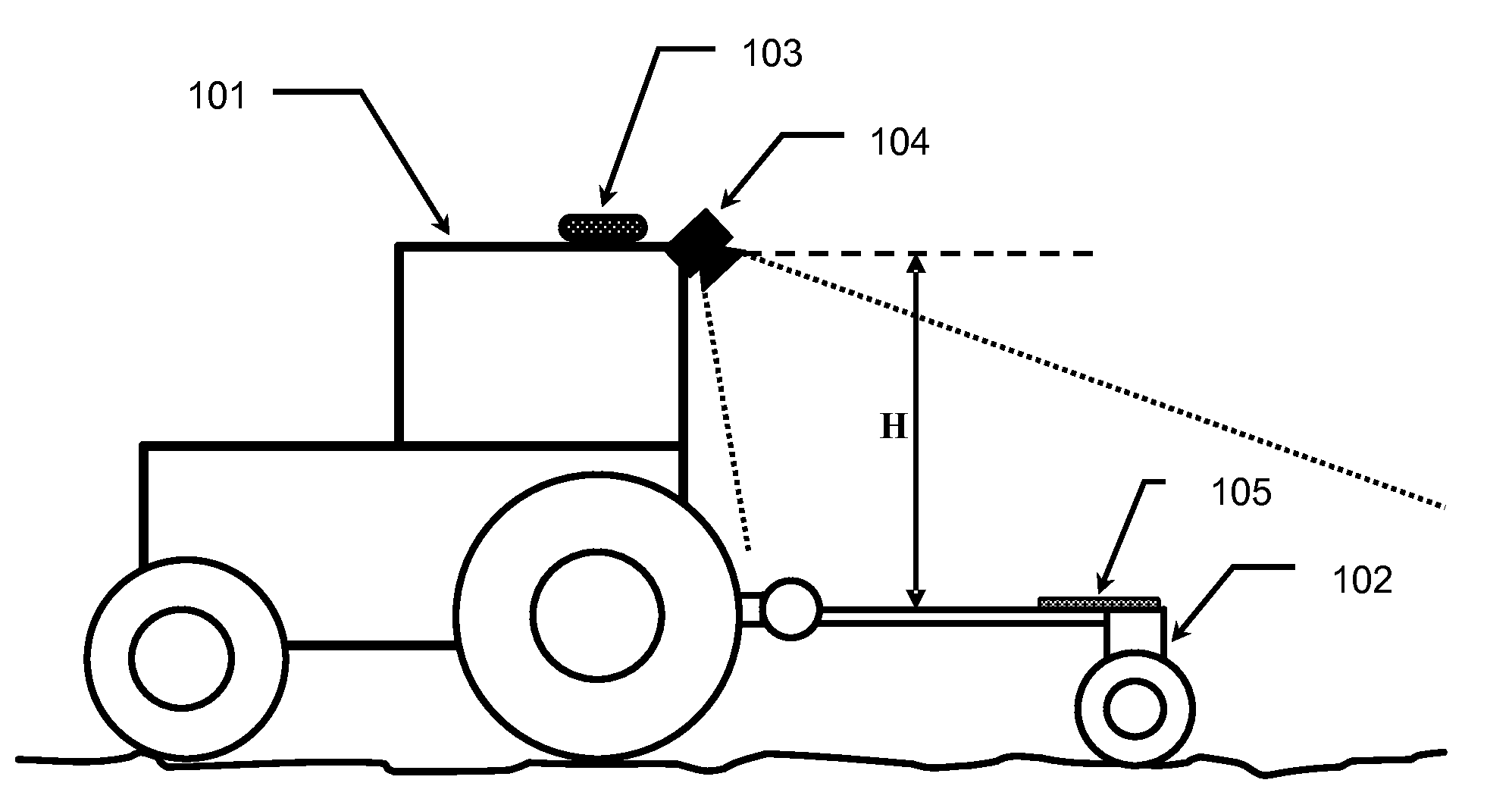
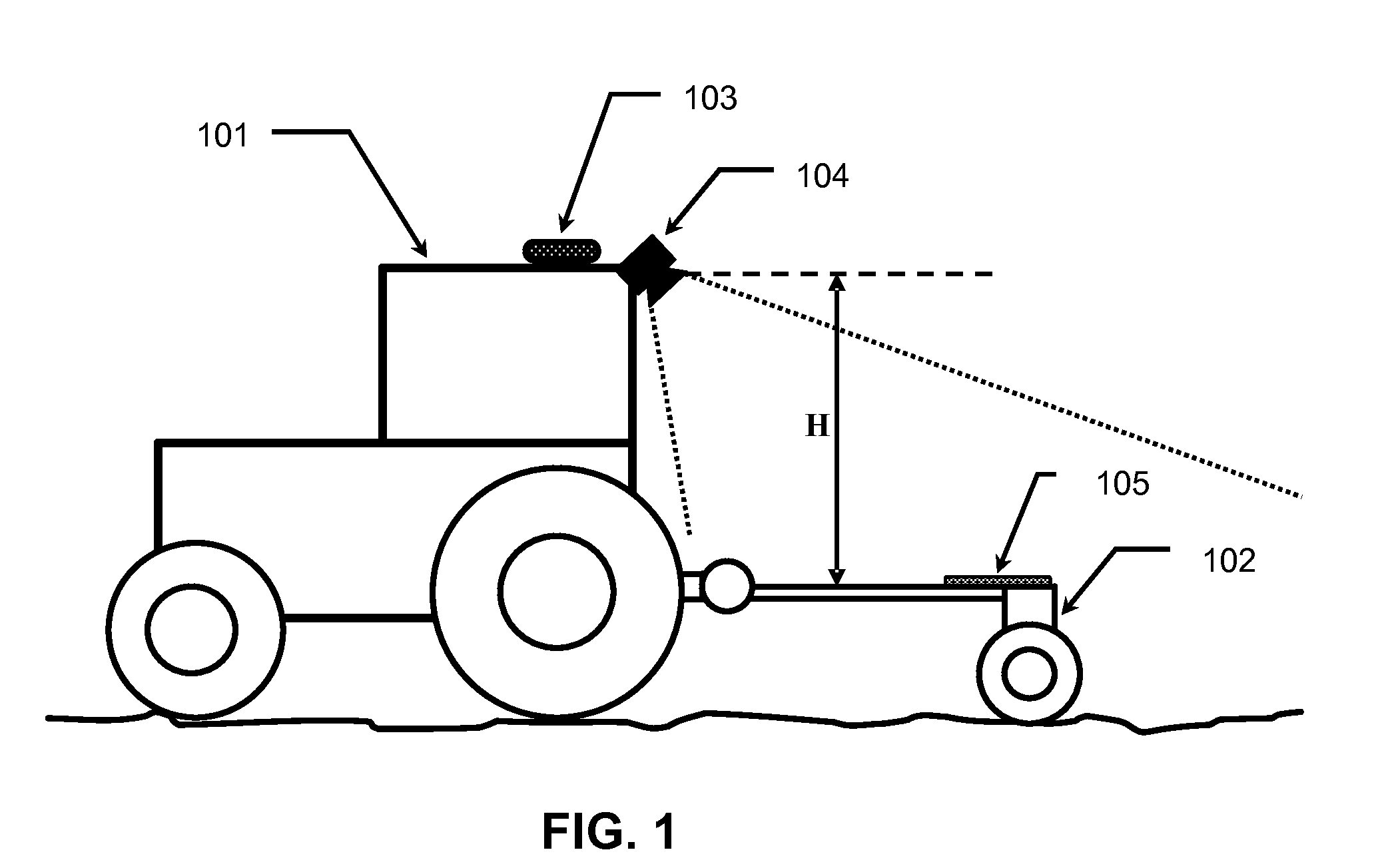
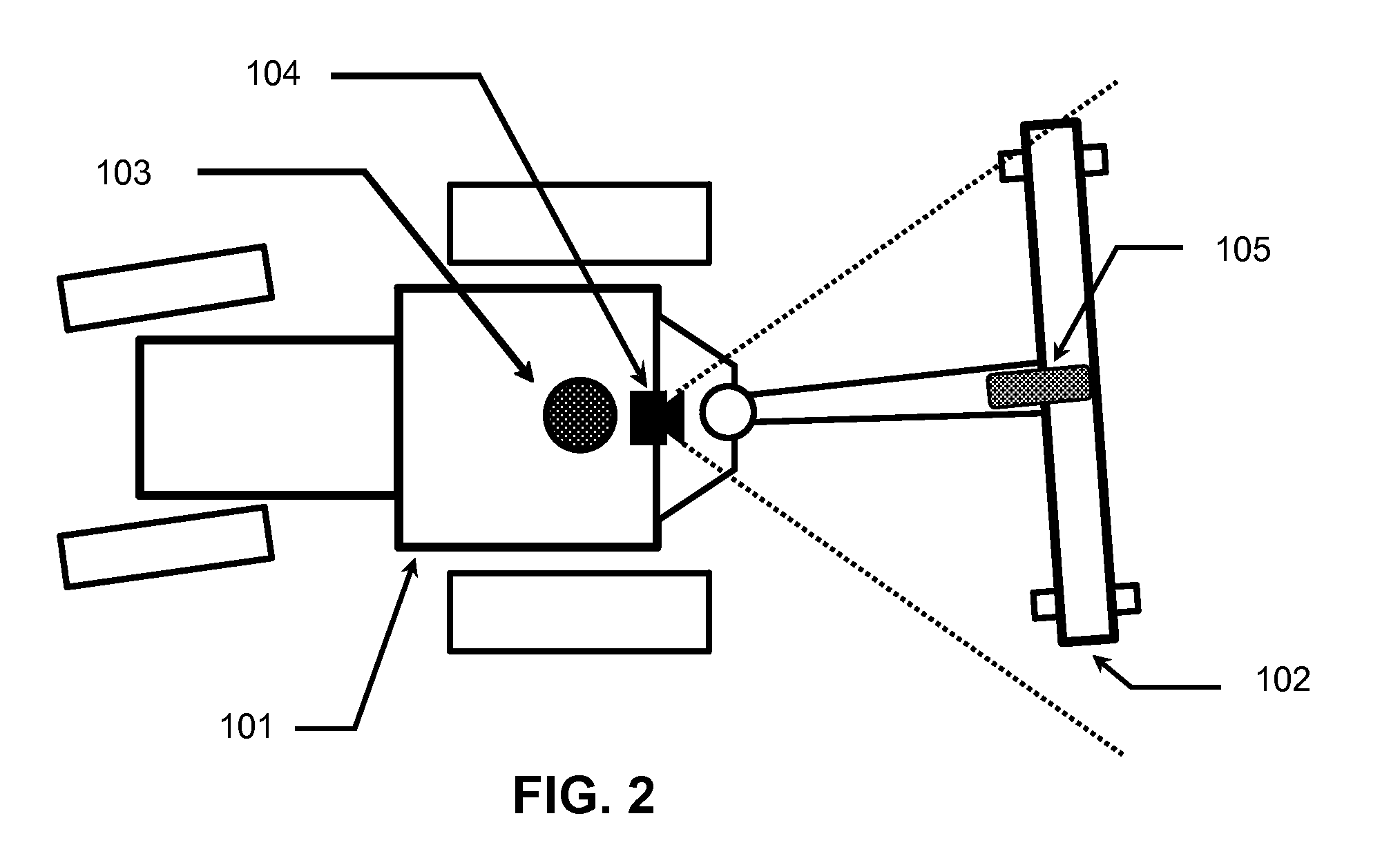
Patents
Literature
705 results about "Spatial Orientations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods for use in dental articulation
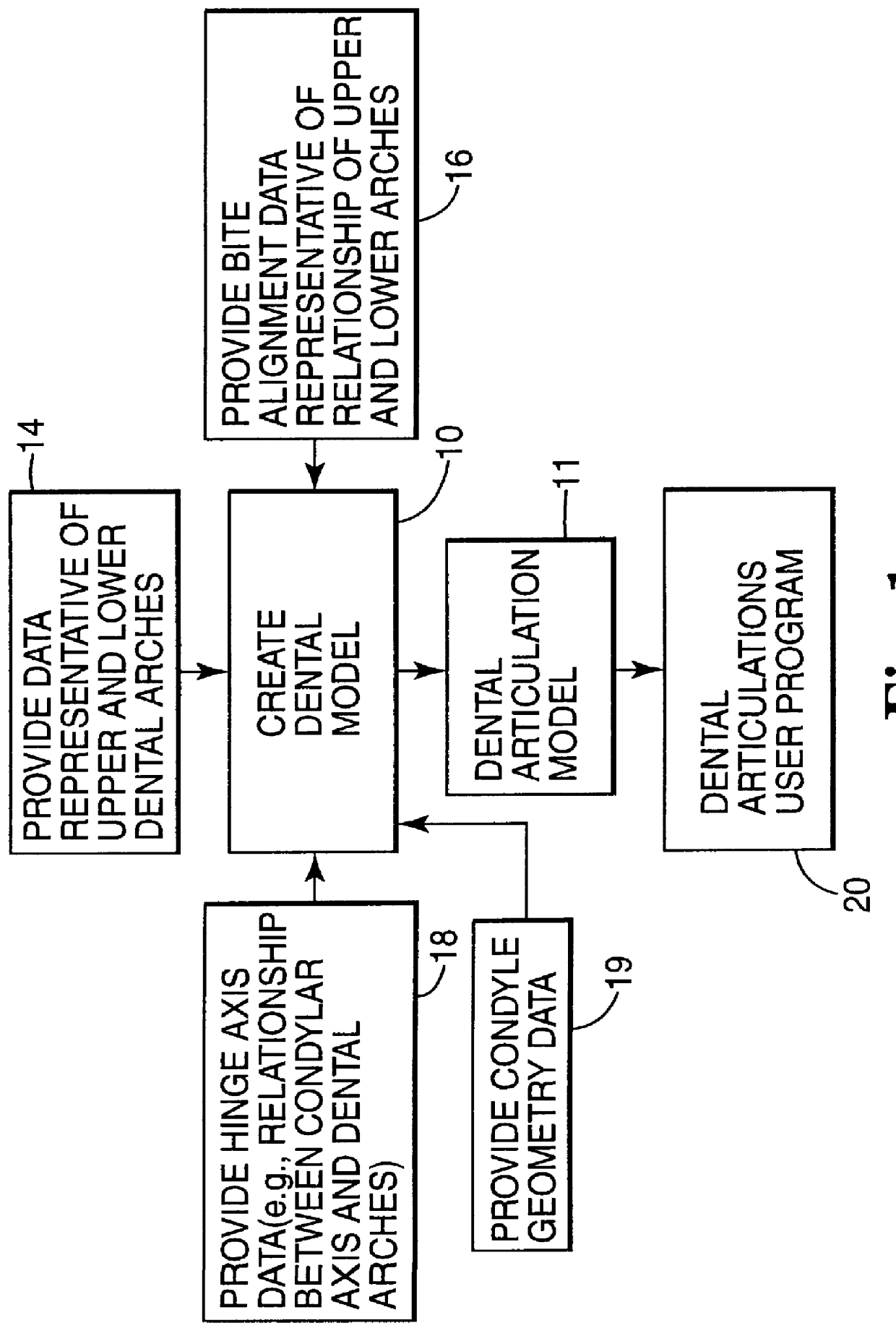
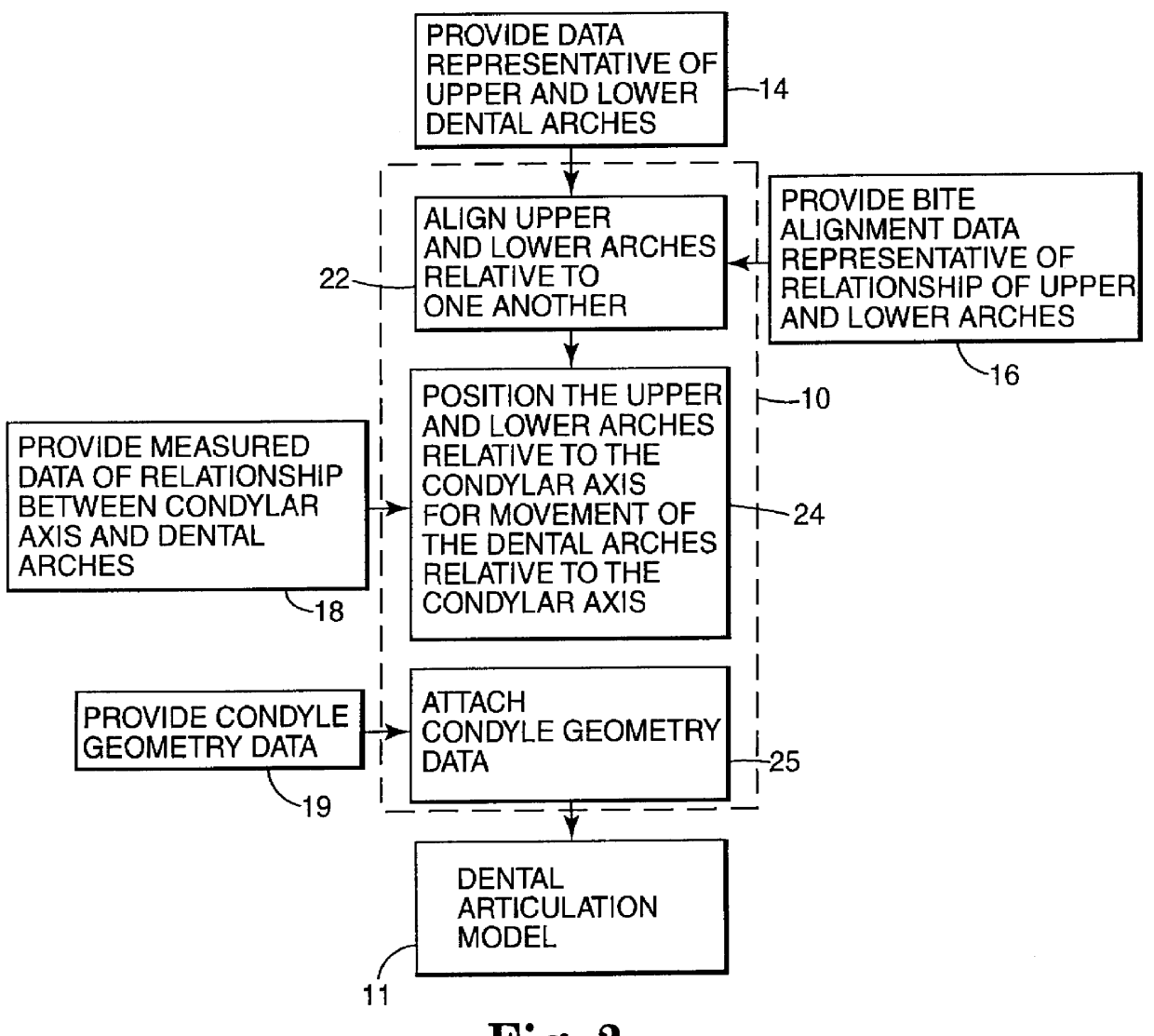
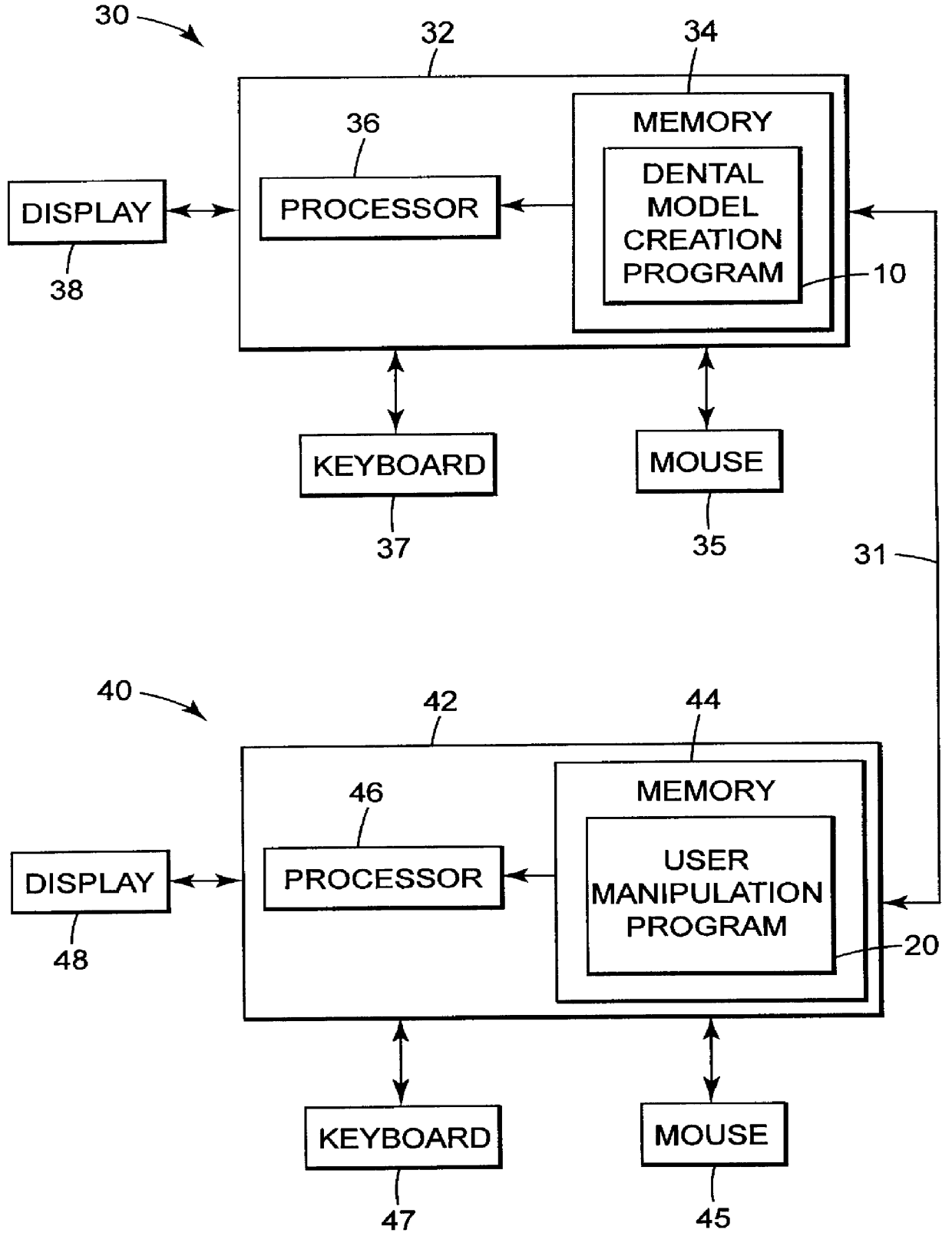
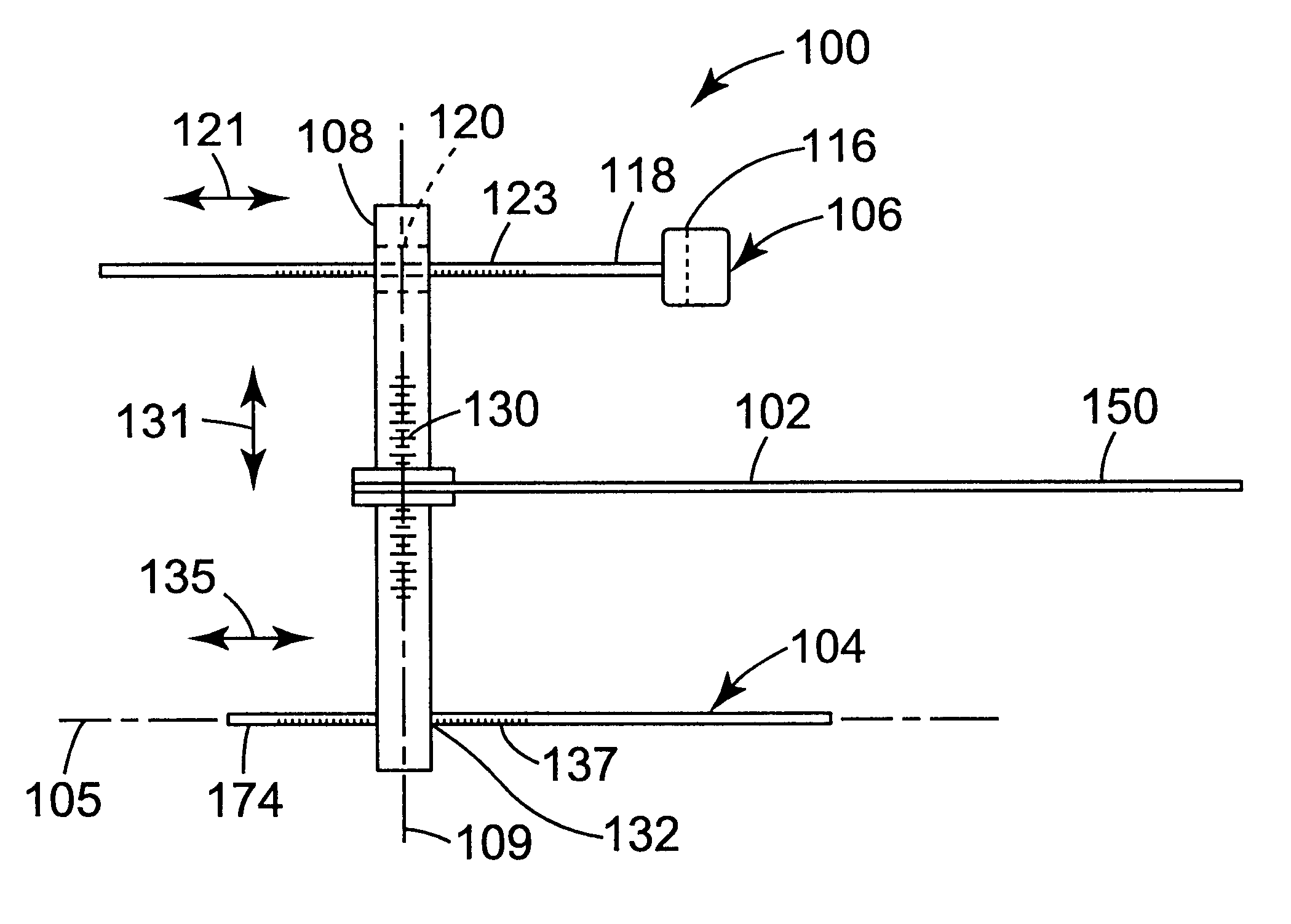
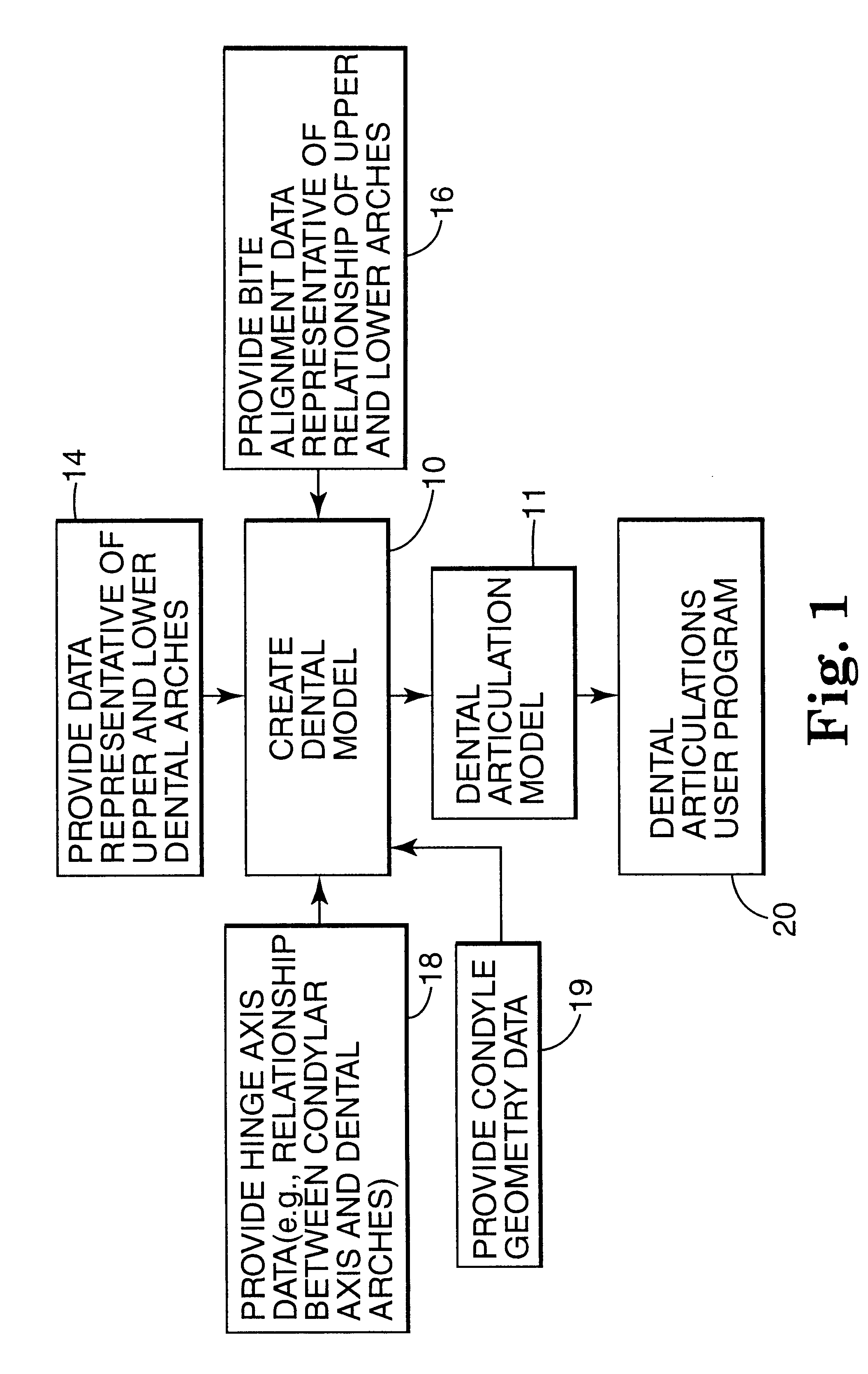
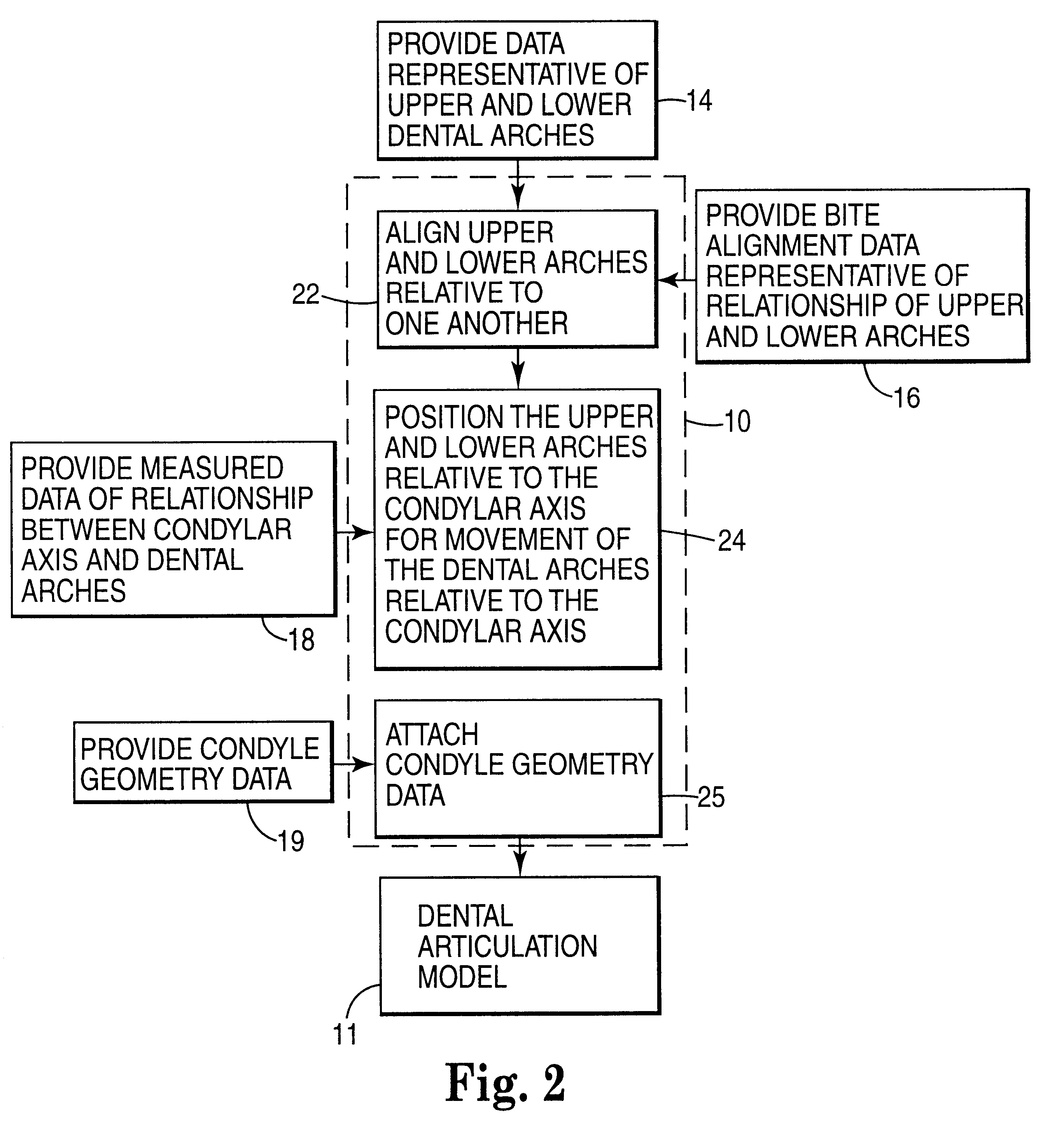
A computer implemented method of creating a dental model for use in dental articulation includes providing a first set of digital data corresponding to an upper arch image of at least a portion of an upper dental arch of a patient, providing a second set of digital data corresponding to a lower arch image of at least a portion of a lower dental arch of the patient, and providing hinge axis data representative of the spatial orientation of at least one of the upper and lower dental arches relative to a condylar axis of the patient. A reference hinge axis is created relative to the upper and lower arch images based on the hinge axis data. Further, the method may include bite alignment data for use in aligning the lower and upper arch images. Yet further, the method may include providing data associated with condyle geometry of the patient, so as to provide limitations on the movement of at least the lower arch image when the arch images are displayed. Further, a wobbling technique may be used to determine an occlusal position of the lower and upper dental arches. Various computer implemented methods of dental articulation are also described. For example, such dental articulation methods may include moving at least one of the upper and lower arch images to simulate relative movement of one of the upper and lower dental arches of the patient, may include displaying another image with the upper and lower dental arches of the dental articulation model, and / or may include playing back recorded motion of a patient's mandible using the dental articulation model.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO +1
Methods for use in dental articulation
A computer implemented method of creating a dental model for use in dental articulation includes providing a first set of digital data corresponding to an upper arch image of at least a portion of an upper dental arch of a patient, providing a second set of digital data corresponding to a lower arch image of at least a portion of a lower dental arch of the patient, and providing hinge axis data representative of the spatial orientation of at least one of the upper and lower dental arches relative to a condylar axis of the patient. A reference hinge axis is created relative to the upper and lower arch images based on the hinge axis data. Further, the method may include bite alignment data for use in aligning the lower and upper arch images. Yet further, the method may include providing data associated with condyle geometry of the patient, so as to provide limitations on the movement of at least the lower arch image when the arch images are displayed. Further, a wobbling technique may be used to determine an occlusal position of the lower and upper dental arches. Various computer implemented methods of dental articulation are also described. For example, such dental articulation methods may include moving at least one of the upper and lower arch images to simulate relative movement of one of the upper and lower dental arches of the patient, may include displaying another image with the upper and lower dental arches of the dental articulation model, and / or may include playing back recorded motion of a patient's mandible using the dental articulation model.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Pattern Transfer Printing by Kinetic Control of Adhesion to an Elastomeric Stamp
ActiveUS20090199960A1Keep the distanceEasy transferFinal product manufactureDecorative surface effectsSpatial OrientationsElastomer
The present invention provides methods, systems and system components for transferring, assembling and integrating features and arrays of features having selected nanosized and / or microsized physical dimensions, shapes and spatial orientations. Methods of the present invention utilize principles of ‘soft adhesion’ to guide the transfer, assembly and / or integration of features, such as printable semiconductor elements or other components of electronic devices. Methods of the present invention are useful for transferring features from a donor substrate to the transfer surface of an elastomeric transfer device and, optionally, from the transfer surface of an elastomeric transfer device to the receiving surface of a receiving substrate. The present methods and systems provide highly efficient, registered transfer of features and arrays of features, such as printable semiconductor element, in a concerted manner that maintains the relative spatial orientations of transferred features.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
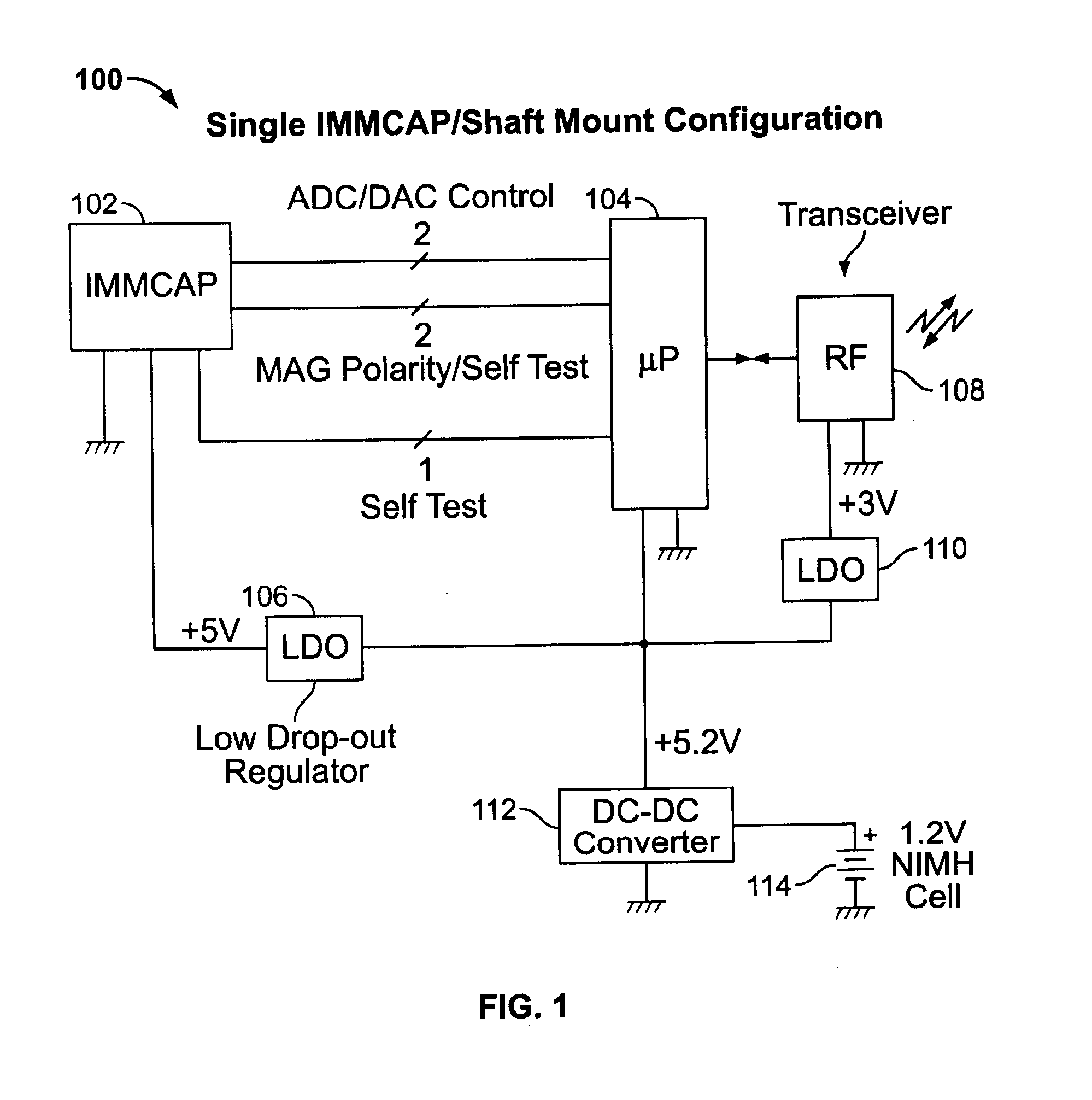
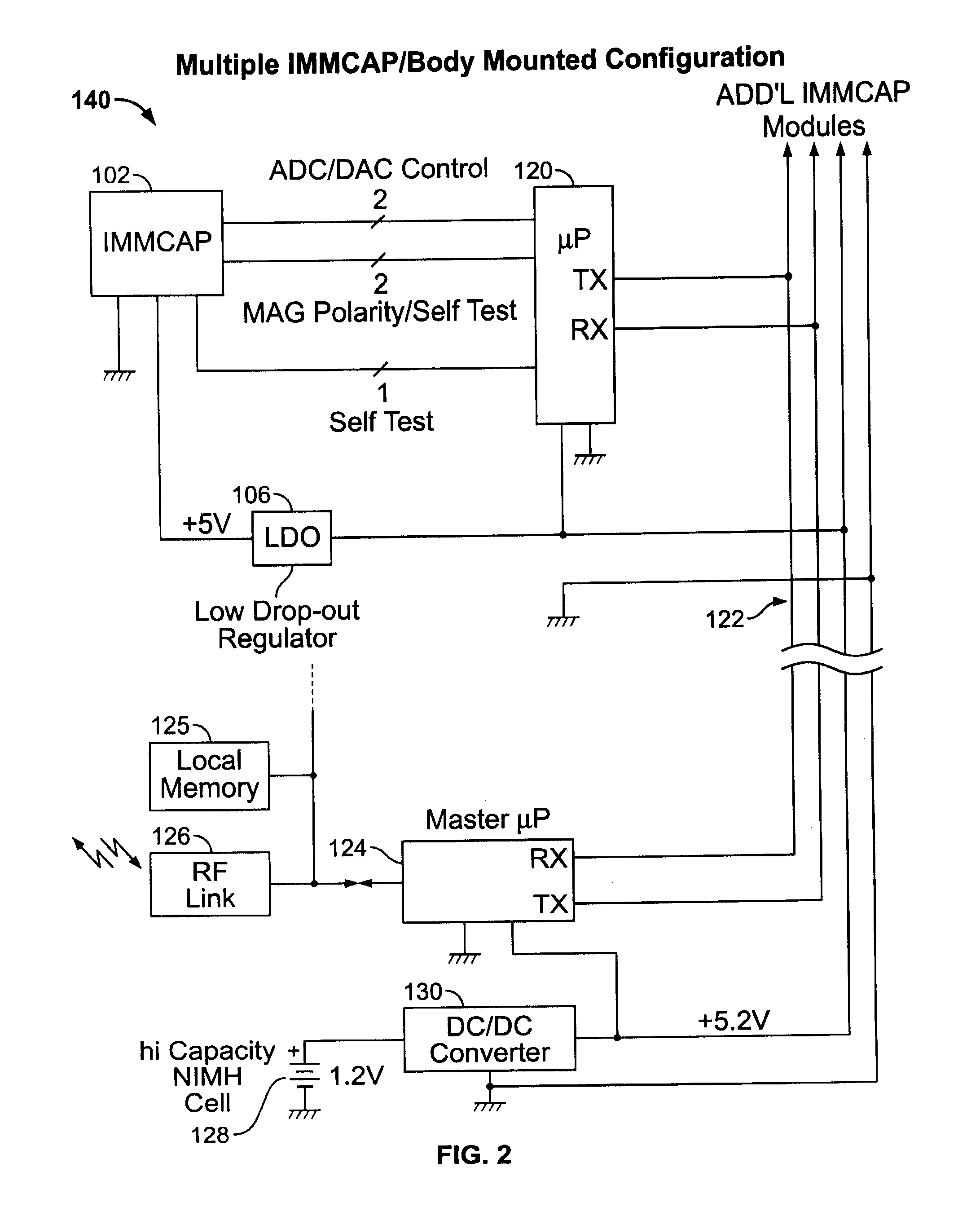
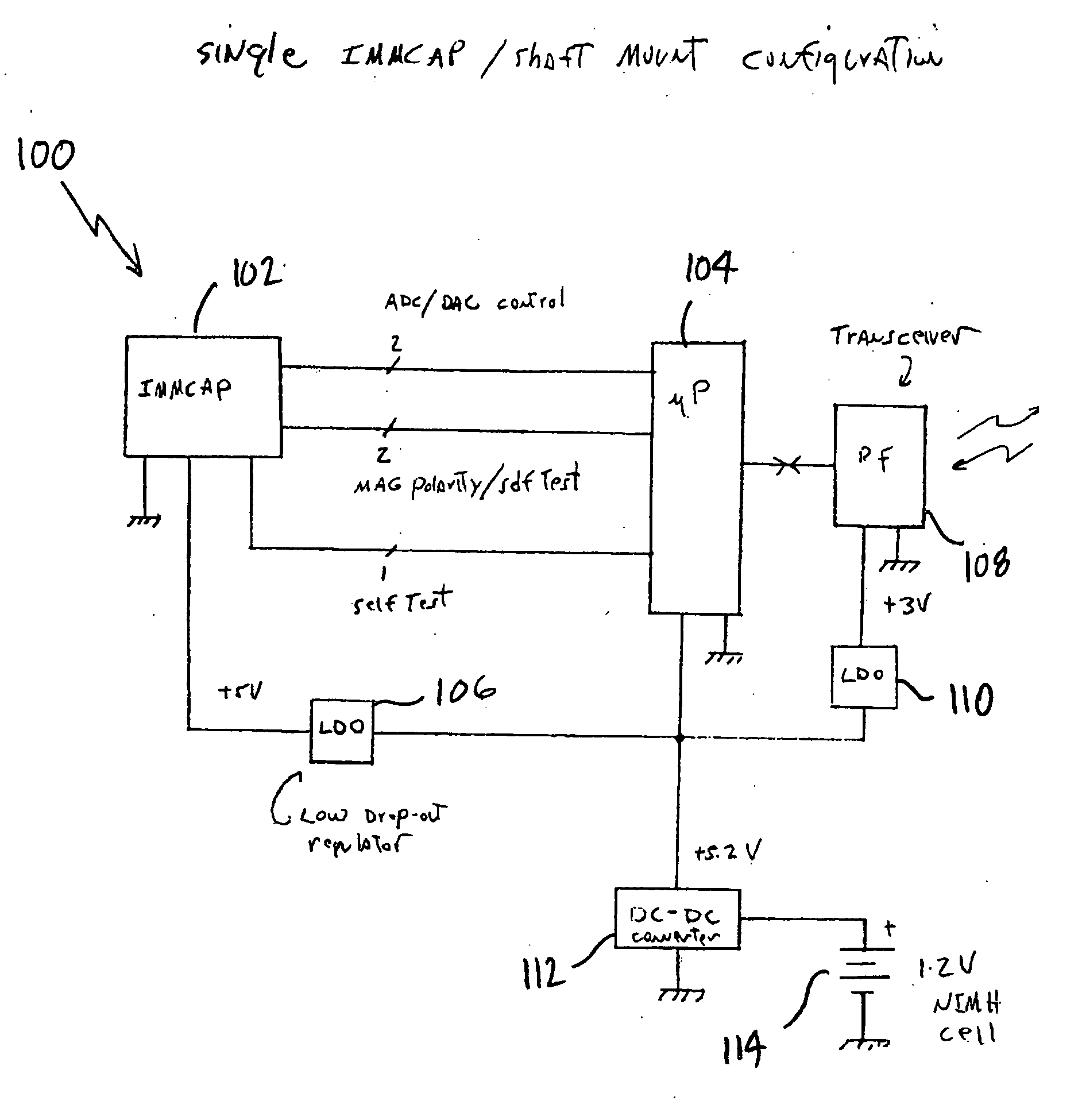
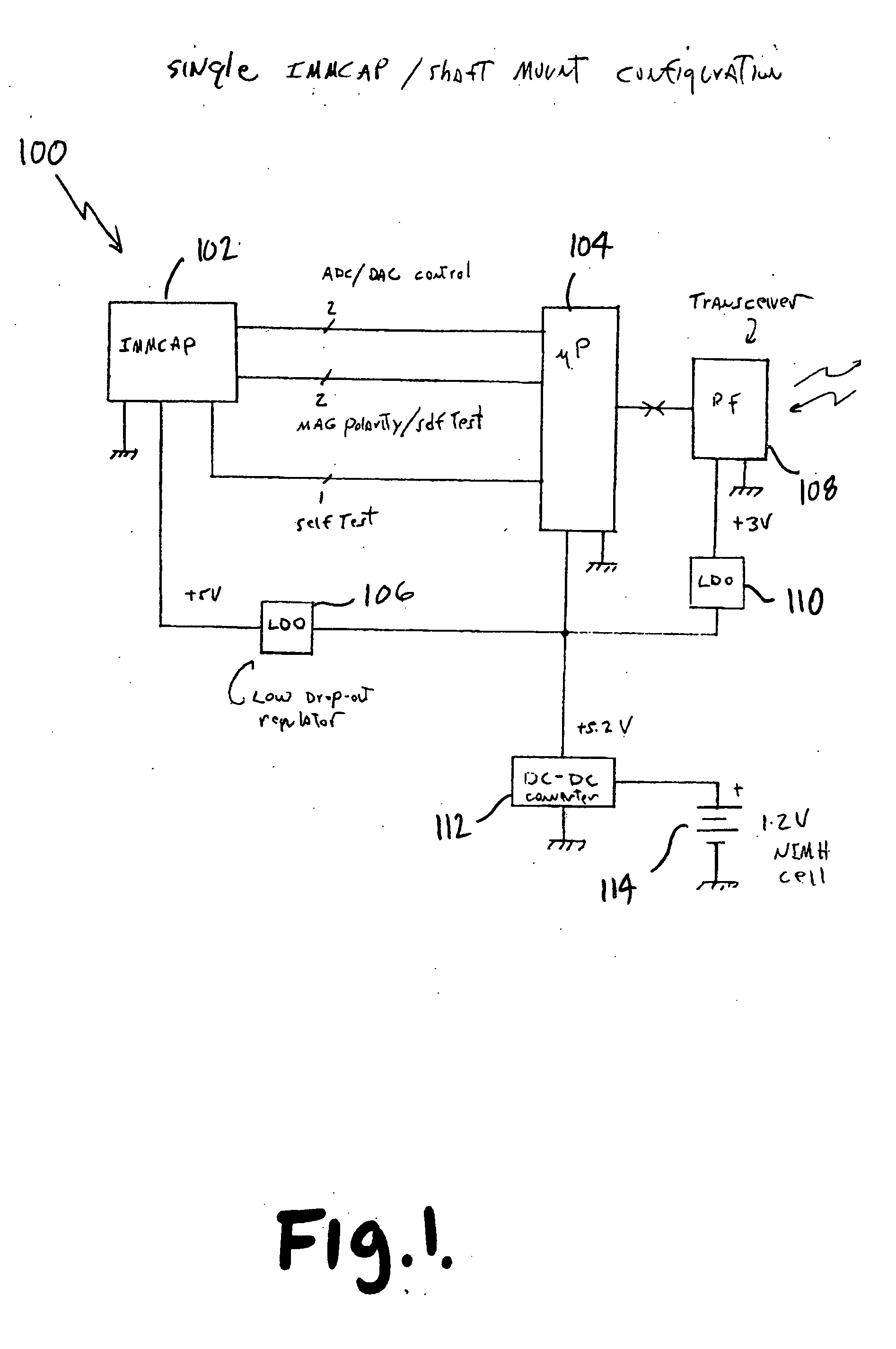
Single/multiple axes six degrees of freedom (6 DOF) inertial motion capture system with initial orientation determination capability
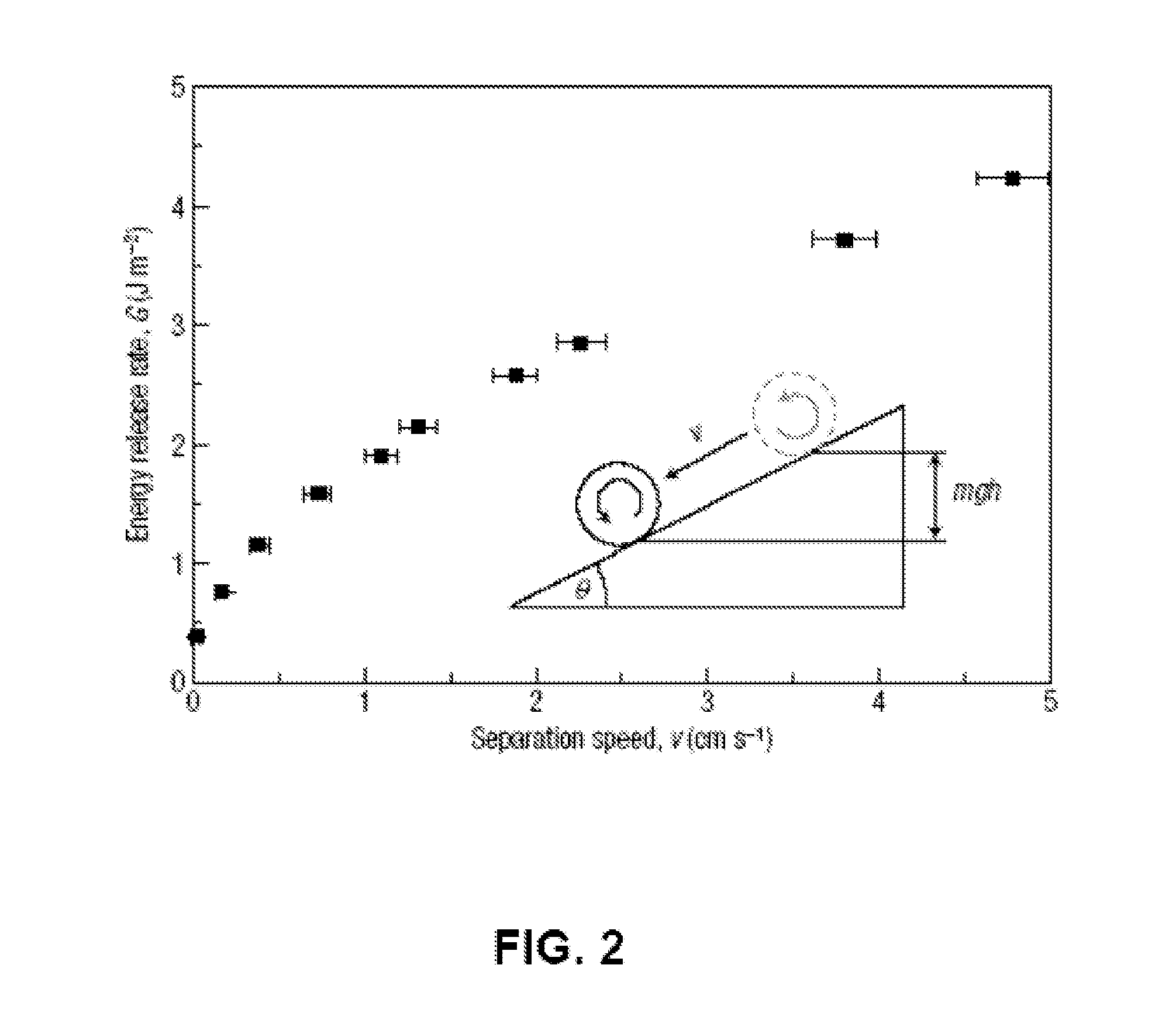
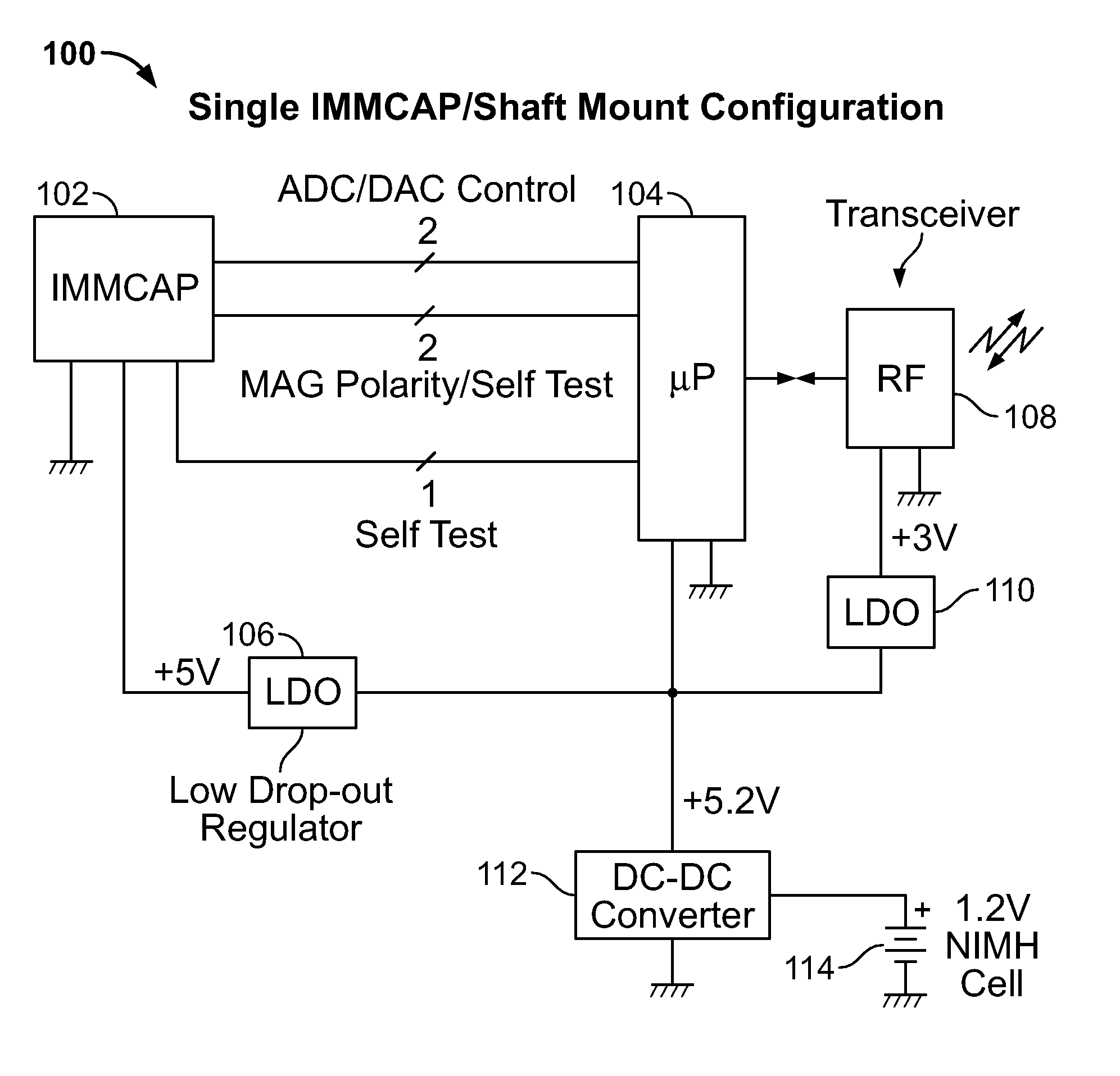
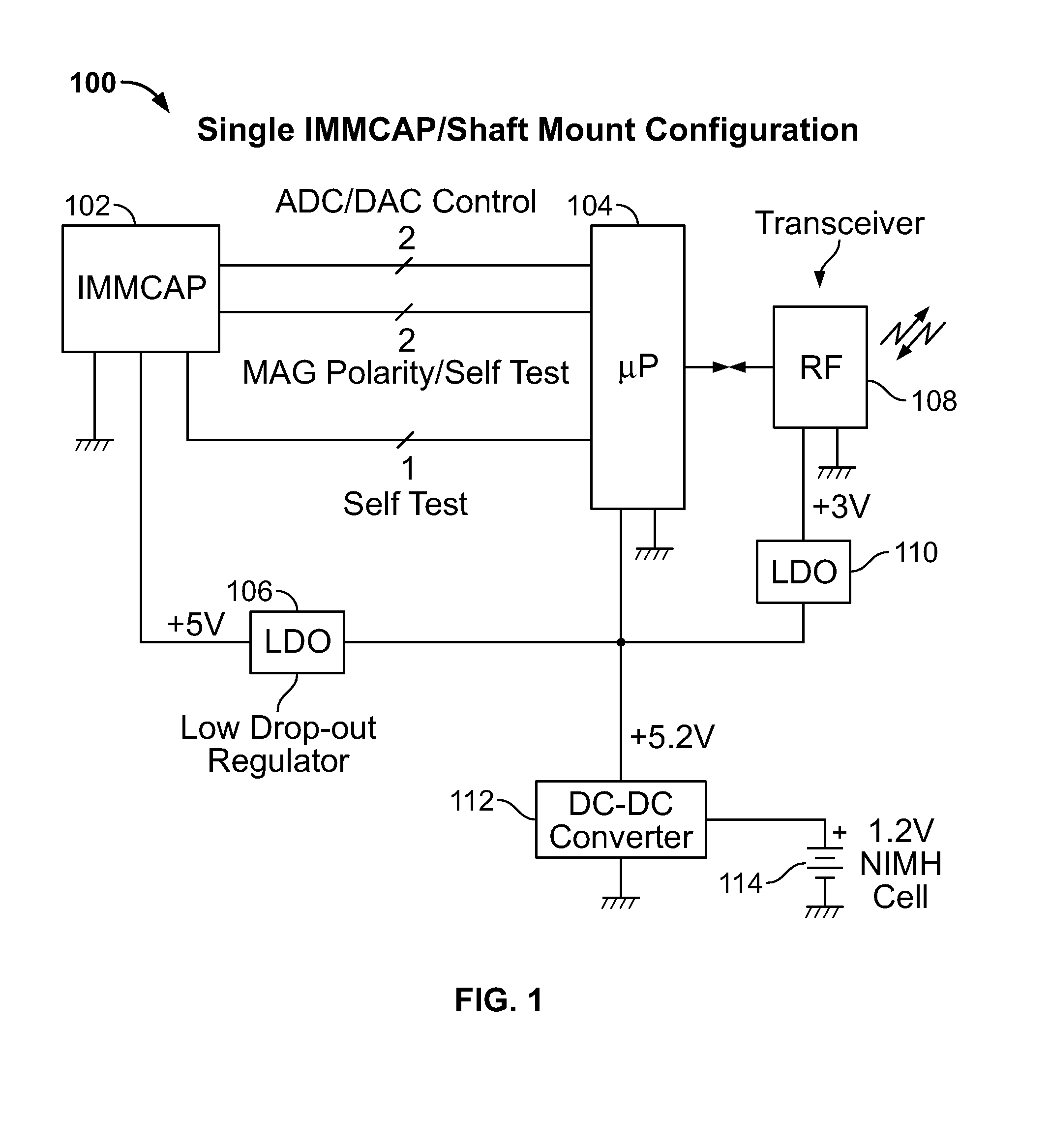
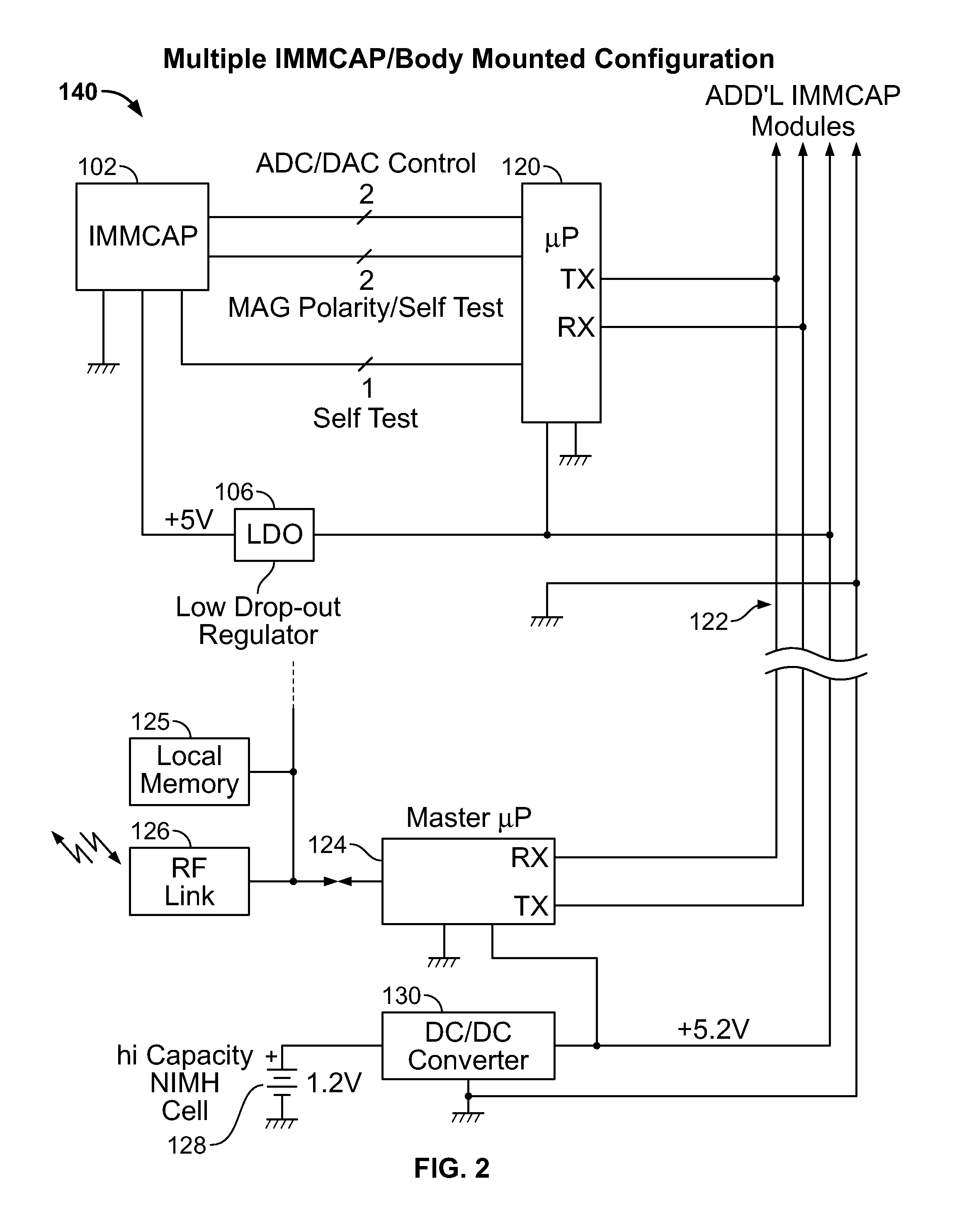
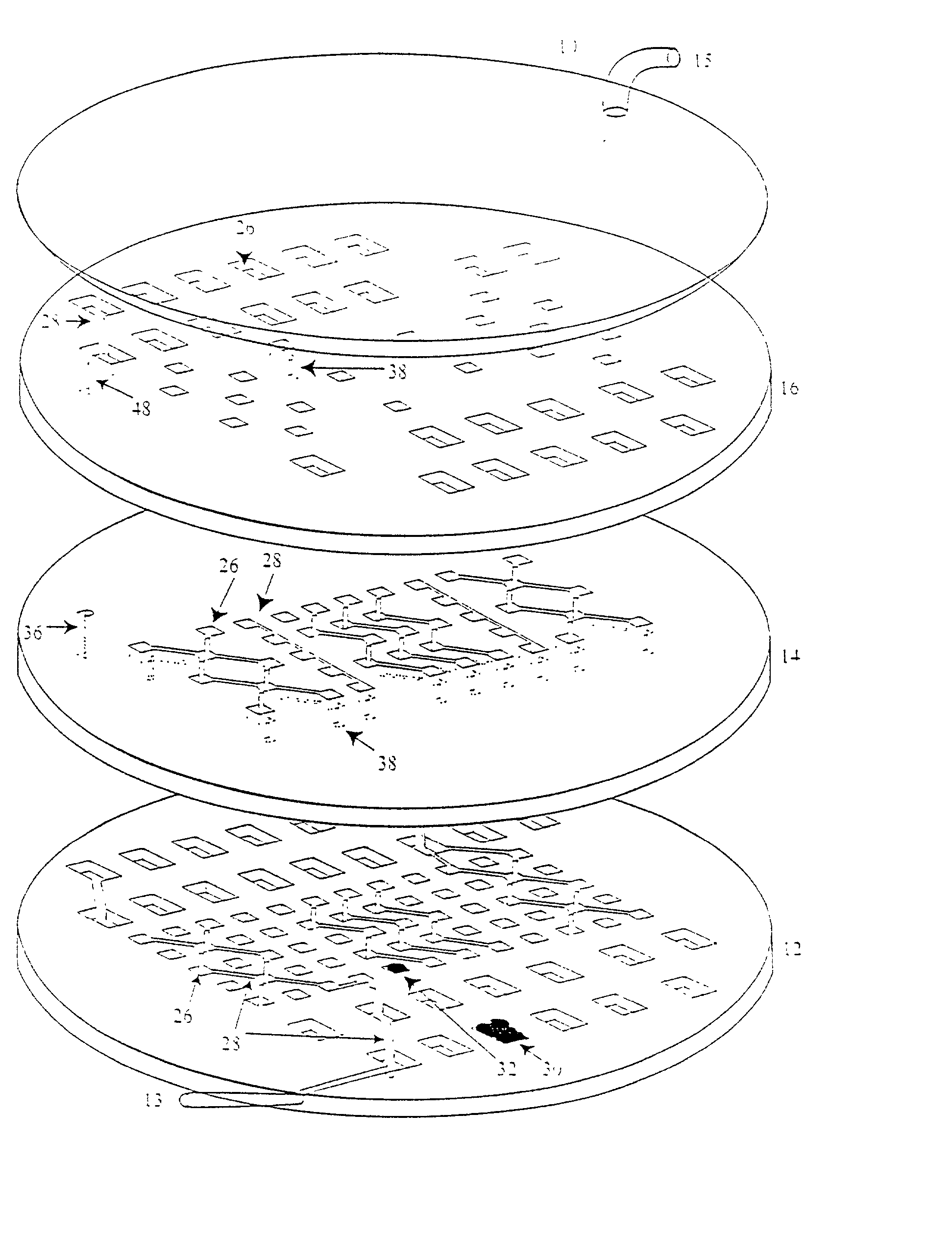
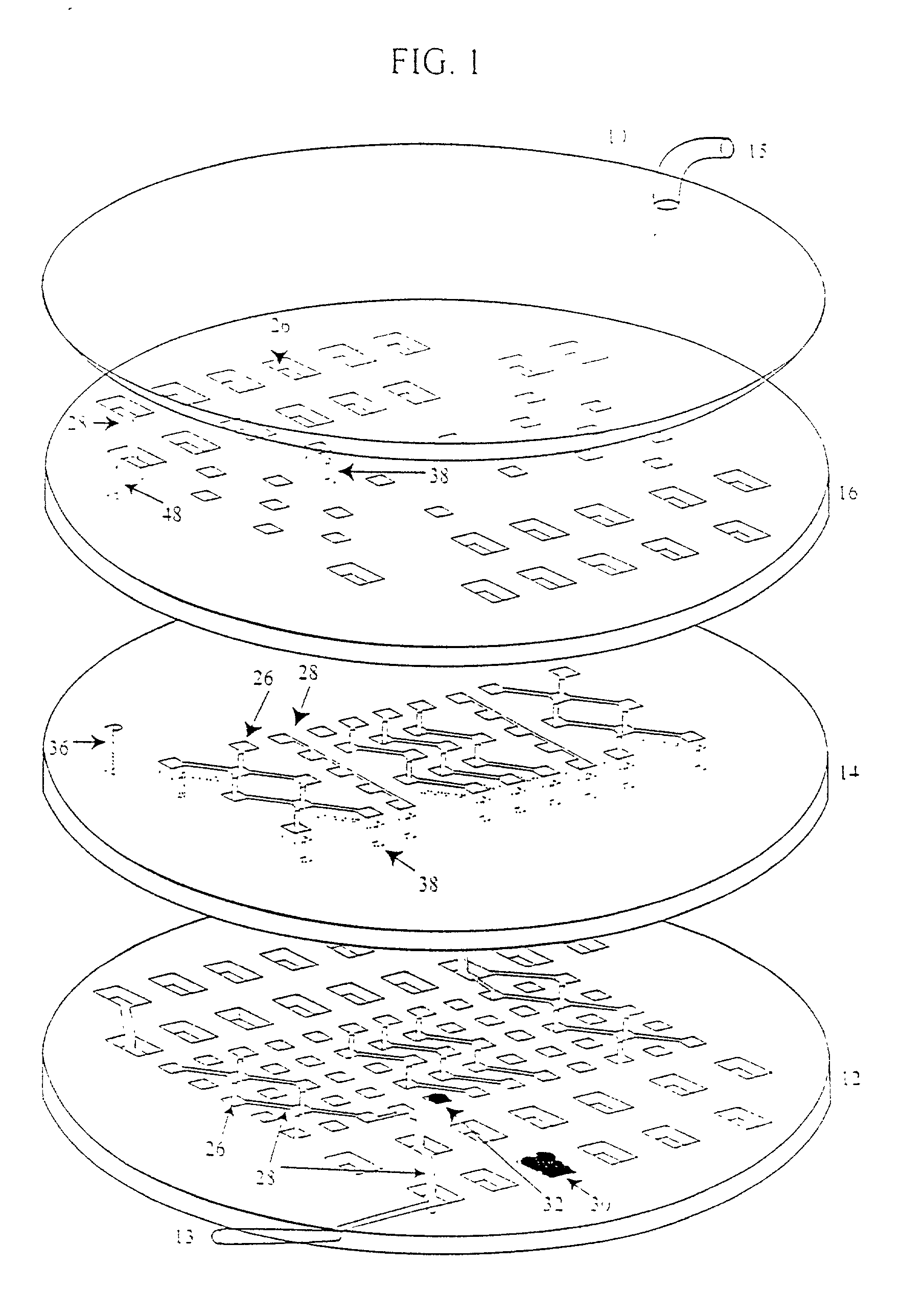
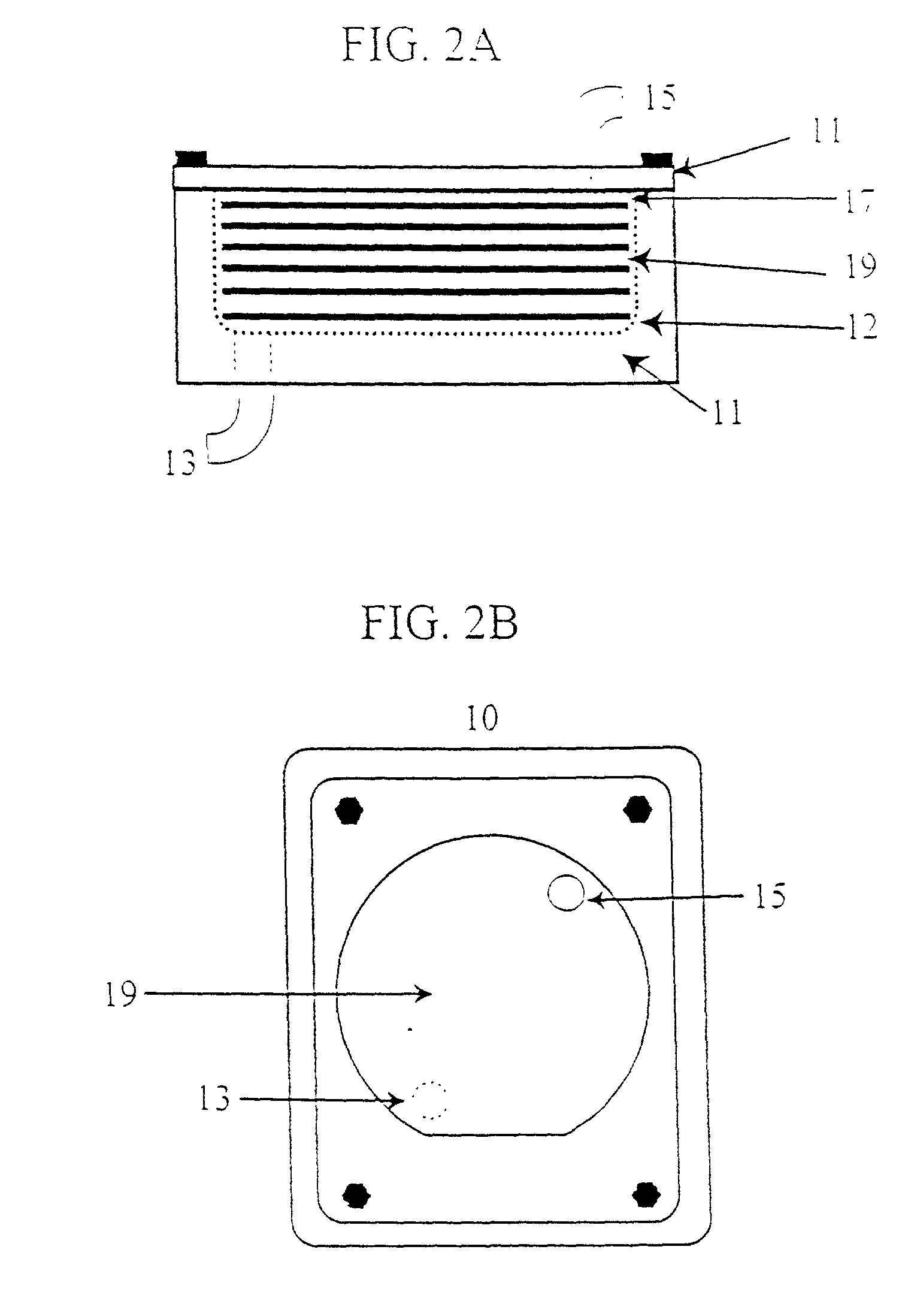
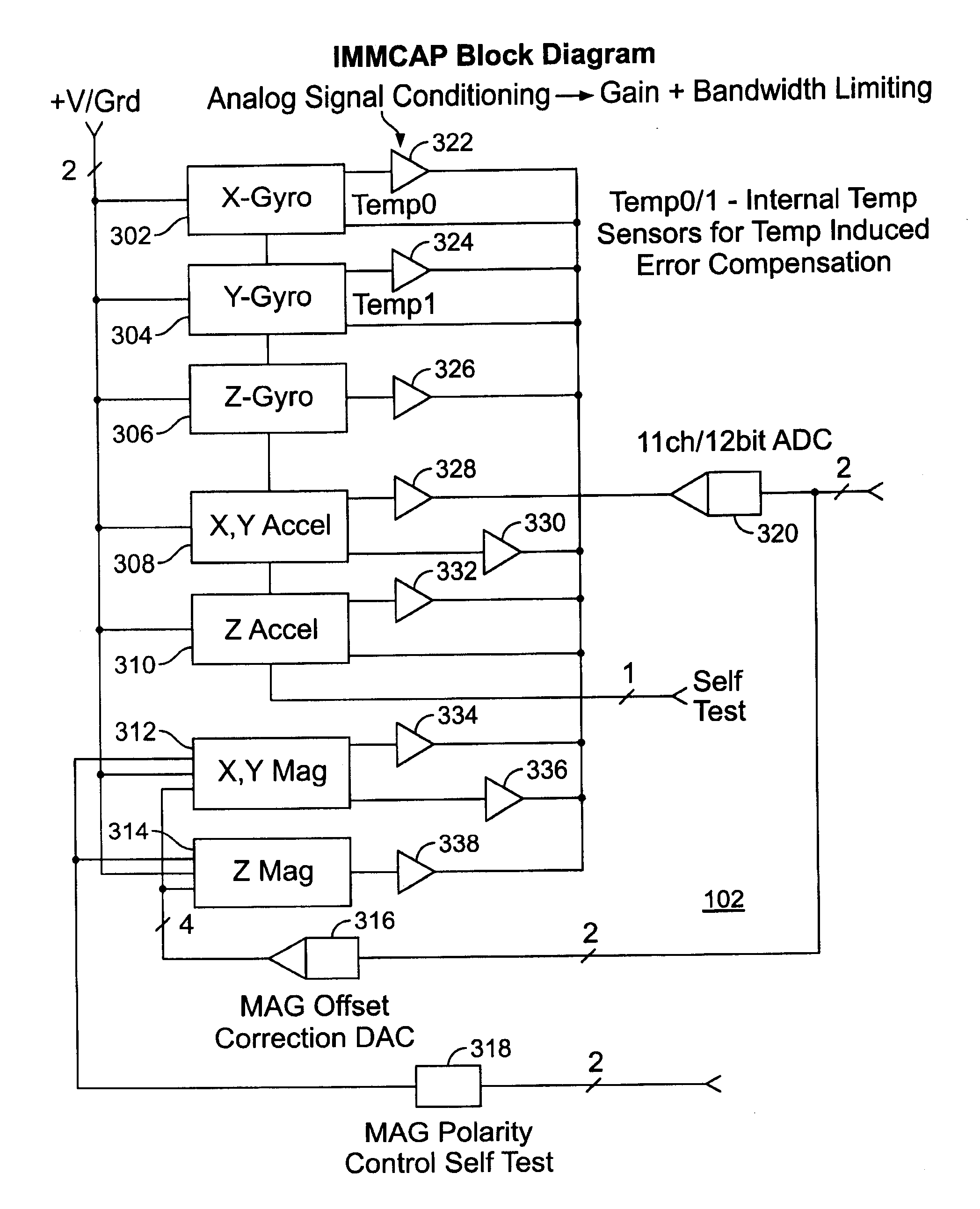
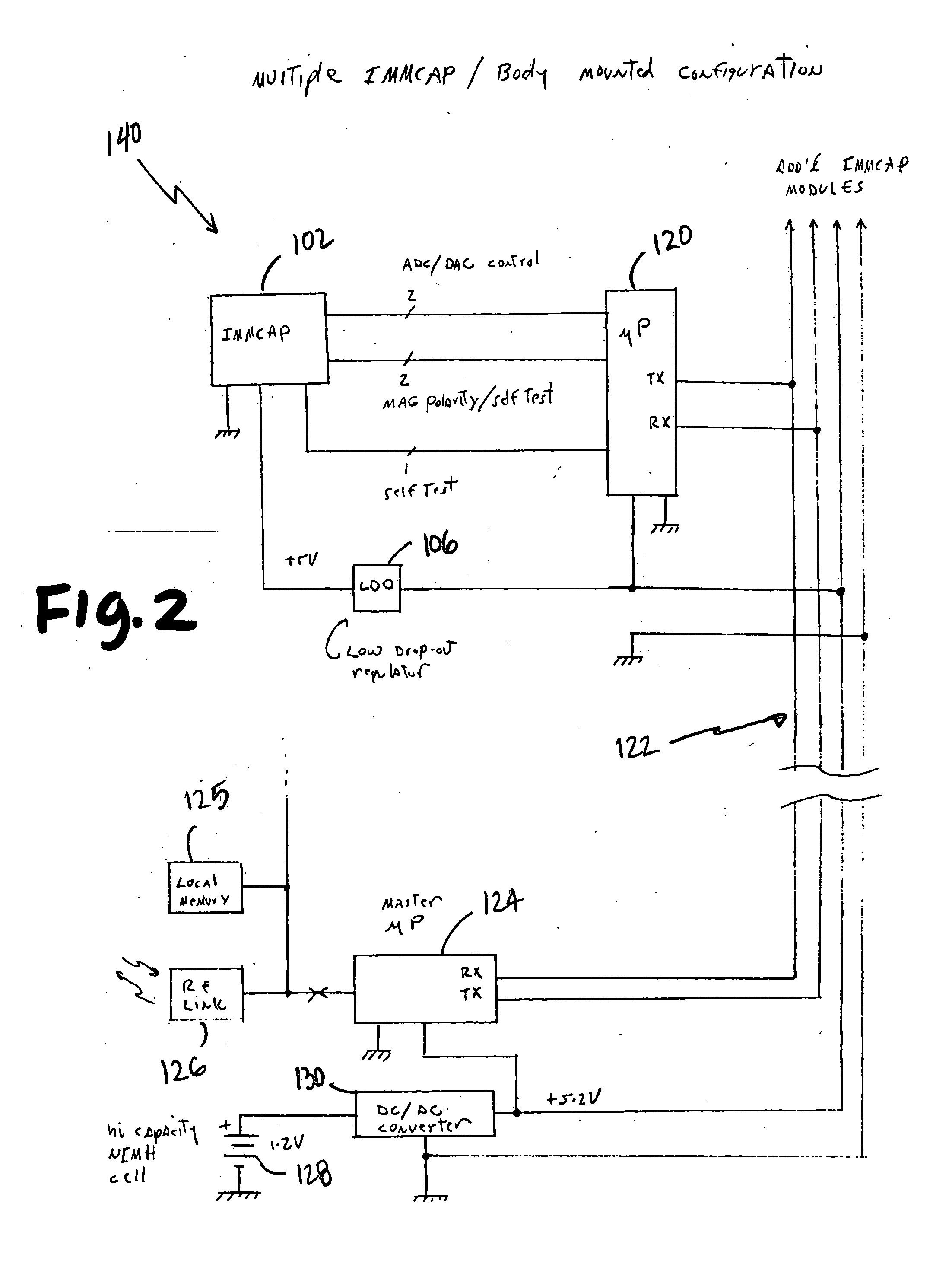
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:MAGNETO INERTIAL SENSING TECH
Device and method or three-dimensional spatial localization and functional interconnection of different types of cells
InactiveUS20020173033A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpatial OrientationsMetabolite
A device, method and process for three-dimensional spatial localization and functional interconnection of the same or different types of cells. The two or three-dimensional device comprising multiple layers containing wells for cell deposition where both the wells and layers are interconnected through microfluidic channels. A process for fabricating the three-dimensional device and a method for depositing different types of cells within the device in a functional interdependent spatial orientation thereby mimicking physiological functions. The device is useful for diagnostic assays, determination of dysfunction of certain cells in the system, quantification of production of cellular proteins, metabolites, hormones or other cellular products, for organ or tissue replacement, for co-culturing different cells, for testing pharmaceutical agents and as a bioreactor for production of biologicals.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Motion sensing apparatus, systems and techniques
InactiveUS20070219744A1Gymnastic exercisingNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDigital data3d print
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:C LAN WIRELESS
Single/multiple axes six degrees of freedom (6 DOF) inertial motion capture system with initial orientation determination capability
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:MAGNETO INERTIAL SENSING TECH
Scrolling and zooming of a portable device display with device motion
InactiveUS20110102455A1Quickly and easily viewReduces and eliminates deficiencyDevices with sensorCathode-ray tube indicatorsSpatial OrientationsAccelerometer
A portable computing device (10) with a display screen (26) that may be scrolled and / or zoomed in response to changes in the spatial orientation of the computing device. Changes in the spatial orientation of the computing device are sensed by accelerometers (20) contained in the device. Software converts signals sent by the accelerometers to scrolling or zooming commands that scroll and / or zoom the display screen. Motion of the computing device in the plane of the display screen of the computing device results in scrolling the display screen in the opposing direction of the motion of the computing device a distance greater than the distance the computing device is moved. Motion of the computing device perpendicular to the plane of the display screen zooms the display screen in or out. Motion of the computing device toward the user results in the display screen being zoomed in to reveal greater detail. Motion of the computing device away from the user results in the display screen being zoomed out to reveal more content.
Owner:TEMPLE WILL JOHN
Grid and rotatable cube guide localization fixture for biopsy device
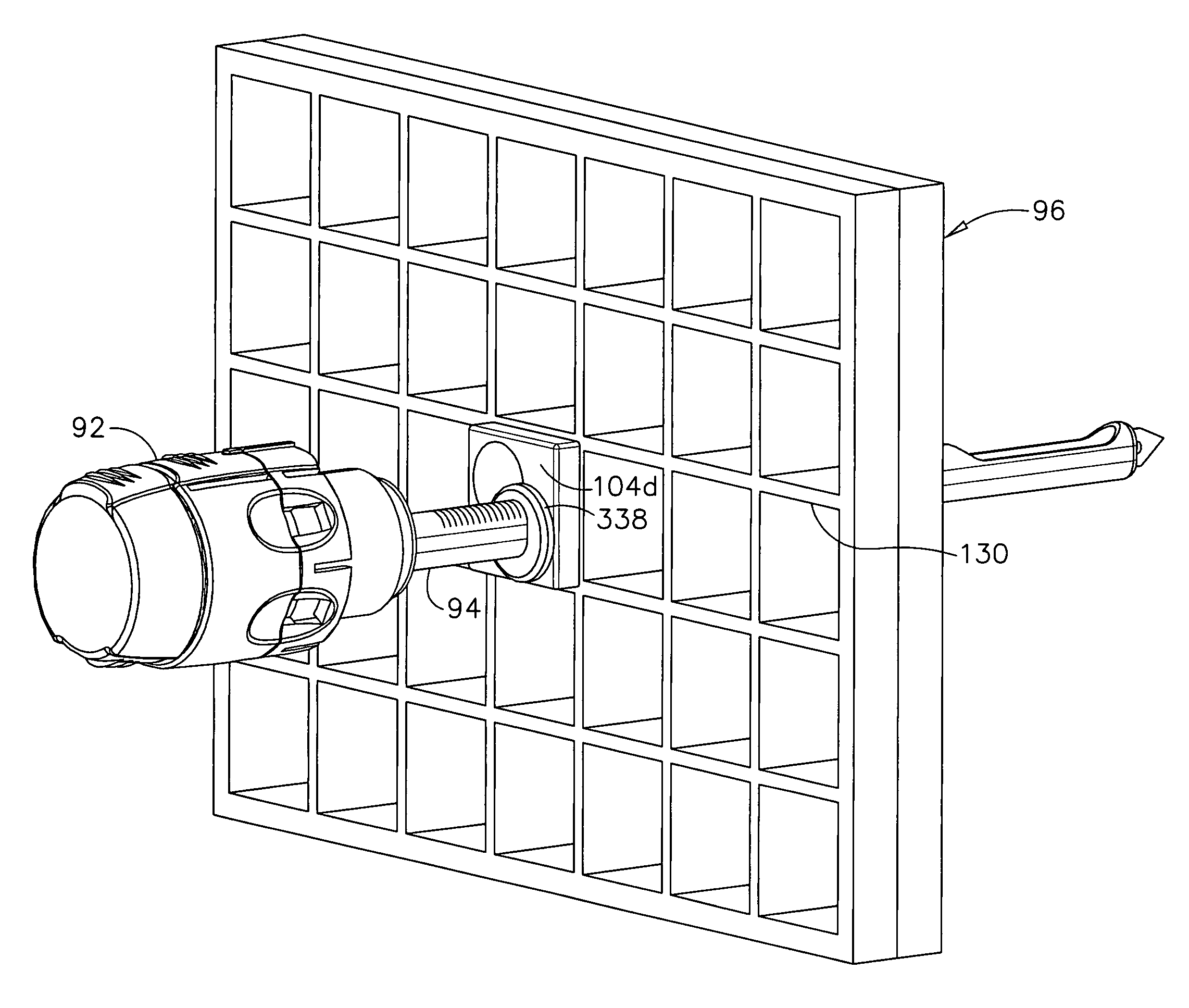
InactiveUS20070255168A1Widen the optionsAdd optionsSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSpatial OrientationsBiopsy instruments
A biopsy system with a grid plate used as either a lateral or medial compression plate of a localization fixture used with a breast coil includes a rotatable guide cube that may be inserted into a desired rectangular recess in the grid plate after rotating to position a selected guide hole in the desired spatial orientation. Versions of a guide cube include those rotatable in two axes to provide additional hole positions, angled holes, enlarged circular holes that function with a rotating guide to support a noncircular biopsy instrument cannula (e.g., trocar / sleeve combination, core biopsy probe of a biopsy device) for rotation. A rotating guide may have an unlocked state for easily sliding to a selected longitudinal position thereon. Thereafter, the rotating guide is locked to serve as a positive depth stop (e.g., quarter turn locking elastomeric rings, triangular and scissor clips, and shutter depth stops).
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Magnetic sensor assembly
ActiveUS7301332B2Low costSmall profileSurgeryMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpatial OrientationsMagneto
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
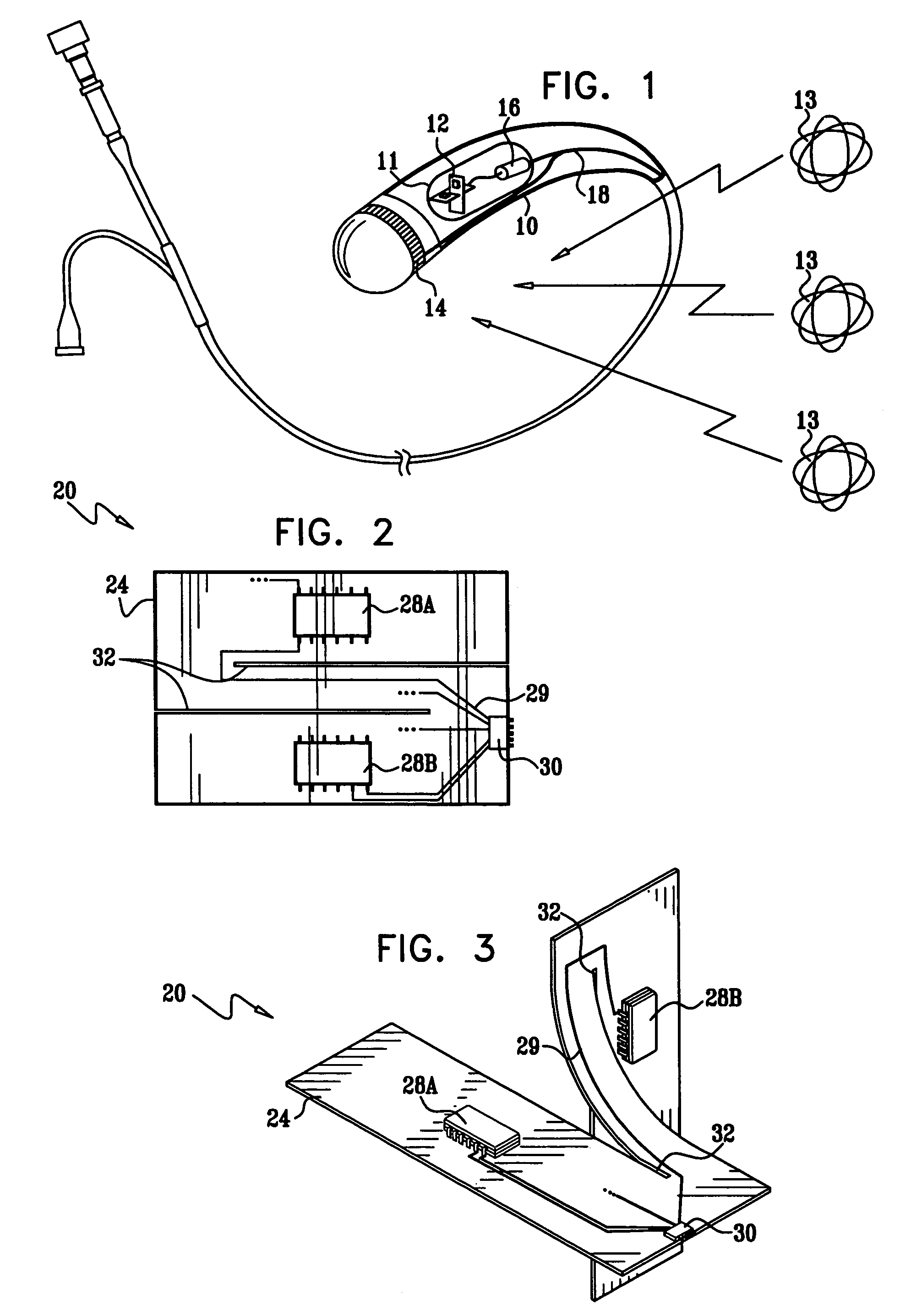
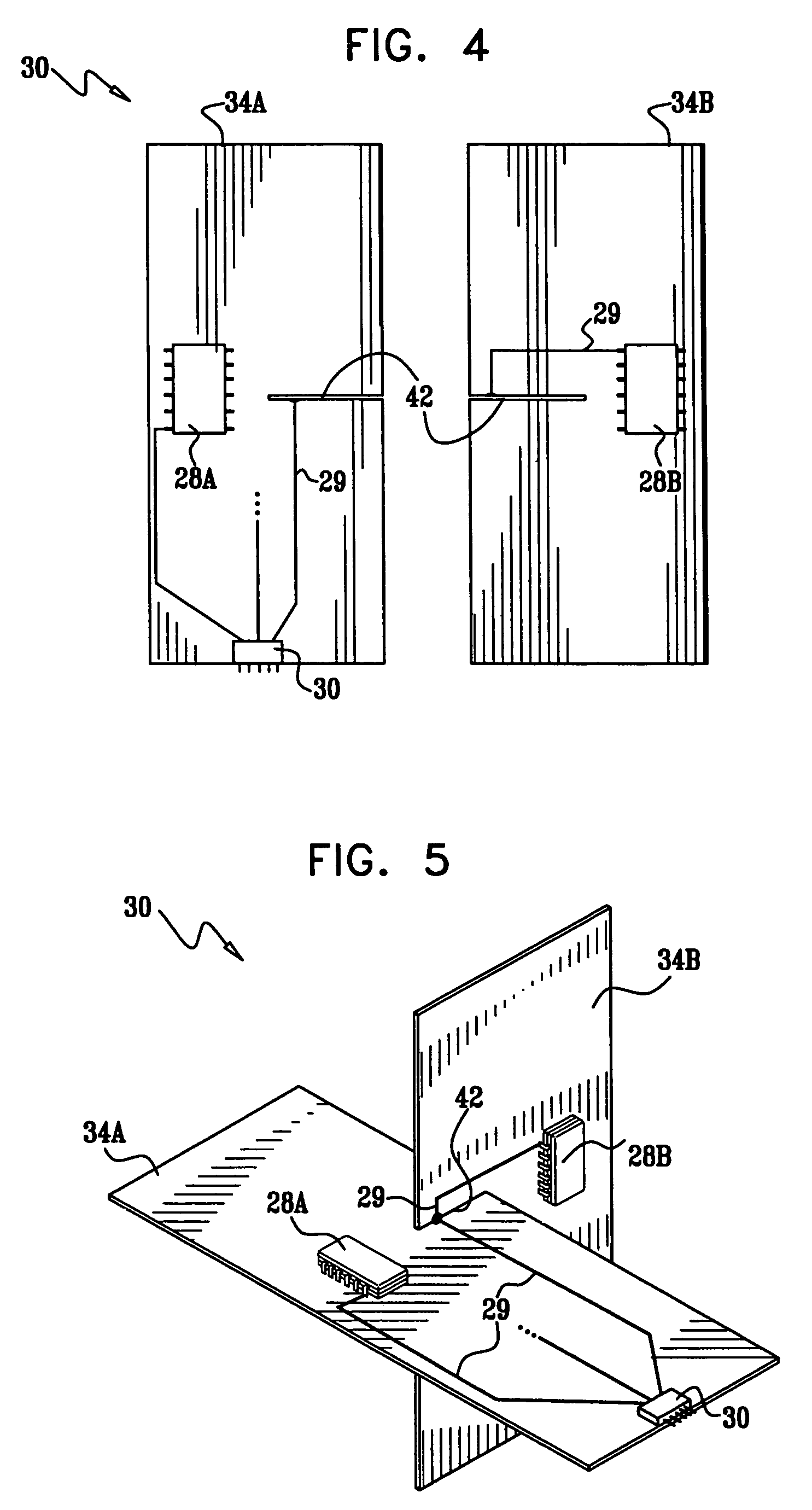
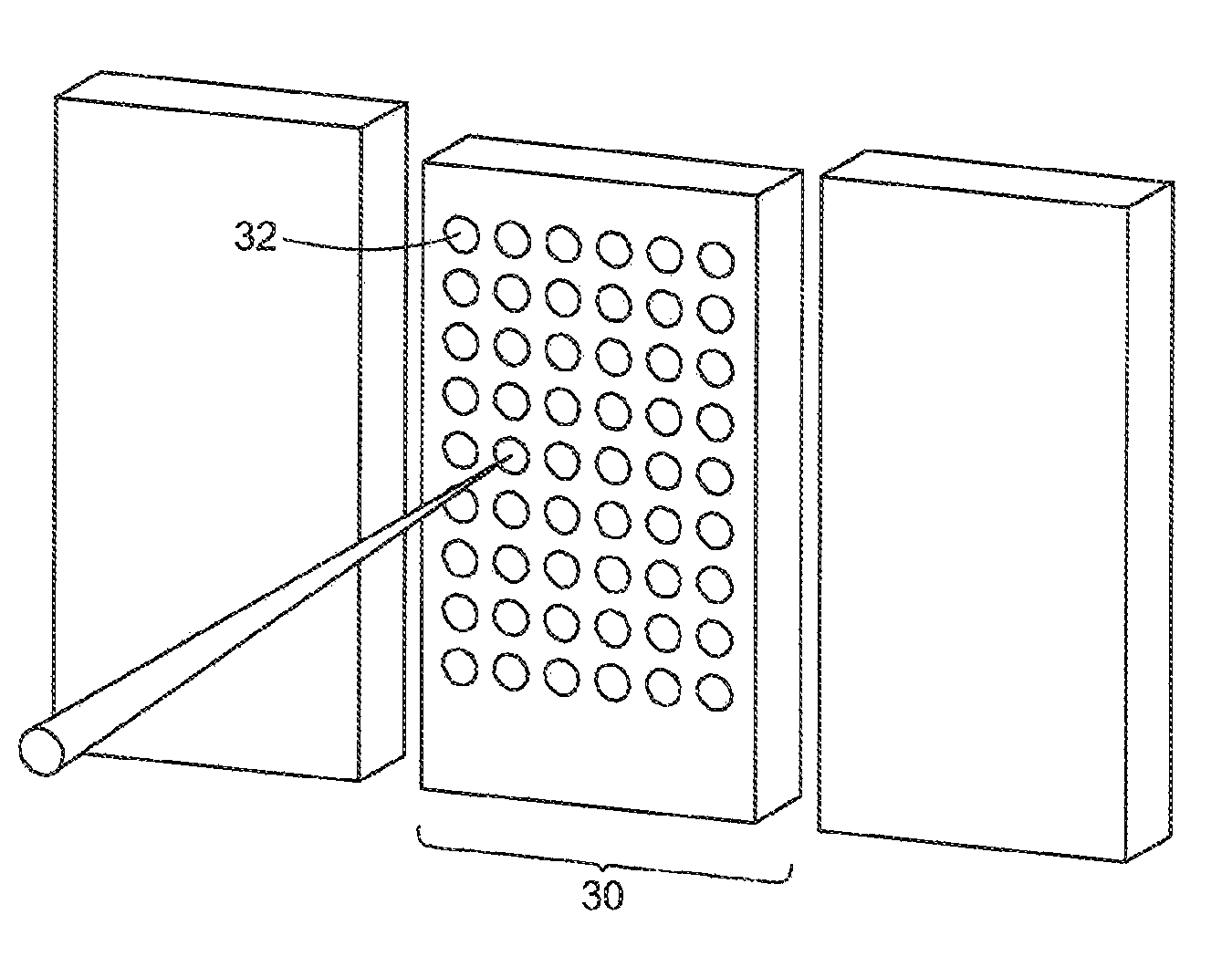
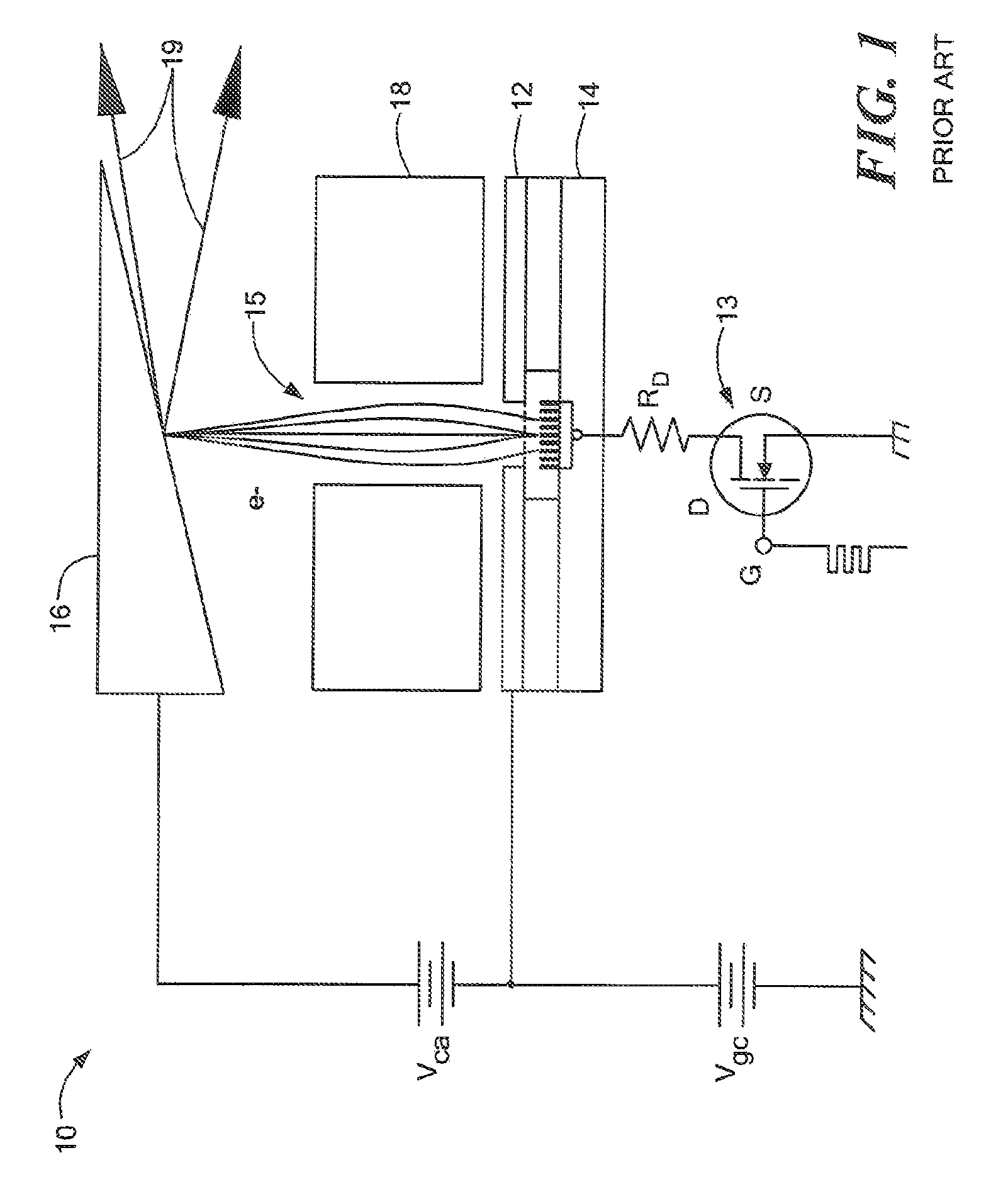
X-ray imaging of baggage and personnel using arrays of discrete sources and multiple collimated beams
ActiveUS7505562B2Material analysis by transmitting radiationNuclear radiation detectionSpatial OrientationsCarbon nanotube
A system and methods are provided for imaging an object, based on activating an array of discrete X-ray sources in a prescribed temporal pattern so as to illuminate the object with a beam varying in spatial orientation, and detecting X-rays of the beam after interaction with the object and generating a detector signal. An image of the object may then be constructed on the basis of the time variation of the detector signal. The discrete X-ray sources may be moved during the course of inspection, moreover, the prescribed temporal pattern may constitute a Hadamard code. The discrete sources may be carbon nanotube x-ray sources.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
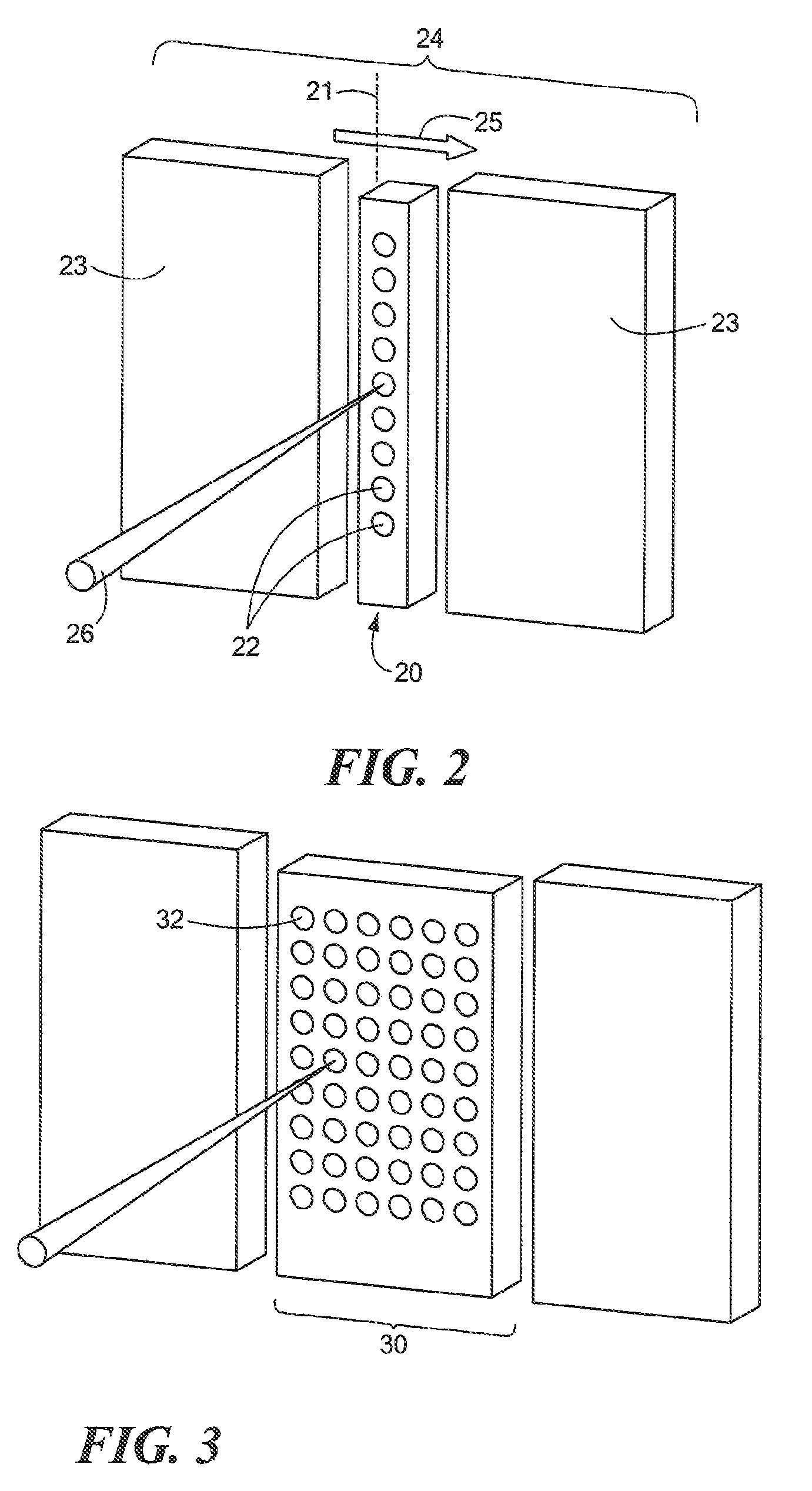
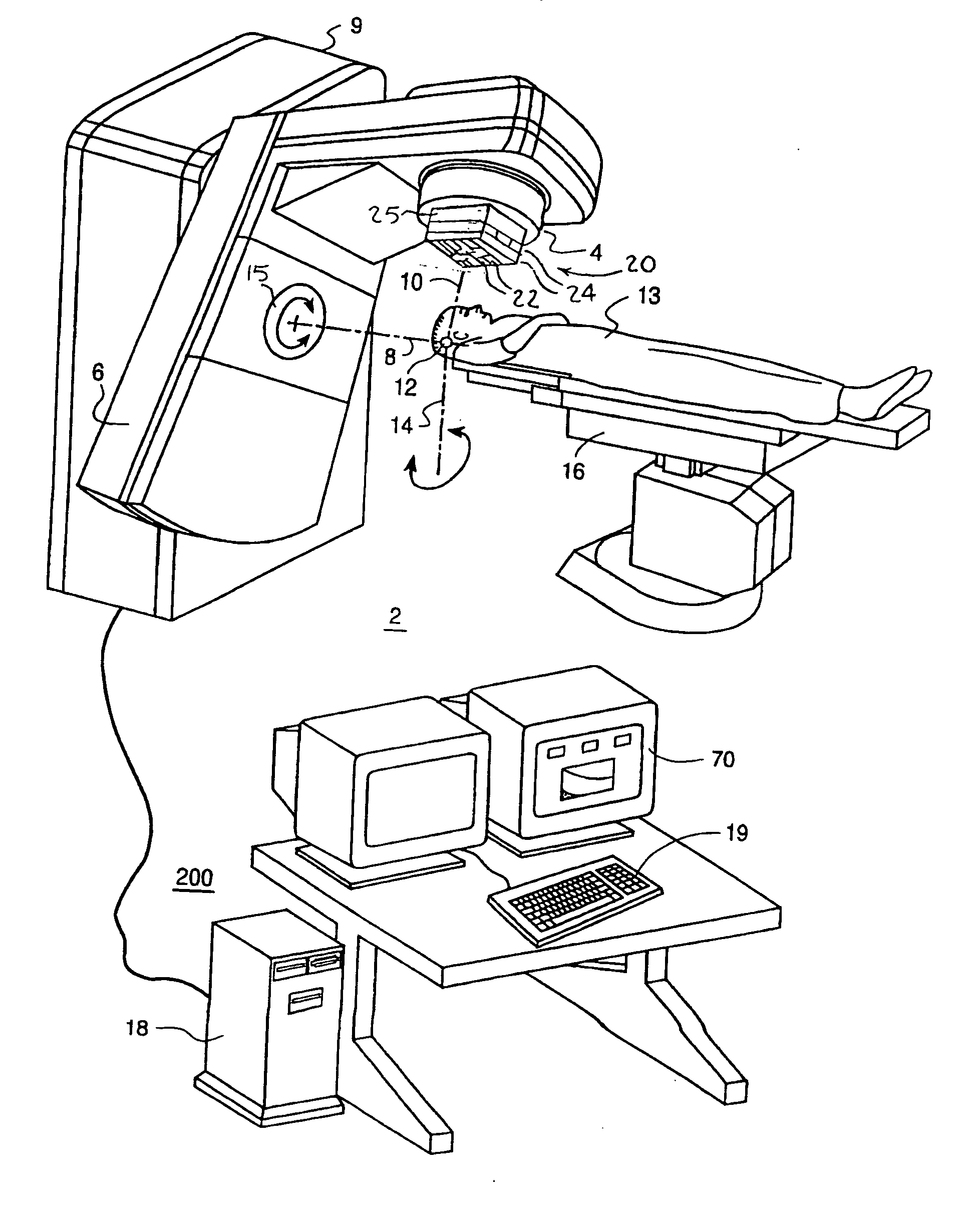
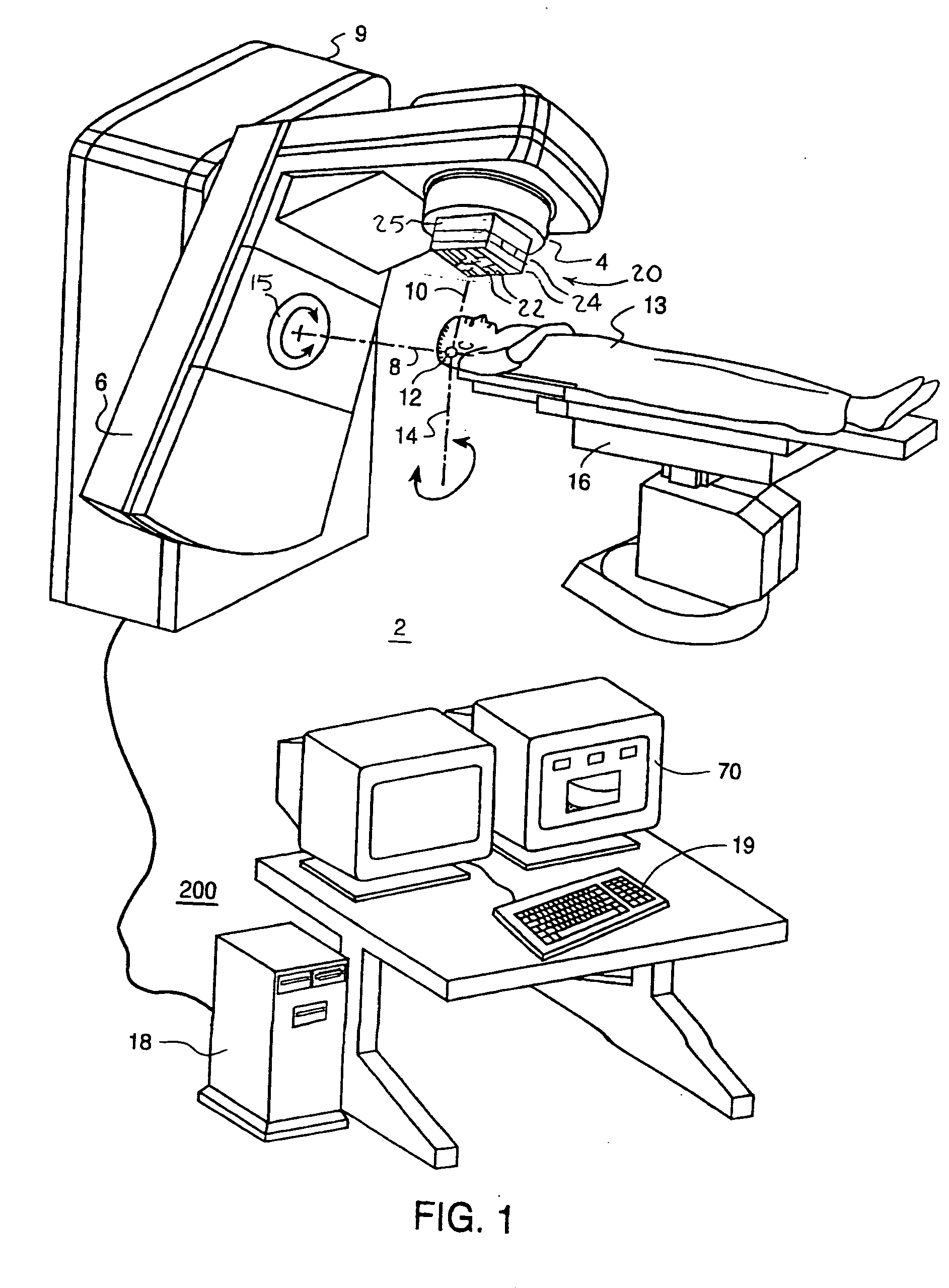
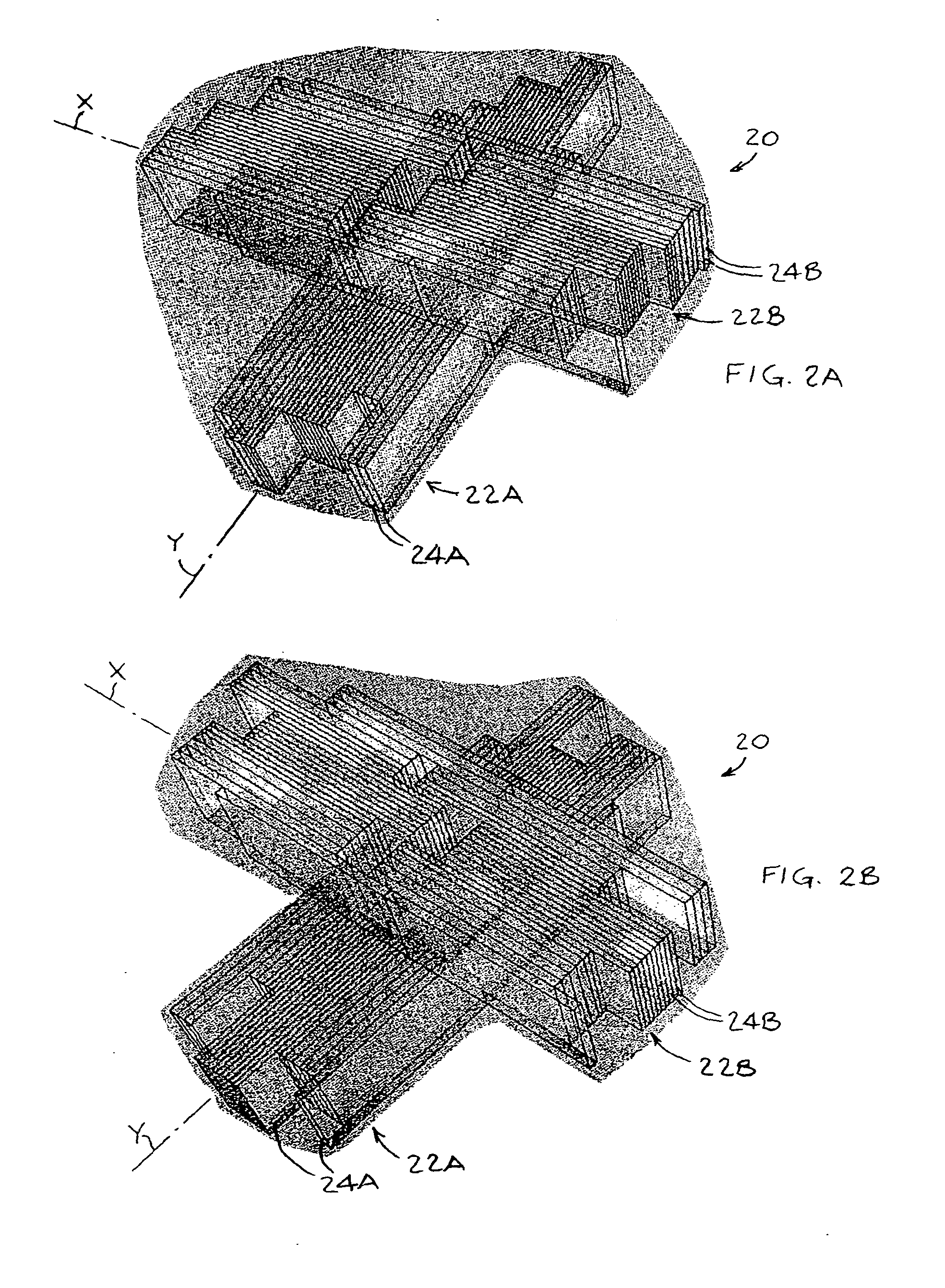
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy with a multilayer multileaf collimator
InactiveUS20050058245A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySpatial OrientationsControl system
An intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) system including a radiation beam delivery device positionable in a plurality of spatial orientations, an IMRT control system adapted to modulate at least an intensity of a radiation beam emanating from the radiation beam delivery device depending on at least one of the spatial orientations of the radiation beam delivery device and in accordance with an IMRT intensity map, and a multilayer multileaf collimator placed in a path of the radiation beam emanating from the radiation beam delivery device, the multilayer multileaf collimator including a plurality of layers of radiation blocking leaves, the layers being at different positions along the path of the radiation beam generally traverse to the radiation beam.
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
Biopsy cannula adjustable depth stop
InactiveUS7507210B2Prevent overshootSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSpatial OrientationsBiopsy instruments
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Augmented-reality-based three-dimensional interactive learning system and method
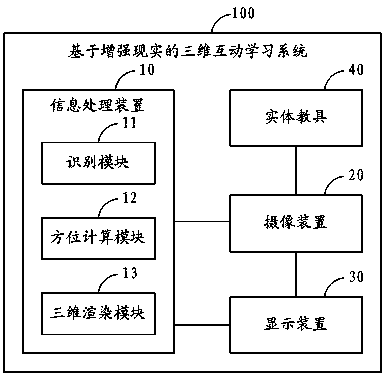
ActiveCN103366610AImprove learning effectEnhance memoryImage data processingElectrical appliancesInformation processingSpatial Orientations
The invention provides an augmented-reality-based three-dimensional interactive learning system and an augmented-reality-based three-dimensional interactive learning method. The system comprises an information processing device, a photographic device, a display device and at least one physical teaching aid, wherein the physical teaching aid is provided with identification information; the photographic device is used for performing video acquisition on a real environment after augmented reality application is started; and the information processing device comprises an identification module for identifying the identification information on the physical teaching aid, an orientation calculation module for calculating the spatial orientation information of the physical teaching aid, and a three-dimensional rendering module for acquiring a three-dimensional model corresponding to the identification information, rendering and generating a corresponding virtual object, and placing the virtual object at a corresponding position in a video image for display according to the spatial orientation information of the physical teaching aid. According to the system and the method, the real environment and the virtual object are overlapped in the same scenario in real time, so that a more vivid sensory experience is provided for a user, and meanwhile, a teaching effect is improved by utilizing the instinct of a person for the recognition of a three-dimensional space.
Owner:YANGSHU WENHUA SHANGHAI
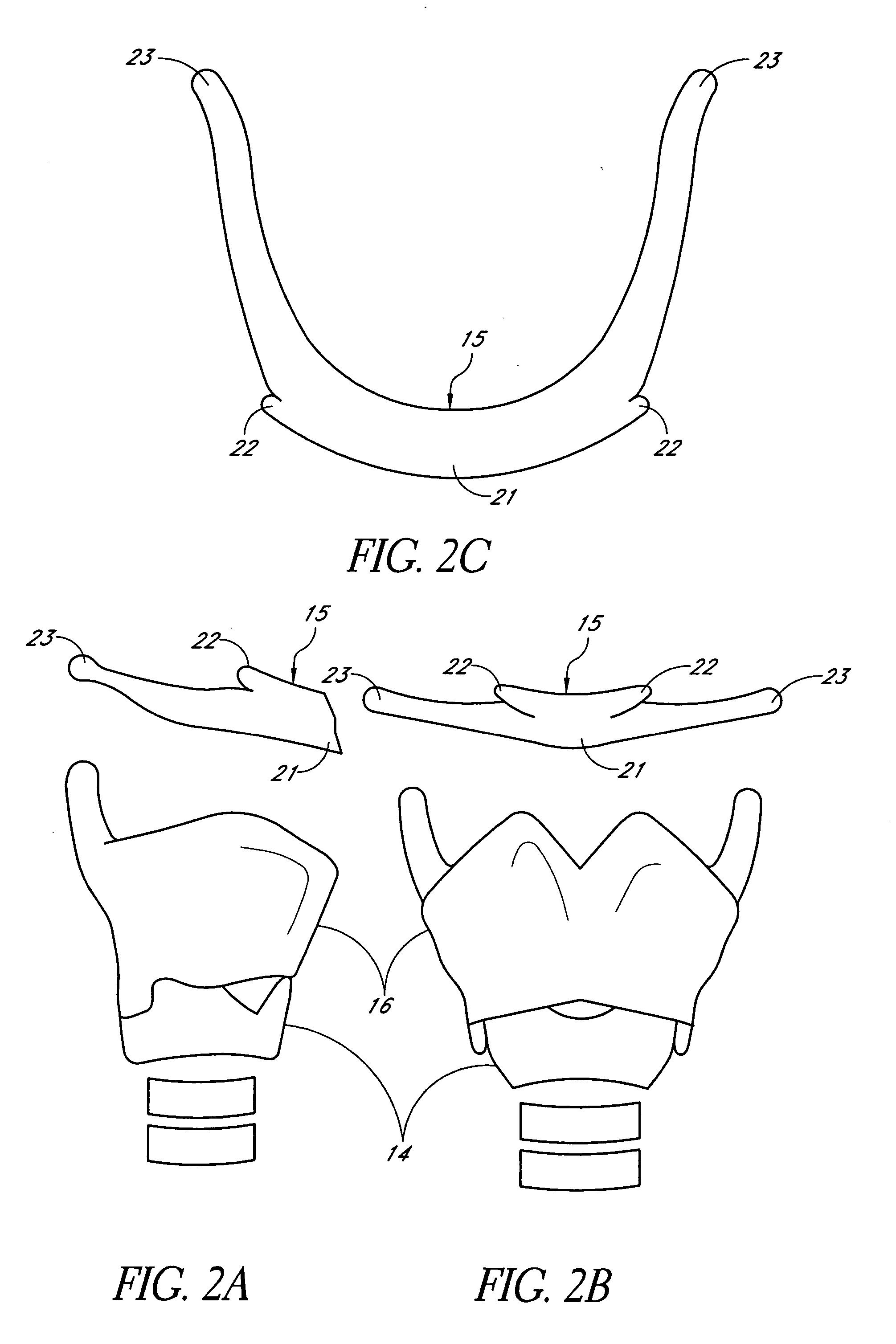
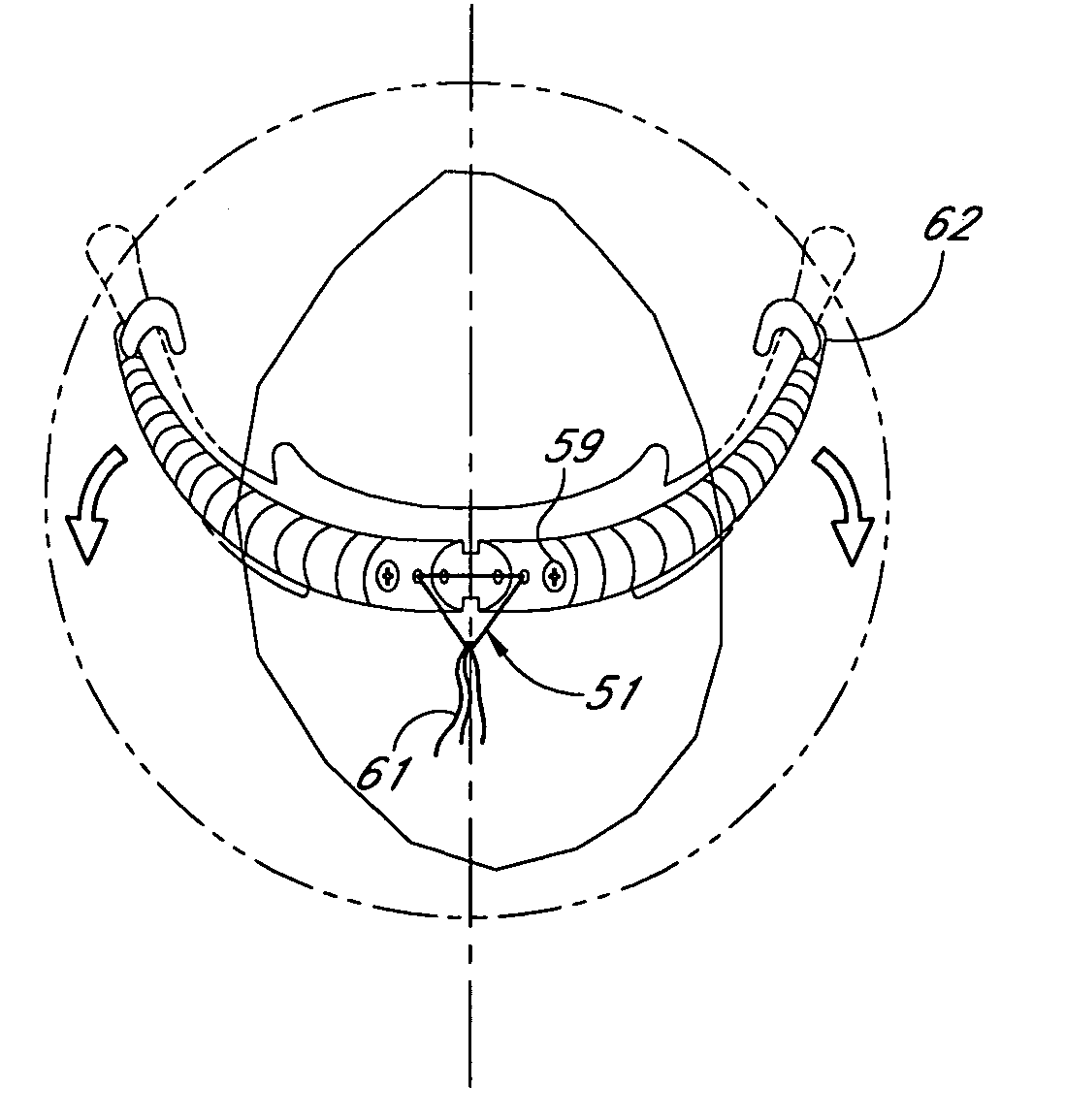
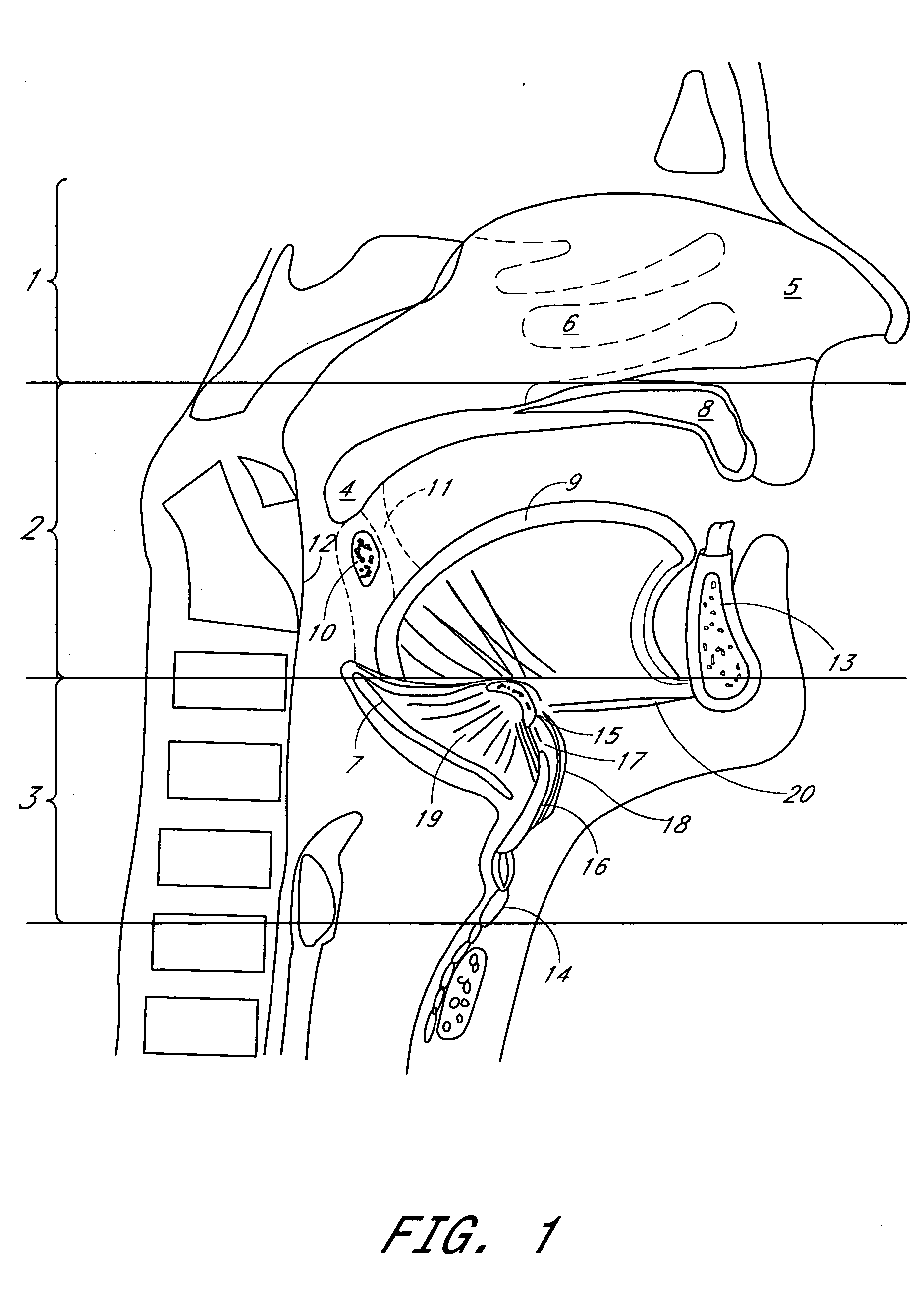
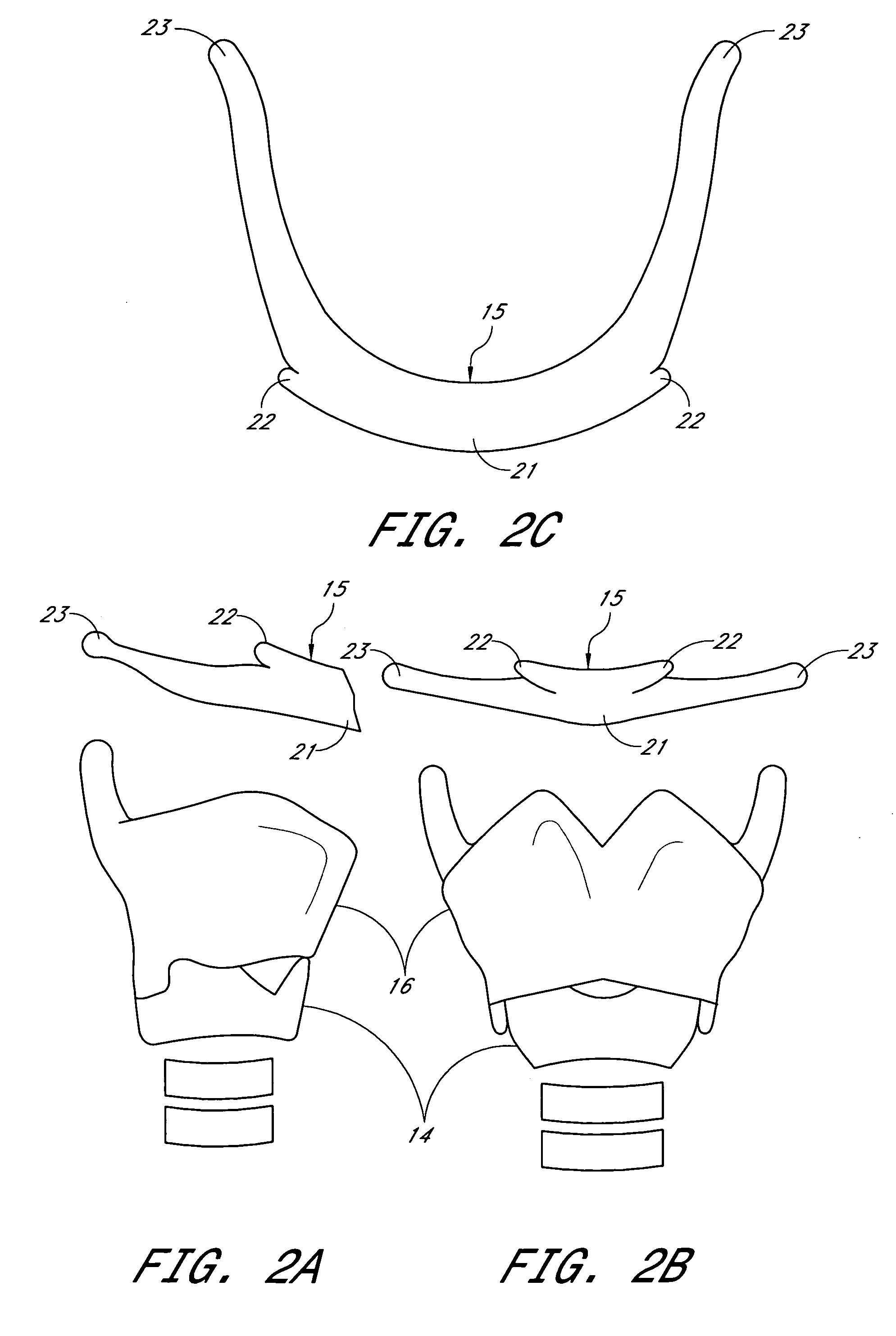
System and method for hyoidplasty
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating the hyoid bone, such as to treat obstructive sleep apnea. A conformable implant is positioned adjacent a hyoid bone. The spatial orientation of the hyoid bone is manipulated, to affect the configuration of the airway. The implant restrains the hyoid bone in the manipulated configuration. The implant is positioned adjacent to pharyngeal structures to dilate the pharyngeal airway and / or to support the pharyngeal wall against collapse. The implant may be attached to the hyoid bone using a clamp delivery tool that is adapted to releasably engage the implant.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
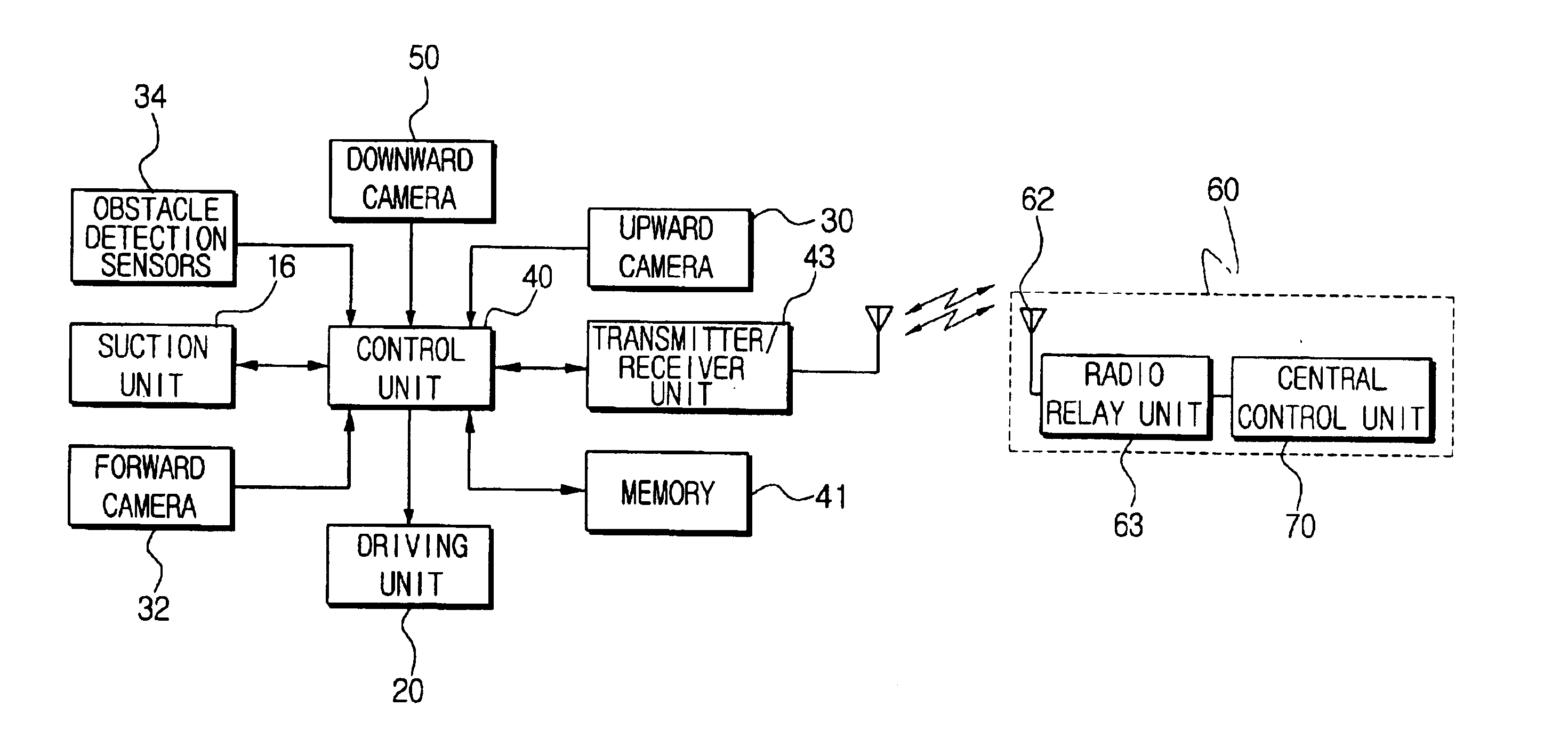
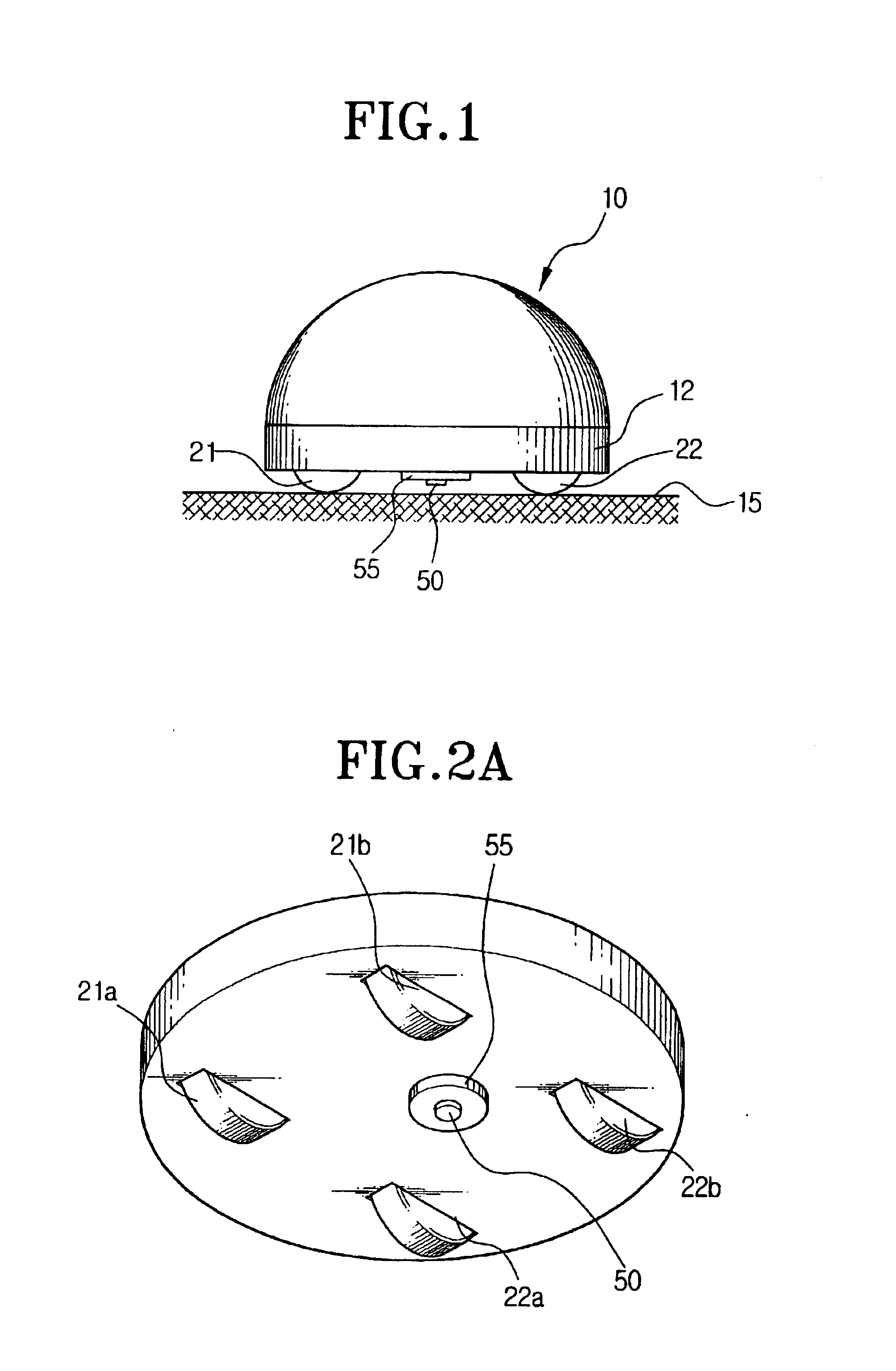
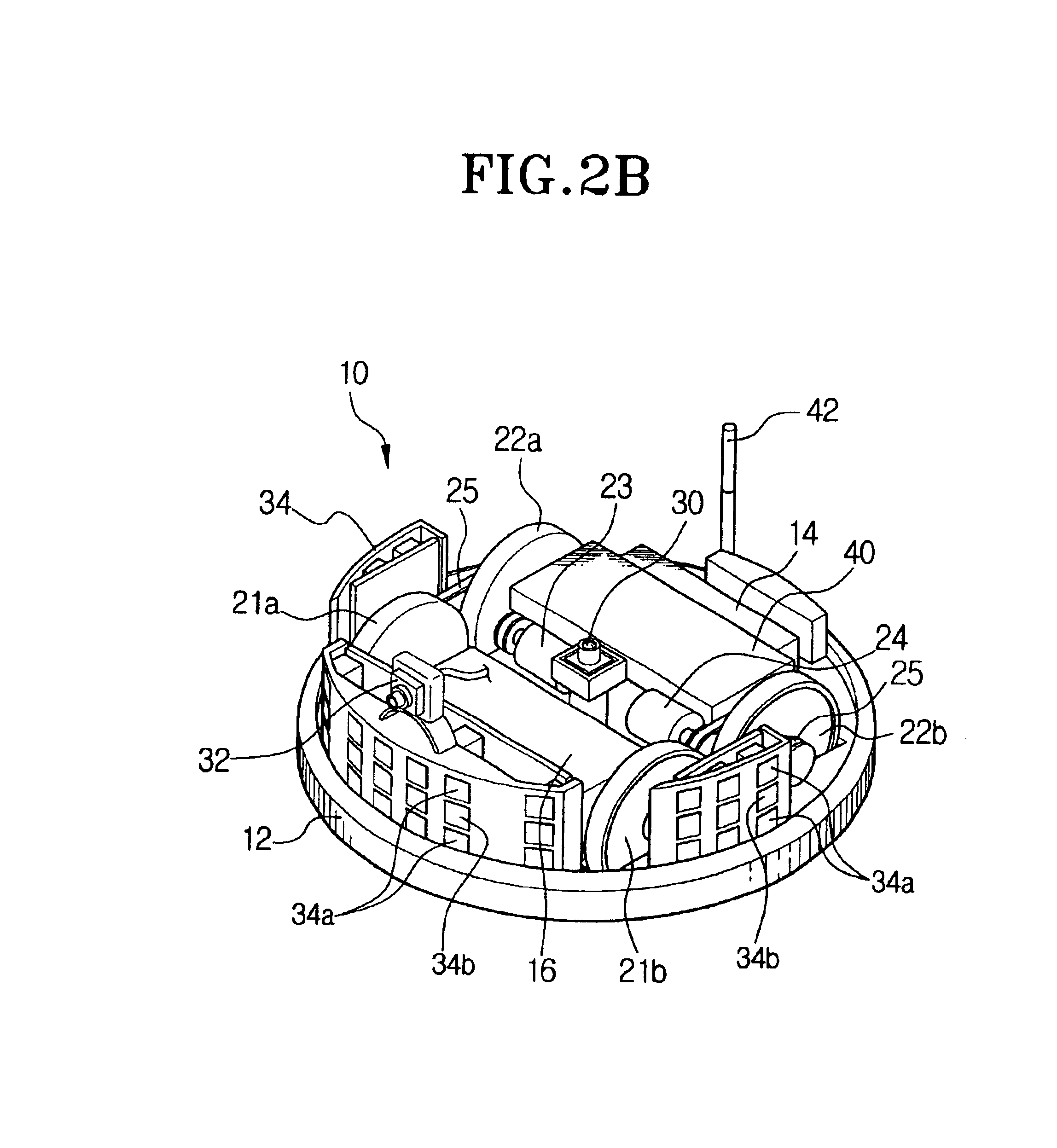
Robot cleaner, robot cleaning system and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS6868307B2Efficient executionAutomatic obstacle detectionProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpatial OrientationsEngineering
A robot cleaner, a robot cleaning system and a method for controlling the same capable of efficiently performing work on command by recognizing the driving distance and direction of the robot cleaner regardless of a of wheel slippage or irregularity in the floor. The robot cleaner performs a working operation while moving about a floor, and comprises a main body, a driving unit for driving a plurality of wheels disposed on a bottom portion of the main body, a downward-looking camera disposed among the wheels on the bottom portion of the main body for photographing images of the floor perpendicular to the driving direction of the robot cleaner, and a control unit for recognizing driving distance and direction of the wheels using image information of the floor photographed by the downward-looking camera, and for controlling the driving unit corresponding to a target work by using the recognized distance and direction of the wheels. An upward-looking camera can photograph and use information relating to spatial orientation for determining and correcting driving distance and direction.
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
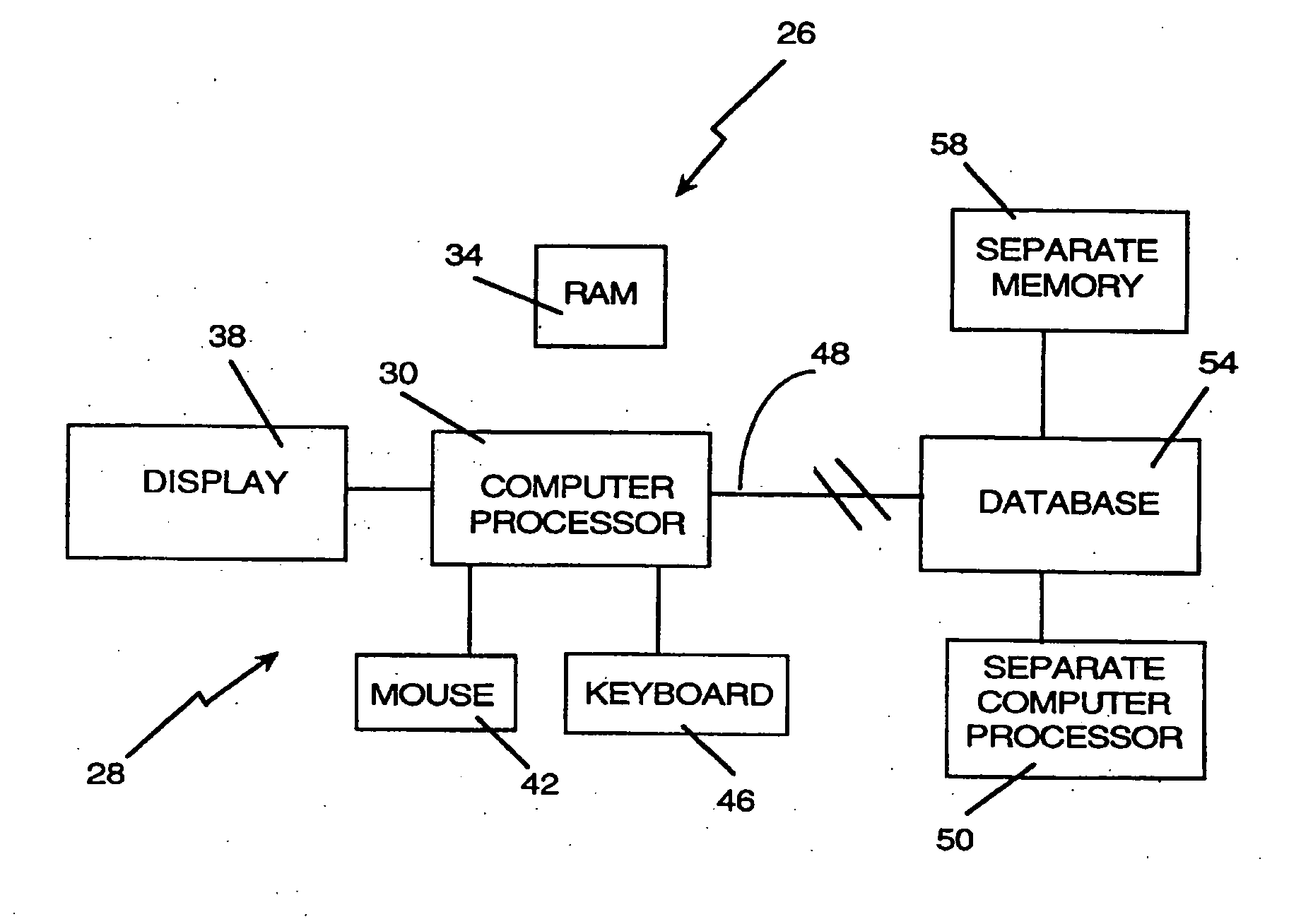
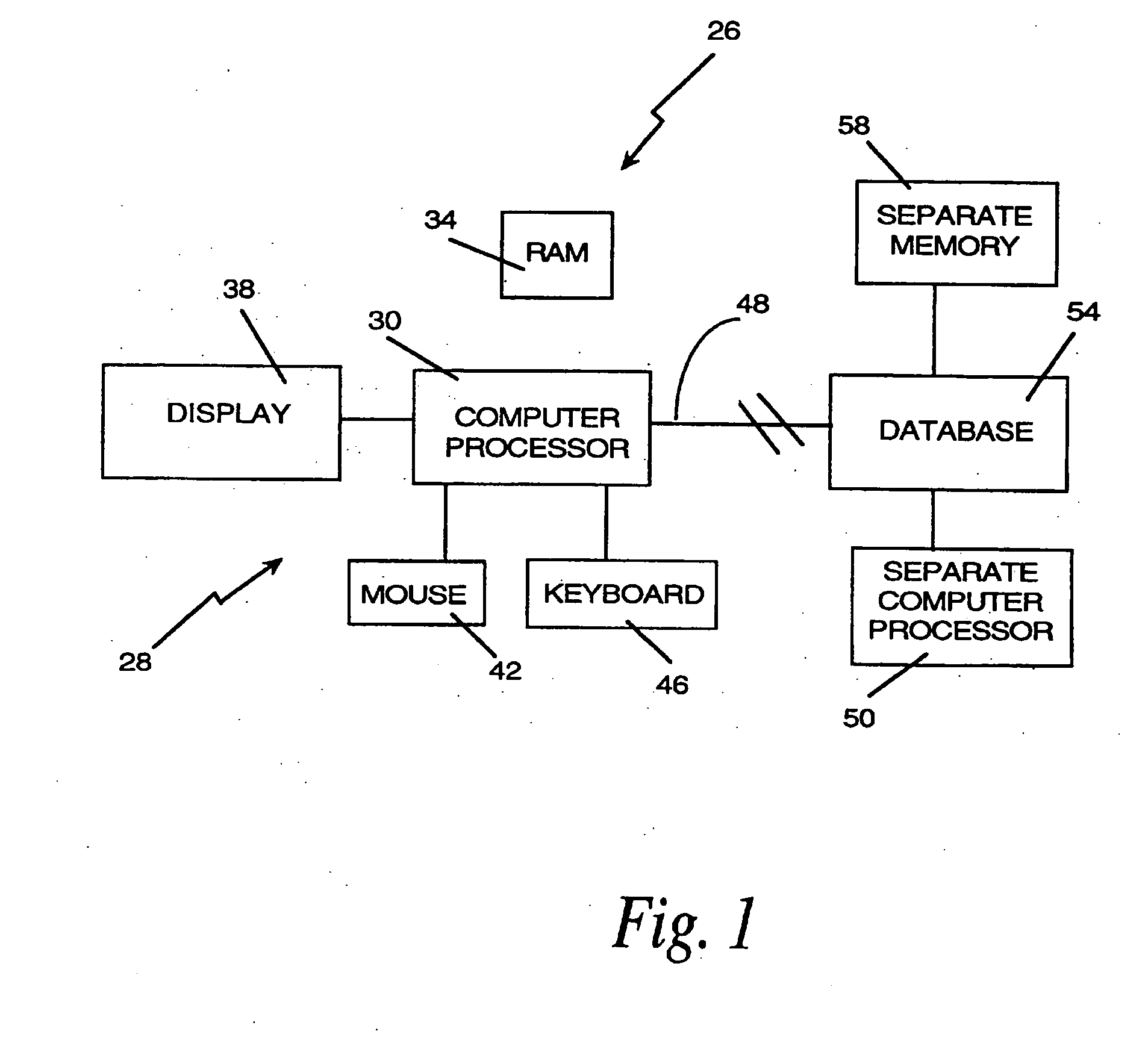
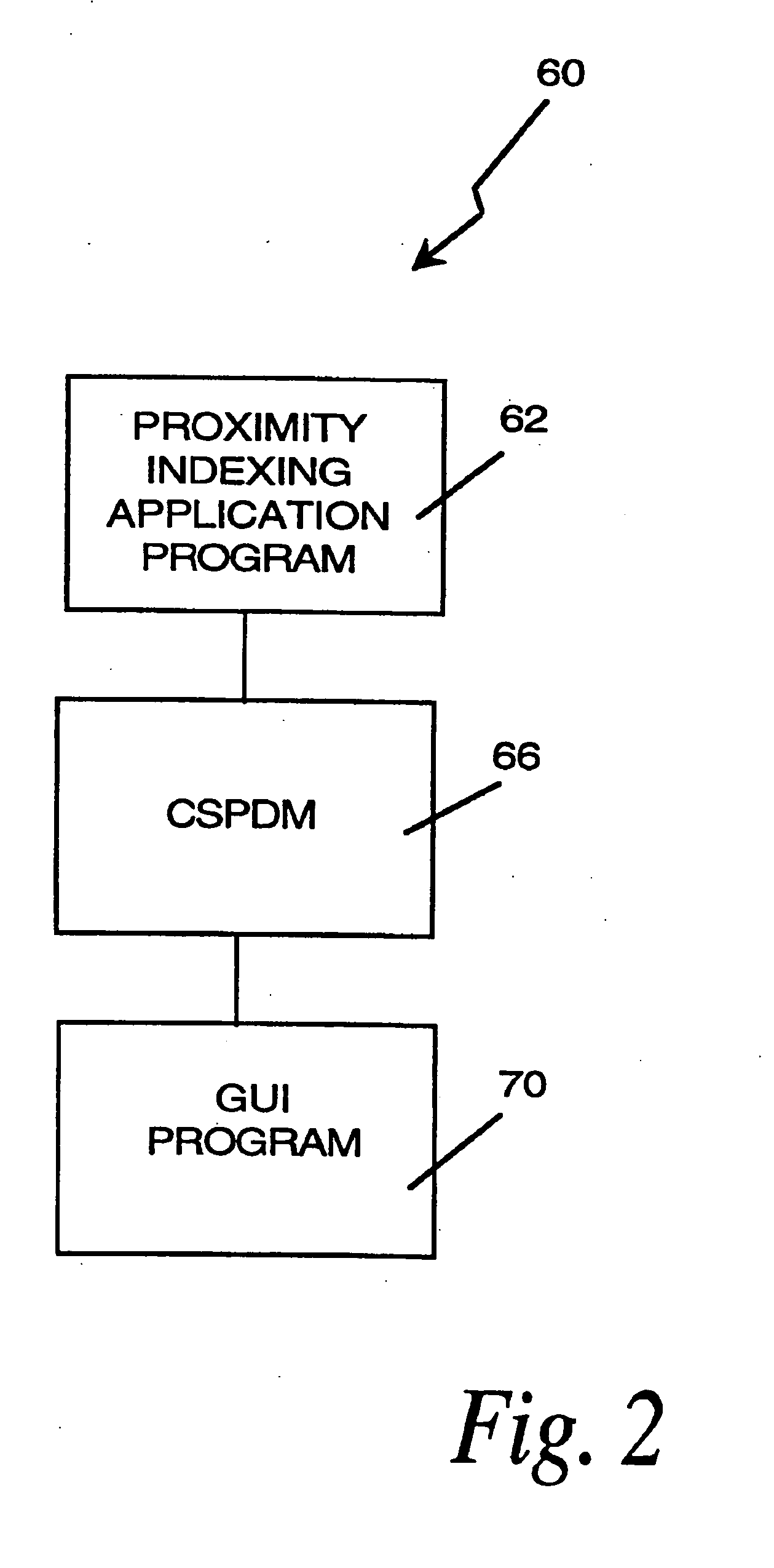
Method and apparatus for indexing, searching and displaying data
InactiveUS20060242564A1Simplifies research taskEasy to demonstrateData processing applicationsWeb data indexingSpatial OrientationsGraphics
A computer research tool for indexing, searching and displaying data is disclosed. Specifically, a computer research tool for performing computerized research of data including textual objects in a database or a network and for providing a user interface that significantly enhances data presentation is described. Textual objects and other data in a database or network is indexed by creating a numerical representation of the data. The indexing technique called proximity indexing generates a quick-reference of the relations, patterns and similarity found among the data in the database. Proximity indexing indexes the data by using statistical techniques and empirically developed algorithms. Using this proximity index, an efficient search for pools of data having a particular relation, pattern or characteristic can be effectuated. The Computer Search program, called the Computer Search Program for Data represented in Matrices (CSPDM), provides efficient computer search methods. The CSPDM rank orders data in accordance with the data's relationship to time, a paradigm datum, or any similar reference. An alternative embodiment of the invention employs a cluster link generation algorithm which uses links and nodes to index and search a database or network. The algorithm searches for direct and indirect links to a search node and retrieves the nodes which are most closely related to the search node. The user interface program, called the Graphical User Interface (GUI), provides a user friendly method of interacting with the CSPDM program and prepares and presents a visual graphical display. The graphical display provides the user with a two or three dimensional spatial orientation of the data.
Owner:LIBERTECH
Systems and methods for three-dimensional ultrasound mapping
ActiveUS20080119727A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsSpatial OrientationsSonification
An automated medical system comprises a first instrument assembly including a first ultrasound transducer having a first transducer field of view that transmits and receives ultrasound signals in imaging planes disposed circumferentially about a guide instrument, and a second instrument assembly including a second ultrasound transducer having a second transducer field of view coupled to one of a second flexible guide instrument and a working instrument. A computing system is operatively coupled to the respective first and second transducers and configured to determine a relative spatial orientation of the respective first and second transducers based at least in part on detecting a signal transmitted by one of the first and second transducers and received by the other of the first and second transducers, the received signal having an amplitude indicating the receiving one of the transducers is in the field of view of the transmitting one of the transducers.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
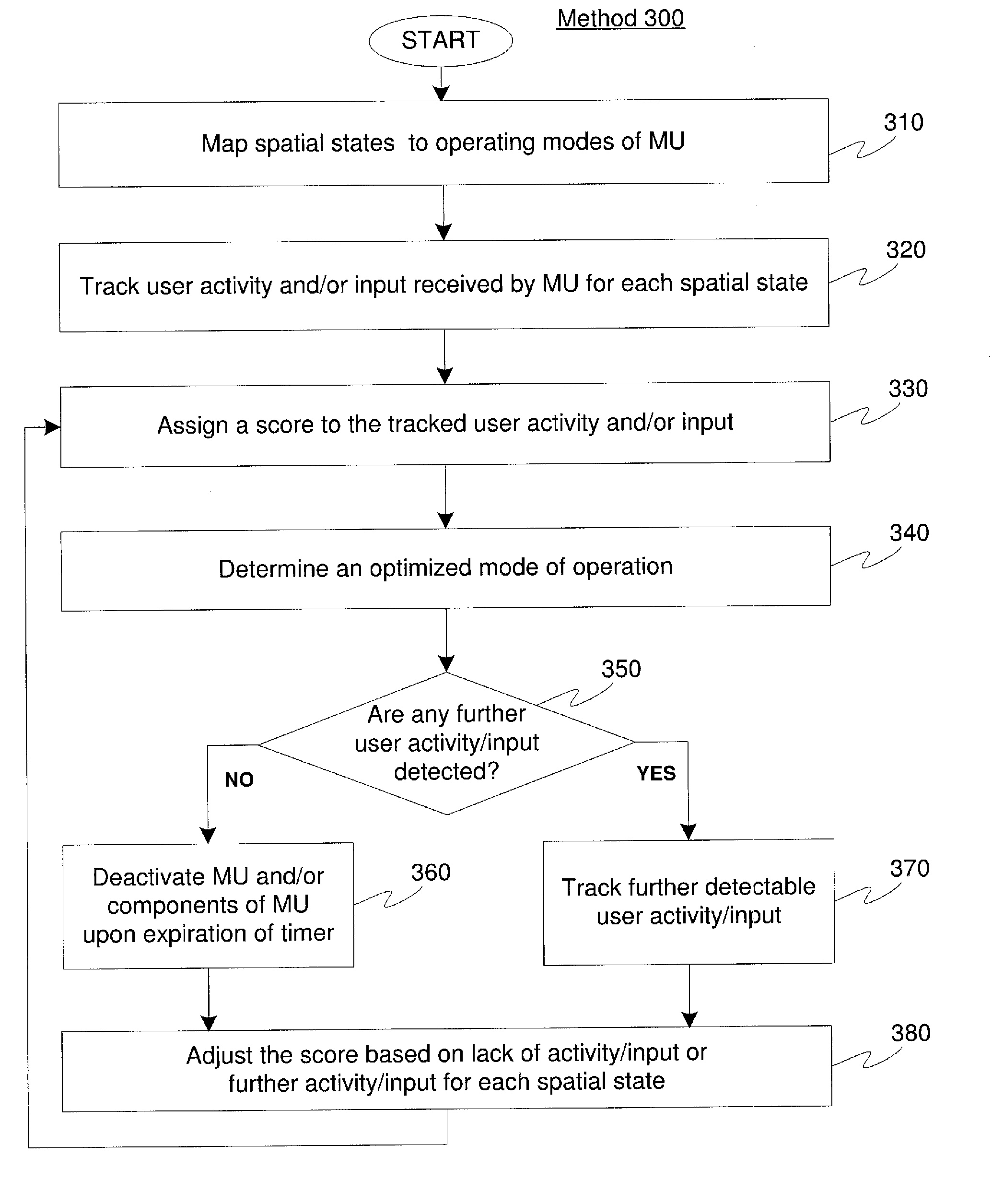
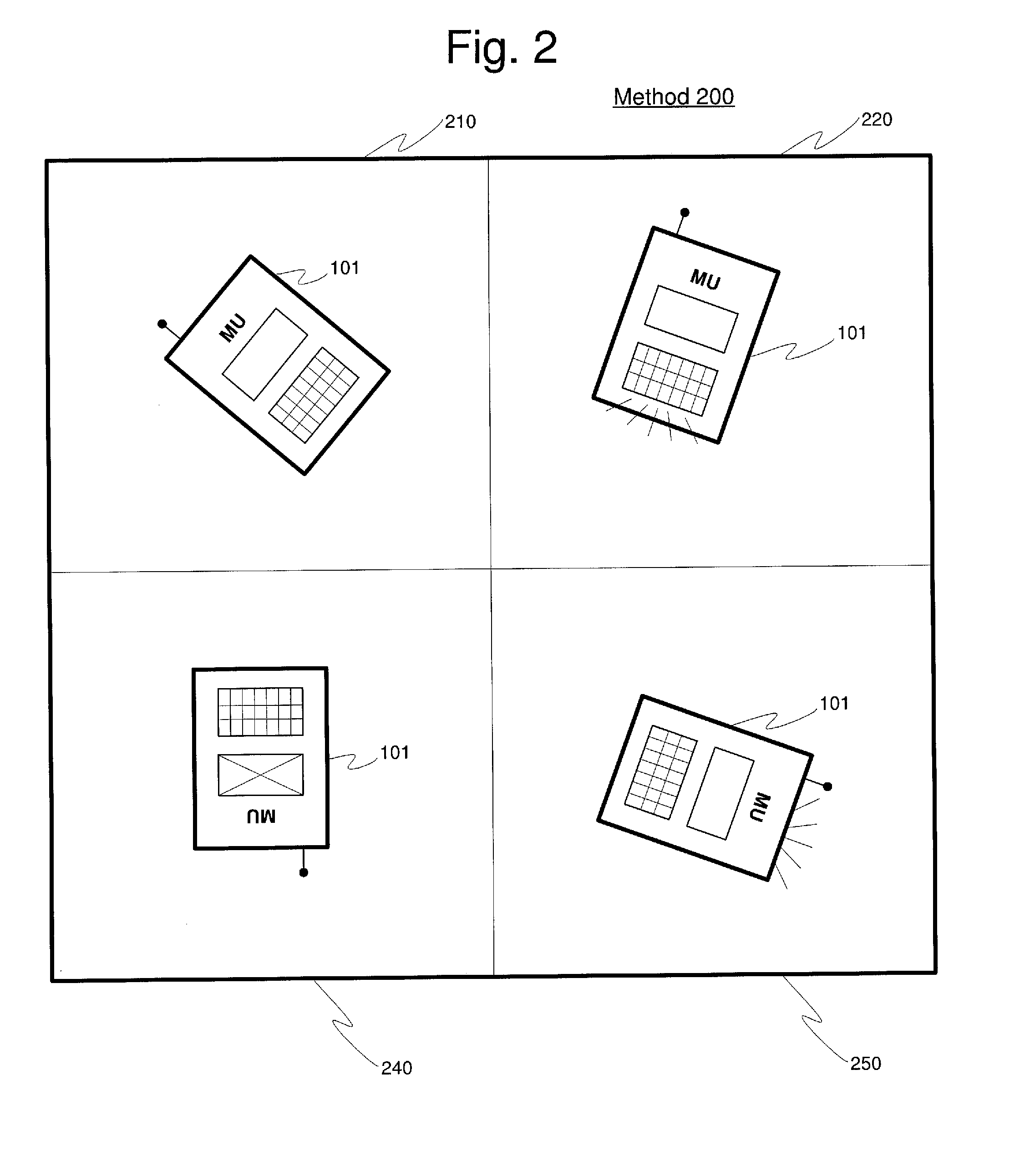
Method and System for Correlating User/Device Activity with Spatial Orientation Sensors
ActiveUS20080254822A1Power managementDigital data processing detailsSpatial OrientationsComputer graphics (images)
A system and method for determining an operating mode for a mobile unit (“MU”), comprising defining a plurality of spatial regions, tracking at least one activity of the MU when the MU is oriented within the one of the plurality of spatial regions, determining an orientation of the mobile unit, and selecting the operating mode based on the at least one of the orientation and an activity of the MU when the MU is oriented within the one of the plurality of spatial regions.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Systems and methods for three-dimensional ultrasound mapping
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Method for determining position and orientation of vehicle trailers
InactiveUS20110050903A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsSpatial OrientationsSpatial positioning
A method and system for determining orientation and positioning of a vehicle trailer. A digital camera is placed on a vehicle. The camera is pointed to a trailer attached to the vehicle. The camera acquires images of the trailer. These images are processed and spatial positioning and orientation of the trailer is determined based on image processing. A special marker visible by the camera is set on the trailer. Relative positions of devices attached to the vehicle—global positioning receiver, spatial orientation measuring device and the digital camera are measured. When each digital frame is formed, coordinates and orientation data of the camera are measured. Pixels corresponding to the marker in the image are determined. A simplified copy of the image, containing only the data related to the marker pixels, is generated. The marker pixels are used for calculating position and azimuth orientation of the marker. The azimuth orientation of the trailer is calculated based on calculated azimuth orientation of the marker.
Owner:TOPCON POSITIONING SYST INC
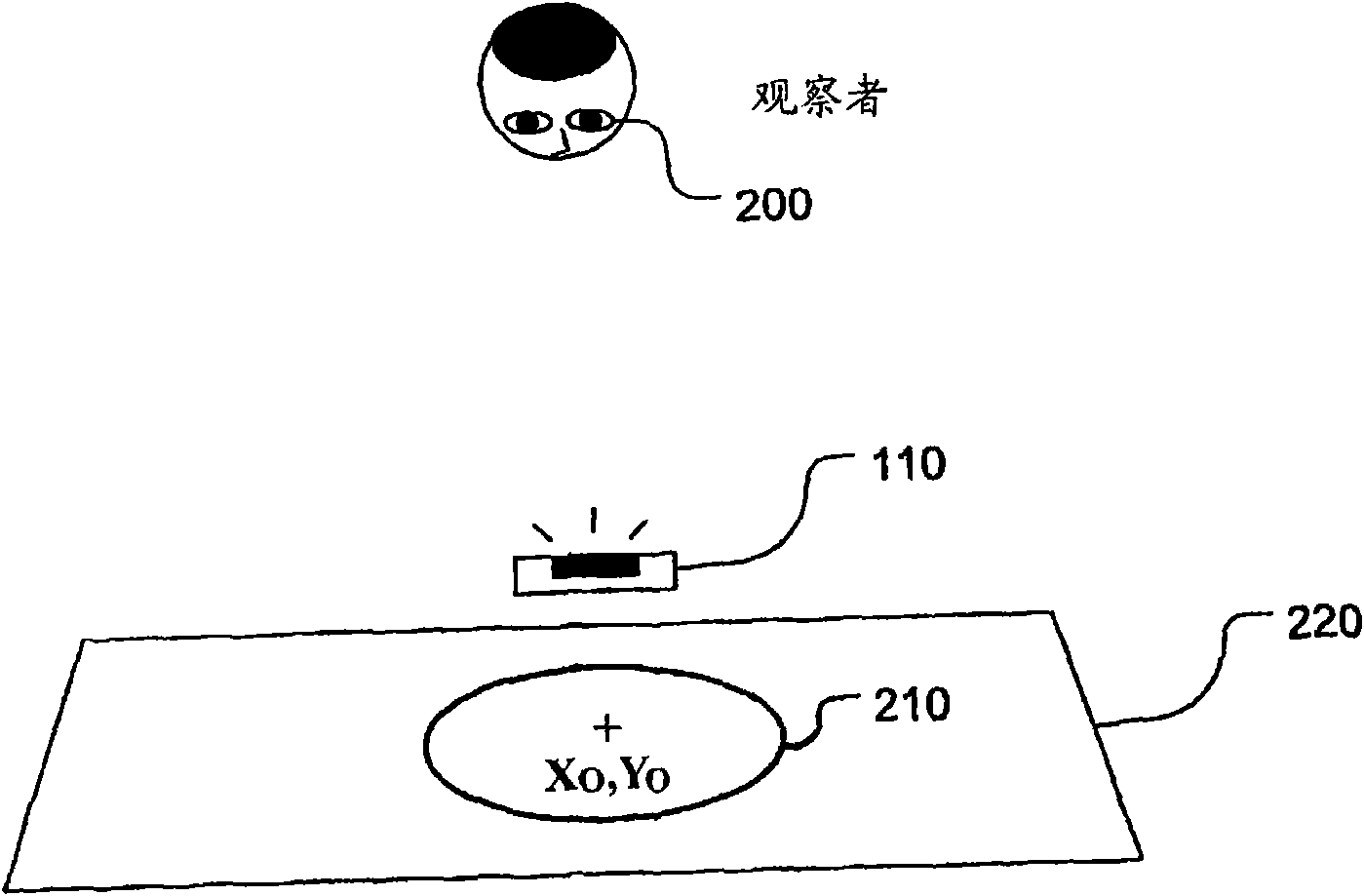
Apparatus and method for determining spatial orientation
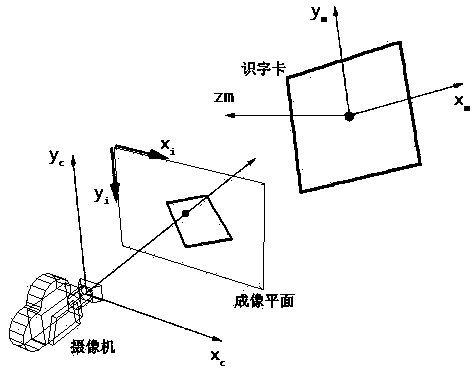
InactiveUS20020048404A1Reduce in quantityInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial OrientationsPattern recognition
A system and a corresponding method for determining a spatial relationship between a surface having a predetermined pattern and an apparatus are disclosed. A portion of the surface may be imaged and compared with the predetermined pattern. The comparison produces at least one reference measurement that may be used to determine a spatial relationship expressed in at least parameters that define an orientation of the surface. By using knowledge of the predetermined pattern together with an algebraic model of the image formation by the apparatus, a numerical adaptation can be performed. Parameters obtained from the adaptation can then be used to calculate the spatial relationship between the apparatus and the surface in terms of, for example, a distance between the apparatus and the surface or an angle between the surface and an axis extending through the apparatus.
Owner:ANOTO AB
Biopsy cannula adjustable depth stop
InactiveUS20070255170A1Prevent overshootSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSpatial OrientationsBiopsy instruments
A biopsy system with a grid plate used as either a lateral or medial compression plate of a localization fixture used with a breast coil includes a rotatable guide cube that may be inserted into a desired rectangular recess in the grid plate after rotating to position a selected guide hole in the desired spatial orientation. Versions of a guide cube include those rotatable in two axes to provide additional hole positions, angled holes, enlarged circular holes that function with a rotating guide to support a noncircular biopsy instrument cannula (e.g., trocar / sleeve combination, core biopsy probe of a biopsy device) for rotation. A rotating guide may have an unlocked state for easily sliding to a selected longitudinal position thereon. Thereafter, the rotating guide is locked to serve as a positive depth stop (e.g., quarter turn locking elastomeric rings, triangular and scissor clips, and shutter depth stops).
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
3D audio delivery accompanying 3D display supported by viewer/listener position and orientation tracking
InactiveUS20110157327A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsStereoscopic photographySpatial OrientationsSound sources
Techniques are described herein for supporting 3D audio delivery accompanying 3D display supported by viewer / listener position and orientation tracking. For example, audio content is configured to have a spatial orientation that accords with an orientation of a viewer. A spatial orientation of audio content is a configuration of the audio content in which characteristics of respective portions of the audio content, which correspond to respective speakers, indicate an orientation of ears of a viewer / listener with respect to sound source(s) that correspond to (e.g., are depicted in) a three-dimensional view. Such a characteristic may include an amplitude of sound that corresponds to a sound source and / or a delay associated with the sound that corresponds to the sound source.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
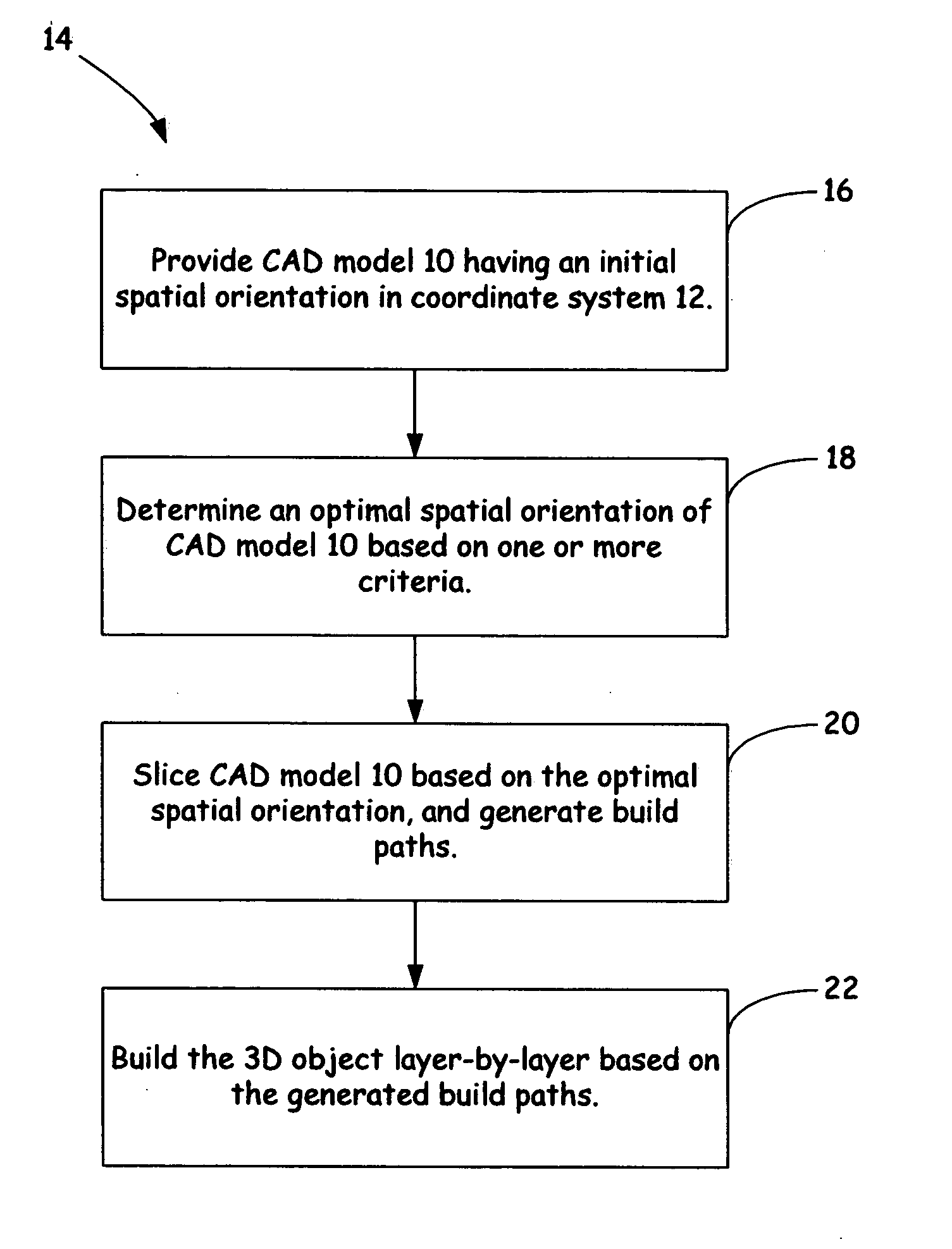
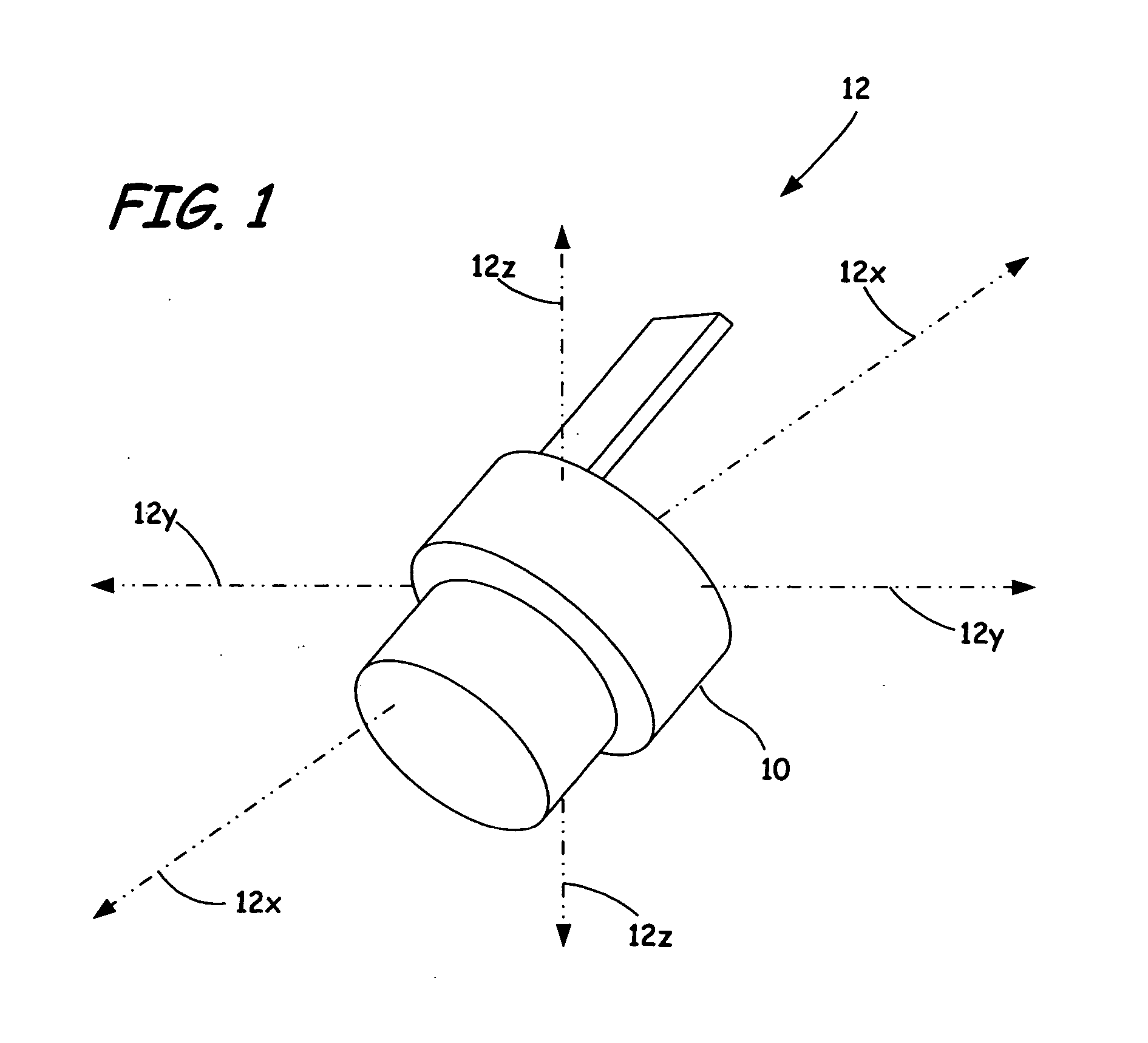
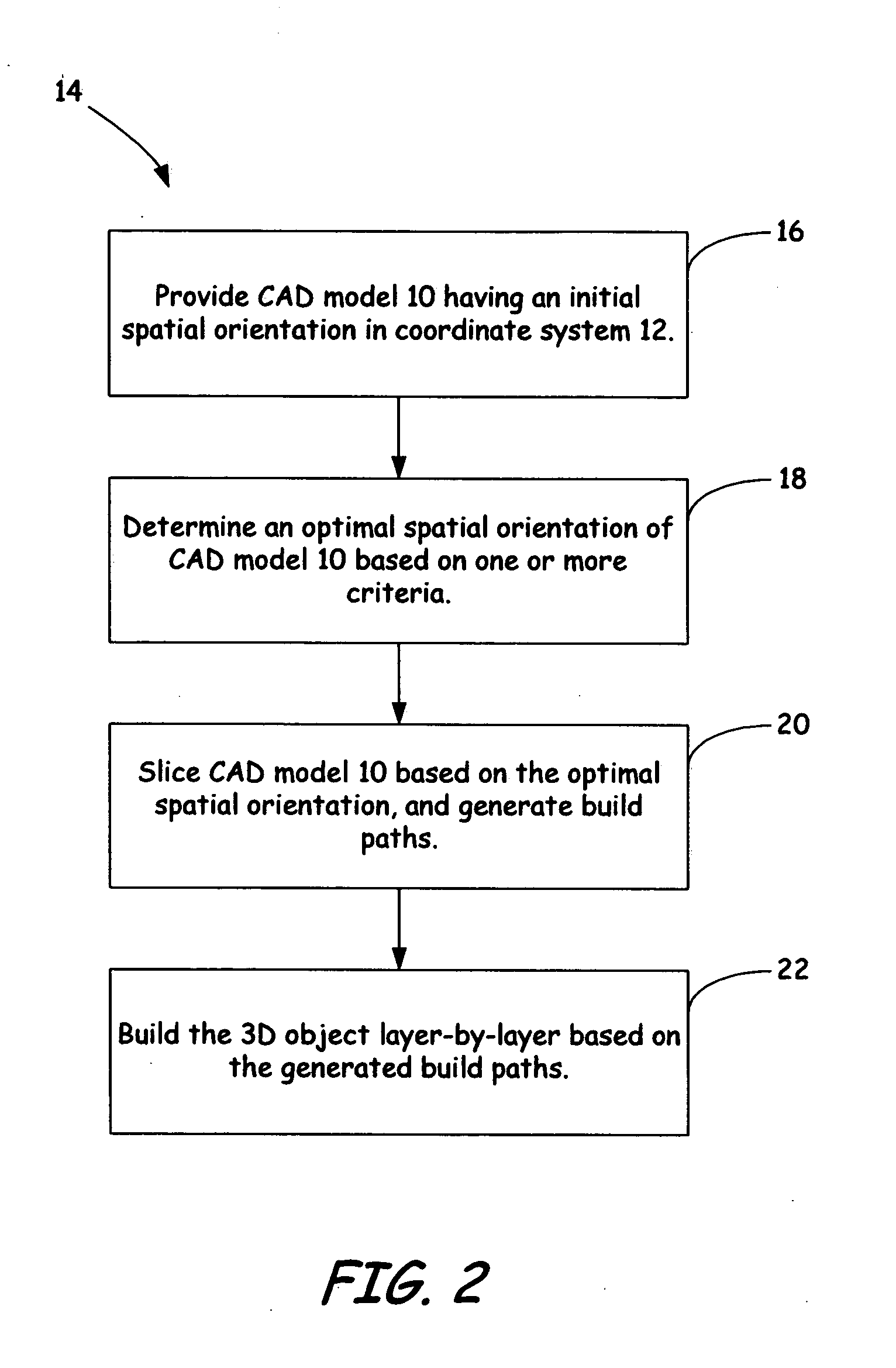
Method for optimizing spatial orientations of computer-aided design models
ActiveUS20070233298A1Improve the build effectAdditive manufacturing apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationComputer Aided DesignSpatial Orientations
A method and system for building one or more three-dimensional objects, where the method includes providing a computer-aided design model of a three-dimensional object having an initial spatial orientation in a coordinate system, and determining an optimal spatial orientation of the computer-aided design model in the coordinate system based on one or more criteria.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
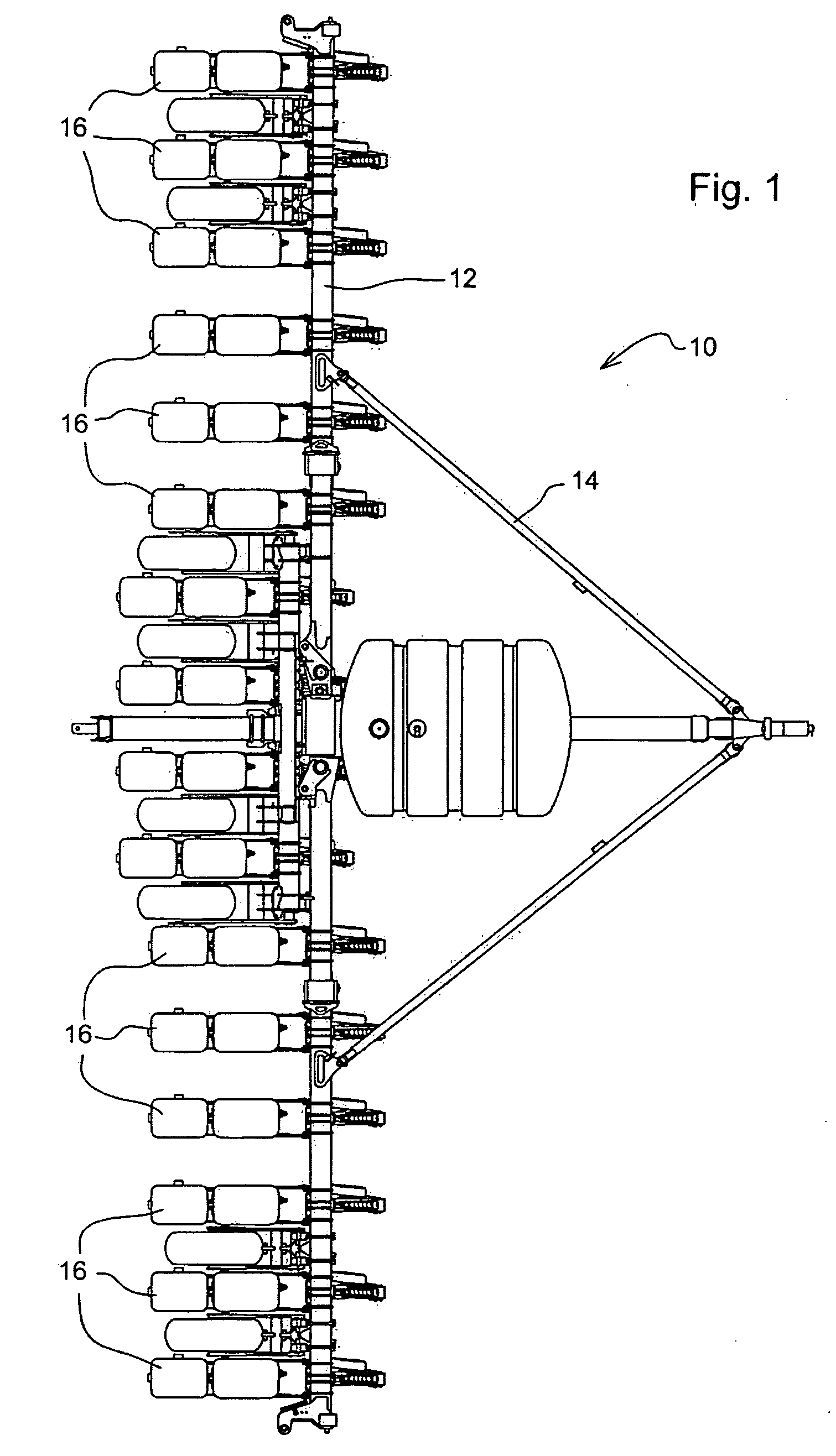
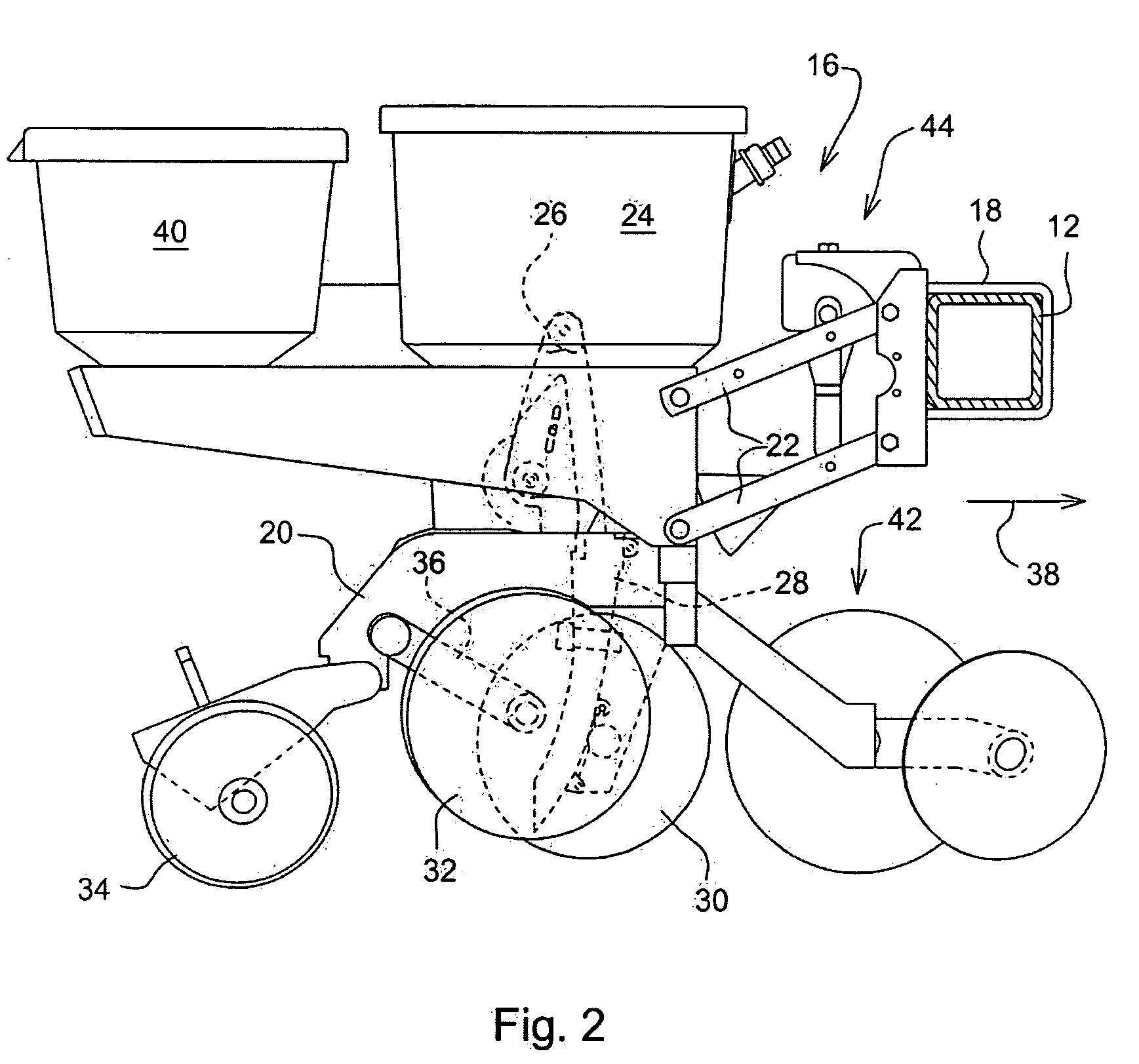
Differential Pressure Seed Meter With An Endless Belt Seed Transport Member
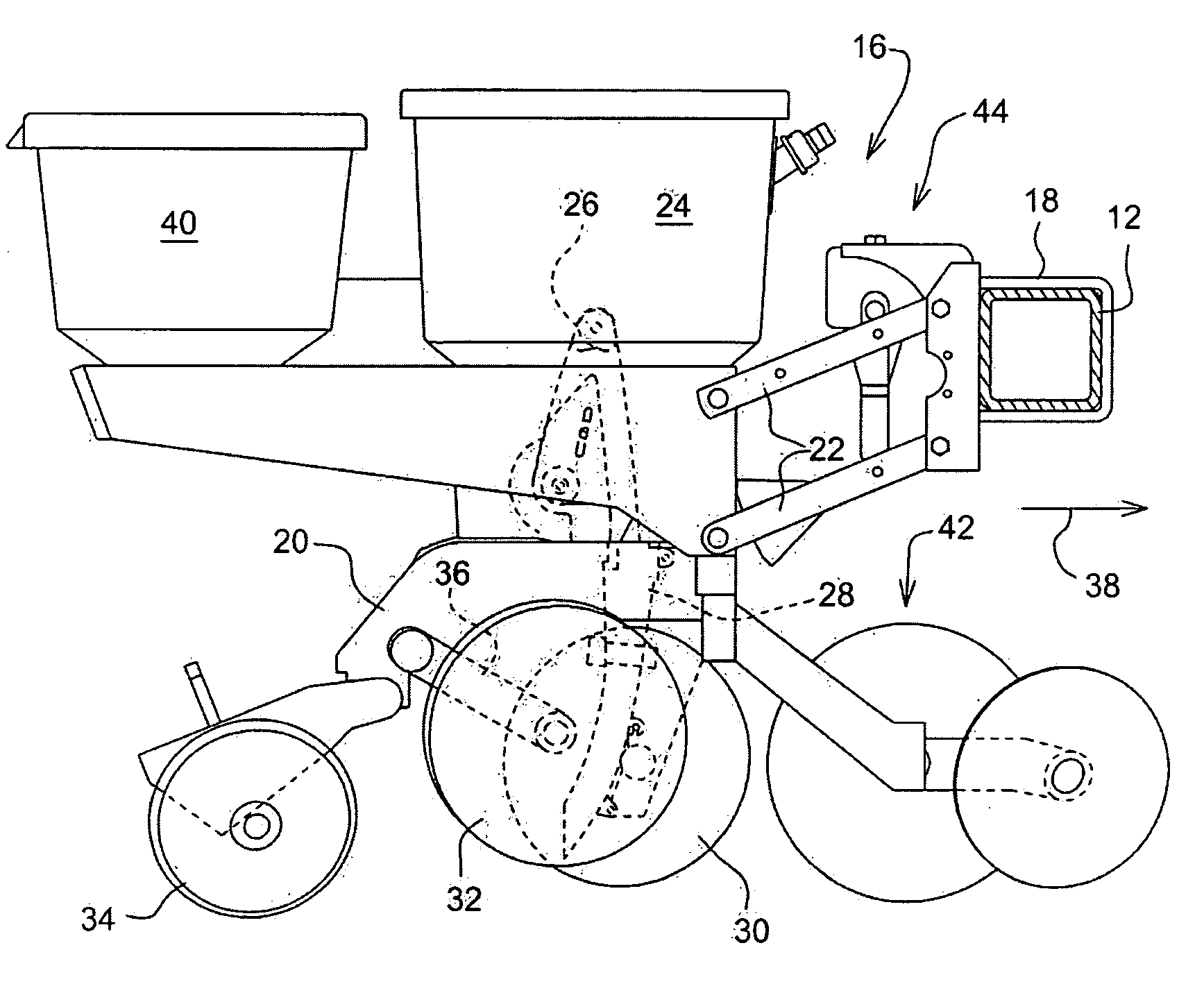
ActiveUS20100192818A1Great freedomFertiliser distributersPotato plantersSpatial OrientationsDifferential pressure
A seed meter is provided having an endless belt as a seed transport member together with a pressure differential to hold the seed onto the belt. The use of an endless belt as the seed transport member enables the spatial orientation of the seed transport member to vary from location to location along the path of the belt where different seed meter functions are performed. The belt allows greater freedom in determining the location of the seed pick-up region and the seed release or removal region beyond the constraints of a fixed diameter seed disk. The belt further allows for a narrow envelope seed meter which can cross-feed seed into a substantially vertically oriented delivery device.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Method for manipulating image based on tracked eye movements
ActiveCN101943982AInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingSpatial OrientationsEye movement
The invention discloses a method for controlling and manipulating an object displayed on a device based on tracked eye movements of an observer, which comprises the steps of: when the object is displayed according to an initial view, tracking and processing the eye movements of the observer to determine the attention of the observer or the focus gazed on the image by the observer; then, amending the displayed image to provide a better view of the most interesting part of the object for the observer. The invention is realized by at lease one condition of the spatial orientation of the object, the perspective of the object and the observation direction of the object in the observing area.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
System and method for hyoidplasty
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating the hyoid bone, such as to treat obstructive sleep apnea. An implant is positioned adjacent a hyoid bone. The spatial orientation of the hyoid bone is manipulated, to affect the configuration of the airway. The implant restrains the hyoid bone in the manipulated configuration. The implant is positioned adjacent to pharyngeal structures to dilate the pharyngeal airway and / or to support the pharyngeal wall against collapse.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
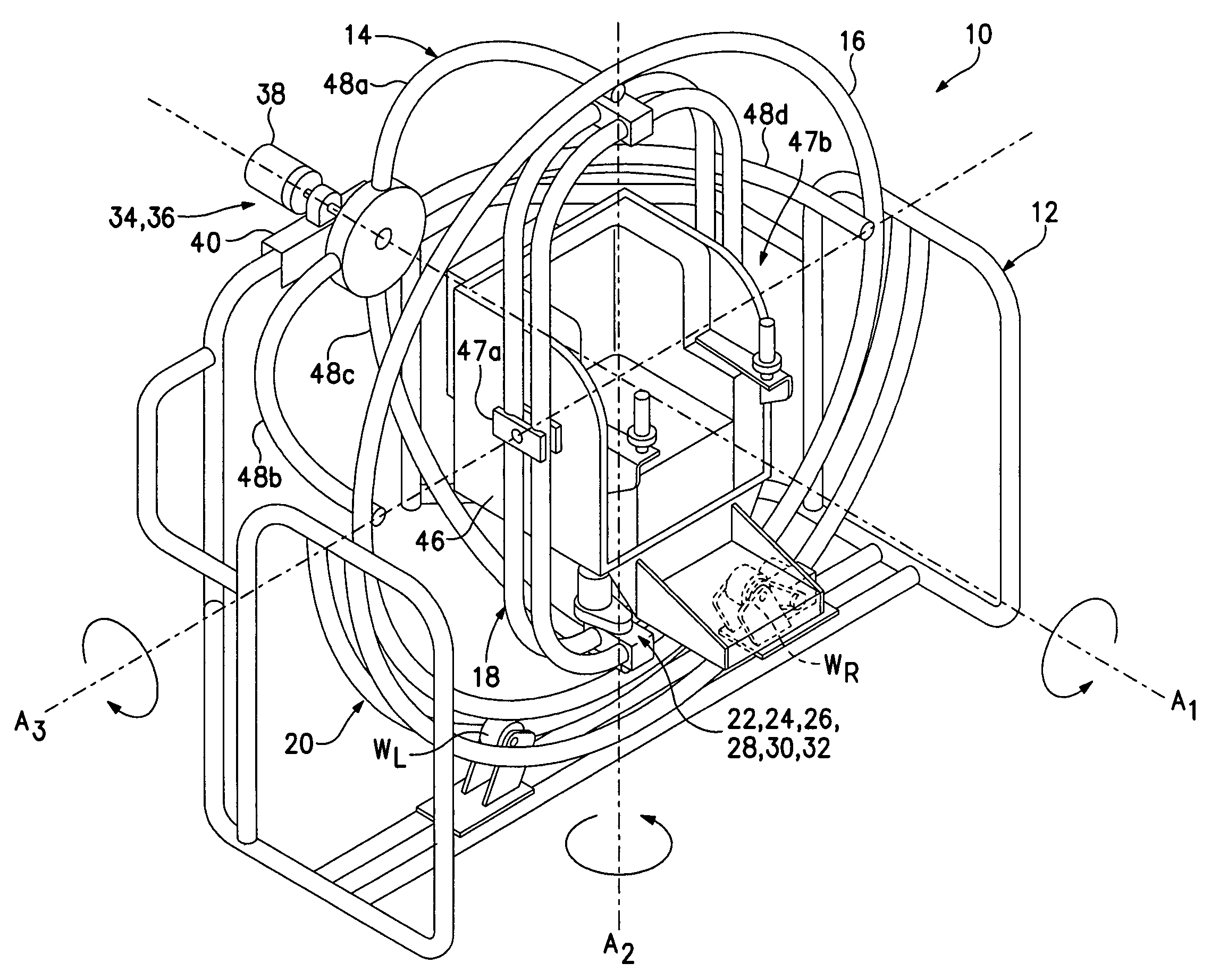
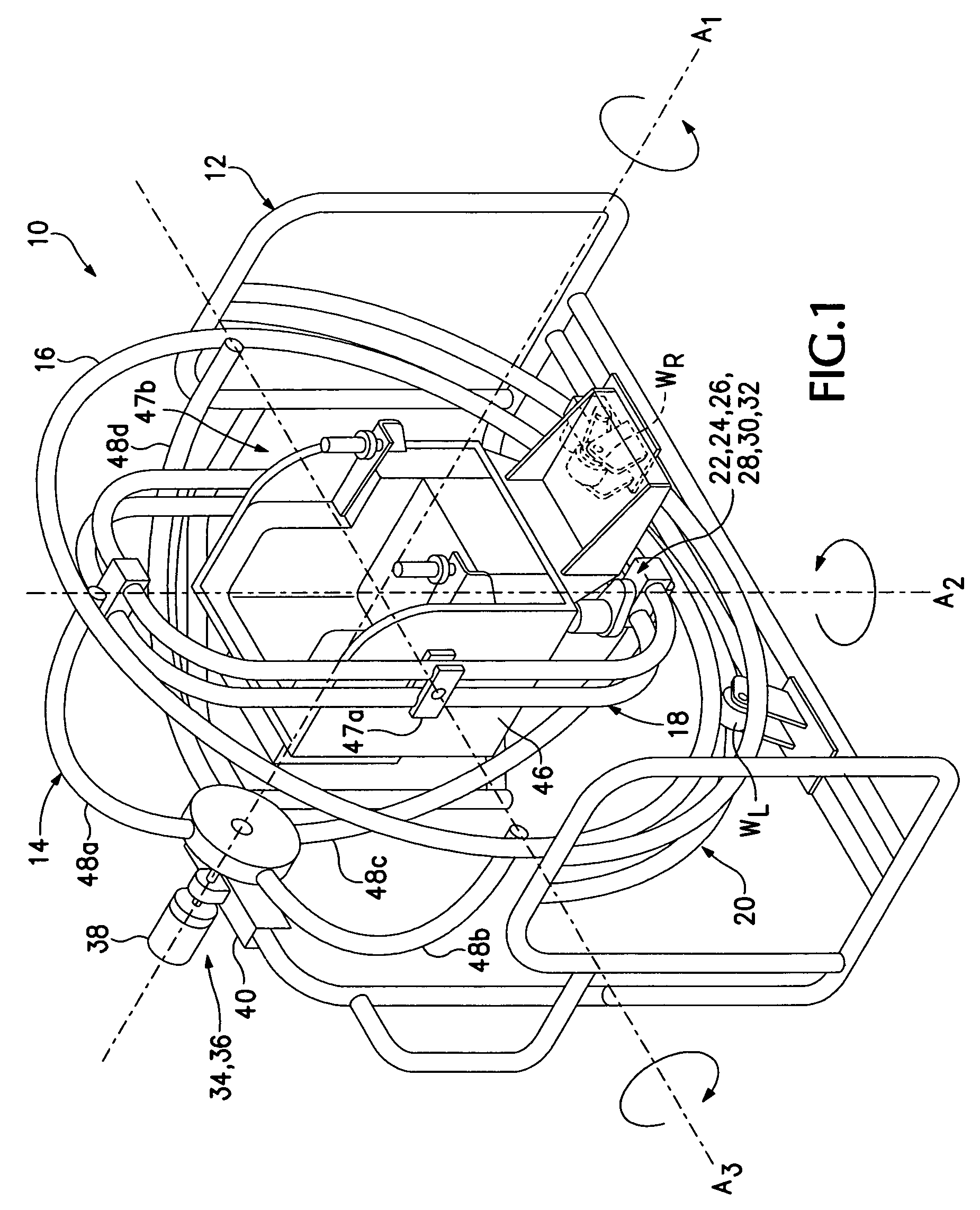
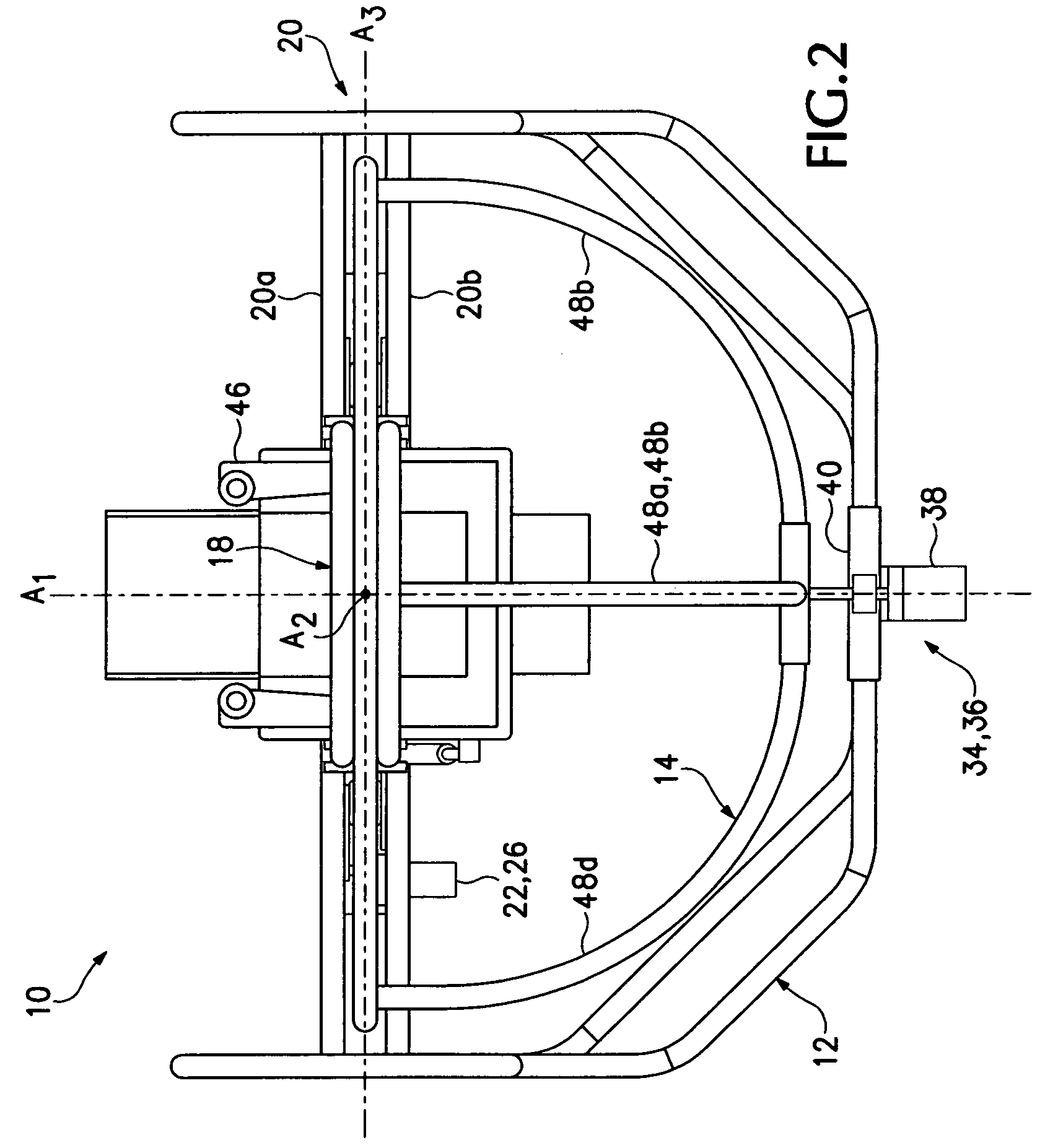
Hemispheroidal-truss spatial manipulator system and apparatus
ActiveUS7559766B2Cosmonautic condition simulationsHoop exercising devicesSpatial OrientationsRotational axis
Spatial manipulator apparatus for a mammalian subject includes a stabilizing base; a hemispheroidal truss frame mounted for rotation on the stabilizing base, the truss frame supporting and stabilizing an outer generally circular rim in relation to a non-concentric hub located at its rotational axis; and a second frame mounted orthogonally within the outer rim on a second rotational axis, the second frame being configured to support a mammalian subject during spatial manipulation thereof by rotation about one or more of the orthogonal rotational axes. Preferably, the truss frame and the second frame are driven for rotation about the orthogonal rotational axes to achieve a desired mammalian-subject spatial orientation within a chair-like structure pivotally adjustably mounted within the second frame. Preferably, the truss frame includes a substantially circular rim member mounting the second frame for rotation therein; three or more struts connecting from circumferential substantially evenly spaced locations along the circular rim member to a point of convergence on the truss frame through which the first axis extends; and a hub at the point of convergence mounting the three or more struts.
Owner:WEST TEXAS PCS LLC
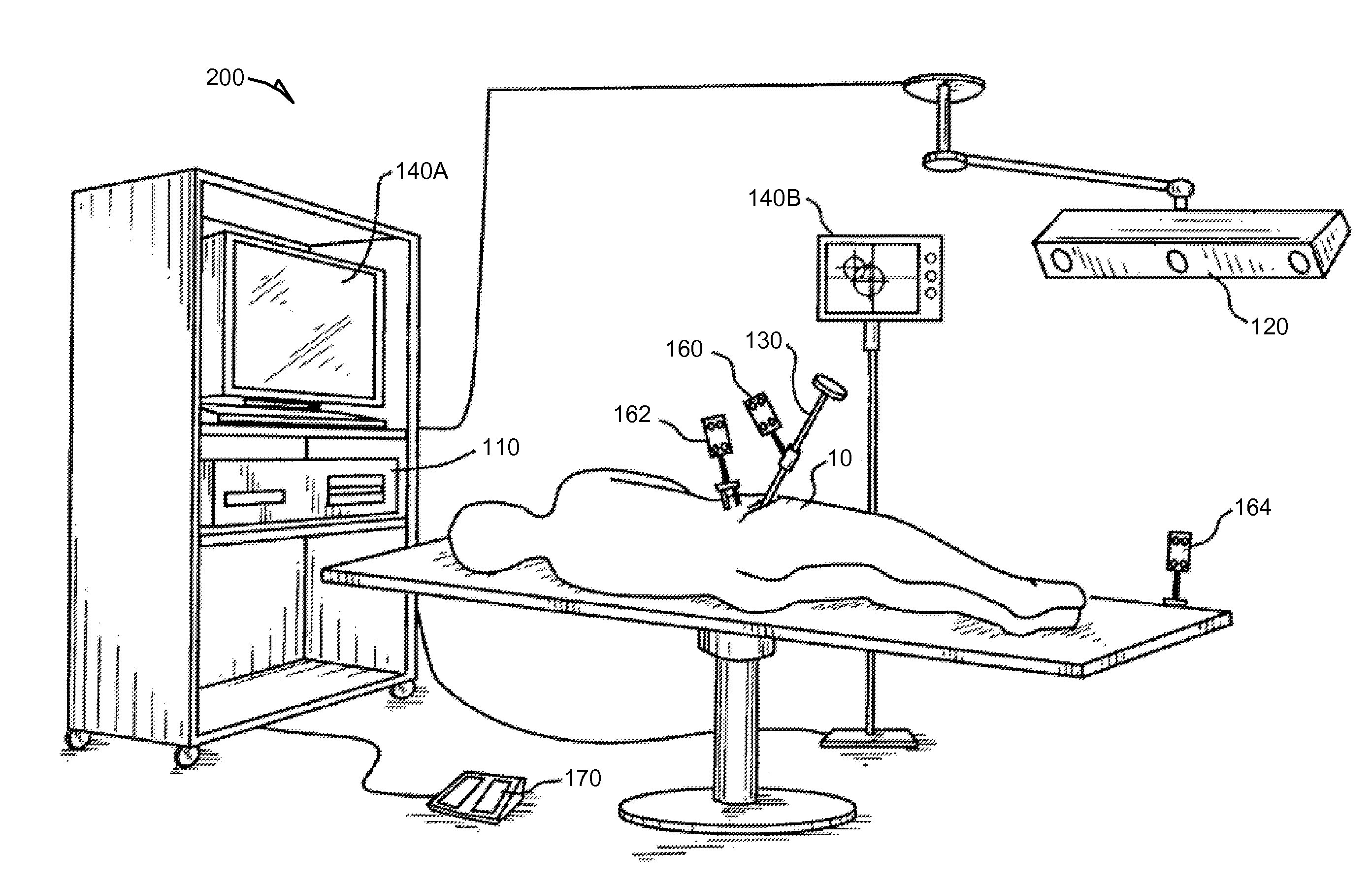
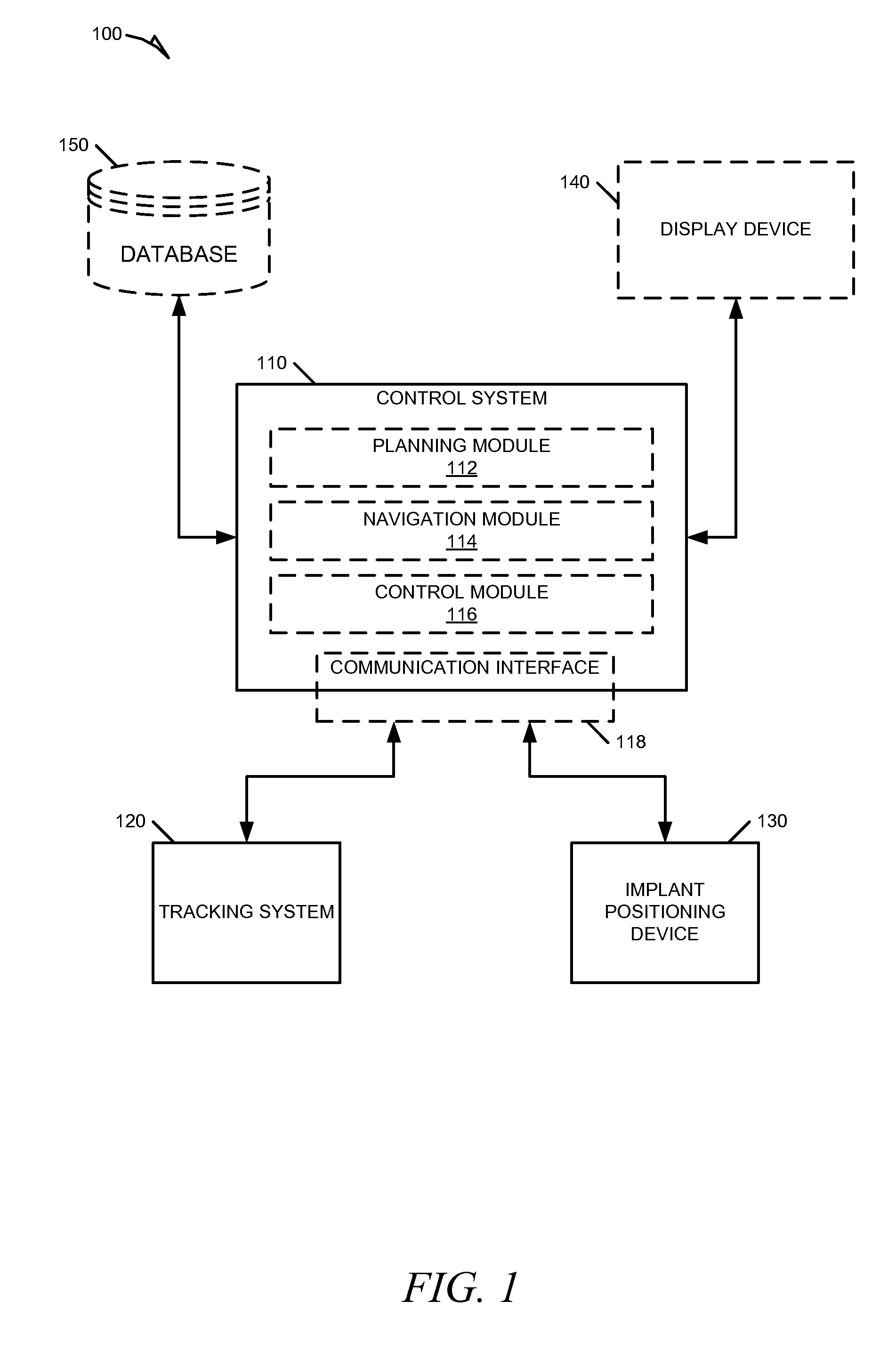
Systems and methods for navigation and control of an implant positioning device
Systems and methods for navigation and control of an implant positioning device are discussed. For example, a method can include operations for accessing an implant plan, establishing a 3-D coordinate system, receiving tracking information, generating control signals, and sending the control signals to the implant positioning device. The implant plan can include location and orientation data describing an ideal implant location and orientation in reference to an implant host. The 3-D coordinate system can provide spatial orientation for the implant positioning device and the implant host. The tracking information can identify current location and orientation data within the 3-D coordinate system for the implant positioning device and implant host during a procedure. The control signals can control operation of the implant positioning device to assist a surgeon in positioning the implant according to the implant plan.
Owner:BLUE BELT TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com