Patents
Literature
1251 results about "Motion range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Range of motion is measured with the palm facing the side of the body and the arm straight. It is measured from neutral to the highest point the arm can be lifted behind the back. Normal range of motion is between 45 and 60 degrees.
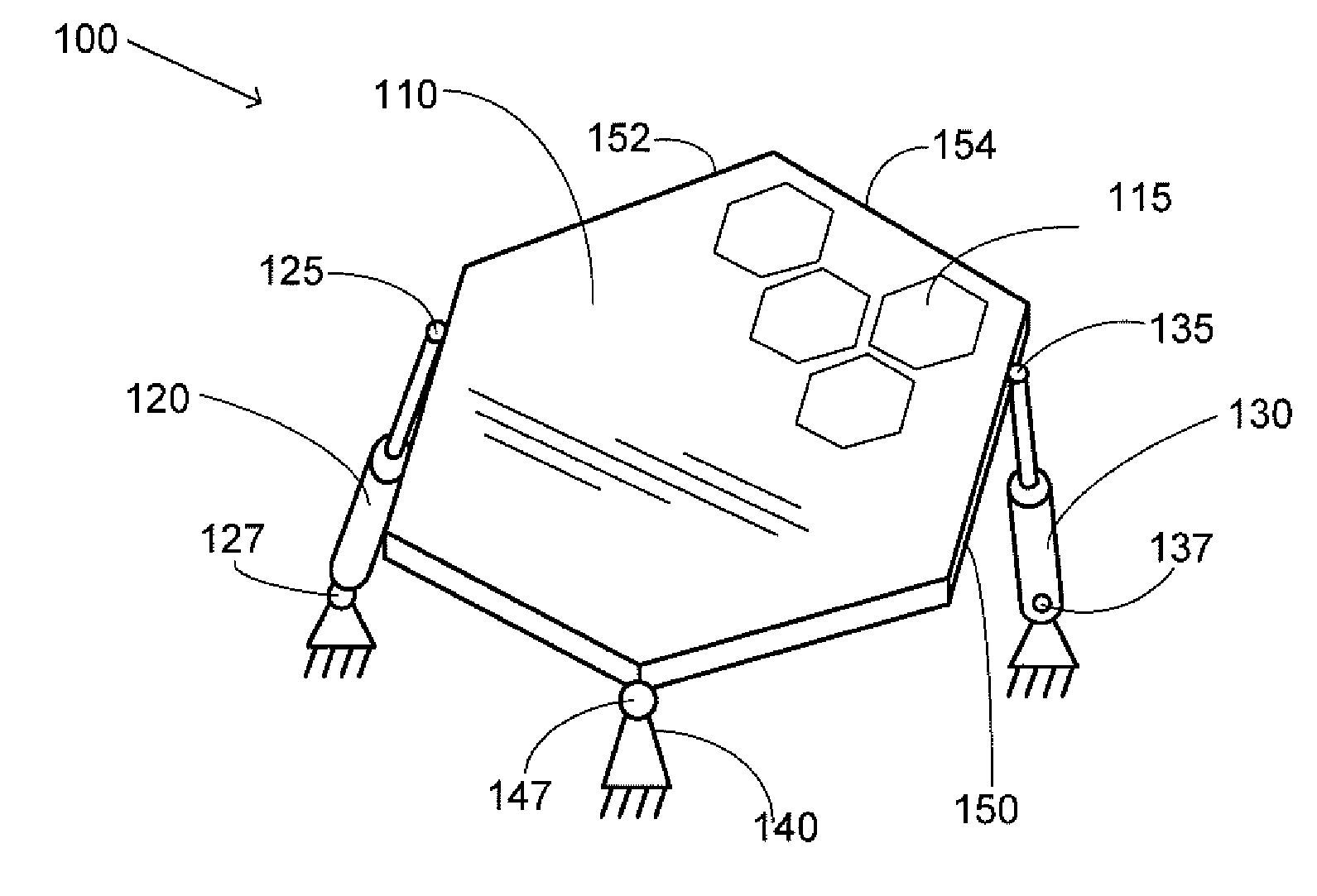
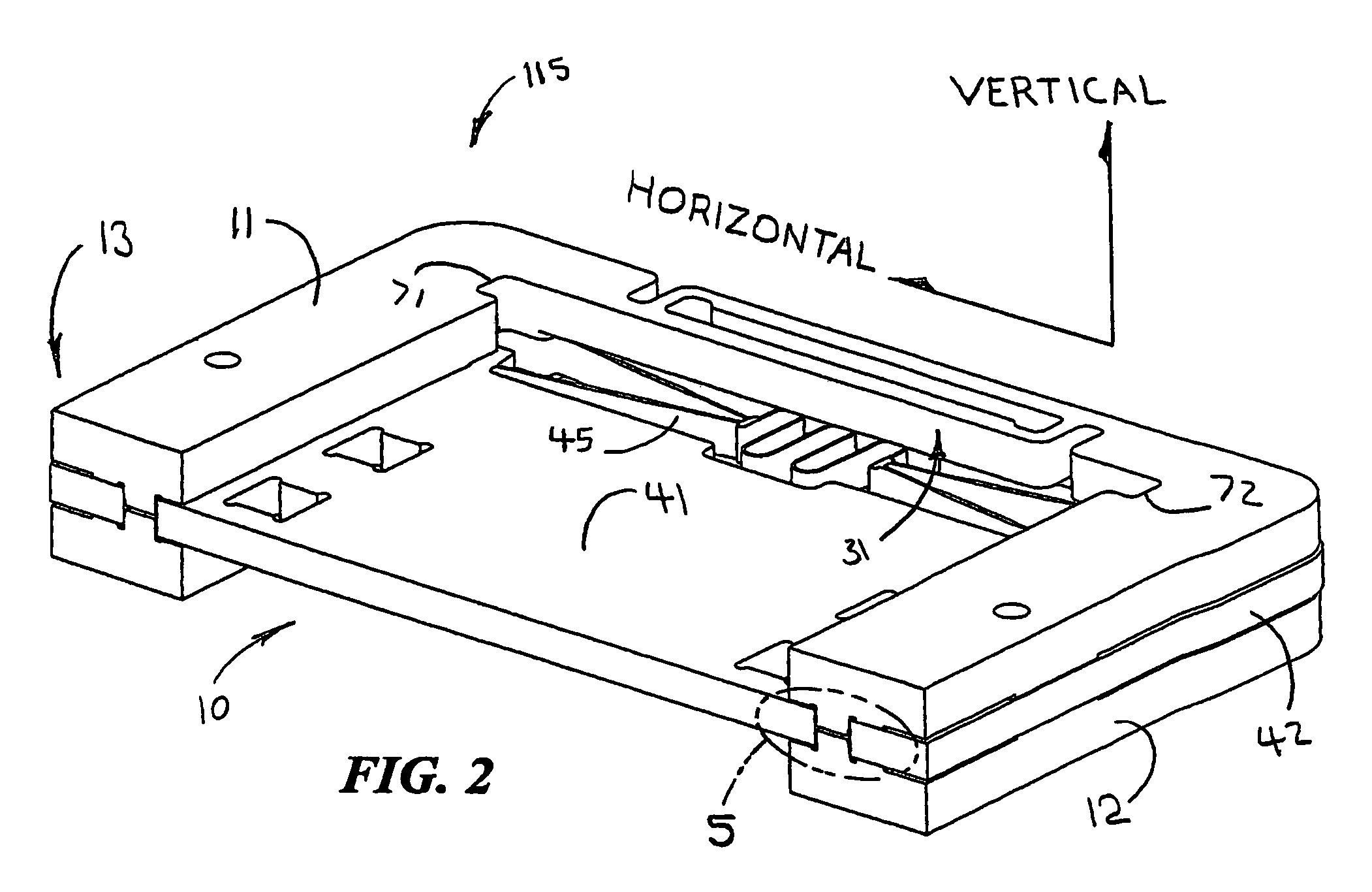
Parallel mechanism
InactiveUS6330837B1Reduce inertiaHigh speedMechanical apparatusJointsRange of motionDegrees of freedom
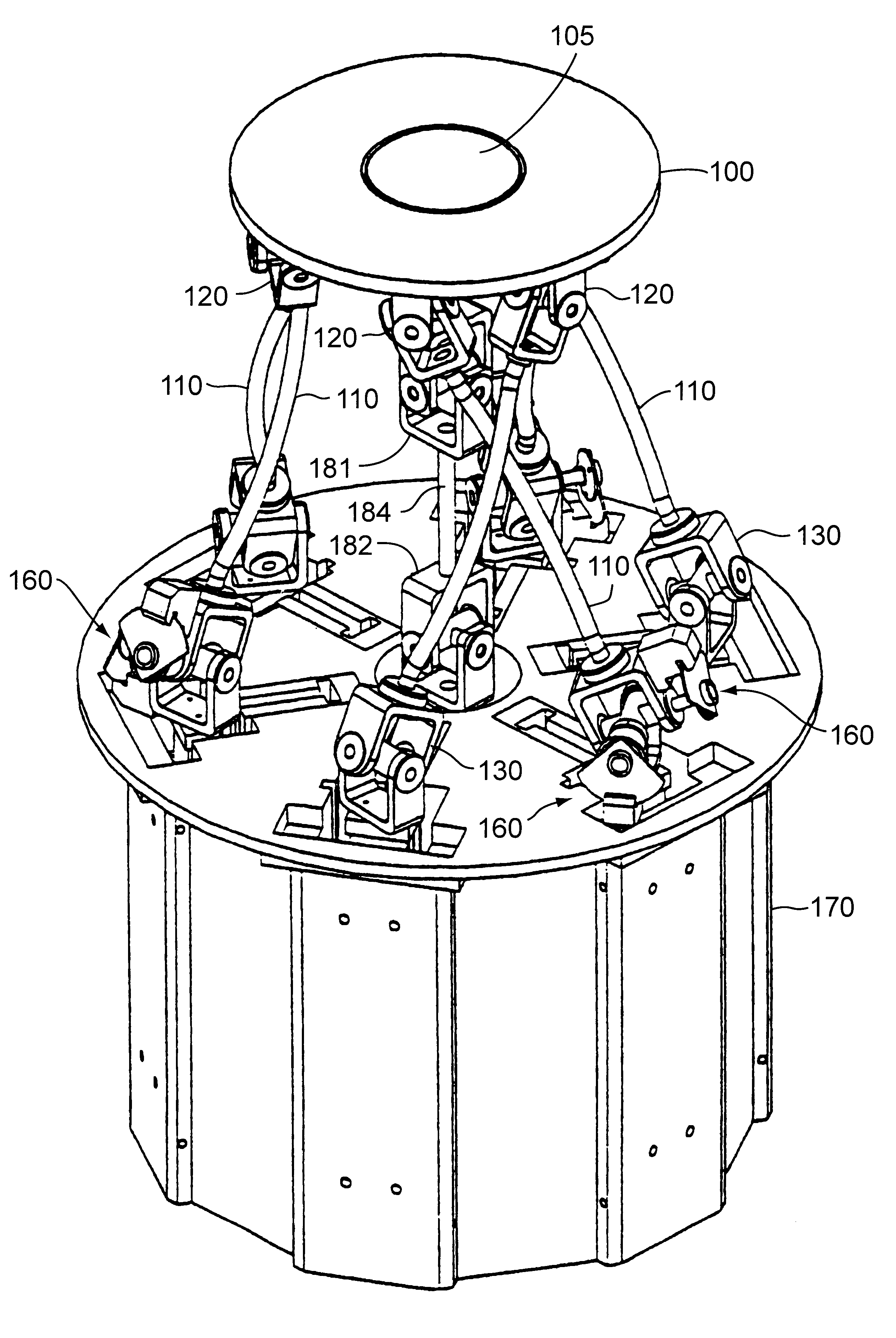
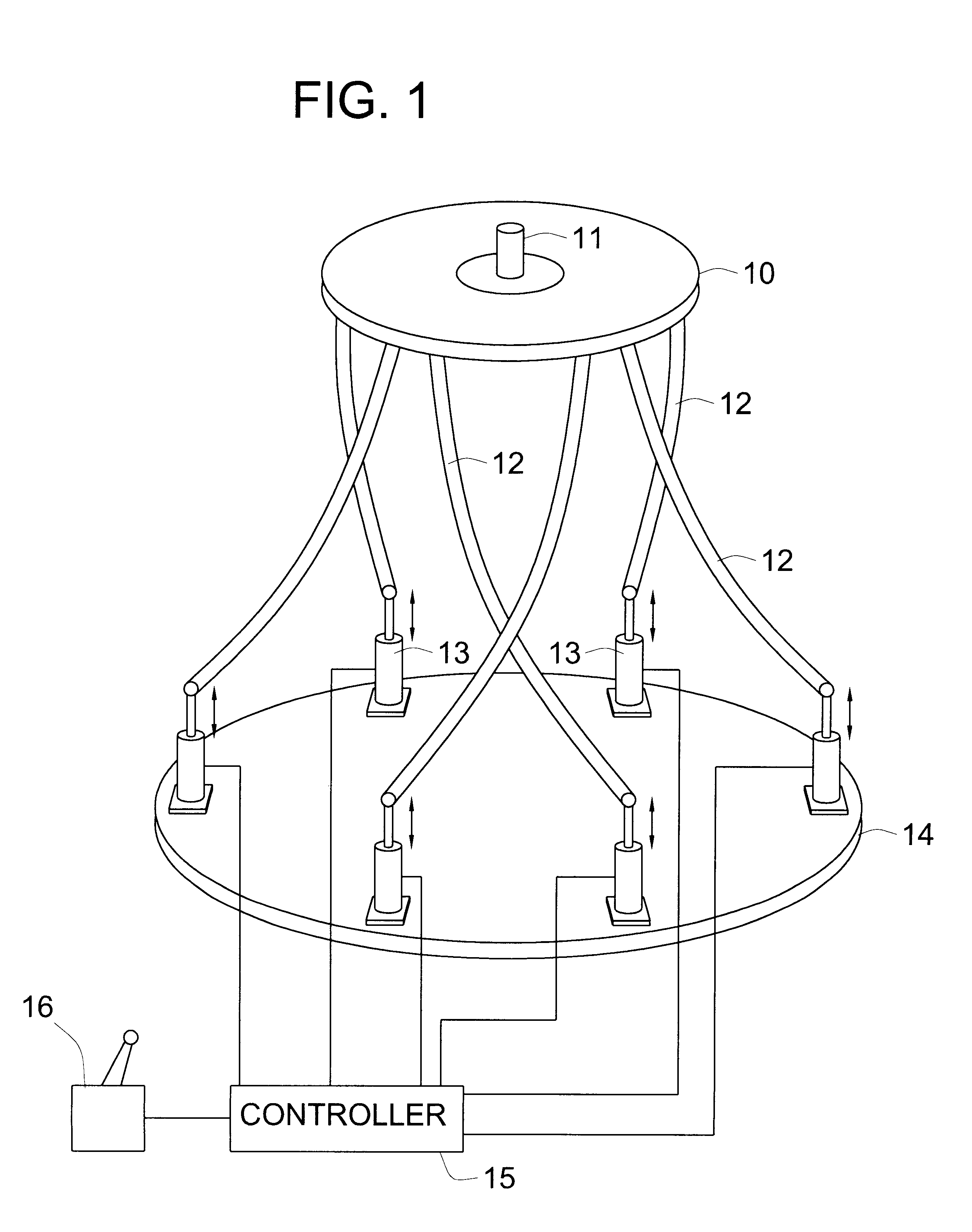
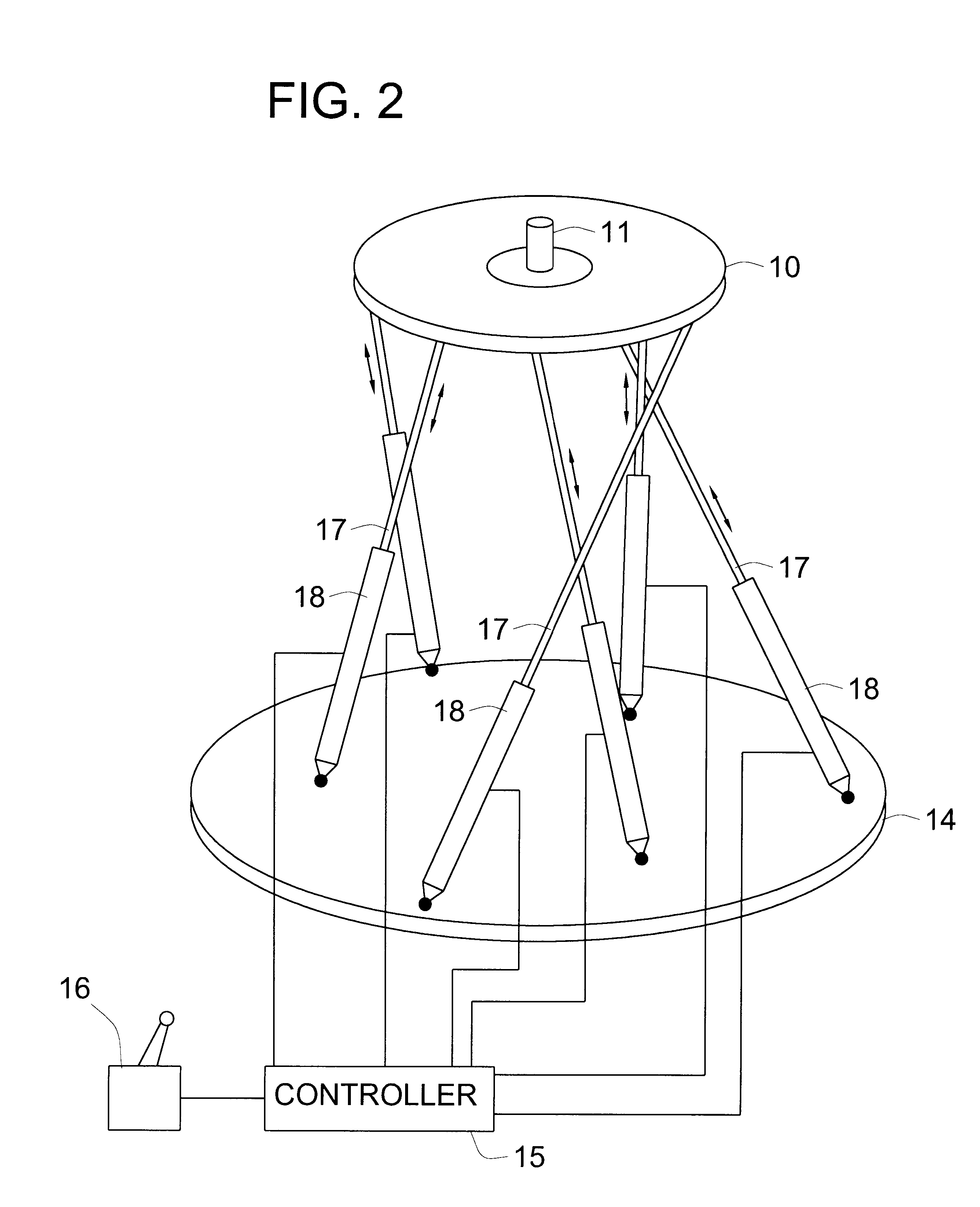
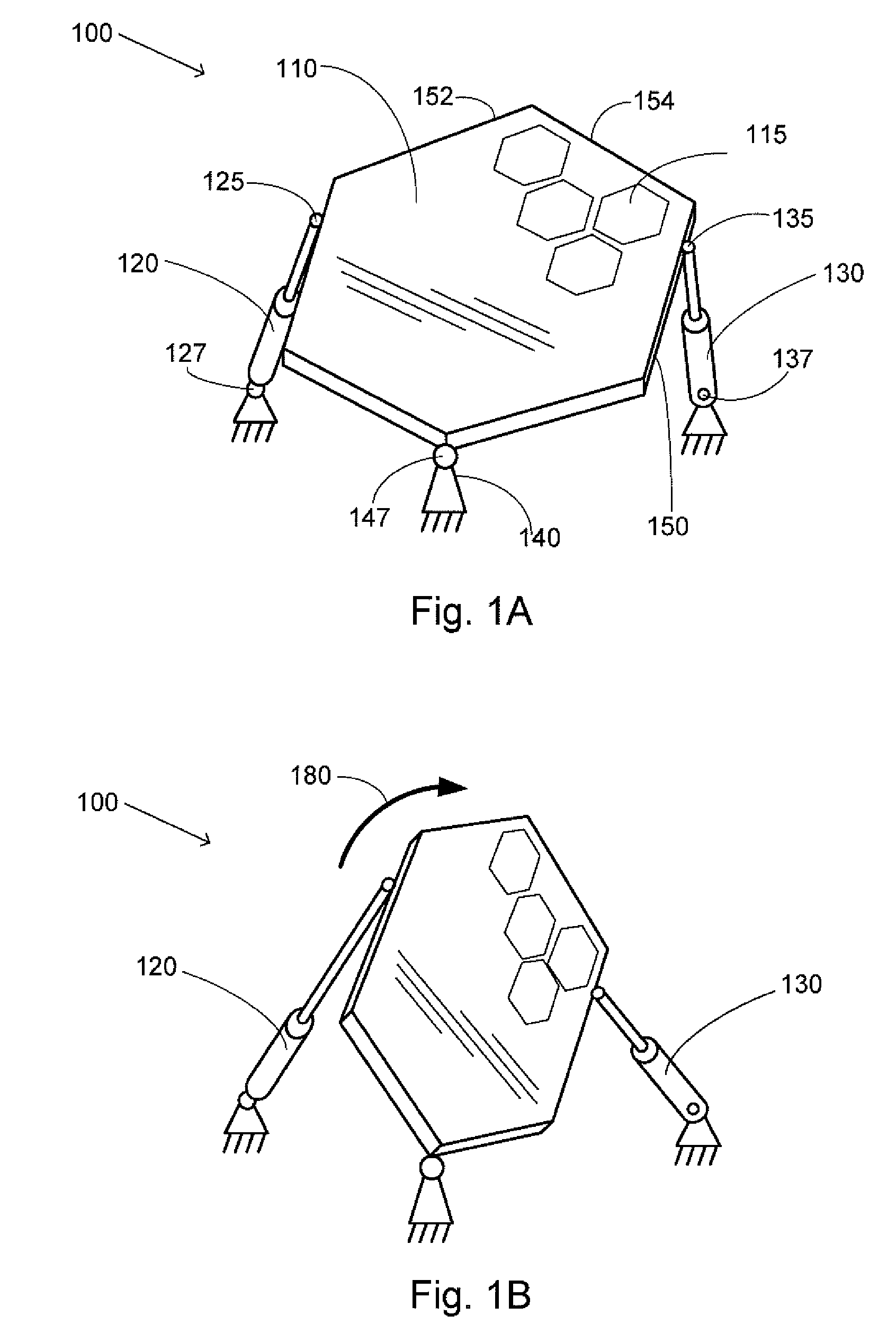
A parallel mechanism is capable of positioning and orienting an end platform with up to six or more degrees of freedom. In preferred embodiments, the mechanism includes six links having a first and second ends. The first end is connected to an end platform for supporting a tool, while the second end is connected to an actuator capable of translating the second end. A rotational drive mechanism may be provided for rotating an object mounted on the end platform at varying orientations of the end platform independently of movement of the end platform as a whole. The links may be curved in order to avoid interference between adjoining links, thereby permitting an increased range of motion and improved dexterity of the mechanism.
Owner:MOORE RUSSELL
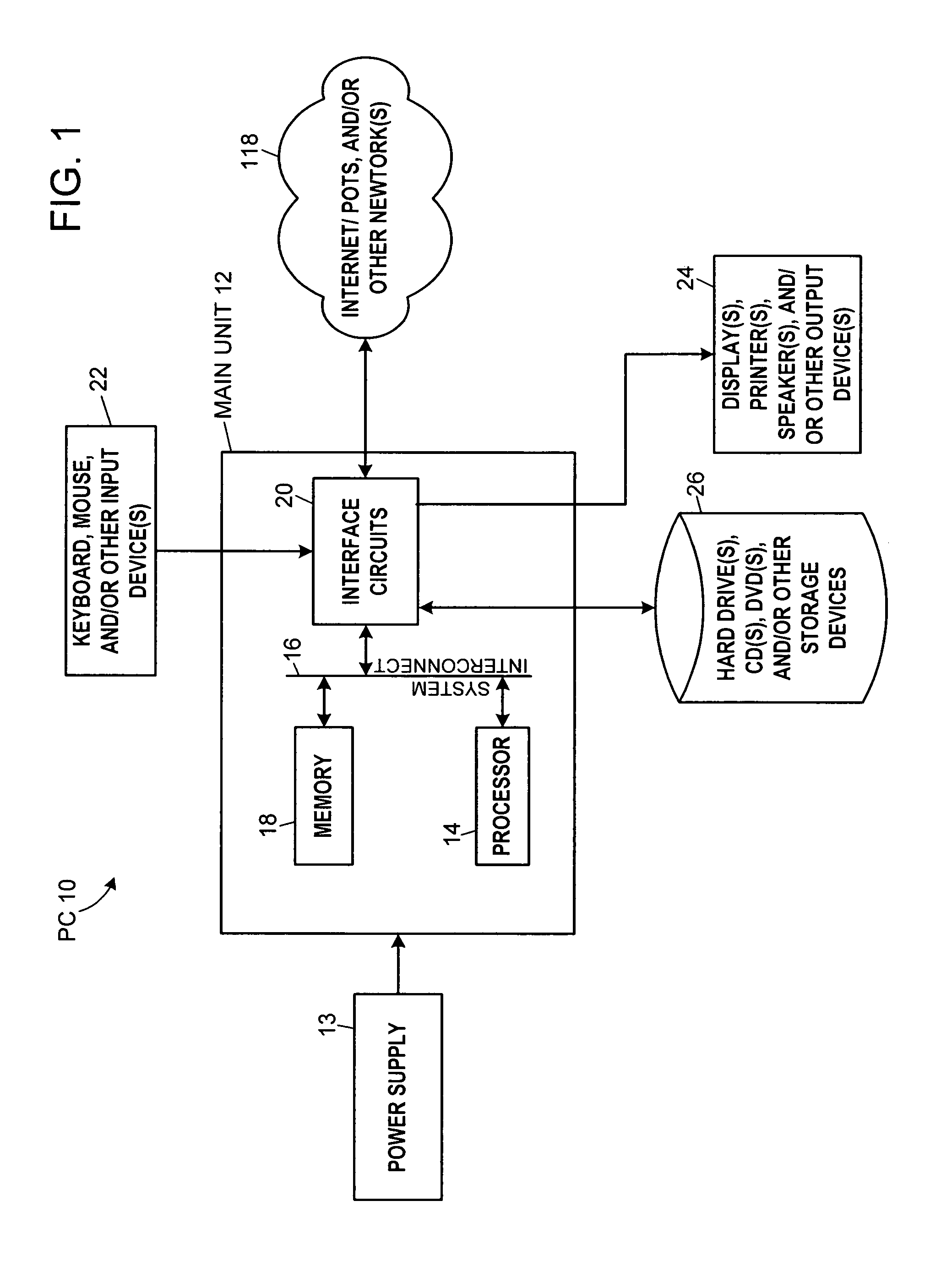
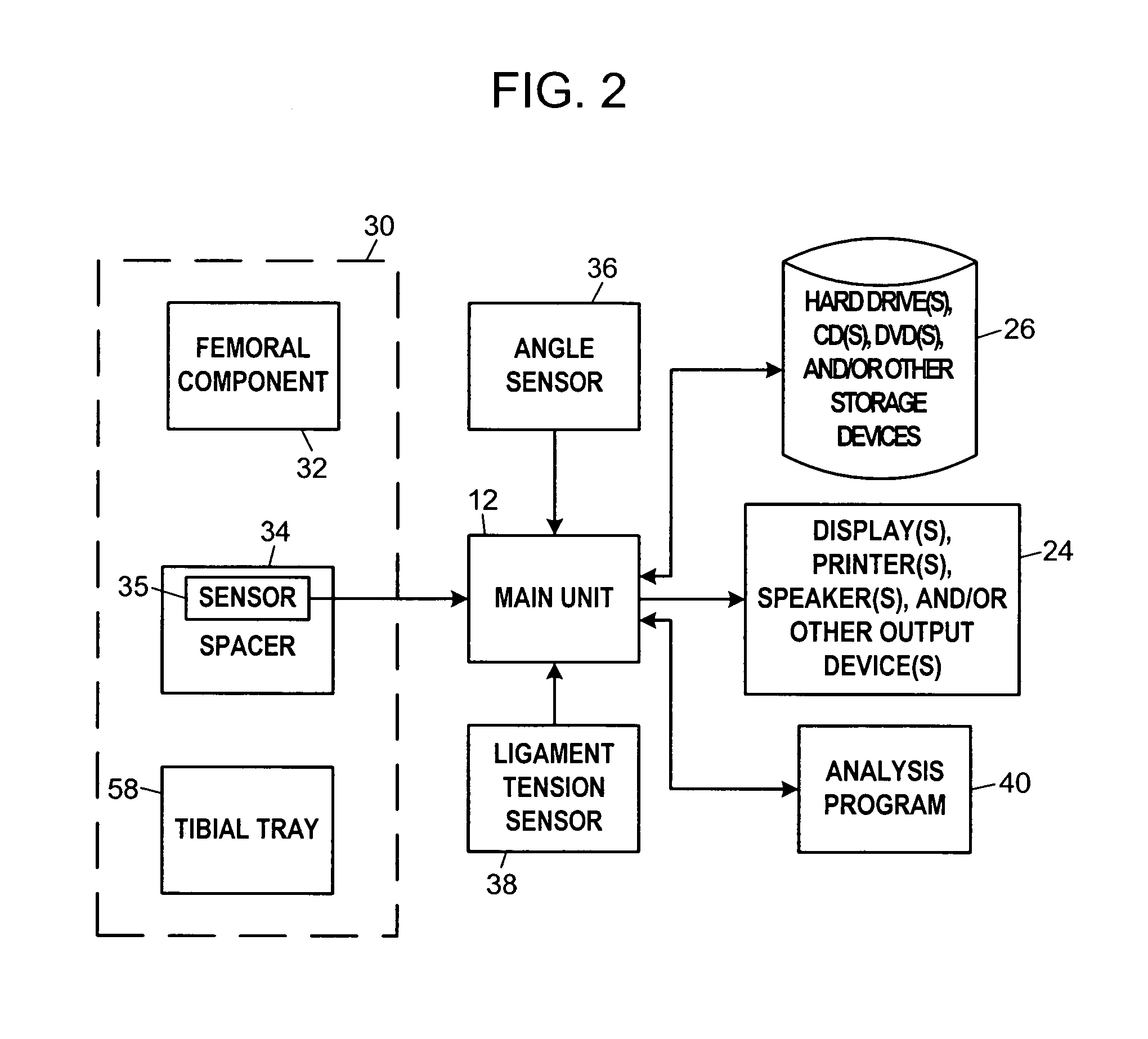
System and method for prosthetic fitting and balancing in joints
InactiveUS7575602B2Physical therapies and activitiesFinger jointsProsthesis fittingArtificial joints
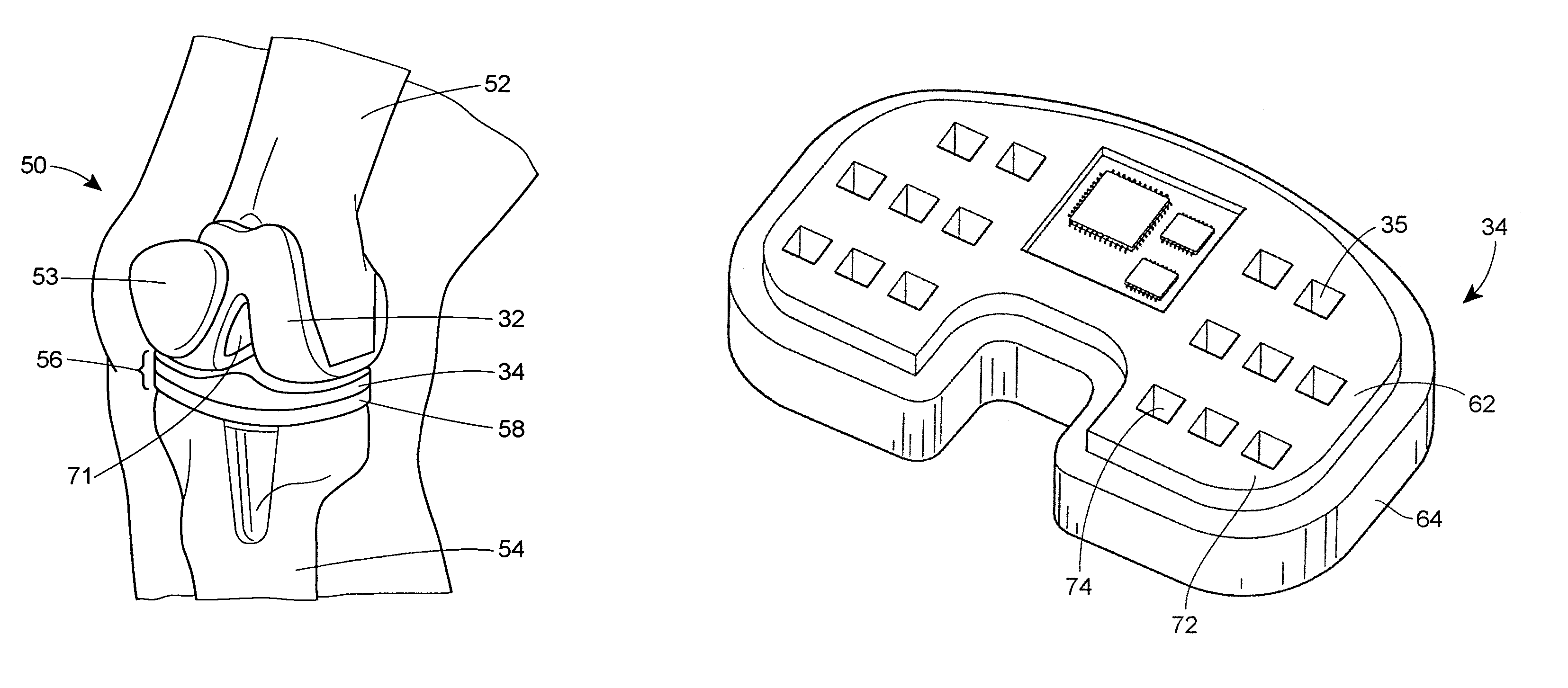
A system and method for prosthesis fitting in joints comprising an artificial condyle and a spacer which cooperates with the condyle to form an artificial joint. The spacer embedded with at least one sensor which is responsive to a force generated between the condyle and the spacer. The artificial joint is adapted to move between a flexed position and an extended position defining a range of motion. The sensor is responsive to the force and generates an output representative of that force. The output is transmitted, either wirelessly or other, to a processor which utilizes an analysis program to display a representation of the forces applied. A practitioner utilizing the displayed analysis may intraoperatively determine the adjustments and balancing required within the artificial joint. The system may also utilize a ligament tension sensor which generates data representative of tension on a ligament of the artificial joint, and a joint angle sensor responsive to the range of motion of the artificial joint. The processor may be adapted to store the outputted sensor data to provide the practitioner with statistically relevant historical data.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
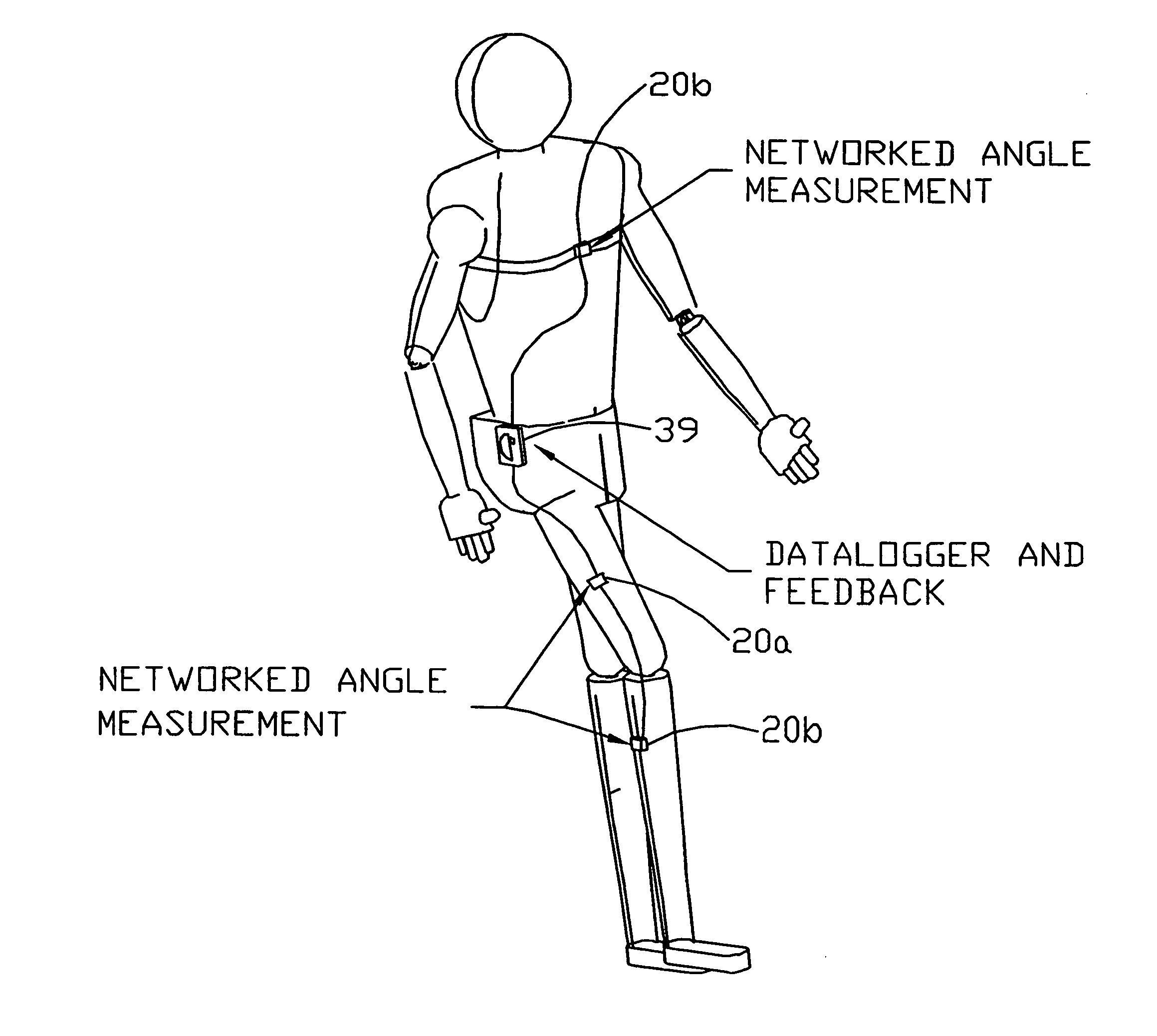
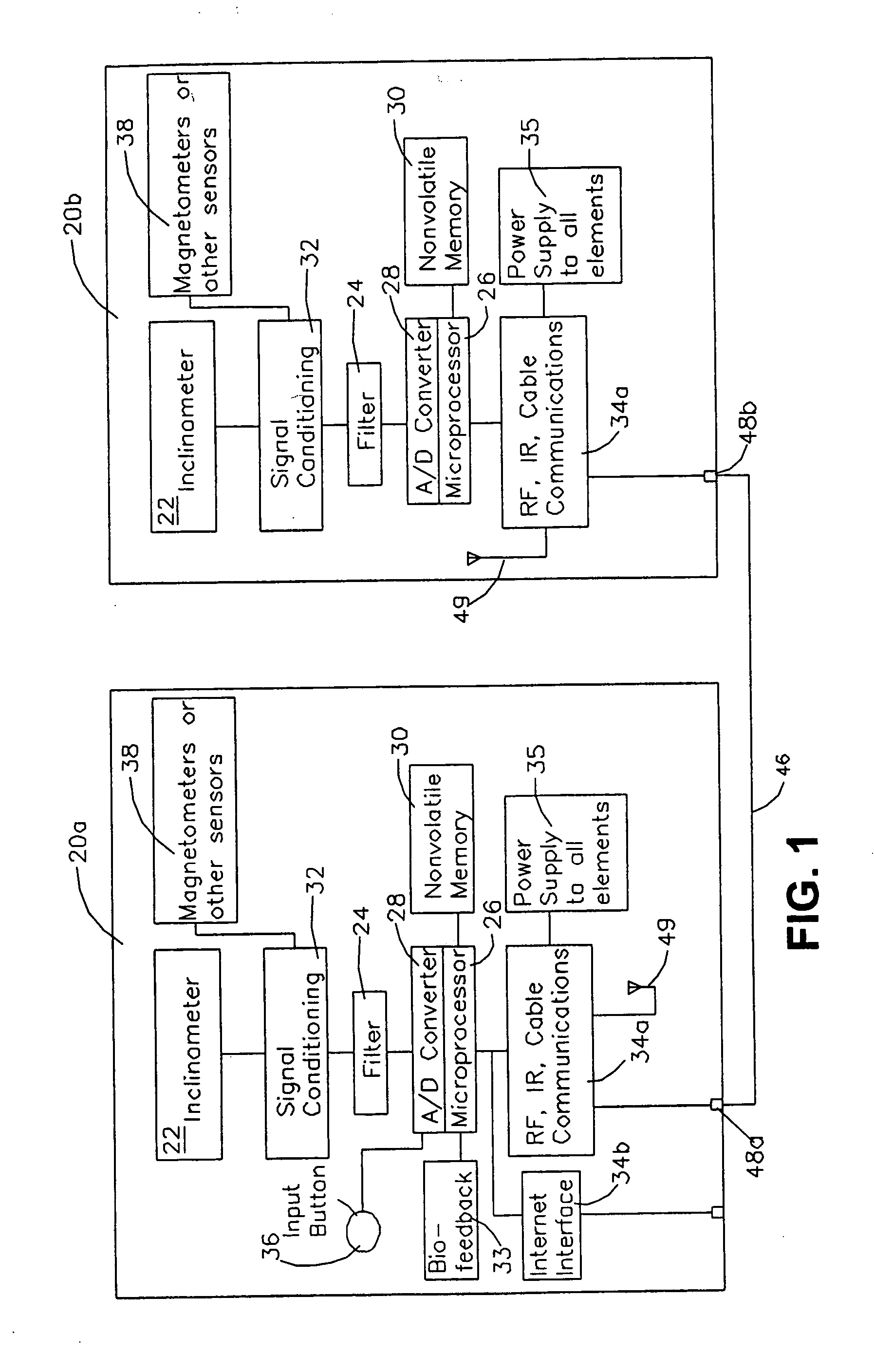
Posture and body movement measuring system
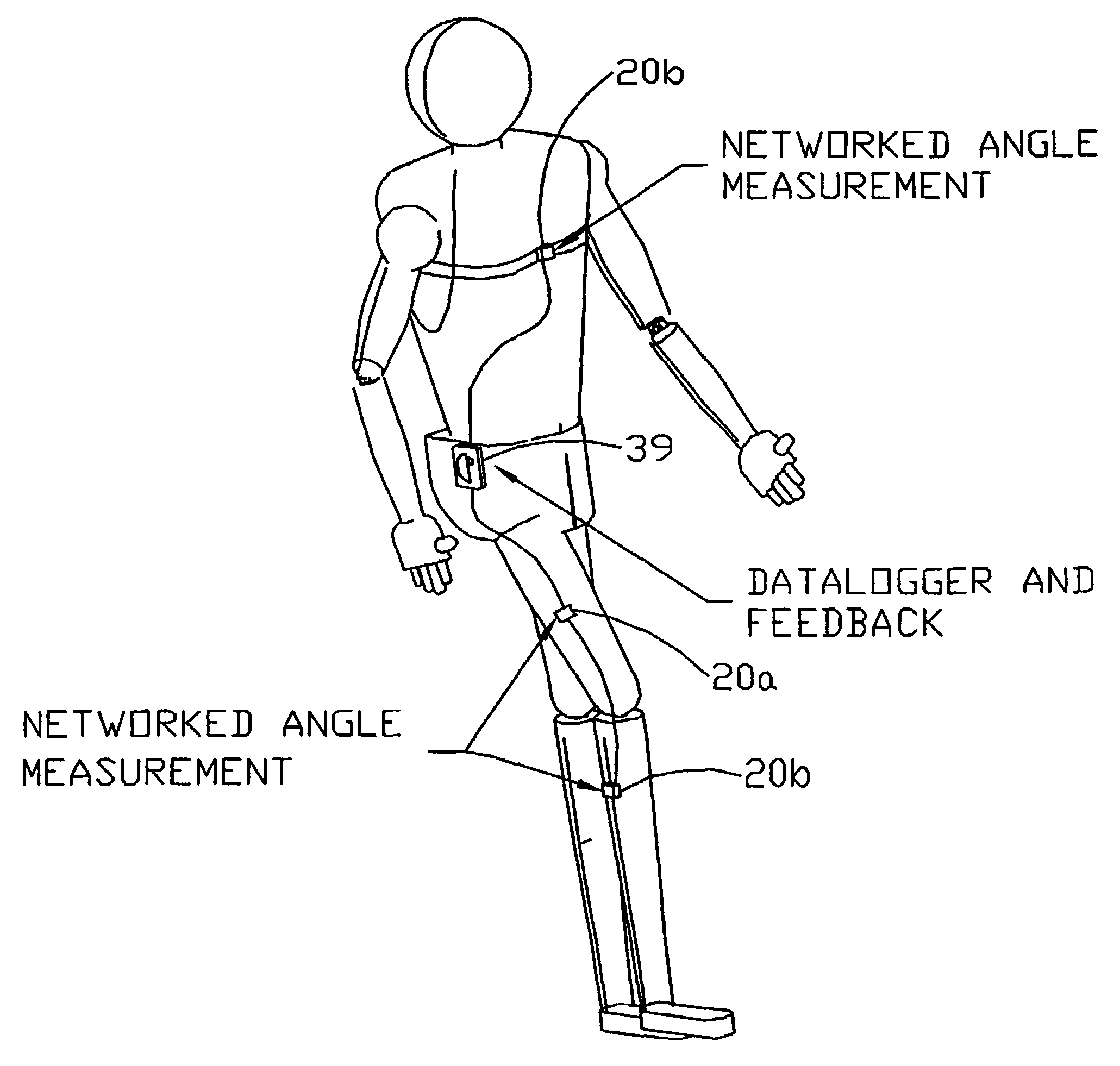
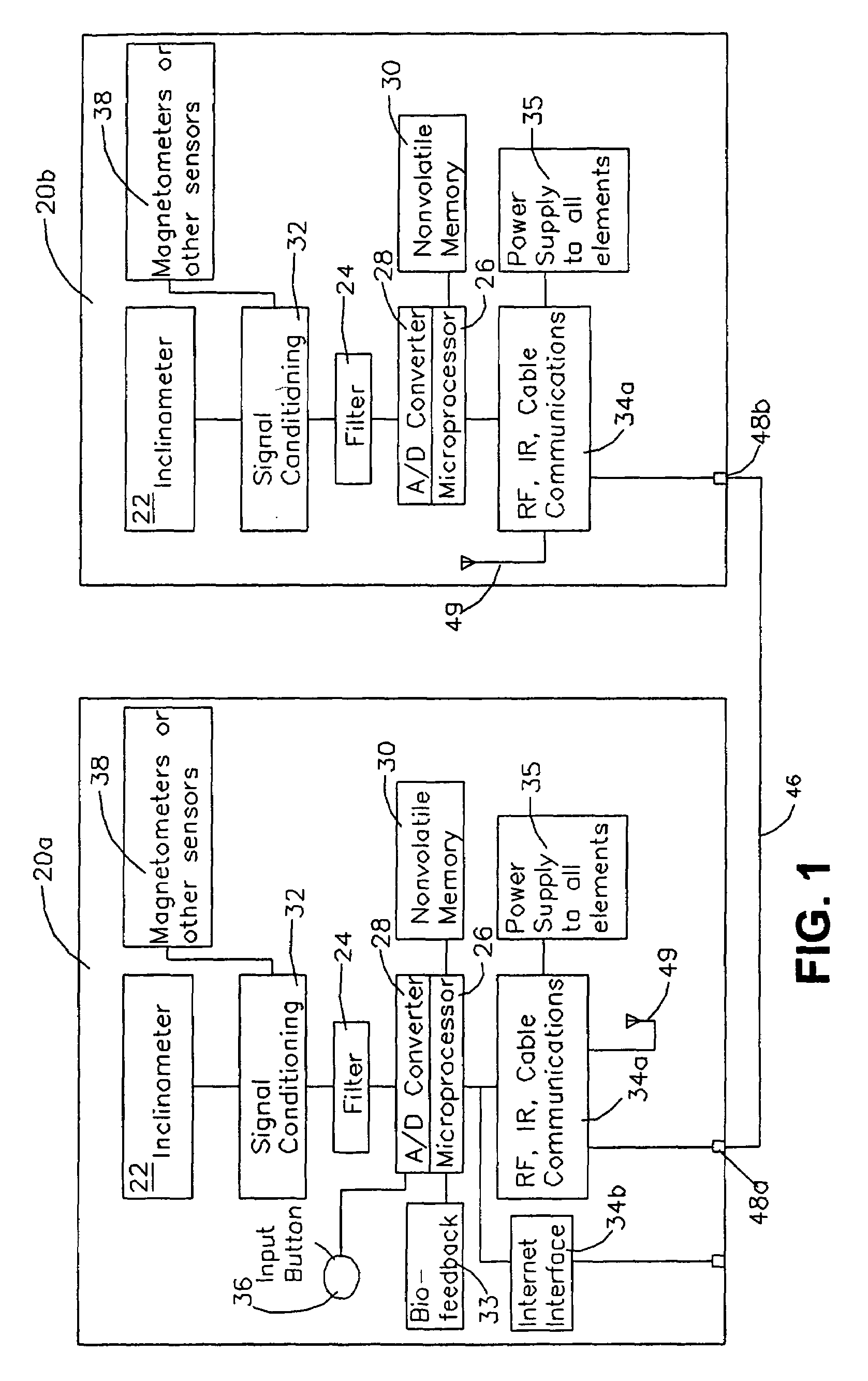
A sensing device is attached to a living subject that includes a first sensors for distinguishing lying, sitting, and standing positions. In another embodiment, sensor data is stored in a storage device as a function of time. Multiple points or multiple intervals of the time dependent data are used to direct a feedback mechanism to provide information or instruction in response to the time dependent output indicating too little activity, too much time with a joint not being moved beyond a specified range of motion, too many motions beyond a specified range of motion, or repetitive activity that can cause repetitive stress injury.
Owner:LORD CORP
Ergonomic computer mounting device permitting extensive vertical, horizontal and angular ranges of motion
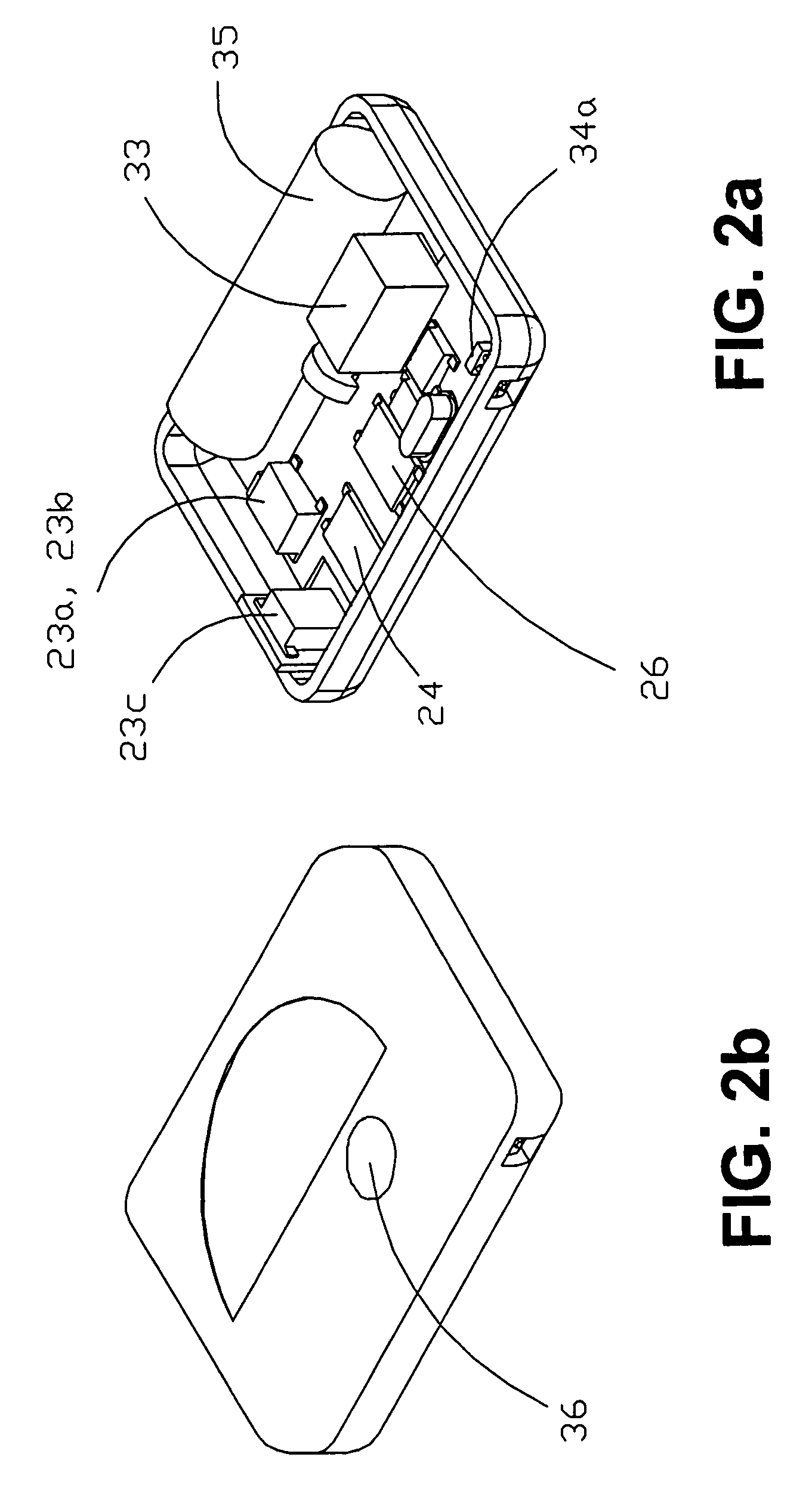
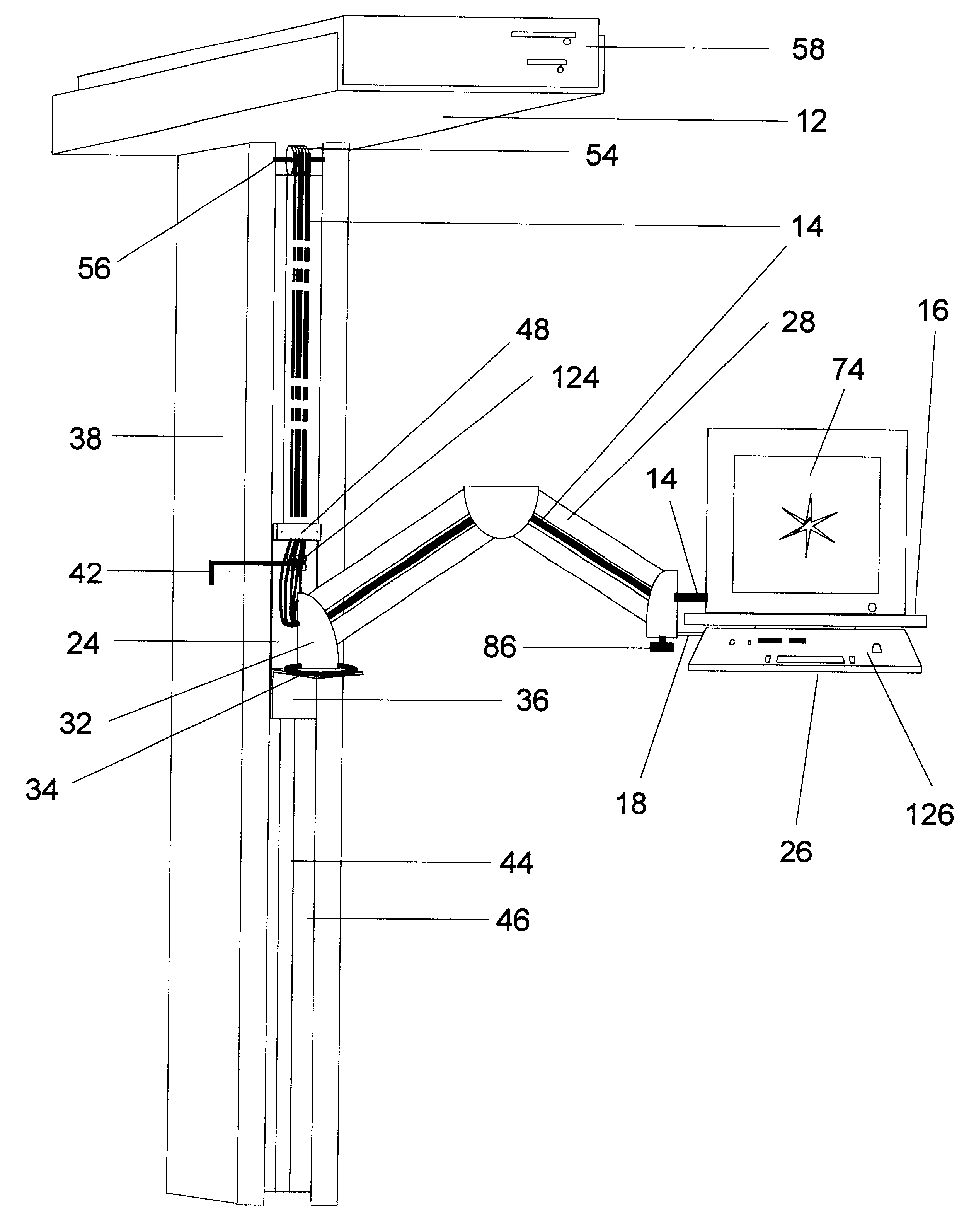
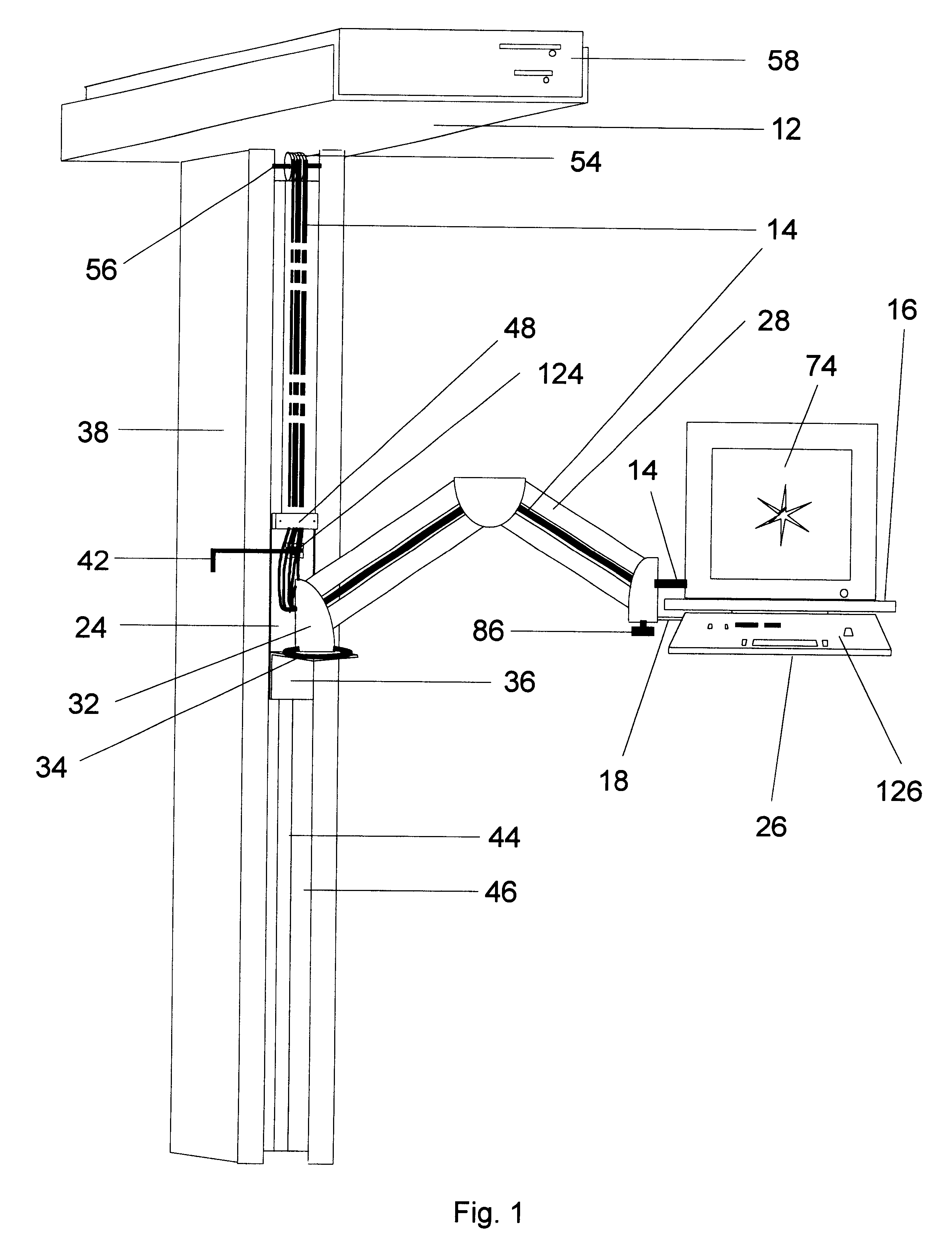
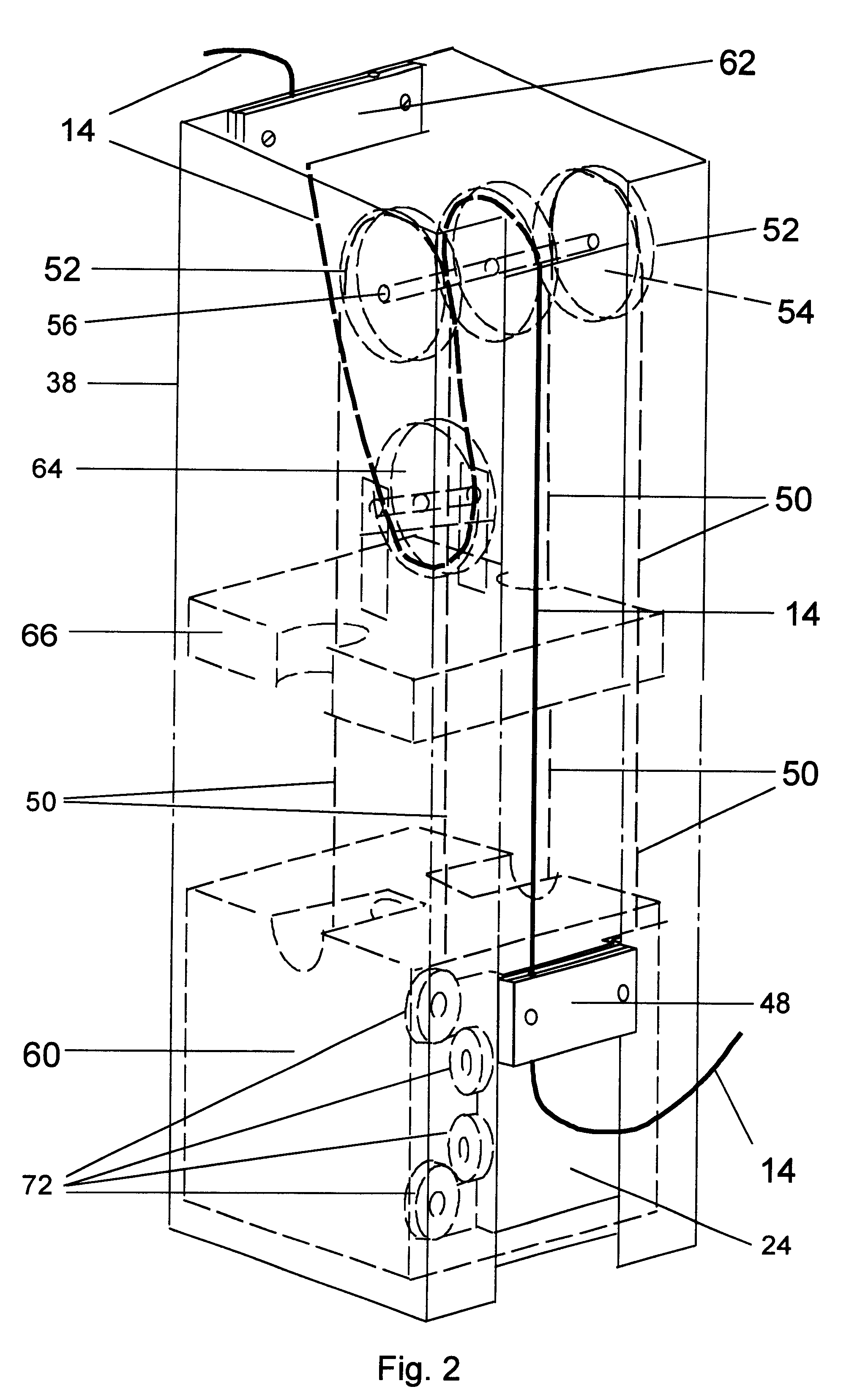
A computer workstation mounting device is provided which permits devices to be accessed by operators in a variety of positions including sitting, standing, or from a wheelchair. The invention permits said devices to be moved in a wide variety of vertical, horizontal, and rotational ranges of motion, and permits the devices to be moved clear of the work area while performing other tasks, or safely moved to a position near the ceiling for security or additional workspace conservation. The invention uses a simple, low maintenance counterweight principle for its vertical travel. It also possesses a simple tilt and swivel mechanism, swivel bracket (32), and dual parallelogram arm assembly for its horizontal and rotational ranges of motion. The invention also incorporates the counterweight principle for maintaining the data cables (14) in an organized, aesthetically pleasing manner without loops or kinks through all ranges of motion. Additionally provided is a friction lock (124) for stability of the monitor arm assembly in its vertical travel. Provision for the central processing unit (58) to be mounted atop the column (38) increases computer security.
Owner:HARBIN BRADLEY
Tilting wheeled vehicle
ActiveUS7487985B1Complex control systemWheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionControl systemCaster angle
A tilting, preferably three-wheeled, vehicle is disclosed that has a tilting mechanism that allows the vehicle to have leaning characteristics substantially similar to those offered by an in-line two-wheeled vehicle, but that does not require complex linkages and / or control systems to operate effectively. A tilting linkage is operably secured to a frame to allow a pair of spaced apart wheels to remain substantially aligned with the plane of the vehicle throughout its range of movement while still allowing the steering axes of each wheel to intersect the substantially vertical centerline of each wheel. The linkage also allows the caster angle of each wheel's pivot axis can be optimized independently of the angle of the vehicle's handlebar steering shaft.
Owner:ARCIMOTO
Remotely controlled catheter insertion system
A remotely controlled insertion system for a medical device is described. The system comprises a robotic device and a remote control mechanism. The robotic device has a handle controller to receive and hold the control handle or proximal end of a medical device. The medical device is capable of moving in up to six ranges of motion. In ione embodiment a first motor is connected through a drive screw to a handle controller to move the medical device forward and backward. A second motor is connected to drive wheels effective to rotate the medical device clockwise and counter-clockwise. A third motor drives a series of gears that are connected to one or more control members on the medical device, this being effective to deflect a tip of the medical device so that movement of the third motor causes such deflection. A control unit is connected to all three motors.
Owner:CATHETER PRECISION INC
Retractable vehicle step
InactiveUS6942233B2Easy to storeSimple stepsThigh restsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementRange of motionEngineering
A retractable step for use with a vehicle comprises a stepping member having a stepping deck, a first arm, a second arm, a motor and a stop. The first arm has a first end pivotally attached to the vehicle, and a second end pivotally attached to the stepping member. The second arm also has a first end pivotally attached to the vehicle, and a second end pivotally attached to the stepping member. The motor is drivingly connected to the first arm such that a rotation of the motor causes rotation of the first arm about its first end and moves the stepping member from a retracted position to an extended position, or vice versa. The stop is located within the range of motion of the second arm such that the second arm bears against the stop when the stepping member is in the extended position. The first and second arms are situated such that the first arm is loaded in compression and the second arm is loaded in tension when the stepping member is in the extended position and a load is placed upon it. In another embodiment, a retractable vehicle step assist comprises a rigid frame, a forward planar linkage pivotably connected to the frame along a forward upper connection width, and a rearward planar linkage pivotably connected to the frame along a rearward upper connection width. The retractable vehicle step further comprises a rigid step member having a stepping deck. The step member is pivotably connected to the forward planar linkage along a forward lower connection width, and is pivotably connected to the rearward planar linkage along a rearward lower connection width and on a side of the forward planar linkage opposite the stepping deck. The stepping deck is substantially wider than any of the forward upper connection width, the rearward upper connection width, the forward lower connection width, and the rearward lower connection width.
Owner:LUND MOTION PRODS
Position adjustable load support mechanism
InactiveUS6857610B1Precise positioningLarge range of motionStands/trestlesKitchen equipmentRange of motionGas spring
An improved mechanism for positioning loads of varying magnitudes, such as LCD displays, etc. The position of the load can be varied in height and angle according to the requirements of the user. The mechanism incorporates an adjustable sliding fulcrum, a support arm, a housing with four generally perpendicular channels, and a gas spring. The mechanism is initially manually adjusted for a particular load and then it automatically adjusts proportionally for the varying moments generated as the position of the load changes. The load is therefore evenly counterbalanced throughout its range of motion, and its position is maintained.
Owner:CONNER JOHN P +1
Posture and body movement measuring system
InactiveUS20050126026A1Many timesLittle activityMeasurement devicesSurgeryRange of motionStress injury
A sensing device is attached to a living subject that includes a first sensors for distinguishing lying, sitting, and standing positions. In another embodiment, sensor data is stored in a storage device as a function of time. Multiple points or multiple intervals of the time dependent data are used to direct a feedback mechanism to provide information or instruction in response to the time dependent output indicating too little activity, too much time with a joint not being moved beyond a specified range of motion, too many motions beyond a specified range of motion, or repetitive activity that can cause repetitive stress injury.
Owner:LORD CORP
Exercise device
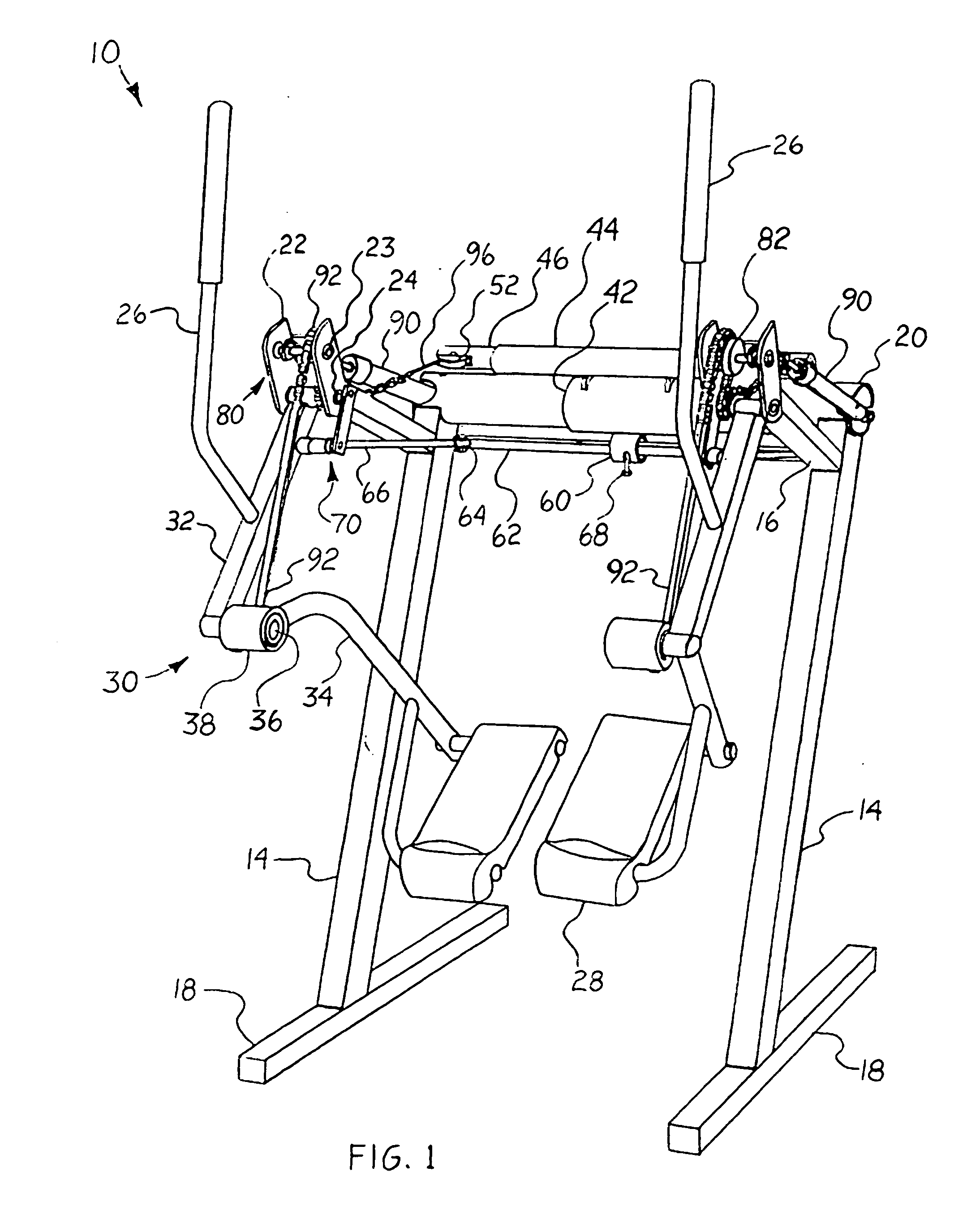
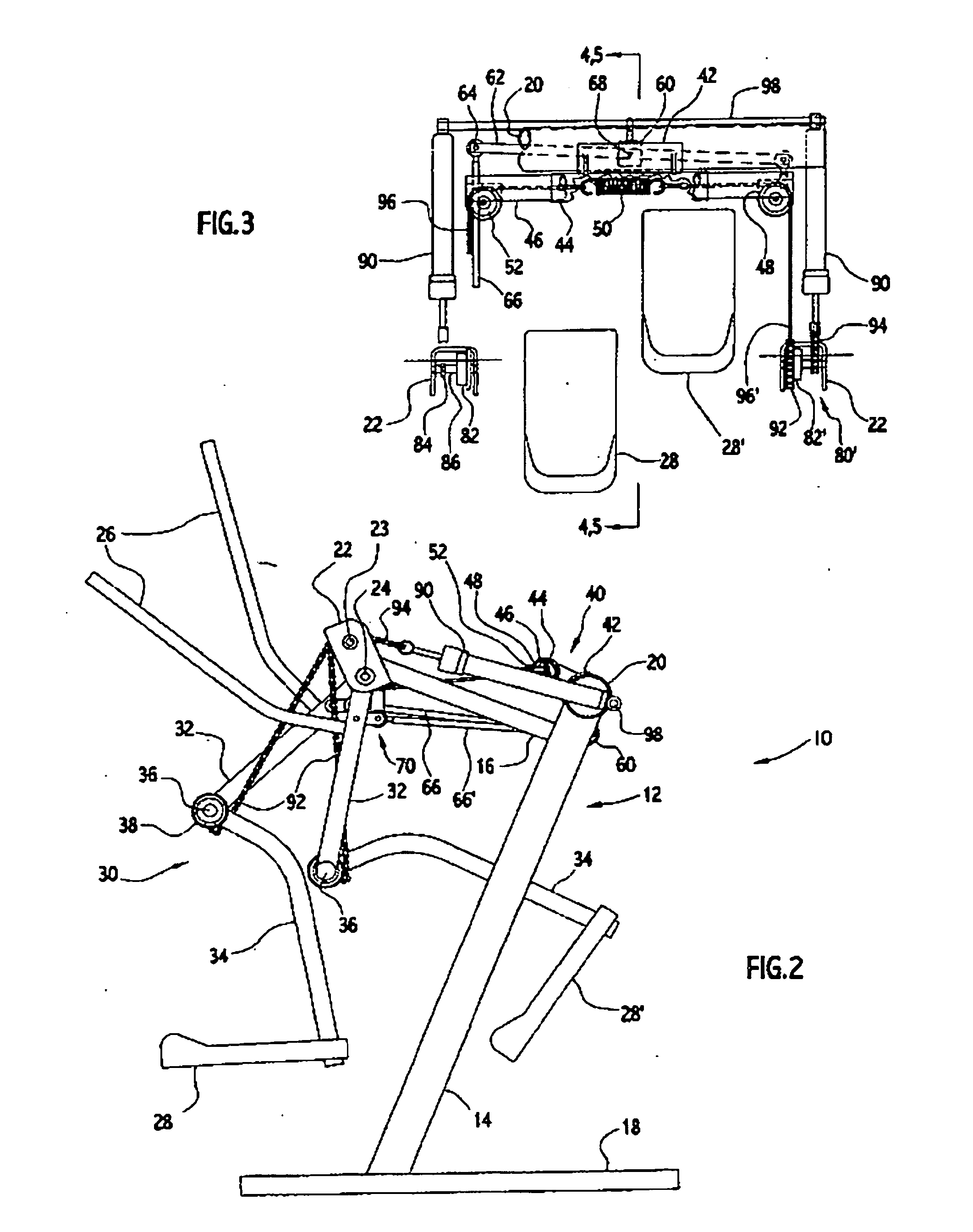
InactiveUS20070037667A1Great degreeHigh simulationRider propulsionMuscle exercising devicesVertical planeLeg exercise
An exercise device upon which a user generally standing upright supported by foot platforms suspended from a frame via linkages in which the linkage lengths and pivot points correspond generally to the users upper and lower legs and hip and knee joints. This device not only allows natural free and spontaneous leg movement, able to simulate such exercises as walking, jogging, running, stepping, skiing or gliding, bicycling, climbing, reverse action and various isolated leg exercises, where the exercises can be performed at random generally without the need to reconfigure the device. This device preferably includes an isolation system capable of simulating natural forces throughout the entire range of movement in the horizontal and / or vertical plane. A safety / suspension system can be provided, alone or in combination with the isolation system, to resist sudden foot movement in the same direction, yet allows a slow and controlled tilting of the linkages whereby the user may simulate uphill and downhill travel.
Owner:EXERCITING
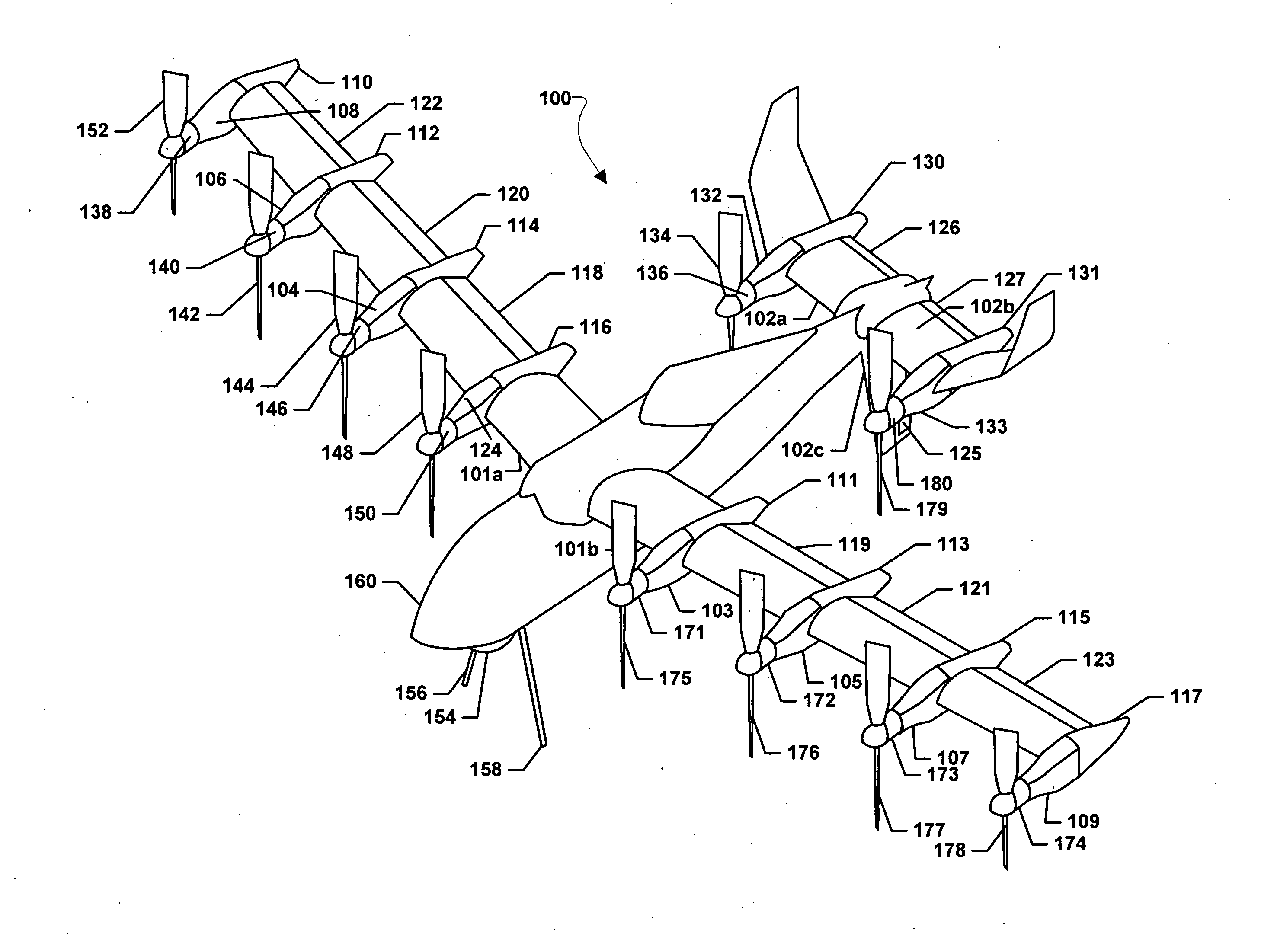
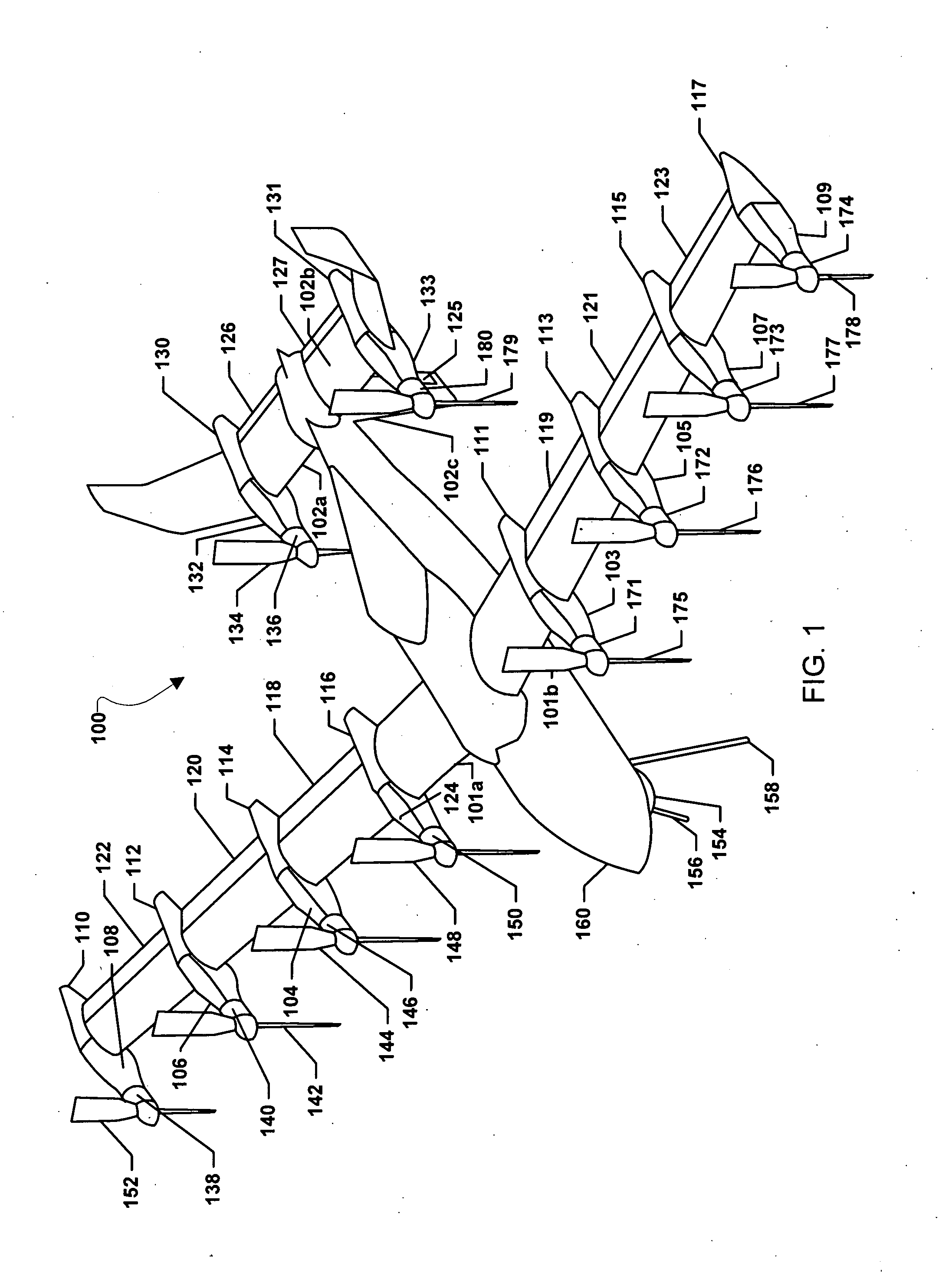
Vertical take-off and landing vehicle with increased cruise efficiency
Systems, methods, and devices are provided that combine an advance vehicle configuration, such as an advanced aircraft configuration, with the infusion of electric propulsion, thereby enabling a four times increase in range and endurance while maintaining a full vertical takeoff and landing (“VTOL”) and hover capability for the vehicle. Embodiments may provide vehicles with both VTOL and cruise efficient capabilities without the use of ground infrastructure. An embodiment vehicle may comprise a wing configured to tilt through a range of motion, a first series of electric motors coupled to the wing and each configured to drive an associated wing propeller, a tail configured to tilt through the range of motion, a second series of electric motors coupled to the tail and each configured to drive an associated tail propeller, and an electric propulsion system connected to the first series of electric motors and the second series of electric motors.
Owner:NASA
Maneuvering system having inner force sense presenting function
ActiveUS20100139436A1Easy to operateHighly accurate and broadband positional controlMechanical apparatusJointsElectricityRange of motion
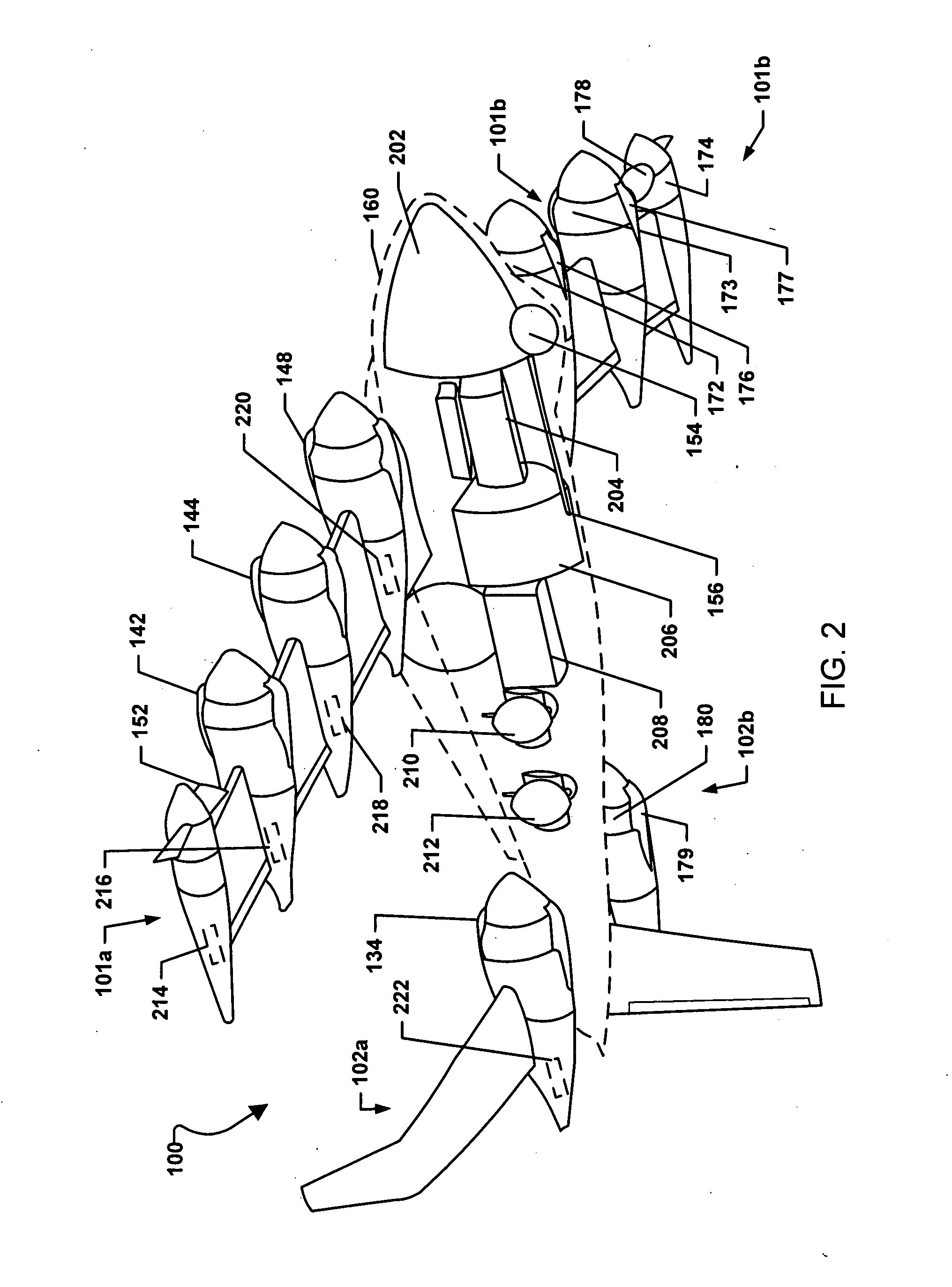
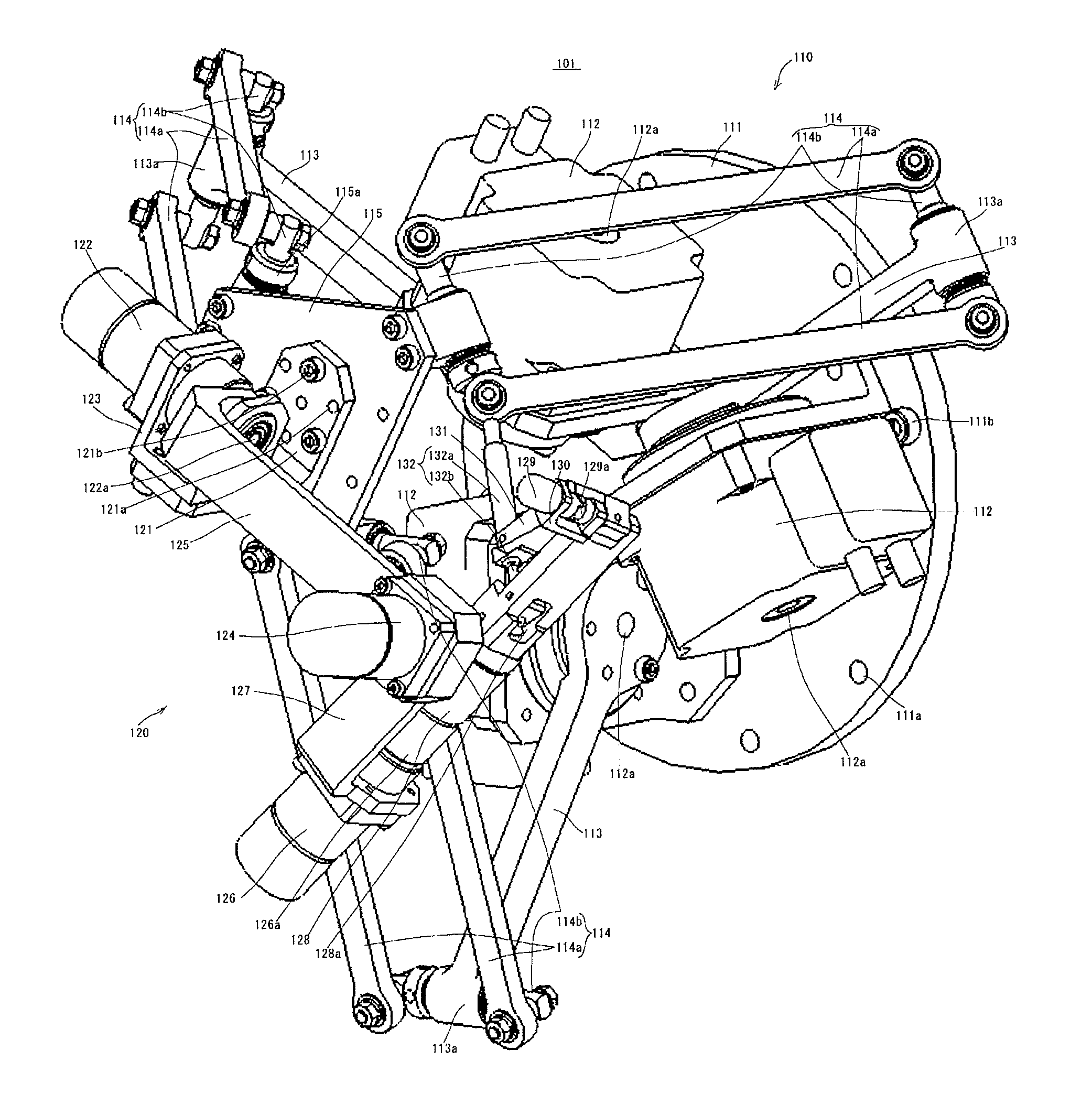
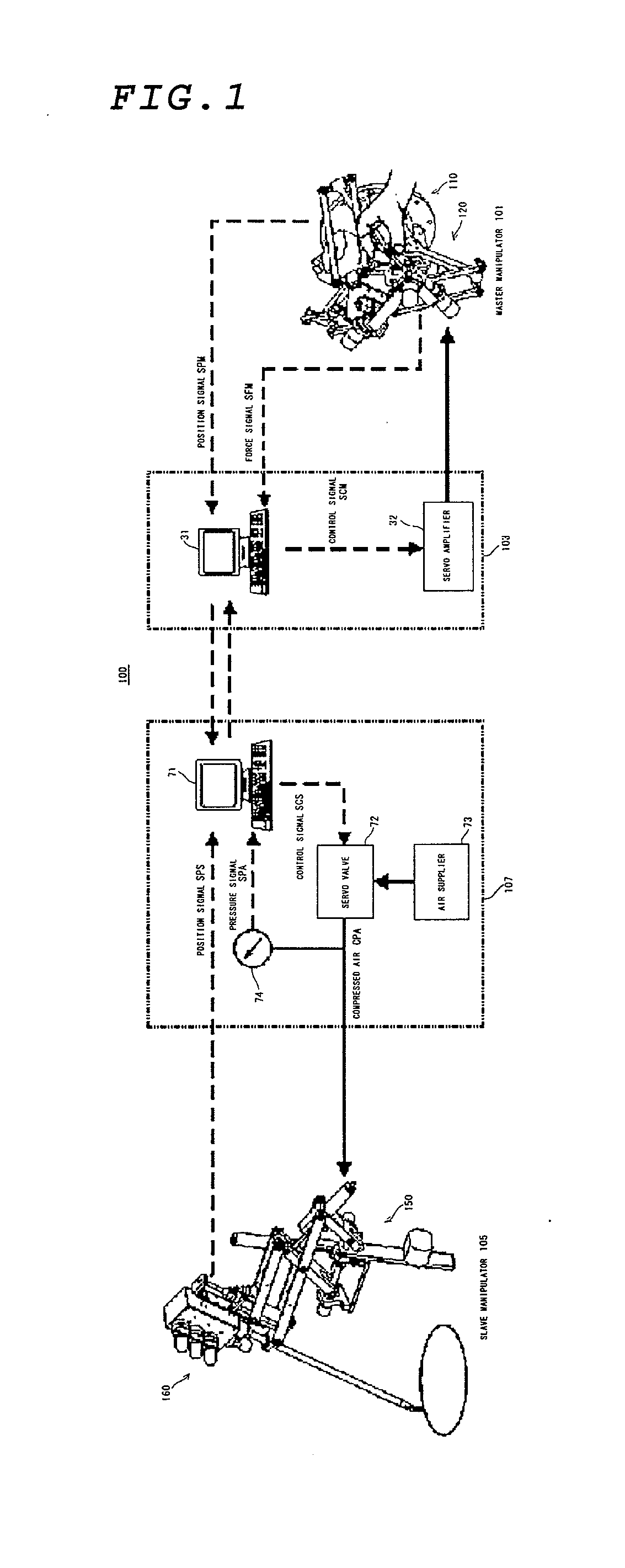
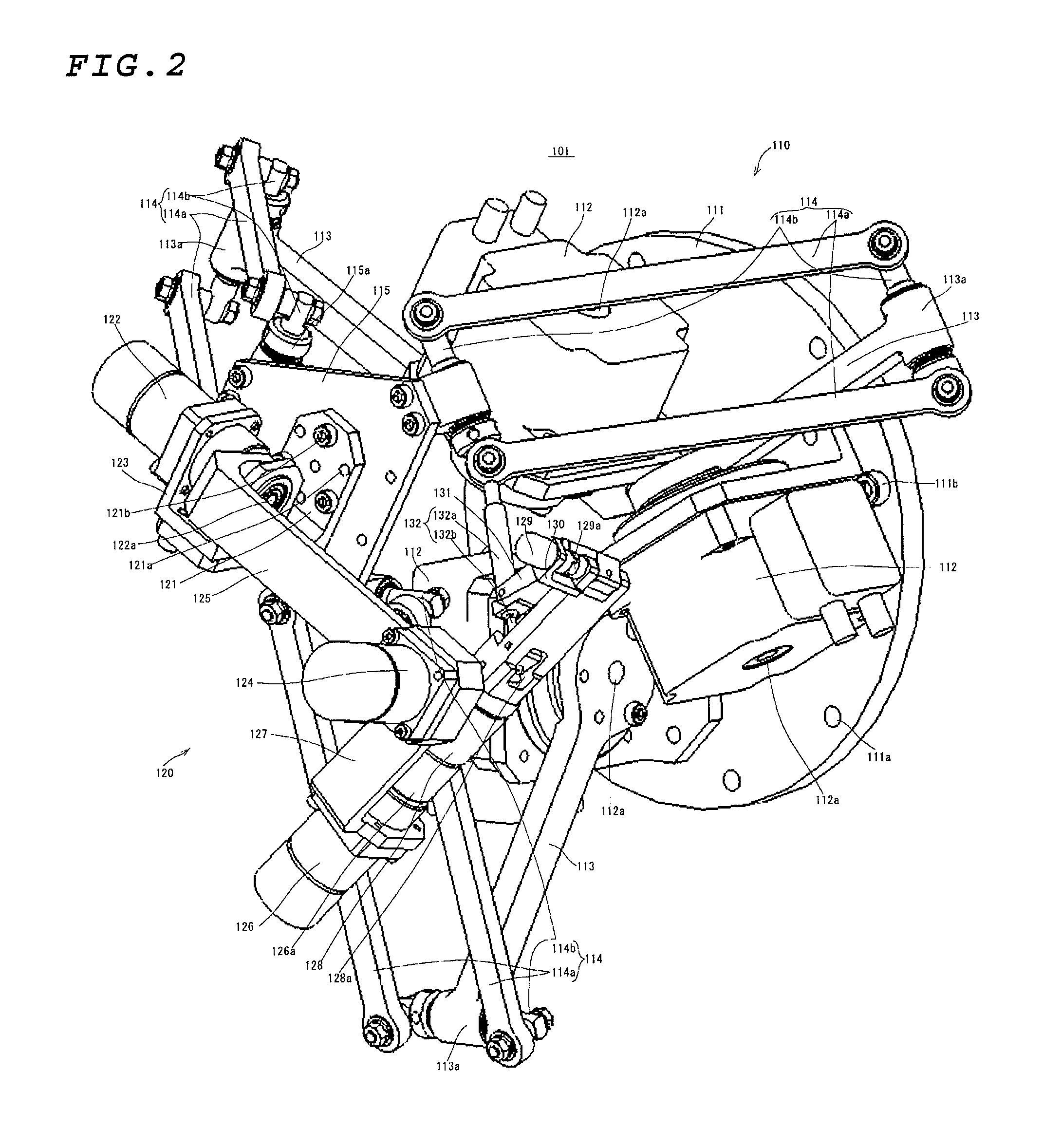
A compact, lightweight manipulation system that excels in operability and has a force feedback capability is provided.When automatic operation of a slave manipulator105 that follows manual operation of a master manipulator 101 is bilaterally controlled by means of communication, the force acting on the slave manipulator is fed back to the master manipulator by operating the master manipulator primarily under electrically-driven speed control and the slave manipulator primarily under pneumatically-driven force control. Therefore, in the master manipulator, it is not necessary to compensate for the dynamics and the self-weight of the master manipulator in the motion range of a user, allowing highly accurate, broadband positional control, which is specific to an electrically-driven system, and in the slave manipulator, nonlinearity characteristics specific to a pneumatically-driven system presents passive softness, provides a high mass-to-output ratio, and produces a large force.
Owner:RIVERFIELD
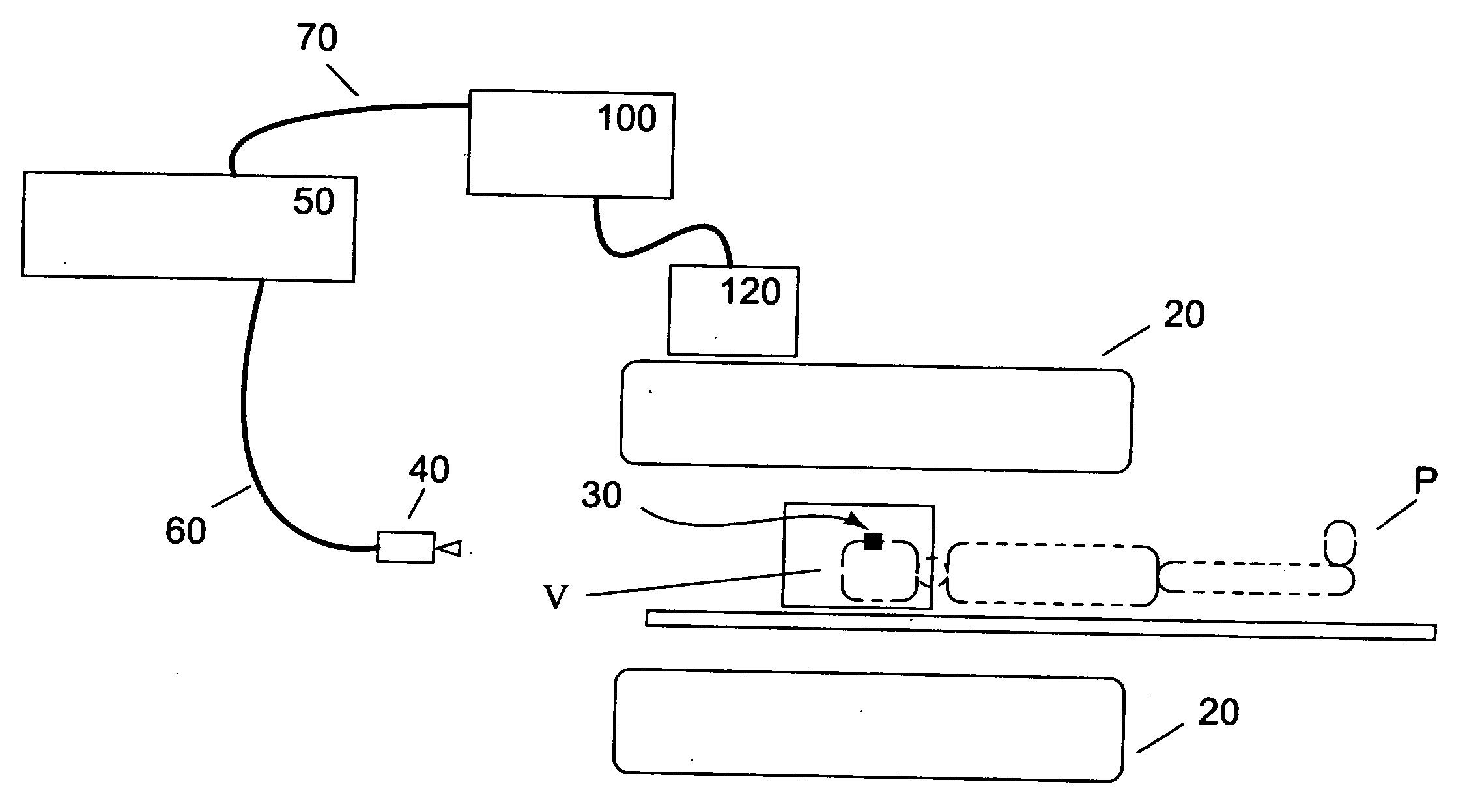
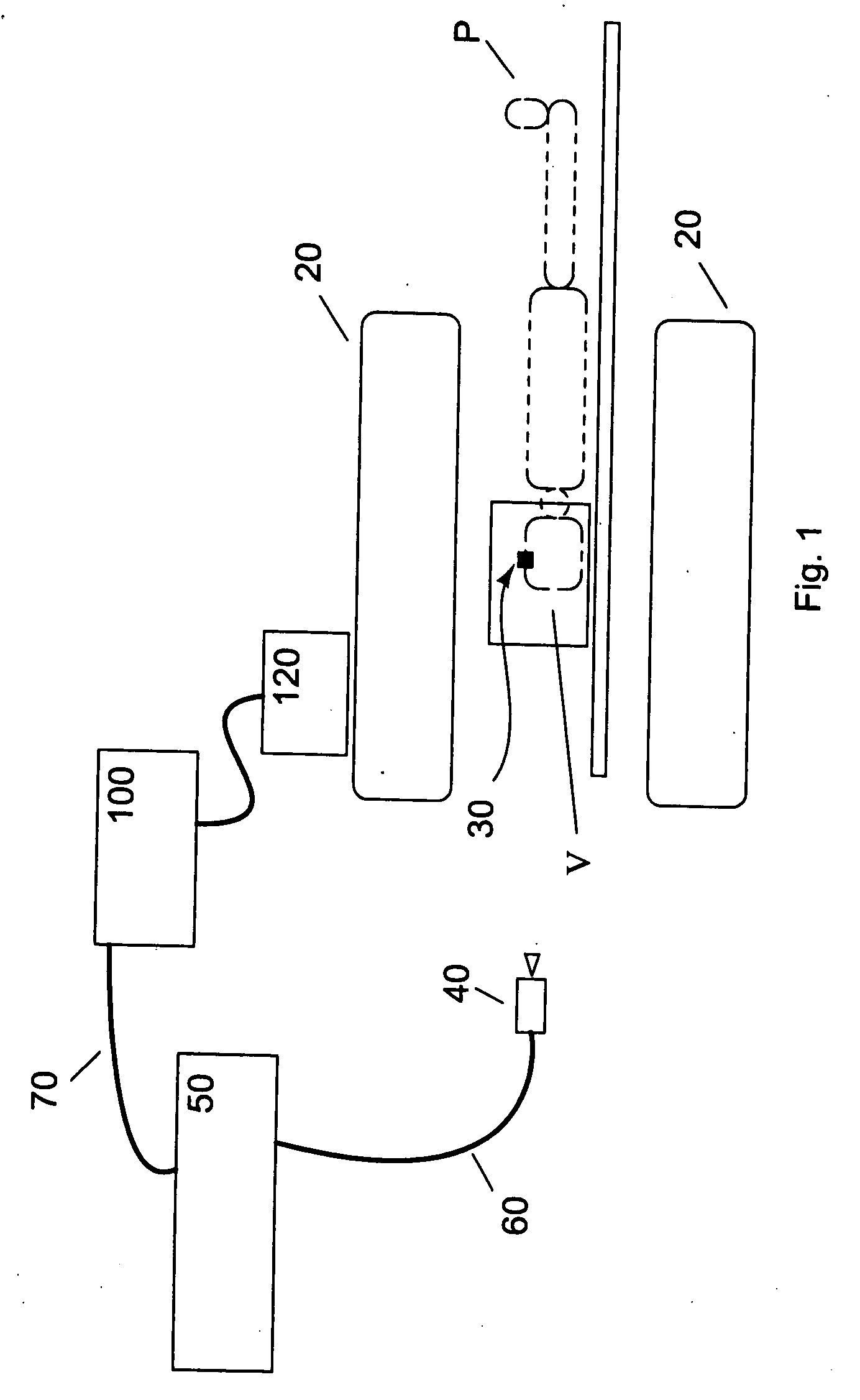
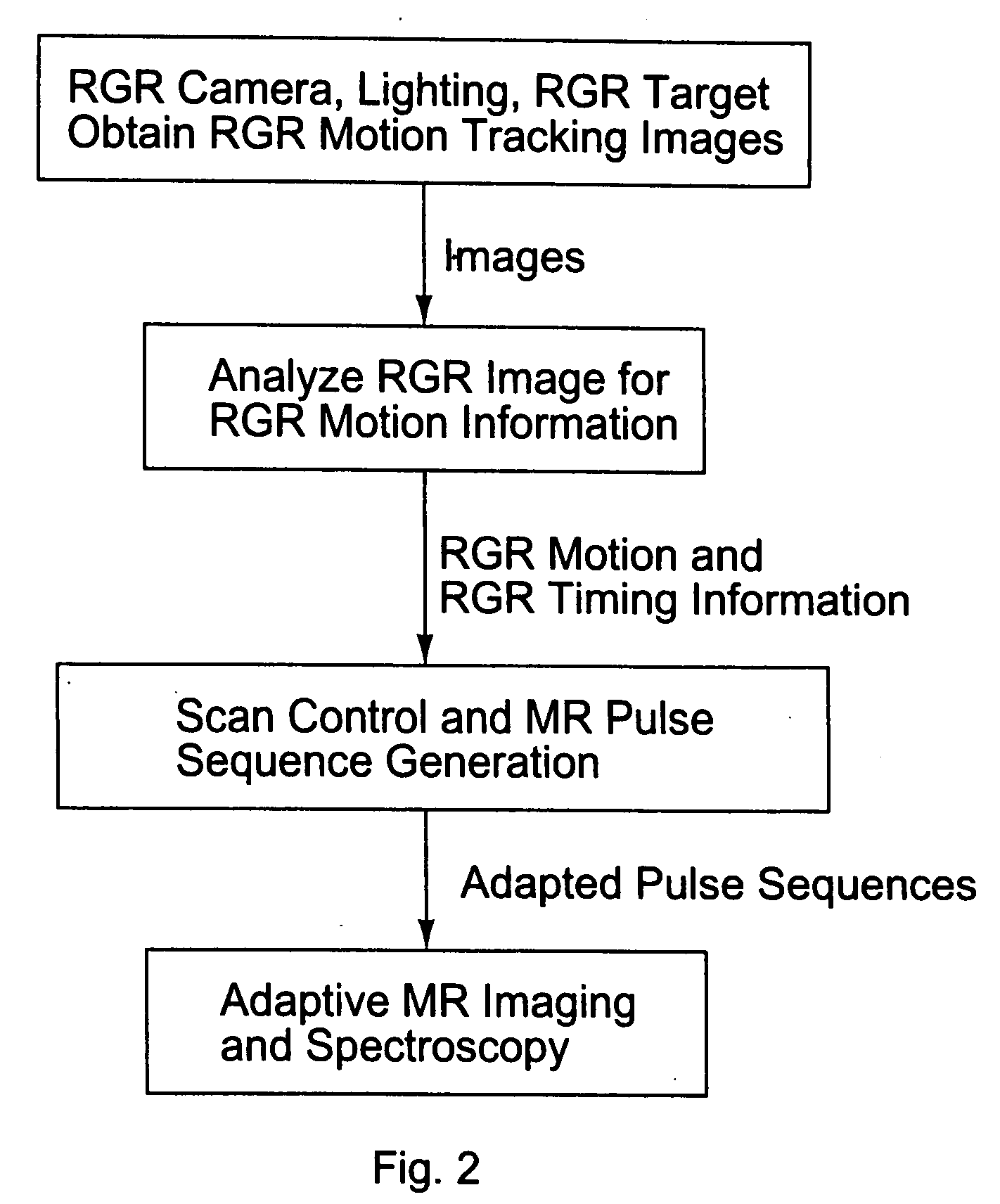
Motion tracking system for real time adaptive imaging and spectroscopy
ActiveUS20070280508A1Improve performanceImprove accuracyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive imagingUsability
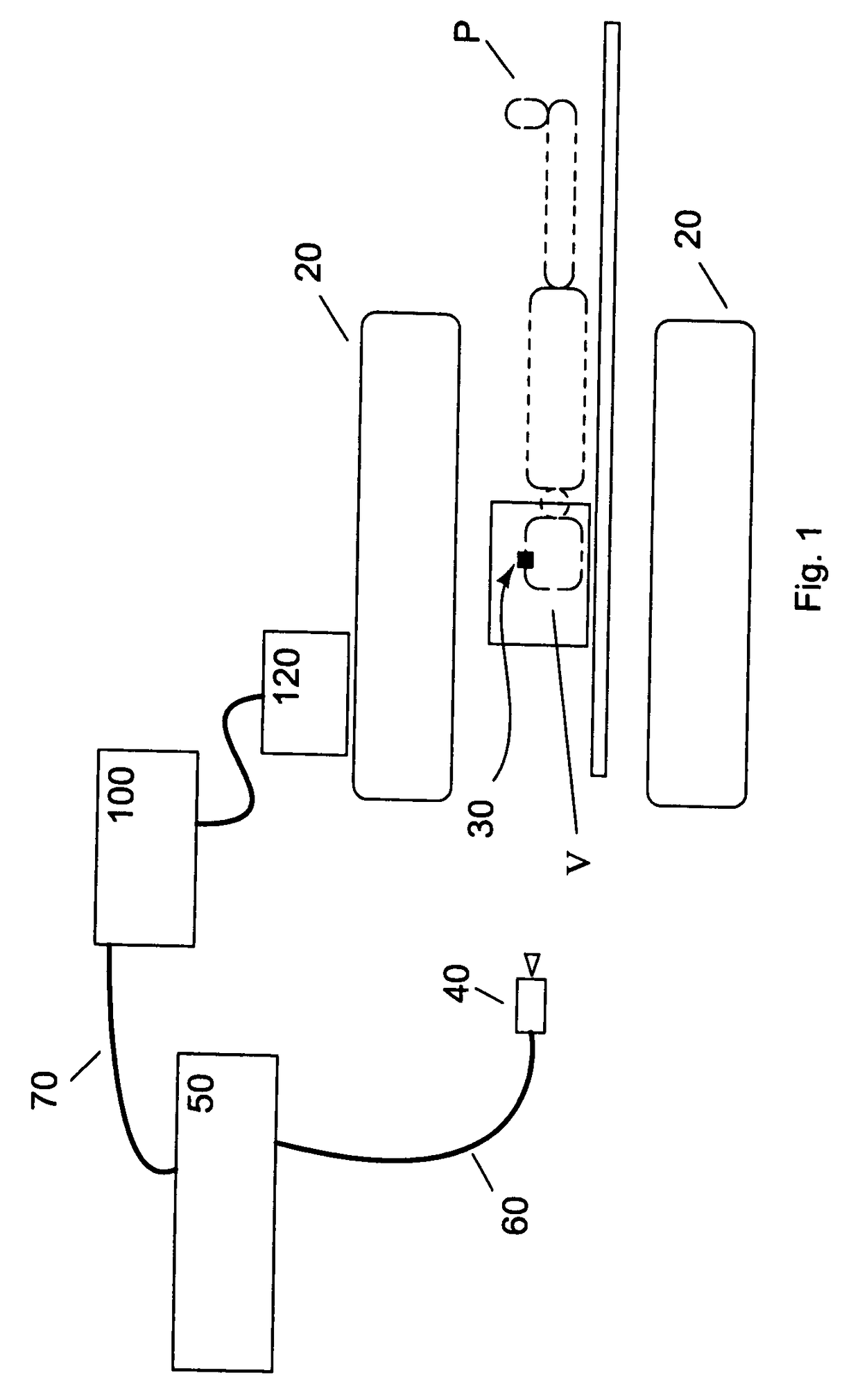
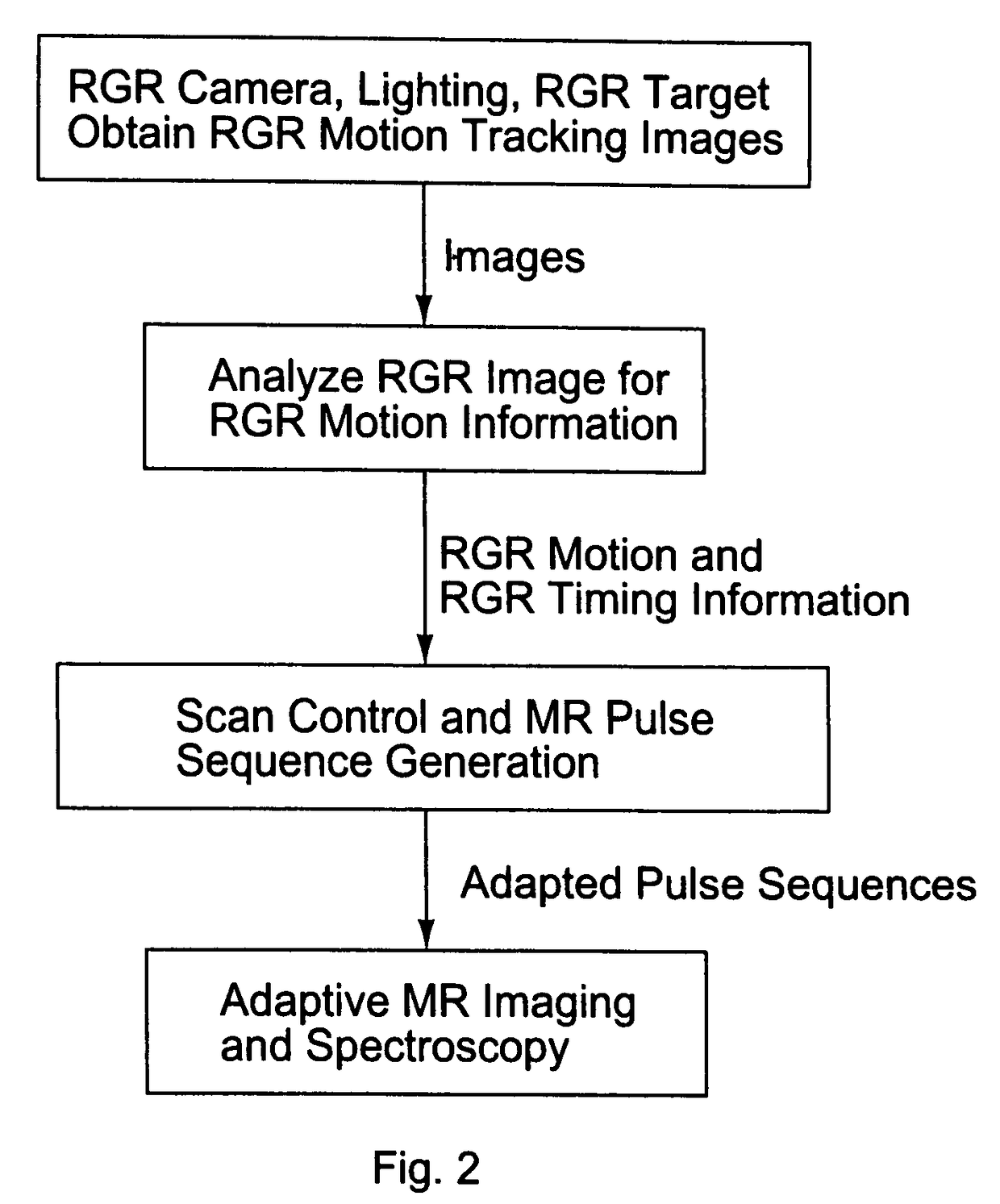
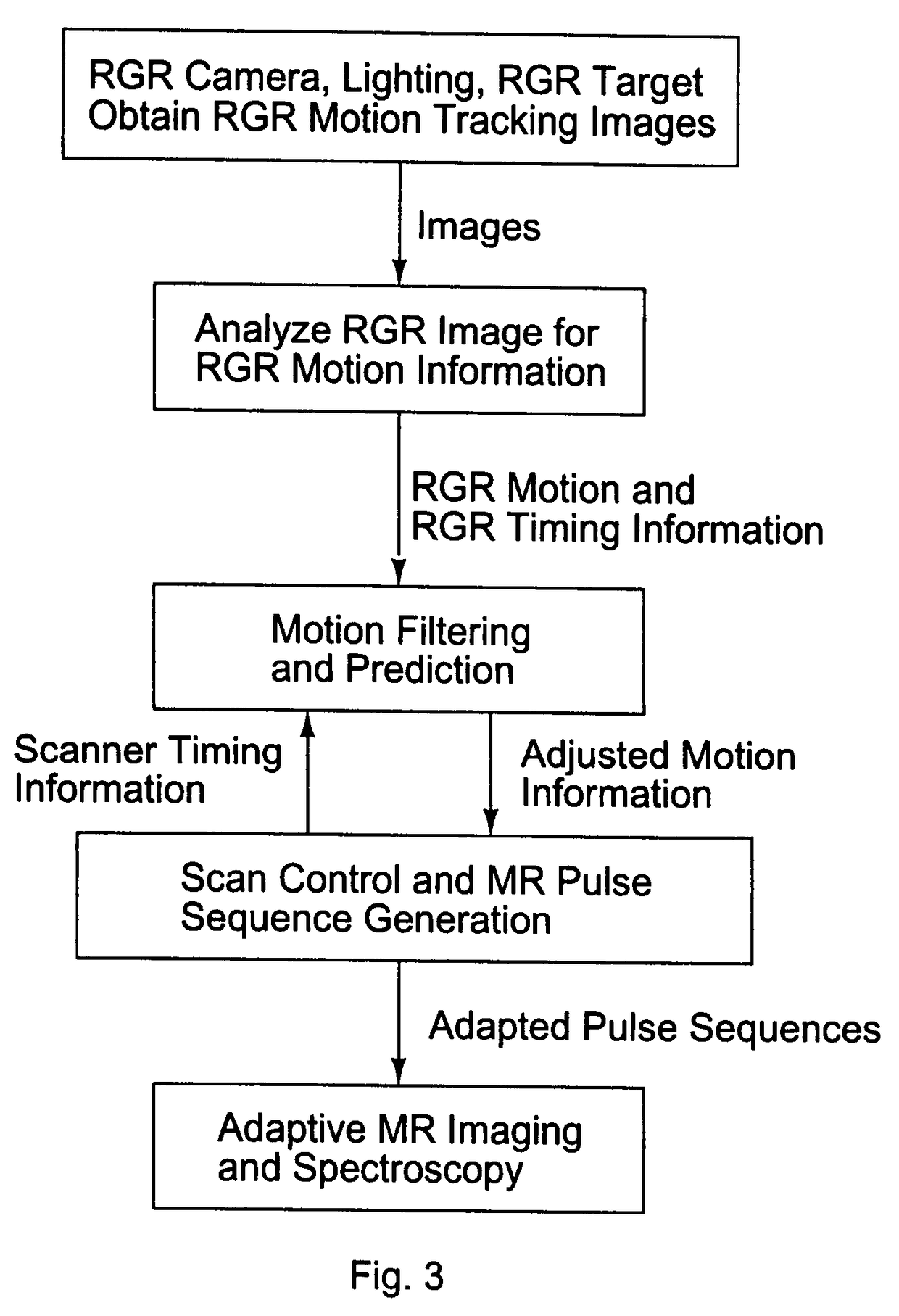
Current MRI technologies require subjects to remain largely motionless for achieving high quality magnetic resonance (MR) scans, typically for 5-10 minutes at a time. However, lying absolutely still inside the tight MR imager (MRI) tunnel is a difficult task, especially for children, very sick patients, or the mentally ill. Even motion ranging less than 1 mm or 1 degree can corrupt a scan. This invention involves a system that adaptively compensates for subject motion in real-time. An object orientation marker, preferably a retro-grate reflector (RGR), is placed on a patients' head or other body organ of interest during MRI. The RGR makes it possible to measure the six degrees of freedom (x, y, and z-translations, and pitch, yaw, and roll), or “pose”, required to track the organ of interest. A camera-based tracking system observes the marker and continuously extracts its pose. The pose from the tracking system is sent to the MR scanner via an interface, allowing for continuous correction of scan planes and position in real-time. The RGR-based motion correction system has significant advantages over other approaches, including faster tracking speed, better stability, automatic calibration, lack of interference with the MR measurement process, improved ease of use, and long-term stability. RGR-based motion tracking can also be used to correct for motion from awake animals, or in conjunction with other in vivo imaging techniques, such as computer tomography, positron emission tomography (PET), etc.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII +3
System and Method for Solar Tracking
InactiveUS20090050191A1Easy to installStable and cost-effective designSolar heating energyPhotometry using reference valueRange of motionComputer module
Owner:SOLFOCUS
Continuous passive motion apparatus
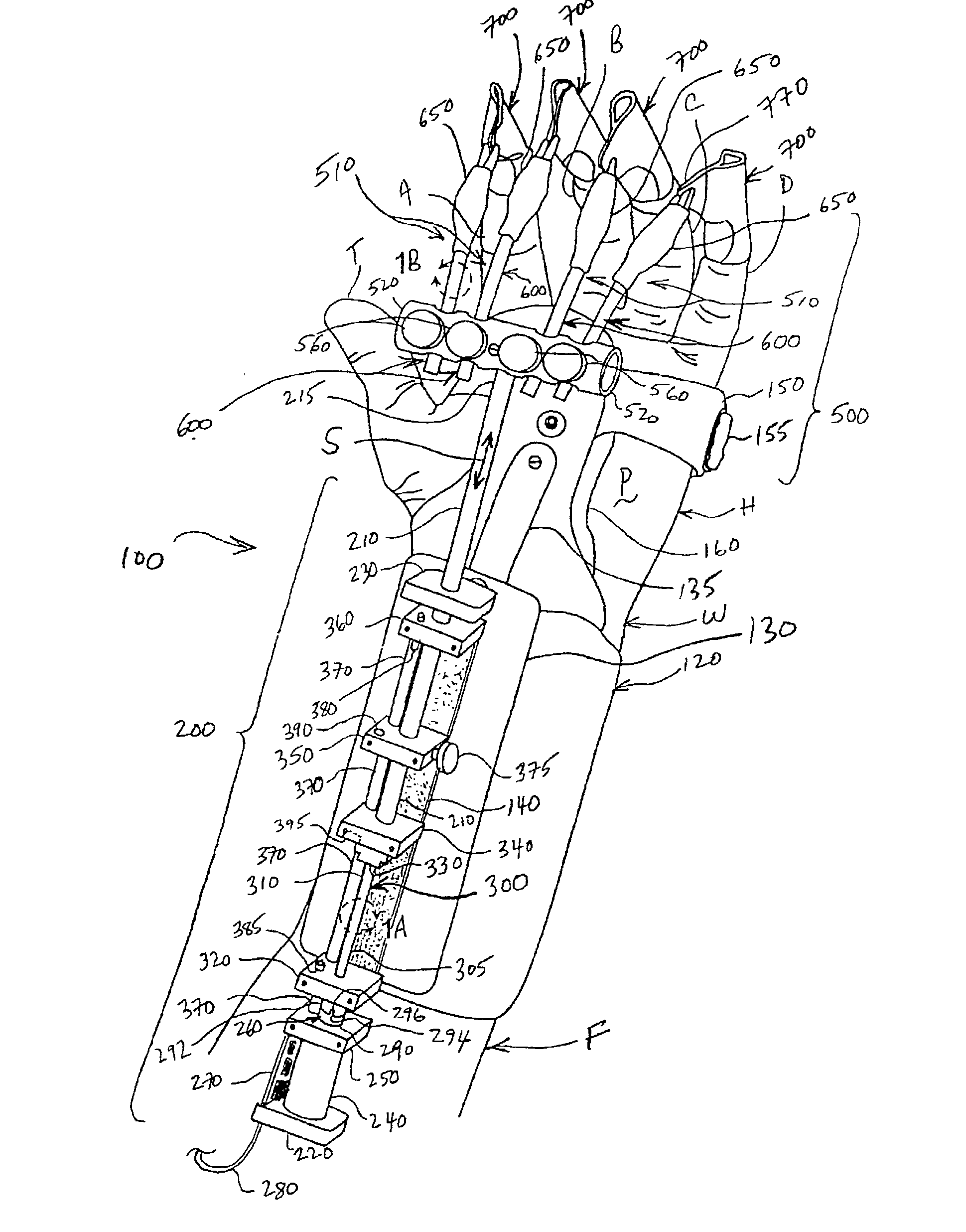
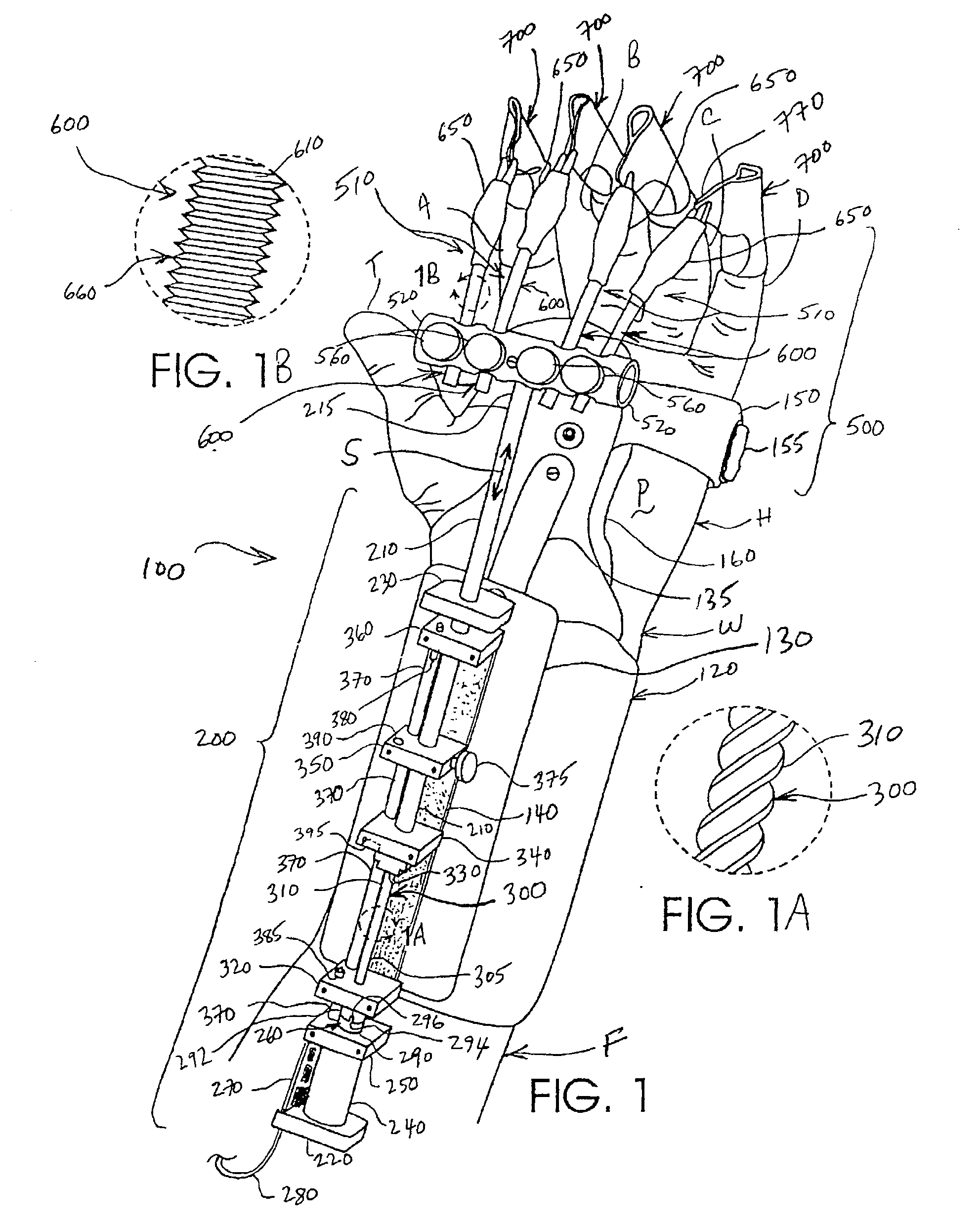
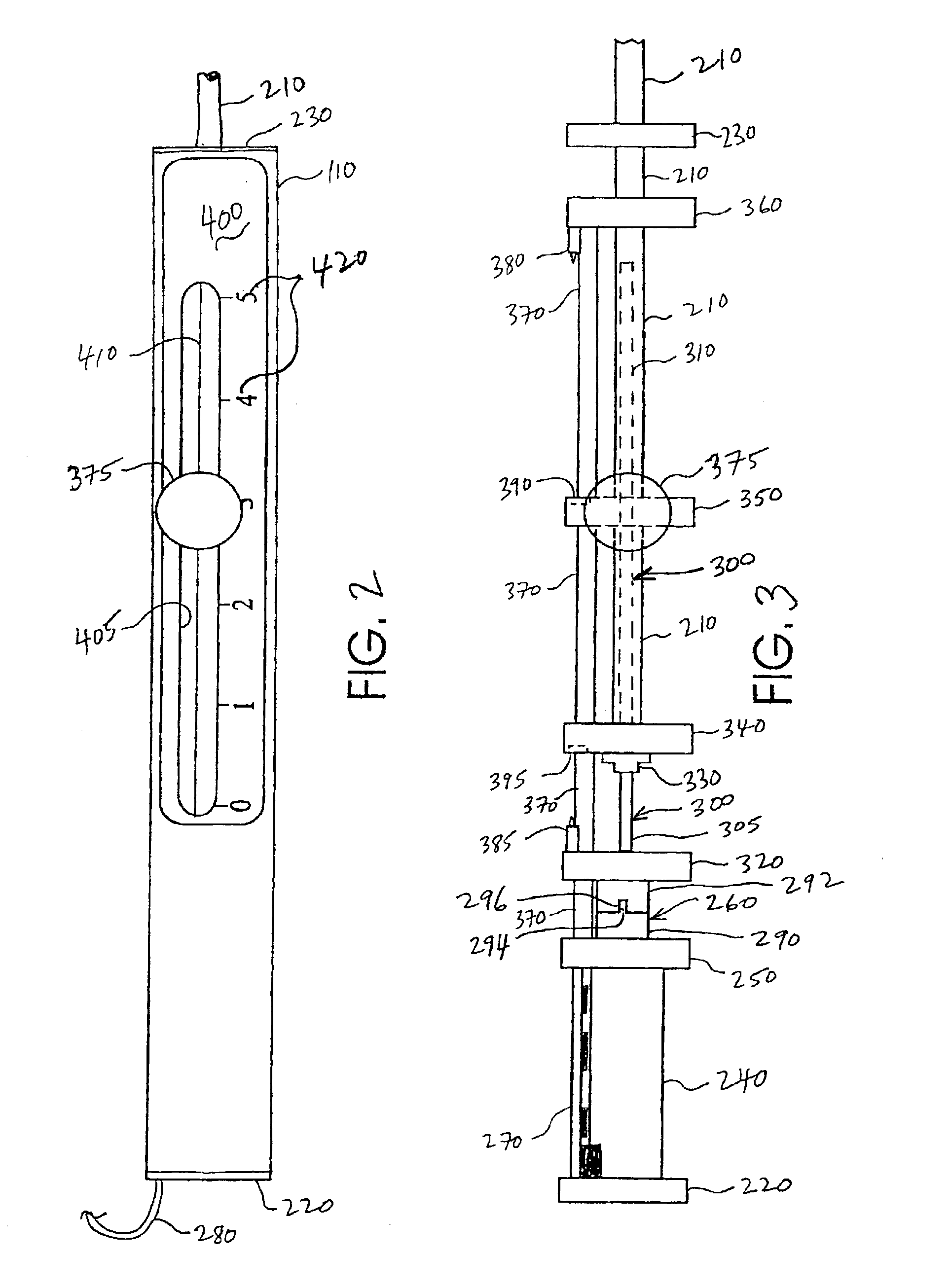
A continuous passive motion apparatus for therapeutic treatment of the fingers of a patient's hand that includes a forearm hand splint. A drive unit is mounted on a palmer aspect of the splint and incorporates a motorized drive tube actuatable over a selectable range of motion. A flexion and extension assembly is connected to the tube and includes at least one finger motion assembly. The finger motion assembly is pivotally interconnected to a proximal end of the drive tube by a coupler adapted to enable movement in at least 2 degrees of freedom relative to the coupler. The coupler is further adapted to releasably engage the at least one finger motion assembly after adjustment to optimally accommodate the anatomical arrangement, size, and range and path of motion of the fingers. The finger motion assembly includes a resilient prime mover selected to be repeatedly bendable without damage but with a bend memory so that it can be adjusted to have an angle of up to about 90 degrees. In variations of the exemplary embodiment, the prime mover is interconnected to the coupler by at least one pivot ball received within the coupler and configured to move about multiple axes of motion. At least one finger splint is releasably connected to a distal end of the finger motion assembly and is adapted to receive a distal phalanx of the finger. The finger splint is preferably formed from a flexible sheet material that incorporates one or more stiffening, bend memory, and hypo-allergenic adhesive layers.
Owner:TAYLOR ROBIN L +1
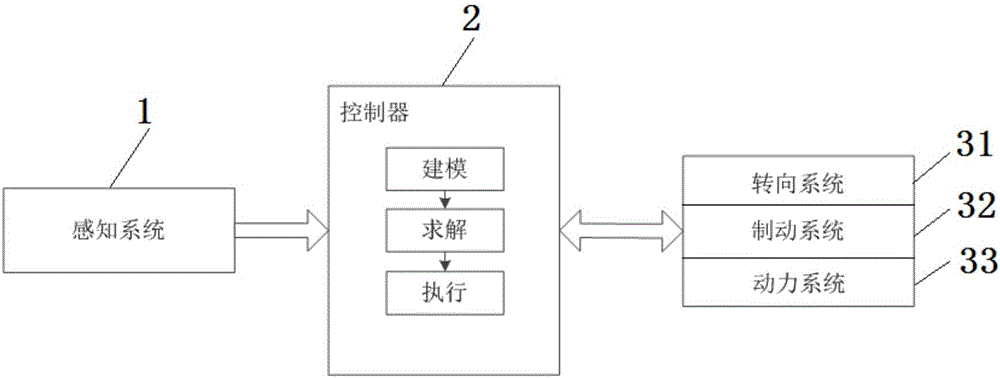
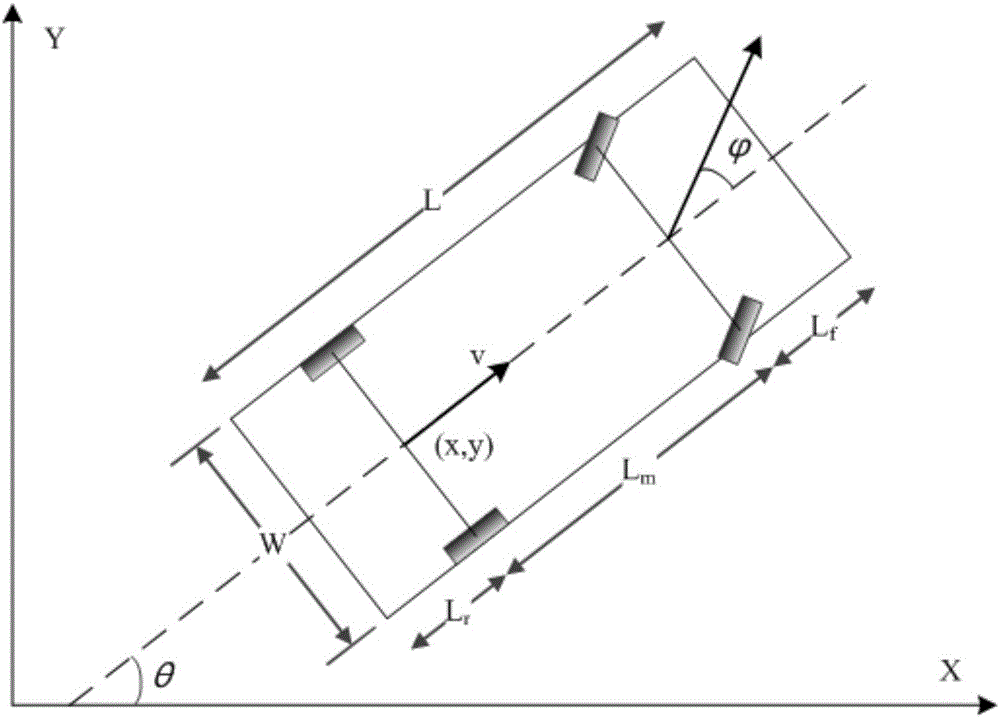
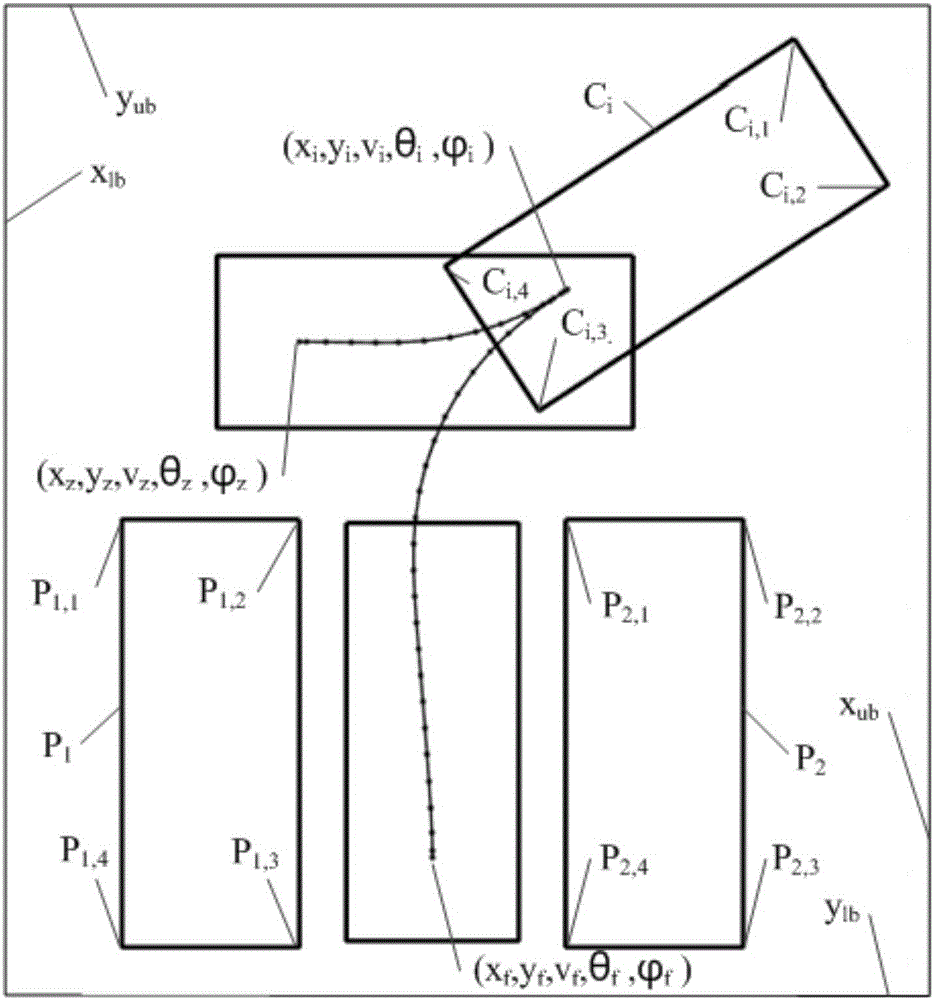
Vehicle autonomous parking path programming method used for multiple parking scenes
ActiveCN105857306APlanning results are safe and feasibleEasy to trackControl devicesRange of motionParking guidance and information
The invention provides a vehicle autonomous parking path programming method used for multiple parking scenes. The method is used for automatically parking a vehicle in a parking space through an autonomous parking system when the autonomous parking system detects the available parking space. The method includes the steps that target parking space information is detected, and a parking scene is determined; the initial state and target state of the to-be-parked vehicle are determined; a vehicle kinematics differential equation is established; state variables and control variables of the vehicle are segmented, equidistance sampling is performed on each segment according to certain time step, and to-be-optimized variables are obtained; an equality constraint, boundary constraints and inequality constraints of the to-be-optimized variables are formed; motion range constraints of the to-be-parked vehicle are formed according to the motion range limit in the parking process of the vehicle; an optimization objective is determined, and an objective function is established; and by means of a nonlinear programming solver, an optimal solution of a parking path is obtained. The vehicle autonomous parking path programming method is suitable for the multiple parking scenes, the design is reasonable, abundant information can be provided so as to control autonomous parking of the vehicle, and the security coefficient is high.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Parallel manipulator having backlash-free gearnings
InactiveUS20060182602A1Improve rigidityEasy to controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsEngineeringParallel manipulator
A delta robot has motor / gearing units, which are respectively assigned to an arm and which are disposed on one side each of a triangle. Each motor / gearing unit has a gearing, by virtue of material-locking and / or positive-locking connection of gearing components, is free from backlash over the whole of the motional range of the gearing, allowing virtually all aspects fundamental to the delta robot to be optimized, especially the rigidity, the control characteristics, the spatial requirement, the speed and the positioning accuracy.
Owner:SIG TECH AG +1
Method and device for controlling the closing movement of a chassis component for vehicles
ActiveUS20090217596A1Improve protectionReduce decreaseBuilding braking devicesWing fastenersRange of motionEngineering
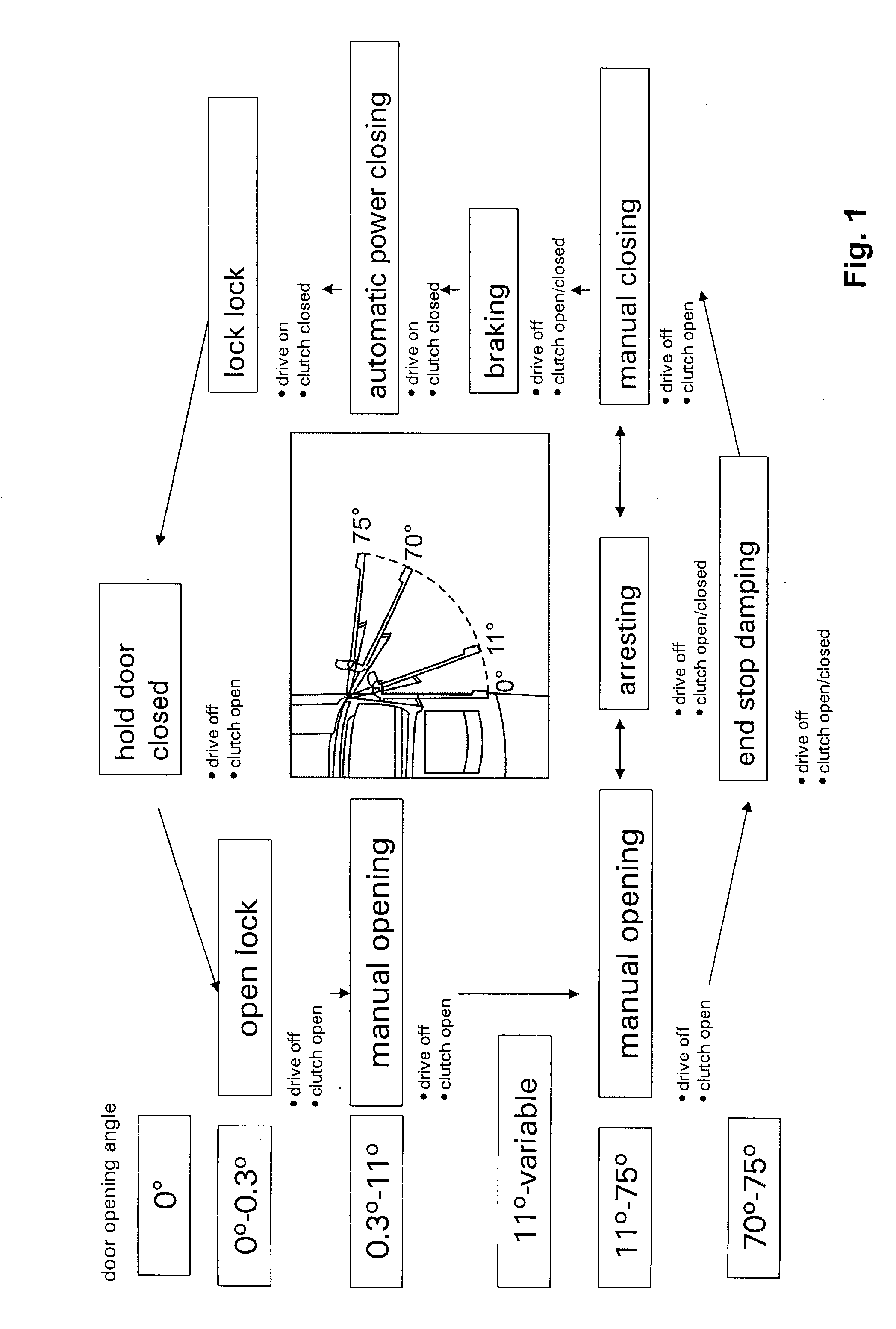
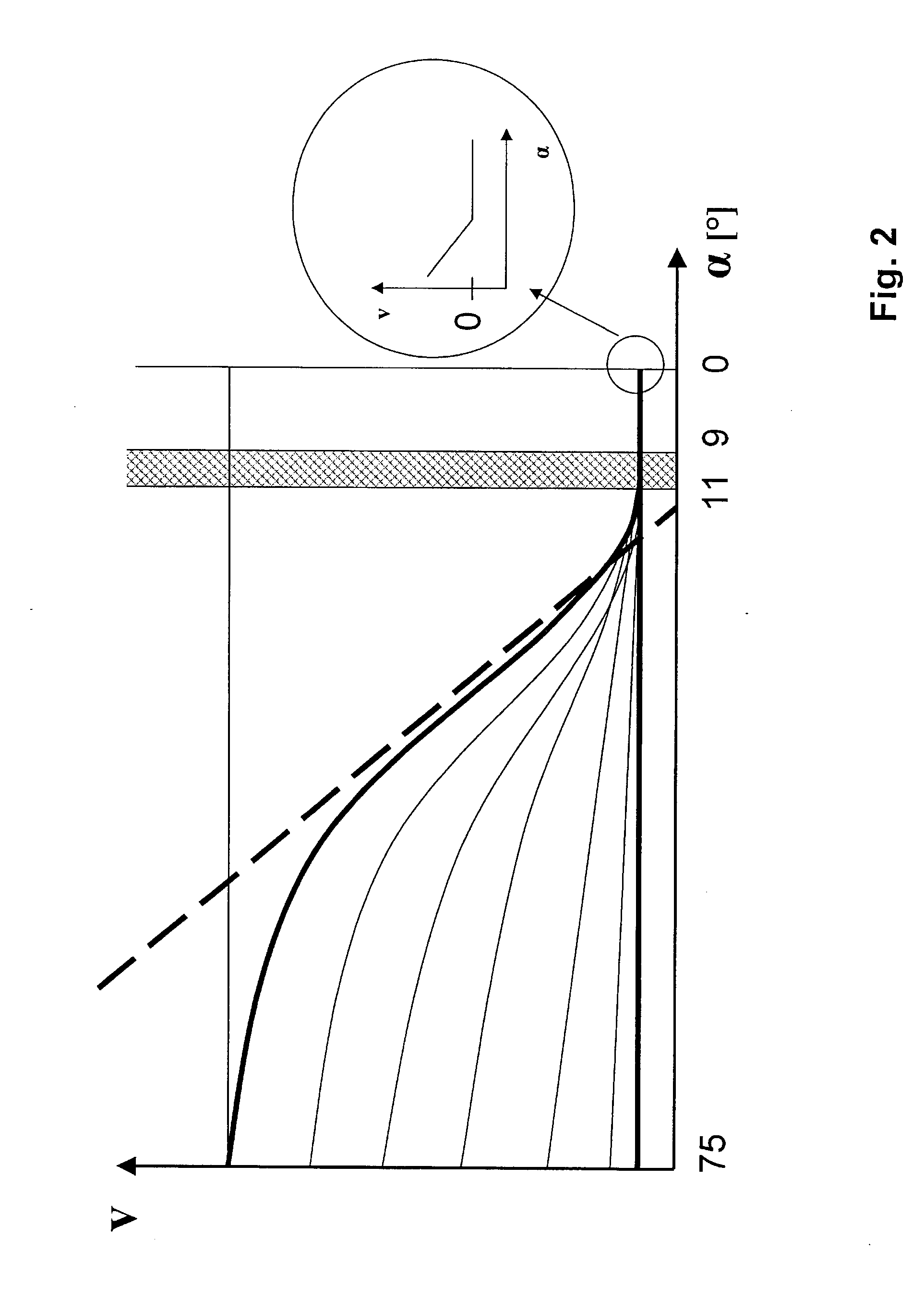
In order to reduce the stresses occurring during the closing of a manually closable body component, e.g. a door, a method of controlling the closing movement is proposed in which,during the closing movement, departing from an opened position, the body component passes through a first movement range in which the body component is moved towards the closed position without any action by a control member, and,following the first movement range, the body component passes through a second movement range in which the closing movement of the body component is varied in such a manner by the action of the control member that the residual kinetic energy of the body component does not exceed a predetermined limit value after passing through the second movement range, irrespective of the initial speed.The residual kinetic energy is not sufficient to close the body component automatically. The body component is therefore automatically drawn in a third movement range following the second movement range until a pre catch or main catch of a lock is reached.The invention relates furthermore to a corresponding control device.
Owner:BROSE FAHRZEUGTEILE SE & CO KG COBURG
Retractable vehicle step
InactiveUS7487986B2Easy to storeFacilitates self-energizingSteps arrangementRange of motionEngineering
A retractable step for use with a vehicle comprises a stepping member having a stepping deck, a first arm, a second arm, a motor and a stop. The first arm has a first end pivotally attached to the vehicle, and a second end pivotally attached to the stepping member. The second arm also has a first end pivotally attached to the vehicle, and a second end pivotally attached to the stepping member. The motor is drivingly connected to the first arm such that a rotation of the motor causes rotation of the first arm about its first end and moves the stepping member from a retracted position to an extended position, or vice versa. The stop is located within the range of motion of the second arm such that the second arm bears against the stop when the stepping member is in the extended position. The first and second arms are situated such that the first arm is loaded in compression and the second arm is loaded in tension when the stepping member is in the extended position and a load is placed upon it. In another embodiment, a retractable vehicle step assist comprises a rigid frame, a forward planar linkage pivotably connected to the frame along a forward upper connection width, and a rearward planar linkage pivotably connected to the frame along a rearward upper connection width. The retractable vehicle step further comprises a rigid step member having a stepping deck. The step member is pivotably connected to the forward planar linkage along a forward lower connection width, and is pivotably connected to the rearward planar linkage along a rearward lower connection width and on a side of the forward planar linkage opposite the stepping deck. The stepping deck is substantially wider than any of the forward upper connection width, the rearward upper connection width, the forward lower connection width, and the rearward lower connection width.
Owner:LUND MOTION PRODS
Hydraulic Actuator Control System
InactiveUS20080228323A1Slow motionFluid couplingsControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsElectronic controllerControl signal
A system for controlling motion of a hydraulic actuator during a portion of its range of motion is described, including a sensor on the hydraulic actuator for providing a signal indicating that the actuator is near a portion of its range of motion, and a pneumatic control valve that is configured to selectively modify a pressurized air control signal to in turn restrict flow of pressurized hydraulic fluid to the hydraulic actuator. The hydraulic actuator control system further includes an electronic controller for controlling the pneumatic control valve in response to a signal from the sensor. The hydraulic actuator control system thereby slows the motion of the hydraulic actuator near the portion of its range of motion.
Owner:HARTFIEL AUTOMATION
Medical robotic system providing an auxiliary view including range of motion limitations for articulatable instruments extending out of a distal end of an entry guide
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Sliding and nesting console system
A console system which may translate longitudinally in a vehicle includes a forward end which is capable of being at least partially nested with a vehicle instrument panel. The range of movement may extend to the front seats or further toward the rear of the vehicle to provide functionality for occupants of second or even third row seats. The translation mechanism preferably includes a track similar to those employed in the vehicle art for manual seat adjustment. In the most preferred embodiment, a storage drawer is included in the instrument panel which may be used when the console is in any position, including its nested position.
Owner:YANFENG CZECHIA AUTOMOTIVE INTERIOR SYST SRO
Elastically-driven modular joint with force feedback control
ActiveCN102632509AIncrease flexibilityImprove compactnessJointsMechanical energy handlingReduction driveRange of motion
The invention discloses an elastically-driven modular joint with force feedback control. comprising assembly components such as a motor stator, a motor rotor, a harmonic speed reducer and the like, so that the design flexibility and compactedness of the joint can be increased; and due to the design of an air routing shaft, the joint is convenient to route, so that the joint is more succinct, the moving range of the joint can be preferably enlarged, and the running reliability of the joint can be improved. Due to the introduction of a first absolute type angle sensor and a second absolute type angle sensor, the angle deviation between an output shaft and an output end cover can be obtained, and the angle deviation is multiplied by the elasticity coefficient of an elastic torsion spring, so that a moment value applicable to the joint can be obtained, for an input feedback value of a joint signal; and a reliable moment feedback signal can be provided for the joint, so that the elastic torsion spring can be deformed, the smoothness can be provided for the joint, and an energy storing mechanism can be further provided for the joint, and the elastically-driven modular joint is applicable to a robot, so that the interaction capability between the robot and the environment can be enhanced, and the running efficiency of the robot can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Apparatus and method for coating pipes
InactiveUS6881266B1Minimizes amount of wasteReduce riskMovable spraying apparatusVacuum evaporation coatingRange of motionSpray coating
Apparatus for spraying a coating onto the outside of a pipe includes a body for mounting on a pipe to be coated. A spray gun is mounted on the body such that it can move relative to the body to spray coating completely around the periphery of the pipe. The apparatus may include only a single spray gun which is able to travel in a 360 degree range of motion around the periphery of the pipe. The apparatus is particularty suited to coating girth welds of a pipeline.
Owner:PIPELINE INDUCTION HEAT
Motion tracking system for real time adaptive imaging and spectroscopy
ActiveUS8121361B2Accurately determinedAccurately determineImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive imagingSpectroscopy
Current MRI technologies require subjects to remain largely motionless for achieving high quality magnetic resonance (MR) scans, typically for 5-10 minutes at a time. However, lying absolutely still inside the tight MR imager (MRI) tunnel is a difficult task, especially for children, very sick patients, or the mentally ill. Even motion ranging less than 1 mm or 1 degree can corrupt a scan. This invention involves a system that adaptively compensates for subject motion in real-time. An object orientation marker, preferably a retro-grate reflector (RGR), is placed on a patients' head or other body organ of interest during MRI. The RGR makes it possible to measure the six degrees of freedom (x, y, and z-translations, and pitch, yaw, and roll), or “pose”, required to track the organ of interest. A camera-based tracking system observes the marker and continuously extracts its pose. The pose from the tracking system is sent to the MR scanner via an interface, allowing for continuous correction of scan planes and position in real-time. The RGR-based motion correction system has significant advantages over other approaches, including faster tracking speed, better stability, automatic calibration, lack of interference with the MR measurement process, improved ease of use, and long-term stability. RGR-based motion tracking can also be used to correct for motion from awake animals, or in conjunction with other in vivo imaging techniques, such as computer tomography, positron emission tomography (PET), etc.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII +3
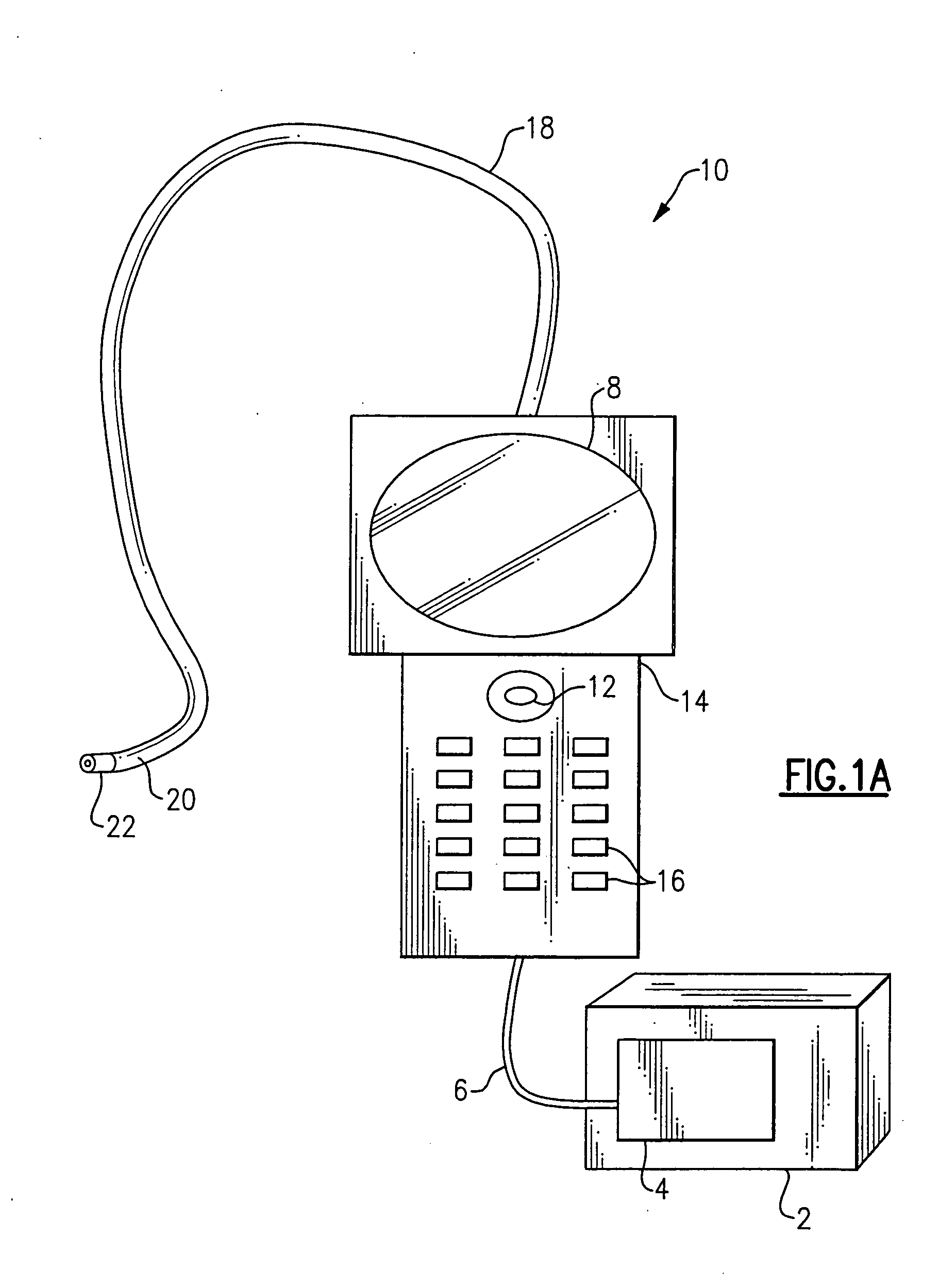
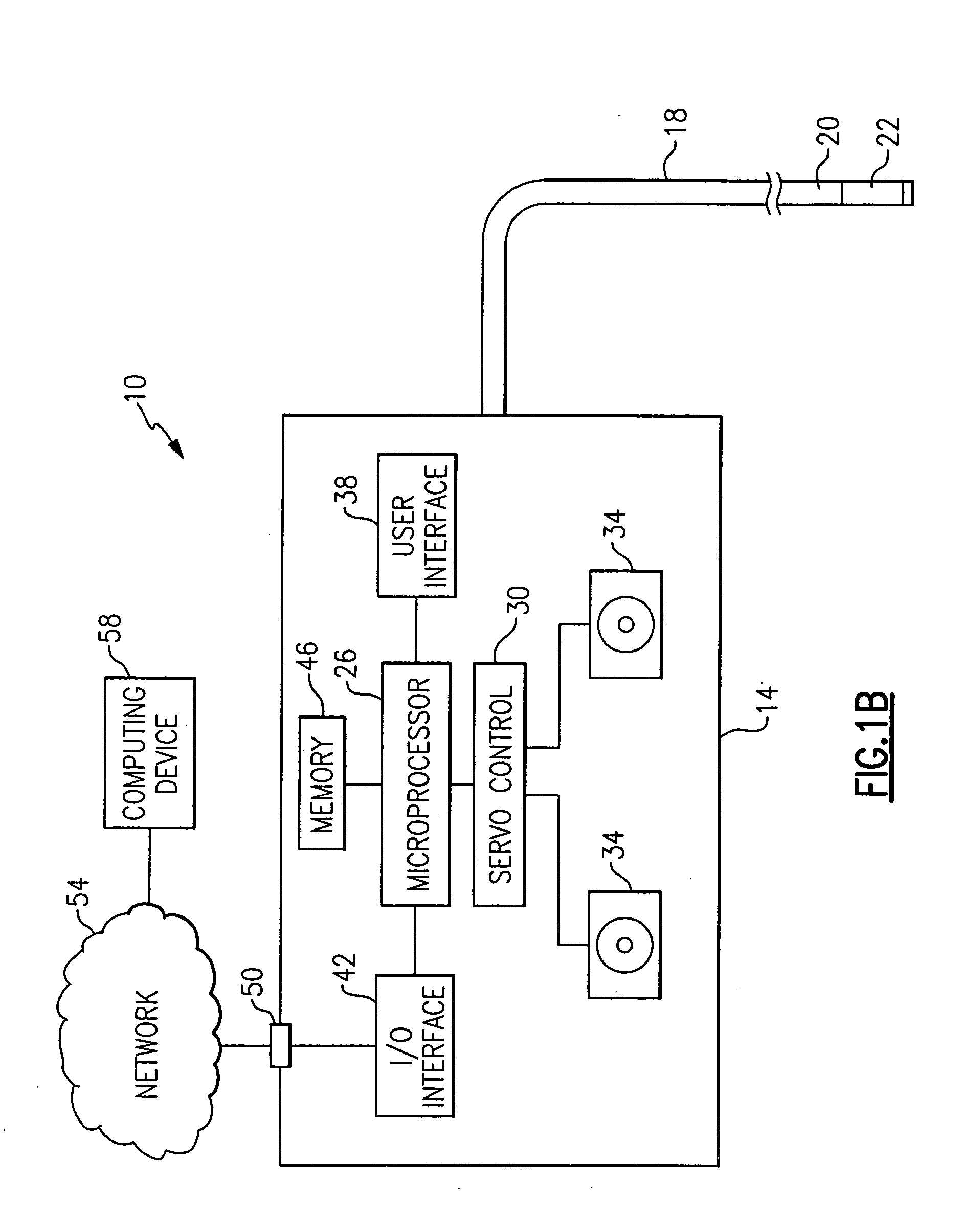
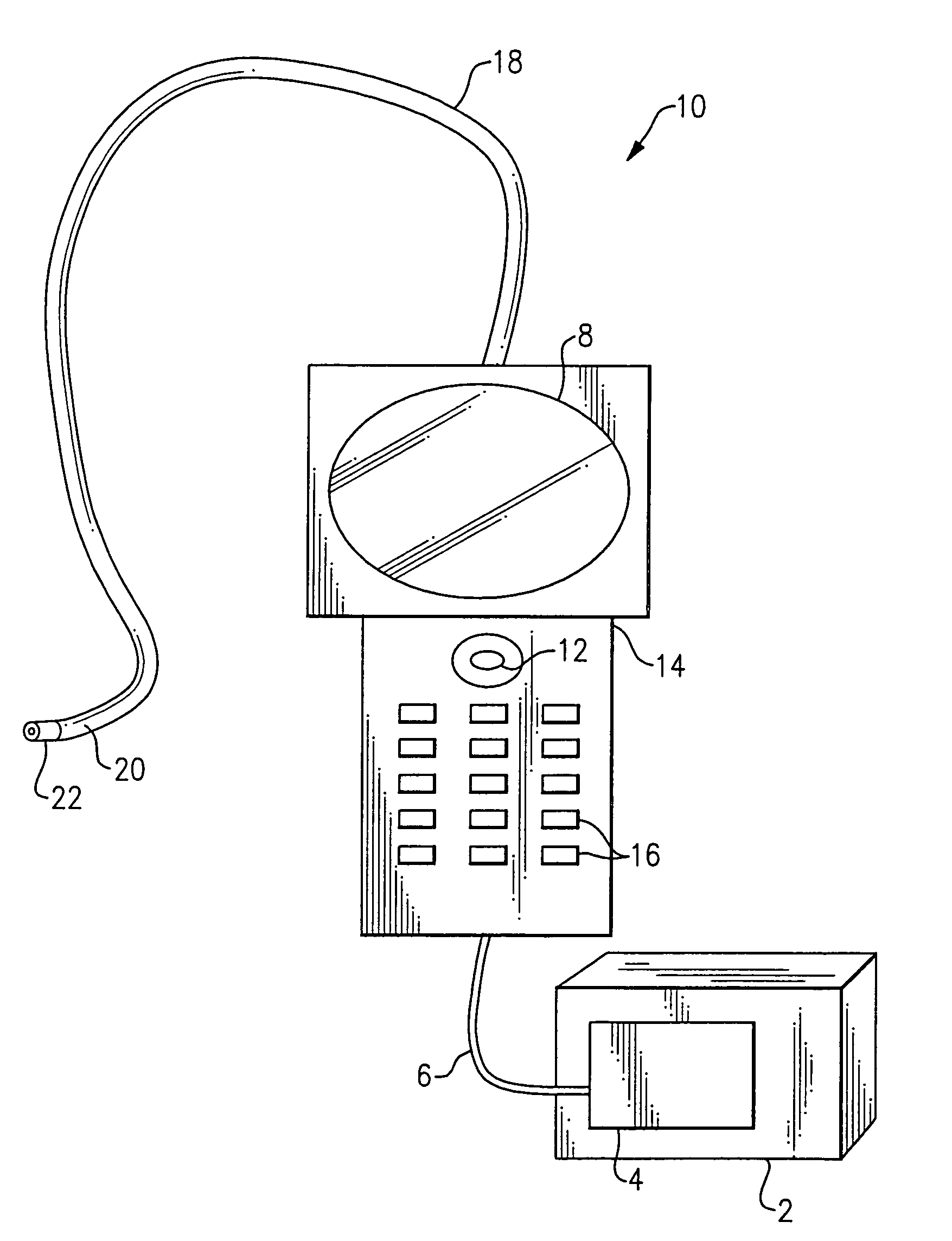
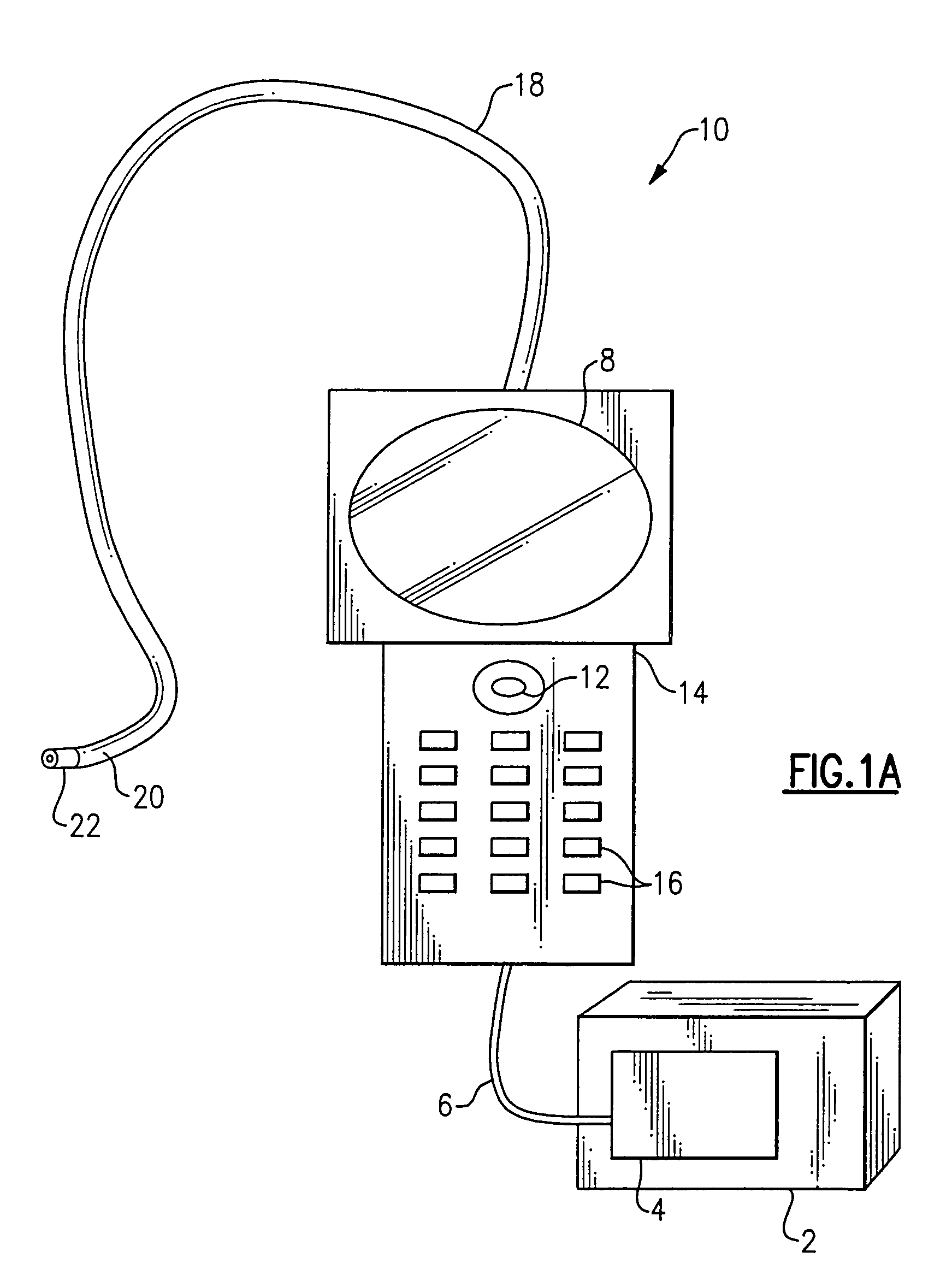
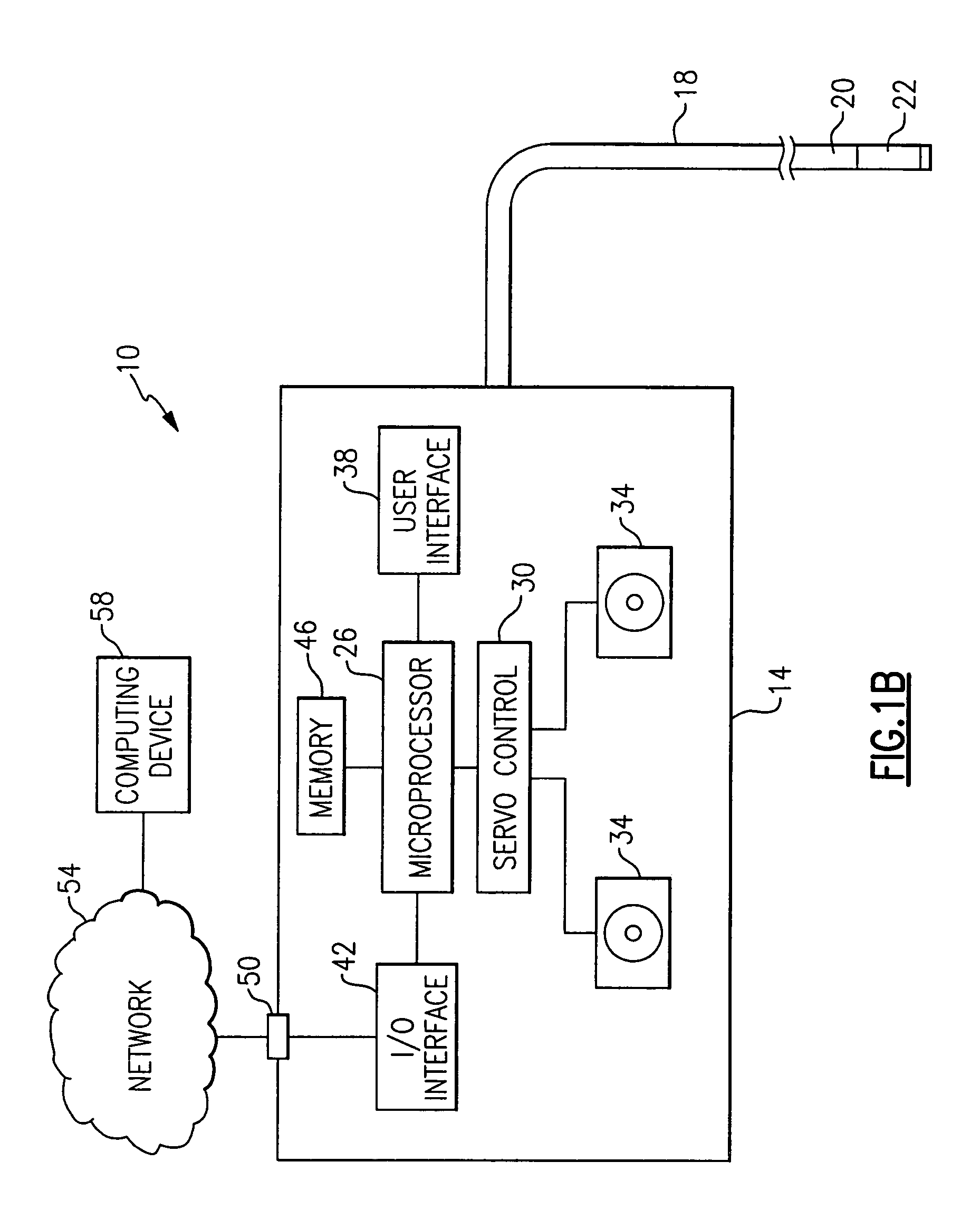
Method and apparatus for improving the operation of a remote viewing device
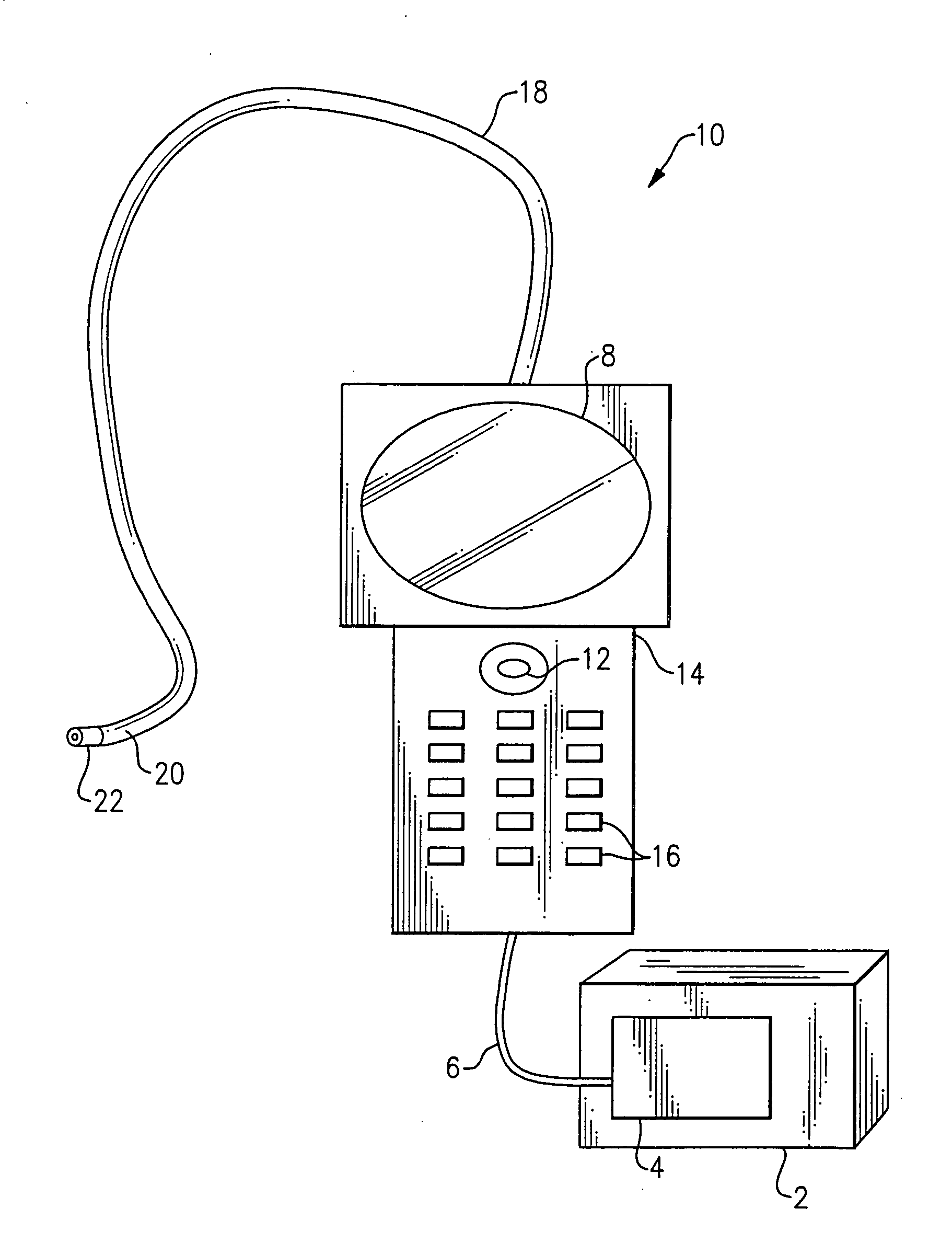
ActiveUS20050168571A1Convenient remote operationImprove viewing effectSurgeryEndoscopesRange of motionEngineering
The present invention features a remote viewing device that is capable of improving its operation by removing slack in its control cables and / or by increasing the range of motion of its viewing head. In one embodiment, the method for improving the operation involves removing at least a portion of the slack in at least one control cable attached to a servo motor. The removal of at least a portion of the slack includes changing the position of a servo motor relative to a flexible tube termination block until a specified tension is encountered in at least one of the control cables. The method further includes determining first and second servo control signal values corresponding to no angular deflection and a specified deflection in a viewing head.
Owner:GE INSPECTION TECH LP
Axial snubbers for camera
ActiveUS7555210B2Reduce contactReduce stressProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementRange of motionSnubber
Owner:DIGITALPTICS MEMS
Method and apparatus for improving the operation of a remote viewing device by changing the calibration settings of its articulation servos
ActiveUS7134993B2Convenient remote operationImprove viewing effectSurgeryEndoscopesRange of motionControl theory
The present invention features a remote viewing device that is capable of improving its operation by removing slack in its control cables and / or by increasing the range of motion of its viewing head. In one embodiment, the method for improving the operation involves removing at least a portion of the slack in at least one control cable attached to a servo motor. The removal of at least a portion of the slack includes changing the position of a servo motor relative to a flexible tube termination block until a specified tension is encountered in at least one of the control cables. The method further includes determining first and second servo control signal values corresponding to no angular deflection and a specified deflection in a viewing head.
Owner:GE INSPECTION TECH LP
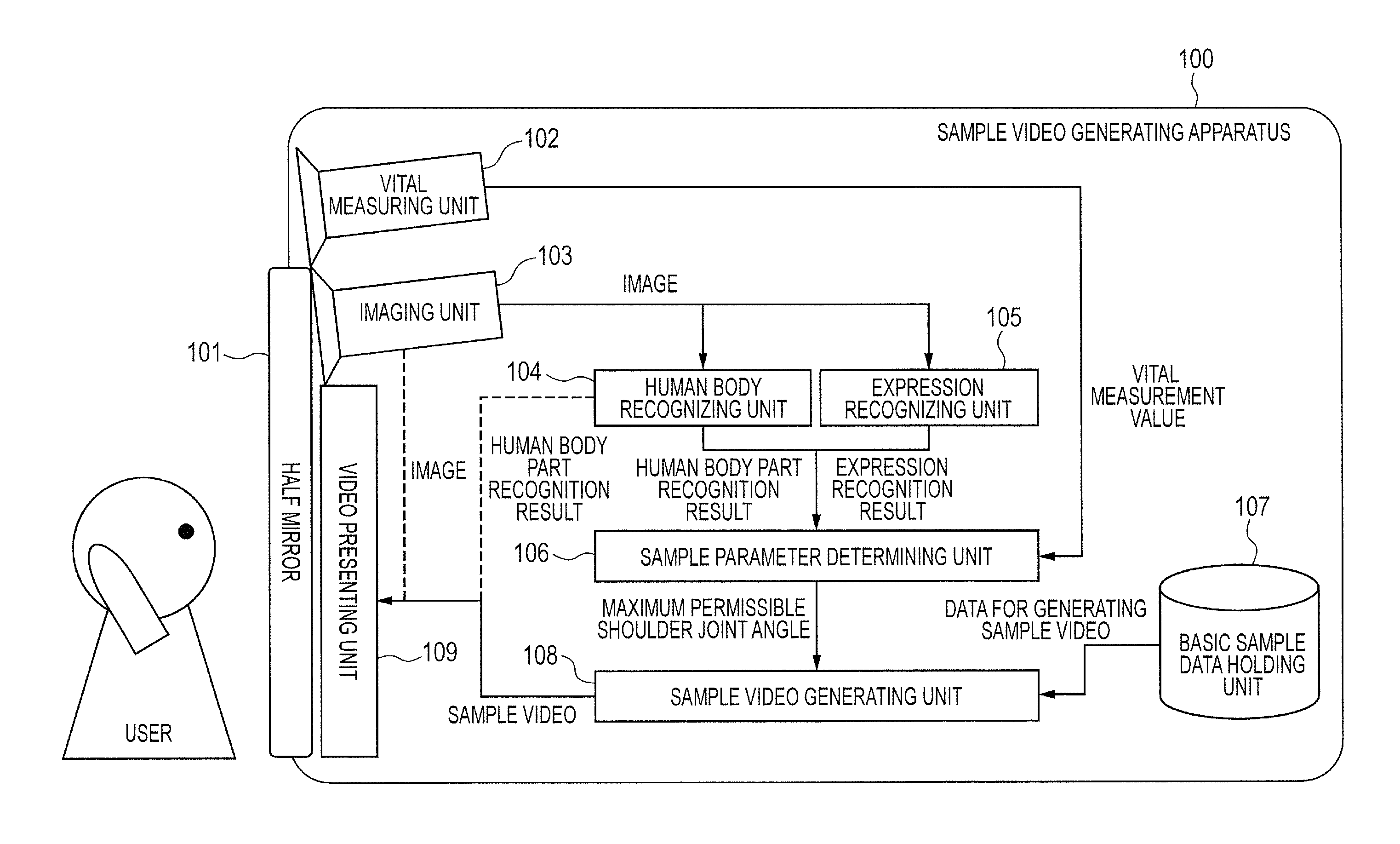
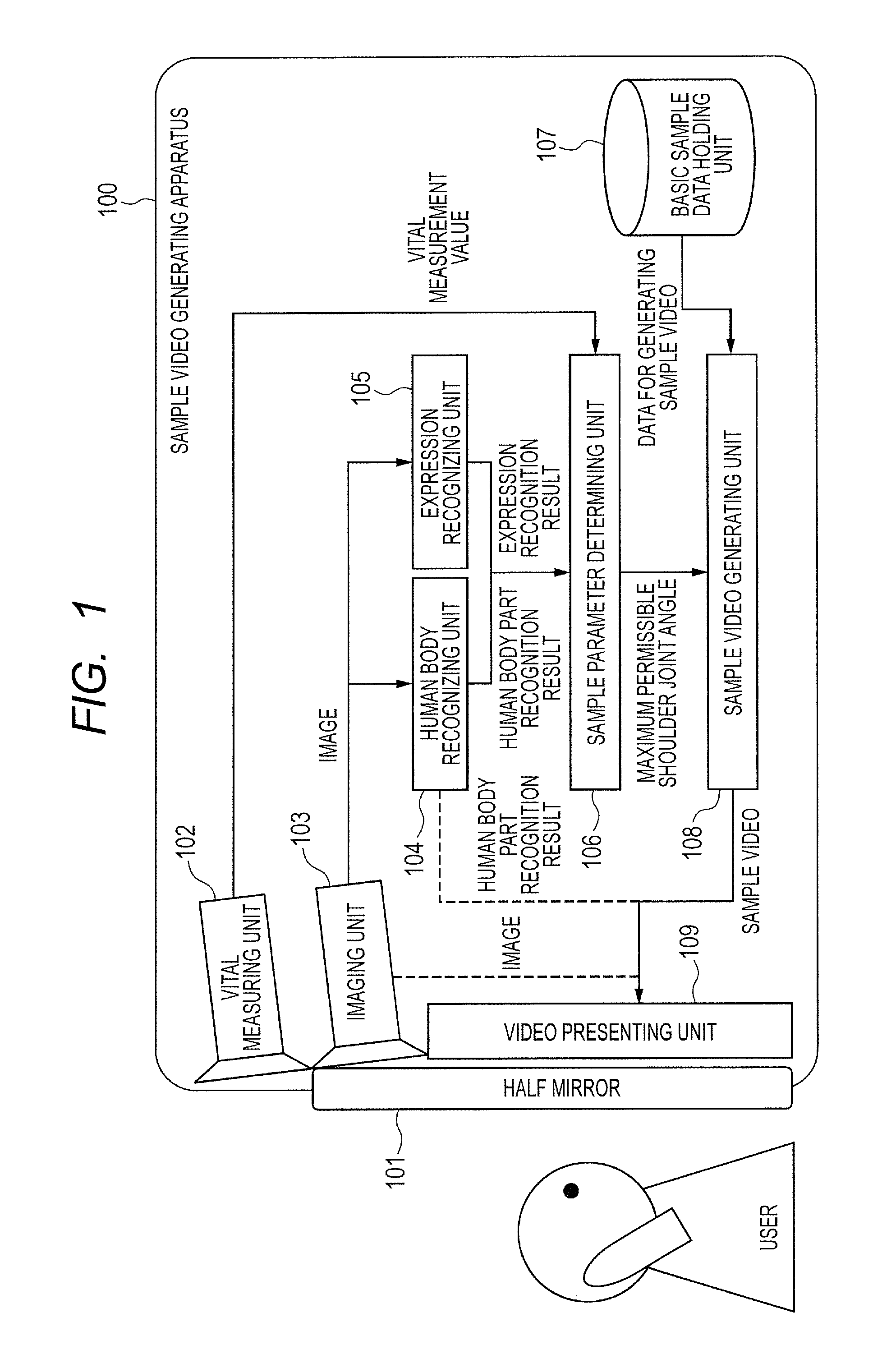
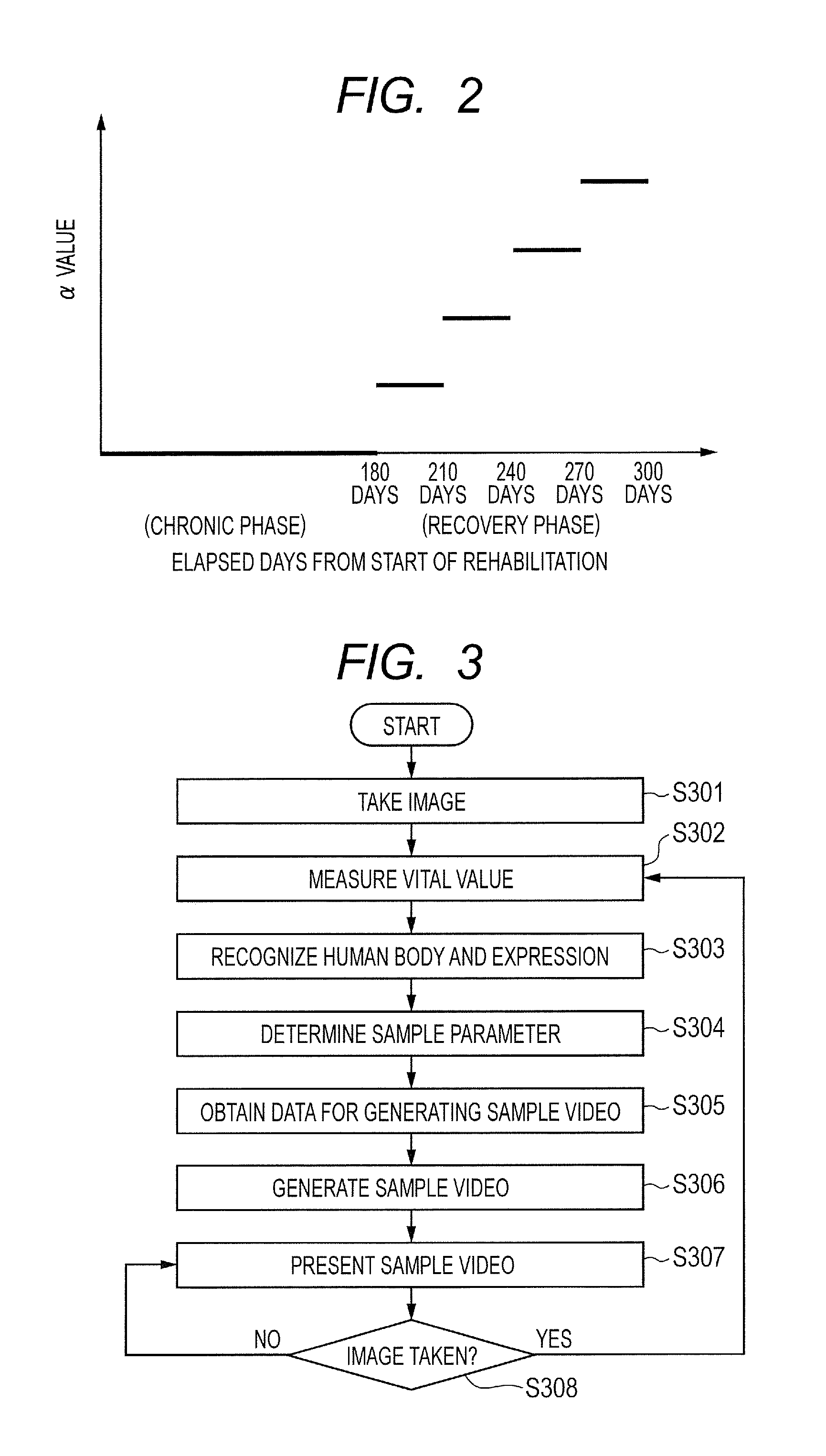
Video generating apparatus and method
ActiveUS20130141607A1Small timeLittle effortTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRange of motionComputer vision
A video generating apparatus comprises: an obtaining unit for obtaining an image in which a person has been taken; a human body recognizing unit recognizing a part of a human body of the person in the image; a holding unit for holding data concerning a basic video showing that the person exercises; a setting unit for setting a motion range of a specific part in the exercise of the person, on the basis of the recognized parts of the human body of the person; a video generating unit for generating, from the data concerning the basic video, a sample video for the person in the image on the basis of the motion range; and a display controlling unit for displaying the generated sample video on a displaying apparatus. Thus, it is possible to generate and show the sample video suitable for the person.
Owner:CANON KK
Retractable steering column with dual actuators
According to one exemplary embodiment of the present invention a steering column assembly is provided. The steering column assembly includes a steering column shaft. The steering column assembly further includes a retraction actuator to translate an adjustment actuator mounting plate within a retraction range. The steering column further includes an adjustment actuator mounted on the adjustment actuator mounting plate to translate a steering column bracket within an adjustment range. The steering column bracket translates the steering column shaft within a steering column shaft movement range. The steering column shaft movement range is a sum of the retraction range and the adjustment range.
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com