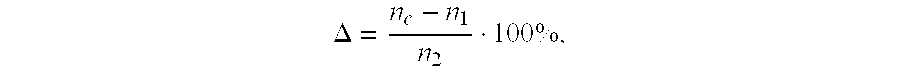Patents
Literature
459 results about "Double-clad fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
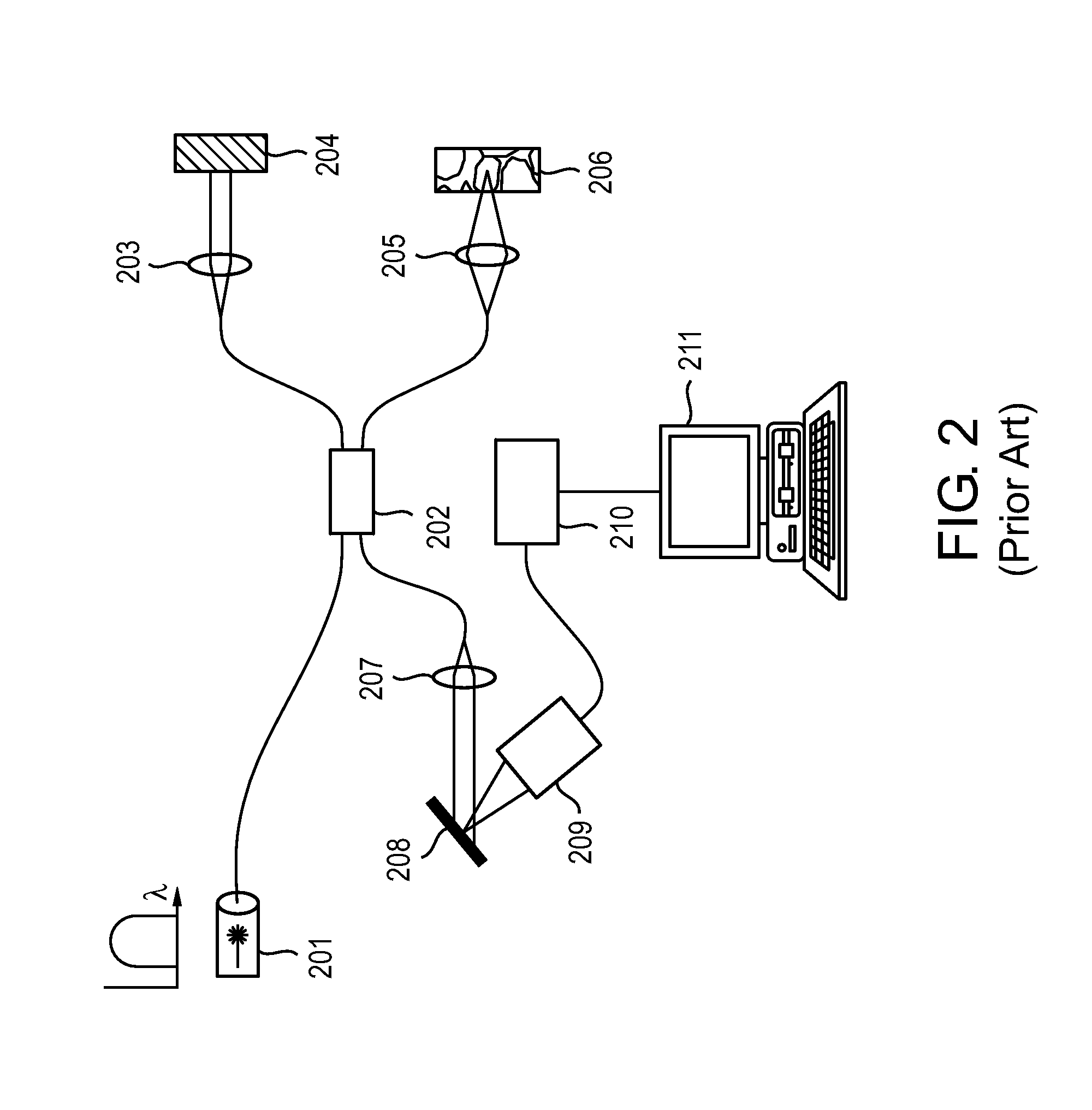
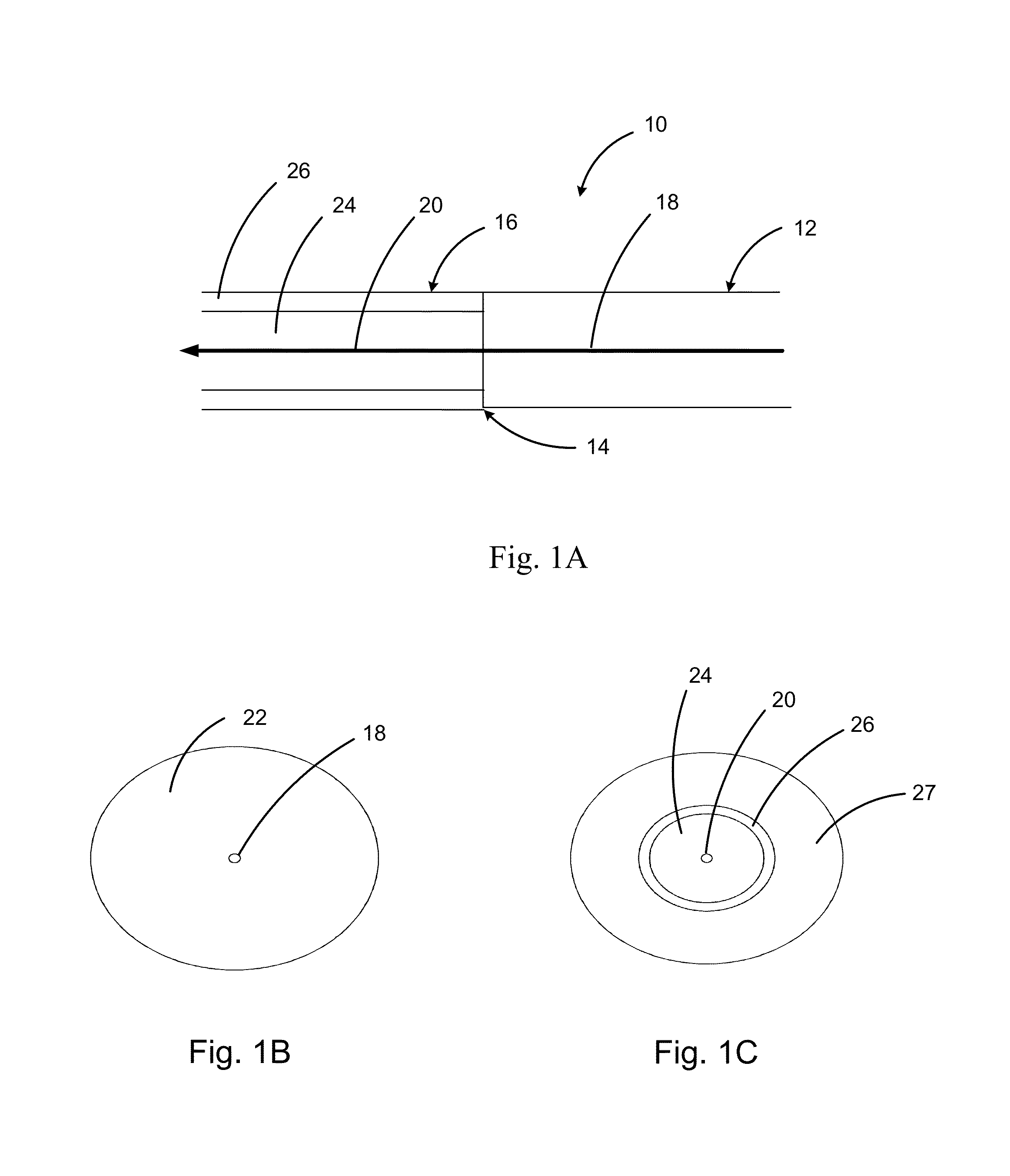
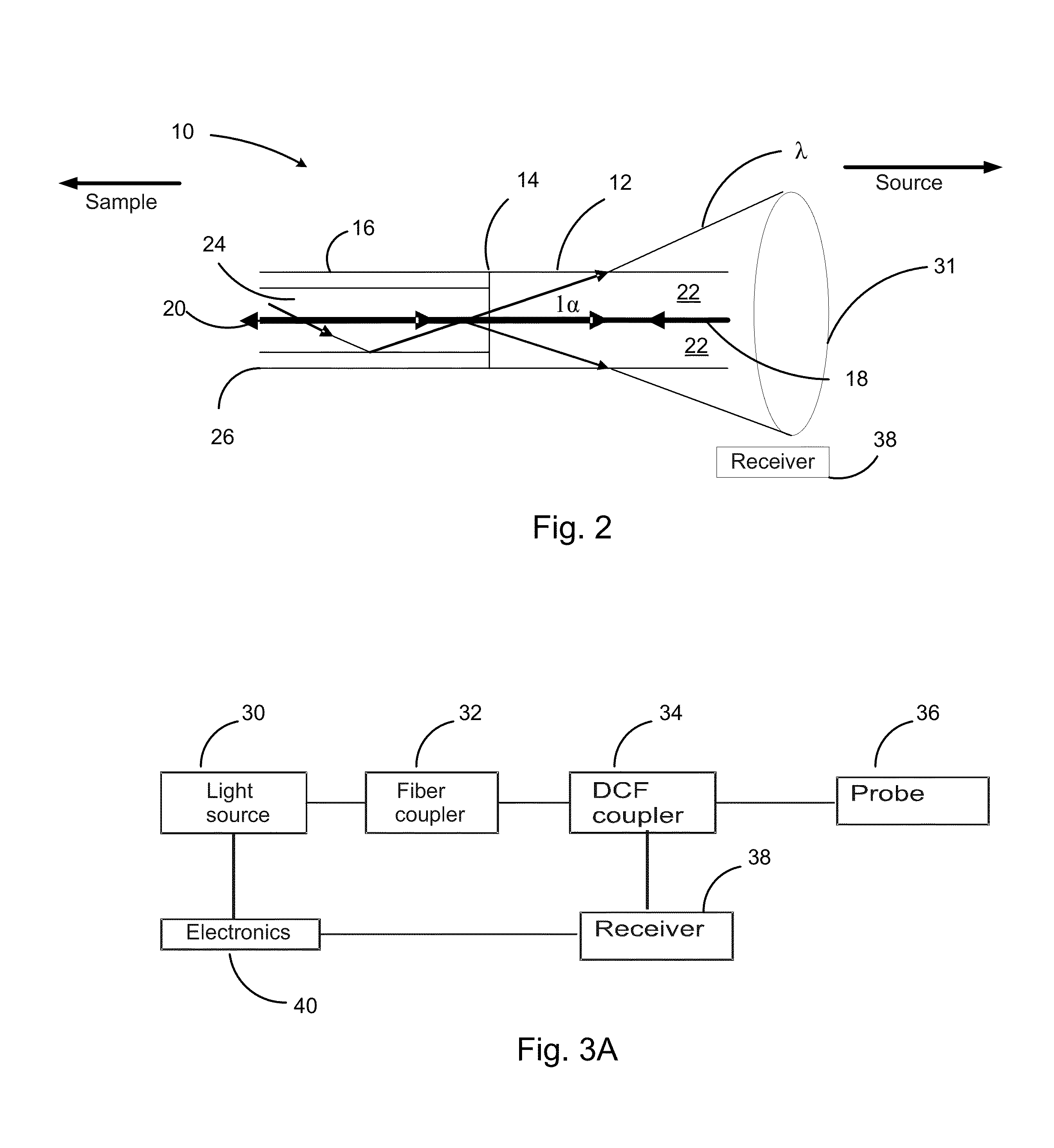
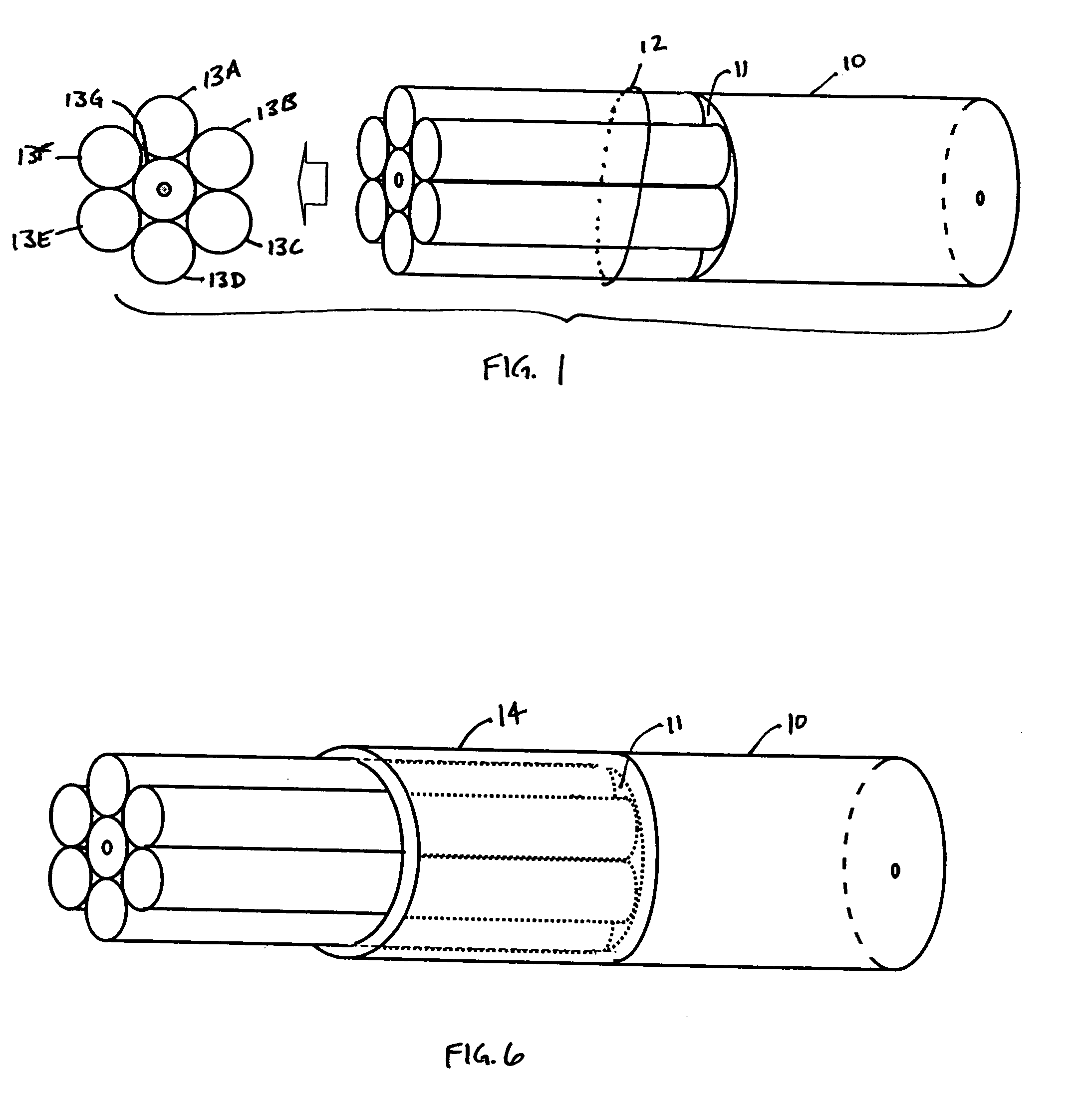
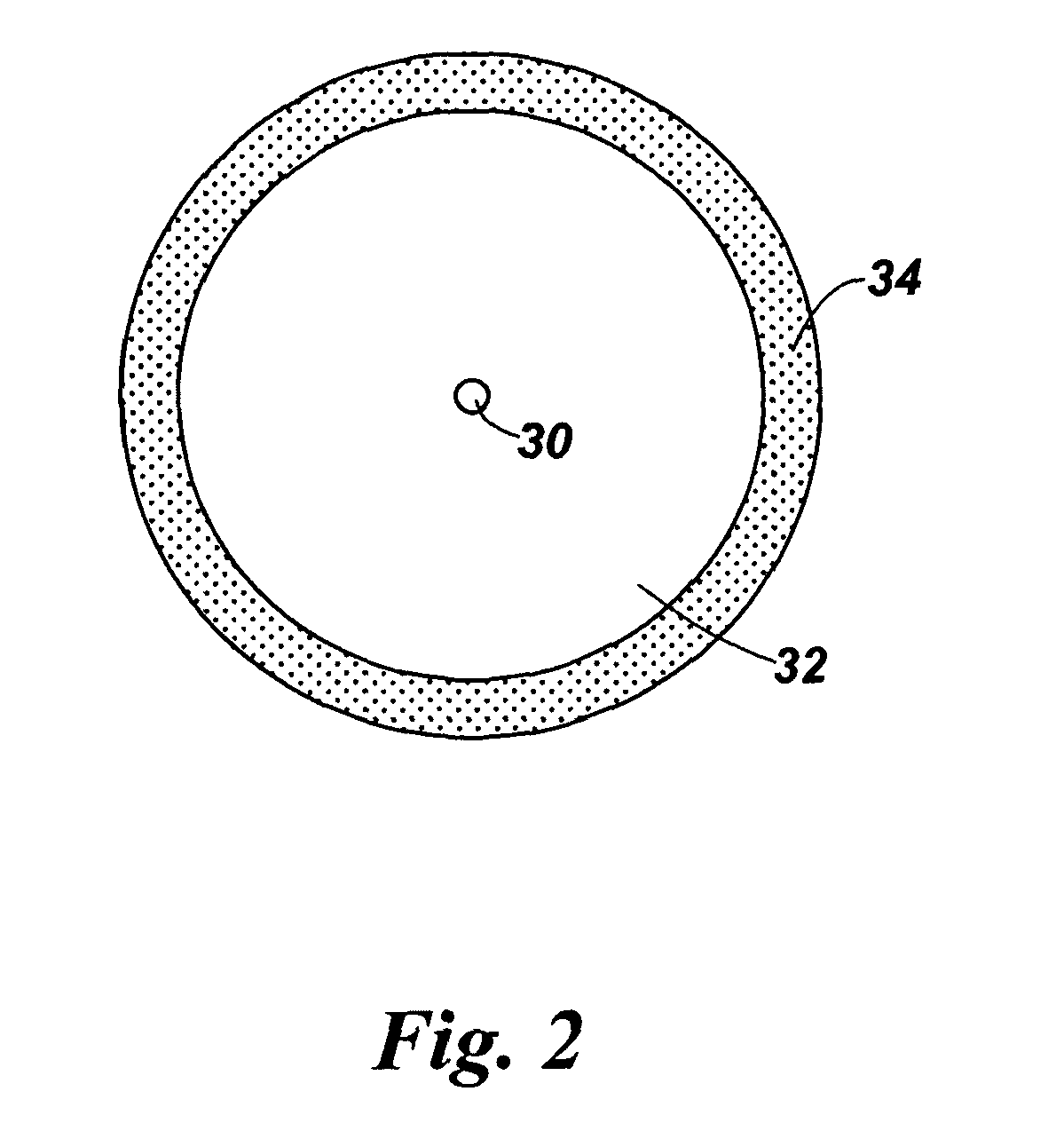
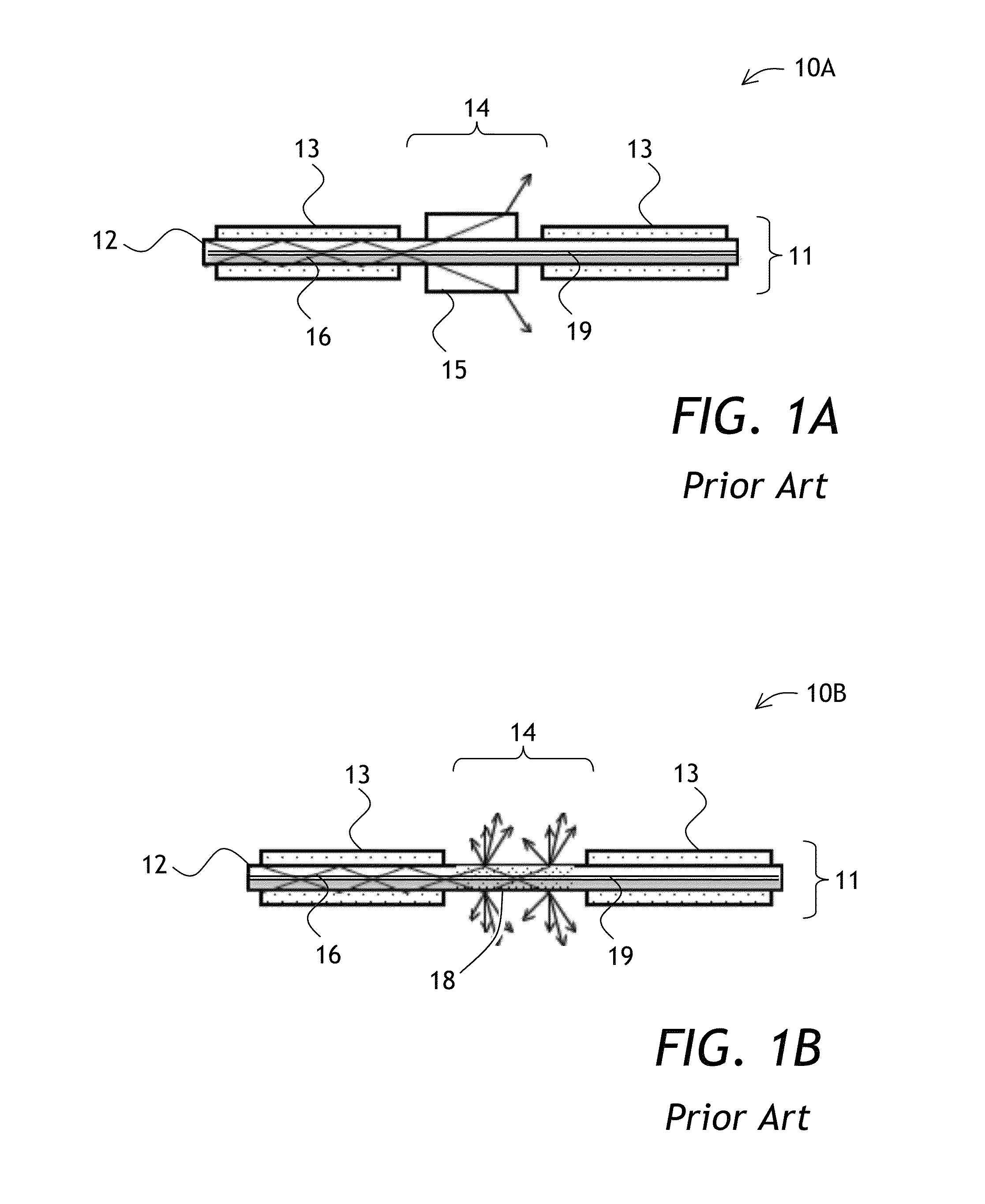
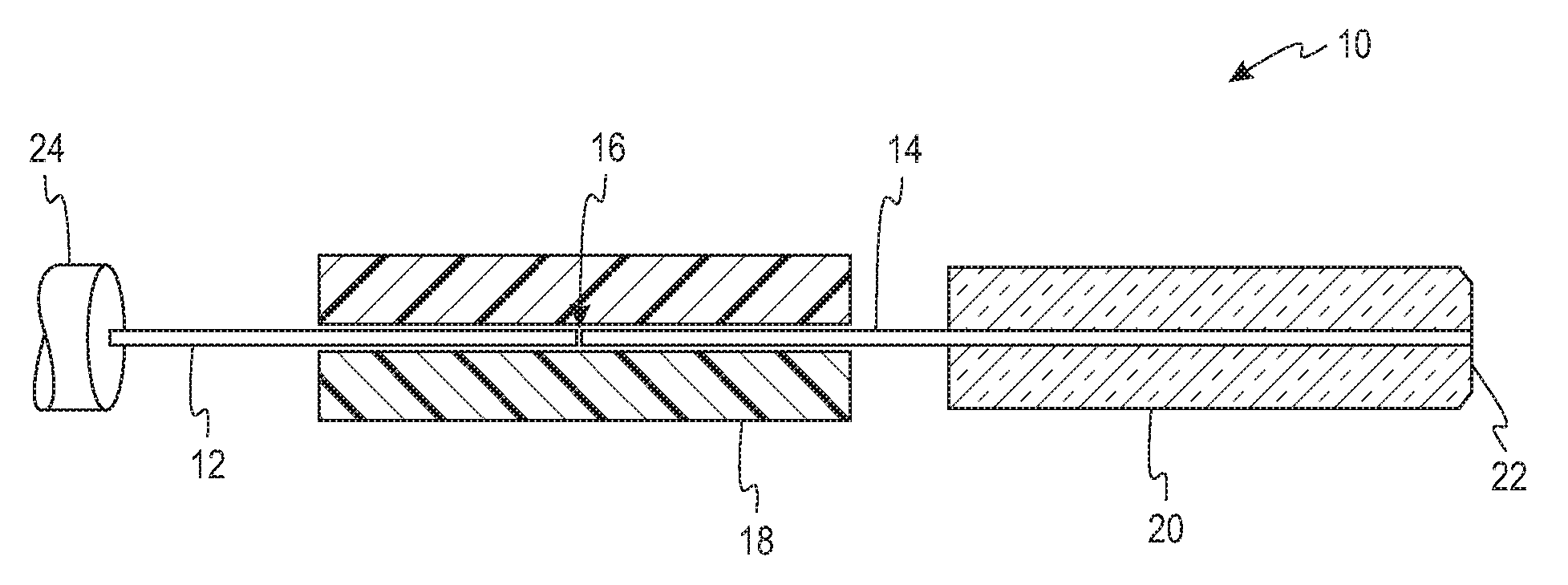
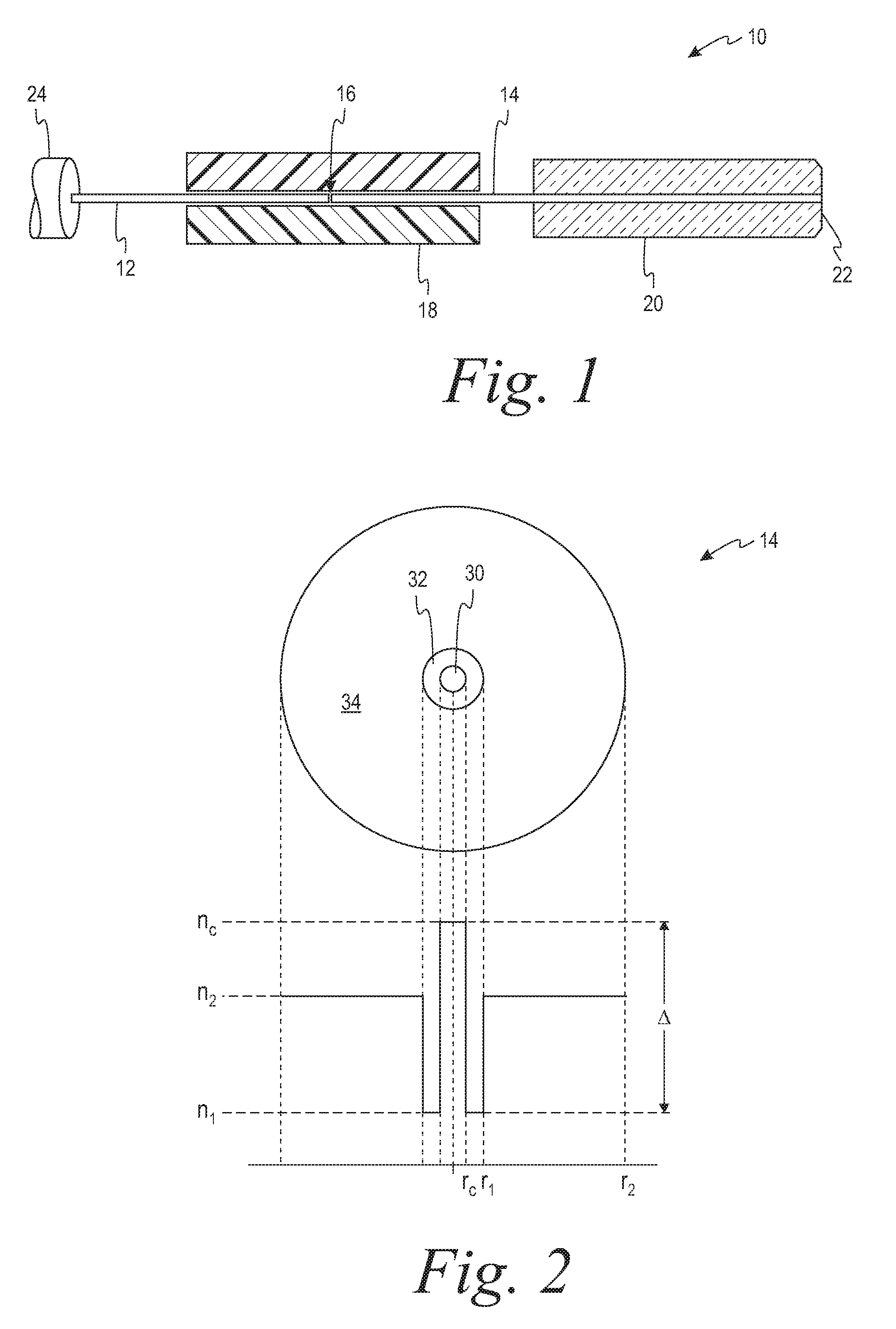
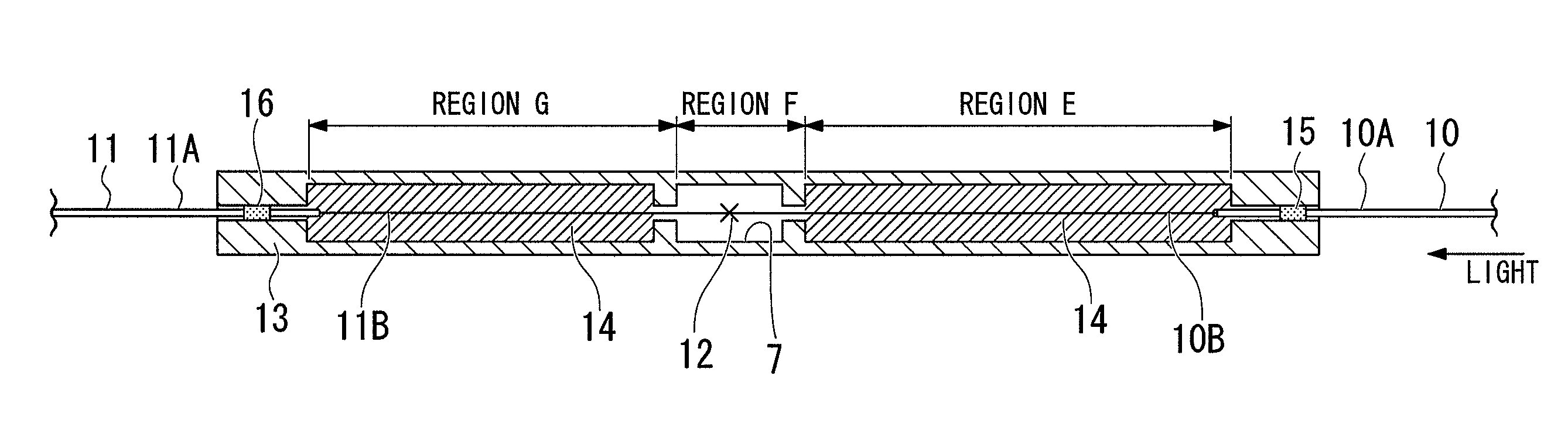
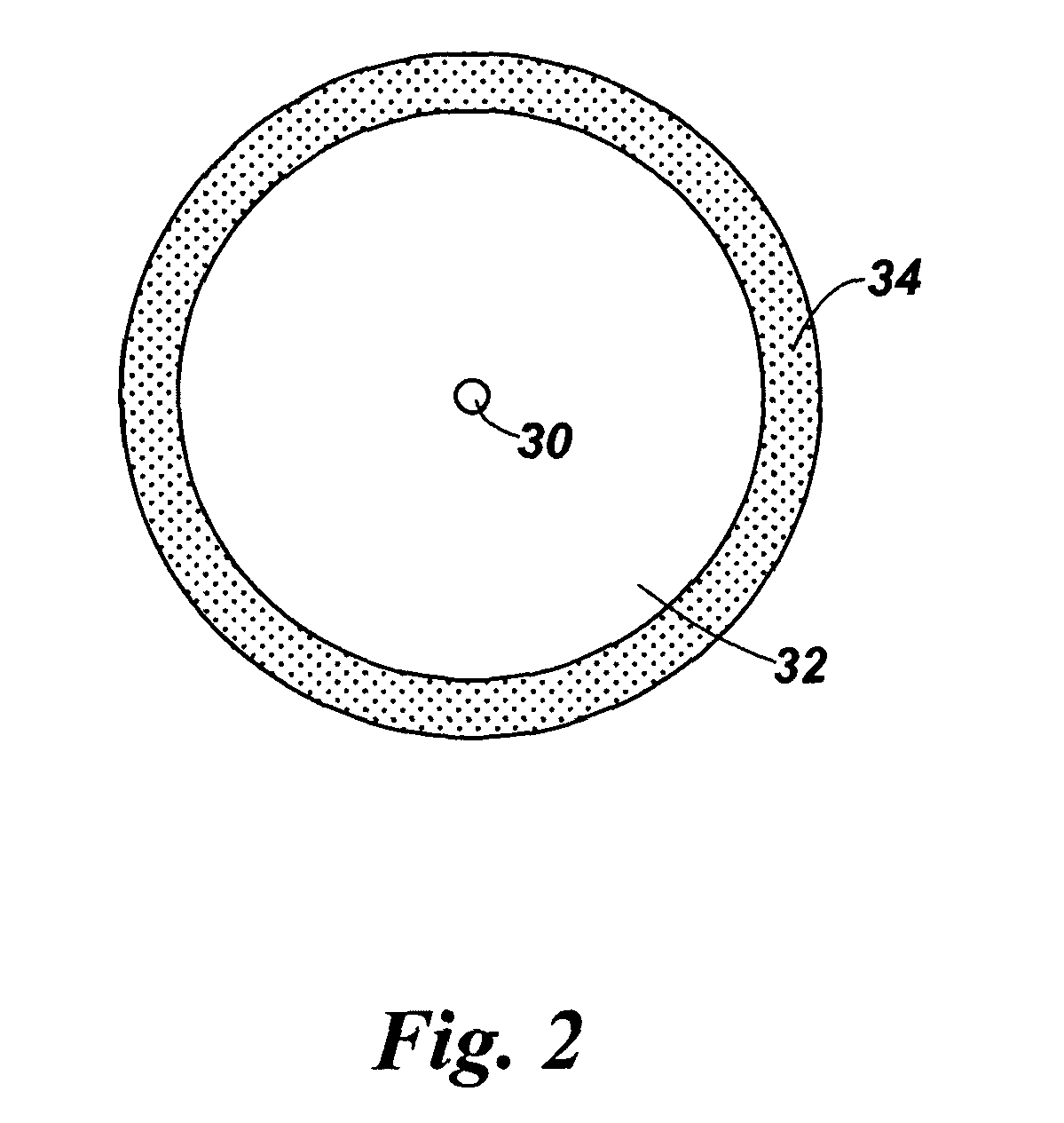
Double-clad fiber (DCF) is a class of optical fiber with a structure consisting of three layers of optical material instead of the usual two. The inner-most layer is called the core. It is surrounded by the inner cladding, which is surrounded by the outer cladding. The three layers are made of materials with different refractive indices.
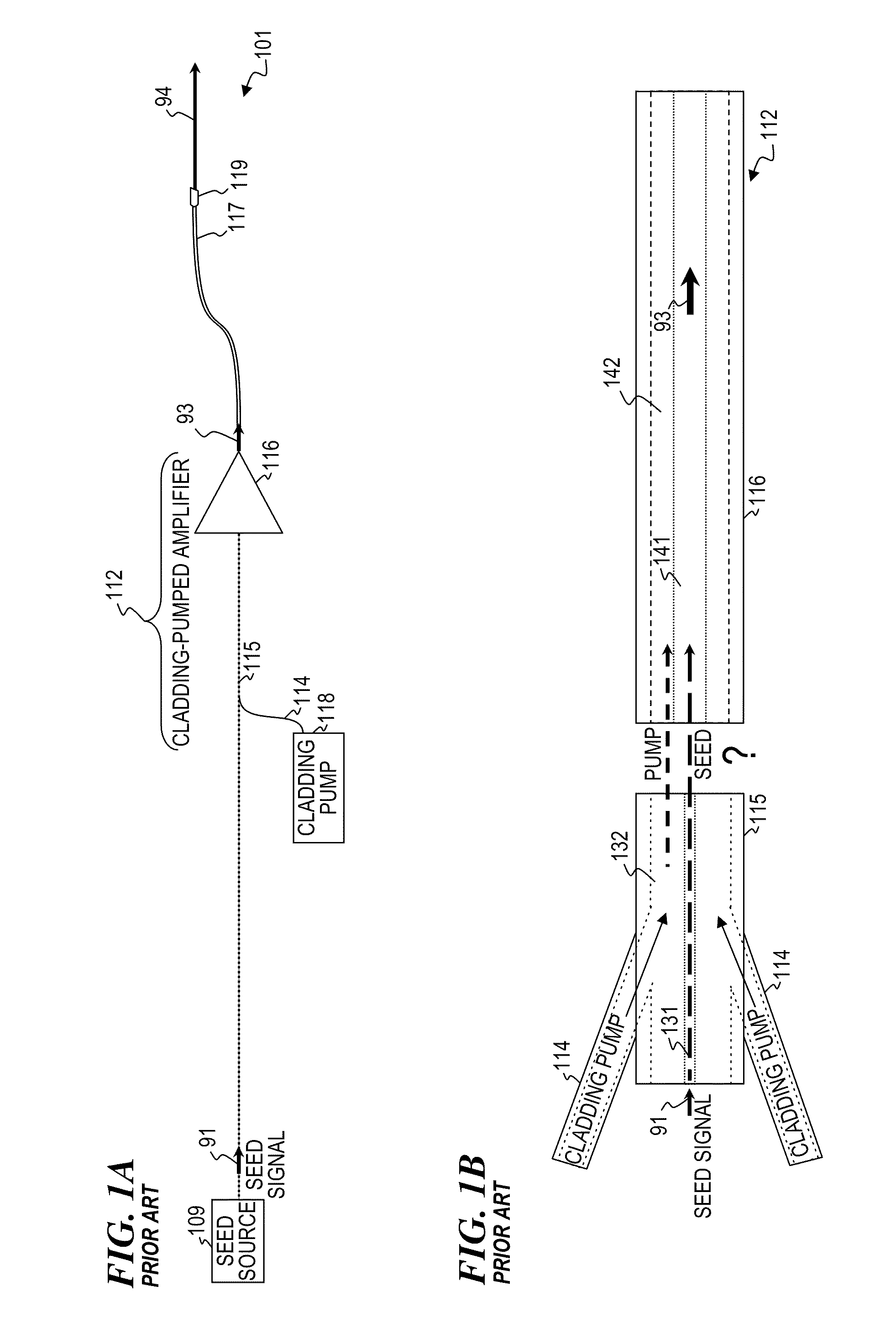
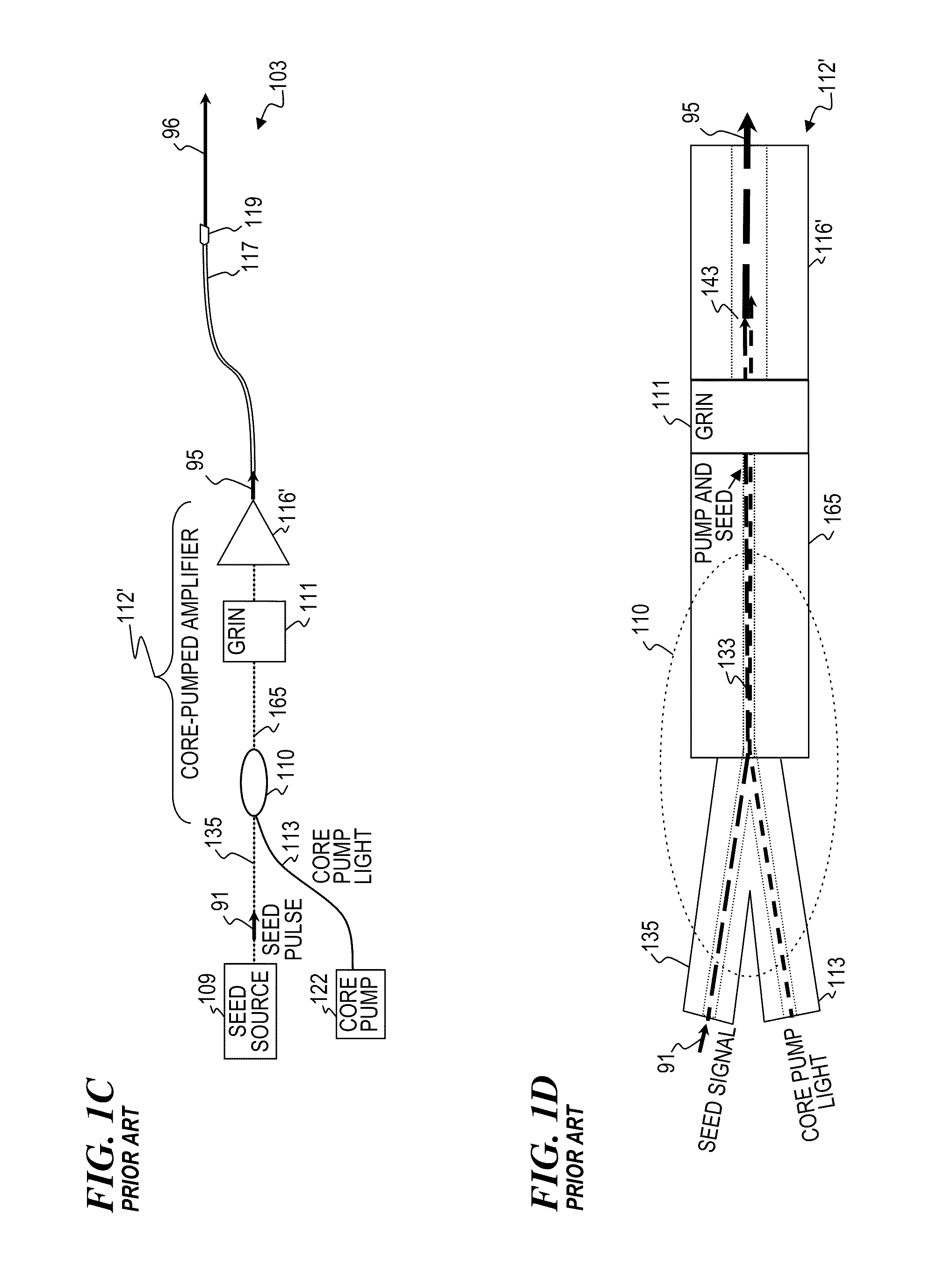
Apparatus and method for the generation of high-power femtosecond pulses from a fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6014249ALong pulse widthLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
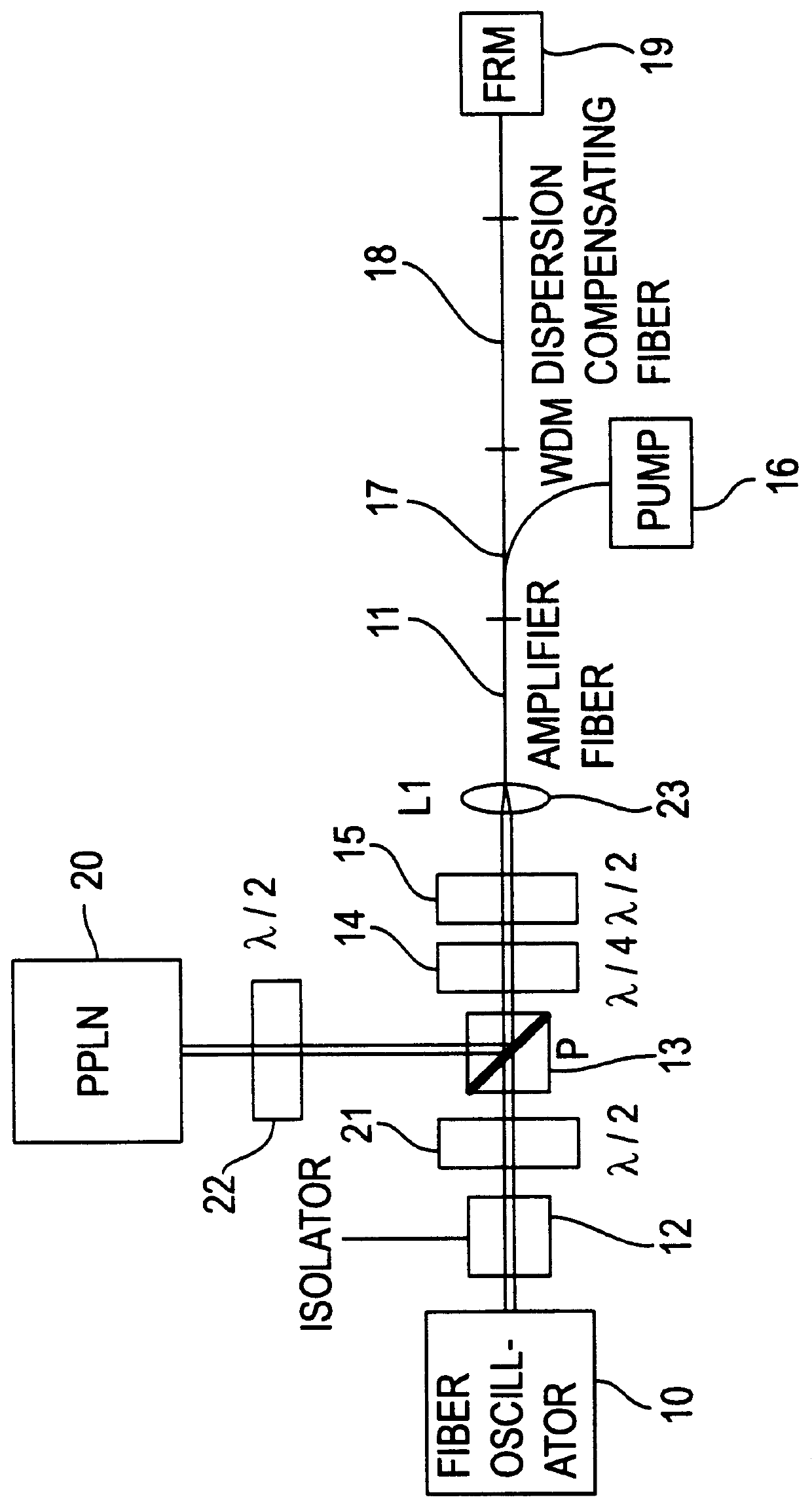
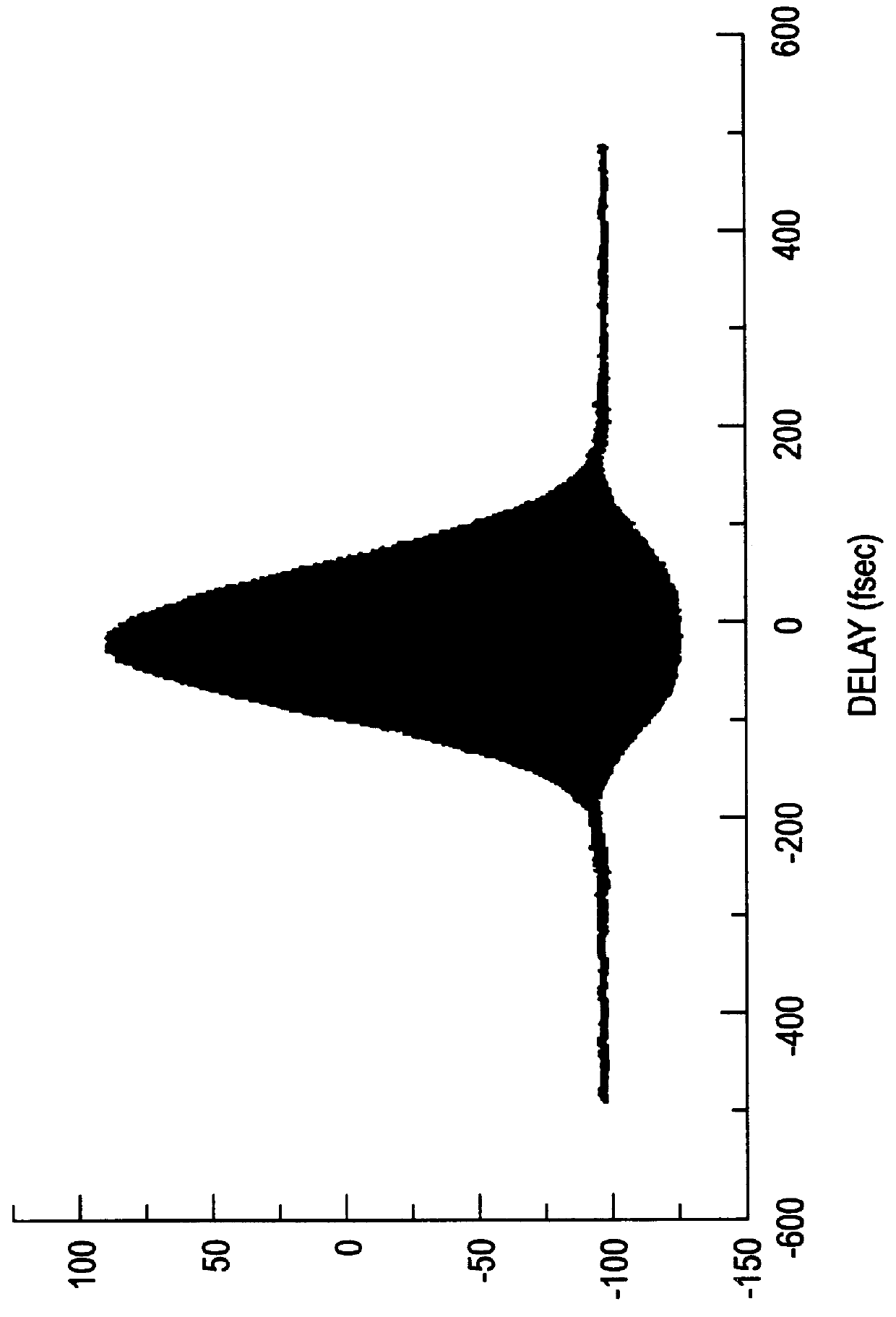
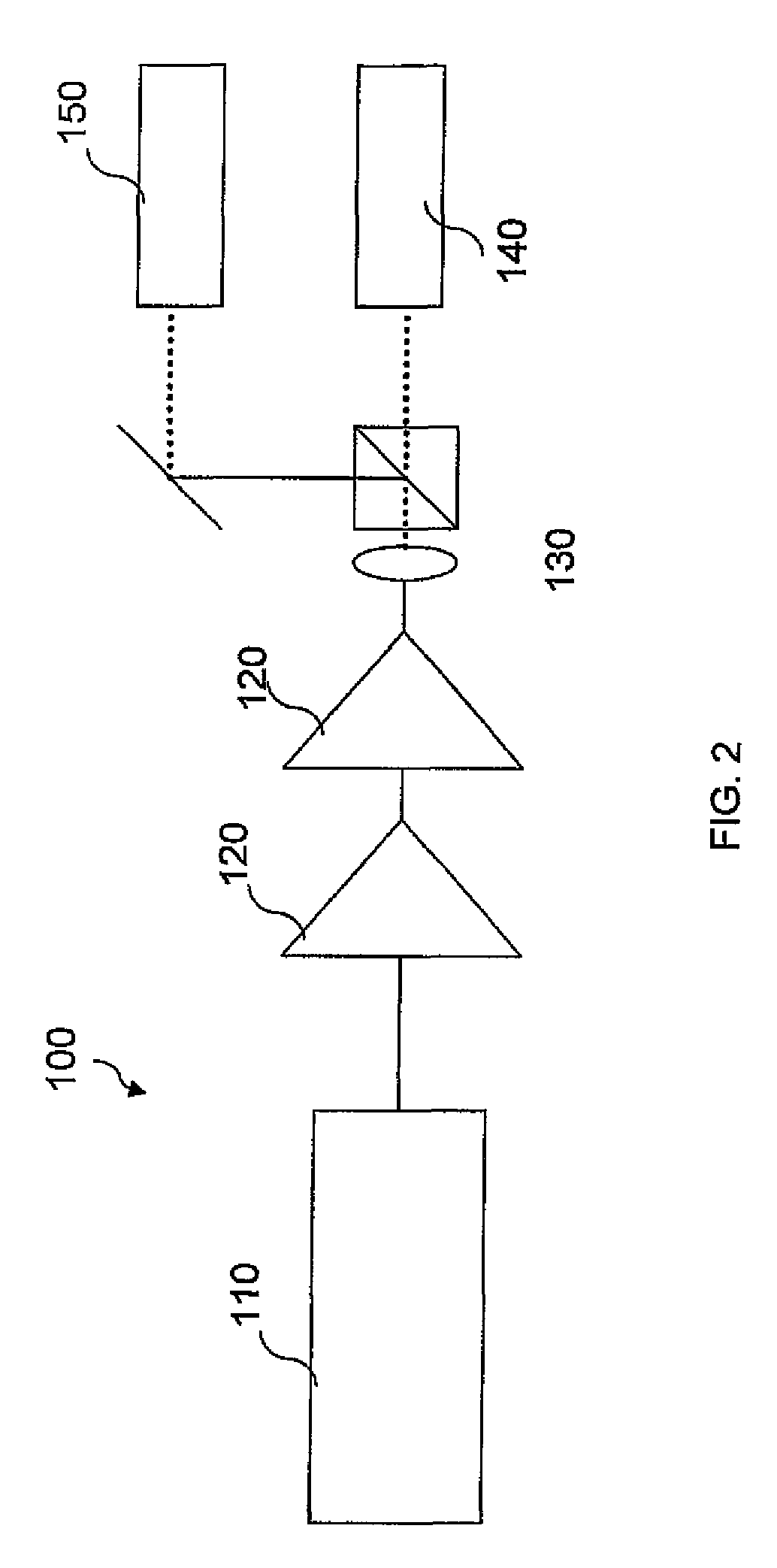
An apparatus generates femtosecond pulses from laser amplifiers by nonlinear frequency conversion. The implementation of nonlinear frequency-conversion allows the design of highly nonlinear amplifiers at a signal wavelength (SW), while still preserving a high-quality pulse at an approximately frequency-doubled wavelength (FDW). Nonlinear frequency-conversion also allows for limited wavelength tuning of the FDW. As an example, the output from a nonlinear fiber amplifier is frequency-converted. By controlling the polarization state in the nonlinear fiber amplifier and by operating in the soliton-supporting dispersion regime of the host glass, an efficient nonlinear pulse compression for the SW is obtained. The generated pulse width is optimized by utilizing soliton compression in the presence of the Raman-self-frequency shift in the nonlinear fiber amplifier at the SW. High-power pulses are obtained by employing fiber amplifiers with large core-diameters. The efficiency of the nonlinear fiber amplifier is optimized by using a double clad fiber (i.e., a fiber with a double-step refractive index profile) and by pumping light directly into the inner core of this fiber. Periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) is used for efficient conversion of the SW to a FDW. The quality of the pulses at the FDW can further be improved by nonlinear frequency conversion of the compressed and Raman-shifted signal pulses at the SW. The use of Raman-shifting further increases the tuning range at the FDW. For applications in confocal microscopy, a special linear fiber amplifier is used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
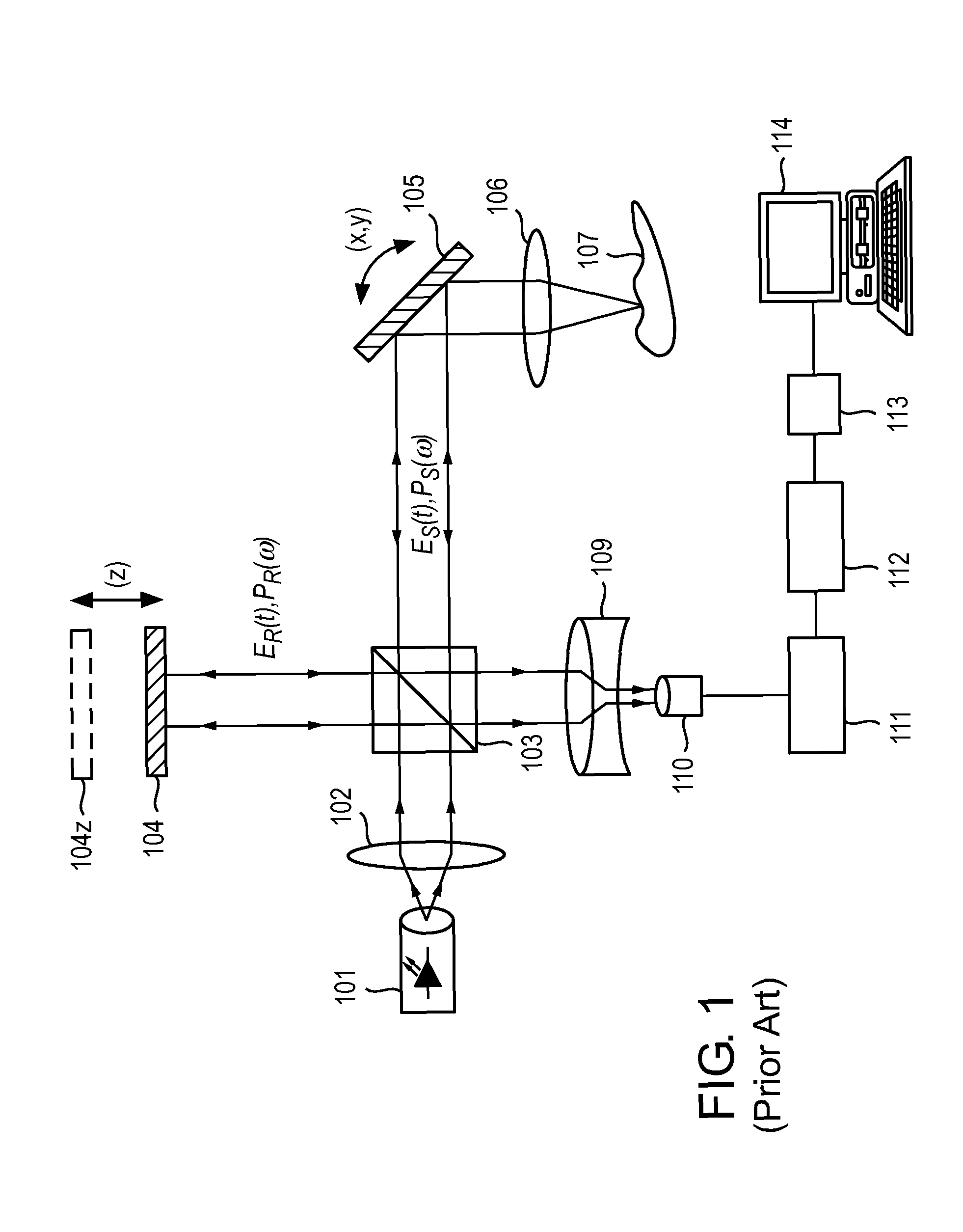
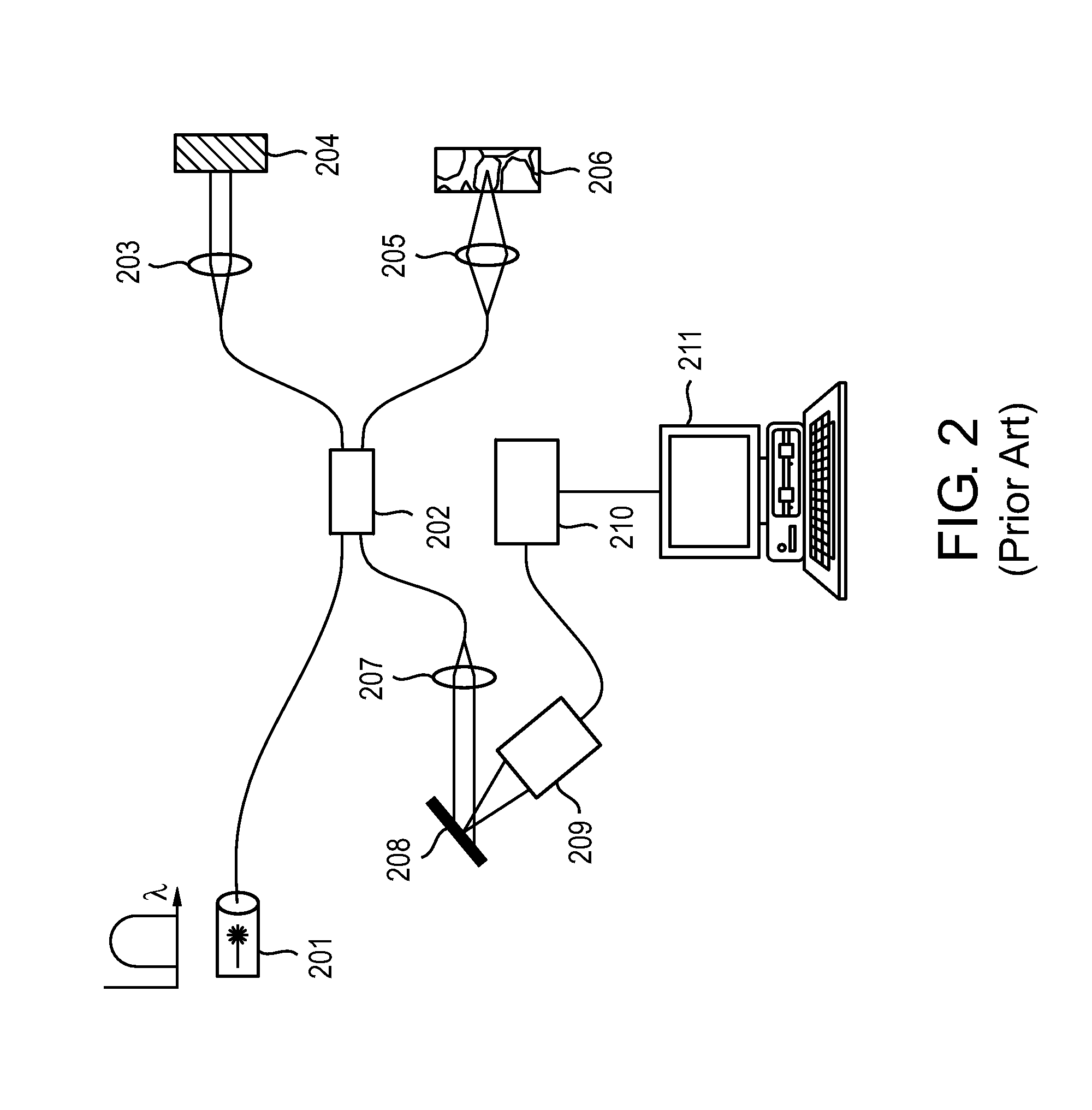
Imaging system and related techniques
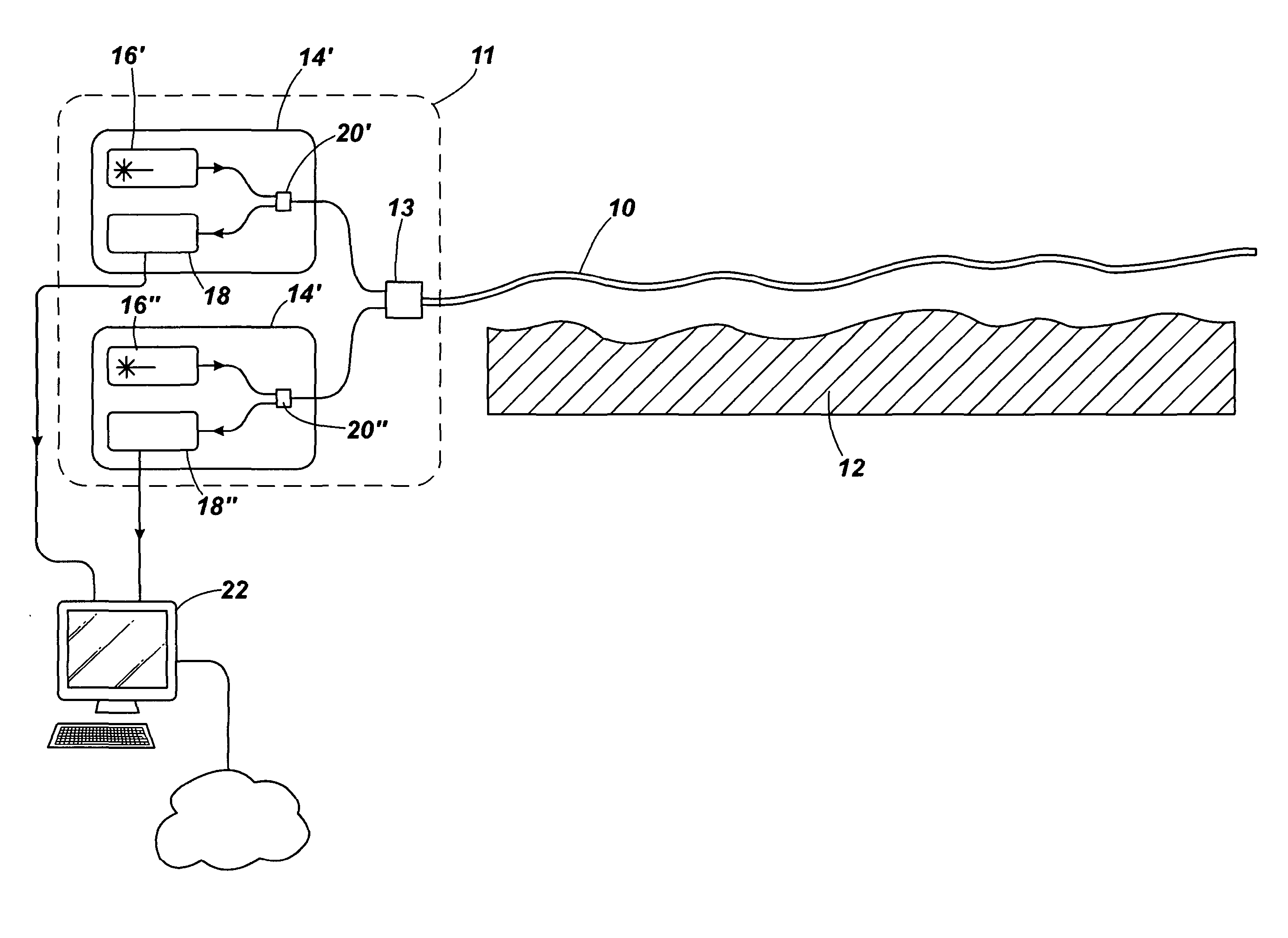
ActiveUS7447408B2Reduces image speckleAdd depthRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDouble-clad fiberComputer science
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
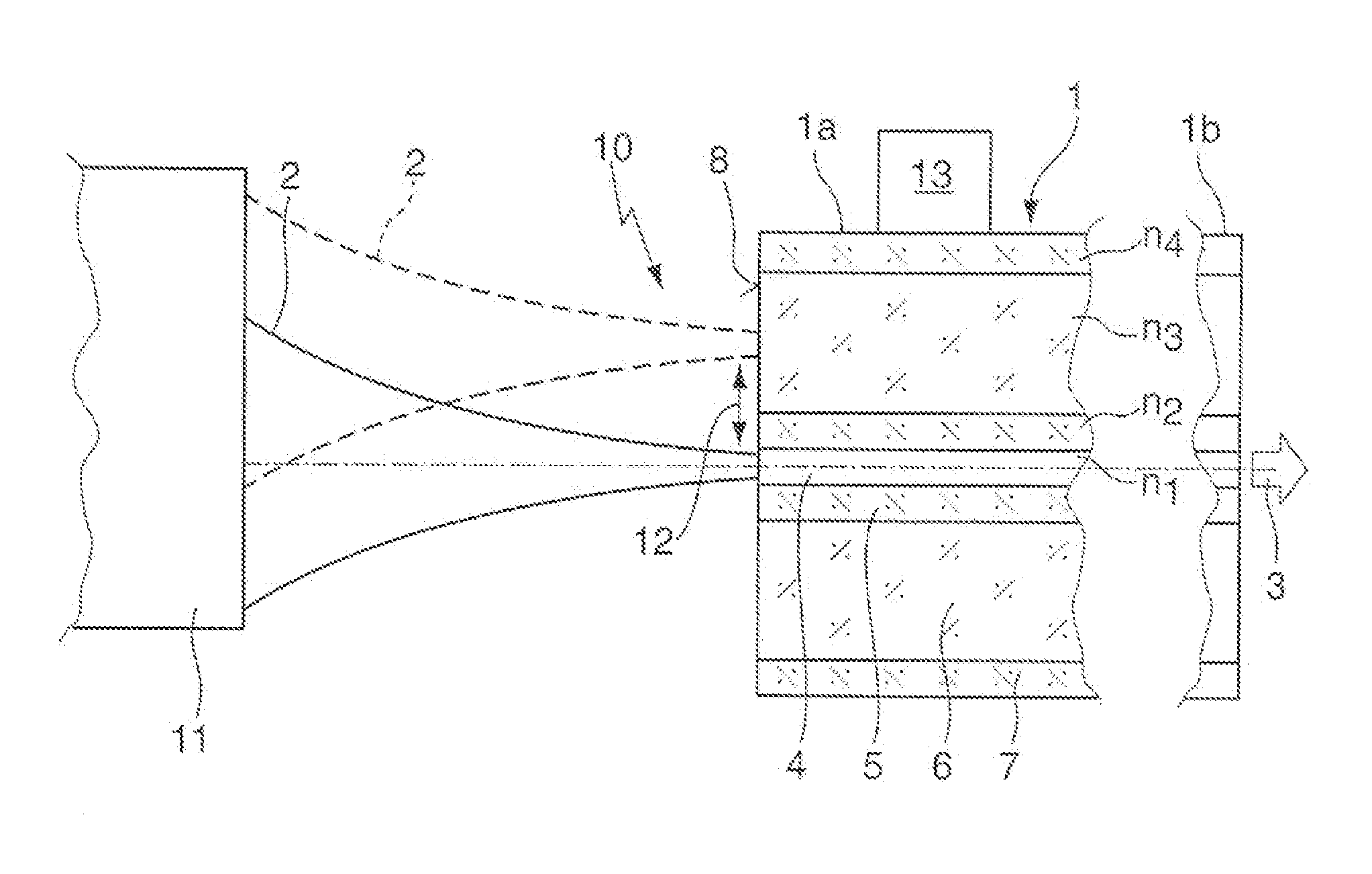
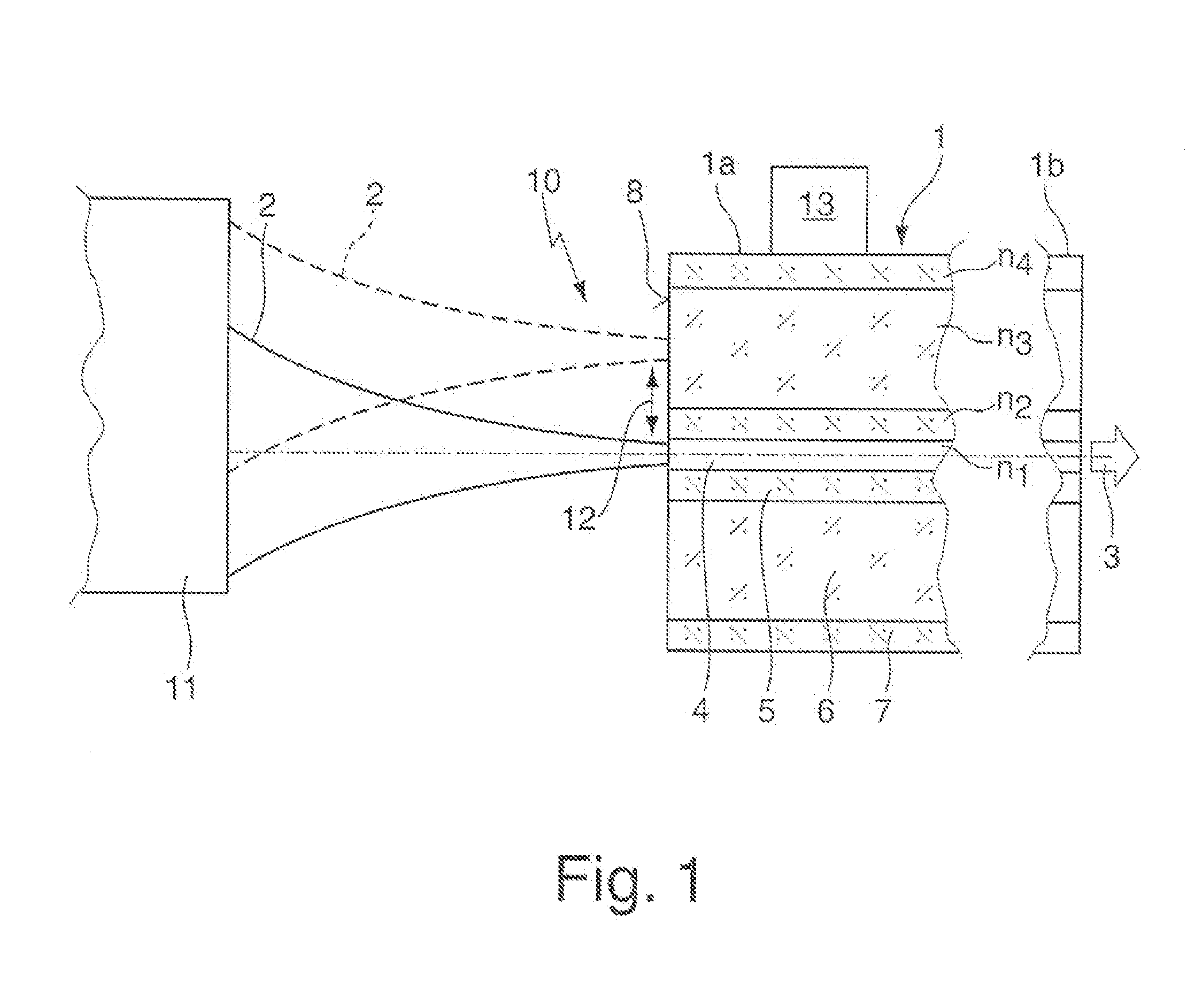
Method and arrangement for generating a laser beam having a differing beam profile characteristic by means of a multi-clad fiber
ActiveUS8781269B2Expand the range of adaptation potential of beam profile characteristicsReduce complexityLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberDouble-clad fiber
The invention concerns a method for generating a laser beam (3) with different beam profile characteristics, whereby a laser beam (2) is coupled into one fiber end (1a) of a multi-clad fiber (1), in particular a double-clad fiber, and emitted from the other fiber end (1b) of the multi-clad fiber (1) and whereby, to generate different beam profile characteristics of the output laser beam (3), the input laser beam (2) is electively coupled either at least into the inner fiber core (4) of the multi-clad fiber (1) or at least into at least one outer ring core (6) of the multi-clad fiber (1), as well as a corresponding arrangement (10).
Owner:TRUMPF LASERSYST FOR SEMICON MFG
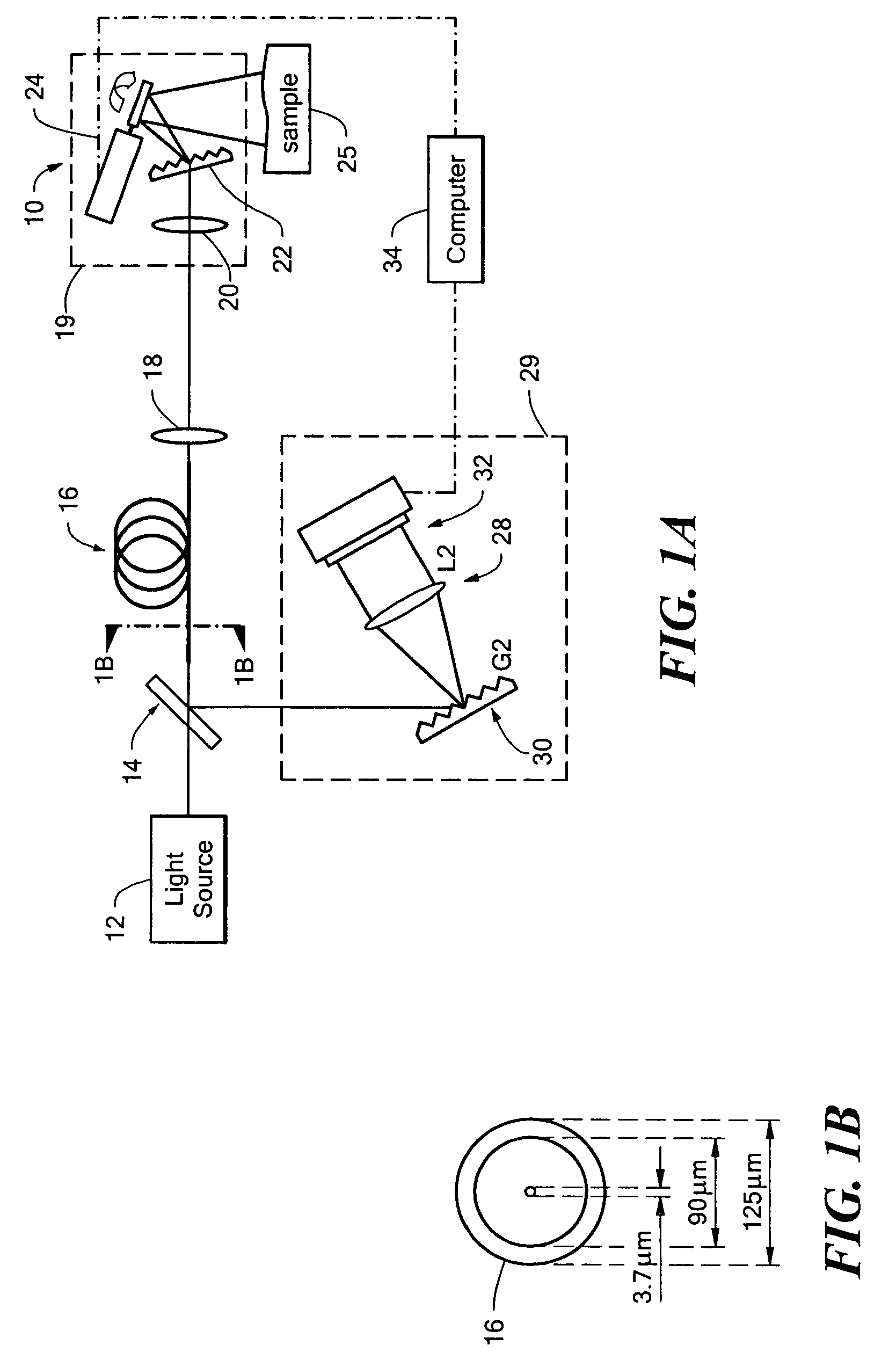
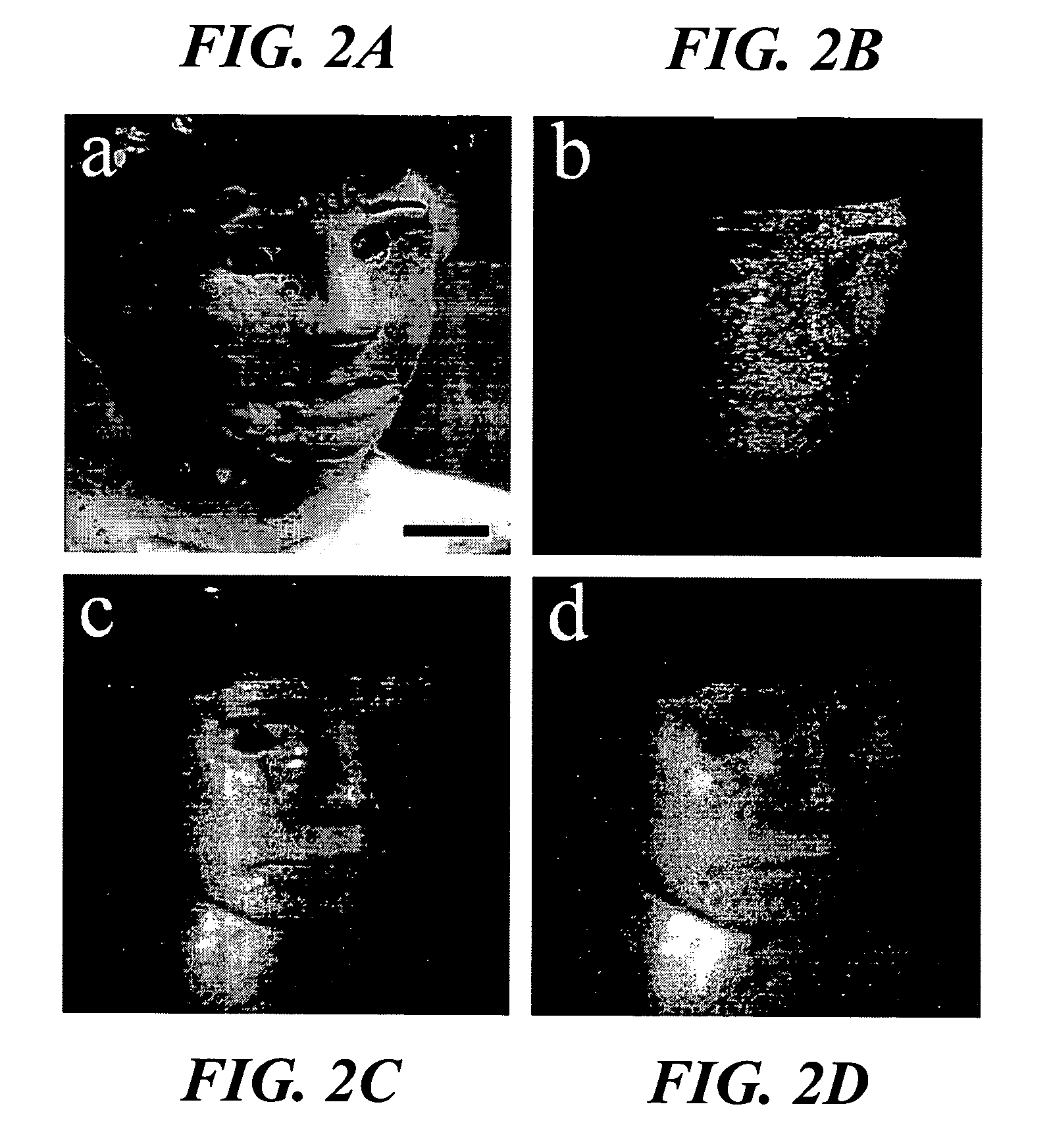
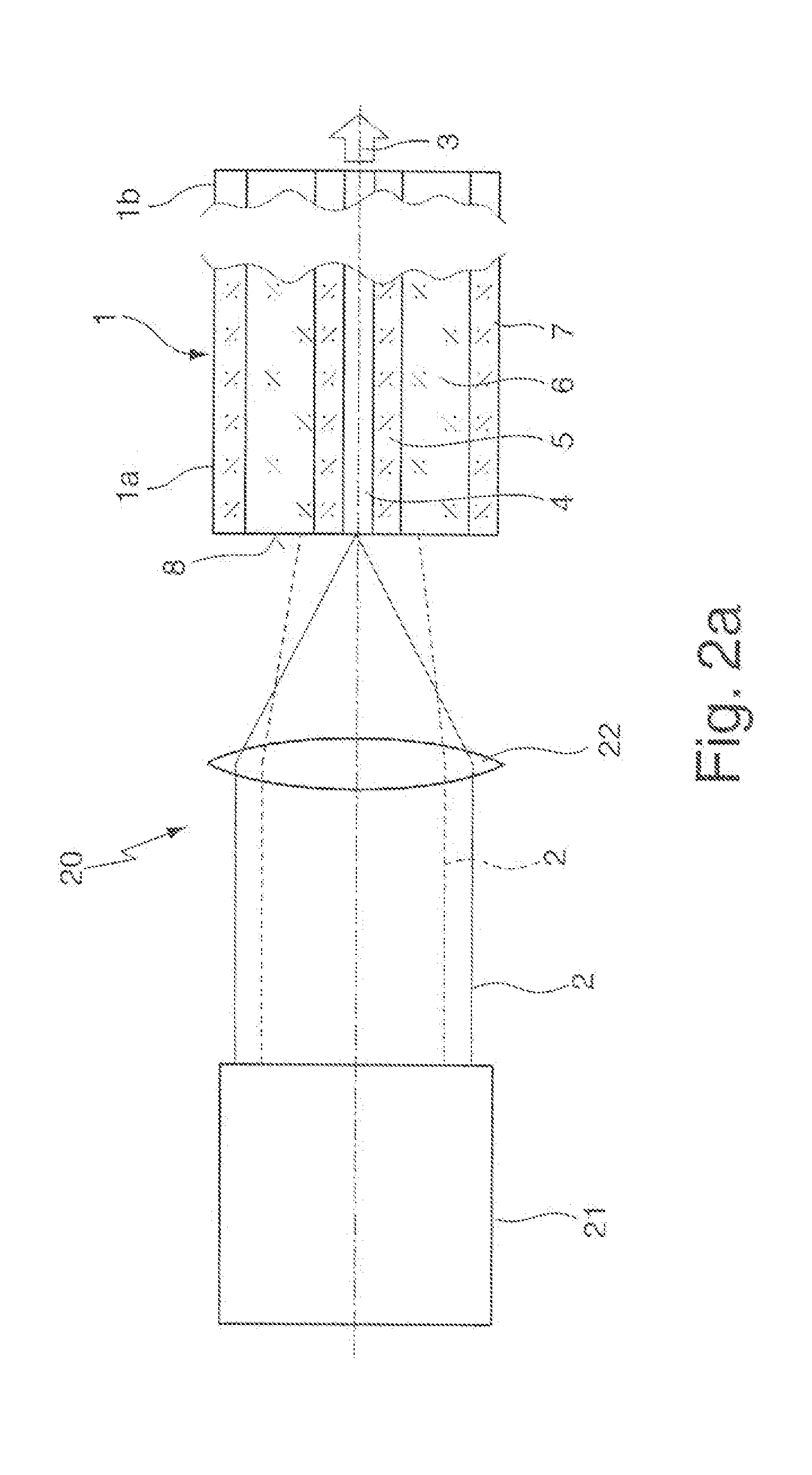
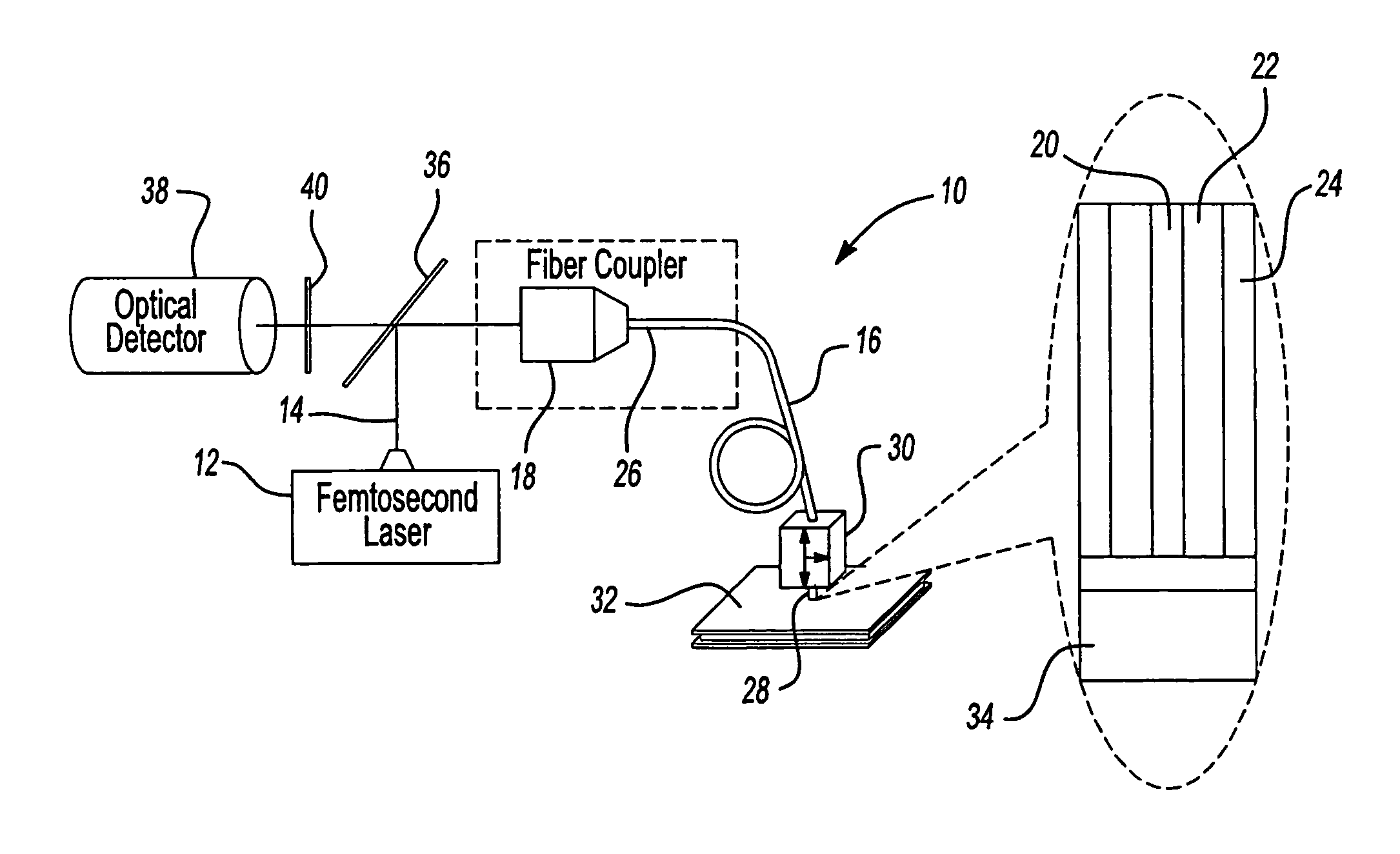
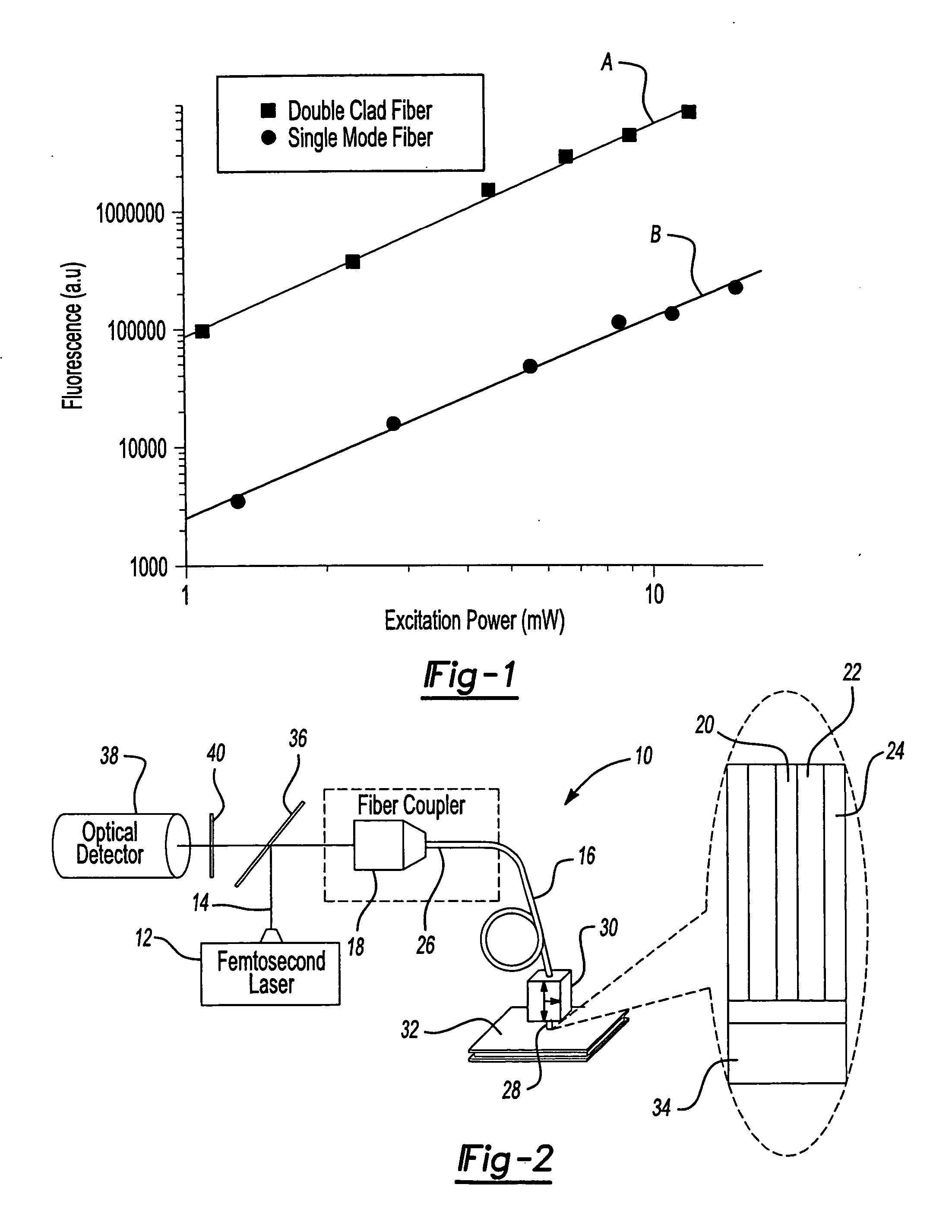
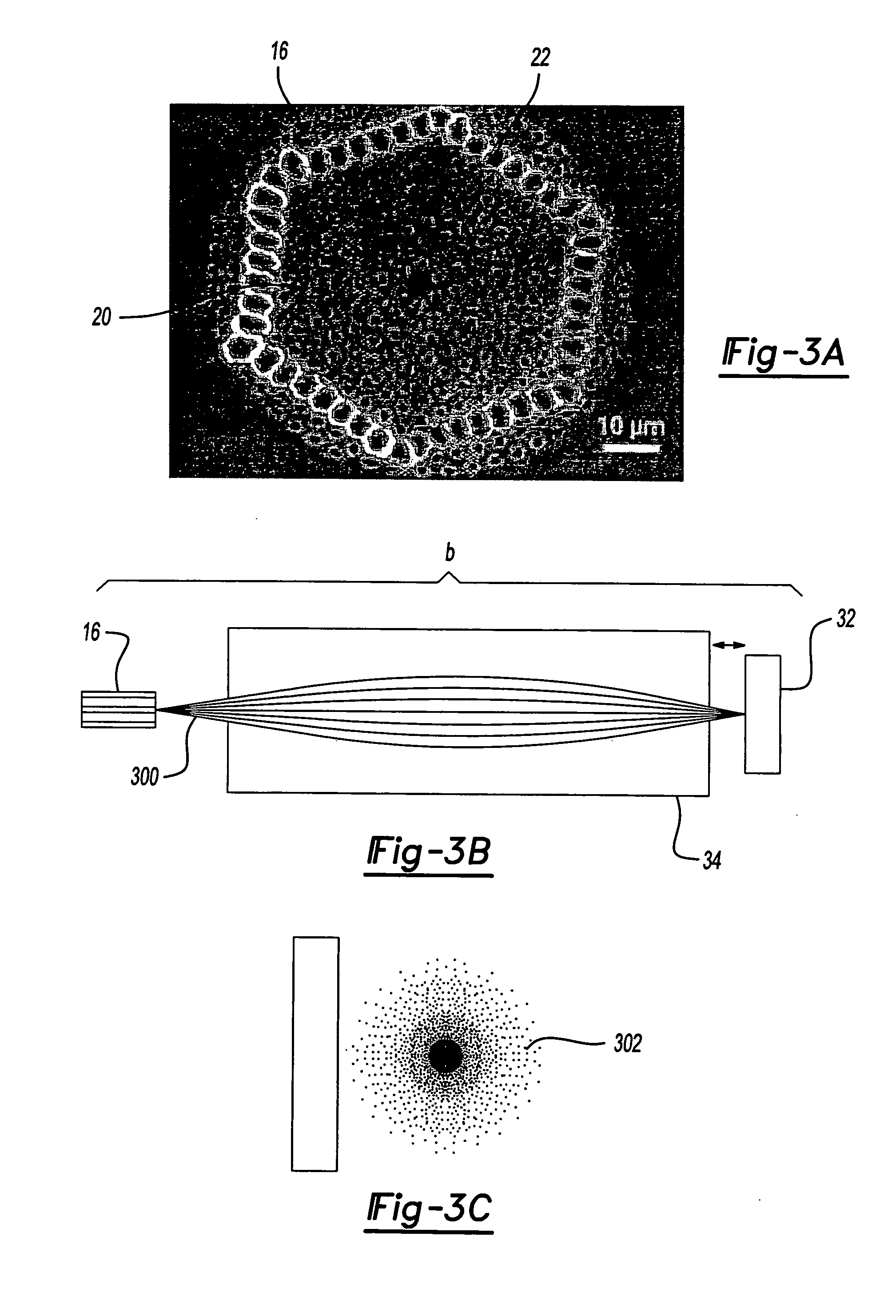
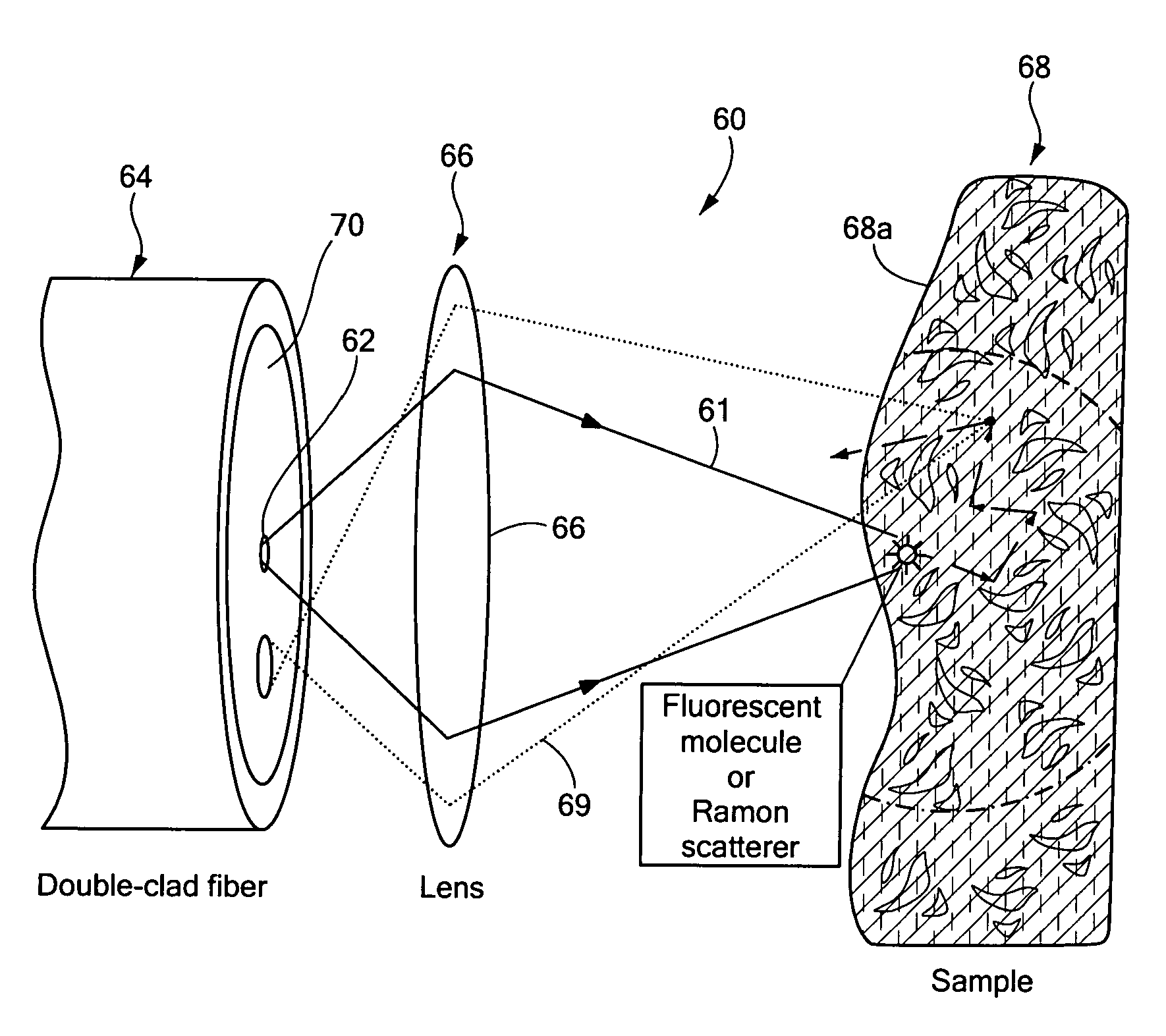
Double-clad fiber scanning microscope
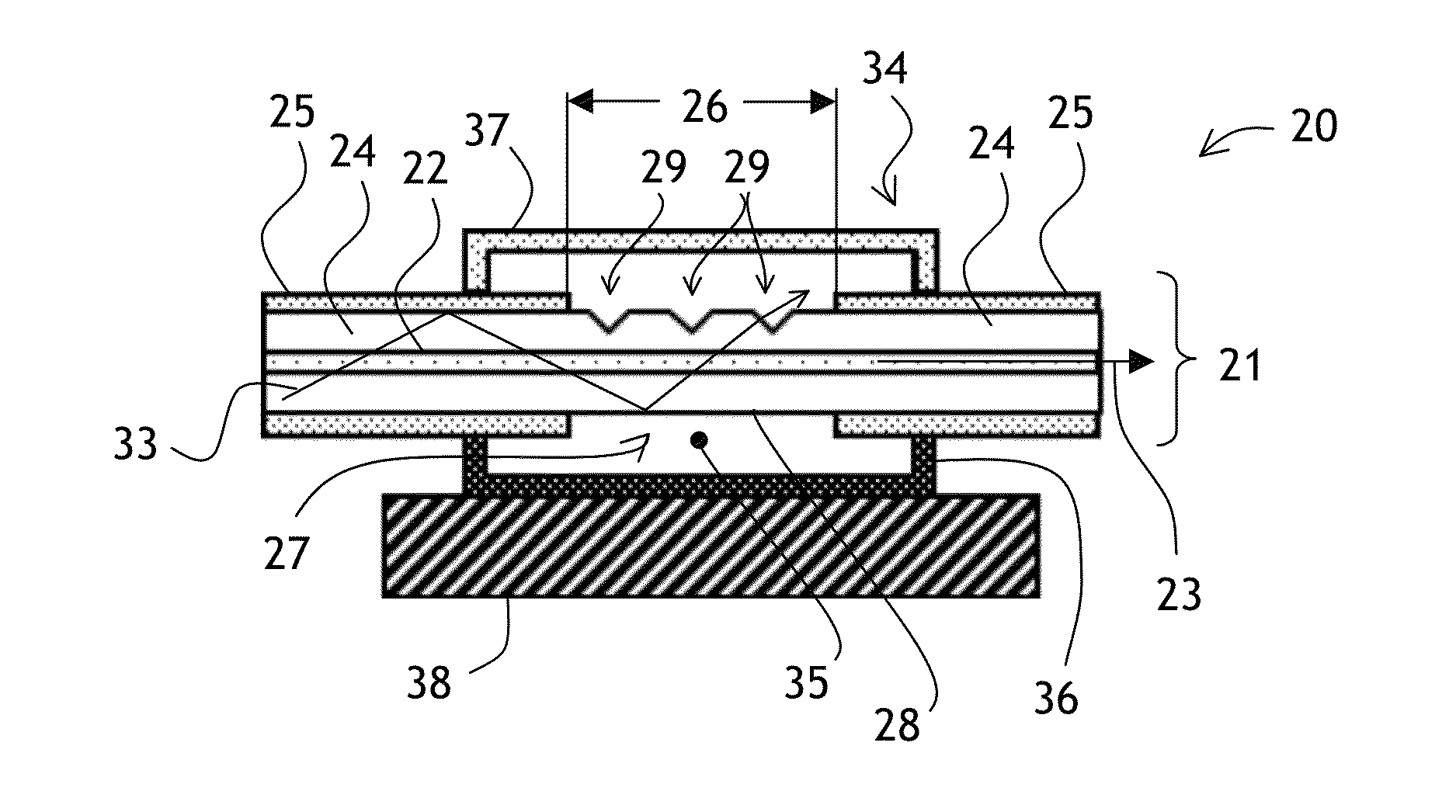
ActiveUS20070002435A1High resolutionImprove detection efficiencyRaman scatteringMicroscopesFiberDouble-clad fiber
A scanning microscope having a laser outputting an excitation laser beam and a fiber member having a first core and a second core. The second core is generally disposed within the first core and is operable to receive the excitation laser beam from the laser and transmit the excitation laser beam to a sample to be tested. A moveable stage supports an end of the fiber member and / or a sample to be tested and is operable to move the end of the fiber member and the sample to be tested relative to each other.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Optical Coupler Devices, Methods of Their Production and Use
InactiveUS20070237453A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDouble-clad fiberWaveguide
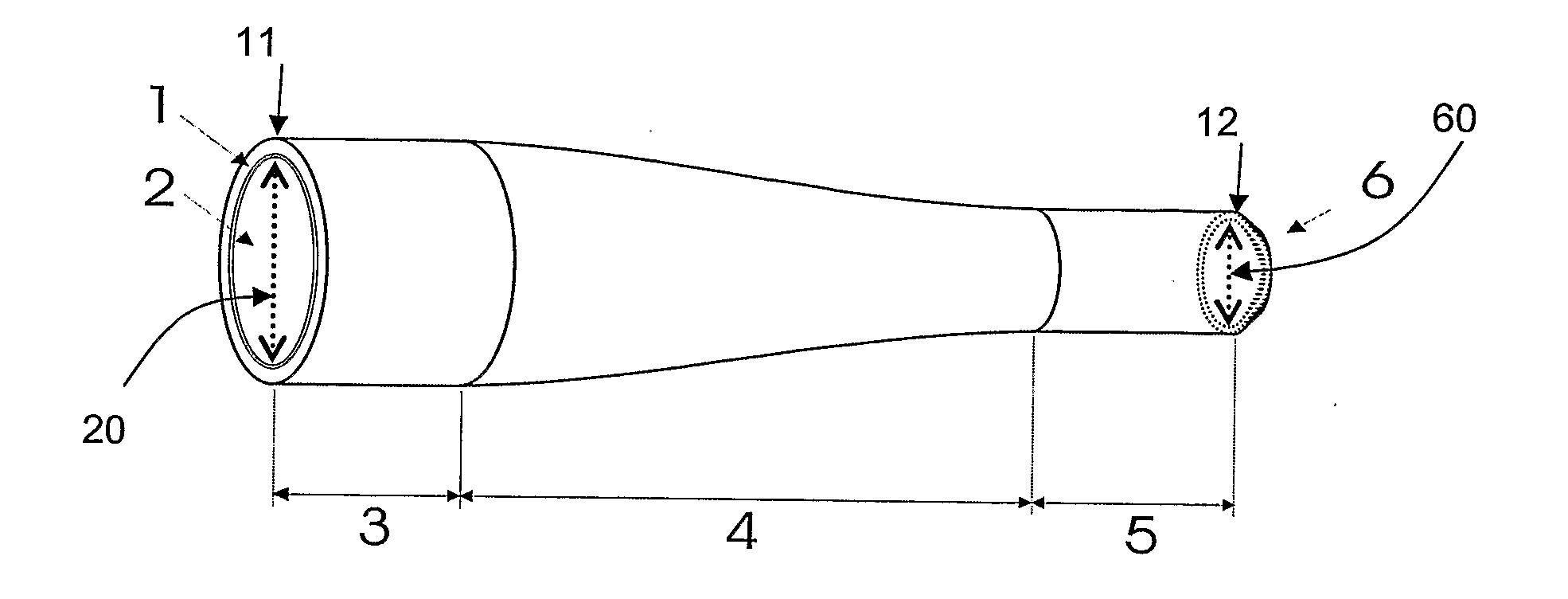
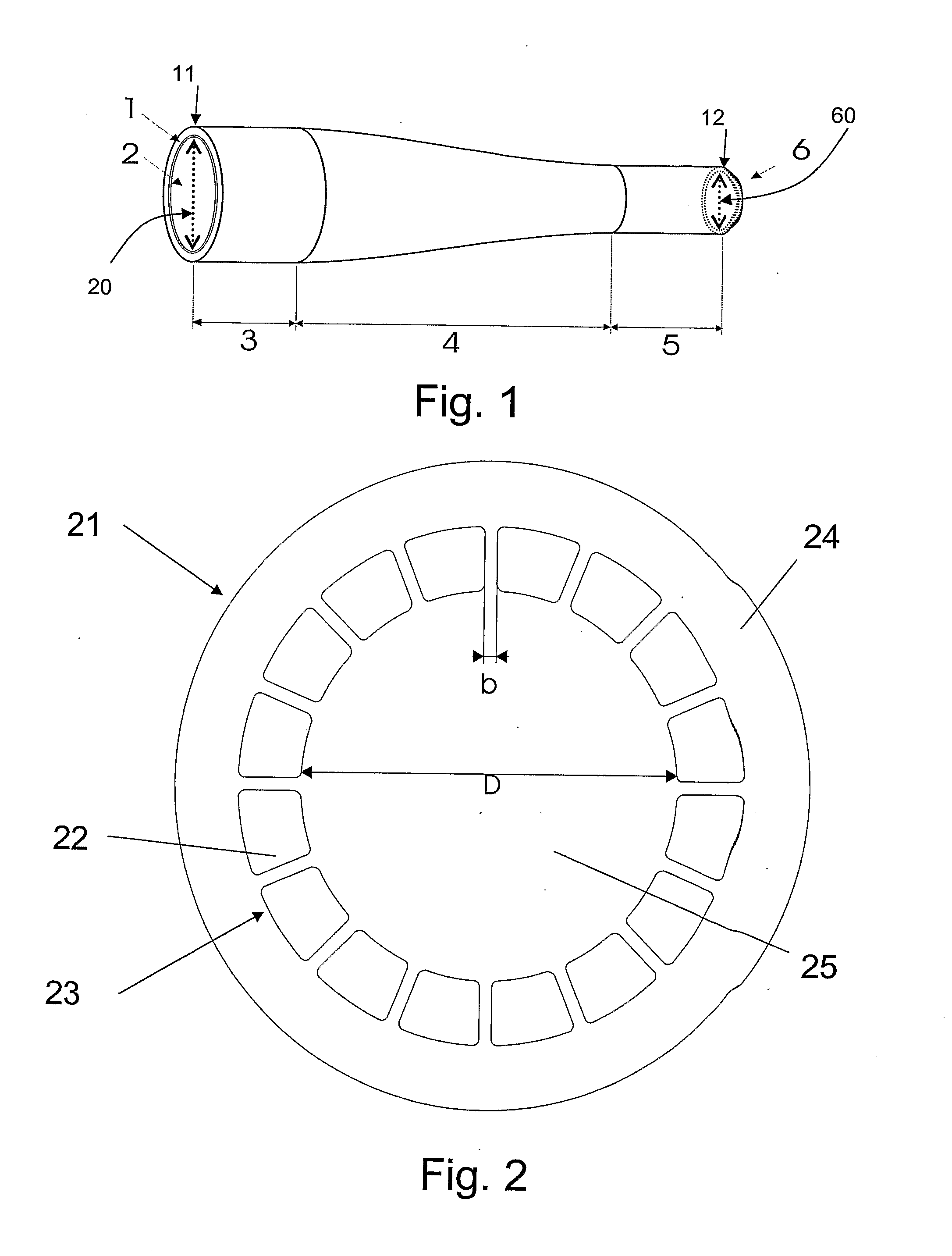
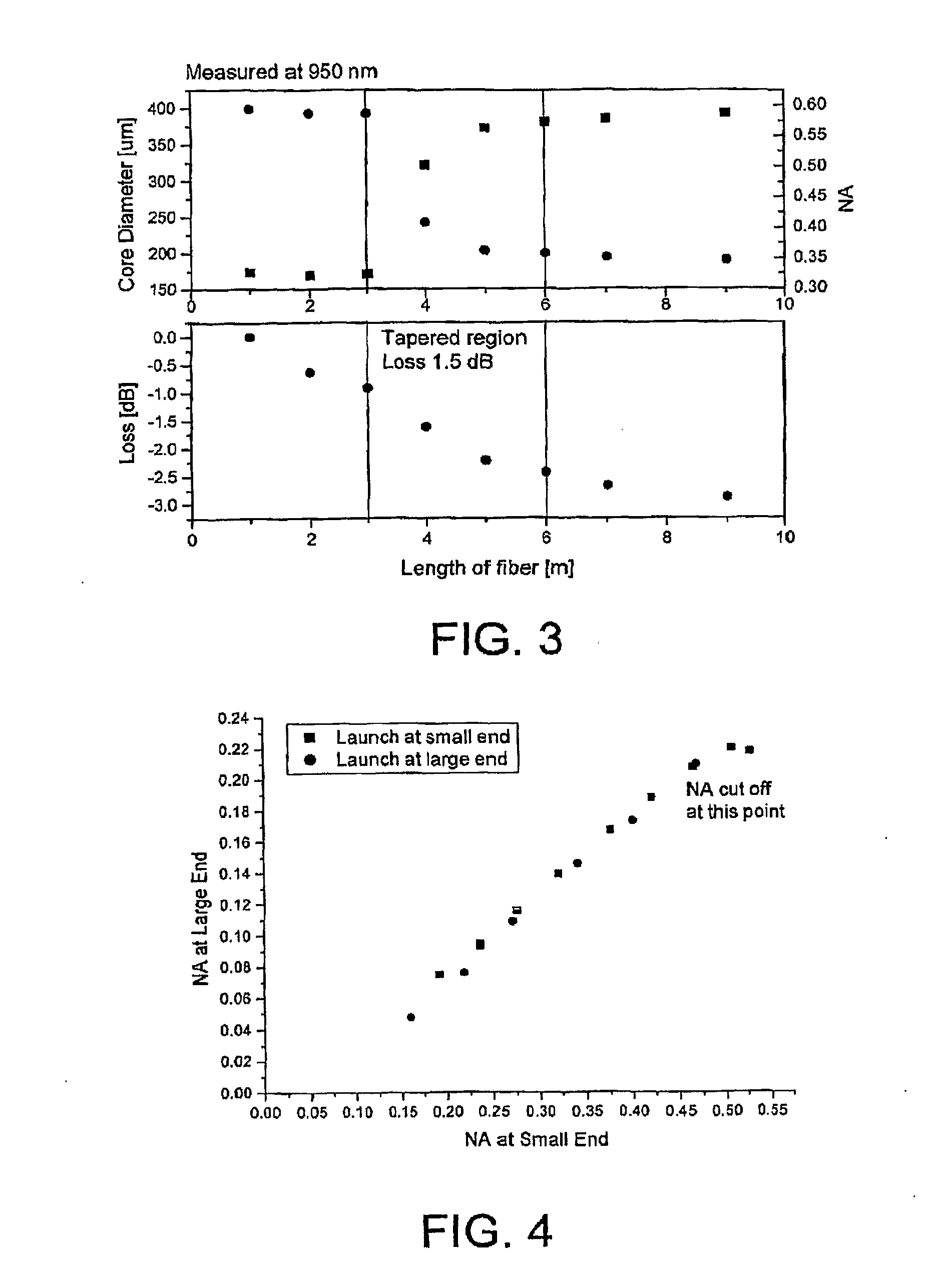
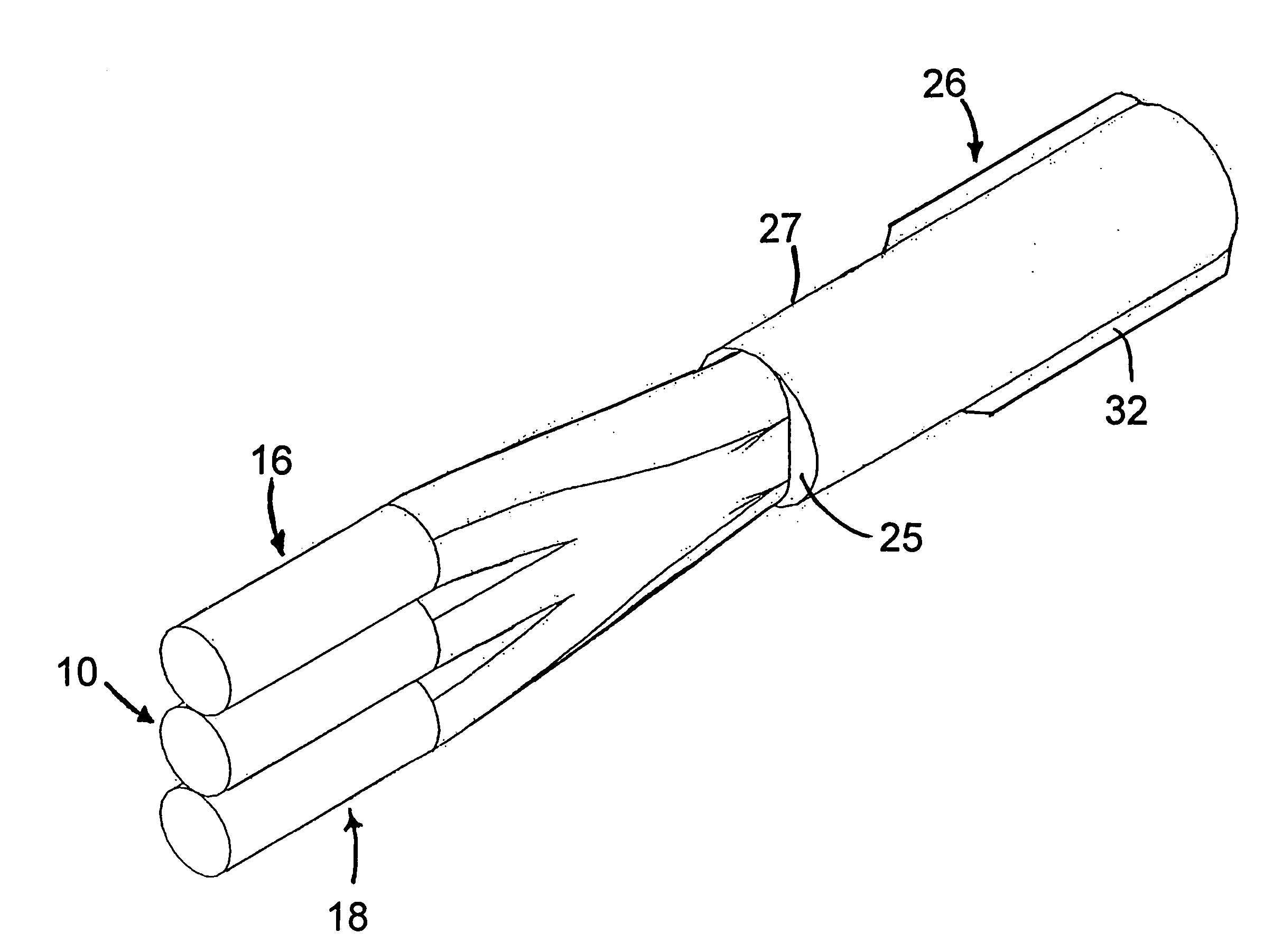
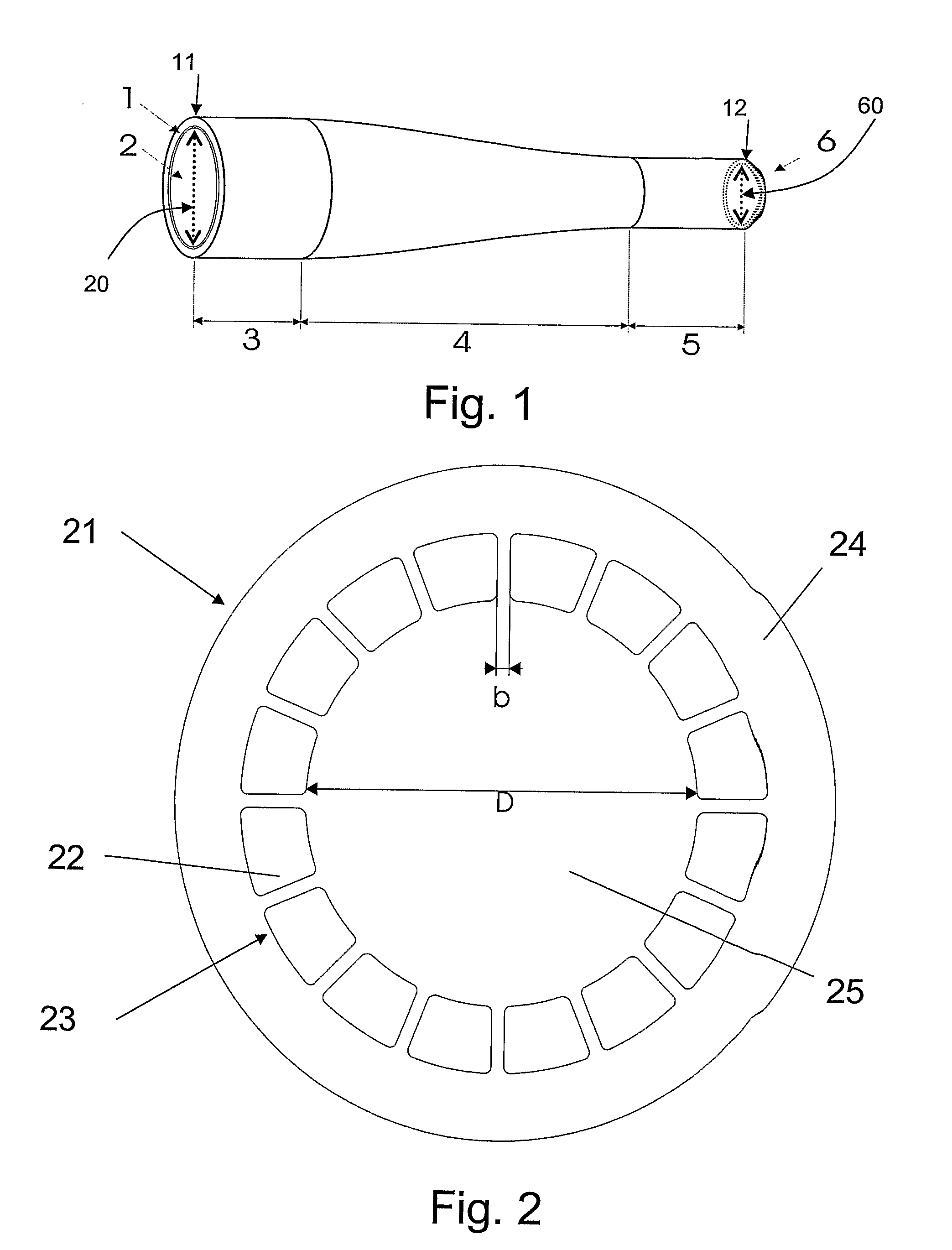
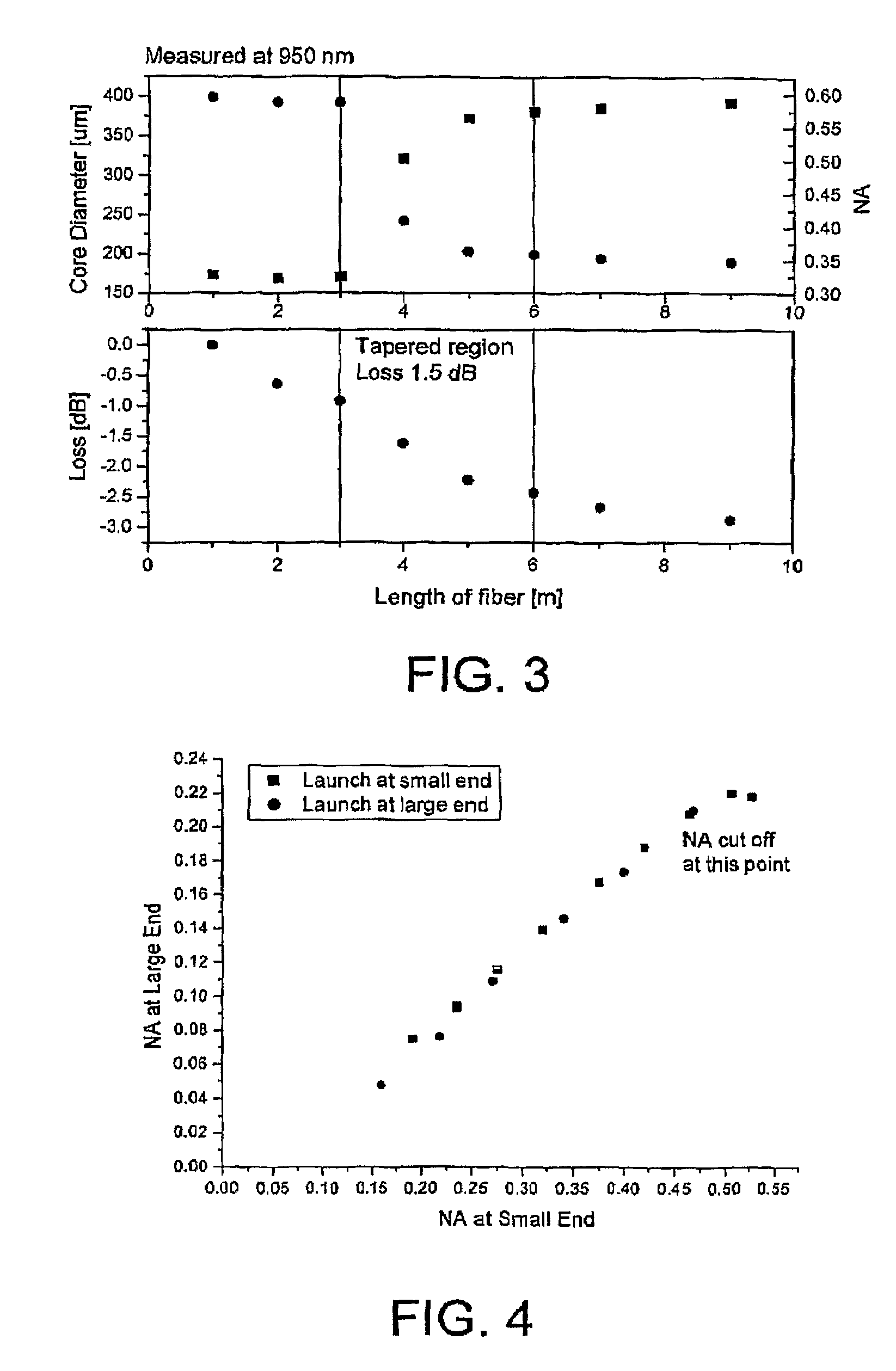
The present invention relates in general to coupling of light from one or more input waveguides to an output waveguide or output section of a waveguide having other physical dimensions and / or optical properties than the input waveguide or waveguides. The invention relates to an optical component in the form of a photonic crystal fibre for coupling light from one component / system with a given numerical aperture to another component / system with another numerical aperture. The invention further relates to methods of producing the optical component, and articles comprising the optical component, and to the use of the optical component. The invention further relates to an optical component comprising a bundle of input fibres that are tapered and fused together to form an input coupler e.g. for coupling light from several light sources into a single waveguide. The invention still further relates to the control of the spatial extension of a guided mode (e.g. a mode-field diameter) of an optical beam in an optical fibre. The invention relates to a tapered longitudinally extending optical waveguide having a relatively larger cross section that over a certain longitudinal distance is tapered down to a relatively smaller cross section wherein the spatial extent of the guided mode is substantially constant or expanding from the relatively larger to the relatively smaller waveguide cross section. The invention may e.g. be useful in applications such as fibre lasers or amplifiers, where light must be coupled efficiently from pump sources to a double clad fibre.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
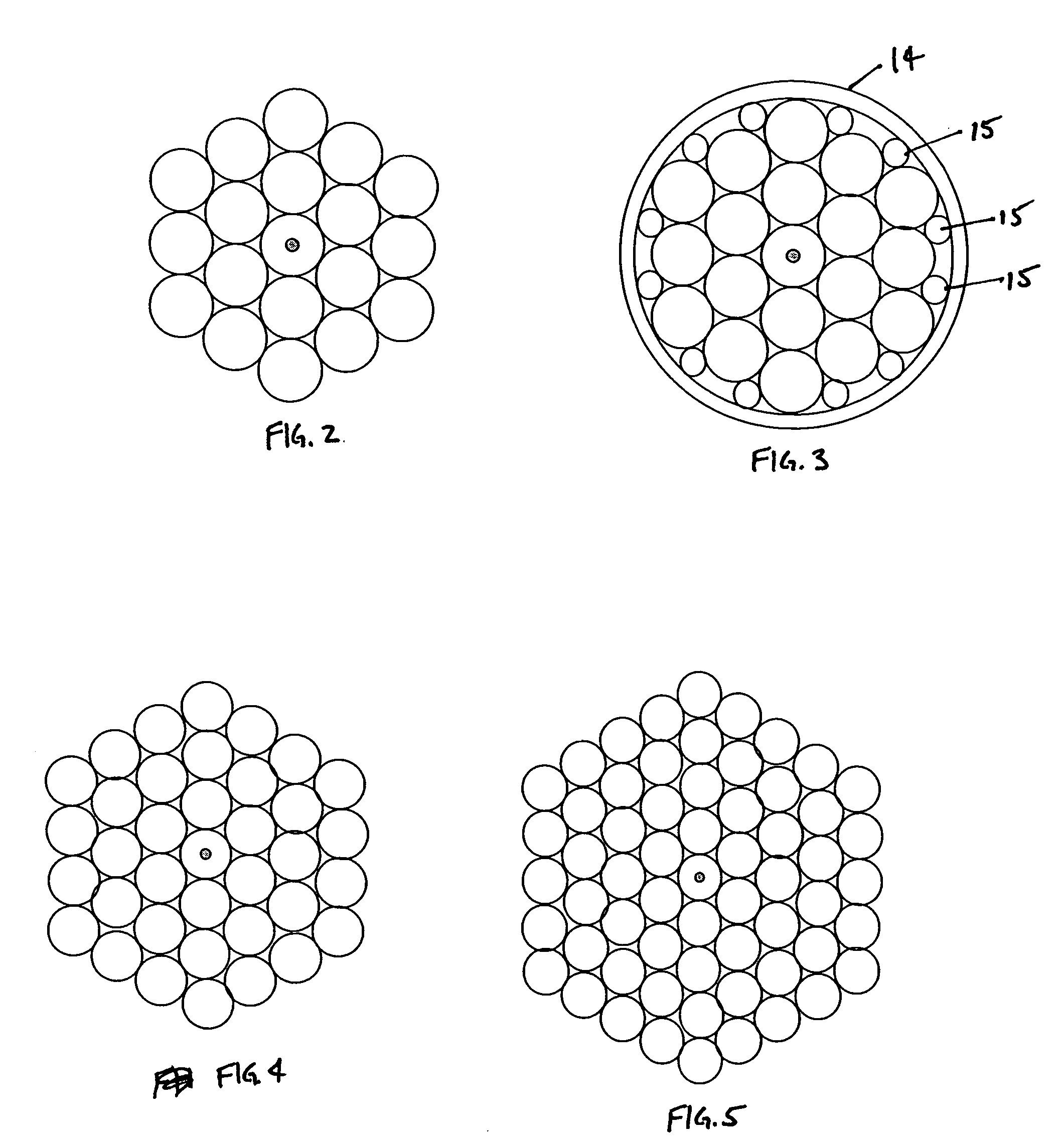
Optical coupler comprising multimode fibers and method of making the same
ActiveUS20050094952A1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesFew mode fiberDouble-clad fiber
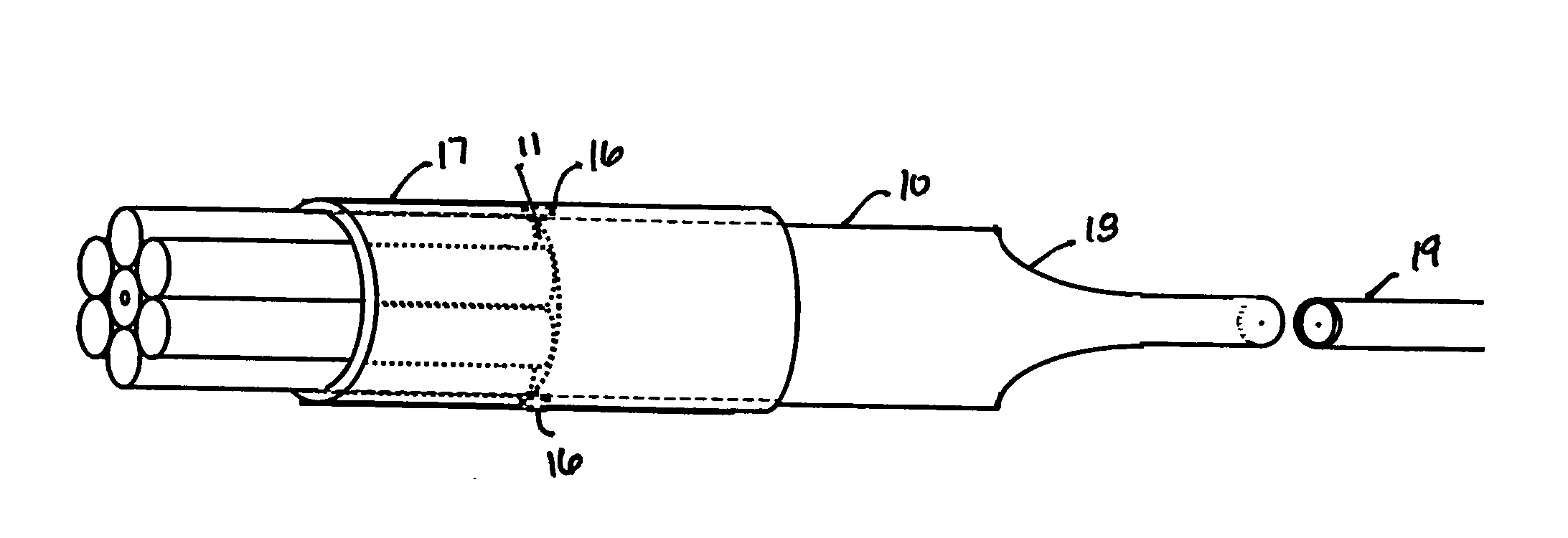
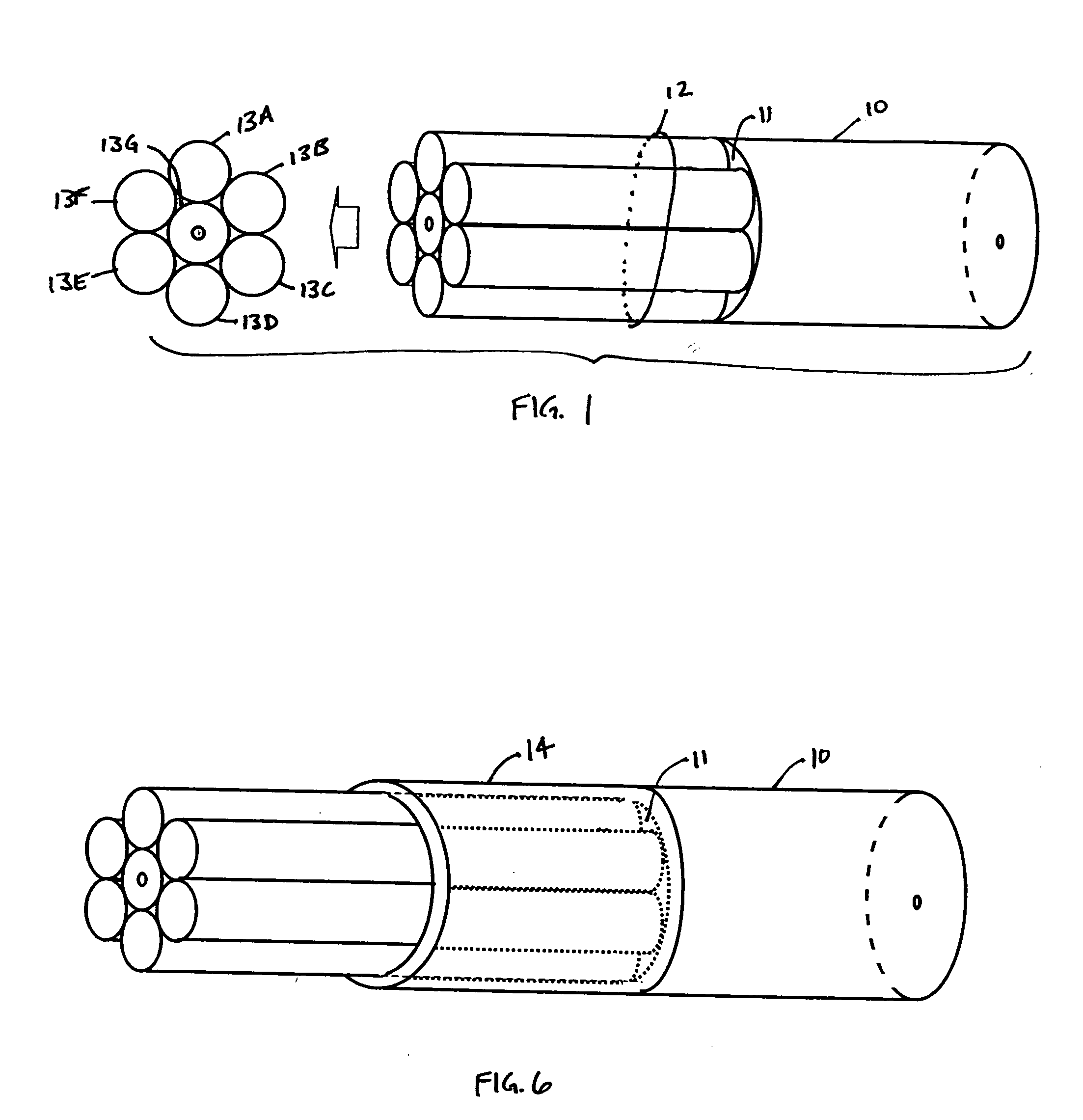
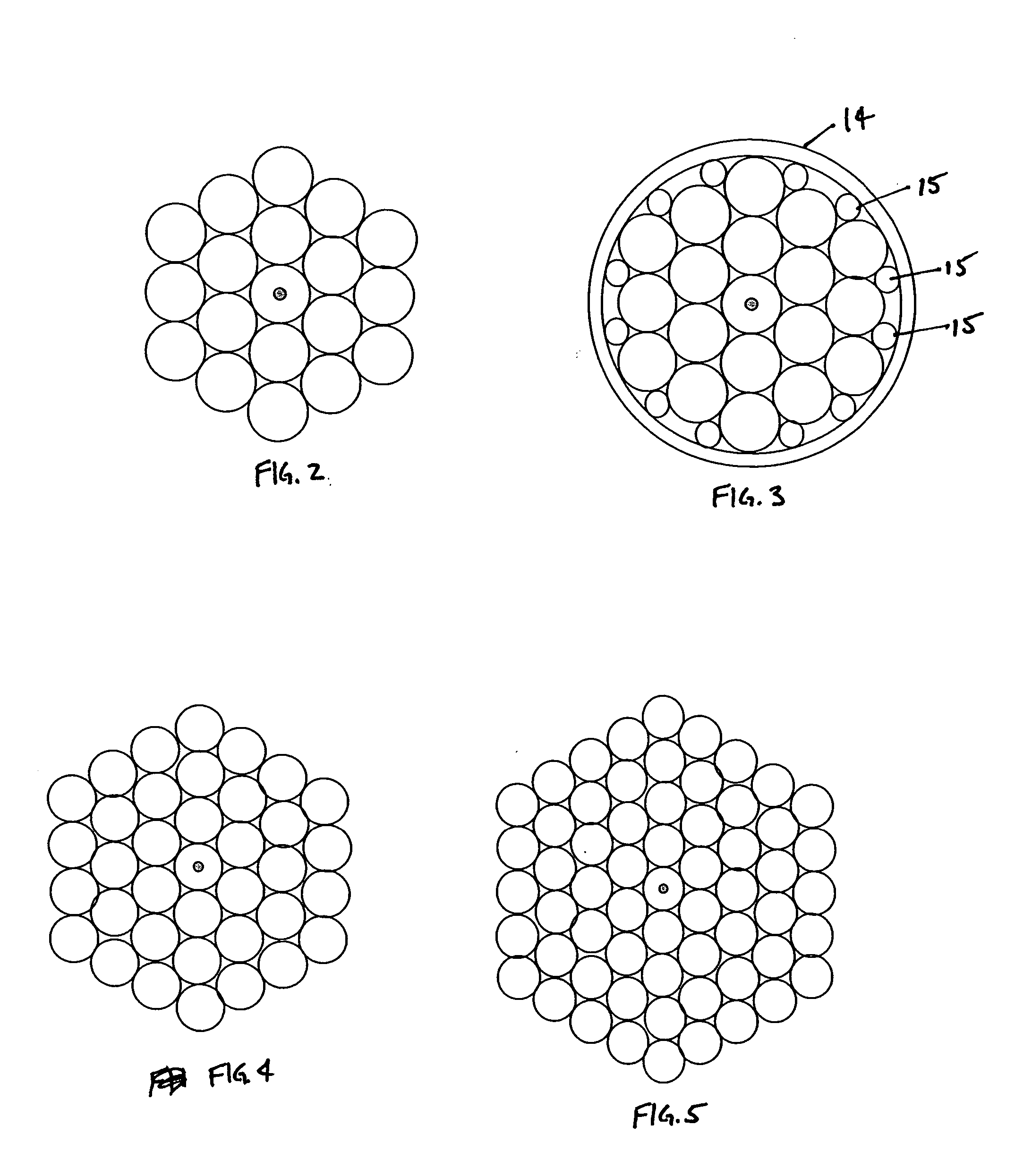
An optical coupler is provided. It has a bundle of multimode fibers with a few-mode fiber in its centre. Such bundle is fused at one end which is the output end for the signal that is transmitted by the few-mode fiber. To make the coupler, this output end of the bundle is aligned and spliced with a large area core double clad fiber while preserving the modal content of the feed-through. A method for making such optical coupler is also provided. It includes the steps of bundling a central few-mode fiber with a plurality of multimode fibers and then fusing one end of such bundle and aligning it and splicing with a large core double clad fiber, while preserving fundamental mode transmission from one to the other.
Owner:ITF TECH +1
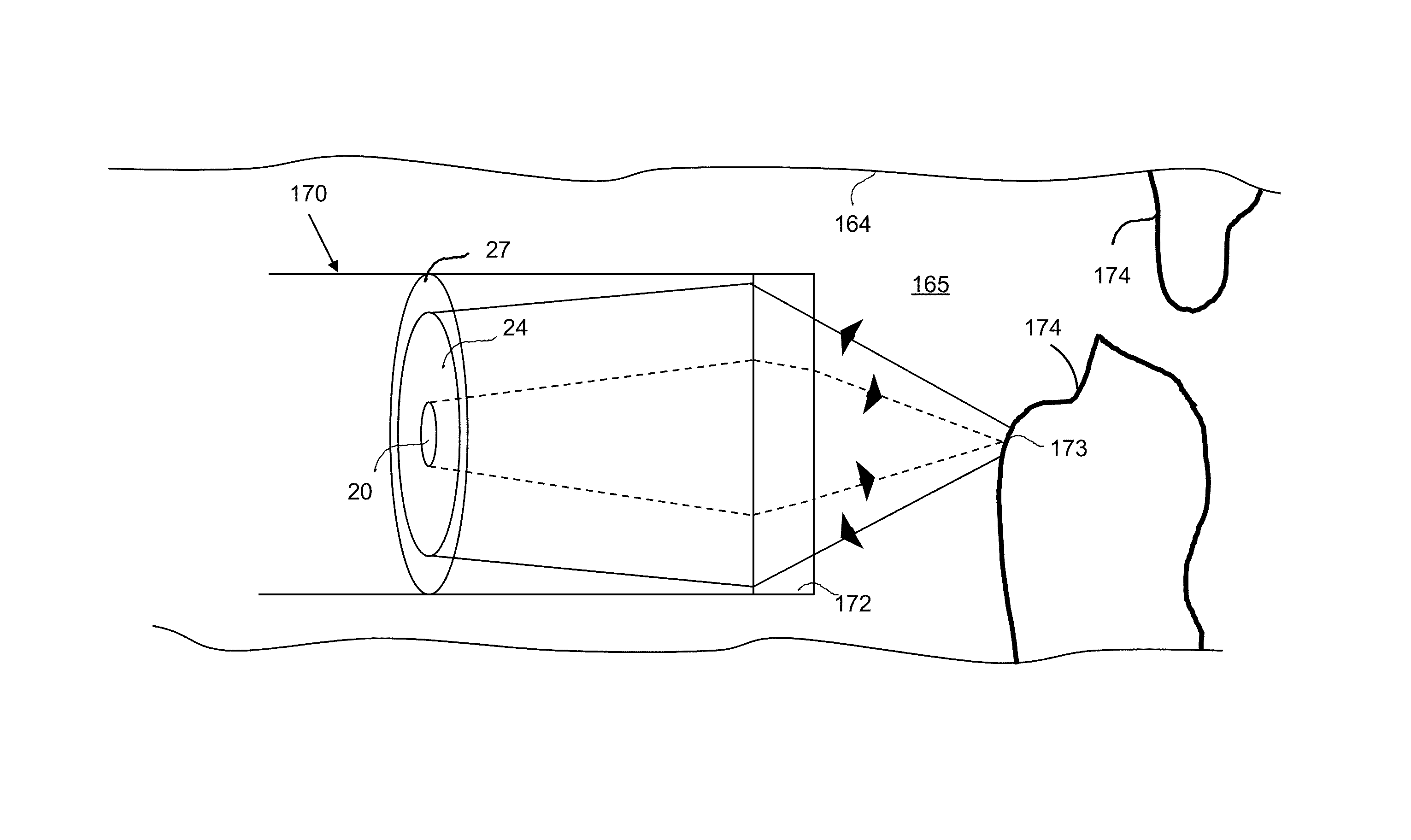
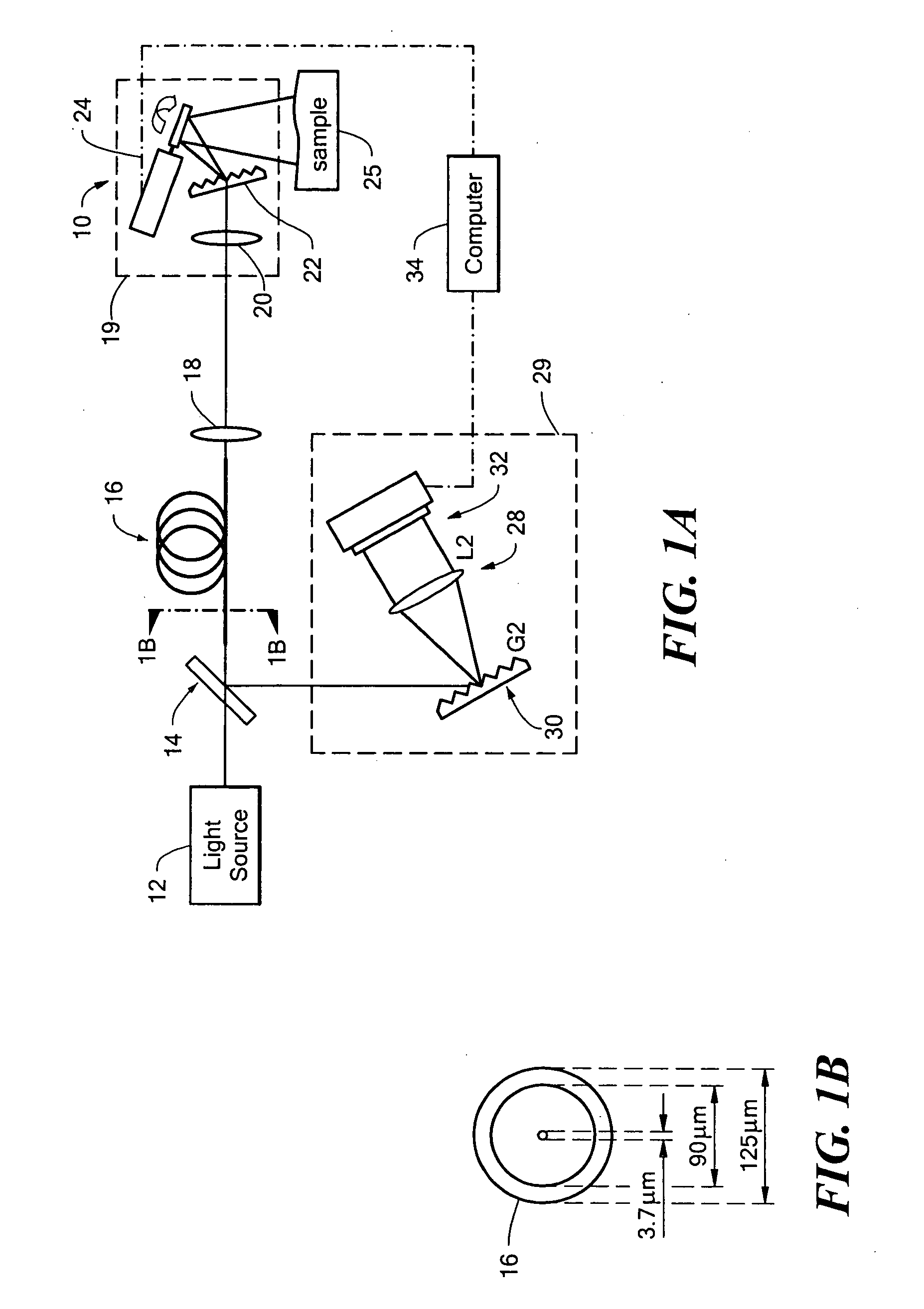
Optical catheter configurations combining raman spectroscopy with optical fiber-based low coherence reflectometry
The present invention provides apparatuses and methods for sample analysis, such as tissue analysis, that integrate high wavenumber (HW) Raman spectroscopy for chemical composition analysis and optical coherence tomography (OCT) to provide depth and morphological information. The invention also provides side-viewing optical probes that are based on a single double clad optical fiber for performing the combined HW Raman spectroscopy and OCT. Intravascular catheter embodiments and related vascular diagnostic methods are also provided.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
Optical fiber pump multiplexer
InactiveUS20050105854A1Lower refractive indexLaser detailsCoupling light guidesSignal waveDouble-clad fiber
One or more single mode few-moded or multimode fibers are incorporated into a bundle to carry input to a fiber amplifier or output from a fiber amplifier or a fiber laser. The input is at the signal wavelength, which is the wavelength where amplification or lasing occurs. Each of the fibers in the bundle is cleaved individually or as a group and fiber ends are aligned in the same plane. The fiber amplifier or fiber laser may include a double clad fiber and the other fibers of the bundle couple light for cladding pumping. The device may also include a mode filter for controlling the output mode.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Spectroscopic imaging probes, devices, and methods
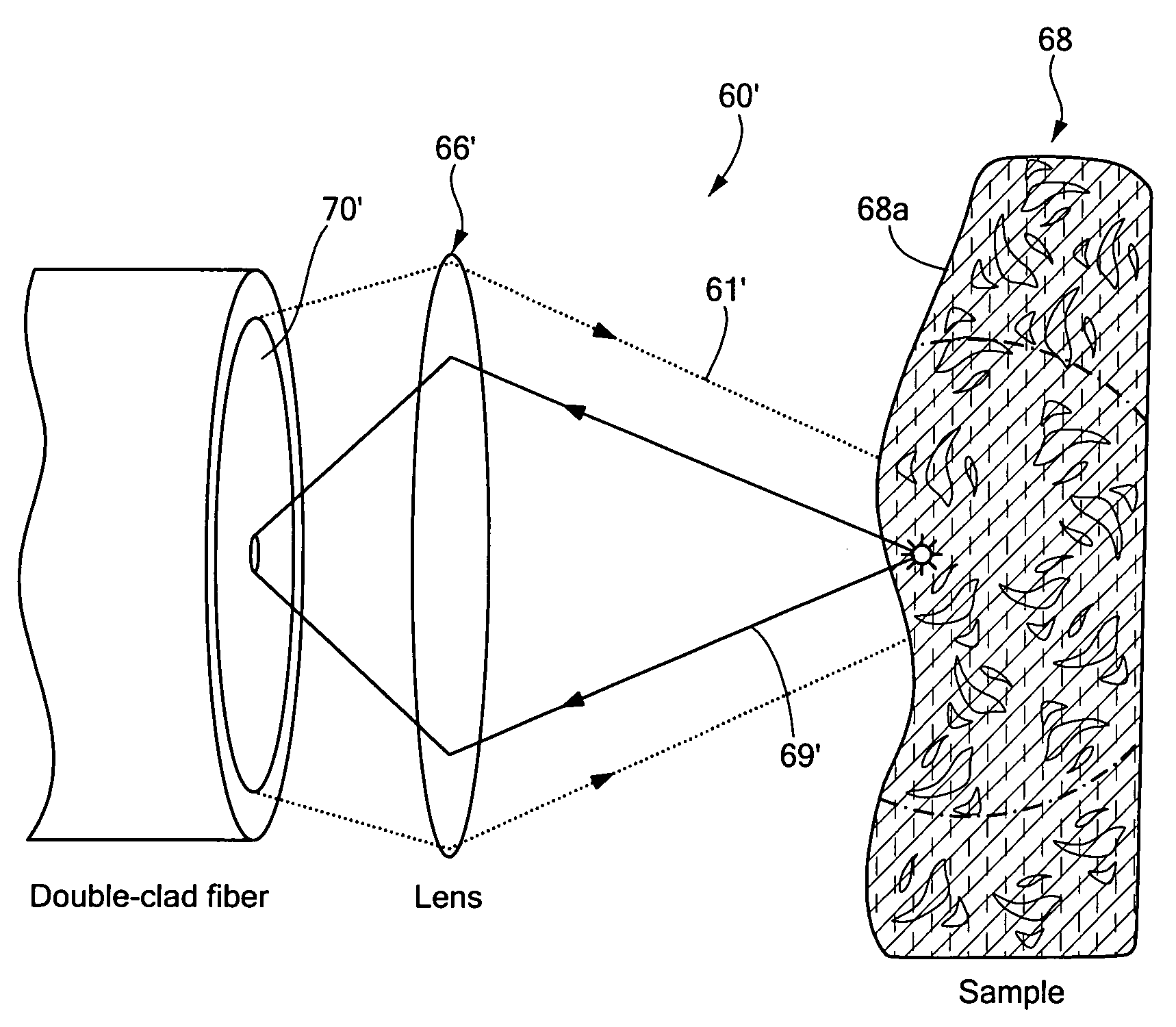
In part, the invention relates to a single clad fiber to multi-clad optical fiber connector for use in applying excitation light to a sample and obtaining reflected light from the sample. The connector can include a dual clad optical fiber portion and a single clad optical fiber portion in optical communication with the dual clad optical fiber portion. In one embodiment, a core of the dual clad optical fiber portion and a core of the single clad optical fiber portion have substantially similar indices of refraction. In one embodiment, excitation light is propagated by the core of the dual clad optical fiber. Further, in one embodiment, light reflected by the sample is propagated by the first cladding layer of the dual clad optical fiber portion.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Optical fiber pump multiplexer
InactiveUS7016573B2Lower refractive indexLaser detailsCoupling light guidesDouble-clad fiberMultiplexer
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Fiber lasers
ActiveUS7778290B2Improve conversion efficiencyImprove abilitiesLaser using scattering effectsDouble-clad fiberPolarizer
Fiber lasers for producing Band I wavelengths include a laser cavity having an optical fiber with specific parameters in length and thickness and doping concentration, and having high reflectivities. Examples show the feasibility of producing such fiber lasers. Fiber lasers for producing Band IV wavelengths include a depolarized laser oscillator, at least one amplifier and a polarizer. Depolarized laser oscillator is an inherently depolarized CW laser, or a depolarized laser diode, which is depolarized by a depolarizer. Additional fiber lasers in accordance with embodiments of the present invention include a double clad active optical fiber having a pump power entry point for sending pump energy through the active optical fiber in a first direction, and a loop portion at a second end of the fiber for sending pump energy through the active optical fiber in a second direction which is opposite to the first direction. A system for coupling light into a fiber in accordance with embodiments of the present invention include a first fiber, a second double clad fiber, and a bulk optic component positioned between the first and second fibers. A mode stripper included within the second fiber allows for removal of high power light which is propagated through the outer clad rather than launched into the core of the second fiber.
Owner:ELBIT SYST ELECTRO OPTICS ELOP
Method for stripping residual pump light in double-coated optical fiber
InactiveCN101718916ASimple structureEasy to implementOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingNon-linear opticsDouble-clad fiberOptical fiber amplifiers
The invention relates to a method for stripping residual pump light in a double-coated optical fiber, which comprises the steps of: removing an outer coating and a cladding layer of one section of the double-coated optical fiber at the output end of a full optical fiber laser; covering optical gel with high refractive index outside an inner coating of the section of the optical fiber, wherein the refractive index of the optical gel is higher than that of the inner coating of the double-coated optical fiber; leaking light transmitted in the inner coating out through the optical gel, and fully absorbing the leaded pump light with high power by a heat radiating device. The invention has the characteristics of compact structure and convenient integration, and can be applied to a high-power optical fiber laser or high-power optical fiber amplifier.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Distributed Optical Fibre Sensing
ActiveUS20120127459A1Increase rangeHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansDouble-clad fiberOptoelectronics
There is disclosed a distributed optical fibre sensing system in which the sensor fibre comprises at least first and second waveguides used for separate sensing operations. The sensor fibre may be, for example, a double clad fibre having a monomode core and a multimode inner cladding.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
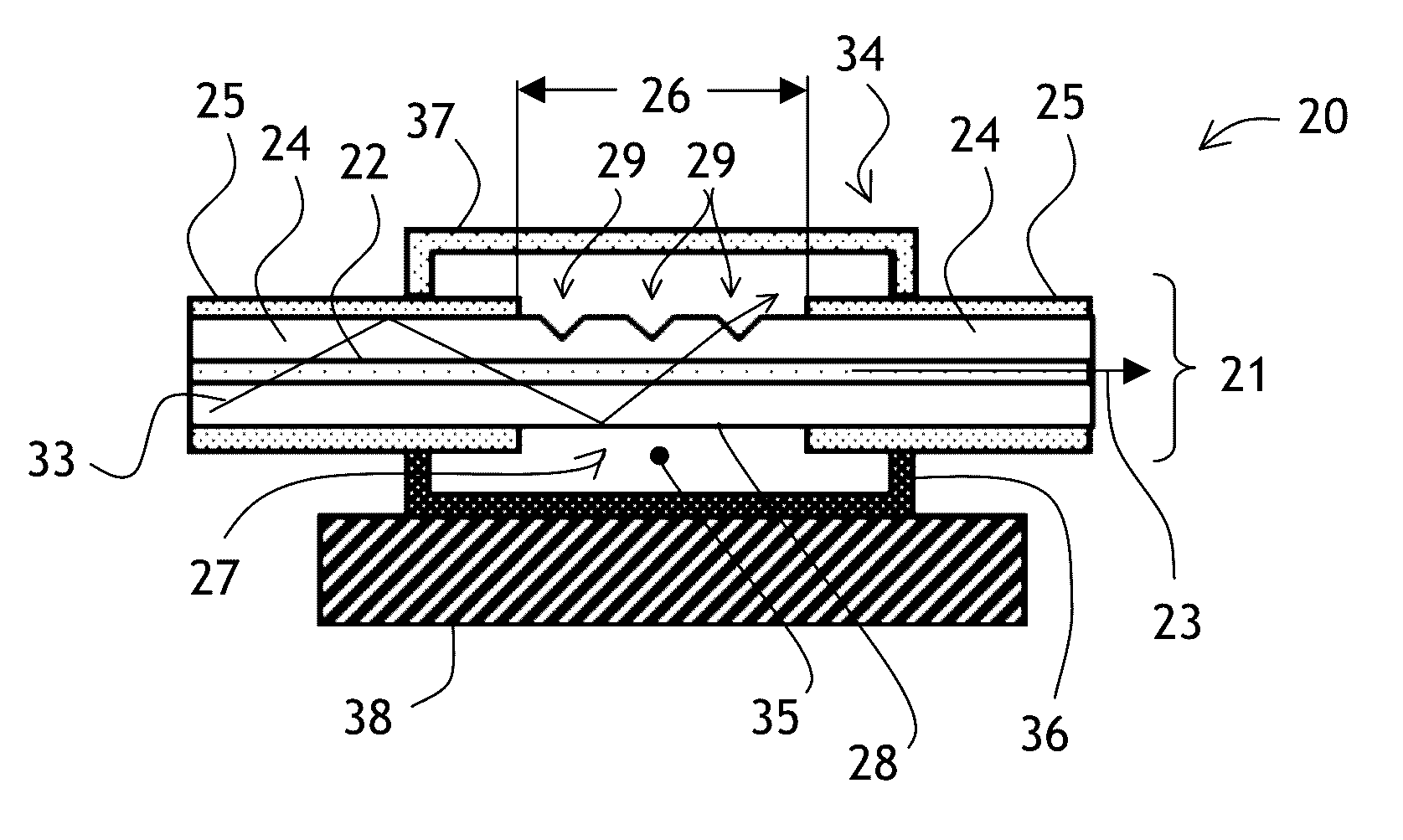
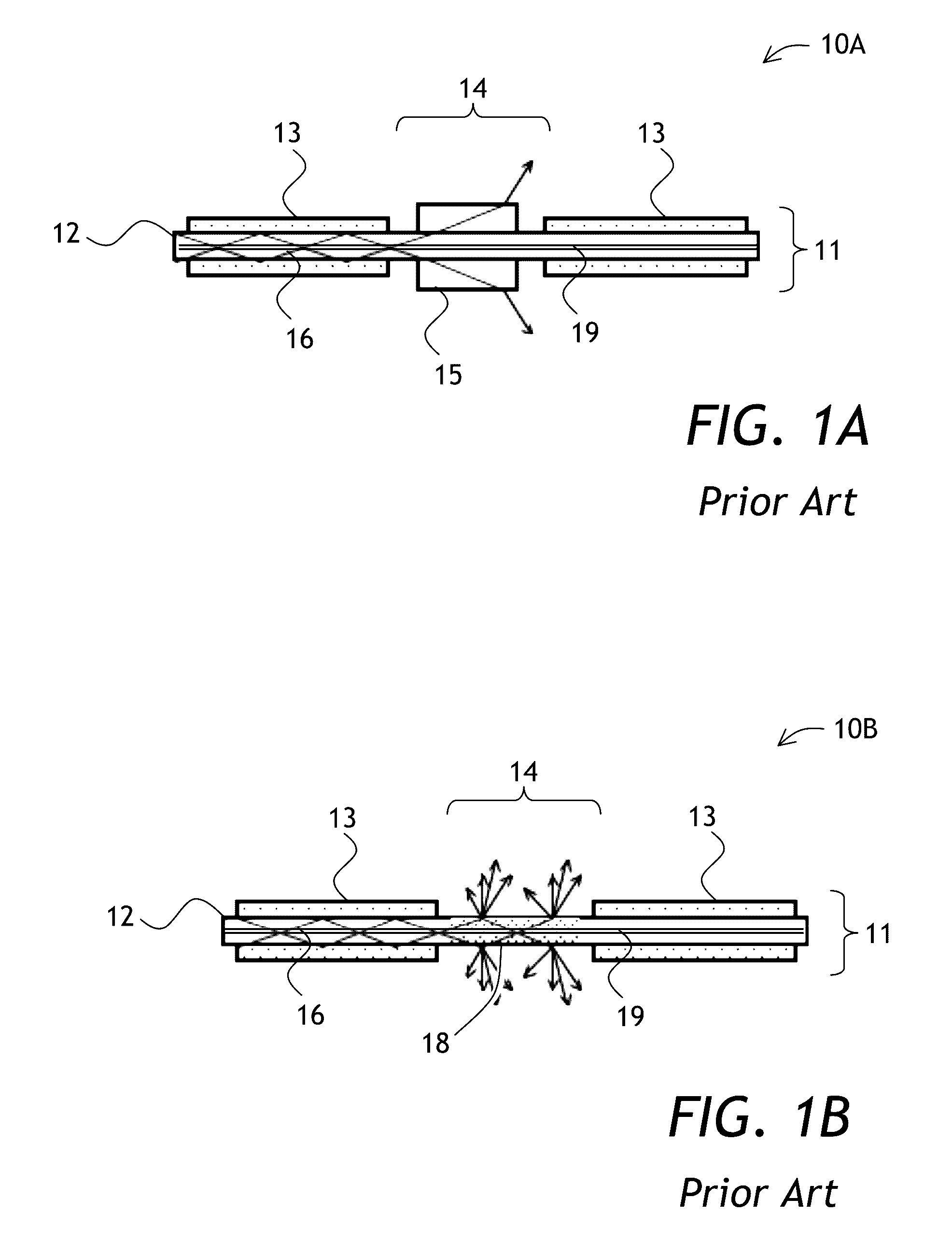
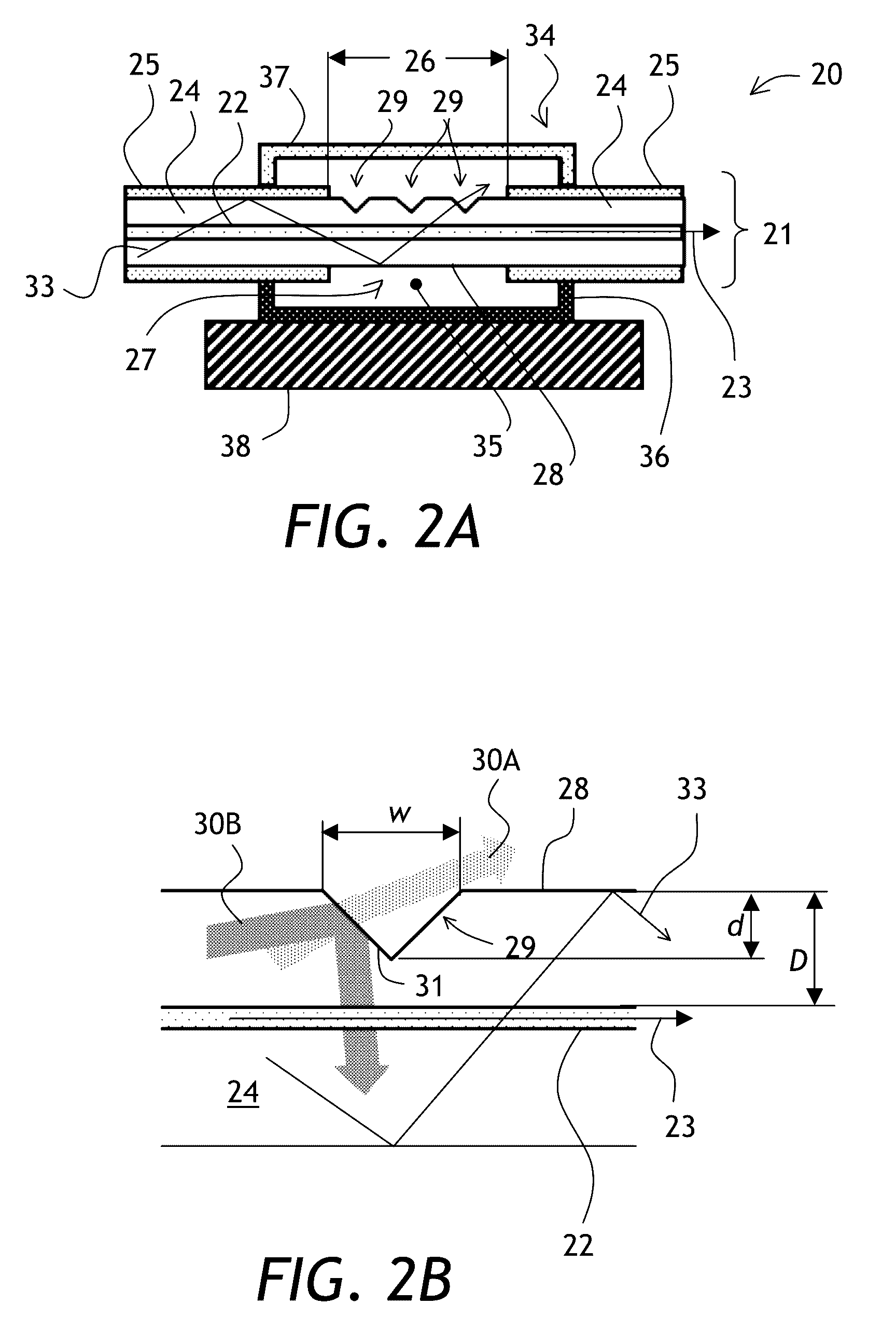
Cladding light stripper and method of manufacturing
ActiveUS20140211818A1High optical power levelHigh levelLaser using scattering effectsOptical articlesDouble-clad fiberLaser ablation
A cladding stripper includes a plurality of transversal notches or grooves in the outer surface of an exposed inner cladding of a double clad optical fiber. Position and orientation of the notches can be selected to even out cladding light release along the cladding light stripper, enabling more even temperature distributions due to released cladding light. The notches on the optical fiber can be made with a laser ablation system.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Fiber cladding light filter and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102255227AIncrease powerAvoid heat damageActive medium shape and constructionDouble-clad fiberOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a fiber cladding light filter and a manufacturing method thereof. In the fiber cladding light filter, a section of coating layer of a single-cladding fiber or a section of coating layer and an outer cladding of a double-cladding fiber are removed; the surface of an exposed cladding or an inner cladding is roughened by using a cutting knife or a chemical agent; total reflection conditions of pumping light and cladding laser in the cladding of the single-cladding fiber and the inner cladding of the double-cladding fiber are destroyed; a section of the fiber is sealed in a metal container with a water inlet and a water outlet; and flowing cooling water is filled into the metal container. The fiber cladding light filter is simple in structure and high in filtering efficiency, can bear filtered cladding light with higher power and prevent thermal damage on a component and can be applied to a high-power fiber laser and a high-power fiber amplifier.
Owner:SHANGHAI FEIBO LASER TECH CO LTD
Optical coupler devices, methods of their production and use
InactiveUS20090080469A1Difficult to packageLess fragileLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingDouble-clad fiberAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates to an optical component comprising an acceptance fibre, e.g. a photonic crystal fibre, for propagation of pump and signal light, a number of pump delivery fibres and a reflector element that reflects pump light from the pump delivery fibres into the acceptance fibre. It is an object of the invention to provide a fibre coupler for coupling two or more light sources into a multi-clad (e.g. double clad) optical fibre, which has practical advantages with respect to handling, loss and back reflection. An object of the invention is achieved by an optical component comprising a) a first fibre having a pump core with an NA1, and a first fibre end; b) a number of second fibres surrounding said pump core of said first fibre, at least one of said second fibres has a pump core with an NA2 that is smaller than NA1, said number of second fibres each having a second fibre end; and c) a reflector element comprising an end-facet with a predetermined profile for reflecting light from at least one of said second fibre ends into the pump core of said first fibre. The invention further relates to articles comprising the optical component (e.g. a laser or amplifier), to methods of its production and use. The invention further relates to a rod-type optical fibre with optimized stiffness to volume ratio. The invention may e.g. be useful in applications such as fibre lasers or amplifiers, where light can be coupled efficiently from pump sources to an acceptance fibre, e.g. a double clad fibre, using the optical component. The invention specifically addresses optical fibre amplifiers where pump light and signal light are propagating in different directions (counter-propagating pump) within a double-clad optical fibre.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Imaging system and related techniques
ActiveUS20060013544A1Improve image qualityReduces image speckleRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDouble-clad fiberComputer science
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Optical coupler devices, methods of their production and use
InactiveUS7526165B2Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDouble-clad fiberWaveguide
The present invention relates in general to coupling of light from one or more input waveguides to an output waveguide or output section of a waveguide having other physical dimensions and / or optical properties than the input waveguide or waveguides. The invention relates to an optical component in the form of a photonic crystal fiber for coupling light from one component / system with a given numerical aperture to another component / system with another numerical aperture. The invention further relates to methods of producing the optical component, and articles comprising the optical component, and to the use of the optical component. The invention further relates to an optical component comprising a bundle of input fibers that are tapered and fused together to form an input coupler e.g. for coupling light from several light sources into a single waveguide. The invention still further relates to the control of the spatial extension of a guided mode (e.g. a mode-field diameter) of an optical beam in an optical fiber. The invention relates to a tapered longitudinally extending optical waveguide having a relatively larger cross section that over a certain longitudinal distance is tapered down to a relatively smaller cross section wherein the spatial extent of the guided mode is substantially constant or expanding from the relatively larger to the relatively smaller waveguide cross section. The invention may e.g. be useful in applications such as fiber lasers or amplifiers, where light must be coupled efficiently from pump sources to a double clad fiber.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Optical catheter configurations combining raman spectroscopy with optical fiber-based low coherence reflectometry
The present invention provides apparatuses and methods for sample analysis, such as tissue analysis, that integrate high wavenumber (HW) Raman spectroscopy for chemical composition analysis and optical coherence tomography (OCT) to provide depth and morphological information. The invention also provides side-viewing optical probes that are based on a single double clad optical fiber for performing the combined HW Raman spectroscopy and OCT. Intravascular catheter embodiments and related vascular diagnostic methods are also provided.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
Cladding light stripper and method of manufacturing
A cladding stripper includes a plurality of transversal notches or grooves in the outer surface of an exposed inner cladding of a double clad optical fiber. Position and orientation of the notches can be selected to even out cladding light release along the cladding light stripper, enabling more even temperature distributions due to released cladding light. The notches on the optical fiber can be made with a laser ablation system.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Quick-response conical micro-nano optical fiber humidity sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103293131AAchieve the purpose of cleaningHigh sensitivityPhase-affecting property measurementsMicro nanoDouble-clad fiber
The invention discloses a quick-response conical micro-nano optical fiber humidity sensor and a preparation method thereof. The humidity sensor comprises a broadband light source, a conical micro-nano optical fiber structure and an optical spectrum analyzer which are sequentially connected, wherein the conical micro-nano optical fiber structure comprises a conical waist region and two conical transitional regions which are positioned at two ends of the conical waist region; the two conical transitional regions are connected with the broadband light source and the optical spectrum analyzer through a standard optical fiber respectively. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) removing a coating layer of a double-clad optical fiber to remain a bare optical fiber containing a fiber core, an inner cladding layer and an outer cladding layer; (2) fusing two ends of the bare optical fiber with the standard optical fiber through an optical fiber welding machine respectively; (3) performing fused biconical taper on the bare optical fiber to obtain the conical micro-nano optical fiber structure; (4) connecting the standard optical fiber of which the two ends are fused with the broadband light source and the optical spectrum analyzer to form the conical micro-nano optical fiber humidity sensor. The quick-response conical micro-nano optical fiber humidity sensor has a simple optical fiber structure, and is high in response speed, wide in measurement range and high in detection sensitivity.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
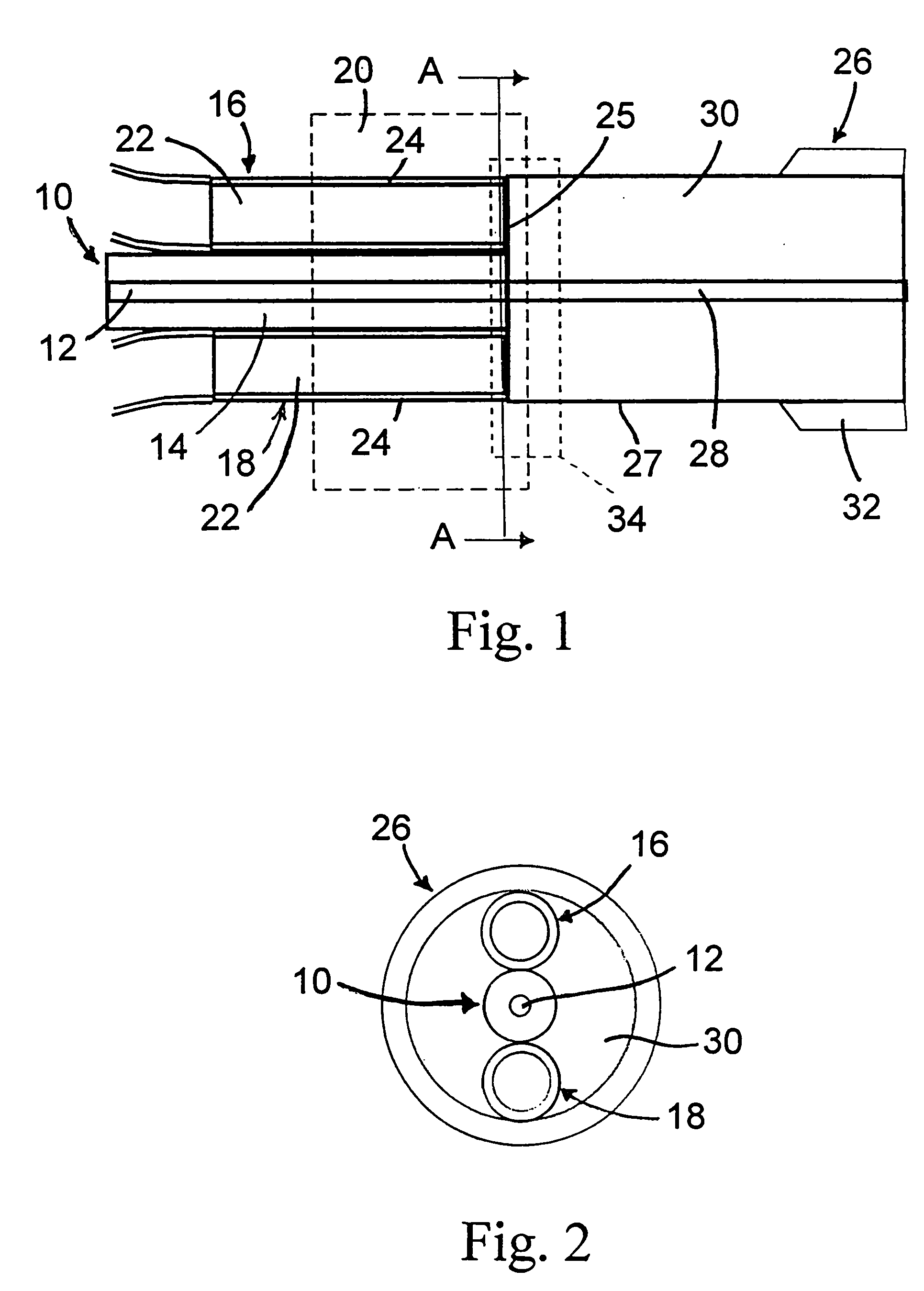
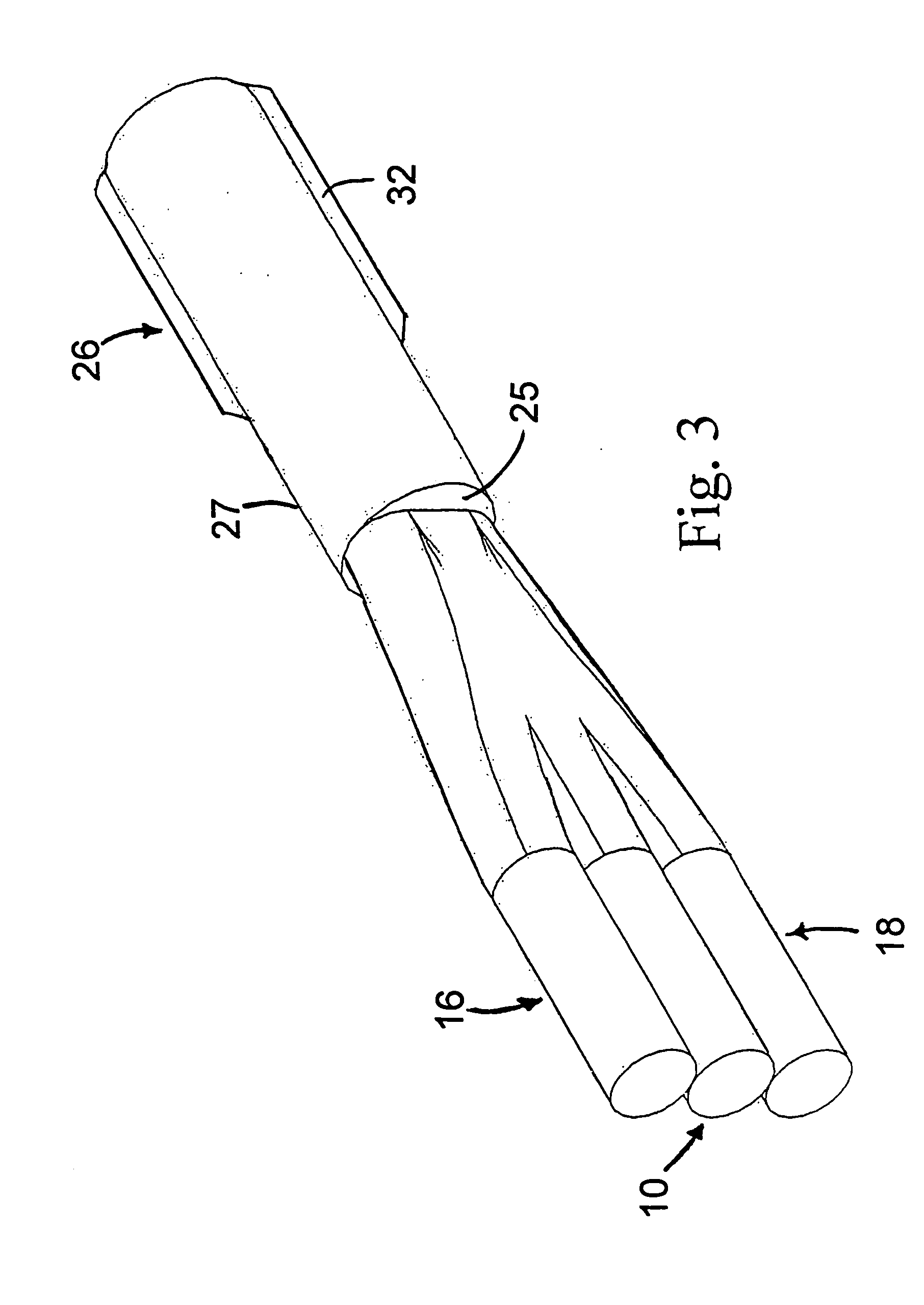
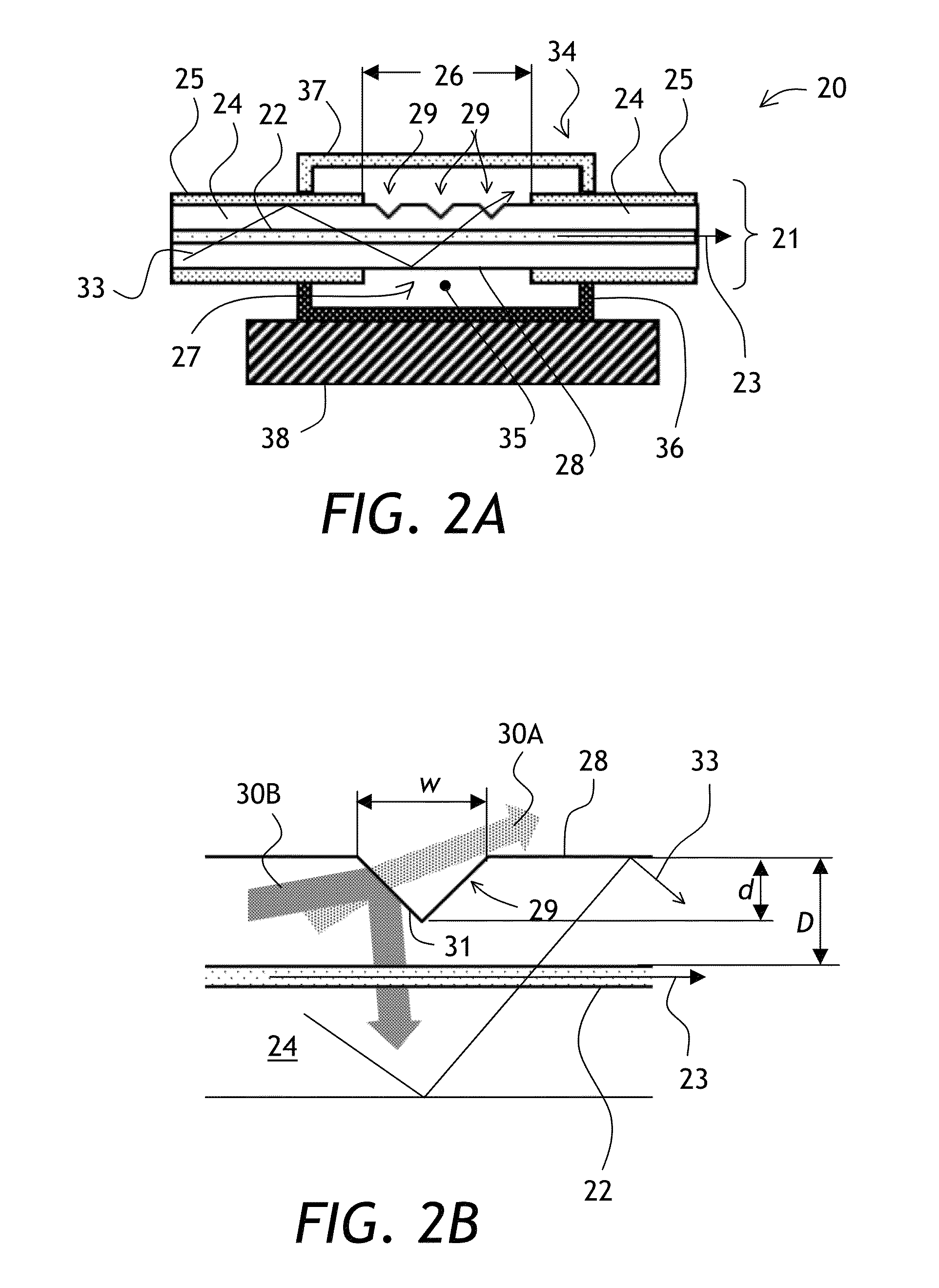
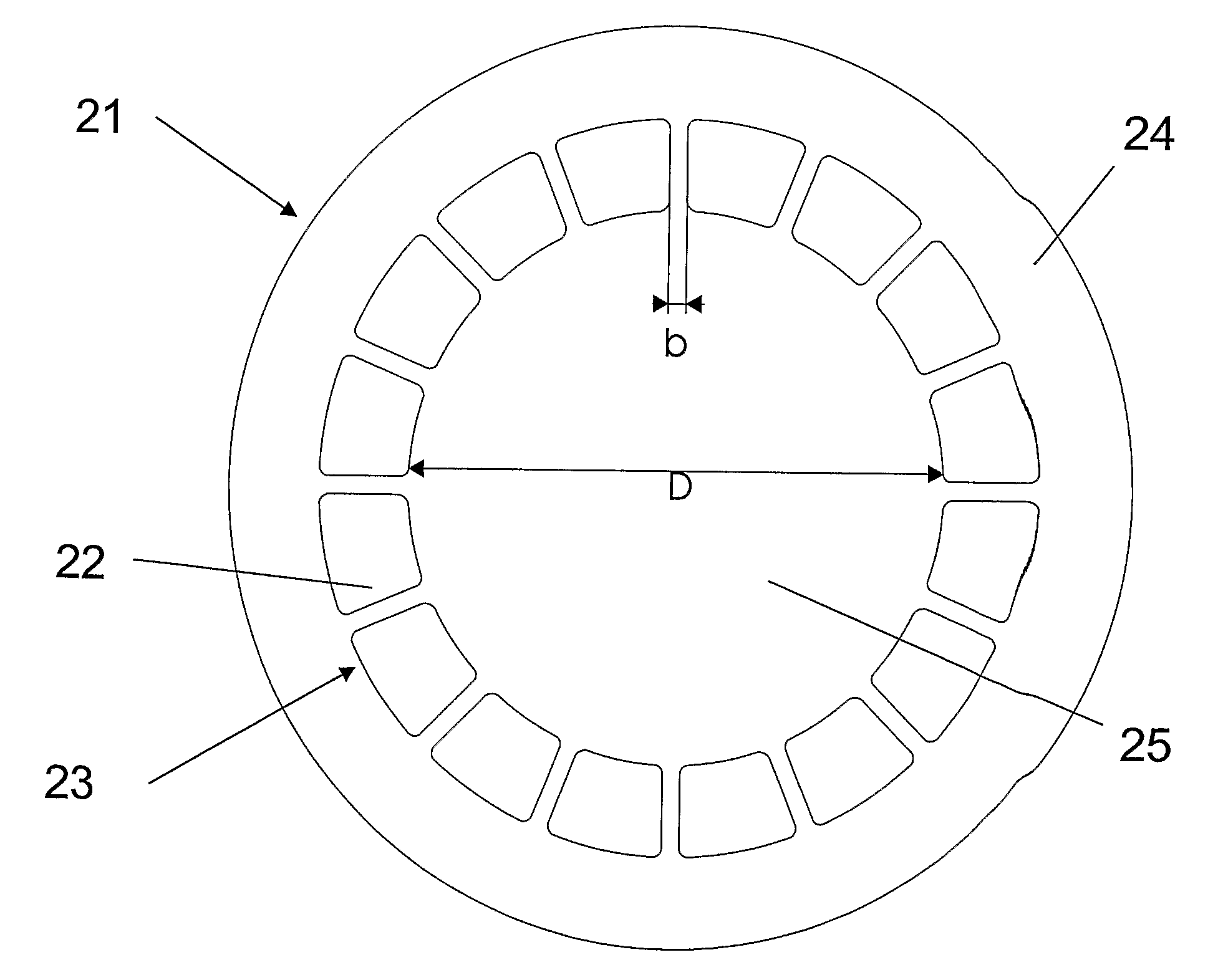
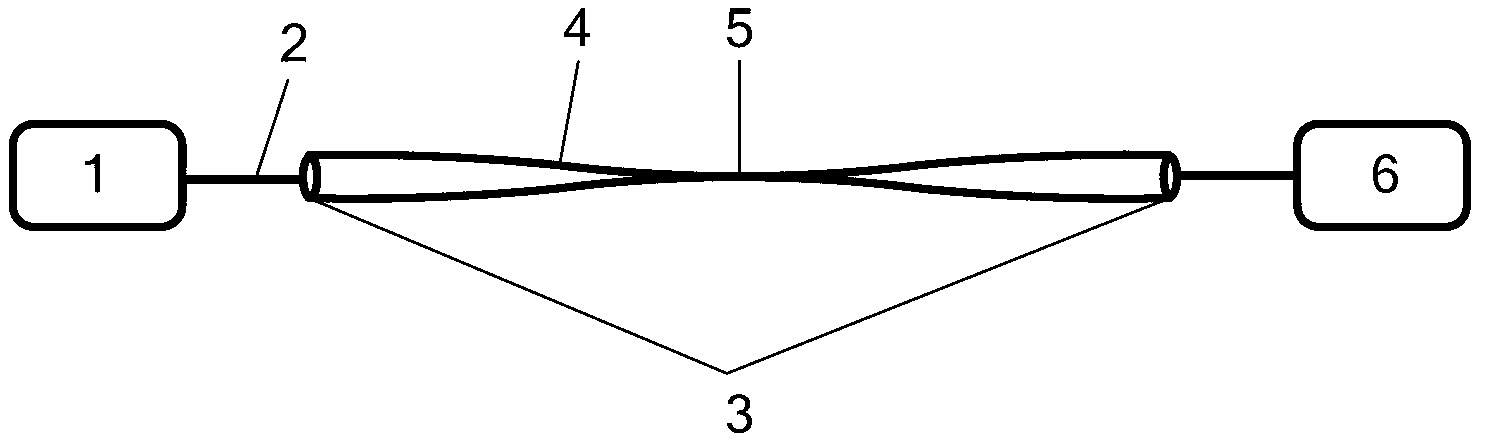
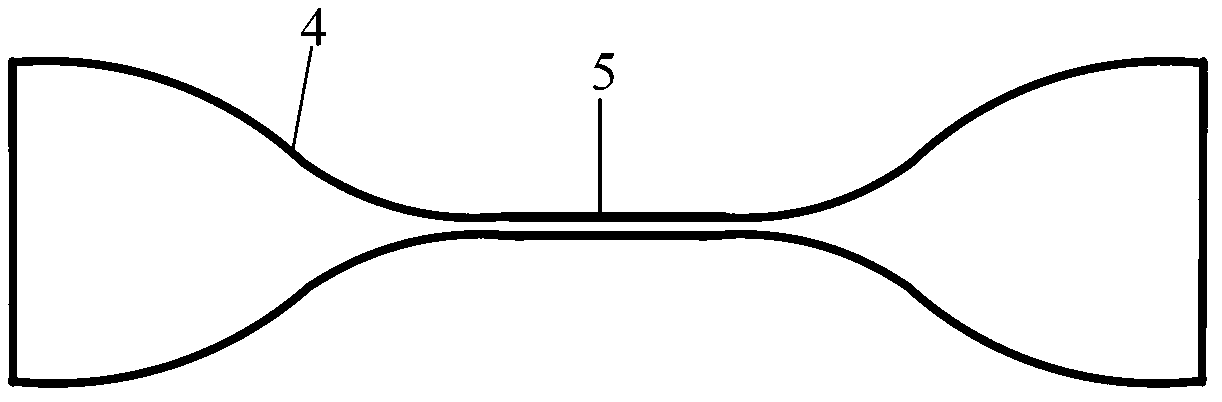
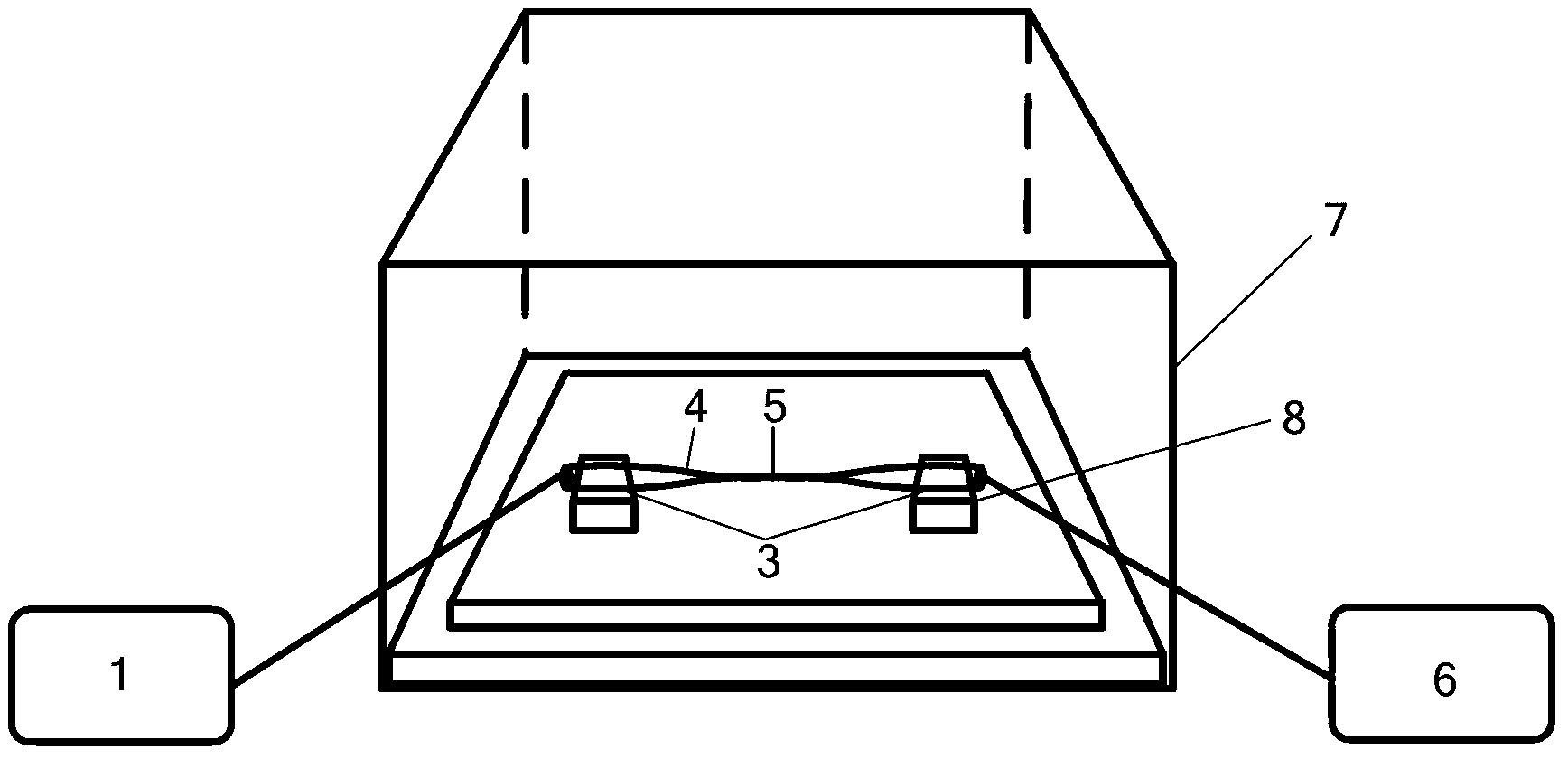
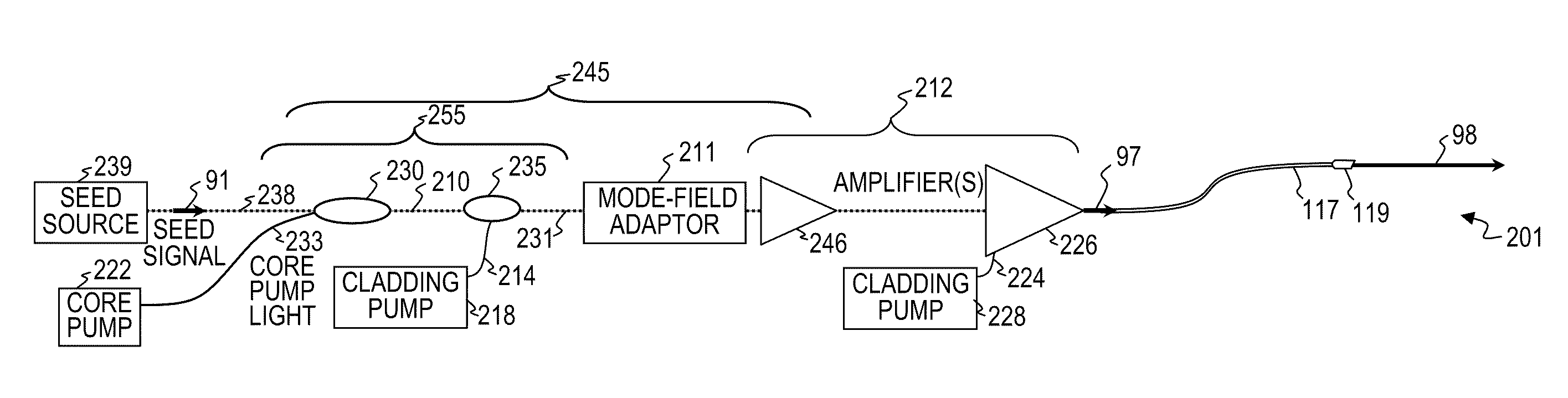
Signal and pump mode-field adaptor for double-clad fibers and associated method
A method and apparatus for mode-matching double-clad fibers. In some embodiments, a first fiber section that has a first core, wherein the first core has a first core diameter connects to a mode-field adaptor, wherein the mode-field adaptor includes a first portion having a central volume that has a substantially constant index-of-refraction radial profile and a diameter larger than the first core diameter, and a second portion that has a graded-index (GRIN) central volume, wherein the GRIN central volume has a central axis and a graded index-of-refraction radial profile having an index that gradually decreases at larger distances from its central axis and a length selected to focus light into the core of a second fiber wherein the second core has a diameter that is larger than the first core diameter, and wherein the second fiber section is double clad. Some embodiments are polarized.
Owner:BDS BV +1
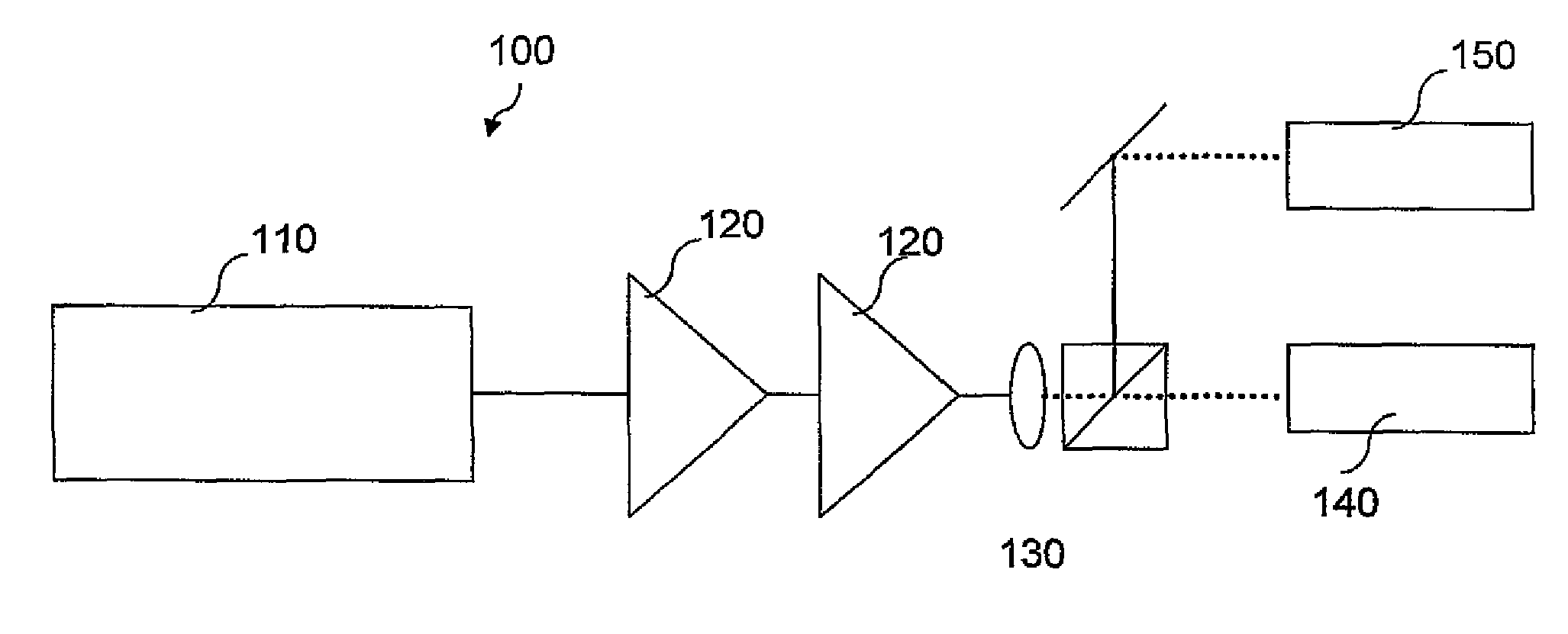
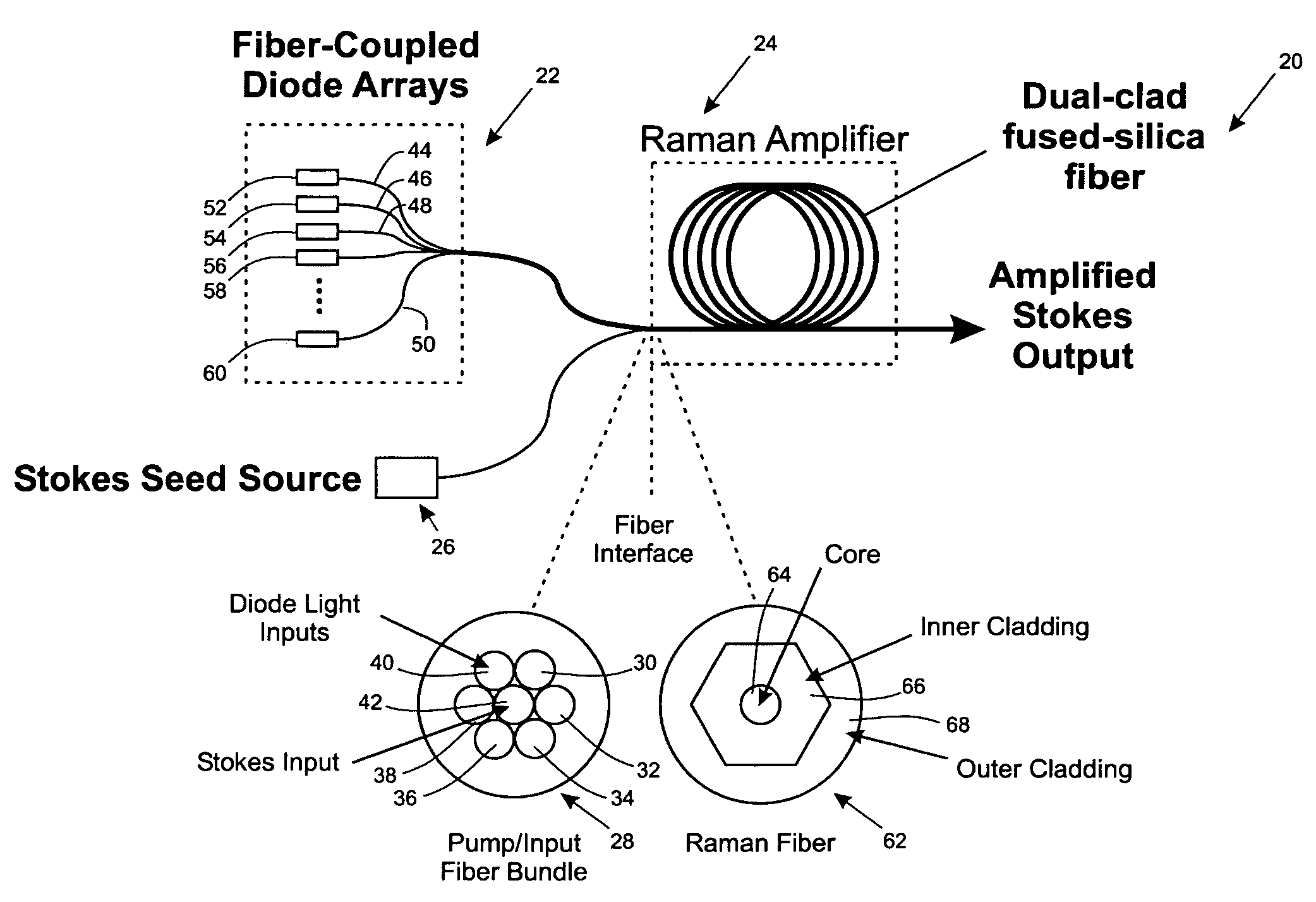
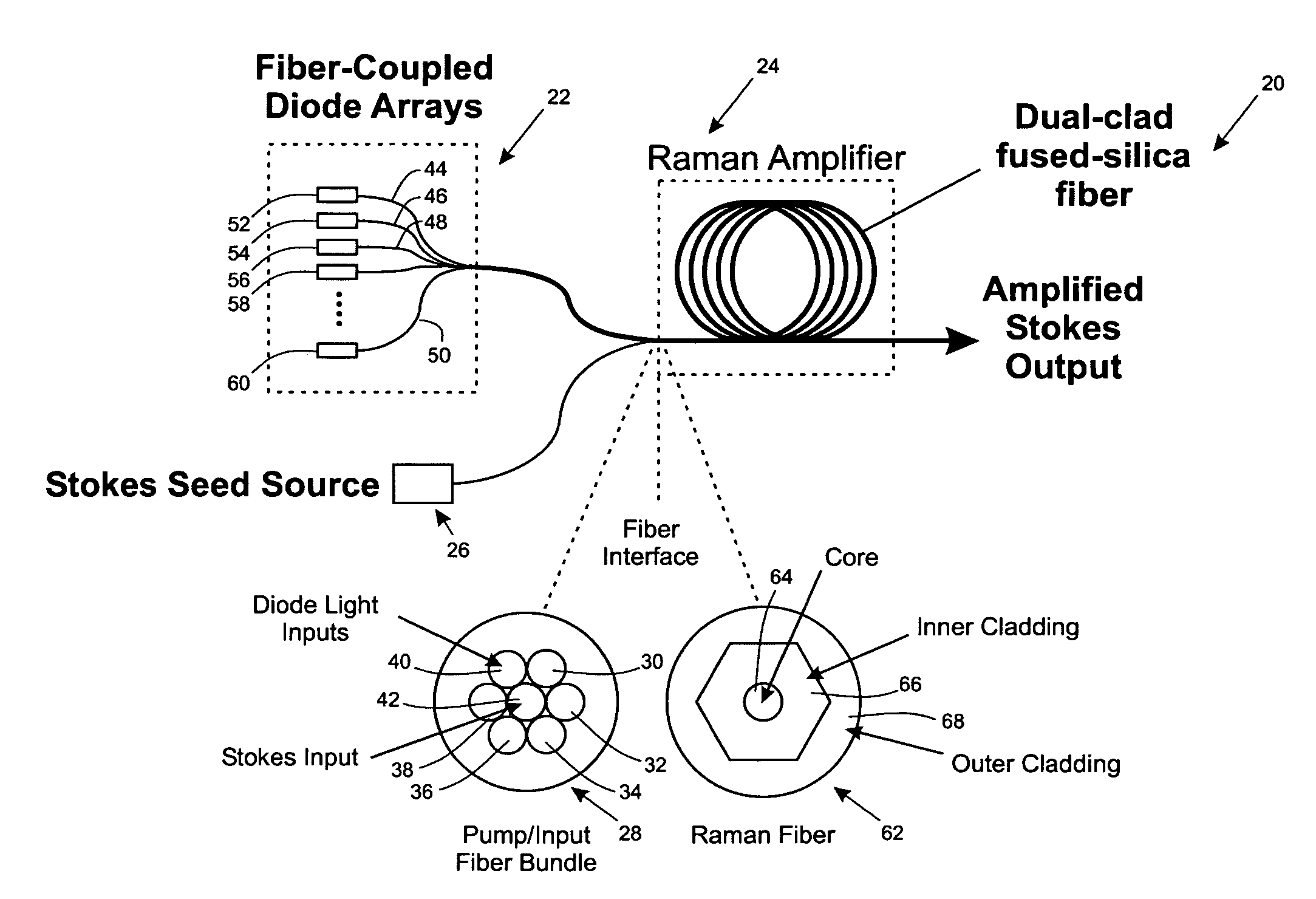
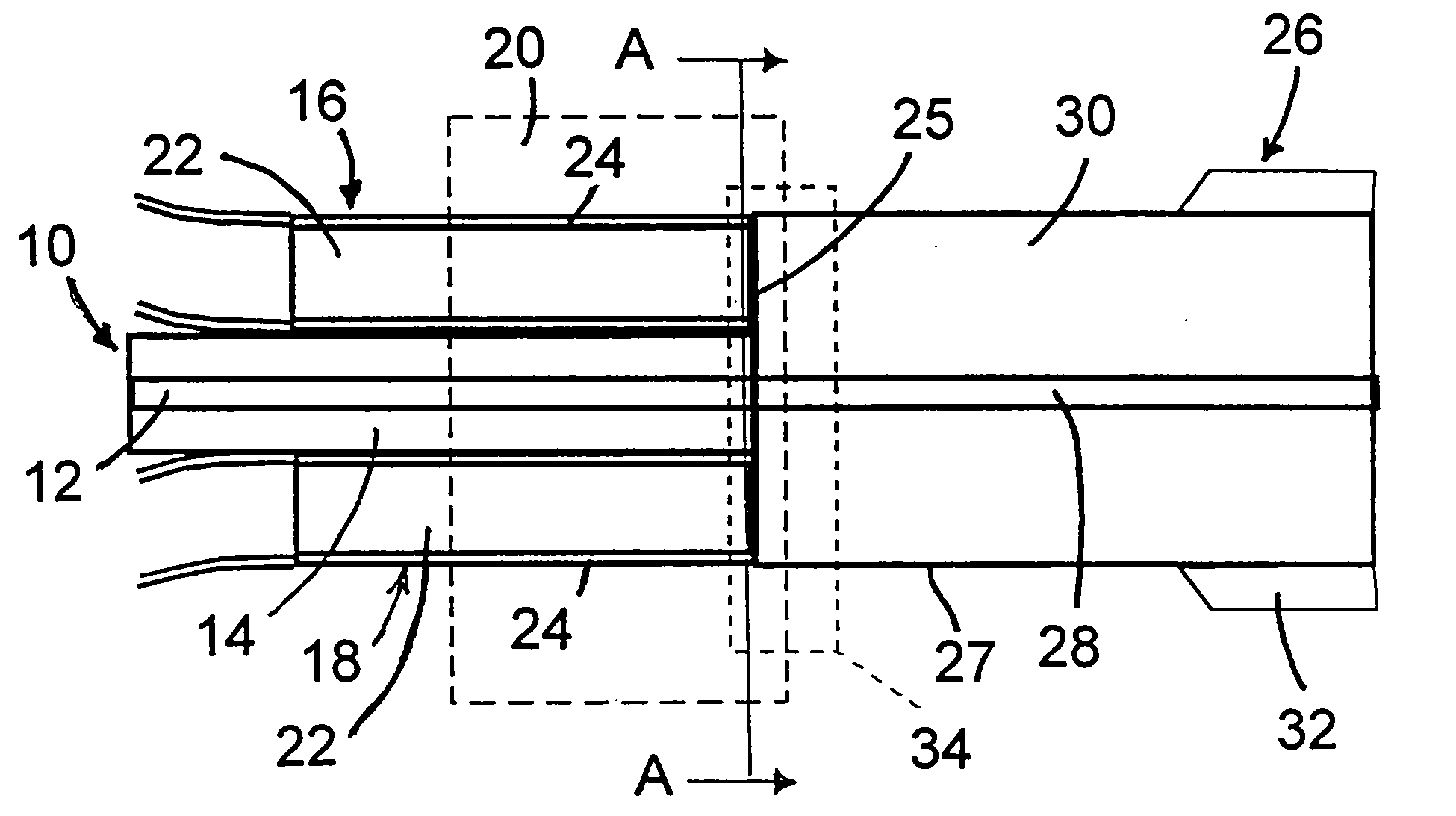
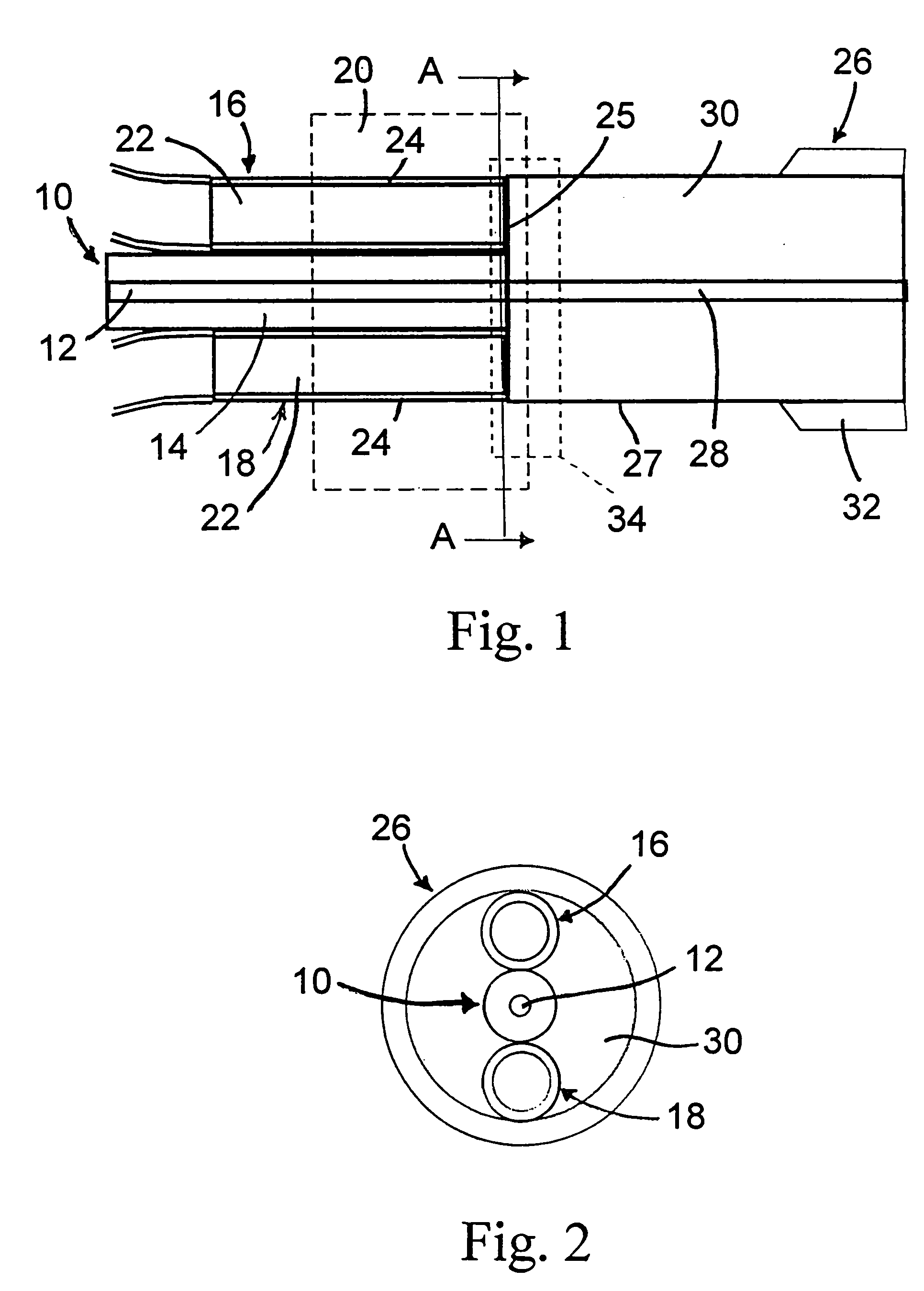
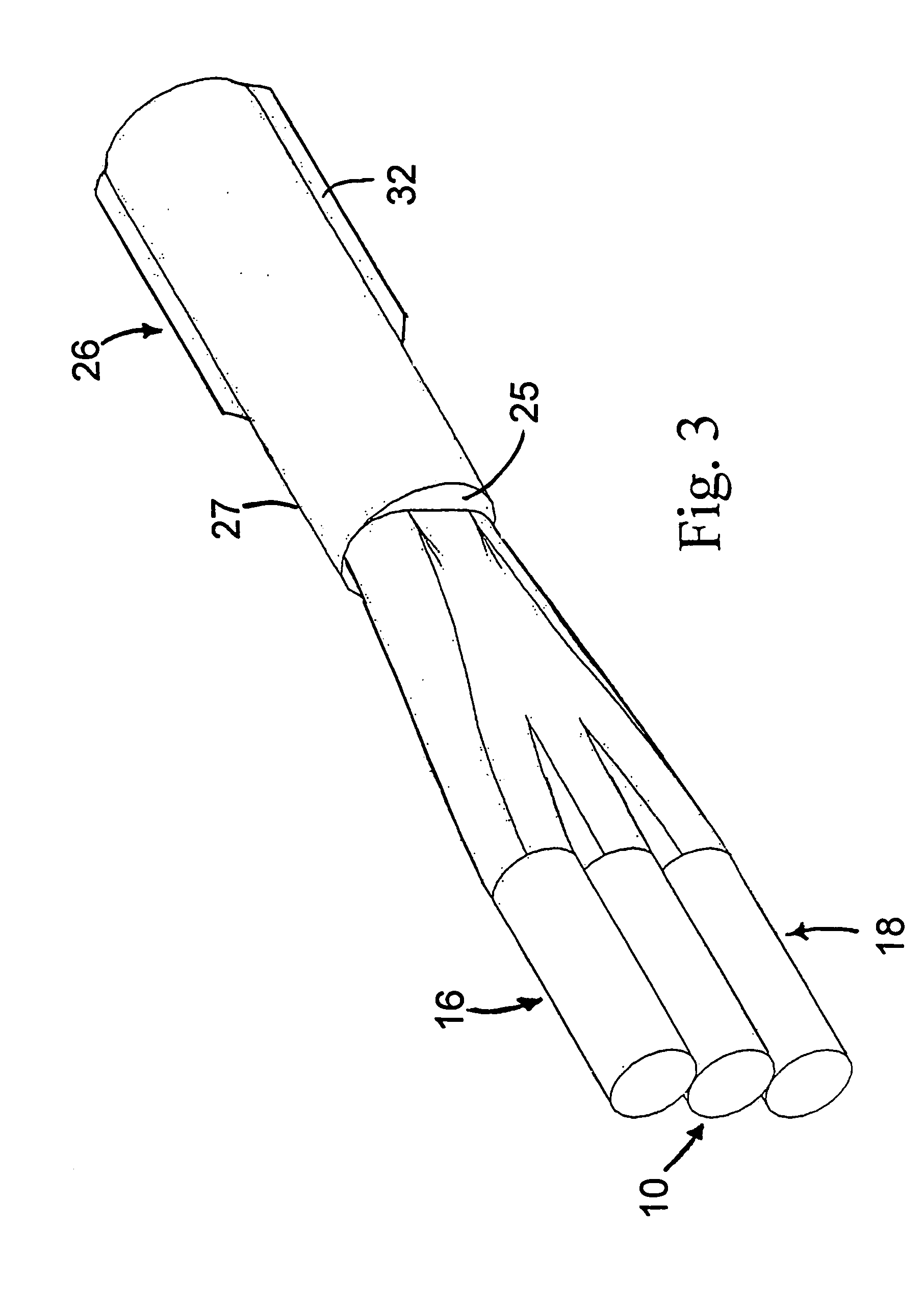
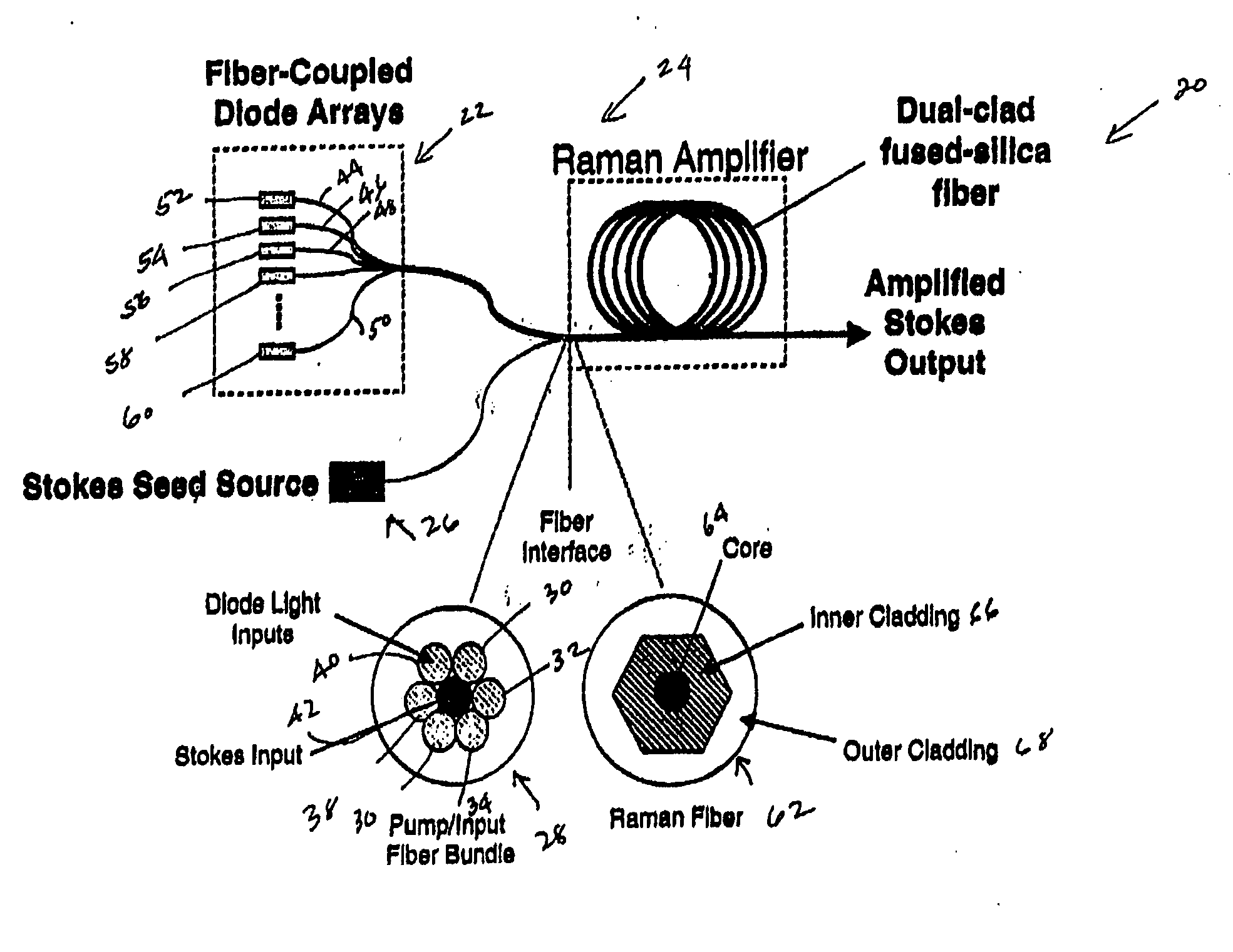
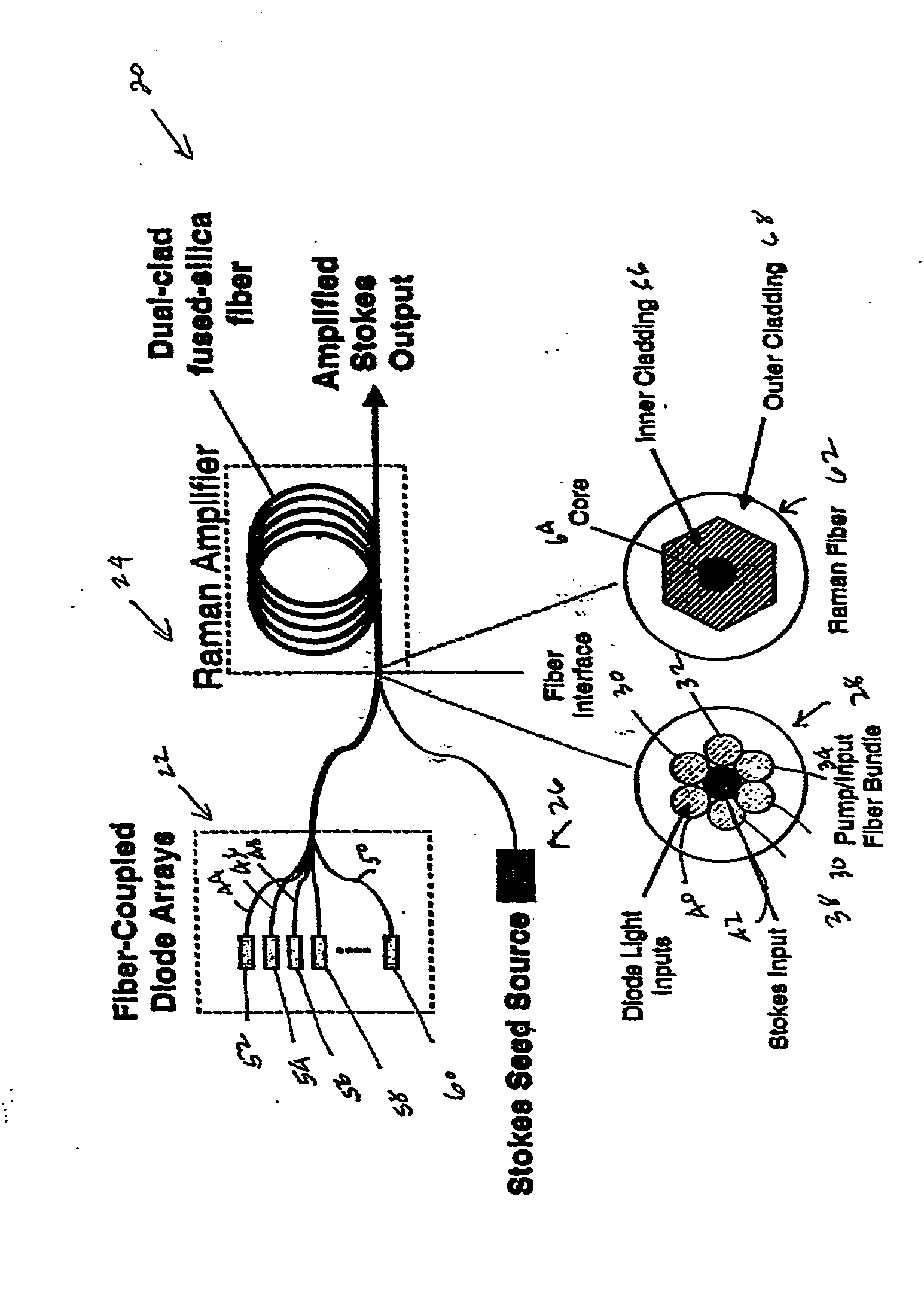
Brightness enhancement of diode light sources
InactiveUS7034992B2Increase brightnessExact costLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDouble-clad fiberStimulate raman scattering
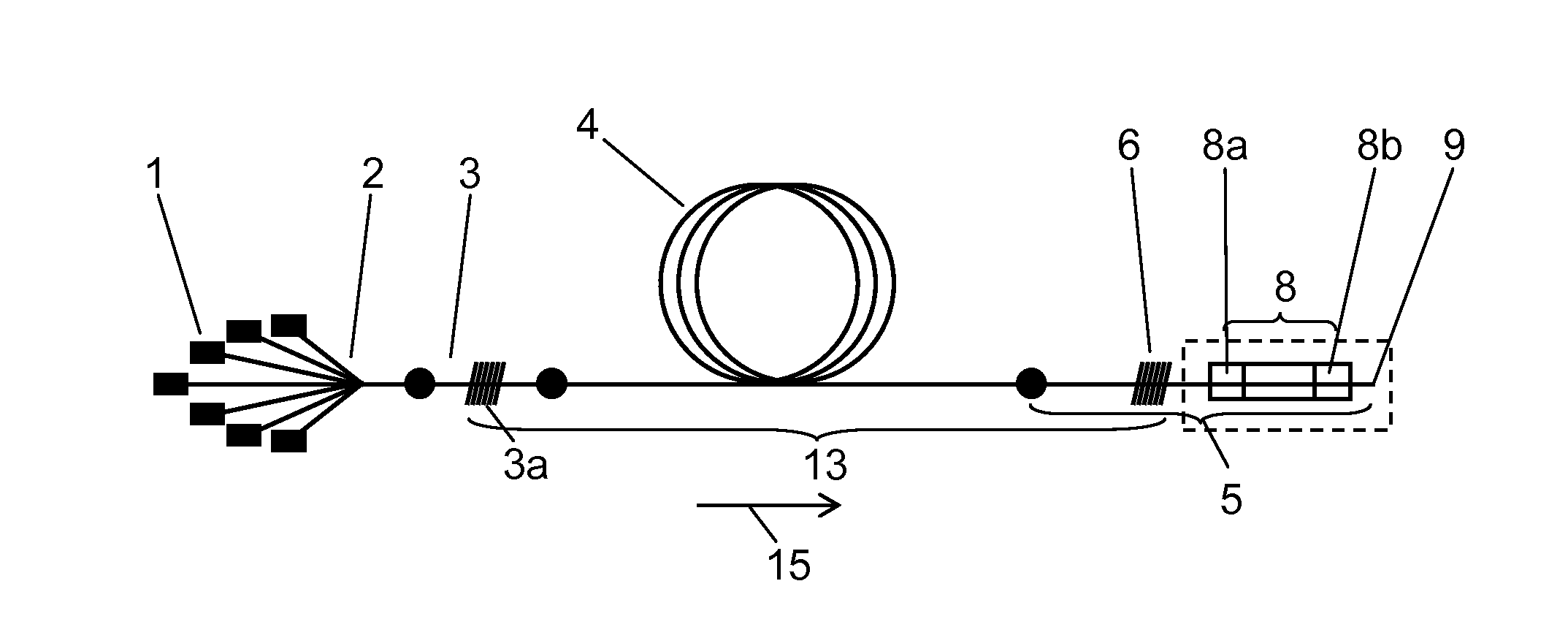
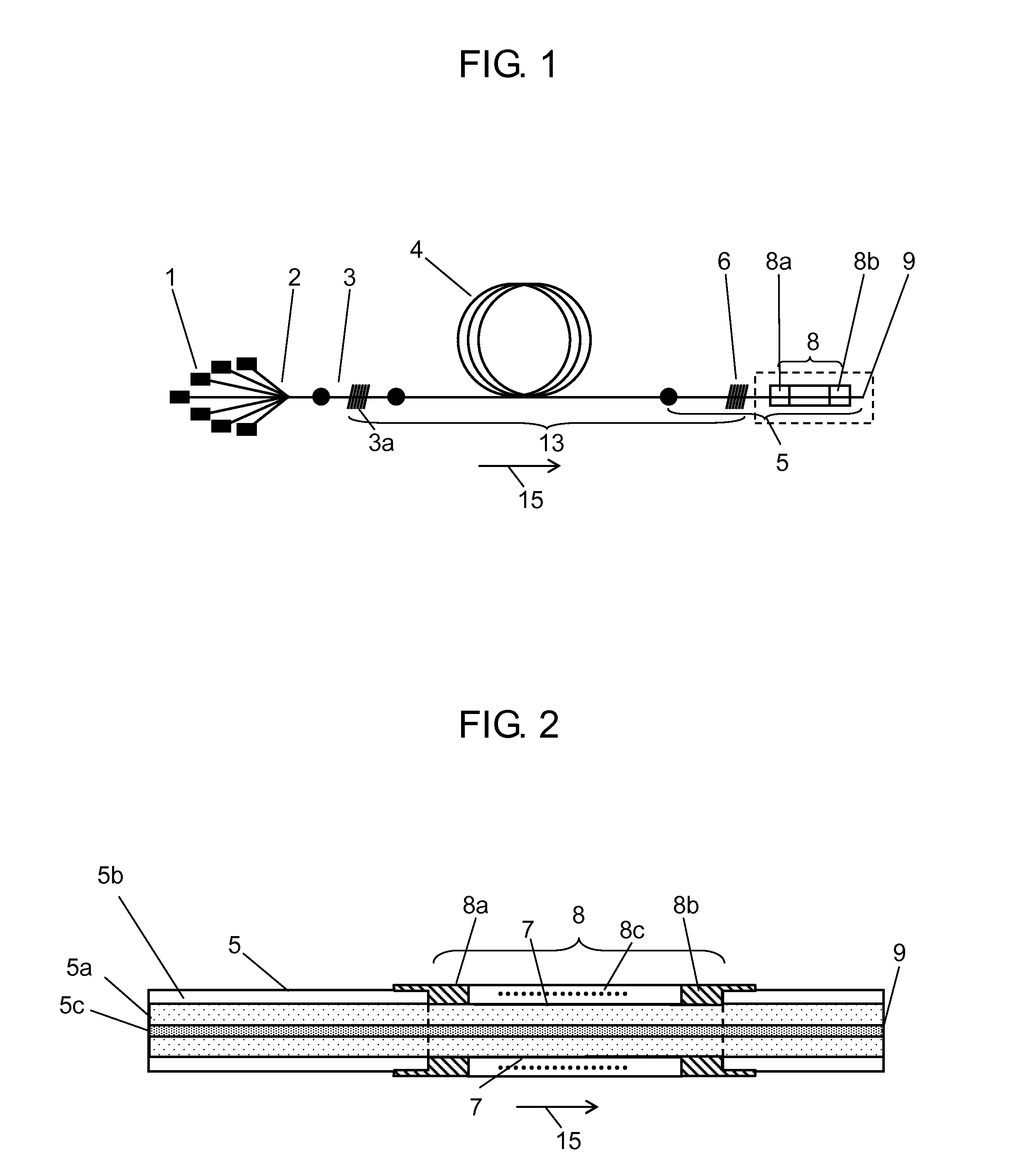
Briefly, the present invention relates to a system for combining the output light beams of a plurality of semiconductor laser diodes, for example, to form a combined light beam with increased brightness. The output light beams from the semiconductor laser diodes are coupled to a plurality of optical fibers forming a fiber coupled diode array. The optical fibers forming the fiber coupled diode array are coupled to a dual clad optical fiber with a central core. The output light beams from the optical fibers from the fiber coupled diode array are coupled to the inner cladding of a dual clad optical fiber. A Stokes seed source is applied to the central core, and the inner-clad diode light acts as a pump source to amplify the Stokes beam by stimulated Ramans scattering, thereby transferring power from the inner cladding into Stokes beam in the central core. The configuration in accordance with the present invention provides a Stokes output light beam with a relatively higher brightness level than known techniques which merely combine the output light beams from a plurality of semiconductor diodes and eliminates the need for a relatively precise alignment and the cost associated with the lenses required by known systems.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
Fiber optic connector with double-clad stub fiber
InactiveUS20080219624A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberDouble-clad fiber
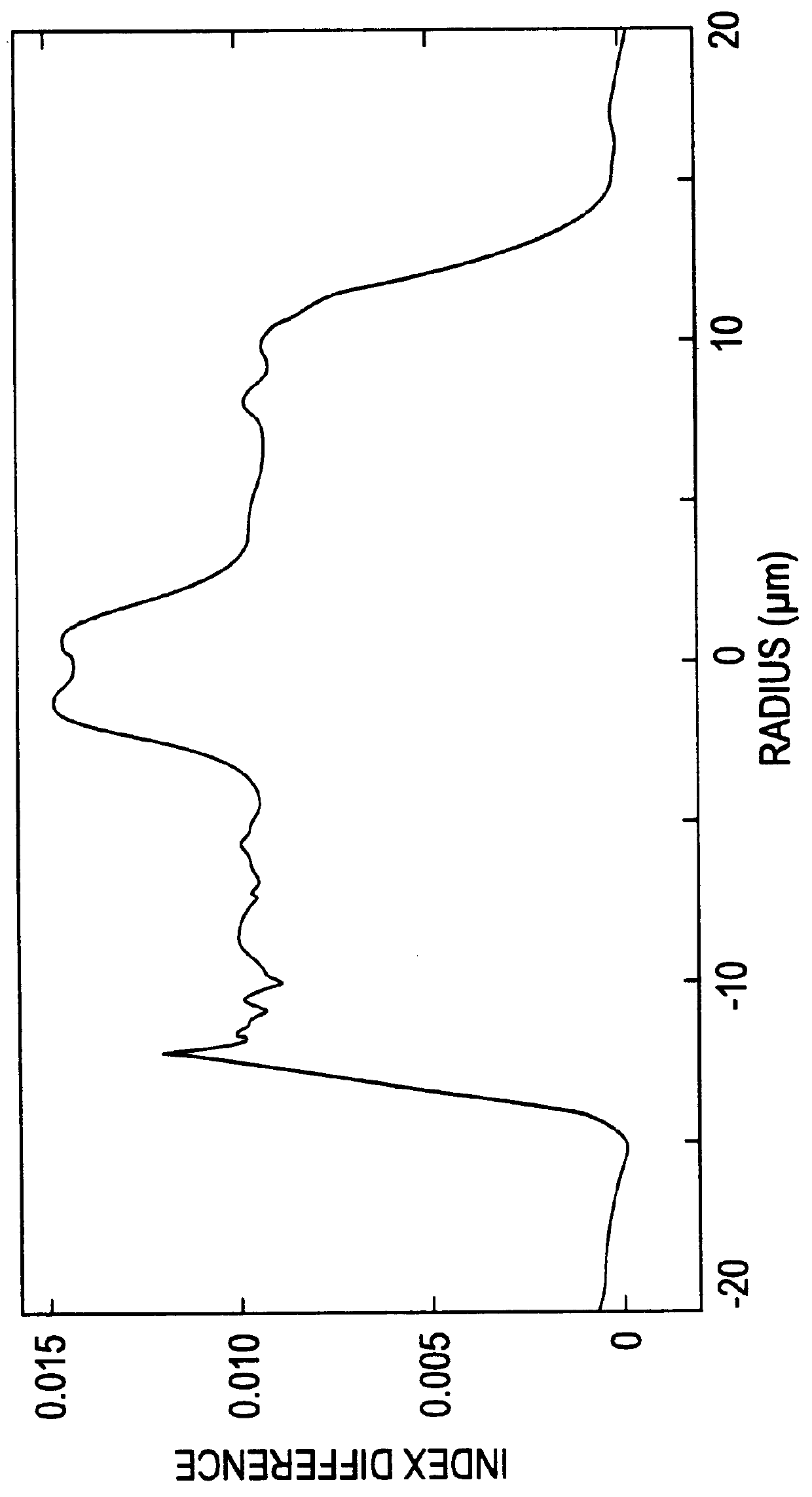
A fiber optic connector having a double-clad specialty optical stub fiber with a deep index core-to-inner-cladding profile and a raised index outer-cladding profile. The double-clad optical stub fiber abuts against a single-clad field optical fiber of the single-mode type to form an interface across which the primary mode traverses without significantly interfering with higher-order modes. The ratio of the radius of the inner cladding to the radius of the core of the stub fiber is less than 6.5:1. The index profile of the refractive index of the inner cladding is deep relative to the refractive index of the core to confine the primary mode within the core. The raised refractive index of the outer-cladding pulls the higher-order modes deeper into that region, reducing interference with the primary mode. The respective core diameters of the field and stub fibers are matched to avoid mode-field diameter mismatch.
Owner:PANDUIT
Fusion splicing structure of optical fibers
InactiveUS7748913B2Inhibit deteriorationEasy to useOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesDouble-clad fiberSingle fiber
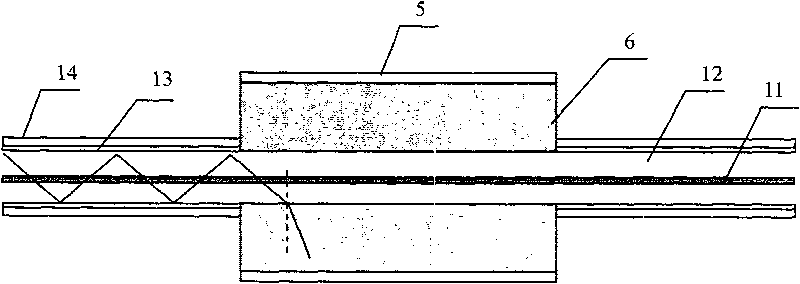
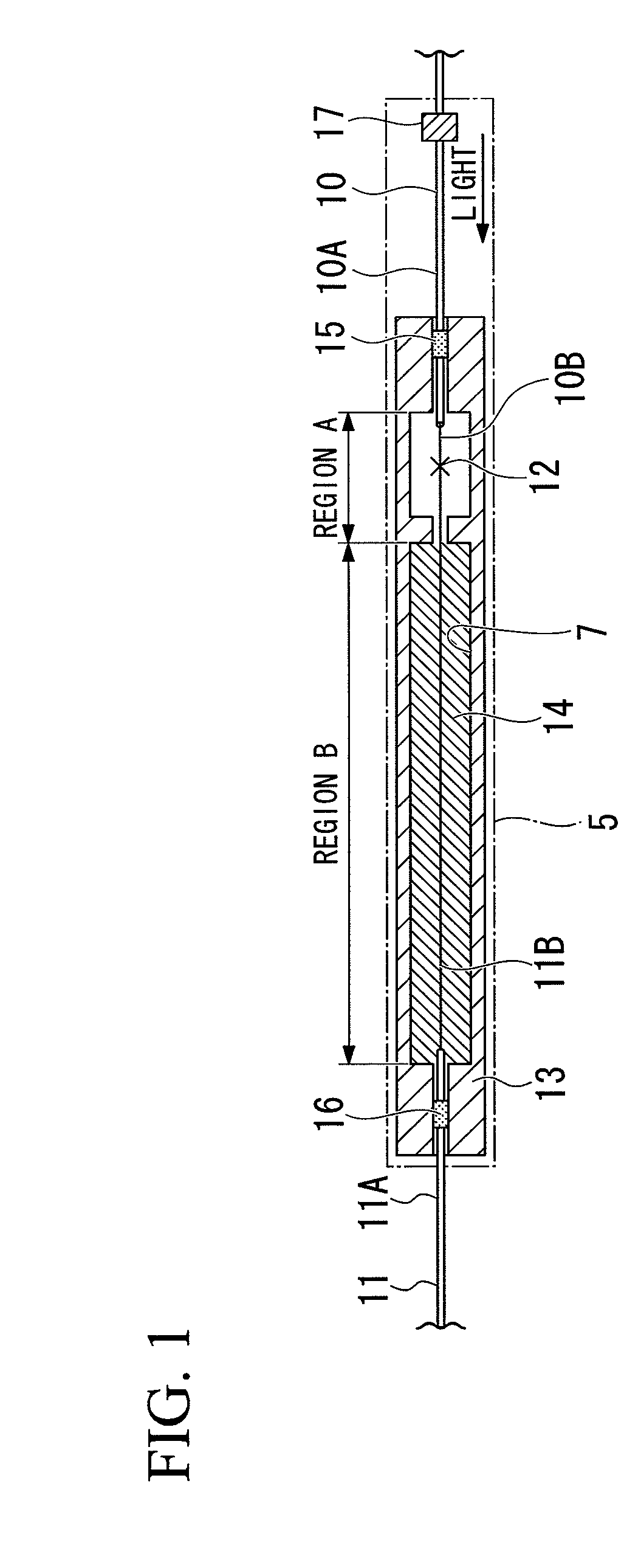
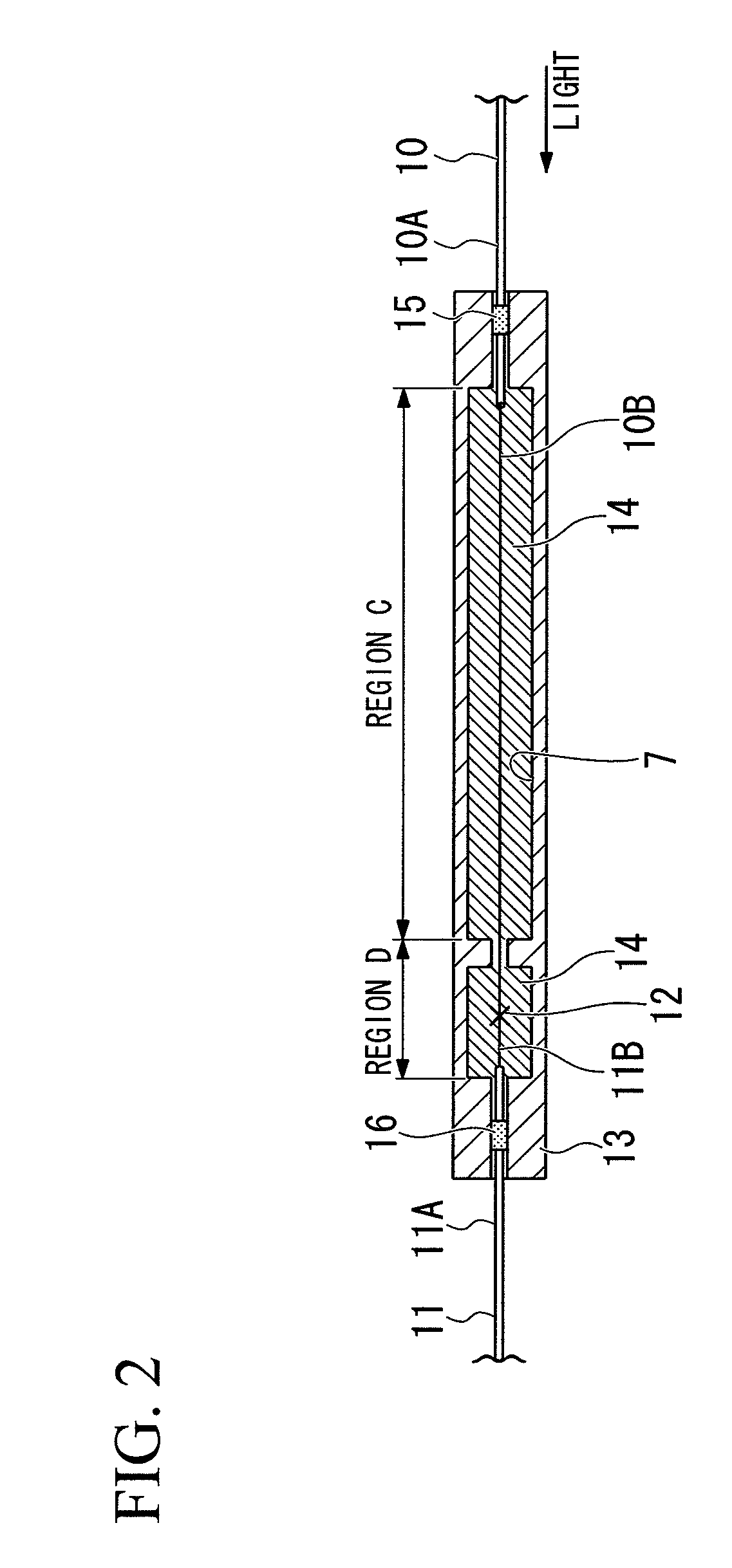
The present invention is a splicing structure of optical fibers for fusing a double clad fiber and a single clad fiber, the splicing structure is provided with a block covering a fusion splicing point of the double clad fiber and the single clad fiber, and which is made of a highly thermal conductive material.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD
Fiber laser
ActiveUS20130308661A1Improve reliabilityHigh refractive indexLaser optical resonator constructionLaser using scattering effectsDouble-clad fiberRefractive index
The optical fiber of the present invention has an input double-clad fiber containing high-reflection FBG, an oscillation double-clad fiber, and an output double-clad fiber containing low-reflection FBG. The output double-clad fiber is formed of a core, a first clad, and a second clad. In the output double-clad fiber, a high refractive-index resin coat section recoated with high refractive-index resin whose refractive index is the same as that of the second clad or greater is disposed at a part where the second clad is partly removed between an output end and the low-reflection FBG. The refractive index of the high refractive-index resin coat section gradually increases along the direction in which light travels through the first clad.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Distributed optical fibre sensing
ActiveUS8520197B2Increase rangeHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansSeismology for water-loggingFiberDouble-clad fiber
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Optical coupler comprising multimode fibers and method of making the same
ActiveUS7046875B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesFew mode fiberDouble-clad fiber
An optical coupler is provided. It has a bundle of multimode fibers with a few-mode fiber in its centre. Such bundle is fused at one end which is the output end for the signal that is transmitted by the few-mode fiber. To make the coupler, this output end of the bundle is aligned and spliced with a large area core double clad fiber while preserving the modal content of the feed-through. A method for making such optical coupler is also provided. It includes the steps of bundling a central few-mode fiber with a plurality of multimode fibers and then fusing one end of such bundle and aligning it and splicing with a large core double clad fiber, while preserving fundamental mode transmission from one to the other.
Owner:ITF TECH +1
Brightness enhancement of diode light sources
InactiveUS20050078353A1Increase brightnessExact costLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDouble-clad fiberSeeds source
Briefly, the present invention relates to a system for combining the output light beams of a plurality of semiconductor laser diodes, for example, to form a combined light beam with increased brightness. The output light beams from the semiconductor laser diodes are coupled to a plurality of optical fibers forming a fiber coupled diode array. The optical fibers forming the fiber coupled diode array are coupled to a dual clad optical fiber with a central core. The output light beams from the optical fibers from the fiber coupled diode array are coupled to the inner cladding of a dual clad optical fiber. A Stokes seed source is applied to the central core, and the inner-clad diode light acts as a pump source to amplify the Stokes beam by stimulated Ramans scattering, thereby transferring power from the inner cladding into Stokes beam in the central core. The configuration in accordance with the present invention provides a Stokes output light beam with a relatively higher brightness level than known techniques which merely combine the output light beams from a plurality of semiconductor diodes and eliminates the need for a relatively precise alignment and the cost associated with the lenses required by known systems.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
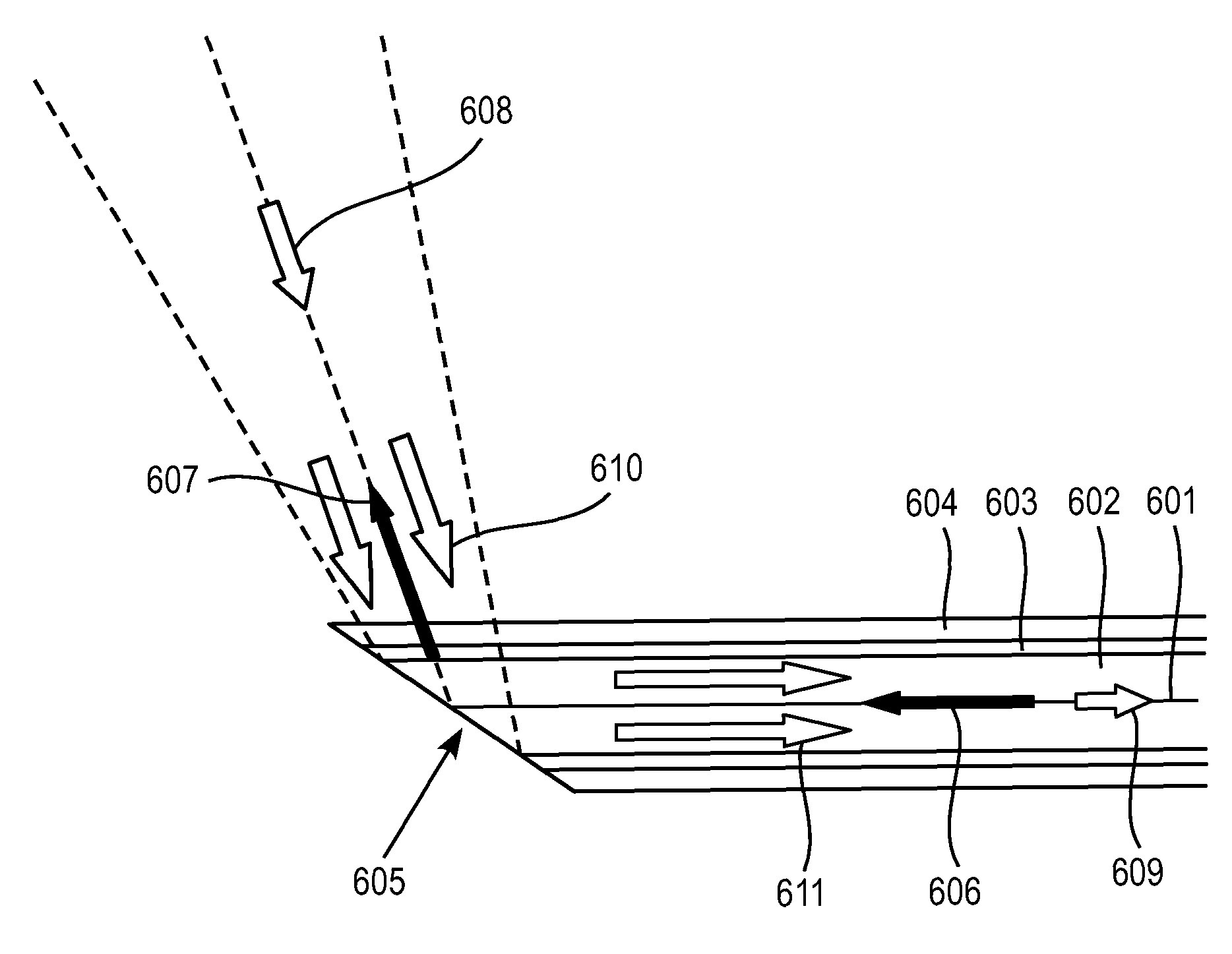
Device and method for endovascular optical coherence tomography - opto-acoustic - ultrasonic multimode imaging
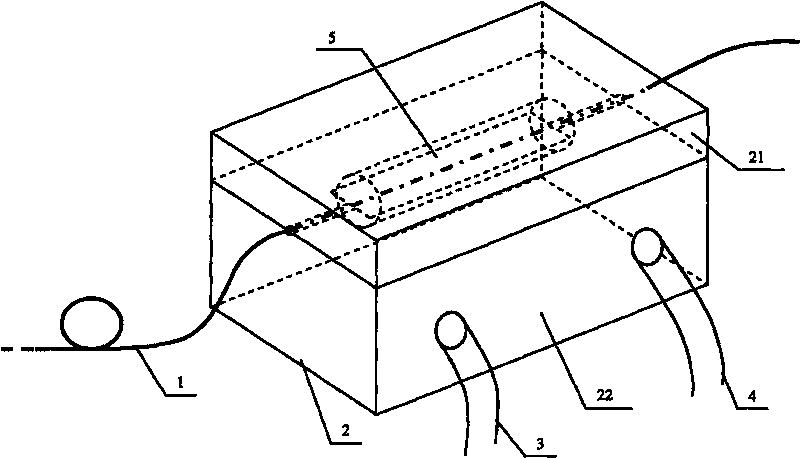
ActiveCN106361294ASimplify testing proceduresReduce the difficulty of detectionSurgeryCatheterDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySonification
The invention belongs to the field of blood vessel endoscopic imaging and discloses a device and method for endovascular optical coherence tomography - opto-acoustic - ultrasonic multimode imaging. The device comprises a computer, an optical coherence tomography (OCT) excitation and collection system, an opto-acoustic signal excitation and collection system, an ultrasonic signal excitation and collection system and an integrated probe. The OCT excitation and collection system comprises a field programmable logic array (PFGA) panel, a superluminescent diode, an isolator, a first optical fiber coupler, a reference arm, a linear array charge coupled device (CCD) and a first collecting card. The opto-acoustic signal excitation and collection system comprises a pulsed laser, a diaphragm, a second optical fiber coupler and a doubly clad optical fiber. The ultrasonic signal excitation and collection system comprises a pulse ultrasonic emitter / receiver, a signal amplifier, a signal filter and a second collecting card. The OCT, opto-acoustic and ultrasonic tri-modal blood vessel endoscopic imaging system integrates three imaging modes and respective advantages thereof, and multi-parameter physiological function information and multiscale structural information of a blood vessel can be obtained.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com