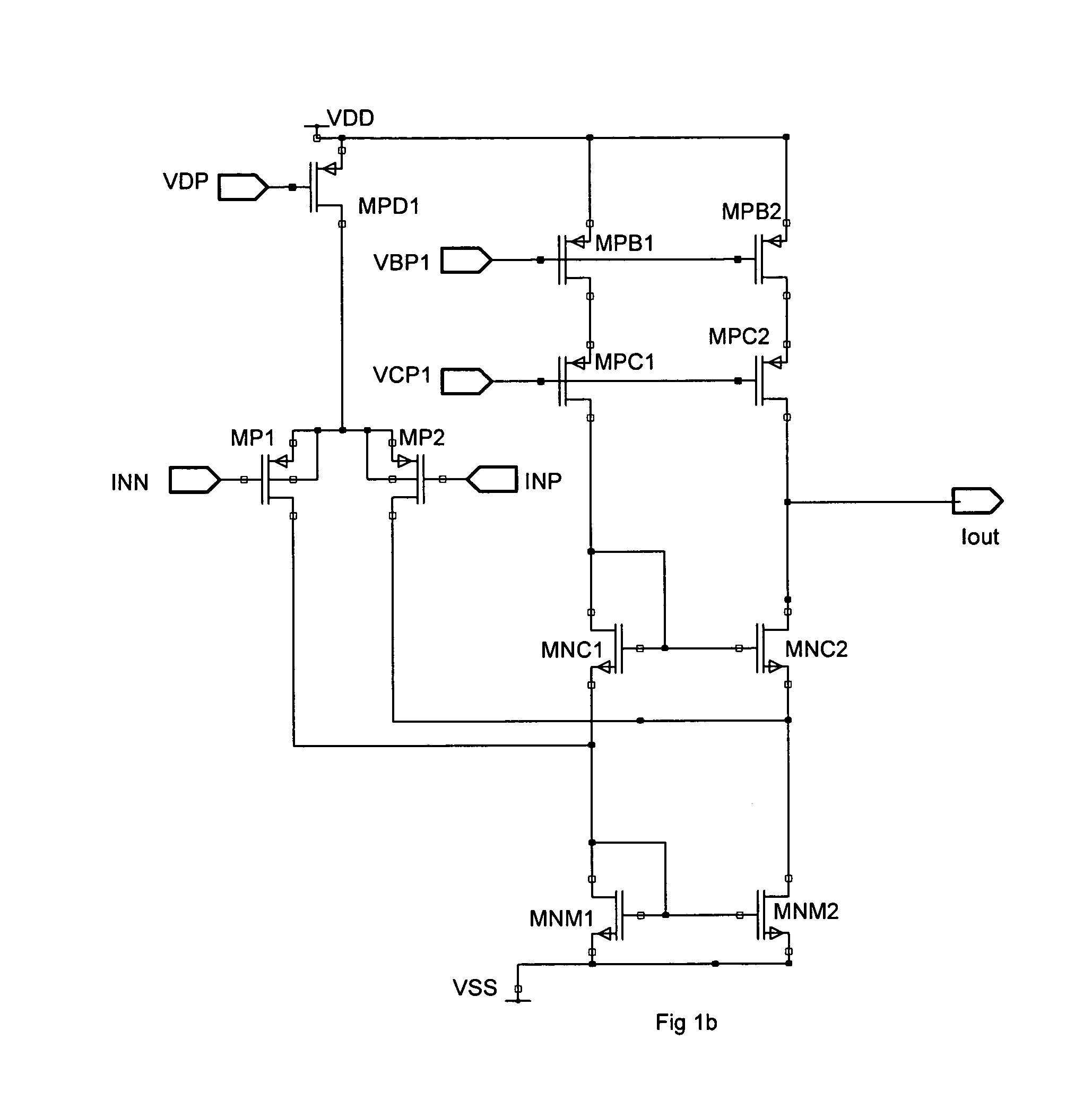
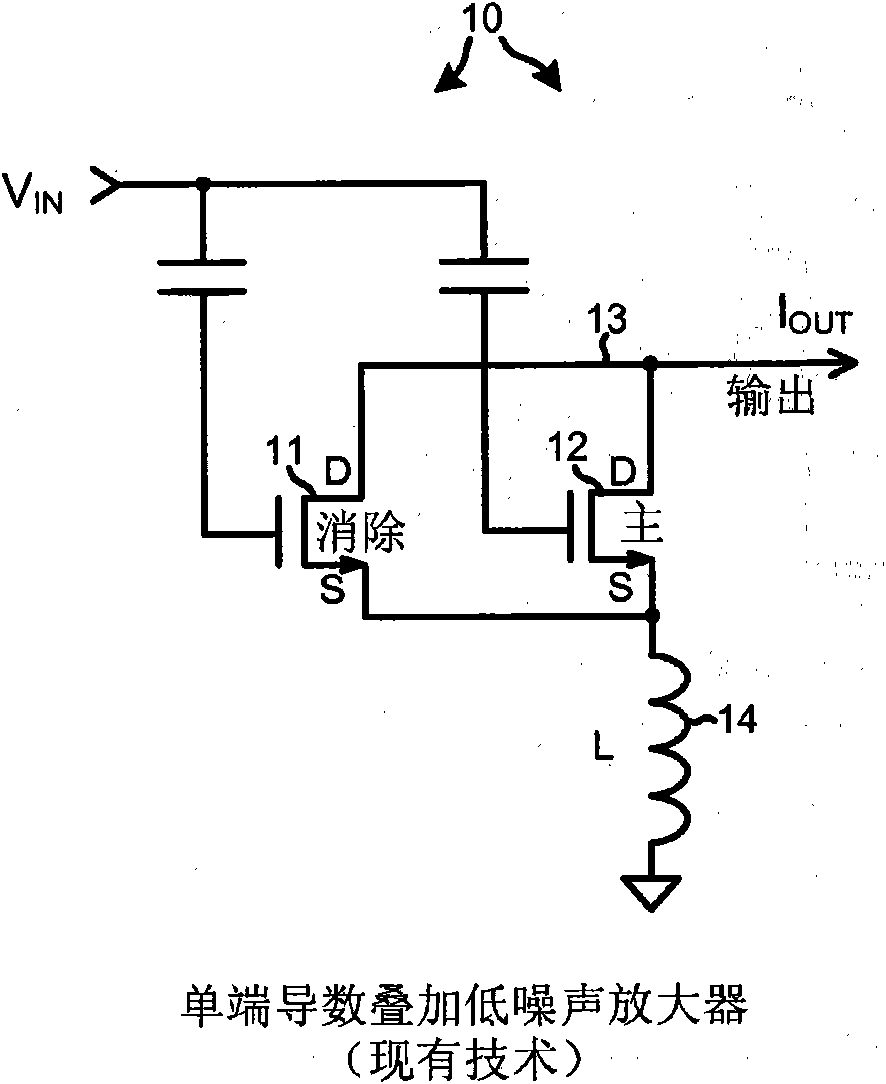
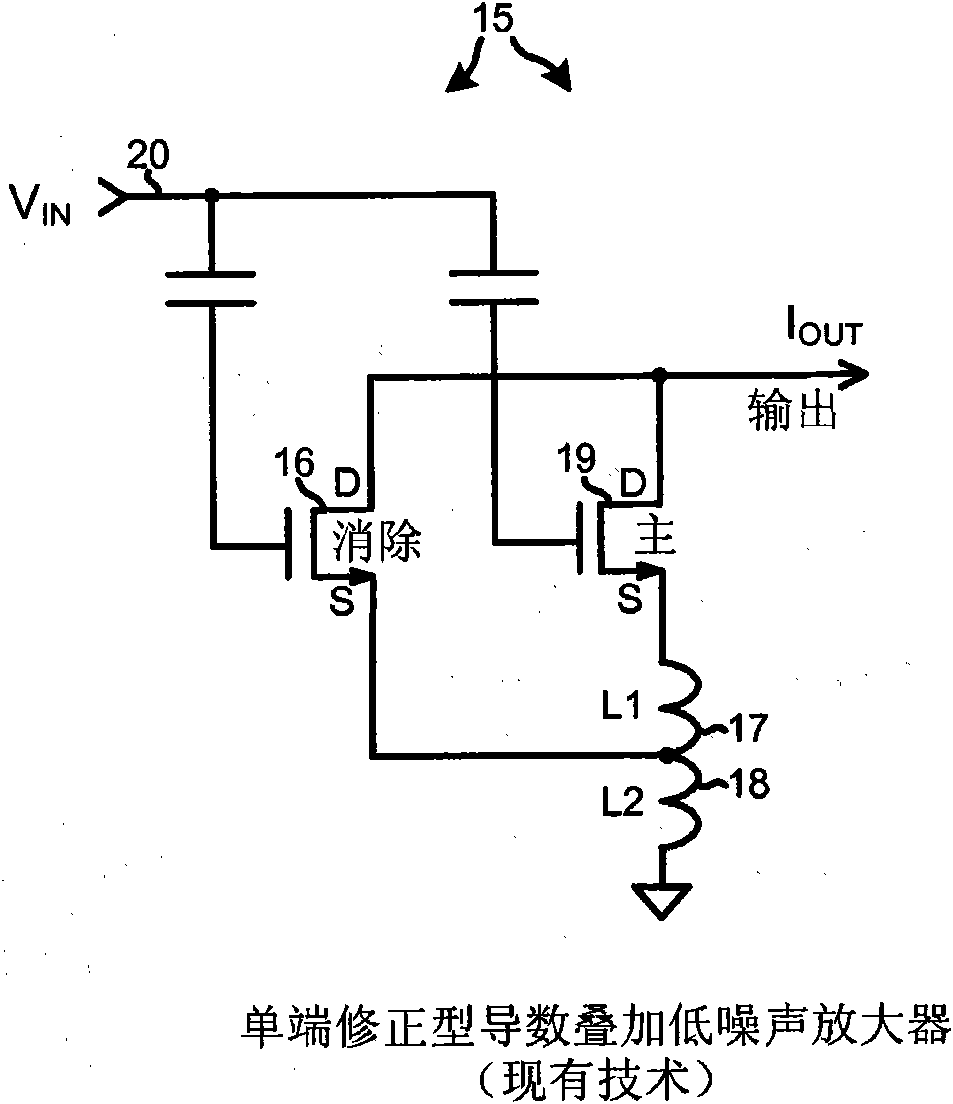
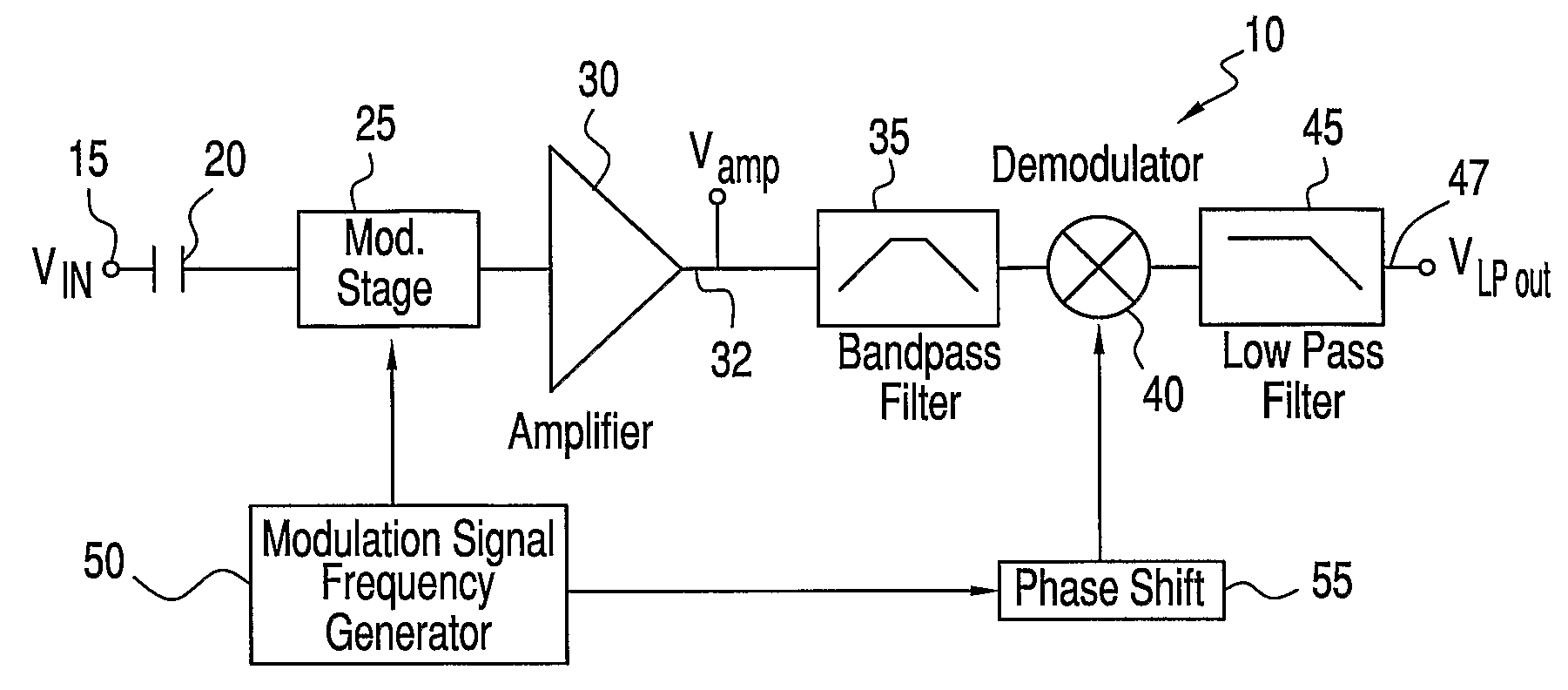
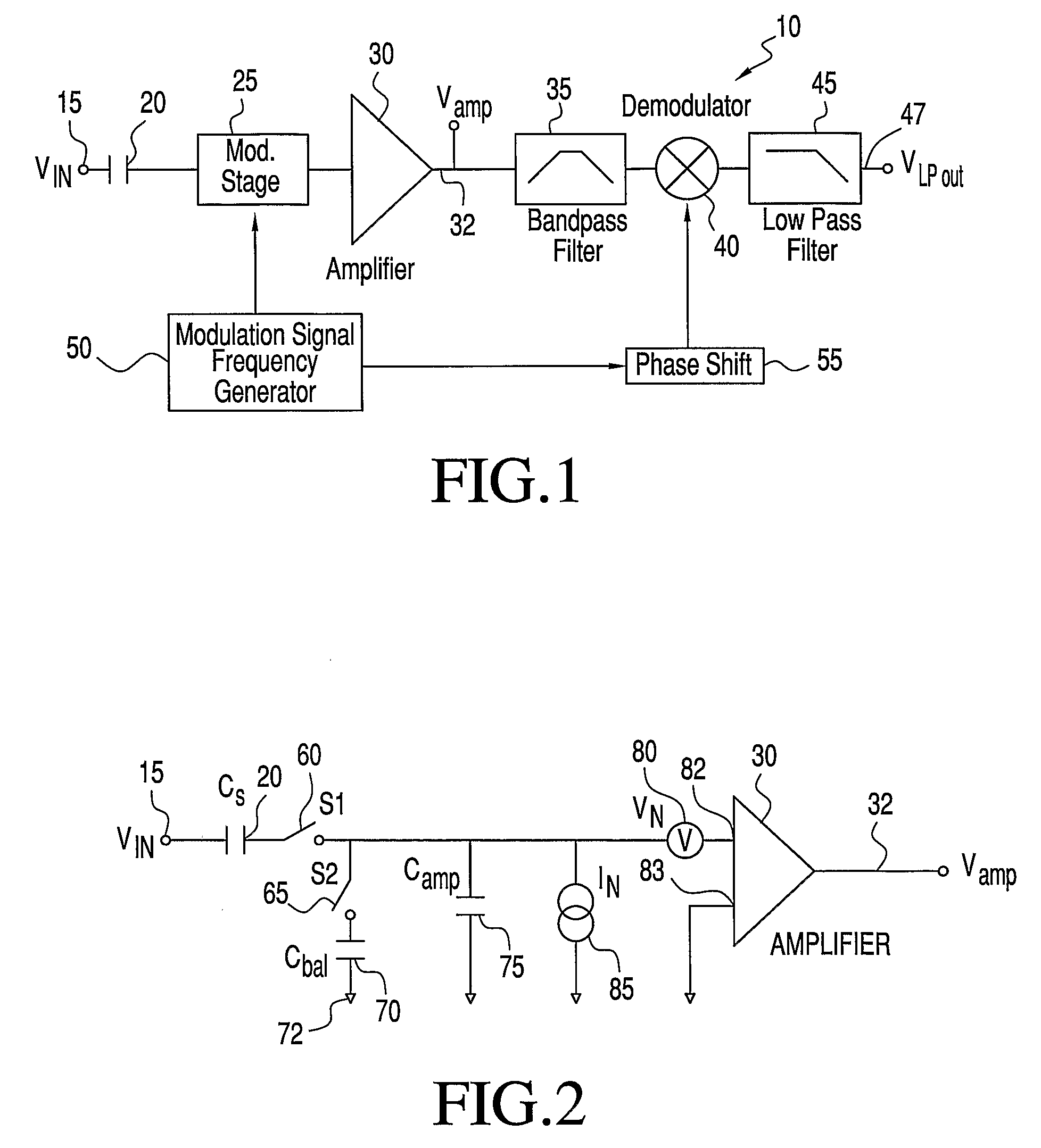
Patents
Literature
75results about How to "Reduce noise contribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
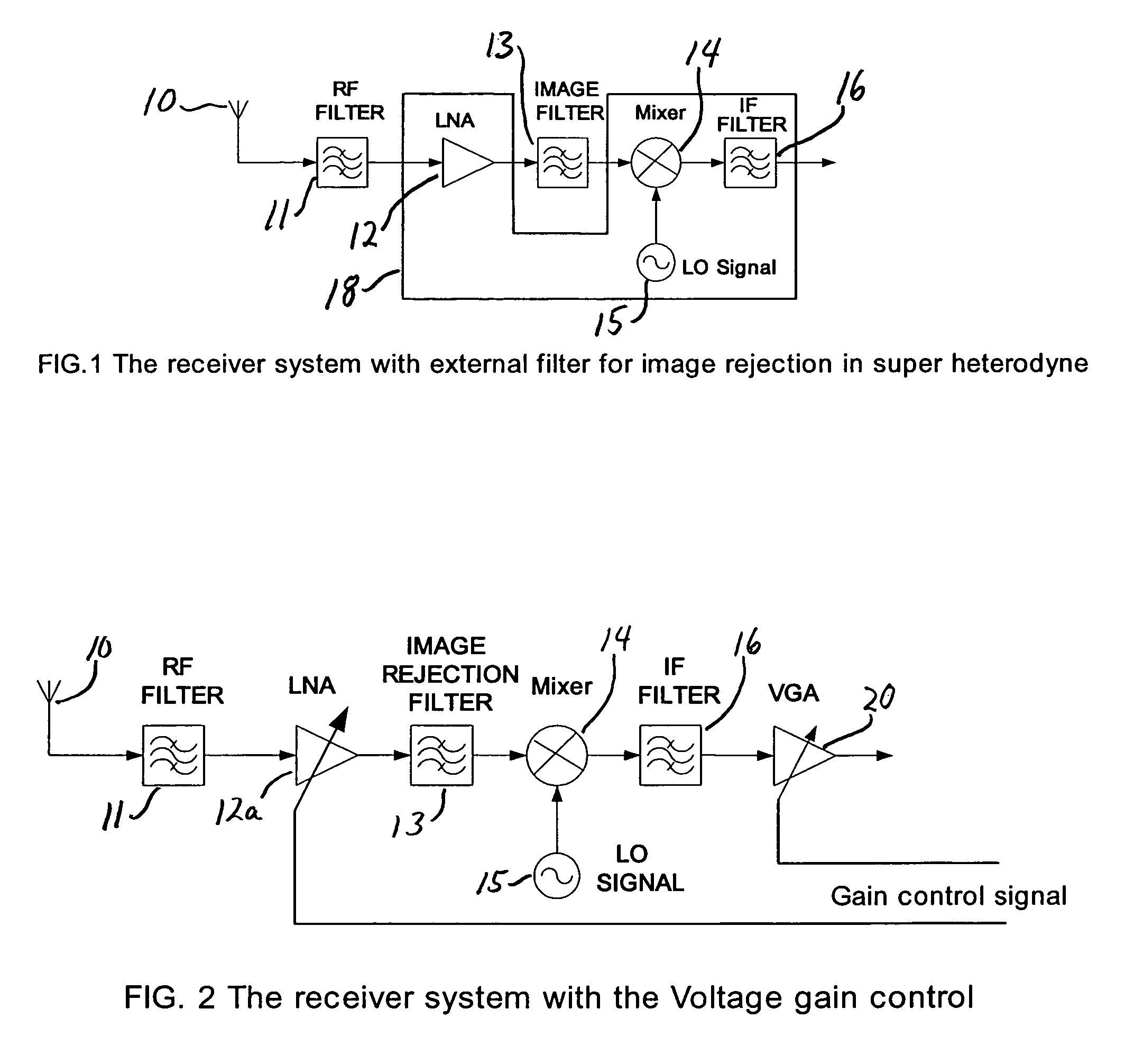
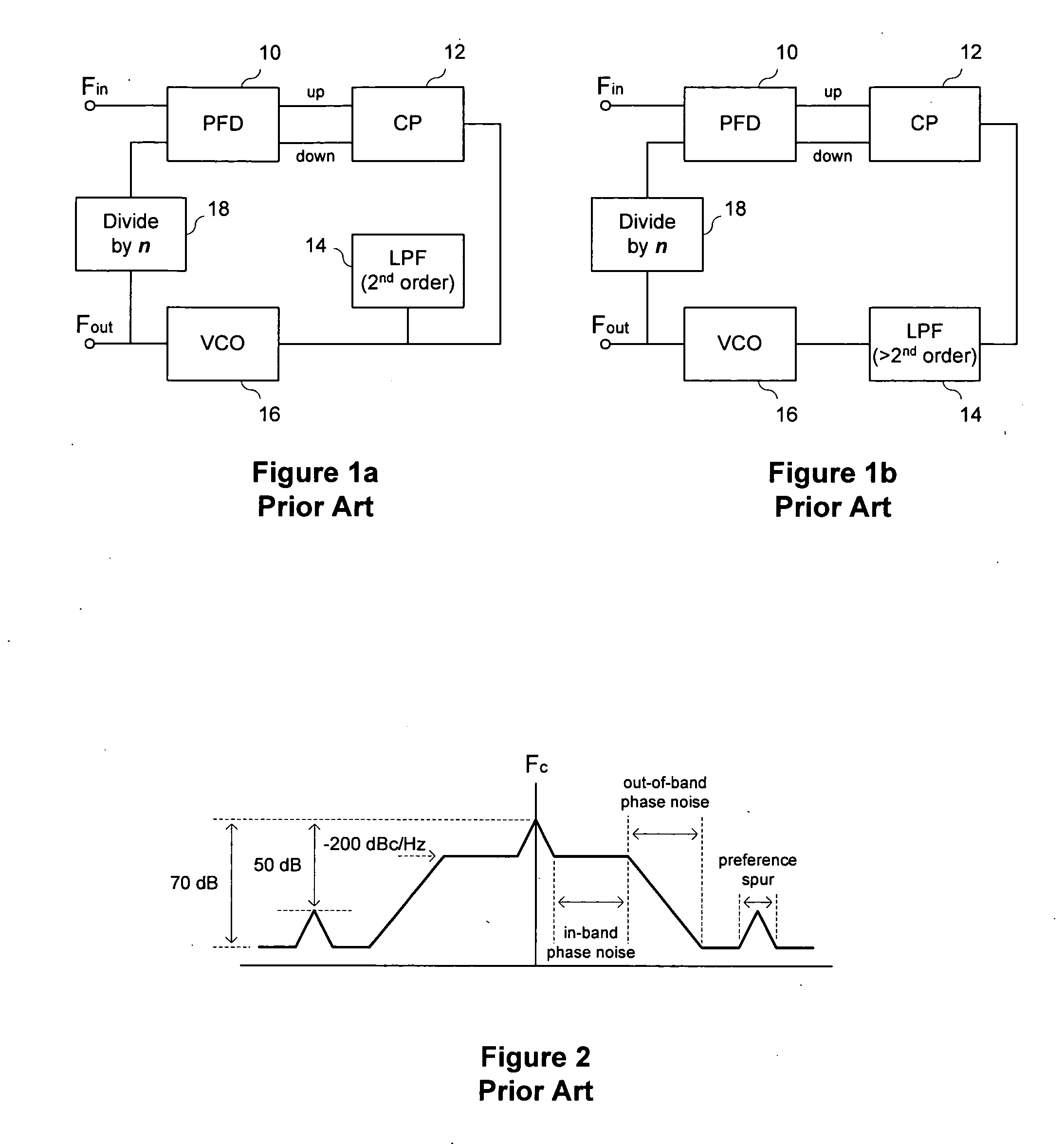
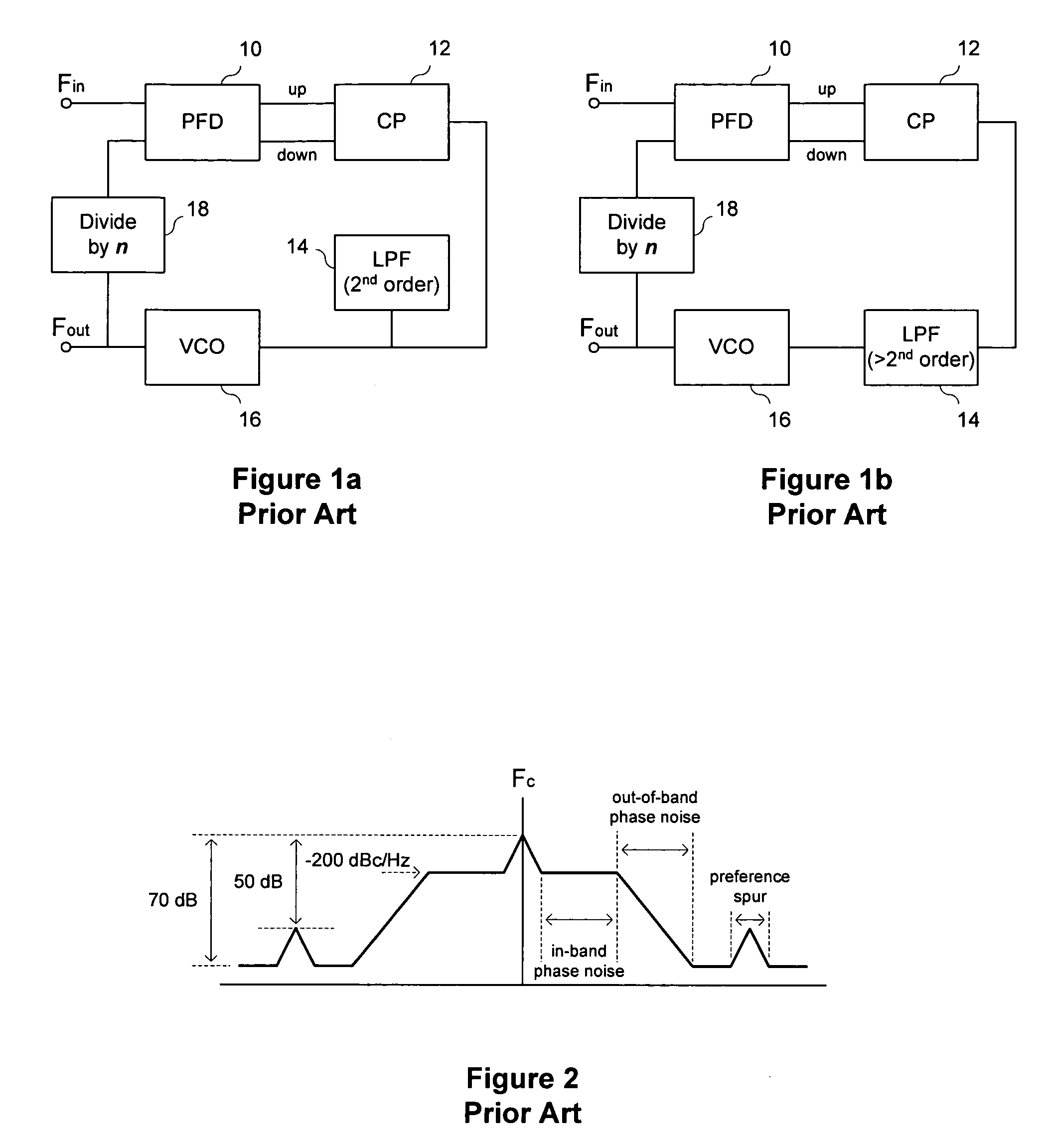
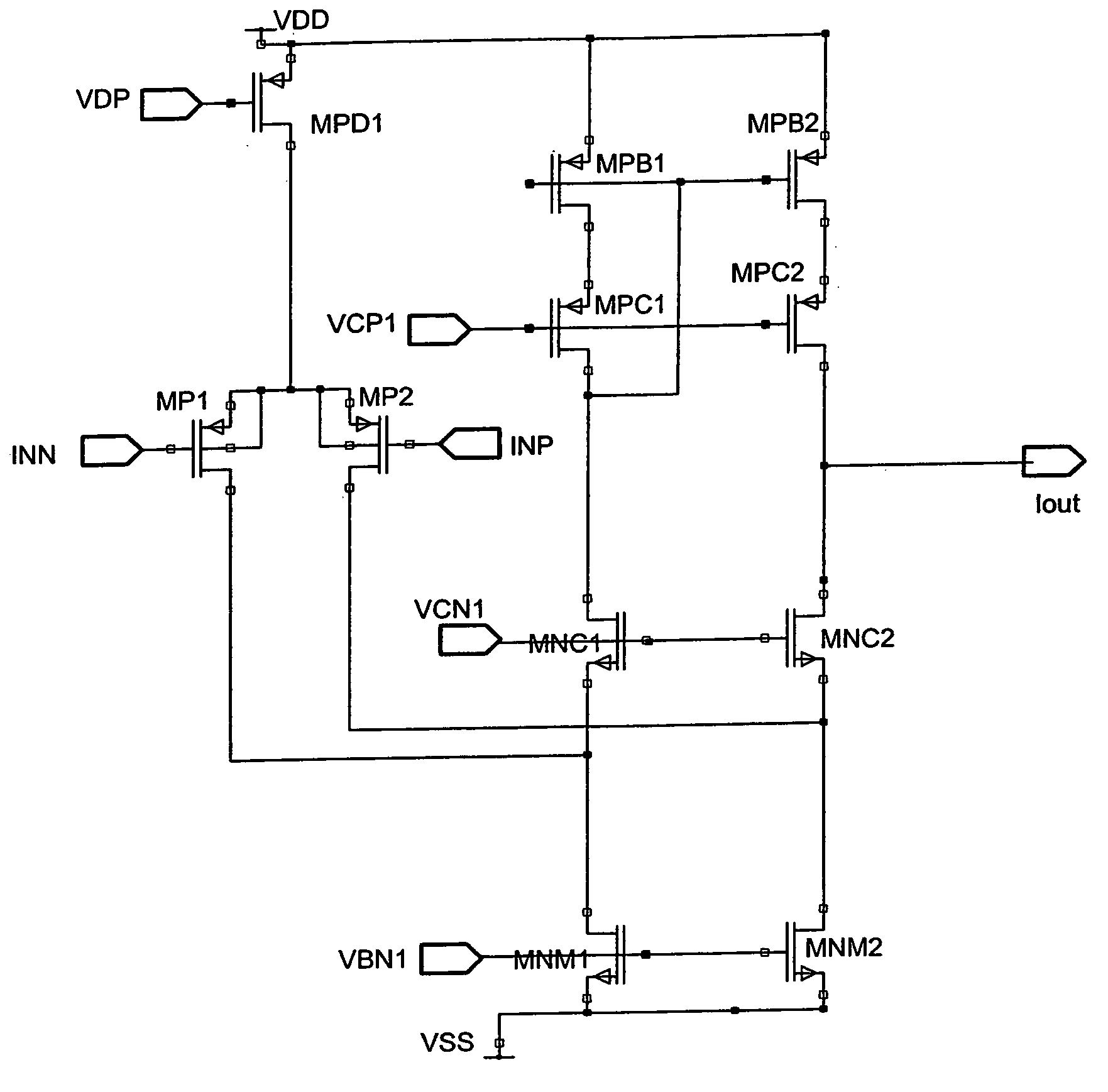
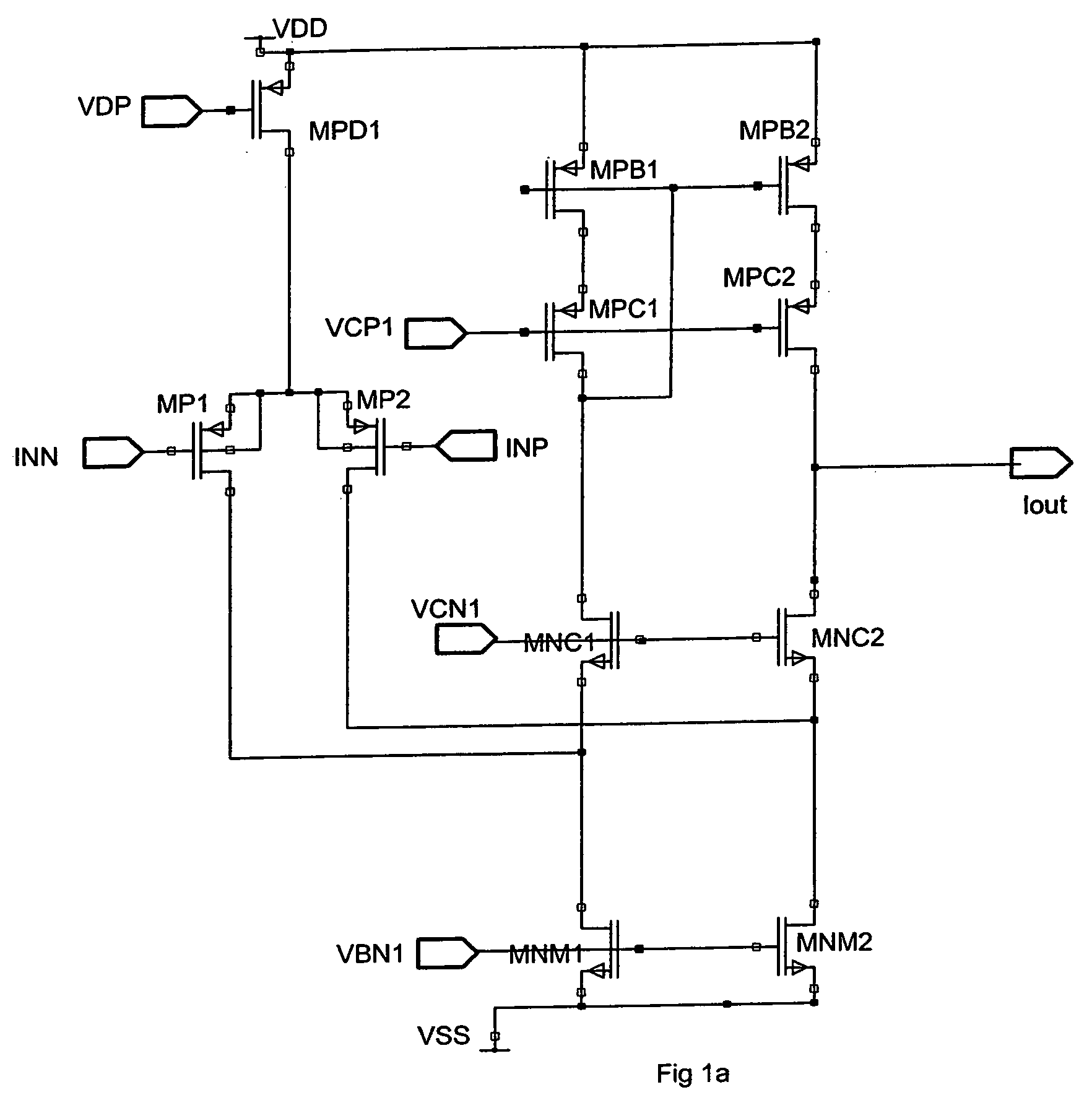
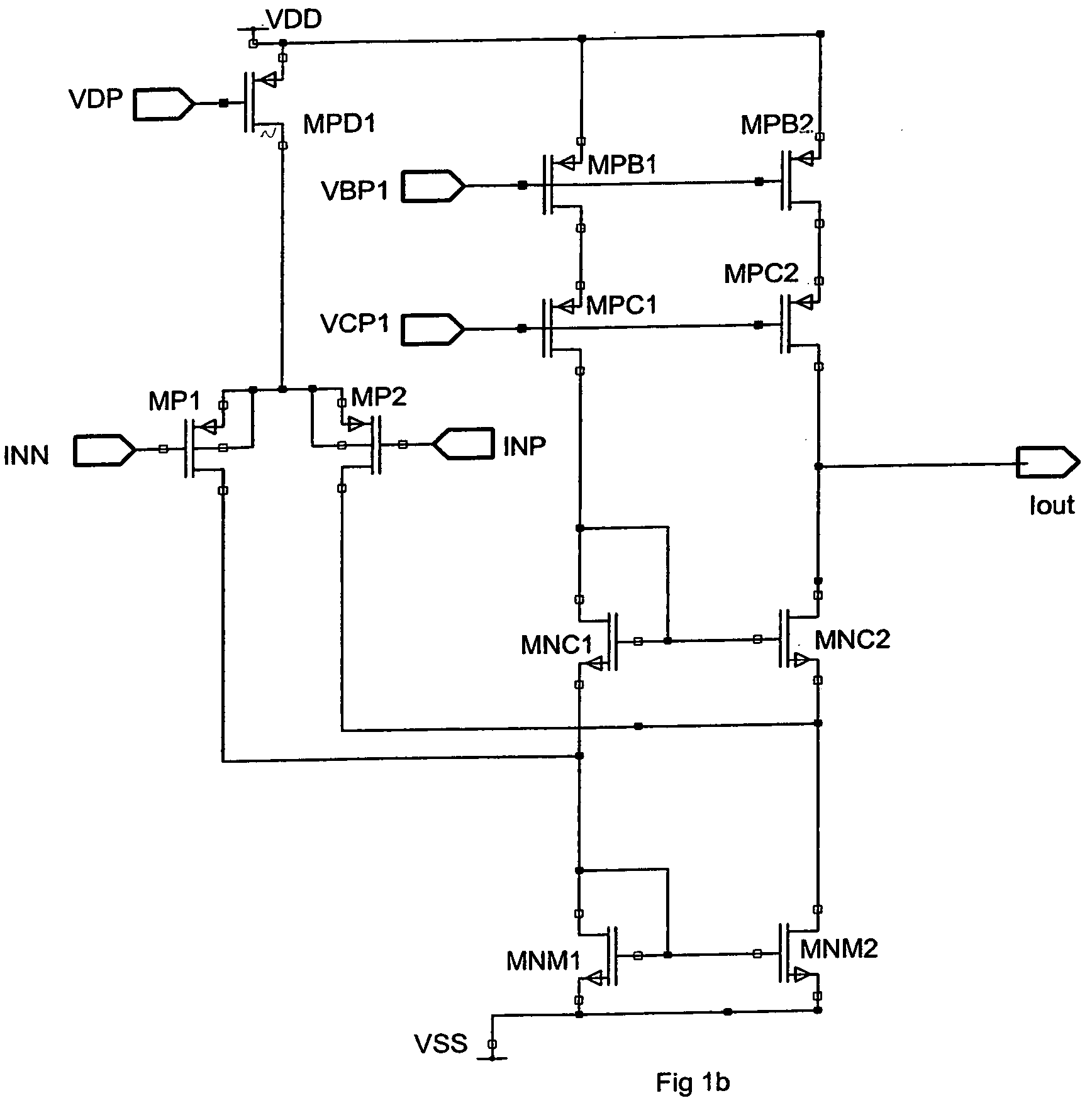
Method and apparatus to reduce the jitter in wideband PLL frequency synthesizers using noise attenuation
InactiveUS20060141963A1Reduce noise contributionReduce phase noisePulse automatic controlTransmissionMOSFETCapacitance
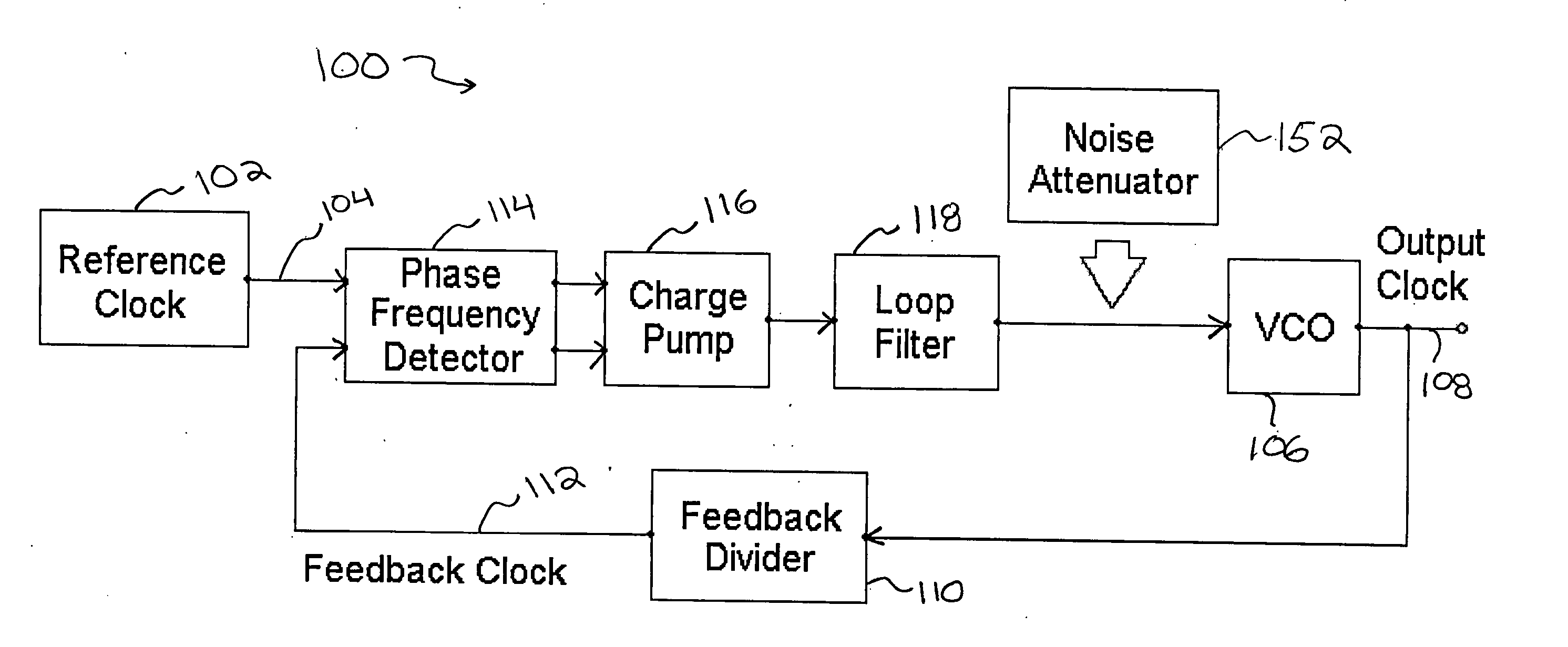
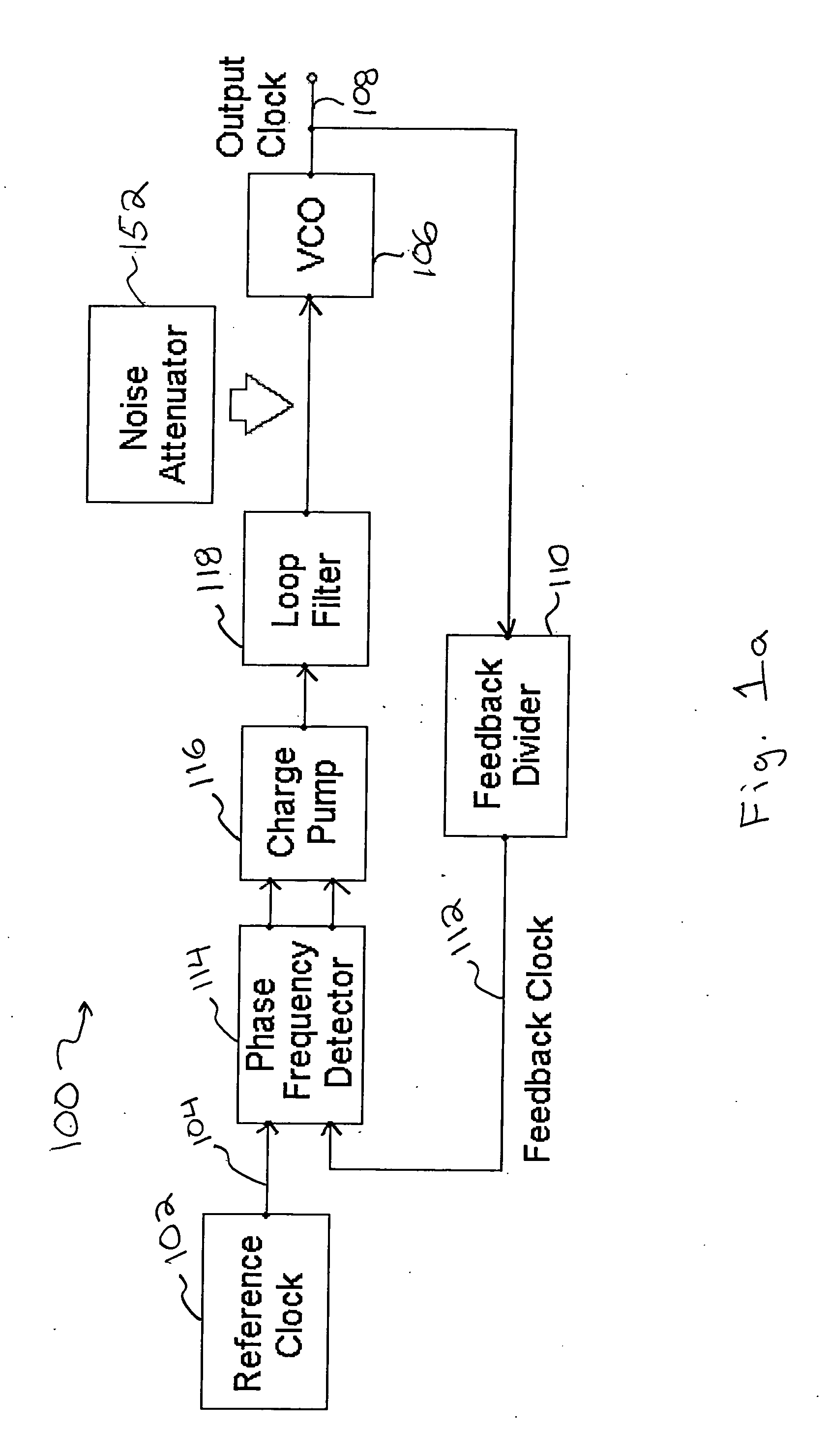
A noise attenuator loop filter for PLL applications that allows a full on-chip integration of the loop filter capacitors, while ensuring a low output clock phase noise (jitter) is disclosed. A voltage attenuator (A) is inserted between the loop filter (passive or active) and the controlled oscillator. The attenuator attenuates the noise coming from the loop filter. In case of a passive RC filter, the series resistor noise power is attenuated by A2 times, allowing the usage of a resistor that is A2 times larger and therefore the loop filter capacitors result A2 times smaller (easy to integrate on-chip). The relatively low value capacitor allows the usage of thick-oxide accumulation-mode MOSFET capacitors that take a reasonable low area, have a good linearity, are isolated from the substrate by the grounded N-well, and have negligible gate leakage current. Several embodiments of the noise attenuator are proposed for different practical applications: clock generation for digital circuits, frequency translation, low or high supply voltage, narrow or wide frequency range, processes with or without isolated well devices, processes with or without polysilicon resistors, and medium or high reference spurs rejection.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
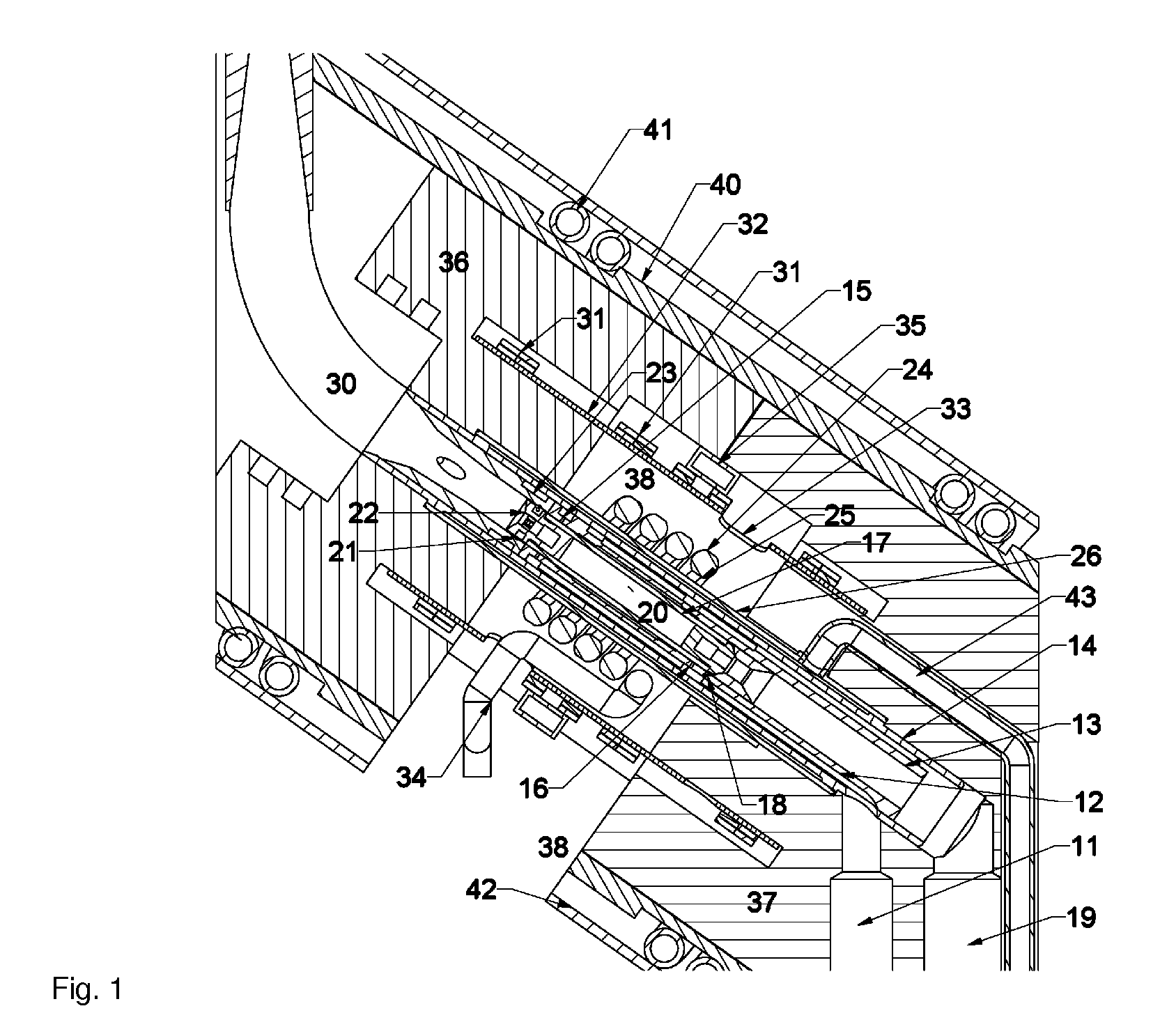
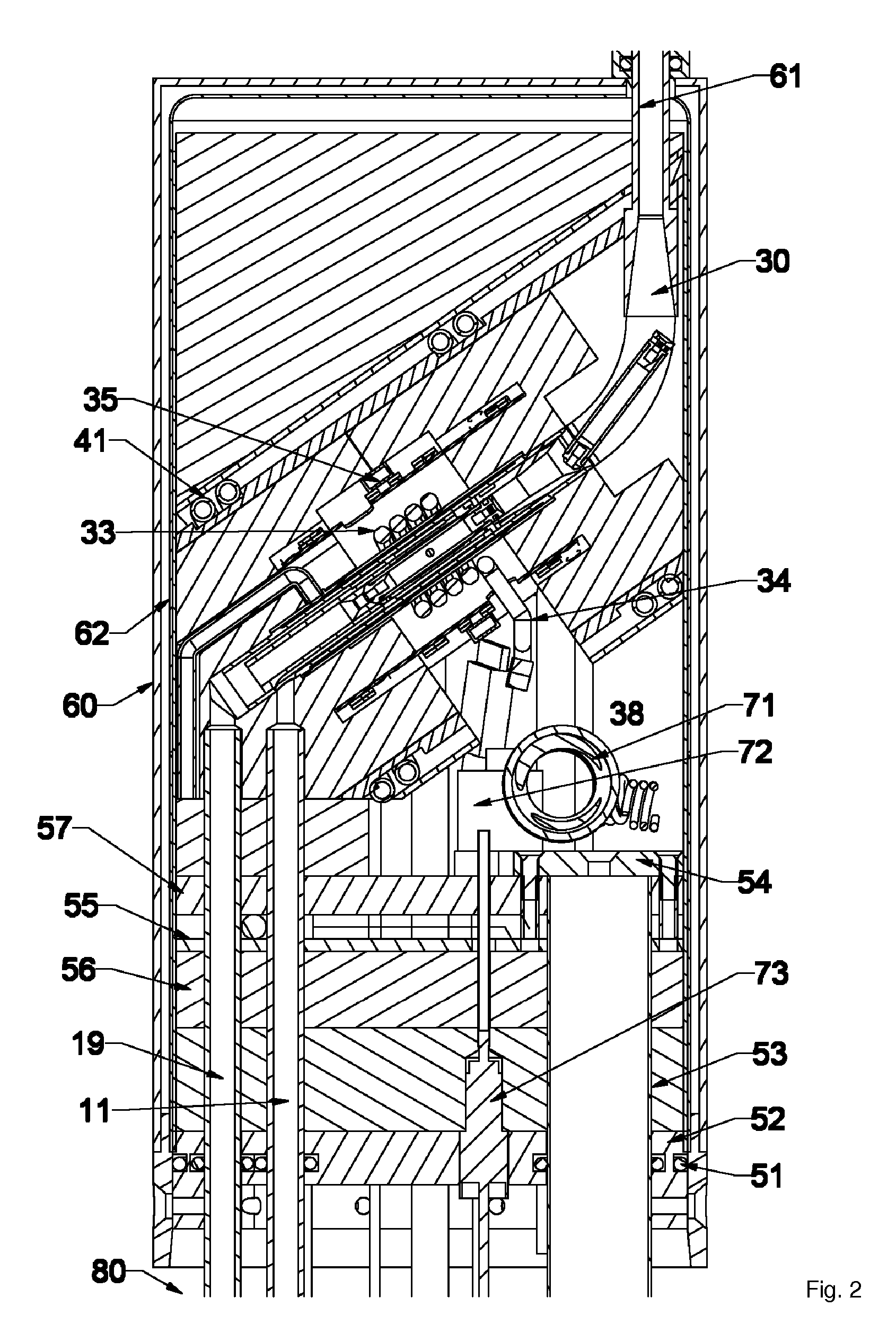
NMR CryoMAS probe for high-field wide-bore magnets
InactiveUS7282919B2Reduce riskAvoid flowElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningNitrogen gas
Owner:DOTY SCI
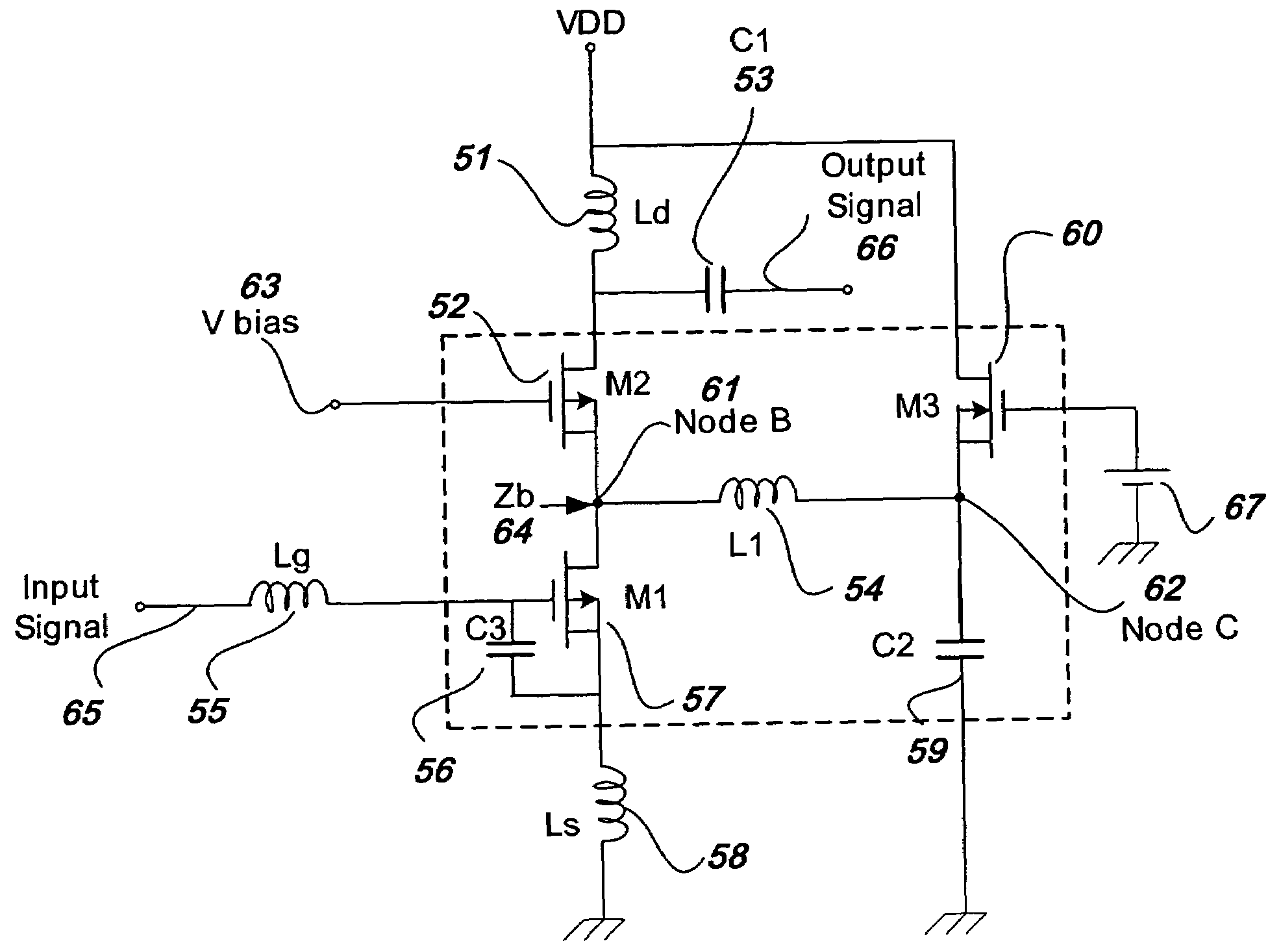
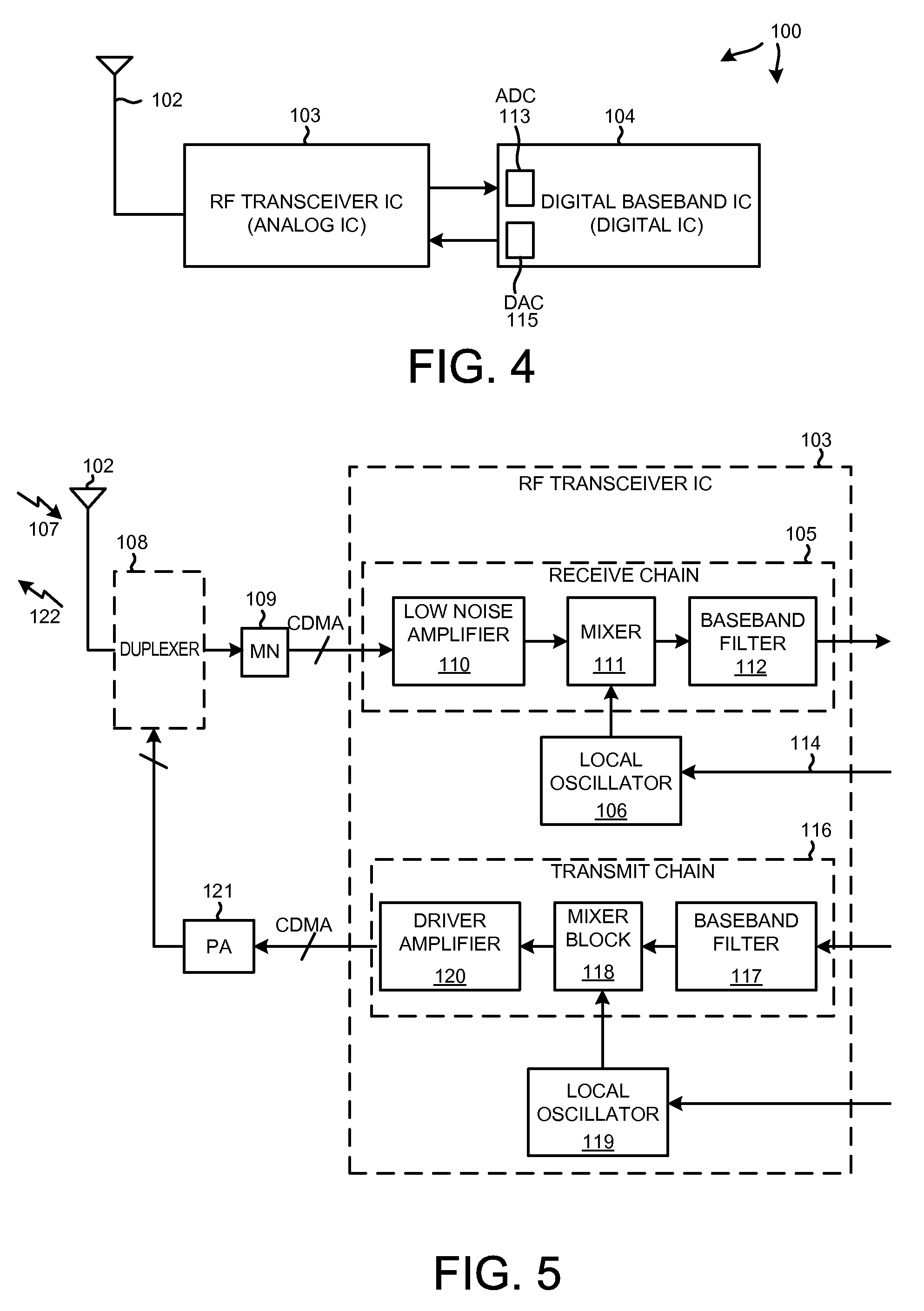
Low noise amplifier for wireless communications
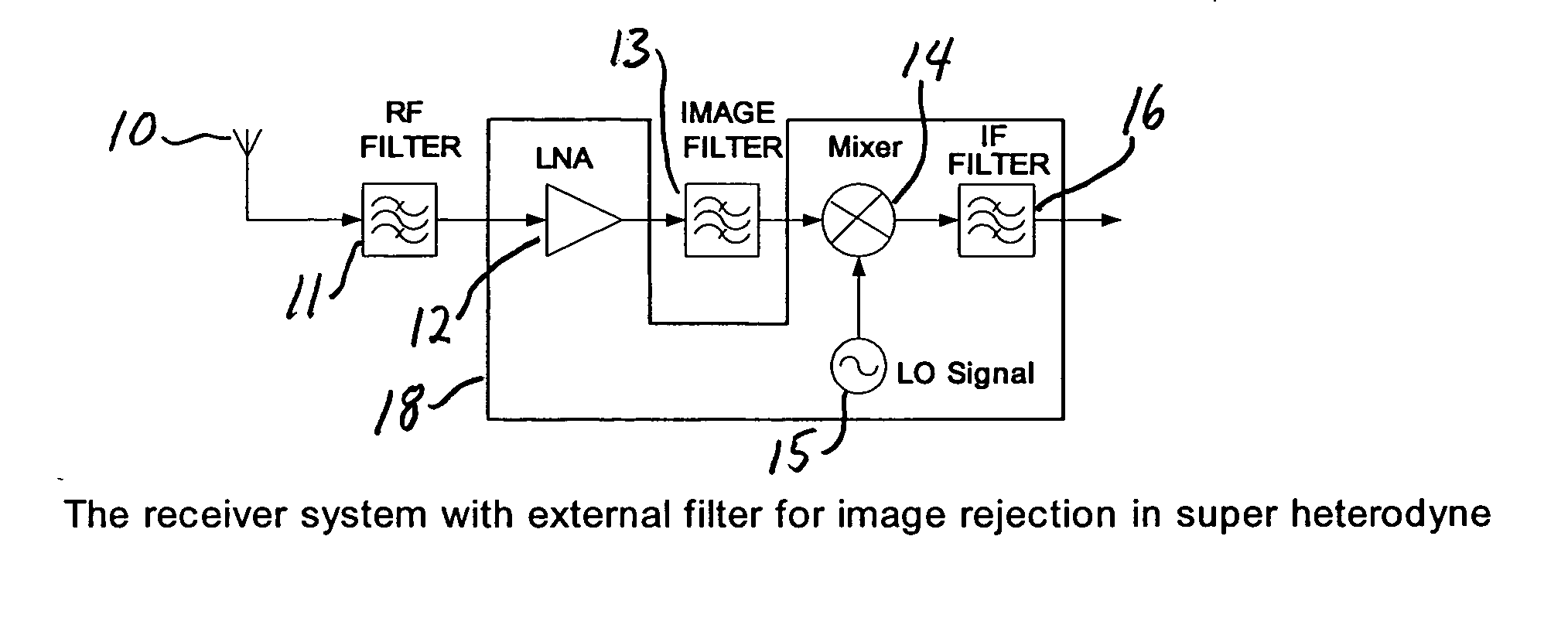
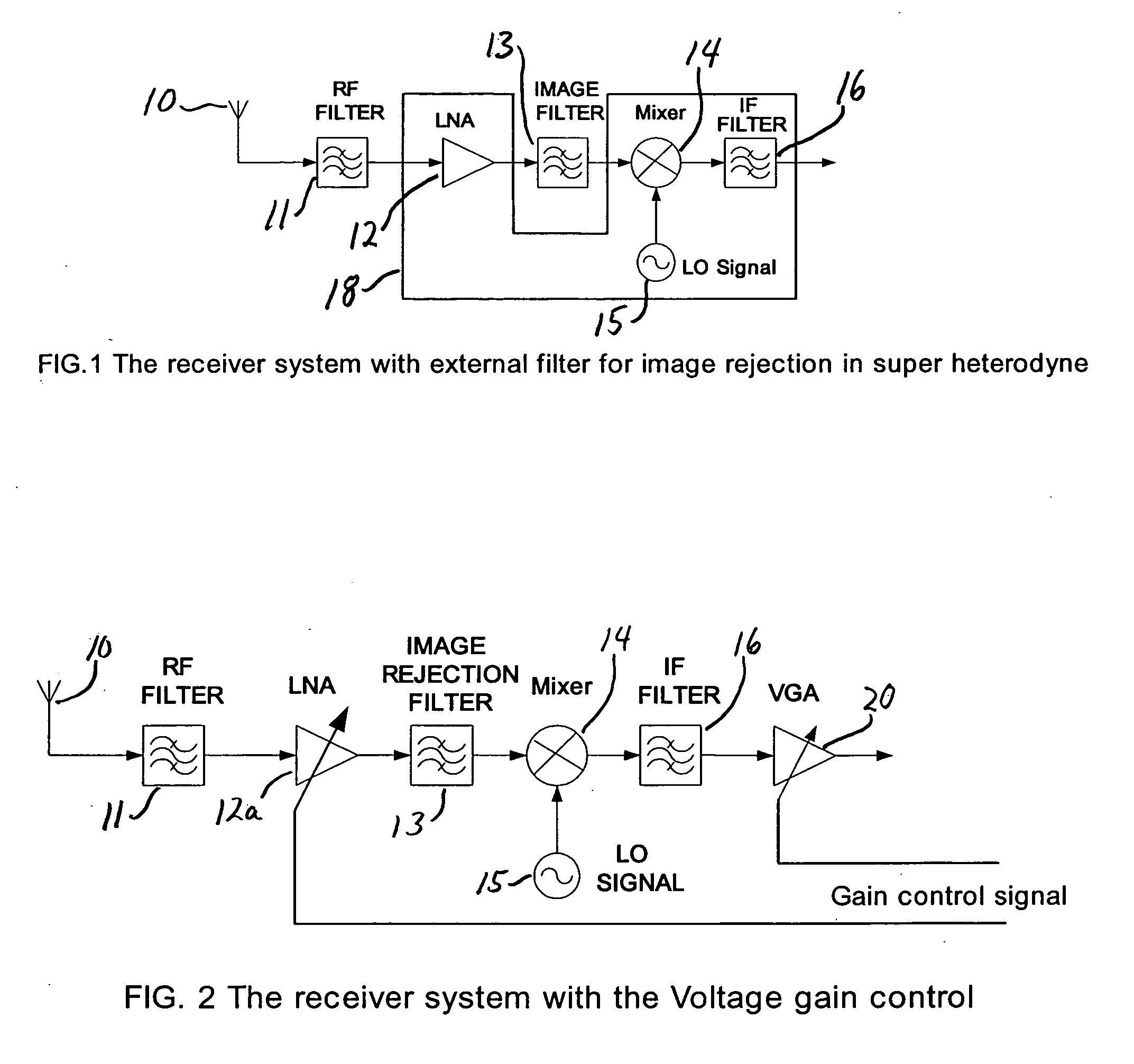
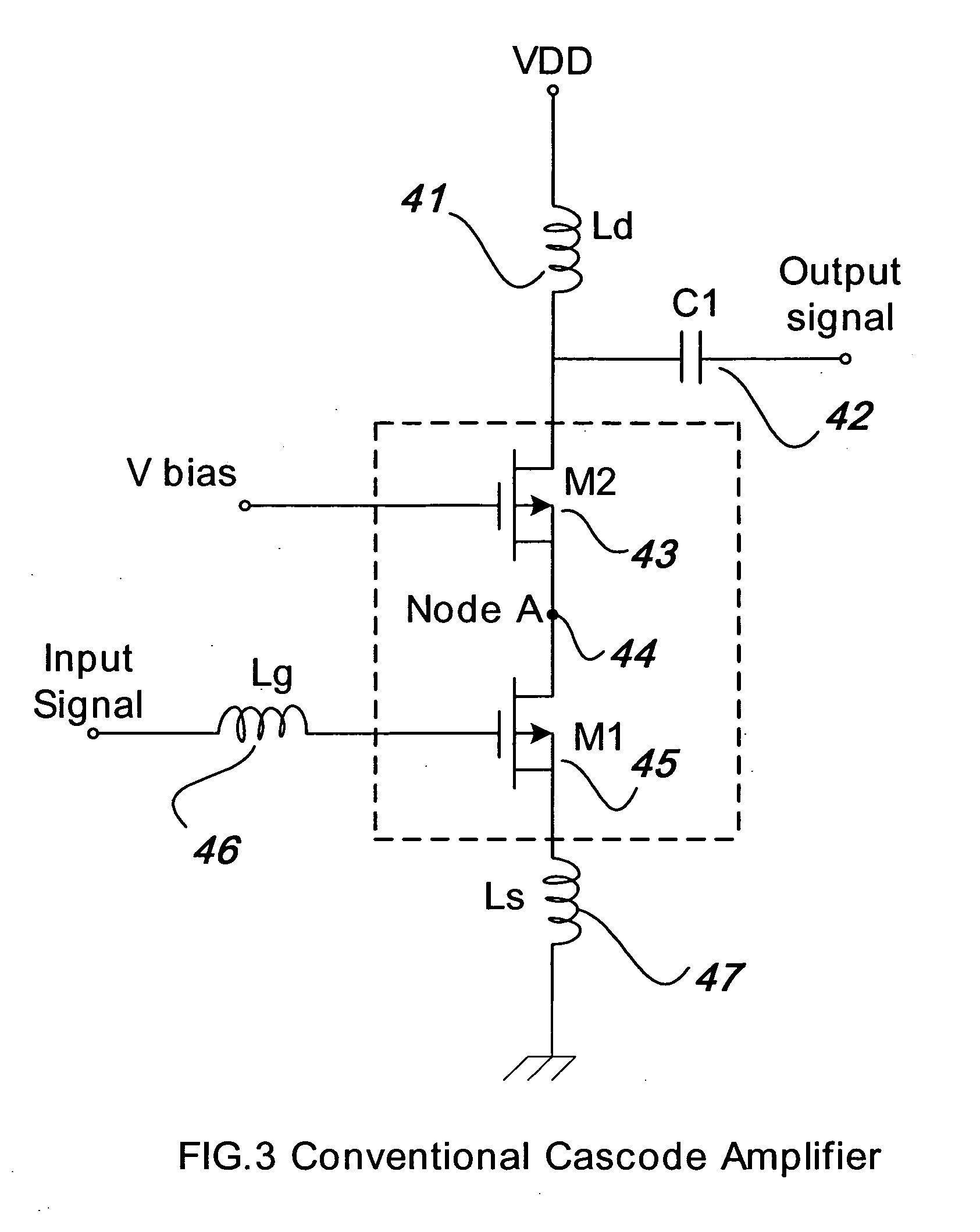
InactiveUS7266360B2Reduce noiseLow noise characteristicsMultiple-port networksGain controlCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
A low noise amplifier is provided for the receiver of a wireless communications system. The amplifier incorporates an image rejection function by incorporating a notch filter formed by an inductor and capacitor connected at a node between two active elements of the amplifier. The amplifier also incorporates a gain control function by adding a further active element connected to, on one hand, a node between the inductor and capacitor and, on the other hand, a voltage supply. A gain control signal is connected to the control input of the further active element has an input connected to a feedback lead of the receiver to provide the gain control.
Owner:NEOREACH INC
Method of and system for determining distances between loudspeakers
InactiveUS20100135118A1Without disturbingEconomical and simpleDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesLoudspeakersEngineeringLoudspeaker
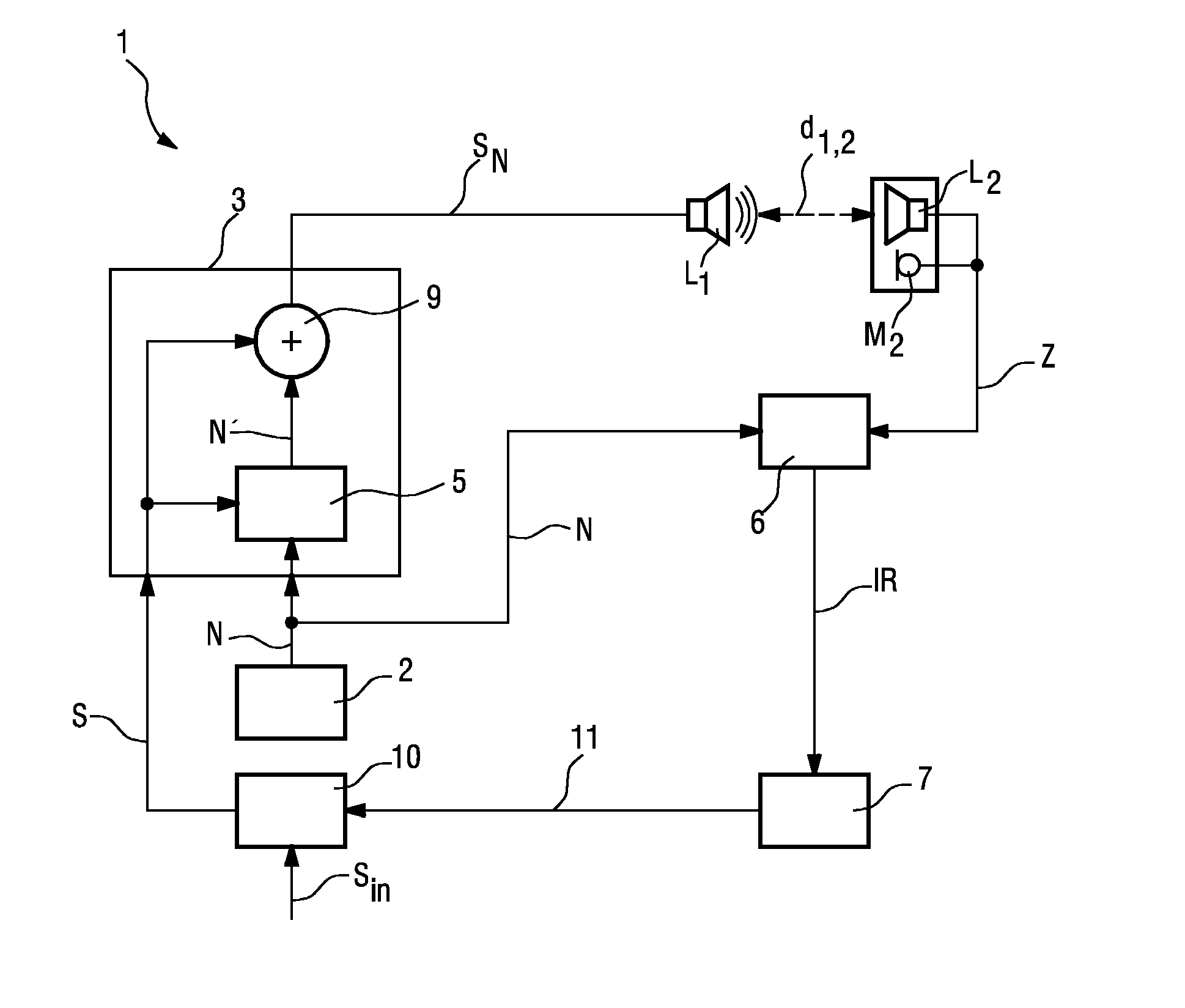
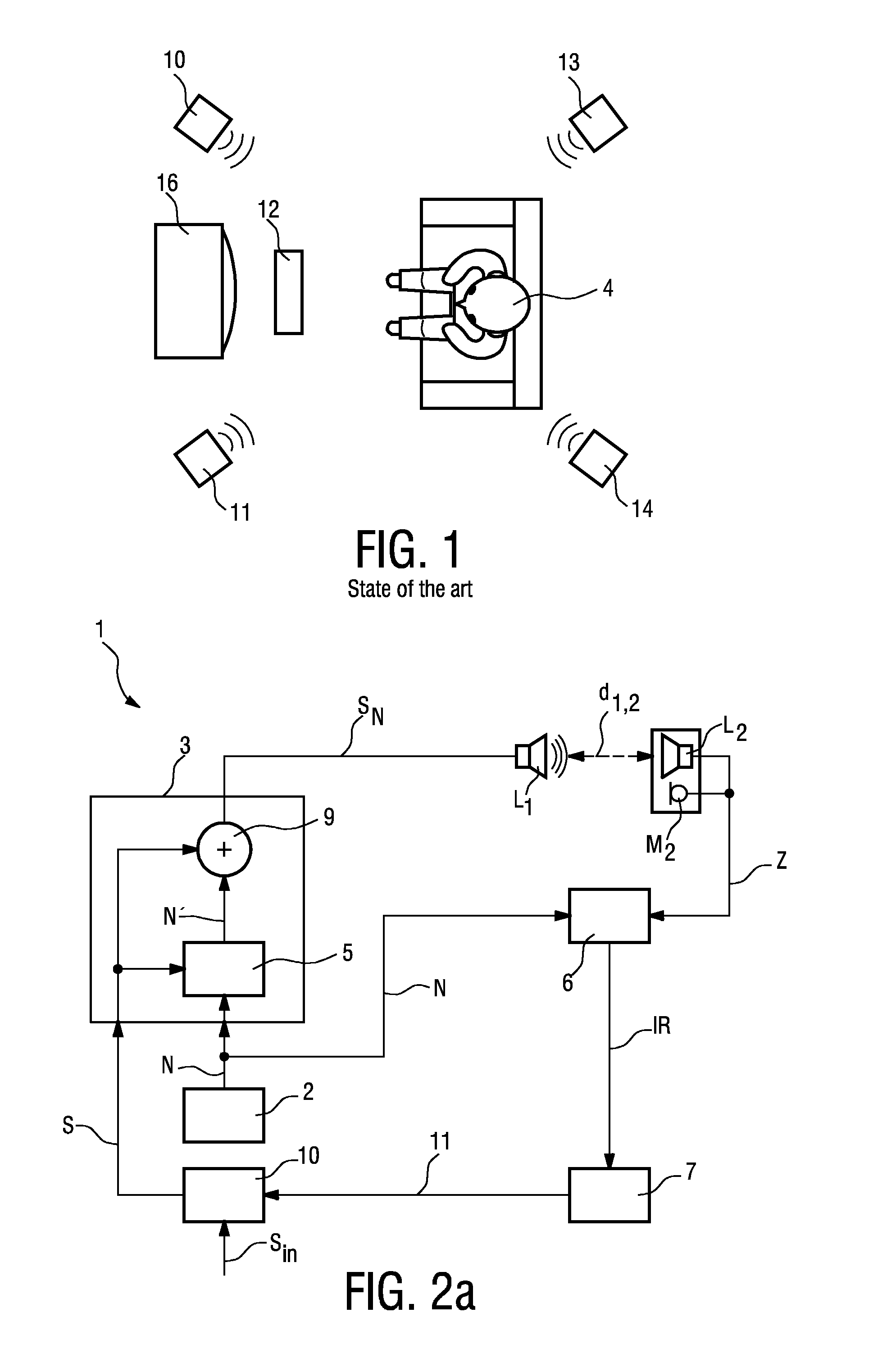
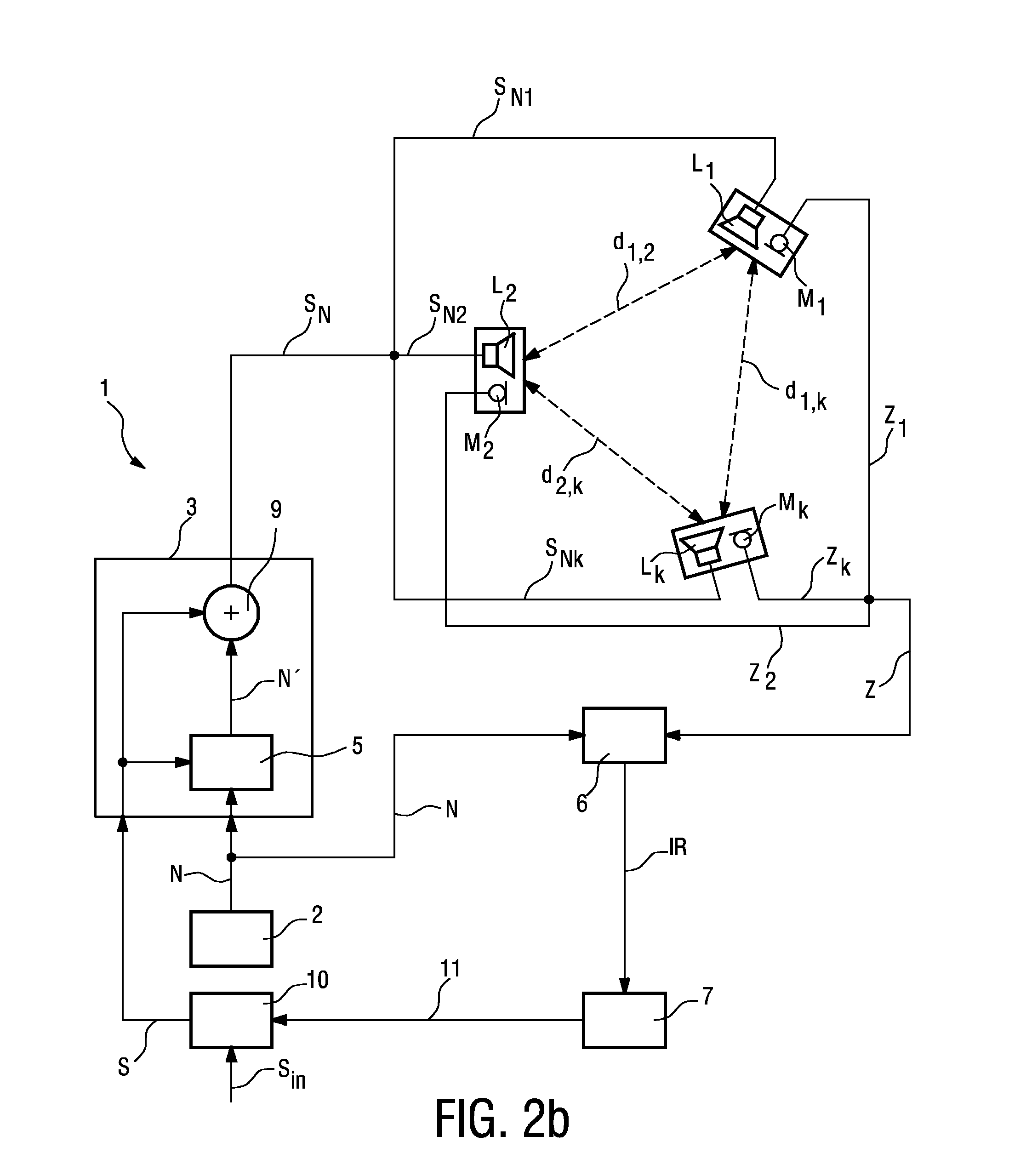
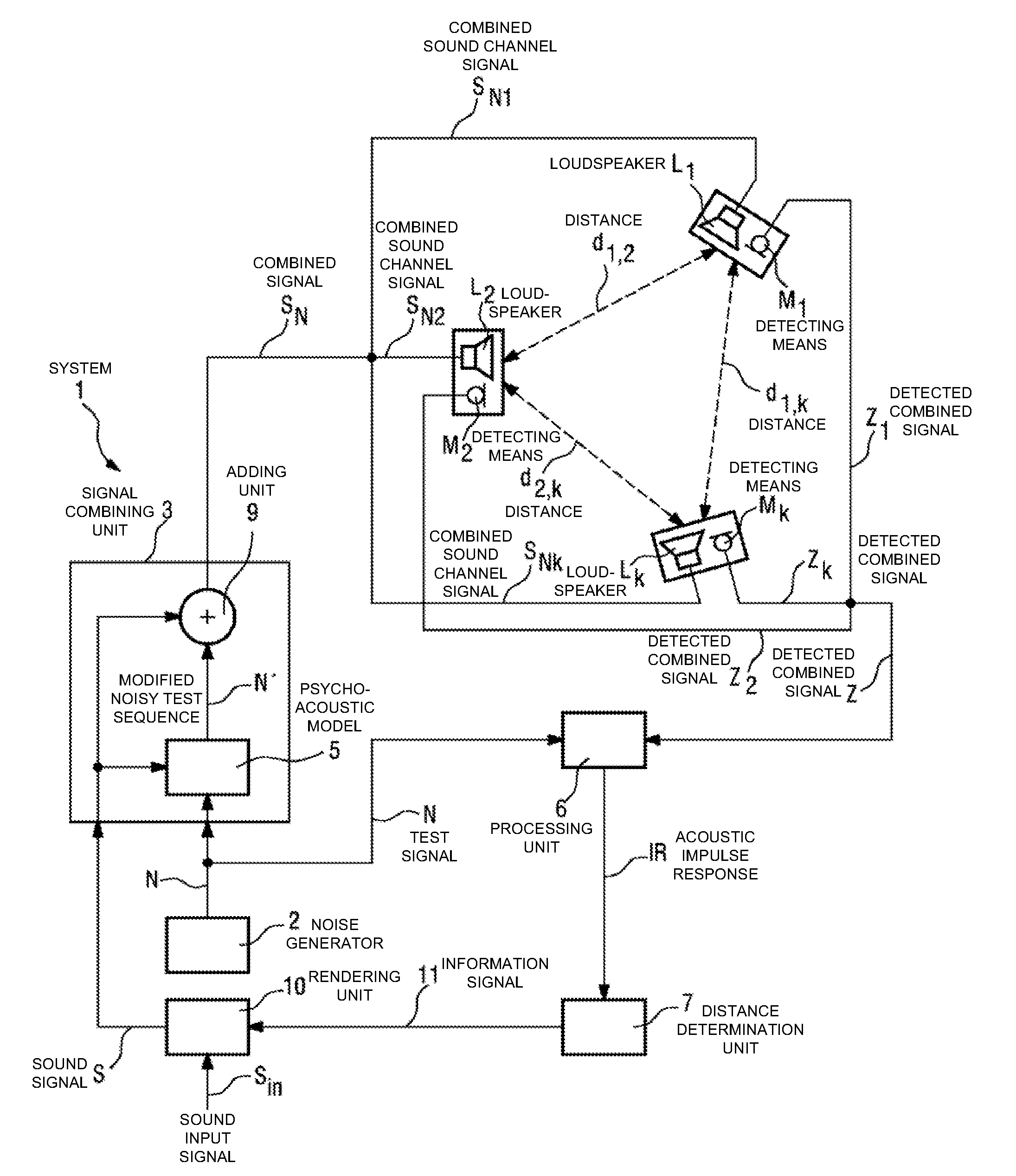
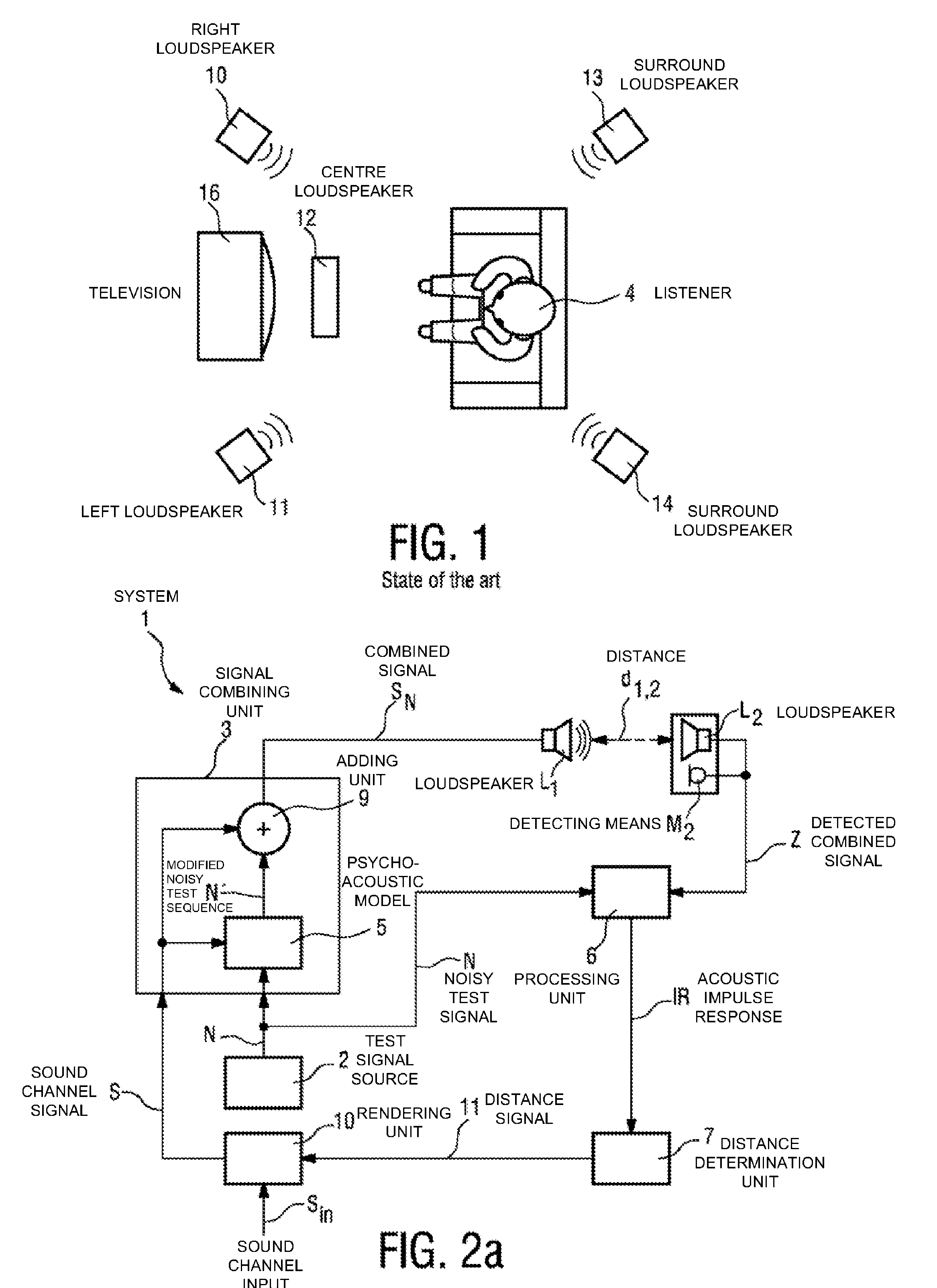
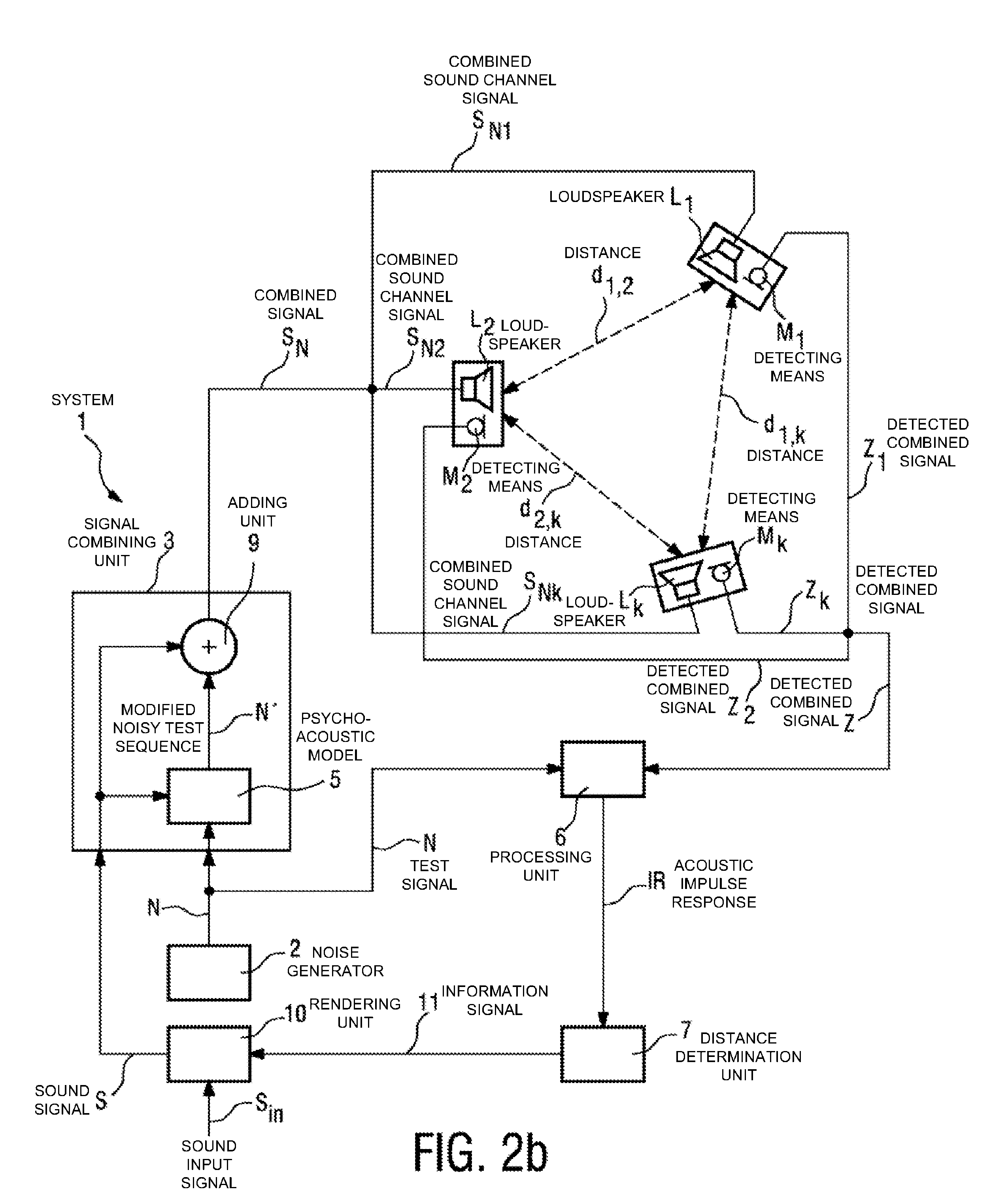
The invention describes a method of determining the distance (d12) between two loudspeakers (L1, L2), wherein the method comprises the steps of providing a test signal (N), combining the test signal (N) with a sound signal (S) to give a combined signal (SN) in which the test signal is imperceptible to a listener (4), and issuing the combined signal (SN) by means of a first loudspeaker (L1). The combined signal (SN) is detected by a detecting means (M2) associated with the second loudspeaker (L2) and processed to obtain an acoustic impulse response (IR), which is used to determine the distance (d1,2) between the first loudspeaker (L1) and the second loudspeaker (L2). The invention further describes a system (1) for determining the distance (d1,2) between two loudspeakers (L1, L2) and an acoustic sound system, comprising a number of loudspeakers (L1, L2, . . . , Lk) for reproduction of multi-channel sound, and a system (1) for determining the distances (d1,2, d2,3, . . . , dk-i,k) between the loudspeakers (L1, L2, . . . , Lk) in order to automatically configure the loudspeakers (L1, L2, . . . , Lk) for that acoustic sound system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Low noise amplifier for wireless communications
InactiveUS20050227652A1Reduce noiseLow noise characteristicsGain controlPower amplifiersCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
A low noise amplifier is provided for the receiver of a wireless communications system. The amplifier incorporates an image rejection function by incorporating a notch filter formed by an inductor and capacitor connected at a node between two active elements of the amplifier. The amplifier also incorporates a gain control function by adding a further active element connected to, on one hand, a node between the inductor and capacitor and, on the other hand, a voltage supply. A gain control signal is connected to the control input of the further active element has an input connected to a feedback lead of the receiver to provide the gain control.
Owner:NEOREACH INC
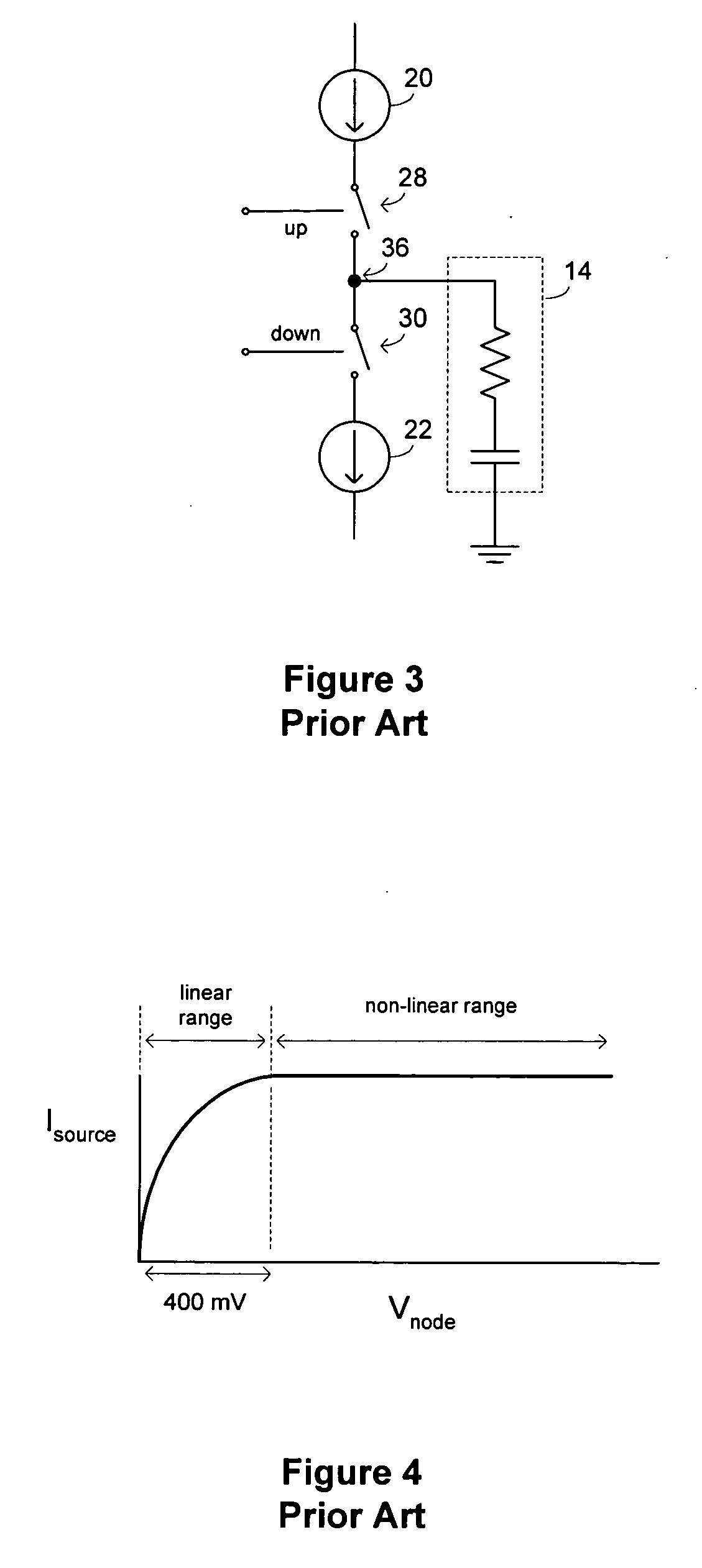
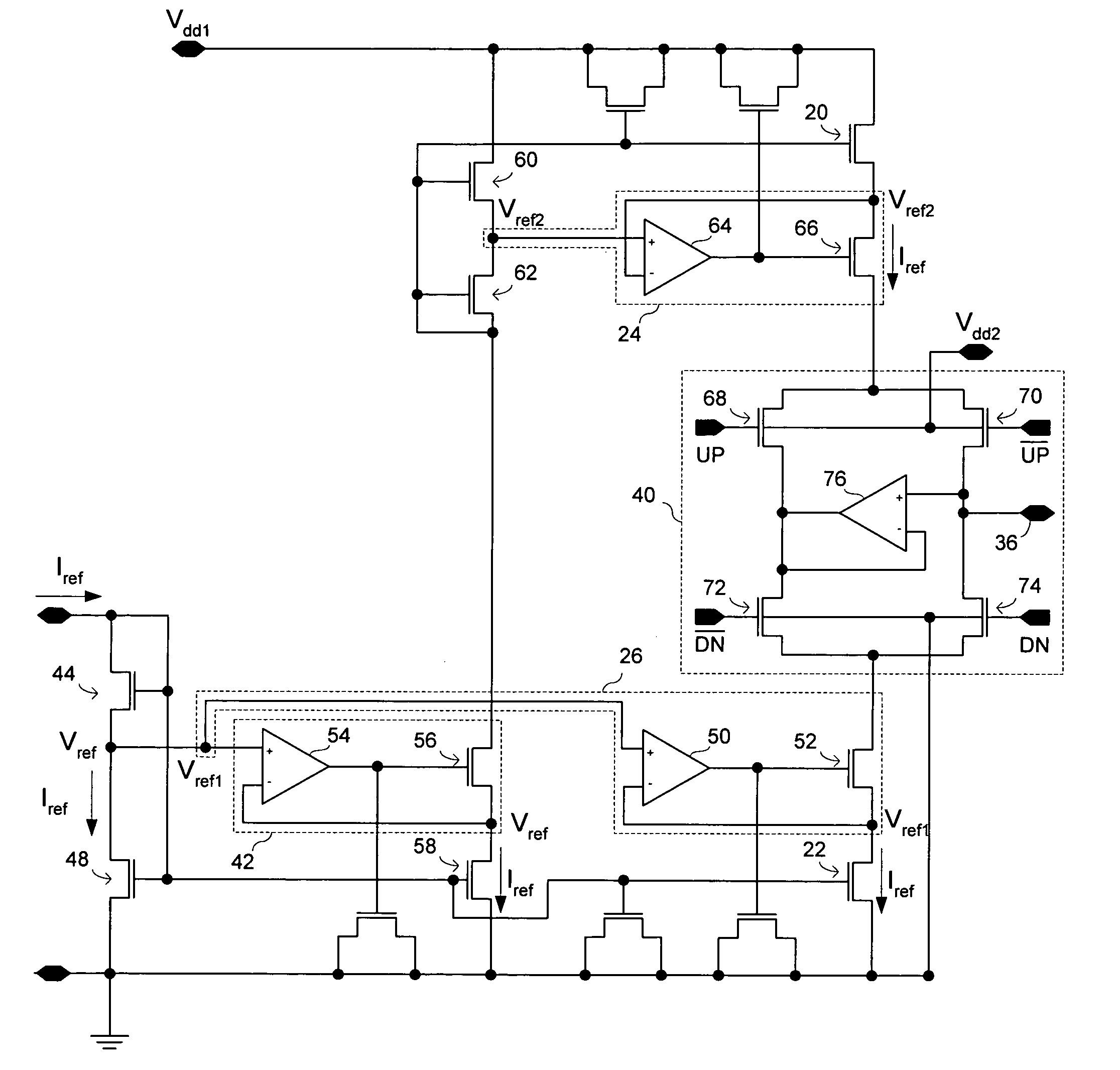
Charge pump circuit using active feedback controlled current sources
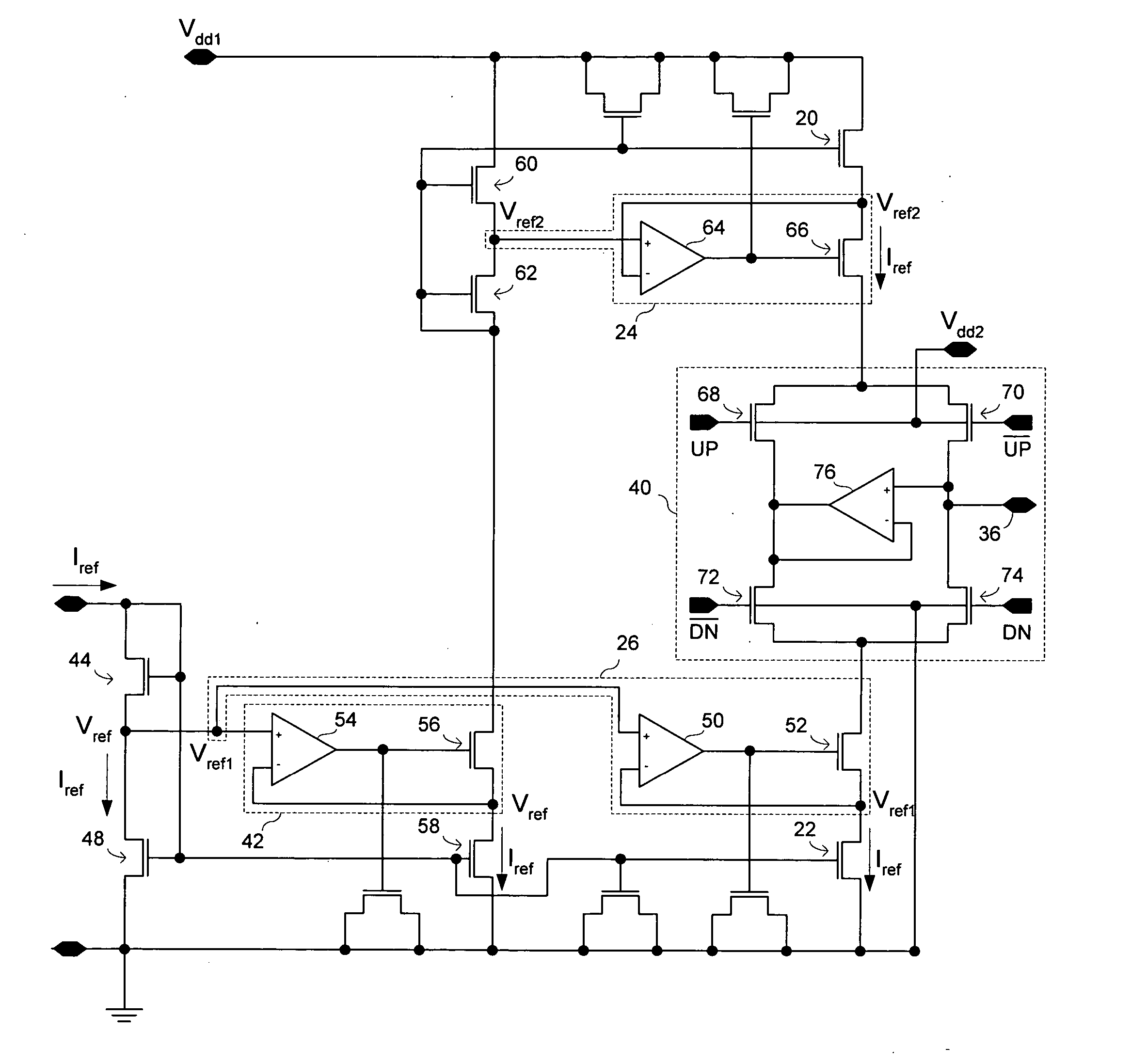
ActiveUS20050195003A1Reduce noise contributionRaise the gate voltageAc-dc conversion without reversalPulse automatic controlActive feedbackDriving current
A charge pump circuit utilizes active feedback control circuits to control the currents produced by sinking and sourcing current sources. The feedback control circuits may regulate the drain voltages of sinking and sourcing current source transistors to make them approximately equal to respective reference voltages received by the feedback control circuits. The charge pump circuit may utilize multiple supply voltages, with a higher supply voltage such as a 3.3 V supply voltage being used to drive current source transistors, and a lower supply voltage such as a 1.8 V supply voltage being used to drive switches in a switching section.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP +1
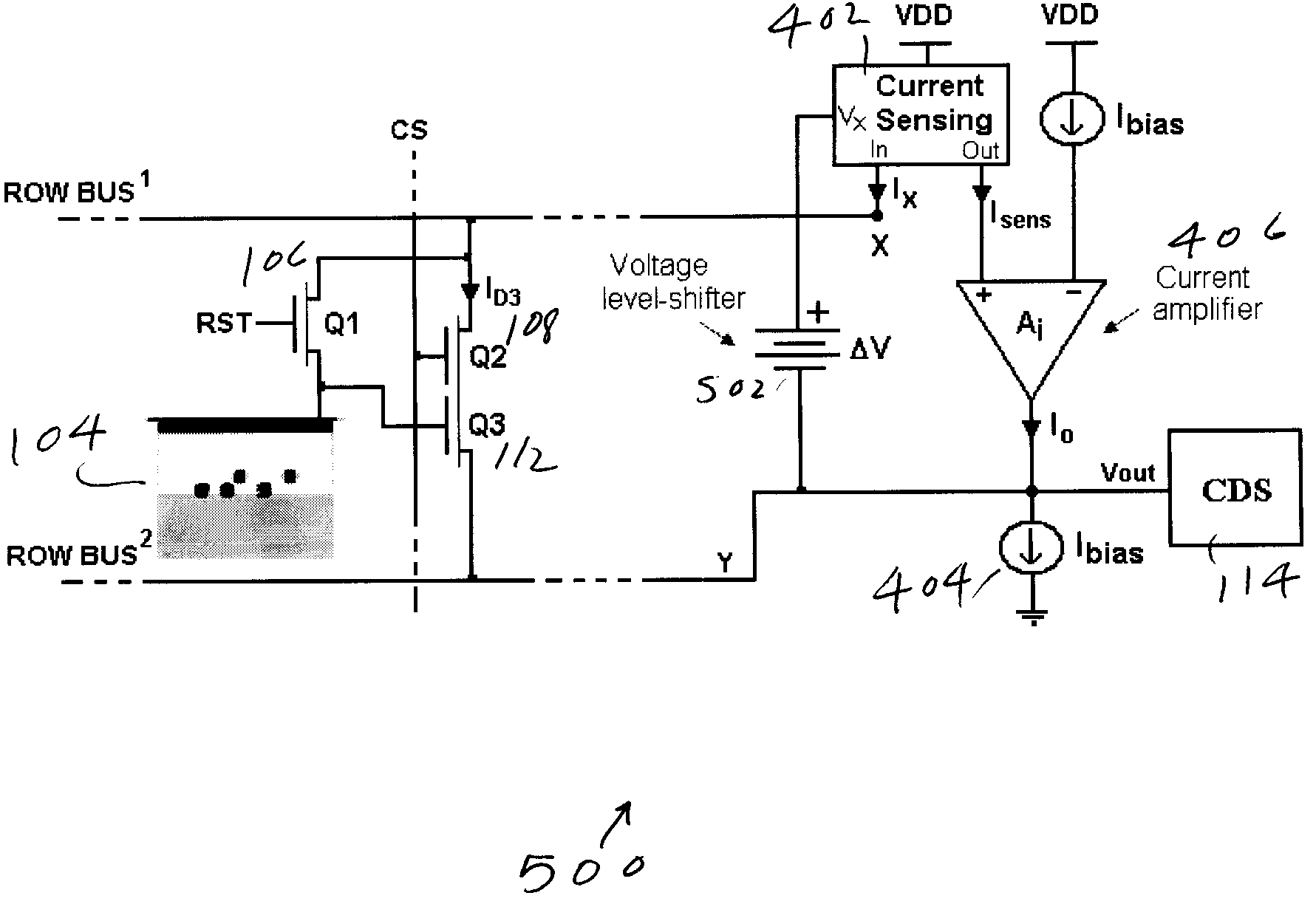
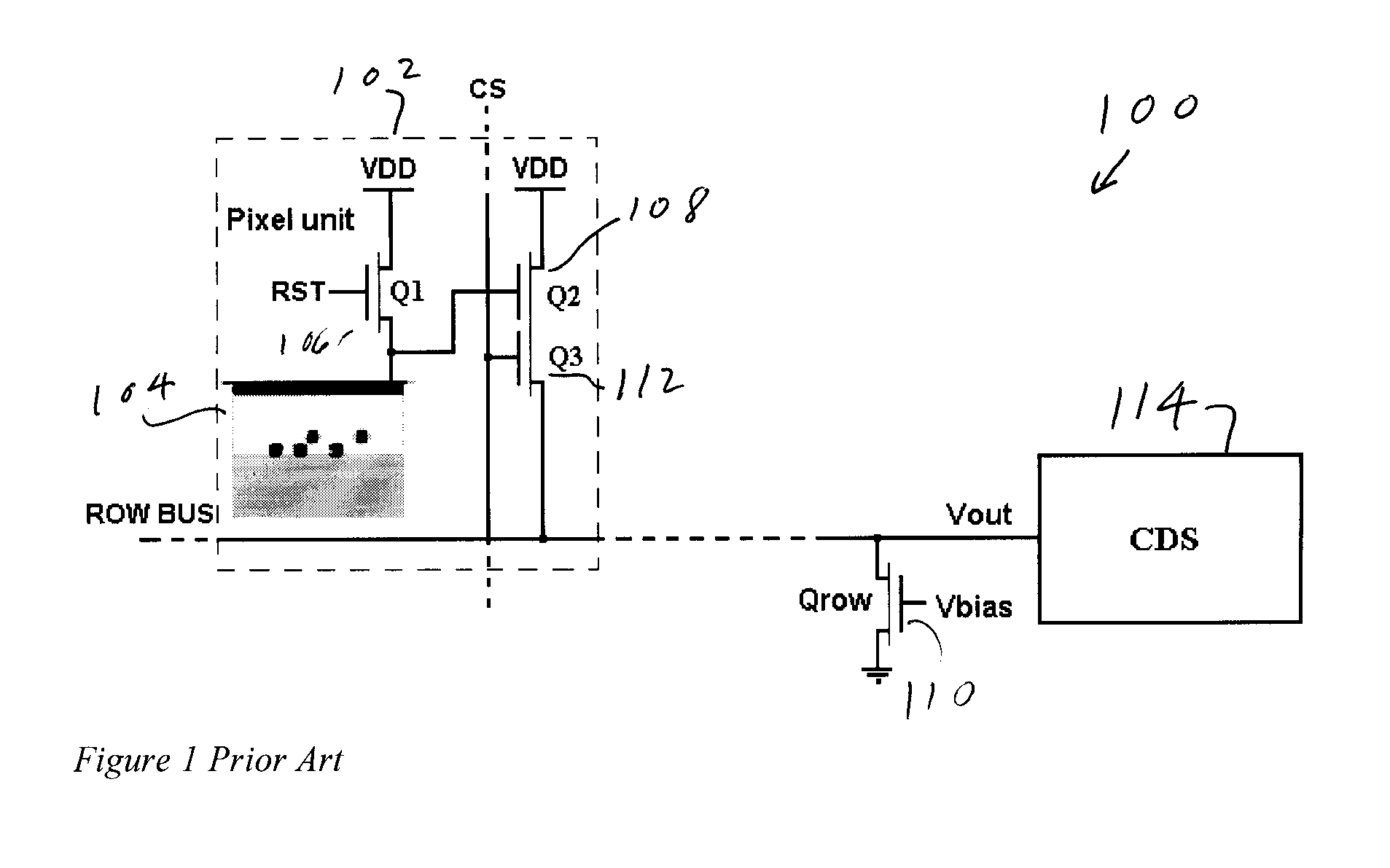
CMOS image sensor readout employing in-pixel transistor current sensing
ActiveUS7847846B1Reduce read noiseIncrease frame rateTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSParasitic capacitance
In an image sensor, the current through the in-pixel readout transistor is sensed by a circuit that is external to the pixel, and according to the measured current value a feedback current is supplied to charge the read-line parasitic capacitance. The feedback current is supplied by a circuit that also is external to the pixel area. The amplifier structure is reconfigurable so that it can be used both to read out and to reset the pixel.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
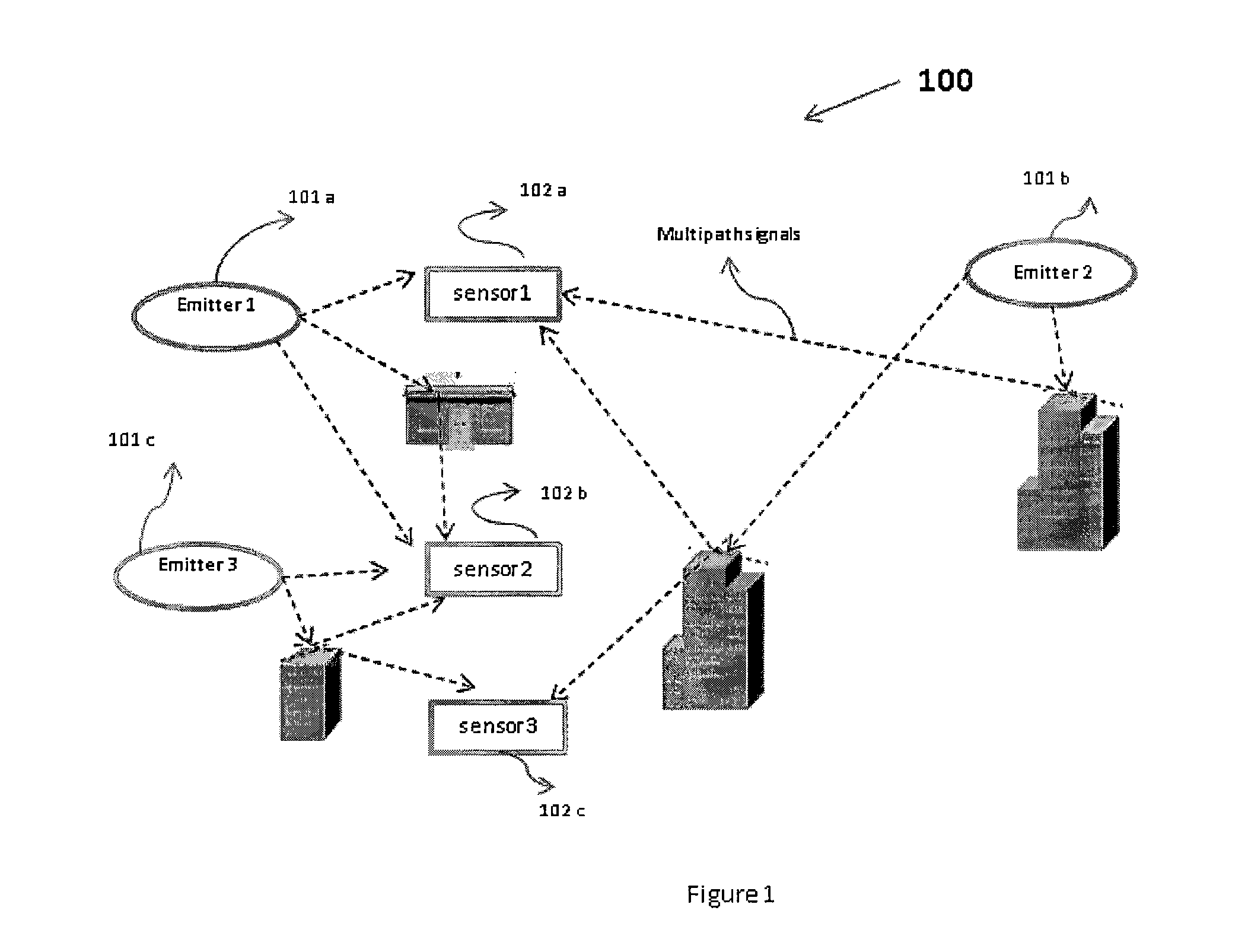
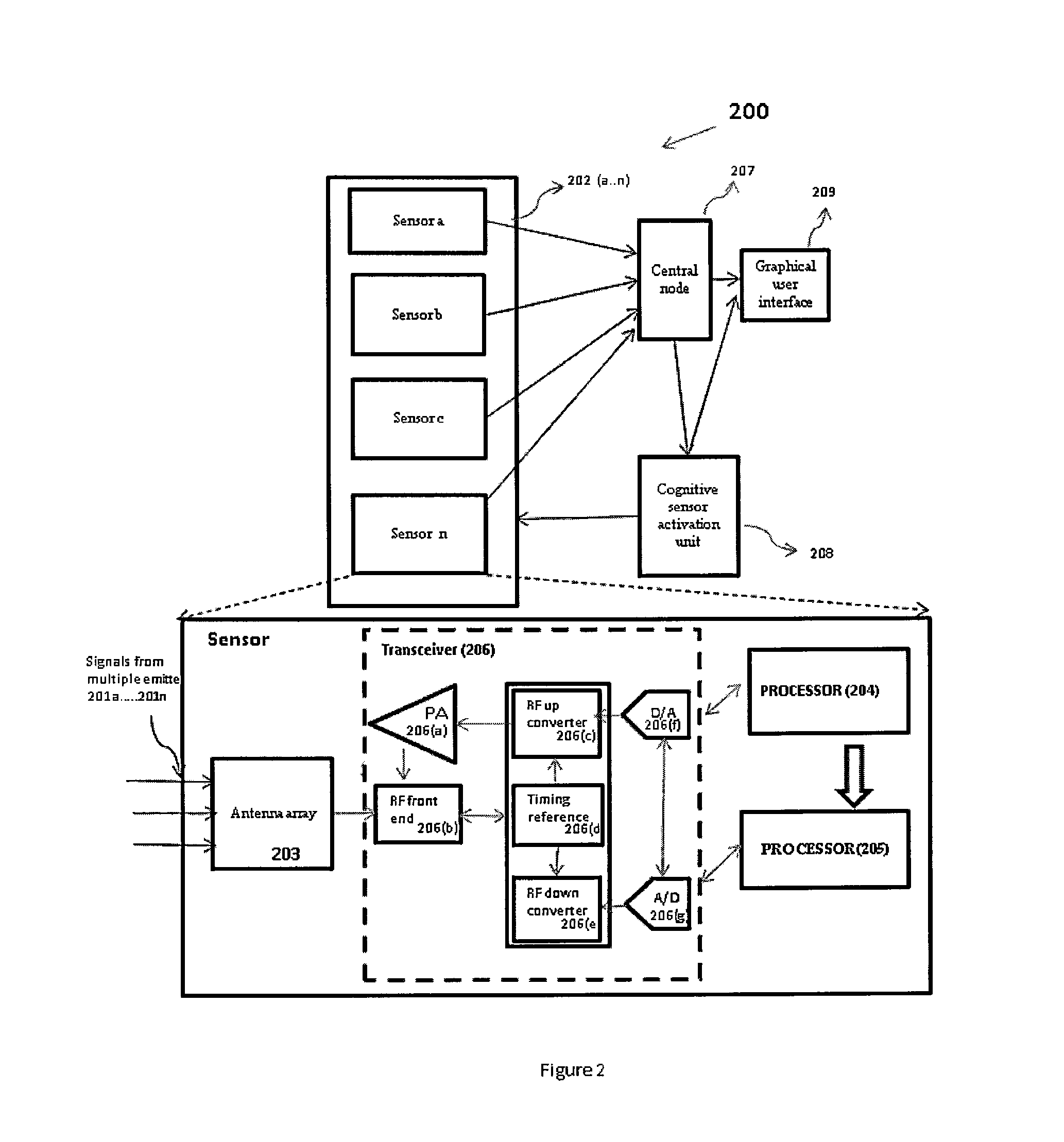
System and Methods for Non-Parametric Technique Based Geolocation and Cognitive Sensor Activation
ActiveUS20150009072A1High resolutionLarge power saveRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPosition fixationCluster basedAngle of arrival
The present invention relates to a geolocation system and method for a multi-path environment. The geolocation system comprises one or more emitters (201a . . . 201n), one or more sensors (202a . . . 202n) comprising at least one processor. A first processor (204) estimates angle of arrival (AOA) and time of arrival (TOA) from the signals received from said one or more emitters (201a . . . 201n). A second processor (205) determines clusters based on the (AOA) and (TOA) data. The system also comprises a central node (207) in communication with at least one sensor (202a . . . 202n) and configured to estimate geolocation of one or more emitters (201a . . . 201n) wherein, said second processor (205) clusters data for the one or more emitters (201a . . . 201n) by executing a non-parametric Bayesian technique and said central node (207) utilizes hybrid angle of arrival-time difference of arrival (AOA-TDOA) technique to determine geolocation of each of the emitters (201a . . . 201n).
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Method and system for fuel vapor control
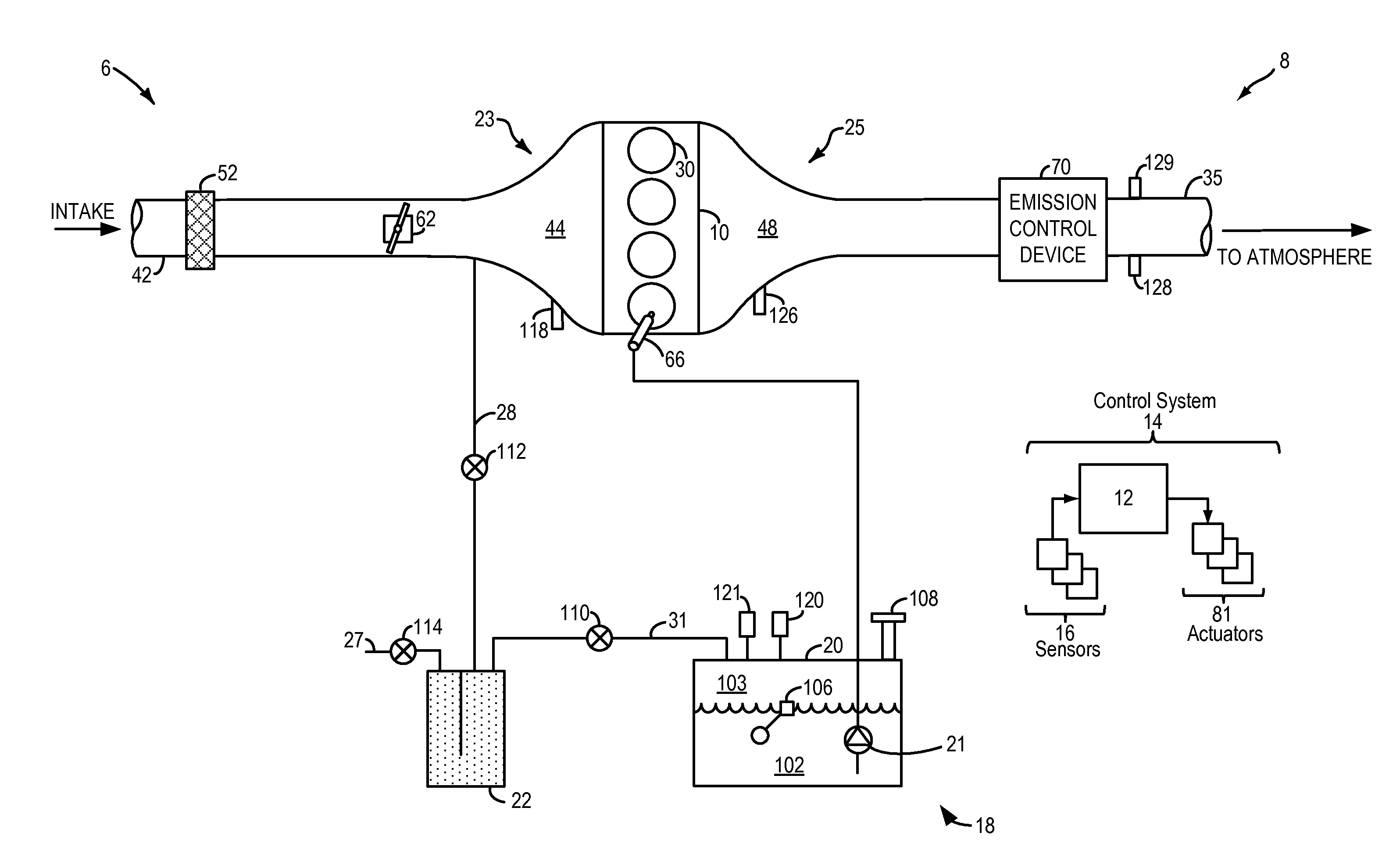
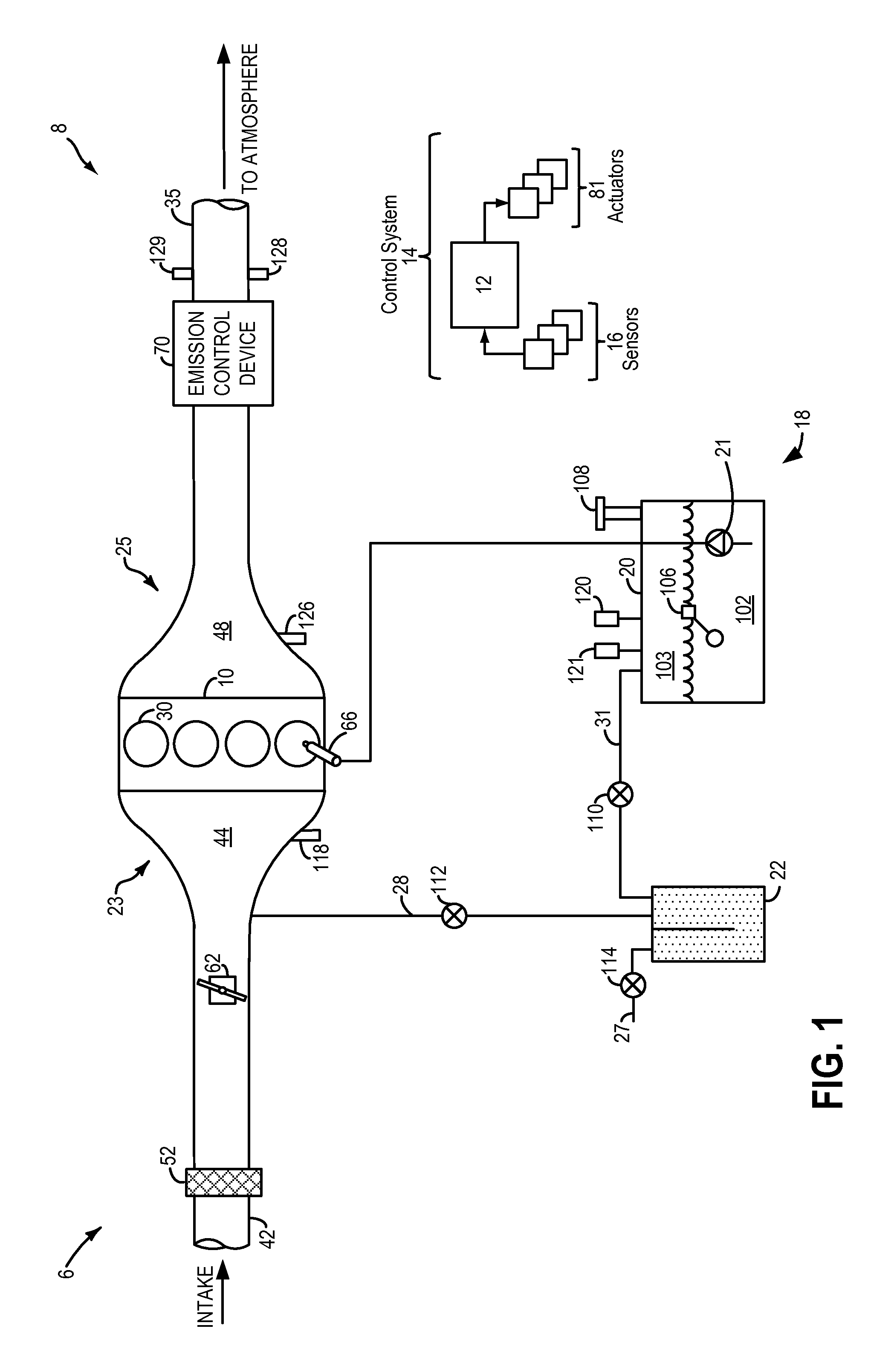
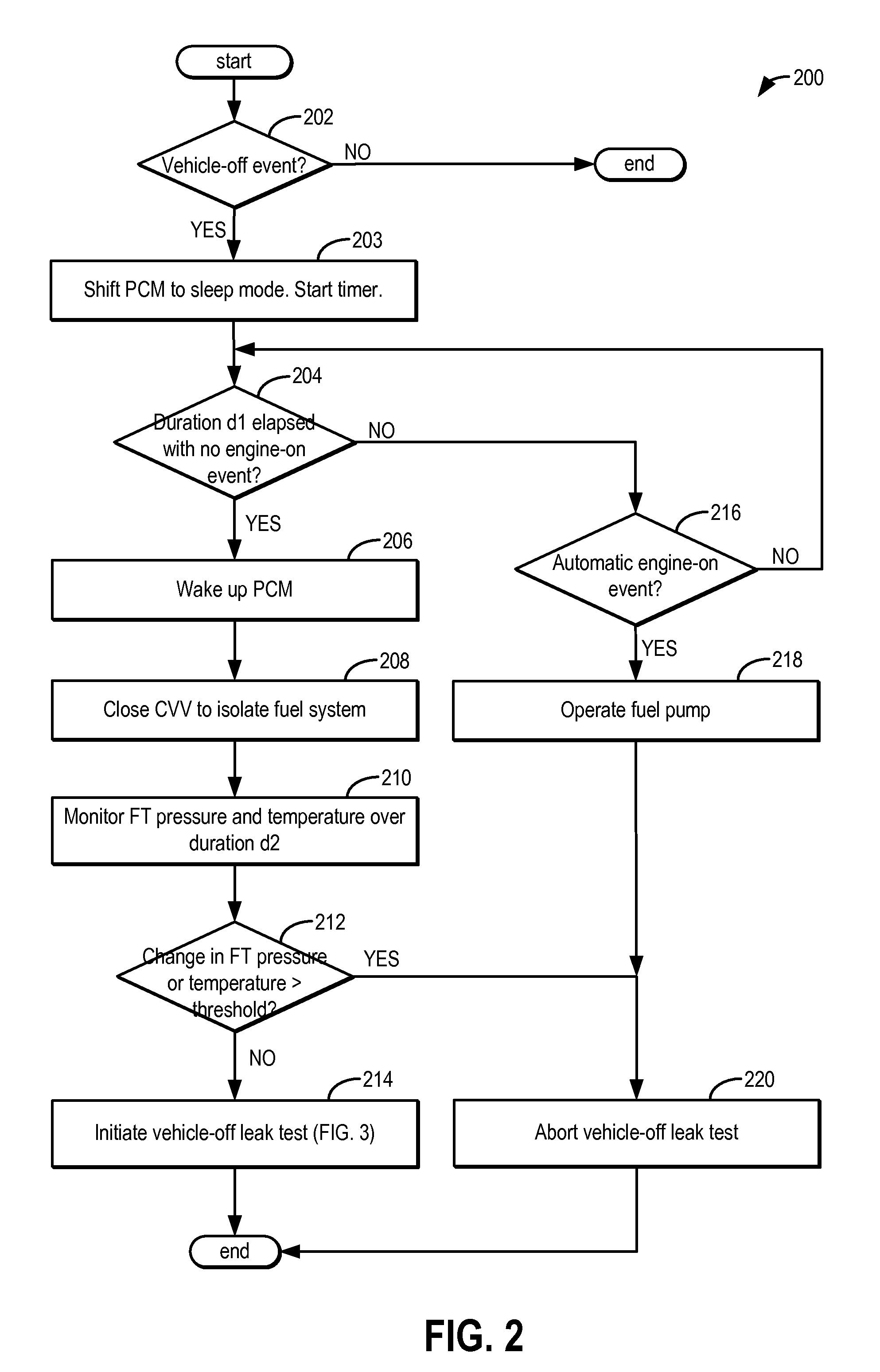
InactiveUS20140074385A1Reduce noise contributionReduce noiseDetection of fluid at leakage pointAnalogue computers for vehiclesFuel vaporPressure decay
Methods and systems are provided for performing a vehicle-off fuel system leak test. A vehicle controller may be woken up after a vehicle has been in a key-off condition for a sufficient amount of time to monitor a fuel tank for pressure and temperature stabilization. If the pressure and temperature of the fuel tank is stable, a fuel pump may be operated to raise a fuel tank vapor pressure, and fuel system leaks are identified based on a rate of pressure decay from the fuel tank.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
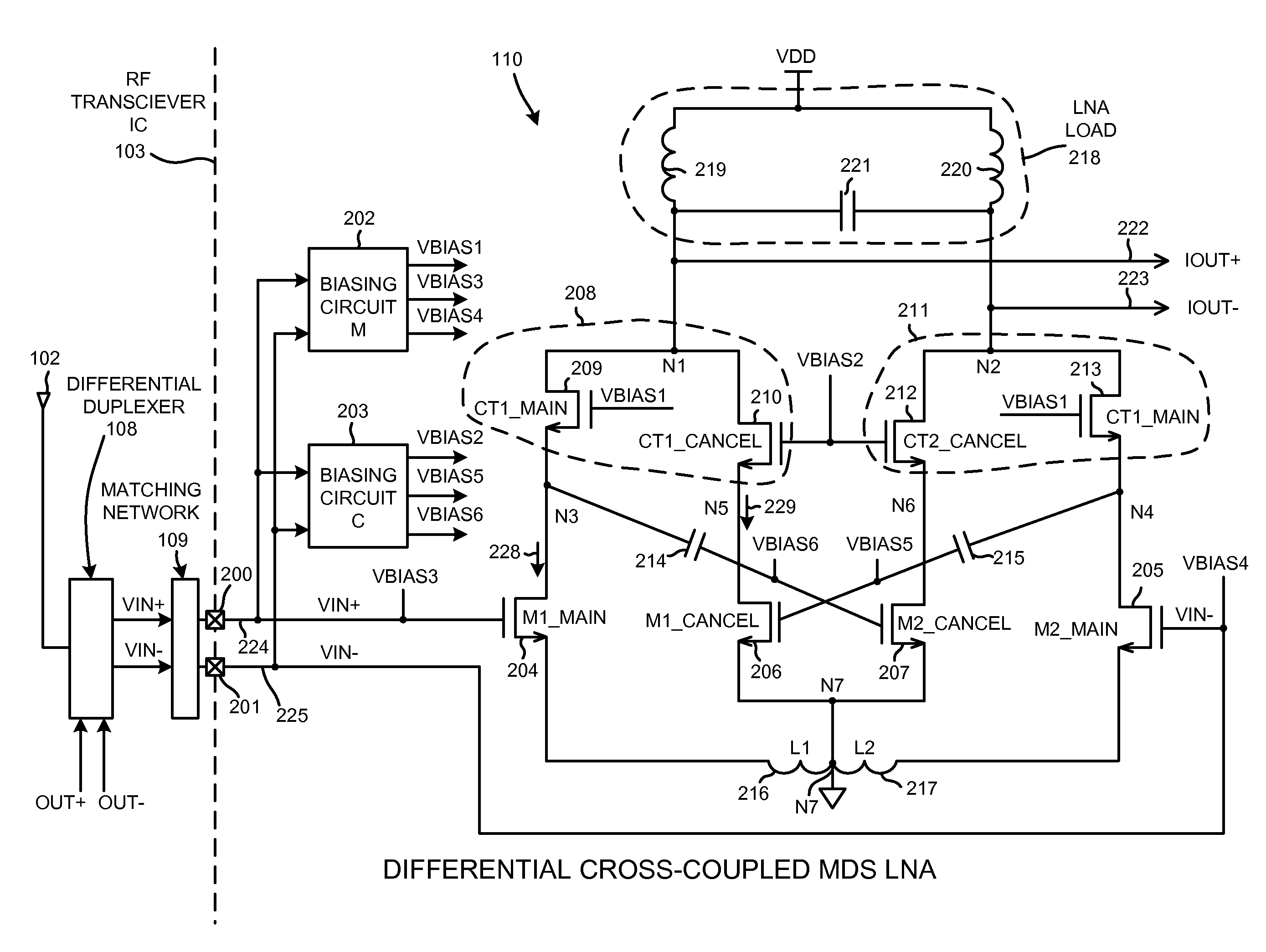
Low noise and low input capacitance differential MDS LNA
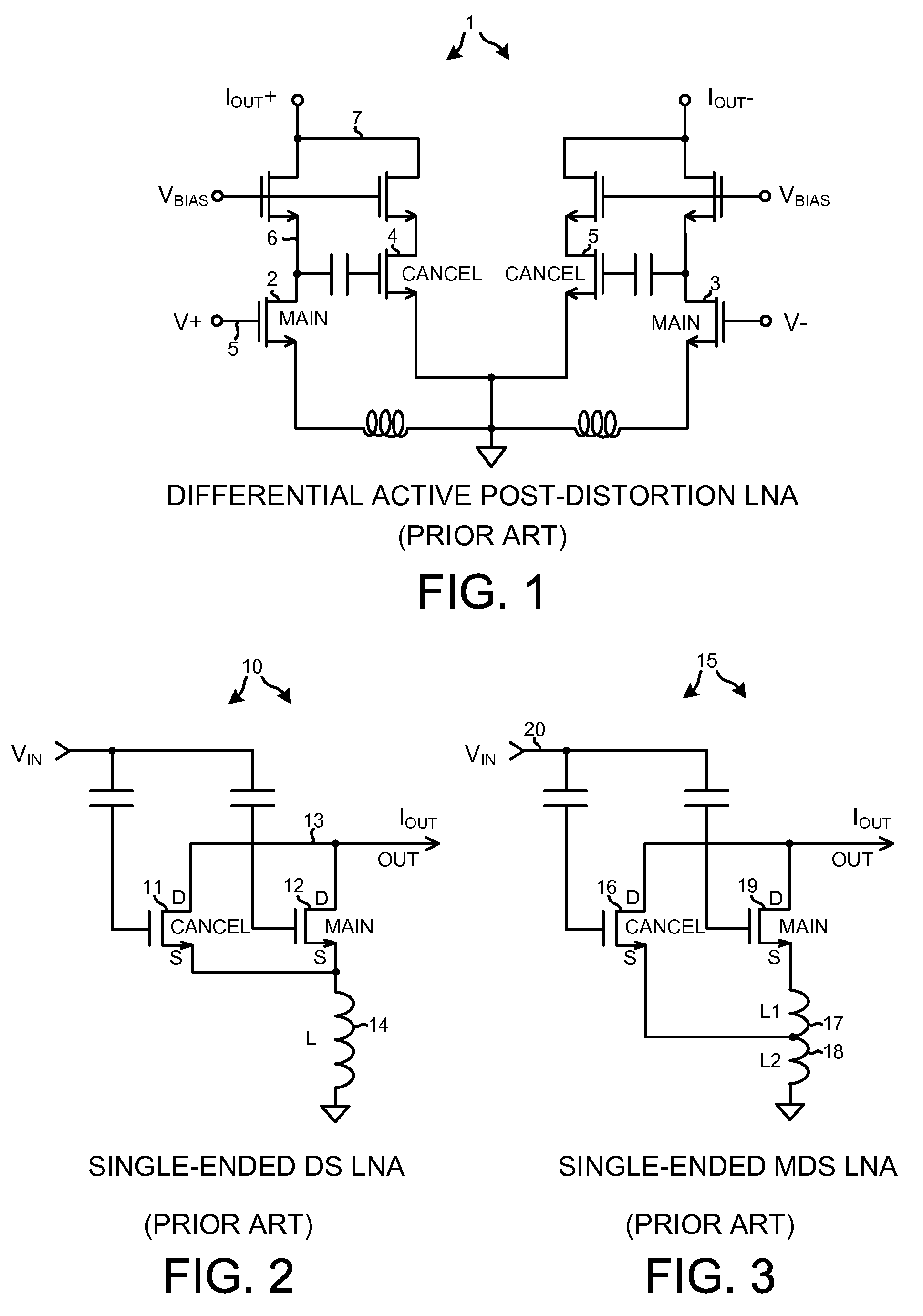
ActiveUS7944298B2Weakening rangeReduce input capacitanceGain controlDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceLow noise
A differential low noise amplifier (LNA) involves two main amplifying transistors biased in saturation, and two cancel transistors biased in sub-threshold. In one example, the gates of the cancel transistors are coupled to the drains of main transistors, in a symmetrical and cross-coupled fashion. The main transistors are source degenerated. Because the gates of cancel transistors are not coupled to the differential input leads of the LNA, the input capacitance of the LNA is reduced. Noise introduced into the LNA output due to the cancel transistors being biased in the sub-threshold region is reduced because there are two stages. The first stage involves the main transistors, and the second stage involves the cancel transistors. By increasing the gain of the first stage and decreasing the gain of the second stage, overall LNA gain is maintained while reducing the noise that the sub-threshold biased transistors contribute to the LNA output.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
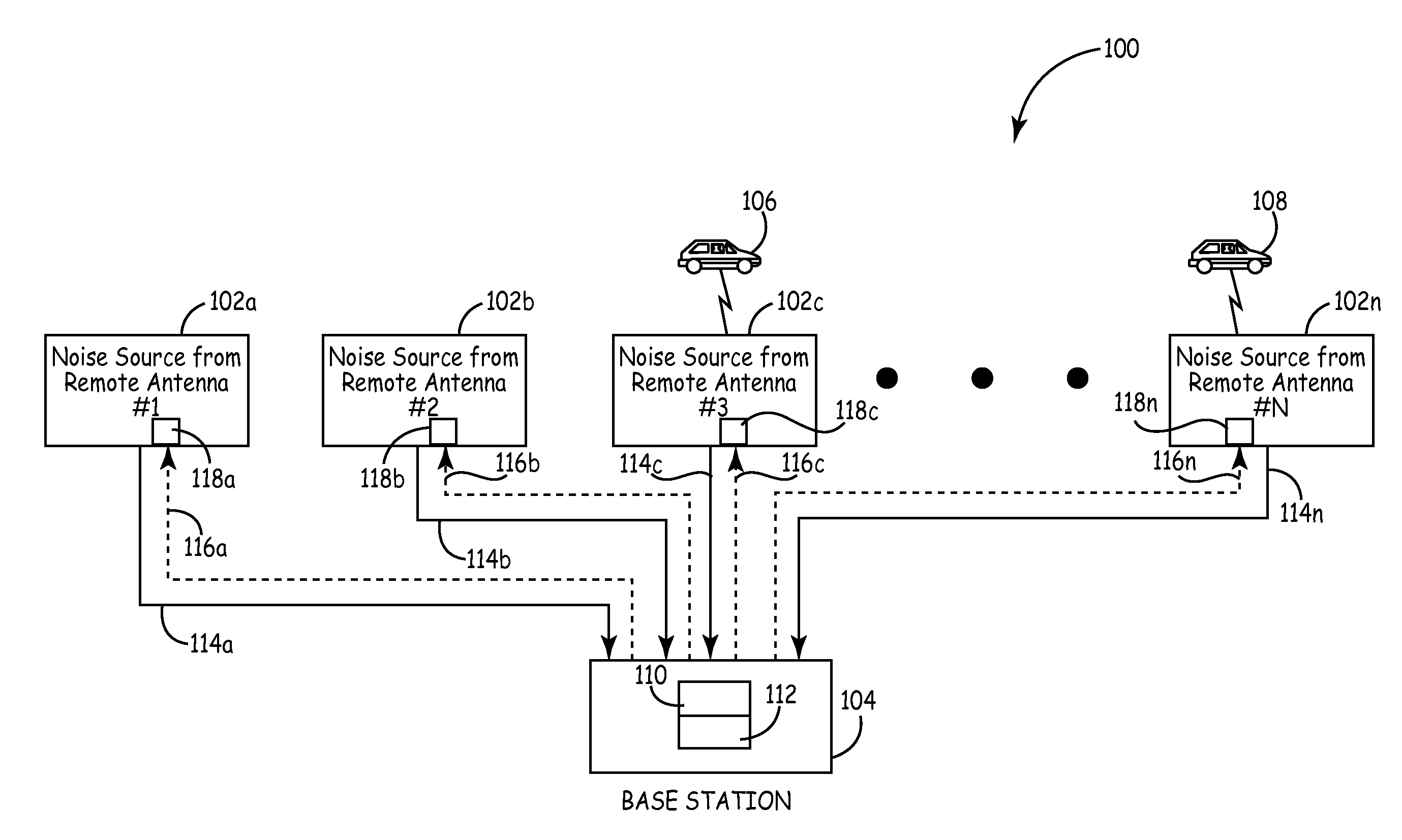
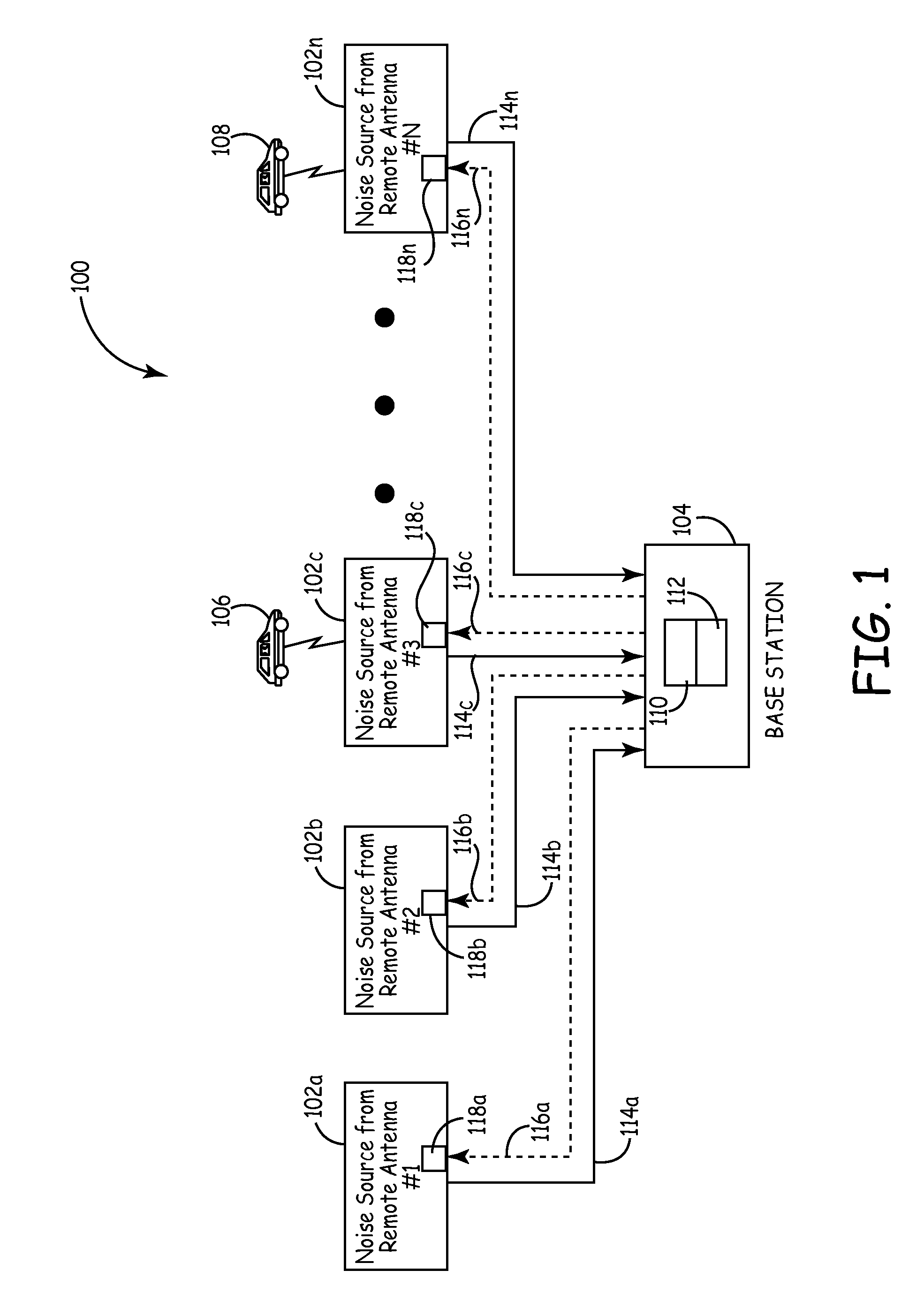
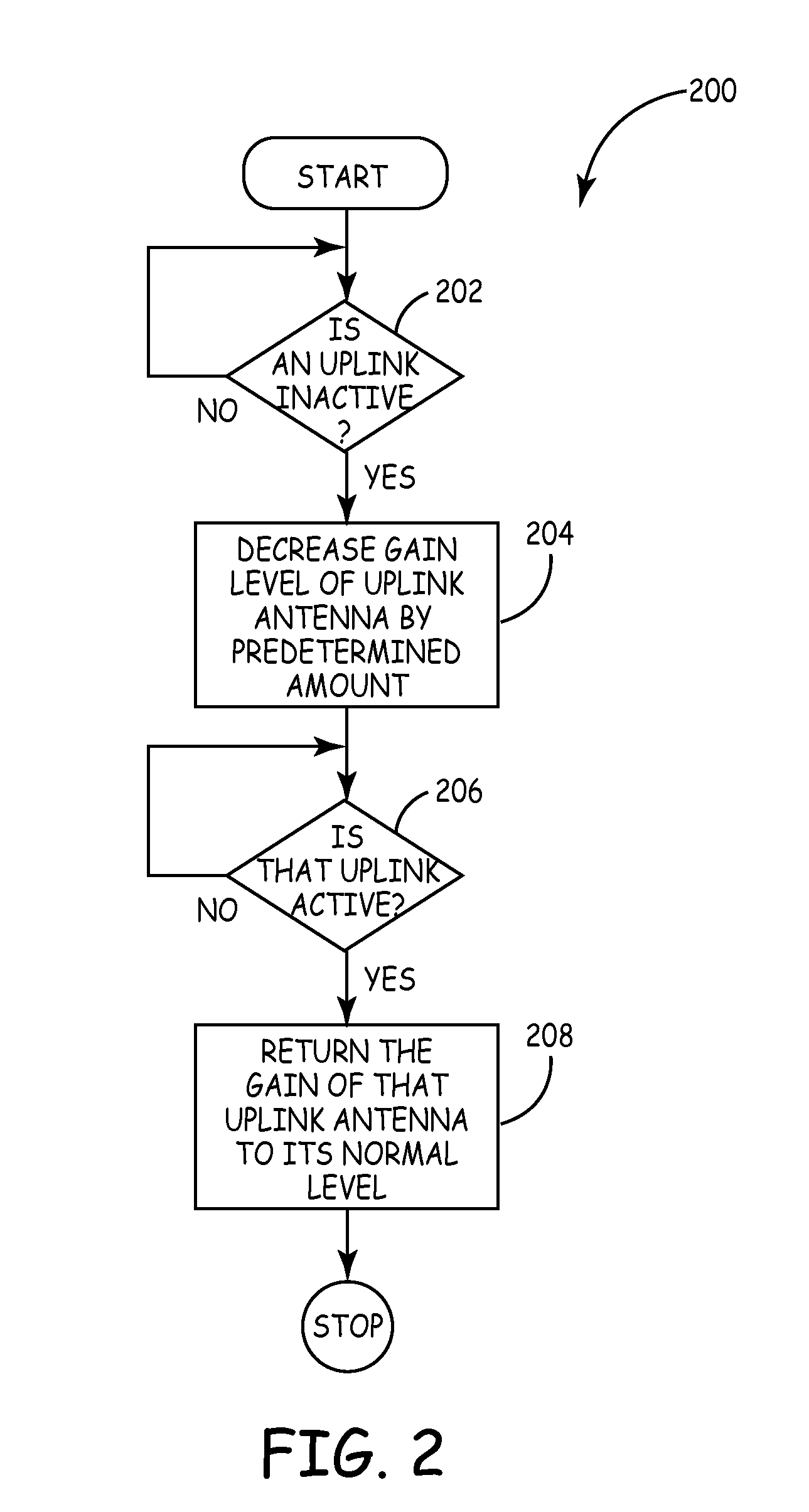
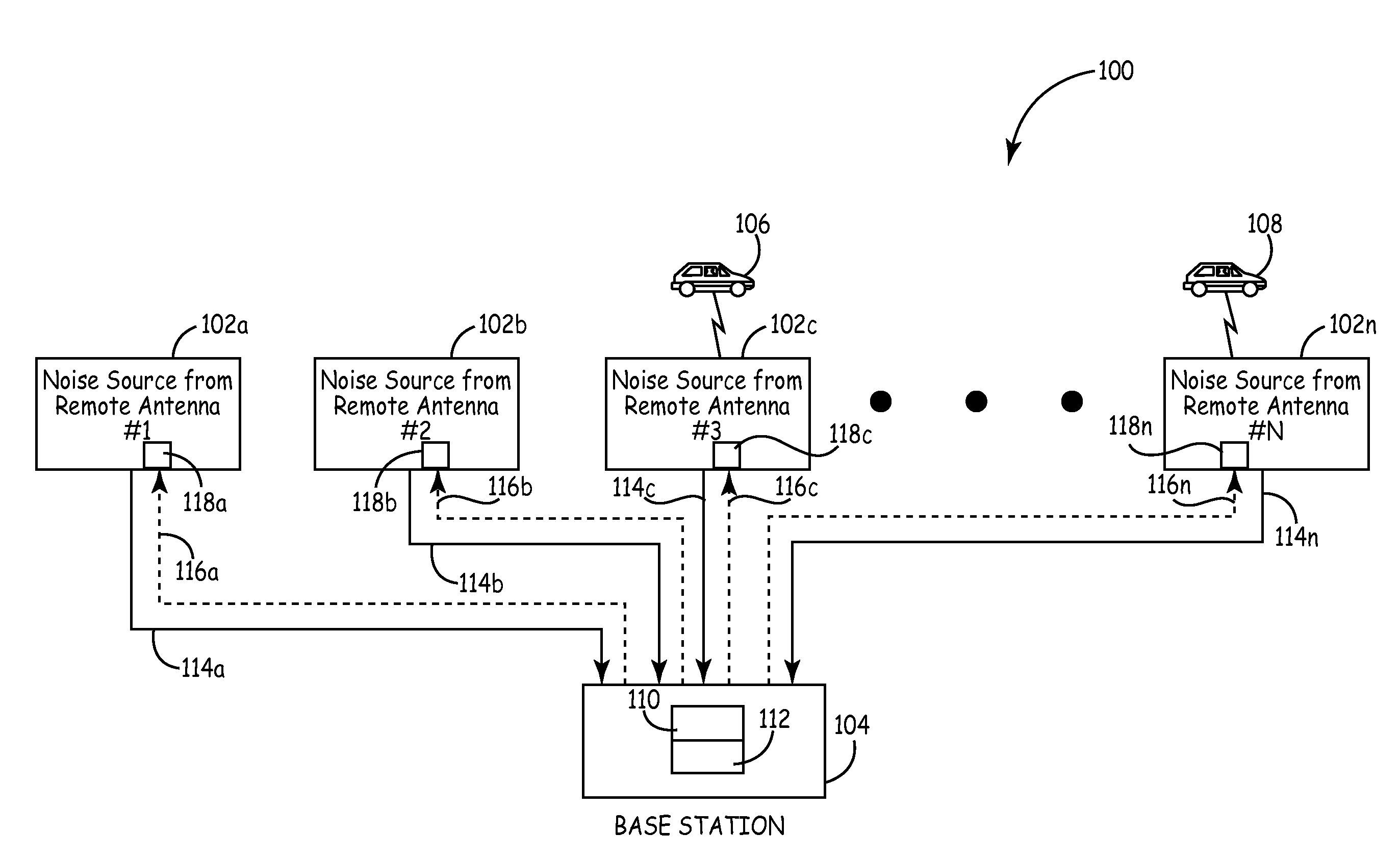
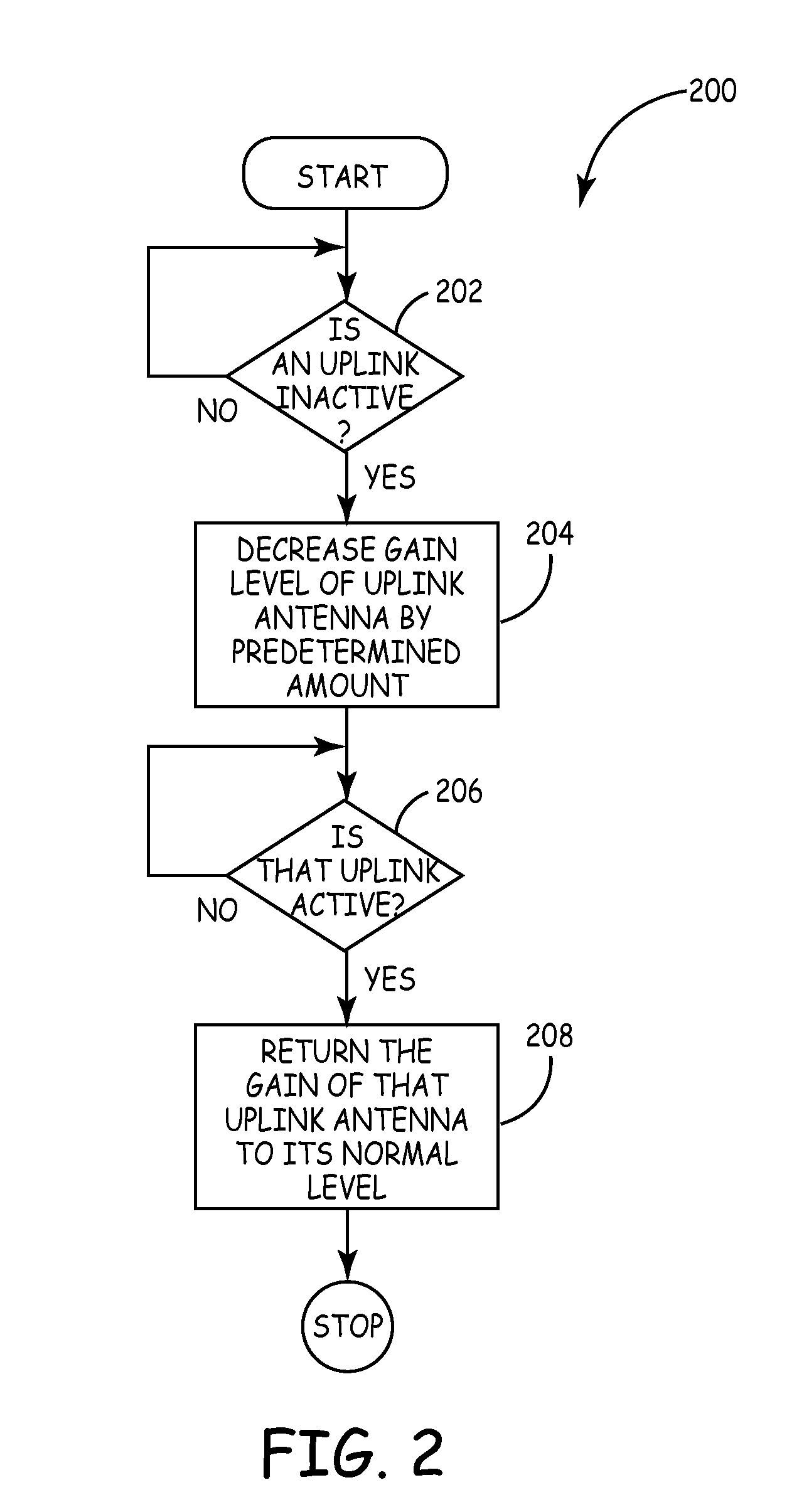
Method and system for reducing uplink noise in wireless communication systems
ActiveUS7974244B2Reduce the noise floorReduce noise contributionSubstation equipmentWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemTransmitter
A method and system for reducing the overall noise floor in a wireless communication system, subsystem or network are disclosed, which reduces the output gain levels of specific uplink antenna transmitters during non-signal time periods (e.g., rest mode) when no communication signals are being conveyed between the mobile unit(s) and base station involved. The output gain level of each such uplink antenna's transmitter is decreased by a predetermined amount, which reduces the noise contribution of that uplink antenna, but also maintains the gain at a high enough level so that a signal can still pass from a mobile unit to the base station via that link, for example, during a call initiation attempt.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Active noise cancellation in hearing devices
ActiveUS8229127B2Reduce and attenuate and block audio signalEnhanced signalEar treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationHearing apparatusEngineering
Disclosed is a hearing device system comprising at least one hearing aid circuitry and at least one active noise cancellation unit, the at least one hearing aid circuitry comprises at least one input transducer adapted to convert a first audio signal to an electric audio signal; a signal processor connected to the at least one input transducer and adapted to process said electric audio signal by at least partially correcting for a hearing loss of a user; an output transducer adapted to generate from at least said processed electric audio signal a sound pressure in an ear canal of the user, whereby the generated sound pressure is at least partially corrected for the hearing loss of the user; the at least one active noise cancellation unit being adapted to provide an active noise cancellation signal adapted to perform active noise cancellation of an acoustical signal entering the ear canal in addition to said generated sound pressure, wherein the hearing device system further comprises a combiner unit adapted to combine the processed electric audio signal with the active noise cancellation signal, to obtain a combined signal and to provide the combined signal to the output transducer.
Owner:OTICON
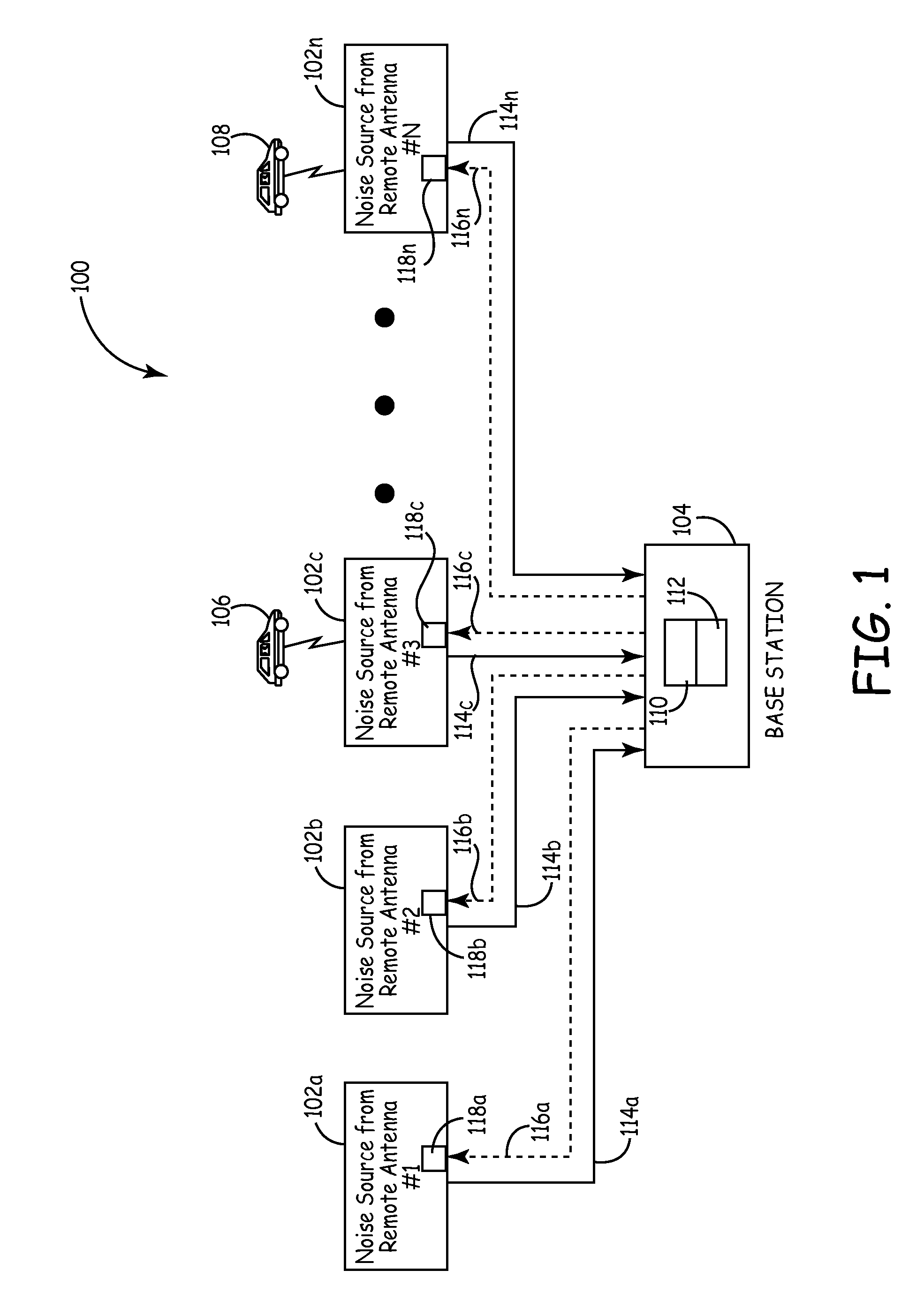
Method and system for reducing uplink noise in wireless communication systems
ActiveUS20090054105A1Reduce the noise floorReduce noise contributionSubstation equipmentWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemTime segment
A method and system for reducing the overall noise floor in a wireless communication system, subsystem or network are disclosed, which reduces the output gain levels of specific uplink antenna transmitters during non-signal time periods (e.g., rest mode) when no communication signals are being conveyed between the mobile unit(s) and base station involved. The output gain level of each such uplink antenna's transmitter is decreased by a predetermined amount, which reduces the noise contribution of that uplink antenna, but also maintains the gain at a high enough level so that a signal can still pass from a mobile unit to the base station via that link, for example, during a call initiation attempt.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
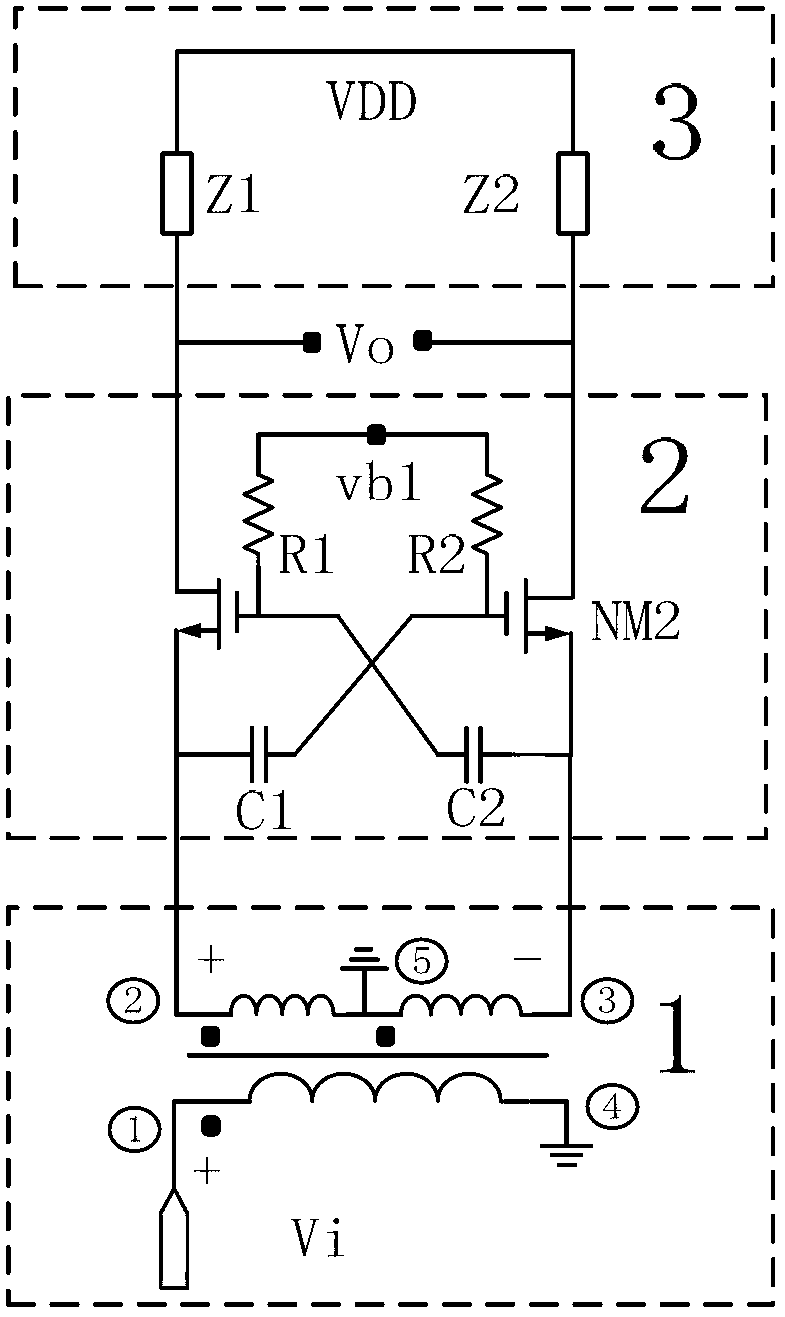
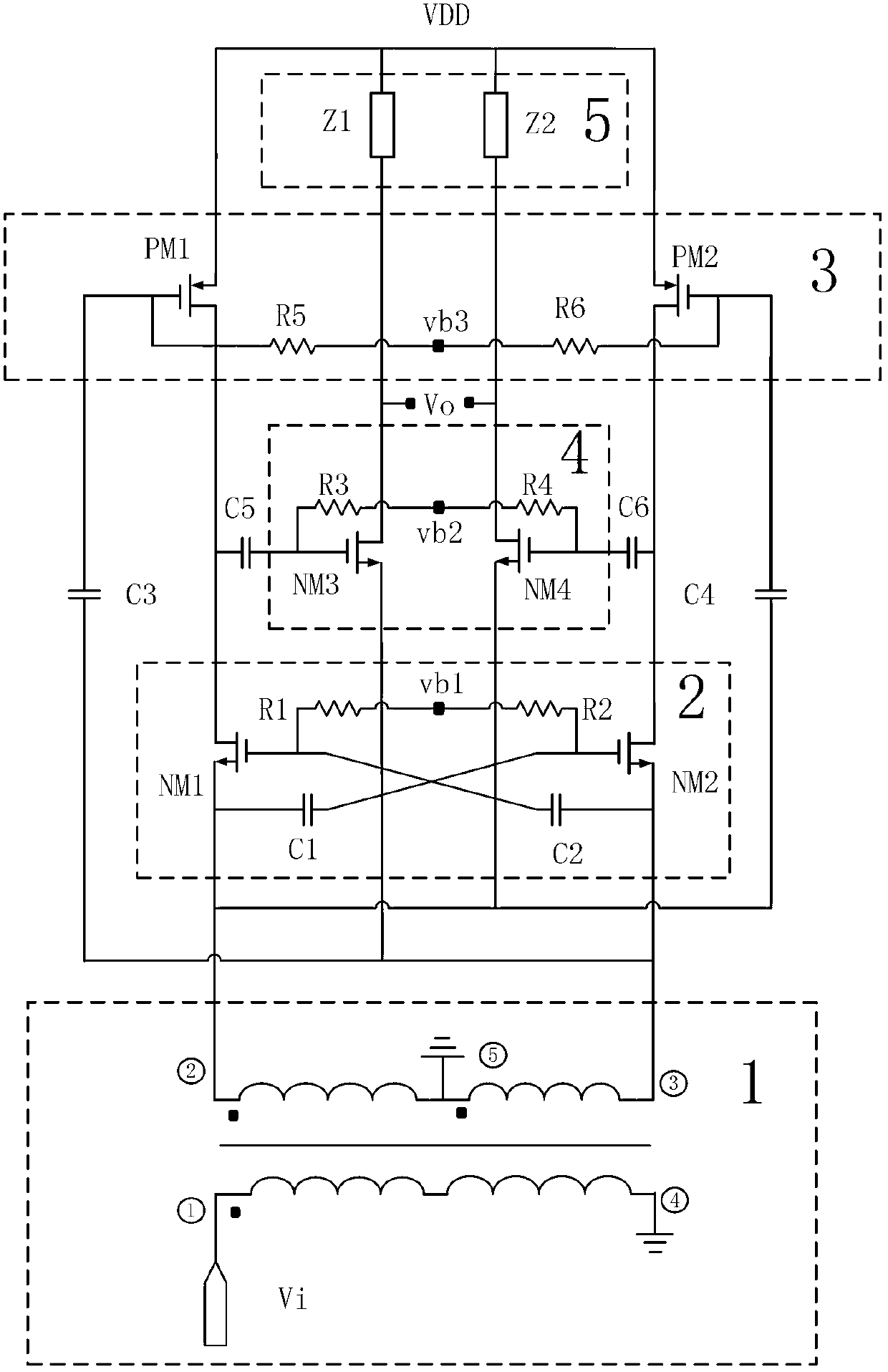
Low-power consumption and low-noise amplifier adopting noise cancellation technology
InactiveCN103219951AReduce circuit power consumptionReduce noise contributionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTransconductanceCapacitance
The invention provides a low-power consumption and low-noise amplifier adopting a noise cancellation technology. The amplifier comprises a balanced-unbalanced transformer (1), a capacitance cross coupling common-gate amplification stage (2), a feedforward noise cancellation stage (3), a main common-gate amplification stage (4) and a load impedance (5). A mode of cascading the capacitance cross coupling common-gate amplification stage with the main common-gate amplification stage is adopted to enhance transconductance twice, and the higher equivalent transconductance is realized through low power consumption; the noise contribution of the capacitance cross coupling common-gate amplification stage can be reduced through the feedforward noise cancellation stage; and the noise contribution of the main common-gate amplification stage can be inhibited through the gains provided by the capacitance cross coupling common-gate amplification stage and the feedforward noise cancellation stage. The twice transconductance enhancement and a feedforward noise cancellation technology are combined together so as to realize low noise factor and low power consumption.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Charge pump circuit using active feedback controlled current sources
ActiveUS6980046B2Reduce noise contributionRaise the gate voltageAc-dc conversion without reversalPulse automatic controlDriving currentActive feedback
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP +1
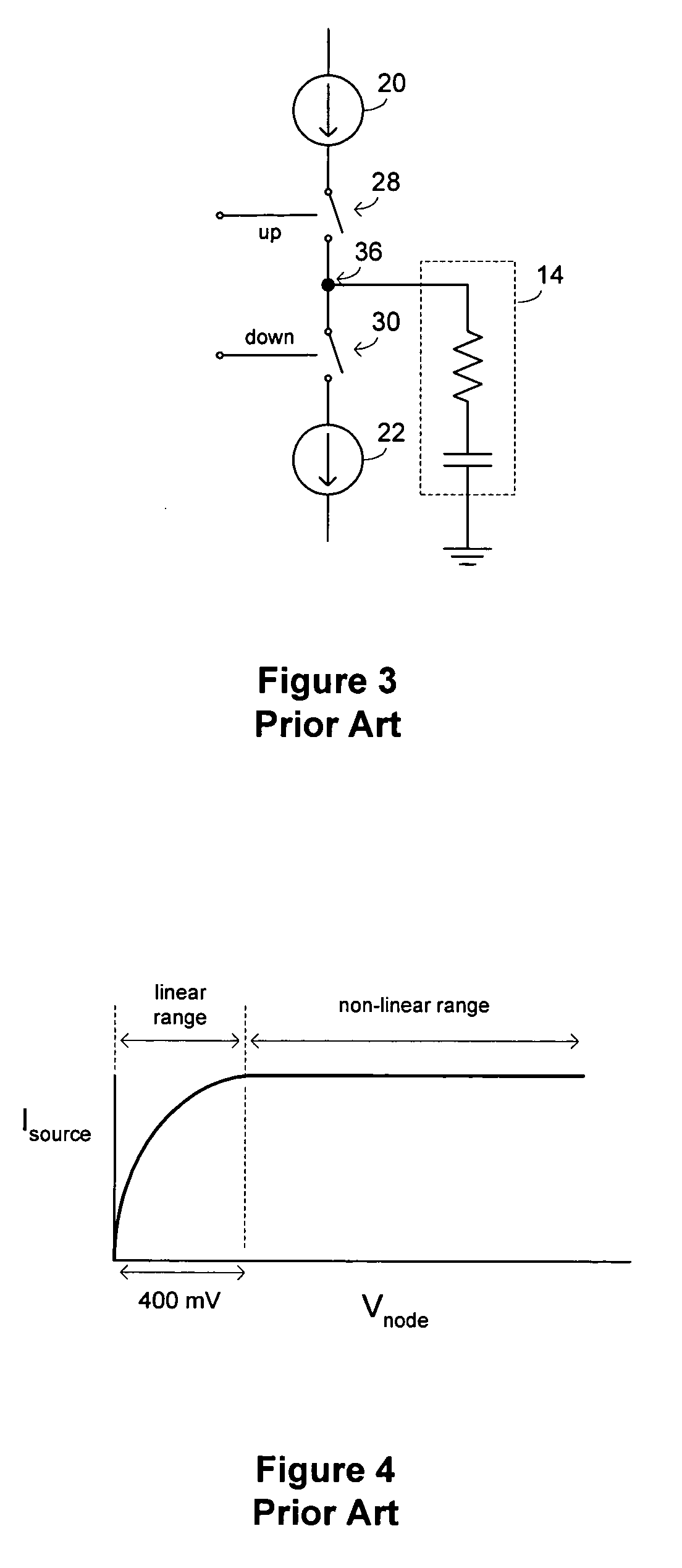
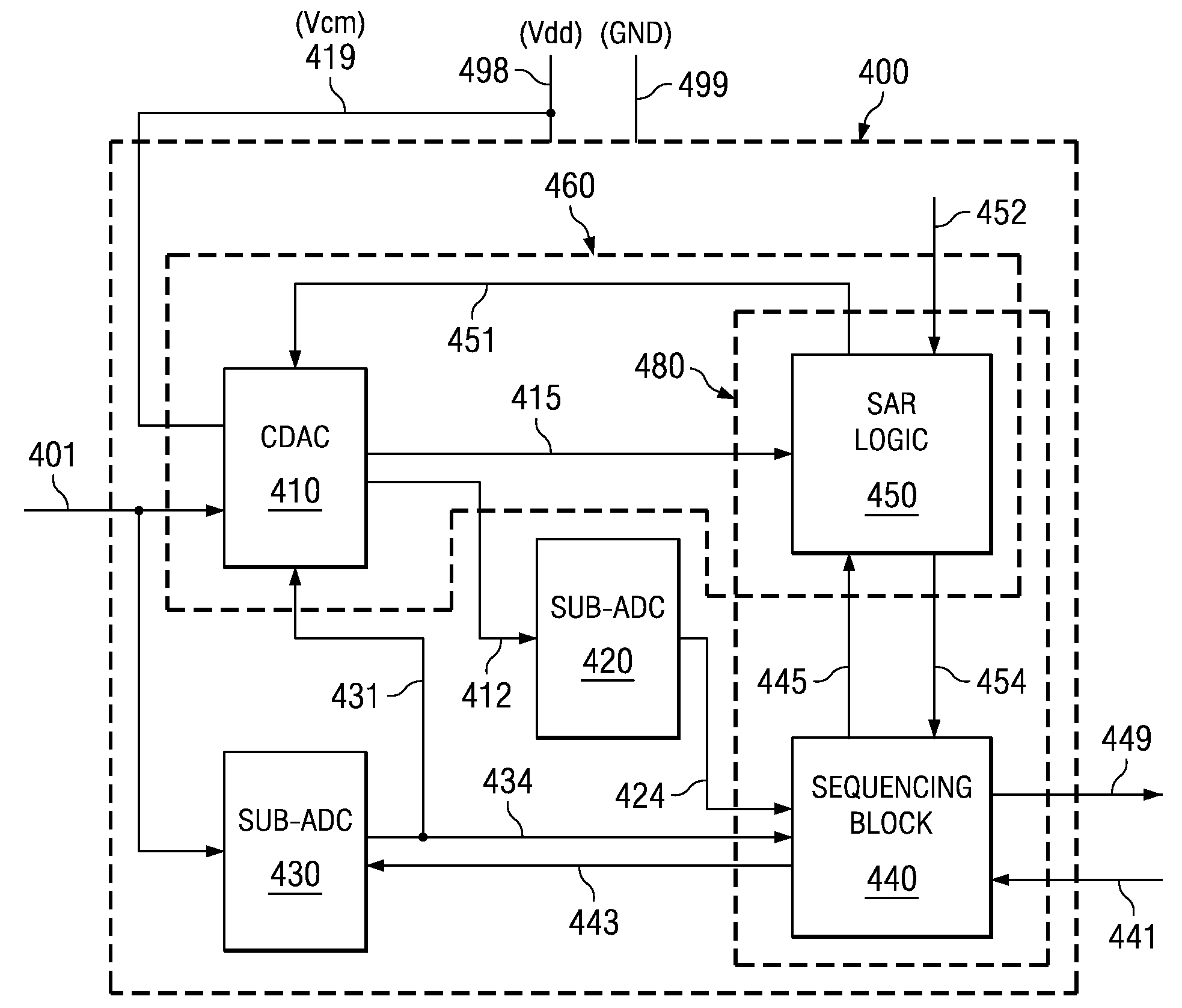
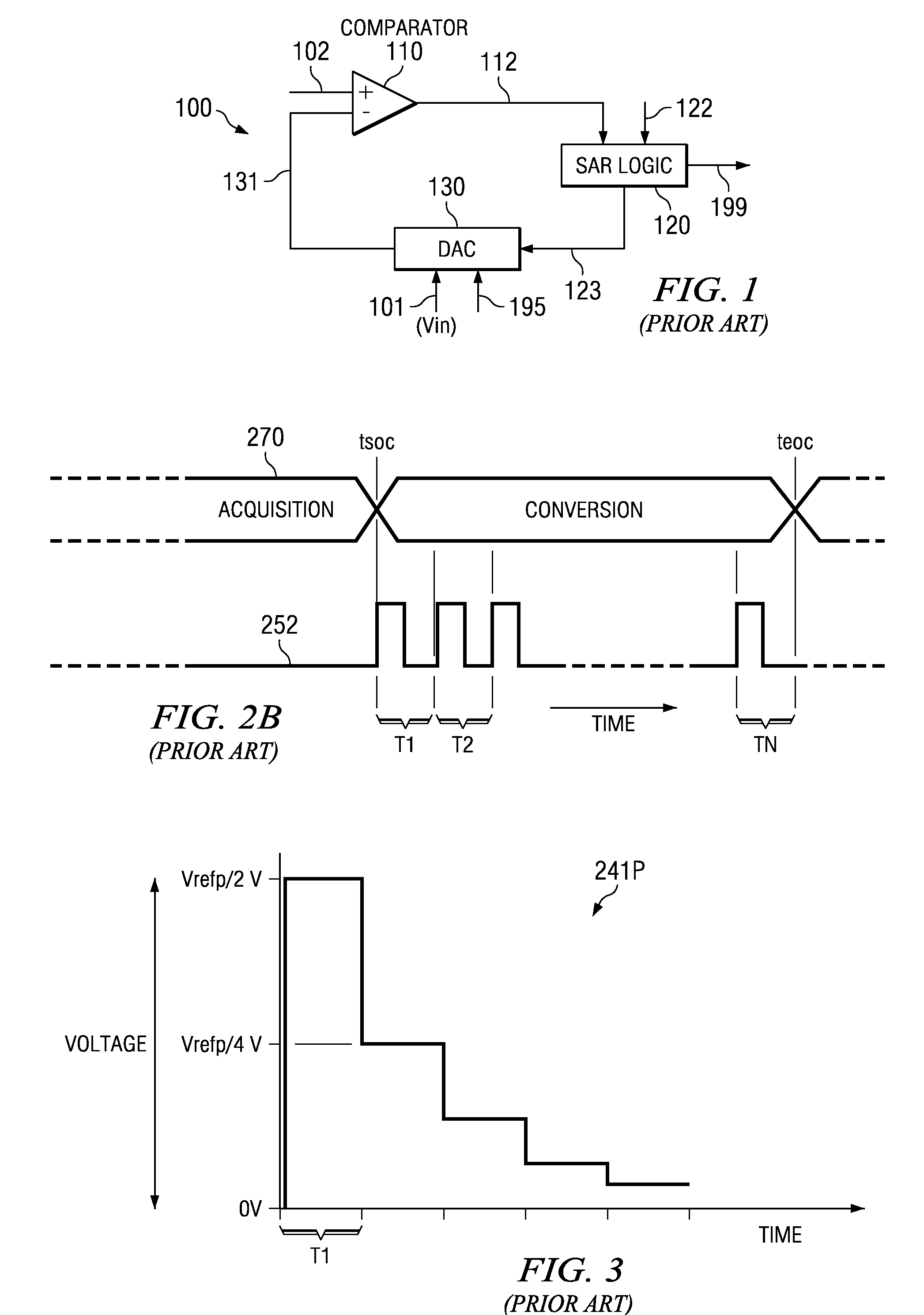
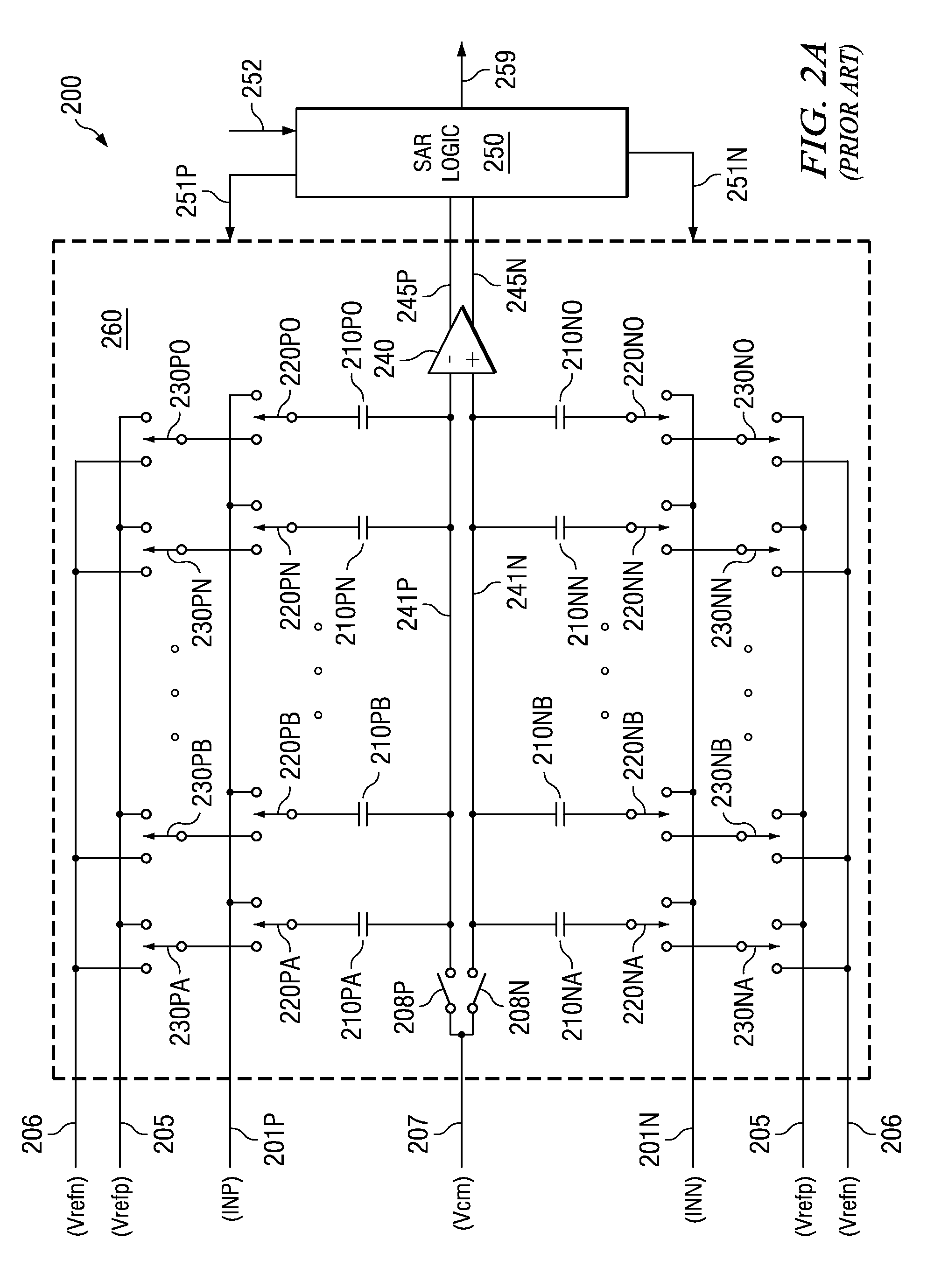
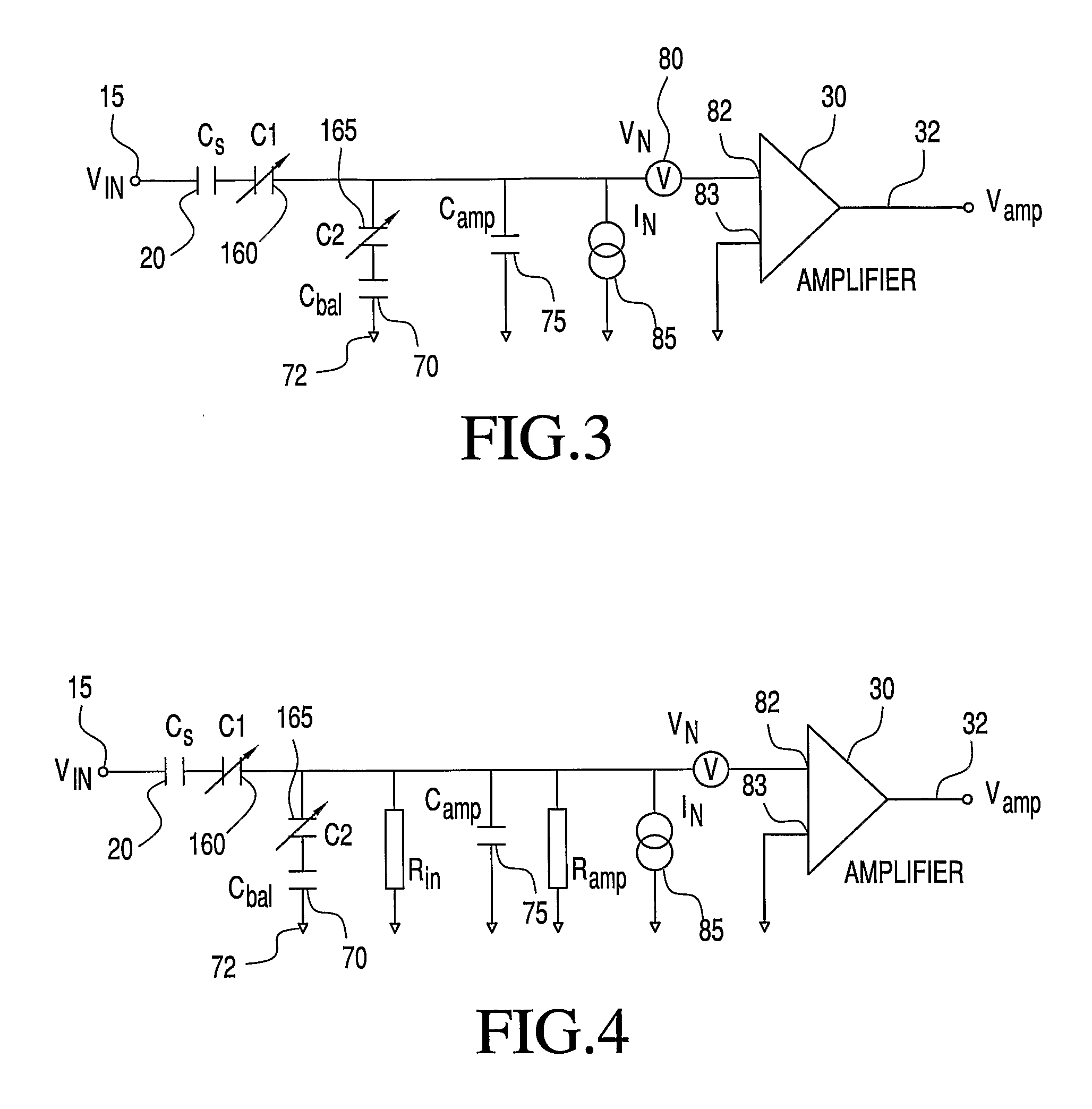
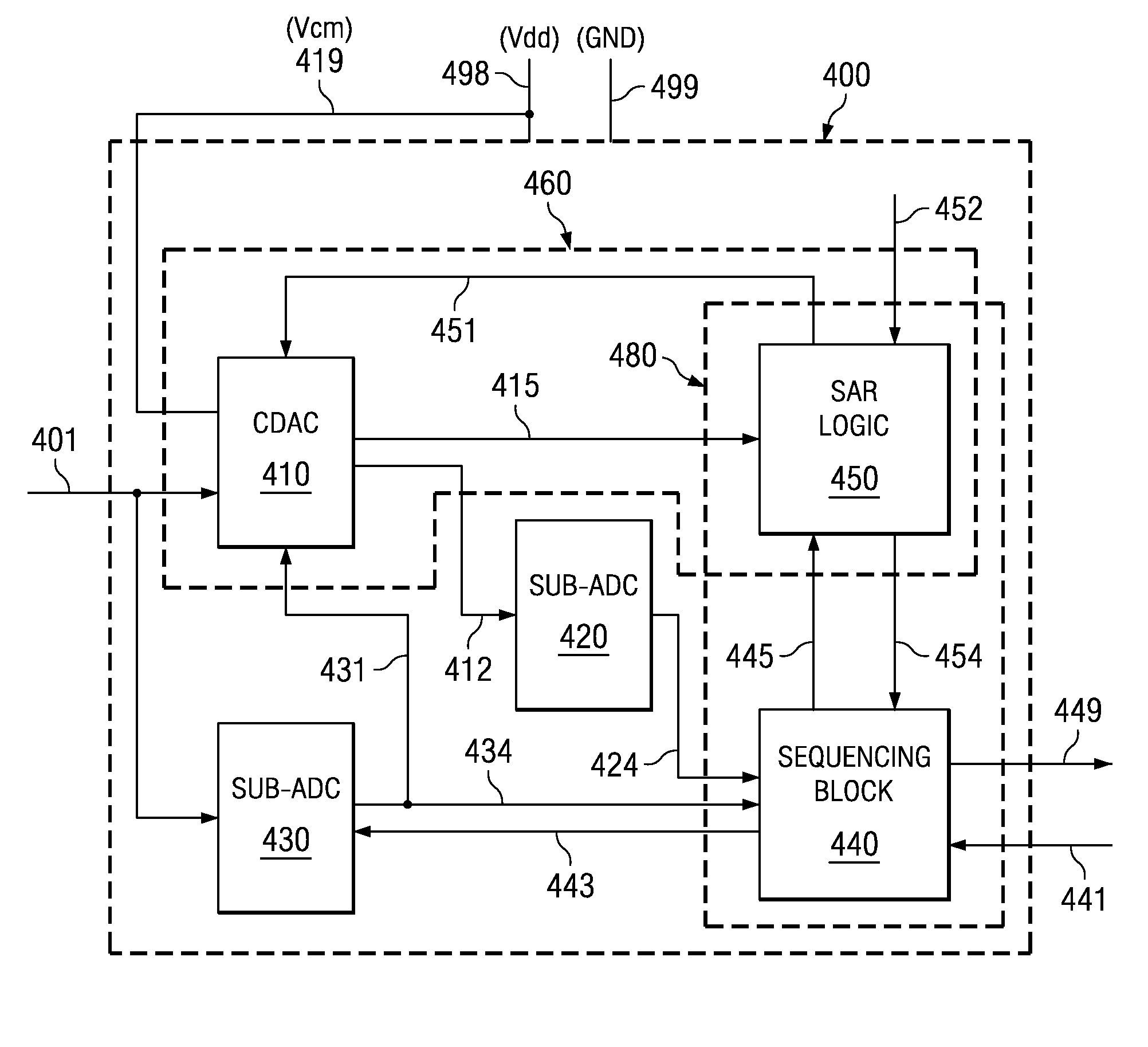
High Speed High Resolution ADC Using Successive Approximation Technique
ActiveUS20090073018A1Improve conversion speedIncrease speedElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierEngineering
An analog to digital converter (ADC) containing a sub-ADC to resolve at least some of the bits using successive approximation principle (SAP), while providing various improvements. According to one aspect, another sub-ADC is used to resolve some of the bits in parallel. According to another aspect, the sub-ADC using SAP is implemented using a charge redistribution principle, while another sub-ADC does not rely on charge conservation. According to yet another aspect of the present invention, a same component operates as a comparator when the sub-ADC using SAP resolves the corresponding bits, and operates as an amplifier when the sub-ADC generates a residue signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Low noise op amp
ActiveUS20050206454A1Reduce flicker noiseReduce thicknessAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceEmergency protective circuit arrangementsLow noiseAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates amplifiers using metal oxide semiconductor based integrated circuits. The present invention is particularly but not exclusively related to audio application mixed signal chips. The present invention provides an analogue circuit for processing analogue signals in an integrated circuit comprising a number of metal oxide semiconductor transistor devices, the circuit stage comprising a first said transistor device having a first oxide thickness, and a second said transistor device having a second and different oxide thickness. Preferably a cascode based op amp structure is implemented.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
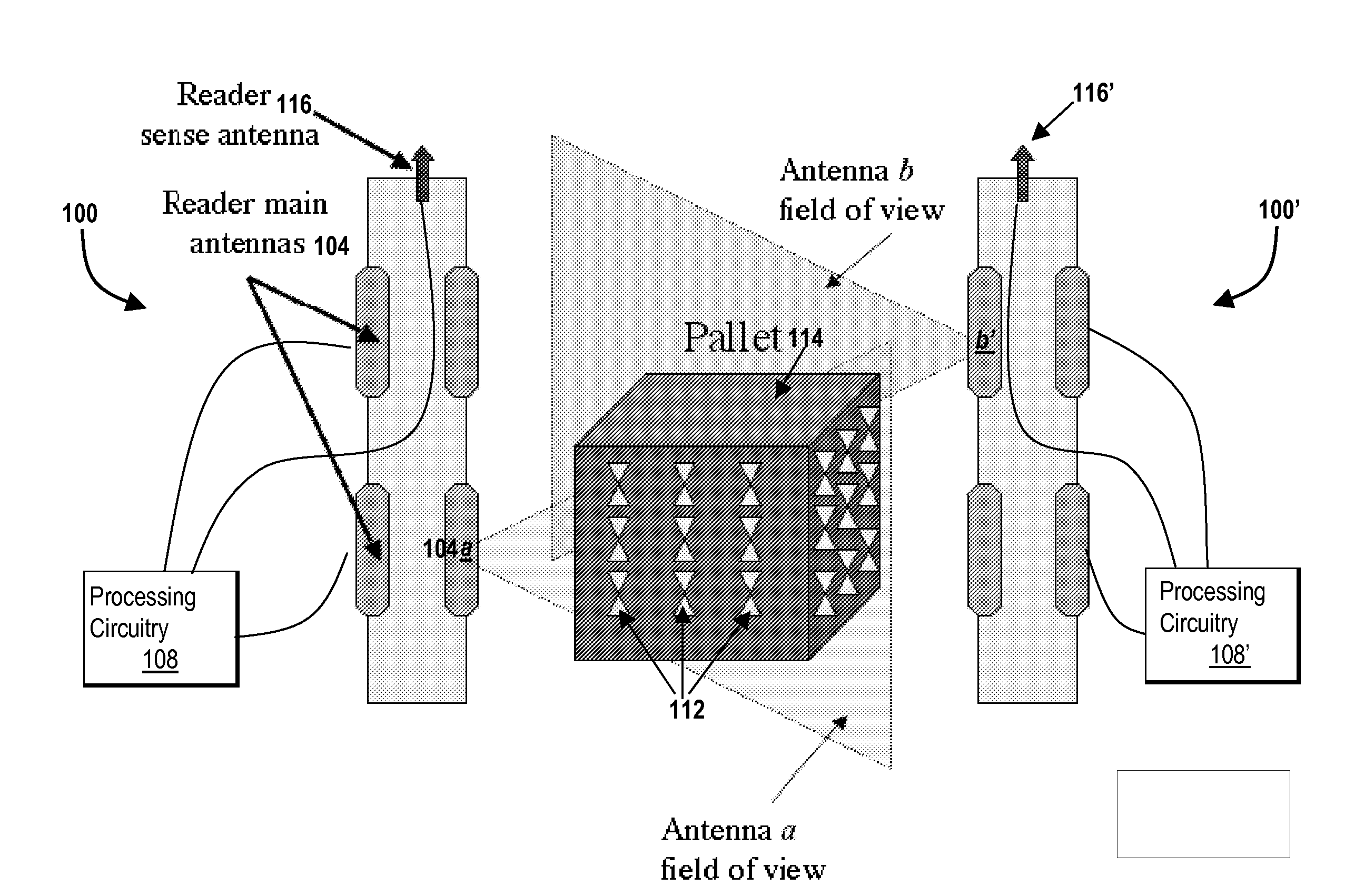
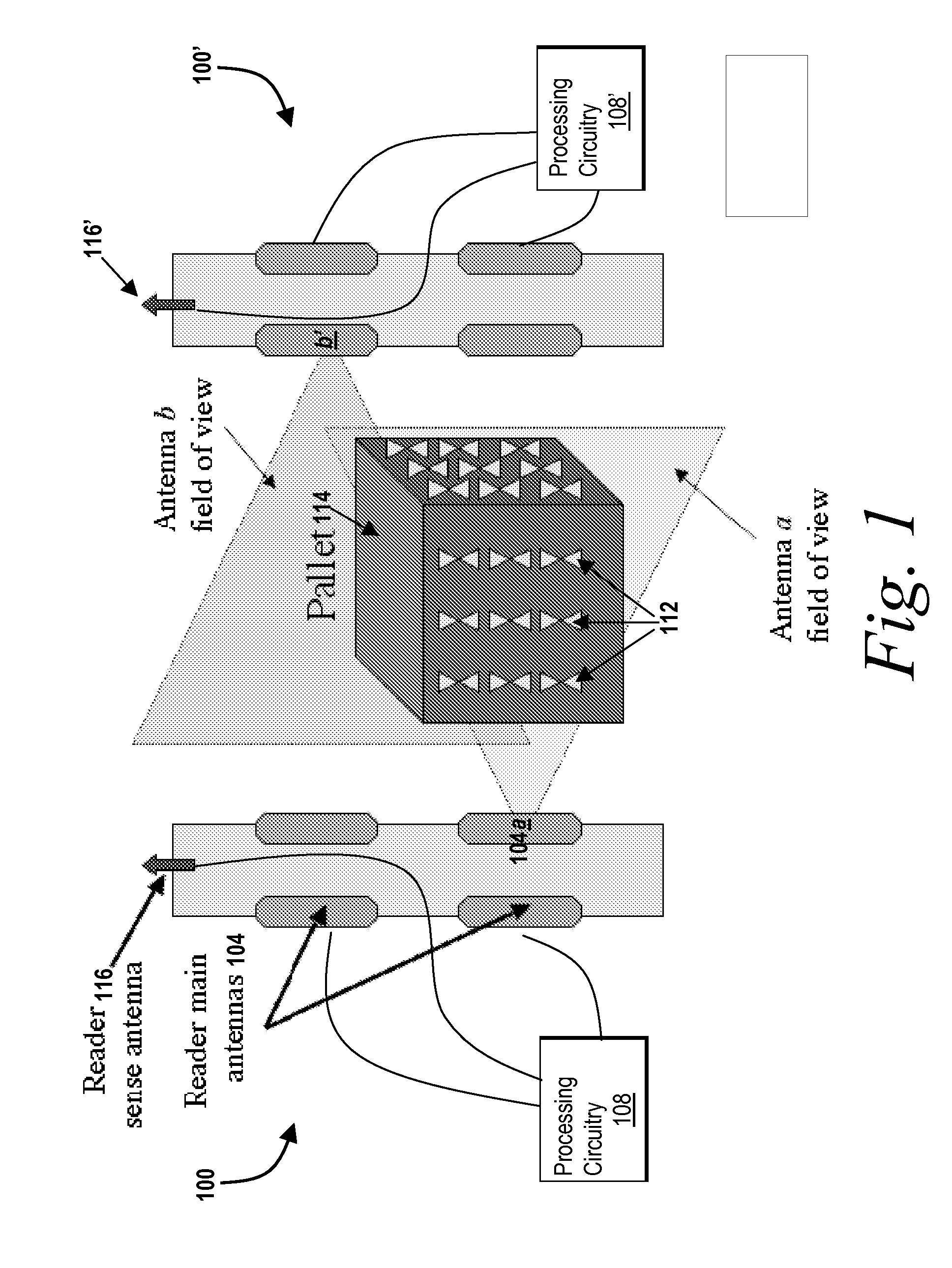
Systems and methods for active noise cancellation in an RFID tag reader
InactiveUS20070280369A1Reduce noise contributionIncrease a signal-to-noise-plus-interference ratioPolarisation/directional diversityNear-field in RFIDSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Interference ratio
Systems and methods for providing active noise cancellation in an RFID tag reader are described. In one aspect, the method features increasing the signal-to-noise-plus-interference ratio of a radio frequency tag response. The method includes receiving, with a first antenna element of a radio frequency tag reader, a radio frequency tag response having a noise-plus-interference portion and a response portion, receiving a noise-plus-interference signal with a second antenna element of the radio frequency tag reader, and processing the received radio frequency tag response and the noise-plus-interference signal to increase a signal-to-noise-plus-interference ratio of the received radio frequency tag response.
Owner:NOVANTA CORP
Low noise op amp
ActiveUS7301401B2Reduce flicker noiseReduce thicknessAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceLow noiseVoltage pulse
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
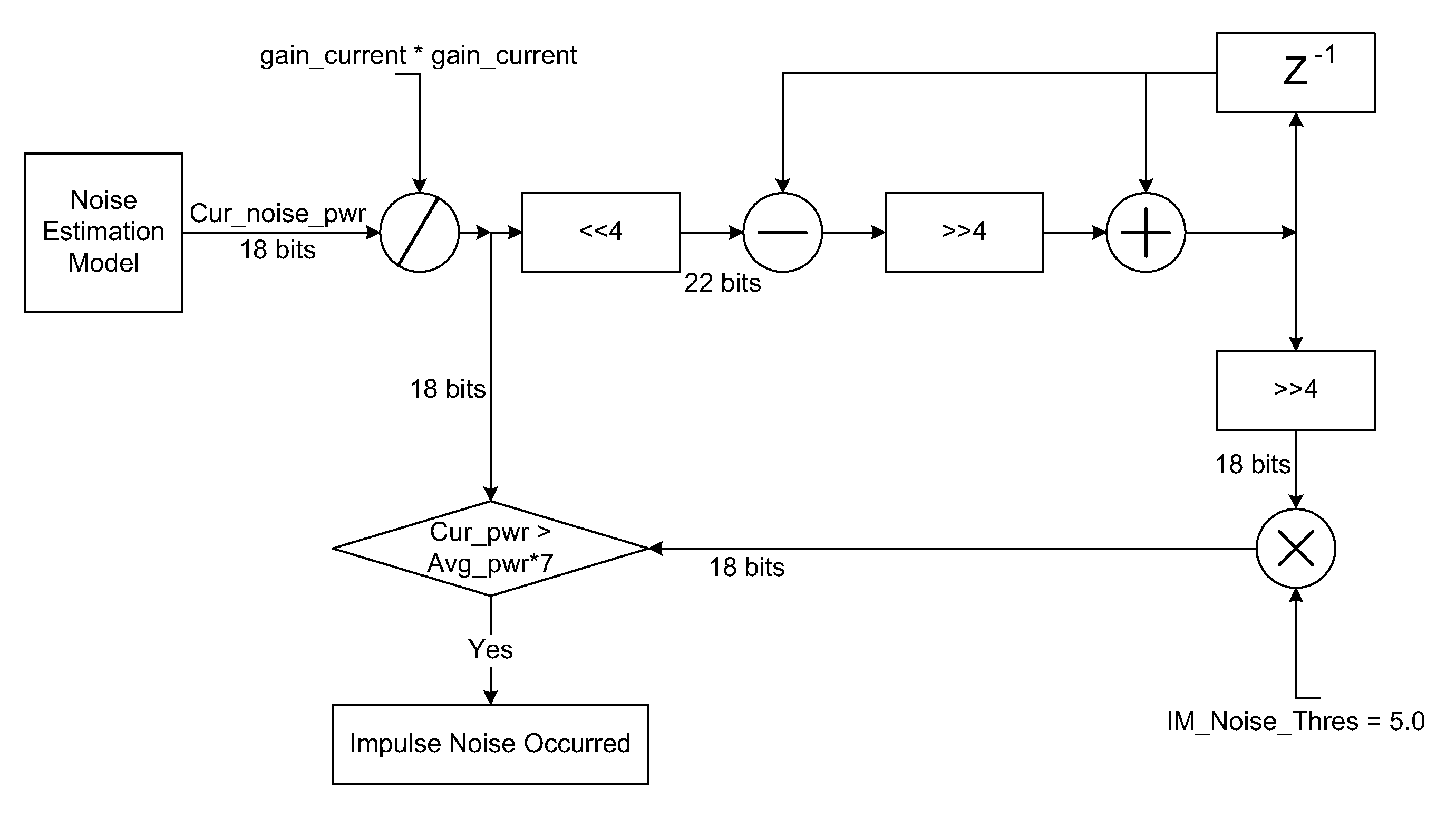
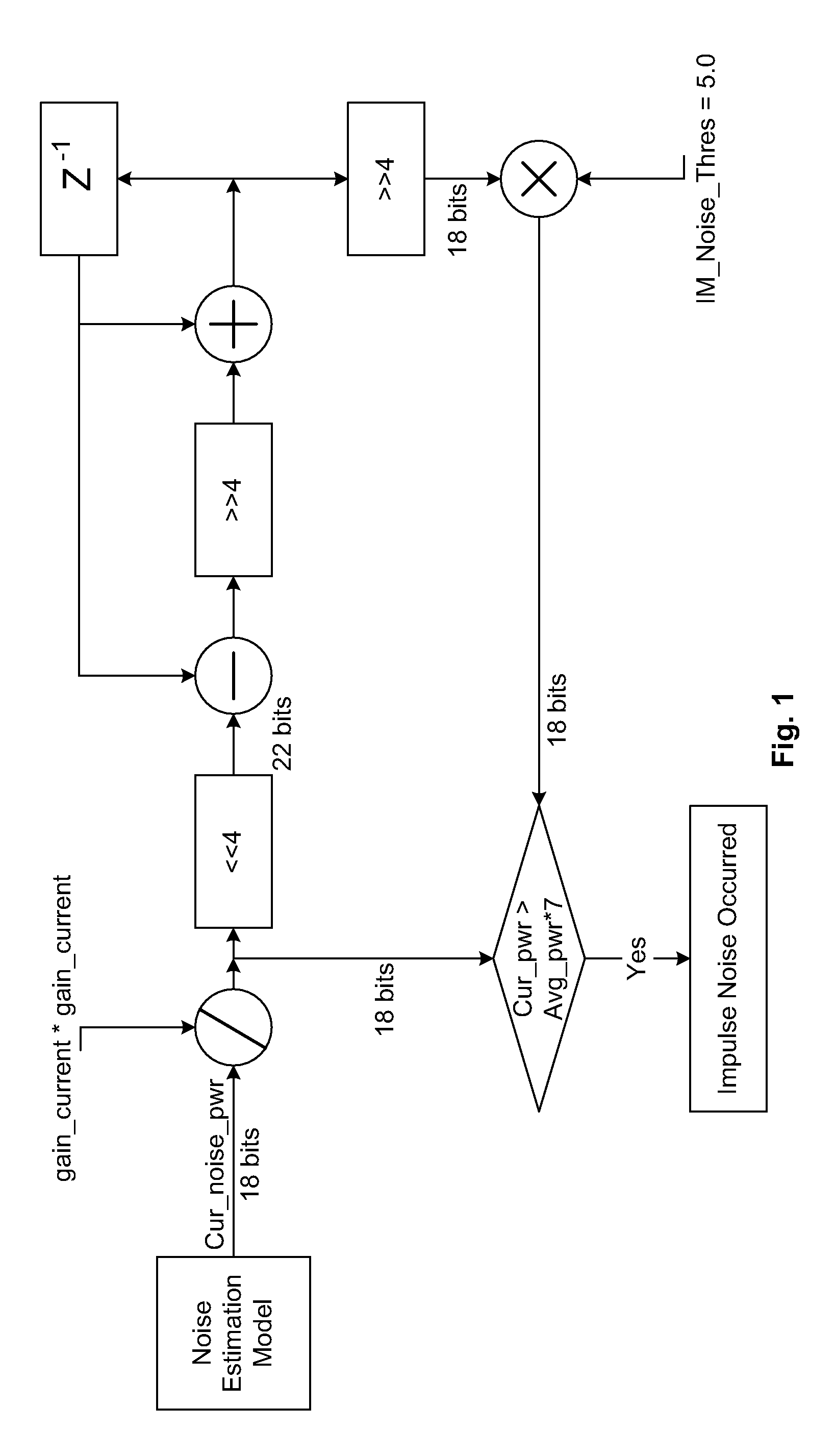
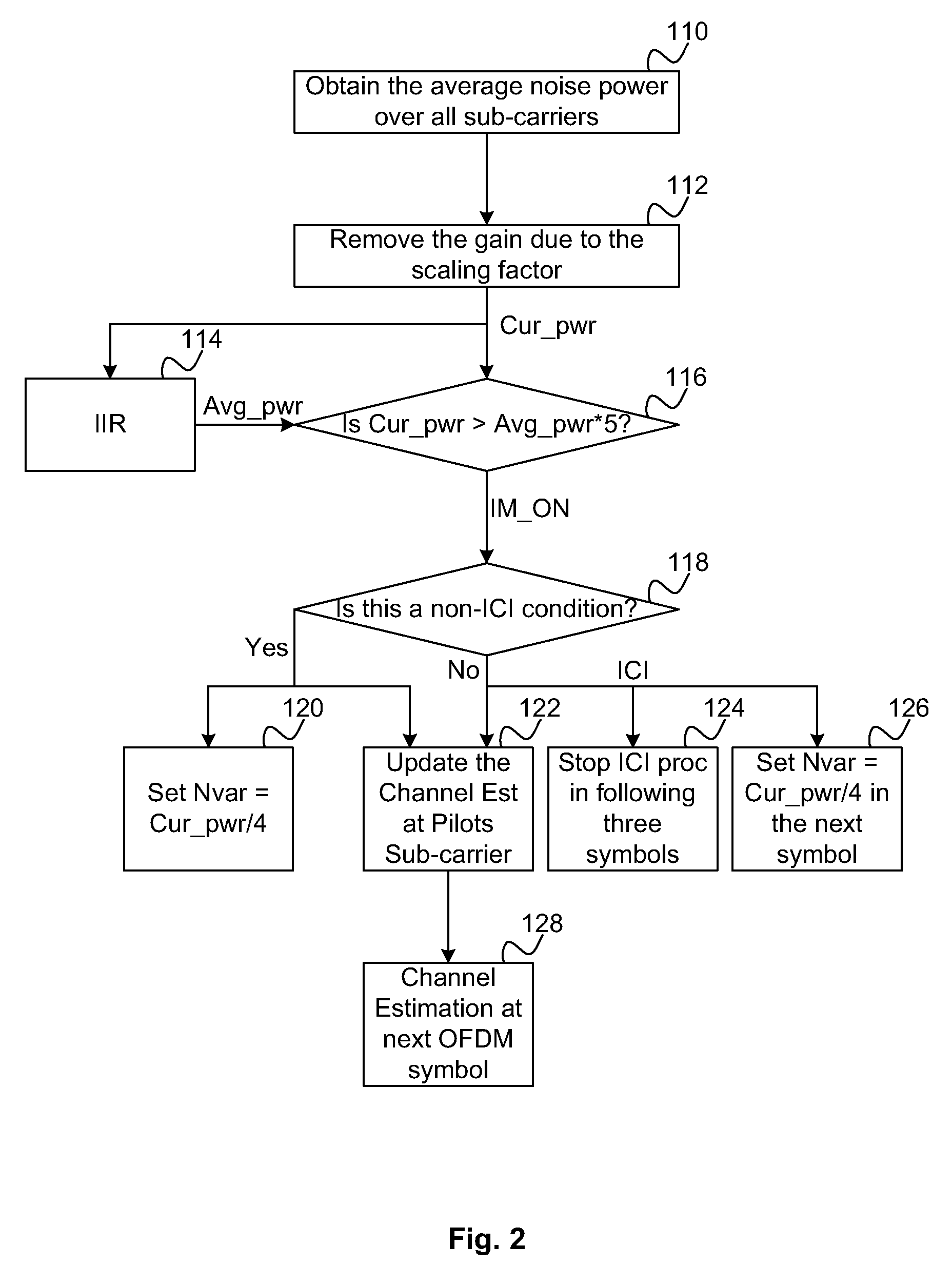
Methods and Systems for Impulse Noise Compensation for OFDM Systems
InactiveUS20090097596A1Reducing bit error number in errorReducing impulse noise contributionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationViterbi decoderBurst error
Methods and systems are provided to reduce the effects of impulse noise in decoding a received OFDM signal by reducing the bit error number in burst error positions and by reducing the impulse noise contribution to channel estimation. In order to reduce the performance degradation due to impulse noise, it is important to find the position or the OFDM symbol where impulse noise occurs. The high noise variance gain can then be used for a Viterbi decoder to reduce the bit error number in burst error position, and also to reduce the contribution of the channel estimation by impulse noise in future channel estimations. Accordingly, the performance of the system can be greatly improved.
Owner:AUGUSTA TECHNOLOGIE
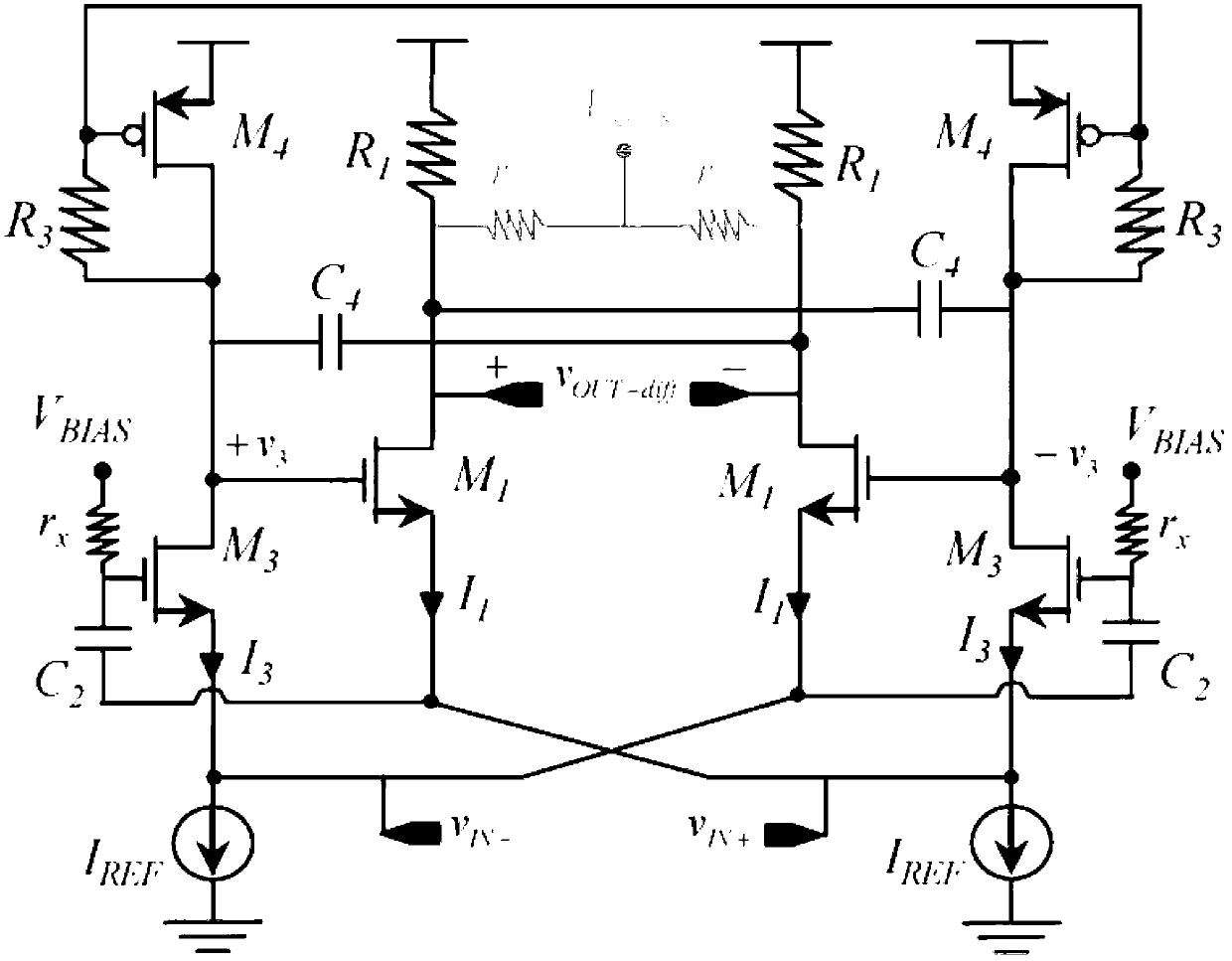
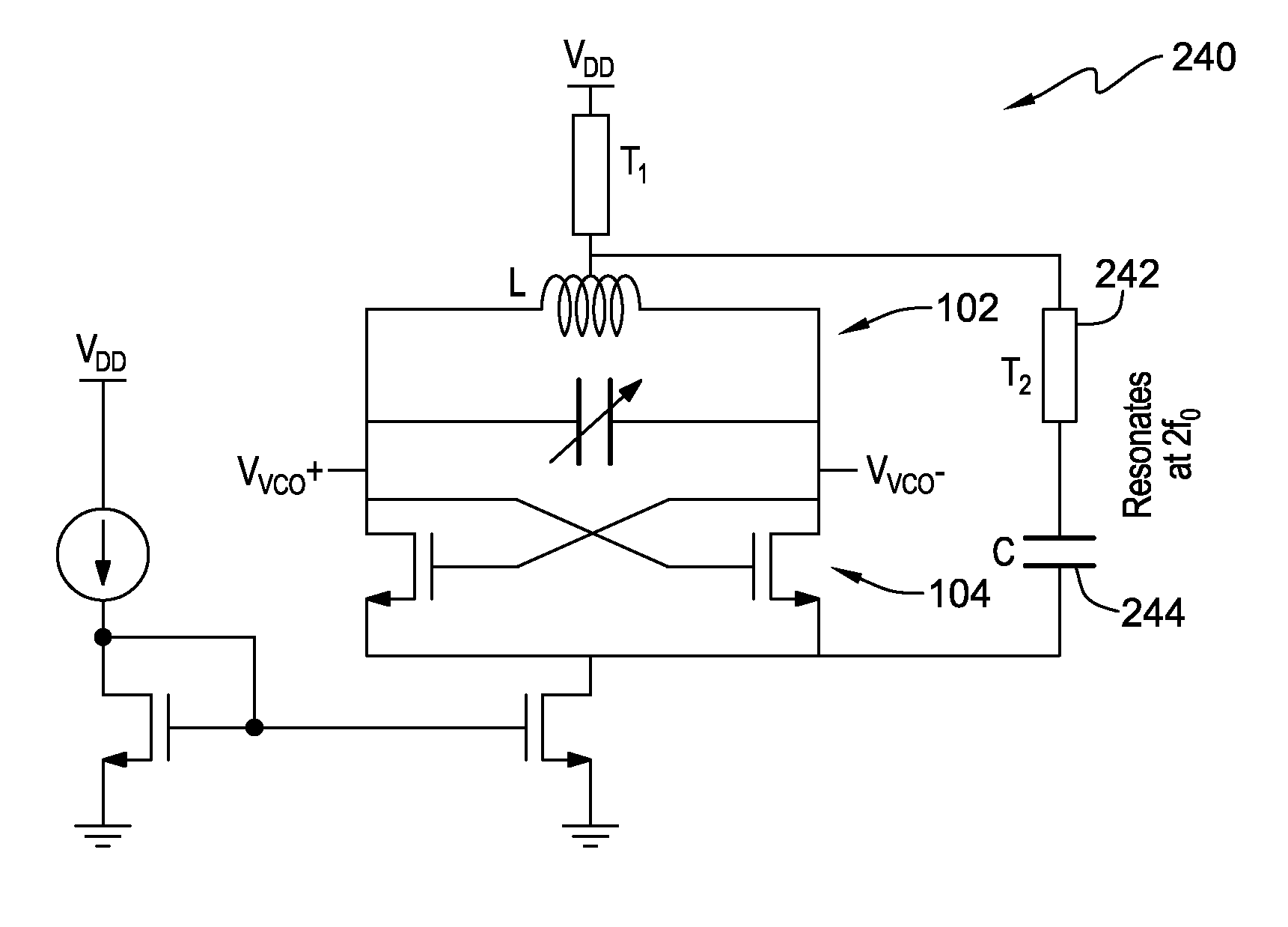
Phase noise reduction in voltage controlled oscillators
ActiveUS9330214B2Reduce noise contributionCAD circuit designOscillations generatorsPhase noiseEngineering
A voltage controlled oscillator (VCO), a method of designing a voltage controlled oscillator, and a design structure comprising a semiconductor substrate including a voltage controlled oscillator are disclosed. In one embodiment, the VCO comprises an LC tank circuit for generating an oscillator output at an oscillator frequency, and an oscillator core including cross-coupled semiconductor devices to provide feedback to the tank circuit. The VCO further comprises a supply node, a tail node, and a noise by-pass circuit connected to the supply and tail nodes, in parallel with the tank circuit and the oscillator core. The by-pass circuit forms a low-impedance path at a frequency approximately twice the oscillator frequency to at least partially immunize the oscillator core from external noise and to reduce noise contribution from the cross-coupled semiconductor devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
Low noise and low input capacitance differential MDS LNA
ActiveCN101904091AEliminate the first distorted signalReduce input capacitanceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCapacitanceLow noise
A differential low noise amplifier (LNA) involves two main amplifying transistors biased in saturation, and two cancel transistors biased in sub-threshold. In one example, the gates of the cancel transistors are coupled to the drains of main transistors, in a symmetrical and cross-coupled fashion. The main transistors are source degenerated. Because the gates of cancel transistors are not coupled to the differential input leads of the LNA, the input capacitance of the LNA is reduced. Noise introduced into the LNA output due to the cancel transistors being biased in the sub-threshold region is reduced because there are two stages. The first stage involves the main transistors, and the second stage involves the cancel transistors. By increasing the gain of the first stage and decreasing the gain of the second stage, overall LNA gain is maintained while reducing the noise that the sub-threshold biased transistors contribute to the LNA output.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Amplifier Circuit and Method for Reducing Voltage and Current Noise
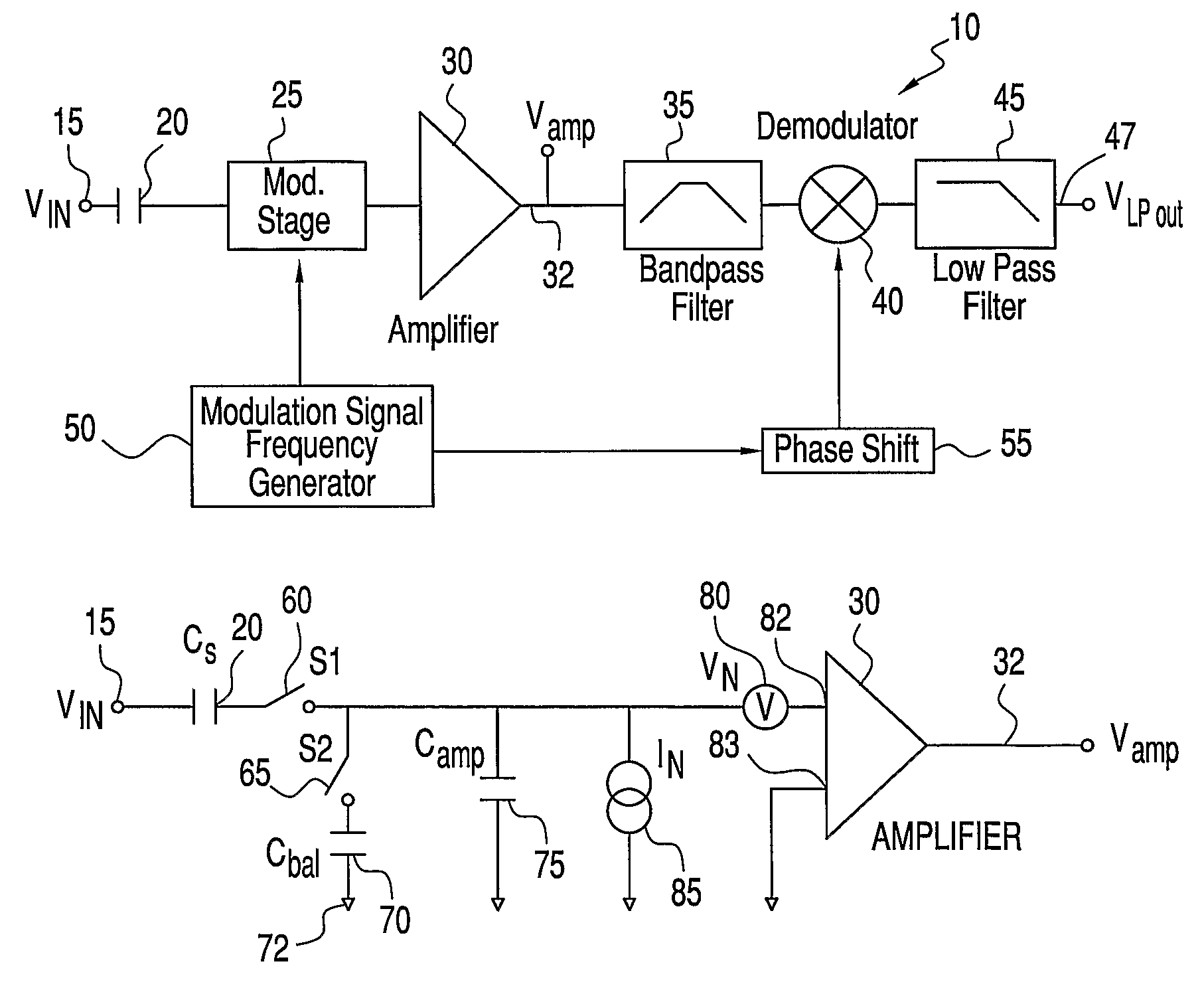
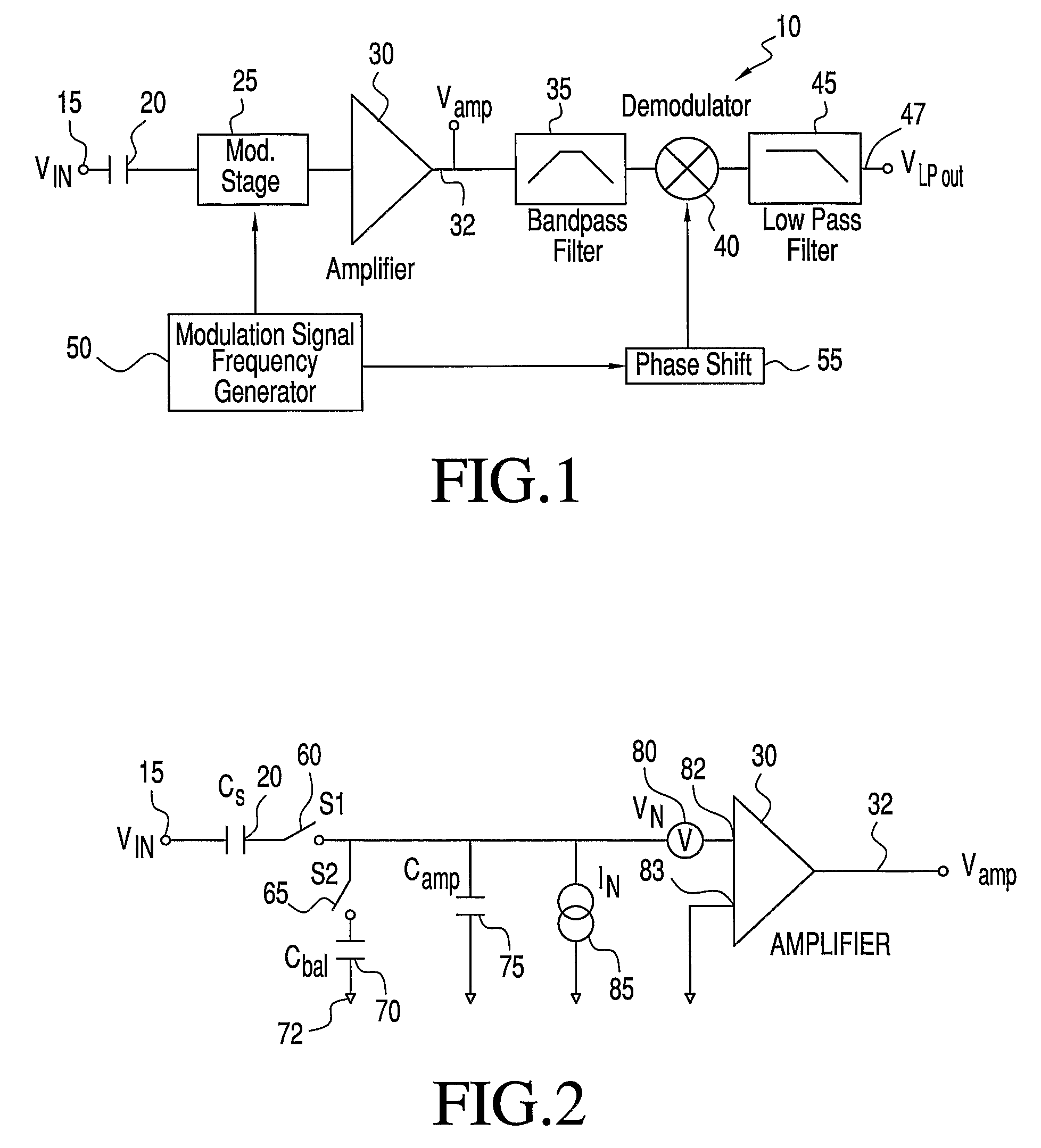
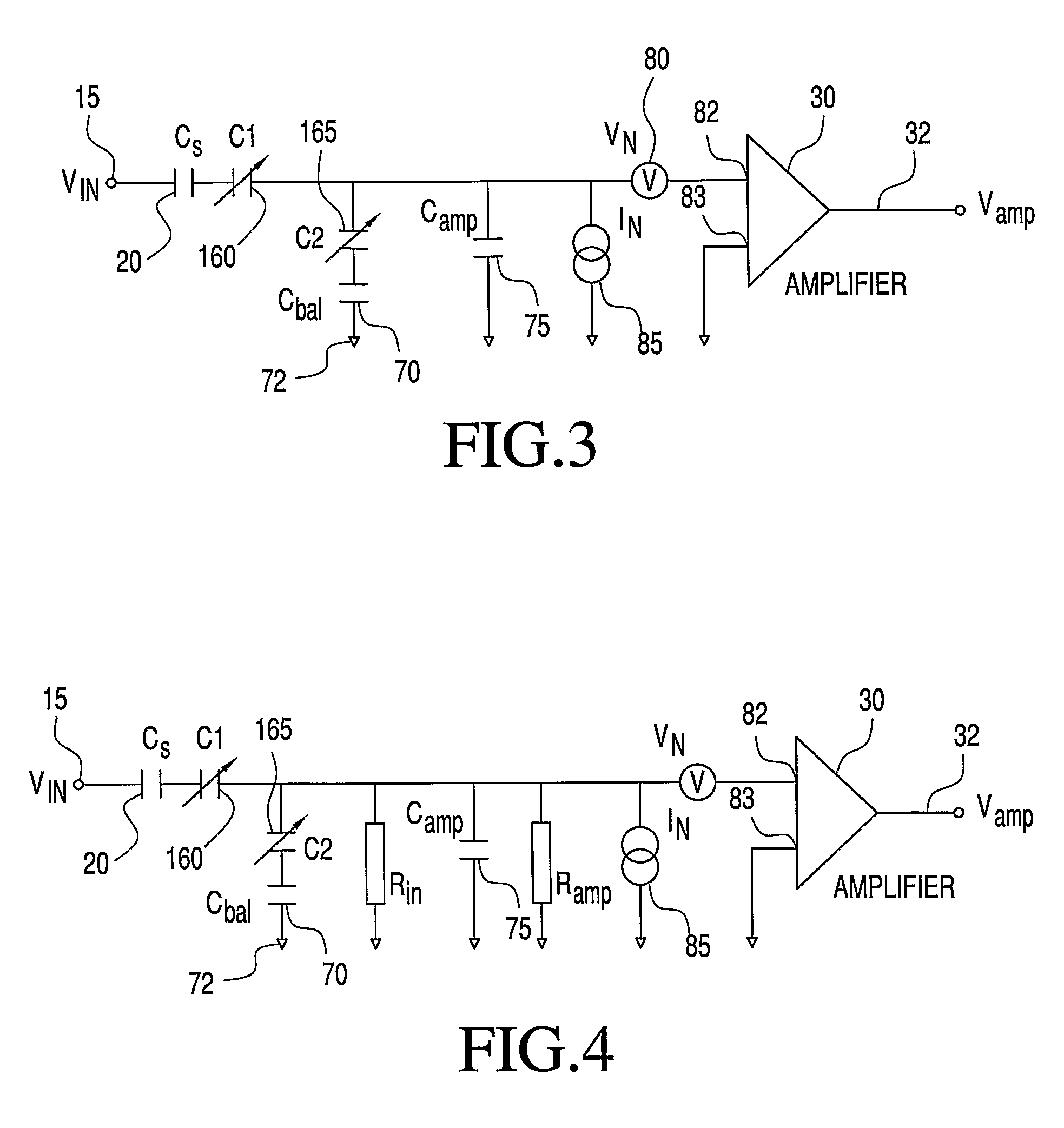
ActiveUS20080111621A1Reduce impactEffective voltage noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyBandpass filteringCurrent noise
An amplifier circuit with current noise reduction employs first and second variable impedance devices between a signal source and an amplifier. A modulation frequency generator establishes a modulation frequency fmod to alter the first and second impedance values out of phase from one another at the modulation frequency so that the sum of the first and second impedance values at the input of the amplifier is relatively constant. The modulation at frequency fmod shifts the signal to side bands about the modulation frequency. The output from the amplifier is passed to a bandpass filter centered on the modulation frequency in order to remove all frequencies outside the bandwidth of interest. The signal itself is recovered by demodulating the output of the bandpass filter using a synchronization signal that is derived from the modulation signal.
Owner:QUANTUM APPLIED SCI & RES
High speed high resolution ADC using successive approximation technique
ActiveUS7796077B2Improve conversion speedIncrease speedElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierEngineering
An analog to digital converter (ADC) containing a sub-ADC to resolve at least some of the bits using successive approximation principle (SAP), while providing various improvements. According to one aspect, another sub-ADC is used to resolve some of the bits in parallel. According to another aspect, the sub-ADC using SAP is implemented using a charge redistribution principle, while another sub-ADC does not rely on charge conservation. According to yet another aspect of the present invention, a same component operates as a comparator when the sub-ADC using SAP resolves the corresponding bits, and operates as an amplifier when the sub-ADC generates a residue signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Temperature sensitive circuit
InactiveUS20090058391A1High voltageTotal current dropThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansEngineeringTemperature sensitive
A circuit for use in a current source or a proportional to absolute temperature sensor or in a bandgap regulator, the circuit comprising at least two PTAT cells the operating Voltages of whose components overlap, the PTAT contribution to the output including the sum of the outputs of the two PTAT cells.
Owner:ADAPTALOG
Method and a Touch Sensing Device for Implementing the Method
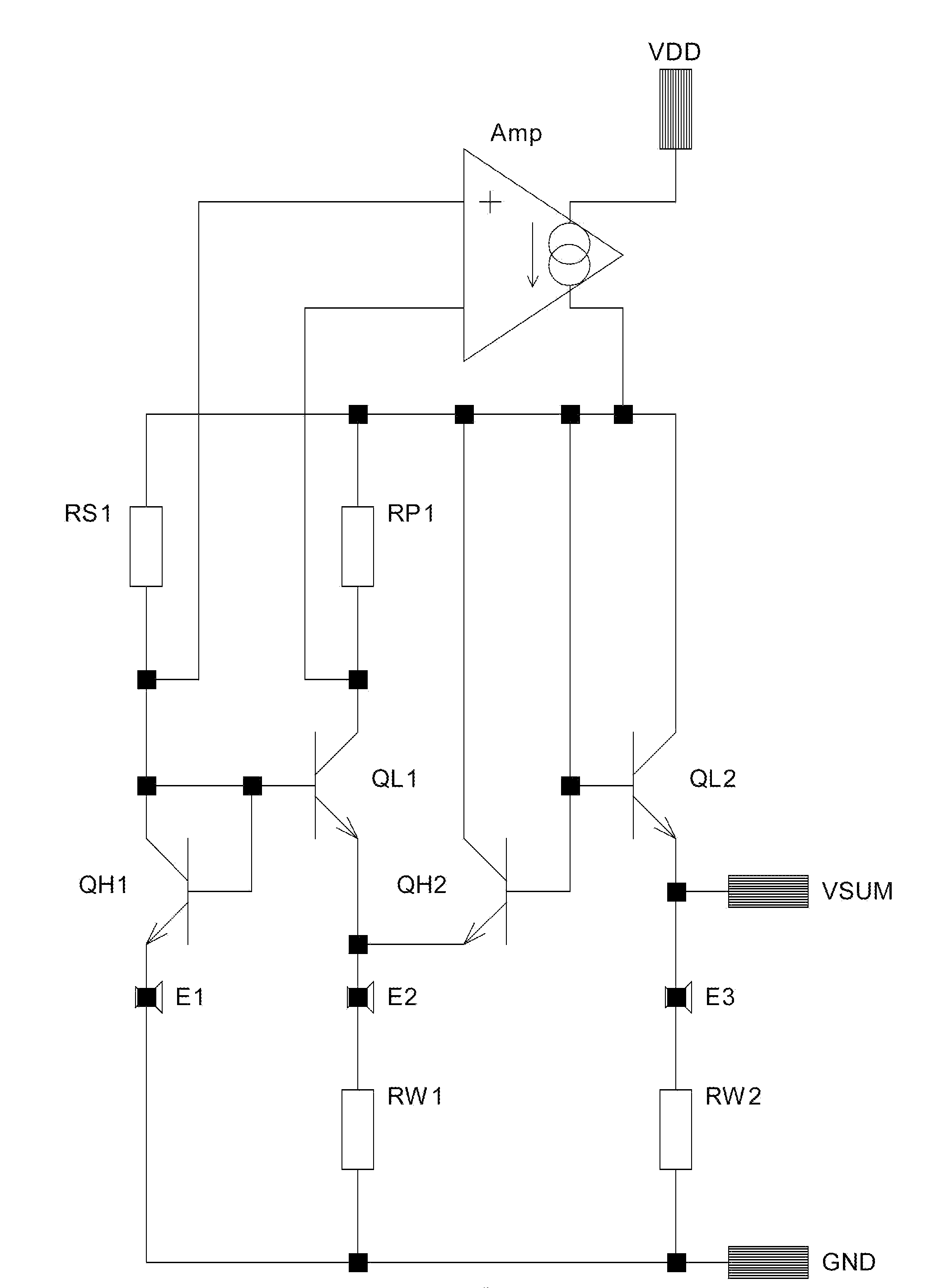
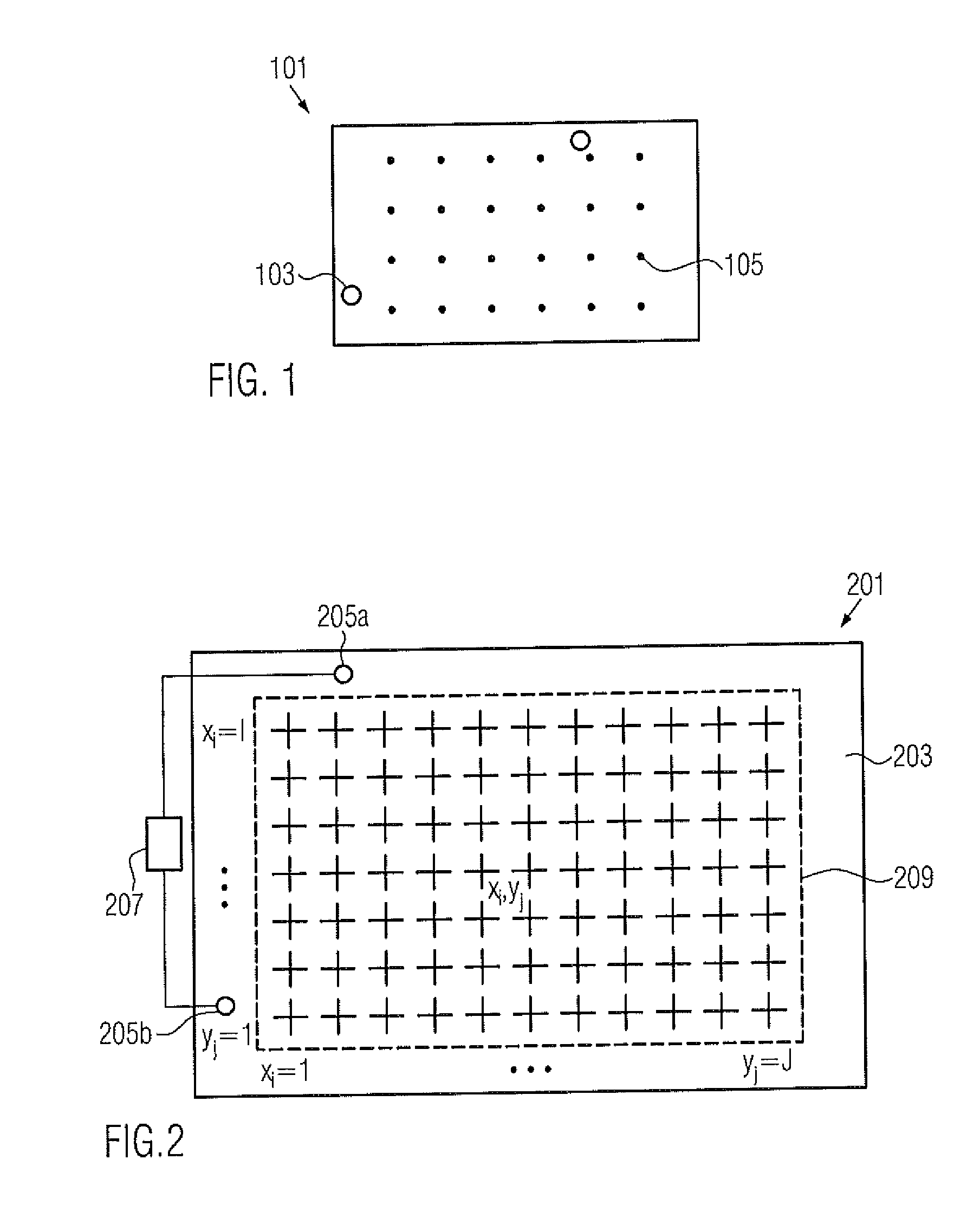
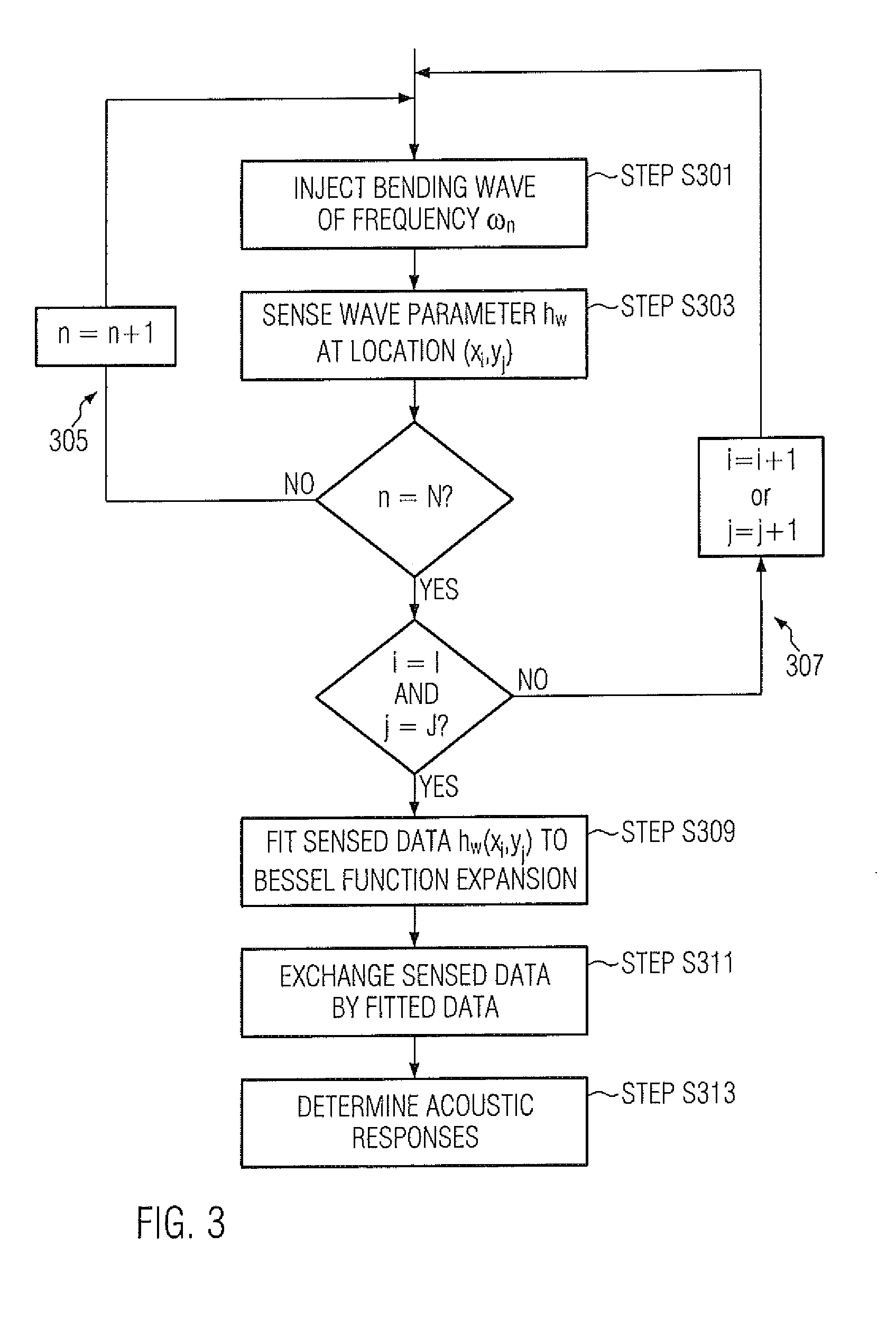
ActiveUS20120166145A1Reduce noise signalReduce noise contributionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Touch Senses
The present invention relates to a method for reducing noise in a signal sensing a bending wave propagating in an object comprising the steps of: receiving a sensed signal representative of a plurality of locations of the object, and fitting a function satisfying bending wave propagation properties to the sensed signals, thereby reducing noise contributions to the sensed signals not satisfying the bending wave propagation properties. By doing so, noise contributions not satisfying the wave propagation properties can be suppressed from the sensed signal, thereby improving the signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:ELO TOUCH SOLUTIONS INC
Method of and system for determining distances between loudspeakers
InactiveUS7864631B2Without disturbingEconomical and simpleDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesLoudspeakersEngineeringLoudspeaker
The invention describes a method of determining the distance (d12) between two loudspeakers (L1, L2), wherein the method comprises the steps of providing a test signal (N), combining the test signal (N) with a sound signal (S) to give a combined signal (SN) in which the test signal is imperceptible to a listener (4), and issuing the combined signal (SN) by means of a first loudspeaker (L1). The combined signal (SN) is detected by a detecting means (M2) associated with the second loudspeaker (L2) and processed to obtain an acoustic impulse response (IR), which is used to determine the distance (d1,2) between the first loudspeaker (L1) and the second loudspeaker (L2). The invention further describes a system (1) for determining the distance (d1,2) between two loudspeakers (L1, L2) and an acoustic sound system, comprising a number of loudspeakers (L1, L2, . . . , Lk) for reproduction of multi-channel sound, and a system (1) for determining the distances (d1,2, d2,3, . . . , dk-i,k) between the loudspeakers (L1, L2, . . . , Lk) in order to automatically configure the loudspeakers (L1, L2, . . . , Lk) for that acoustic sound system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Amplifier circuit and method for reducing voltage and current noise
ActiveUS7518443B2Reduce impactEffective voltage noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyBandpass filteringCurrent noise
An amplifier circuit with current noise reduction employs first and second variable impedance devices between a signal source and an amplifier. A modulation frequency generator establishes a modulation frequency fmod to alter the first and second impedance values out of phase from one another at the modulation frequency so that the sum of the first and second impedance values at the input of the amplifier is relatively constant. The modulation at frequency fmod shifts the signal to side bands about the modulation frequency. The output from the amplifier is passed to a bandpass filter centered on the modulation frequency in order to remove all frequencies outside the bandwidth of interest. The signal itself is recovered by demodulating the output of the bandpass filter using a synchronization signal that is derived from the modulation signal.
Owner:QUANTUM APPLIED SCI & RES
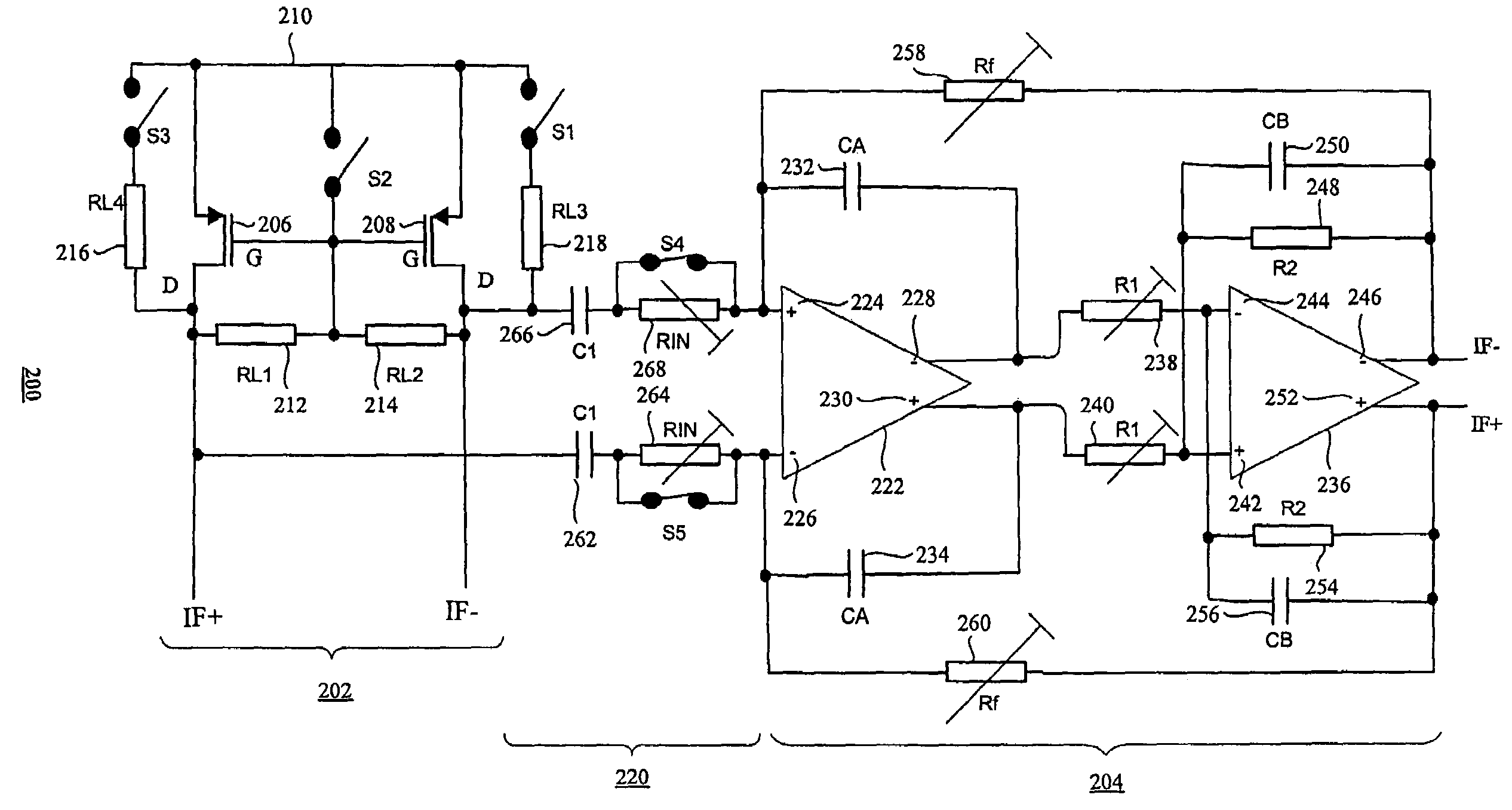
Radio receiver/transceiver including an interface circuit selectively operable in a current mode or a voltage mode
InactiveUS7392028B2Reduce noise contributionReduce gainPower managementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverRadio reception
A radio receiver is selectively operable in a current mode or a voltage mode according to conditions prevailing within a wireless environment. If the signal levels within the wireless environment are relatively low, the radio receiver is operable in current mode. If the signal levels within the wireless environment are relatively high, the radio receiver is operable in voltage mode. The radio receiver is switchable between current and voltage mode of operation via selectively actuable switches that bringing into effect or remove from effect corresponding resistances.
Owner:BREAKWATERS INNOVATIONS
Low noise op amp
ActiveUS7113042B2Reduce flicker noiseReduce thicknessAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceEmergency protective circuit arrangementsLow noiseAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates amplifiers using metal oxide semiconductor based integrated circuits. The present invention is particularly but not exclusively related to audio application mixed signal chips. The present invention provides an analog circuit for processing analog signals in an integrated circuit comprising a number of metal oxide semiconductor transistor devices, the circuit stage comprising a first said transistor device having a first oxide thickness, and a second said transistor device having a second and different oxide thickness. Preferably a cascode based op amp structure is implemented.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com