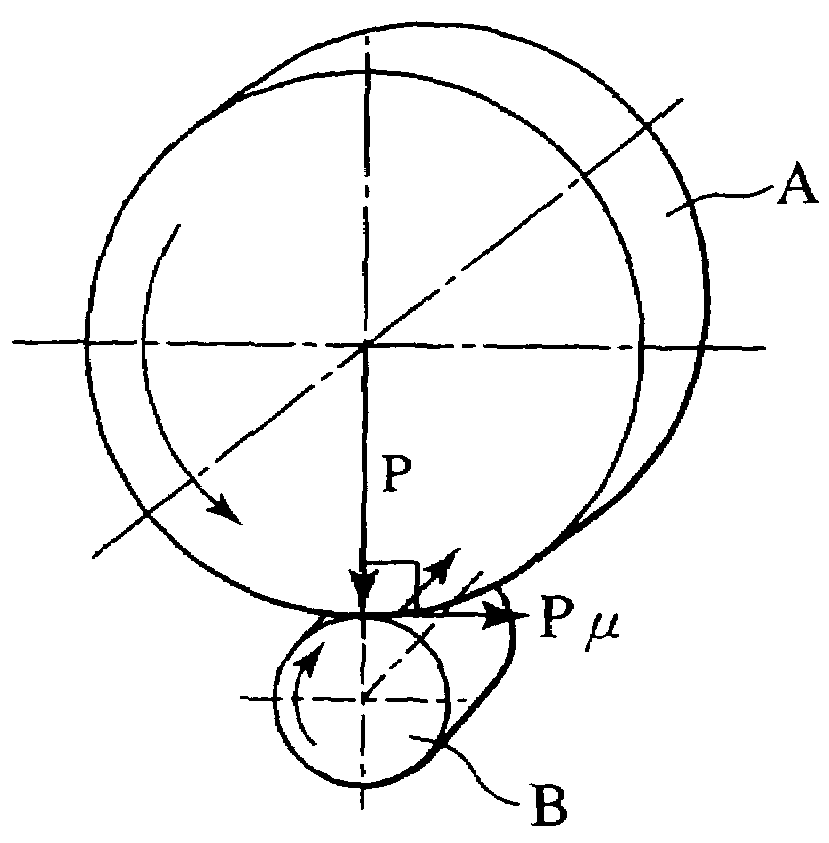Patents
Literature
453 results about "Beam delivery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
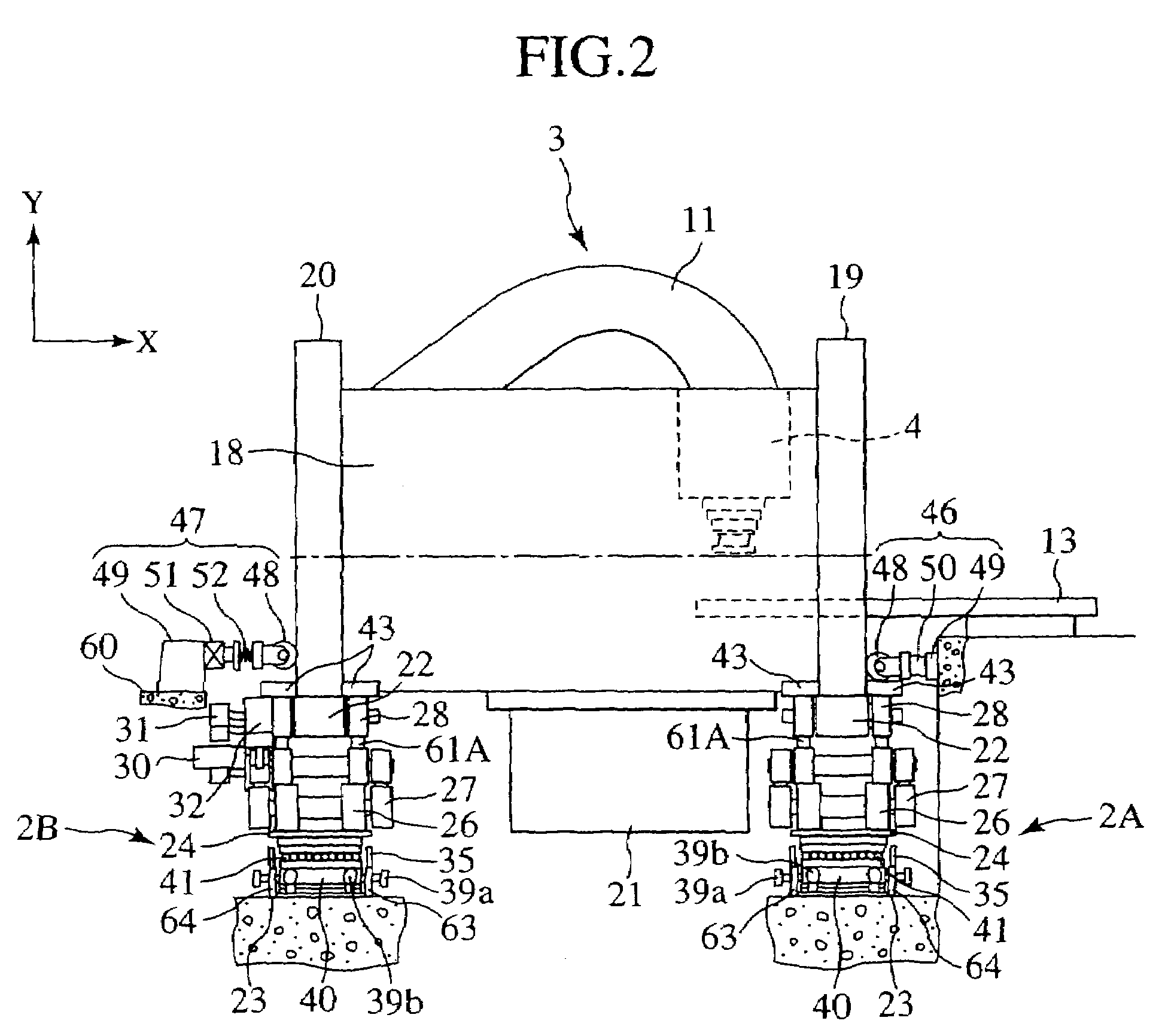
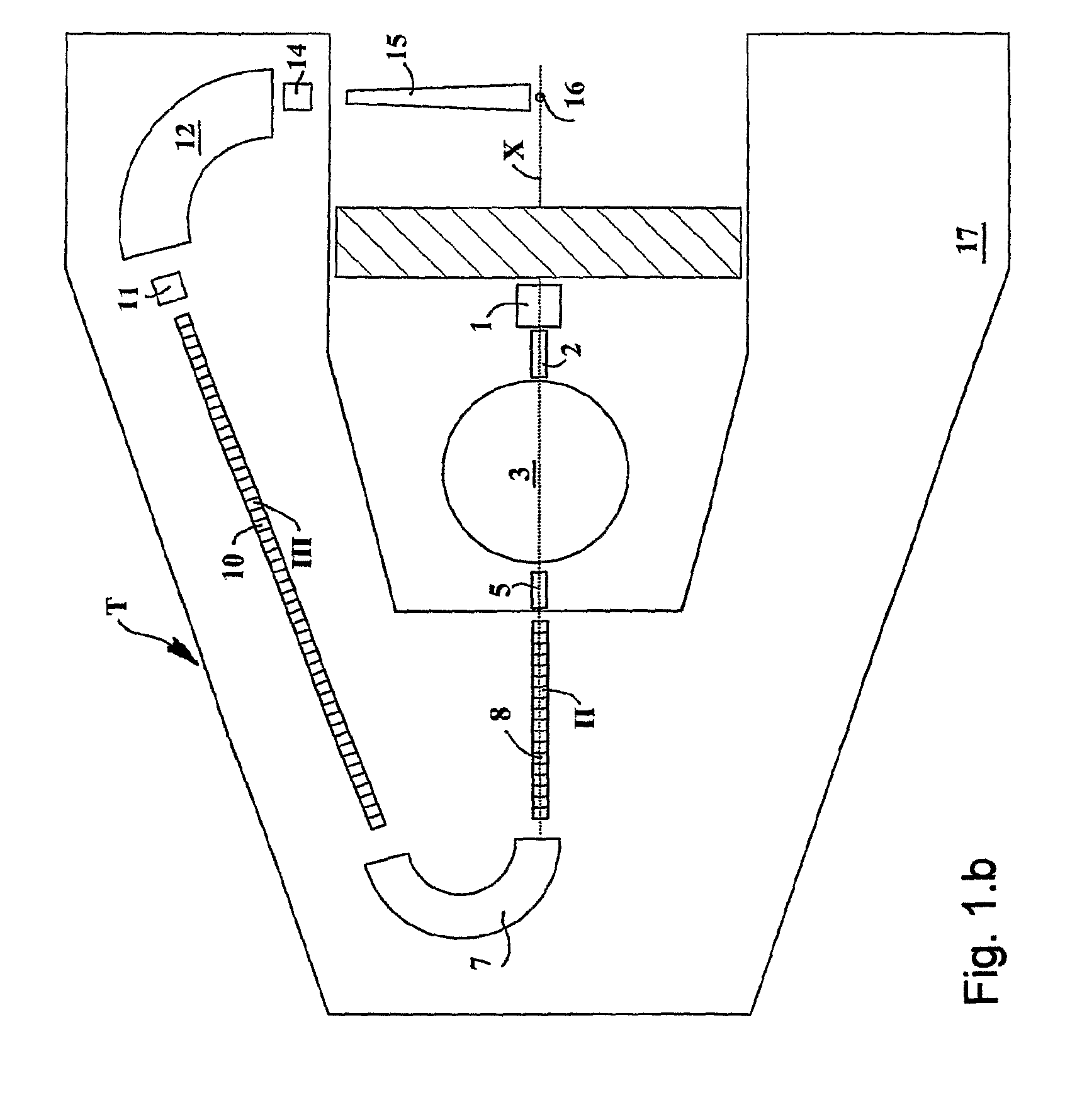
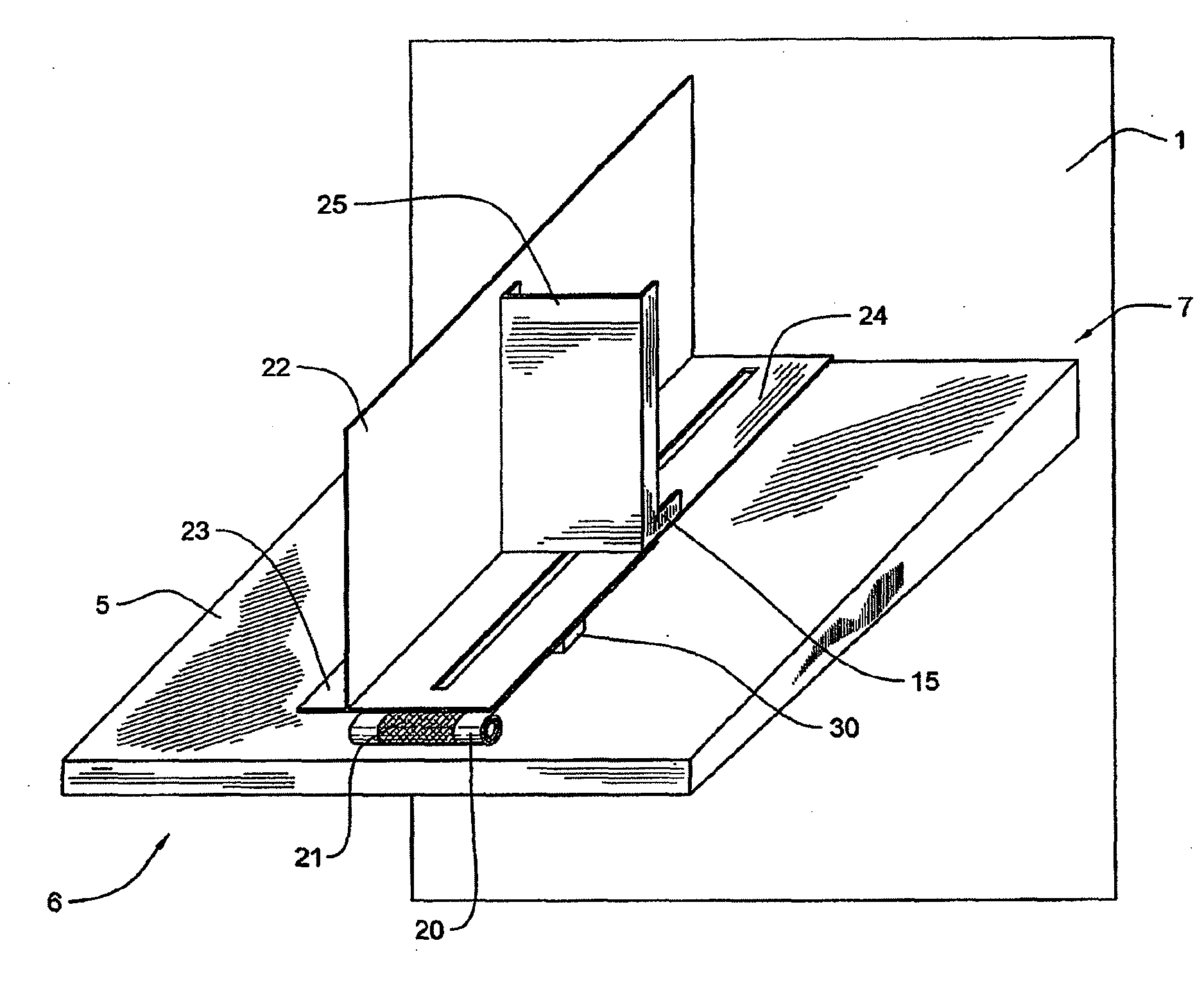
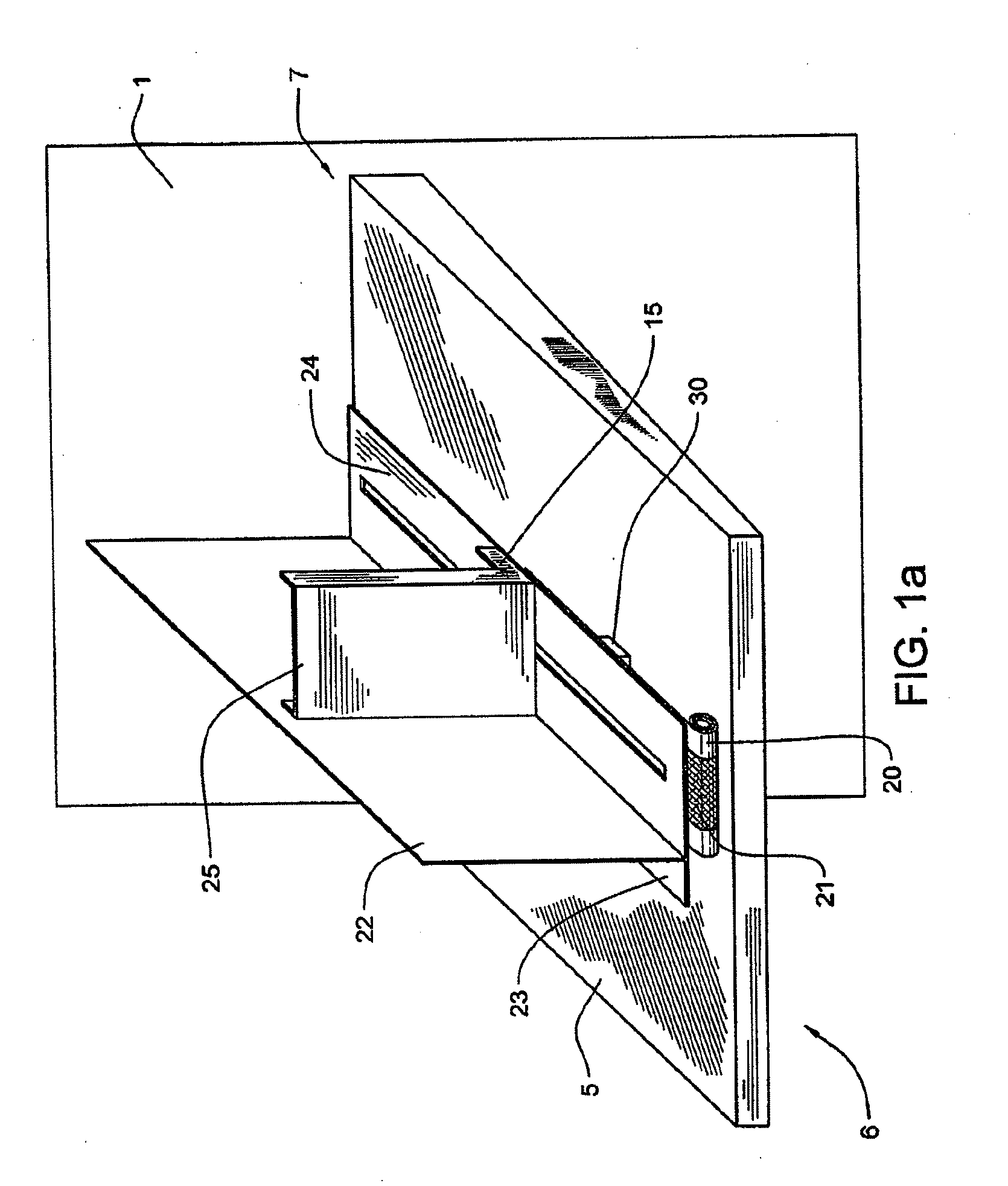
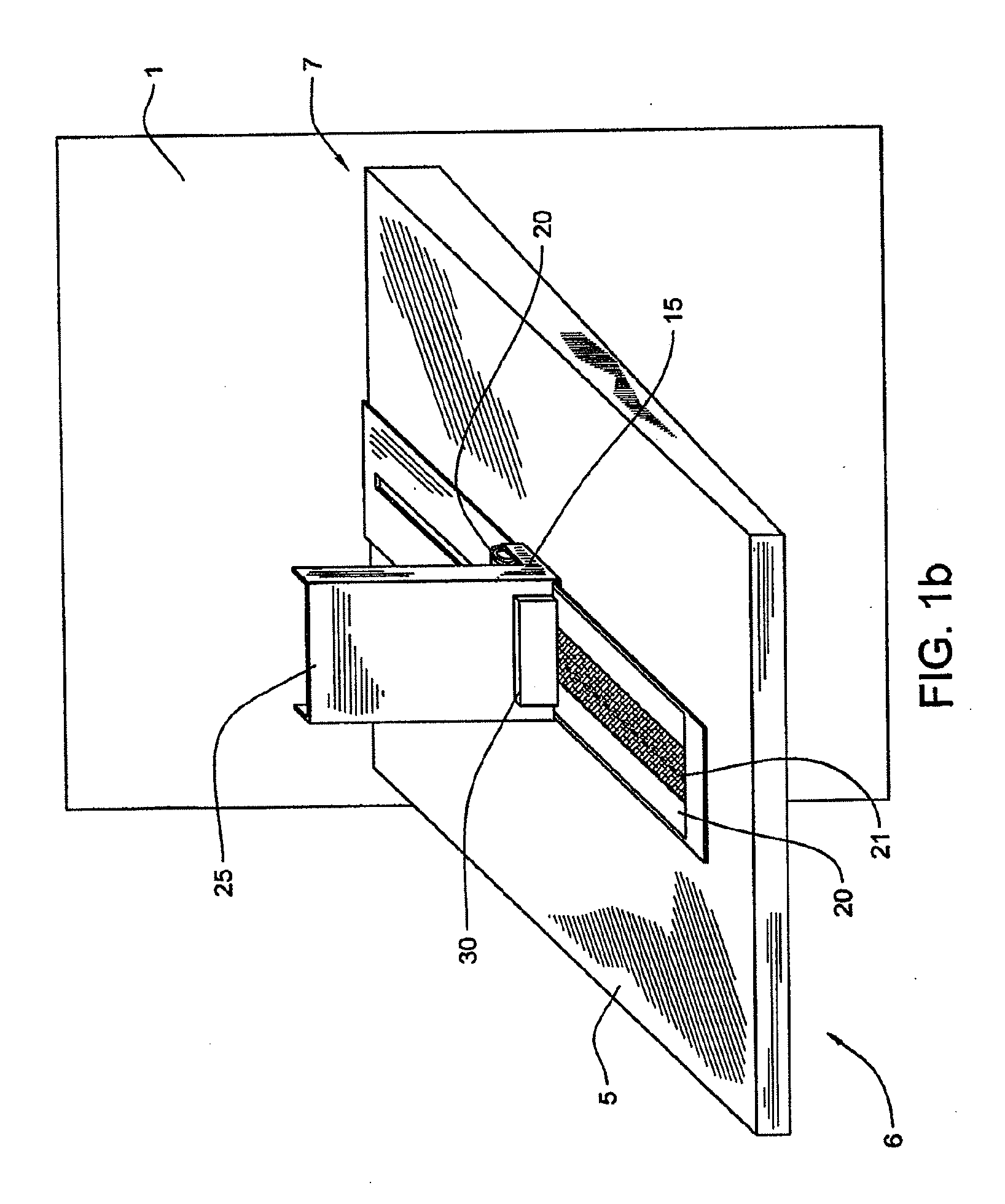
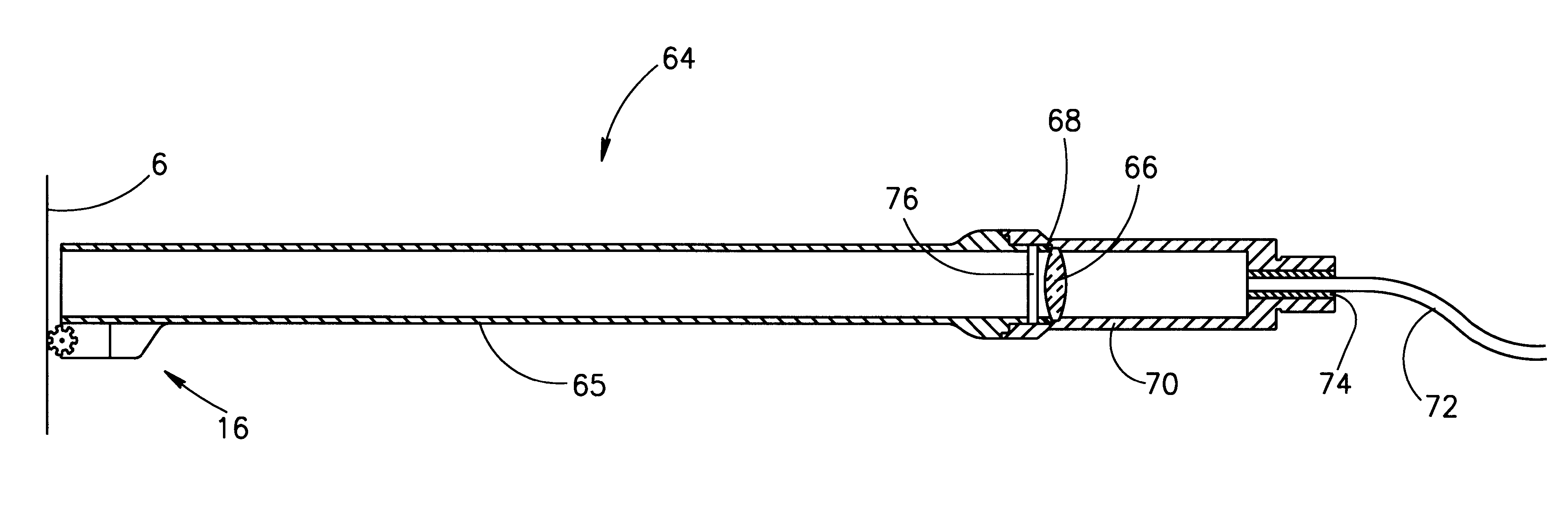
Rotating irradiation apparatus
ActiveUS7381979B2Increase the number ofHigh positioning accuracyRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsParticle radiotherapyRotational axis
A rotating irradiation apparatus includes a rotating gantry 3 including a front ring 19 and a rear ring 20 and is provided with a beam delivery device 11 and an irradiation device 4. The beam delivery device 11 delivers an ion beam used for particle radiotherapy. Radial support devices 61A and 61B support the front ring 19 and radial support devices 61A and 61B support the rear ring 20. Each radial support device includes a linear guide 41, an upper support structure disposed above the linear guide 41, and a lower support structure disposed below the linear guide 41. The upper support structure is movably mounted on the lower support structure and is movable in the direction of the rotational axis of the rotating gantry 3.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
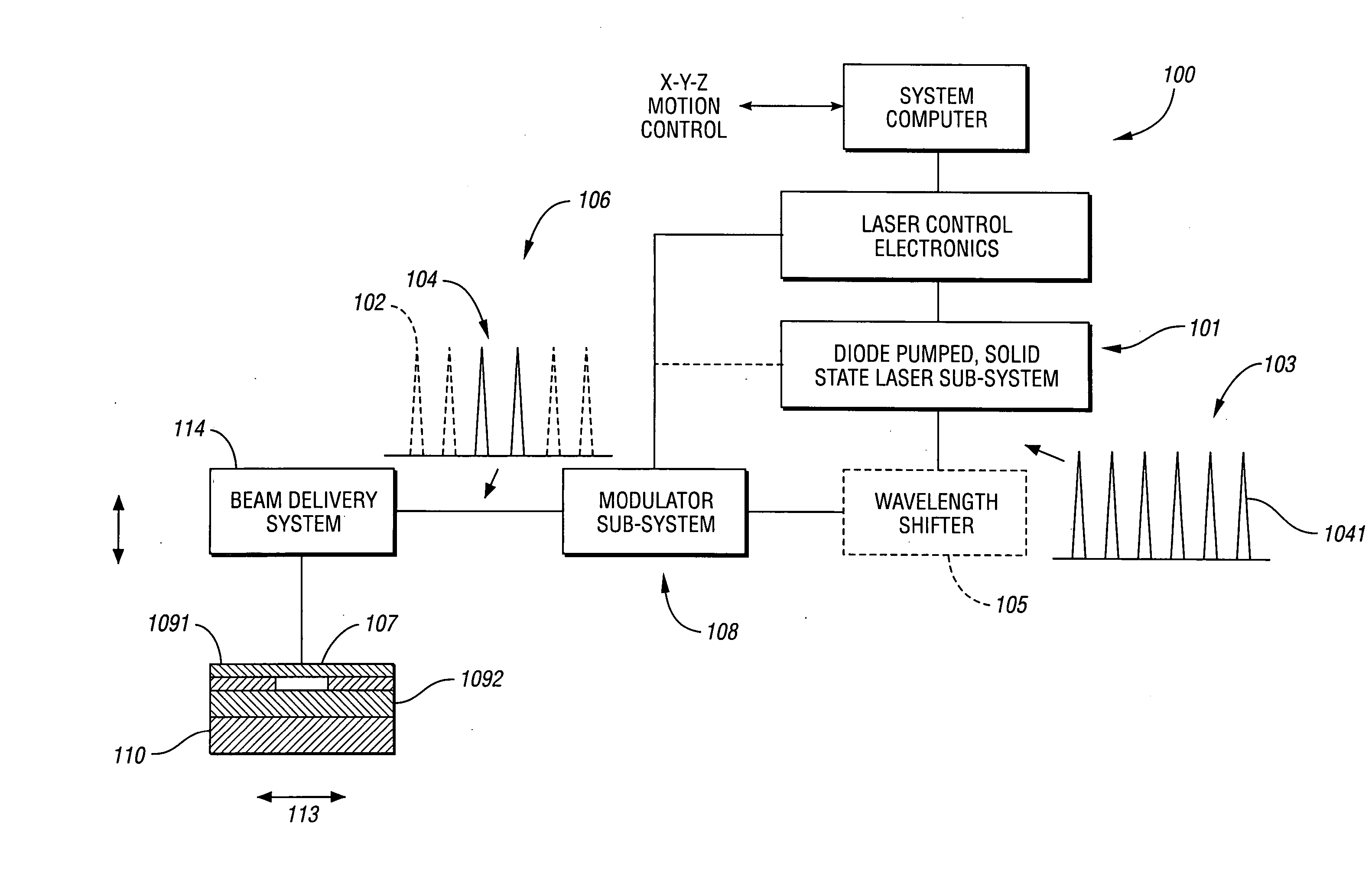
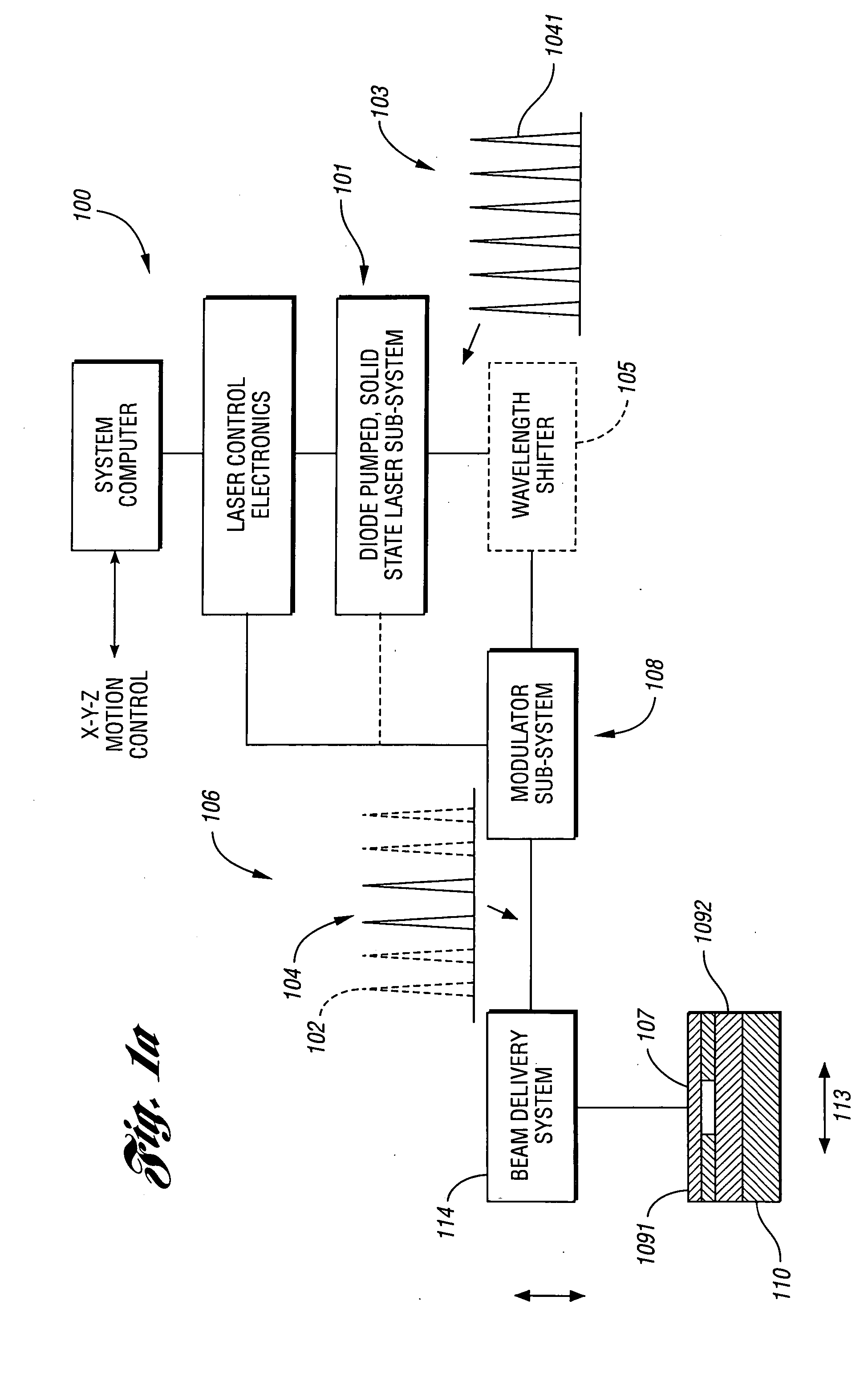
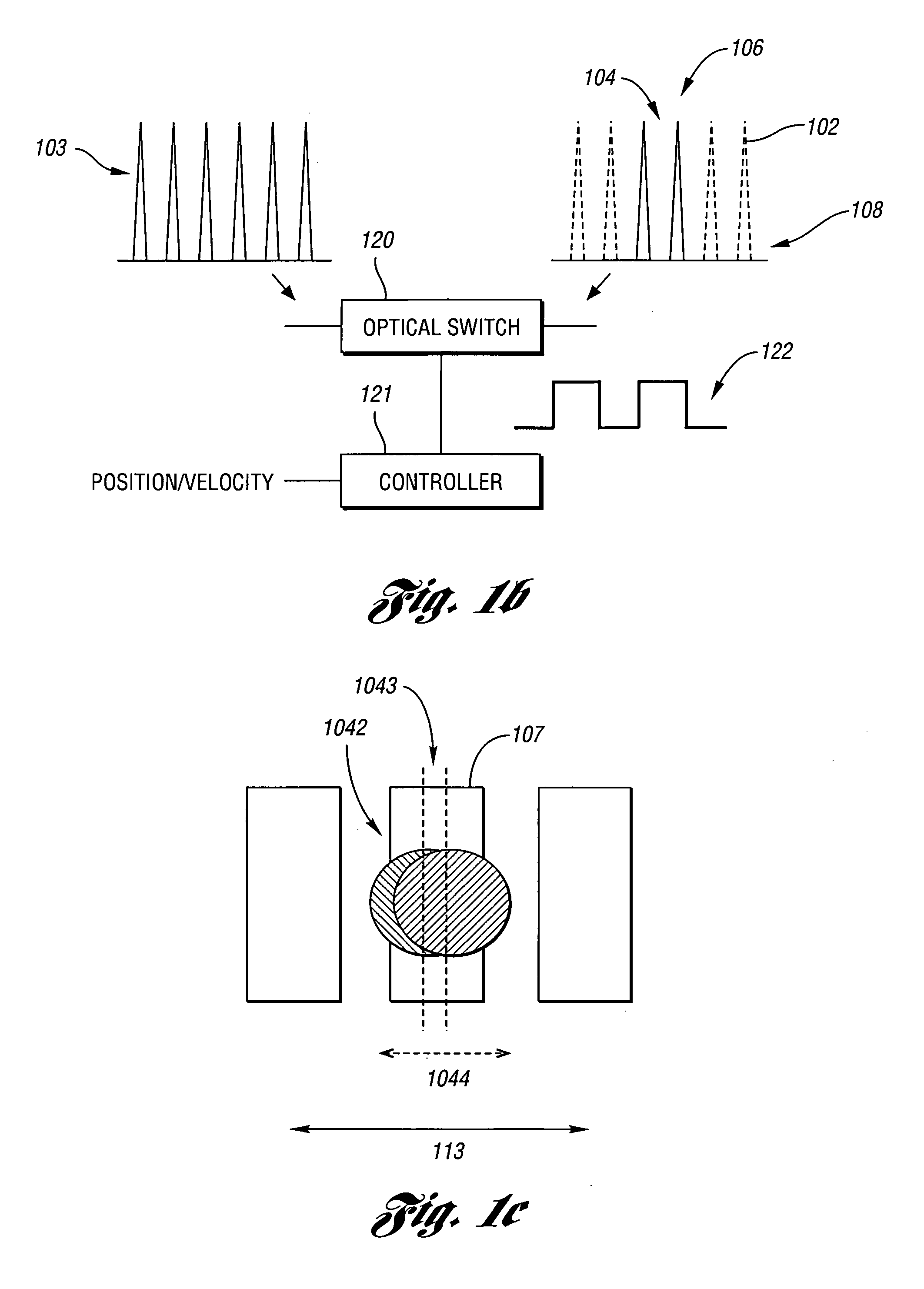
Laser-based system for memory link processing with picosecond lasers
InactiveUS20040134894A1Quality improvementReduce reflectivitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPicosecond laserMicroscopic scale
A laser-based system for processing target material within a microscopic region without causing undesirable changes in electrical or physical characteristics of at least one material surrounding the target material, the system includes a seed laser, an optical amplifier, and a beam delivery system. The seed laser for generating a sequence of laser pulses having a first pre-determined wavelength. The optical amplifier for amplifying at least a portion of the sequence of pulses to obtain an amplified sequence of output pulses. The beam delivery system for delivering and focusing at least one pulse of the amplified sequence of pulses onto the target material. The at least one output pulse having a pulse duration in the range of about 10 picoseconds to less than 1 nanosecond. The pulse duration being within a thermal processing range. The at least one focused output pulse having sufficient power density at a location within the target material to reduce the reflectivity of the target material and efficiently couple the focused output into the target material to remove the target material.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS CORP
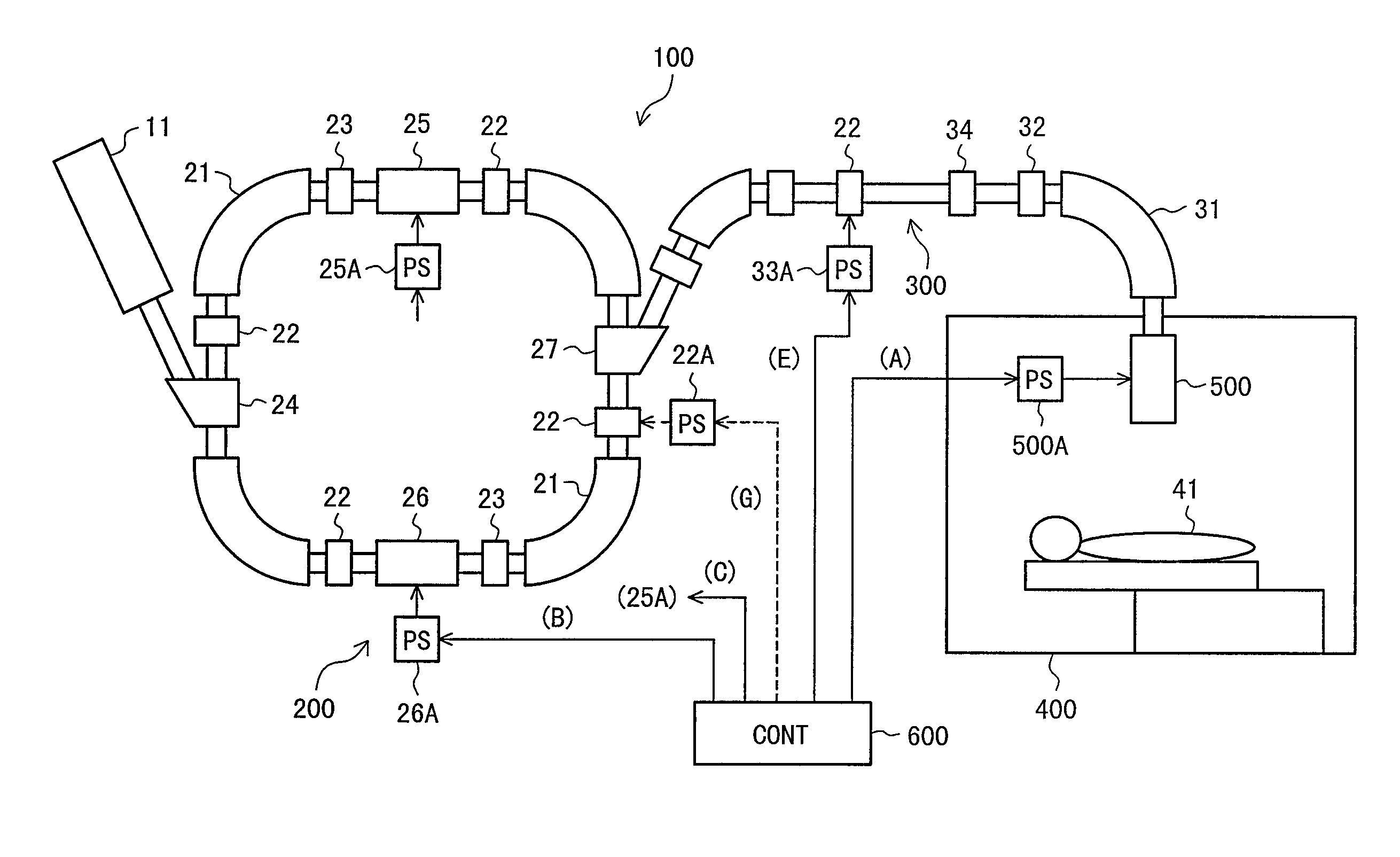
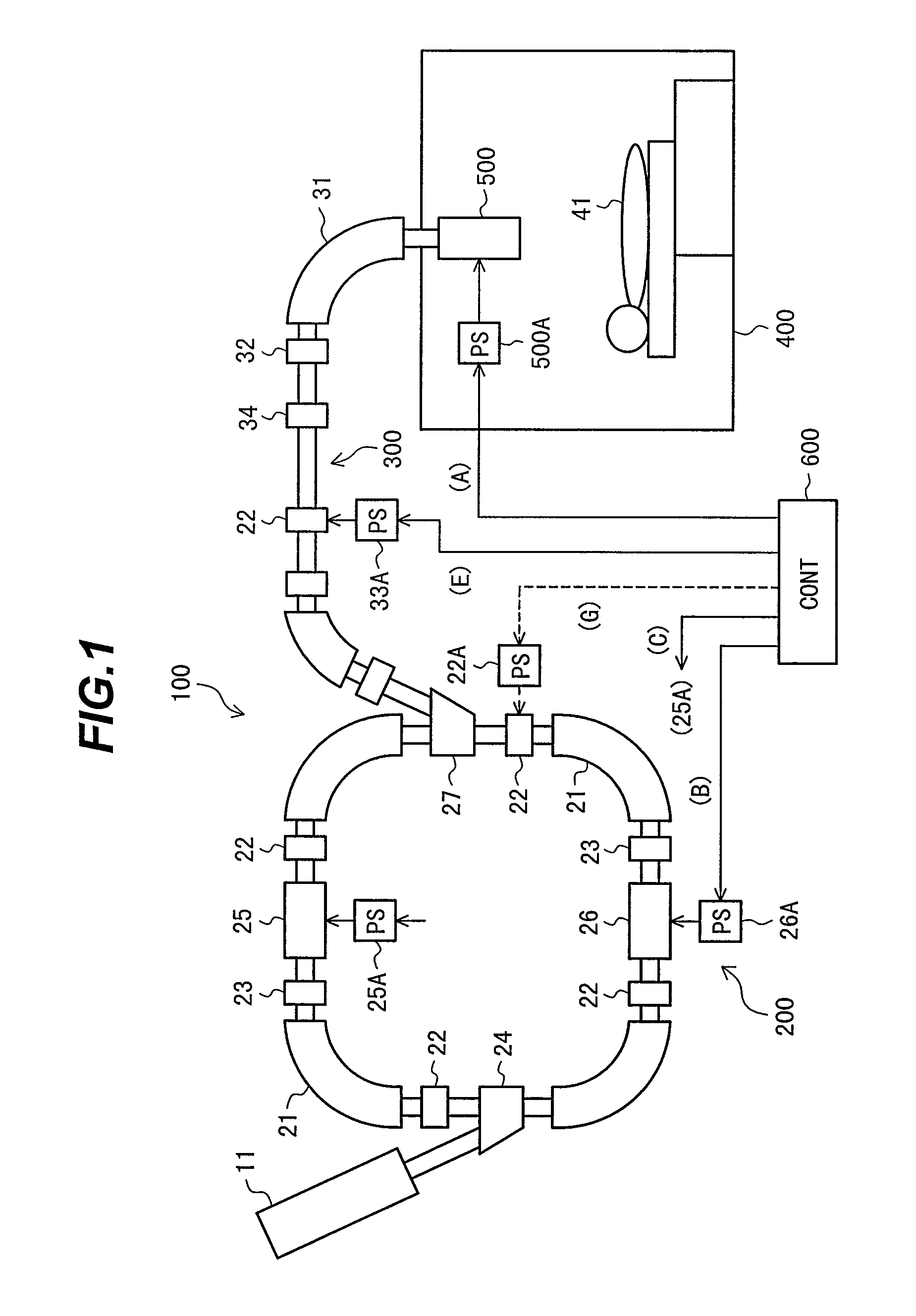
Particle beam therapy system
ActiveUS7772577B2Quality improvementLow costElectrode and associated part arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansTransport systemSynchrotron
A particle beam therapy system using a spot scanning method includes a synchrotron, a beam transport system, an irradiation system, and a controller. A controller is configured to turn on a radio frequency electromagnetic field to be applied to an extraction system when a charged particle beam is to be supplied to the irradiation system, and turn off the radio frequency electromagnetic field to be applied to the extraction system when the supply of the charged particle beam to the irradiation system is to be blocked by means of an electromagnet provided in the beam transport system or in the synchrotron. The controller is also adapted to turn off a radio frequency acceleration voltage to be applied to an acceleration cavity in synchronization with the turning-off of the radio frequency electromagnetic field to be applied to the extraction device.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Beam delivery system for laser dark-field illumination in a catadioptric optical system
A method and apparatus for inspecting a specimen are provided. The apparatus comprises a primary illumination source, a catadioptric objective exhibiting central obscuration that directs light energy received from the primary illumination source at a substantially normal angle toward the specimen, and an optical device, such as a prism or reflective surface, positioned within the central obscuration resulting from the catadioptric objective for receiving further illumination from a secondary illumination source and diverting the further illumination to the specimen. The method comprises illuminating a surface of the specimen at a variety of angles using a primary illumination source, illuminating the surface using a secondary illumination source, the illuminating by the secondary illumination source occurring at a substantially normal angle of incidence; and imaging all reflected, scattered, and diffracted light energy received from the surface onto a detector.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Laser produced plasma EUV light source
ActiveUS20060219957A1Increase the rate of chemical reactionsRadiation pyrometryNanoinformaticsLine tubingLight beam
An EUV light source is disclosed that may include a laser source, e.g. CO2 laser, a plasma chamber, and a beam delivery system for passing a laser beam from the laser source into the plasma chamber. Embodiments are disclosed which may include one or more of the following; a bypass line may be provided to establish fluid communication between the plasma chamber and the auxiliary chamber, a focusing optic, e.g. mirror, for focusing the laser beam to a focal spot in the plasma chamber, a steering optic for steering the laser beam focal spot in the plasma chamber, and an optical arrangement for adjusting focal power.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Bi-polar treatment facility for treating target cells with both positive and negative ions
A system for treating target cells with both positive and negative ions comprises a bi-polar beam delivery system configured to create and deliver both positive ion beams and negative ion beams. The bi-polar beam delivery system comprises a bi-polar accelerator configured to accelerate positive and negative ions in the same direction making such a bi-polar beam delivery system practical.
Owner:NANOLIFE SCI
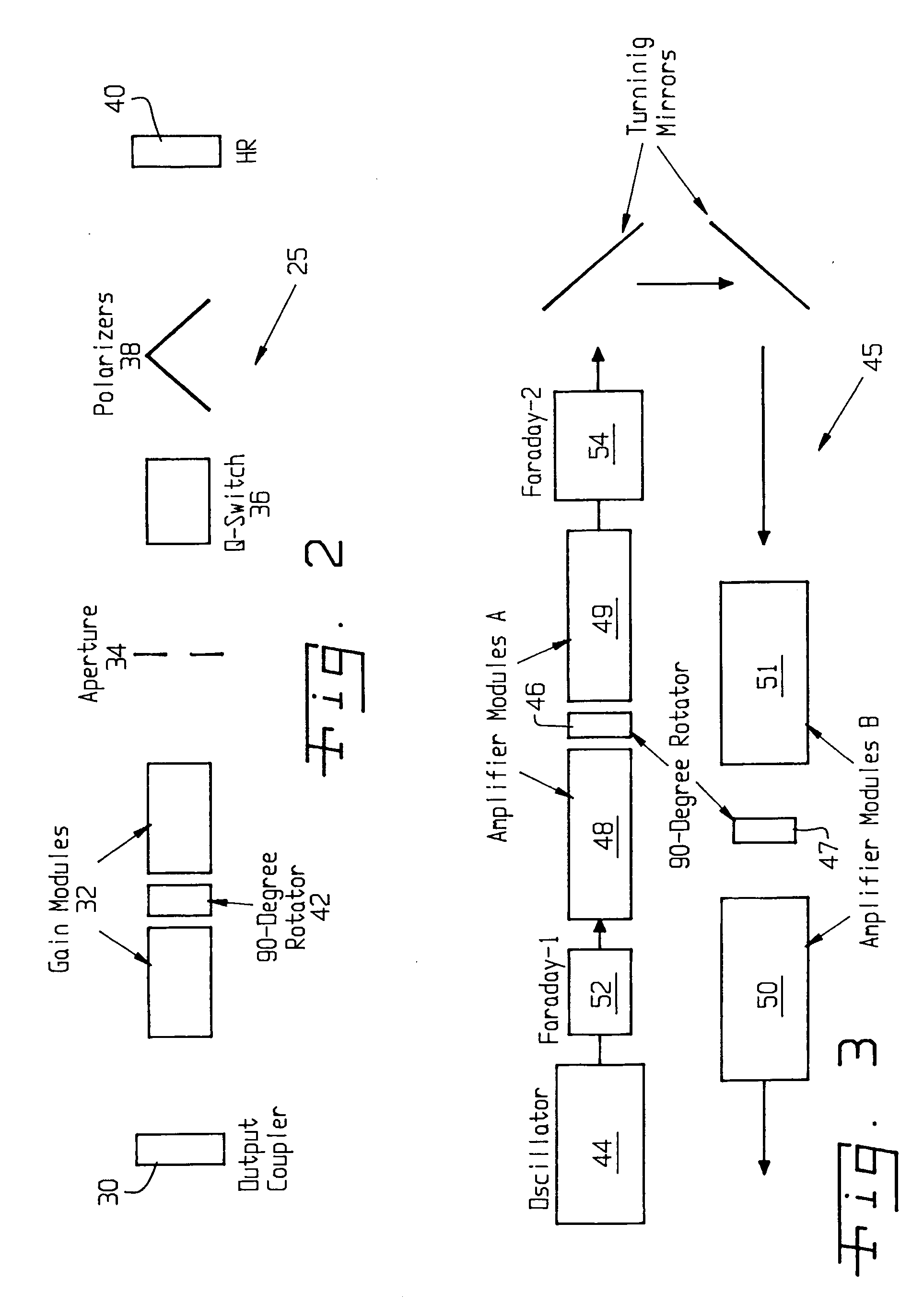
Long delay and high TIS pulse stretcher
A method and apparatus for laser light pulse stretching is disclosed which may comprise a beam splitter in the path of a laser output light pulse beam; selected to pass a first percent of the energy of a first input pulse of the laser output light pulse beam along a laser output light pulse beam output path as a first output pulse and to reflect a second percent of the energy of the laser output light pulse beam into a first delayed beam; an optical delay path receiving the first delayed beam and returning the first delayed beam to the beam splitter in an orientation such that a third percent of the first delayed beam is reflected into the output path as a second output pulse and a fourth percent is passed into the optical delay path as a second delayed beam; the optical delay path receiving the second delayed beam and returning the second delayed beam to the beam splitter in an orientation such that the third percent of the second delayed beam is reflected into the output path as a third output pulse and the fourth percent of the second delayed beam is passed into the optical delay path as a third delayed beam; the optical delay path receiving the third delayed beam and returning the third delayed beam to the beam splitter in an orientation such that the third percent of the third delayed beam is reflected into the output path as a fourth output pulse; the first input pulse being a first pulse in a plurality of pulses output from a prior pulse stretcher, each of a plurality of succeeding input pulses comprising the output of the prior pulse stretcher resulting from the stretching of a narrow band laser light output pulse, forming successive first, second, third and fourth output pulses, the combination of which forms a pulse stretcher having an output with TIS of at least 200 ns. The optical delay path may be formed of a plurality of at least eight reflecting mirrors and contained in an elongated enclosure having first and second end plates mounting a first group of at least four of the at least eight reflecting mirrors mounted on the first mounting surface symmetrically about a center axis of the optical delay path and a second group of at least four of the at least eight reflecting mirrors mounted on the second mounting surface symmetrically about the center axis. The mirrors may be staggered in a predefined pattern, e.g., a circular pattern. The delay path may lie in a plurality of planes. The apparatus may be part of a laser system, part of a beam delivery system or an interface between the two.
Owner:CYMER INC
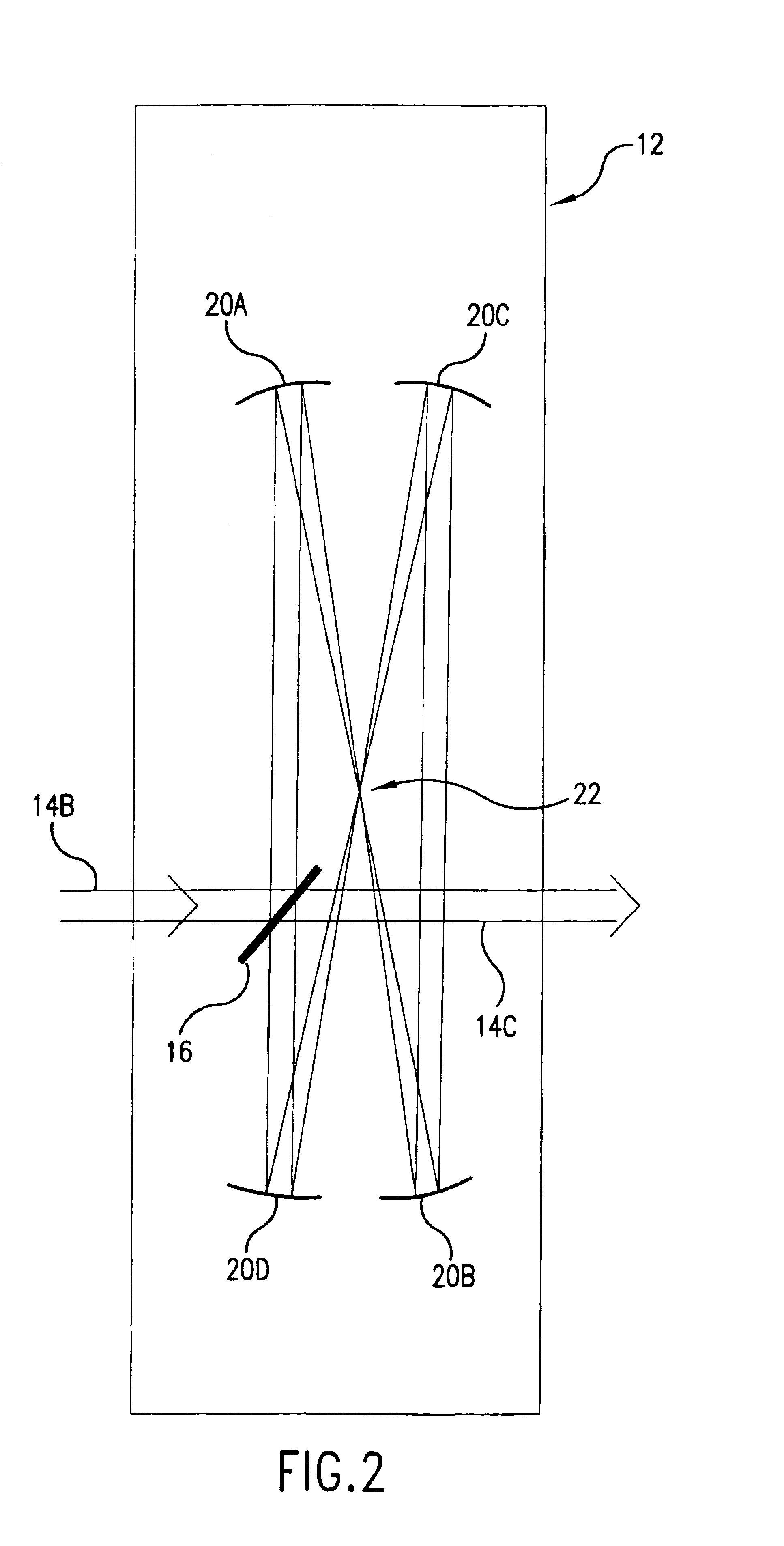
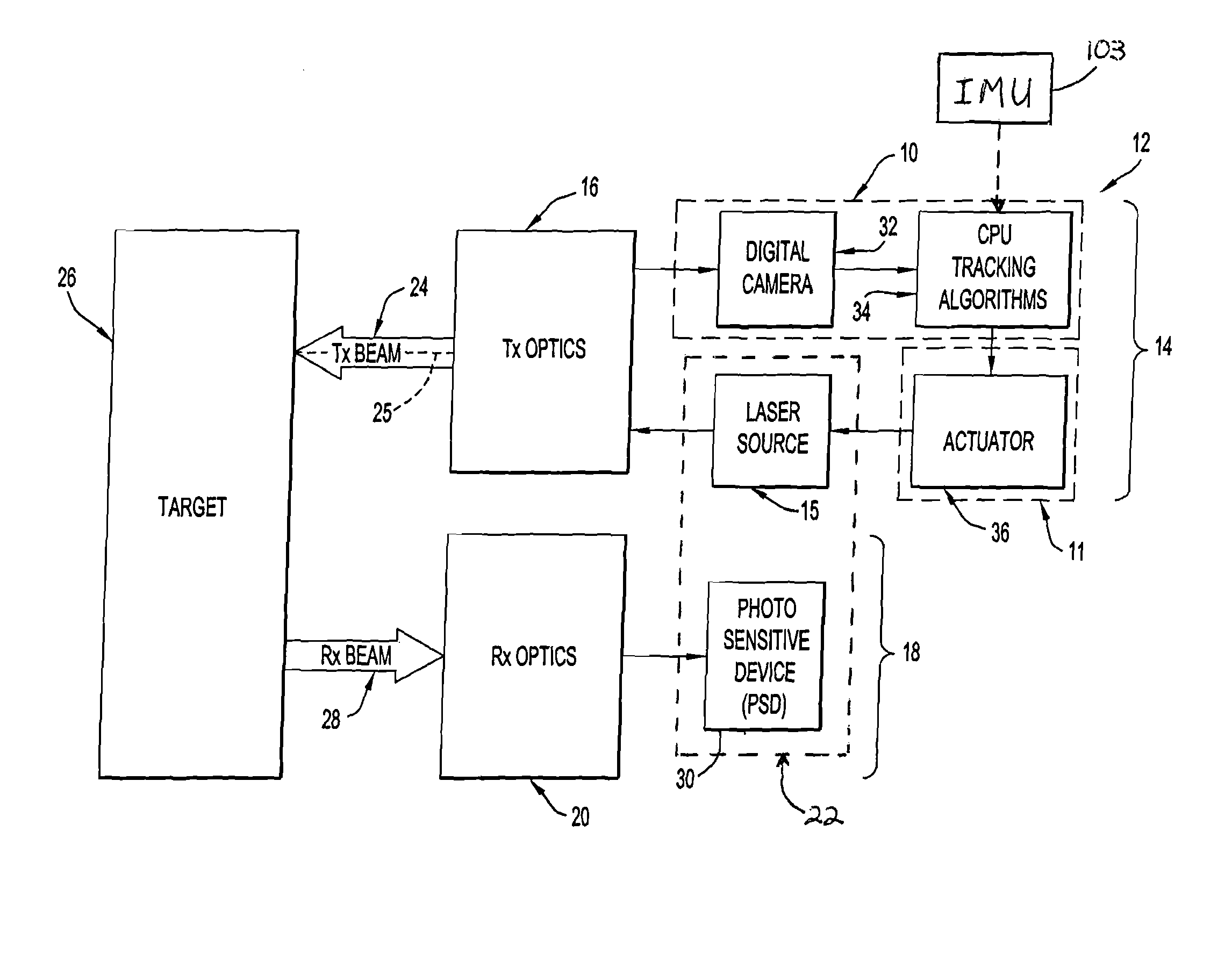
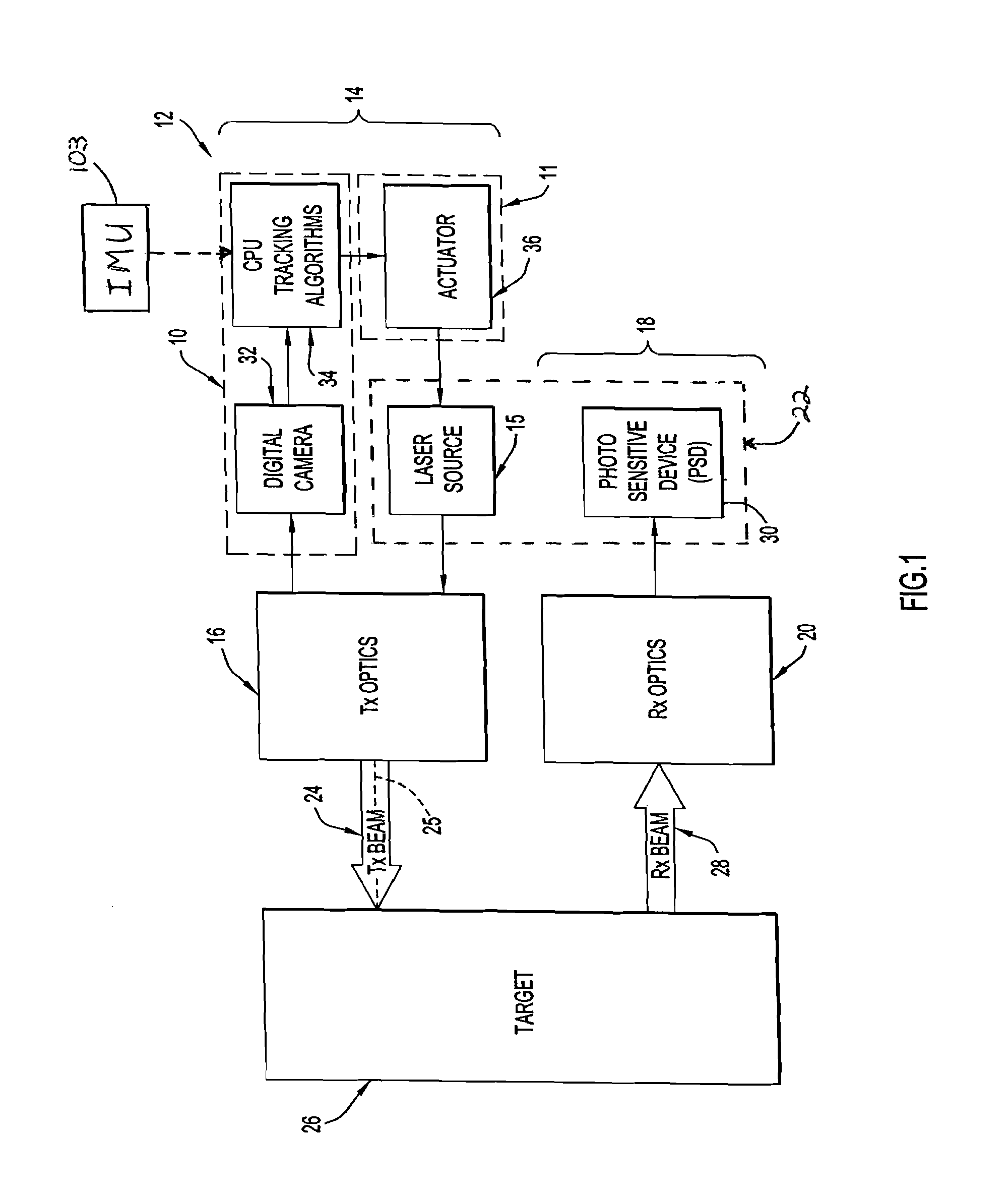
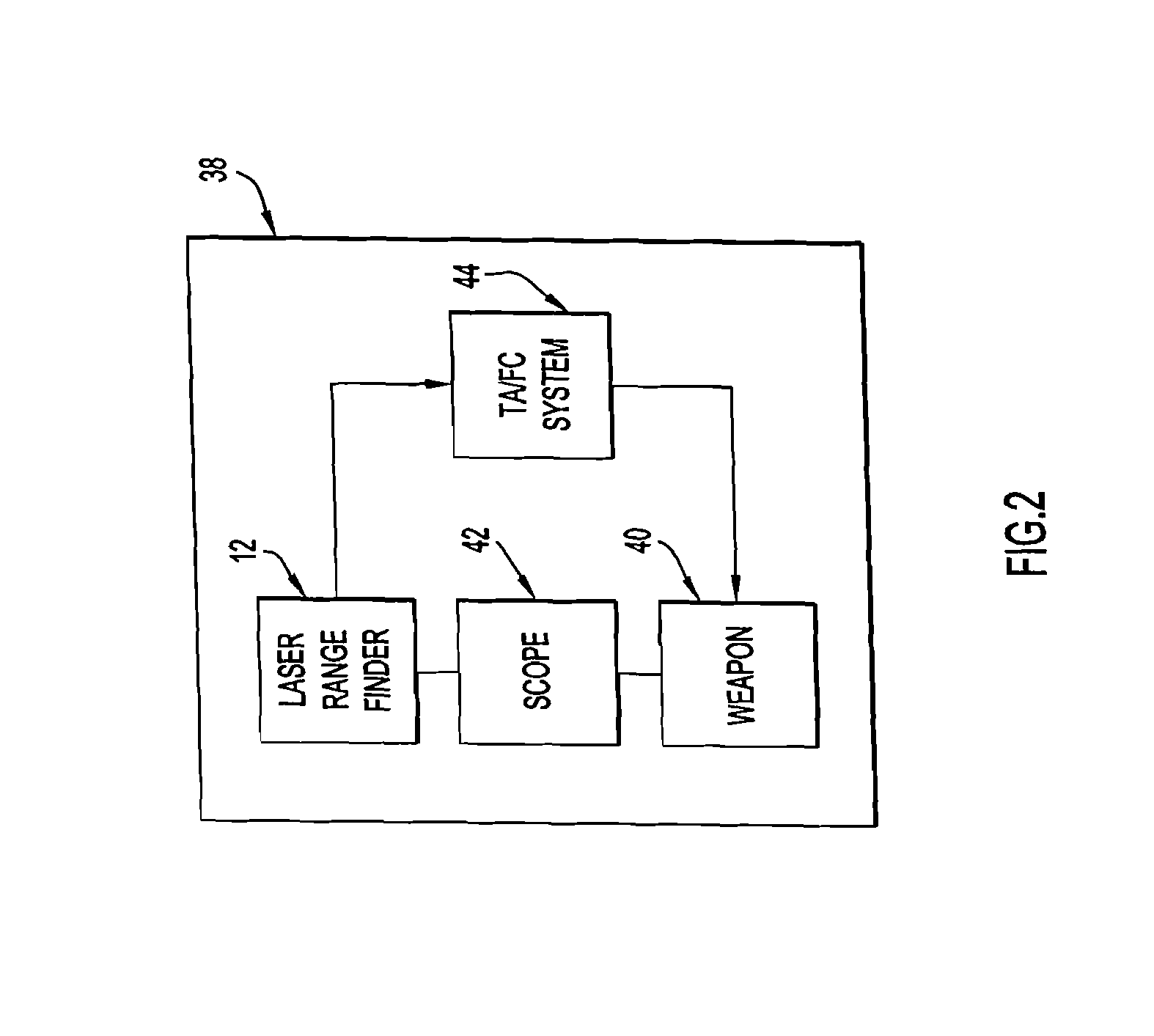
Systems and methods for automatic target tracking and beam steering
An automatic target tracking system and method employ an image capturing system for acquiring a series of images in real time of a distant area containing a remote target, and a processing system for processing the acquired images to identify the target and follow its position across the series of images. An automatic beam steering and method operate in conjunction with a laser source for emitting a laser beam to be transmitted in the form of a transmitted laser beam extending along a steerable beam transmission axis to the remote target. The beam steering system is controlled by the processing system to steer the beam transmission axis to be aimed at the target being tracked by the target tracking system, so that the transmitted laser beam will be transmitted at the appropriate angle and in the appropriate direction to be aimed at the tracked target.
Owner:INTELLIGENT AUTOMATION LLC
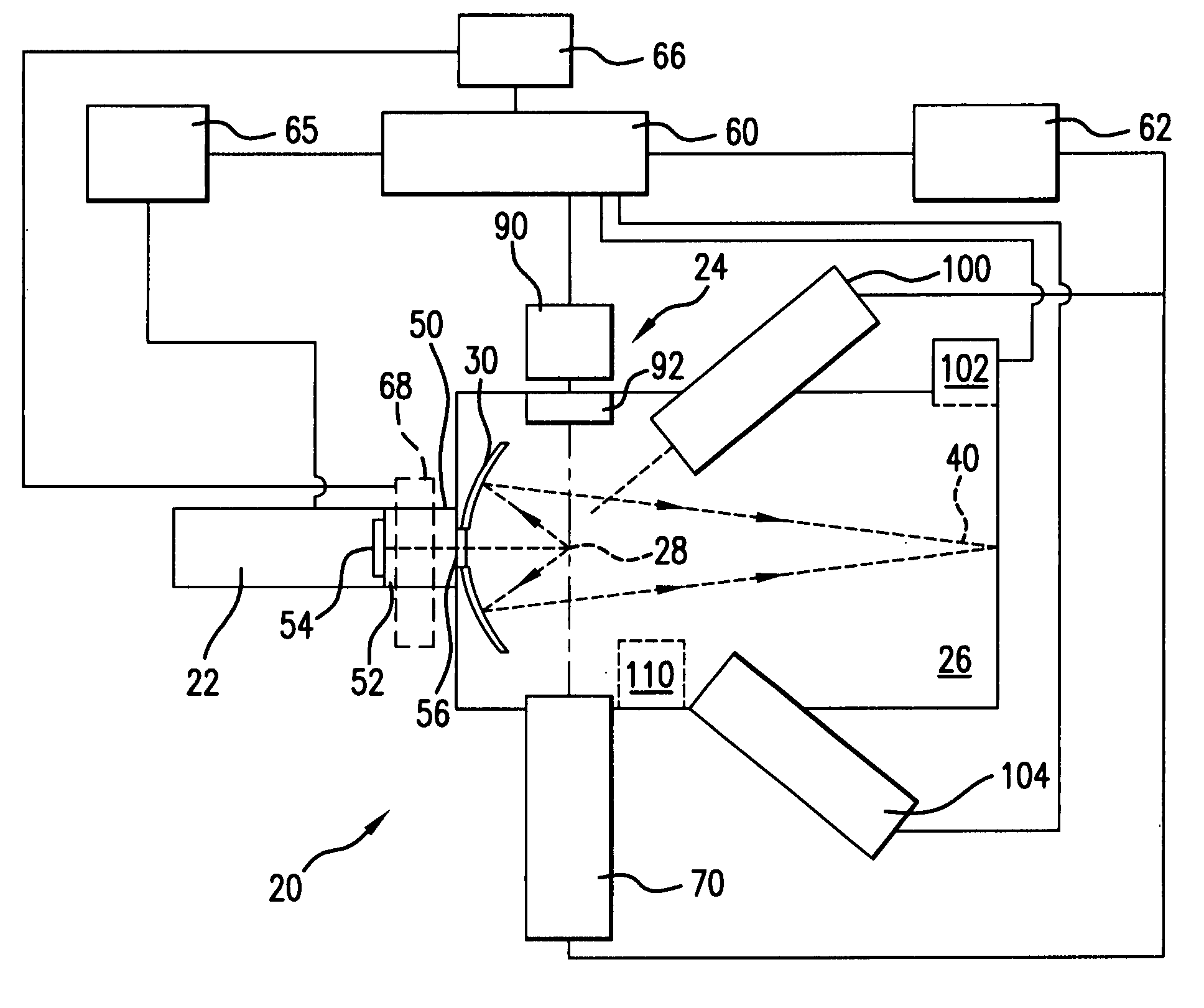
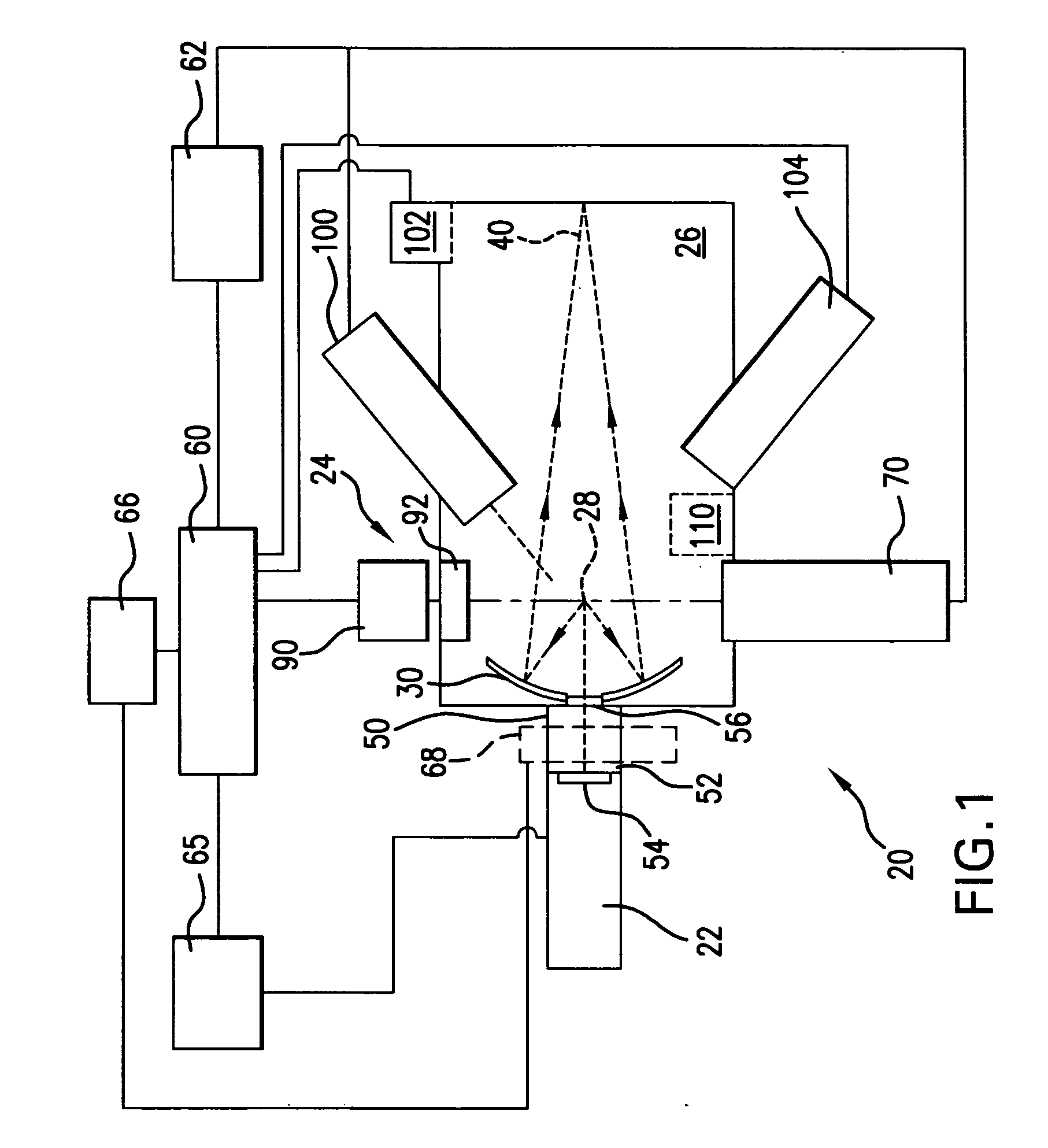
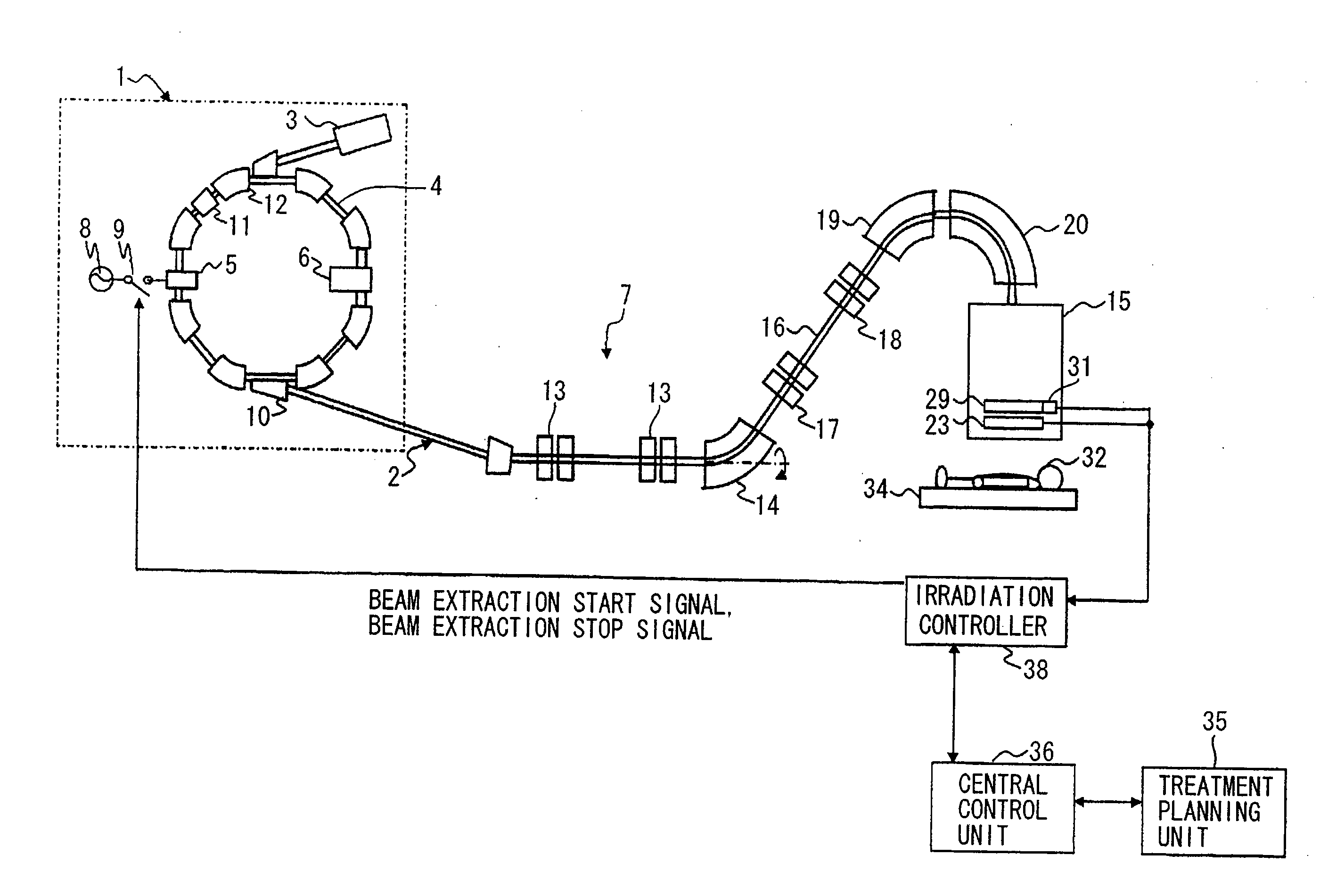
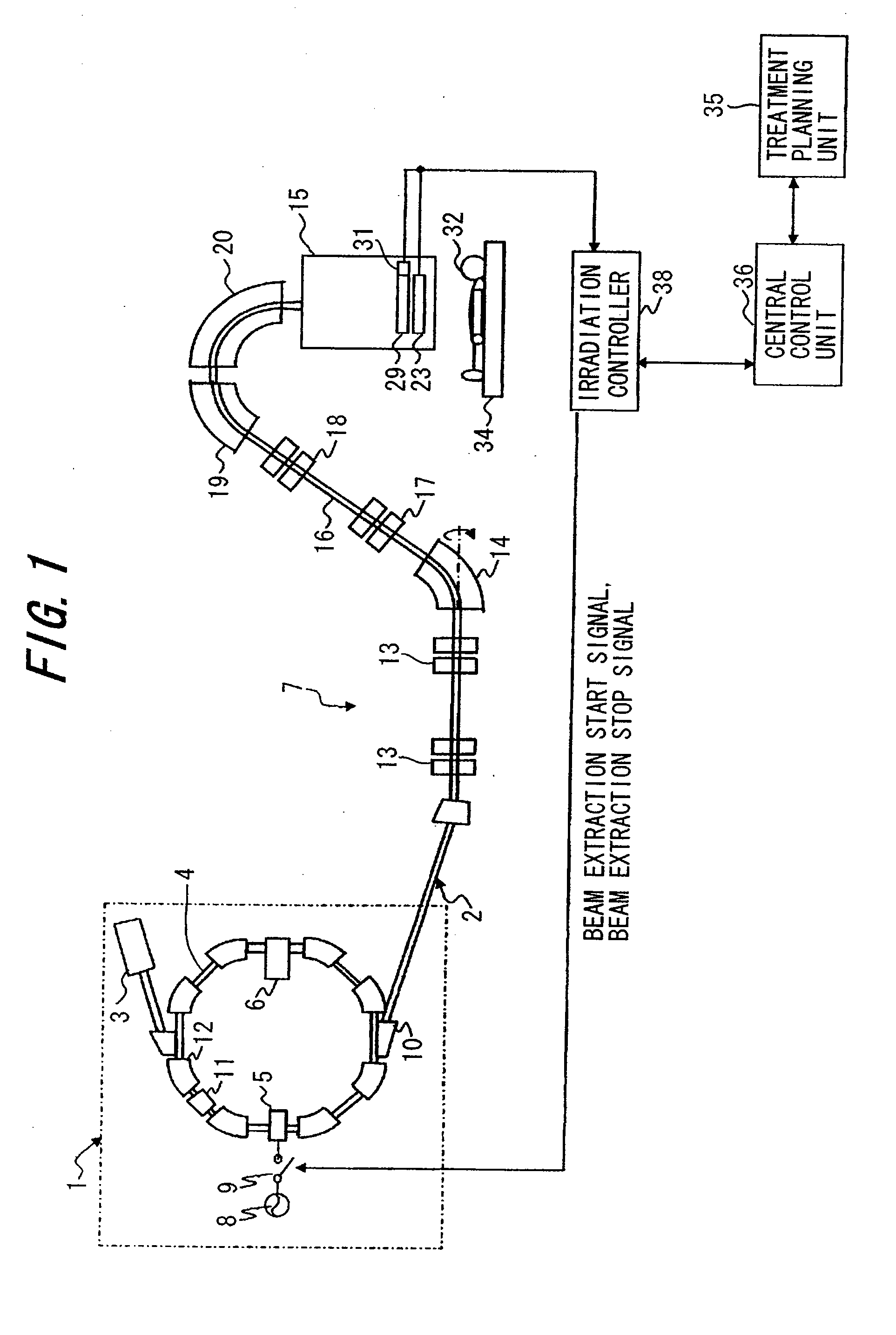
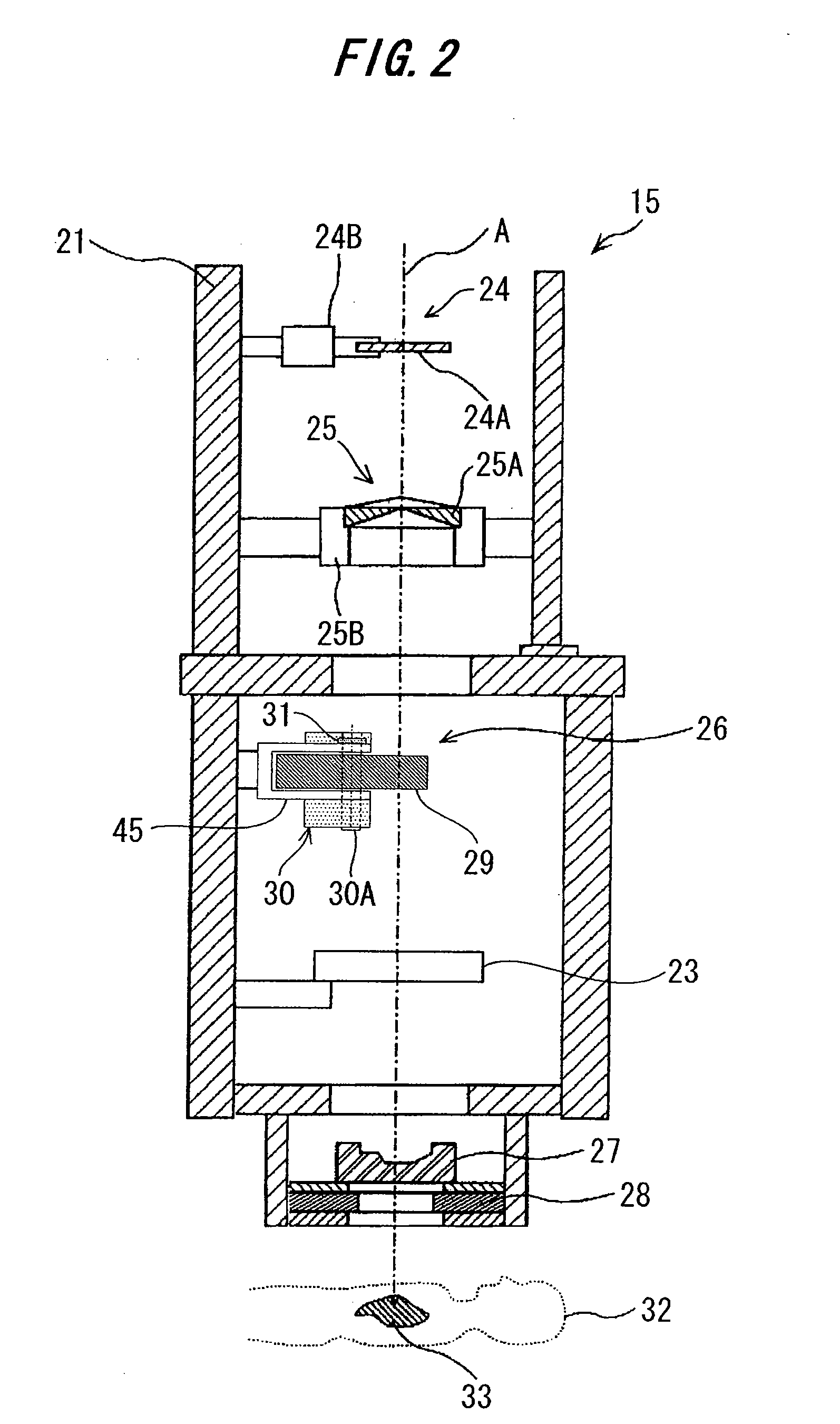
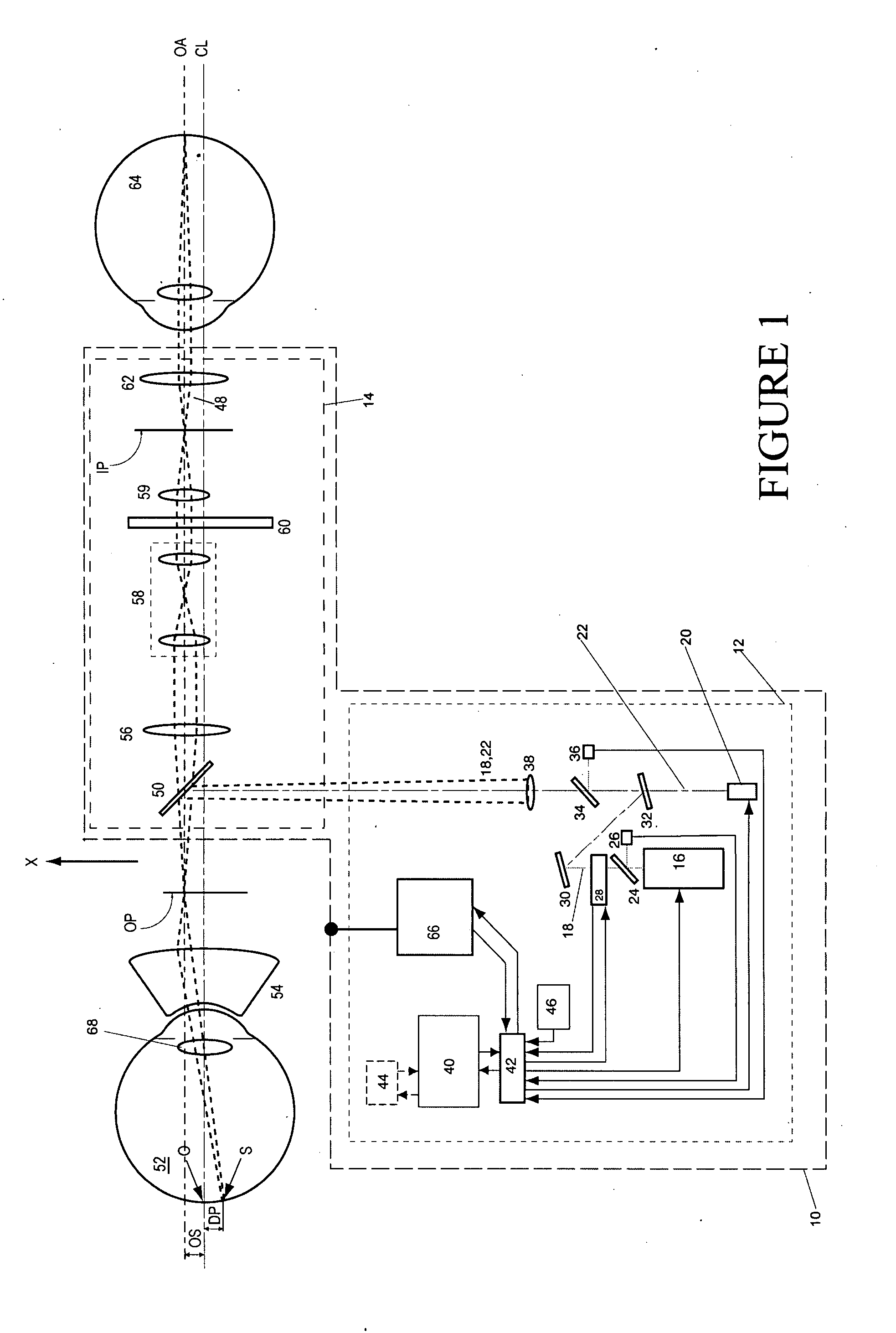
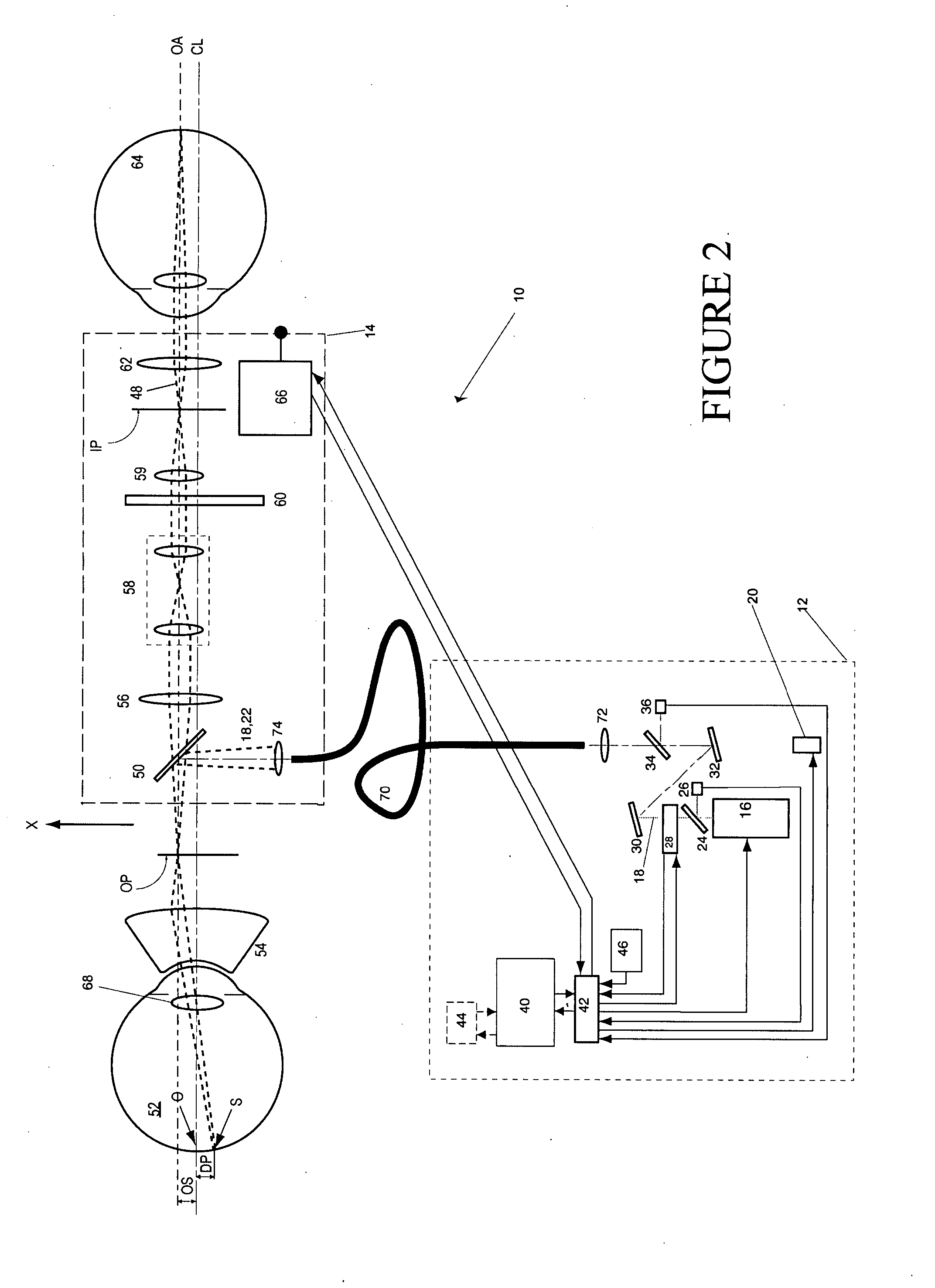
Charged Particle Beam Irradiation System
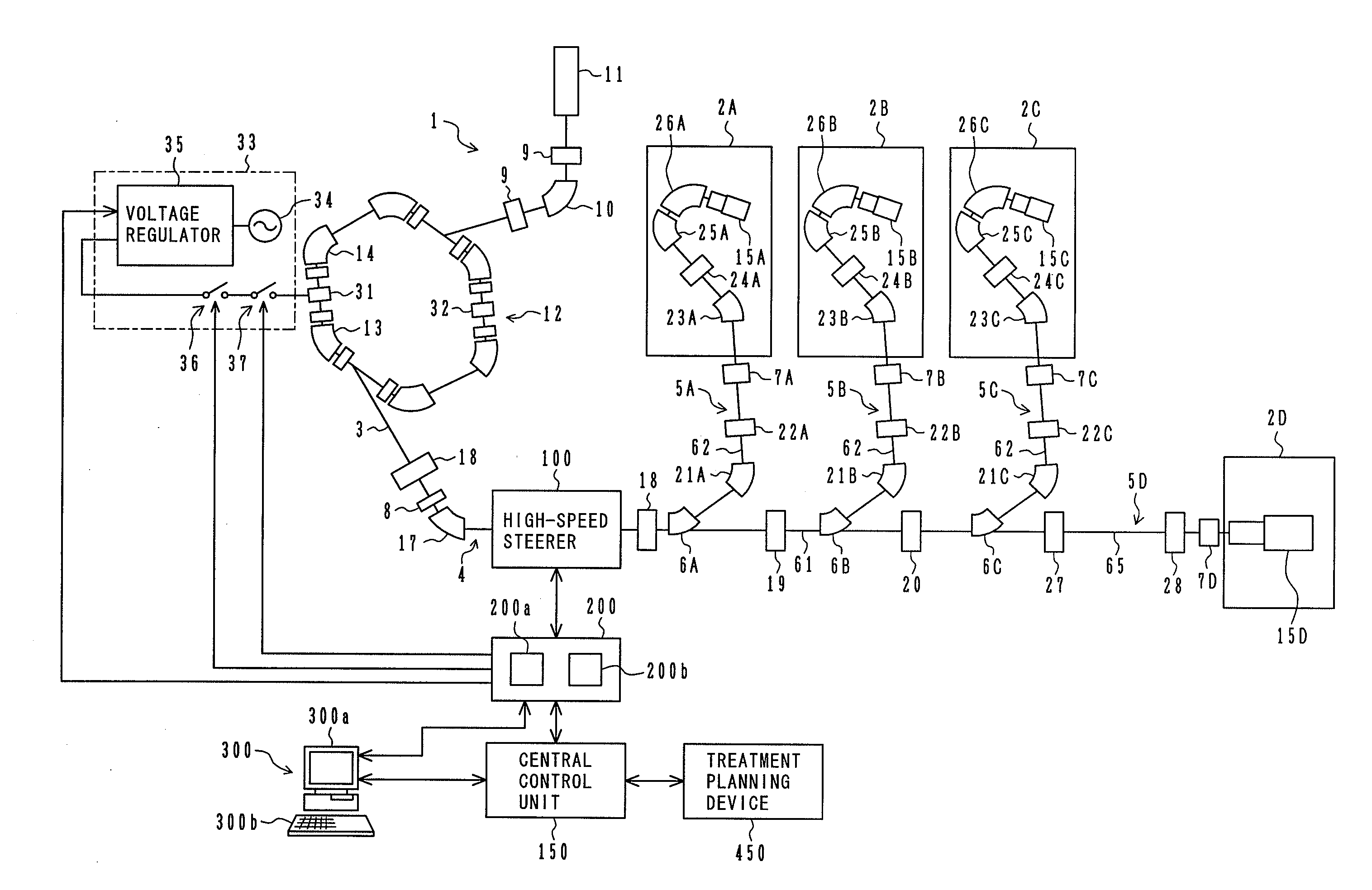
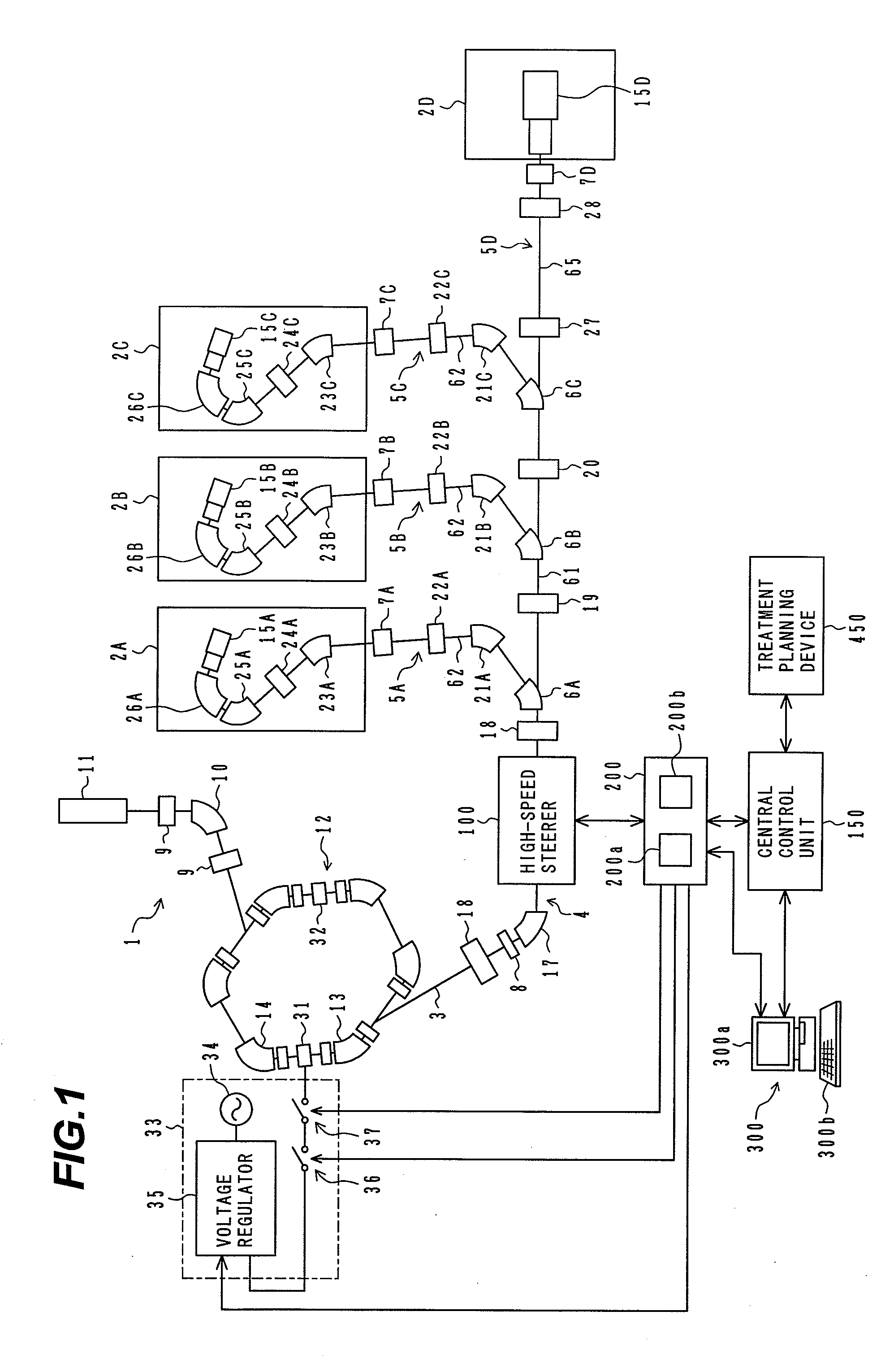
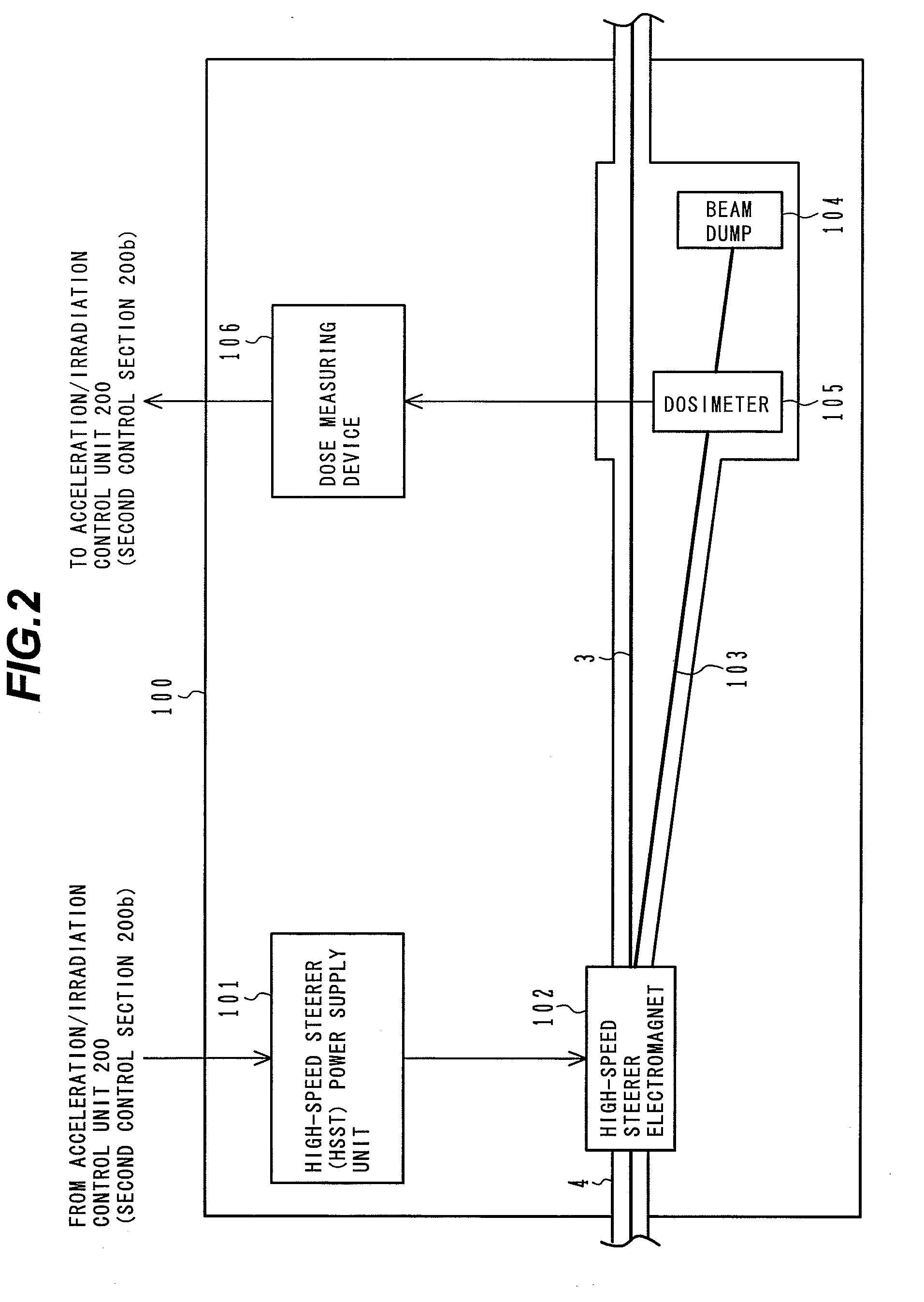
ActiveUS20090184263A1Shorten the timeImprove accuracyThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsBeam dumpLight beam
A charged particle beam irradiation system comprises a high-speed steerer (beam dump device) 100 disposed in a course of a beam transport line 4 through which an ion beam is extracted from a charged-particle beam generator 1. The beam dump device 100 is provided with dose monitoring devices 105, 106 for measuring a dose of an ion beam applied to a beam dump 104 so that the intensity of the ion beam can be measured without transporting the ion beam to irradiation nozzles 15A through 15D. Thus, the system is capable of adjusting the intensity of an ion beam extracted from a synchrotron without operating each component of a beam transport line, and an irradiation nozzle.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
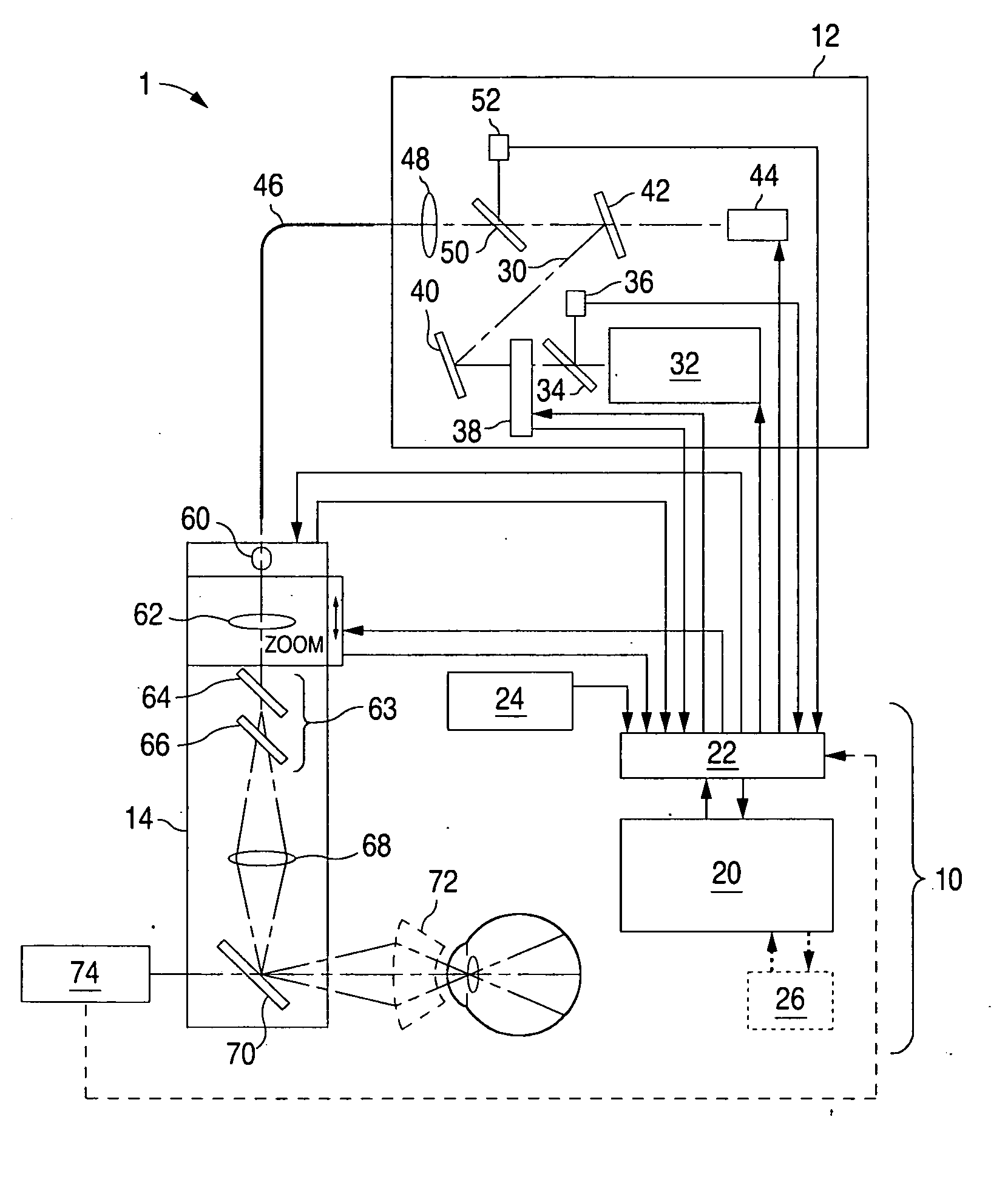
System and method for minimally traumatic ophthalmic photomedicine
ActiveUS20070129709A1Good treatment effectLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLight beamTarget tissue
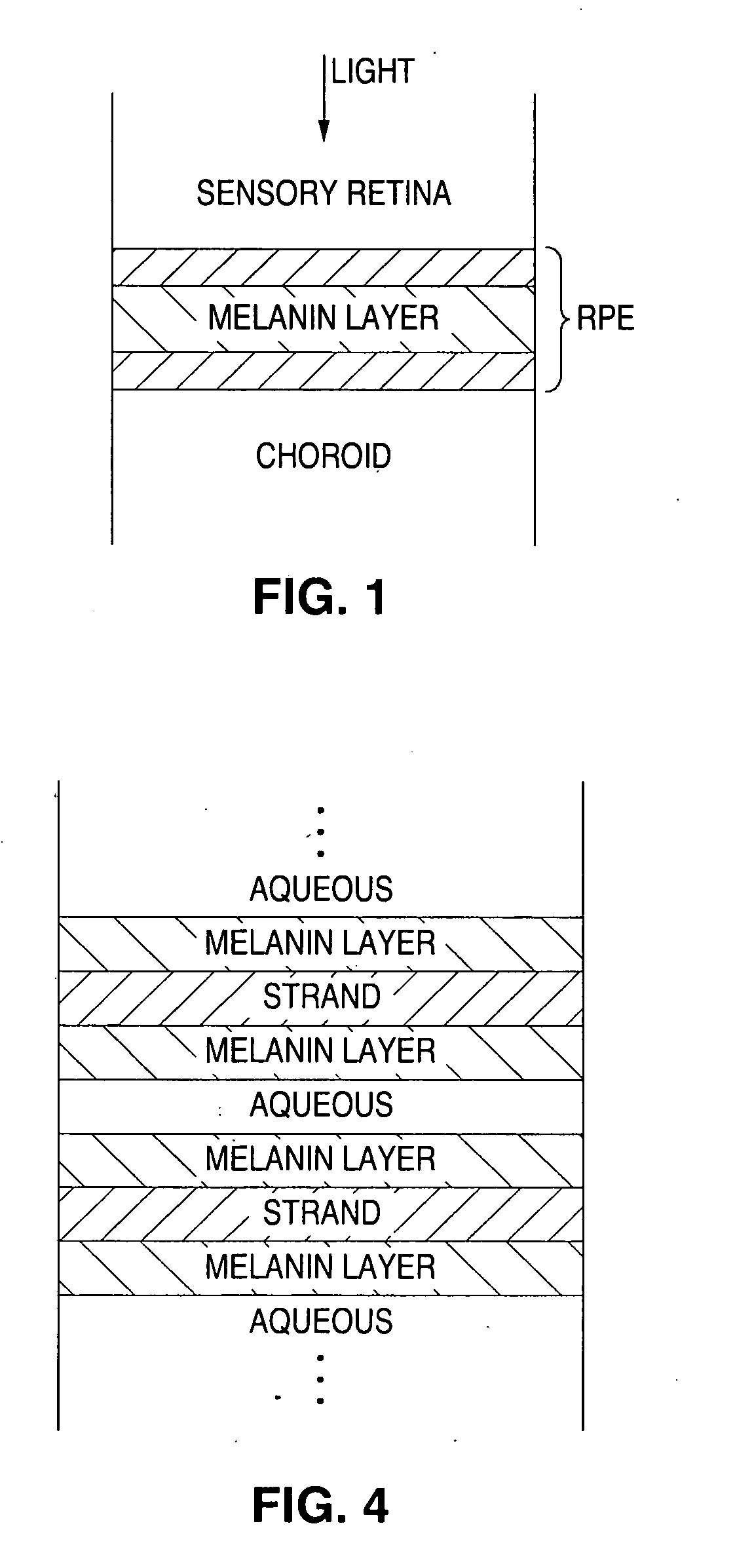
A system and method for treating ophthalmic target tissue in which a light source generates a beam of light, a scanner unit deflects the beam of light into a pattern, a beam delivery unit for delivering the pattern to ophthalmic target tissue. The light is either pulsed or moved across the target tissue such that the light pulses having a duration of, or the light dwells on any given point of target tissue for, between 30 μs and 10 ms.
Owner:IRIDEX CORP
Ion acceleration system for medical and/or other applications
ActiveUS8405056B2Enhanced couplingWeaken energyStability-of-path spectrometersConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMedicineEngineering
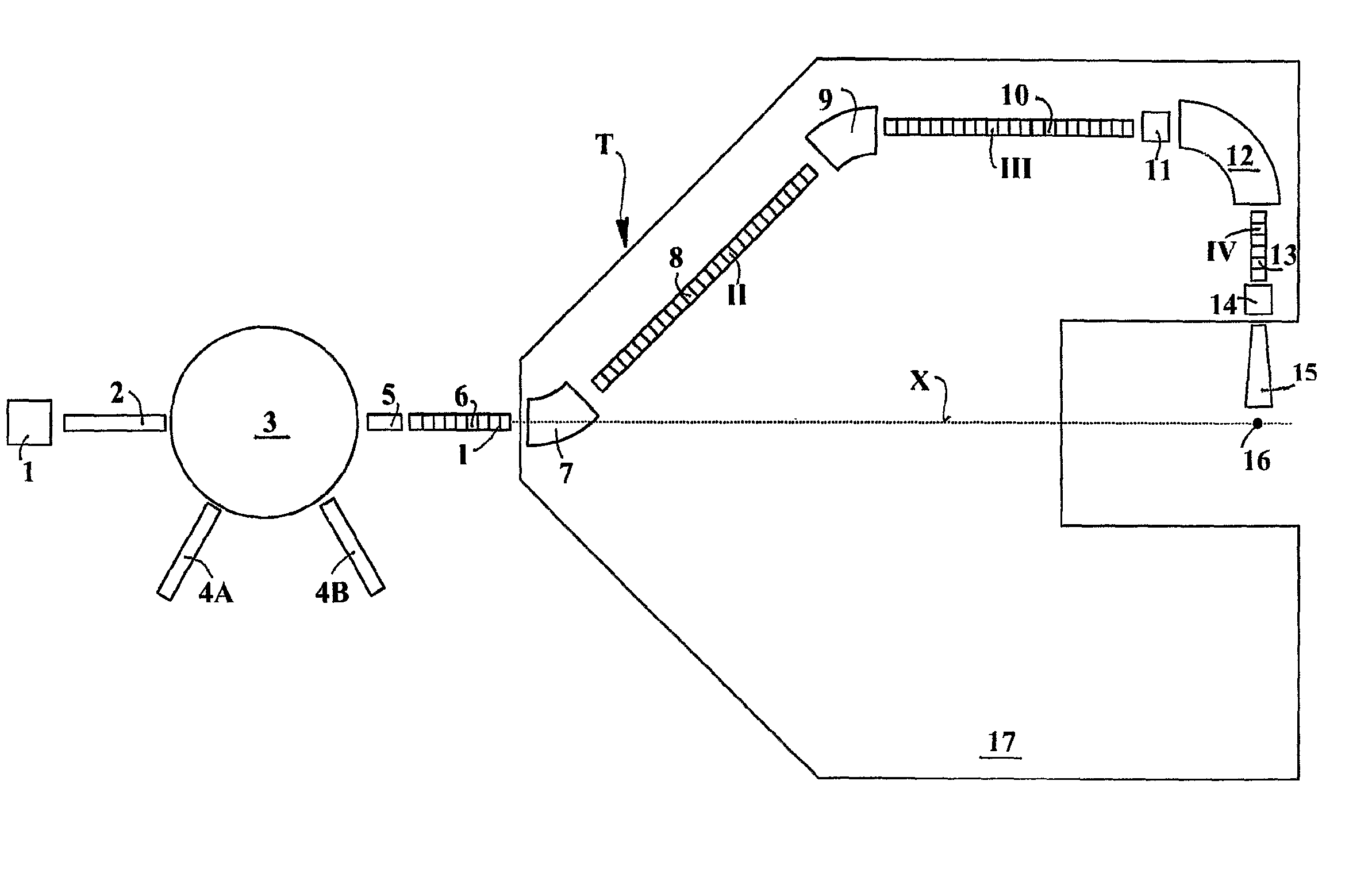
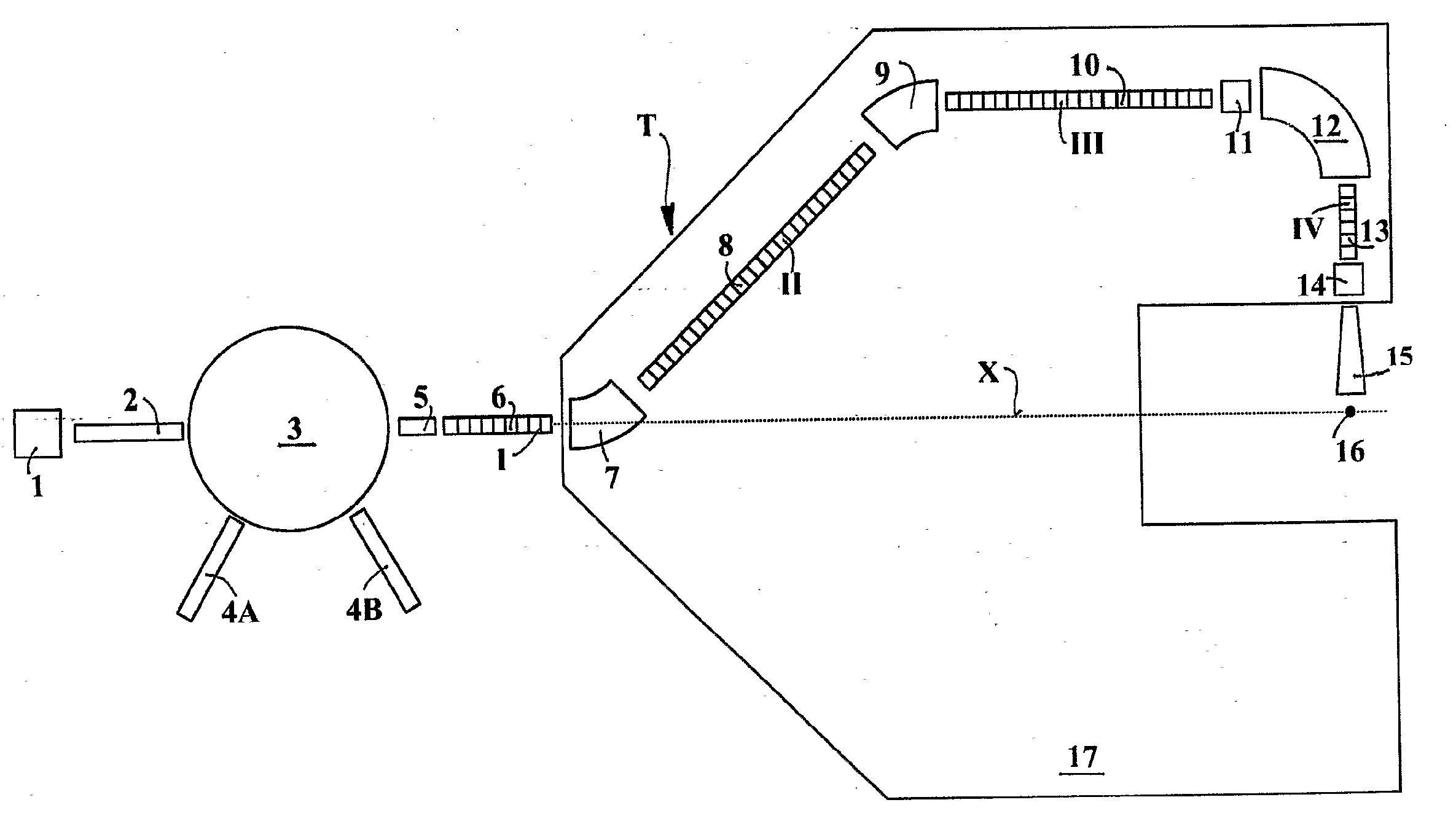
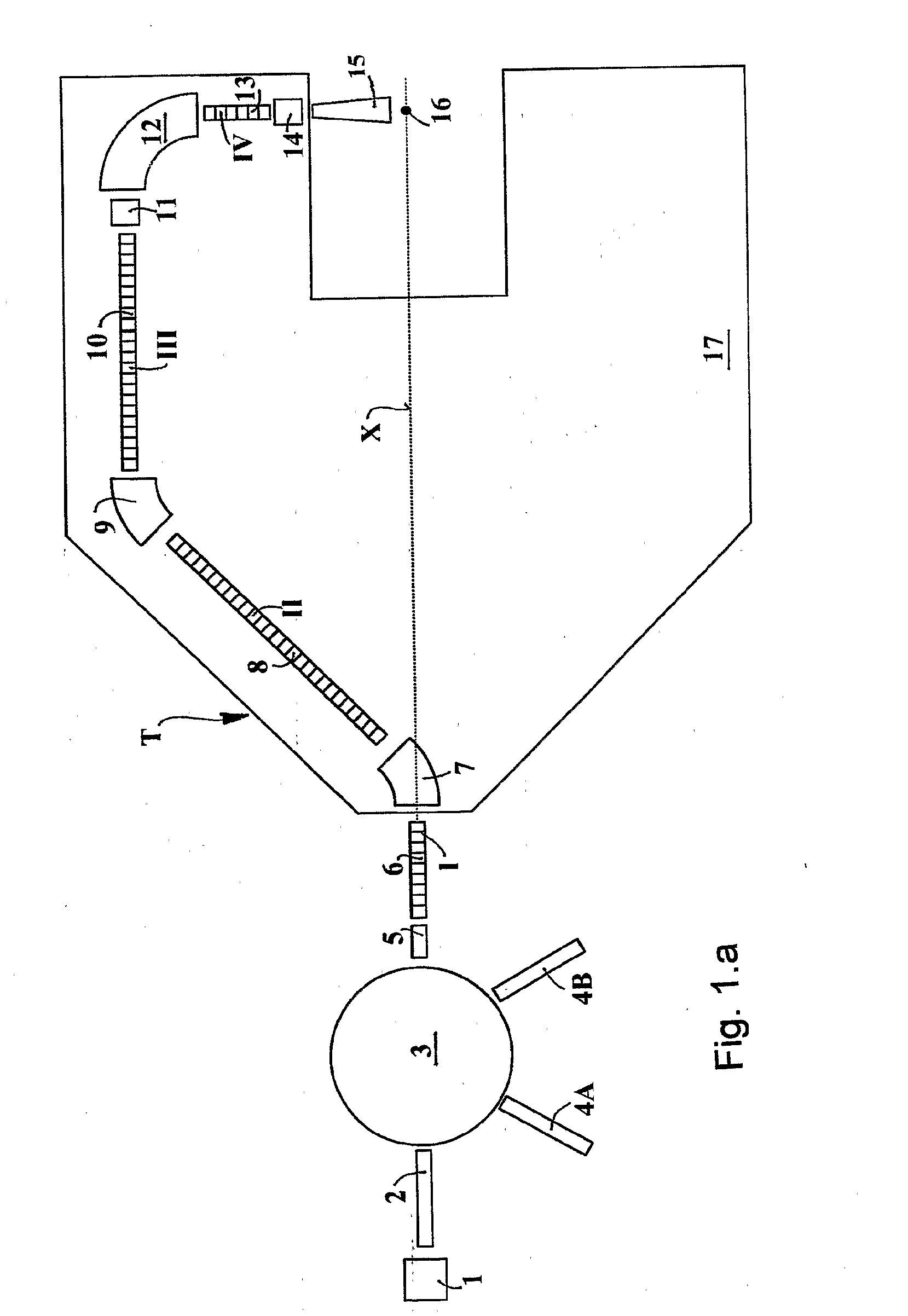
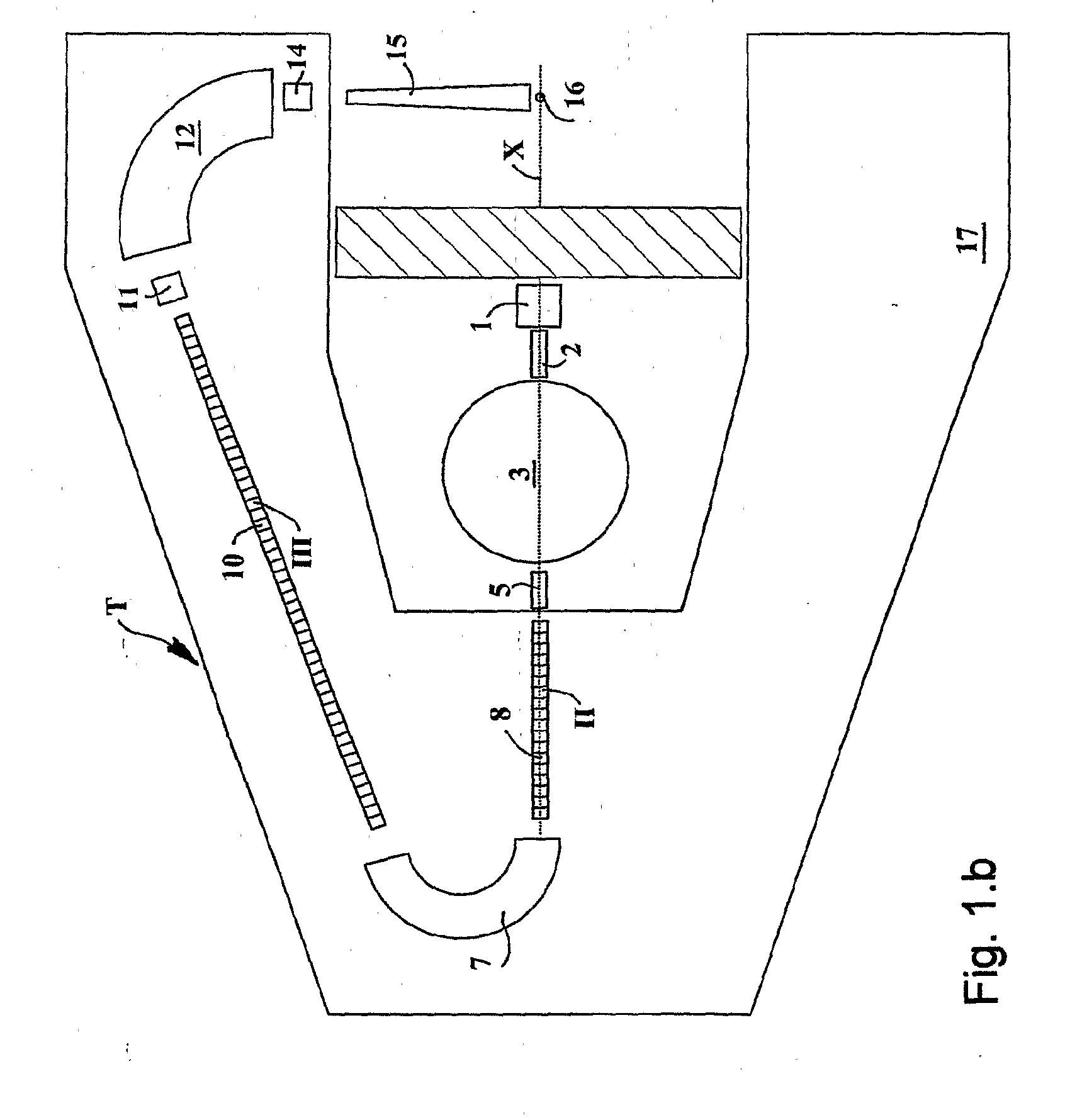
The ion acceleration system or complex (T) for medical and / or other applications is composed in essence by an ion source (1), a pre-accelerator (3) and one or more linear accelerators or linacs (6, 8, 10, 13), at least one of which is mounted on a rotating mechanical gantry-like structure (17). The isocentrical gantry (17) is equipped with a beam delivery system, which can be either ‘active’ or ‘passive’, for medical and / or other applications. The ion source (1) and the pre-accelerator (3) can be either installed on the floor, which is connected with the gantry basement, or mounted, fully or partially, on the rotating mechanical structure (17). The output beam can vary in energy and intensity pulse-by-pulse by adjusting the radio-frequency field in the accelerating modules of the linac(s) and the beam parameters at the input of the linear accelerators.
Owner:ADVANCED ONCOTHERAPY PLC
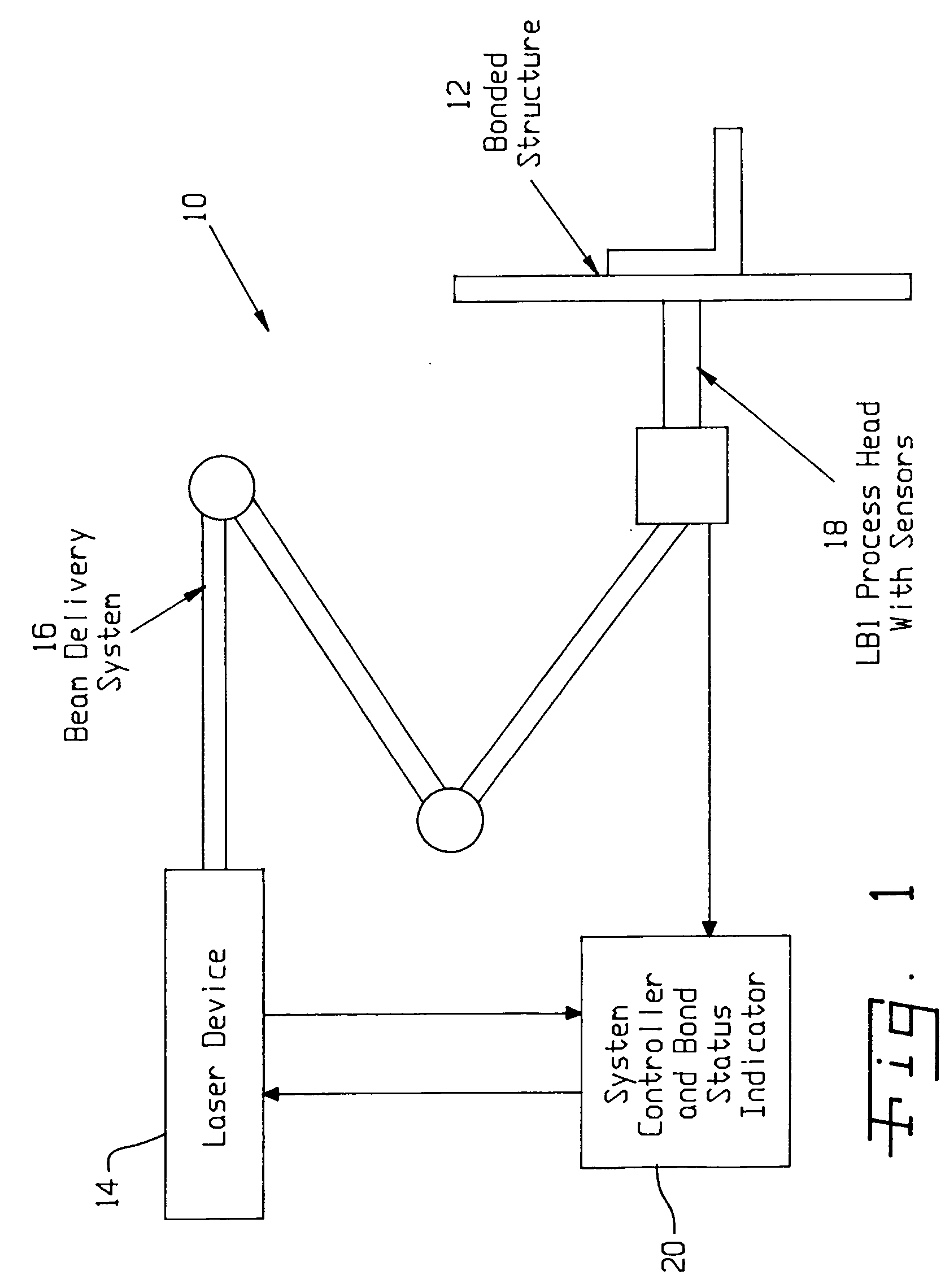
Laser system and method for non-destructive bond detection and evaluation
ActiveUS20050120803A1Easy to collectAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesNon destructiveLight beam
A system for evaluating the integrity of a bonded joint in an article includes a laser configured in a laser shock processing arrangement to perform a laser shock processing treatment on the article. A beam delivery system employs an articulated arm assembly to communicate the radiant energy emitted by the laser to a process head proximate the article. The laser shock processing treatment causes the formation of shockwaves that propagate through the article, inducing internal stress wave activity that characteristically interacts with the bonded joint. A sensor detects a stress wave signature emanating from the article, which is indicative of the integrity of the bond. A detector such as a non-contact electromagnetic acoustic transducer provides a measure of the stress wave signature in the form of surface motion measurements.
Owner:LSP TECH INC
Beam delivery system for laser dark-field illumination in a catadioptric optical system
A method and apparatus for inspecting a specimen are provided. The apparatus comprises a primary illumination source, a catadioptric objective exhibiting central obscuration that directs light energy received from the primary illumination source at a substantially normal angle toward the specimen, and an optical device, such as a prism or reflective surface, positioned within the central obscuration resulting from the catadioptric objective for receiving further illumination from a secondary illumination source and diverting the further illumination to the specimen. The method comprises illuminating a surface of the specimen at a variety of angles using a primary illumination source, illuminating the surface using a secondary illumination source, the illuminating by the secondary illumination source occurring at a substantially normal angle of incidence; and imaging all reflected, scattered, and diffracted light energy received from the surface onto a detector.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
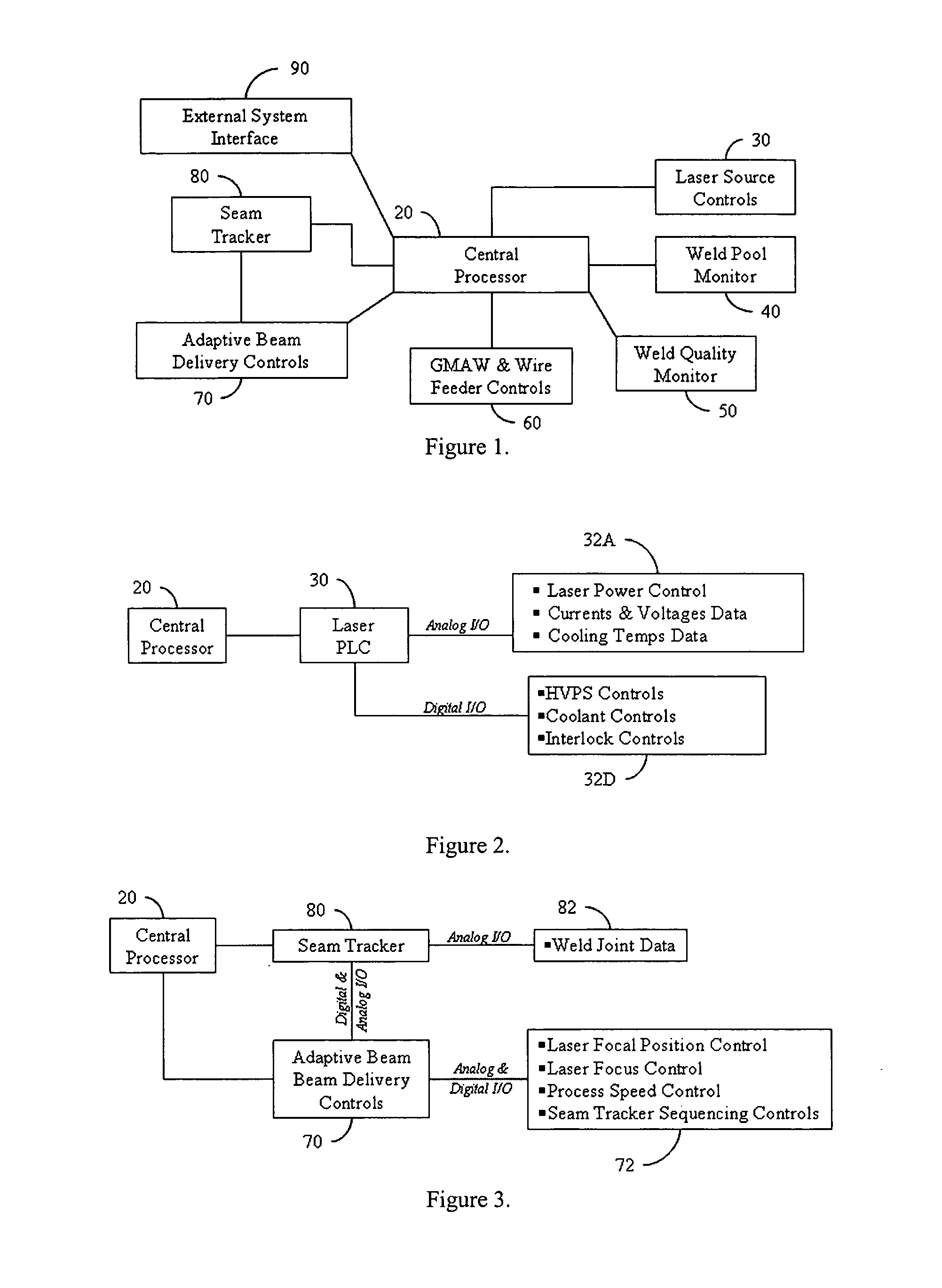
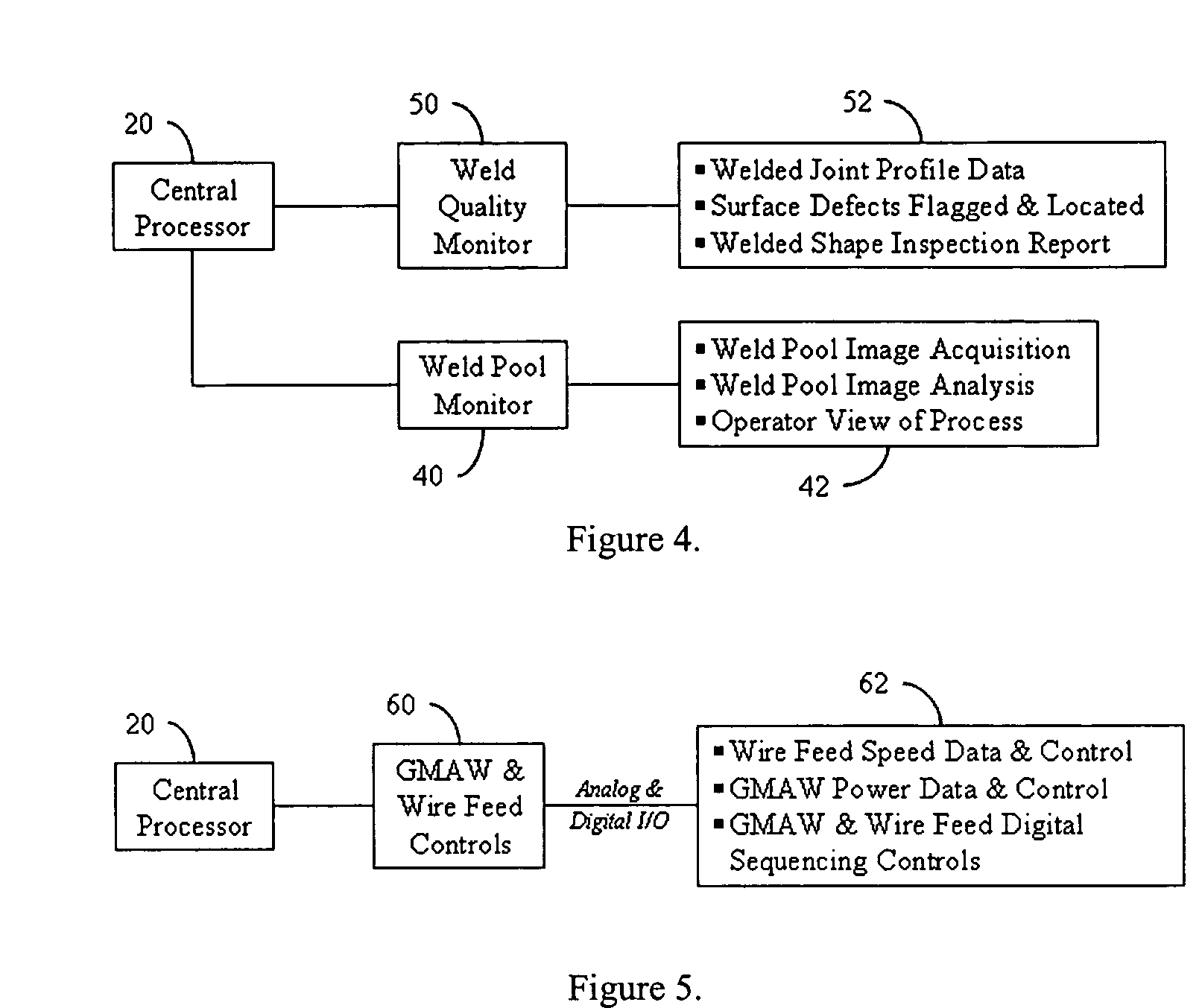
Laser welding control system
ActiveUS7107118B2Improve reliabilityReduce the amount requiredProgramme controlElectrical apparatusClosed loopVision based
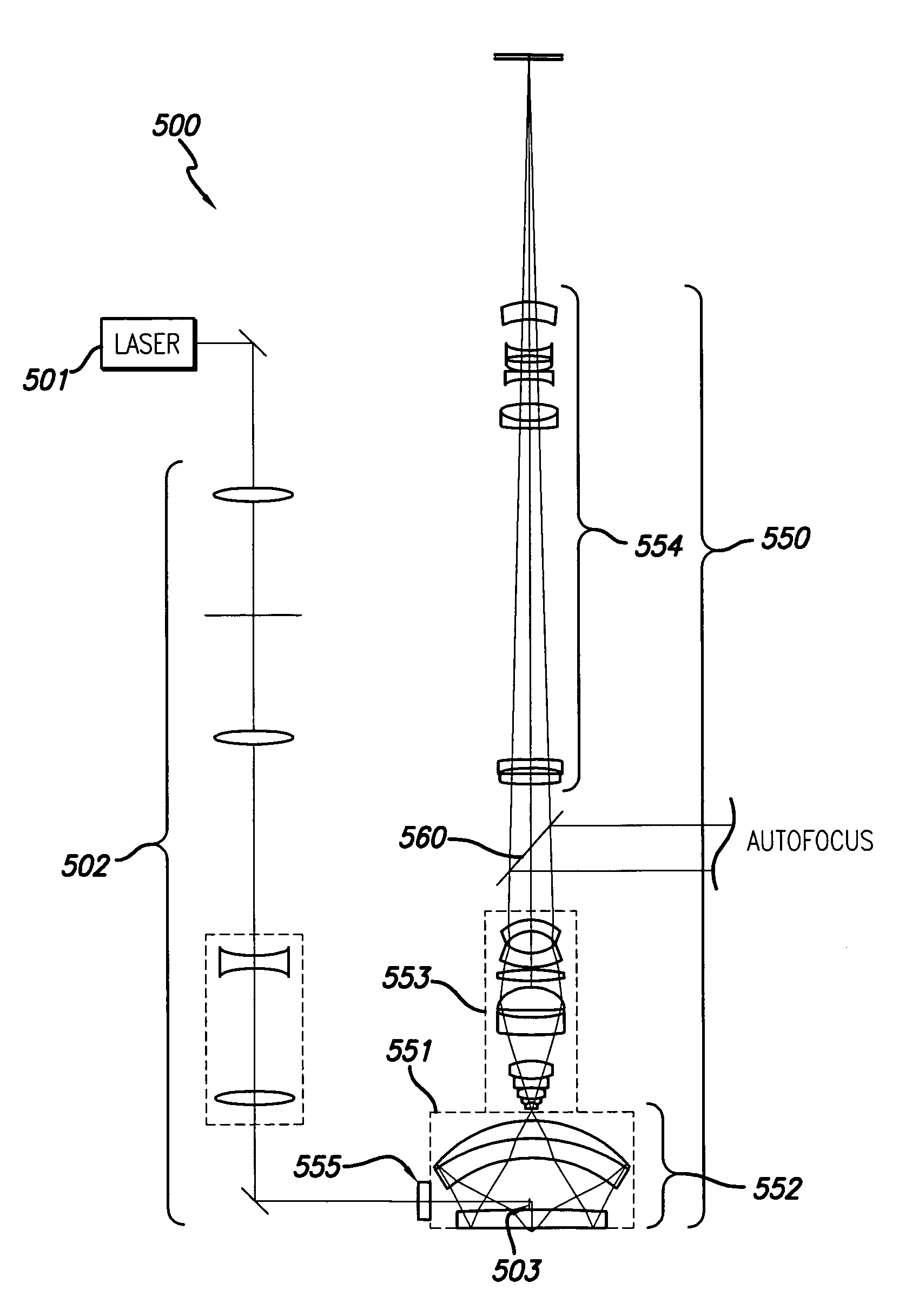
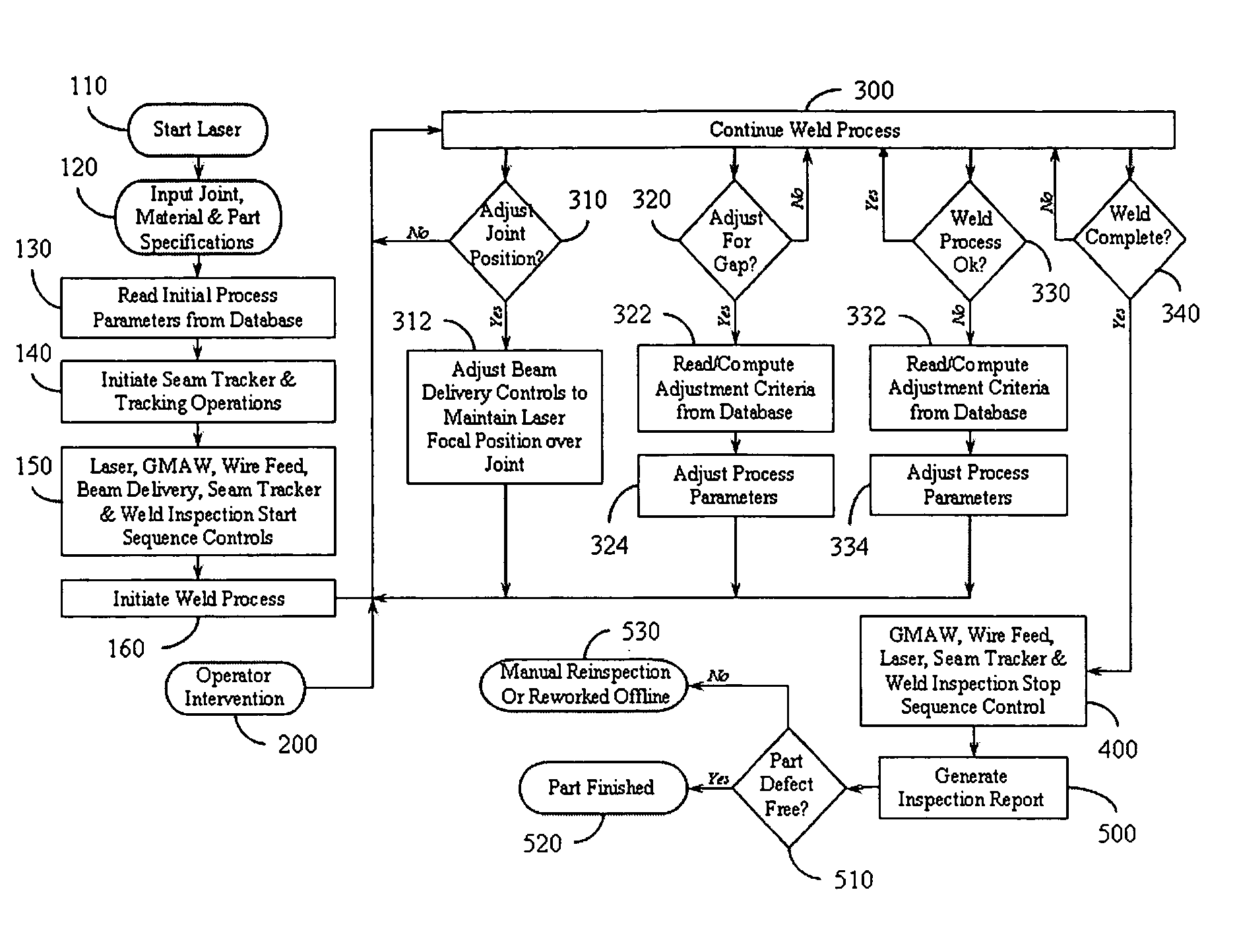
A fully integrated automated laser weld process control system (LWPCS) and method of controlling the fabrication of structural parts, particularly for shipbuilding and other industries. The LWPCS defines joint and weld quality attributes as process control variables and integrates these weld quality variables, along with the more traditional process parameters such as laser power, wire feed, GMAW voltage and active seam tracking, into a closed-loop monitoring and control system. The LWPCS includes a central processor and a plurality of subsystems that control laser beam positioning, vision-based monitoring and image processing, active weld-quality monitoring and inspection, adaptive beam delivery, and seam tracking. Cross-communication between subsystems is managed by the central processor. In addition to process control, the system extracts weld quality attributes during the weld process and provides immediate documentation of the weld quality.
Owner:ESAB AB
Ion beam delivery equipment and ion beam delivery method
ActiveUS20070228291A1Increase the number ofRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsVarying thicknessIrradiation
The invention is intended to increase the number of patients treatable using one wheel having a thickness varied in the rotating direction to change energy of an ion beam passing the wheel. Ion beam delivery equipment for irradiating an ion beam to a patient for treatment comprises a beam generator for producing and accelerating the ion beam, an beam delivery nozzle including a range modulation wheel which has a predetermined thickness distribution in the rotating direction and is rotated on a travel passage of the ion beam generated from the beam generator to control a range of the ion beam, and an irradiation controller for controlling the beam producing and accelerating operation of the beam generator in accordance with the phase of rotation of the range modulation wheel.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Damage isolation by shaped beam delivery in laser scribing process
ActiveUS20120322240A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingShaped beamOptoelectronics
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High-speed, precise, laser-based material processing method and system
InactiveUS20060191884A1Delay minimizationLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLight beamMaterials processing
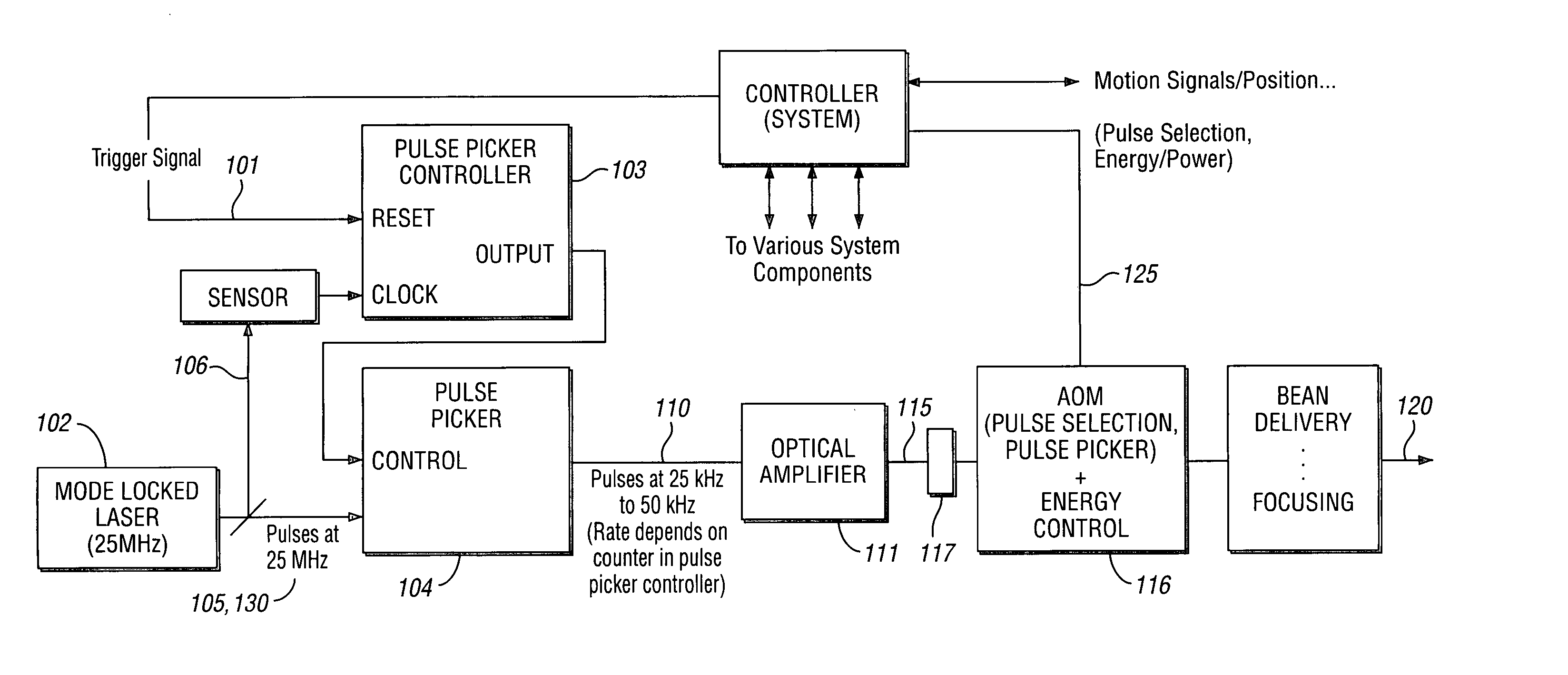
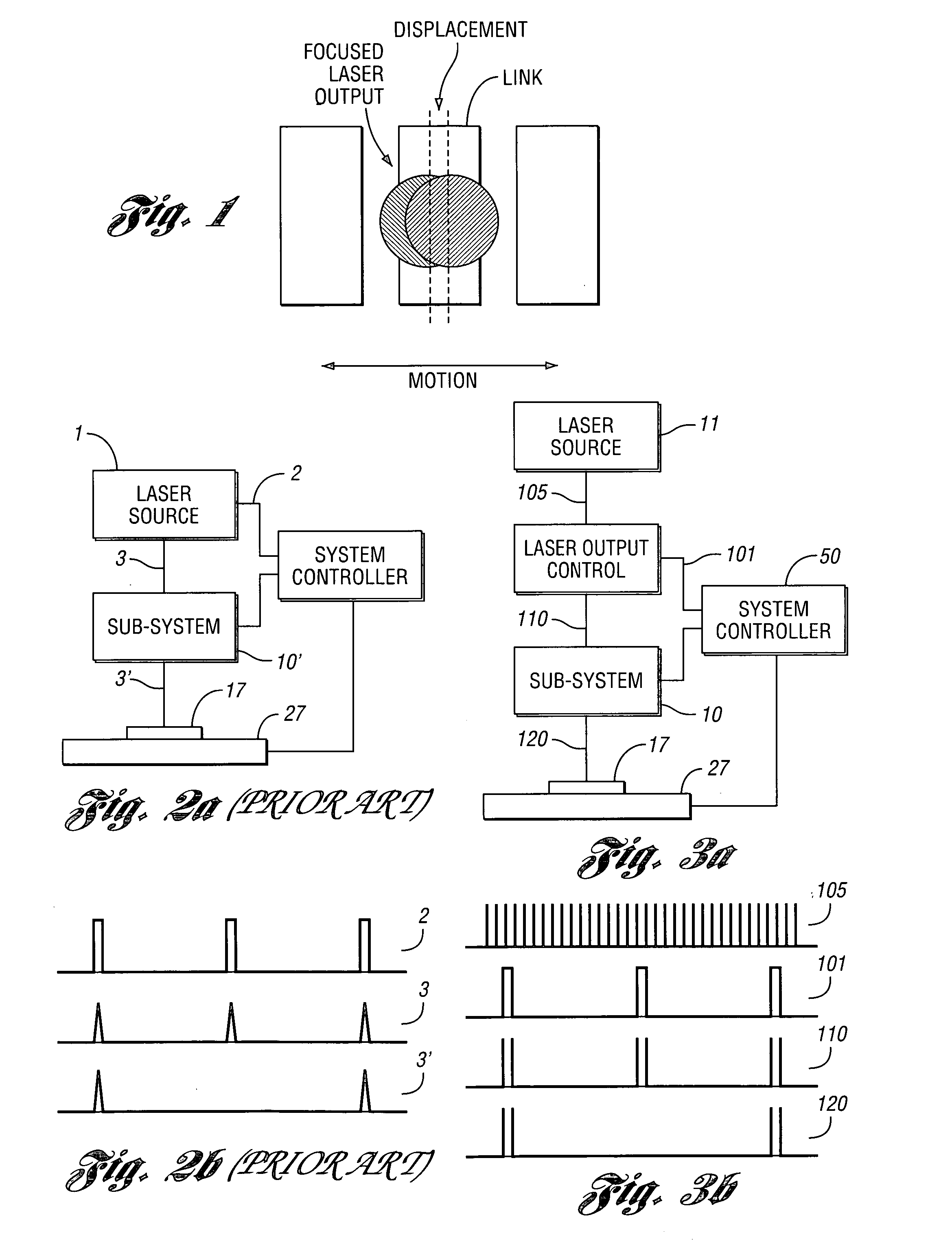
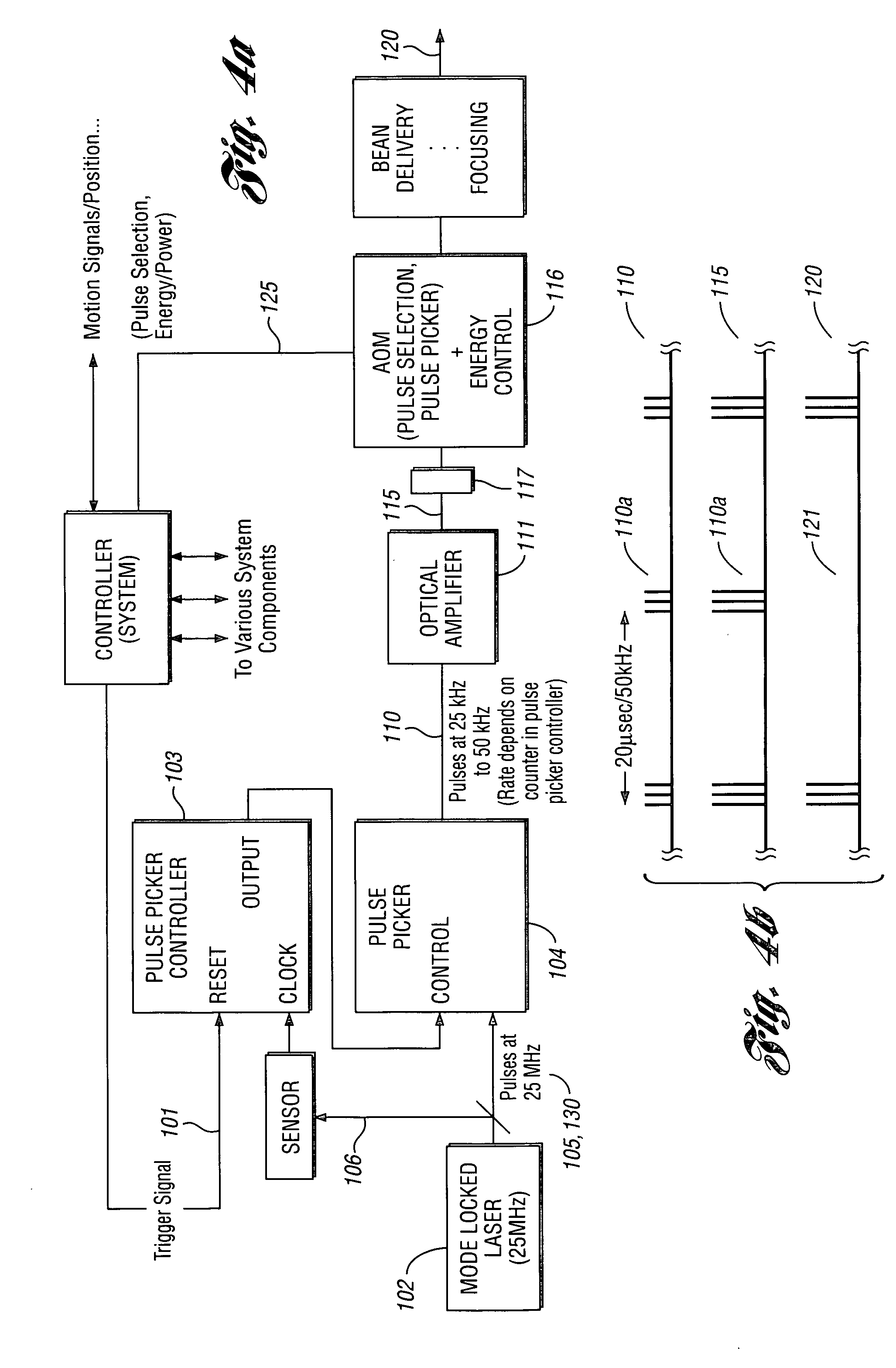
A high-speed, precise, laser-based material processing method and system are provided wherein relative movement of target material and a pulsed laser output used to process the material are synchronized. The laser-based system includes a pulsed laser source for generating a set of laser pulses, and a laser output control that controllably selects a subset of pulses from the set of laser pulses at a position beyond the laser source to obtain the pulsed laser output. The laser-based system further includes a mechanism for synchronizing the pulsed laser output with relative movement of the target material. A beam delivery and focusing subsystem delivers at least a portion of the synchronized pulsed laser output to the target material as a laser material processing output to process the target material. A positioning subsystem moves the target material relative to the pulsed laser output.
Owner:THE GSI GRP LLC
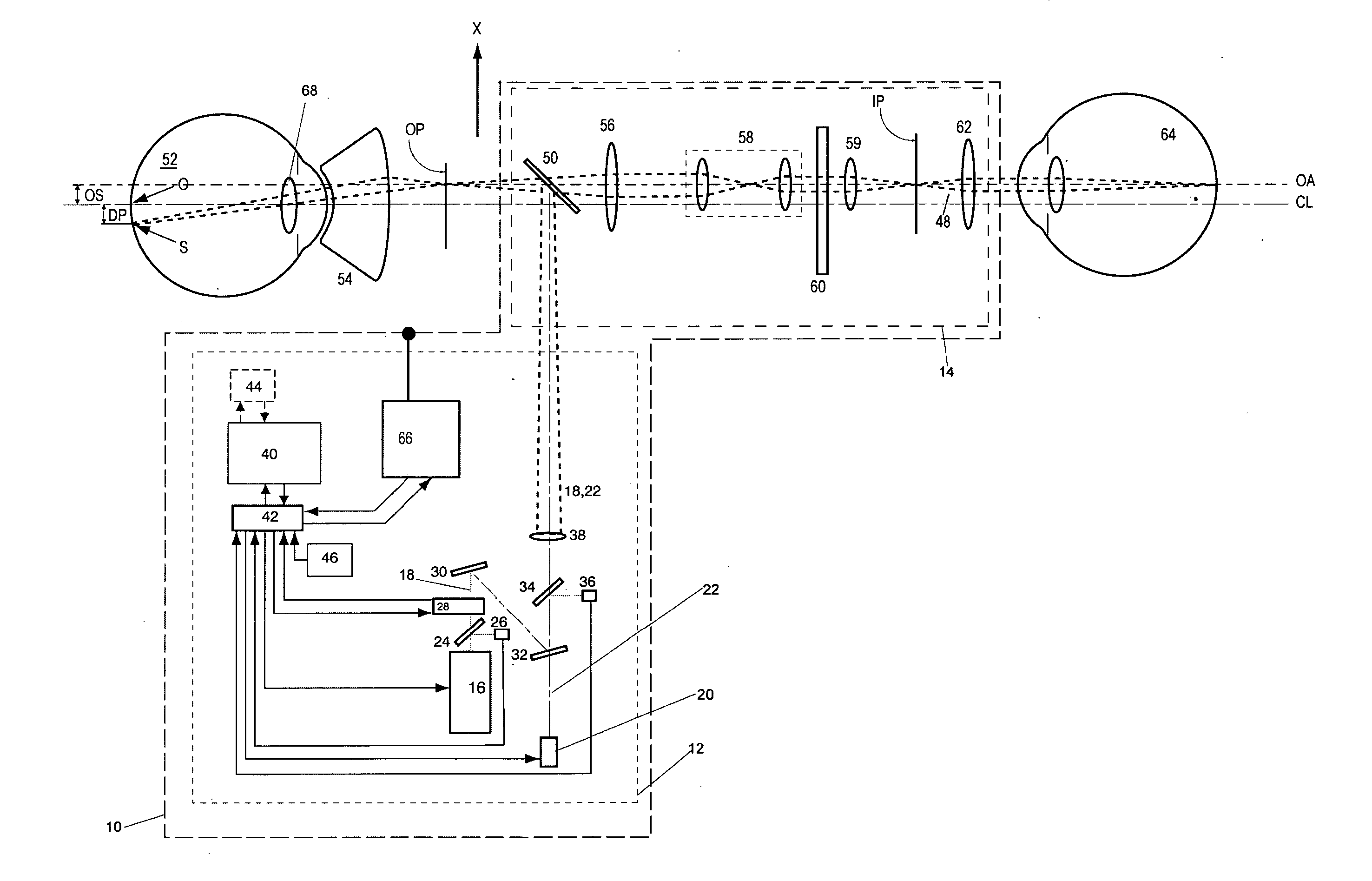
Dynamic optical surgical system utilizing a fixed relationship between target tissue visualization and beam delivery
A system and method of treating target tissue that includes generating a treatment beam of light using a light source, directing the treatment beam onto target tissue using an optical element, generating an image of the target tissue from light emanating from the target tissue using a plurality of optical elements, and translating the light source, the optical element and / or the plurality of optical elements relative to the target tissue (using a translation device) to simultaneously move the treatment beam along the target tissue and the field of view of the target tissue as defined by the plurality of optical elements. Control electronics control the translation device to cause the treatment beam to move along the target tissue in a predetermined pattern.
Owner:IRIDEX CORP
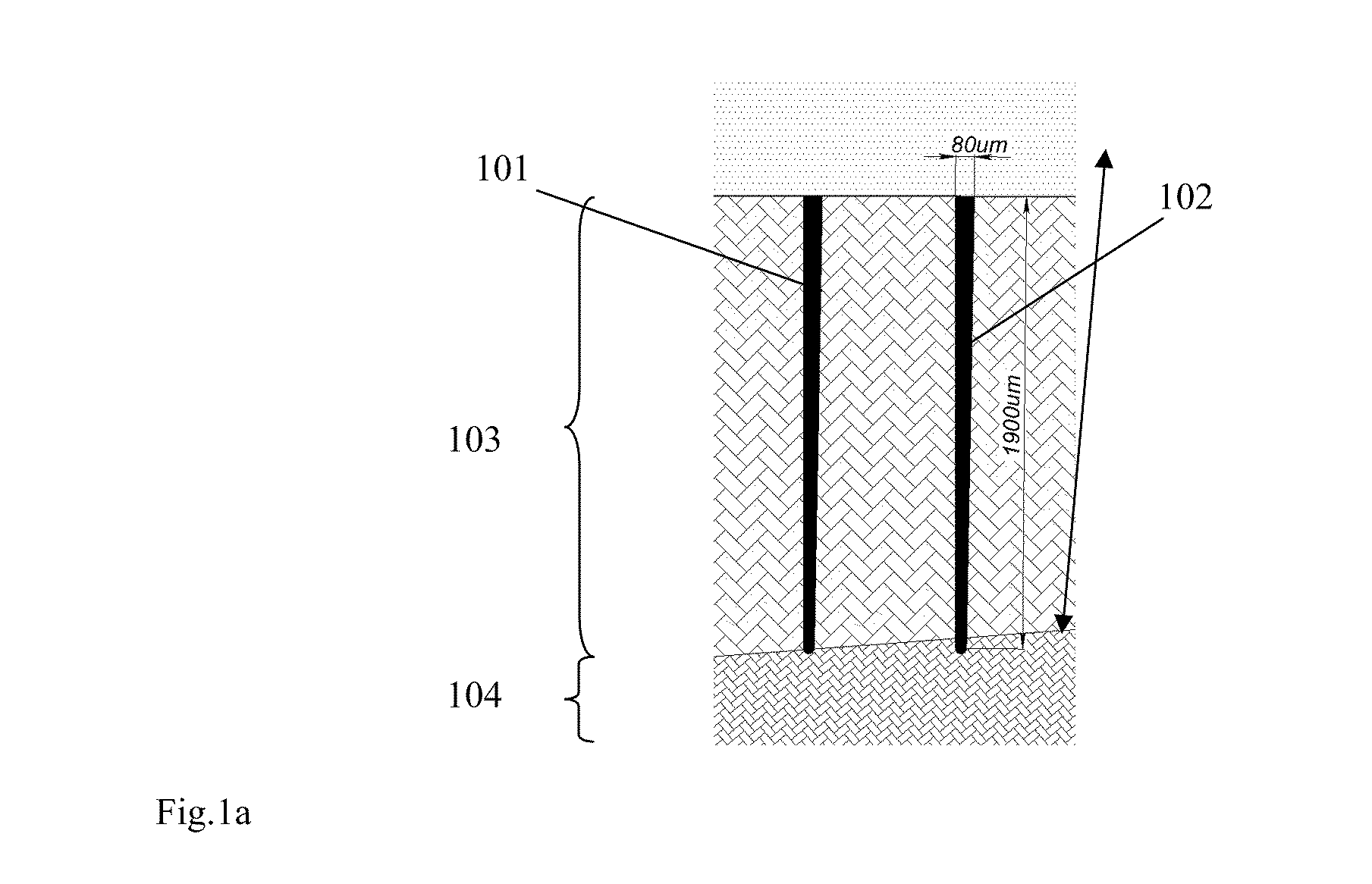
Method and apparatus for diagnostic and treatment using hard tissue or material microperforation
InactiveUS20100015576A1Reliable and minimally invasive fasteningControlled diffusionTeeth fillingDiagnostic recording/measuringPulse energyLight beam
A method of modifying or treating biological tissue by microperforating hard tissue is disclosed. The method comprises identifying a target area associated with the hard tissue, using a laser beam to perforate at least one incision in the hard tissue, wherein at least one incision has a diameter from a range of 0.001 mm to 0.5 mm and an aspect ratio from a range of 1 to 100 times, introducing a treatment substance into the incision, and causing the treatment substance to interact with the target area. Also a device for microperforating hard biological tissue is disclosed, comprising a laser pump system and a laser head coupled to the laser pump system for generating a pulsed laser having ranges of wavelengths, a pulse duration, pulse energy from a selected range, a beam divergence factor less than 5, a repetition rate higher than 50 Hz; and a beam delivery system comprised of a focusing system for creating a beam having a diameter from a range of 0.001 mm to 0.5 mm.
Owner:REJUVEDENT
Ion acceleration system for medical and/or other applications
ActiveUS20100320403A1Minimal volumeEasy to installConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsElectrode and associated part arrangementsBasementEngineering
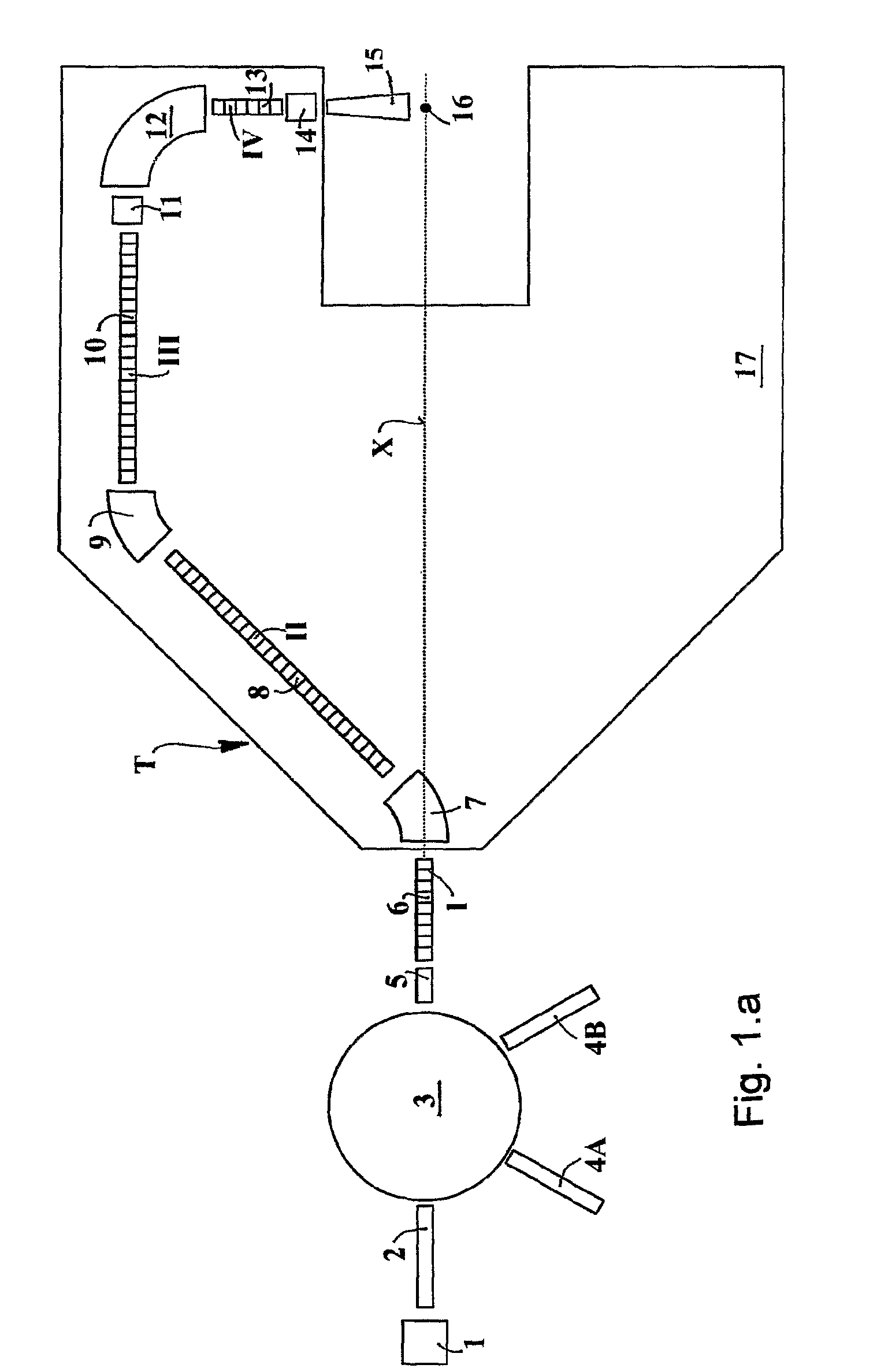
The ion acceleration system or complex (T) for medical and / or other applications is composed in essence by an ion source (1), a pre-accelerator (3) and one or more linear accelerators or linacs (6, 8, 10, 13), at least one of which is mounted on a rotating mechanical gantry-like structure (17). The isocentrical gantry (17) is equipped with a beam delivery system, which can be either ‘active’ or ‘passive’, for medical and / or other applications. The ion source (1) and the pre-accelerator (3) can be either installed on the floor, which is connected with the gantry basement, or mounted, fully or partially, on the rotating mechanical structure (17). The output beam can vary in energy and intensity pulse-by-pulse by adjusting the radio-frequency field in the accelerating modules of the linac(s) and the beam parameters at the input of the linear accelerators.
Owner:ADVANCED ONCOTHERAPY PLC
System for Inventory Management
The present invention relates to a system for detecting and communicating the position of a pusher assembly on a shelf. In an embodiment, a system includes a control module, a pusher assembly, and a laser scanner. The laser scanner is configured to transmit a swept beam to a mirrored reflective surface located behind the pusher assembly. The control module analyzes the laser beam at the laser scanner to detect the position of the pusher assembly on the shelf. In another embodiment, a system includes a control module, a pusher assembly, and an infrared transceiver that sends and receives infrared signals. The transceiver may be located behind the pusher assembly. The control module analyzes the infrared signals to determine the position of the pusher assembly on the shelf.
Owner:RTC IND
Apparatus and method including a handpiece for synchronizing the pulsing of a light source
The present application discloses an apparatus and a method for synchronizing the activation of a light source with the position of a hand piece on a surface and for providing a substantially homogenous exposure of a surface to light irradiation. The apparatus includes a light source, a handpiece for delivering light pulses to the irradiated surface, and a beam delivery system for delivering light from the light source to the handpiece. The handpiece, which is moved along the surface by an operator, includes a sensor for sensing the distance traversed by the handpiece on the surface. The sensor sends signals to a signal processing unit which calculates the distance traversed by the handpiece on the surface and controls the activation of the light source either by automatically activating the light source or by providing the operator with a signal indicating that the light source should be pulsed. The handpiece can also include a device for cooling the irradiated surface and for marking the irradiated part of the surface with a visible marker. The handpiece may be constructed to be movable along a surface in a predetermined orientation relative to the handpiece. Alternatively, the handpiece may be freely movable along the surface in any desired orientation. The light source can be a pulsed laser, a continuous wave laser or a non-coherent light source.
Owner:TALPALRIU GERARD +4
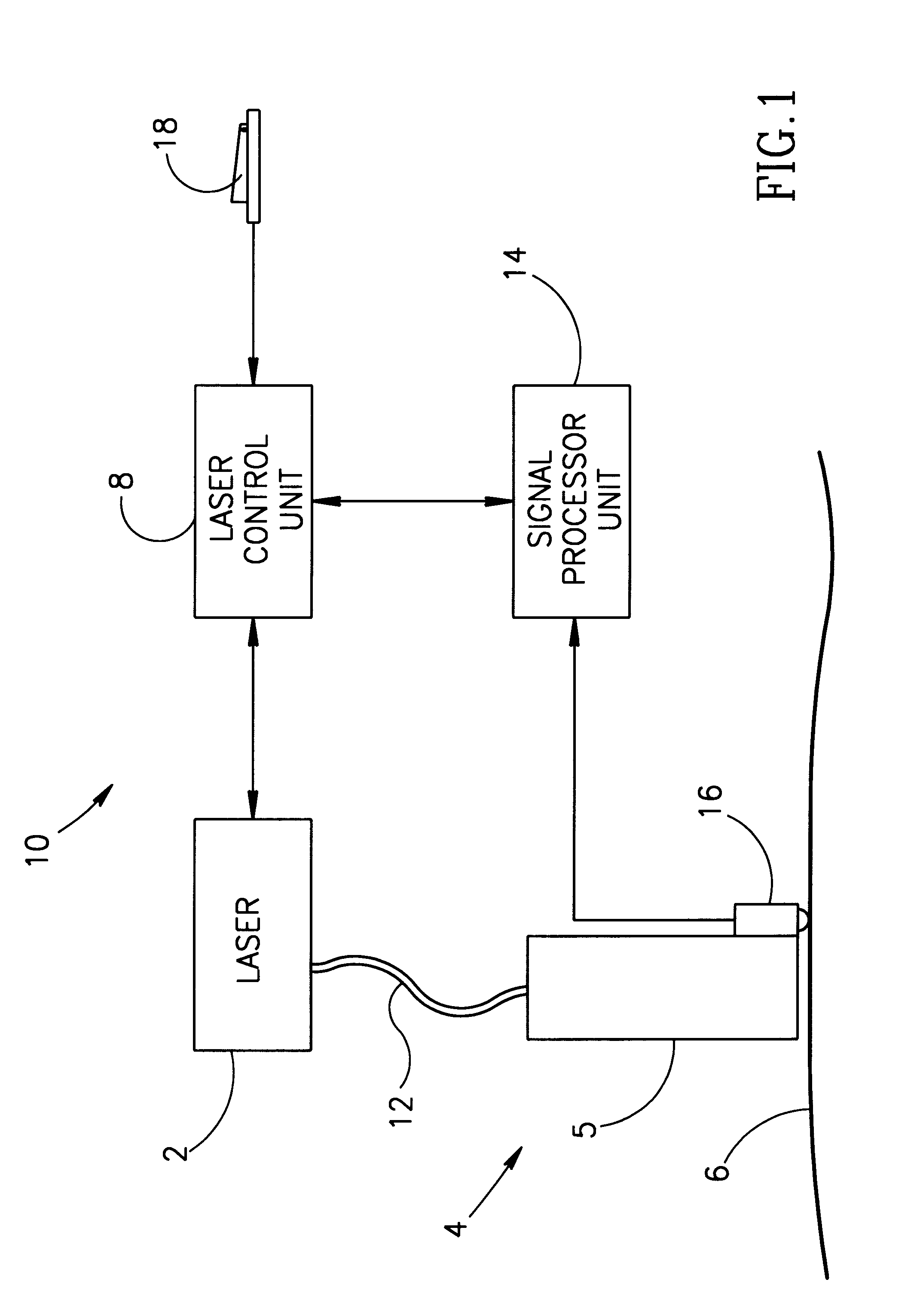
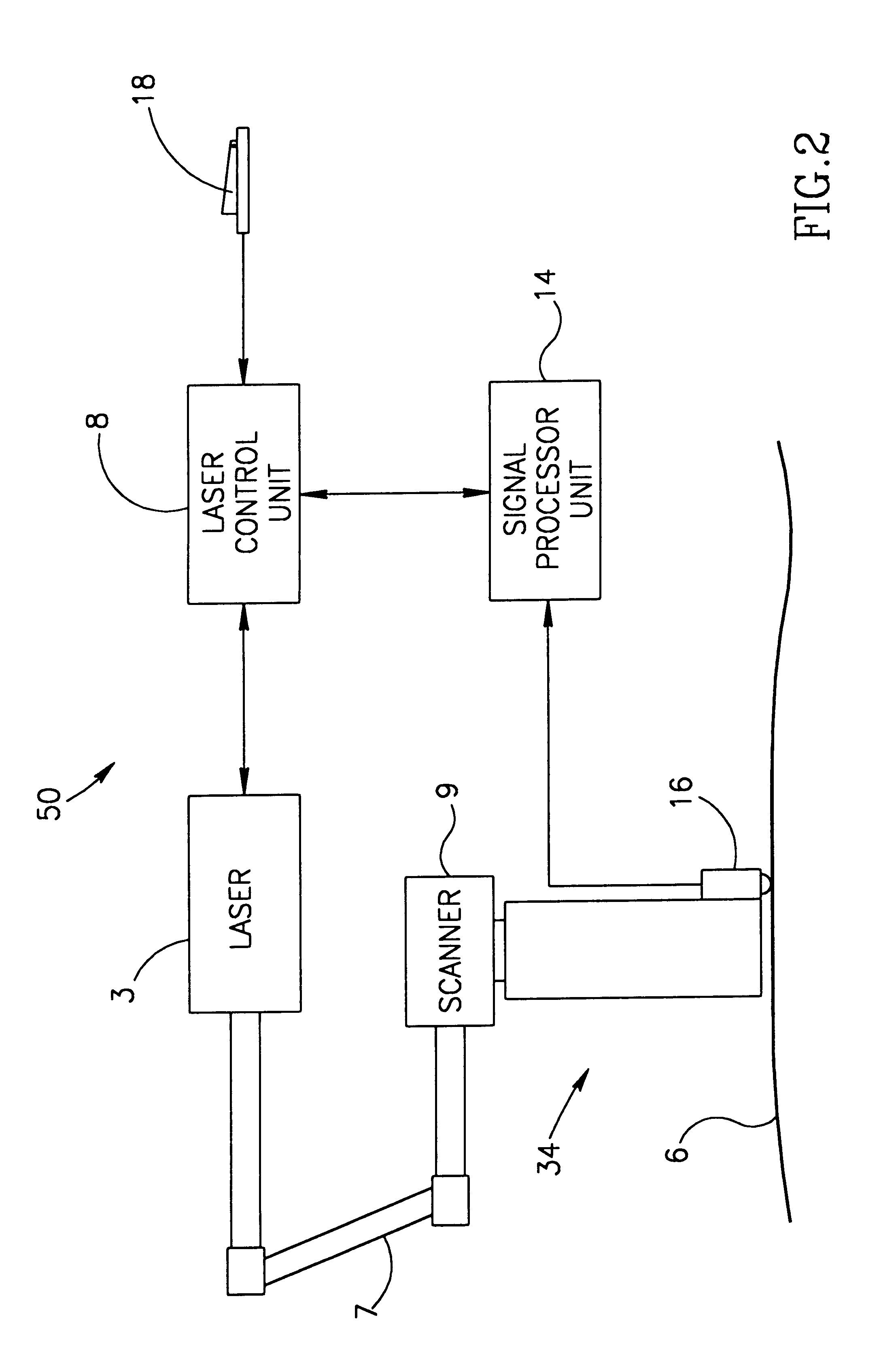
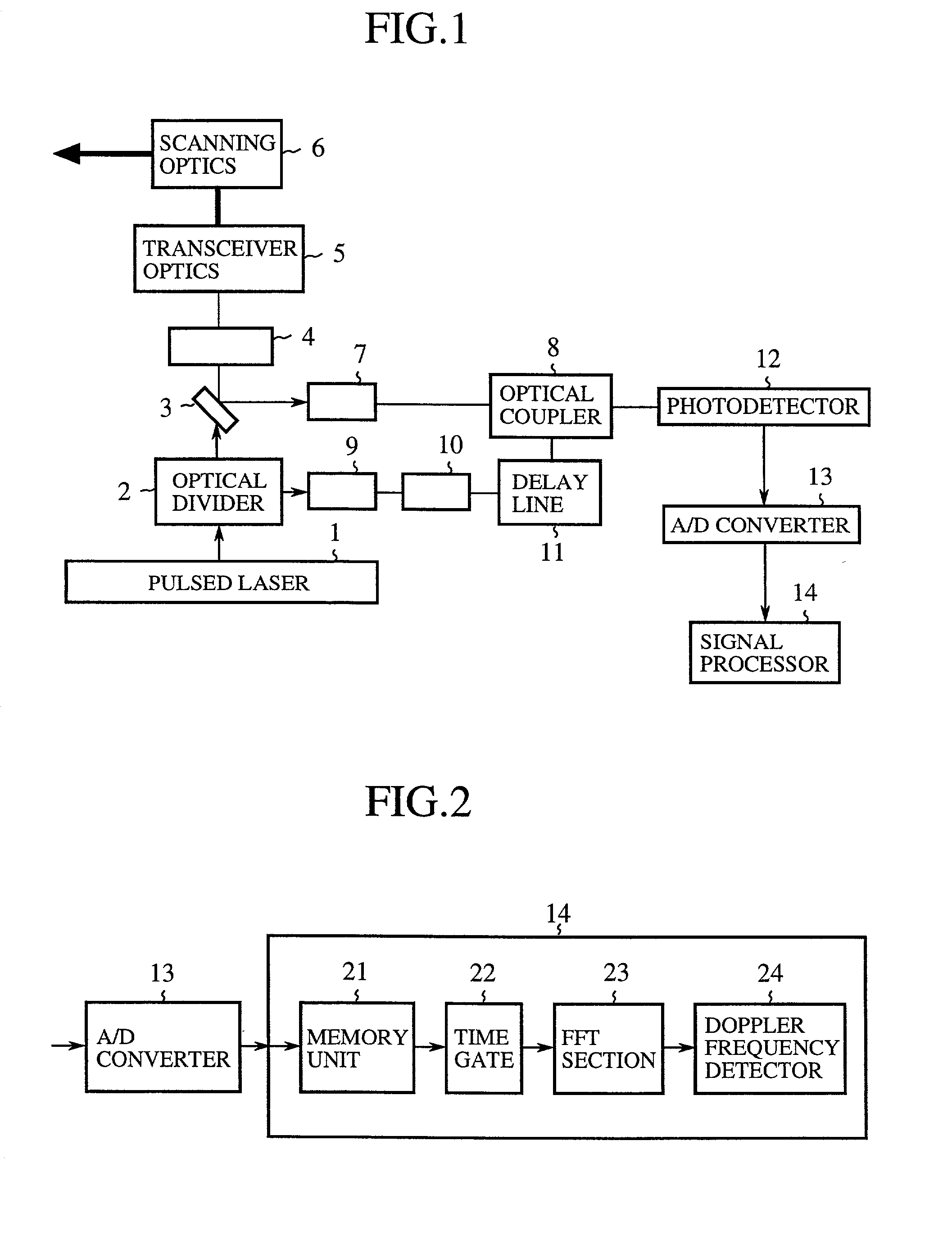
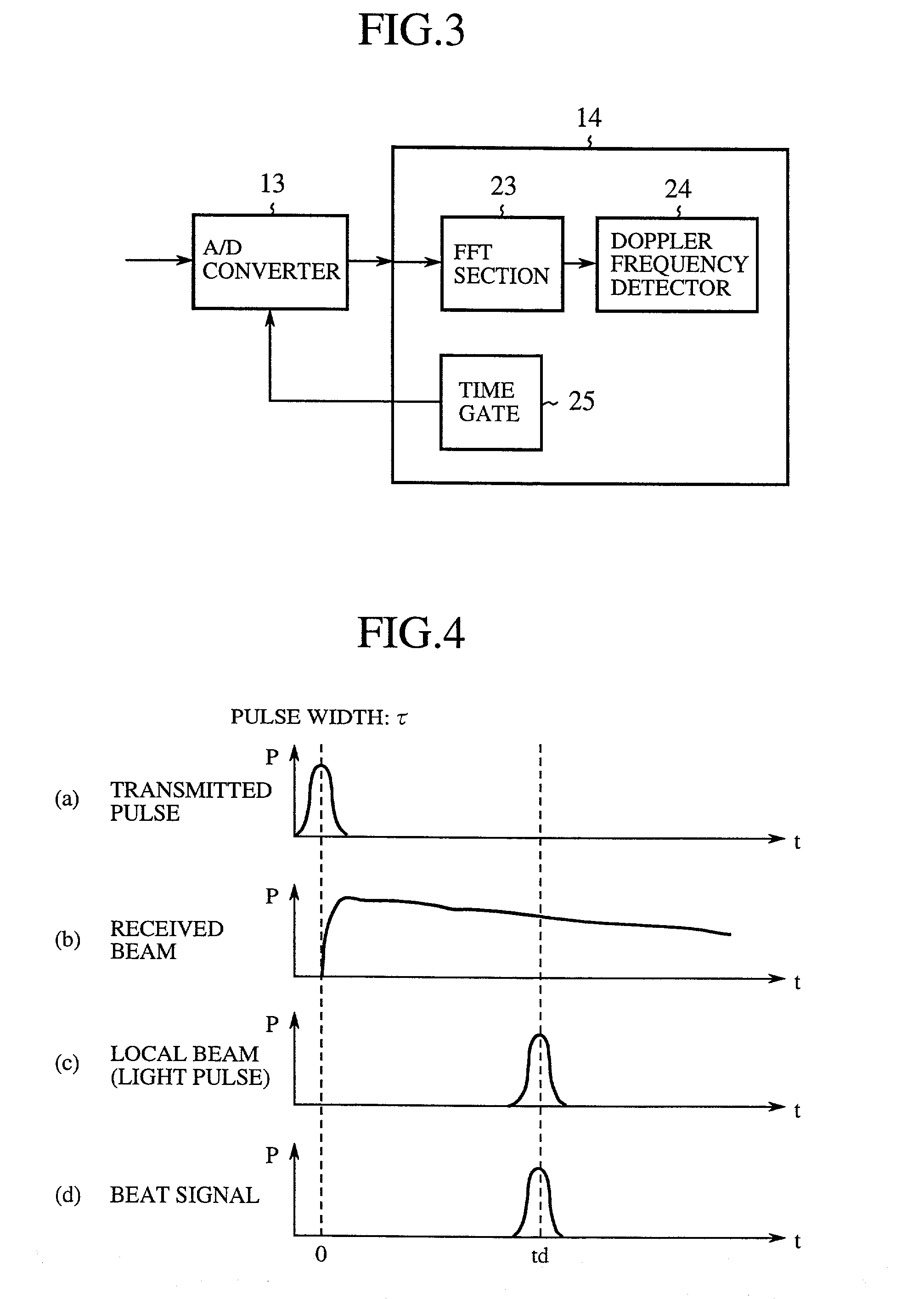
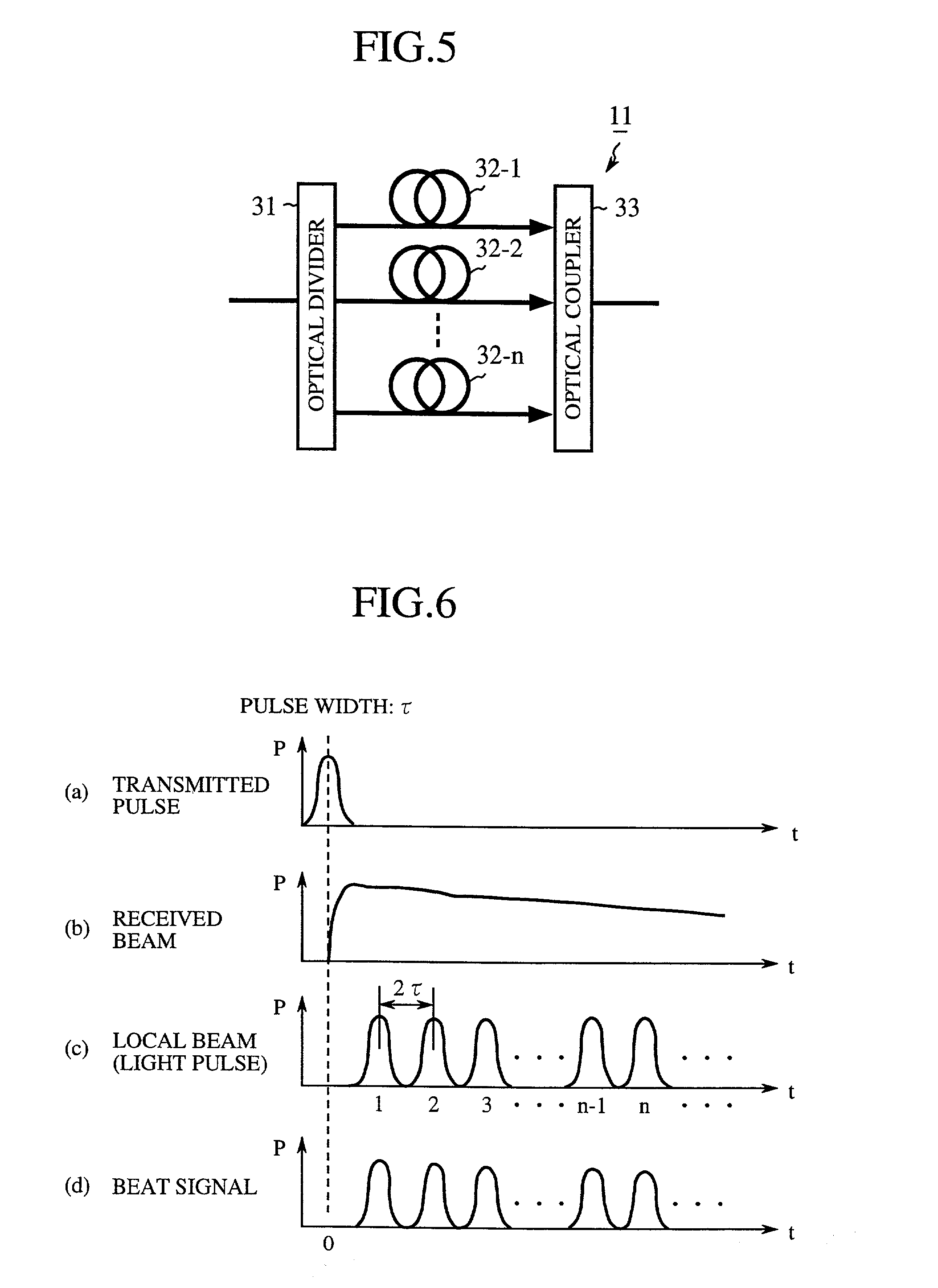
Coherent laser radar system and target measurement method
A coherent laser radar system includes a pulsed laser oscillating a pulsed laser beam which is split into two parts by an optical divider. A first part of the two is transmitted as a transmitted beam via a beam splitter. A second part is supplied to a delay line via a coupling optics and others to be delayed by a predetermined time as a local beam, and is incident onto an optical coupler. The received beam from the target is incident onto the optical coupler via a scanning optics and so on. A photodetector carries out the coherent detection of the light beam coupled by the optical coupler. A signal processor computes a target velocity and the like from a signal generated by the detection and converted into a digital signal by an A / D converter. This makes it possible to solve a problem of a conventional system in that the system configuration is complicated and expensive.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
High average power ultra-short pulsed laser based on an optical amplification system
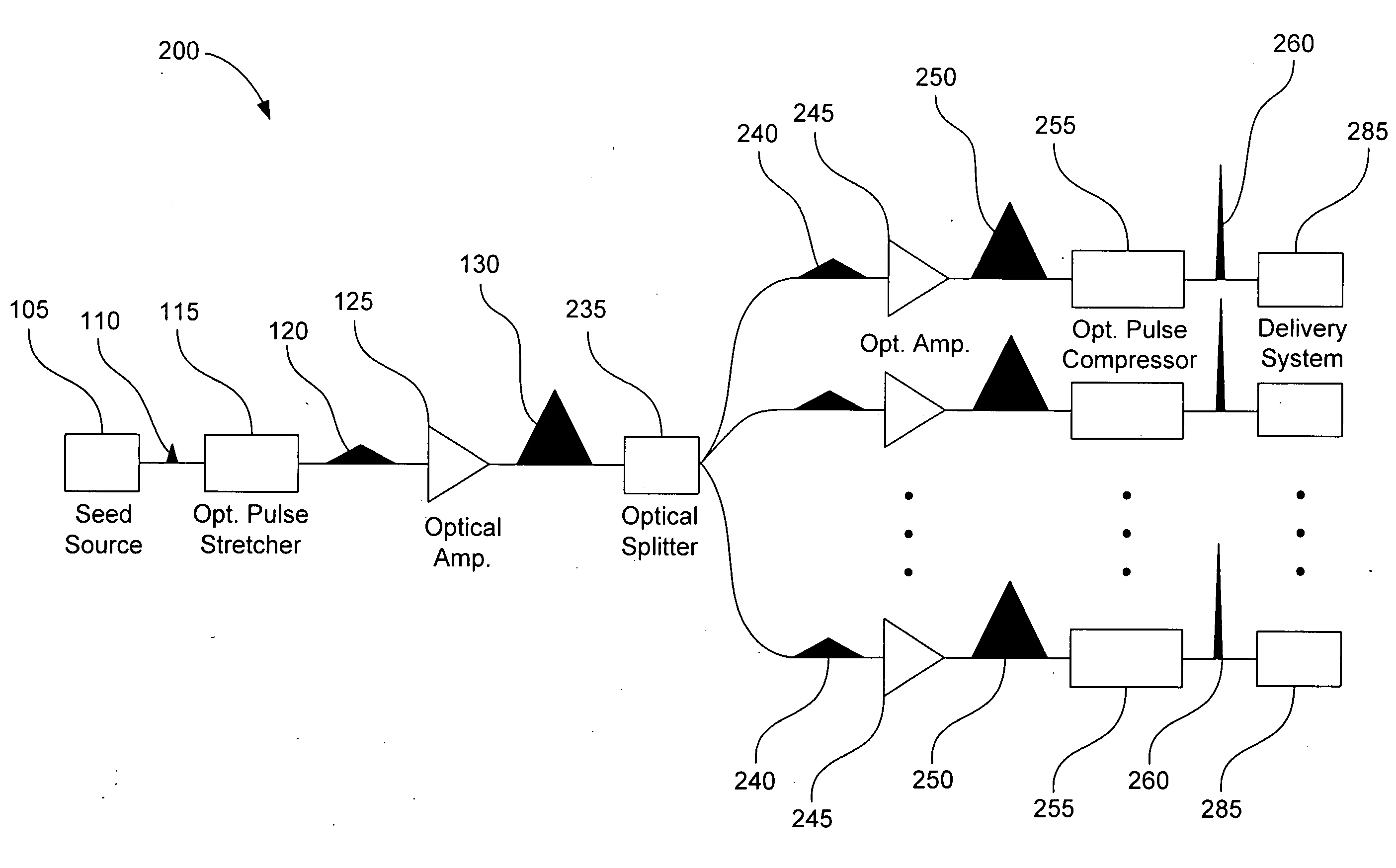
The present invention includes an apparatus and the method to scale the average power from high power ultra-short pulsed lasers, while at the same time addressing the issue of effective beam delivery and ablation, by use of an optical amplification system.
Owner:RAYDIANCE
Apparatus and method for combining multiple laser beams in laser material processing systems
InactiveUS6423925B1Easy to useIncrease flexibilitySemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser optical deviceOptical axisLight beam
Each one of multiple laser sources are independently separately mounted on a laser material processing platform and their beam paths are combined by a combiner which includes one or more optical elements mounted in the laser material processing platform which make the beam paths parallel and colinear. The combined beams are then moved in X and Y planes relative to a workpiece supported in the laser material processing platform under the control of a computer in the performance of work in accordance with a work program. The beam path of each laser source and the optical axis of the beam delivery system are each pre-aligned to the same predetermined reference and automatically coincide upon installation such that these components are rapidly and interchangeably interfaceable. The beams are orthogonally polarized and the optical elements of the combiner transmit one beam while reflecting another beam. While two laser beams are shown, an infinite number of laser beams may be used.
Owner:UNIVERSAL LASER SYST
System And Method For Determining Dosimetry In Ophthalmic Photomedicine
ActiveUS20080167642A1Efficiently determinedMore treatment resultLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsDosimetry radiationUser input
A system and method for treating ophthalmic target tissue, including a light source for generating a beam of light, a beam delivery system that includes a scanner for generating patterns, and a controller for controlling the light source and delivery system to create a dosimetry pattern of the light beam on the ophthalmic target tissue. One or more dosage parameters of the light beam vary within the dosimetry pattern, to create varying exposures on the target tissue. A visualization device observes lesions formed on the ophthalmic target tissue by the dosimetry pattern. The controller selects dosage parameters for the treatment beam based upon the lesions resulting from the dosimetry pattern, either automatically or in response to user input, so that a desired clinical effect is achieved by selecting the character of the lesions as determined by the dosimetry pattern lesions.
Owner:IRIDEX CORP
System and method for cutting using a variable astigmatic focal beam spot
ActiveUS7388172B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLeading edgeLight beam
A variable astigmatic focal beam spot is formed using lasers with an anamorphic beam delivery system. The variable astigmatic focal beam spot can be used for cutting applications, for example, to scribe semiconductor wafers such as light emitting diode (LED) wafers. The exemplary anamorphic beam delivery system comprises a series of optical components, which deliberately introduce astigmatism to produce focal points separated into two principal meridians, i.e. vertical and horizontal. The astigmatic focal points result in an asymmetric, yet sharply focused, beam spot that consists of sharpened leading and trailing edges. Adjusting the astigmatic focal points changes the aspect ratio of the compressed focal beam spot, allowing adjustment of energy density at the target without affecting laser output power. Scribing wafers with properly optimized energy and power density increases scribing speeds while minimizing excessive heating and collateral material damage.
Owner:IPG PHOTONICS CORP
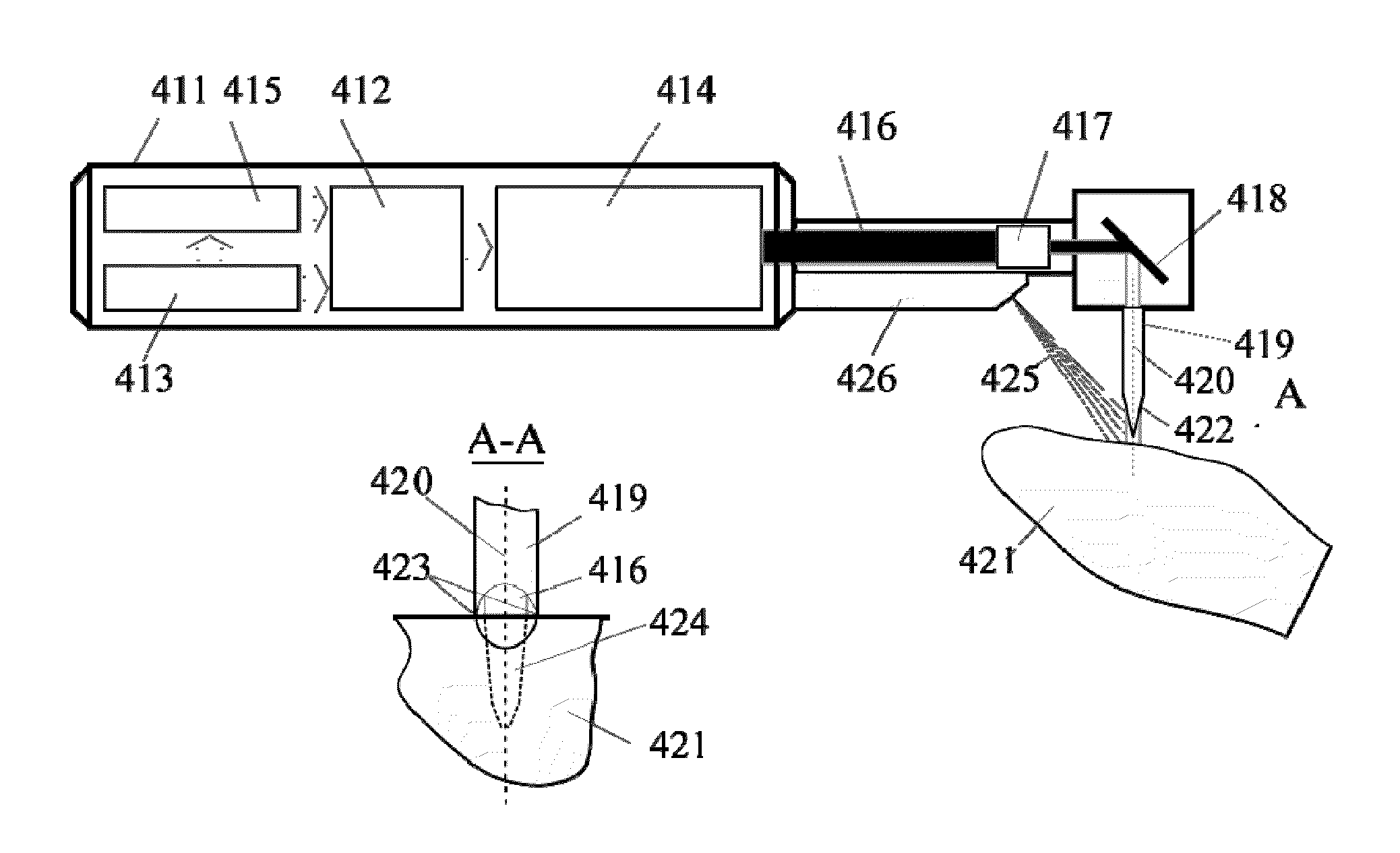
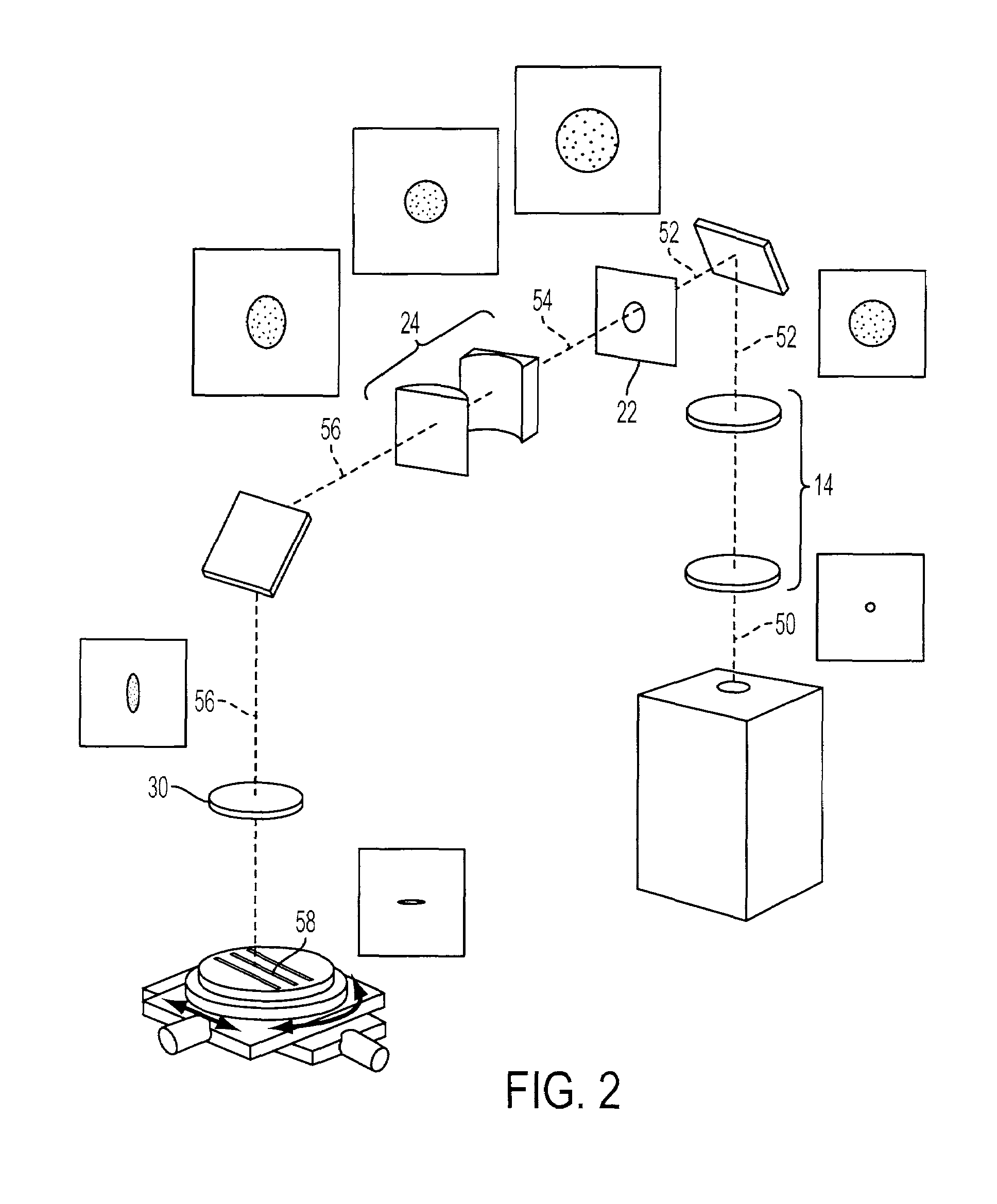
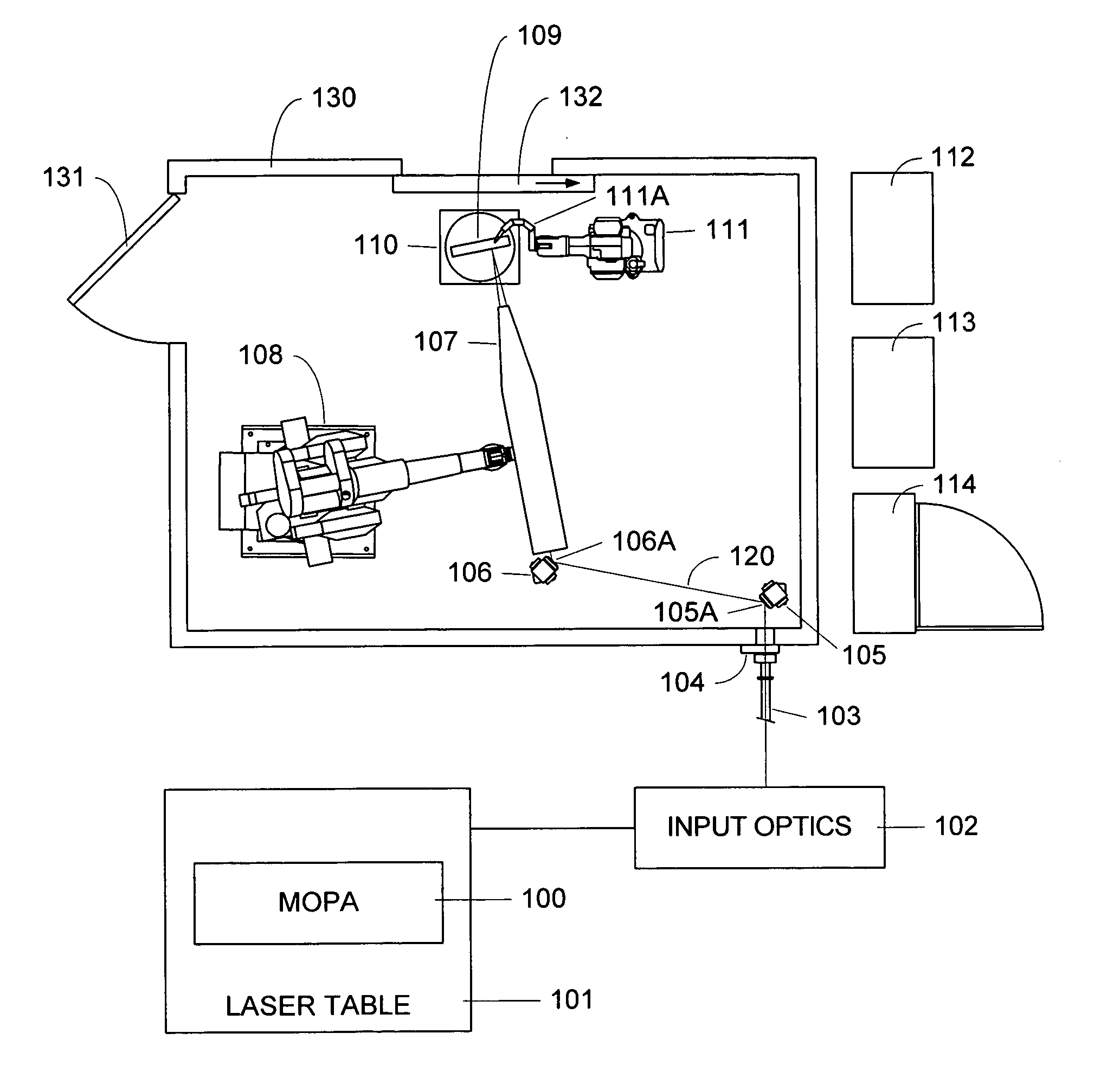
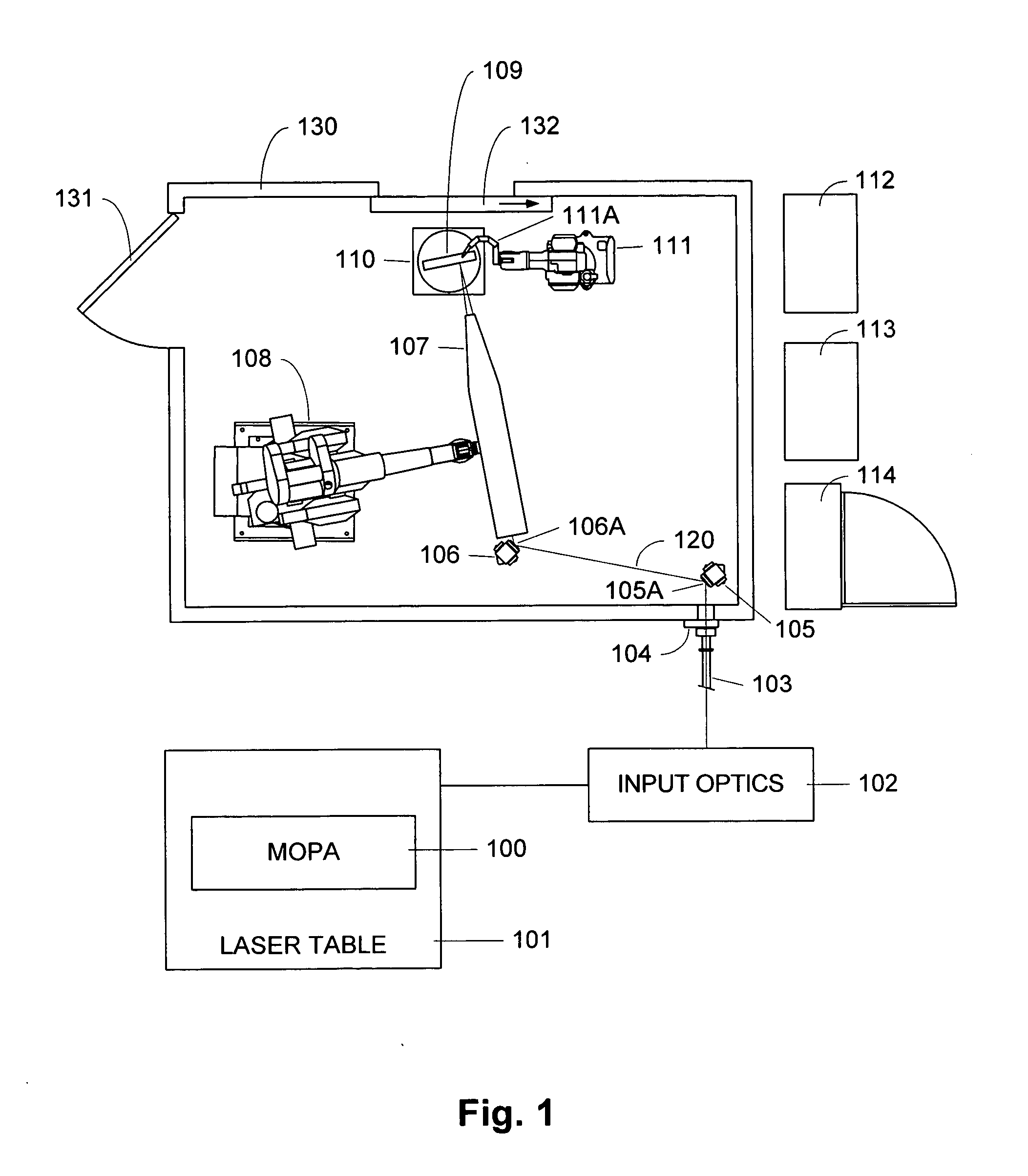
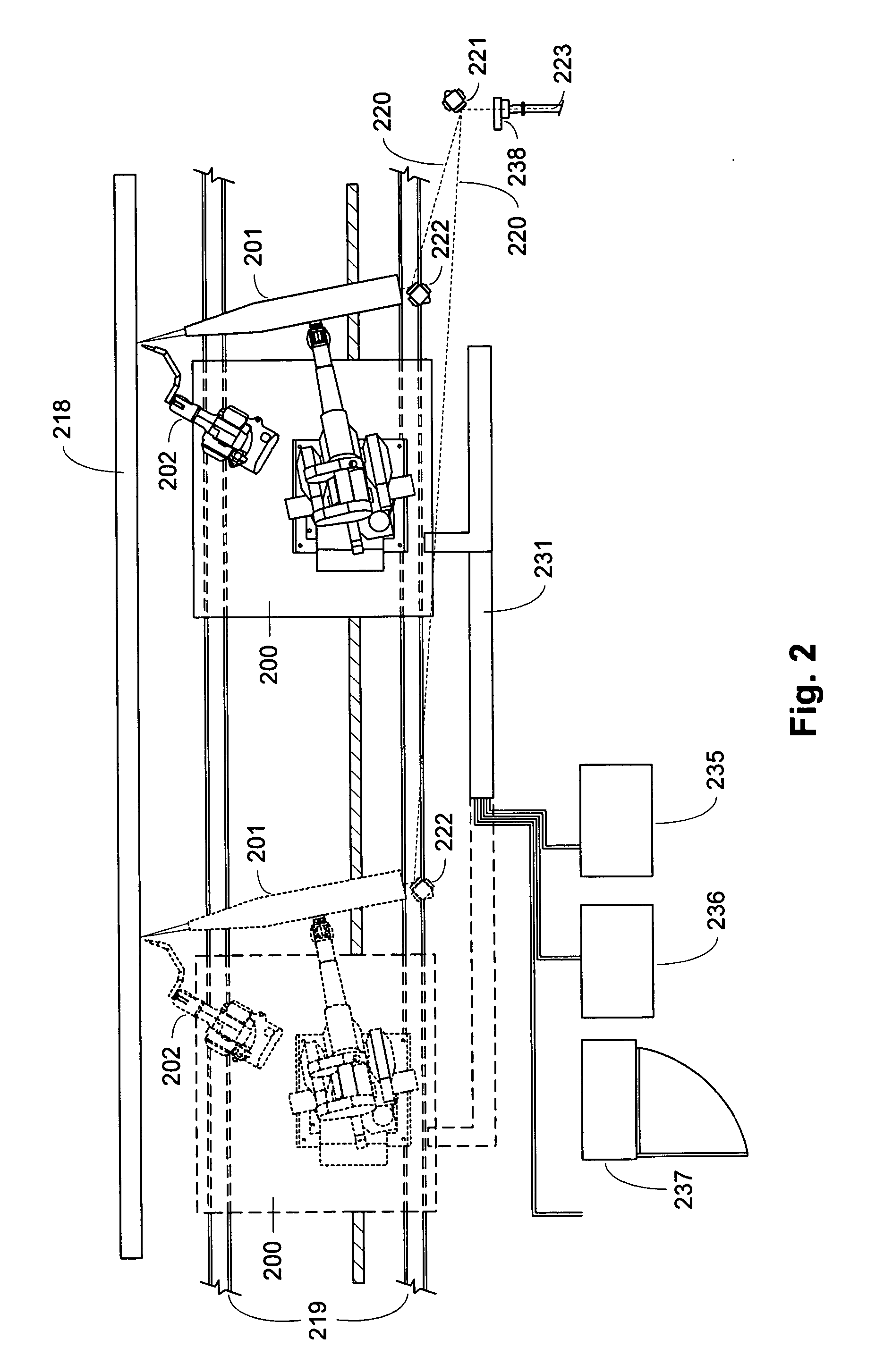
Active beam delivery system for laser peening and laser peening method
ActiveUS20060102609A1Minimizes holding fixtureMinimizes work piece moving complexityWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesAngle of incidenceVariable length
A laser peening method and system allows the work piece to be fixed, while moving and directing the laser beam. A laser energy delivery system includes a relay imaging system. Input optics arranged to receive the laser energy, a transmitting mirror having adjustable angle of incidence relative to the input optics, and a robot mounted processing head including an optical assembly are configured to direct laser energy toward the movable target image plane. The laser energy follows an optical path including an essentially straight segment from the transmitting mirror to the receiving mirror, having a variable length and a variable angle relative to the input optics. Diagnostics on the processing head facilitate operation.
Owner:METAL IMPROVEMENT CO INC
Laser processing device and method thereof
ActiveCN104162741AShort duration of actionImprove work efficiencyLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingOptical axis
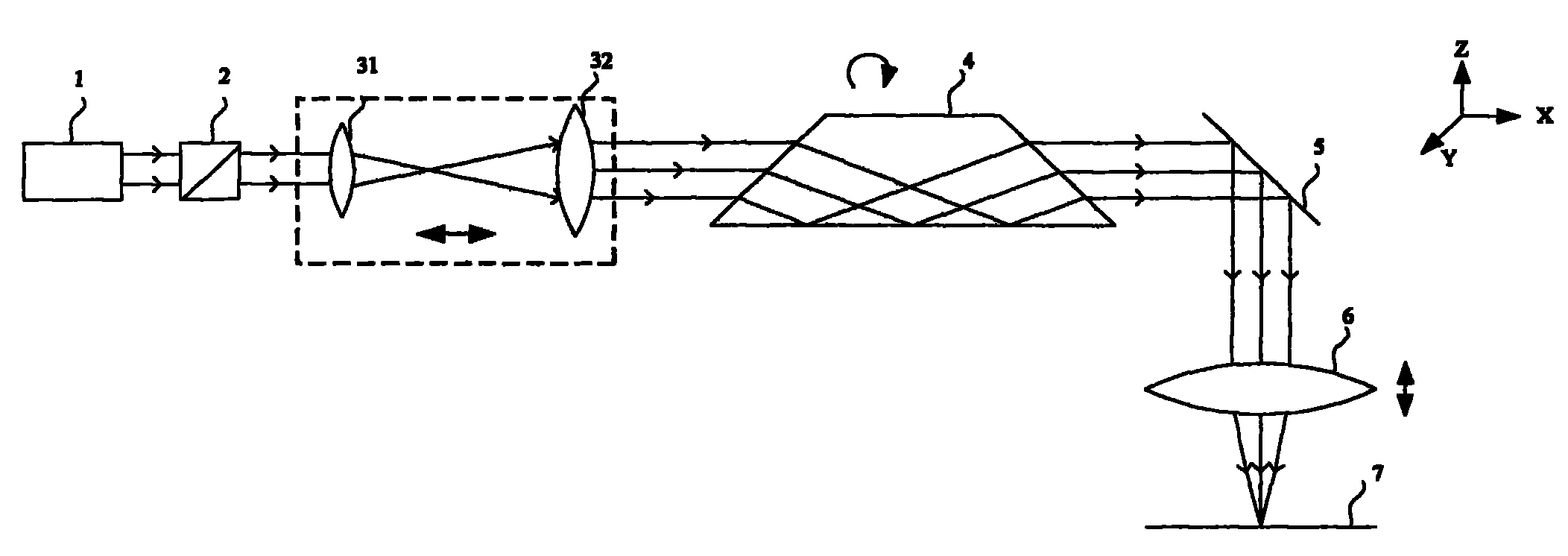
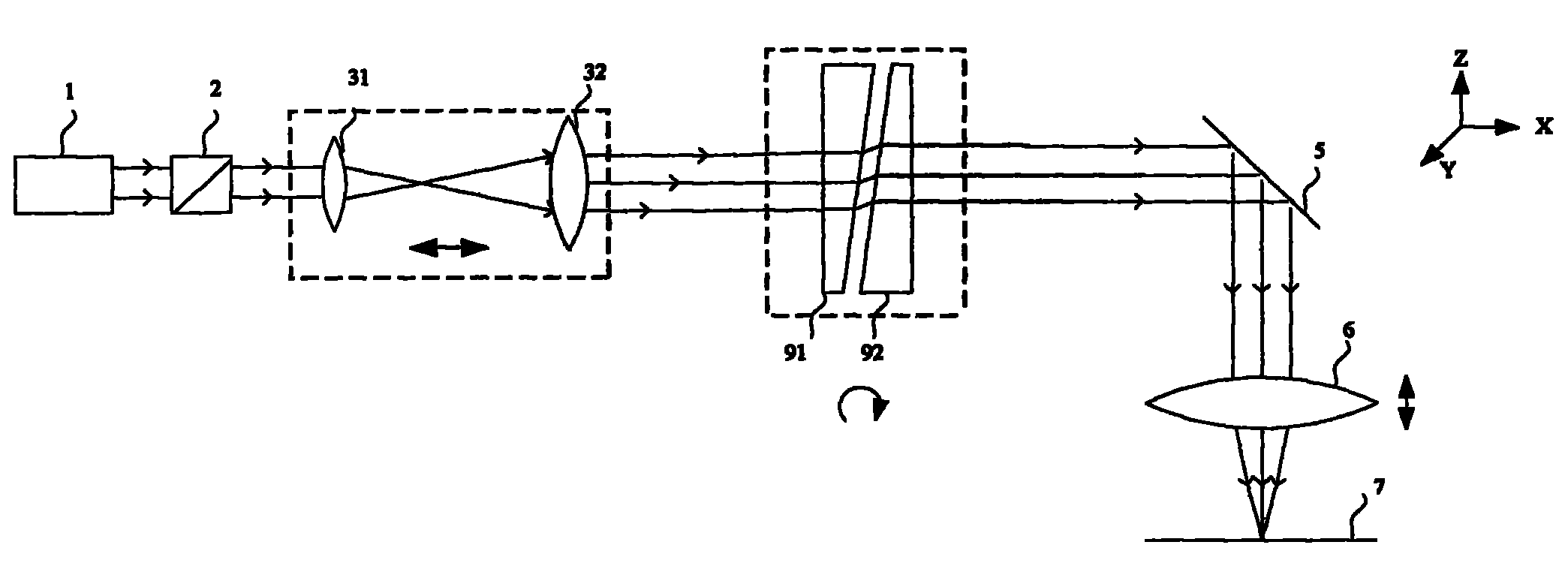
The invention provides a laser processing device and a method of the laser processing device. The laser processing device comprises a laser, a lens set, a Dove prism, a plane mirror, a focus lens and a workpiece to be processed which are all sequentially arranged in the direction of an optical axis, wherein the lens set is composed of two lenses, and the distance between the two lenses can be adjusted so that the spot sizes and the divergence angles of outgoing beams of the laser can be adjusted; the Dove lens is installed in a rotary motor and rotates with the optical axis as the center, and the beams going out from the Dove lens also rotate with the optical axis as the center; the plane mirror is used for deflecting the transmission direction of the beams; the position of the focus lens in the beam transmission direction can be adjusted, and the beams are focused on the surface of the workpiece to be processed after passing through the focus lens; the workpiece to be processed is placed on an electric displacement platform and can make two-dimensional movement in the plane perpendicular to the transmission direction of the beams.
Owner:北京中科镭特电子有限公司
Photonic milling using dynamic beam arrays
A laser processing system includes a beam positioning system to align beam delivery coordinates relative to a workpiece. The beam positioning system generates position data corresponding to the alignment. The system also includes a pulsed laser source and a beamlet generation module to receive a laser pulse from the pulsed laser source. The beamlet generation module generates a beamlet array from the laser pulse. The beamlet array includes a plurality of beamlet pulses. The system further includes a beamlet modulator to selectively modulate the amplitude of each beamlet pulse in the beamlet array, and beamlet delivery optics to focus the modulated beamlet array onto one or more targets at locations on the workpiece corresponding to the position data.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com