Patents
Literature
1025 results about "Wave propagation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wave propagation is any of the ways in which waves travel. With respect to the direction of the oscillation relative to the propagation direction, we can distinguish between longitudinal wave and transverse waves.
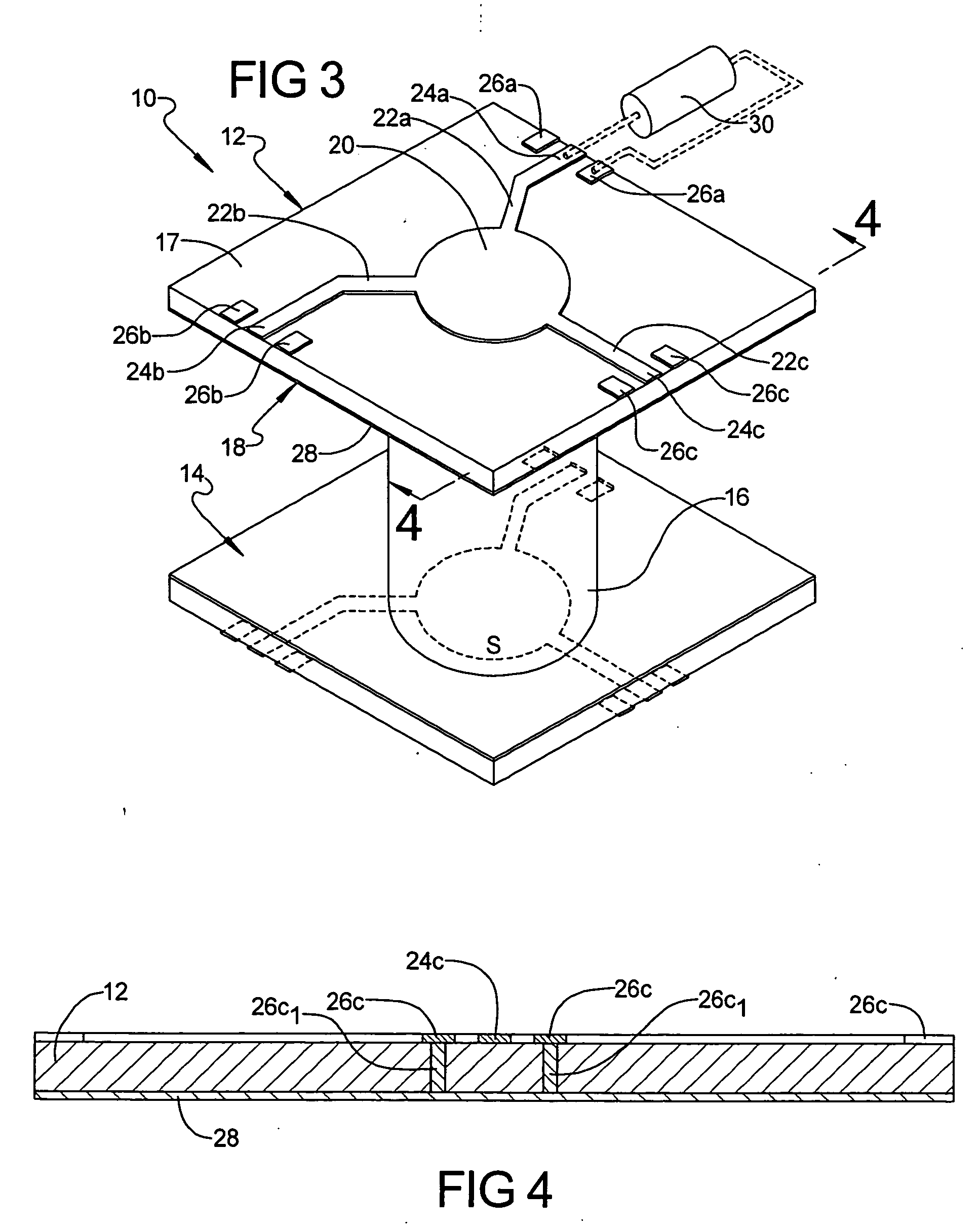
Electromagnetic wave propagation path and electromagnetic wave propagation device
InactiveUS20140167882A1Increase resistanceHighly reliable communicationOne-port networksWaveguidesDielectricElectrical conductor
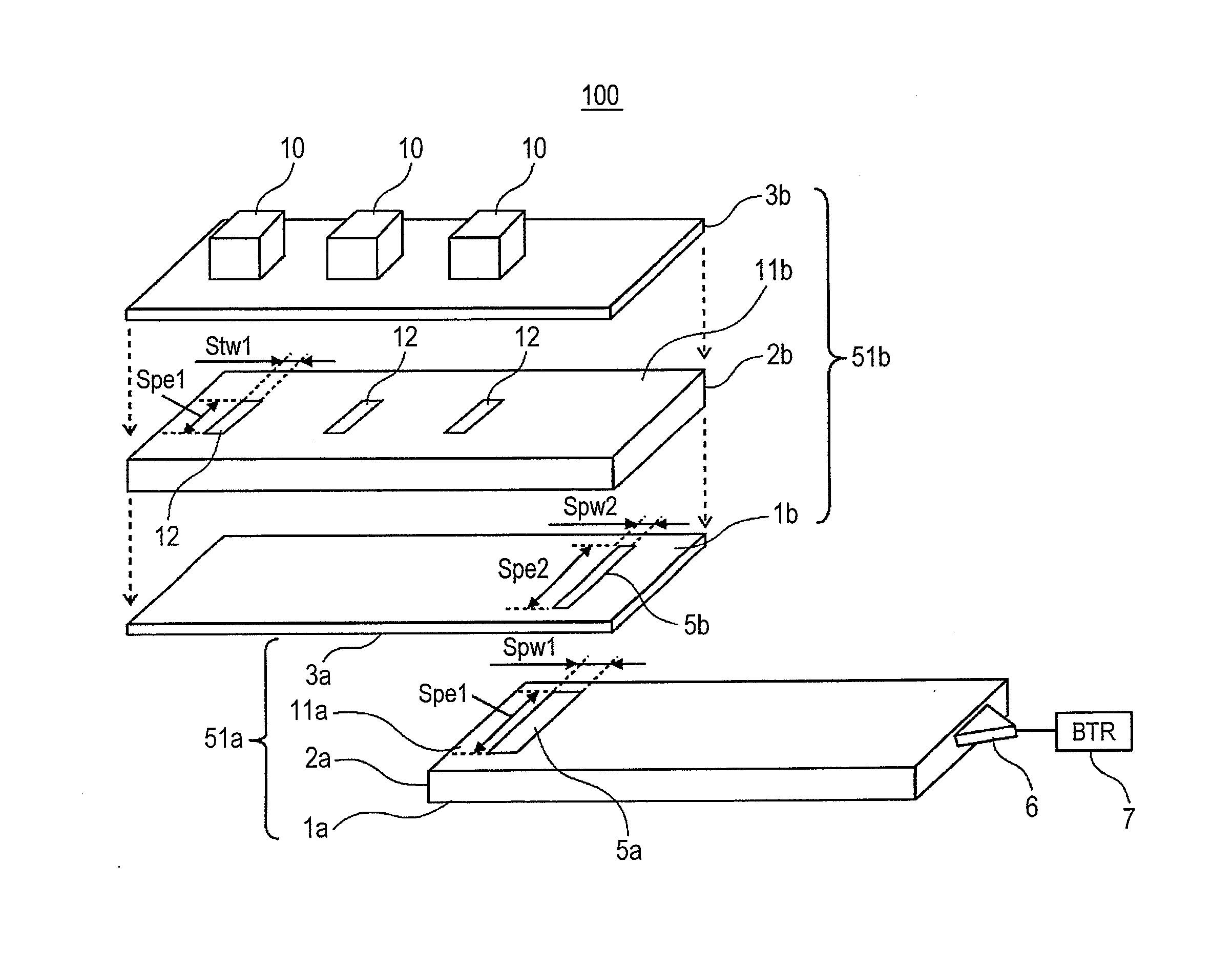
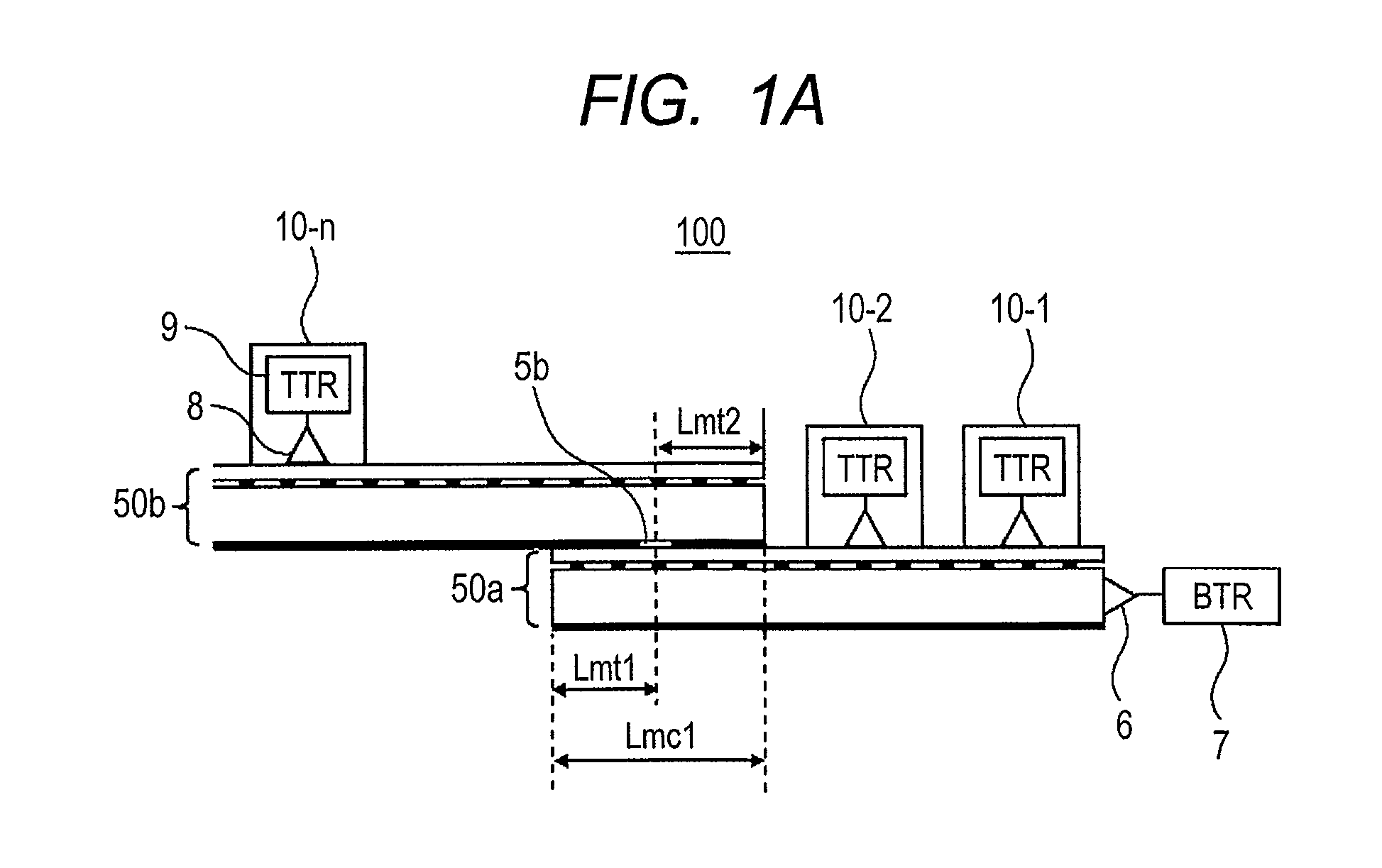
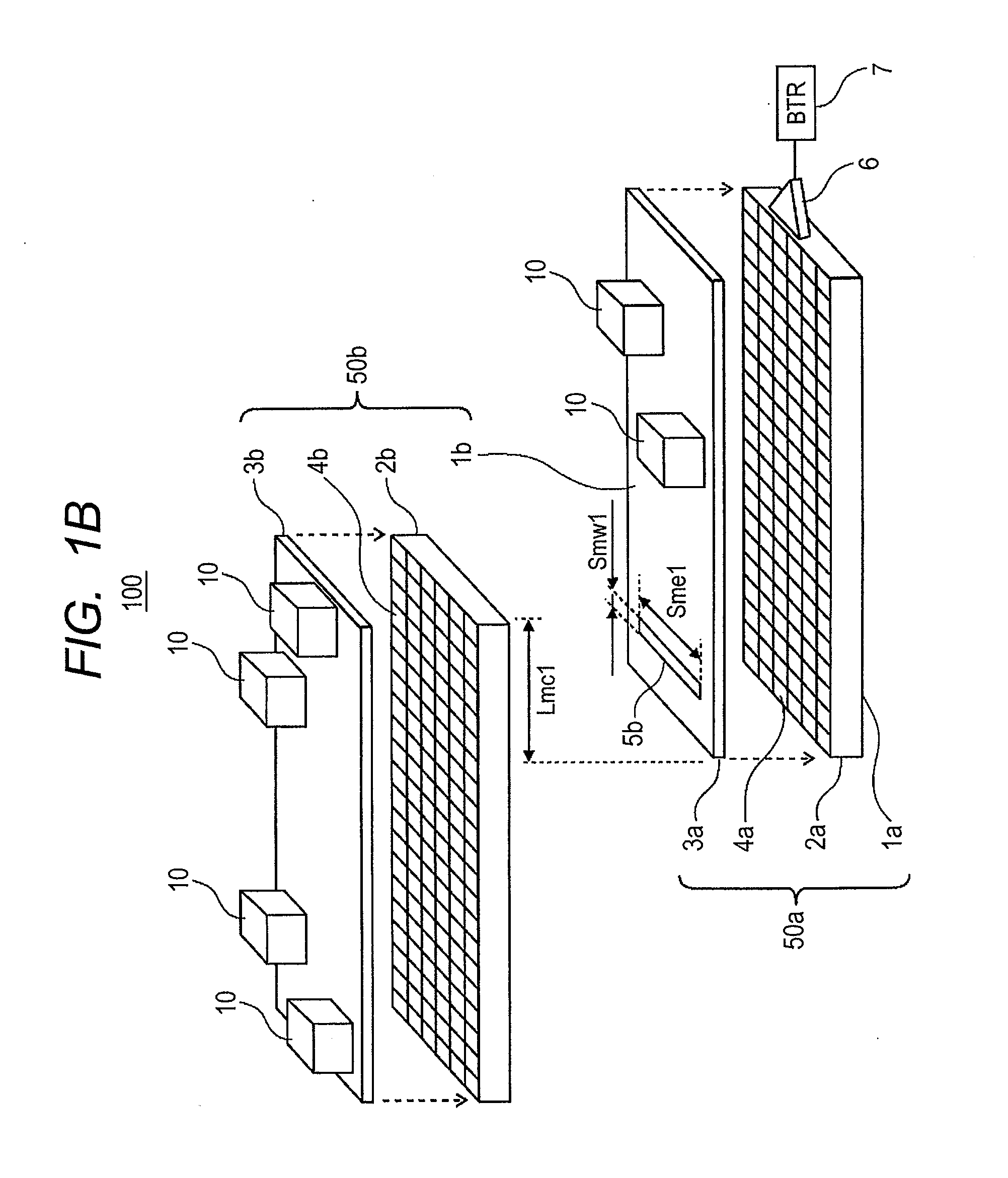
An electromagnetic wave propagation device includes multiple planar propagation media each formed by laminating at least one planar conductor and at least one planar dielectric, multiple transceivers for transmitting and receiving information among electronic apparatuses, and a first interface for transmitting and receiving the electromagnetic wave between the transceivers and the planar propagation media. Planar dielectric spacers are provided for isolating the multiple planar propagation media from one another. The planar propagation medium is disposed to have an overlapped part with at least the other of the planar propagation media so that an obverse face of the medium and a reverse face of the other medium are at least partially overlapped with each other. The planar conductor is provided with an electromagnetic wave linking unit at the overlapped part that transmits and receives the electromagnetic wave between the planar propagation media.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
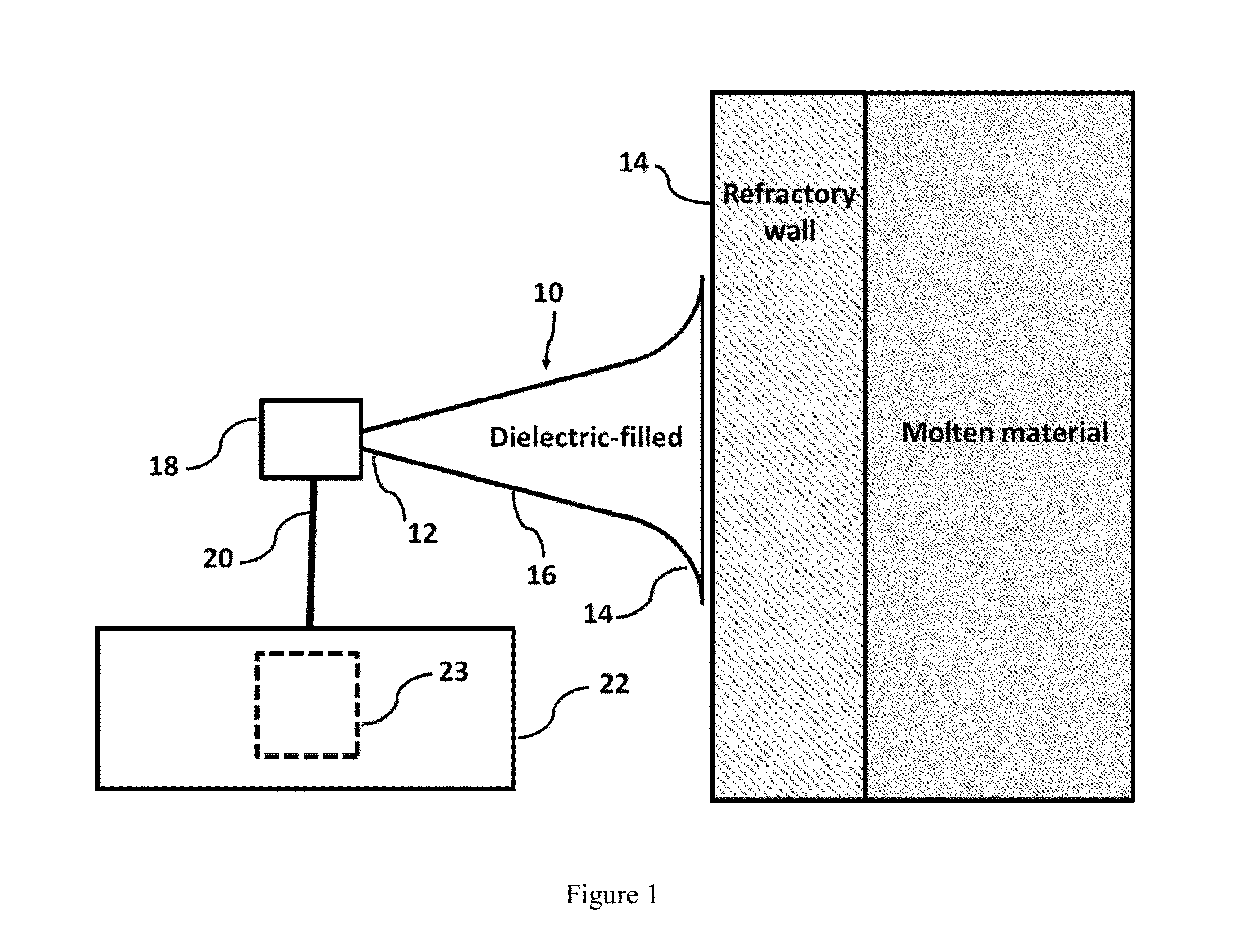
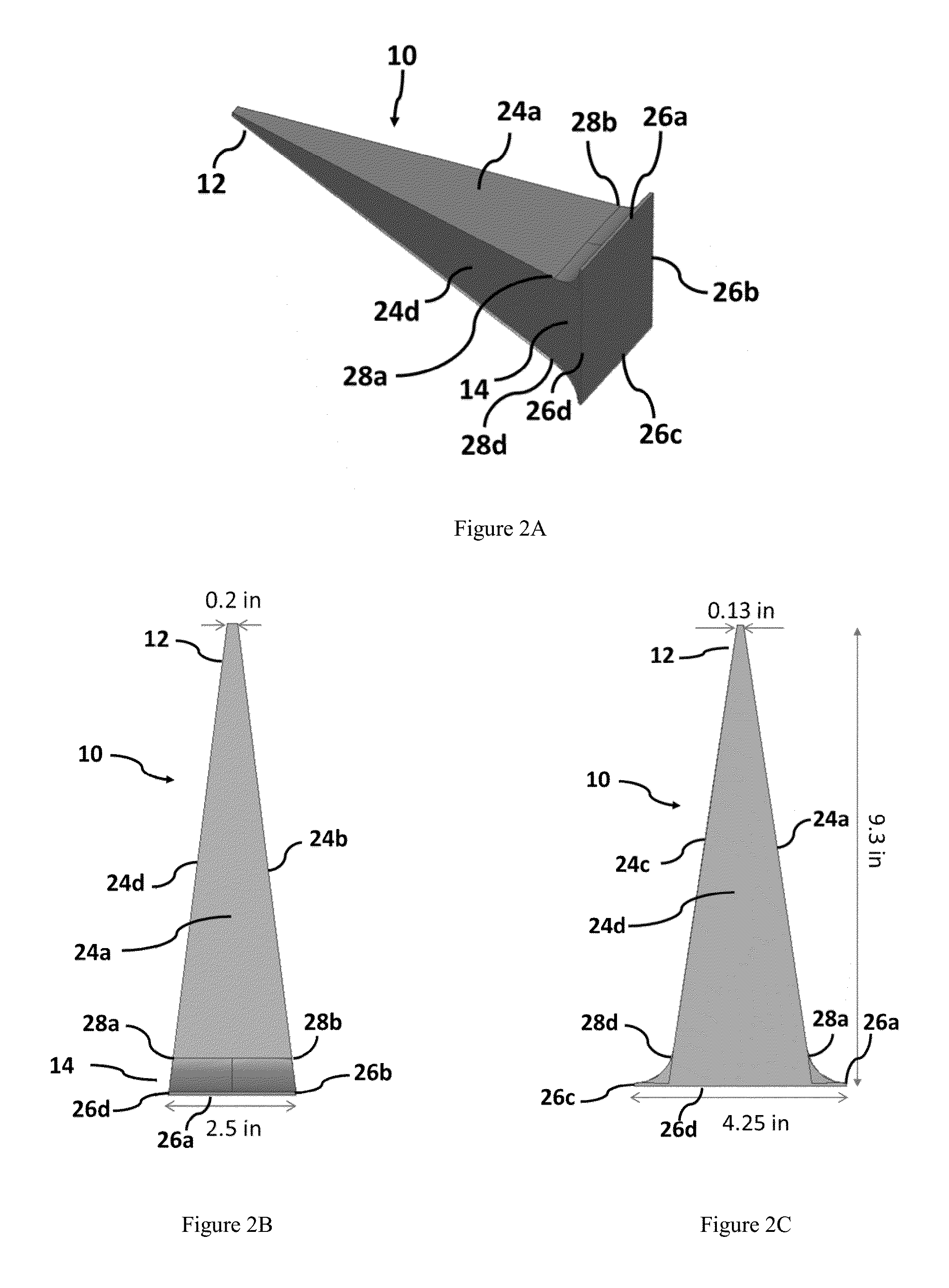
Material erosion monitoring system and method
ActiveUS20150276577A1Reduce confusionMultiple EffectsFurnace componentsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial ErosionMonitoring system
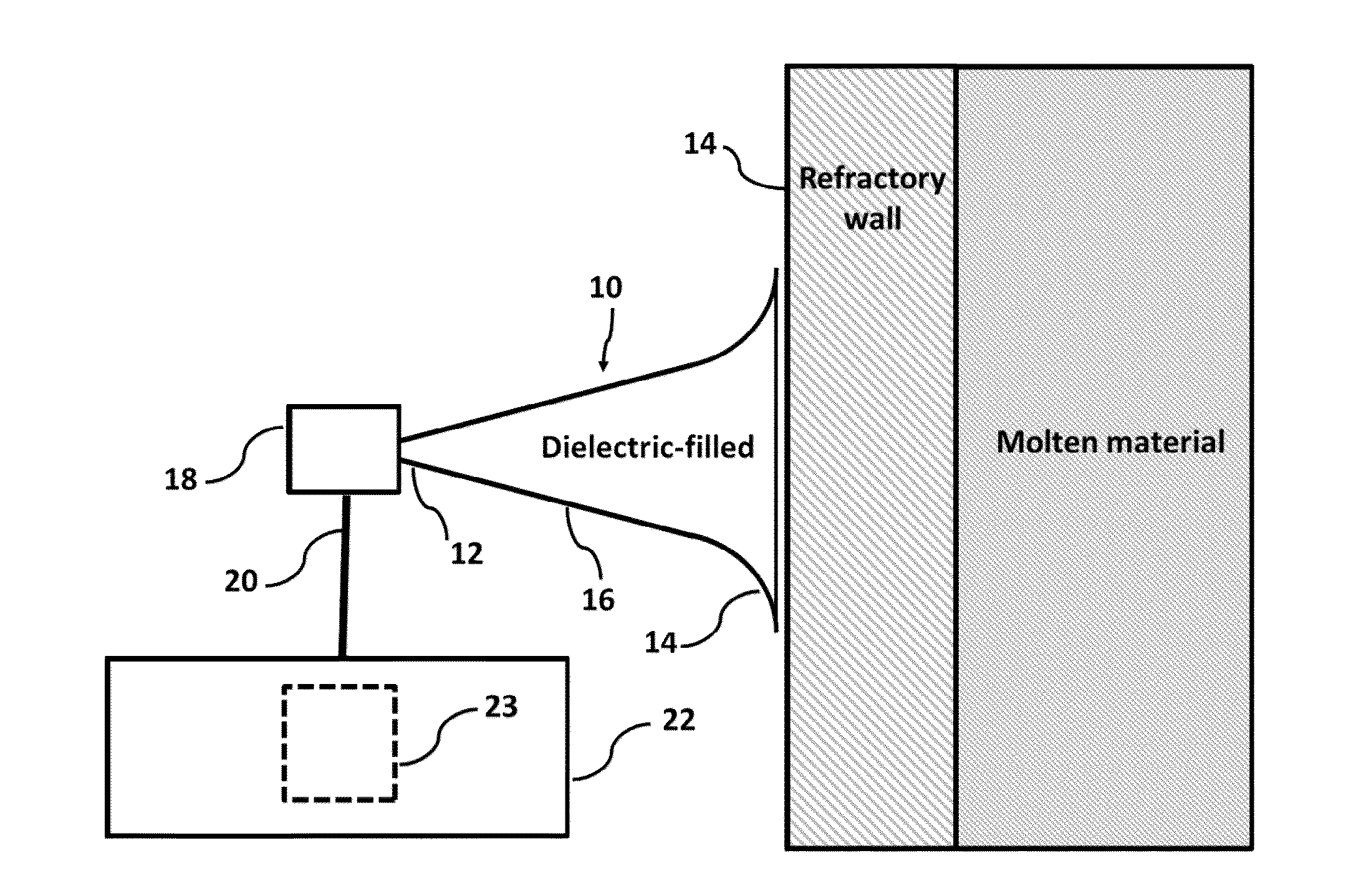
Disclosed is an improved system and method to evaluate the status of a material. The system and method are operative to identify flaws and measure the erosion profile and thickness of different materials, including refractory materials, using electromagnetic waves. The system is designed to reduce a plurality of reflections, associated with the propagation of electromagnetic waves launched into the material under evaluation, by a sufficient extent so as to enable detection of electromagnetic waves of interest reflected from remote discontinuities of the material. Furthermore, the system and method utilize a configuration and signal processing techniques that reduce clutter and enable the isolation of electromagnetic waves of interest. Moreover, the launcher is impedance matched to the material under evaluation, and the feeding mechanism is designed to mitigate multiple reflection effects to further suppress clutter.
Owner:PANERATECH
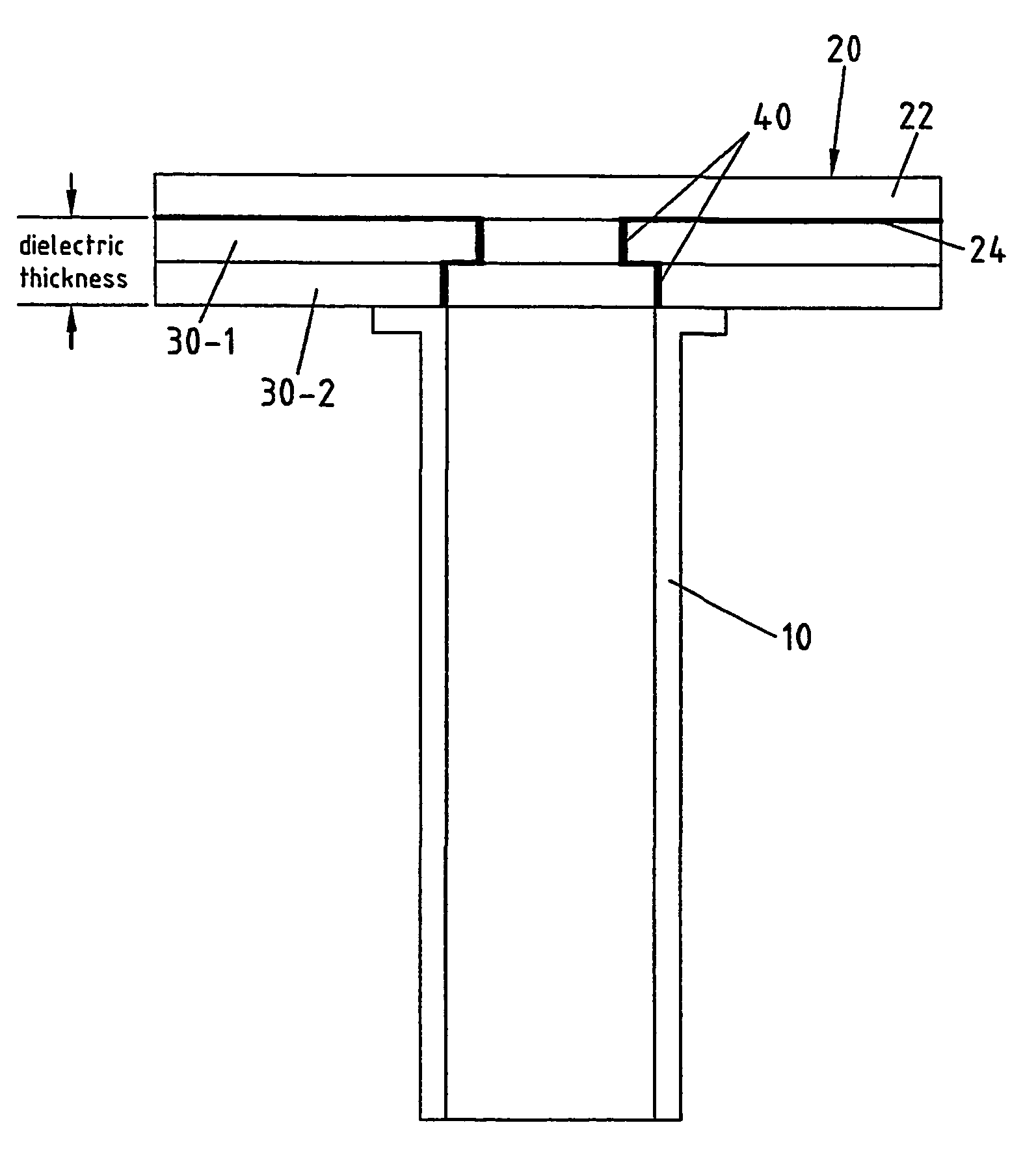
Waveguide to stripline transition with via forming an impedance matching fence
InactiveUS6958662B1Easy to manufactureLess expensiveMultiple-port networksOne-port networksMulti bandCoupling
The invention relates to a device for guiding electromagnetic waves from a wave guide (10), in particular a multi-band wave guide, to a transmission line (20), in particular a micro strip line, arranged at one end of the wave guide (10), comprising coupling means (30-1, . . . , 30-7) for mechanical fixation and impedance matching between the wave guide (10) and the transmission line (20). It is the object of the invention to improve such a structure in the way that manufacturing is made easier and less expensive than according to prior art. According to the present invention that object is solved in the way that the coupling means comprises at least one dielectric layer (30) being mechanically connected with the main plane of the transmission line, the geometric dimension of that at least one dielectric layer extending along the propagation direction of the electromagnetic waves being correlated with the center frequency of electromagnetic waves in order to achieve optimised impedance matching.
Owner:RPX CORP
Optical plasmon-wave structures
Optical plasmon-wave attenuator and modulator structures for controlling the amount of coupling between an guided optical signal and a surface plasmon wave. Optical power coupled to the plasmon wave mode is dissipated in varying amounts producing an intensity modulation effect on the optical signal. For electrical modulation, an additional dielectric (or polymer) layer with variable refractive index in optical contact with a metal layer supporting at least one plasmon wave mode is used to perturb or vary the propagation constant of plasmon wave. Propagation constant variation results in the power coupling variation between the surface plasmon wave and the optical wave. The refractive index variation of the dielectric (or polymer) layer can be accomplished via an electro-optic traveling-wave, a lump-element, or any other integrated optics modulator configuration situated to affect the layer, thereby permitting data rates into tens of GHz. Because of the extremely small interaction lengths needed, the optical plasmon-wave modulator is a very compact device which can be implemented on the top of a fiber or as an integrated optical planar structure.
Owner:VERIFIBER TECH
Efficient wave propagation for terahertz imaging and sensing
A method of wave propagation from 100–10000 GHz. The currently disclosed method and apparatus adapts micro-opto-electro-mechanical systems (MOEMS) technologies and processes to construct Kinoform optical components from microwave to terahertz range. The method uses induced coupled plasma (ICP) and gray scale processes for upper terahertz band; LIGA-based high aspect ratio (HAR) and gray scale processes are for the mid band; and computer numerical control (CNC) for lower band. In all cases, the thickness of any processed components is about the respective wavelength and system efficiency is about 95%. A Kinoform lens element is designed at 5000 GHz. However, the method is applicable for the entire terahertz band.
Owner:MOTAMEDI MANOUCHEHR E +1
Direct bonding method with reduction in overlay misalignment
ActiveUS20120077329A1Reduce appearance problemsReduce and minimize overlay microcomponent misalignmentLamination ancillary operationsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementEngineeringParaboloid
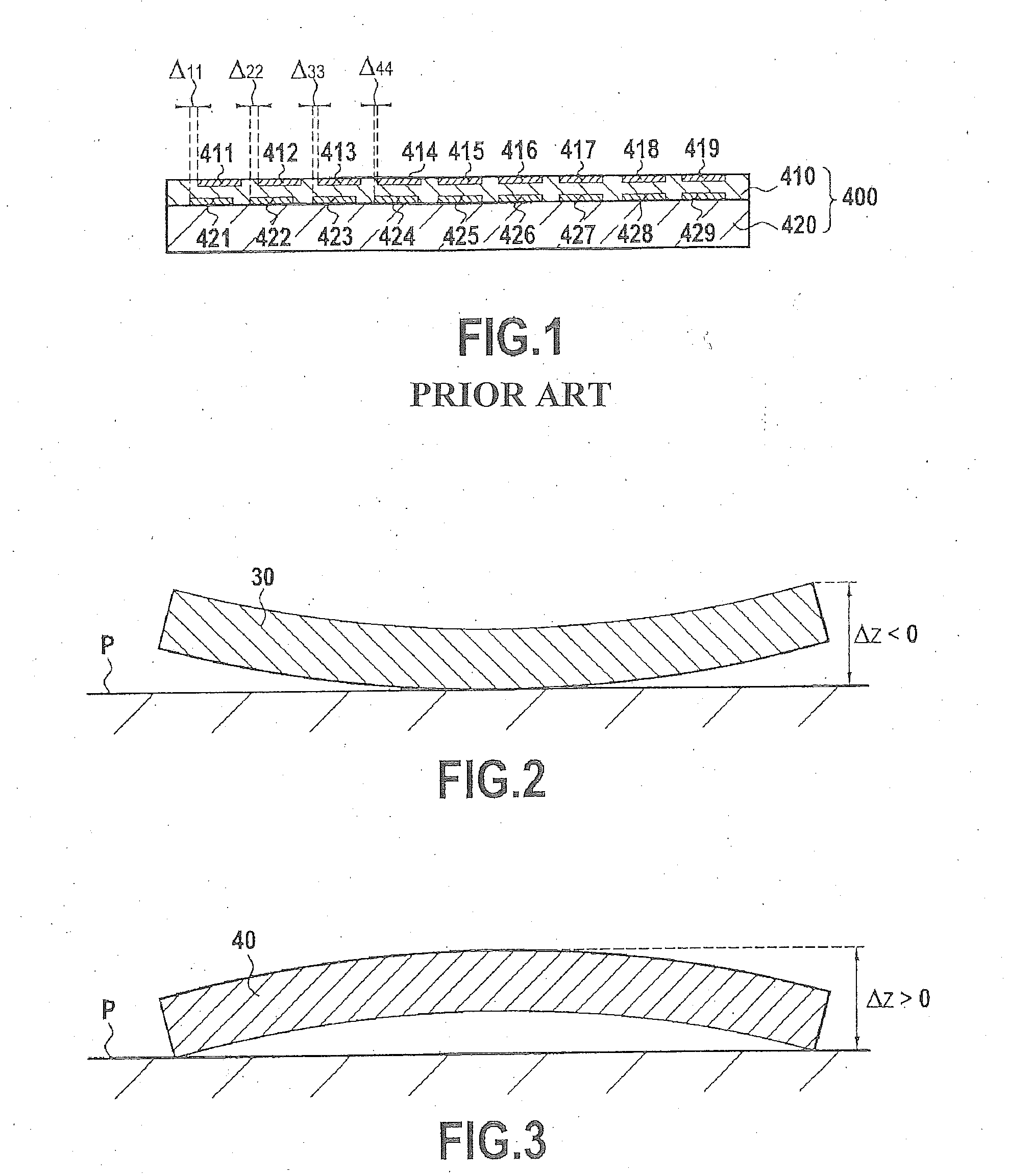
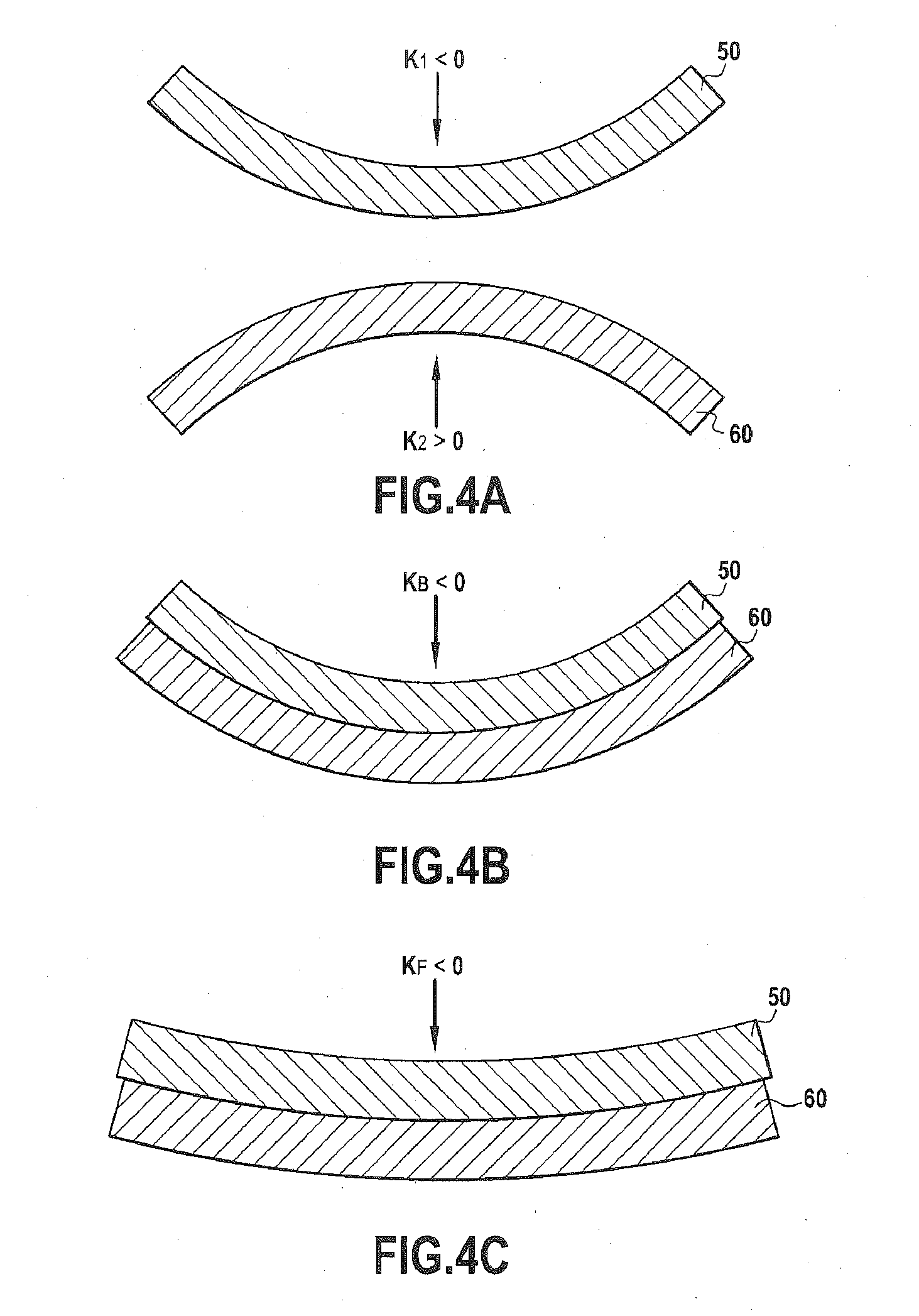
A method for the direct bonding of a first wafer having an intrinsic curvature before bonding to a second wafer having an intrinsic curvature before bonding, at least one of the two wafers comprising at least one series of microcomponents. The method includes of bringing the two wafers into contact with each other so as to initiate the propagation of a bonding wave therebetween while imposing a predefined bonding curvature in the form of a paraboloid of revolution on one of the two wafers depending at least upon the intrinsic curvature before bonding of the wafer that includes the microcomponents, with the other wafer being free to conform to the predefined bonding curvature.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Electromagnetic wave propagation disruption device and method for producing same
An electromagnetic wave propagation disruption device with a metamaterial structure including: a plurality of conductive elements arranged on a top face of a substrate; a plurality of interconnection networks electrically interconnecting at least some of these conductive elements, wherein these networks are not electrically connected to each other. At least two of these networks are dimensioned differently to each other, thus involving that distances between interconnected conductive elements are different from one network to another, to generate phase shifts, between the conductive elements interconnected thereby, different from one network to the other. A ground plane with holes is arranged on a bottom face of the substrate and metallic vias are formed in the substrate, each of them including an upper end in contact with a conductive elements and a lower end arranged facing one of the holes of the ground plane, with no electrical contact with the ground plane.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
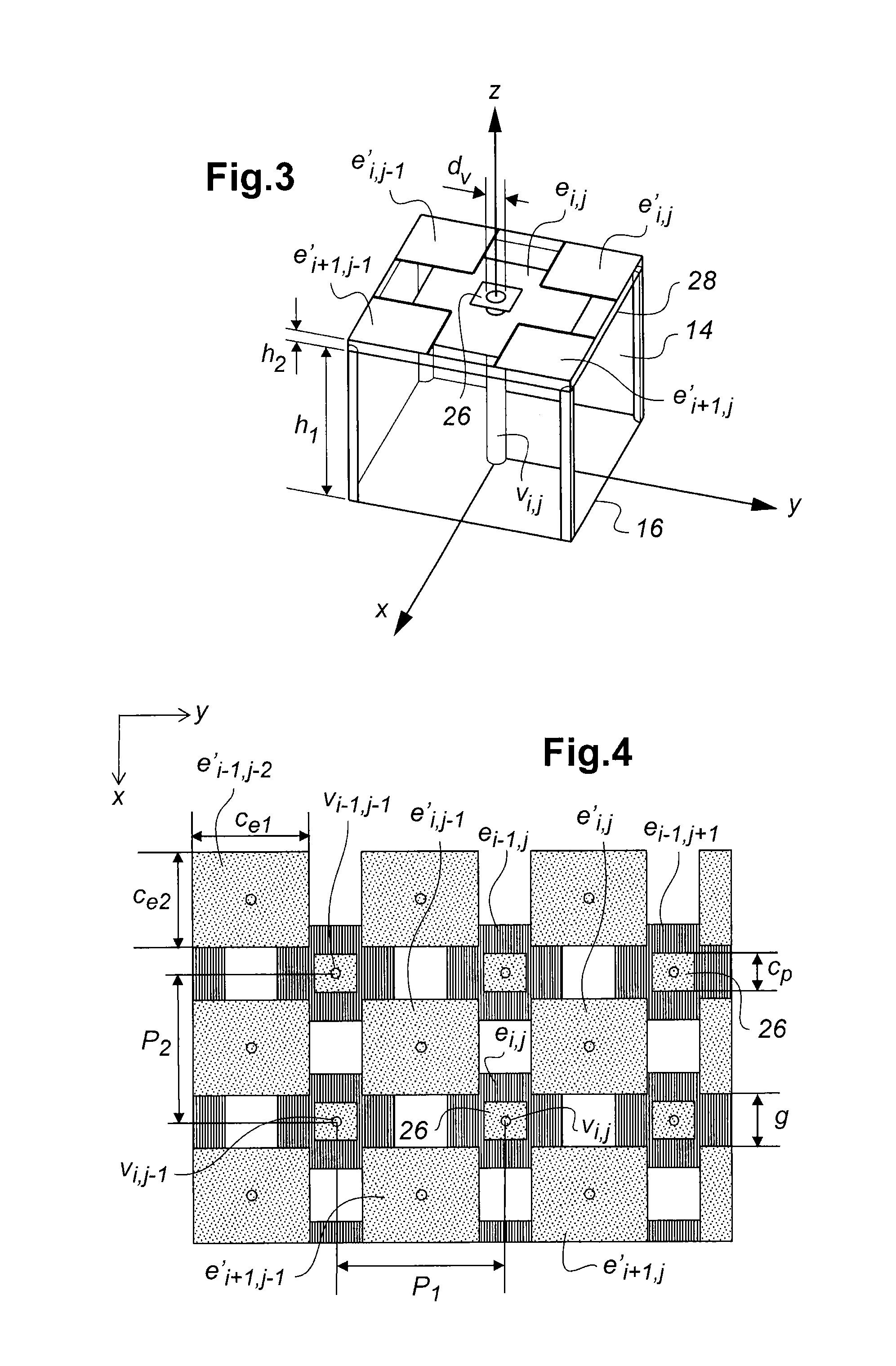
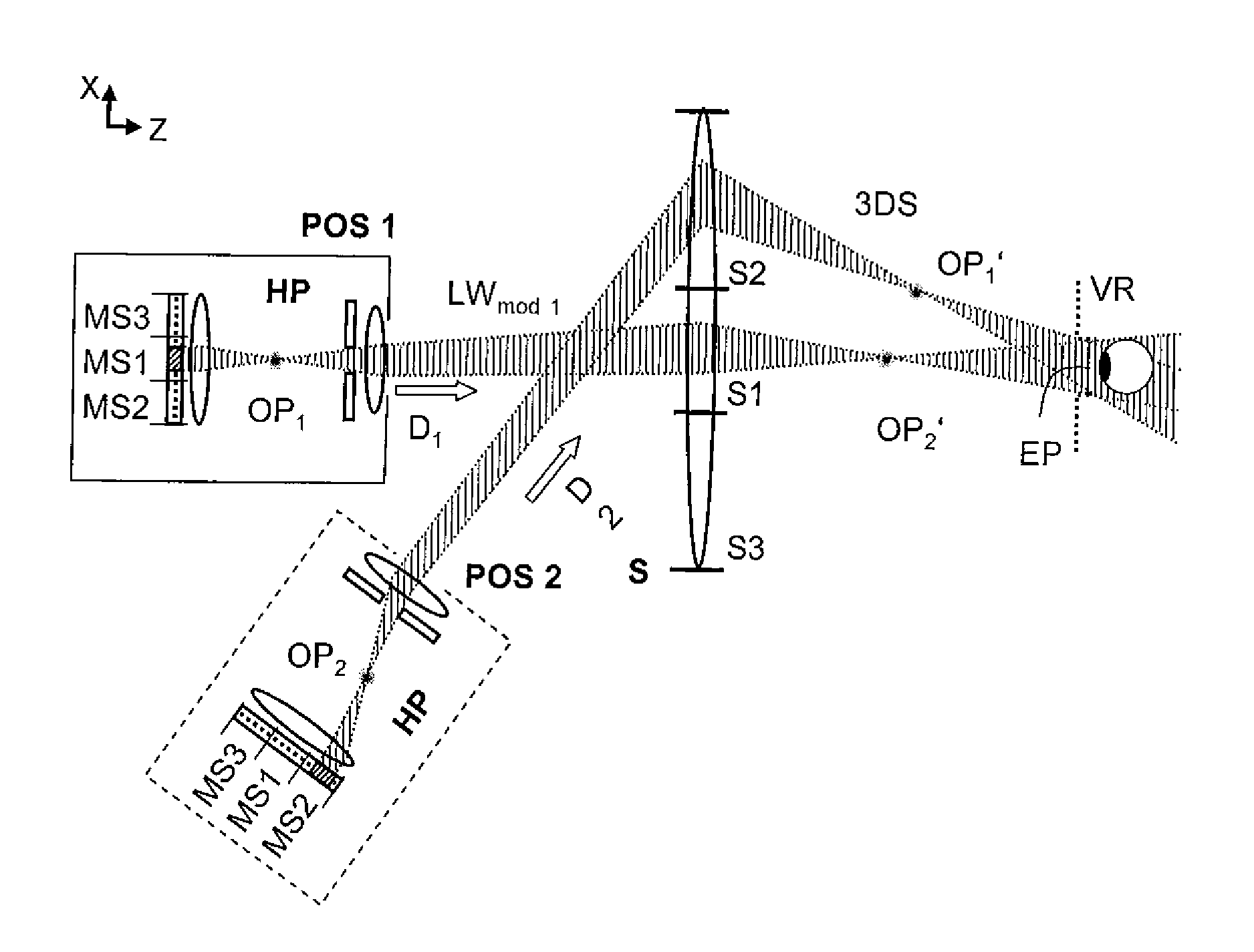
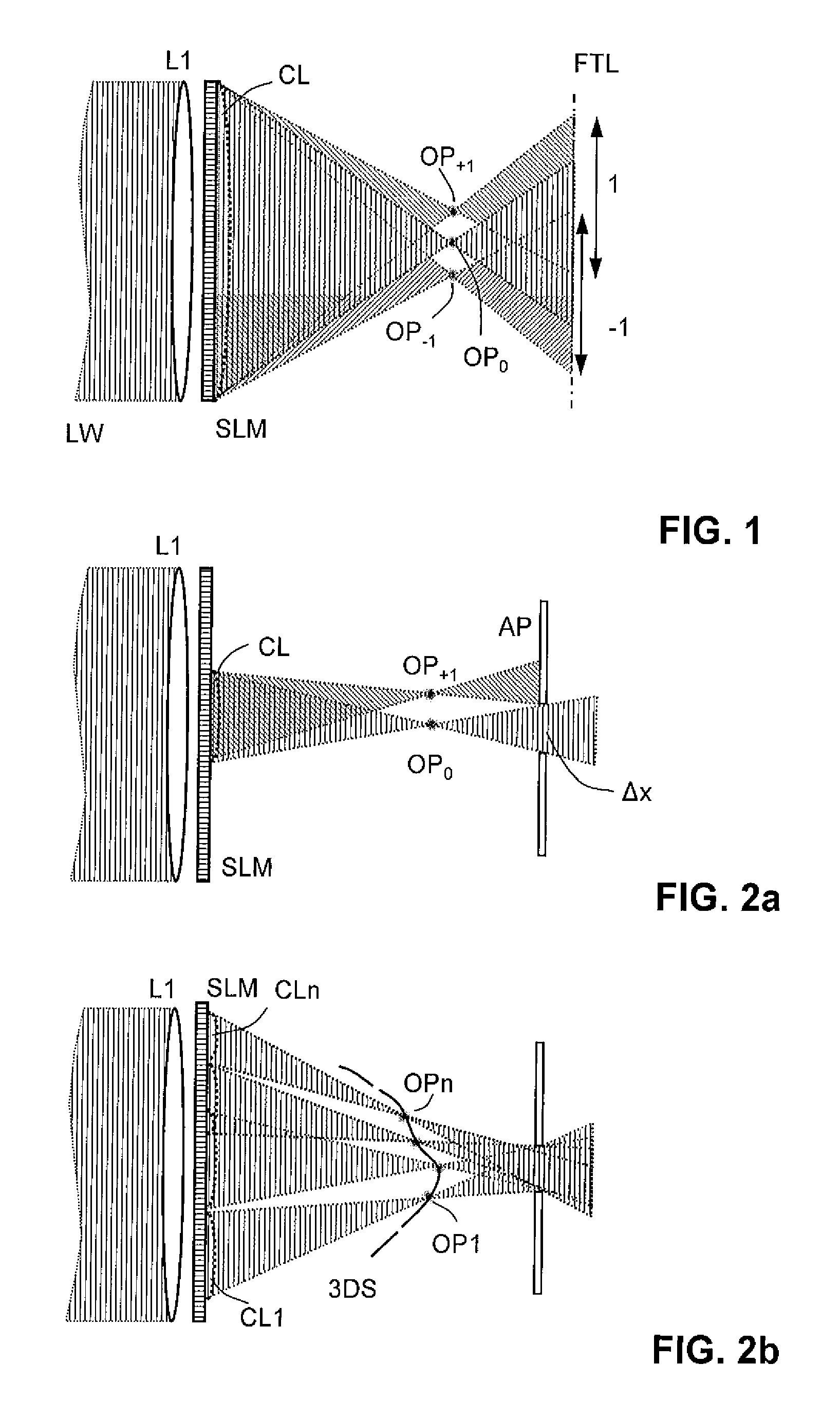
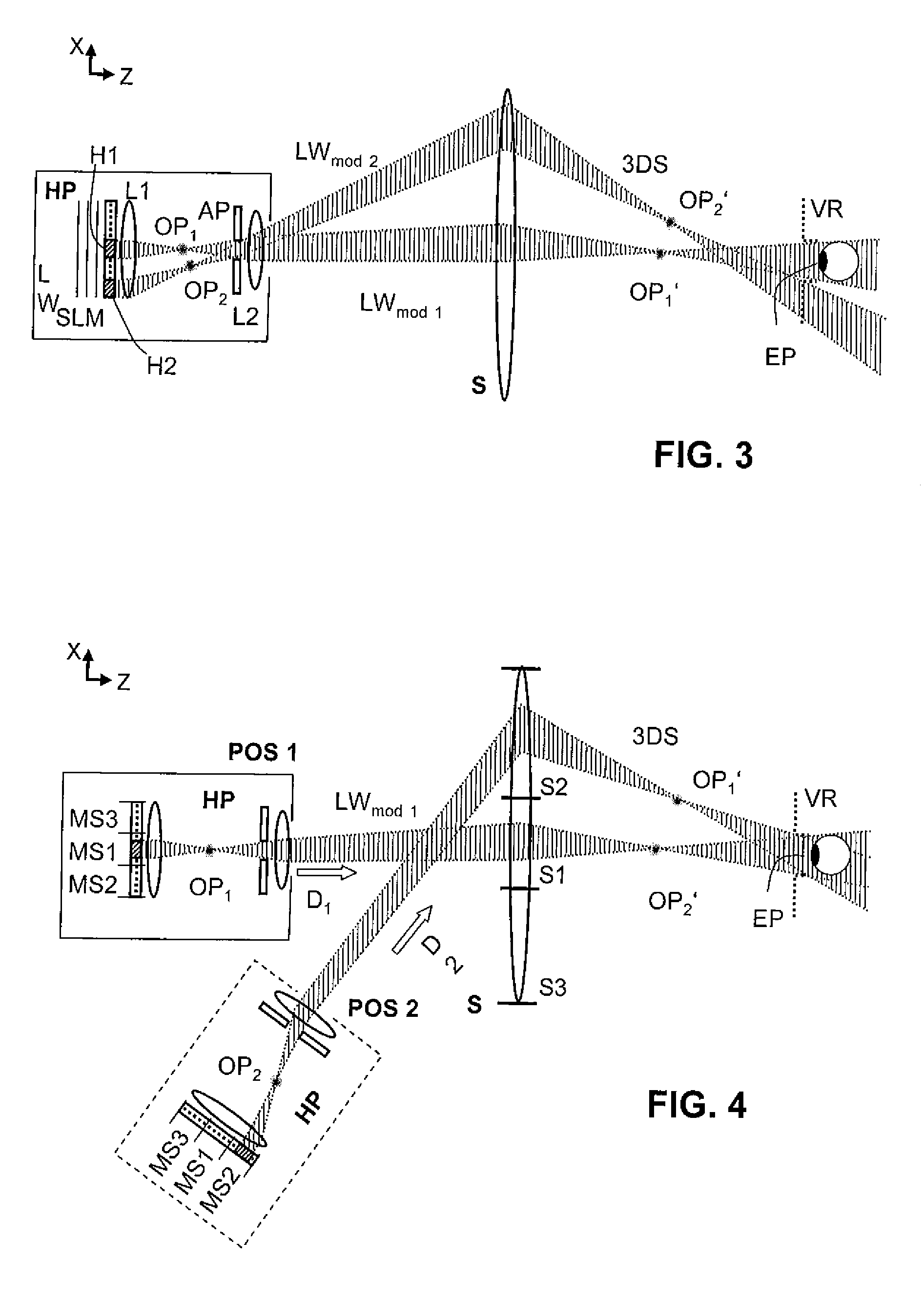
Holographic Projection System with Optical Wave Tracking and with Means for Correcting the Holographic Reconstruction
ActiveUS20100103246A1Reduce the effect of aberrationSmall aberrationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVisibilityProjection system
A holographic projection system with a display screen and an optical wave tracking means for controlling the direction of propagation of a modulated wave uses a position controller and an eye finder. An extremely wide tracking range is realised in the projection system for simultaneous viewing of the reconstruction by multiple observers, which are situated beside one another. The reconstruction of the scene is reconstructed for each eye position of an observer such that the entire scene is visible in the visibility region in a large tracking range with minimal errors. The projection system reconstructs the scene with the help of modulated partial waves. Projection means direct these partial waves with separately holographically reconstructed segments of the scene at the desired eye position through a structure of screen segments which are at least horizontally staggered on the display screen.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
High-precision measuring method and apparatus
InactiveUS7080554B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhase locked loop circuitTransmission channel
Owner:NEXENSE
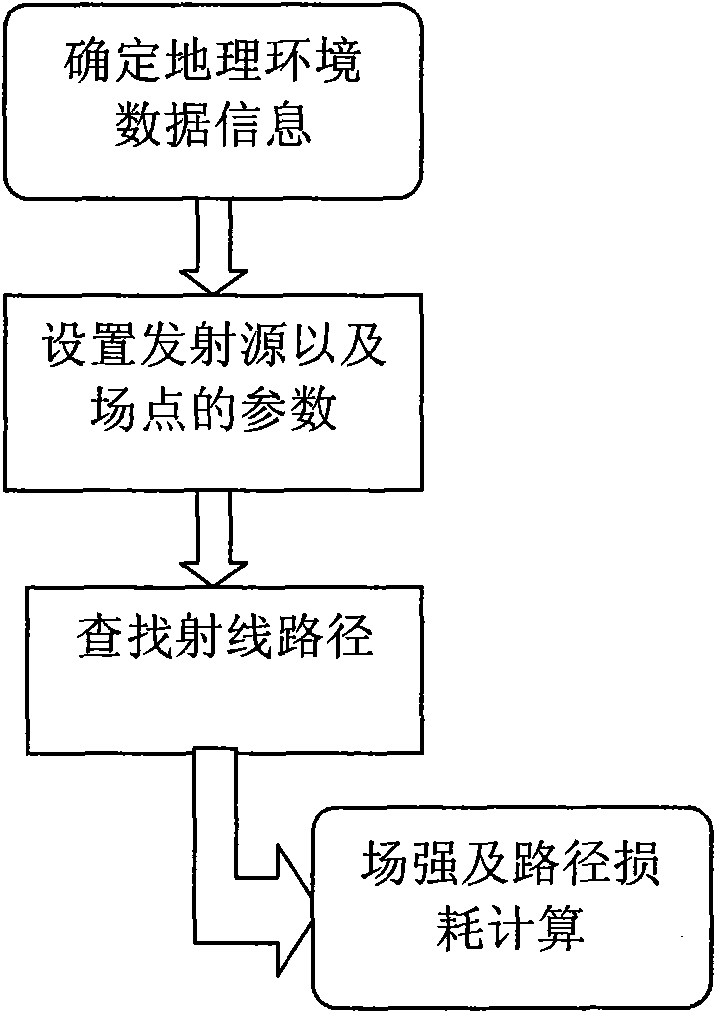
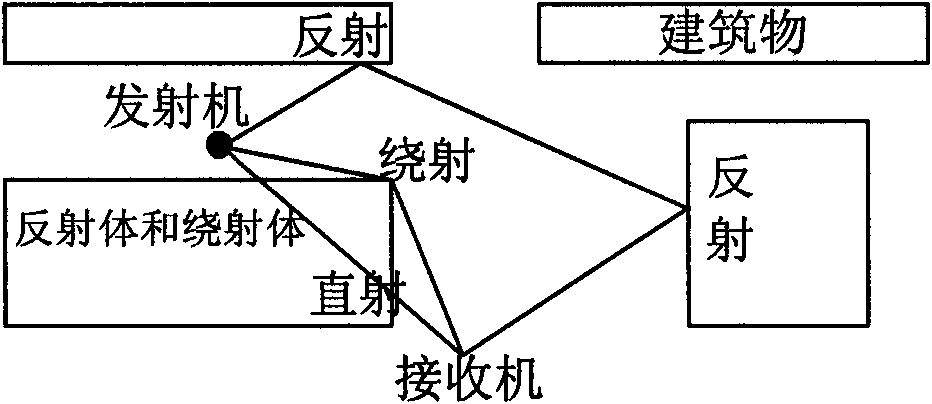
Method for predicting electromagnetic wave propagation based on ray tracking method
InactiveCN101592690AImprove adaptabilityTransmission monitoringElectromagentic field characteristicsFresnel equationsCommunications system
The invention relates to a method for predicting electromagnetic wave propagation based on a ray tracking method, which comprises the steps of ray path searching, reflected and diffracted ray calculation, field intensity receiving, and path loss calculation. The conception of the method comprises the following steps: firstly, determining the position of an emission source, and finding out all propagation paths from the emission source to the ray of each test point according to building characteristics and distribution on a 3D map; secondly, determining reflection and diffraction losses and the like according to a Fresnel equation, a geometrical diffraction theory / uniform diffraction theory and the like so as to correspondingly obtain the field intensity from each path to each test point; and finally, performing coherence stack on the field intensities of all the arrived paths at the same test point to obtain the total received field intensity at each test point. The method has the advantage of better adaptability compared with the conventional statistical model. The method can be applied to predicting the electric wave propagation in a wireless communication system and adapts to the requirements on wireless network programming and designing.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Waveguides and transmission lines in gaps between parallel conducting surfaces
ActiveUS20170084971A1Improve performanceProduced cost efficientlyWaveguide hornsParallel-plate/lens fed arraysElectricityMicrowave
A microwave device, such as a waveguide, transmission line, waveguide circuit, transmission line circuit or radio frequency part of an antenna system, is disclosed. The microwave device comprises two conducting layers arranged with a gap there between, and a set of periodically or quasi-periodically arranged protruding elements fixedly connected to at least one of said conducting layers, thereby forming a texture to stop wave propagation in a frequency band of operation in other directions than along intended waveguiding paths, thus forming a so-called gap waveguide. All protruding elements are connected electrically to each other at their bases at least via the conductive layer on which they are fixedly connected, and some or all of the protruding elements are in conductive or non-conductive contact also with the other conducting layer. A corresponding manufacturing method is also disclosed.
Owner:GAPWAVES
3D prestack seismic data migration method
InactiveUS6311133B1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainSeismic trace
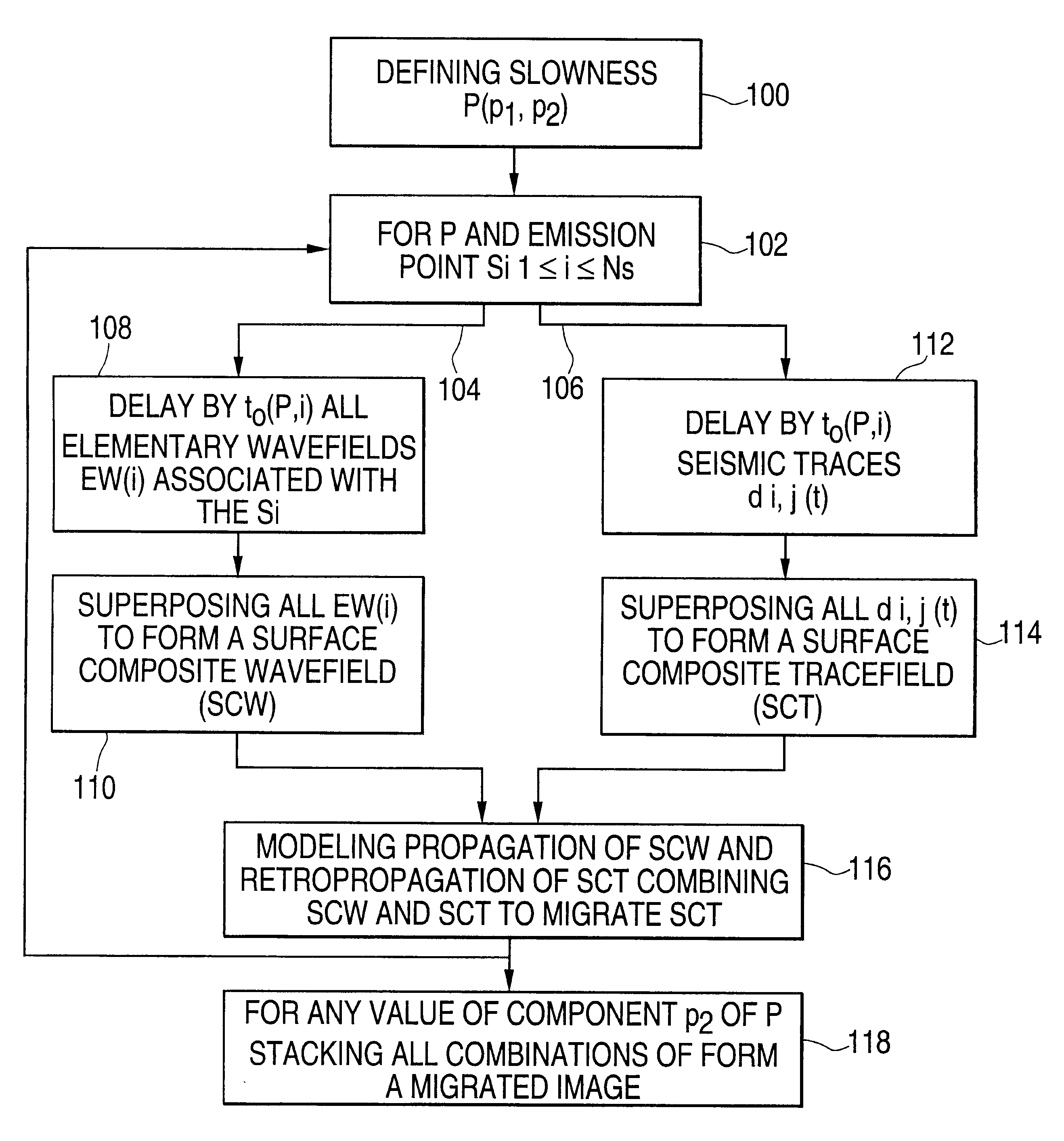
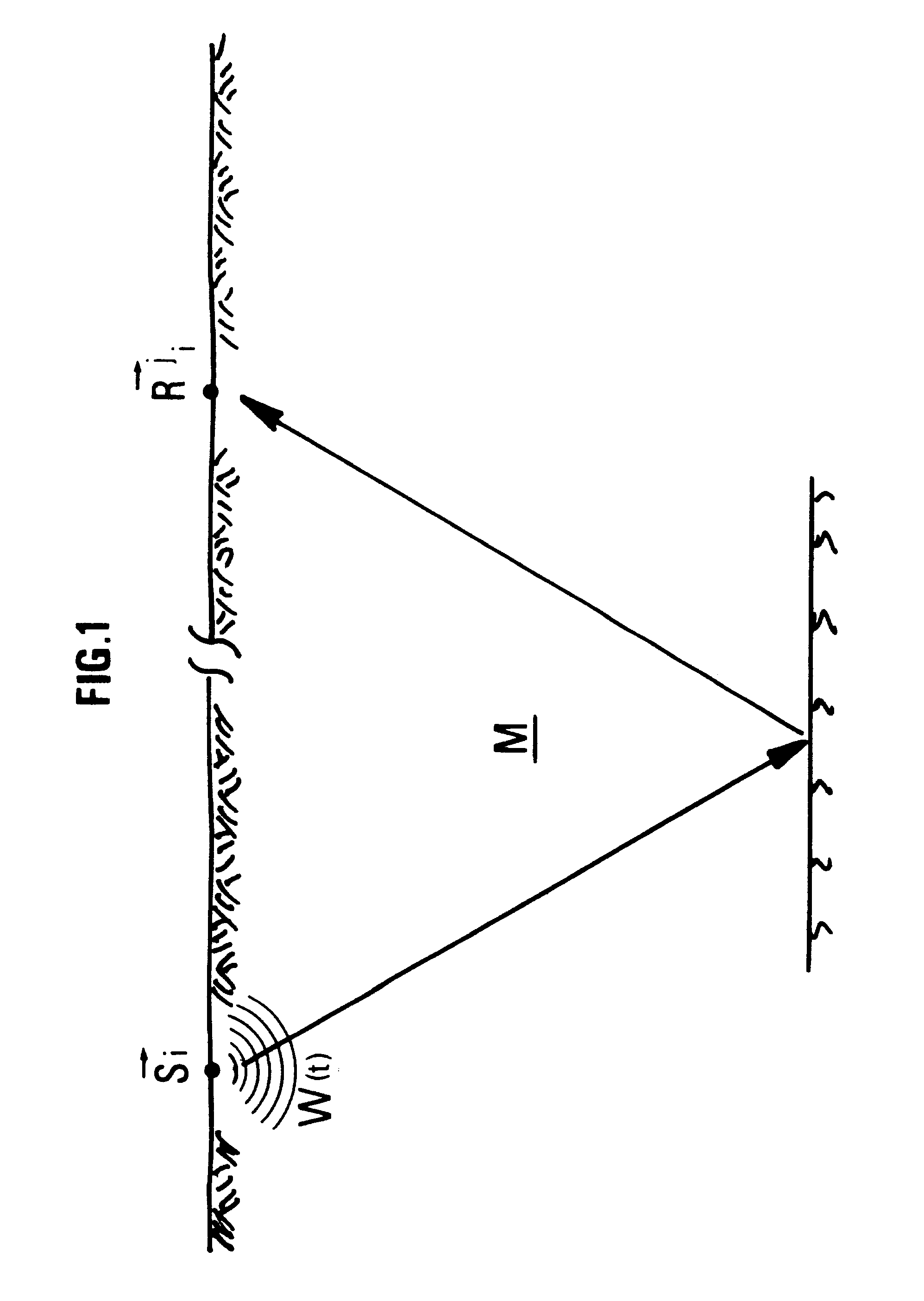
A prestack migration method allowing imaging of an underground zone, for a given velocity model of arbitrary complexity. By means of conventional wave propagation and retropropagation modelling tools, the method allows to obtain elementary migrated images associated with the values assumed by a parameter and the sum of the images obtained for the different values of the parameter (post-migration stacking), in the depth domain as well as in the time domain. This migration is obtained at an attractive price (calculation cost) because it is independent of the volume of the results calculated and of the number of seismic traces recorded. Only the volume of the zone in which the waves are propagated, the complexity of the events to be imaged and the desired accuracy have an effect on the calculation cost. Volume images are thus obtained by taking account of all the seismic traces. It is thus possible to implement a plane wave migration procedure in cases where acquisition does not allow synthesis of the subsurface response to a plane wave excitation, a response required from the outset in conventional plane wave migration algorithms. The method can be applied for imaging of geologic interfaces or heterogeneities of a part of an underground zone.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Drill bit tracking apparatus and method
An apparatus is provided for assessing the location of a drill bit underground. The apparatus includes an acoustic sound generator that is driven by the drilling mud supplied to the drill bit. The sound generator a characteristic string of pulses, which may be termed a signature or key. The key is repeated over and over. Monitors (i.e., sensors) at the surface listen for this key. The key is distorted by the inconstant angular velocity of the drill bit. Thus the observed data do not precisely match the key. On the basis of numerical algorithms, a digitally revised reference signal or key, is identified to map the known reference key onto the best fitting observed data. The correction factors are then applied to map the modified reference key onto the data observed at other sensors of an array of sensors mounted on the surface. By determining the phase shift and travel time of the signals at the various sensors, and having determined the speed of wave propagation in the geological media, the position of the bit, or a fairly close approximation thereof, may be obtained. The correction factors applied to the reference key may also tend to permit the actual rotational speed of the drill bit to be determined.
Owner:ATHENA IND TECH
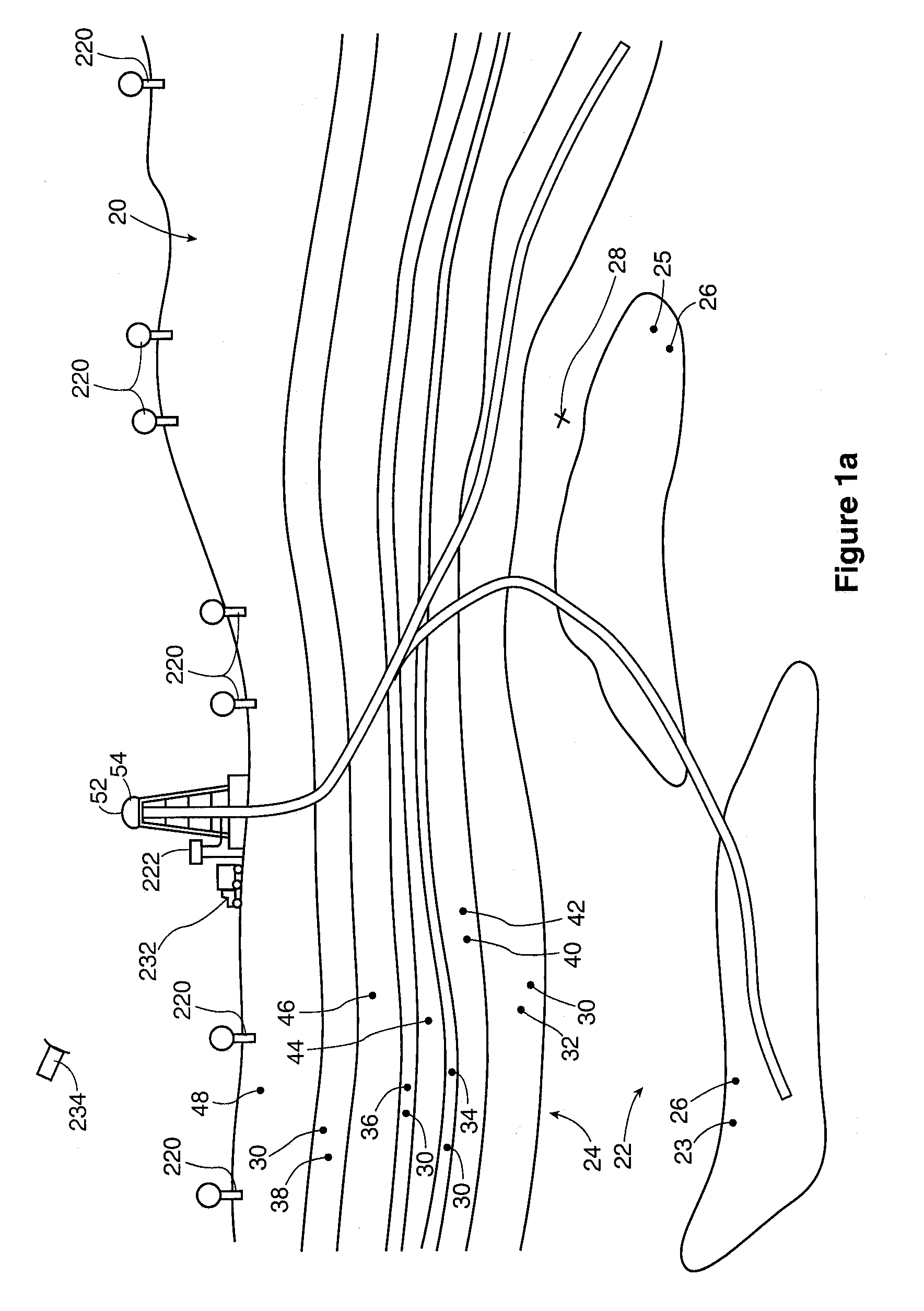
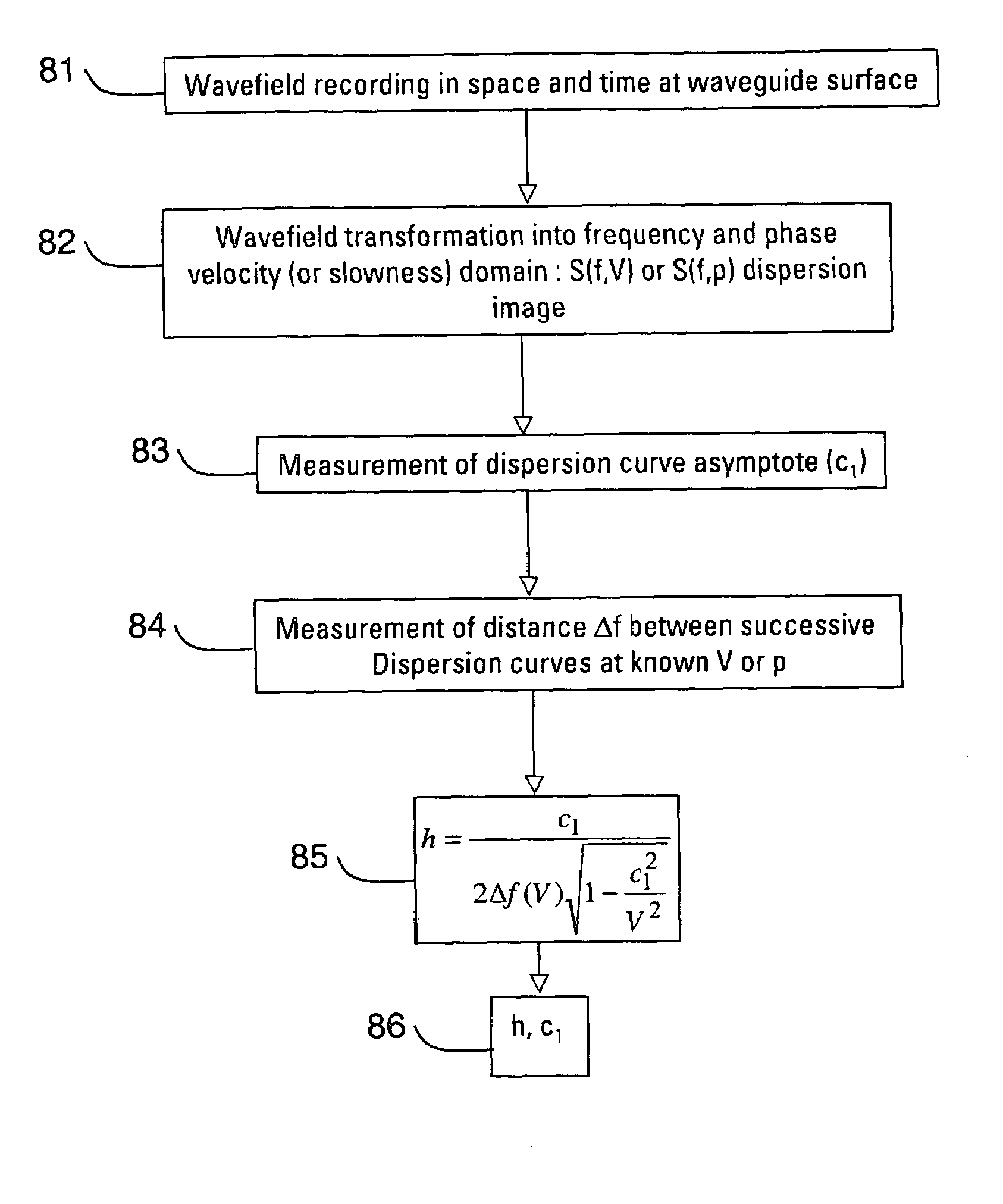
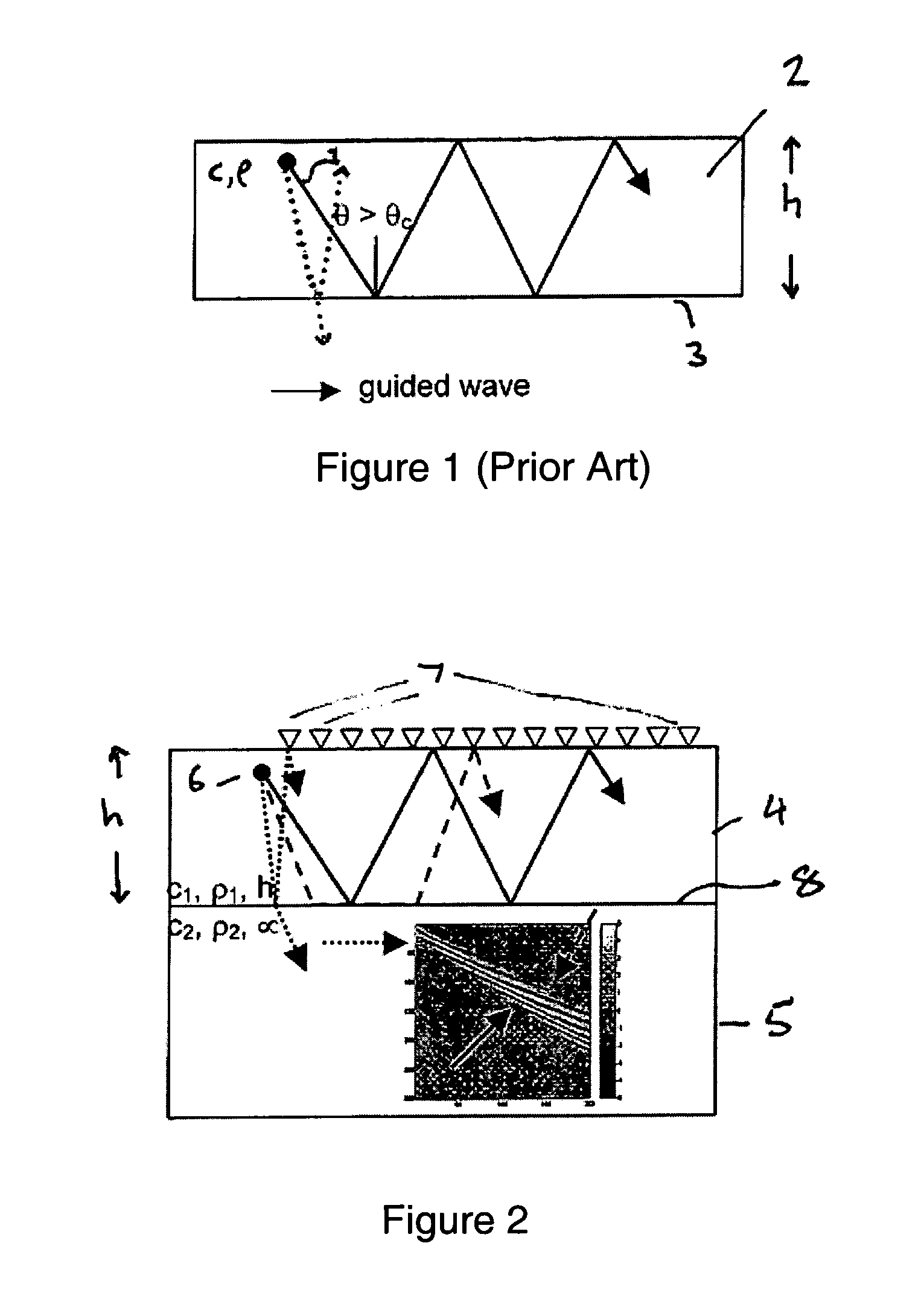
Determination of waveguide parameters
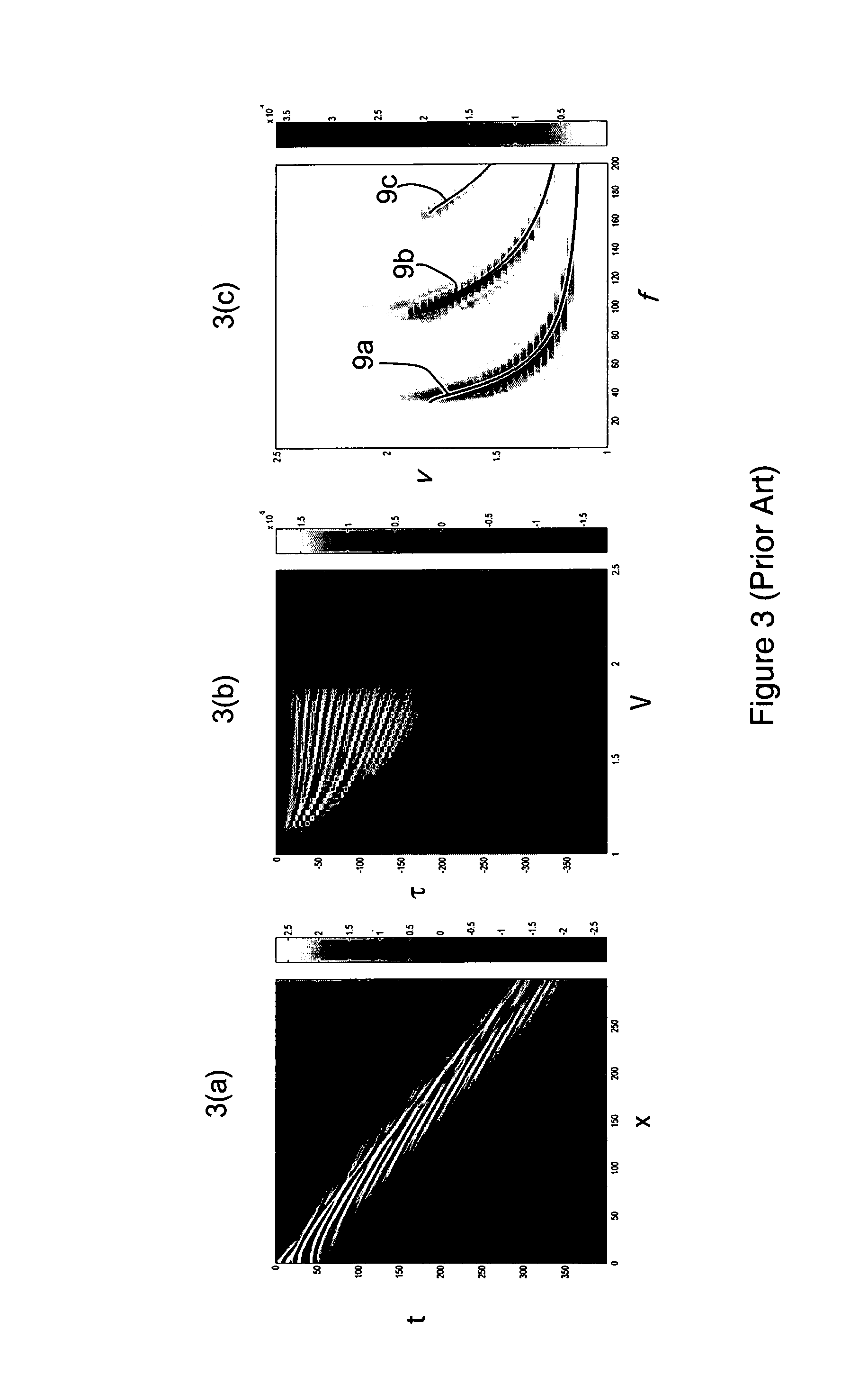
ActiveUS7110900B2Spectral/fourier analysisDigital variable/waveform displayDispersion curveClassical mechanics
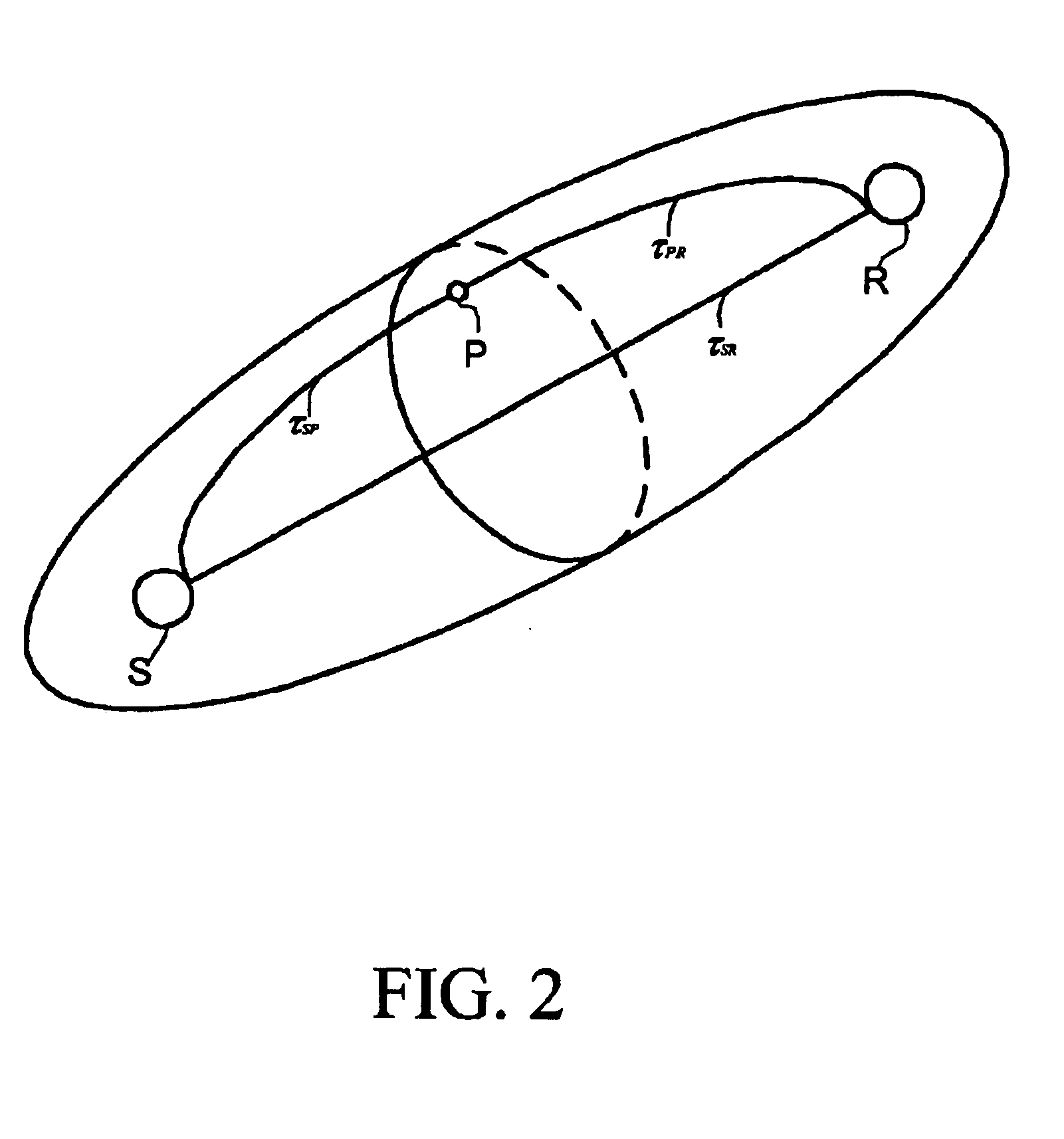
A method of determining at least one parameter of a waveguide (3) from wavefield data acquired from wave propagation in the waveguide including obtaining first and second dispersion curves (9a, 9b, 9c) in the frequency domain from the wavefield data. A frequency interval between the first dispersion curve and the second dispersion curve is found, and this is used in the determination of at least one parameter of the waveguide. The frequency separation Δƒ(V) between the first and second dispersion curves may be found at a particular value of the phase velocity V, and the thickness h of the waveguide can be found using:Δf(V)=c12h1-c12V2Here, c1 is the velocity of wave propagation in the waveguide. This may be found from the asymptotic velocity values of the dispersion curves.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Watermark information embedment device and watermark information detection device
There are disclosed a watermark information embedment device capable of accurately embedding secret information, and a watermark information detection device. In the watermark information embedment device, there are prepared a plurality of different sorts of dot patterns in which the wave propagation direction and the wave length are changed depending on the dot arrangement. Each dot pattern of the same sort is given the same symbol, and the secret information is represented by combining these dot patterns. In the watermark information detection device, there are provided 2-dimensional wavelet filters having the same wave propagation direction and the wave length as the different sorts of dot patterns. There is computed convolution between an arbitrary region in the watermarked image and plural 2-dimensional wavelet filters, and it is judged that the dot pattern corresponding to a particular one of the 2-dimensional wavelet filters is embedded in the region where the computed convolution indicates a maximum value.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
System for conversion of the whole kinetic energy of sea wave into electricity by one-way direct drive shaft converter, (ODSC system)
ActiveUS10514018B2No more energy loss from free run rotationEfficient conversionReaction enginesEngine componentsOcean bottomSea waves
ODSC system is a system for conversion of the whole kinetic energy of sea wave, both in propagation and oscillation direction, into electricity. The ODSC system comprises 2 main structures, a tower and a floating power plant. A tower is utilized as a site station and a pivot of the floating power plant. The floating power plant with a triangle based pyramid framework keeps afloat along with the sea tide and always turns its front toward to the wave propagation direction. This self-alignment maximizes effectiveness of energy conversion by ODSC converter installed in the floating power plant. The ODSC converter comprises 3 main structures, a plurality of attenuators, a one-way clutch and meshing gear system, and a drive shaft, wherein the whole kinetic energy of the sea wave is captured, transformed, converted and integrated together into a powerful one-way driving torque. The powerful torque then drives an electric generation system directly. The electricity then is transmitted ashore via a submarine power cable.
Owner:WICHITAMORNLOET ARTHRON +1
Acoustic transducer and image generation apparatus
ActiveUS20100251823A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTransducerReflected waves
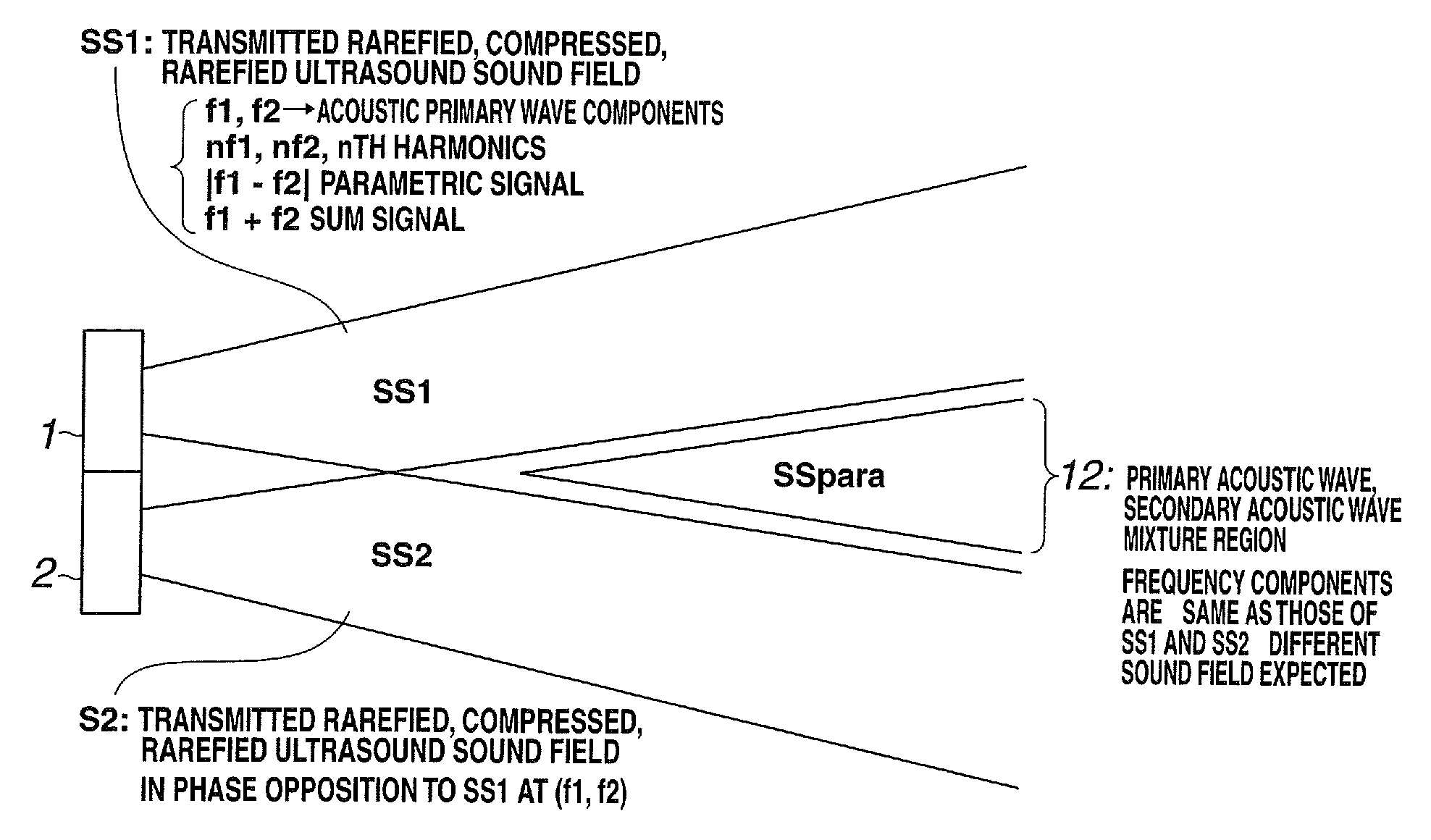
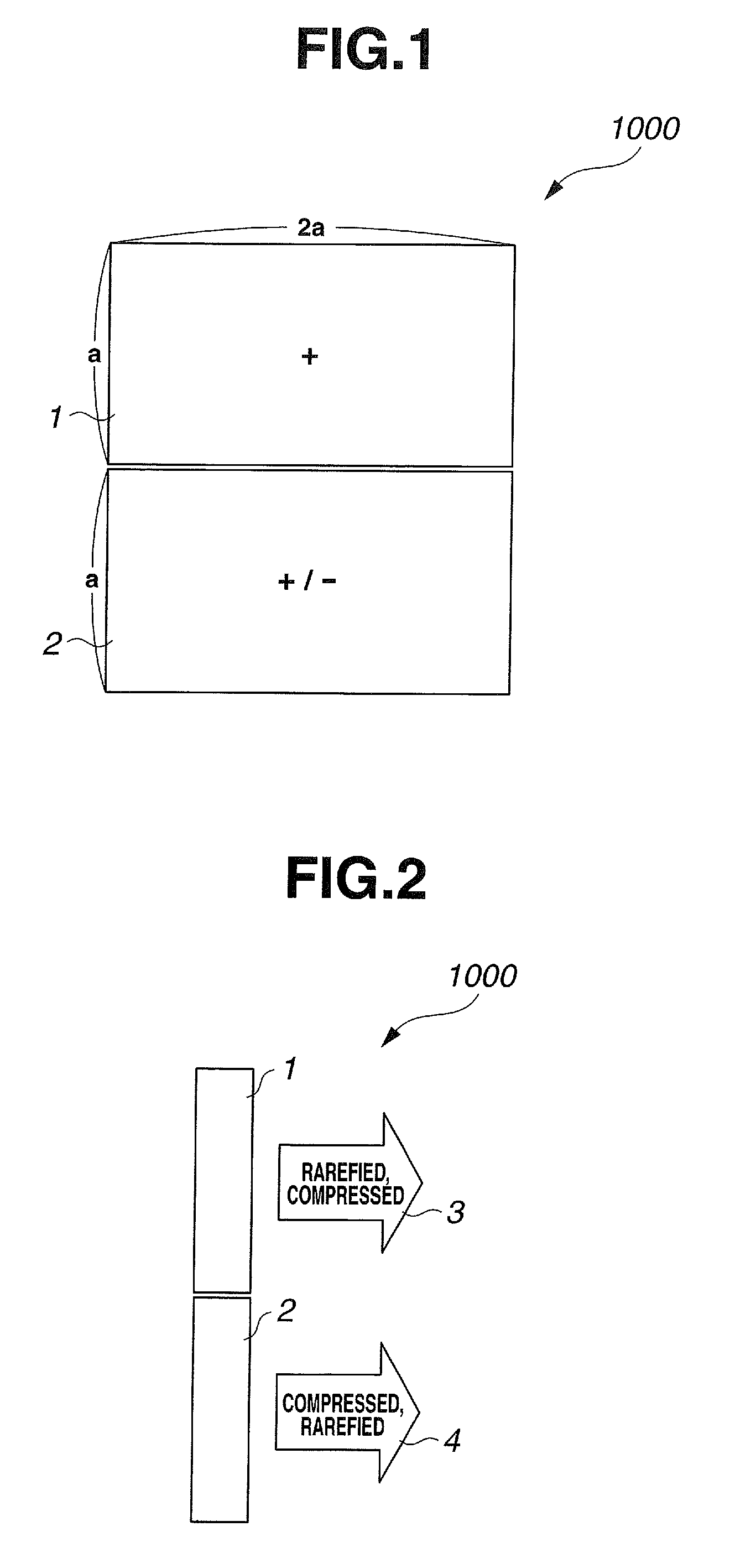
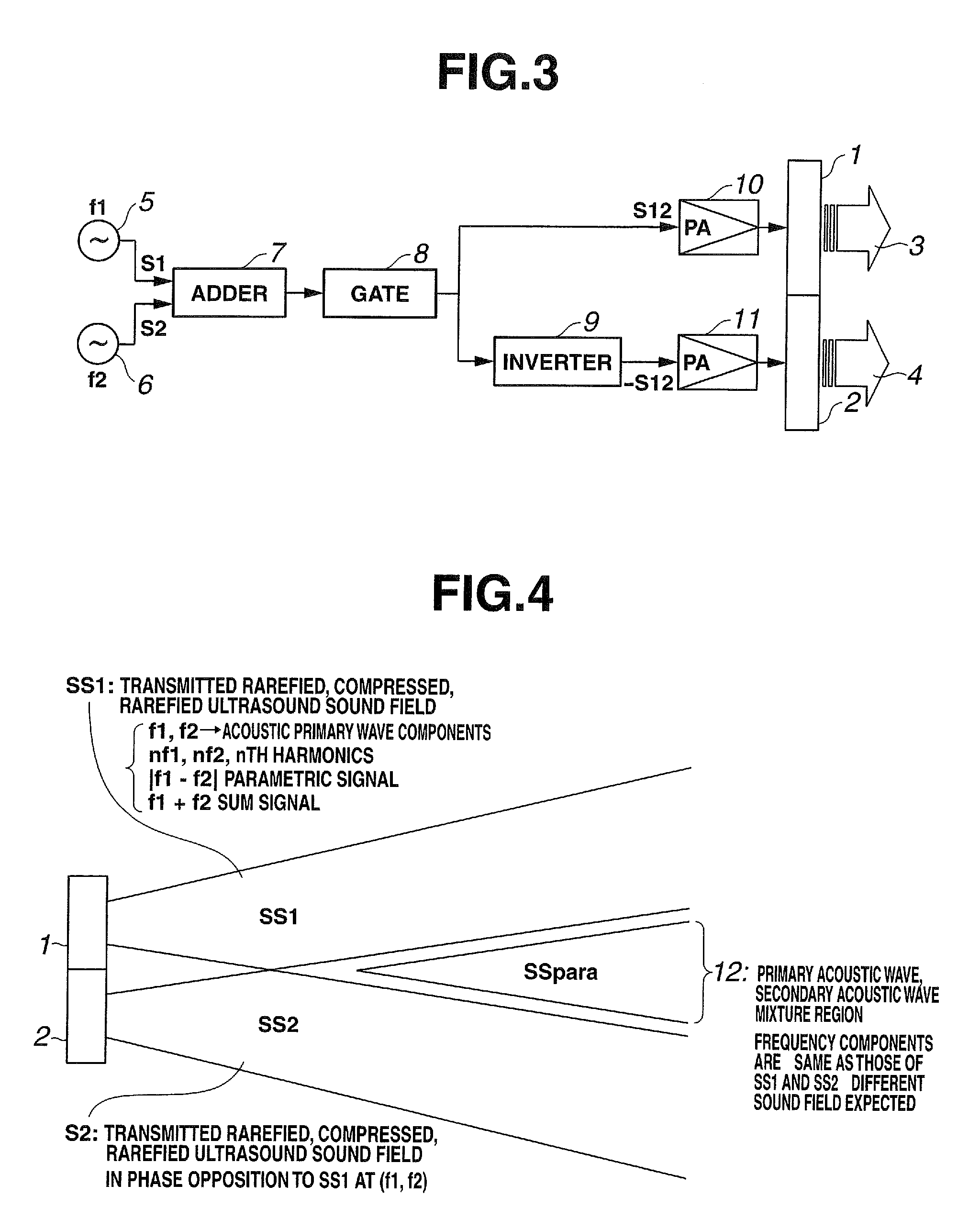
An acoustic transducer has a first transducer which transmits an acoustic primary wave having two frequency components, and a second transducer which, in order to receive a reflected wave of an acoustic secondary wave generated with propagation of the acoustic primary wave, is disposed so that a region for receiving the reflected wave is superimposed on the first transducer as seen along the direction of transmission of the acoustic primary wave.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
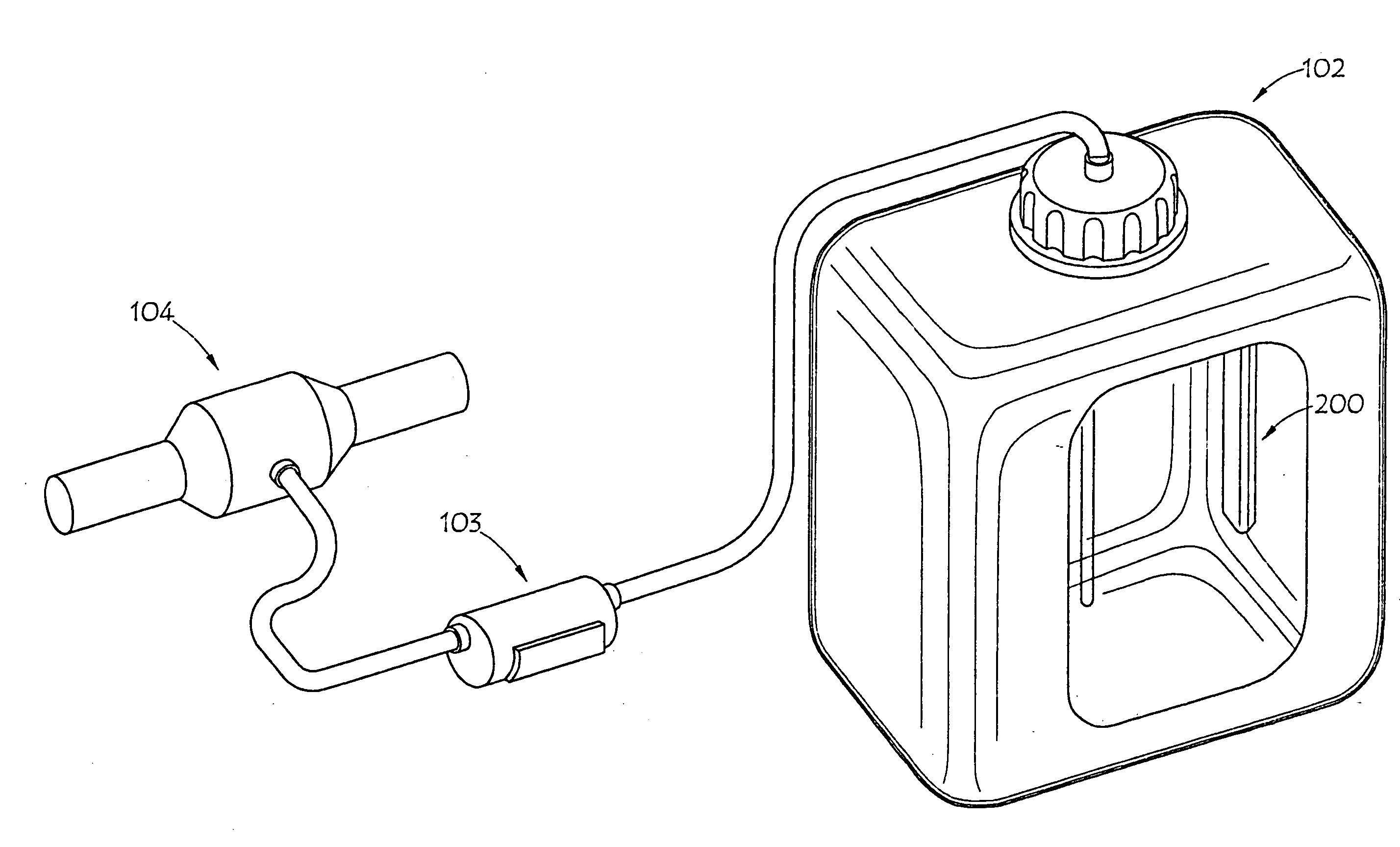
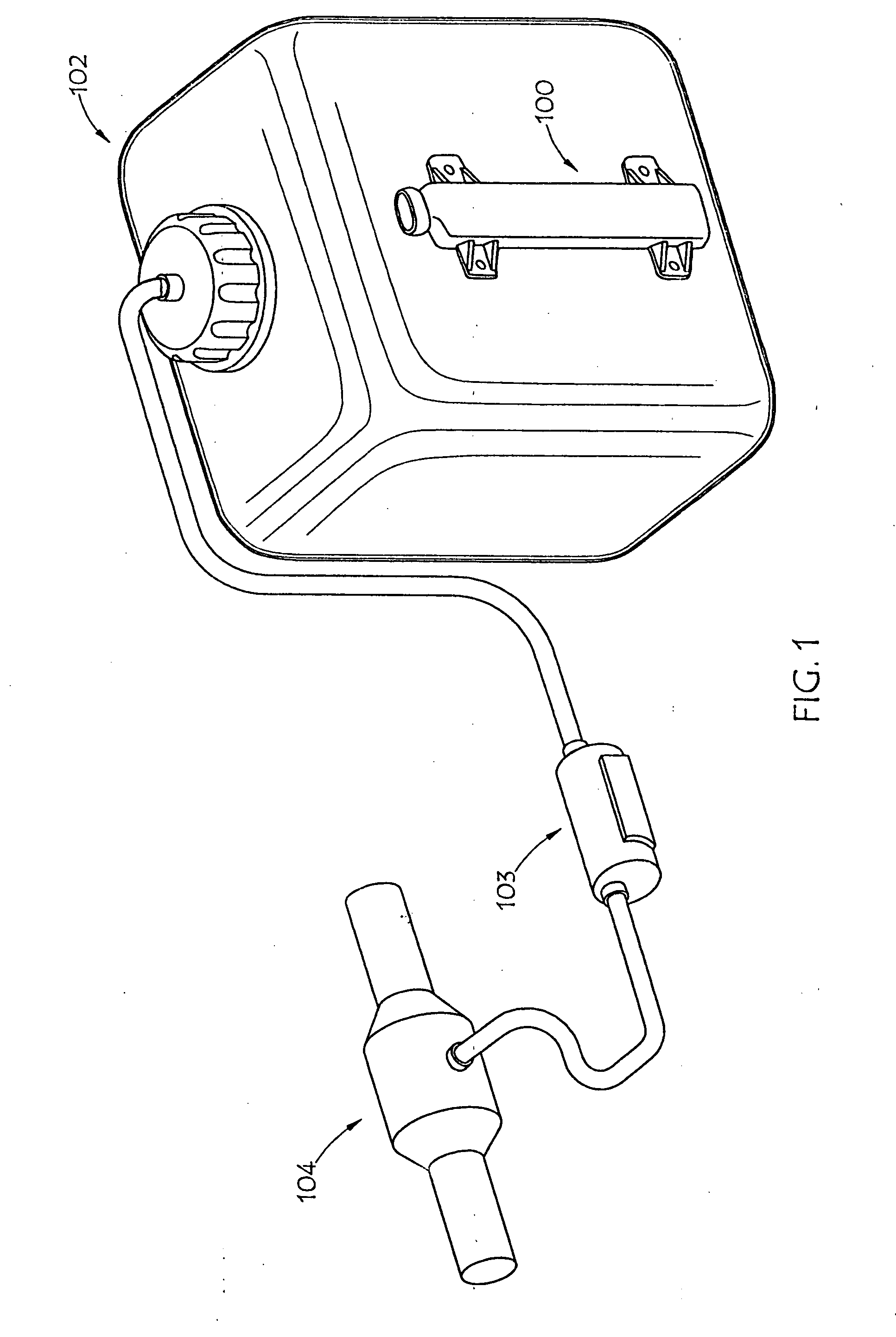
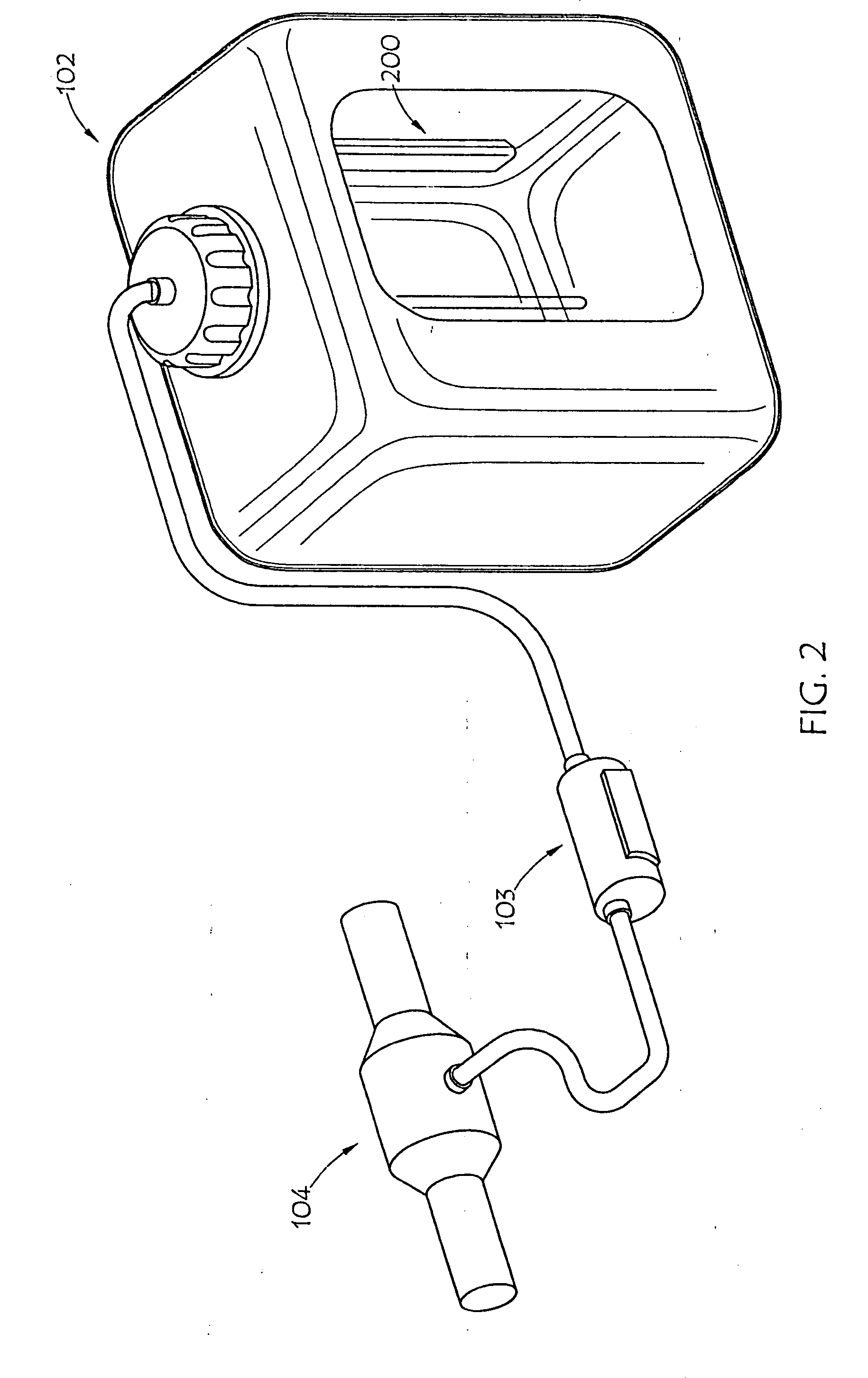
Liquid level and quality sensing apparatus, systems and methods using EMF wave propagation
InactiveUS20100327884A1Reduce and negate dependenceReduce and eliminate effectInternal combustion piston enginesResistance/reactance/impedenceResonanceRefractive index
A liquid level, composition and contamination sensor generates an RF signal across a resonant circuit that includes a variable inductor and capacitor. The resulting electromagnetic radiation is propagated into the liquid and changes in impedance and resonance of the resonant circuit that result from changes in the conductivity and dielectric properties of the liquid, which are proportional to liquid content and volume, are detected. The conductivity and dielectric properties of the liquid are measured, based on the changed impedance and resonance of the resonant circuit, and are compared to determine aging and contamination of the urea solution by other liquids. Also, an optical sensor may be submerged in the liquid to determine the refractive index of the liquid. The refractive index of the liquid may be used to determine: if the liquid is water or a urea solution; the concentration of a urea solution.
Owner:SCHRADER ELECTRONICS LTD
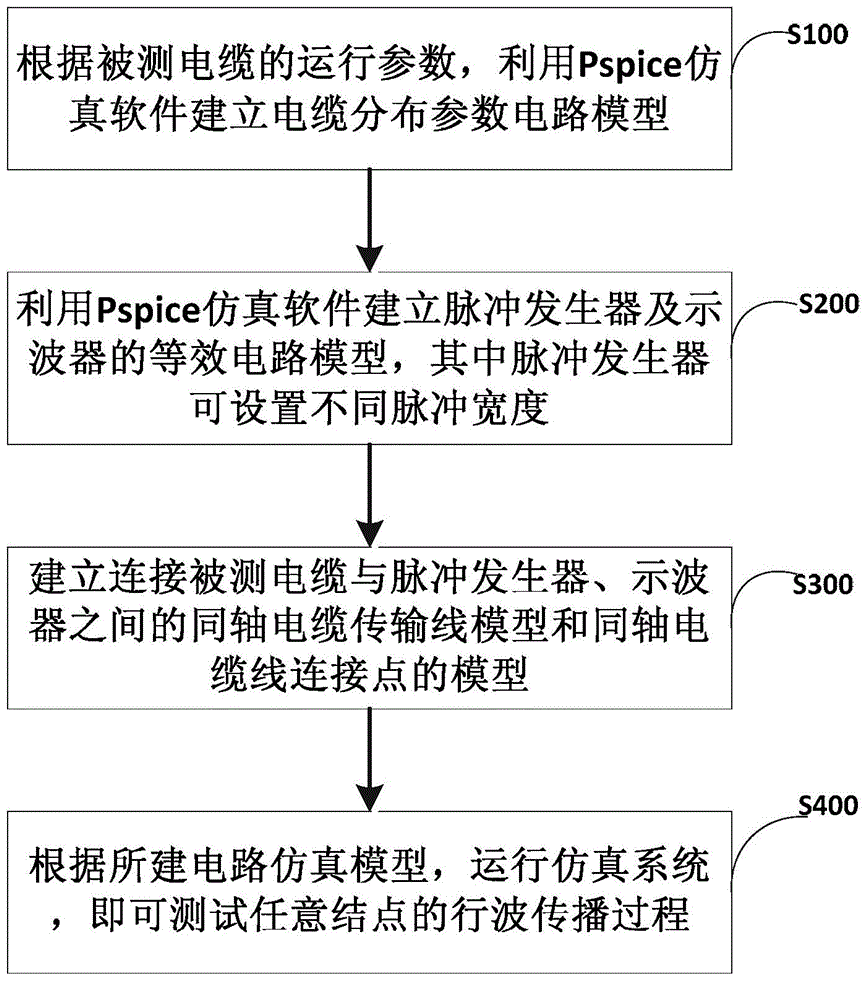
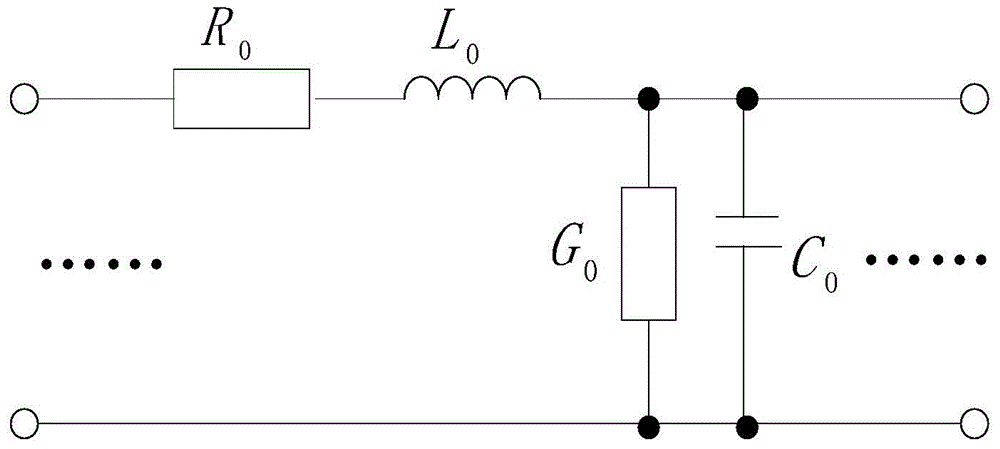
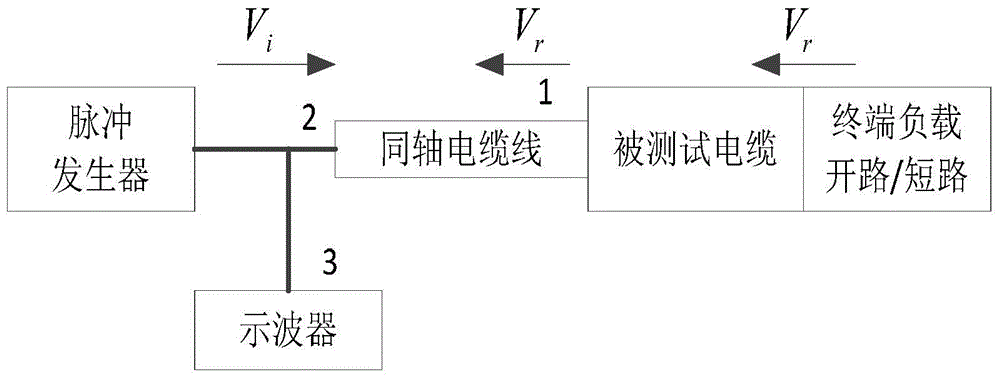
Cable fault positioning simulation method using time domain reflectometry
InactiveCN103954886AEasy to observe intuitivelyEasy to analyzeFault location by pulse reflection methodsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTime domainCoaxial cable
The invention discloses a cable fault positioning simulation method using time domain reflectometry. The method includes the following steps that S100, a cable distributed parameter circuit model is established through Pspice simulation software according to the operating parameter of a cable to be detected; S200, an equivalent circuit model of a pulse generator and an equivalent circuit model of an oscilloscope are established through the Pspice simulation software, wherein different pulse widths can be set in the pulse generator; S300, the model of coaxial cable transmission lines connected among the cable to be detected, the pulse generator and the oscilloscope and the model of coaxial cable transmission line connecting points are established; S400, the simulation system is made to operate according to an established artificial circuit model, the traveling wave propagation process of any node is tested, and meanwhile the actual reflected impulse waveform of the cable to be detected can be tested. By the adoption of the cable fault positioning simulation method, the operation accuracy of simulation experiments is improved, and extremely high application value is achieved to application and study of a time domain pulse method.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
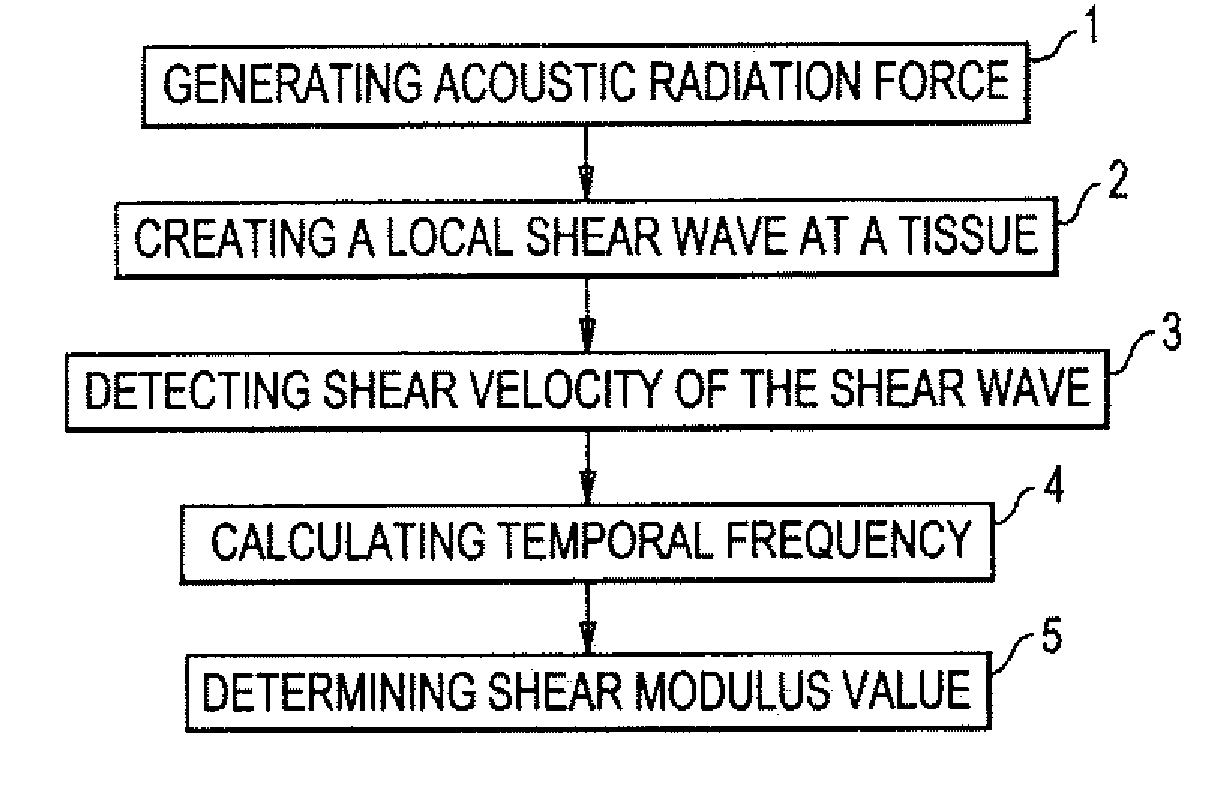
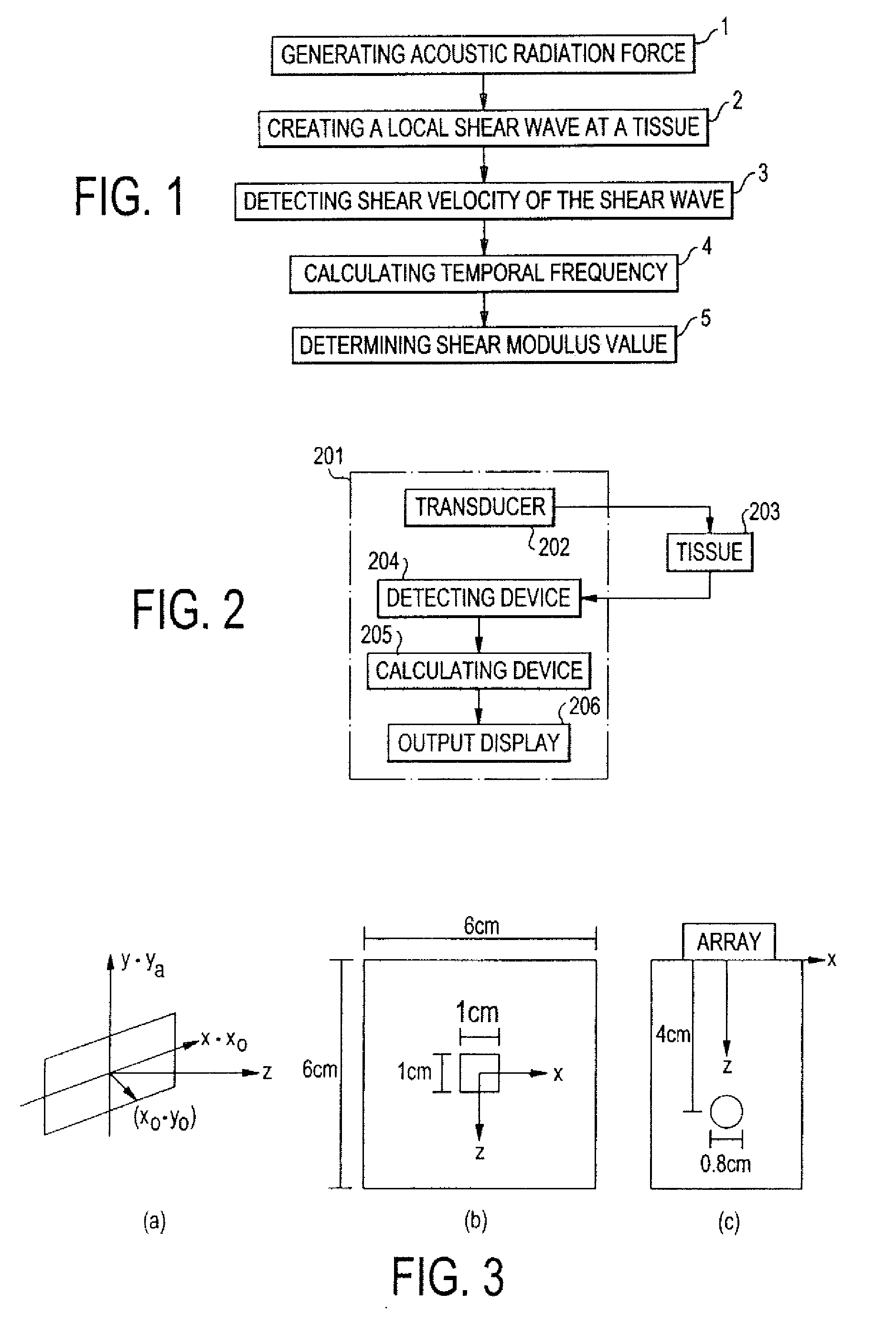
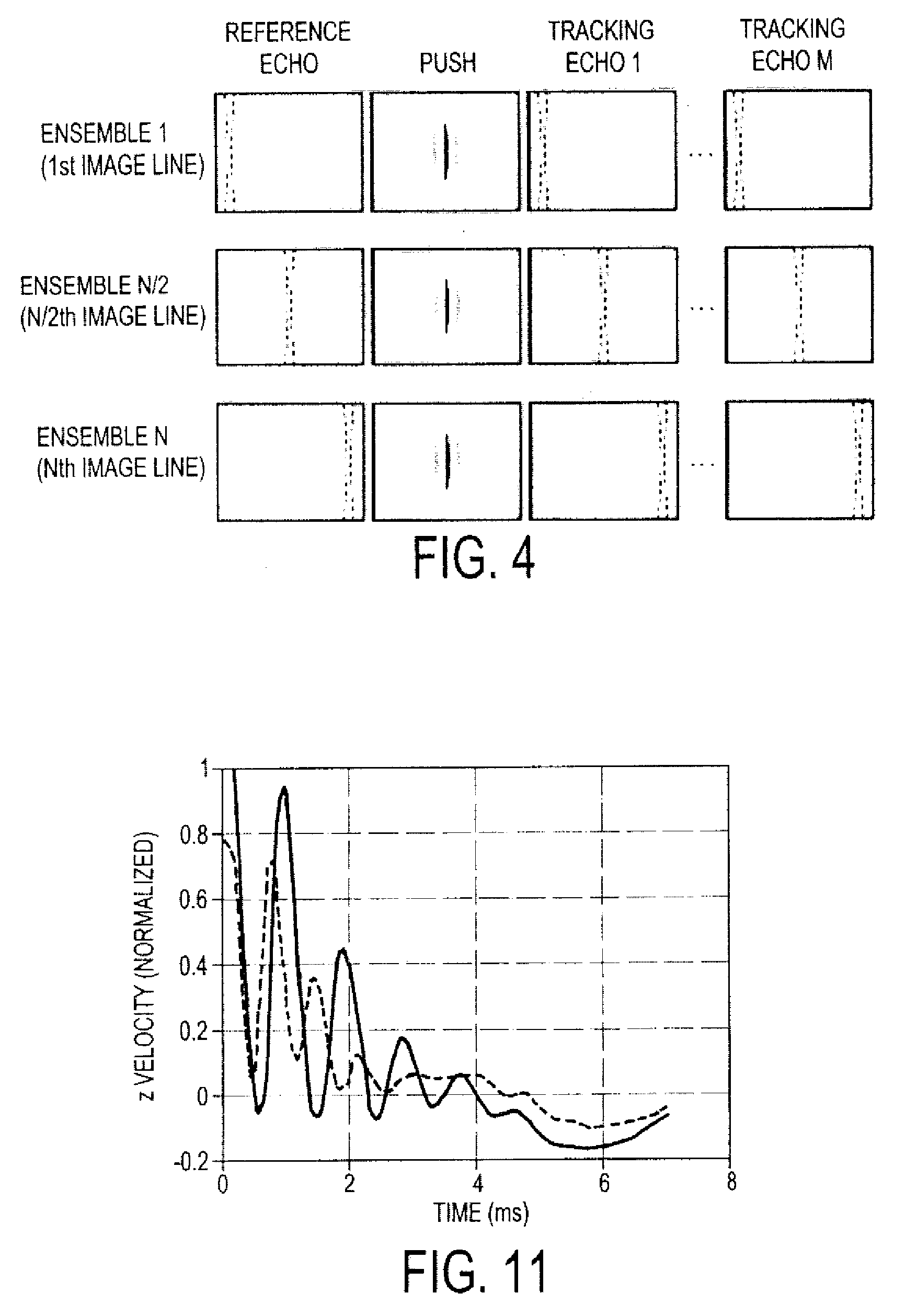
Shear modulus estimation by application of spatially modulated impulse acoustic radiation force approximation
ActiveUS20090056453A1Quantitative measurement of the shear modulus of the tissueVibration measurement in solidsVibration measurement in fluidShear modulusSonification
A method for determining a shear modulus of an elastic material with a known density value is provided. In this method, a spatially modulated acoustic radiation force is used to initially generate a disturbance of known spatial frequency or wavelength. The propagation of this initial displacement as a shear wave is measured using ultrasound tracking methods. A temporal frequency is determined based on the shear wave. The shear modulus of the elastic material at the point of excitation may be calculated using the values of the spatial wavelength, material density, and temporal frequency.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
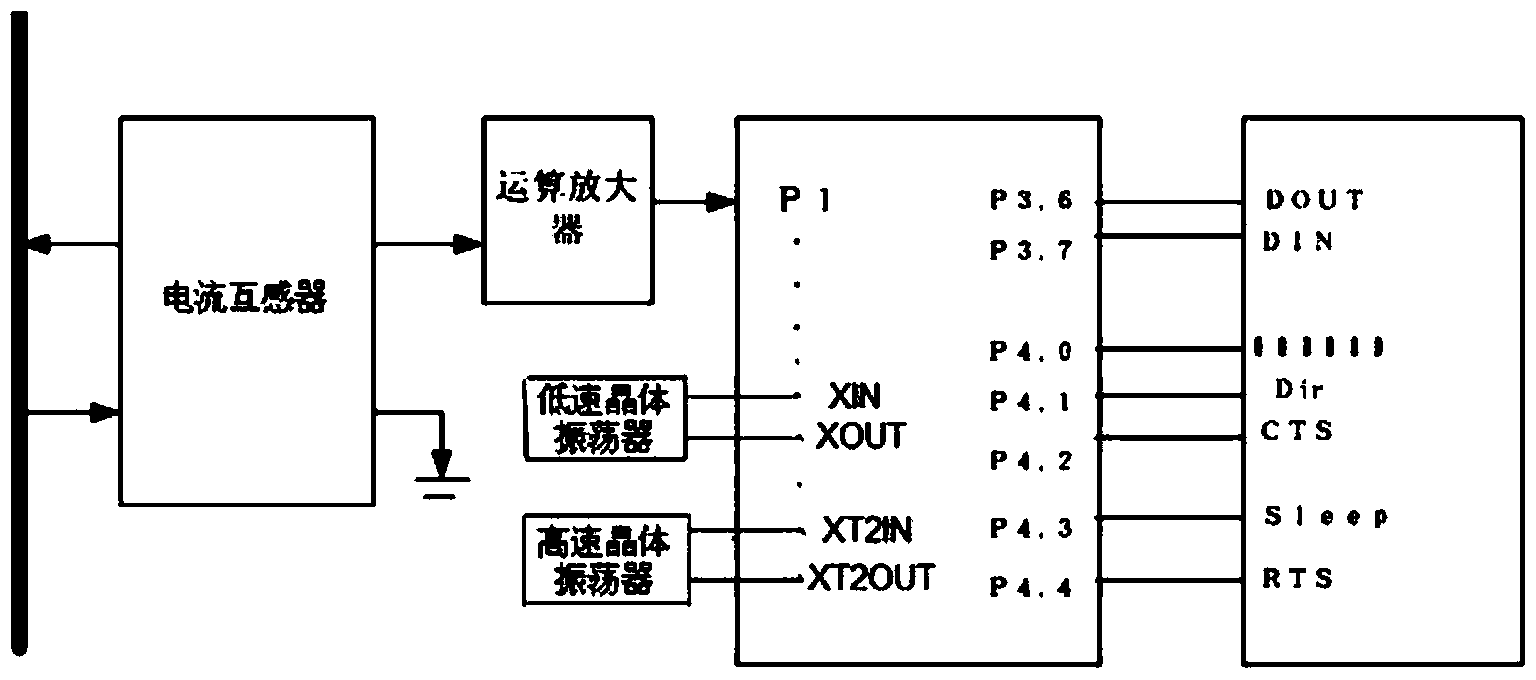
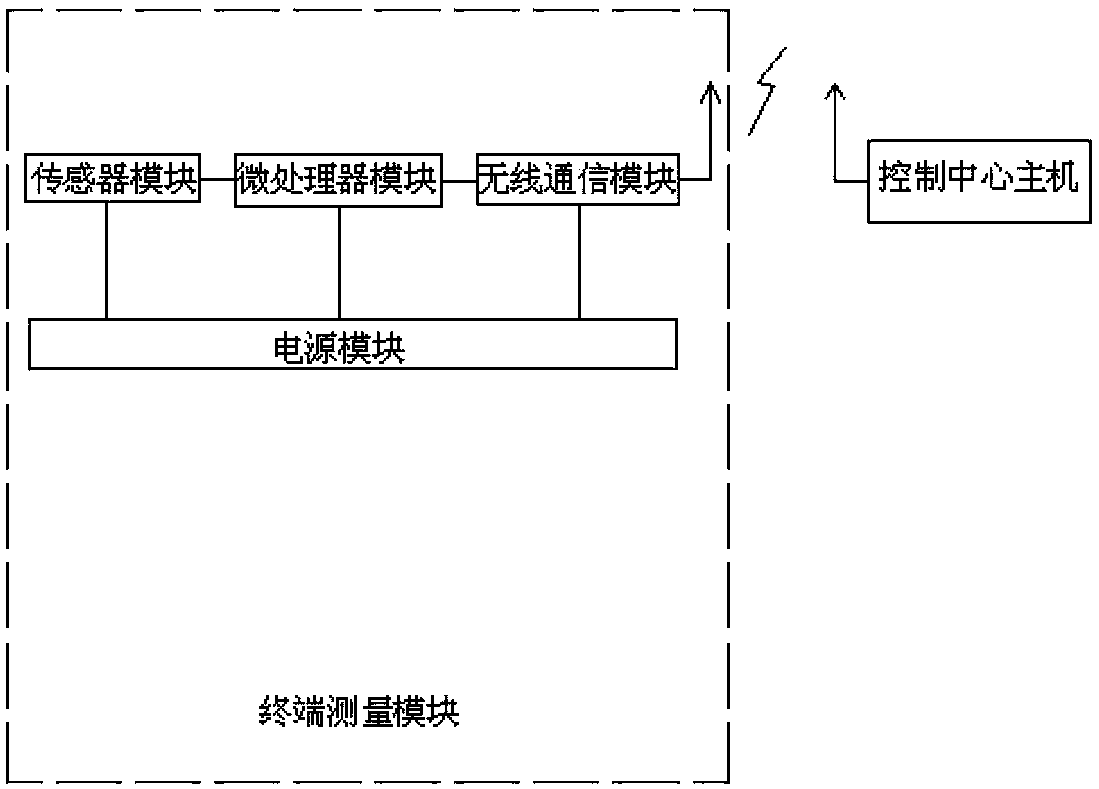
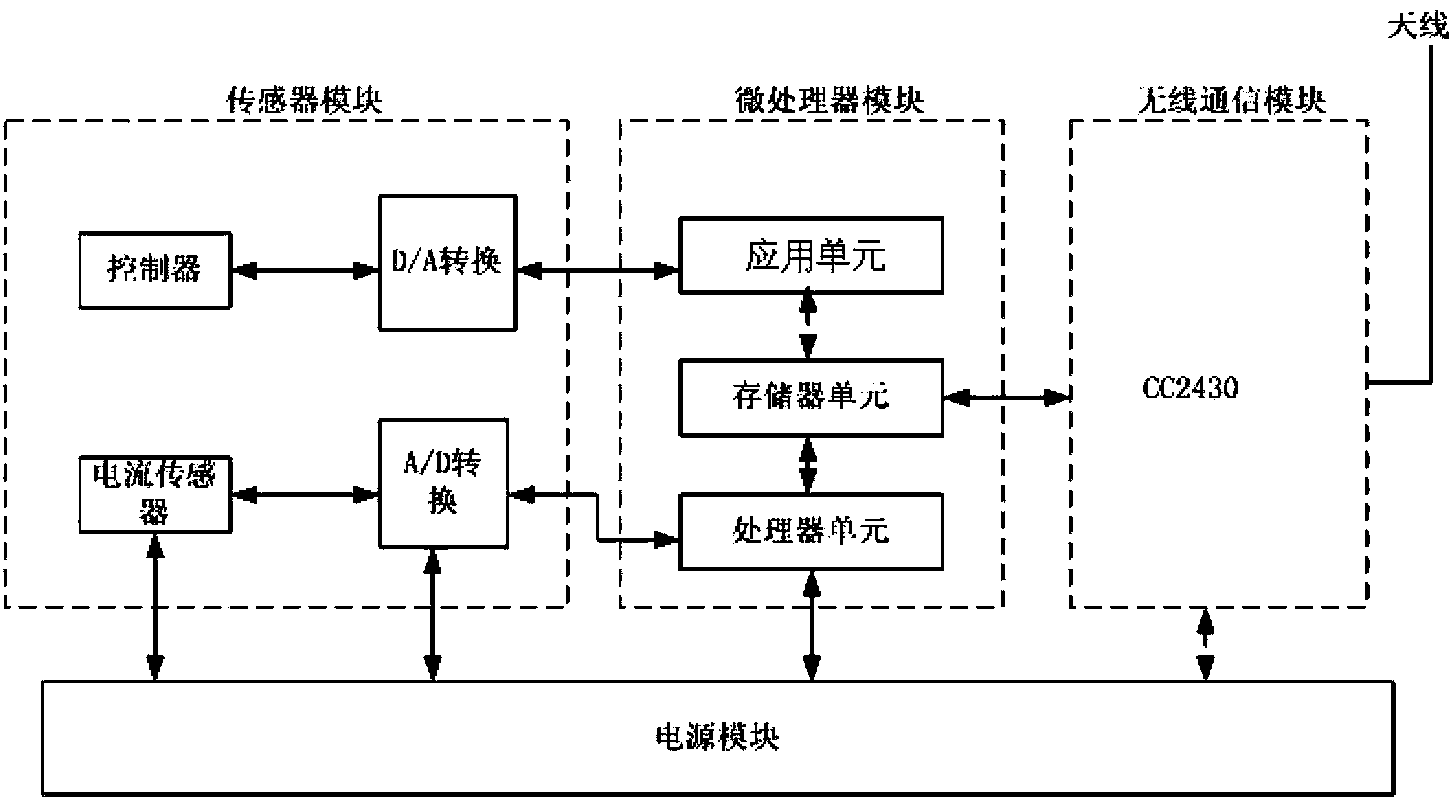
System and method for distribution network fault locating based on improved double-terminal traveling wave method
InactiveCN104166073ASolve the real problemImprove detection accuracyFault locationInformation technology support systemPhase currentsMeasurement point
The invention relates to a system and a method for distribution network fault locating based on an improved double-terminal traveling wave method. The system comprises a terminal measurement module and a control center host computer, wherein the terminal measurement module is composed of a sensor module, a microprocessor module, a wireless communication module and a power supply module. The method comprises the following steps: a current traveling wave signal measured by a current transformer is calculated to obtain each current phase with a time scale; the phase current is decoupled, and a line mode component is selected as a traveling wave propagation mode for fault locating; an obtained traveling wave signal is uploaded to the control center host computer; the head of a travelling wave is detected, and rapid intrinsic mode decomposition is carried out on the line mode component; the arrival time of the travelling wave is determined; the wave speed is measured; and a fault is located. By adopting the system and the method of the invention, higher detection accuracy is achieved, the consistency of wave speeds of a fault traveling wave in three line sections formed by a fault point and three measuring points is ensured, and accurate online fault traveling wave speed determination is realized.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Liquid level and composition sensing systems and methods using EMF wave propagation
ActiveUS20080143345A1Accurately measure levelRisk minimizationResistance/reactance/impedenceExhaust apparatusLiquid ChangeMicrocontroller
An automotive urea solution monitoring device is deployed in conjunction with the urea tank of a selective catalytic reduction vehicle. An RF signal of a constant frequency may be generated across a resonant circuit, which may be comprised of an inductor and a PCB trace capacitor, or the like. Electromagnetic radiation is propagated into the automotive urea solution in the urea tank. The conductivity and dielectric properties of the liquid change the impedance of the discrete / trace capacitor and or the discrete / trace inductor. These changes are proportional to ammonia content, temperature, and / or level of the automotive urea solution in the urea tank and are preferably detected by a microcontroller, or the like, and then transmitted to a selective catalytic reduction vehicle engine management system, or the like.
Owner:SCHRADER ELECTRONICS LTD
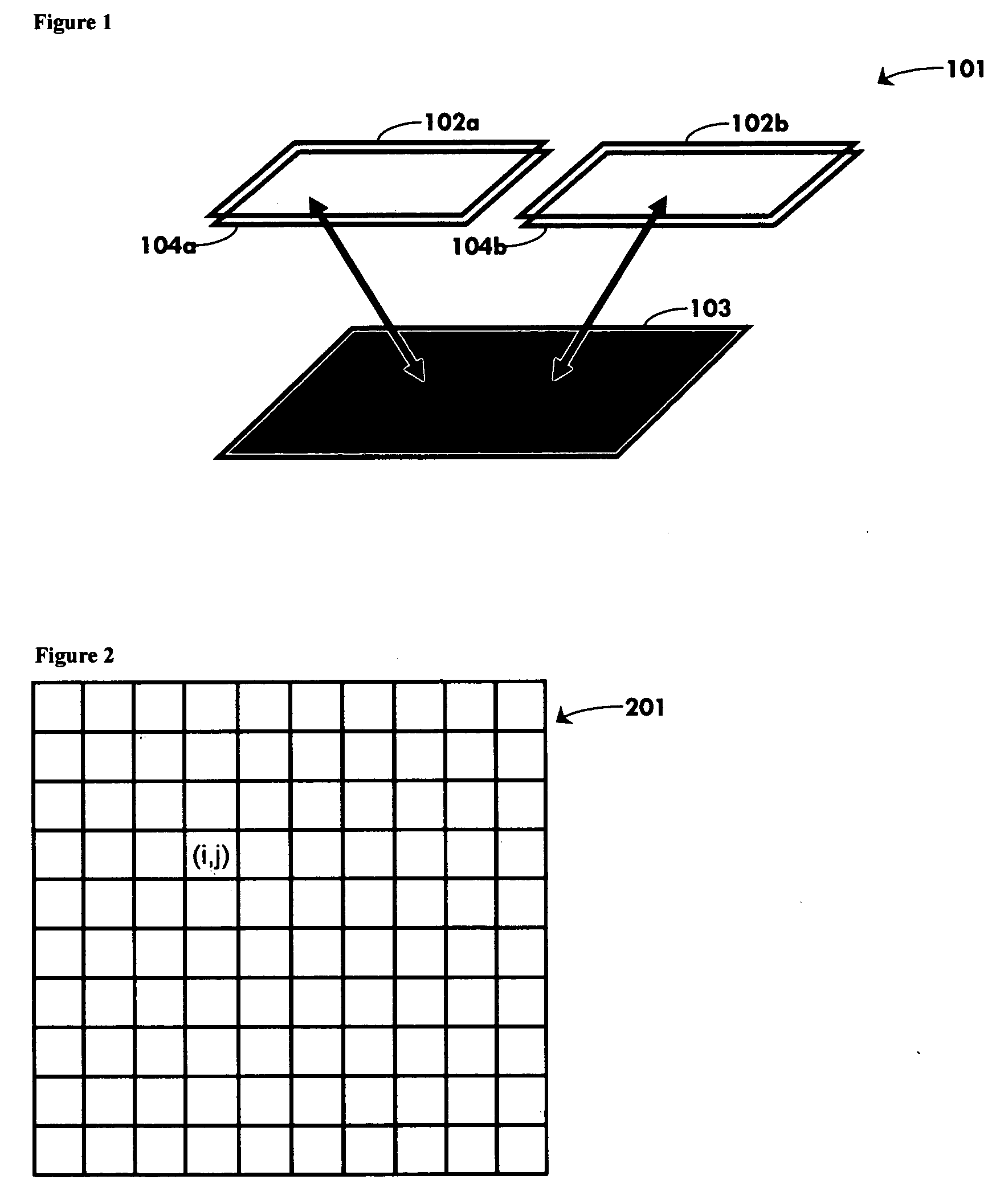
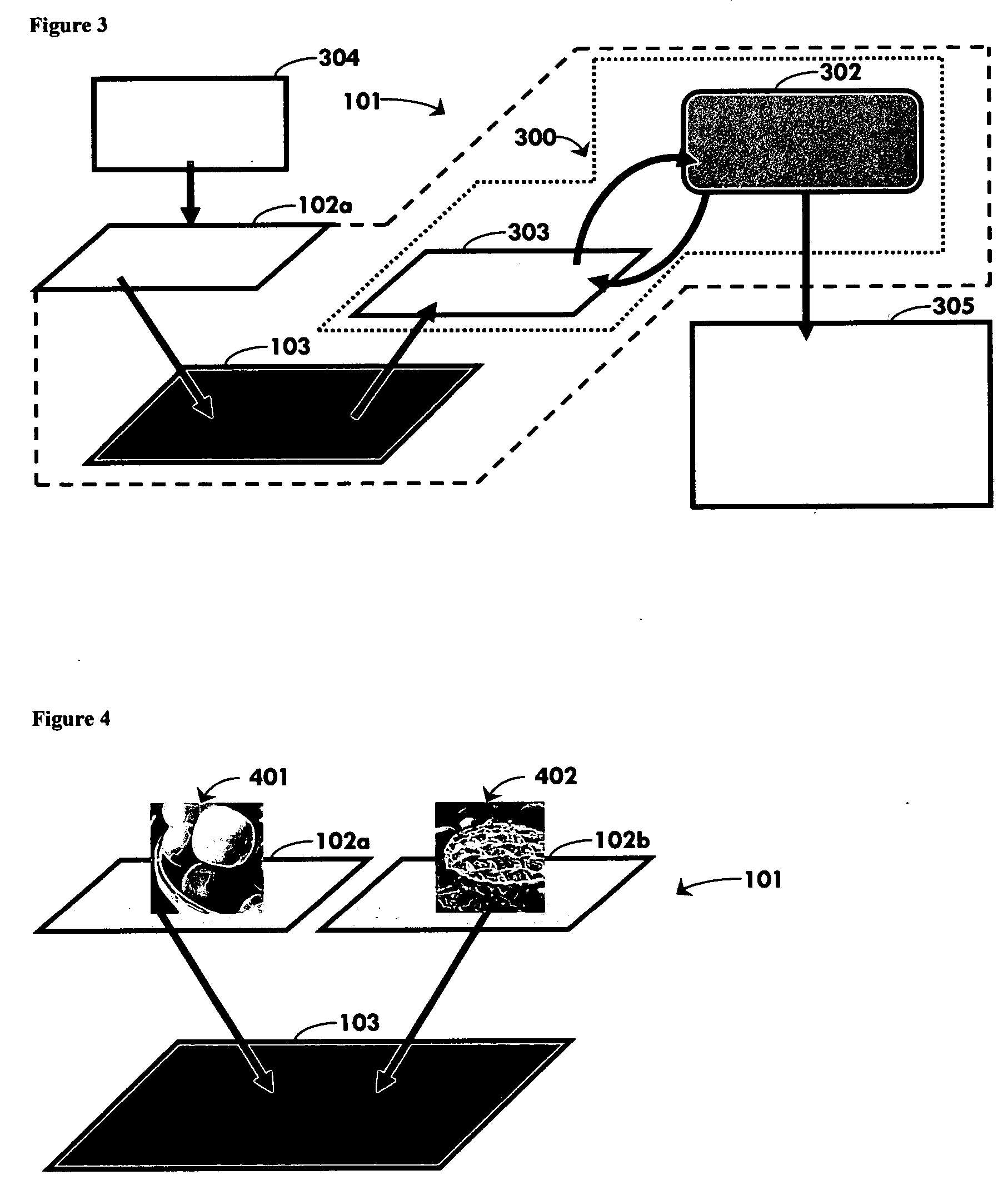
Associative memory device and method based on wave propagation
ActiveUS20040193789A1Successful and recognitionMemory loss protectionDigital computer detailsBrain functionComputer science
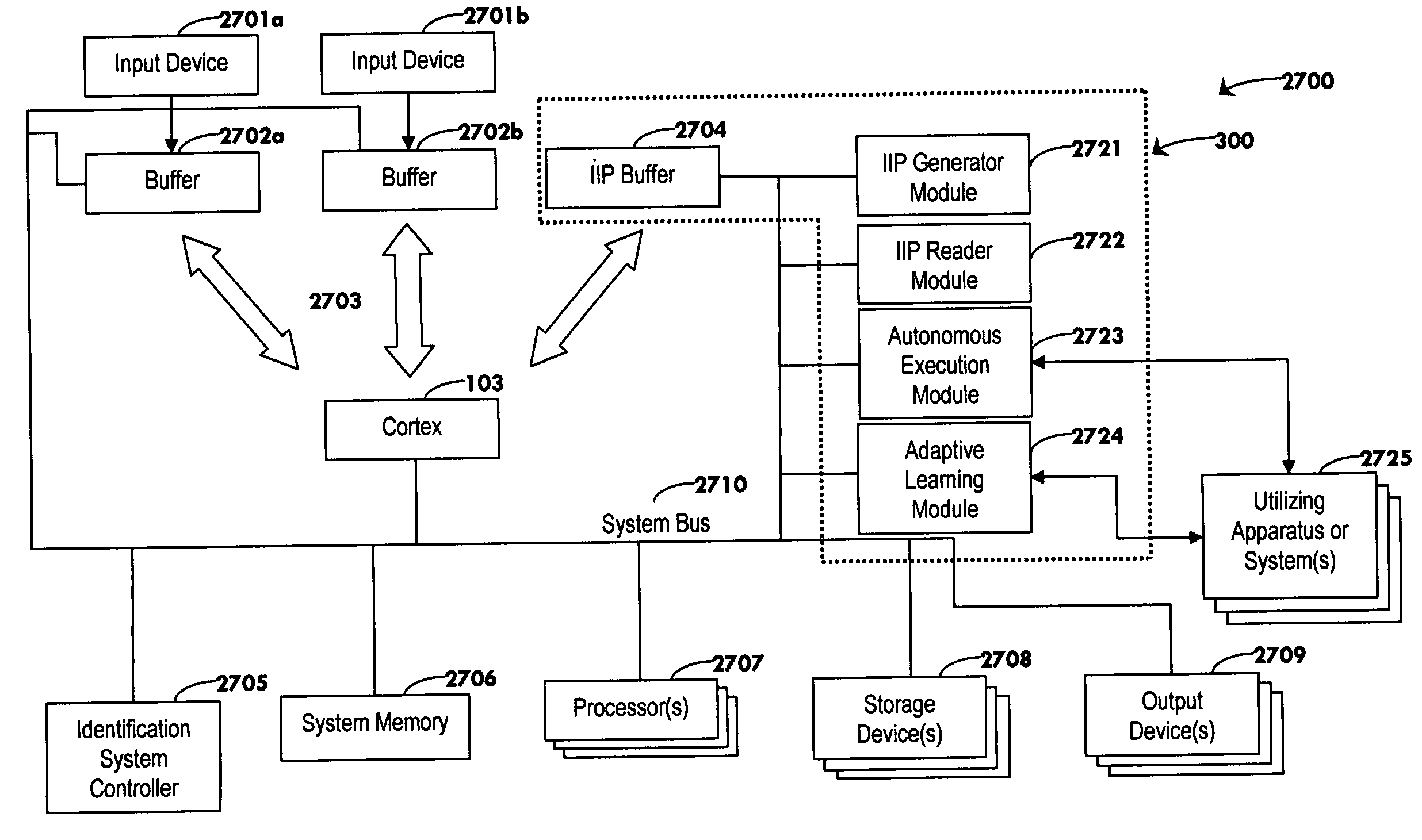
An associative, or content-addressable, memory device (101) and method based on waves is described. In this invention, arbitrary inputs are written as patterns which are interpreted as values of complex waves, discretized or analog, on one or more buffers (102,104). Information is transported via wave propagation from the buffers (102,104) to a cortex (103) or to multiple cortices, where the patterns are (1) associated using a mathematical operation for storage purposes or (2) de-associated through the corresponding inverse operation for retrieval purposes. The present associative memory is shown to emulate important behavioral properties of the human brain, including higher-brain functions such as learning from experience, forming generalizations or abstractions, and autonomous operation.
Owner:RUDOLF PAUL
Multi-channel circulator/isolator apparatus and method
A multi-channel circulator or isolator well suited for use in phased array antennas or other RF devices where space and packaging constraints make the implementation of a conventional circular or isolator difficult or impossible. The multi-channel circulator / isolator can be configured as an isolator by the inclusion of one or more load resistors at one of its ports. In various configurations two or more ferrite substrates are provided that each provide a plurality of transmission ports. One or more permanent magnets are used to simultaneously provide the magnetic flux field through both of the substrates. The substrates can be configured such that they are spaced apart by a small distance, or positioned face to face in contact with one another. One or a plurality of magnets can be used depending upon RF requirements. Each substrate forms an independent electromagnetic wave propagation channel that limits the propagation of RF energy between its ports in one direction only.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
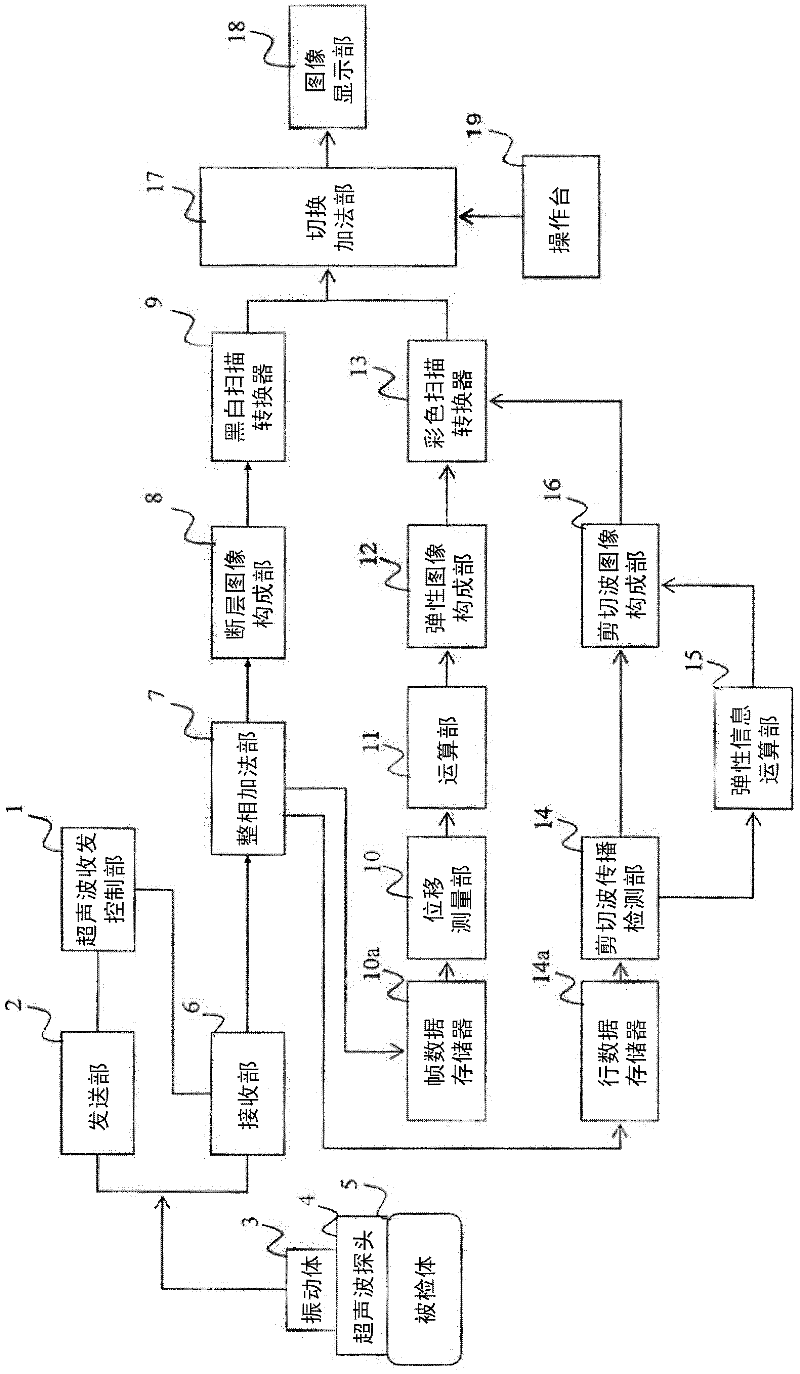
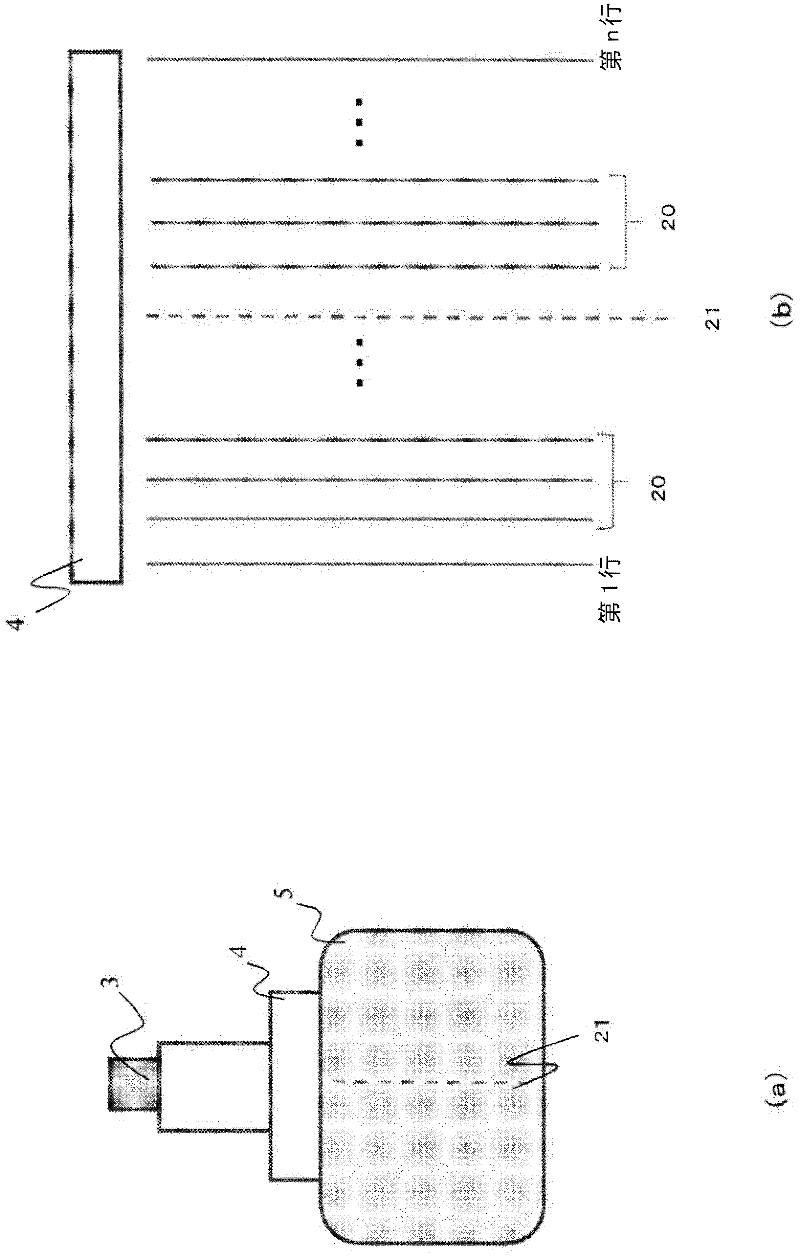
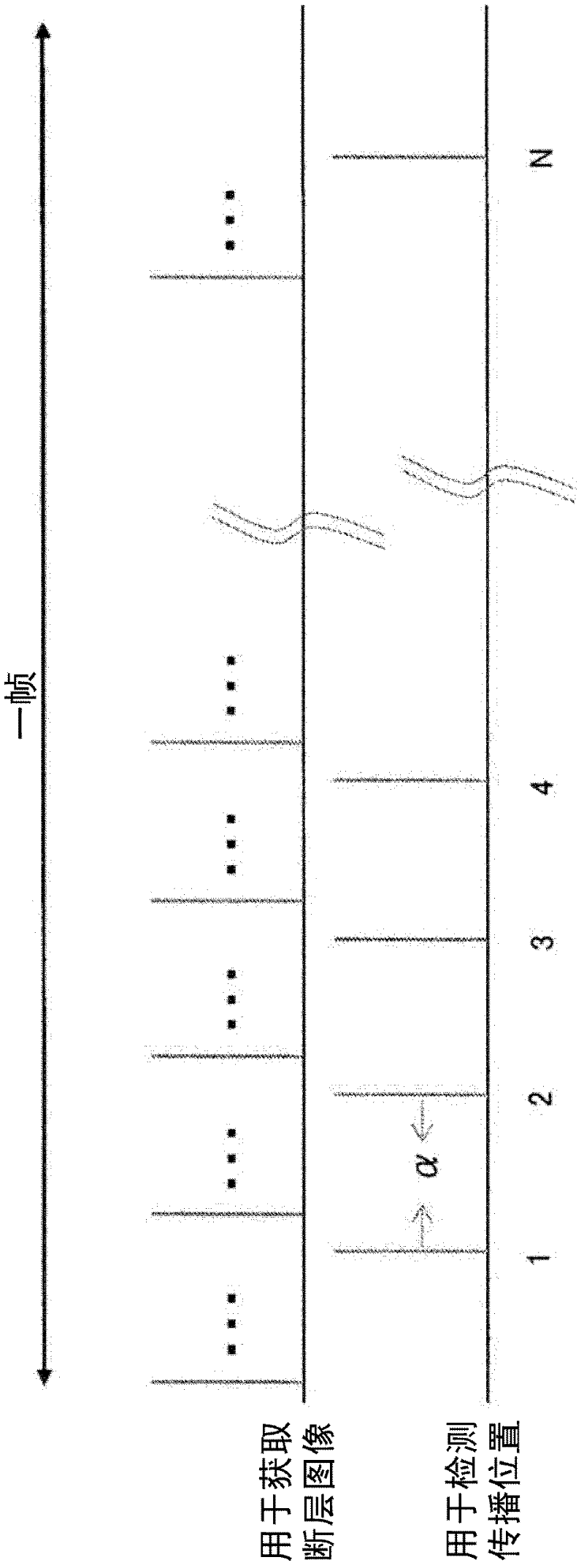
Ultrasonic diagnosis apparatus and ultrasonic measurement method
InactiveCN102469989AEasy accessDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionPropagation timeShear wave imaging
Disclosed are an ultrasonic diagnosis apparatus and an ultrasonic measurement method enabling easy acquisition of elasticity information by means of a shear wave. The ultrasonic diagnosis apparatus is provided with an ultrasonic probe (4) for transmitting / receiving an ultrasonic wave to / from a subject (5), a vibrator (3) for generating a shear wave, a transmitting / receiving unit (2, 6) for transmitting / receiving an ultrasonic wave to / from the ultrasonic probe (4), a shear wave propagation detecting unit (14) for determining the propagation position of the shear wave and the propagation time of the shear wave, a shear wave image constructing unit (16) for constructing a shear wave image showing the relation between the propagation position and propagation time of the shear wave, and an elasticity information computing unit (15); for computing elasticity information on the basis of the boundary of the shear wave image.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
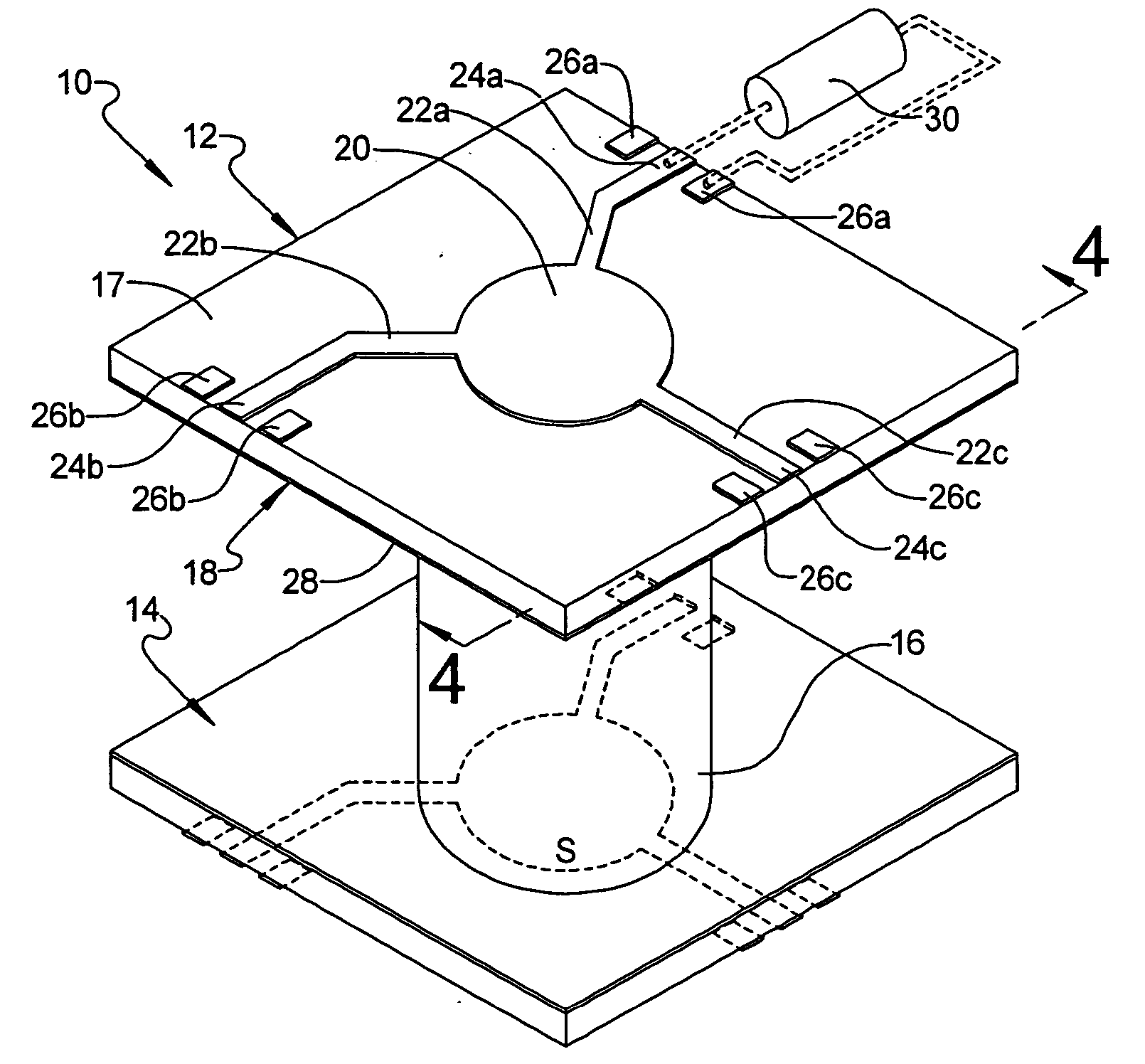
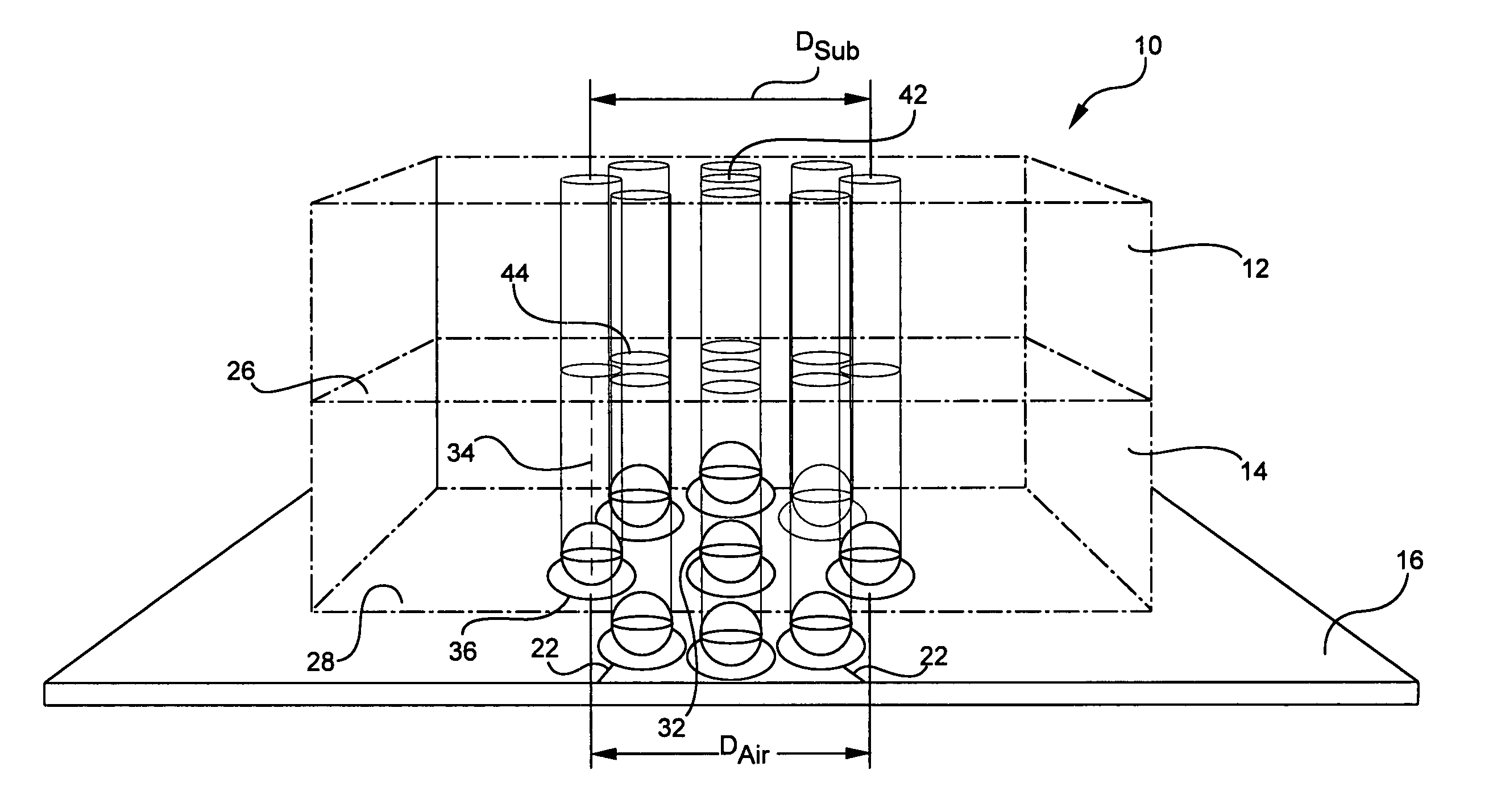
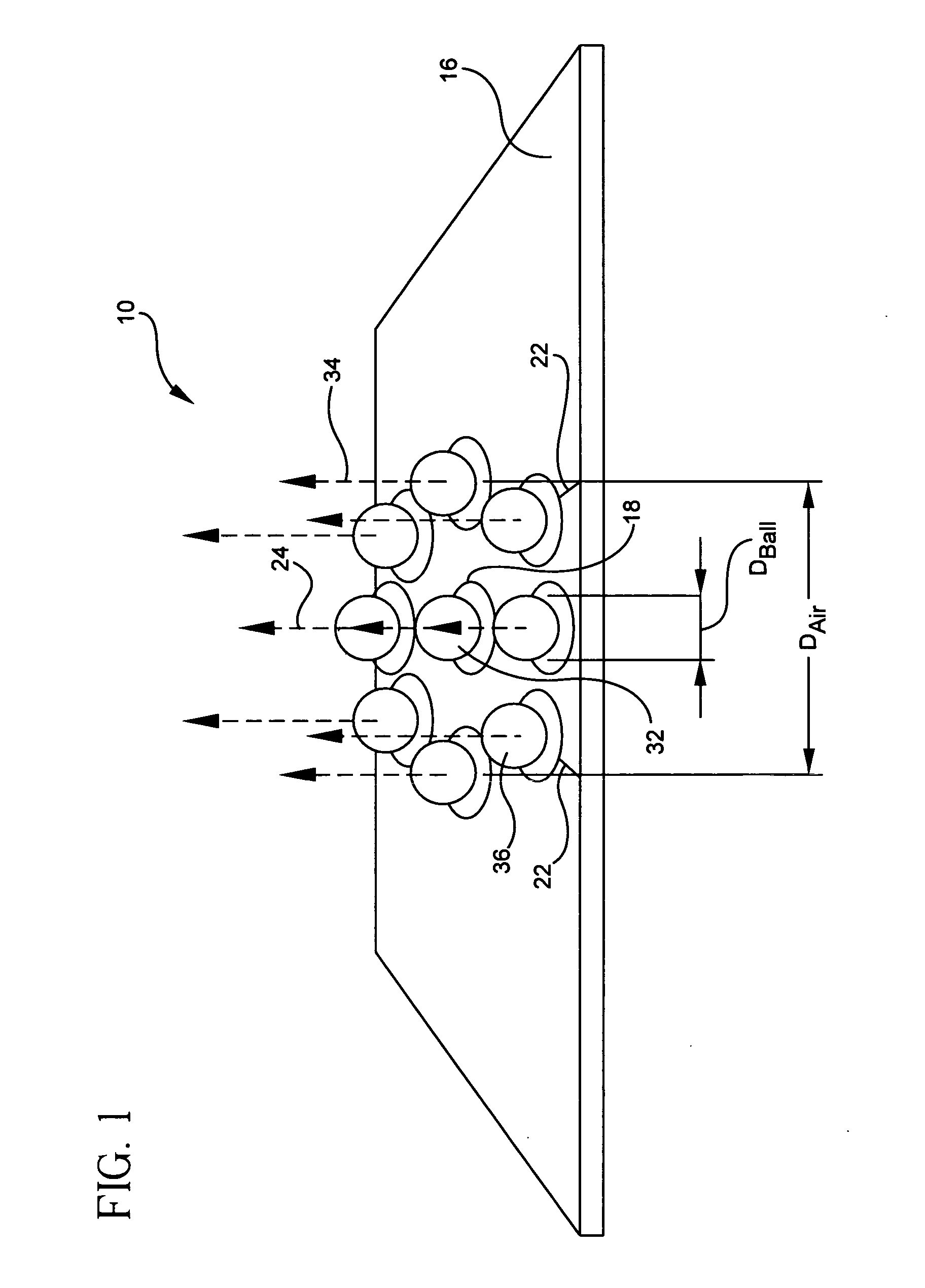
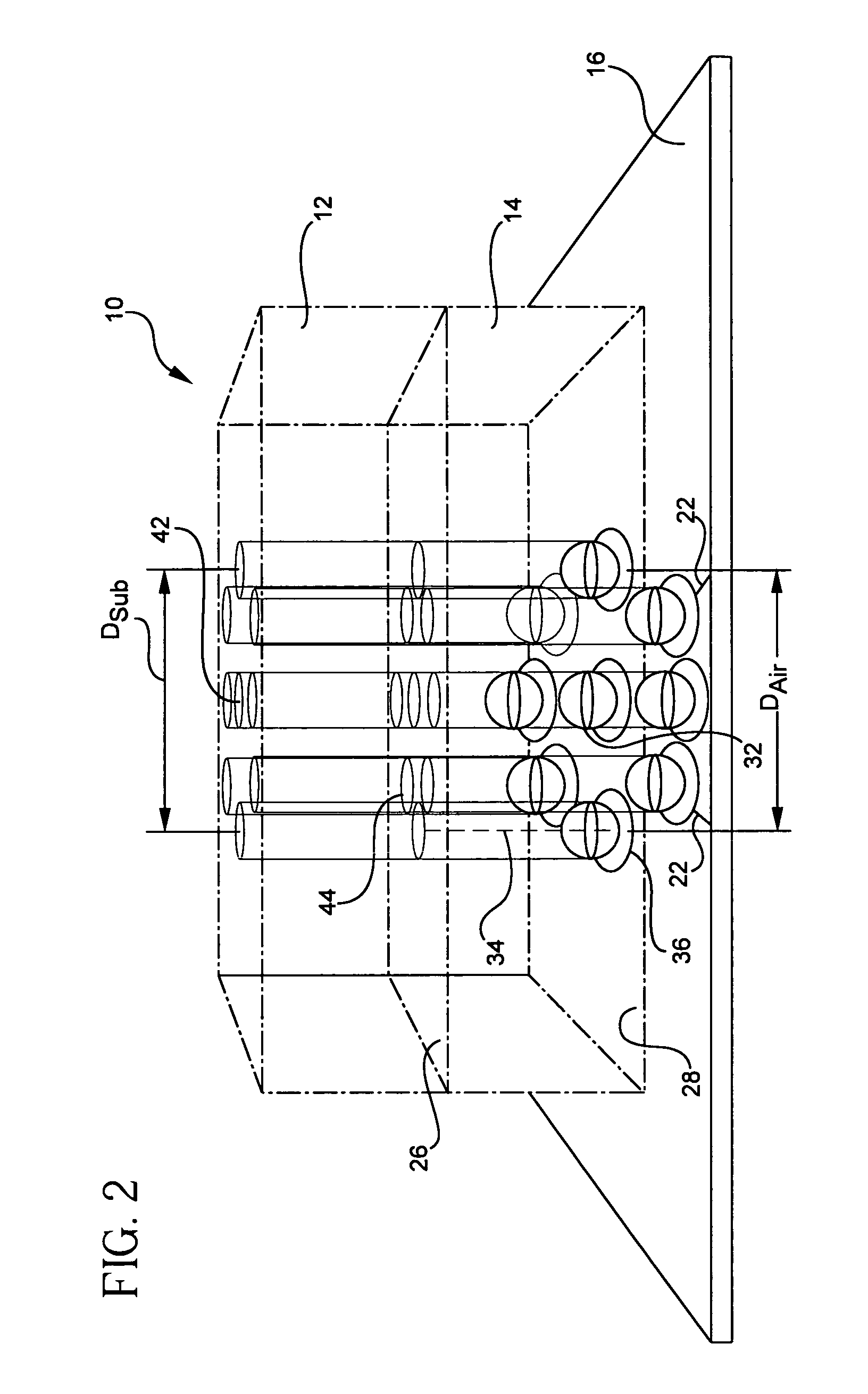
Ball coax interconnect
InactiveUS20060226928A1Multiple-port networksPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringCharacteristic impedance
A pseudo-coaxial vertical transition (10) includes a substrate (16). A bump array is disposed in a substantially concentric bump pattern upon the substrate (16) for simulating a pseudo-coaxial vertical electromagnetic wave propagation. The bump array is formed from a centrally disposed bump (32) having a predetermined bump diameter, and a plurality of at least five ground bumps (36) substantially equi-distant and circularly disposed about the centrally disposed bump (32). The predetermined bump diameter and a bump spacing of the centrally disposed bump are determined in relation to the plurality of ground bumps and a dielectric constant of air for providing a characteristic impedance.
Owner:CORNING INC
Reconfigurable base station antenna
InactiveUS20090312057A1Increase battery capacityPivotable antennasSubstation equipmentEngineeringBase station antennas
A reconfigurable base station (BS) antenna permits increasing cell capacity by dynamically varying an antenna's configuration according to a wave propagation environment and subscriber distribution. At least two reflective plates each have at least one radiator, a ray dome accommodates the two reflective plates in a hollow interior, and upper and lower caps are combined with upper and lower portions of the ray dome, respectively. Reflective connection members are connected to the respective two reflective plates and the upper and lower caps, so that the two reflective plates are rotatable, and at least one force generator provides a rotation force, and at least one force transfer mechanical portion transfers the rotation force received from the force generator to at least one reflective plate and controls a rotation angle of the at least one reflective plate. At least one of the force generator and the force transfer mechanical portion is combined with the two reflective plates.
Owner:KMW INC
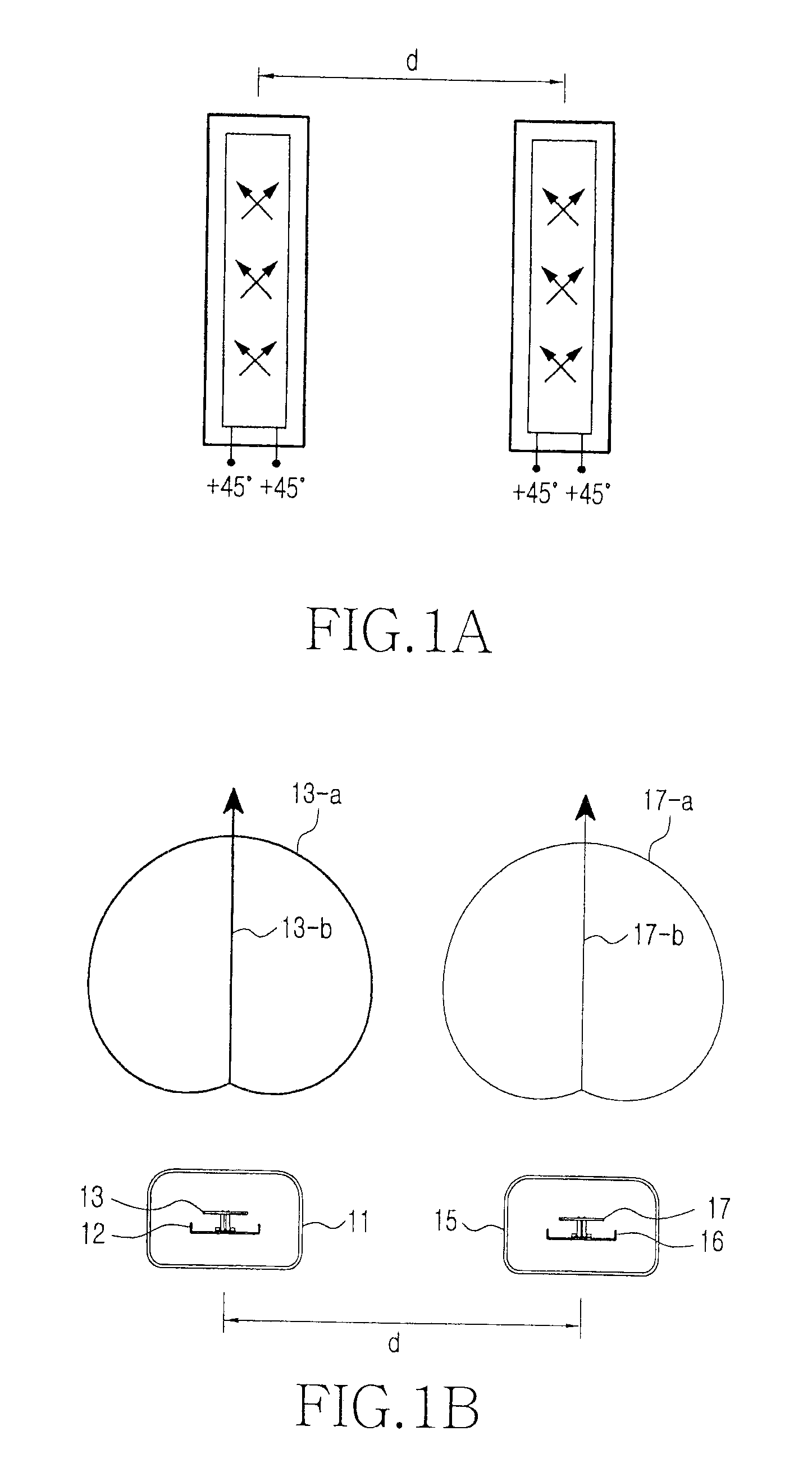
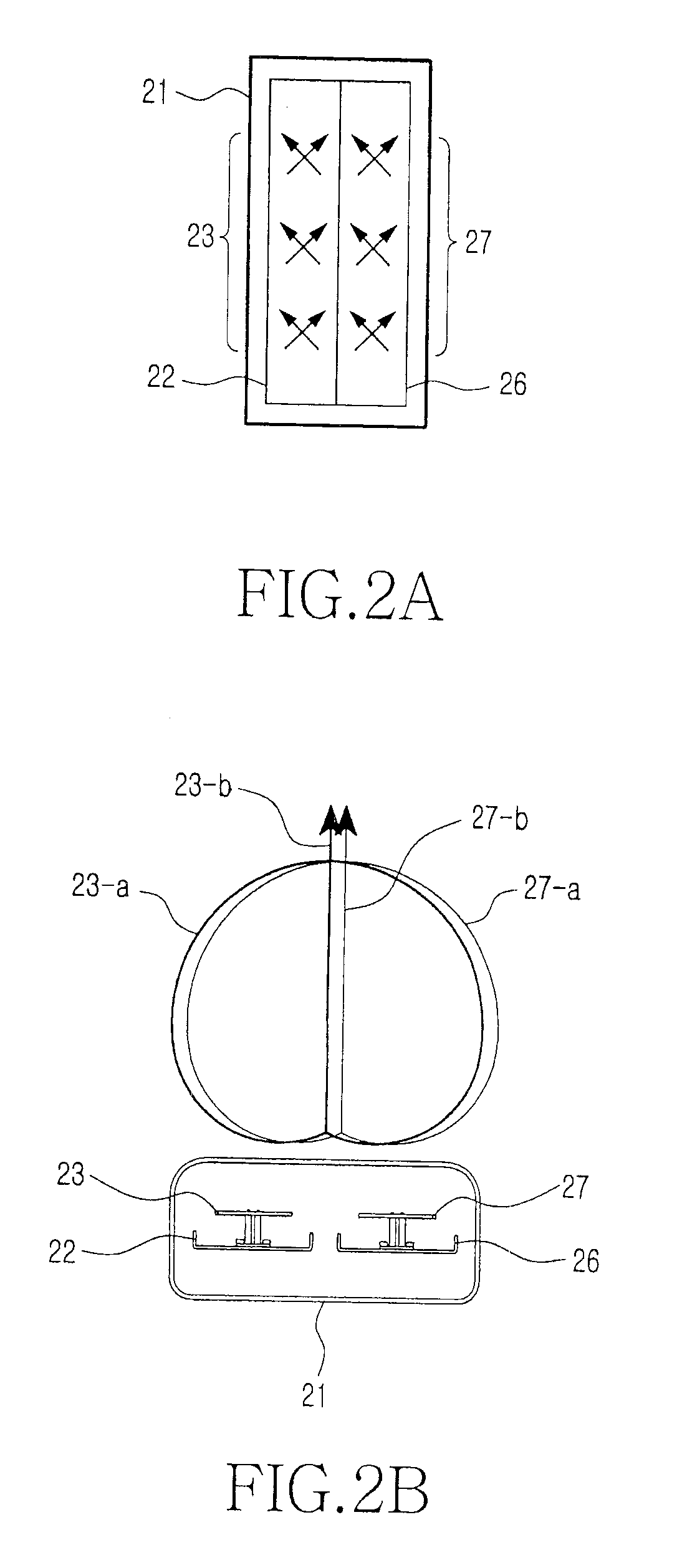
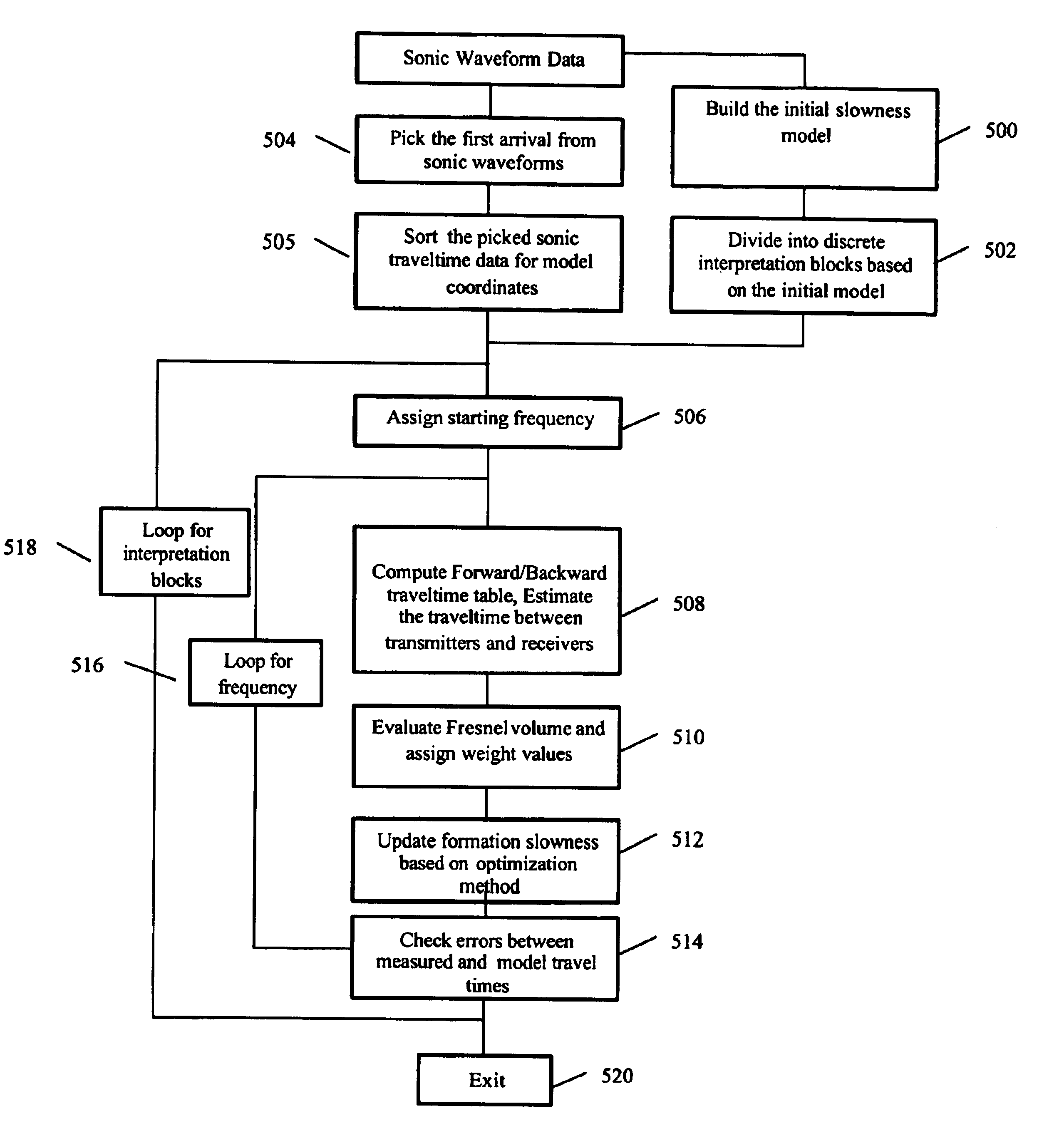
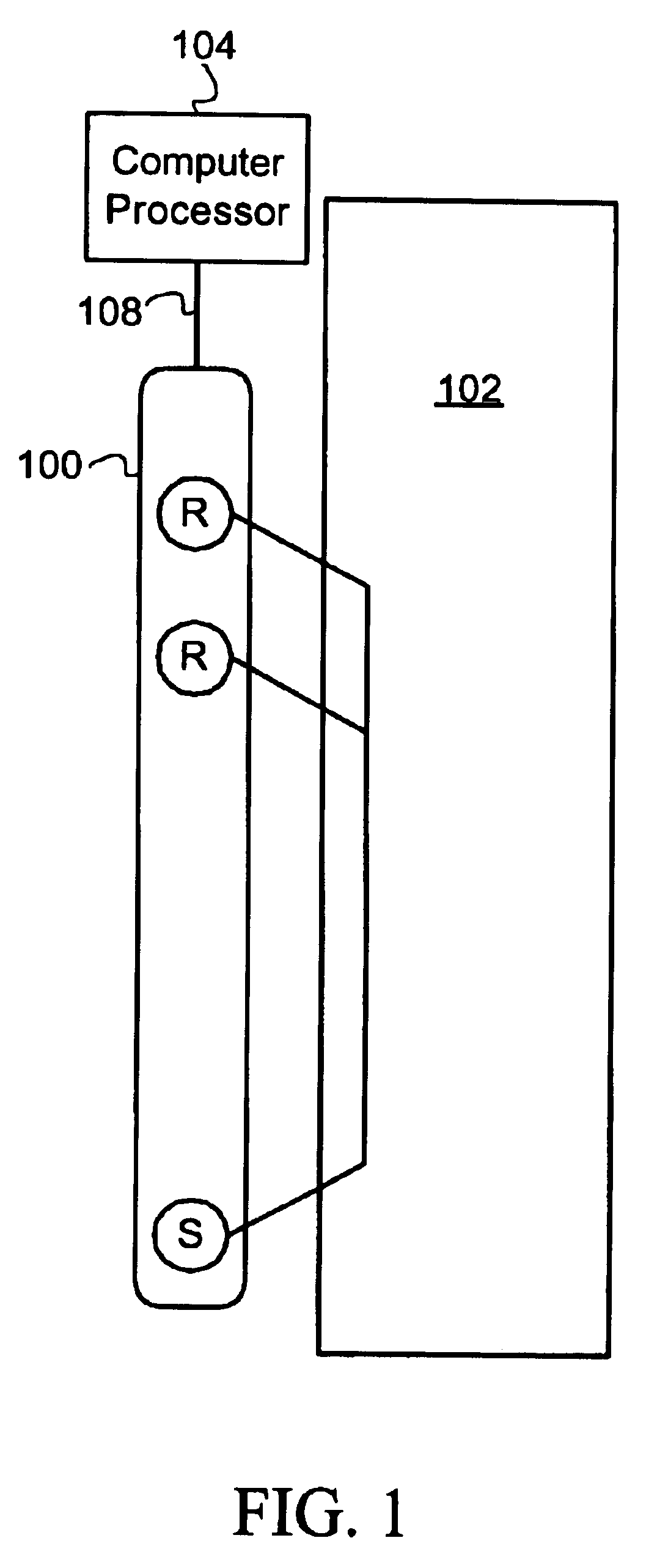
Methods for determining formation and borehole parameters using fresnel volume tomography
InactiveUS7027927B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingBack projectionTomography
A method and apparatus for determining formation slowness around a borehole are provided. The Fresnel volume concept is applied for traveltime tomography. The Fresnel volume represents a sonic wave propagation path about the borehole. The application of Fresnel volume to sonic data provides for a stable inversion and makes practical 3-D tomography. Inversion is accomplished by an iterative back-projection method.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Underground personnel positioning system and method based on radio frequency identification technology
ActiveCN102890767AHigh precisionEasy to identifyMining devicesSensing record carriersUltrasound attenuationEngineering
The invention discloses an underground personnel positioning system based on a radio frequency identification technology. The system comprises tag card readers, electronic tags, a switch, an upper personal computer (PC), a central display screen and optical fibers; at least three tag card readers are arranged in underground laneways and are connected with the electronic tags which are worn by underground personnel through radio frequency electromagnetic waves; the conventional ranging algorithm is improved by adopting an electromagnetic wave propagation model and an attenuation index which are in accordance with an underground environment; distance between the underground personnel and each tag card reader is measured accurately by an improved ranging algorithm by the tag card readers; measurement results are transmitted to the ground upper PC after being collected by the switch; coordinate positions of the underground personnel are determined accurately by a trilateral positioning method according to the distance value of every three same identifiers by the upper PC; a positioning result is displayed on the central display screen in real time; and position reference is provided for ground management personnel and personnel who is about to go down for operating. By the improved system and the improved algorithm, the problem of coal mine underground positioning difficulties is solved effectively.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Three-dimensional hot spot localization
ActiveUS20110297829A1Improve depth resolutionImprove measurement reliabilityInvestigating semiconductor impuritiesSamplingTime delaysData acquisition
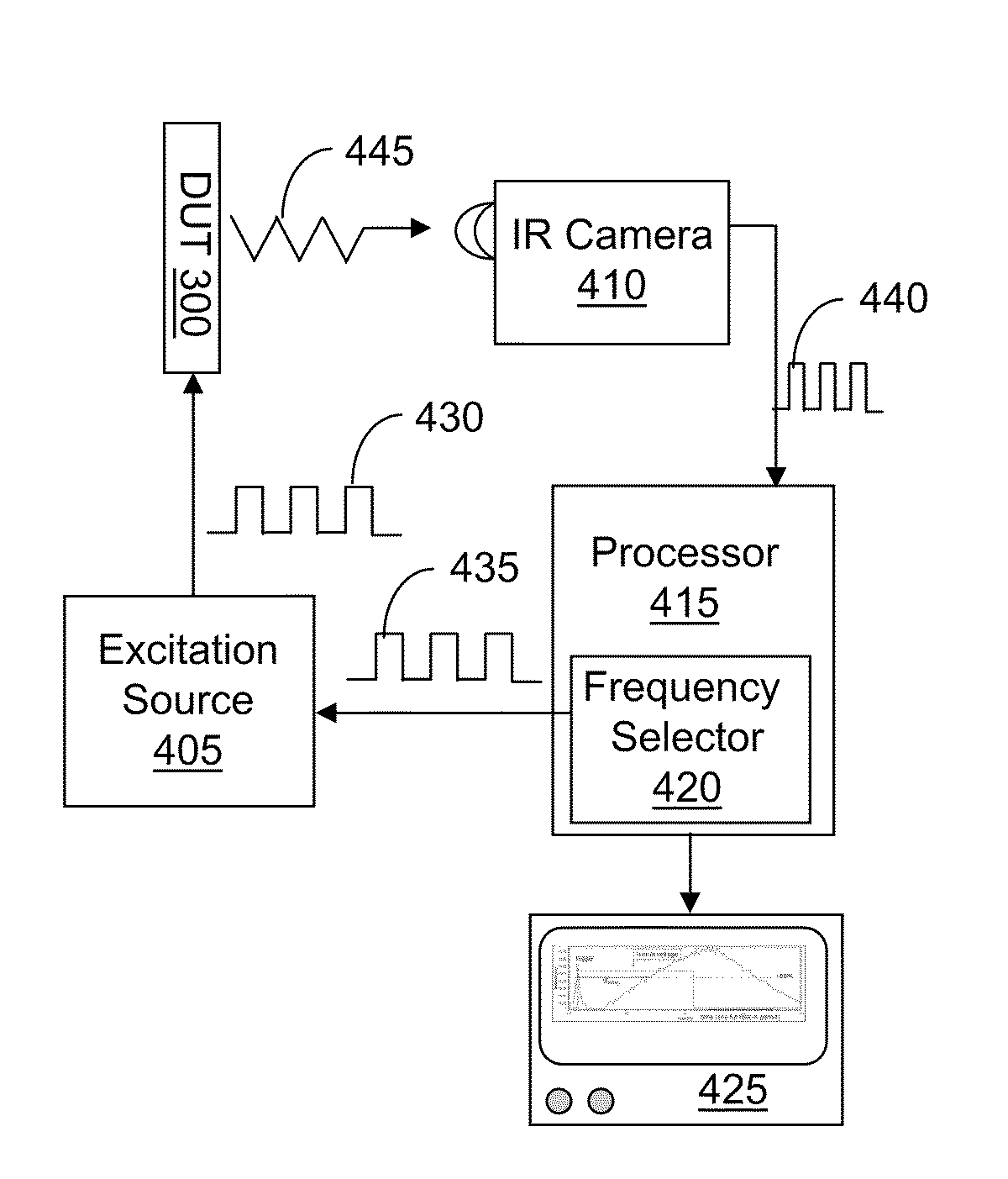
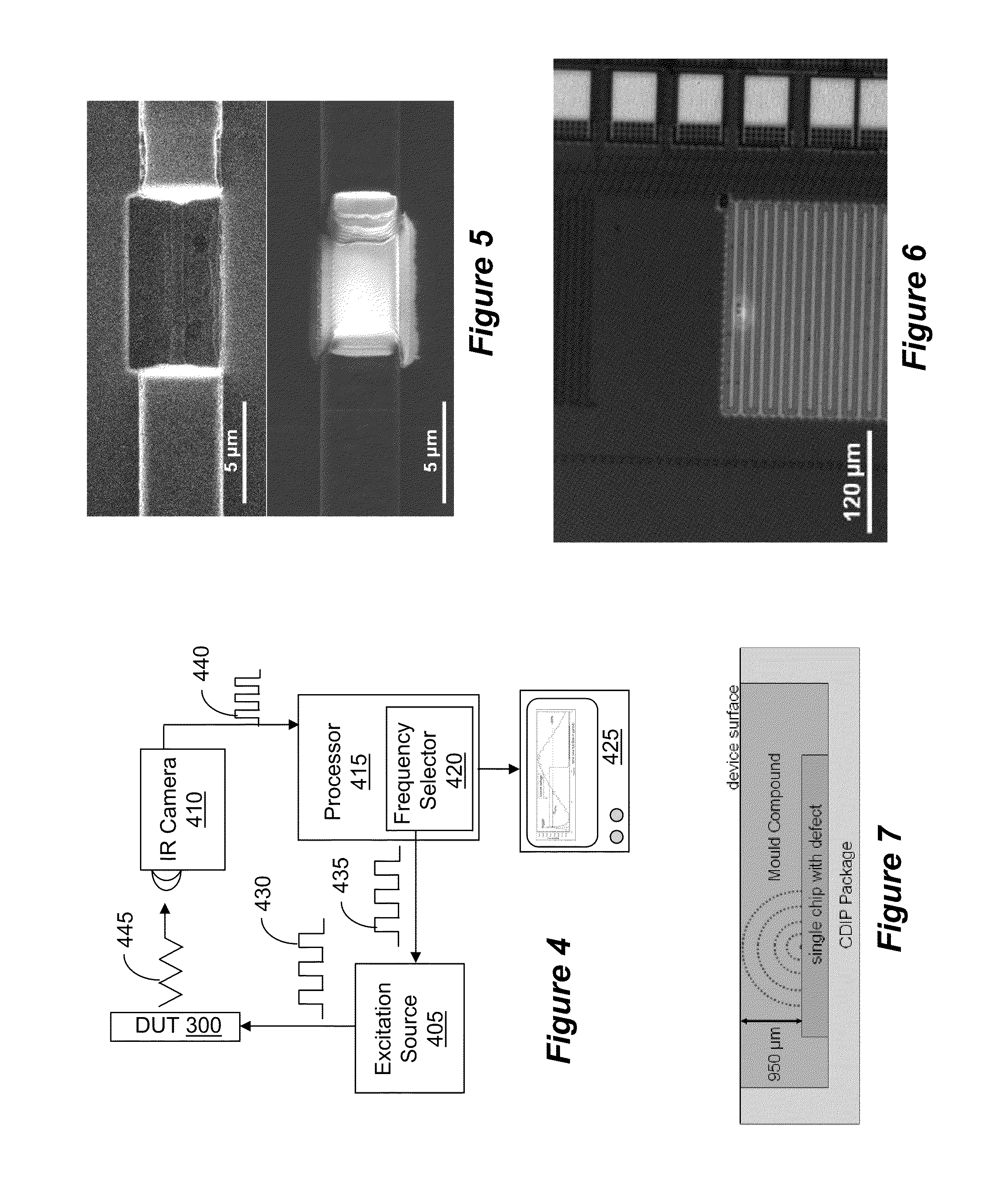
A non-destructive approach for the 3D localization of buried hot spots in electronic device architectures by use of Lock-in Thermography (LIT). The 3D analysis is based on the principles of thermal wave propagation through different material layers and the resulting phase shift / thermal time delay. With more complex multi level stacked die architectures it is necessary to acquire multiple LIT results at different excitation frequencies for precise hot spot depth localization. Additionally, the use of multiple time-resolved thermal waveforms, measured in a minimized field of view on top of the hot spot location, can be used to speed up the data acquisition. The shape of the resulting waveforms can be analyzed to further increase the detection accuracy and confidence level.
Owner:DCG SYST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com