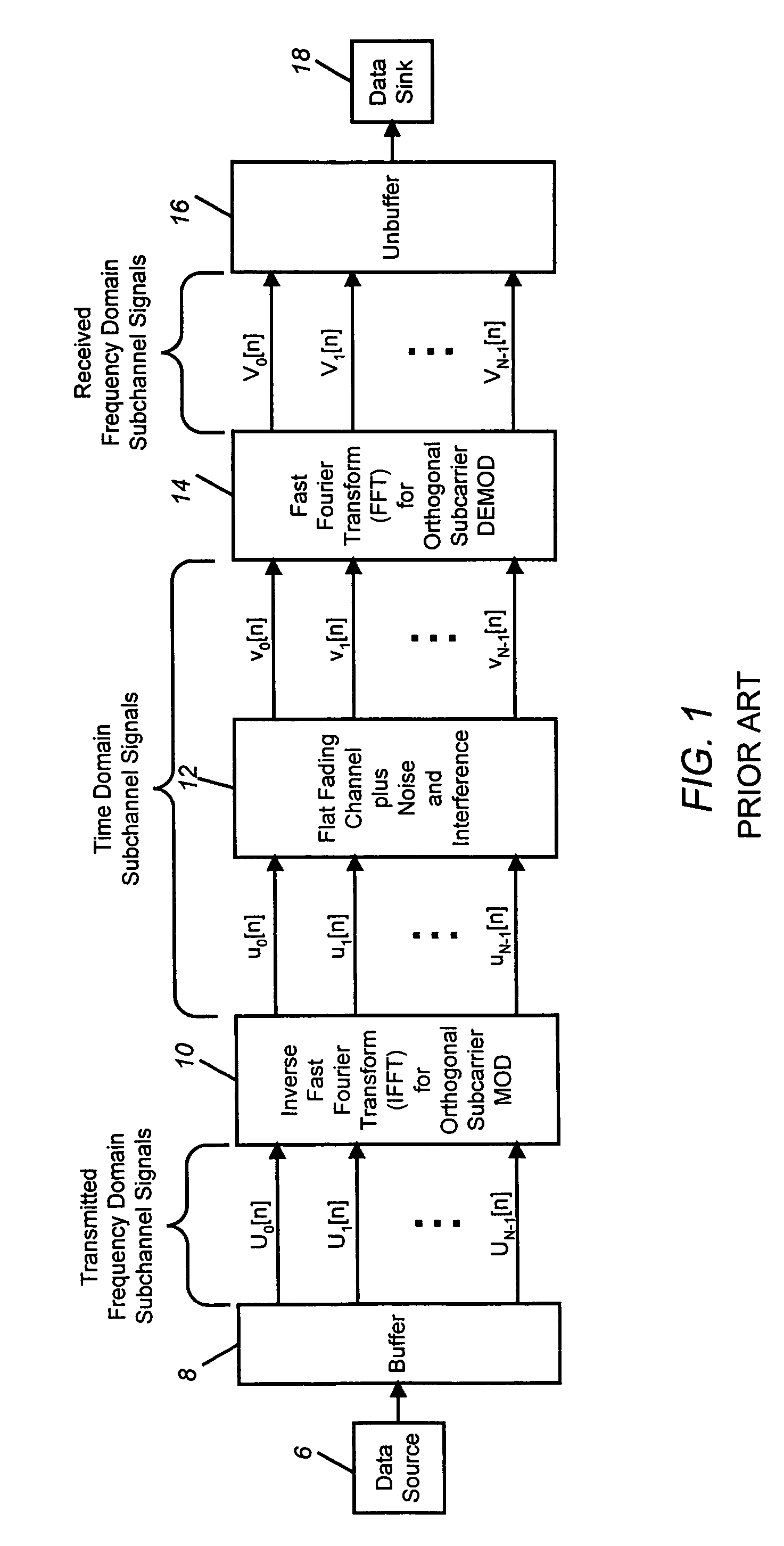
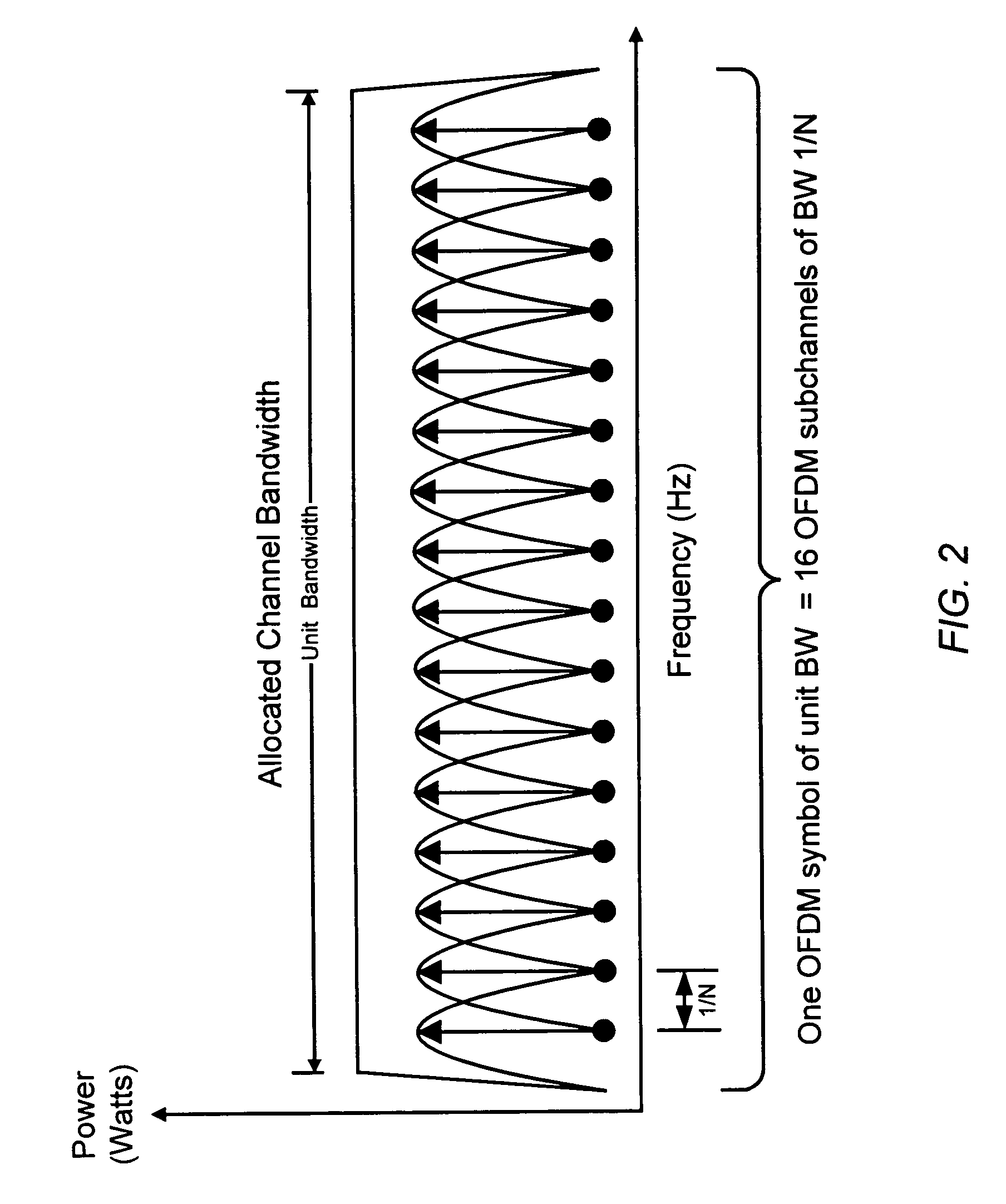
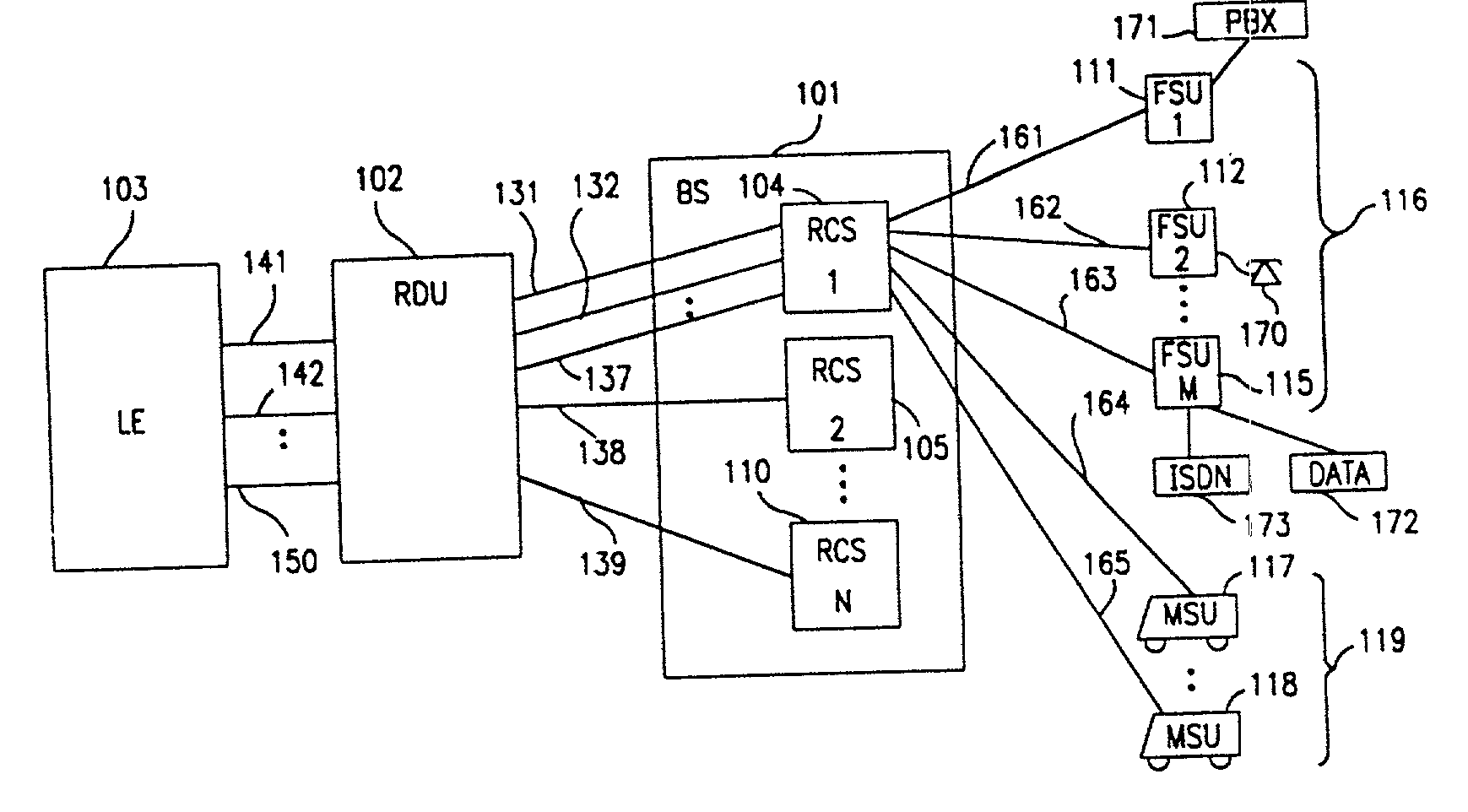
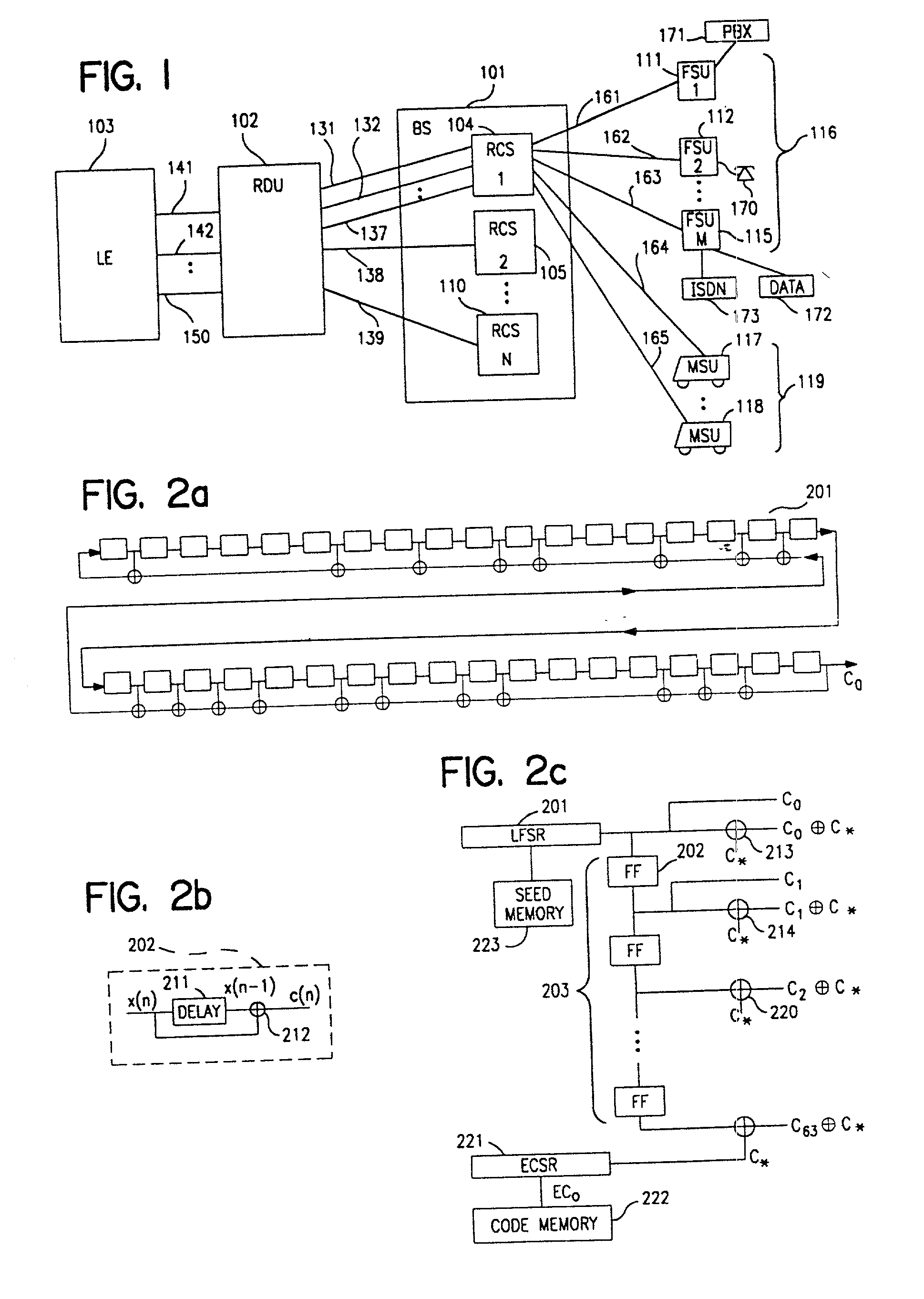
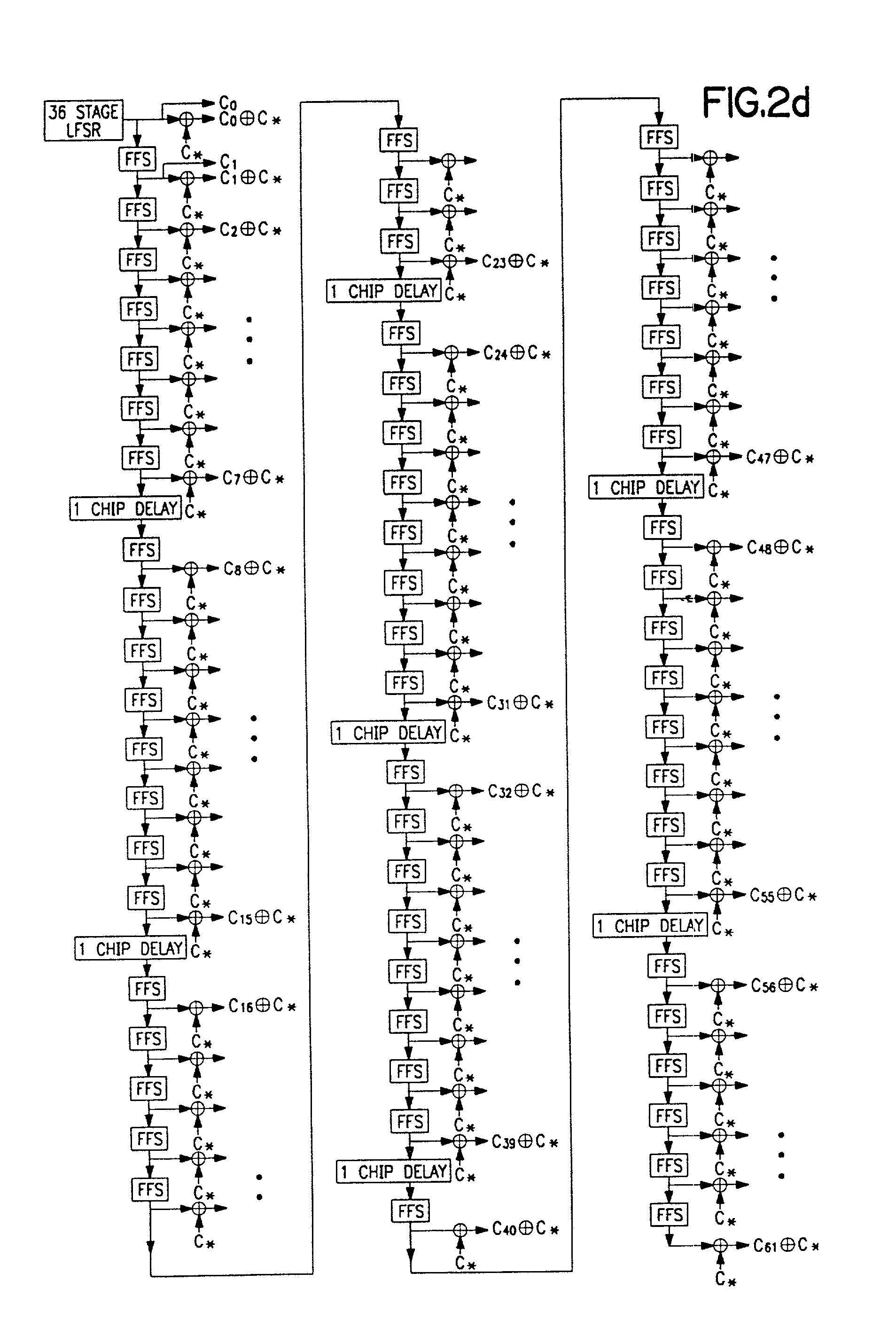
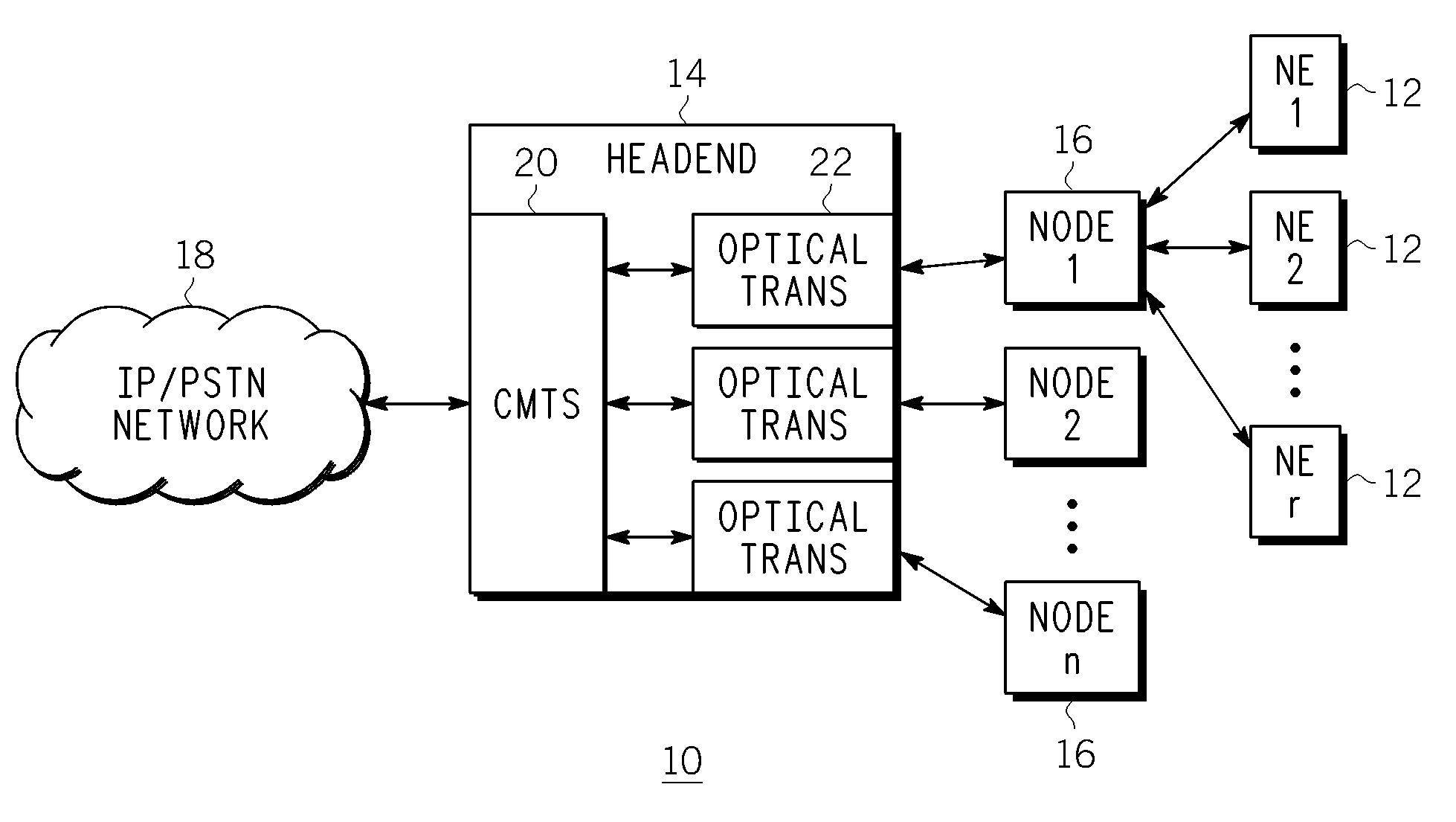
Patents
Literature
1733 results about "Noise power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
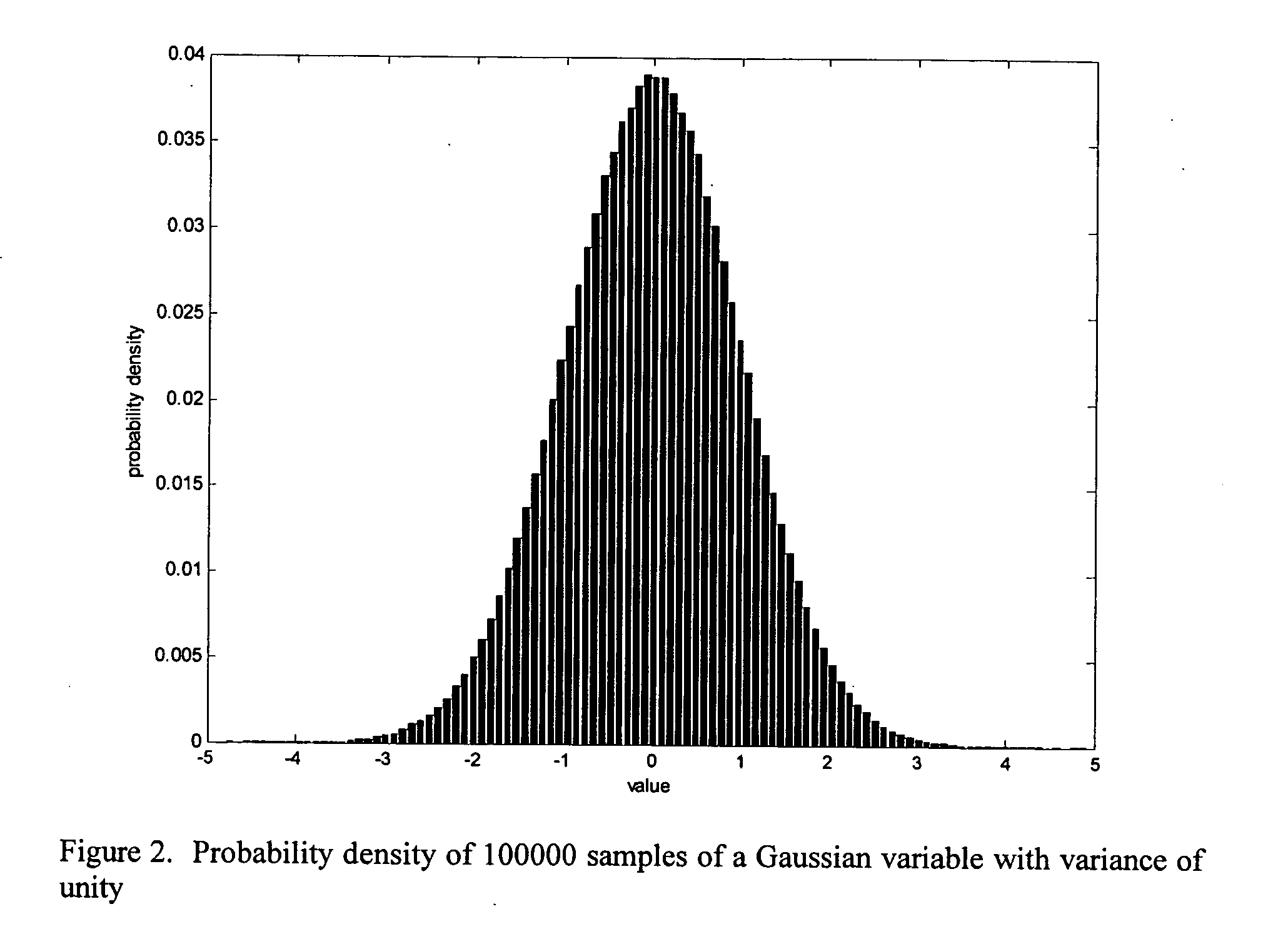
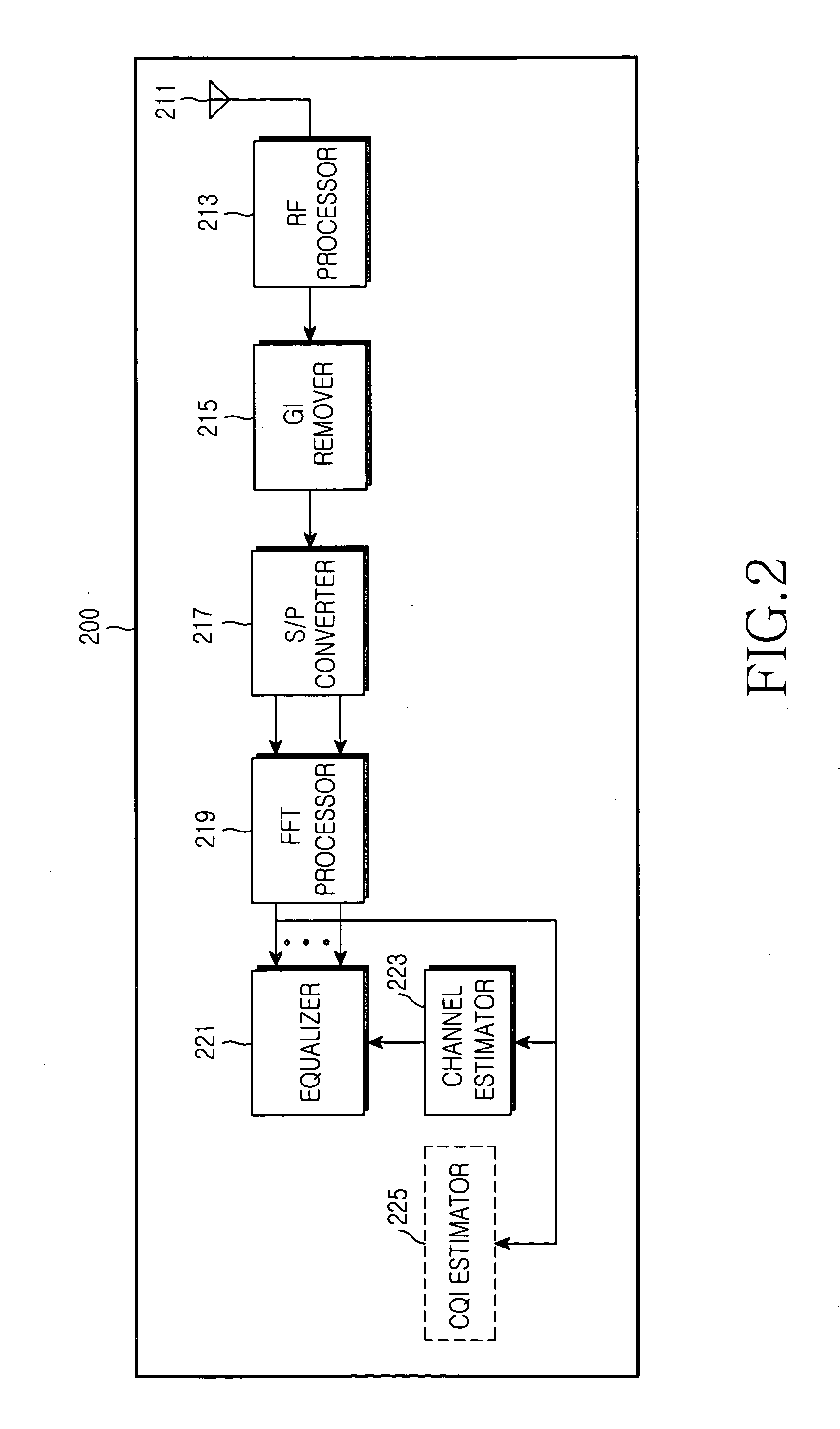
In telecommunication, the term noise power has the following meanings: The measured total noise per bandwidth unit at the input or output of a device when the signal is not present. The power generated by a random electromagnetic process. Interfering and unwanted power in an electrical device or system. In the acceptance testing of radio transmitters, the mean power supplied to the antenna transmission line by a radio transmitter when loaded with noise having a Gaussian amplitude-vs.-frequency distribution.
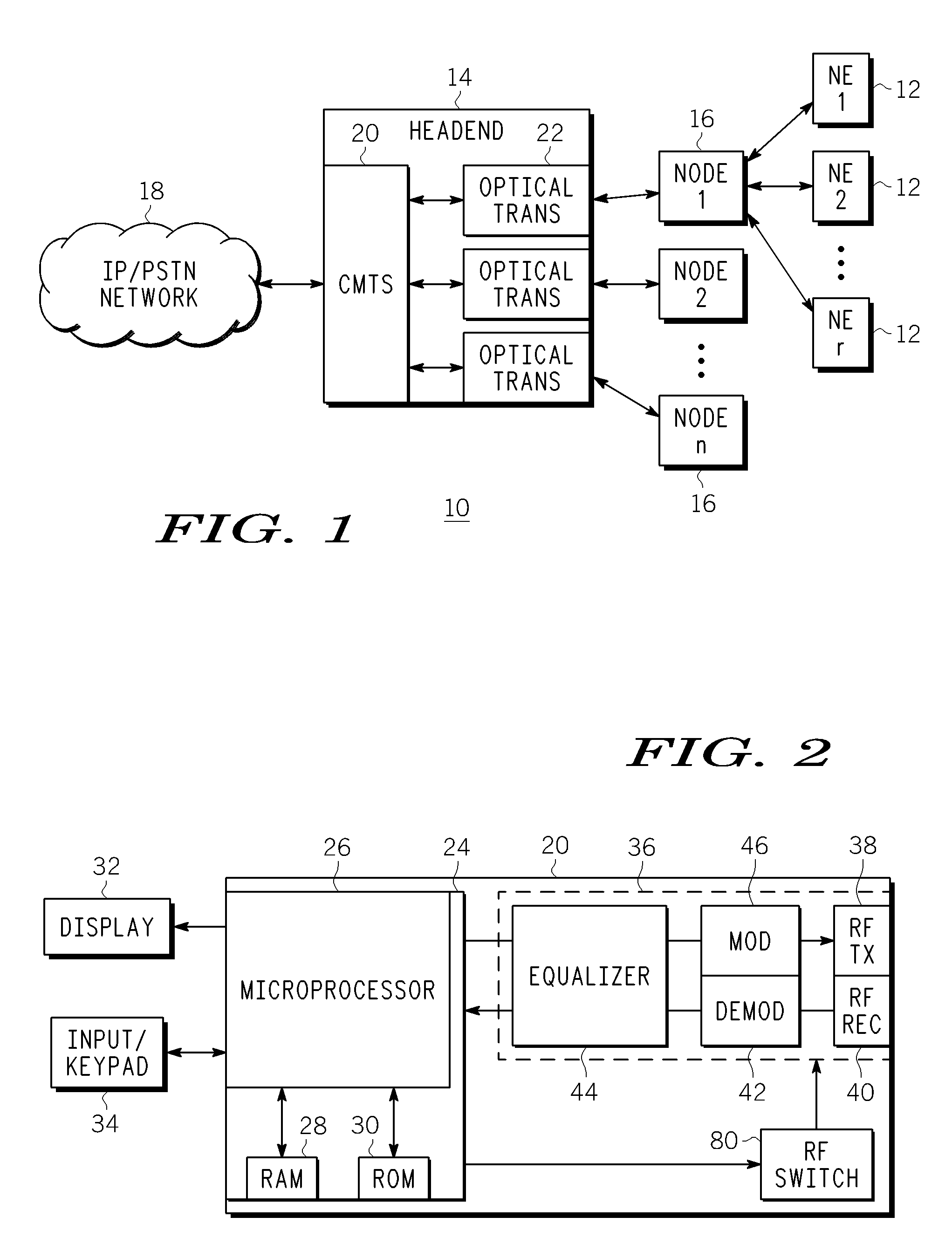
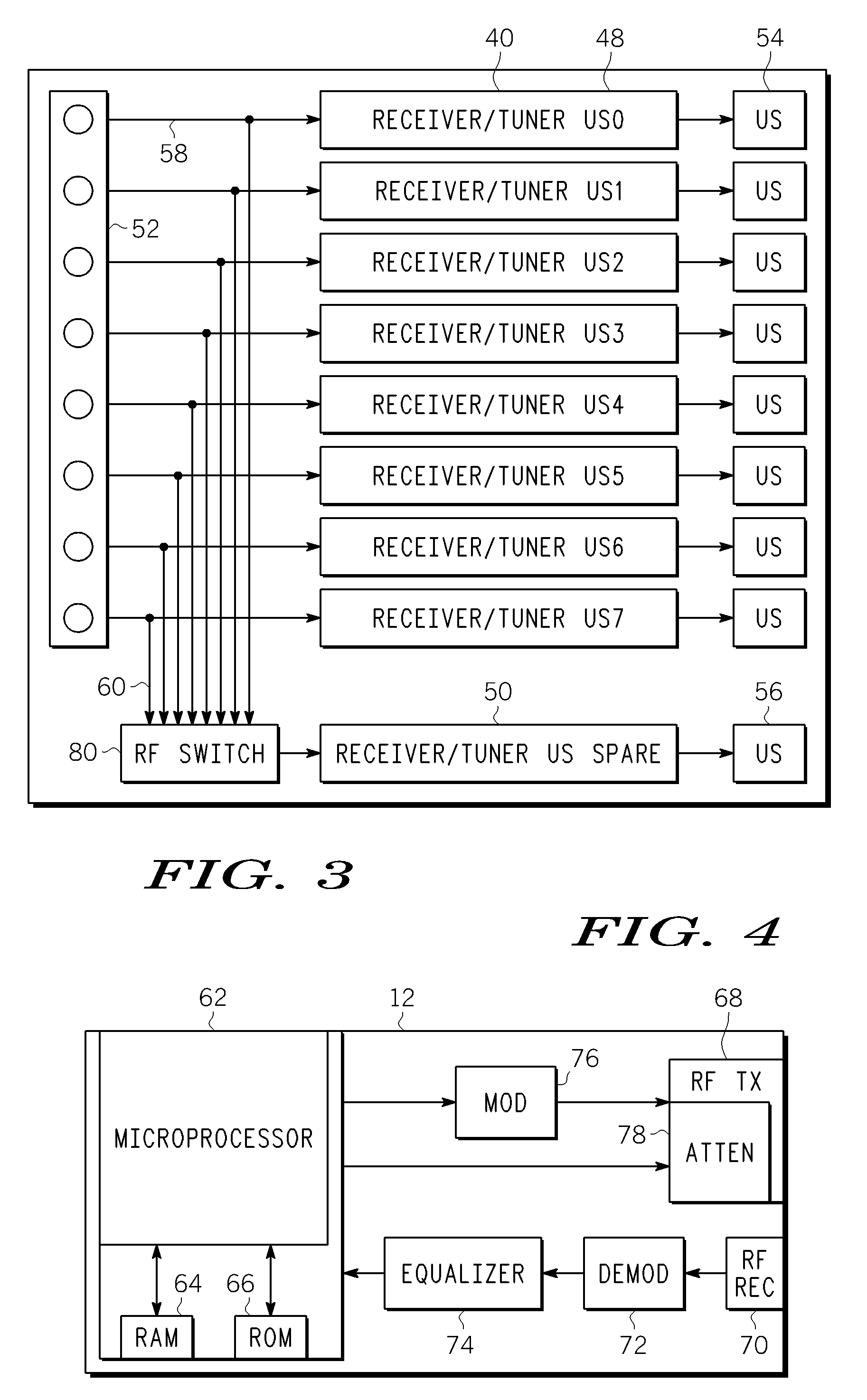
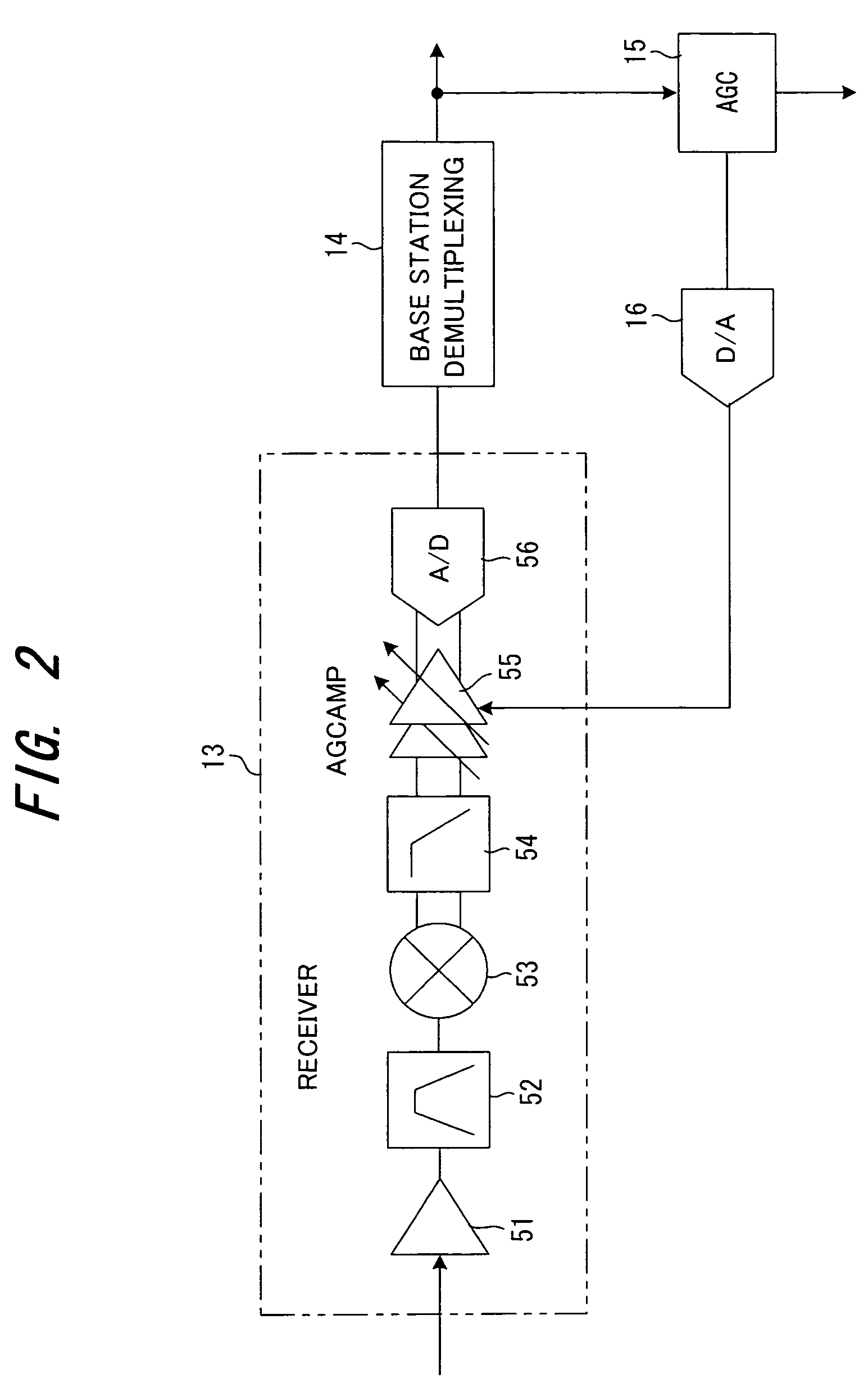
Radio communication apparatus, base station and system
InactiveUS20060013285A1Modulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexSignal to noise power ratioTransmitter
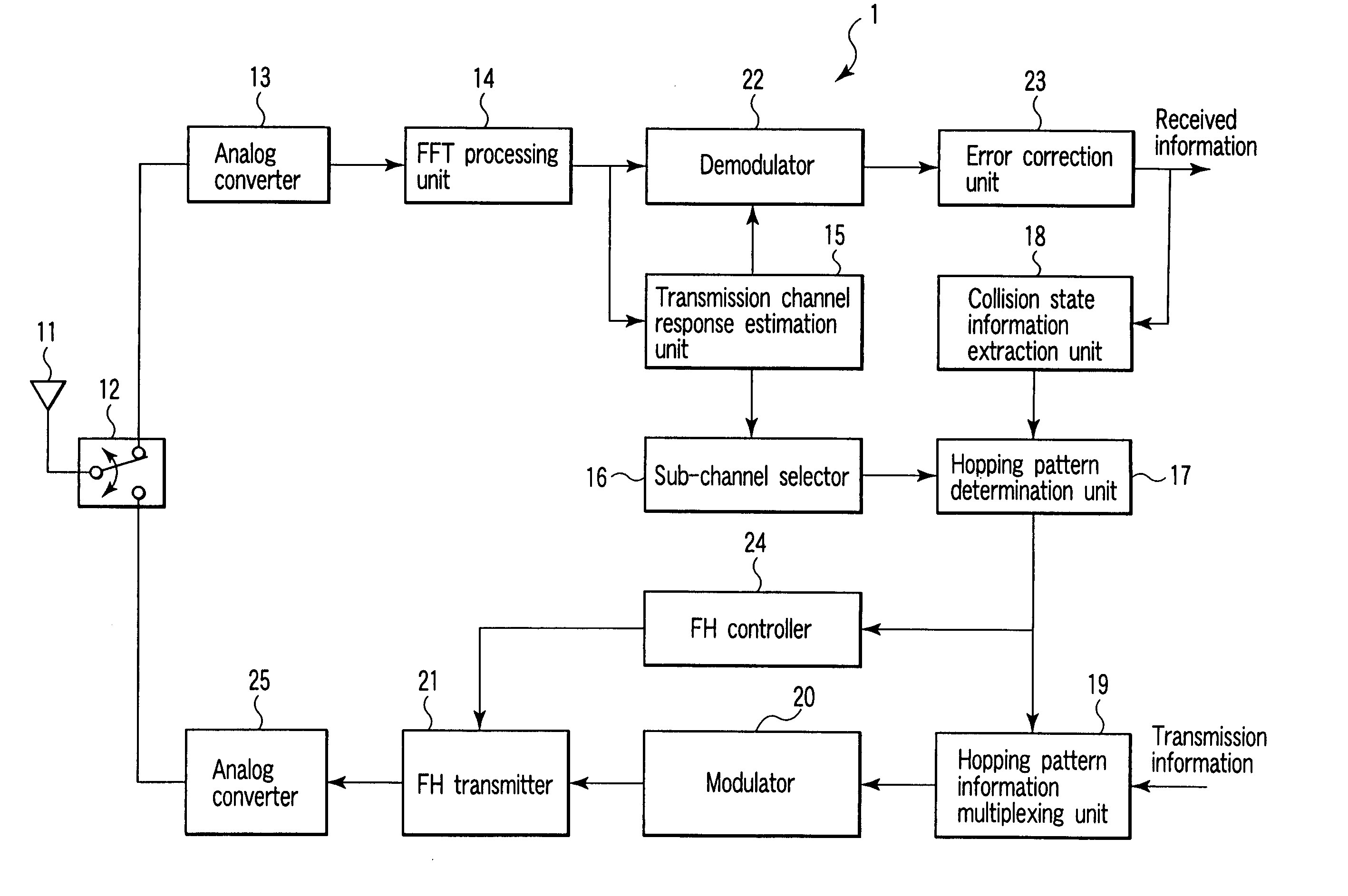
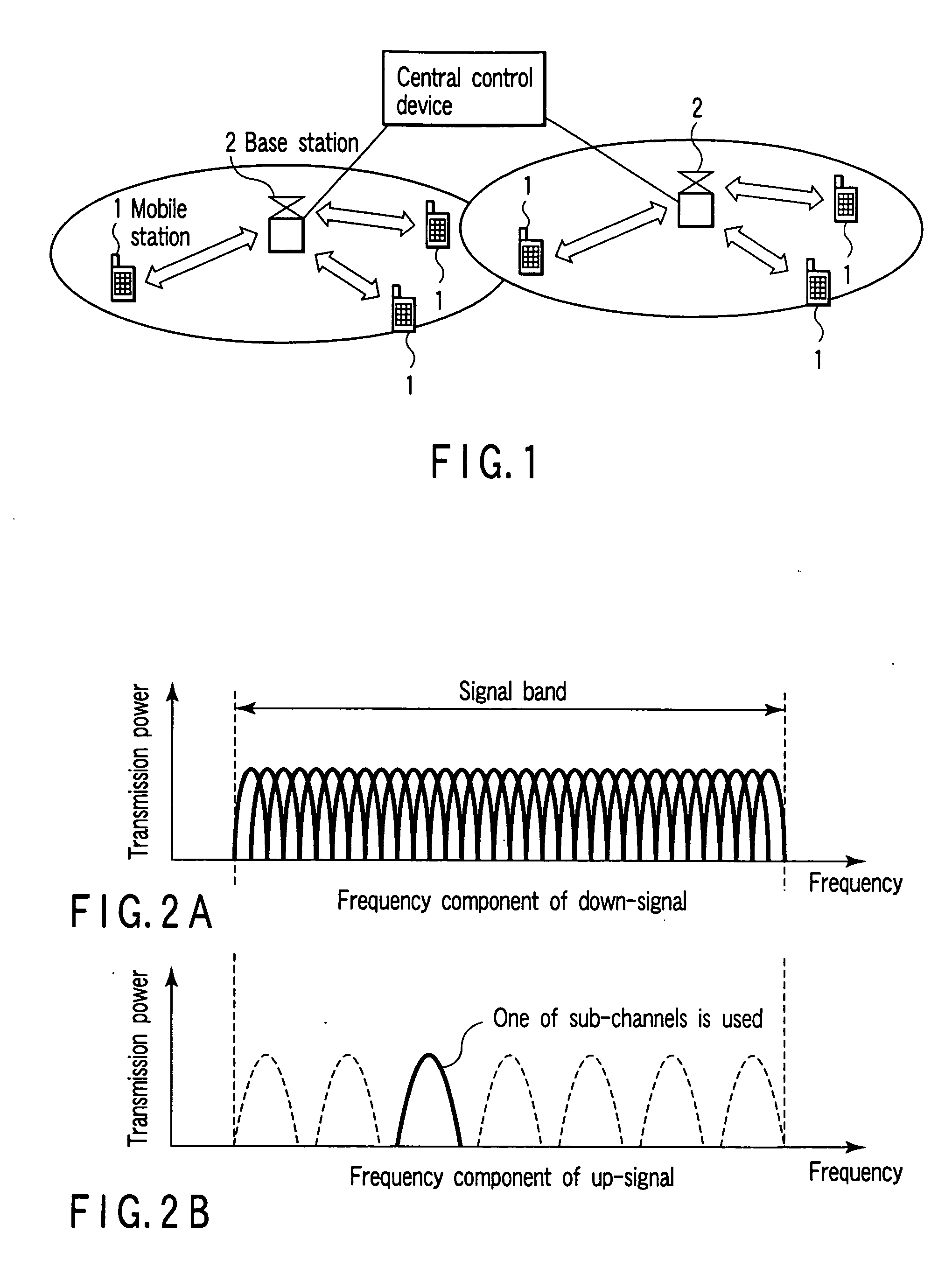
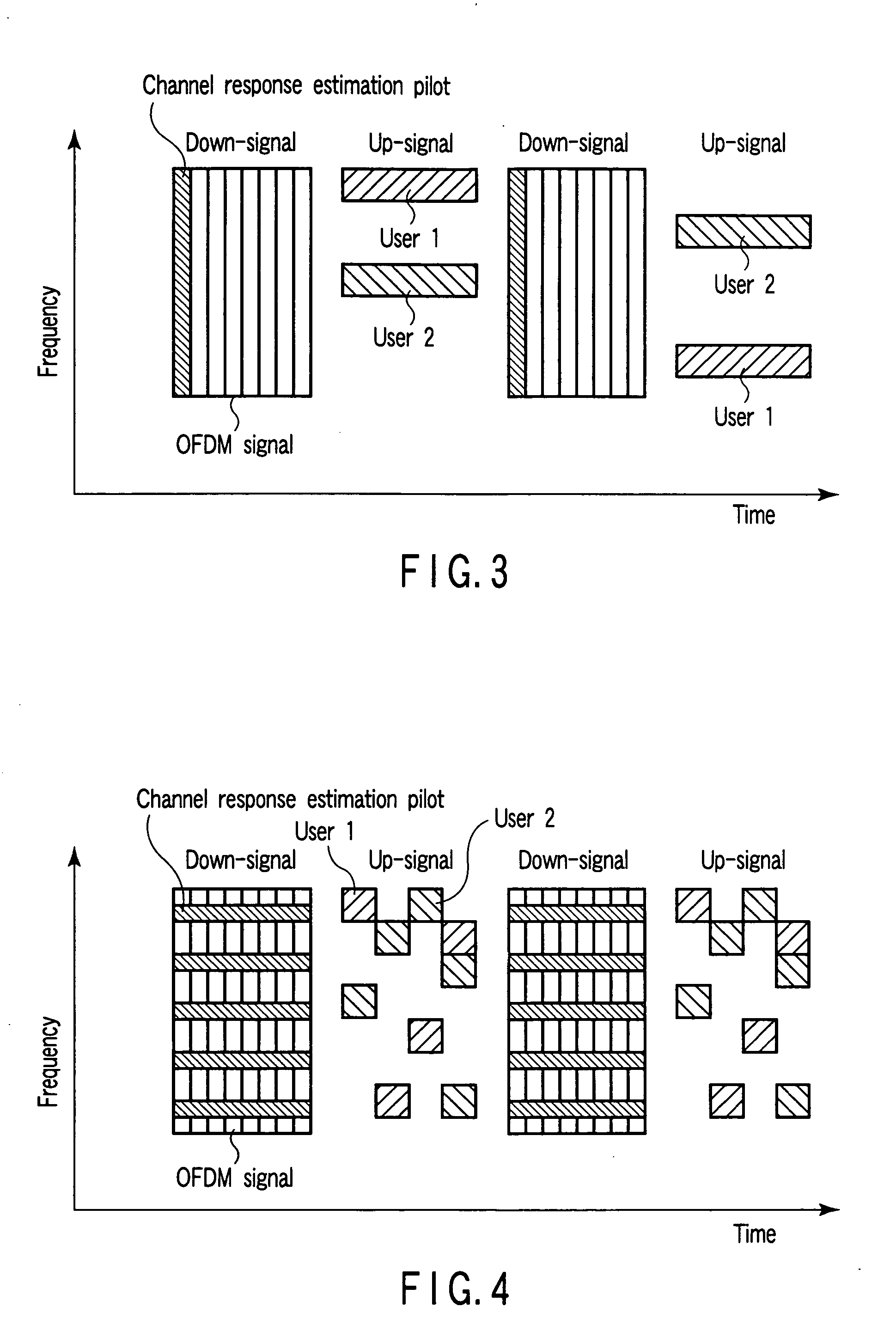
Radio communication apparatus for receiving OFDM signal from base station and transmitting FH signal to base station, using sub-channels, base station comparing hopping pattern information items indicating hopping patterns from radio communication apparatuses including radio communication apparatus, and generating collision information when hopping patterns include colliding hopping patterns, includes estimation unit configured to estimate channel response values of sub-channels based on OFDM signal, selector which selects, from sub-channels, several sub-channels which have higher channel response values than a value, each of channel response values being expressed by power level, signal-to-noise power ratio, or signal-to-interference ratio, determination unit configured to determine hopping pattern from selected sub-channels, transmitter which transmits, to base station, hopping pattern information item indicating determined hopping pattern, receiver which receives collision information from base station, and correction unit configured to correct hopping pattern based on collision information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
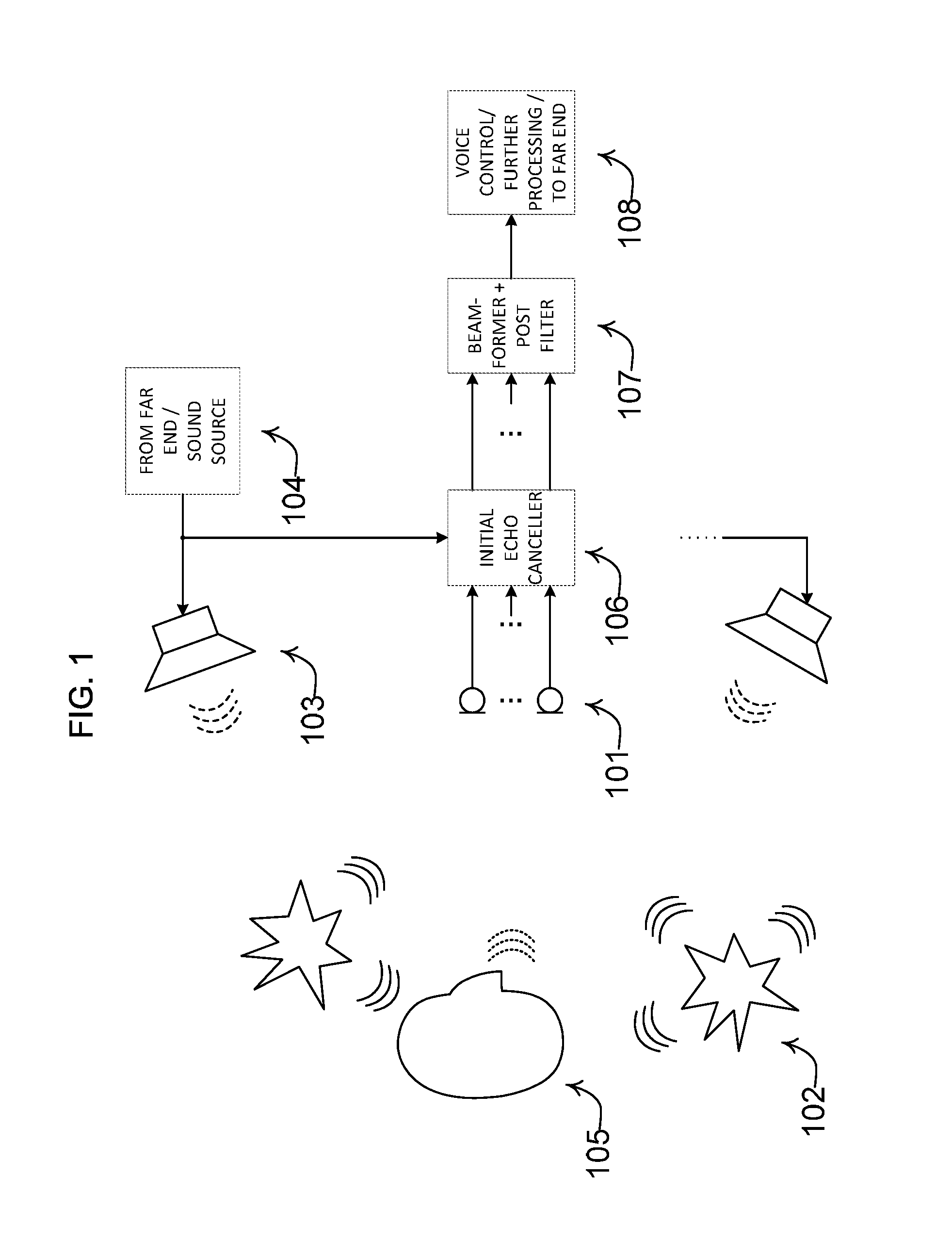
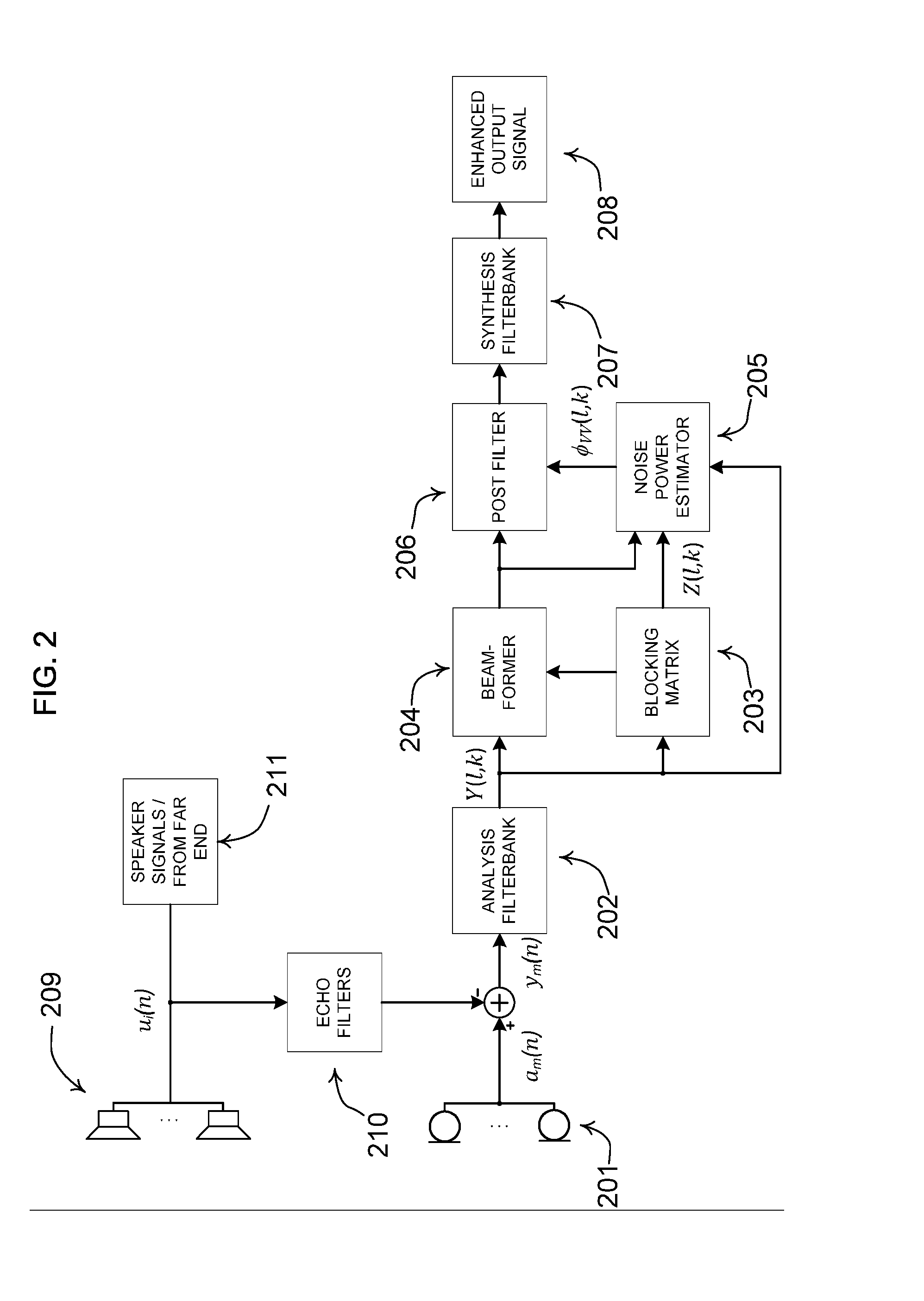
Noise estimation for use with noise reduction and echo cancellation in personal communication
ActiveUS20140056435A1Improve recognition rateImprove sound qualityInterconnection arrangementsEar treatmentNoise correctionEngineering
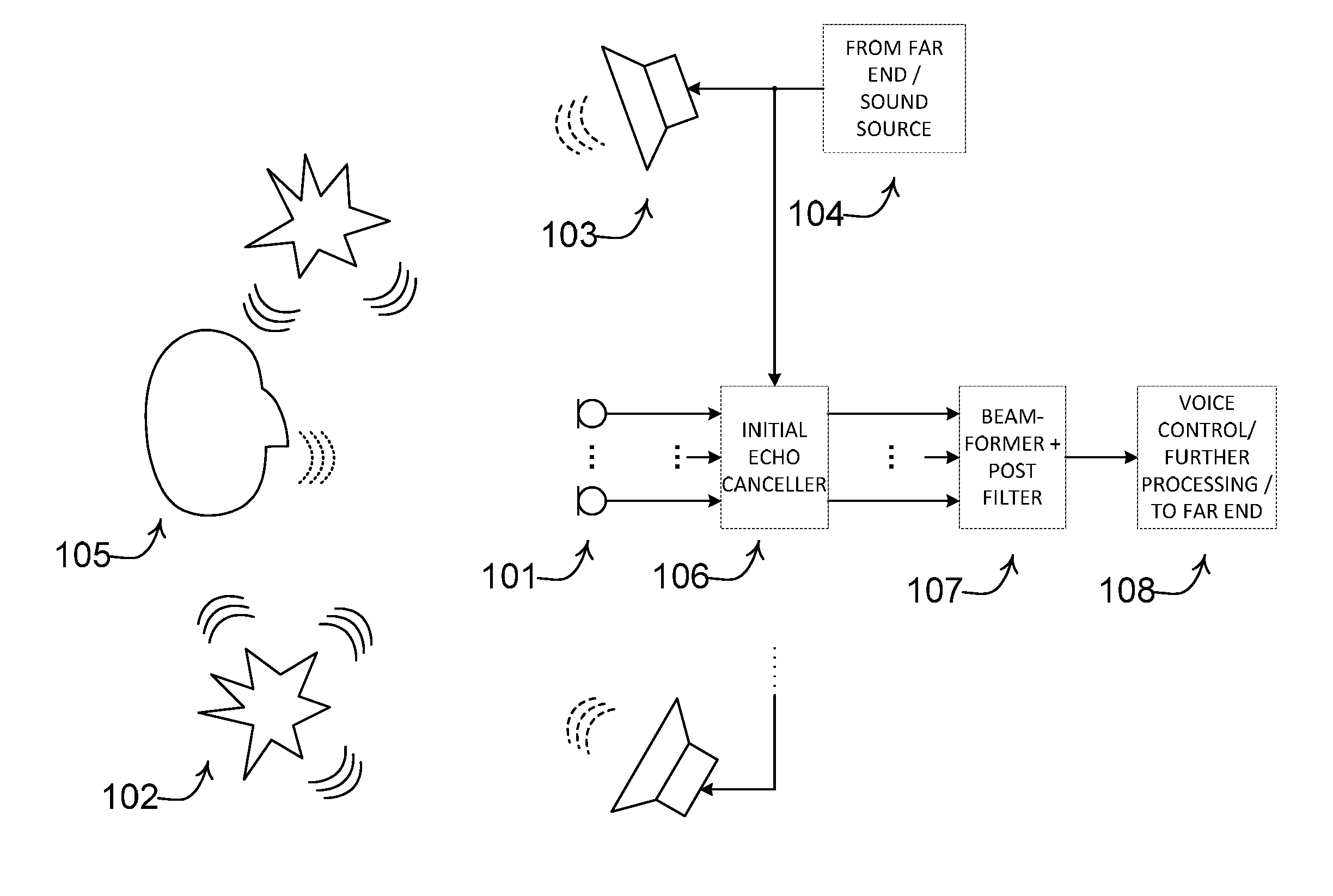
A method comprises processing M subband communication signals and N target-cancelled signals in each subband with a set of beamformer coefficients to obtain an inverse target-cancelled covariance matrix of order N in each band; using a target absence signal to obtain an initial estimate of the noise power in a beamformer output signal averaged over recent frames with target absence in each subband; multiplying the initial noise estimate with a noise correction factor to obtain a refined estimate of the power of the beamformer output noise signal component in each subband; processing the refined estimate with the magnitude of the beamformer output to obtain a postfilter gain value in each subband; processing the beamformer output signal with the postfilter gain value to obtain a postfilter output signal in each subband; and processing the postfilter output subband signals to obtain an enhanced beamformed output signal.
Owner:OTICON
Apparatus and method for adaptive 3D artifact reducing for encoded image signal
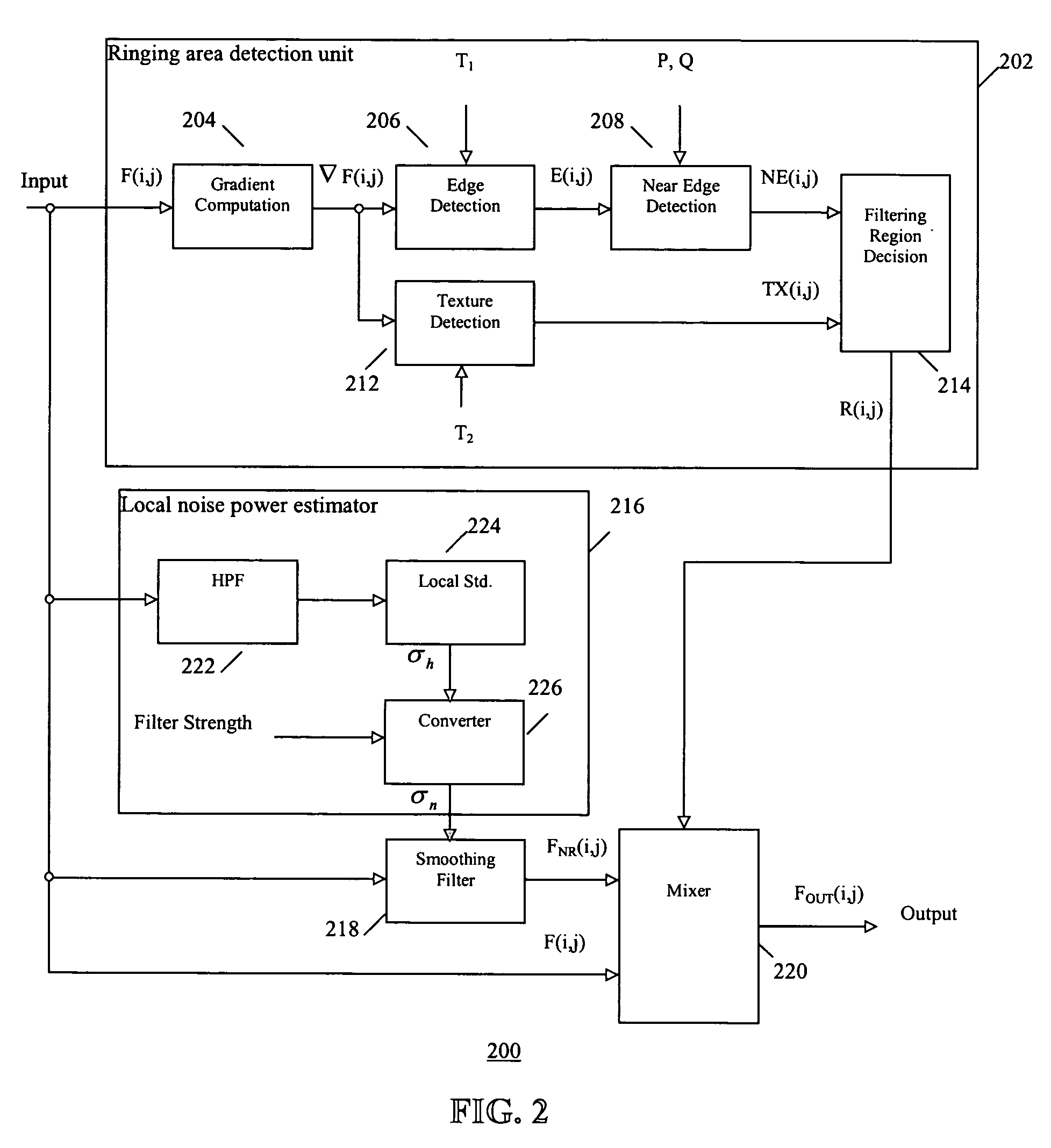
InactiveUS20060050783A1Efficient reductionReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementRandom noiseNoise reduction
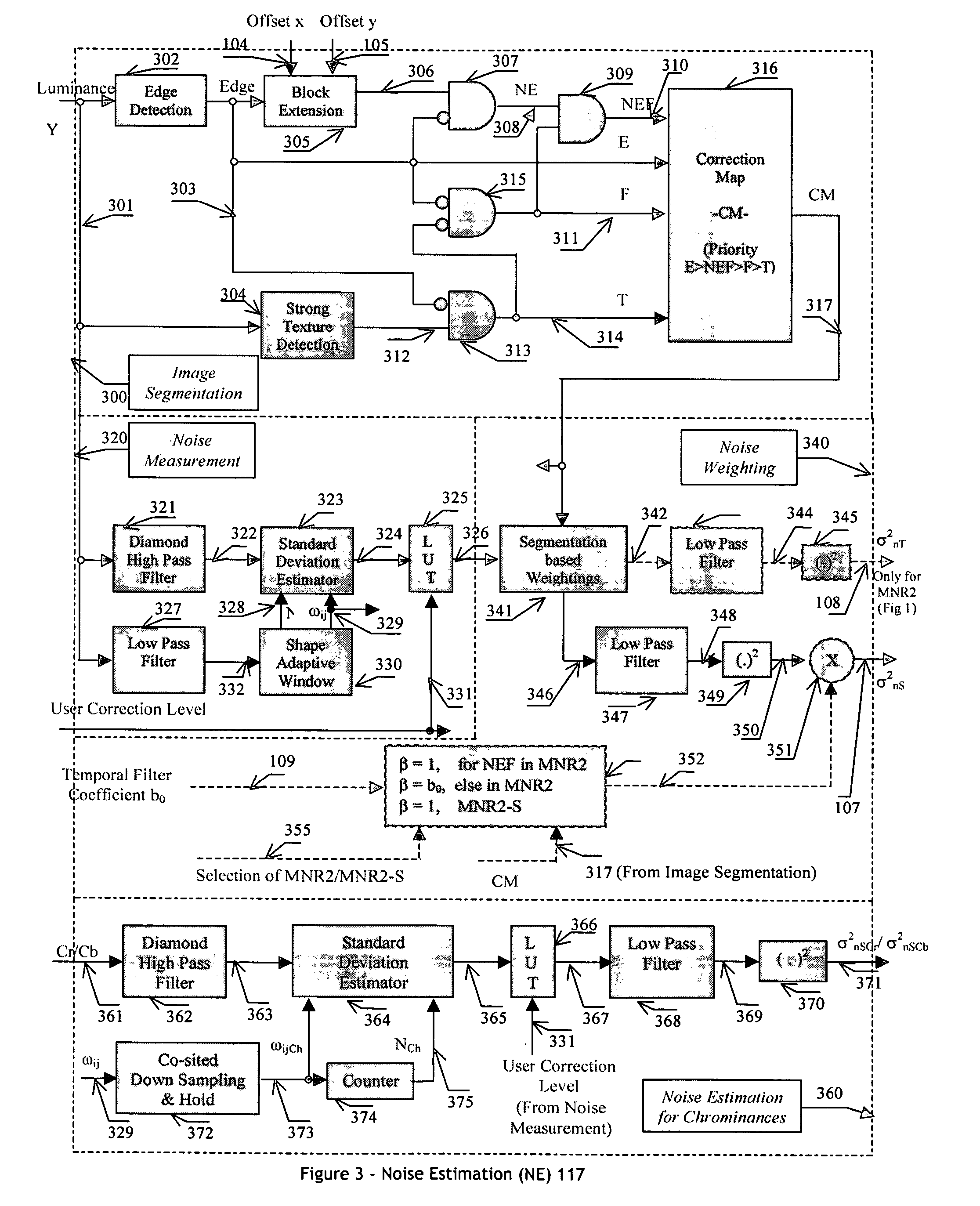
An efficient and non-iterative 3D post processing method and system is proposed for mosquito noise reduction, block localization and correction in DCT block-based decoded images. The 3D post processing is based on a simple classification that segments a picture in multiple regions such as Edge, Near Edge, Flat, Near Flat and Texture regions. The proposed technique comprises also an efficient and shape adaptive local power estimation for equivalent additive noise and provides simple noise power weighting for each above cited region. Temporal filtering configurations using Minimum Noise Variance Criterion are proposed for reducing temporally varying coding artifacts. A Minimum Mean Square Error or Minimum Mean Square Error-like noise reduction with robust and effective shape adaptive windowing is utilized for smoothing mosquito and / or random noise for the whole image, particularly for Edge regions. The proposed technique comprises also signal domain histogram analysis based Block Localization and adaptive edge based Block artifact correction. Finally, is also proposed an optional adaptive detail enhancer which can enhances the luminance signal in eight directions differently.
Owner:SENSIO TECHNOLOGIES
Active noise control algorithm that requires no secondary path identification based on the SPR property
InactiveUS20100284546A1Reduce vibration and noiseReduce residual noise powerEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlControl system
A control system for reducing noise or vibration in a target zone. The noise or vibration is produced by a source and transferred to the target zone by a main path. The control system is provided with an actuator, at least one error sensor and a controller. The actuator is positioned to deliver actuated signals into at least a portion of the target zone. The at least one error sensor monitors the residual noise or vibration power in the target zone and produces an error signal representative thereof. The controller receives a reference signal representative of noise or vibration produced by the source, and the error signal representative of the residual noise power in the target zone. The controller analyzes sub-bands of the reference signal and the error signal without identification of a secondary path, and provides drive signals to the actuator to cause the actuator to deliver the actuated signals into the target zone so as to reduce the residual noise power in the target zone.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Signal processing apparatus and signal processing method
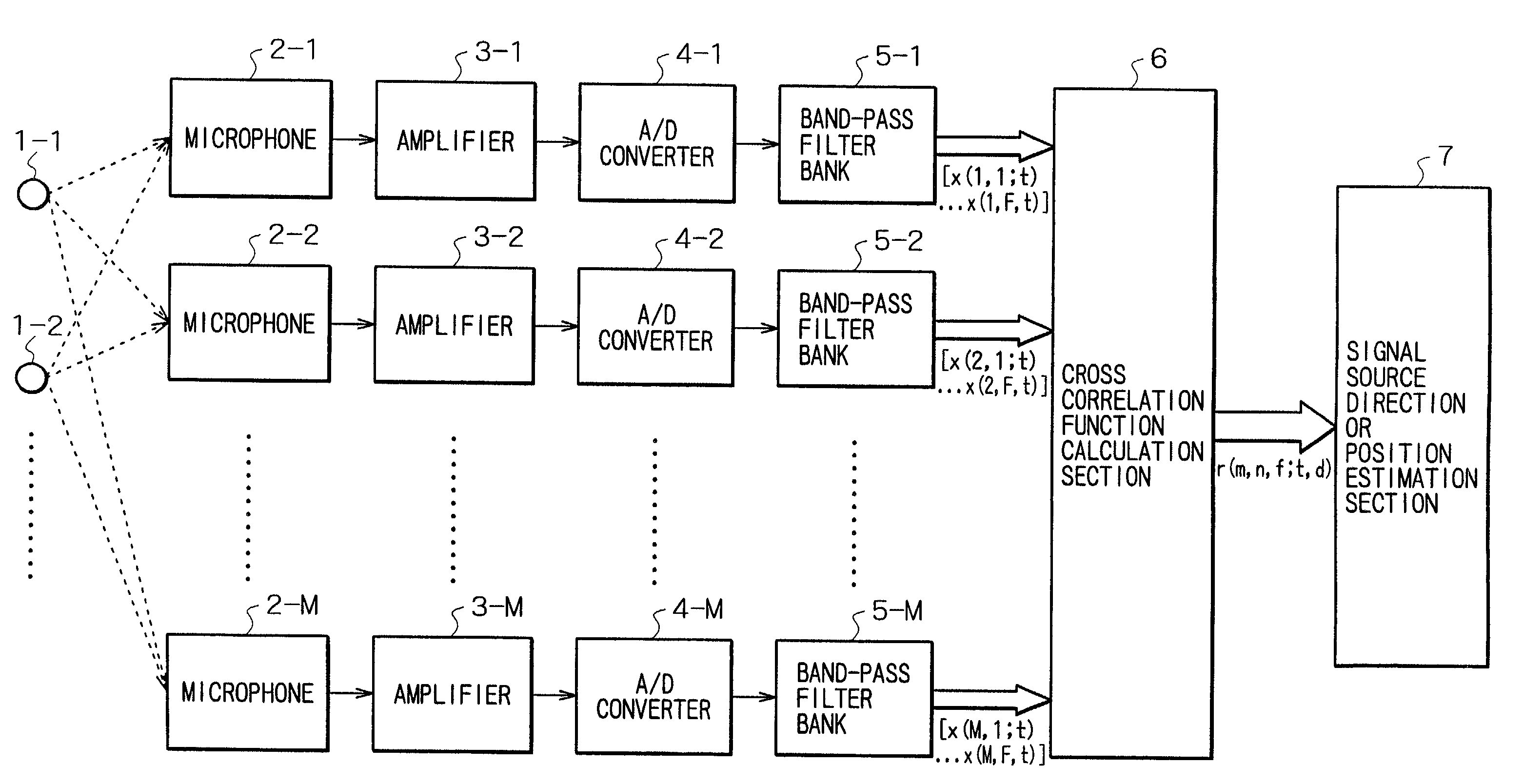
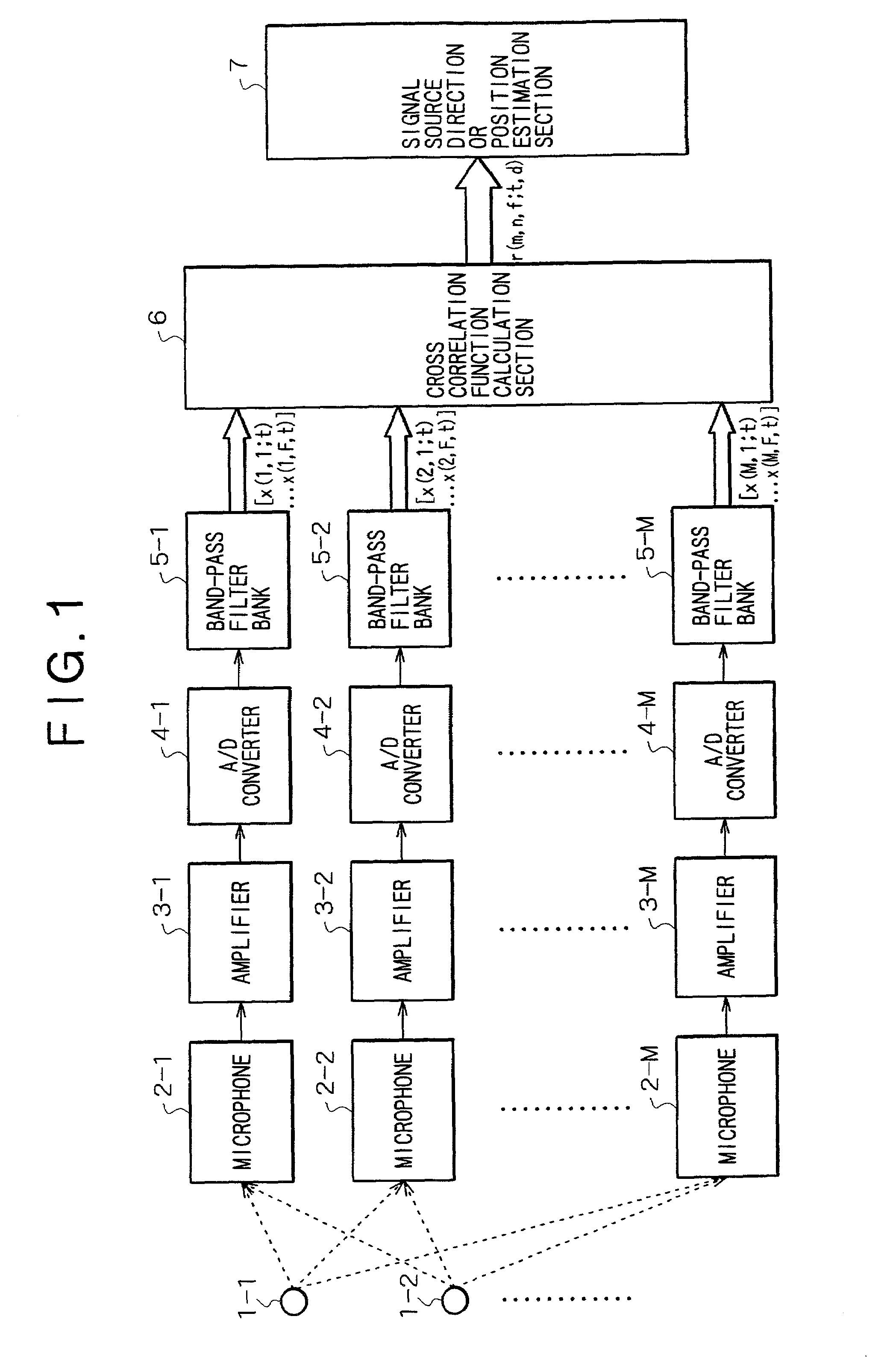
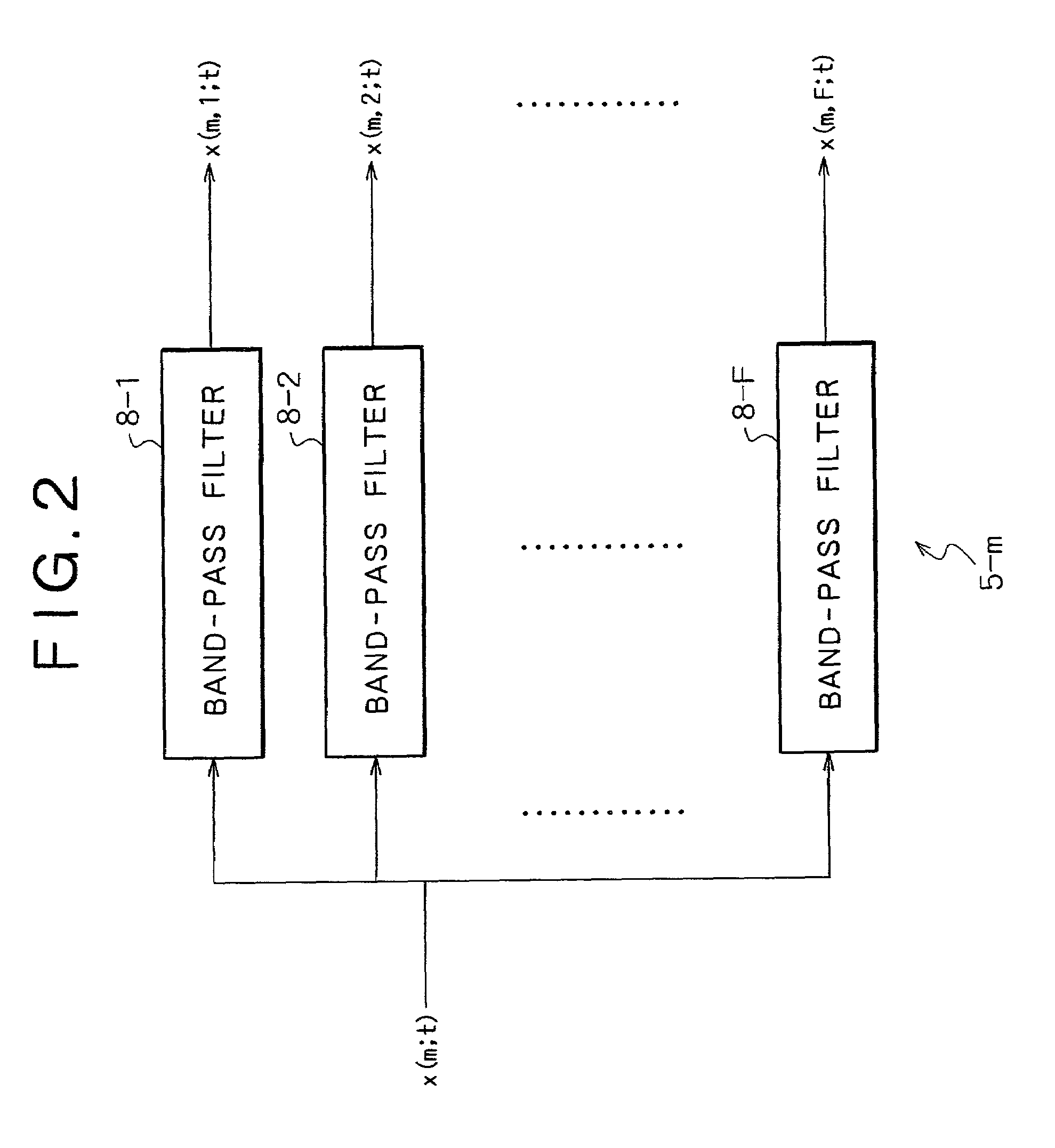
InactiveUS7054452B2Influence of noise can be suppressedTelevision conference systemsPosition fixationSound sourcesBand-pass filter
The invention provides a method and apparatus by which the direction in or the position at which a signal source such as a sound source is present is estimated. A signal or signals from a signal source or a plurality of signal sources are received by a plurality of reception apparatus, and the received signals are decomposed into signals of different frequency bands by a plurality of band-pass filters. Then, cross correlation functions between the different frequency band signals are calculated for individual combinations of the reception apparatus for the individual corresponding frequency bands. If the power of noise having no directivity is high in some of the frequency bands, then the cross correlation functions of the frequency band do not exhibit a maximum value. Therefore, an influence of the noise can be suppressed effectively when delay times of the individual reception apparatus which depend upon the direction or directions or the position or positions of the signal source or sources are estimated.
Owner:SONY CORP
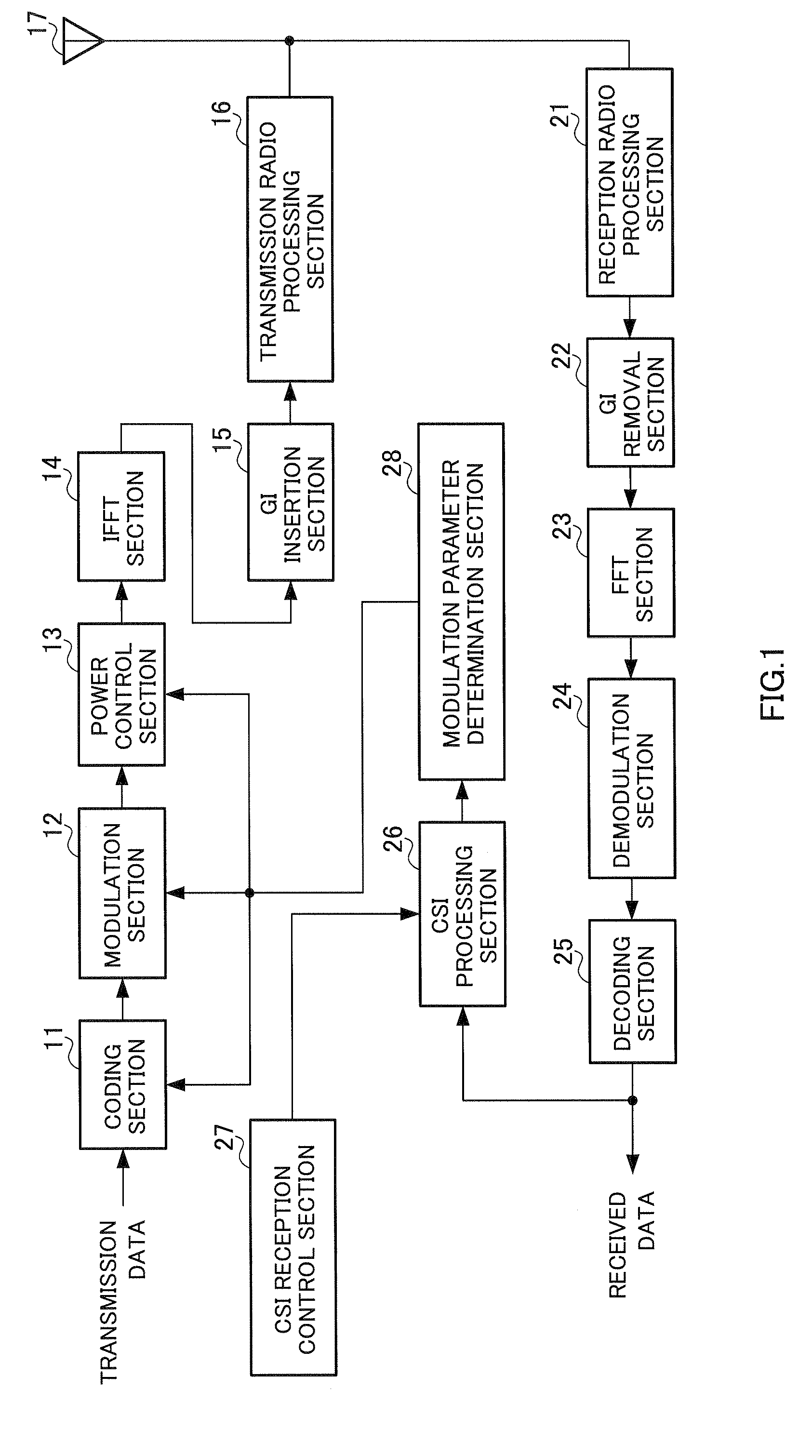
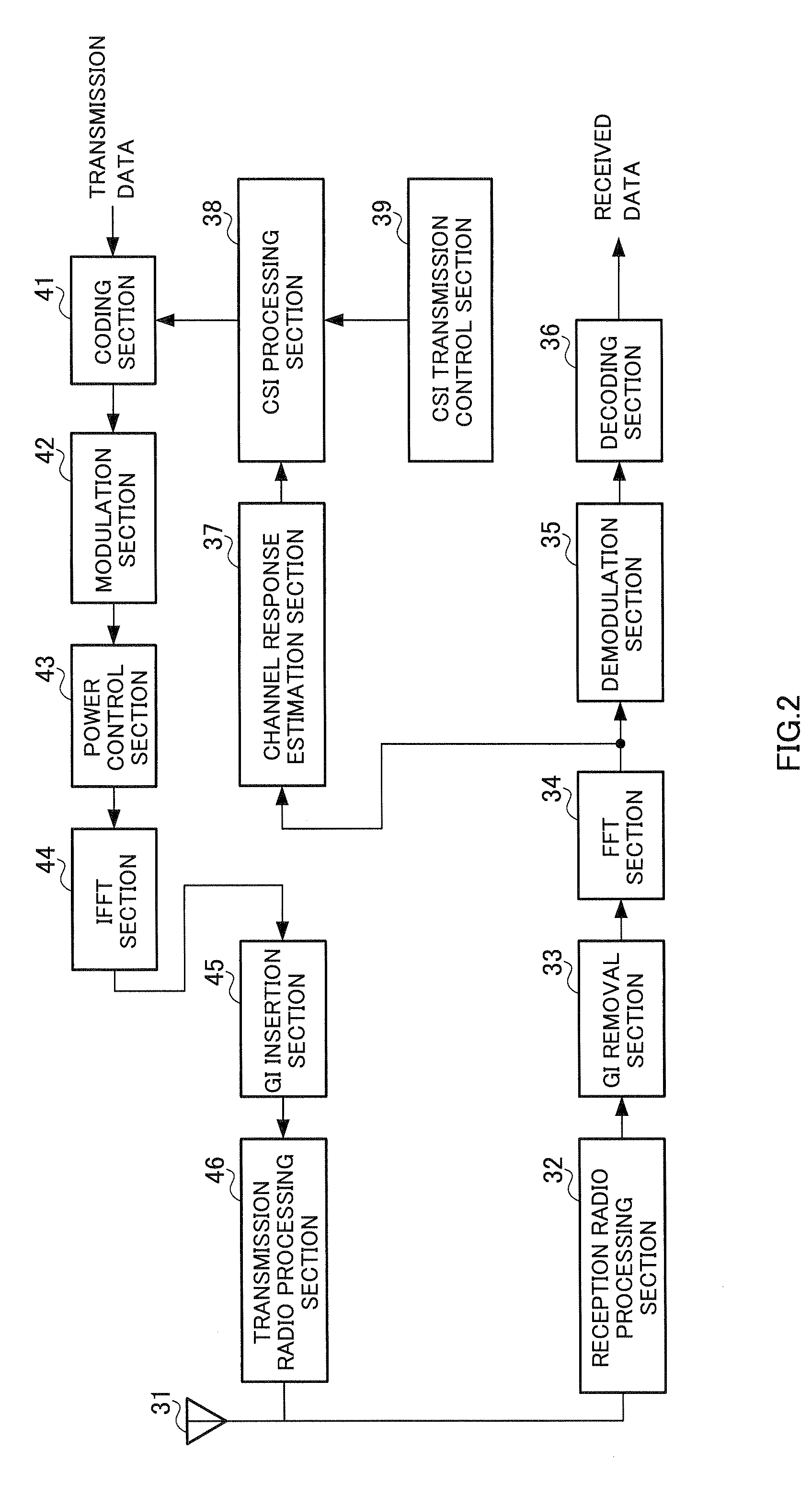
Wireless Communication Apparatus and Wireless Communication Method
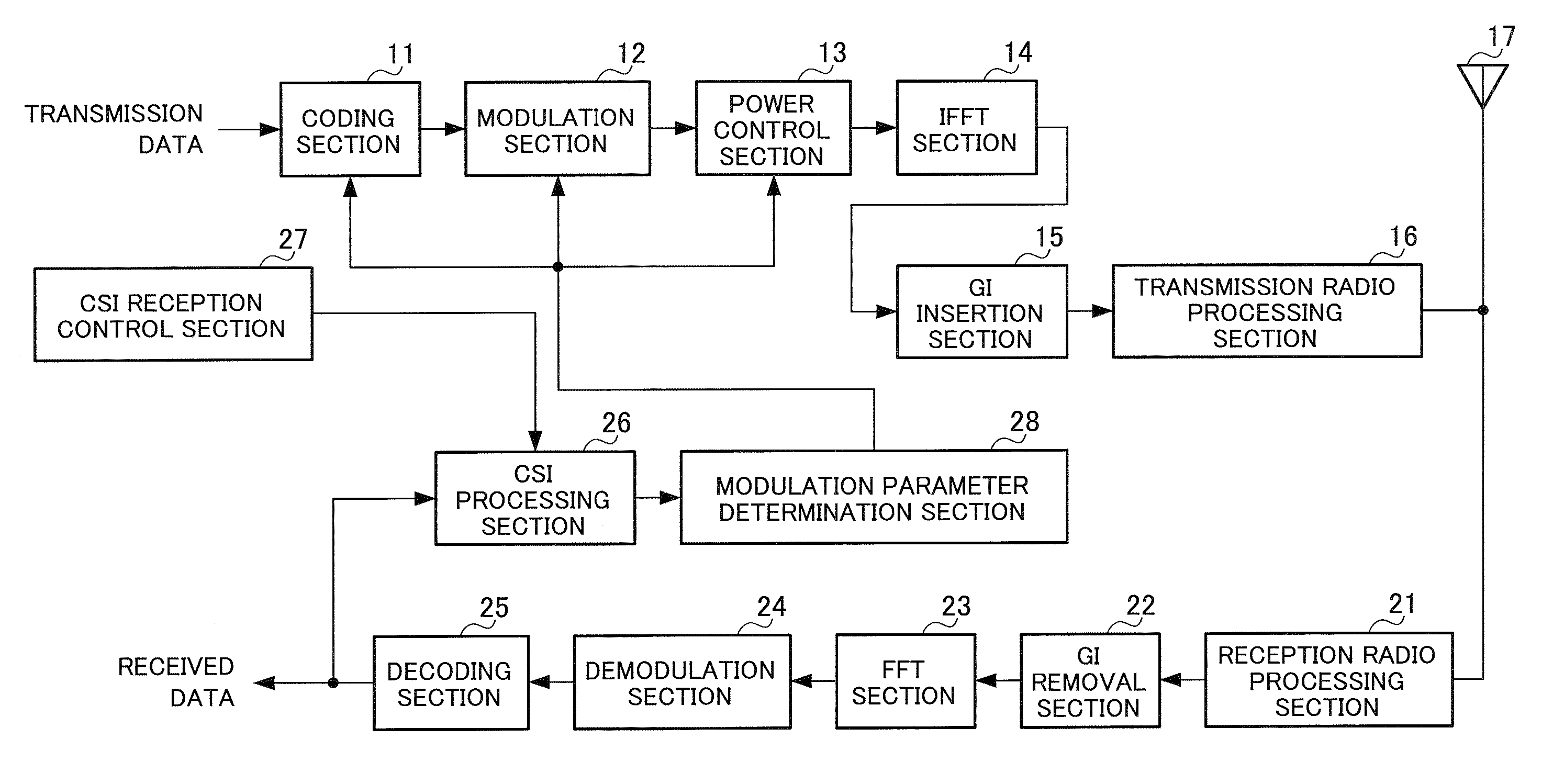
InactiveUS20070298728A1Improve throughputReduce data volumeModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionInformation processingChannel state information
A wireless communication apparatus wherein the data amount of feedback information can be reduced, while a high throughput being maintained. In this apparatus, a CSI (Channel State Information) processing part (38) generates a CSI frame based on an SNR (Signal power to Noise power Ratio) for each of measured subcarriers, and a CSI transmission control part (39) generates a timing signal and control information required for generating the CSI frame, and controls the CSI processing part (38). The CSI processing part (38) generates a first frame (CSI1) which comprises the CSI of a subcarrier whose SNR variation amount is less than a threshold value, in a generation period that is greater than the generation period of a second frame (CSI2) comprising the CSI of a subcarrier whose SNR variation amount is equal to or greater than the threshold value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Multicarrier modulation systems
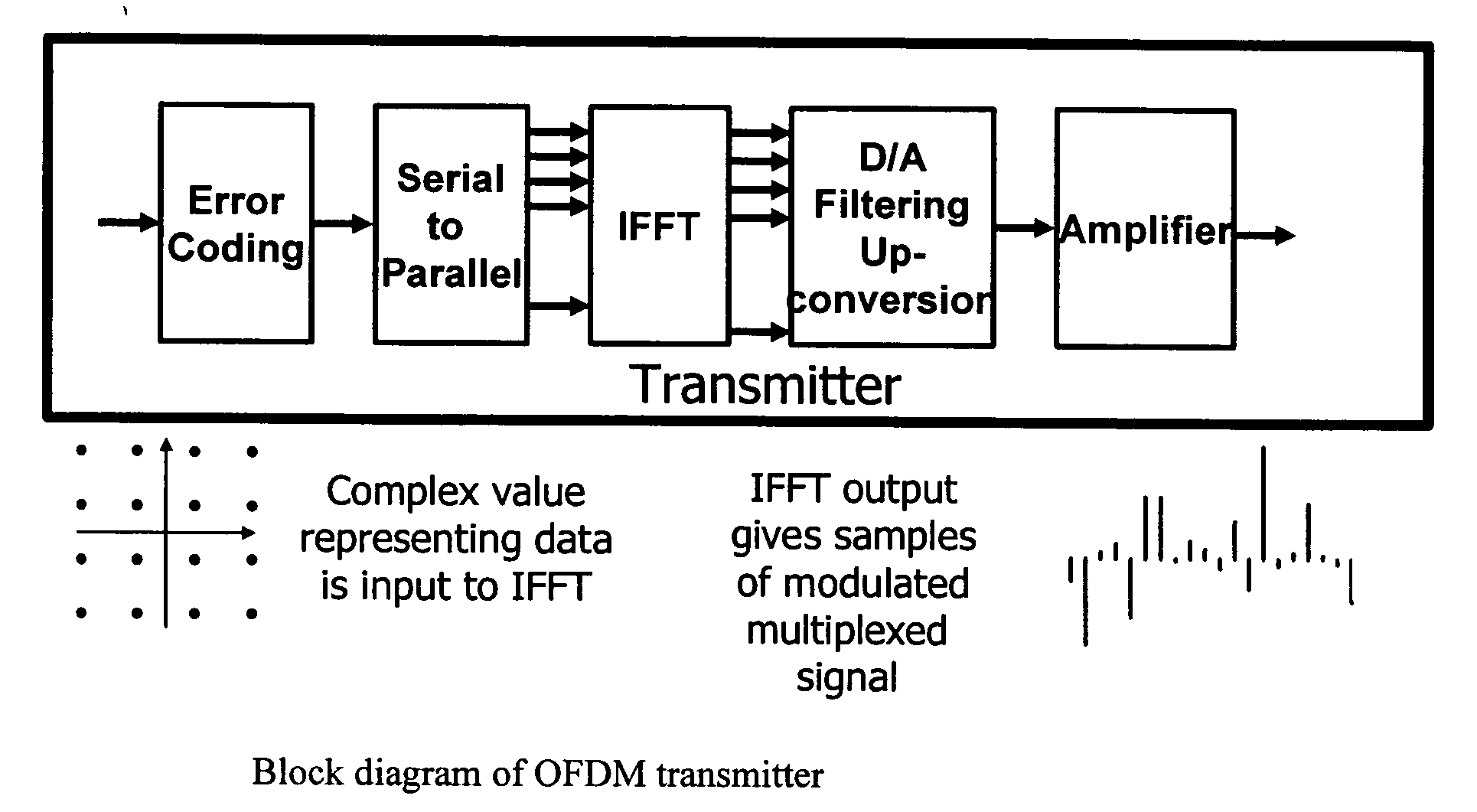
ActiveUS20050243938A1Reduce probabilityMinimize degradationDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationCarrier signalEngineering
The invention provides a new approach which is better suited to FFT design as applied to multicarrier modulation systems such as OFDM. The signals are scaled so that overflow, rather than being completely avoided, occurs with low probability throughout the IFFT and FFT structures. The size of the error that results from an overflow depends on how overflow is handled in the DSP. To minimize the degradation, overflow should result in saturation of the value at the maximum positive or negative value option. This is equivalent to clipping the signal. Using the new technique, signals within the FFT structure are scaled to balance the effect of clipping and round-off. Clipping may result in comparatively large errors in a few signal values but because of the spreading effect of the FFT and because OFDM systems typically include error coding / correction, system performance depends on the total error or, in other words the total noise power, across all of the FFT outputs rather than on any individual value.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Method and apparatus for reducing mosquito noise in decoded video sequence
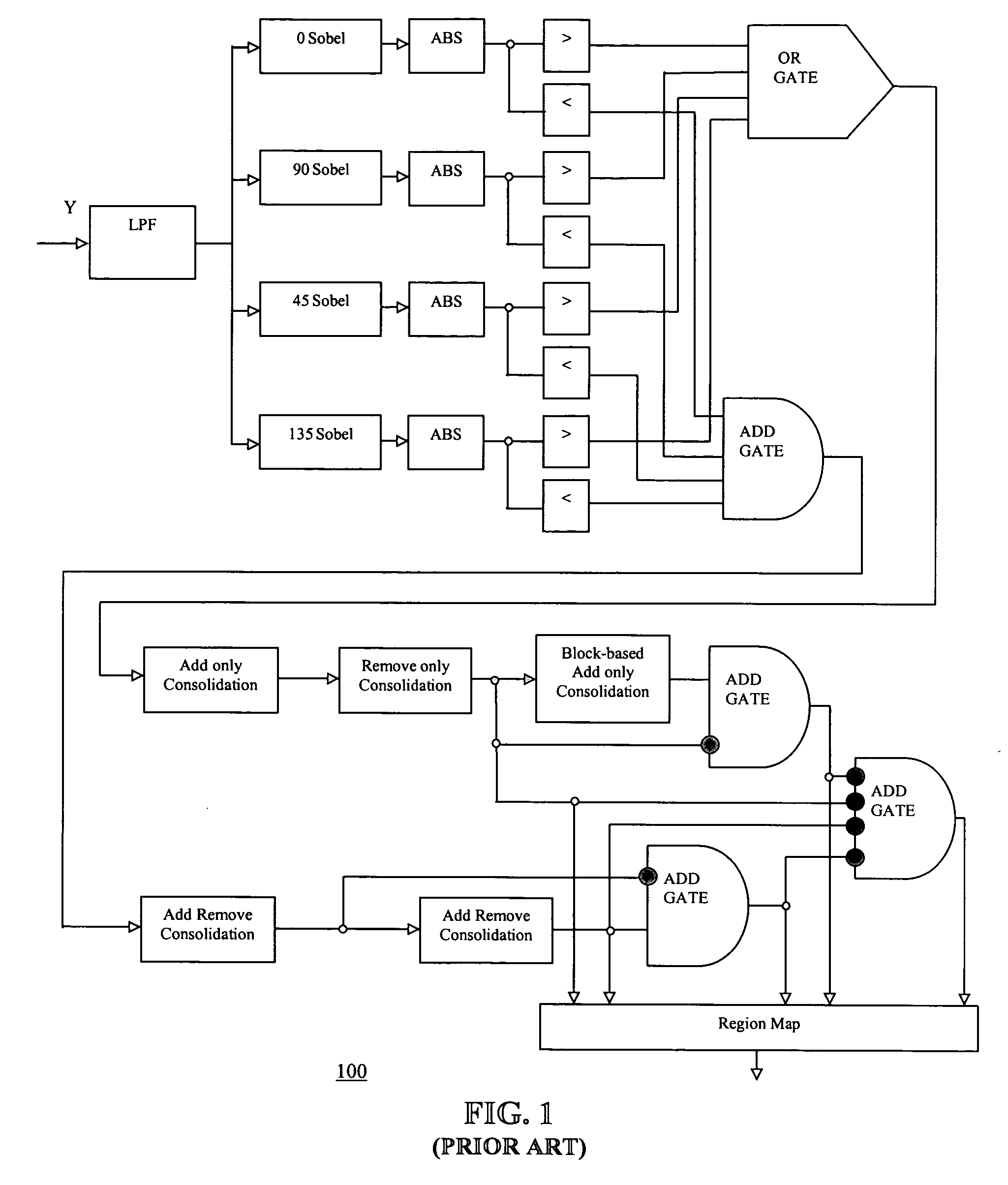
InactiveUS20060245506A1Reducing mosquito noiseSimple ringing (mosquito noise)Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVideo sequenceArea detector
A ringing area detector classifies the input image into two regions: a mosquito noise region (i.e. filtering region) and a non-mosquito noise region (i.e. non-filtering region), and uses this classification information to adaptively remove the mosquito noise in a mosquito noise reduction system. The mosquito noise reduction system includes a ringing area detector, a local noise power estimator, a smoothing filter, and a mixer. The ringing area detector includes an edge detector, a near edge detector, a texture detector, and a filtering region decision block. The ringing detection block detects the ringing area where the smoothing filter is to be applied. The local noise power estimator controls the filter strength of the smoothing filter. The smoothing filter smoothes the input image. The mixer mixes the smoothed image and the original image properly based on the region information from the ringing area detection block.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
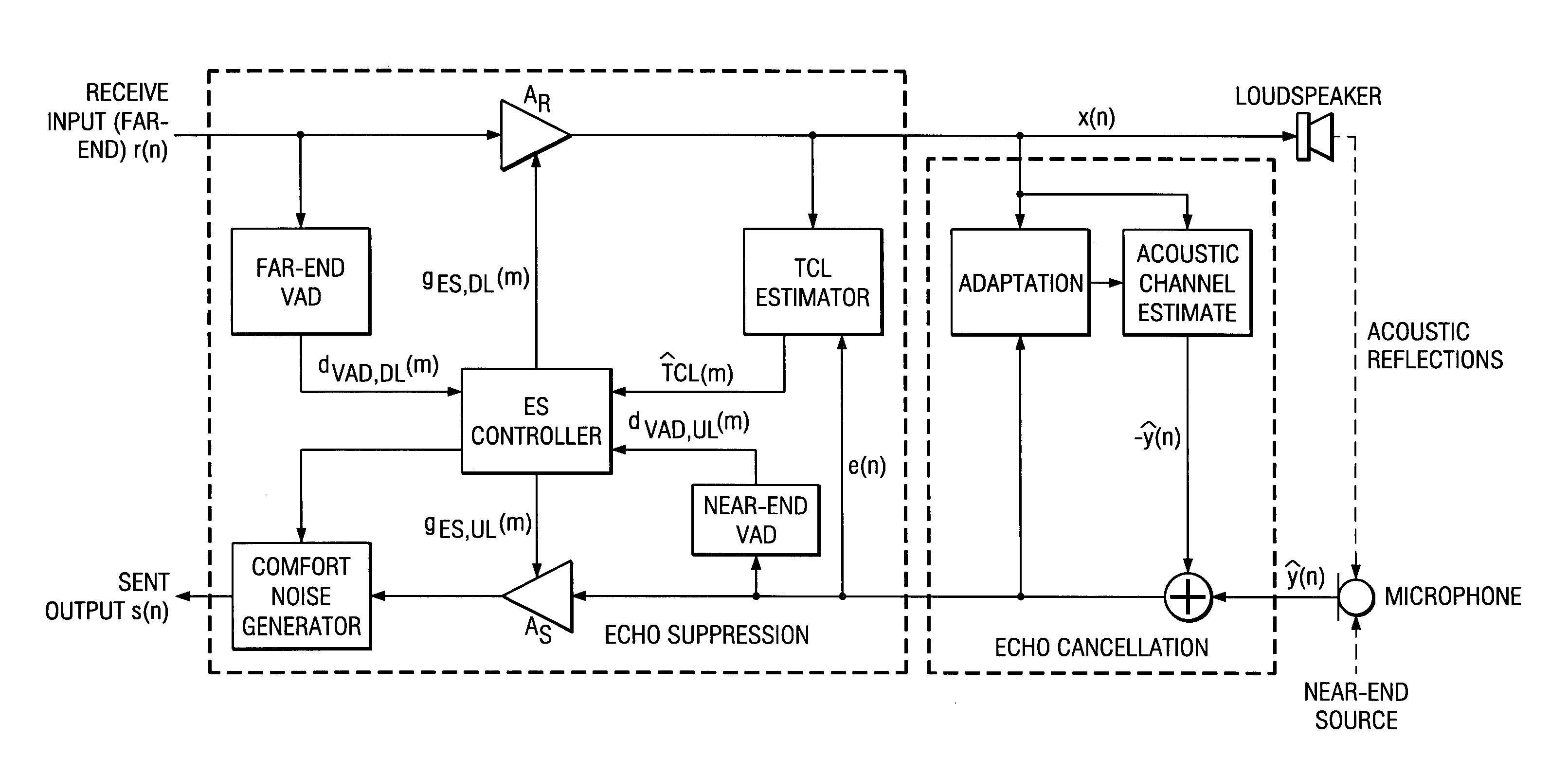
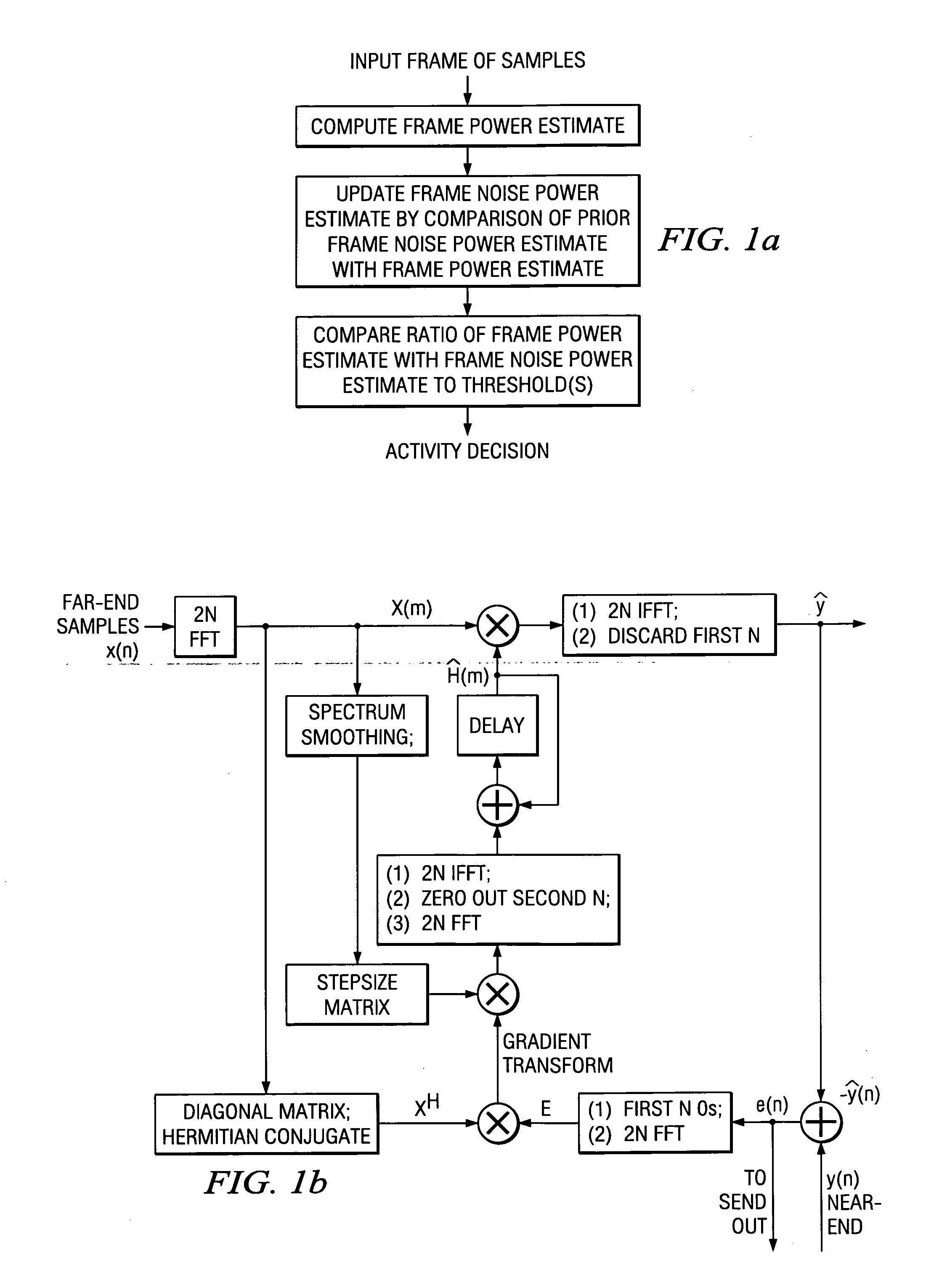
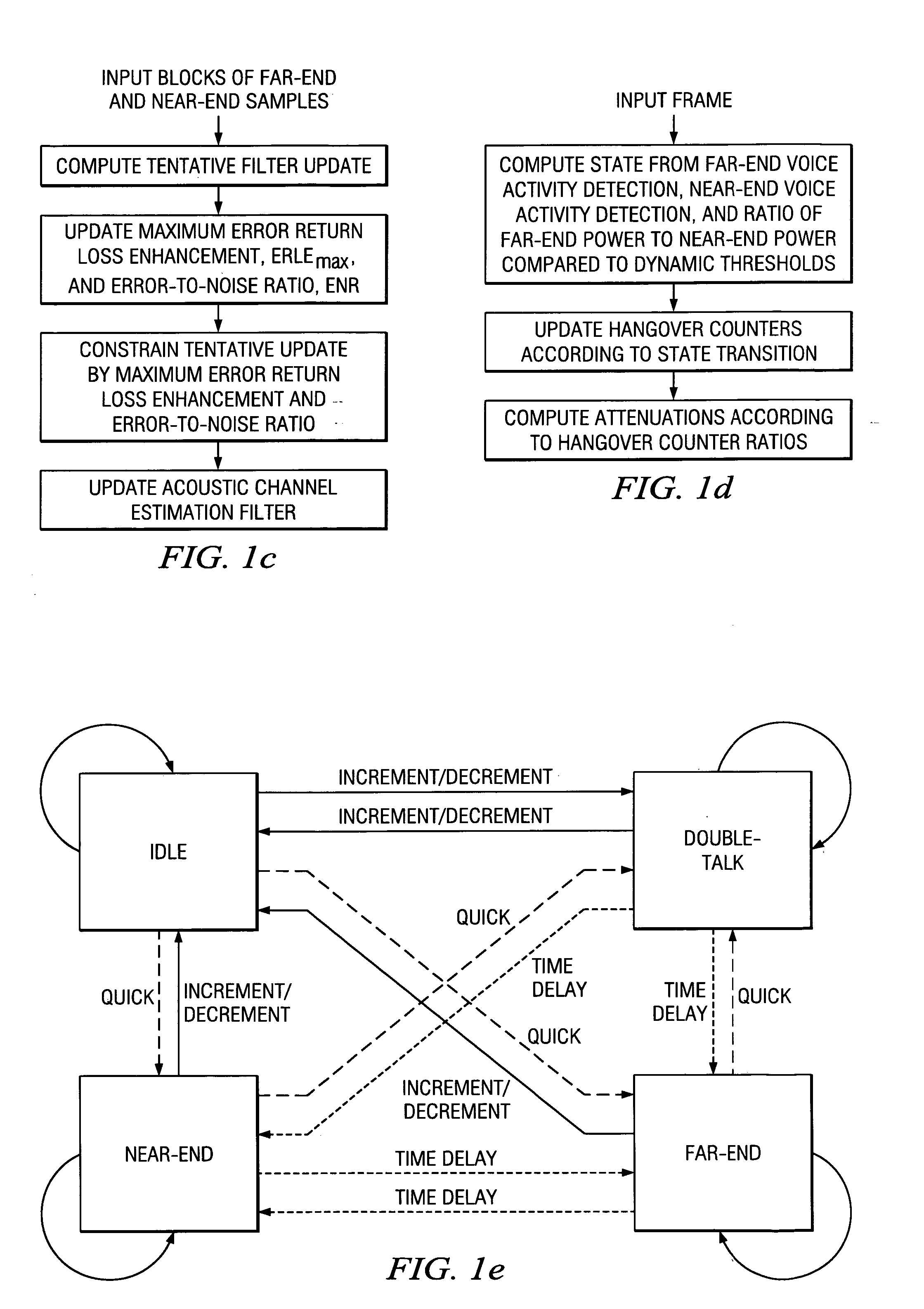
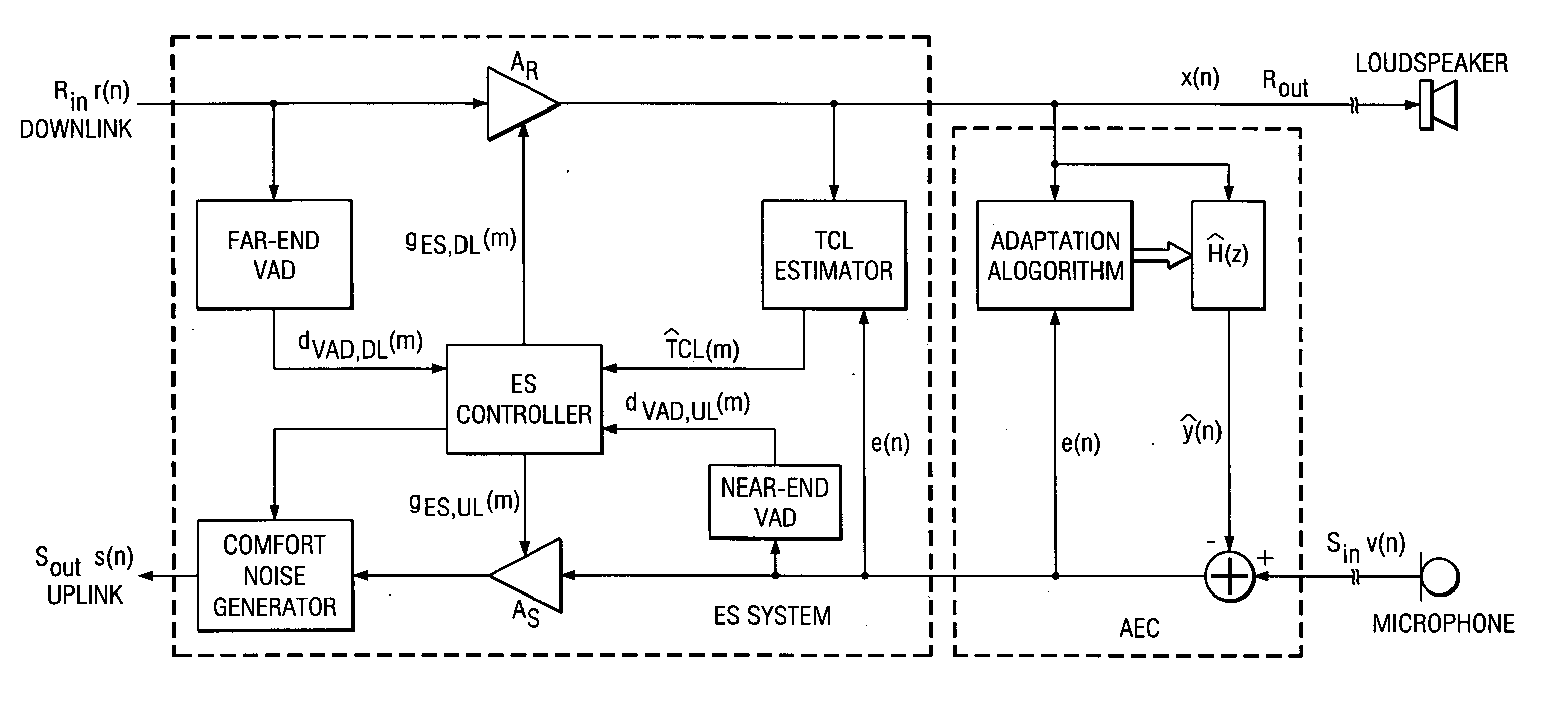
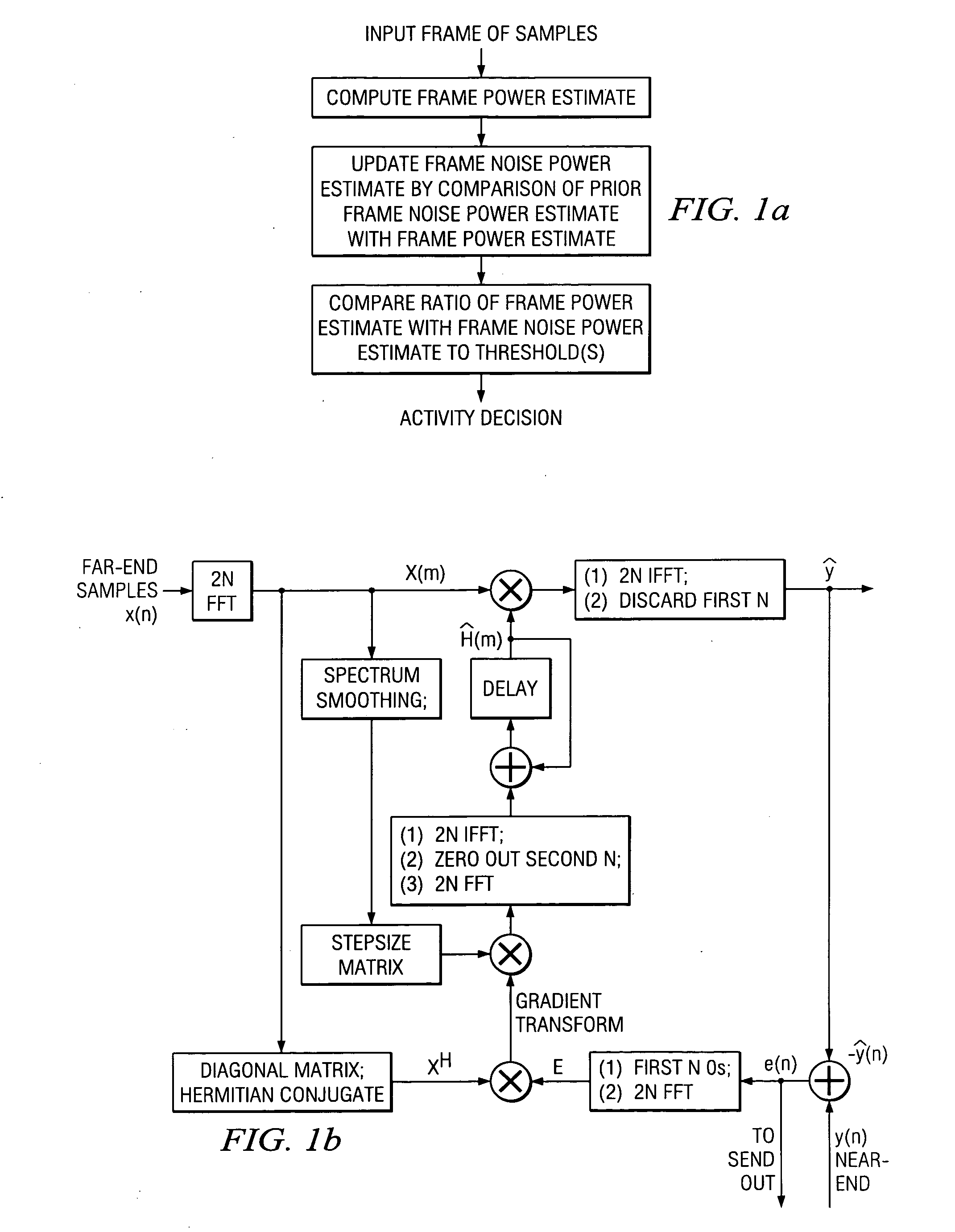
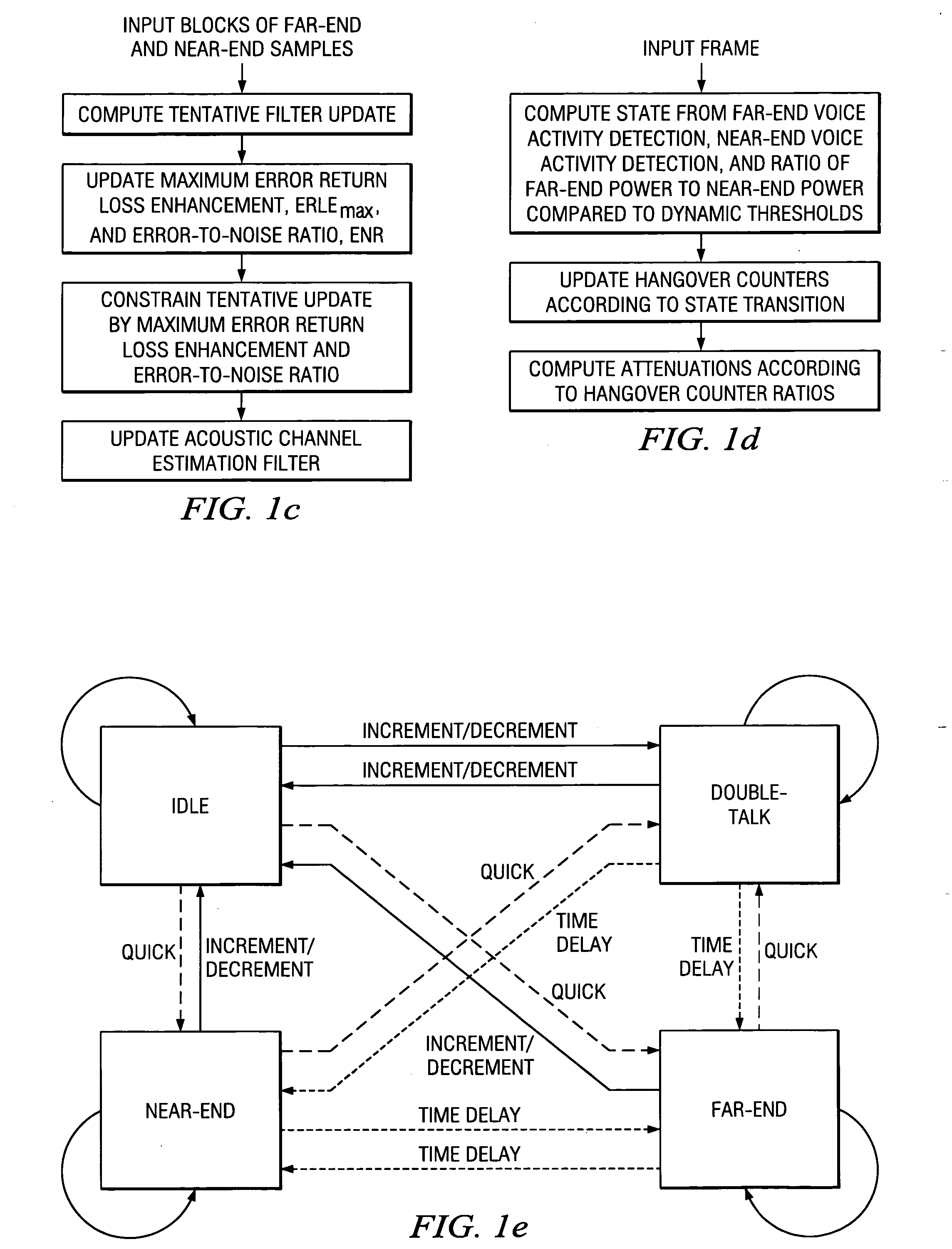
Acoustic echo devices and methods
Hands-free phones with voice activity detection using a comparison of frame power estimate with an adaptive frame noise power estimate, automatic gain control with fast adaptation and minimal speech distortion, echo cancellation updated in the frequency domain with stepsize optimization and smoothed spectral whitening, and echo suppression with adaptive talking-state transitions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method for solving high papr problem of mcm communication system using unitary transform
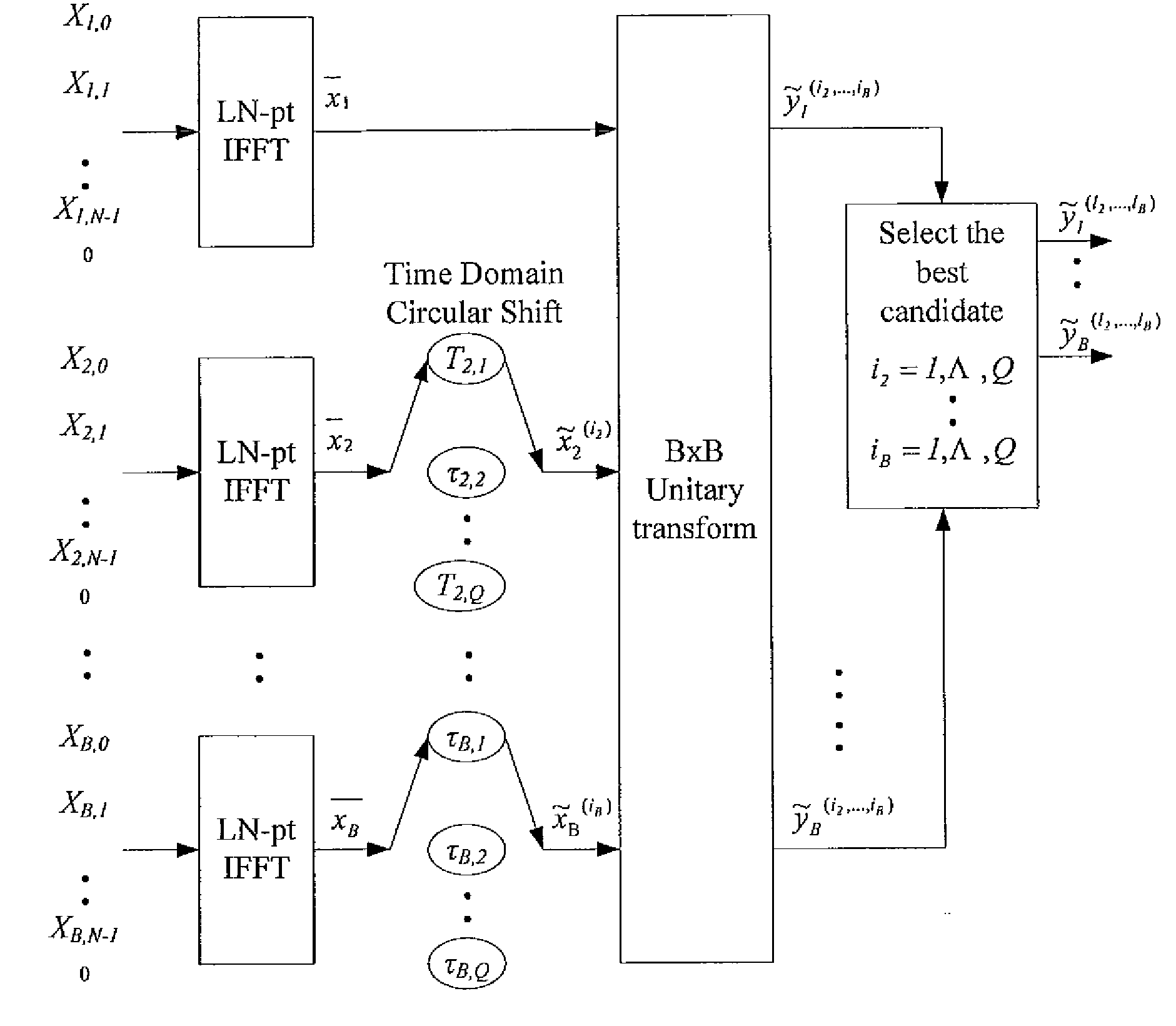
ActiveUS20090147870A1Sacrificing error rateLess complexSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainCommunications system
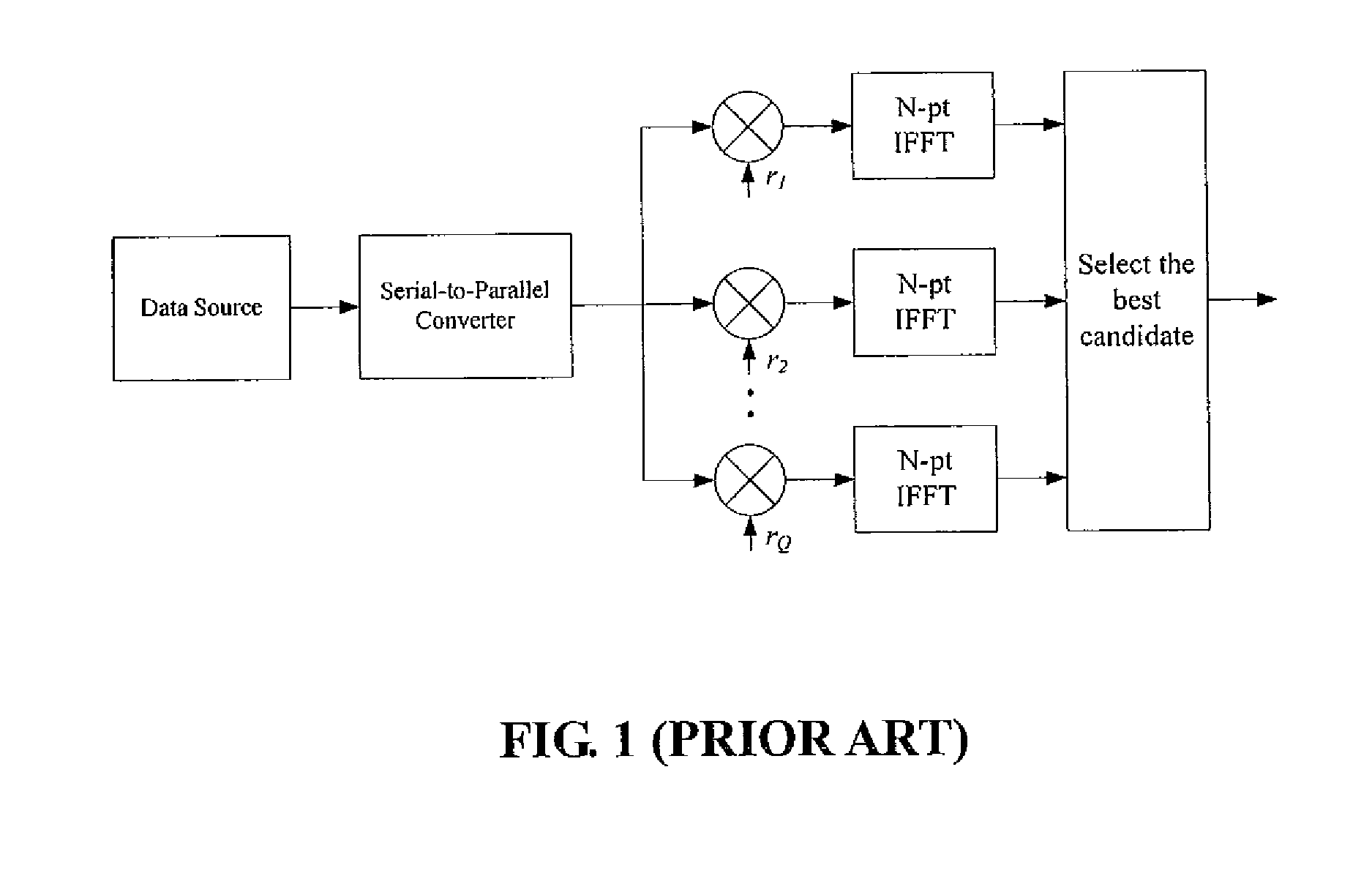
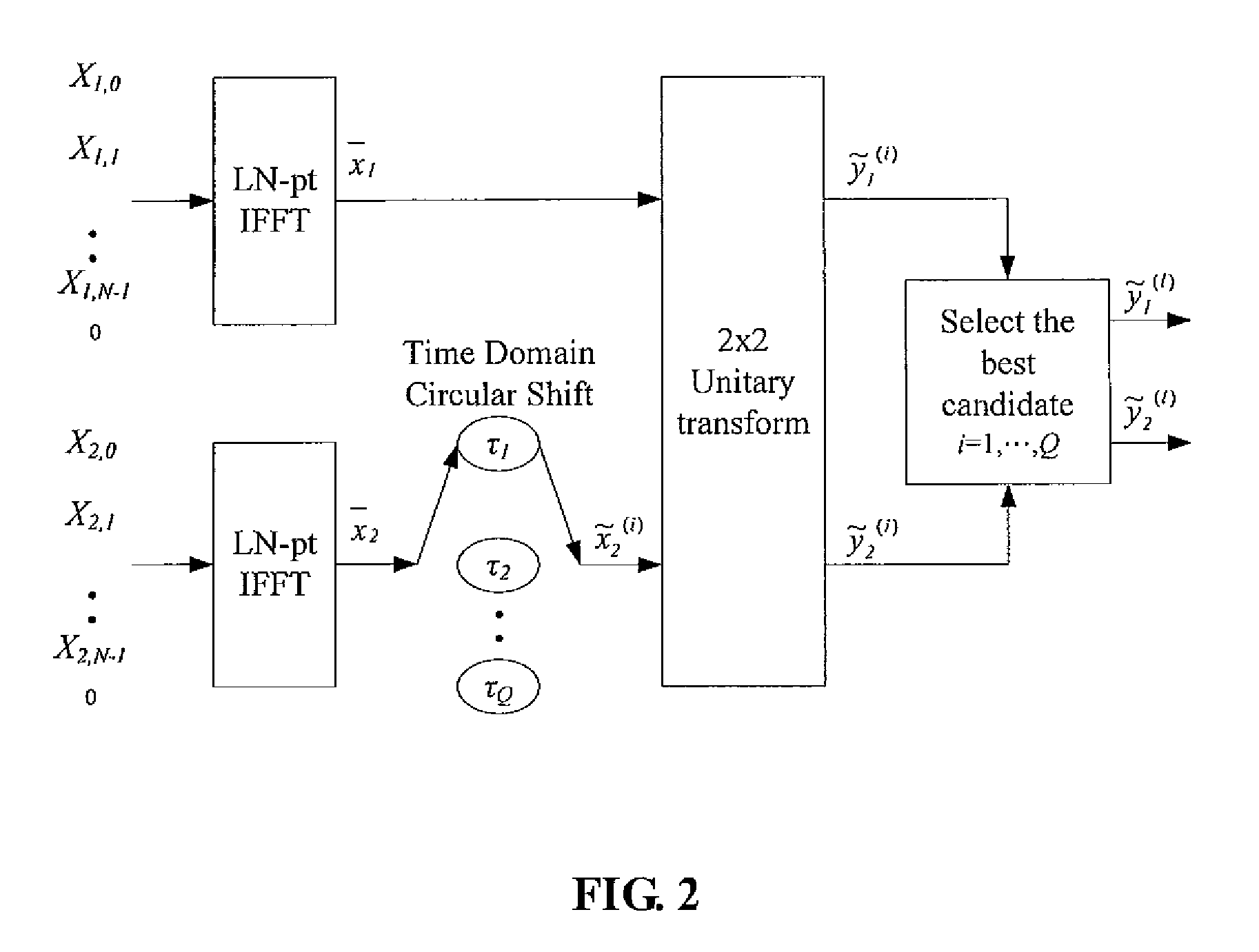
The method contains the following steps. First, in a MCM system with N sub-carriers, the baseband signal blocks Xj, j=1, 2, . . . ,B are supplemented with zeros and processed with LN-point IFFT, respectively, to obtain L-time oversampled time-domain signal blocks xj, j=1,2, . . . ,B. Then, xj undergoes Q Time Domain Circular Shifts or Frequency Domain Circular Shifts to obtain Q signal blocks {tilde over (x)}j(i<sub2>j< / sub2>), ij=1,Λ,Q. Subsequently, a B×B unitary transform is performed against ( x1,{tilde over (x)}2(i<sub2>2< / sub2>), . . . ,{tilde over (x)}B(i<sub2>B< / sub2>)). After the unitary transform, for each (i2, . . . ,iB) a combination having B time-domain signal blocks is obtained as follows: ({tilde over (y)}1(i<sub2>2< / sub2>, . . . ,i<sub2>B< / sub2>),{tilde over (y)}2(i<sub2>2< / sub2>, . . . ,i<sub2>B< / sub2>), . . . ,{tilde over (y)}B(i<sub2>2< / sub2>, . . . ,i<sub2>B< / sub2>)=( x1,{tilde over (x)}2(i<sub2>2< / sub2>), . . . ,{tilde over (x)}B(i<sub2>B< / sub2>)) cU where U is the B×B unitary matrix, and c is an arbitrary constant (c≠0). Finally, the total QB-1 combinations are compared against each other to select a best candidate for transmission that could produce the lowest peak value, or the smallest PAPR, or the lowest clipping noise power.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
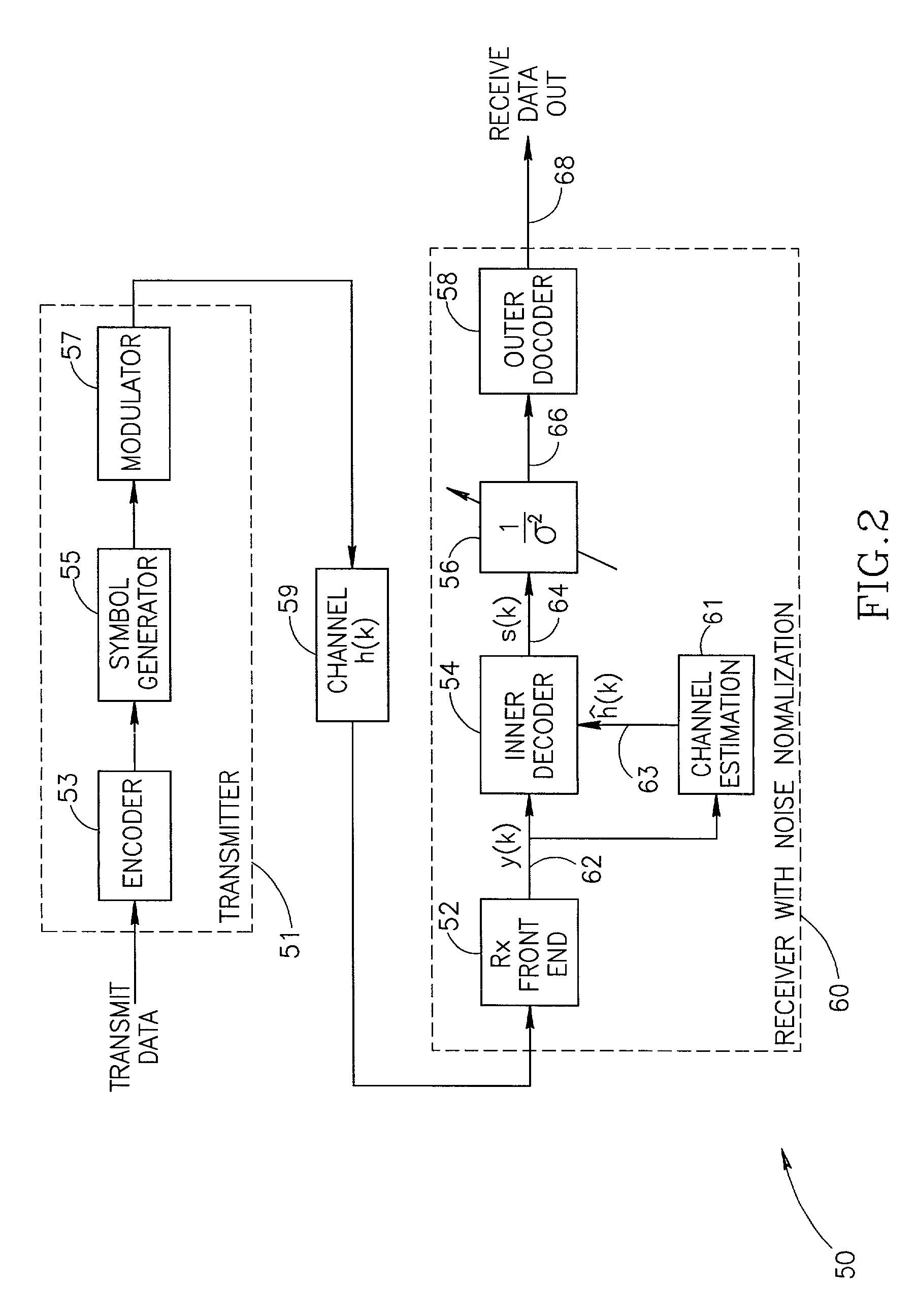
Normalization of equalizer soft output for channels with varying noise power
InactiveUS6980602B1Overcome disadvantagesSuitable for useData representation error detection/correctionError preventionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Computer science
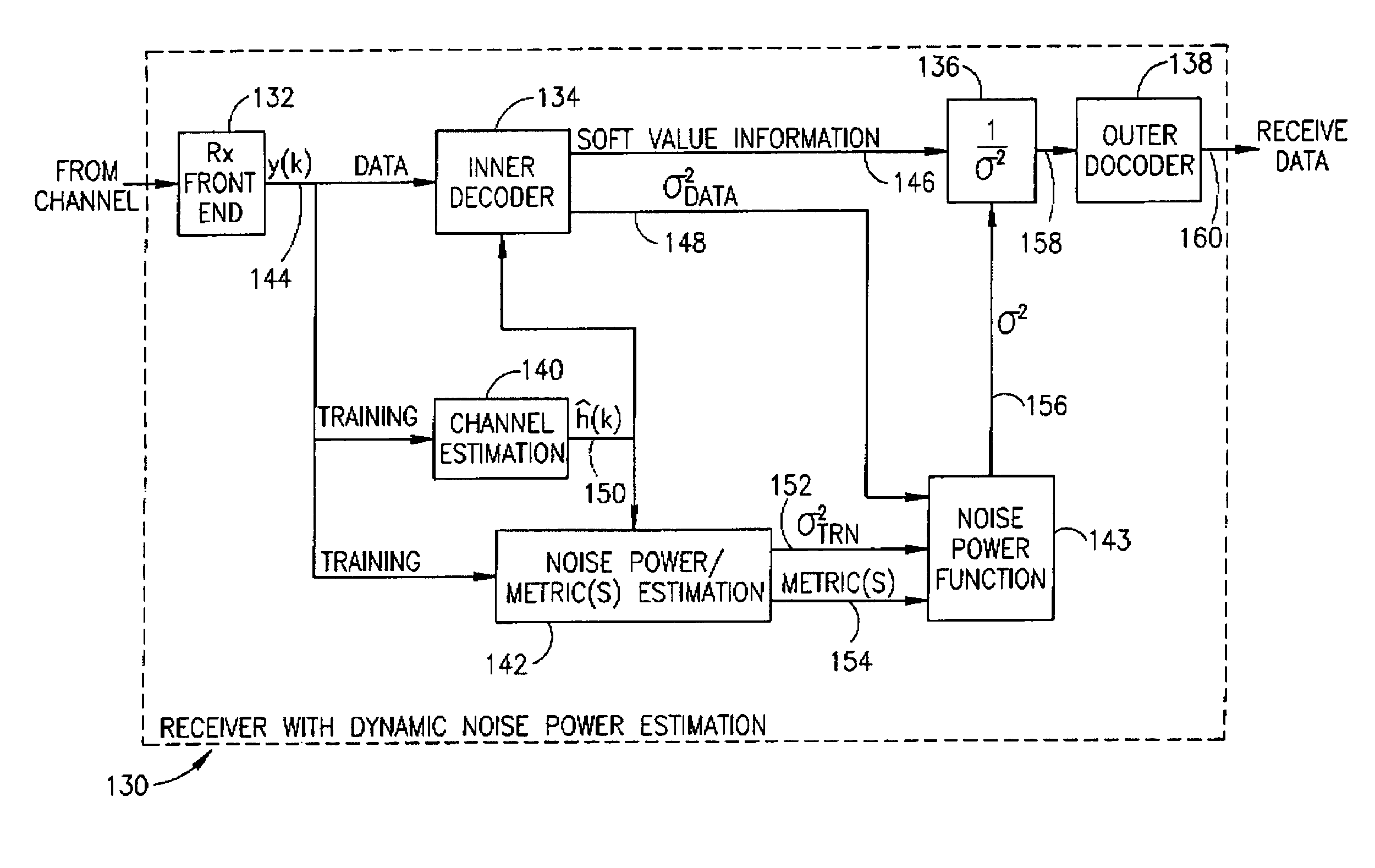
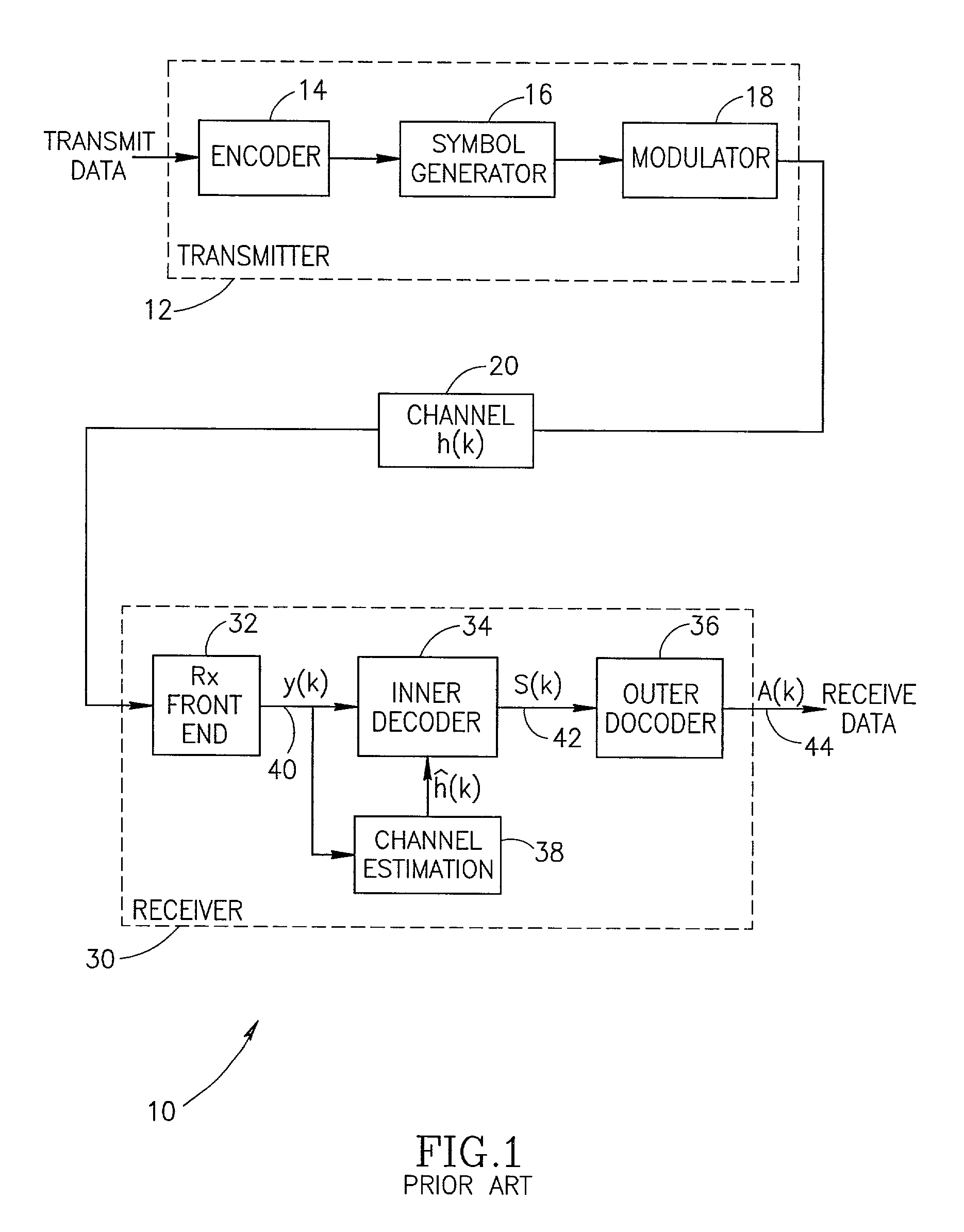
An apparatus for and method of generating normalized soft decision information output from an inner decoder (i.e. equalizer) in a communications receiver. The invention is operative to normalize the soft decision information before it enters a soft outer decoder. The normalization is performed using a noise power estimate that is dynamically calculated in response to changing noise statistics on the channel. The normalized soft decision output is then applied to the soft outer decoder thus realizing maximum performance therefrom. The noise power estimate is derived from the training sequence and / or the data portion of the received signal. Both types of estimates are calculated. A binary or smoothly weighted average is calculated using both types of estimates. The weighting factor is determined based on one or more performance metrics, such as the Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR).
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
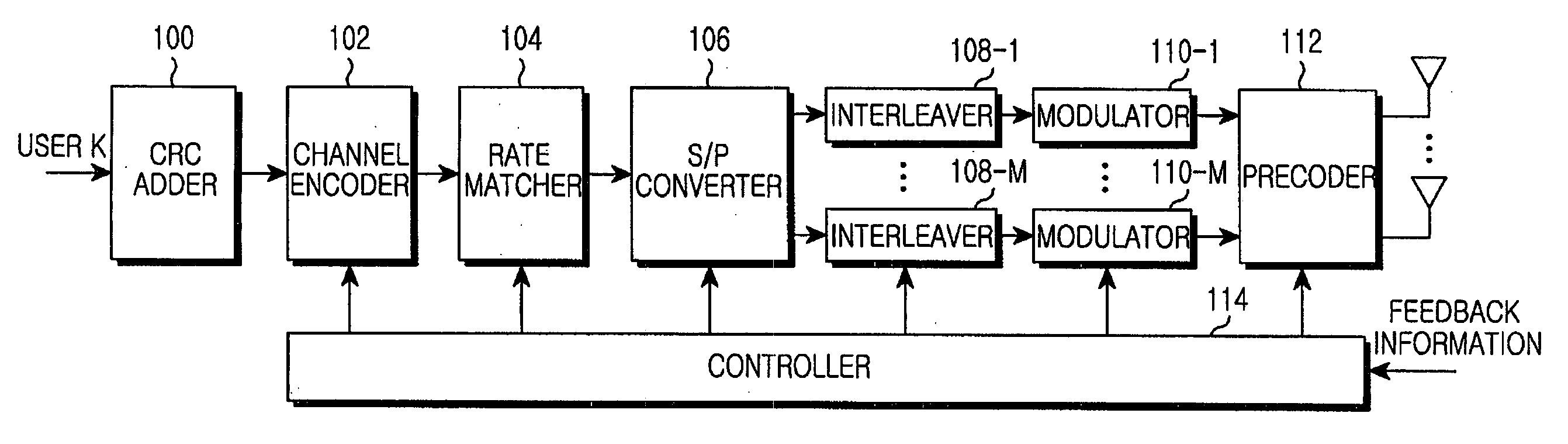
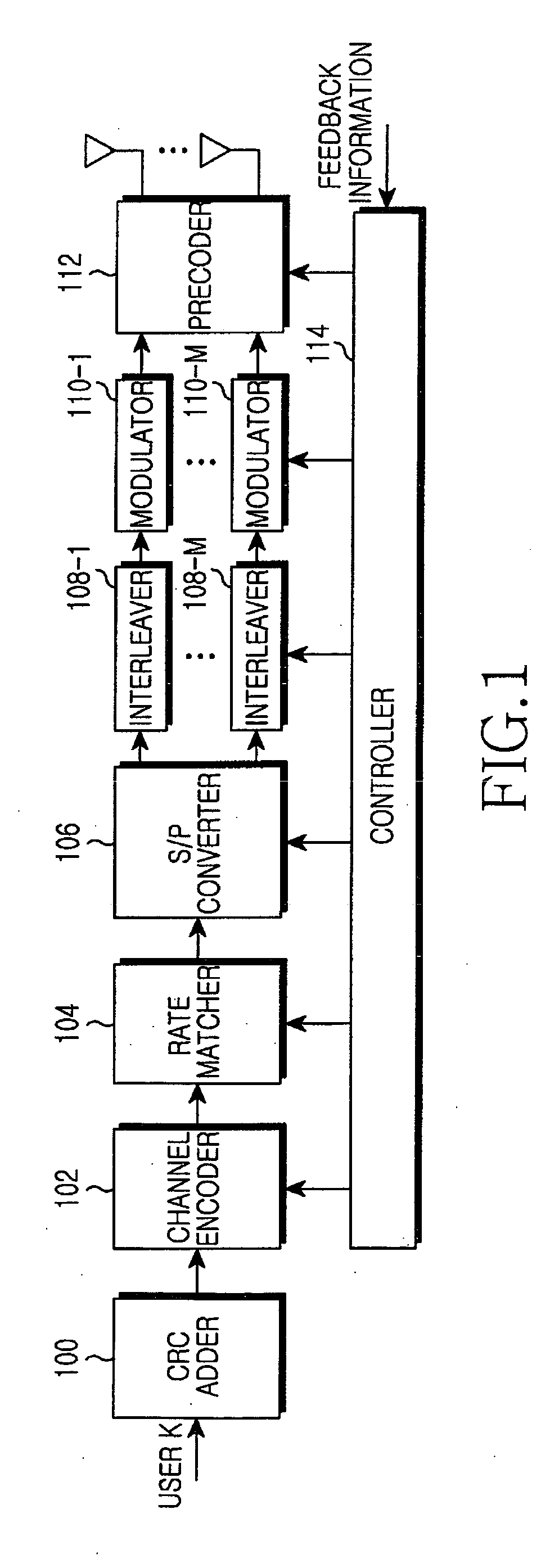
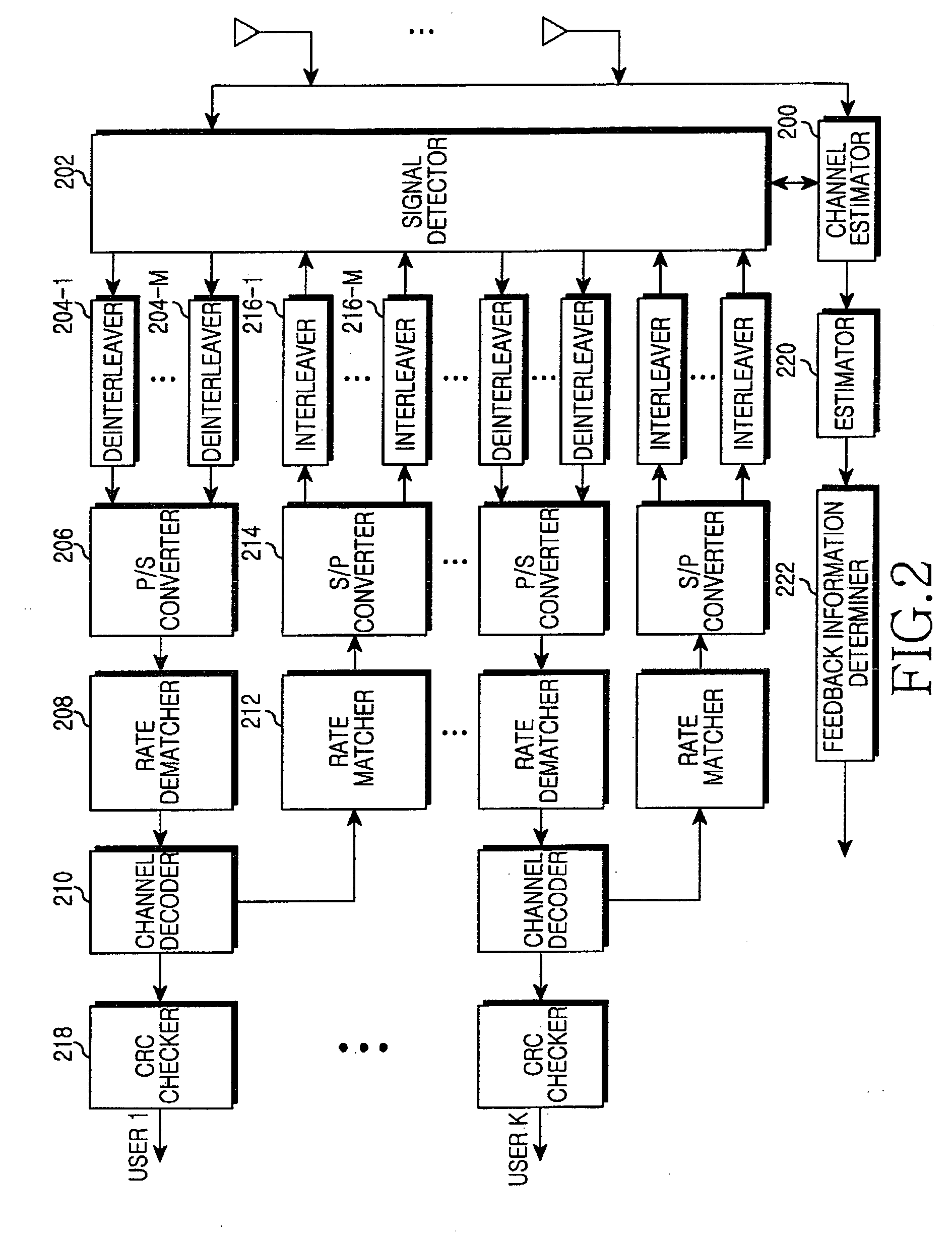
Transmitting/receiving apparatus and method for interleaver division multiple access system
InactiveUS20090060094A1Maximize transfer efficiencyChannel estimationAmplitude demodulationEngineeringNoise power
Provided is a transmitting / receiving apparatus and method for an IDMA system. The receiving apparatus includes a channel estimator, an estimator, and a determiner. The channel estimator estimates a channel using a multi-user signal received through at least one RX antenna. The estimator estimates the noise power and the signal power for each transmission layer of each user by using the estimated channel value from the channel estimator. The determiner determines the number of transmission layers for each user and an MCS level for each transmission layer by using the signal power and the noise power estimated by the estimator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optimization of channel equalizer
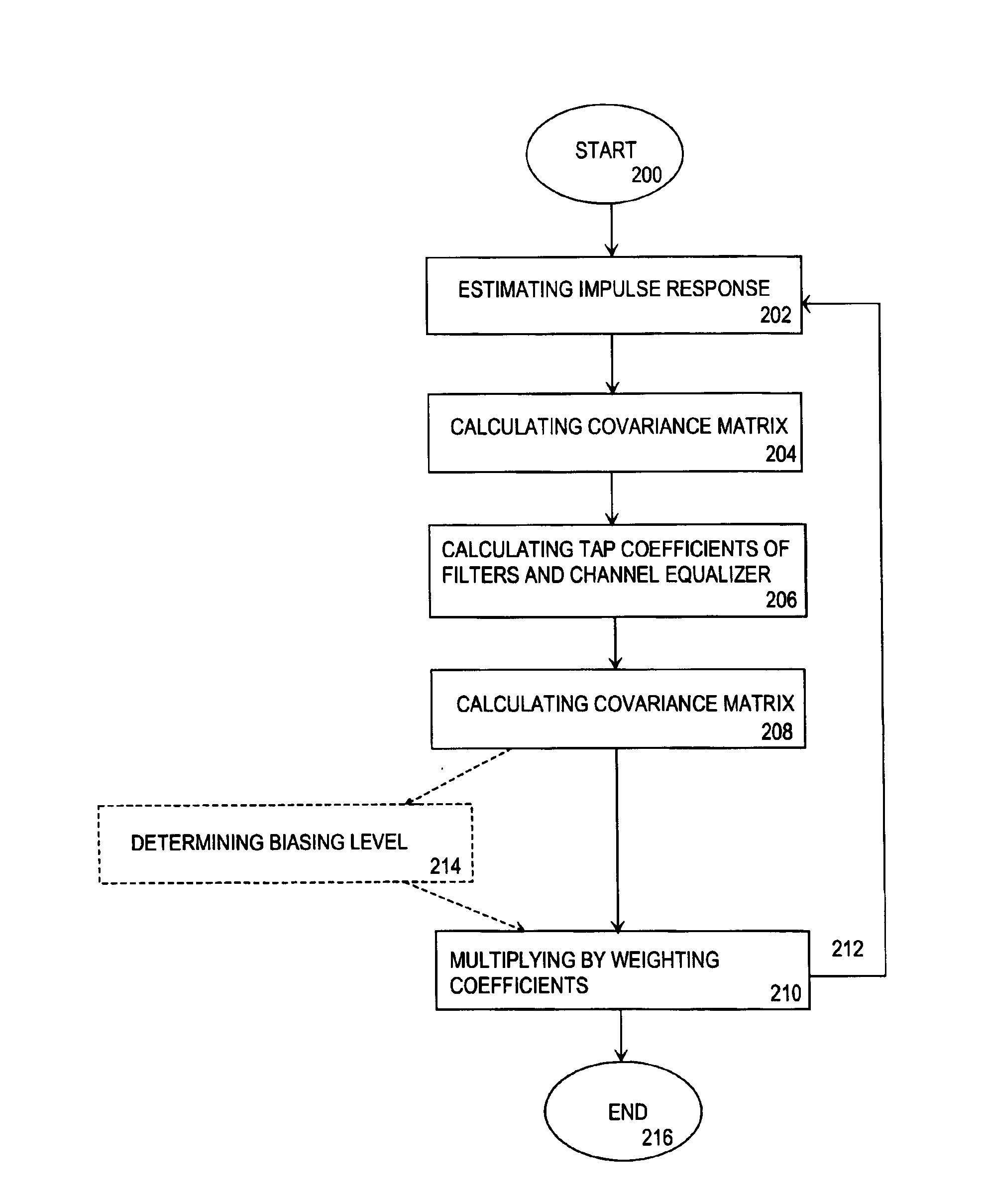
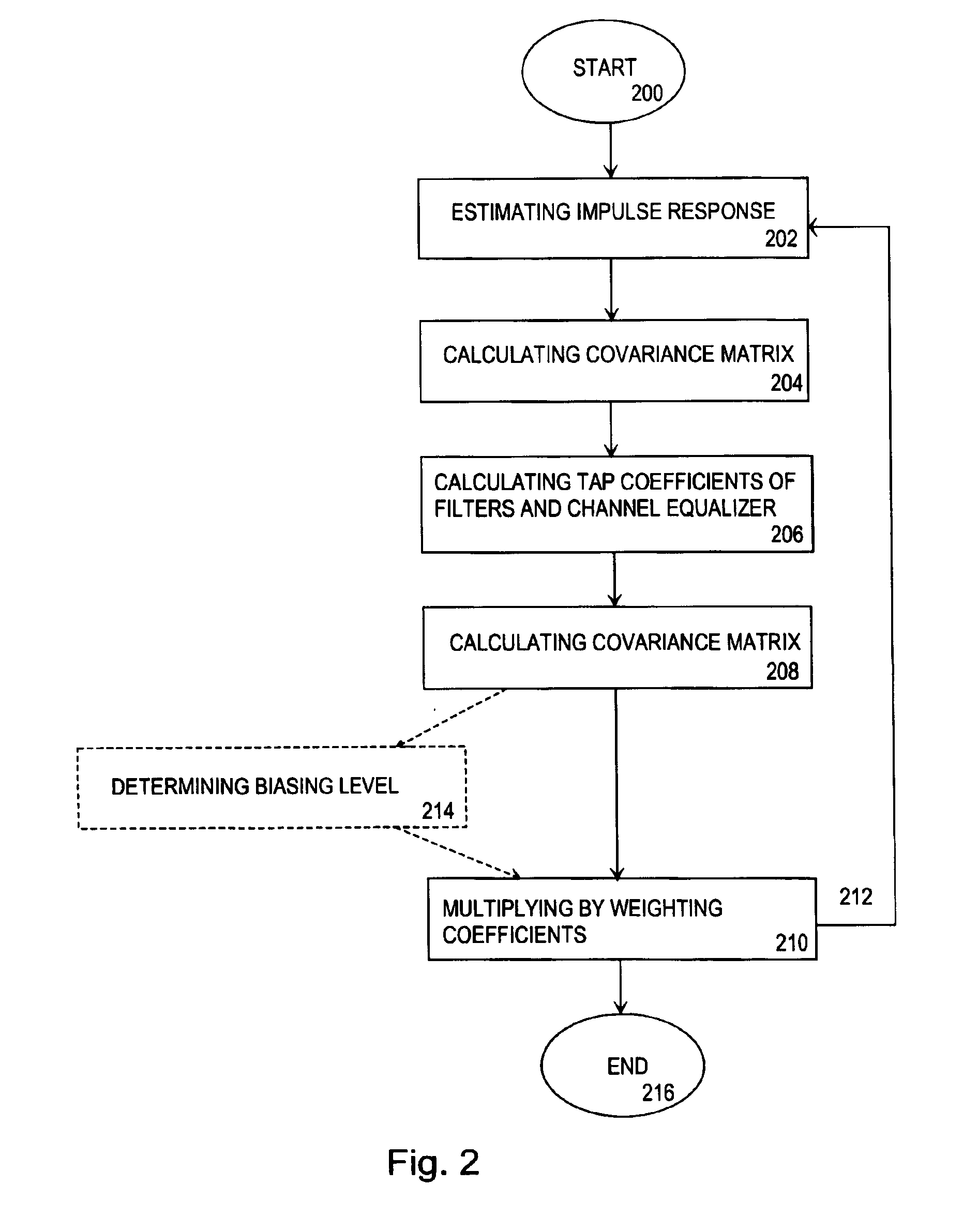
InactiveUS6954495B2Improve channel performanceImprove performanceMultiple-port networksError preventionWeight coefficientRadio receiver
A method for carrying out channel equalization in a radio receiver wherein an impulse response is estimated, noise power is determined by estimating a co-variance matrix of the noise contained in a received signal before prefiltering, and tap coefficients of prefilters and an equalizer are calculated. The method comprises determining the noise power after prefiltering by estimating a noise covariance matrix, after which input signals of the channel equalizer are weighted by weighting coefficients obtained from the noise covariance estimation.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
SINR measurement method for OFDM communications systems
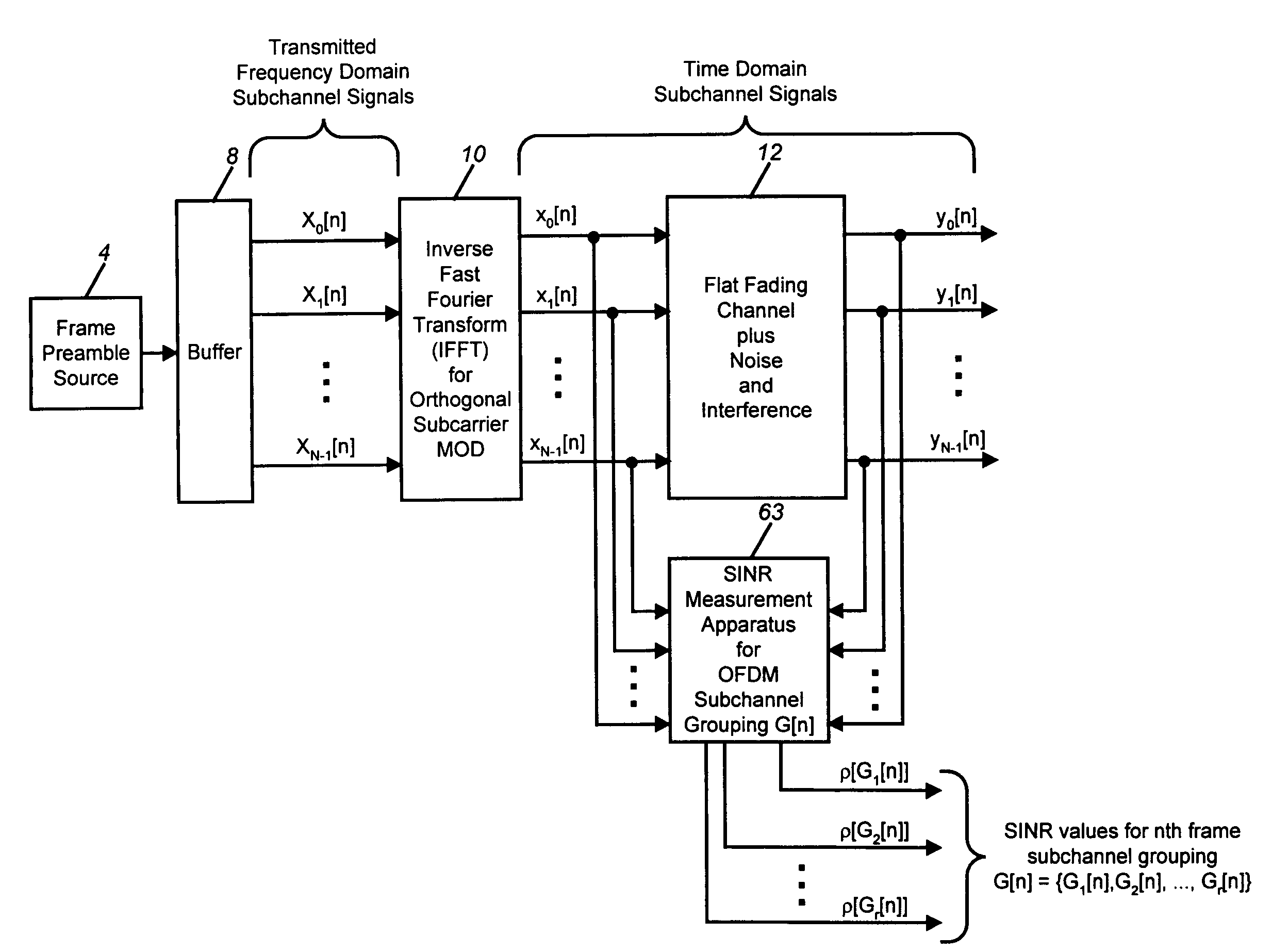
ActiveUS7260054B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency-division multiplexEngineeringMulti carrier
A signal to interference-plus-noise power ratio (SINR) measurement method for wireless communications systems which employ orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) for multicarrier data transmission is disclosed. Fast-Fourier transform (FFT)-based SINR measurements can be computed on frame-by-frame or greater interval for individual or groupings of subchannel signals. Given a known transmitted time-domain OFDM frame preamble, and the corresponding channel and interference-plus-noise (IPN) corrupted received time-domain frame preamble, the disclosed method first computes the power spectral densities of the received signal of interest and of a received unwanted interference-plus-noise signal. The FFT-computed power spectral densities are then used to compute average received signal and received IPN power measurements for specified individual or groupings of OFDM subchannel signals. The power measurements are then frame-averaged using a recursive exponential smoothing method. The frame-averaged signal and IPN power measurements are then used to form quantized measurements of SINR for the specified OFDM subchannel signals of the received frame.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Apparatus and method for estimating interference and noise in a communication system
ActiveUS20050152480A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemCarrier signal
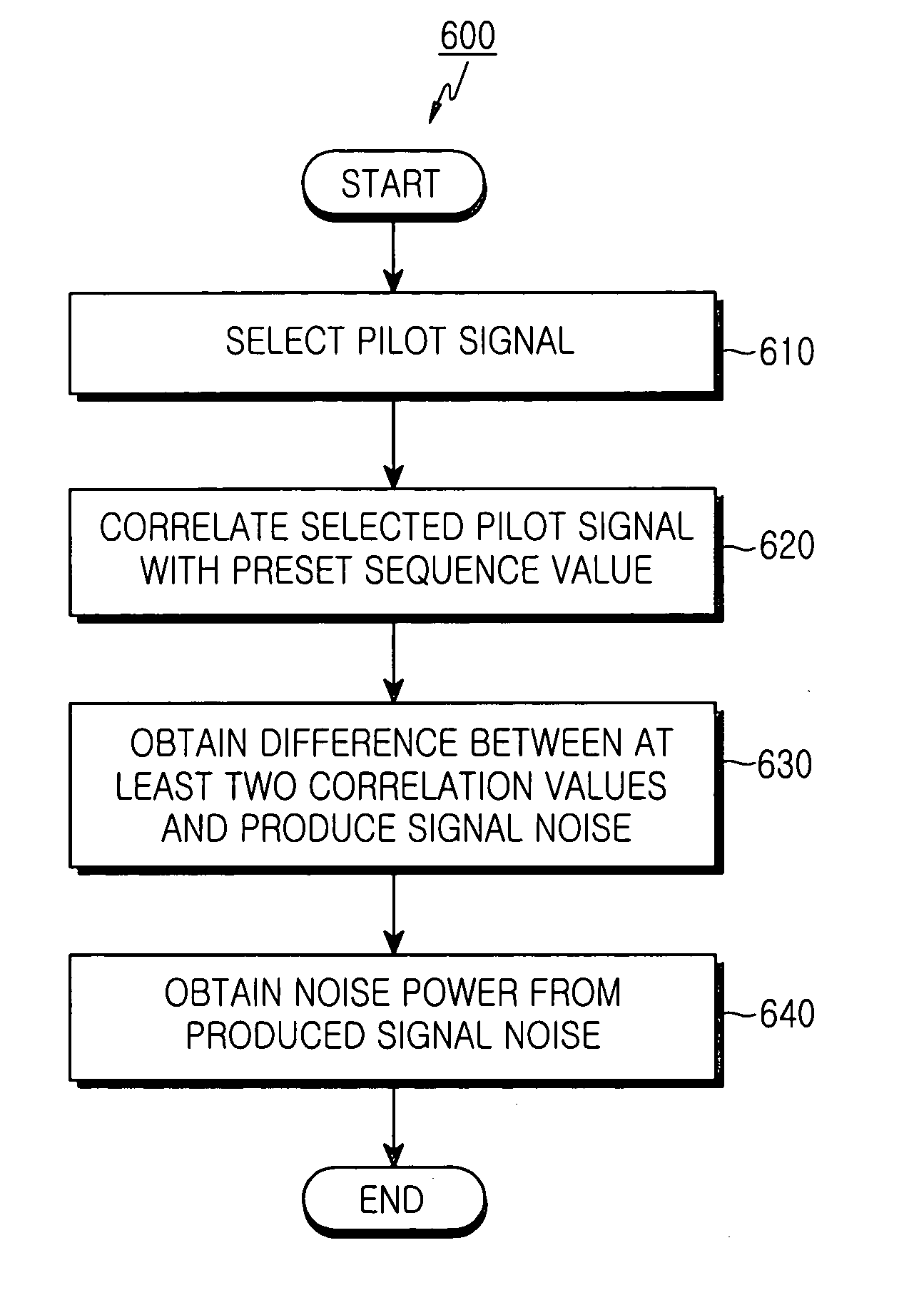
A method and apparatus for estimating interference and noise power in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing / orthogonal frequency division multiple access / discrete multi-tone (OFDM / OFDMA / DMT) system is disclosed. A correlator correlates a plurality of sub-carriers with a preset reference sequence on an element-by-element basis and outputs a result of the correlation. A signal noise producer calculates a difference between a correlation value associated with each of the plurality of sub-carriers output from the correlator and a correlation value produced from at least one adjacent sub-carrier and outputs a result of the calculation. An interference and noise power producer produce interference and noise power from the difference between the correlation values calculated by the signal noise producer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method, and computer program
InactiveUS20100008406A1Avoid mistakesReduce estimation errorTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityEqualizationComputer science
A wireless communication apparatus compensates for phase and amplitude imbalances existing among transmit and receive branches, while also preventing likelihood information and SNR estimation error produced by such imbalance compensation. In an apparatus having a plurality of transmit and receive antennas and respective branches for each antenna, a calibration processor multiplies receive signals in each receive branch by antenna calibration coefficients, in order to correct phase and amplitude imbalances existing among the receive branches. A transmit beamforming matrix estimator then estimates a transmit beamforming matrix by using the multiplied receive signals. An estimator then solves for estimated values such as the noise power, likelihood information, and channel waveform equalization values for each receive branch, and in addition, derives a final estimated value that takes the multiplication by correction coefficients into account when averaging the estimated values for each receive branch or when computing a weighted average according to likelihood.
Owner:SONY CORP
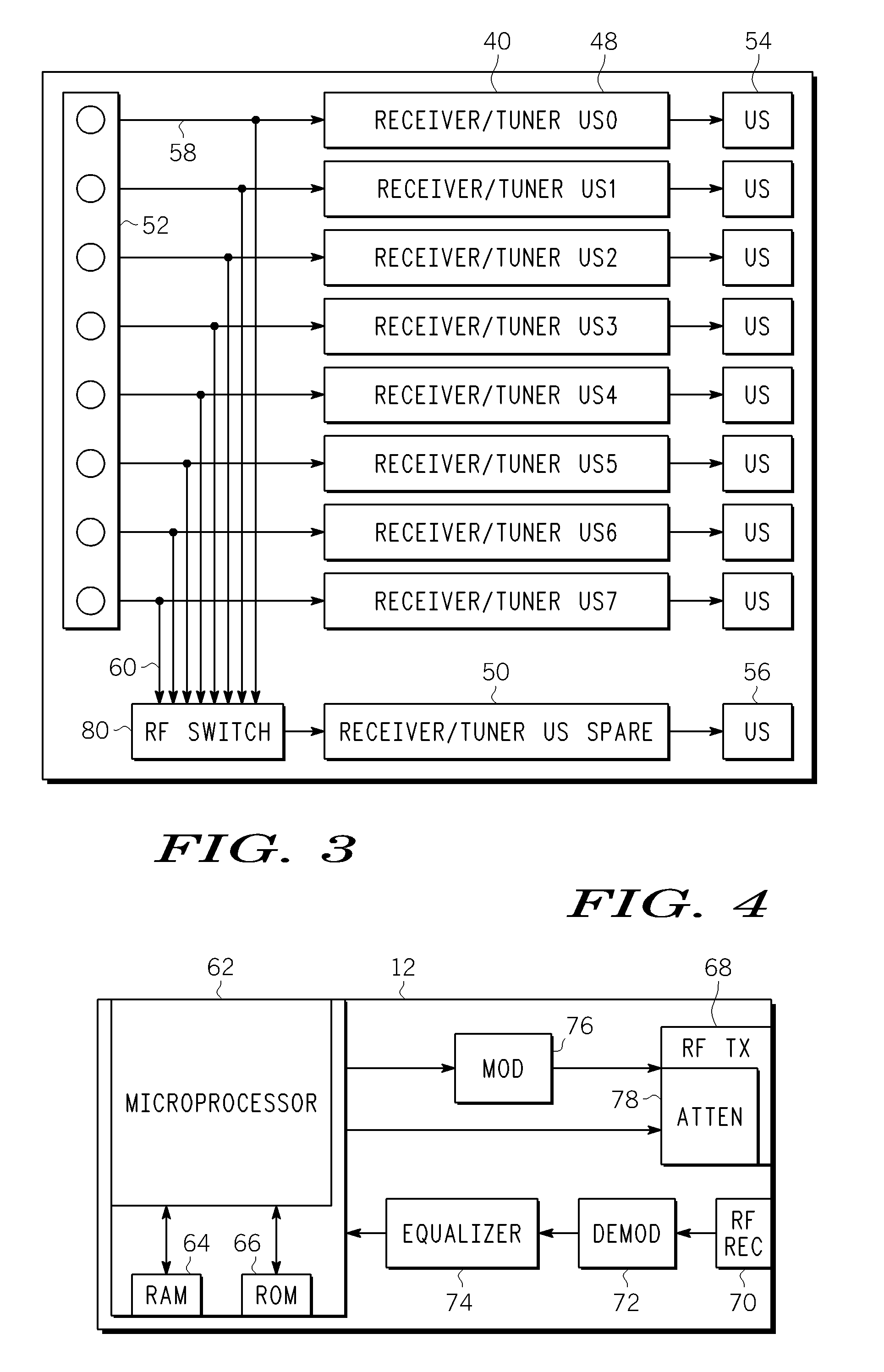
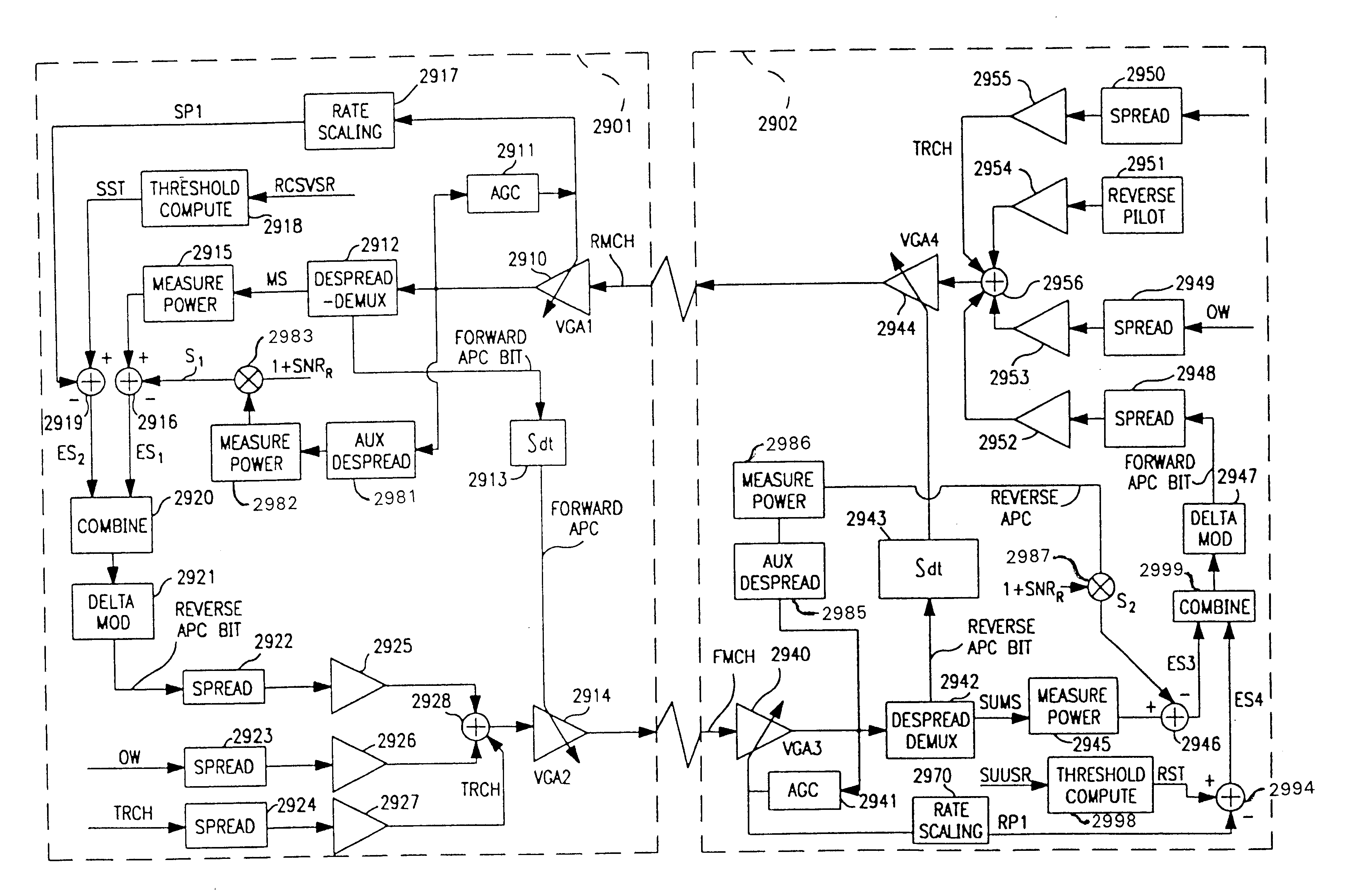
Apparatus for adaptive forward power control for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20020057659A1Easy to liftShortens channel acquisition timeError preventionRadio transmission for post communicationSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioSet point
A code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) system employing spread-spectrum modulation. The CDMA system has a base station (BS), and a plurality of subscriber units. The signals transmitted between the base station and subscriber unit use spread-spectrum modulation. The improvement apparatus for adaptive forward power control (APC) from a base station (BS) to a subscriber unit (SU), includes sending from the base station, using spread-spectrum modulation, a BS-spreading code on a forward channel. The subscriber unit despreads the BS-spreading code on the forward channel as a despread signal, determines a first power level Pd which includes power of the despread signal plus noise and a second power level PN, which includes despread-noise power. The subscriber unit determines a first error signal e1, from the first power level Pd, the second power level PN, and a required signal-to-noise ratio SNRREQ for service type, and a second error signal e2, from a measure of total received power Pr and an automatic gain control (AGC) set point Po. The subscriber unit forms a combined error signal from the first error signal e1, the second error signal e2, a first weight a1 and a second weight a2, and hard limits the combined error signal to form a single APC bit. The APC bit is transmitted to the base station. In response to the APC bit, the base station adjusts transmitter power to the subscriber unit.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Methods and System for Determining a Dominant Impairment of an Impaired Communication Channel
InactiveUS20100157824A1Easy to identifyEasy to distinguishError preventionTransmission systemsEngineeringReview of systems
Methods are described for identifying a dominant impairment on a communication channel impaired by an interference issue. The methods include systematic examination of total power loading, systematic examination of signal power reduction, statistical examination of communication channel noise power, and systematic examination of interleaver effectiveness. Each relates to automatically diagnosing and characterizing distortion-based interference issues by monitoring the performance of a communication channel during a testing procedure. These methods enable a technician or engineer to remotely diagnose distortion-based interference issues relatively quickly without having to use external test equipment and without having to deploy technicians to various locations within the cable plant. A system by which these methods can be implemented is also disclosed.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Apparatus for adaptive reverse power control for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS6940840B2Increase profitRadio transmission for post communicationLink quality based transmission modificationSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioAutomatic gain control
A code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) system employing spread-spectrum modulation. The CDMA system has a base station (BS), and a plurality of subscriber units. The signals transmitted between the base station and subscriber unit use spread-spectrum modulation. The improvement method for adaptive reverse power control (APC) from a subscriber unit (SU) to a base station (BS), comprises the steps of sending from the subscriber unit, using spread-spectrum modulation, a SU-spreading code on a reverse channel. The base station despreads the SU-spreading code on the reverse channel as a despread signal, determines a first power level Pd which includes power of the despread signal plus noise and a second power level PN, which includes despread-noise power. The base station determines a first error signal e1, from the first power level Pd, the second power level PN, and a required signal-to-noise ratio SNRREQ for service type, and a second error signal e2, from a measure of total received power Prt at the base station, and an automatic gain control (AGC) set point Po. The base station forms a combined error signal from the first error signal e1, the second error signal e2, a first weight a1, and a second weight a2, and hard limits the combined error signal to form a single APC bit. The APC bit is transmitted to the subscriber unit. In response to the APC bit, the subscriber adjusts transmitter power to the base station.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
System and method for estimating noise power level in a multi-signal communications channel
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Communication environment measurement method for mobile station and the mobile station
InactiveUS20060211391A1Prevent drop in communication throughputQuick controlAssess restrictionRadio transmissionCommunications systemData signal
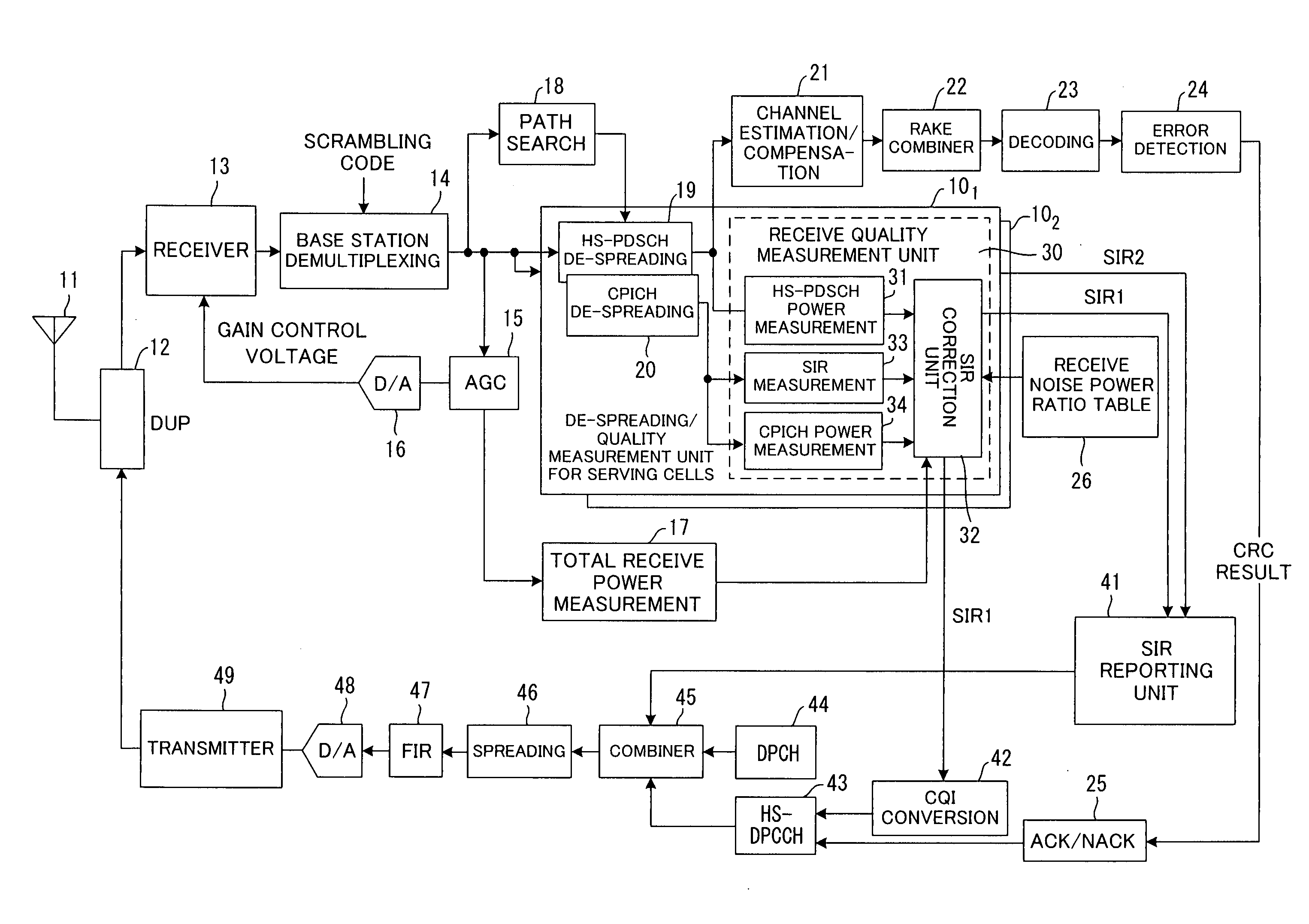
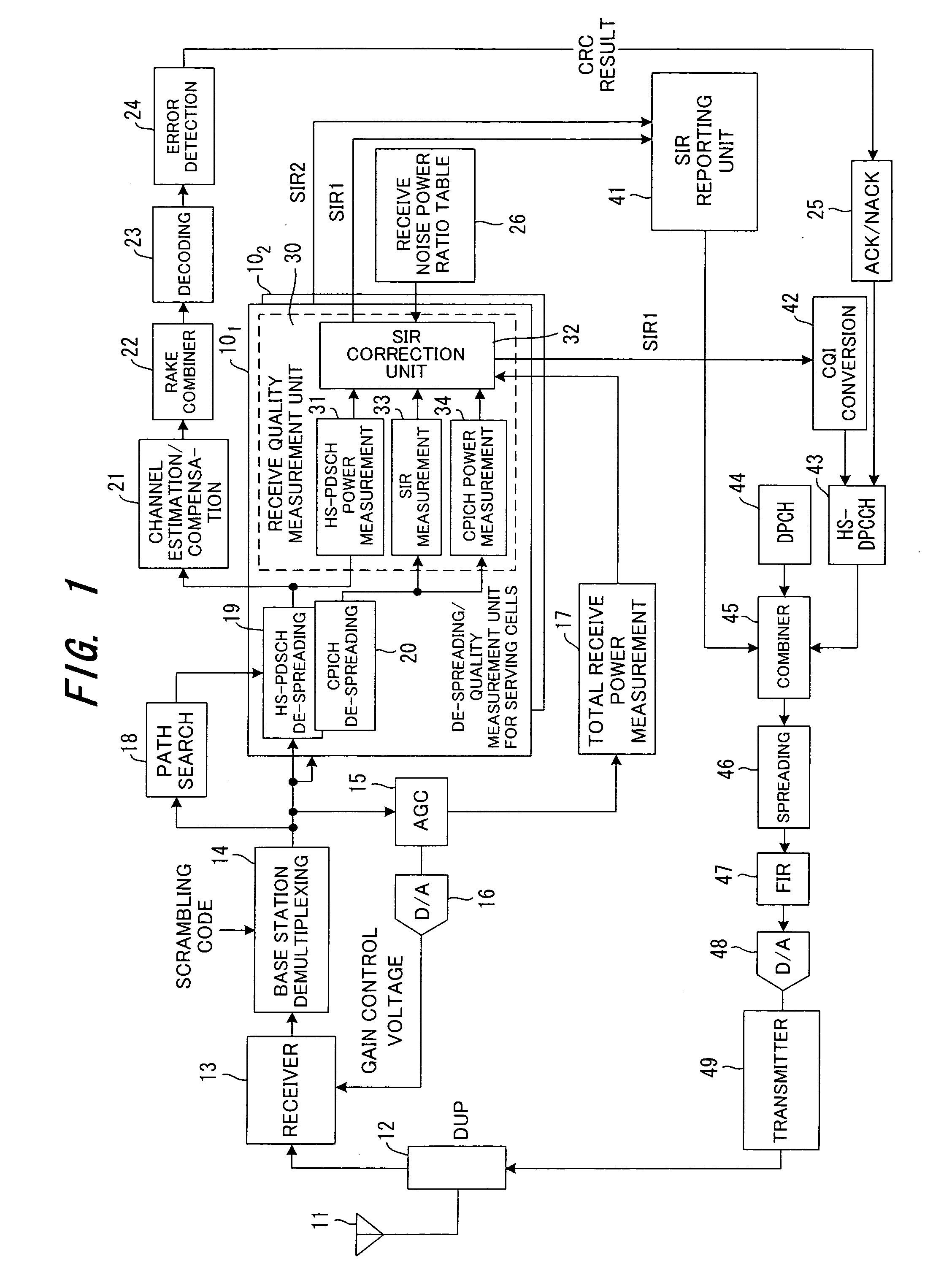
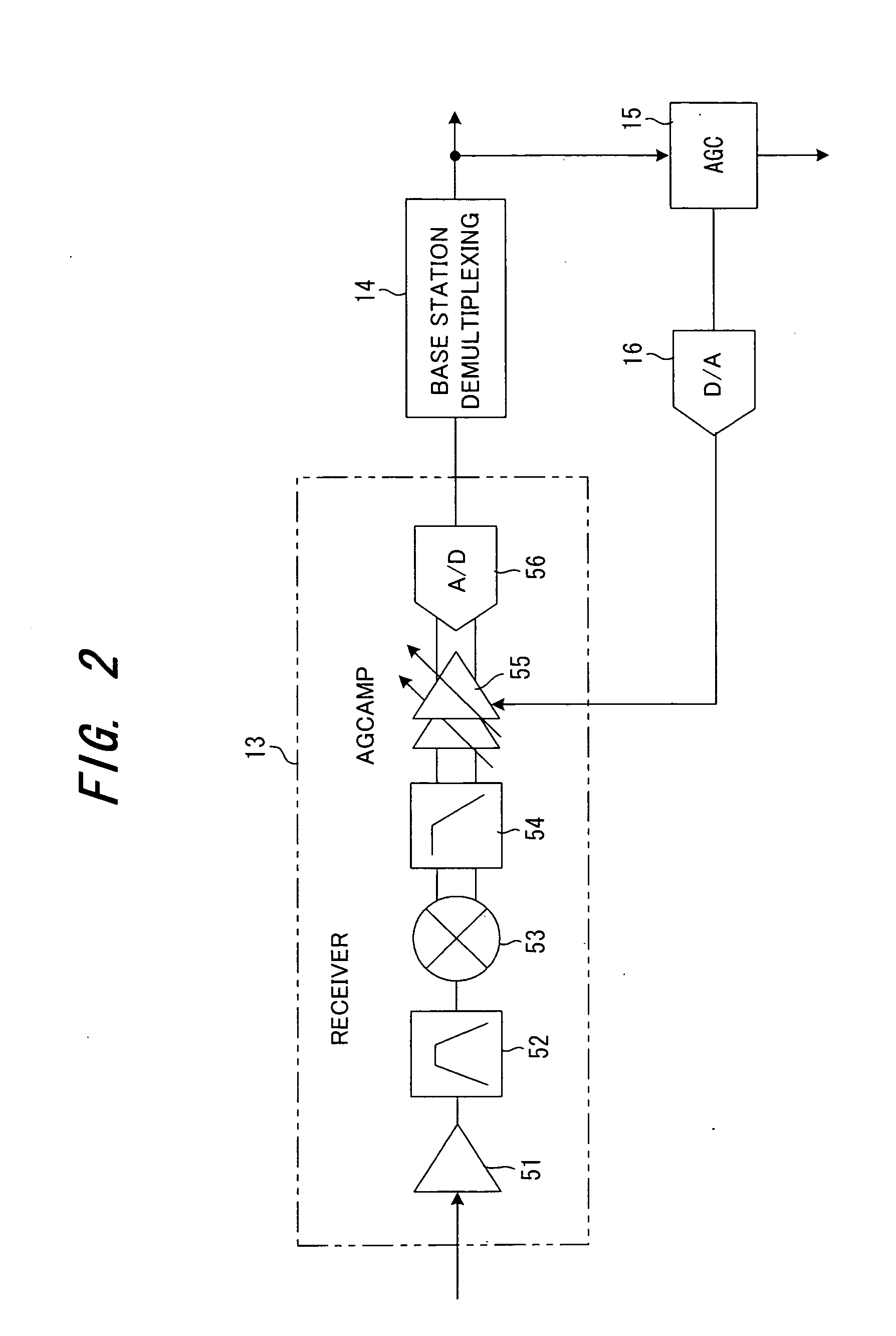
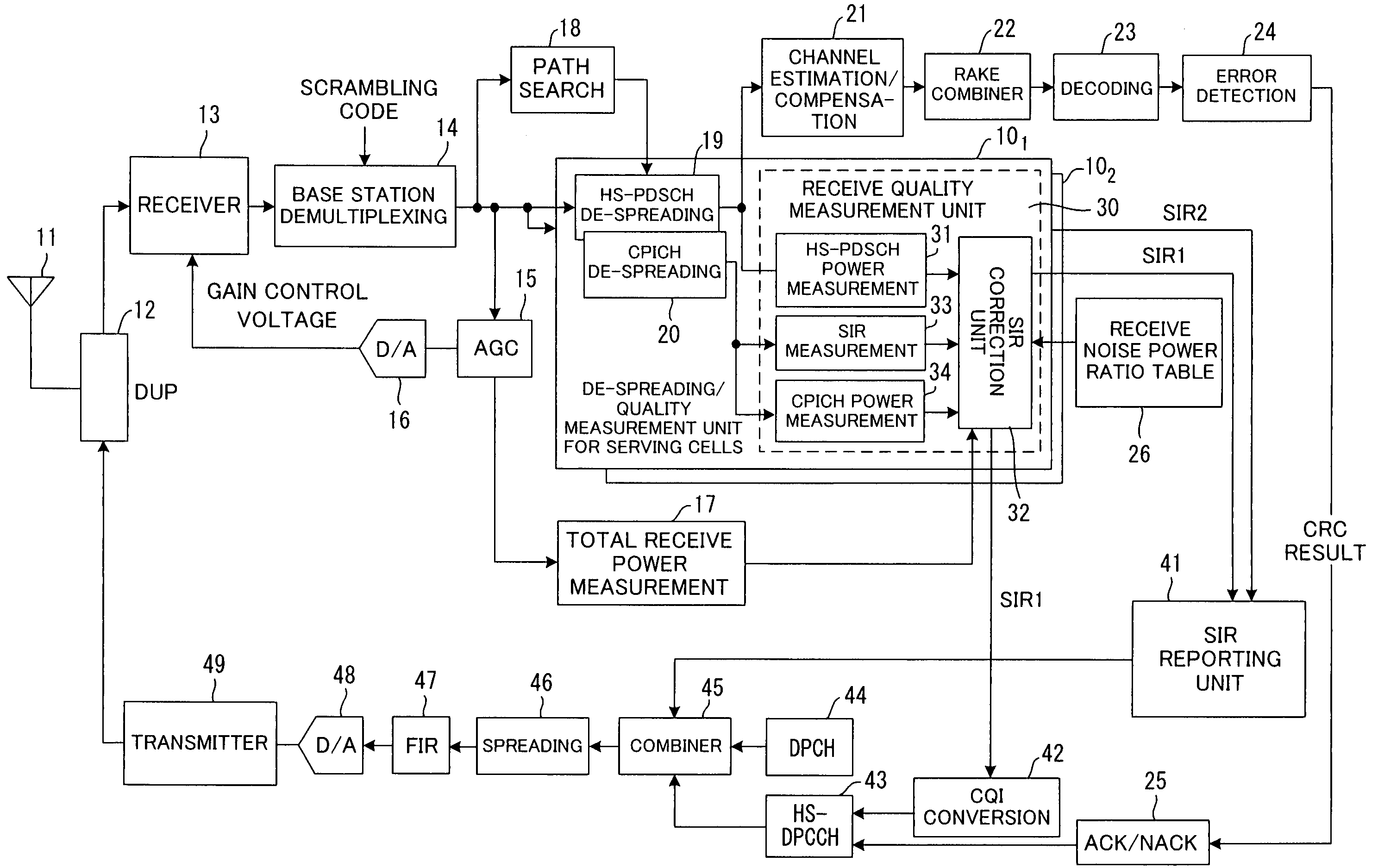
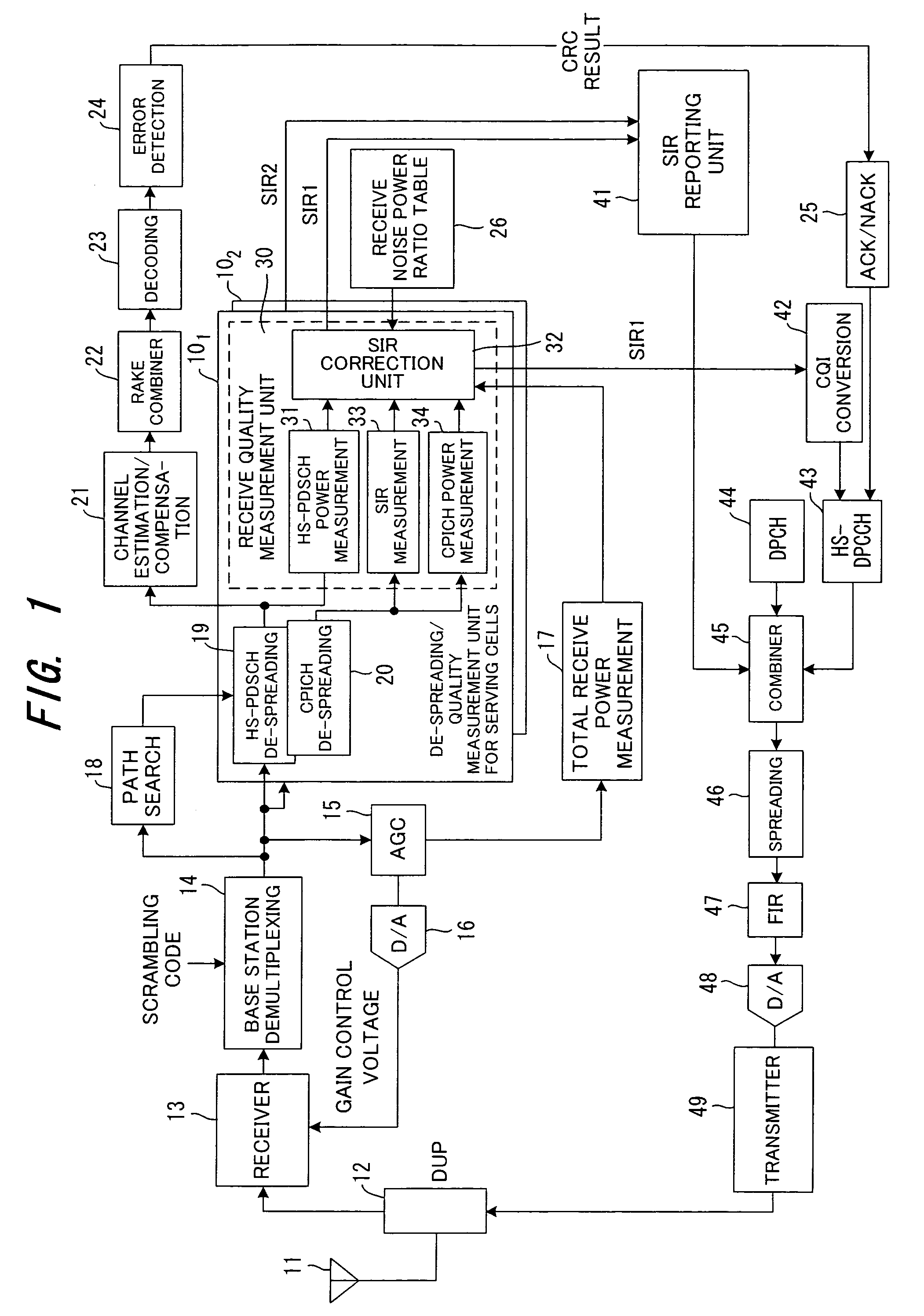
In a communication system for respectively transmitting pilot signals from a plurality of base stations to a mobile station via a first channel and also for transmitting data from one base station to a mobile station via a second channel, the mobile station corrects total receive power at the time of handover by subtracting power of the data signal received via the second channel from the total receive power of the signals received from a base station in communication (serving cells) via the second channel, then corrects the total noise power based on the total receive power after the correction, and measures the communication environment between the base station and the mobile station using the power of the pilot signal received from the base station in-communication and the corrected total noise power.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus to reduce the jitter in wideband PLL frequency synthesizers using noise attenuation
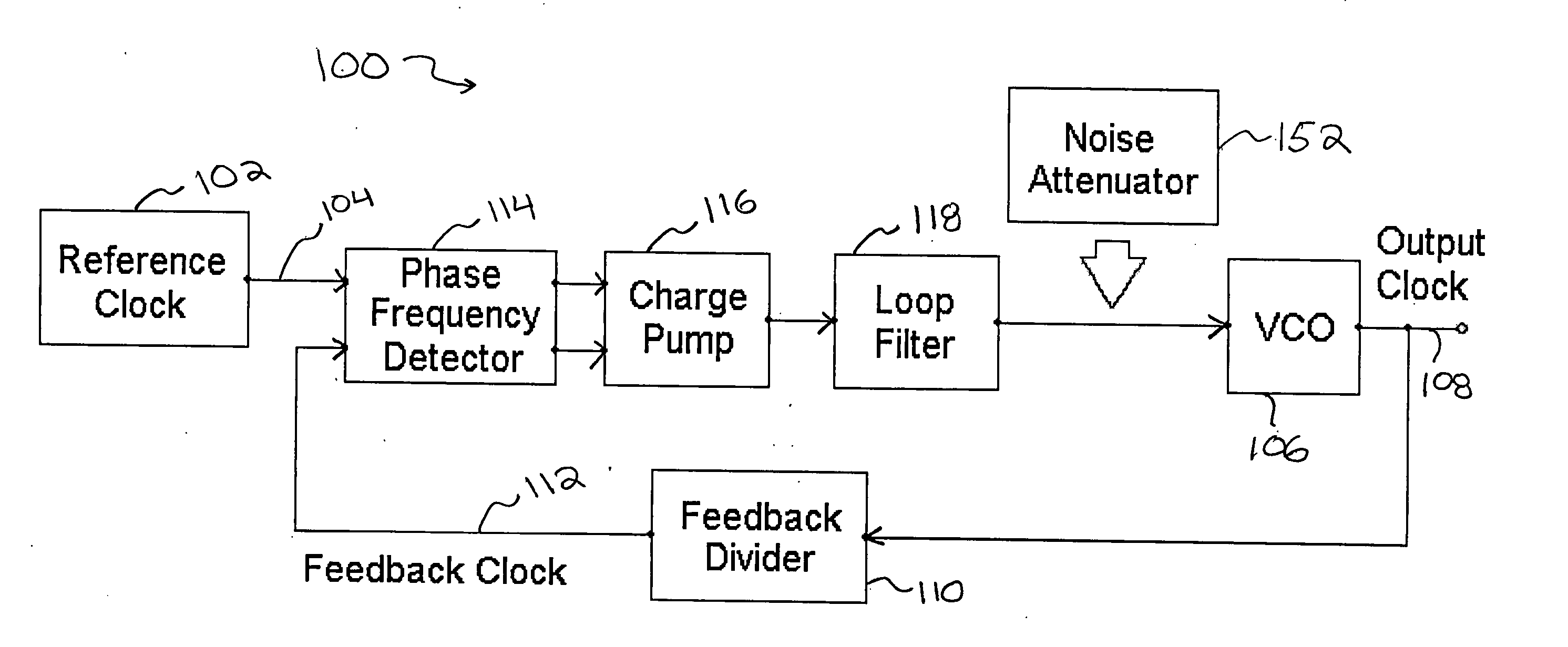
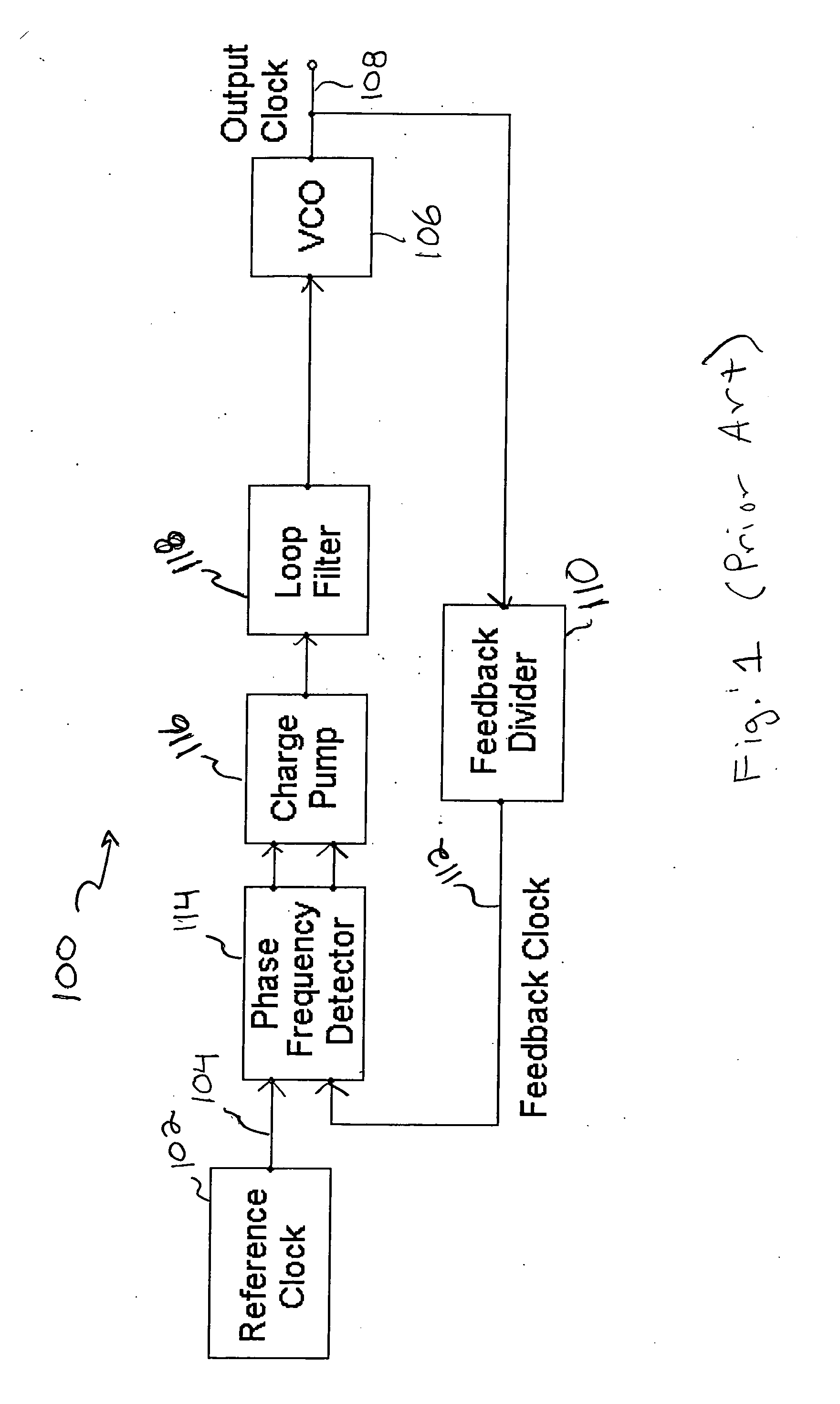
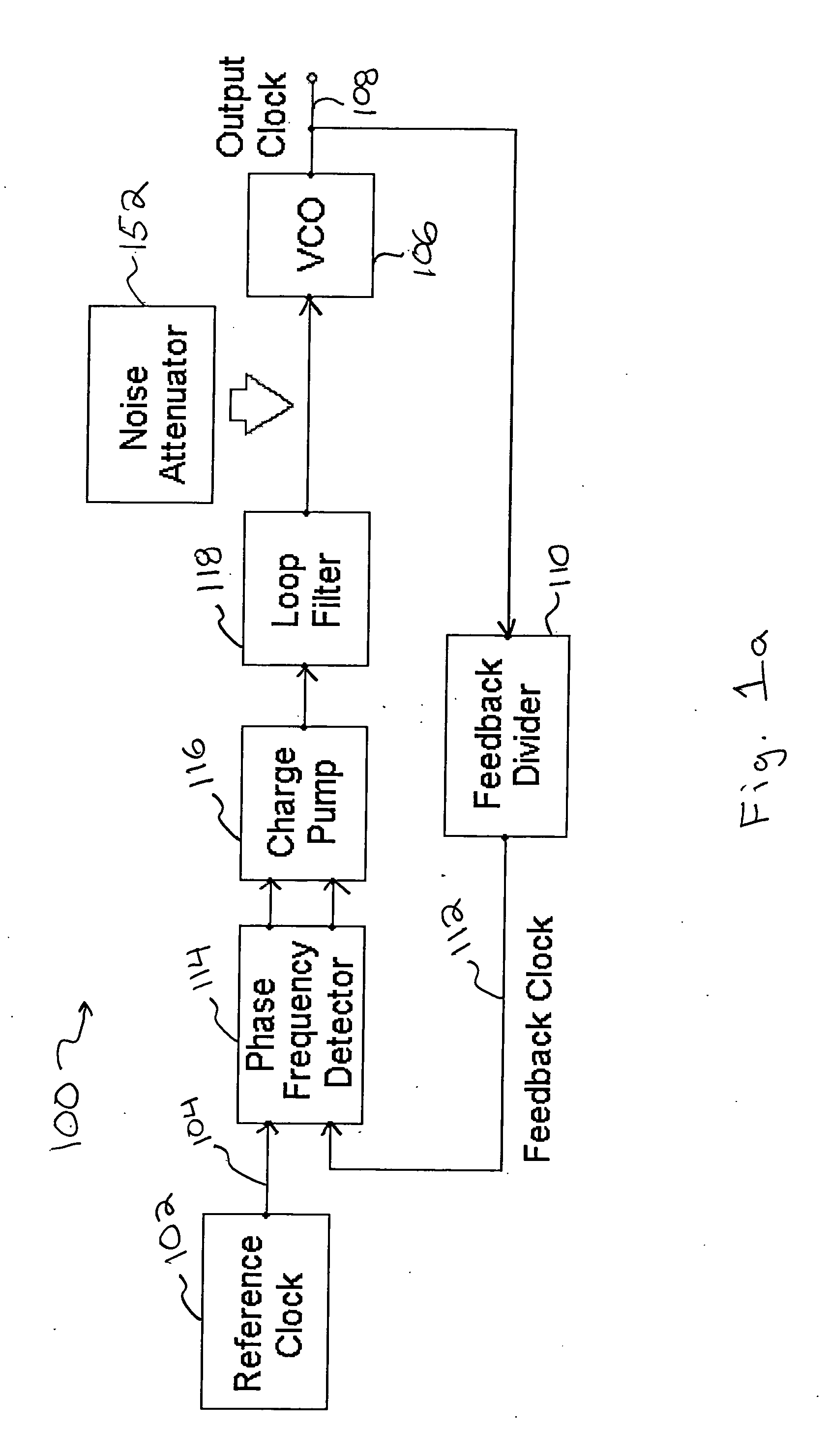
InactiveUS20060141963A1Reduce noise contributionReduce phase noisePulse automatic controlTransmissionMOSFETCapacitance
A noise attenuator loop filter for PLL applications that allows a full on-chip integration of the loop filter capacitors, while ensuring a low output clock phase noise (jitter) is disclosed. A voltage attenuator (A) is inserted between the loop filter (passive or active) and the controlled oscillator. The attenuator attenuates the noise coming from the loop filter. In case of a passive RC filter, the series resistor noise power is attenuated by A2 times, allowing the usage of a resistor that is A2 times larger and therefore the loop filter capacitors result A2 times smaller (easy to integrate on-chip). The relatively low value capacitor allows the usage of thick-oxide accumulation-mode MOSFET capacitors that take a reasonable low area, have a good linearity, are isolated from the substrate by the grounded N-well, and have negligible gate leakage current. Several embodiments of the noise attenuator are proposed for different practical applications: clock generation for digital circuits, frequency translation, low or high supply voltage, narrow or wide frequency range, processes with or without isolated well devices, processes with or without polysilicon resistors, and medium or high reference spurs rejection.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Methods and System for Determining a Dominant Impairment of an Impaired Communication Channel
Methods are described for identifying a dominant impairment on a communication channel impaired by an interference issue. The methods include systematic examination of total power loading, systematic examination of signal power reduction, statistical examination of communication channel noise power, and systematic examination of interleaver effectiveness. Each relates to automatically diagnosing and characterizing distortion-based interference issues by monitoring the performance of a communication channel during a testing procedure. These methods enable a technician or engineer to remotely diagnose distortion-based interference issues relatively quickly without having to use external test equipment and without having to deploy technicians to various locations within the cable plant. A system by which these methods can be implemented is also disclosed.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
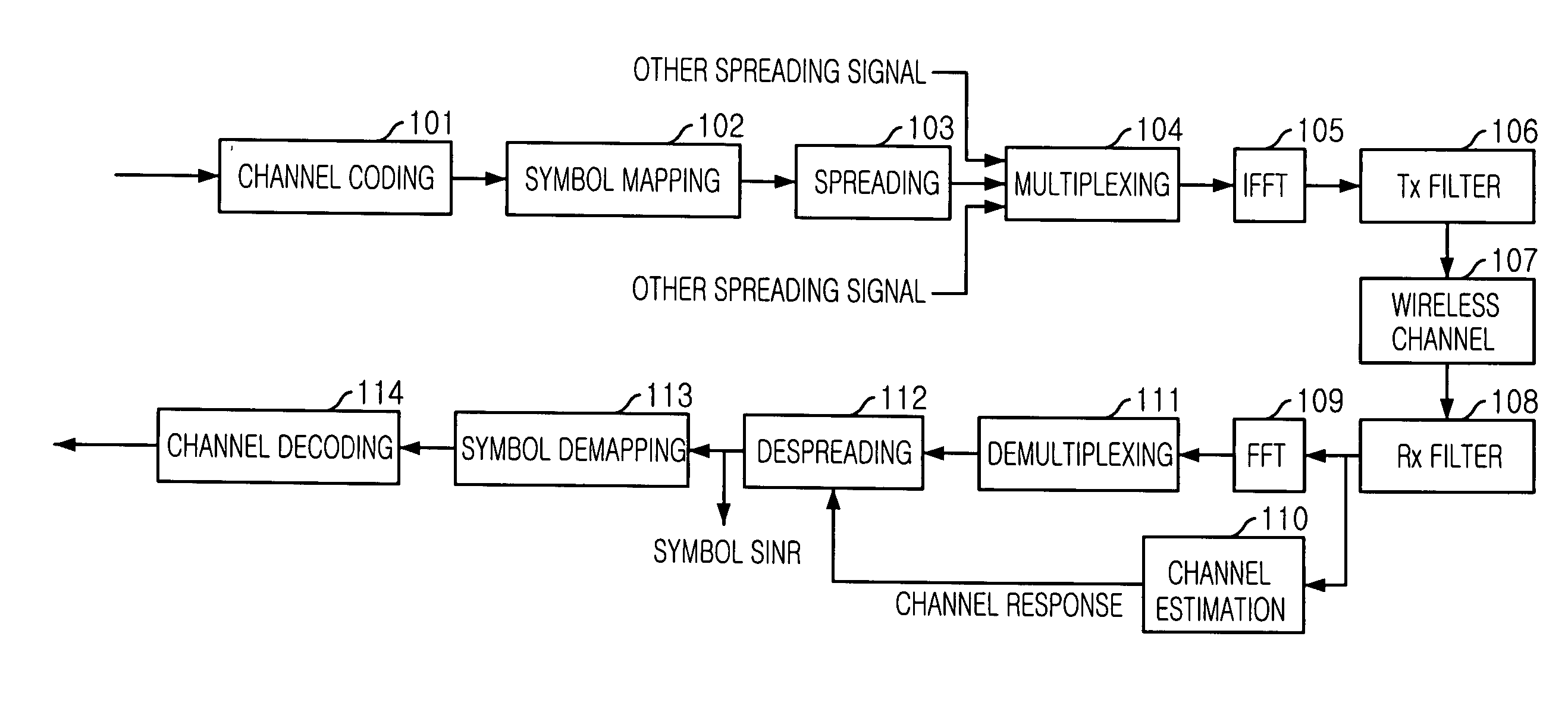
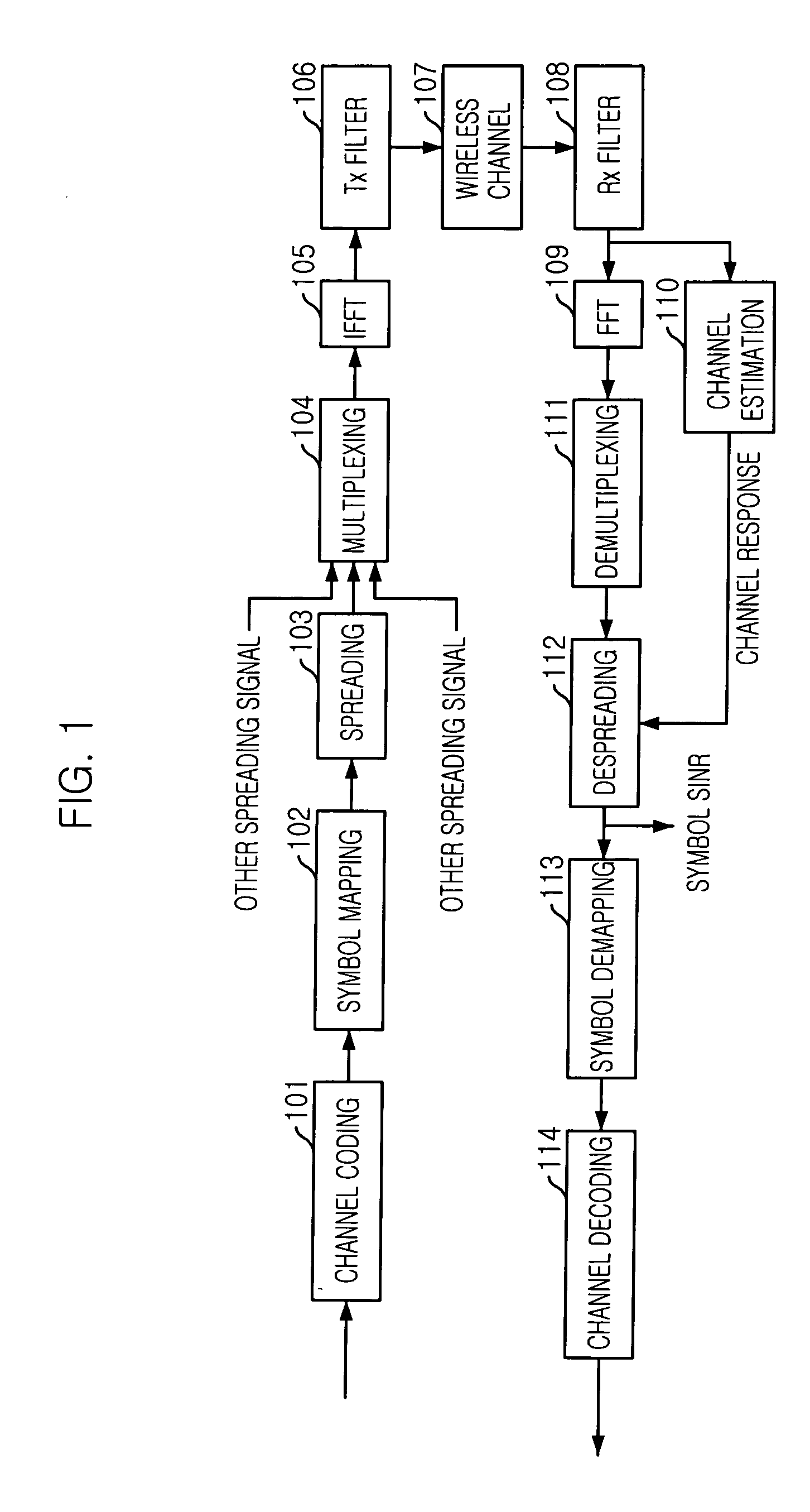
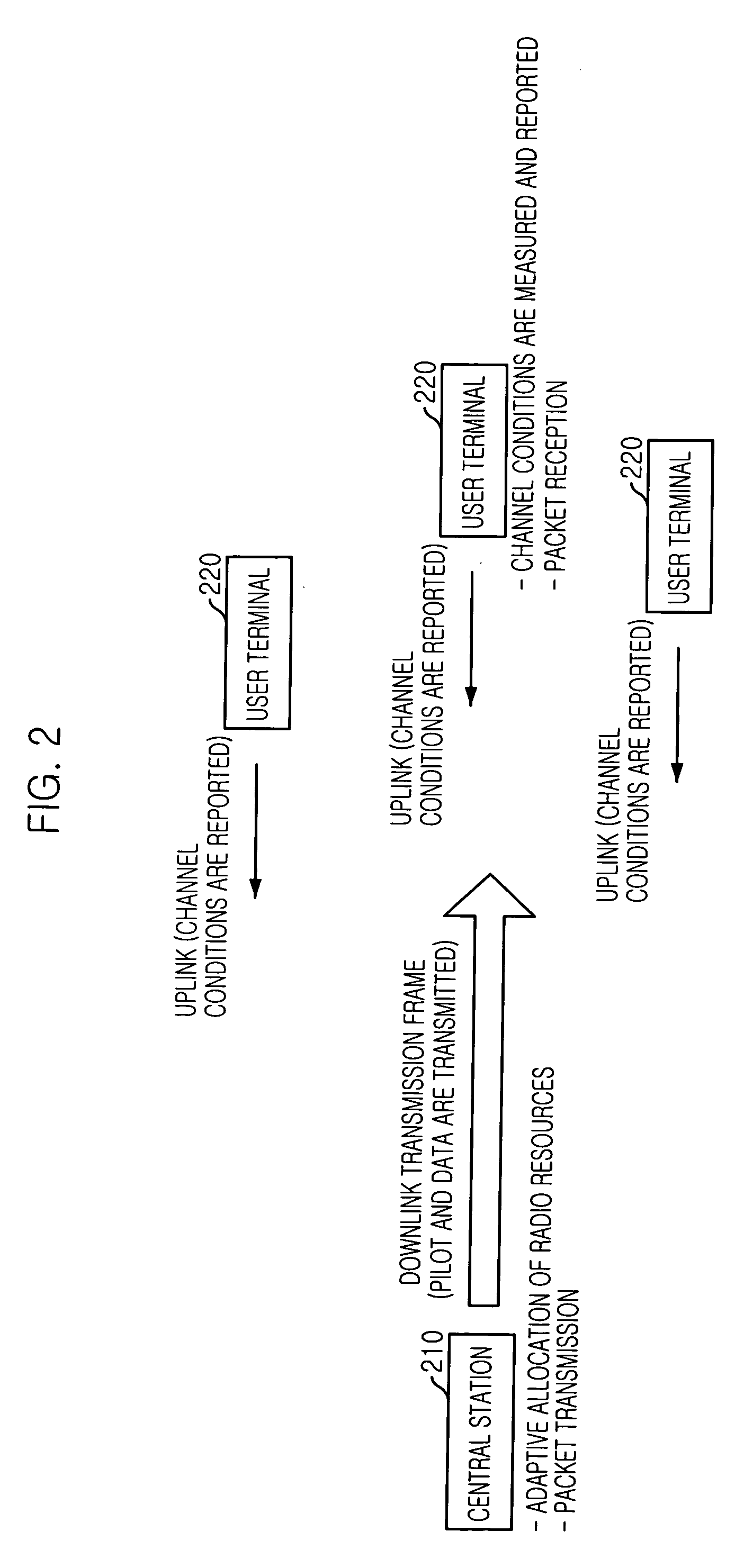
Adaptive downlink packet transmission method in multicarrier CDMA system
InactiveUS20050141473A1Minimize interferenceRadio resource efficientlyPower managementBaseband system detailsInterference factorEqualization
Disclosed is an adaptive downlink packet transmission method for a multicarrier Code Division Multiple Access (MC-CDMA) system. The method can allocate radio resources efficiently according to the variations of channel conditions for each user terminal, allocate transmission power appropriately according to the interference from the same cell, and minimize interference to adjacent cells. The adaptive downlink packet transmission method includes the steps of: a) estimating a signal-to-interference-and-noise ratio (SINR) in a user terminal after channel equalization and despreading by measuring a downlink pilot channel; b) measuring an average interference factor and an average noise power; and c) allocating radio resources adaptively in the central station by determining transmission slots in a transmission frame, the number of spreading codes to be used in each transmission slot, symbol energy for each spreading code, and a transmission method, until transmission slots and packets to be allocated are not available.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
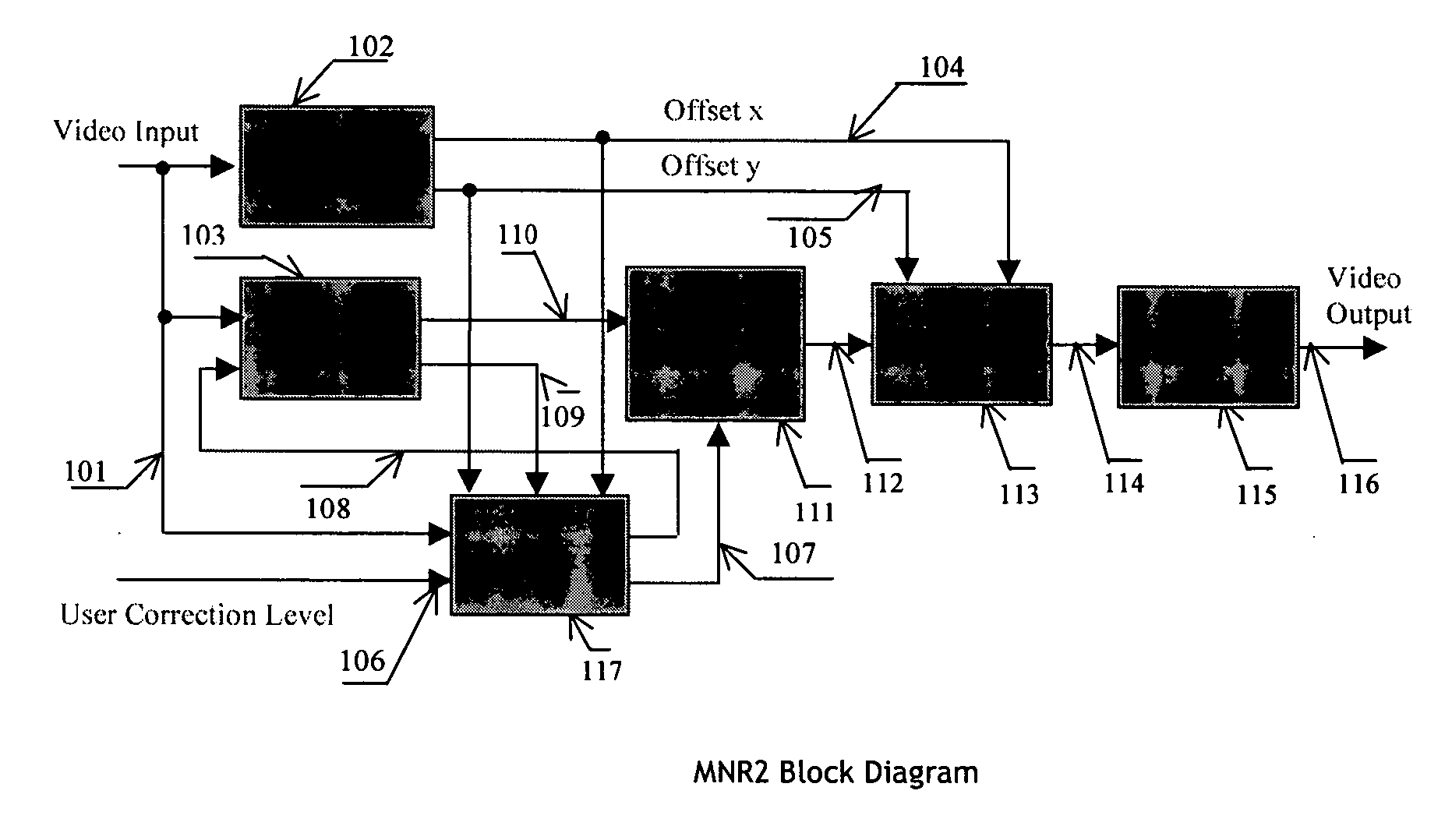
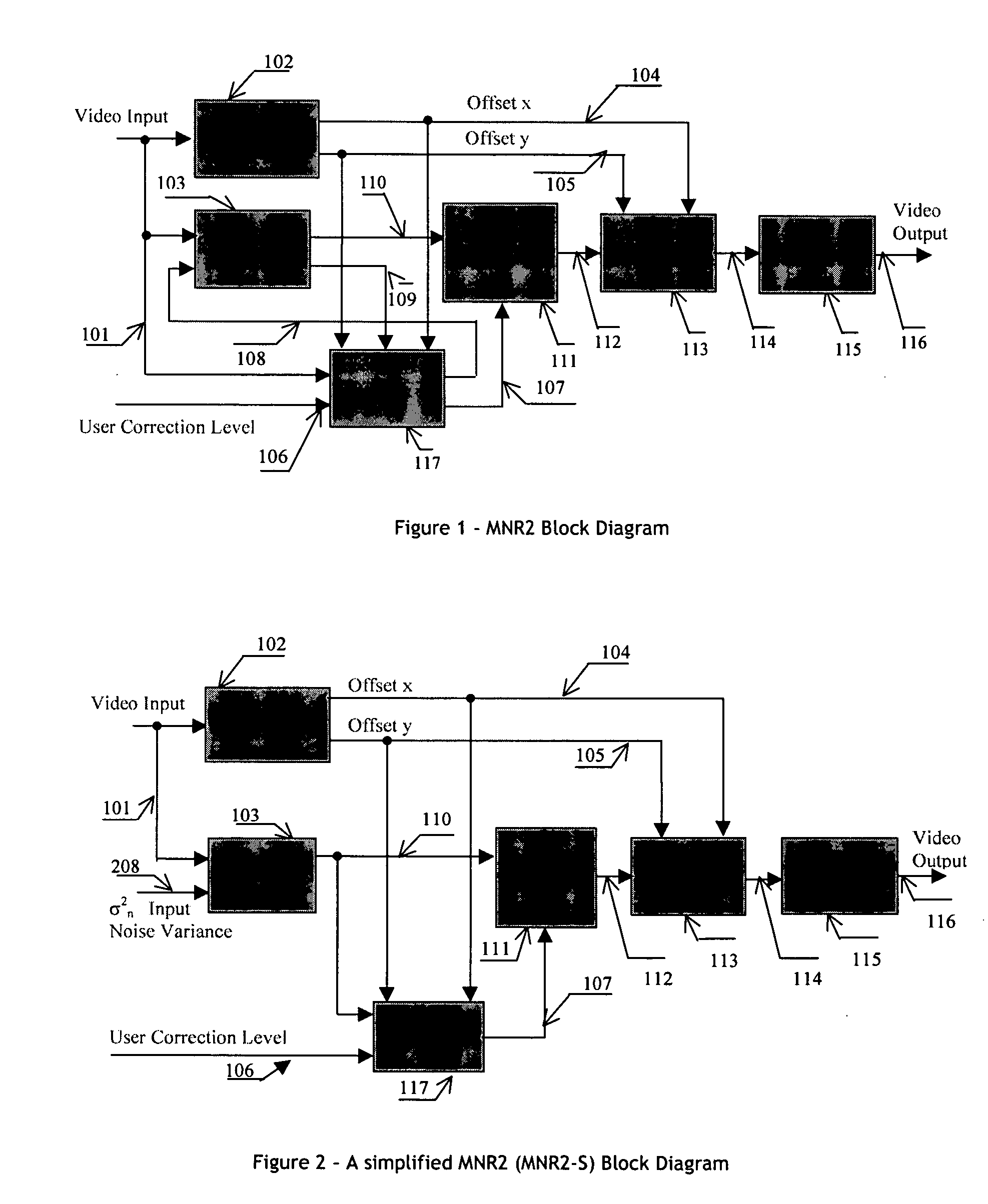
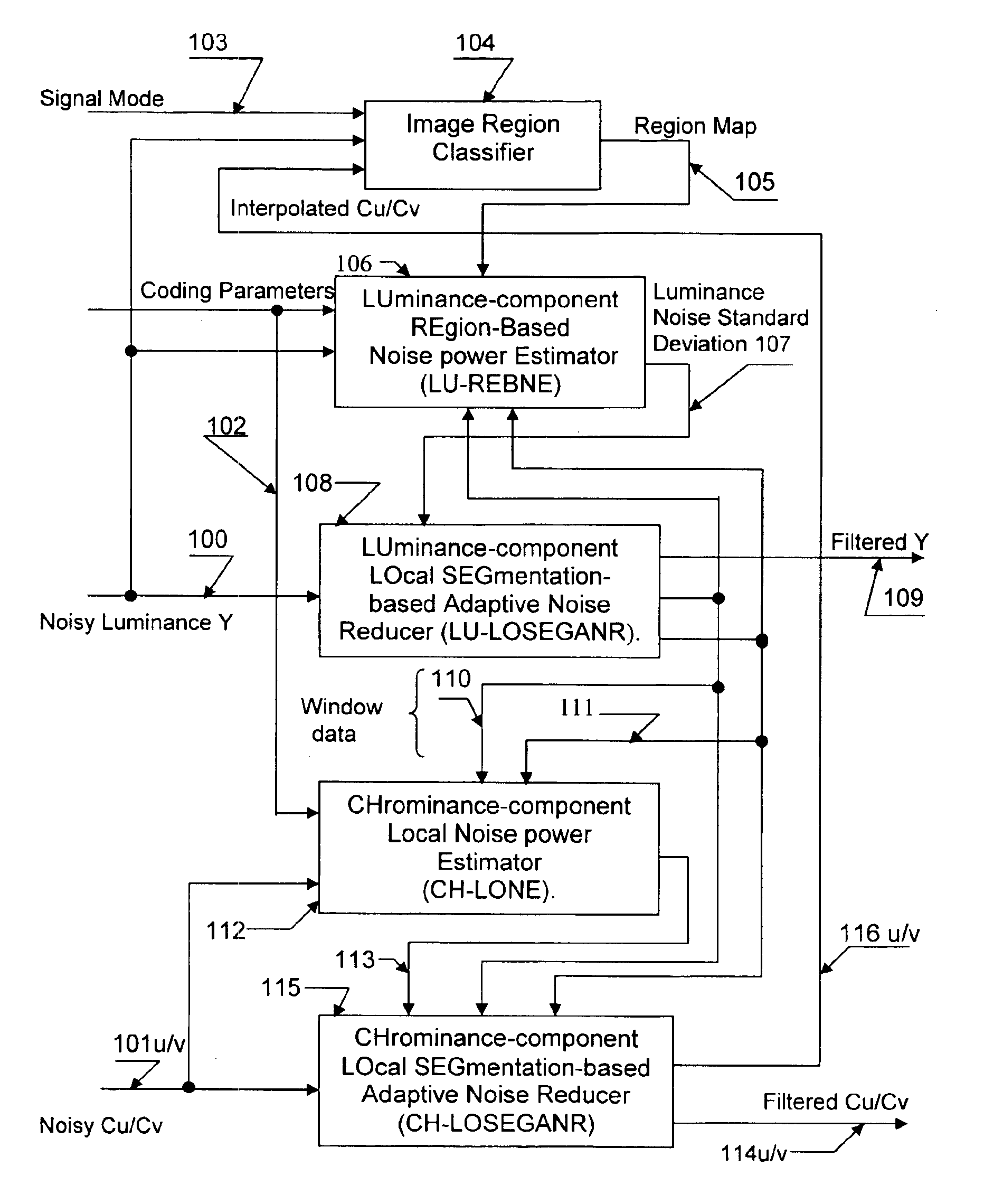
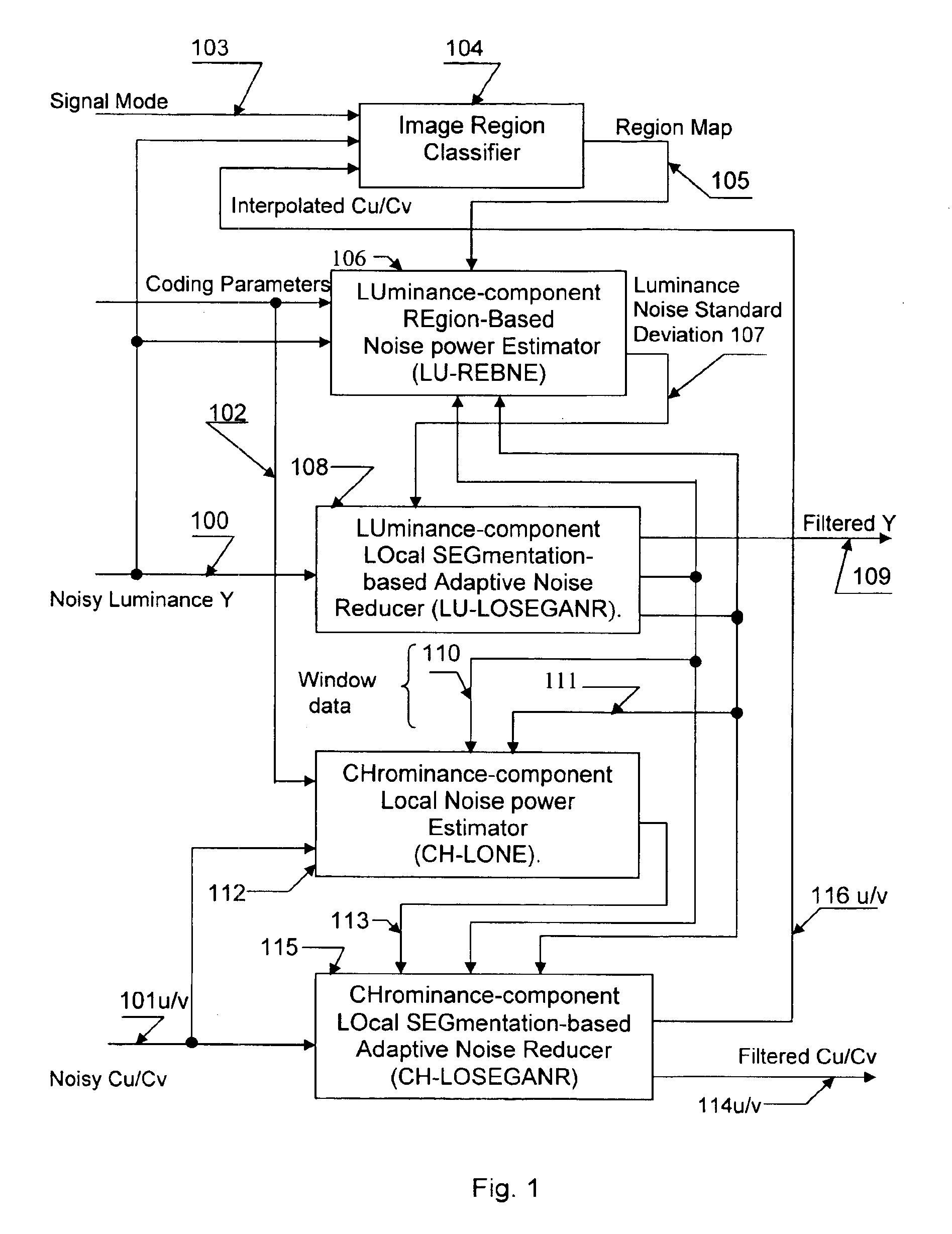
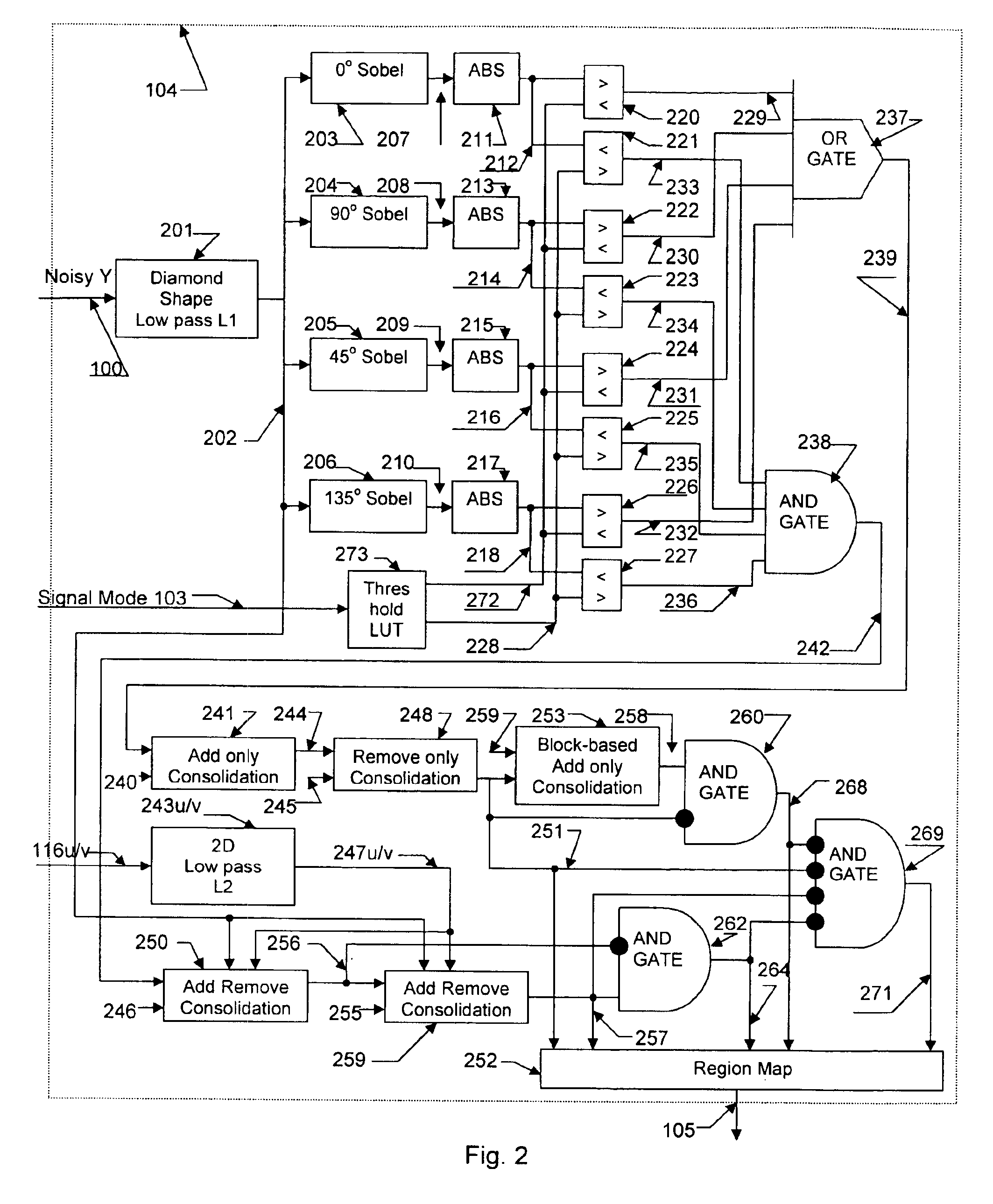
Apparatus and method for adaptive spatial segmentation-based noise reducing for encoded image signal
InactiveUS7076113B2Reduce noiseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionRandom noise
An efficient and non-iterative post processing method and system is proposed for mosquito noise reduction in DCT block-based decoded images. The post-processing is based on a simple classification that segments a picture in multiple regions such as Edge, Near Edge, Flat, Near Flat and Texture regions. The proposed technique comprises also an efficient and shape adaptive local power estimation for equivalent additive noise and provides simple noise power weighting for each above cited region. An MMSE or MMSE-like noise reduction with robust and effective shape adaptive windowing is utilized for smoothing mosquito and / or random noise for the whole image, particularly for Edge regions. Finally, the proposed technique comprises also, for chrominance components, efficient shape adaptive local noise power estimation and correction.
Owner:BANK OF MONTREAL +1
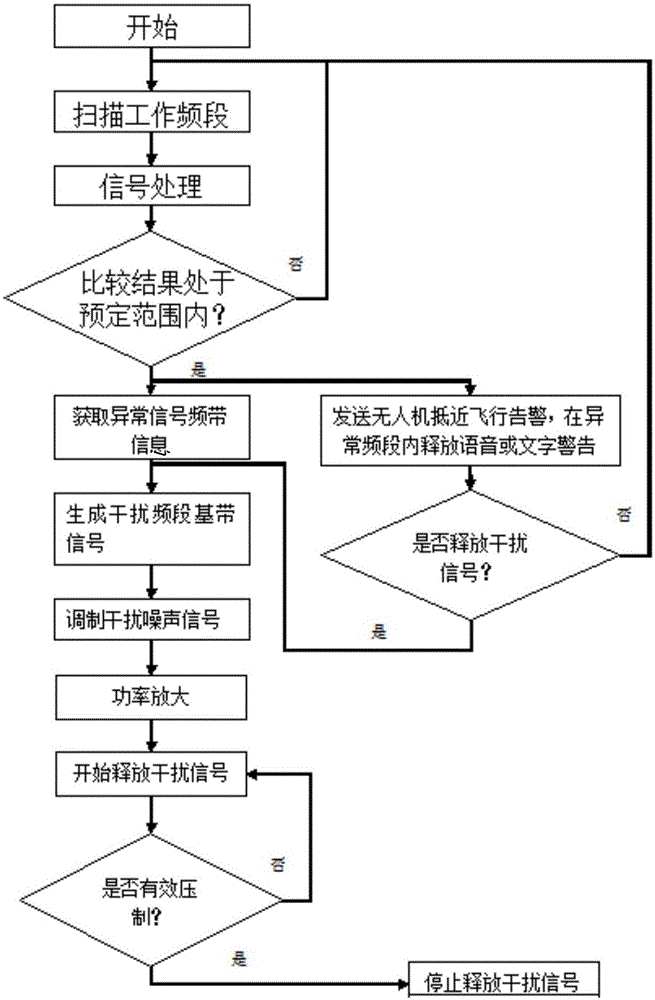
Unmanned aerial vehicle signal processing device and signal processing method
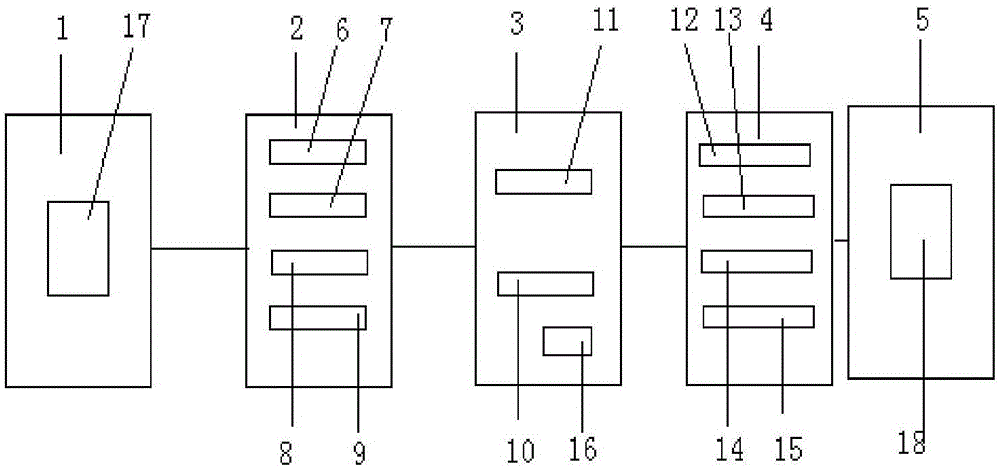
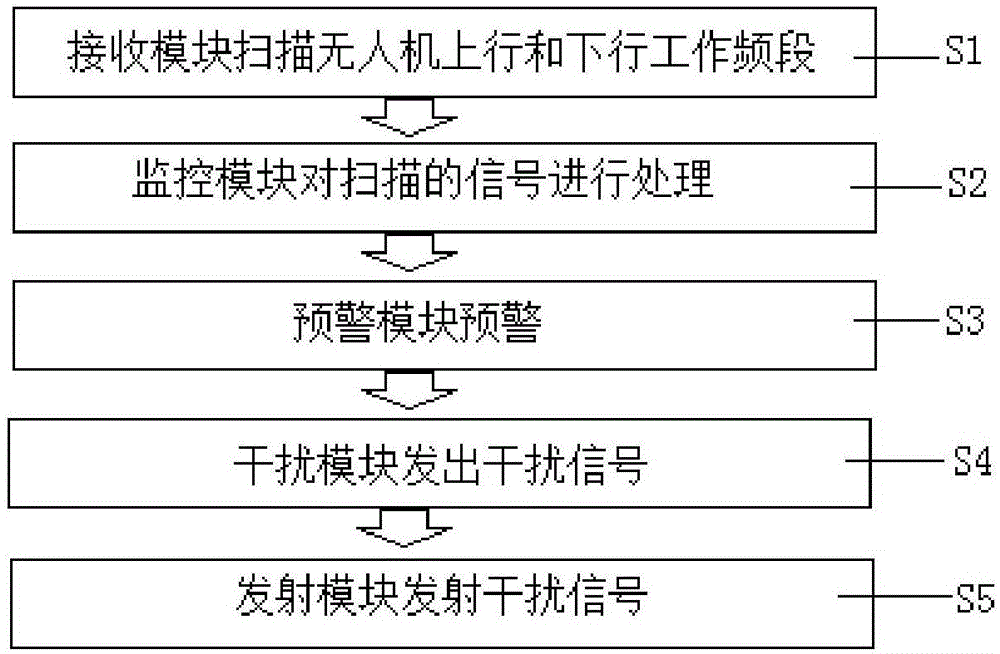
ActiveCN105099585AStop approachingPrevent leakageCommunication jammingPropogation channels monitoringAudio power amplifierSignal generator
The invention provides an unmanned aerial vehicle signal processing device and a processing method thereof. The device comprises a receiving module (1), a monitoring module (2), an early warning module (3), an interference module (4) and a transmitting module (5). The early warning module (3) comprises a storage unit (10) which stores unmanned aerial vehicle frequency domain data and a comparison unit (11) which compares current frequency domain data transmitted by a frequency spectrum analysis unit (9) with the unmanned aerial vehicle frequency domain data stored in the storage unit (10). The early warning module (3) alarms when the comparison result is in the preset range. The interference module (4) comprises a baseband signal generator (12) which sets baseband signal frequency, an interference modulator (13) which modulates a baseband signal into a noise signal, a working amplifier (14) which increases noise power and a combiner (15) which combines different noise frequency bands. Close-up flight of an unmanned aerial vehicle can be warned in advance by detecting working frequency range of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and close-up flight of the unmanned aerial vehicle to the protected security area can be prevented.
Owner:陈昊
Communication environment measurement method for mobile station and the mobile station
InactiveUS7328019B2Prevent drop in communication throughputQuick controlAssess restrictionTransmission monitoringCommunications systemData signal
In a communication system for respectively transmitting pilot signals from a plurality of base stations to a mobile station via a first channel and also for transmitting data from one base station to a mobile station via a second channel, the mobile station corrects total receive power at the time of handover by subtracting power of the data signal received via the second channel from the total receive power of the signals received from a base station in communication (serving cells) via the second channel, then corrects the total noise power based on the total receive power after the correction, and measures the communication environment between the base station and the mobile station using the power of the pilot signal received from the base station in-communication and the corrected total noise power.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
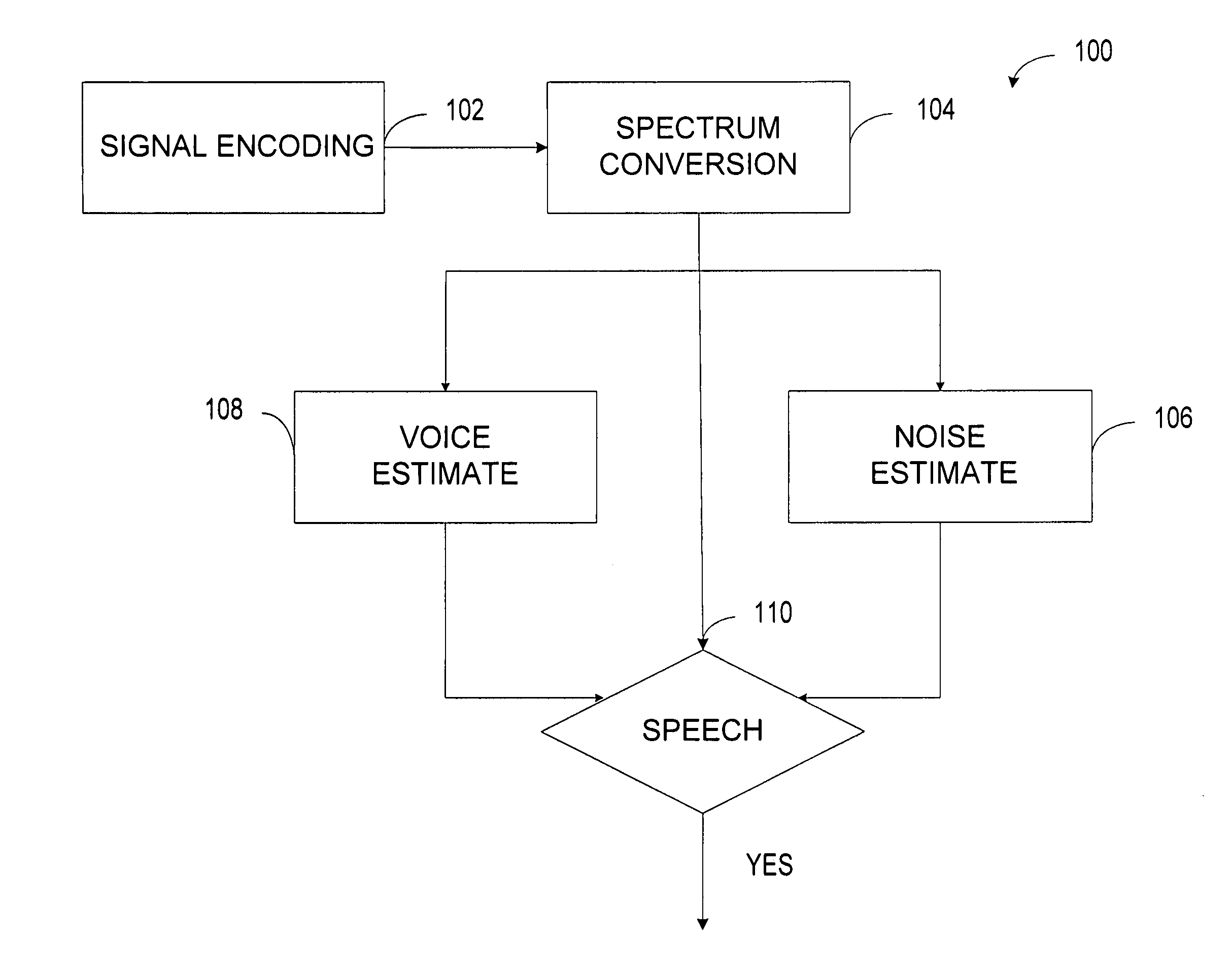
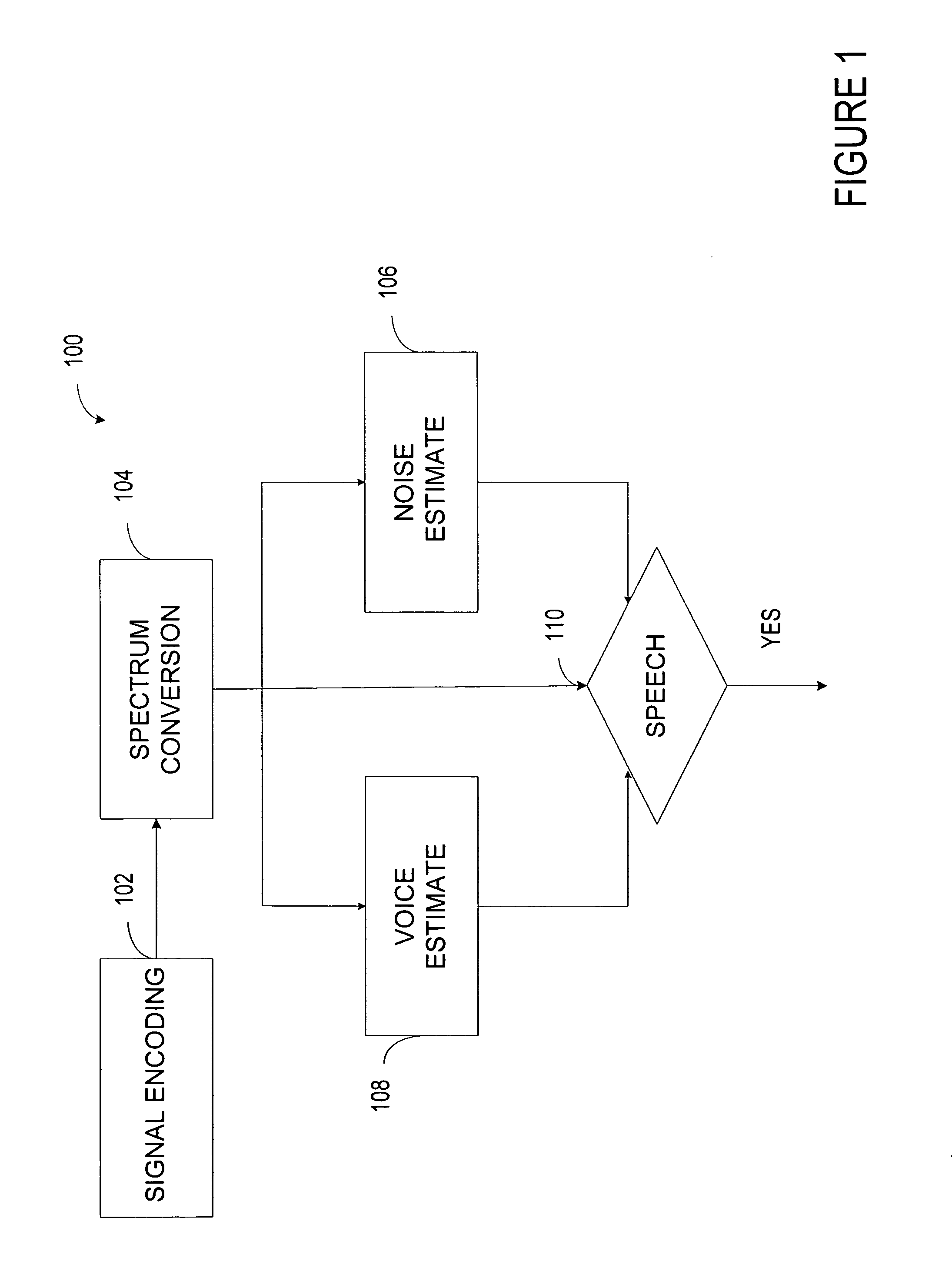
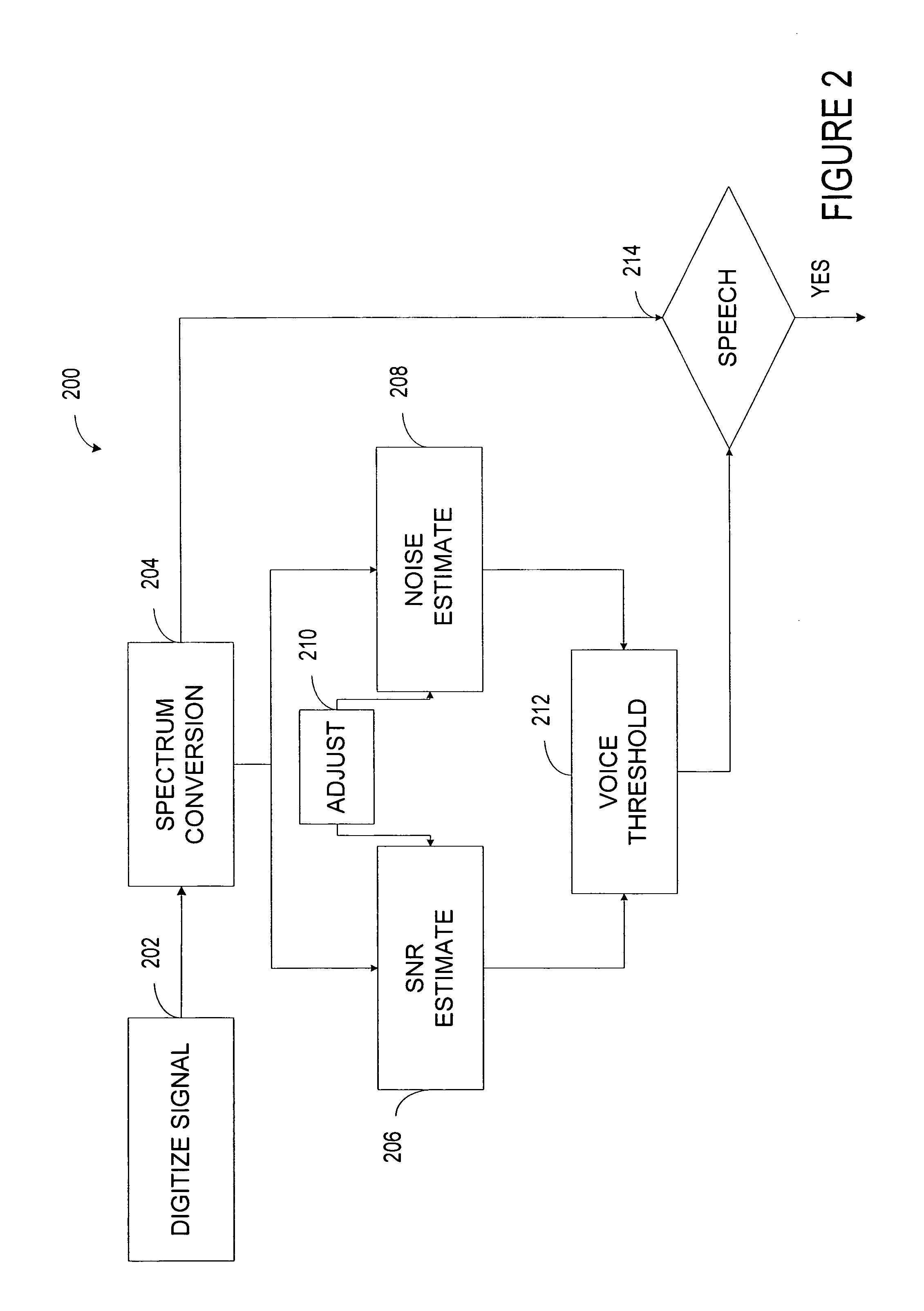
Targeted speech
A system detects a speech segment that may include unvoiced, fully voiced, or mixed voice content. The system includes a digital converter that converts a time-varying input signal into a digital-domain signal. A window function passes signals within a programmed aural frequency range while substantially blocking signals above and below the programmed aural frequency range when multiplied by an output of the digital converter. A frequency converter converts the signals passing within the programmed aural frequency range into a plurality of frequency bins. A background voice detector estimates the strength of a background speech segment relative to the noise of selected portions of the aural spectrum. A noise estimator estimates a maximum distribution of noise to an average of an acoustic noise power of some of the plurality of frequency bins. A voice detector compares the strength of a desired speech segment to a criterion based on an output of the background voice detector and an output of the noise estimator.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Acoustic echo devices and methods
Hands-free phones with voice activity detection using a comparison of frame power estimate with an adaptive frame noise power estimate, automatic gain control with fast adaptation and minimal speech distortion, echo cancellation updated in the frequency domain with stepsize optimization and smoothed spectral whitening, and echo suppression with adaptive talking-state transitions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
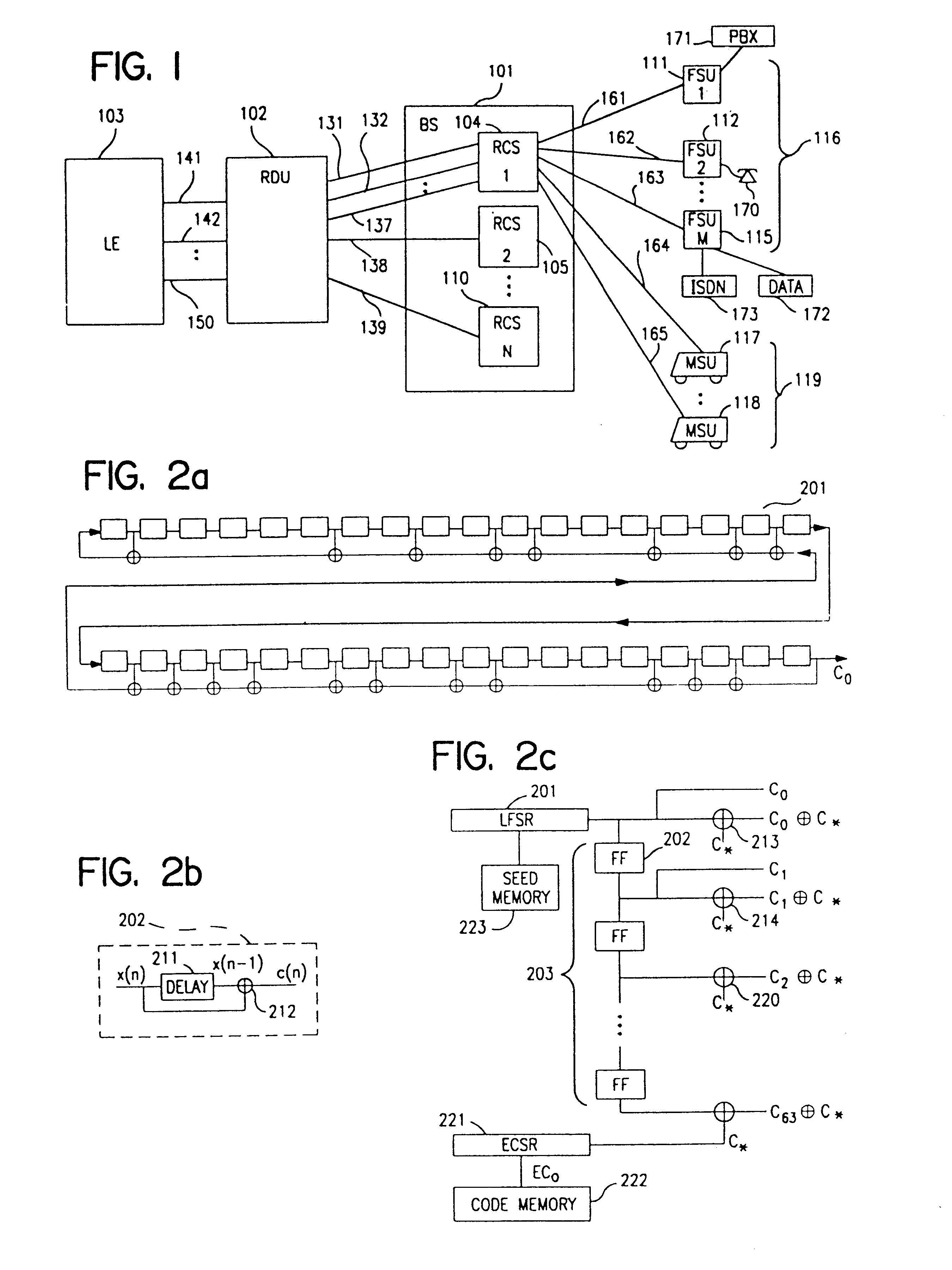
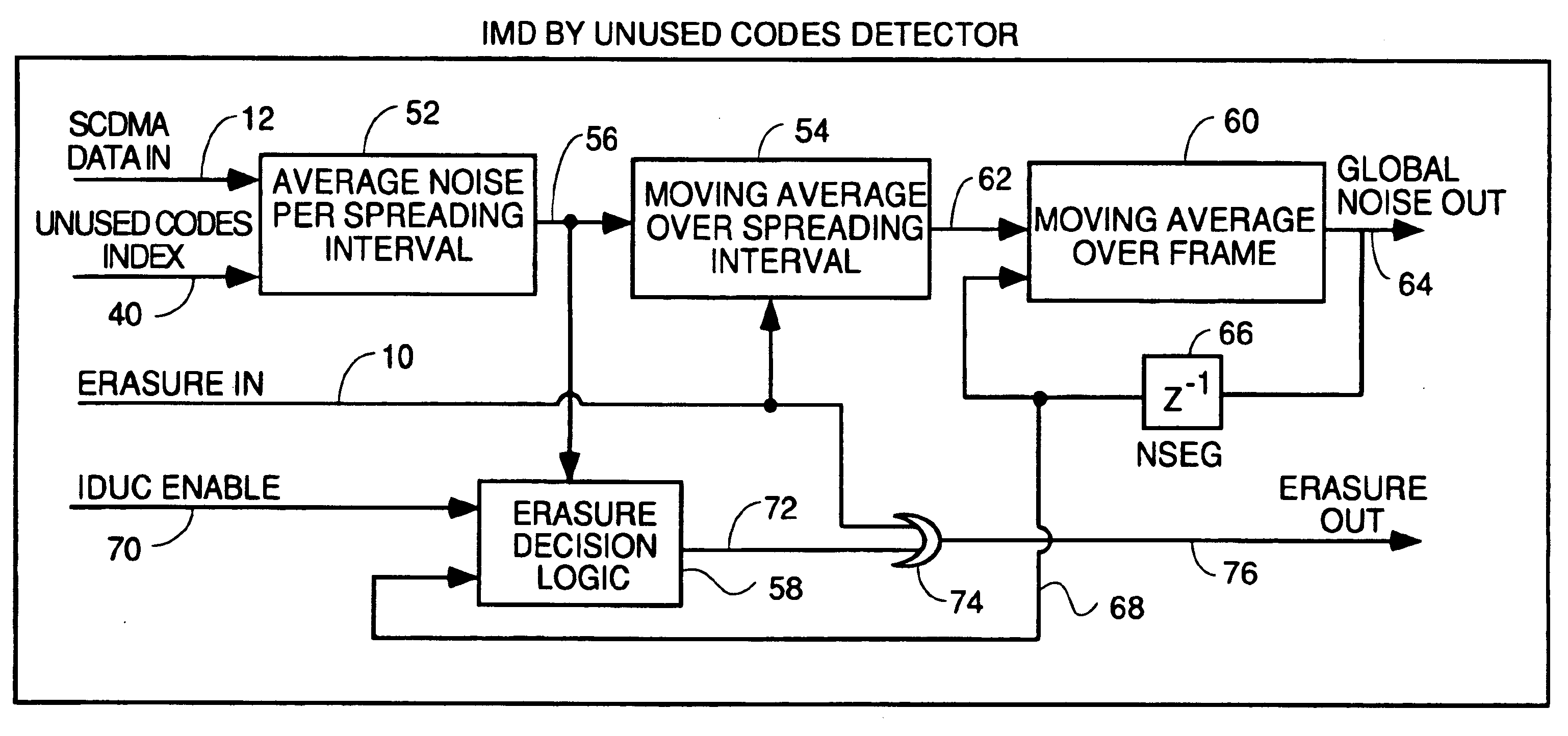
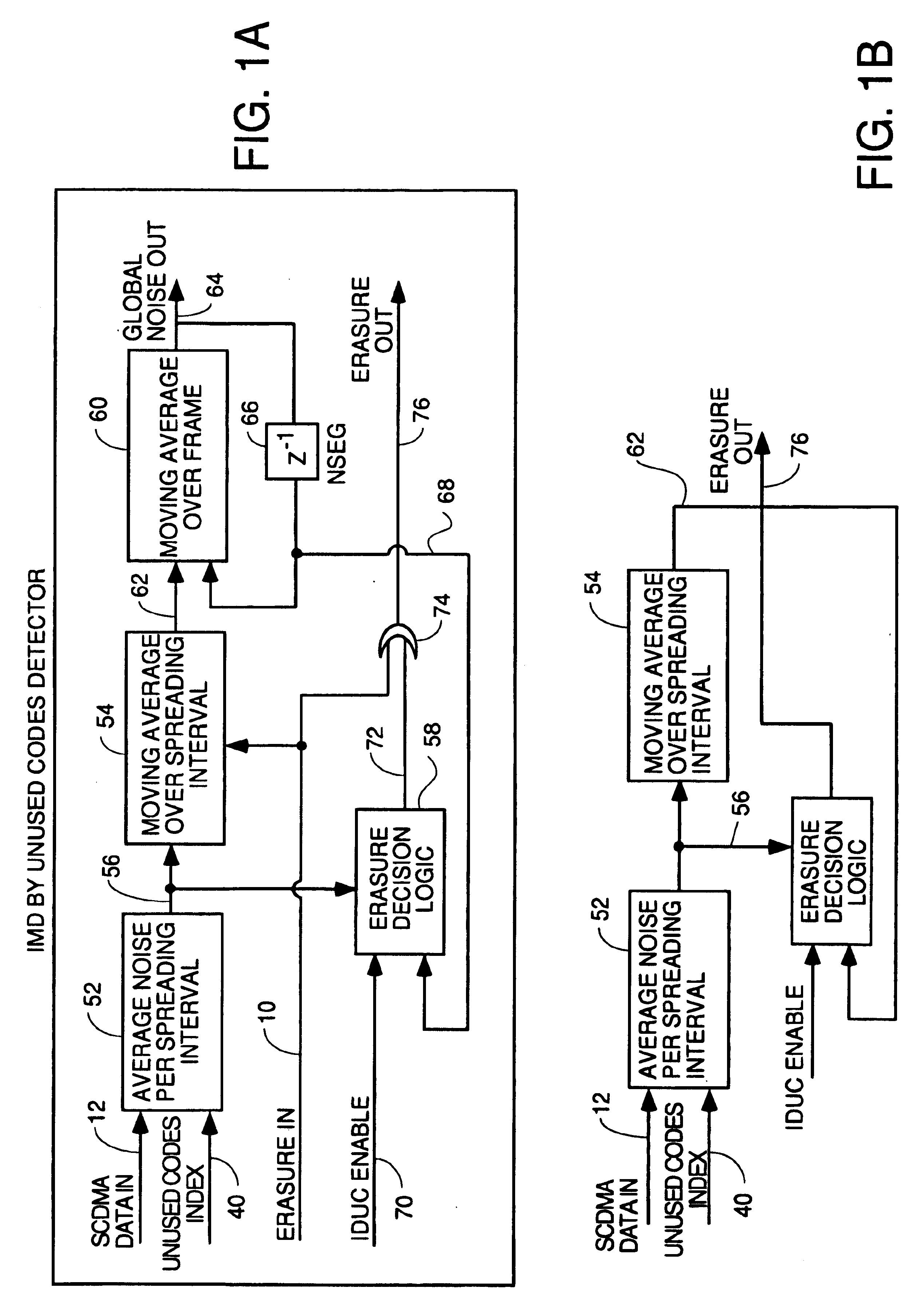
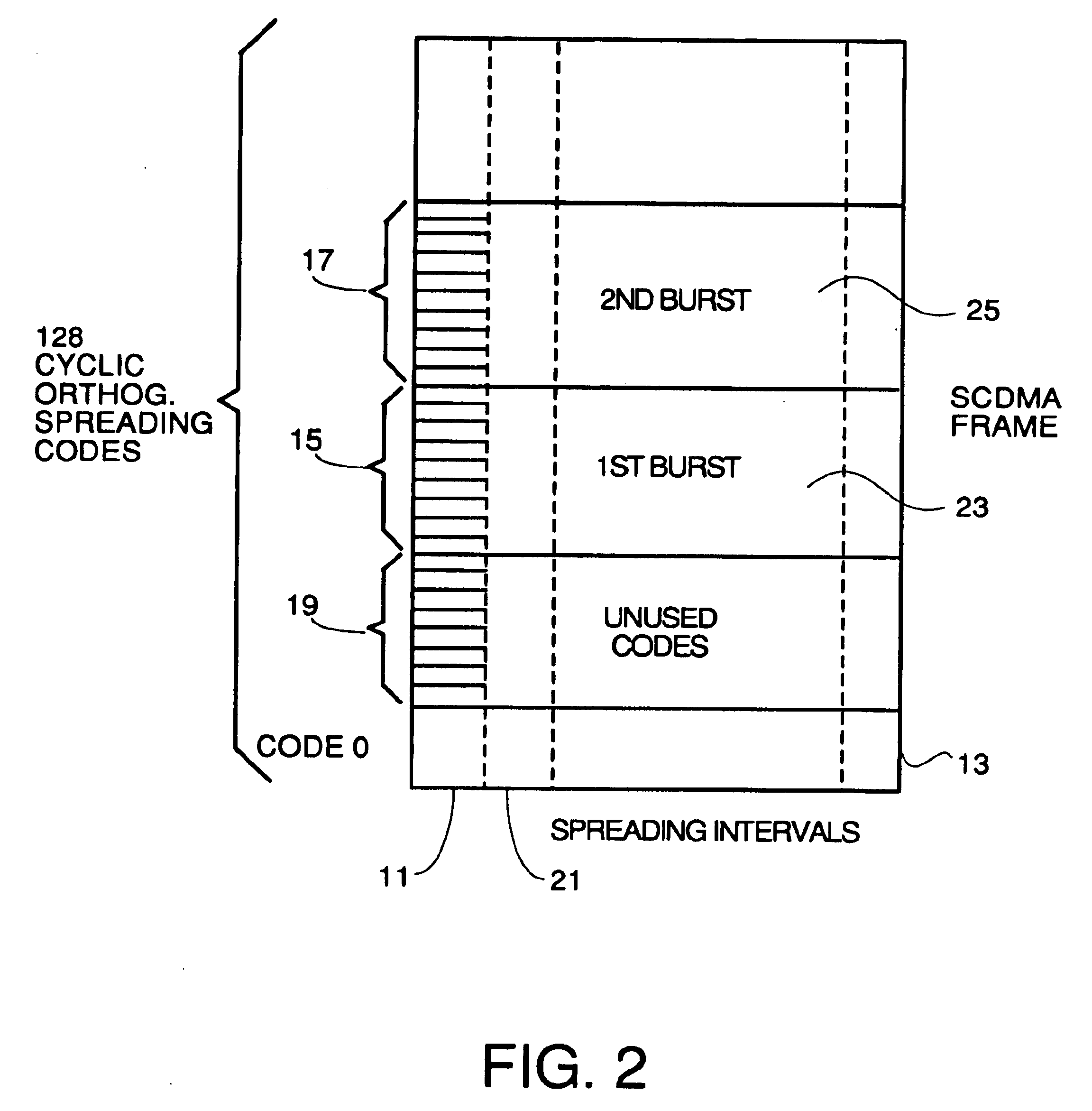
Detection of impulse noise using unused codes in CDMA systems
InactiveUS6859488B2Improving error correction capability of error correctionCancel noiseError preventionSpeech analysisDiscrimination thresholdEngineering
An impulse detector which can detect both low and high levels of impulse noise in a CDMA system is comprised of circuitry to calculate the background noise level in unused codes. Another circuit calculates the average noise power in the unused codes of each spreading interval to output the noise power per spreading interval. This average is continuously averaged over spreading intervals by another circuit which outputs the average background noise power. A comparator compares the noise power in the current spreading interval with the background noise power plus a programmable threshold and generates an erasure indication if the background noise power plus a discrimination threshold is exceeded.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com