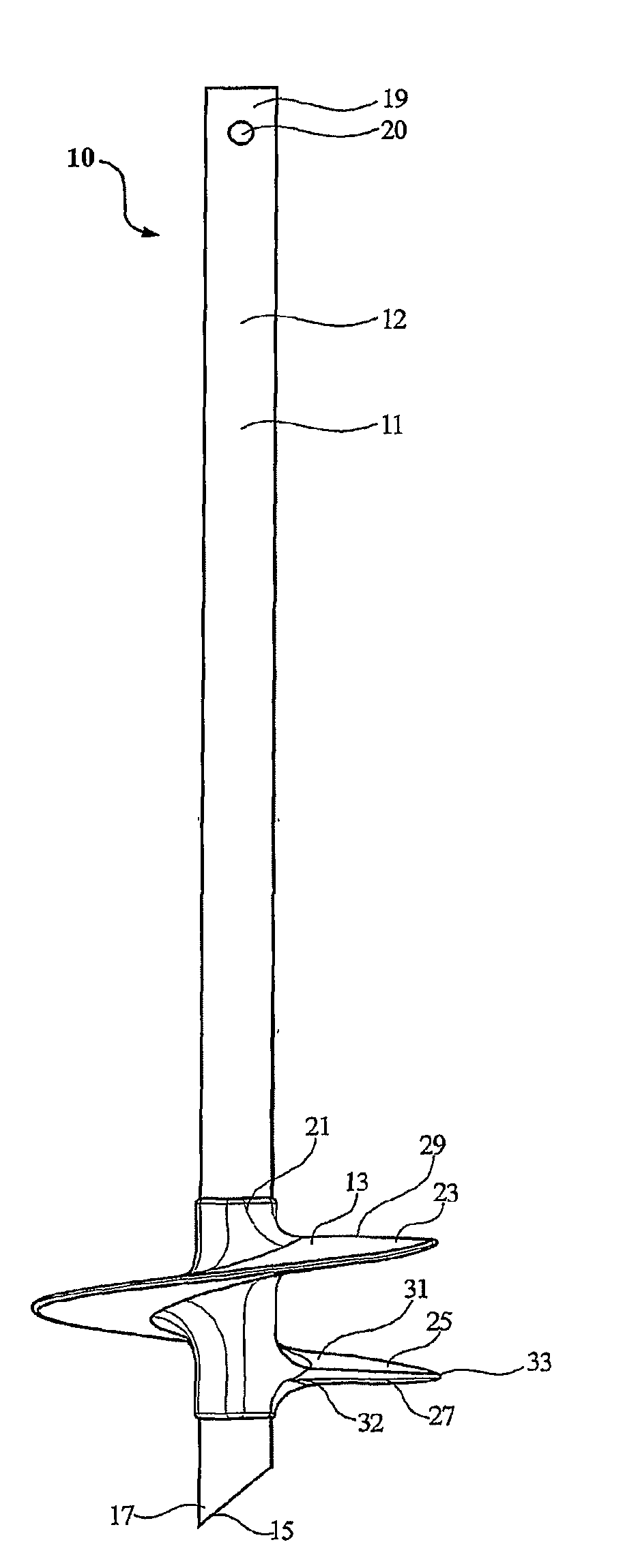Patents
Literature
684 results about "Embedment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
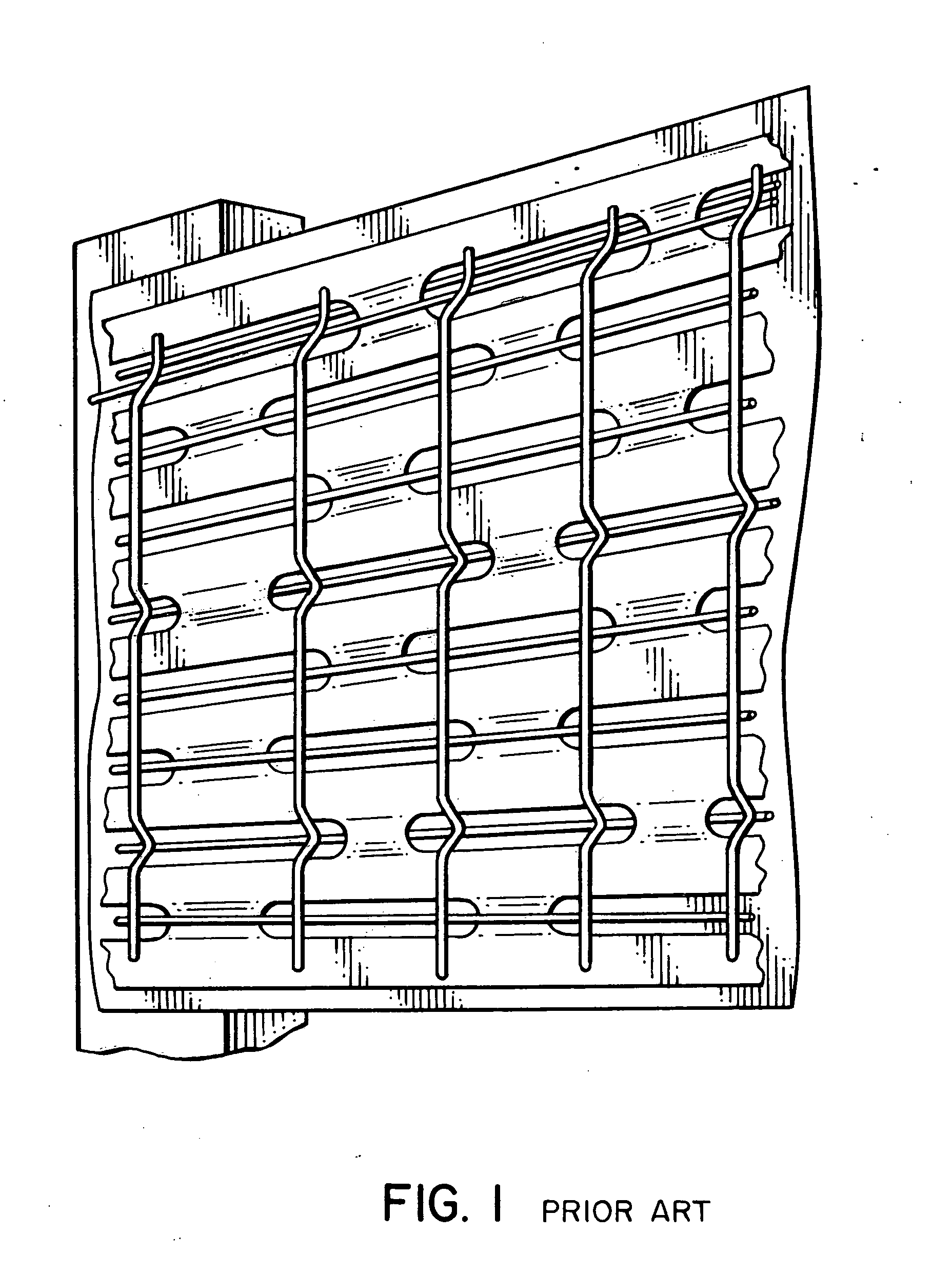
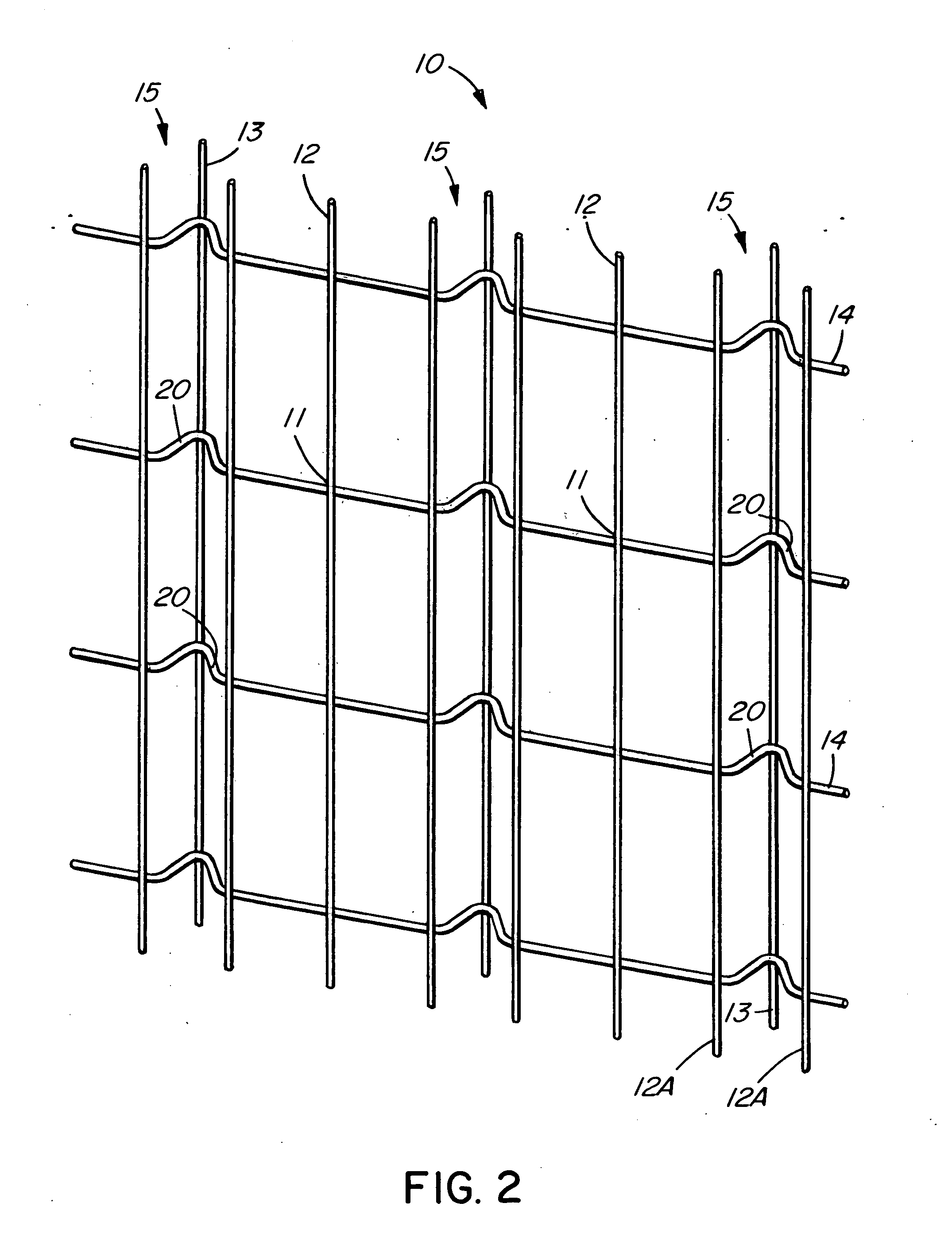
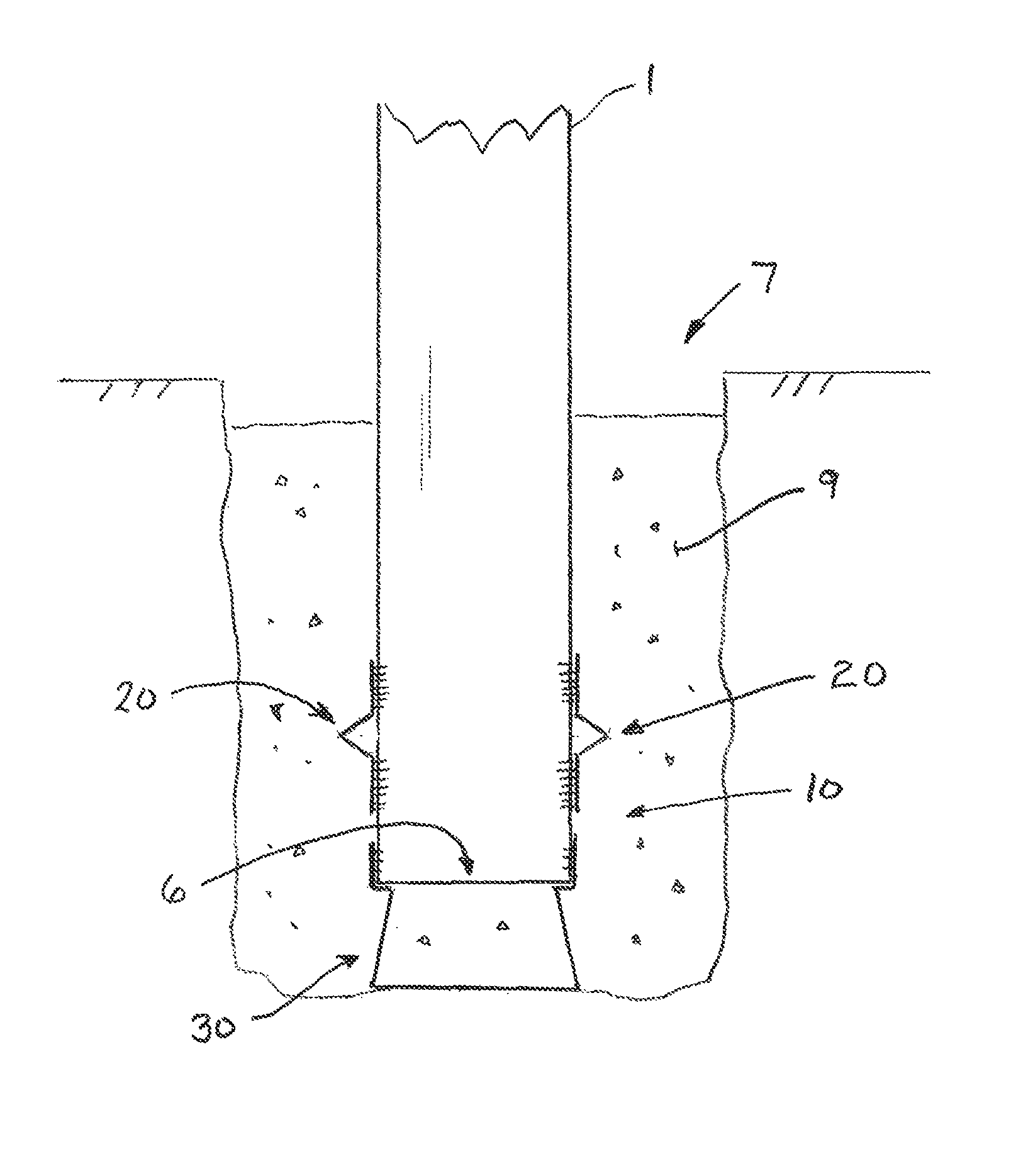
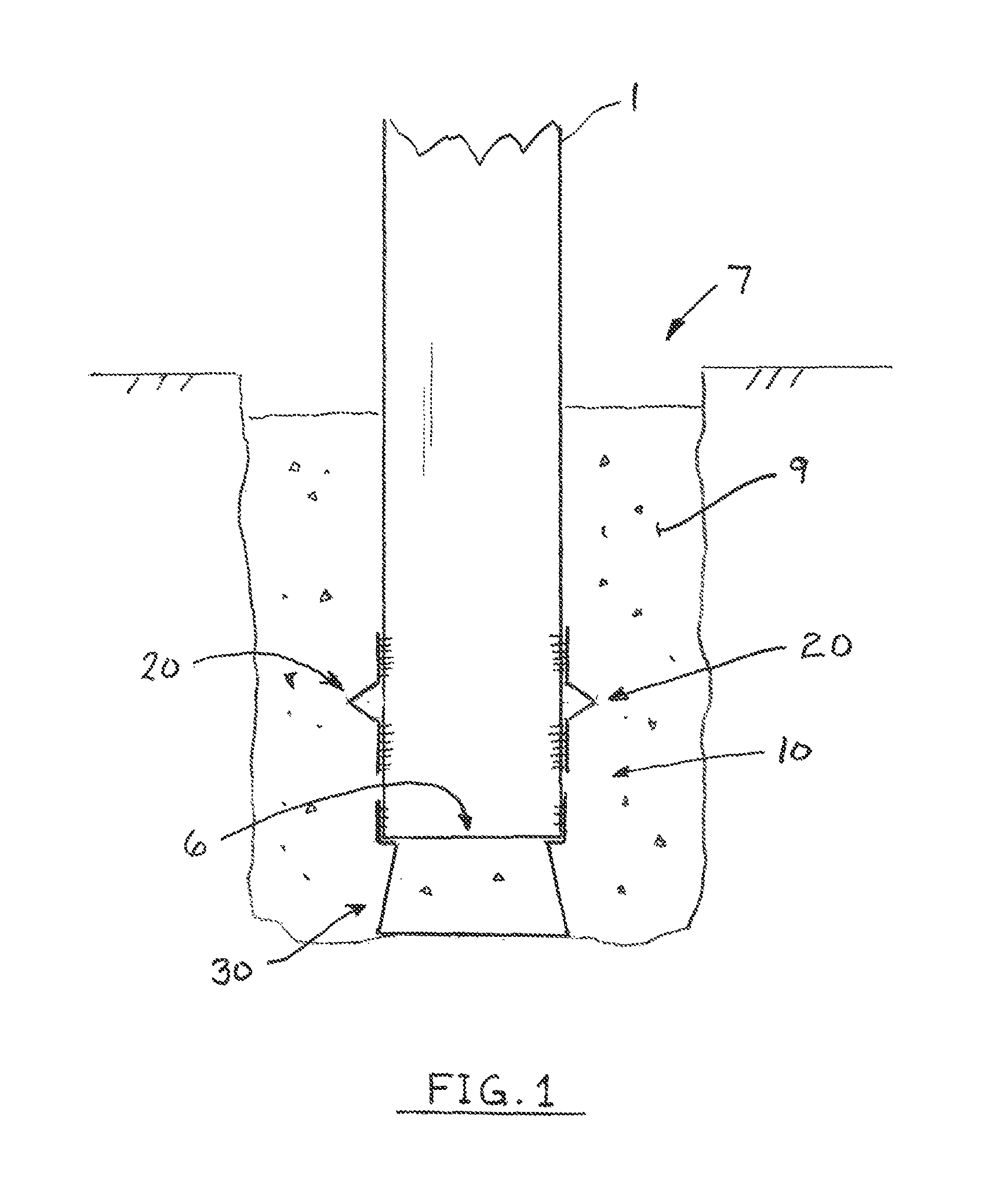
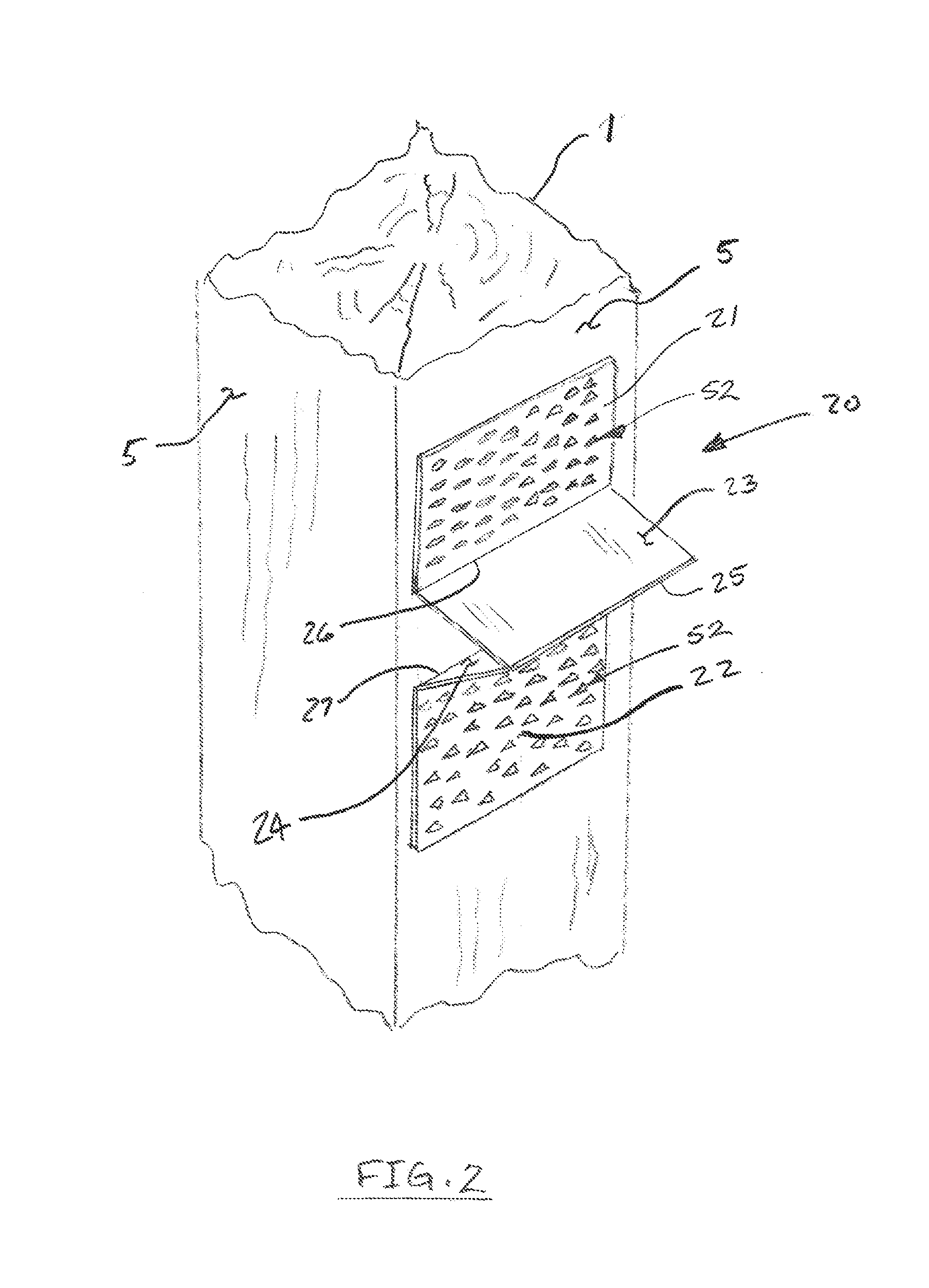
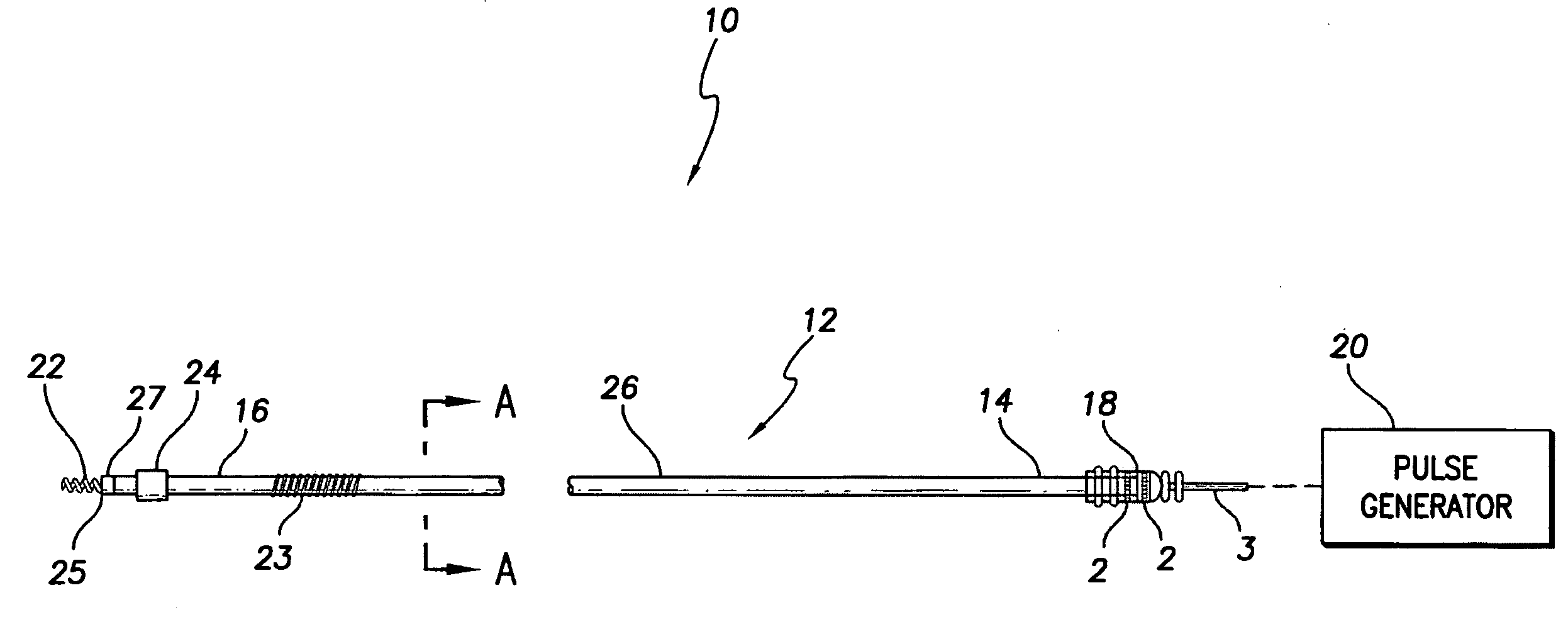
Embedment is a phenomenon in mechanical engineering in which the surfaces between mechanical members of a loaded joint embed. It can lead to failure by fatigue as described below, and is of particular concern when considering the design of critical fastener joints.
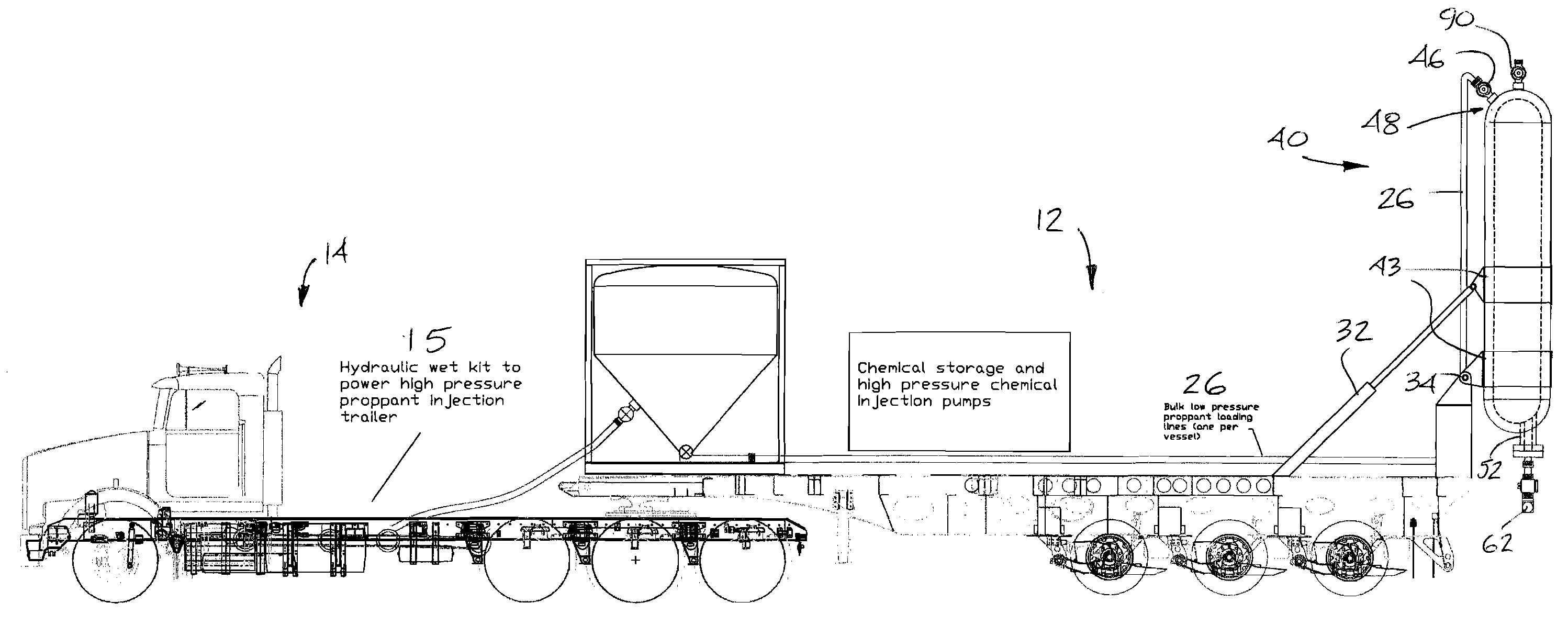
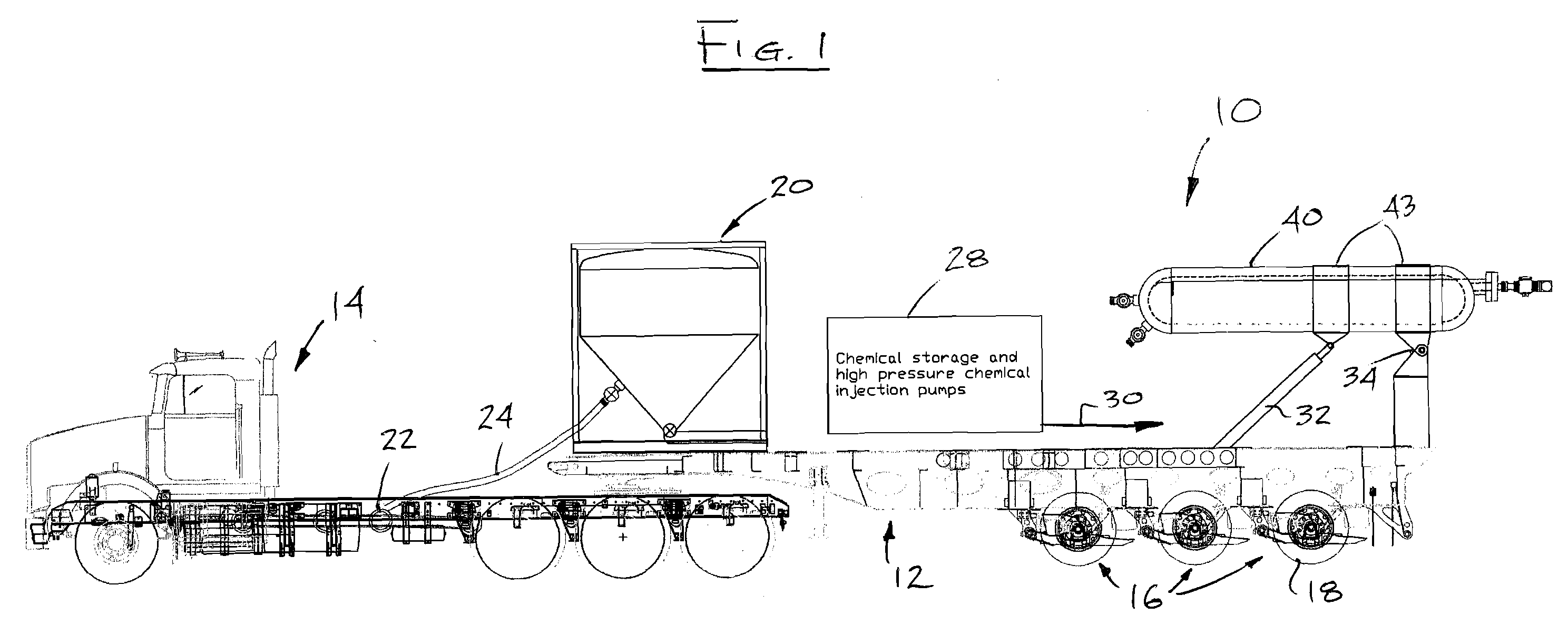
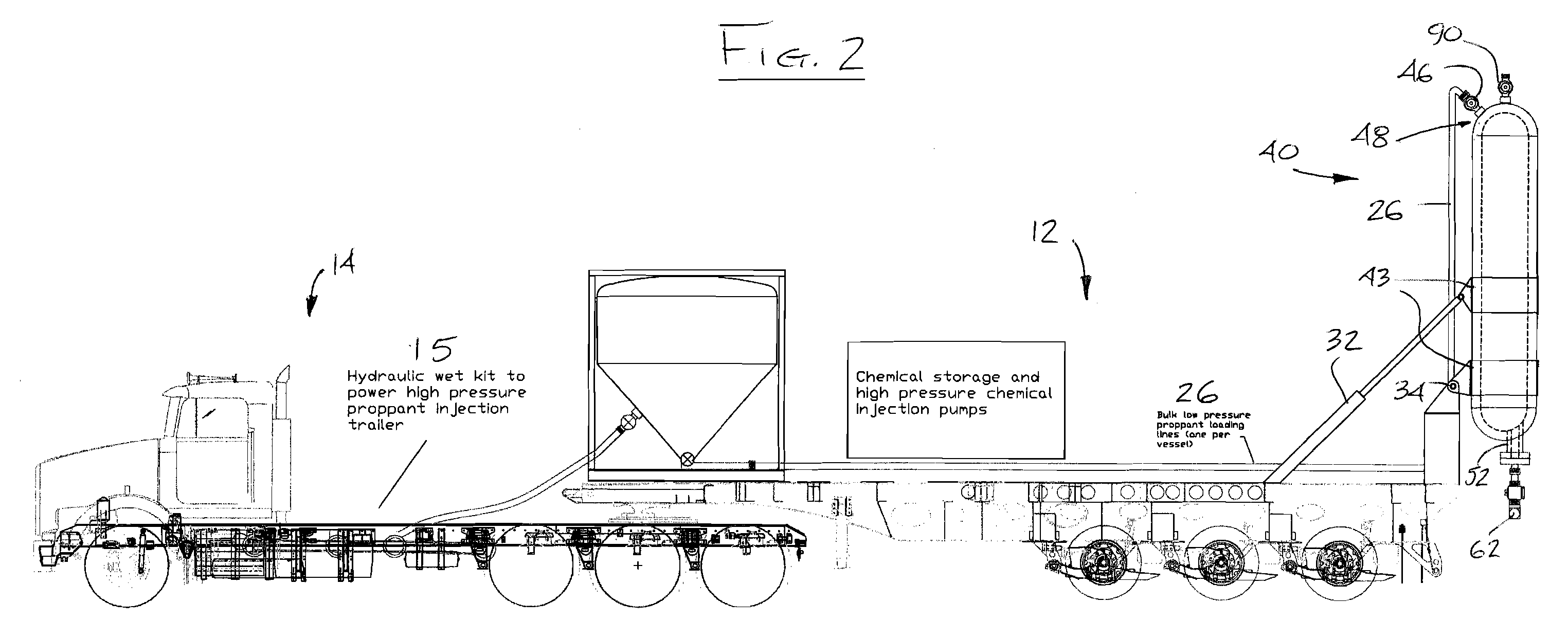
High-pressure Injection Proppant System
Owner:FRAC SOURCE
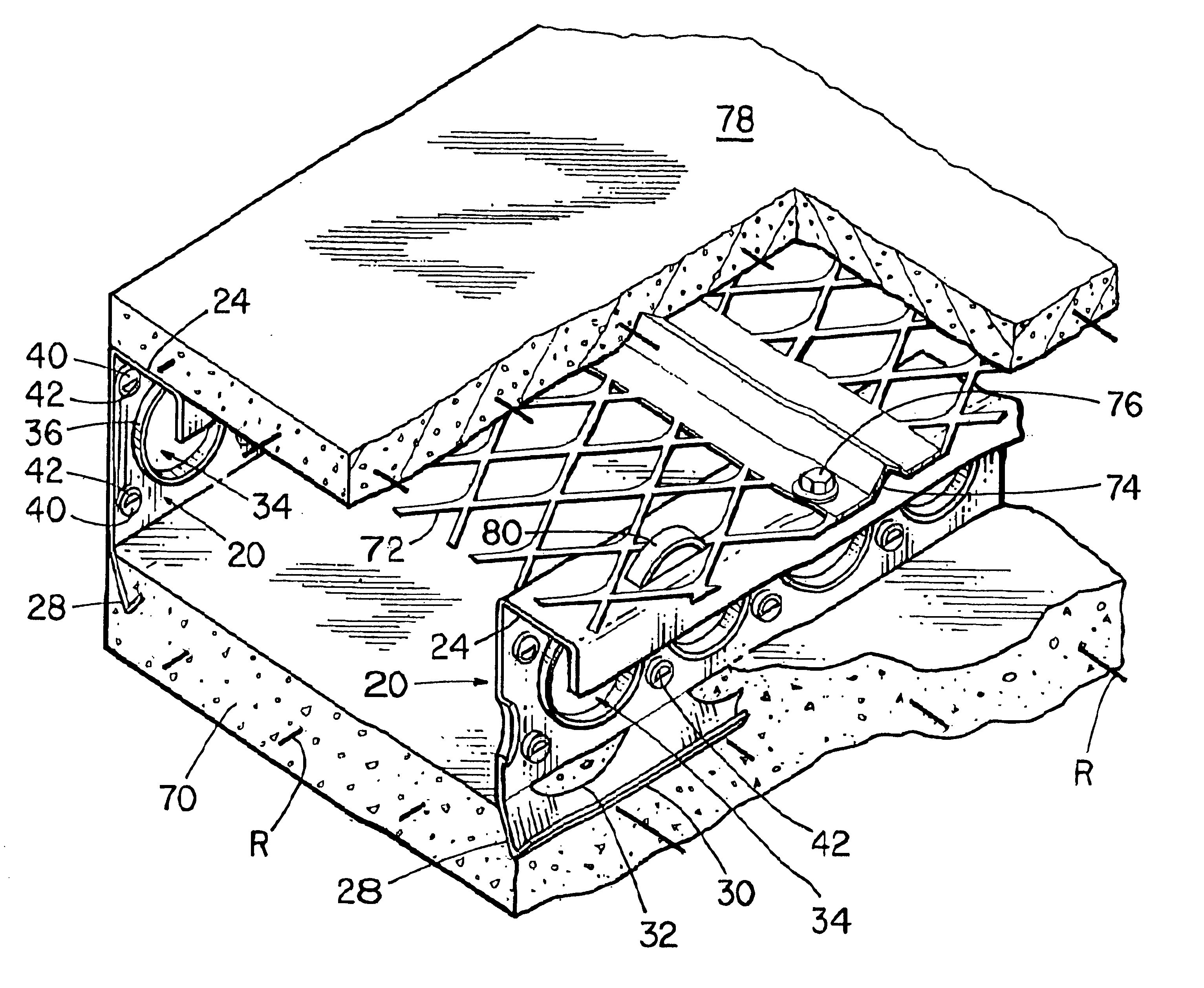
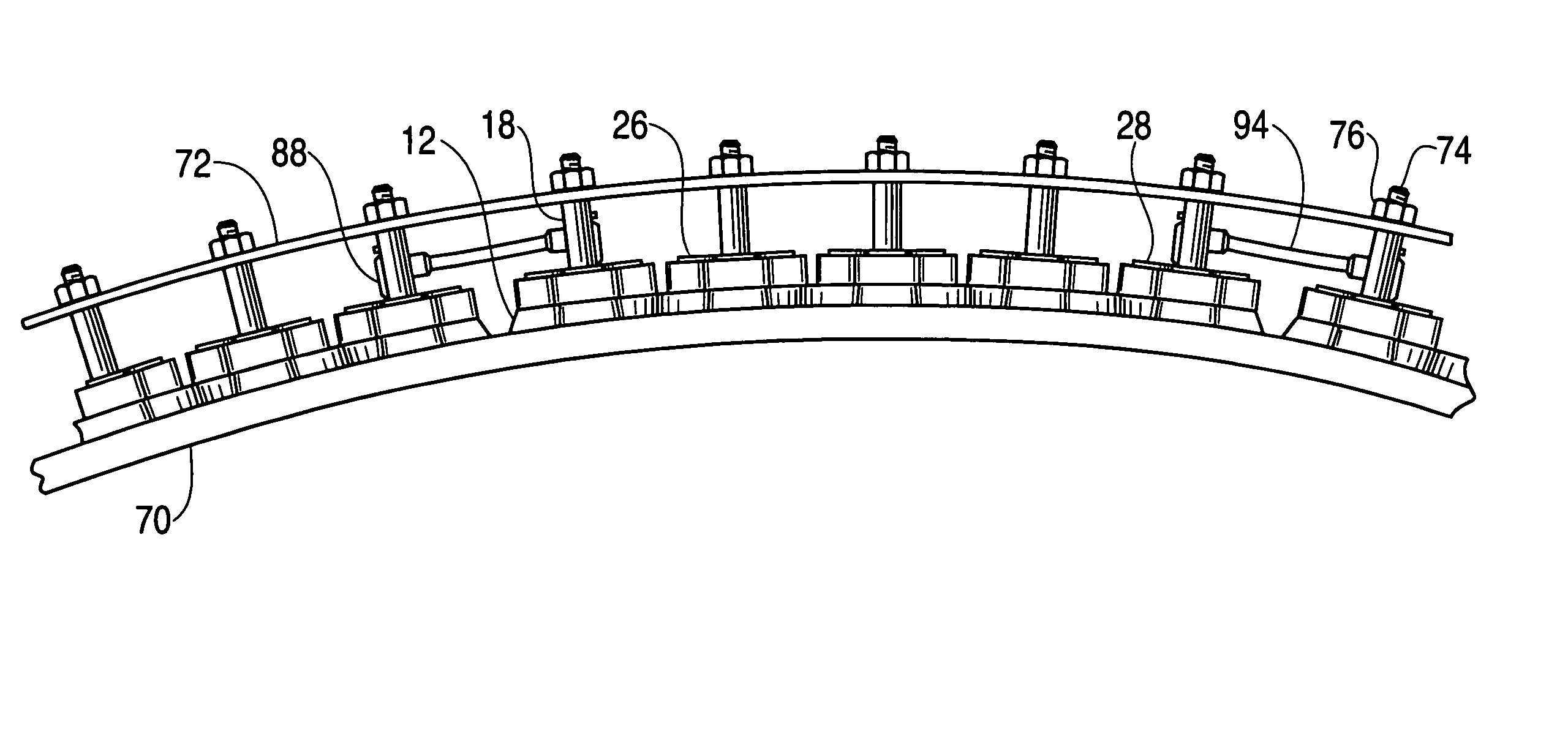
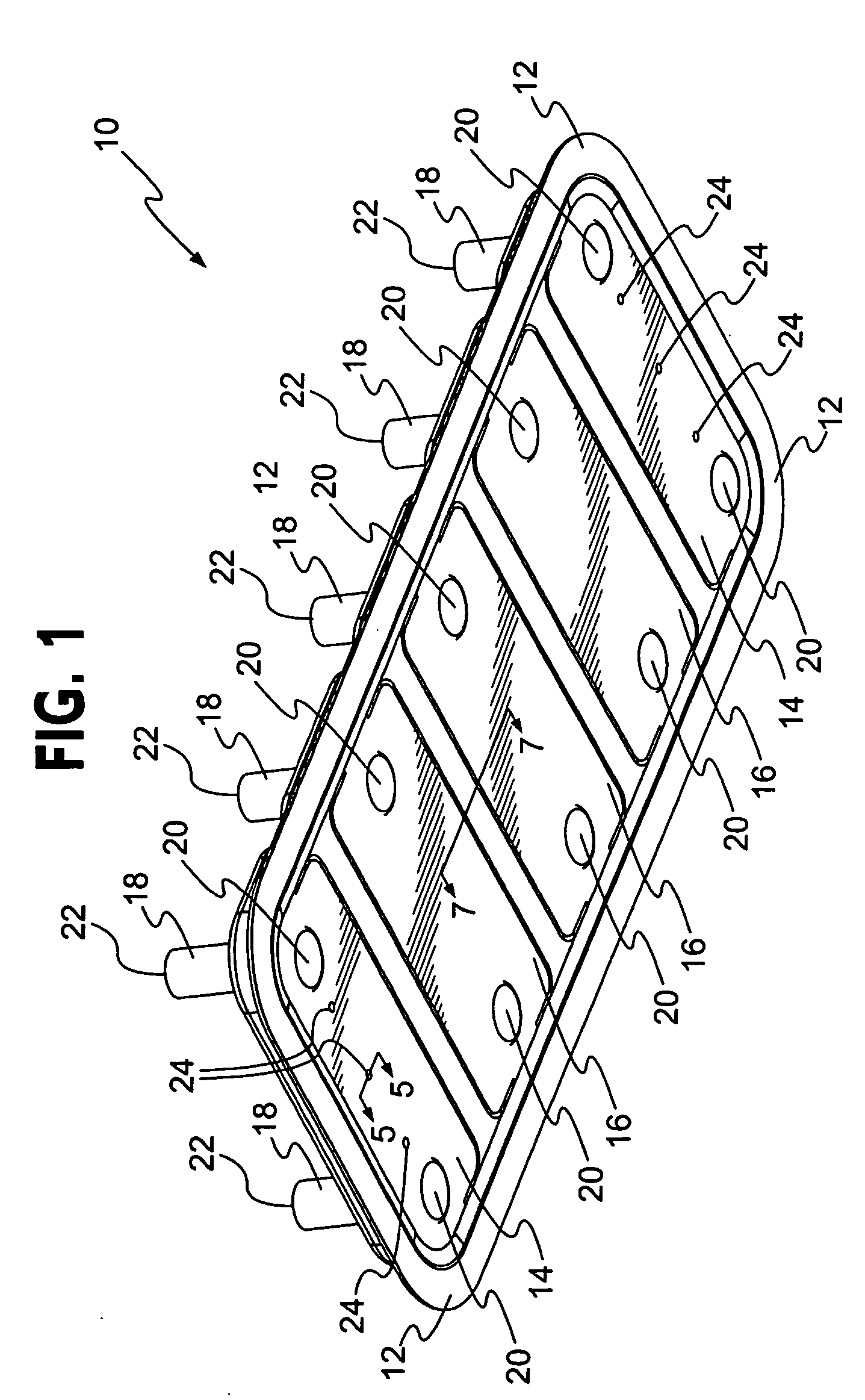
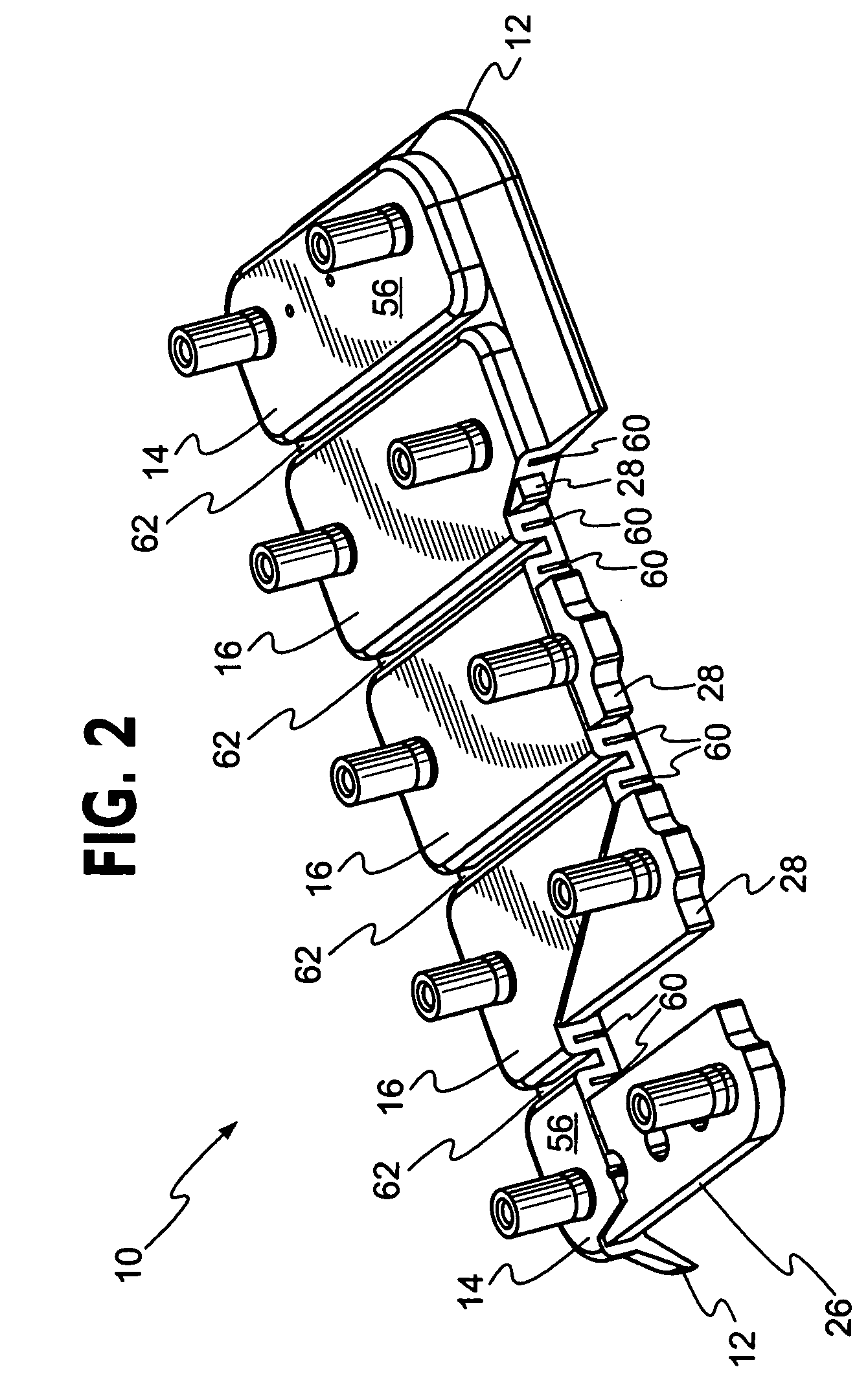
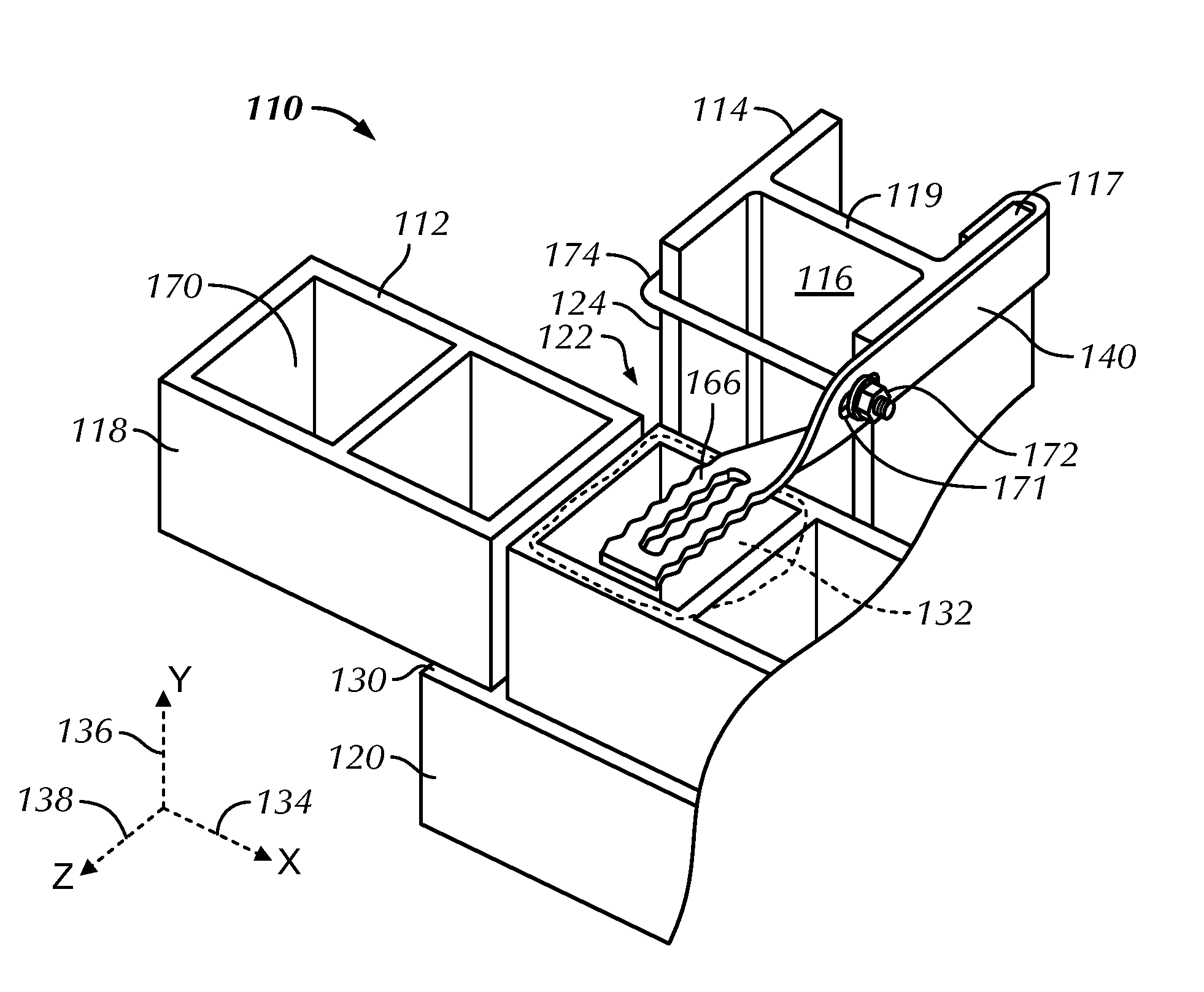
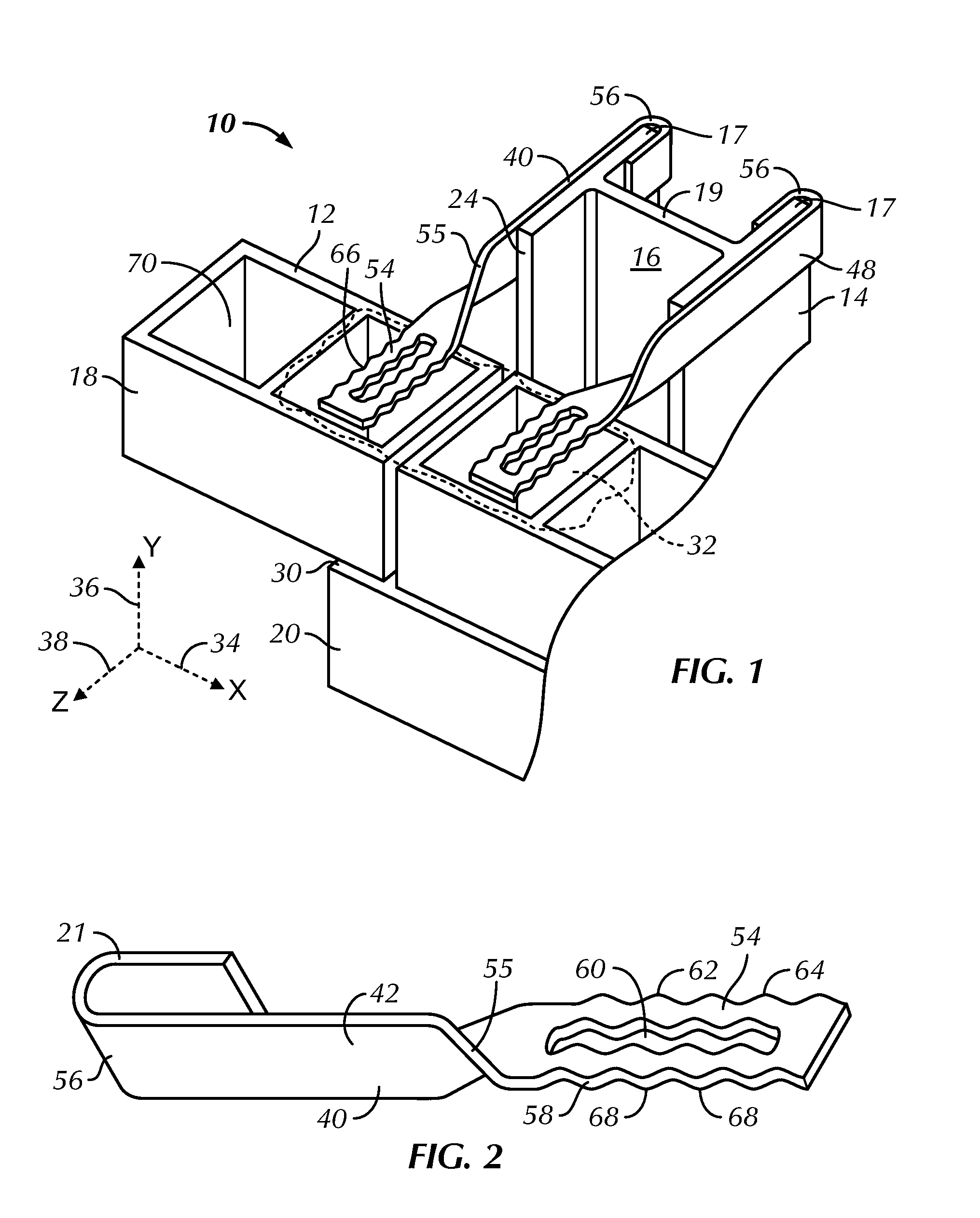
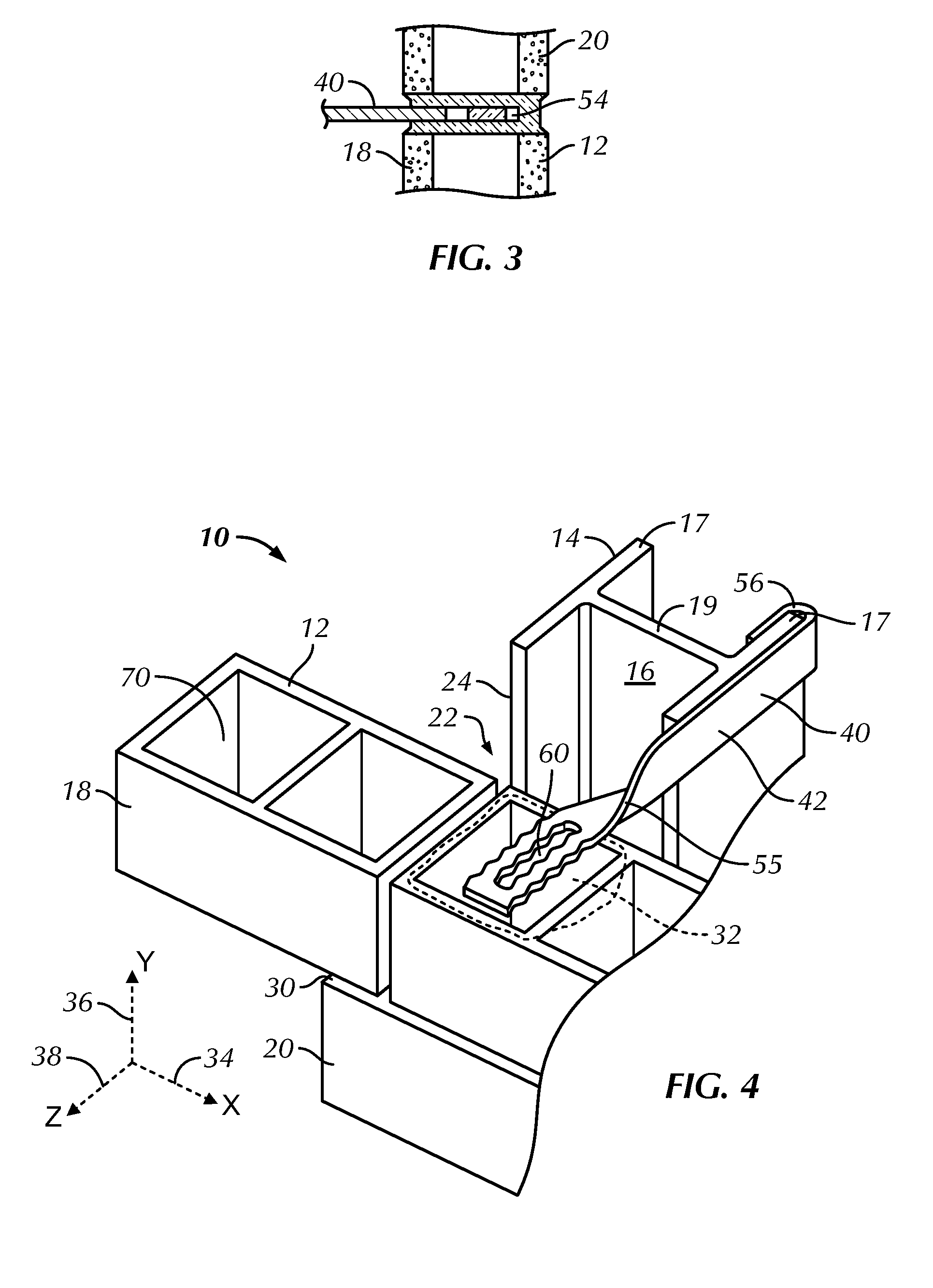
Sheet metal stud and composite construction panel and method
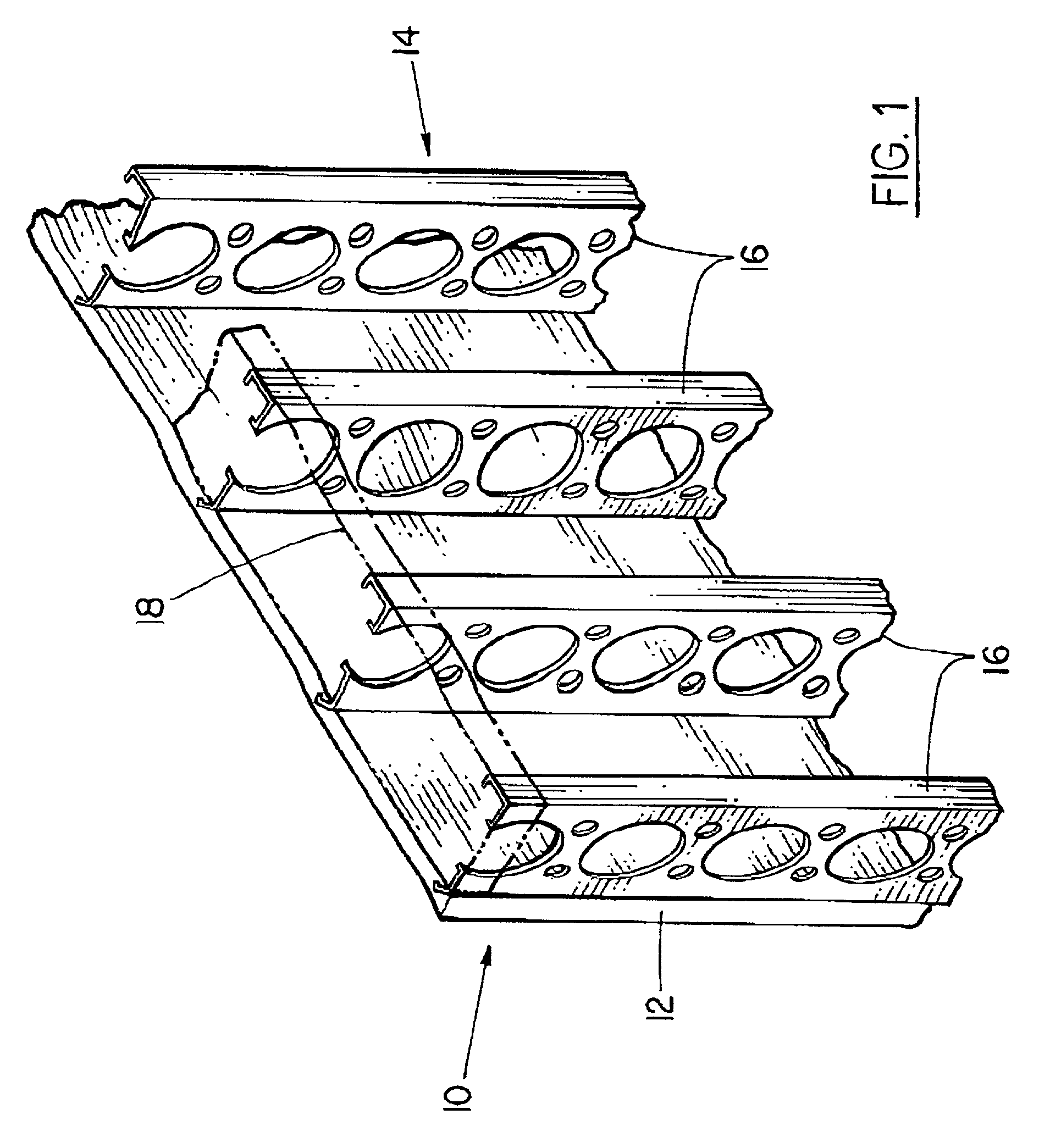
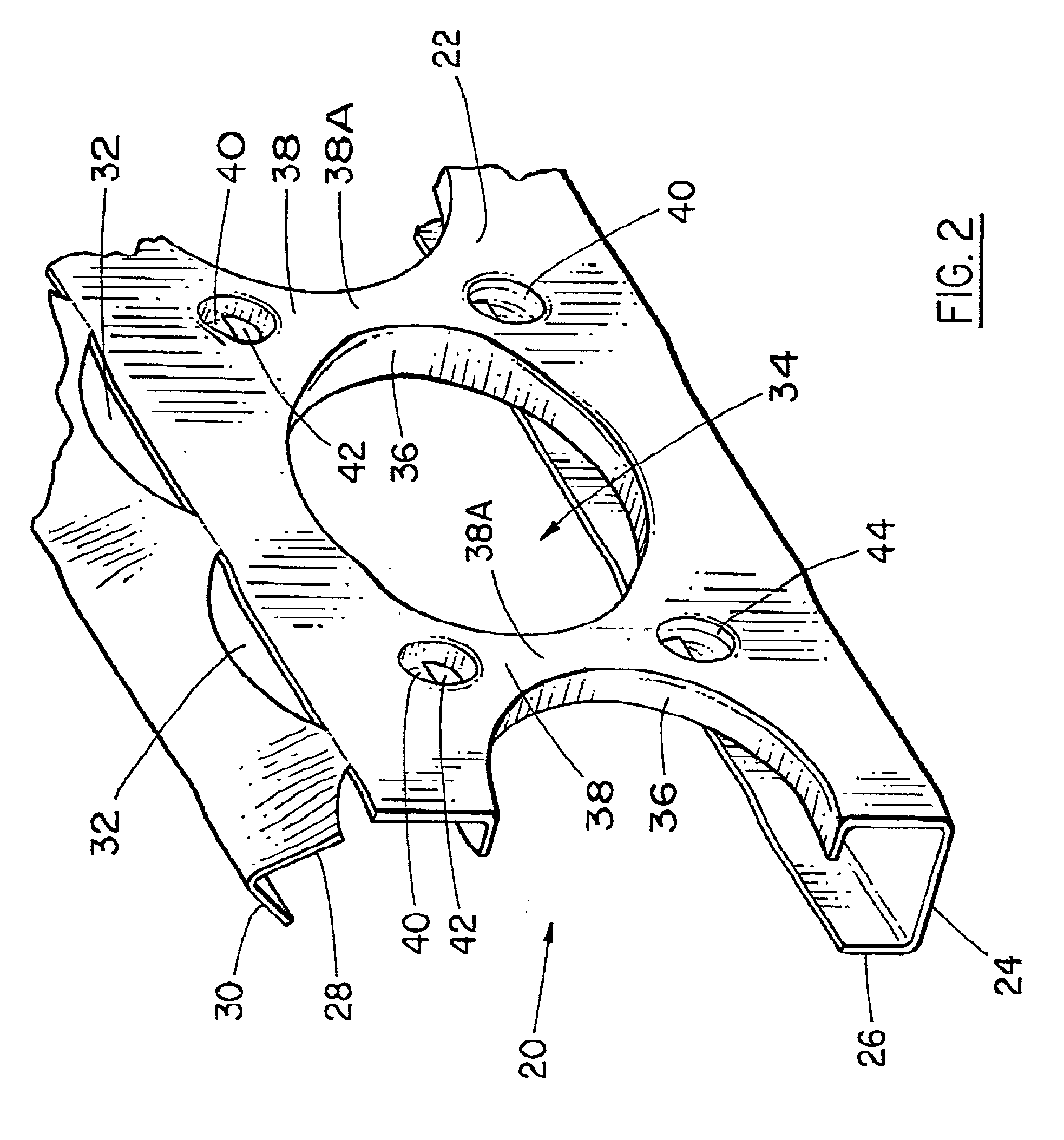
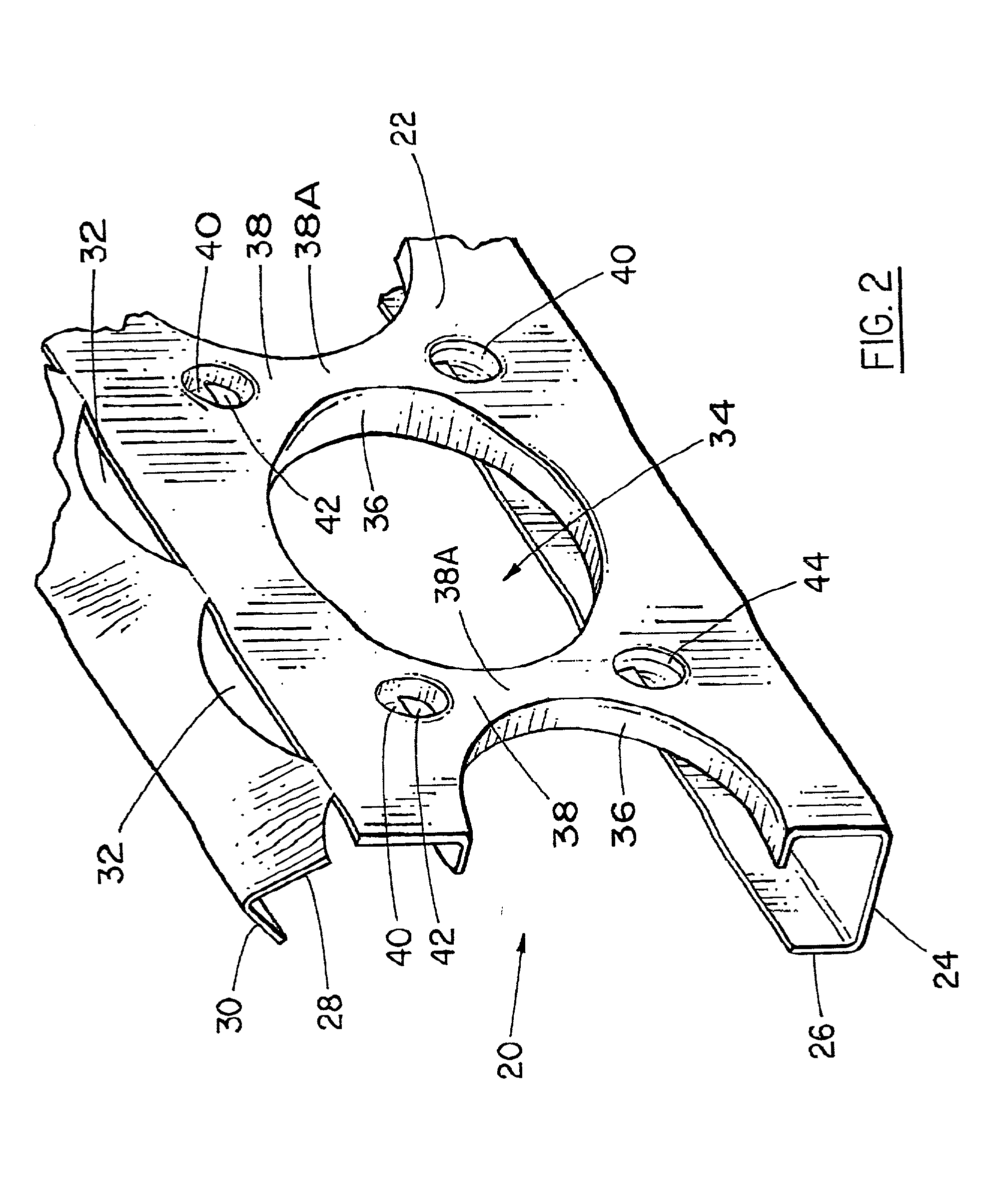
A composite construction panel having a thin panel of concrete material and a reinforcing grid of sheet metal studs with embedment portions which are actually embedded into the concrete panel, each of the studs having a web, main web openings through the web, a right angular flange formed on a free edge of the web, an embedment angled flange portion formed along the opposite edge of the web, an edge strip formed on the angled flange at an angle thereto; and, spaced apart angled flange openings formed in the angled flange for flow of concrete therethrough. An alternate form of stud has a triangular tube structure along one edge of the web. Another form of stud has a discontinuous webs defining spaces between them. In one embodiment two concrete panels may be secured to the studs in spaced relation to create a hollow structure.
Owner:GCG HLDG
Hemming method and apparatus
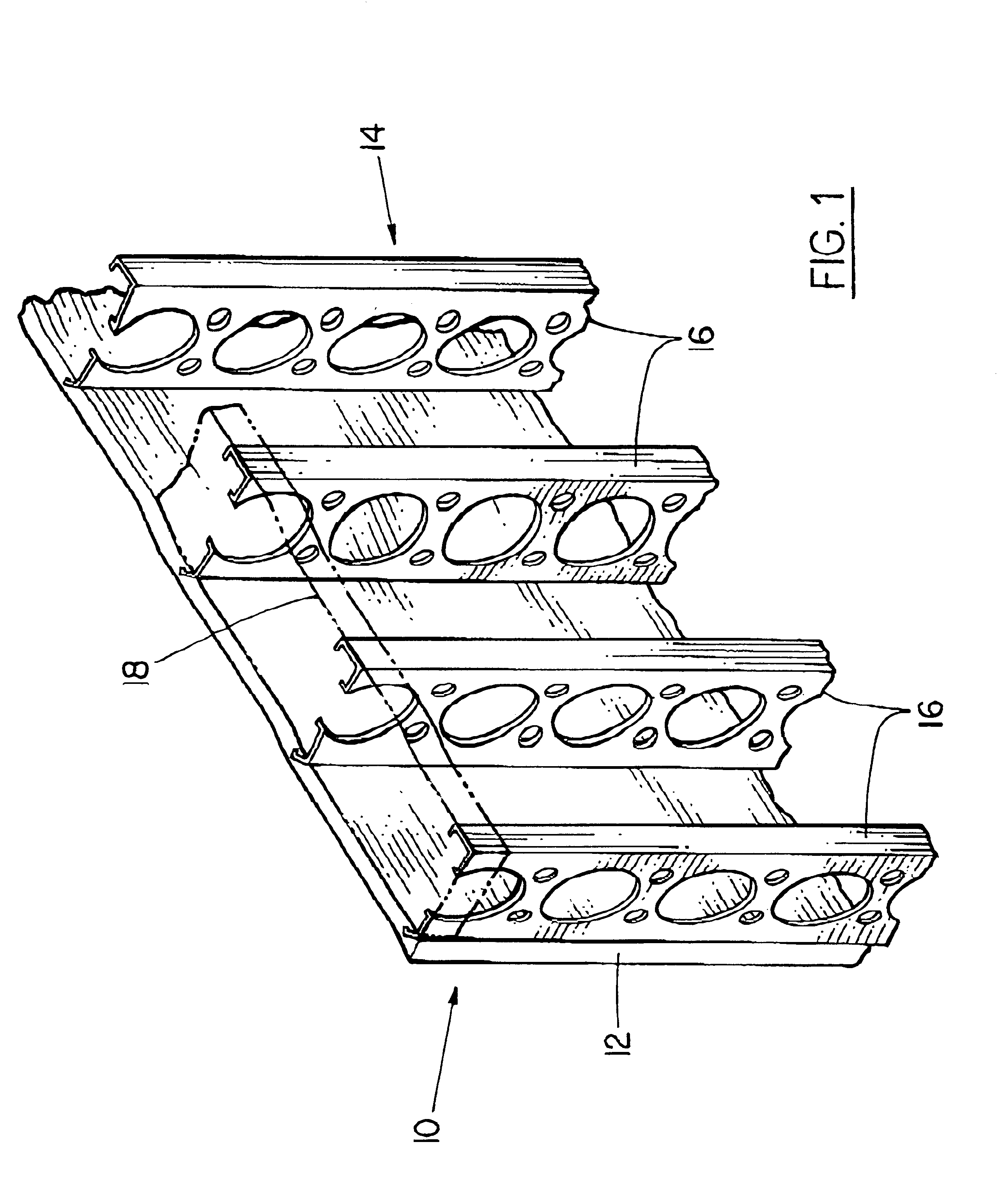
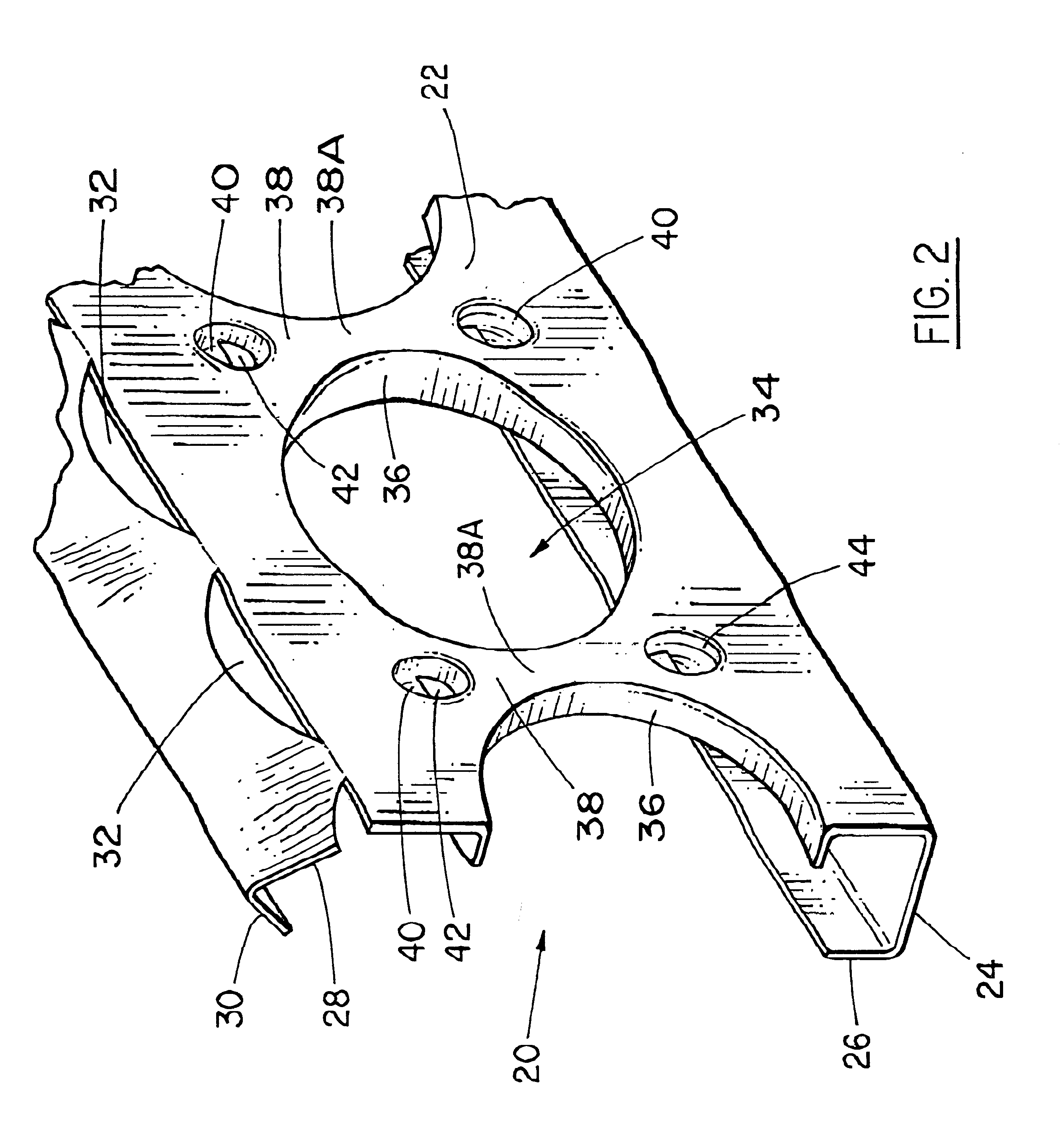
InactiveUS6029334AImprove appearance qualityEliminate the problemForging hammersAssembly machinesEmbedmentRead through
Improved method and apparatus for interlocking hemmed together edges of inner and outer vehicle body panels with an improved interlock joint. The inner panel blank is draw stamped and provided with PLP holes in a stamping press. A plurality of conventional hardware components are then welded to the inner panel. Then interlock holes are formed by a piercing tool moving through the inner panel border from its outboard to its inboard side while the inner panel is held by clamps and PLP pins. The hole piercing punch thus leaves cold worked upset material slightly raised inboard, rather than outboard, around the pierced interlock hole margin. Then the inner panel subassembly is married to the outer panel and transferred to a hemming station and again precisely clamped and positioned by PLP pins, whereupon hemming press gates are operable for hemming the flange lip of the outer panel over the inner panel border. The final hemming steel of each gate carries staking punches that individually strike a precision registered portion of such hemmed lip to deform it into locking engagement with the associated interlock hole. The upset material is thus flattened and accurately worked into embedment into the interior surface of the hemmed flange lip, rather than into the interior surface of the outer panel, thereby avoiding creating read through problems on the outer panel.
Owner:UNOVA IP
Panel smoothing process and apparatus for forming a smooth continuous surface on fiber-reinforced structural cement panels
InactiveUS20080099133A1Remove pock marks or groovesA large amountSolid waste managementTransportation and packagingProduction lineSurface layer
A vibrating flexible smoothing sheet or shroud disposed transversely of a direction of travel of a formed fiber panel including gypsum-cementitious slurry and embedded chopped fibers. The sheet is used to smooth the surface of the panel as it exits a fiber embedment station of a structural cementitious panel production line to remove grooves and other non-uniform surface imperfections to reduce the need for costly finishing after the panels are cured and cut to size. The flexible sheet is designed to float over the surface of the formed panel without tearing or otherwise damaging the surface of the heavily fiber reinforced surface layers of the panel. The vibrating sheet is pivotally mounted on the side dams of the web production line so it can float over the panel surface during use, but be raised off the line when not in use.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
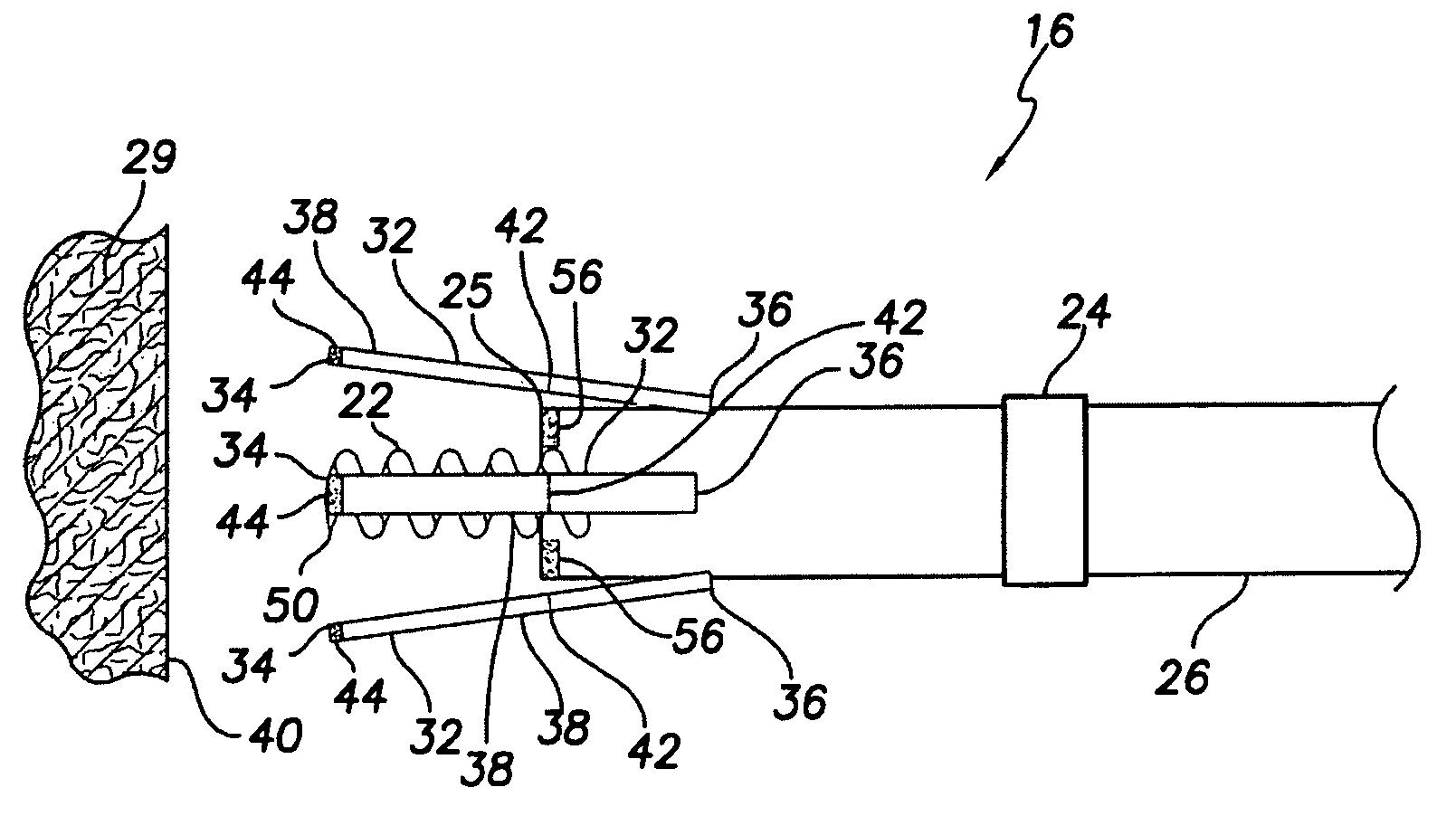
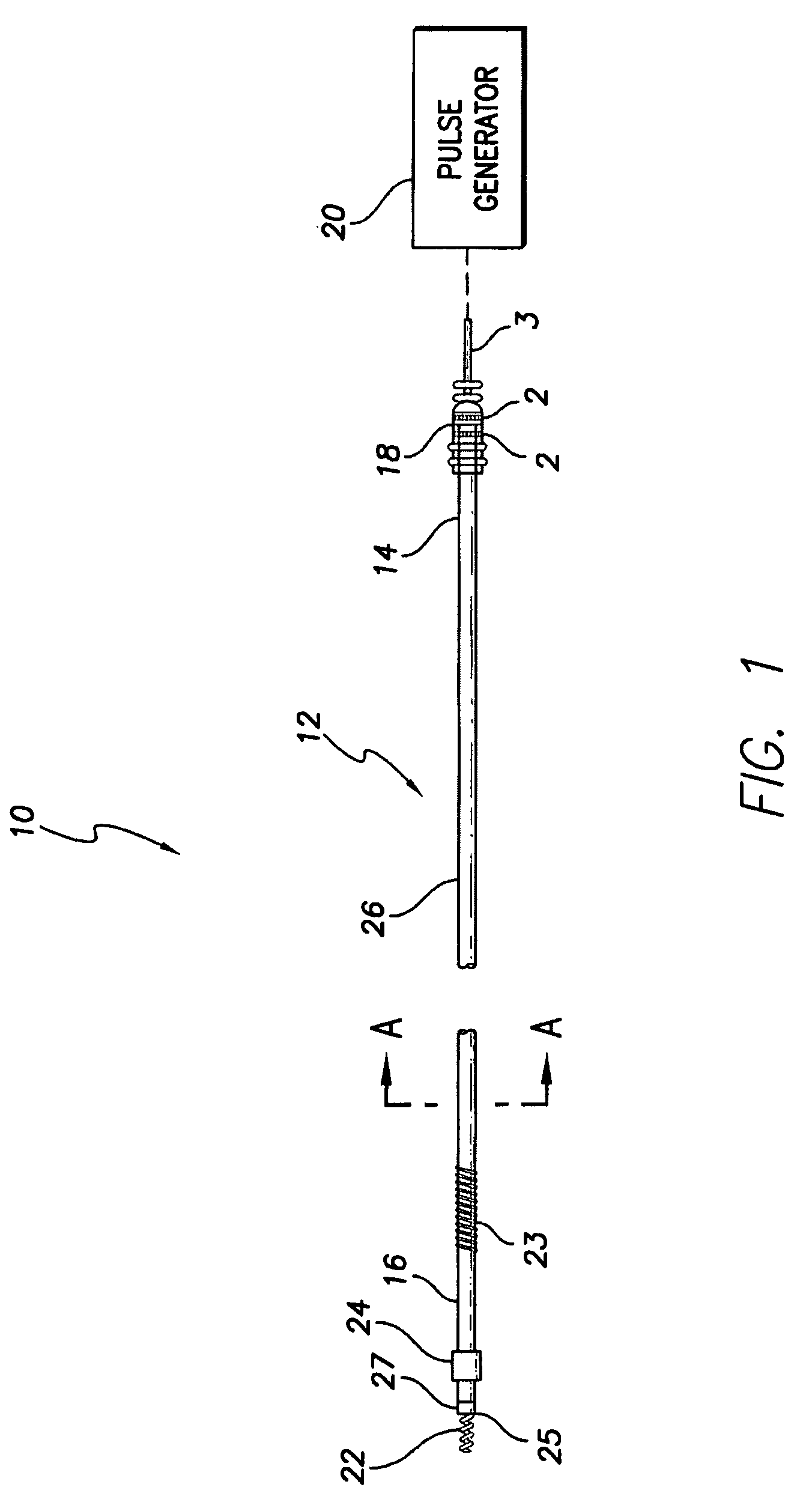
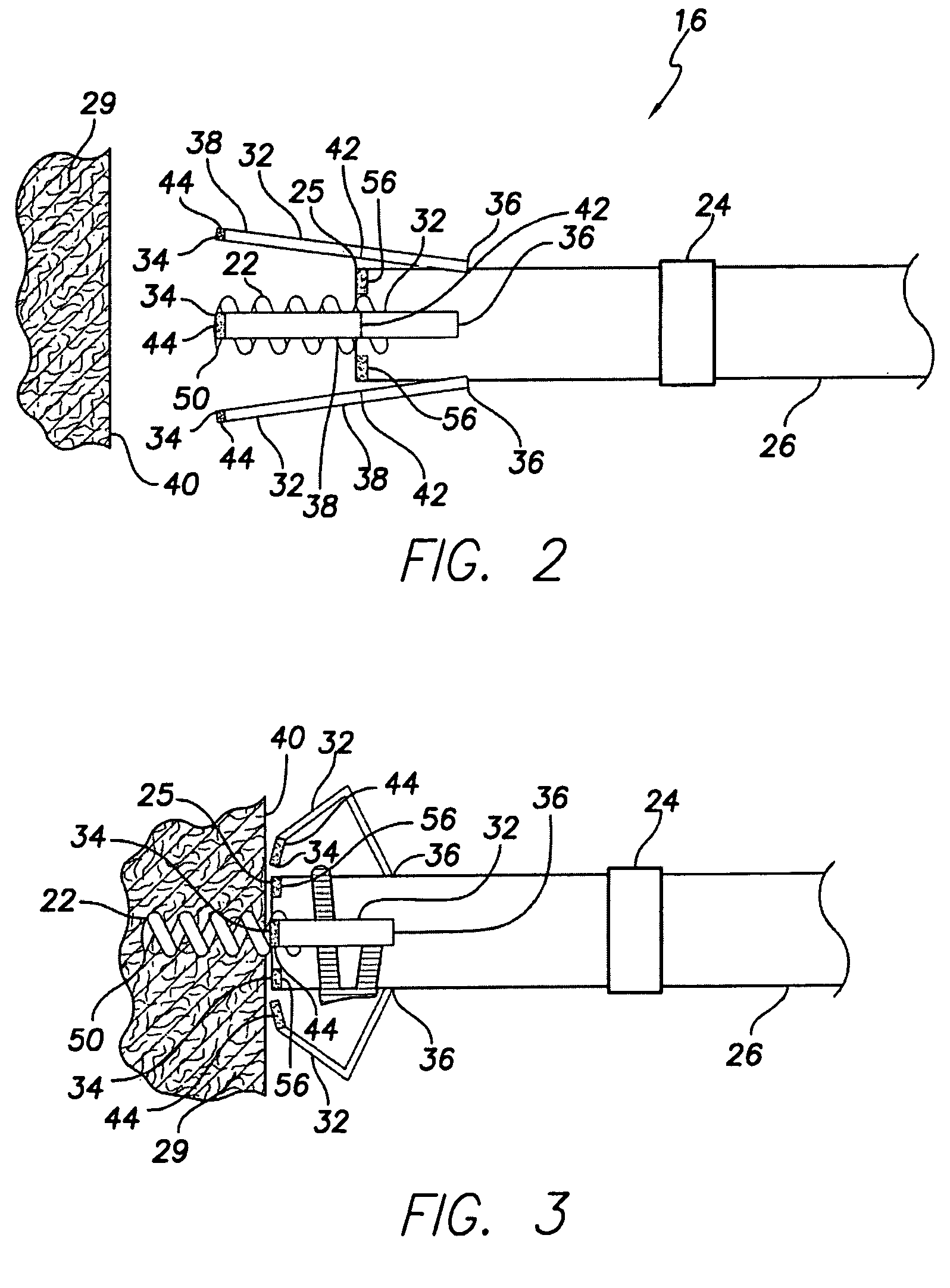
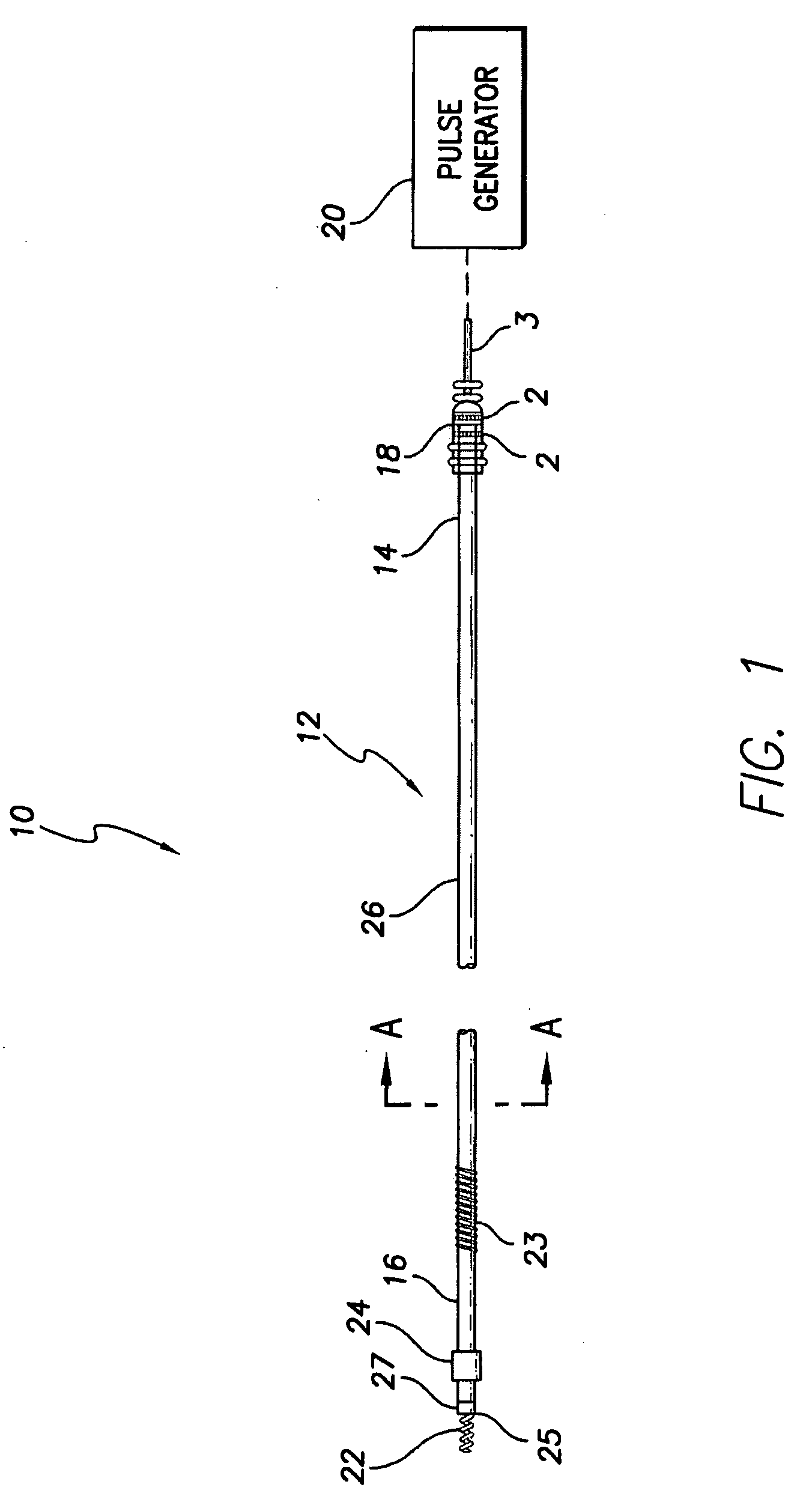
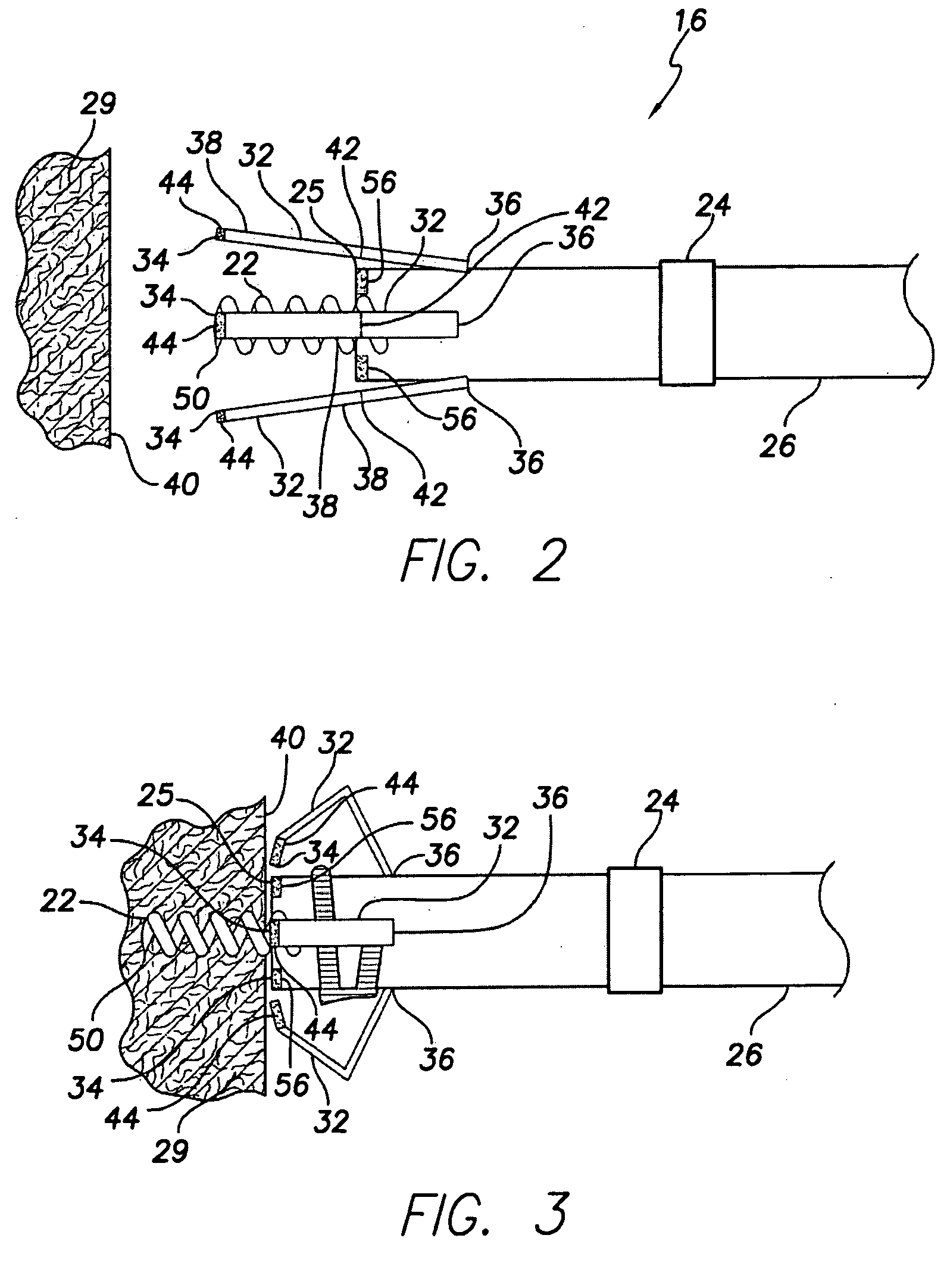
Active fixation implantable medical lead configured to indicate via fluoroscopy embedment of helical anchor in cardiac tissue
An implantable medical lead for active fixation to cardiac tissue is disclosed herein. The lead may include a lead body distal end, a tissue fixation helical anchor and a structure. The tissue fixation helical anchor may be coupled to the lead body distal end and include a distal tip. The structure may be coupled to the lead body distal end and include a structure distal end including a first radiopaque marker. The structure may be biased to project the structure distal end near the distal tip. When the tissue fixation helical anchor is progressively embedded in the cardiac tissue, the cardiac tissue progressively displaces the structure distal end proximally.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Transfer coping for dental implants
An impression coping is provided for taking an impression of an implant installed in a patient's mouth. The impression coping comprises an engagement portion, a cover and an impression portion. The engagement portion is adapted to be inserted within an internal cavity of the implant. The engagement portion has a plurality of axially extending protrusions positioned around the periphery for engaging corresponding channels within the internal cavity of the implant. The engagement shaft is thus configured to register the internal orientation of the implant within a patient's jaw. The impression portion of the coping includes one or more embedment features adapted to be embedded in a dental impression material for taking a dental impression thereof.
Owner:NOBEL BIOCARE SERVICES AG
Construction method of shallow buried underground excavating tunnel super large section using PBA method
ActiveCN101225742ASolve comprehensive technical problemsSolve processing problemsUnderground chambersTunnel liningShotcreteTerrain
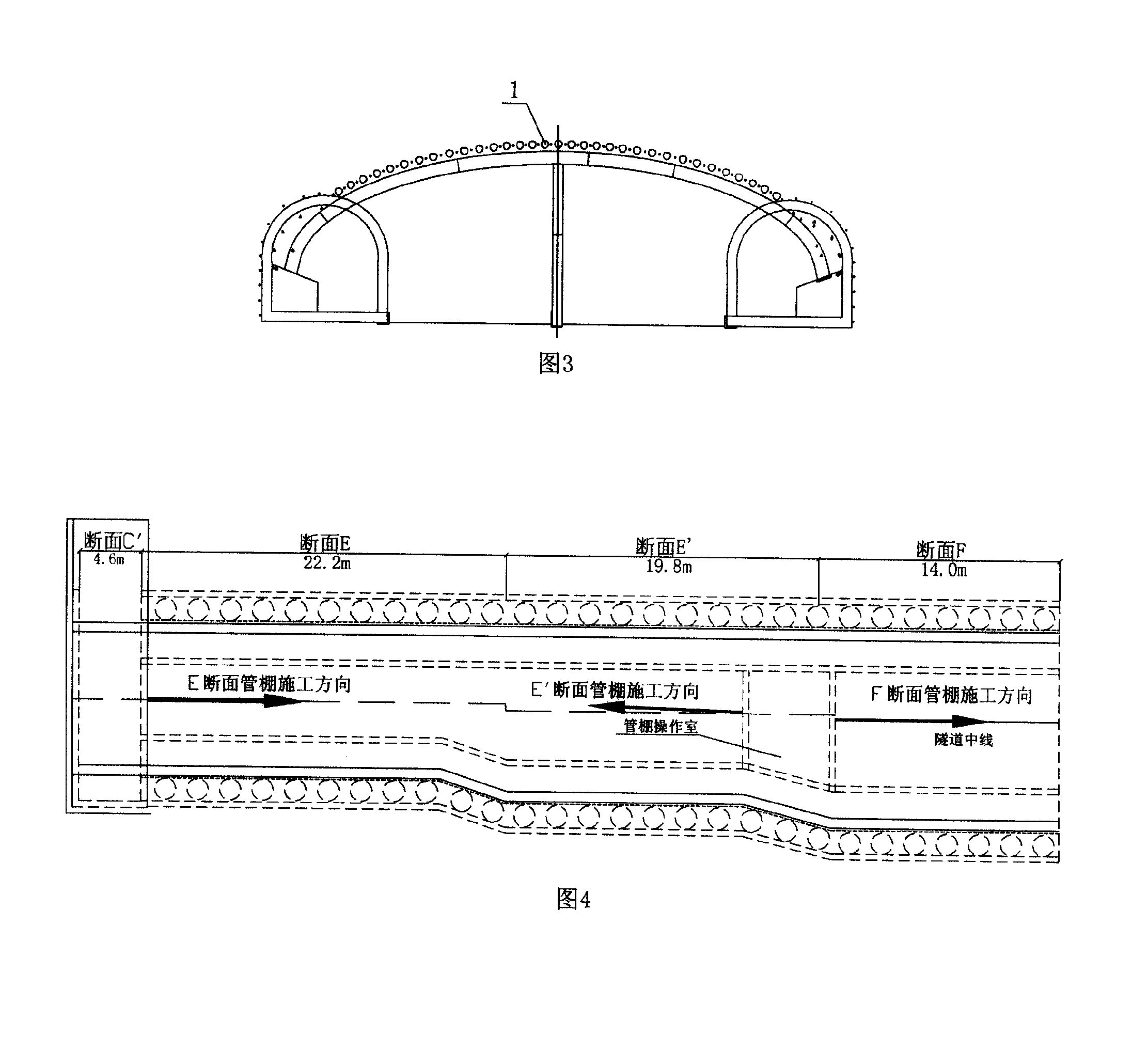
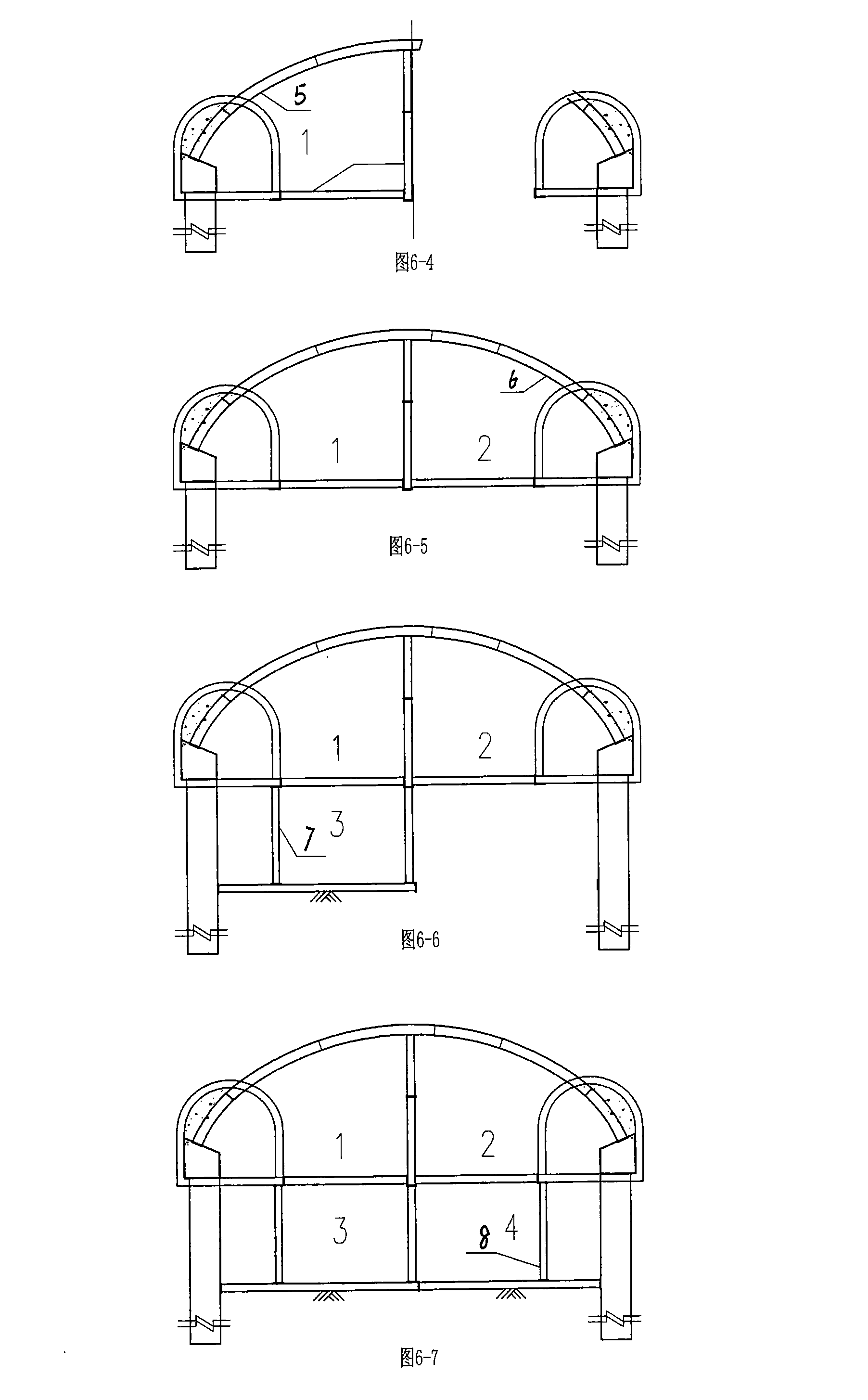
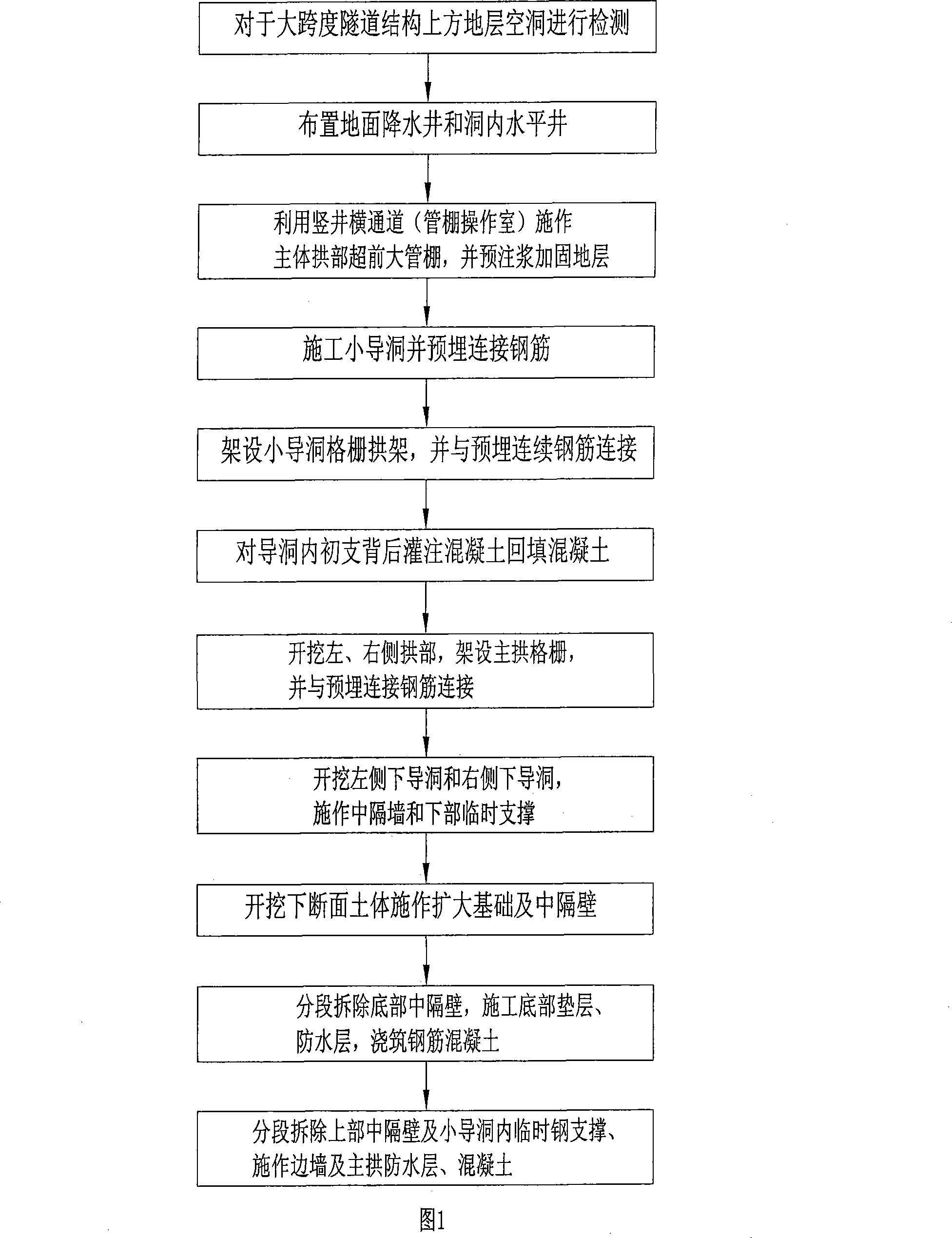
The invention relates to a method of shallow embedment and concealed excavation based on the PBA method for construction on super large cross-section of tunnel, comprising the following steps: 1. to detect the geologic cavity over the wide span tunnel structure; 2. to arrange the ground dewatering well and the tunnel horizontal well; 3. to take the horizontal channels of vertical well as the front large pipe shed on the arch part of the main body and to inject for strengthening the terrain formation; 4. to carry out the supporting arch construction on the side span of small pilot tunnel and the supporting major arch construction on the main body; 5. to excavate the soil mass of lower cross section as the extended foundation and the central partition wall; 6. to remove the bottom central partition wall section by section, construct bottom underlayer and waterproof layer, pour the reinforced concrete; 7. to remove the central partition wall of the upper part section by section and temporary steel shotcrete in the small pilot tunnel, construct the waterproof layer and concrete of the side wall and the main arch. The method of shallow embedment and concealed excavation based on the PBA method for construction on super large cross-section of tunnel has the advantages of guaranteeing the safety, quality and time limit of the construction, saving cost and enhancing work efficiency.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY 18TH BUREAU GRP CO LTD
Fiberglass mesh scrim reinforced cementitious board system
InactiveUS20120148806A1High densityGood field performanceSolid waste managementWarp knittingSpatial OrientationsYarn
A cementitious board system which is reinforced on its opposed surfaces by an improved glass fiber mesh scrim with thicker yarn and larger mesh openings to provide a cementitious board with improved handling properties while retaining tensile strength and long term durability. The fabric is constructed as a mesh of high modulus strands of bundled glass fibers encapsulated by alkali and water resistant material, e.g. a thermoplastic material. The composite fabric also has suitable physical characteristics for embedment within the cement matrix of the panels or boards closely adjacent the opposed faces thereof. The fabric provides a board system with long-lasting, high strength tensile reinforcement and improved handling properties regardless of their spatial orientation during handling. Included as part of the invention are methods for making the reinforced board.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Sheet metal stud and composite construction panel and method
A composite construction panel having a thin panel of concrete material and a reinforcing grid of sheet metal studs with embedment portions which are actually embedded into the concrete panel, each of the studs having a web, right angular flange formed on a free edge of the web, an angled edge strip formed along the free edge of the right angular flange, an embedment angled flange portion formed along the opposite edge of the web, an edge strip formed on the angled flange at an angle thereto; and, spaced apart angled flange openings formed in the angled flange for flow of concrete therethrough. An alternate form of stud has a triangular tube structure along one edge of the web. Another form of stud has a discontinuous webs defining spaces between them. In one embodiment two concrete panels may be secured to the studs in spaced relation to create a hollow structure.
Owner:BODNAR ERNEST R
Lateral earth pressure sensor embedment method and device in earth
InactiveCN101358455ALow priceLow bending stiffnessArtificial islandsForce measurementSteel jacketData acquisition
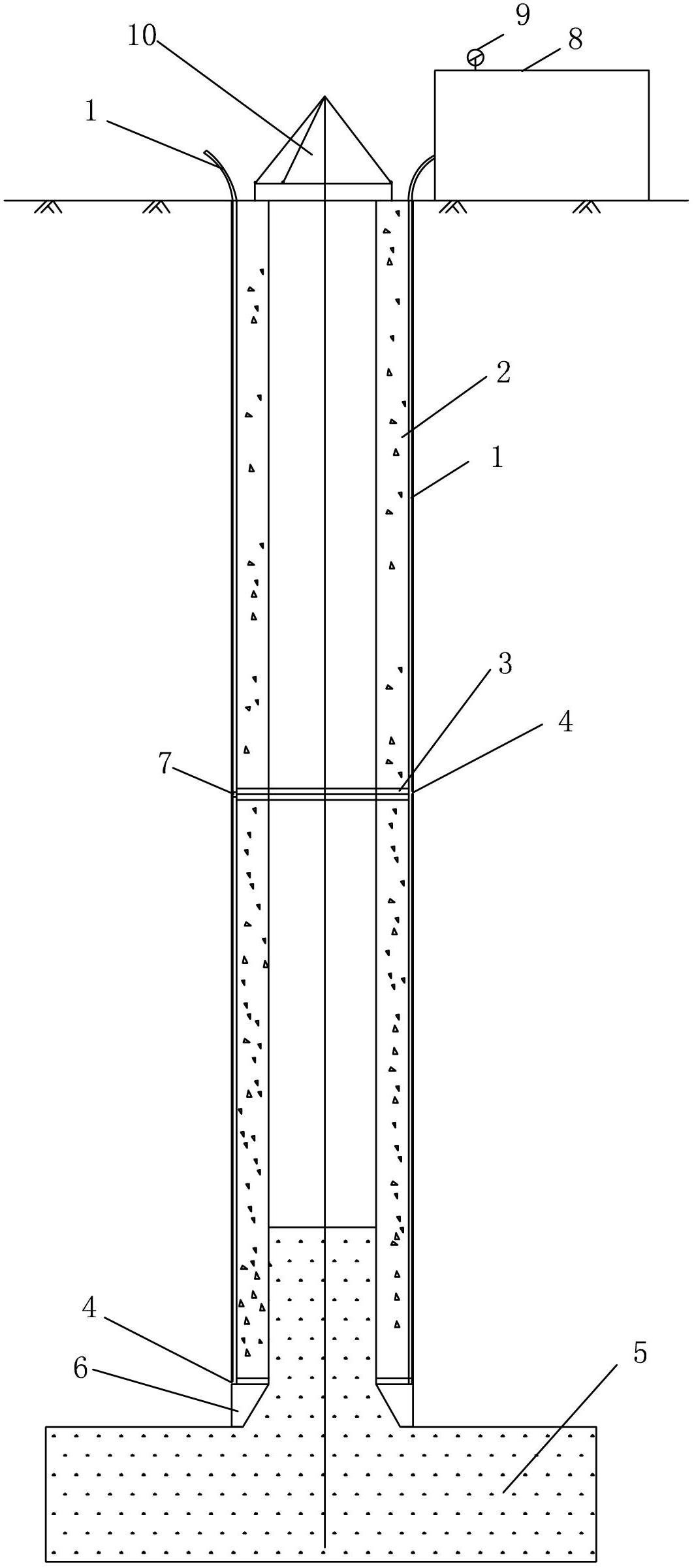
The invention relates to a method for embedding a side-direction soil pressure sensor in the soil and a device thereof, which belongs to the technical field of construction engineering. The device comprises a sensor installation pipe, an extension pipe, a soil pressure sensor, a protective steel jacket, a U-shaped protective steel clip, a rigging screw, a connector pipe, a data transmission guide wire and a data collection instrument. The data transmission guide wire of the soil pressure sensor is connected with the data collection instrument. A notch is arranged in the center of the sensor installation pipe; the soil pressure sensor is put into the protective steel jack and then the soil pressure sensor and the protective steel jack are embedded in the notch; the U-shaped protective steel clip and the rigging screw are used to fix; the connector pipe is used to extend the sensor installation pipe and the extension pie to the design length; the pipes are put into a soil drilling hole; the guide pipes are fixed temporarily, and then fine sand is backfilled into the drilling hole; after the fine sand is consolidated, and the side direction soil pressure test is carried out. The invention has the advantages of convenient installation and operation, economy and practicality, high survival rate of the sensor embedded, capability of quite accurately measuring the side direction soil pressure in the soil, and accurate and reliable test result.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Hydraulic Fracturing Proppants
ActiveUS20110180259A1Increase contact areaImprove stress distributionFluid removalDrilling compositionStress distributionEmbedment
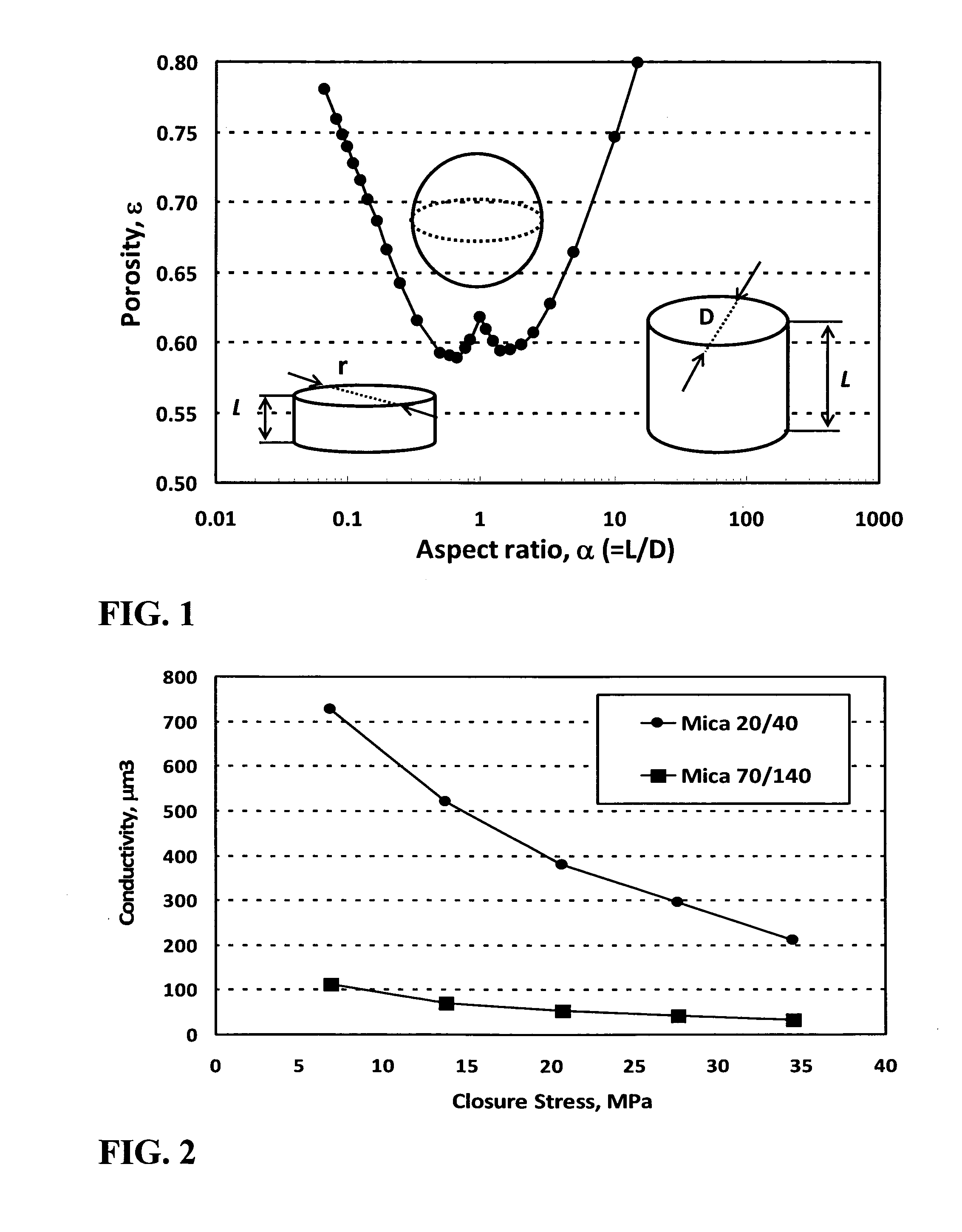
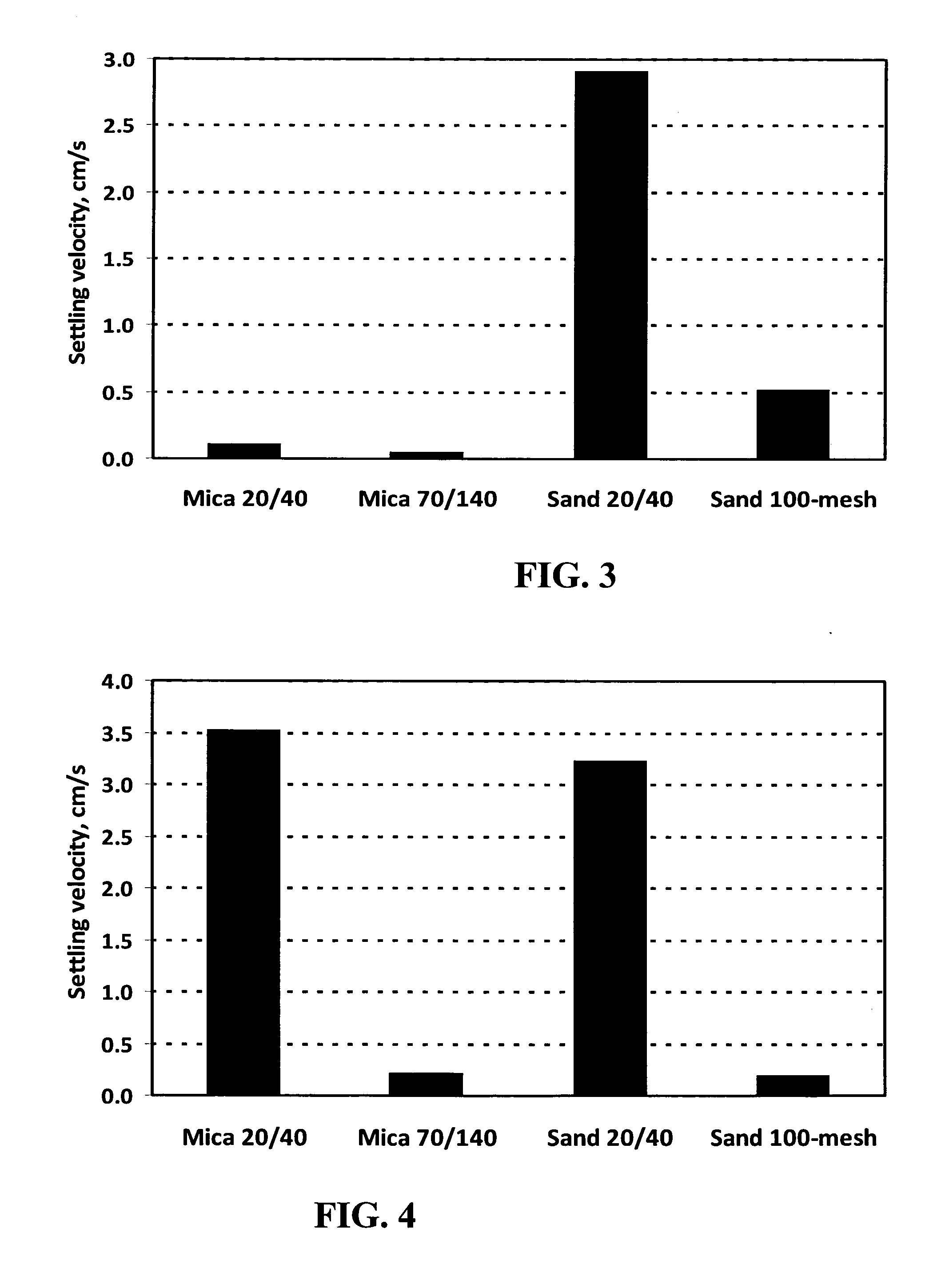
A method is given for treating a wellbore in a subterranean formation by hydraulic fracturing, slickwater fracturing, gravel packing, and the like, by using plate-like materials as some or all of the proppant or gravel. The plate-like materials are particularly useful in complex fracture systems, for example in shales. They may be used as from about 20 to about 100% of the proppant. Relative to conventional proppants, plate-like proppants demonstrate (a) enhanced crush resistance of the proppant due to better stress distribution among proppant particles, (b) diminished proppant embedment into formation fracture faces due to the greater contact surface area of proppant particles with the formation, (c) better proppant transport due to lower proppant settling rates, (d) deeper penetration into branched and fine fracture networks, and (e) enhanced proppant flowback control. Preferred plate-like proppants are layered rocks and minerals; most preferred is mica.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Porous silicon-based cathode for lithium battery and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101894940AIncrease capacityGood high current discharge performanceCell electrodesCopper foilSolvent
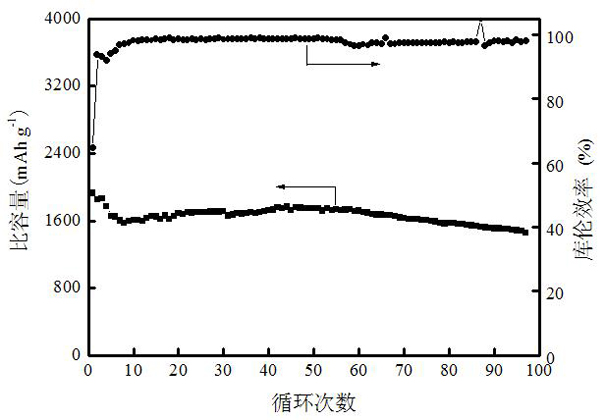
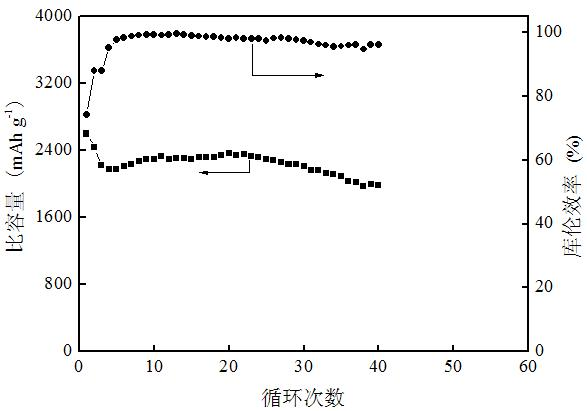
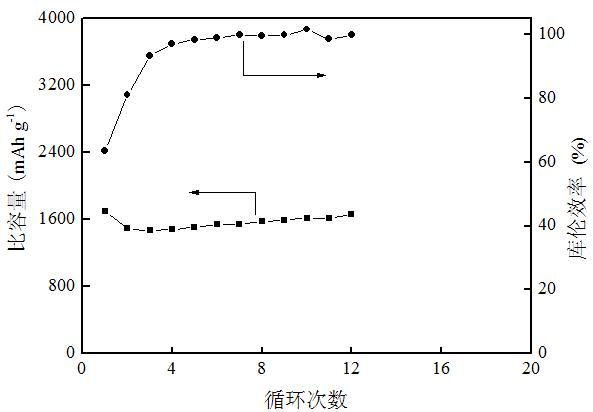
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous silicon-based cathode for a lithium battery and relates to a battery cathode and a preparation method thereof. In the invention, the problem that the great volume change produced in battery cathodes made of the conventional silicon-based materials during Li embedment and removal leads to destruction of the internal structure of the material and influences the circulation performance of electrode materials is solved. The porous silicon-based cathode for the lithium battery consists of a conductive current collector layer and a high-porosity active layer. The preparation method comprises: dissolving a bonder in a solvent; adding a conductive agent, a silicon active material and a pore forming agent; coating an electrode on the surface of a metal copper foil; and drying, rolling and performing heat treatment in an atmosphere of a protective gas. In the porous silicon-based cathode of the invention, gaps can buffer the volume change of silicon effectively, improve the circulation performance of the silicon-based cathode obviously and improve the contact area between the silicon material and electrolyte; and thus, the lithium ion embedding and removing speeds are improved, and the volume and high-current discharge performance of the silicon cathode can be improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Power embedment anchor with high-frequency small amplitude vibration
The invention relates to a power embedment anchor with high-frequency micro-amplitude vibration in the ship and ocean engineering technical field. The embedment anchor comprises an anchor cover, an anchor shank, an anchor hammer, a lifting lug, a high-frequency micro-amplitude vibration device, a main fin, an anchor chain, a power source and a cable, wherein the anchor cover is arranged on the upper part of the anchor shank; the anchor hammer is arranged on the lower part of the anchor shank; the lifting lug is arranged on the surface of the outer wall of the anchor shank; the anchor chain is connected with the lifting lug; the high-frequency micro-amplitude vibration device is arranged inside the anchor shank; the main fin consists of two to four sheets which are uniformly and symmetrically arranged on the surface of the outer wall of the anchor shank; the power source supplies power to the high-frequency micro-amplitude vibration device through the cable; and the cable is connected with the power source and the high-frequency micro-amplitude vibration device through an outer cover. The embedment anchor has good holding power and underwater anchor weight ratio under different submarine sediment, can rapidly hold seabed, and is little in windlass tension needed in the process of raising anchors.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for grinding soft crisp functional crystal
InactiveCN101376228AAvoid scratchesPrevent embeddingSupport wheelsAqueous dispersionsHigh surfaceGrinding wheel
A soft brittle functional crystal grinding and machining method belongs to the technical field of soft brittle functional crystal machining, and particularly relates to a soft brittle functional crystal ultra-precision grinding and machining method for a semiconductor and a photoelectric crystal. The method is characterized in that a micro-powder diamond segmental variable speed feed and a soft abrasion grinding wheel chemical mechanical grinding method are adopted to machine the soft brittle function crystal. During the crude grinding period and the accurate grinding period, the feeding speed of the grinding wheel is firstly high and then low. A grinding fluid is de-ionized water. A soft abrasive agent grinding wheel is adopted to conduct the chemical mechanical grinding. The soft abrasive agent is a macromolecule polymer or waterproof resin. A filler is NaHCO3 or a refined naphthalene foaming agent. The chemical and mechanical grinding fluid is adopted as a reaction fluid and a cooling fluid. The grinding fluid mainly contains lactic acid, acetic acid and de-ionized water. The pH value of the grinding fluid is 2-4. The invention has the advantages of high grinding and machining efficiency, low machining cost and high surface precision. In addition, no surface / sub-surface damage is caused to the surface of a workpiece, such as small scratches, embedment of free abrasive agent, plastic deformation, residual stress, and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Conformal vacuum cup apparatus and method
A conformal vacuum cup provides a machine tool attachment fitting usable in a flexible-track drill system. Using multiple, independently articulated stiffeners, the conformal vacuum cup conforms to the contour of complex aerostructure surface shapes. The individual stiffeners are decoupled from each other to some extent by grooves and slots molded into resilient overmolding material to support long-axis curving. Spacing pins employ a domed shape consonant with the elastic deformation of the workpiece surface under load. The pins employ a hard material to prevent particle embedment in use and to control position tolerance for drill heads and other tools traveling on the flexible track. Partial holes in each vacuum cup are blocked by diaphragms. Interconnection from a vacuum system manifold to the vacuum cups can be realized by penetrating the diaphragms and inserting barbed fittings connected by vacuum tubing.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
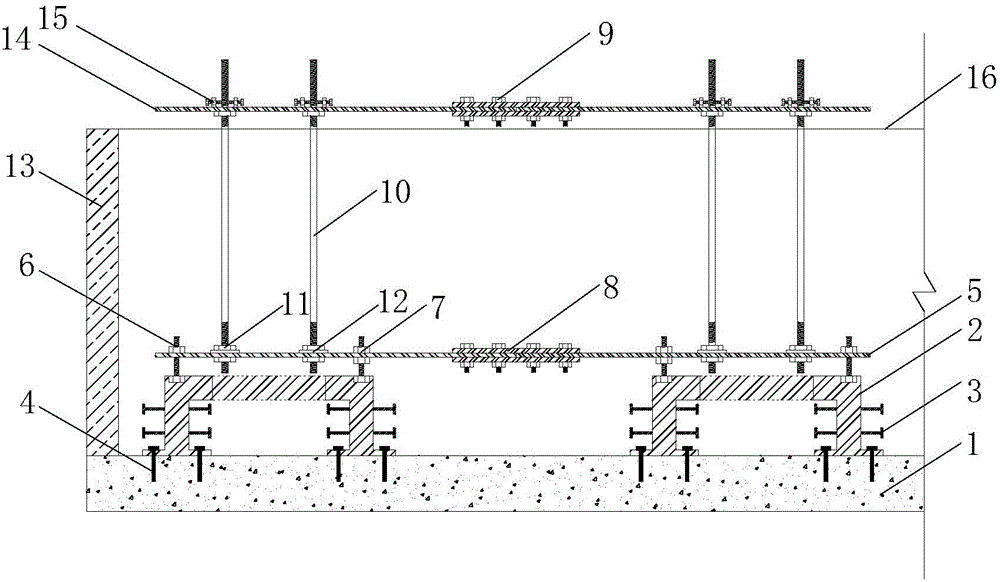
Construction method for raft plate basic high-precision overall pre-embedded large-diameter bolt group structure
InactiveCN104895101AAchieve regulationImprove embedding accuracyFoundation engineeringStructure of the EarthEmbedment
The invention relates to a raft plate basic high-precision overall pre-embedded large-diameter bolt group structure. The structure is characterized in that the structure comprises an upper-layer positioning plate, a lower-layer positioning plate, a bottom support seat, pre-embedded foundation bolts, connecting bolts, fine-adjustment bolts and leveling bolts; unit positioning steel plates are connected and assembled through node plates and the bolts to respectively form the upper- and lower-layer positioning plates, the pre-embedded foundation bolts are disposed between the upper- and lower-layer positioning plates, the pre-embedded foundation bolts and the upper-layer positioning plate are connected through the fine-adjustment bolts, the pre-embedded foundation bolts is in anchor connection with the lower-layer positioning plate; and the leveling bolts are disposed between the lower-layer positioning plate and the bottom support seat to perform connection, and the bottom support seat and a concrete cushion are connected through the pre-embedded bolts. The bolt group structure can perform three-dimensional dynamic adjustments on the pre-embedded bolts, ensures accuracy of center coordinates and scale heights of the bolts, achieves high-precision pre-embedment of a bolt group, and has a good economic technical benefit. The invention further provides a construction method for the raft plate basic high-precision overall pre-embedded large-diameter bolt group structure.
Owner:柳州市建筑工程集团有限责任公司
Sheet metal stud and composite construction panel and method
A composite construction panel having a thin panel of concrete material and a reinforcing grid of sheet metal studs with embedment portions which are actually embedded into the concrete panel, each of the studs having a web, main web openings through the web, a right angular flange formed on a free edge of the web, an embedment angled flange portion formed along the opposite edge of the web, an edge strip formed on the angled flange at an angle thereto; and, spaced apart angled flange openings formed in the angled flange for flow of concrete therethrough. An alternate form of stud has a triangular tube structure along one edge of the web. Another form of stud has a discontinuous webs defining spaces between them. In one embodiment two concrete panels may be secured to the studs in spaced relation to create a hollow structure.
Owner:GCG HLDG
Construction method for large-area irregular floor tile
InactiveCN101565997AShort construction periodReduce management costsBuilding material handlingFlooringBrickSurface layer
Owner:QINGDAO HENGSHENGYUAN GROUP CONSTR
Pipe pile foundation for static-pressure grouting on pile side and rotary jet grouting at pile bottom and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a pipe pile foundation for static-pressure grouting on a pile side and high-pressure rotary jet grouting at a pile bottom and a construction method of the pipe pile foundation. The pipe pile foundation comprises a prestressed concrete pipe pile, a reinforced graphite packing sealing gasket, a pile shoe and a pile bottom high-pressure rotary jet grouting reinforcing body, wherein a grouting pipe is embedded in a pile body of the prestressed concrete pipe pile, and the prestressed concrete pipe pile is connected with and seals the grouting pipe embedded in the pile body corresponding to an upper-section pipe pile and a lower-section pipe pile through a reinforced graphite packing sealing gasket; the pile shoe is connected with the lower end of the lowest-section pipe pile of the pipe pile foundation; the grouting pipe embedded in the pile body is reasonably provided with stock outlets in the connection position of the pipe pile and the pile shoe and the connection position of the upper-section pipe pile and the lower-section pipe pile; and one end of the grouting pipe embedded in the pile body is connected to a high-pressure grouting pump. The pipe pile foundation for static-pressure grouting on the pile side and high-pressure rotary jet grouting at the pile bottom and the construction method thereof, provided by the invention, are especially suitable for filed construction of prestressed concrete pipe pile foundations with poorer geological conditions and deep bed rock embedment, and can effectively reduce the length of a pipe pile, and meanwhile the bearing capacity of the pipe pile foundation is ensured, and thus the construction method is simple and reliable.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INSTITUTE OF BUILDING SCIENCE CO LTD +1
Tactile tile with improved reinforced embedment plate
Disclosed is an embedment tile for producing a tactilely detectable surface in a moldable material and method for using same. The tile comprises a tile member having a pattern of upwardly extending projections on its upper surface forming a tactilely detectable pattern, and a cross beam joined to the lower surface of the tile member. The cross beam defines a hollow chamber and apertures to allow for the release of air and inflow of moldable material to secure the embedment tile when the moldable material hardens. The cross beam can define a lower open portion at a cross beam end portion that eases installation by permitting a more direct flow path into the chamber for moldable material. The embedment tile can also include a reinforcing member joined to the lower surface of the tile member and / or a transverse reinforcing member joined to a lower surface of the tile member.
Owner:METADOME
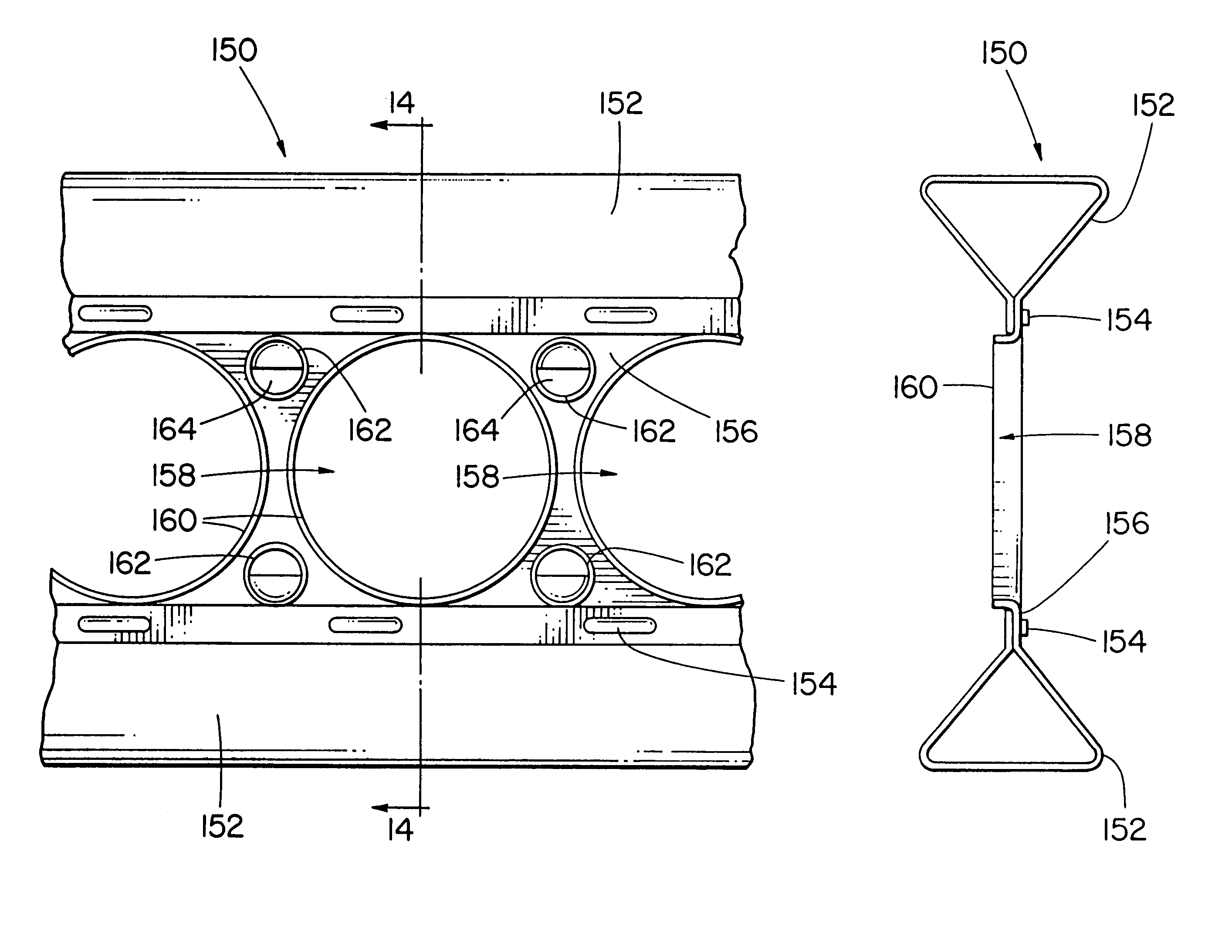
Self-stiffened welded wire lath assembly
A self-furring wire lath comprises a mesh of transverse and longitudinal wires welded at their intersections. Stiffening trusses are formed by bent sections in the transverse wires and longitudinal wires attached to the shoulders of the bent sections. A barrier layer material is retained in the lath between the apex of the bent sections and the principal plane of the lath mesh. The barrier layer material has apertures that coincide with the intersections only at the bent sections to enable mesh size reduction without compromising the barrier layer but still allow the fabrication of the lath. The lath provides good embedment in the stucco, reduces cracking and wastage of stucco while remaining easy to work with.
Owner:SACKS ABRAHAM +4
Construction method for large area concrete terrace angle steel corner protector dividing joint
ActiveCN101476382ASame seam widthImprove the quality of look and feelFlooringResource consumptionEmbedment
The invention discloses a method for constructing an angle steel corner guard dividing joint of a large area concrete pad, which comprises the followings steps: construction preparation; base layer treatment; true joint angle steel corner guard construction; terrace concrete construction; terrace concrete maintenance; dummy joint construction; and joint embedment. The method for constructing the angle steel corner guard dividing joint of the large area concrete pad has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, easy popularization, smaller operation workload, short lasting construction time, less resource consumption and good impression, and effectively avoids the hollowing cracking of the large area concrete pad.
Owner:中建五局第三建设有限公司
Decompression type blocking method for foundation pit dewatering well
ActiveCN103334444AKeep the well closedImprove construction efficiencyFoundation engineeringBasementEmbedment
The invention provides a decompression type blocking method for a foundation pit dewatering well. The method includes the steps of step 1, sleeving a waterproof casing pipe outside a dewatering well pipe and carrying out reinforcement and embedment, step 2, embedding the waterproof casing pipe and pouring the waterproof casing pipe into foundation base plate concrete, step 3, cutting off unnecessary well pipes on the base plate surface after basement base plate concrete reaches a certain strength, inserting one drainage shock tube into the lower portion of the well pipes, and enabling the top end of the drainage shock tube to be communicated with a water conduit, step 4, shutting in the well, lifting a water pump out, then filling well shut-in materials into the dewatering well pipes sequentially, step 5, enabling a cover plate and the waterproof casing pipe to be connected and fixed and enabling a small amount of water to flow out independently from the shock tube, step 6, starting a mud jack pump and compressing curing agents into the dewatering well pipe, and step 7, cutting off the portions, exposed out of the surface of the base plate, of the drainage shock tube, and then using high-intensity concrete to block portions around the well pipe. Thus, blocking of the dewatering well is finished. The decompression type blocking method is wide in application range, high in construction efficiency, convenient to operate, good in water-stop effect and small in later influence.
Owner:CHINA FIRST METALLURGICAL GROUP
Laser configured hook column anchors and anchoring systems utilizing the same
InactiveUS8904731B2Easy to installReduce manufacturing costBuilding reinforcementsRegular patternEmbedment
A high-strength laser configured column anchor and anchoring system is disclosed. The high-strength column anchor provides high-strength pullout resistance when embedded within the wall bed joint. Specially-configured apertures, edging and dimension restrictions provide for flow-through mortar embedment within the wall bed joint. The edging provides irregular and regular patterns ensuring a secure fit within the bed joint. The column anchors include a hook attachment portion for secure attachment to the column flanges and optionally include a securement bar or clamp to further secure the column anchor to the column flanges.
Owner:HOHMANN & BARNARD INC
Easily connectable anchor and pillblock replacement for an embedded wooden post
ActiveUS8584413B1Firmly connectedHigh strengthFoundation engineeringBuilding reinforcementsEmbedmentEngineering
An anchor device having a plurality of teeth protruding from planar surfaces configured for placement adjacent to the post. The teeth may be forced into the wood to secure the anchor in position until the post embedment is completed. The anchor comprises a first portion that protrudes from the surface of the post to engage with backfill, typically concrete, to resist post uplift once the backfill cures. A second portion of the anchor is secured to the side surfaces of the post adjacent to the end of the post that is to be embedded and extends beyond the end of the post. When the anchor is installed and the post inserted into a hole, the second portion of the anchor elevates the end of the post from the bottom of the post hole so that concrete backfill may flow beneath the post to form a suitable post foundation.
Owner:UPELEVATOR PLATE LLC
Active Fixation Implantable Medical Lead Configured to Indicate via Fluoroscopy Embedment of Helical Anchor in Cardiac Tissue
An implantable medical lead for active fixation to cardiac tissue is disclosed herein. The lead may include a lead body distal end, a tissue fixation helical anchor and a structure. The tissue fixation helical anchor may be coupled to the lead body distal end and include a distal tip. The structure may be coupled to the lead body distal end and include a structure distal end including a first radiopaque marker. The structure may be biased to project the structure distal end near the distal tip. When the tissue fixation helical anchor is progressively embedded in the cardiac tissue, the cardiac tissue progressively displaces the structure distal end proximally.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Ecological river interlocking type building blocks and construction method for building protection ridge through building blocks
ActiveCN103758084AImprove frost resistanceGood weather resistanceWater resource protectionCoastlines protectionCrack resistanceArchitectural engineering
The invention discloses ecological river interlocking type building blocks and a construction method for building a protection ridge through the building blocks. Each building block comprises a building block basal body, a first building block connecting body and a second building block connecting body are arranged on the two sides of each building block basal body respectively, and the first building block connecting body and the second building block body are respectively provided with grouting holes. The construction method for building the protection ridge through the building blocks particularly includes the following steps of surveying and setting out, base slot excavation and PVC drain pipe embedment, bottom plate concrete pouring, reinforcing mesh laying and installing, ecological retaining wall installing, steel doweling and grouting, grass planting, earthwork backfilling and geogrid laying. The building blocks have the advantages of being high in strength and crack resistance and few in consumed materials, and therefore the cost for manufacturing the mutually-embedded protection slope building blocks is reduced; bottom plates, retaining walls and earthworks behind the walls form a stable structure, and the structure can resist the load effect and is stable and firm.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Ground Anchor
InactiveUS20080302028A1Improved holding abilityIncrease the effective diameterTowersBuilding constructionsNormal loadPropeller
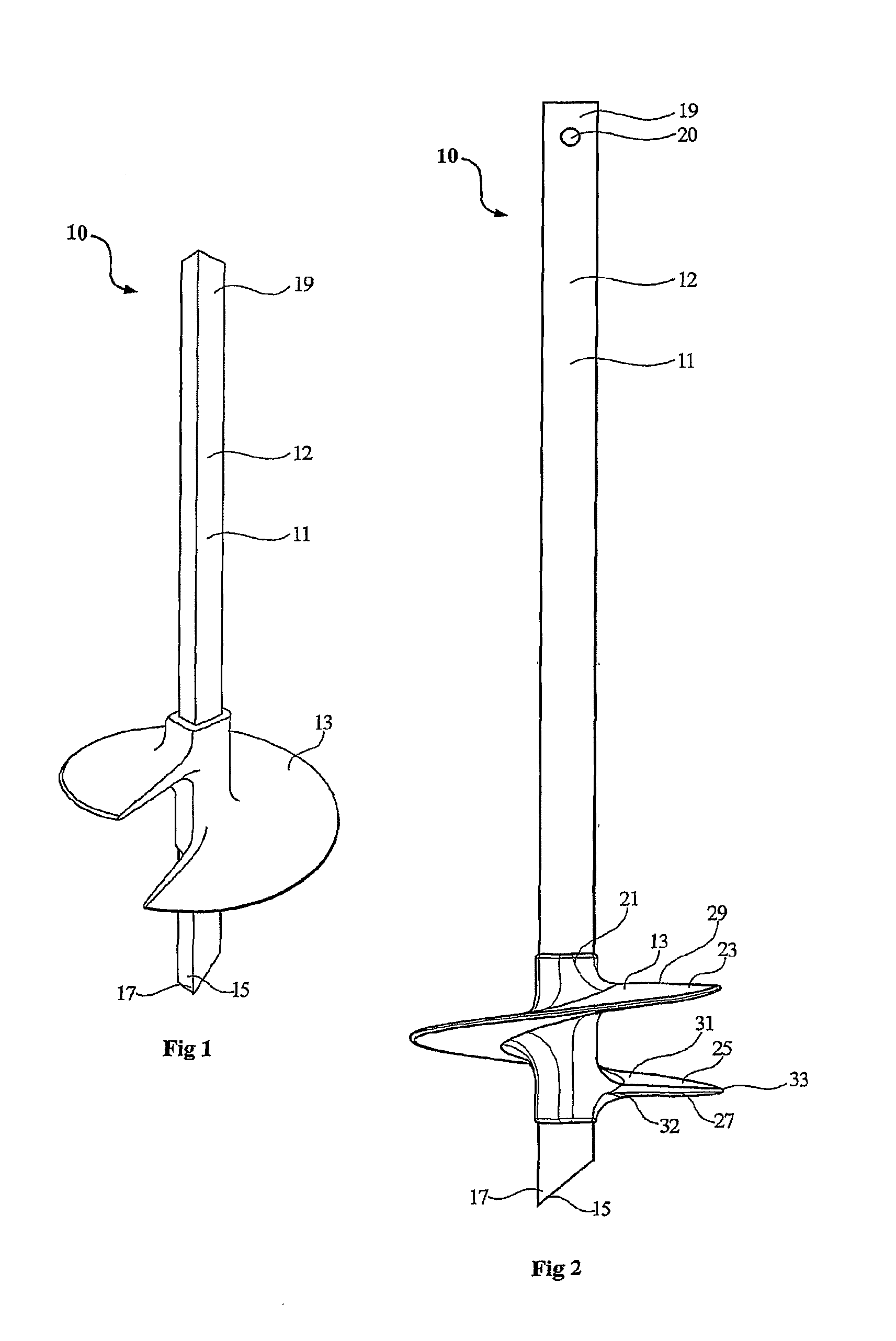
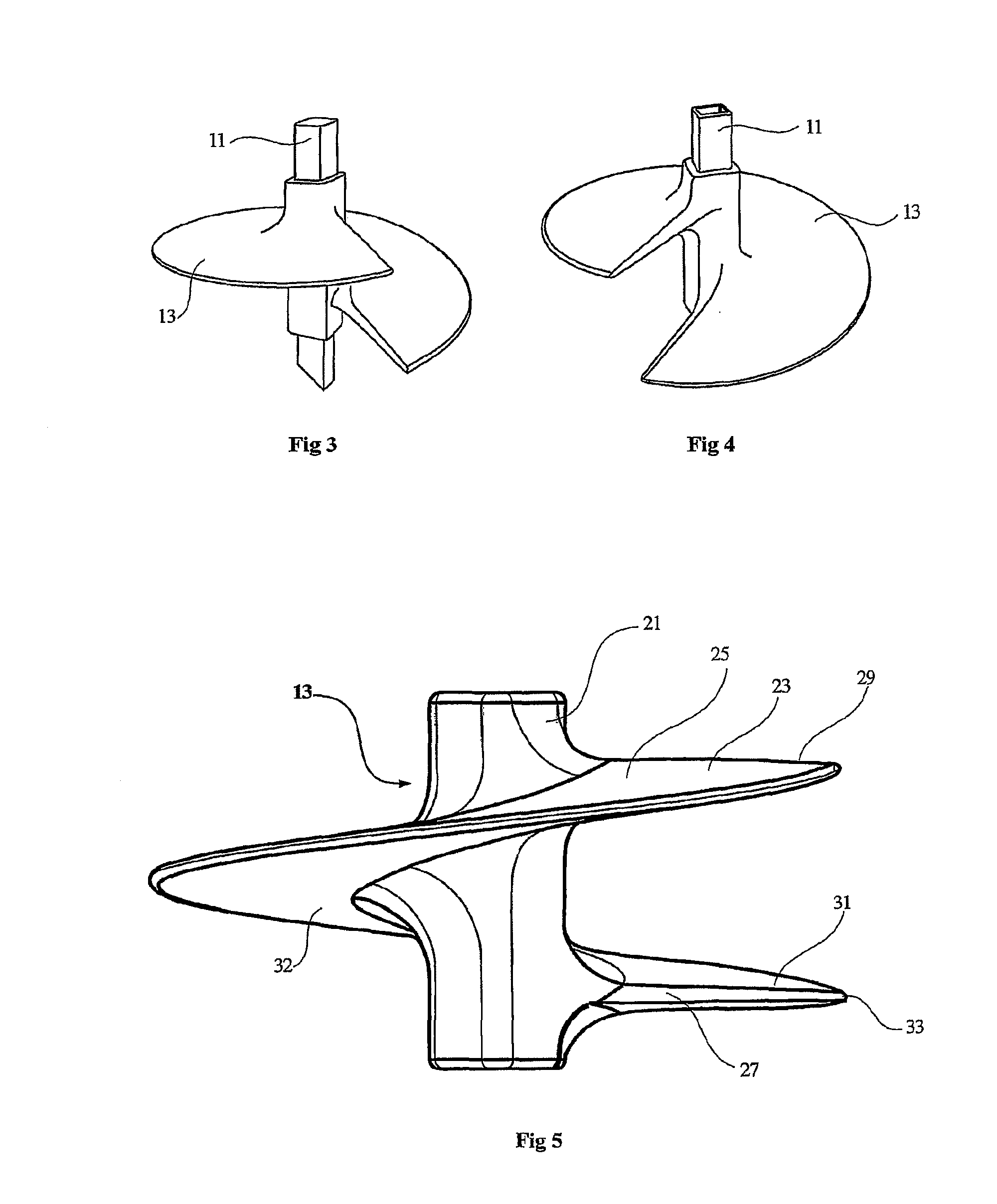
A ground anchor (10) comprising an anchor shaft (11) and an anchoring screw (13) moulded onto the anchoring shaft adjacent the lower end thereof. The anchoring shaft (11) is of a rectangular cross-section with four side walls (12). The anchoring shaft (11) is configured at its bottom end (15) for ground penetration. The upper end (19) of the anchor shaft (11) is configured to receive torque applied thereto. The anchoring screw (13) comprises a hub (21) and a screw flight (23) on the hub. The anchoring screw (13) is moulded onto the anchor shaft (11), and the hub (21) is keyed to the anchor shaft. The anchoring screw (13) is so constructed that the spiral flight (23) is rigid yet has some resilient flexibility which allows the flight to deflect laterally in the direction of the screw axis. Specifically, the screw flight (23) has sufficient rigidity to allow it to penetrate the ground in which it is intended to be used when torque is applied to the anchor shaft (11). Further, the screw flight (23) has sufficient rigidity in order to retain the ground anchor (10) embedded in the ground when subjected to the normal load conditions for which it is intended, as is the case with conventional ground anchors. The resilient flexibility provides the screw flight (23) with a degree of ‘springiness’, so allowing the screw flight (23) to deflect laterally in the direction of the screw axis when subjected to the loadings to which it is exposed when winding into the ground. With this arrangement, the pitch of the helical screw (25) is permitted to alter during ground embedment as ground pressure increases.
Owner:LEWENHOFF STEPHEN MARK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com