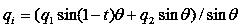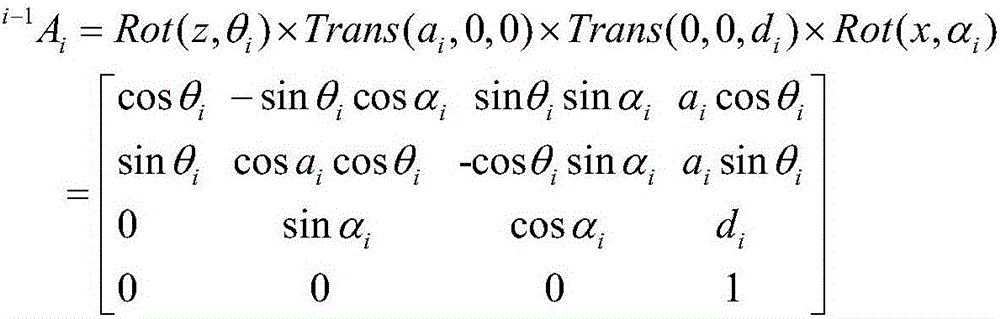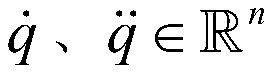Patents
Literature
816 results about "Joint angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
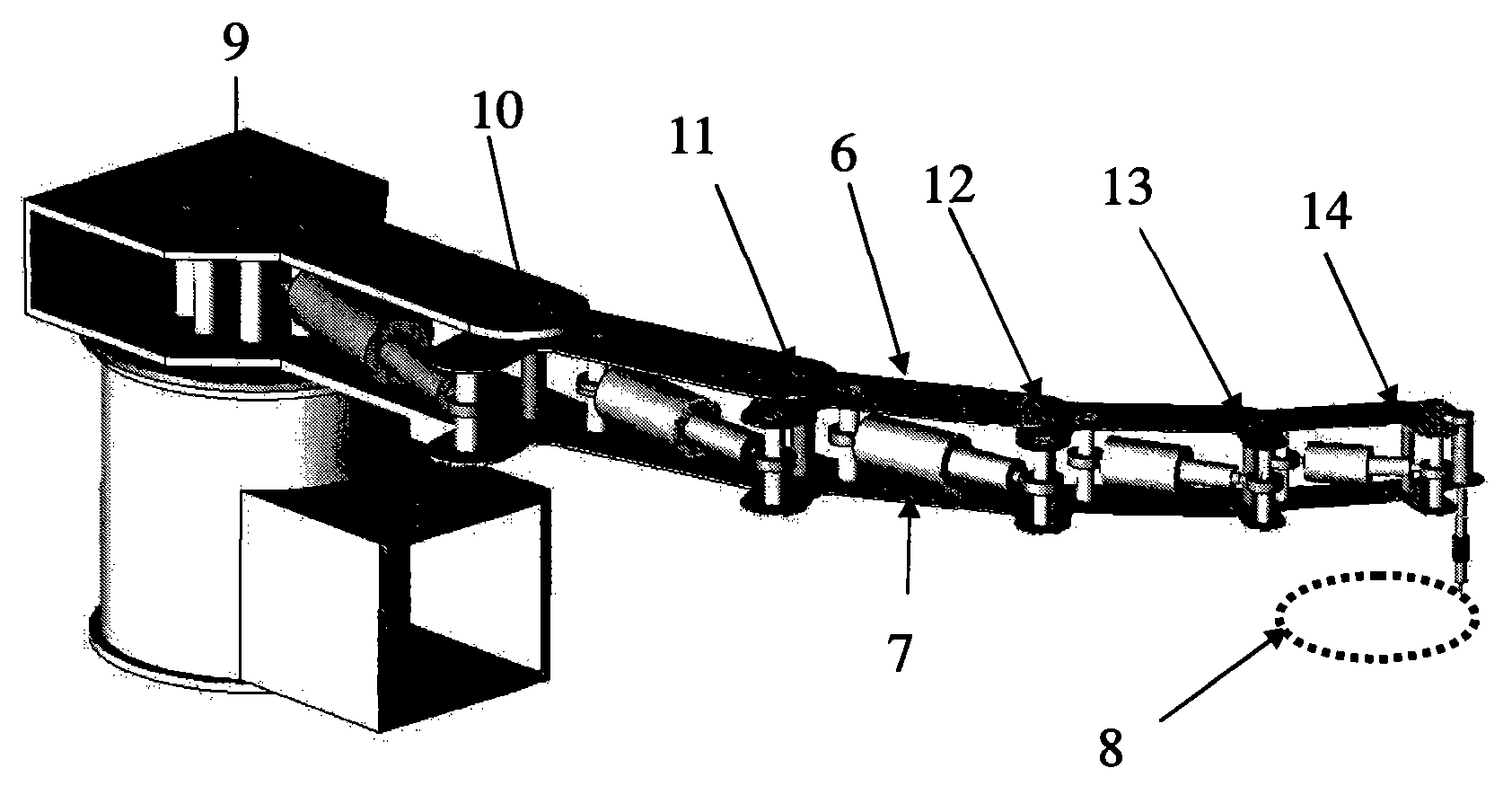
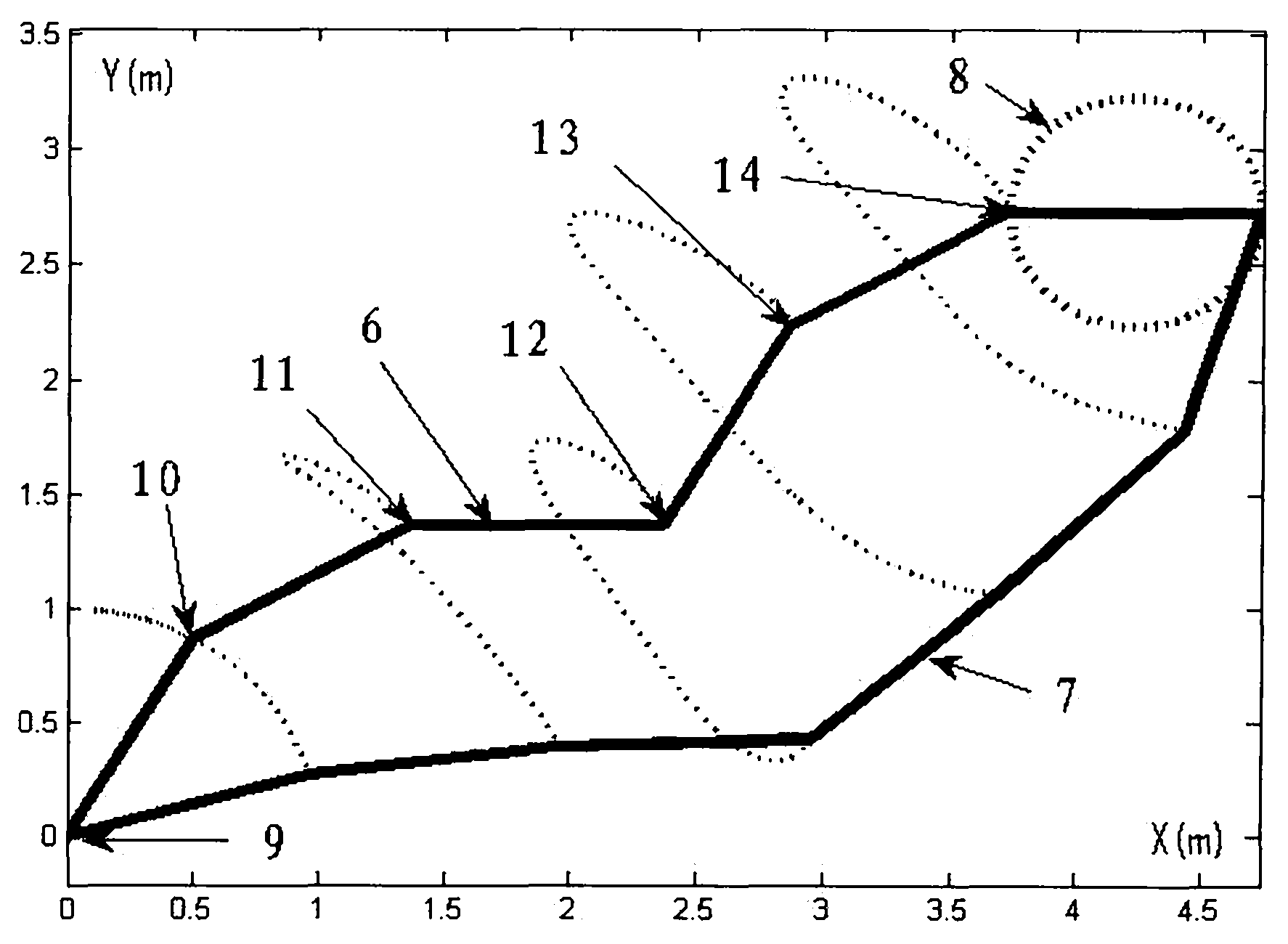
An angle joint is a generic term for a wide classification of connection methods where one piece enters the joint in a specific direction and another piece leaves in a different direction.
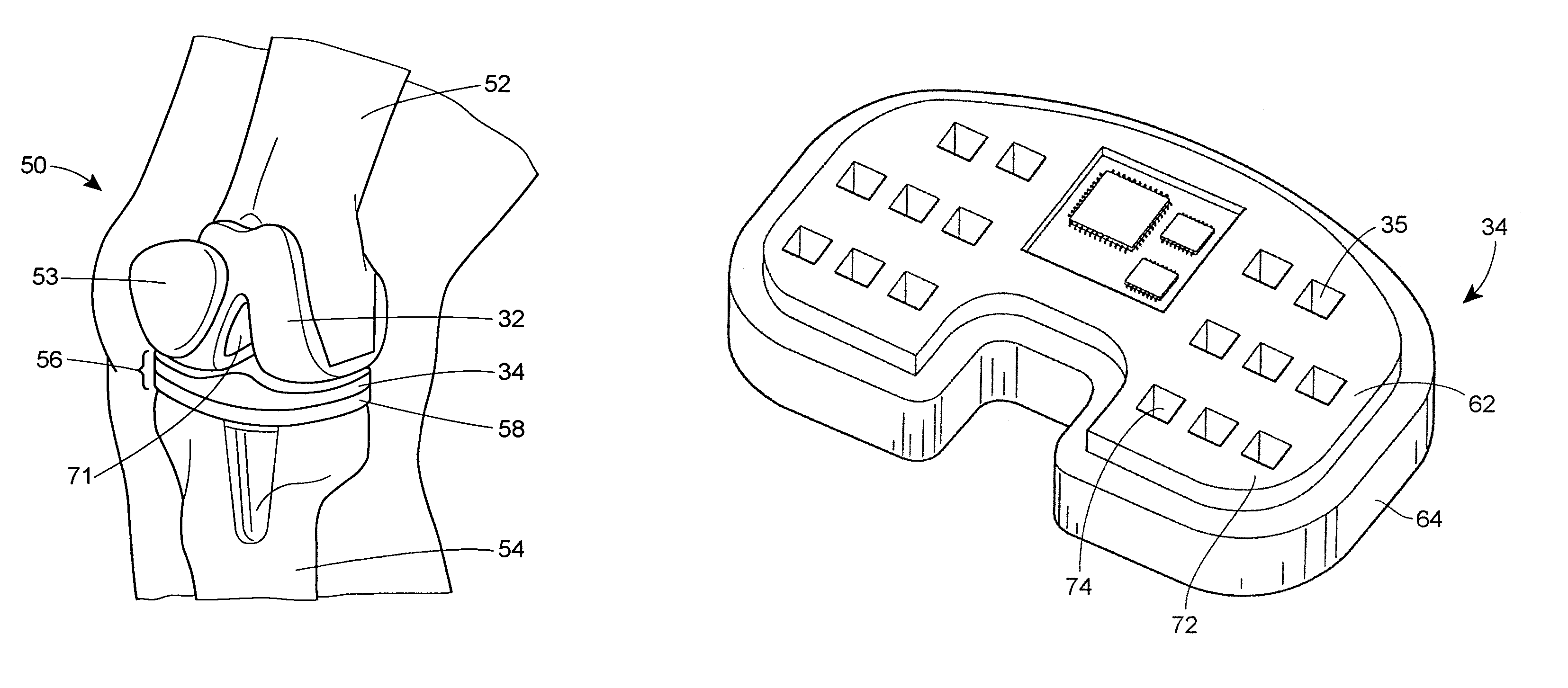
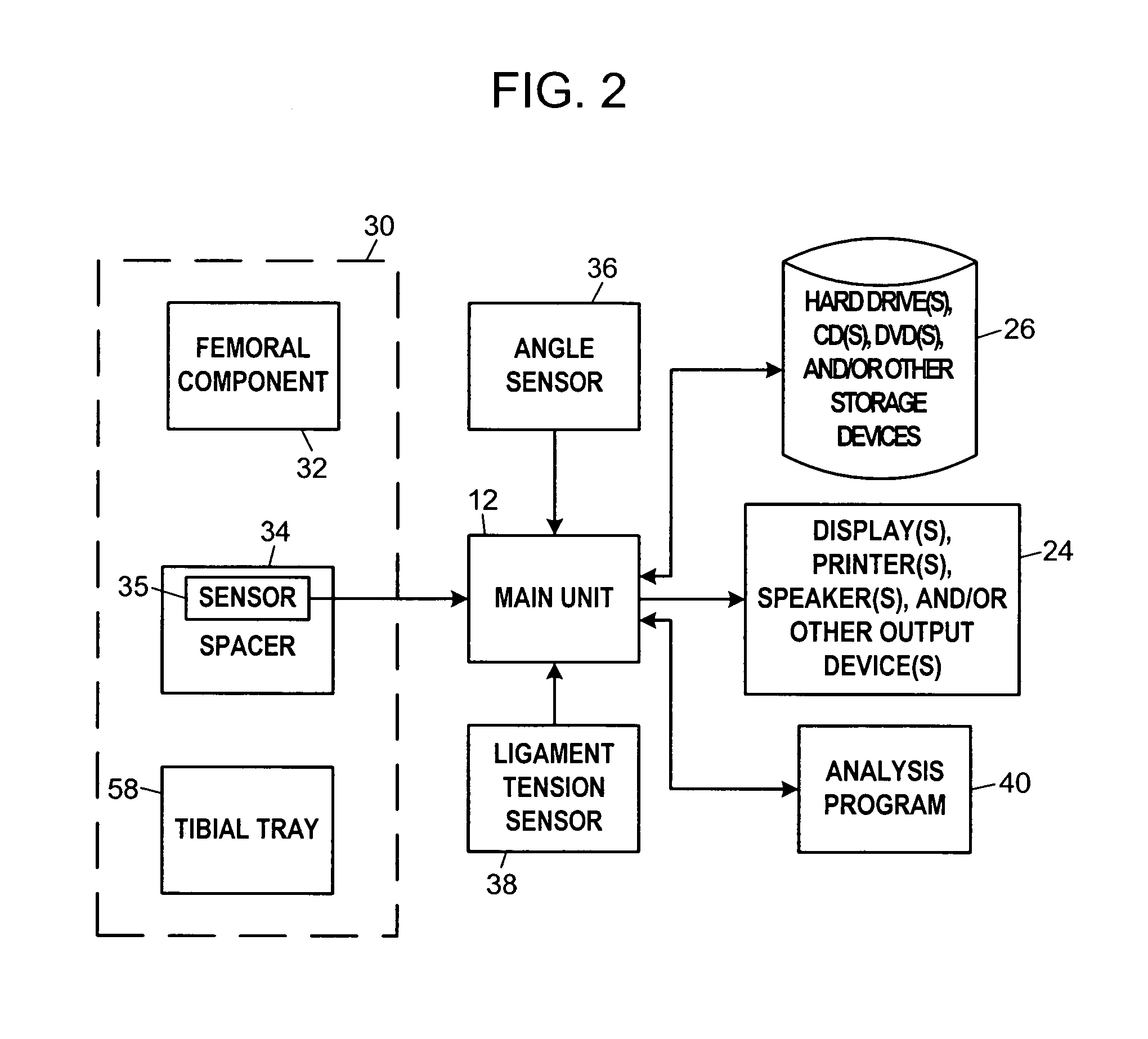
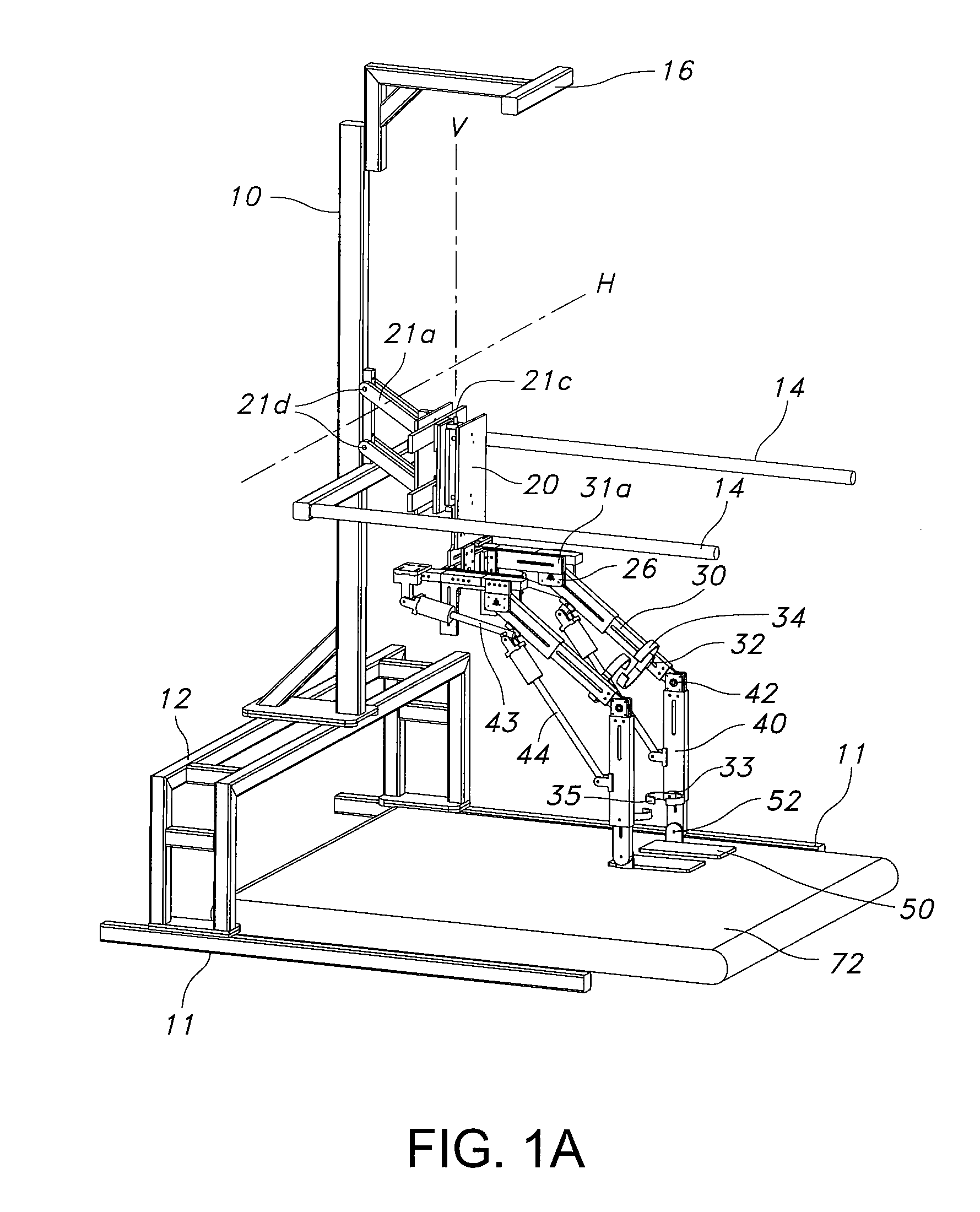
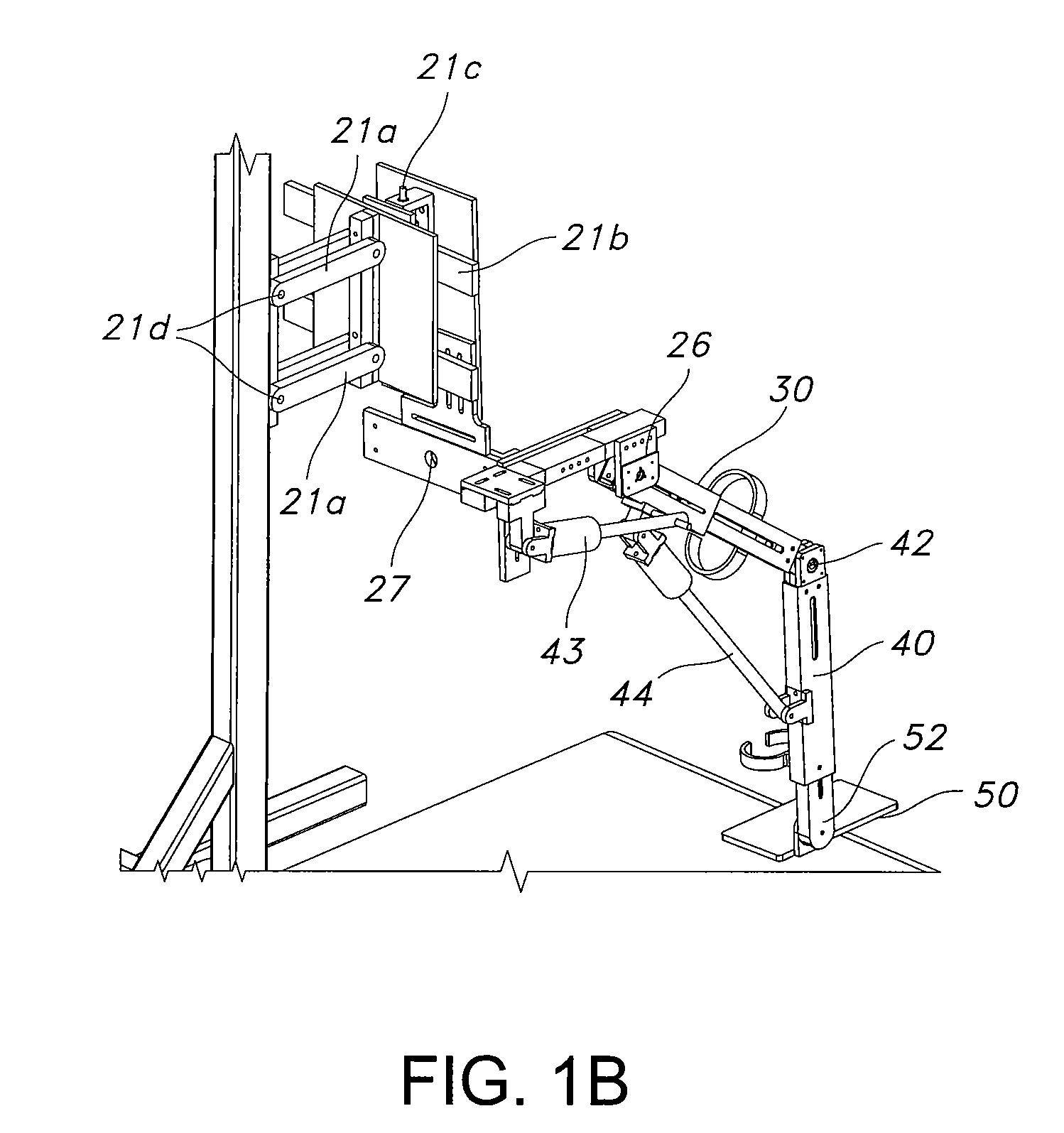
System and method for prosthetic fitting and balancing in joints
InactiveUS7575602B2Physical therapies and activitiesFinger jointsProsthesis fittingArtificial joints
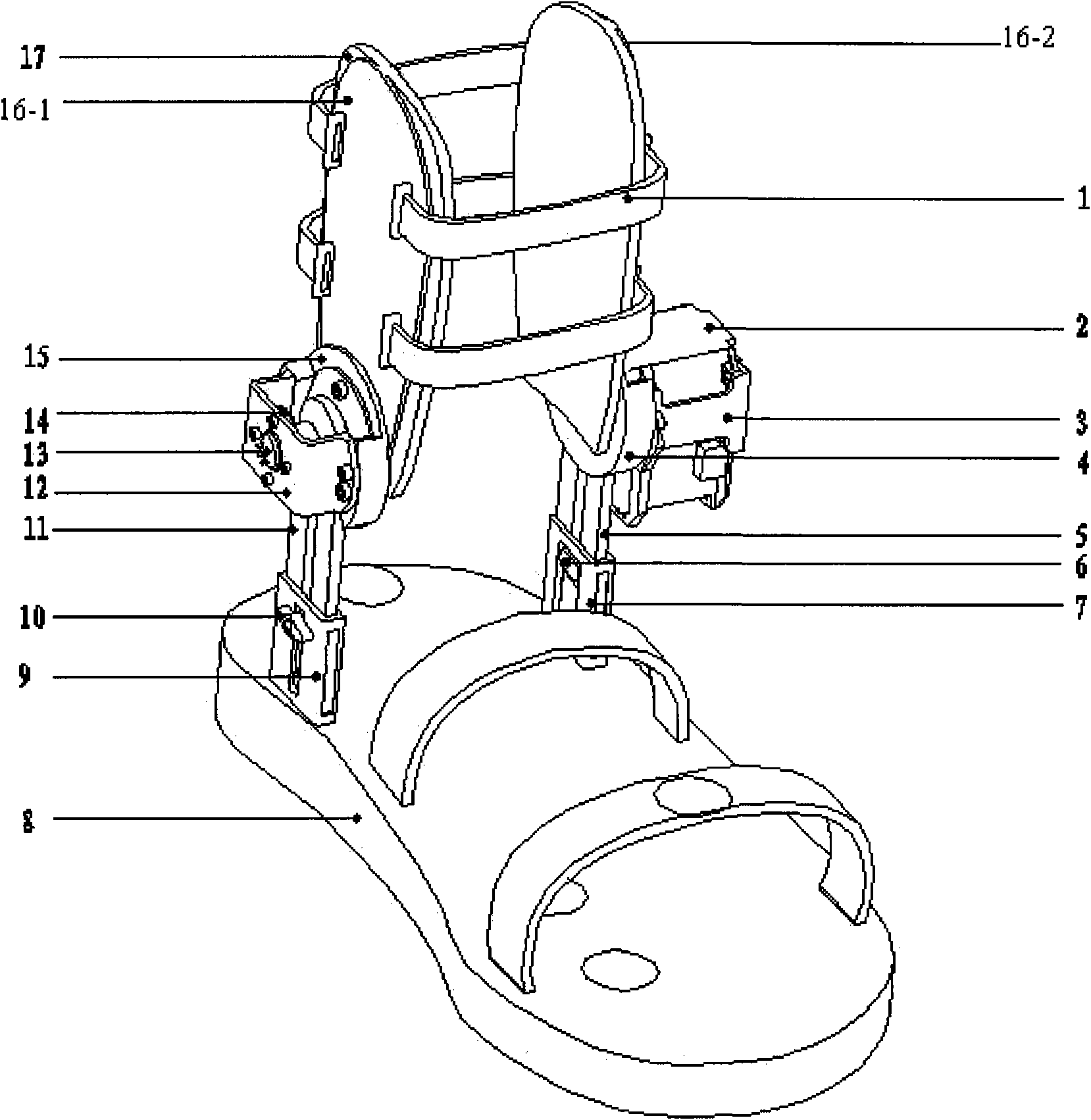
A system and method for prosthesis fitting in joints comprising an artificial condyle and a spacer which cooperates with the condyle to form an artificial joint. The spacer embedded with at least one sensor which is responsive to a force generated between the condyle and the spacer. The artificial joint is adapted to move between a flexed position and an extended position defining a range of motion. The sensor is responsive to the force and generates an output representative of that force. The output is transmitted, either wirelessly or other, to a processor which utilizes an analysis program to display a representation of the forces applied. A practitioner utilizing the displayed analysis may intraoperatively determine the adjustments and balancing required within the artificial joint. The system may also utilize a ligament tension sensor which generates data representative of tension on a ligament of the artificial joint, and a joint angle sensor responsive to the range of motion of the artificial joint. The processor may be adapted to store the outputted sensor data to provide the practitioner with statistically relevant historical data.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Goniometer-based body-tracking device and method
A sensing system is provided for measuring various joints of a human body for applications for performance animation, biomechanical studies and general motion capture. One sensing device of the system is a linkage-based sensing structure comprising rigid links interconnected by revolute joints, where each joint angle is measured by a resistive bend sensor or other convenient goniometer. Such a linkage-based sensing structure is typically used for measuring joints of the body, such as the shoulders, hips, neck, back and forearm, which have more than a single rotary degree of freedom of movement. In one embodiment of the linkage-based sensing structure, a single long resistive bend sensor measures the angle of more that one revolute joint. The terminal ends of the linkage-based sensing structure are secured to the body such that movement of the joint is measured by the device. A second sensing device of the sensing system comprises a flat, flexible resistive bend sensor guided by a channel on an elastic garment. Such a flat sensing device is typically used to measure various other joints of the body which have primarily one degree of freedom of movement, such as the elbows, knees and ankles. Combining the two sensing devices as described, the sensing system has low sensor bulk at body extremities, yet accurately measures the multi-degree-of-freedom joints nearer the torso. Such a system can operate totally untethered, in real time, and without concern for electromagnetic interference or sensor occlusion.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
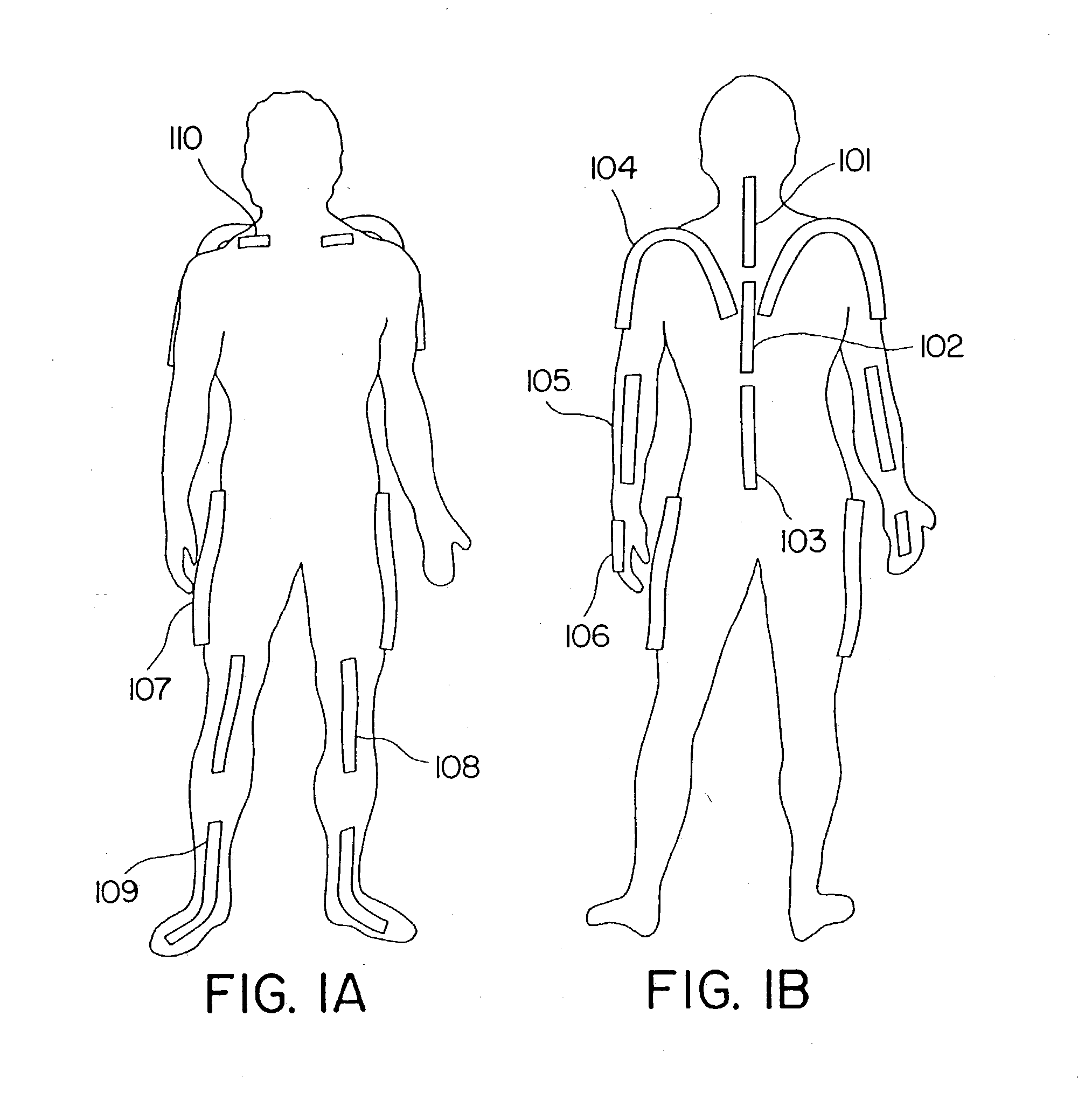
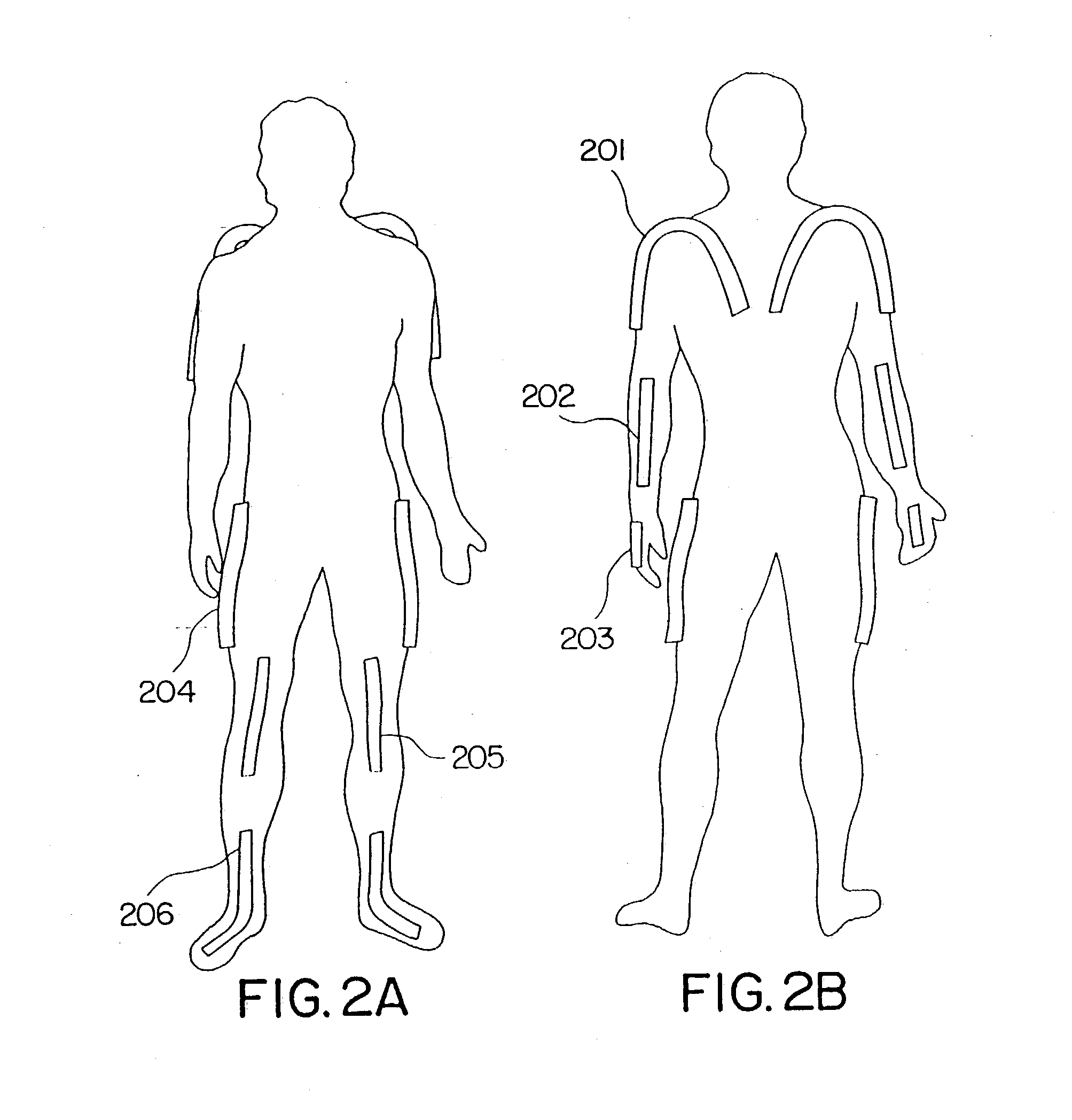
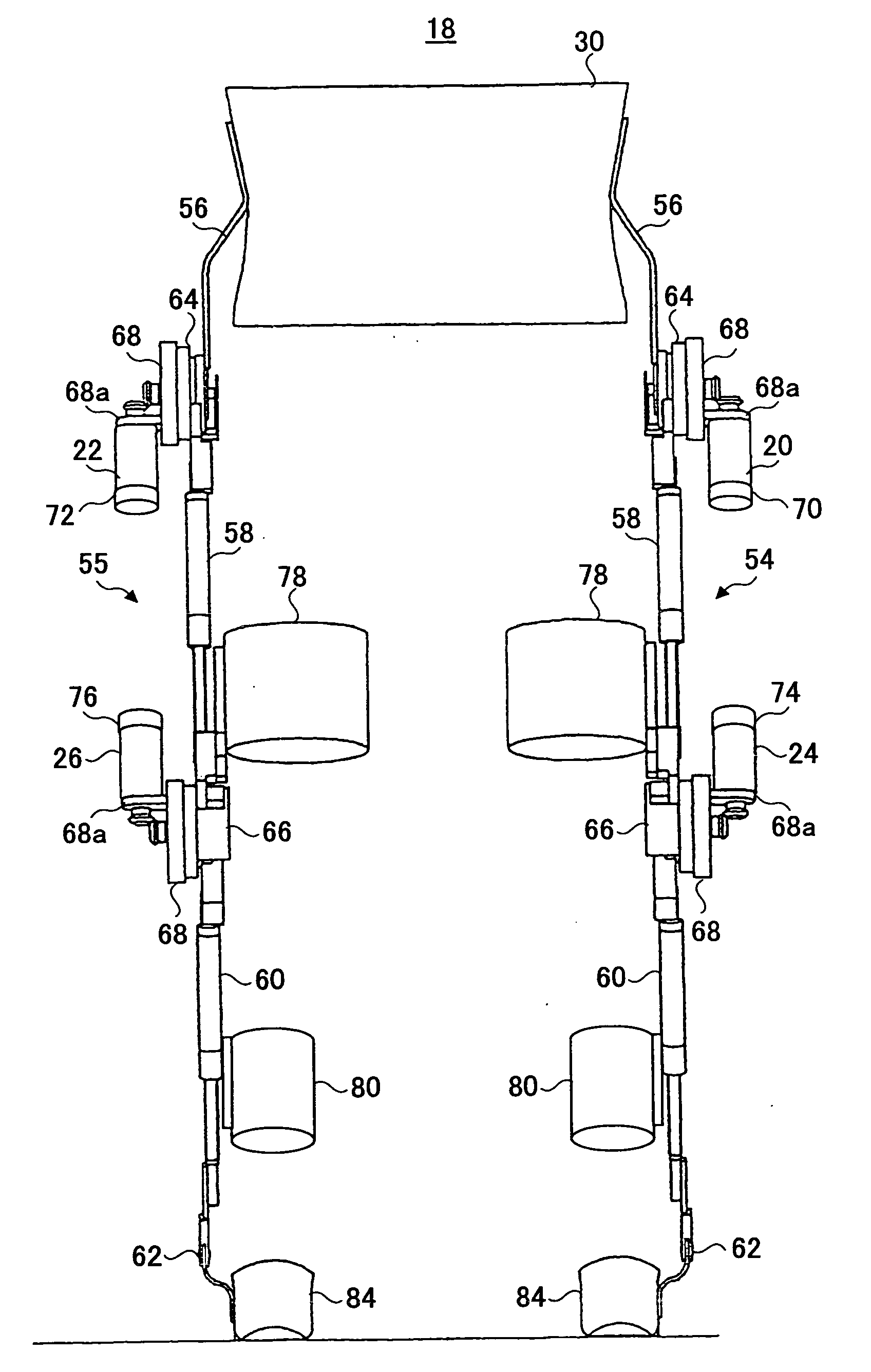
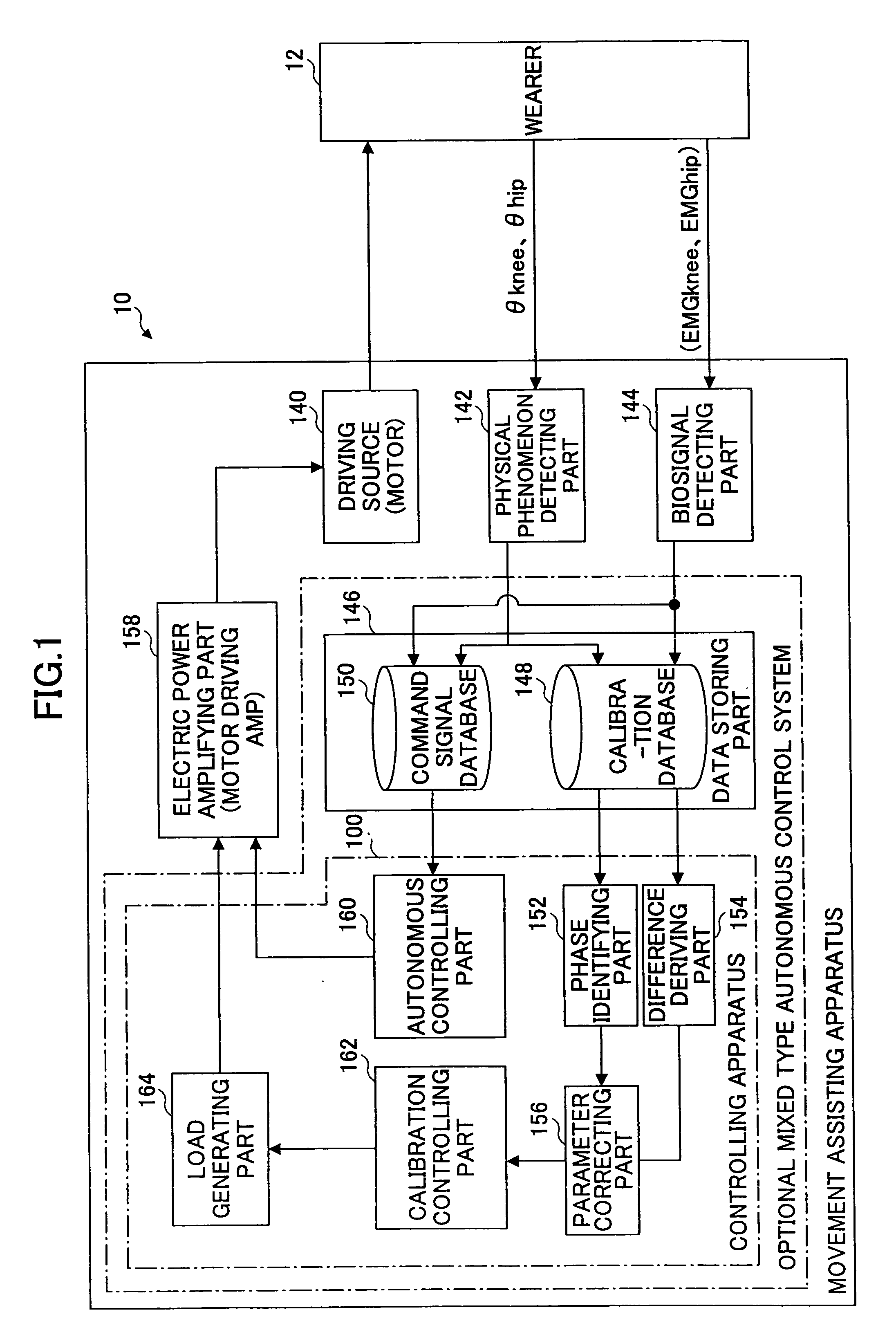
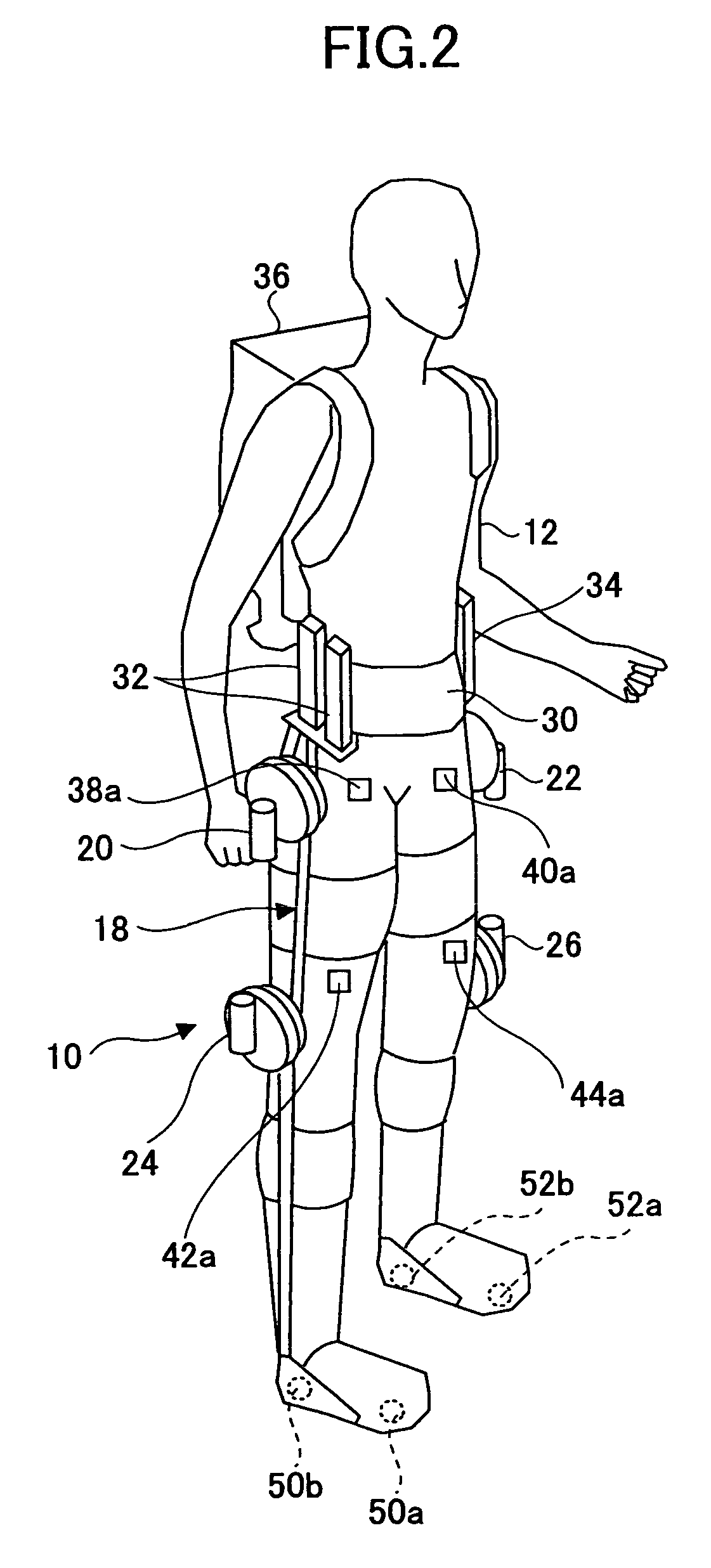
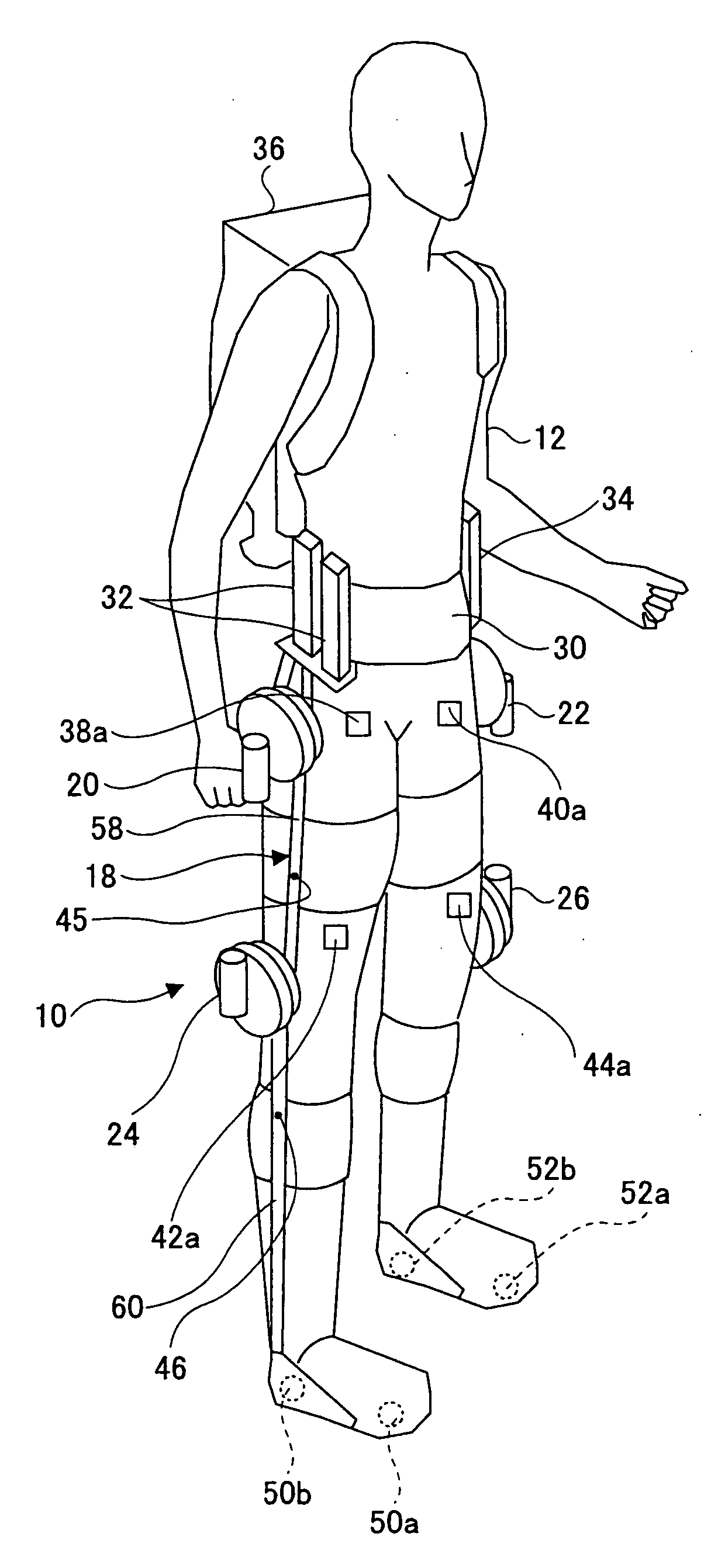
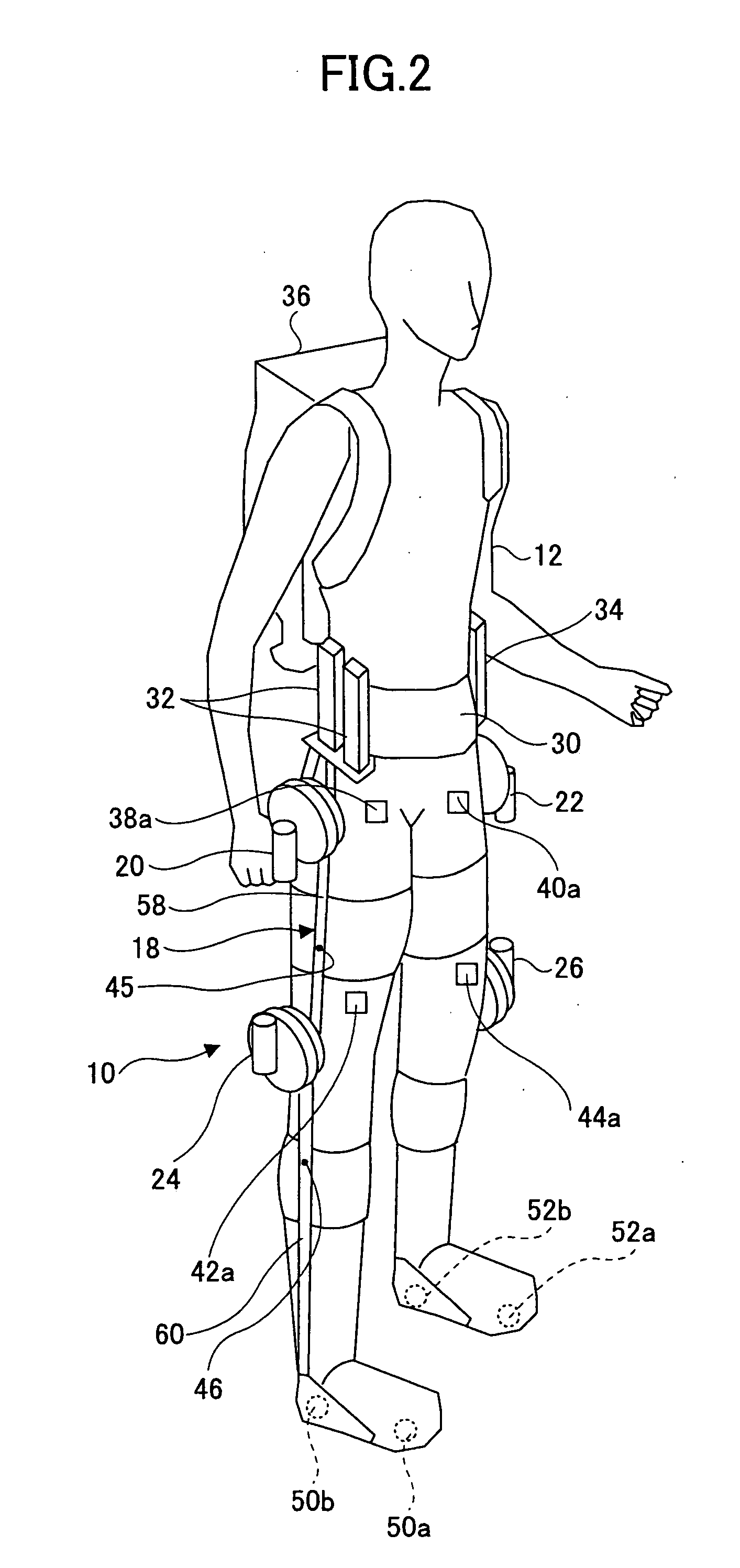
Wearing Type Behavior Help Device, Wearing Type Behavior Help Device Calibration Device, and Calibration Program
ActiveUS20080234608A1Precise applicationReliable typeProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectromyographyEngineeringSkeletal muscle
[Problem to be Solved]The problem to be solved by the present invention is to reduce the load applied to the wearer by correcting a parameter in correspondence with detectivity of biosignals.[Means to Solve Problem]The calibration controlling part 162 of the movement assisting apparatus 10 enables the power amplifying part 158 to apply a driving force of the driving source 140 as a load (input torque) from the load generating part 164 to the wearer 12 when the wearer 12 wears the movement assisting wearing device. Then, the wearer 12 applied with the driving force of the driving source 140 generates power from the skeletal muscles by performing a predetermined calibration operation. Accordingly, the physical phenomenon detecting part 142 detects joint angle along with the calibration operation, and the biosignal detecting part 144 detects myoelectric signals. In the parameter correction part 156, a parameter K is corrected based on the difference between the load (input torque) and the driving force (muscular strength) being calculated by the difference deriving part 154 with respect to the phase identified by the phase identifying part 152.
Owner:TSUKUBA UNIV OF +1
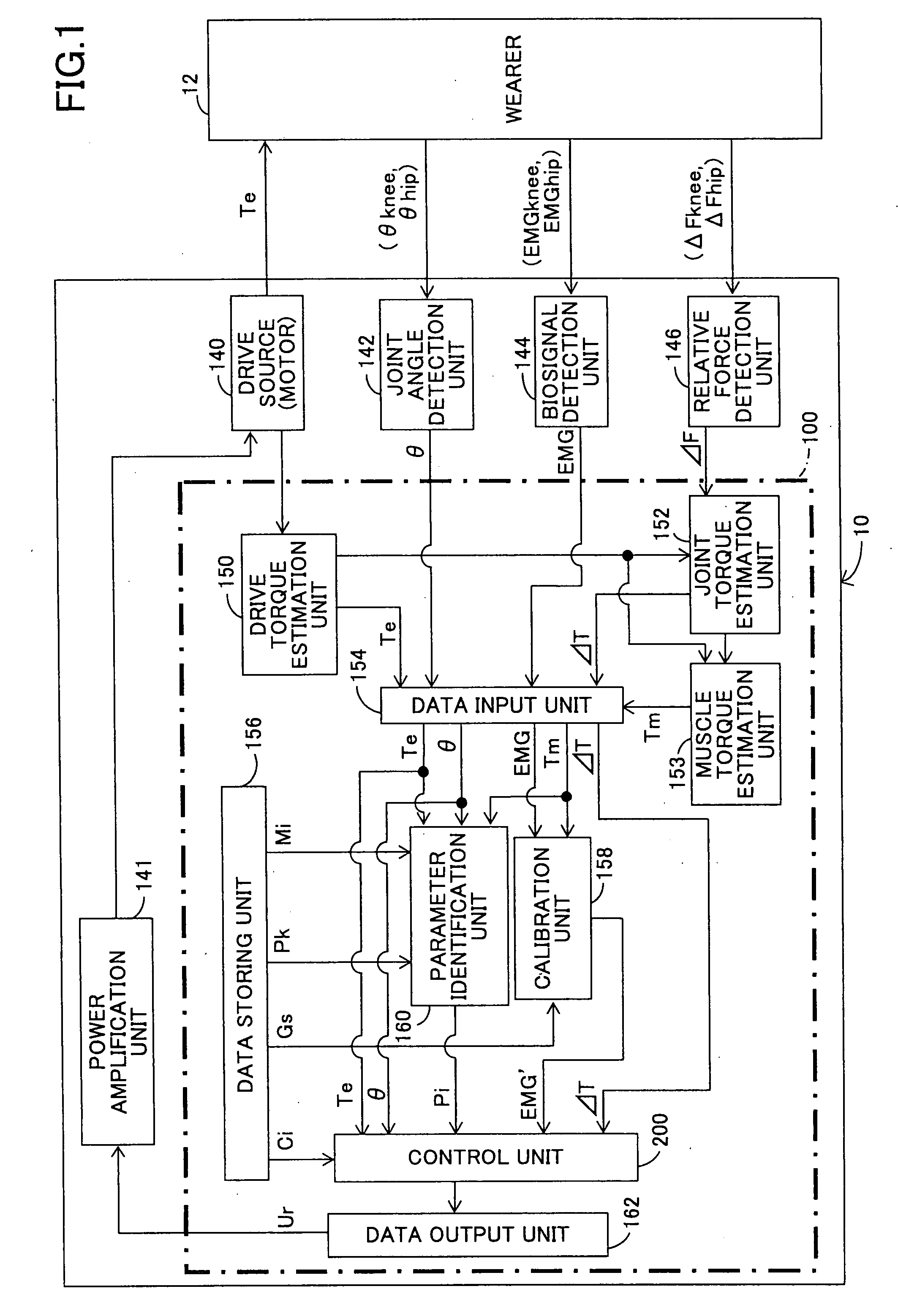
Wearing-Type Motion Assistance Device and Program for Control
ActiveUS20080161937A1Sufficient effect in conformityAvoid it happening againProgramme-controlled manipulatorGymnastic exercisingEngineeringParametric identification
A motion assistance device has a biological signal detection means for detecting a biological signal from the wearer of the device; a motion assistance device installation member having a drive source for applying torque acting to the wearer by use of each joint of the wearer as a rotating shaft; a control means for controlling the drive source to generate torque corresponding to the biological signal detected by the biological signal detection mean; a drive torque estimation means for estimating the drive torque generated by the drive source; a joint angle detection means for detecting angular displacement of a joint; and a parameter identification means for substituting the drive torque estimated by the drive torque estimation means and the angular displacement detected by the joint angle detection means into an equation of motion to specify the wearer-specific dynamics parameter, the equation relating to the entire system and including wearer-specific dynamics parameter. The control means controls the drive source according to a predetermined control method, based on the equation of motion into which the dynamics parameter identified by the parameter identification means is substituted.
Owner:CYBERDYNE INC
Goniometer-based body-tracking device
InactiveUS7070571B2Binding can be eliminatedReduce resistanceInput/output for user-computer interactionStrain gaugeHuman bodyBiomechanics
A sensing system is provided for measuring various joints of a human body for applications for performance animation, biomechanical studies and general motion capture. One sensing device of the system is a linkage-based sensing structure comprising rigid links interconnected by revolute joints, where each joint angle is measured by a resistive bend sensor or other convenient goniometer. Such a linkage-based sensing structure is typically used for measuring joints of the body, such as the shoulders, hips, neck, back and forearm, which have more than a single rotary degree of freedom of movement. In one embodiment of the linkage-based sensing structure, a single long resistive bend sensor measures the angle of more than one revolute joint. A second sensing device of the sensing system comprises a flat, flexible resistive bend sensor guided by a channel on an elastic garment.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Powered Orthosis
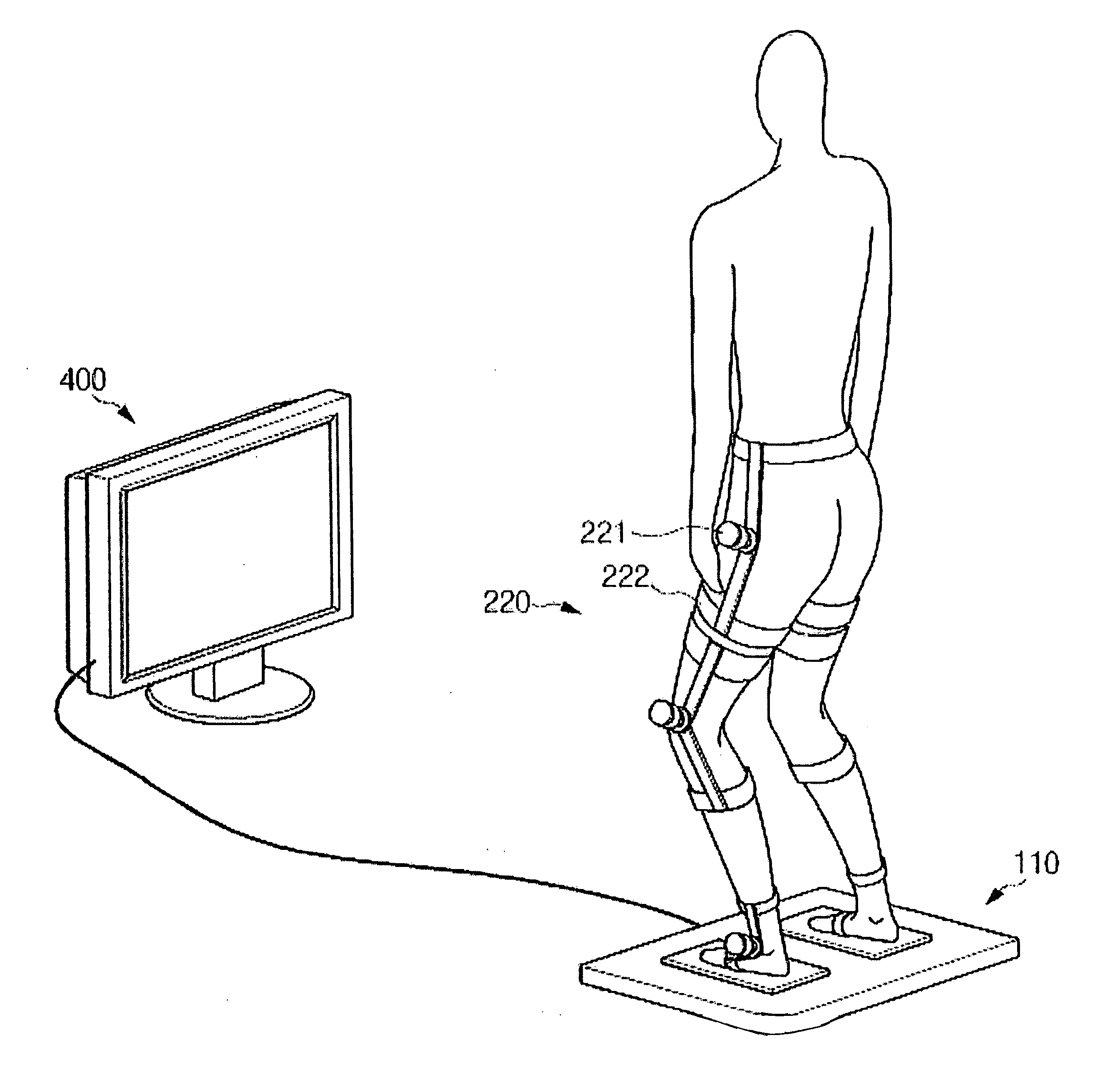
A powered orthosis, adapted to be secured to a corresponding body portion of the user for guiding motion of a user, the orthosis comprising a plurality of structural members and one or more joints adjoining adjacent structural members, each joint having one or more degrees of freedom and a range of joint angles. One or more of the joints each comprise at least one back-drivable actuator governed by a controller for controlling the joint angle. The plurality of joint controllers are synchronized to cause the corresponding actuators to generate forces for assisting the user to move the orthosis at least in part under the user's power along a desired trajectory within an allowed tolerance. One embodiment comprises force-field controllers that define a virtual tunnel for movement of the orthosis, in which the forces applied to the orthosis for assisting the user may be proportional to deviation from the desired trajectory.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
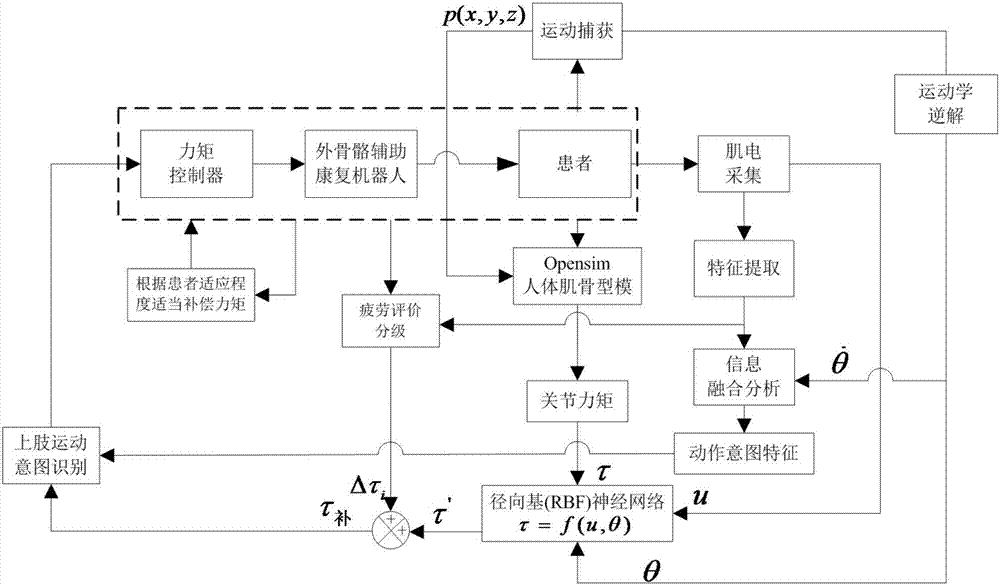
Upper limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot control method based on radial basis neural network
ActiveCN107397649ARealize interactive intelligent rehabilitationImprove rehabilitation effectChiropractic devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringUpper limb muscleNetwork model
The invention discloses an upper limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot control method based on a radial basis neural network. The method includes the steps that a human body upper limb musculoskeletal model is established; upper limb muscle myoelectric signals and upper limb movement data are collected, the movement data are imported into the upper limb musculoskeletal model, upper limb joint torque is obtained, the radial basis neural network is established and a neural network model is given out; the patient movement intention is recognized, the joint angular speed is subjected to fusion analysis, the result is used for recognizing the training object joint stretching state, and the limb movement intention is determined; and myoelectric signals and joint angles in affected side rehabilitation training are collected in real time, affected side joint torque is obtained through the neural network, joint torque needing to be compensated by an exoskeleton mechanical arm is calculated, myoelectric signal fatigue characteristics are analyzed, the compensation torque magnitude can be adjusted by classifying the degree of fatigue, and a torque controller can be controlled to achieve the effect that an upper limb rehabilitation robot assists patients in rehabilitation training by combining the movement intention. By means of the upper limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot control method, the rehabilitation training process is made to be more suitable for the patients, man-machine interaction is strengthened, and the rehabilitation effect is improved.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
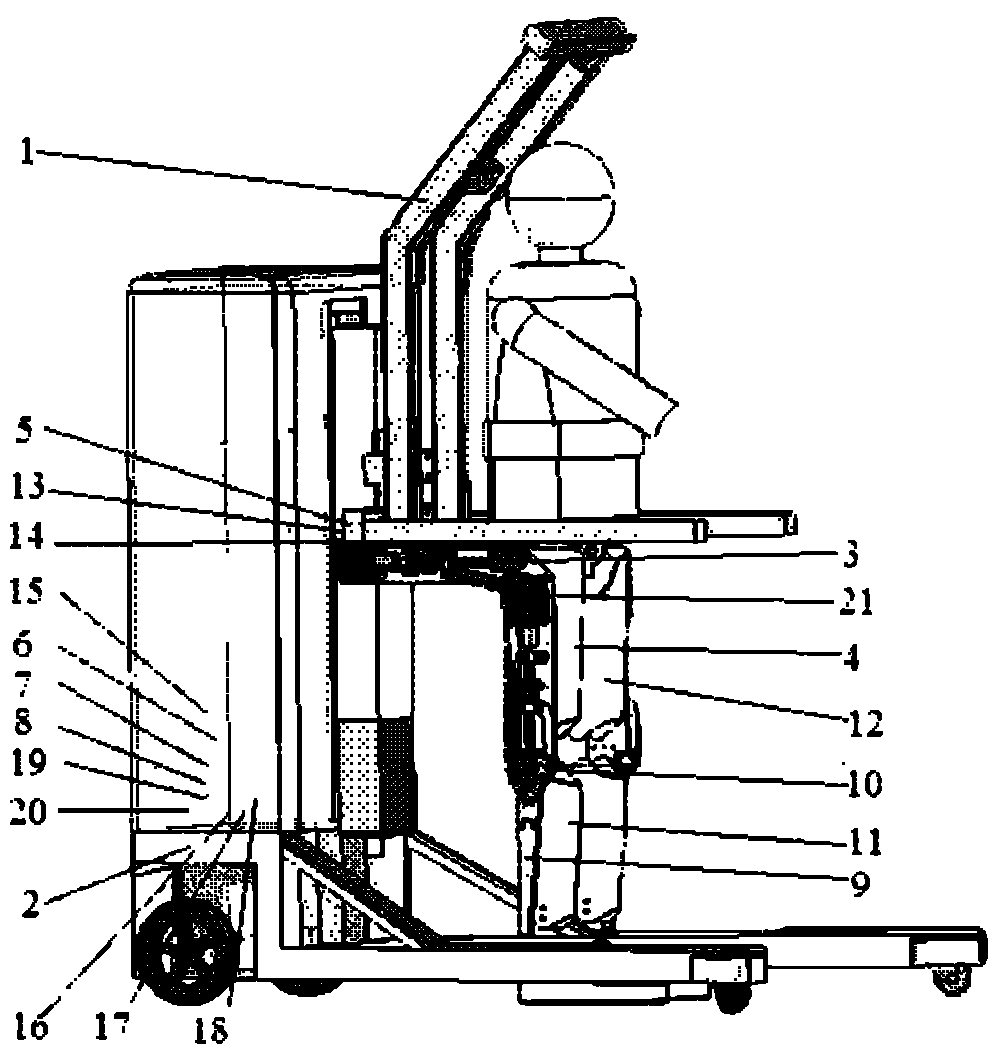
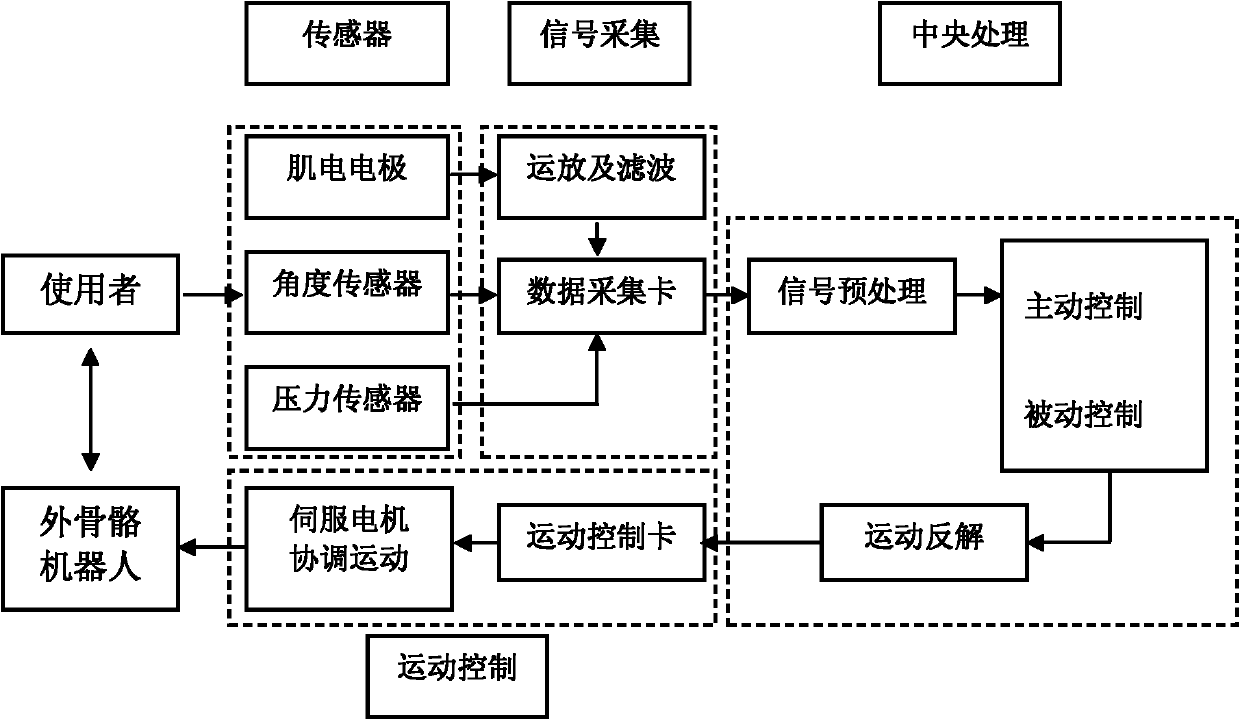
Walk-aiding exoskeleton robot system and control method
InactiveCN101791255ACompact designMeet the actual sports requirementsWalking aidsArtificial legsHuman bodyExoskeleton robot
The invention relates to a walk-aiding exoskeleton robot system and a control method, which belong to the technical field of rehabilitation engineering. The system comprises a hanging support, a moving platform, joints, protecting sleeves, a sensor module, a signal acquisition module, a central processing module and a motion control module, wherein the hanging support is fixed on the moving platform, the joints are connected with the hanging support to form an exoskeleton robot, the sensor module, the signal acquisition module, the central processing module and the motion control module are sequentially connected, the sensor module is used for acquiring joint angles, the interacting force of the exoskeleton robot and the human being and the myoelectric signals of the muscles of the human body, the signal acquisition module carries out signal conditioning and digital-to-analog conversion, the central processing module carries out action generation and the reverse solution of motion, and transmits an action command to the motion control module, and the motion control module is connected with the exoskeleton robot and generates a pulse signal to control the coordinated motion of the exoskeleton robot. The invention realizes the synchronous motion of the exoskeleton robot and the human body and real-time active control.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
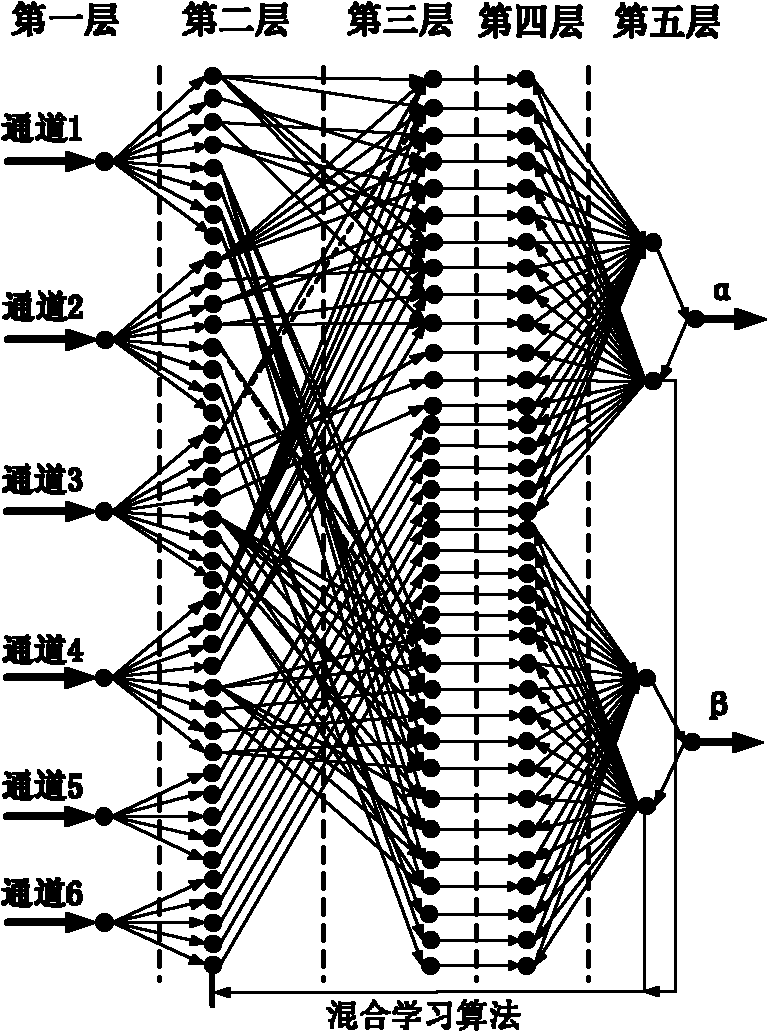
Man-machine interactive manipulator control system and method based on binocular vision
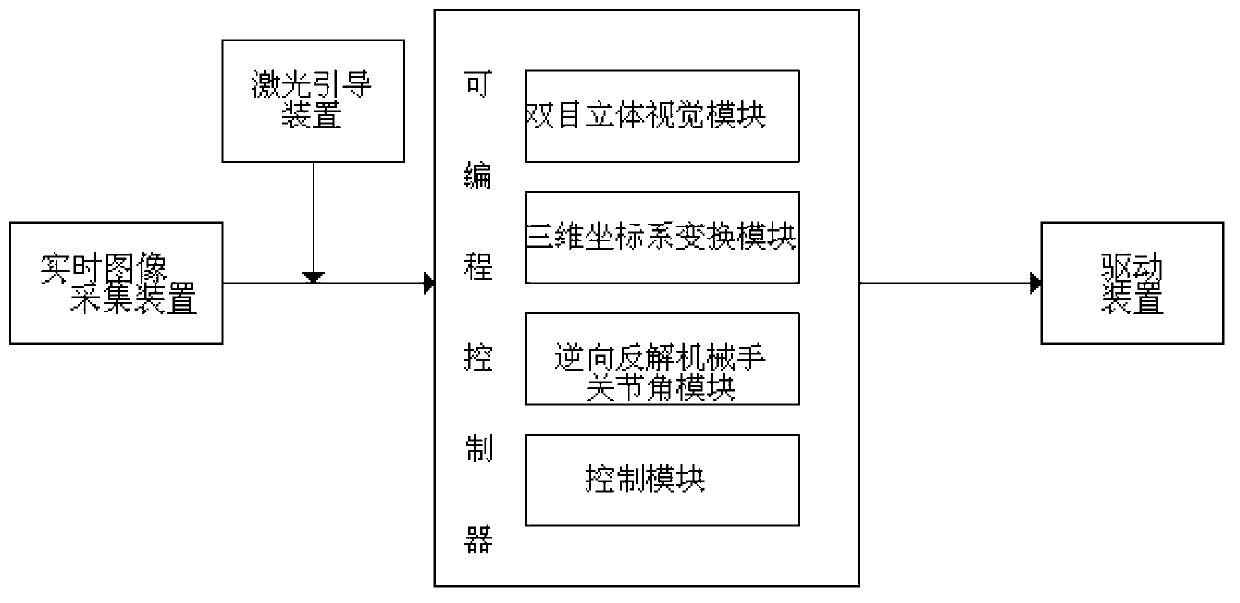
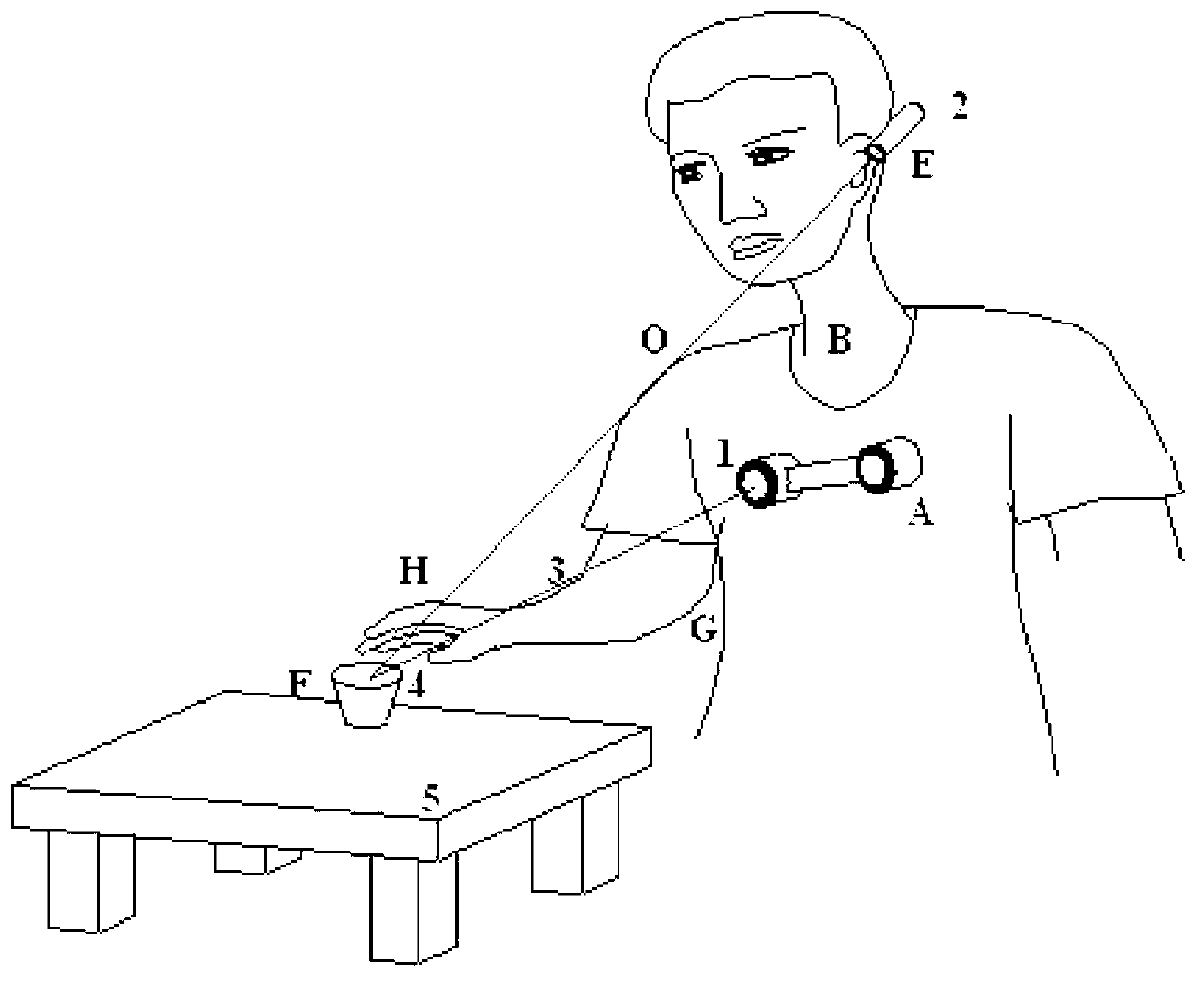
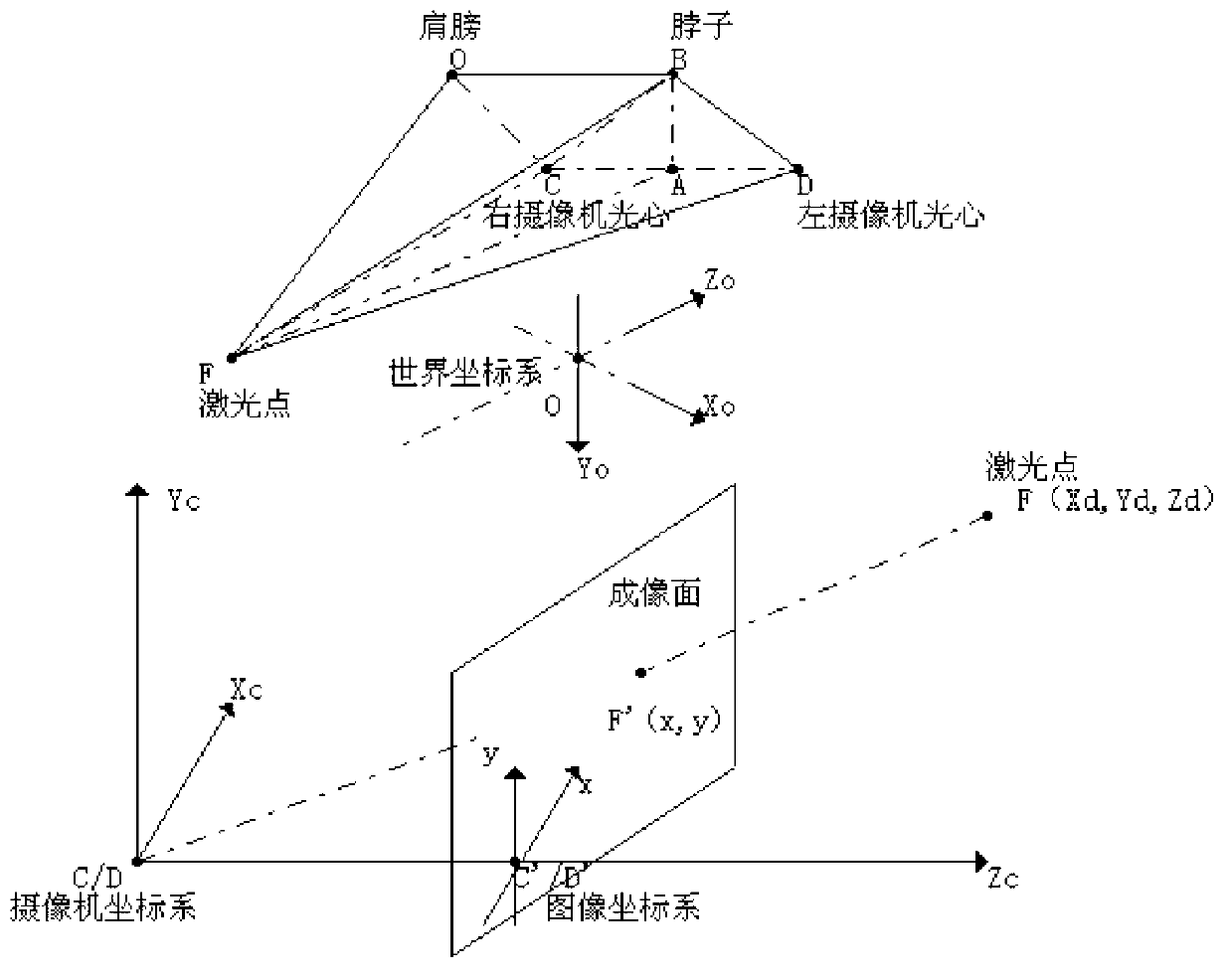
InactiveCN103271784AControl tension reductionImprove participationProgramme-controlled manipulatorProsthesisSystem transformationVisual perception
The invention discloses a man-machine interactive manipulator control system and method based on binocular vision. The man-machine interactive manipulator control system is composed of a real-time image collecting device, a laser guiding device, a programmable controller and a driving device. The programmable controller is composed of a binocular three-dimensional vision module, a three-dimensional coordinate system transformation module, an inverse manipulator joint angle module and a control module. Color characteristics in a binocular image are extracted through the real-time image collecting device to be used as a signal source for controlling a manipulator, and three-dimensional information of red characteristic laser points in a view real-time image is obtained through transformation and calculation of the binocular three-dimensional vision system and a three-dimensional coordinate system and used for controlling the manipulator to conduct man-machine interactive object tracking operation. The control system and method can effectively conduct real-time tracking and extracting of a moving target object and is wide in application fields such as intelligent artificial limb installing, explosive-handling robots, manipulators helping the old and the disabled and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Parallel kinematic machine trajectory planning method
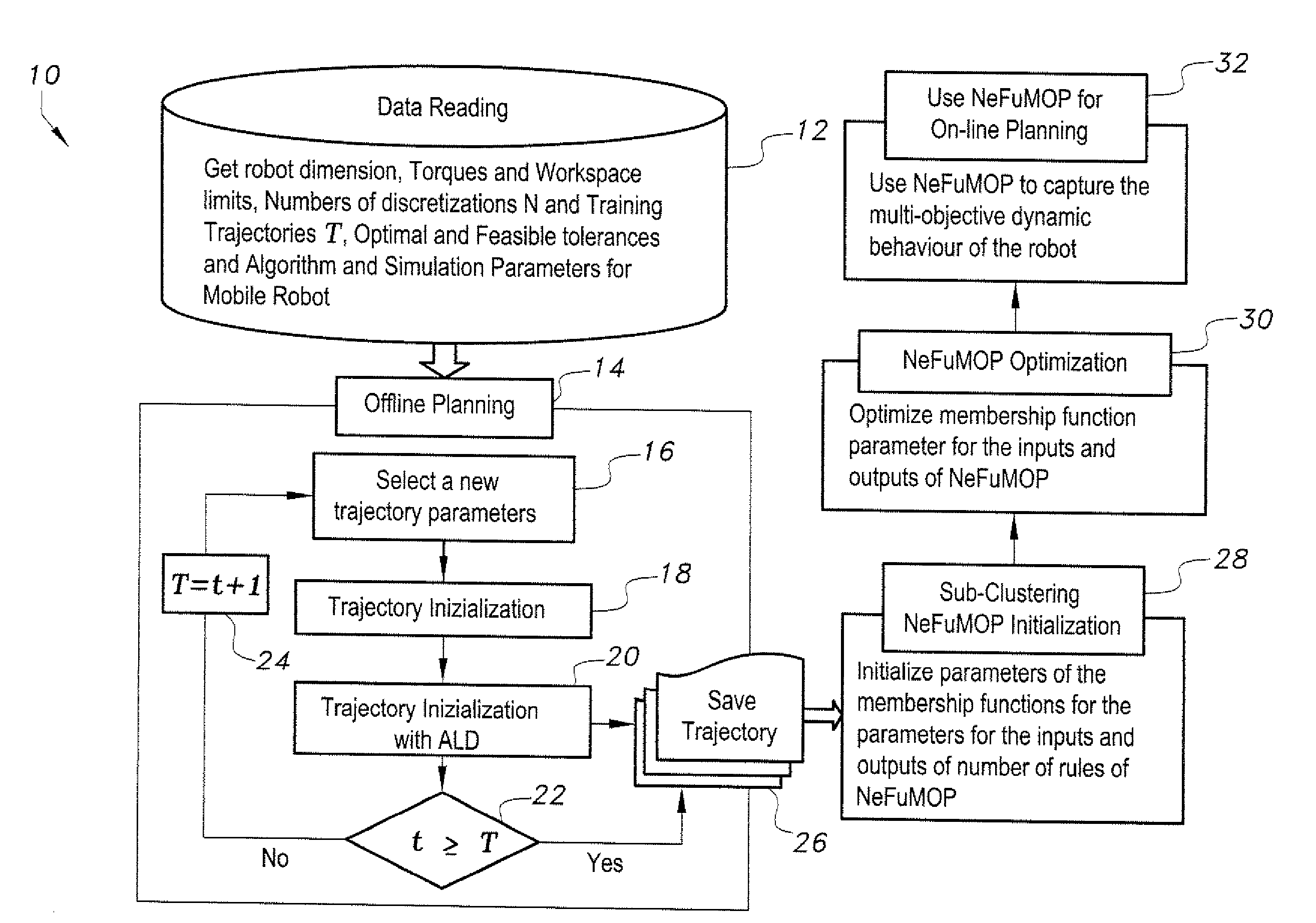
InactiveUS20120290131A1Minimize timeMinimizing energyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlData setParallel kinematics
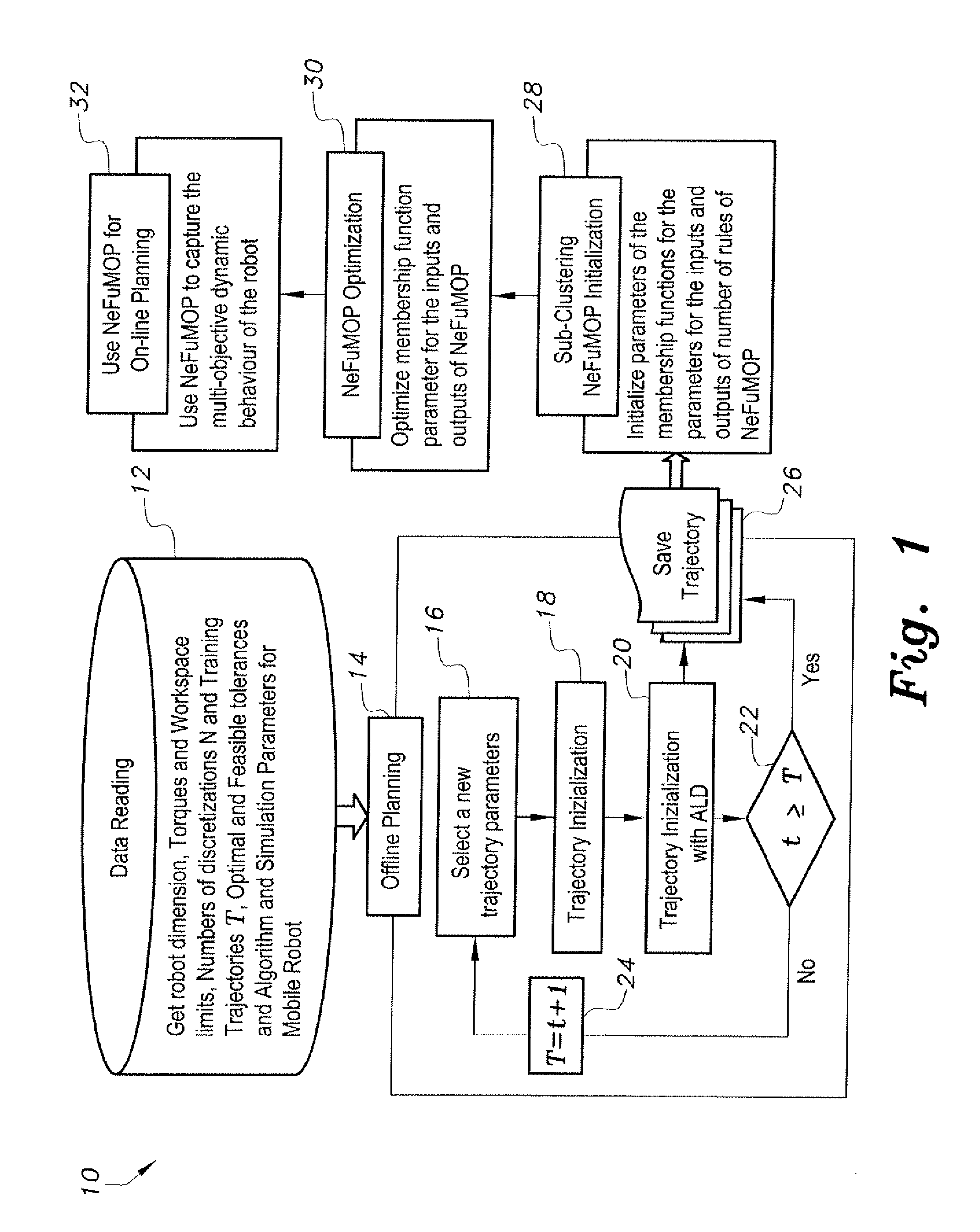
The parallel kinematic machine (PKM) trajectory planning method is operable via a data-driven neuro-fuzzy multistage-based system. Offline planning based on robot kinematic and dynamic models, including actuators, is performed to generate a large dataset of trajectories, covering most of the robot workspace and minimizing time and energy, while avoiding singularities and limits on joint angles, rates, accelerations and torques. The method implements an augmented Lagrangian solver on a decoupled form of the PKM dynamics in order to solve the resulting non-linear constrained optimal control problem. Using outcomes of the offline-planning, the data-driven neuro-fuzzy inference system is built to learn, capture to and optimize the desired dynamic behavior of the PKM. The optimized system is used to achieve near-optimal online planning with a reasonable time complexity. The effectiveness of the method is illustrated through a set of simulation experiments proving the technique on a 2-degrees of freedom planar PKM.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
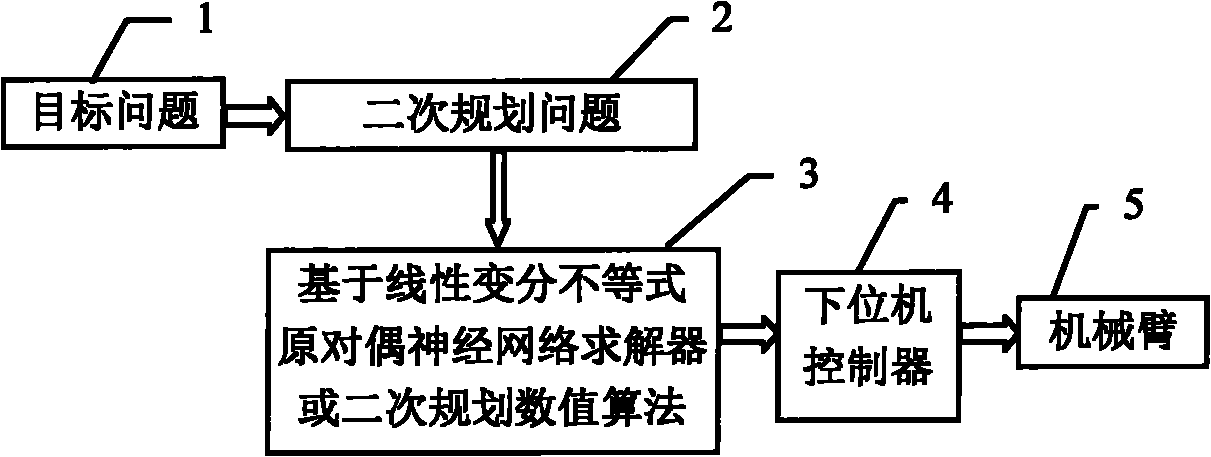
Redundant manipulator motion planning method
InactiveCN101804627AImprove computing efficiencyStrong real-timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorAngular velocityEngineering
The invention provides a redundant manipulator motion planning method which comprises the following steps that: (1) an upper computer analyzes the inverse kinematics of a manipulator on a velocity layer through quadratic optimization, the designed minimum performance index can be velocity norm, repetitive motion or kinetic energy and is bound by a velocity jacobian equation, an inequation and a joint angular velocity limit, and the angular velocity limit changes with a joint angle; (2) the quadratic optimization of step (1) is optimized into a quadratic programming problem; (3) the quadratic programming problem in step (2) is calculated by a linear variational inequation primal-dual neural network solver or a numerical method; and (4) the calculation result in step (3) is transmitted to a lower computer controller to drive the manipulator to move. The redundant manipulator motion planning method is based on the primal-dual neural network of the linear variational inequation, has global exponential convergence, does not involve matrix inversion and other complicated operations, greatly improves the calculation efficiency, and simultaneously has strong real-time performance, and can adapt to the changes to the joint angular velocity limit.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Powered orthosis
A powered orthosis, adapted to be secured to a corresponding body portion of the user for guiding motion of a user, the orthosis comprising a plurality of structural members and one or more joints adjoining adjacent structural members, each joint having one or more degrees of freedom and a range of joint angles. One or more of the joints each comprise at least one back-drivable actuator governed by a controller for controlling the joint angle. The plurality of joint controllers are synchronized to cause the corresponding actuators to generate forces for assisting the user to move the orthosis at least in part under the user's power along a desired trajectory within an allowed tolerance. One embodiment comprises force-field controllers that define a virtual tunnel for movement of the orthosis, in which the forces applied to the orthosis for assisting the user may be proportional to deviation from the desired trajectory.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
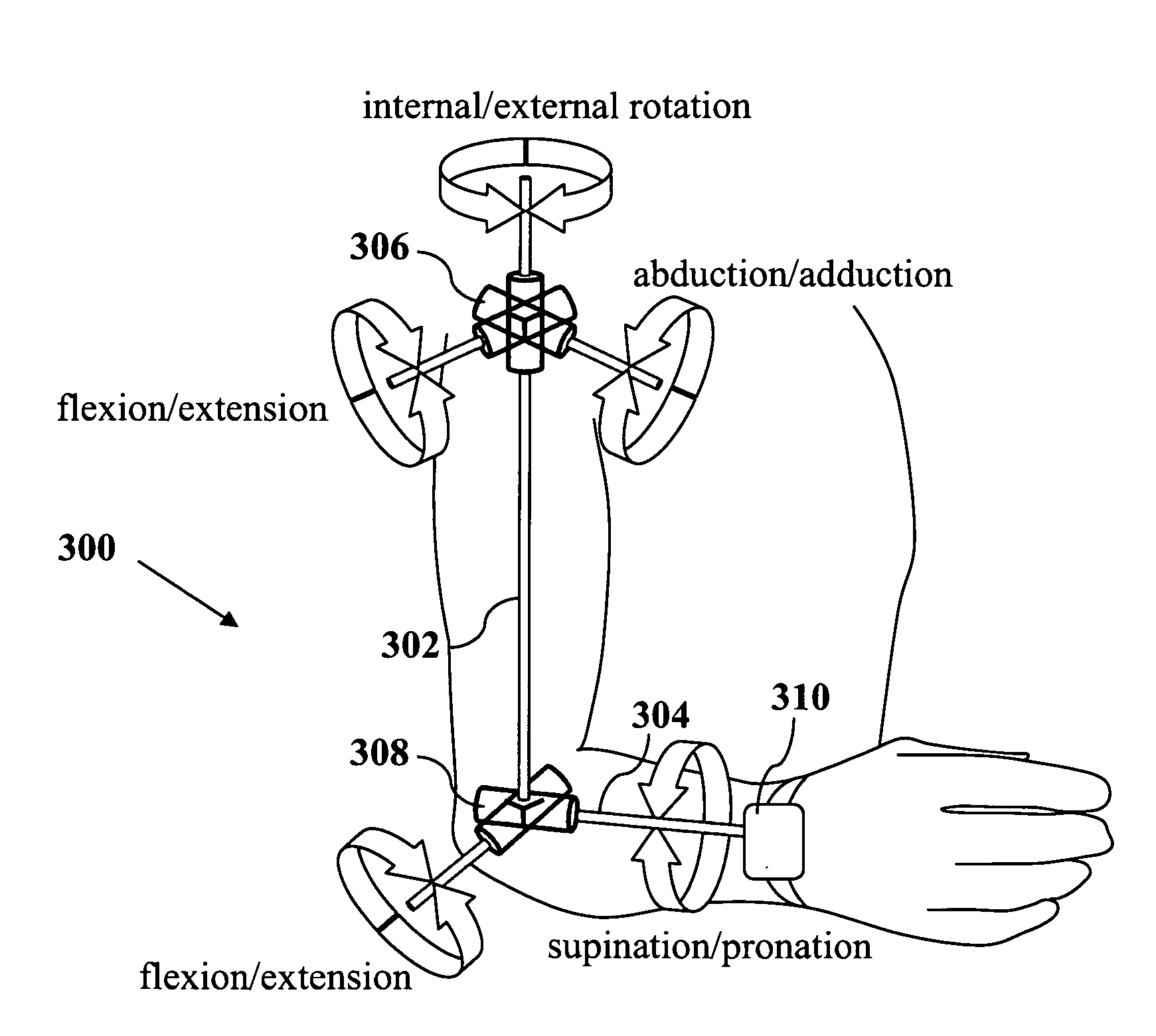
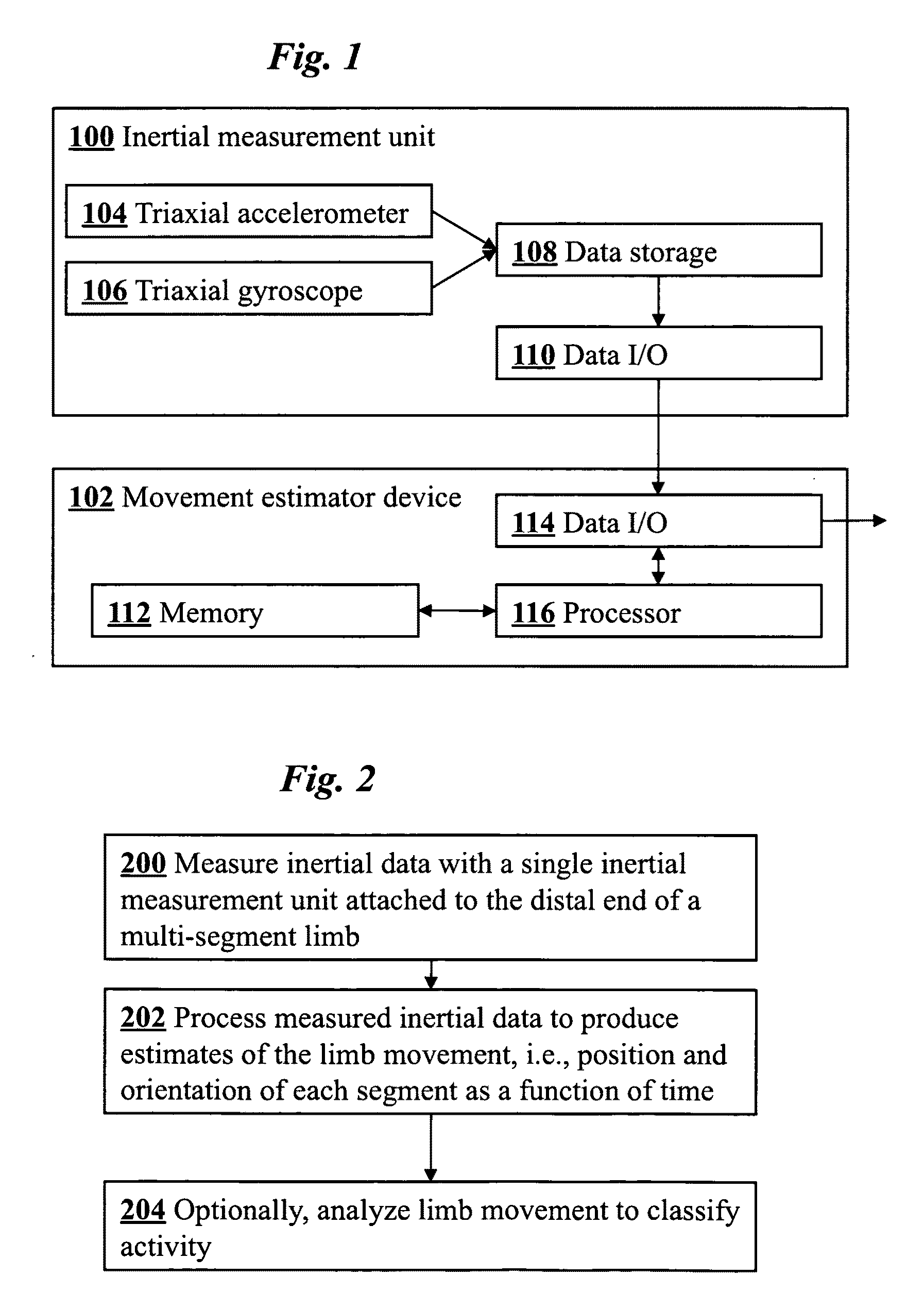
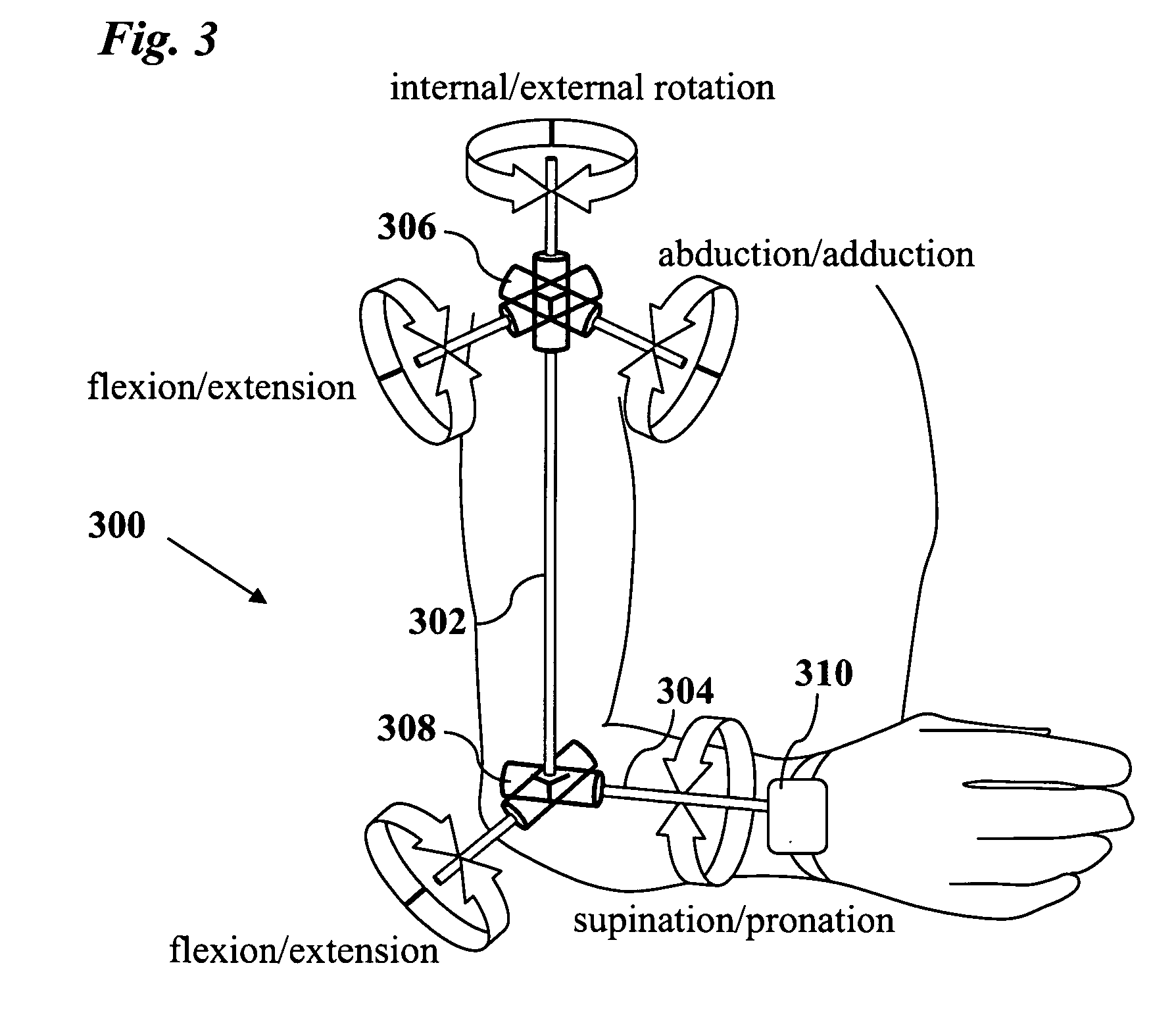
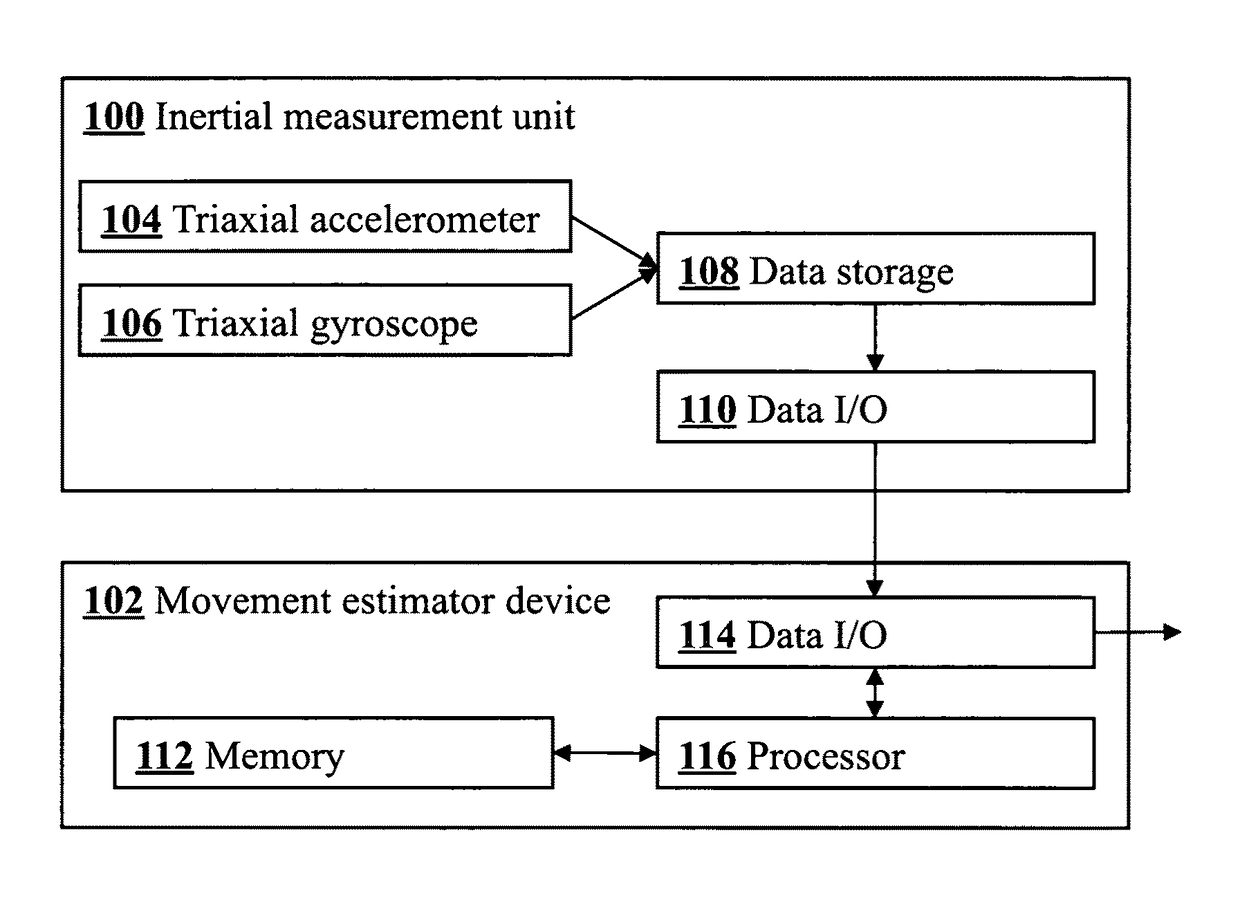
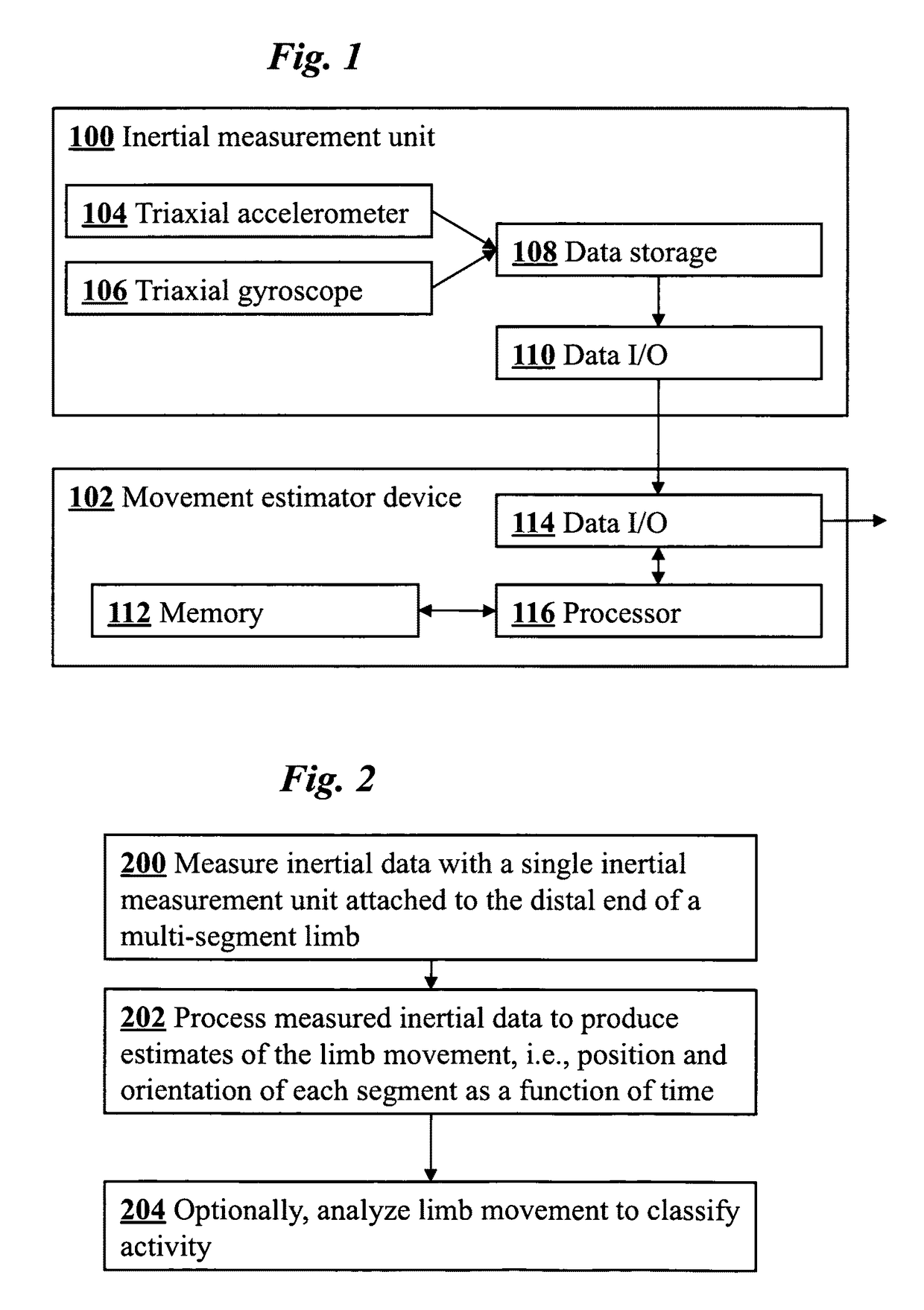
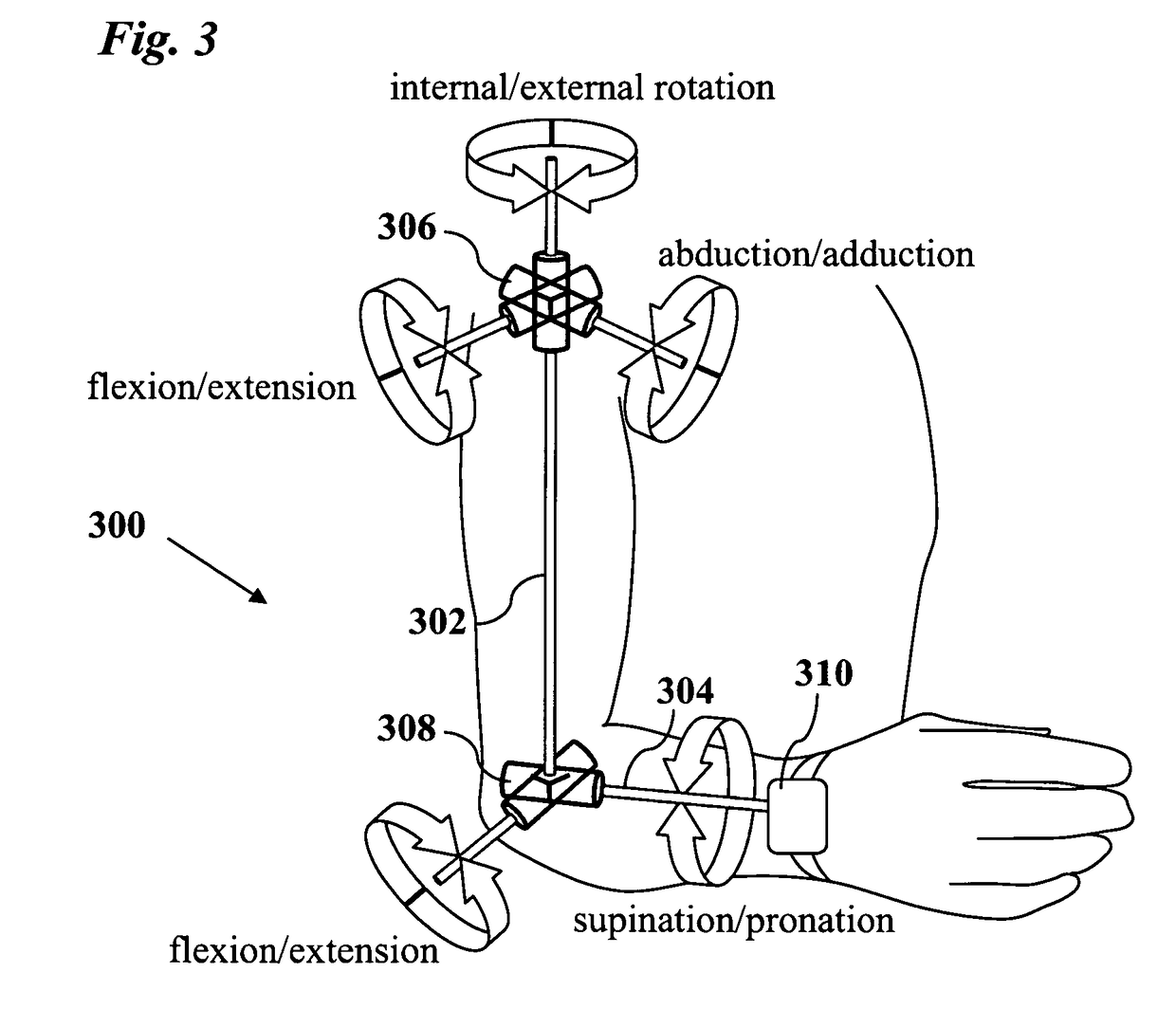
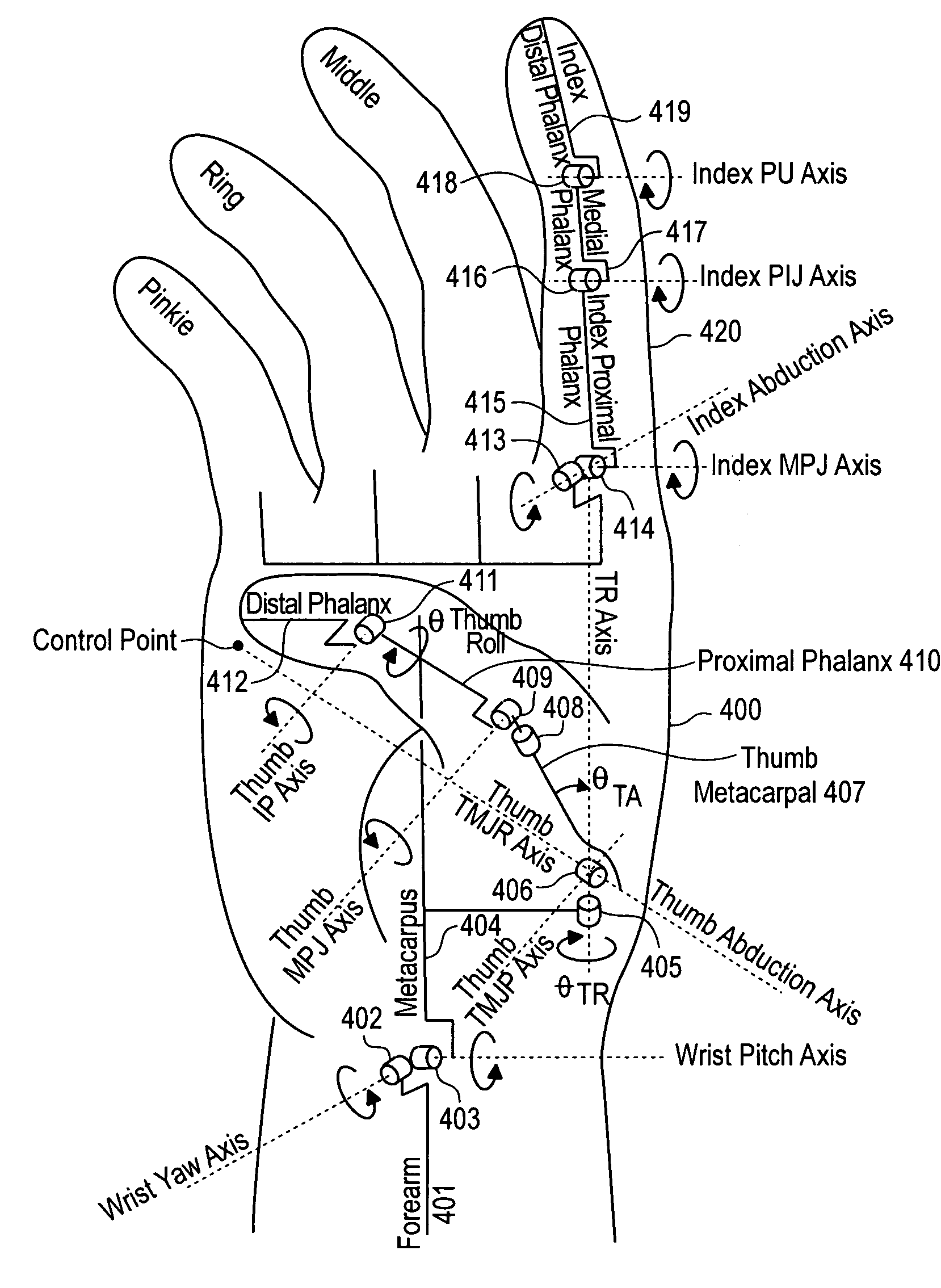
Joint angle tracking with inertial sensors
ActiveUS20090204031A1Accurate estimateAccurate trackingPerson identificationInertial sensorsEngineeringMulti segment
A method for estimating joint angles of a multi-segment limb from inertial sensor data accurately estimates and tracks the orientations of multiple segments of the limb as a function of time using data from a single inertial measurement unit worn at the distal end of the limb. Estimated joint angles are computed from measured inertial data as a function of time in a single step using a nonlinear state space estimator. The estimator preferably includes a tracking filter such as an unscented Kalman filter or particle filter. The nonlinear state space estimator incorporates state space evolution equations based on a kinematic model of the multi-segment limb.
Owner:OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE PORTLAND STATE UNIV THE STATE OF
Offline programming and modifying method of six-axis grinding and polishing industrial robot
ActiveCN105269565ASimplified offline programming processPracticalProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsComputer moduleWorking environment
The invention discloses an offline programming and modifying method of a six-axis grinding and polishing industrial robot. The offline programming and modifying method particularly includes the steps of building a model, extracting workpiece machining path information, performing point data processing, generating a robot working motion joint angle, generating a robot working motion trail, performing robot grinding and polishing working motion simulation, generating a robot motion key parameter conversion module and a code, modifying the position of an abrasive belt, modifying the position, posture and singularity and modifying the grinding and polishing work environment. The offline programming and modifying method enables the offline programming process of the six-axis grinding and polishing industrial robot to be simplified, has practicability, can quickly generate programs applicable to the six-axis grinding and polishing industrial robot which grinds and polishes workpieces with complex surfaces, and improves the grinding and polishing uniformity.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG IND
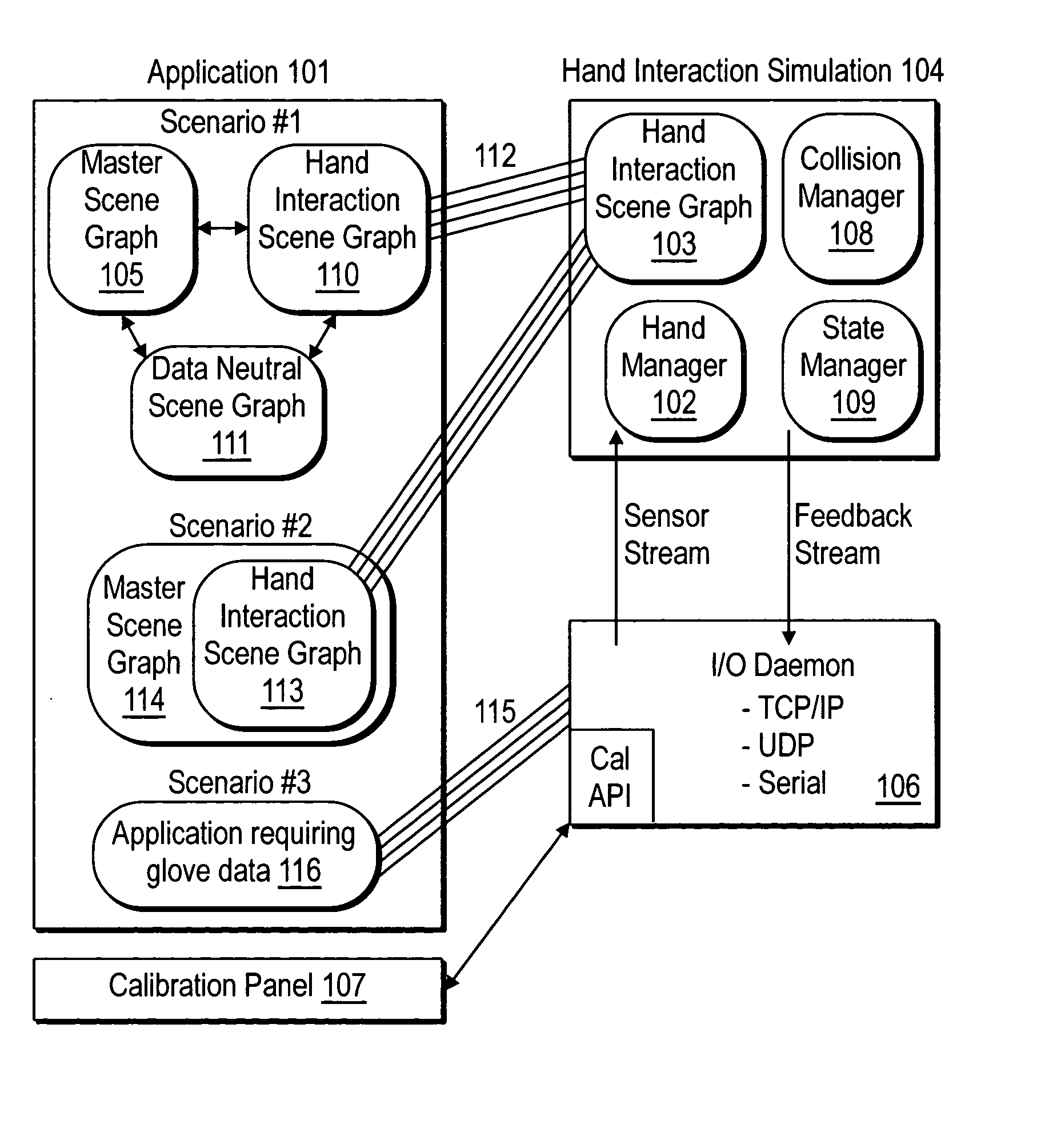
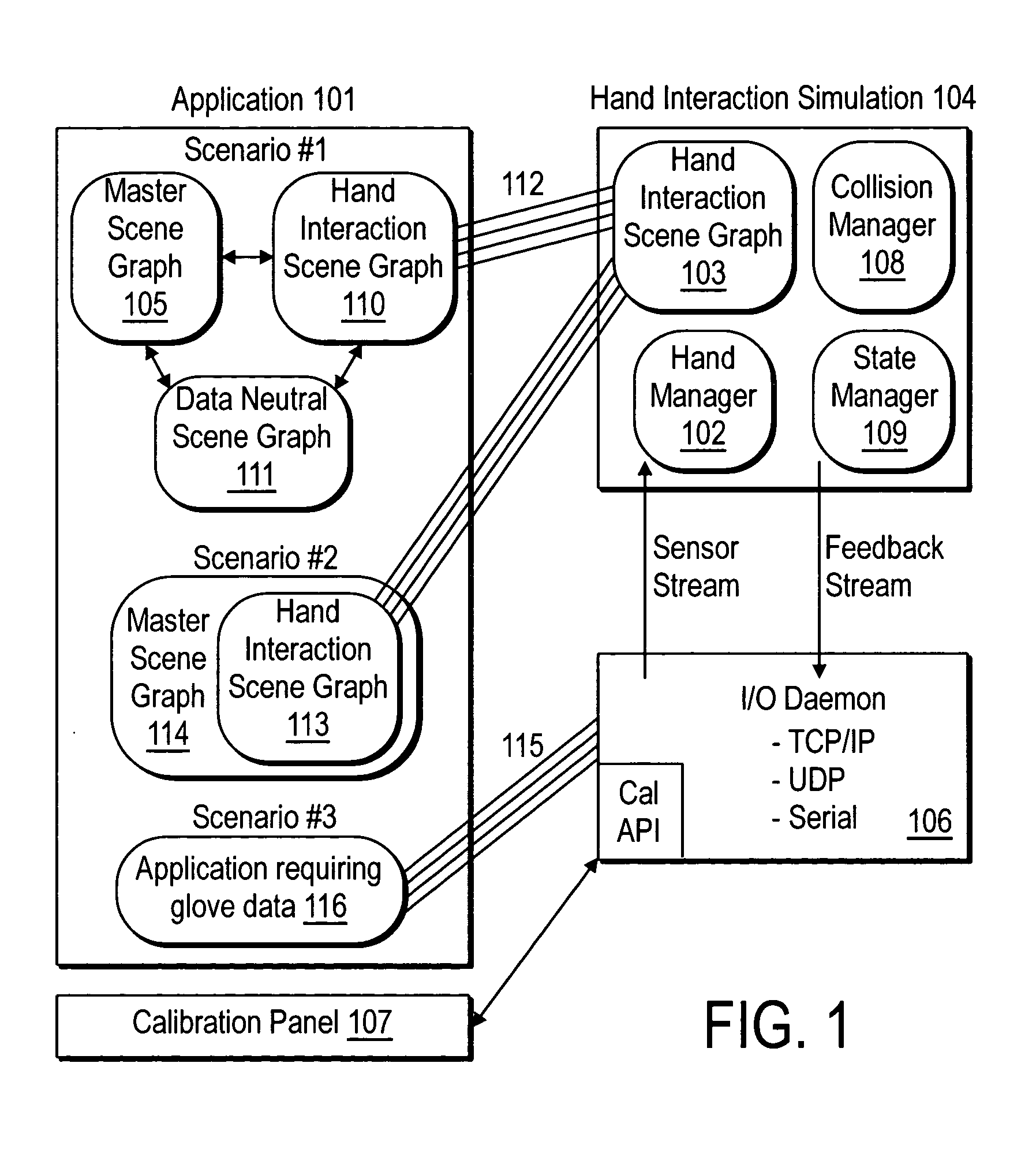
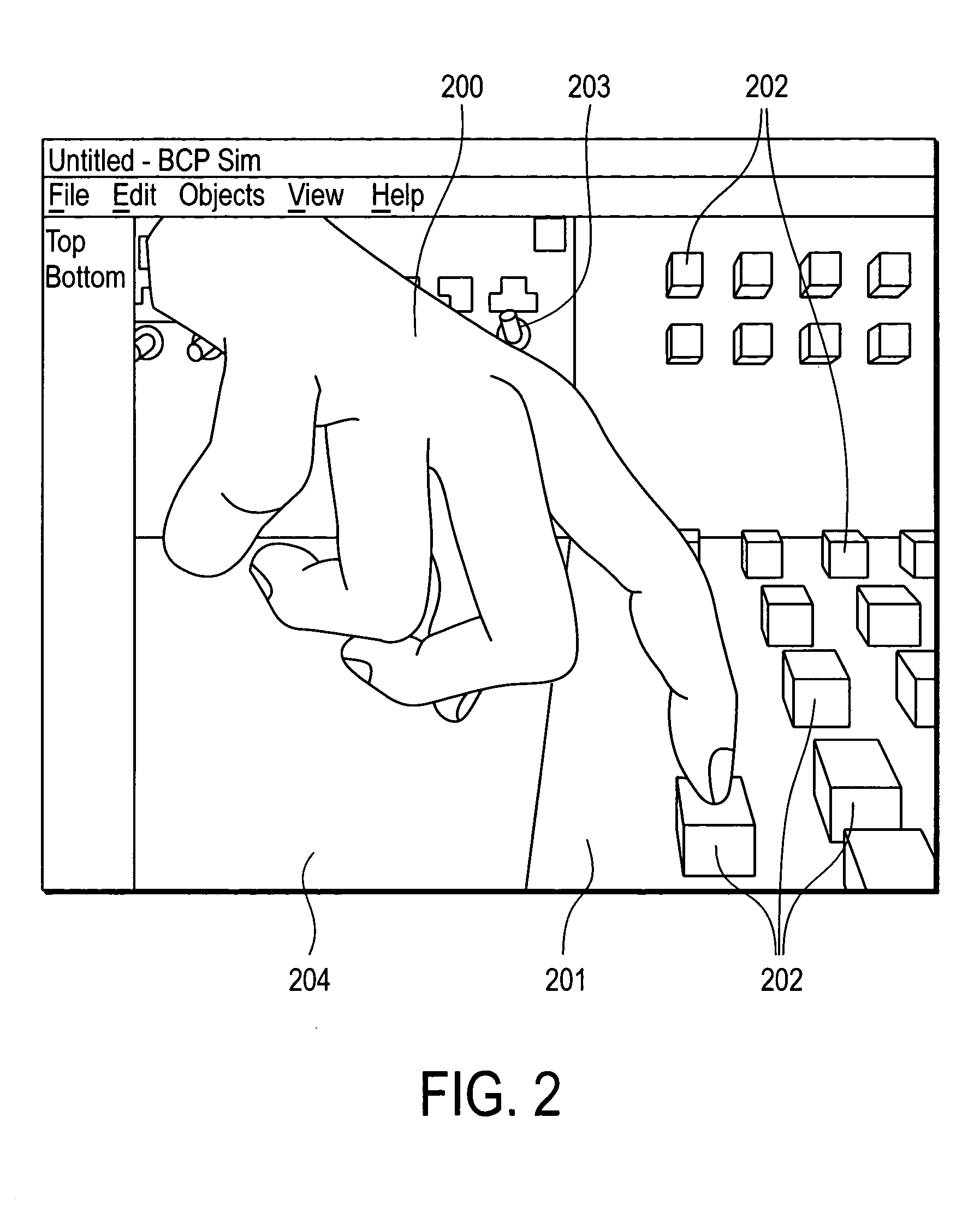
System and method for constraining a graphical hand from penetrating simulated graphical objects
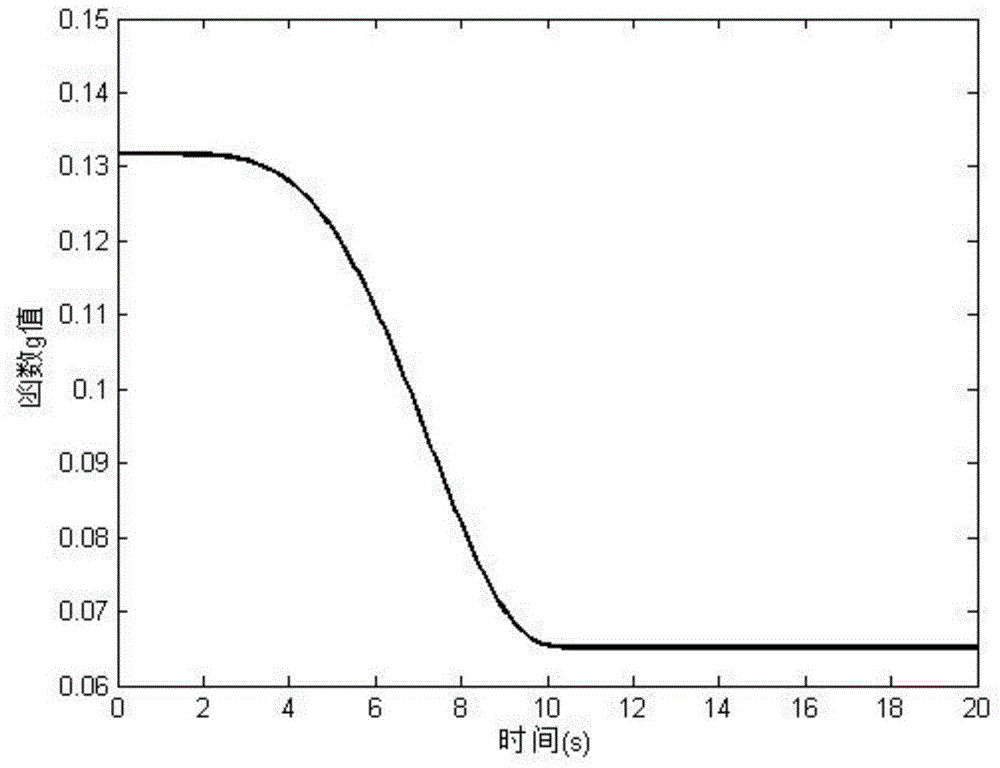
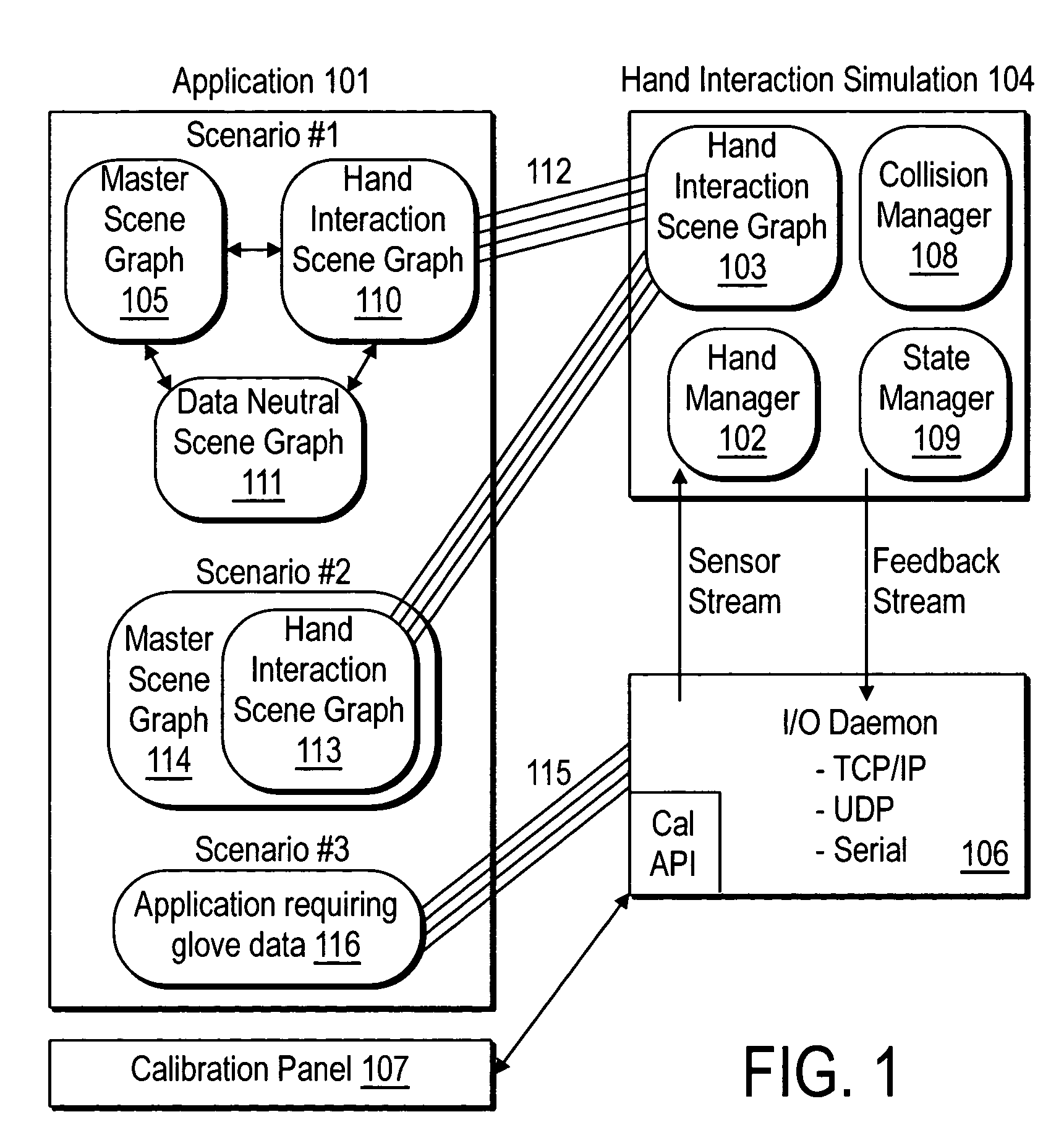
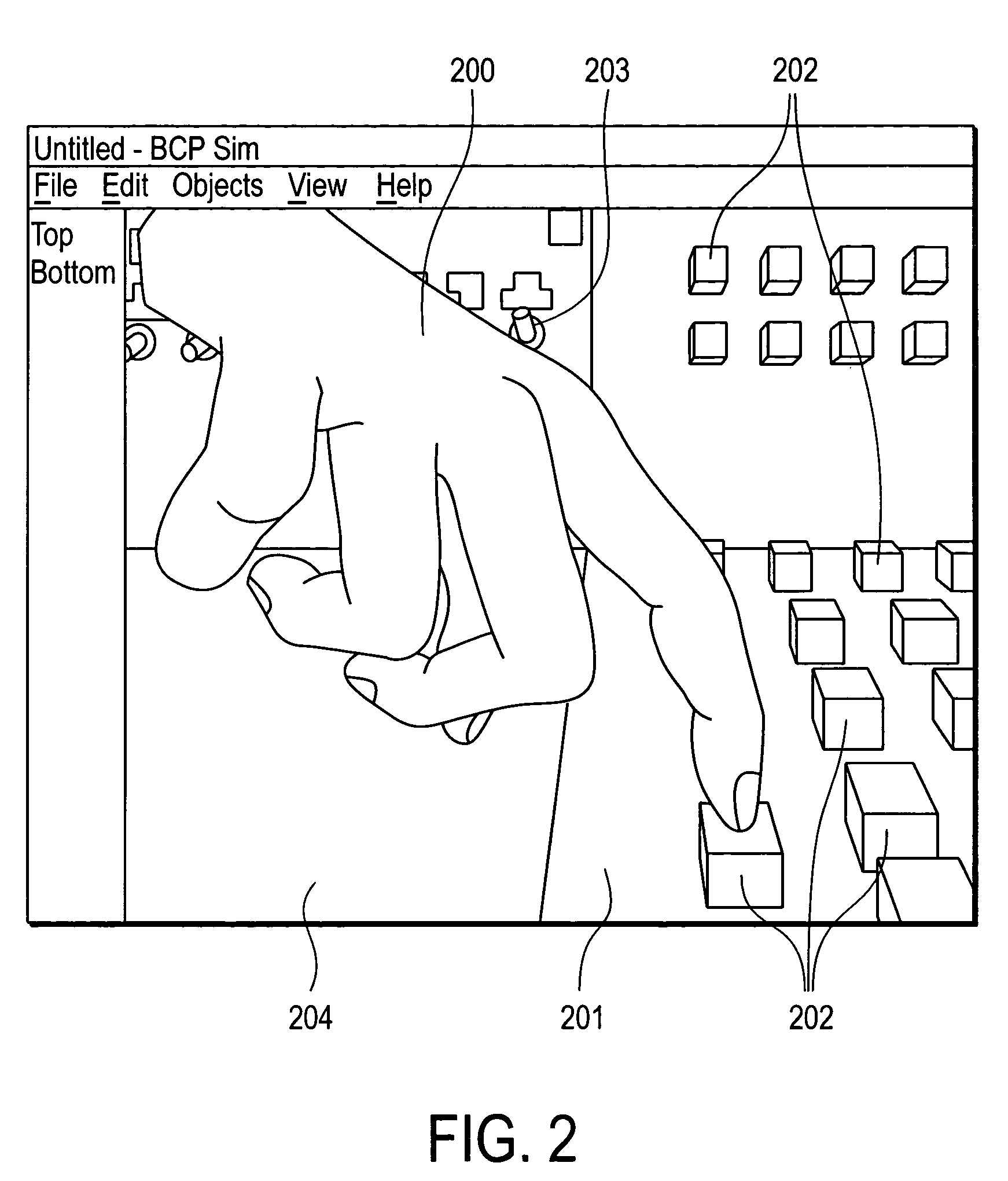
An apparatus, system, method, and computer program and computer program product are provided for constraining the movement of a graphical hand when the physical hand controlling the graphical hand does not have a similar physical constraint. The constraining technique may comprise use and analysis of a revolute-joint-link-spring model. In such a model, an uncompressed / unextended spring position represents the corresponding measured joint angle or link position. In addition to linear springs which follow Hook's Law, i.e., F=k*x, non-linear springs or other non-linear force functions may be employed to obtain the desired result of allowing a graphical joint or link to deviate from what the corresponding measured joint or link provides. In particular, if a graphical hand configuration corresponding to measured joint and link positions causes a portion of the hand to penetrate a simulated graphical solid object, a mathematical determination is used to compute modified joint and link positions such that the graphical hand part will no longer penetrate the graphical solid object. Such a constraint technique may include solving a spring model such that the various joint and link springs compress or extend to produce modified joint and link positions. Such a constraint technique may also be applied to constrain other graphical body parts and graphical inanimate objects, where corresponding physical controlling, i.e., measured, body parts and inanimate objects do not possess a similar constraint or impediment.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Joint angle tracking with inertial sensors
ActiveUS9597015B2Accurately estimate and trackImprove usabilityPerson identificationInertial sensorsKaiman filterState space
A method for estimating joint angles of a multi-segment limb from inertial sensor data accurately estimates and tracks the orientations of multiple segments of the limb as a function of time using data from a single inertial measurement unit worn at the distal end of the limb. Estimated joint angles are computed from measured inertial data as a function of time in a single step using a nonlinear state space estimator. The estimator preferably includes a tracking filter such as an unscented Kalman filter or particle filter. The nonlinear state space estimator incorporates state space evolution equations based on a kinematic model of the multi-segment limb.
Owner:OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE PORTLAND STATE UNIV THE STATE OF
Gait phase detection apparatus with ankle joint angle self-rectification function
InactiveCN101548925ASimple structureEasy to useChiropractic devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringGait trainingDeformity
The invention discloses a gait phase detection apparatus with ankle joint angle self-rectification function, which comprises a shank fixing mechanism, a ankle joint angle control mechanism, a ankle joint angle measuring mechanism and a thenar pressure measuring footwear. The invention can control ankle joint motor rotation angle according to thenar pressure signal, regulate ankle joint angle for foot drop patient in weight reduction walking training, prevent the damage to foot due to the towing and impacting caused by foot drop, and improve the dorsiflexion ability of foot drop patient; a pressure sensor and an angle sensor collects thenar pressure signal and ankle joint angle signal timely, an upper computer performs fuzzy logic algorithm to realize to detect gait phase smoothly and submissively. patient with walking ability defects or normal person with some degree of gait deformity can wear the invention while walking, detect the gait phase information in walking, estimate gait recovery degree scientifically, and optimize gait training strategy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
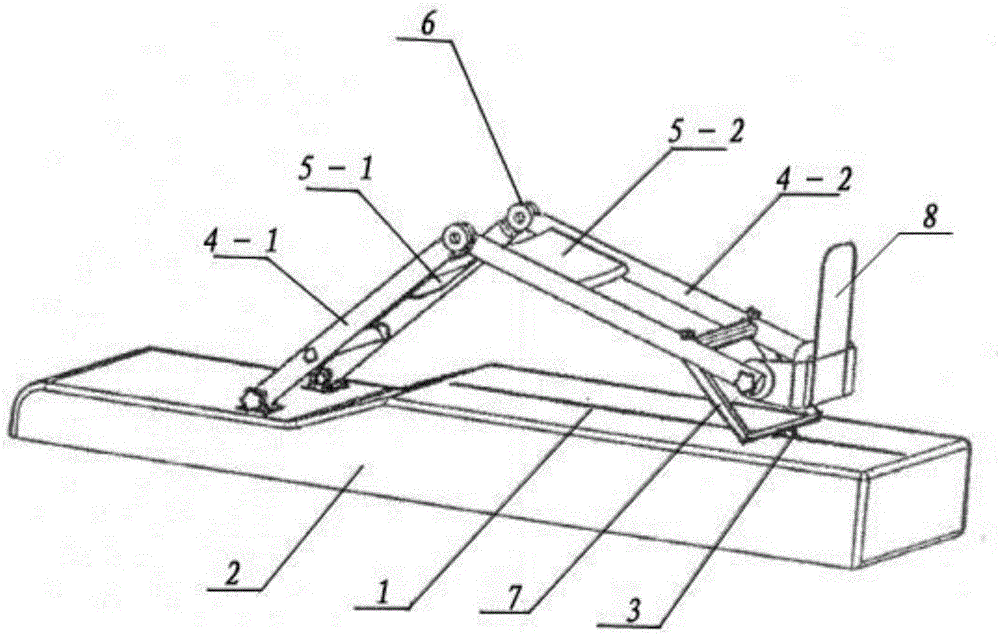
Apparatus and method for lower-limb rehabilitation training using weight load and joint angle as variables
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for lower-limb rehabilitation training of a patient with lower limb paralysis. The invention measures the usage of the paralyzed lower limb, and based upon the measurement, forces patients with lower limb paralysis to use partially paralyzed muscles which they are not likely to use. The apparatus can measure the weight load and the angle of the joint, and by using the measure values as variables, display the condition of paralysis to the patient so that he / she can recognize his / her present condition of paralysis, and enable the user to training through feedback. The joint includes all of knee joint, ankle joint and hip joint of the lower limb, and the movement of important muscles of the lower limb can be detected. With the apparatus attached, the patient can perform a balance training of alternatively raising the paralyzed lower limb and the normal limb, a standing training of bending and straightening both knees of the lower limbs and a walking training of using the both lower limbs.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
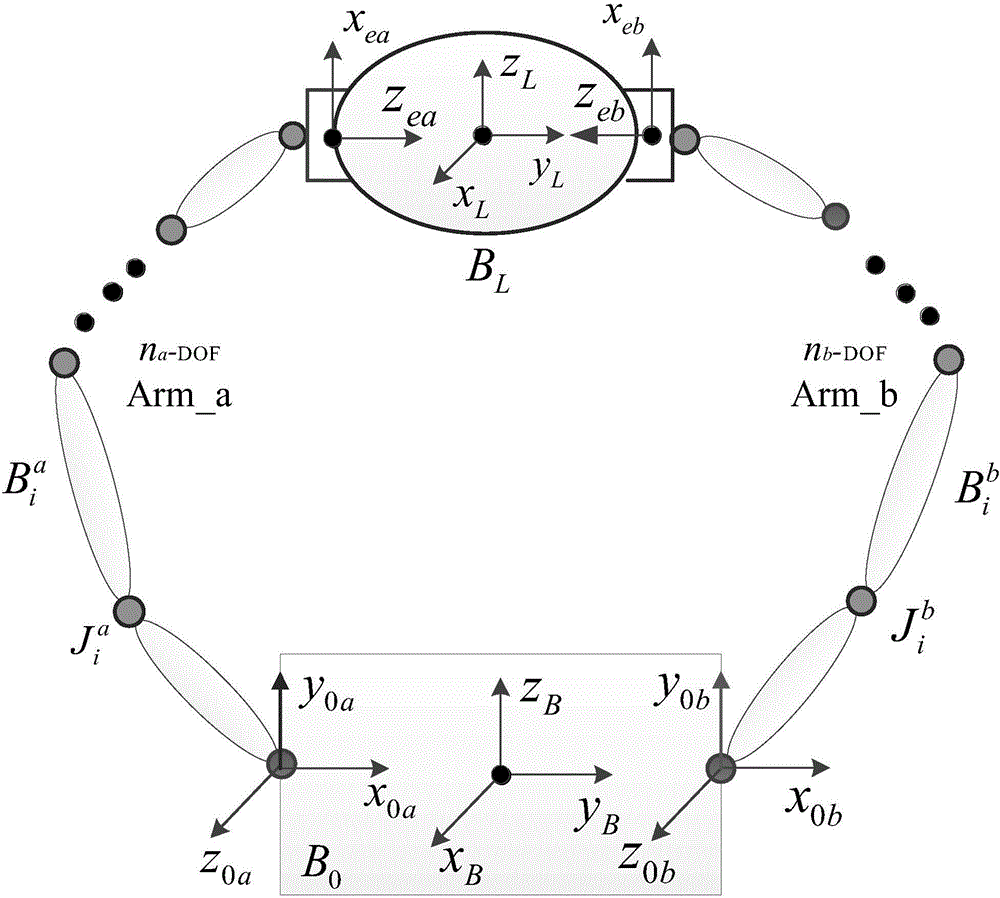
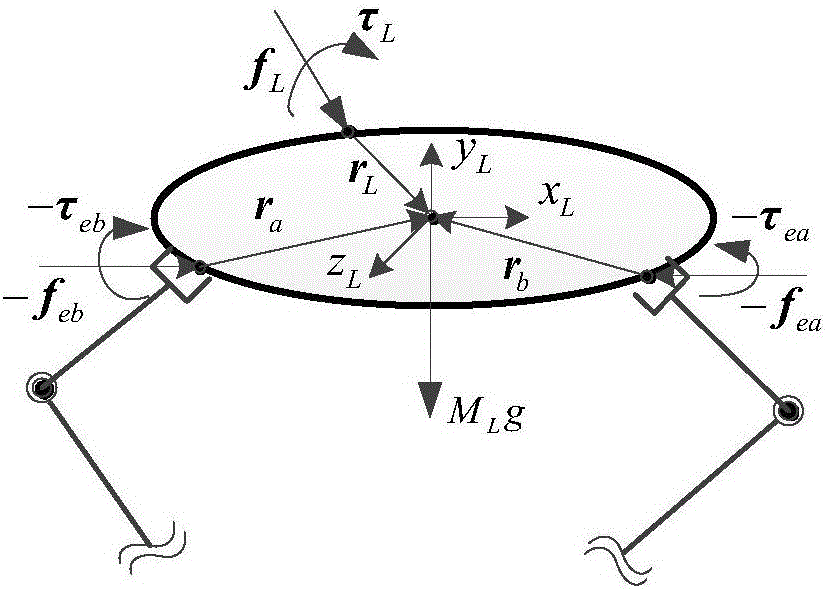
Compliance control method and system based on collaborative operation of double-arm robot
ActiveCN106695797ALower requirementSafe and reliable control schemeProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorDynamic modelsControl system
The invention discloses a compliance control method based on collaborative operation of a double-arm robot. The method comprises the steps that a double-arm collaborative control module sets up a dynamic model according to an expected motion trail of target loads and expected force to obtain tail end expected poses and tail end expected force of all mechanical arms; a single-arm control module completes analysis and execution of an expected task instruction to obtain expected angles of all joints of the mechanical arms; and a drive module drives the mechanical arms to complete the task trail according to the planned expected joint angles. The invention further provides a compliance control method based on collaborative operation of the double-arm robot. According to the scheme, master-slave mode and share-based mode strategies are adopted for carrying out public force decomposition on the loads to obtain expected operation force of two mechanical arms, and then a master-slave mode compliance control method and a share-based compliance control method for double-arm collaborative operation are provided. The method is widely applied to the double-arm collaborative control field of robot technologies.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Robot accuracy compensation method synthesizing pose error model and rigidity compensation
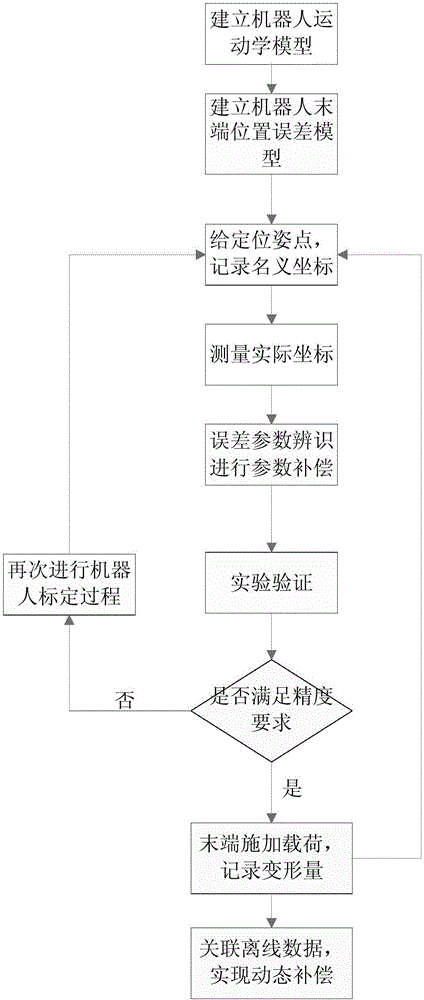
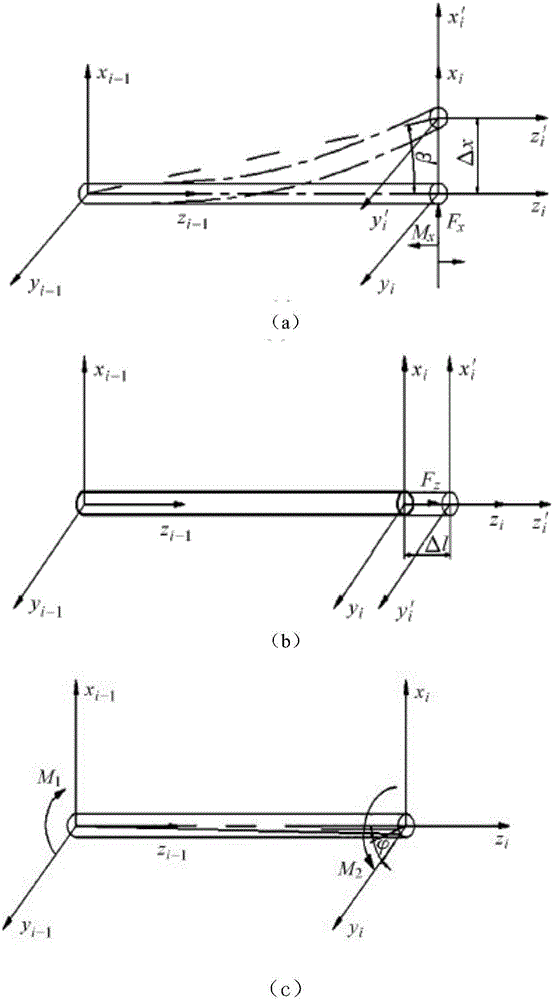
ActiveCN106737855ADescribe wellImprove online productivityProgramme-controlled manipulatorMeasuring instrumentStructural error
The invention discloses a robot accuracy compensation method synthesizing a pose error model and rigidity compensation. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a robot motion model according to structural parameter of a robot; step 2, establishing a robot error model; step 3, in a robot working space, randomly giving a target pose point, and when a tail end of the robot moves a designated point, recording a joint angle at the moment; step 4, using a position measuring instrument to measure actual coordinates Pa of the given target pose point; step 5, using a least square method to recognize an error parameter; step 6, applying a load at the tail end of the robot, measuring the deformation amount of the robot, then returning to step 3, compensating a re-recognized structural error for the motion model again, thereby eliminating the pose error of the tail end due to the deformation caused by the load, and meanwhile, data of the deformation amount caused by the load is stored in a database for later accuracy compensation. According to the invention, the absolute positioning accuracy of the robot can be improved remarkably, and high simplicity and high efficiency are realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
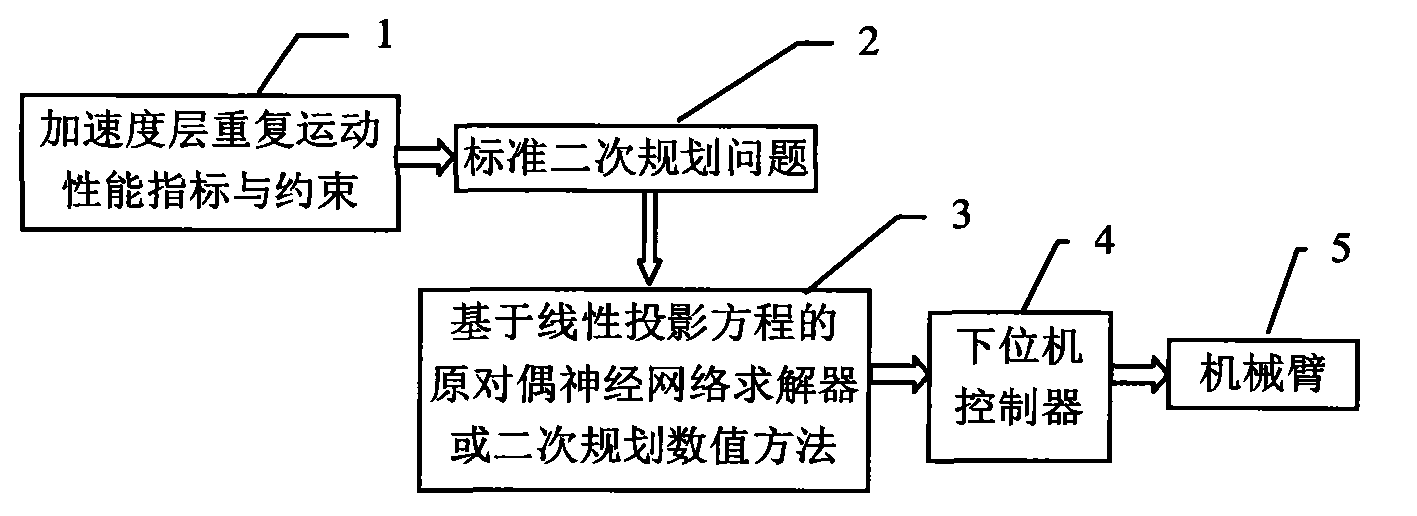
Repetitive motion planning method for redundant manipulator
The invention provides a repetitive motion planning method for a redundant manipulator, which comprises the following steps of: 1) resolving a manipulator repetitive motion scheme on an acceleration layer by adopting quadratic model optimization through an upper computer, designing the minimum performance index as repetitive motion, and restraining by an acceleration Jacobian equation, a joint angle limit, a joint speed limit and a joint acceleration limit; 2) converting the quadratic model optimization in the step 1) into standard quadratic programming; 3) solving the standard quadratic programming in the step 2) by using a linear projection equation-based primal-dual neural-network solver or quadratic programming numerical method; and 4) transmitting a solving result in the step 3) to acontroller of a lower computer for driving the manipulator to move. The method realizes the repetitive motion of the manipulator on the acceleration layer, has good control effect on the redundant manipulator inconvenient to control, and can effectively prevent the manipulator from exceeding the limits and being physically damaged according to various joint limits.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Mechanical arm trajectory tracking control method based on high-order sliding-mode observer
ActiveCN109927032AAccurate trackingReduce lossProgramme-controlled manipulatorAngular velocityDrive motor
The invention discloses a mechanical arm trajectory tracking control method based on a high-order sliding-mode observer. The method comprises the following steps of 1, establishing a dynamical model of an n-degree-of-freedom rotary joint rigid mechanical arm system; 2, acquiring measurement information of joint angles q of a mechanical arm by utilizing a photoelectric encoder, and calculating a mechanical arm trajectory tracking error e = q - qd according to a set expected joint angle qd; 3, establishing a global integral fast terminal sliding mode surface according to e; 4, determining control torque tau of joint driving motors of the mechanical arm according to the sliding mode surface and establishing a control gain self-adaptive rate capable of being dynamically adjusted; and 5, establishing the output feedback high-order sliding mode observer according to the control torque tau and the joint angles q of the mechanical arm, and estimating current angular velocity of joints and lumped disturbance. According to the method, under the situation that nonlinear uncertain items such as system parameter perturbation, external torque interference and damping friction exist in the mechanical arm system, the trajectory tracking control of the mechanical arm is realized only based on the measurement information of all the joint angles, and robustness of whole control process is ensured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
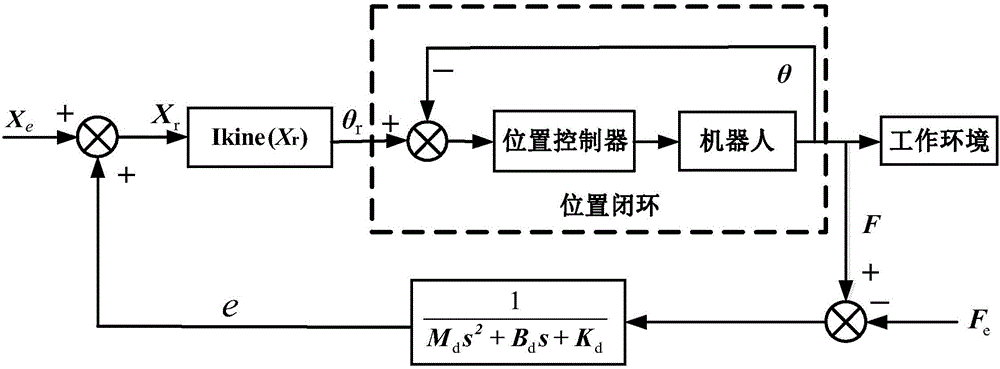
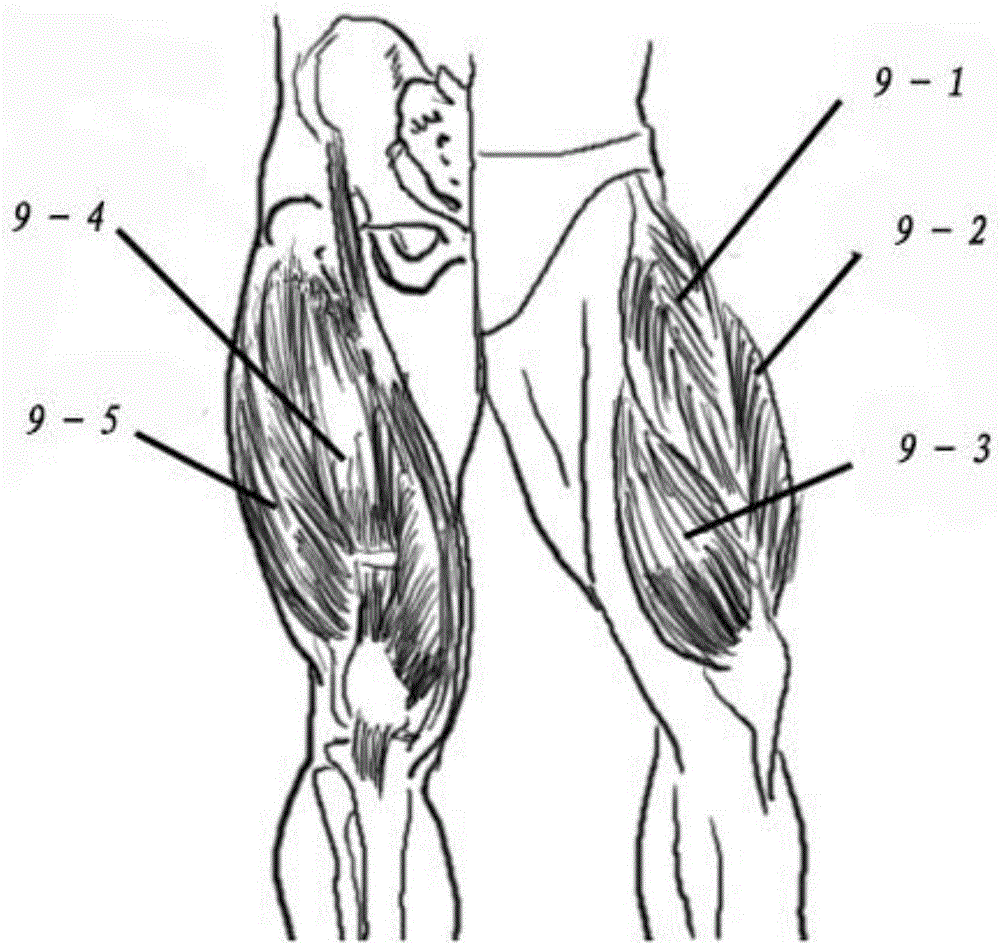
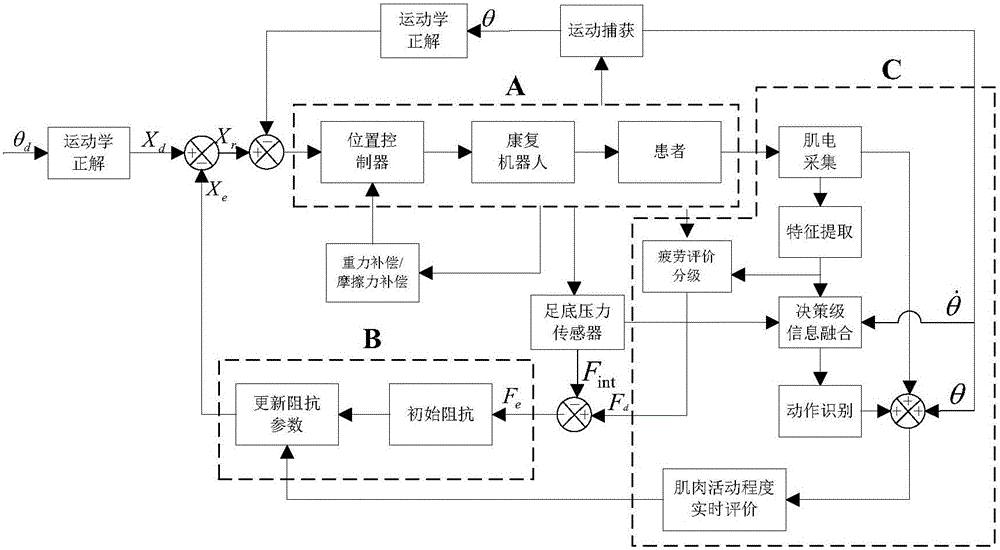
A rehabilitation robot control method based on electromyography feedback type impedance self-adaption
ActiveCN106109174ARealize flexible switchingHighlight interactionChiropractic devicesSensorsObject basedAngular velocity
The invention provides a rehabilitation robot control method based on electromyography feedback type impedance self-adaption. The method comprises the steps of identifying the joint extension and flexion states of a training object based on electromyography signal characteristics values, plantar pressure signals and angular velocity signals, determining limb movement intention, and giving electromyography signal characteristic quantities used for describing the active level of the muscles of an affected side by using a method of affected side-mirroring-unaffected side; setting a target impedance equation, describing the function relation between extremity movement track differences and extremity stress, and establishing an impedance function capable of self-adaptive adjustment according to the active level of the muscles of the affected side and joint angles; according to initial anticipated static balance force, analyzing electromyography signals to obtain fatigue degree levels, and finely adjusting the anticipated static balance force. Self-adaptive tracking of anticipated tracks of a lower limb rehabilitation robot is realized by using a position controller. By establishing the self-adaptive adjustment impedance function and adjusting the static balance force by level, rehabilitation training processes can adapt to individuals and control processes are more natural, smooth and reliable and safer.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Repetitive movement planning method for redundancy mechanical arm
ActiveCN106945041AAddressing non-repetitive motion problemsImprove real-time performanceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRepetitive movementsPlanning method
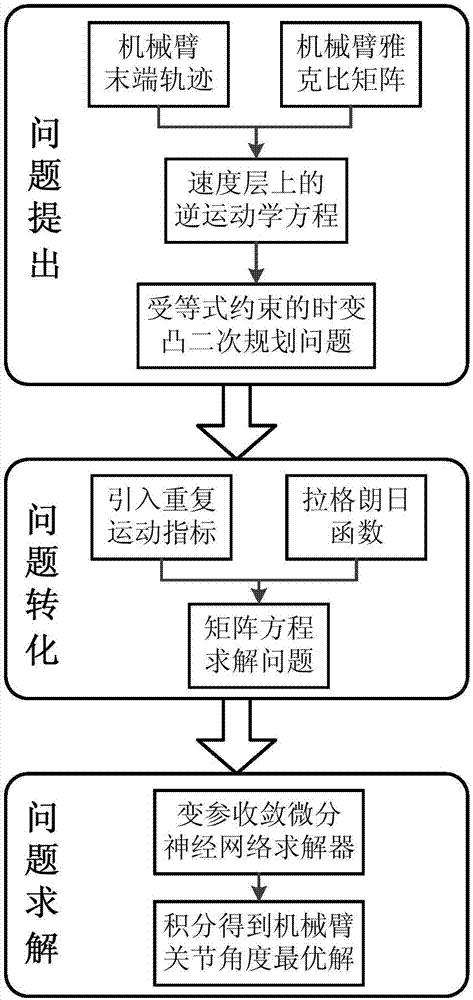
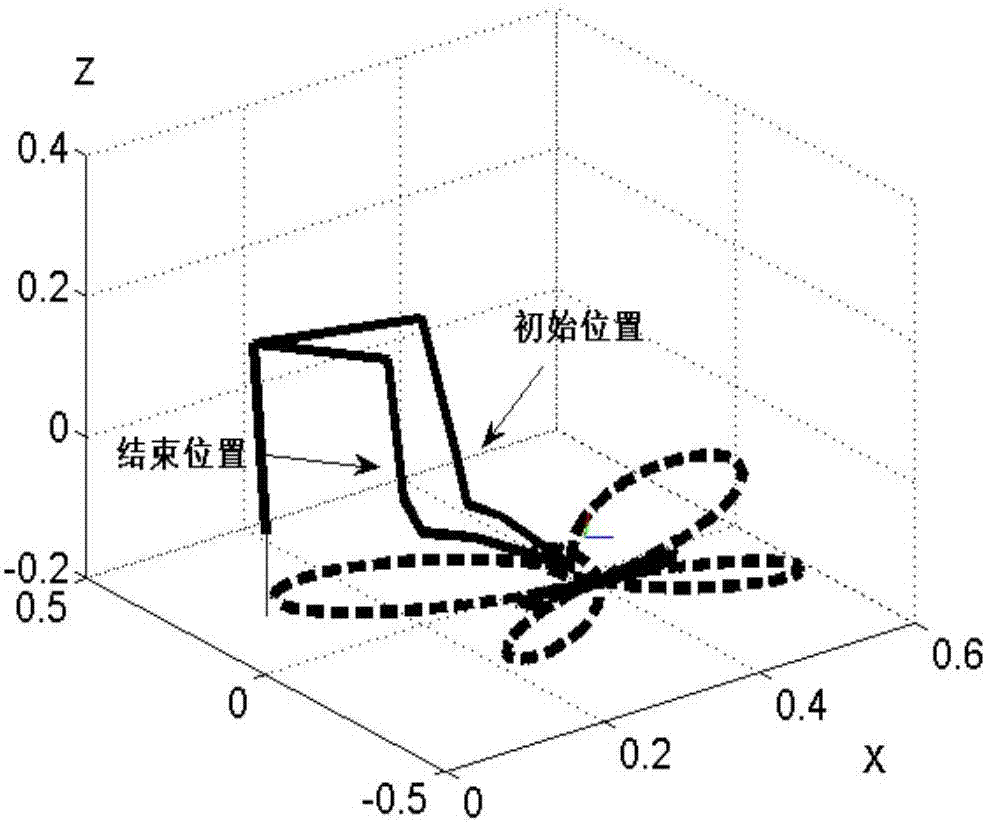
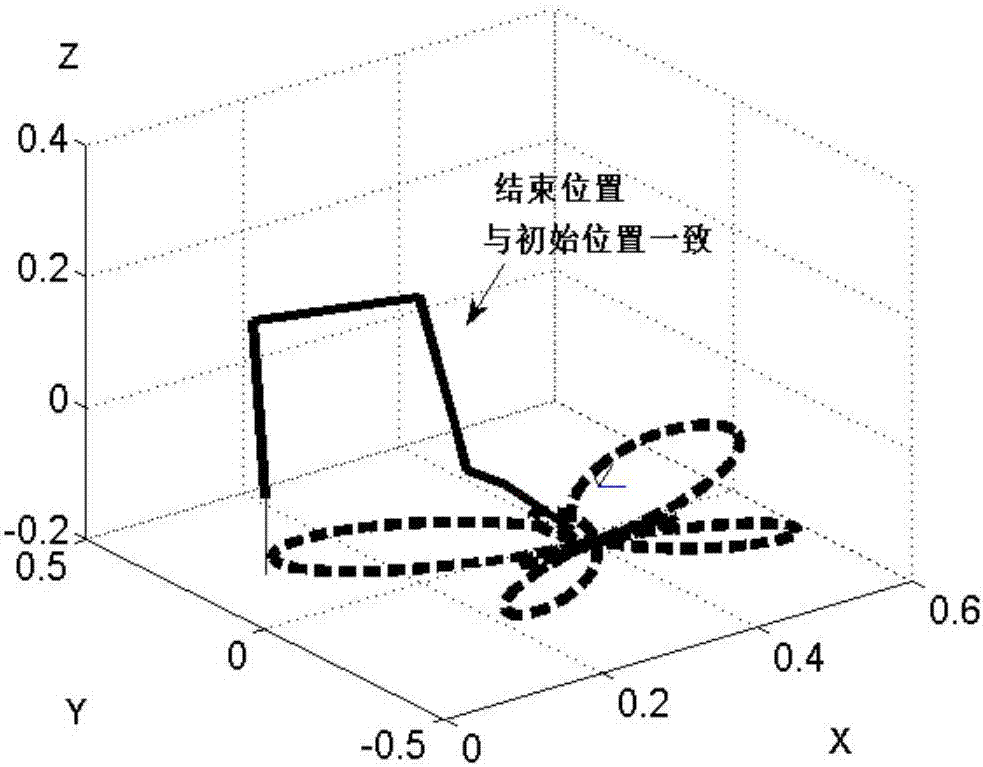
The invention discloses a repetitive movement planning method for a redundancy mechanical arm based on a variable-parameter convergence differential neural network. The repetitive movement planning method includes the following steps that firstly, a redundancy mechanical arm inverse kinematics equation is established on a speed layer through the track of the tail end of the redundancy mechanical arm; secondly, the inverse kinematics problem in the first step is designed as a time-varying convex quadratic programming problem constrained by the equation; thirdly, a repetitive movement index is introduced in the time-varying convex quadratic programming problem; fourthly, the time-varying convex quadratic programming problem in which the repetitive movement index is introduced is converted into a time-varying matrix equation through a lagrangian function; fifthly, the time-varying matrix equation is solved through the variable-parameter convergence differential neural network; and sixthly, integration is conducted on the optimal solution, obtained in the fifth step, on the speed layer of the redundancy mechanical arm, and the optimal solution of the joint angle is obtained. By means of the repetitive movement planning method for the redundancy mechanical arm based on the variable-parameter convergence differential neural network, the variable-parameter convergence differential neural network is adopted for solving the repetitive movement of the redundancy mechanical arm, and the beneficial effects of the high calculating efficiency, high real-time performance and good robustness are achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Robot trace tracking control method and system
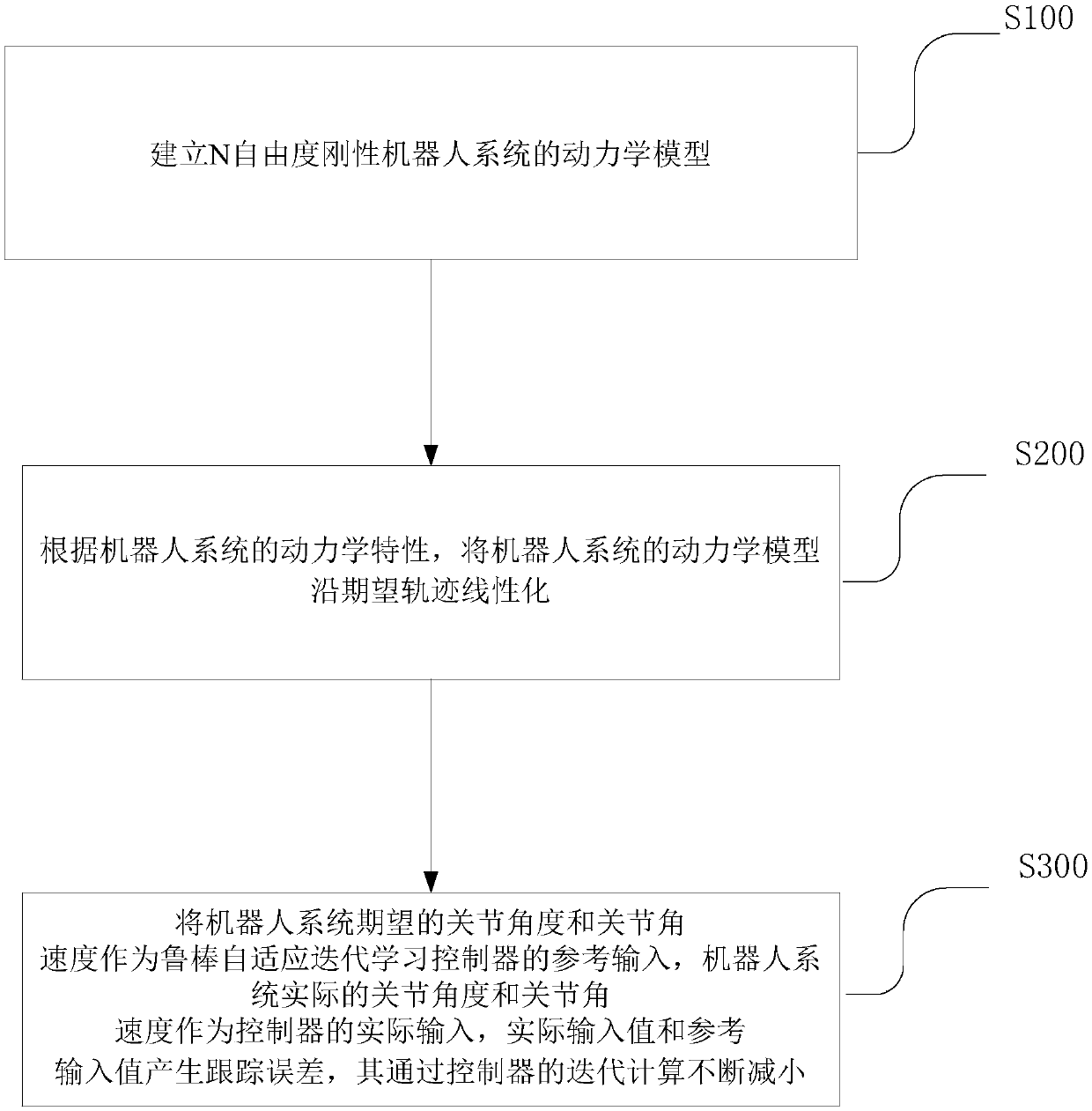
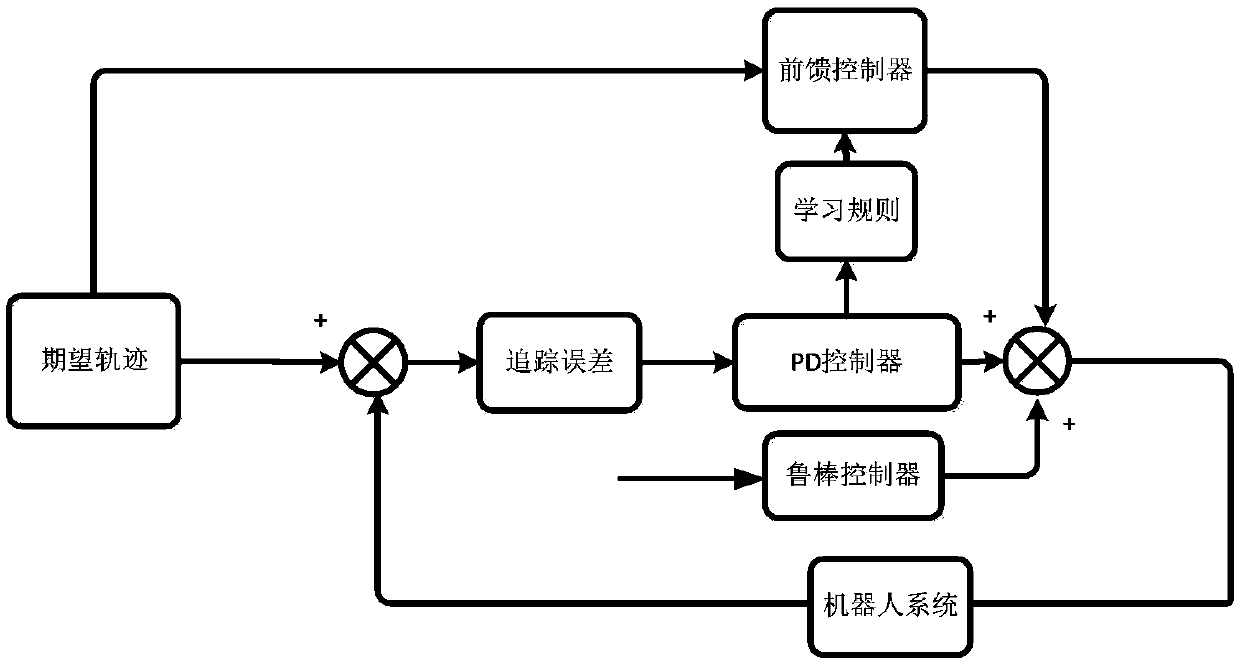
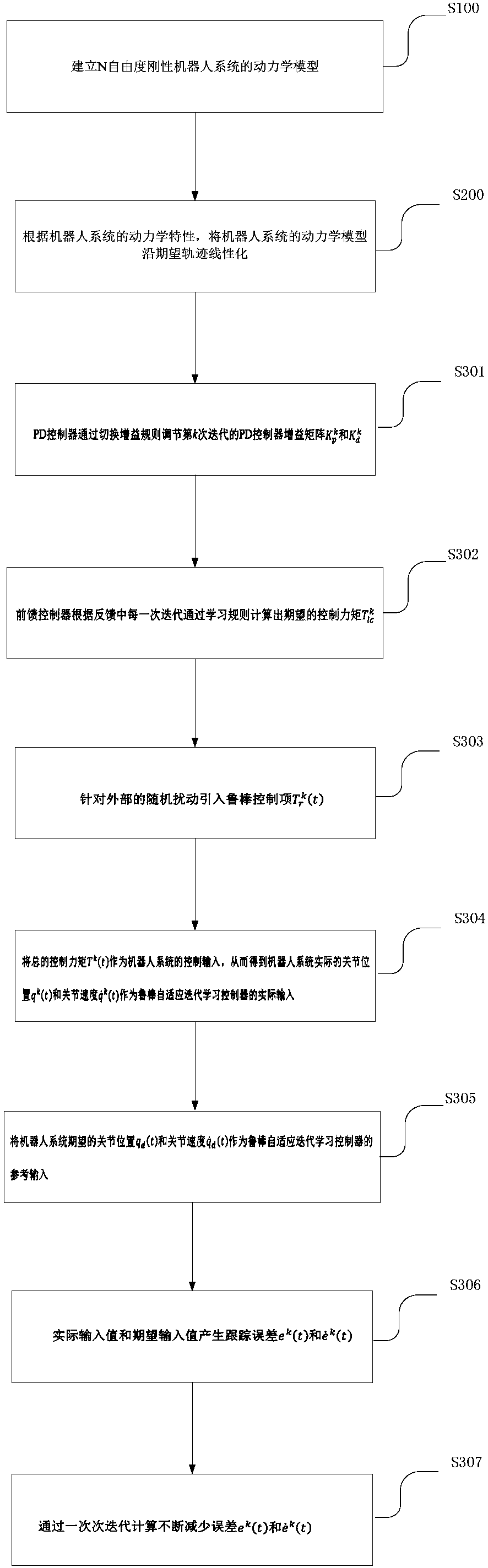
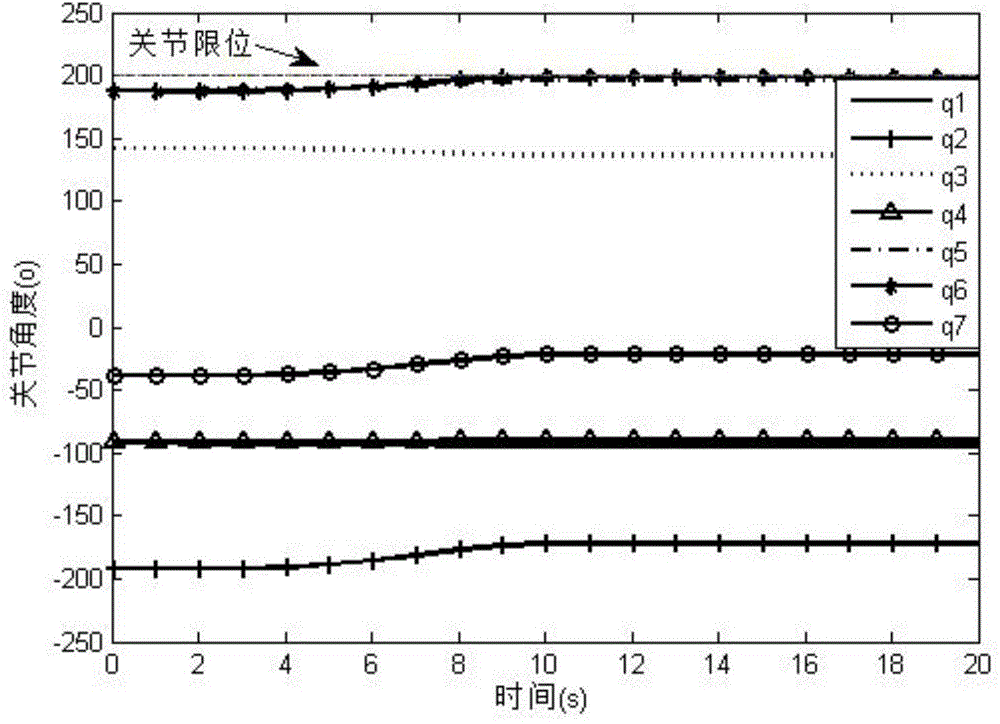
ActiveCN108319144AGuaranteed certaintyGuaranteed stabilityAdaptive controlRobotic systemsLearning controller
The present invention discloses a robot trace tracking control method and system. The method comprises the following steps of: the step S100: establishing a dynamical model of an N-degree-of-freedom rigid robotic system; the step S200: according to dynamic characteristics of the robotic system, performing linearization of the dynamical model of the robotic system along an expected trace; and the step S300: taking expected joint angle and joint angular speed of the robotic system as reference input of a robustness adaptive iteration learning controller, taking actual joint angle and joint angular speed of the robotic system as actual input of the controller, generating tracking errors between the actual input and the reference input, and gradually decreasing the tracking errors through iteration calculation of the controller. The robot trace tracking control method and system can perform tracking control of a robot of uncertainty modeling and random disturbance, can improve the rate ofconvergence and the control precision of tracking control and can meet the requirement of the work speed and the precision of the robot.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Space manipulator track planning method for minimizing base seat collision disturbance
InactiveCN104526695AAccurate pose captureReduce base attitude disturbanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematics equationsEngineering
The invention discloses a space manipulator track planning method for minimizing base seat collision disturbance, and belongs to the technical field of manipulator control. The space manipulator track planning method for minimizing the base seat collision disturbance includes: deriving a manipulator base seat attitude disturbance equation on the basis of establishing a space manipulator kinematical equation and a dynamical equation; designing a comprehensive optimized operator on the premise of considering tail capture pose accuracy and joint displacement limiting of a space manipulator, and optimizing manipulator configuration in a null space so as to achieve minimization of the base seat disturbance caused by collision; finally, using a particle swarm optimization algorithm to achieve track planning before the collision of the space manipulator from an initial pose to an ideal pose. The space manipulator track planning method for minimizing the base seat collision disturbance solves problems in the track planning before the collision of the space manipulator, achieves a simple and pellucid control process, performs novel and practical design of the comprehensive optimized operator, can achieve the purpose of reducing the base seat pose disturbance caused by the collision to the utmost on the premise of guaranteeing the accurate tail capture pose of the manipulator and preventing joint angles from exceeding limits.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
System and method for constraining a graphical hand from penetrating simulated graphical objects
Movement of a graphical hand is constrained when the physical hand controlling the graphical hand does not have a similar physical constraint. An analysis of a revolute-joint-link-spring model in which an uncompressed / unextended spring position represents the corresponding measured joint angle or link position is used. Linear springs , non-linear springs, or the like may be employed to obtain the desired result of allowing a graphical joint or link to deviate from what the corresponding measured joint or link provides. If a graphical hand configuration causes a portion of the hand to penetrate a simulated graphical solid object, a mathematical determination is used to compute modified joint and link positions such that the graphical hand part will no longer penetrate the solid object. Such a constraint technique may include solving a spring model such that the various joint and link springs compress or extend to produce modified joint and link positions.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Manipulator apparatus and medical device system
ActiveUS20090112316A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsManipulatorSacroiliac joint
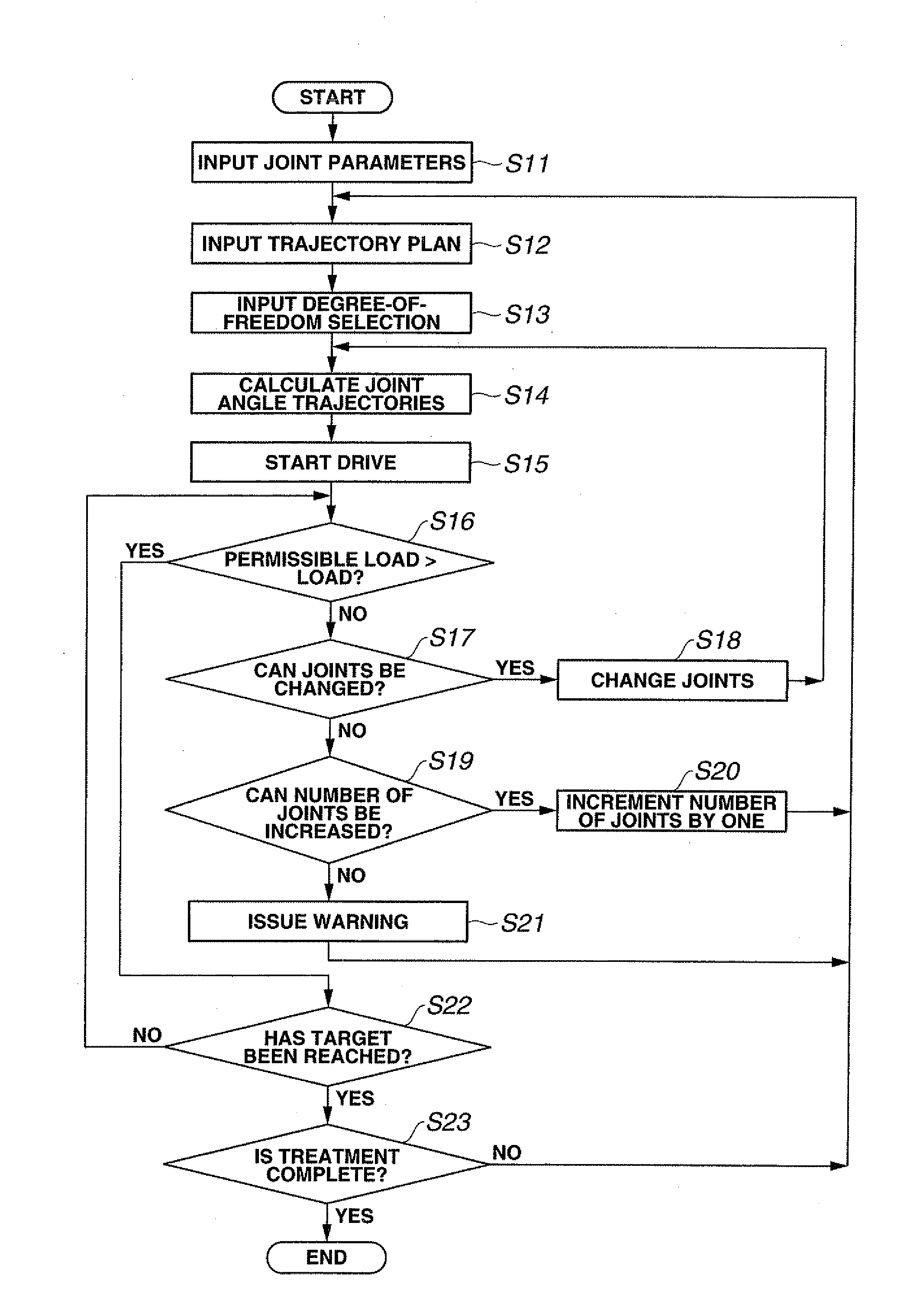
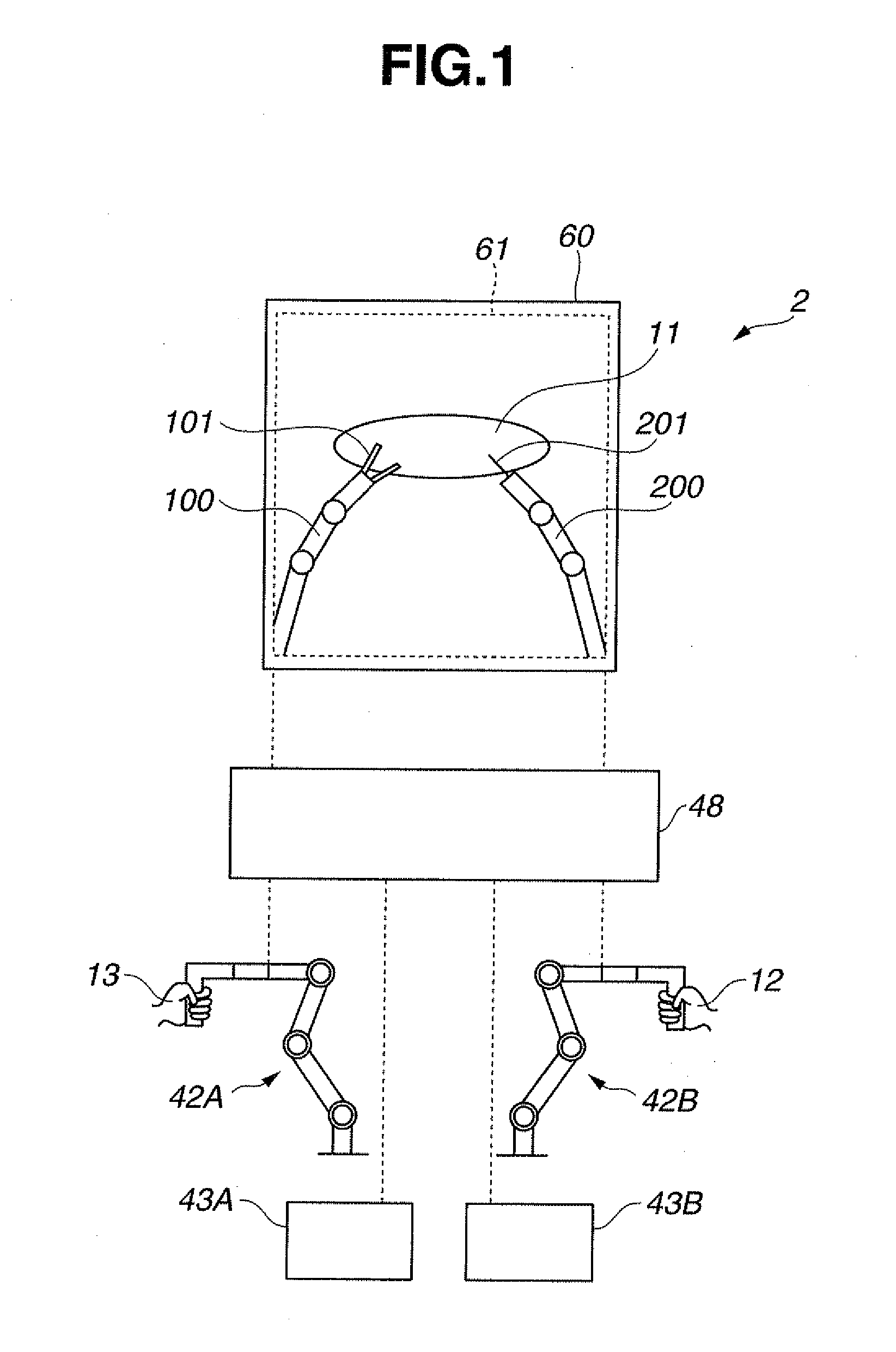
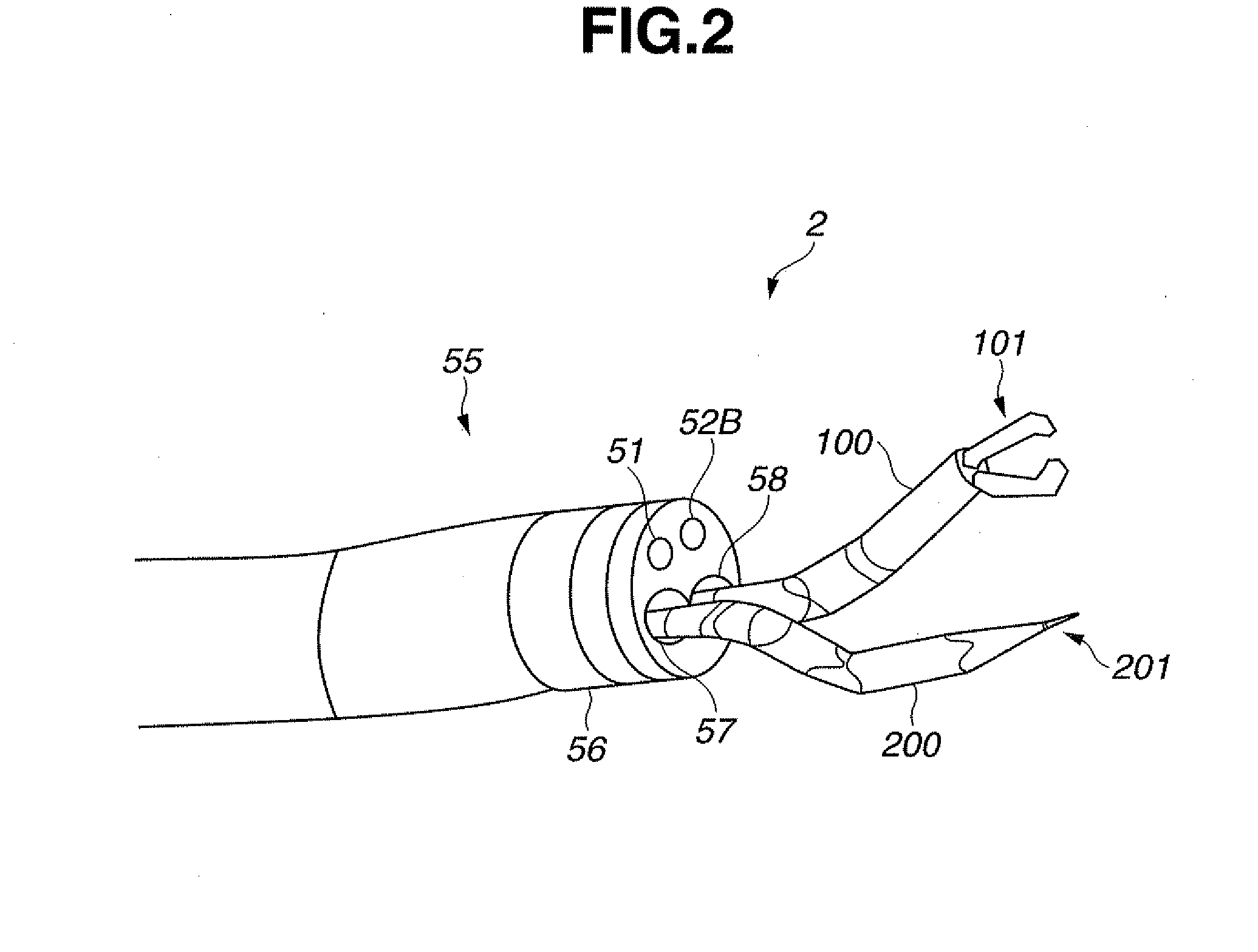
A medical device system includes a manipulator including a plurality of joints, a parameter storing portion for storing joint parameters, including a largest available force, of each joint of the plurality of joints, a trajectory inputting portion for inputting, as a trajectory plan, trajectories for moving a distal end of the manipulator from a current position and attitude to a target position and attitude, a trajectory setting portion for setting a joint angle trajectory for each joint providing a largest available force from among joint angle trajectories which allow movement to the target position and attitude with a minimum number of driven joints based on a largest available force parameter for the each joint stored in the parameter storing portion and the trajectory plan.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
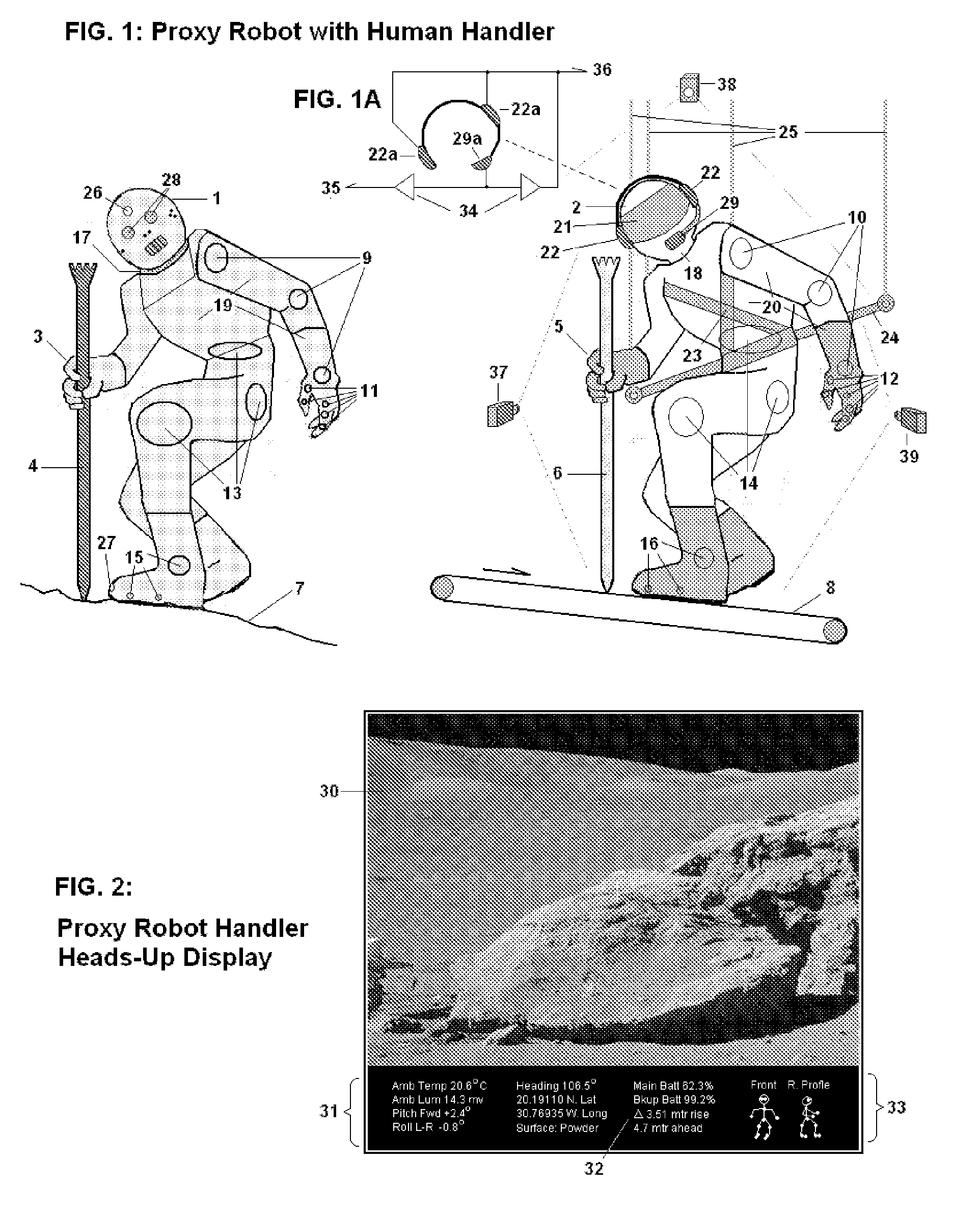
Proxy Robots and Remote Environment Simulator for Their Human Handlers
InactiveUS20130211594A1Improve stabilityAvoiding inherent risk and enormous costProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorAnimationSimulation
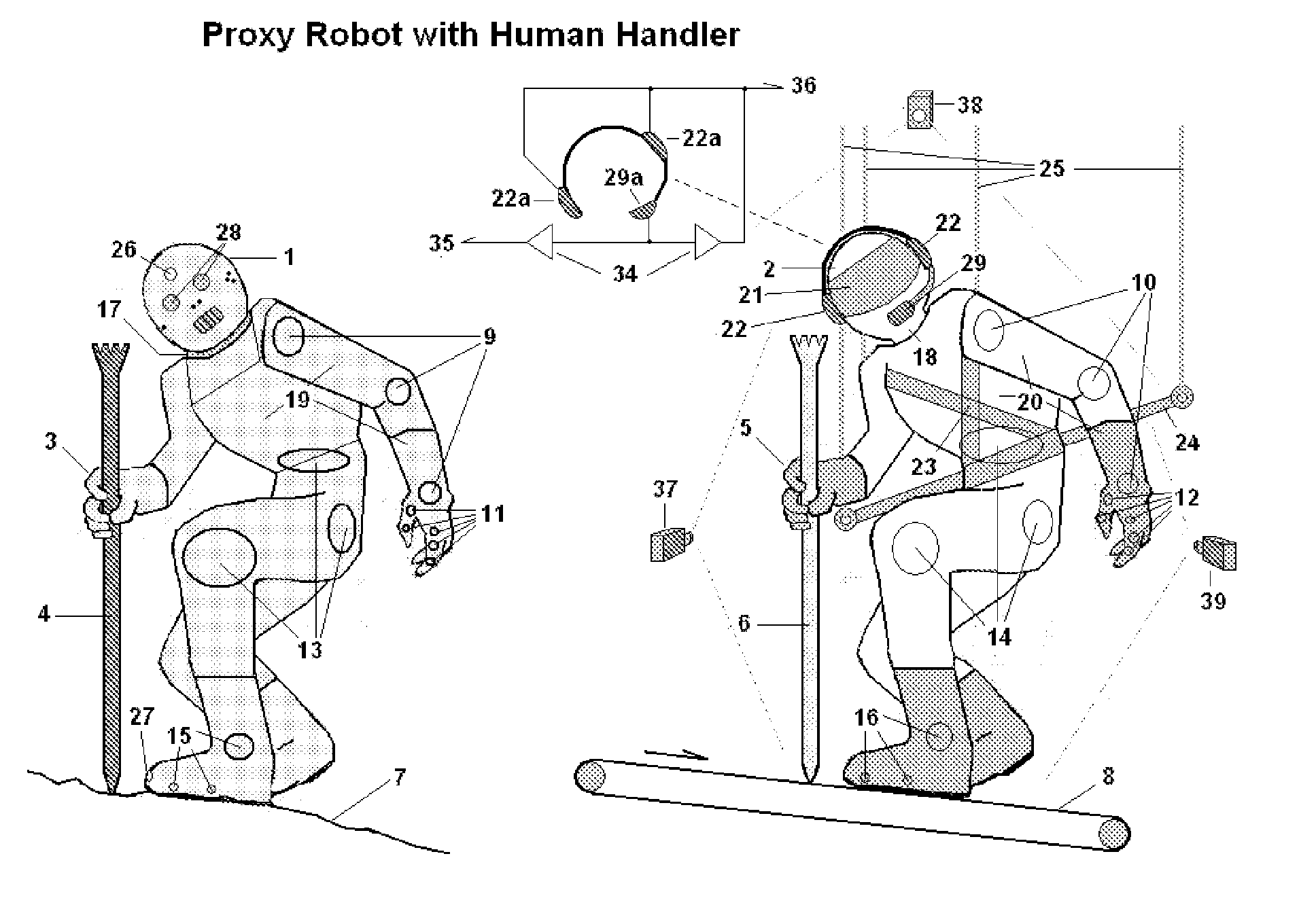
A system for controlling a human-controlled proxy robot surrogate is presented. The system includes a plurality of motion capture sensors for monitoring and capturing all movements of a human handler such that each change in joint angle, body posture or position; wherein the motion capture sensors are similar in operation to sensors utilized in motion picture animation, suitably modified to track critical handler movements in near real time. A plurality of controls attached to the proxy robot surrogate is also presented that relays the monitored and captured movements of the human handler as “follow me” data to the proxy robot surrogate in which the plurality of controls are configured such that the proxy robot surrogate emulates the movements of the human handler.
Owner:STEPHENS JR KENNETH DEAN
Method for quick solution of six-degree-of-freedom humanoid dexterous arm inverse kinematics
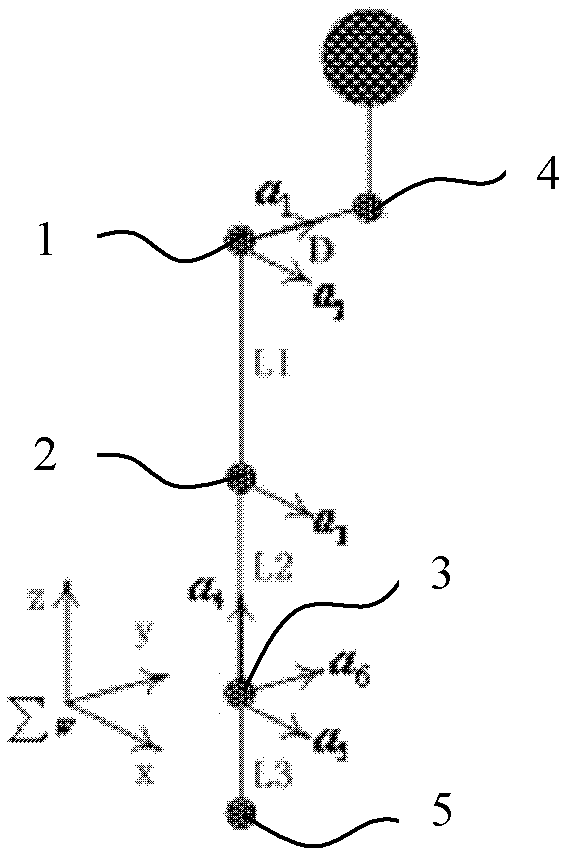
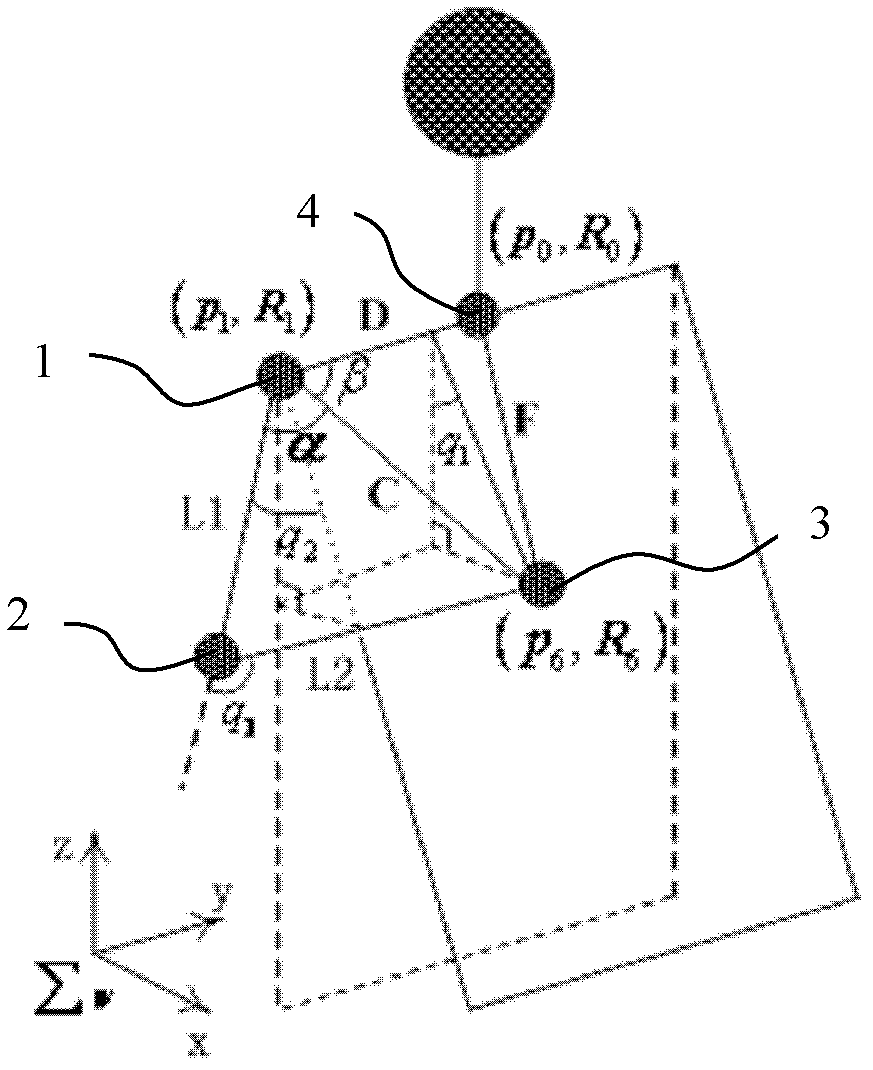
InactiveCN102509025AImprove computing efficiencyHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringShoulder joint capsule
The invention discloses a method for quick solution of six-degree-of-freedom humanoid dexterous arm inverse kinematics. The method includes: firstly, setting up a six-degree-of-freedom human arm simulated joint structural model, solving an elbow joint angle and two joint angles of the shoulder joint according to a planar relation formed by the shoulder center, the elbow center, the wrist center and the neck center of the dexterous arm and the tail end position of the dexterous arm, and further solving three joint angles of the wrist joint by the aid of the dexterous arm tail-end posture relation; and calculating position error of a dexterous arm target link to prove effectiveness of the solution of the inverse kinematics by means of a positive kinematic model. Compared with a numerical solving method for robot inverse kinematics, the method for quick solution of six-degree-of-freedom humanoid dexterous arm inverse kinematics is high in precision and quick in speed, and can be used for humanoid dexterous arm operational tasks having high requirements on precision and instantaneity.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com