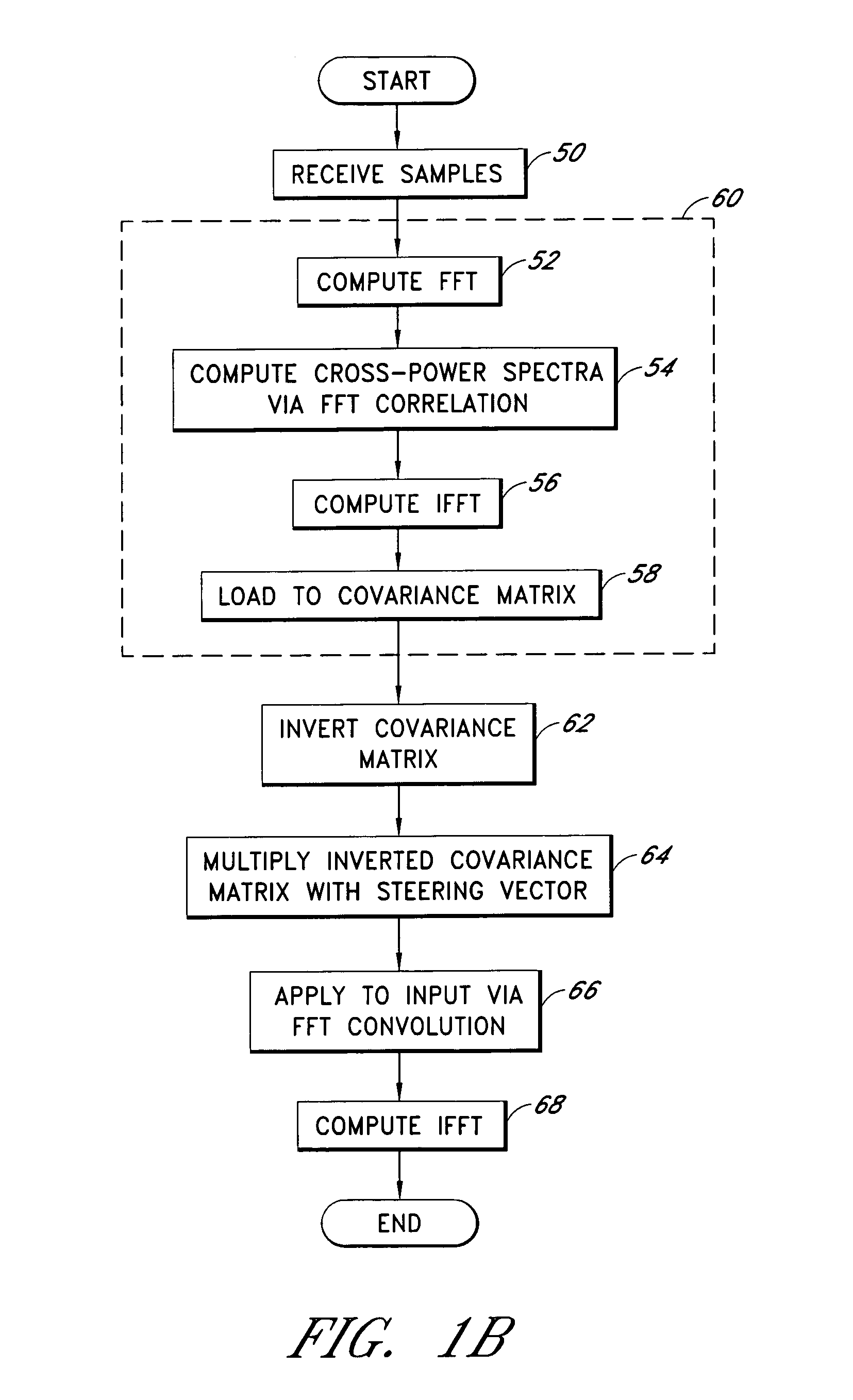
A system for efficiently filtering interfering signals in a front end of a GPS receiver is disclosed. Such interfering signals can emanate from friendly, as well as unfriendly, sources. One embodiment includes a GPS receiver with a space-time adaptive processing (STAP) filter. At least a portion of the interfering signals are removed by applying weights to the inputs. One embodiment adaptively calculates and applies the weights by Fourier Transform convolution and Fourier Transform correlation. The Fourier Transform can be computed via a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). This approach advantageously reduces computational complexity to practical levels. Another embodiment utilizes redundancy in the covariance matrix to further reduce computational complexity. In another embodiment, an improved FFT and an improved Inverse FFT further reduce computational complexity and improve speed. Advantageously, embodiments can efficiently null a relatively large number of jammers at a relatively low cost and with relatively low operating power.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Smart antenna beamforming device in communication system and method thereof
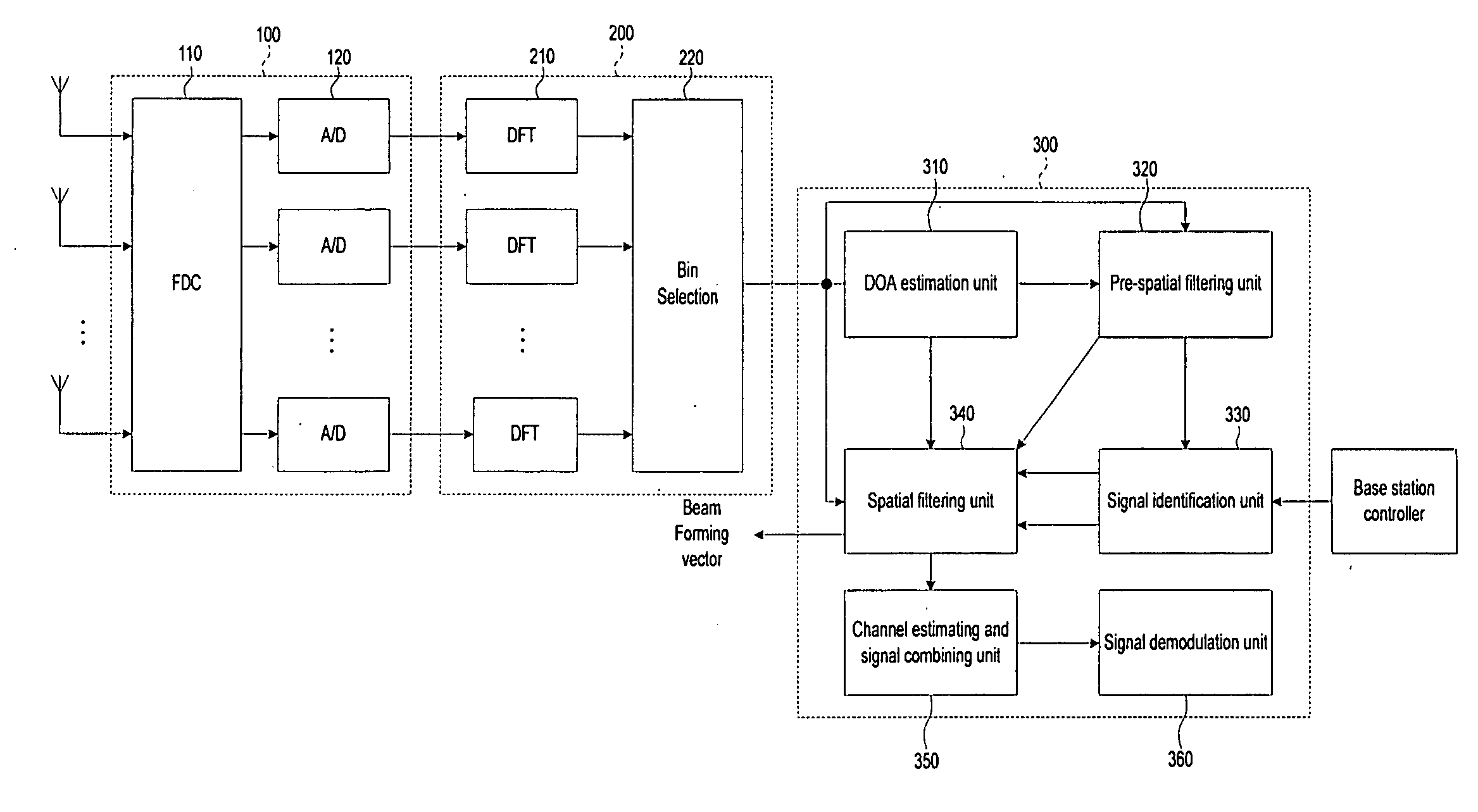
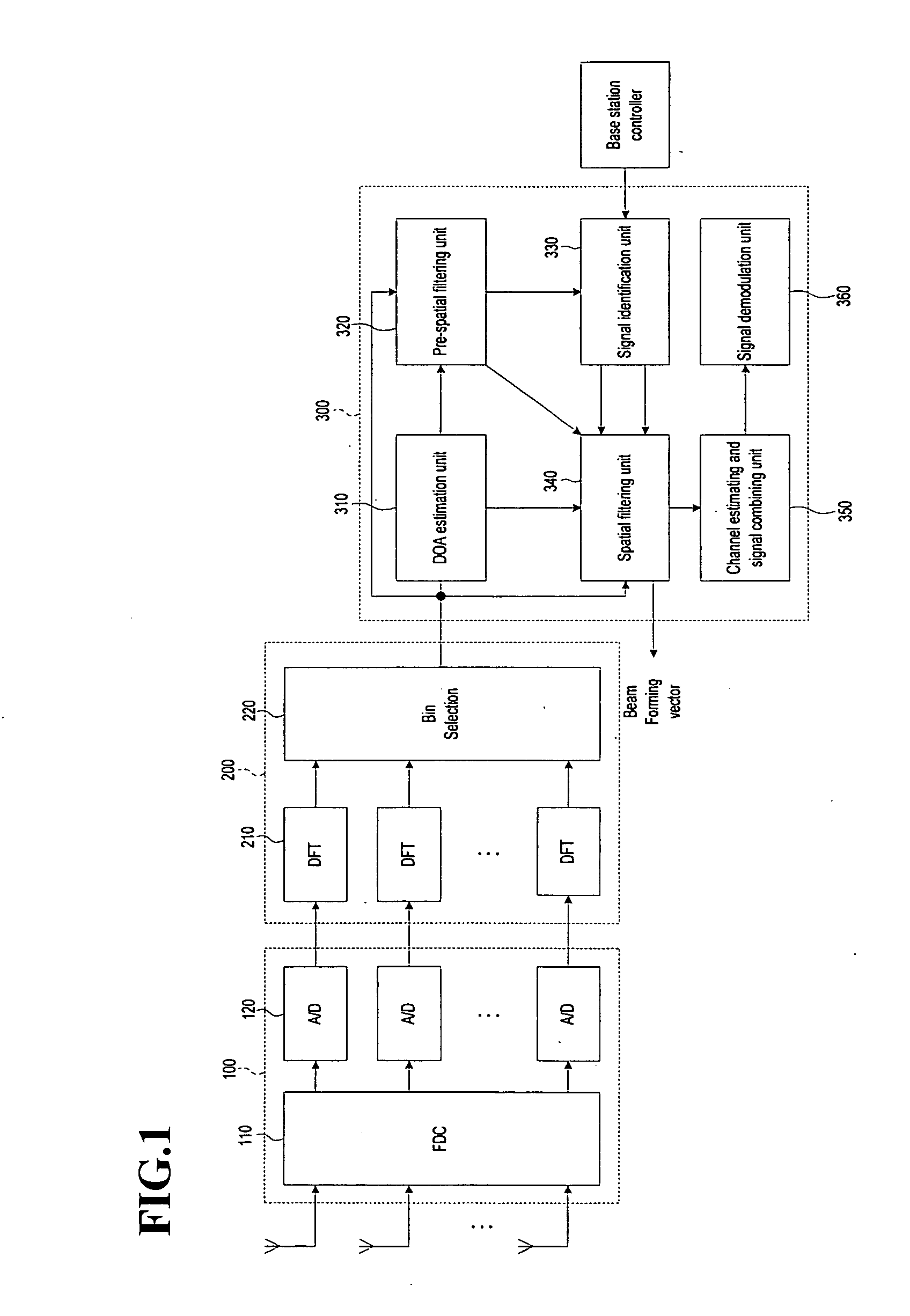
ActiveUS20070164902A1Maximizing signal to interferenceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemSmart antenna
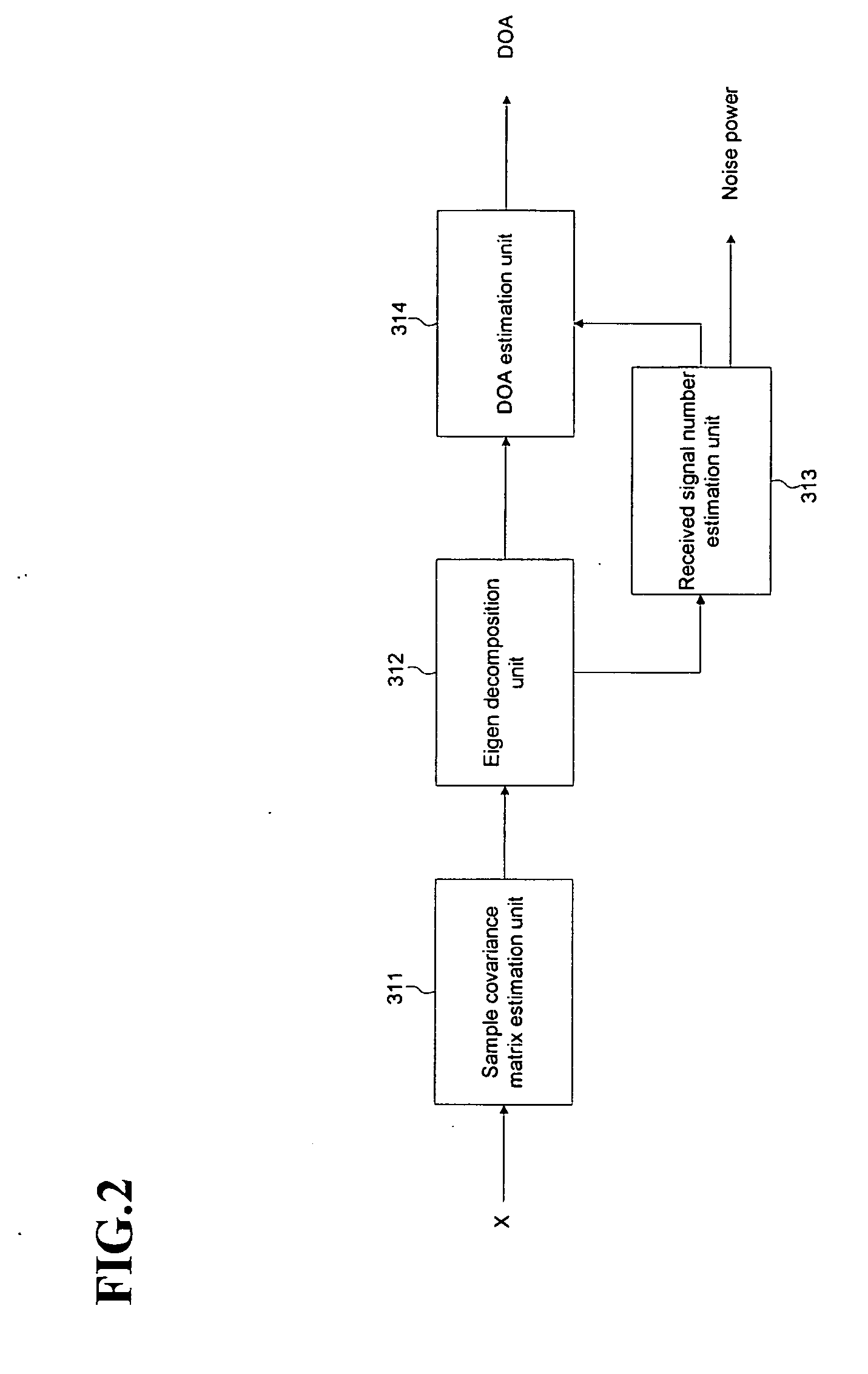
A beamforming device includes a Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation unit for estimating DOAs of the received signals based on a data subcarrier matrix; a pre-spatial filtering unit for using the estimated DOA, performing a filtering operation for the data subcarrier matrix, and generating filtering matrixes; a signal identification unit for using a data sequence, identifying original and interference signals, and generating the DOAs of the original and interference signals; a spatial filtering unit for generating an interference-plus-noise covariance matrix by using the DOA of the interference signal, eliminating the interference signal by using the covariance matrix and the DOA of the original signal, and forming final beams for the original signal; and a channel estimating and signal combining unit for performing a maximal ratio combining operation so that the final beams are combined as one combined final beam.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +4
Robust multiple chain receiver
InactiveUS7012978B2Easy to implementEasy to receiveSpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysCarrier signalTransmission channel
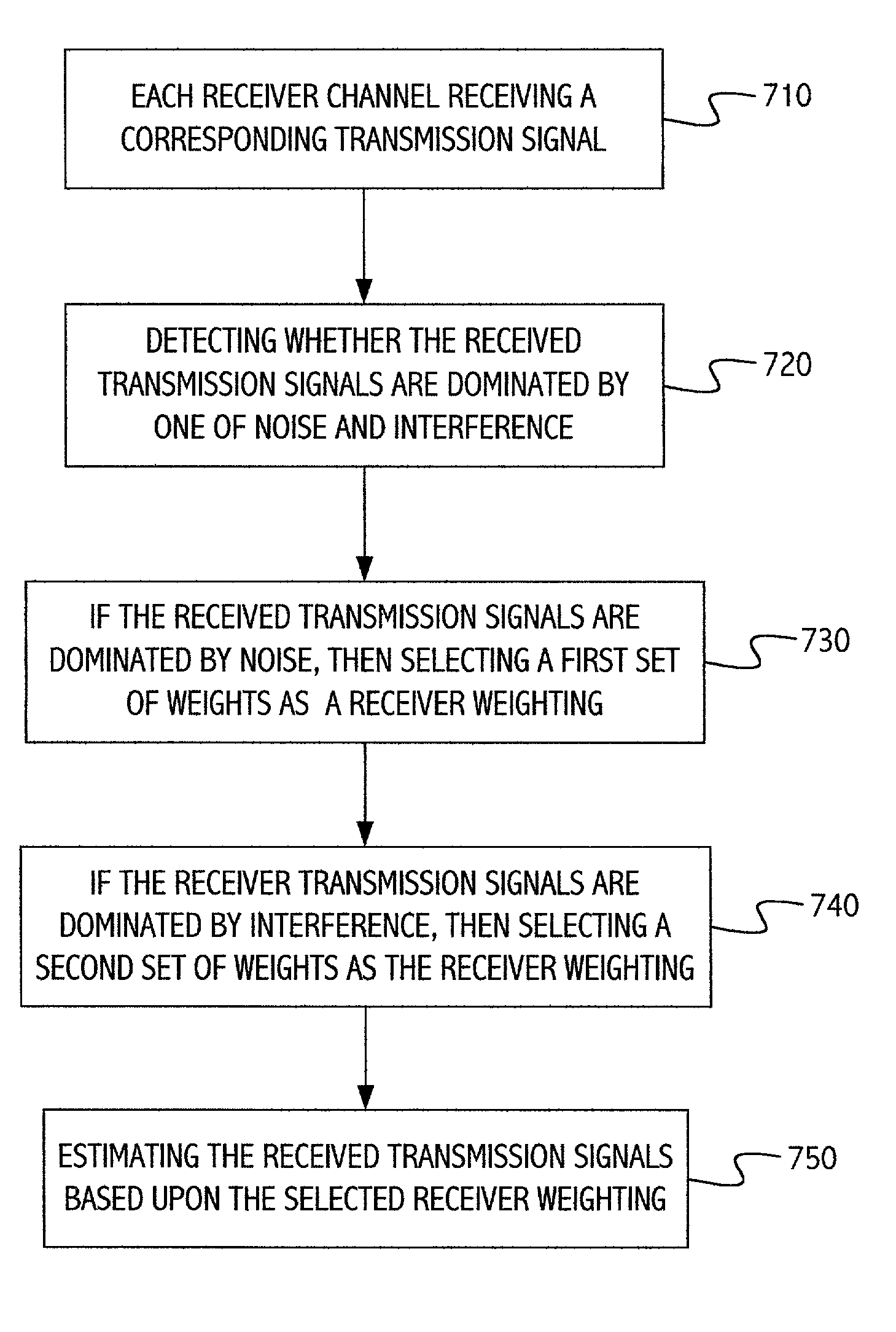
The present invention provides a method and system for receiving a plurality of transmission signals at a receiver, the transmission signals each traveling through a corresponding transmission channel. The receiver includes a plurality of receiver channels, a receiver channel corresponding to each transmission channel. Each receiver channel receives a corresponding transmission signal. The received transmission signals are detected to determine whether the received transmission signals are dominated by noise or interference. If the received transmission signals are dominated by noise, then a first set of weights are selected as a receiver weighting. If the received transmission signals are dominated by interference, then a second set of weights are selected as the receiver weighting. The received transmission signals are estimated based upon the receiver weighting. Detecting whether the received transmission signals are dominated by noise or interference includes determining a level of correlation between the received transmission signals. Detecting whether the received transmission signals are dominated by noise or interference can be determined during a time slot of nulled transmission signals. If the transmission signals are multiple carrier signals, then detecting whether the received transmission signals are dominated by noise or interference can be determined during a frequency and time slot of a nulled carrier of the transmission signals. The first set of weights can be based upon a first covariance matrix, wherein the first covariance matrix represents received noise and interference covariance. The second set of weights can be based upon the second covariance matrix, wherein the second covariance matrix represents interference covariance. The first set of weights and the second set of weights can also be used for transmission mode selection and receiver soft decoding.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Buried object locating and tracing method and system employing principal components analysis for blind signal detection
ActiveUS7136765B2Eliminates usual ambiguityResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage-current phase angleSensor arrayMaximum eigenvalue
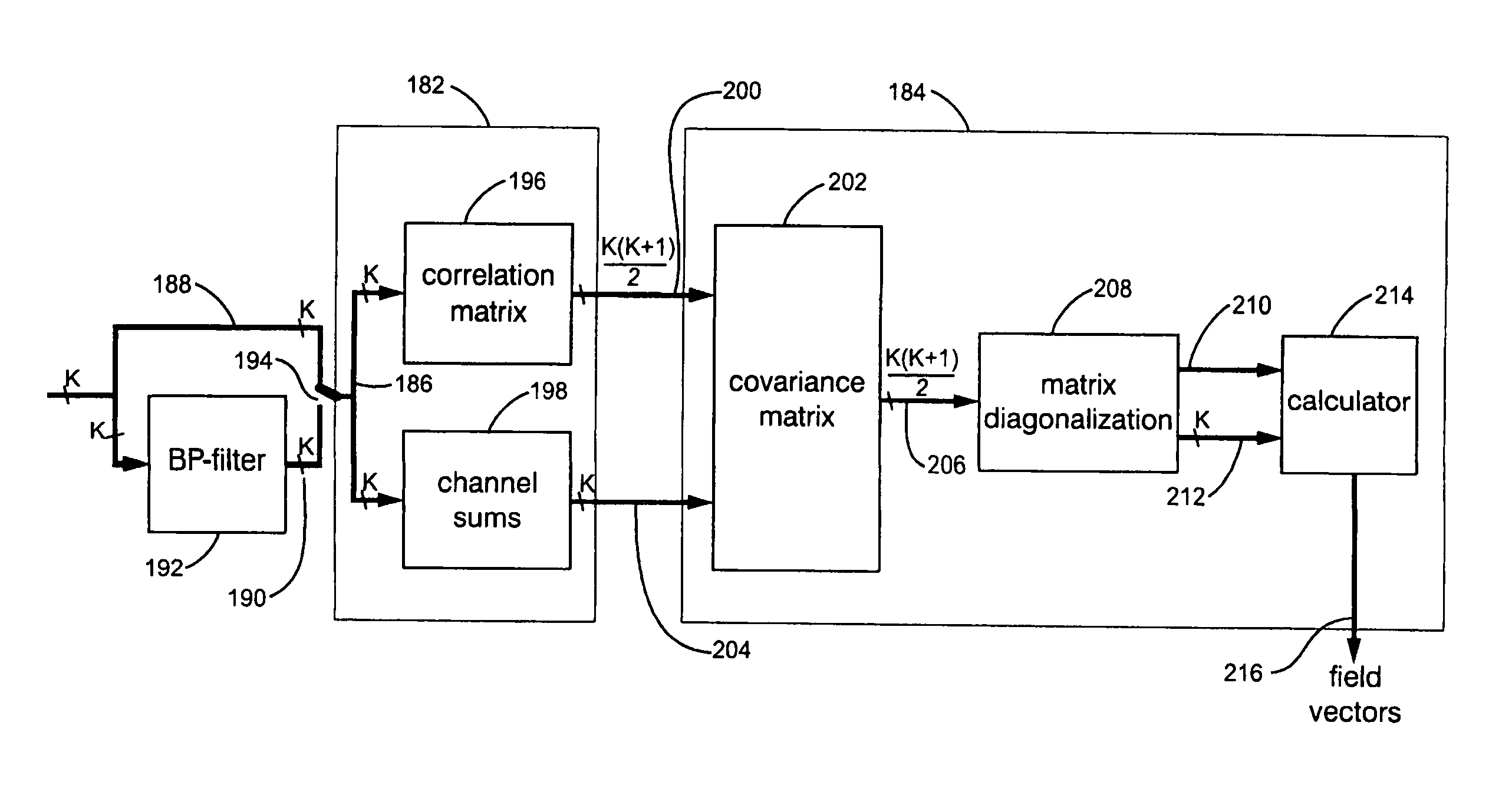
A blind locating system for finding and tracing buried objects such as utility lines, conductive pipes and sondes. A sensor array is coupled to a signal processor, which determines a field vector for one or more buried objects by producing a data signal representing a covariance matrix corresponding to the covariances of the time-varying sensor array signals over a selected frequency band and accumulation interval. The covariance matrix is characterized by eigenvalues and associated eigenvectors and a user interface (UI) indicates the field vector associated with the eigenvector having the largest eigenvalue. Using several different frequency bands, a plurality of underground objects may be simultaneously detected and indicated in the UI without foreknowledge of their existence or characteristics.
Owner:SEESCAN
Optimization of channel equalizer
InactiveUS6954495B2Improve channel performanceImprove performanceMultiple-port networksError preventionWeight coefficientRadio receiver
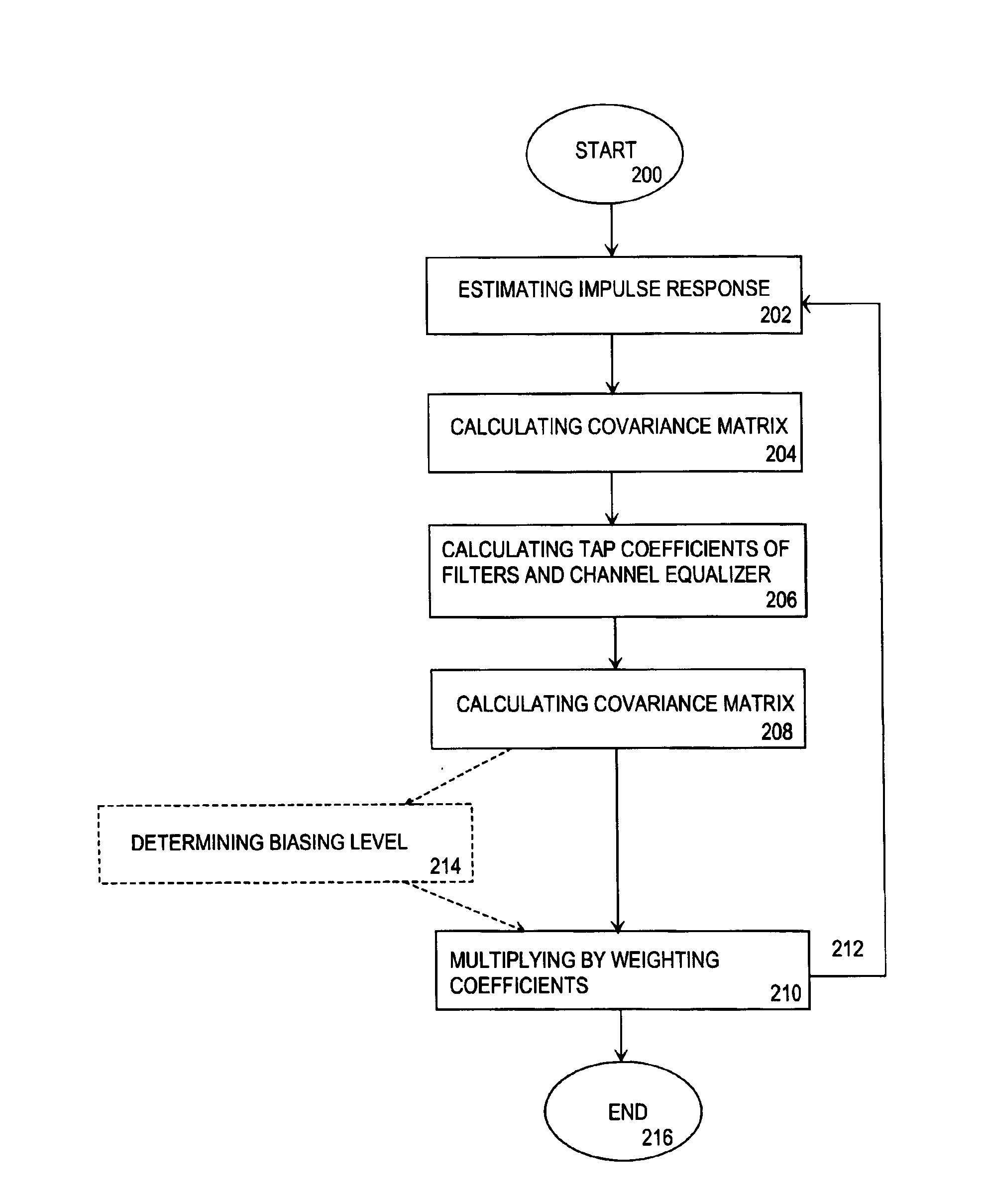
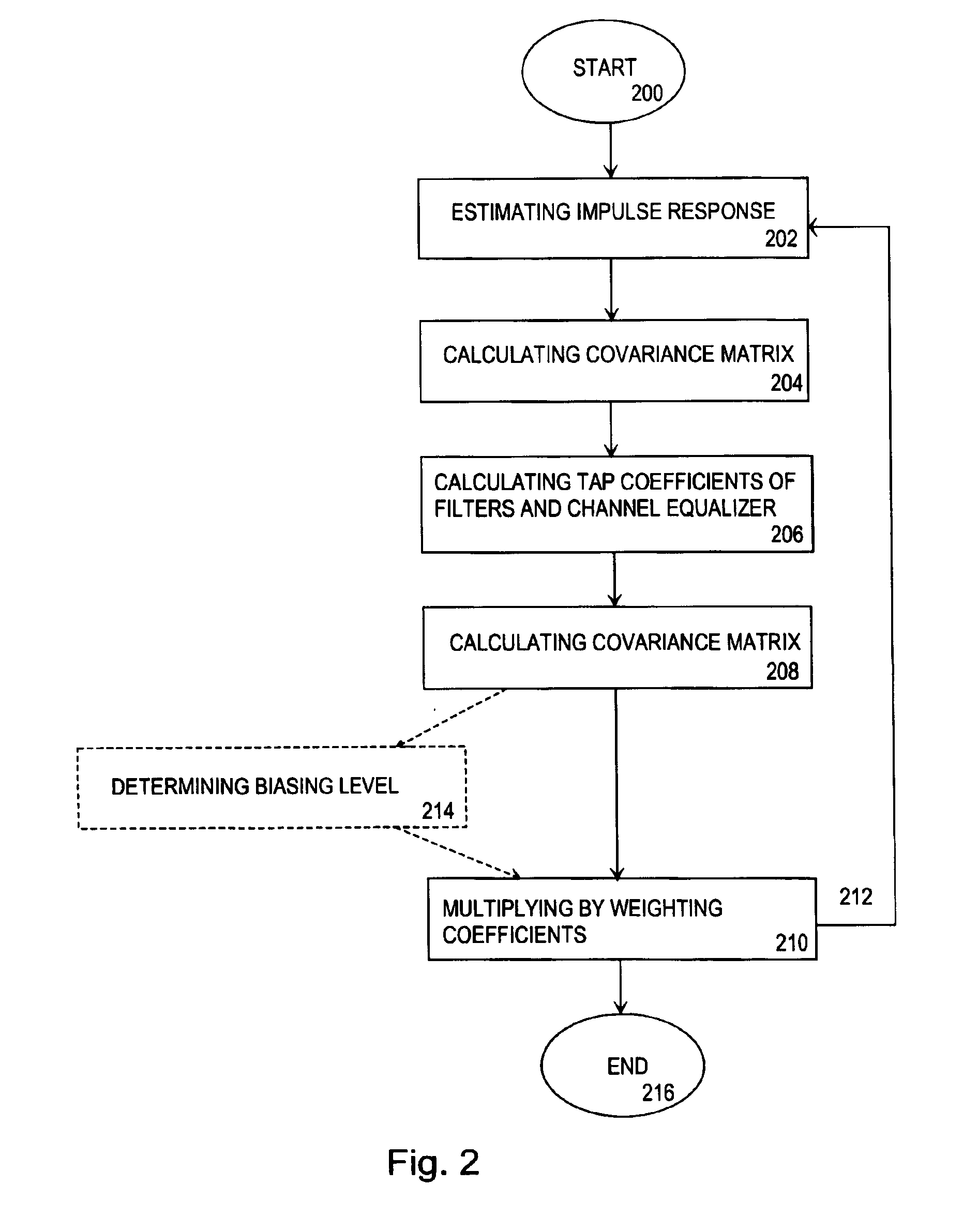
A method for carrying out channel equalization in a radio receiver wherein an impulse response is estimated, noise power is determined by estimating a co-variance matrix of the noise contained in a received signal before prefiltering, and tap coefficients of prefilters and an equalizer are calculated. The method comprises determining the noise power after prefiltering by estimating a noise covariance matrix, after which input signals of the channel equalizer are weighted by weighting coefficients obtained from the noise covariance estimation.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
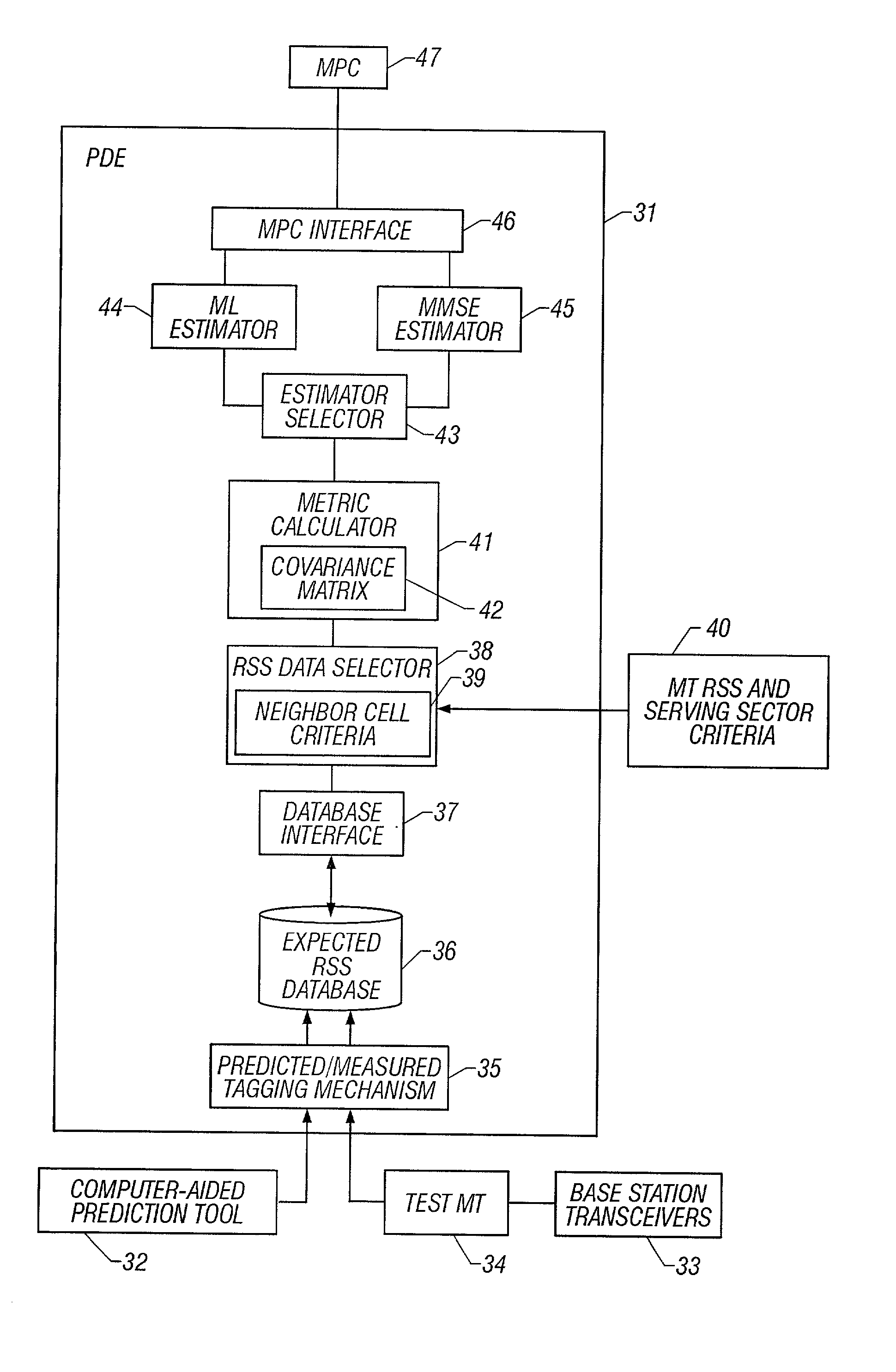
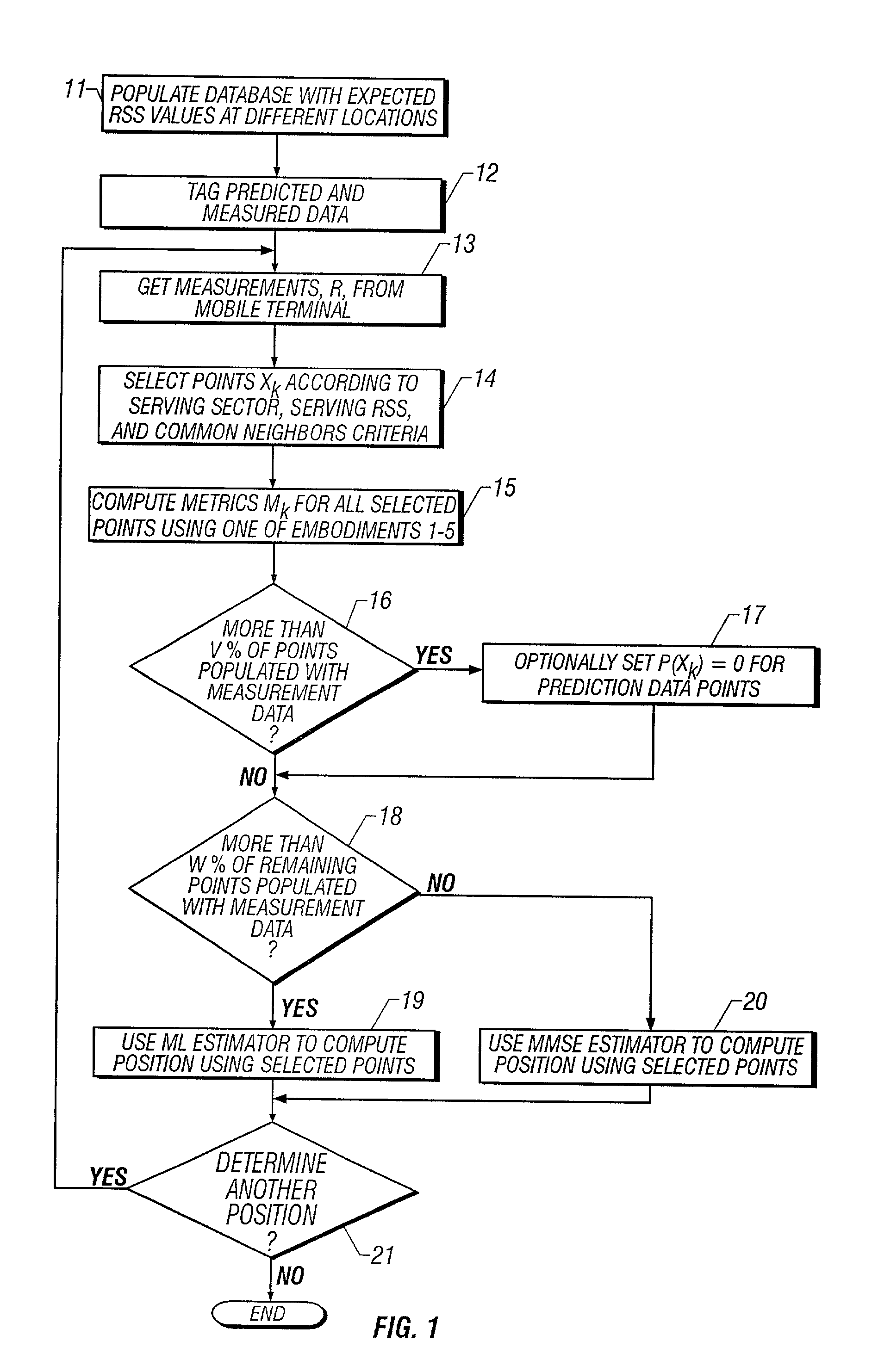
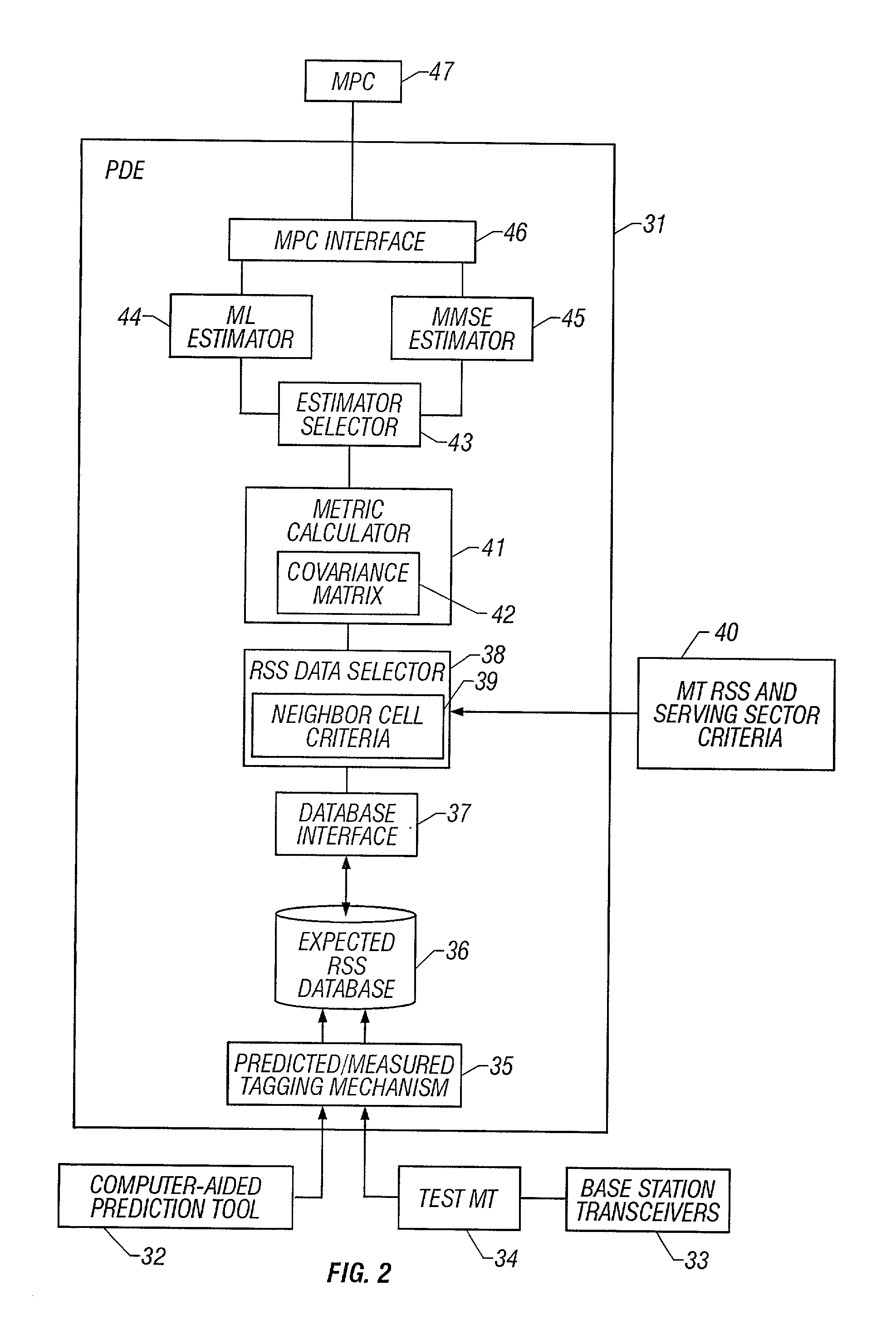
System and method of estimating the position of a mobile terminal in a radio telecommunications network
InactiveUS20030129992A1Direction finders using radio wavesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverTelecommunications network
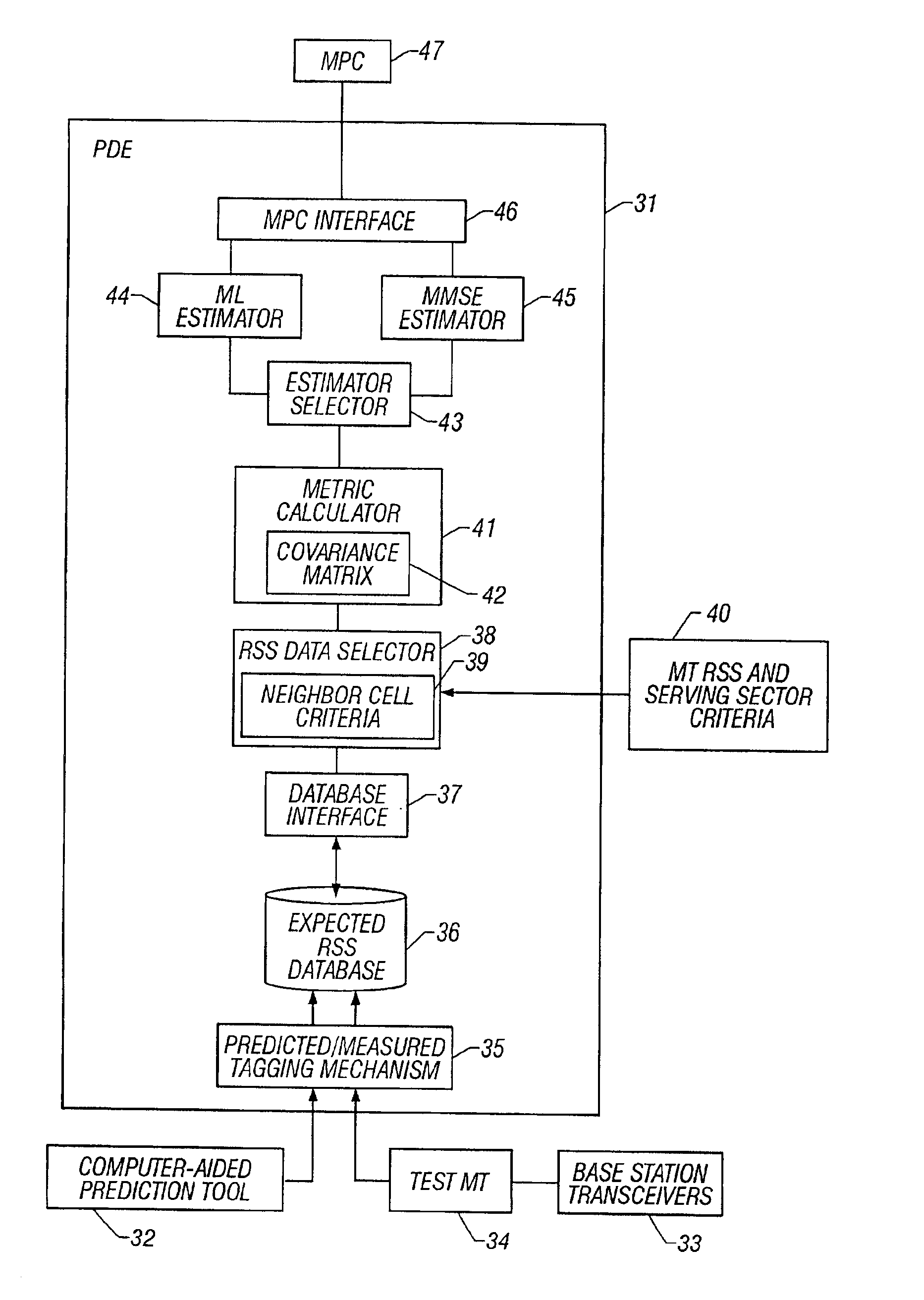
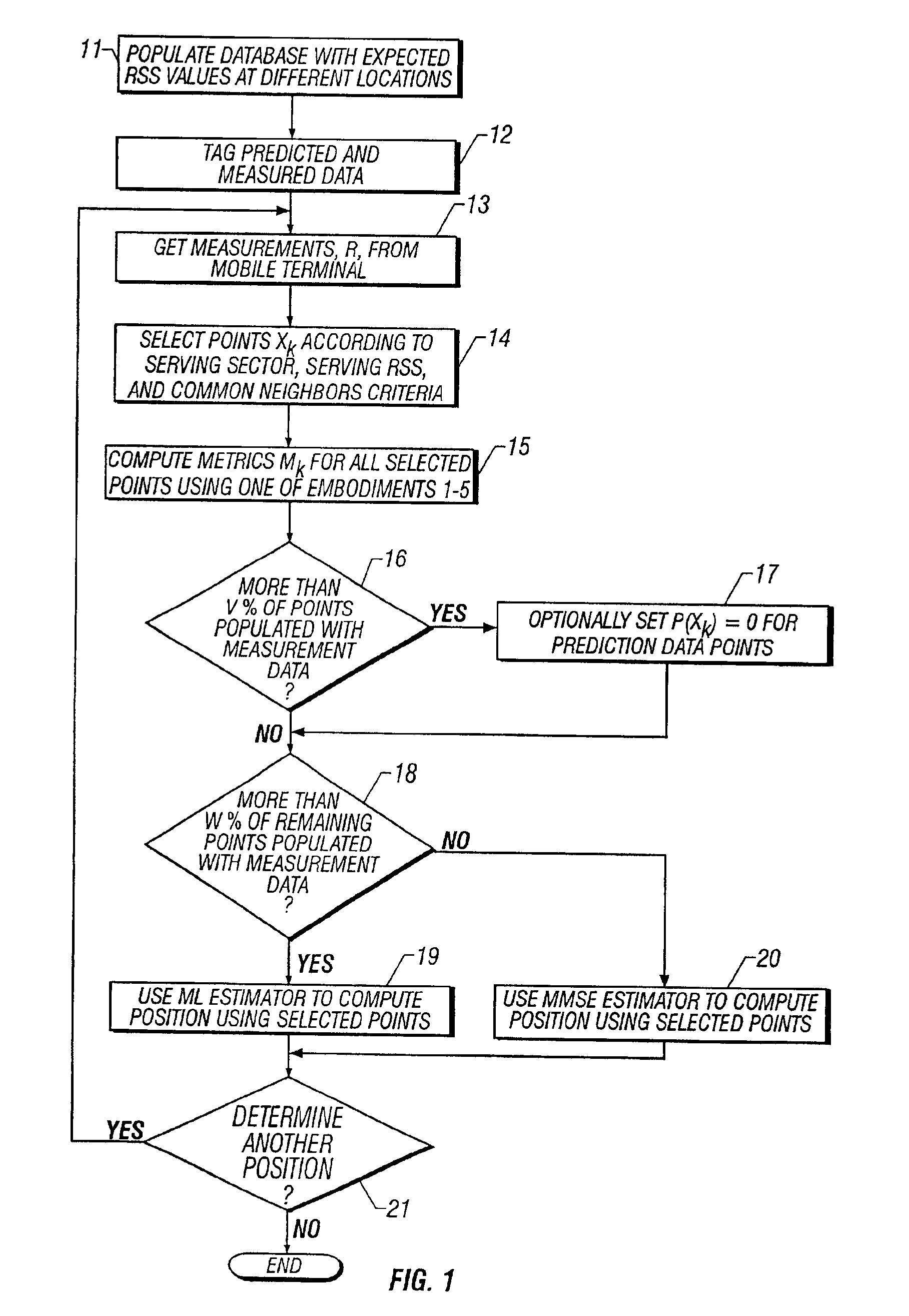
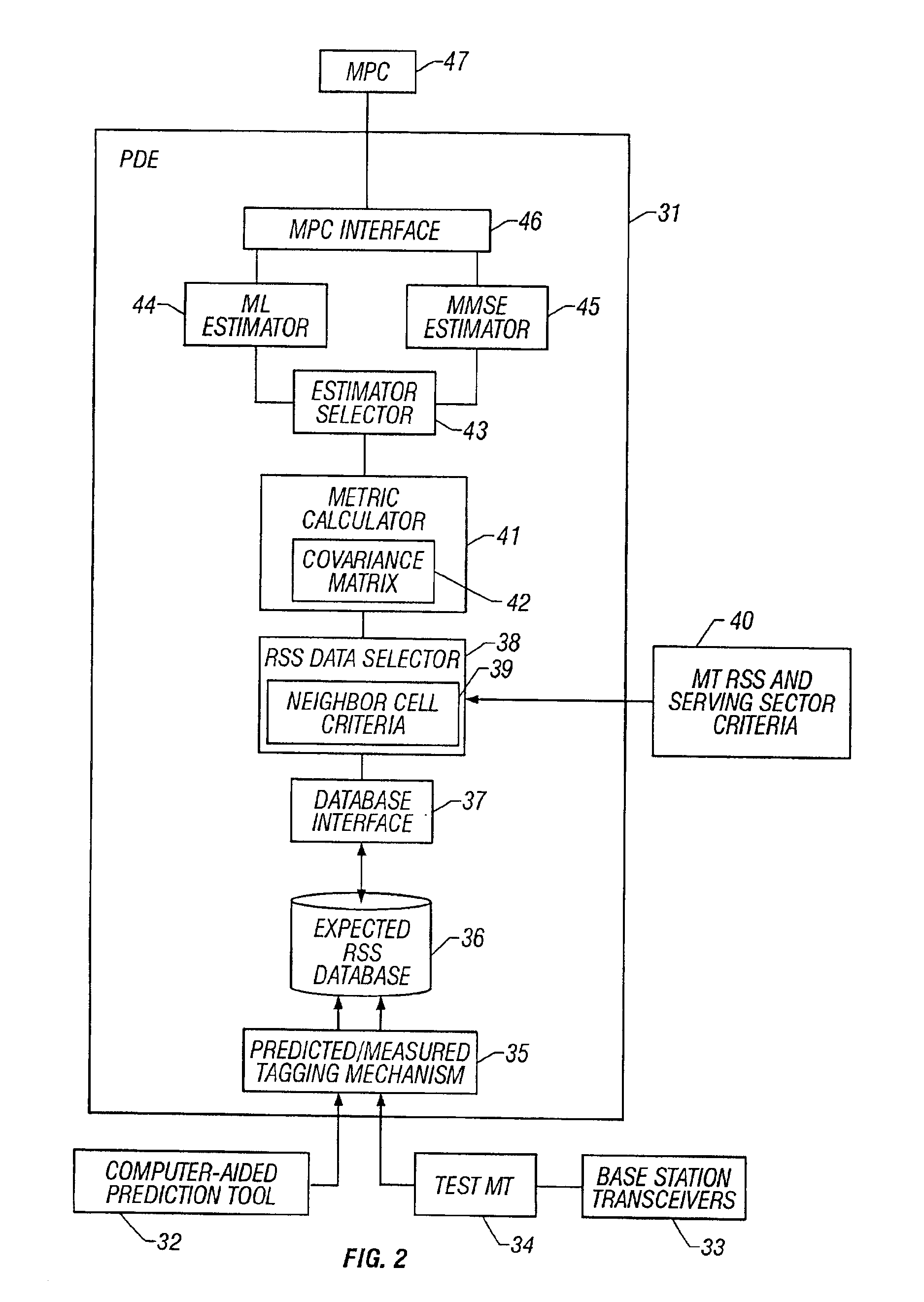
A system and method of estimating the position of a mobile terminal (MT) operating in a radio telecommunications network. Expected Received Signal Strength (RSS) values are predicted by a computer-aided prediction tool, and / or are measured by a test MT from base station transceivers. The predicted and measured RSS values are then tagged to indicate whether each value was predicted or measured. The RSS values are then stored at a plurality of locations in a database. When RSS measurements are received from the MT being located, a covariance matrix is used to compute metrics for the locations in the database. If more than a threshold percentage of the locations were populated with measured values, a Maximum-Likelihood (ML) estimator is used to estimate the position of the MT. If fewer than the threshold percentage of locations were populated with measured values, a Minimum-Mean-Square-Error (MMSE) estimator is used to estimate the position.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Method and apparatus for scheduling in multiple-input multiple-output communication system
ActiveUS20110182375A1Efficient executionEffectively control interferenceSecret communicationRadio transmissionCommunications systemComputer science
In a Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) communication system, a serving evolved Node B (eNB) receives a channel covariance matrix of the serving eNB and a channel covariance matrix for a first neighbor eNB with the highest interference among neighbor eNBs, from a User Equipment (UE). Received signal power information is generated for each subband-beam pair. Interference signal power information is generated for each subband-beam pair for the first neighbor eNB. The generated interference signal power information is exchanged with the first neighbor eNB for each subband-beam pair. Beam coordination information indicating a use status of each beam in each subband is generated for the UE, using the interference signal power information of the first neighbor eNB. The generated beam coordination information is exchanged with the neighbor eNB. Scheduling is performed on the UE using the generated beam coordination information and the beam coordination information of the first neighbor eNB.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dynamic digital pre-distortion system
ActiveUS20080260066A1Simplify reduce numberImprove efficiencyTransmitters monitoringPower managementAudio power amplifierLinear filter
A Dynamic Digital Pre-Distortion (DDPD) system is disclosed to rapidly correct power amplifier (PA) non-linearity and memory effects. To perform pre-distortion, a DDPD engine predistorts an input signal in order to cancel PA nonlinearities as the signal is amplified by the PA. The DDPD engine is implemented as a composite of one linear filter and N-1 high order term linear filters. The bank of linear filters have programmable complex coefficients. To compute the coefficients, samples from the transmit path and a feedback path are captured, and covariance matrices A and B are computed using optimized hardware. After the covariance matrices are computed, Gaussian elimination processing may be employed to compute the coefficients. Mathematical and hardware optimizations may be employed to simplify and reduce the number of multiplication operands and other operations, which can enable the DDPD system to fit within a single chip.
Owner:MICROELECTRONICS TECH INC
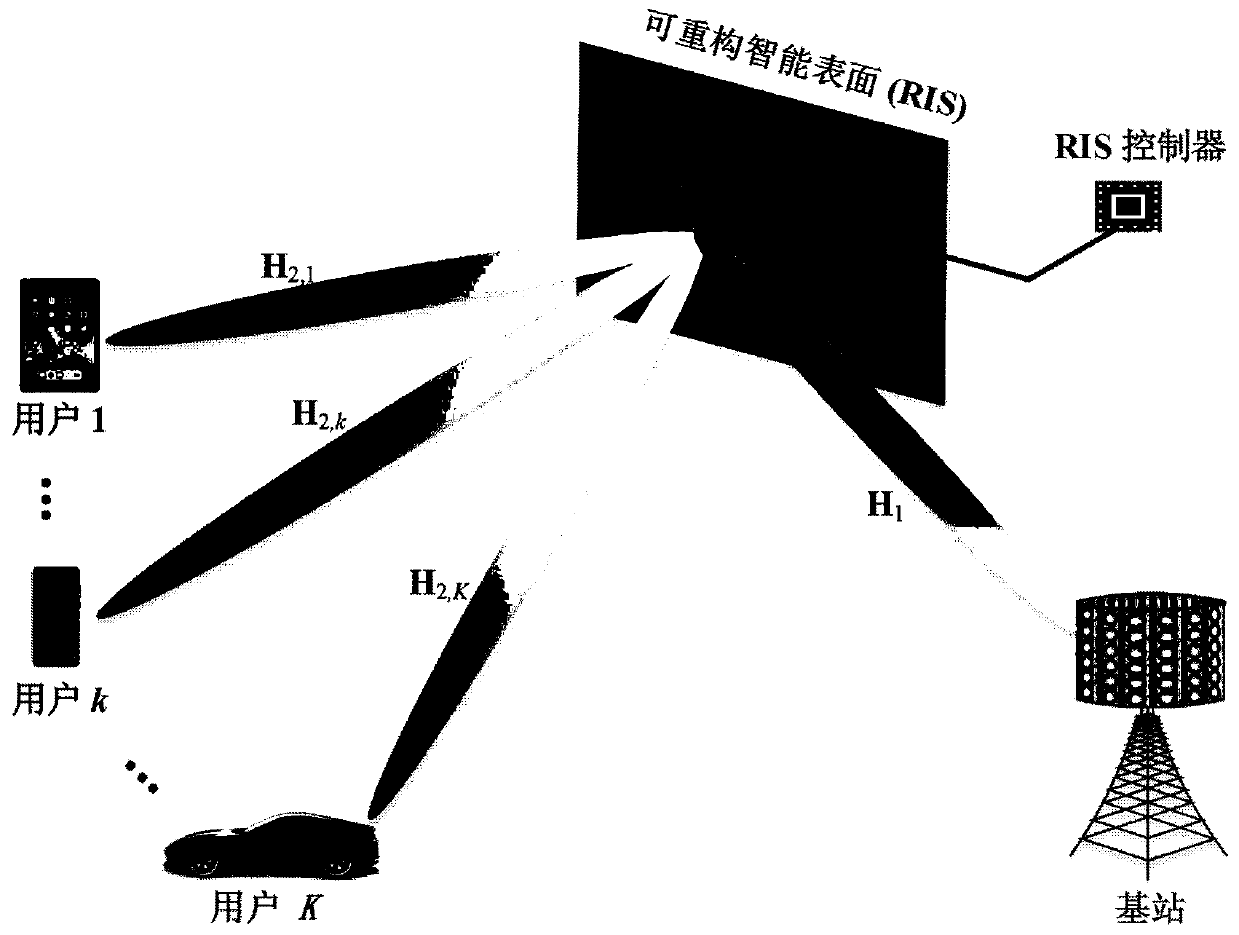
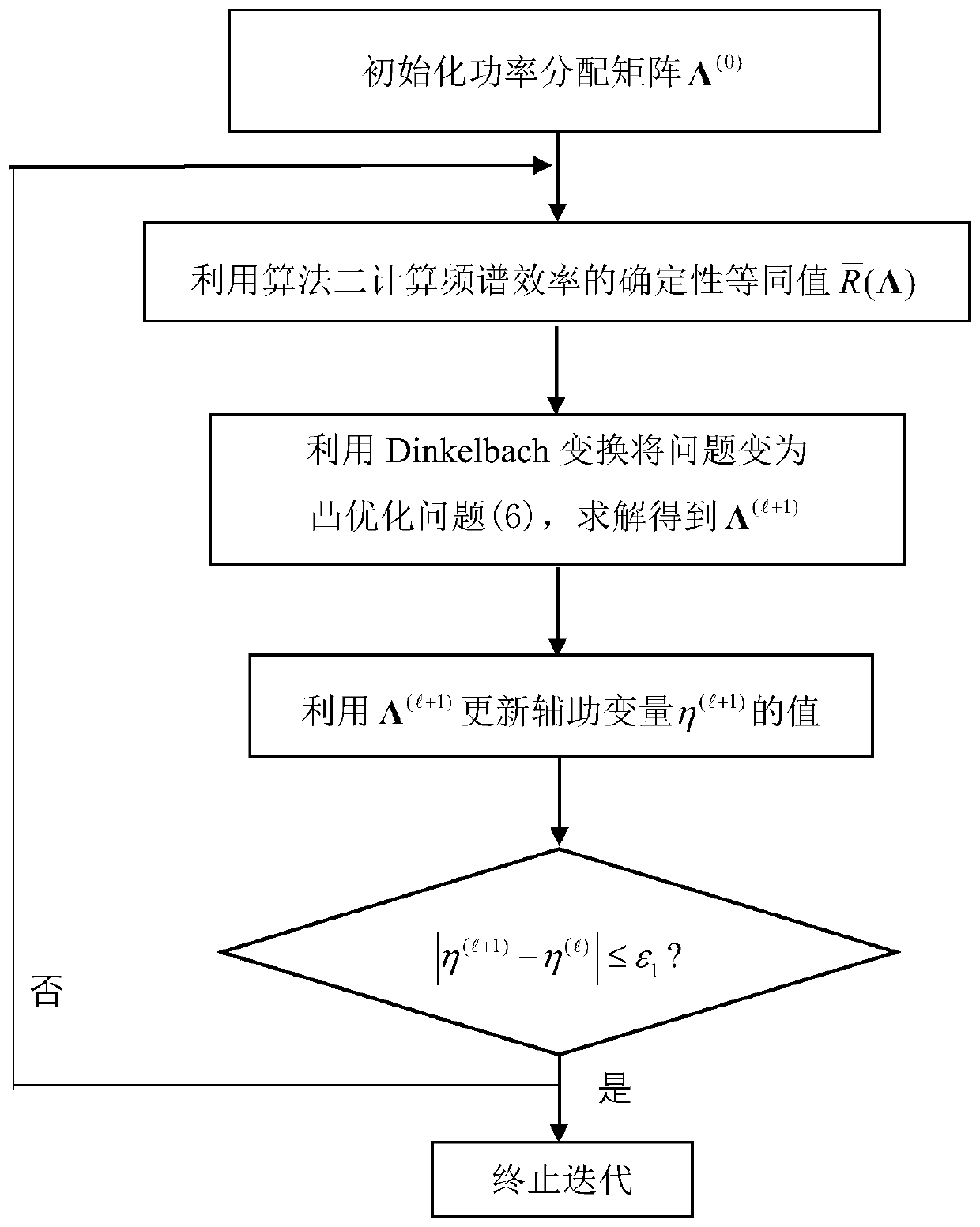
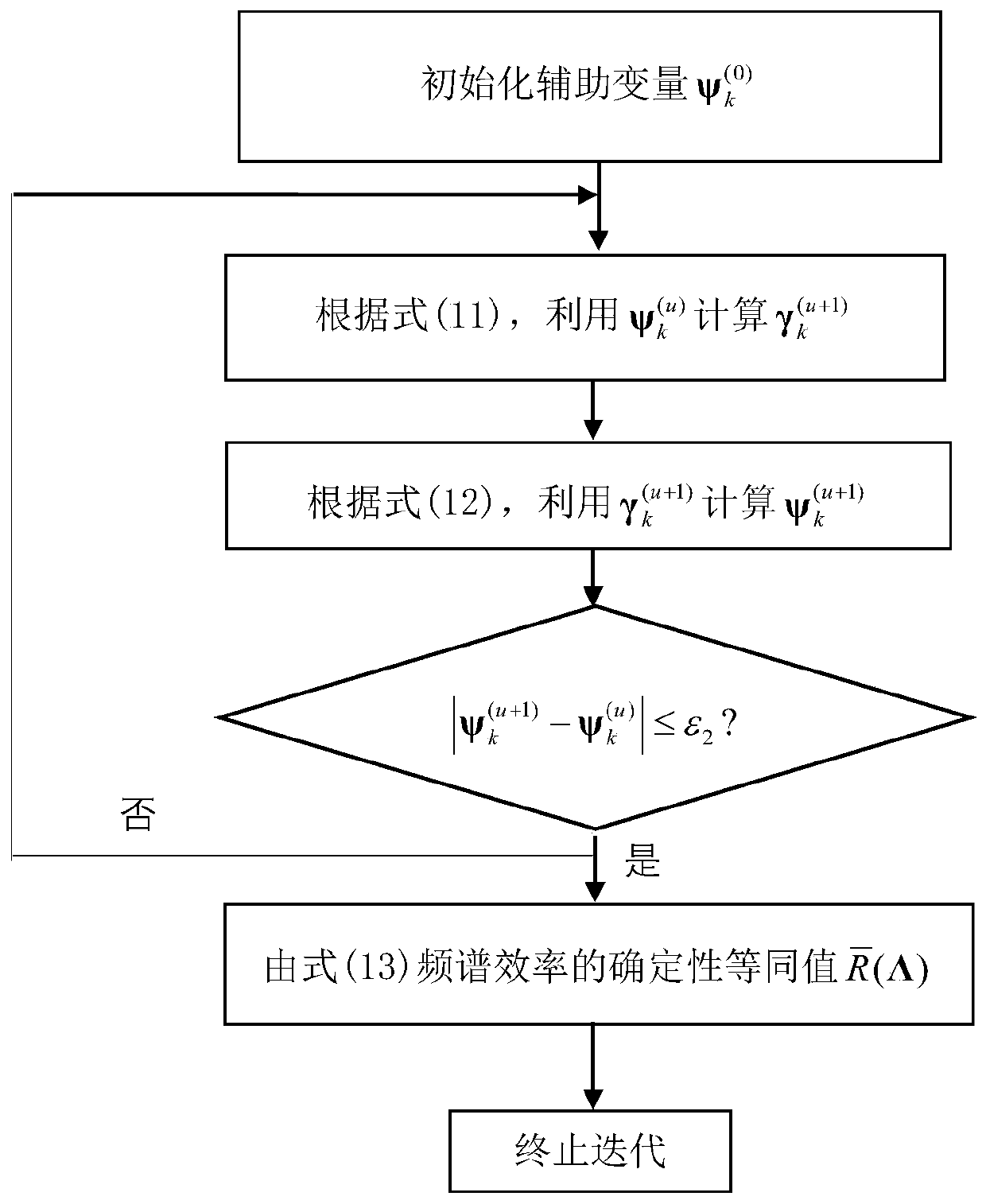
Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multi-user MIMO uplink transmission method
ActiveCN111010219AReduce complexityMitigate multipath propagationSpatial transmit diversityHigh level techniquesChannel state informationMimo transmission
The invention provides a reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multi-user MIMO uplink transmission method. According to the transmission method, a signal sent by a user side is reflected to a base station through an RIS, and the RIS can change the phase of the signal incident on the RIS. Aiming at a bottleneck problem of channel information acquisition of an RIS-assisted multi-user MIMO transmission system, only partial channel state information is utilized, including instantaneous channel state information from the RIS to a base station channel and statistical channel state informationfrom a user to the RIS channel; through an alternate optimization method, a deterministic equivalence principle, a block coordinate descent method, an MM method and the like, a sending covariance matrix and an RIS phase shift matrix of a user are jointly designed to maximize the global energy efficiency of the system or traverse the spectral efficiency; when the channel state information is changed, the user side dynamically implements transmission power distribution with maximum energy or spectral efficiency, and the RIS dynamically adjusts the phase shift matrix. According to the invention,the implementation complexity is low, and the performance of multi-user MIMO uplink transmission can be effectively improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Self-adapting interactive multiple model mobile target tracking method
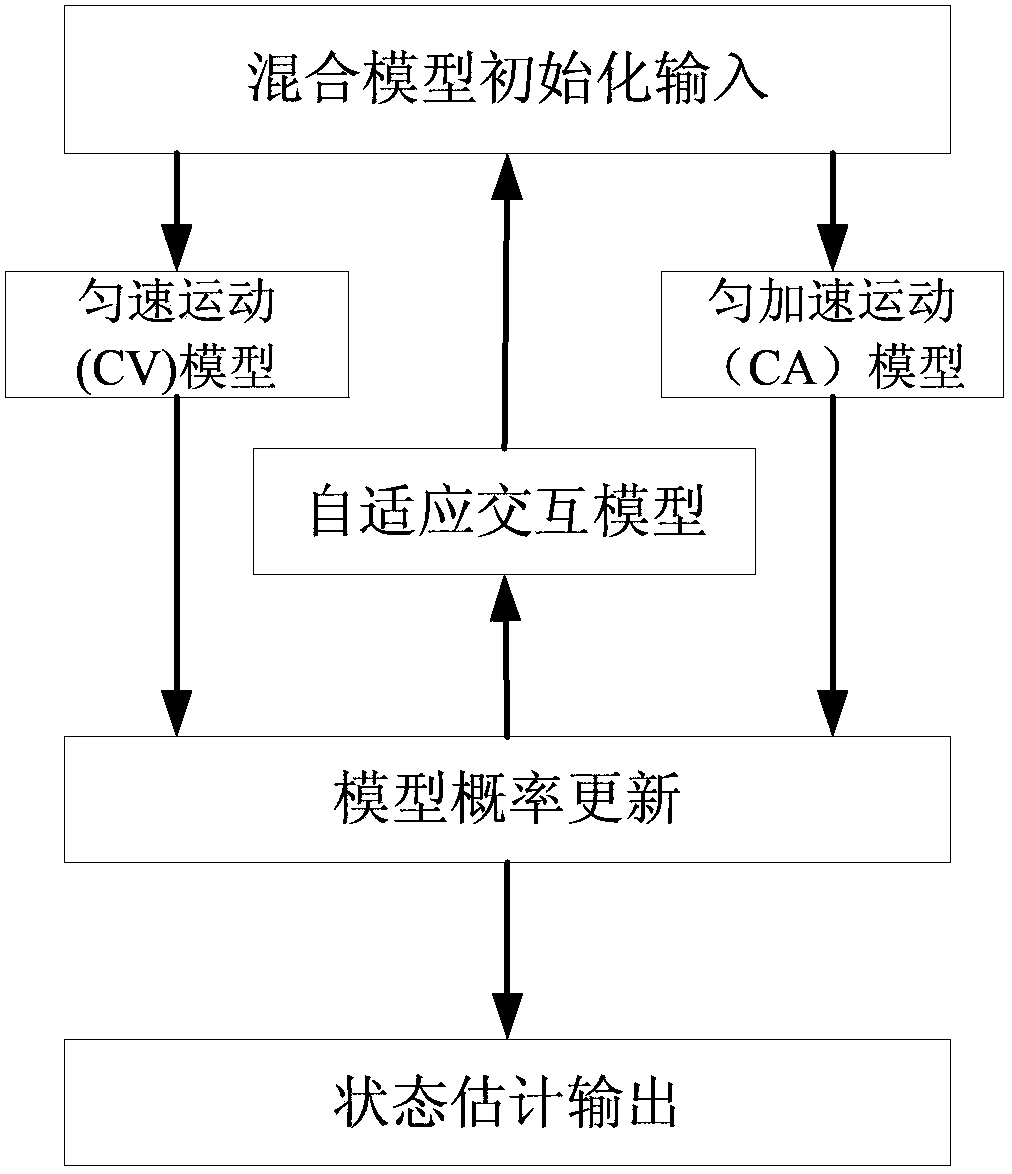
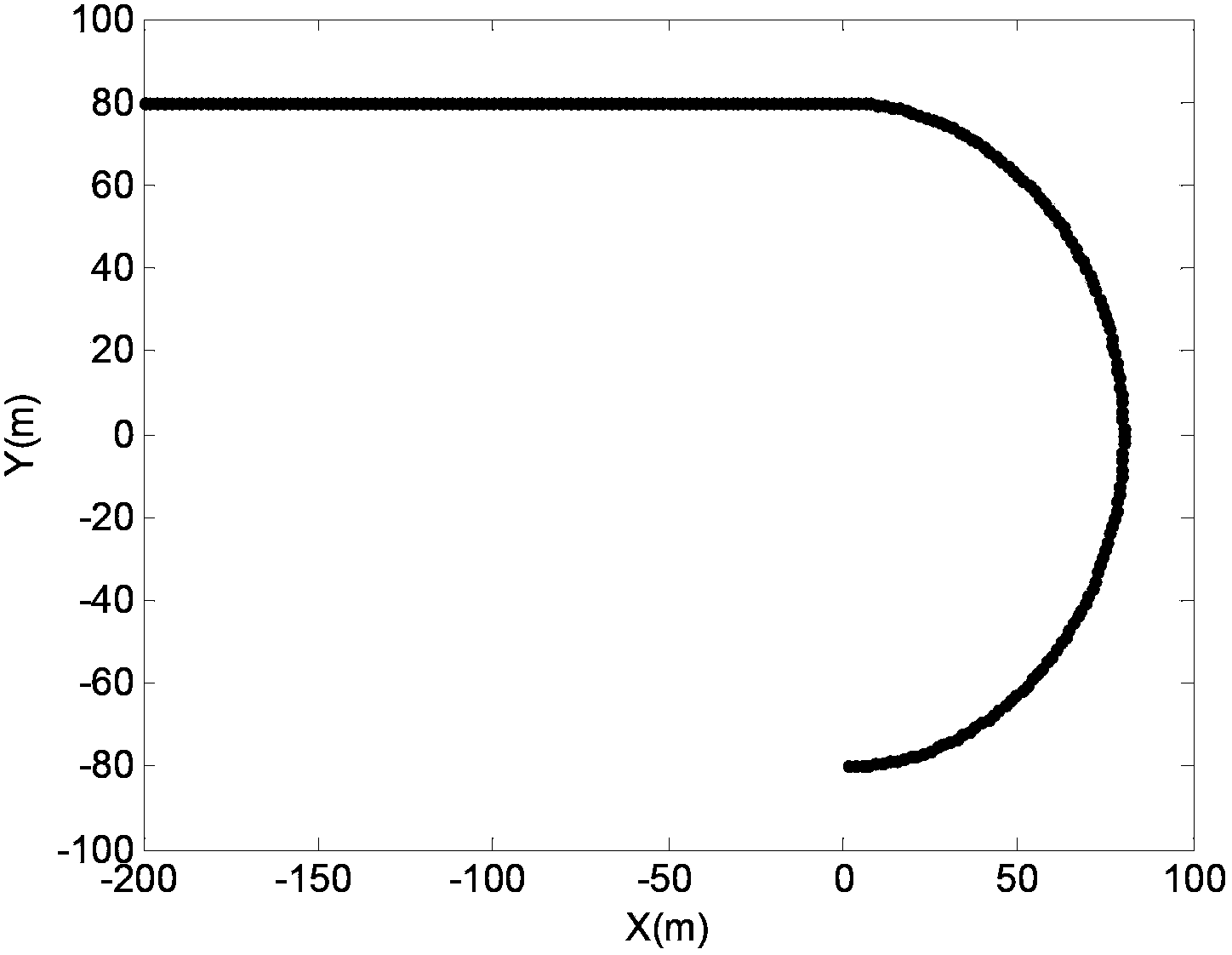
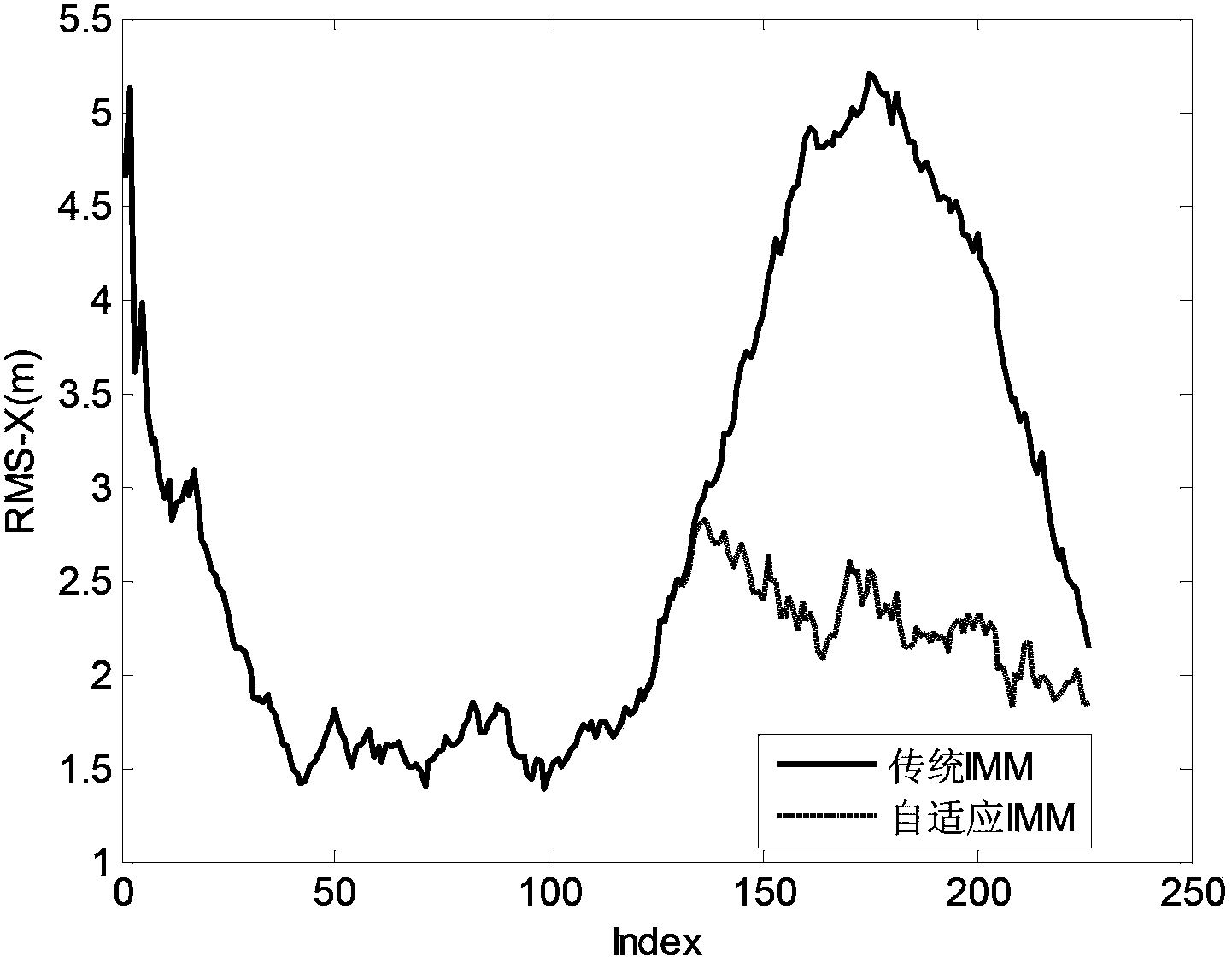
InactiveCN103853908AReduce complexityImprove real-time performanceNavigation instrumentsSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexitySelf adaptive
The invention relates to mobile tracking of vehicle targets in the communication and transportation field. A self-adapting interactive multiple model mobile target tracking method comprises the following steps of establishing mixed initialized input. including a covariance matrix of a mixed initial condition and a mixed initial state. of each model; establishing constant velocity (CV) and constant acceleration (CA) motion models; updating: calculating covariance matrix and innovation of an error according to a Kalman filter formulation; constructing a likelihood function of a target motion module by utilizing the innovation of a Kalman filter result, and calculating a Markov state transition probability matrix; carrying out estimation output after being fused by utilizing the Markov state transition probability matrix as weight of switch among each motion model. According to the self-adapting interacting multiple model mobile target tracking method disclosed by the invention, the problem that the error is increased or the tracking is failed caused by non-matching of a filter model and a target motion model due to the motion of a target in the traditional interactive multiple model algorithm is solved; the self-adapting interacting multiple model mobile target tracking method has the advantages of low calculation complexity and good tracking effect, and can be applied to target tracking of motor vehicles in the communication and transportation field.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
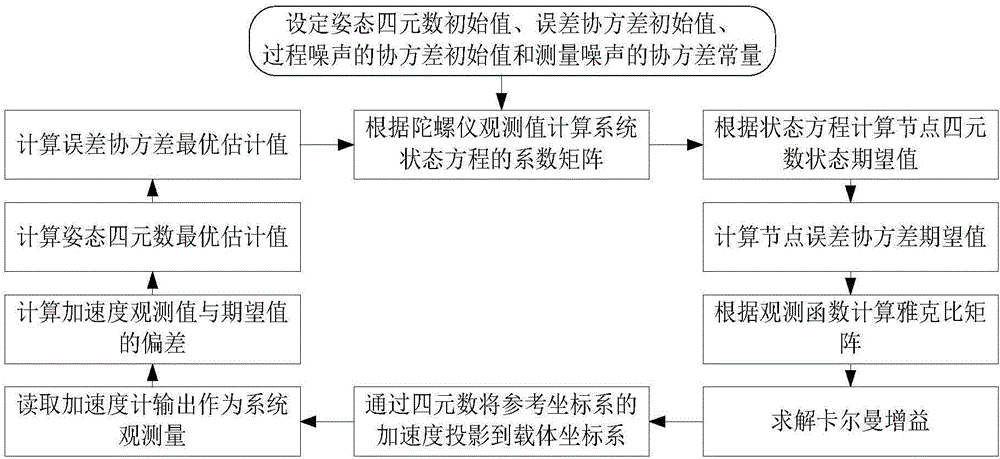
Human body posture recognition method based on self-adaptive extension Kalman filtering
ActiveCN106500695ANavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsHuman bodyArea network
The invention discloses a human body posture recognition method based on self-adaptive extension Kalman filtering, belonging to the field of body-area networks. The method comprises a model design step and a parameter design step. In the model design step, the angular speed and accelerated speed of the motion of a human body and the peripheral magnetic field intensity are collected by virtue of an inertial sensor through the characteristic that the motion angle of limbs of the human body can be reflected by a quaternion, and posture resolving is carried out based on a self-adaptive extension Kalman filtering method so as to obtain a posture quaternion. In the parameter design step, by utilizing a theoretical analysis and experiment method, a process noise covariance matrix is determined, and the value of a noise covariance matrix, a state initial value and an initial value of a state covariance matrix are measured, so that the continuous iteration of the self-adaptive extension Kalman filtering method can be realized, and the motion posture of the human body is continuously recognized in real time. The human body posture recognition method can be used as a human body posture recognition method in the fields of physical training, medical care, game design and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Image saliency detection method based on region description and priori knowledge
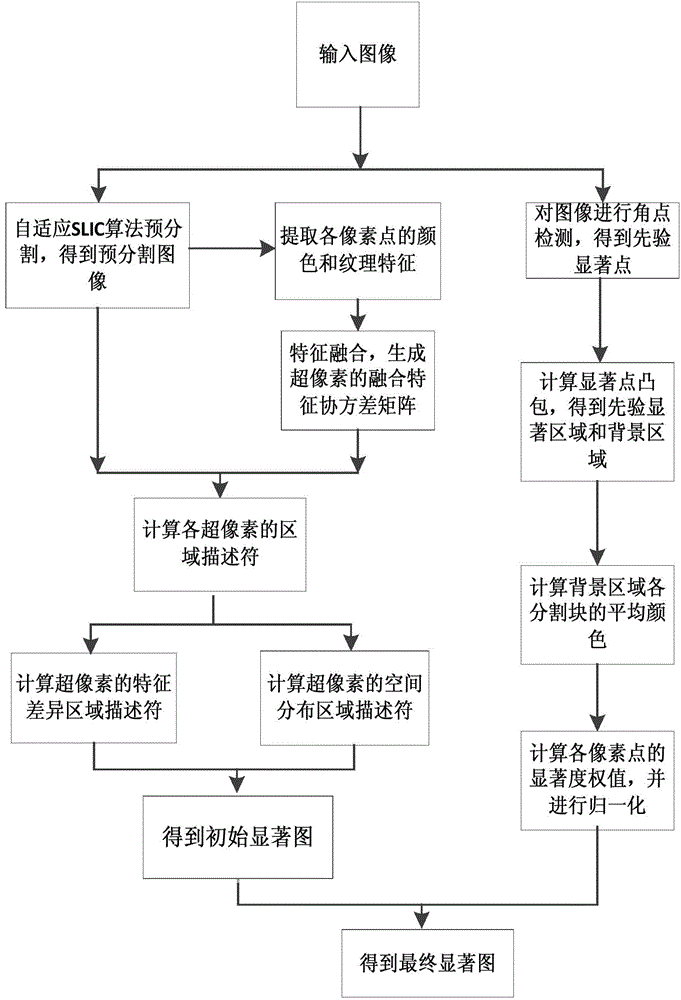
InactiveCN104103082APreserve edge detailSignificance detection is goodImage analysisPattern recognitionSaliency map
The invention discloses an image saliency detection method based on region description and priori knowledge. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) an image to be detected is subjected to pre-segmentation, superpixels are generated, and a pre-segmentation image is obtained; (2) a fusion feature covariance matrix of the superpixels is generated; (3) feature different region descriptors and space distribution region descriptors of each superpixel are calculated; (4) the initial saliency value of each pixel point of the image to be detected is calculated; (5) a priori saliency region and a background region of the image are obtained; (6) the saliency weight of each pixel point of the image to be detected is calculated; and (7) the final saliency value of each pixel point is calculated. The image saliency detection method has the advantages that the saliency region can be uniformly highlighted in an obtained final saliency map; the background noise interference is inhibited; a good saliency detection effect can be achieved in ordinary images, and the processing on the saliency detection of complicated images can also be realized; and the processing on subsequent image key region extraction and the like can also be favorably carried out.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Kernels and methods for selecting kernels for use in learning machines
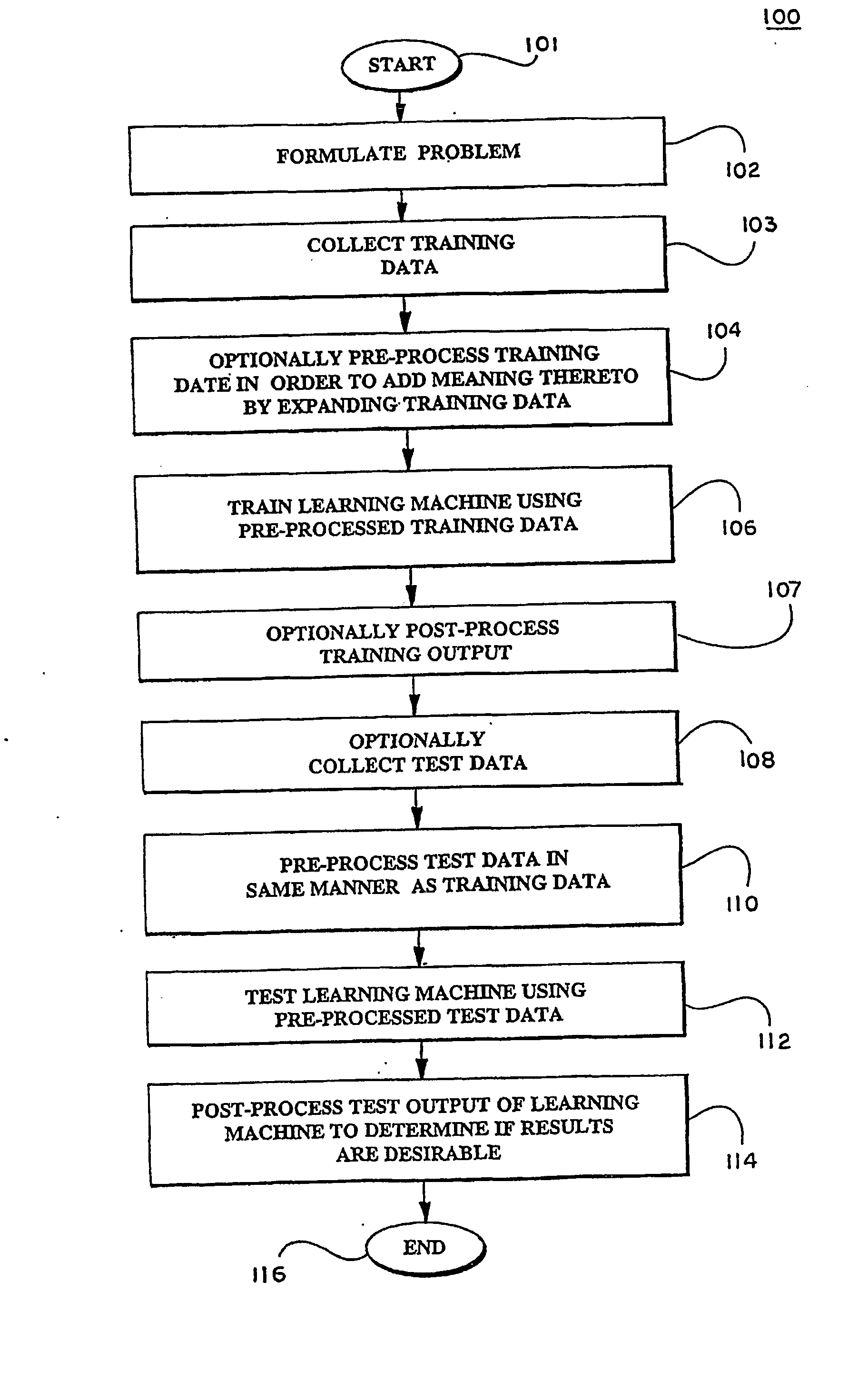
InactiveUS20050071300A1Enhancing knowledge discoveryDigital data processing detailsKernel methodsLearning machineEcg signal
Kernels (206) for use in learning machines, such as support vector machines, and methods are provided for selection and construction of such kernels are controlled by the nature of the data to be analyzed (203). In particular, data which may possess characteristics such as structure, for example DNA sequences, documents; graphs, signals, such as ECG signals and microarray expression profiles; spectra; images; spatio-temporal data; and relational data, and which may possess invariances or noise components that can interfere with the ability to accurately extract the desired information. Where structured datasets are analyzed, locational kernels are defined to provide measures of similarity among data points (210). The locational kernels are then combined to generate the decision function, or kernel. Where invariance transformations or noise is present, tangent vectors are defined to identify relationships between the invariance or noise and the data points (222). A covariance matrix is formed using the tangent vectors, then used in generation of the kernel.
Owner:BIOWULF TECH +1
Broadband signal DOA estimation method based on co-prime array
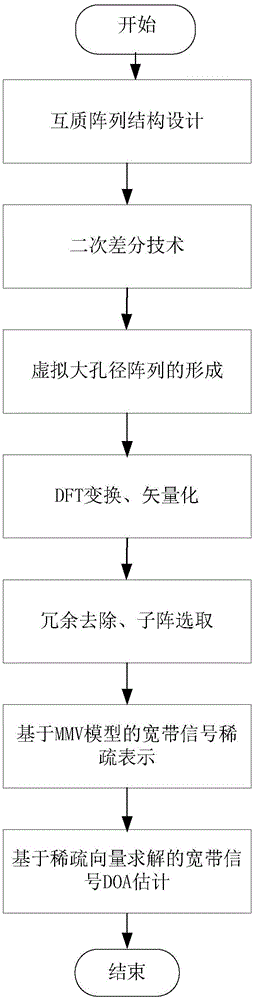
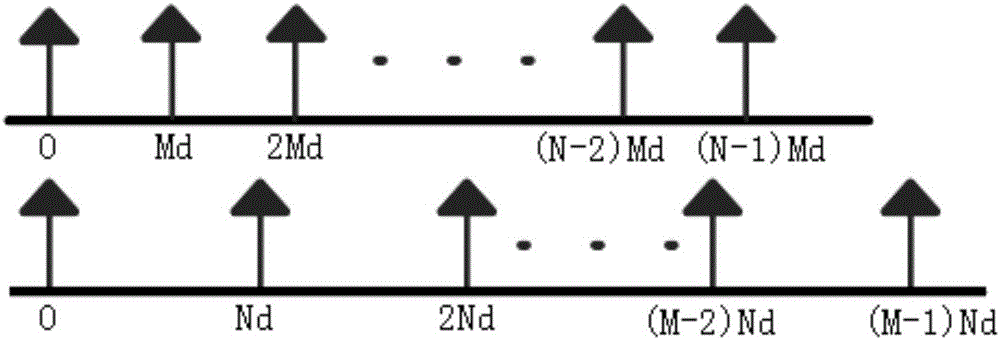
ActiveCN106324558AHigh-resolutionEasy to detectDirection findersSparse constraintSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a broadband signal DOA estimation method based on a co-prime array, and the method comprises the steps: S1, designing a co-prime array structure through an antenna; S2, carrying out the sampling and discrete Fourier transform of a broadband signal received by an antenna in the co-prime array, and obtaining a frequency domain signal output model; S3, calculating an autocorrelation matrix of the frequency domain signal output model, carrying out the vectorization of the frequency domain signal output model, and obtaining a new signal model; S4, carrying out the processing of the new signal model, and obtaining a spatial smooth covariance matrix of the broadband signal; Sa5, dividing a space domain grid, constructing a dictionary, carrying out the sparse representation of the spatial smooth covariance matrix through employing the dictionaries of a plurality of frequency points of the broadband signal, and forming a multi-measurement-vector sparse representation model of a plurality of dictionaries of the broadband signal; S6, achieving the arrival direction estimation of the broadband signal in a mode of solving a sparse inverse problem through the joint sparse constraint of the sparse representation coefficients of the plurality of dictionaries. The method can improve the estimation precision of the direction angle of the broadband signal under the condition of low signal to noise ratio, and reduces the direction finding error.
Owner:东北大学秦皇岛分校
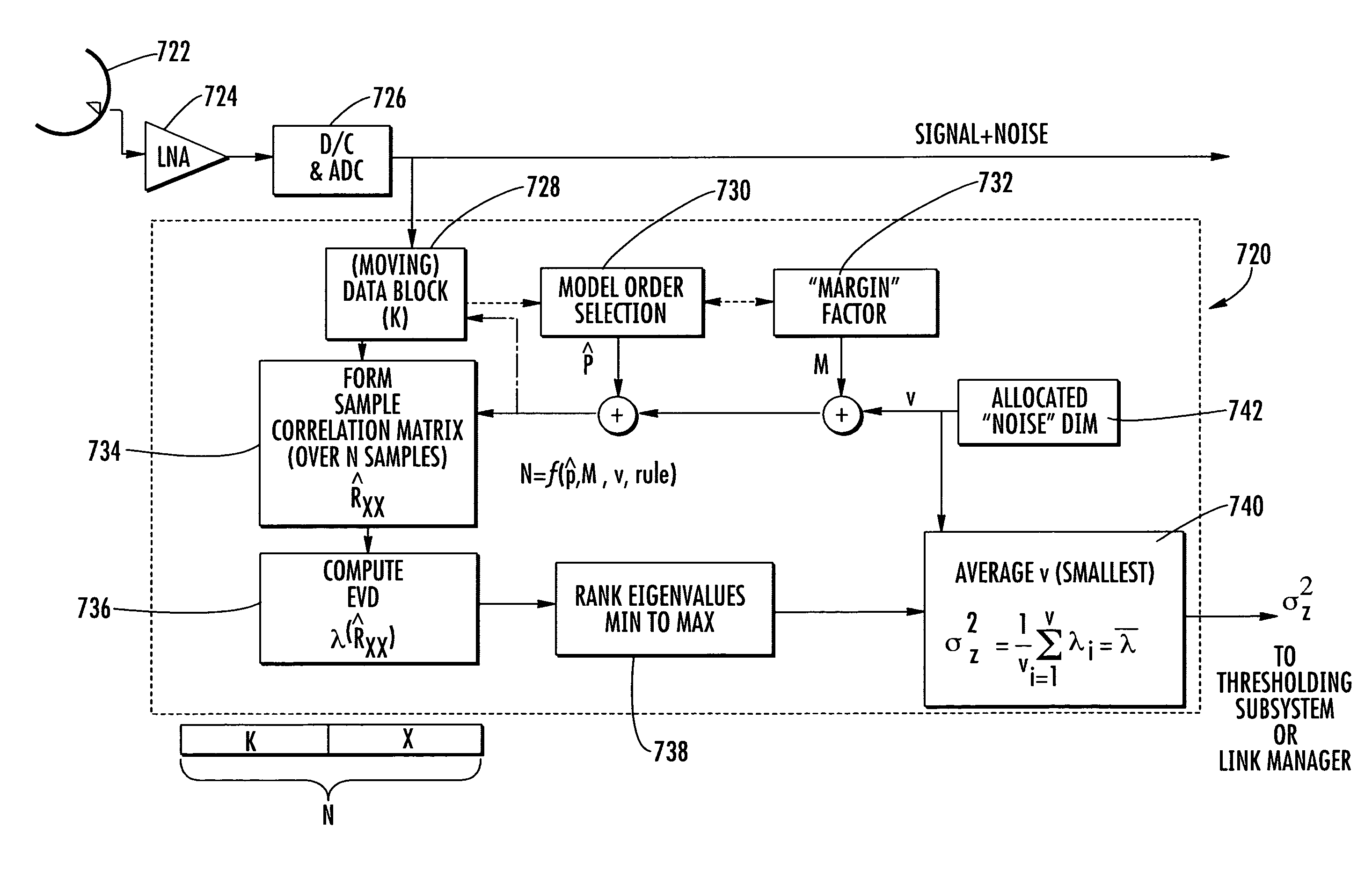
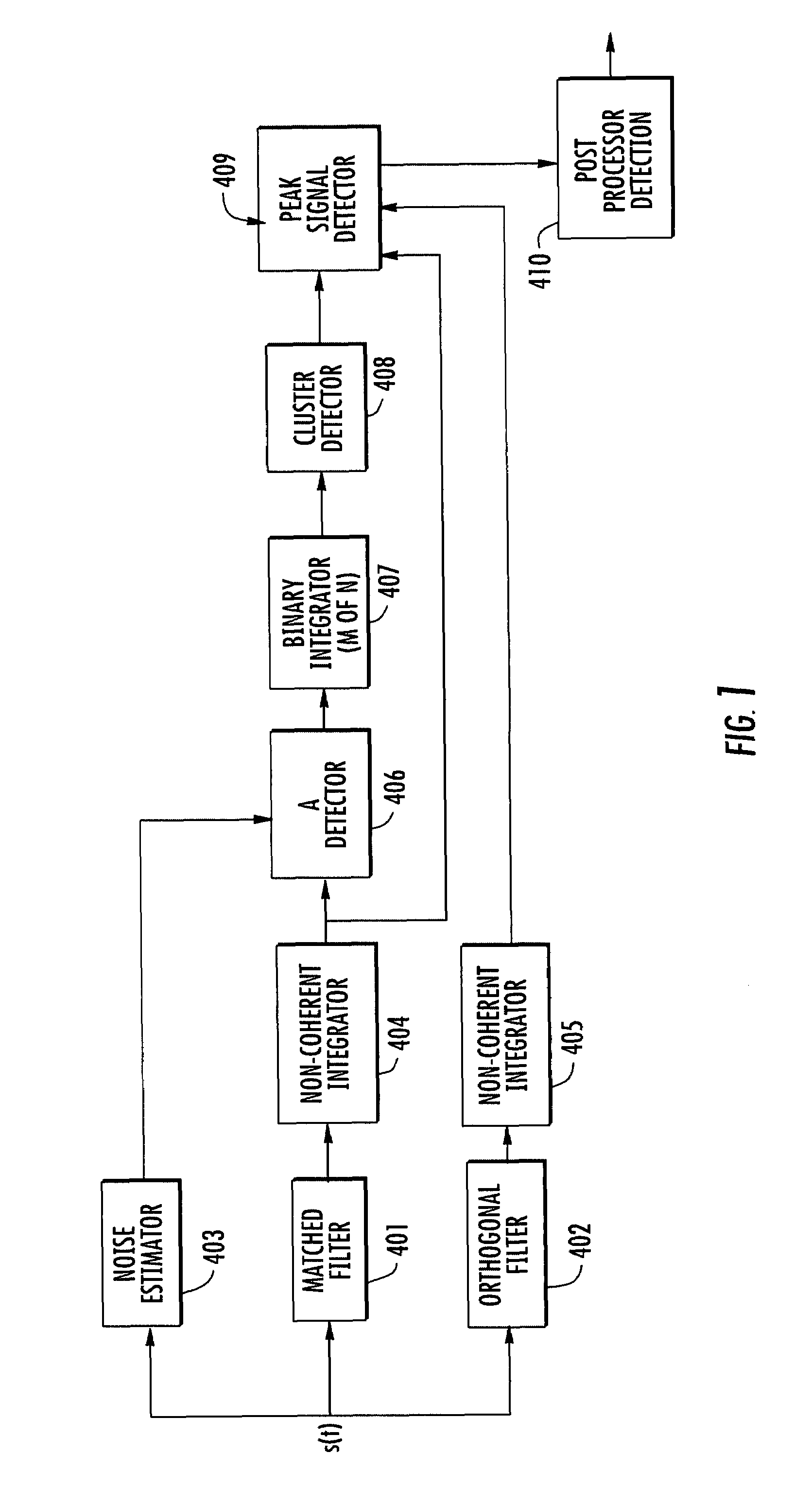
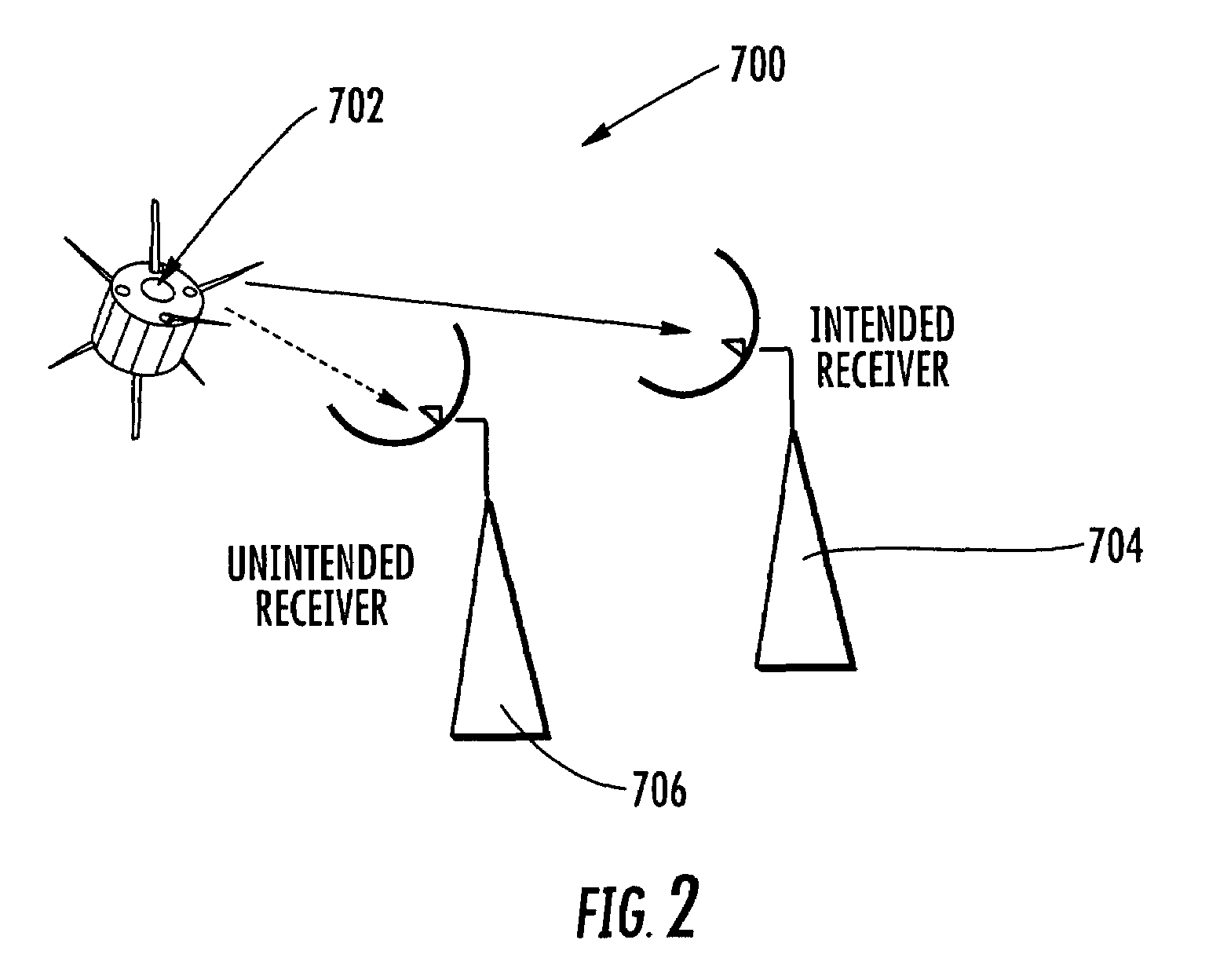
System and method for estimating noise power level in a multi-signal communications channel
Owner:HARRIS CORP
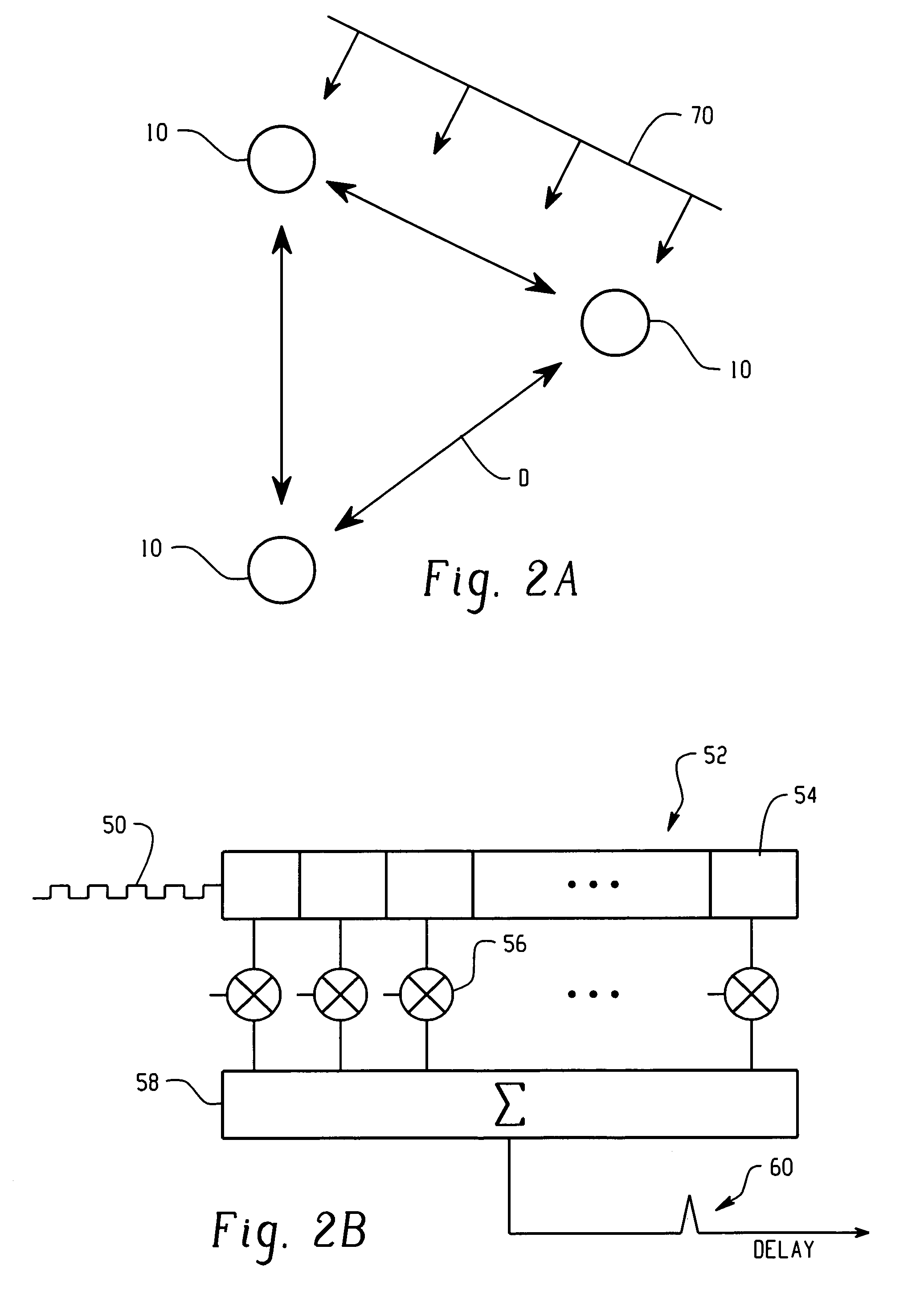
Multipath resolving correlation interferometer direction finding
ActiveUS20070273576A1Improve accuracyRobust and accurateMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWater useCovariance
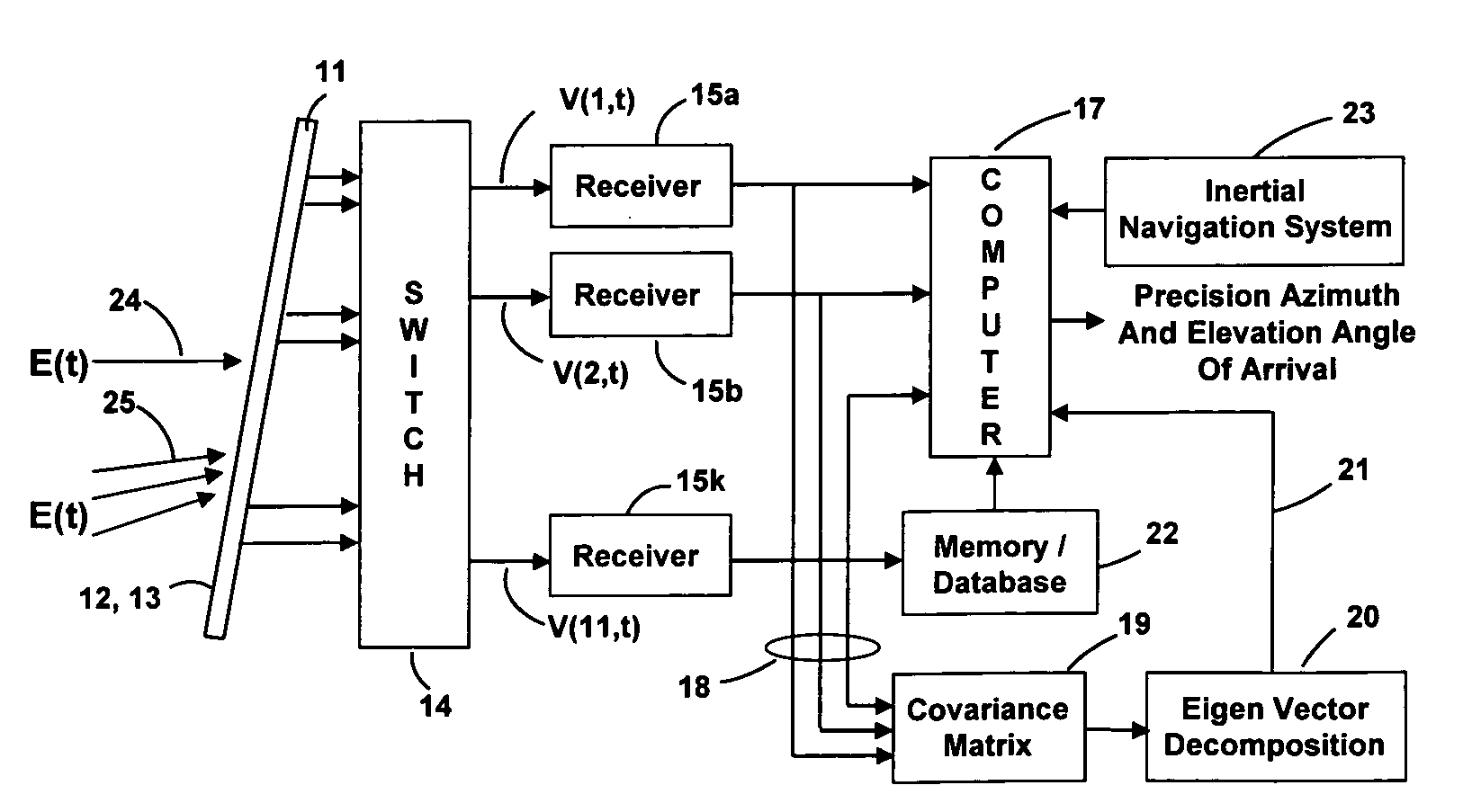
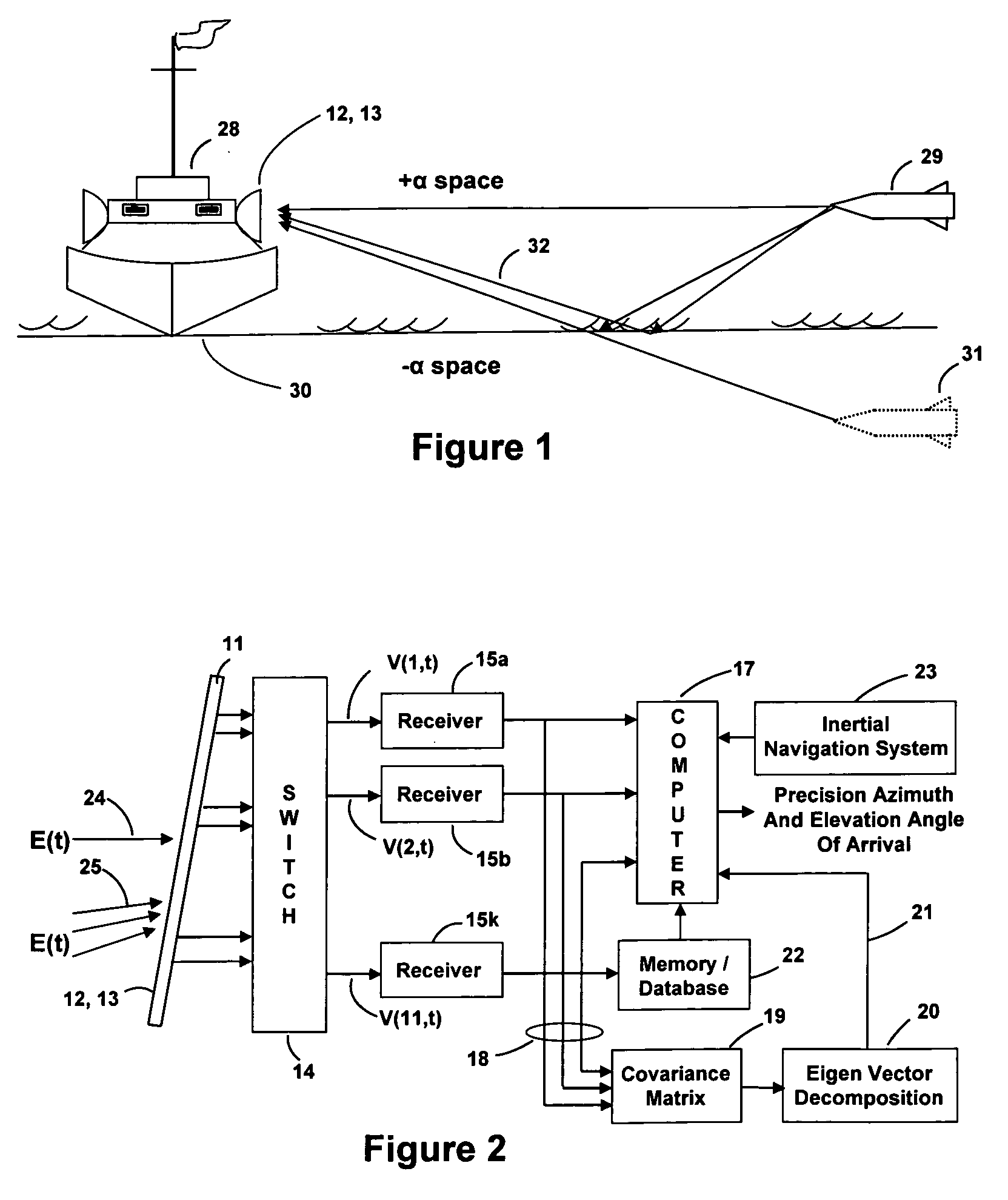
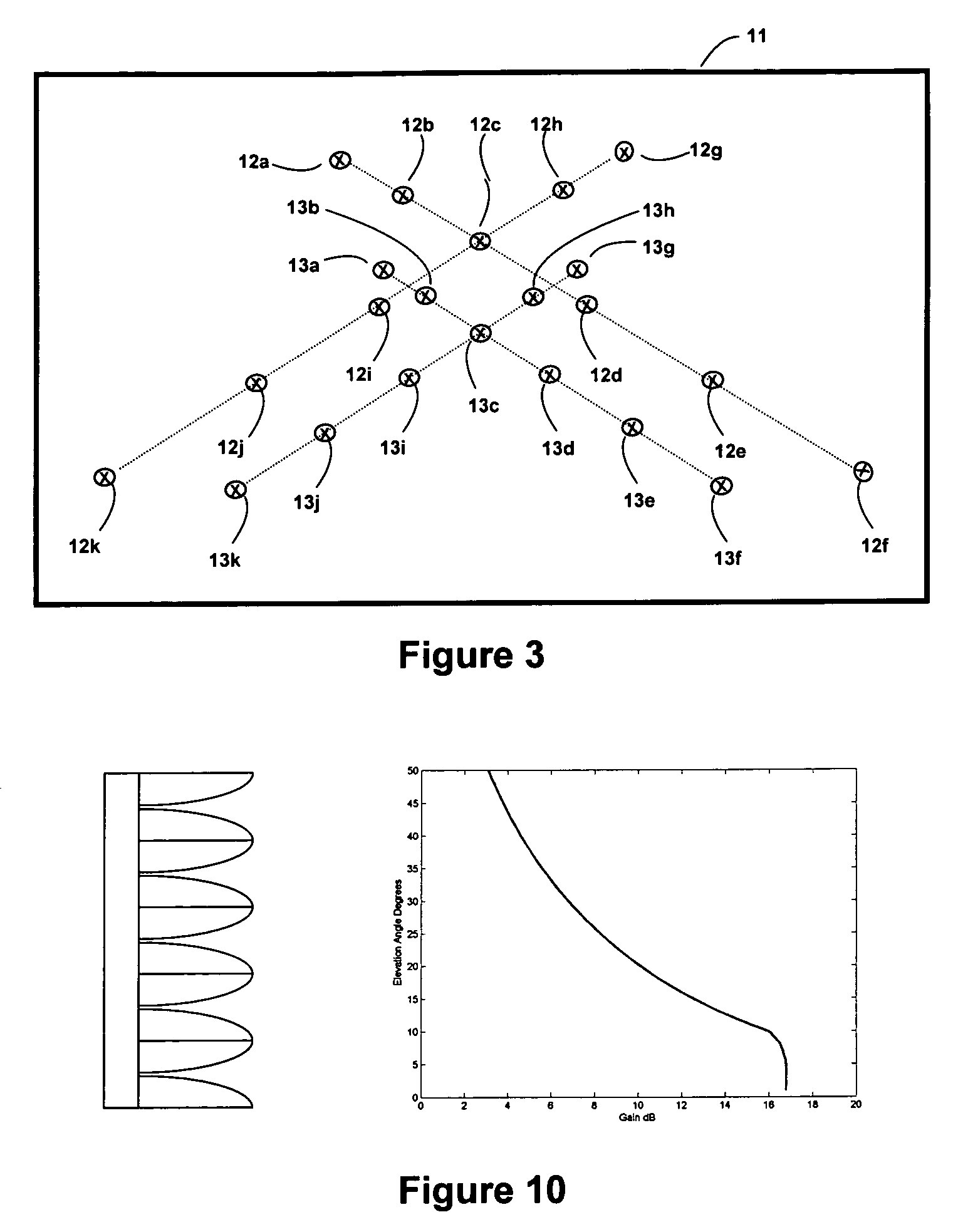
Apparatus and a method utilizing correlation interferometer direction finding for determining the azimuth and elevation to an aircraft at long range and flying at low altitudes above water with a transmitting radar while resolving multipath signals. The signals from the radar are received both directly and reflected from the surface of the water using horizontally polarized and vertically polarized antenna arrays, are digitized and are stored in separate covariant matrices. Eigenvalues for the eigenvectors of the matrices processed on signal samples recorded on horizontally polarized X arrays are compared to the eigenvalues for the eigenvectors of the covariance matrices processed on signal samples recorded on vertically polarized X arrays. Incident field polarization is associated with the antenna array measurements that yield the strongest eigenvalue. The eigenvector and eigenvalues for the strongest signal are selected and used for subsequent signal processing. An initial global search assuming mirror sea-state reflection conditions using the signal eigenvector having the strongest eigenvalue is performed to yield an approximate elevation α and azimuth β to the aircraft. The approximate values are then used as the starting point for a subsequent conjugate gradient search to determine accurate elevation α and azimuth β to the aircraft.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
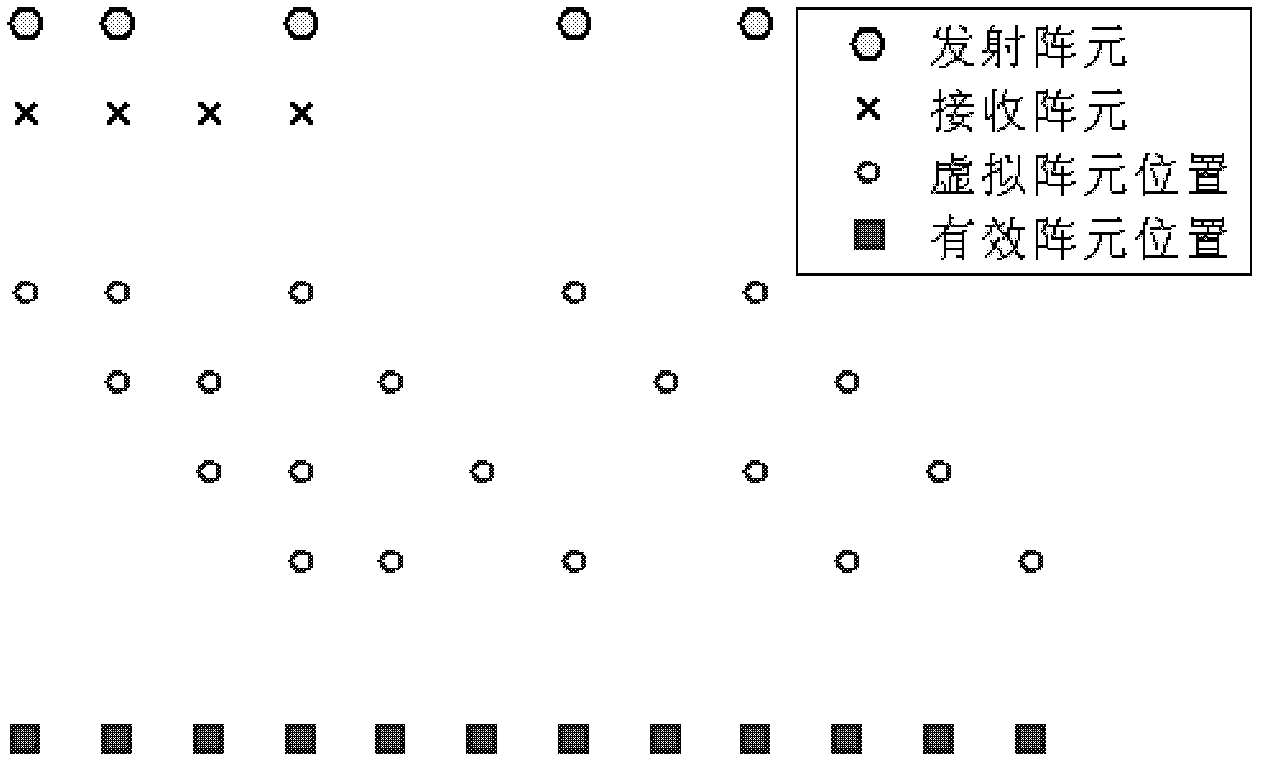
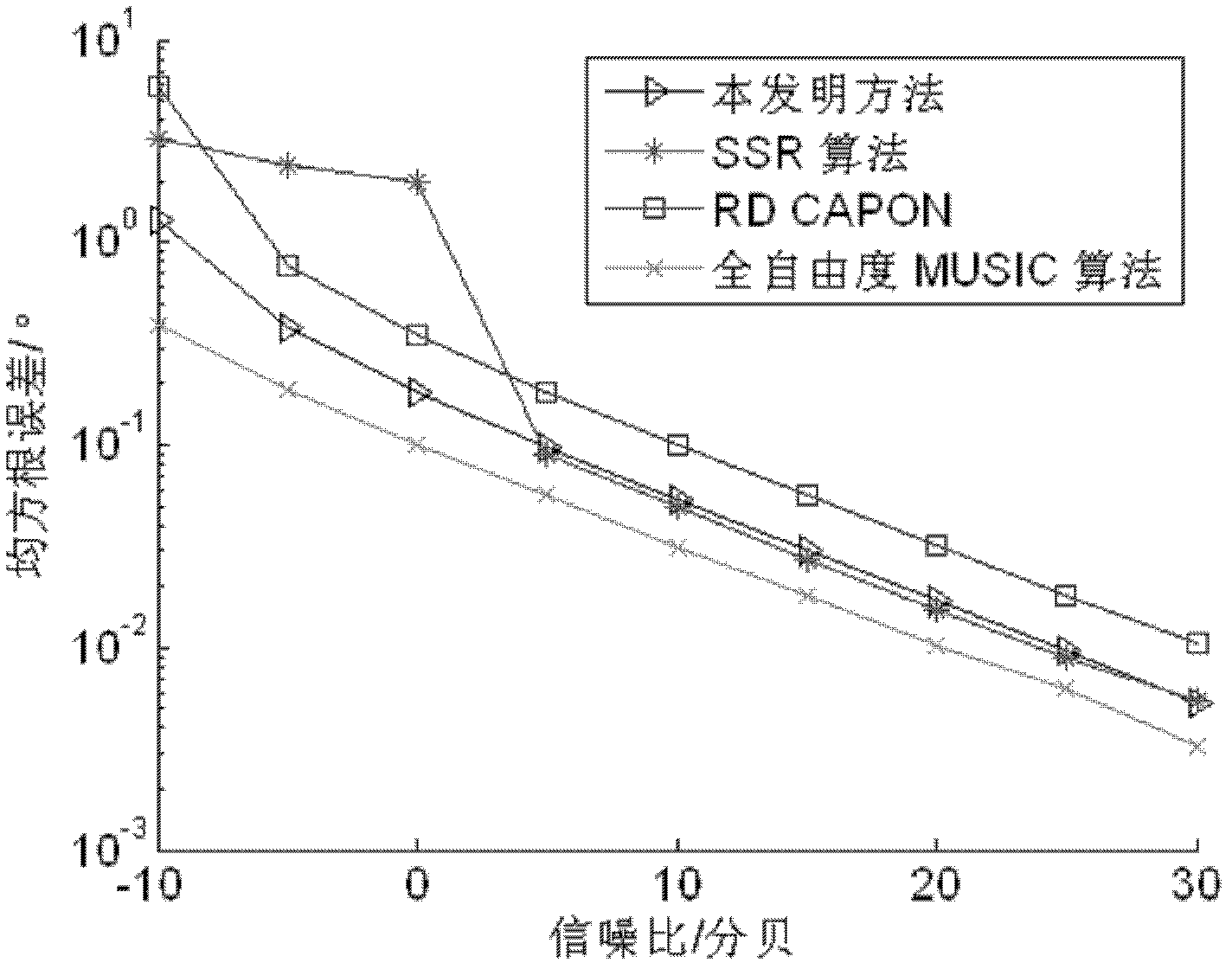
Target angle of arrival estimation method for mimo radar
ActiveCN102279387ASimple methodVersatilityWave based measurement systemsMatched filter bankSignal subspace
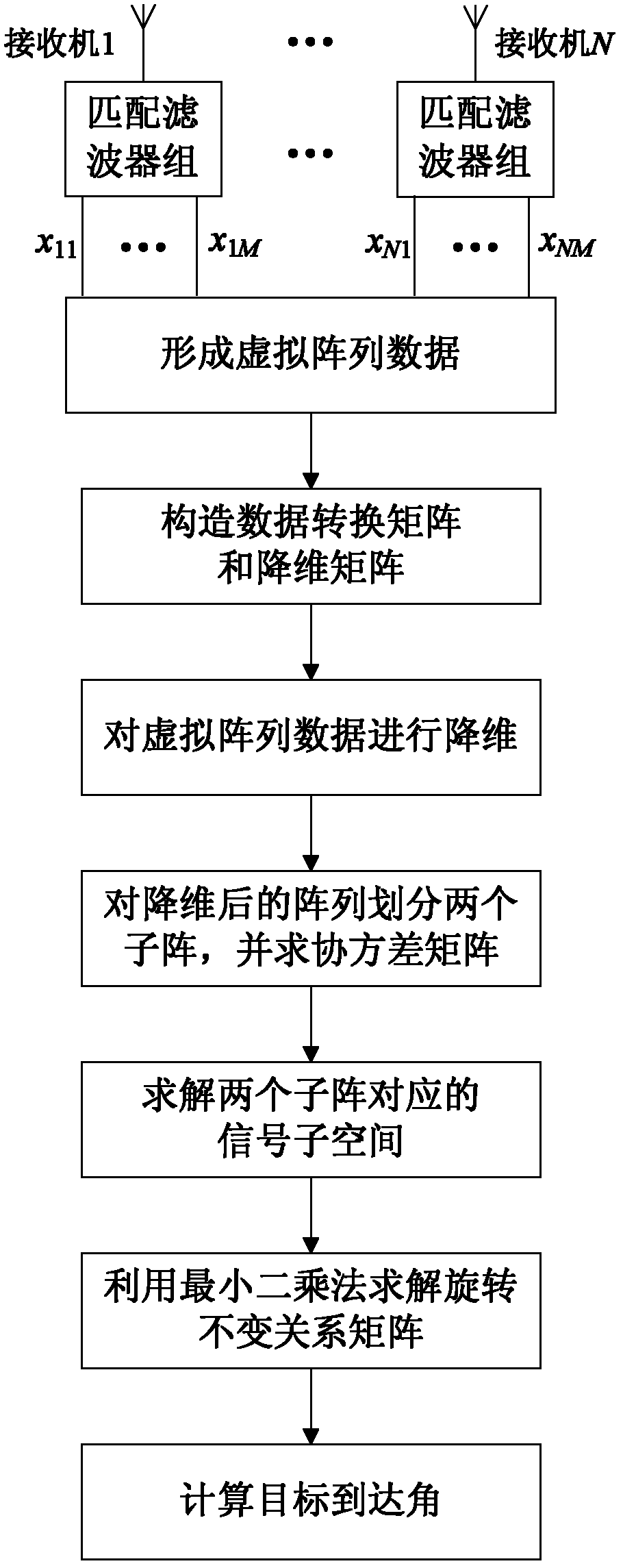
The invention discloses a method for estimating target arrival angle of a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) radar, which mainly solves the problem of large signal processing capacity in the target positioning process of MIMI radar. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) obtaining a virtual array of echo of each receiving antenna by a matched filter bank; 2) constructing a data conversion matrix and a dimension reduction array according to position of transmitting and receiving array; (3) reducing dimension of the virtual array data by the dimension reduction array to obtain an effective array after dimension reduction; 4) constructing two sub-arrays by rotational variance of effective array, and deriving covariance matrix of data; 5) decomposing eigenvalue of covariance matrix to obtain signal sub-spaces corresponding to two sub-arrays; 6) deriving rotational invariant relationship matrix by least square method to obtain arrival angle of target. The dimension reduction matrix form constructed by the method has versatility; the computation quantity is reduced by the dimension reduction of data and the ESPRIT (estimating signal parameter via rotational invariance techniques) algorithm; the computation speed of MIMO radar is increased; and the real-time signal processing of the MIMO radar is made easier.
Owner:XIAN CETC XIDIAN UNIV RADAR TECH COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION INST CO LTD
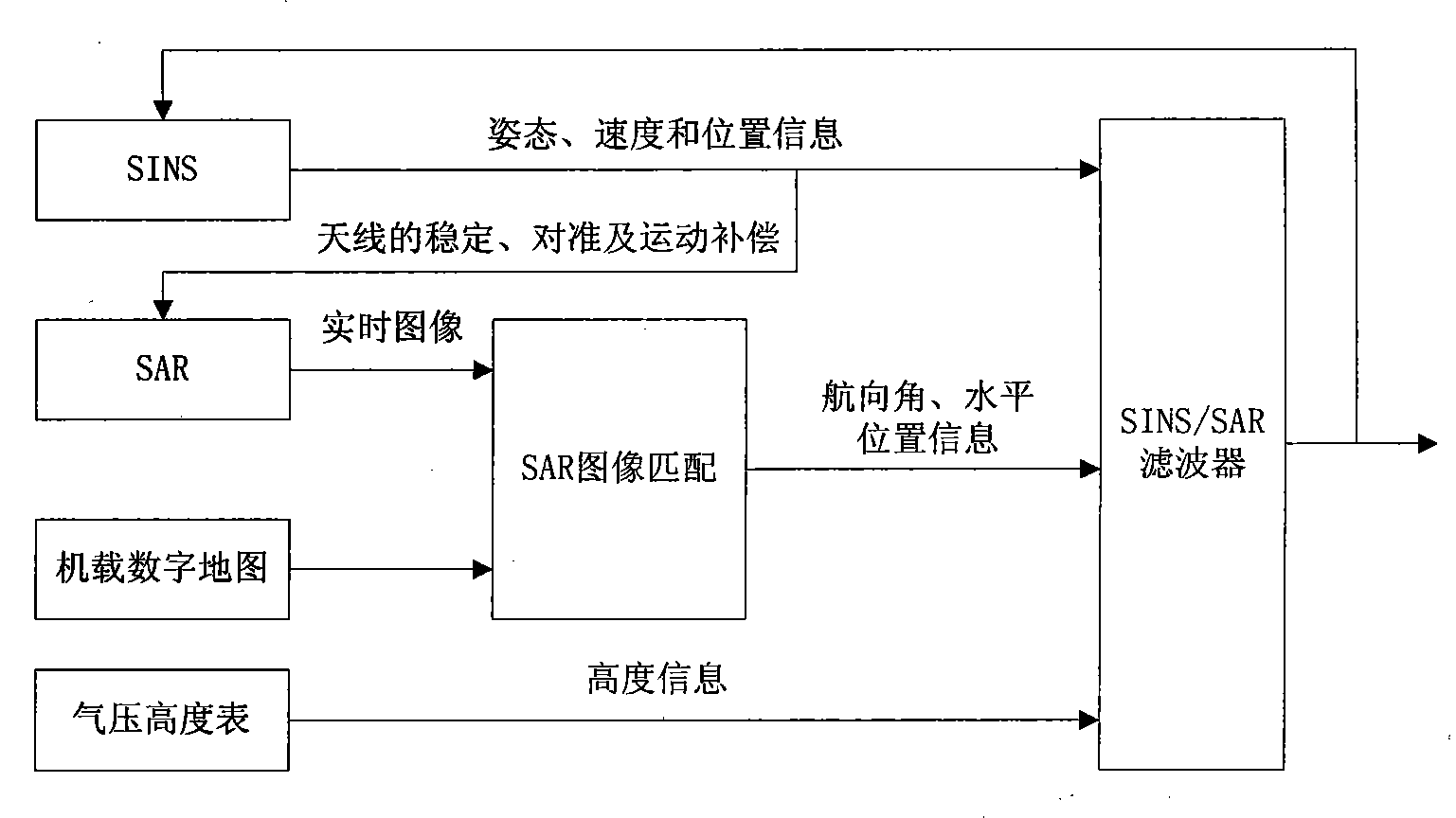
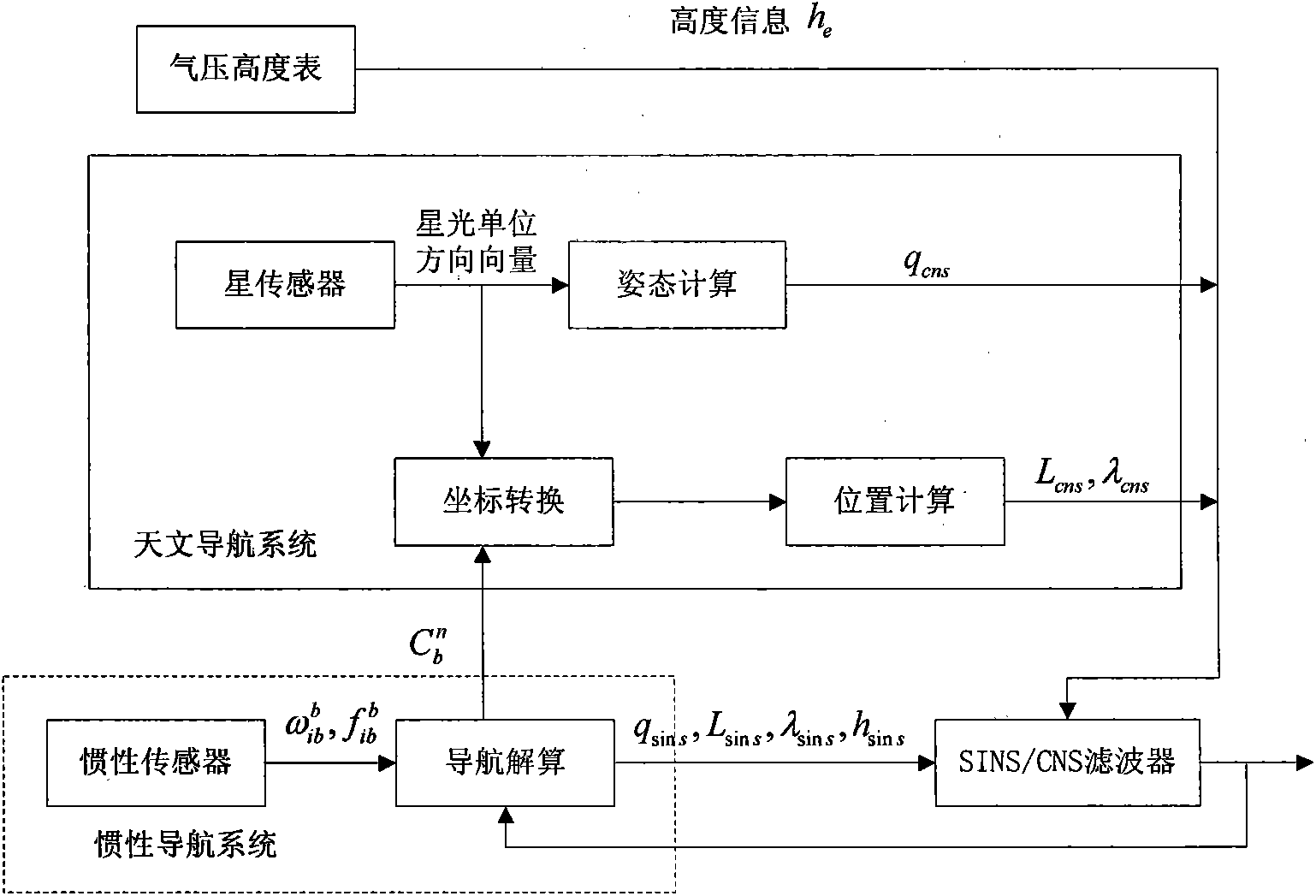
Autonomous integrated navigation system
InactiveCN103528587AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsSynthetic aperture radarCovariance
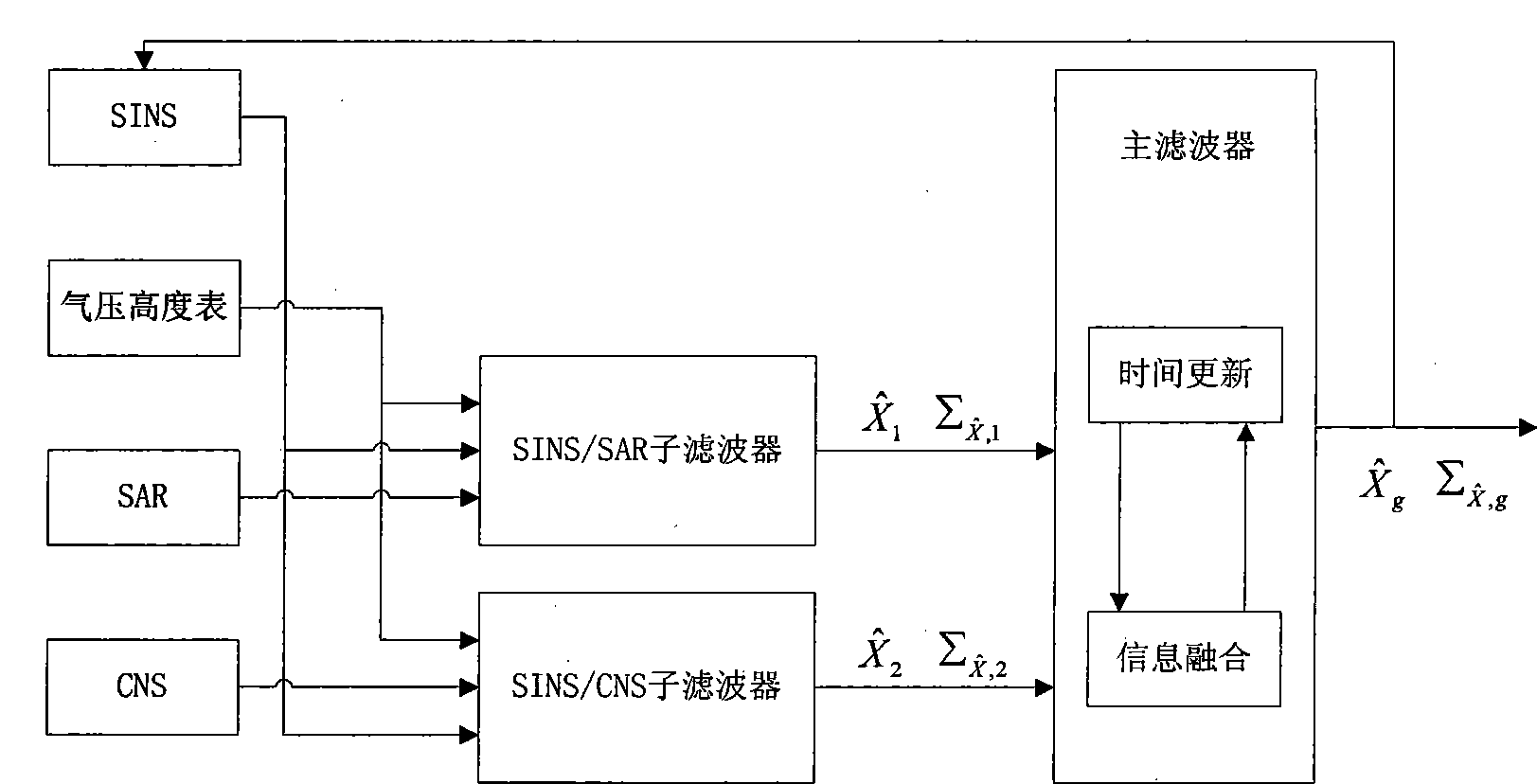
The invention relates to an autonomous integrated navigation system which belongs to the technical field of navigation systems. The SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System) / SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) / CNS (Celestial Navigation System) integrated navigation system takes SINS as a main navigation system and SAR and CNS as aided navigation systems and is established by the following steps: firstly, designing SINS / SAR and SINS / CNS navigation sub-filters, calculating to obtain two groups of local optimal estimation values and local optimal error covariance matrixes of the integrated navigation system state, then transmitting the two groups of local optimal estimation values into a main filter by a federal filter technology for fusion to obtain an overall optimal estimation value and an overall optimal error covariance matrix, and finally, performing real-time correction on the error according to the overall optimal estimation value so as to obtain an optimal estimation fusion algorithm of the SINS / SAR / CNS integrated navigation system. The autonomous integrated navigation system, disclosed by the invention, is less in calculation amount and high in reliability, is applicable to aircrafts in near space, aircrafts flying back and forth in the aerospace, aircrafts for carrying ballistic missiles, orbit spacecrafts and the like, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
System and method of estimating the position of a mobile terminal in a radio telecommunications network
InactiveUS6873852B2Direction finders using radio wavesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunications networkTransceiver
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
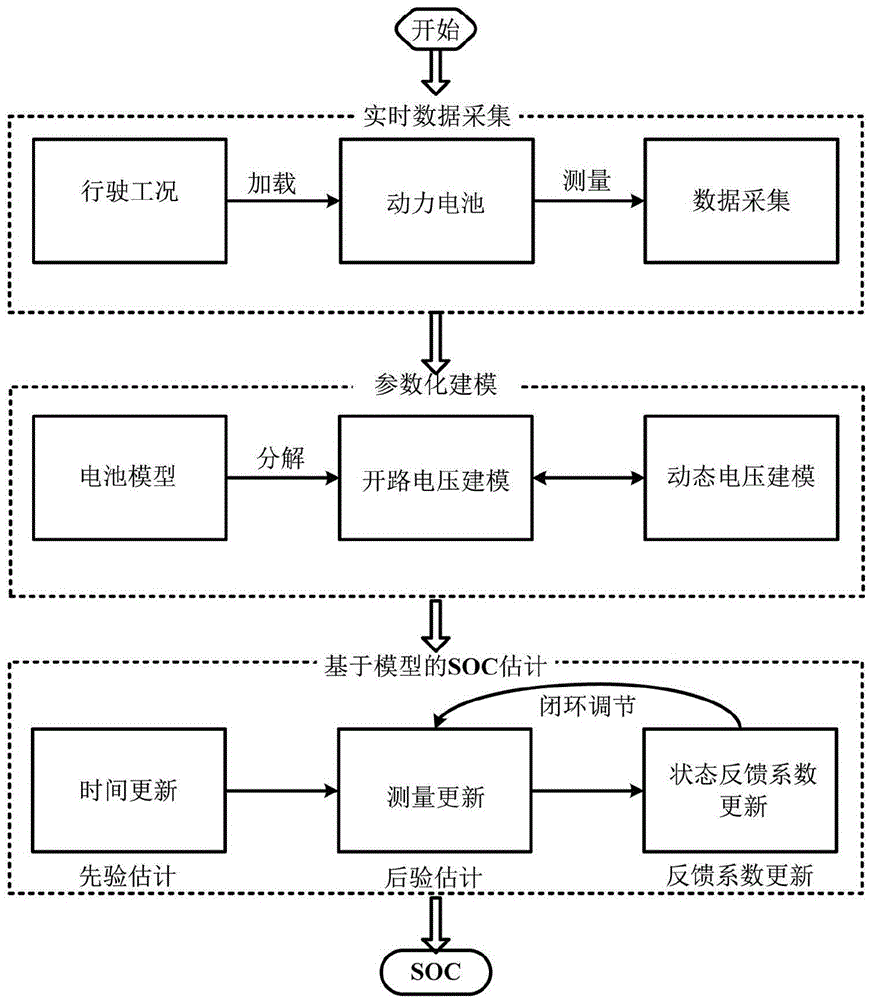
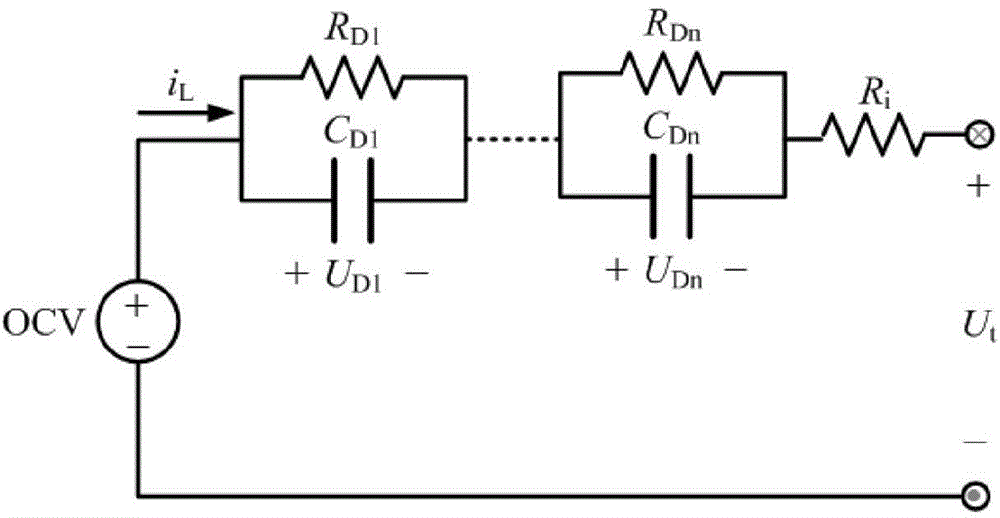
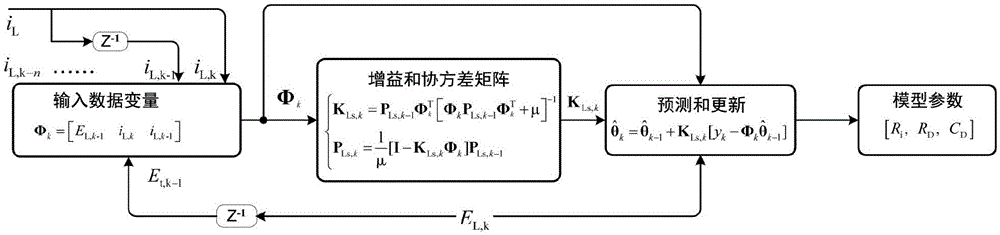
Method for estimating state of charge of power battery of electric automobile
InactiveCN104569835AImprove estimation accuracyEstimated Accuracy DecreasedElectrical testingPower batteryState observer
The invention relates to a power battery management system of an electric automobile. In order to improve the estimating precision, the invention provides a method for estimating a charge state of a power battery of the electric automobile. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the terminal voltage, the charging and discharging current and the battery surface temperature of the power battery; according to a corresponding relationship between the open-circuit voltage and the state of charge of the power battery, analyzing to obtain an open-circuit voltage model, and according to an input matrix, a parameter matrix and an output matrix of a dynamic voltage system of the power battery, establishing a dynamic voltage model of the dynamic voltage system; updating time and measurement of a state observer to obtain priori estimated values and posteriori estimated values of a system state as well as a covariance matrix of a system state estimating error at a time point k, and circulating the updating operation till the end of estimation to obtain the state of charge (SoC) of the power battery. By the method, the estimating precision of the SoC can be improved to be within 5%, and when a set value of the SoC of the power battery is deviated from a reference value of the SoC of the power battery, the SoC is rapidly converged to the reference value.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
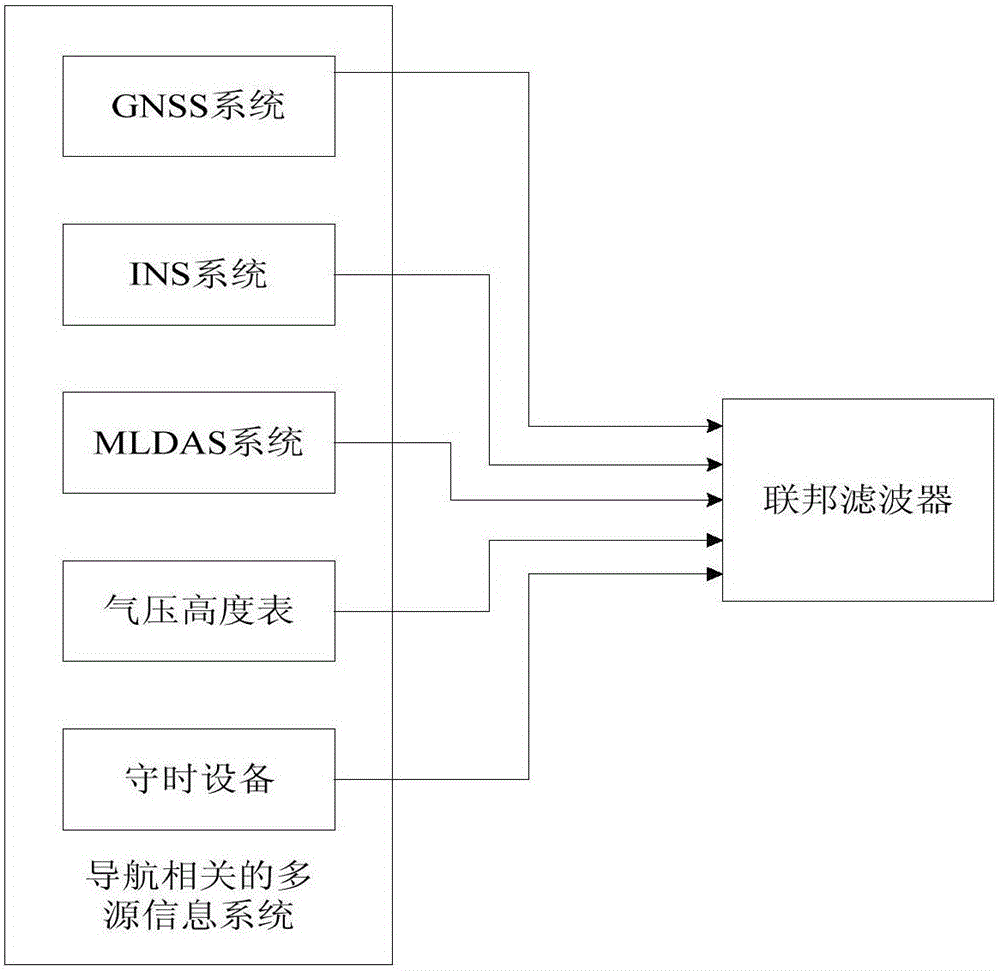
Integrated navigation method and equipment based on multisource information fusion
InactiveCN105758401ANavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingOn boardCovariance
The invention provides an integrated navigation method and equipment based on multisource information fusion. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining multisource navigation information, namely obtaining navigation related information from one or more of a global satellite navigation system GNSS, an inertial navigation system INS, a multimode region difference augmentation system MLDAS, a pressure altimeter and timekeeping equipment, which are arranged on an aircraft; performing fusion treatment on multisource information by using a federal wave filter, wherein the federal wave filter comprises a main wave filter and a plurality of local wave filters connected with the main wave filter, and each kind of the multisource navigation information and a reference signal are jointly input to one local wave filter; triggering the local wave filters to respectively calculate local estimation values and error covariance matrixes; triggering the main wave filter to perform wave filtering on the reference signal, and performing optimal infusion on the wave filtering results of the reference signal according to output results of the local wave filters and the local wave filters, so as to obtain a global optimum estimation value. Therefore, the availability and the integrity of on-board navigation equipment are improved.
Owner:ZHONGWEI IOT CHENGDU TECH CO LTD
Wireless communication system with interference compensation
InactiveUS7006795B2Reduce the amount of calculationMaximized through complex calculationsPower managementPolarisation/directional diversityCommunications systemData rate
A method and apparatus for assigning the data rate and / or power level to the mobile terminals without determining the highest theoretical system throughput, and without determining the highest weighted system throughput. An order is imposed on the terminals and the data rate and / or power covariance matrices are assigned such that the data rates of the terminals having a lower index in the order will not be decreased due to the presence of the terminals having a higher index in the order, and this is accomplished without changing the power covariance matrixes of the antennas involved in the communication with the lower index terminals. Thus, the assignment is made to the terminals based on the terminals requirements without regard to the interference introduced by the terminals with a higher index in the order since this interference will be compensated for by the compensation technique when the compensation technique process the terminals in accordance with the order. The invention reduces the amount of computation necessary to implement such compensation techniques on an ongoing, real-time basis in a real-world system.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
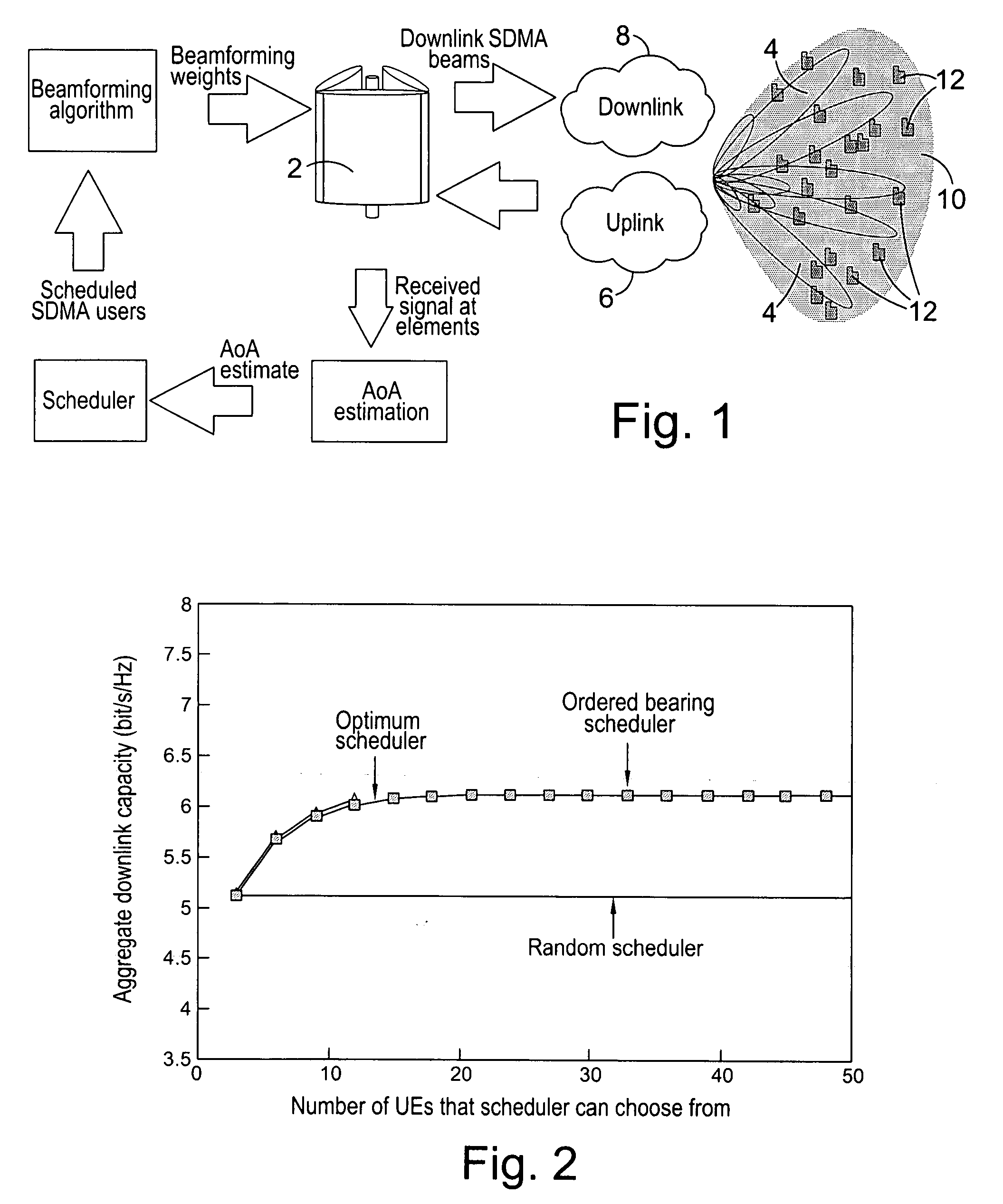
Downlink beamforming for broadband wireless networks
ActiveUS20060281494A1Multiplicative spectral efficiency gainHigh trafficSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionDownlink beamformingFrequency spectrum
Spatial Division Multiple Access (SDMA) offers multiplicative spectral efficiency gains in wireless networks. An adaptive SDMA beamforming technique is capable of increasing the traffic throughput of a sector, as compared to a conventional tri-cellular arrangement, by between 4 and 7 times, depending on the environment. This system uses an averaged covariance matrix of the uplink signals received at the antenna array to deduce the downlink beamforming solution, and is equally applicable to Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) and Time Division Duplex (TDD) systems. A scheduling algorithm enhances the SDMA system performance by advantageously selecting the users to be co-scheduled.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for fusing signals with partially known independent error components
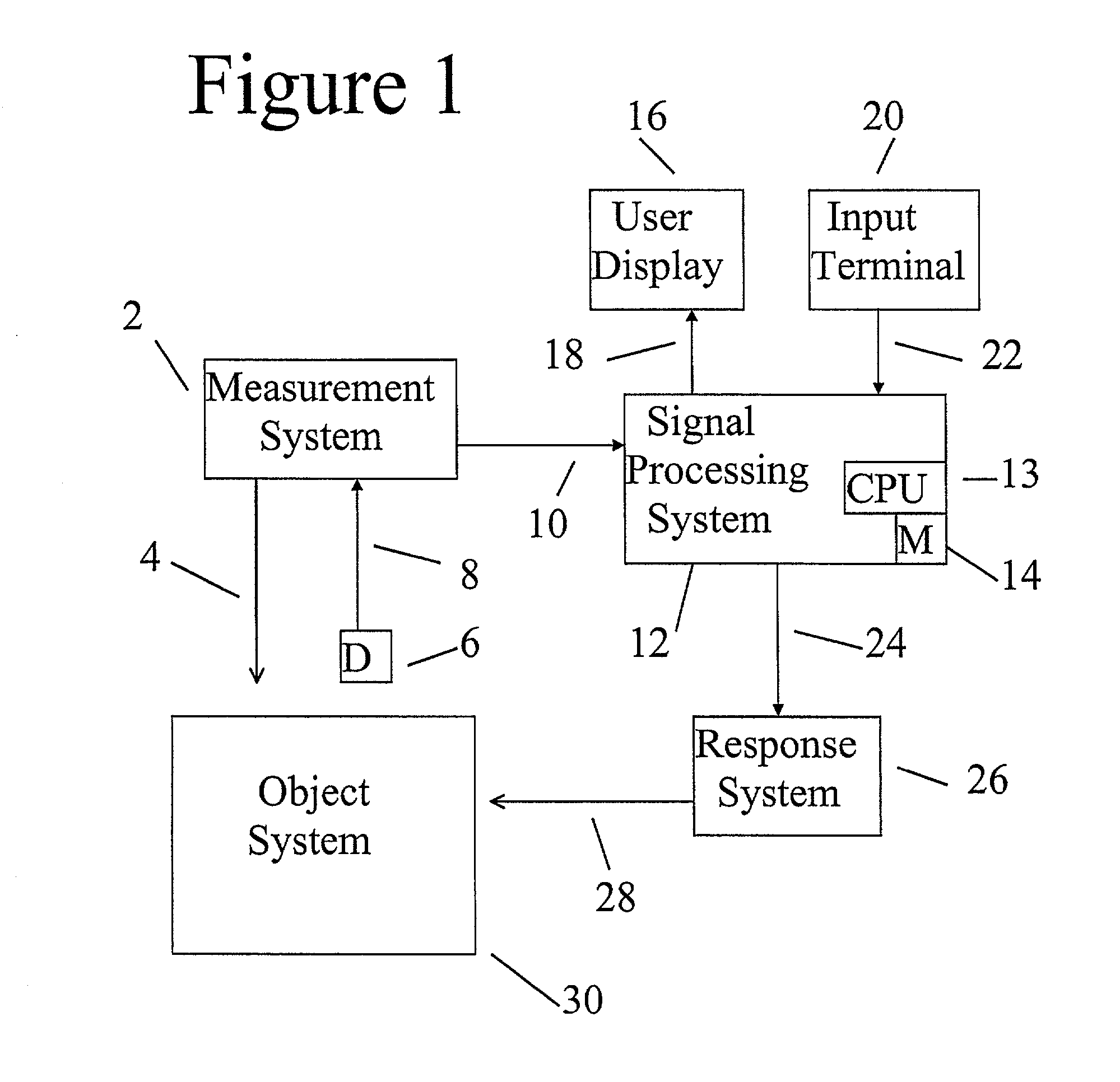
InactiveUS20030204382A1Reduce in quantityImprove numerical propertyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsErrors and residualsComputer science
A method and apparatus is described for fusing a plurality of signals corresponding to estimates of the state of an object, system, or process. The method and apparatus is specialized or programmed for (1) receiving estimates, each of which can be expressed in the form of a state vector and an error covariance matrix, at least one estimate of which can be decomposed into a sum of an independent error covariance matrix and a potentially correlated error covariance matrix, and (2) transmitting a resulting signal corresponding to an estimate, which can be expressed in the form of a state vector and an error matrix, in order to evoke a physical response from a system receiving the signal. The method and apparatus provides advantages over the prior art by improving the accuracy of fused estimates while guaranteeing consistency.
Owner:JULIER SIMON JUSTIN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com