Patents
Literature
145 results about "Nonlinear fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
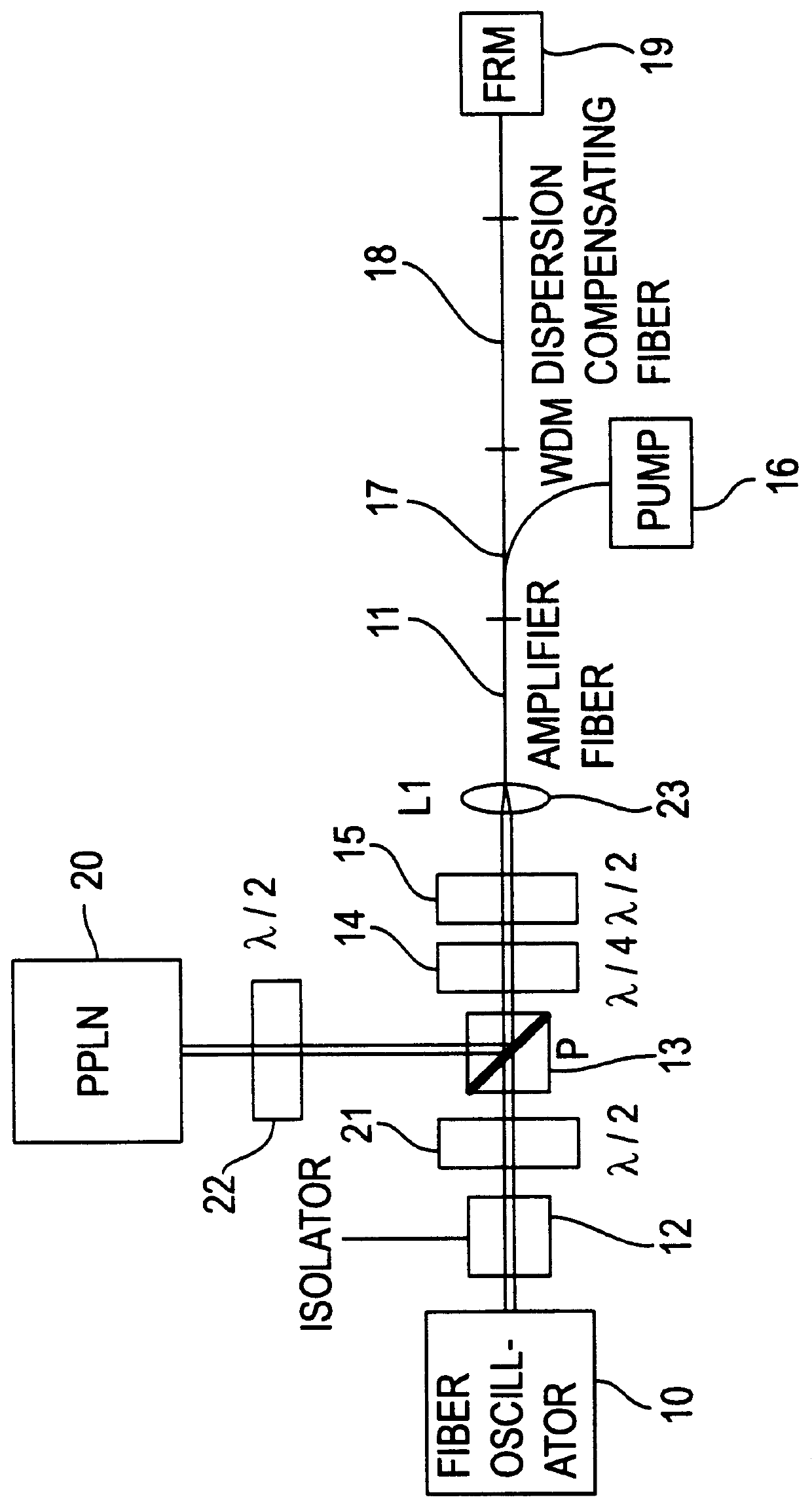
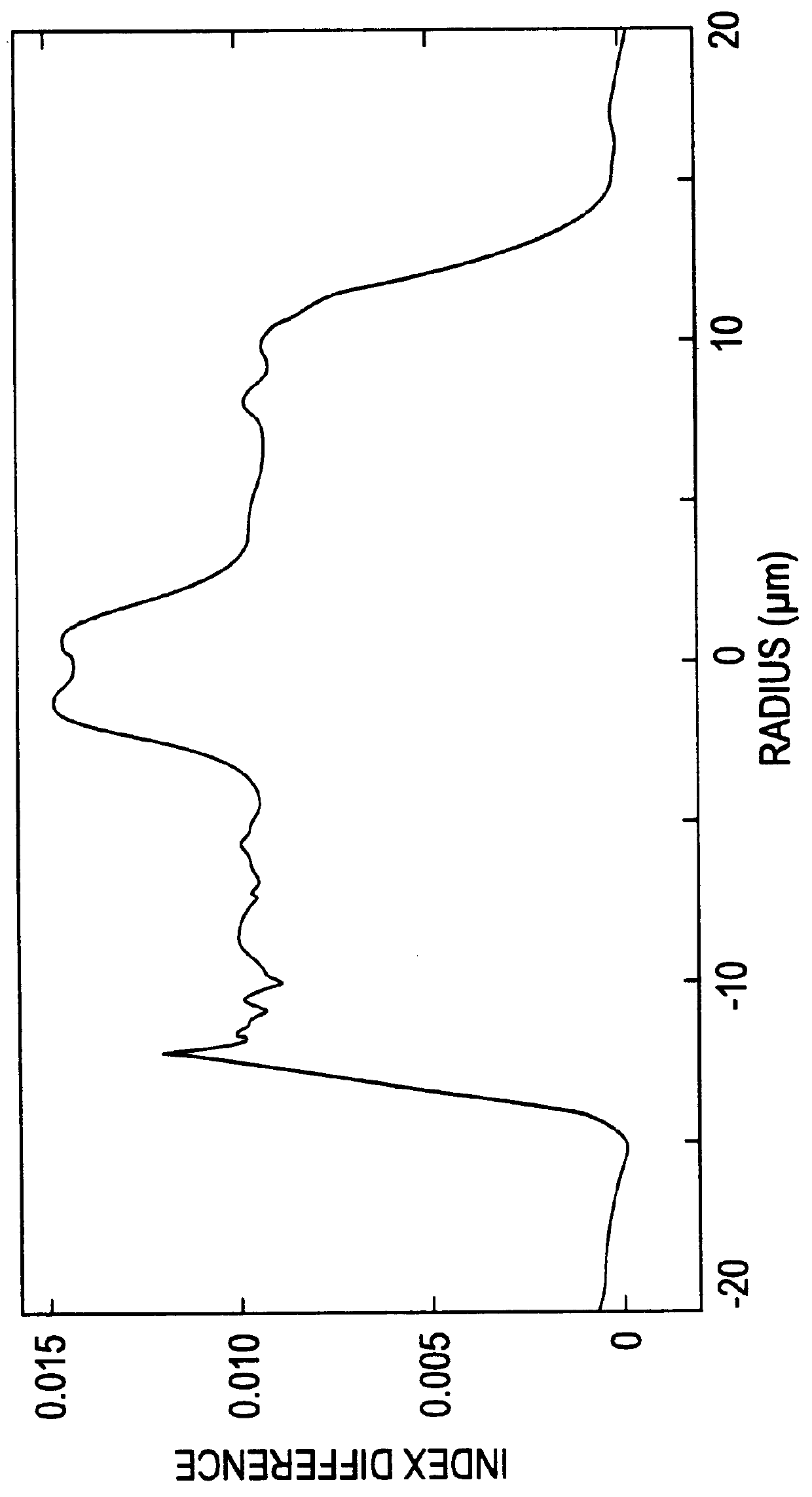
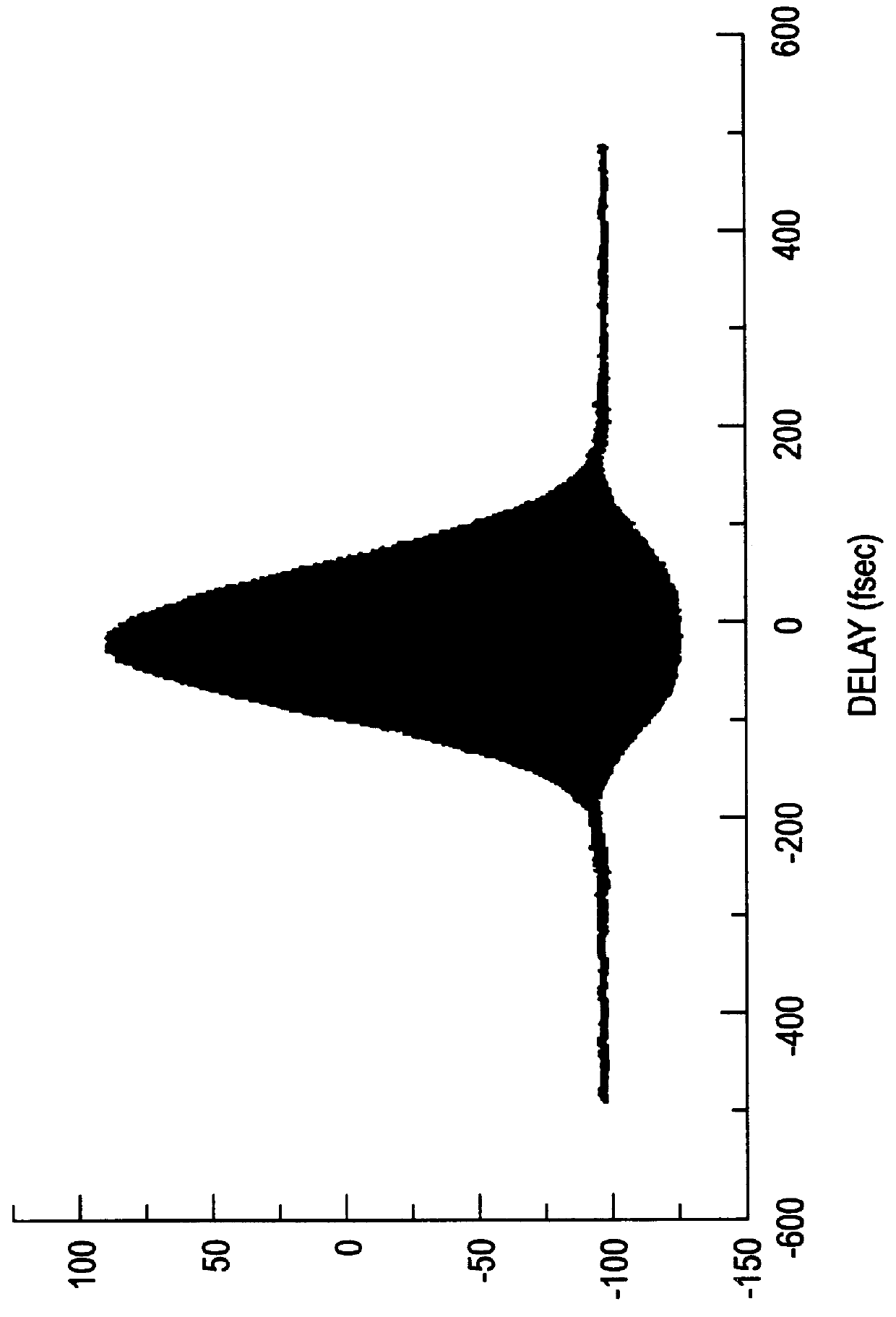
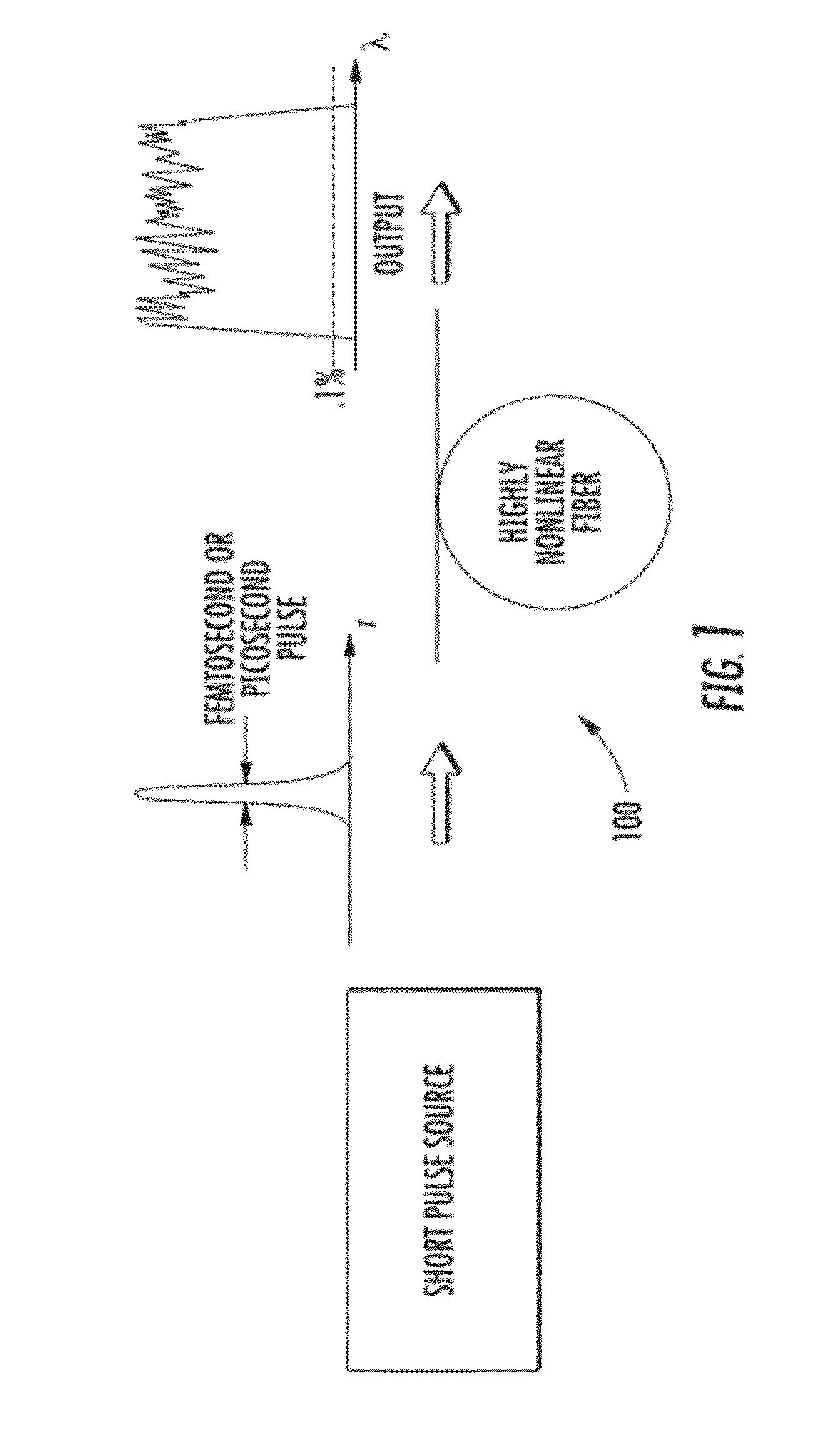
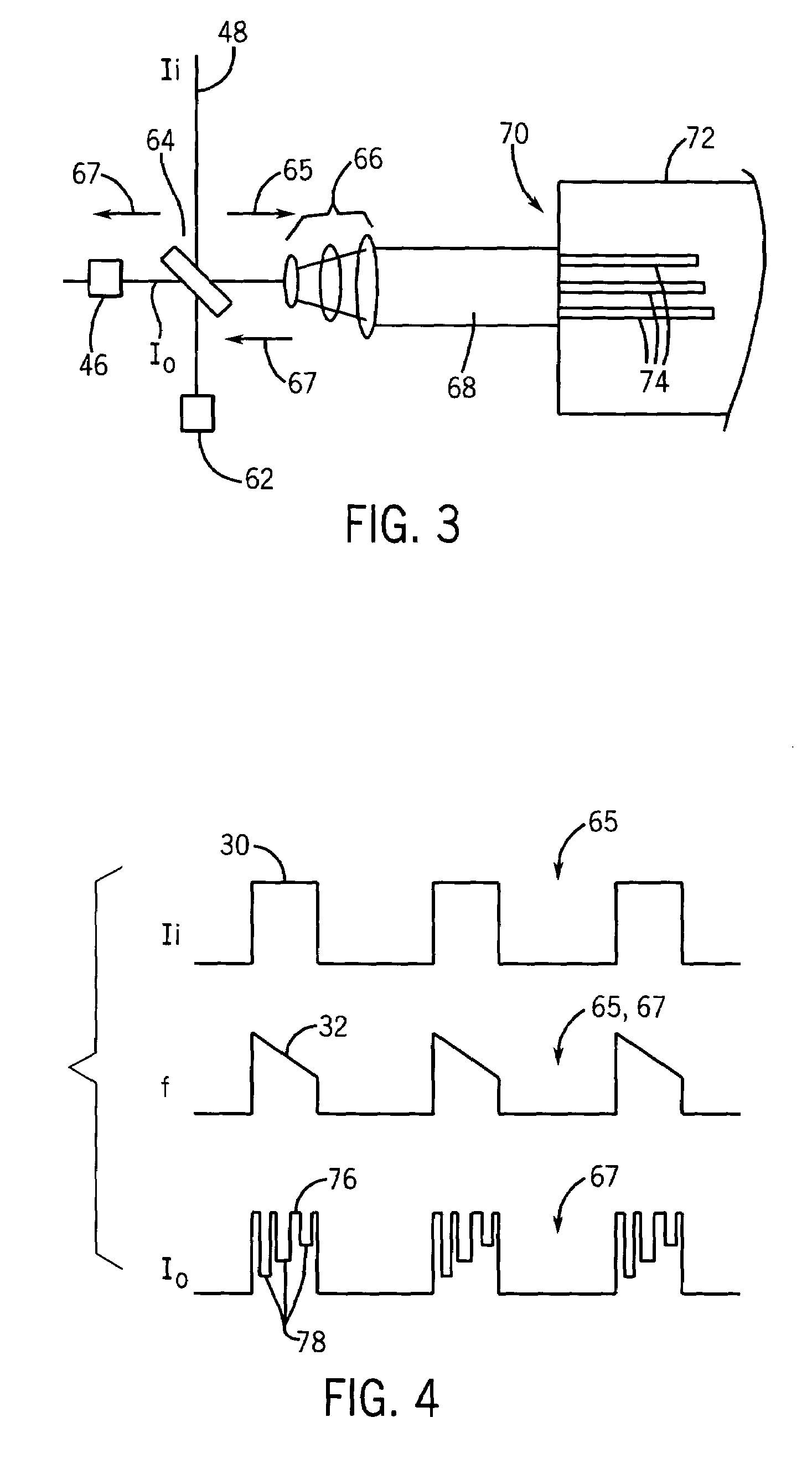
Apparatus and method for the generation of high-power femtosecond pulses from a fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6014249ALong pulse widthLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
An apparatus generates femtosecond pulses from laser amplifiers by nonlinear frequency conversion. The implementation of nonlinear frequency-conversion allows the design of highly nonlinear amplifiers at a signal wavelength (SW), while still preserving a high-quality pulse at an approximately frequency-doubled wavelength (FDW). Nonlinear frequency-conversion also allows for limited wavelength tuning of the FDW. As an example, the output from a nonlinear fiber amplifier is frequency-converted. By controlling the polarization state in the nonlinear fiber amplifier and by operating in the soliton-supporting dispersion regime of the host glass, an efficient nonlinear pulse compression for the SW is obtained. The generated pulse width is optimized by utilizing soliton compression in the presence of the Raman-self-frequency shift in the nonlinear fiber amplifier at the SW. High-power pulses are obtained by employing fiber amplifiers with large core-diameters. The efficiency of the nonlinear fiber amplifier is optimized by using a double clad fiber (i.e., a fiber with a double-step refractive index profile) and by pumping light directly into the inner core of this fiber. Periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) is used for efficient conversion of the SW to a FDW. The quality of the pulses at the FDW can further be improved by nonlinear frequency conversion of the compressed and Raman-shifted signal pulses at the SW. The use of Raman-shifting further increases the tuning range at the FDW. For applications in confocal microscopy, a special linear fiber amplifier is used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Broadband generation of mid ir, coherent continua with optical fibers
ActiveUS20120236314A1Improve fluencyBroad spectral coverageLaser detailsUsing optical meansLow noiseFiber
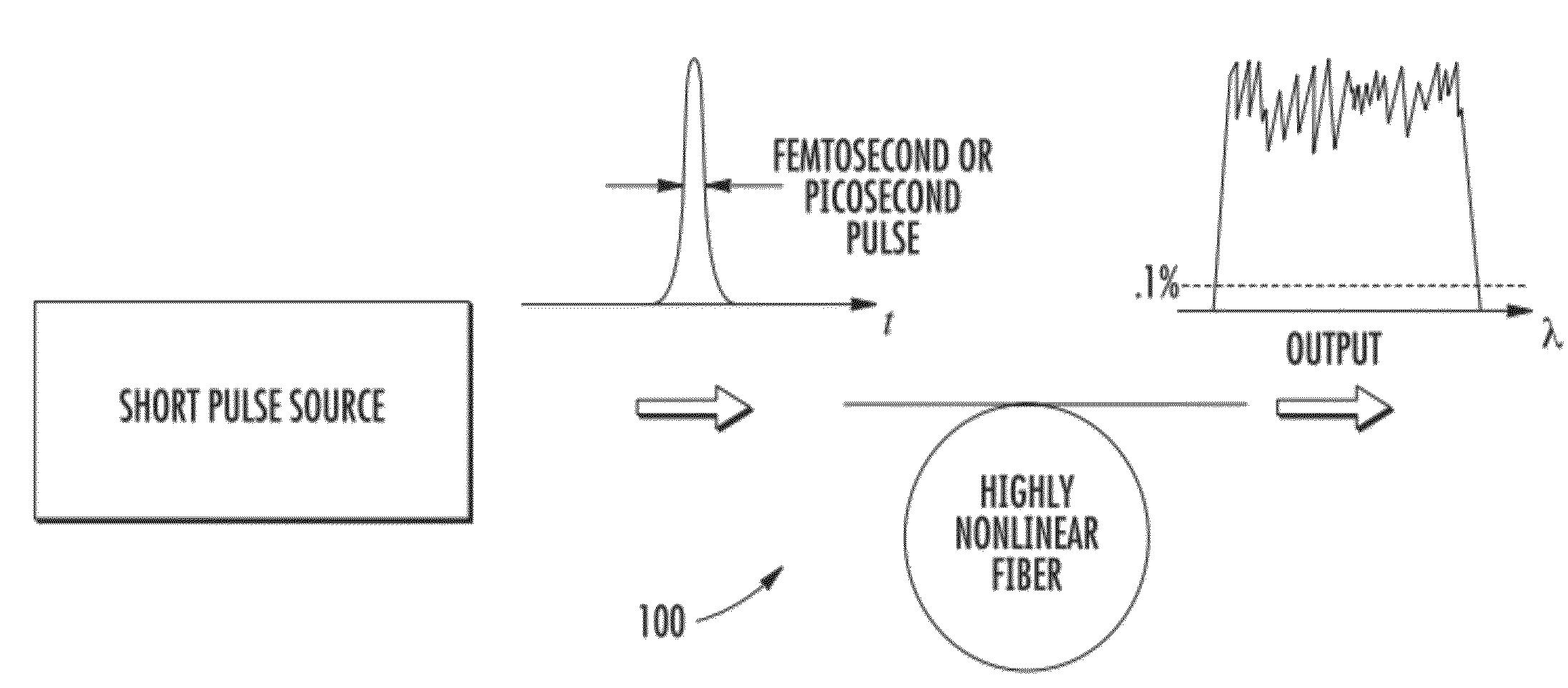
Coherent and compact supercontinuum light sources for the mid IR spectral regime are disclosed and exemplary applications thereof. The supercontinuum generation is based on the use of highly nonlinear fibers or waveguides. In at least one embodiment the coherence of the supercontinuum sources is increased using low noise mode locked short pulse sources. Compact supercontinuum light sources can be constructed with the use of passively mode locked fiber or diode lasers. Wavelength tunable sources can be constructed using appropriate optical filters or frequency conversion sections. Highly coherent supercontinuum sources further facilitate coherent detection schemes and can improve the signal / noise ratio in lock in detection schemes.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
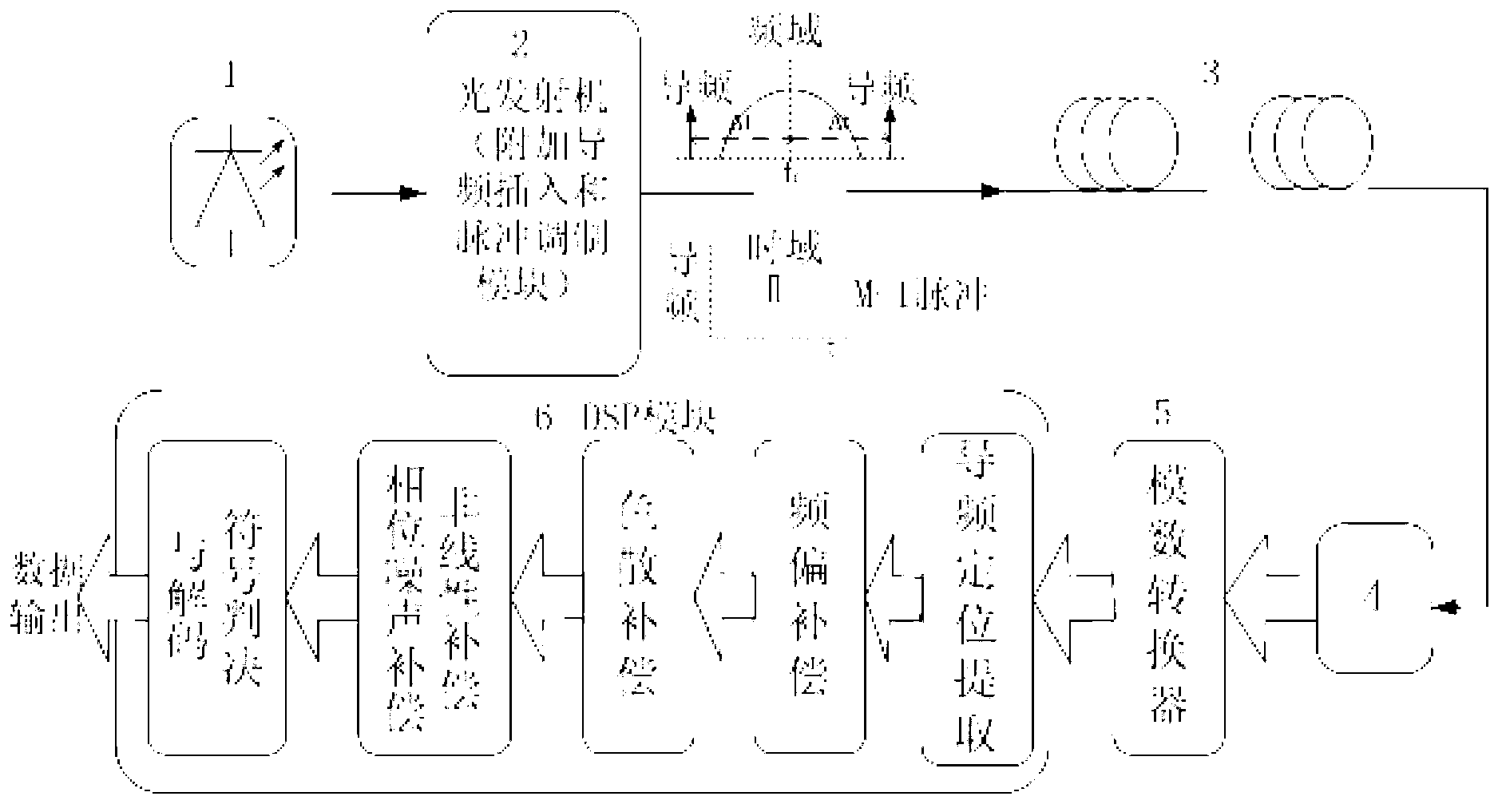
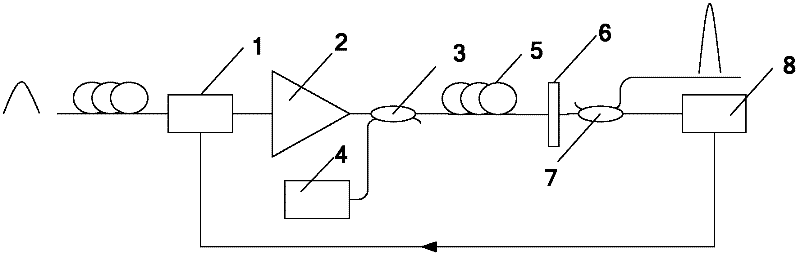
Self-adaptive damage compensation method and system for digital-related optical communication system
InactiveCN103312645AImprove reliabilityImprove practicalityFibre transmissionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFiberFourier transform on finite groups
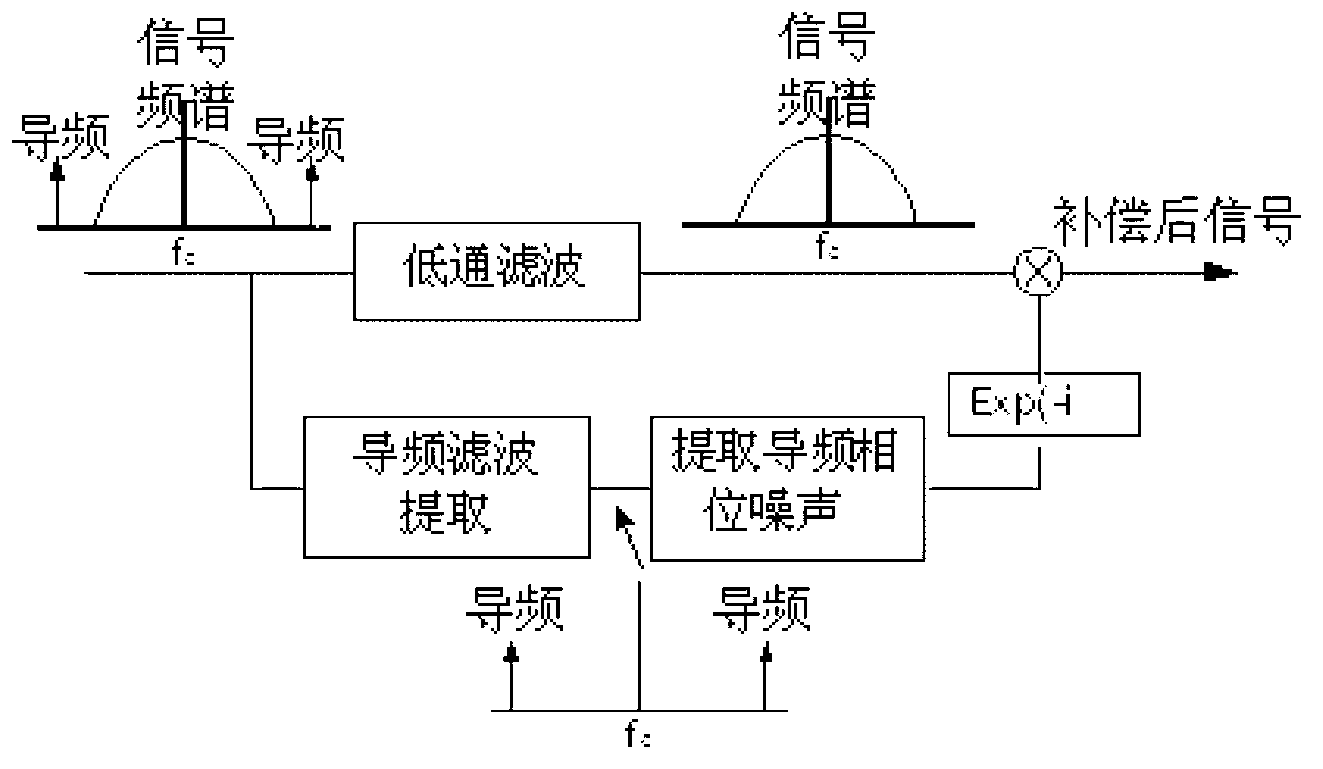
The invention relates to a self-adaptive damage compensation method and system for a digital-related optical communication system. The self-adaptive damage compensation method includes inserting two pulse modulation pilot frequency signals symmetrically distributed on an input signal frequency fc (fiber channel) at a transmitting terminal; acquiring an input signal power spectrum by the Fourier transform at a receiving terminal, and receiving the pilot frequency signals of a signal power spectrum and subjecting the pilot frequency signals to location and filtering extraction; calculating size of frequency offset of a vibration laser and performing compensation by a pilot frequency; acquiring pilot time domain waveforms by the Fourier transform and calculating a delay delta tau between two pilot light pulses, and calculating size of dispersion by the delta tau and performing the compensation; finally extracting pilot phase noises and subtracting the same from a signal phase so as to eliminate laser phase noises and nonlinear fiber damages. The self-adaptive damage compensation method has the advantages of high accuracy, low complexity, small occupation of bandwidth and fast response speed, so that self-adaptive compensation of various damages can be realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
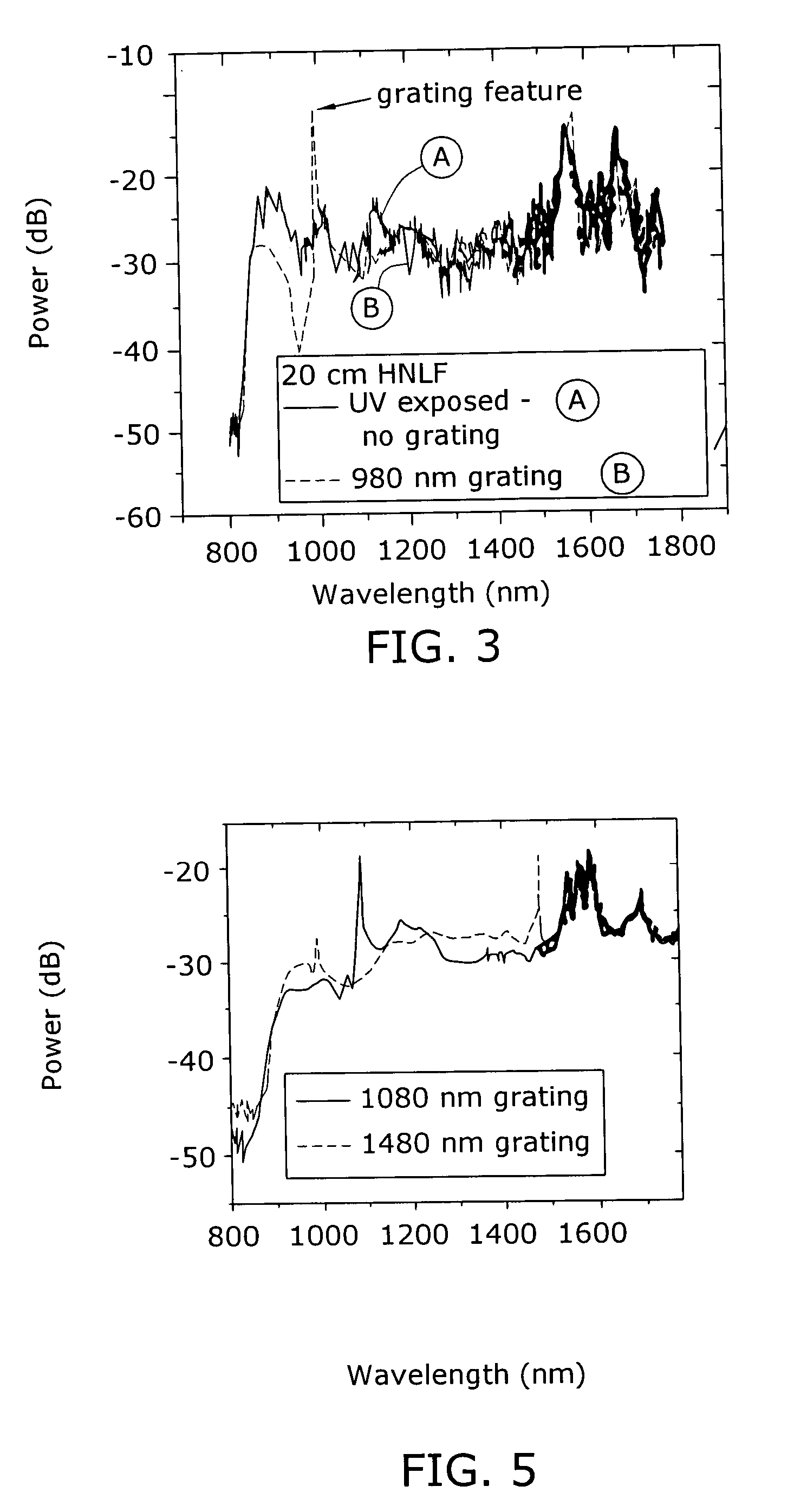
Enhanced supercontinuum generation in highly nonlinear fibers using post-fabrication processing
ActiveUS20050226576A1Alteration in dispersionAlteration in effective areaLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringNonlinear fiber
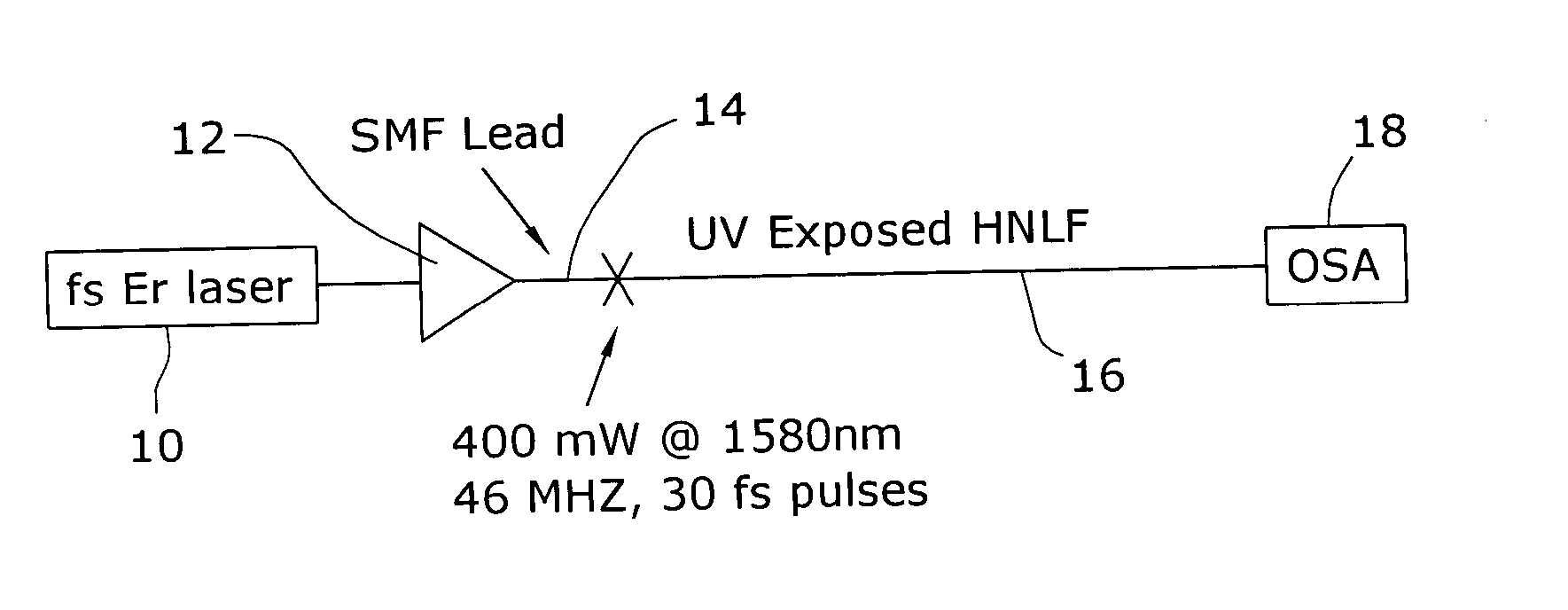
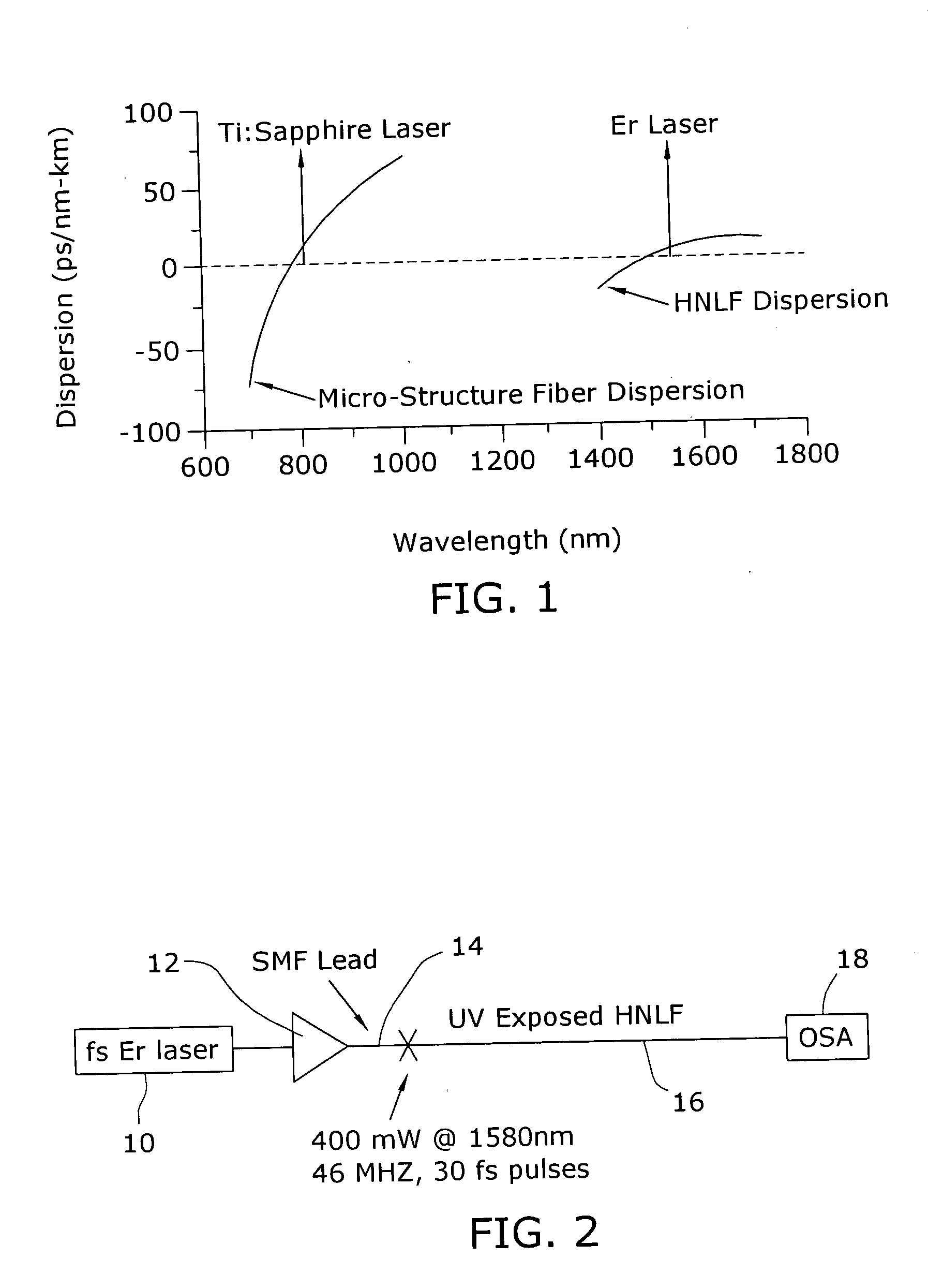
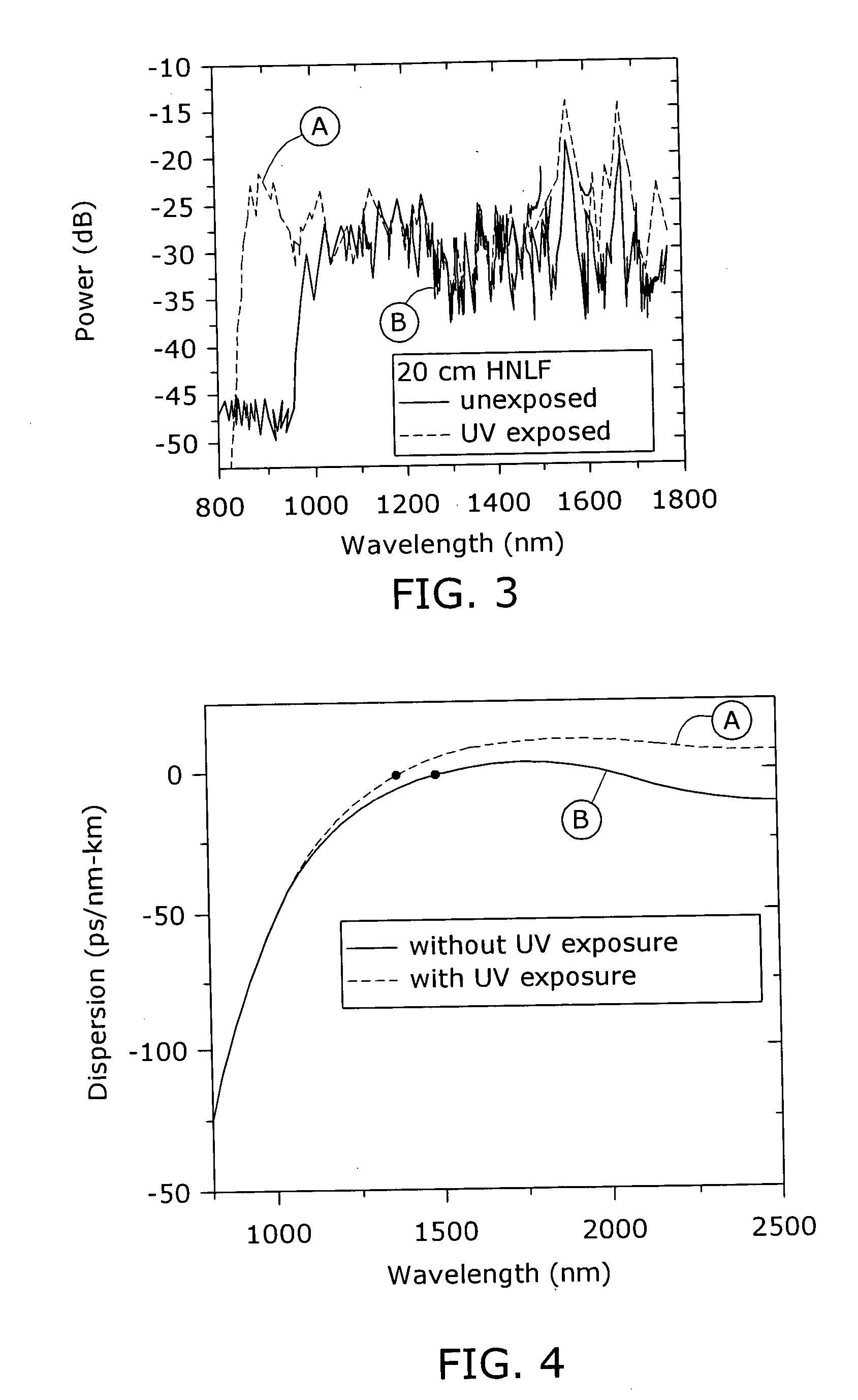
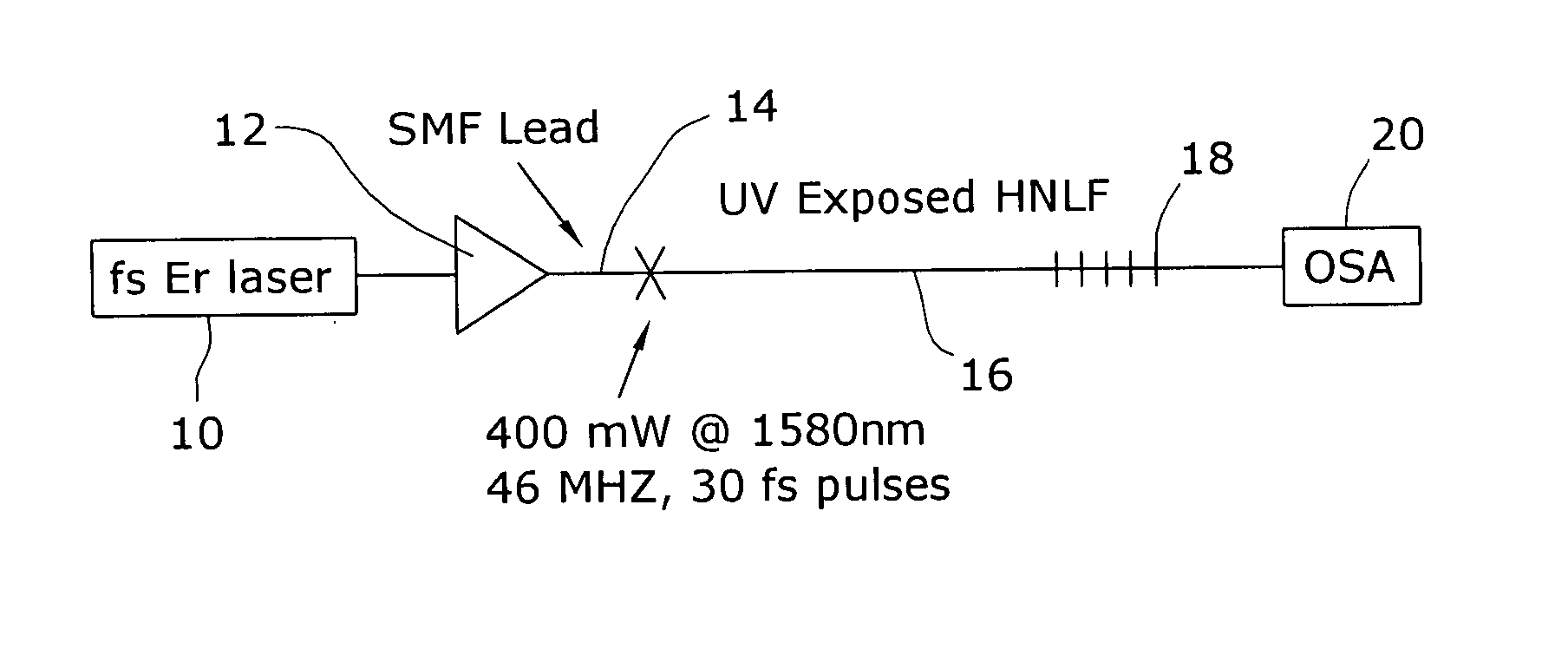
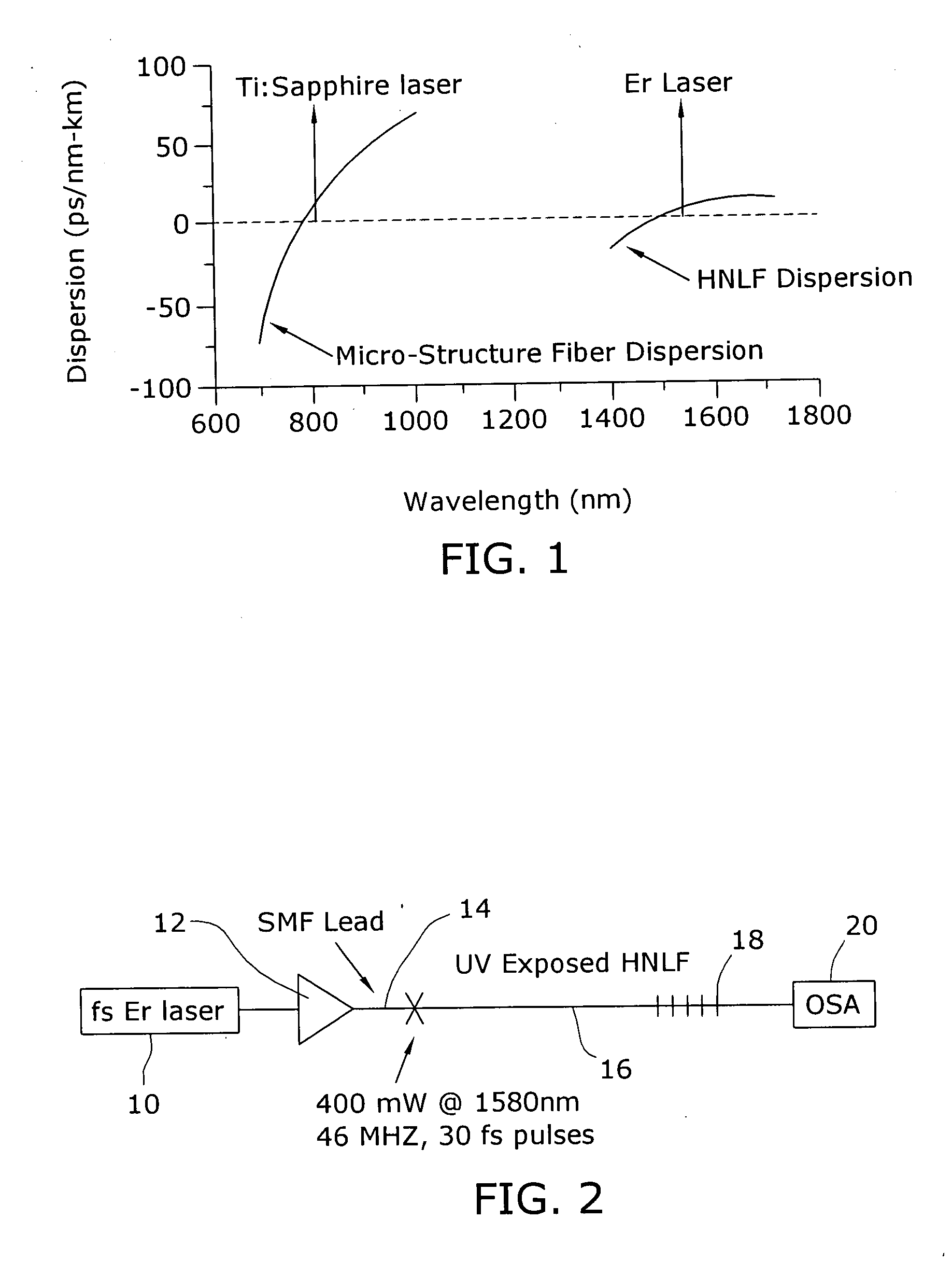
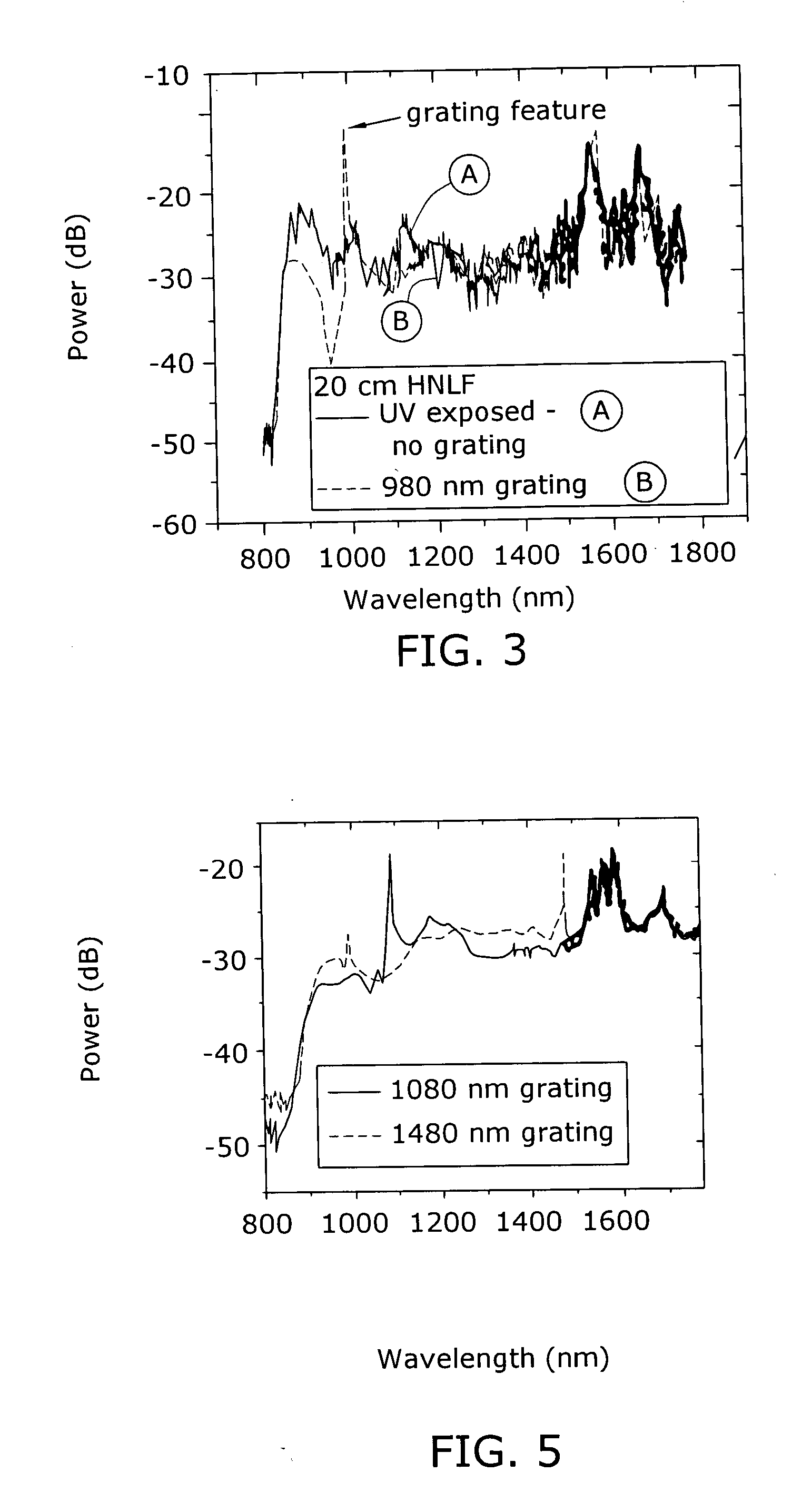
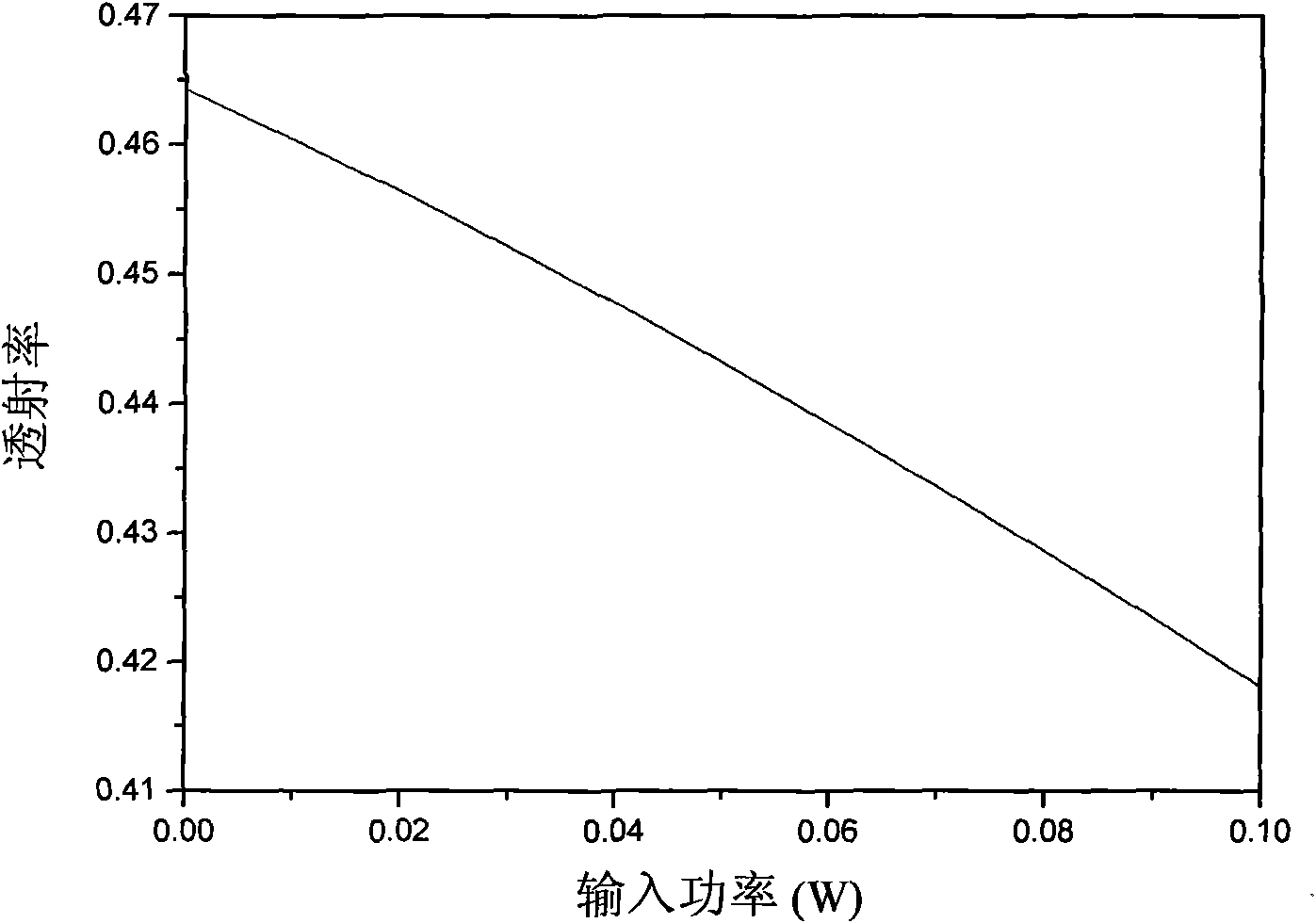
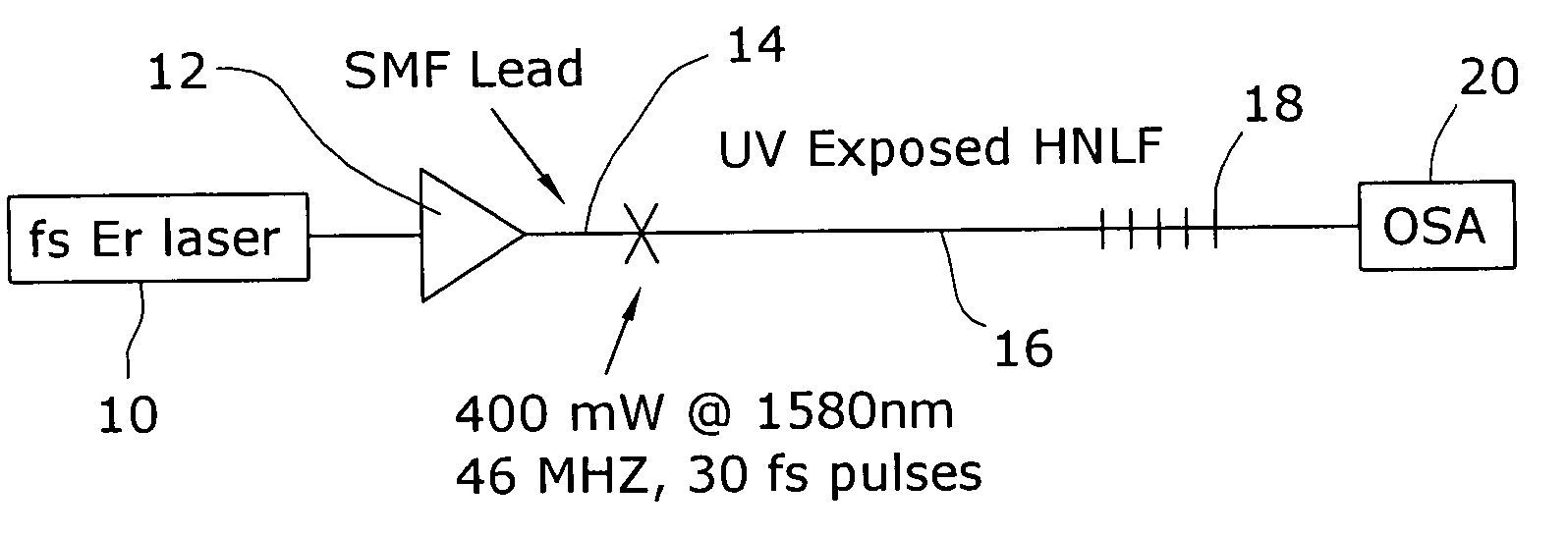
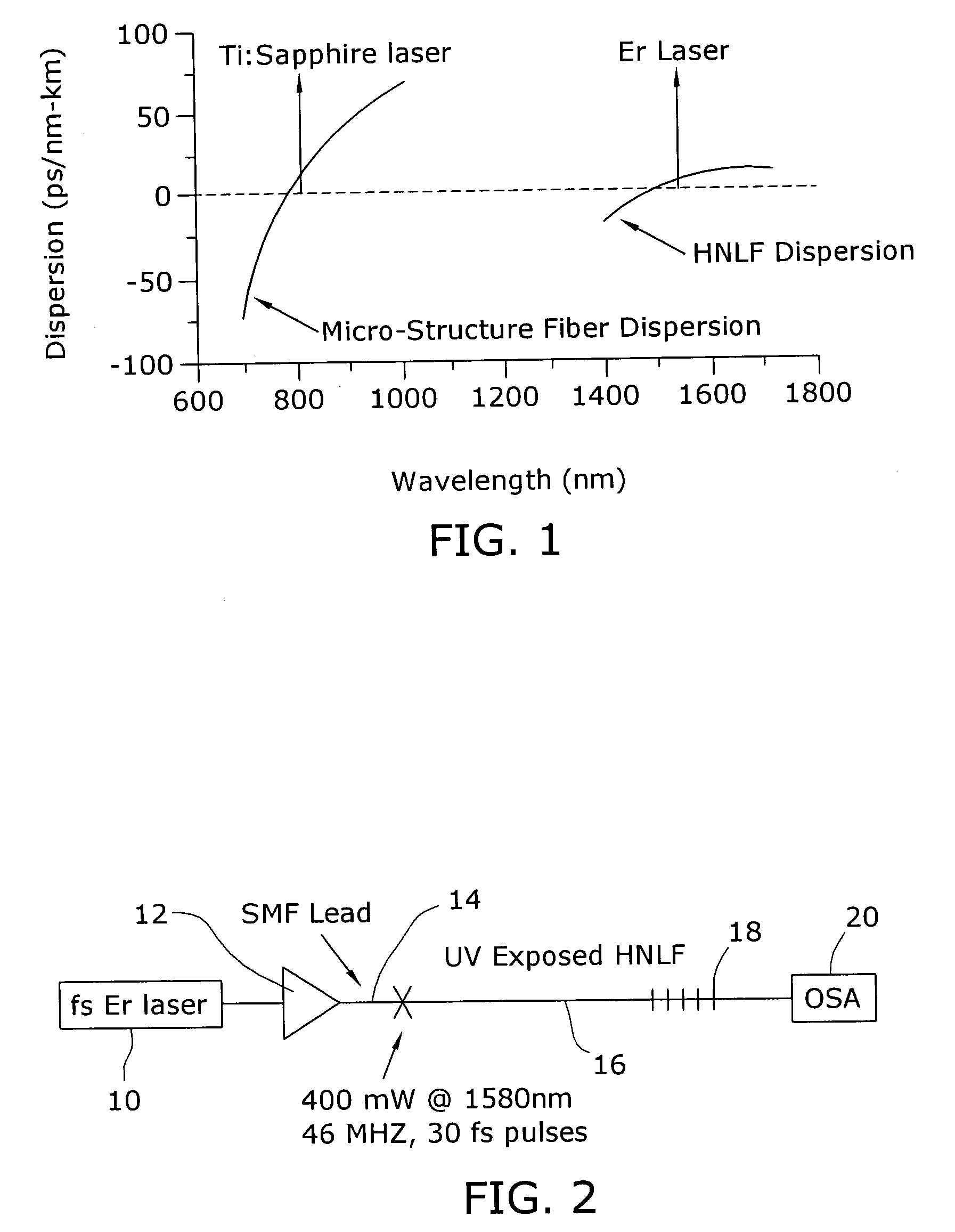
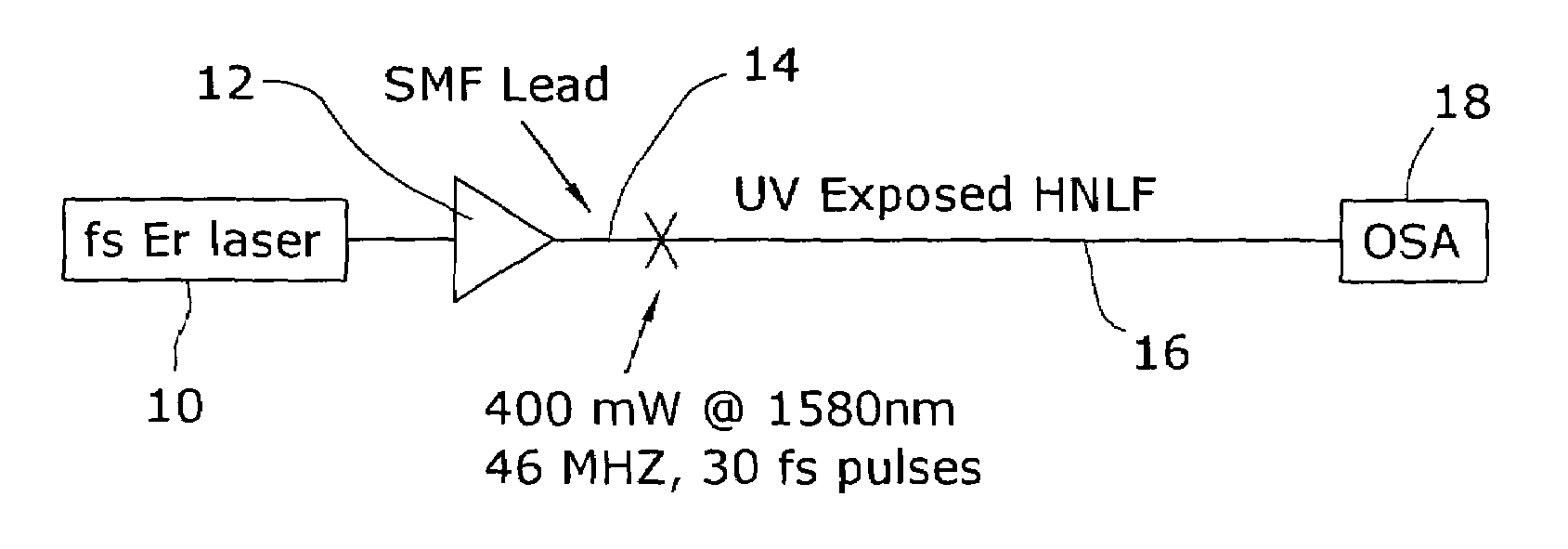
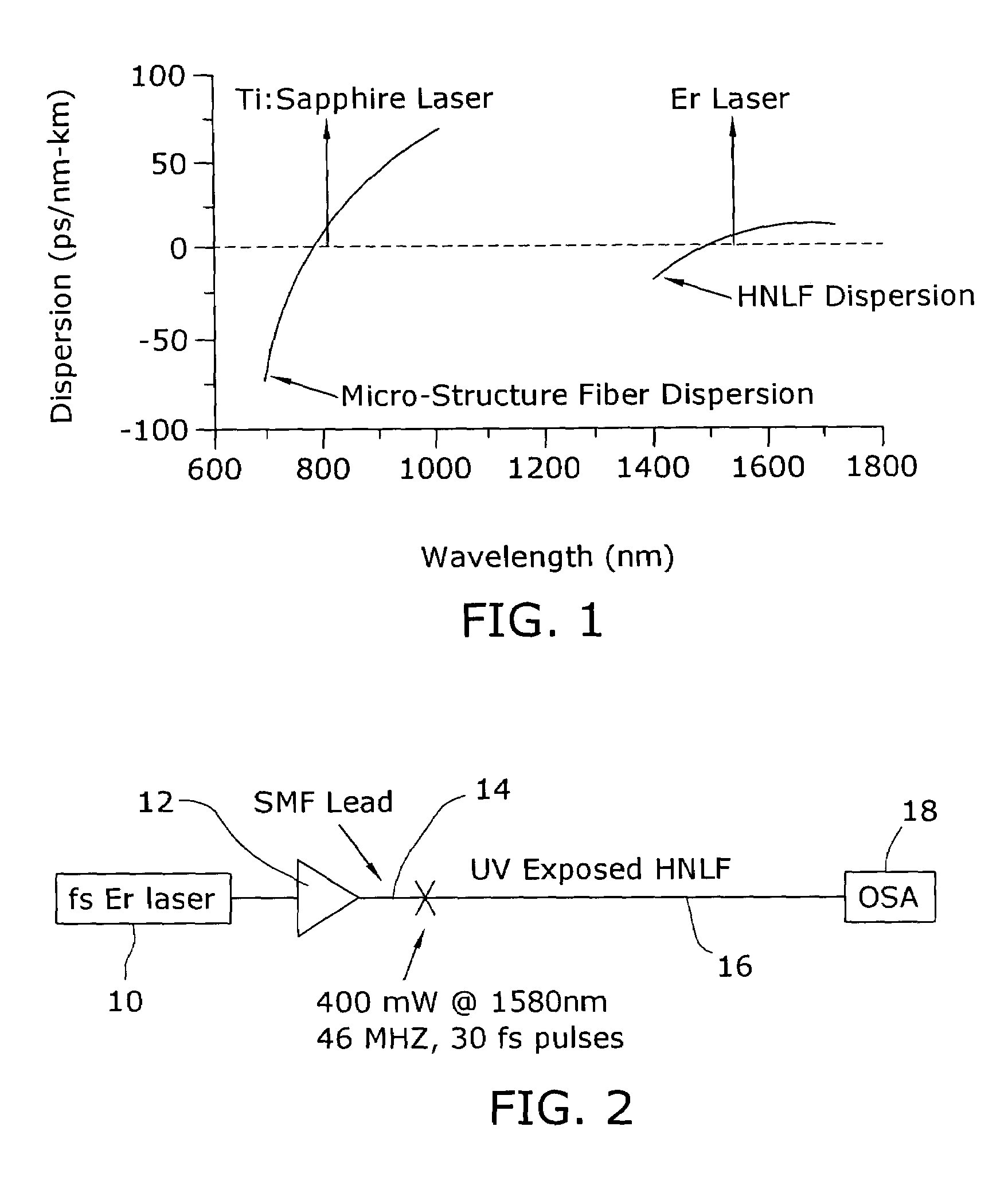
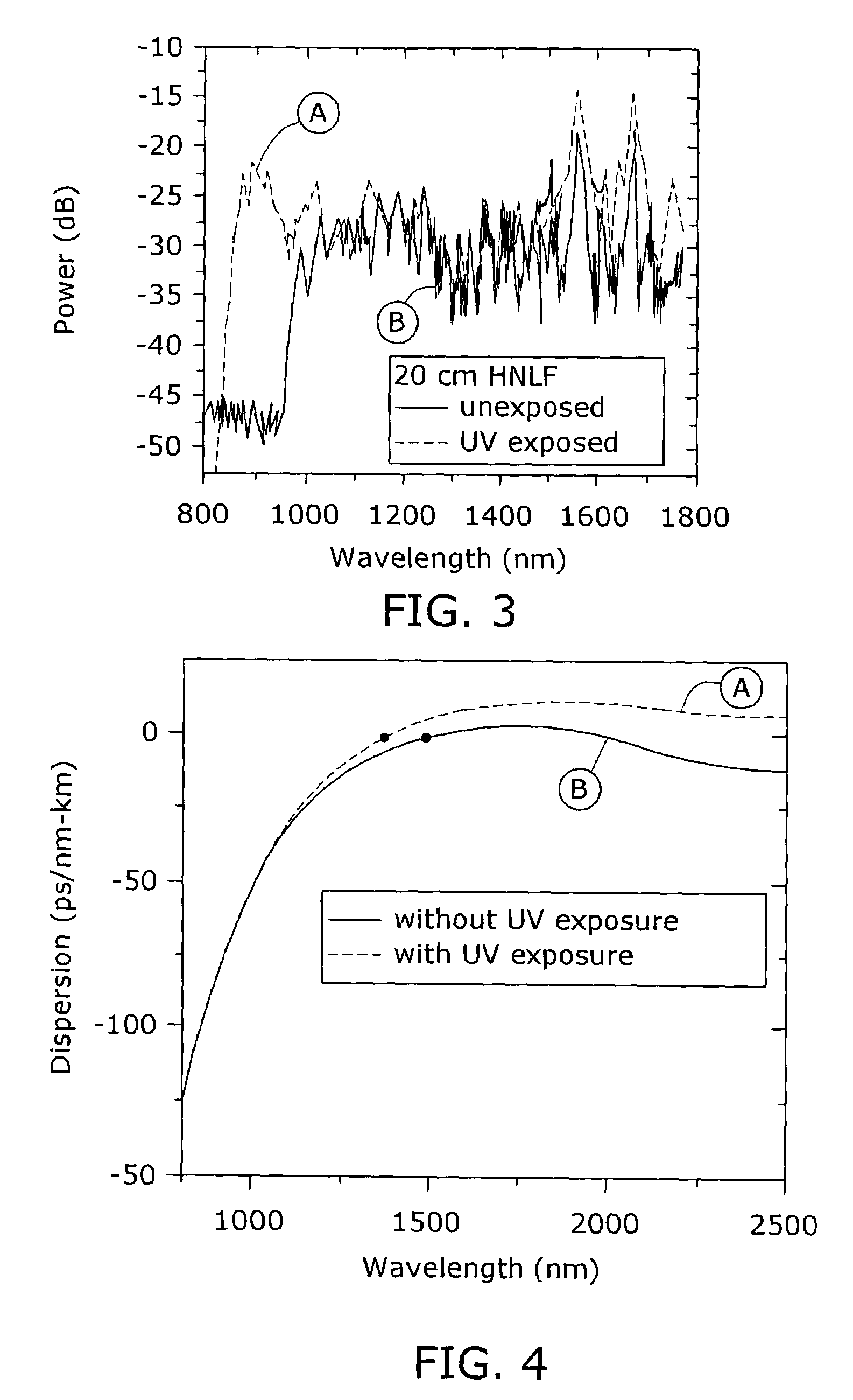
Enhancement of the supercontinuum generation performance of a highly-nonlinear optical fiber (HNLF) is accomplished by performing at least one post-processing treatment on the HNLF. Particularly, UV exposure of the HNLF will modify its dispersion and effective area characteristics so as to increase its supercontinuum bandwidth, without resorting to techniques such as tapering or introducing unwanted reflections into the HNLF. The UV exposure can be uniform, slowly varying or aperiodic along the length of the HNLF, where the radiation will modify the nonlinear properties of the HNLF. Various other methods of altering these properties may be used. The output from the HNLF can be monitored and used to control the post-processing operation in order to achieve a set of desired features in the enhanced supercontinuum spectrum.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Supercontinuum emitting device
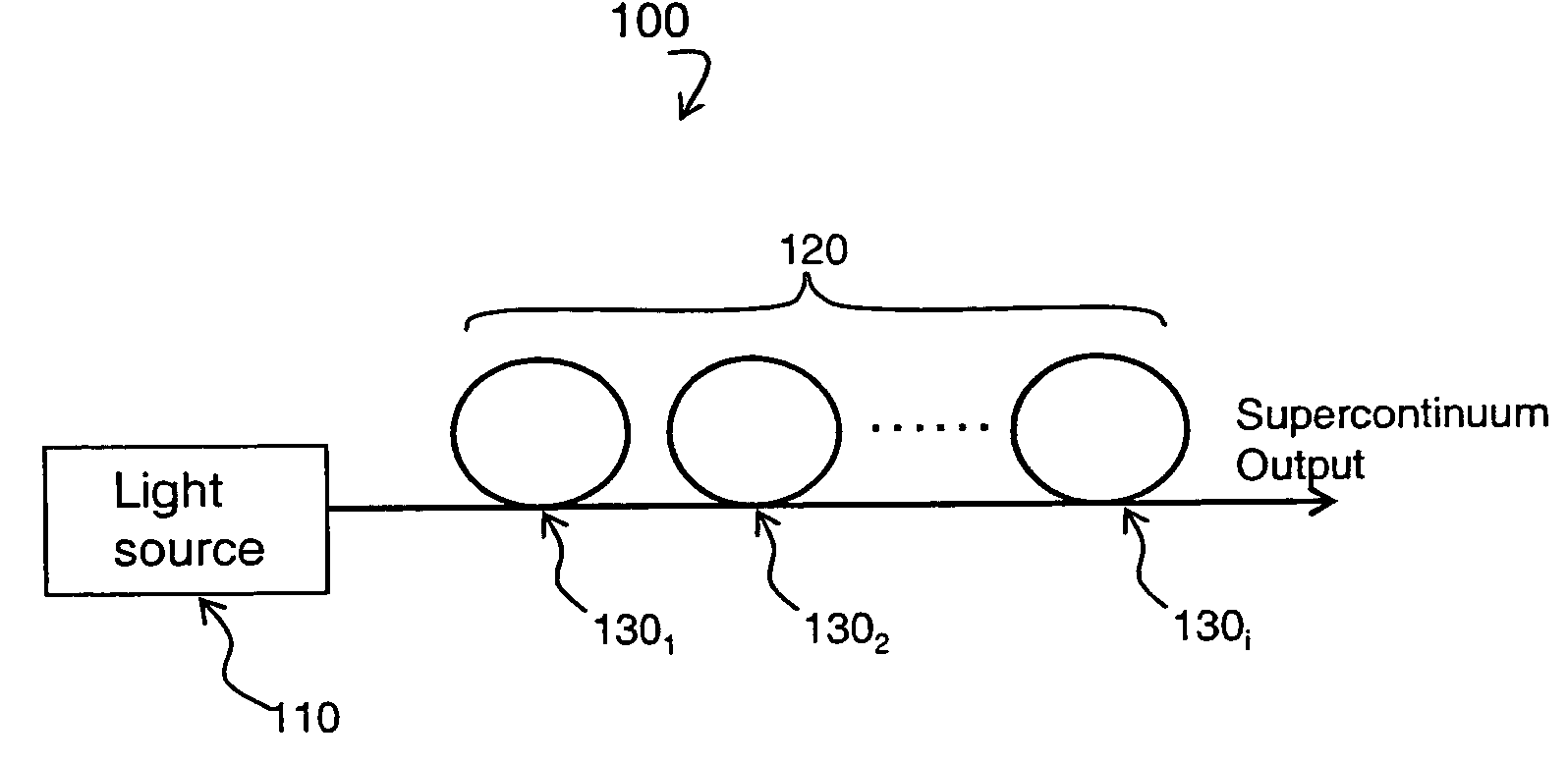
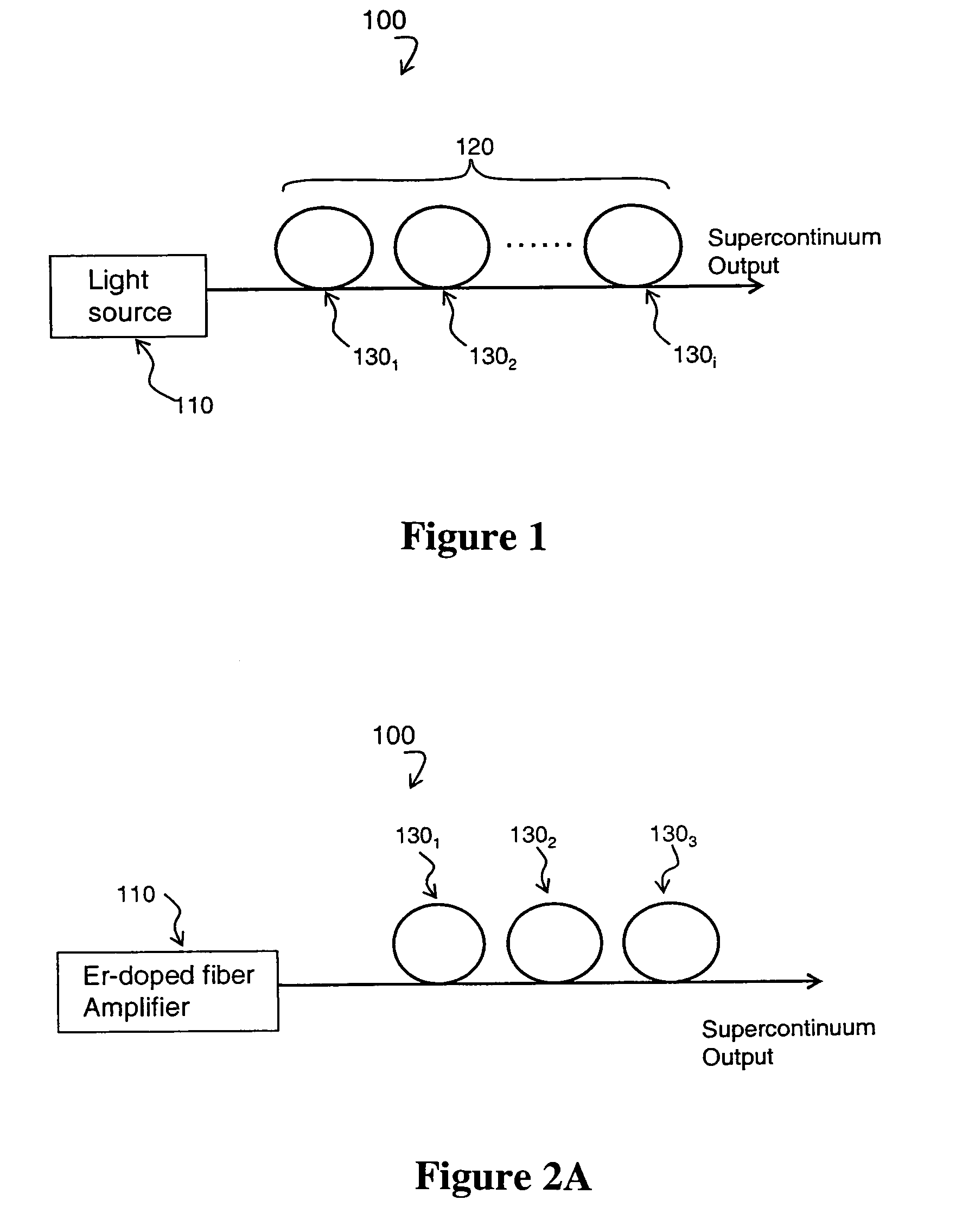
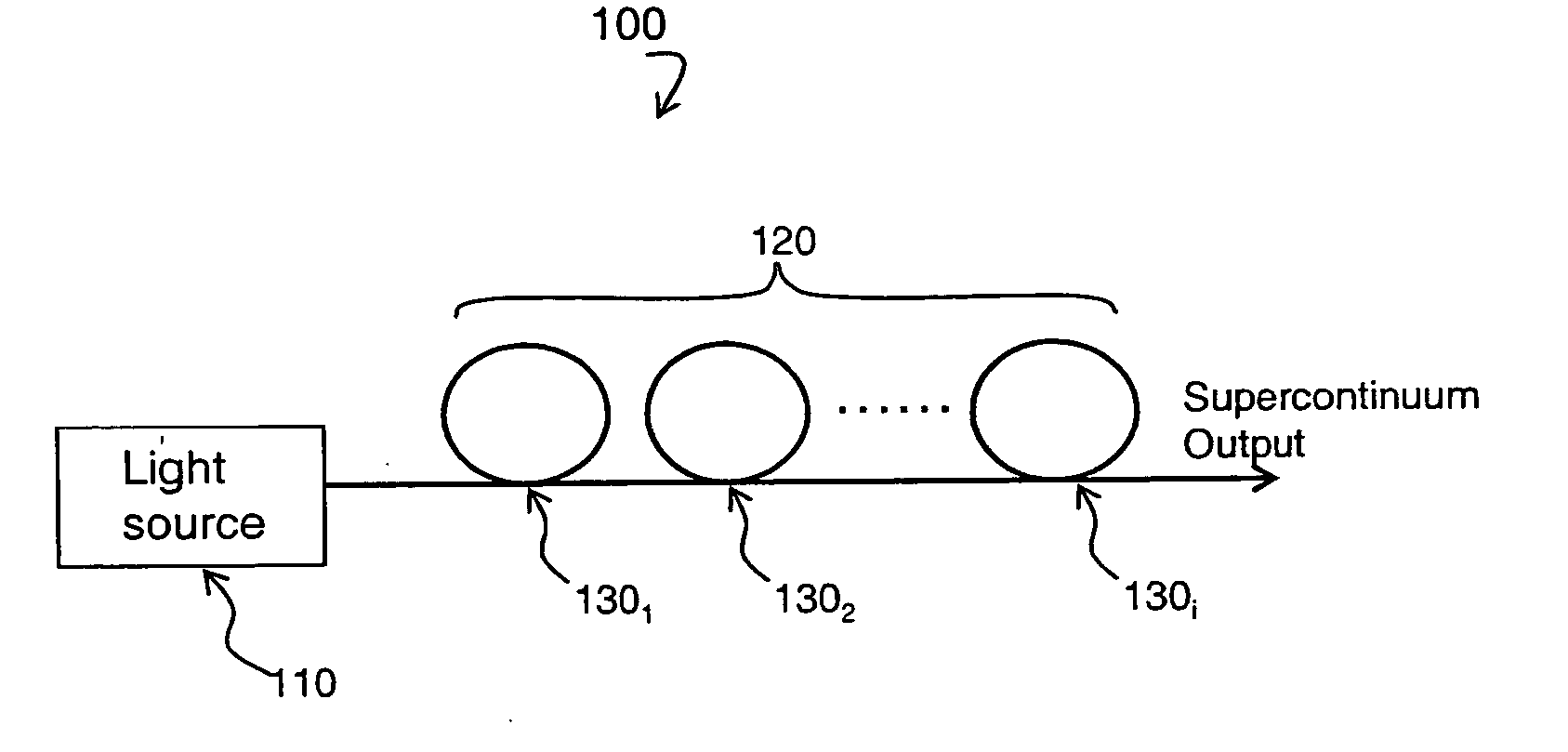
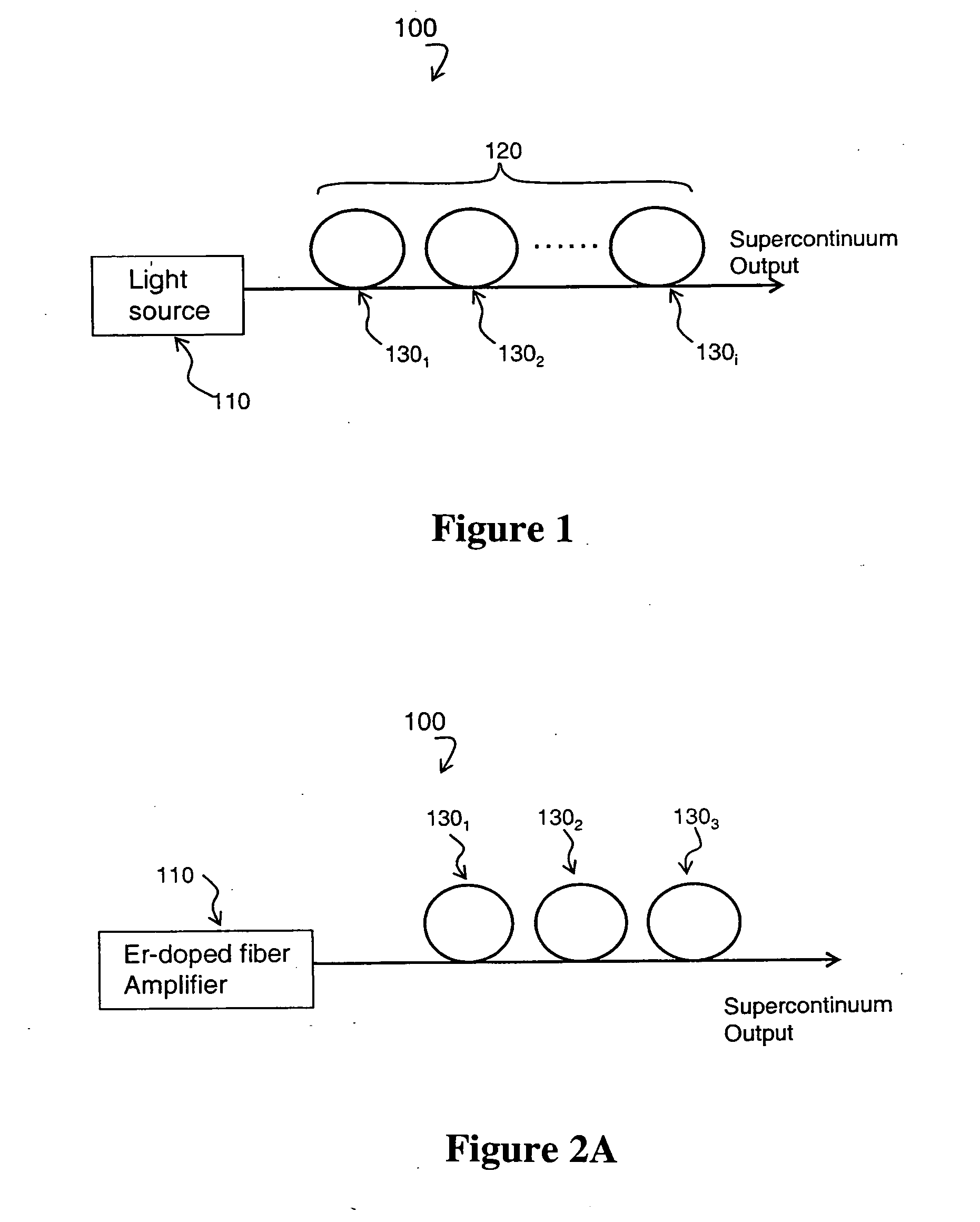
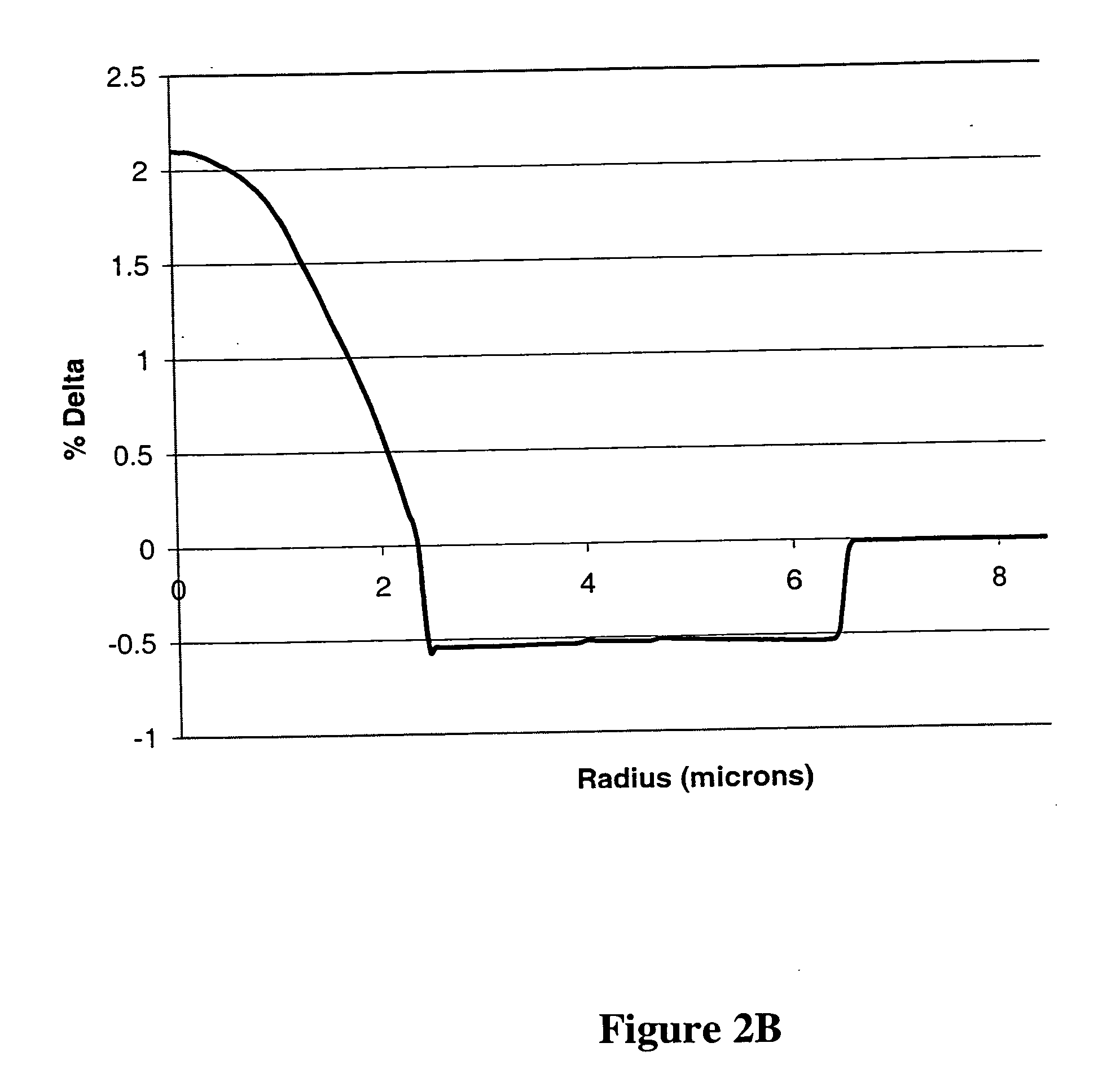
A supercontinuum light emitting device comprises an effectively CW light source producing light of wavelength λ1 within a specified bandwidth and a nonlinear fiber optically coupled to the light source. The nonlinear fiber has a plurality of fiber segments with different zero dispersion wavelengths λoi, where each successive fiber segment has zero dispersion wavelength λoi which is larger than the zero dispersion wavelength of the preceding fiber and the zero dispersion wavelength of the first fiber segment is within ±20 nm of λ1.
Owner:CORNING INC
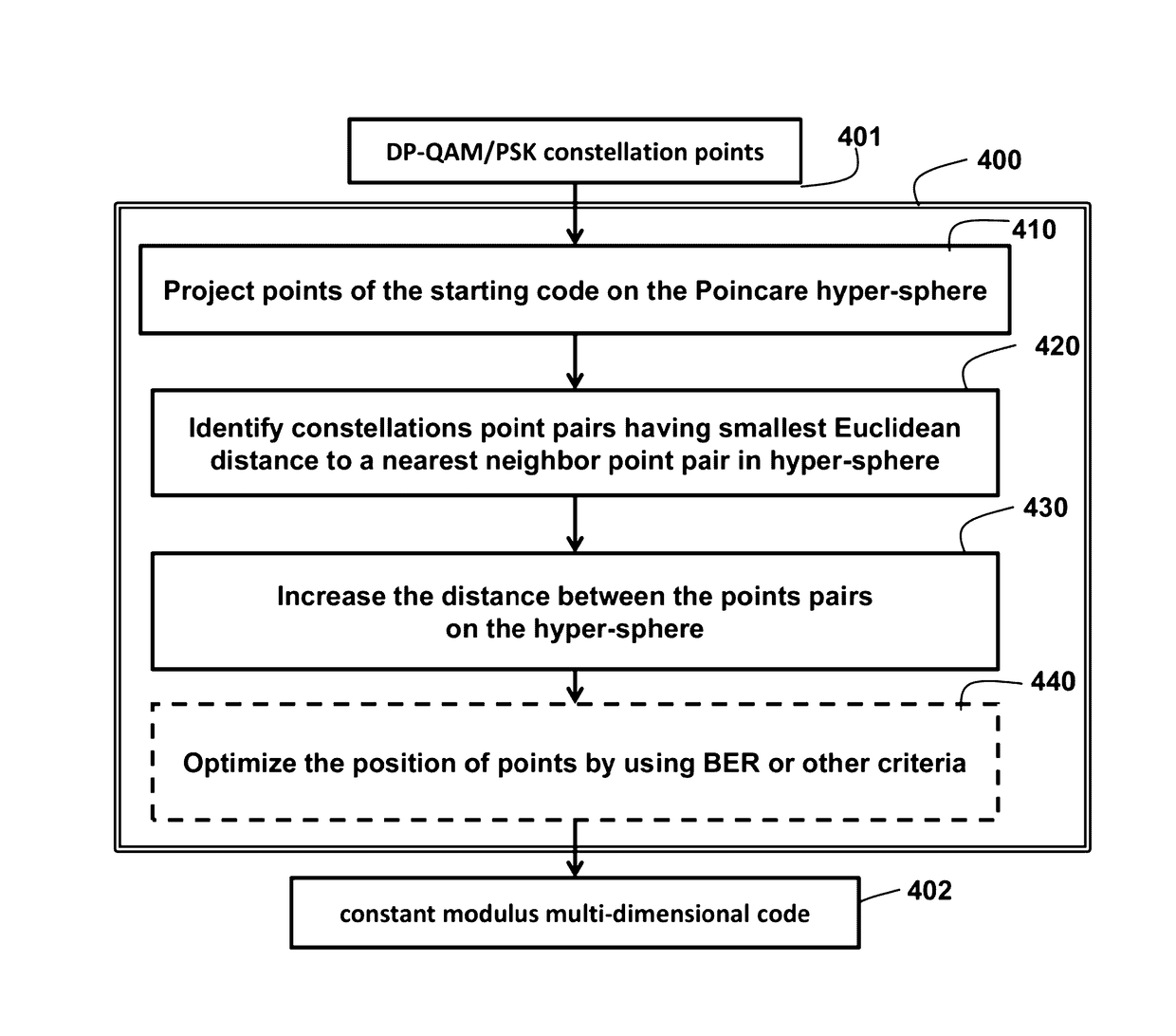
Method for Generating Constant Modulus Multi-Dimensional Modulations for Coherent Optical Communications
ActiveUS20160006515A1Improve spectral efficiencyConstant modulusElectromagnetic transmittersMultiple carrier systemsPhase noiseBlock code
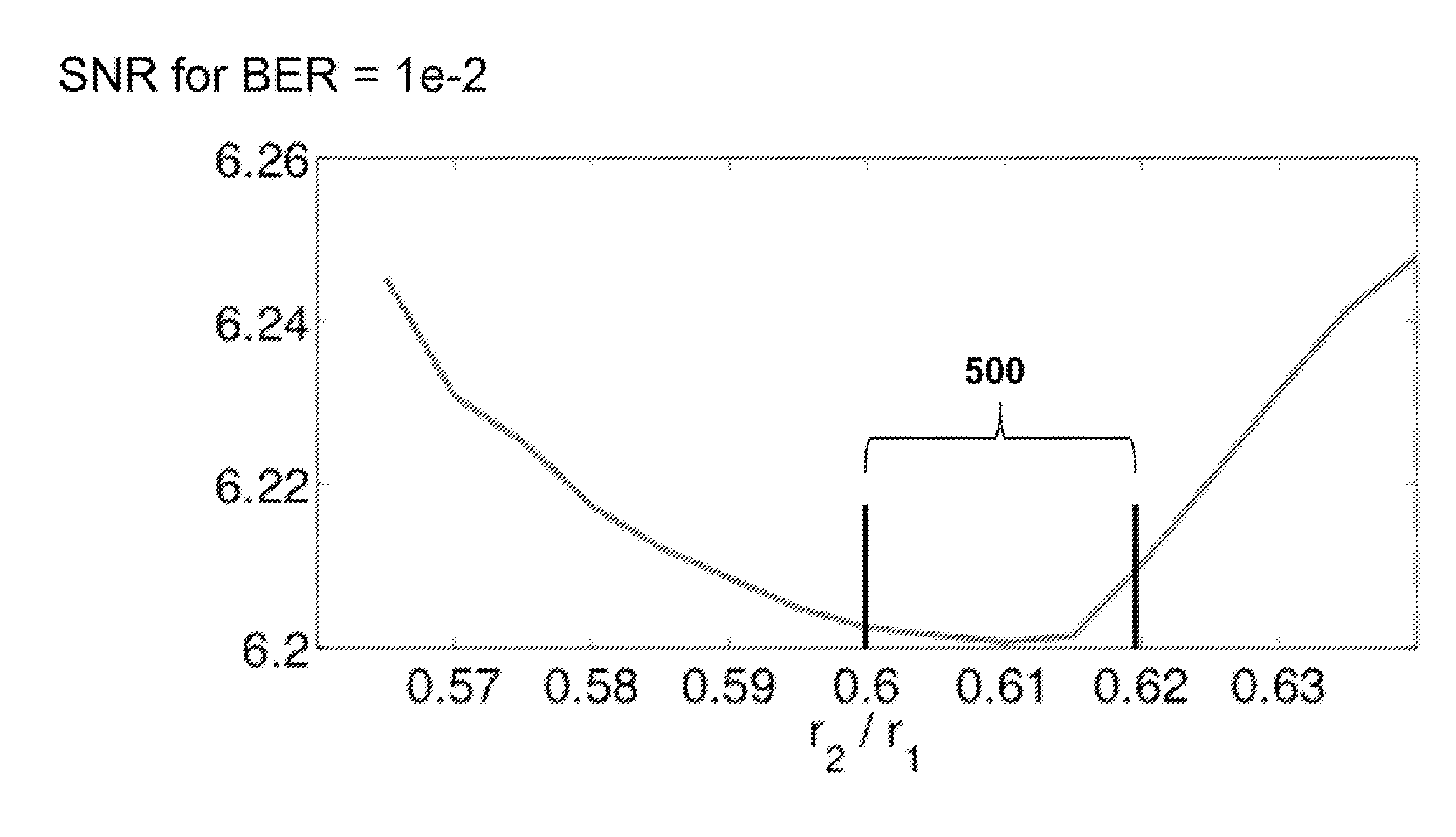
A method generates constant modulus multi-dimensional modulations for coherent optical communications by first projecting points in a constellation of the code onto a Poincare sphere or its higher-dimensional hyper-sphere. By using meta-heuristic procedures, nonlinear programming and gradient search methods, constellation points in the hyper-sphere are optimized in certain criteria, such as maximizing the minimum Euclidean distance, minimizing the union bound, minimizing the bit-error rate, minimizing the required signal-to-noise ratio, maximizing the nonlinear fiber reach, maximizing the phase noise tolerance, and maximizing the mutual information. Some methods use parametric unitary space-time block codes such as Grassmannian packing, and filter impulse response as well as unitary rotation over adjacent code blocks to generate near-constant modulus waveform, not only at the symbol timing, but also over the entire time.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Phase-sensitive amplification in a fiber
A method of and device for generating an amplified optical signal directly in an optical fiber by way of phase-sensitive amplification based on one or more four-wave mixing (FWM) processes. In one embodiment, an input signal and two pump waves are applied to a highly nonlinear fiber (HNLF). The input signal is amplified in the HNLF due to energy transfer from the pump waves to the input signal via a degenerate phase-conjugation (PC) process. In another embodiment, an input signal and first and second pump waves are applied to a first HNLF to generate, via a Bragg scattering (BS) process, an idler signal corresponding to the input signal. The second pump wave is then filtered out and the first pump wave, a third pump wave, and the input and idler signals are applied to a second HNLF, where they interact via a non-degenerate PC process to produce an amplified output signal.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
SBS suppressed nonlinear optical fiber
InactiveUS6959135B1Increase powerMore nonlinear behaviorOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideLength waveWaveguide
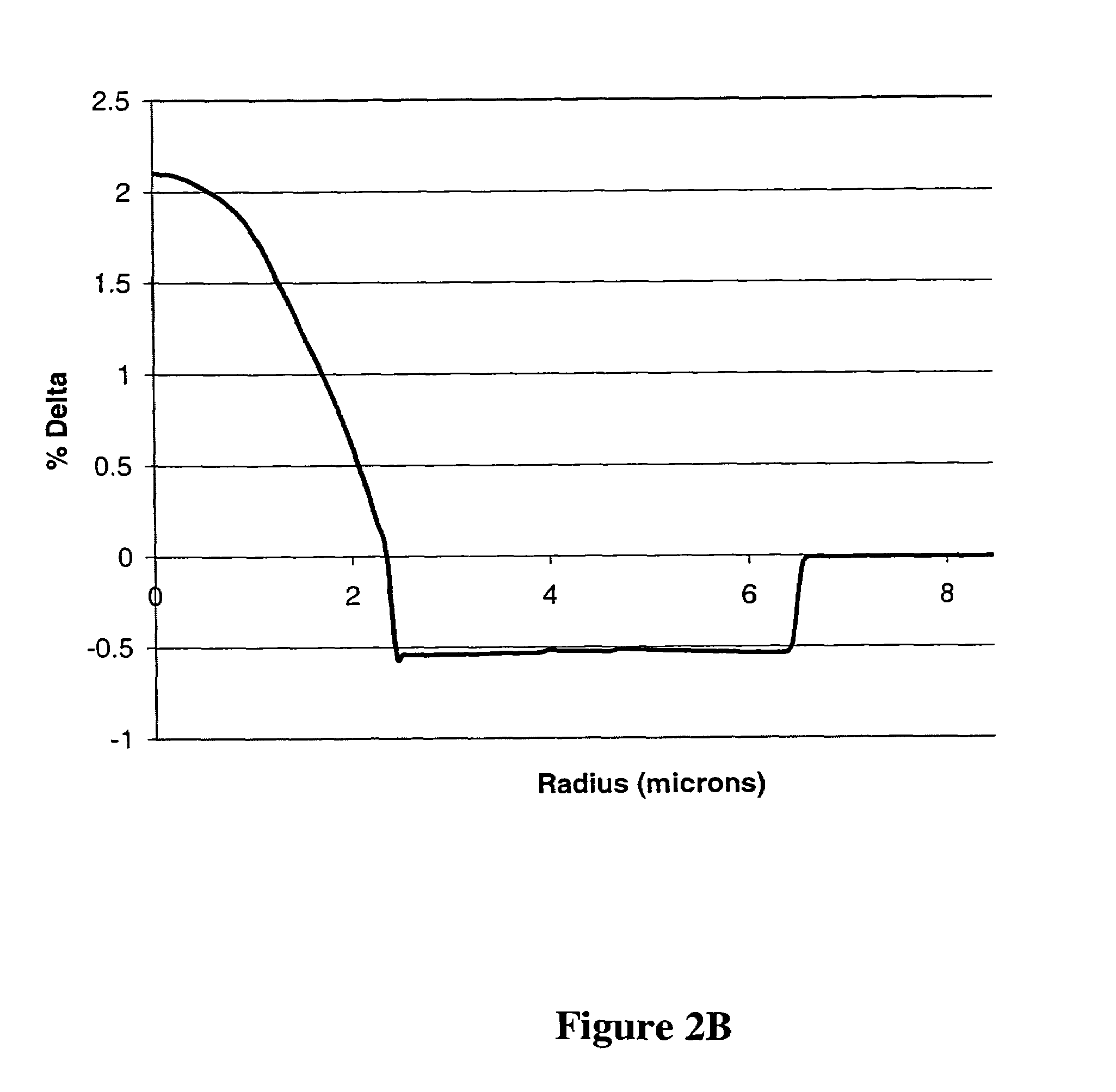
An optical waveguide fiber having a high threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering is disclosed which is suitable as a nonlinear fiber. The optical fiber has a core with one or more core segments. The optical effective area at a wavelength of 1550 nm is less that 30 μm2.
Owner:CORNING INC
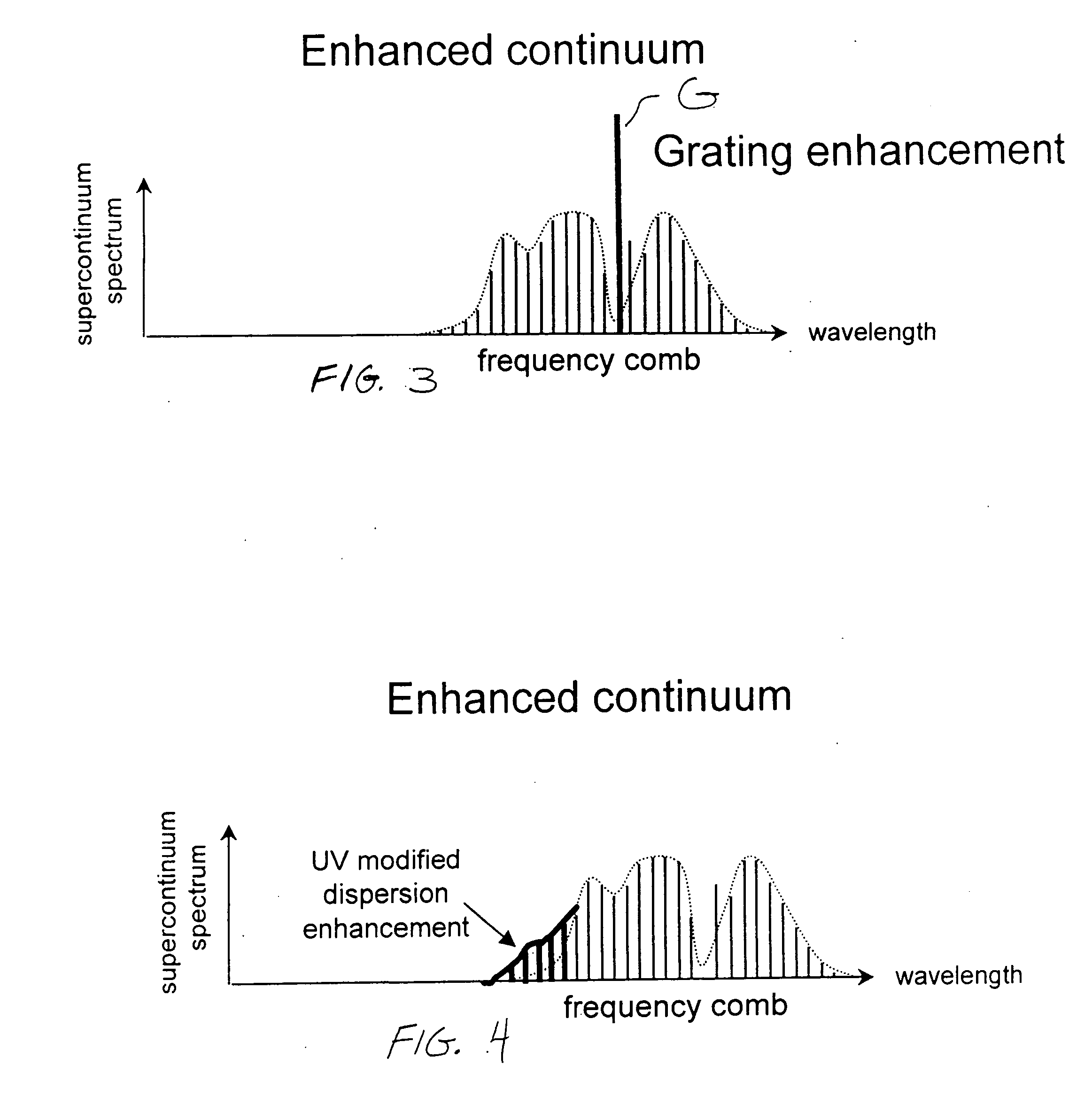
Enhanced supercontinuum generation in highly nonlinear fibers using strong bragg gratings
ActiveUS20050226575A1Enhance generated supercontinuumGenerate and outputWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesGratingResonance
Enhancement of the supercontinuum generation performance of a highly-nonlinear optical fiber (HNLF) is accomplished by incorporating at least one Bragg grating structure in the HNLF. The Bragg grating results in reflecting a core-guided signal into signal which also remains core-guided. The supercontinuum radiation generated by such an arrangement will exhibit a substantial peak in its energy at the grating resonance of the Bragg grating and a region of increased radiation in a narrow wavelength band on the long wavelength side of the peak. A number of such Bragg gratings may be formed so as to “tailor” the enhancements provided in the supercontinuum radiation. Various, well-known Bragg grating modifications (tuning, chirped, blazed, etc.) may also be used in the inventive structure to enhance the generated supercontinuum.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC +1
Erbium doped fiber laser with convertible multi-wavelength and mode locking and realization method thereof
InactiveCN101557071AMeet needsSwitchable wavelength tunableActive medium shape and constructionMode-lockingLaser light
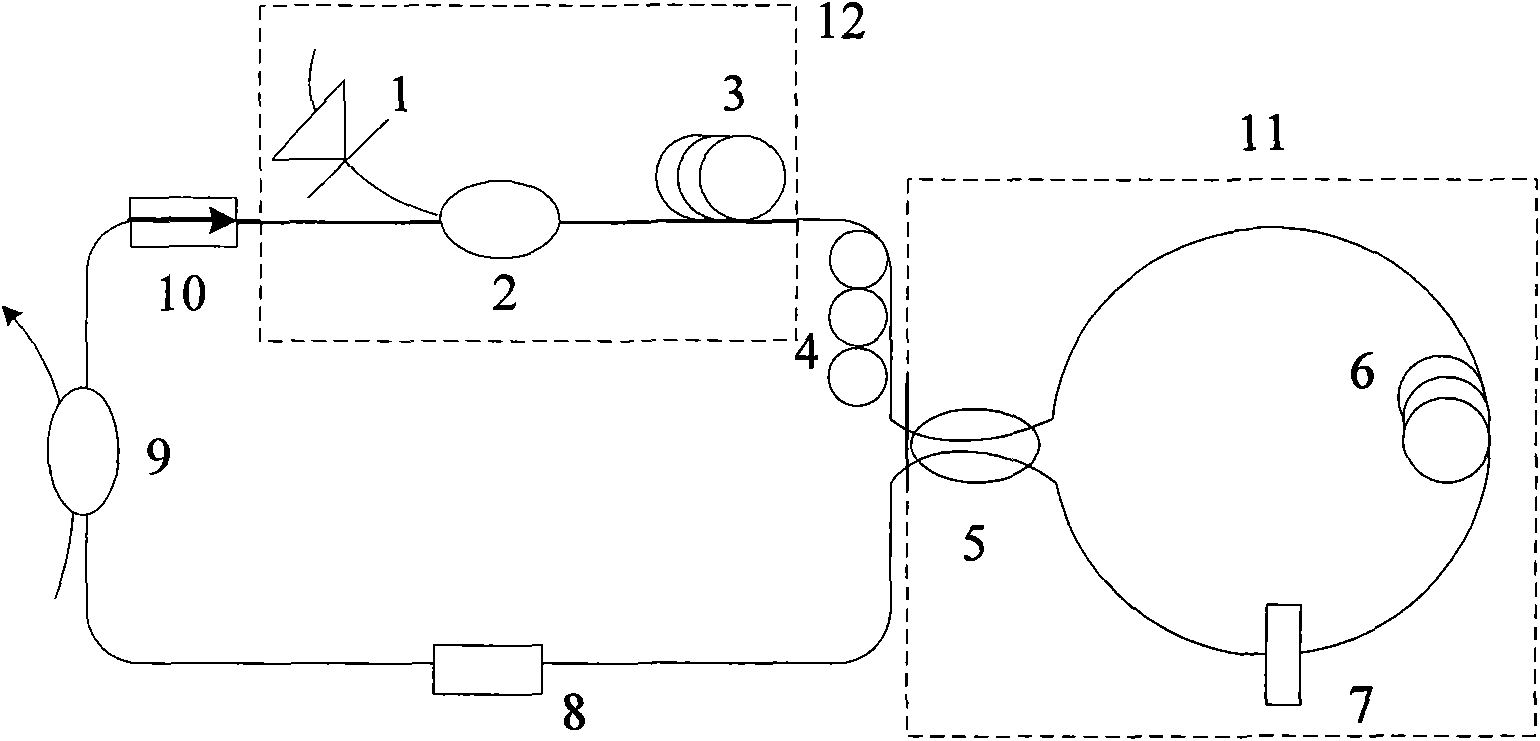
The invention relates to an erbium doped fiber laser with multi-wavelength and mode locking functions and convertible working state and a realization method thereof, in particular to a laser which can realize switching conversion between multi-wavelength and mode locking, has adjustable output wavelength position of multi-wavelength, and can stably work at room temperature and a realization method thereof. The laser comprises: a gain amplification unit, a polarization control unit, an output coupling unit, a comb filtering unit, an optical isolation unit and a nonlinear fiber loop mirror. The realization method of the laser includes the following steps: incident polarization state and double refraction are adjusted to lead the nonlinear fiber loop mirror inserted in the cavity of the laser to be in different working states, and the multi-wavelength and mode locking functions of the laser are respectively realized according to the different working conditions of the nonlinear fiber loop mirror. The invention has the advantages of convenient toning, low cost, being capable of realizing the two functions of stable multi-wavelength continuous output and mode locking pulse output, and the like, and can satisfy the demand for multifunctional laser light sources of optical time division multiplex / wavelength division multiplex communication technology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Stabilized optical fiber continuum frequency combs using post-processed highly nonlinear fibers
ActiveUS20060251424A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioMaintain propertiesElectromagnetic transmittersLight demodulationFrequency combNonlinear fiber
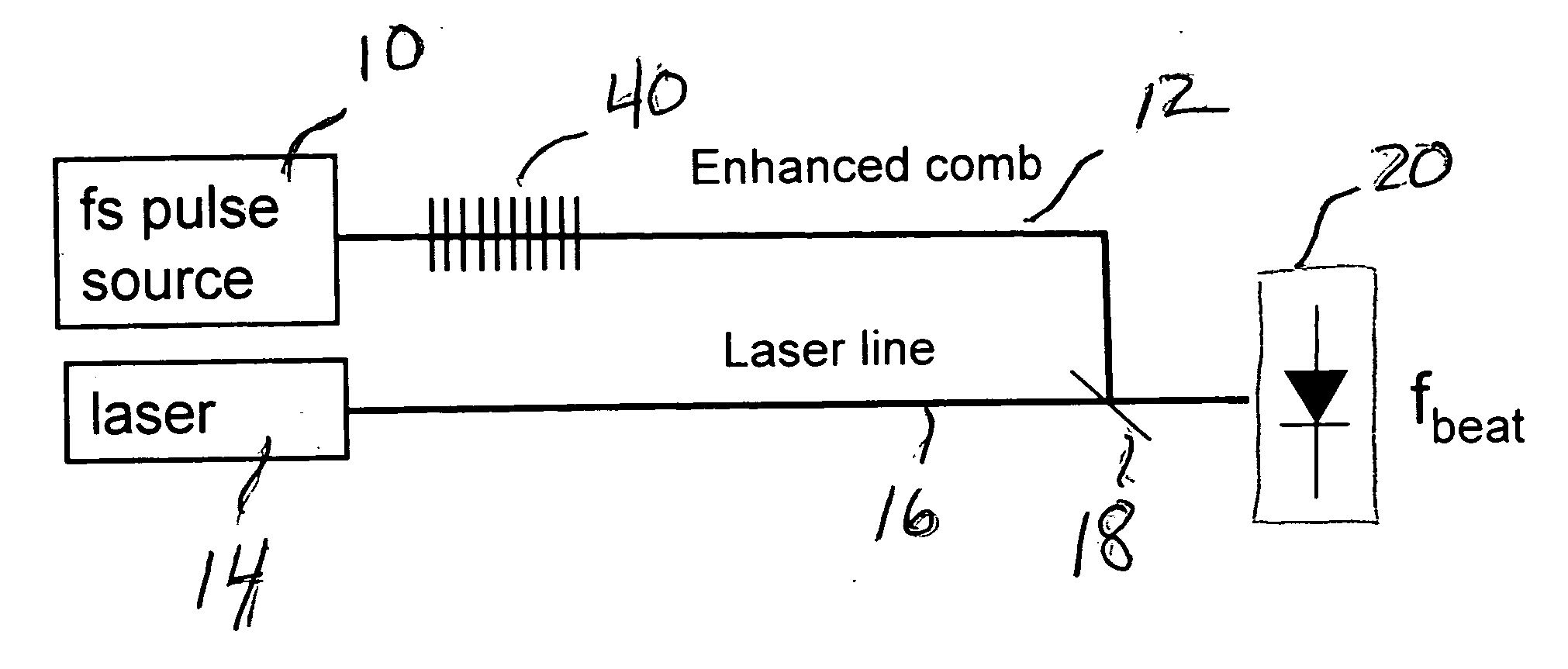
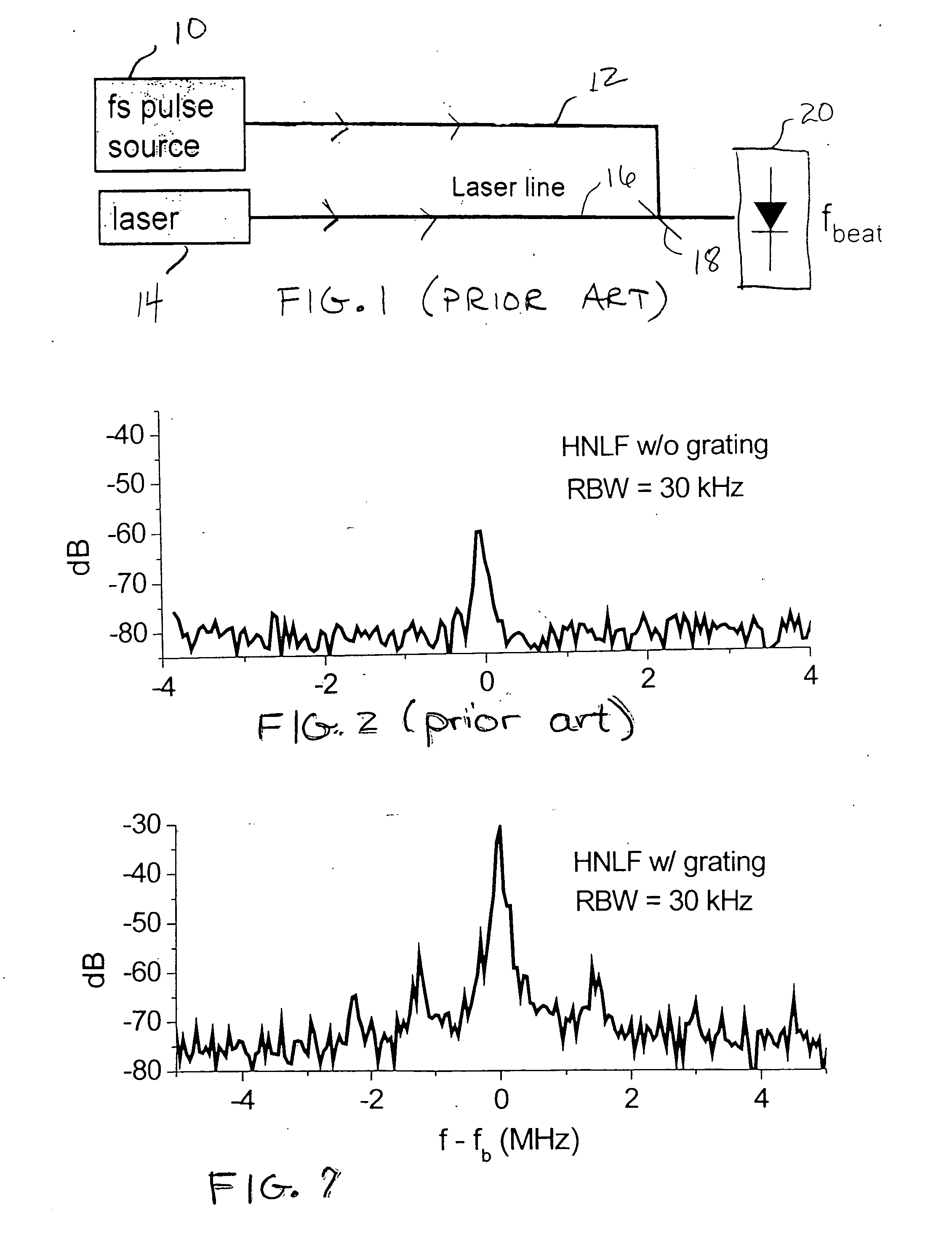
An arrangement for generating beat notes with a relatively high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) utilizes a pulsed laser source coupled into a section of post-processed highly-nonlinear optical fiber (HNLF) to generate a frequency comb having one or more regions of enhanced spectral power. A second laser signal source is overlapped with the frequency comb to form one or more “beat notes” at difference frequencies(y) between the second source and the continuum comb. By virtue of the post-processing, areas of spectral enhancement are formed along the comb, and are positioned to interact with the second laser signal to generate optical beat notes. The second laser signal may be from an external source (forming beat notes from a signal “outside” of the comb), or may be a frequency-multiplied version of the generated supercontinuum (forming beat notes from a signal “within” the comb).
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
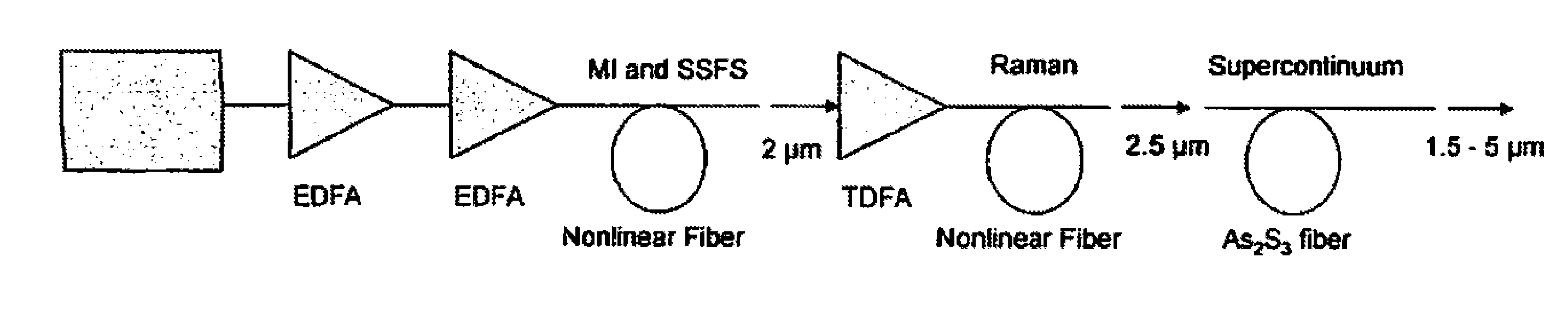
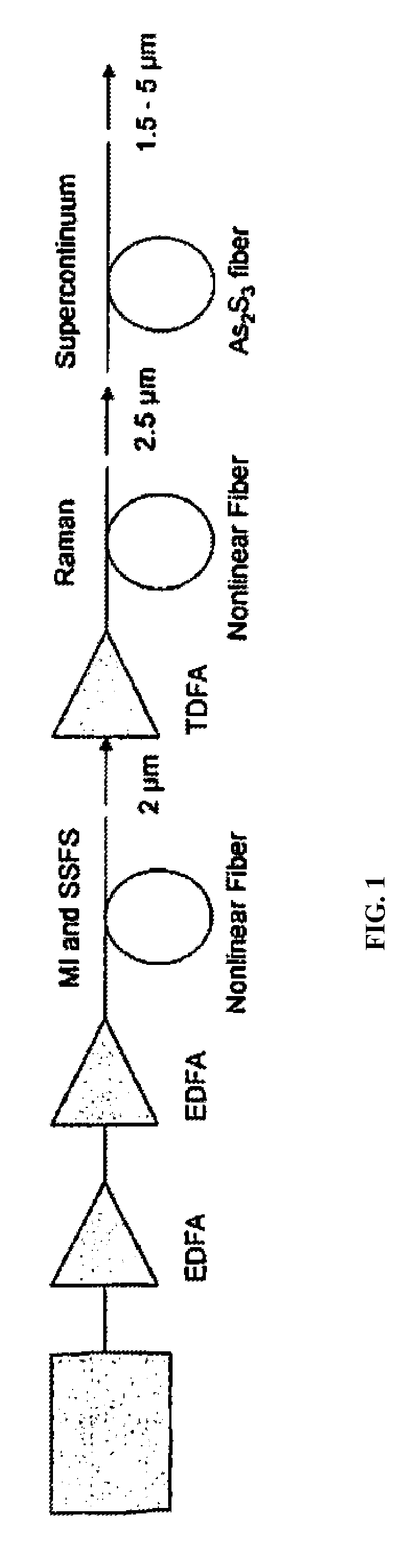
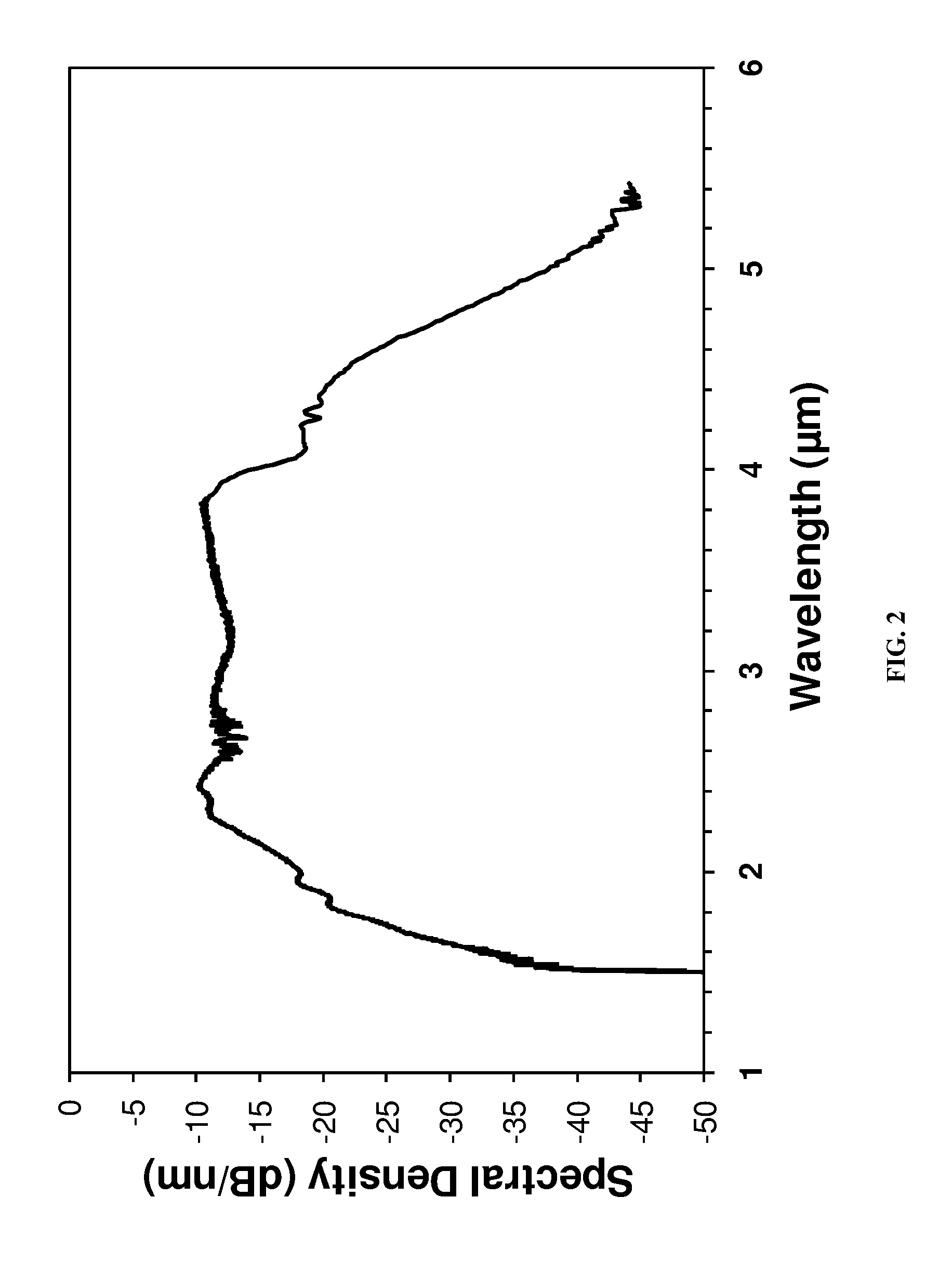
Ir fiber broadband mid-ir light source
ActiveUS20130188240A1Power scalableCompact and rugged and highly efficientLight demodulationNon-linear opticsBroadbandLength wave
A method of generating a supercontinuum in chalcogenide fiber with a pump light comprising a short pulse fiber laser or diode laser operating with a wavelength of 1.0μm or greater that is wavelength shifted through a nonlinear fiber one or more times and amplified one or more times and launched into a chalcogenide fiber whereby the spectrum is broadened in the chalcogenide fiber through various nonlinear processes to generate a supercontinuum within the mid-IR from 1.5 to greater than 5μm.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Supercontinuum emitting device
A supercontinuum light emitting device comprises an effectively CW light source producing light of wavelength λ1 within a specified bandwidth and a nonlinear fiber optically coupled to the light source. The nonlinear fiber has a plurality of fiber segments with different zero dispersion wavelengths λoi, where each successive fiber segment has zero dispersion wavelength λoi which is larger than the zero dispersion wavelength of the preceding fiber and the zero dispersion wavelength of the first fiber segment is within ±20 nm of λ1.
Owner:CORNING INC
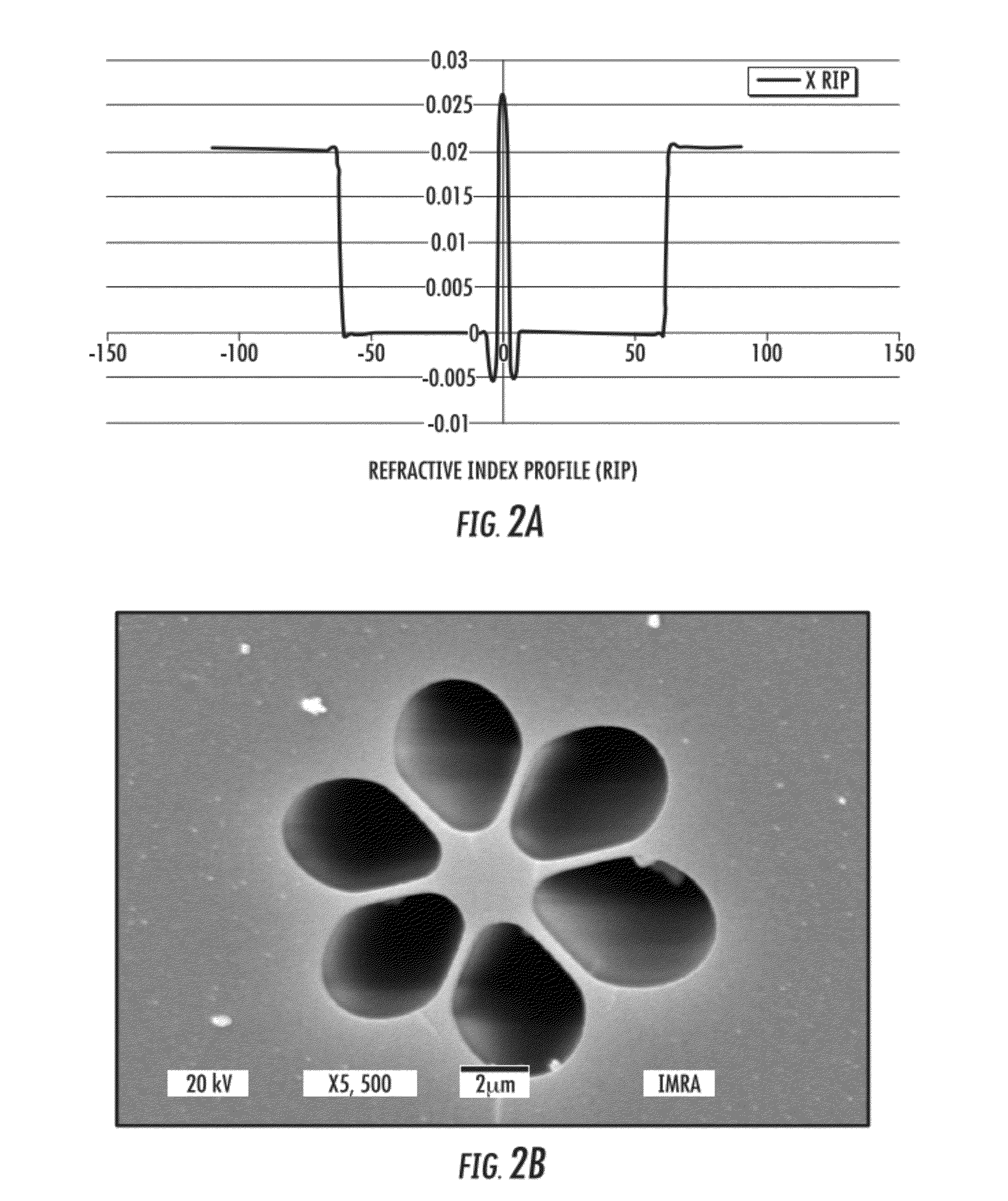
Holey optical fibres of non-silica based glass
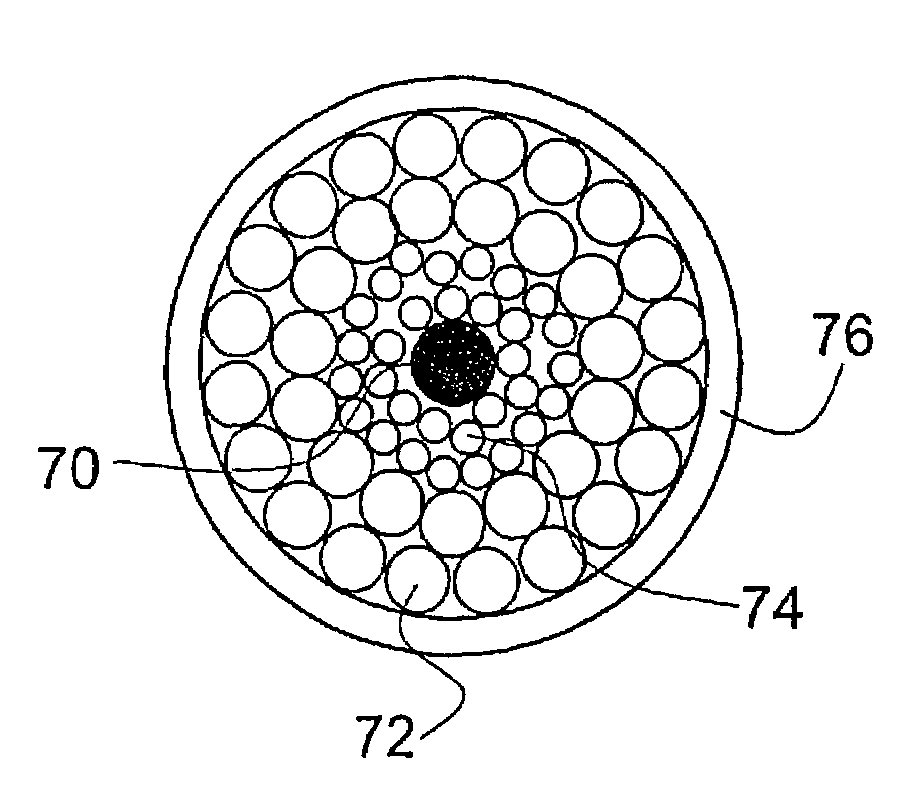
InactiveUS7155099B2Mismatch problemMinimal numberGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFibre typeRare earth
To overcome problems of fabricating conventional core-clad optical fibre from non-silica based (compound) glass, it is proposed to fabricate non-silica based (compound) glass optical fibre as holey fibre i.e. one contining Longitudinal holes in the cladding. This removes the conventional problems associated with mismatch of the physical properties of the core and clad compound glasses, since a holey fibre can be made of a single glass composition. With a holey fibre, it is not necessary to have different glasses for the core and cladding, since the necessary refractive index modulation between core and cladding is provided by the microstructure of the clad, i.e. its holes, rather than by a difference in materials properties between the clad and core glasses. Specifically, the conventional thermal mismatch problems between core and clad are circumvented. A variety of fibre types can be fabricated from non-silica based (compounds) glasses, for example: single-mode fibre; photonic band gap fibre; highly non-linear fibre; fibre with photosensitivity written gratings and other refractive index profile structures; and rare-earth doped fibres (e.g. Er, Nd, Pr) to provide gain media for fibre amplifiers and lasers.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
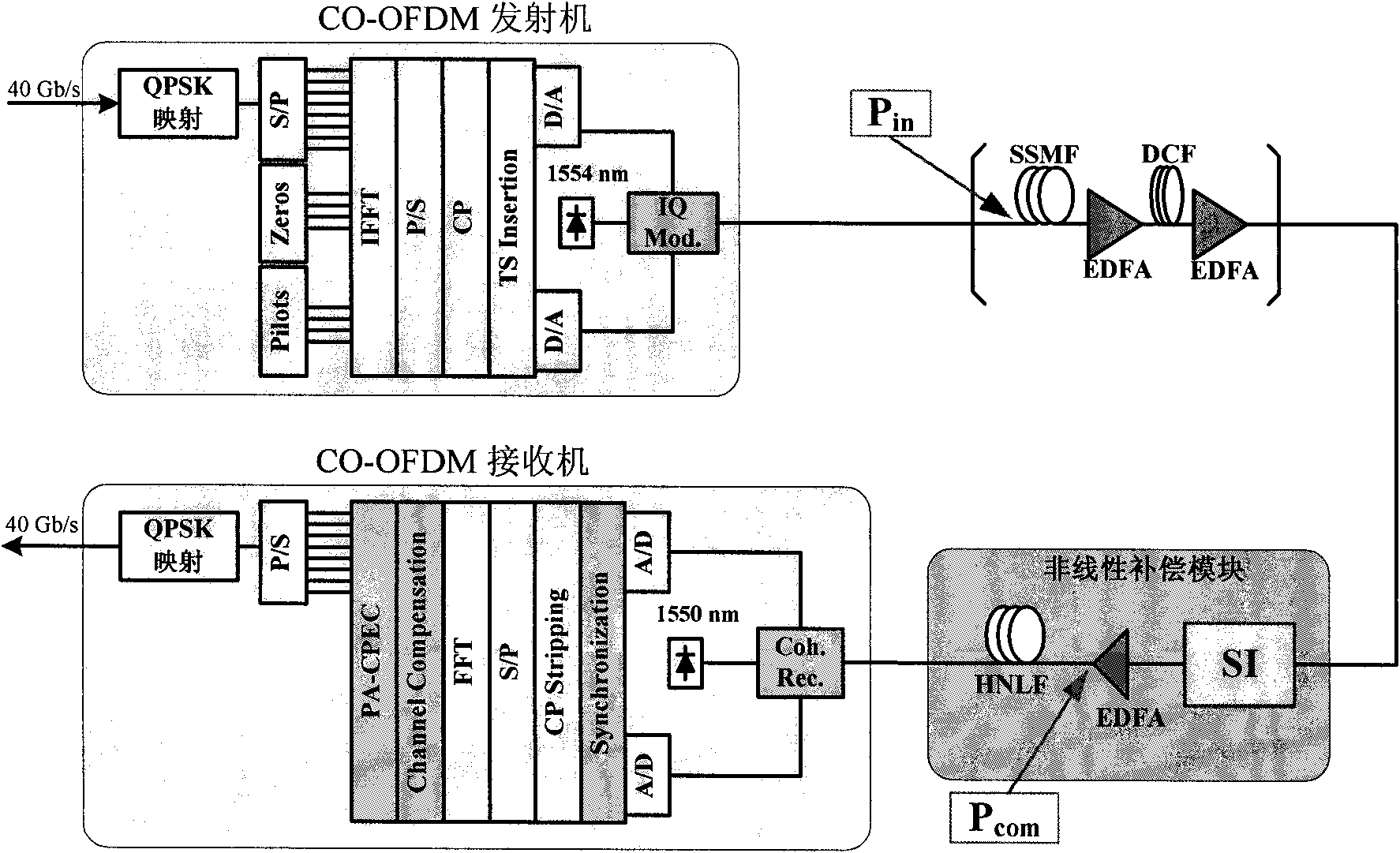
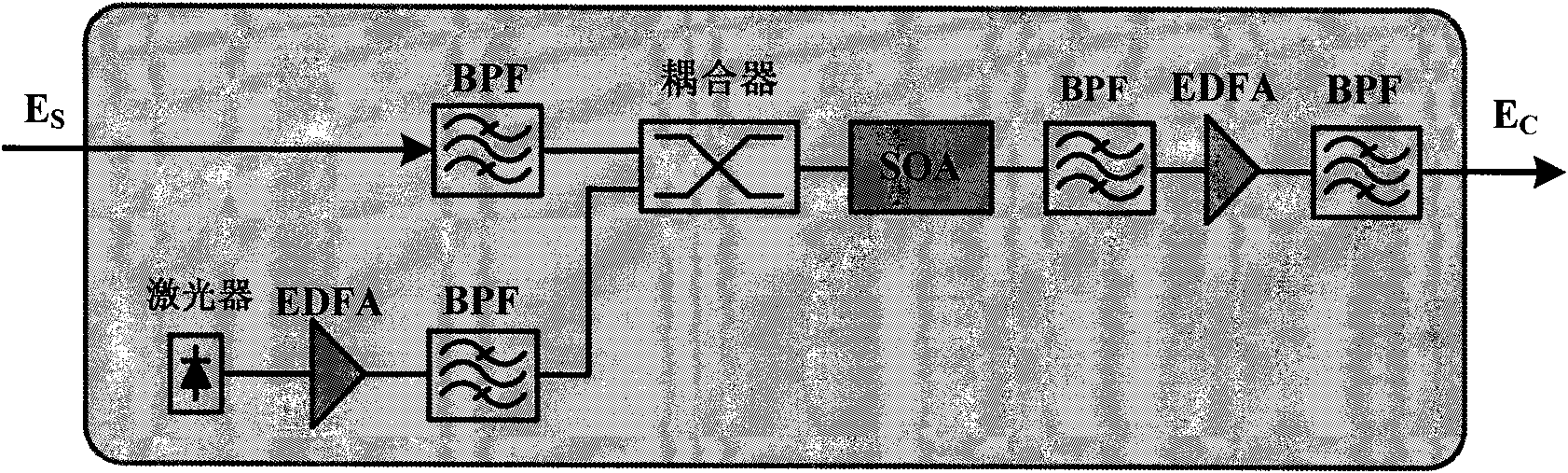
SI (Spectrum Inversion)-based nonlinear fiber damage compensation method and device in OFDM system
The invention relates to SI (Spectrum Inversion)-based nonlinear fiber damage compensation method and device in an O-OFDM (Optical-Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) system, belonging to the field of optical communication and applied to the O-OFDM system for nonlinear fiber damage compensation. The whole compensation module is arranged in front of a receiver of the O-OFDM system and comprises an SI unit and an HNLF (Highly Non-Linear Fiber) which has a certain length and is arranged behind the SI unit, wherein SI is realized by an SOA (Semiconductor Optical Amplifier) based on FWM (Four Wave Mixing) effect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
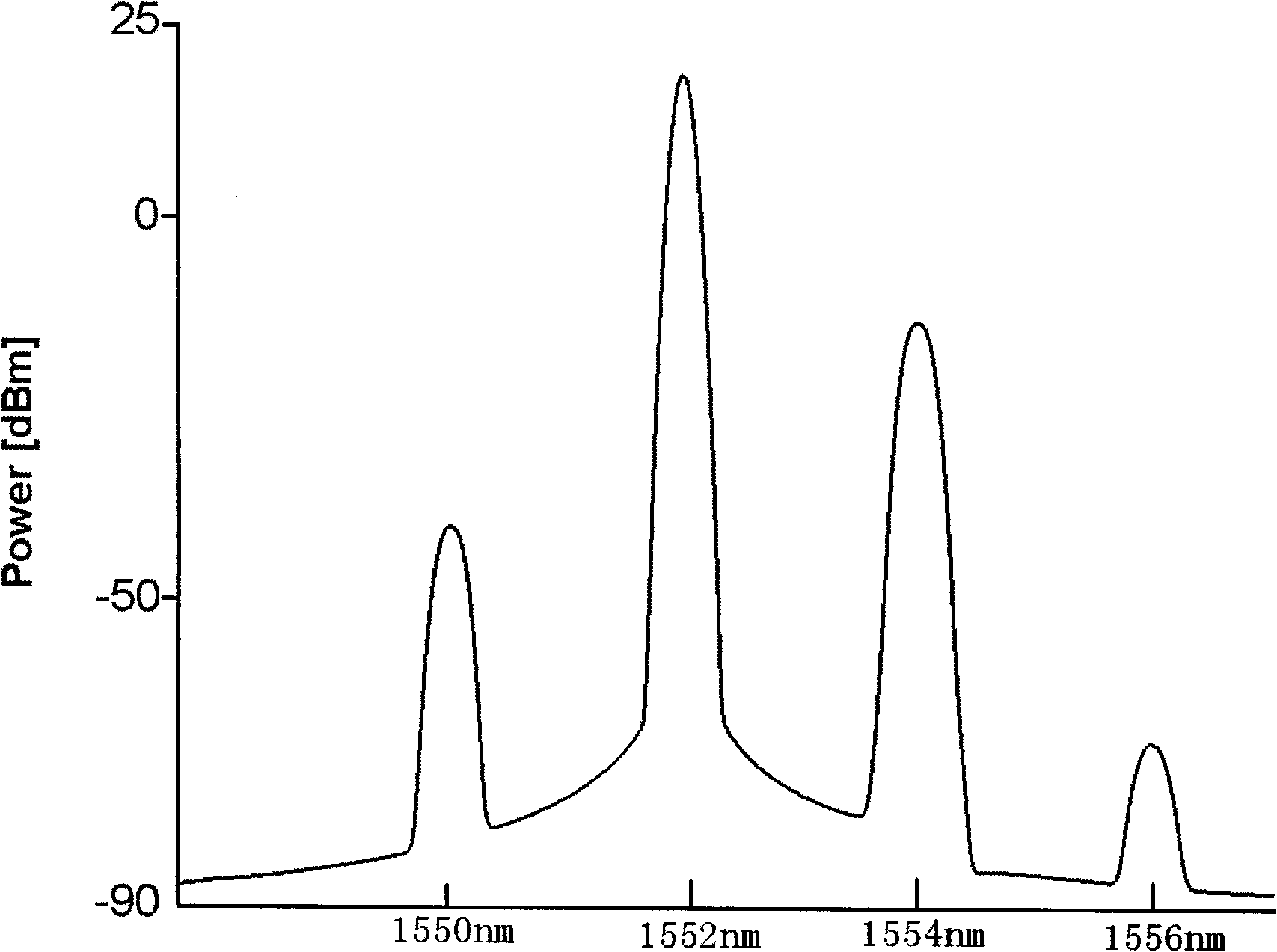
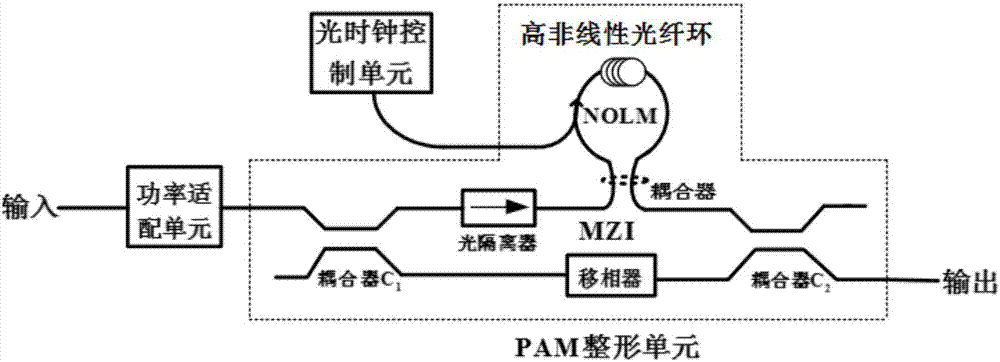
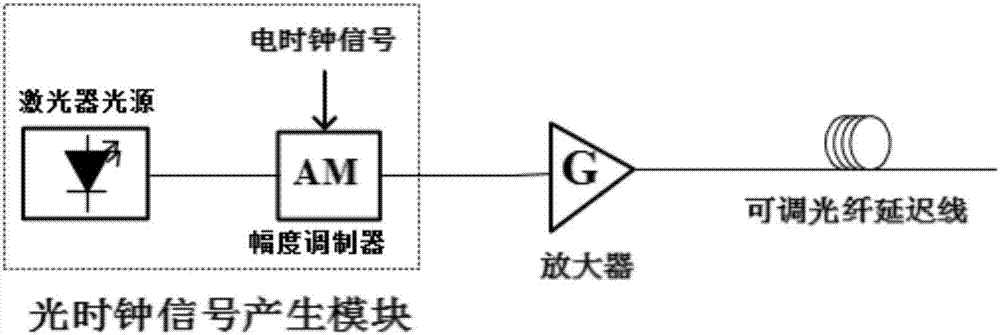
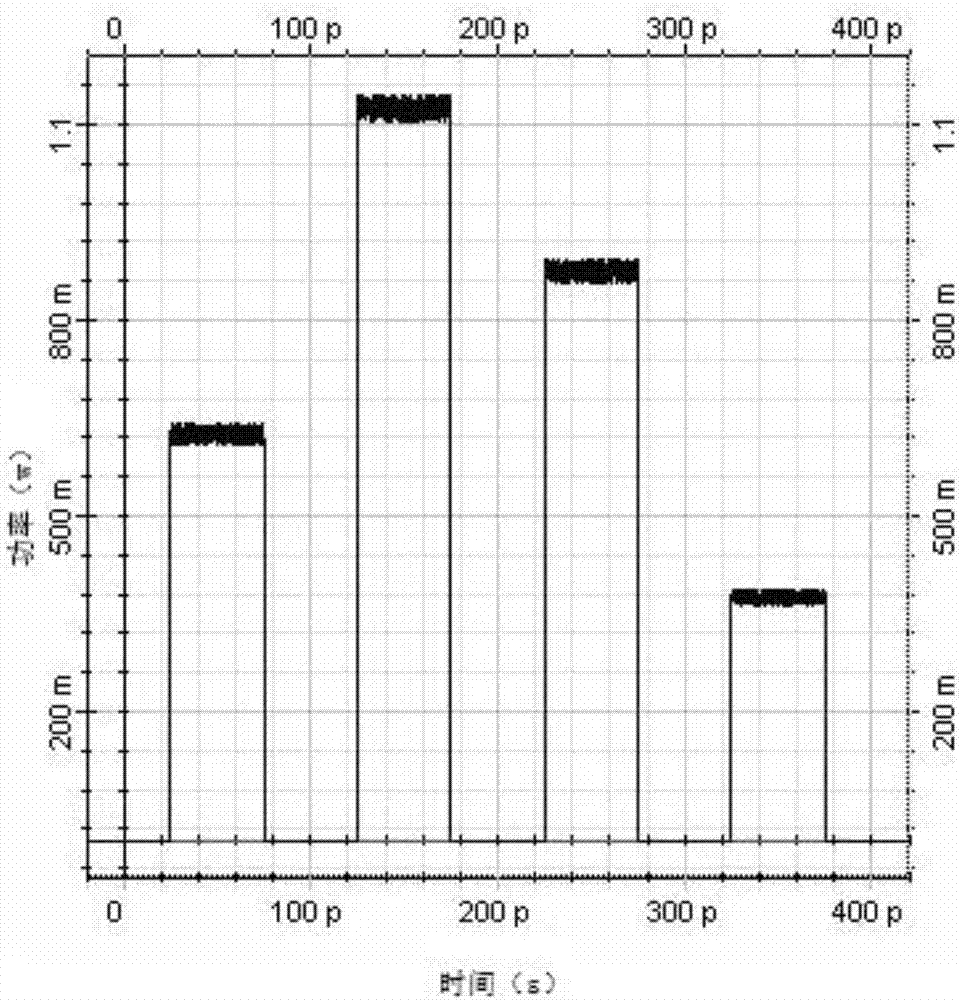
Optically controlled optical PAM signal regeneration device
InactiveCN106972890AFlexible designTime-division multiplexElectromagnetic transmittersOptical clockSignal regeneration
The invention discloses an optically controlled optical PAM signal regeneration device comprising a power adapting unit, an optical clock control unit and a PAM reshaping unit, wherein the PAM reshaping unit is the core of a regenerator and is composed of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer MZI and a highly nonlinear fiber ring NOLM, for a to-be-regenerated degraded optical PAM signal, the level matching between the input degraded optical PAM signal and the PAM reshaping unit is accomplished by the power adapting unit, the optical clock signal power and the delay output by the optical clock control unit and a phase shifter in the MZI structure are adjusted, so that the PAM reshaping unit works normally, the loss coefficient, the optical fiber length, the nonlinear coefficient and other parameters of a highly nonlinear optical fiber in the NOLM structure, and the coupling coefficients of front and back couplers in the MZI structure are changed to design PAM reshaping units with different level numbers, and then the regeneration of the degraded optical PAM signal is accomplished. Therefore, the optically controlled optical PAM signal regeneration device disclosed by the invention can execute a reshaping and a re-timing function and has the advantages of flexible design of regeneration level numbers.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
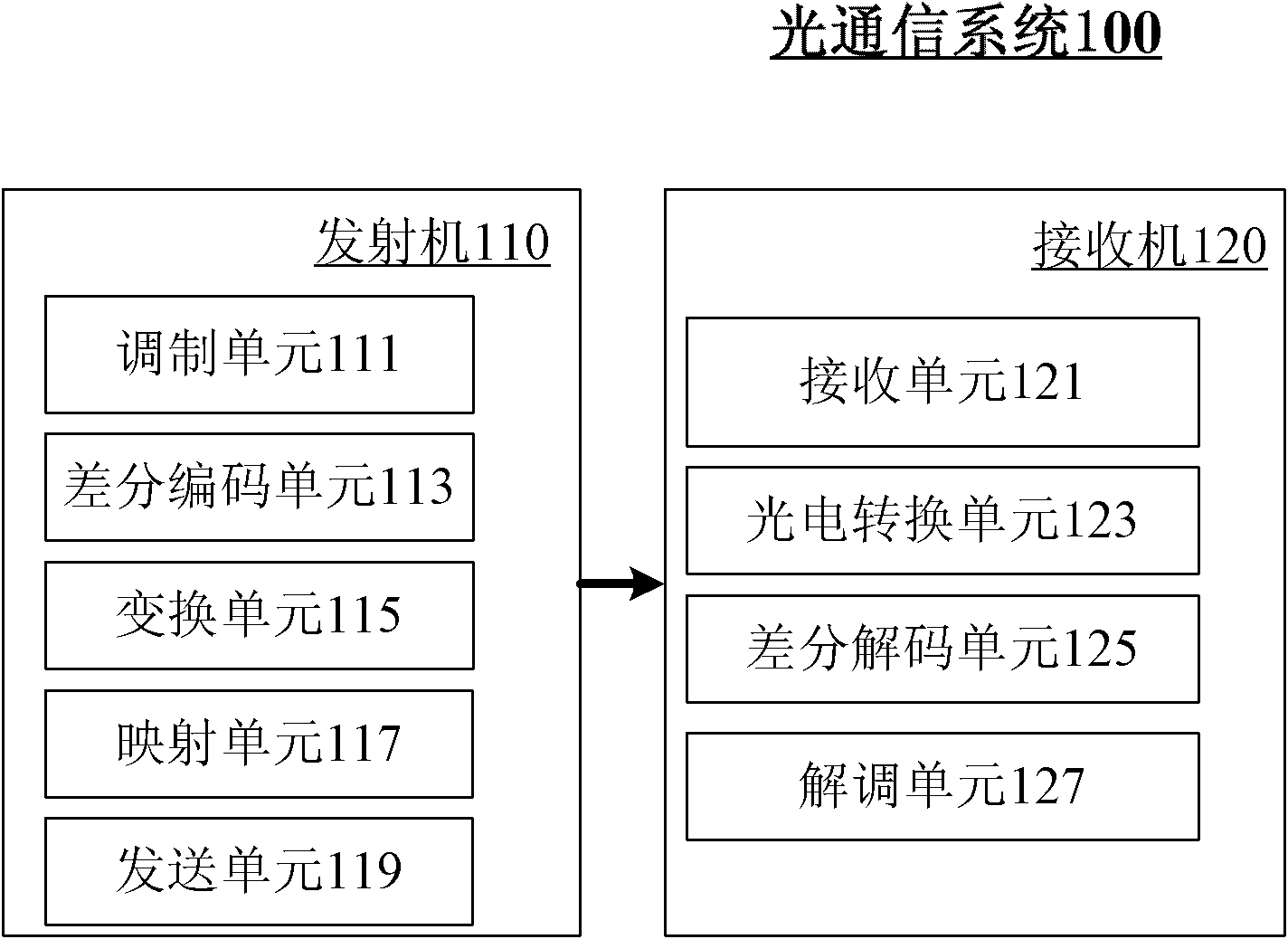
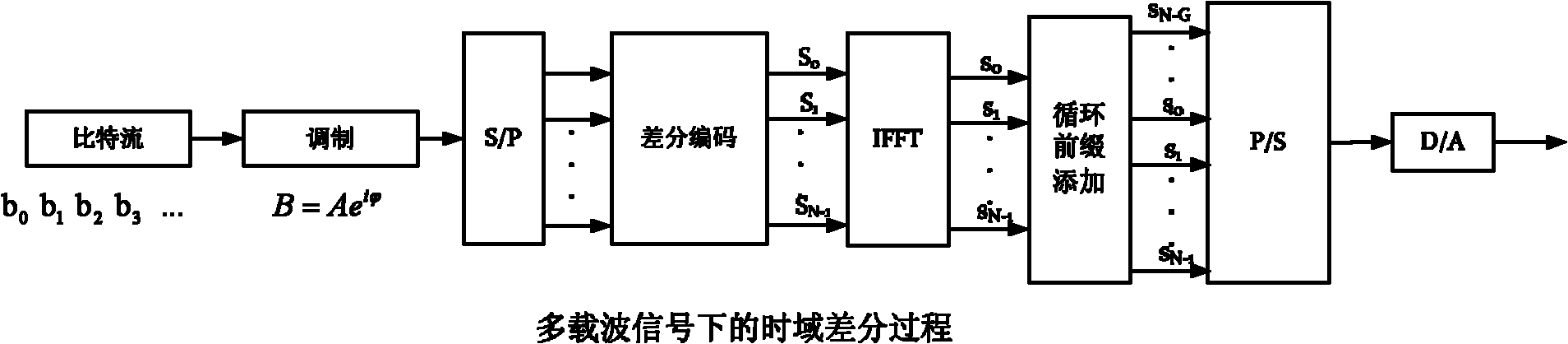
Optical communication method and system
InactiveCN102427387AIncrease line widthEnhanced ability to resist inter-carrier interferenceBaseband system detailsElectromagnetic transmissionFrequency spectrumStream data
The invention provides an optical communication method which comprises the steps of: modulating obtained bit stream data to obtain a modulating signal; carrying out differential coding on the modulating signal to obtain a differential coding signal; converting the differential coding signal into an electrical signal; mapping the electrical signal on an optical carrier to form an optical signal; and then transmitting the optical signal. By using the method, on the premise that a frequency spectrum utilization rate is not reduced, the system capability of resisting disturbance among carriers is enhanced; thus, the tolerance of the existing optical communication sysem for resisting laser linewidth, quick change PMD (Physical Media Dependent), nonlinear fiber, disturbance among channels and other damage is enhanced; and system performance is greatly enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multifunctional optical signal processing system
InactiveCN102347797AAchieving Dynamic Dispersion CompensationTransparent rateDistortion/dispersion eliminationOptical power meterTransport system
The invention relates to a multifunctional optical signal processing system. In the system, continuous detection light and signal light are combined through a first coupler and injected into a high nonlinear optical fiber; idle light generated in the high nonlinear optical fiber due to a fourwave mixing effect is divided into two paths through an optical filter and an optical coupler and are output, wherein one output path is connected to an optical power meter, the optical power output performs feedback control on a tunable dispersion compensator so as to realize dynamic dispersion compensation, while the other output path is used as a system output signal to generate an optical signal with high extinction ratio and no dispersion; and the wavelength of the output optical signal is changed by regulating the wavelength of the detection light, so that tunable wavelength conversion is realized. The multifunctional optical signal processing system can realize HNLF (High Nonlinear Fiber), dispersion detection, extinction ratio enhancement and wavelength conversion, has the advantages of multifunction integration, high response speed, high sensitivity of dispersion detection, wide working wave band and transparency to signal speed and modulation format and can be applied to an optical transmission system with channel rate of over 40Gb / s.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Enhanced supercontinuum generation in highly nonlinear fibers using strong bragg gratings
ActiveUS7116874B2Generate and outputEnhance the generated supercontinuumWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesGratingFiber Bragg grating
Enhancement of the supercontinuum generation performance of a highly-nonlinear optical fiber (HNLF) is accomplished by incorporating at least one Bragg grating structure in the HNLF. The Bragg grating results in reflecting a core-guided signal into signal which also remains core-guided. The supercontinuum radiation generated by such an arrangement will exhibit a substantial peak in its energy at the grating resonance of the Bragg grating and a region of increased radiation in a narrow wavelength band on the long wavelength side of the peak. A number of such Bragg gratings may be formed so as to “tailor” the enhancements provided in the supercontinuum radiation. Various, well-known Bragg grating modifications (tuning, chirped, blazed, etc.) may also be used in the inventive structure to enhance the generated supercontinuum.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC +1
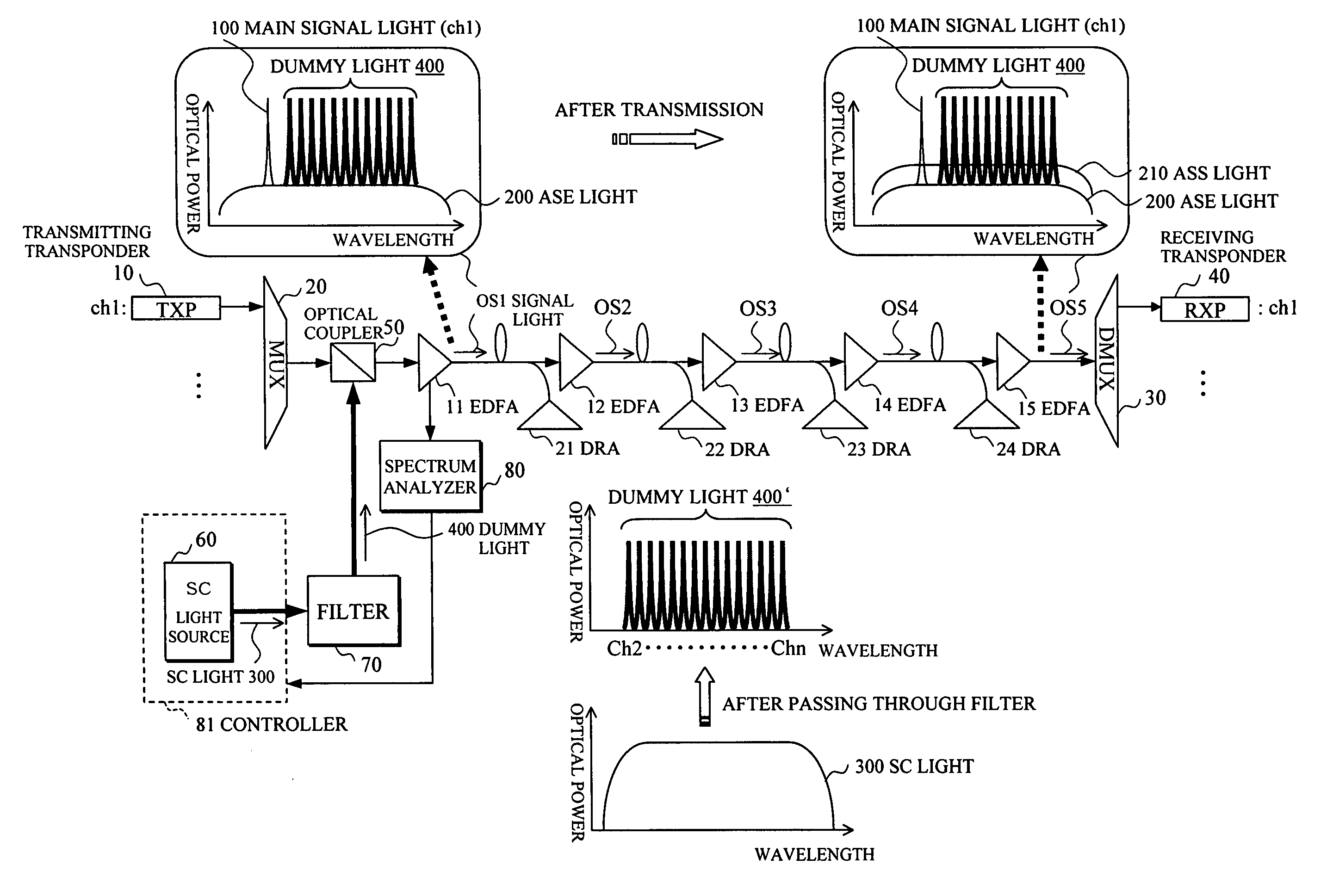
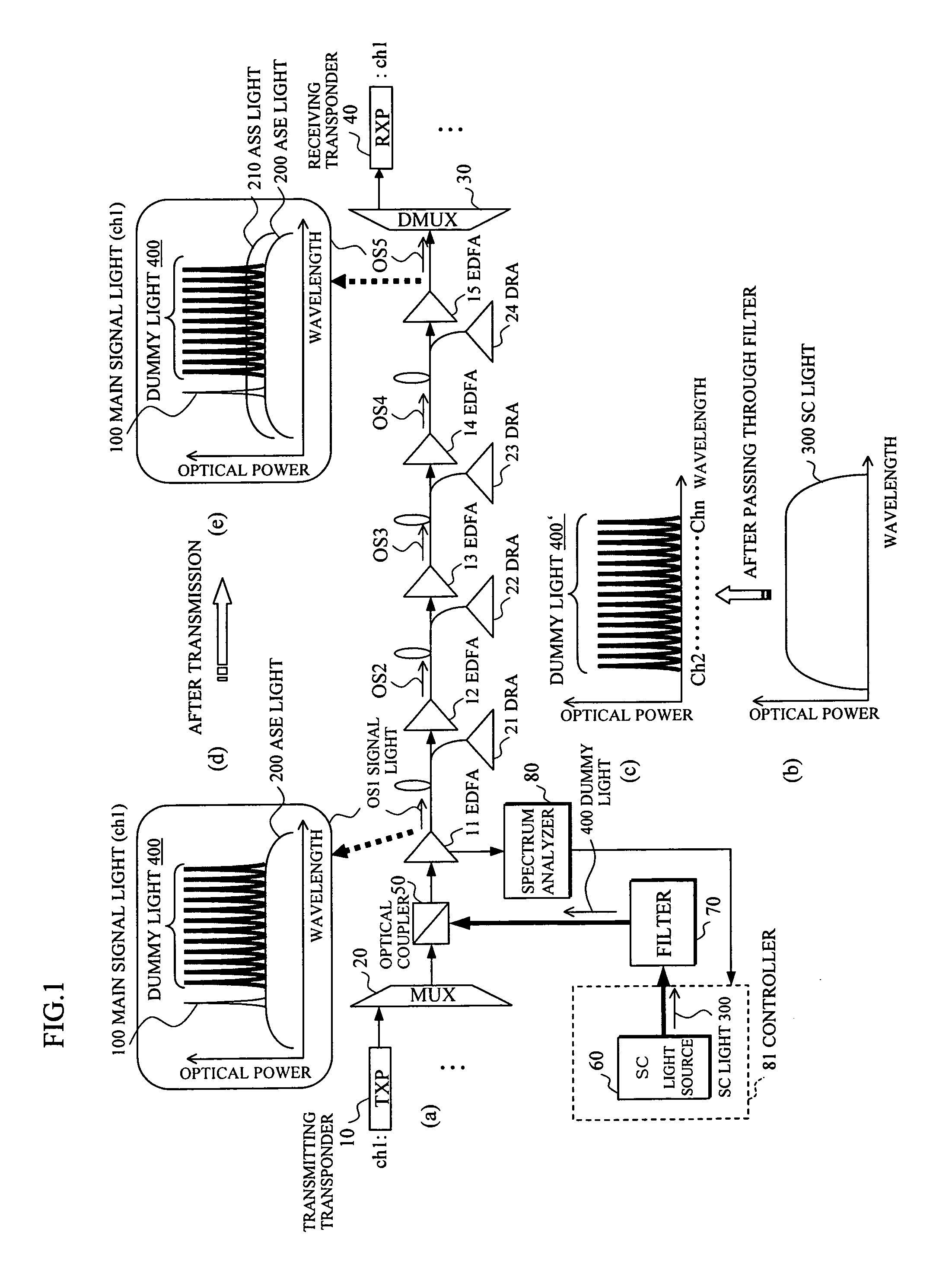
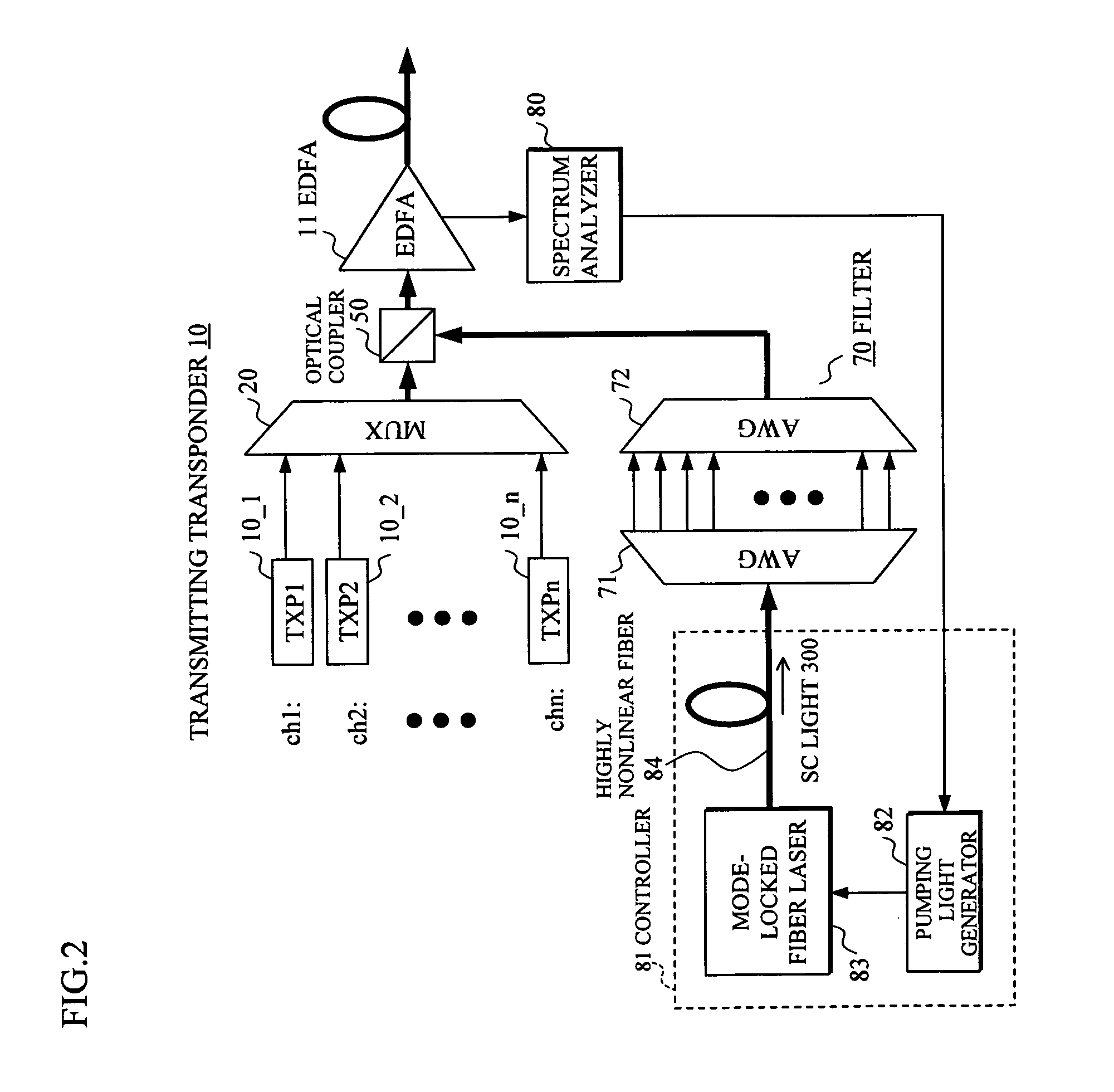
Optical transmission apparatus
InactiveUS20070230968A1Increase speedImprove stabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsSpectrum analyzerOptical power
In an optical transmission apparatus, a number of wavelengths of an output light to an optical transmission line and an optical power of each of the wavelengths are detected by a spectrum analyzer, and a power of a super continuum light outputted to a highly nonlinear fiber is controlled by a controller so as to confine the number of wavelengths and the optical power within predetermined ranges. A wavelength component corresponding to a signal light is removed by a filter from the output light from the highly nonlinear fiber, and an output light of the filter and the signal light is coupled by an optical coupler.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Double-pump Fourier domain mode-locked fiber optical parametric oscillator
InactiveCN102749785AAchieve laser outputFlexible tuning range controlNon-linear opticsOptical tomographyGrating
The invention relates to a fiber optical parametric oscillator for achieving Fourier domain mode-locked laser output. Seed light output by two semiconductor lasers is modulated by phase and amplified by a high power optical amplifier to serve as pump light, the pump light is output from the pump output end of a wavelength division multiplexer and enters high nonlinear fiber through a polarization controller, and a part of the pump light is transferred into signal light in the high nonlinear fiber due to fiber nonlinear effect. After the signal light passes through a second optical isolator, dispersion-shifted fiber and a tunable filter, most energy is fed back to the high nonlinear fiber from a high power shunt ratio output end of an optical coupler with 9:1 power shunt ratio through the wavelength division multiplexer so as to form resonance laser output. When modulation frequency of the tunable filter is equal to fundamental frequency of a laser resonant cavity, the Fourier domain mode-locked laser output can be obtained. The fiber optical parametric oscillator achieves the Fourier domain mode-locked laser output, has significant application value in the fields of optical tomography, fiber bragg grating sensing and the like, and has the advantages of being high in wavelength scanning frequency, flexible in laser output spectrum tuning range control and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
High speed swept frequency spectroscopic system
A high scan rate spectroscopic system converts a narrow-band laser pulse into a multispectral pulse, using, for example, a nonlinear fiber. The multispectral pulse is then converted to a swept frequency pulse through a second fiber impressing a frequency-dependent delay in the light beam which is then applied to the object to be tested.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
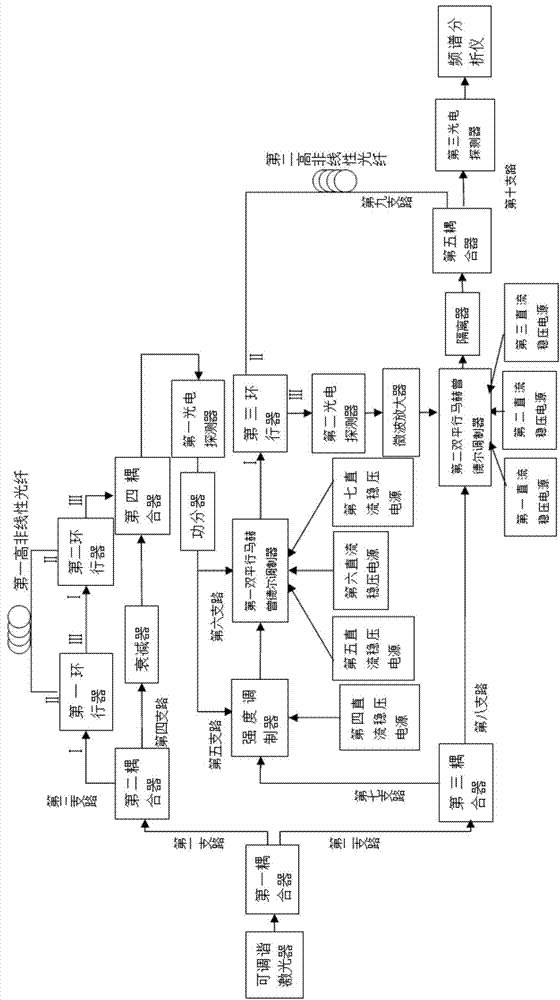
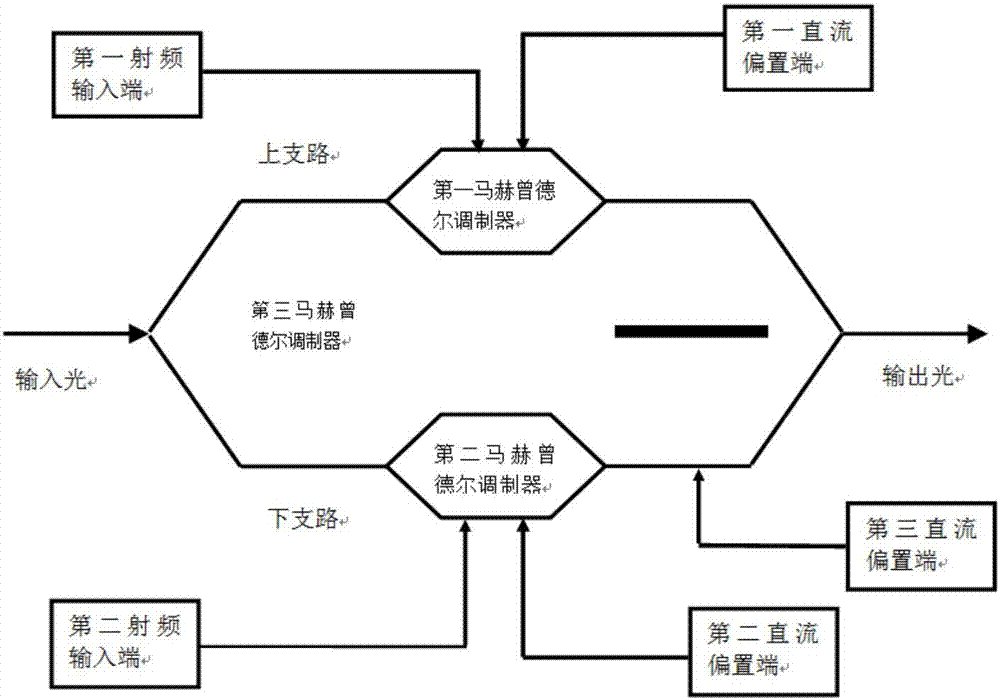
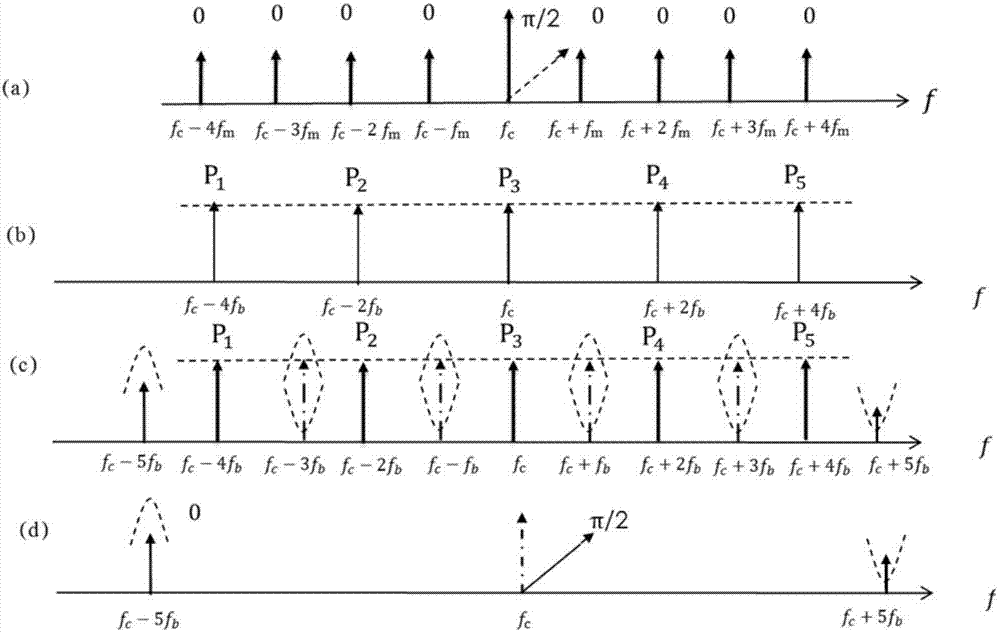
Microwave-signal generating method and device based on excited brillouin scattering effect and optical frequency comb
Provided is a microwave-signal generating method and device based on the excited brillouin scattering effect and the optical frequency comb in high nonlinear fibers. The invention belongs to the technical field of microwave photonics. The device comprises a tunable laser, a first coupler, a second coupler, a first circulator, a second circulator, a first high nonlinear fiber, an attenuator, a fourth coupler, a first photoelectric detector, a power divider, an intensity modulator, a fourth DC voltage regulator, a first double parallel mach-zehnder modulator, a fifth DC voltage regulator, a sixth DC voltage regulator, a seventh DC voltage regulator, a third circulator, a second high nonlinear fiber, a third coupler, a second photoelectric detector, a microwave amplifier, a second double parallel mach-zehnder modulator, a first DC voltage regulator, a second DC voltage regulator, a third DC voltage regulator, an isolator, a fifth coupler, a third photoelectric detector and a frequency analyzer. Due to the advantages of mode selection and positive feedback of a photoelectric oscillator, the microwave signals which are output by the device have the advantages of good spectrum purity and low noises.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
High-power and tunable pulse fiber laser device
InactiveCN104300344AIncrease powerSimple structureActive medium shape and constructionMode locked fiber laserFiber coupler
The invention belongs to the technical field of laser devices, and provides a high-power and tunable pulse fiber laser device and a super-continuum spectrum light source pumped through the high-power and tunable pulse fiber laser device. The high-power and tunable pulse fiber laser device sequentially comprises a tunable passive mode-locking fiber laser device based on the fiber nonlinear effect, a broadband fiber coupler, a power pre-amplification stage and a power main amplification stage in the light path direction. The output end of the high-power and tunable pulse fiber laser device is connected with photonic crystal fibers or high nonlinear fibers or other super-continuum spectrum generating fibers with zero-dispersion wavelength located in the pumping laser gain area, precise matching of the pumping laser and the zero-dispersion wavelength of the super-continuum spectrum generating fibers can be achieved, and accordingly, a broadband and high flatness super-continuum spectrum light source can be obtained. The device has the advantages that the structure is simple, the tuning of the pumping laser wavelength is convenient, cost is low, and full fiber is achieved, and the device can be applied to the fields such as biomedicine, remote sensing, environment monitoring, multi-channel fiber communication and spectroscopy.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
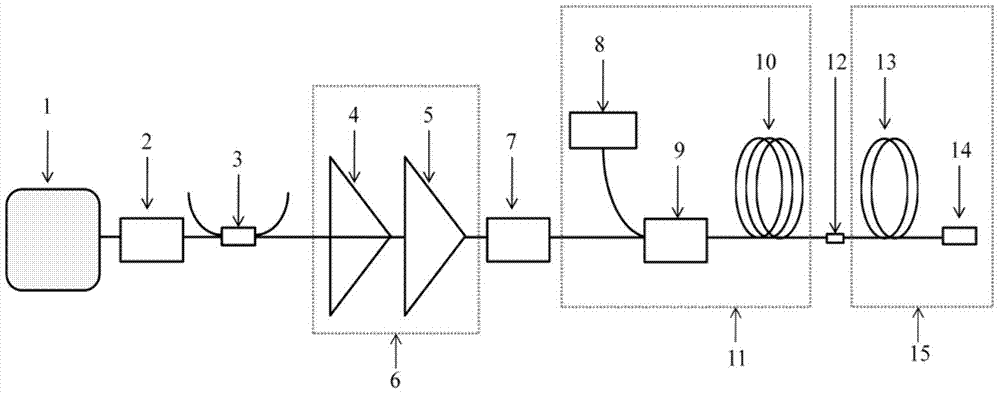
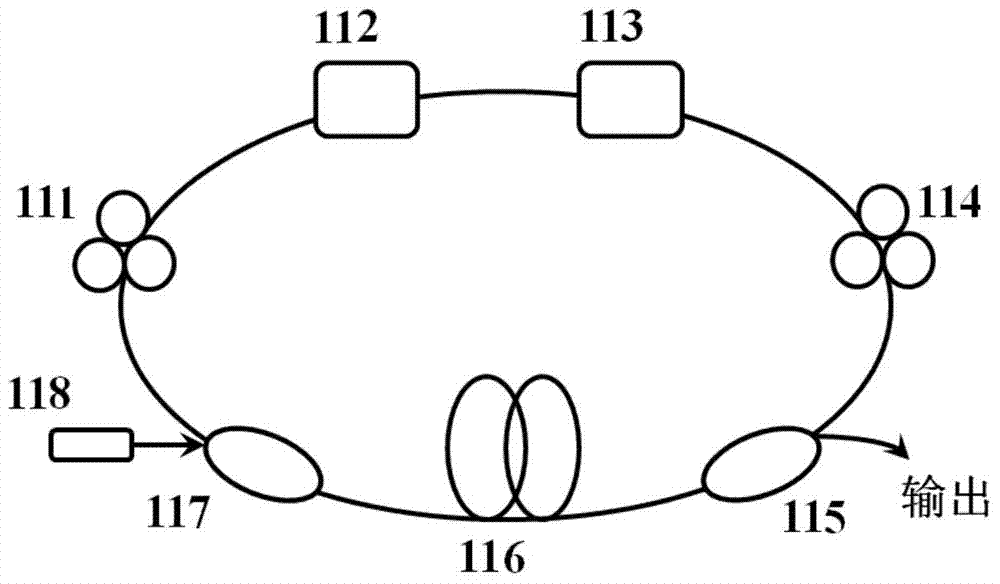
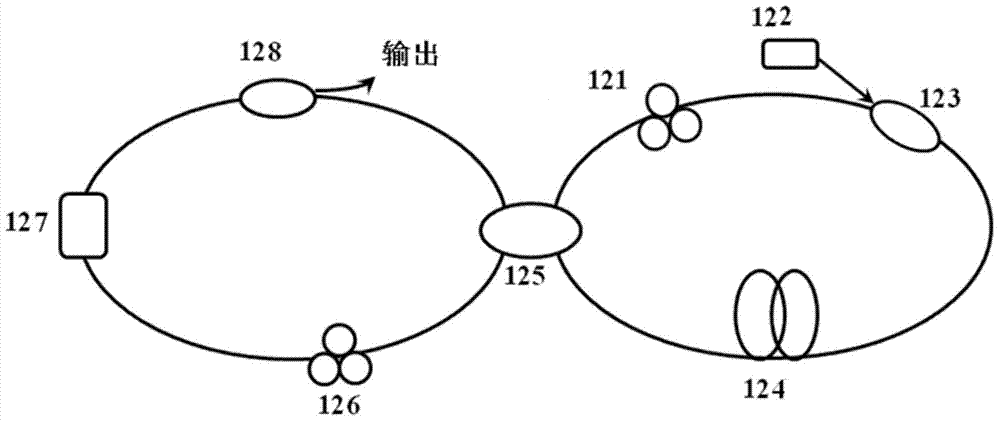
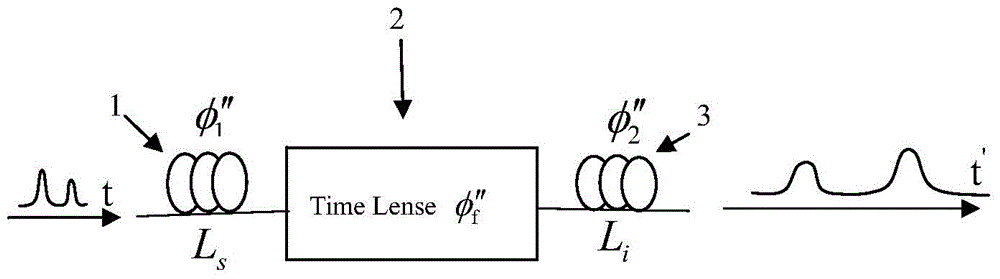
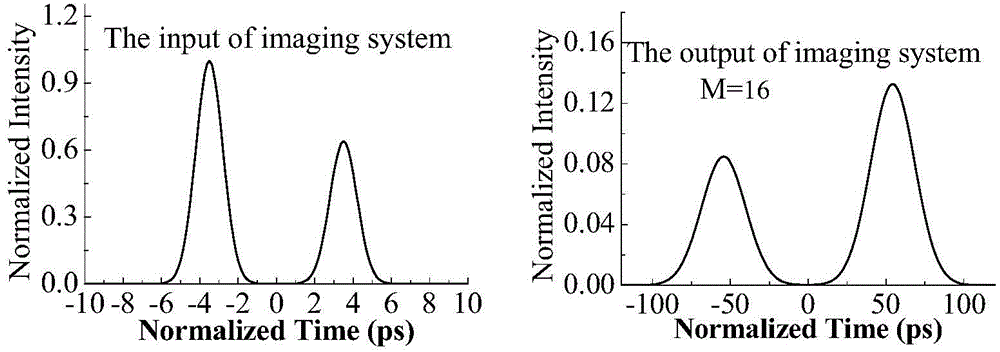
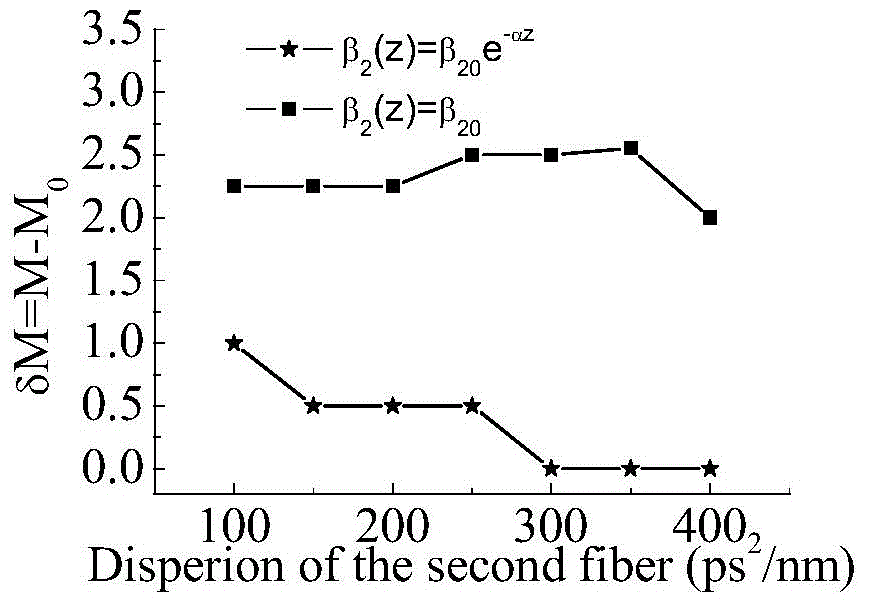
Time-lens image-forming system
The invention discloses an image-forming system of time-lens. The image-forming system comprises an input-section dispersive fiber, a time-lens, and an output-section dispersive fiber. The time-lens is implemented by a four-wave mixing effect of signal light and pump light in a high nonlinear fiber. Second-order dispersive parameters of the input-section dispersive fiber and the outlet-section dispersive fiber both decrease gradually according to the exponential law, and a decreasing index is equal to the loss coefficient of the fibers. According to the image-forming system of time-lens, the dispersive parameters of the inlet-section dispersive fiber and the outlet-section dispersive fiber are improved, an optimal match of a dispersion and a nonlinear effect during the transmission of signals is achieved for the signals, the magnification times of the output signals of the image-forming system of time-lens are closer to a theoretical value, and thereby the imaging effect of the time-lens is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for generating constant modulus multi-dimensional modulations for coherent optical communications
ActiveUS9621275B2Improve spectral efficiencyConstant modulusElectromagnetic transmissionMultiple carrier systemsPhase noiseBlock code
A method generates constant modulus multi-dimensional modulations for coherent optical communications by first projecting points in a constellation of the code onto a Poincare sphere or its higher-dimensional hyper-sphere. By using meta-heuristic procedures, nonlinear programming and gradient search methods, constellation points in the hyper-sphere are optimized in certain criteria, such as maximizing the minimum Euclidean distance, minimizing the union bound, minimizing the bit-error rate, minimizing the required signal-to-noise ratio, maximizing the nonlinear fiber reach, maximizing the phase noise tolerance, and maximizing the mutual information. Some methods use parametric unitary space-time block codes such as Grassmannian packing, and filter impulse response as well as unitary rotation over adjacent code blocks to generate near-constant modulus waveform, not only at the symbol timing, but also over the entire time.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Enhanced supercontinuum generation in highly nonlinear fibers using post-fabrication processing
ActiveUS7171089B2Alteration in areaAlteration in dispersionLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsReady to useNonlinear fiber
Enhancement of the supercontinuum generation performance of a highly-nonlinear optical fiber (HNLF) is accomplished by performing at least one post-processing treatment on the HNLF. Particularly, UV exposure of the HNLF will modify its dispersion and effective area characteristics so as to increase its supercontinuum bandwidth, without resorting to techniques such as tapering or introducing unwanted reflections into the HNLF. The UV exposure can be uniform, slowly varying or aperiodic along the length of the HNLF, where the radiation will modify the nonlinear properties of the HNLF. Various other methods of altering these properties may be used. The output from the HNLF can be monitored and used to control the post-processing operation in order to achieve a set of desired features in the enhanced supercontinuum spectrum.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Phase-sensitive amplification in a fiber
A method of and device for generating an amplified optical signal directly in an optical fiber by way of phase-sensitive amplification based on one or more four-wave mixing (FWM) processes. In one embodiment, an input signal and two pump waves are applied to a highly nonlinear fiber (HNLF). The input signal is amplified in the HNLF due to energy transfer from the pump waves to the input signal via a degenerate phase-conjugation (PC) process. In another embodiment, an input signal and first and second pump waves are applied to a first HNLF to generate, via a Bragg scattering (BS) process, an idler signal corresponding to the input signal. The second pump wave is then filtered out and the first pump wave, a third pump wave, and the input and idler signals are applied to a second HNLF, where they interact via a non-degenerate PC process to produce an amplified output signal.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
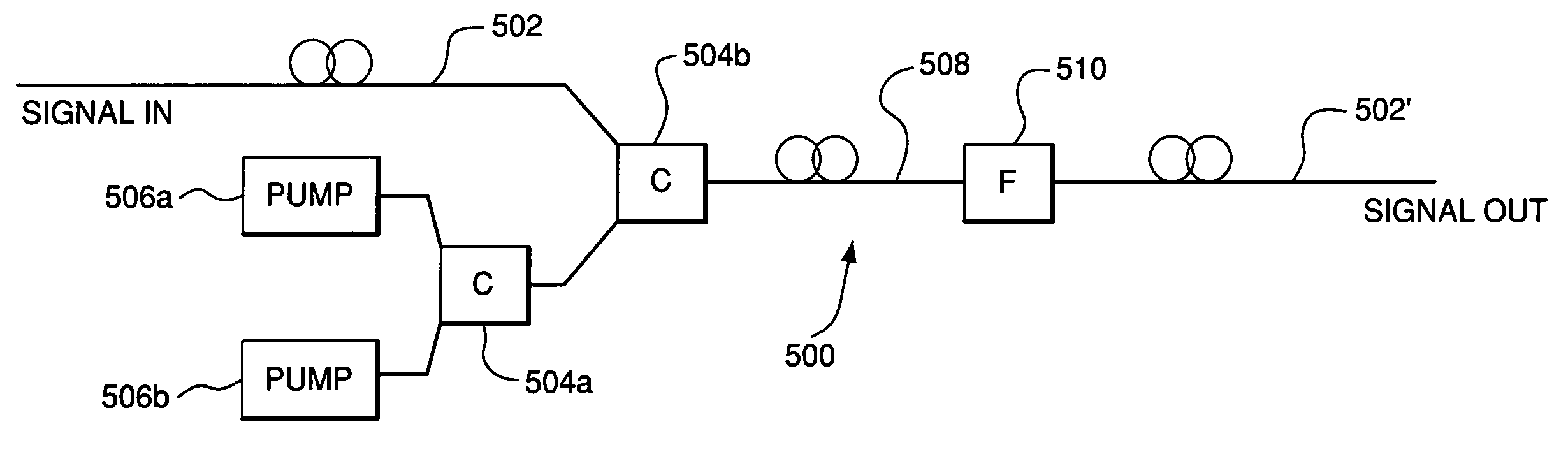
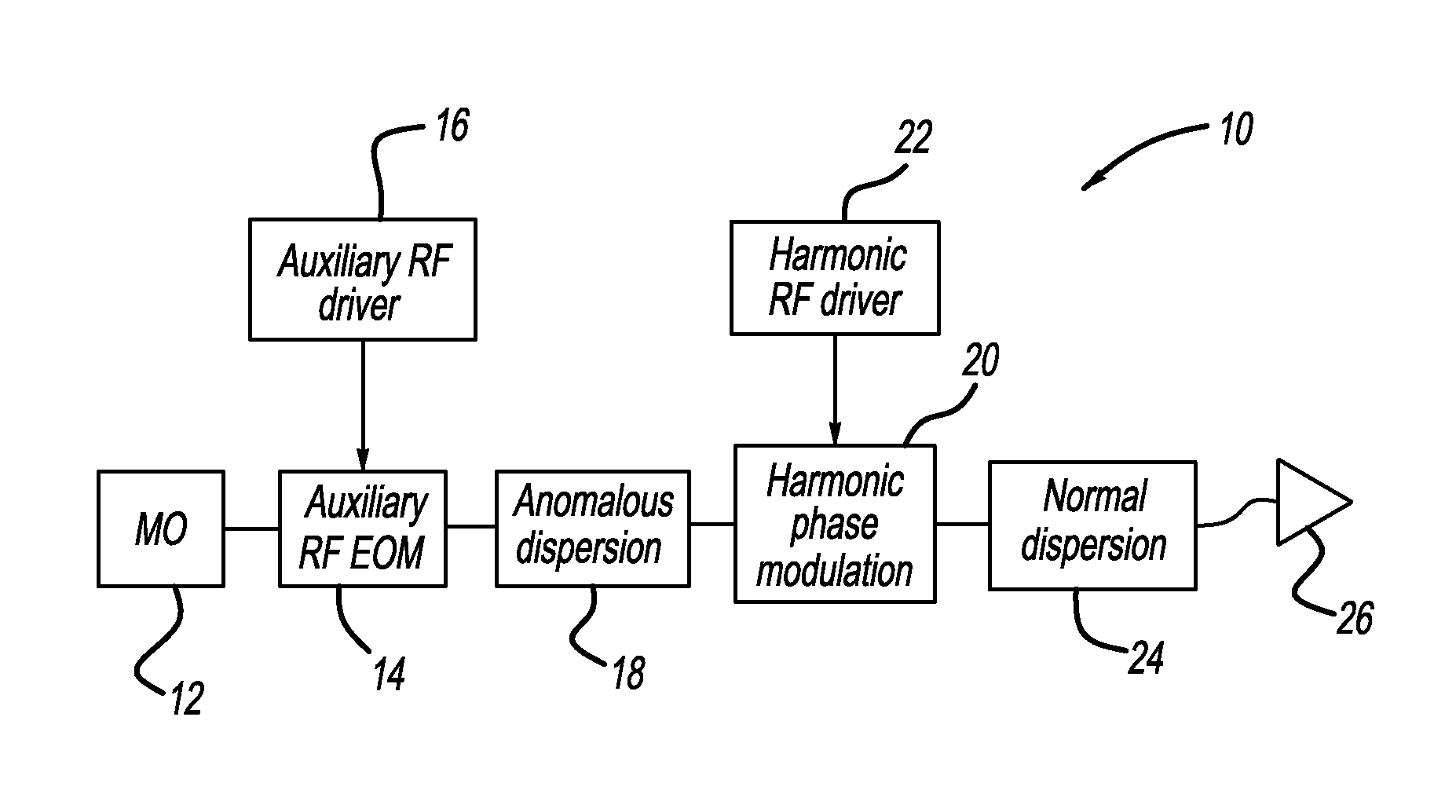
Nonlinear spectrally narrowed fiber amplifier
ActiveUS9036252B1Laser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionFiber amplifierFrequency modulation
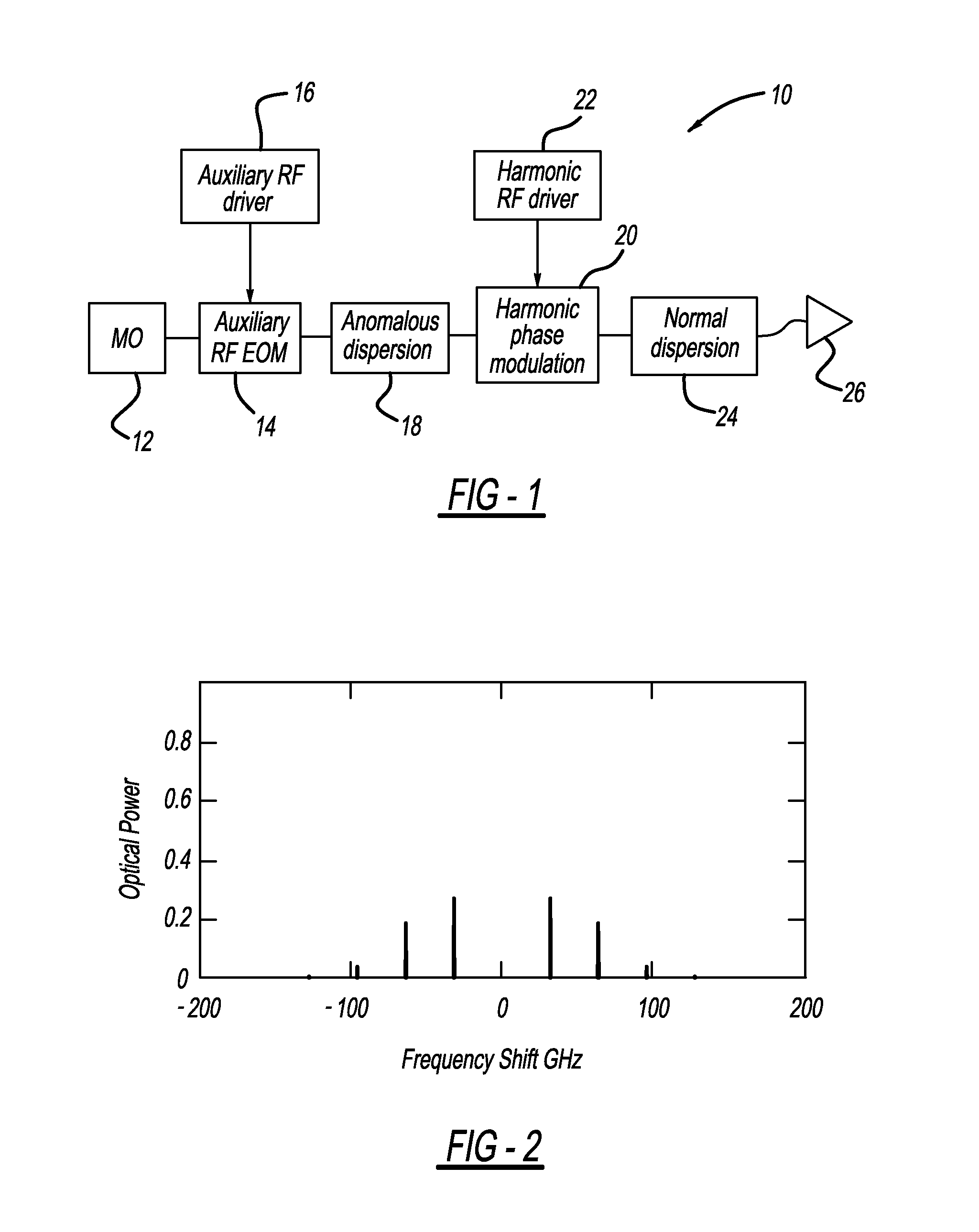
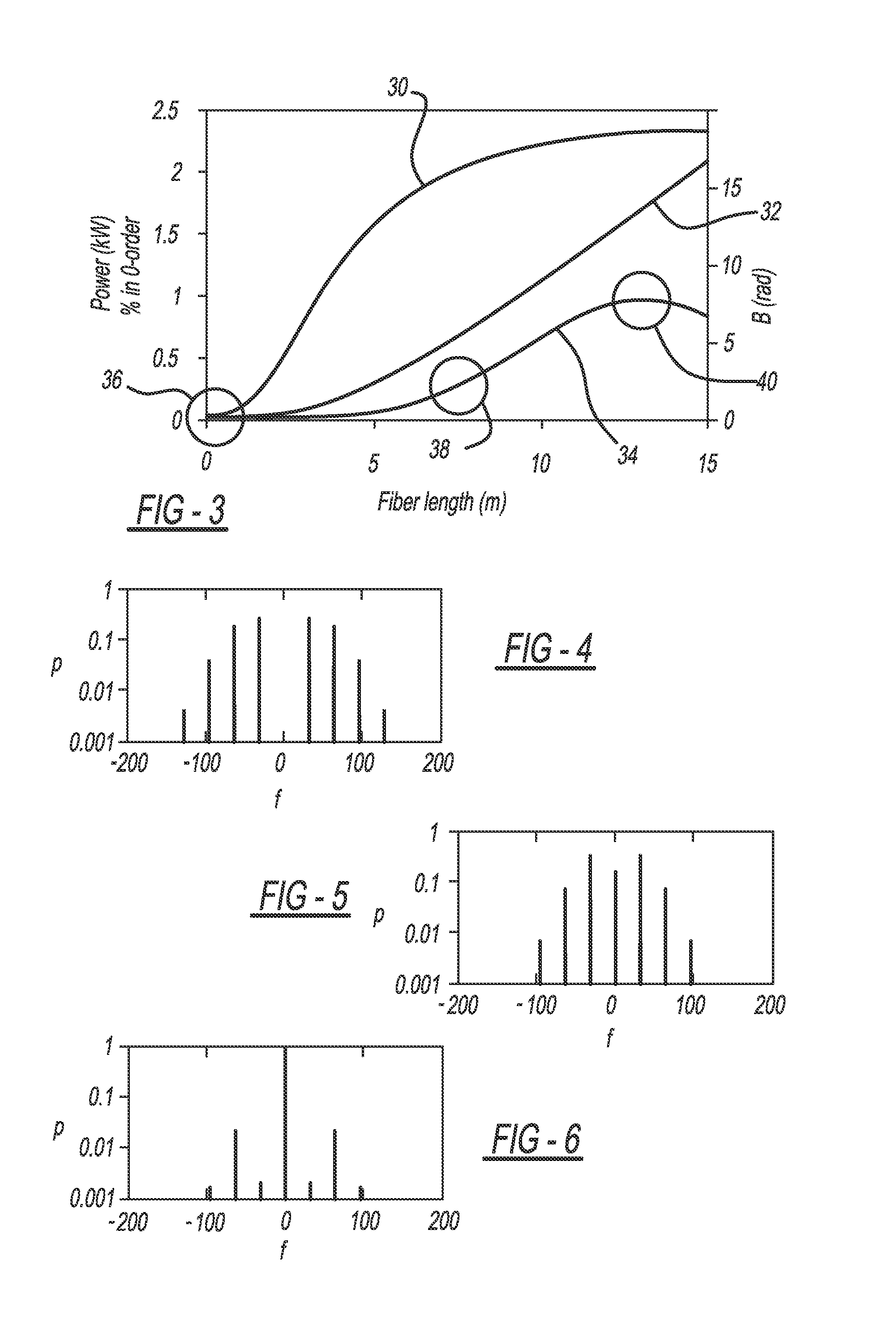
A fiber amplifier system including at least one seed source providing an optical seed beam and a harmonic driver providing a sinusoidal drive signal at a predetermined frequency. The system also includes a harmonic phase modulator that receives the seed beam and the drive signal, where the harmonic phase modulator frequency modulates the seed beam using the drive signal so as to remove optical power from a zeroth-order frequency of the seed beam and create sidebands separated by the frequency of the drive signal. A dispersion element receives the frequency modulated seed beam and provides temporal amplitude modulation to the seed beam and a nonlinear fiber amplifier receives the amplitude modulated seed beam from the dispersion element and amplifies the seed beam, where the dispersion element and the fiber amplifier combine to remove optical power from the sidebands and put optical power back into the zeroth-order frequency.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Random fiber laser
InactiveCN102801091AImprove stabilityImprove efficiencyActive medium shape and constructionRayleigh scatteringRefractive index
The invention discloses a random fiber laser system. According to the system, an optical fiber serves as a laser medium, and a fiber laser comprising a crystal fiber laser, a nonlinear fiber laser, a rare earth doped fiber laser and a plastic fiber laser serves as pump light to be coupled into the optical fiber. Because the refractive index of the optical fiber has non-uniformity and is randomly distributed along the optical fiber, so that the photon is subjected to rayleigh scattering during transmission in the optical fiber; and moreover, the pump light provides gain for the backward scattered light along the optical fiber, when the overall gain is greater than the total loss, the backward scattered light is amplified to form random laser. A discrete optical component is not arranged in the light path of the system, so that all-fiber connection is realized. In the system, the residual pump light is returned to the optical fiber, and the distributed weak scattered light is amplified, and therefore, according to the random fiber laser system, the threshold power of the pump light can be reduced, the utilization rate of the pump light can be improved, and the slope efficiency of the laser is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com