Patents
Literature
2296 results about "Ready to use" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
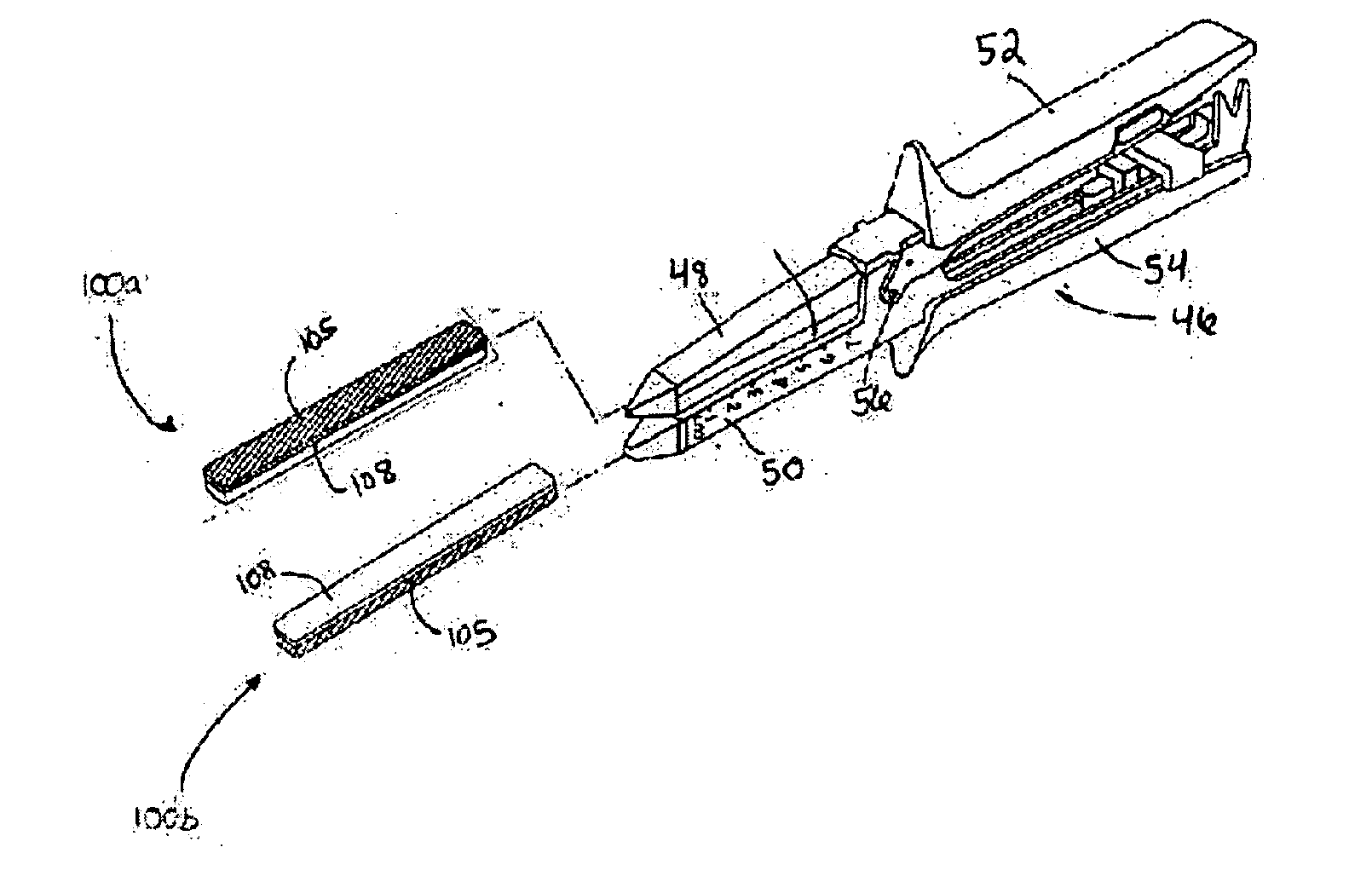
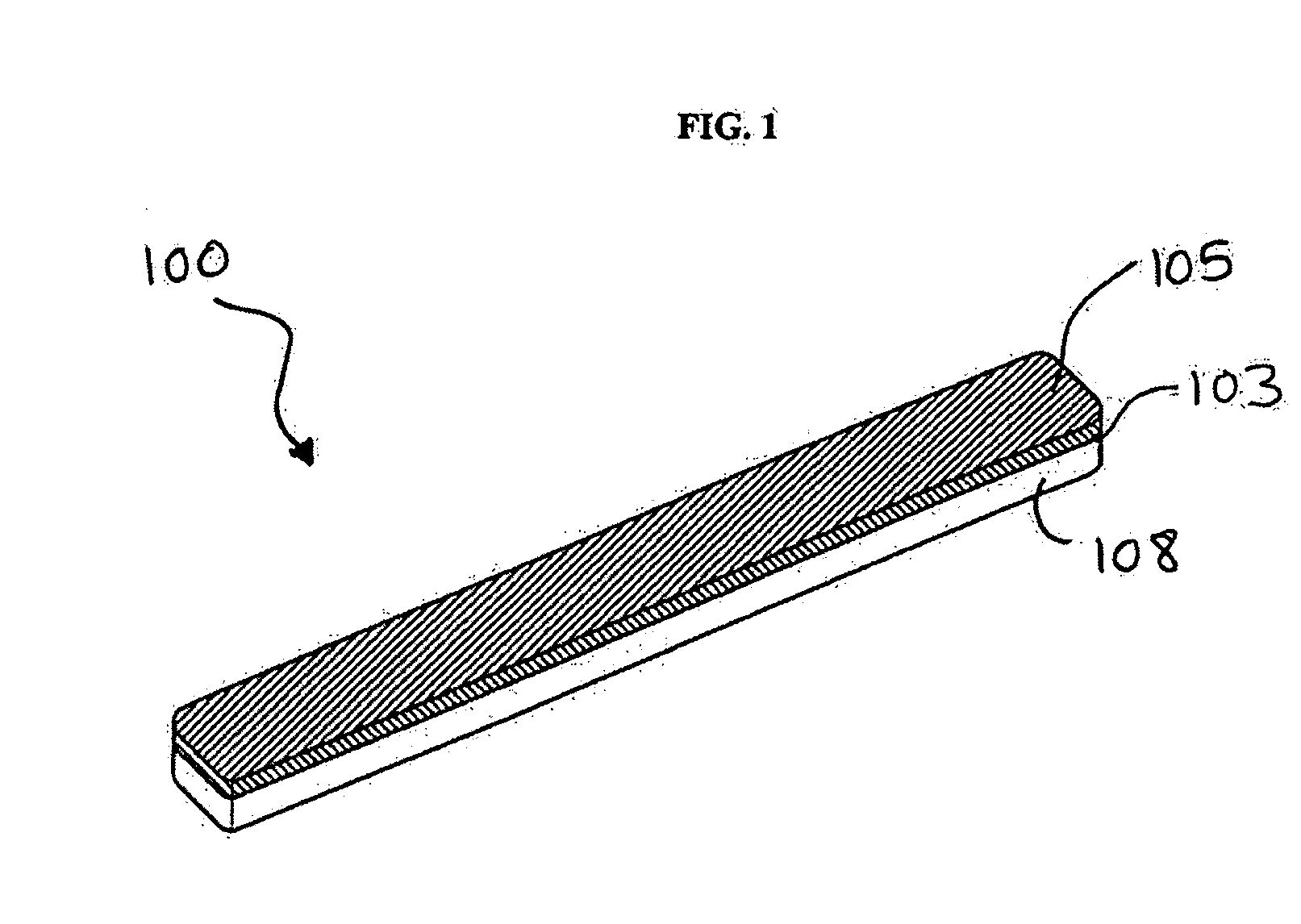
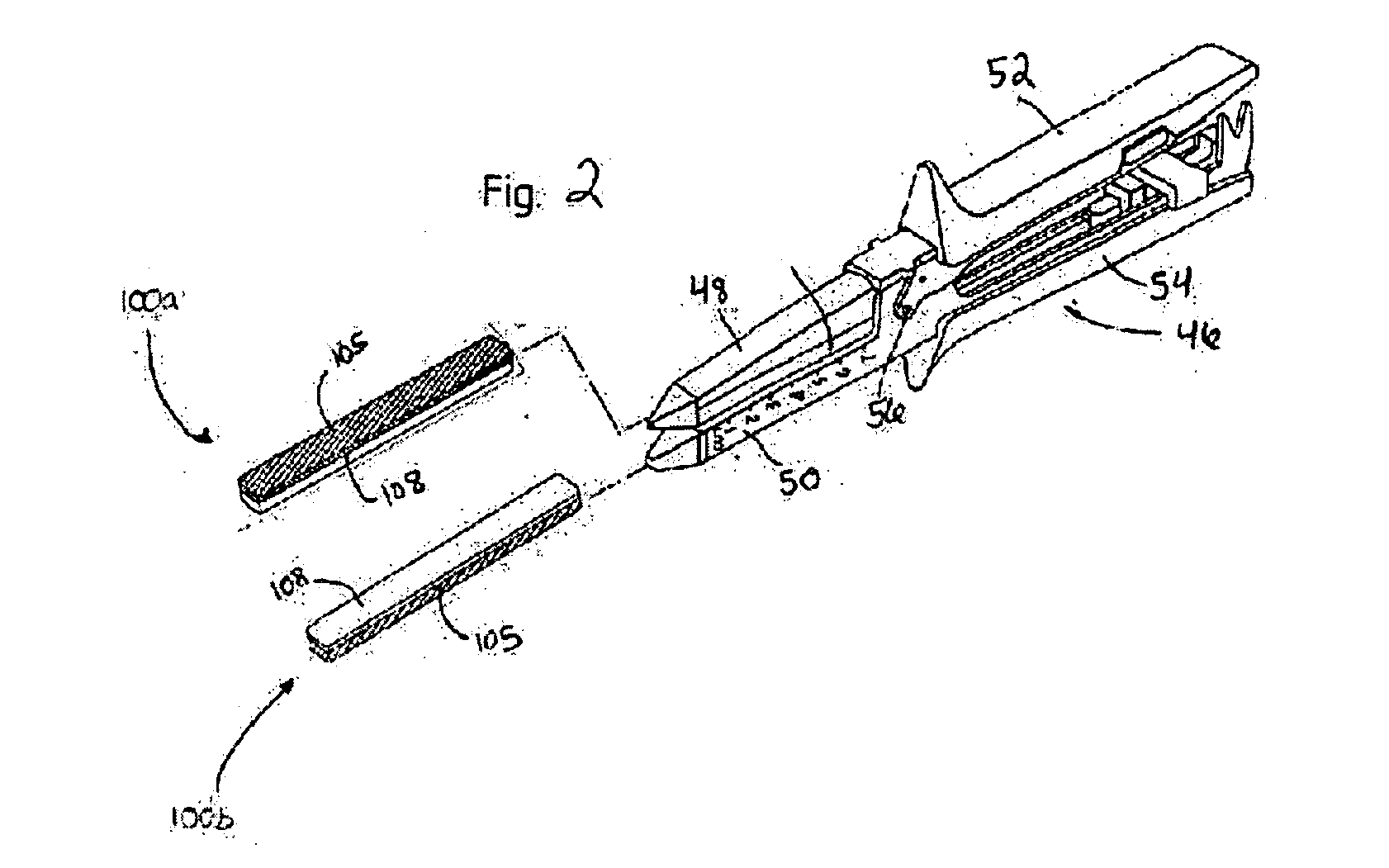
Surgical fastener buttress material
InactiveUS20060173470A1Easy to optimizeReduce misalignmentSurgical staplesWound clampsButtressStaple line
A staple line buttress material having an adhesive surface, packaged and provided in sterile, ready-to-use form. The material can be used to retrofit surgical staplers to provide an improved staple line, and with improved ease of use.
Owner:SYNOVIS LIFE TECH
Apparatus and method for altering generator functions in an ultrasonic surgical system
InactiveUS6908472B2Avoid mistakesNew system functionalityIncision instrumentsDiagnosticsDriving currentElectricity
The present invention provides a system for implementing surgical procedures which includes an ultrasonic surgical hand piece having an end-effector, a console having a digital signal processor (DSP) for controlling the hand piece, an electrical connection connecting the hand piece and the console, and a memory, such as an EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory), disposed in the electrical connection. The console sends a drive current to drive the hand piece which imparts ultrasonic longitudinal movement to the blade. The console reads the memory and authenticates the hand piece for use with the console if particular or proprietary data are present in the memory. Moreover, to prevent errors in operating the hand piece, the memory can store certain diagnostic information which the console can utilize in determining whether the operation of the hand piece should be handicapped or disabled. Furthermore, the memory can be used to reprogram the console, if needed.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Drug releasing anastomosis devices and methods for treating anastomotic sites
ActiveUS7108701B2Reduce drug toxicityGood curative effectSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesBiological bodyReady to use
Medical devices, and in particular implantable medical devices, may be coated to minimize or substantially eliminate a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. The medical devices may be coated with any number of biocompatible materials. Therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may be mixed with the biocompatible materials and affixed to at least a portion of the medical device. These therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may also further reduce a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. Various materials and coating methodologies may be utilized to maintain the drugs, agents or compounds on the medical device until delivered and positioned.
Owner:WYETH
Coated endovascular AAA device
InactiveUS6852122B2Reduce drug toxicityGood curative effectSuture equipmentsStentsBiological bodyReady to use
Medical devices, and in particular implantable medical devices, may be coated to minimize or substantially eliminate a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. The medical devices may be coated with any number of biocompatible materials. Therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may be mixed with the biocompatible materials and affixed to at least a portion of the medical device. These therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may also further reduce a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. In addition, these therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds may be utilized to promote healing, including the formation of blood clots. Various materials and coating methodologies may be utilized to maintain the drugs, agents or compounds on the medical device until delivered and positioned.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Attachment and optical probe
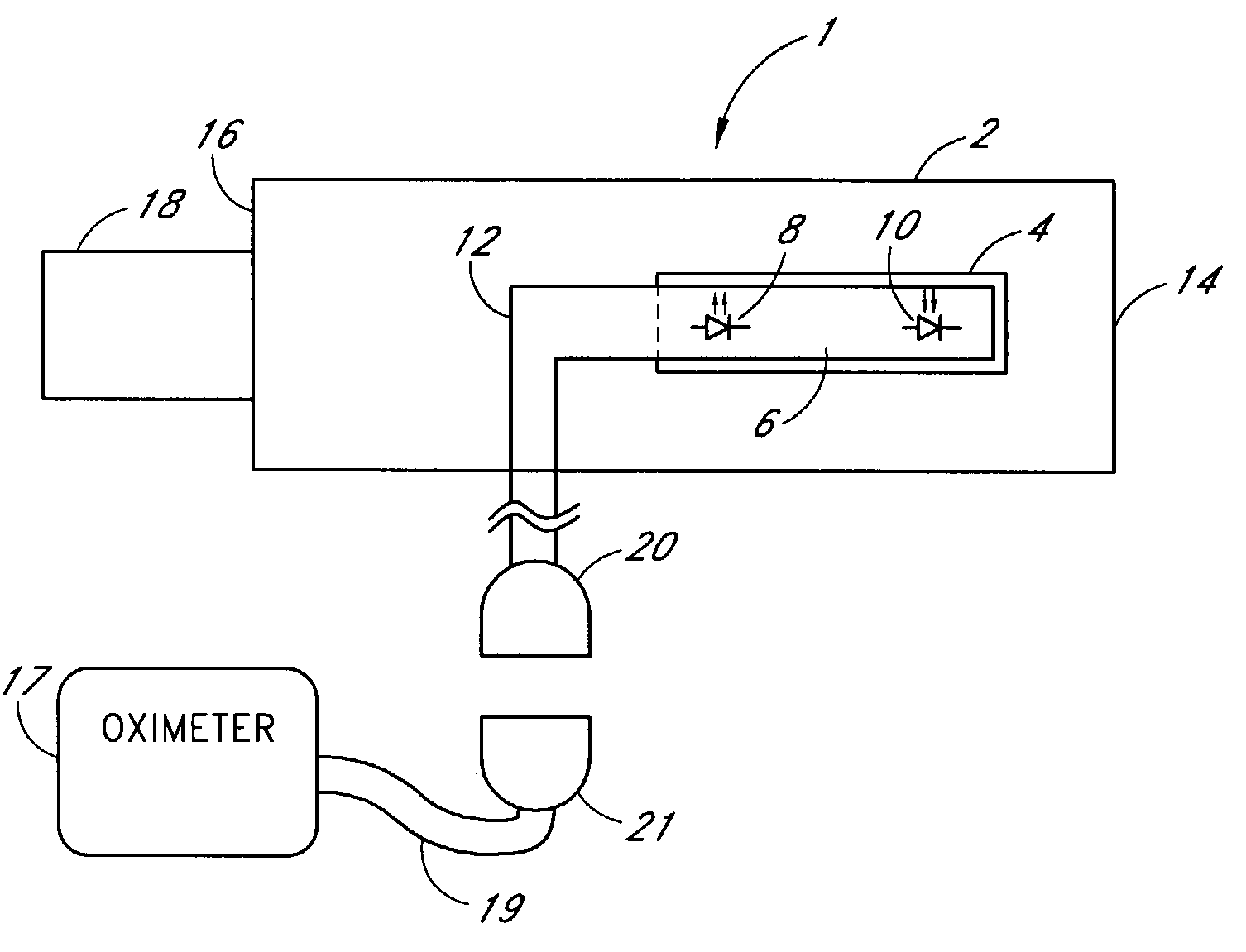
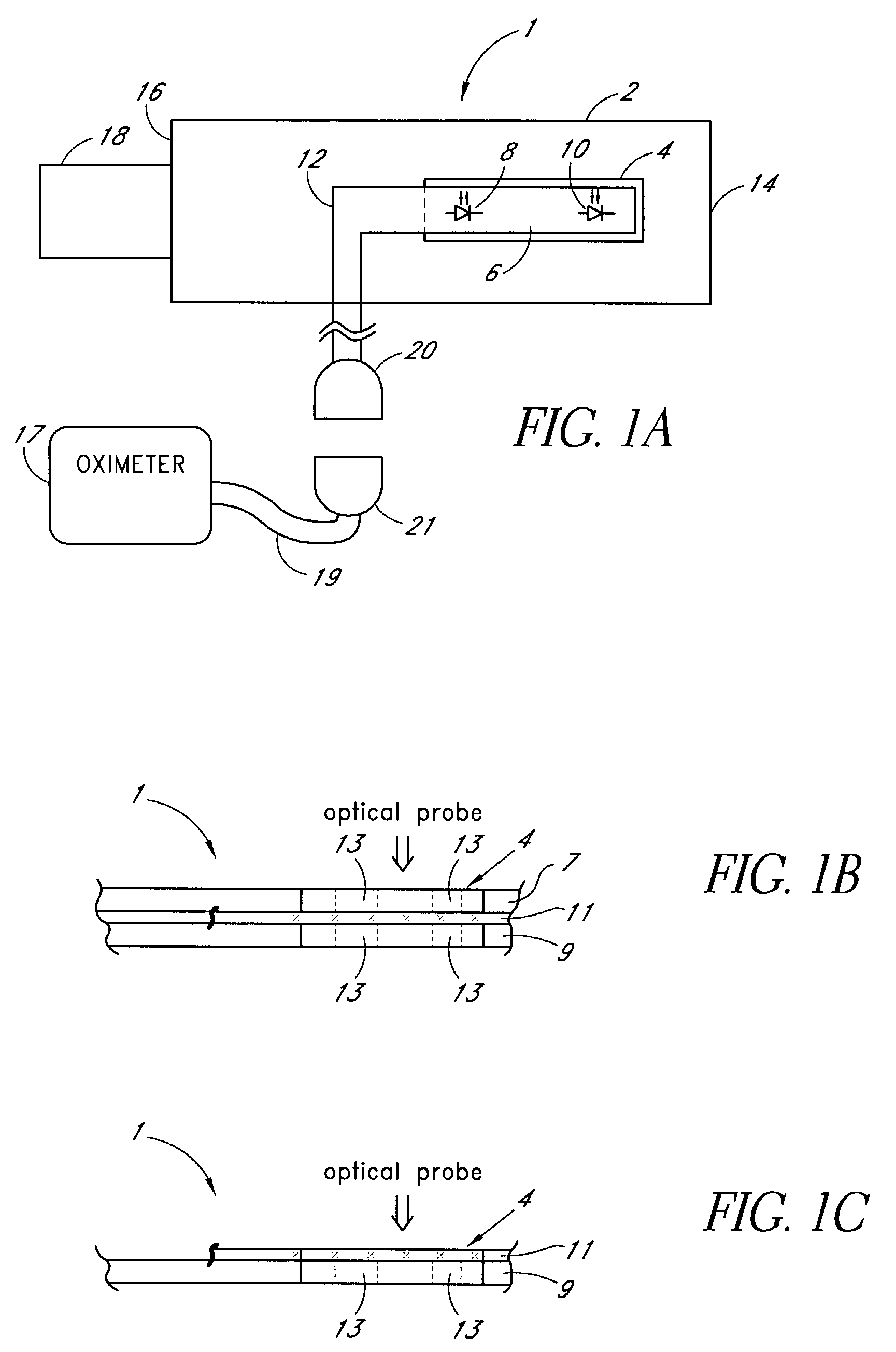
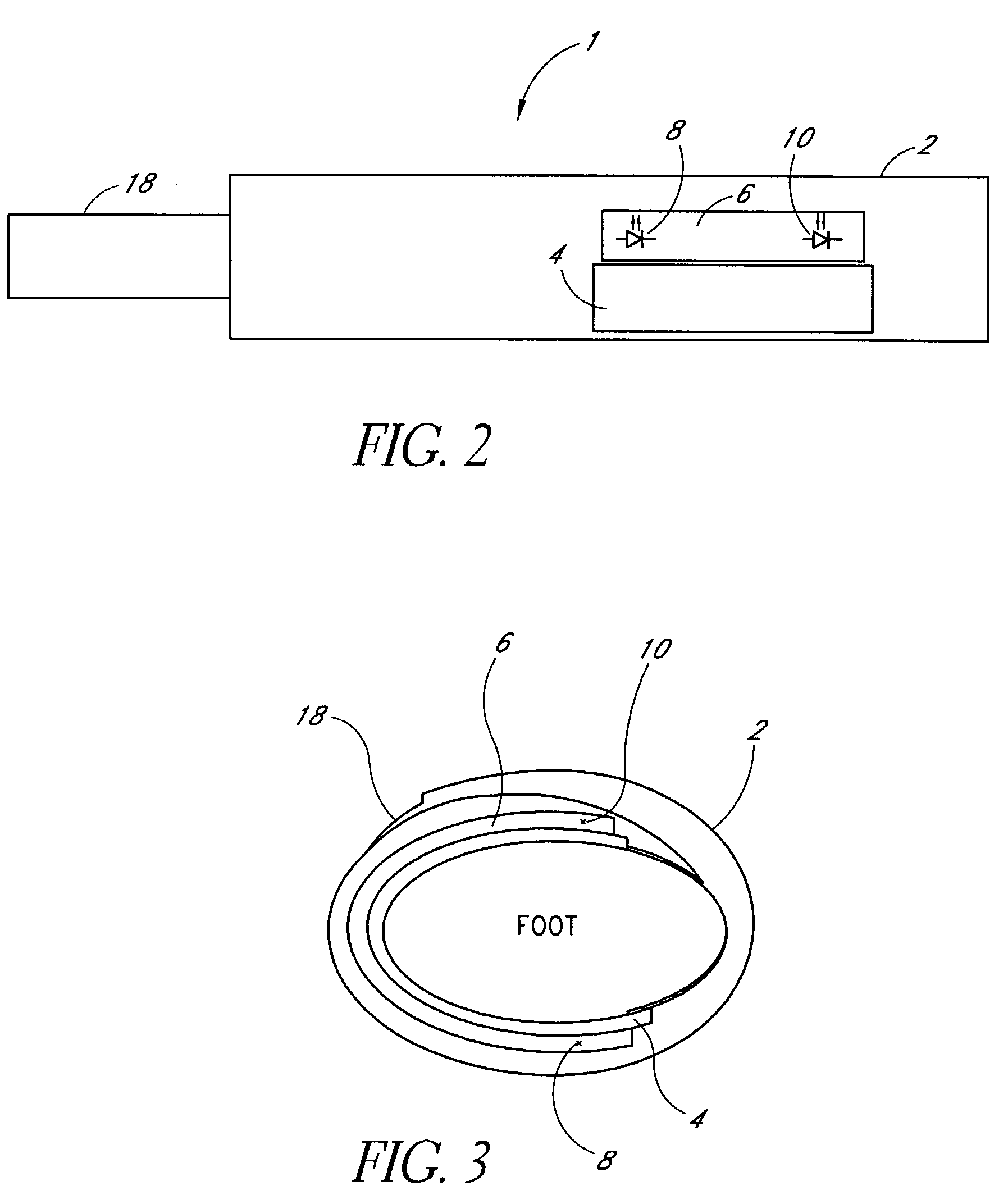
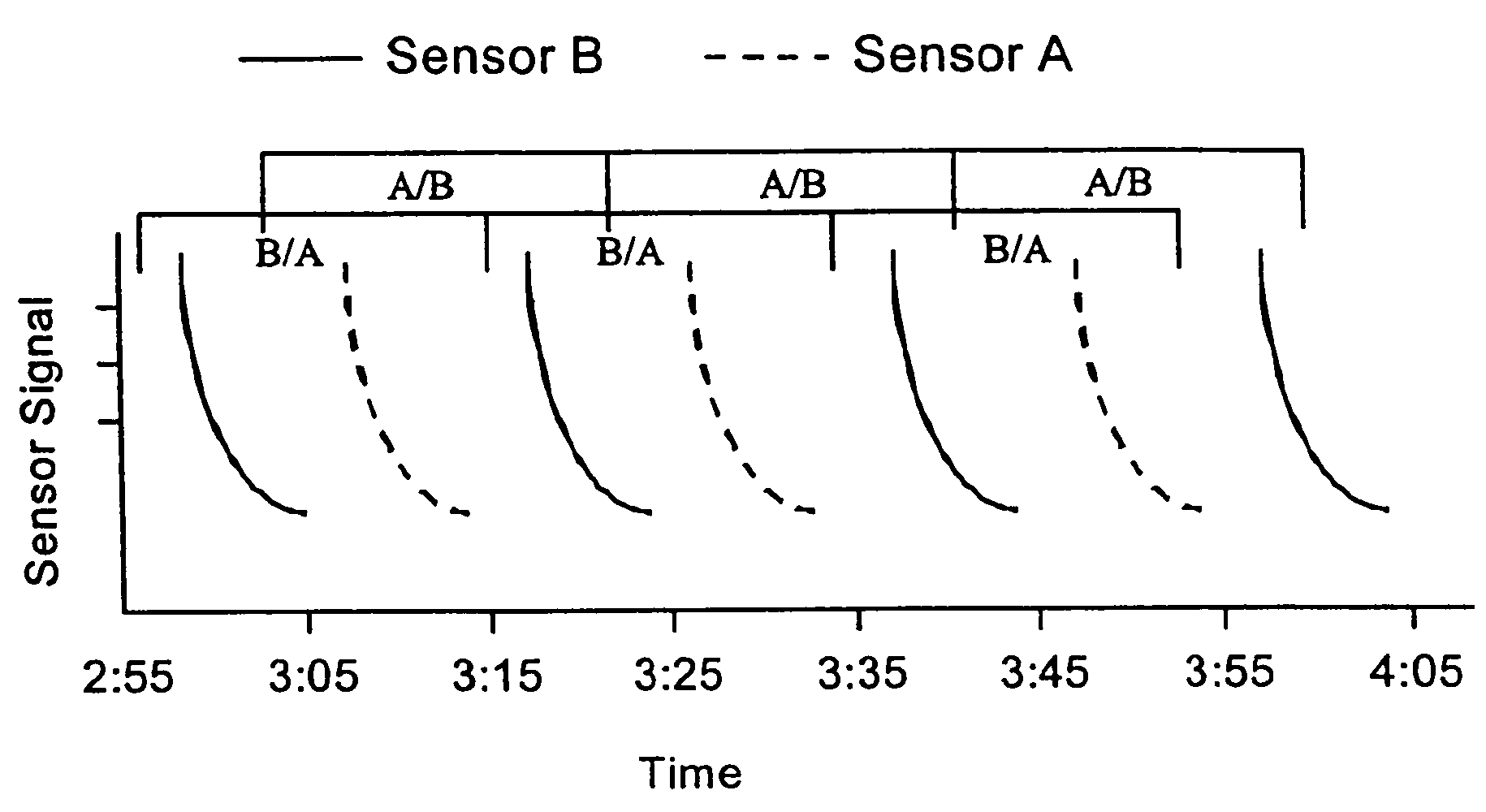
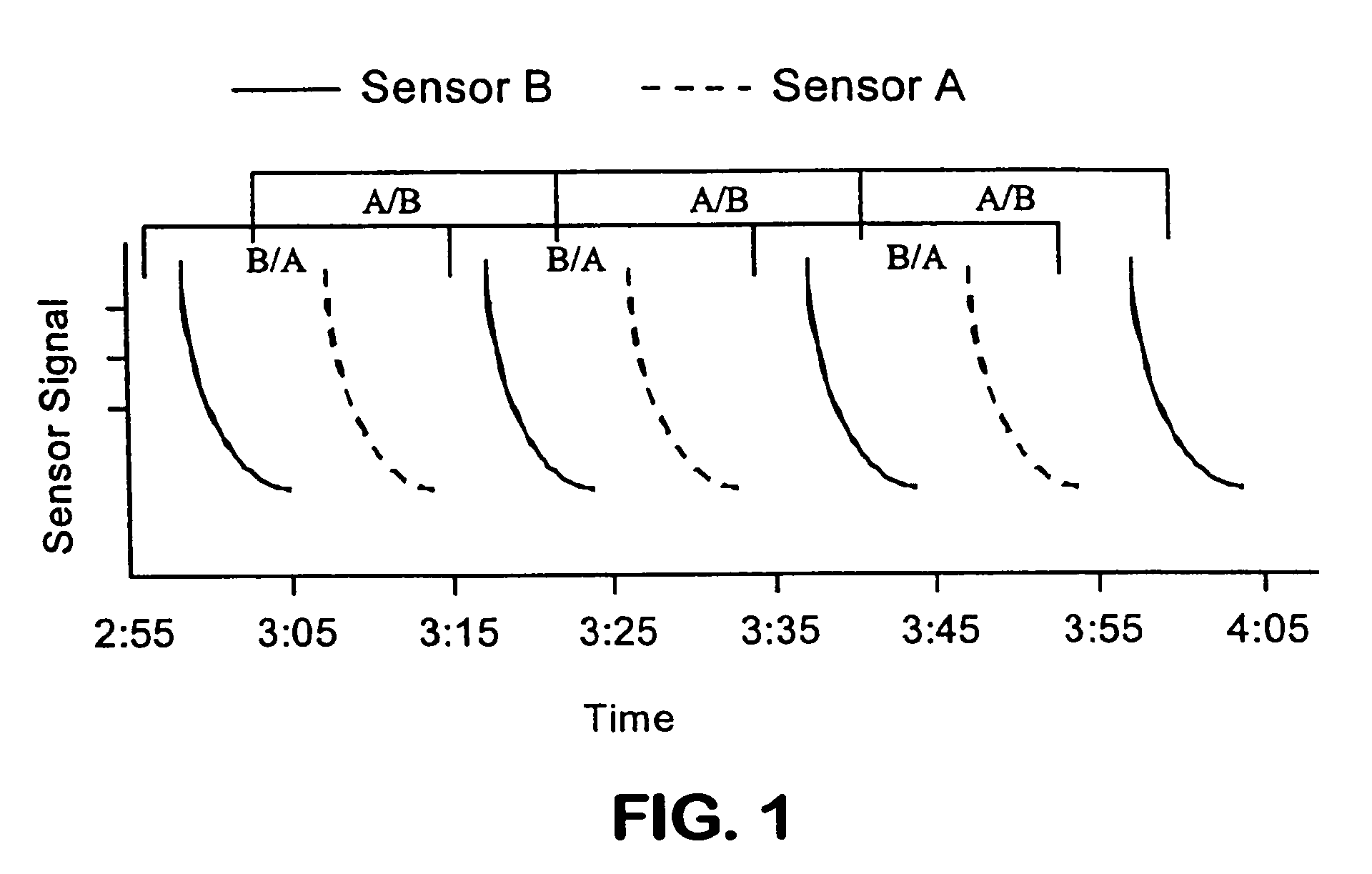
A medical monitoring system, such as an oximetry system, applies an attachment for securing an optical probe to a measurement site. The attachment has an elongated support with a first end and a second end, and a dedicated area in proximity of the first end. The dedicated area receives an optical probe and includes a material that is transparent for light emitted and received by the optical probe. The dedicated area mountably receives the optical probe on the material so that in use, the material is positioned between the optical probe and a surface of a measurement site. The optical probe may be factory-mounted to the dedicated area of the attachment as a ready-to-use sensor. In the alternative, the attachment may be available as an individual component, or as a part of a kit including the attachment and the optical probe.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Methods for computing rolling analyte measurement values, microprocessors comprising programming to control performance of the methods, and analyte monitoring devices employing the methods
InactiveUS7011630B2Reduce morbidityReduce the probability of failureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteMonitoring system
The present invention relates to methods to increase the number of analyte-related signals used to provide analyte measurement values, e.g., when two or more analyte-related signals are used to obtain a single analyte measurement value a “rolling” value based on the two or more signals can be employed. In another aspect, interpolation and / or extrapolation methods are used to estimate unusable, missing or error-associated analyte-related signals. Further, interpolation and extrapolation of values are employed in another aspect of the invention that reduces the incident of failed calibrations. Further, the invention relates to methods, which employ gradients and / or predictive algorithms, to provide an alert related to analyte values exceeding predetermined thresholds. The invention includes the above-described methods, one or more microprocessors programmed to execute the methods, one or more microprocessors programmed to execute the methods and control at least one sensing and / or sampling device, and monitoring systems employing the methods described herein.
Owner:ANIMAS TECH +1
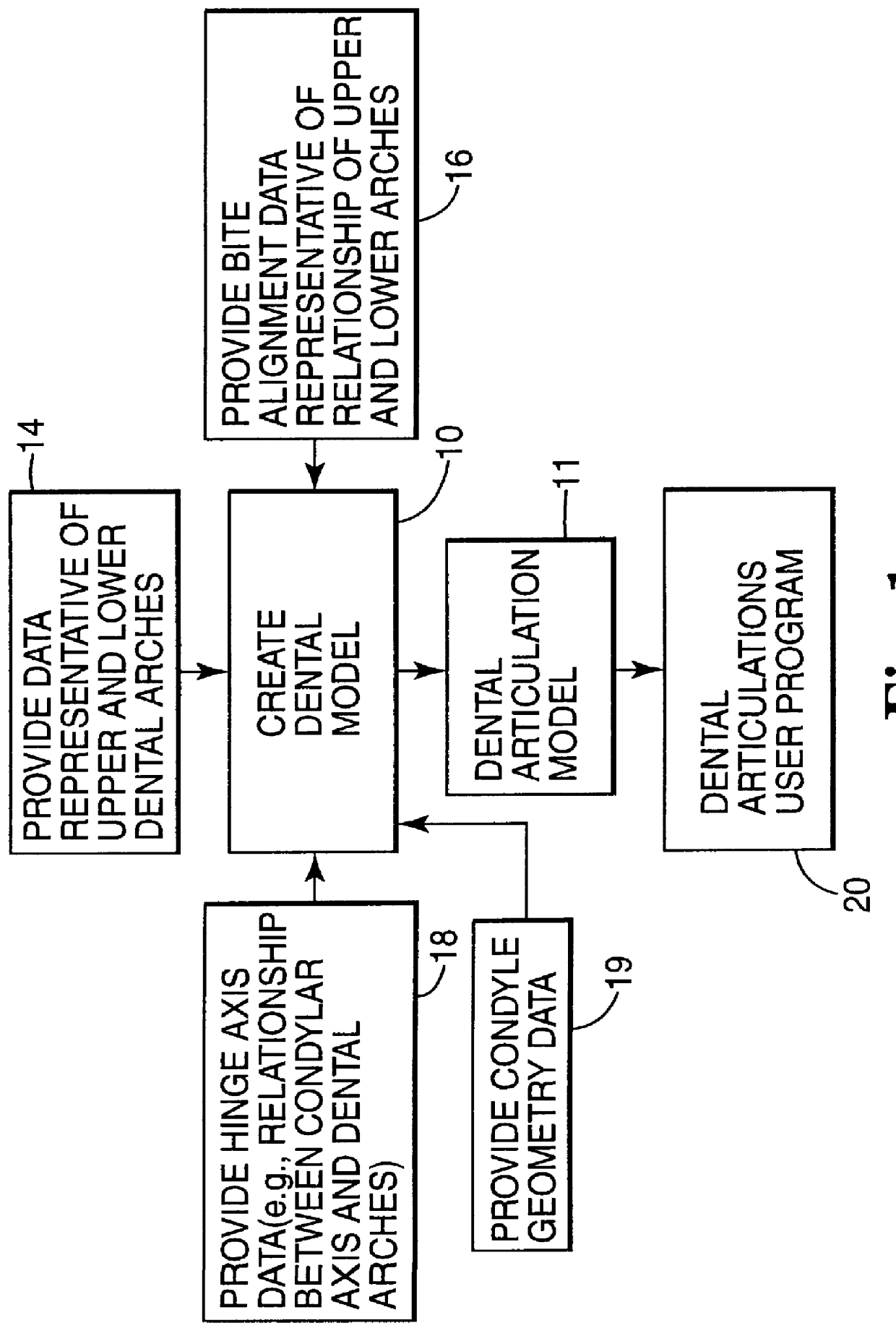
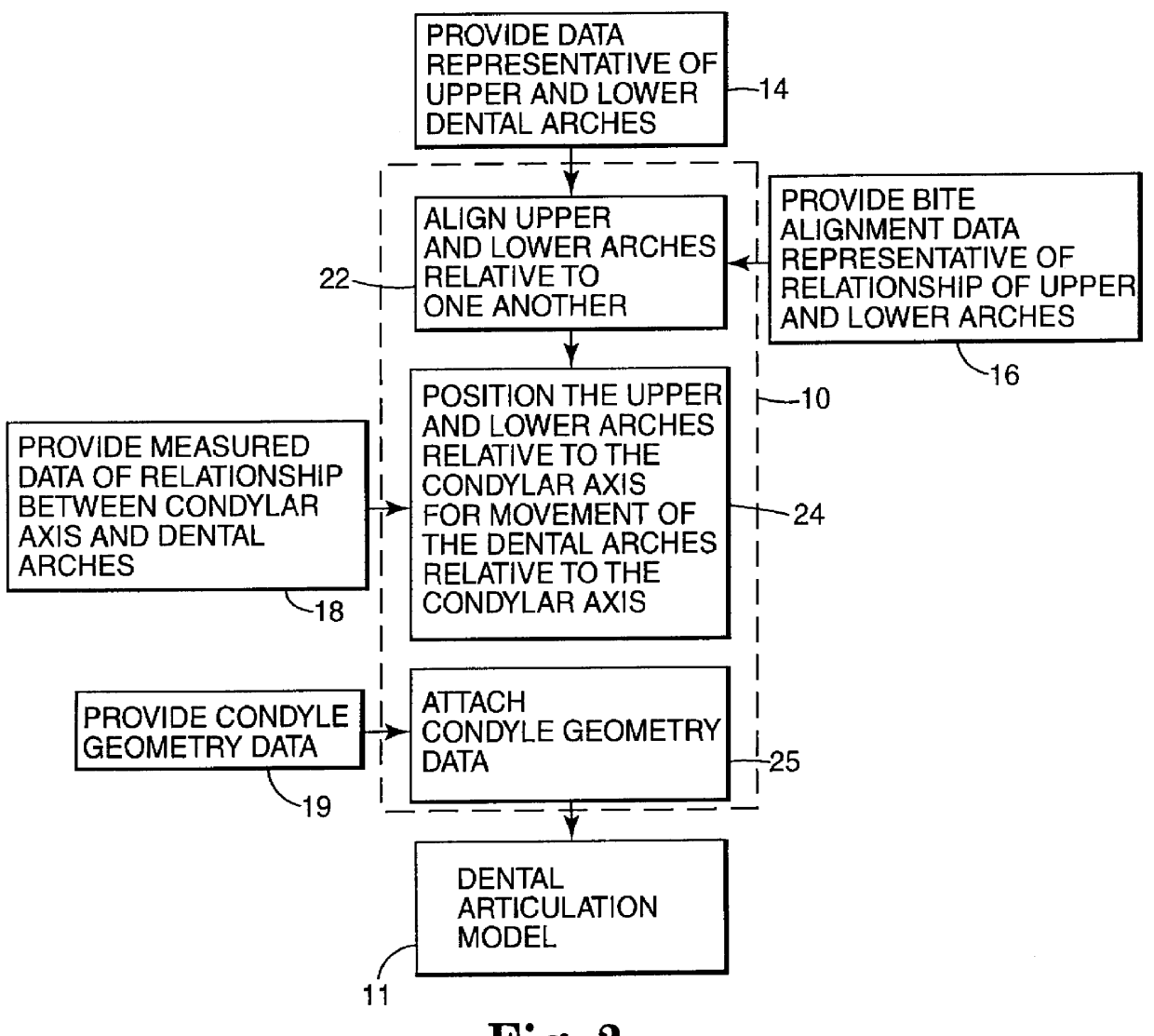
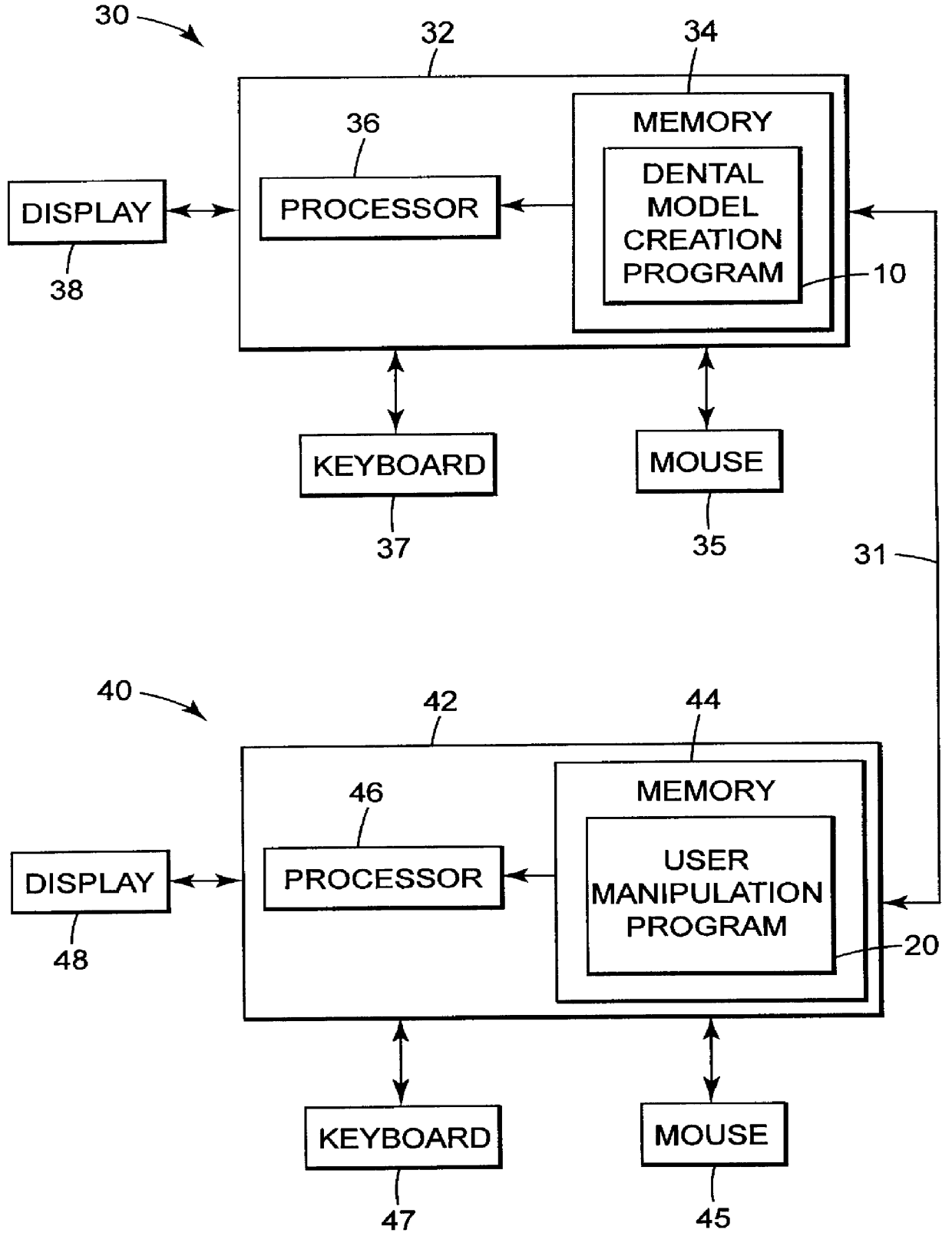
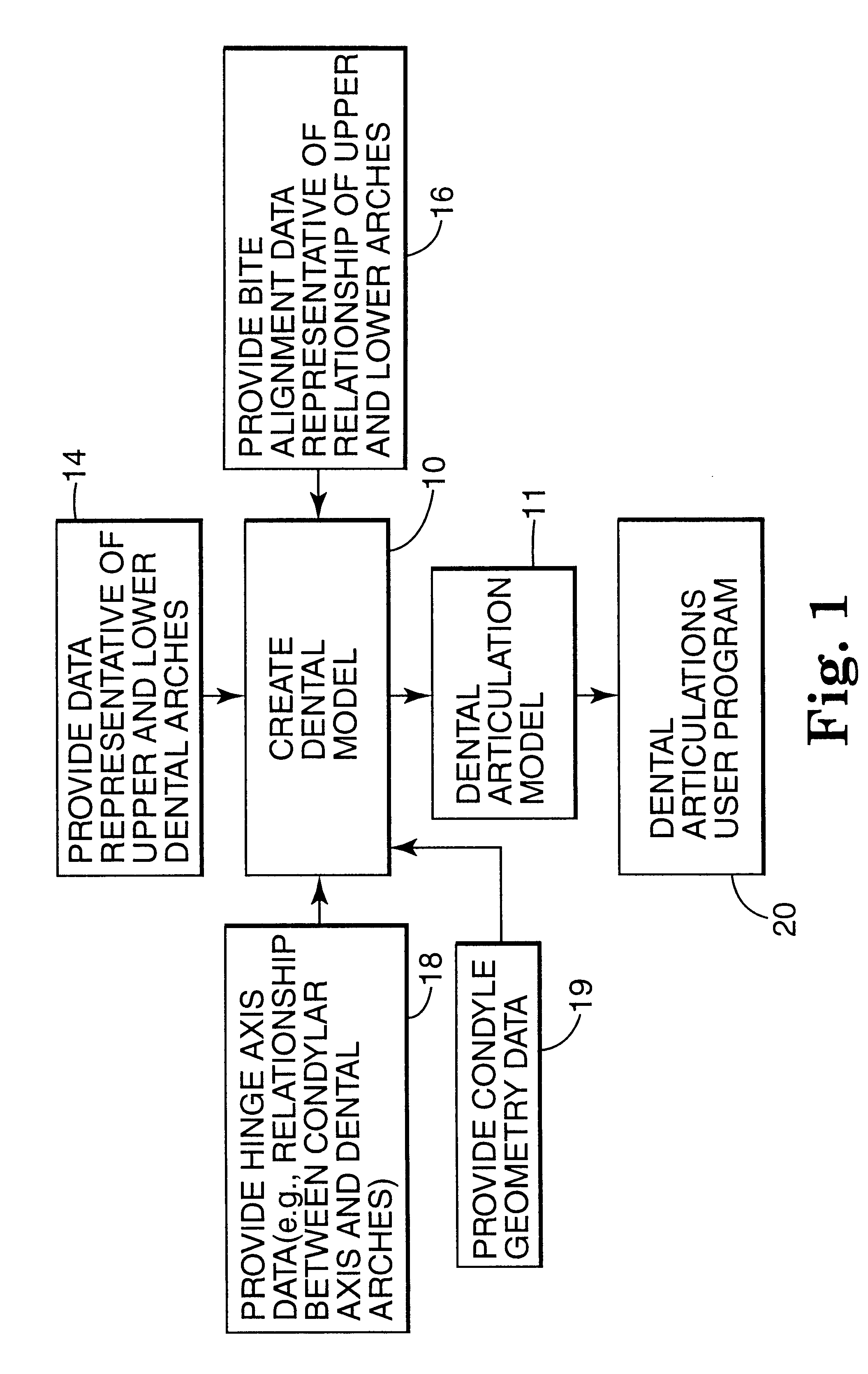
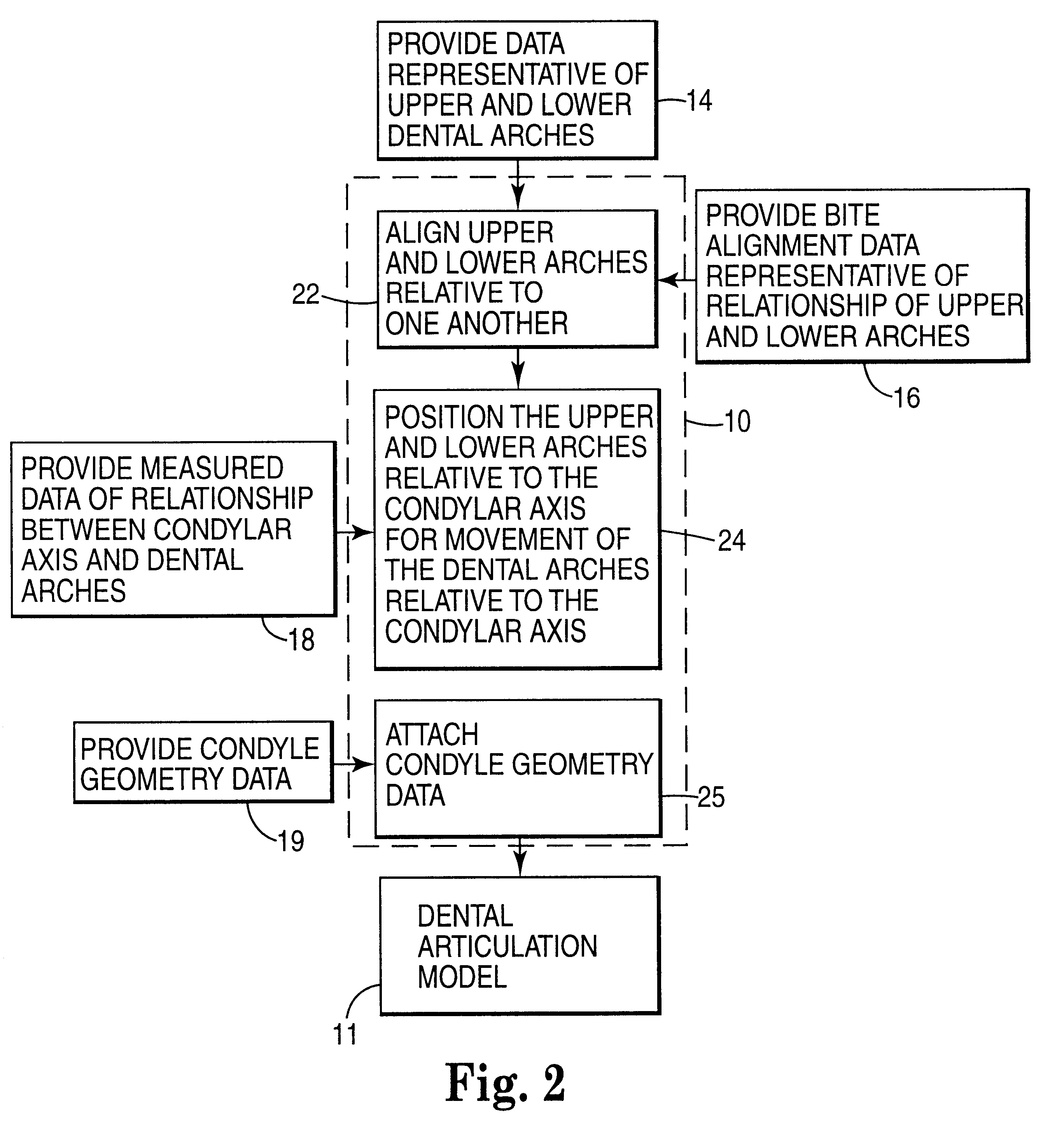
Methods for use in dental articulation
A computer implemented method of creating a dental model for use in dental articulation includes providing a first set of digital data corresponding to an upper arch image of at least a portion of an upper dental arch of a patient, providing a second set of digital data corresponding to a lower arch image of at least a portion of a lower dental arch of the patient, and providing hinge axis data representative of the spatial orientation of at least one of the upper and lower dental arches relative to a condylar axis of the patient. A reference hinge axis is created relative to the upper and lower arch images based on the hinge axis data. Further, the method may include bite alignment data for use in aligning the lower and upper arch images. Yet further, the method may include providing data associated with condyle geometry of the patient, so as to provide limitations on the movement of at least the lower arch image when the arch images are displayed. Further, a wobbling technique may be used to determine an occlusal position of the lower and upper dental arches. Various computer implemented methods of dental articulation are also described. For example, such dental articulation methods may include moving at least one of the upper and lower arch images to simulate relative movement of one of the upper and lower dental arches of the patient, may include displaying another image with the upper and lower dental arches of the dental articulation model, and / or may include playing back recorded motion of a patient's mandible using the dental articulation model.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO +1
Removable wound closure
InactiveUS7381859B2Promote wound healingMinimizes adhesion formationNon-adhesive dressingsWound drainsElastomerPorosity
A system and method for the temporary closure of a wound, especially an abdominal wound, to facilitate re-entry, final closure, and long term healing of the wound. An abdominal wound dressing and methods of use are described that enable the application of negative pressure to the wound site in a site healing promoting manner while also limiting the formation of adhesions that would prevent the removal of the dressing. The dressing comprises a layer of porous foam material (36) enclosed by sheets of elastomeric material (38) punctuated by a number of appropriately placed holes (34). Multiple layers of porous foam may also be used. A suction tube connector (16) is provided on an upper surface of a layer of foam (12) for connection to a negative pressure source. At least one layer of foam is enclosed in elastomeric material and is placed in direct contact with the tissue within the open wound. Fluids are drawn by negative pressure through the holes positioned in the elastomeric envelope, and through the foam. If multiple foam layers are employed, the lower layer(s) of foam are of a finer porosity while the upper layer of foam is coarse. An adhesive elastomeric sheet (14) covers the entire wound dressing and seals the edges to the skin surrounding the wound. An appropriate vacuum device is attached to the suction tube connector.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Active and semi-active damping in a telesurgical system
ActiveUS10058395B2Reduce vibrationPrevent movementDiagnosticsSurgical robotsSurgical operationSemi active
Methods and systems for damping vibrations in a surgical system are disclosed herein. The surgical system can include one or several moveable set-up linkages. A damper can be connected with one or several of the set-up linkages. The damper can be a passive, active, or semi-active damper. The damper can mitigate a vibration arising in one of the set-up linkages, and the damper can prevent a vibration arising in one of the linkages from affecting another of the set-up linkages. The active and semi-active dampers can be controlled with a feedback model and a feed-forward model.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Apparatus and methods for providing interactive entertainment
InactiveUS20080014835A1Increase learning and entertainment opportunityImprove creativityComputerized toysVideo gamesReady to useSpecial effects
Embodiments of the invention provide a unique interactive game that includes multiple dynamic layers in which a participant may complete a variety of challenges and / or tasks. For example, the participant may obtain a toy “wand” from a retail phase that is usable in an interactive entertainment phase. The interactive entertainment phase may include multiple interrelated layers such that progress in one or more layers may affect the participant's experience in one or more other layers. The participant may also receive training on how to use the wand and / or complete one or more special effects, adventures and / or quests. During or following the interactive entertainment phase, the participant may use accumulated points and / or powers to redeem prizes and / or compete against other participants, such as in a duel.
Owner:MQ GAMING
Implantable device and methods for delivering drugs and other substances to treat sinusitis and other disorders
Implantable devices and methods for delivering drugs and other substances to locations within the body of a human or animal subject to treat or diagnose sinusitis and a variety of other disorders. The invention includes implantable substance delivery devices that comprise reservoirs and barriers that control the rate at which substances pass out of the reservoirs. The delivery devices may be advanced into the body using guidewires, catheters, ports, introducers and other access apparatus. In some embodiments the delivery devices may be loaded with one or more desired substance before their introduction into the body. In other embodiments the delivery devices are loaded and / or reloaded with a desired substance after the delivery device has been introduced into the body.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
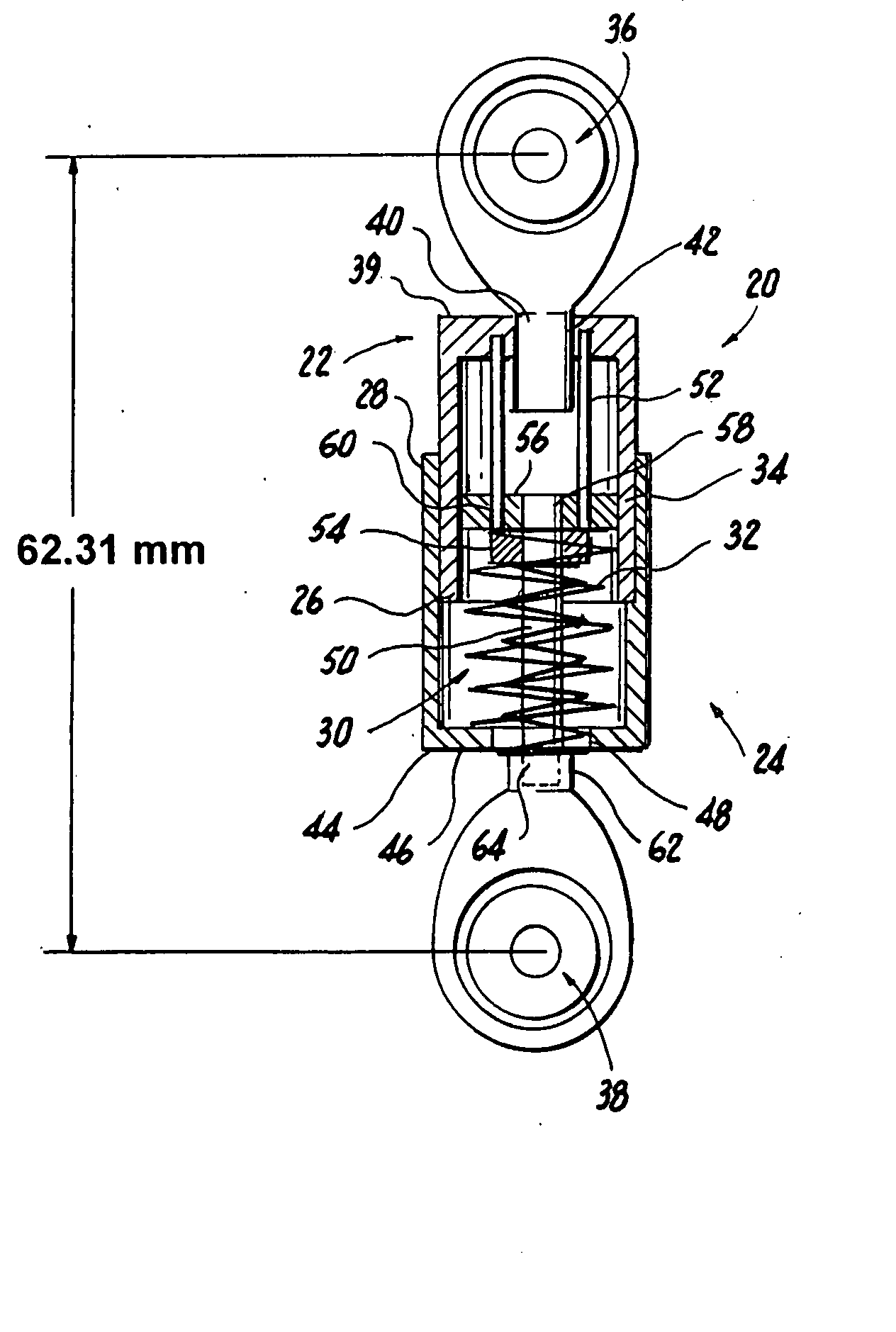
Spine stabilization systems and associated devices, assemblies and methods
InactiveUS20050171543A1Easy to installImprove clinical outcomesInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRotational freedomReady to use
A system and method for effecting multi-level spine stabilization is provided. The system includes a plurality of pedicle screws which are joined relative to each other by elongated members, e.g., rods. At least one of the rods includes a dynamic stabilizing member. The pedicle screw junctions are dynamic, i.e., free relative movement of a socket member is permitted relative to a fixed spherical element. Placement of the spherical element may be facilitated using a guidewire system that includes a guidewire and a tapered guide member. A spine stabilization assembly is also provided that includes an attachment member that includes an opening. At least one spherical element that includes a rod-receiving channel is movably mounted within the opening with three degrees of rotational freedom. The spherical element generally defines an elliptical rod-receiving channel that is deformable to a circular opening to firmly engage a rod positioned therein. Multi-level stabilization systems that combine / mix dynamic and non-dynamic stabilization modalities are also provided. The multi-level spine stabilization system offers efficacious clinical results at least in part due to the inclusion of dynamic stabilizing member(s).
Owner:APPLIED SPINE TECH
Methods for use in dental articulation
A computer implemented method of creating a dental model for use in dental articulation includes providing a first set of digital data corresponding to an upper arch image of at least a portion of an upper dental arch of a patient, providing a second set of digital data corresponding to a lower arch image of at least a portion of a lower dental arch of the patient, and providing hinge axis data representative of the spatial orientation of at least one of the upper and lower dental arches relative to a condylar axis of the patient. A reference hinge axis is created relative to the upper and lower arch images based on the hinge axis data. Further, the method may include bite alignment data for use in aligning the lower and upper arch images. Yet further, the method may include providing data associated with condyle geometry of the patient, so as to provide limitations on the movement of at least the lower arch image when the arch images are displayed. Further, a wobbling technique may be used to determine an occlusal position of the lower and upper dental arches. Various computer implemented methods of dental articulation are also described. For example, such dental articulation methods may include moving at least one of the upper and lower arch images to simulate relative movement of one of the upper and lower dental arches of the patient, may include displaying another image with the upper and lower dental arches of the dental articulation model, and / or may include playing back recorded motion of a patient's mandible using the dental articulation model.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
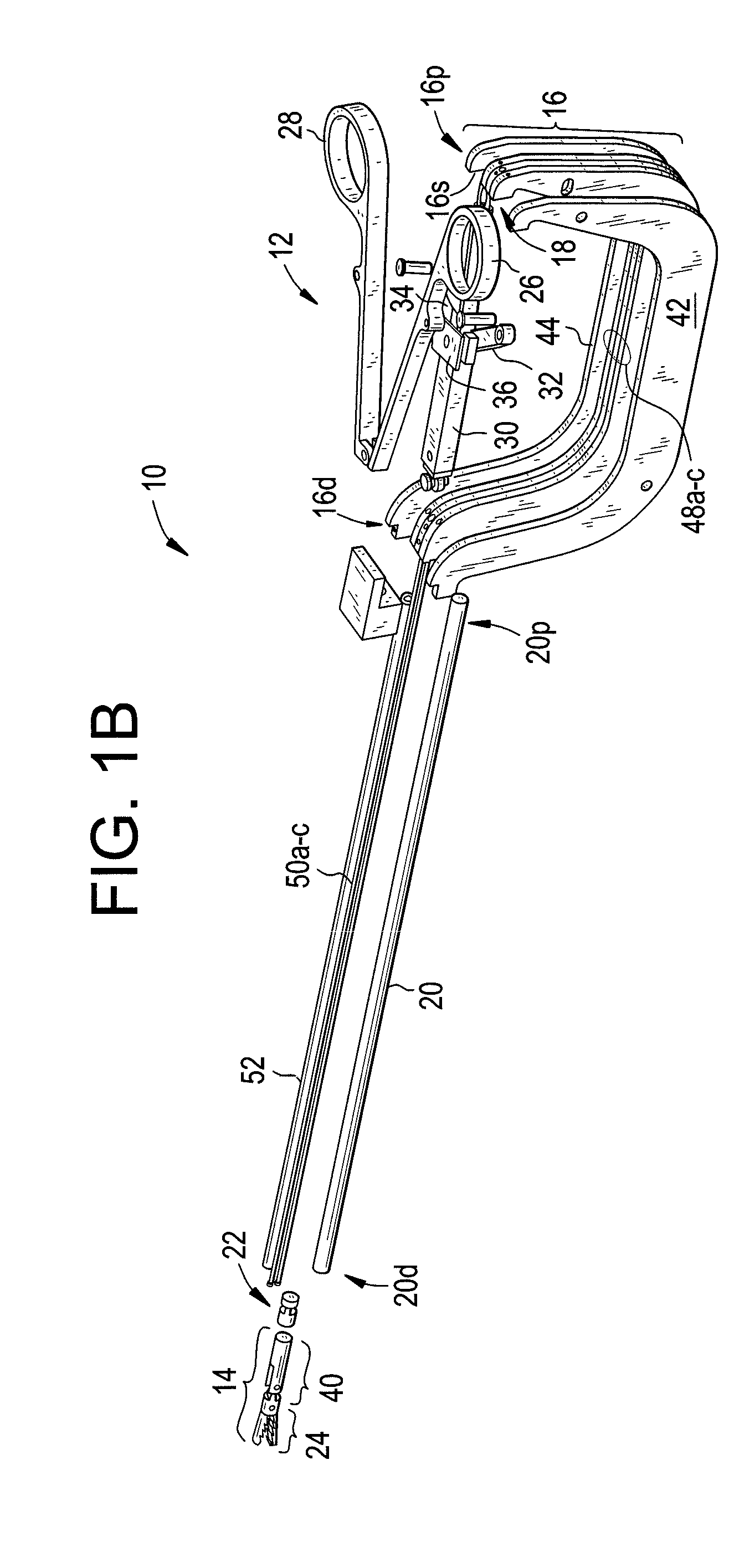
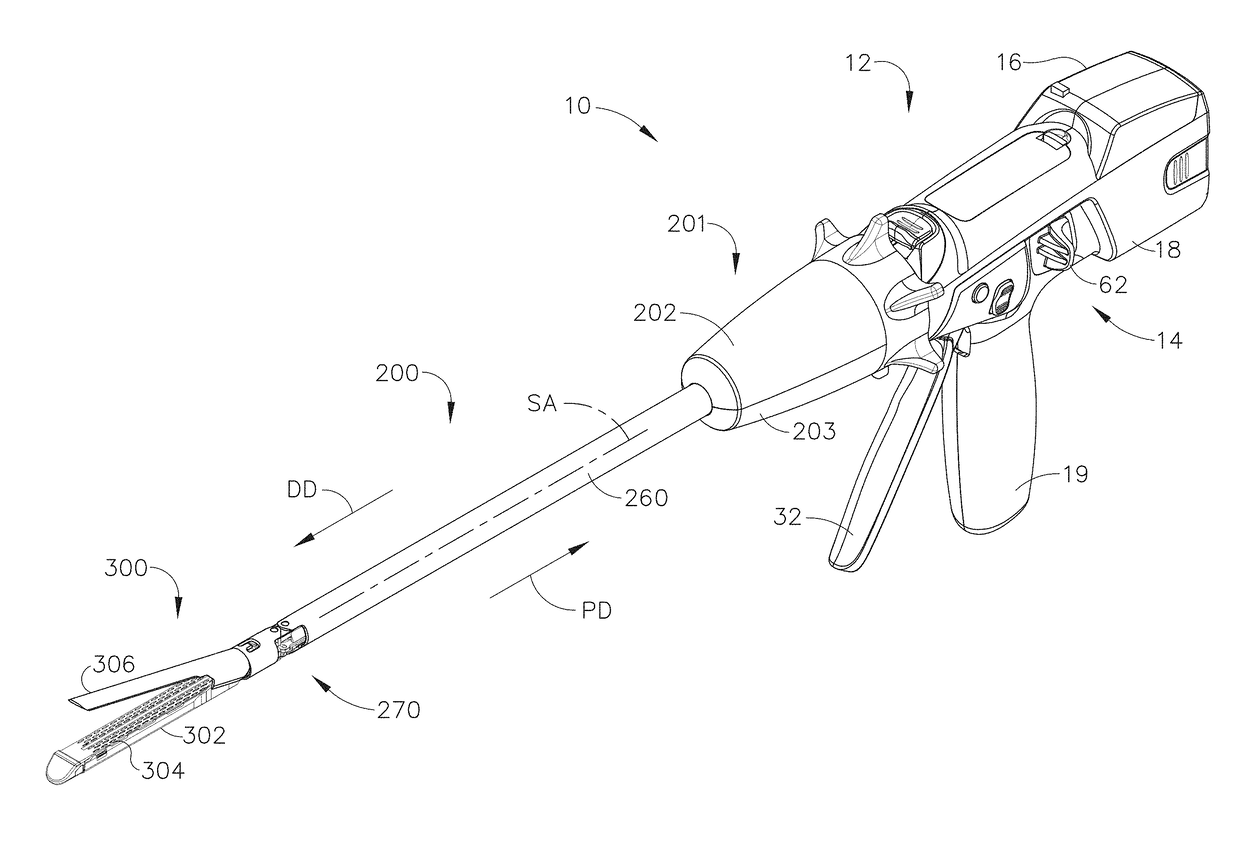
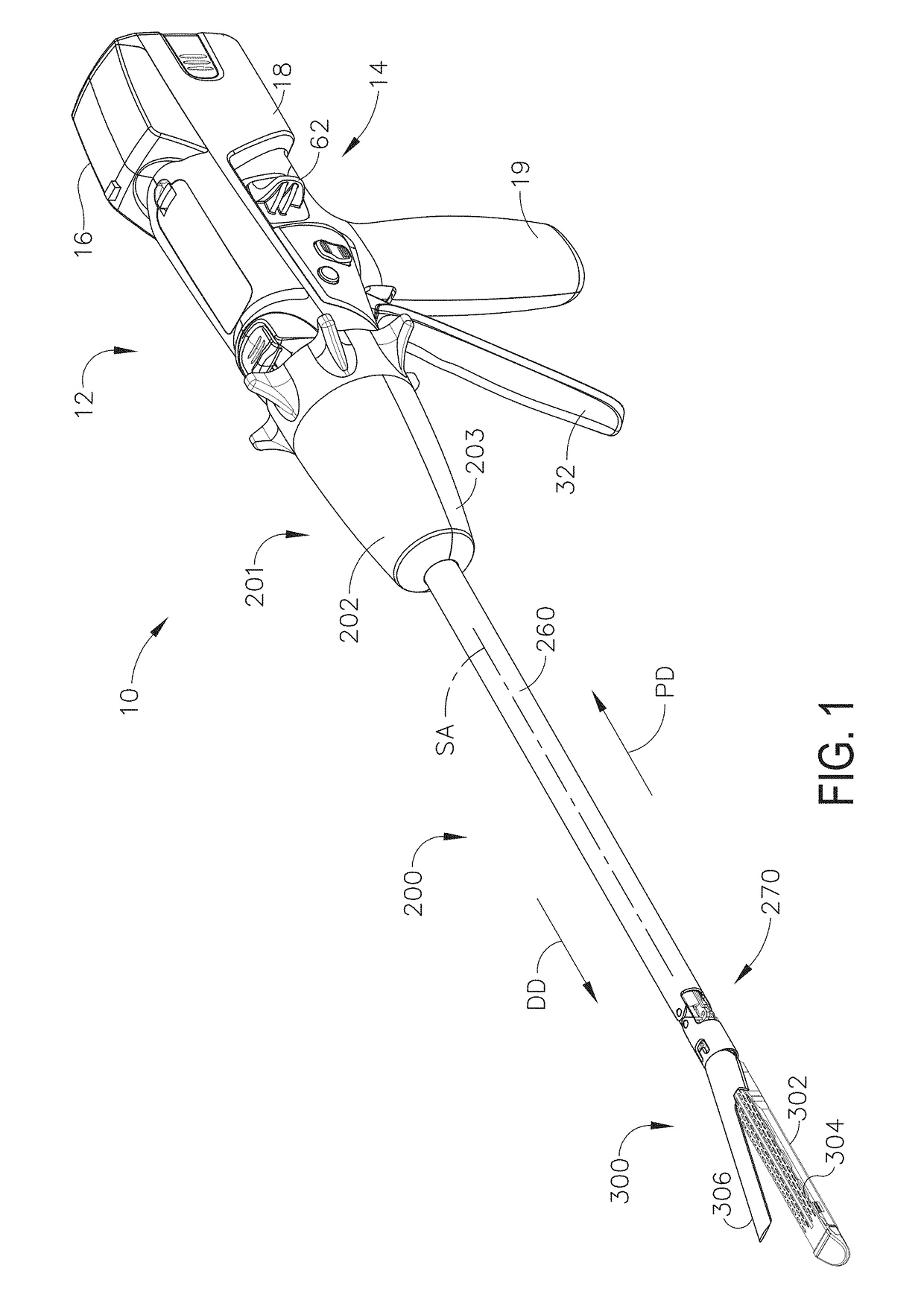
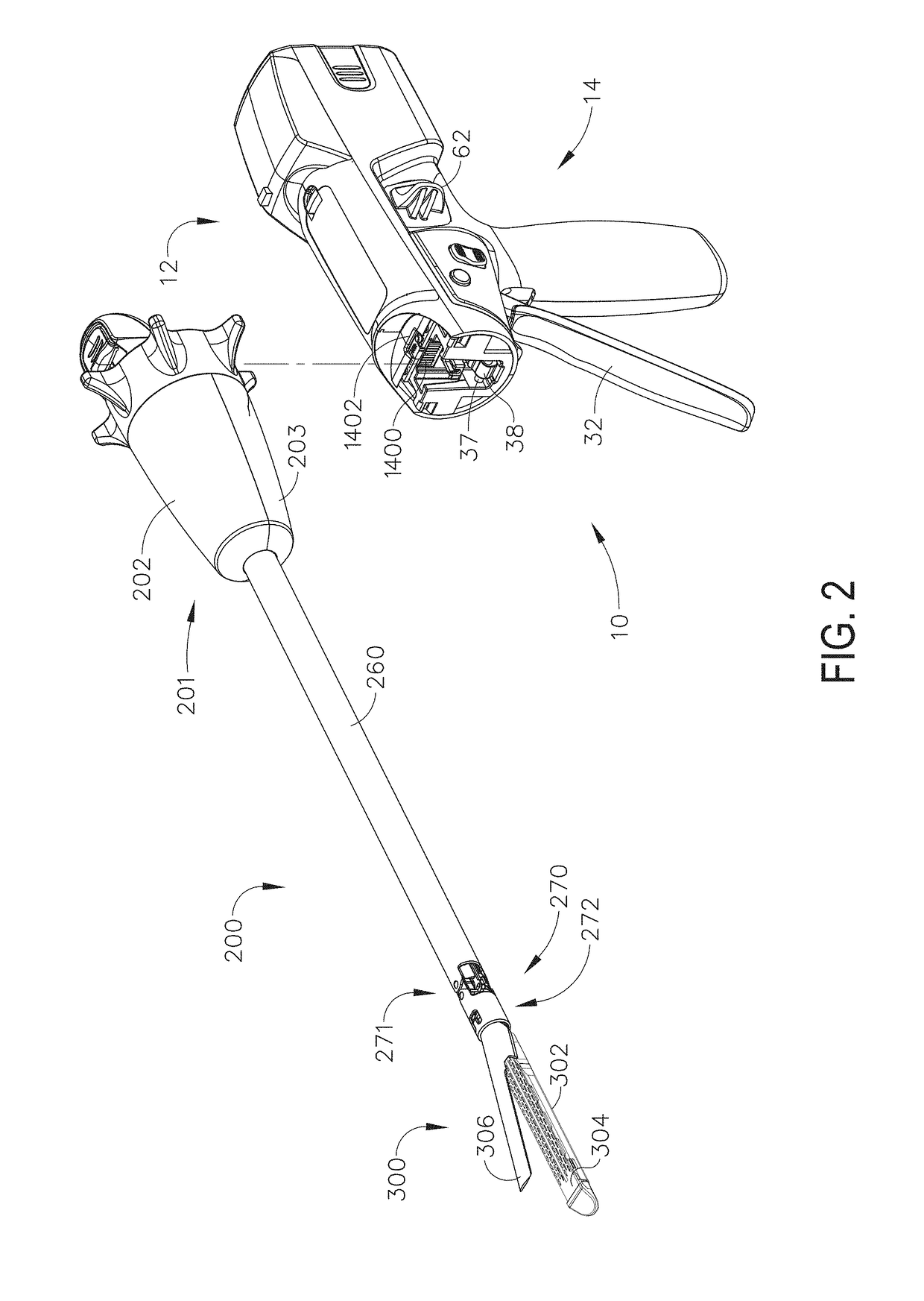
Laparoscopic device with distal handle
Methods and devices are provided for controlling movement of an end effector assembly, and in particular for causing mimicking motion between a handle and an end effector assembly. In an exemplary embodiment, a surgical device is provided having a handle or actuator, an elongate shaft, and an end effector assembly coupled to a distal end of the elongate shaft. The handle or actuator is configured such that movement of the handle is mimicked, not mirrored, by the end effector assembly. The mimicking motion can be achieved using various techniques, but in an exemplary embodiment the handle is located distal to an input joint, and motion is transferred to the end effector assembly through an output joint at a distal end of the elongate shaft. The motion is preferably transferred using a mechanical transmission coupled between the input and output joints.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Apparatus and methods for treating tissue
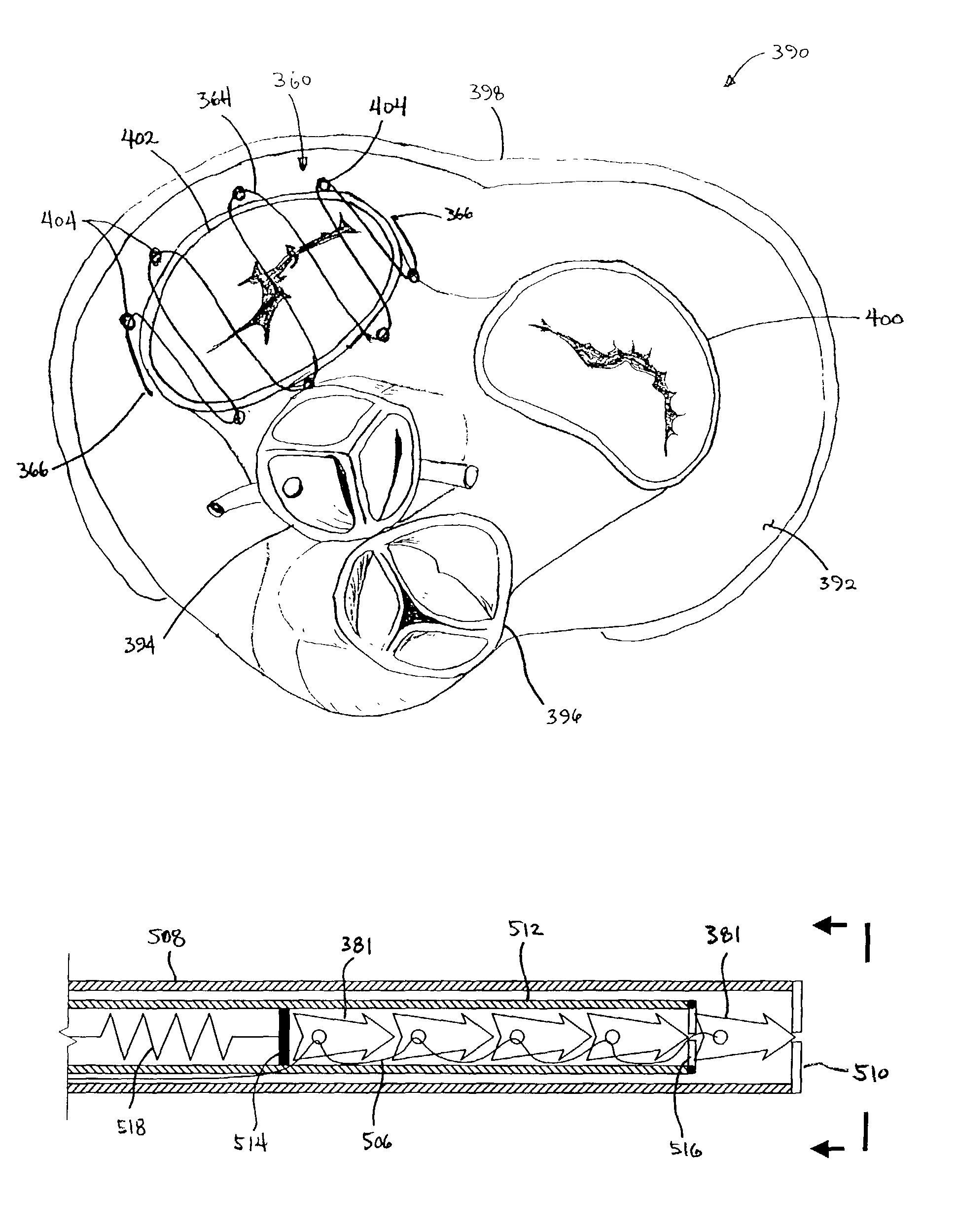
InactiveUS7186262B2Reducing valve diameterFunction increaseSuture equipmentsUltrasound therapyControl mannerTransducer
Apparatus and methods are provided for thermally and / or mechanically treating tissue, such as valvular structures, to reconfigure or shrink the tissue in a controlled manner. Mechanical clips are implanted over the leaflets of a valve, e.g., in the heart, either alone or after thermal treatment to cause the valve to close more tightly. The clips are delivered by a catheter and may be configured to traverse directly over the valve itself or to lie partially over the periphery of the valve to prevent obstruction of the valve channel. The clips can be coated with drugs or a radiopaque coating. Alternatively, individual anchors with a tensioning element, like a suture, may be used to approximate the valves towards each other. The catheter can also incorporate sensors or energy delivery devices, e.g., transducers, on its distal end.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Surgical instrument with detection sensors
ActiveUS20170296178A1Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using pressureSmall form factorSurgical site
Aspects of the present disclosure are presented for a surgical instrument having one or more sensors at or a near an end effector and configured to aide in the detection of tissues and other materials and structures at a surgical site. The detections may then be used to aide in the placement of the end effector and to confirm which objects to operate on, or alternatively, to avoid. Examples of sensors include laser sensors used to employ Doppler shift principles to detect movement of objects at the surgical site, such as blood cells; resistance sensors to detect the presence of metal; monochromatic light sources that allow for different levels of absorption from different types of substances present at the surgical site, and near infrared spectrometers with small form factors.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Minimally-Invasive Approach to Bone-Obstructed Soft Tissue
InactiveUS20080177268A1Improve shielding effectLow magnetic susceptibilitySurgeryMagnetic susceptibilityImaging quality
The subject invention pertains to a method and apparatus for placing a minimally-invasive access with respect to a patient's bone or other non-soft tissue. The subject invention can use a drilling machine incorporating an ultrasound motor. The subject drilling machine can be applied to sample, for example, bone biopsies under MRI control. In a specific embodiment, the subject ultrasound motor can be completely manufactured of non-magnetic materials, such as plastics, titanium, and titanium alloy, or ceramics and piezoceramics. The subject drilling apparatus can be placed into an MRI near field without influencing the image quality, and without the drilling apparatus itself being disturbed by the MRI magnet, gradient, or high-frequency field. The subject invention can incorporate good shielding with the subject drilling apparatus use of these materials, and can achieve minimal, if any, image distortions or so-called artifacts. Thus, the subject invention can involve the problem by use of non-magnetic materials of low magnetic susceptibility for the design of an actuation unit.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data for sensor calibration
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data are disclosed, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. The sensor can be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. Reference data resulting from benchtop testing an analyte sensor prior to its insertion can be used to provide initial calibration of the sensor data. Reference data from a short term continuous analyte sensor implanted in a user can be used to initially calibrate or update sensor data from a long term continuous analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
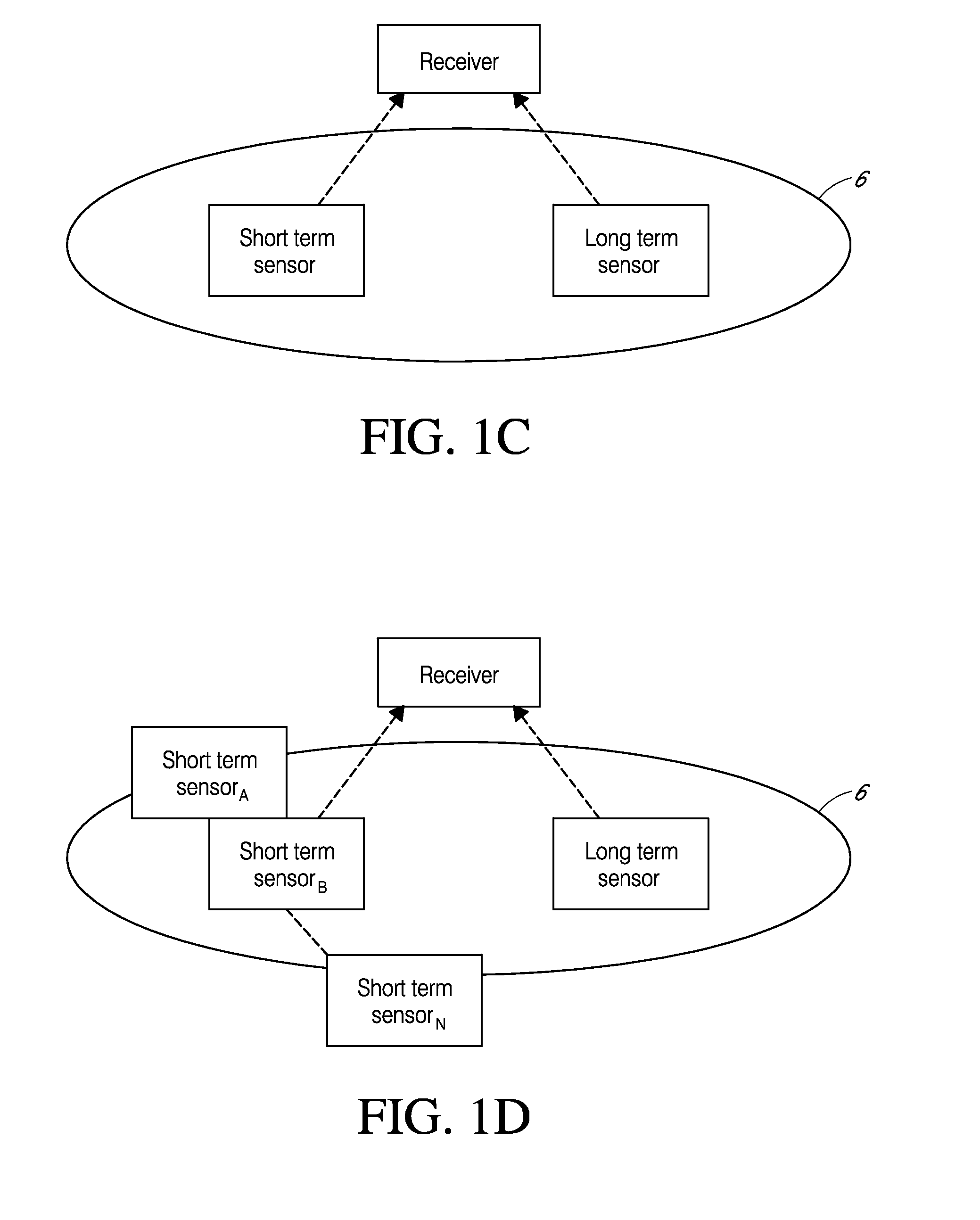
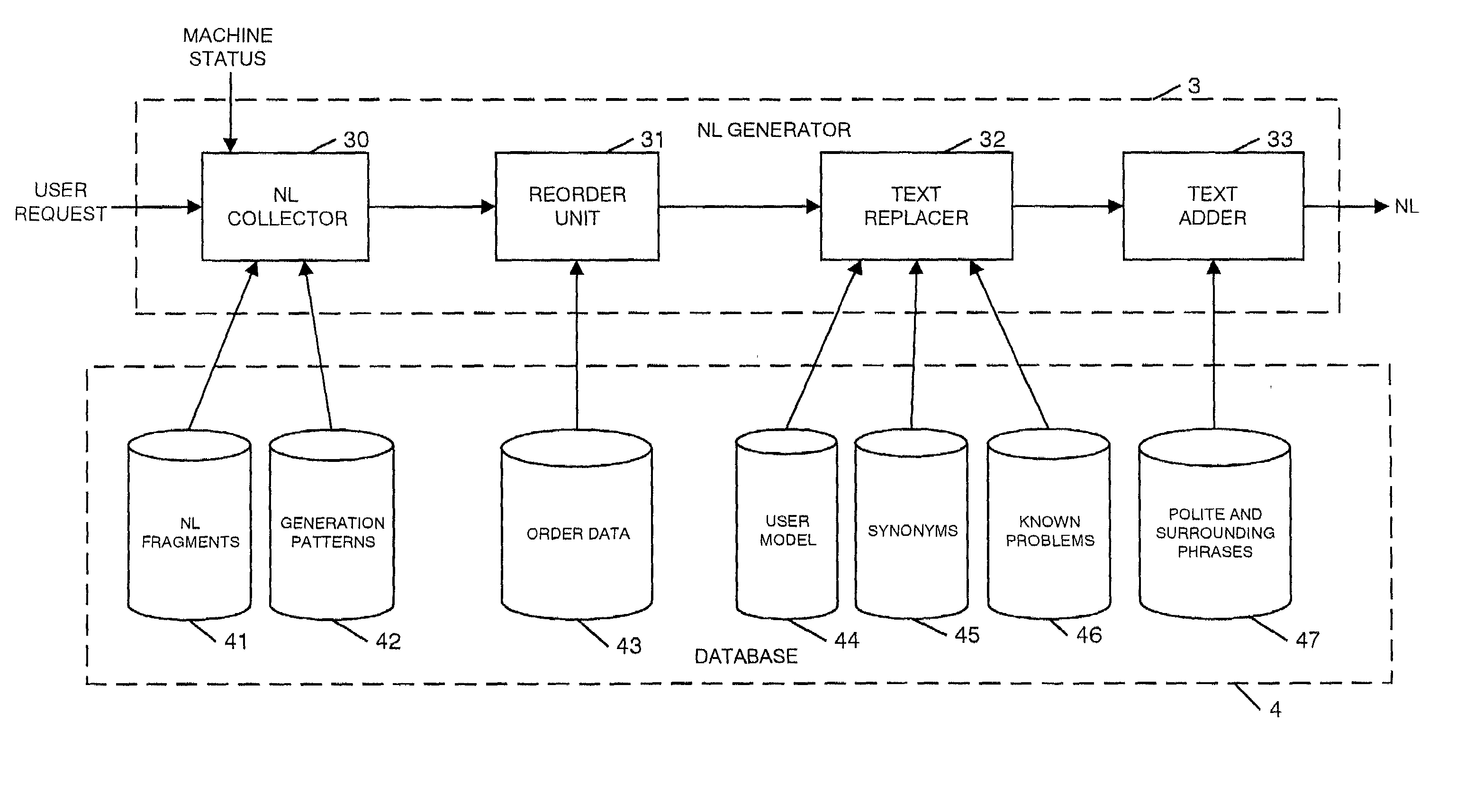
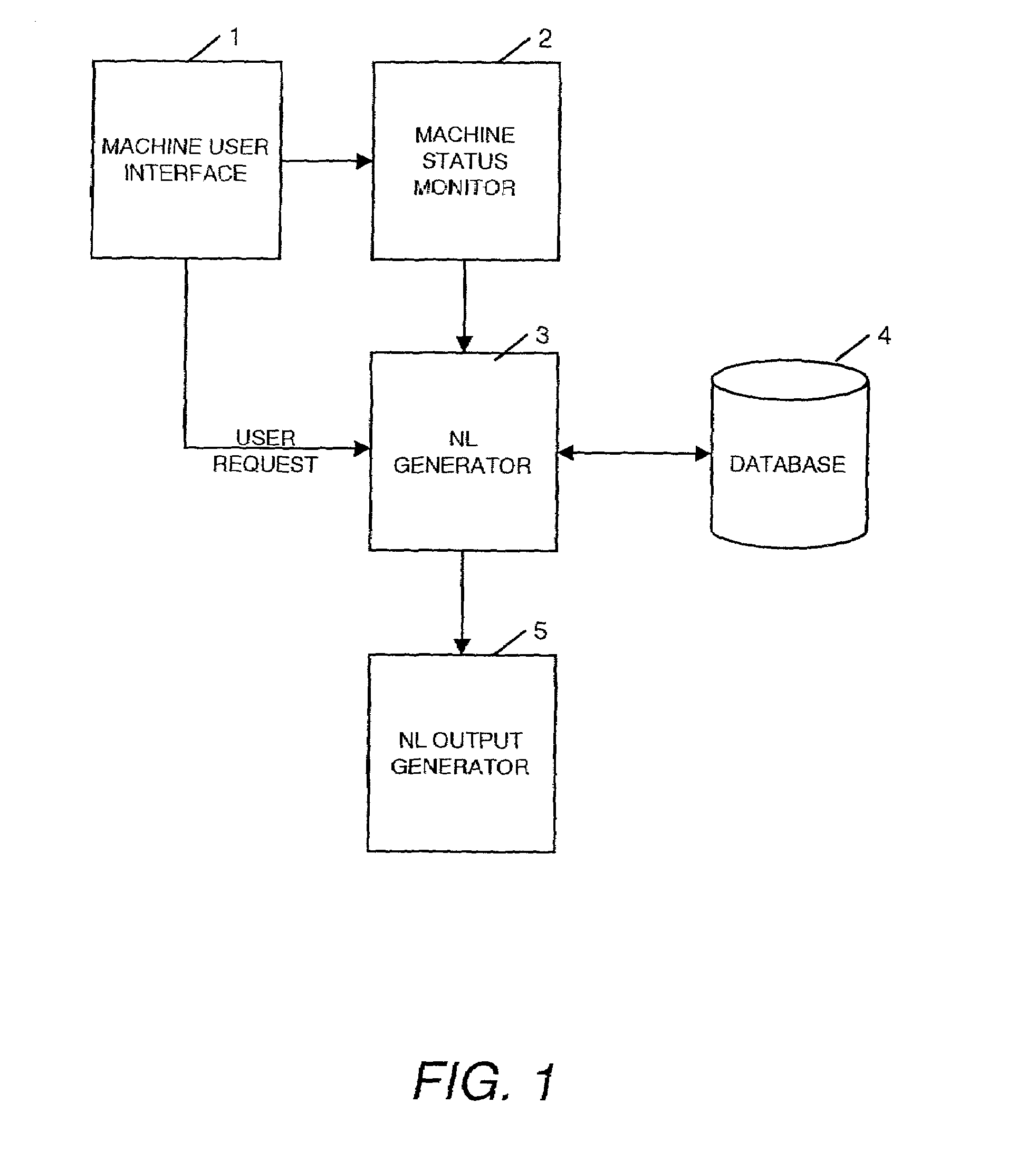
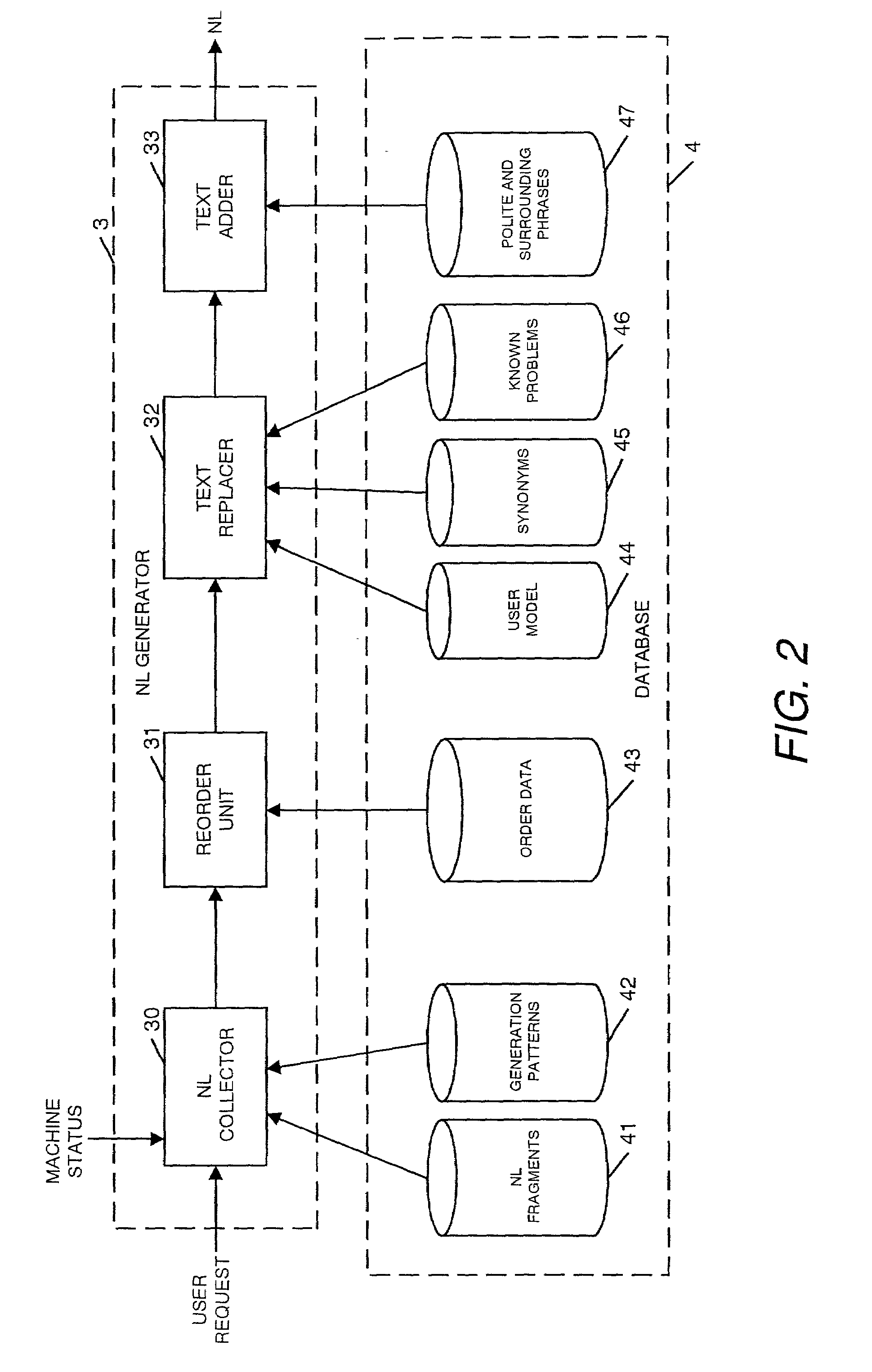
Natural language machine interface
InactiveUS7062428B2Input/output for user-computer interactionNatural language translationReady to useComputer science
A user interface is provided for use with a machine which can use a number of natural language instructions to reach one of a plurality of possible machine states. In order to provide information to a user to enable them to more efficiently achieve the current machine state using natural language instructions, the current state of the machine is determined and used to generate information to inform the user of a natural language instruction which can be input to a machine to achieve the current state of the machine.
Owner:CANON KK
Microfluidic particle-analysis systems
ActiveUS7312085B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReady to useMixed group
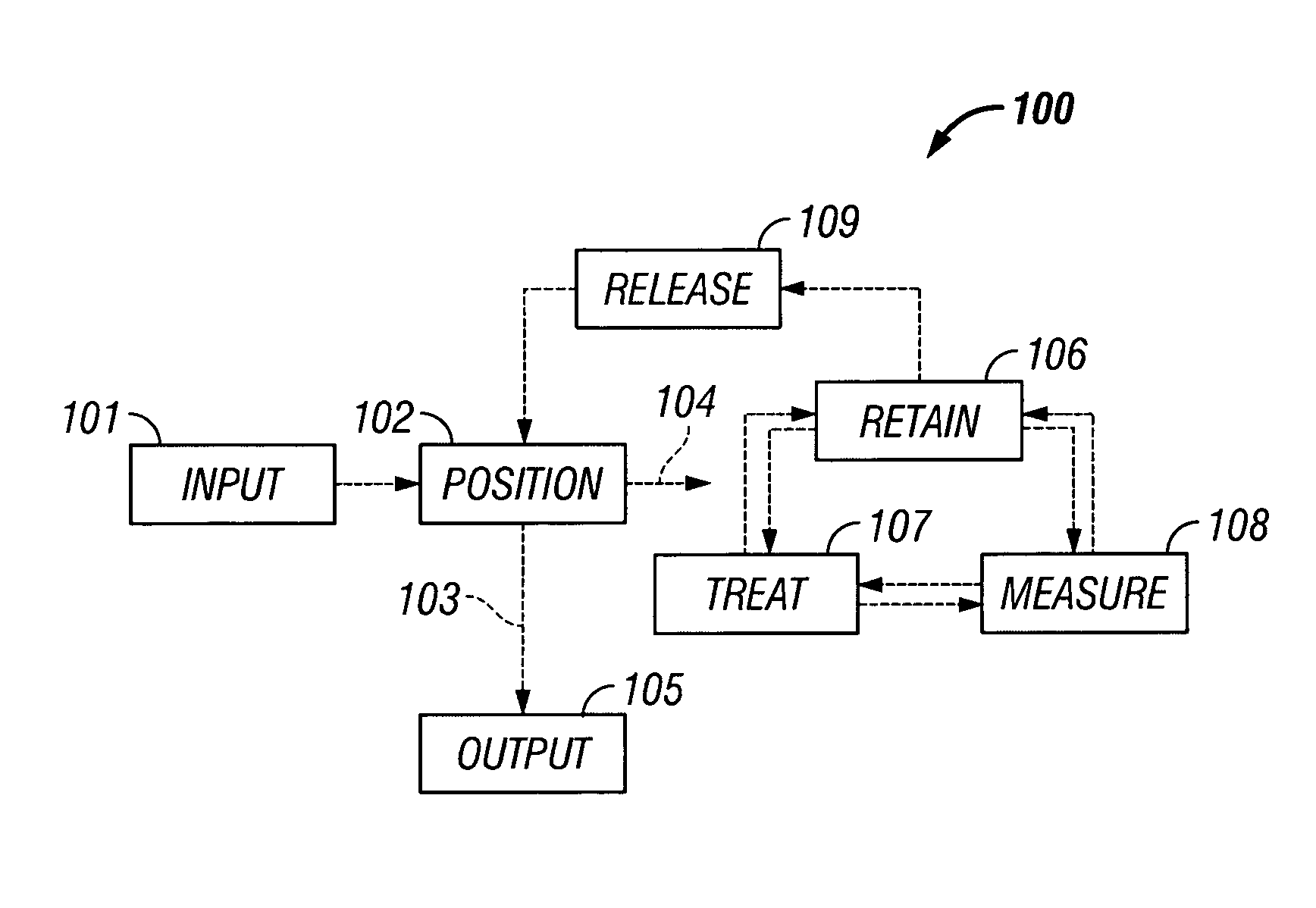
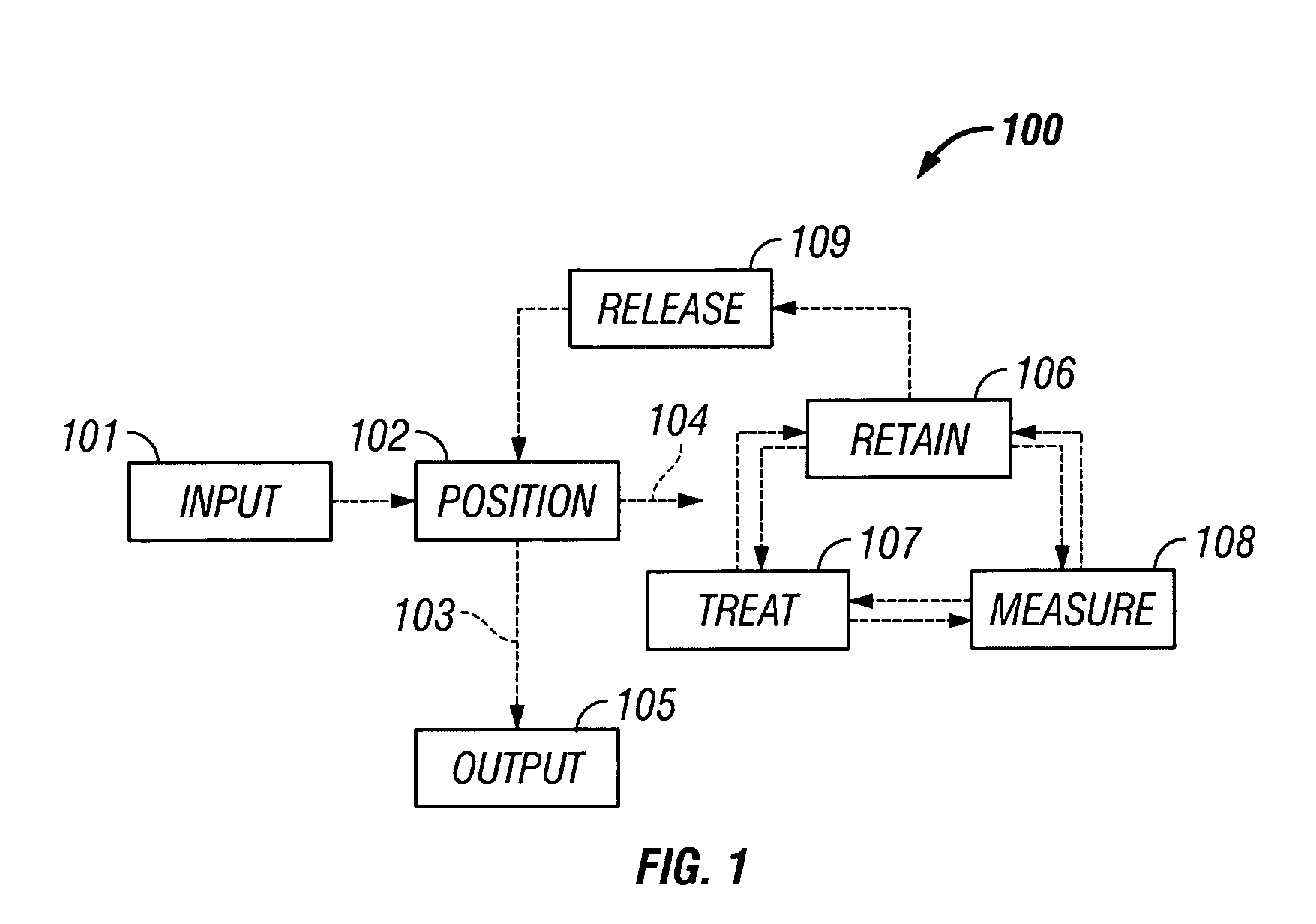
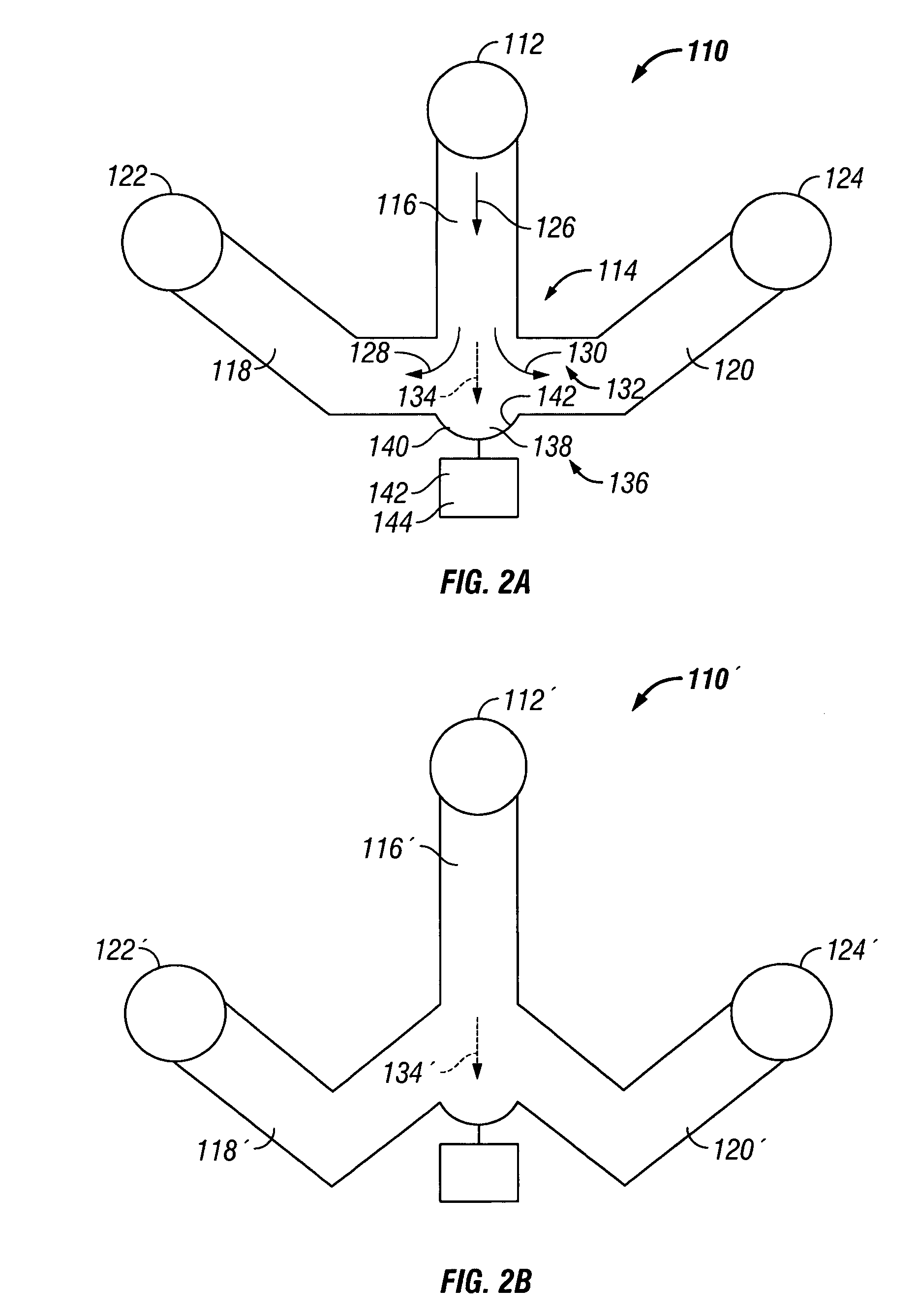
The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or detection of particles, such as cells and / or beads. The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or analysis of particles, such as cells, viruses, organelles, beads, and / or vesicles. The invention also provides microfluidic mechanisms for carrying out these manipulations and analyses. These mechanisms may enable controlled input, movement / positioning, retention / localization, treatment, measurement, release, and / or output of particles. Furthermore, these mechanisms may be combined in any suitable order and / or employed for any suitable number of times within a system. Accordingly, these combinations may allow particles to be sorted, cultured, mixed, treated, and / or assayed, among others, as single particles, mixed groups of particles, arrays of particles, heterogeneous particle sets, and / or homogeneous particle sets, among others, in series and / or in parallel. In addition, these combinations may enable microfluidic systems to be reused. Furthermore, these combinations may allow the response of particles to treatment to be measured on a shorter time scale than was previously possible. Therefore, systems of the invention may allow a broad range of cell and particle assays, such as drug screens, cell characterizations, research studies, and / or clinical analyses, among others, to be scaled down to microfluidic size. Such scaled-down assays may use less sample and reagent, may be less labor intensive, and / or may be more informative than comparable macrofluidic assays.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
Printable electronic display
InactiveUS6980196B1Easy to manufactureLow costElectromagnetic wave systemStatic indicating devicesMicroparticleNonlinear element
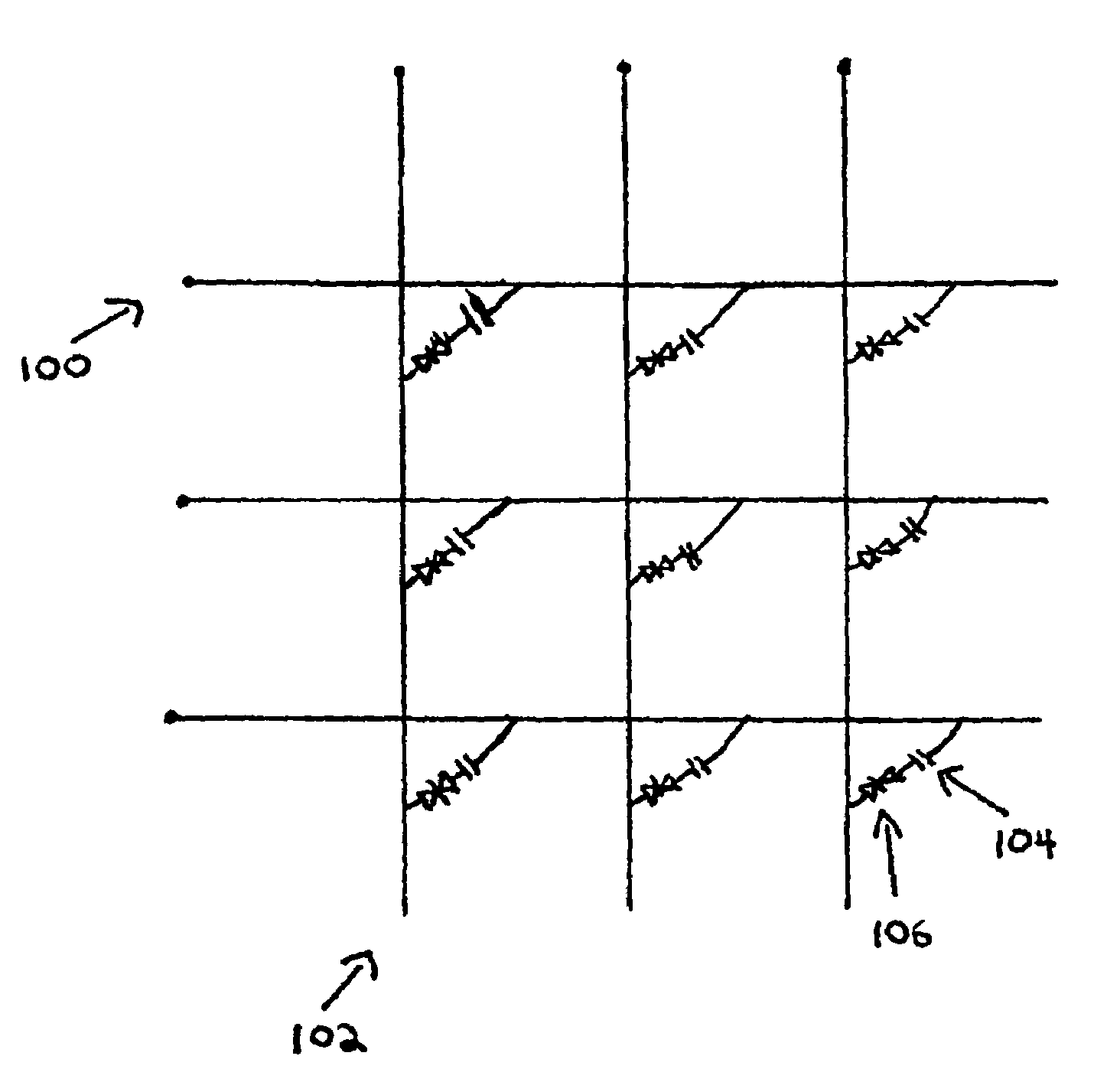
A display system includes a substrate upon which the display system is fabricated; a printable electrooptic display material, such as a microencapsulated electrophoretic suspension; electrodes (typically based on a transparent, conductive ink) arranged in an intersecting pattern to allow specific elements or regions of the display material to be addressed; insulating layers, as necessary, deposited by printing; and an array of nonlinear elements that facilitate matrix addressing. The nonlinear devices may include printed, particulate Schottky diodes, particulate PN diodes, particulate varistor material, silicon films formed by chemical reduction, or polymer semiconductor films. All elements of the display system may be deposited using a printing process.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Intraoperative Tissue Mapping and Dissection Systems, Devices, Methods, and Kits
Intraoperative devices are described that assist the surgeon in identifying the location and characteristics of tissues and structures. Devices are also described that have the added capability of marking the location of the identified tissues and structures. This invention also includes devices that can selectively ablate adjacent tissues while avoiding damage and trauma to the identified tissues and structures by combining ablation with sensing, where sensing of either tissue properties, markings made by another device or surgeon, or a reference probe can be used. Devices are also described that protect tissue in the proximity of reference markings or probes by closed loop inhibition of the ablation process. The devices, systems, methods and kits described are adapted and configured to facilitate locating a target structure or target tissue within a body of a mammal, including nerves, peripheral nerves, blood vessels, and tubes such as the ureter. The devices, systems and methods may discriminate between different tissues by exploiting the electrical, mechanical, and physiological properties of the body.
Owner:TRILLIUM PRECISION SURGICAL
Methods and apparatus for filtering an optical fiber
InactiveUS6222970B1Improve responseReduce sensitivityCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHigh energyPhotonics
Filtering of optical fibers and other related devices. High-energy methods for depositing thin films directly onto the ends of optical fibers can be used to produce high-quality, high-performance filters in quantity at a reasonable cost. These high-quality filters provide the high performance needed for many demanding applications and often eliminate the need for filters applied to wafers or expanded-beam filtering techniques. Having high-quality filters applied directly to optical fiber and faces permits production of high-performance, micro-sized devices that incorporate optical filters. Devices in which these filters may be used include spectroscopic applications including those using fiber optic probes, wavelength division multiplexing, telecommunications, general fiber optic sensor usage, photonic computing, photonic amplifiers, pump blocking and a variety of laser devices.
Owner:CIRREX SYST
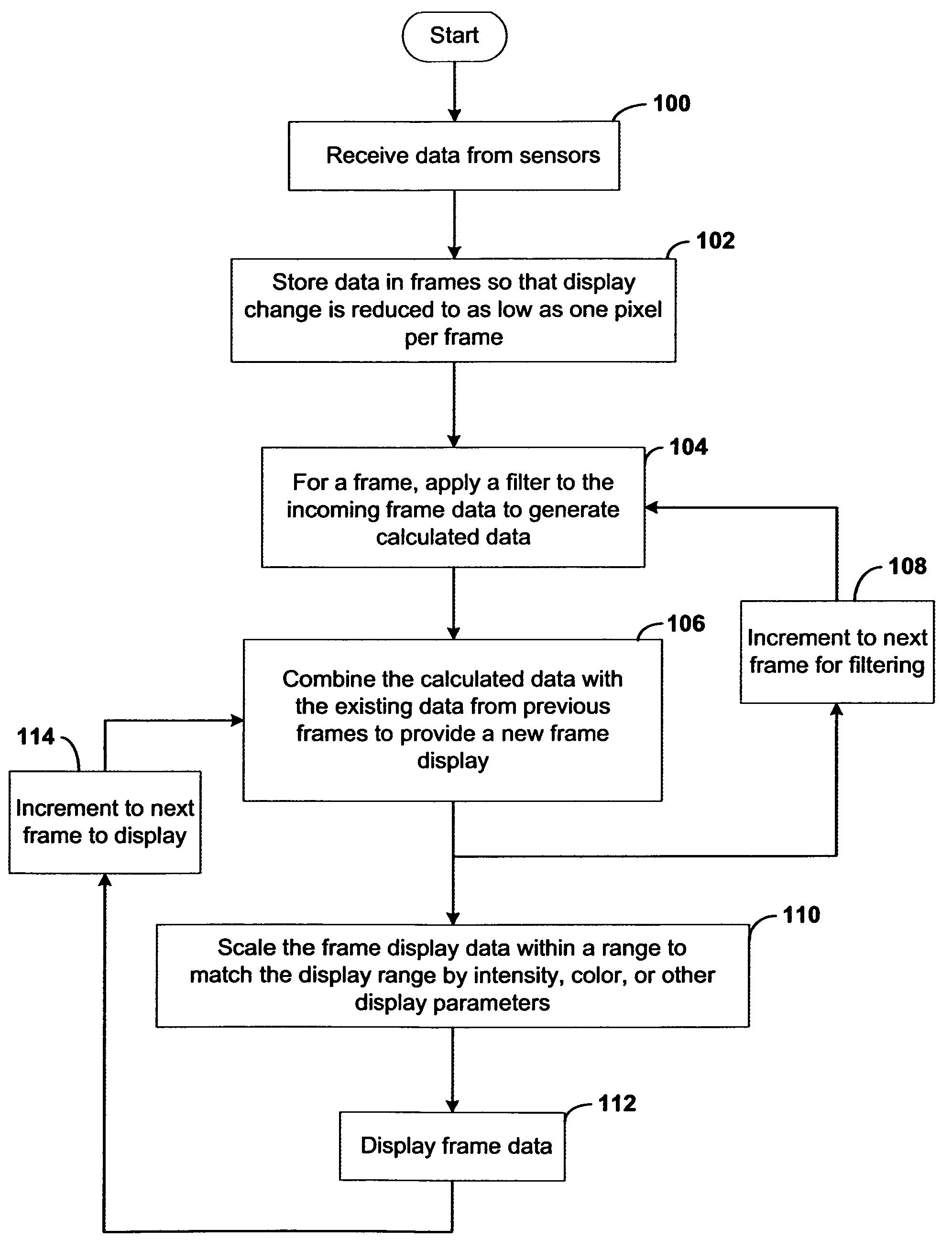
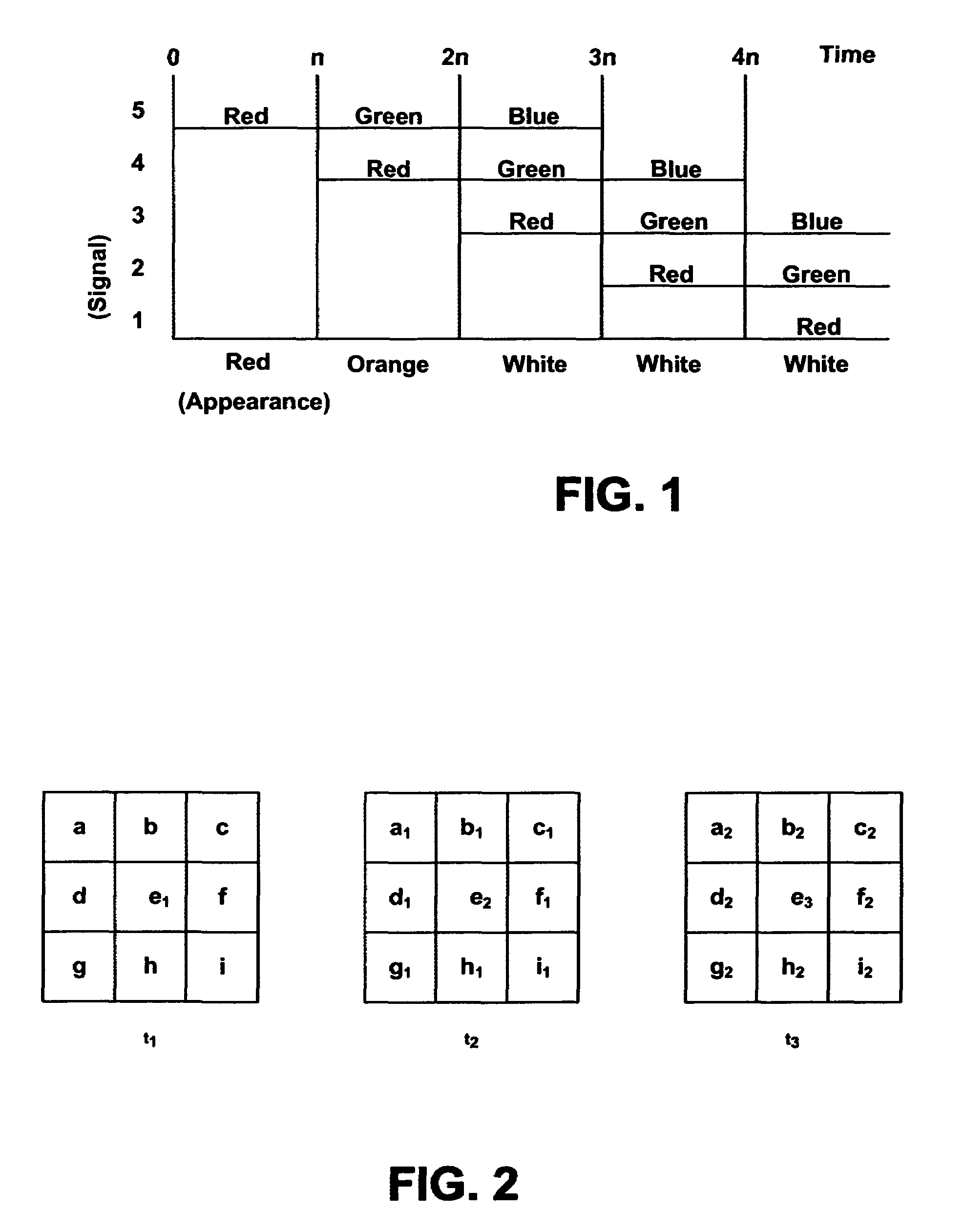
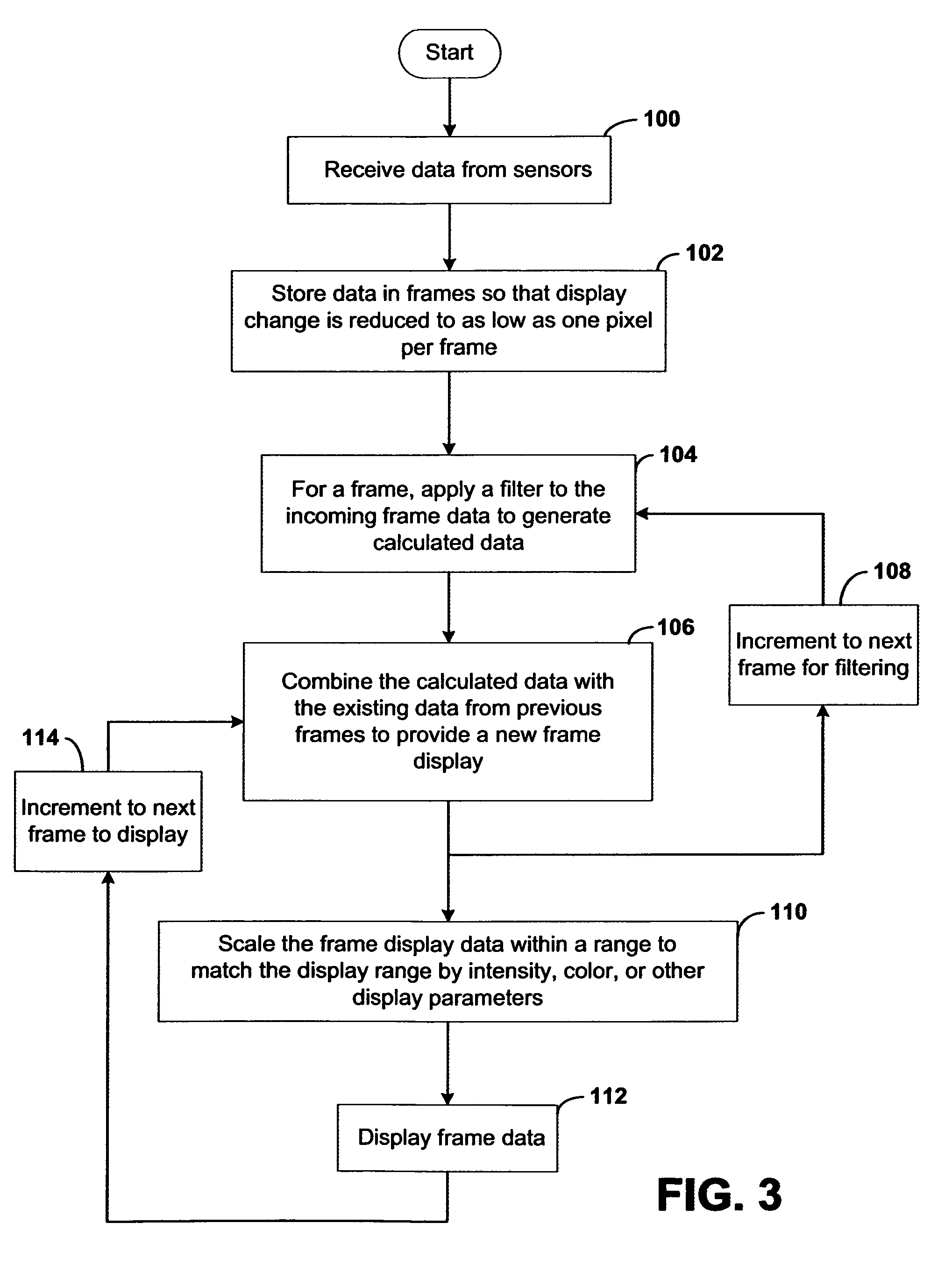
Systems and methods for displaying changes in biological responses to therapy
InactiveUS7720306B2Better convey information to the viewerImprove visibilityDrawing from basic elementsPerson identificationCorrelation functionDisplay device
Systems and methods of this invention display data using pixels with information indicated by color and intensity changes, particularly used for monitoring of physiological variables in real time. For certain methods, physiological data can be acquired by sensors, acquired data can be stored in data frames, data frames can be processed using computer-implemented methods, and processed data frames can be scaled to a display frame for display on a display device. Using such methods, a spot made up of a group of pixels can be updated during a time frame, or cycle using a computer-implemented method, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division or a time dependent function. Newly received data can be combined with prior received data to indicate time-dependent changes. In this way, each spot contains a cumulative history of data starting at some initial time. In other embodiments, visual contrast can be enhanced between desired data and other data. In further embodiments, two or more different types of data can be plotted together to indicate relationships between variables. Real time monitoring of signals during therapeutic treatment using light, electricity or other nerve or muscle stimuli can allow a user to monitor physiological responses during stimulation and to make rapid decisions about medical treatment.
Owner:PHOTOMED TECH
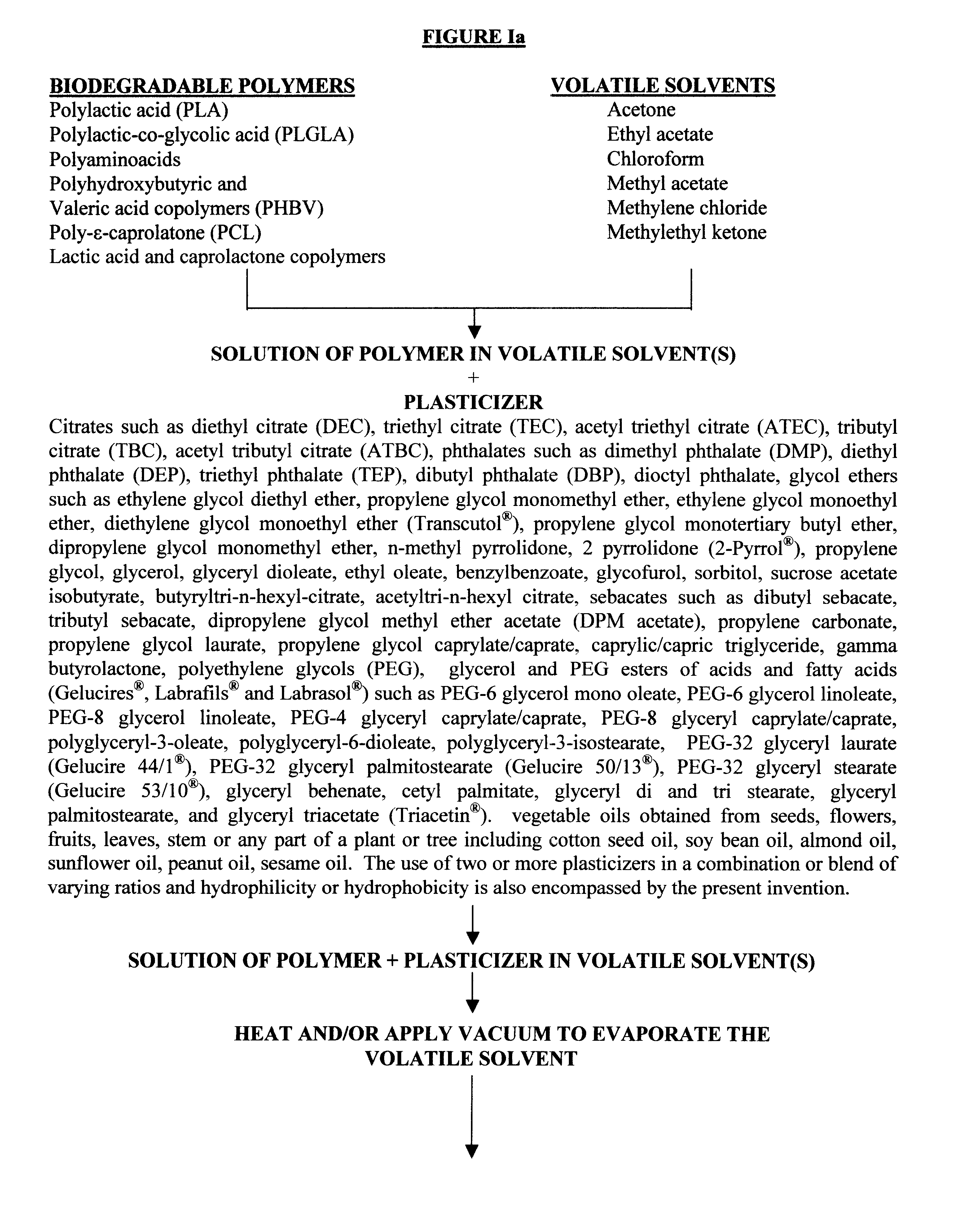
Biodegradable vehicle and filler
InactiveUS6432438B1Improve stabilityWell mixedOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolymer sciencePlasticizer
A biodegradable vehicle and filler (referred to in this invention as biodegradable vehicle), which can be mixed with one or more biologically active substances (BAS), or can be used as a biodegradable filler to fill in cavities or body tissues in animals, birds and humans. The consistency and rheology, hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity, and in vivo degradation rates of the biodegradable vehicle is controlled by modulating the molecular weight of polymers and copolymers, concentration of plasticizers, ratios of two or more plasticizer in the blends, types of polymers and copolymers, copolymer ratios, and ratios of blends of polymers with different molecular weights or different copolymers. The biodegradable vehicle is mixed with one or more BAS (which is separately stored away from the biodegradable vehicle in an appropriate container) just prior to use. Mixing of the BAS with the biodegradable vehicle can be accomplished by simply stirring the mixture with a stirring device, or by triturating the mixture or employing an ointment mill or a suitable device or apparatus or equipment that can be used for blending / mixing. Alternatively, a device, which resembles two syringes, attached together with a removable partition or a valve assembly can also be used to uniformly mix the BAS with the biodegradable vehicle. The mixing is performed in order to dissolve or uniformly suspend the BAS particles in the biodegradable vehicle. Modulating the polymer to plasticizer ratio, polymer molecular weight, copolymer ratio, and hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of the plasticizer controls the release of the BAS from the biodegradable vehicle.
Owner:SHUKLA ATUL J
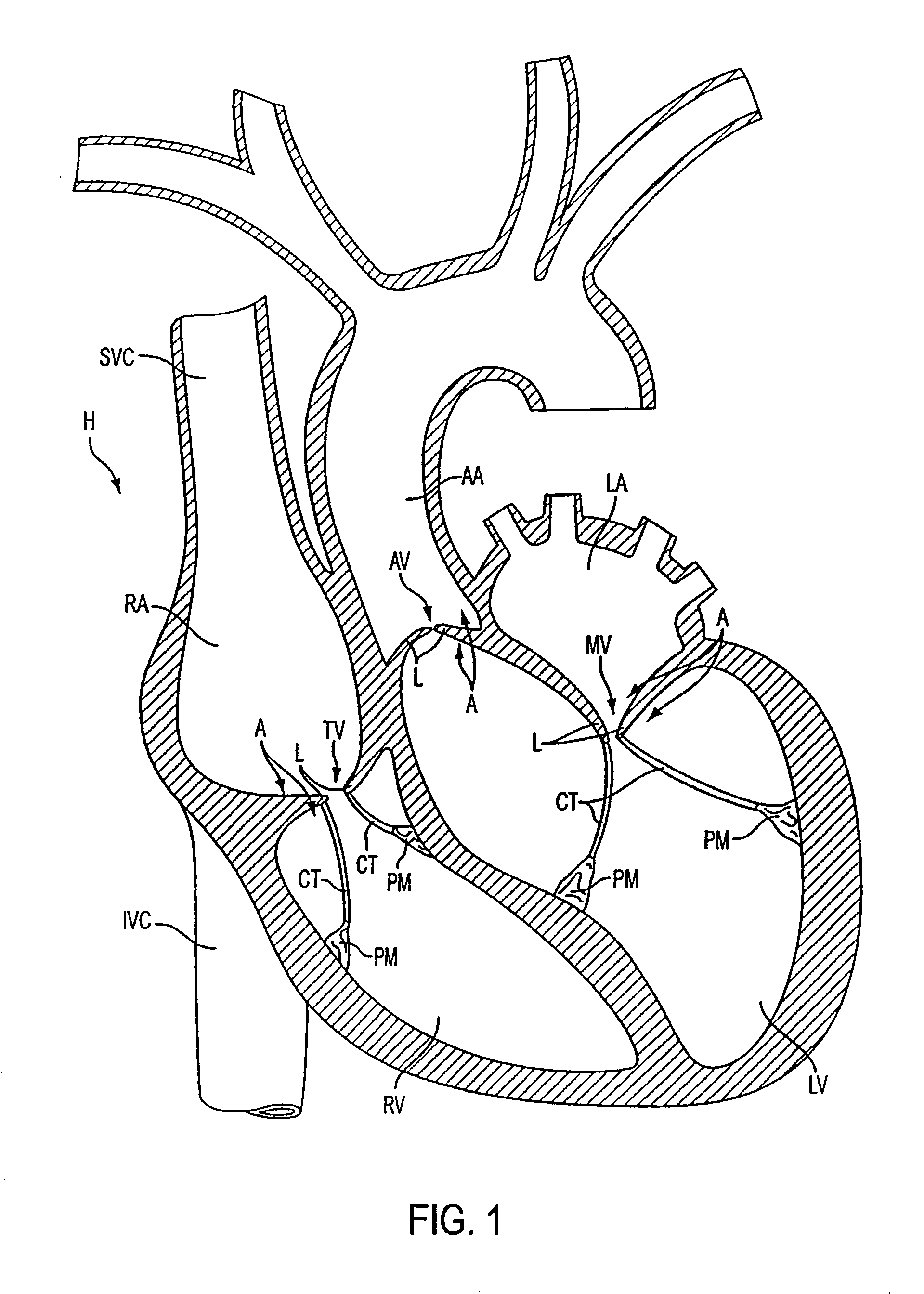
System and method of surgical imagining with anatomical overlay for navigation of surgical devices
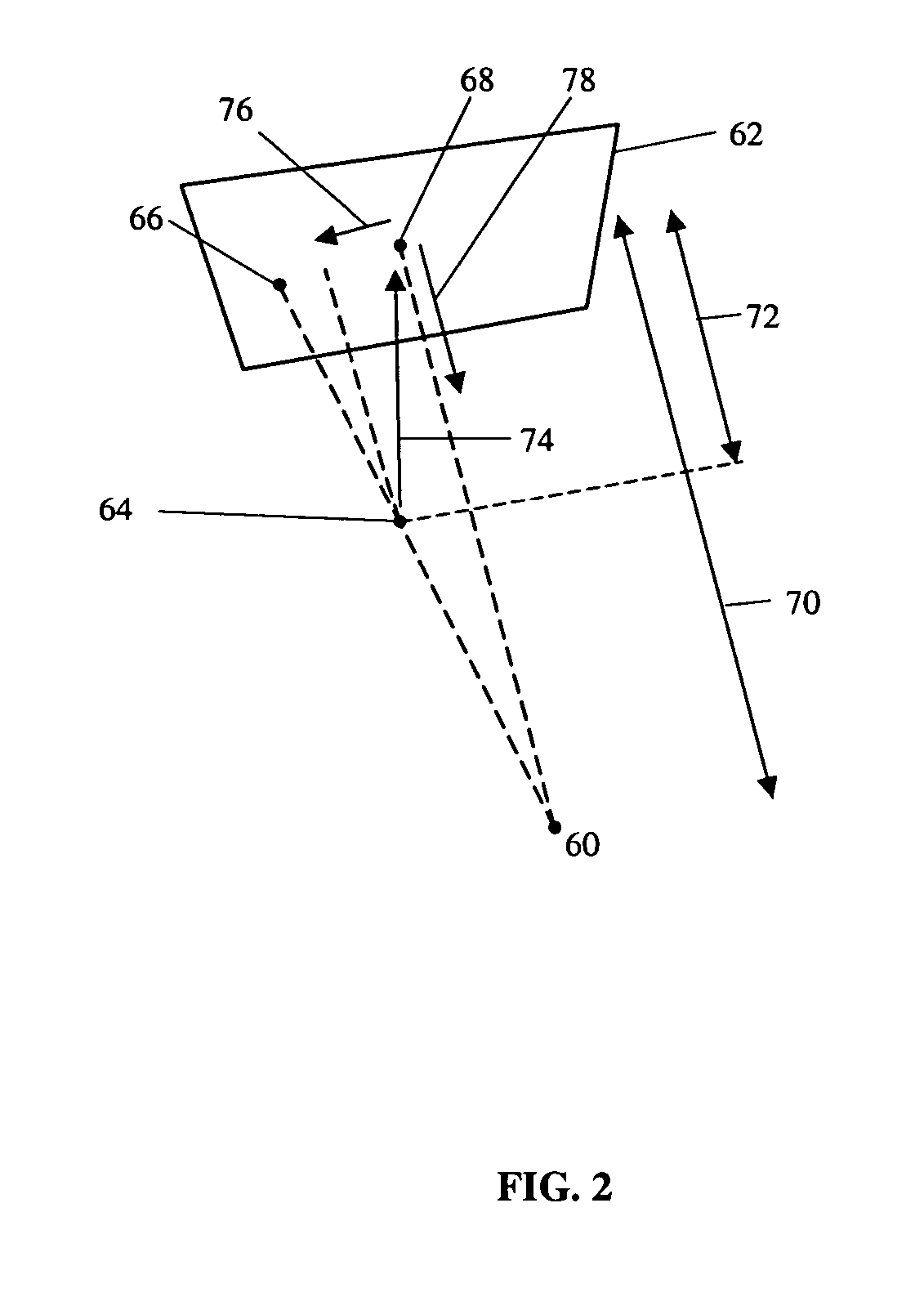
ActiveUS7831294B2Improve the display effectPrecise positioningMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayDisplay device
A system and method are provided for control of a navigation system for deploying a medical device within a subject, and for enhancement of a display image of anatomical features for viewing the projected location and movement of medical devices, and projected locations of a variety of anatomical features and other spatial markers in the operating region. The display of the X-ray imaging system information is augmented in a manner such that a physician can more easily become oriented in three dimensions with the use of a single-plane X-ray display. The projection of points and geometrical shapes within the subject body onto a known imaging plane can be obtained using associated imaging parameters and projective geometry.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
System and elements for managing therapeutic gas administration to a spontaneously breathing non-ventilated patient
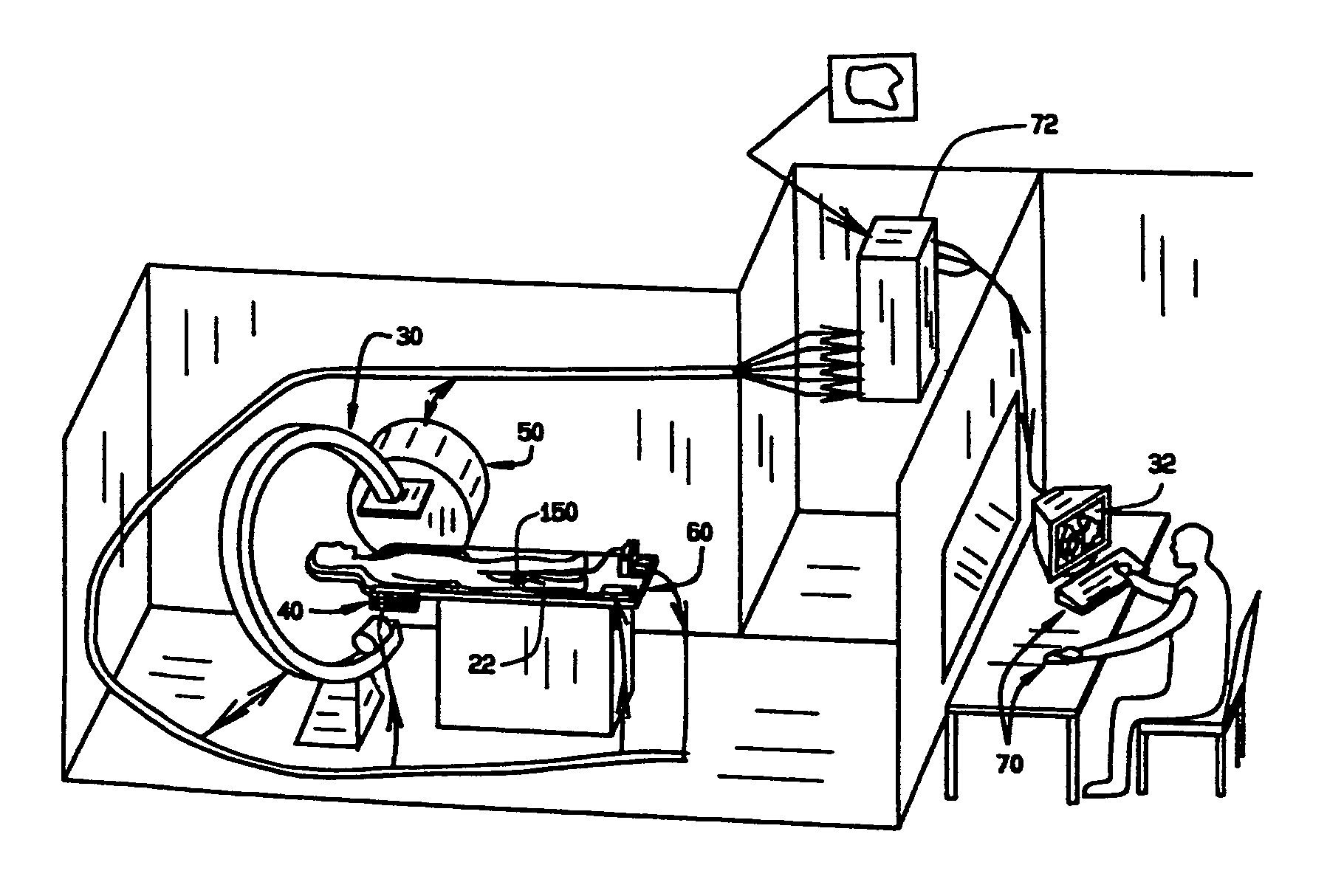
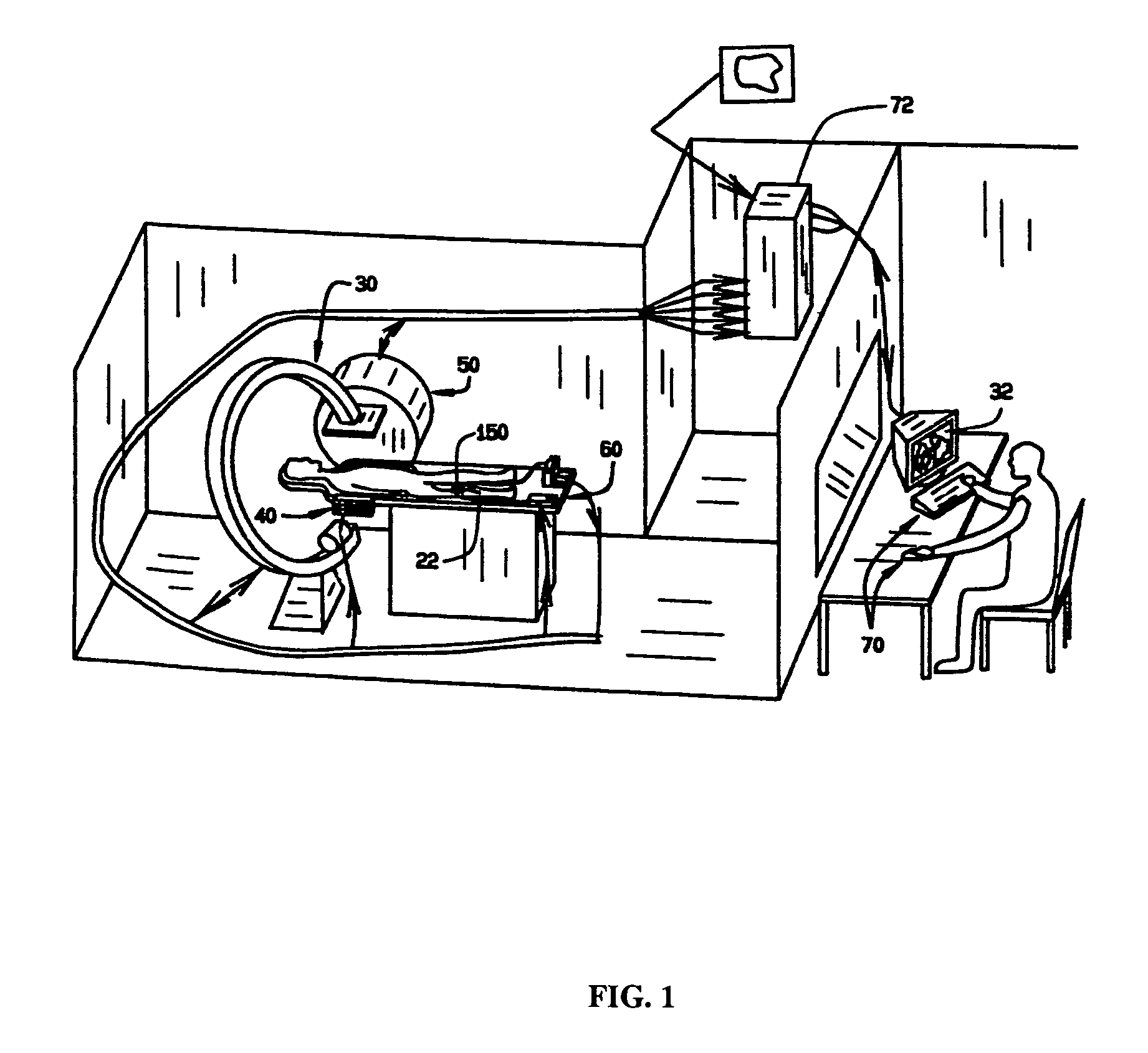
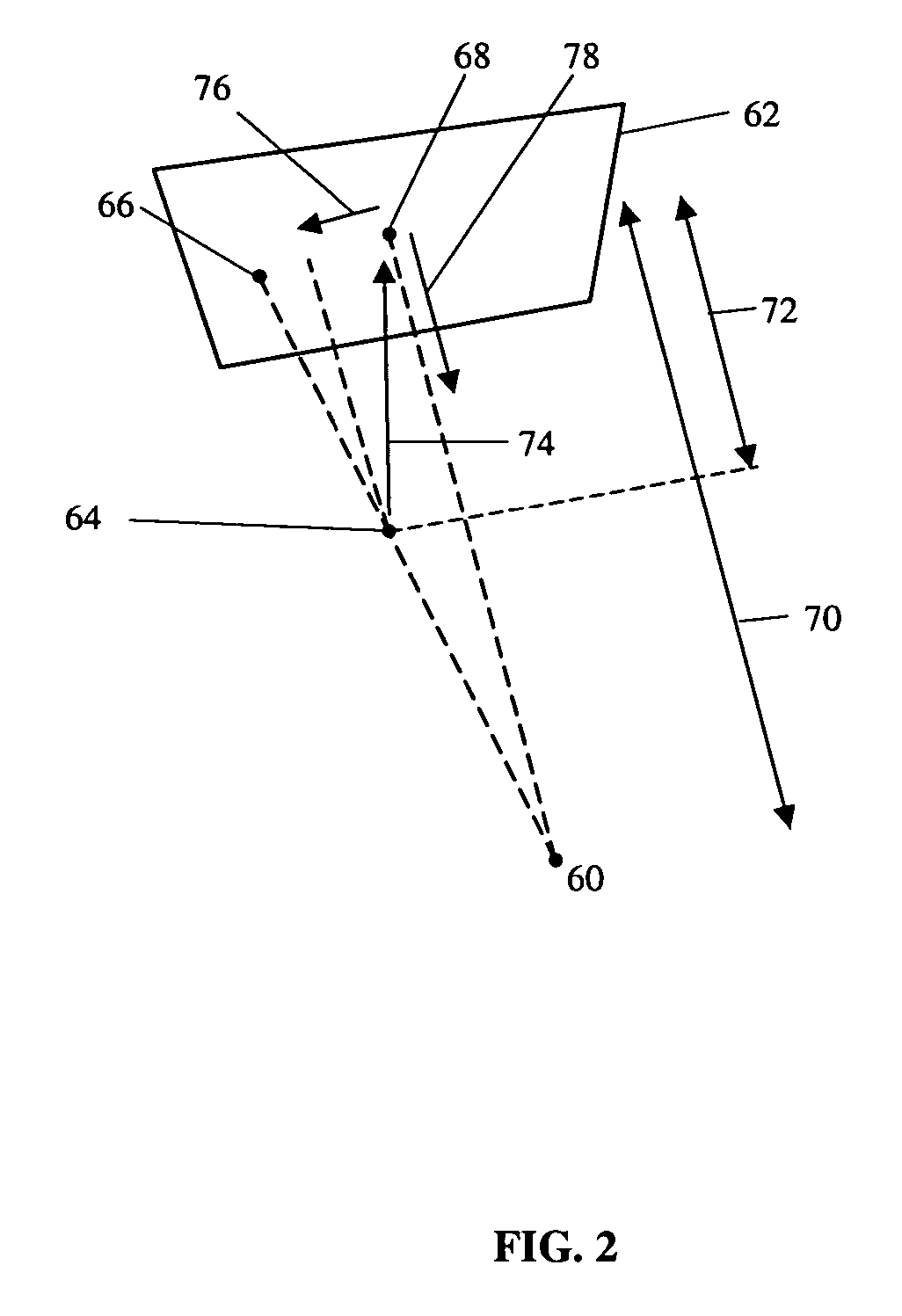
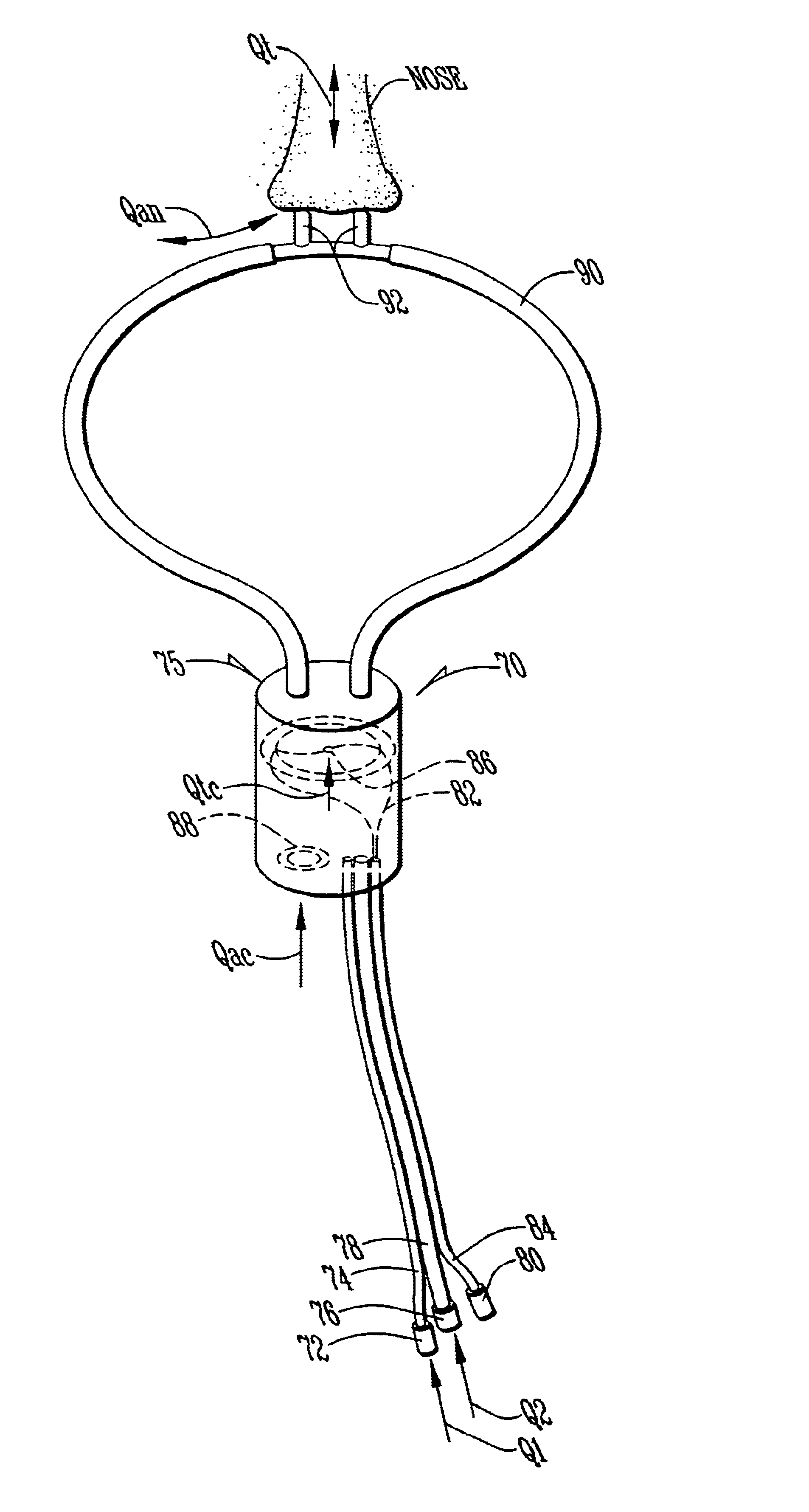
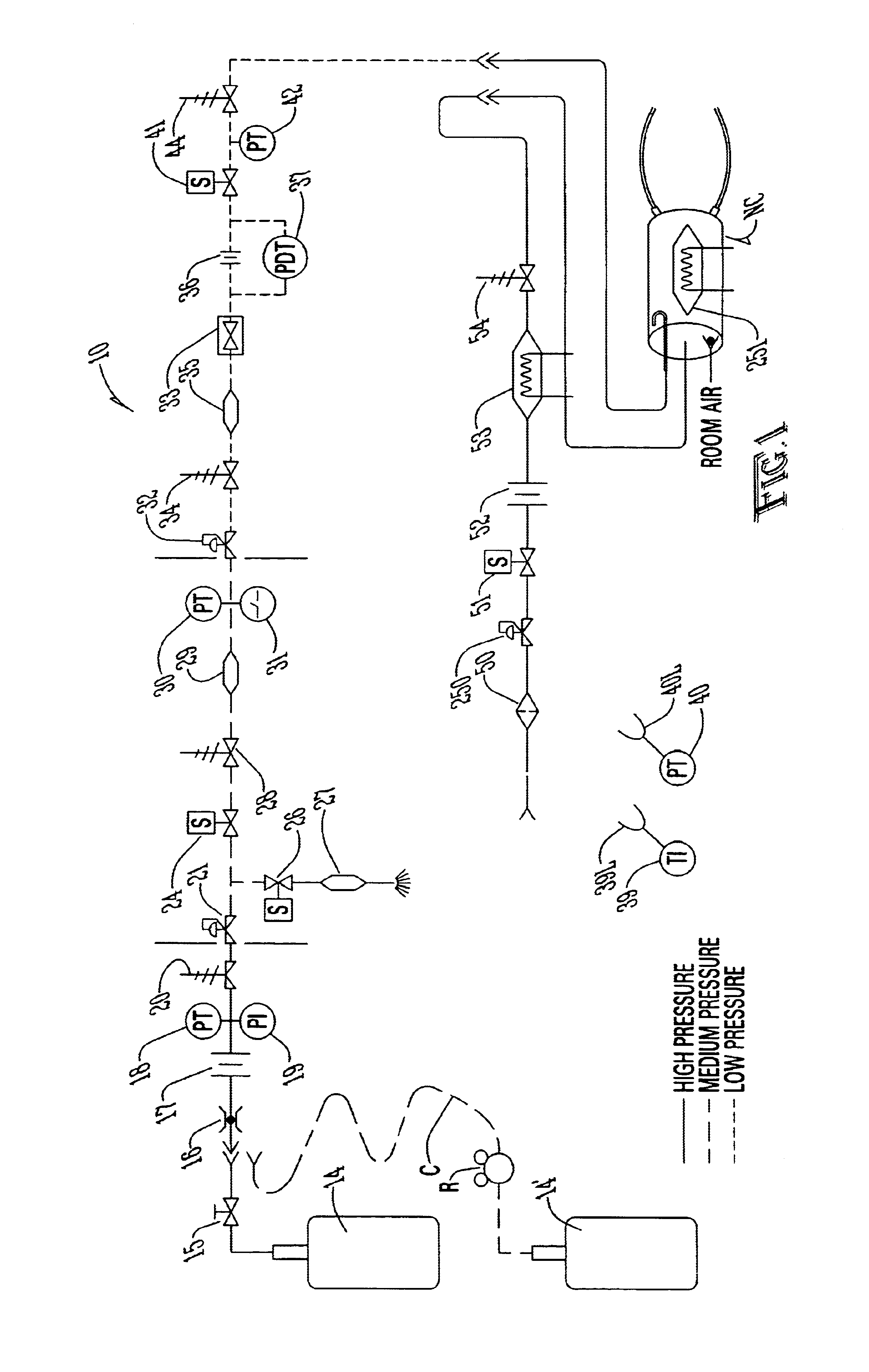
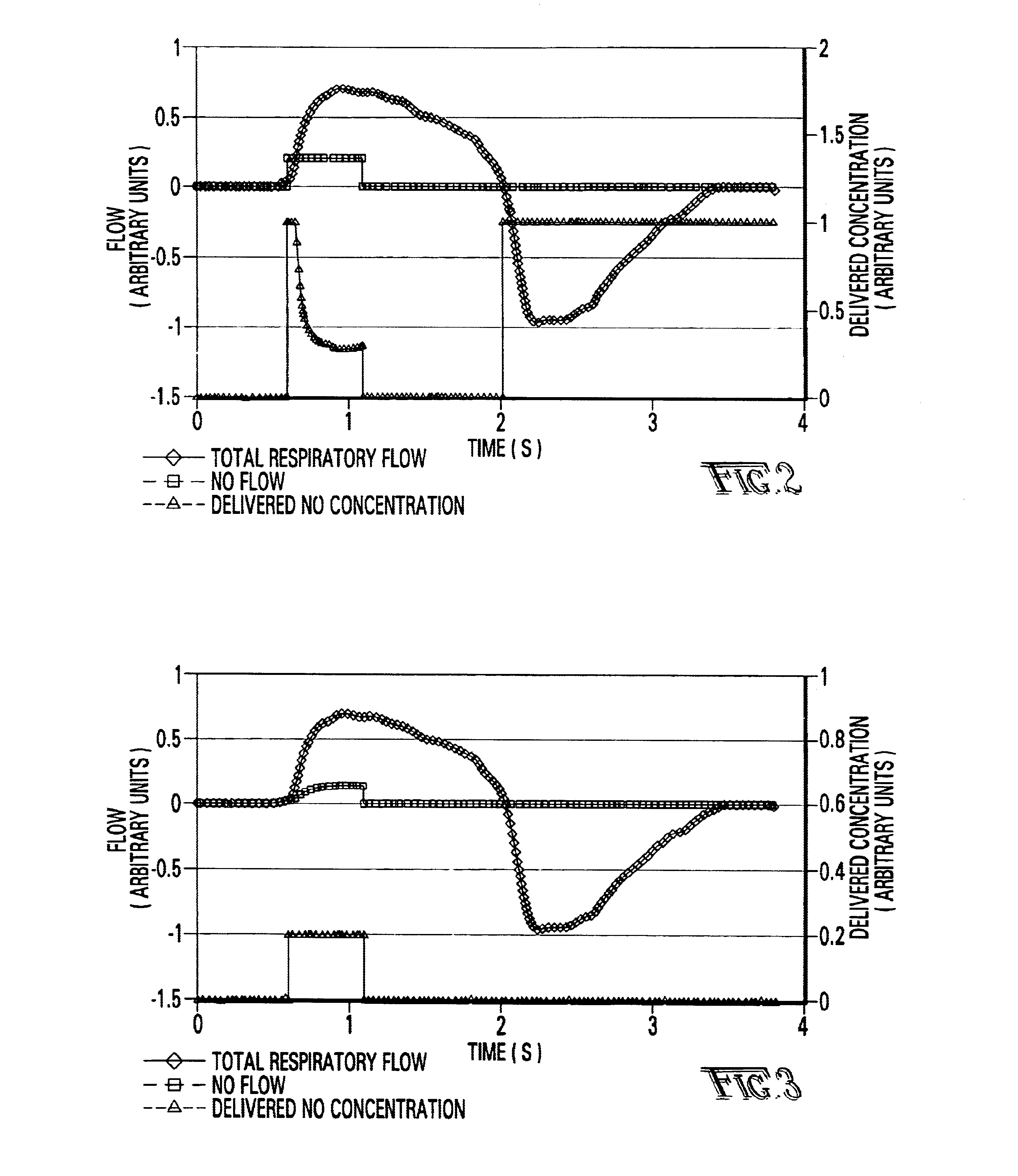
InactiveUS6668828B1Reduce in quantityLower the volumeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksDistal portionNose
A system controls and manages administration of a therapeutic gas, such as NO, O2, or the like, to a spontaneously breathing, non-ventilated patient such that concentrated NO is as low as reasonably possible while delivering the desired amount of NO to the distal portions of the lungs. The system includes an entrainment cell that provides remote, turbulent mixing with low temporal latency and can be used with a nasal cannula or a mask. The entrainment cell uses room air to dilute the therapeutic gas; however, supplementary gases can also be used. A baffle can be included to promote mixing and a flow sensor can also be used if desired. Multiple ports can be included in the entrainment cell. An equalizing valve is also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED INHILATION THERAPIES AIT LTD
Surgical navigation with overlay on anatomical images
ActiveUS20060079745A1Enhance displayed imagePrecise positioningMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayDisplay device
A system and method are provided for control of a navigation system for deploying a medical device within a subject, and for enhancement of a display image of anatomical features for viewing the projected location and movement of medical devices, and projected locations of a variety of anatomical features and other spatial markers in the operating region. The display of the X-ray imaging system information is augmented in a manner such that a physician can more easily become oriented in three dimensions with the use of a single-plane X-ray display. The projection of points and geometrical shapes within the subject body onto a known imaging plane can be obtained using associated imaging parameters and projective geometry.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
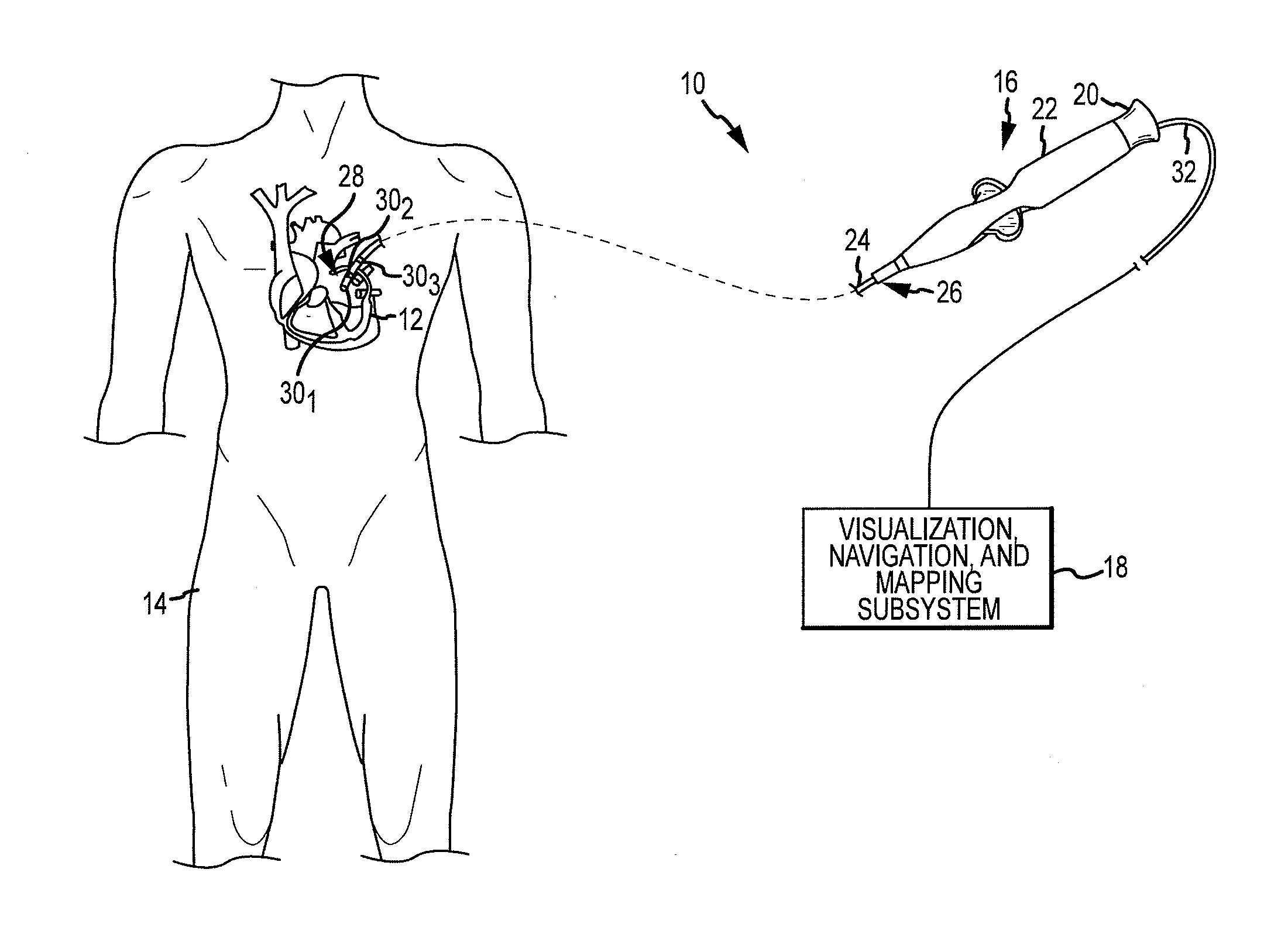
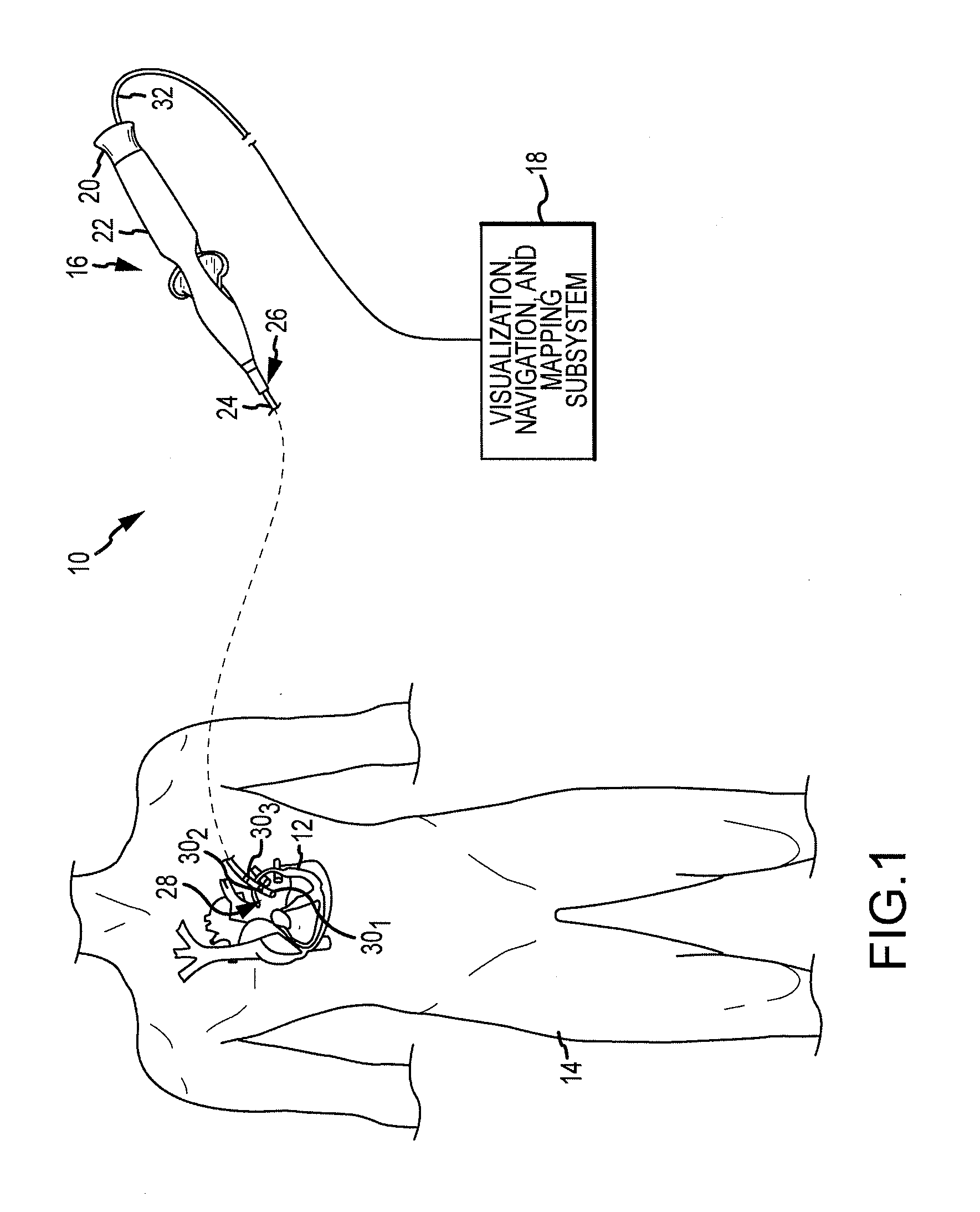
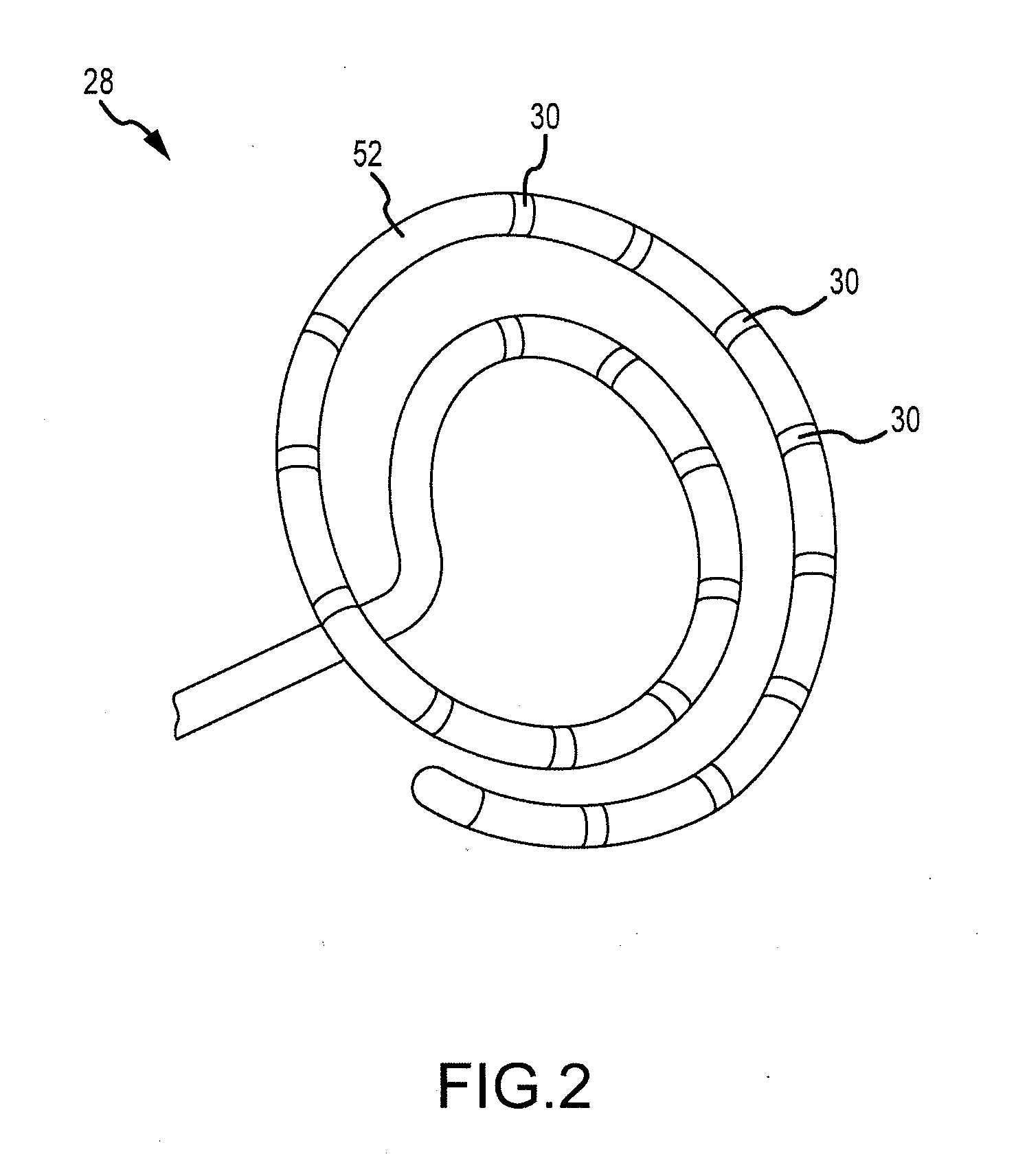
System and Method for Diagnosing Arrhythmias and Directing Catheter Therapies
An efficient system for diagnosing arrhythmias and directing catheter therapies may allow for measuring, classifying, analyzing, and mapping spatial electrophysiological (EP) patterns within a body. The efficient system may further guide arrhythmia therapy and update maps as treatment is delivered. The efficient system may use a medical device having a high density of sensors with a known spatial configuration for collecting EP data and positioning data. Further, the efficient system may also use an electronic control system (ECU) for computing and providing the user with a variety of metrics, derivative metrics, high definition (HD) maps, HD composite maps, and general visual aids for association with a geometrical anatomical model shown on a display device.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com