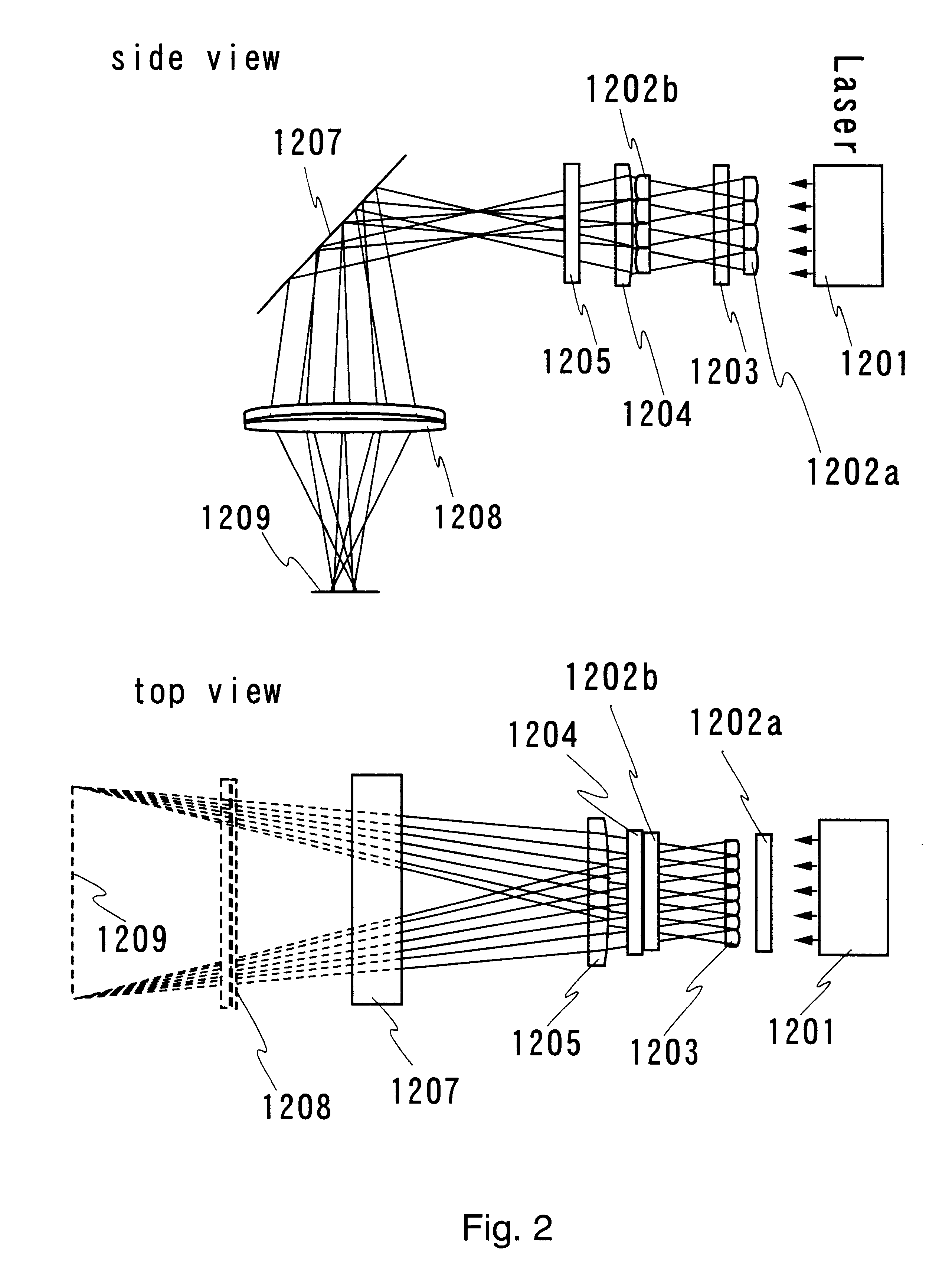
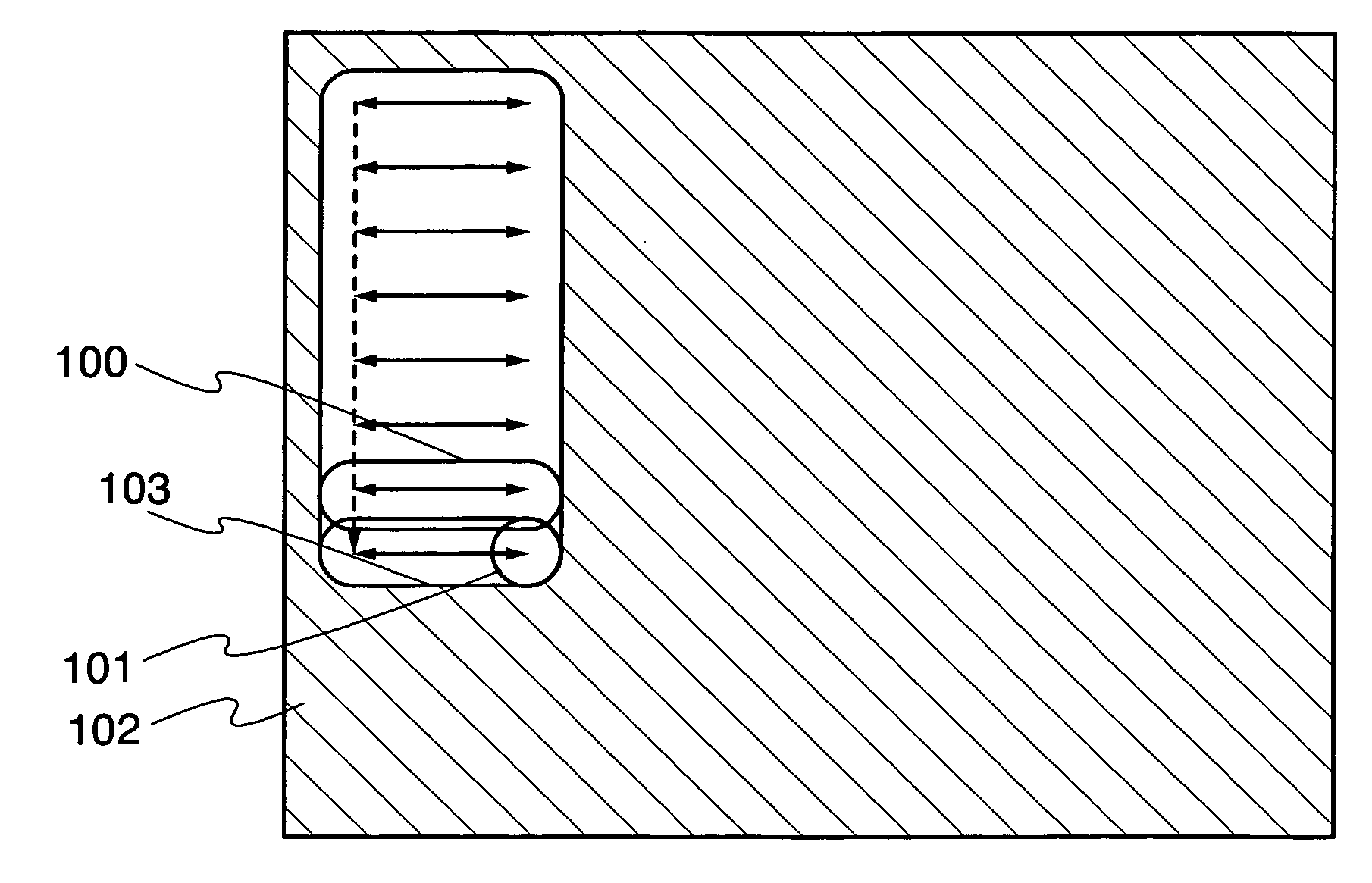
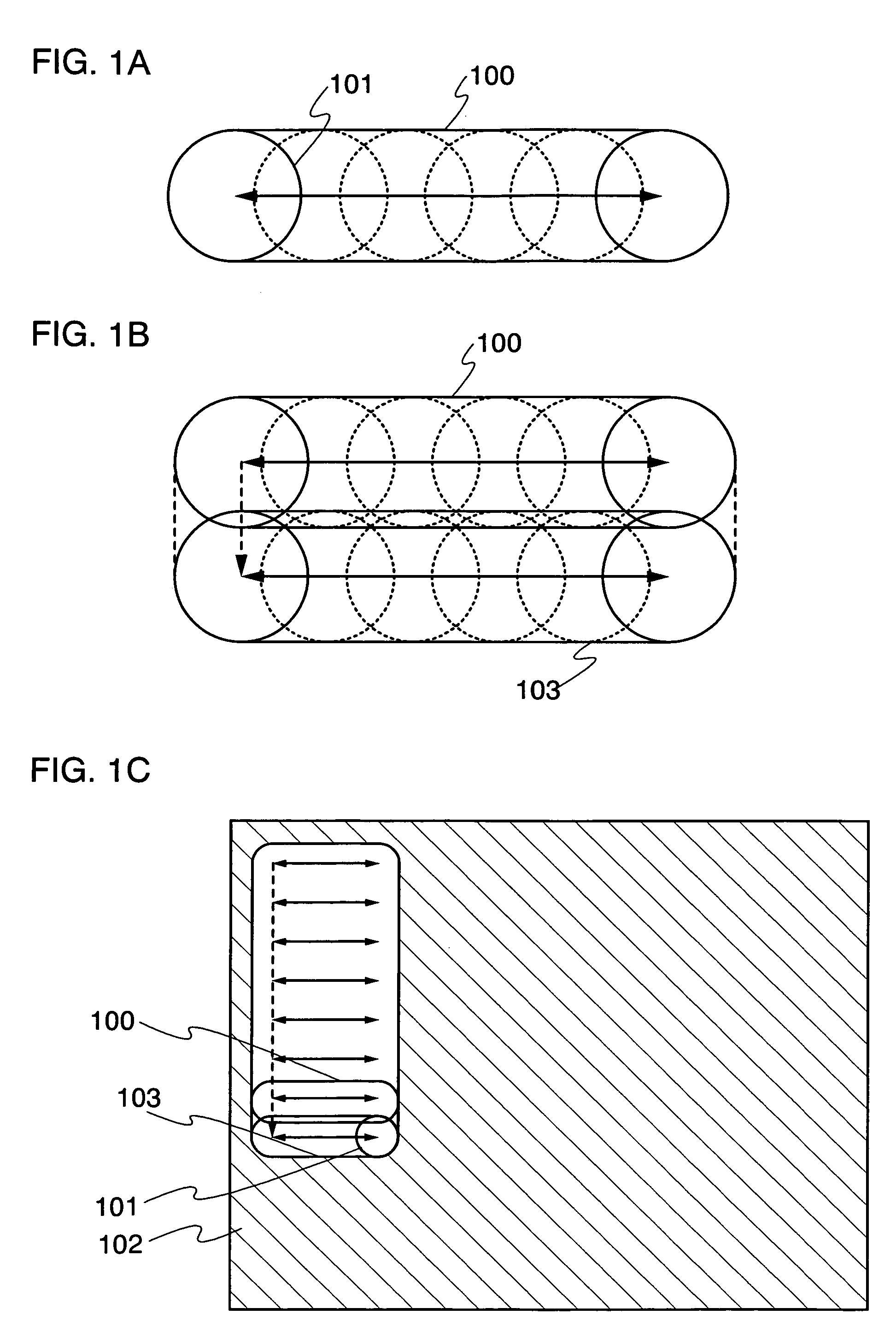
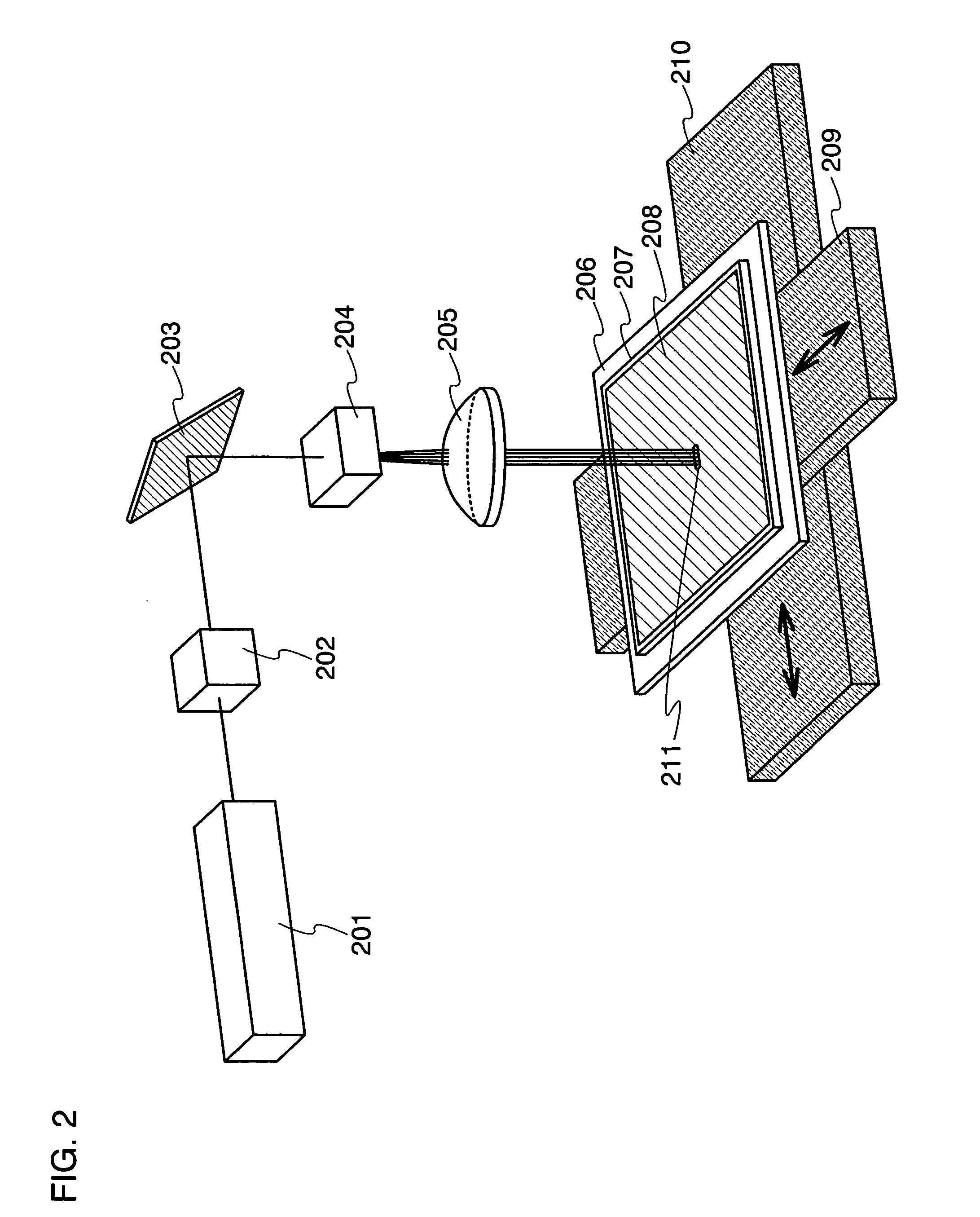
Patents
Literature
1244 results about "Laser oscillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
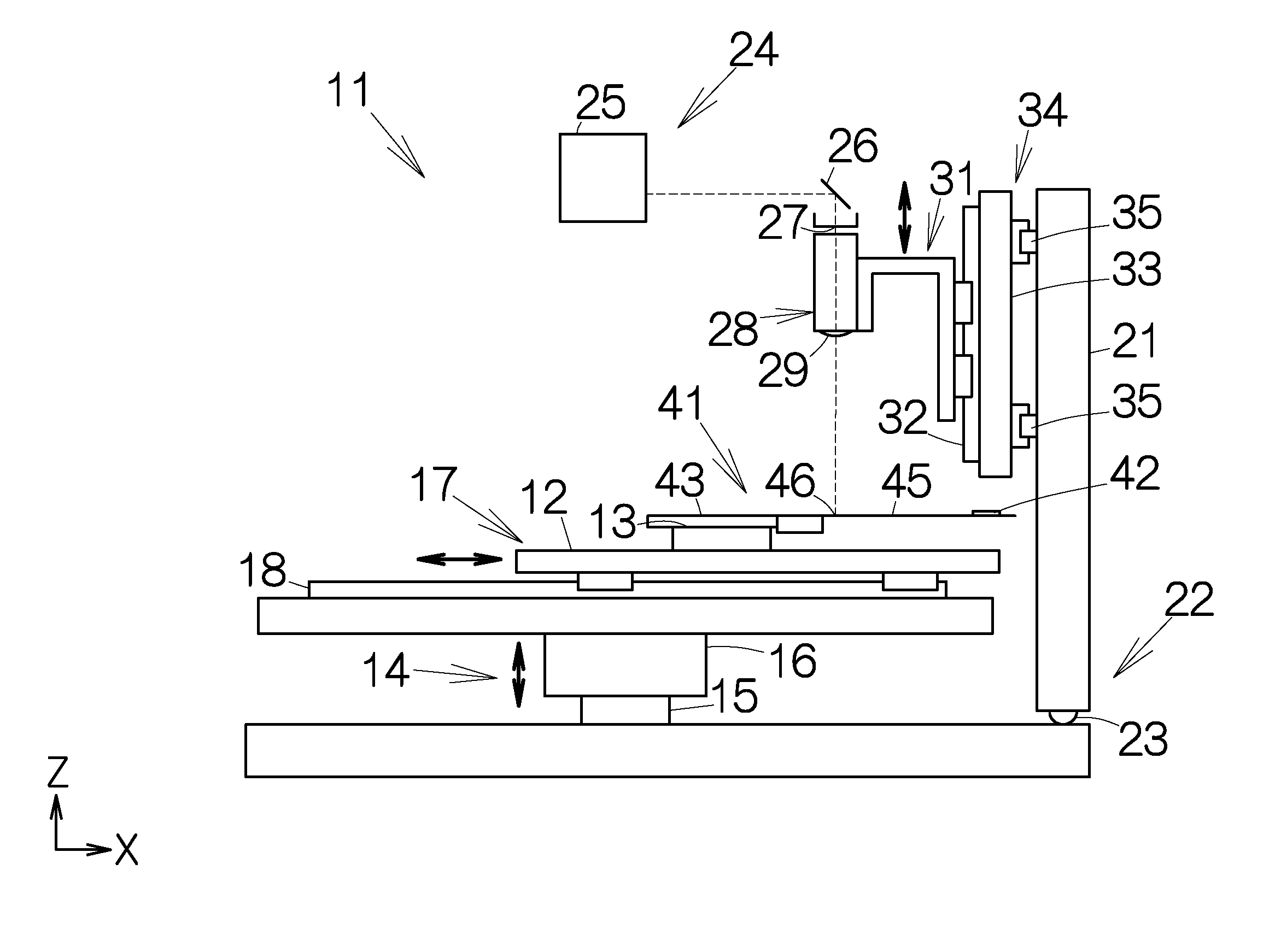
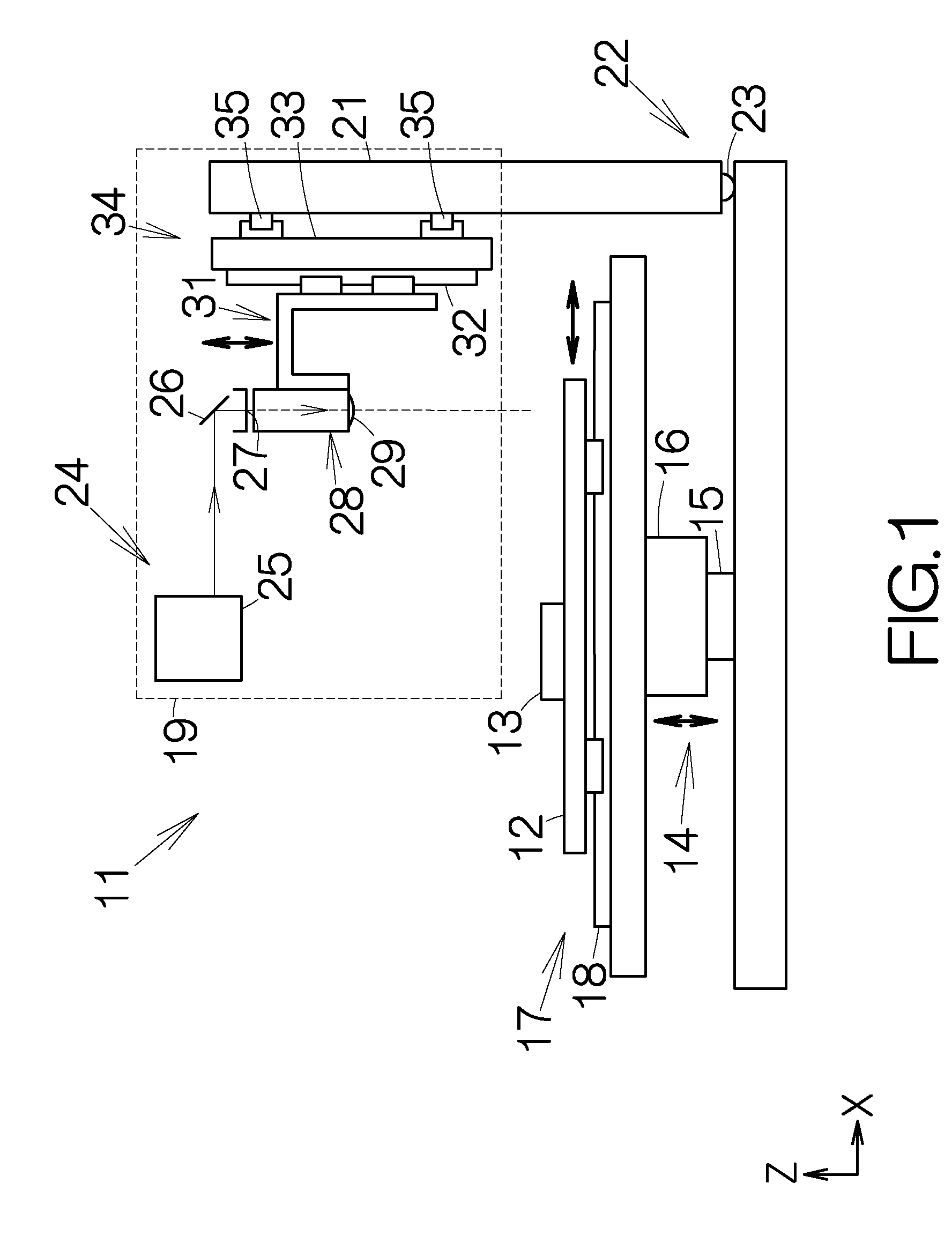
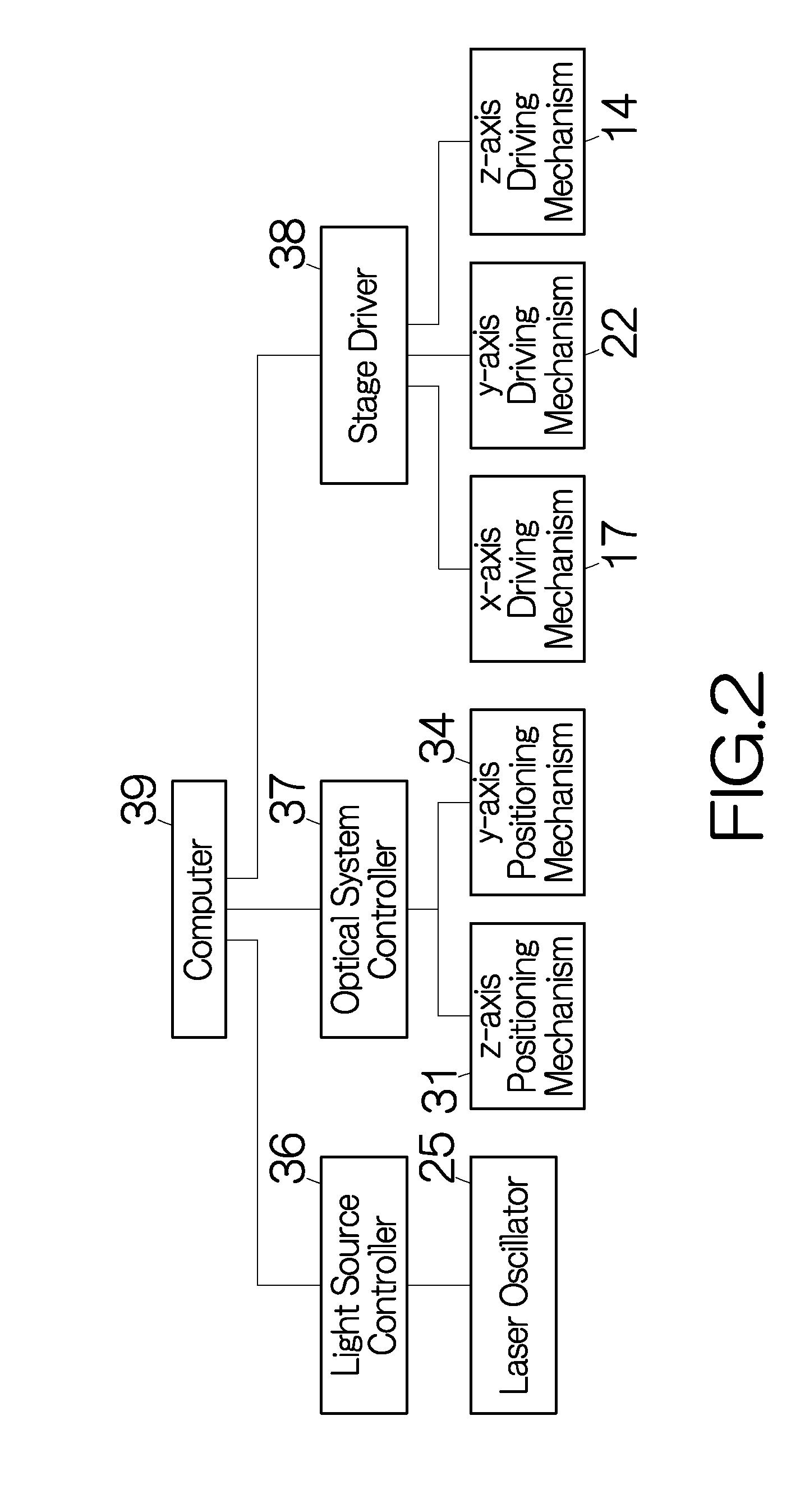
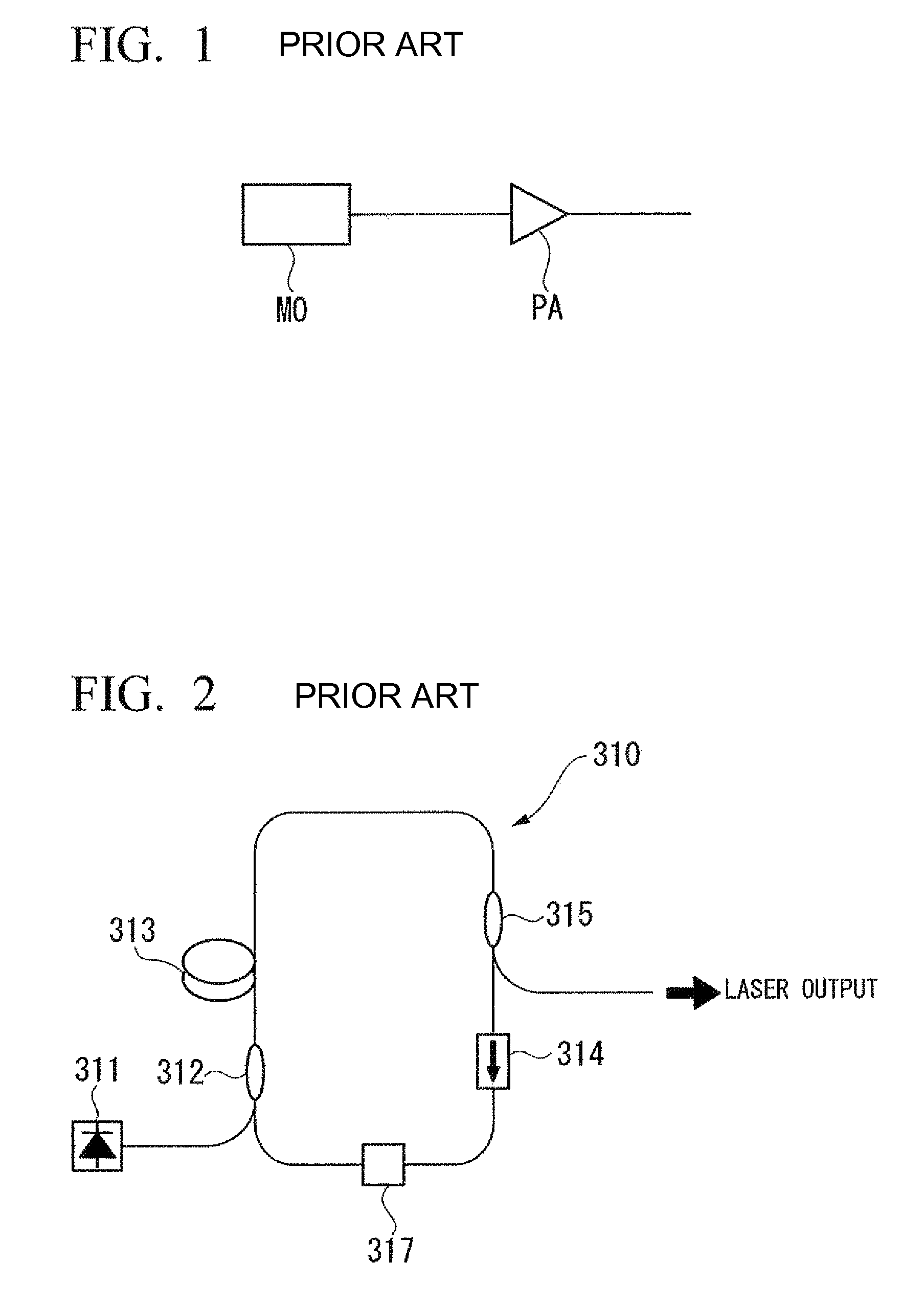
In laser physics, the term laser oscillator is sometimes used for a laser device in order to distinguish it explicitly from an amplifier, where there is amplification by stimulated emission but no laser oscillation.
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS20050274702A1Improve inner wall qualityImprove surface qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserFacula
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin simiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
Laser machining device
InactiveUS6875951B2Low costSmall sizeWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingGalvanometer
A laser machining device according to the invention is provided with a laser oscillator for generating a laser beam, a main deflecting galvannometer mirror, an Fθ lens, and a sub-deflecting means arranged in an optical path between the laser oscillator and the main deflecting galvanometer mirror. A means for splitting a laser beam is provided, and the sub-deflecting means is inserted into the optical path of one of the split laser beams. At the same time, both the split laser beams are incident from the same main deflecting galvannometer mirror to the Fθ lens, and a numerical aperture in the optical system constituted by the main deflecting galvannometer mirror, the Fθ lens, and an object is set to be not more than 0.08.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS7804043B2Minimize heating effectImprove machine qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserBeam polarization
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin semiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
Exposure apparatus with laser device
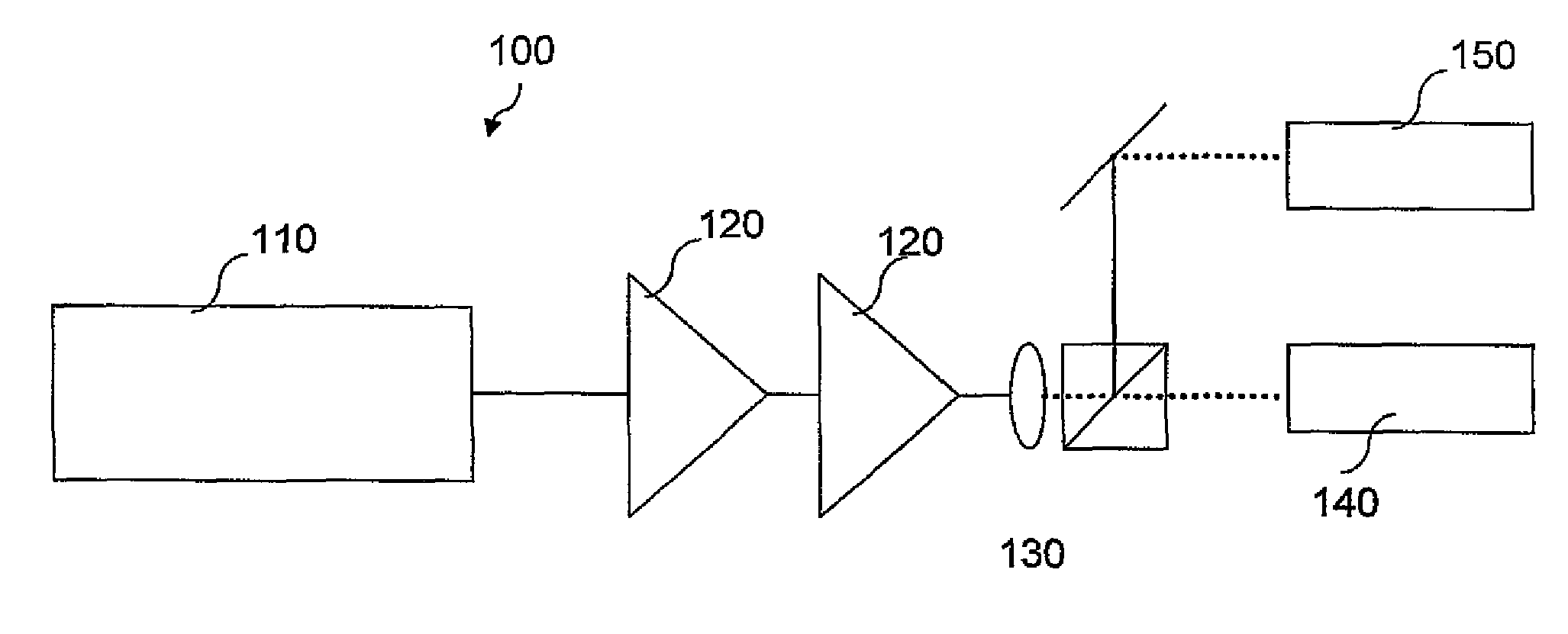
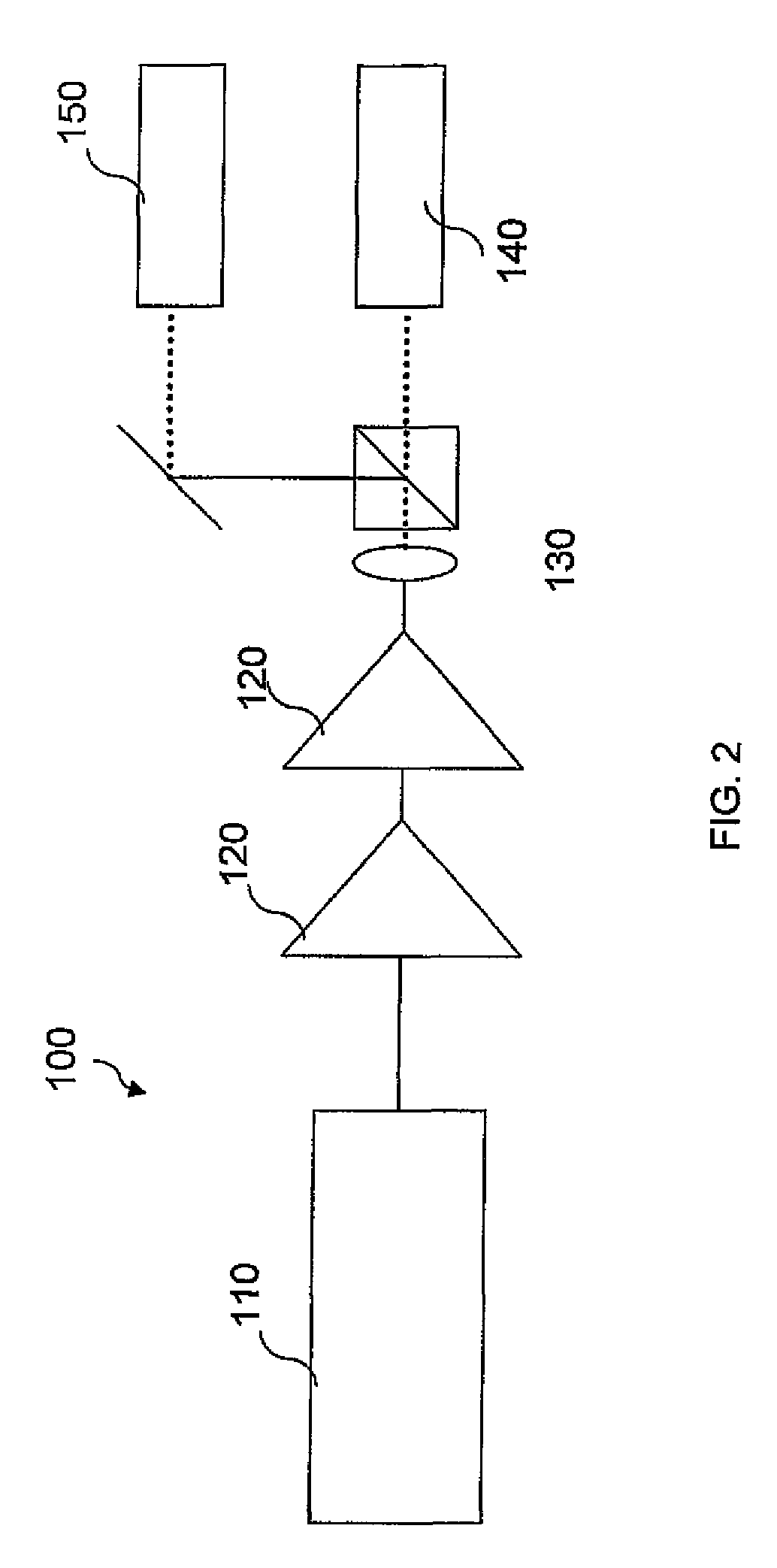
InactiveUS6901090B1Improve maintainabilityEasy alignmentLaser detailsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusFiber bundleAudio power amplifier
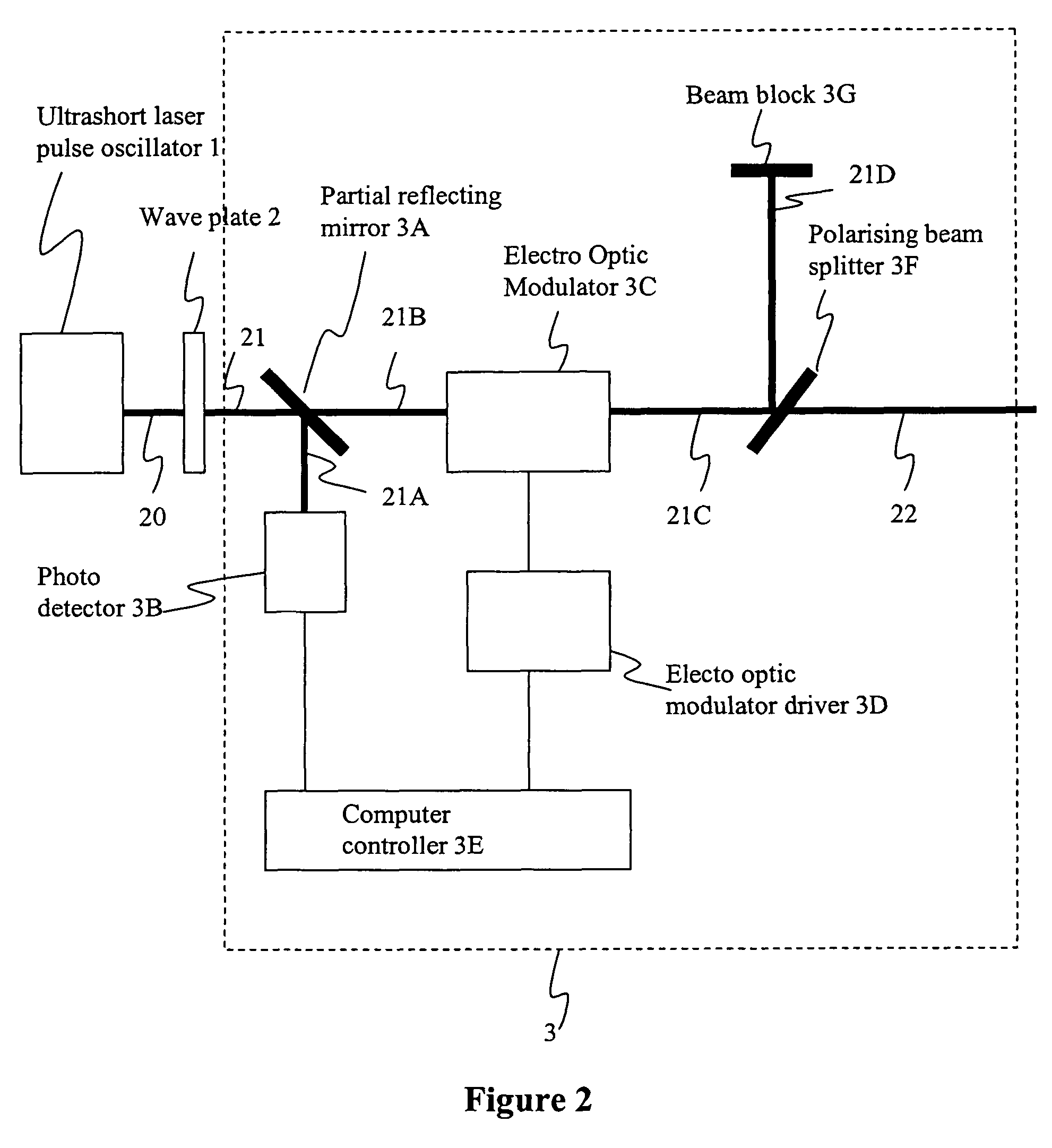
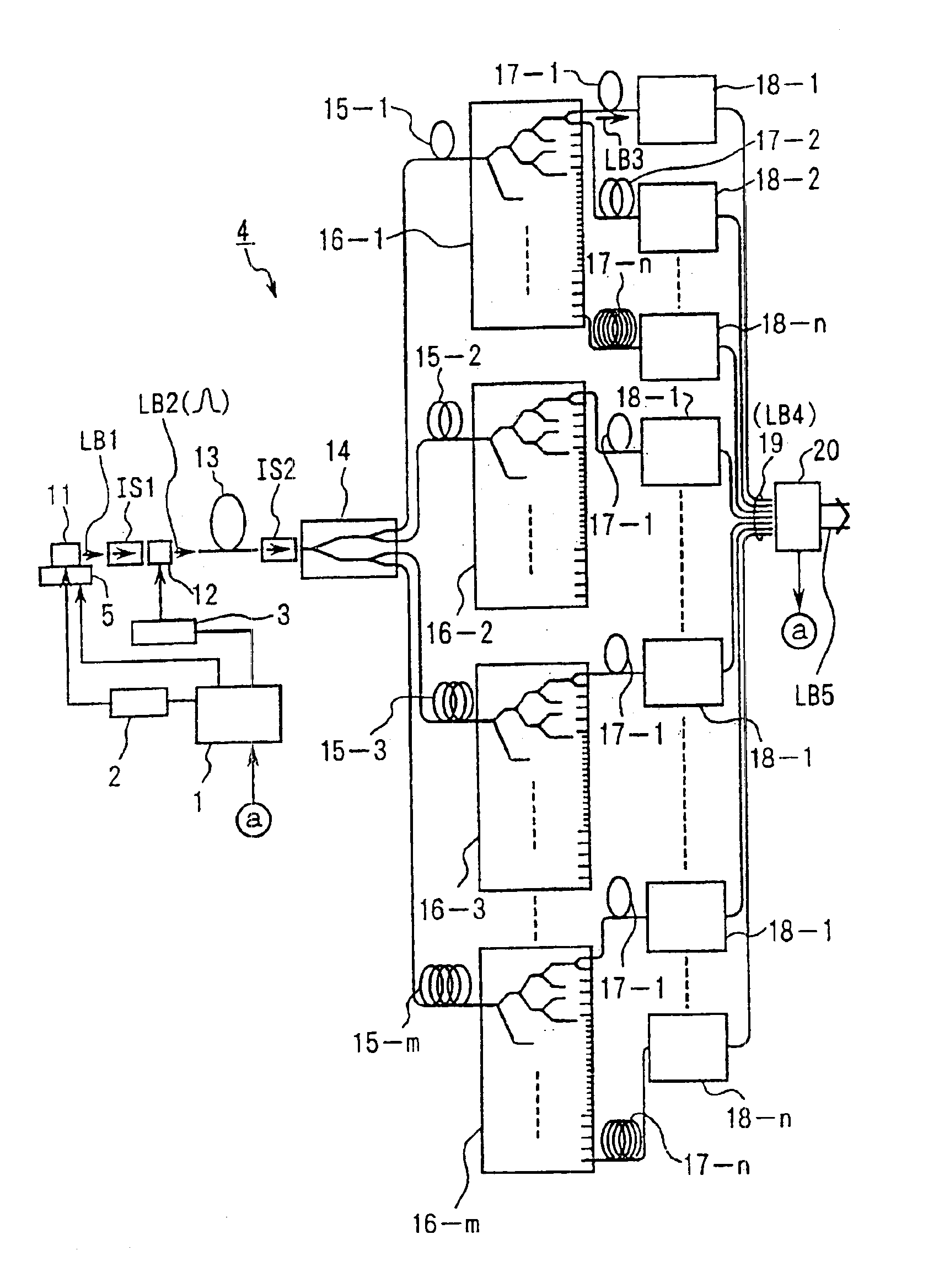
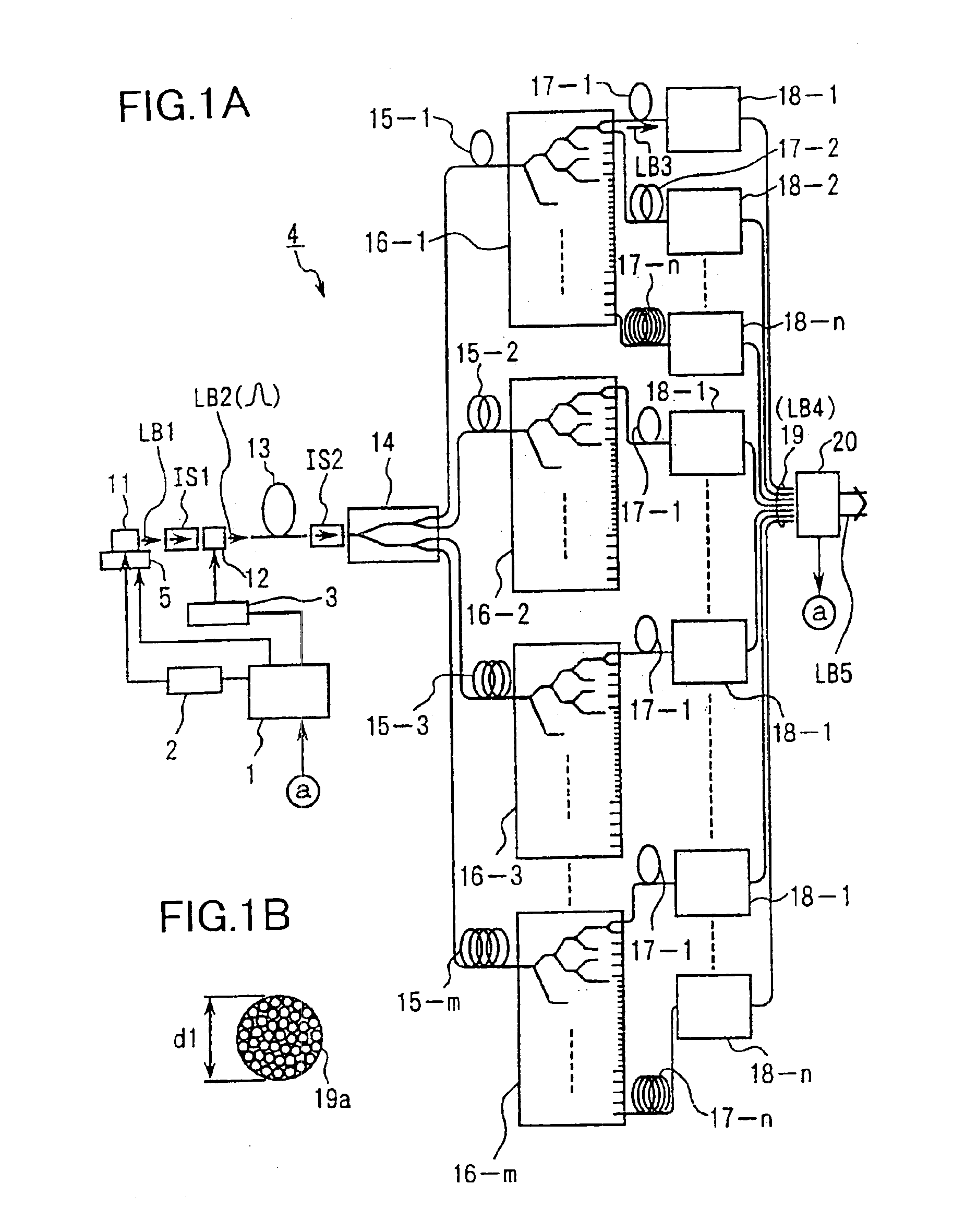
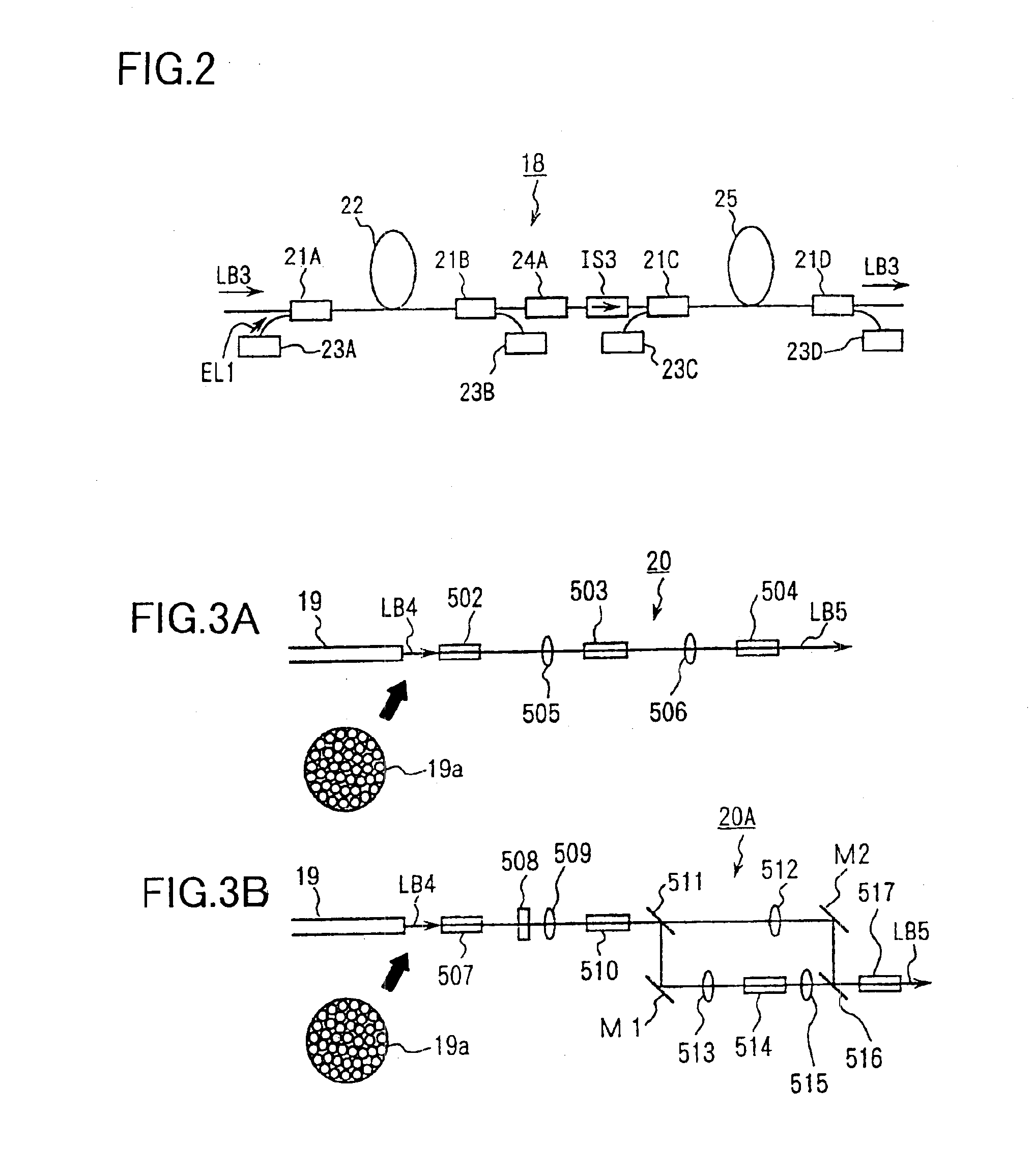
An exposure apparatus has a laser device that is small, easy to maintain, and capable of producing an output that is unlikely to be affected by optical surges occurring in the beginning of operation. A single-wavelength laser oscillator (11) supplies a laser beam (LB1) to a fiber optic amplifier (13) through an optical modulator (12). The amplified laser beam is split by splitters (14, 16-1 to 16-m), amplified by optical amplifier units (18-1 to 18-n) and supplied through a fiber bundle (19) to a wavelength converter (20), which in turn converts the split beams into ultraviolet laser radiation (LB5) for use as exposure light. The optical modulator (12) outputs light pulses during the generation of ultraviolet light. The optical modulator (12) also produces laser radiation during the absence of ultraviolet light, but the laser radiation has substantially the same average output and a considerably low peak compared with that during the generation of ultraviolet light.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Control system and apparatus for use with ultra-fast laser
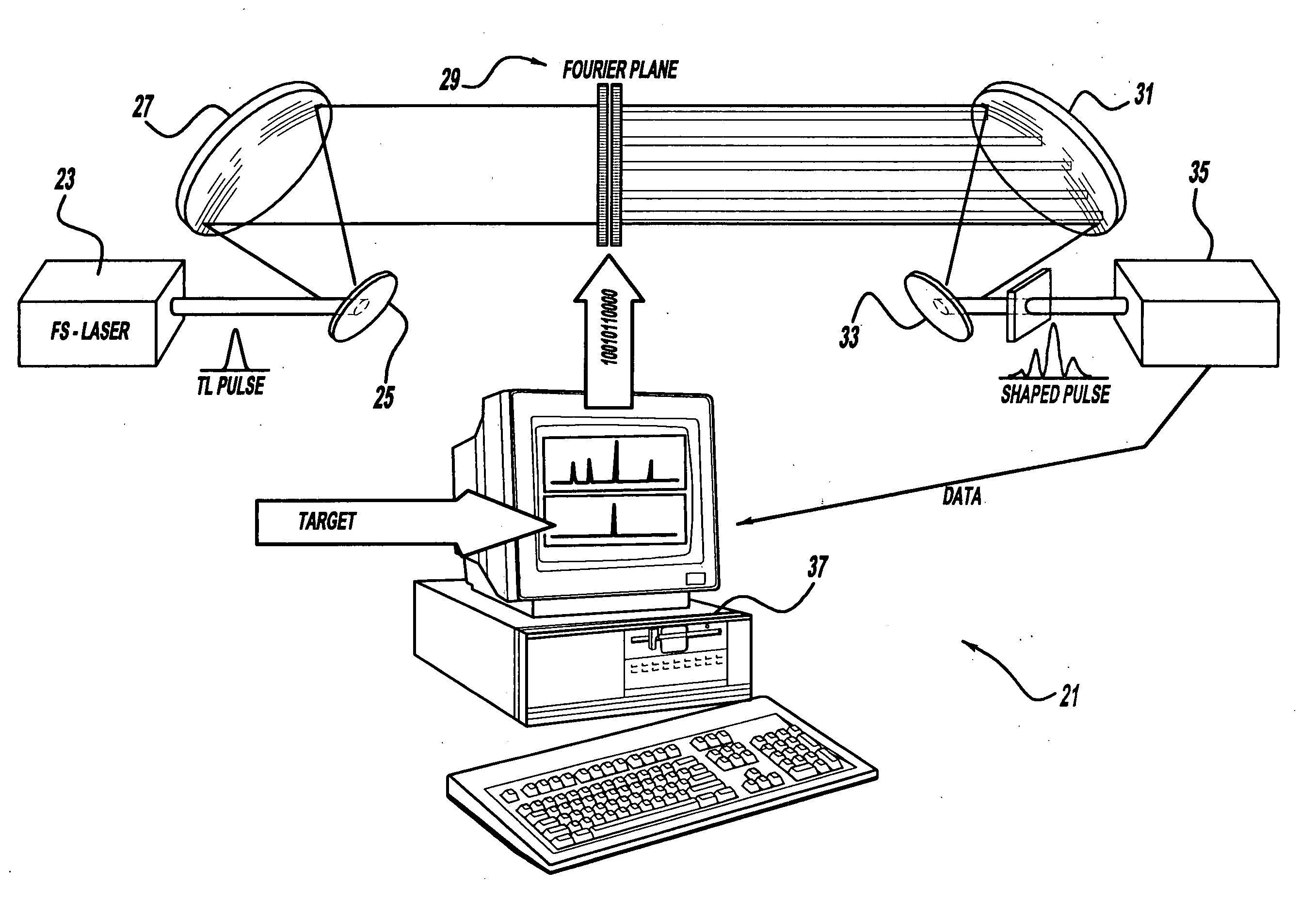
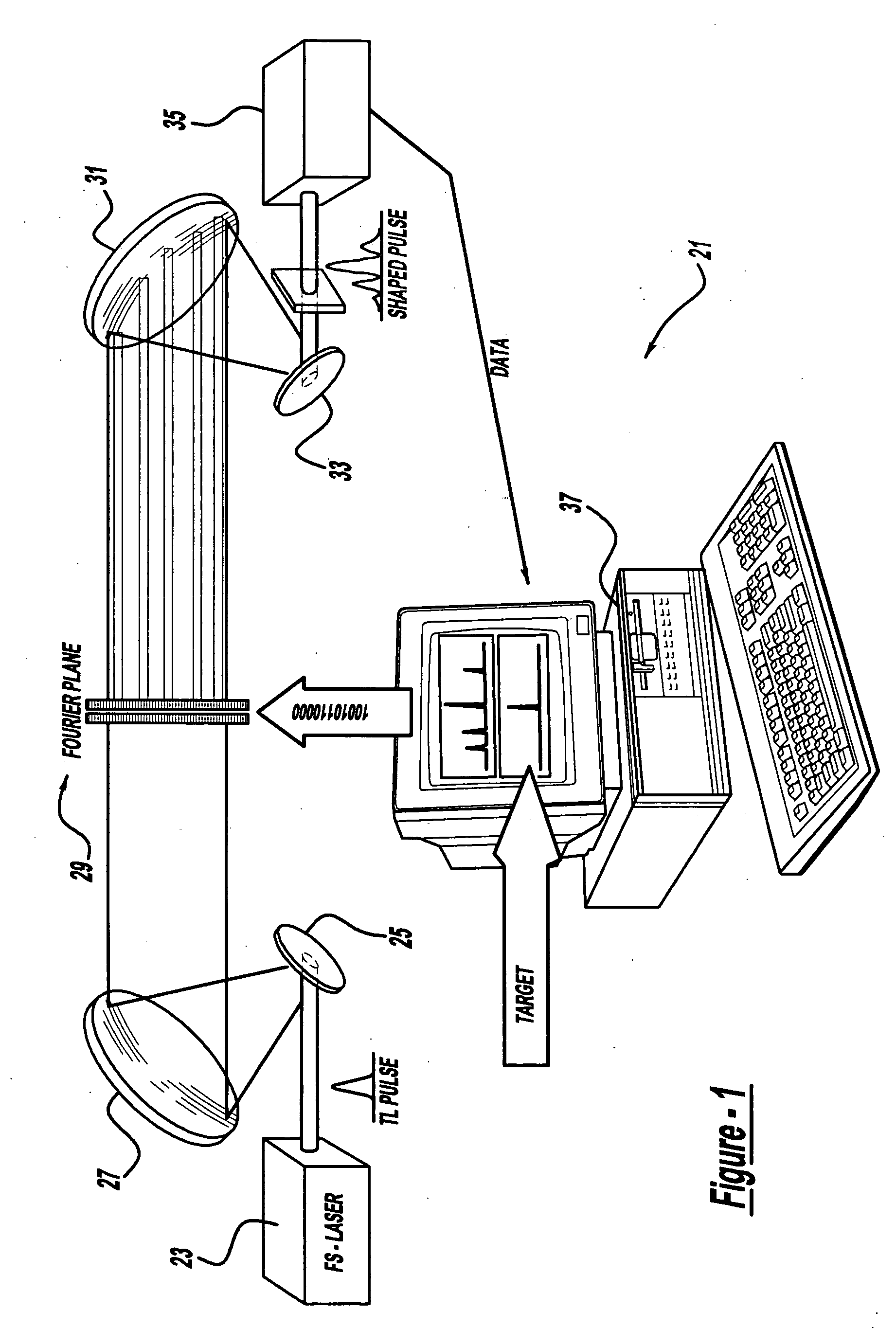
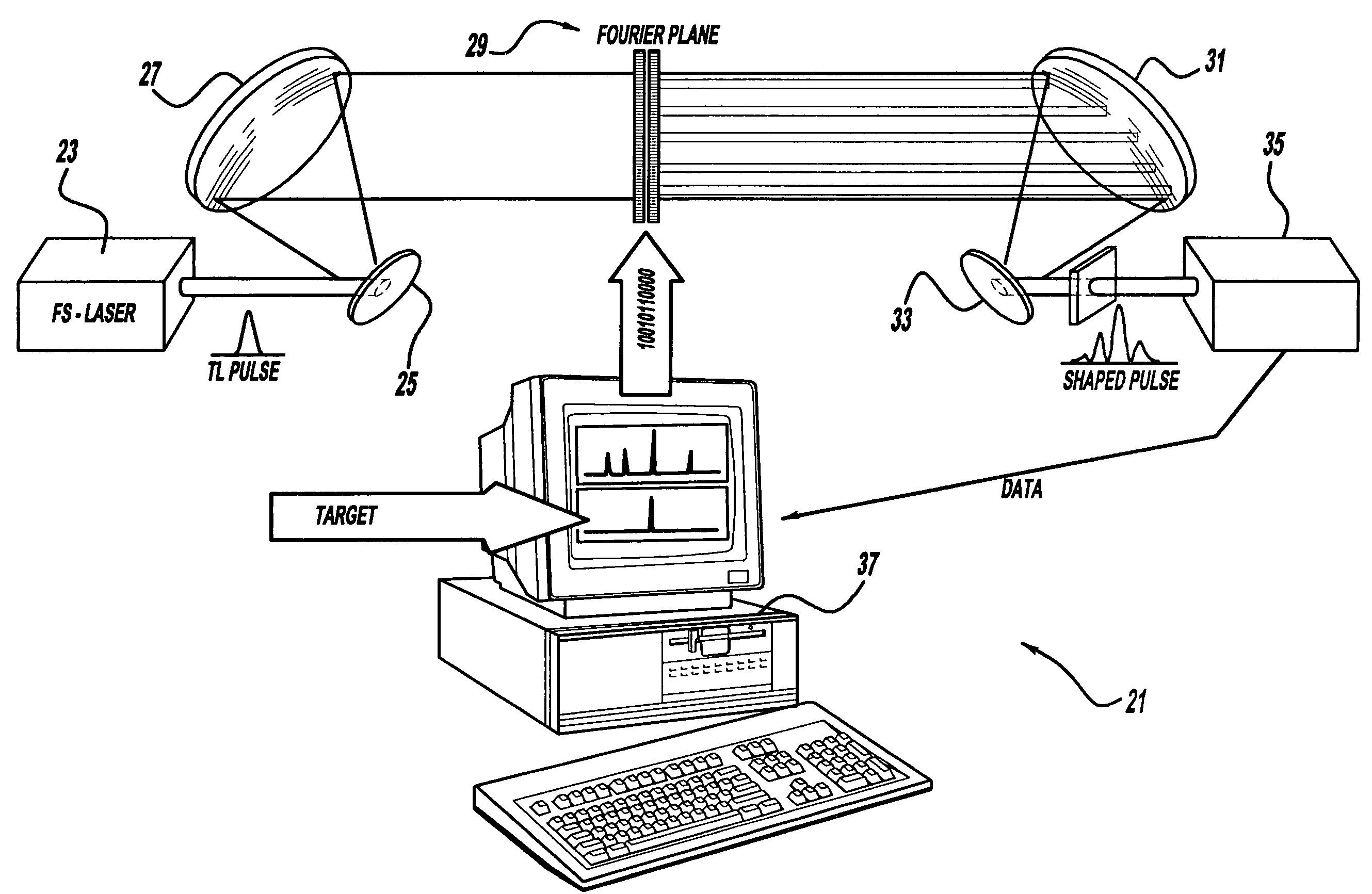
InactiveUS20060056468A1Easy to set upEasy to useLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansAudio power amplifierControl system
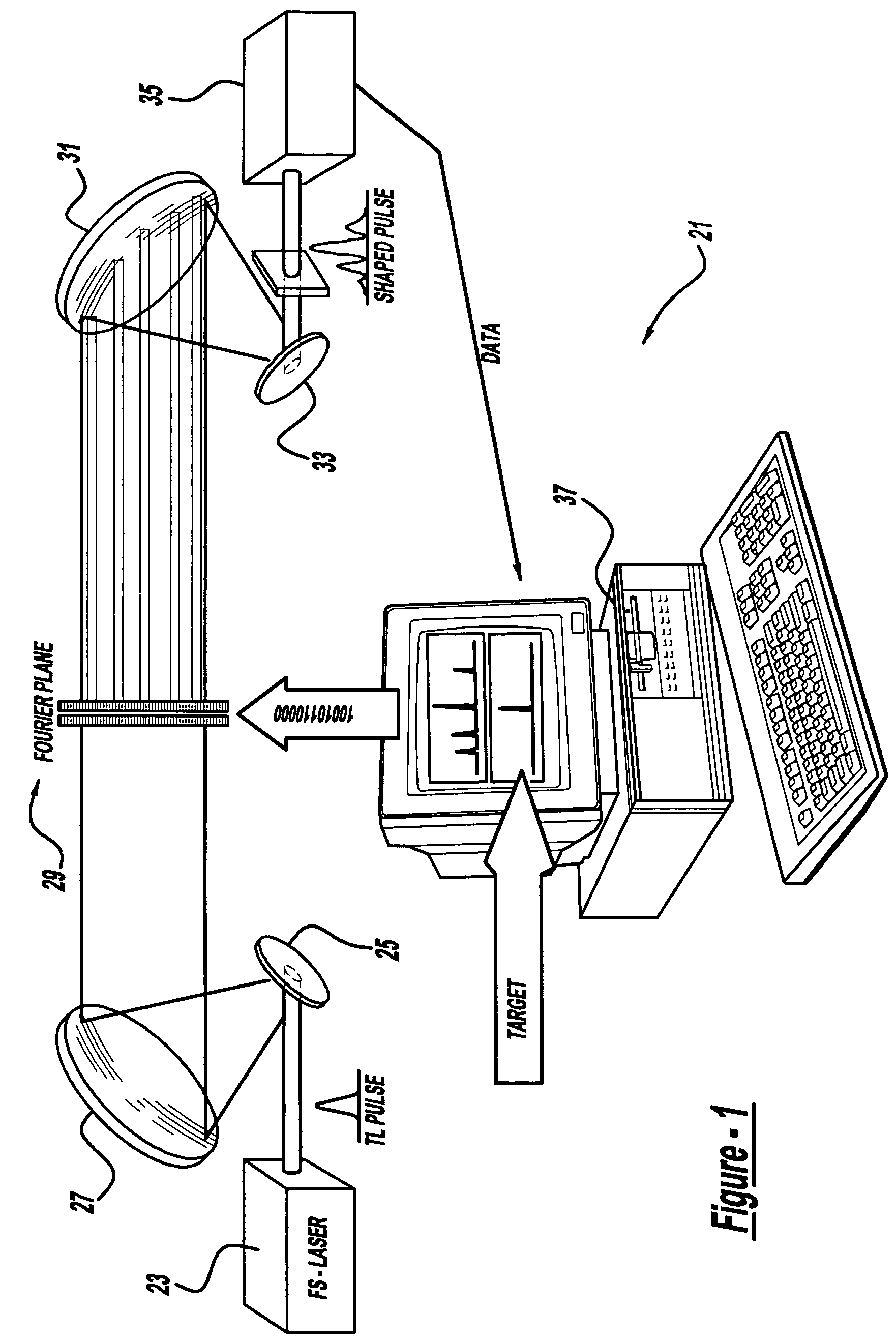
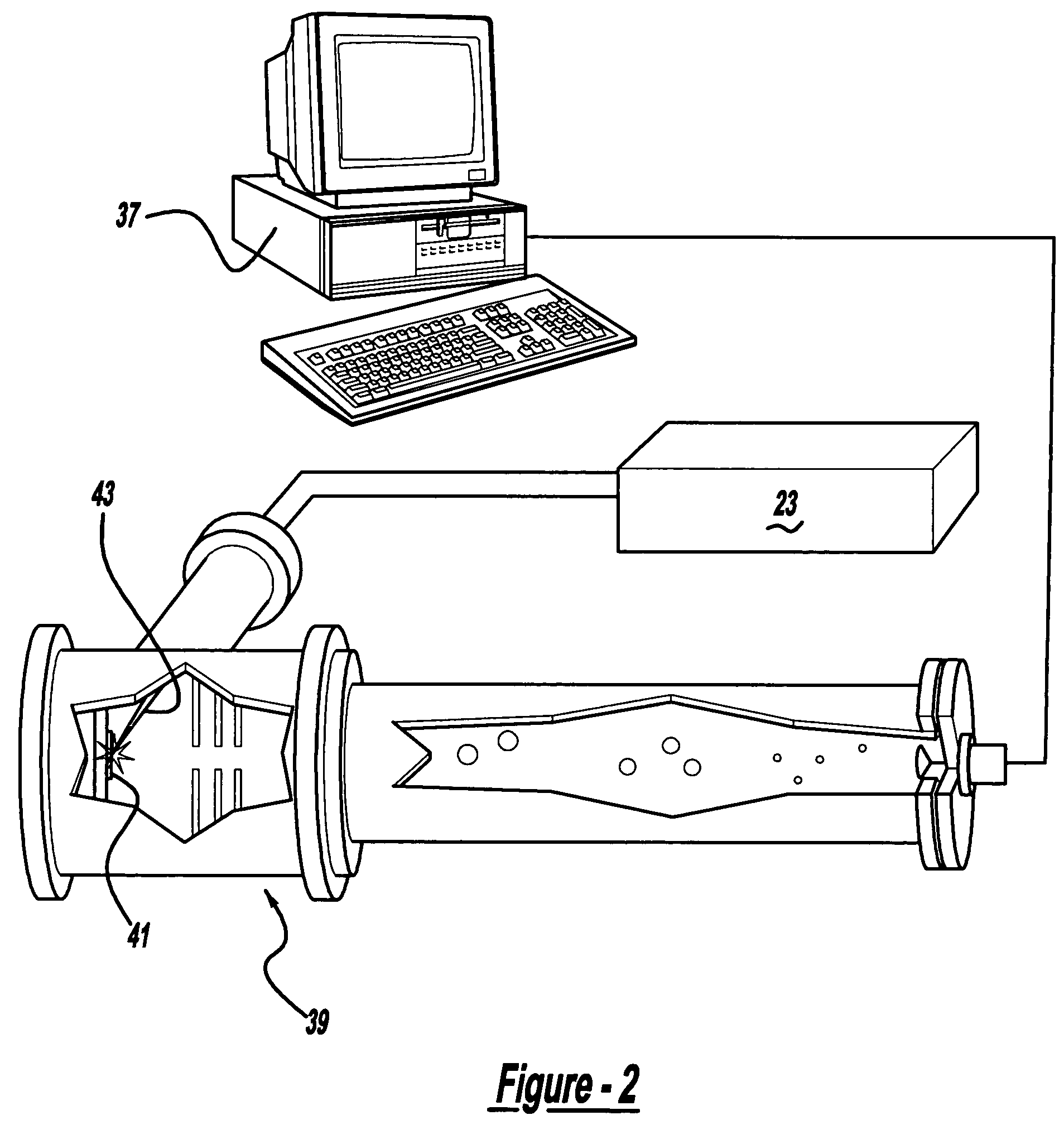
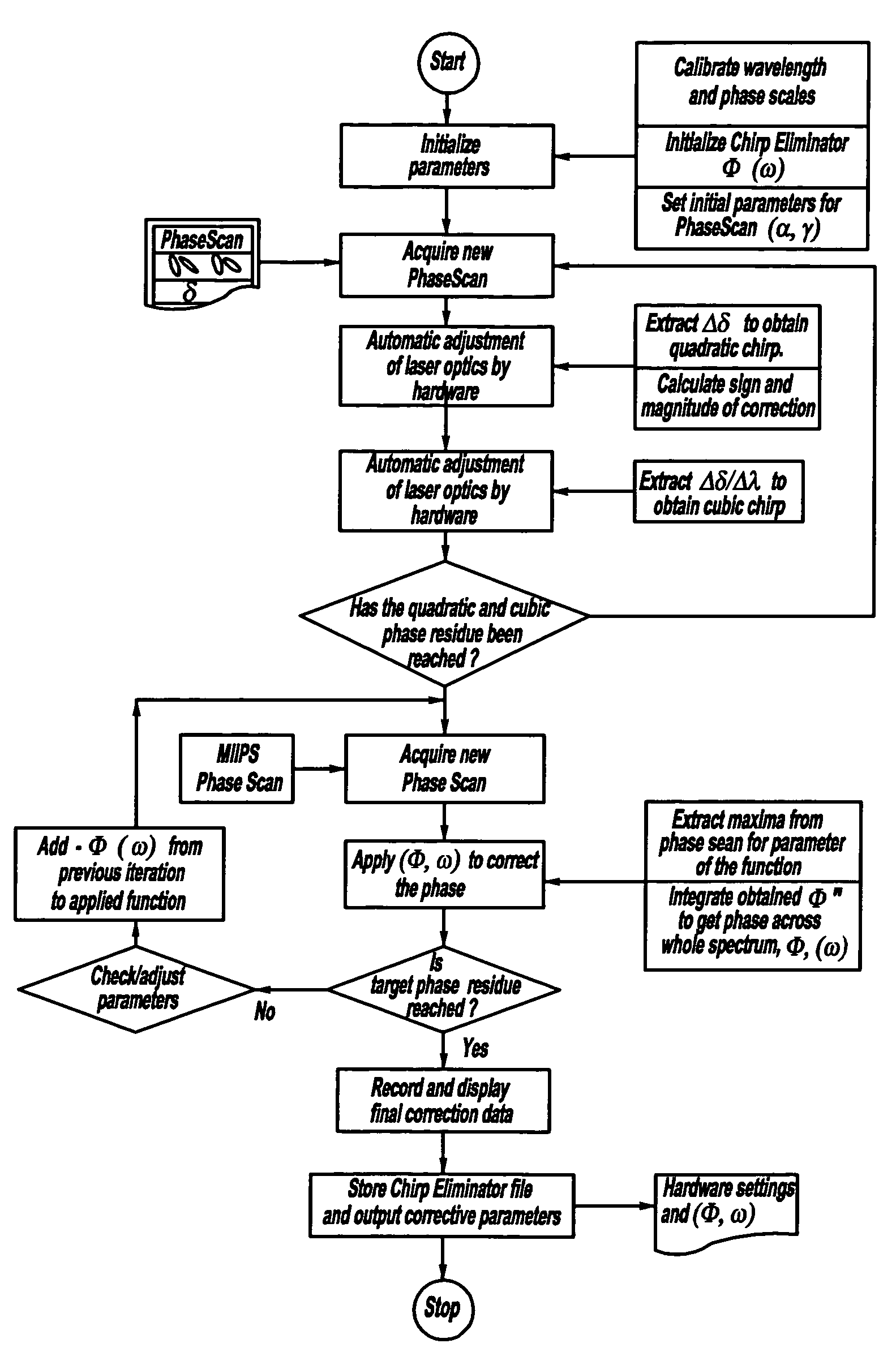
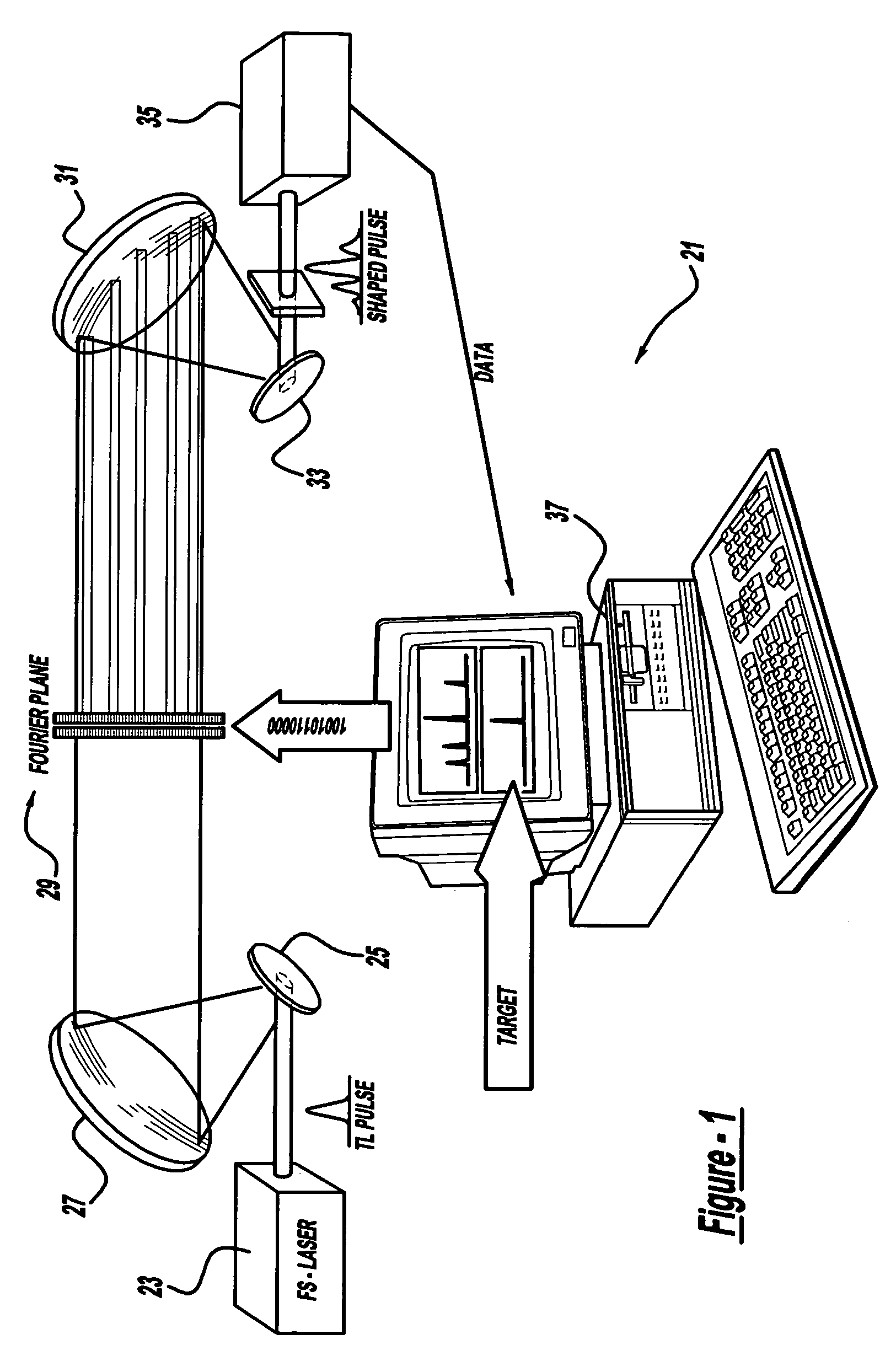
A control system and apparatus for use with an ultra-fast laser is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the apparatus includes a laser, pulse shaper, detection device and control system. A multiphoton intrapulse interference method is used to characterize the spectral phase of laser pulses and to compensate for any distortions in an additional aspect of the present invention. In another aspect of the present invention, a system employs multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan. Furthermore, another aspect of the present invention locates a pulse shaper and / or MIIPS unit between a spectral dispersion point in a laser oscillator and an output of a laser amplifier.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Control system and apparatus for use with ultra-fast laser
InactiveUS7567596B2Easy to set upEasy to useLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansAudio power amplifierControl system
A control system and apparatus for use with an ultra-fast laser is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the apparatus includes a laser, pulse shaper, detection device and control system. A multiphoton intrapulse interference method is used to characterize the spectral phase of laser pulses and to compensate for any distortions in an additional aspect of the present invention. In another aspect of the present invention, a system employs multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan. Furthermore, another aspect of the present invention locates a pulse shaper and / or MIIPS unit between a spectral dispersion point in a laser oscillator and an output of a laser amplifier.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Control system and apparatus for use with ultra-fast laser
ActiveUS7973936B2Easy to set upEasy to useRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryAudio power amplifierMultiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan
A control system and apparatus for use with an ultra-fast laser is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the apparatus includes a laser, pulse shaper, detection device and control system. A multiphoton intrapulse interference method is used to characterize the spectral phase of laser pulses and to compensate any distortions in an additional aspect of the present invention. In another aspect of the present invention, a system employs multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan. Furthermore, another aspect of the present invention locates a pulse shaper and / or MIIPS unit between a laser oscillator and an output of a laser amplifier.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Control system and apparatus for use with ultra-fast laser
ActiveUS20060187974A1Easy to set upEasy to useLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryAudio power amplifierControl system
A control system and apparatus for use with an ultra-fast laser is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the apparatus includes a laser, pulse shaper, detection device and control system. A multiphoton intrapulse interference method is used to characterize the spectral phase of laser pulses and to compensate any distortions in an additional aspect of the present invention. In another aspect of the present invention, a system employs multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan. Furthermore, another aspect of the present invention locates a pulse shaper and / or MIIPS unit between a laser oscillator and an output of a laser amplifier.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
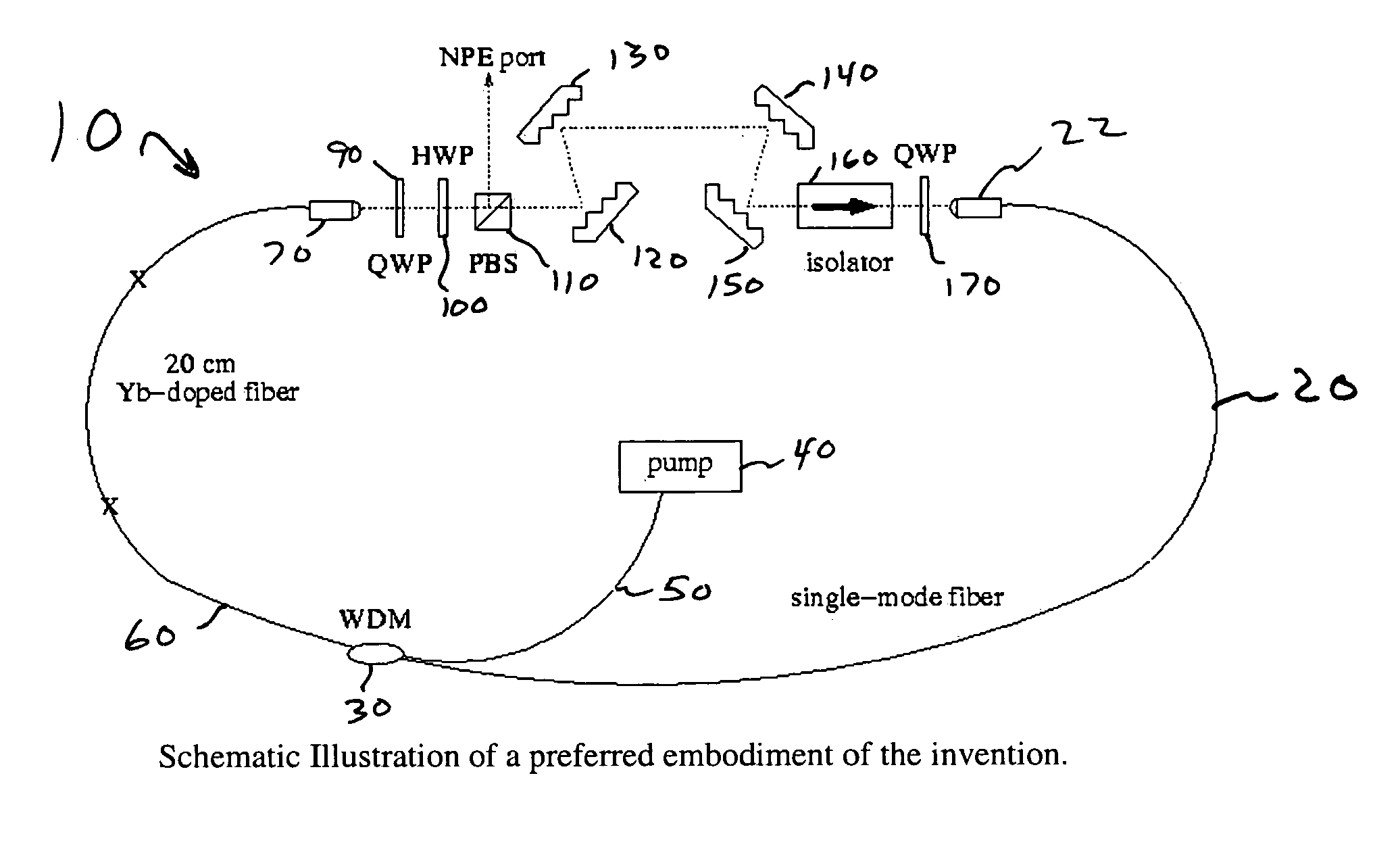
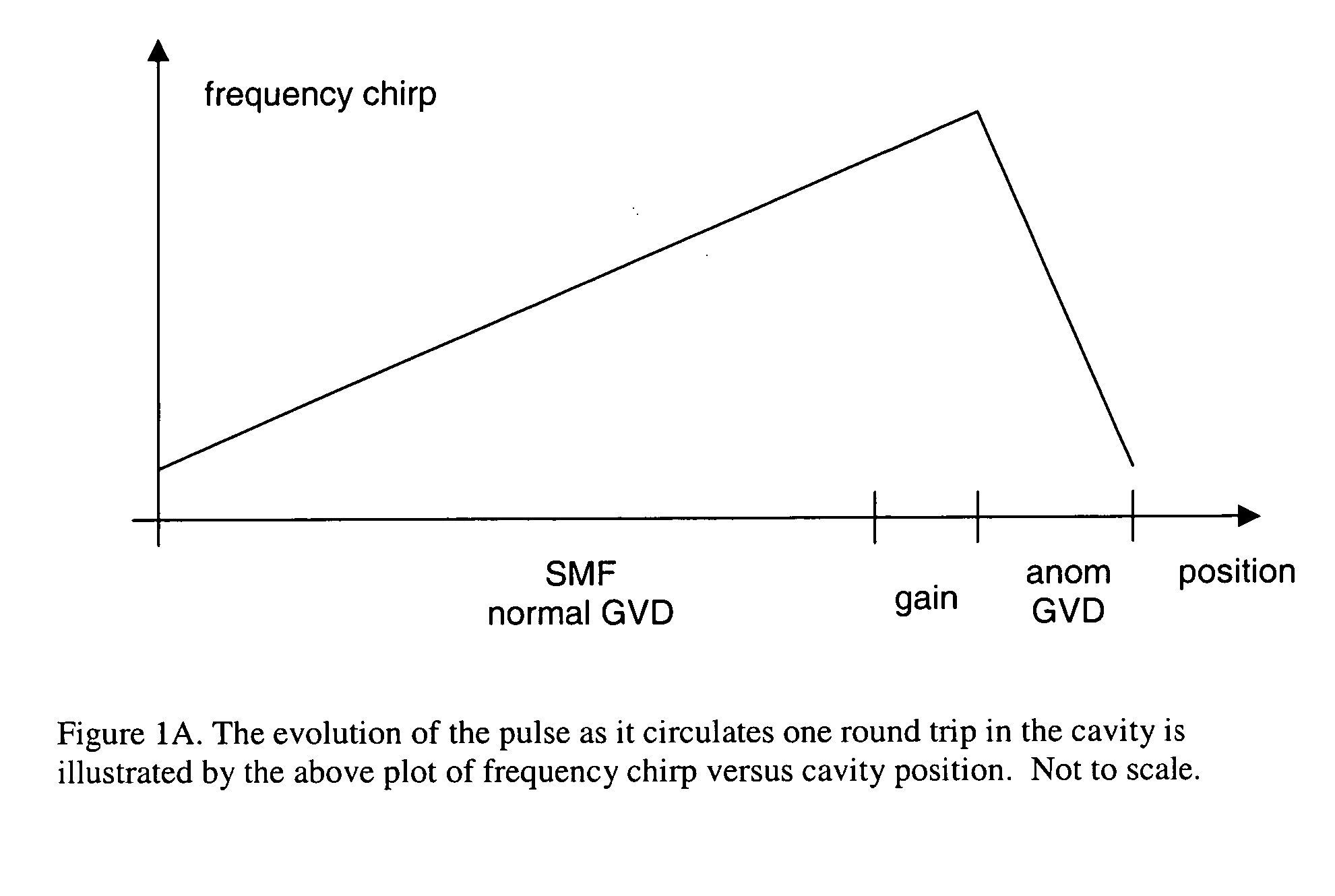
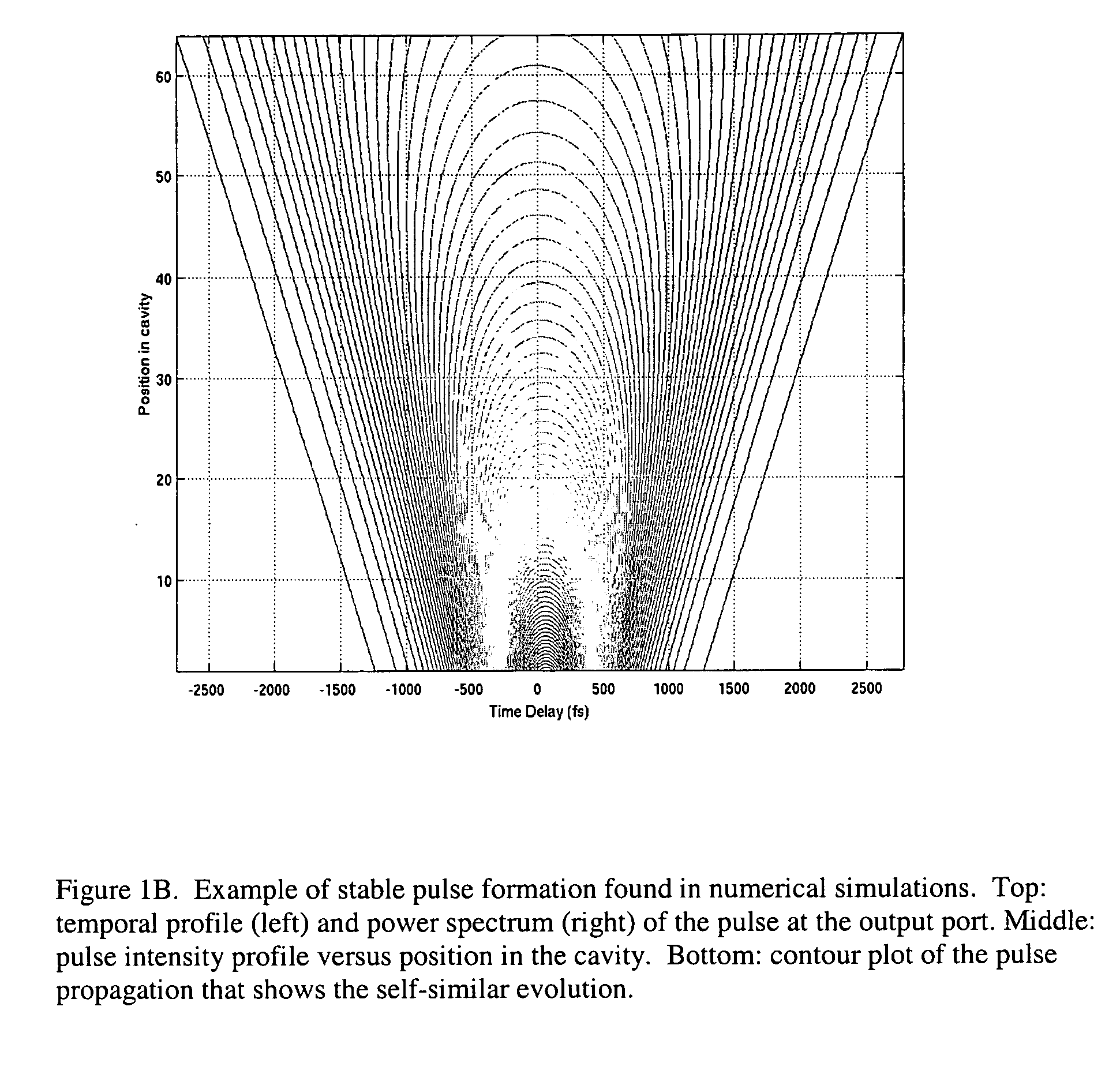
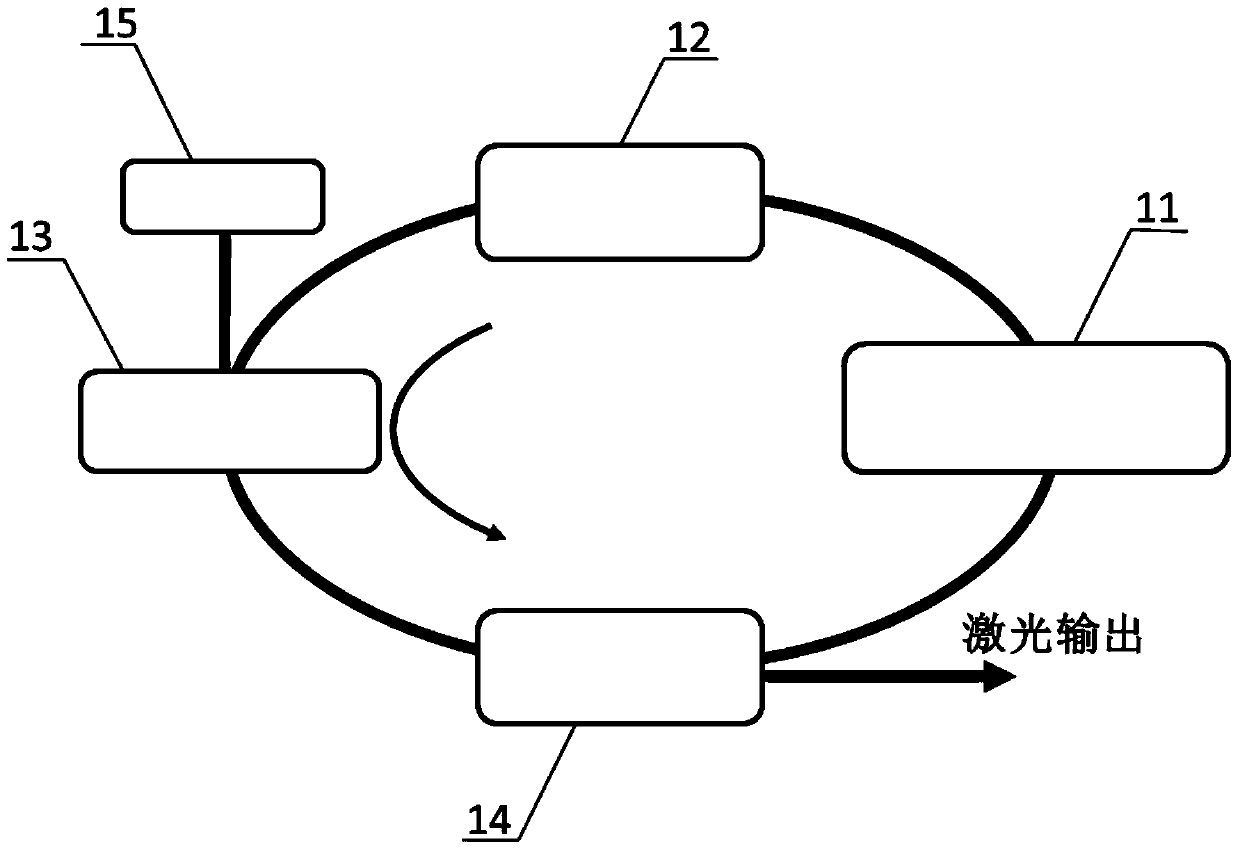
Self-similar laser oscillator
InactiveUS20050169324A1Stable operation of laserHigh bandwidthLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialState of artHigh energy
A laser producing high energy ultrashort laser pulses comprises a normal dispersion segment, a gain segment, an anomalous dispersion segment with negligible nonlinearity and an effective saturable absorber arranged to form a laser cavity. Each segment is optically interconnected so that a laser pulse will propagate self-similarly therein. (A pulse that propagates in a self-similar manner is sometimes referred to as a “similariton.”) With this laser the limitations of prior art laser oscillators are avoided. Also provided are means for pumping the gain medium in the laser cavity, and means for extracting laser pulses from the laser cavity. The laser cavity is preferably a ring cavity. Preferably the laser is configured to achieve unidirectional circulation of laser pulses therein. This configuration is scalable to much higher pulse energy than lasers based on soliton-like pulse shaping.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
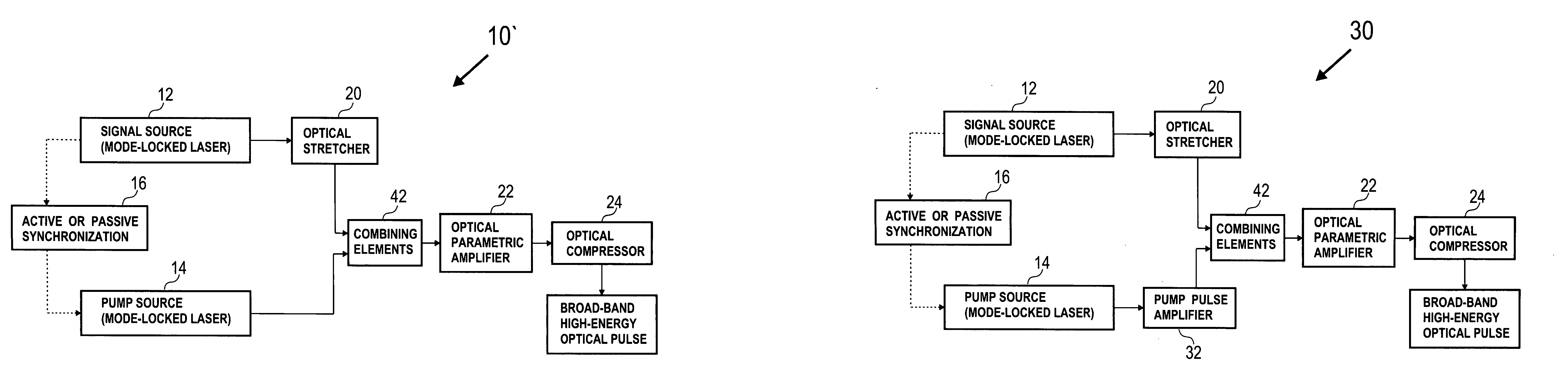
Method and apparatus for high power optical amplification in the infrared wavelength range (0.7-20 mum)
InactiveUS20050271094A1Laser detailsNon-linear opticsAcousto-optic programmable dispersive filterAdemetionine
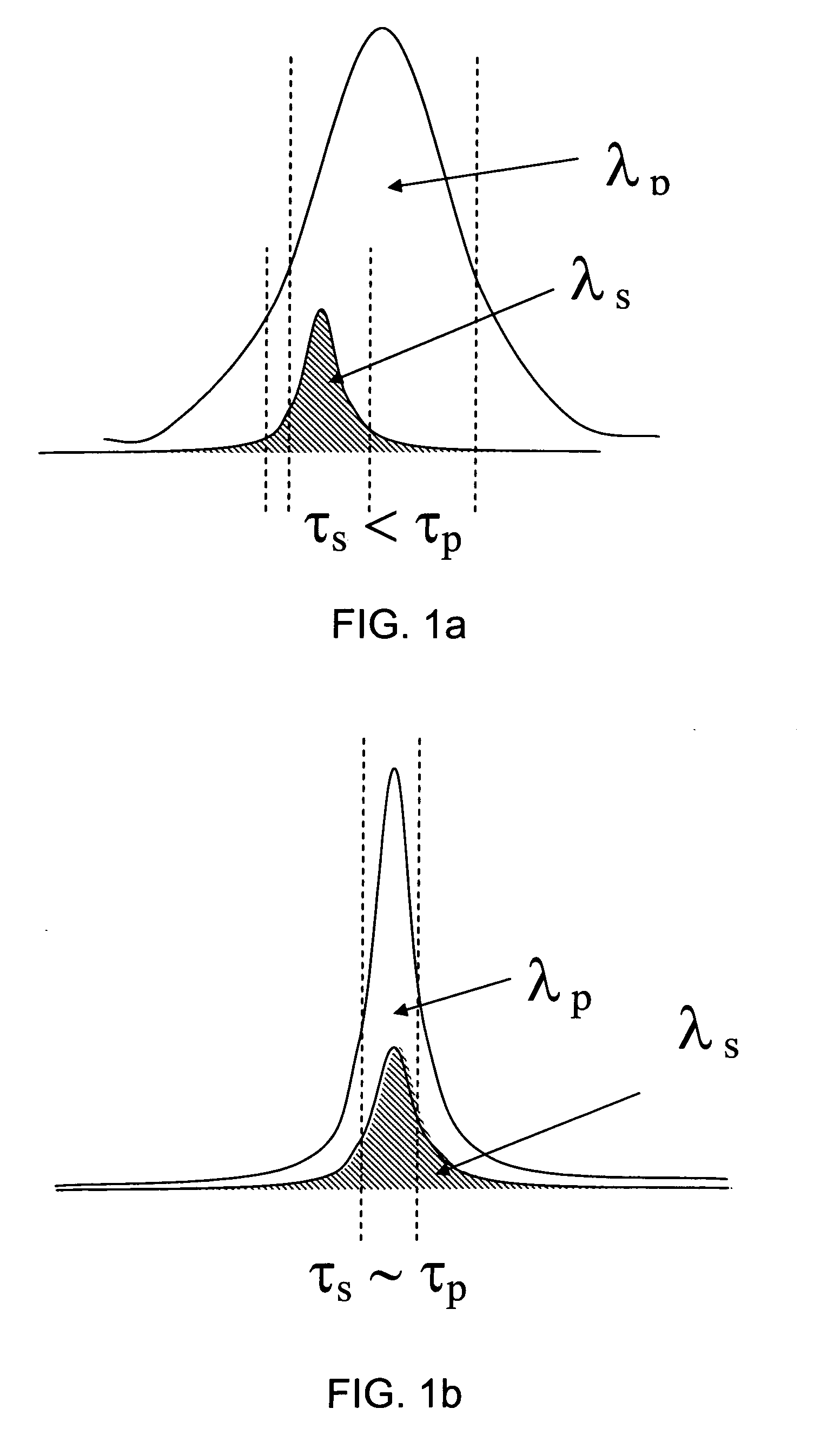
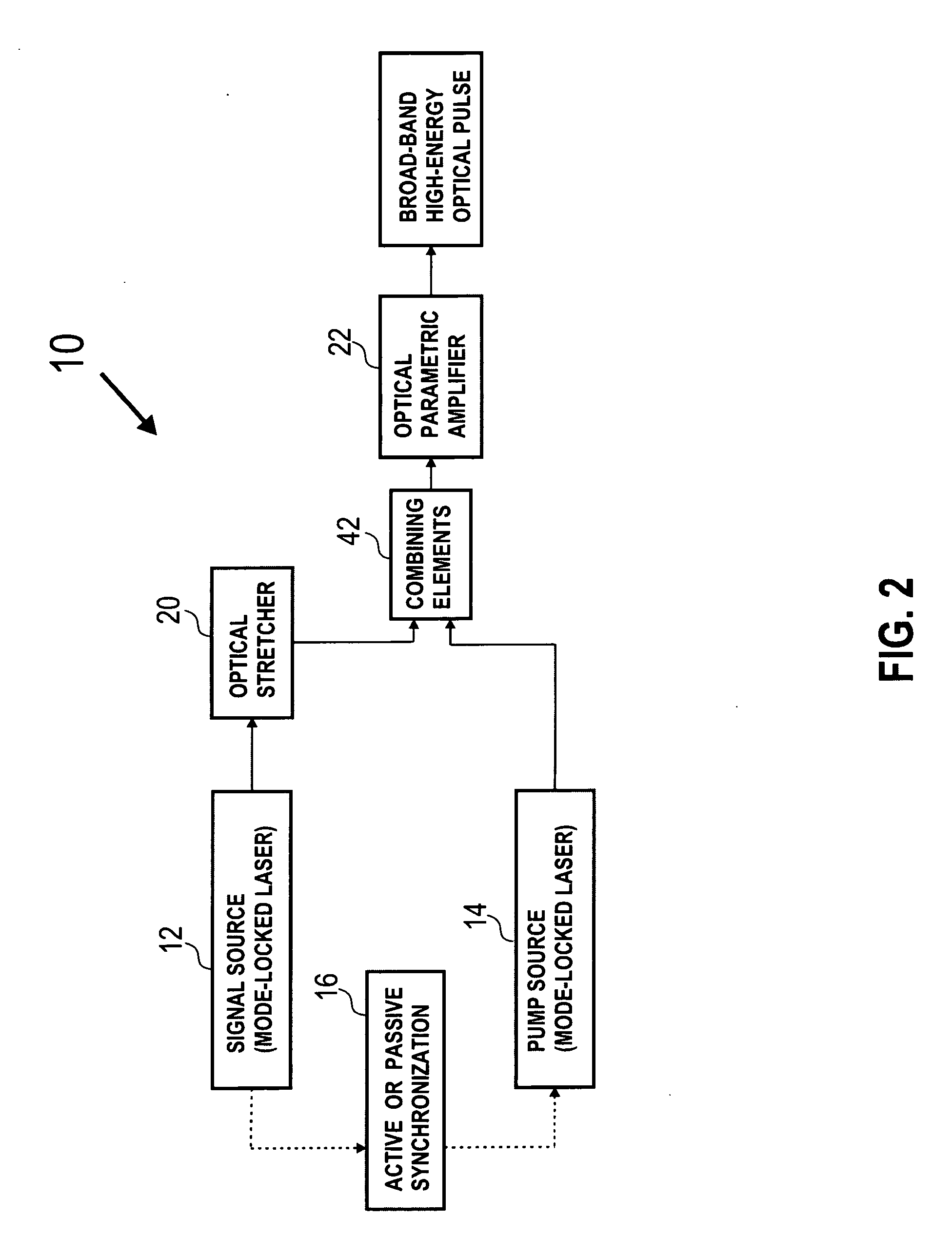
A novel method for high power optical amplification of ultrashort pulses in IR wavelength range (0.7-20 Ãm) is disclosed. The method is based on the optical parametric chirp pulse amplification (OPCPA) technique where a picosecond or nanosecond mode locked laser system synchronized to a signal laser oscillator is used as a pump source or alternatively the pump pulse is created from the signal pulse by using certain types of optical nonlinear processes described later in the document. This significantly increases stability, extraction efficiency and bandwidth of the amplified signal pulse. Further, we disclose five new practical methods of shaping the temporal and spatial profiles of the signal and pump pulses in the OPCPA interaction which significantly increases its efficiency. In the first, passive preshaping of the pump pulses has been made by a three wave mixing process separate from the one occurring in the OPCPA. In the second, passive pre-shaping of the pump pulses has been made by spectral filtering in the pump mode-locked laser or in its amplifier. In the third, the temporal shape of the signal pulse optimized for OPCPA interaction has been actively processed by using an acousto-optic programmable dispersive filter (Dazzler) or liquid crystal light modulators. In the fourth alternative method, the signal pulse intensity envelope is optimized by using passive spectral filtering. Finally, we disclose a method of using pump pulses which interact with the seed pulses with different time delays and different angular orientations allowing the amplification bandwidth to be increased. In addition we describe a new technique for high power IR optical beam delivery systems based on the microstructure fibres made of silica, fluoride or chalcogenide glasses as well as ceramics. Also we disclose a new optical system for achieving phase matching geometries in the optical parametric interactions based on diffractive optics. All novel methods of the ultrashort optical pulse amplification described in this disclosure can be easily generalized to other wavelength ranges.
Owner:MILLER ROBERT JOHN DWAYNE +3
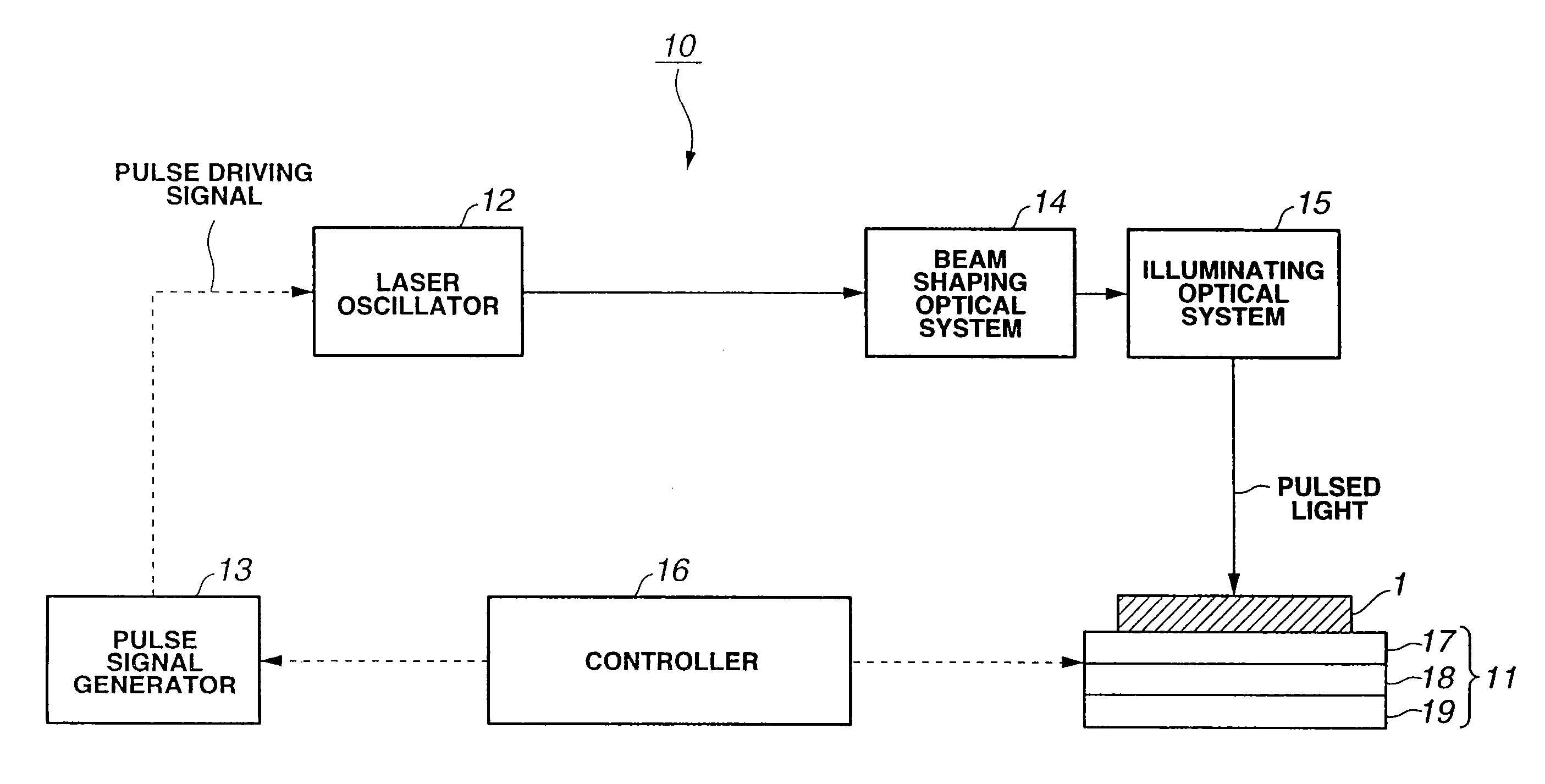
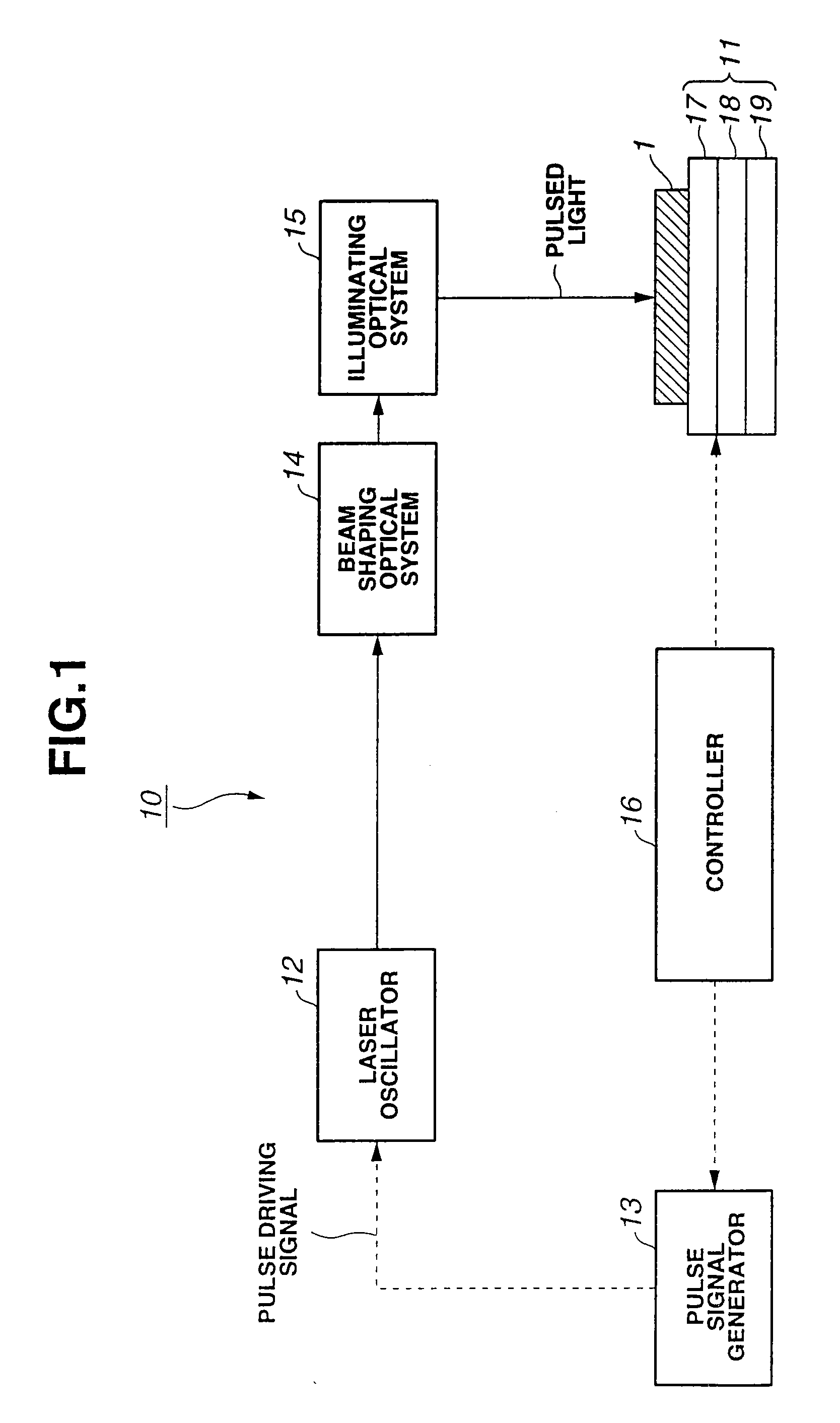
Laser irradiation method, laser irradiation apparatus and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070178672A1High output powerImprove mobilityPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsNonlinear opticsDevice material
In conducting laser annealing using a CW laser or a quasi-CW laser, productivity is not high as compared with an excimer laser and thus, it is necessary to further enhance productivity. According to the present invention, a fundamental wave is used without putting laser light into a non linear optical element, and laser annealing is conducted by irradiating a semiconductor thin film with pulsed laser light having a high repetition rate. A laser oscillator having a high output power can be used for laser annealing, since a non linear optical element is not used and thus light is not converted to a harmonic. Therefore, the width of a region having large grain crystals that is formed by scanning once can be increased, and thus the productivity can be enhanced dramatically.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Spectrally tailored pulsed fiber laser oscillator
ActiveUS20100128744A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical devices for laserPhase variationOptical property
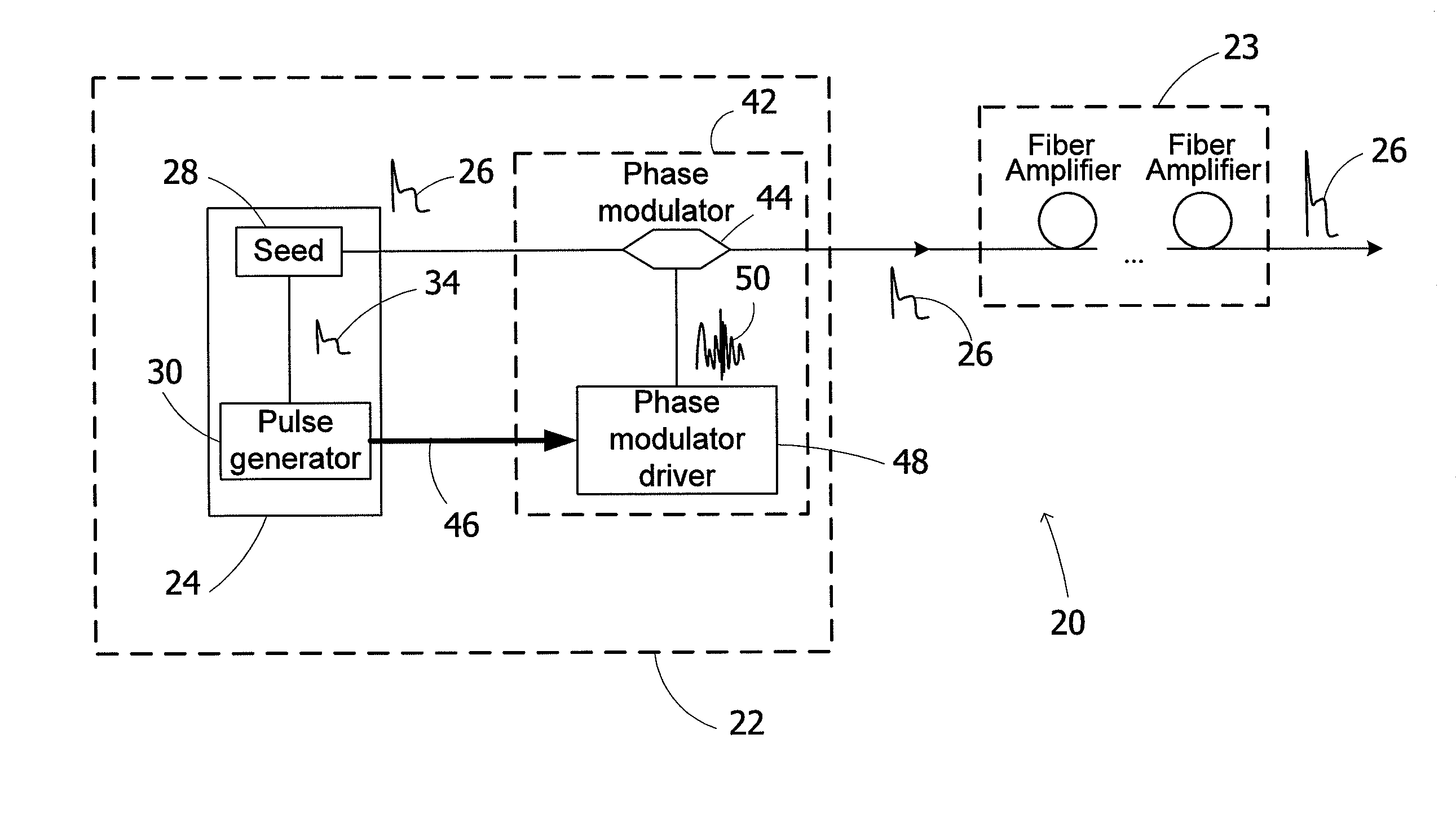
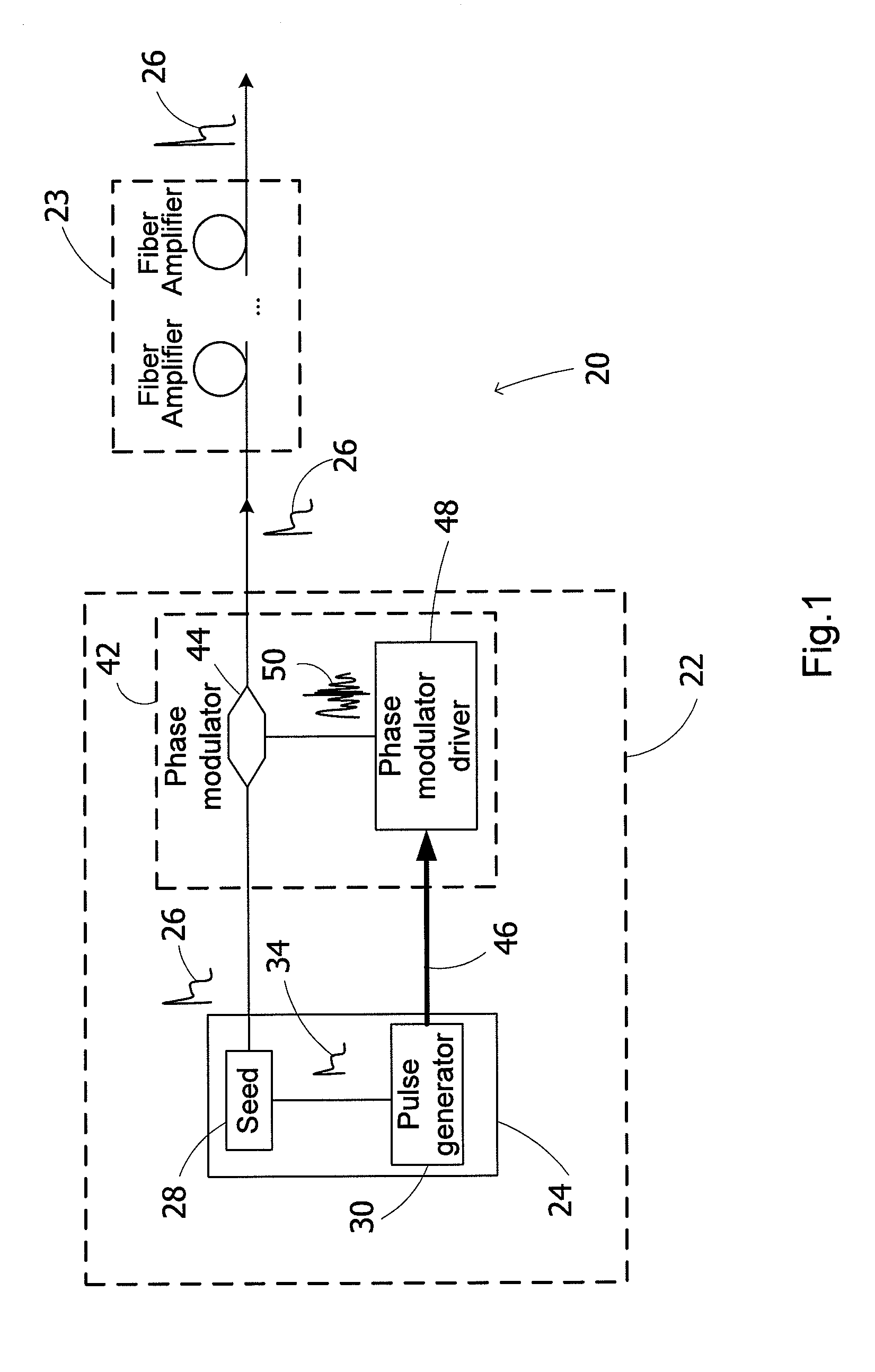
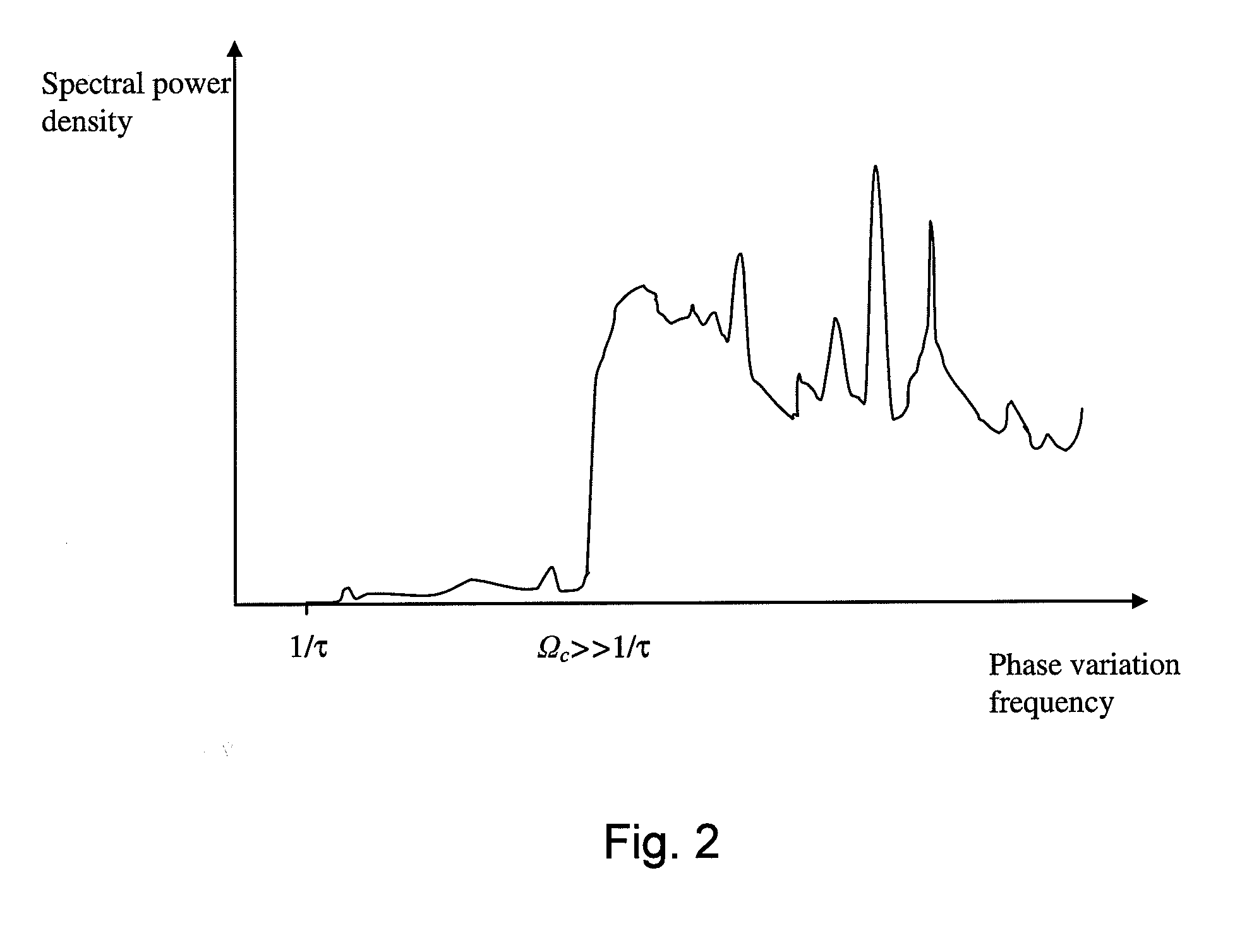
High power optical pulses generating methods and laser oscillators are provided. A light generating module generates seed optical pulses having predetermined optical characteristics. A spectrum tailoring module is then used to tailor the spectral profile of the optical pulses. The spectral tailoring module includes a phase modulator which imposes a time-dependent phase variation on the optical pulses. The activation of the phase modulator is synchronized with the passage of the optical pulse therethough, thereby efficiently reducing the RF power necessary to operate the device.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Laser apparatus
InactiveUS7257136B2Guaranteed uptimeWithout usingLaser detailsLaser beam welding apparatusPower sensorLaser light
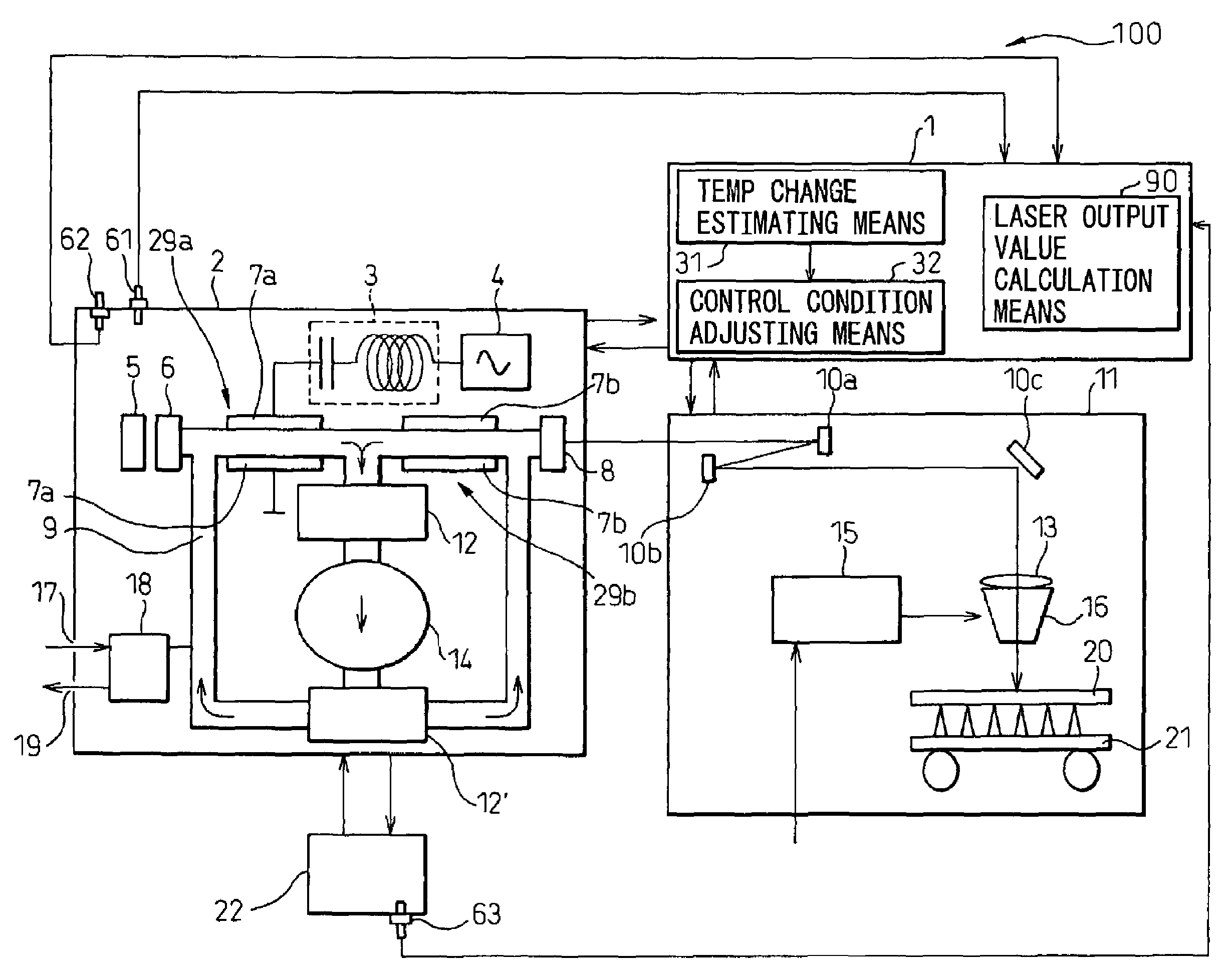
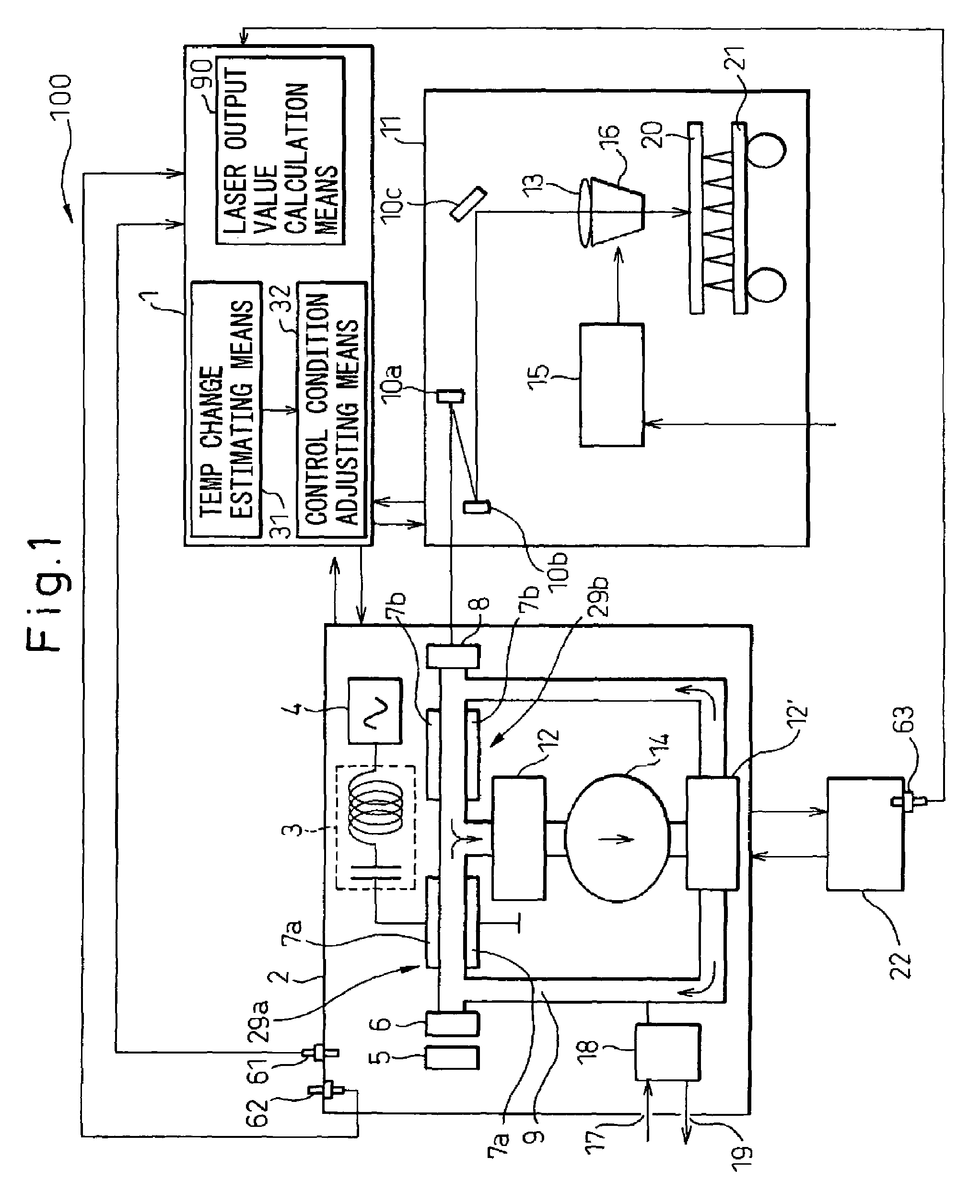
A laser apparatus (100) for performing the laser machining operation by condensing the laser light output from a laser oscillator (3) is disclosed. A laser output value calculation unit calculates a laser output value (L1) based on a command value (L0) issued to a laser oscillator (2). A temperature change estimating unit (31) estimates the temperature change or the temperature (Te) of specified component element(s) (7a, 7b) of the laser apparatus based on the elapsed time (t) and the laser output value calculated by the laser output value calculation unit. An adjusting unit (32) adjusts the conditions for controlling the laser or the conditions for laser machining based on the temperature change or the temperature of the specified component element estimated by the temperature change estimating unit. A stable laser machining operation is performed without a temperature sensor. The laser output value (L1) may be measured by a laser power sensor (5).
Owner:FANUC LTD
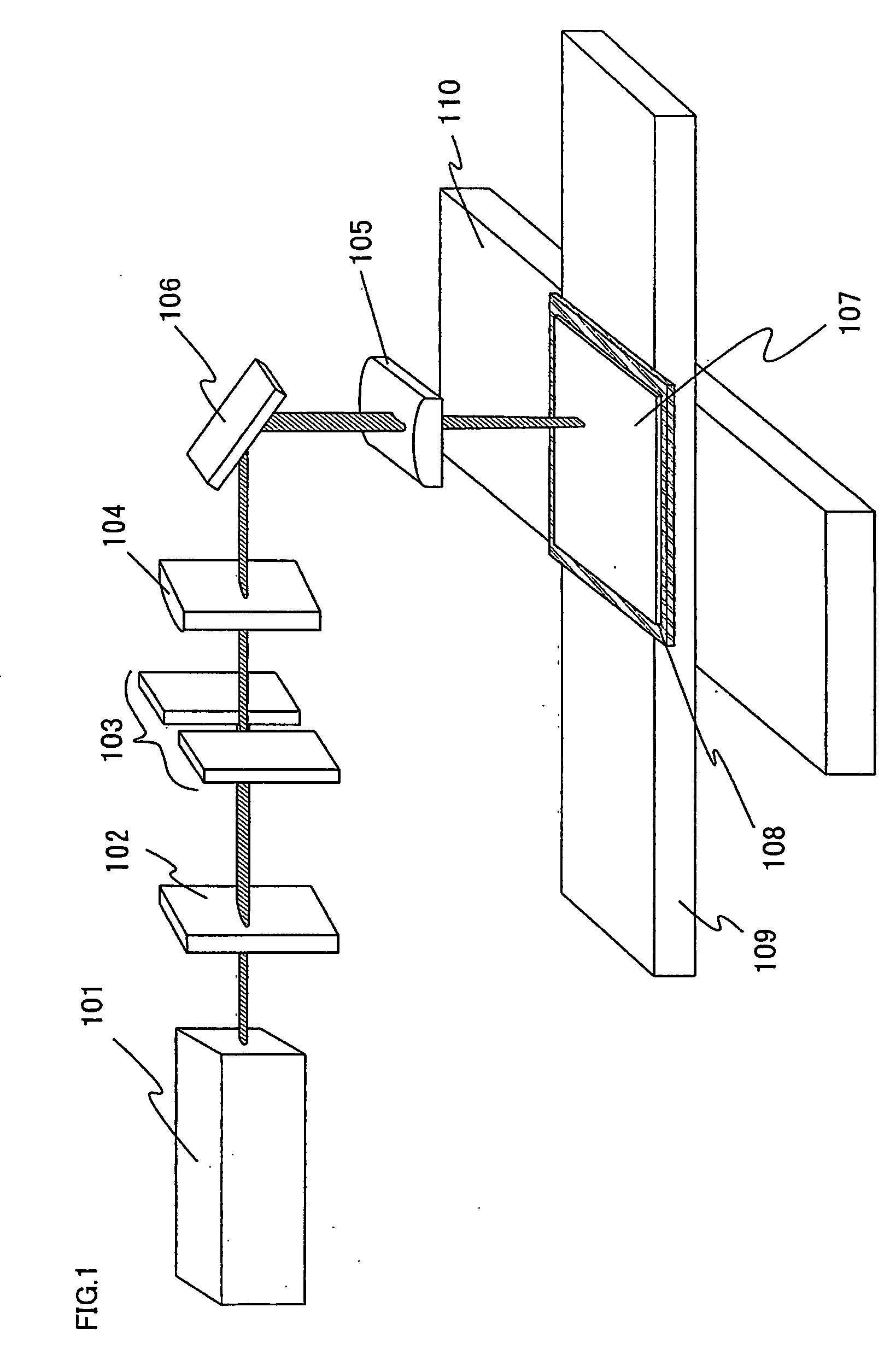
Laser irradiation apparatus and laser irradiation method
ActiveUS20090127477A1High repetition rateImprove conversion efficiencyElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesLight beamOptoelectronics
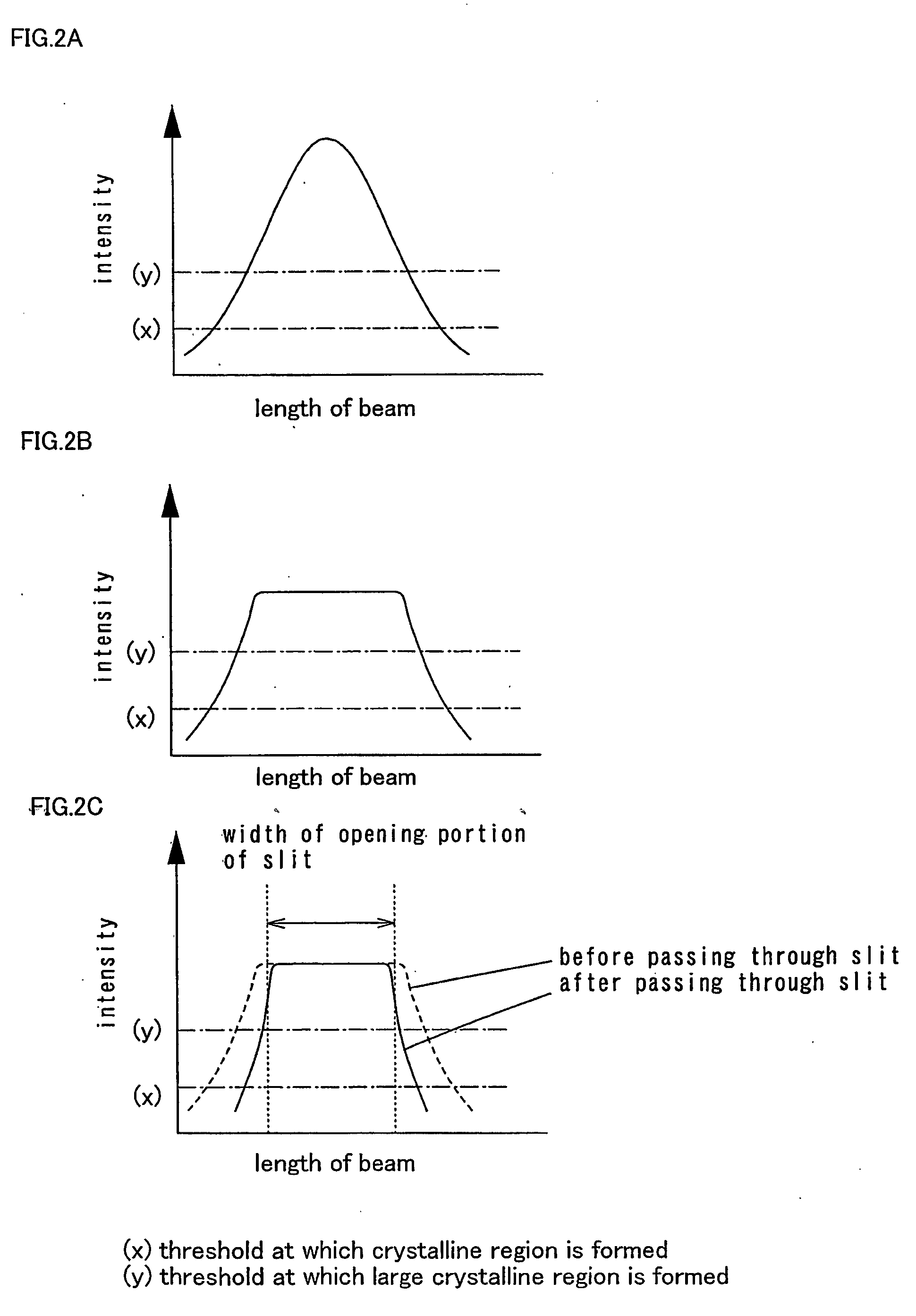
A laser beam having homogeneous intensity distribution is delivered without causing interference stripes of a laser to appear on an irradiation surface. A laser beam emitted from a laser oscillator passes through a diffractive optical element so that the intensity distribution thereof is homogenized. The beam emitted from the diffractive optical element then passes through a slit so that low-intensity end portions in a major-axis direction of the beam are blocked. Subsequently, the beam passes through a projecting lens and a condensing lens, so that an image of the slit is projected onto the irradiation surface. The projecting lens is provided so that the slit and the irradiation surface are conjugated. Thus, the irradiation surface can be irradiated with the laser having homogeneous intensity while preventing the diffraction by the slit.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Laser annealing device and method for producing thin-film transistor
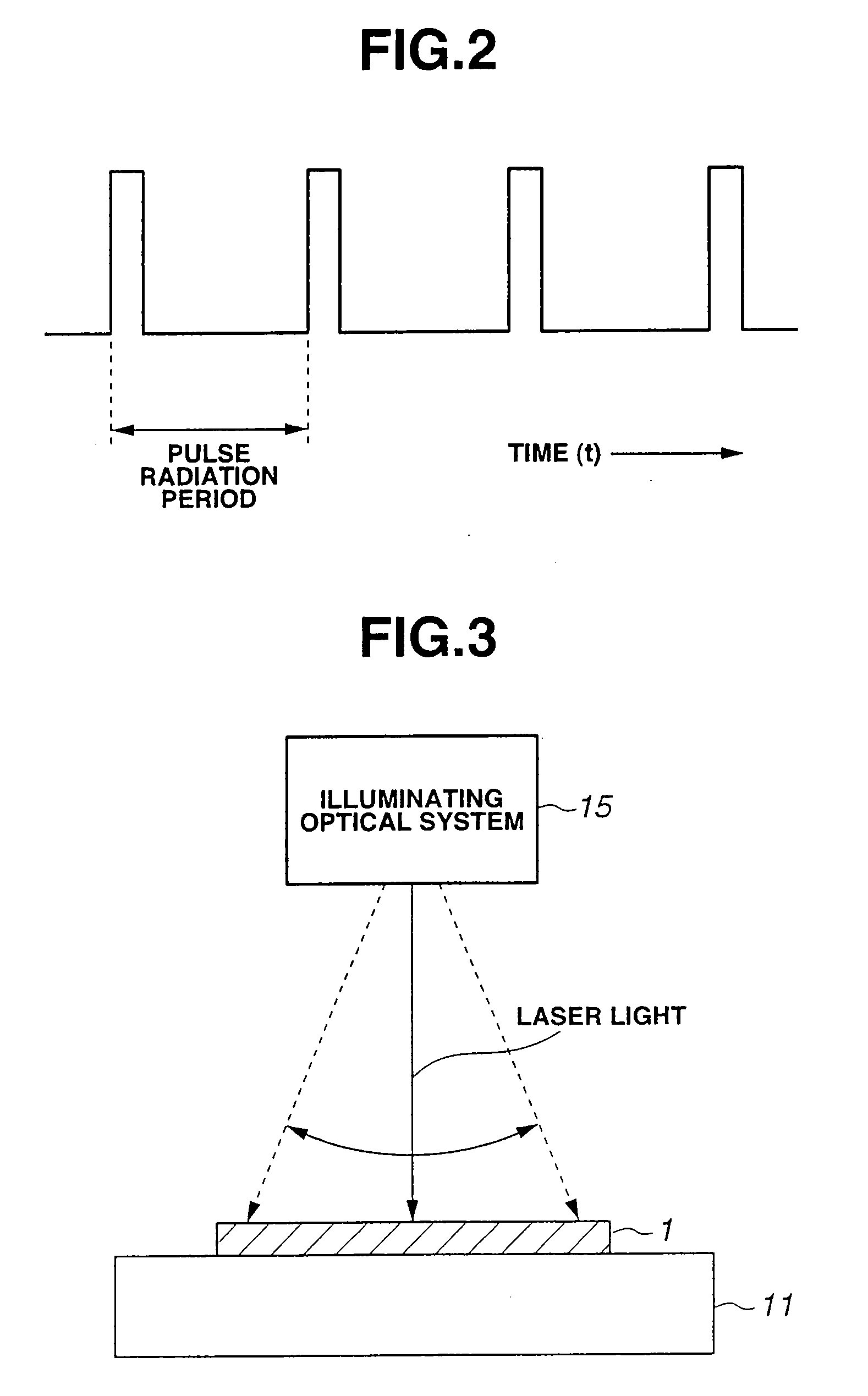
InactiveUS20070178674A1Increase in sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesReference PeriodAmorphous silicon
A laser annealing device (10) includes a laser oscillator (12), radiating a pulsed laser light beam of a preset period, and an illuminating optical system (15) for illuminating a pulsed laser light beam to an amorphous silicon film (1). The illuminating optical system (15) manages control for moving a laser spot so that a plural number of light pulses will be illuminated on the same location on the amorphous silicon film (1). The laser oscillator (12) radiates a laser light beam of a pulse generation period shorter than the reference period. The reference period is a time interval as from the radiation timing of illumination of a pulsed laser light beam on the surface of the film (1) until the timing of reversion of the substrate temperature raised due to the illumination of the laser light beam to the original substrate temperature.
Owner:SONY CORP
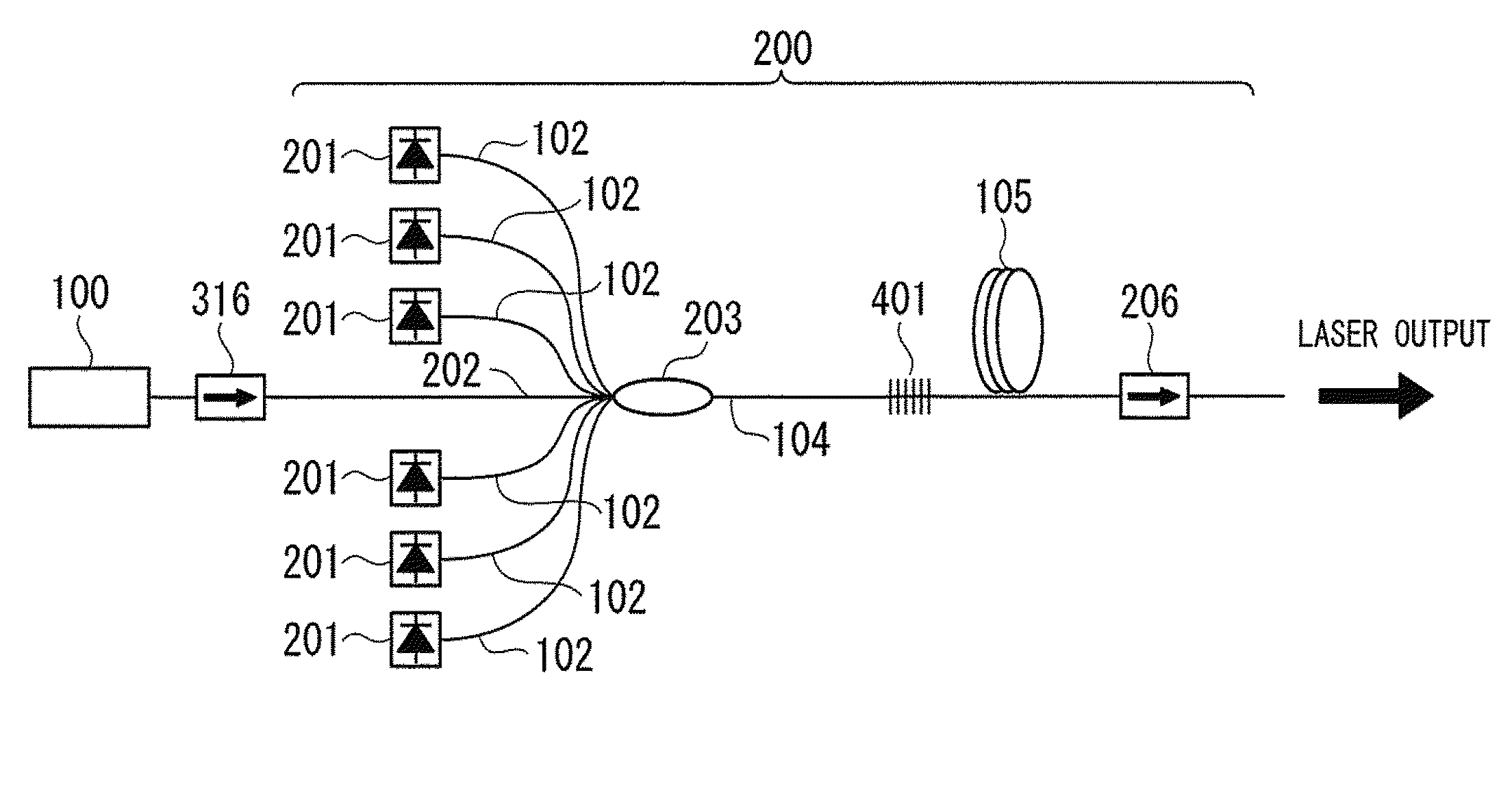
Fiber lasers
ActiveUS7778290B2Improve conversion efficiencyImprove abilitiesLaser using scattering effectsDouble-clad fiberPolarizer
Fiber lasers for producing Band I wavelengths include a laser cavity having an optical fiber with specific parameters in length and thickness and doping concentration, and having high reflectivities. Examples show the feasibility of producing such fiber lasers. Fiber lasers for producing Band IV wavelengths include a depolarized laser oscillator, at least one amplifier and a polarizer. Depolarized laser oscillator is an inherently depolarized CW laser, or a depolarized laser diode, which is depolarized by a depolarizer. Additional fiber lasers in accordance with embodiments of the present invention include a double clad active optical fiber having a pump power entry point for sending pump energy through the active optical fiber in a first direction, and a loop portion at a second end of the fiber for sending pump energy through the active optical fiber in a second direction which is opposite to the first direction. A system for coupling light into a fiber in accordance with embodiments of the present invention include a first fiber, a second double clad fiber, and a bulk optic component positioned between the first and second fibers. A mode stripper included within the second fiber allows for removal of high power light which is propagated through the outer clad rather than launched into the core of the second fiber.
Owner:ELBIT SYST ELECTRO OPTICS ELOP
Processing apparatus and method of processing and method of making leaf spring
InactiveUS20090103579A1Improve accuracyHigh precision machiningLaser detailsLaser beam welding apparatusVoltage regulationLight beam
A light source emits a laser beam to the object through an output end. An optical system is placed between the output end and the object. The optical system adjusts the energy of the laser beam emitted, through the output end, onto a unit area for a unit time. The energy of the beam spot on the object enables cutting or bending of the object. The optical system serves to adjust the energy of the laser beam irradiated to the object. The energy of the laser beam instantly changes as compared with the case where the energy of the laser beam is adjusted based on a driving voltage applied to a laser oscillator. The object is thus processed by using the laser beam with high accuracy.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for generation and amplification of light in a semi-guiding high aspect ratio core fiber
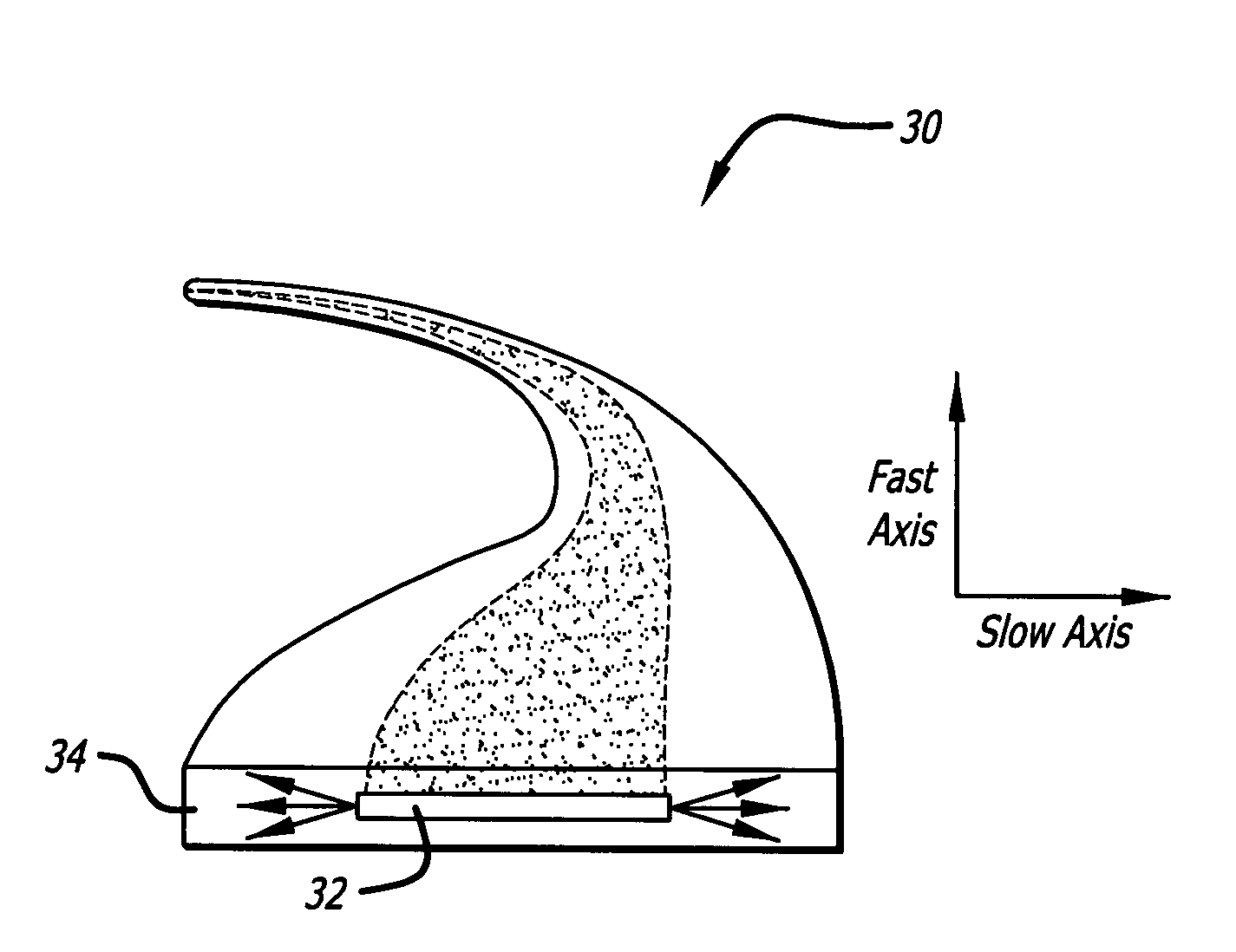
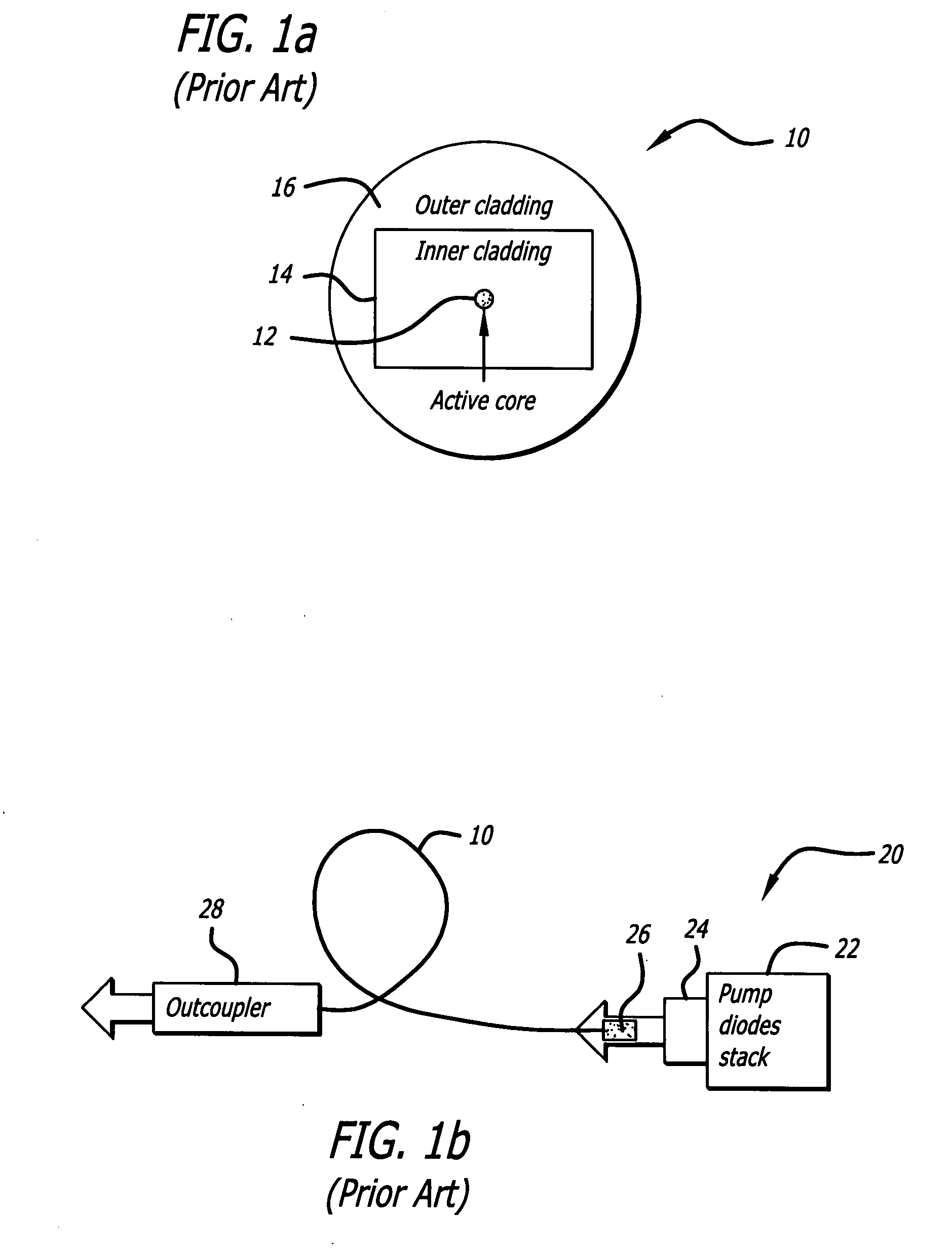
ActiveUS20090041061A1High aspect ratioHigh beam qualityGlass making apparatusLaser using scattering effectsFiberActive core
A planar laser gain medium and laser system. The novel laser gain medium includes an active core having a high aspect ratio cross-section with a fast-axis dimension and a slow-axis dimension, signal claddings adapted to form reflective boundaries at fast-axis boundaries of the core, and a material adapted to minimize reflections at slow-axis boundaries of the core. In an illustrative embodiment, the laser gain medium is an optical fiber. The core and claddings form a waveguide adapted to control modes propagating in the fast-axis direction. When the laser gain medium is employed as a laser oscillator, a high reflectivity mirror and an outcoupler are positioned at opposite ends of the core to form a laser resonator adapted to control modes in the slow-axis direction.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
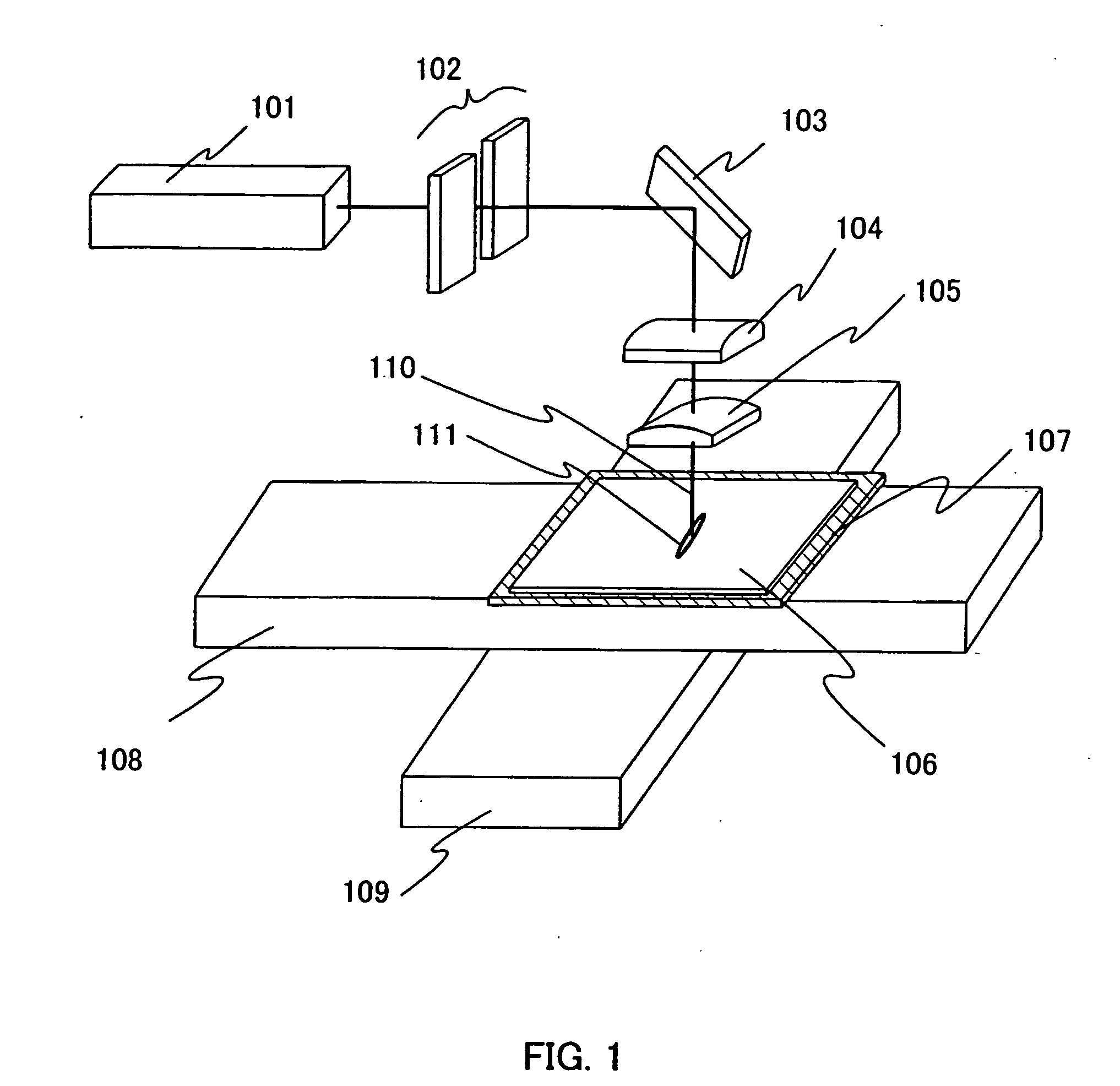
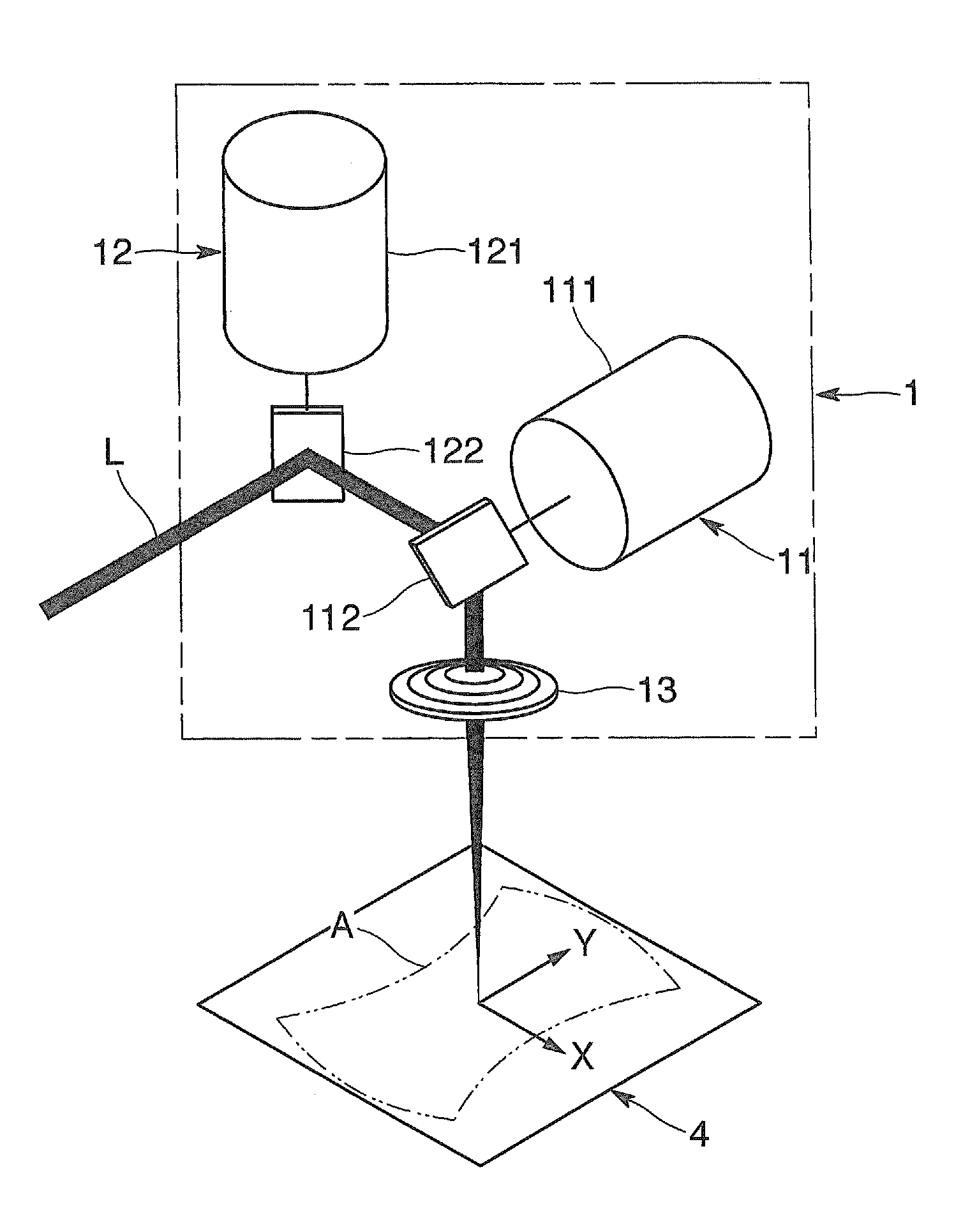
Laser irradiation stage, laser irradiation optical system, laser irradiation apparatus, laser irradiation method, and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6707614B2Shorten the lengthSmall footprintTransistorSemiconductor laser arrangementsLight beamOptical pathlength
As the output of laser oscillators become higher, it becomes necessary to develop a longer linear shape beam for a process of laser annealing of a semiconductor film. However, if the length of the linear shape beam is from 300 to 1000 mm, or greater, then the optical path length of an optical system for forming the linear shape beam becomes very long, thereby increasing its footprint size. The present invention shortens the optical path length. In order to make the optical path length of the optical system as short as possible, and to increase only the length of the linear shape beam, curvature may be given to the semiconductor film in the longitudinal direction of the linear shape beam. For example, if the size of the linear shape beam is taken as 1 mx0.4 mm, then it is necessary for the optical path length of the optical system to be on the order of 10 m. If, however, the semiconductor film is given curvature with a radius of curvature of 40,000 mm, then the optical path length of the optical system can be halved to approximately 5 m, and a linear shape beam having an extremely uniform energy distribution can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Laser irradiation apparatus and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050237895A1Improve throughputSimple processLaser detailsFilamentary/web record carriersOptoelectronicsIrradiation
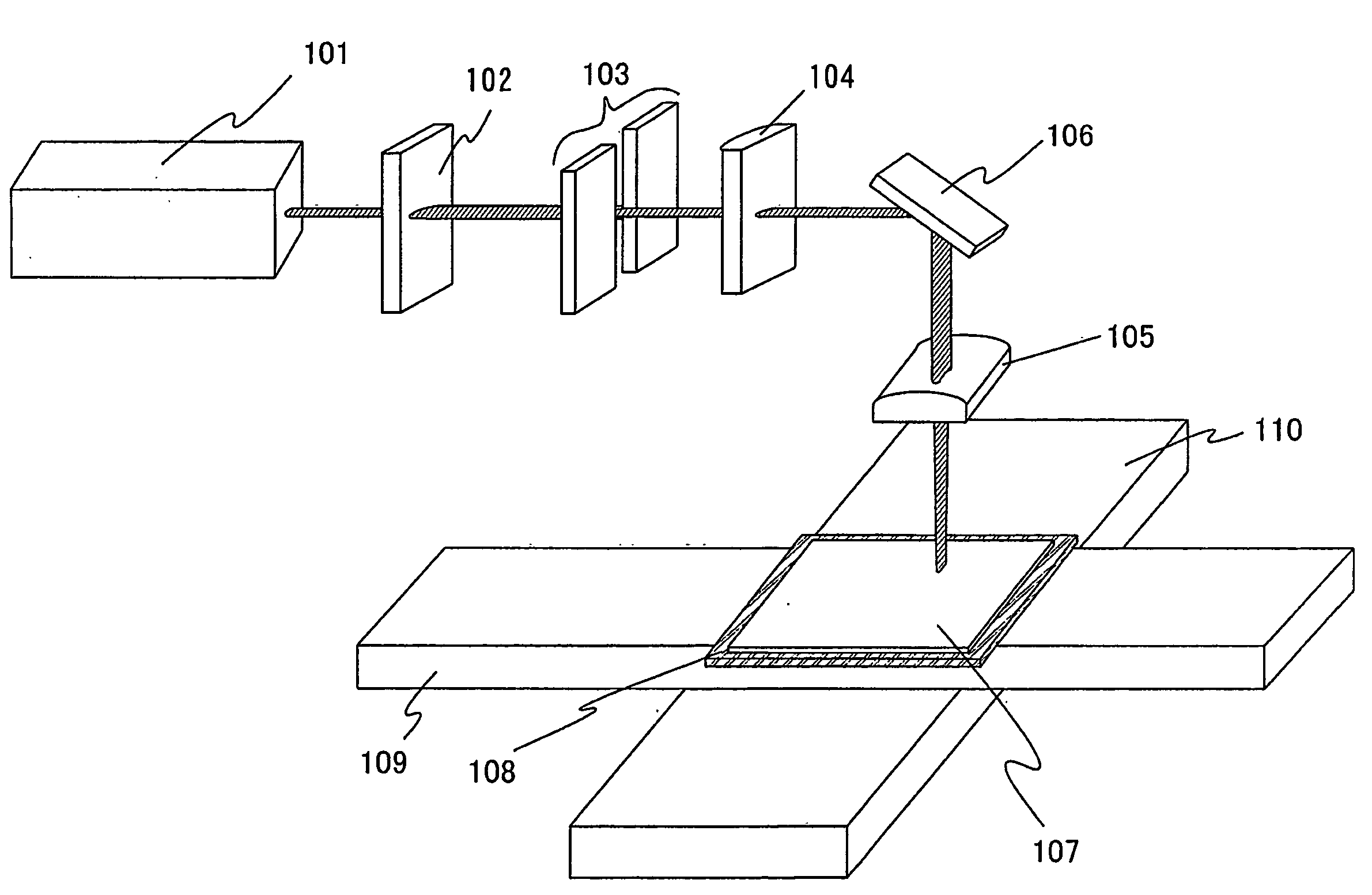
It is an object of the present invention to provide a laser irradiation apparatus being able to irradiate the irradiation object with the laser beam having homogeneous energy density without complicating the optical system. The laser irradiation apparatus of the present invention comprises a laser oscillator, an optical system for scanning repeatedly a beam spot of the laser beam emitted from the laser oscillator in a uniaxial direction over the surface of the irradiation object, and a position controlling means for moving the position of the irradiation object relative to the laser beam in a direction perpendicular to the uniaxial direction.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
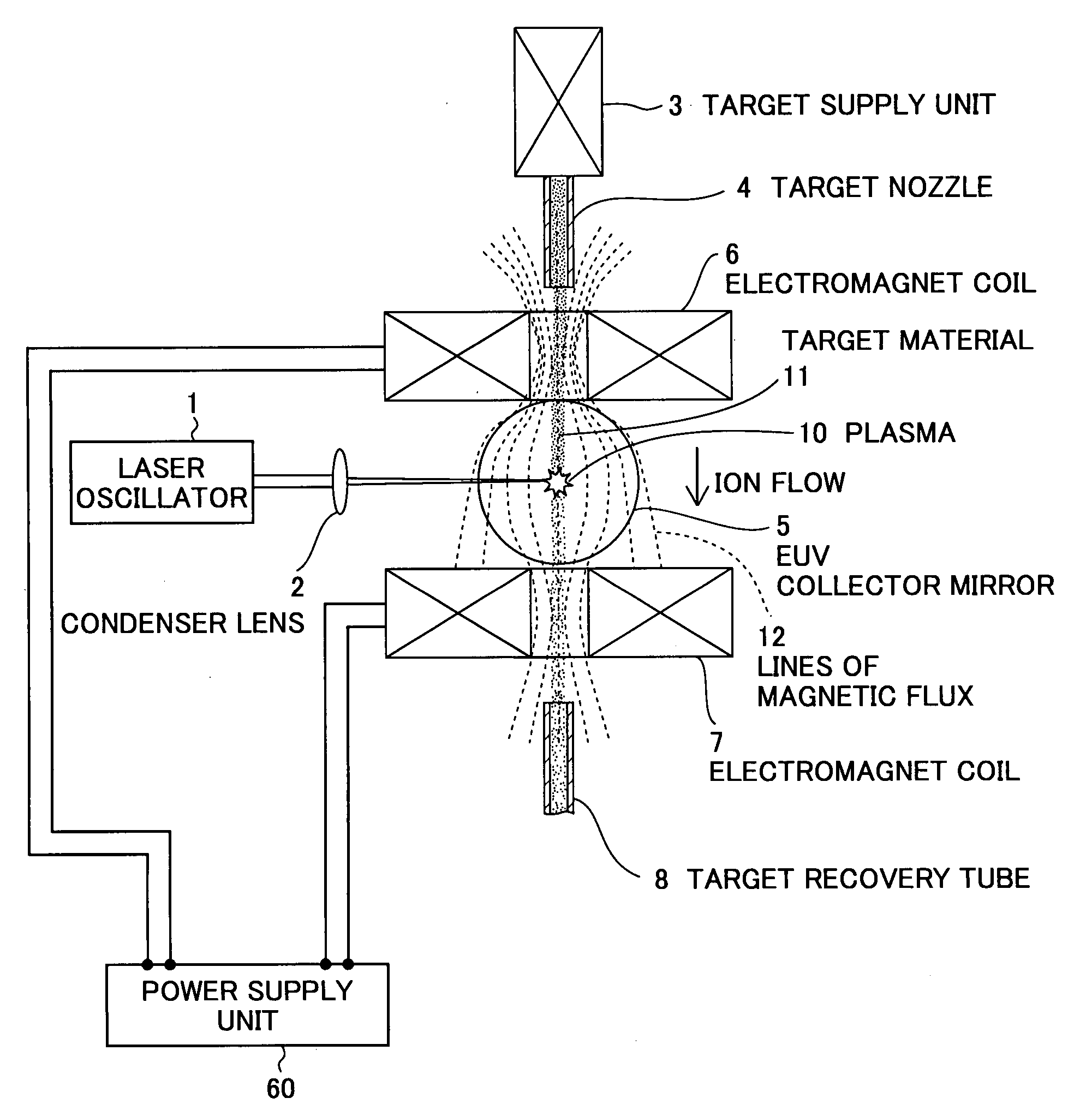
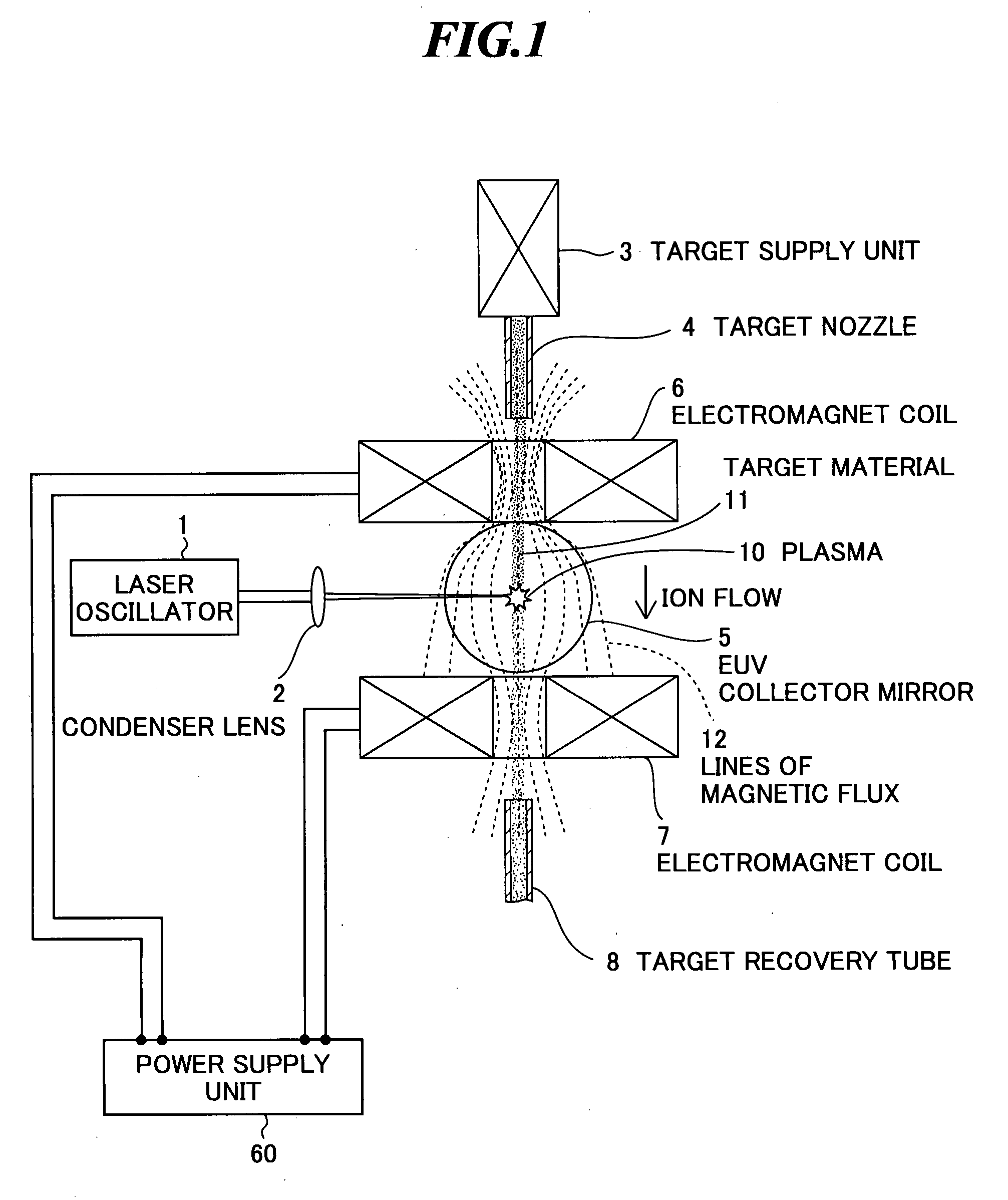
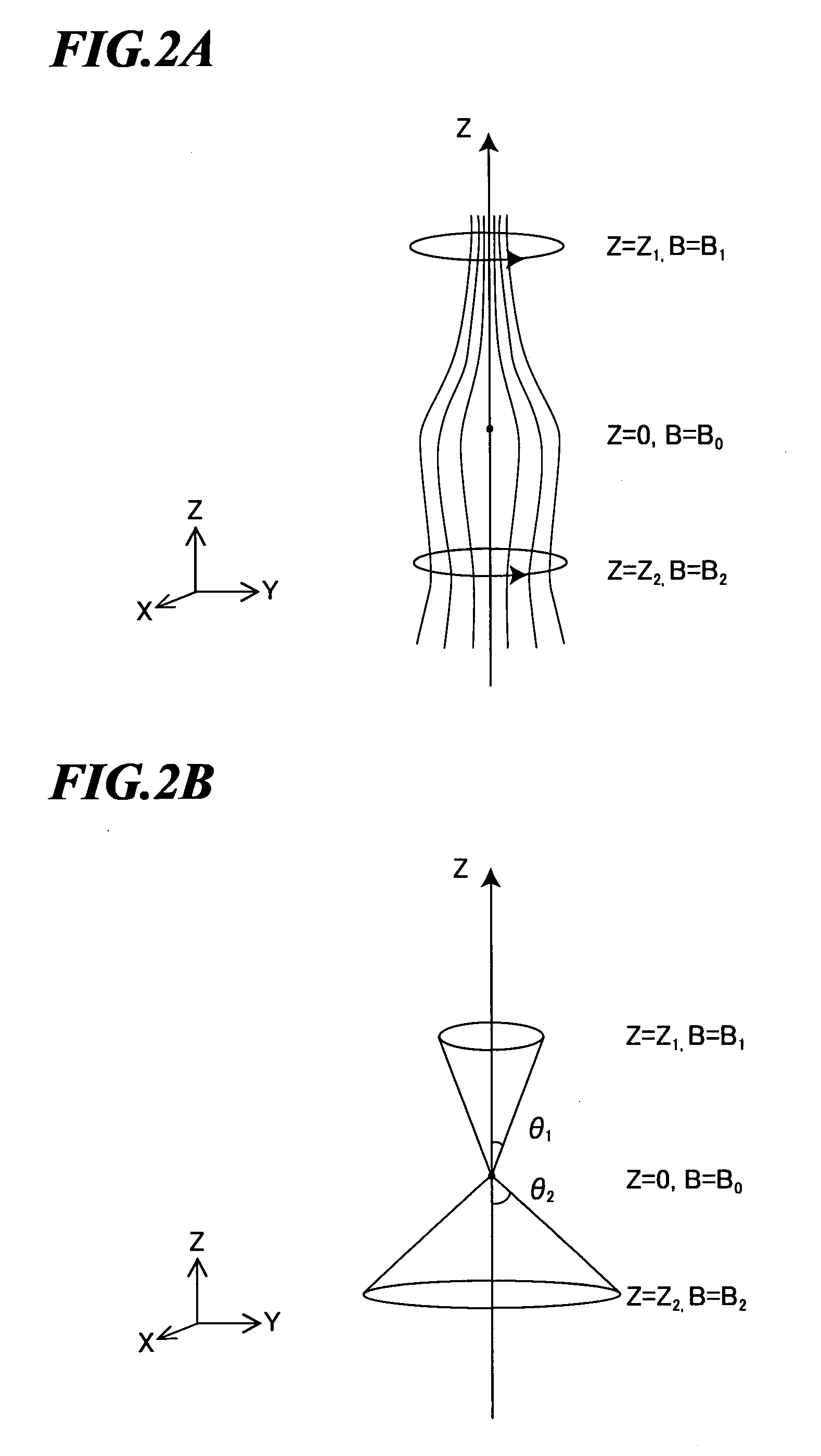
Extreme ultra violet light source device
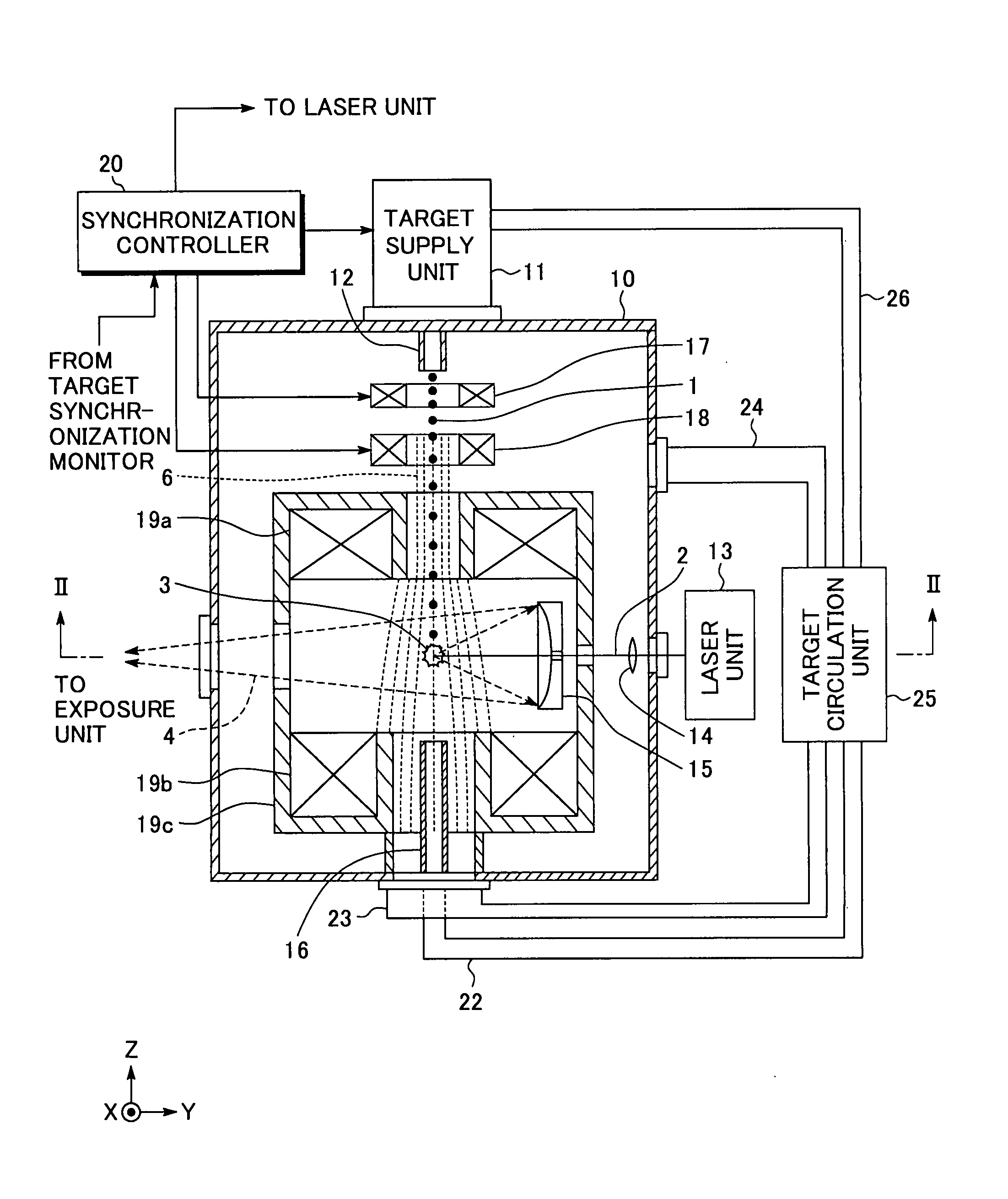
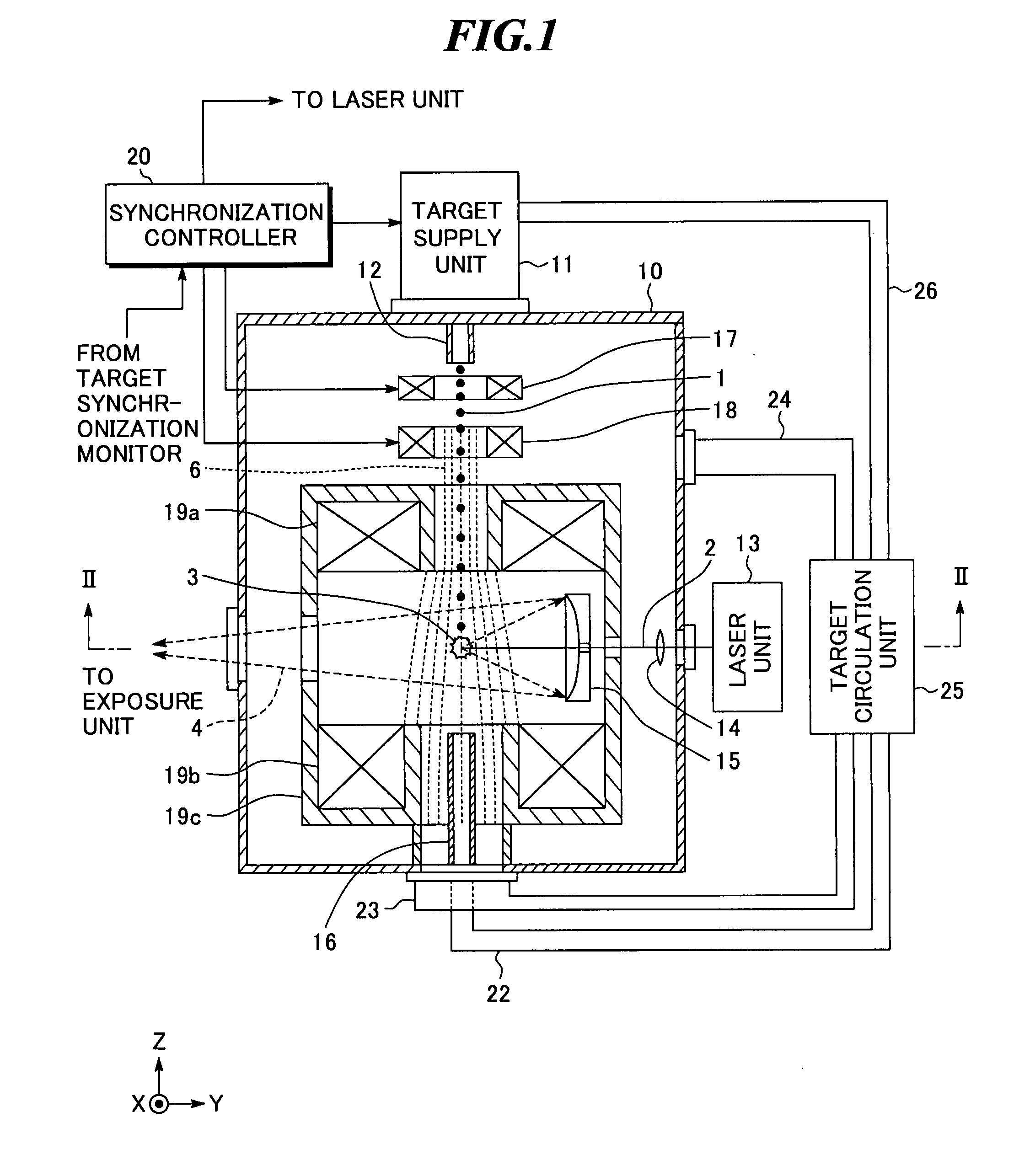
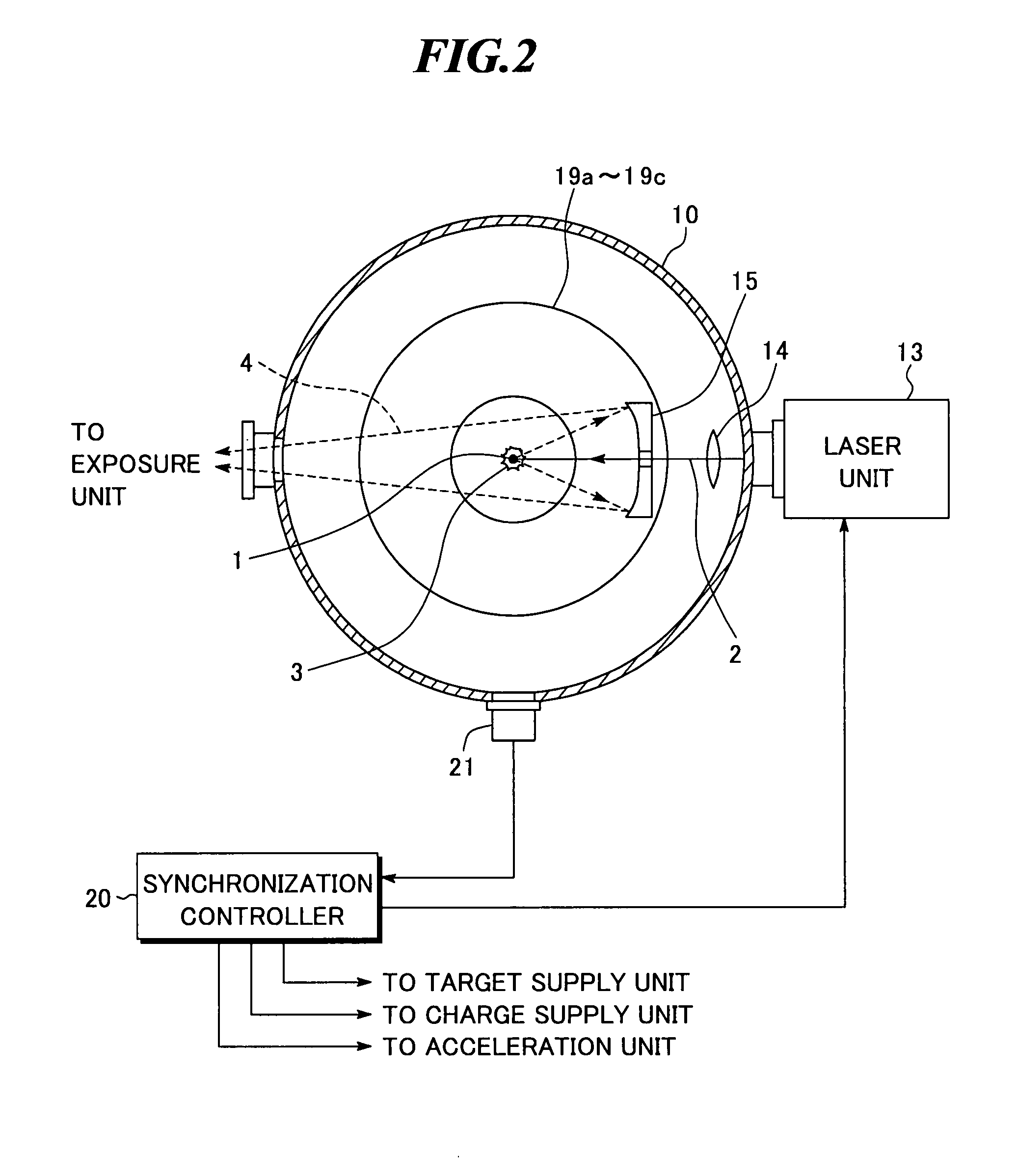
InactiveUS20080035865A1Increase speedAvoid changeRadiation pyrometryLight therapyMagnetic fluxAtomic physics
An extreme ultra violet light source apparatus in which both a mechanism of supplying a droplet target to a laser application position at a high speed and a mechanism of trapping charged particles generated from plasma are managed without disturbing a track of the target. The apparatus includes: a target nozzle that injects a target material toward a plasma generation point; an electric charge supply unit that charges the injected target material; an acceleration unit that accelerates the charged target material; a laser oscillator that applies a laser beam to the target material at the plasma generation point to generate plasma; and electromagnets that form a magnetic field at the plasma generation point such that the magnetic field has substantially straight lines of magnetic flux in substantially parallel with a traveling direction of the target material in the track of the target material.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
Fiber laser
InactiveUS8279899B2Prevent degradationReduce peak powerLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionSelf-oscillationPeak value
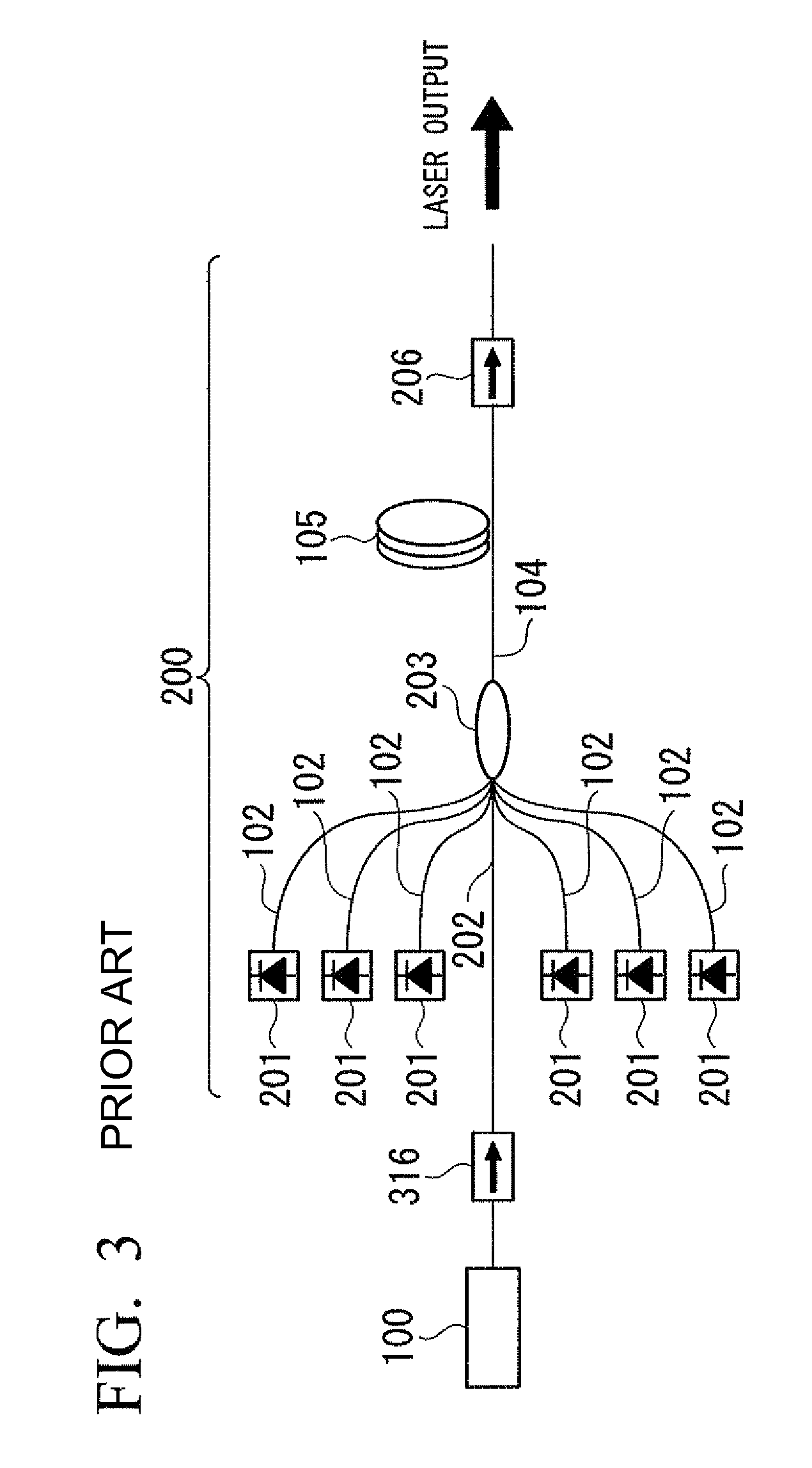
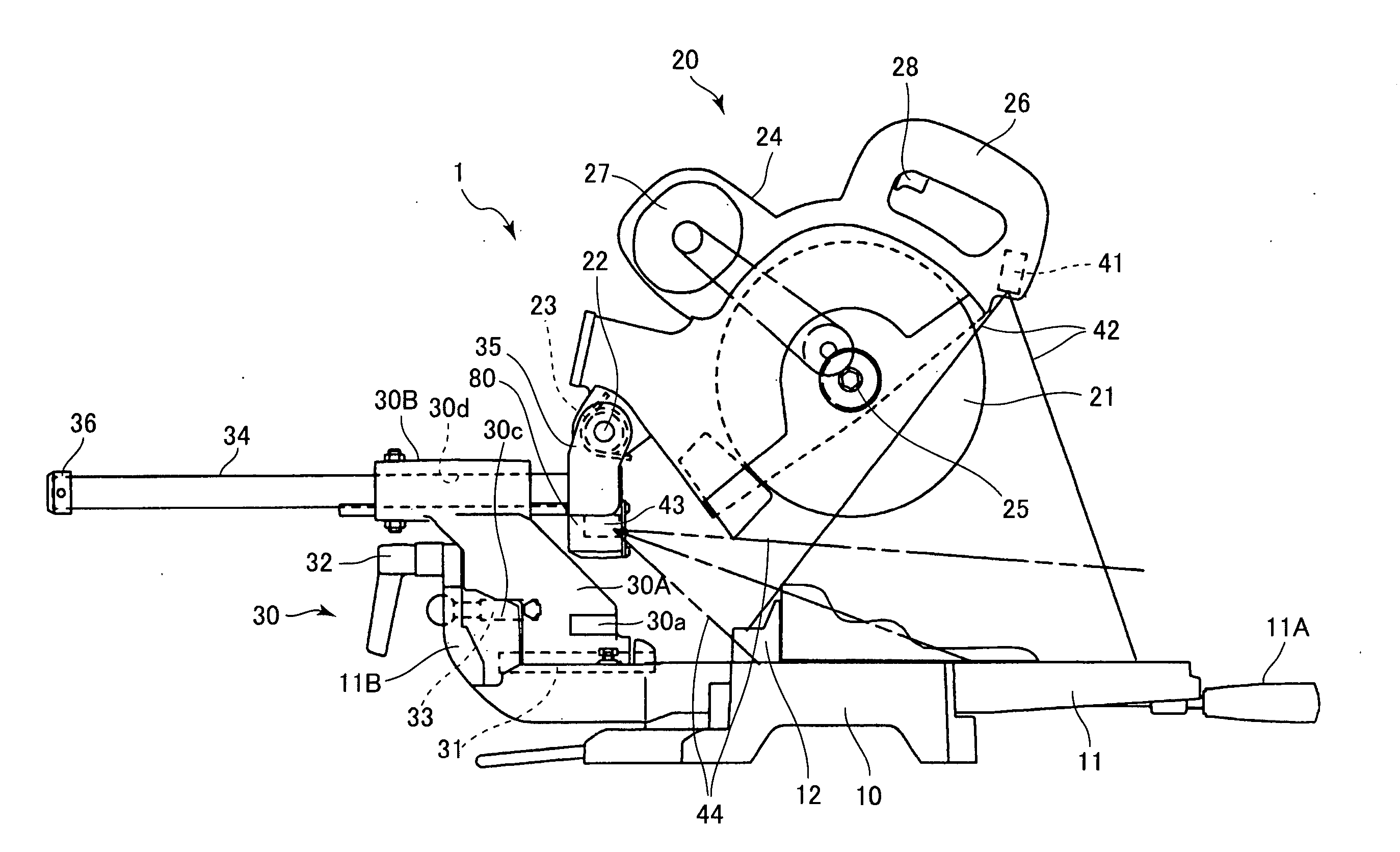
A fiber laser of an MOPA type includes an MO which is a laser oscillator for generating seed light, a PA which is a light amplifier connected to a rear stage of the MO, for amplifying and outputting laser light emitted from the MO, and a reflection device which is provided between the MO and the PA. According to the present invention, the MOPA type fiber laser can decrease the peak value of the pulse which is emitted toward the MO or the pump light source by self-oscillation or reflection, and makes it unlikely that the pump light source or the MO will be damaged.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
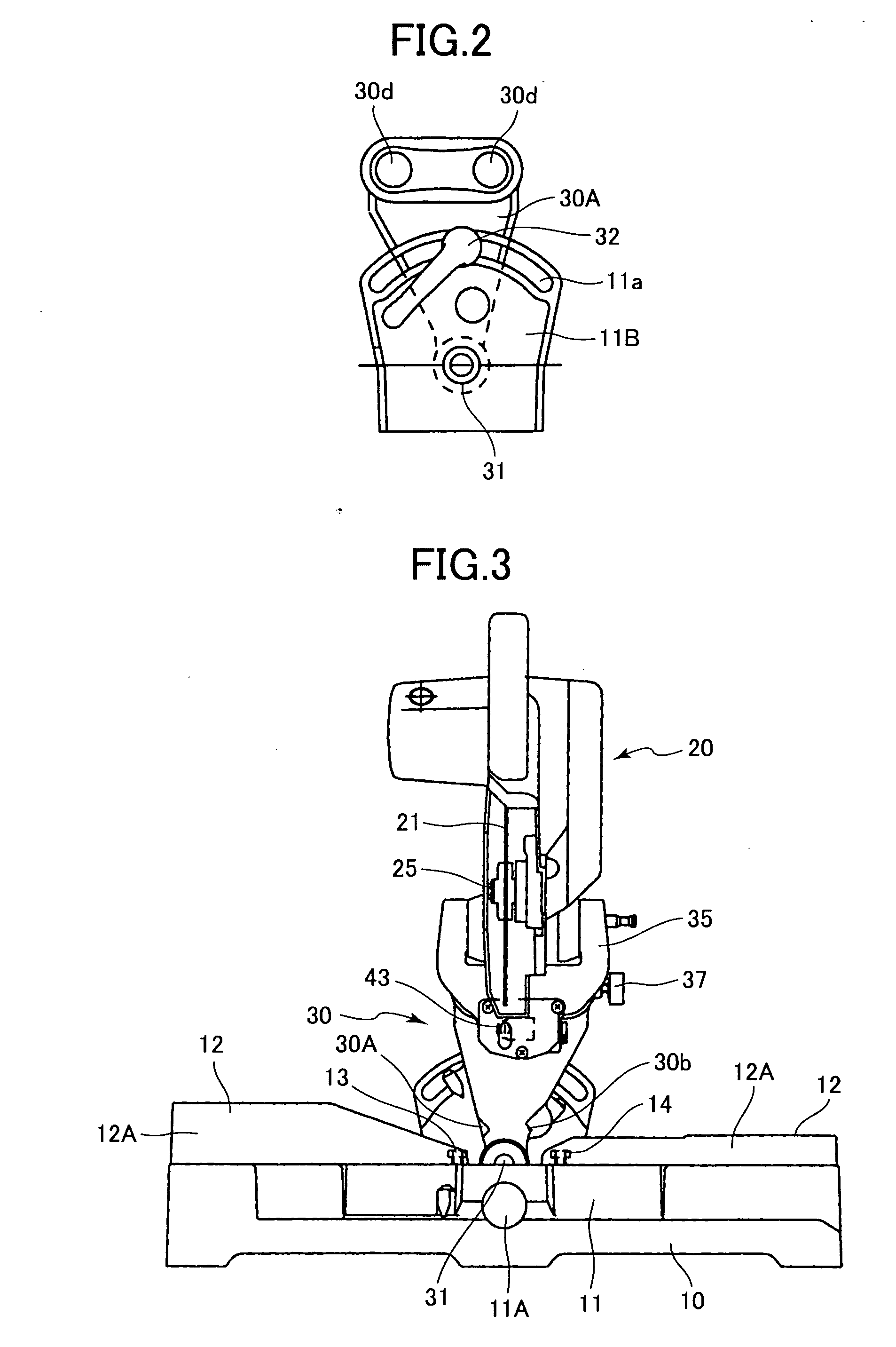
Miter saw having two laser oscillators
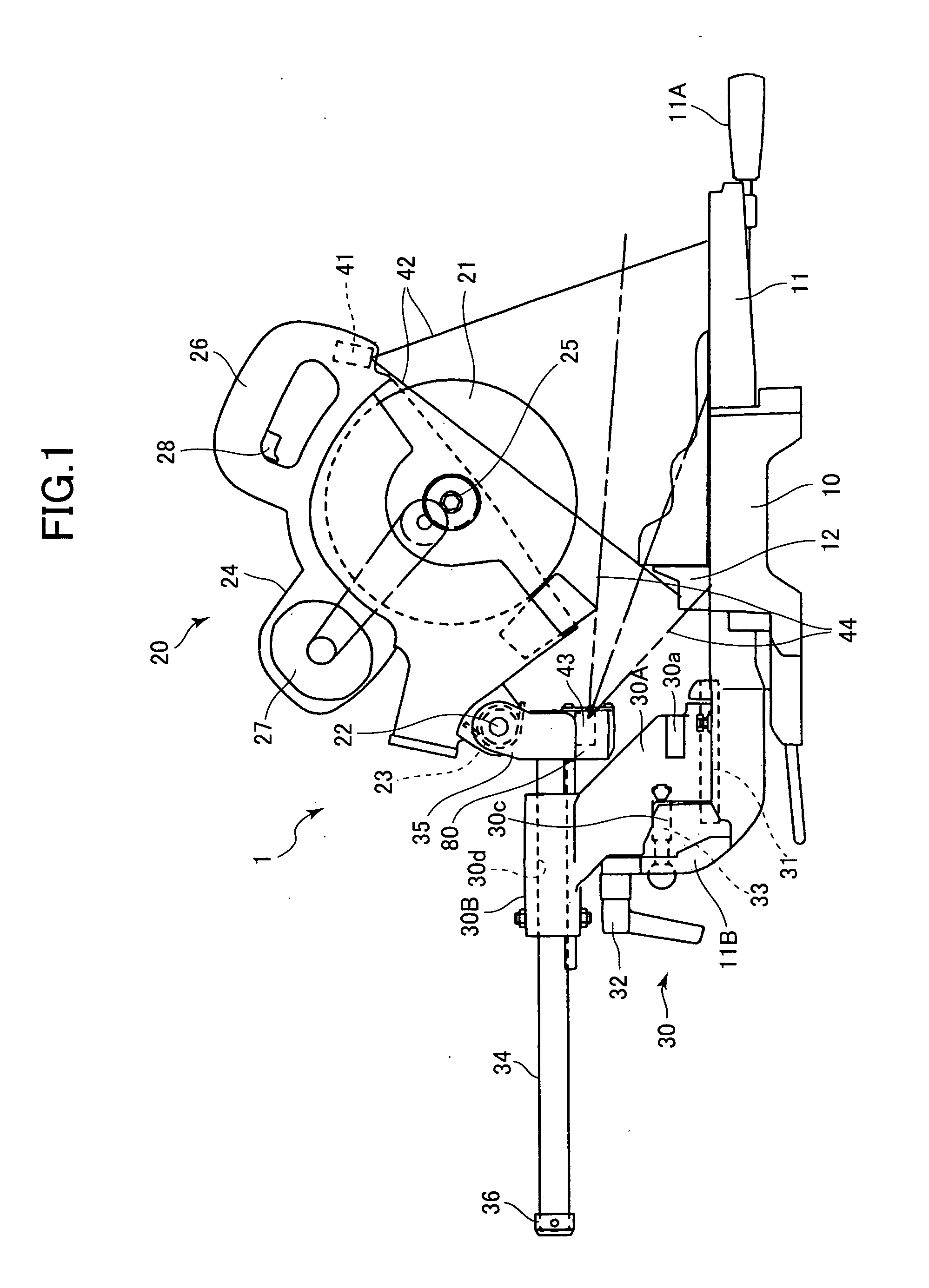
InactiveUS20060042444A1Clear projectionMetal sawing accessoriesMetal working apparatusCircular sawEngineering
A miter saw having first and second laser oscillators. A base is provided for mounting a worpiece. A fence extends in a lateral direction and is fixed to the base and has a front surface to which the workpiece is to be abutted. A cutting unit rotatably supports a circular saw blade. A support section is supported on the base and is pivotably supports the cutting unit movable toward and away from the base. The first laser oscillator is provided at the base for irradiating a first laser beam to the front side of the workpiece. The second laser oscillator is provided at the support section for irradiating a second laser beam to a rear side of the workpiece.
Owner:HITACHI KOKI CO LTD
Extreme ultra violet light source device
ActiveUS20070228298A1Efficiently ejectedImprove concentrationRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsExtreme ultravioletMaterial supply
An extreme ultra violet light source device of a laser produced plasma type, in which charged particles such as ions emitted from plasma can be efficiently ejected. The extreme ultra violet light source device includes: a target nozzle that supplies a target material; a laser oscillator that applies a laser beam to the target material supplied from the target nozzle to generate plasma; collector optics that collects extreme ultra violet light radiated from the plasma; and a magnetic field forming unit that forms an asymmetric magnetic field in a position where the laser beam is applied to the target material.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
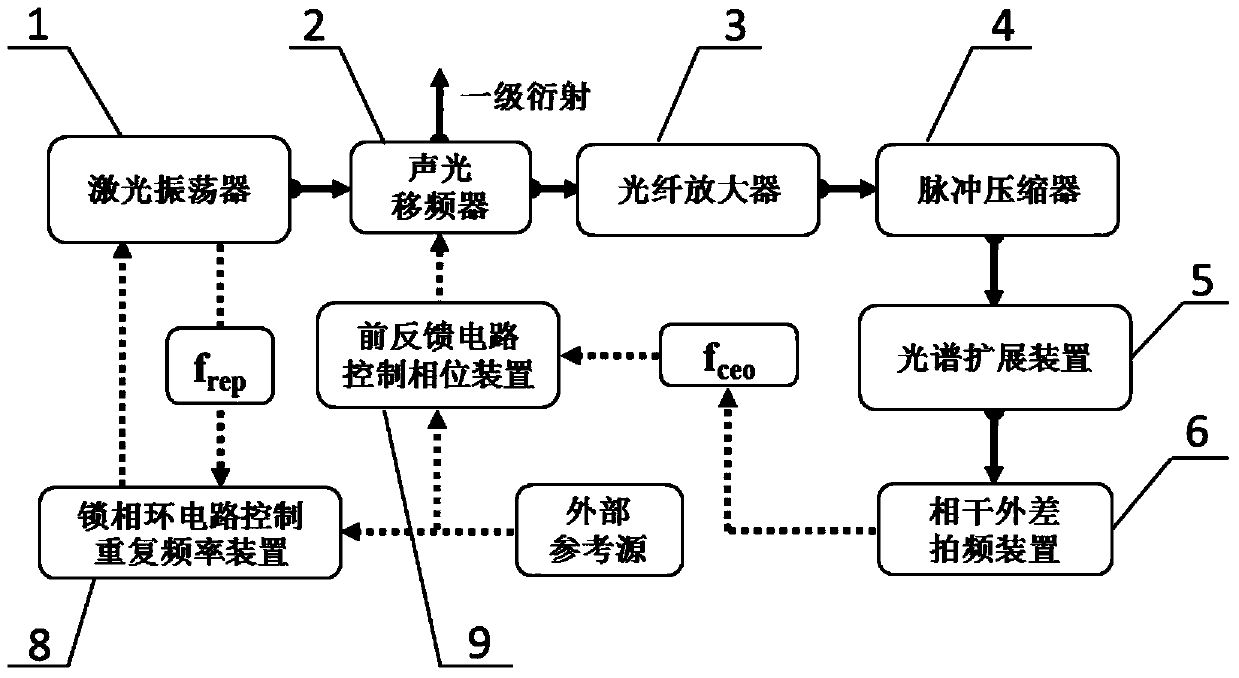
Low noise fiber laser frequency combs device with controllable carrier envelope phase shift frequency
ActiveCN103633537AImprove stabilityCarrier envelope phase shift frequency precise controlOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionLow noisePhase locked loop circuit
The application provides a low noise fiber laser frequency combs device with controllable carrier envelope phase shift frequency. The low noise fiber laser frequency combs device with controllable carrier envelope phase shift frequency comprises an optical path structure and a circuit structure, wherein the optical path structure comprises an oscillator, an acousto-optic frequency shifter, an optical fiber amplifier, a pulse compressor, an optical fiber spread spectrum device and a coherent heterodyne beat device; and the circuit structure comprises a feed-forward circuit control phase device and a phase-locked loop circuit control repetition frequency device. The fiber laser oscillator can ensure long-time operation of a system, so that the stability of the system is superior to that of a system adopting a solid laser oscillator; through the technologies of optimizing intracavity net dispersion of the fiber oscillator, introducing an inner cavity modulator in the oscillator, adopting the feed-forward acousto-optic frequency shifter, and the like, the low noise fiber laser frequency combs device can be realized; and meanwhile, due to the application of the acousto-optic frequency shifter, the carrier envelope phase shift frequency of the optical frequency combs can be accurately regulated, so that the optical frequency combs device with precise phase position regulation and secular stability is provided for realizing applications such as optical frequency standard, attosecond science and non-linear optics.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser processing machine
ActiveUS20130186871A1Solve precise positioningCalibration can be slowLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingOptical axis
A processing machine includes mirrors and to reflect a beam L oscillated from a laser oscillator to a predetermined surface on which a workpiece is arranged, optical axis operating mechanisms and to position an optical axis of the beam L at a desired target irradiation position by changing directions of the mirrors and, a camera sensor to capture an image of the target irradiation position and its periphery reflected in the mirror, and an error calibration mechanism to detect an error between the target irradiation position instructed to the optical axis operating mechanisms and an actual position of the optical axis of the beam L in the predetermined surface by referring to the image captured by the camera sensor. A correction amount to the optical axis operating mechanisms and is determined based on the error to irradiate the target irradiation position with the beam L during processing.
Owner:KATAOKA
Method of and apparatus for machining groove with laser beam
A casing houses therein a laser oscillator for emitting a laser beam, and a tubular head is disposed coaxially with the laser oscillator and coupled to the casing. The laser beam emitted from the laser oscillator is converged by a condenser lens mounted on the head, and then reflected in a direction substantially perpendicular to the axis of the head by a reflecting mirror that is disposed in the head. The reflected laser beam is applied substantially perpendicular to the inner circumferential surface of a workpiece, forming grooves therein with the heat of the laser beam.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Semiconductor thin film crystallization device and semiconductor thin film crystallization method
InactiveUS20060019474A1Flat surfaceFew defectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSemiconductor thin films
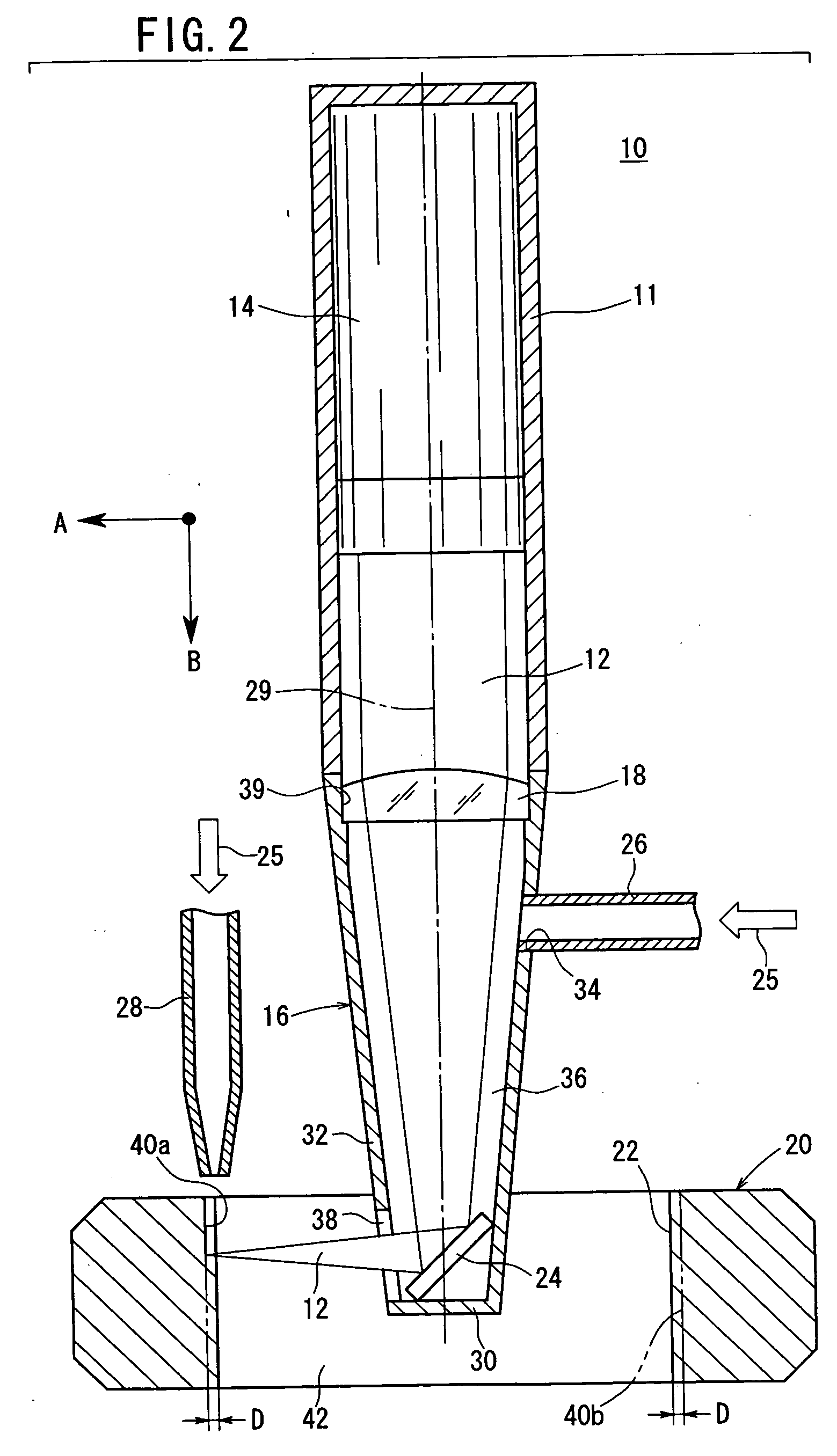
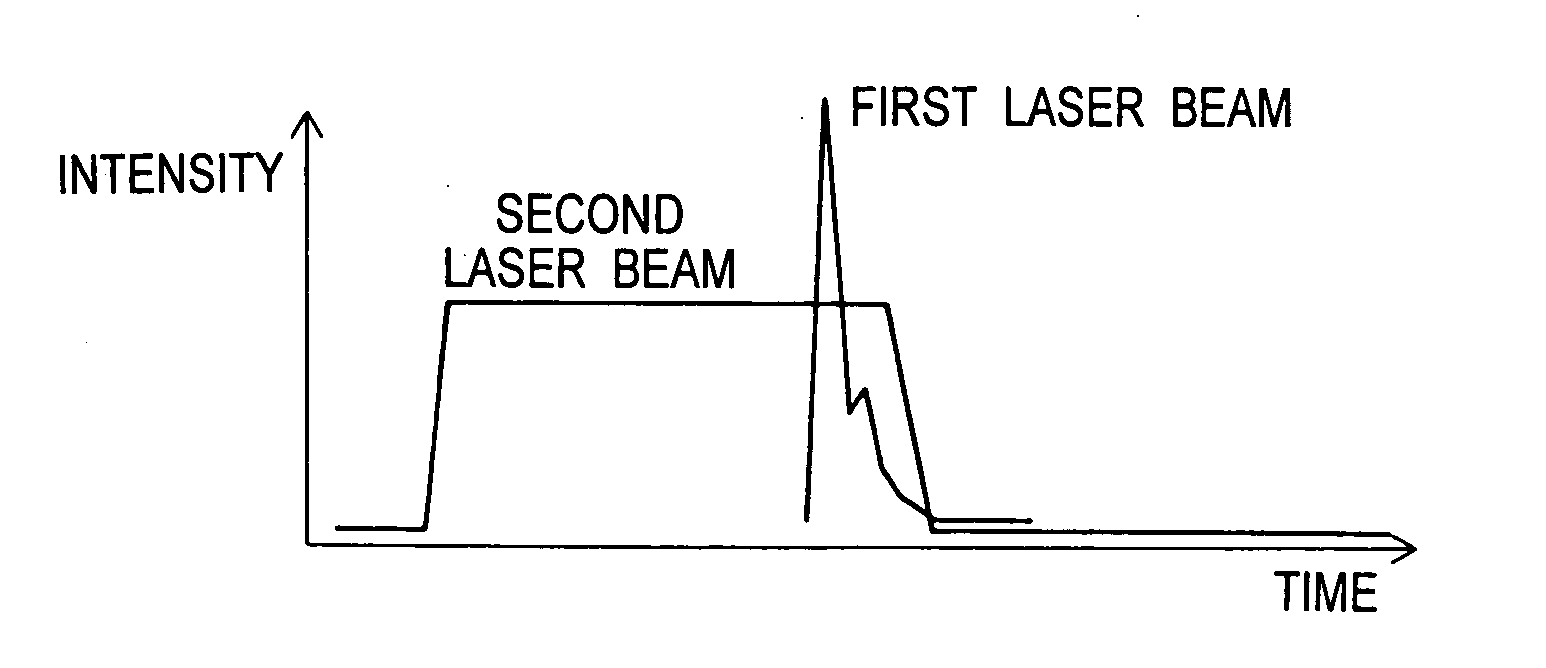
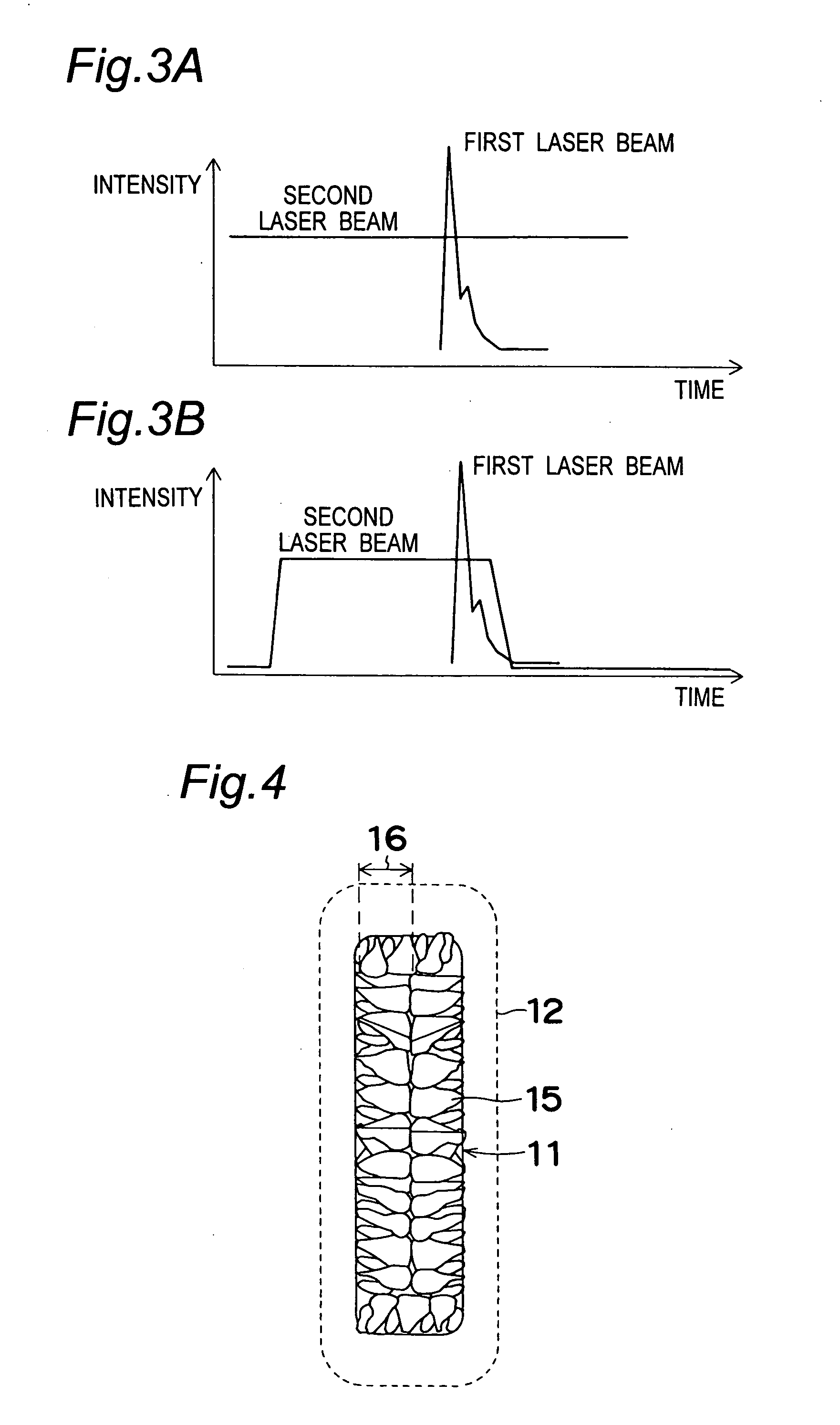
A first laser beam is emitted from a first laser oscillator in a pulsed manner at a high repetition frequency, and converged onto a substrate by a first intermediate optical system 2 so as to form a slit-like first beam spot. A second laser beam is emitted from a second laser beam oscillator in a pulsed manner to rise precedent to and fall subsequent to the first laser beam, and converged onto the substrate by a second intermediate optical system so as to form a second beam spot similar in configuration to the first beam spot and to contain the first beam spot. Crystallization of a semiconductor thin film on the substrate is carried out while the substrate or the first, second beam spots are moved. Thereby, the whole semiconductor thin film is formed into a crystal surface that has grown in one direction and free from ridges. Thus, the semiconductor thin film has an extremely flat surface, extremely few defects, large crystal grains and high throughput.
Owner:SHARP KK
Laser processor and laser processing method
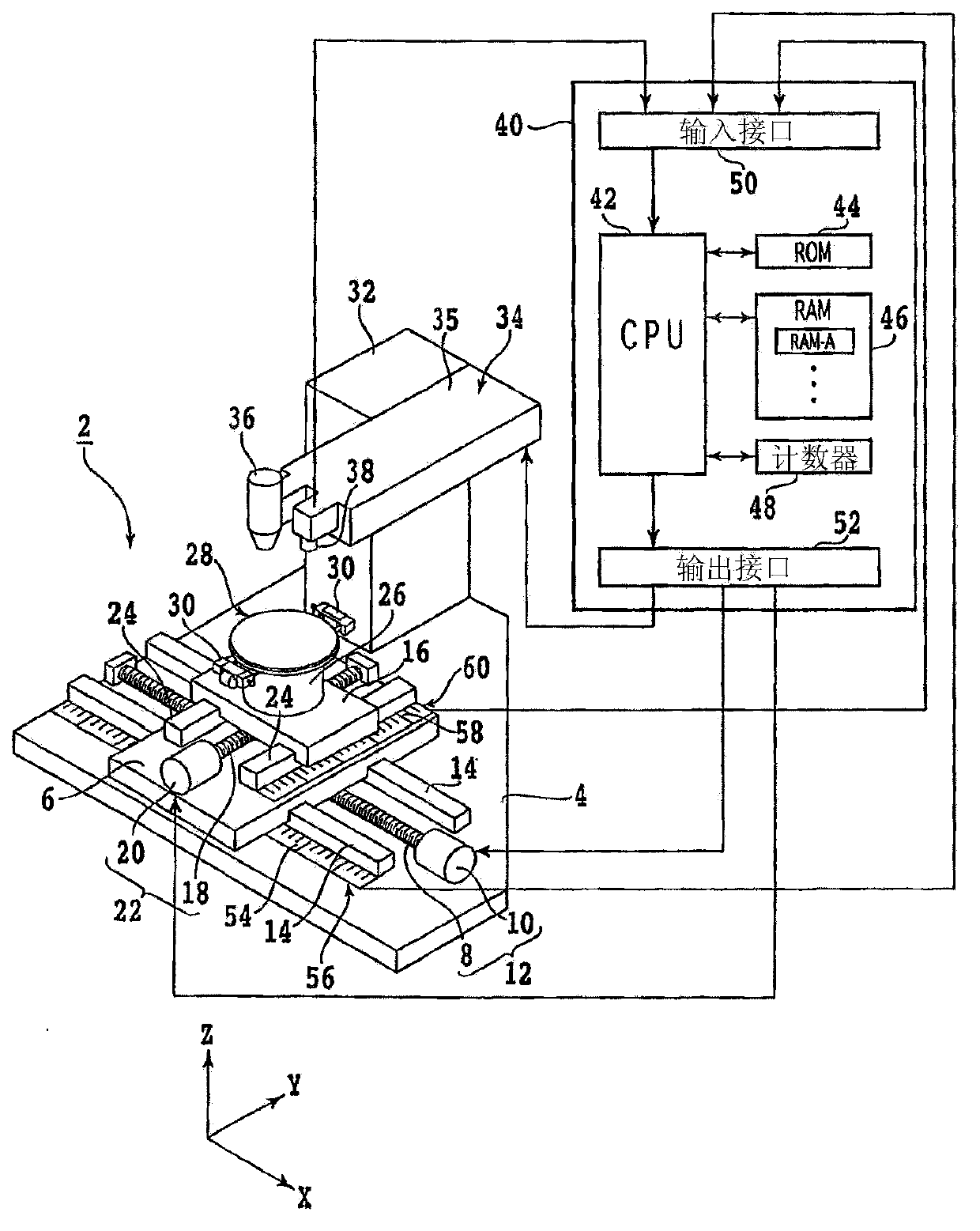
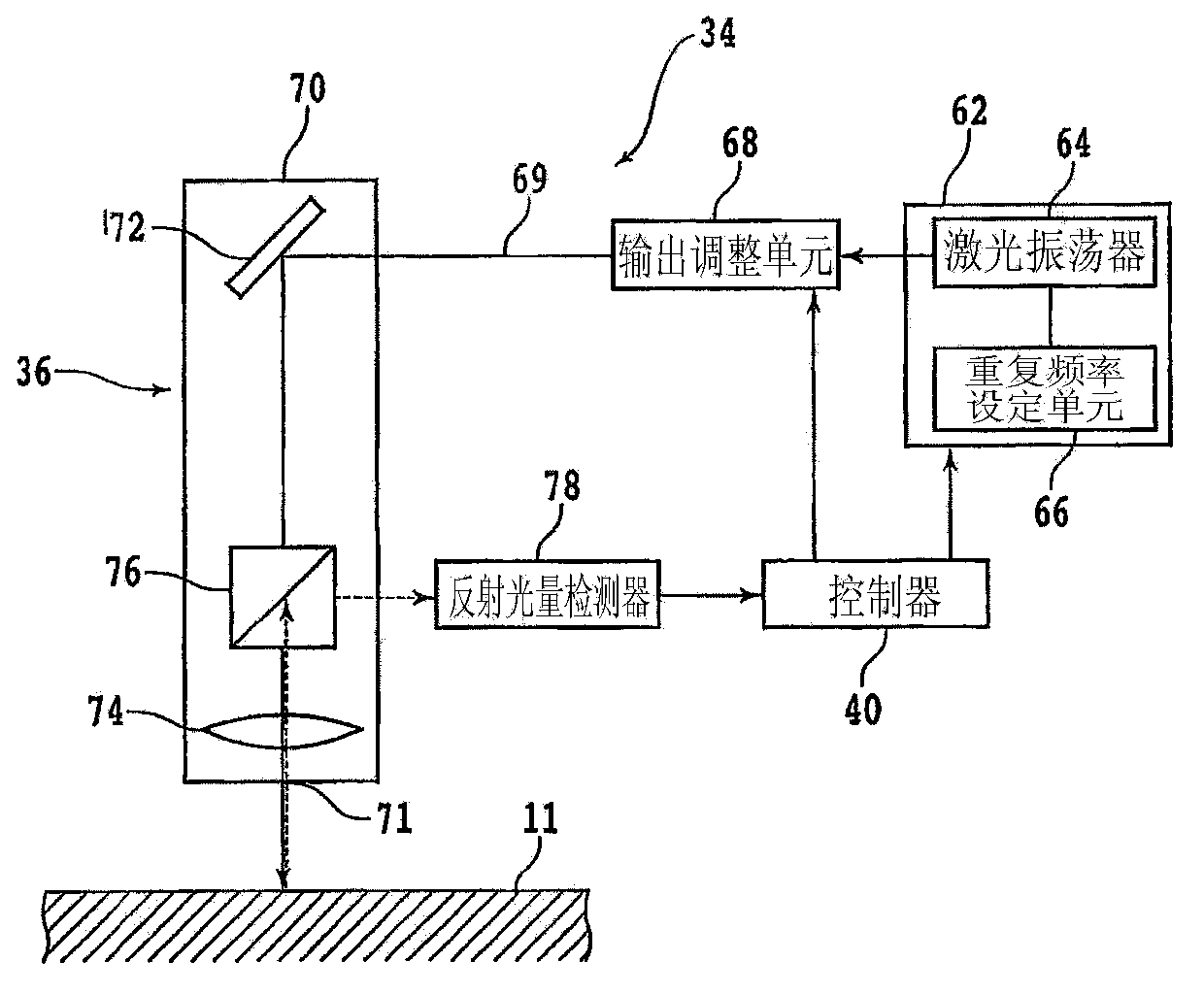
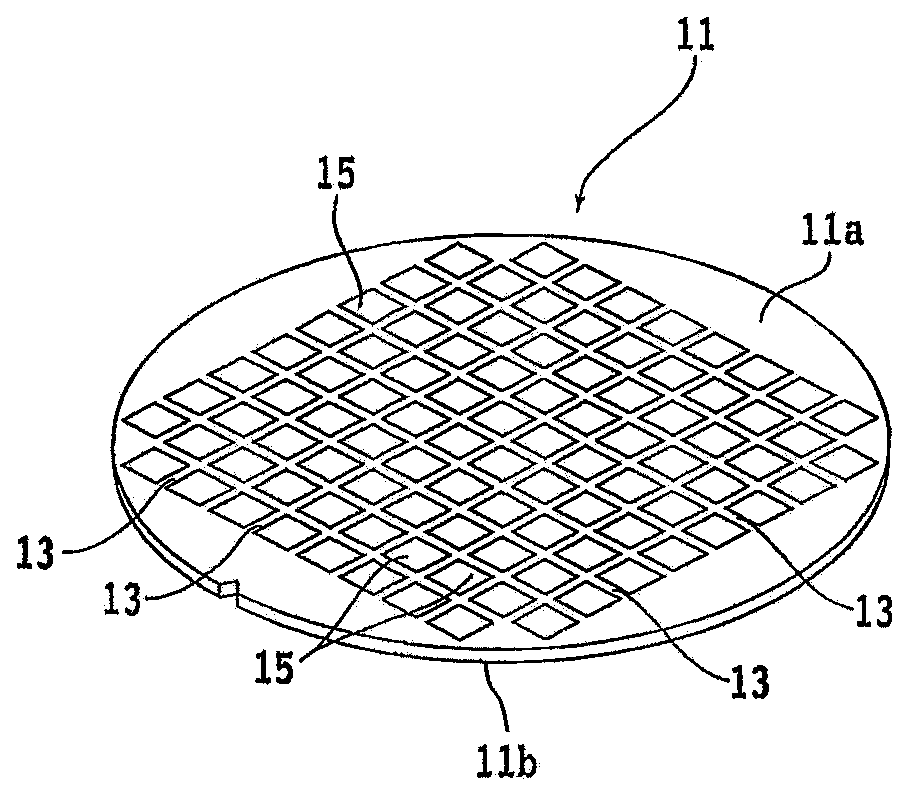
ActiveCN103372720AUniform laser processingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesLaser processingLight beam
The invention provides a laser processor and a laser processing method, and uniform laser processing can be done whatever the laser irradiated surface state of a processed object is. The laser processor that applies laser processing to the processed object is characterized in comprising a chunk table that holds the processed object; a laser beam irradiation member that includes a laser oscillator and a processing head, wherein the processing head a condenser lens that condenses laser beam oscillated by the laser oscillator; a reflected light amount detection member that detects reflected light amount of the laser beam that is irradiated from the laser beam irradiation member to the processed object held on the chunk table; and an output adjusting member that adjusts output of the laser beam oscillated by the laser oscillator based on the reflected light amount detected by the reflected light amount detection member.
Owner:DISCO CORP
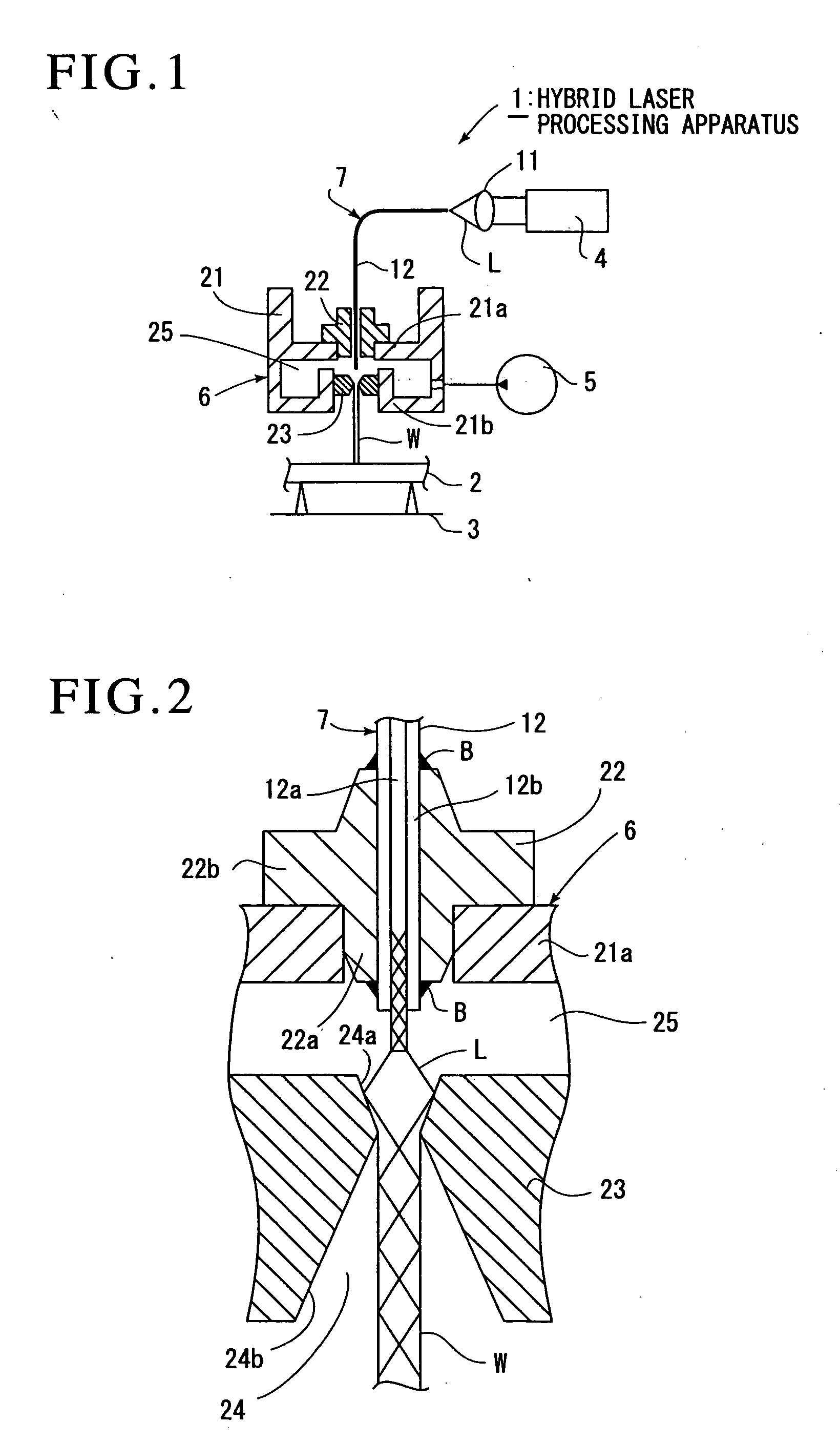
Hybrid Laser Processing Apparatus
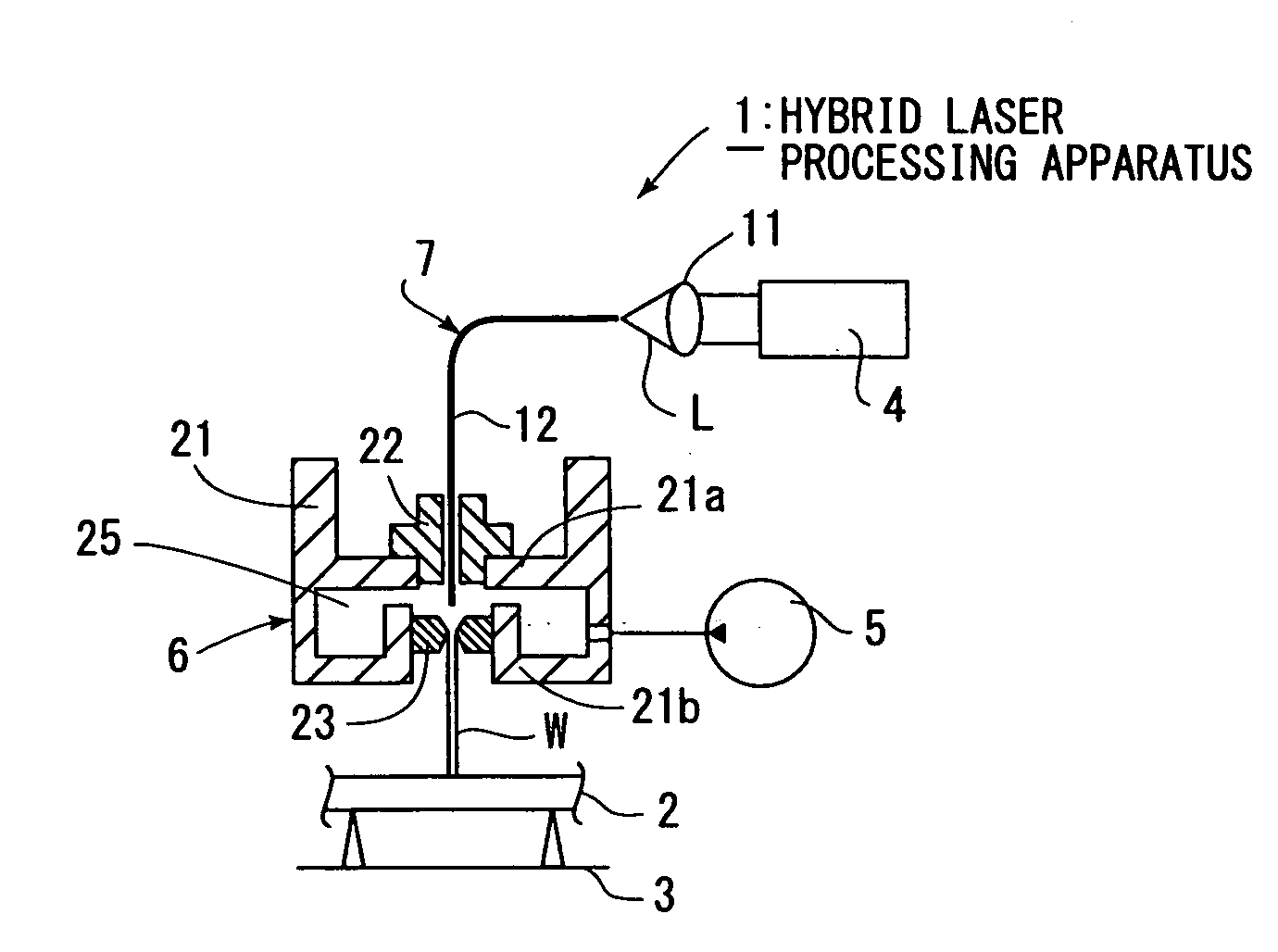
InactiveUS20090045177A1Easy to adjustEasily be guidedMetal working apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusFiberLaser processing
Laser beam L oscillated by a laser oscillator 4 is guided by an optical fiber 12 constituting laser-guiding means 7 to a processing head 6, a liquid passageway 25 to which a high-pressure liquid is supplied by a high-pressure pump 5 is formed in the processing head, and this high-pressure liquid is jetted in the form of a liquid column W from a jet hole 24 of a jet nozzle 23 provided at a lower end of the processing head 6. The optical fiber is exposed inside of the liquid passageway, and a tip of a fiber core 12a of the optical fiber projects beyond a fiber clad 12b, and is close to the vicinity of the jet hole.The laser beam irradiated from the fiber core is guided to the liquid column after it is reflected on a first inclined surface 24a formed on the jet hole, and processing on the workpiece 2 is performed.The laser beam can easily be guided to the liquid column.
Owner:SHIBUYA IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com