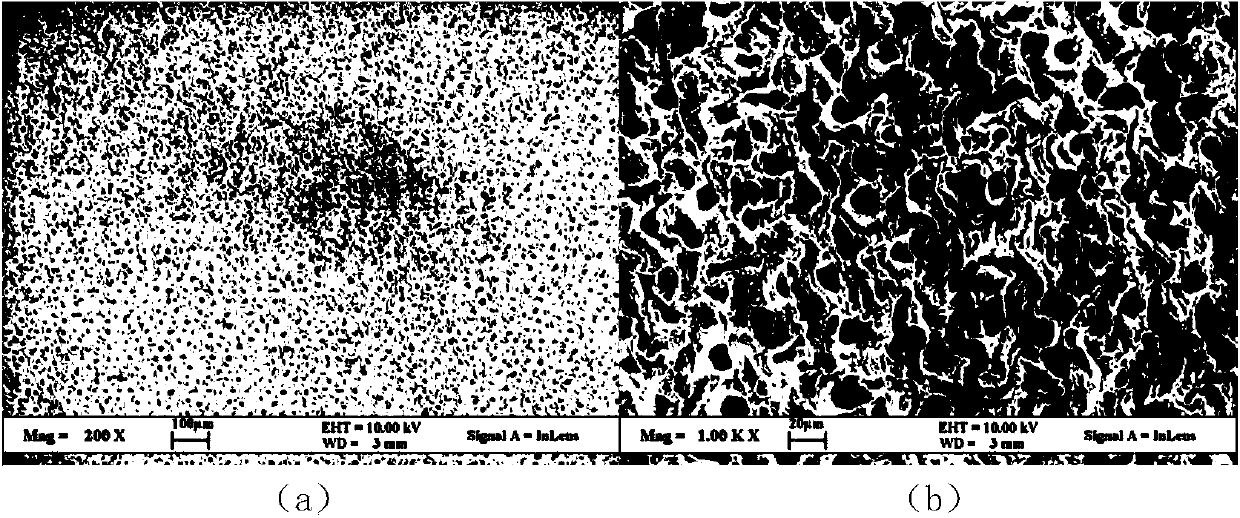
Patents
Literature
414 results about "Picosecond laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
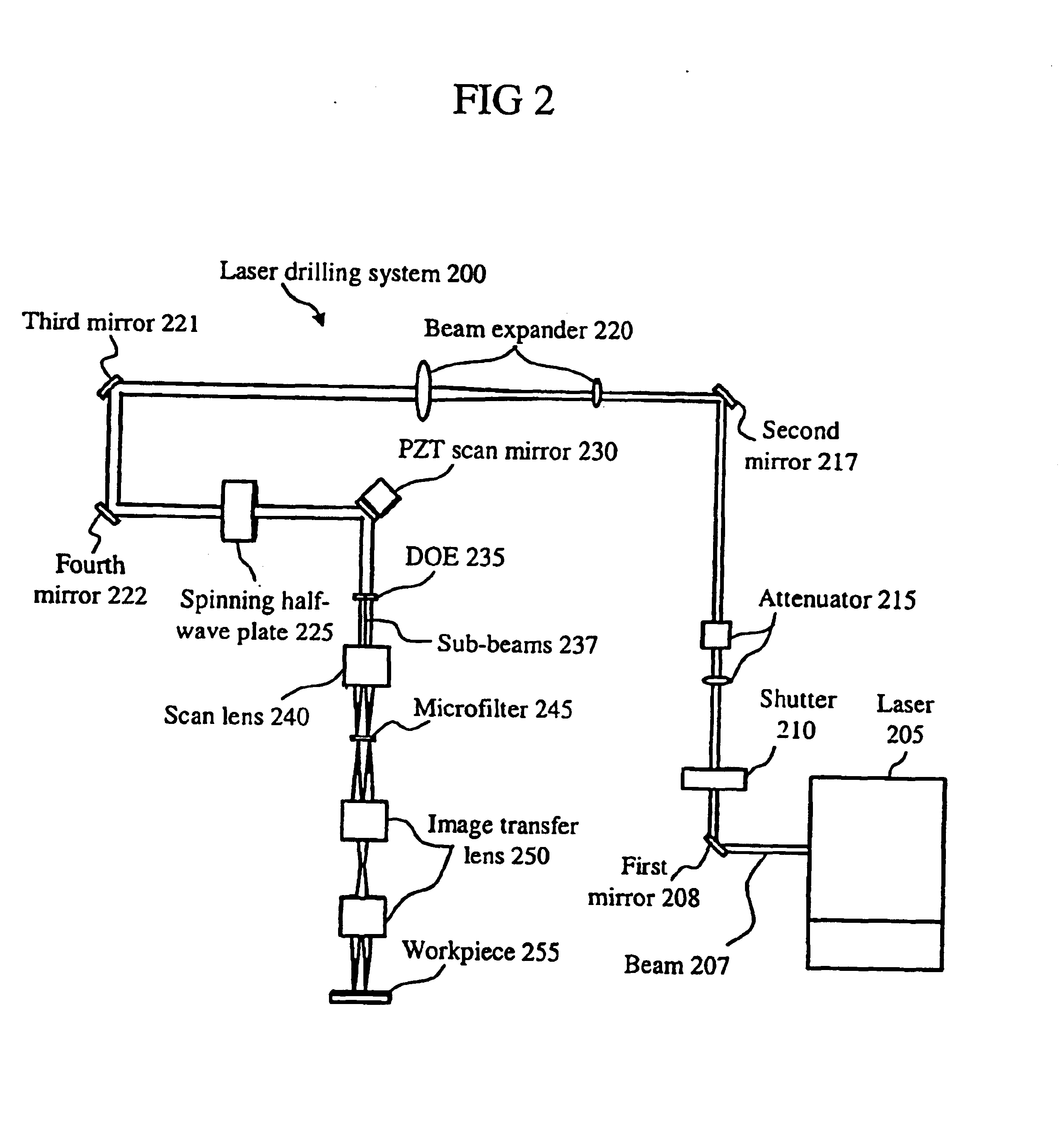
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS20050274702A1Improve inner wall qualityImprove surface qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserFacula
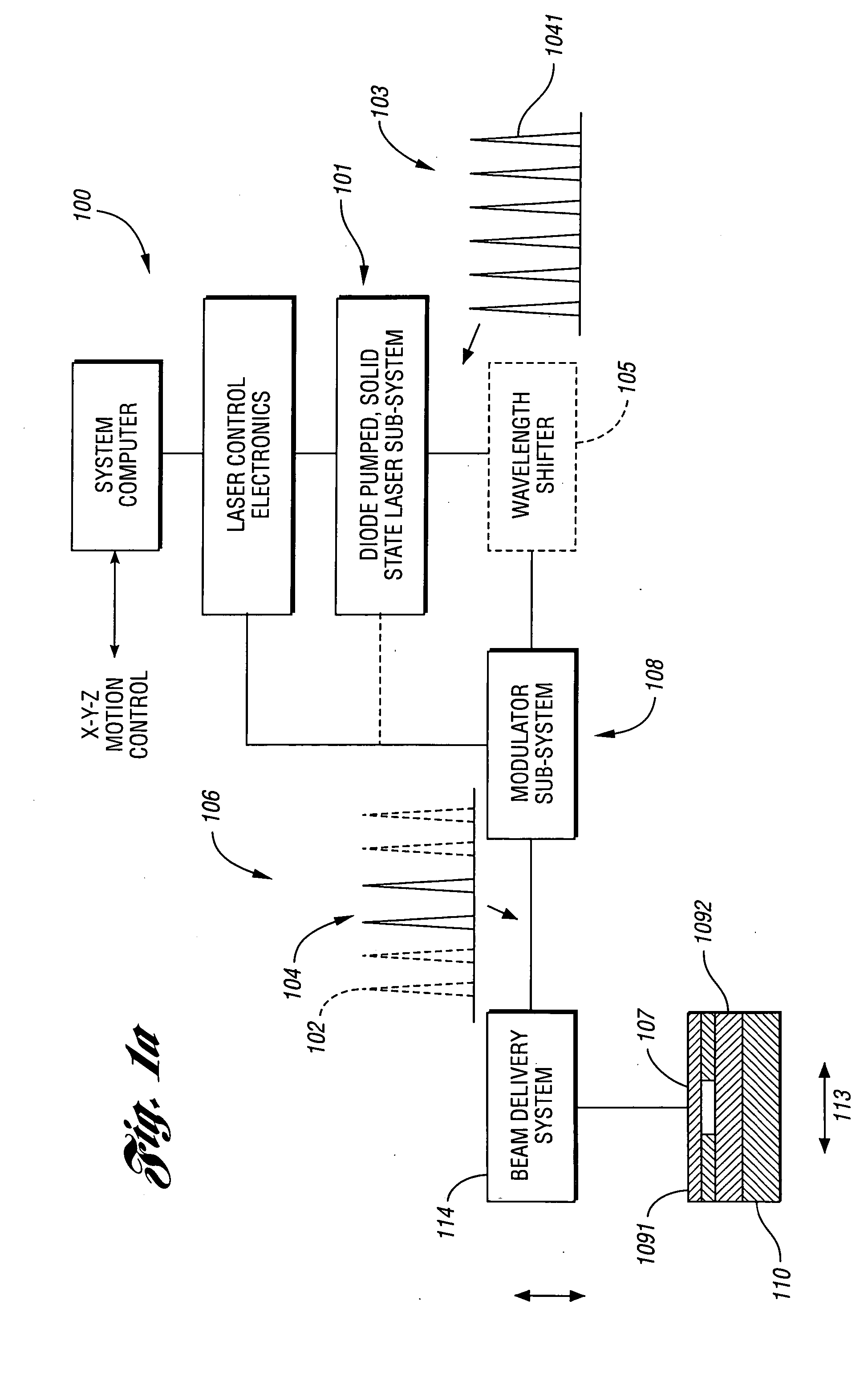
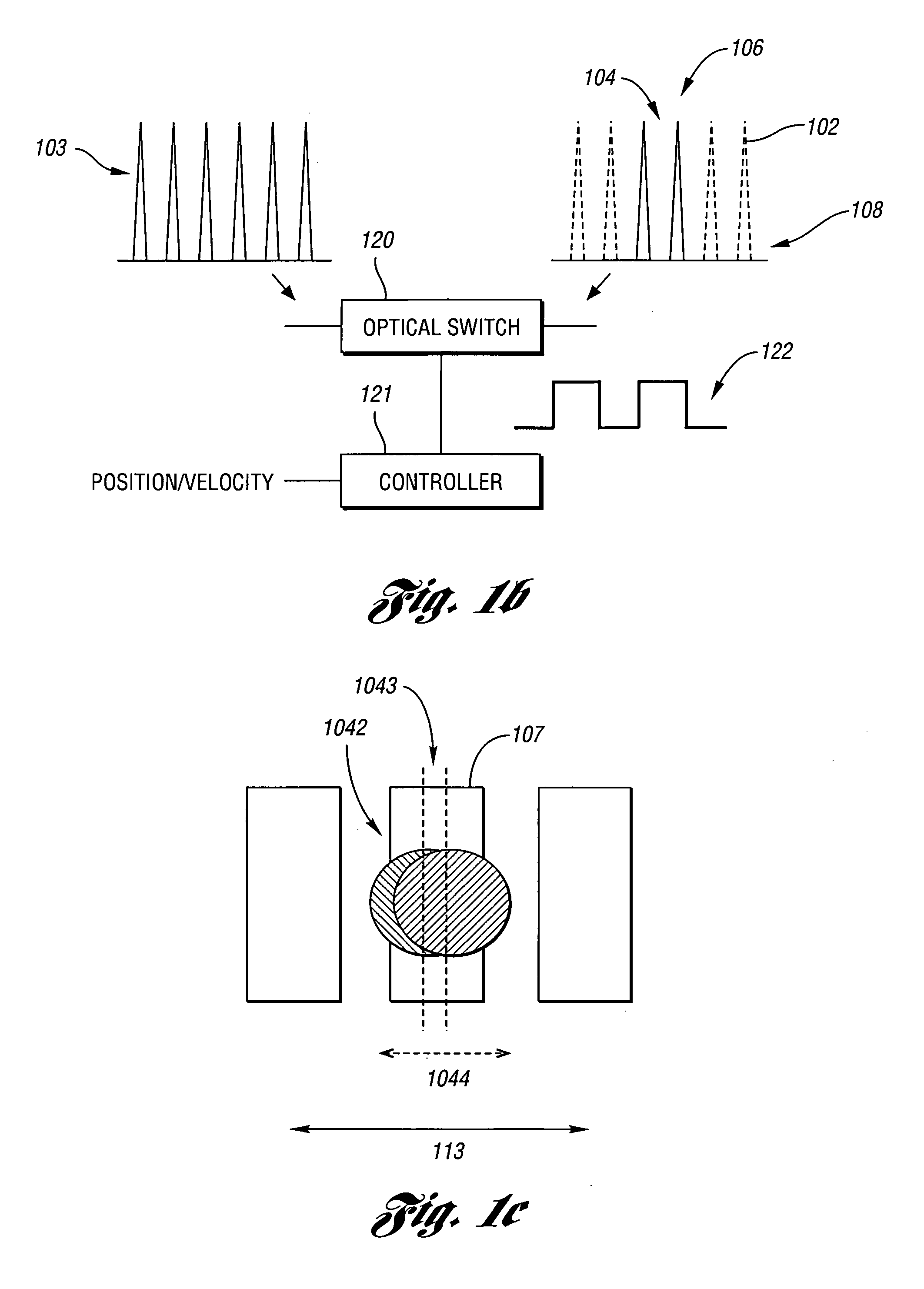
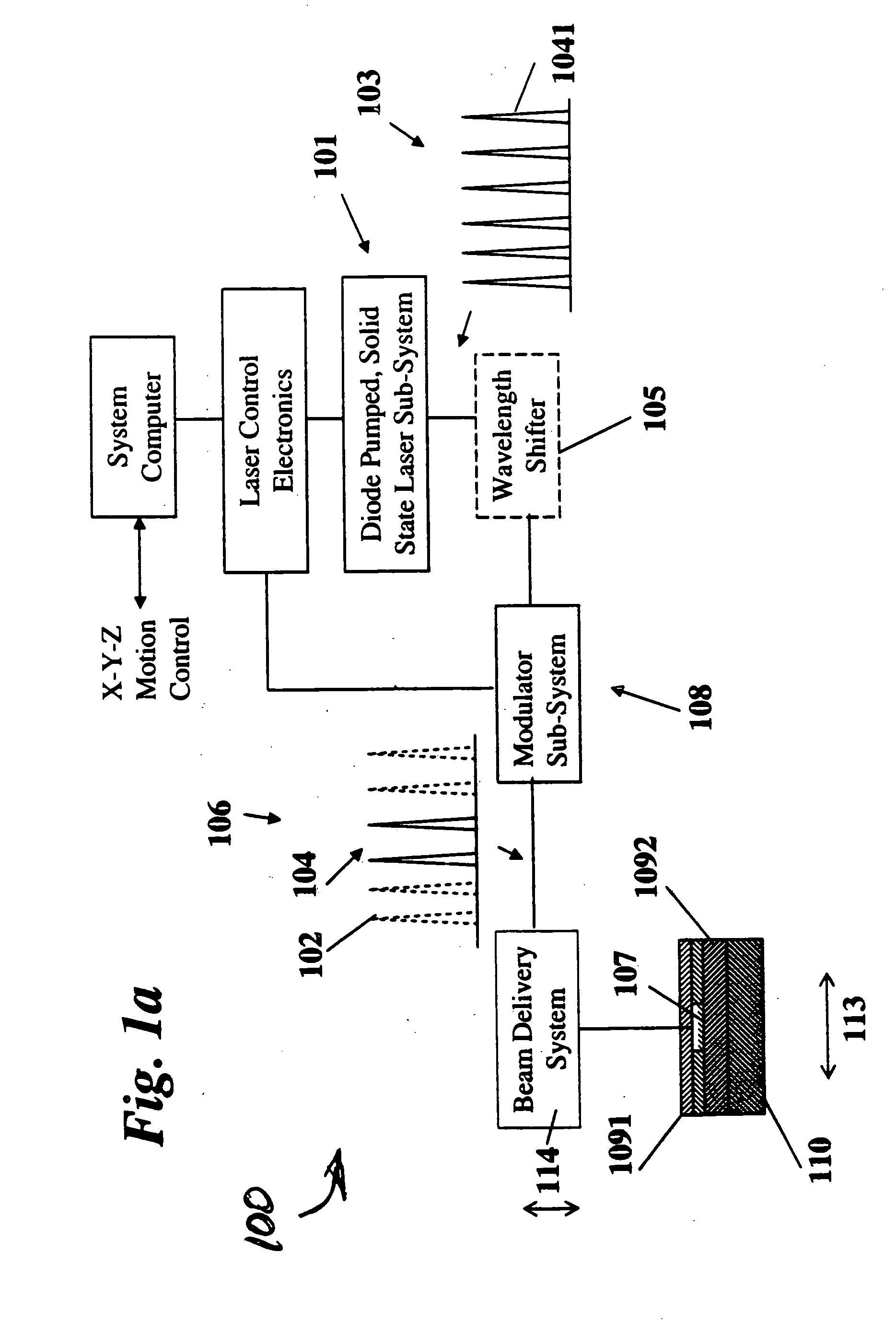
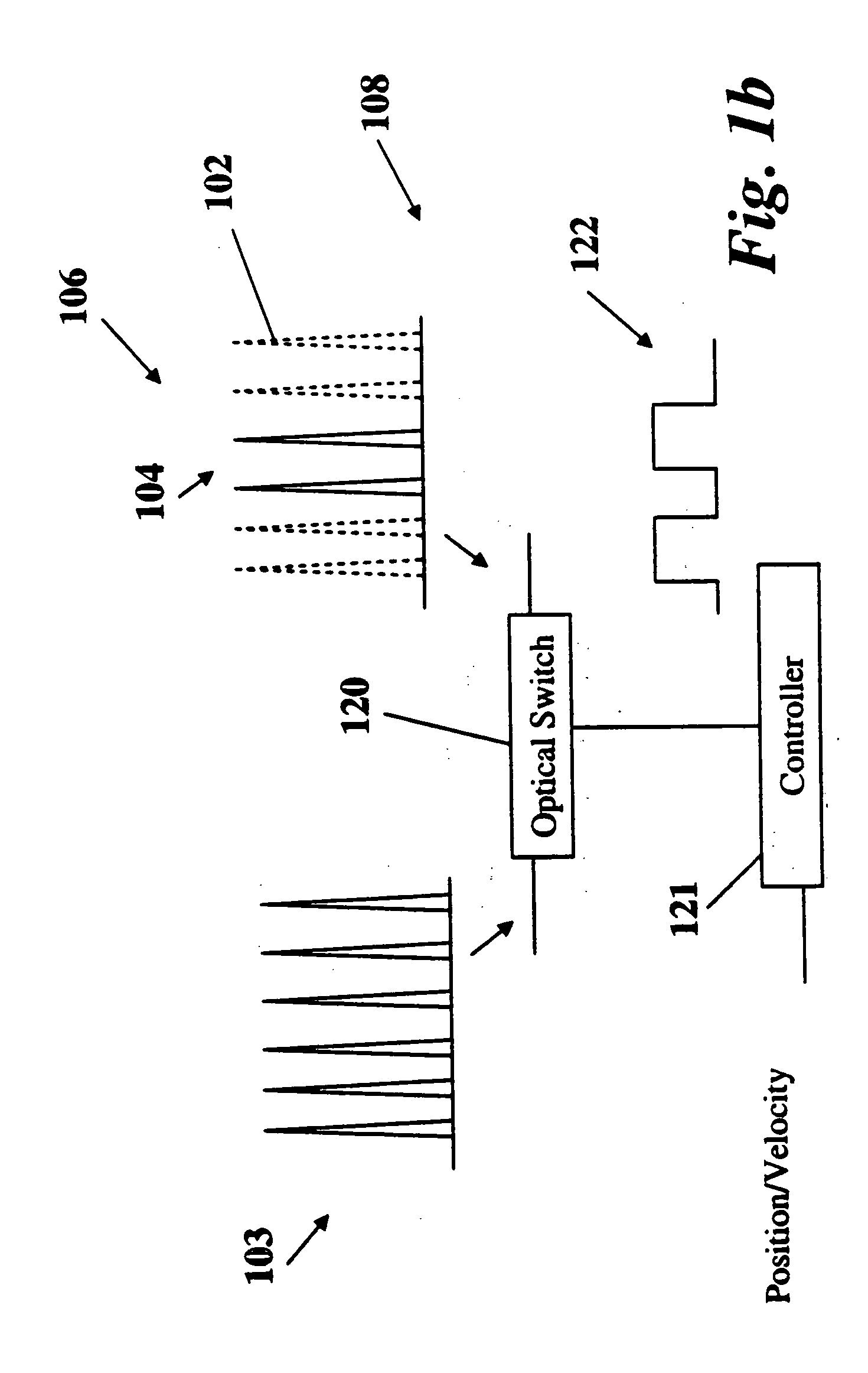
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin simiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
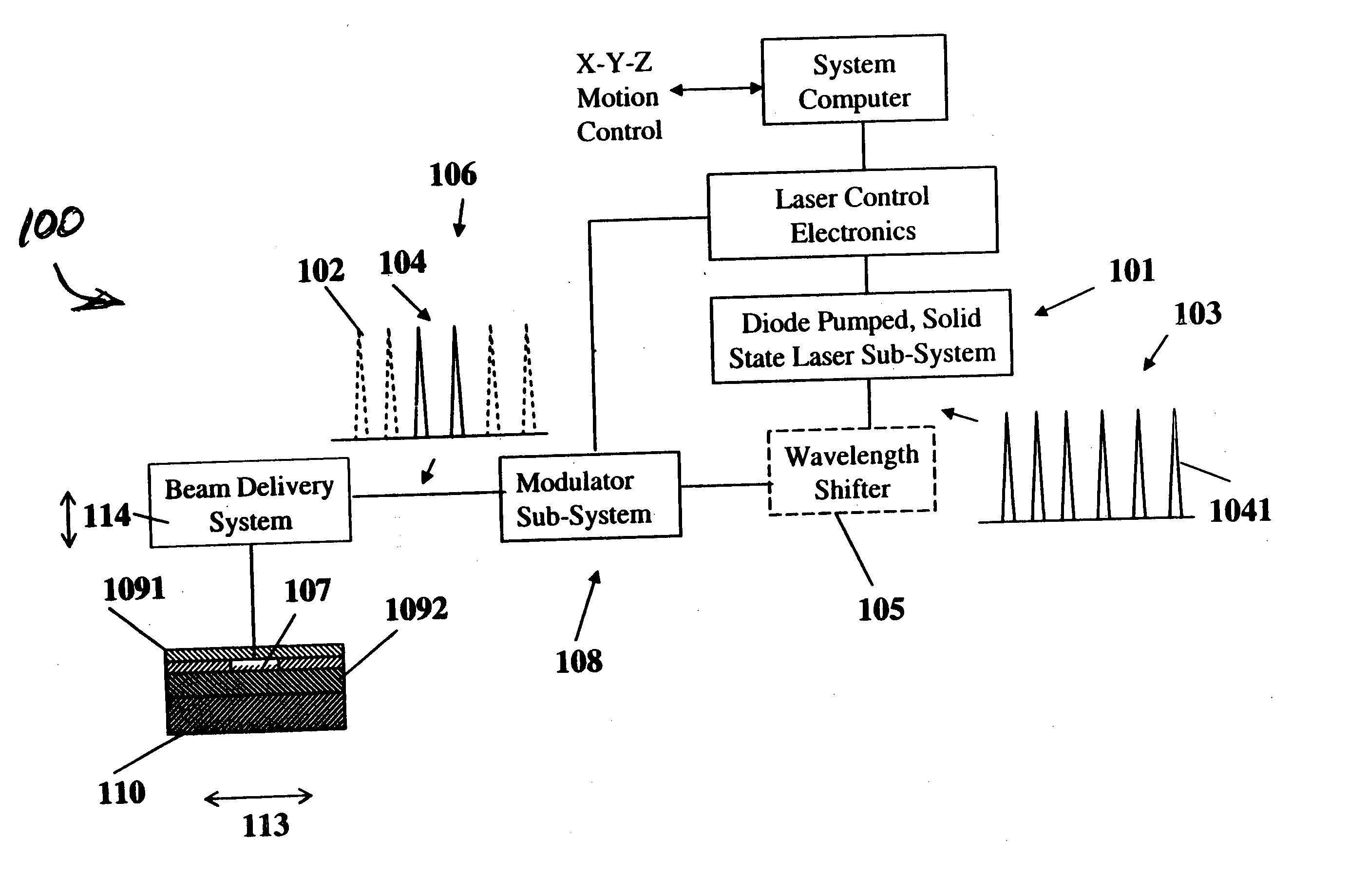
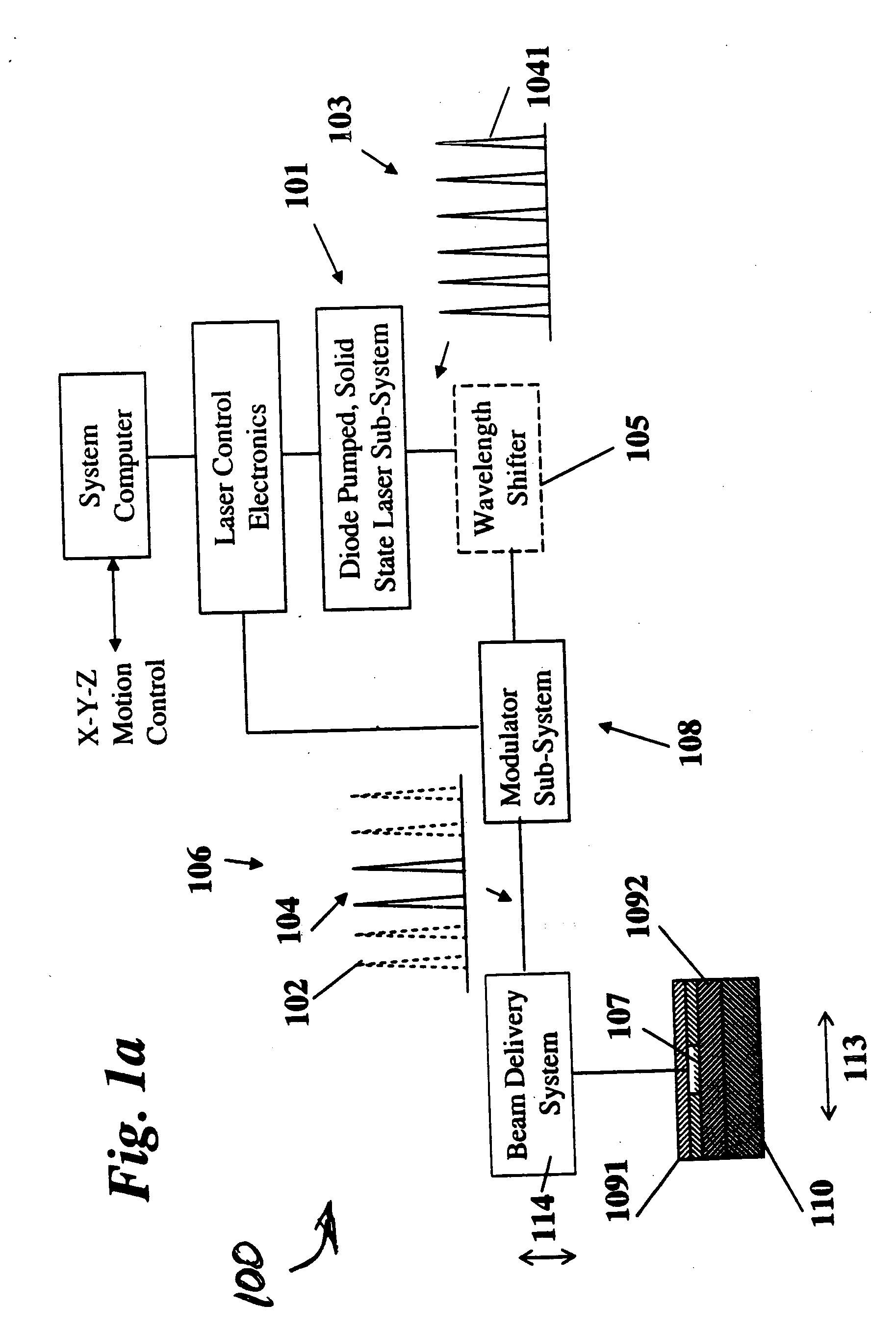
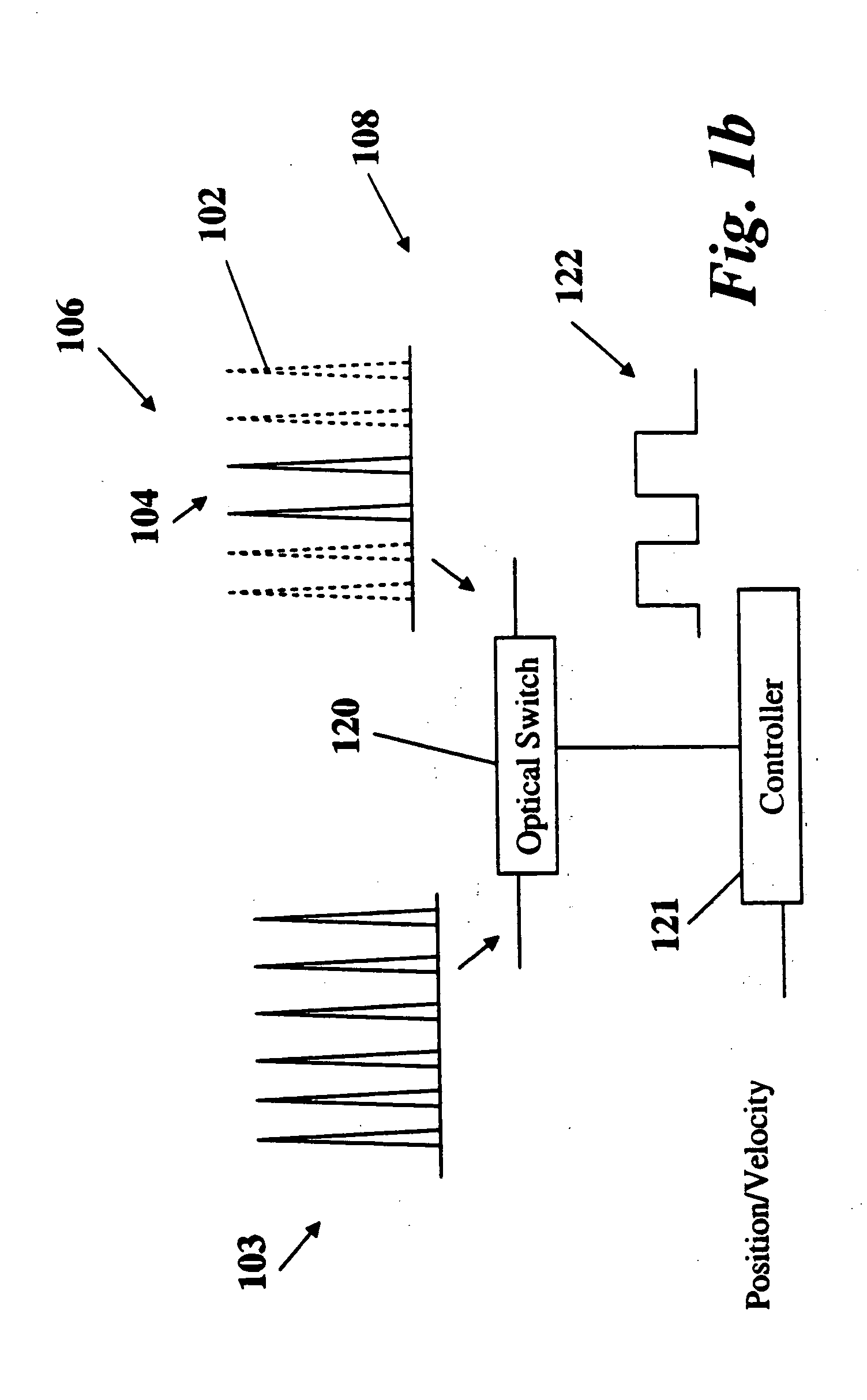
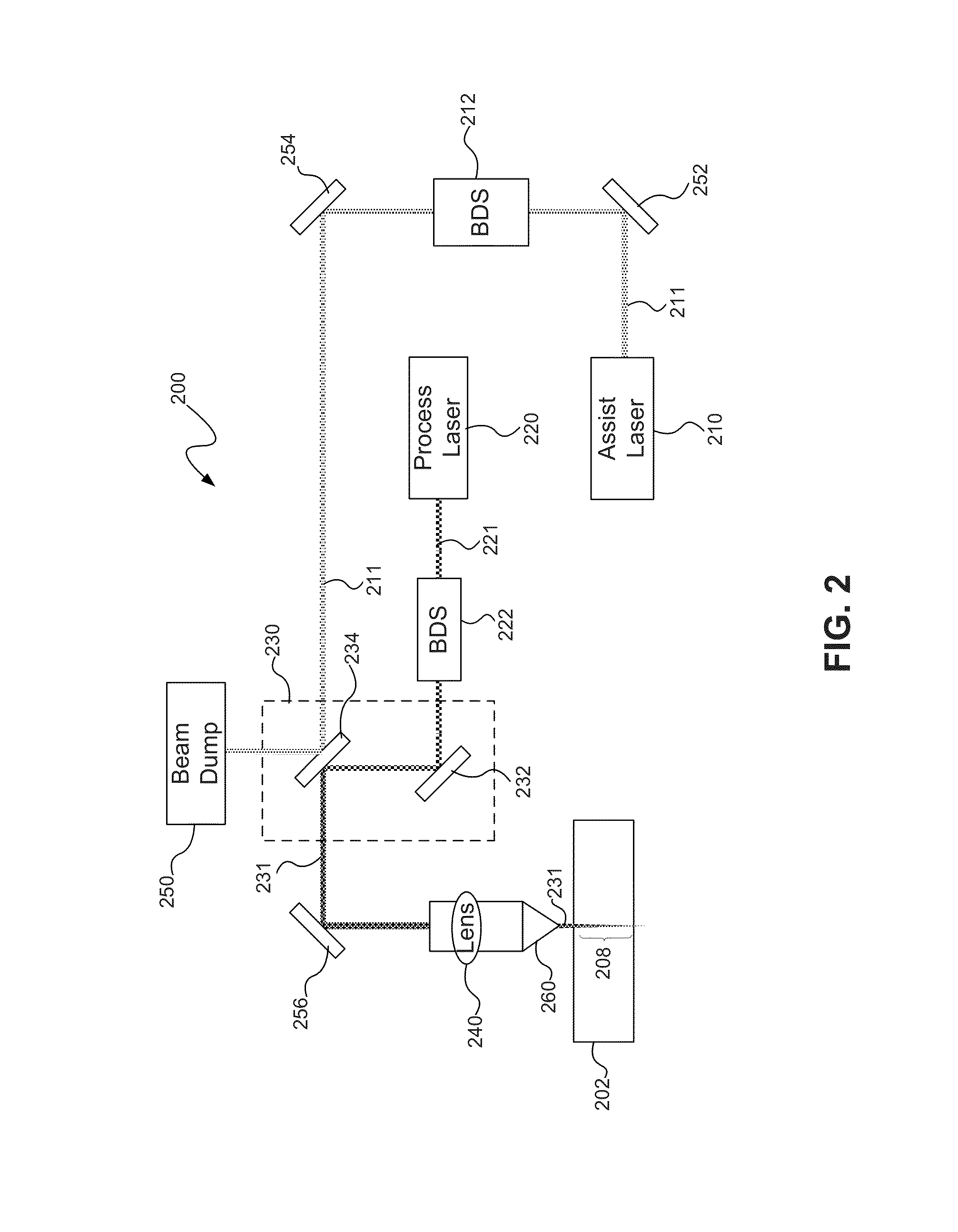
Laser-based system for memory link processing with picosecond lasers
InactiveUS20040134894A1Quality improvementReduce reflectivitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPicosecond laserMicroscopic scale
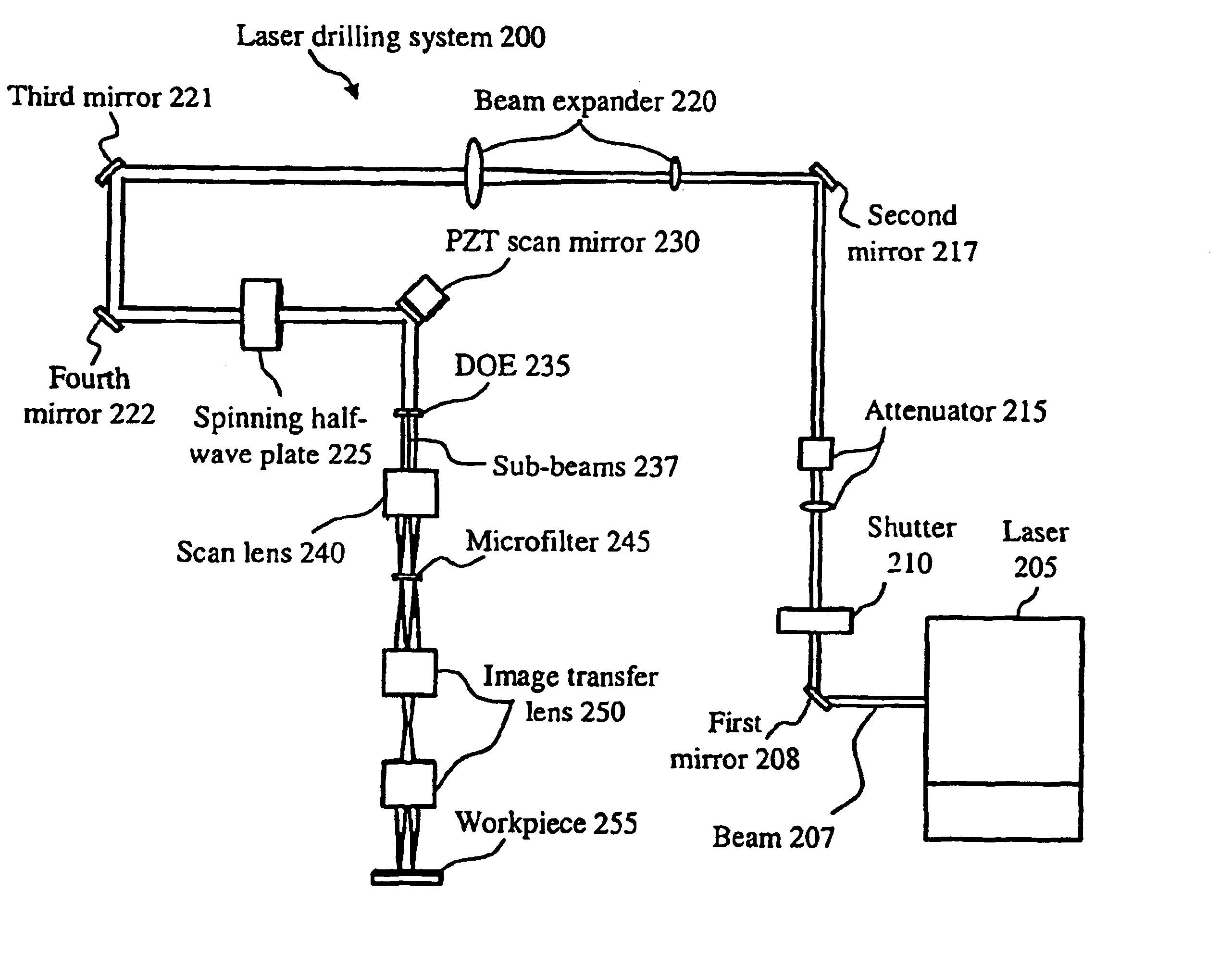
A laser-based system for processing target material within a microscopic region without causing undesirable changes in electrical or physical characteristics of at least one material surrounding the target material, the system includes a seed laser, an optical amplifier, and a beam delivery system. The seed laser for generating a sequence of laser pulses having a first pre-determined wavelength. The optical amplifier for amplifying at least a portion of the sequence of pulses to obtain an amplified sequence of output pulses. The beam delivery system for delivering and focusing at least one pulse of the amplified sequence of pulses onto the target material. The at least one output pulse having a pulse duration in the range of about 10 picoseconds to less than 1 nanosecond. The pulse duration being within a thermal processing range. The at least one focused output pulse having sufficient power density at a location within the target material to reduce the reflectivity of the target material and efficiently couple the focused output into the target material to remove the target material.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS7804043B2Minimize heating effectImprove machine qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserBeam polarization
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin semiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
Laser-based method and system for memory link processing with picosecond lasers
InactiveUS20040134896A1Quality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPicosecond laserNanosecond
A laser-based method of removing a target link structure of a circuit fabricated on a substrate includes generating a pulsed laser output at a pre-determined wavelength less than an absorption edge of the substrate. The laser output includes at least one pulse having a pulse duration in the range of about 10 picoseconds to less than 1 nanosecond, the pulse duration being within a thermal laser processing range. The method also includes delivering and focusing the laser output onto the target link structure. The focused laser output has sufficient power density at a location within the target structure to reduce the reflectivity of the target structure and efficiently couple the focused laser output into the target structure to remove the link without damaging the substrate.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Method for hole machining with picosecond laser
ActiveCN103143841AImprove forming qualityGood processing designabilityLaser beam welding apparatusPicosecond laserOptoelectronics
A method for hole machining with picosecond laser realizes hole machining on CMC-SiC (Ceramic Matrix Composite-Silicon Carbide) material according to the characteristics of fiber composite materials and the machining feature that picosecond laser is suitable for various materials due to superhigh peak power of picosecond laser. According to the method, round holes or square holes are machined in the CMC-SiC material layer by layer in a distributed machining mode; the influence of tiny cracks can be ignored during machining; the stability is good; and the method is particularly suitable for mass repeated micro-hole machining. Layer-by-layer machining in a heliciform way is adopted when round holes are machined; and layer-by-layer machining in a linear scanning way is adopted when square holes are machined. The method has the advantages of good stability of the machining technology, strong designability, high precision and the like.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method of laser milling using constant tool path algorithm
InactiveUS6897405B2Quality improvementGood repeatabilityPrinted circuit manufacturePrintingPicosecond laserLight energy
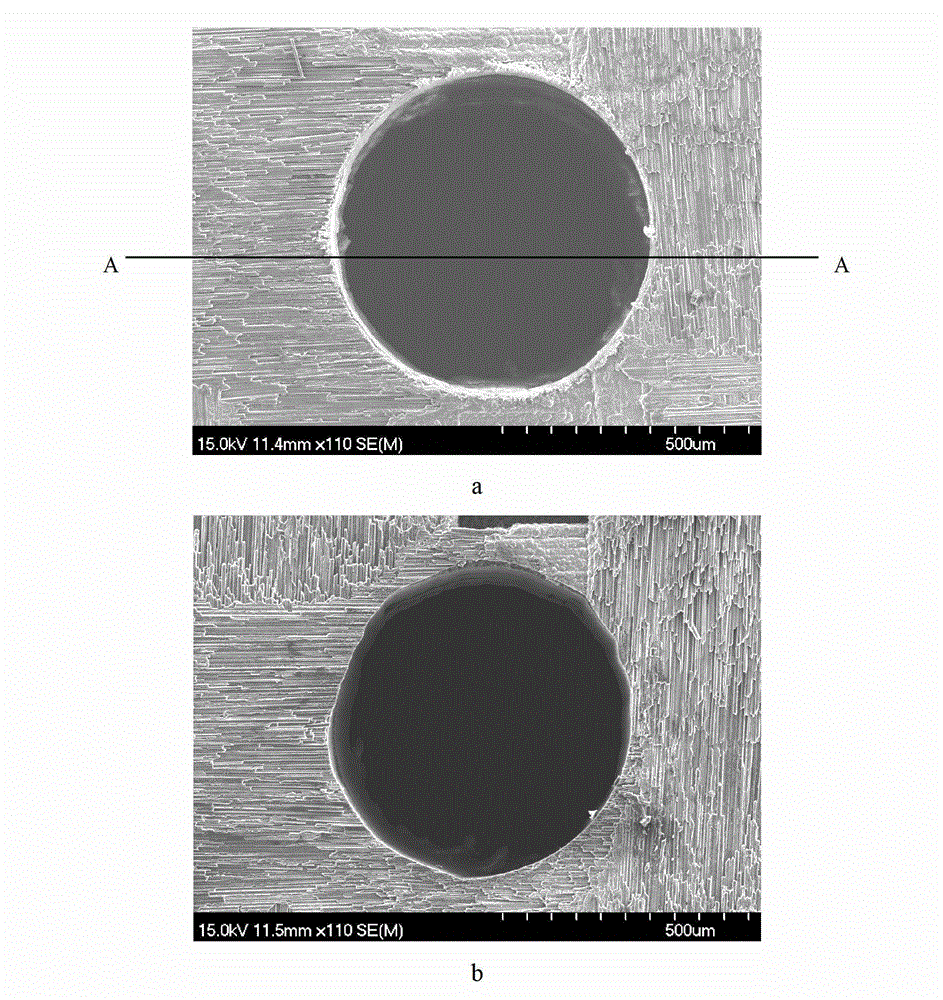
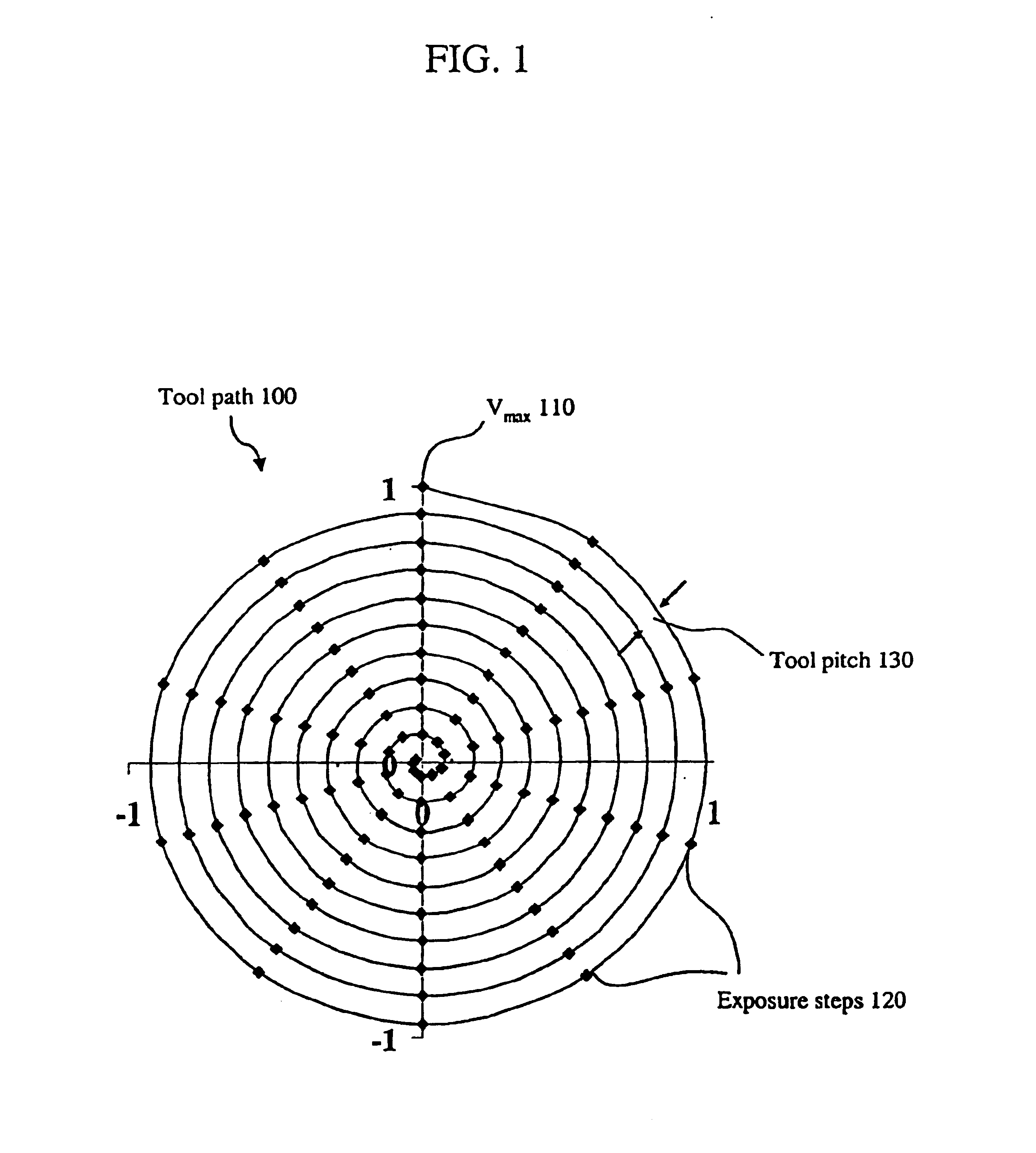
A method of creating a milled structure in a fixed material using a moving laser beam is disclosed, where a picosecond laser provides short pulses of light energy to produce required exposure steps, where a variable rate of laser beam movement conducts the milling upon the material, where the laser beam tool path directs the milling process to produce a milled hole of high quality and repeatability, and where the knowledge of how to measure these 3 quantities is returned as feedback into the laser system. The present invention is further embodied as a spiral milled tool path structured to achieve the customer specified tapered hole shape. The constant arc speed tool path is required to produce tapered holes to customer specification.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Laser-based method and system for memory link processing with picosecond lasers
InactiveUS20050092720A1Quality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPicosecond laserLaser processing
A laser-based method of removing a target link structure of a circuit fabricated on a substrate includes generating a pulsed laser output at a pre-determined wavelength less than an absorption edge of the substrate. The laser output includes at least one pulse having a pulse duration in the range of about 10 picoseconds to less than 1 nanosecond, the pulse duration being within a thermal laser processing range. The method also includes delivering and focusing the laser output onto the target link structure. The focused laser output has sufficient power density at a location within the target structure to reduce the reflectivity of the target structure and efficiently couple the focused laser output into the target structure to remove the link without damaging the substrate.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS CORP
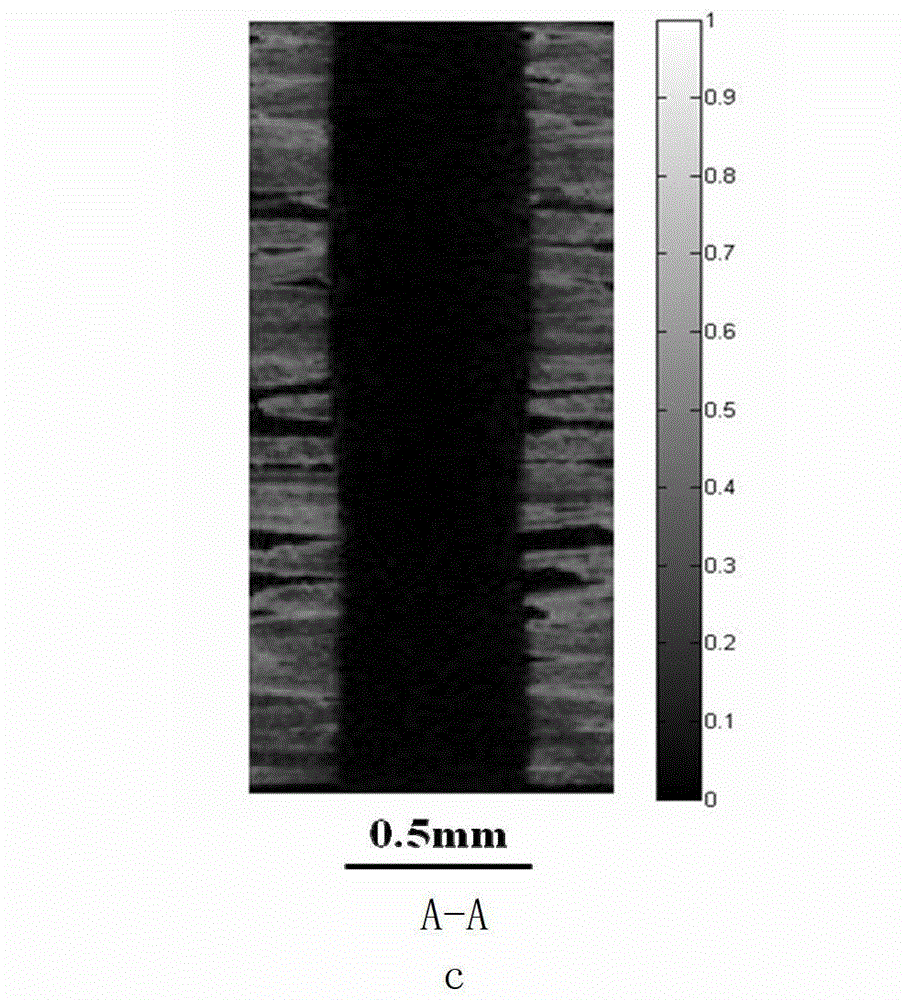
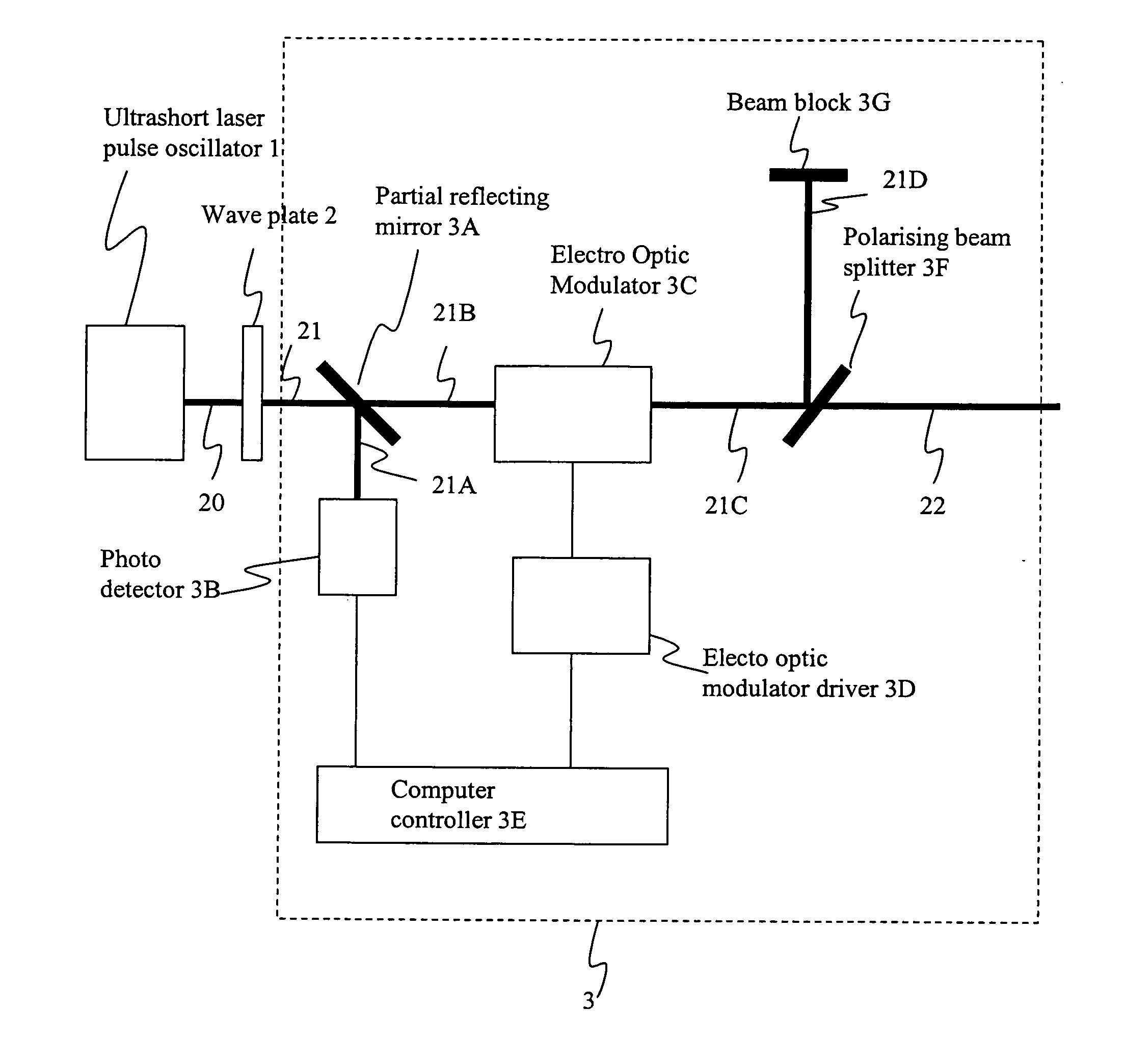
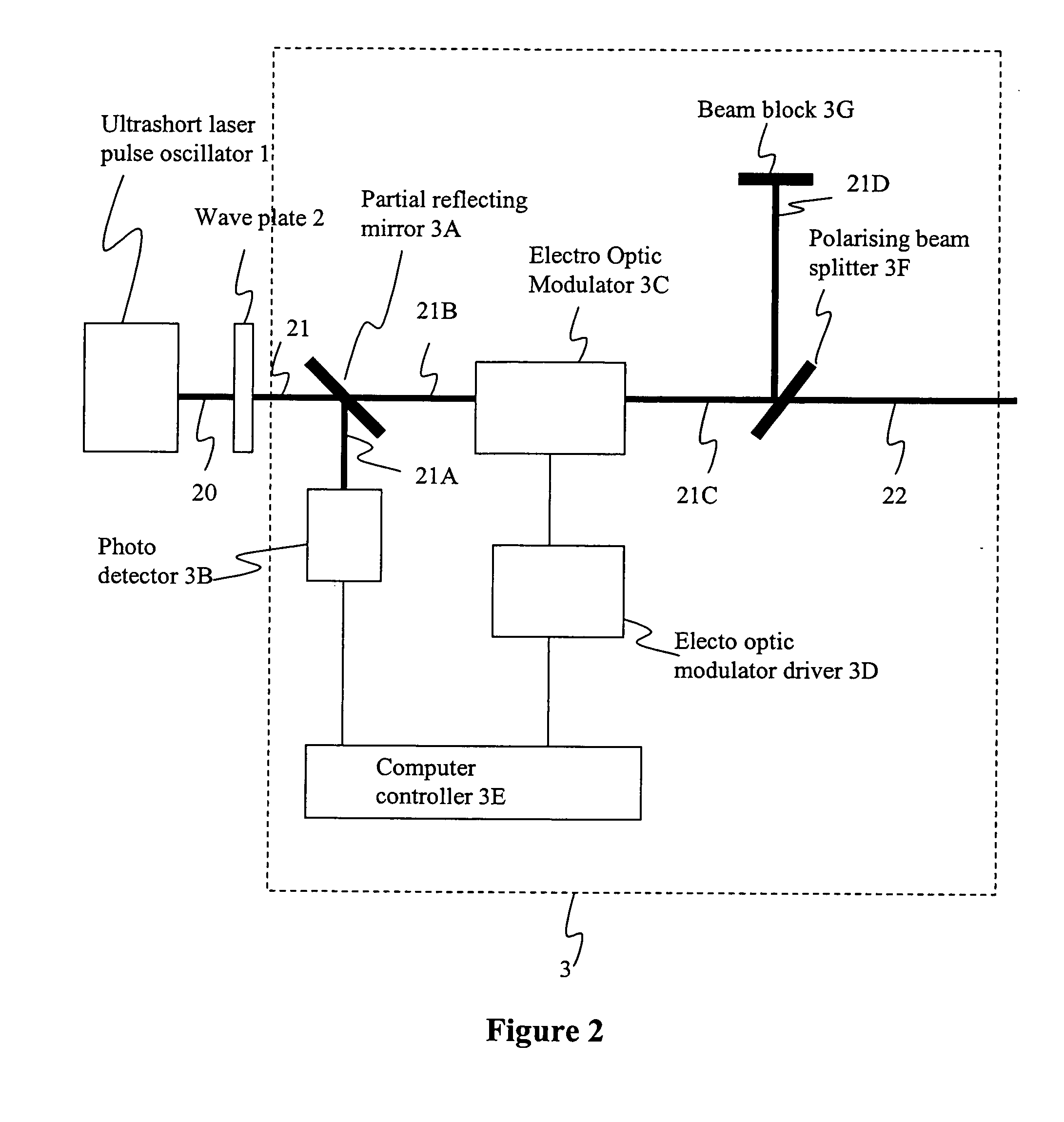
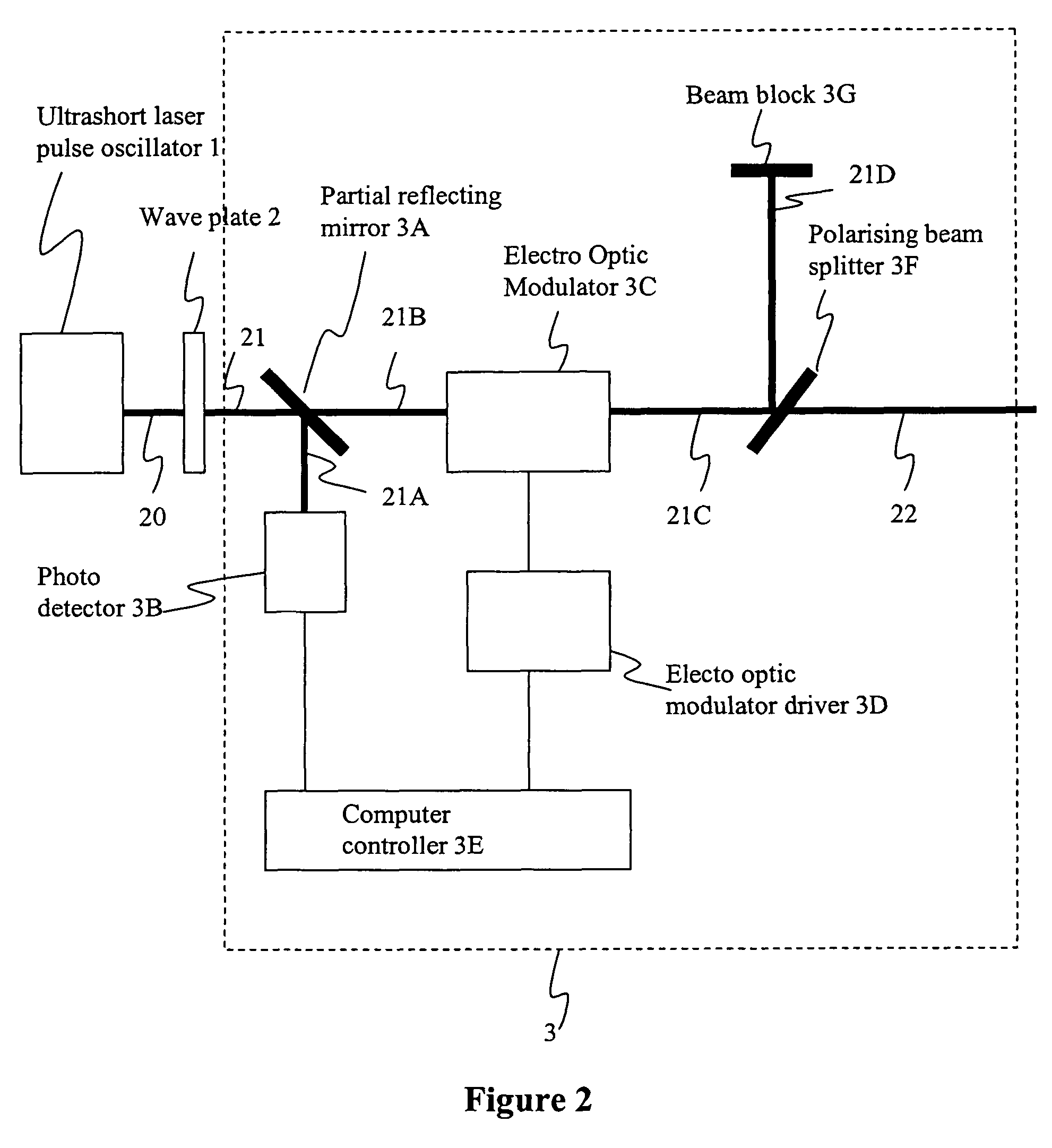
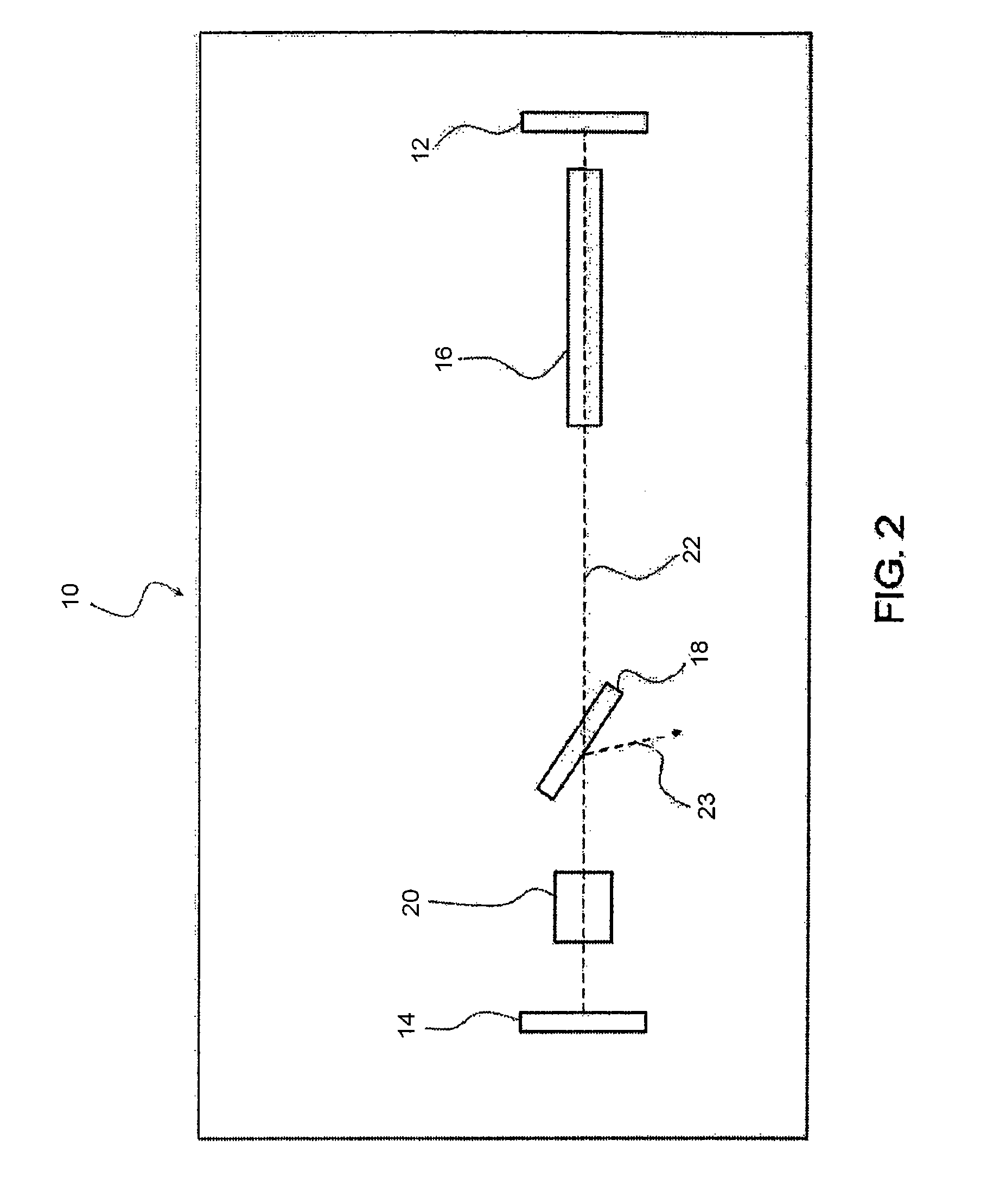
Picosecond laser apparatus and methods for its operation and use
ActiveUS7929579B2Apparatuses may be further simplifiedSimple componentsLaser detailsSurgical instrument detailsPicosecond laserHigh energy
Apparatuses and methods are disclosed for applying laser energy having desired pulse characteristics, including a sufficiently short duration and / or a sufficiently high energy for the photomechanical treatment of skin pigmentations and pigmented lesions, both naturally-occurring (e.g., birthmarks), as well as artificial (e.g., tattoos). The laser energy may be generated with an apparatus having a resonator with the capability of switching between a modelocked pulse operating mode and an amplification operating mode. The operating modes are carried out through the application of a time-dependent bias voltage, having waveforms as described herein, to an electro-optical device positioned along the optical axis of the resonator.
Owner:CYNOSURE
Probes with high current carrying capability and laser machining methods
ActiveUS20120286816A1High strengthElectrical measurement instrument detailsManufacture of electrical instrumentsPicosecond laserNanosecond
The present invention is a probe having a distal end made of one material, a tip and a portion disposed between the distal end and the tip that is a different second material. The probe is laser machined manufactured using a nanosecond or picosecond laser.
Owner:MICRO PROBE
Picosecond pulse laser cutting preparation method for grid-control traveling wave tube grid mesh
ActiveCN103531414AHigh dimensional accuracyImprove consistencyNon-emitting electrodes manufacturePicosecond laserPicosecond pulsed laser
The invention discloses a picosecond pulse laser cutting preparation method for a grid-control traveling wave tube grid mesh. The method comprises the following steps of performing cleaning, hydrogen burning and annealing on a grid mesh material, then pressing the grid mesh material through a die on a punching machine to form a spherical grid mesh blank with high curvature radius precision, performing destressing hydrogen burning on the blank to eliminate stress during processing to guarantee the stability of the curvature radius of a spherical cap of a grid mesh, and finally cutting the grid mesh by adopting picosecond pulse laser of an optimized technology to prepare the grid-control traveling wave tube grid mesh with high size precision and high consistency. According to the preparation method for the grid mesh of a grid-control traveling wave tube, specific technical parameters of picosecond laser cutting are screened through a large number of experiments, the operability is high, the technical design is reasonable, and the application range is large; the prepared grid mesh is high in size precision, high in consistency, high in yield and high in reliability and has an important application value; the shortcoming of an existing electric spark grid mesh processing technology can be effectively overcome.
Owner:NANJING SANLE GROUP
A method for etching extremely-thin electrical isolation grooves on the surface of an ITO conductive thin film
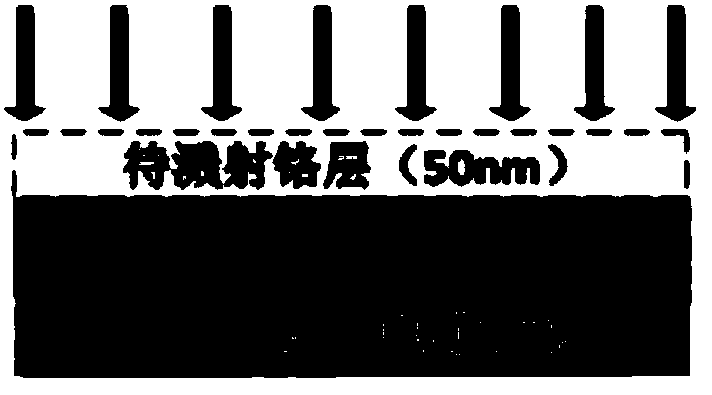
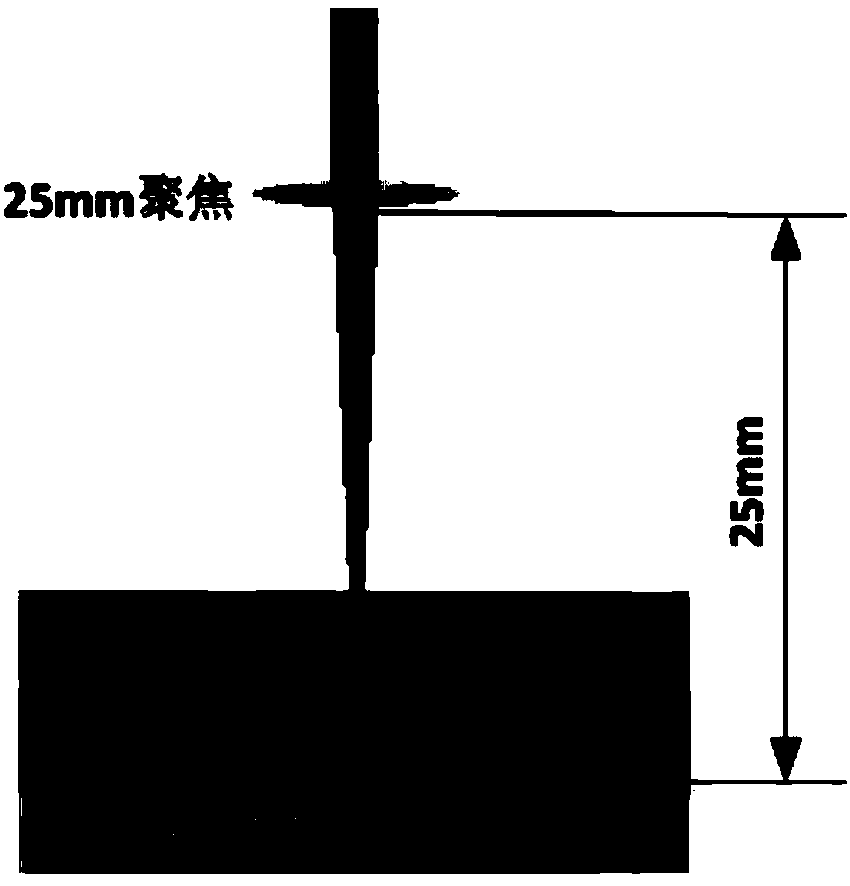
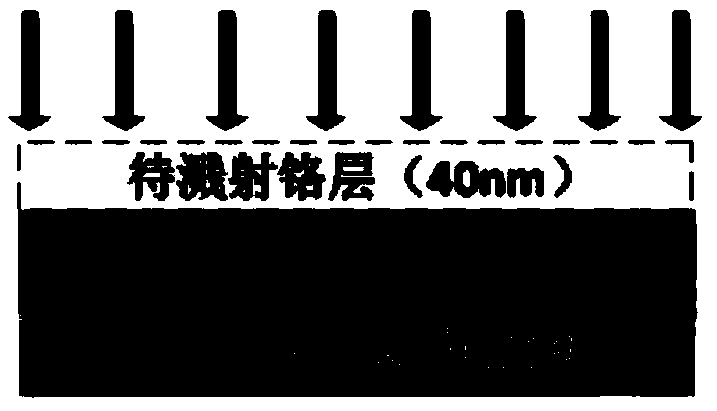
ActiveCN103746027AEasy to limitHigh material utilizationFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationPicosecond laserLight beam
The invention provides a method for etching extremely-thin electrical isolation grooves on the surface of an ITO conductive thin film. The method is characterized in that, to begin with, sputtering metal chromium on the reverse side of an ITO conductive thin film glass substrate; fixing the ITO conductive thin film glass substrate on an object bearing table, with the side having the metal chromium being on the side of laser emission area and keeping the area needing etching on one side of the ITO conductive thin film not to be contacted with the object bearing table; and at last, utilizing picoseconds laser to etch ITO conductive thin film backwardly, wherein the center line of the picoseconds laser beam must keep perpendicular to the surface of the ITO conductive thin film and the focal position of the picoseconds laser must be on the ITO conductive thin film in the whole processing process. The method in the invention effectively reduces the width of the grooves in the surface of the ITO conductive thin film in a thin-film solar cell, guarantees processing efficiency of the picoseconds laser, and improves the overall level of the thin-film solar cell manufacture.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
High-precision Z-axis carrier platform of picosecond laser process equipment
ActiveCN101637849AAddress dynamic thrustSolve the problem of insufficient static holding forceLaser beam welding apparatusPicosecond laserGrating
The invention relates to a high-precision Z-shaft carrier platform of picosecond laser process equipment. A Z fixed plate is fixed on the base plate of a Z platform, a vertical guide rail is installedon the Z fixed plate, an elevating plate capable of moving upwards and downwards along the guide rail is installed on the guide rail, a piezoelectric ceramic motor for controlling the elevating plateto move upwards and downwards is installed on the base plate of the Z platform, a vertical front side plate is fixed on the front side surface of the elevating plate, a vertical back side plate is fixed on the back side surface of the elevating plate, and the front side plate and the back side plate are arranged symmetrically in parallel; a sensor is arranged on the Z fixed plate, and the internal surface of the front side plate or the back side plate is provided with a sensing plate of the sensor; a reading head is arranged on the Z fixed plate, and a grating gage is stuck to the internal surface of the front side plate or the back side plate; and fixture plates are arranged on the front side plate and the back side plate. The high-precision Z-shaft carrier platform of the picosecond laser process equipment controls the Z-shaft to start, stop and elevate by using the high-resolution piezoelectric ceramic motor. The grating gage ensures the precision of elevation and positioning. Thebalancing mechanism solves the problems of insufficient thrust and static retaining force of the piezoelectric ceramic motor.
Owner:SUZHOU DELPHI LASER
Laser-based method and system for memory link processing with picosecond lasers
InactiveUS20050115936A1Quality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPicosecond laserLaser processing
A laser-based method of removing a target link structure of a circuit fabricated on a substrate includes generating a pulsed laser output at a pre-determined wavelength less than an absorption edge of the substrate. The laser output includes at least one pulse having a pulse duration in the range of about 10 picoseconds to less than 1 nanosecond, the pulse duration being within a thermal laser processing range. The method also includes delivering and focusing the laser output onto the target link structure. The focused laser output has sufficient power density at a location within the target structure to reduce the reflectivity of the target structure and efficiently couple the focused laser output into the target structure to remove the link without damaging the substrate.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS CORP
System and method for laser beveling and/or polishing
ActiveUS20160059354A1Edge defects are reducedReduce the edge defectsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusPicosecond laserLaser light
Laser processing of hard dielectric materials may include cutting a part from a hard dielectric material using a continuous wave laser operating in a quasi-continuous wave (QCW) mode to emit consecutive laser light pulses in a wavelength range of about 1060 nm to 1070 nm. Cutting using a QCW laser may be performed with a lower duty cycle (e.g., between about 1% and 15%) and in an inert gas atmosphere such as nitrogen, argon or helium. Laser processing of hard dielectric materials may further include post-cut processing the cut edges of the part cut from the dielectric material, for example, by beveling and / or polishing the edges to reduce edge defects. The post-cut processing may be performed using a laser beam with different laser parameters than the beam used for cutting, for example, by using a shorter wavelength (e.g., 193 nm excimer laser) and / or a shorter pulse width (e.g., picosecond laser).
Owner:IPG PHOTONICS CORP
Picosecond laser apparatus and methods for its operation and use
ActiveUS7586957B2Apparatuses may be further simplifiedSimple componentsLaser detailsSurgical instrument detailsPicosecond laserHigh energy
Apparatuses and methods are disclosed for applying laser energy having desired pulse characteristics, including a sufficiently short duration and / or a sufficiently high energy for the photomechanical treatment of skin pigmentations and pigmented lesions, both naturally-occurring (e.g., birthmarks), as well as artificial (e.g., tattoos). The laser energy may be generated with an apparatus having a resonator with the capability of switching between a modelocked pulse operating mode and an amplification operating mode. The operating modes are carried out through the application of a time-dependent bias voltage, having waveforms as described herein, to an electro-optical device (e.g., a Pockels cell) positioned along the optical axis of the resonator.
Owner:CYNOSURE
Ceramic drilling method of composite nanosecond-picosecond-femtosecond laser technology
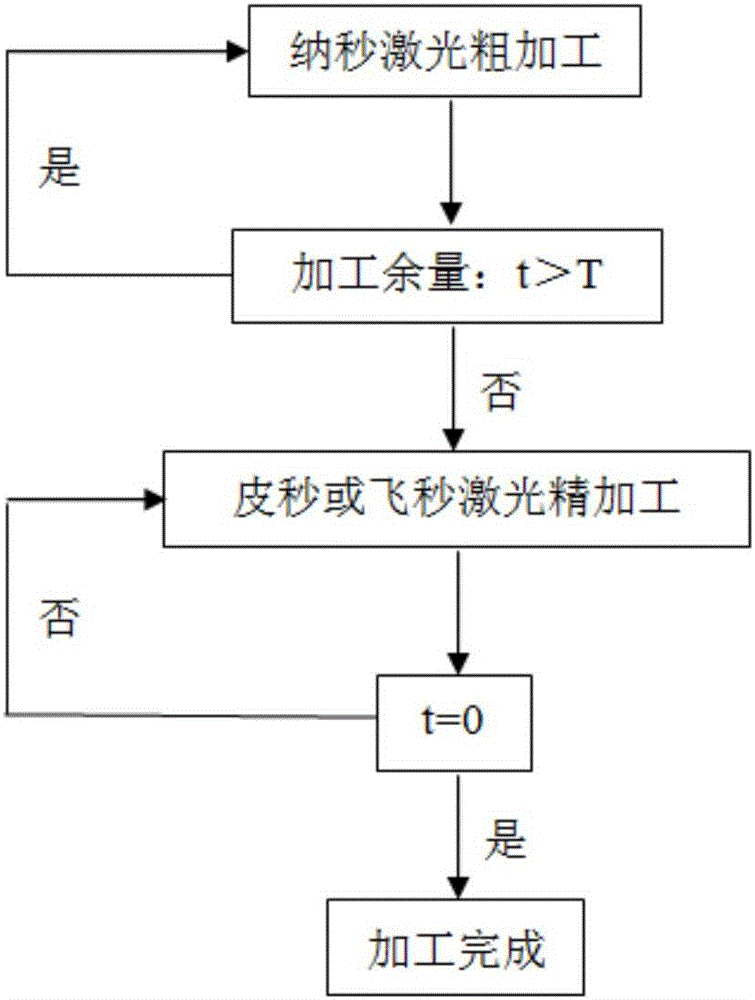
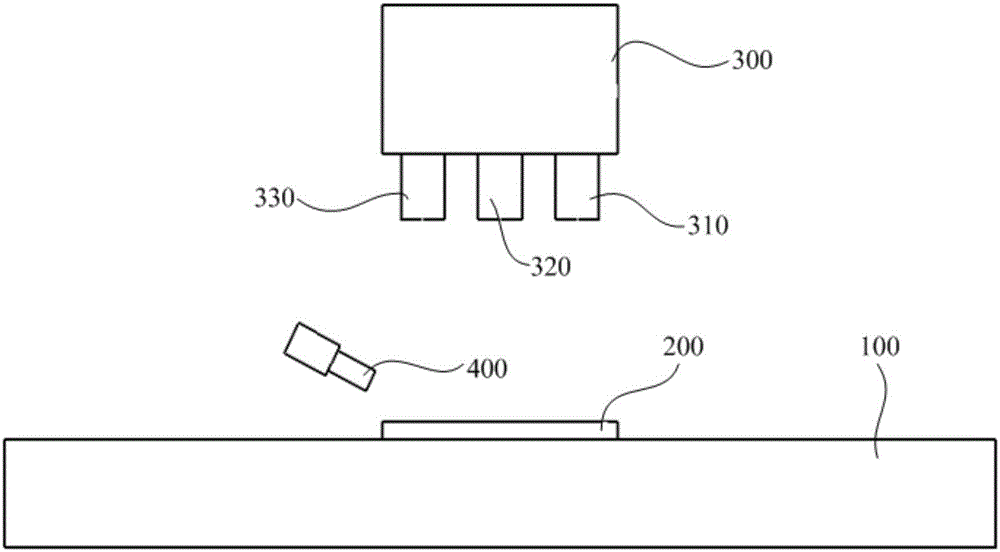
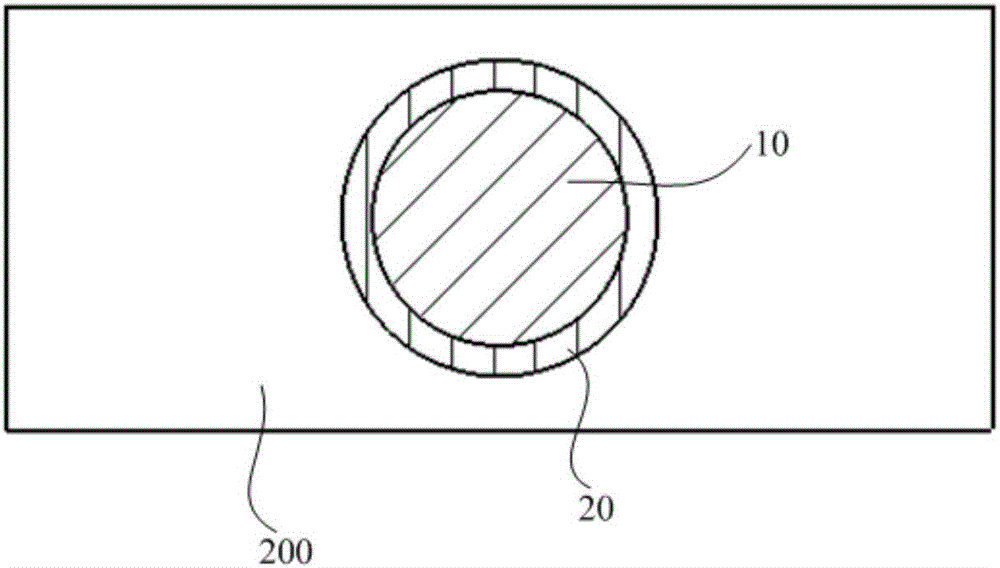
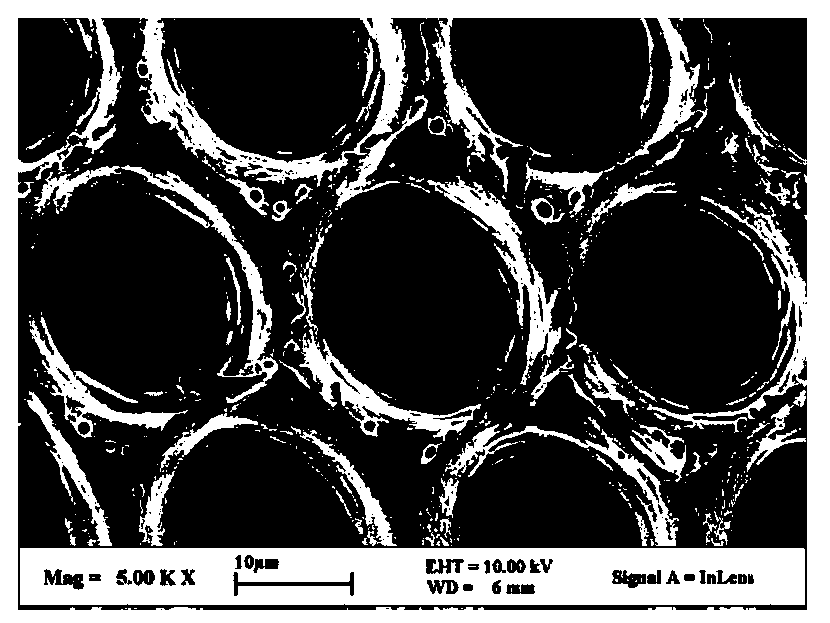
ActiveCN106425125AReduce the temperatureReduce recast layersWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusNanosecond laserPicosecond laser
The invention discloses a ceramic drilling method of a composite nanosecond-picosecond-femtosecond laser technology. The ceramic drilling mechanism of the composite nanosecond-picosecond-femtosecond laser technology comprises the following steps: S10, providing multi-pulse-width fiber laser devices which comprise a nanosecond laser device, a picosecond laser device and a femtosecond laser device, roughly machining a ceramic workpiece fixed on a working table by using the nanosecond laser device, and meanwhile, spraying auxiliary gas at a position nearby a machining position; S20, carrying out finish machining on the ceramic workpiece which is machined roughly by using the picosecond laser device or the femtosecond laser device, and meanwhile, spraying auxiliary gas at a position nearby the machining position; and S30, presetting allowance for finish machining T, detecting residual allowance for machining t by using a dimension precision measurement instrument, repeating the step S10 when t is greater than T, repeating the step S20 when t is greater than 0 and smaller than or equal to T, and repeating in such a way until t is equal to 0. The auxiliary gas is sprayed at the position nearby the machining position, after rough machining by nanosecond laser, finish machining is implemented by picosecond or femtosecond laser, and therefore, machining precision and machining efficiency of the ceramic workpiece are improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Metal die for coining super-hydrophobic micro-nanometer surface and laser manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103521929AHigh structural fidelityIncrease flexibilityNanotechnologyLaser beam welding apparatusPicosecond laserOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a metal die for coining a super-hydrophobic micro-nanometer surface and a laser manufacturing method thereof. The laser manufacturing method comprises the following steps that an ultra-short pulse laser is used for ablating a metal base material, a symmetrical negative structure of a lotus leaf micro-nanometer structure is obtained on the surface of the metal base material through laser ablating removing, and then the metal die is obtained; the symmetrical negative structure of the lotus leaf micro-nanometer structure is a micrometer-level pit and a nanometer-level substructure on the inner surface of the micrometer-level pit. The invention provides the micro-nanometer coining metal die for coining a non-metal material or a light-metal material so as to form the lotus leaf micro-nanometer structure with the surface being super hydrophobic and the laser manufacturing method of the metal die, and particularly relates to the micro-nanometer coining metal die which is manufactured efficiently in a large area by the utilization of high-power picosecond lasers and the manufacturing method of the metal die. The metal die for coining the super-hydrophobic micro-nanometer surface and the laser manufacturing method of the metal die have the comprehensive advantages that the manufacturing efficiency is high, the micro-nanometer coining die is high in temperature resistance, high in pressure resistance and wide in coning material range, the micro-nanometer structure is precise and adjustable in parameter and the lotus structure is vivid. Moreover, the manufacturing method is far superior than other methods.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Picosecond Laser Apparatus and Methods for its Operation and Use
ActiveUS20100296531A1Short durationHigh energyLaser detailsSurgical instrument detailsPicosecond laserPigmented lesion
Apparatuses and methods are disclosed for applying laser energy having desired pulse characteristics, including a sufficiently short duration and / or a sufficiently high energy for the photomechanical treatment of skin pigmentations and pigmented lesions, both naturally-occurring (e.g., birthmarks), as well as artificial (e.g., tattoos). The laser energy may be generated with an apparatus having a resonator with the capability of switching between a modelocked pulse operating mode and an amplification operating mode. The operating modes are carried out through the application of a time-dependent bias voltage, having waveforms as described herein, to an electro-optical device positioned along the optical axis of the resonator.
Owner:CYNOSURE
Microstructures and methods of fabricating
A process of making a microstructure, is described. The process comprises the steps of forming a plurality of fillable features in a first material, to form a template; and applying a second material to the template so that the second material at least partially fills at least some of the fillable features in the template so as to form the microstructure, said second material being different from the first material. The process of forming a template uses a laser selected from a picosecond laser, a femtosecond laser and a nanosecond UV laser. The invention includes a photonic crytal made by this process.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
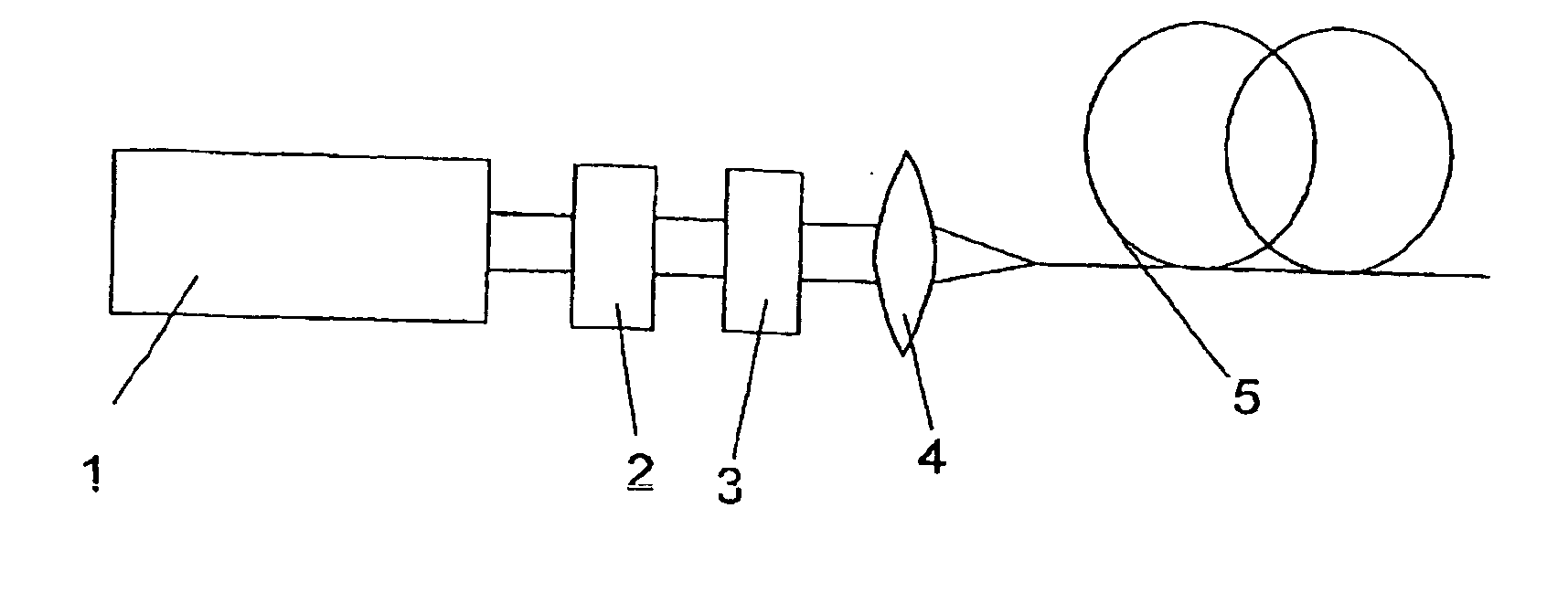
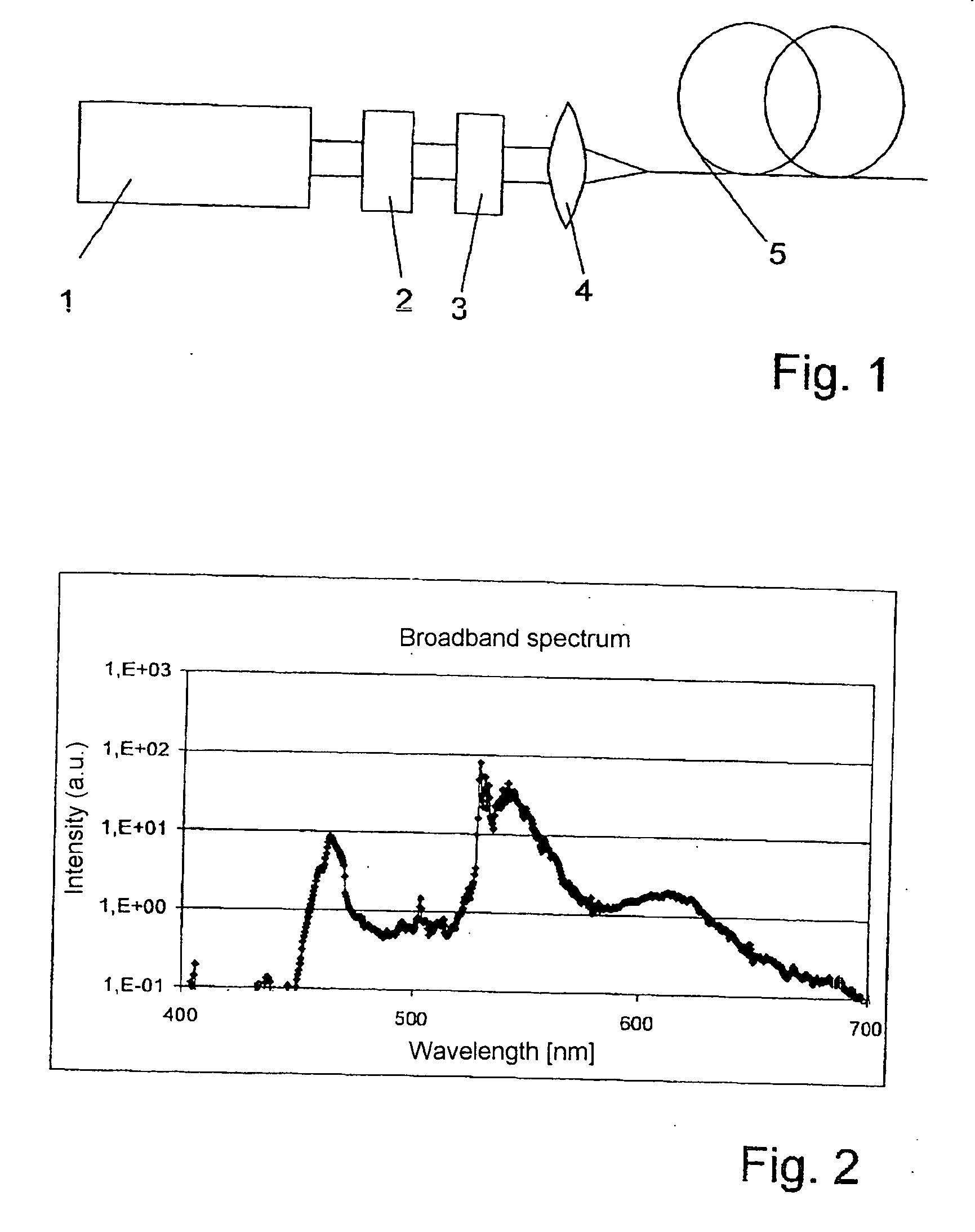
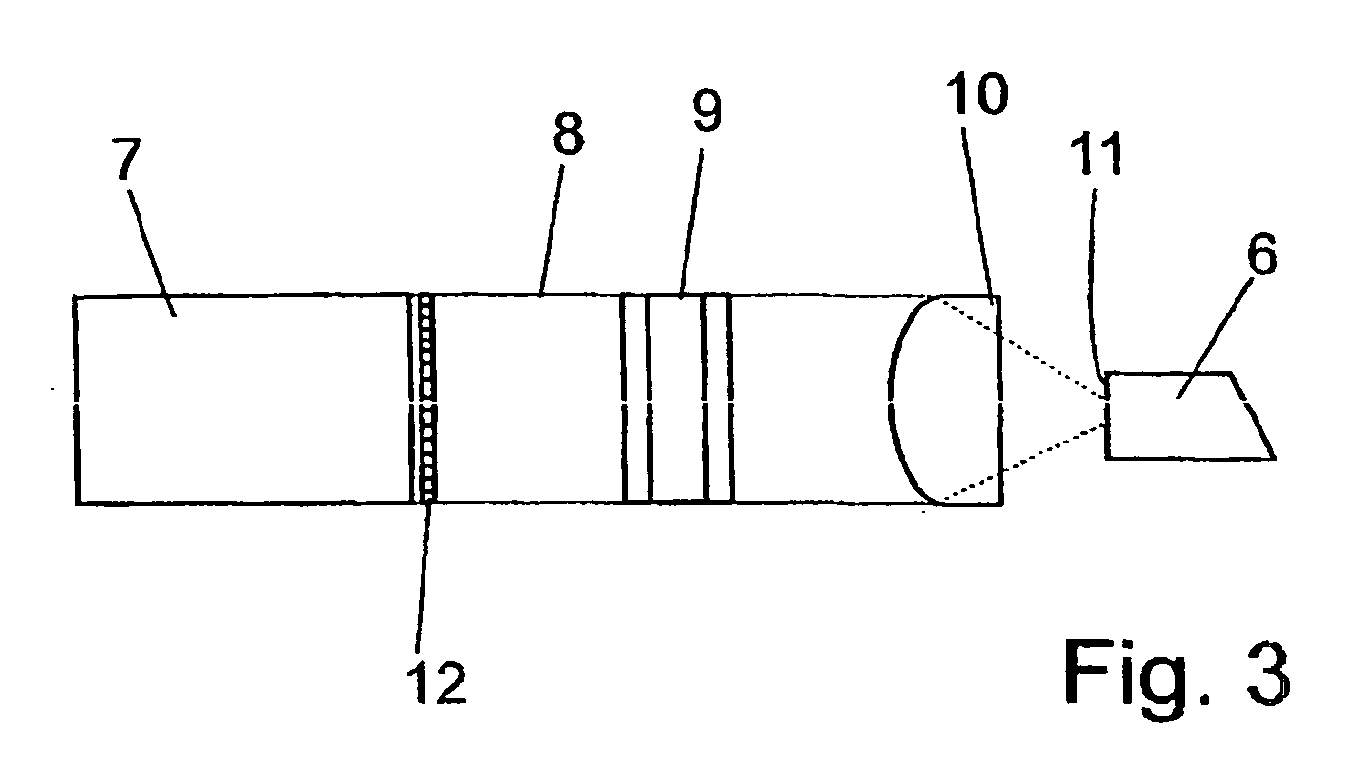
Method and optical arrangement for the generation of a broadband spectrum
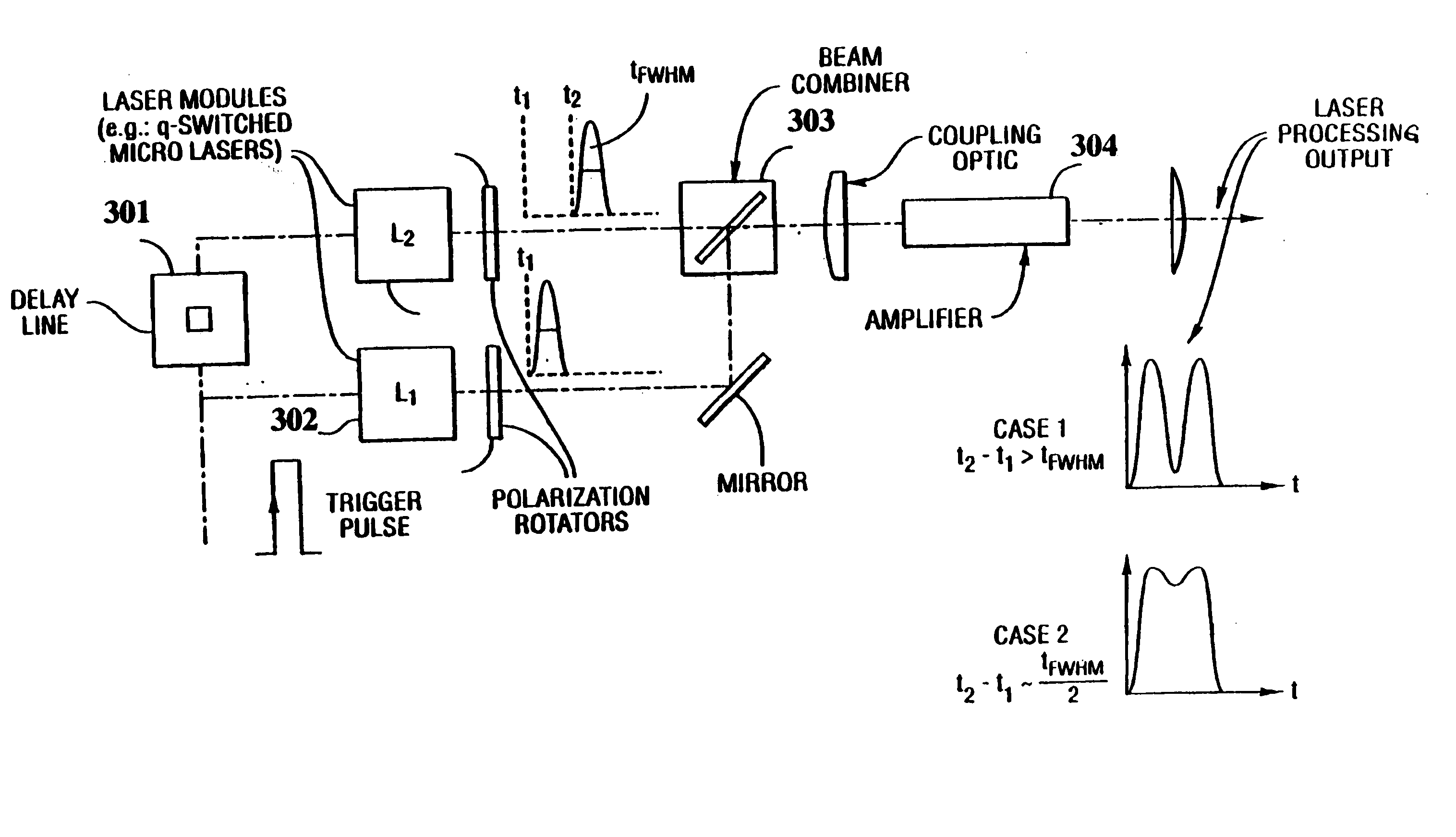
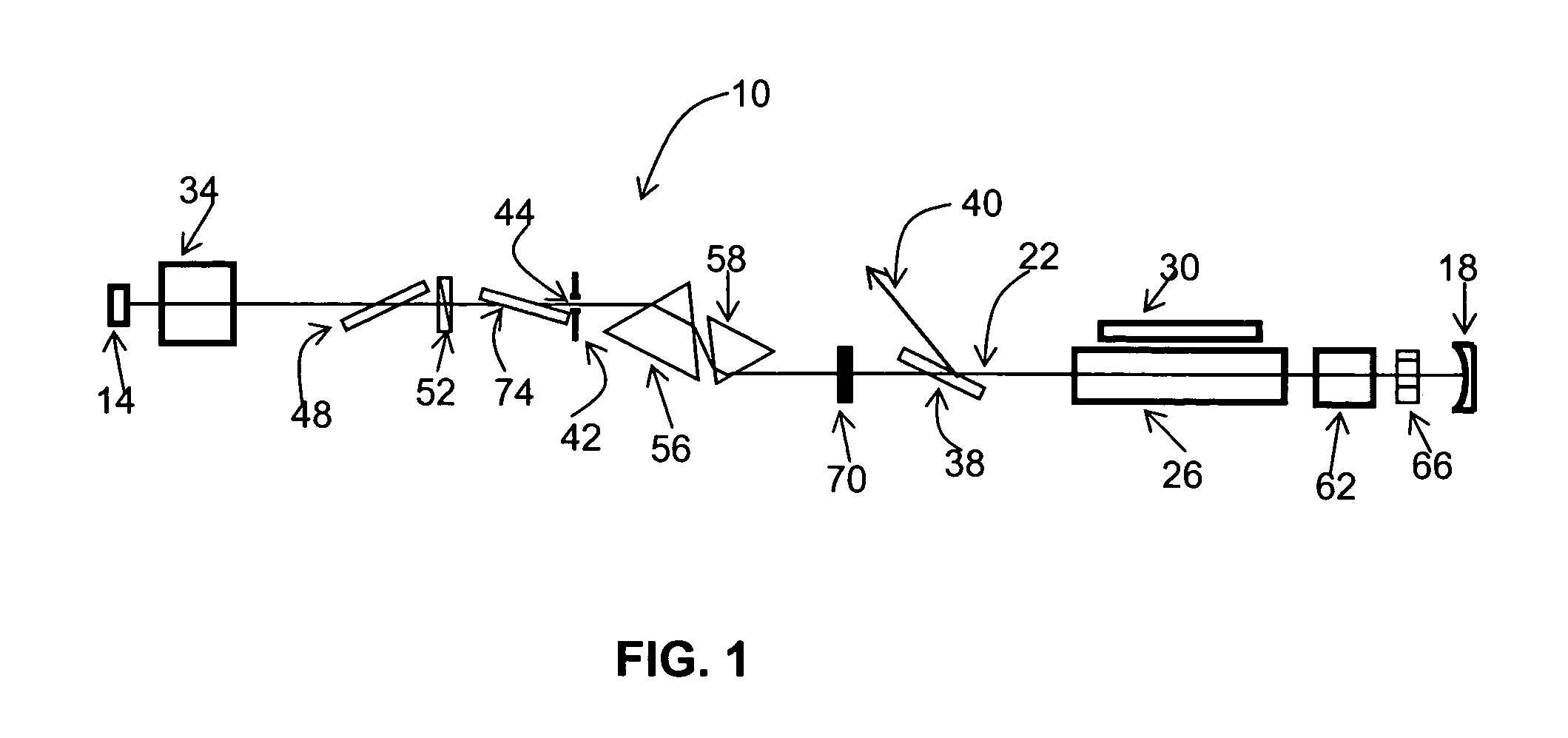
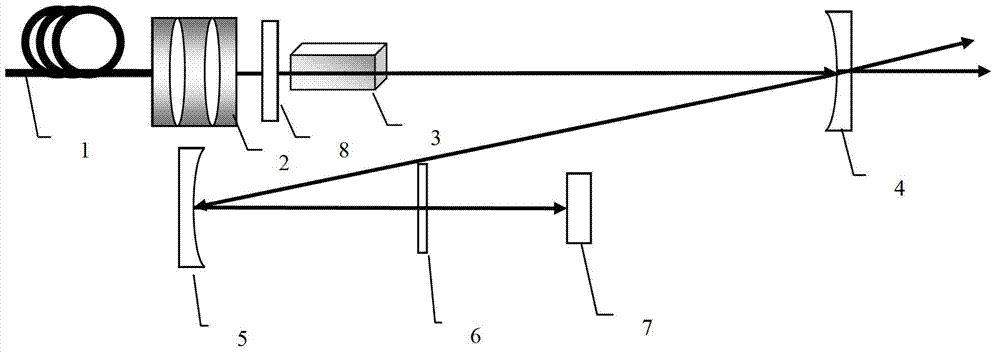
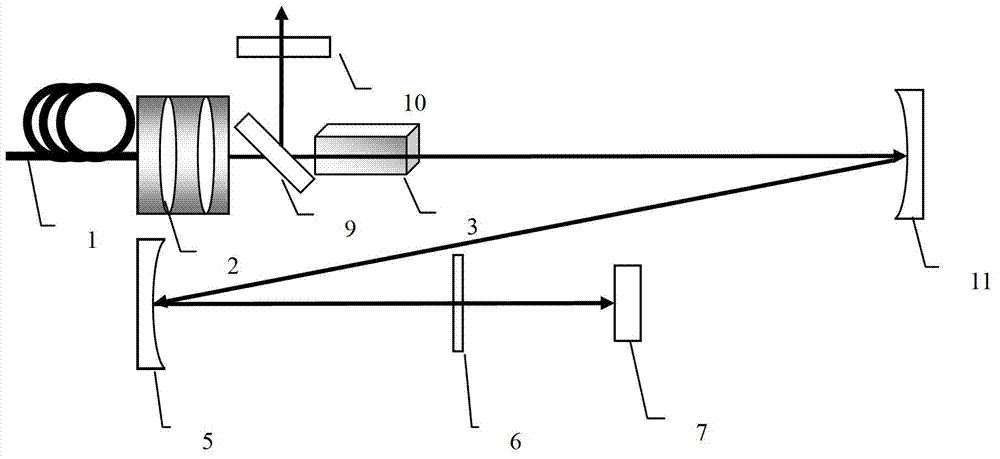
InactiveUS20060002437A1Easy to operateEasy constructionLaser detailsNon-linear opticsPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
The invention is directed to a method and an optical arrangement for the generation of a broadband spectrum in which wavelength regions are selected in an application-oriented manner already during spectrum generation in order to provide increased laser power. A passively mode-coupled solid-state laser provides picosecond laser pulses with an infrared output wavelength which is transformed to a secondary wavelength in the visible spectral range by nonlinear optical processes. The picosecond laser pulses are coupled into a nonlinear optical fiber which is optically adapted to the secondary wavelength with respect to dispersion and nonlinear characteristics, so that a radiation output interval comprising a visible wavelength region is selectively generated. The broadband spectrum has high brilliance and can be used, for example, in spectroscopy, microscopy, cytometry or for array readers.
Owner:JENOPTIK OPTICAL SYST
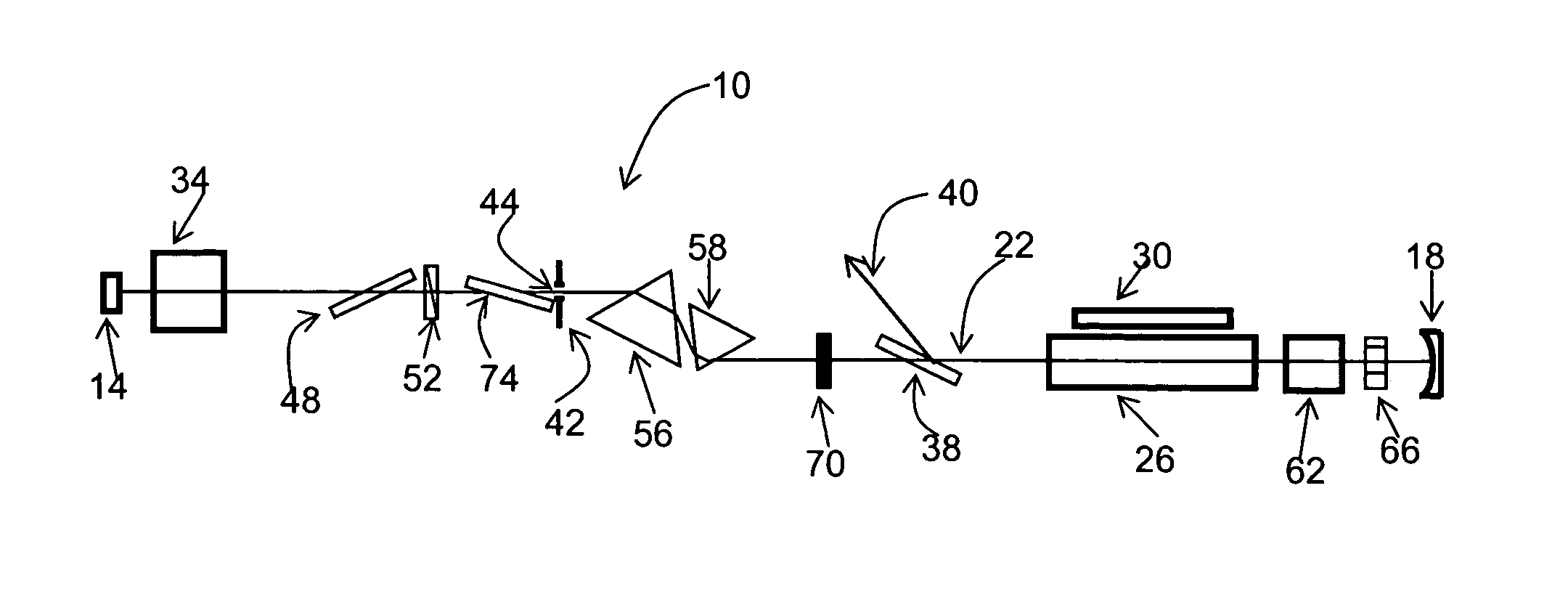
Mode-locked laser with variable pulse duration
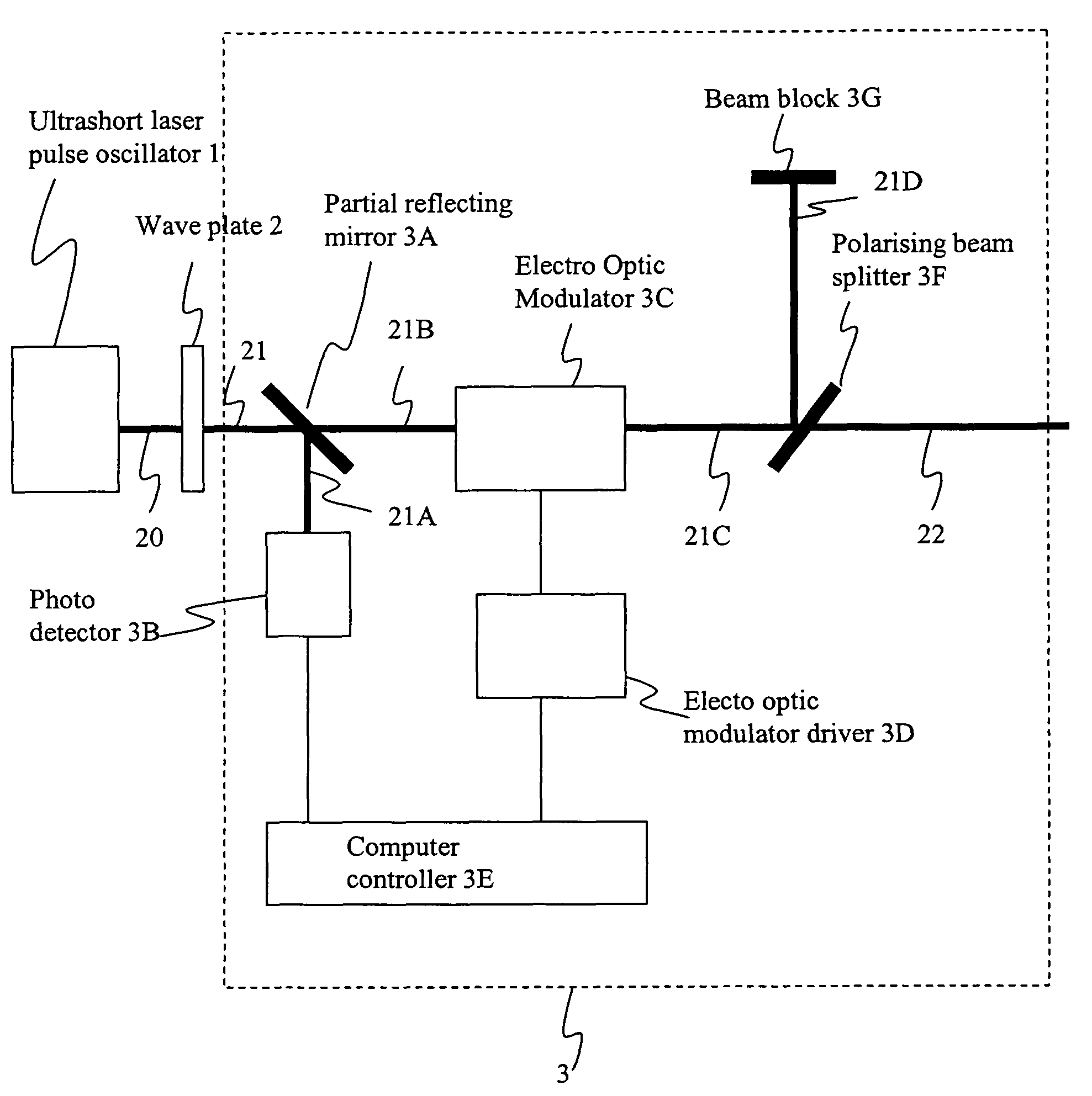
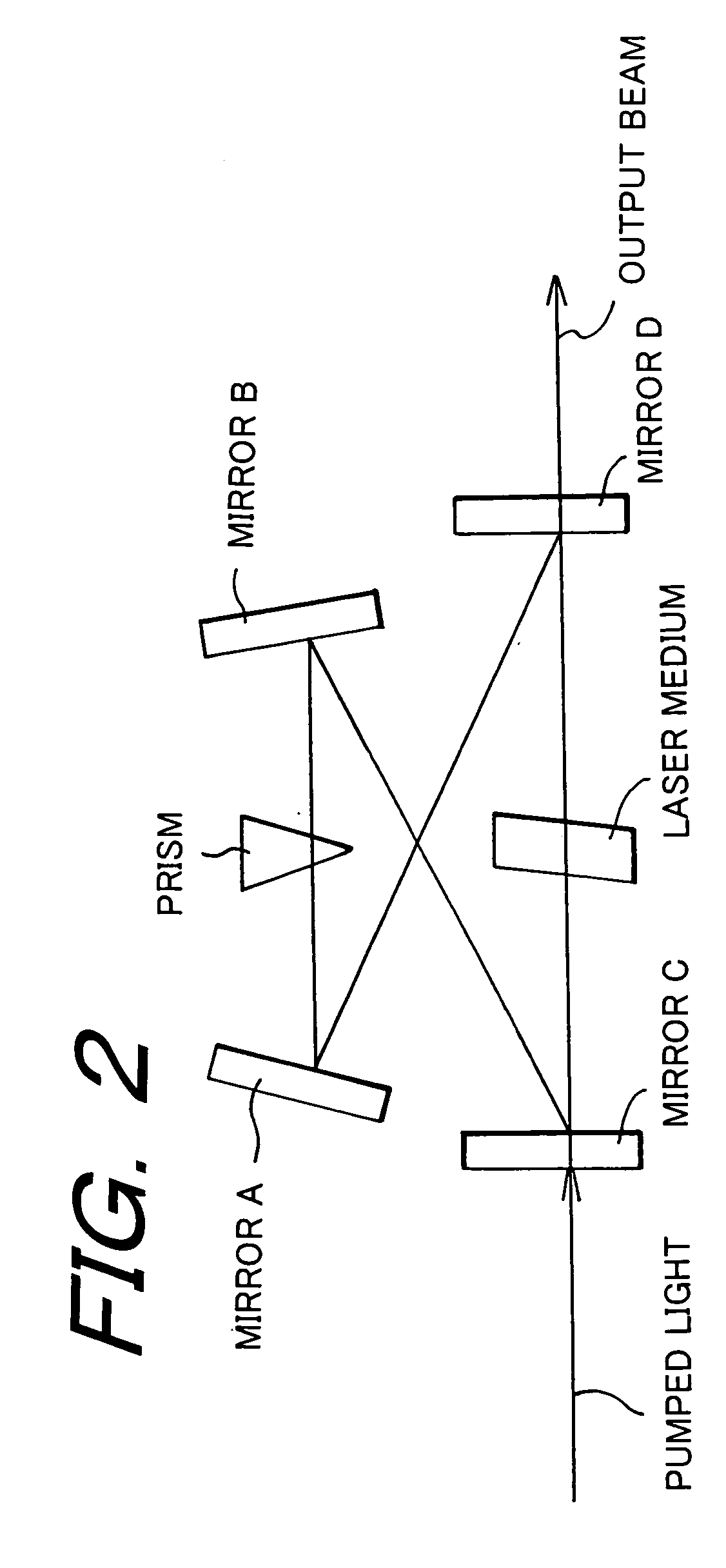
ActiveUS20050074038A1Fine pulse duration variabilityCoarse pulse duration variabilityActive medium materialNegative feedbackPicosecond laser
A pulsed, mode-locked, picosecond laser having a solid-state laser medium, a saturable absorber (SA), and a passive negative feedback (PNF) element. The SA is “slow,” having an absorption recovery time which is longer than a desired duration of an output pulse. The SA and the PNF element together mode-lock the laser to produce an output pulse or pulses of a given duration. The position of the SA along the beam path and the orientation of the SA with respect to the beam path can be varied to vary the output pulse duration over a wide range.
Owner:CONTINUUM ELECTRO OPTICS
Method of regulating and controlling light absorption property of metal surface by picosecond pulse laser
The invention discloses a method of regulating and controlling light absorption property of a metal surface by picosecond pulse laser. The method comprises the following steps: irradiating the metal surface by picosecond pulse laser; carrying out laser ablation for removal and self-assembly of the metal surface induced by picosecond pulse laser to obtain a micro-nano dual-scale structure on the metal surface thus realizing regulation and control of the light absorption property of the metal surface. The method disclosed by the invention fully exerts a picosecond laser preparation rule or the micron structure in random distribution as well as capacity of forming the self-assembled nanostructure, and is agile and controllable in processing process, low in processing cost and high in efficiency, so that the method is an economical and practical method of regulating and controlling the light absorption property of the metal surface.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
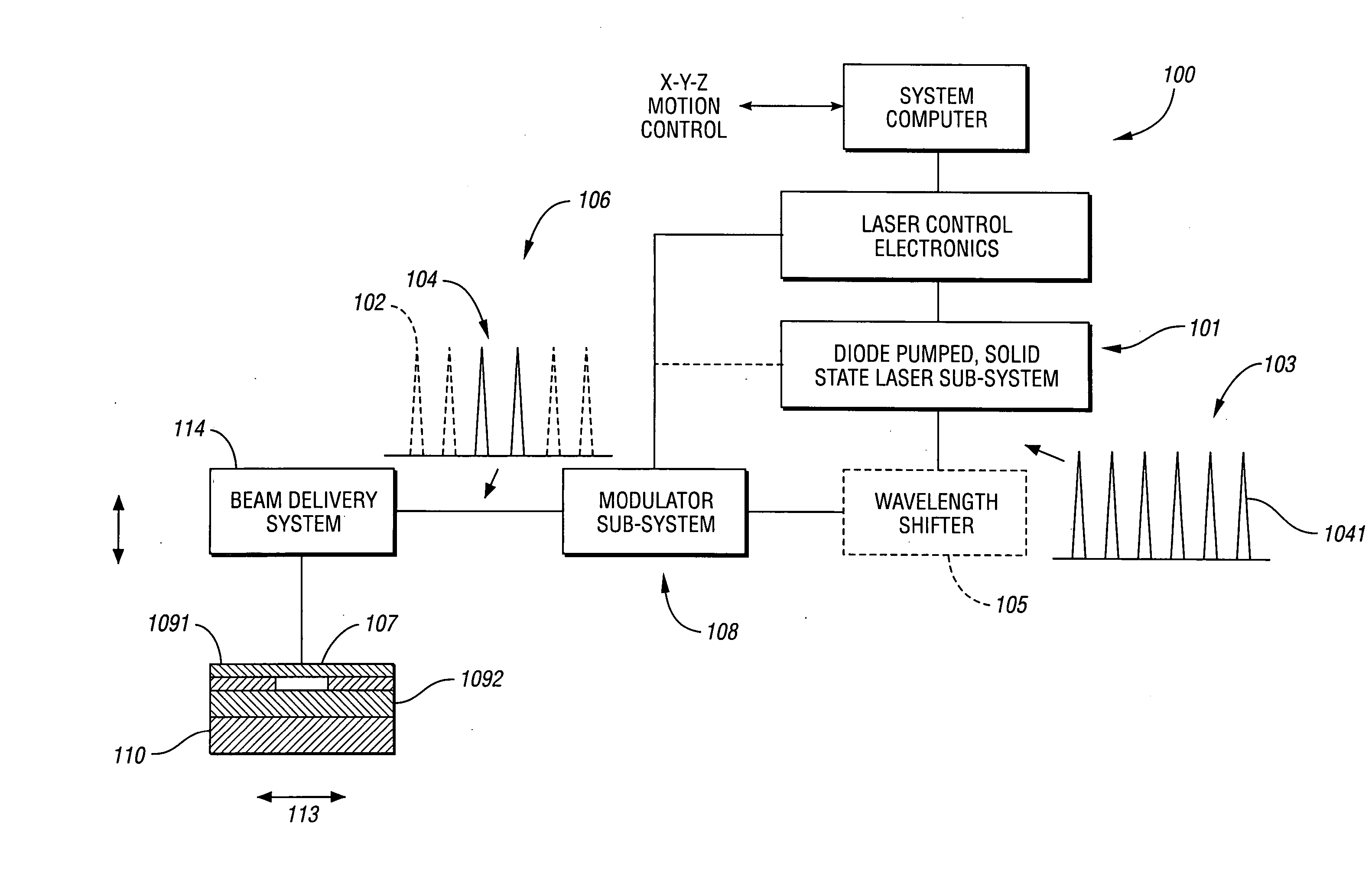
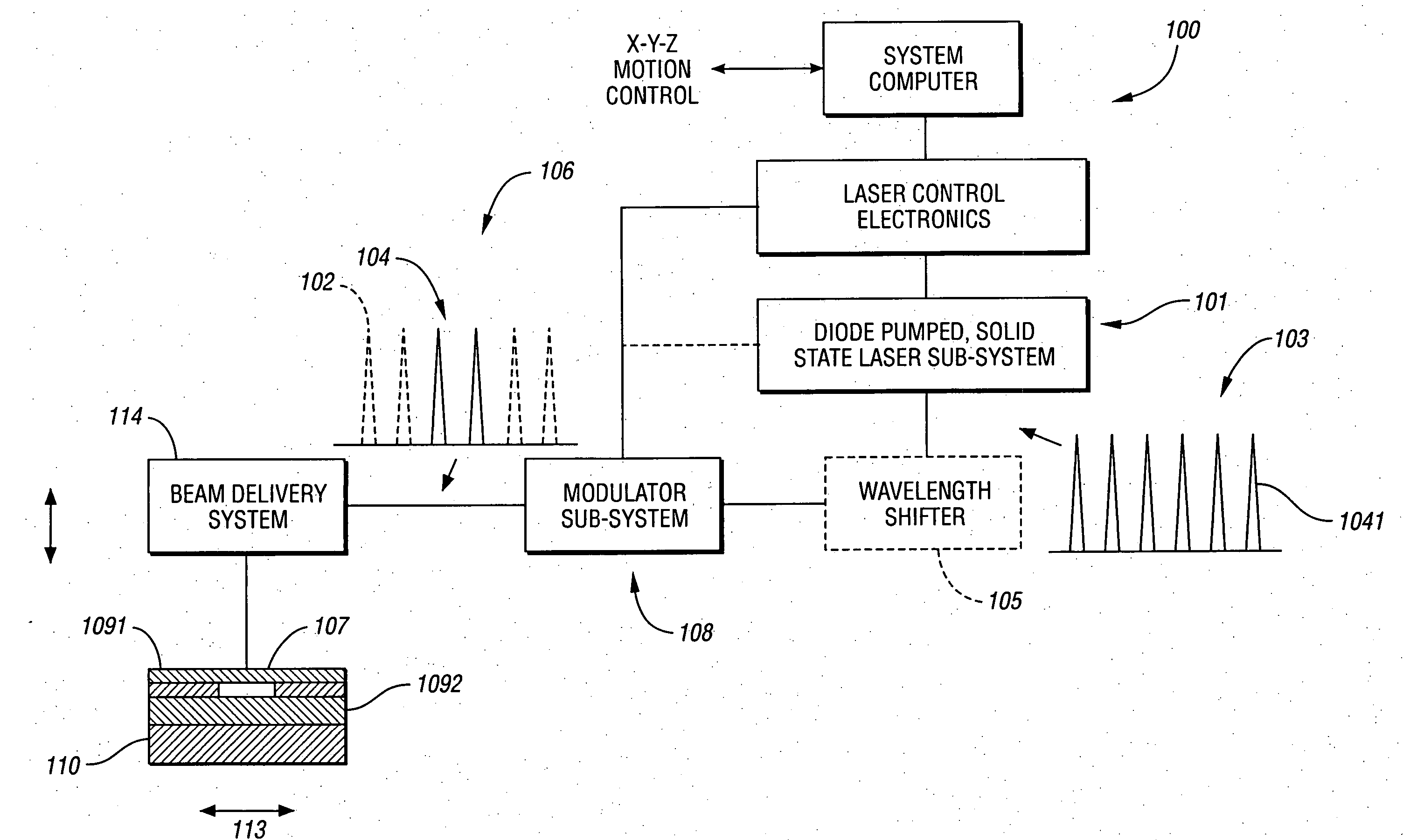
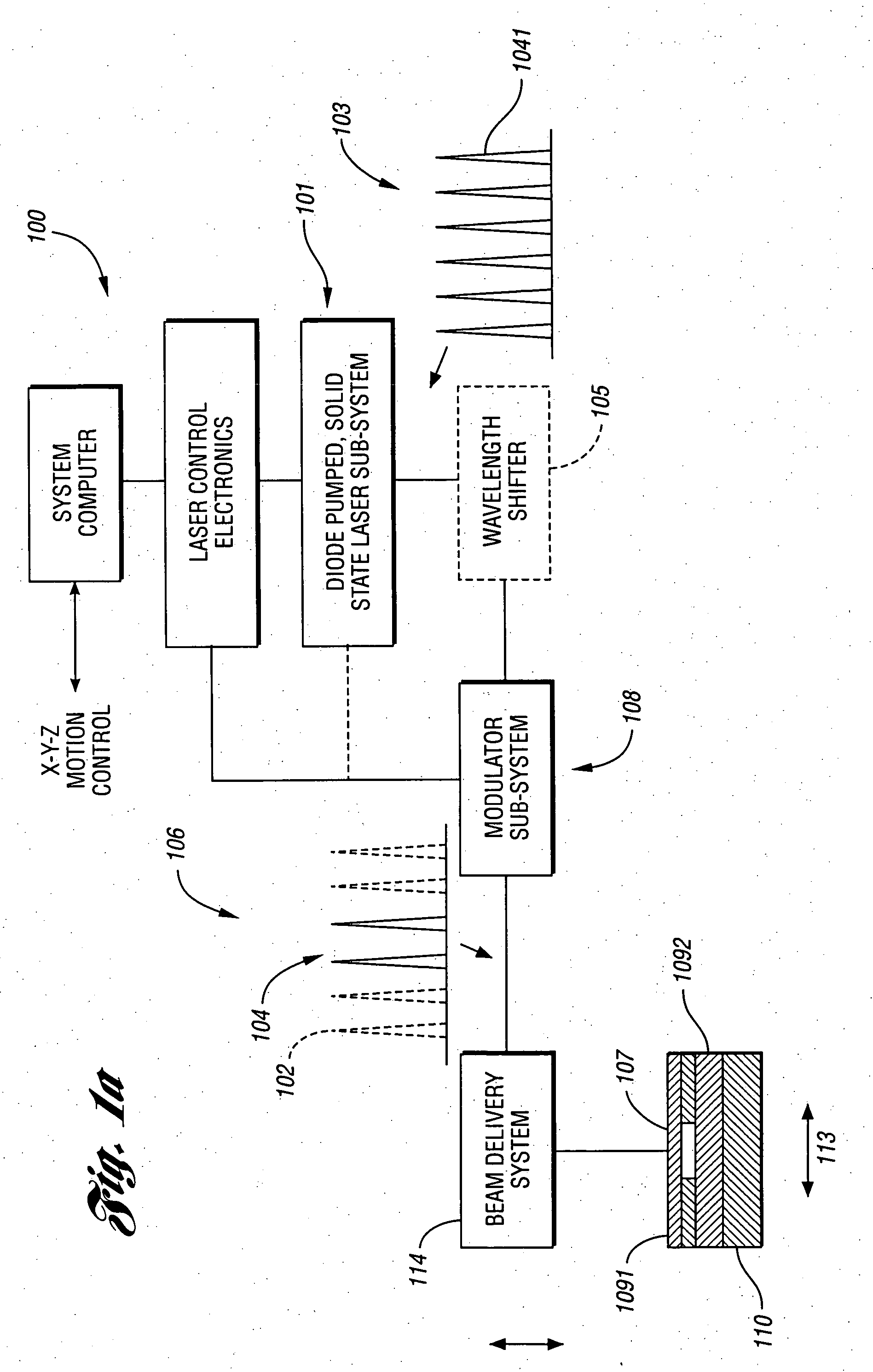
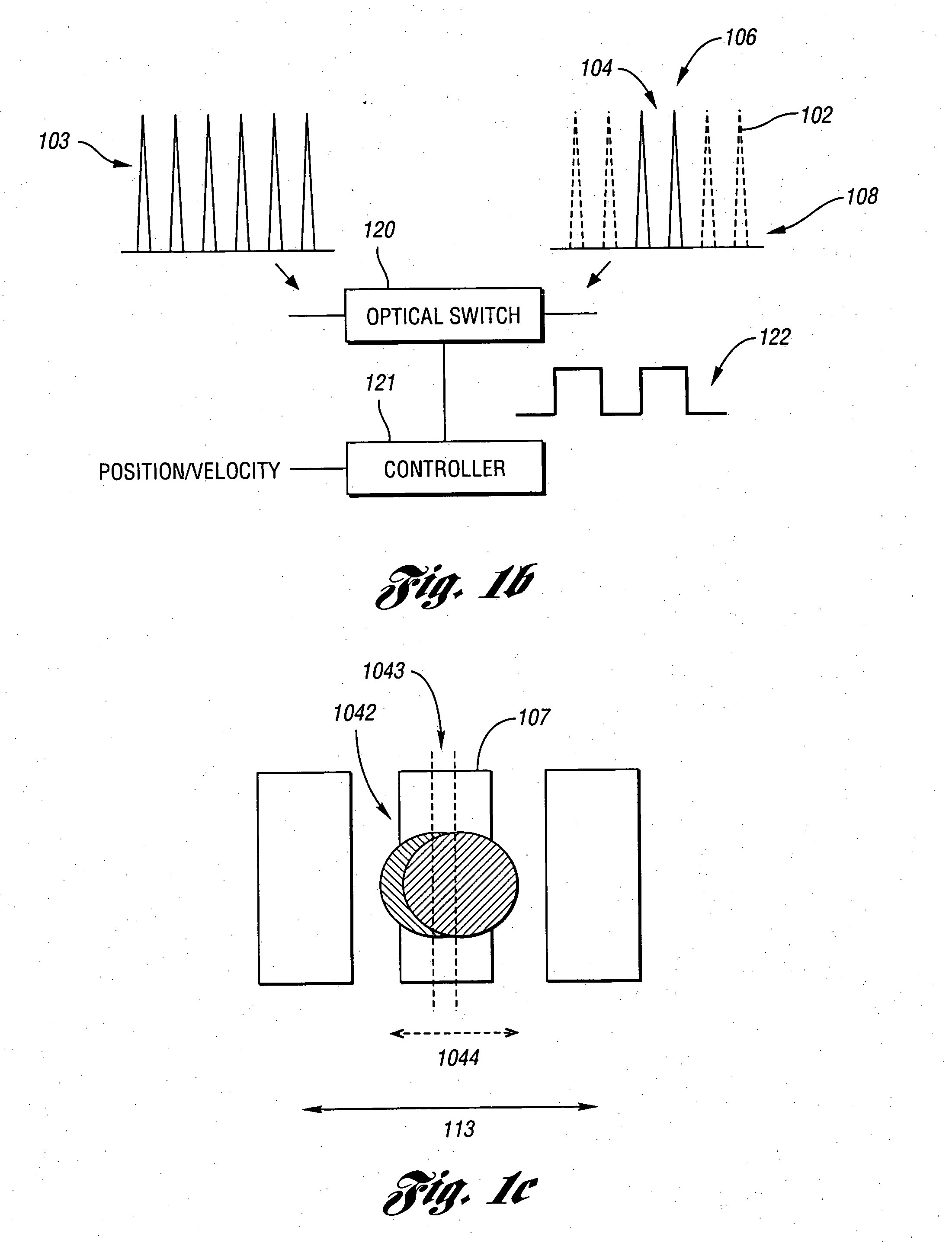
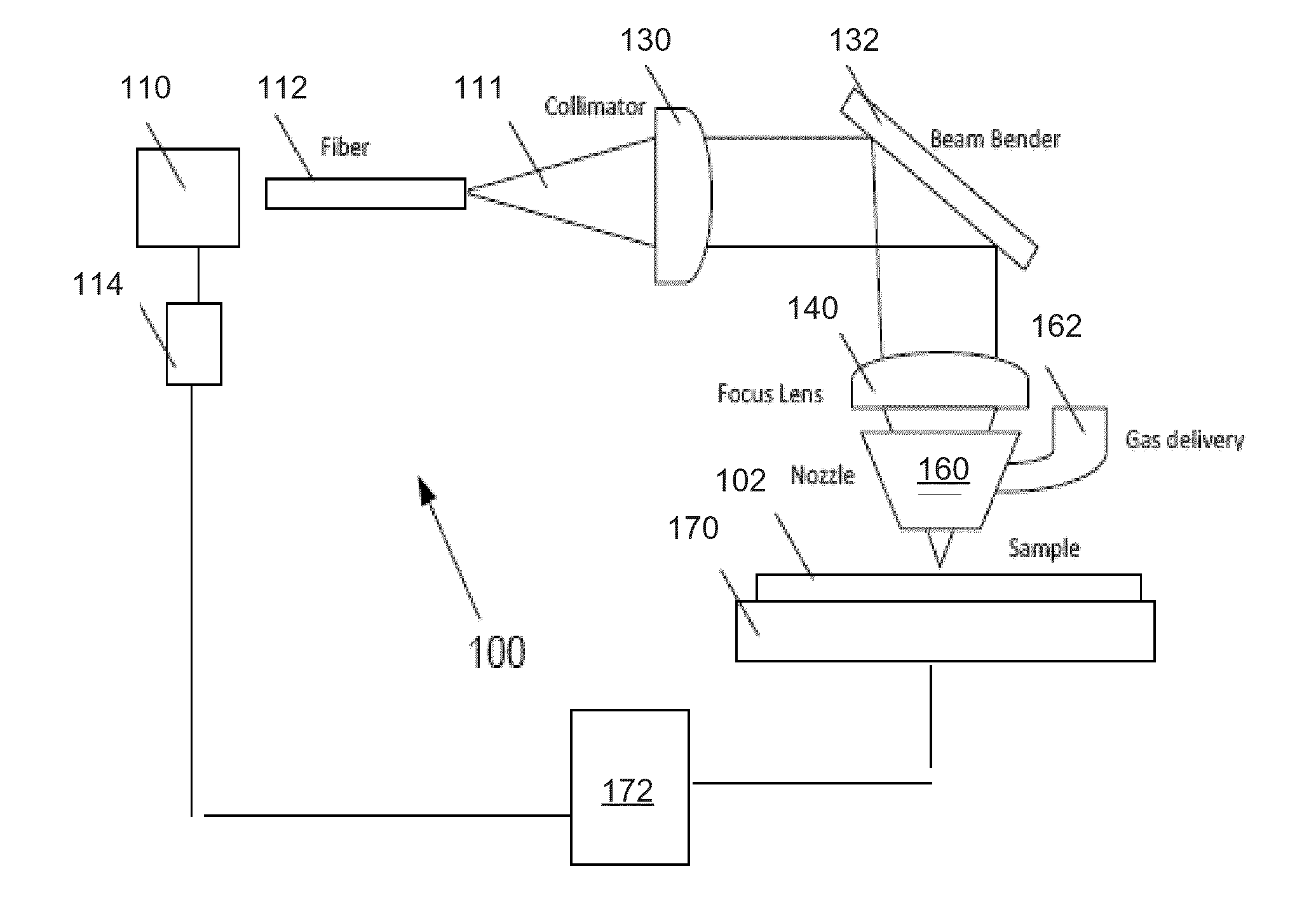
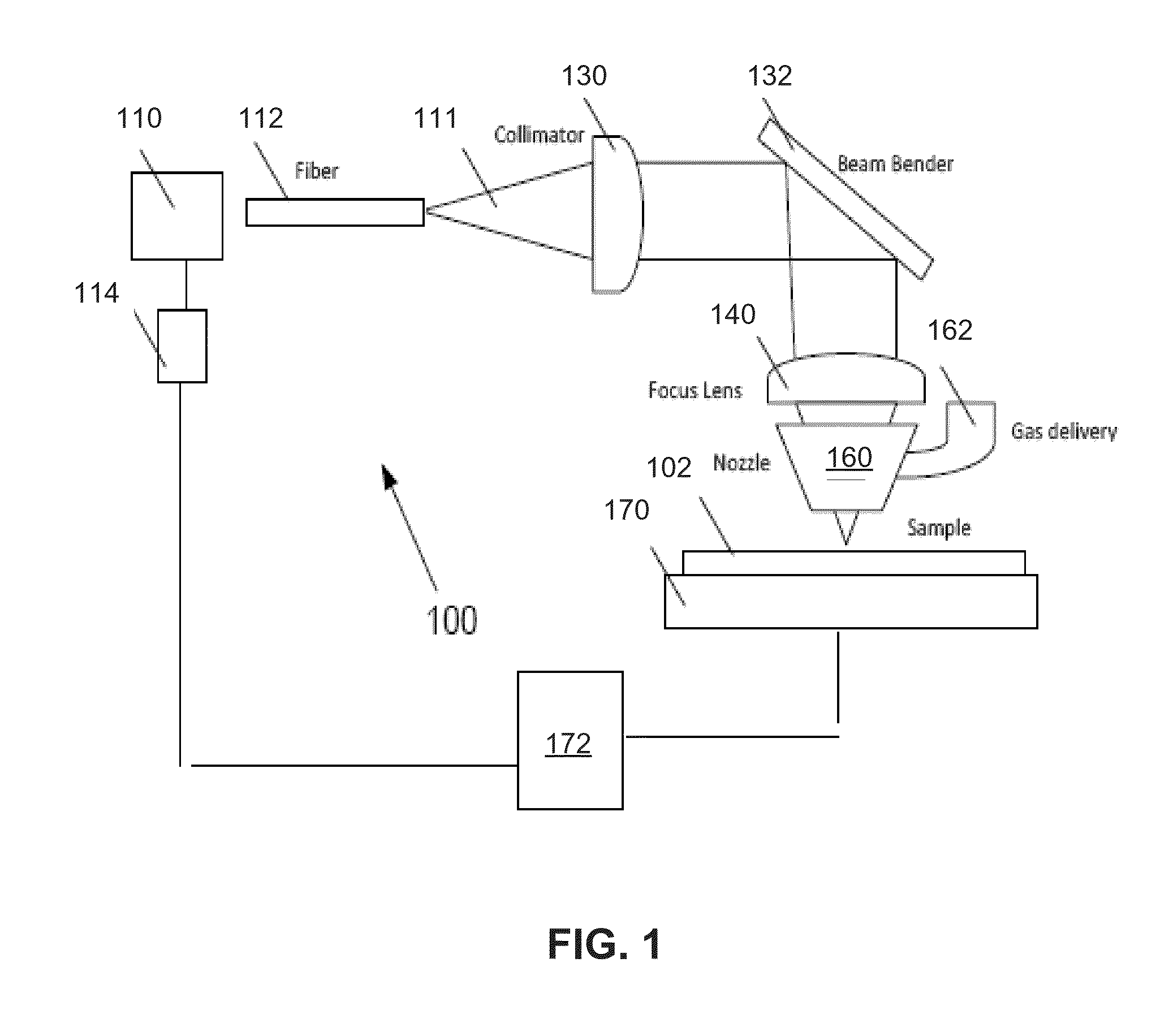
Laser direct ablation with picosecond laser pulses at high pulse repetition frequencies
ActiveUS8648277B2Efficient processingSufficient pulse overlapSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuitsPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
Laser direct ablation (LDA) produces patterns cut into a dielectric layer for the formation of electrically conductive traces with controlled signal propagation characteristics. LDA processing includes selecting a dose fluence for removing a desired depth of material along a scribe line on a surface of a workpiece, selecting a temporal pulsewidth for each laser pulse in a series of laser pulses, and selecting a pulse repetition frequency for the series of laser pulse. The pulse repetition frequency is based at least in part on the selected temporal pulsewidth to maintain the selected dose fluence along the scribe line. The selected pulse repetition frequency provides a predetermined minimum overlap of laser spots along the scribe line. The LDA process further includes generating a laser beam including the series of laser pulses according to the selected dose fluence, temporal pulsewidth, and pulse repetition frequency.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Method of controlling laser oscillation of pulsed laser and pulsed laser system
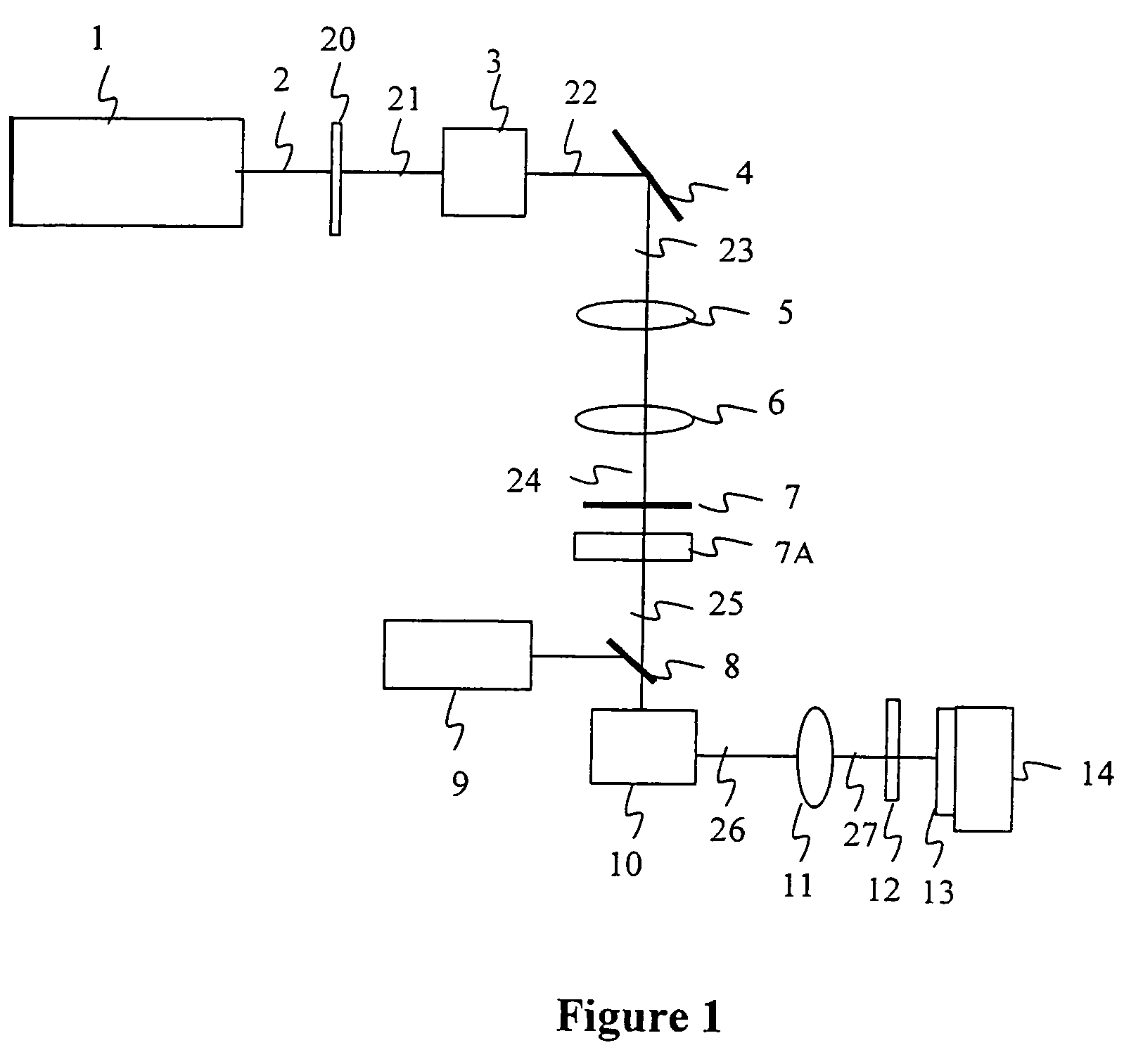
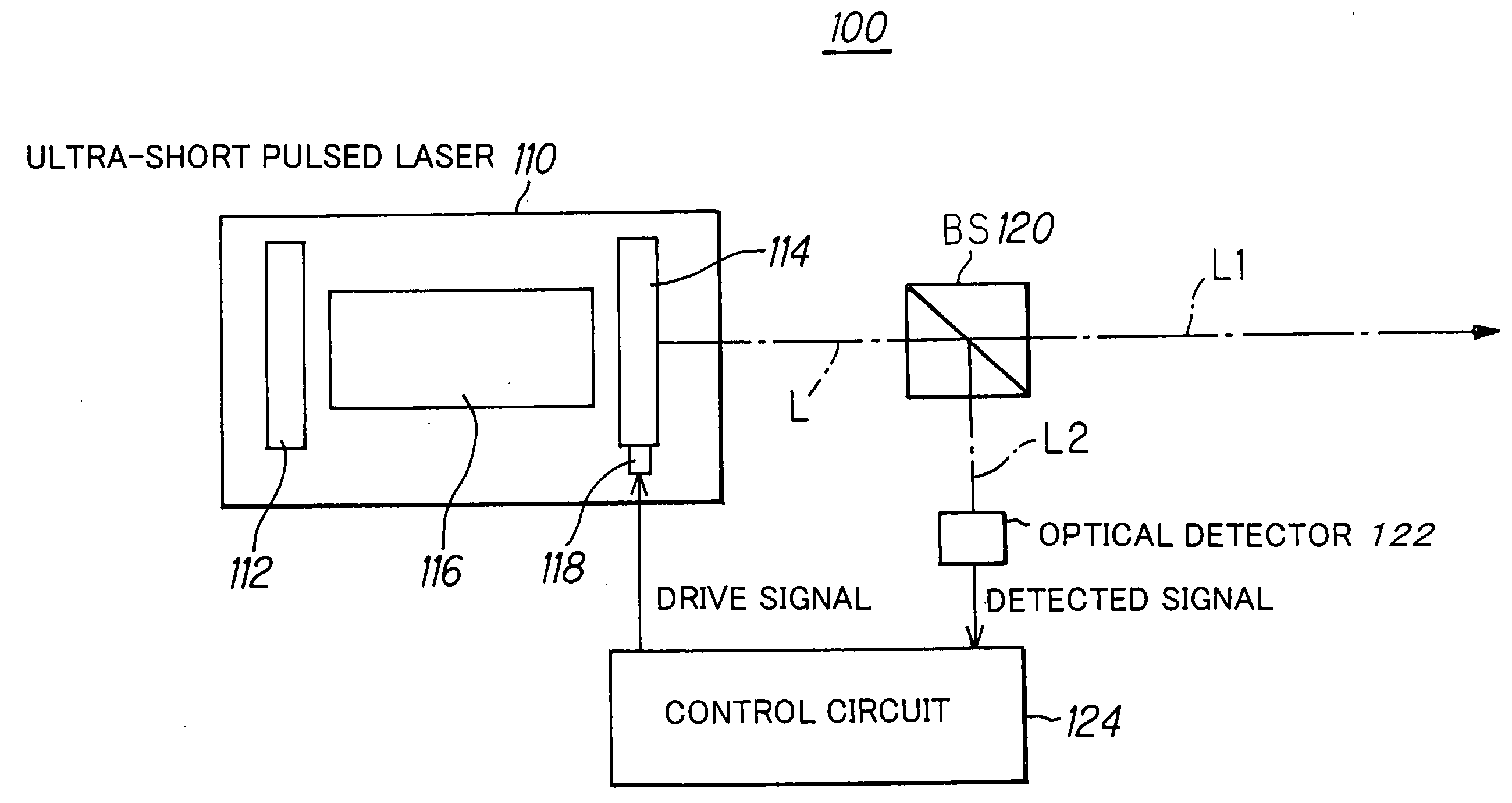
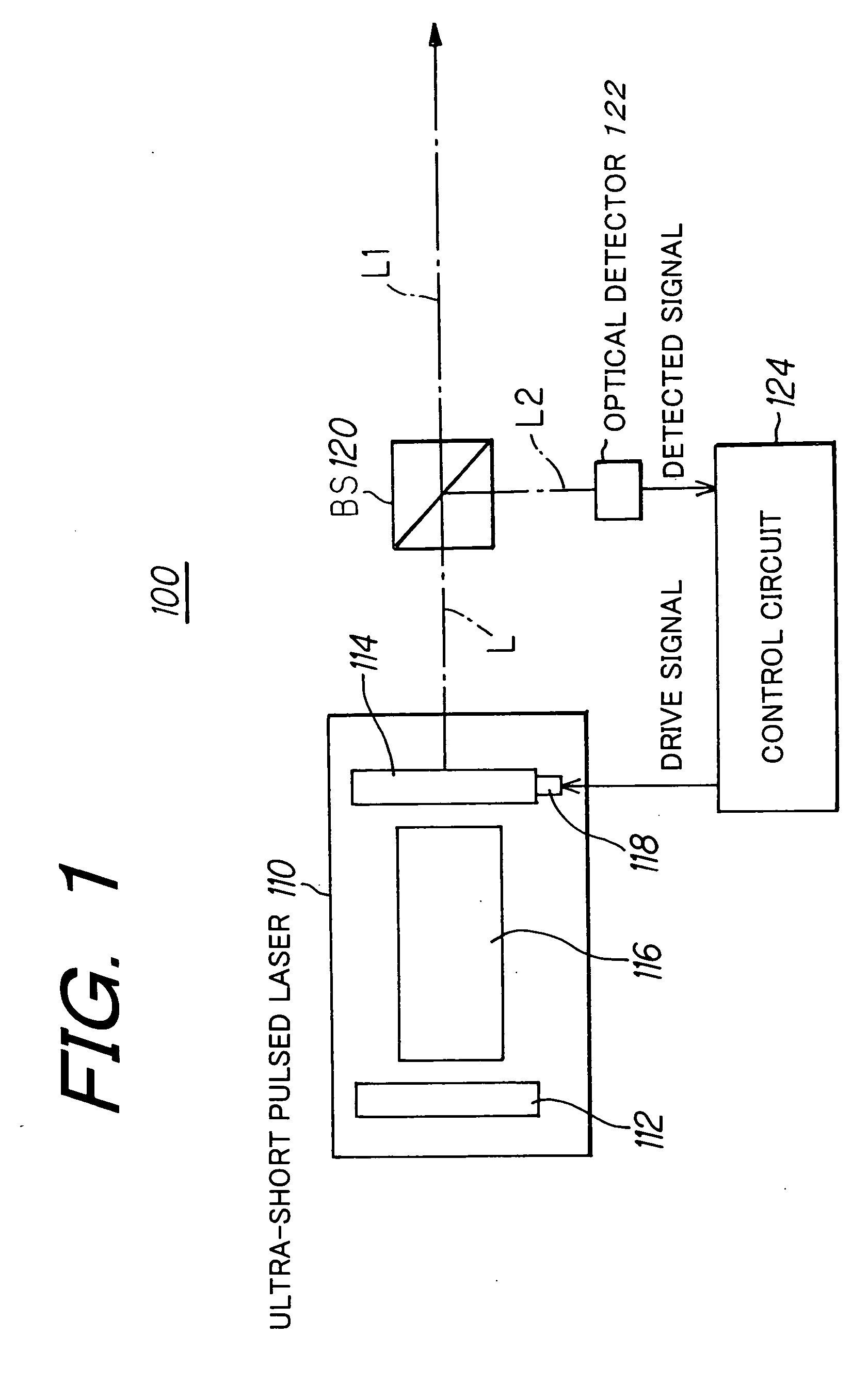
InactiveUS20060182154A1Improve accuracyGood effectLaser detailsLaser beam welding apparatusPicosecond laserOptical processing
In order to perform positional control of a condensing spot of pulsed laser beam highly accurately when performing optical modeling, optical recording or the like in optical machining technology, optical recording technology or the like which uses various kinds of pulsed laser, which are ultra-short pulsed lasers such as a femtosecond laser and short pulsed laser such as a picosecond laser and a sub-picosecond laser, as a light source, a pulsed laser system detects an output beam from a pulsed laser, controls laser oscillation of the pulsed laser based on the detection result such the output beam contains CW laser beam together with pulsed laser beam, and allows the pulsed laser to output the pulsed laser beam and the CW laser beam simultaneously as the output beam from the pulsed laser.
Owner:RIKEN
Method for producing hologram by pico-second laser
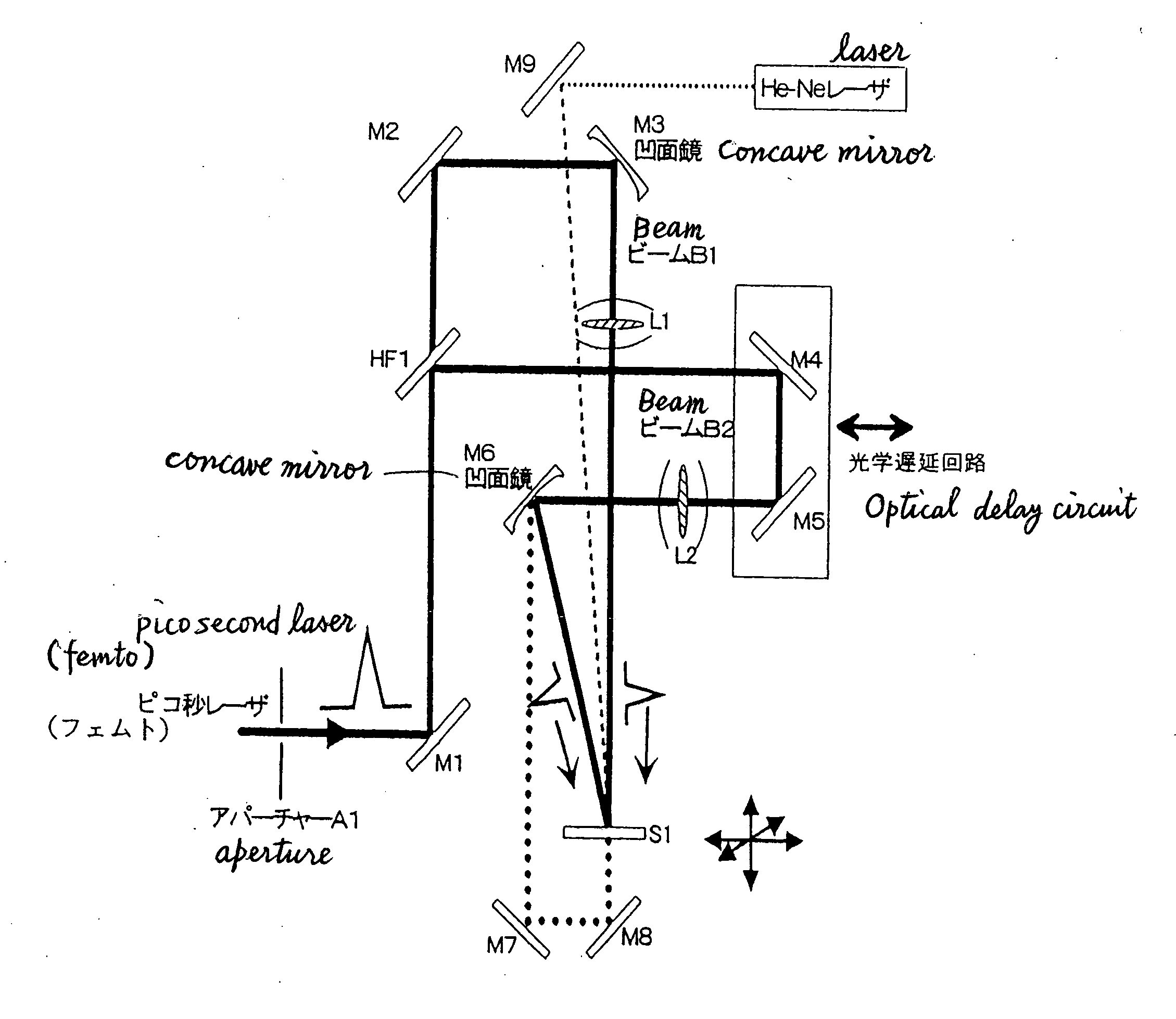
InactiveUS20060019171A1Reduce waveform distortionStable recordHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesPhotomechanical apparatusPicosecond laserOptical interaction
Disclosed is a method of producing a hologram through a two-beam laser interfering exposure process, which comprises emitting a coherent laser light with a pulse width (τ) ranging from greater than 900 femtoseconds to 100 picoseconds and a laser power of 10 μJ / pulse or more using a solid-state laser as a light source, dividing the pulses light from the laser into two beams, controlling the two beams temporally and spatially in such a manner that the two beam are converged on a surface of or inside a workpiece for recording a hologram while matching the respective converged spots of the two beams with one another temporally and spatially to create the interference therebetween so as to record a surface-relief hologram on the surface of the workpiece or an embedded hologram inside the workpiece in an irreversible manner. The present invention can solve a problem with a conventional process of recording a hologram in a non-photosensitive material in an irreversible manner using interfering femtosecond laser pulses, specifically, distortion in the waveforms of pulsed laser beams and resulting instability in recording of an embedded hologram due to a non-linear optical interaction between the femtosecond laser pulses and air / the material.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Picosecond laser apparatus and methods for its operation and use
ActiveUS20080031288A1Short durationHigh energyLaser detailsSurgical instrument detailsPicosecond laserHigh energy
Apparatuses and methods are disclosed for applying laser energy having desired pulse characteristics, including a sufficiently short duration and / or a sufficiently high energy for the photomechanical treatment of skin pigmentations and pigmented lesions, both naturally-occurring (e.g., birthmarks), as well as artificial (e.g., tattoos). The laser energy may be generated with an apparatus having a resonator with the capability of switching between a modelocked pulse operating mode and an amplification operating mode. The operating modes are carried out through the application of a time-dependent bias voltage, having waveforms as described herein, to an electro-optical device (e.g., a Pockels cell) positioned along the optical axis of the resonator.
Owner:CYNOSURE
Resonant cavity for outputting mode-locking picosecond laser and mode-locking picosecond laser device
InactiveCN102832536APeak power controlMeet the requirements of different applicationsOptical resonator shape and constructionPicosecond laserResonant cavity
The invention provides a resonant cavity for outputting mode-locking picosecond laser and a mode-locking picosecond laser device. The mode-locking picosecond laser device comprises a pumping source, a focusing lens and the resonant cavity for outputting the mode-locking picosecond laser, and the pumping source, the focusing lens and the resonant cavity are sequentially arranged along a light path. The resonant cavity is characterized that a laser crystal, a focusing device, a Fabry-Perot etalon and a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror are arranged in the resonant cavity, and the energy density of light beams acting on the semiconductor saturable absorber mirror can be sufficient to realize continuous mode-locking owing to the focusing device. Peak power of the picosecond laser device can be accurately controlled, so that different application requirements can be effectively met advantageously. Besides, pulse width of the picosecond laser device can be controlled, so that different application requirements can be effectively met advantageously. In addition, picosecond pulse width can be tuned, operation is easy, and mode-locking stability is unaffected. A pulse width tunable device is small in size and is beneficial to saving space.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Laser cutting device and cutting method
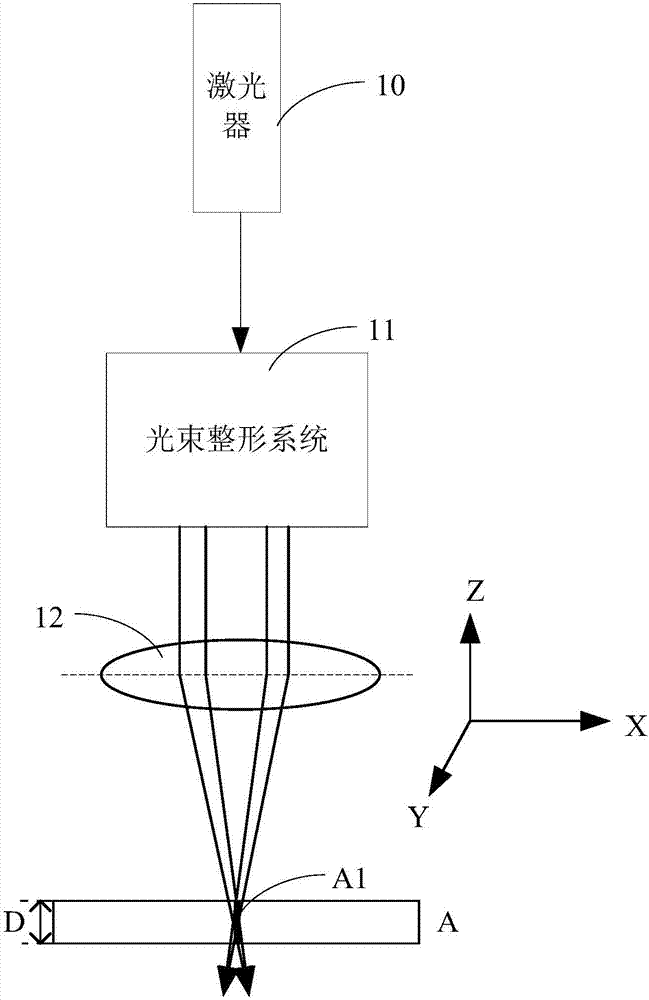
ActiveCN106994564AEfficient cuttingGlass severing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesPicosecond laserGaussian beam
The invention provides a laser cutting device and a cutting method. The laser cutting device comprises a laser, a light beam shaping system and a first collecting lens; the laser is a picosecond laser; the laser is used for emitting laser; the laser is a Gaussian beam; the light beam shaping system is used for converting the Gaussian beam to a Bessel beam; and the first collecting lens is used for focusing the Bessel beam to an area to be cut of samples to be cut, so that the area to be cut is precut by the Bessel beam. As the focused Bessel beam is the focused beam with longer focal depth, compared with the Gaussian beam, the Bessel beam can effectively cut the samples to be cut with greater thicknesses to widen the application range of the laser cutting device.
Owner:东莞市盛雄激光先进装备股份有限公司
Broadly tunable optical parametric oscillator
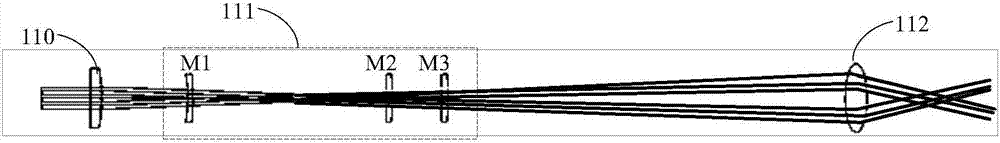
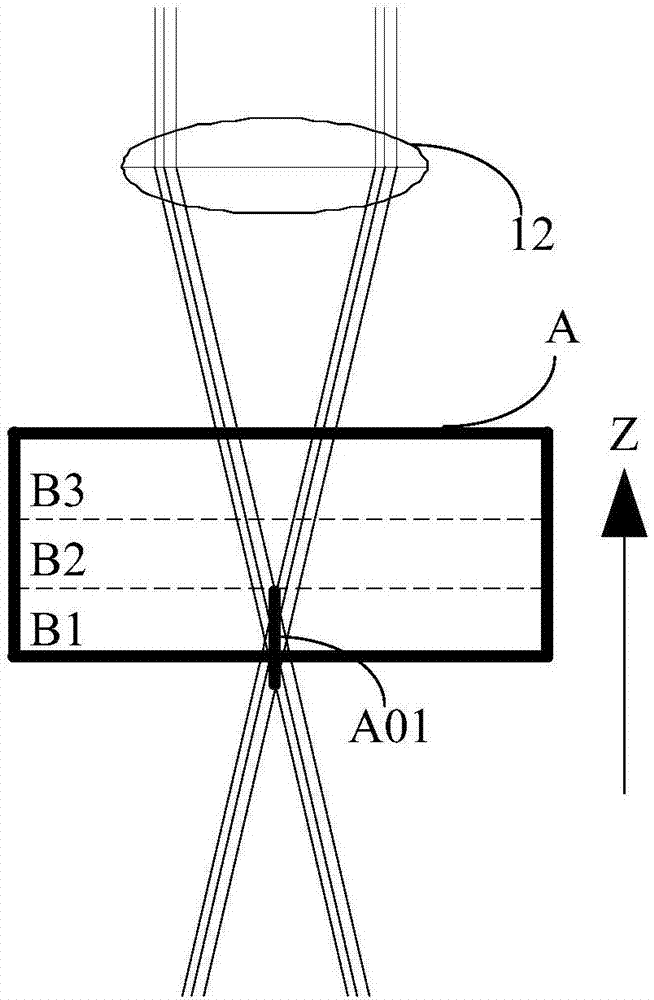
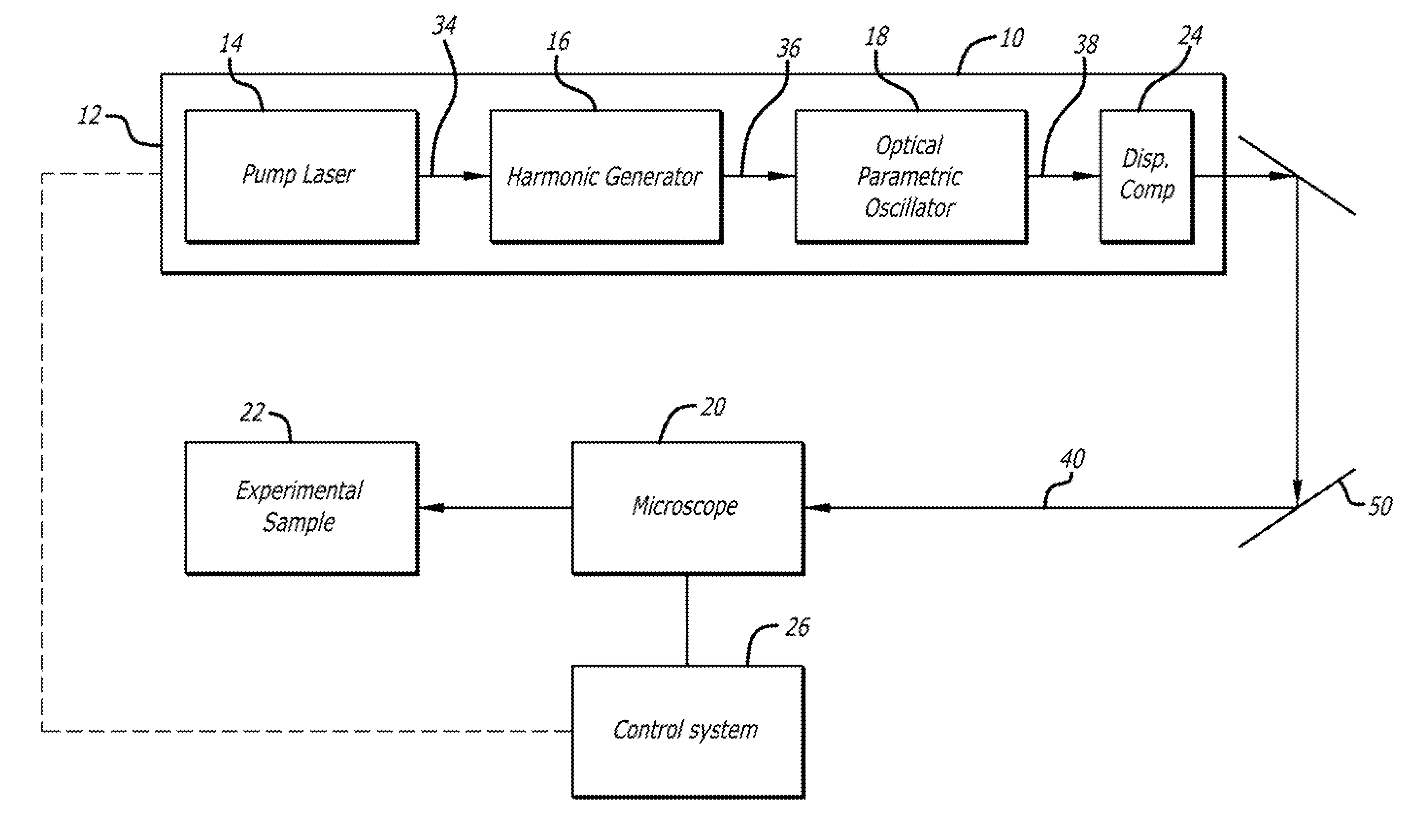
ActiveUS20110180729A1Color/spectral properties measurementsOptical devices for laserPicosecond laserLength wave
A novel broadly tunable optical parametric oscillator is described for use in numerous applications including multi-photon microscopy. The optical parametric oscillator includes at least one sub-picosecond laser pump source configured to output a pump signal having a wavelength of about 650 nm or less and at least one type II optical parametric oscillator in optical communication with the pump source and configured to generate a single widely tunable pulsed optical signal. In one application, an optical system is in optical communication with the optical parametric oscillator and configured to direct at least a portion of the optical signal to a specimen, and at least one analyzing device is configured to receive a signal from the specimen in response to the optical signal.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Method and apparatus for improved singulation of light emitting devices
InactiveUS20120175652A1Reduce the amount requiredAvoid thermal damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesPicosecond laserLaser processing
The present invention is a system and method for laser-assisted singulation of light emitting electronic devices manufactured on a substrate, having a processing surface and a depth extending from the processing surface. It includes providing a laser processing system having a picosecond laser having controllable parameters; controlling the laser parameters to form light pulses from the picosecond laser, to form a modified region having a depth which spans about 50% of the depth and substantially including the processing surface of the substrate and having a width less than about 5% of the region depth; and, singulating the substrate by applying mechanical stress to the substrate thereby cleaving the substrate into said light emitting electronic devices having sidewalls formed at least partially in cooperation with the linear modified regions.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com