Patents
Literature
1967 results about "Radiation beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
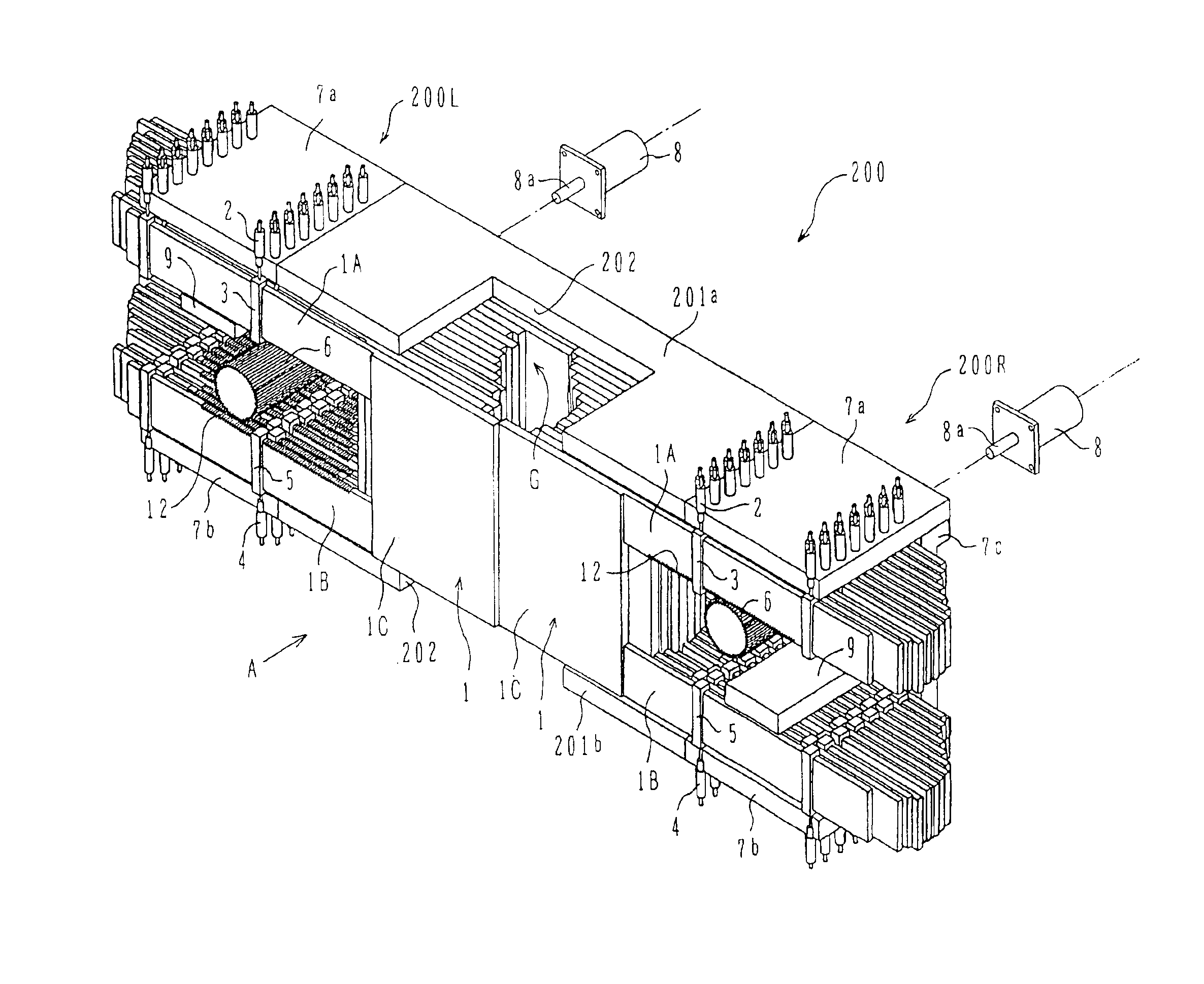
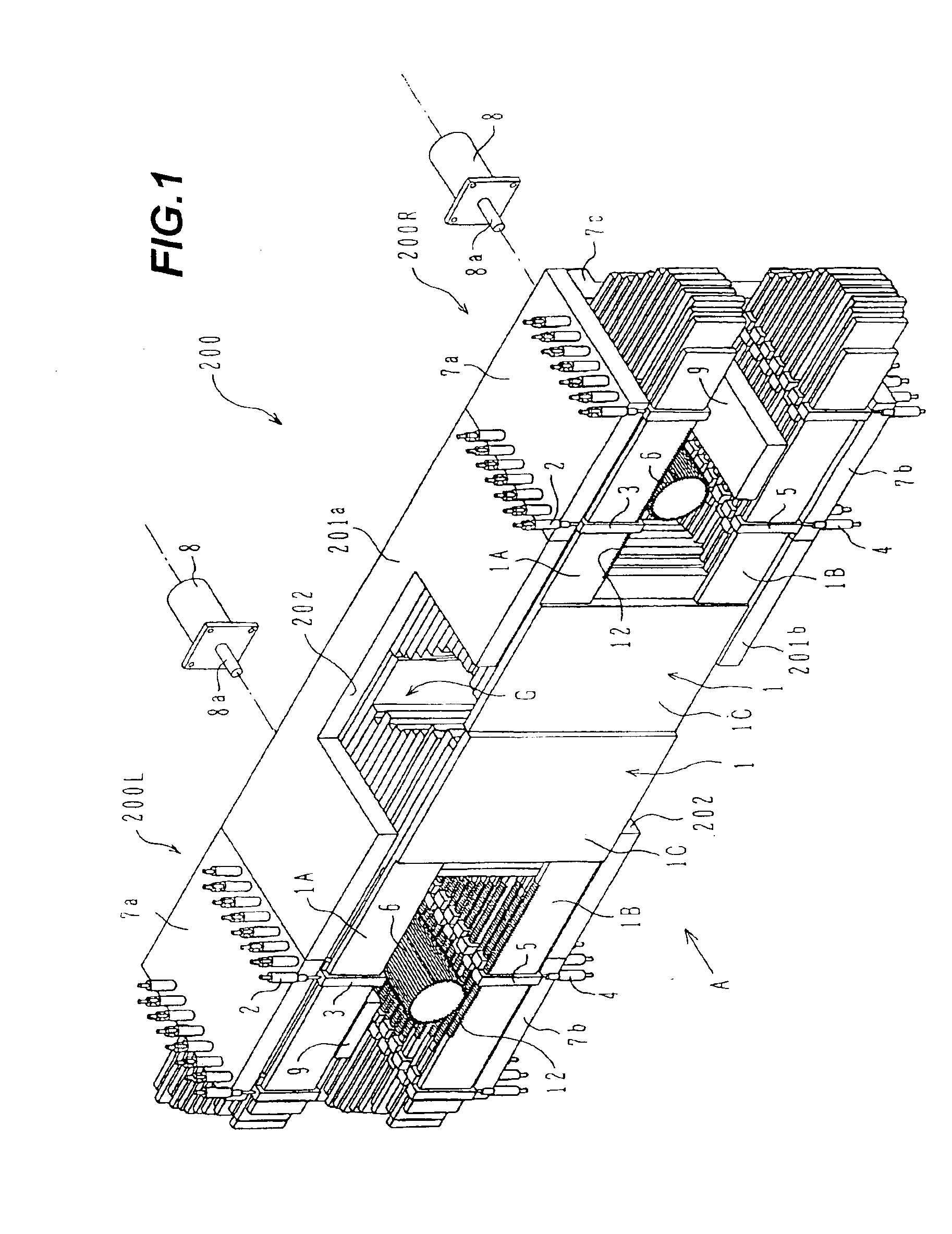
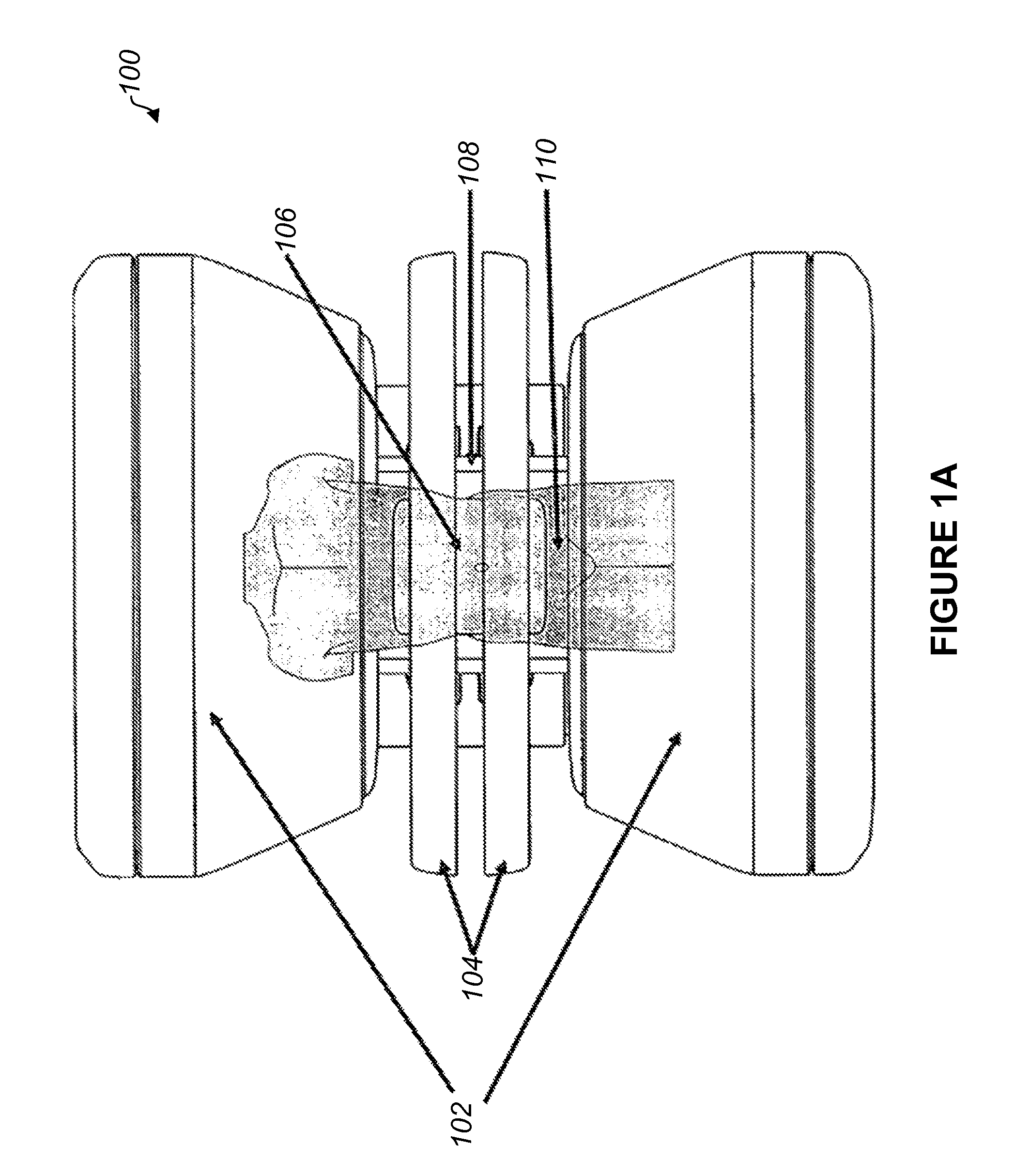
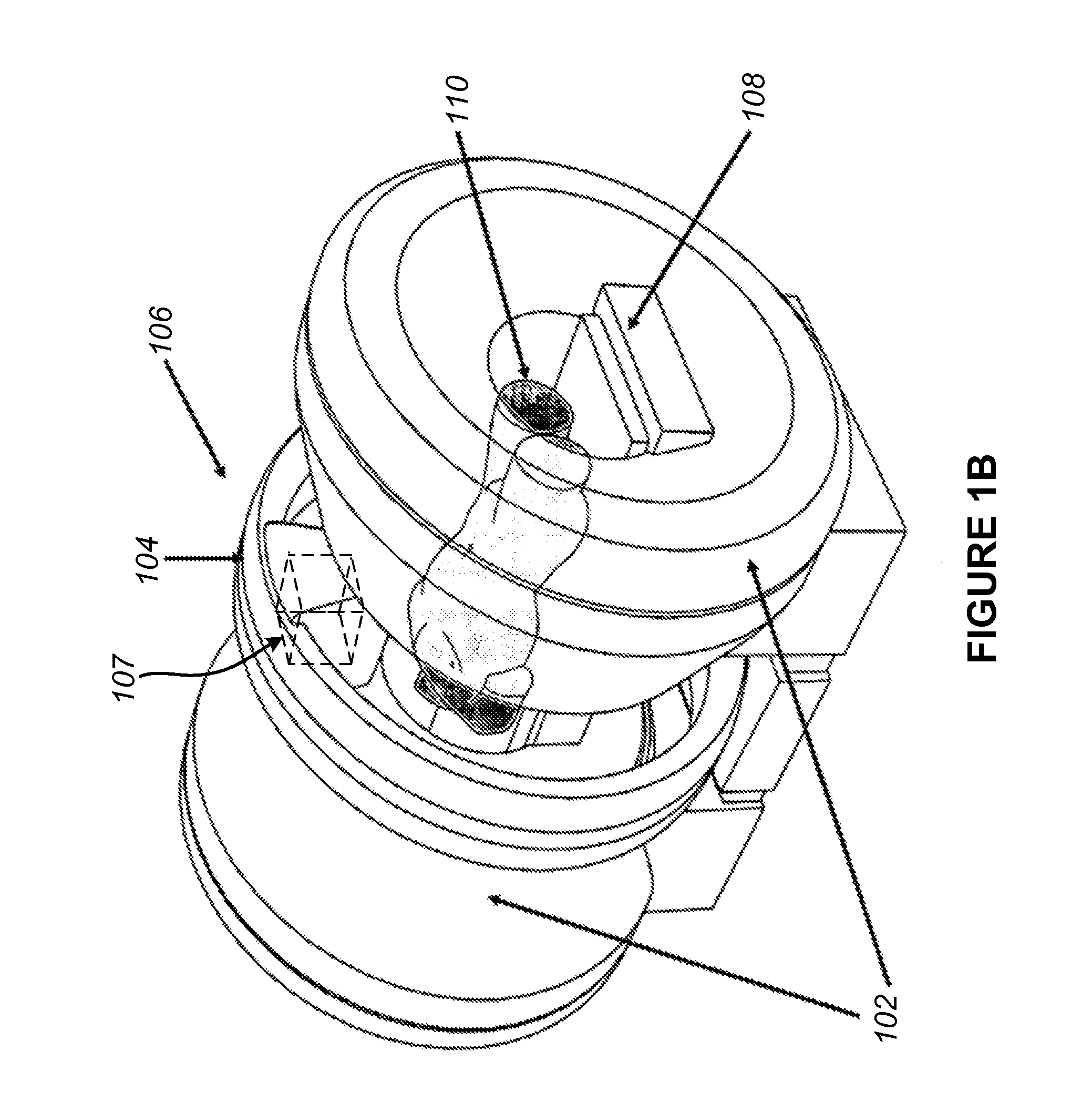
Radio communication system
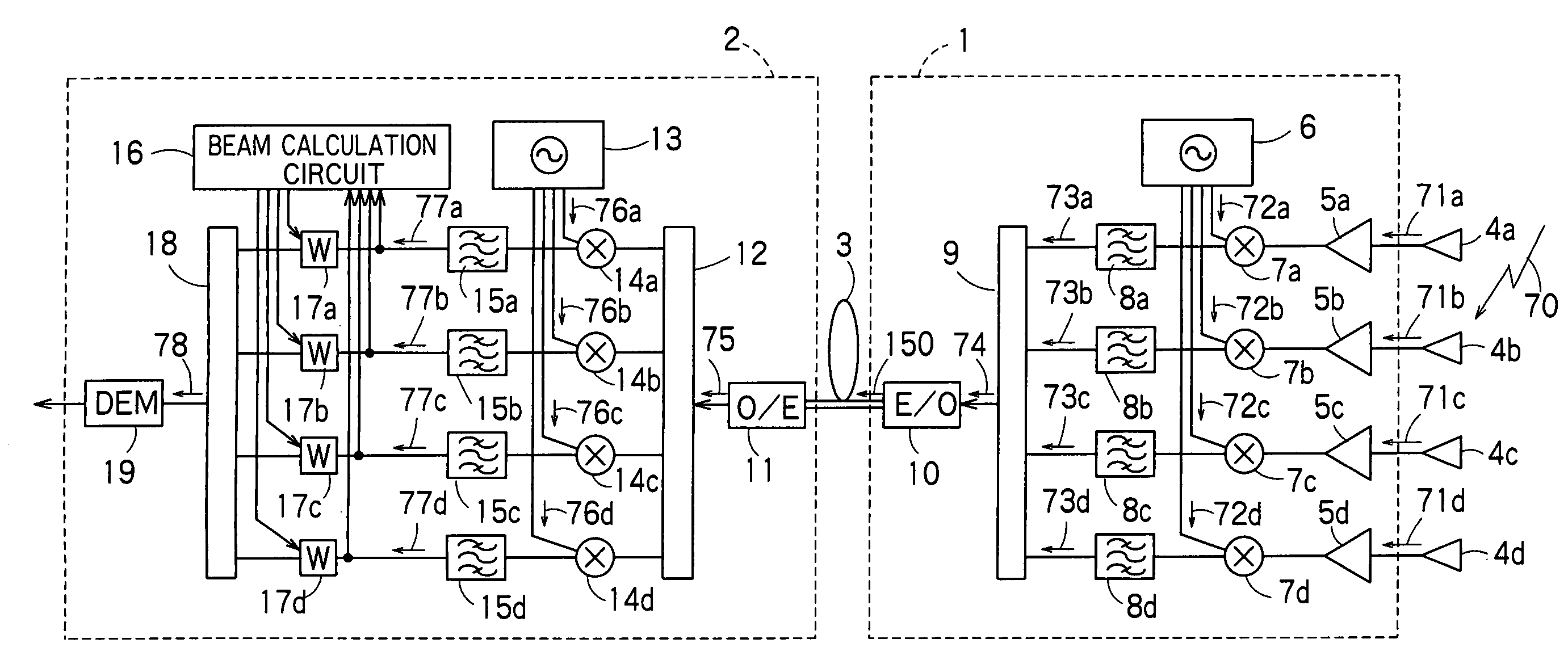
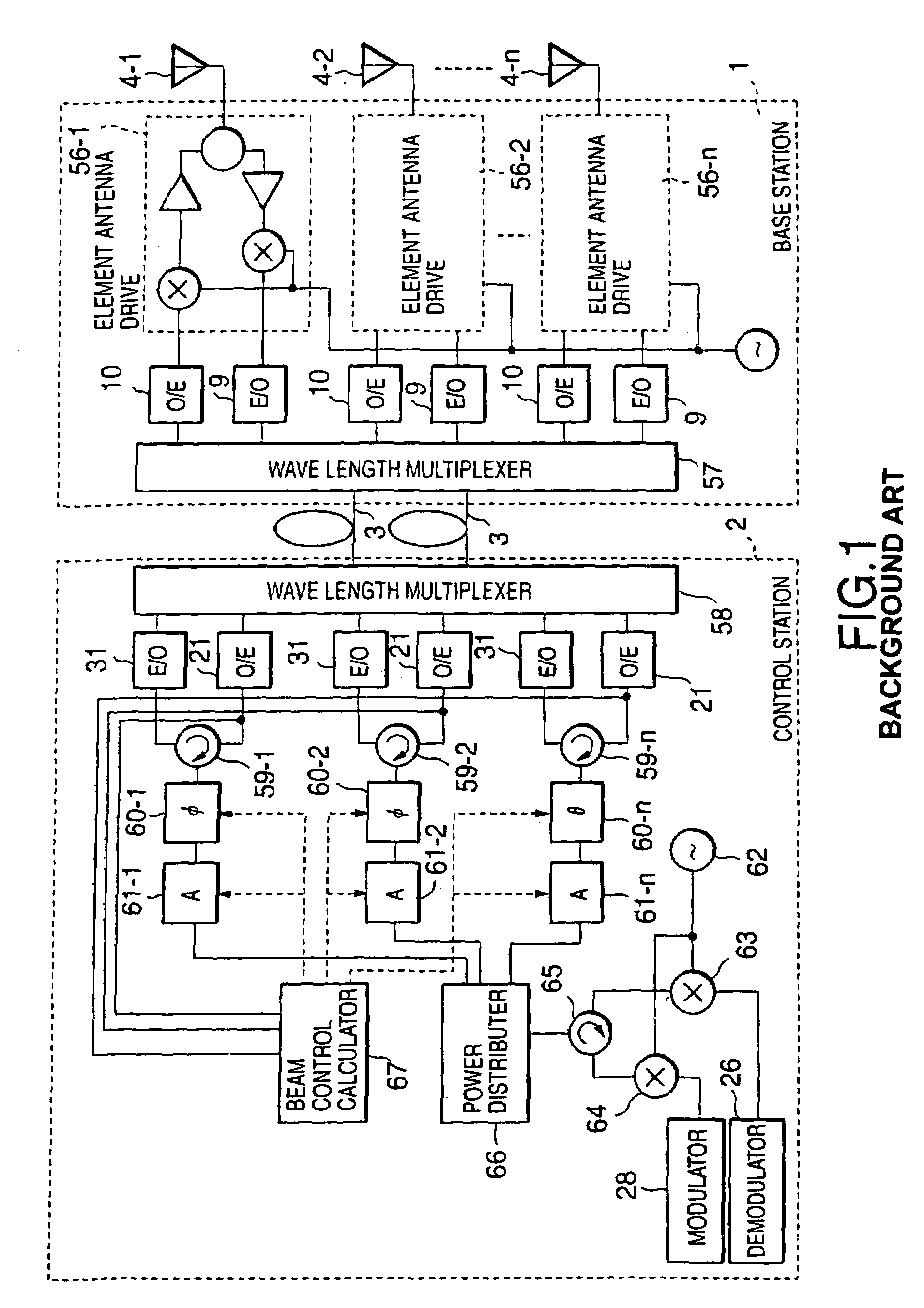
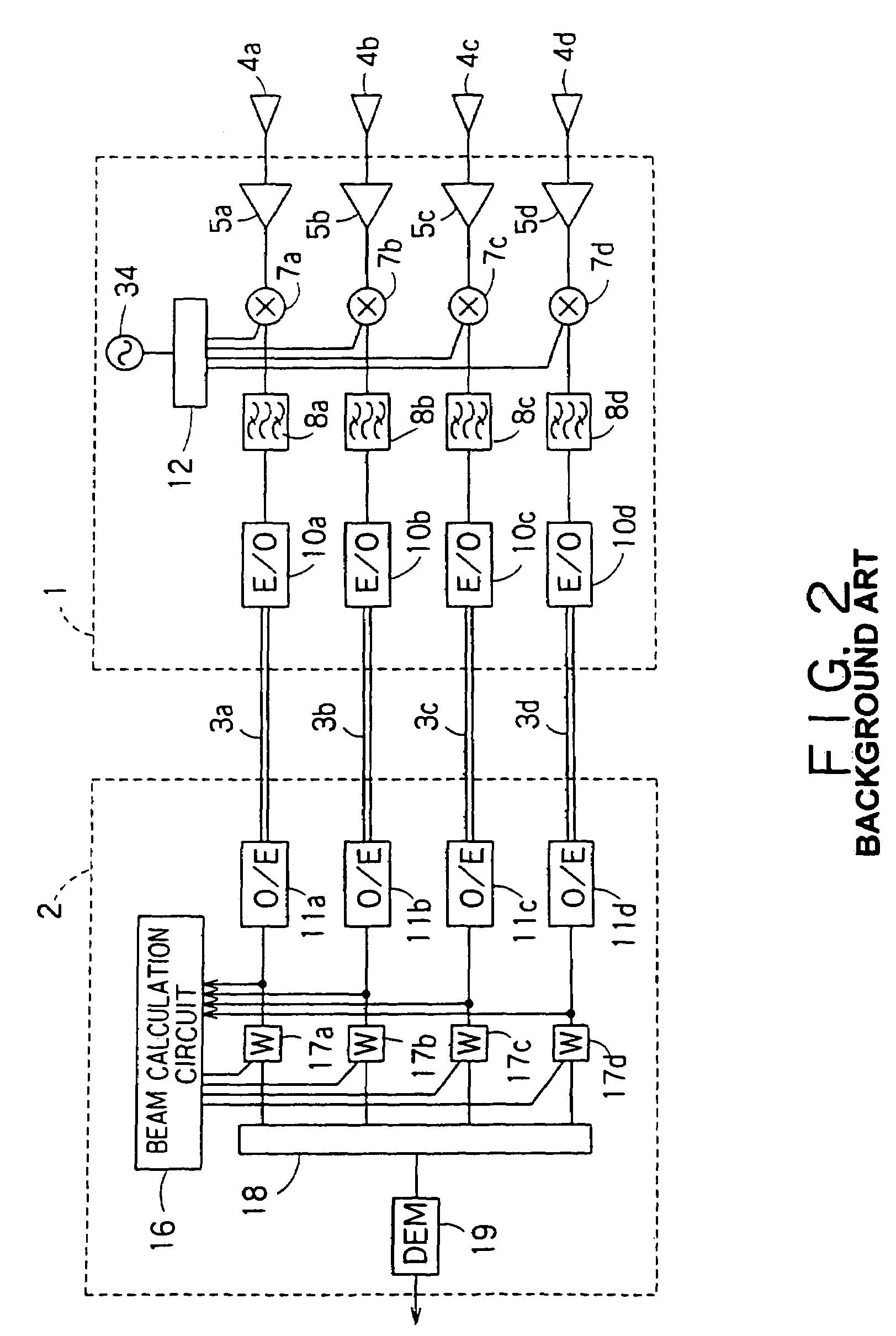
InactiveUS7043271B1Reduce in quantityReduces constitutionTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityCarrier signalEngineering
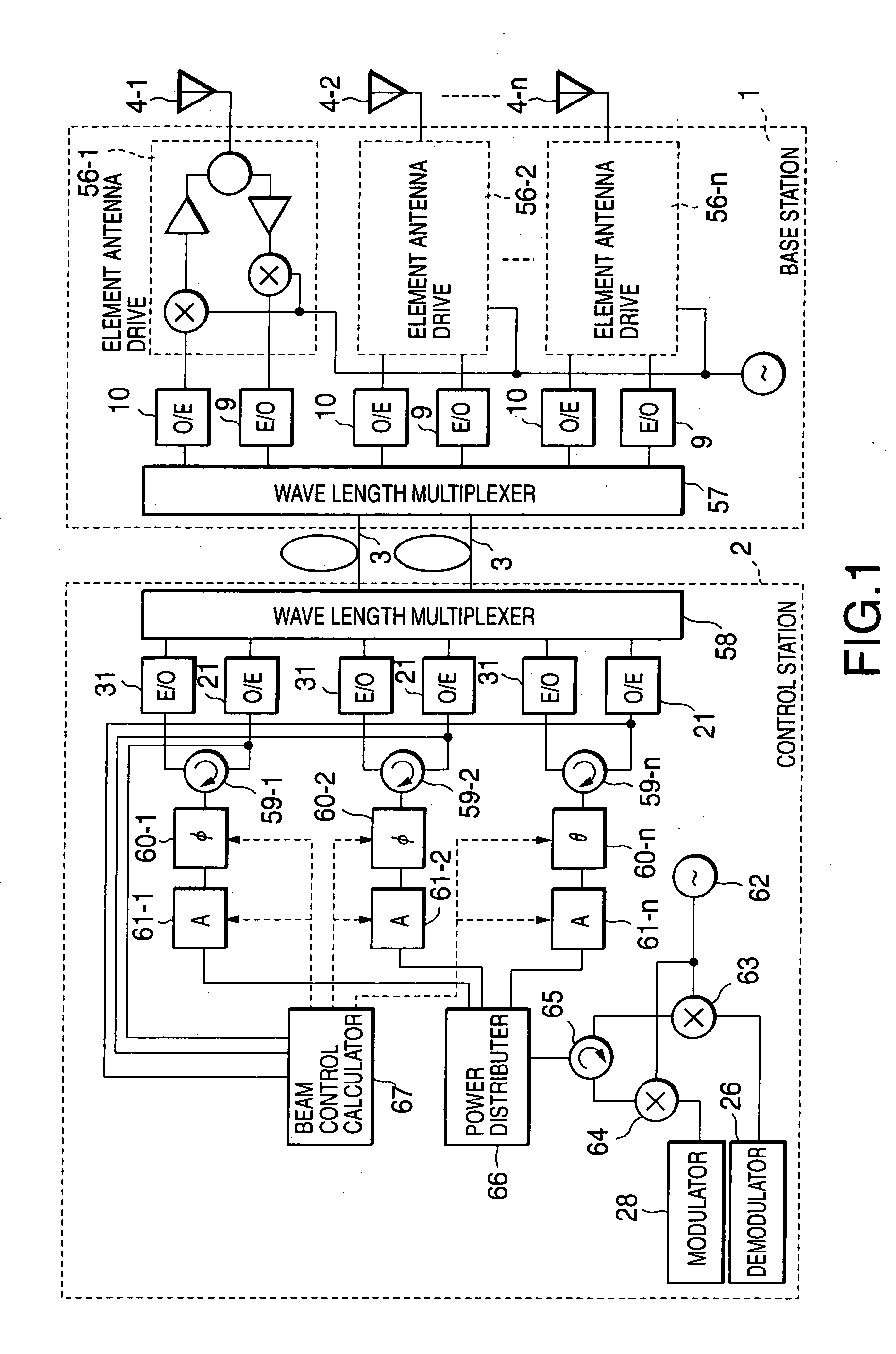
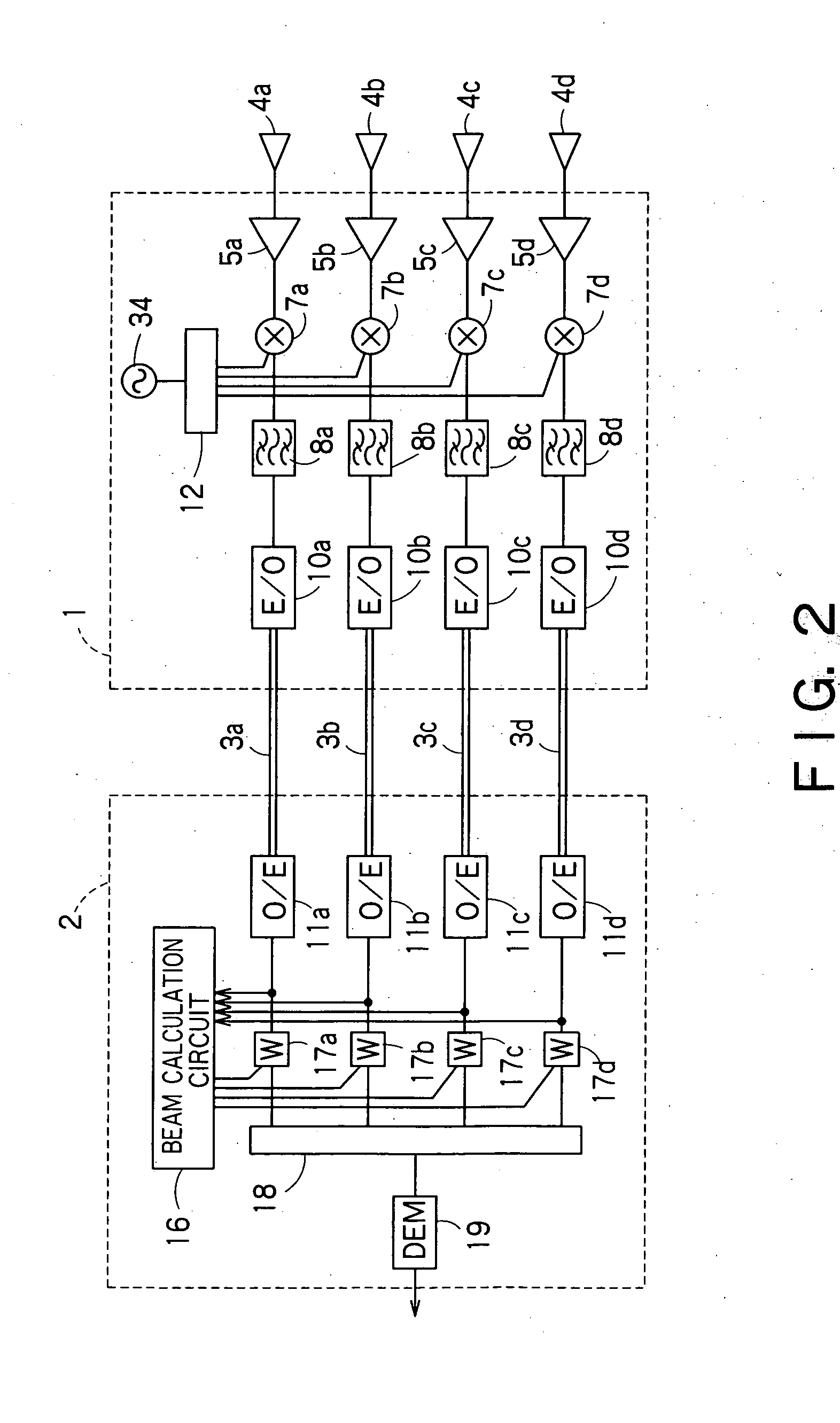
There is disclosed a radio communication system in which a constitution of a base station and further a control station can be simplified. A radio communication system according to the present invention converts a received signal received by a plurality of antenna elements in a base station to a signal of different frequency band, and then conflates the converted signal in order to generate sub-carrier wave multiplex signal. The signal is converted to an optical signal, and then the optical signal is transmitted to a control station via an optical fiber. Or the control station performs weighting to phase of the transmitted signal transmitted from a plurality of antennas of a base station, and then performs frequency conversion to different frequency band, and then conflates the converted signal in order to generate the sub-carrier wave multiplex signal. The signal is converted to an optical signal, and then an optical signal is transmitted to the base station side via the optical fiber. The control station and the base station divides the received sub-carrier wave multiplex signal by each frequency band, and then the frequency of the divided signals are converted to the same frequency band in order to generate the transmitted / received signal of each antenna element. By such a constitution, it is possible to reduce constituent of the optical transmission components to the minimum and to simplify the constitution of the base station. Furthermore, it is possible to maintain the relative phase difference and the relative intensity of the transmitted / received signal of each antenna element. Because of this, it is possible to estimate an arrival direction of the received signal and to control radiation beam pattern of the transmitted signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
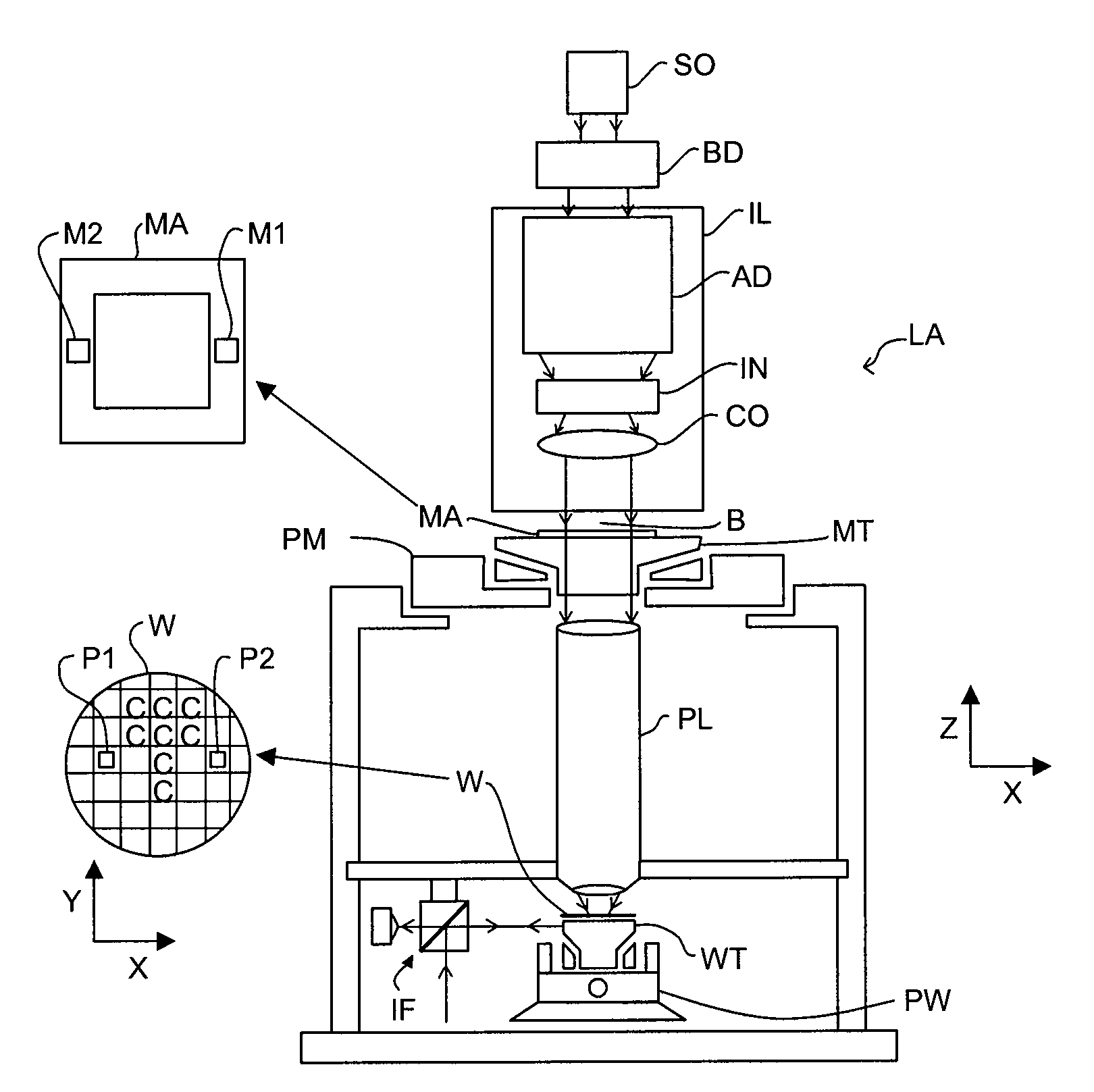
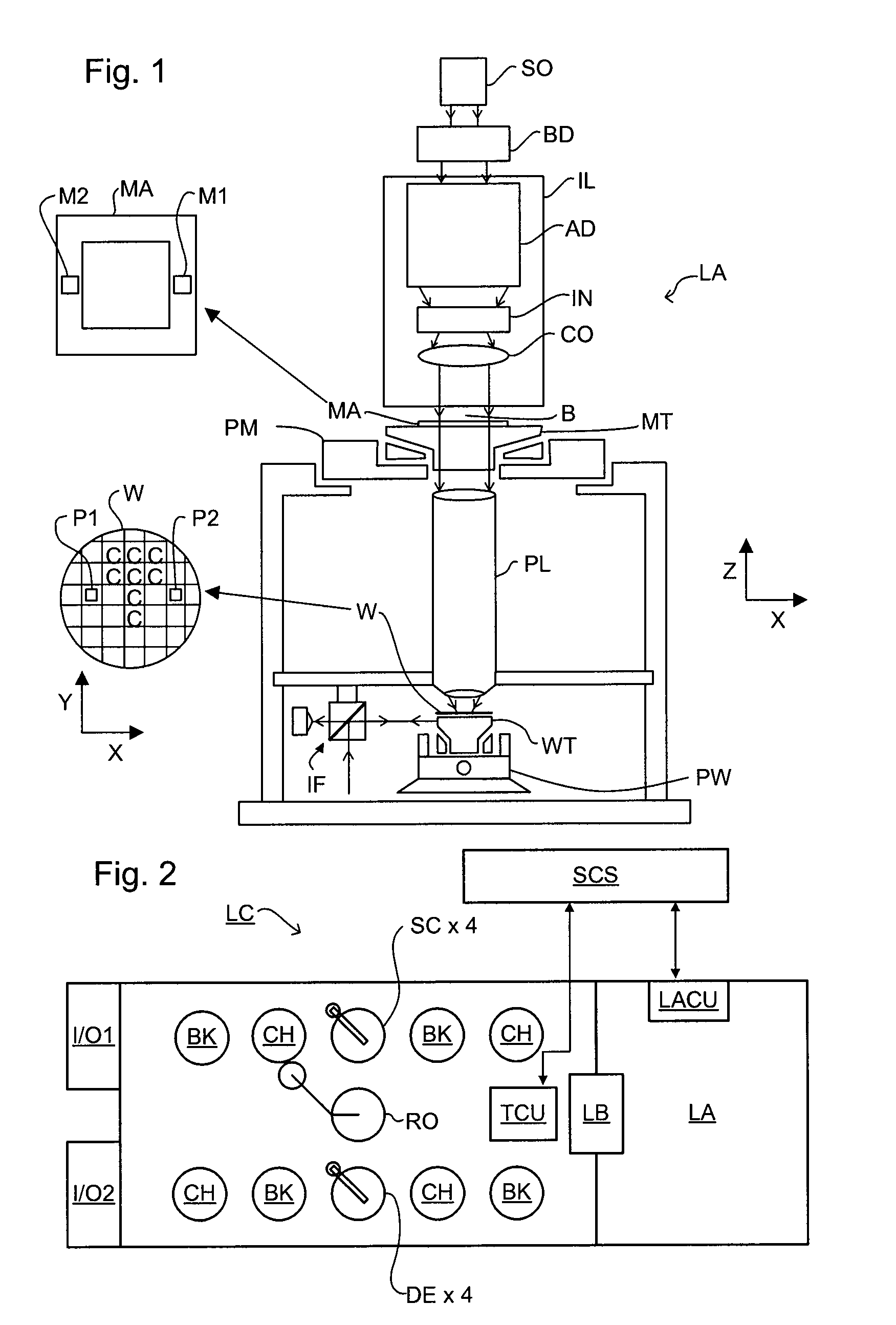
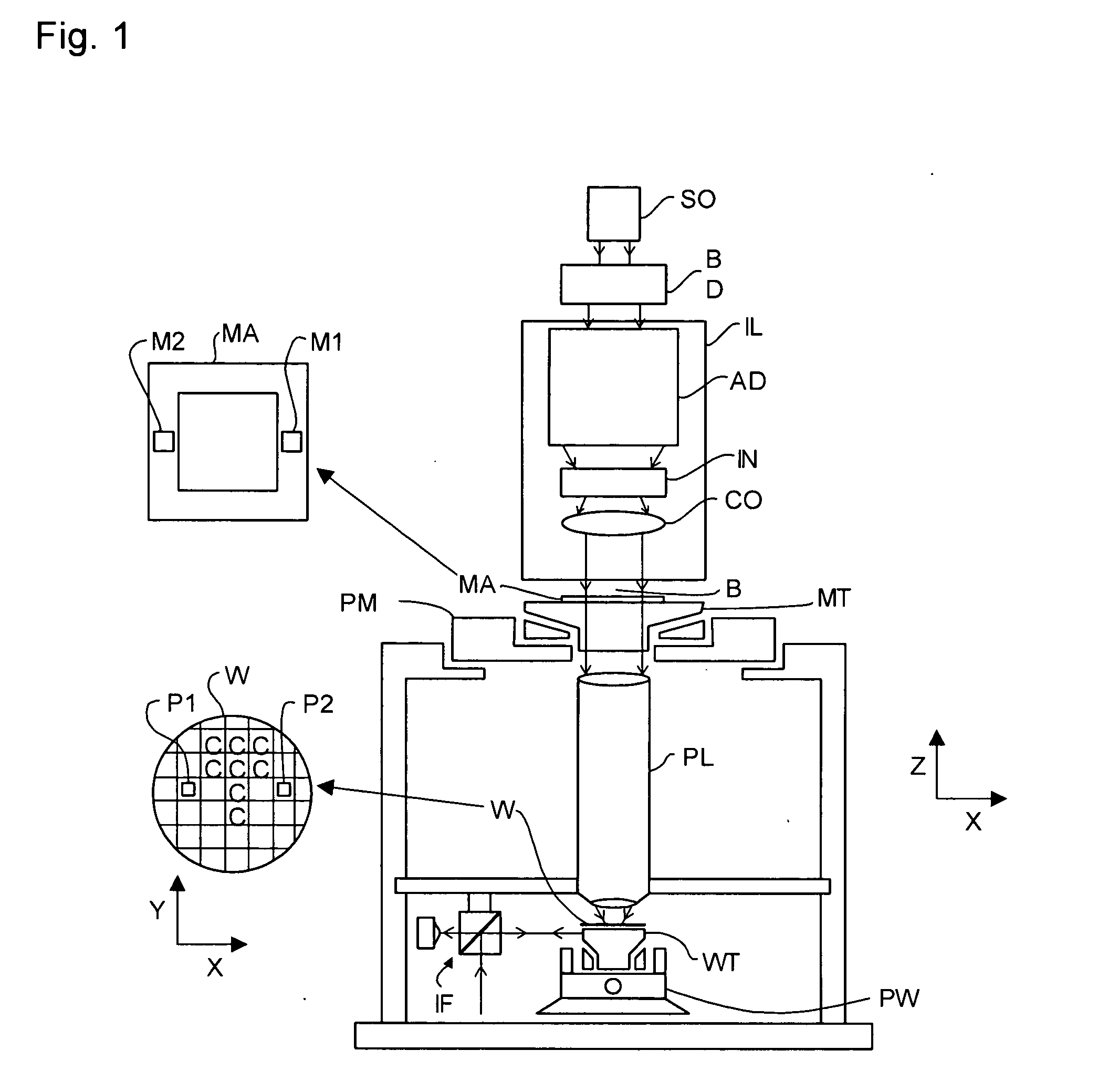
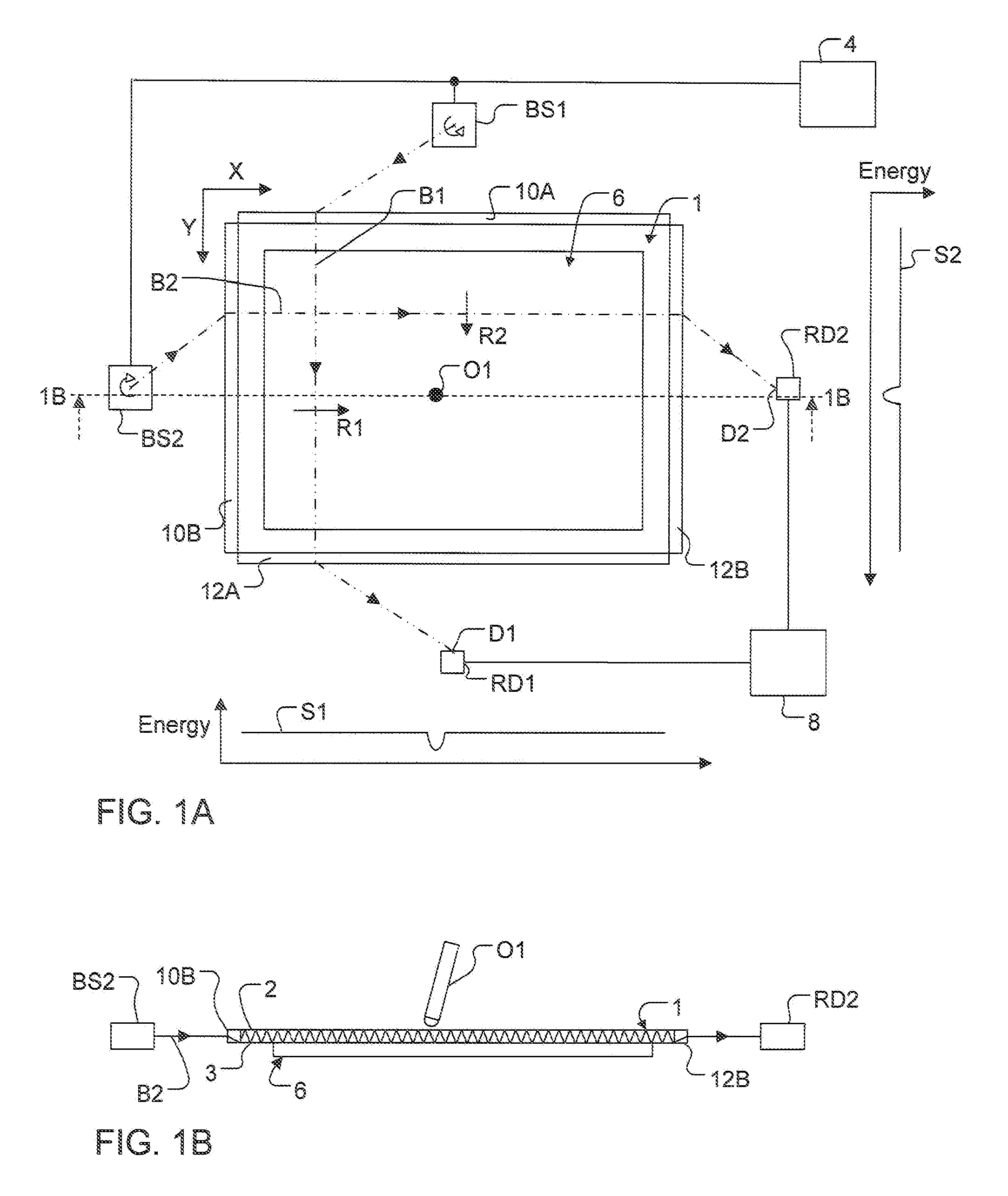
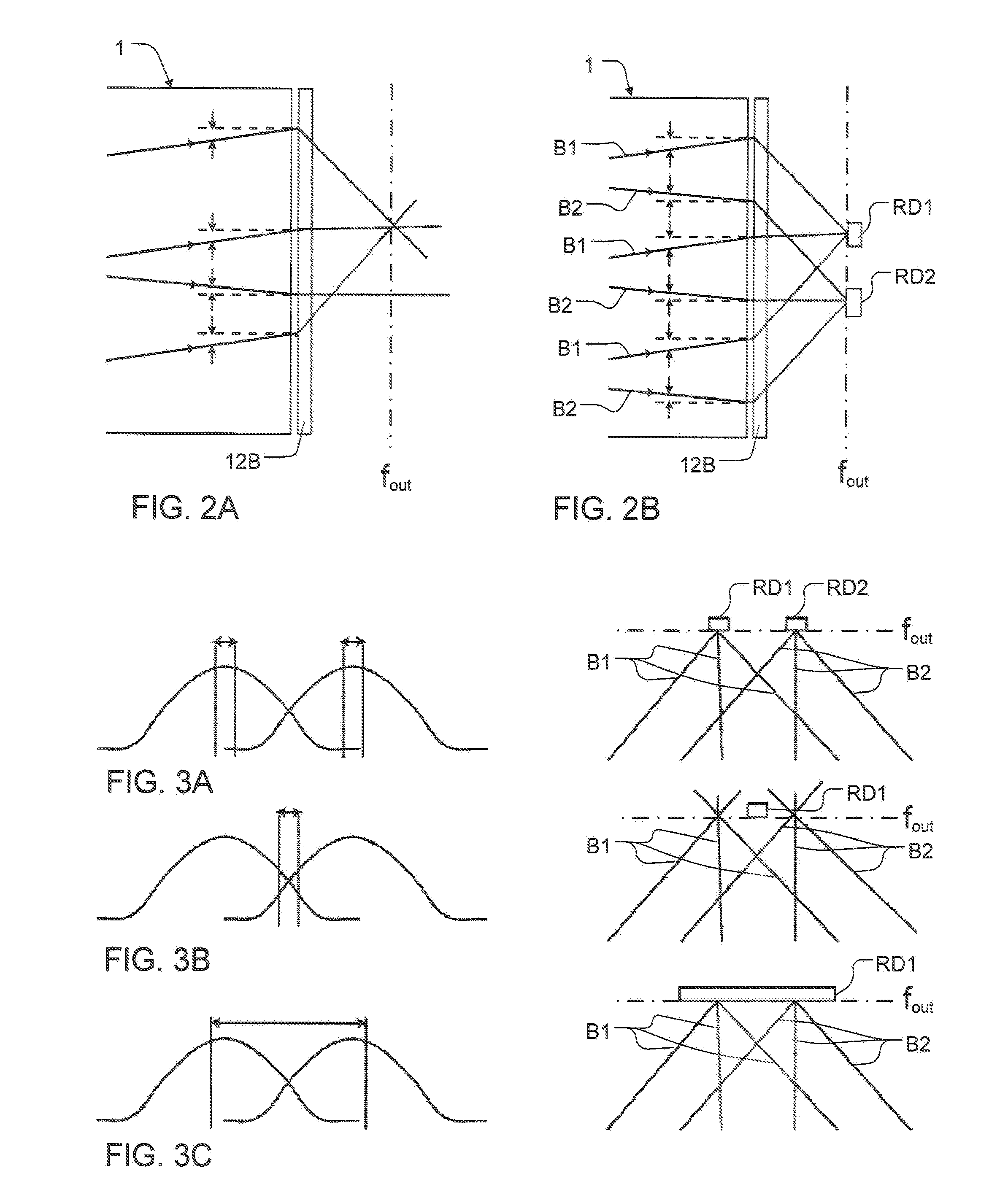
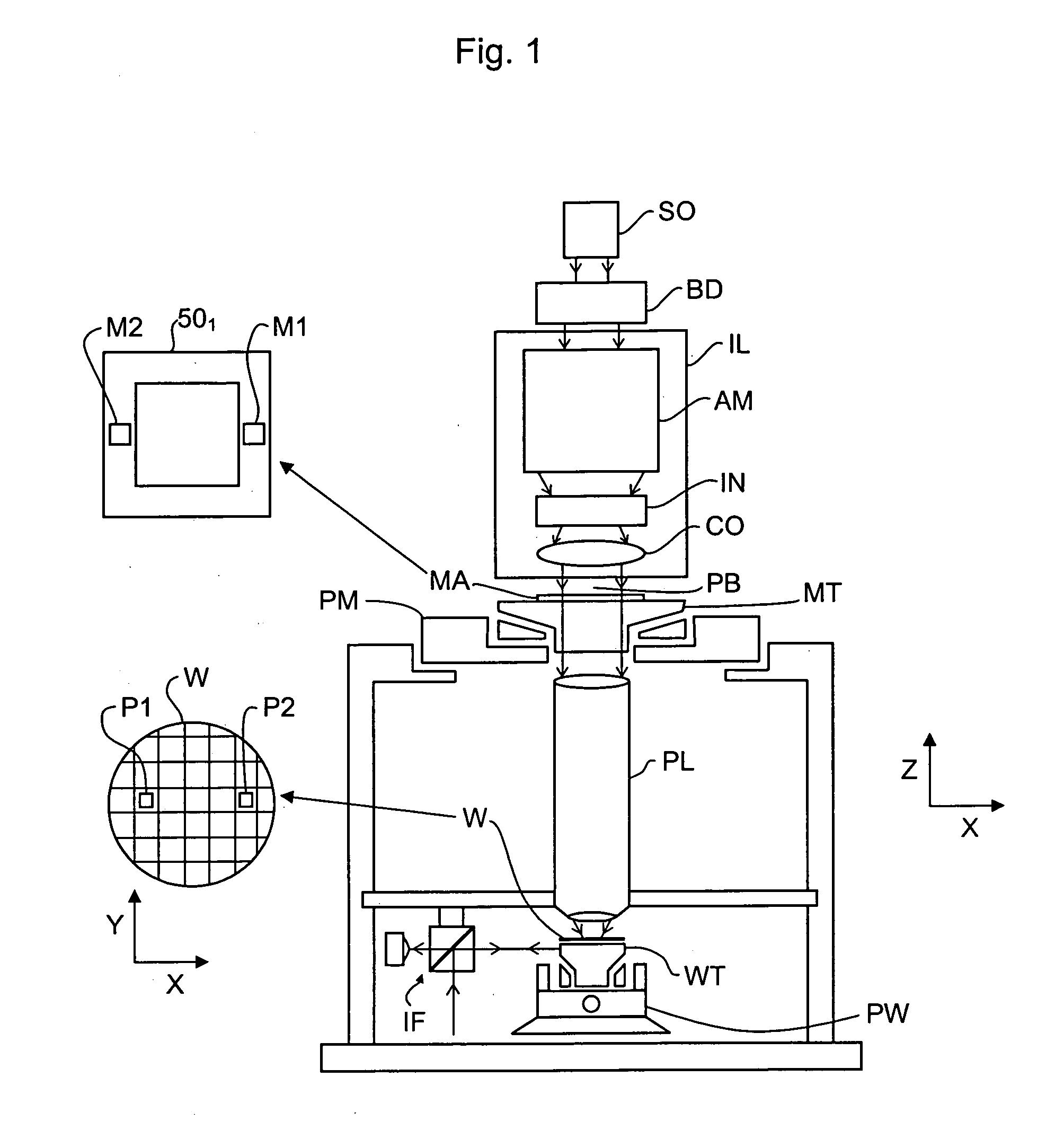
Inspection Apparatus, Lithographic Apparatus, Lithographic Processing Cell and Inspection Method
ActiveUS20100201963A1Increase the number ofPossible to separateRaman/scattering spectroscopySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsFour quadrantsZeroth order
For angular resolved spectrometry a radiation beam is used having an illumination profile having four quadrants is used. The first and third quadrants are illuminated whereas the second and fourth quadrants aren't illuminated. The resulting pupil plane is thus also divided into four quadrants with only the zeroth order diffraction pattern appearing in the first and third quadrants and only the first order diffraction pattern appearing in the second and third quadrants.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Systems and methods for imaging large field-of-view objects
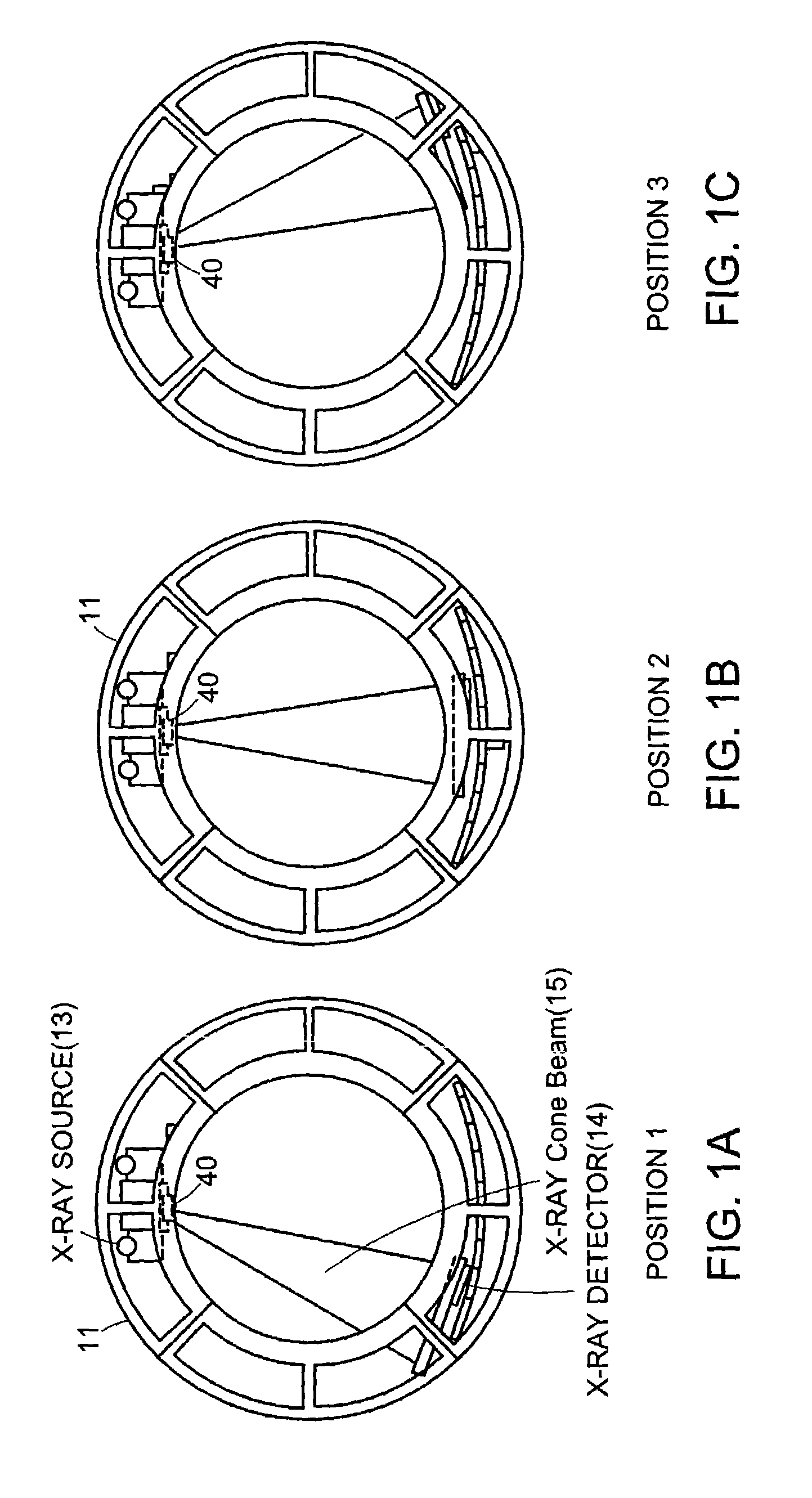
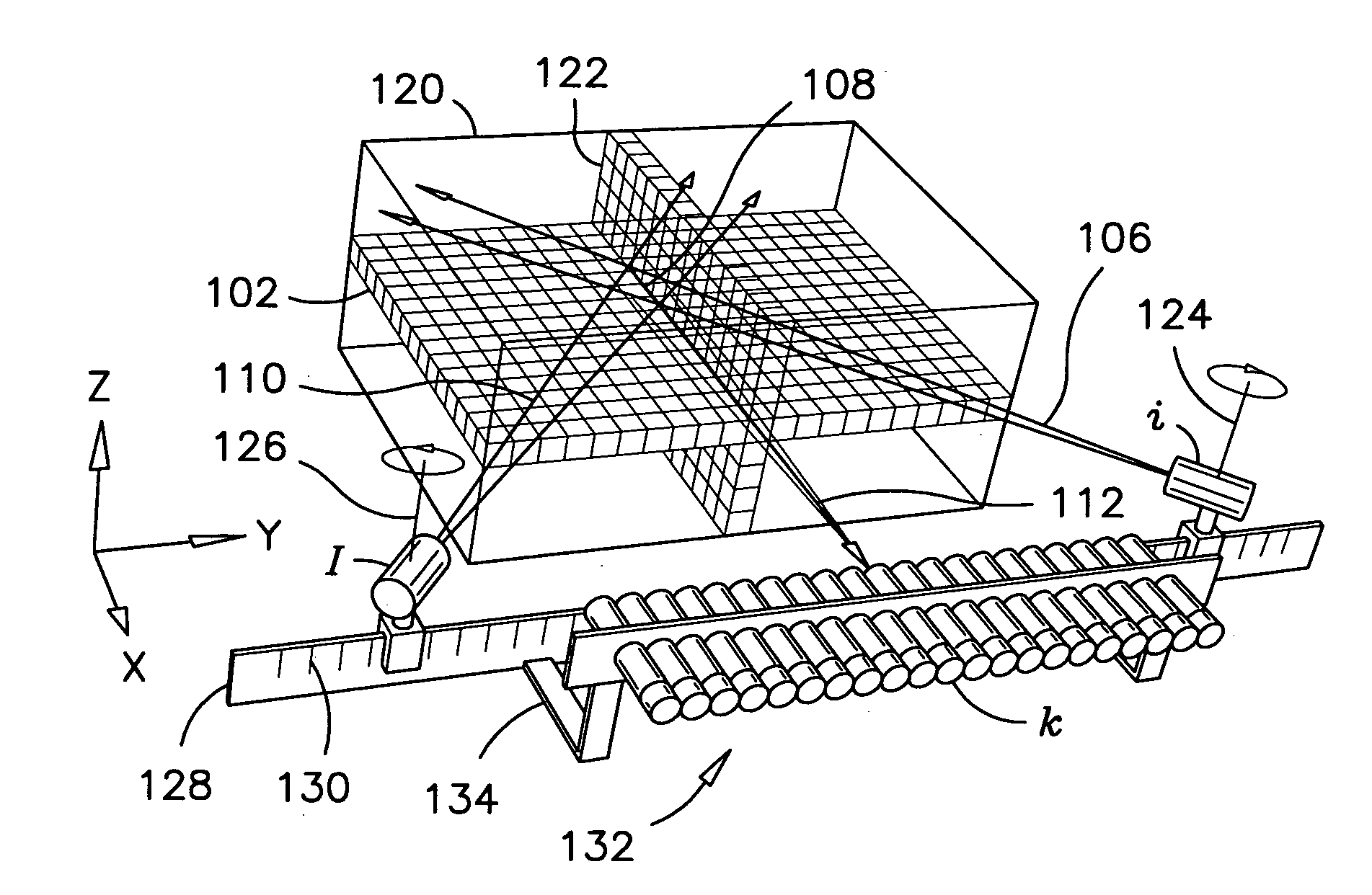
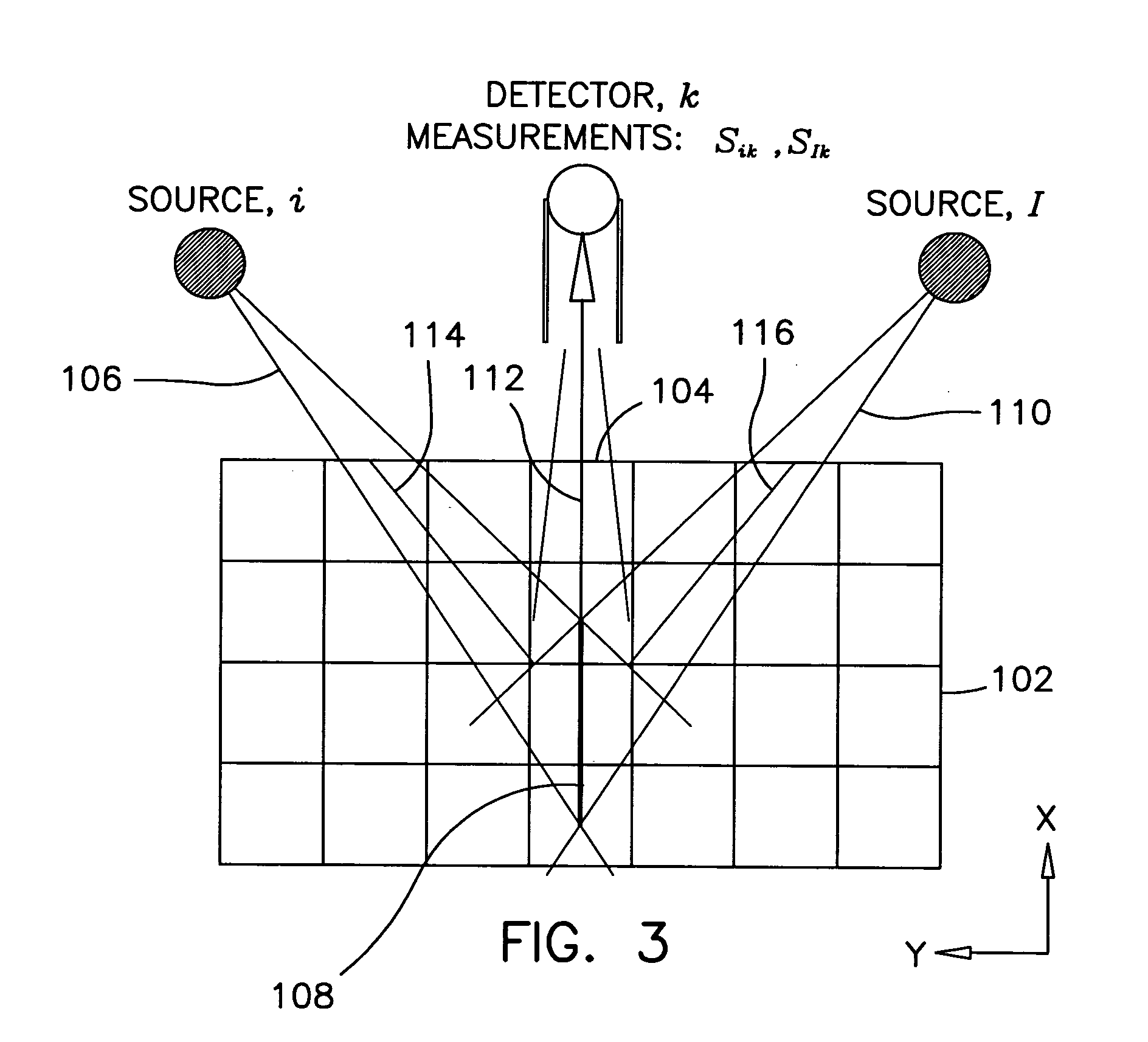
InactiveUS7108421B2Quantity minimizationAvoiding corrupted and resulting artifacts in image reconstructionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingBeam sourceX-ray
An imaging apparatus and related method comprising a source that projects a beam of radiation in a first trajectory; a detector located a distance from the source and positioned to receive the beam of radiation in the first trajectory; an imaging area between the source and the detector, the radiation beam from the source passing through a portion of the imaging area before it is received at the detector; a detector positioner that translates the detector to a second position in a first direction that is substantially normal to the first trajectory; and a beam positioner that alters the trajectory of the radiation beam to direct the beam onto the detector located at the second position. The radiation source can be an x-ray cone-beam source, and the detector can be a two-dimensional flat-panel detector array. The invention can be used to image objects larger than the field-of-view of the detector by translating the detector array to multiple positions, and obtaining images at each position, resulting in an effectively large field-of-view using only a single detector array having a relatively small size. A beam positioner permits the trajectory of the beam to follow the path of the translating detector, which permits safer and more efficient dose utilization, as generally only the region of the target object that is within the field-of-view of the detector at any given time will be exposed to potentially harmful radiation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
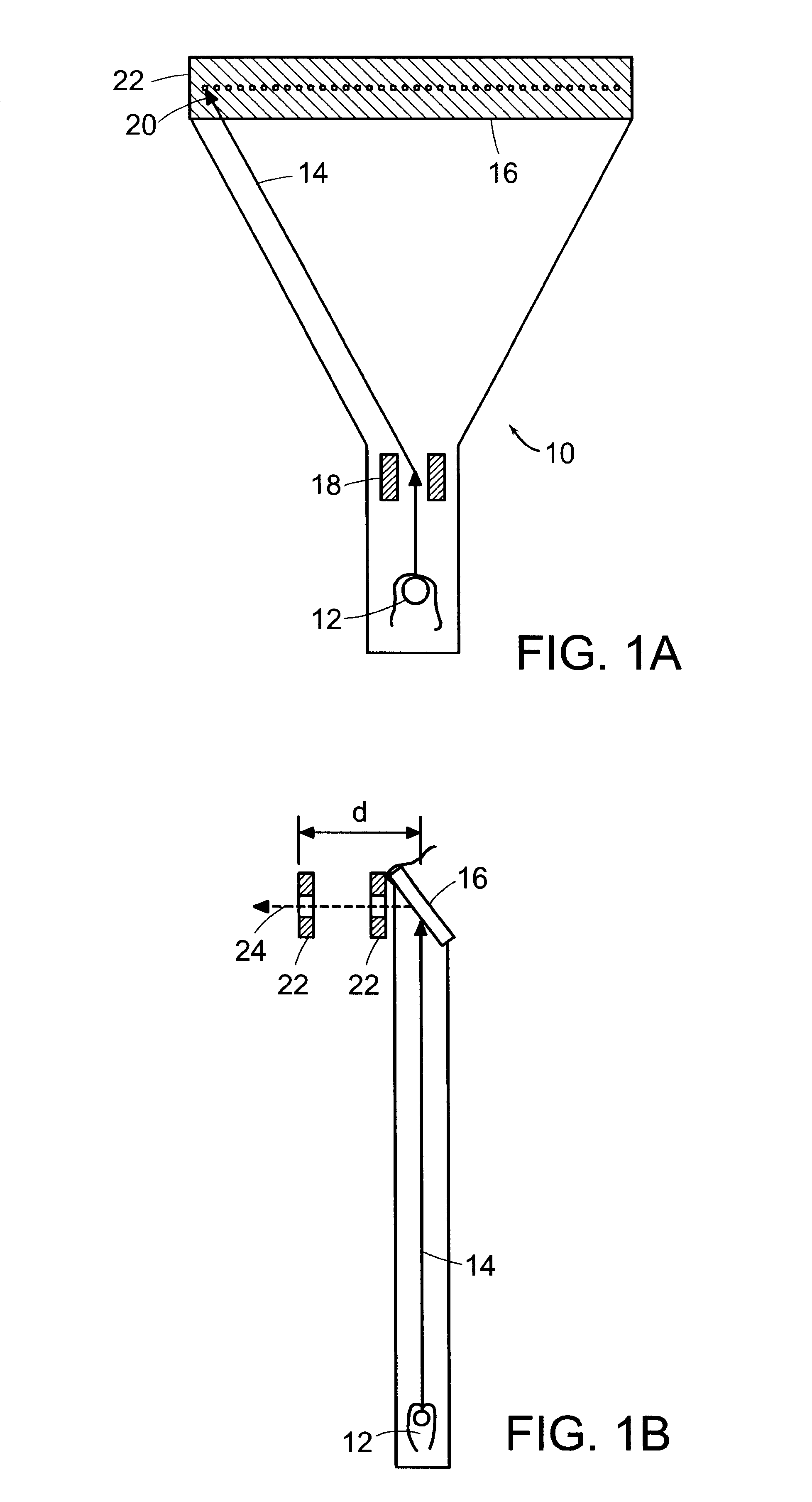
Method and apparatus for irradiating a target
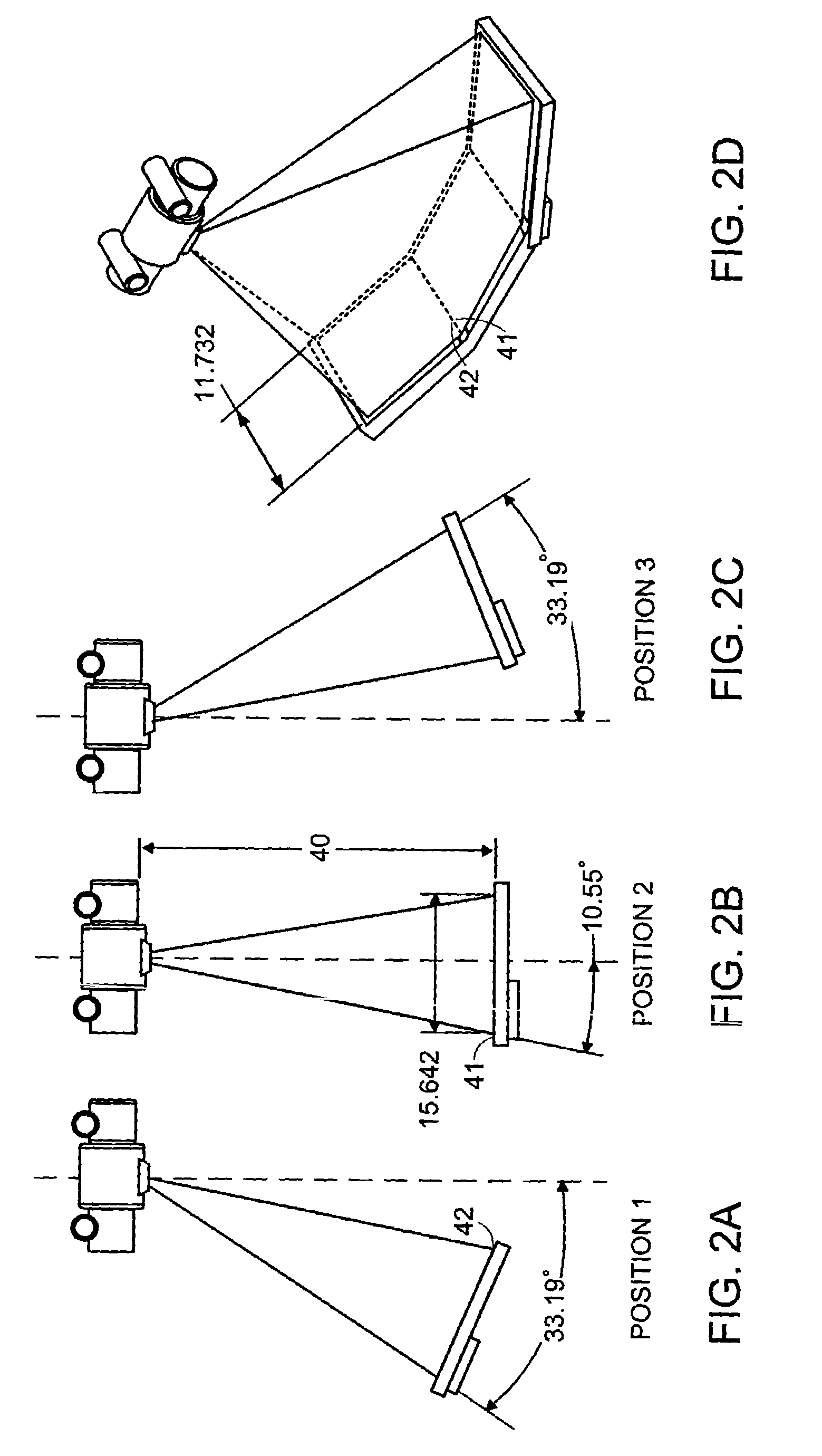
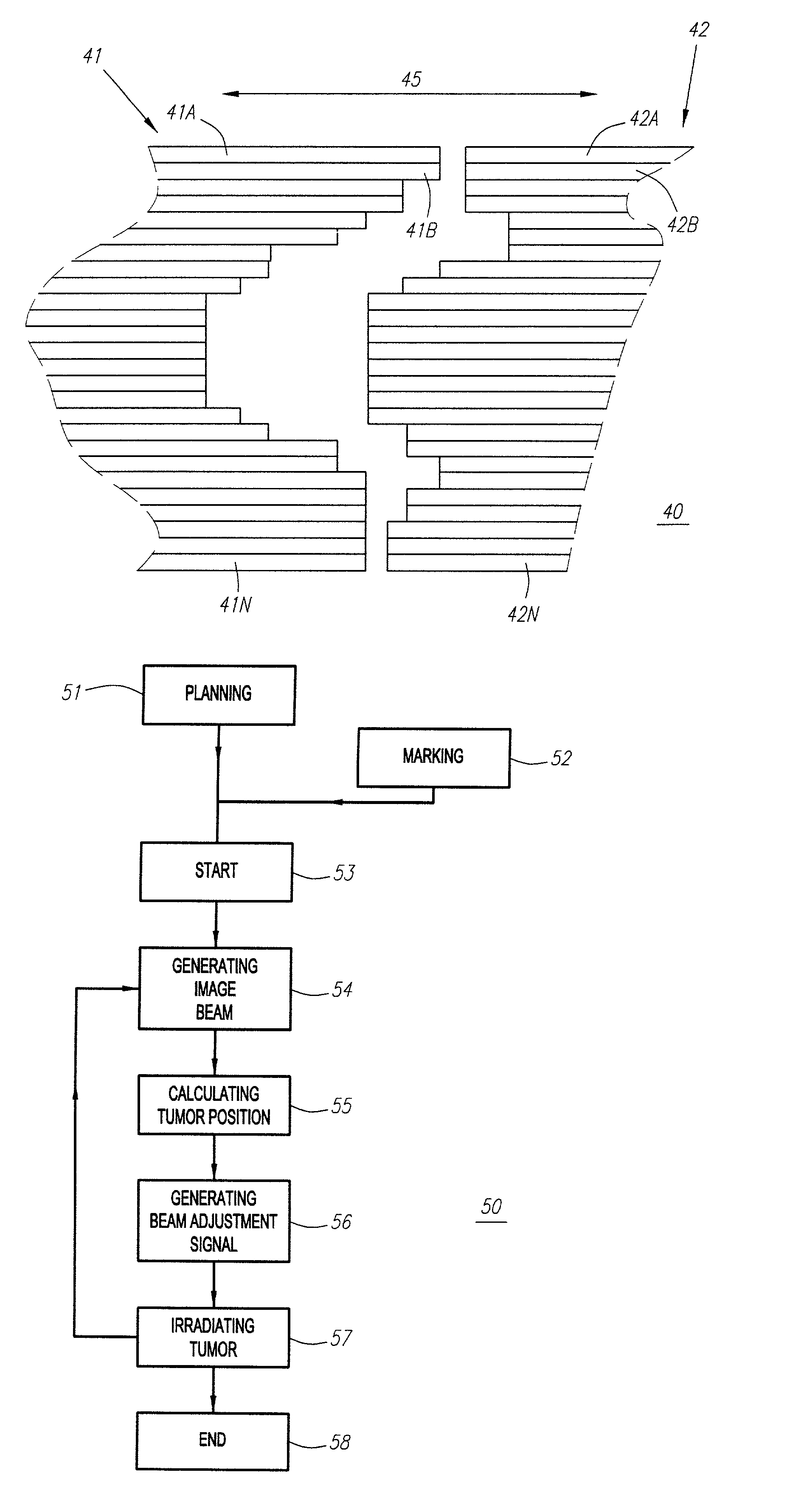
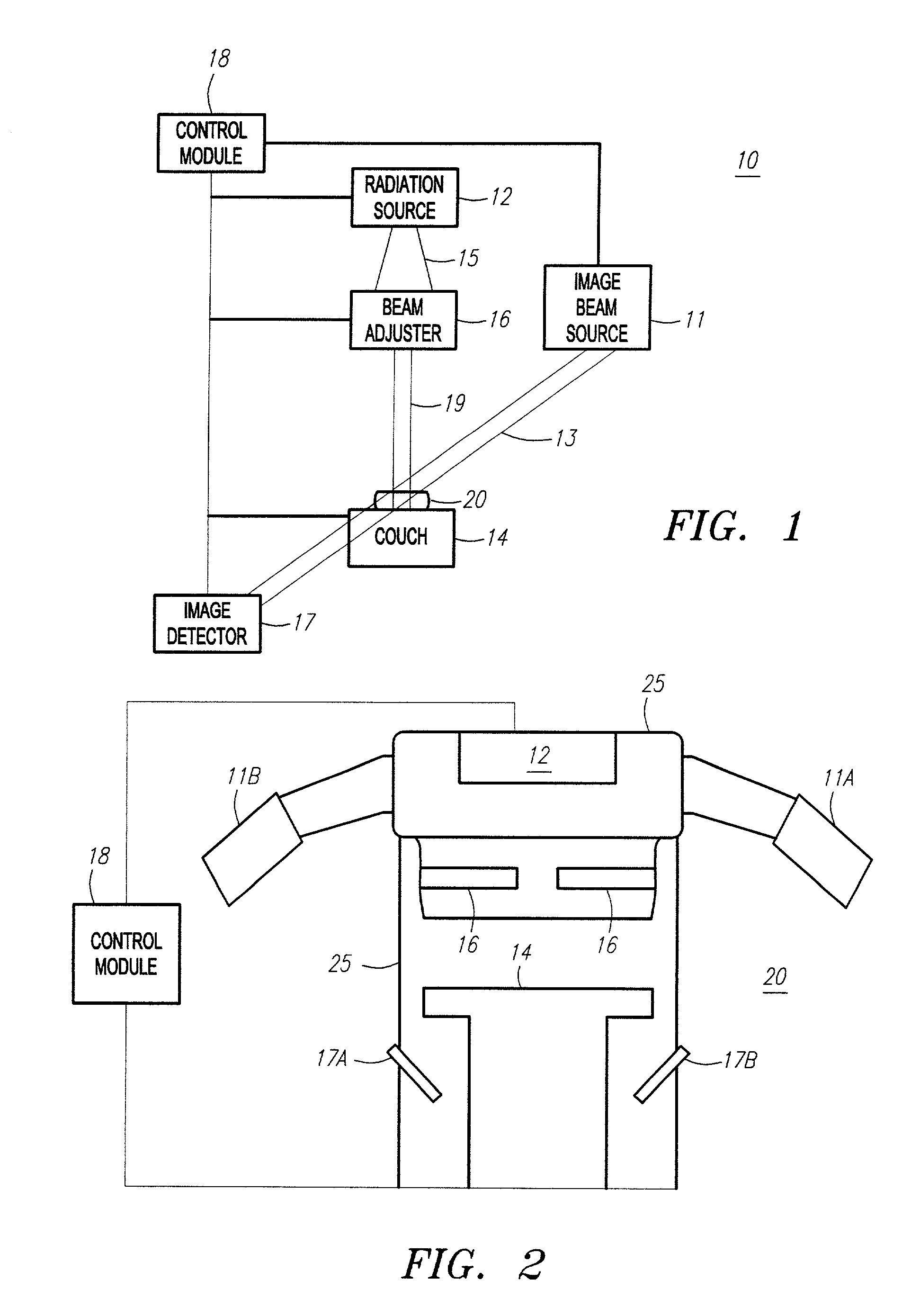
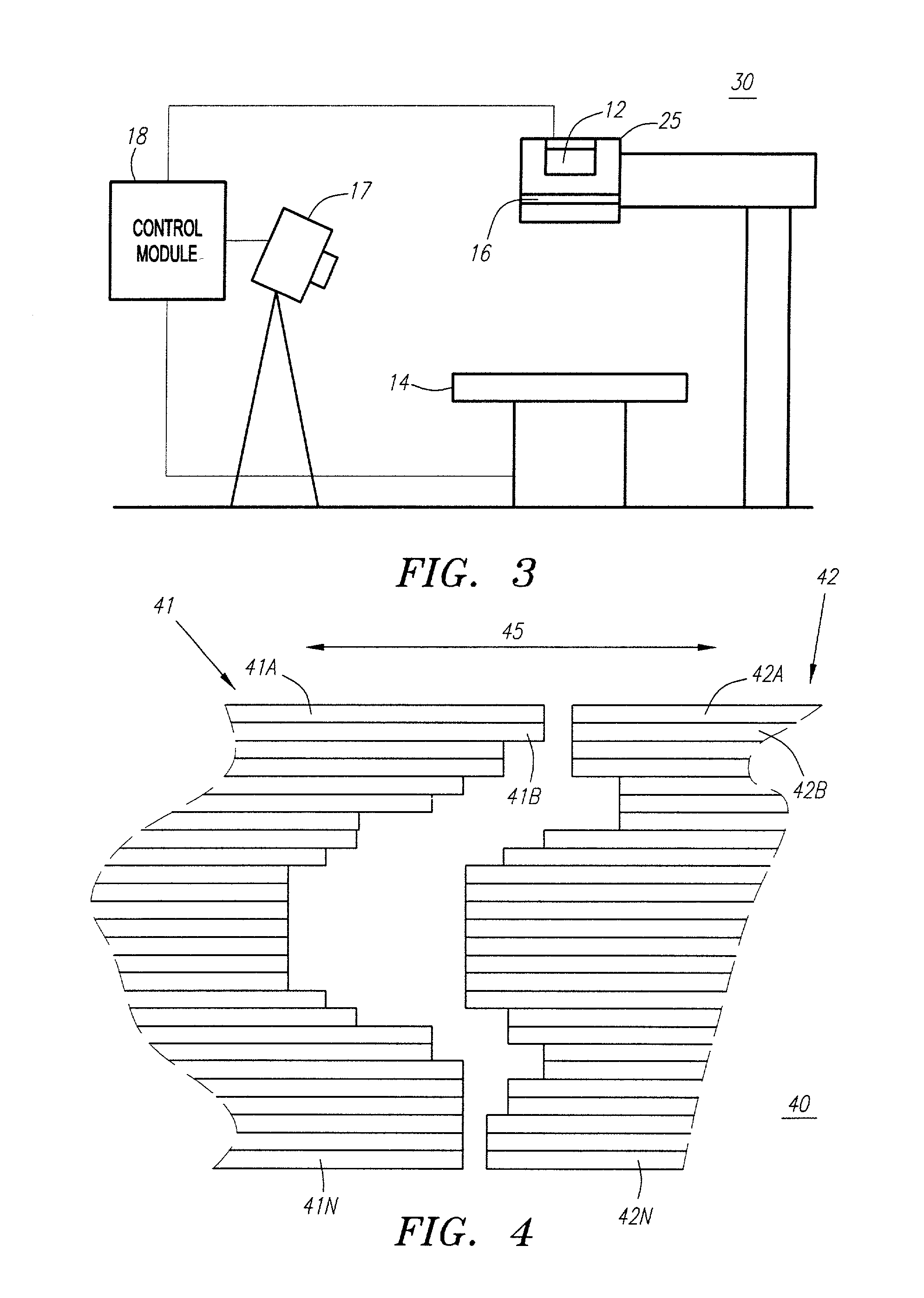
An apparatus (10) for irradiating a target includes a radiation source (12) for generating a radiation beam and a multiple leaf beam adjuster (16) for collimating and adjusting the shape of the radiation beam from the radiation source (12) that would be projected on the target. An image detector (17) detects generates an image signal of the target. In response to the image signal, a control module (18) generate a beam adjustment signal for controlling the beam adjuster (16), thereby enabling the radiation beam from the radiation source (12) to track the movement of the target.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
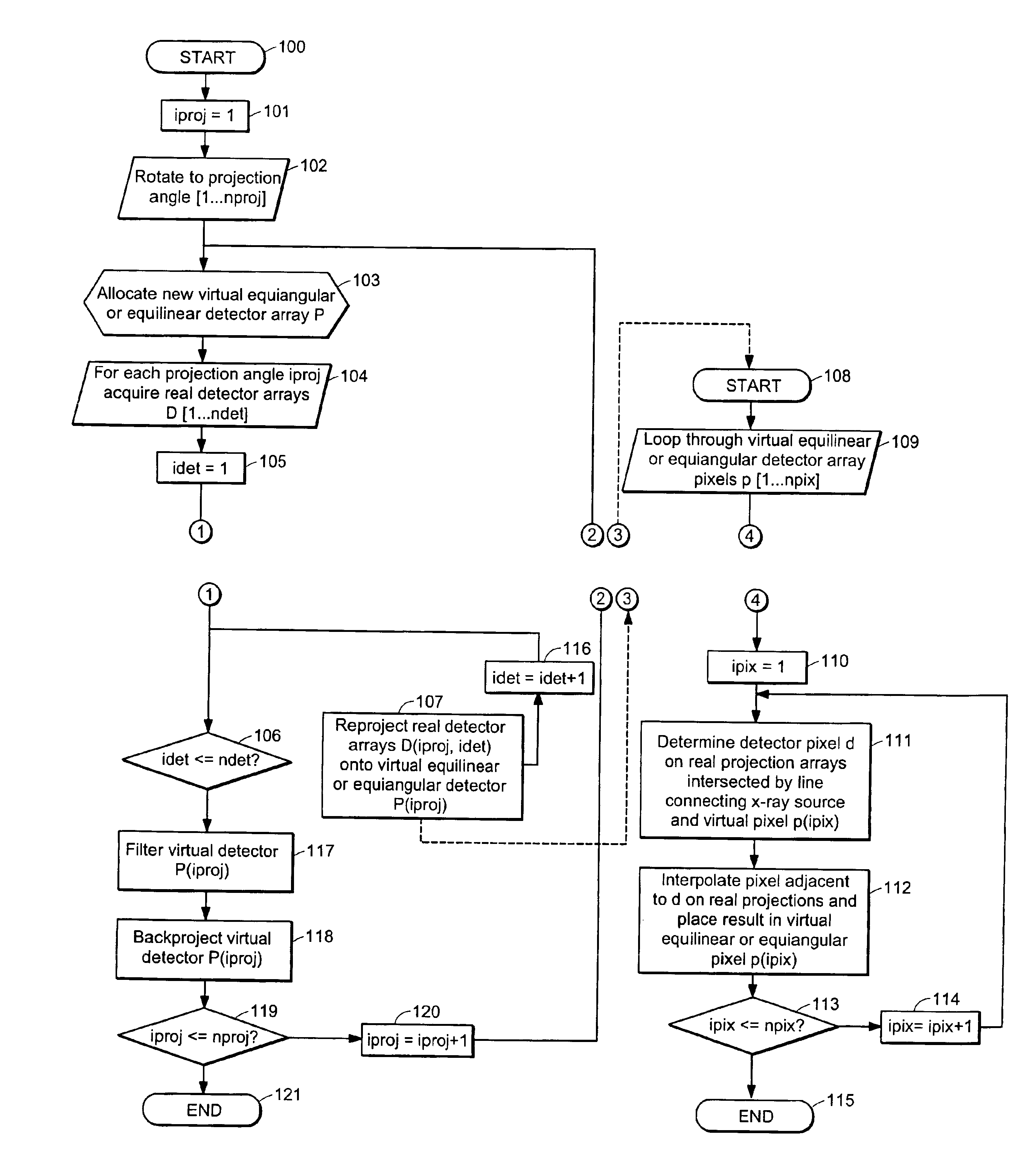
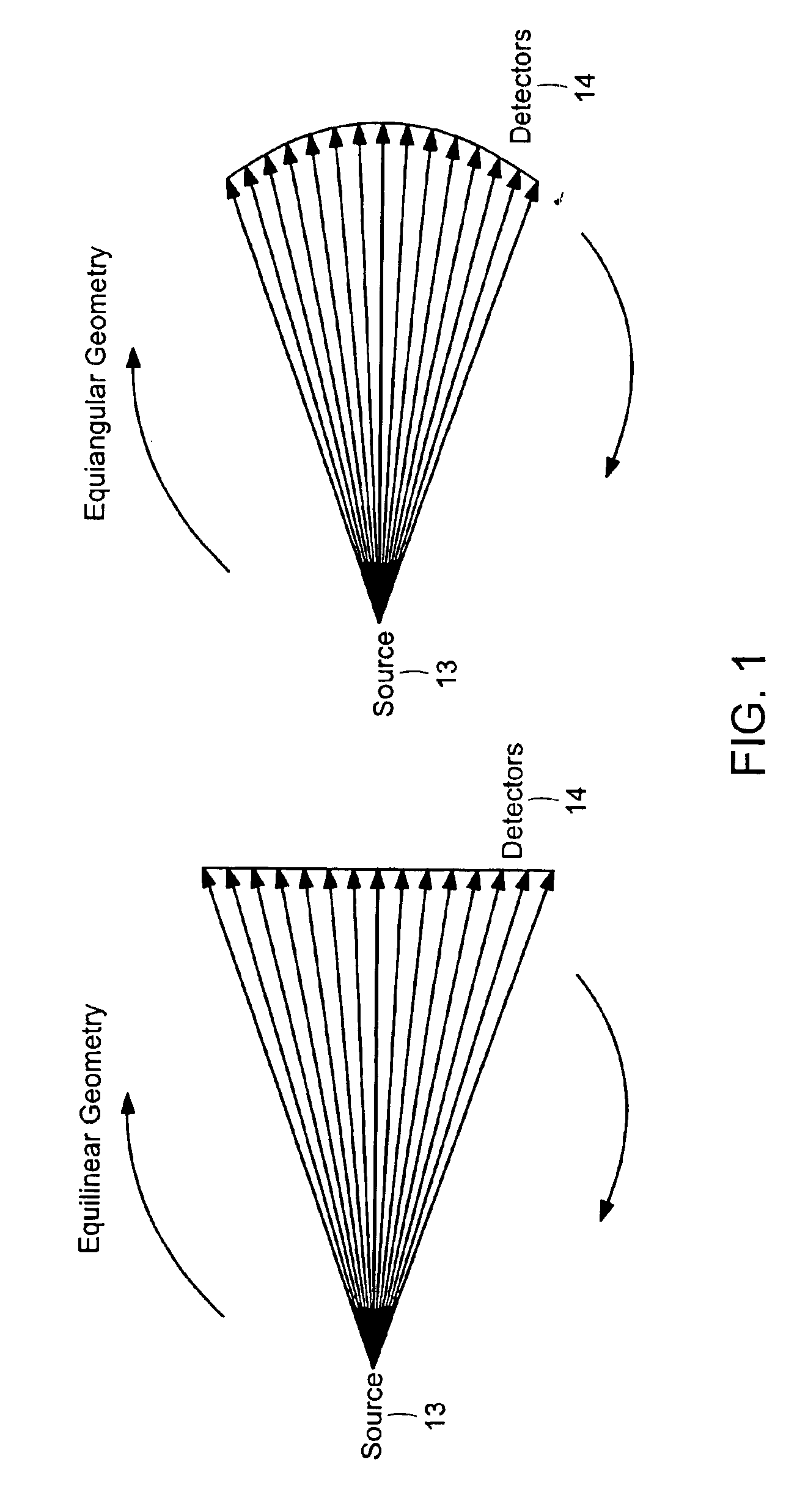
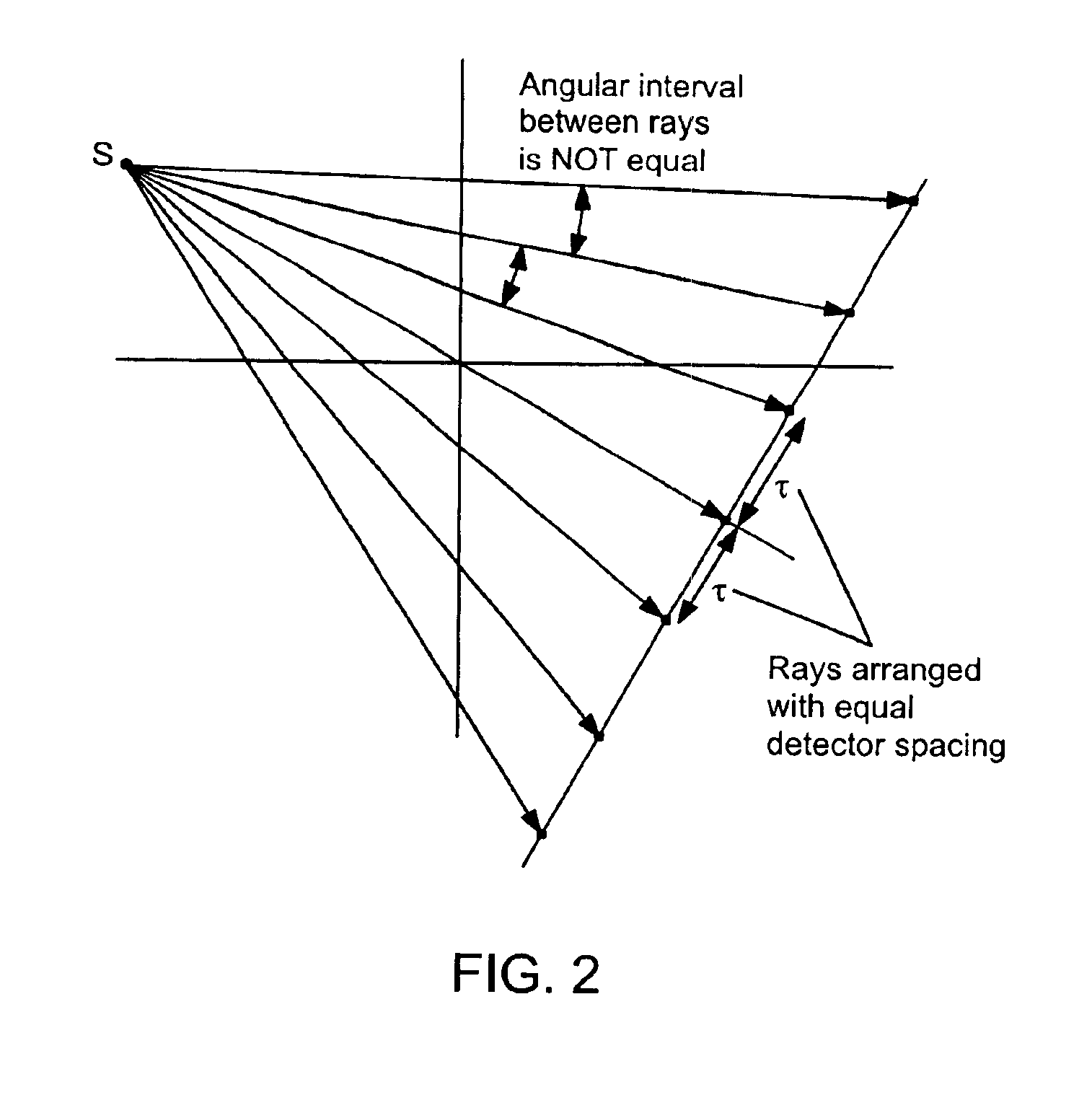
Apparatus and method for reconstruction of volumetric images in a divergent scanning computed tomography system
ActiveUS7106825B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDetector arrayComputing tomography
An apparatus and method for reconstructing image data for a region are described. A radiation source and multiple one-dimensional linear or two-dimensional planar area detector arrays located on opposed sides of a region angled generally along a circle centered at the radiation source are used to generate scan data for the region from a plurality of diverging radiation beams, i.e., a fan beam or cone beam. Individual pixels on the discreet detector arrays from the scan data for the region are reprojected onto a new single virtual detector array along a continuous equiangular arc or cylinder or equilinear line or plane prior to filtering and backprojecting to reconstruct the image data.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
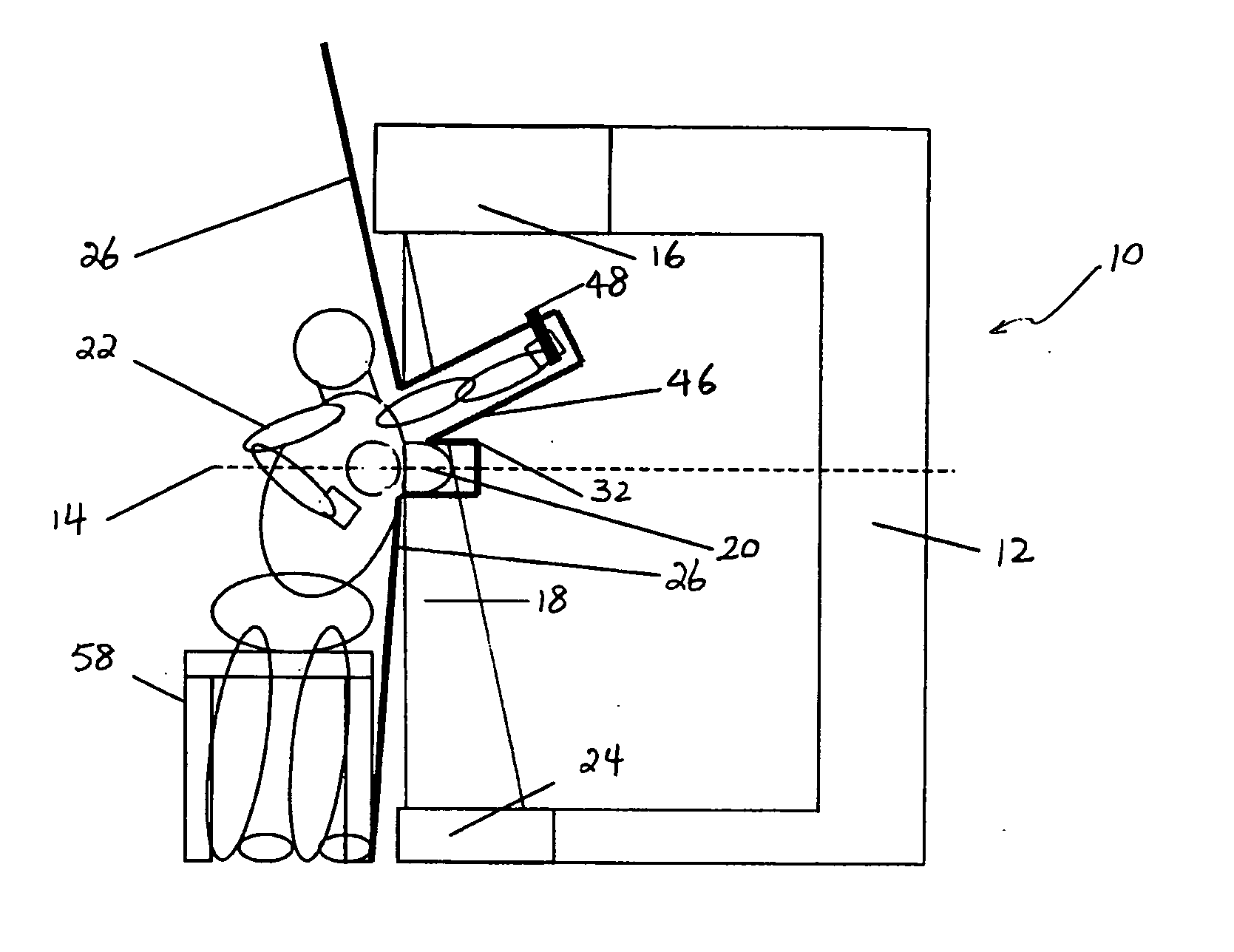
System and method for imaging and treatment of tumorous tissue in breasts using computed tomography and radiotherapy
InactiveUS20060262898A1Preventing formation of vacuumInhibition formationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMuscle tissueTumour tissue
The present invention provides a system 10 for irradiating a breast 20 of a patient 22. The system 10 comprises a gantry 12 rotatable about a horizontal axis 14 and comprising a radiation source 16 for generating a radiation beam 18 and a detector 24 spaced from the radiation source 16, and a barrier 26 disposed between the patient 22 and the gantry 12. The barrier 26 is provided with an opening 30 adapted to allow a breast 20 passing therethrough to be exposed to the radiation beam 18. In some embodiments, the barrier 26 is provided with an opening 30 adapted to allow both the breast 20 and the tissue leading from the breast to axilla and the muscle tissue of the adjacent chest wall passing therethrough to be exposed to the radiation beam 18.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Multi-beam antenna with shared dielectric lens
An integrated multi-beam antenna with a shared dielectric lens is disclosed. The antenna is formed by positioning the feed apertures of a plurality of waveguide feeds at positions located on the surface of the shared dielectric lens. The angular direction and shape of radiation beams produced by the waveguide feeds are determined by the physical and dielectric characteristics of the lens, the location of feed apertures of the waveguide feeds on the surface of the lens, and the frequency of electromagnetic energy propagating in the waveguide feeds. The principles of the invention are applied to realize an inexpensive, integrated multi-feed antenna adapted to provide desired angular areas of coverage for both a long range and short range radar in an automotive radar safety system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Reflector arrangement for attachment to a wireless communications terminal
ActiveUS9270013B2Low production costImproving Impedance MatchingAntenna supports/mountingsLight beamComputer terminal
A reflector arrangement is configured for attachment to a wireless communications terminal having a patch antenna. The patch antenna includes a patch radiator in a substantially parallel relationship with a ground plane, and the patch antenna produces a radiation beam of a predetermined beamwidth. The reflector arrangement is configured, when attached to the terminal, to produce a radiation beam of reduced beamwidth relative to the predetermined beamwidth. The reflector arrangement comprises a main reflector and a sub-reflector for reflecting radiation towards the main reflector, and the reflector arrangement is configured such that, when attached to the terminal, the patch antenna acts as a feed antenna for the sub-reflector. The sub-reflector is arranged to collect the radiation from the patch antenna and to reflect the beam towards the main reflector such that the main reflector produces the radiated beam of reduced beamwidth.
Owner:CAMBIUM NETWORKS
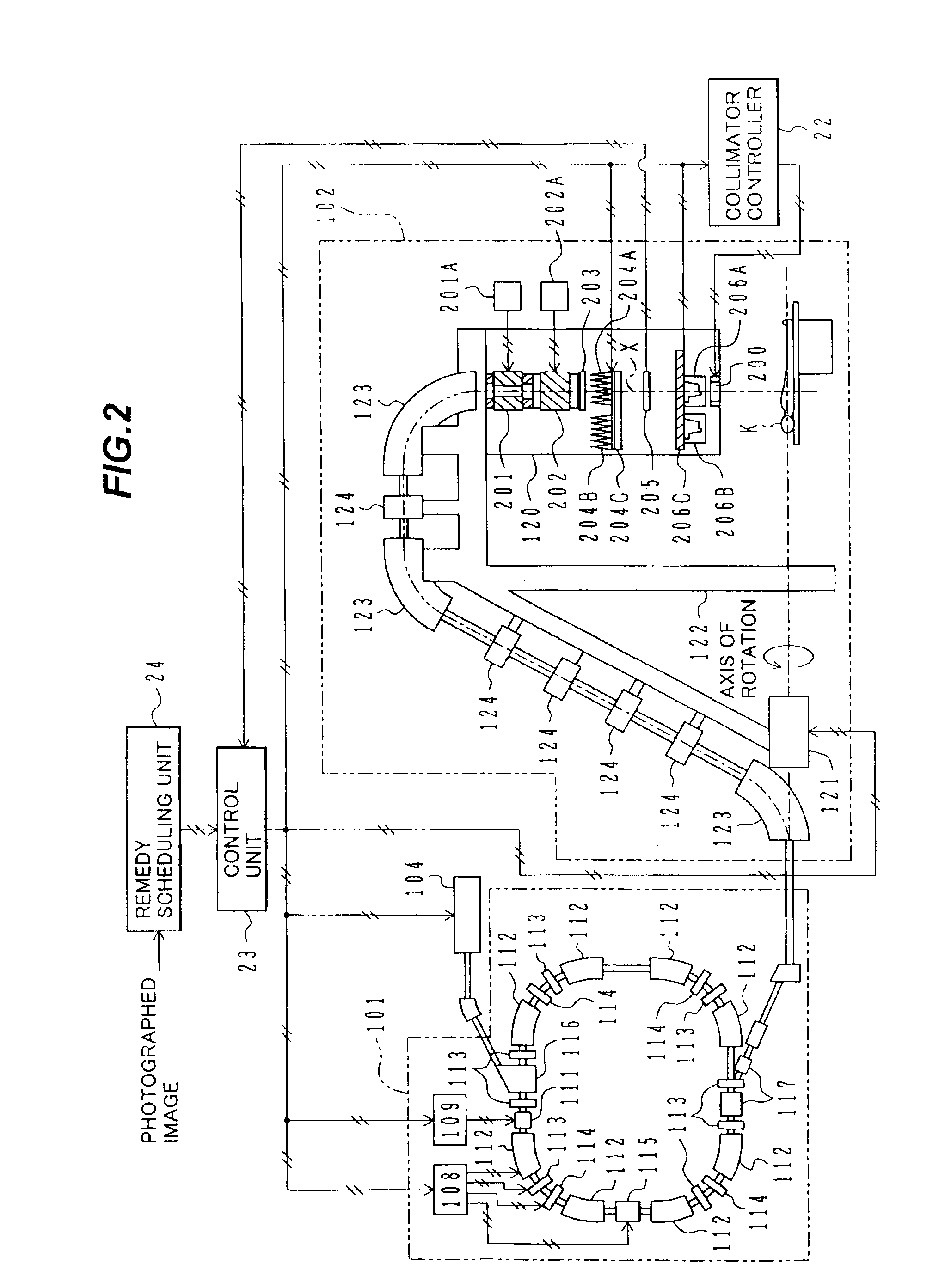
Multi-leaf collimator and medical system including accelerator
InactiveUS6931100B2Reduce physical and mental burdenShorten positioning timeHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorEngineering
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Radio communication system
InactiveUS20060079290A1Reduce in quantityReduces constitutionTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringCarrier signalEngineering
There is disclosed a radio communication system in which a constitution of a base station and further a control station can be simplified. A radio communication system according to the present invention converts a received signal received by a plurality of antenna elements in a base station to a signal of different frequency band, and then conflates the converted signal in order to generate sub-carrier wavemultiplex signal. The signal is converted to an optical signal, and then the optical signal is transmitted to a control station via an optical fiber. Or the control station performs weighting to phase of the transmitted signal transmitted from a plurality of antennas of a base station, and then performs frequency conversion to different frequency band, and then conflates the converted signal in order to generate the sub-carrier wave multiplex signal. The signal is converted to an optical signal, and then an optical signal is transmitted to the base station side via the optical fiber. The control station and the base station divides the received sub-carrier wave multiplex signal by each frequency band, and then the frequency of the divided signals are converted to the same frequency band in order to generate the transmitted / received signal of each antenna element. By such a constitution, it is possible to reduce constituent of the optical transmission components to the minimum and to simplify the constitution of the base station. Furthermore, it is possible to maintain the relative phase difference and the relative intensity of the transmitted / received signal of each antenna element. Because of this, it is possible to estimate an arrival direction of the received signal and to control radiation beam pattern of the transmitted signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
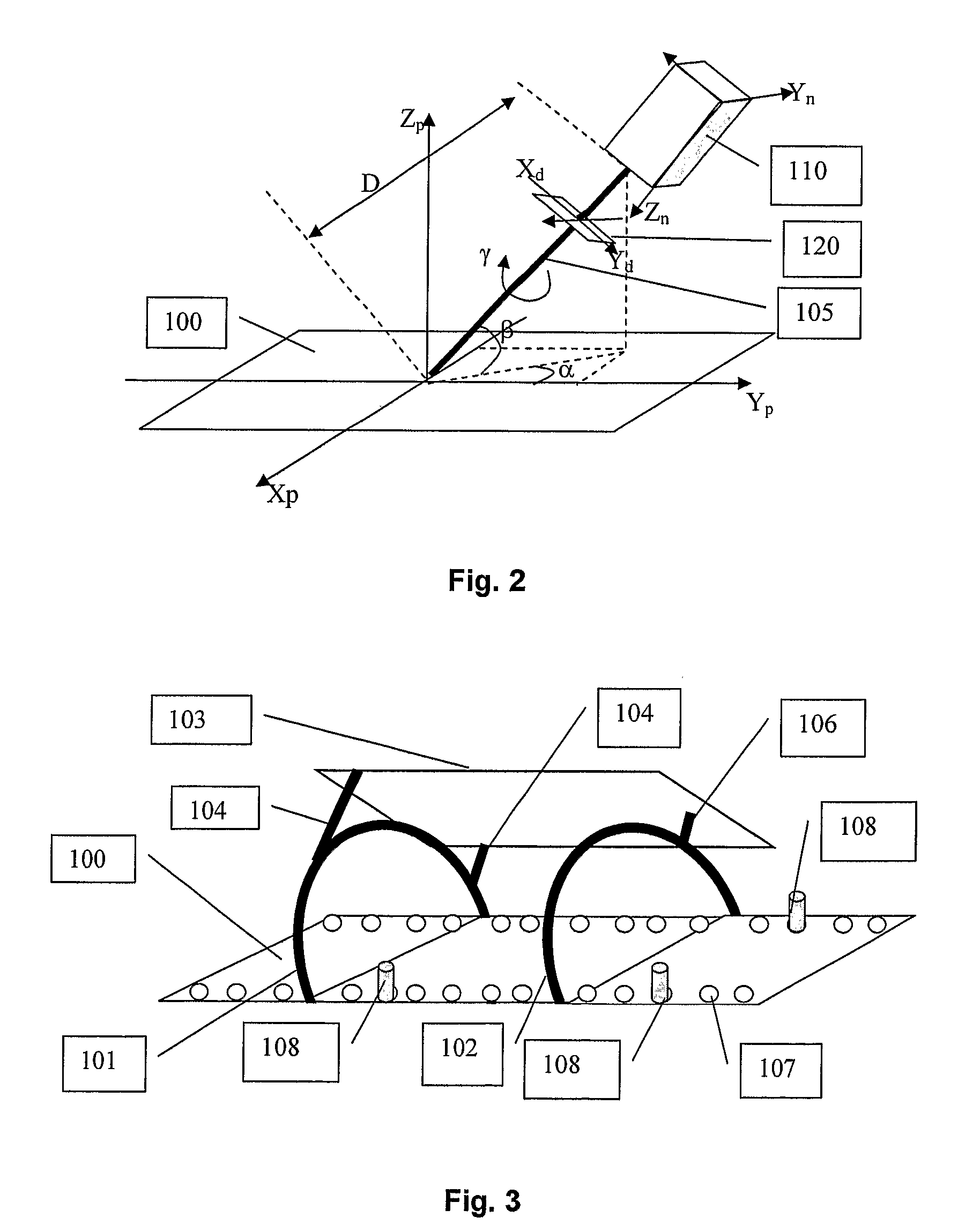
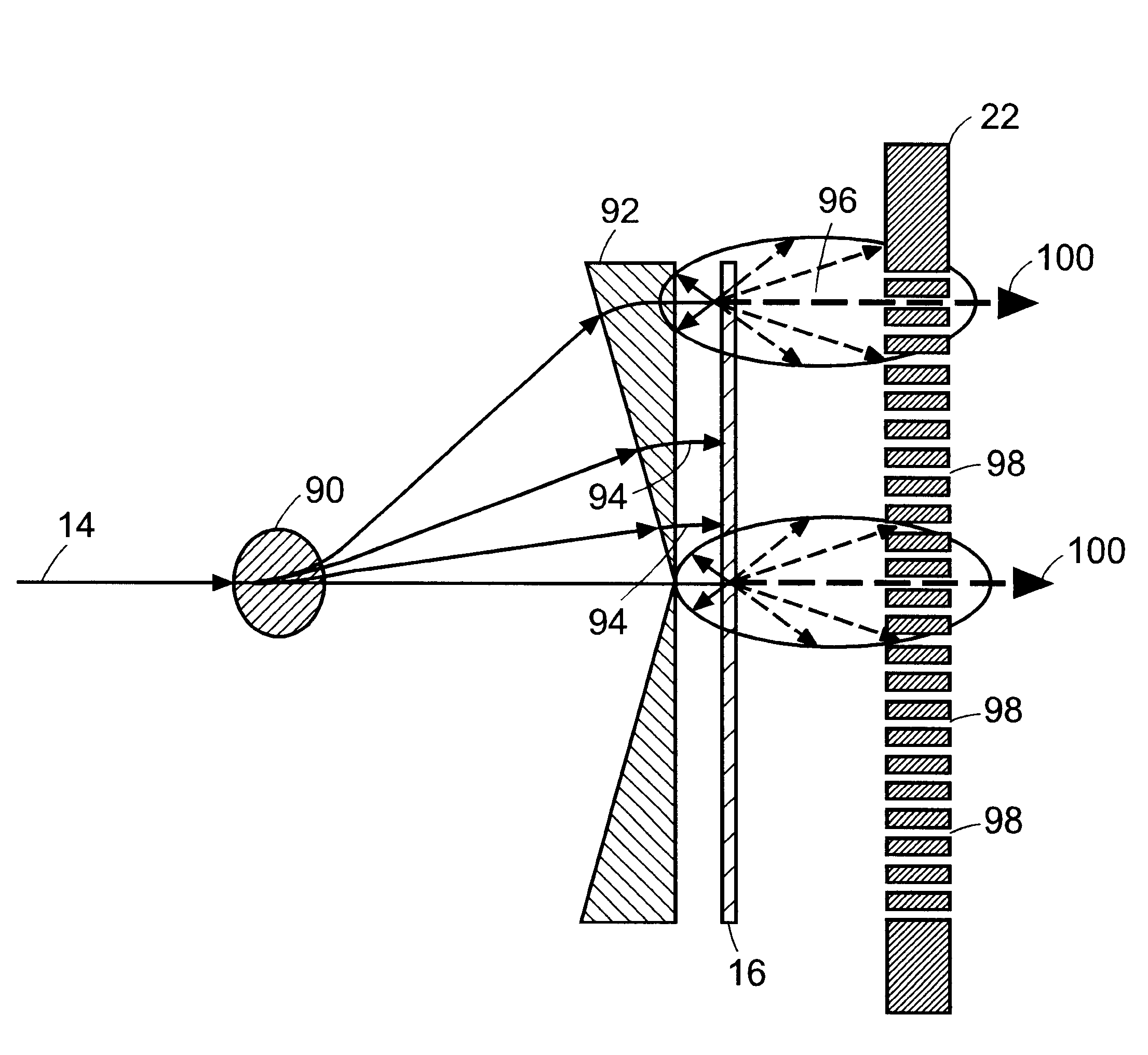
Device and method for positioning a target volume in radiation therapy apparatus
InactiveUS7860216B2Pointing accuratelyThermometers using material expansion/contactionRadiation beam directing meansRadiation beamRT - Radiotherapy
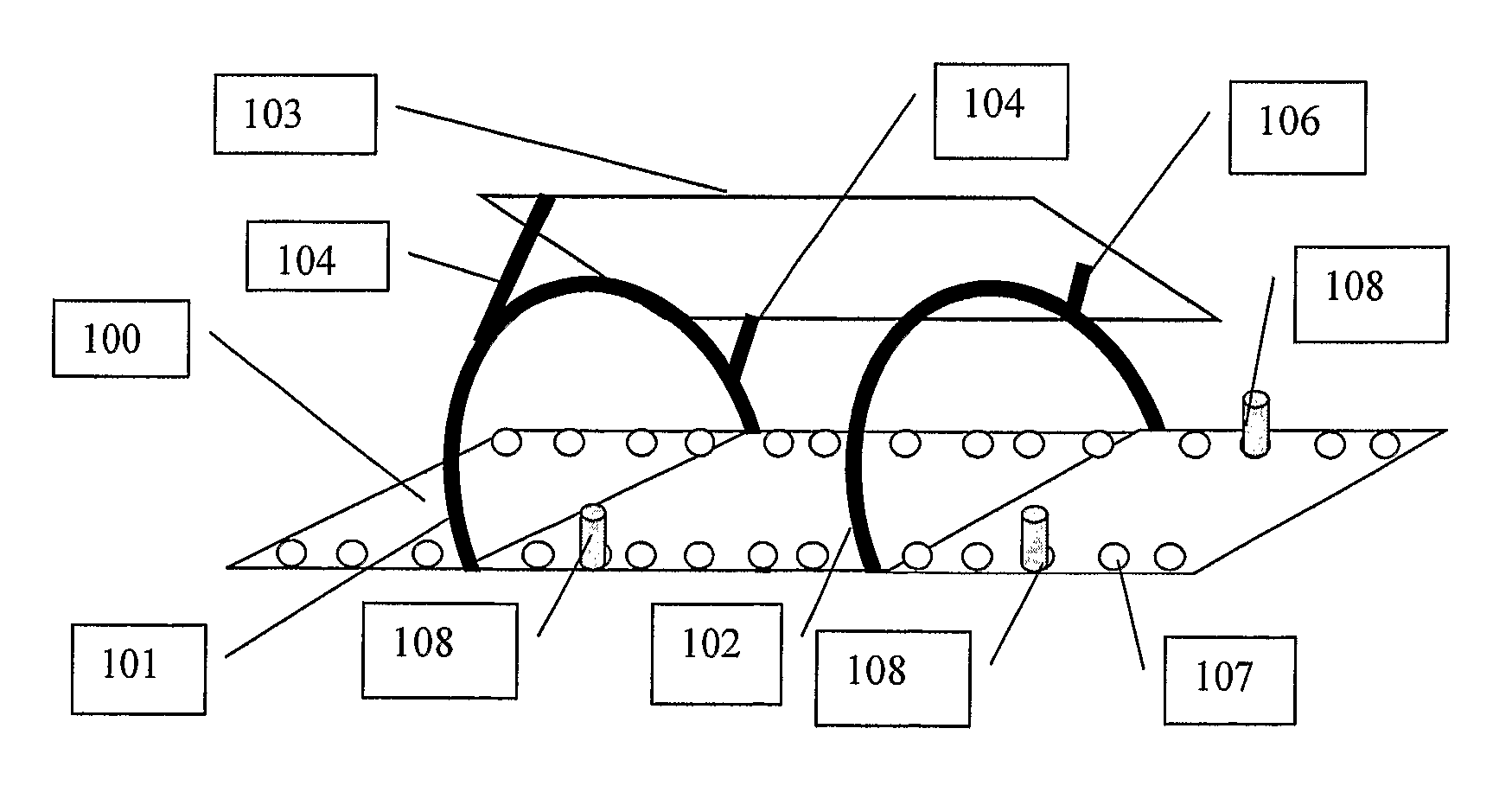
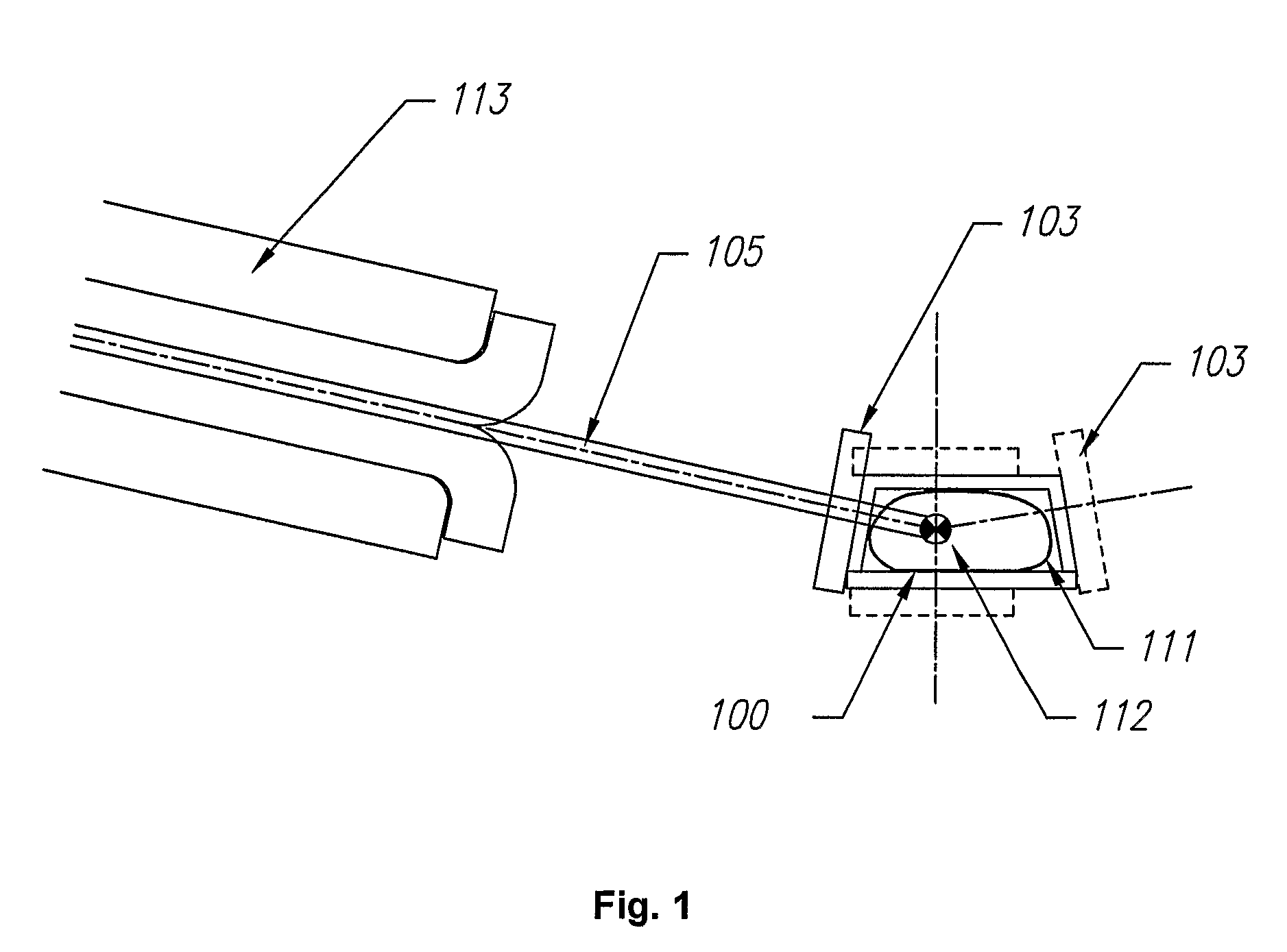
Device for positioning a target volume (112) such, as a phantom or a patient in a radiation therapy apparatus, said apparatus directing a radiation beam (405) towards said target (112), characterized in that it comprises:—a target support (100) whereon the target is immobilized; a two dimensional radiation detector (103) fixed with fixations means (101, 102, 104, 106 107; 301, 302, 304, 305, 306; 208, 209) in a known geometric relationship to said target support (100), said radiation detector (103) being capable of detecting the position of intersection of said radiation beam (105) with said detector (103); correcting means for correcting the relative position of said beam (105) and said target support 100), based on said detected intersection position.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
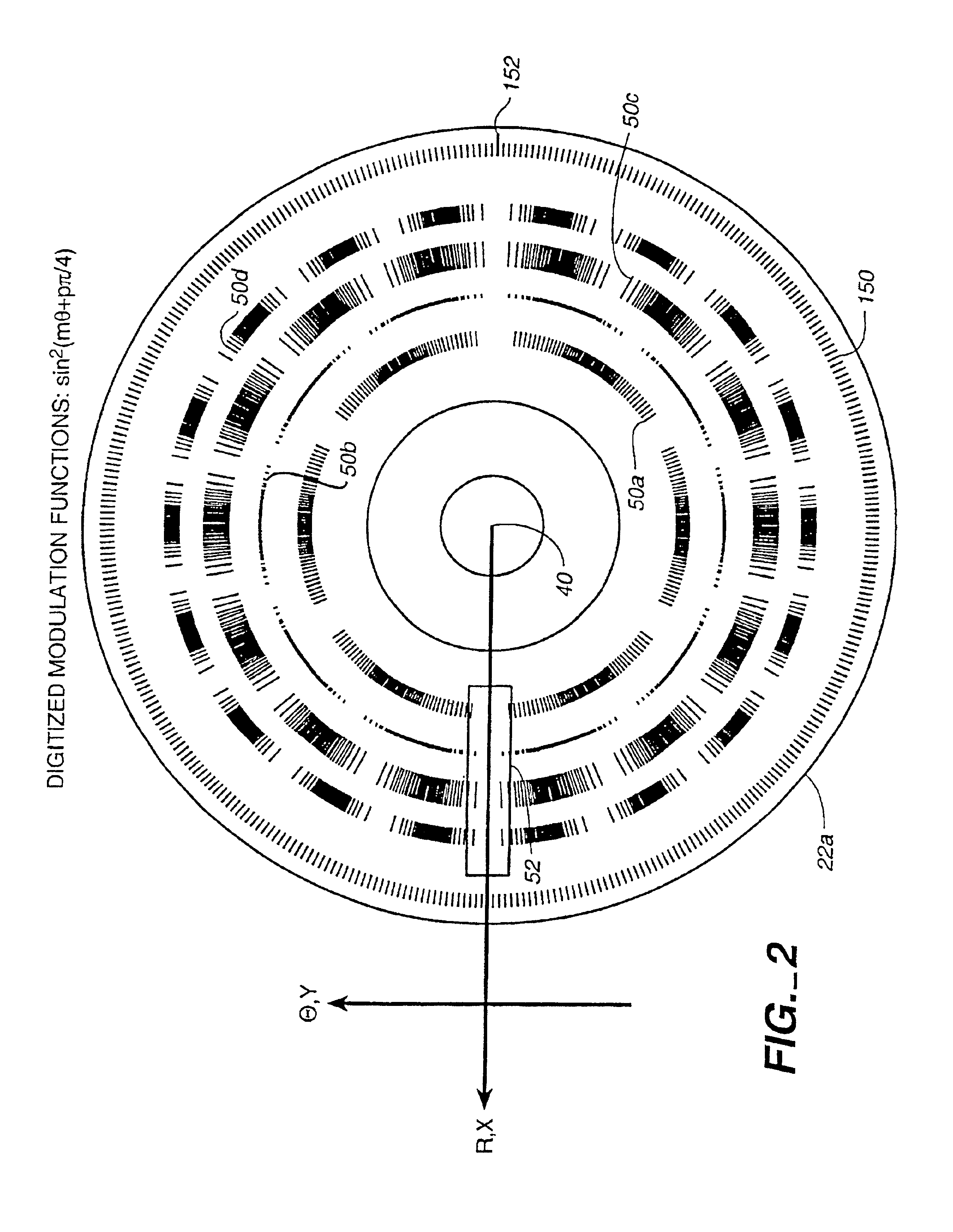
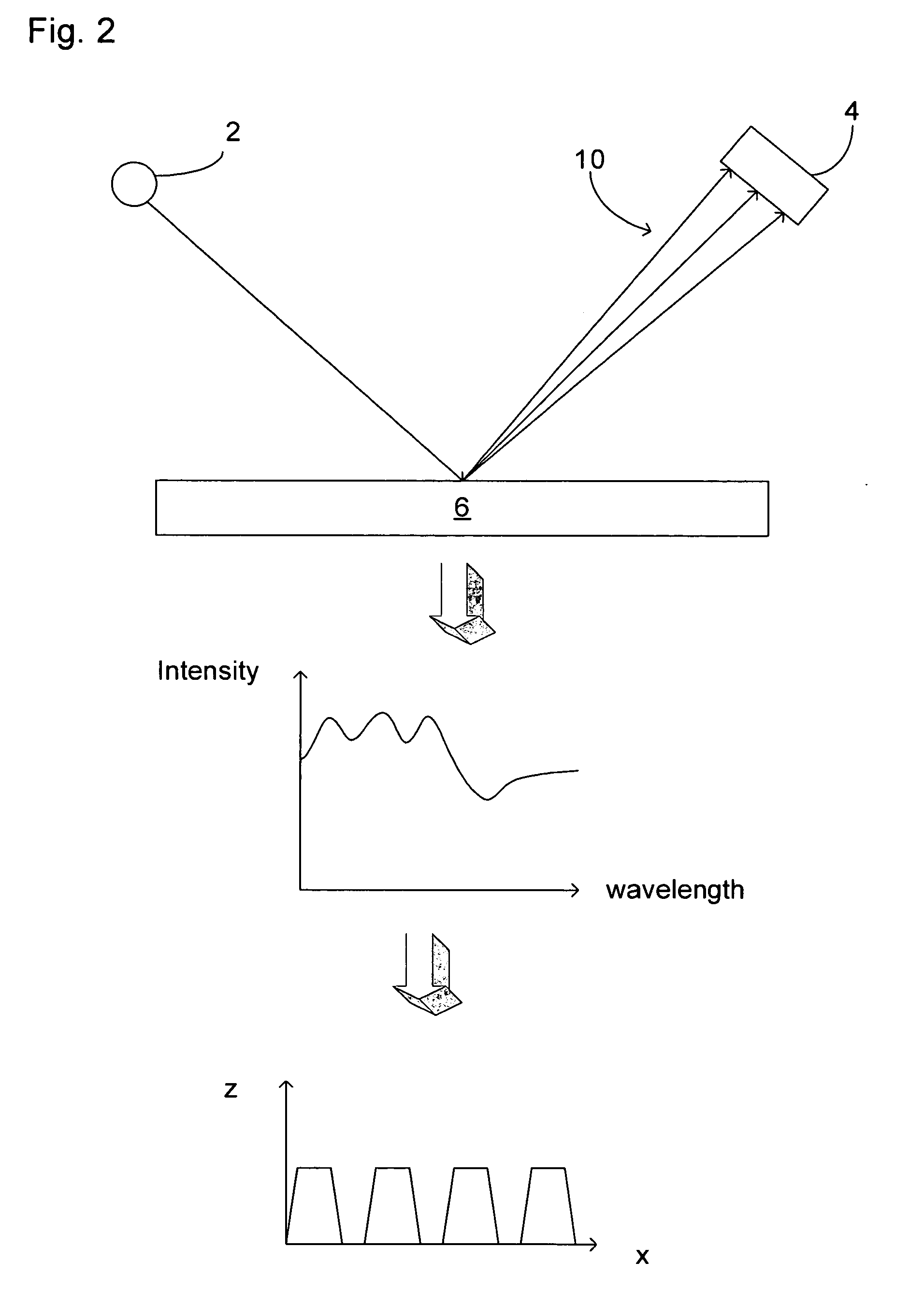
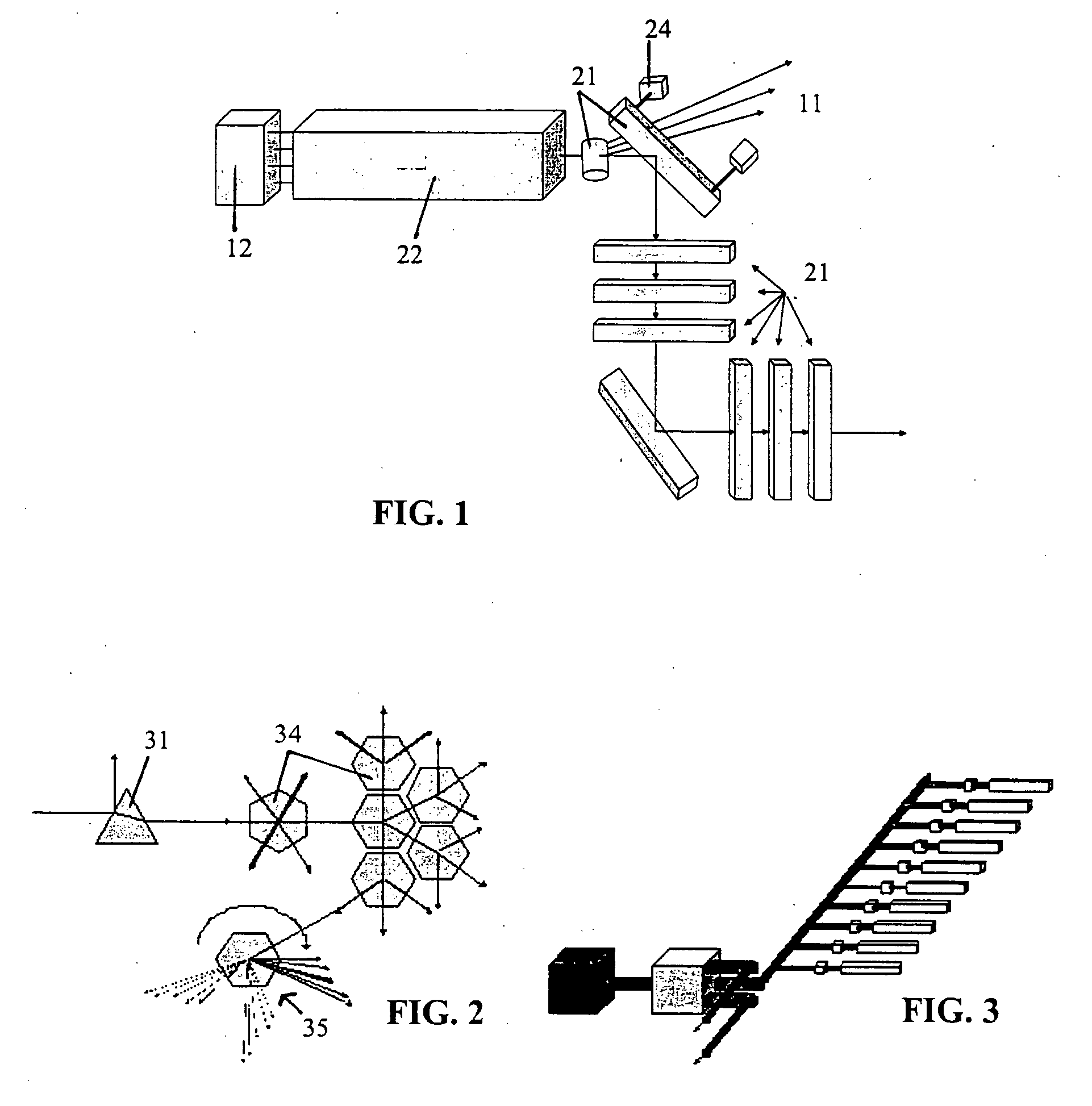
Method and apparatus for spectrum analysis and encoder
InactiveUS6897952B1Increase motor speedReduce motor speedRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsModulation functionFrequency spectrum
A disc serving as a spatial radiation modulator has dispersed radiation filters thereon. Each filter has a transmittance or reflectance modulation function of the form sin2(mθ+pπ / 4), where m is a positive integer and p has one of the four values 0, 1, 2, 3. A radiation beam including selected wavelength components is diffracted into an elongated image dispersed according to wavelength. Different wavelength components are focused onto different filters on the modulator and are encoded by corresponding filters. Since the modulation functions of the filters are orthogonal to one another, it is possible to extract the amplitude of each wavelength component after it has been encoded or modulated by corresponding filter from the total detected signal during one measurement.
Owner:MUDLOGGING SYST
Method and apparatus for generating sequential beams of penetrating radiation
InactiveUS6421420B1Radiation/particle handlingCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingLight beamElectromagnetic radiation
An apparatus and method for generating electronically steerable beams of sequential penetrating radiation. Charged particles from a source are formed into a beam and accelerated to a target. Electromagnetic radiation generated by the target is emitted with an angular distribution which is a function of the target thickness and the energy of the particles. A beam of particles is produced by allowing the radiation to exit from an apparatus through a collimator proximal to the target. The direction of the beam is determined by the point of radiation production and the corresponding array of transmission regions of the collimator.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy with a multilayer multileaf collimator
InactiveUS20050058245A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySpatial OrientationsControl system
An intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) system including a radiation beam delivery device positionable in a plurality of spatial orientations, an IMRT control system adapted to modulate at least an intensity of a radiation beam emanating from the radiation beam delivery device depending on at least one of the spatial orientations of the radiation beam delivery device and in accordance with an IMRT intensity map, and a multilayer multileaf collimator placed in a path of the radiation beam emanating from the radiation beam delivery device, the multilayer multileaf collimator including a plurality of layers of radiation blocking leaves, the layers being at different positions along the path of the radiation beam generally traverse to the radiation beam.
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
Method to track three-dimensional target motion with a dynamical multi-leaf collimator
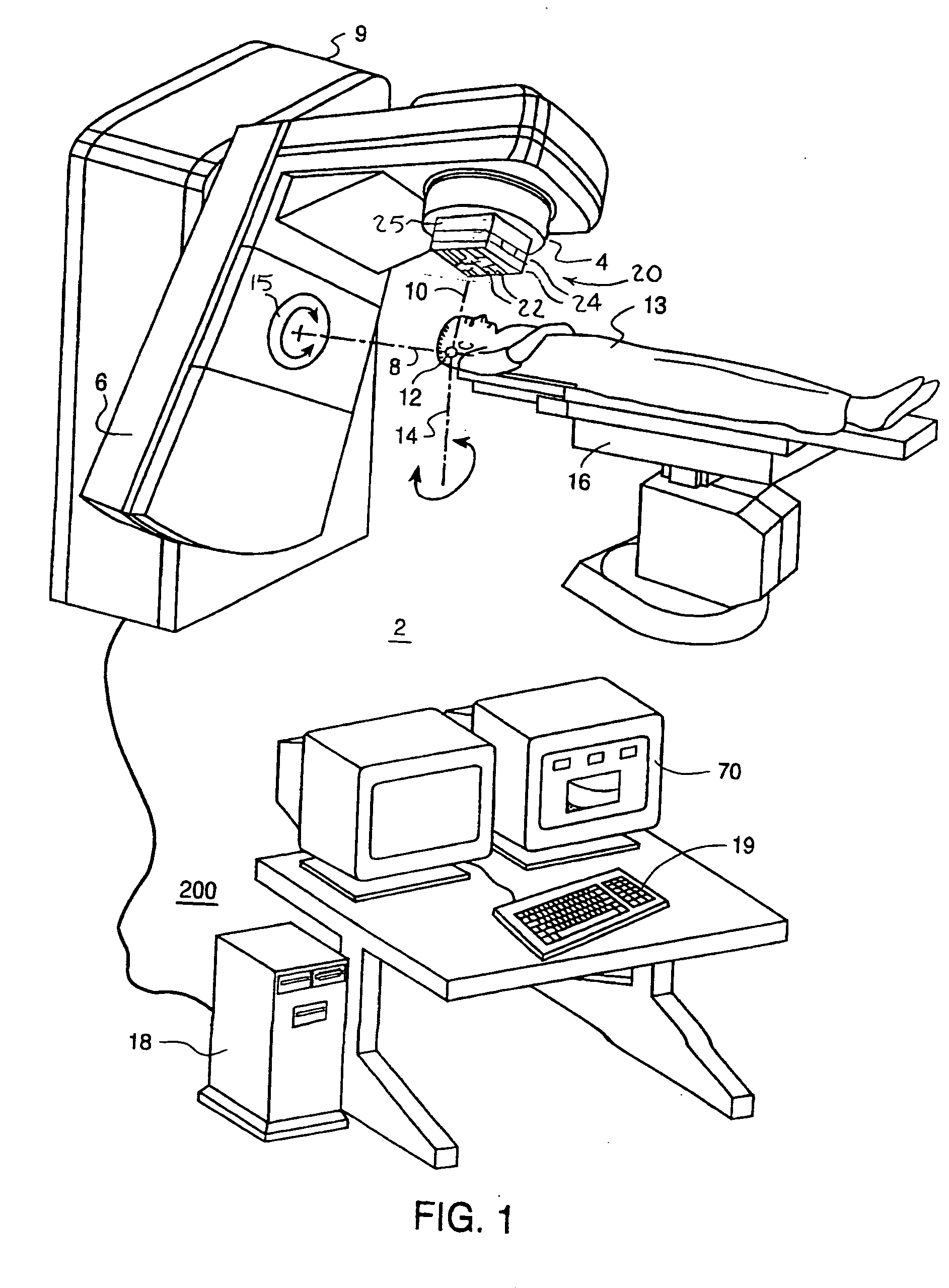
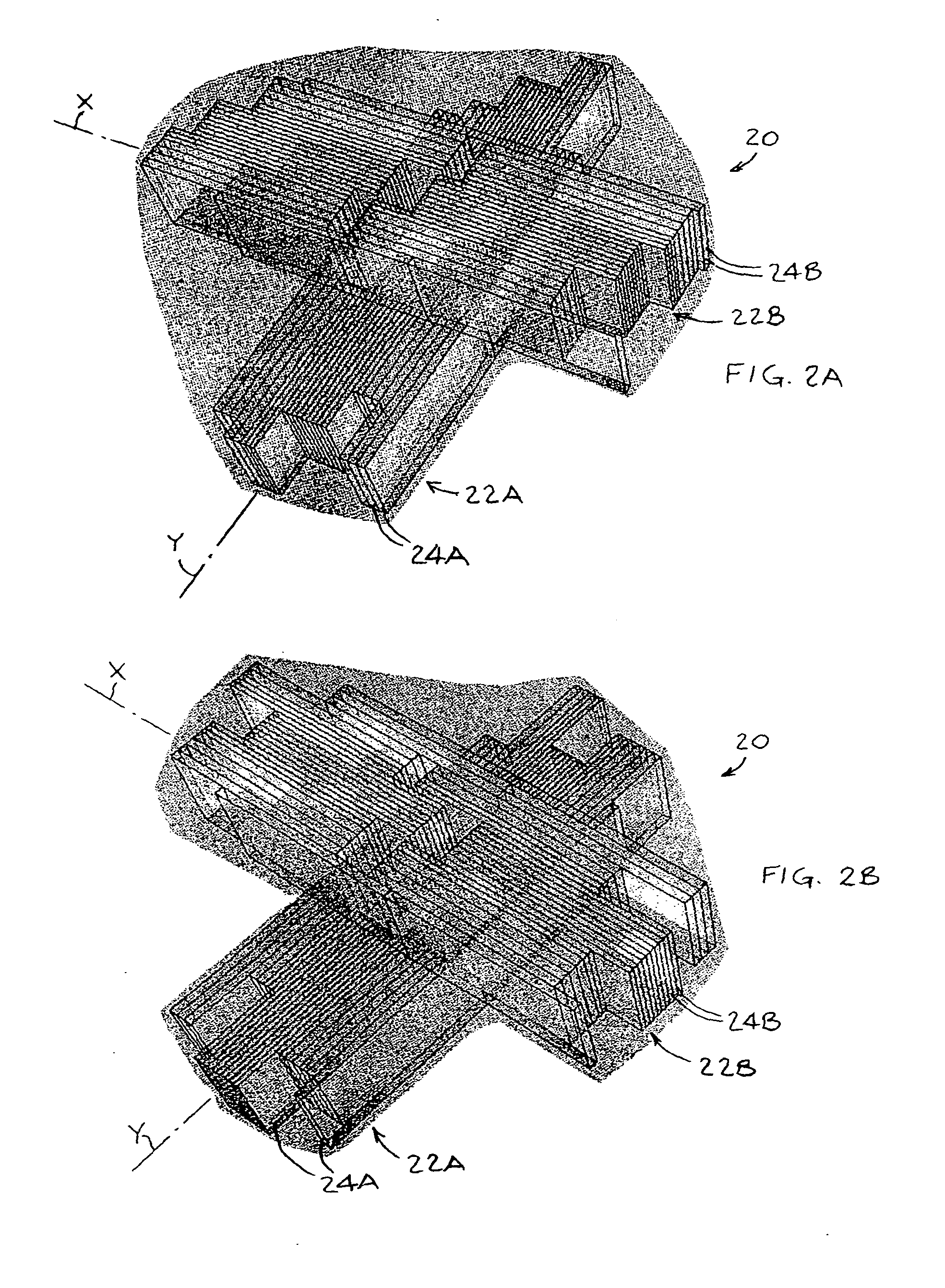
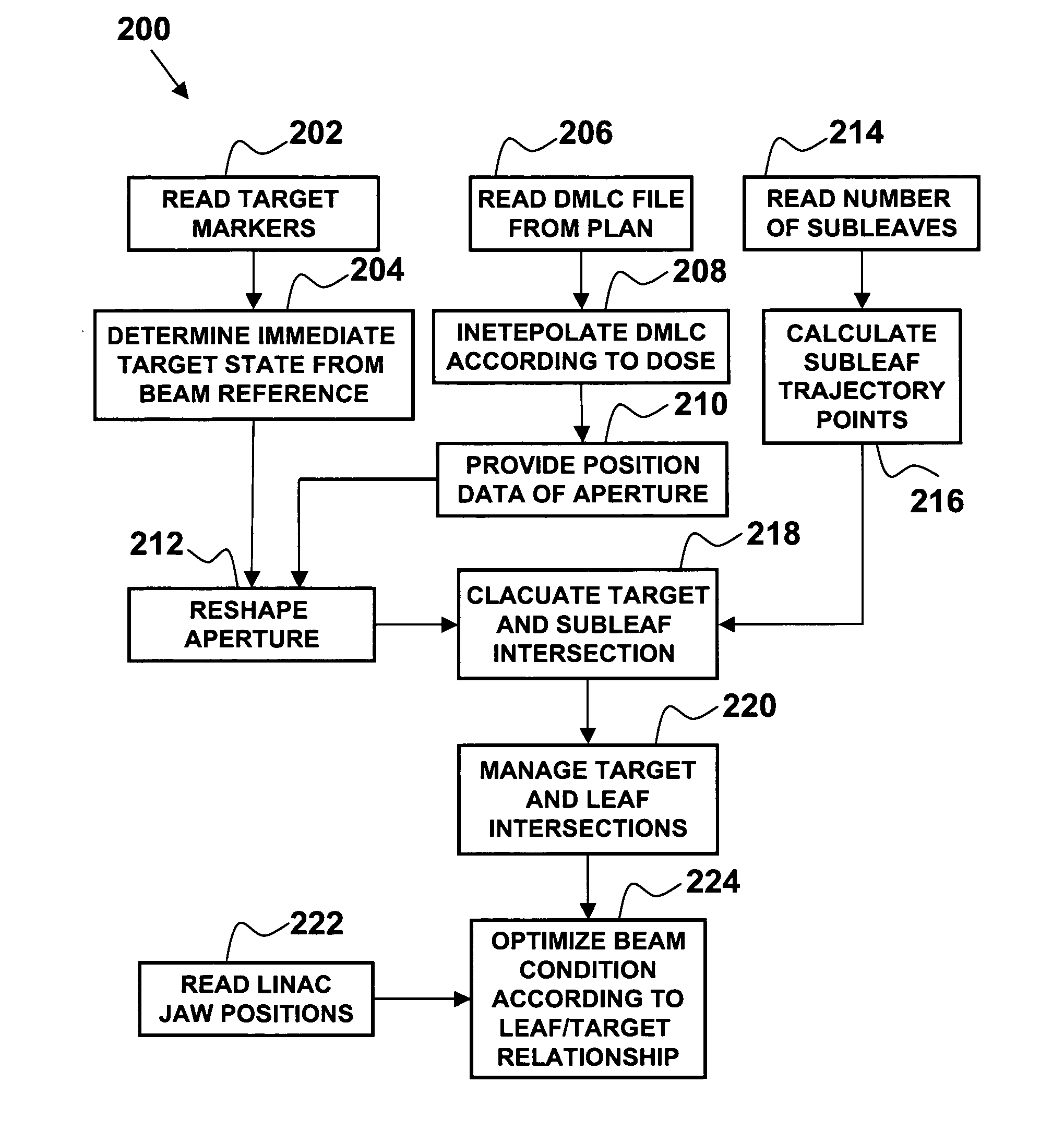
InactiveUS20080159478A1Radiation beam directing meansX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPrediction algorithmsMulti leaf collimator
A method of continuous real-time monitoring and positioning of multi-leaf collimators during on and off radiation exposure conditions of radiation therapy to account for target motion relative to a radiation beam is provided. A prediction algorithm estimates future positions of a target relative to the radiation source. Target geometry and orientation are determined relative to the radiation source. Target, treatment plan, and leaf width data, and temporal interpolations of radiation doses are sent to the controller. Coordinates having an origin at an isocenter of the isocentric plane establish initial aperture end positions of the leaves that is provided to the controller, where motors to position the MLC midpoint aperture ends according to the position and target information. Each aperture end intersects a single point of a convolution of the target and the isocenter of the isocentric plane. Radiation source hold-conditions are provided according to predetermined undesirable operational and / or treatment states.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
Systems for Efficient Staining and Sorting of Populations of Cells
ActiveUS20090176271A1Preventing initiationLow viscosityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStainingControl cell
A multi-channel apparatus for classifying particles according to one or more particle characteristics. The apparatus comprises a plurality of flow cytometry units, each of which is operable to classify particles in a mixture of particles by interrogating a stream of fluid containing the particles with a beam of electromagnetic radiation. The flow cytometry units share an integrated platform comprising at least one of the following: (1) a common supply of particles; (2) a common housing; (3) a common processor for controlling operation of the units; (4) a common processor for receiving and processing information from the units; and (5) a common fluid delivery system. The integrated platform can include a common source of electromagnetic radiation. A method of the invention comprises using a plurality of flow cytometry units sharing the integrated platform to perform a flow kilometric operation, such as analyzing or sorting particles.
Owner:INGURAN LLC
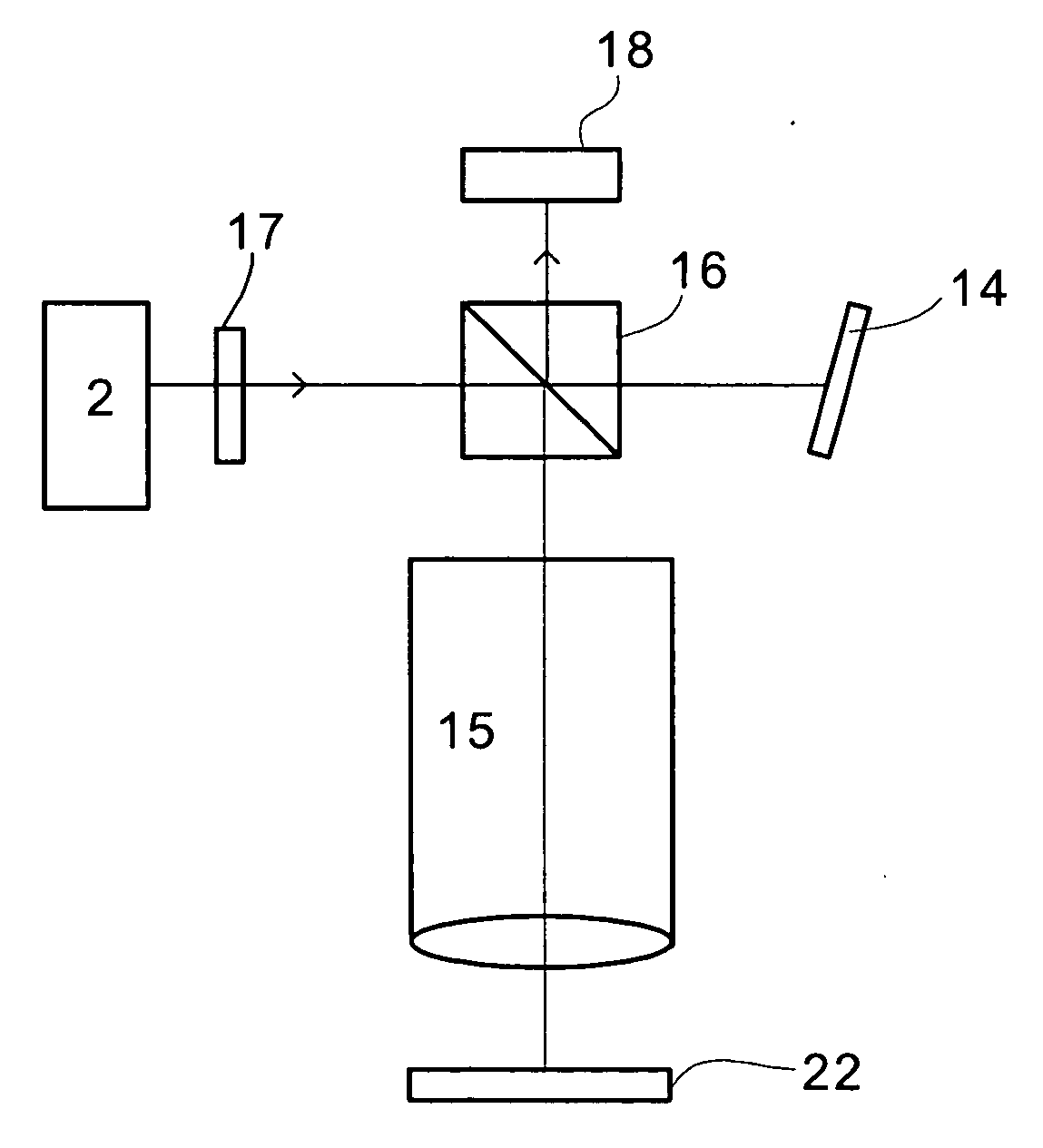
Method of characterising the transmission losses of an optical system
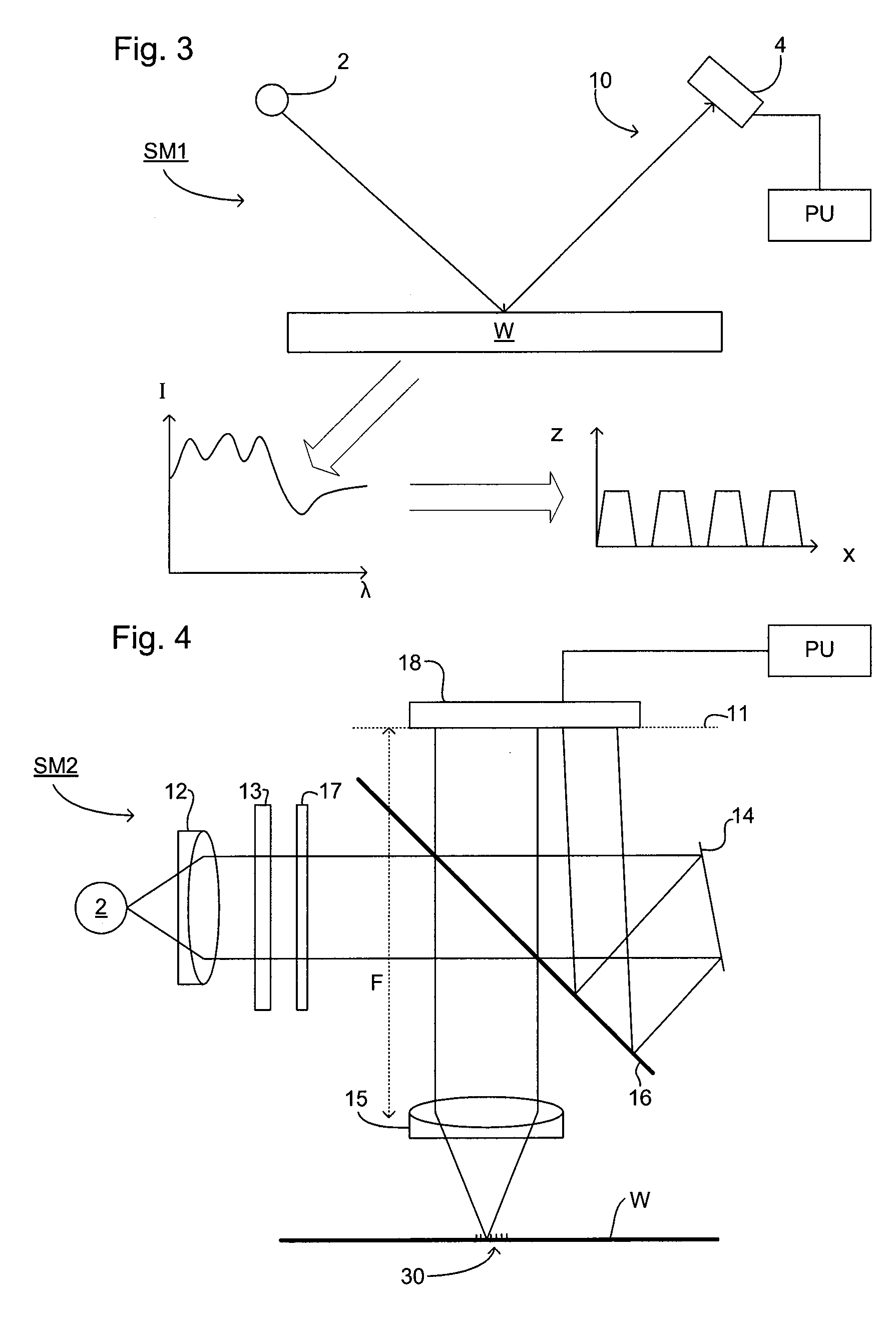
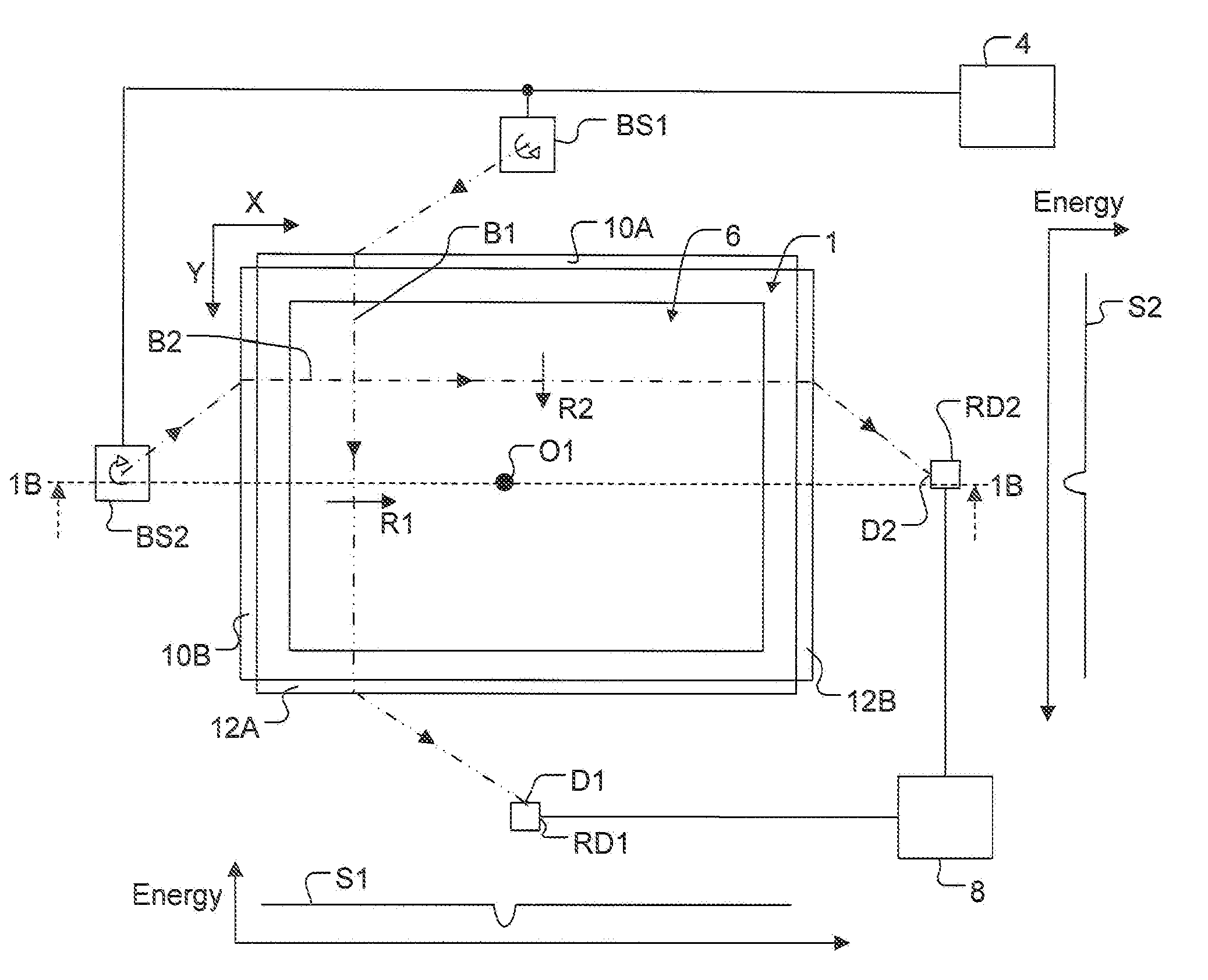
ActiveUS20070296960A1Minimize impactPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransmission lossOptic system
The illumination profile of a radiation beam is initially measured using a CCD detector. A reference mirror is then placed in the focal plane of the high aperture lens and the reflected radiation measured. By comparing the illumination profile and the detected radiation it is possible to determine the transmission losses for S and P polarisation which can then be used in scatterometry modeling.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
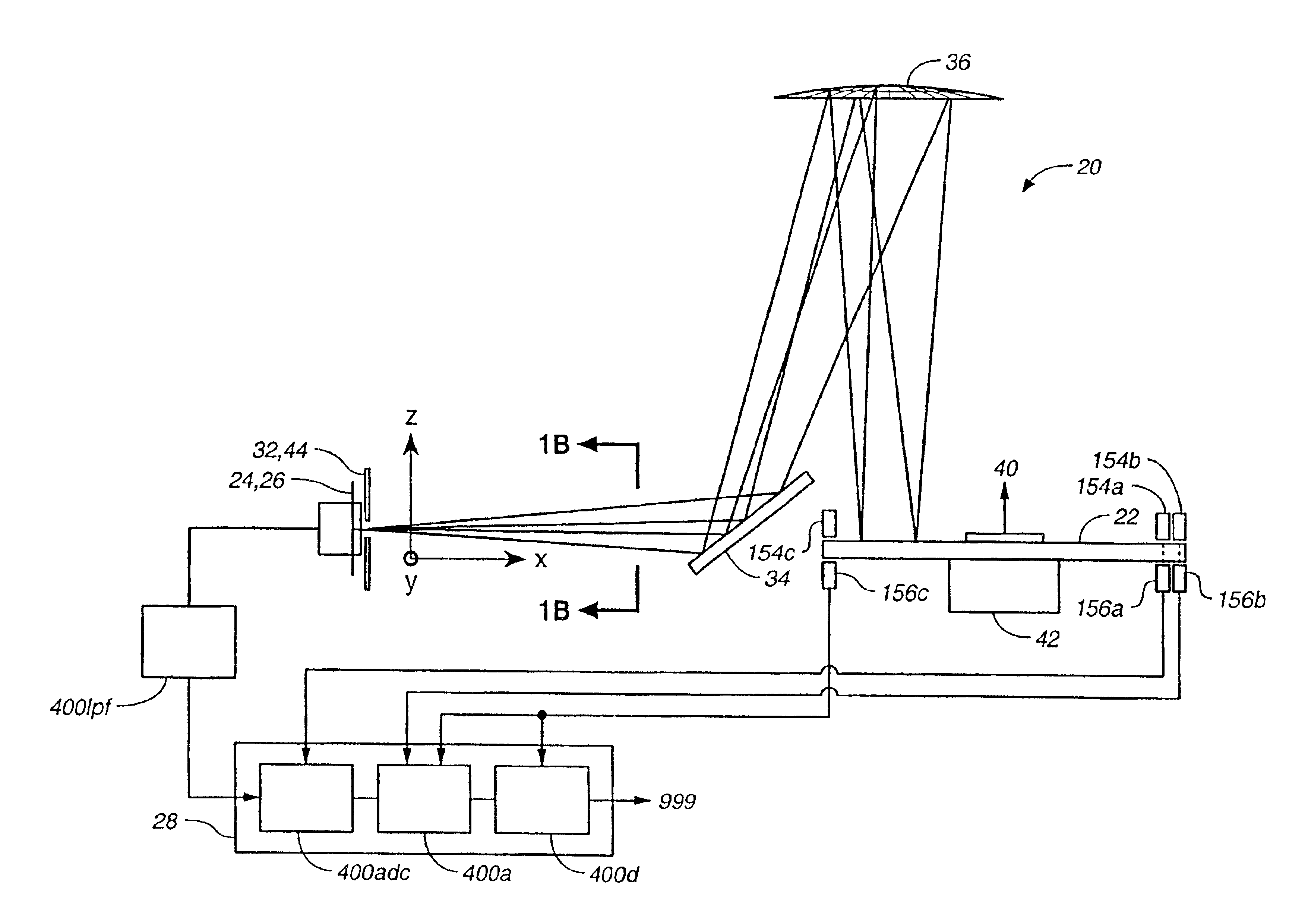
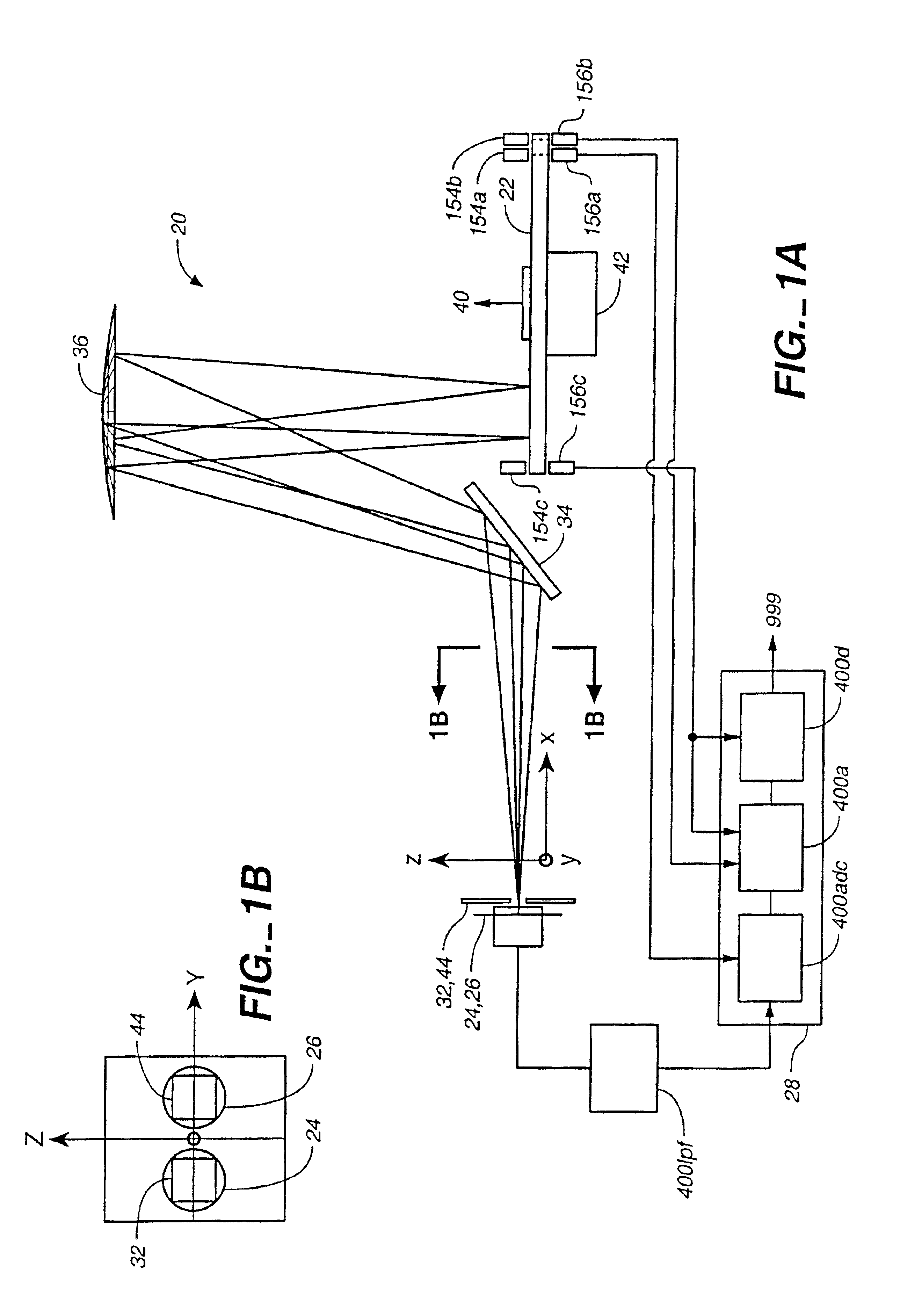
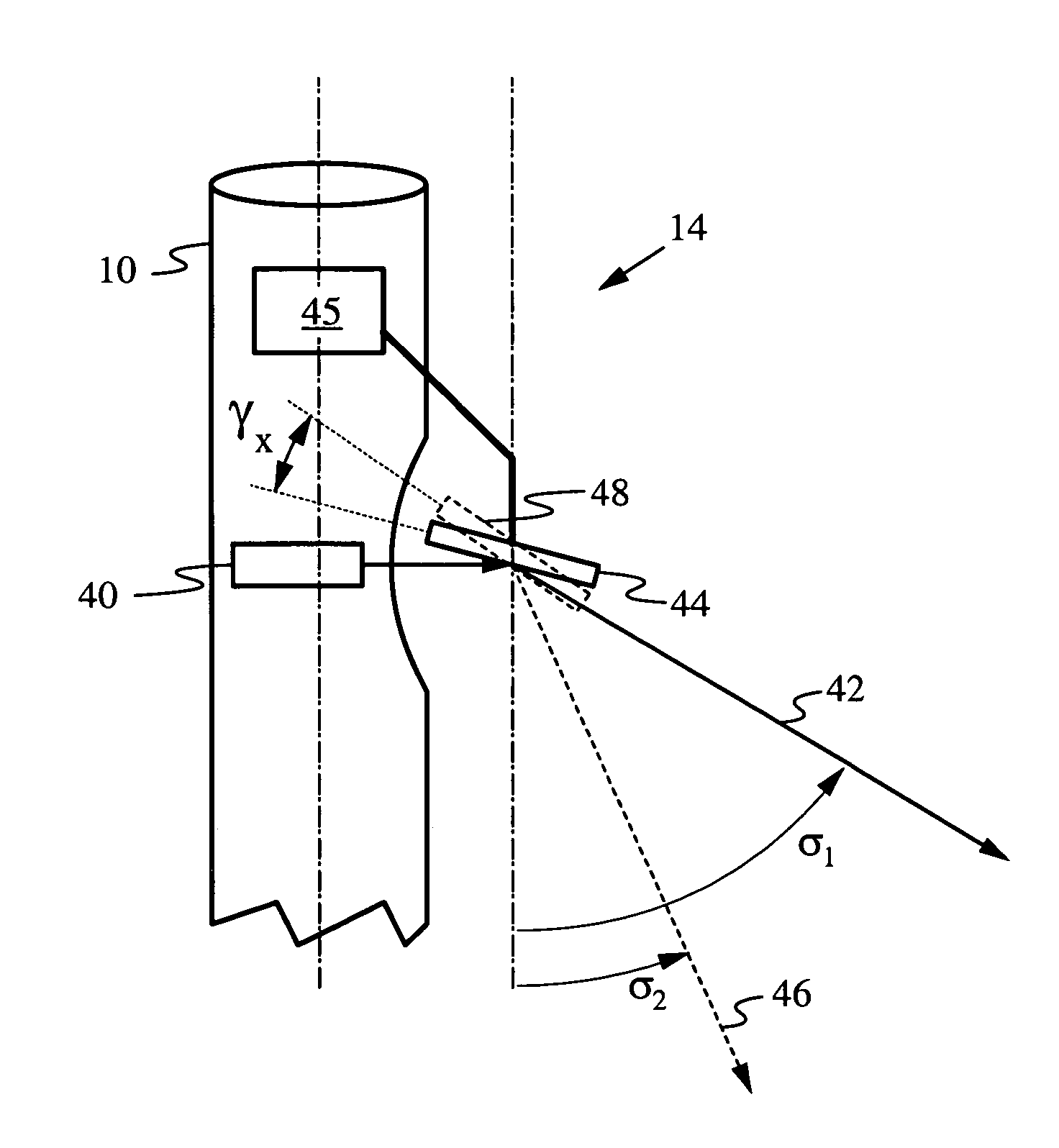
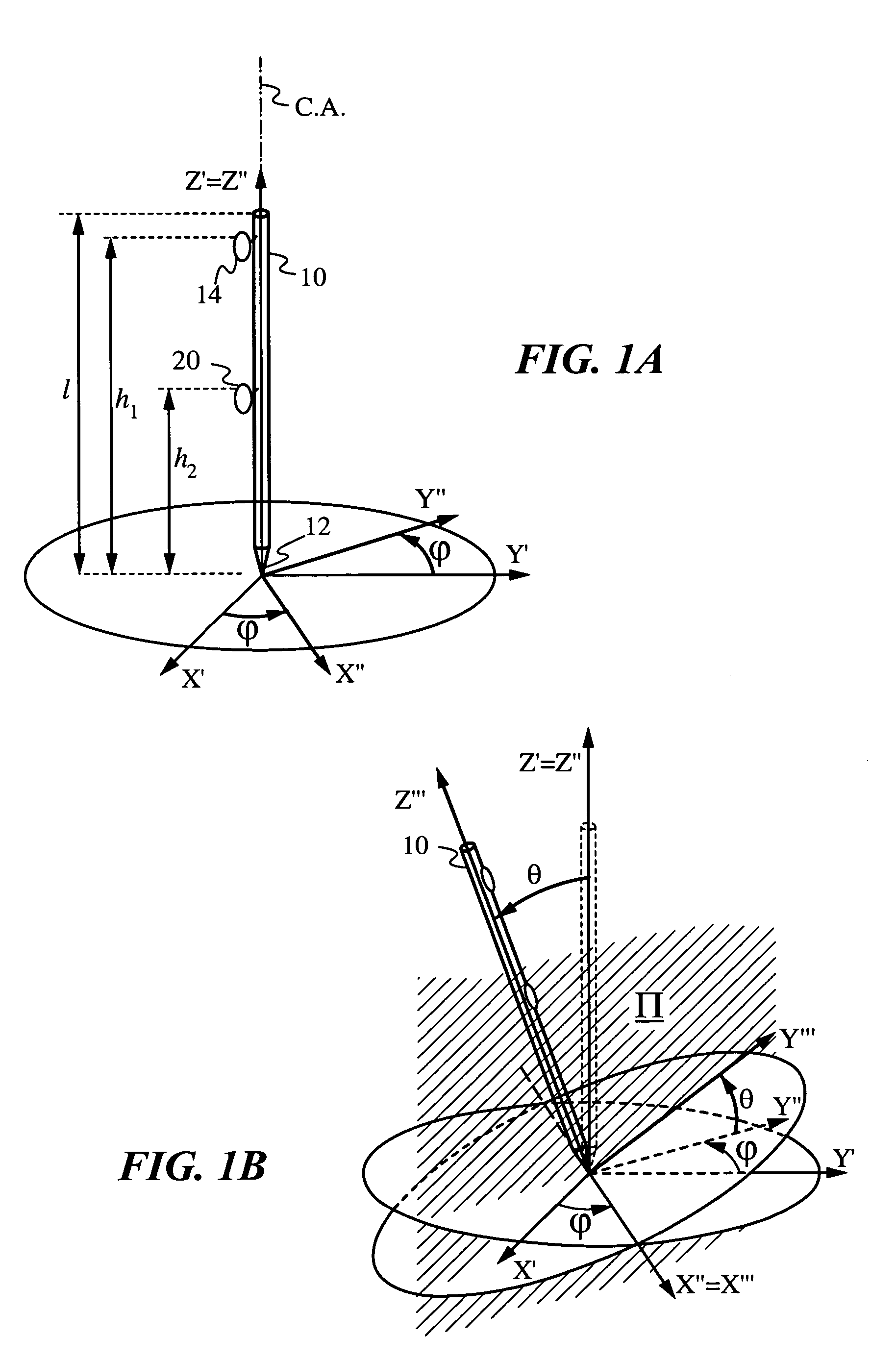
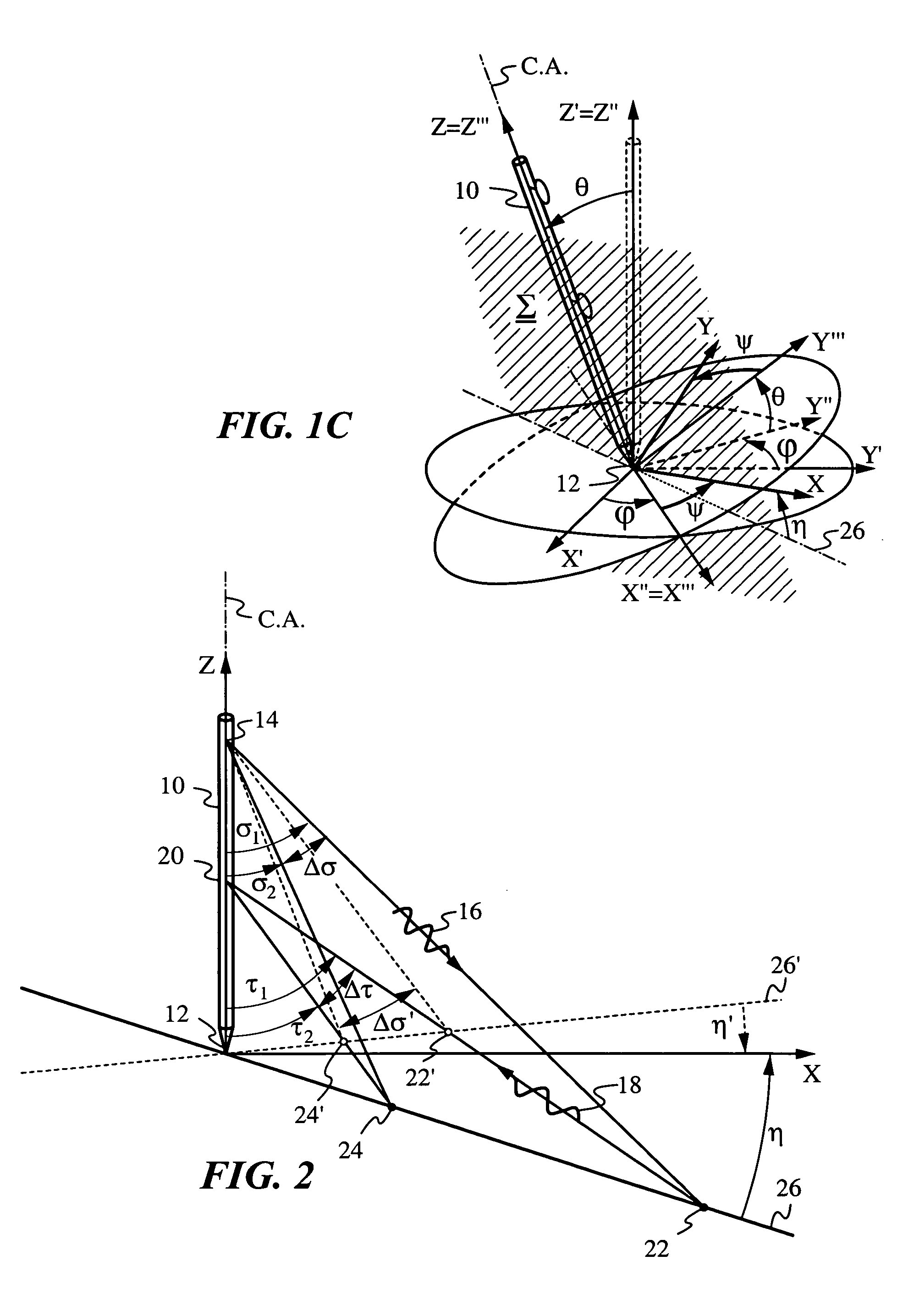
Determination of an orientation parameter of an elongate object with a scan beam apparatus
An elongate object optically determines at least one of its orientation parameters relative to a plane surface. A probe radiation beam is directed from the object at various angles σ to various locations on the plane, where the angle σ is a periodic function of time. Two angularly-selective radiation detectors oriented at fixed angles τ1 and τ2 sense scattered portions of the beam from two locations at two corresponding times. The orientation parameter is computed from a time difference Δt=t2−t1 between the two times.
Owner:ESPI
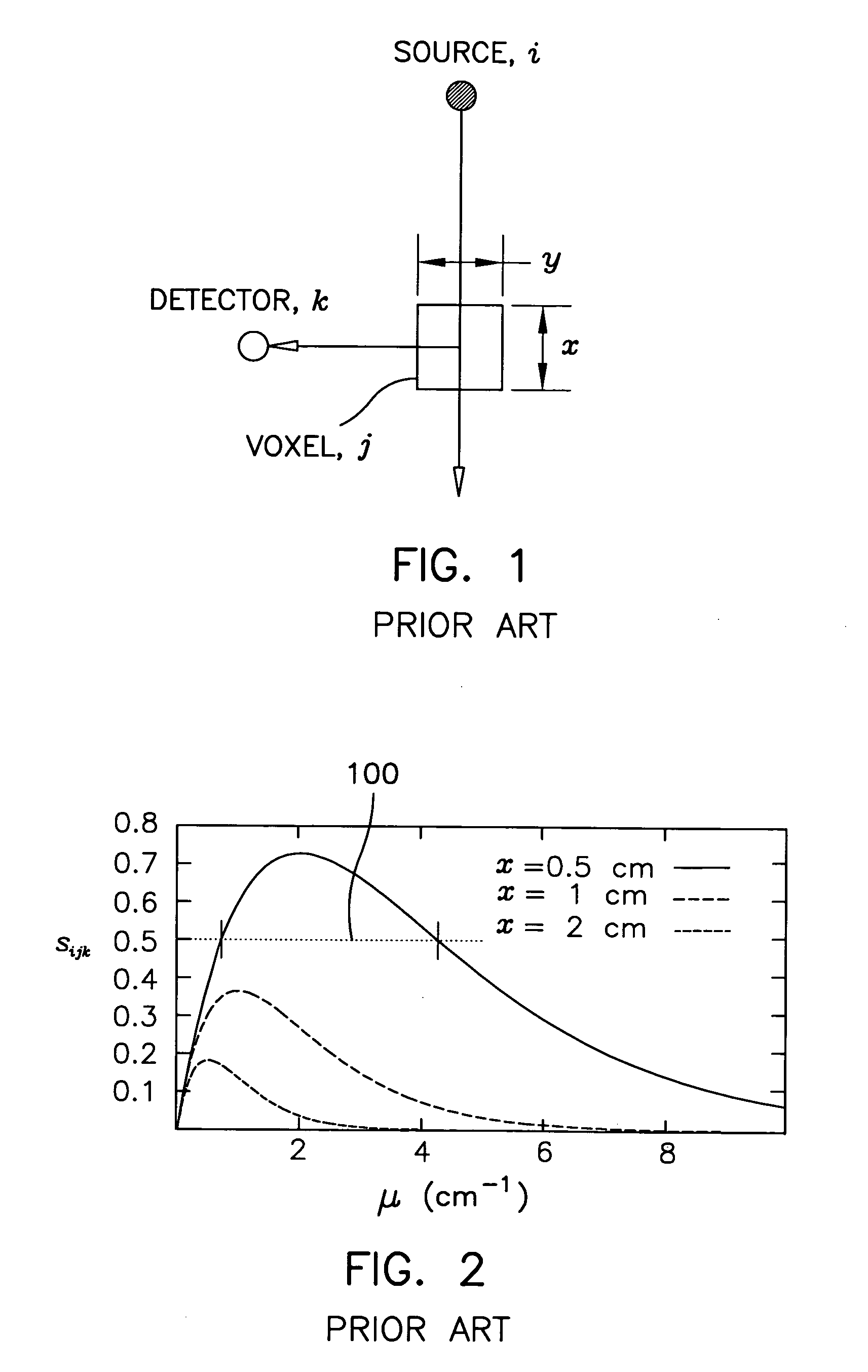
X-ray scatter image reconstruction by balancing of discrepancies between detector responses, and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS7203276B2Duplicity of solutionNon-linearity of the inverse problem andMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
Vehicle mounted inspection systems and methods
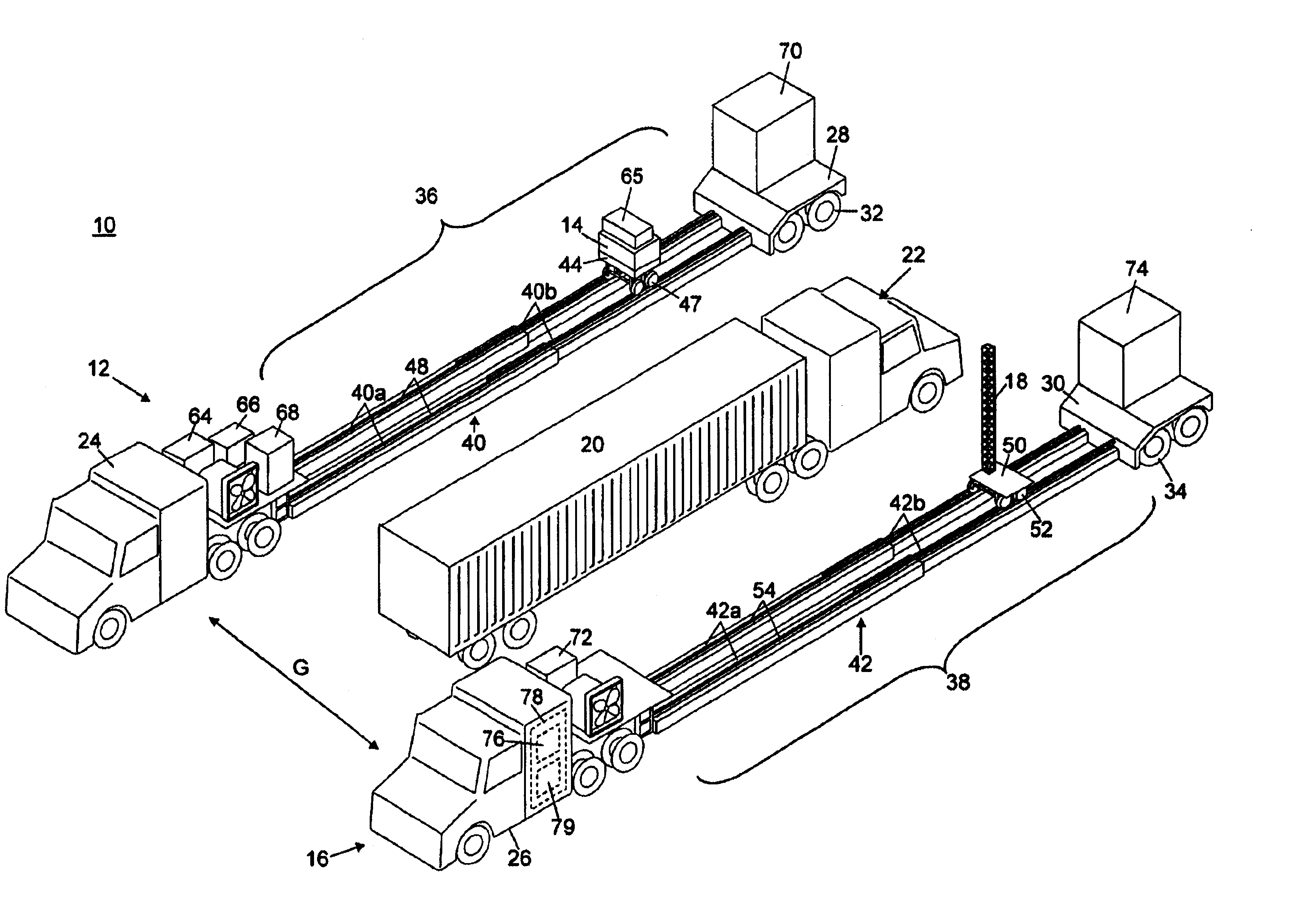
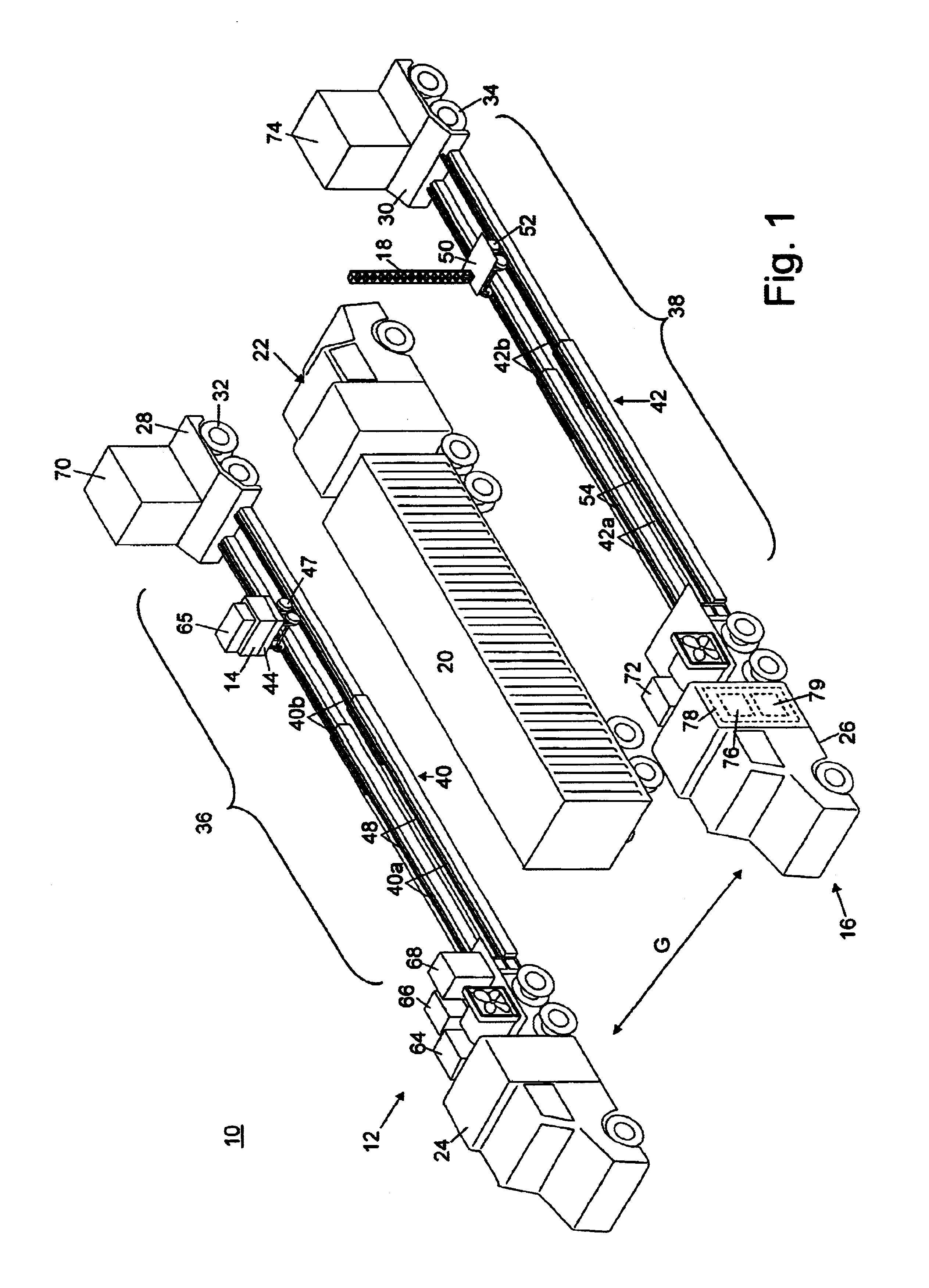
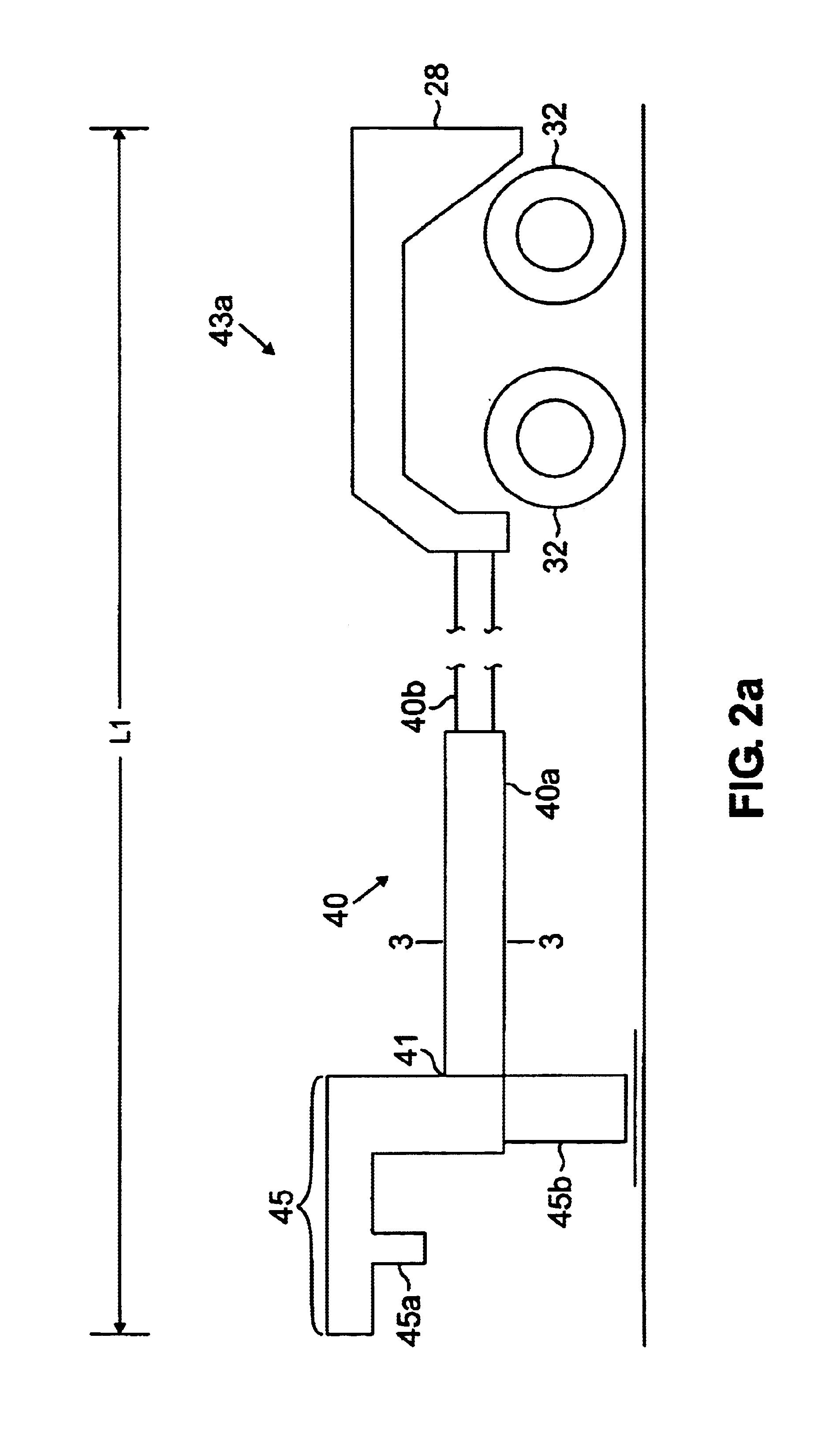
InactiveUS6937692B2Using wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayTruck
Radiation scanning systems to inspect objects are disclosed comprising a first vehicle supporting a radiation source. A second vehicle supports a detector. The source and the detector may be moved to scan an object, such as a cargo conveyance, between the vehicles. The first and second vehicles may having an expandable length and the source and detector may be moved across the expandable length, to scan long objects. The radiation source may be adapted to emit a vertically diverging beam of radiation, such as a fan beam. The radiation may be X-ray radiation, for example. The vehicle may comprise a truck and an expandable trailer releasably coupled to the truck. The trailer may comprise telescoping rails. The first and second vehicles may be driven to an inspection site, where they may be rapidly deployed. Methods of inspecting objects are disclosed, as well.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
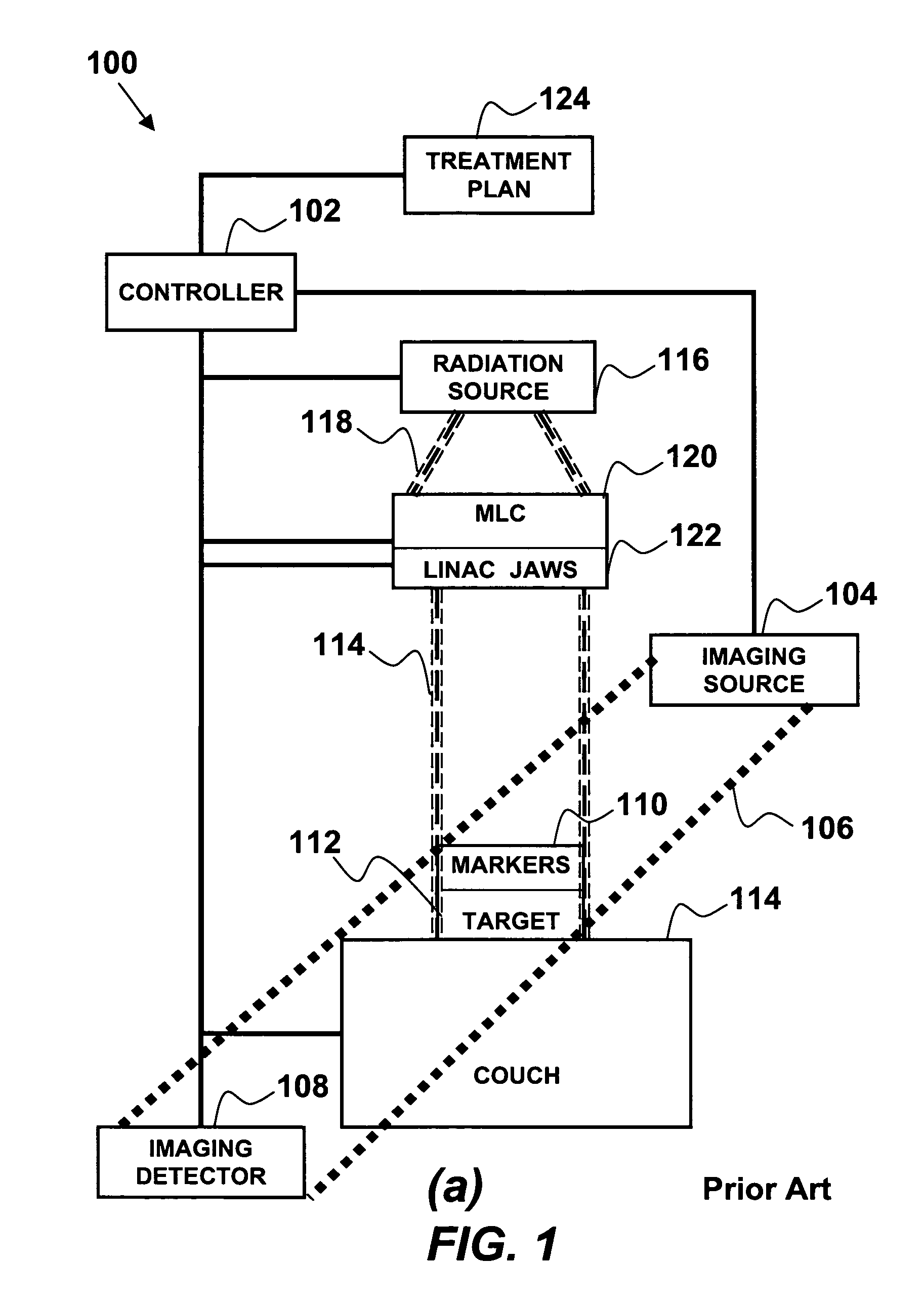
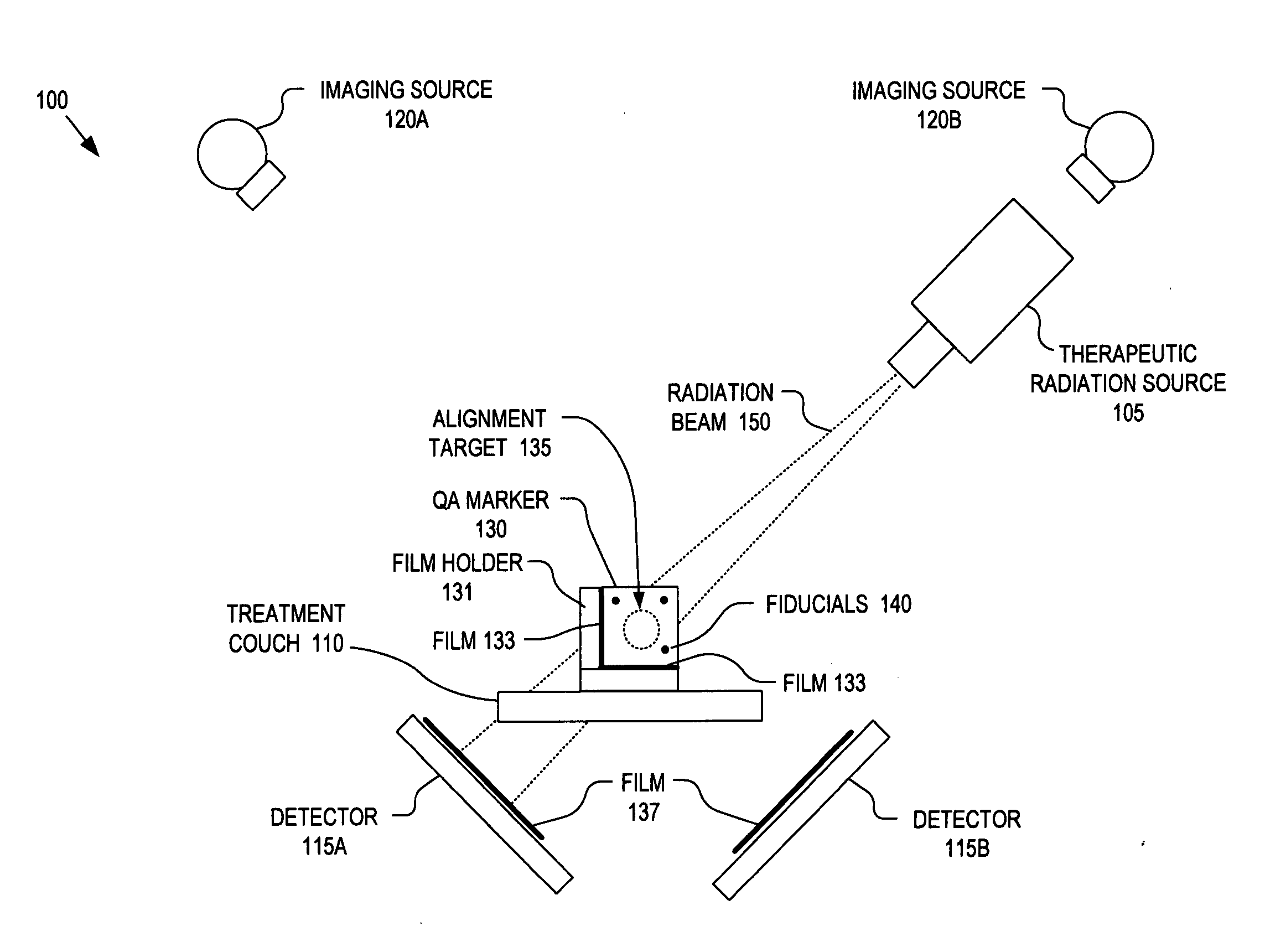
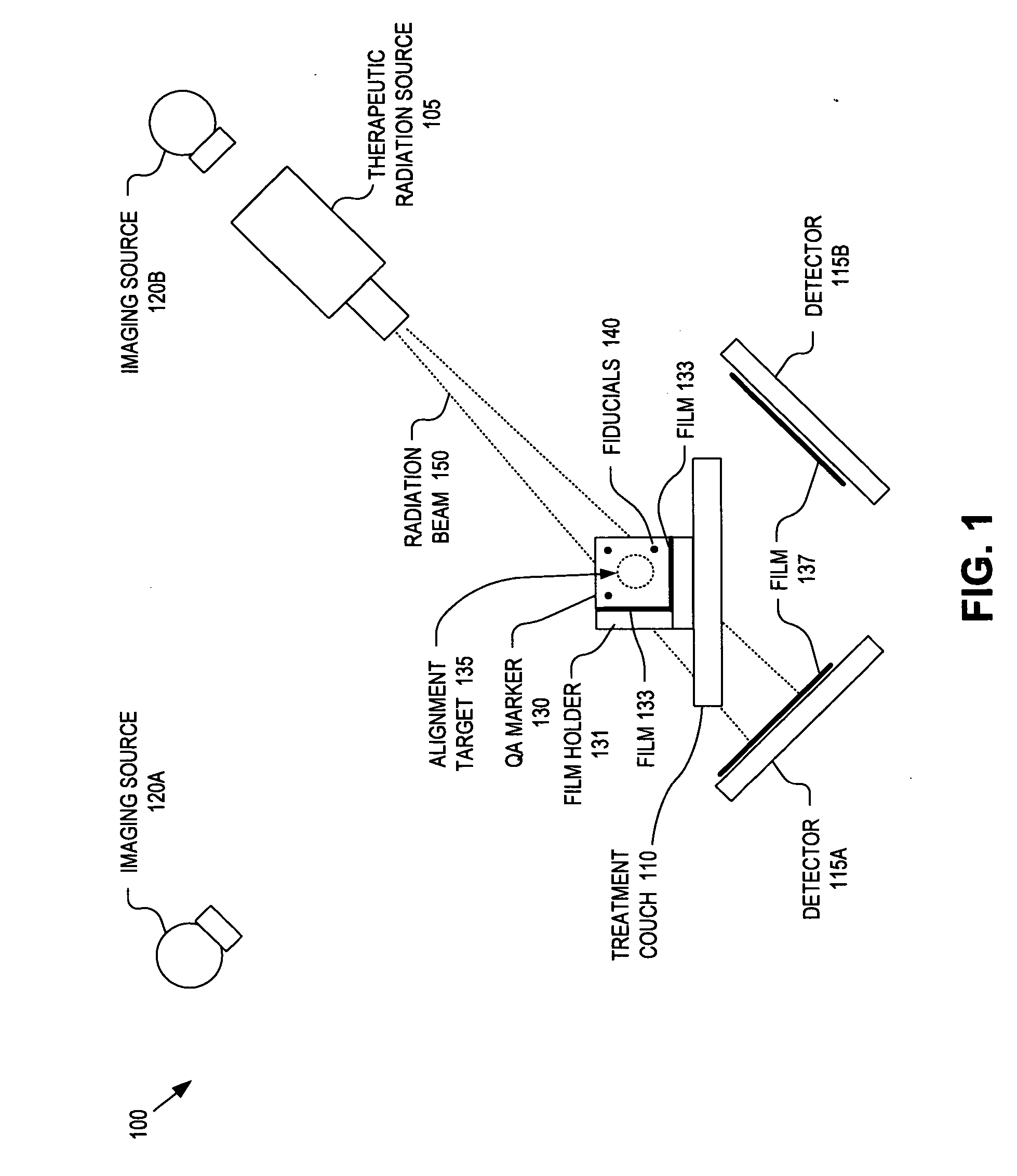
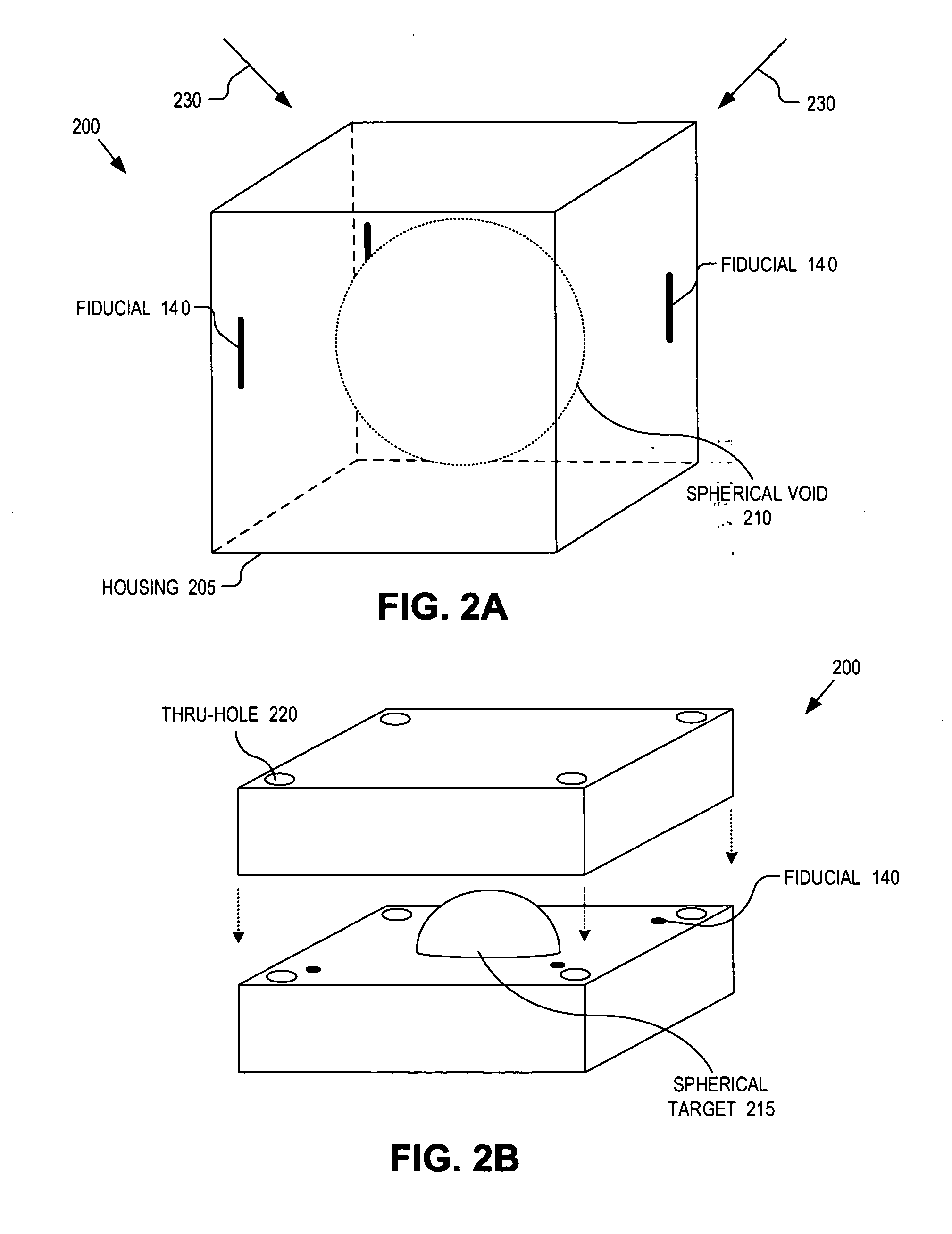
Integrated quality assurance for an image guided radiation treatment delivery system
ActiveUS20070071176A1Calibration apparatusRadiation beam directing meansQuality assuranceImage-guided radiation therapy
A method and apparatus for quality assurance of an image guided radiation treatment delivery system. A quality assurance (“QA”) marker is positioned at a preset position under guidance of an imaging guidance system of a radiation treatment delivery system. A radiation beam is emitted from a radiation source of the radiation treatment delivery system at the QA marker. An exposure image of the QA marker due to the radiation beam is generated. The exposure image is then analyzed to determine whether the radiation treatment delivery system is aligned.
Owner:ACCURAY
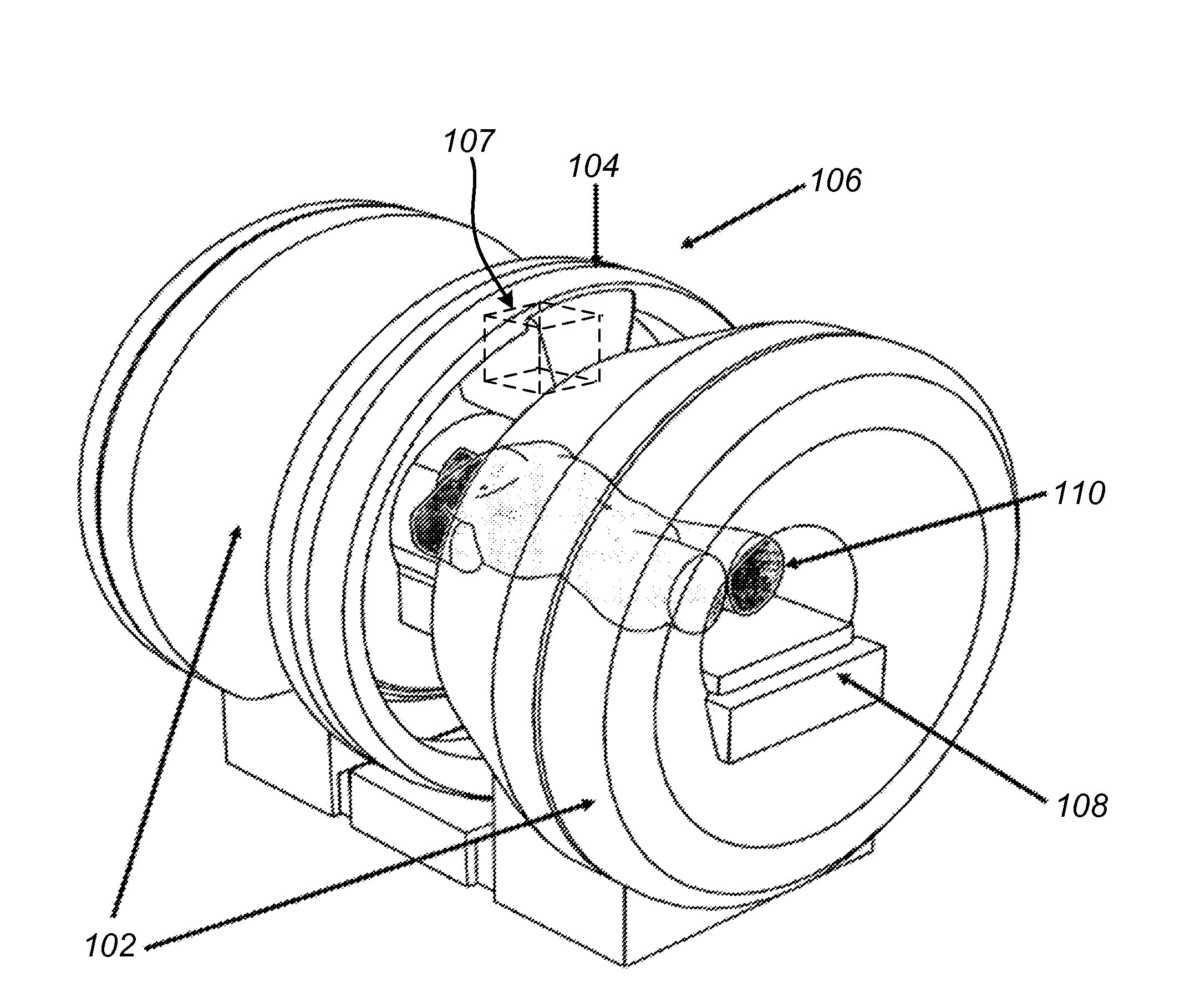
Method and apparatus for shielding a linear accelerator and a magnetic resonance imaging device from each other
InactiveUS20110012593A1Improve permeabilityReduce flux densityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSplit magnetResonance
A radiation therapy system comprises a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system combined with an irradiation system, which can include one or more linear accelerators (linacs) that can emit respective radiation beams suitable for radiation therapy. The MRI system includes a split magnet system, comprising first and second main magnets separated by gap. A gantry is positioned in the gap between the main MRI magnets and supports the linac(s) of the irradiation system. The gantry is rotatable independently of the MRI system and can angularly reposition the linac(s). Shielding can also be provided in the form of magnetic and / or RF shielding. Magnetic shielding can be provided for shielding the linac(s) from the magnetic field generated by the MRI magnets. RF shielding can be provided for shielding the MRI system from RF radiation from the linac.
Owner:VIEWRAY TECH
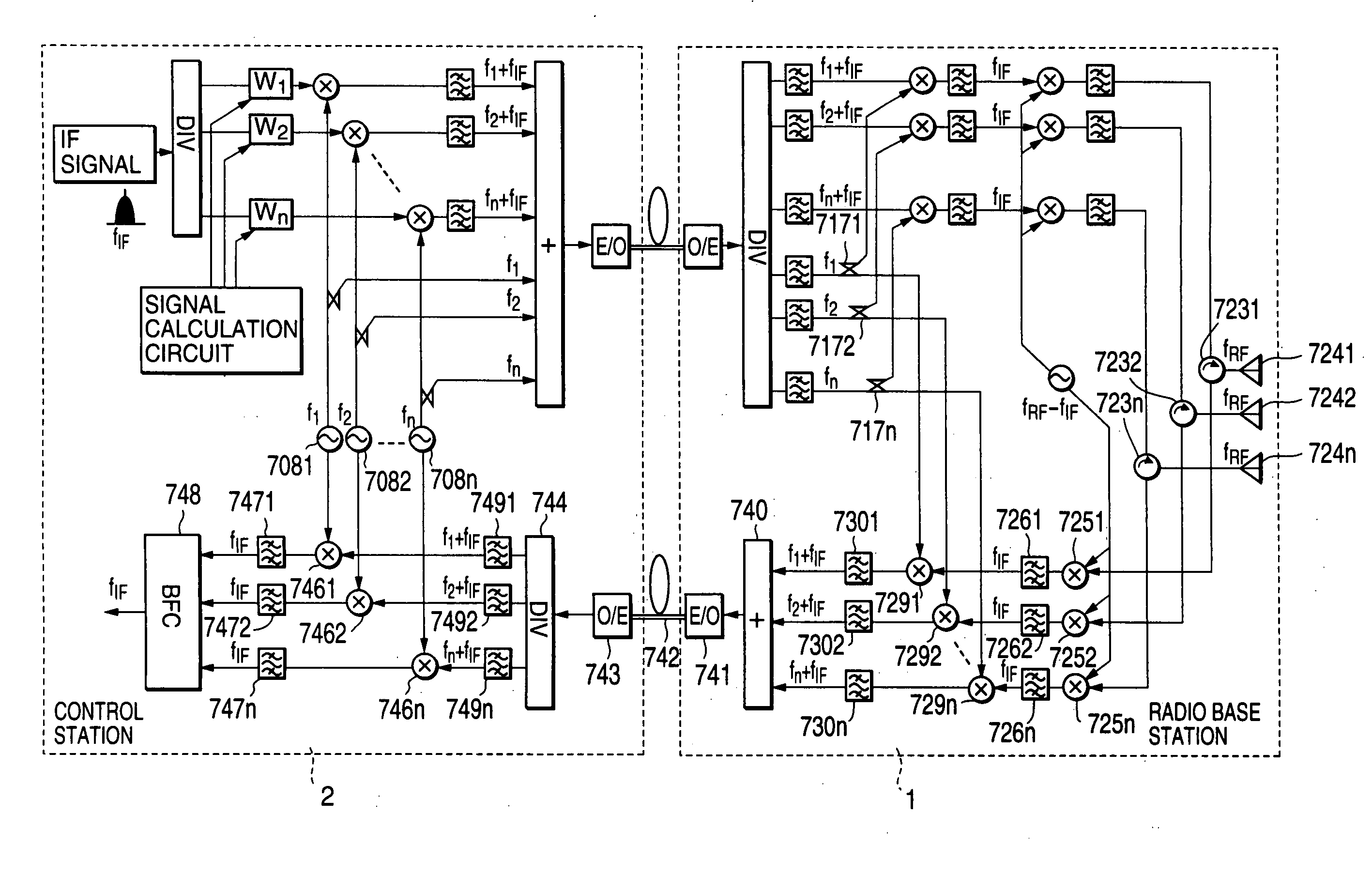
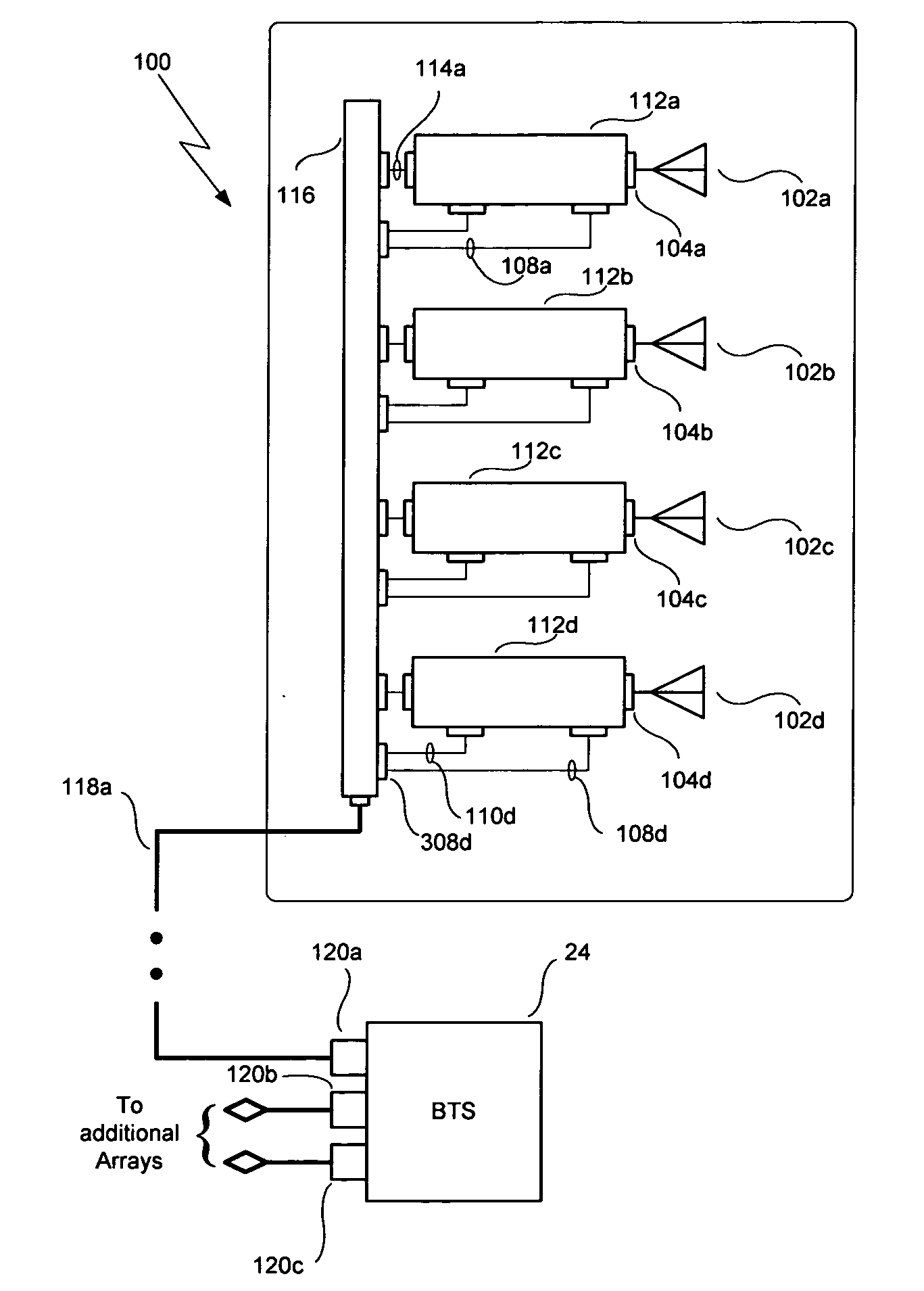
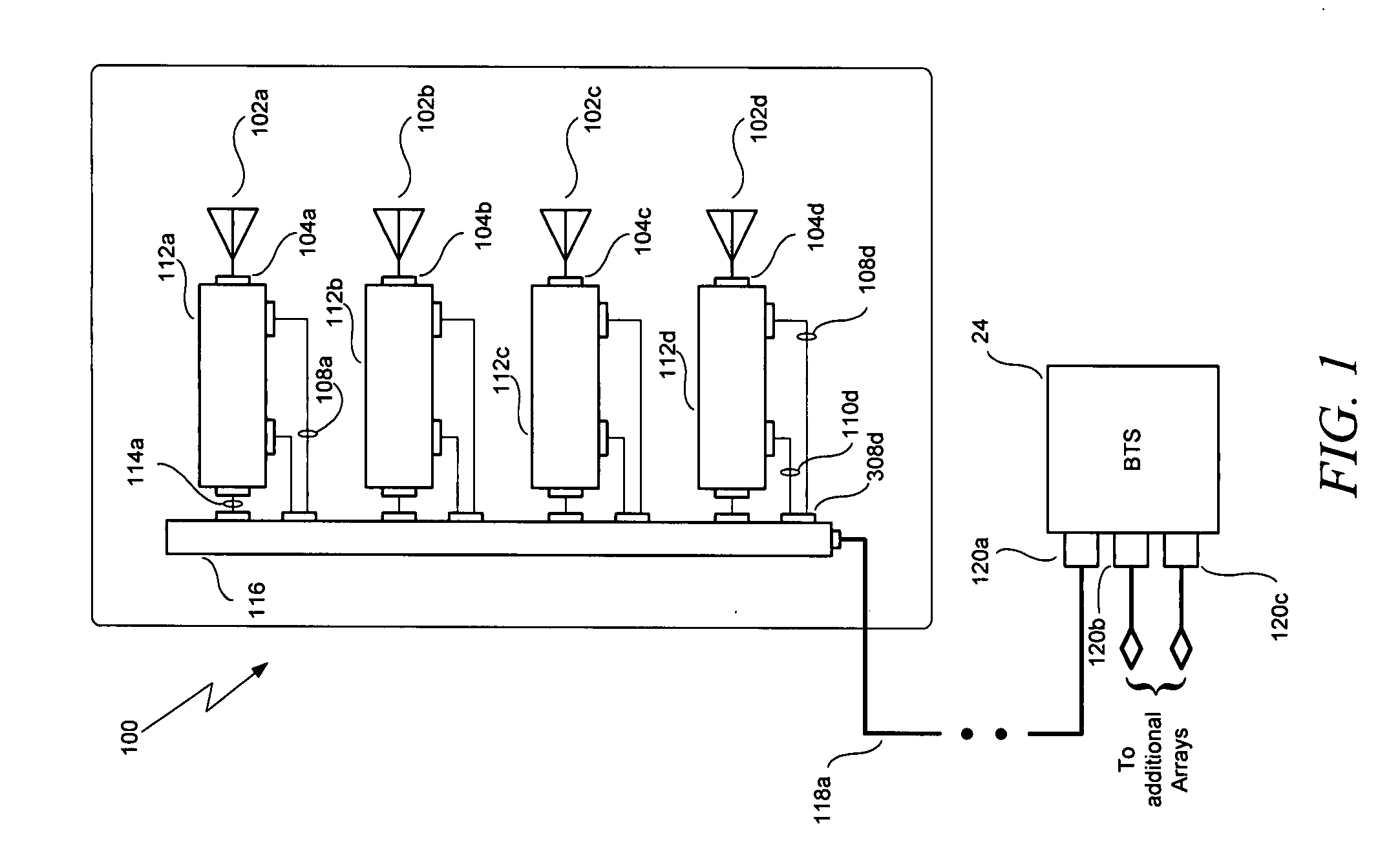
Smart antenna array over fiber
InactiveUS20080007453A1Improve performanceQuality improvementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsModular arraysFiberSmart antenna
A smart antenna system includes a plurality of antennas, a plurality of Transmit—Receive Modules (TRMs) coupled respectively to the plurality of antennas, and a beam steering module coupled to the plurality of TRMs and providing radiation beam steering for the plurality of TRMs. The beam steering module includes a pilot generator for generating a pilot signal and providing it to the TRMs to calibrate a receive (RX) reference plane. The pilot signal is injected at a first location before the receiver section into the RX path, and the pilot signal is sampled at a second location after the receiver section. The TRMs and the beam steering module can also be used to calibrate a transmit (TX) reference plane by sampling output signals from the TRMs. The output signals have a pilot signal component, and are sampled at the first location in the TX path after the transmitter section.
Owner:POWERWAVE TECH INC
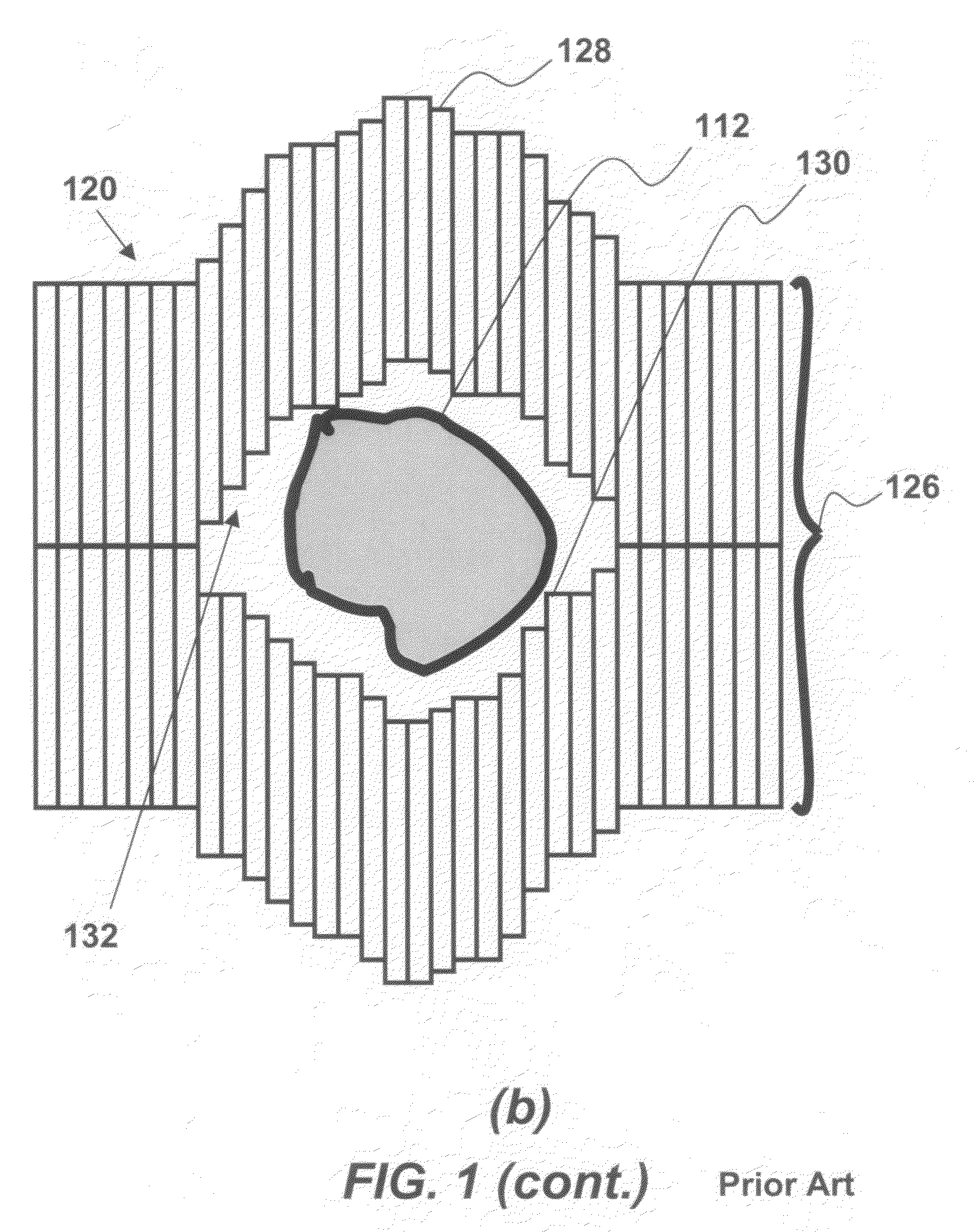
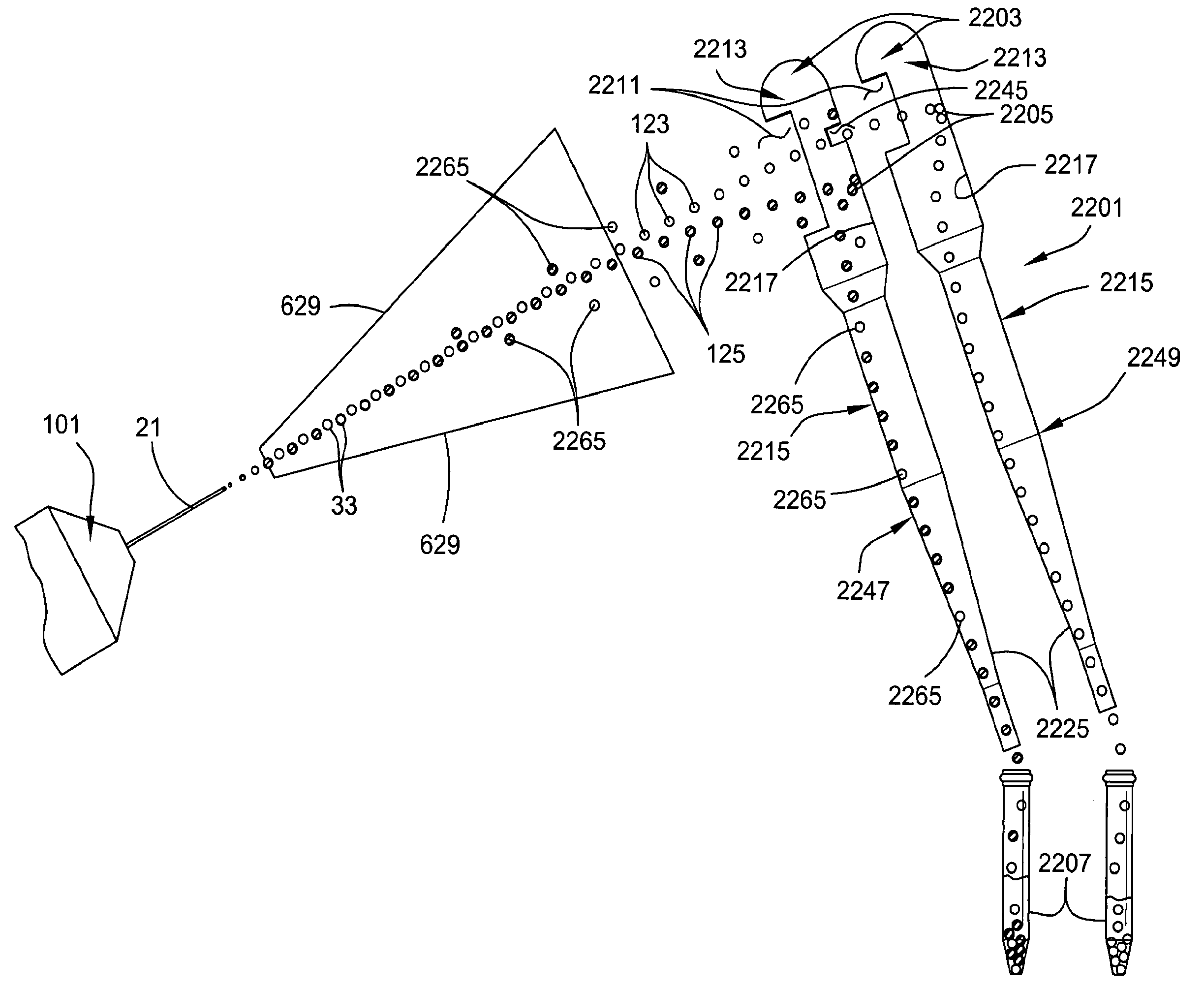
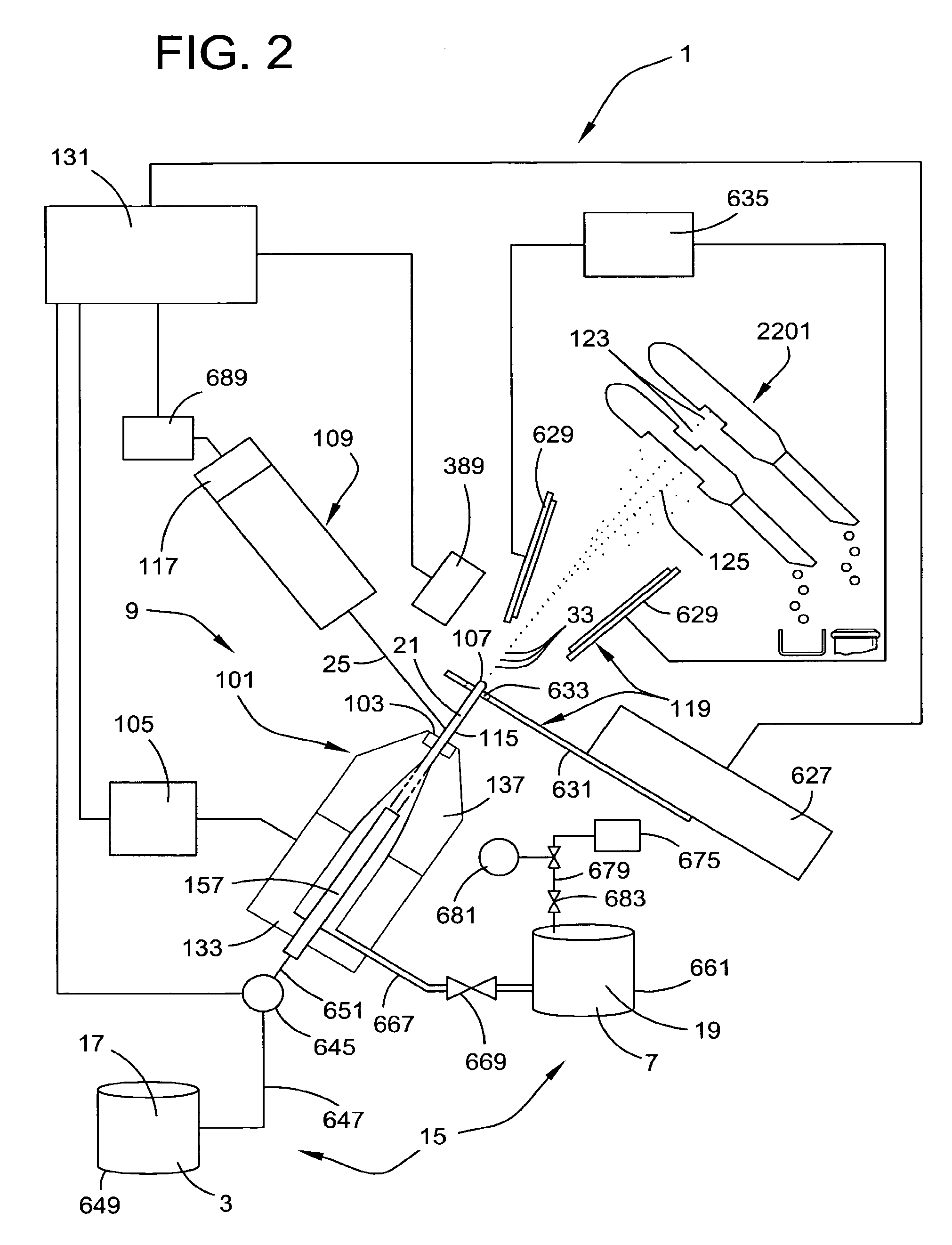
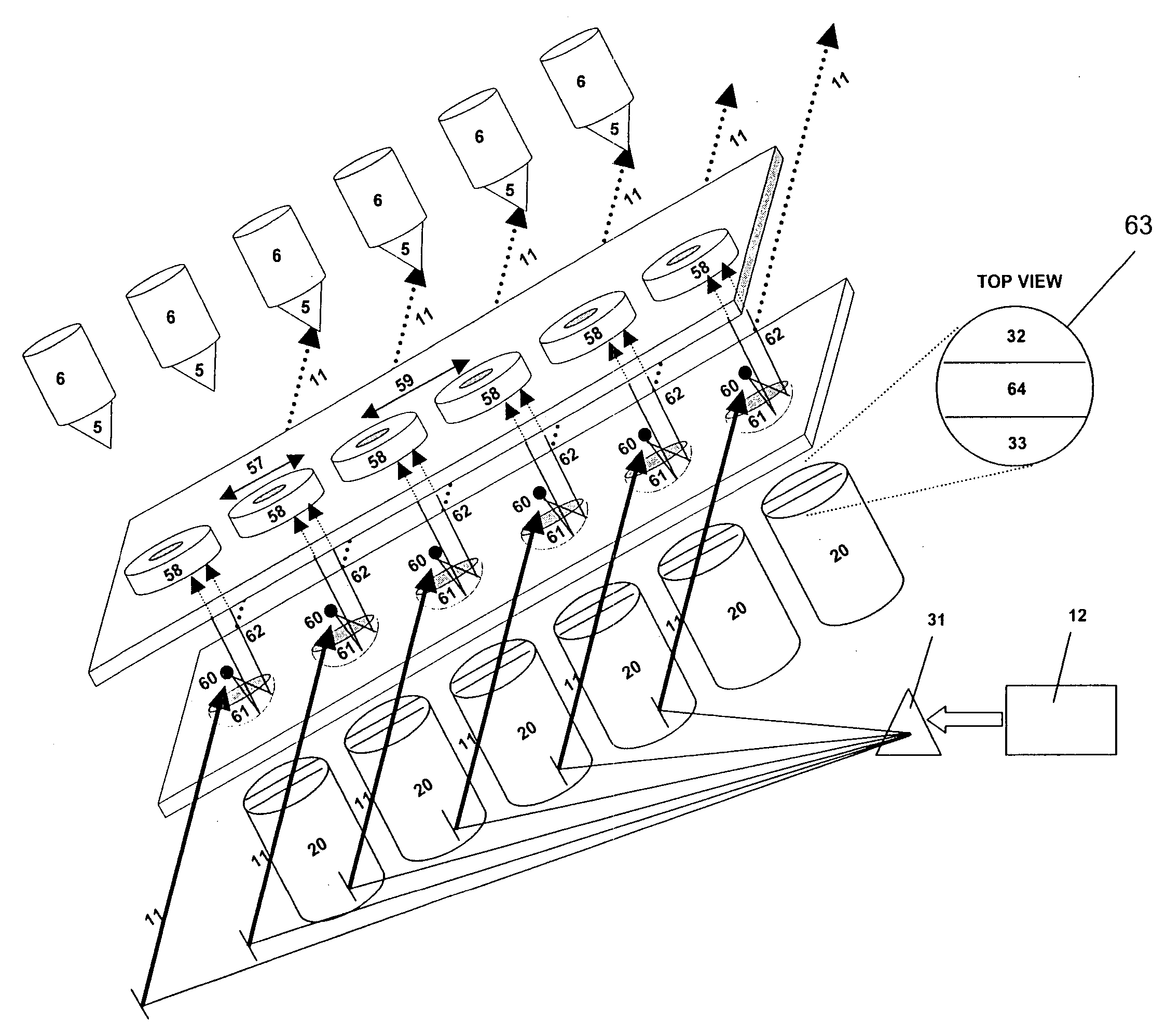
Efficient haploid cell sorting flow cytometer systems
InactiveUS20060263829A1Increase ratingsHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsImage resolutionManipulator
A flow cytometry system (1) for sorting haploid cells, specifically irradiatable sperm cells, with an intermittingly punctuated radiation emitter (56). Embodiments include a beam manipulator (21) and even split radiation beams directed to multiple nozzles (5). Differentiation of sperm characteristics with increased resolution may efficiently allow differentiated sperm cells to be separated higher speeds and even into subpopulations having higher purity.
Owner:XY
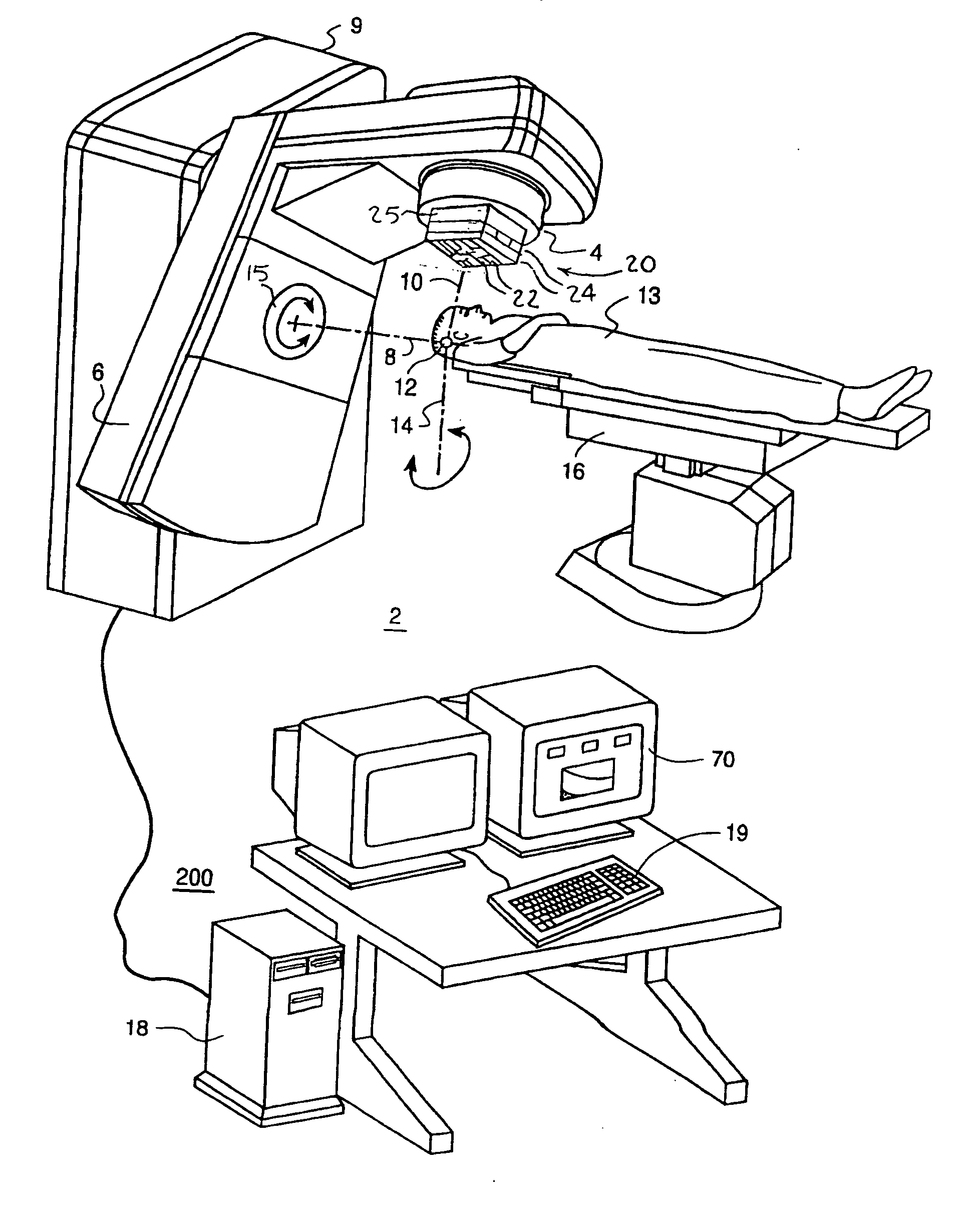
Image processing system for use with a patient positioning device
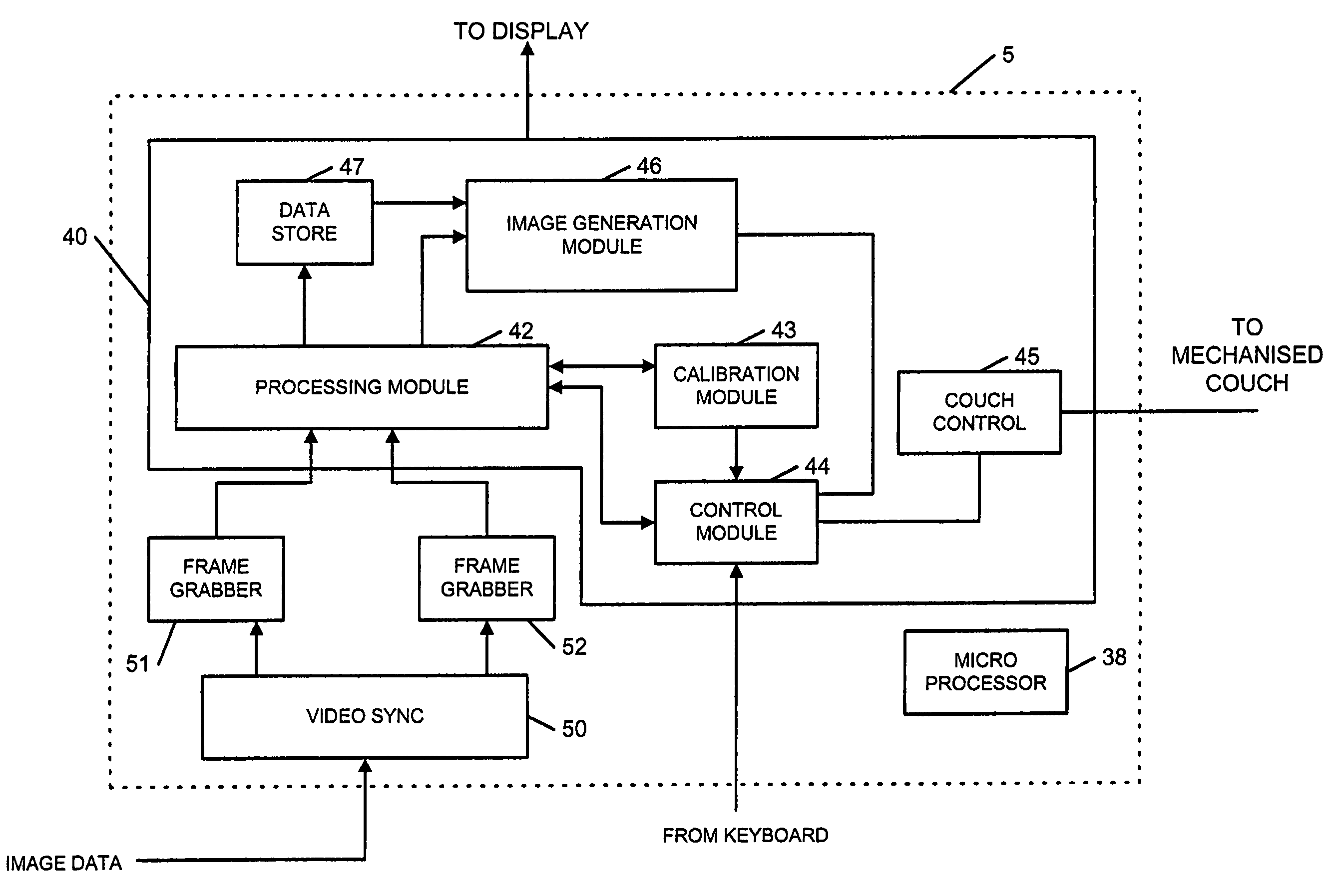
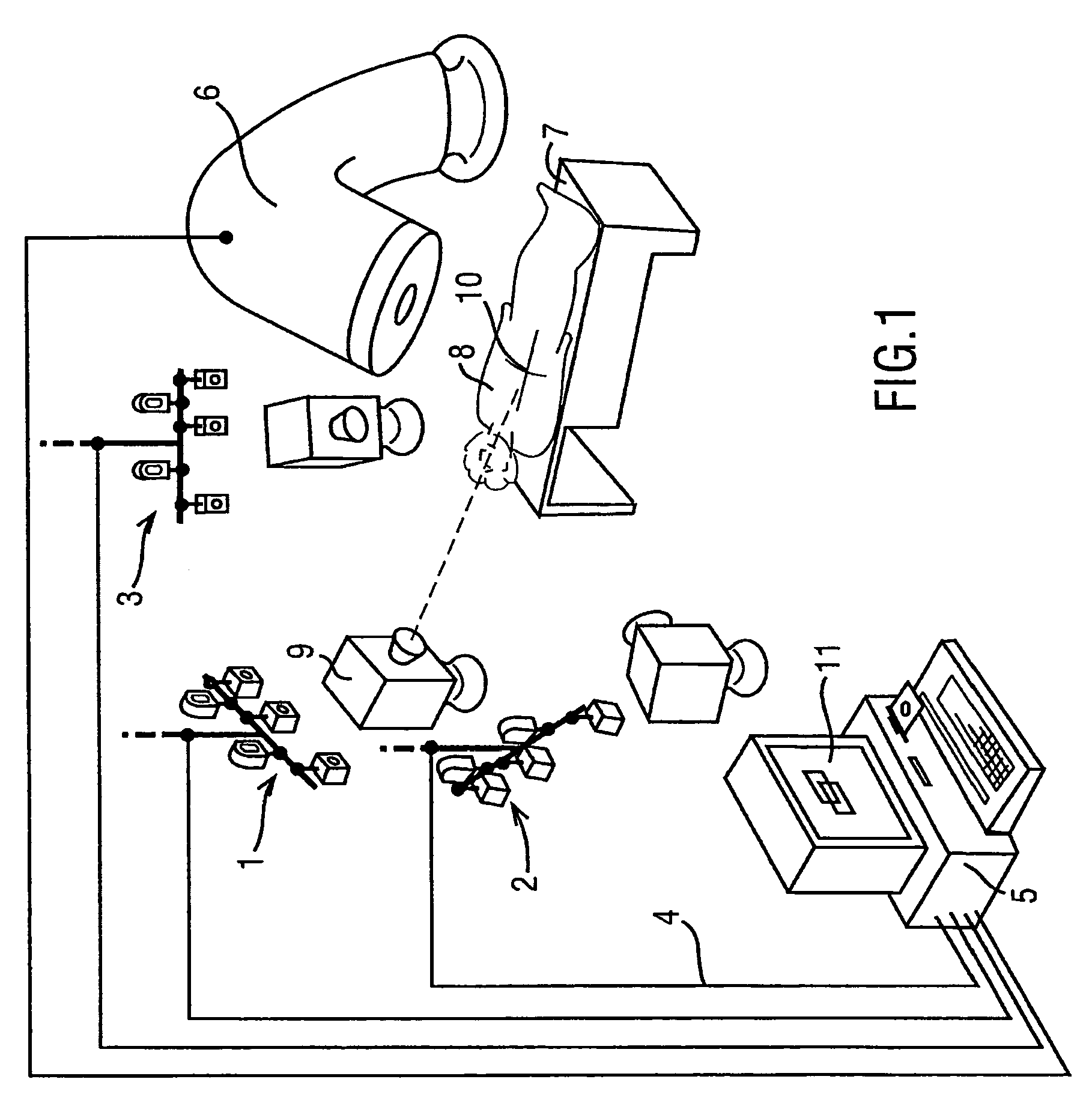
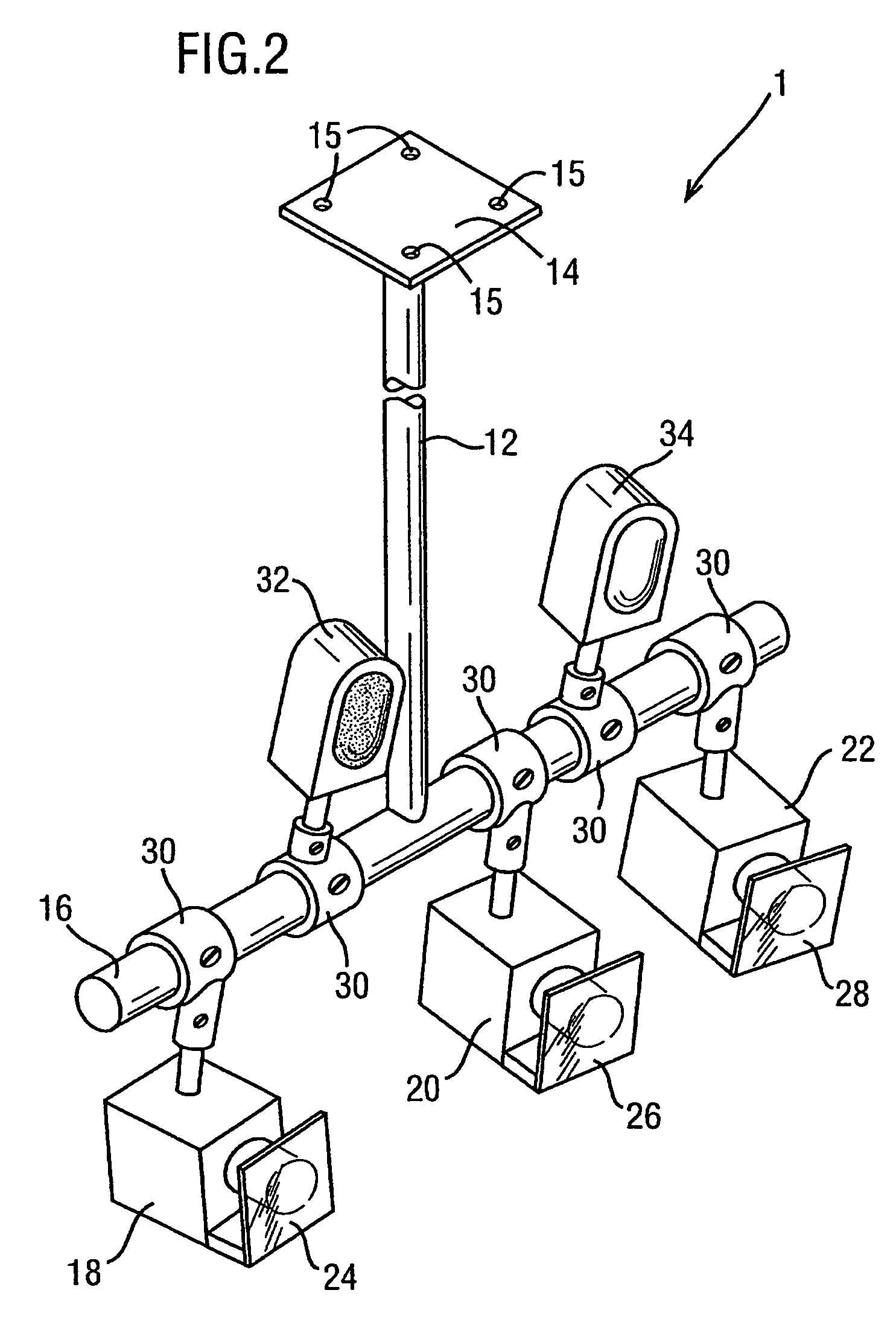
An image processing system (1-5) is provided which obtains images of a patient (8) from multiple view points and which then generates positioning instructions for a mechanical couch (7) to vary the position of a patient. A number of techniques are disclosed in order to calibrate the image processing system so as to enable the image processing system to identify the iso center of radiation beams generated by a treatment apparatus (6). Techniques for processing generated 3 dimensional models to monitor a patient's breathing are also disclosed.
Owner:VISION RT LTD
Detecting the location of an object on a touch surface
InactiveUS20110074734A1Overcome limitationsInput/output processes for data processingUltrasound attenuationData processing
An apparatus is operated to determine the location of at least one object on a touch surface of a light transmissive panel. In the apparatus, an illumination arrangement introduces radiation into the panel for propagation by internal reflection between the touch surface and the opposite surface, so as to generate a grid of intersecting radiation paths in a sensing area, and a detection arrangement measures the transmitted energy in the radiation paths. A data processor then determines, based on the transmitted energy, the location based on an attenuation of two or more radiation paths caused by the object touching the touch surface within the sensing area. In the apparatus, the illumination arrangement generates at least a subset of the radiation paths by sweeping at least one beam of radiation along the touch surface. The detection arrangement comprises a fixed re-directing device which receives and re-directs the beam onto a common detection point while the beam is swept along the touch surface, and a radiation detector which is located at the common detection point to measure the energy of the beam(s).
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Apparatus, methods and processes for sorting particles and for providing sex-sorted animal sperm
ActiveUS20070117086A1Low powerHigh incidenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImage resolutionManipulator
Owner:XY
Radiotherapy system with turntable
A radiotherapy system including a collimator operable to shape and steer a radiation beam in at least one dimension, a turntable for supporting a patient thereupon adapted to rotate the patient about a rotational axis, the patient having a target therein for irradiation by the radiation beam, a detector adapted for measuring a position of the target relative to the radiation beam, and a processor adapted to receive target positional data from the detector, the processor being in communication with the collimator for causing the collimator to steer the radiation beam in a direction to the target.
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
Charged particle cancer therapy imaging method and apparatus
ActiveUS20110147608A1Stability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by optical meansBeam energyBeam trajectory
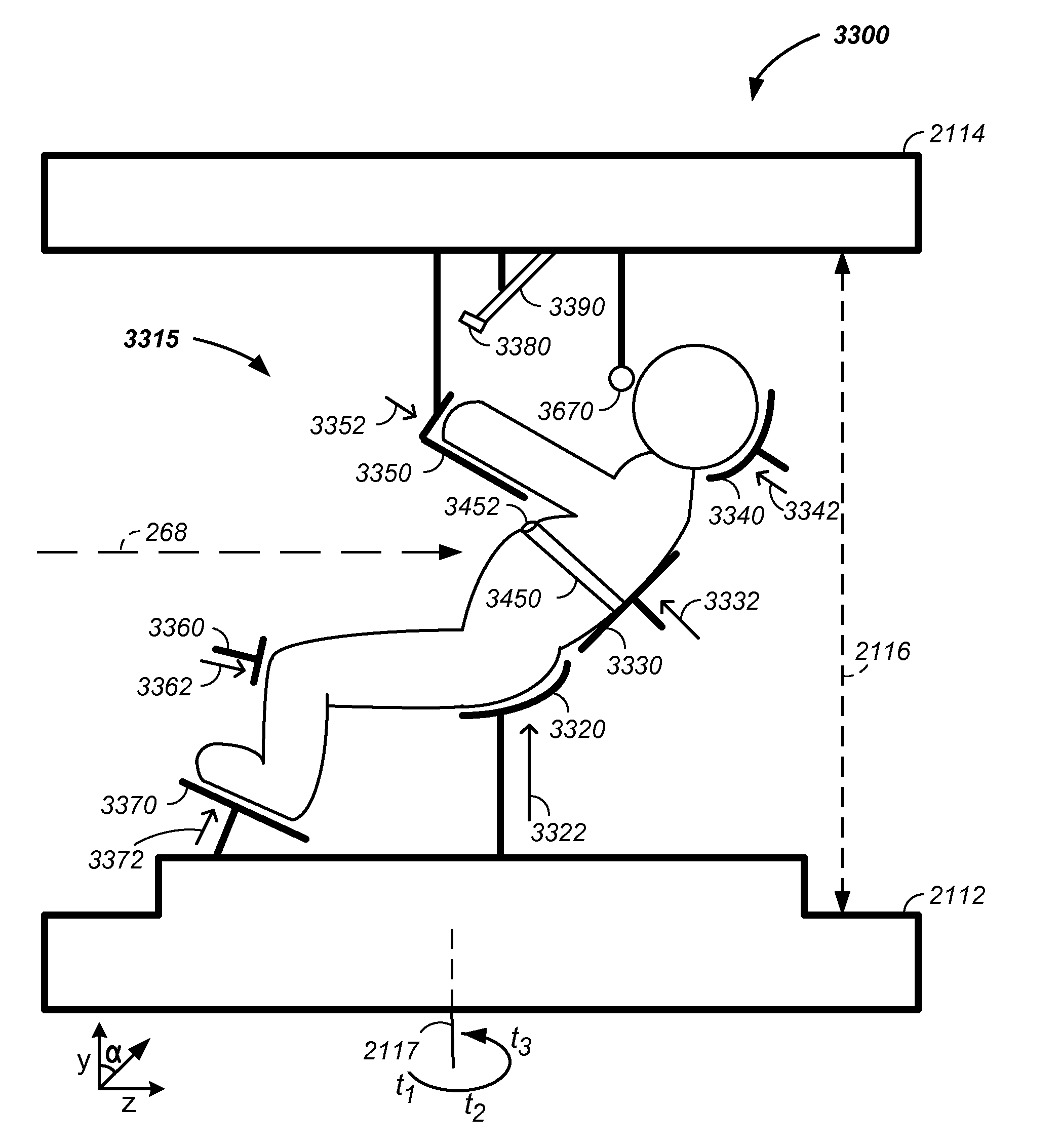
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for treatment of a solid tumor. More particularly, the invention comprises a multi-axis and / or multi-field charged particle cancer therapy system. In one embodiment, the tumor is imaged from multiple directions in phase with patient respiration. The two-dimensional images are combined to produce a three-dimensional picture of the tumor relative to patient features. The resulting three-dimensional image is used in generation of a radiation treatment plan and subsequent radiation therapy with the radiation beam in terms of control of two-dimensional beam trajectory, delivered beam energy, delivered beam intensity, and / or beam velocity each as a function of patient vertical translation position, patient rotation position, and / or patient respiration.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
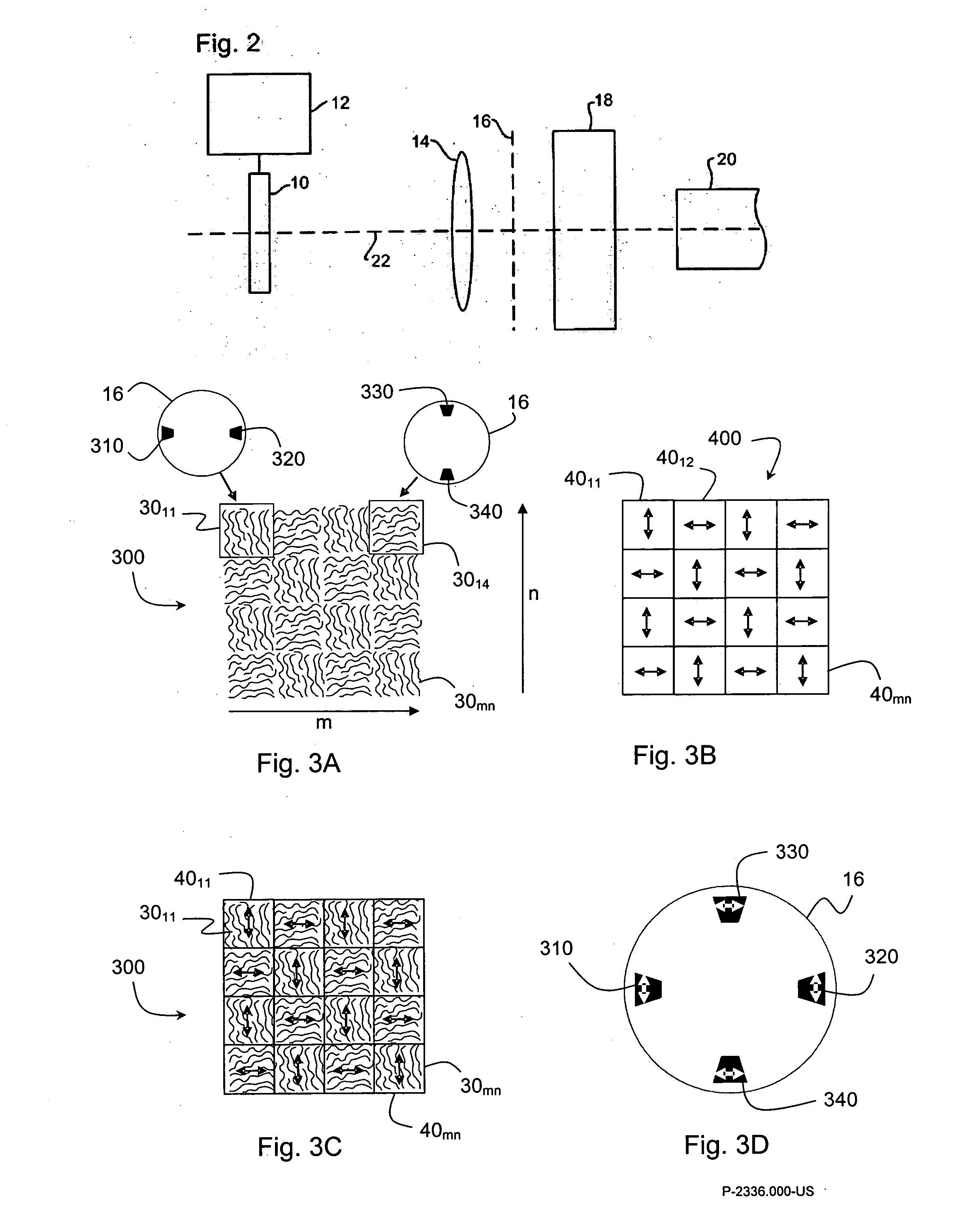
Optical element for use in lithography apparatus and method of conditioning radiation beam
InactiveUS20070058151A1Little loss of strengthPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingLithographic artistLighting system
An optical element for effecting a desired change in incident radiation at a plane of an illumination system of a lithographic apparatus comprises an array of cells manufactured as a single unit, each cell being arranged to redirect the incident radiation in a predetermined direction. An array of polarizing regions is also provided, each polarizing region being associated with a corresponding cell. Each cell arranged to redirect radiation in a first direction has associated with it a polarizing region ensuring that the redirected radiation has a first polarization, so that all of the radiation redirected in the first direction has the same polarization.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com