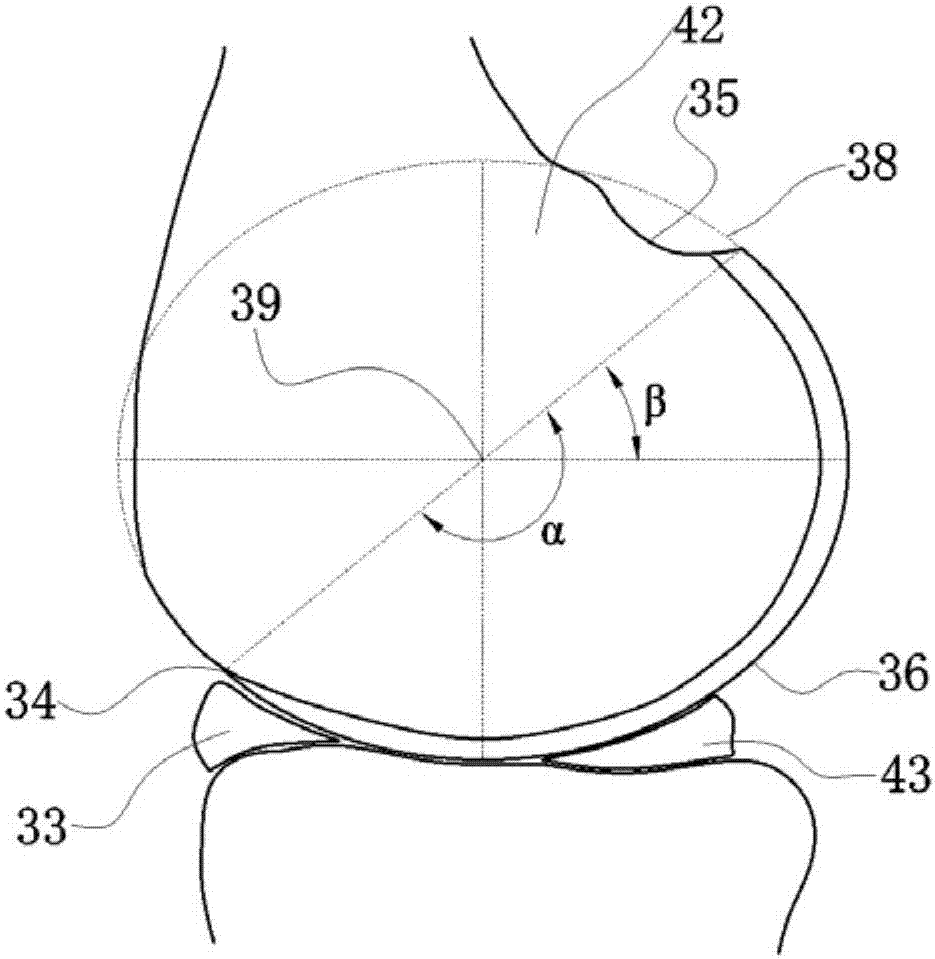
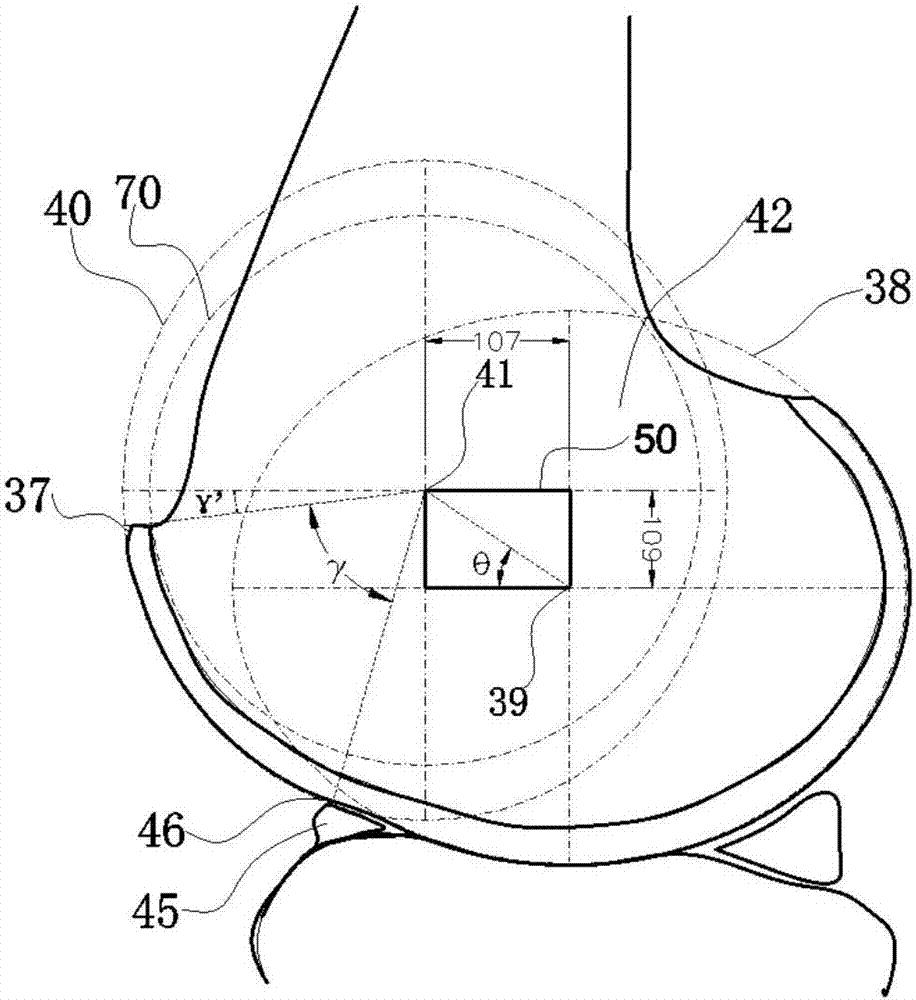
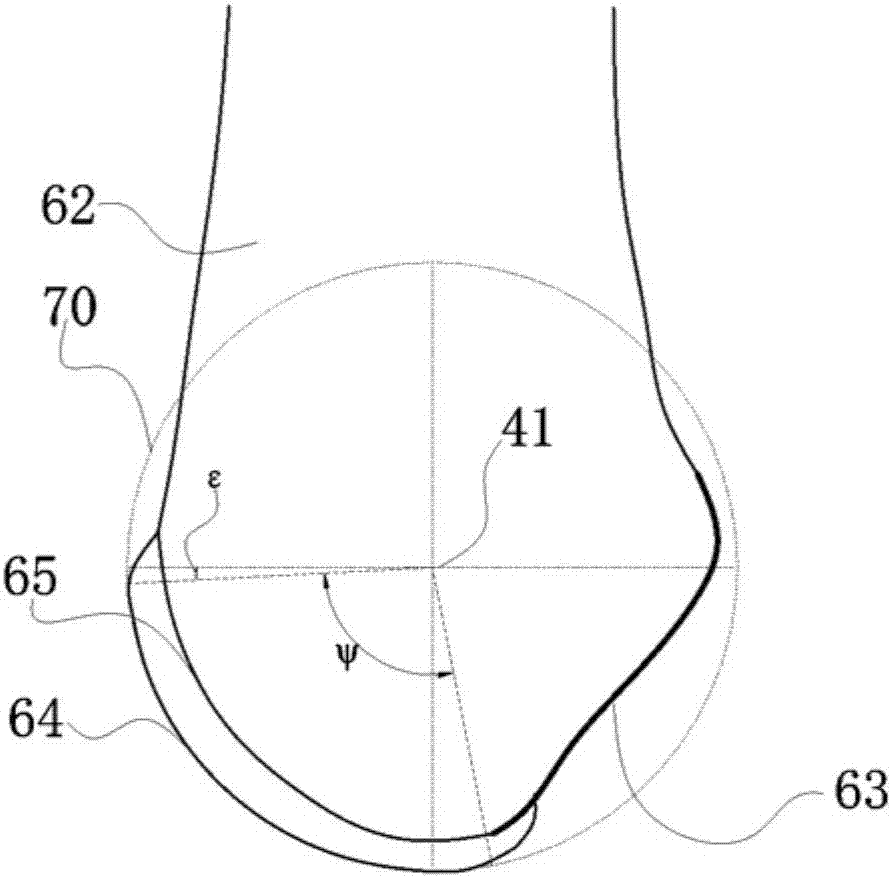
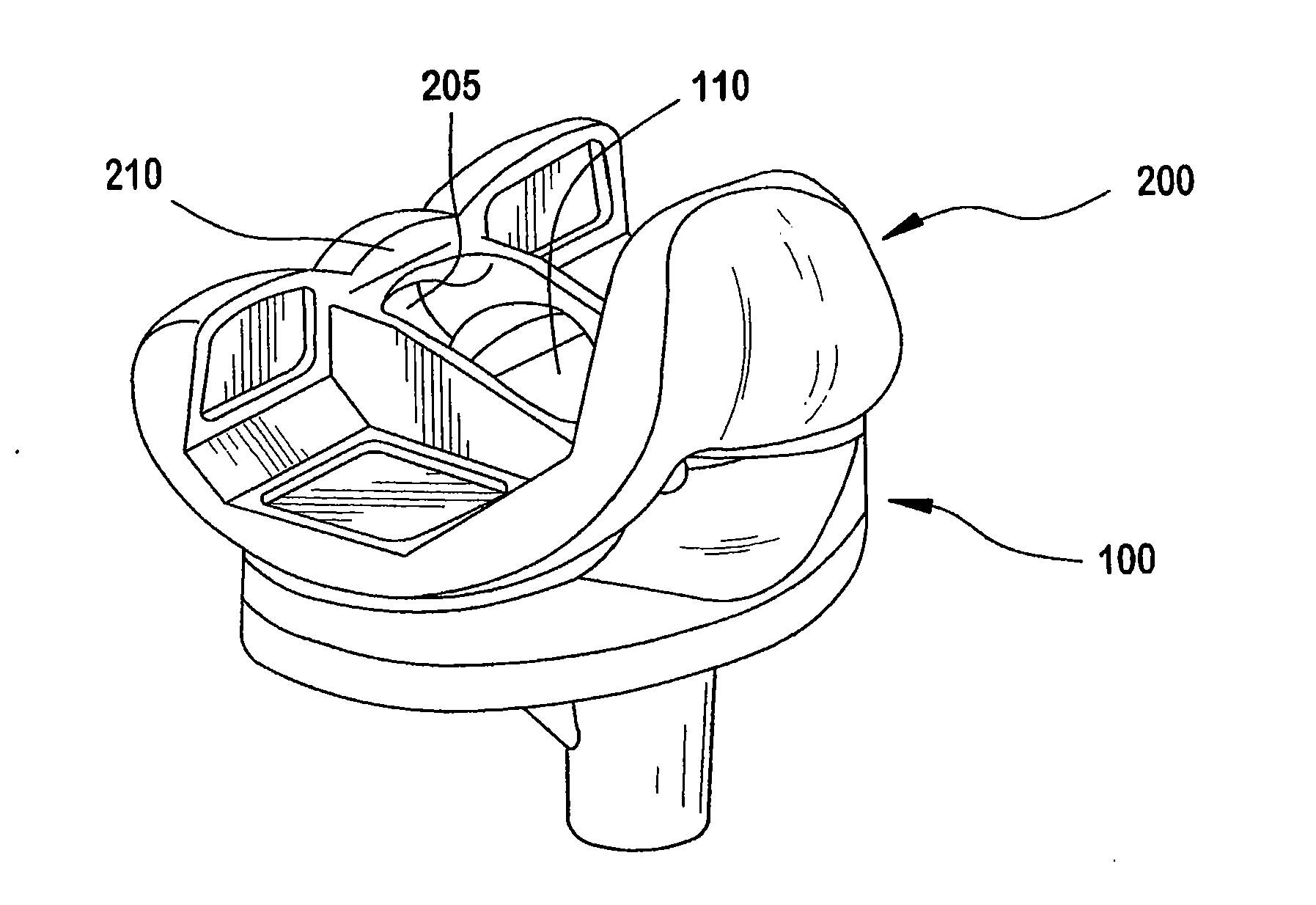
Patents
Literature
135 results about "Condyle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
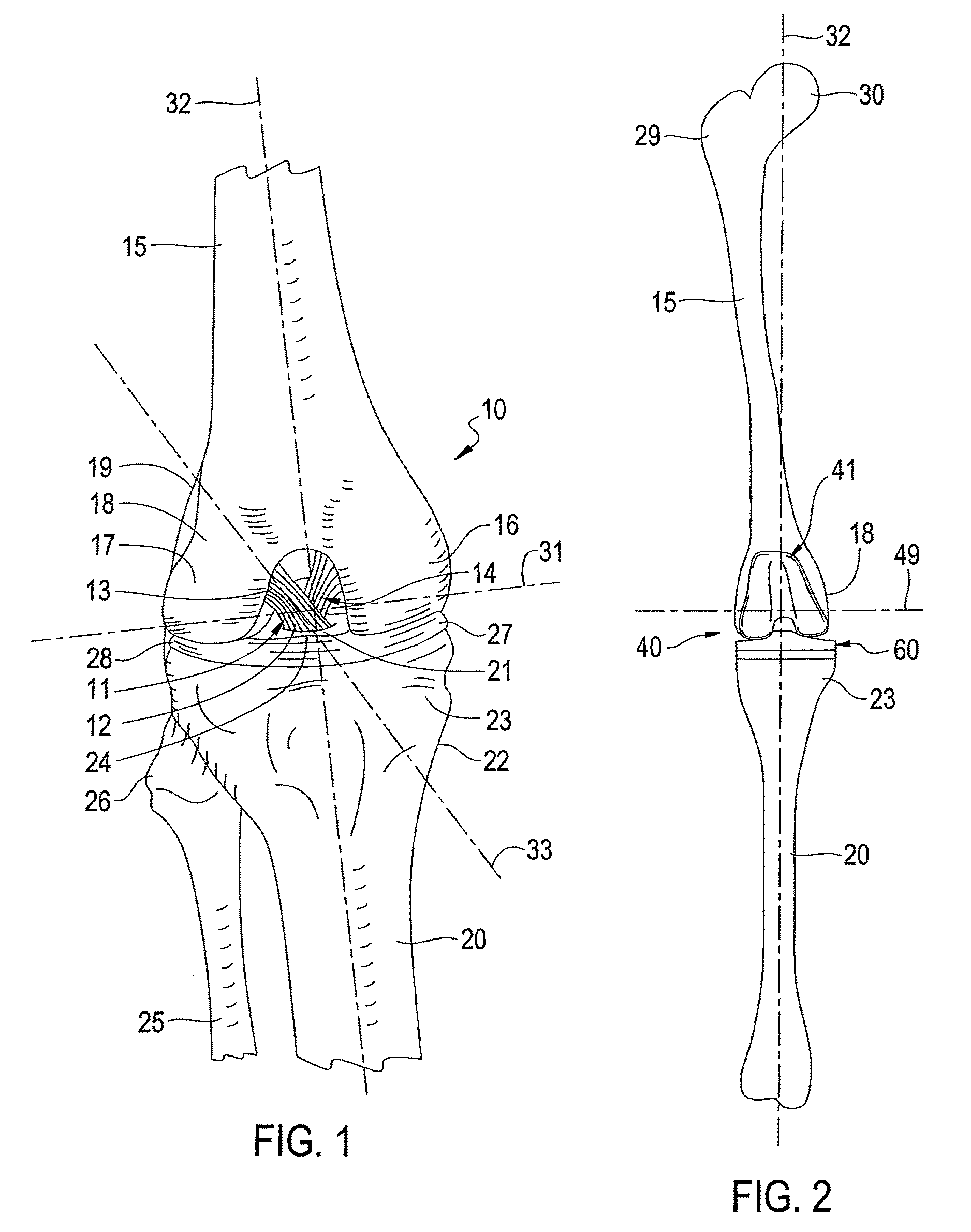
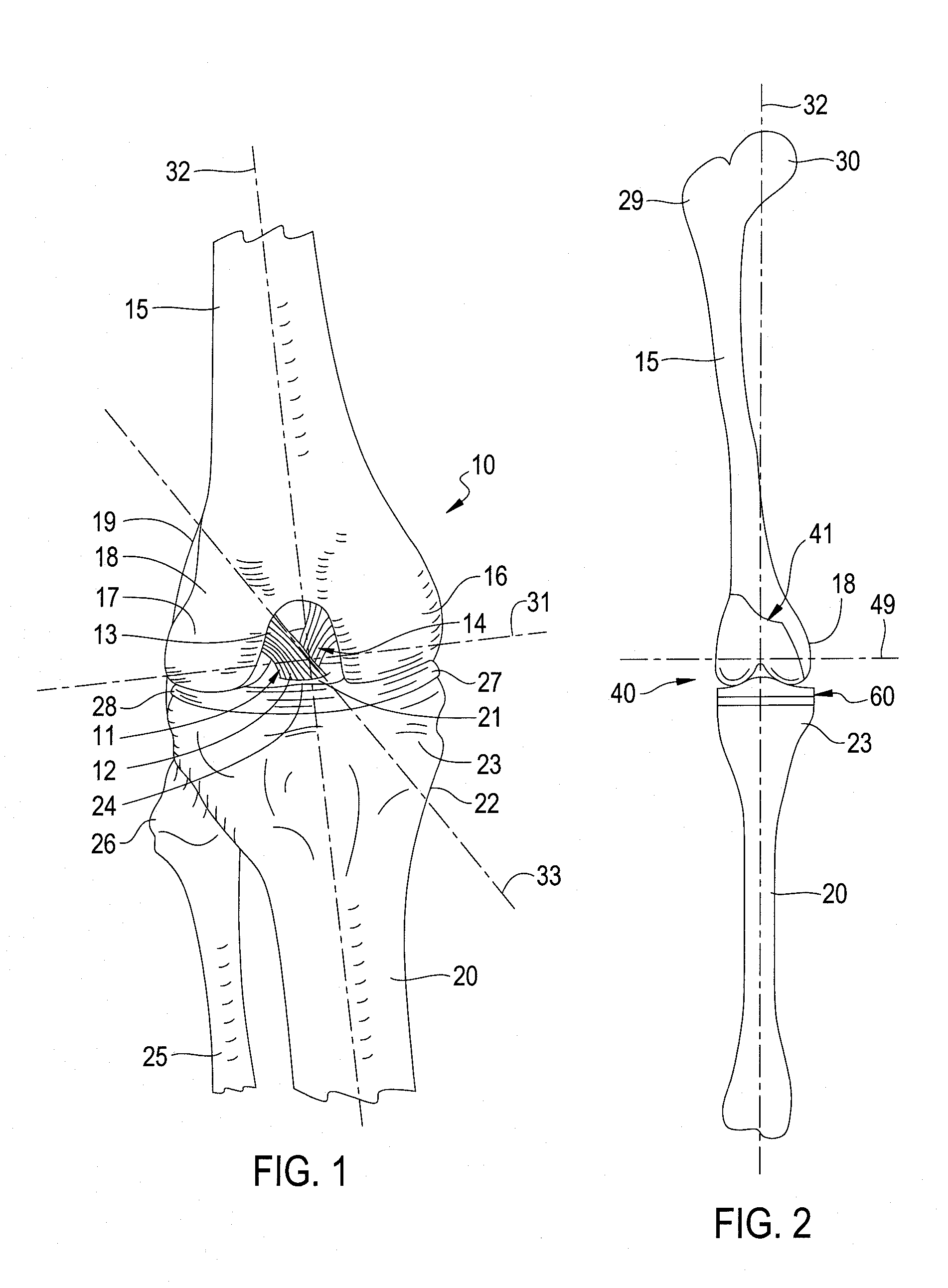
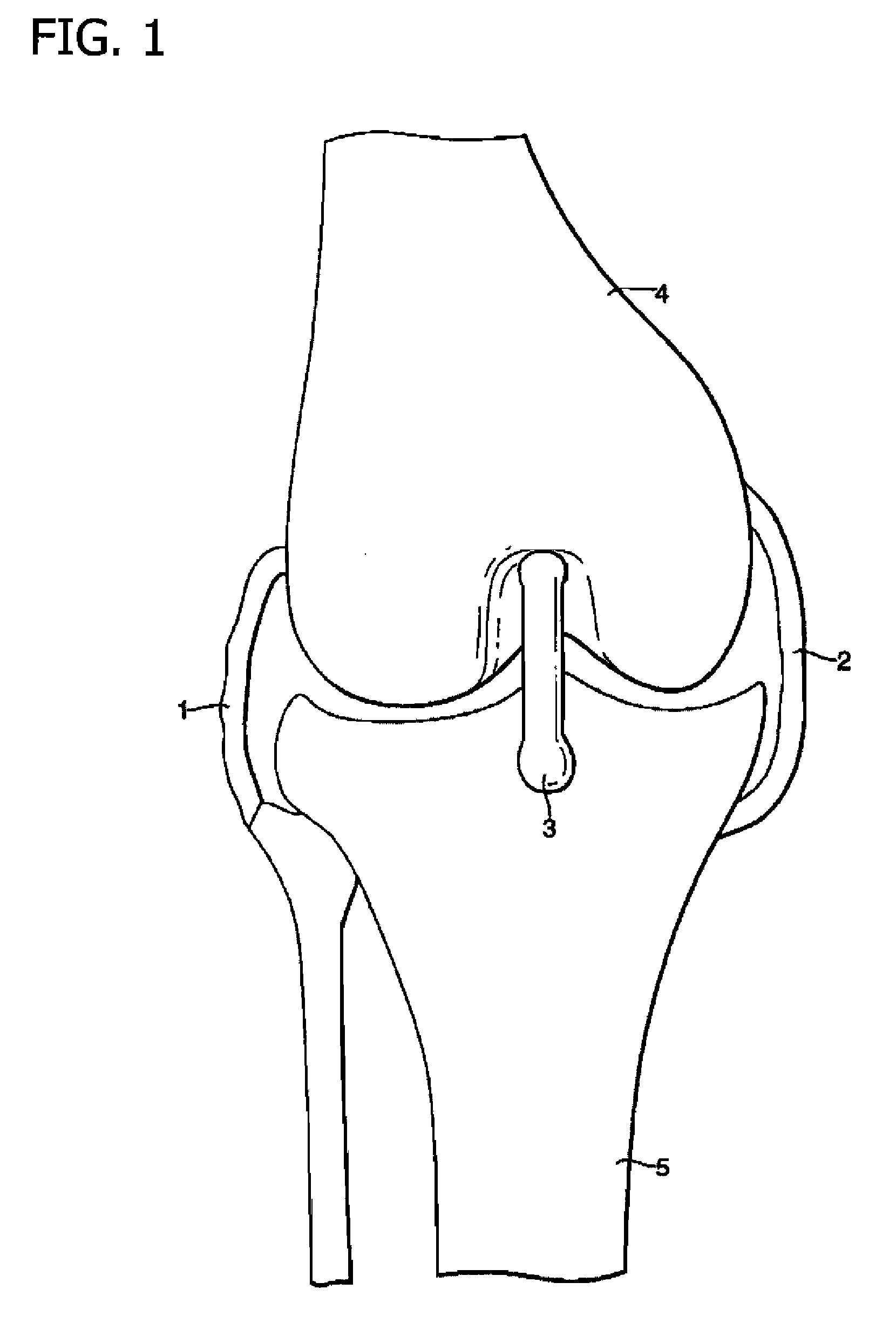
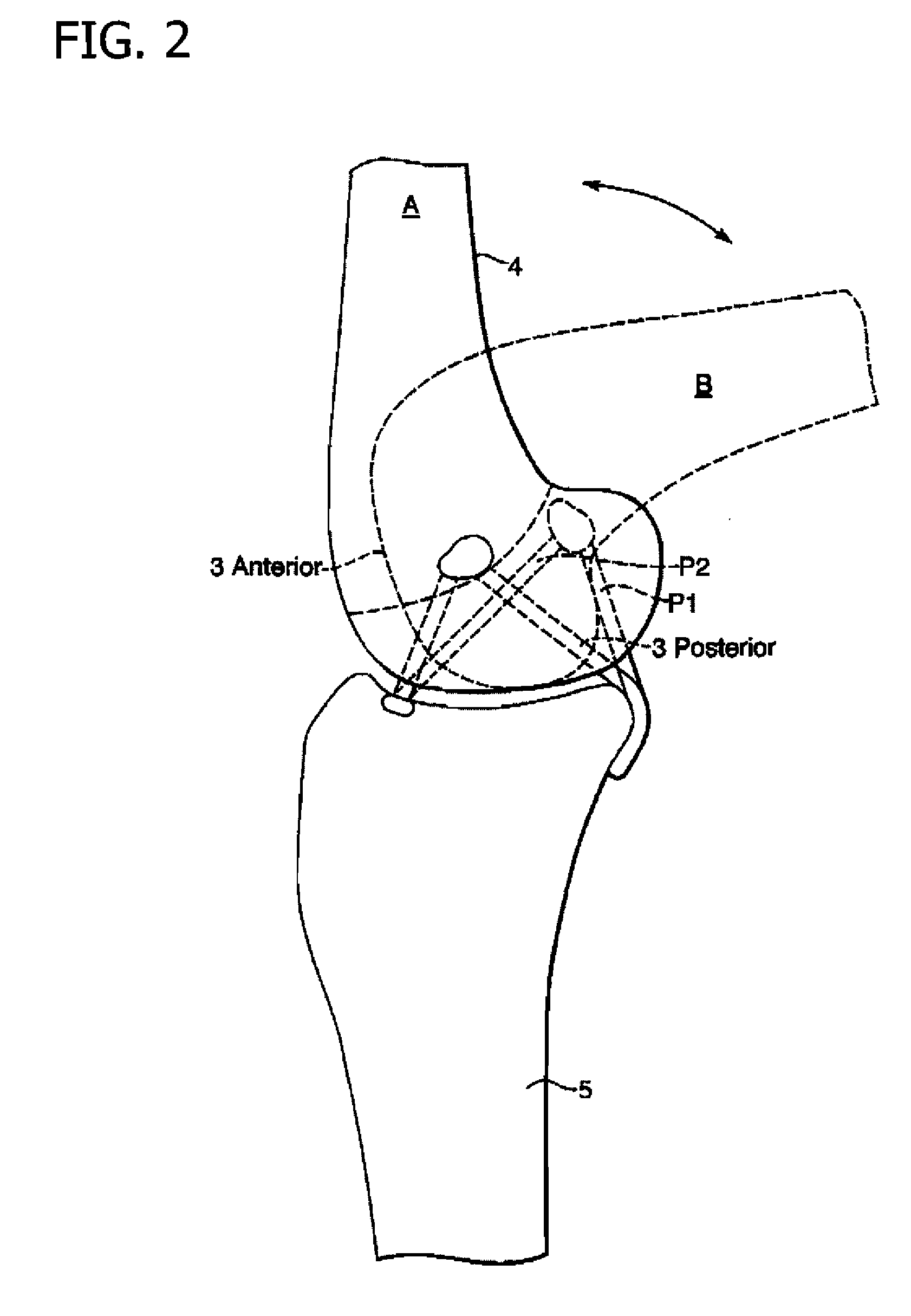
A condyle (/ˈkɒndəl/ or /ˈkɒndaɪl/; Latin: condylus, from Greek: kondylos; κόνδυλος knuckle) is the round prominence at the end of a bone, most often part of a joint - an articulation with another bone.
Methods for use in dental articulation
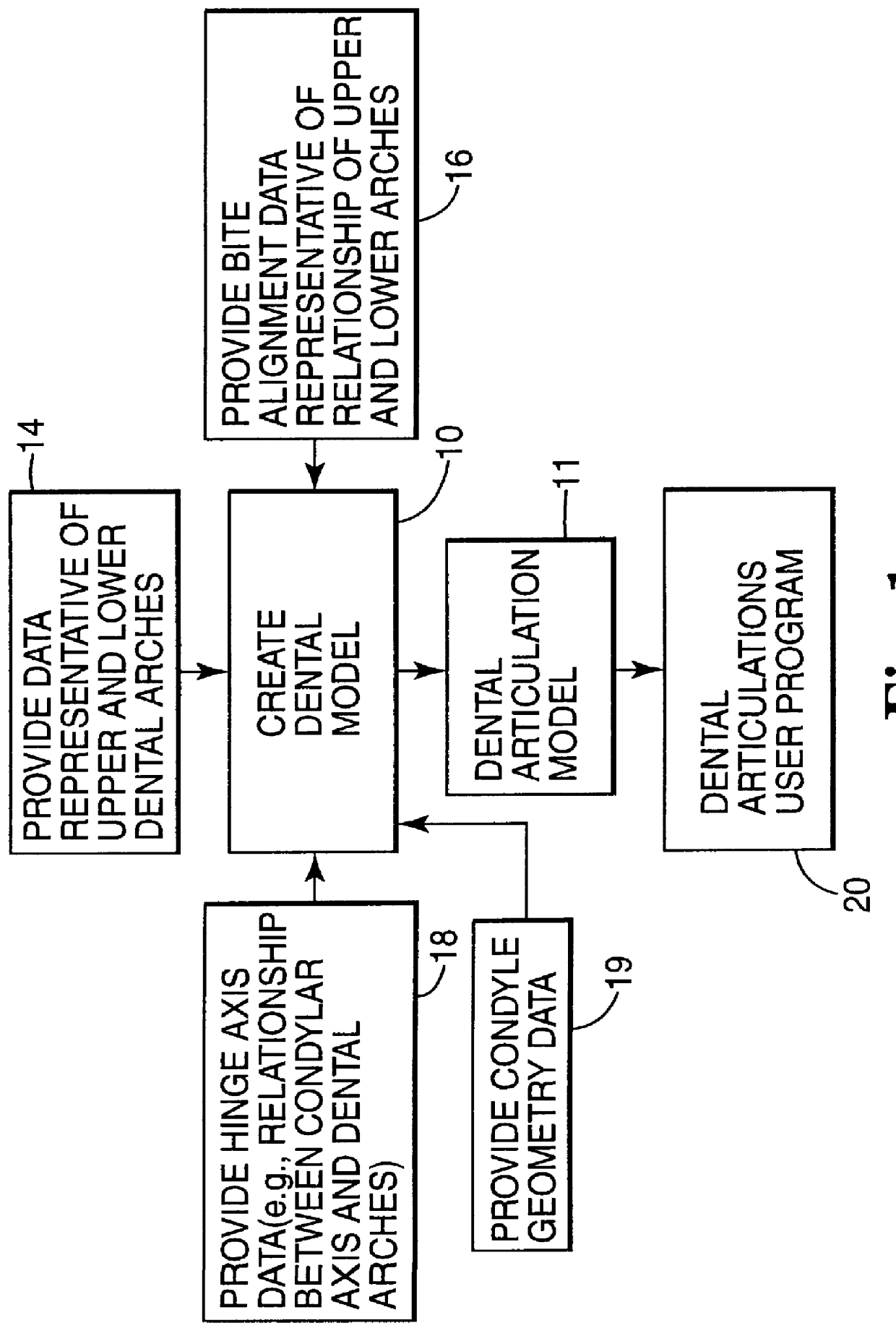
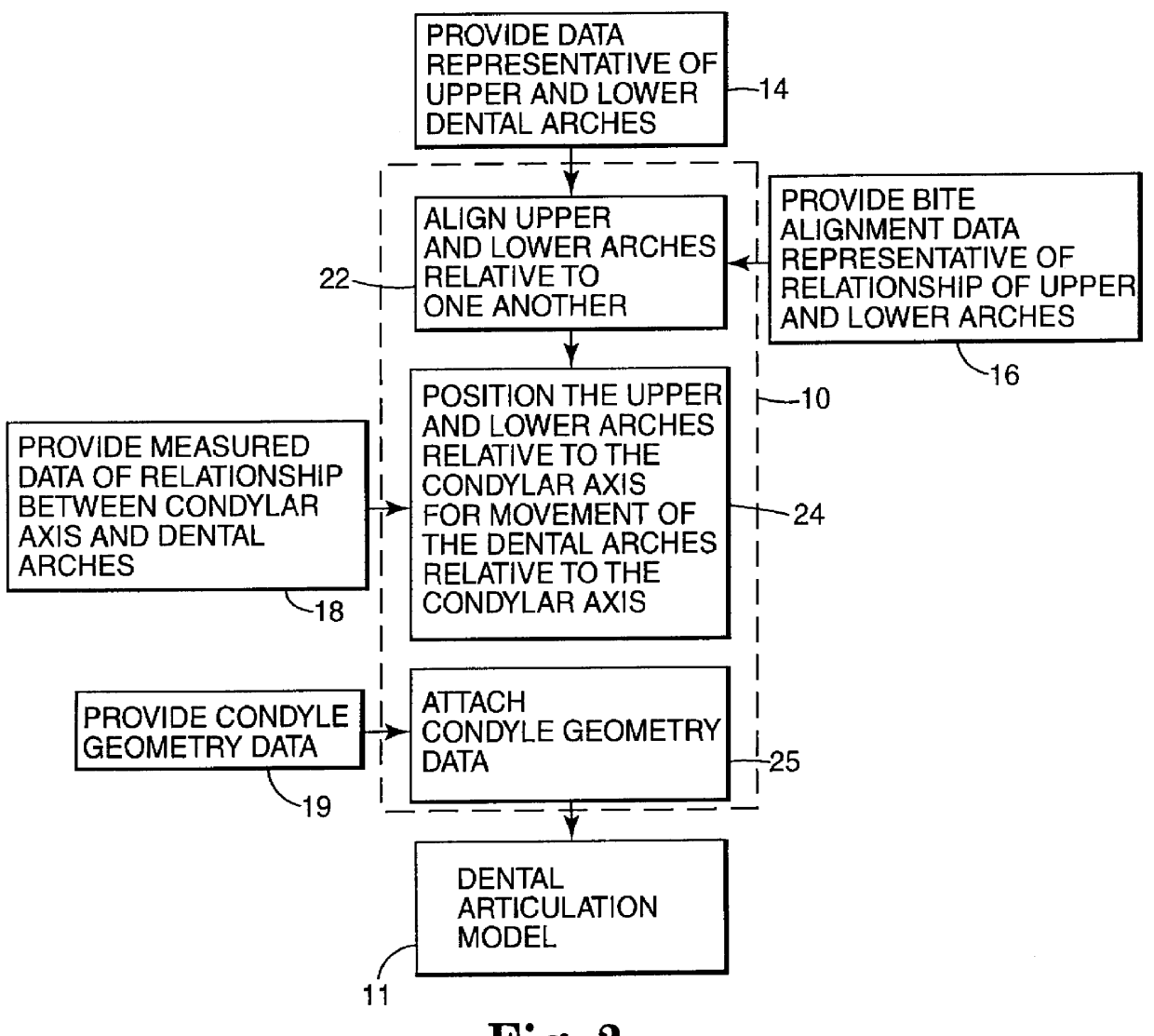
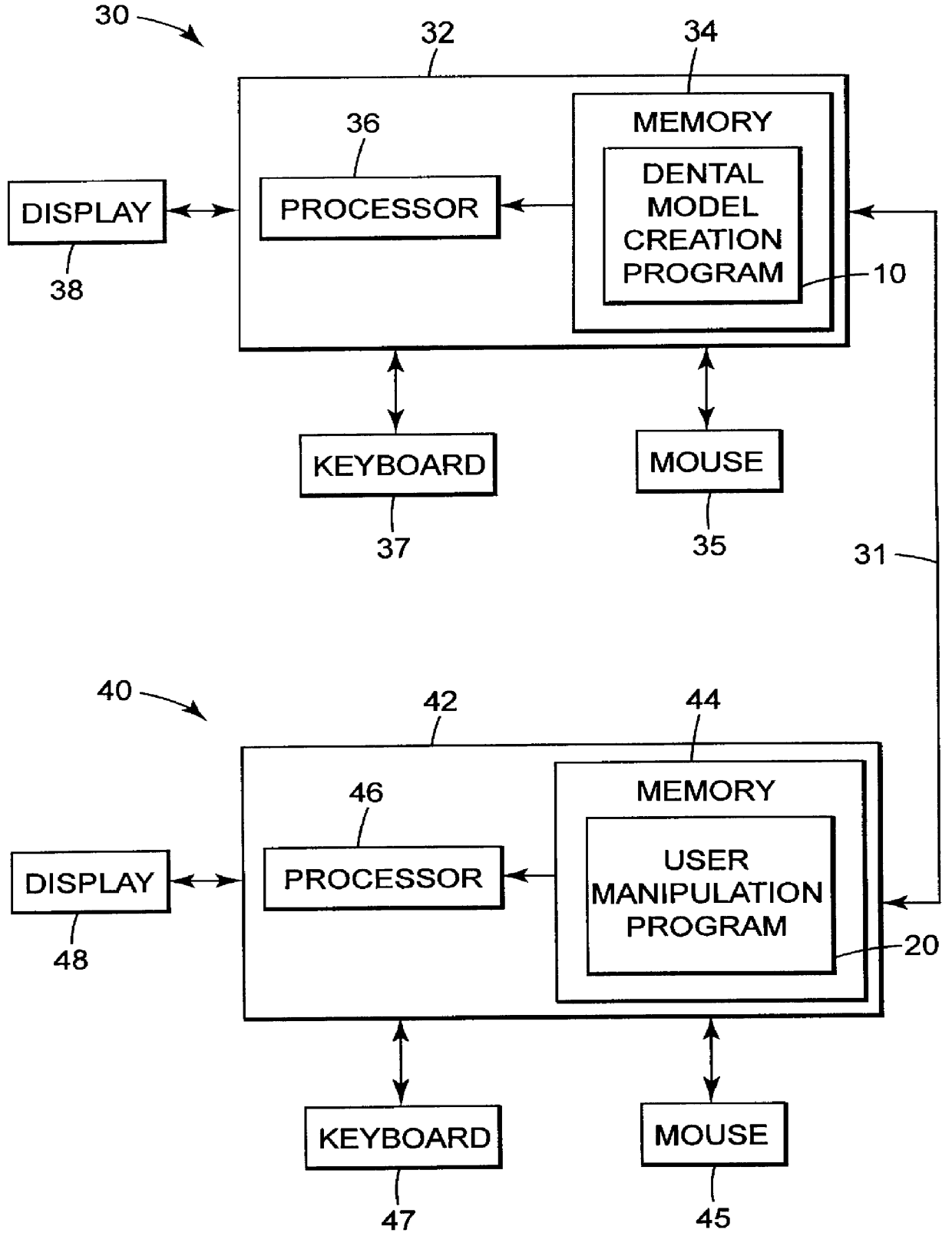
A computer implemented method of creating a dental model for use in dental articulation includes providing a first set of digital data corresponding to an upper arch image of at least a portion of an upper dental arch of a patient, providing a second set of digital data corresponding to a lower arch image of at least a portion of a lower dental arch of the patient, and providing hinge axis data representative of the spatial orientation of at least one of the upper and lower dental arches relative to a condylar axis of the patient. A reference hinge axis is created relative to the upper and lower arch images based on the hinge axis data. Further, the method may include bite alignment data for use in aligning the lower and upper arch images. Yet further, the method may include providing data associated with condyle geometry of the patient, so as to provide limitations on the movement of at least the lower arch image when the arch images are displayed. Further, a wobbling technique may be used to determine an occlusal position of the lower and upper dental arches. Various computer implemented methods of dental articulation are also described. For example, such dental articulation methods may include moving at least one of the upper and lower arch images to simulate relative movement of one of the upper and lower dental arches of the patient, may include displaying another image with the upper and lower dental arches of the dental articulation model, and / or may include playing back recorded motion of a patient's mandible using the dental articulation model.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO +1
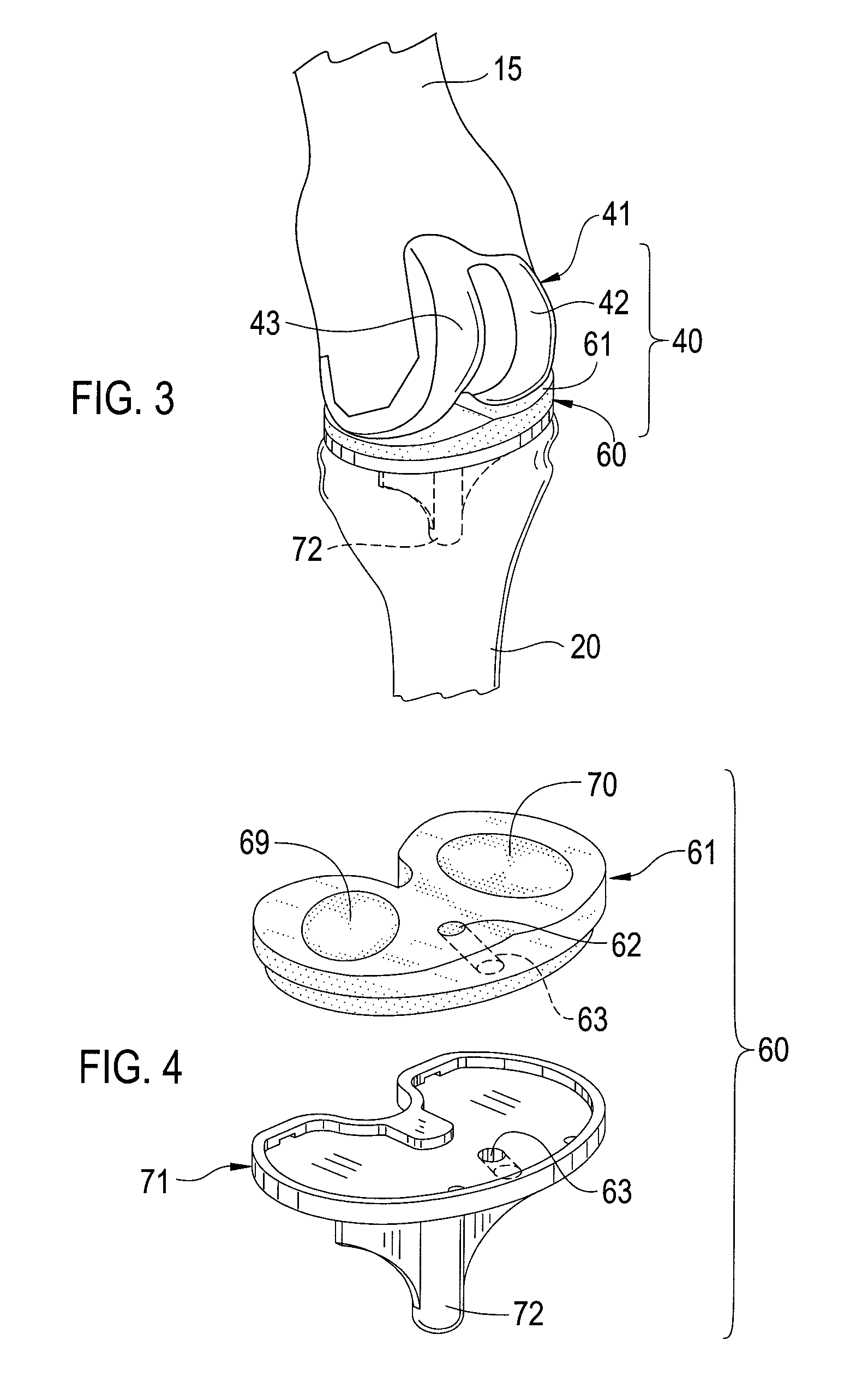
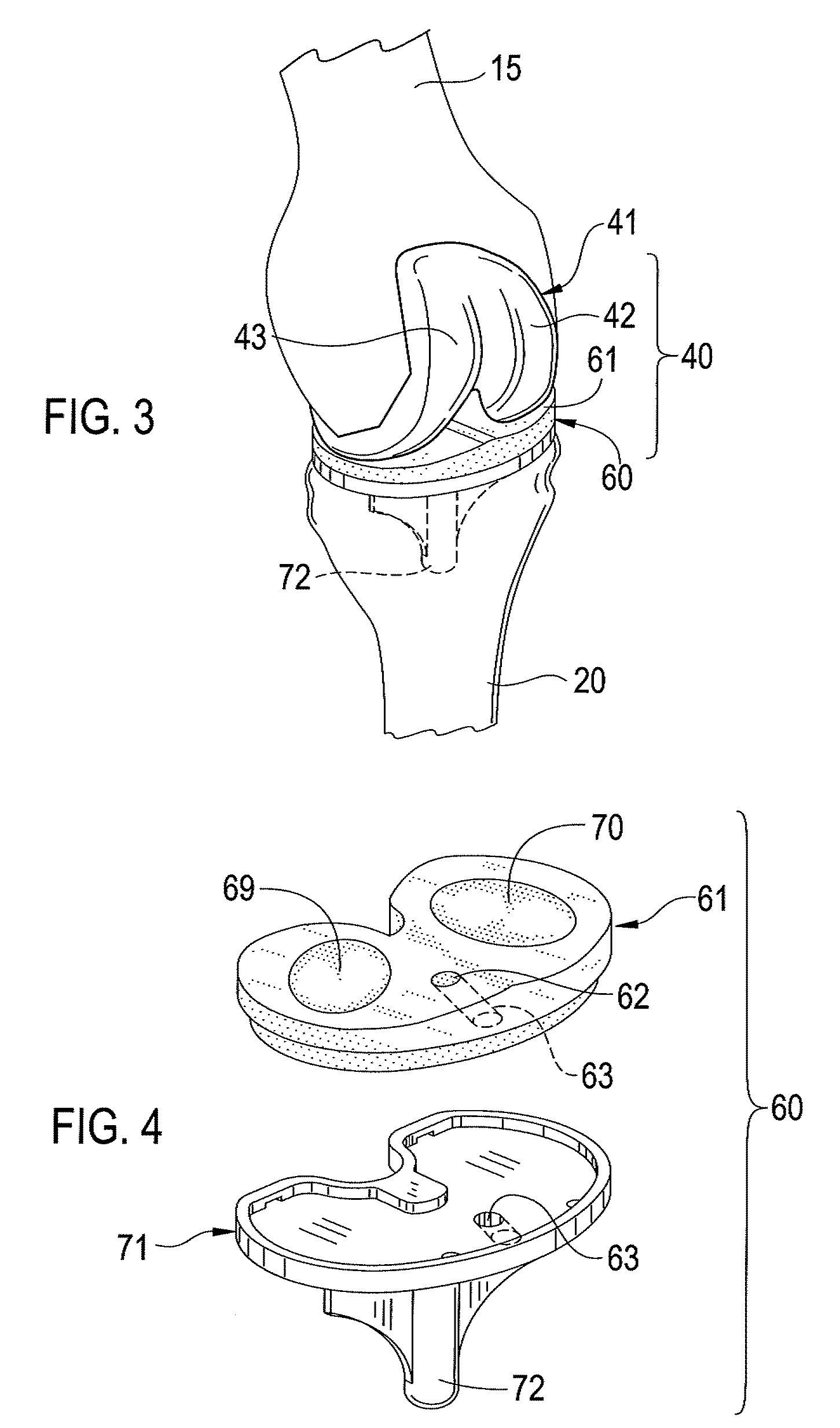
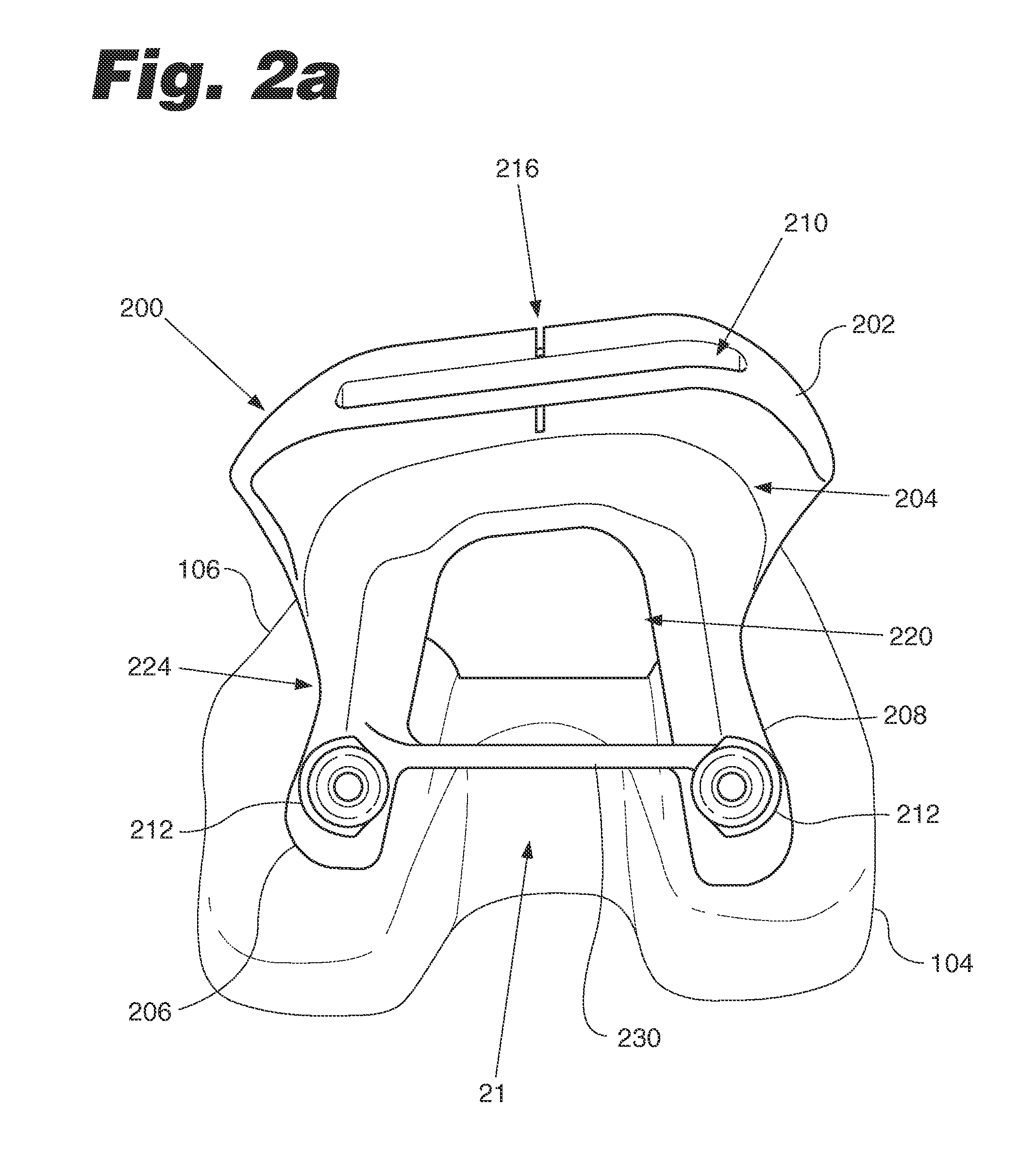
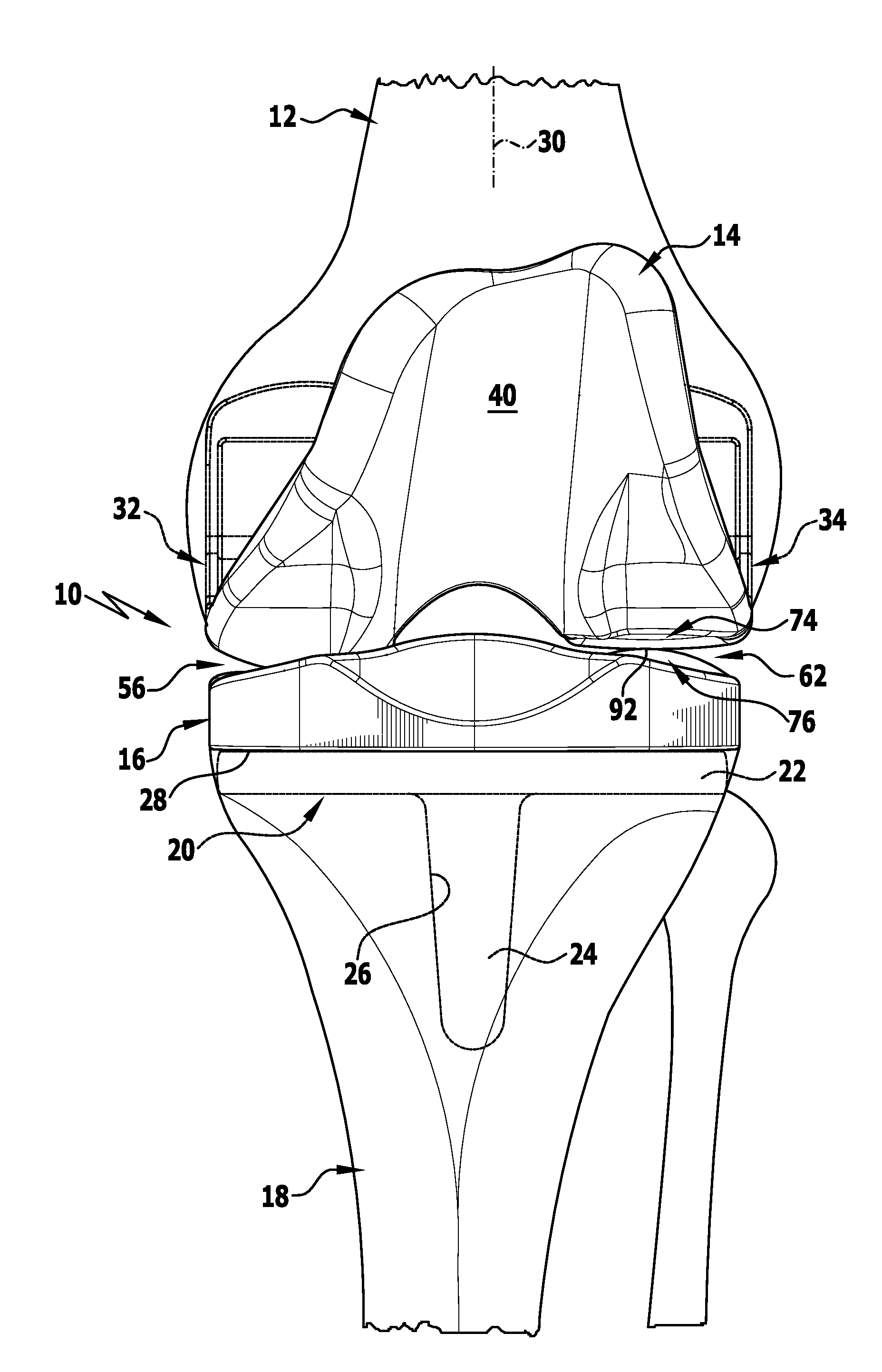
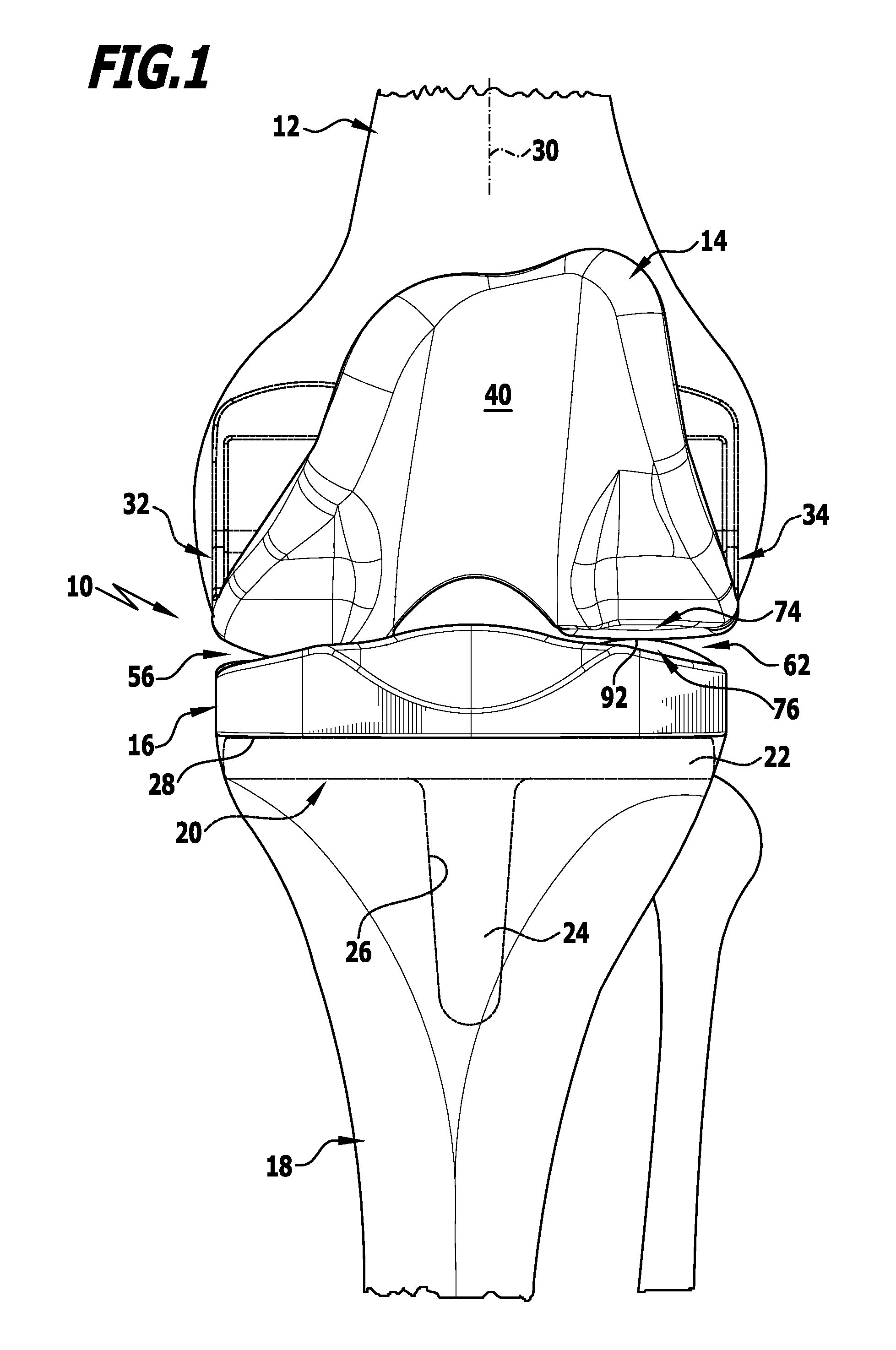
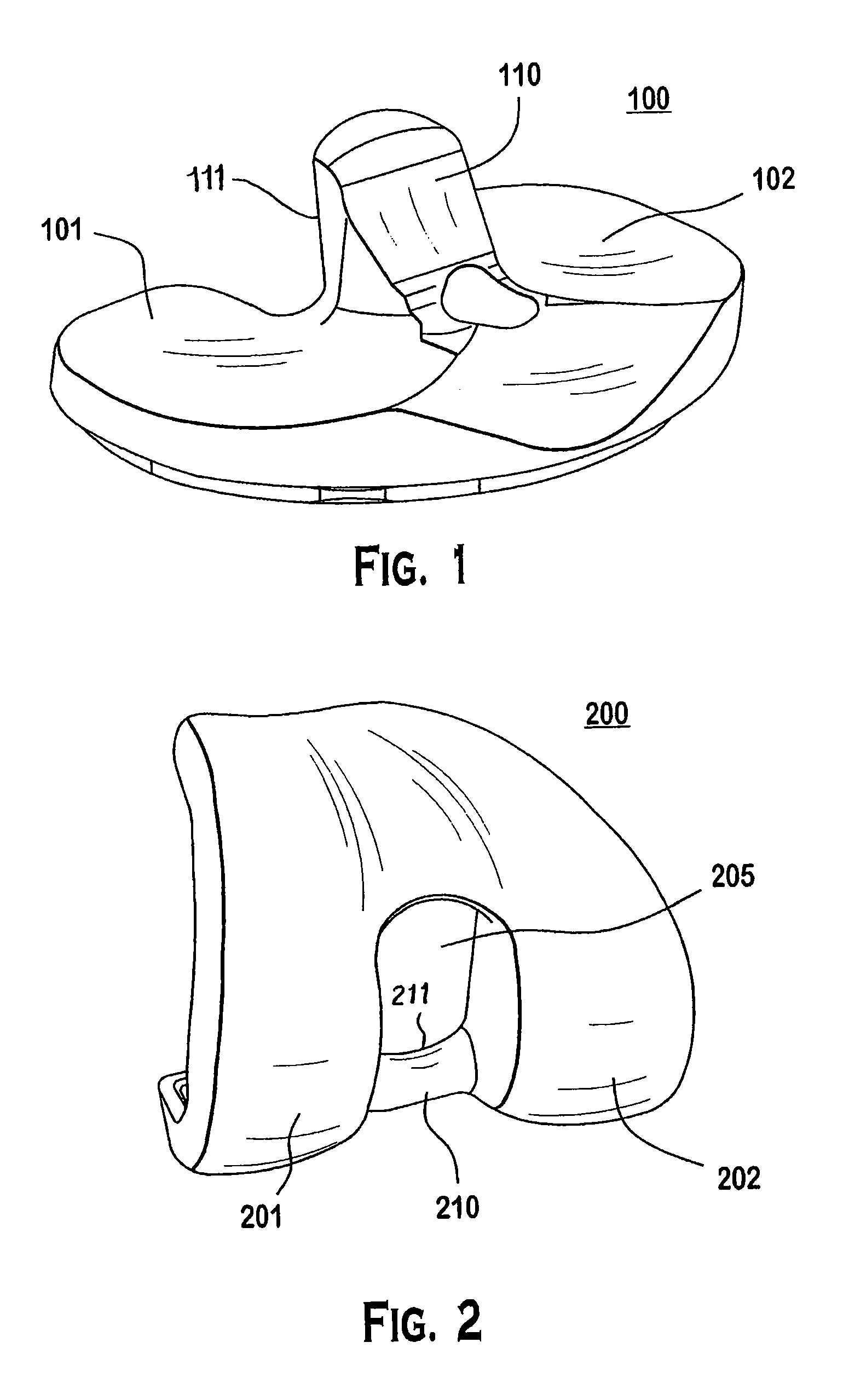
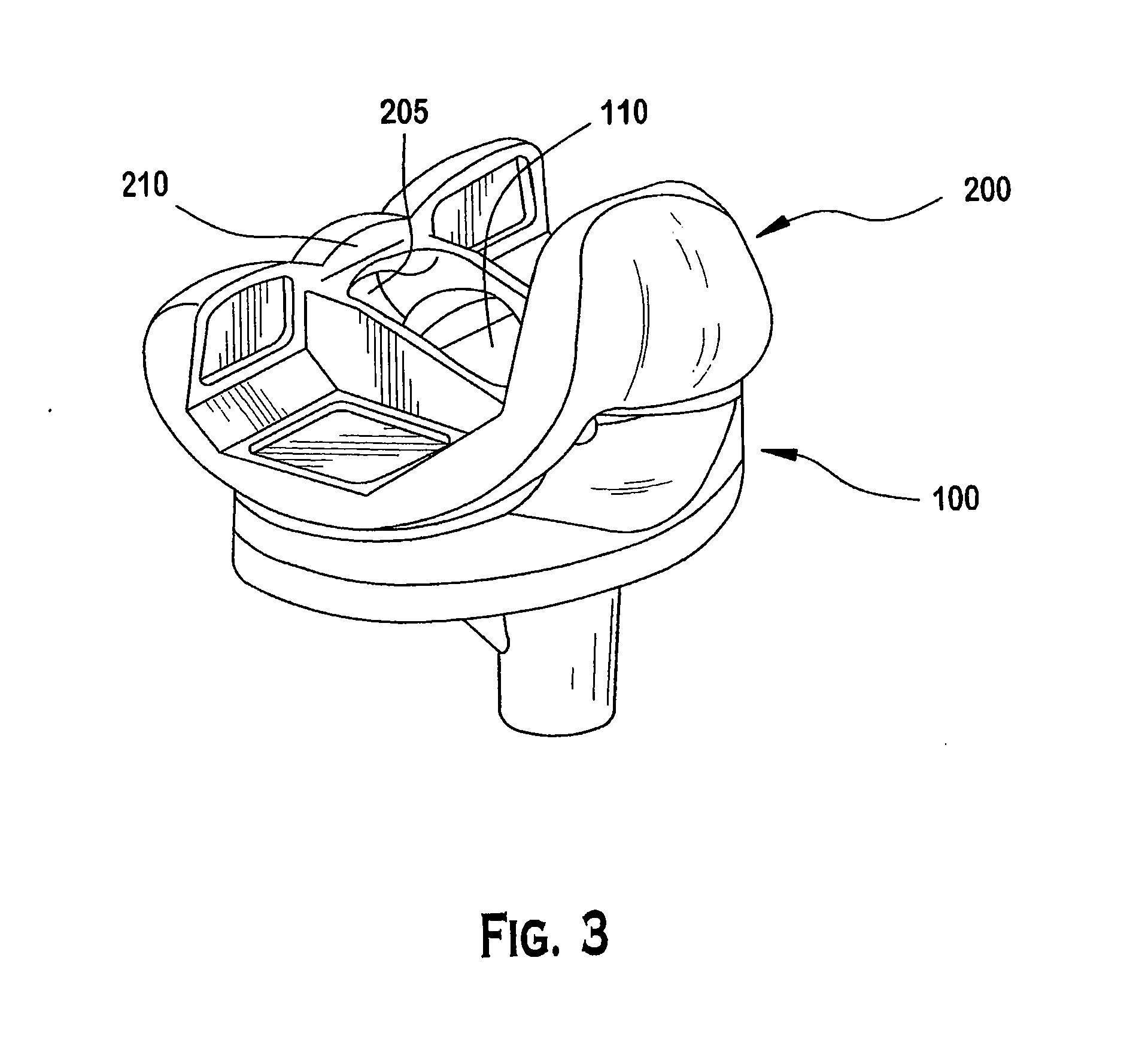
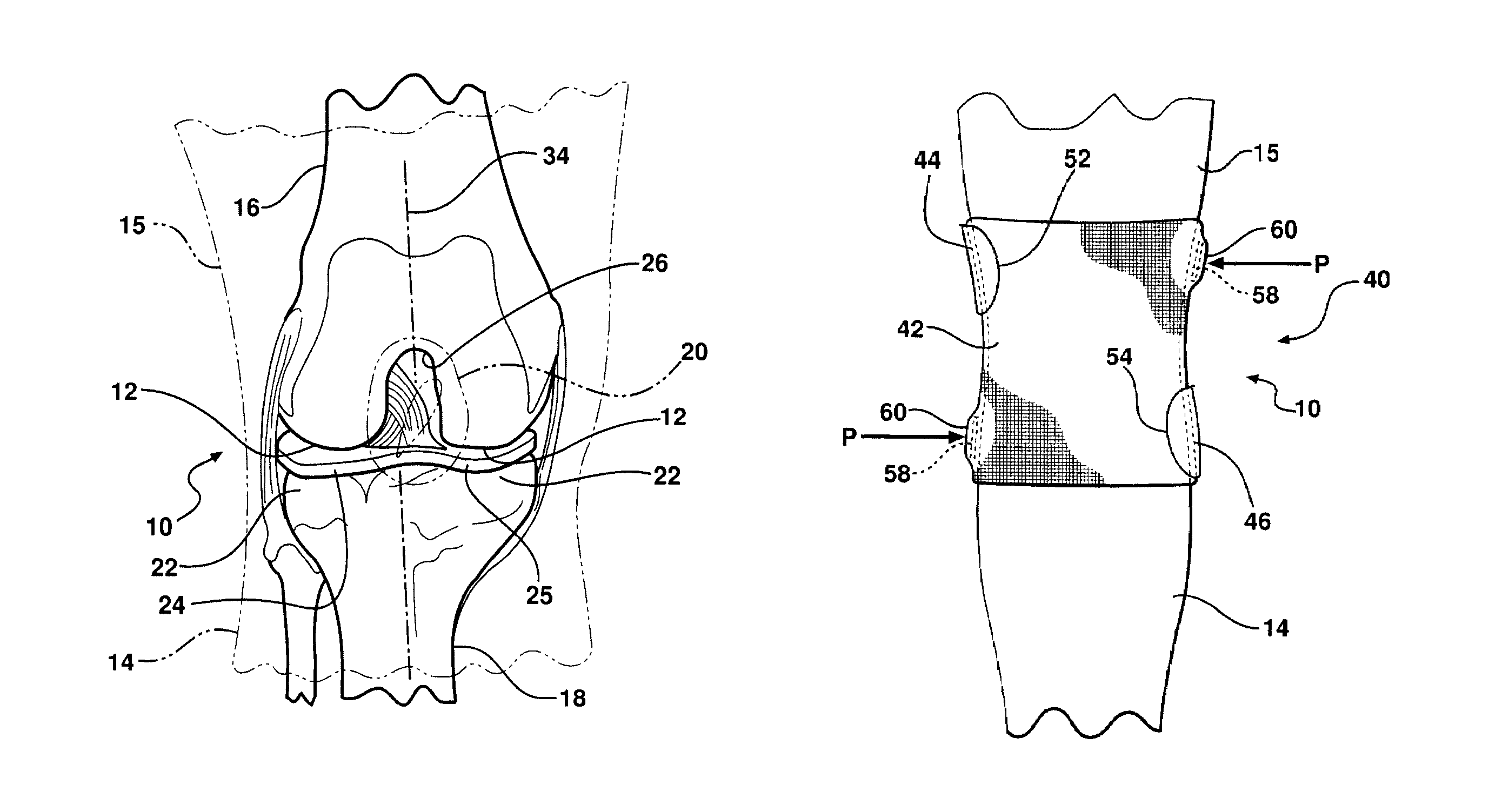
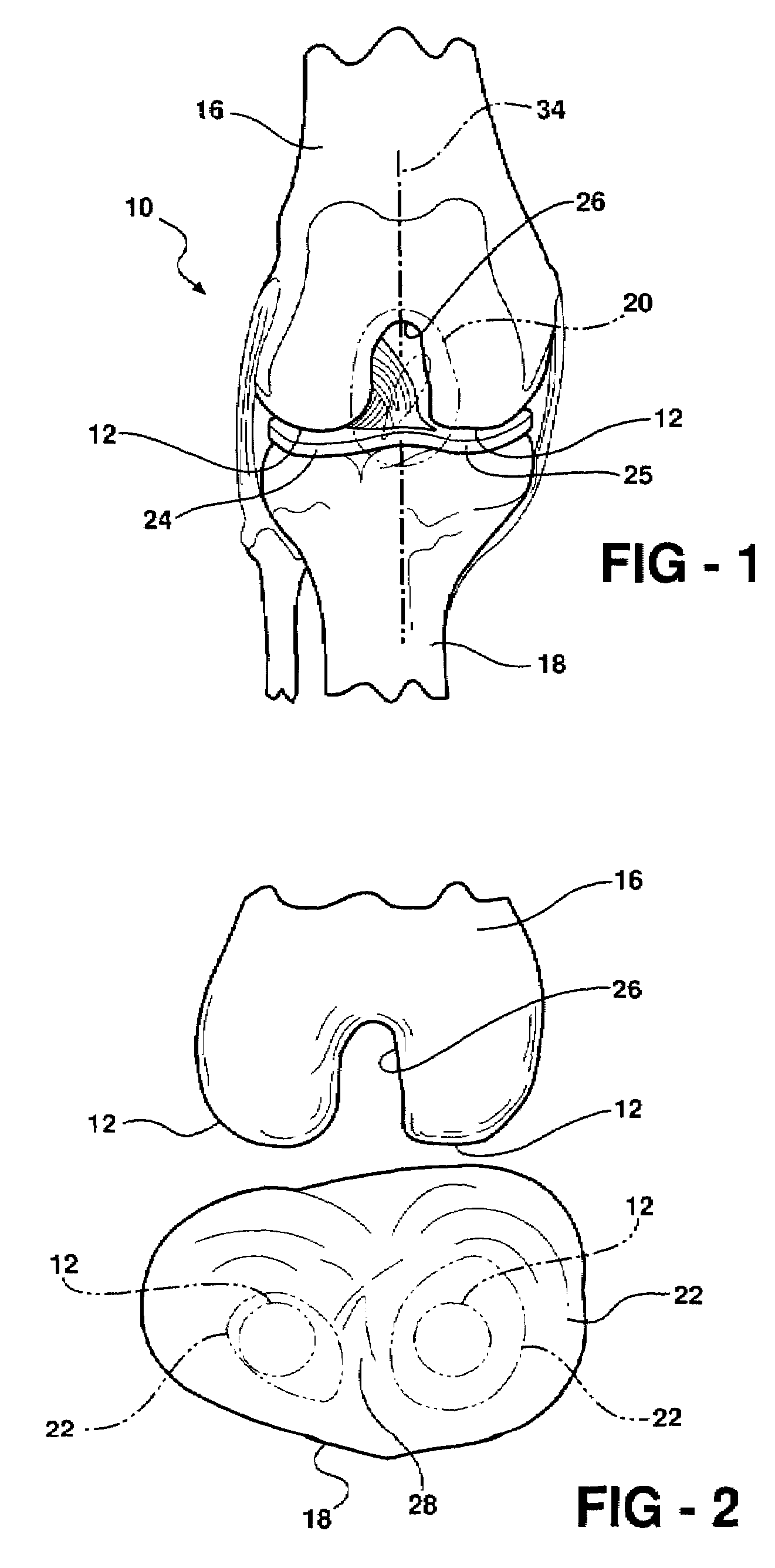
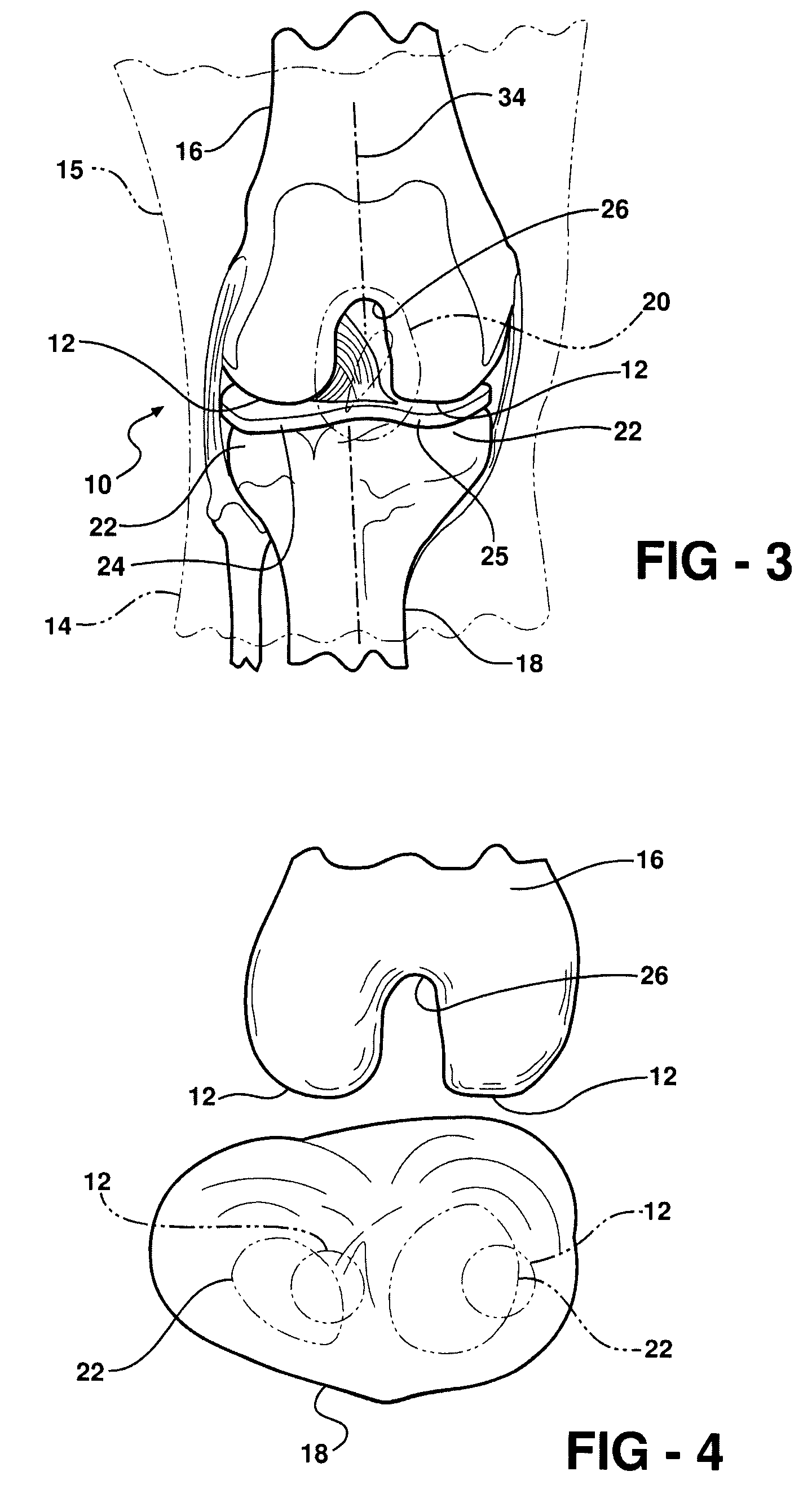
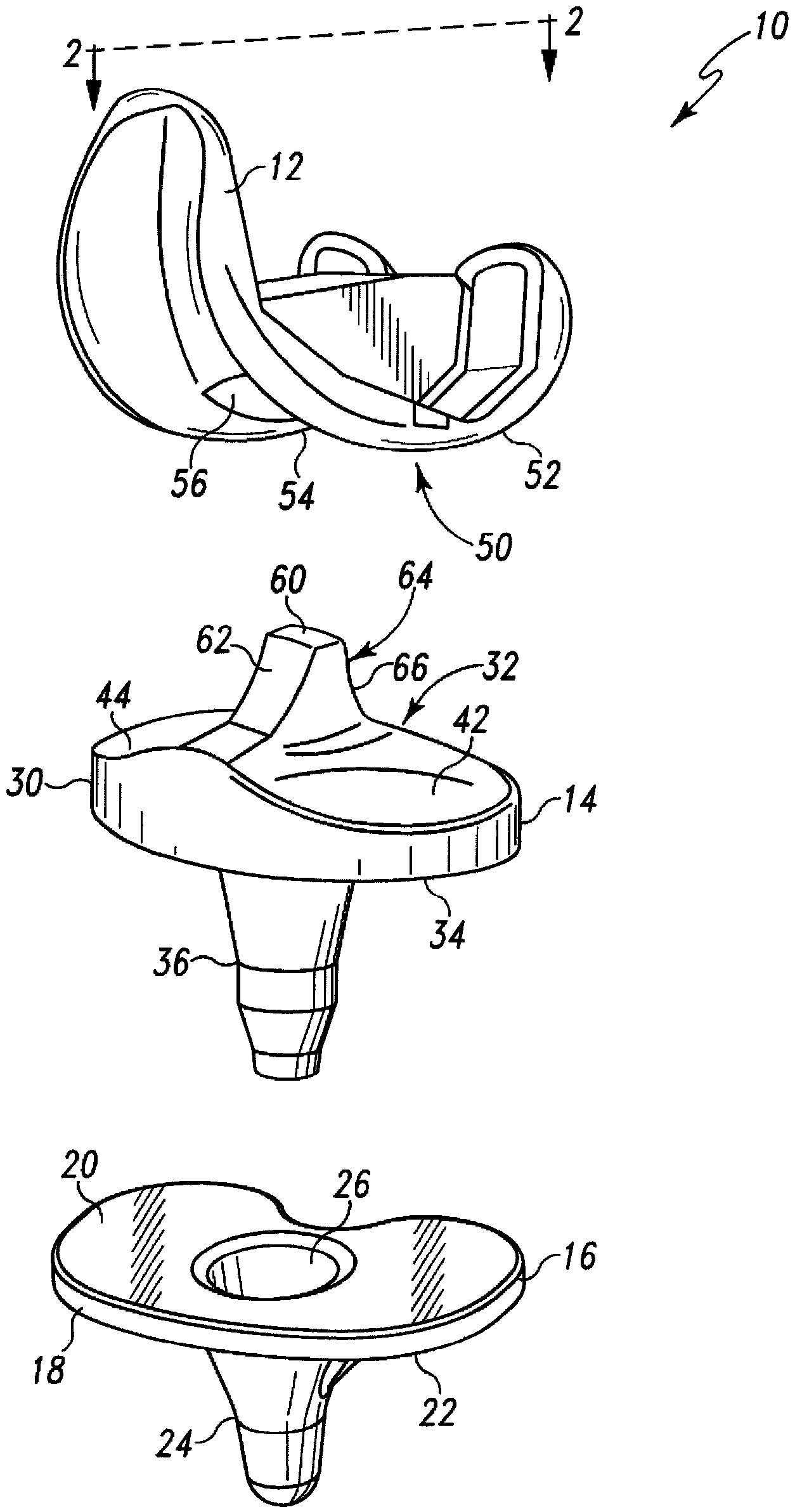
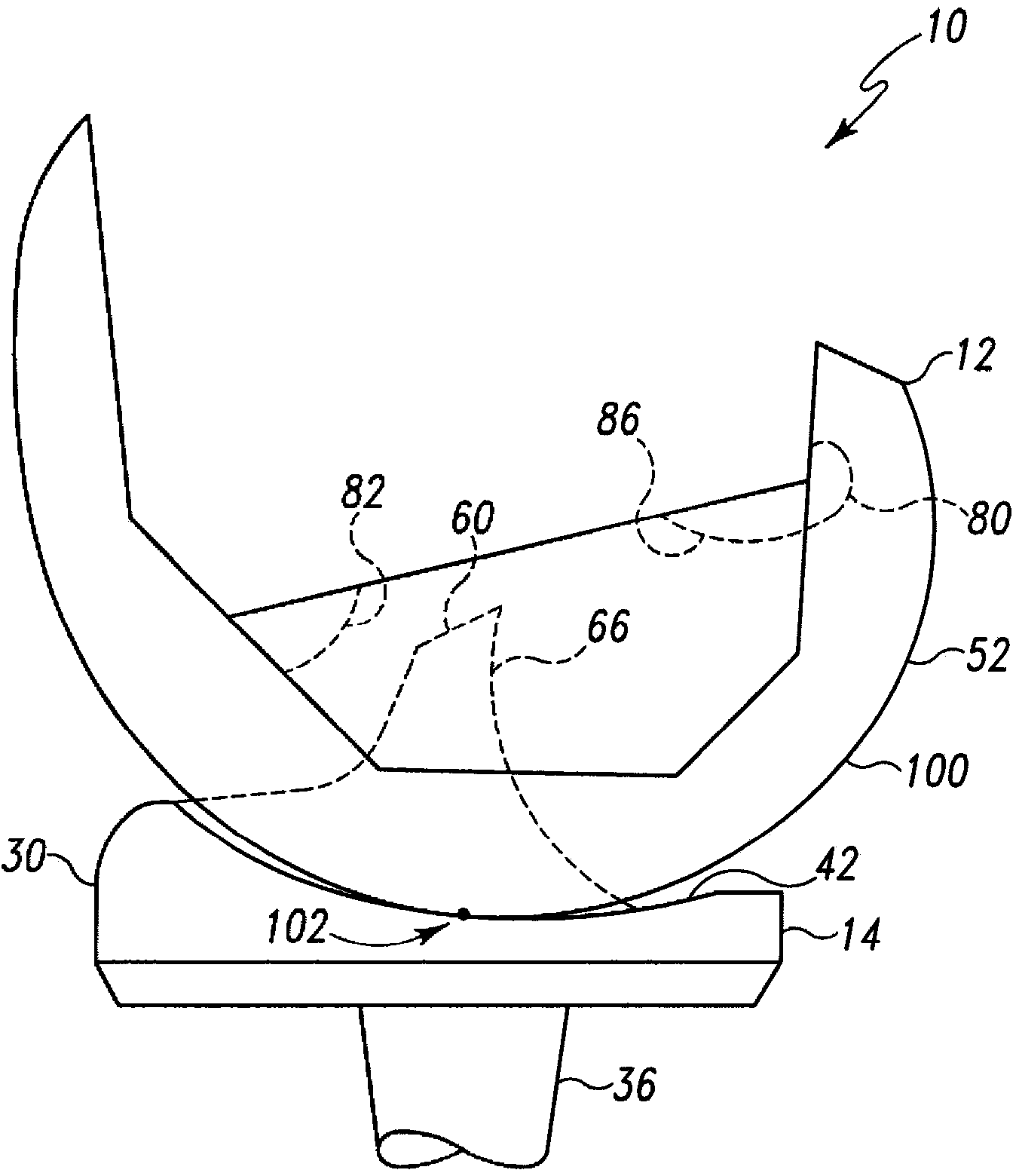
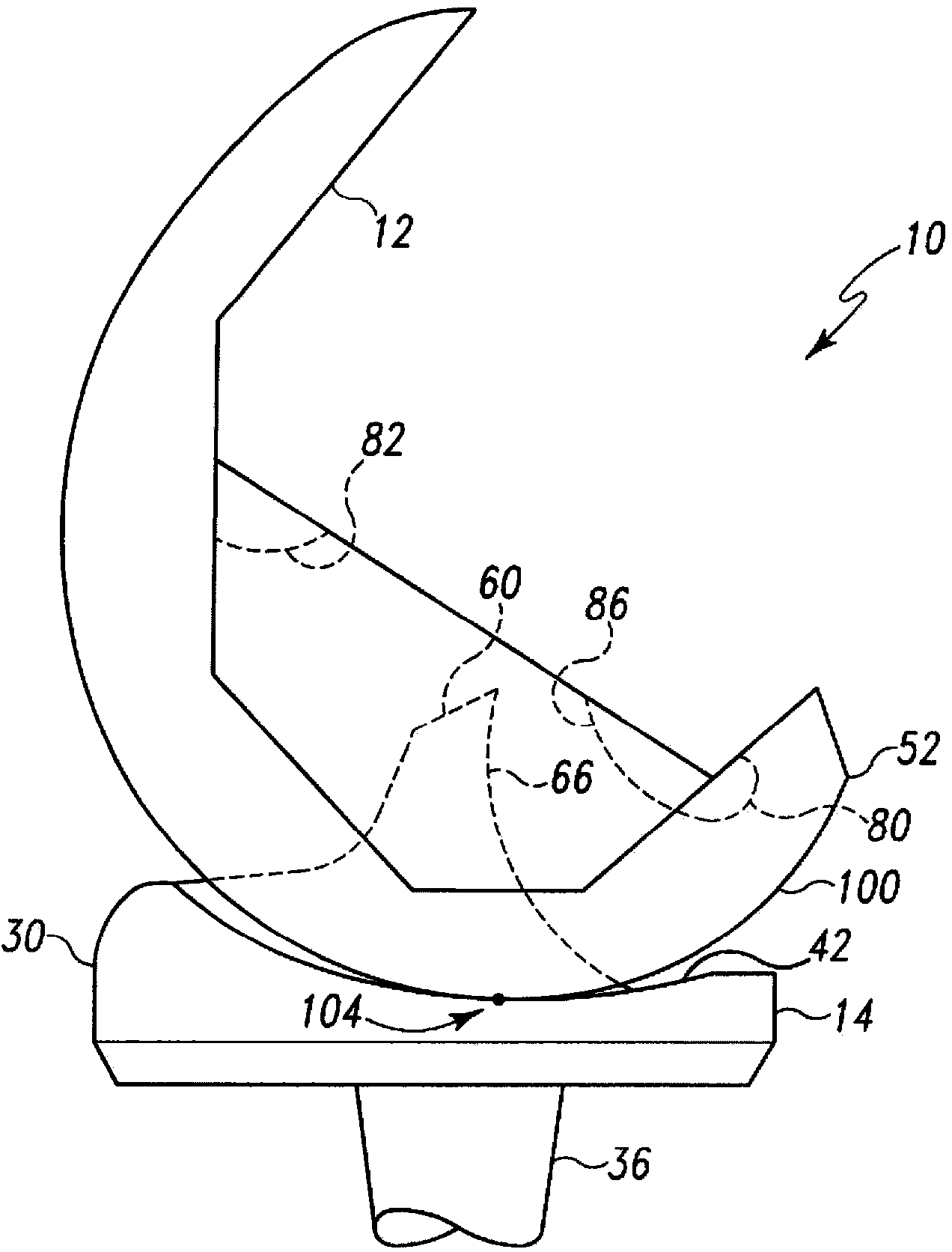
Modular knee prosthesis
A modular prosthetic knee system used to replace the natural knee. The system includes a femoral knee prosthesis and a tibial knee prosthesis. Both prostheses are formed of modular components that are connectable in-vivo to form the prosthetic knee system. The femoral knee prosthesis includes two separate components, a lateral condyle and medial condyle; and the tibial knee prosthesis includes a multiple separate components, a medial baseplate, a lateral baseplate, a medial insert, and a lateral insert. The medial and lateral baseplate are connectable to form a complete baseplate with the medial and lateral inserts connectable to the complete baseplate.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
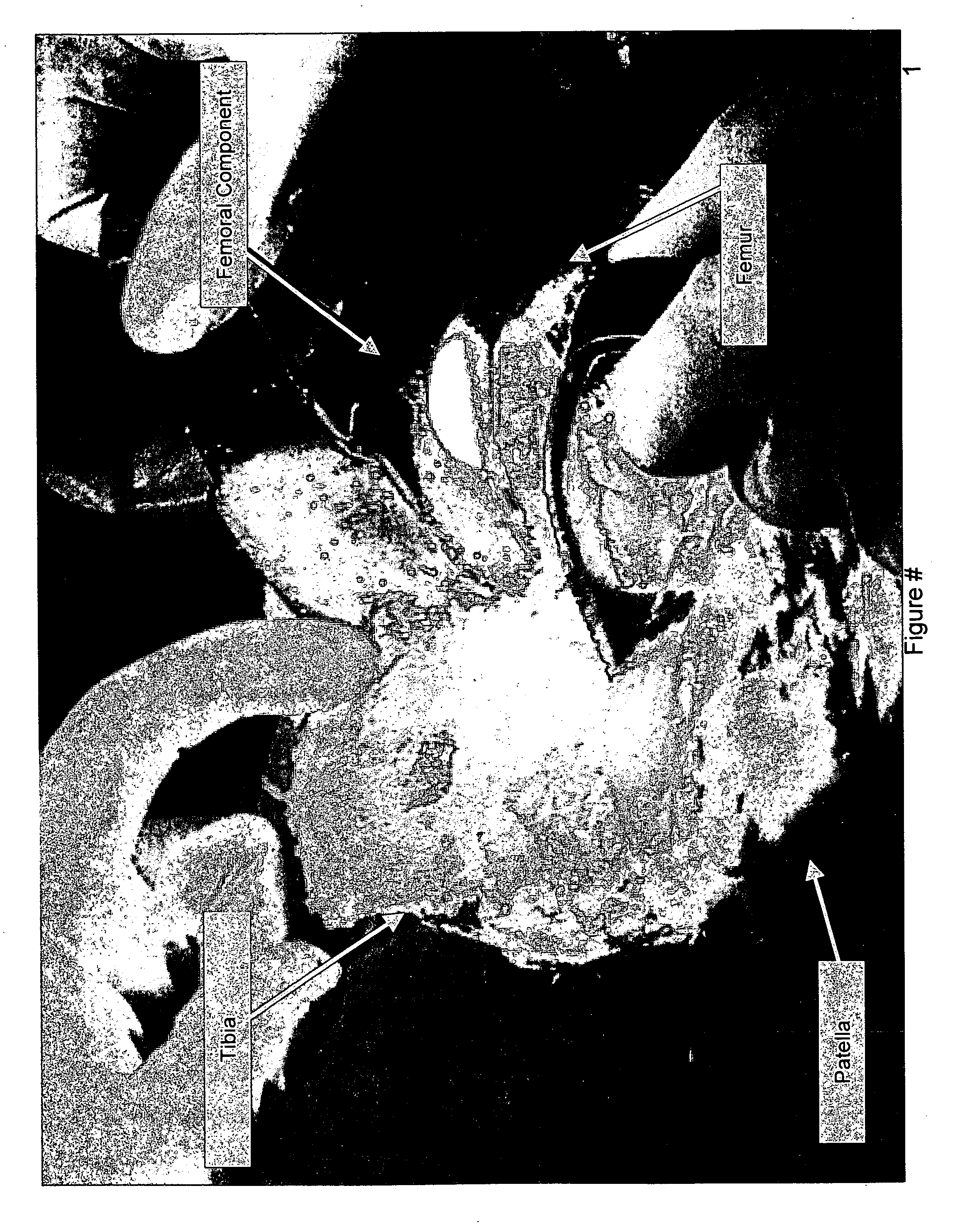
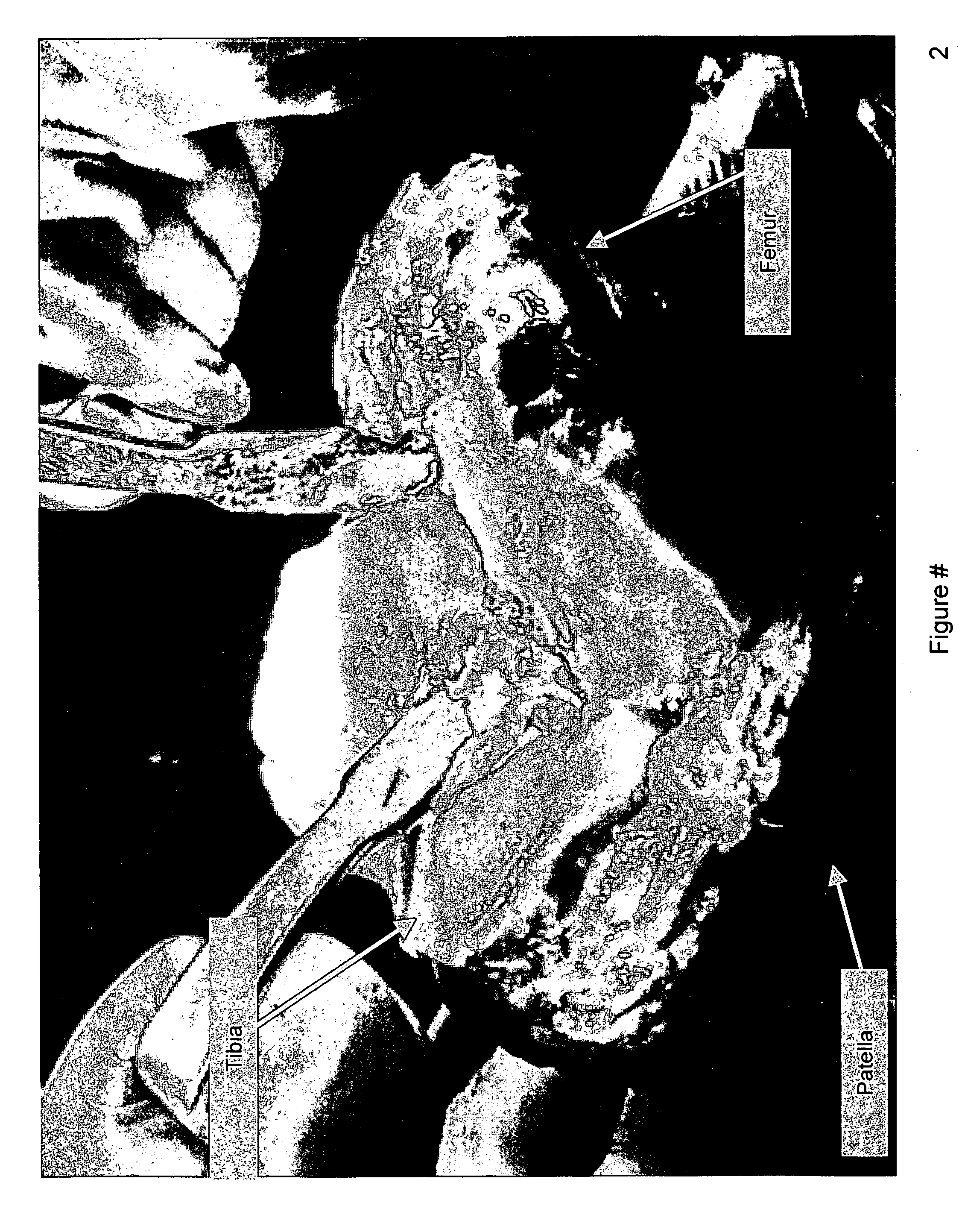
Total knee prosthesis and method for total knee arthroplasty
A prosthetic knee implant for implantation into a mammal, which accommodates an anterior cruciate ligament substitute to provide stability to the knee implant. The prosthetic knee implant includes a femoral component having a pair of condylar surfaces and a tibial component having a surface portion adapted to slidably engage the femoral component upon rotation of the same. The femoral component further includes a recess between the condyles defining an aperture through the femoral component. The tibial component further includes a center portion defining an aperture through the tibial component substantially at its center. The femoral aperture and the tibial aperture are adapted to receive an anterior cruciate ligament substitute for biasing the mammalian femur and tibia together. Also disclosed is a method used to replace the total knee joint in a mammal with the improved prosthetic knee implant of the present invention.
Owner:BLUM MICHAEL F
Methods and apparatus for improved cutting tools for resection
ActiveUS20060015109A1Facilitating intraoperativeFacilitating postoperative efficacyJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaSacroiliac joint
A cutting tool is provided with an arcuate cutting blade that preferably engages a guide tool to create a curved resected surface during an arthorplasty procedure. In one embodiment, a depth of the cutting blade is sufficient to permit the simultaneous creation of resected surfaces on two bones that articulate, such as both the femor and the tibia for a given condyle, without the need to reposition the guide or the leg. In another embodiment, a cutting member has a generally rectangular cross-section along a longitudinal axis with a first and second surface having cutting teeth defined thereon and a third and fourth surface adapted to interface with a cutting guide positioned proximate the bone. In this embodiment, the cutting tool can resect the bone in two different directions without reorienting the cutting member.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Posterior stabilized knee with varus-valgus constraint
ActiveUS20050192672A1Accurately and efficiently emulates kinematicsAccurately and efficiently and functionJoint implantsKnee jointsSpinal columnTibial bone
A femoral component of a knee prosthesis has spaced condyle surfaces defining a notch therebetween. The notch defines an elongated cam housing having an anterior cam and a posterior cam at opposite ends of the housing. The tibial component of the knee prosthesis includes a platform and a bearing supported on the platform, the bearing defining bearing surfaces configured to articulate with the condyle surfaces. The tibial component includes a spine projecting superiorly from the bearing that defines an anterior face and a posterior face. The posterior face and the posterior cam define complementary curved surfaces configured for cooperative engagement when the femoral component and the tibial component are at a predetermined flexion angle. The cam housing is configured to form a gap between the posterior cam and the spine when the knee is normally extended. In another feature, the spine includes a stiffening pin extending therethrough.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Total Knee Prosthesis and Method for Total Knee Arthroplasty
A prosthetic knee implant for implantation into a mammal, which accommodates an anterior cruciate ligament substitute to provide stability to the knee implant. The prosthetic knee implant includes a femoral component having a pair of condylar surfaces and a tibial component having a surface portion adapted to slidably engage the femoral component upon rotation of the same. The femoral component further includes a central femoral recess between the condyles providing access to the femur for drilling a channel through which a cruciate ligament substitute may be integrated into the femur. The tibial component further includes a center portion defining an aperture through which the ligament substitute maybe threaded through the tibia and integrated therein, or anchored upon its surface. Also disclosed is a method used to replace the total knee joint in a mammal with the improved prosthetic knee implant of the present invention.
Owner:BLUM MICHAEL F
Patient match instrument
InactiveUS20140018813A1Good repeatabilityGood reproducibilitySurgical sawsProsthesisTangential contactTrochlear groove
A patient matched instrument for a patient's femur is disclosed. The instrument includes a body having a cutting slot and a patient matched surface that mates with the patient's trochlear groove, a first leg portion extending from the body, a second leg portion extending from the body; and each leg portion has a contacting pad for tangential contact with the patient's femoral medial and lateral condyles.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Total Knee Prosthesis and Method for Total Knee Arthroplasty
A prosthetic knee implant for implantation into a mammal, which accommodates an anterior cruciate ligament substitute to provide stability to the knee implant. The prosthetic knee implant includes a femoral component having a pair of condylar surfaces and a tibial component having a surface portion adapted to slidably engage the femoral component upon rotation of the same. The femoral component further includes a recess between the condyles defining an aperture through the femoral component. The tibial component further includes a center portion defining an aperture through the tibial component substantially at its center. The femoral aperture and the tibial aperture are adapted to receive an anterior cruciate ligament substitute for biasing the mammalian femur and tibia together. Also disclosed is a method used to replace the total knee joint in a mammal with the improved prosthetic knee implant of the present invention.
Owner:BLUM MICHAEL F
Composite performance enhancing tethered mouthguard
InactiveUS8074658B2Preventing possibility of delamination and separationImprove performanceEar treatmentTeeth fillingCustom fittingEngineering
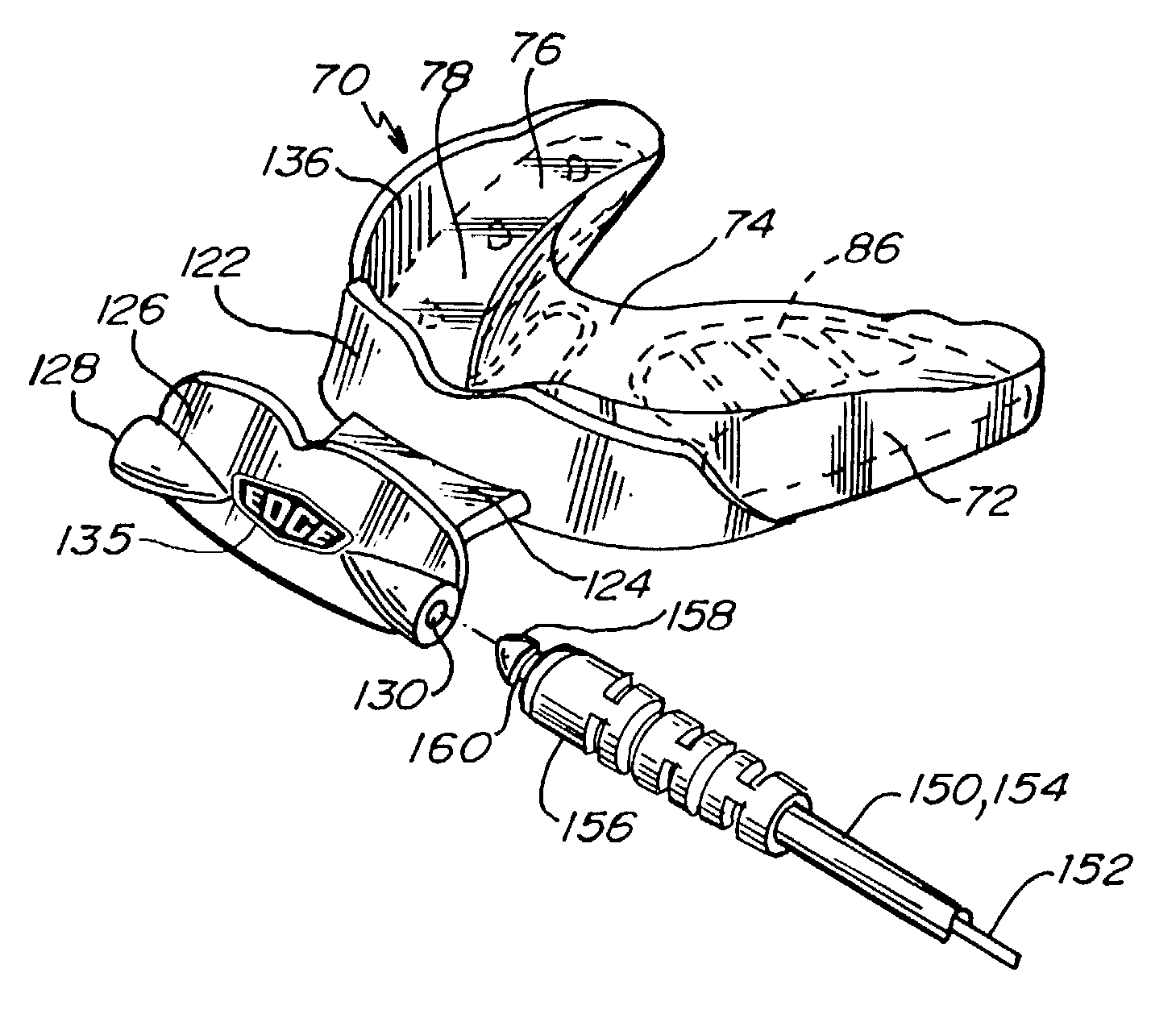
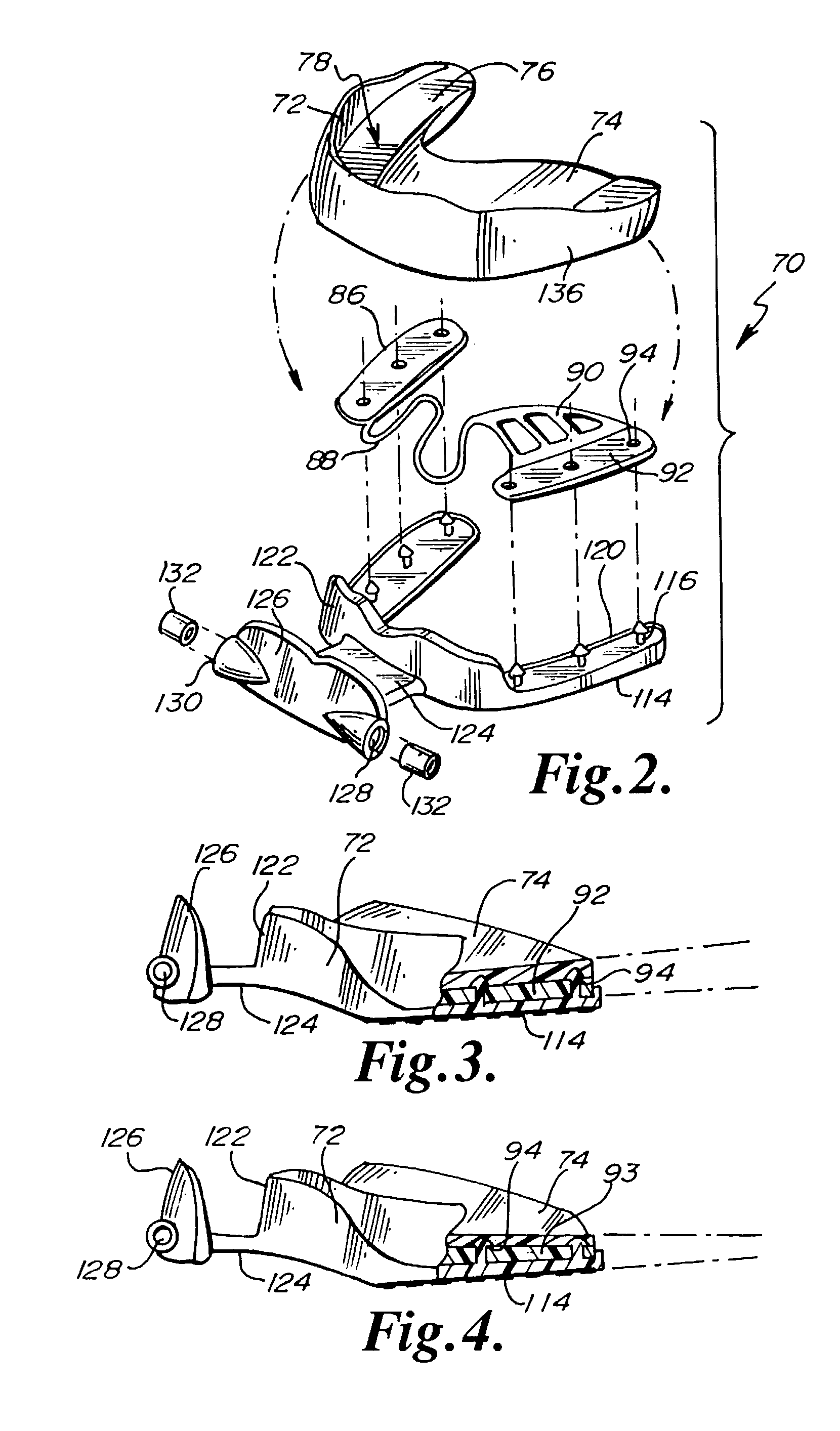
A performance enhancing and force absorbing mouthguard adapted to fit the upper teeth of the mouth of an athlete wherein the mouthguard is unobstructably tethered and of a composite material. The first internal layer is a nonsoftenable flexible framework which will permit the mouthguard to hold its shape during fitting as well as to absorb and dissipate significant impact conveyed to the upper teeth. A hard, durable bite plate wedge lowers the condyle from the temporomandibular joint in a fulcrum action to place the lower jaw in an optimum condition preventing impingement upon the nerves and arteries as well as spacing the upper and lower teeth apart. Elastomeric traction pads are on the bottom of the mouthguard and are grippingly engaged by the posterior teeth of the lower jaw. While the framework, wedge and traction pads are mechanically interlocked, a softenable material is placed over the mouthguard excepting the contact portions of the traction pads to encapsulate the mouthguard and to permit custom fitting. An anterior tab supports a transverse external bumper having left and right ports to unobstructively tether the mouthguard.
Owner:BITE TECH
Prostheses
A replacement ligament prosthesis including an elongate replacement ligament having a femoral end and a tibial end. The prosthesis includes a bar, which in use will extend between the medial and lateral condyles of a femur and across the intercondylar notch, and to which the femoral end of the elongate replacement ligament will be fixed. The prosthesis also includes a fixing means, which in use will fasten the tibial end of the elongate replacement ligament to the tibia.
Owner:FINSBURY DEV
Knee joint endoprosthesis
In accordance with the invention a knee joint endoprosthesis comprises a femoral component and a meniscal component mounted for movement relative to and on said femoral component. Said femoral component comprises a medial and a lateral condyle having a medial and a lateral condylar surface. Said meniscal component comprises a medial and a lateral joint surface on which the medial and lateral condylar surfaces bear at least partially. Said medial condyle and said medial joint surface are shaped so as to form a rotary joint with a rotary joint center. Moreover, a rolling motion guiding device is provided for defined rolling of the lateral condylar surface and the lateral joint surface on each other along a curved path which is defined in dependence upon an angle of flexion between femoral component and meniscal component and extends around the rotary joint center.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
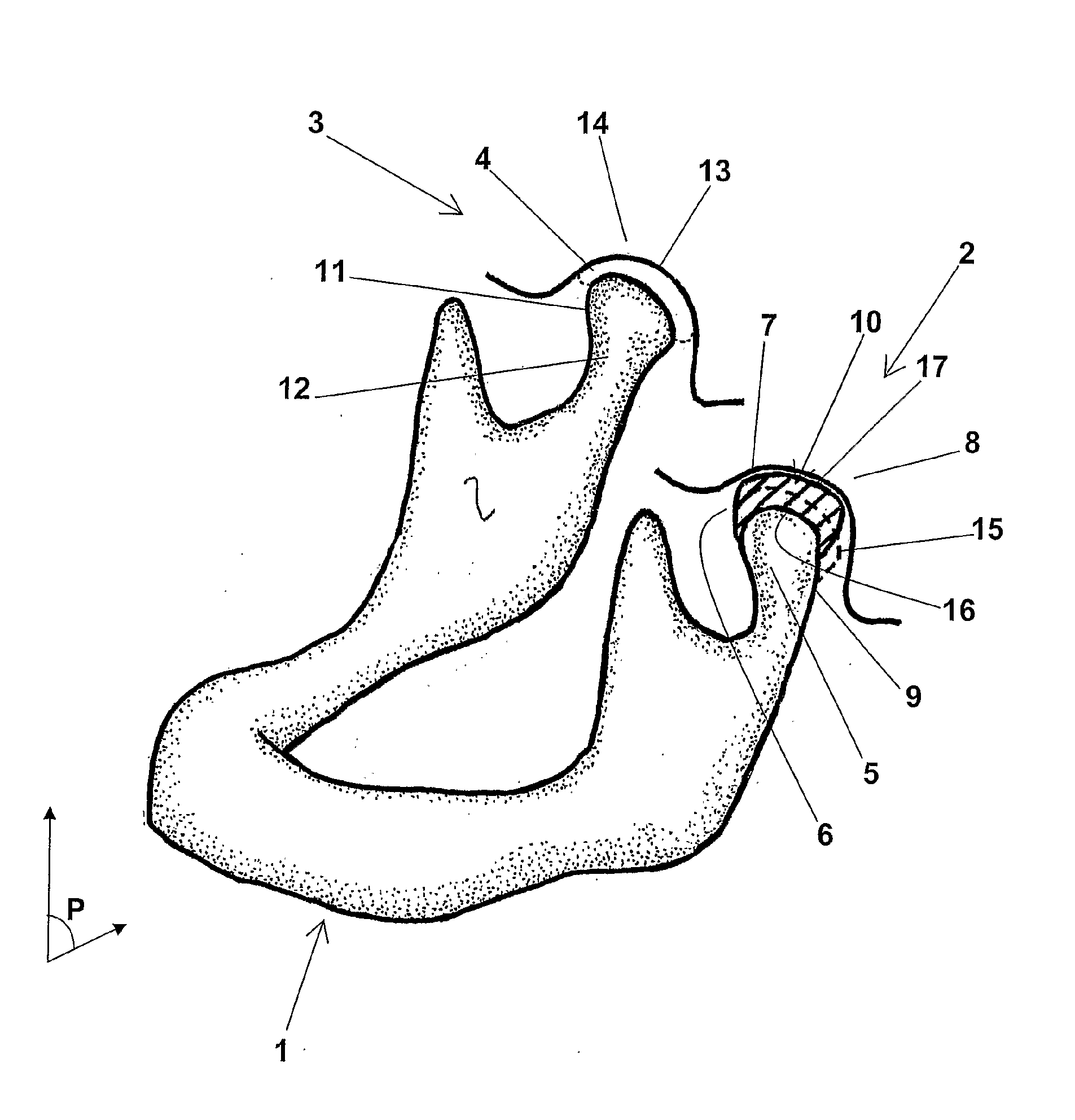
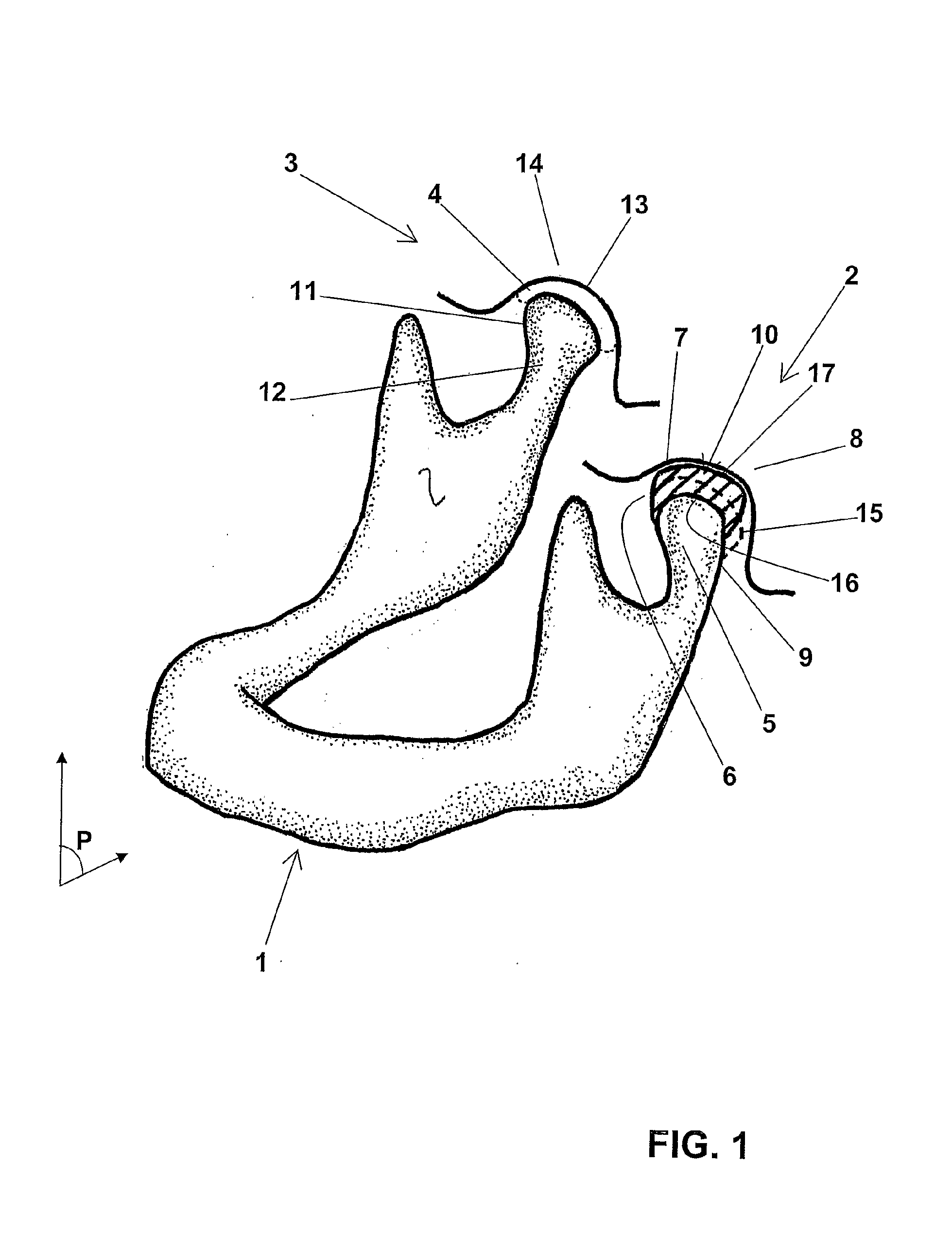
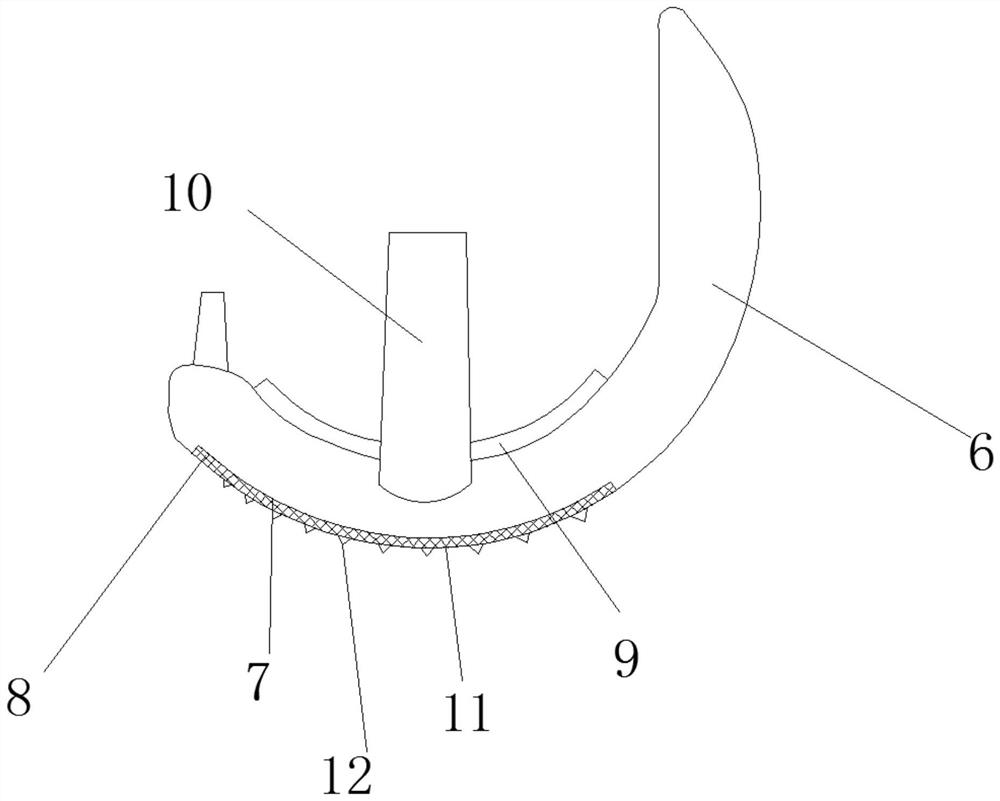
Temporomandibular prosthetic implant, and corresponding production method
ActiveUS20090222102A1Restore bilateral symmetryPromote osseointegrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusJoint implantsData fileMandibular prosthesis implantation
The prosthetic temporomandibular implant (10) comprises a concave surface (16) and a convex surface (17) designed to cooperate, respectively, with the natural outer surface (9) of the condyle (5) and the natural inner surface (7) of the fossa (8) of a damaged joint (2) of a human mandible (1). It is made of a rigid biocompatible material such as ceramic, stainless steel or an aluminum / zirconium alloy.The implant is designed based on an image of the joint (2) generated by a medical imaging system and incorporating an image of a healthy joint (3); these three-dimensional images are processed by a CAD (segmentation, vectorization) system to obtain a vector representation of the implant (10) and a data file capable of controlling a digital milling machine.The invention is applicable to the restoration of a damaged TMJ (2).
Owner:OBL
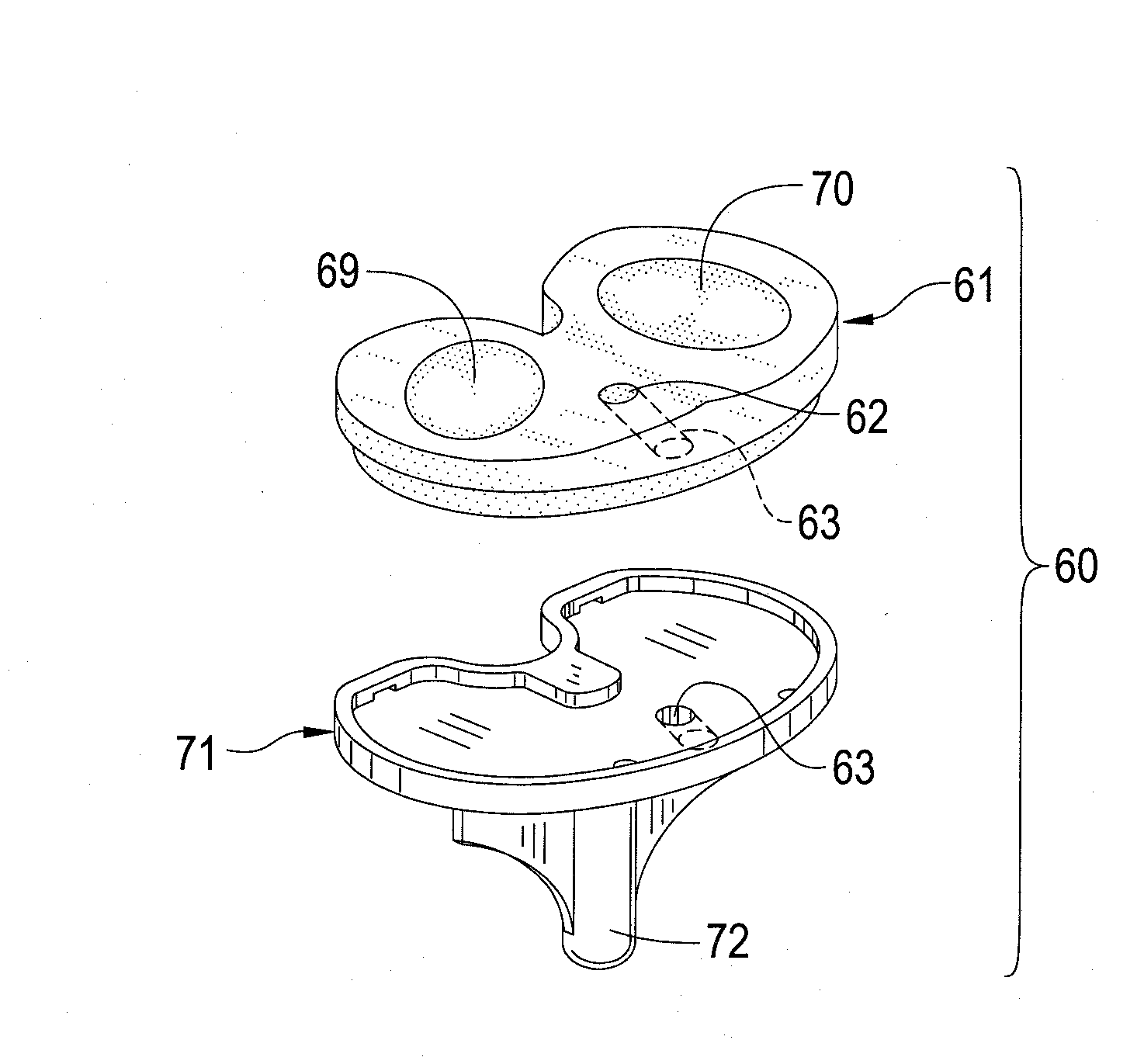
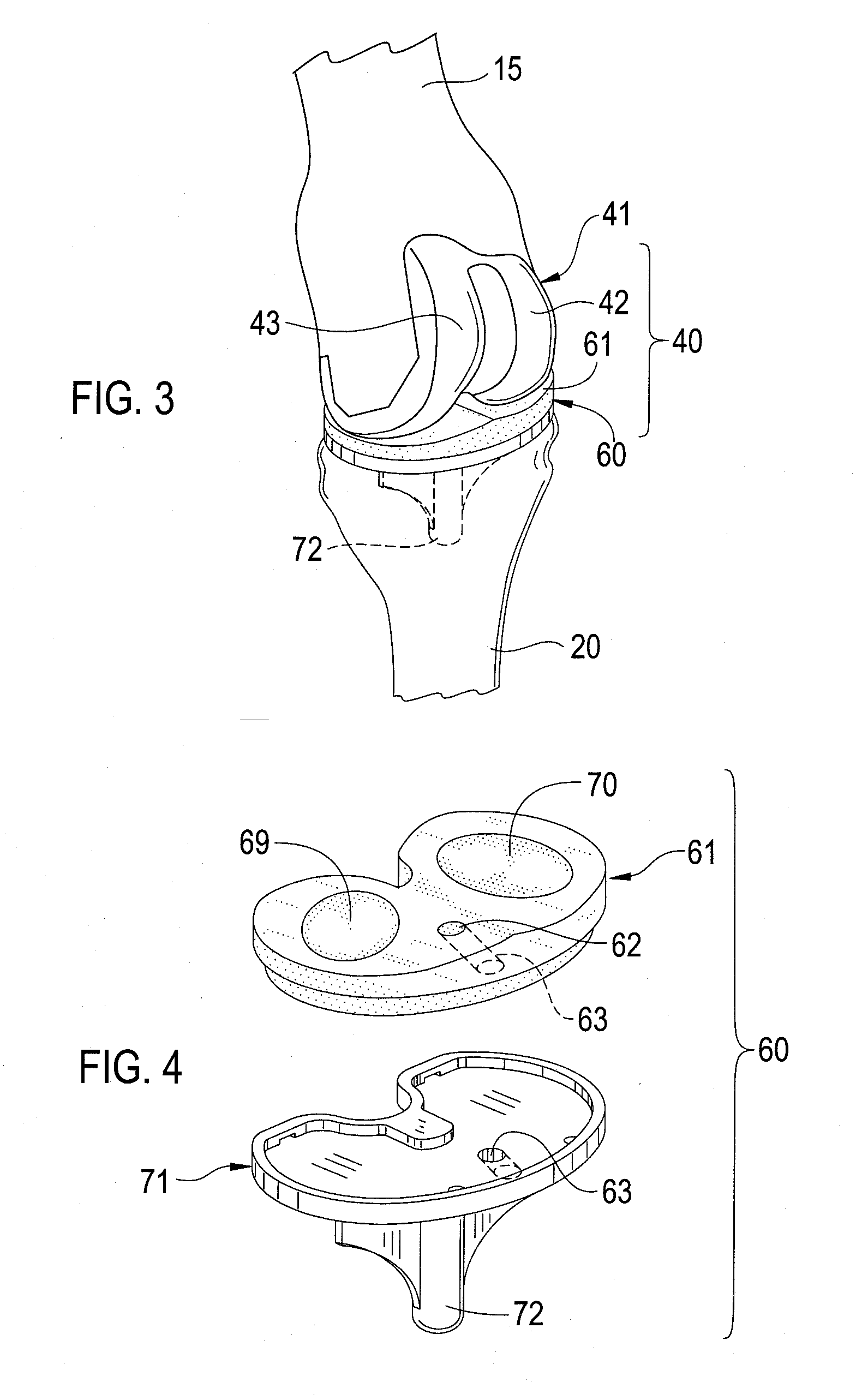
Medial femoral single condyle prosthesis, lateral femoral single condyle prosthesis, and femoral trochlea prosthesis
PendingCN107280817ASimplified Design Parameter ValuesJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
The invention discloses a medial femoral single condyle prosthesis (201), a lateral femoral single condyle prosthesis (301), and a femoral trochlea prosthesis (401). The medial femoral single condyle prosthesis comprises an articular surface which is a surface making contact with the medial patella and the medial tibial plateau during the knee joint motion process, wherein the articular surface is presented as a segmental arc (203) on a first ellipse (38) on the sagittal position, and is presented as a segmental arc (95) on a first circle (94) on a coronal position; and an inside surface, which is the part adjoining femoral condyle cut bone surface and bone cement after prosthesis implantation, and is presented as a medial posterior condyle (202) with a straight line section and a medial distal end (209) consistent with the segmental arc (203). The prosthesis can be closer to the geometric shape of the normal human femoral condyle, and design parameter values of femoral prostheses of various types are simplified.
Owner:温晓玉
Knee prosthesis
A knee prosthesis includes a femoral component having two condyles and an asymmetrical cam extending between the condyles. The cam has a medial end and a lateral end. The knee prosthesis also includes a tibial component having bearing surfaces and a post disposed between the bearing surfaces. The femoral component and tibial component are engageable by contact between the femoral condyles and tibial bearing surfaces, and by contact between the cam and post. The cam includes a first curvature defined by a first plane passing through the cam, and a second curvature defined by a second plane passing through the cam, the first curvature having a first vertex, and the second curvature having a second vertex, the distance between the first vertex and a medial plane being greater than the distance between the second vertex and the medial plane.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Spherical pivot hinge type artificial knee joint prosthesis of rotary platform and use method for spherical pivot hinge type artificial knee joint prosthesis of rotary platform
PendingCN110811936AIncreased risk of long-term looseningReduce aseptic loosening rateJoint implantsFemurTibial boneBone marrow cavity
The invention relates to a spherical pivot hinge type artificial knee joint prosthesis of a rotary platform and a use method for the spherical pivot hinge type artificial knee joint prosthesis of therotary platform. The use method comprises the steps: firstly, cutting a distal-end tumor of a thighbone and a proximal-end bone surface of a shinbone, carrying out marrow cavity reaming, connecting athigh bone medullary nail and a thighbone condyle patch together, injecting bone cement into a thigh bone marrow cavity, then, inserting the thigh bone medullary nail into the thigh bone marrow cavity; connecting a shinbone member and a shin bone medullary nail together, injecting bone cement into a shin bone marrow cavity, and then, inserting the shin bone medullary nail into the shin bone marrowcavity; placing a rotary lining into a lining hole of a connecting part, placing a shinbone gasket on a shinbone component, and placing a hinge rotating sphere in a spherical groove of the rotary lining through an insertion splicing hole; and placing the thighbone component on the shinbone gasket, inserting a lining lock into the lining hole of the connecting part, and fixing the thighbone condyle patch onto the thighbone component through a screw. According to the prosthesis, the amount of cut bones can be reduced to the maximum, the sterile loosening rate of the prosthesis can be remarkablylowered, the lifetime of the prosthesis is prolonged, and certain bone storage is reserved for possible reconditioning.
Owner:胡永成
Knee Prosthesis
ActiveUS20200069432A1Improve wear characteristicsImprove stabilityJoint implantsKnee jointsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationKnee Joint
A knee prosthesis comprises a femoral component for securement to a femur, the femoral component defining medial and lateral J-shaped condyles and an intercondylar groove; and a fixed bearing tibial component for securement to a tibia, the tibial component having respective bearing surfaces which are fixed with respect to both a tibial engaging component and a stabilising peg for securing the tibial component to a tibia, the respective bearing surfaces being shaped to engage with said condyles both when the knee, in use, is extended and also over a range of flexion.
Owner:MCMINN DEREK JAMES WALLACE
Knee brace and methods of use and modification thereof
InactiveUS7666156B2Accurate conditionEasy to adjustFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesFemoral condylesPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A knee brace, method of use thereof, and modification to an existing knee brace facilitates inducing side loads to a knee joint to align upper and lower leg portions relative to one another, thereby allowing the knee joint to function properly over its full dynamic range of motion. The knee brace, whether as manufactured or modified, acts to apply a lateral shear force to the knee joint through application of opposing lateral forces, with one lateral force being above the knee joint in one direction and the other lateral force being below the knee joint in an opposite direction. The counteracting forces act to shift femoral condyles and tibial condyles of the knee joint back into proper lateral alignment without acting directly on the patella to counteract the effects of the patella femoral syndrome.
Owner:BROWN ALICE M
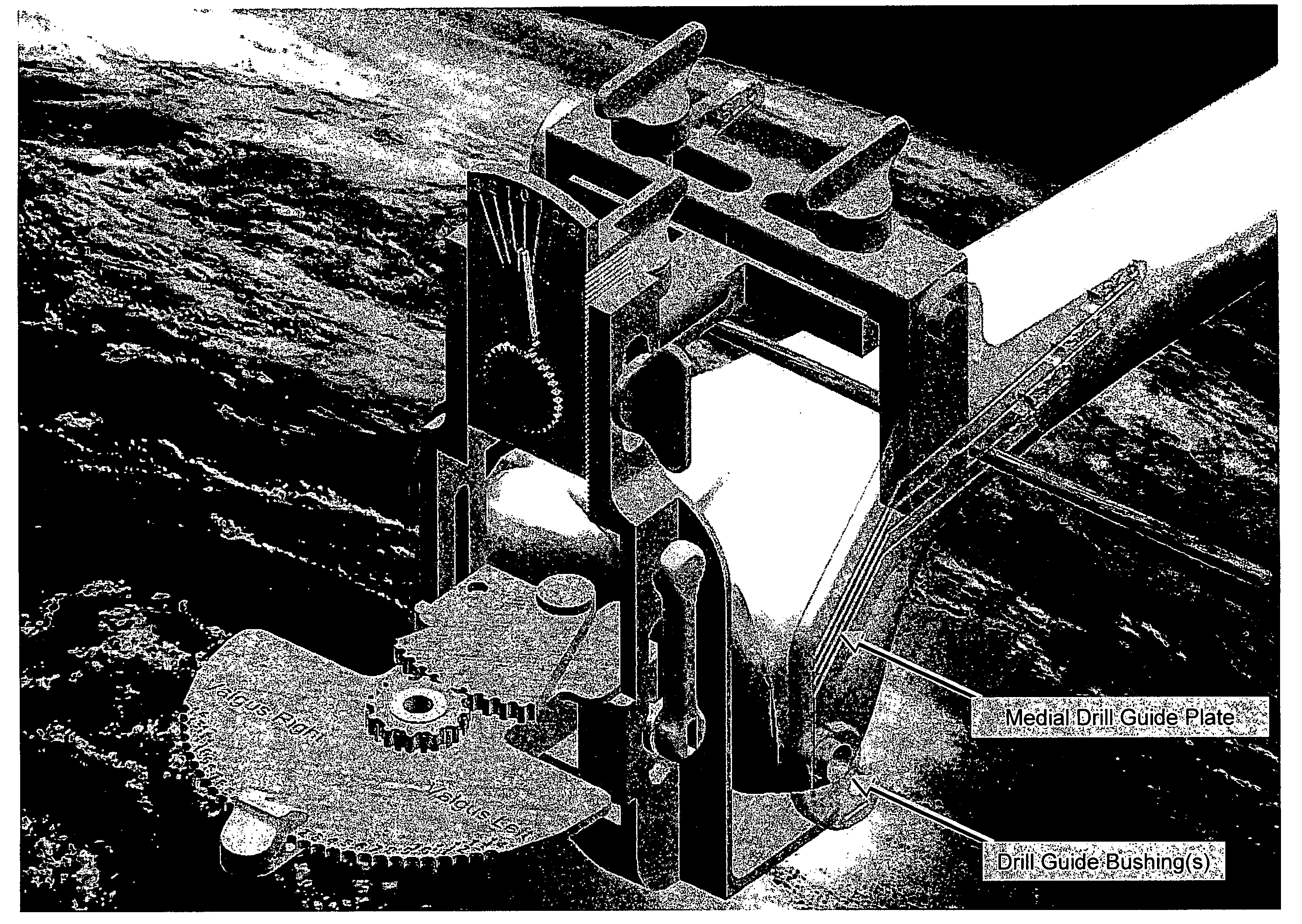
Method for positioning longitudinal osteotomy position of tibia in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
ActiveCN113397651AAvoid collisionGood compatibilityDiagnostic markersBone drill guidesUnicompartmental knee arthroplastyKnee Joint
The invention provides a method for positioning longitudinal osteotomy position of tibia in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, an intramedullary positioning rod and a thighbone drilling guide auxiliary device are used for determining the drilling position of a fixing hole used for mounting a thighbone prosthesis on the thighbone, the fixing hole is prepared under the guiding effect of the thighbone drilling guide auxiliary device, the postartis of the thighbone is cut off, the meniscus is cut off, a thighbone test mold with the appropriate thickness of the distal condyle is selected and installed after bone surface primary forming, the knee joint is bent and stretched repeatedly, and the longitudinal osteotomy position of the tibia is determined through the thighbone test mold. By capturing the motion trail of the tibia joint during relative normal motion, reference is provided for longitudinal osteotomy of the tibia platform, so that the longitudinal osteotomy position of the tibia is determined, the rotation alignment of the tibia prosthesis is closer to the motion trail of the tibia joint, collision between the prostheses is avoided, the motion compatibility and coincidence of the thighbone and tibia prostheses are better, the postartis of the thighbone is preferentially cut off, so that the meniscus on the tibial plateau is cut off more easily, and the collateral ligament is prevented from being damaged.
Owner:袁海浪
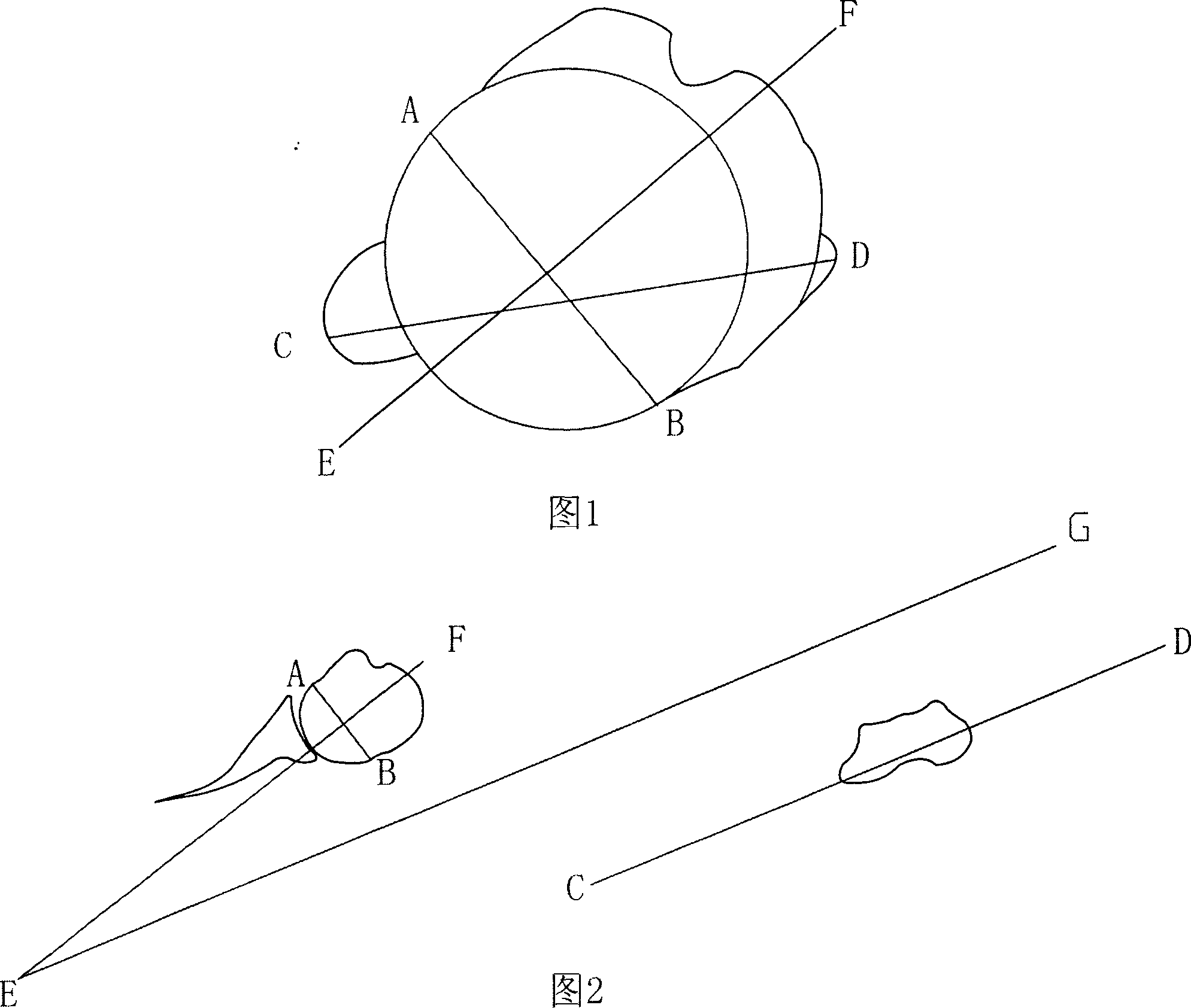
Method for measuring turning angle of humerus by using multiple line of CT three-D remodelling
InactiveCN1903126AReduce the influence of human factorsImprove accuracyComputerised tomographsTomographyCt scannersIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
A 3D reproducing method with multi-row for measuring the torsional angle of humerus head includes such steps as using the shoulder joint mode in volume reproducing technique to cut and separate scapula and obtain the reproduced 3D humerus image, drawing a circle to fit the joint surface of humerus head, drawing a line between dots A and B which are cross points between said circle and joint surface, drawing the midnormal line EF or said line AB to obtain the far-end defining line of said torsional angle, drawing a line CD between the most convex dots of internal and external upper condyles to obtain its near-end defining line, and measuring the included angle between lines EF and CD to obtain said torsional angle.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Tibial shim for knee joint
PendingCN110801315AReduce manufacturing costSmall footprintJoint implantsKnee jointsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationProsthesis
The invention relates to a tibial shim pad for a knee joint. The tibial shim is used in cooperation with a test mode prosthesis and a test condyle prosthesis, and the tibial shim includes a shim basematched with the test mode prosthesis, a shim main body matched with the test condyle prosthesis and a connection mechanism for connecting the shim base and the shim main body, the connection mechanism includes a clamping part for connecting a force line handle, and the clamping part can disconnect from the force line handle after being placed between the test mode prosthesis and the test condyleprosthesis. The assembly and disassembly of the tibial shim can be easily completed with the help of the force line handle, and compared with a manual disassembly and assembly method of an integratedtibial shim in the prior art, the assembly and disassembly method provided by the invention effectively shortens the surgery time; and the tibial shim for the knee joint provided by the application iscomposed of the shim base, the shim main body and the connection mechanism, can realize the mass production of the shim base and the connection mechanism, is beneficial to reducing the preparation costs, effectively reduces the occupied space of the tibial shim during a surgery, and is beneficial to progress of the surgery.
Owner:BEIJING CHUNLIZHENGDA MEDICAL INSTR
System and method for predicting tissue integrity
A system and method of diagnosing tissue integrity related to a joint of a patient may include imaging a first bone of the joint of the patient, determining a bone density profile of the first bone based on results of the imaging step, comparing the bone density profile of the first bone to at least one reference bone density profile of a reference first bone, and predicting an integrity of a tissue with respect to the first bone based on the comparison. The first bone may be a tibia and the bone density profile of the tibia may include a bone density profile of a sulcus of a medial tibial condyle of the tibia. The tissue may be an anterior cruciate ligament (“ACL”) and the predicting step may include predicting the integrity of both an anteromedial bundle and a posterolateral bundle of the ACL.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
3D-printing femoral-condyle five-in-one integration osteotomy device and forming method thereof
PendingCN108784782AIt has the characteristics of not easy to deform under forceFit tightlySurgery3d printFemoral osteotomy
The invention provides a 3D-printing femoral-condyle five-in-one integration osteotomy device and a forming method thereof, and relates to the technical field of medical apparatuses and instruments. For solving the technical problem that errors are easy to generate in existing total knee replacement femoral-condyle osteotomy, the 3D-printing femoral-condyle five-in-one integration osteotomy devicecomprises a femoral osteotomy device model matched with the affected-side femoral condyle of a patient, the femoral osteotomy device model is provided with a femoral-condyle front fitting face, a femoral-medial-condyle fitting face and a femoral-lateral-condyle fitting face, and the femoral-condyle front fitting face is used for fixed with the femoral condyle; the femoral osteotomy device model is subjected to stress and is not front to deformation, and is formed in a 3D-printing mode. Two osteotomy processes can be merged into one process, femoral-condyle osteotomy is completed one time, theusing quantity of osteotomy guiding plates is decreased, and deviations are reduced.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV +1
Manufacturing method and using method of front tooth occlussion blocker based on 3D printing
InactiveCN108836534AEasy to operateEasy to masterAdditive manufacturing apparatusDental articulators3D printingOral cavity
The invention discloses a manufacturing method and a using method of a front tooth occlussion blocker based on 3D printing, and relates to a preparation guiding piece of at least one tooth used for dental restoration preparation. The manufacturing method of the front tooth occlussion blocker based on 3D printing comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a digital model; (2) constructing an occlussion guiding plate; (3) positioning the occlussion guiding plate; (4) adjusting and amending a rudimentary model to obtain an overall model after fine virtual adjustment; (5) carrying out 3D printing, and carrying out subsequent processing according to requirements after the printing is completed. According to the scheme provided in the invention, the blocker does not need to be manufactured directly in the mouth of a patient, solidified self-curing resin does not need to consume much time to be worn into a plane, the operation is simple, the method is easy to grasp, and the materials are saved; occlussion opening distance is accurately controlled in the design process, the phenomena that the separation distance of teeth is too large and the condyle is free of a centric relation are avoided, the lower jaw can freely slide into the centric relation, and repeated adjustment is not needed.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
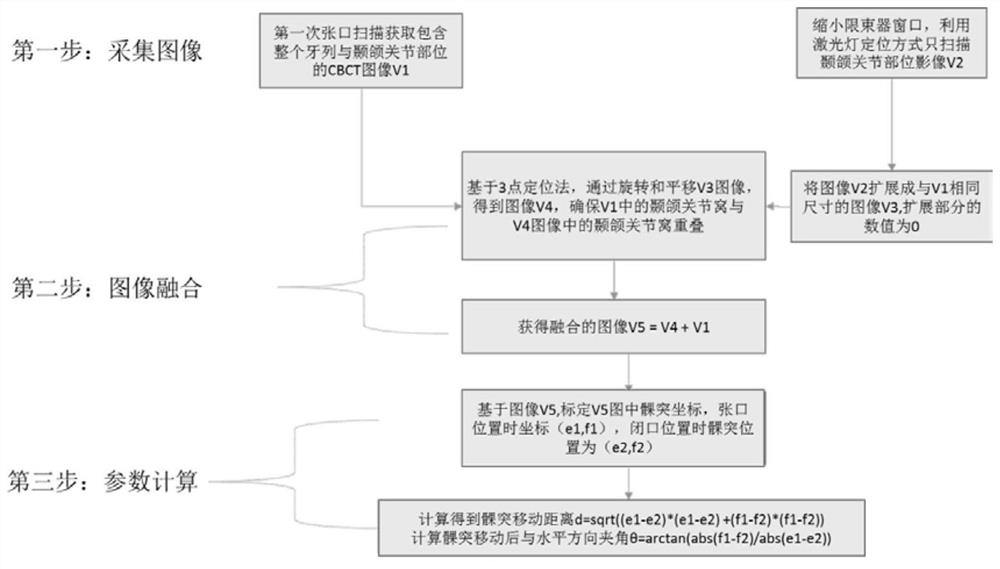
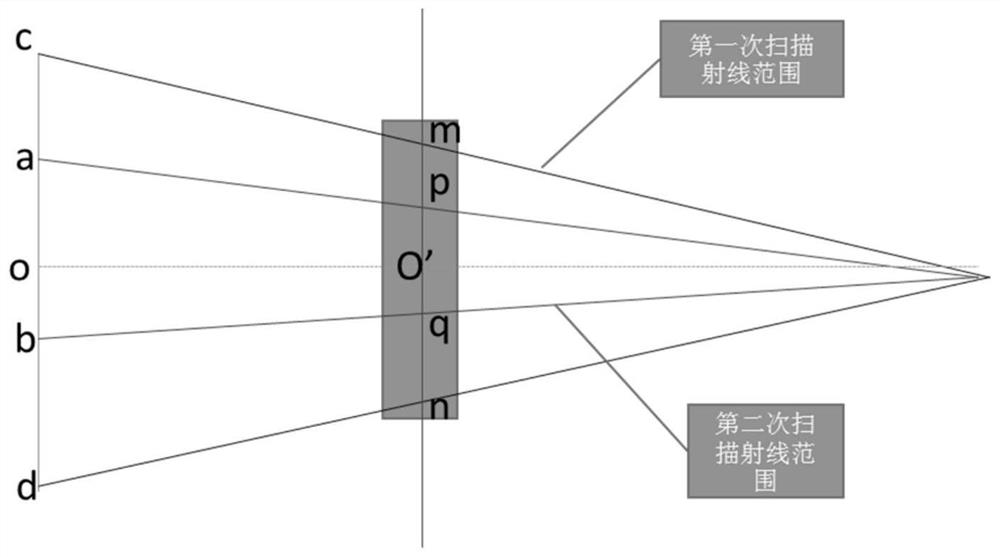
Method for positioning temporomandibular joints based on CBCT
PendingCN111870270APrecise positioningDentistryRadiation diagnostics for dentistryPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPhysical therapy
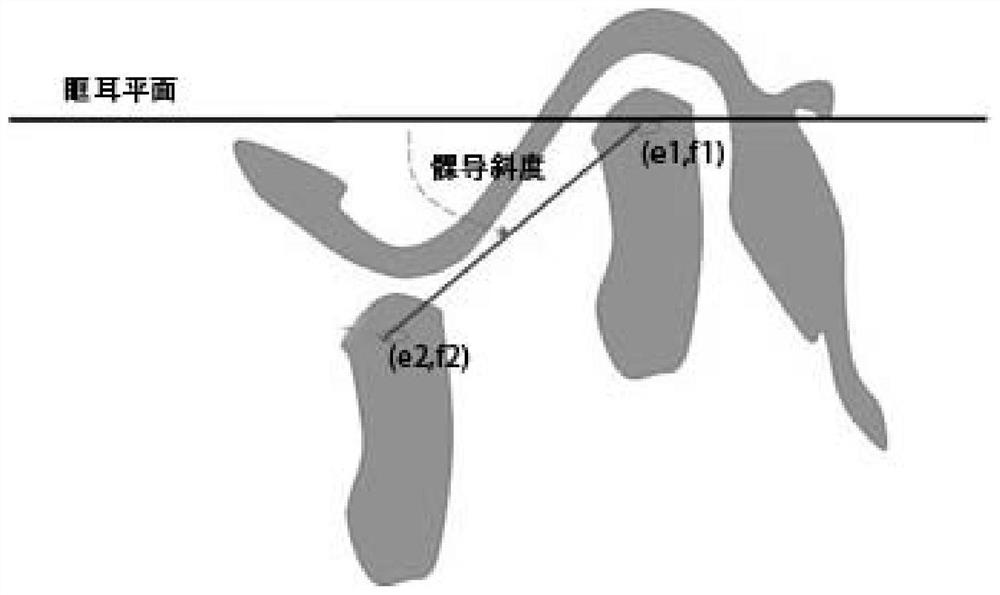
The invention discloses a method for positioning temporomandibular joints based on CBCT. The method comprises the following steps of (1) performing image acquisition; (2) performing image fusion; and(3) performing parameter calculation. The opening and closing images of the temporomandibular joints are fused based on CBCT three-dimensional data, and displacement information of condyles at the temporomandibular joints and angle information of the opening and closing condyles and the horizontal line for diagnosis of doctors are obtained. The opening and closing movement track of a patient is obtained through secondary CBCT irradiation, the rotation center of the condyle process and the condyle guide inclination are determined, and therefore, precise positioning of the temporomandibular joints is achieved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU BOEN ZHONGDING MEDICAL TECH
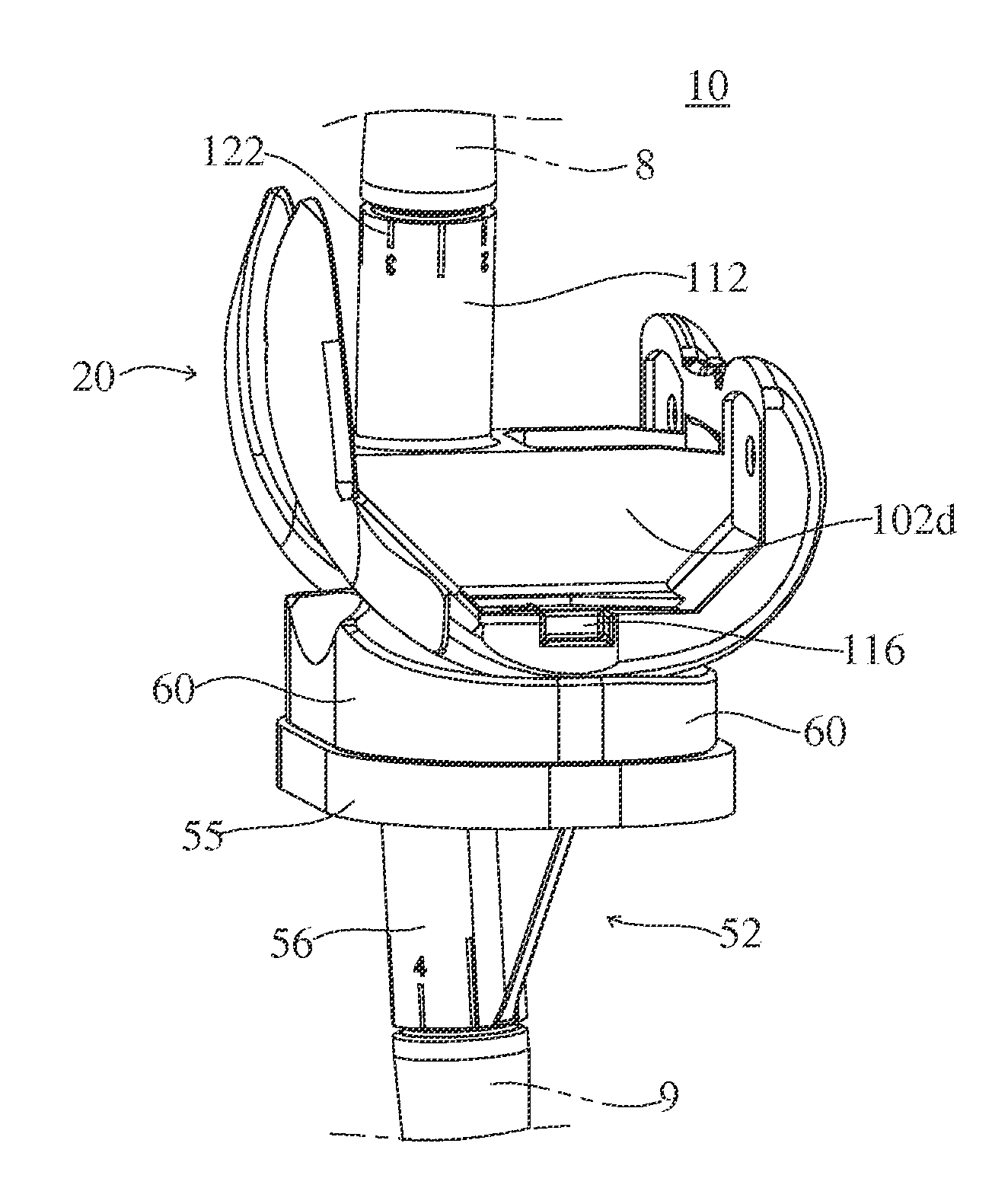
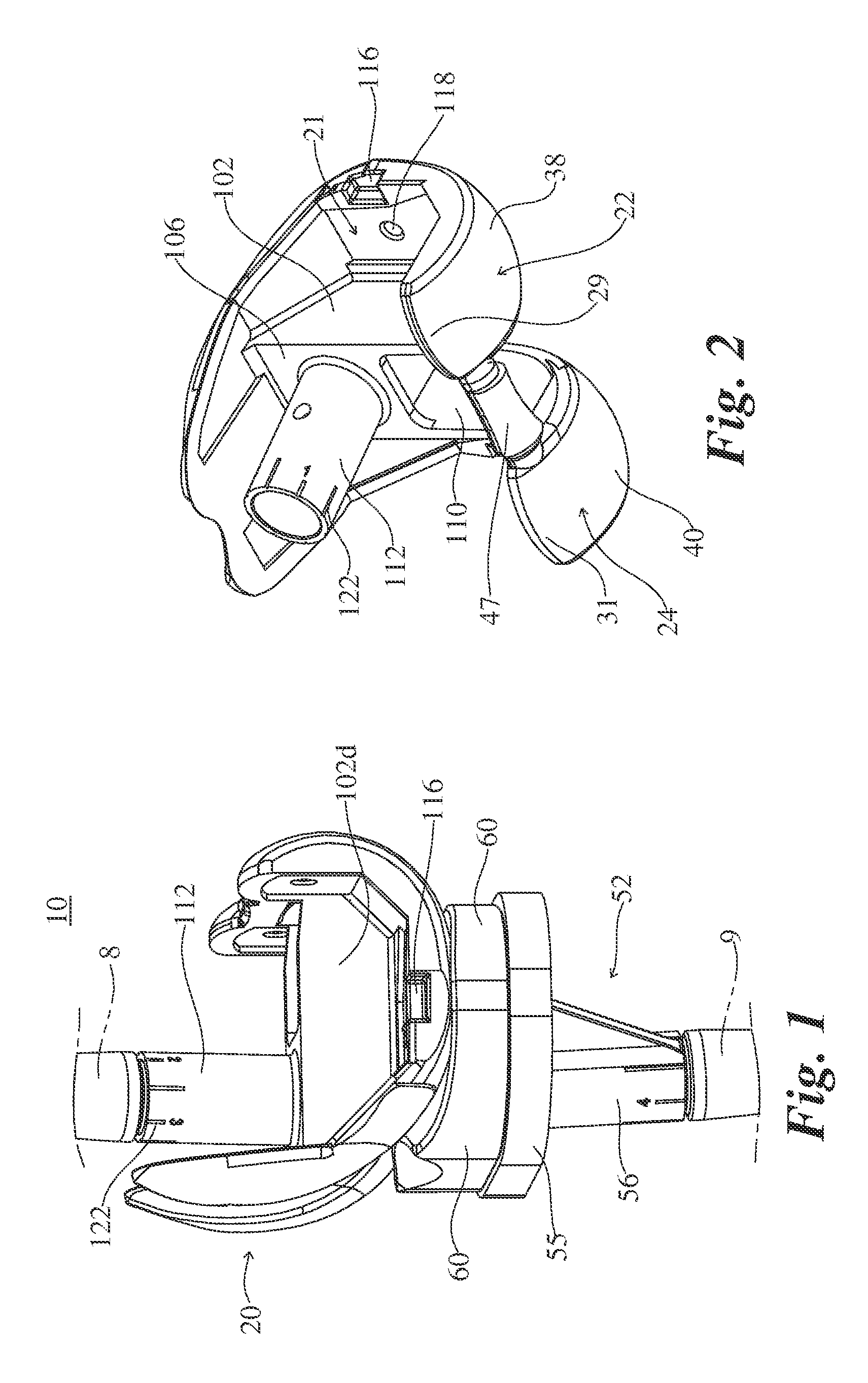
Elbow replacement apparatus
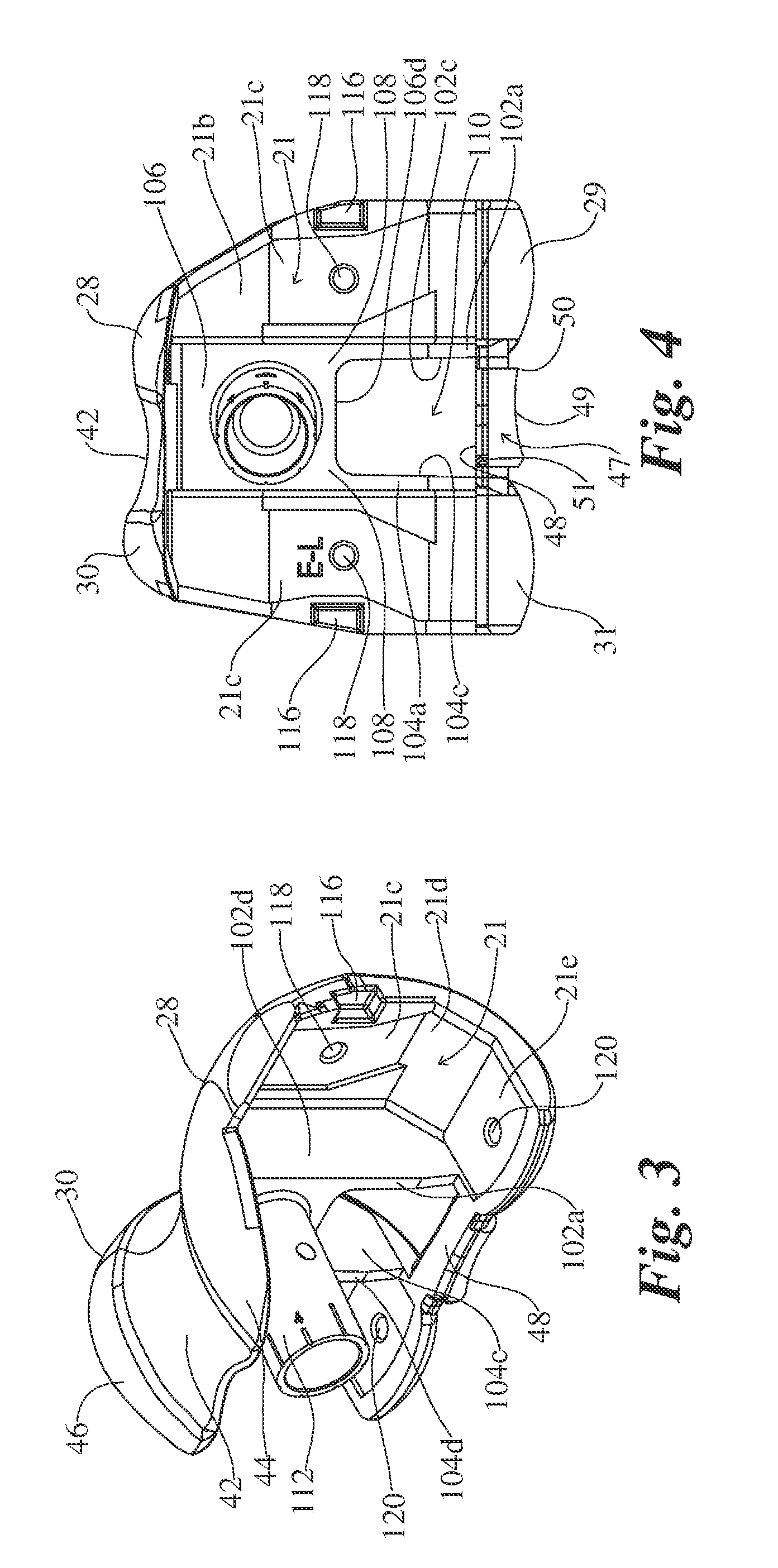
An elbow prosthesis is provided and comprises: a humeral component (119) comprising condyle portions (118) having humeral bushings (103) suitable to receive a hinging axle (106) along a hinging axis (112); and an ulnar component (104) comprising an ulnar bearing (105) and an ulnar body (107) configured for reciprocal coupling in a coupled condition, the condyle portions (118) and the ulnar bearing(105) being configured for reciprocal articulation about the hinging axis (112) in an articulation condition; the ulnar bearing (105) comprising an ulnar hinging hole (145); the ulnar body (107) comprising an ulnar coupling hole (143) aligned to said ulnar hinging hole (145) along said hinging axis (112) in said coupled condition, said hinging axle (106) being fixedly attachable to said ulnar coupling hole (143), the ulnar coupling hole (143) and the ulnar hinging hole (145) being further aligned with said humeral bushings (103) along said hinging axis (112) in said articulation condition, for insertion of said hinging axle (106). The elbow prothesis can be used for total elbow replacement, and allows a surgeon to intraoperatively select a linked or unlinked constraint by utilizing a connection located on the body of the ulnar and / or humeral stem. Additional modularity also allows the selection of a cemented or cementless stem as described herein. The modularity and adjustability provides a number of advantages.
Owner:LIMA CORPORATE SPA
Posterior stabilized orthopaedic knee prosthesis having controlled condylar curvature
An orthopaedic knee prosthesis includes a tibial bearing and a femoral component configured to articulate with the tibial bearing. The femoral component includes a posterior cam configured to contact a spine of the tibial bearing and a condyle surface curved in the sagittal plane. The radius of curvature of the condyle surface decreases gradually between early-flexion and mid-flexion. Additionally, in some embodiments, the posterior cam of the femoral component may include a concave cam surface and a convex cam surface.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
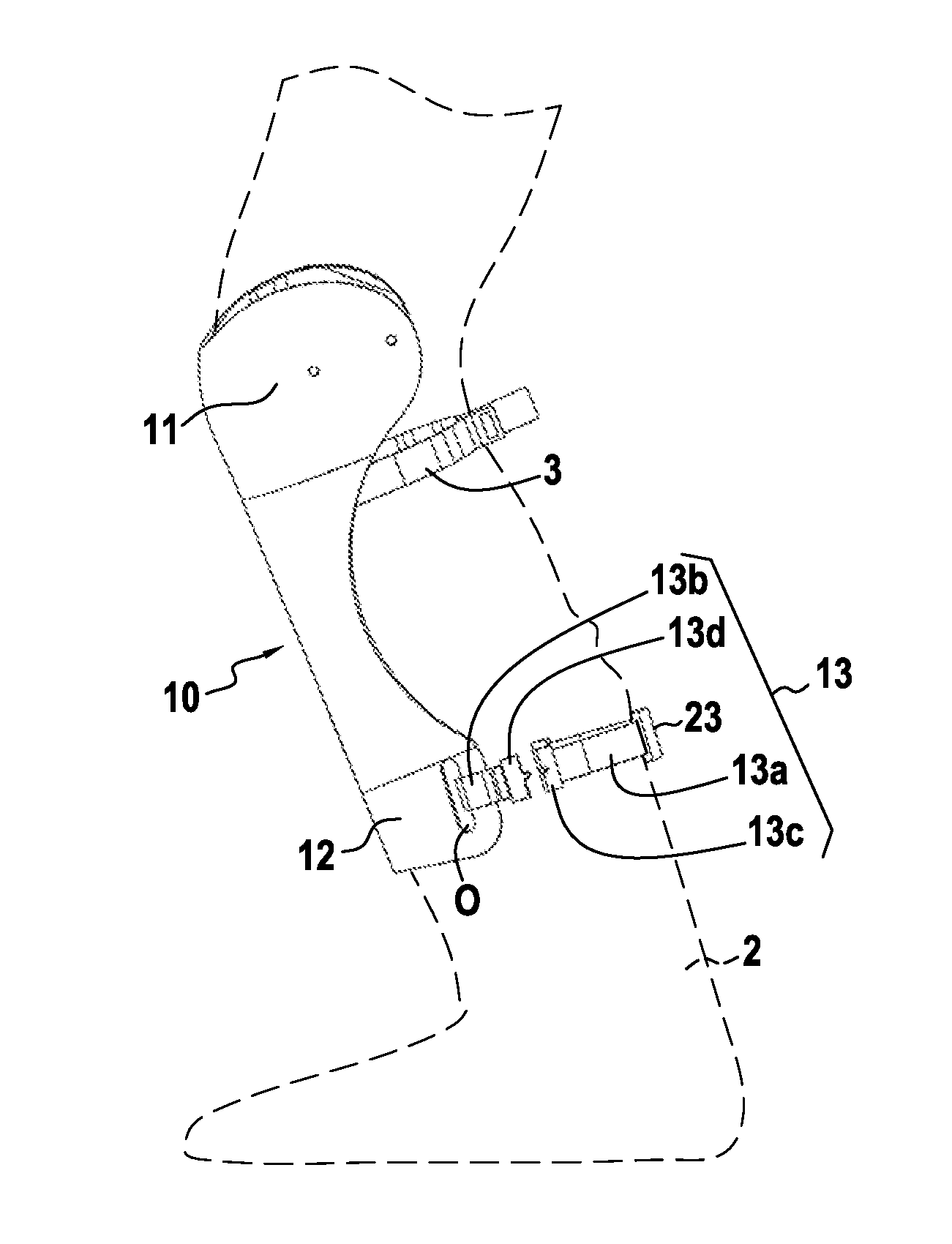
Device for protecting the knee joint with a strap
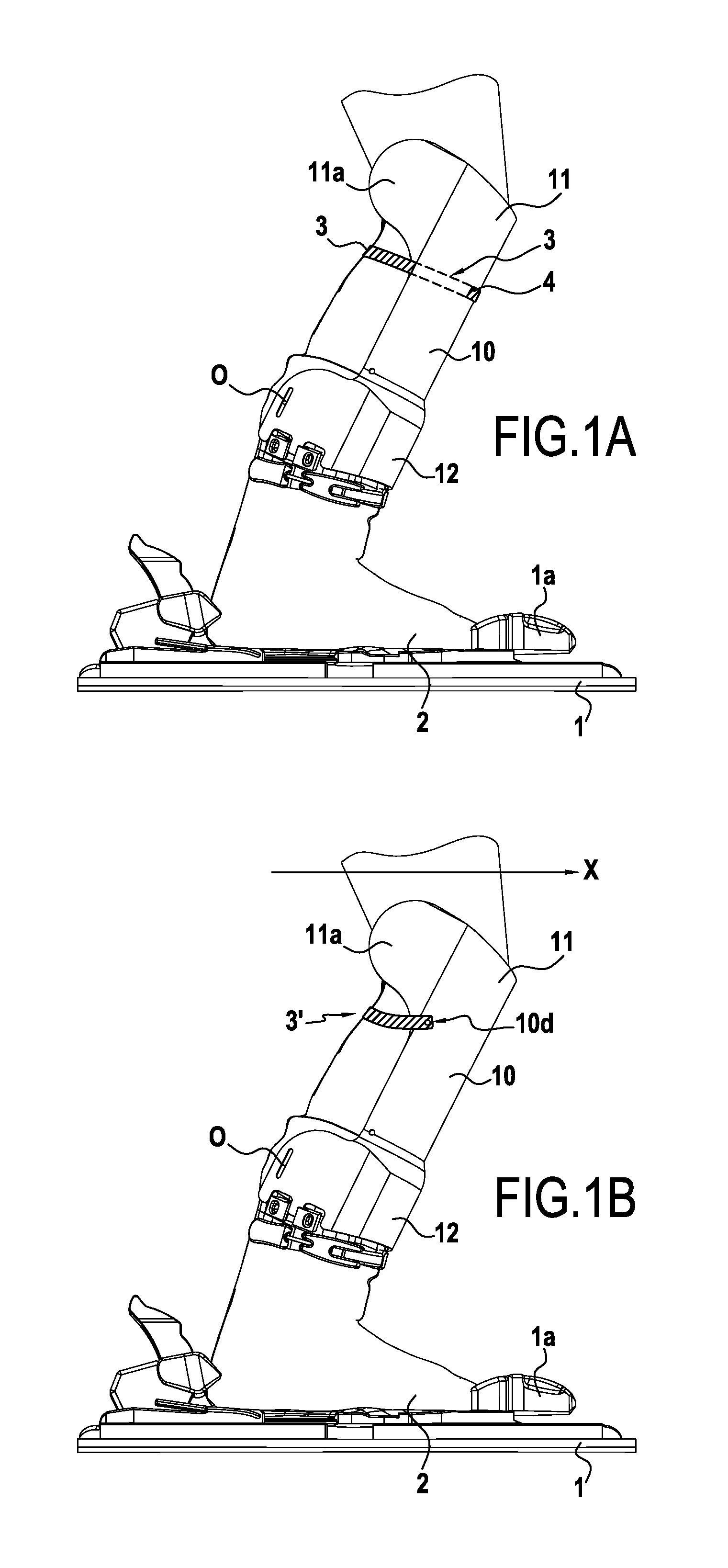
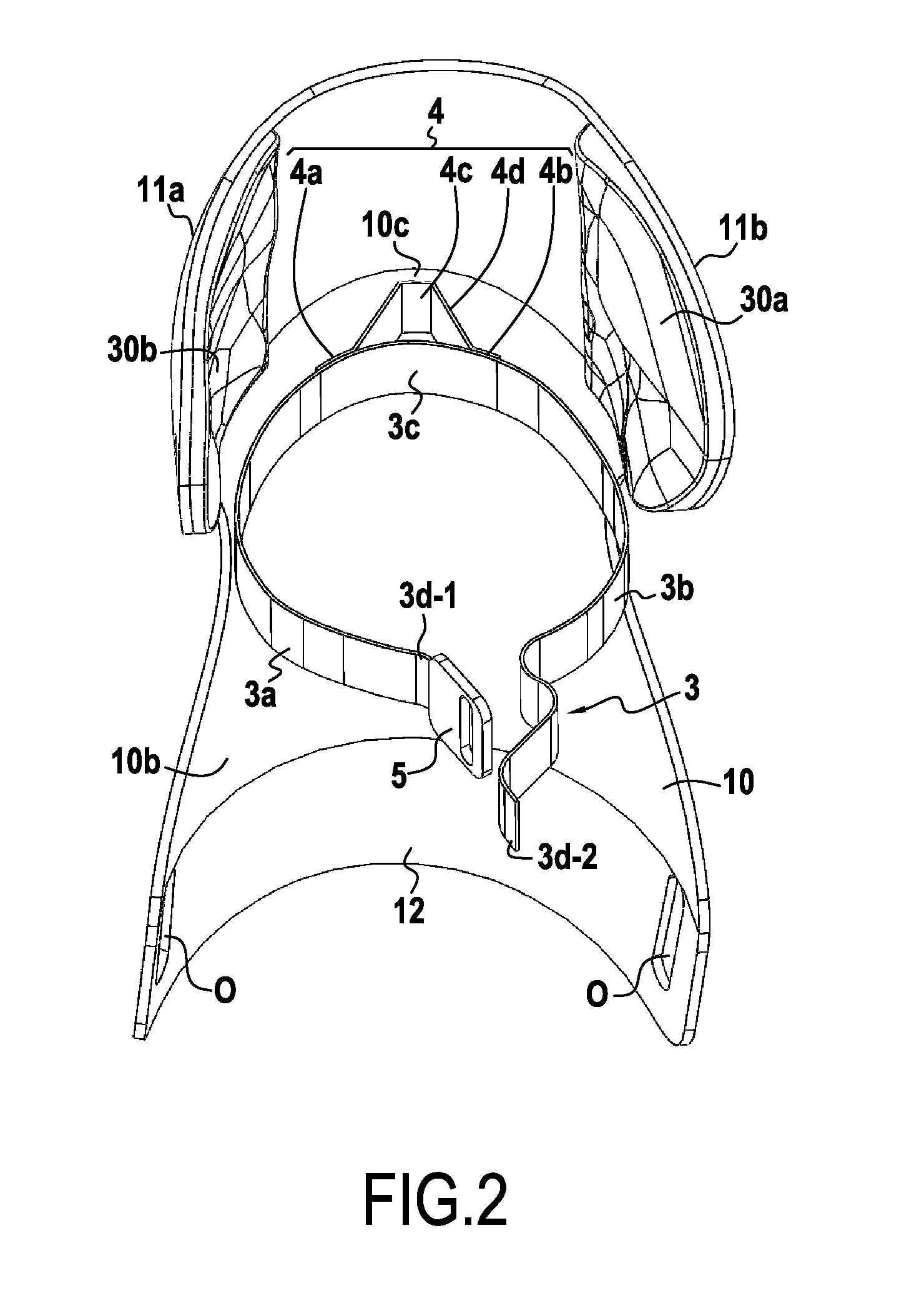
InactiveUS20150106991A1Improve featuresIncrease stiffnessMedical scienceSport apparatusPhysical medicine and rehabilitationFemoral bone
The present invention relates to a device for protecting a user's knee joint, the device being for installing on a sports boot (2) and being characterized in that it comprises a shell (10) provided with an inside surface suitable for covering at least in part an anterior portion of the user's leg, the shell (10) having a top portion (11) for situating at knee level and a bottom portion (12) including connection means suitable for connecting the shell (10) to the sports boot (2), the top portion including side cheeks suitable for being put into contact with the knee on either side of the knee, and coming into contact at least with the condyles of the user's femur, at least one strap (3) for attaching around a zone of the leg and attachment means for attaching the strap (3) to the inside surface of the shell (10).
Owner:GOUNIOT PIERRE
Knee Revision Prosthesis With Progressive Restraint
A knee revision prosthesis that provides decreasing valgus-varus and medial-lateral restraint as the knee rotates from extension to flexion, and then increasing restraint as the knee rotates from flexion to full extension. The prosthesis includes a femoral component and a tibial component. The femoral component includes a guide box fixed to the femoral mounting surfaces intermediate the condyles. The tibial component includes a central post fixed intermediate the tibial concavities, which articulates within the guide box and constrains rotational movement of the femoral and tibial components relative to one another in the coronal plane and transverse planes. The post and guide box are constructed and arranged to provide progressively decreasing and then progressively increasing rotational constraint of the femoral component in the coronal and transverse planes as the femoral component rotates in the sagittal plane between full extension to a position in flexion, and then back to full flexion, respectively.
Owner:MAXX ORTHOPEDICS INC
Tibia platform support and single-condyle knee joint applying tibia platform support
PendingCN110786969ASimple structureExtended service lifeJoint implantsKnee jointsKnee JointArthroplasty knee
The invention relates to the field of medical instruments, and discloses a tibia platform support and a single-condyle knee joint applying the tibia platform support. The single-condyle knee joint applying the tibia platform support comprises a first platform part, as well as a connecting part which is fixed on a bottom surface of the first platform part; the connecting part comprises at least onefixed column and at least one panel which are arranged, with interval between, on the bottom surface of the first platform part; and the panel has a tapered width from the bottom surface of the firstplatform part to a direction that is away from the bottom surface. The single-condyle knee joint applying the tibia platform support disclosed by the invention is capable of realizing better fixationwith human bone tissue, so that the single-condyle knee joint has improved stability after a single-condyle knee replacement surgery; and thus, normal kinematics of the knee joint can be ensured.
Owner:BEIJING CHUNLIZHENGDA MEDICAL INSTR
Hemi-condyle type artificial knee joint
ActiveUS20200383794A1Good effectImprove experienceJoint implantsKnee jointsFemoral boneFemoral prosthesis
A semi-condylar artificial knee joint includes a femoral prosthesis and a tibial prosthesis, and the cross-section of said tibial prosthesis is of a kidney-like type. The tibial prosthesis is disposed at one side of the tibial plateau intercondylar eminence and is located below the femoral prosthesis. The artificial knee joint further includes a locating pin for fixing the tibial prosthesis. The bottom surface of said tibial prosthesis is provided with a prosthetic notch, and below said tibial prosthesis is provided with a tibial notch. Said prosthetic notch corresponds to said tibial notch, and together forming a limiting hole for accommodating the locating pin. The cooperation between the locating pin and the limiting hole can ensure relative position stability and balance between the tibial prosthesis and the tibial plateau intercondylar eminence.
Owner:ZHU HONGWEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com