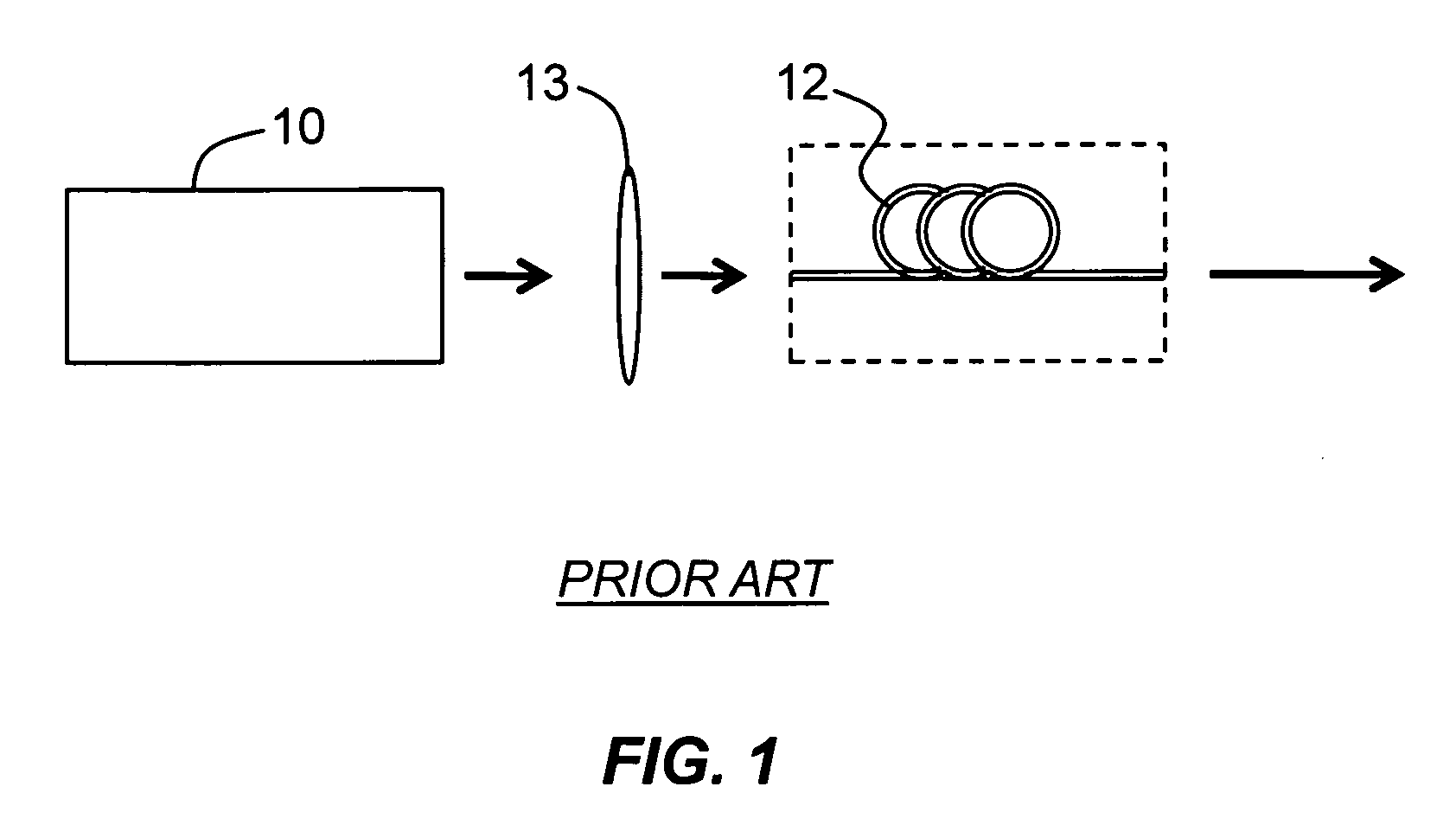
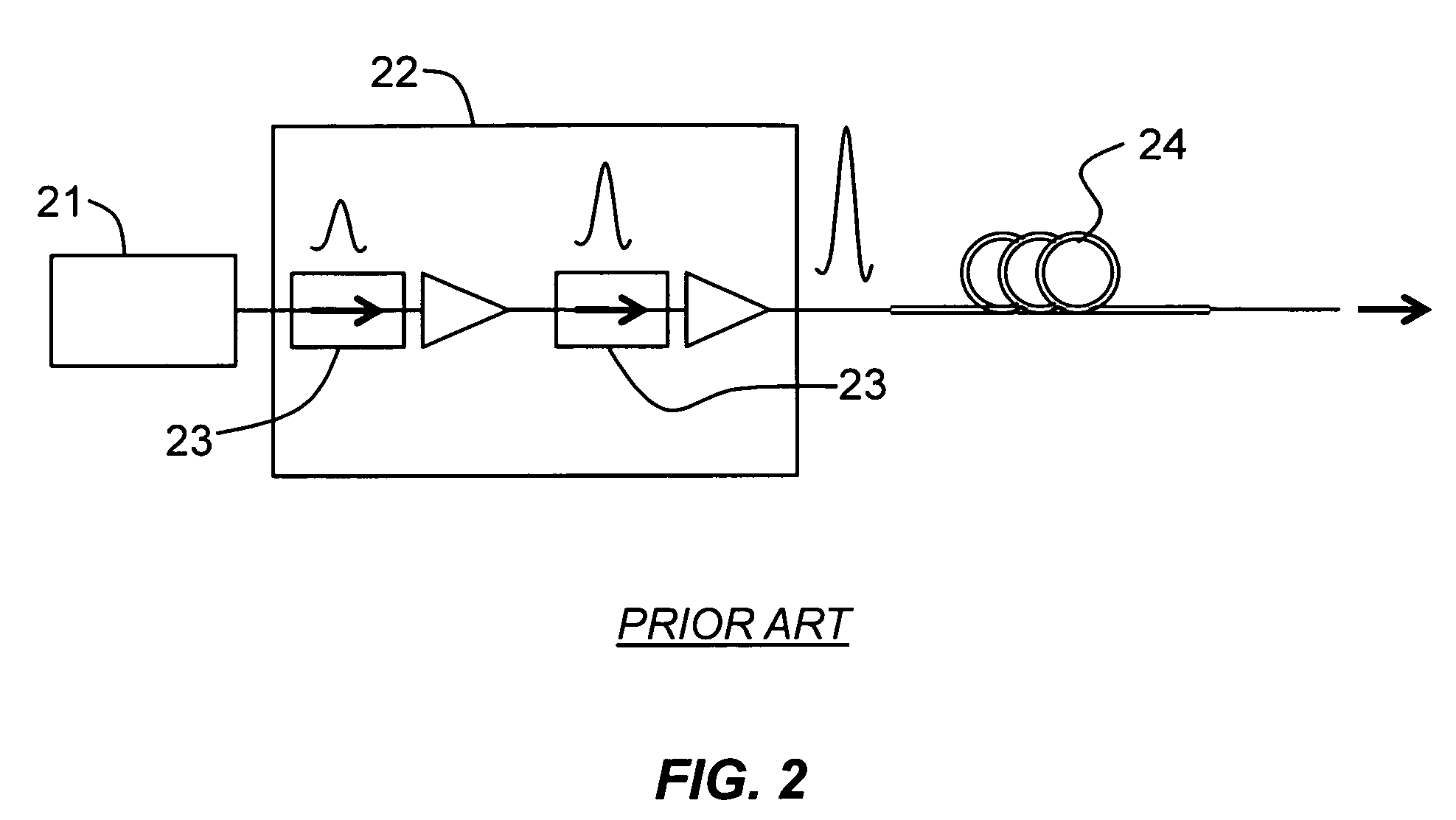
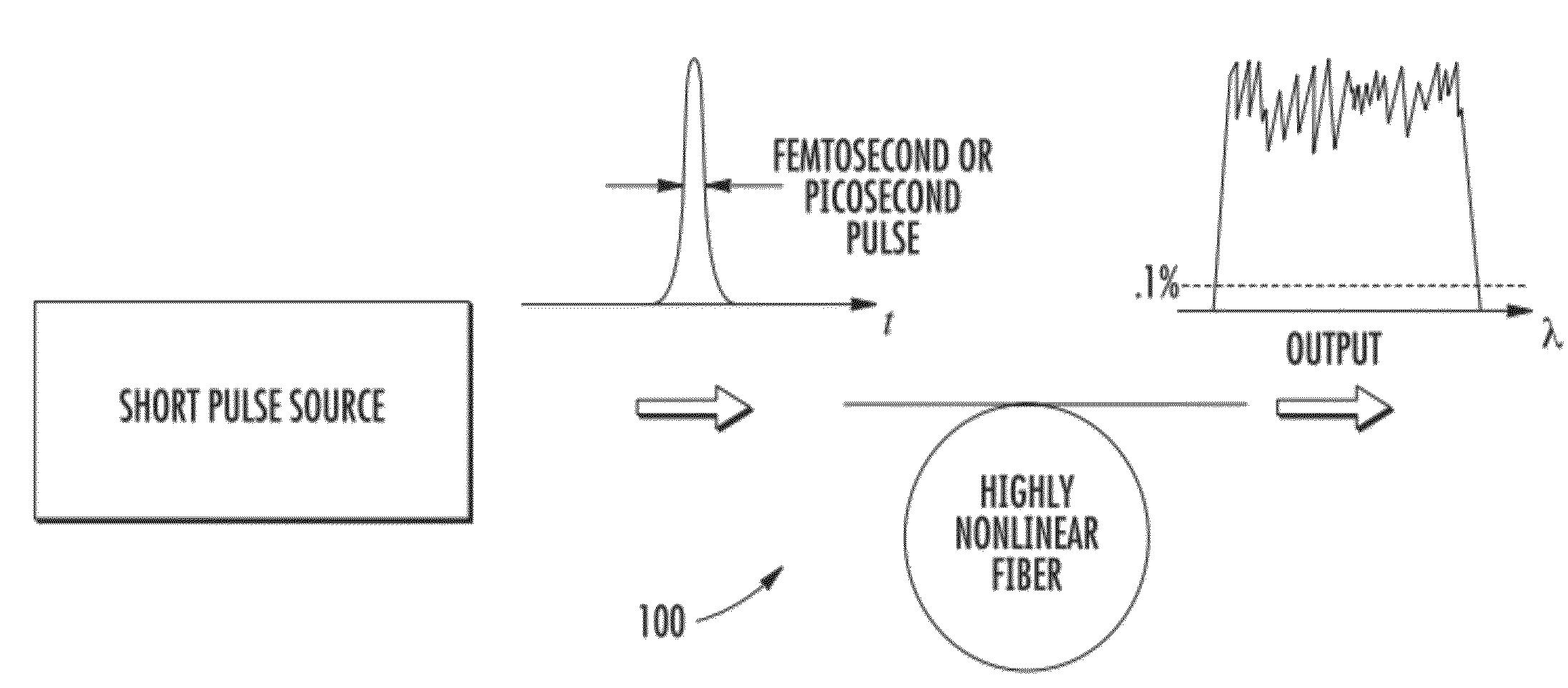
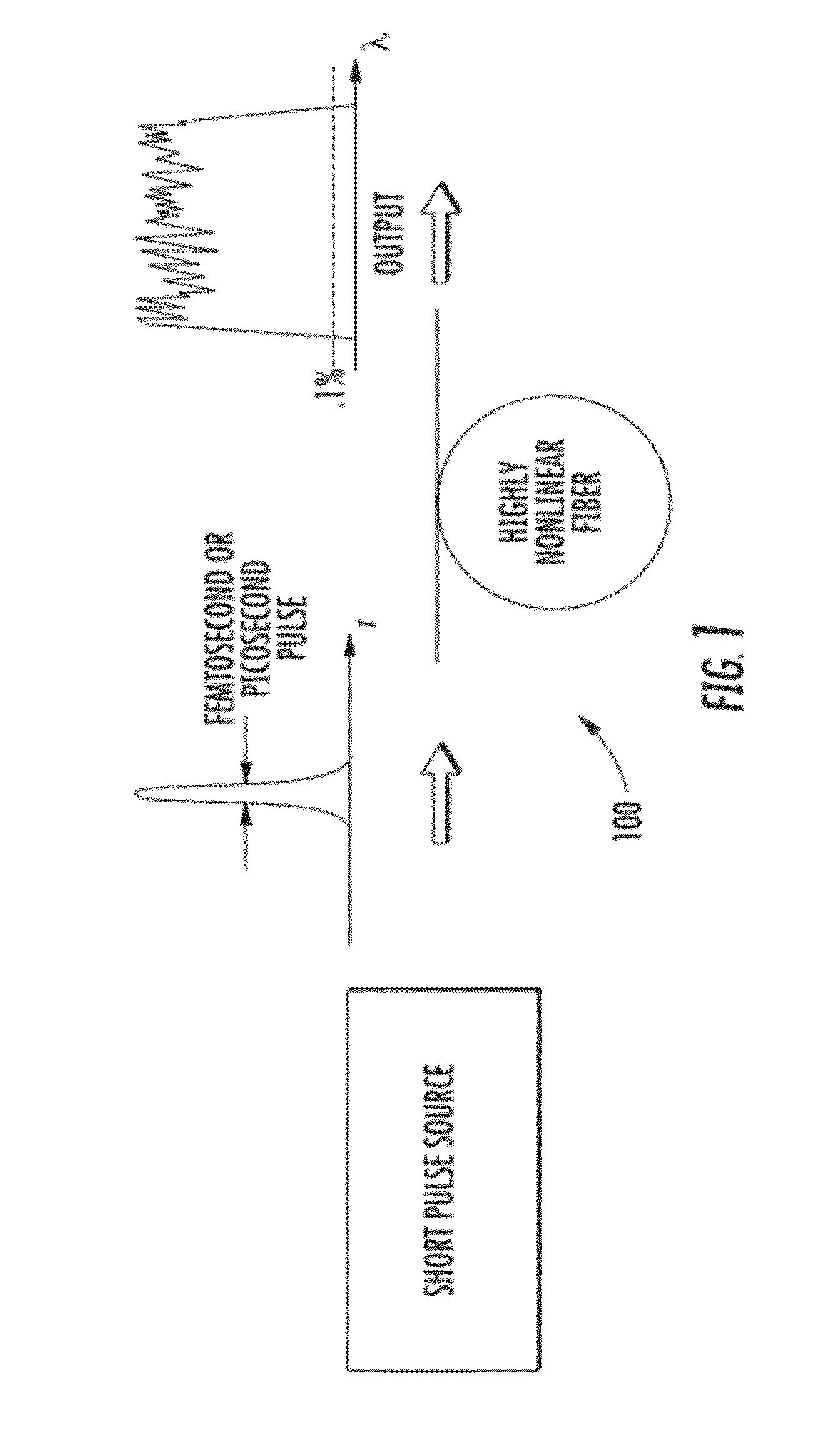
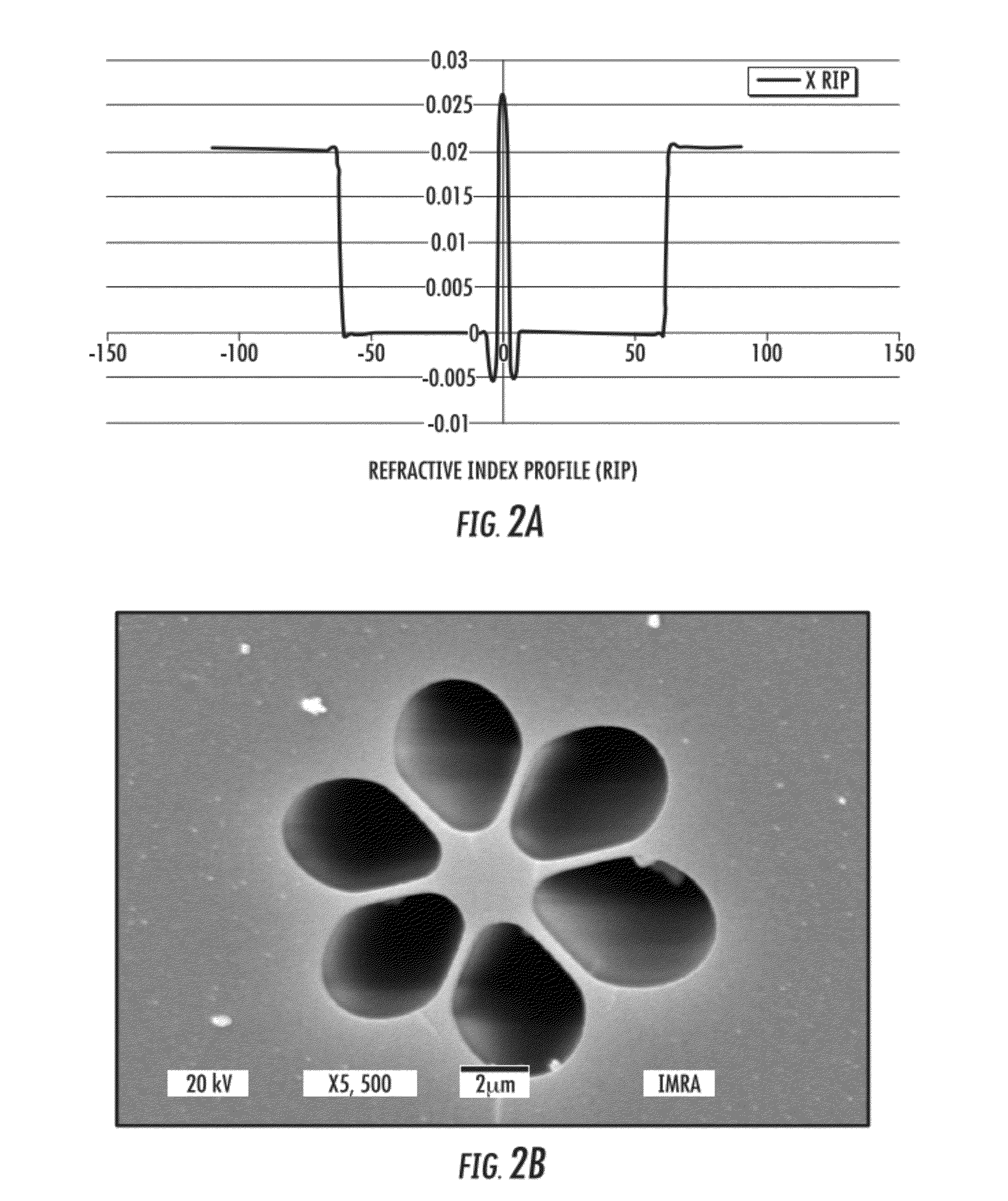
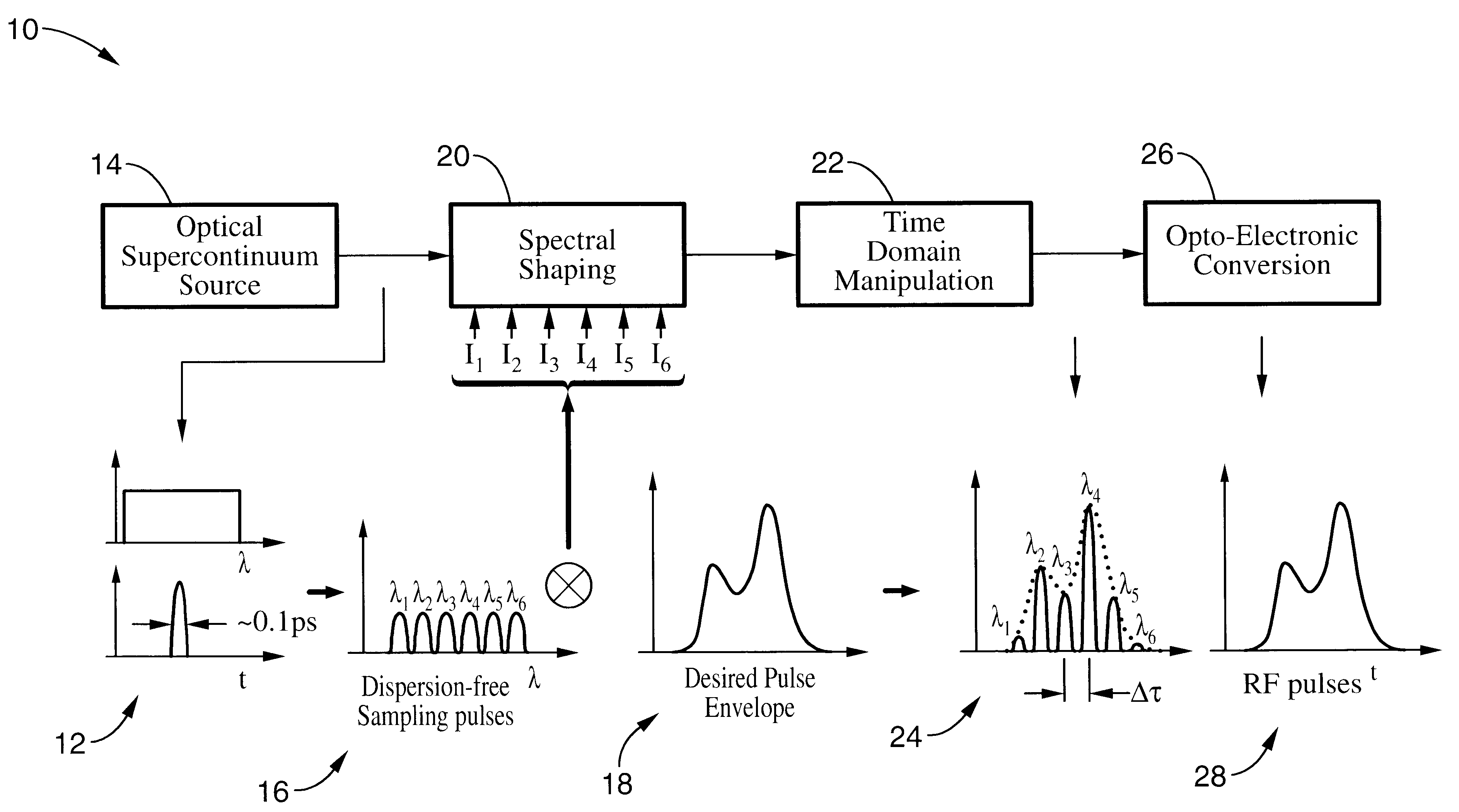
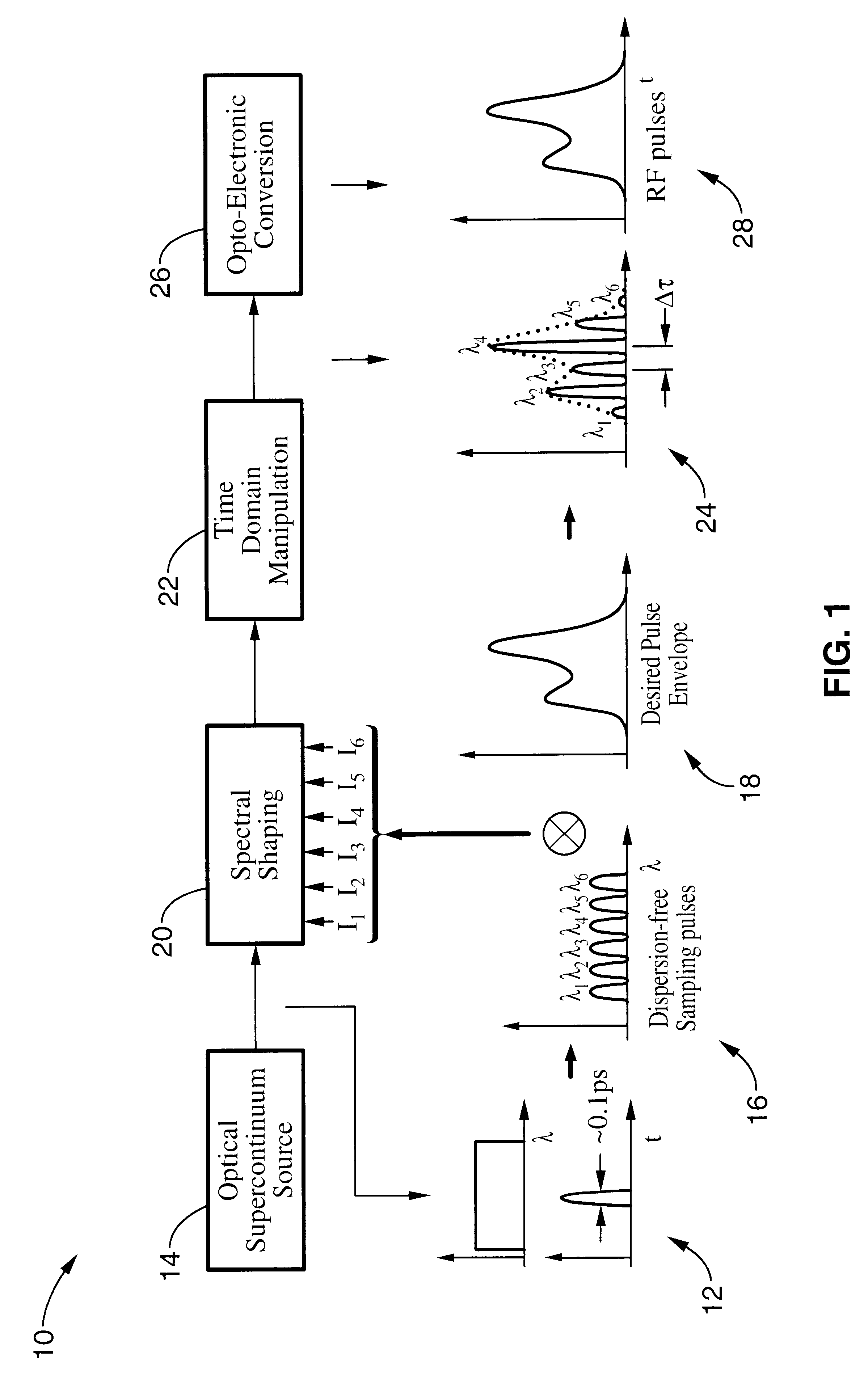
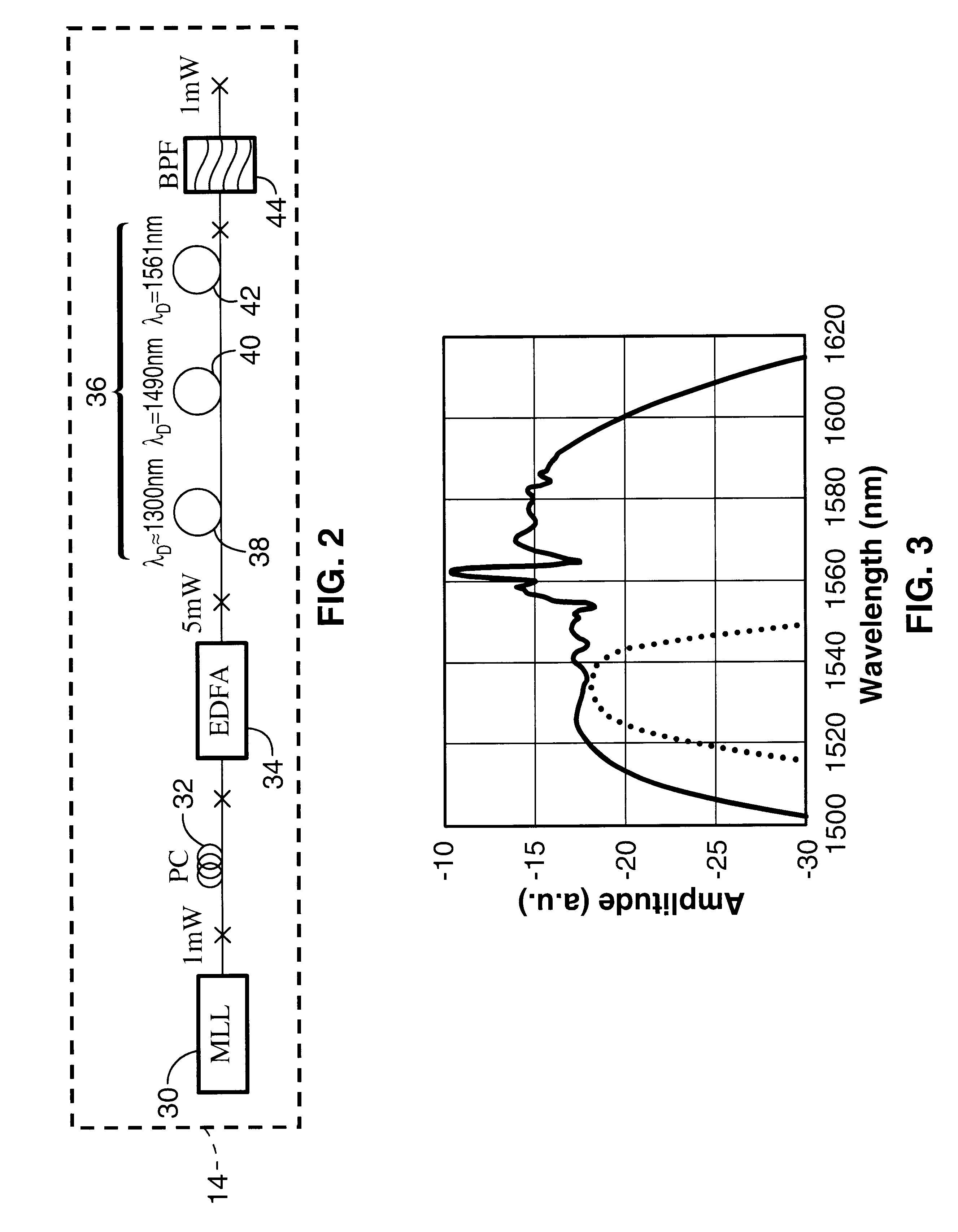
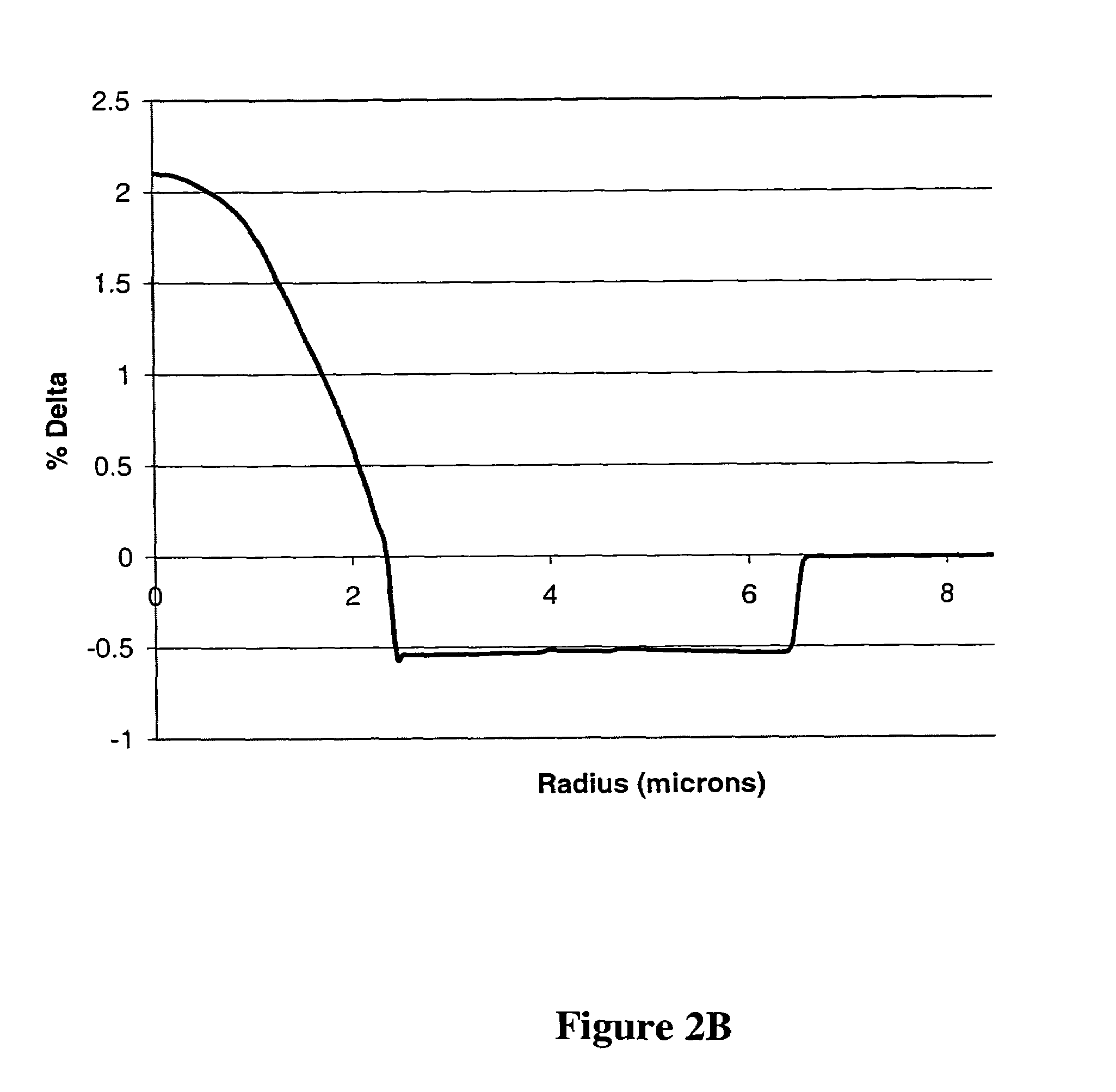
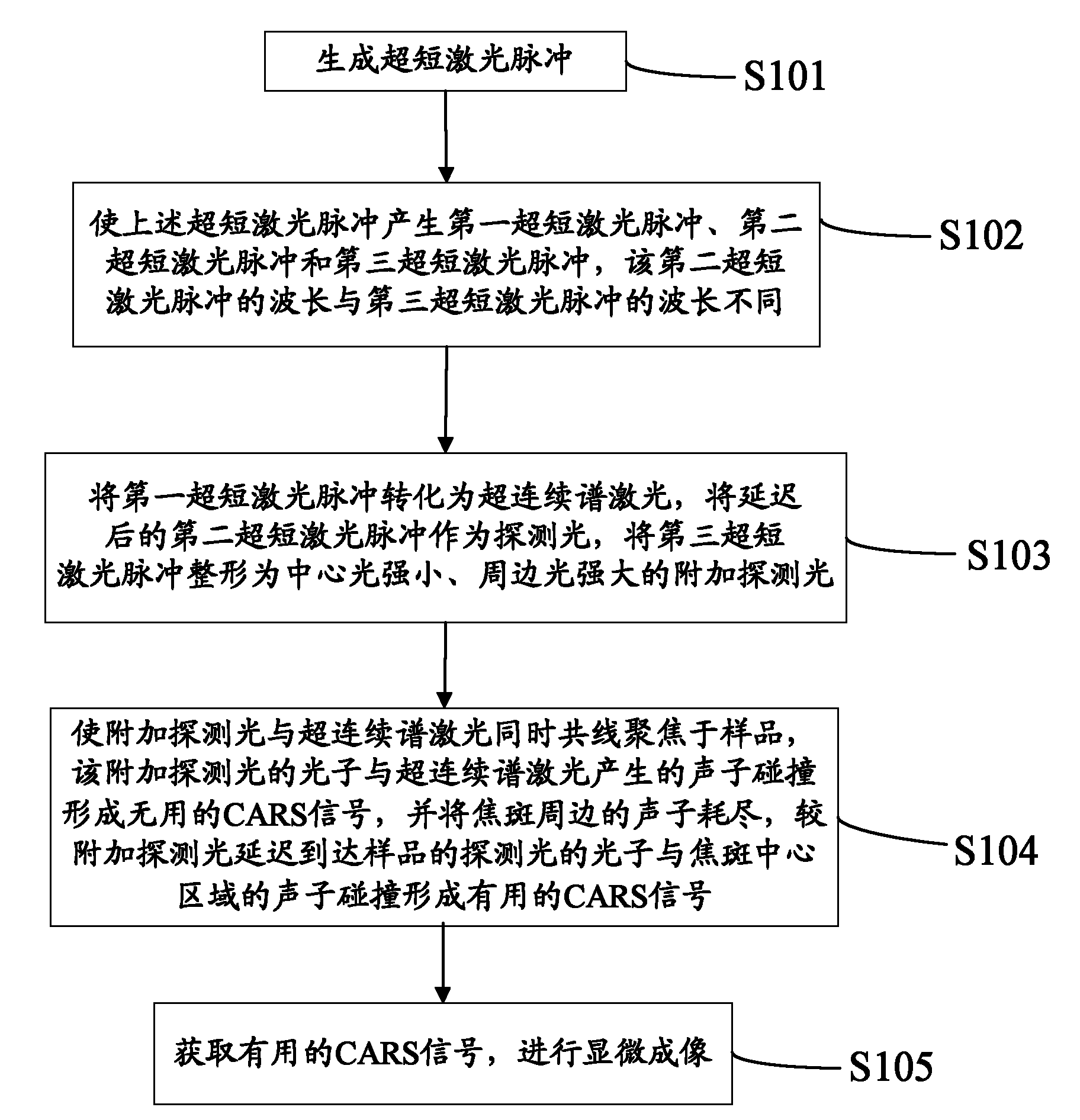
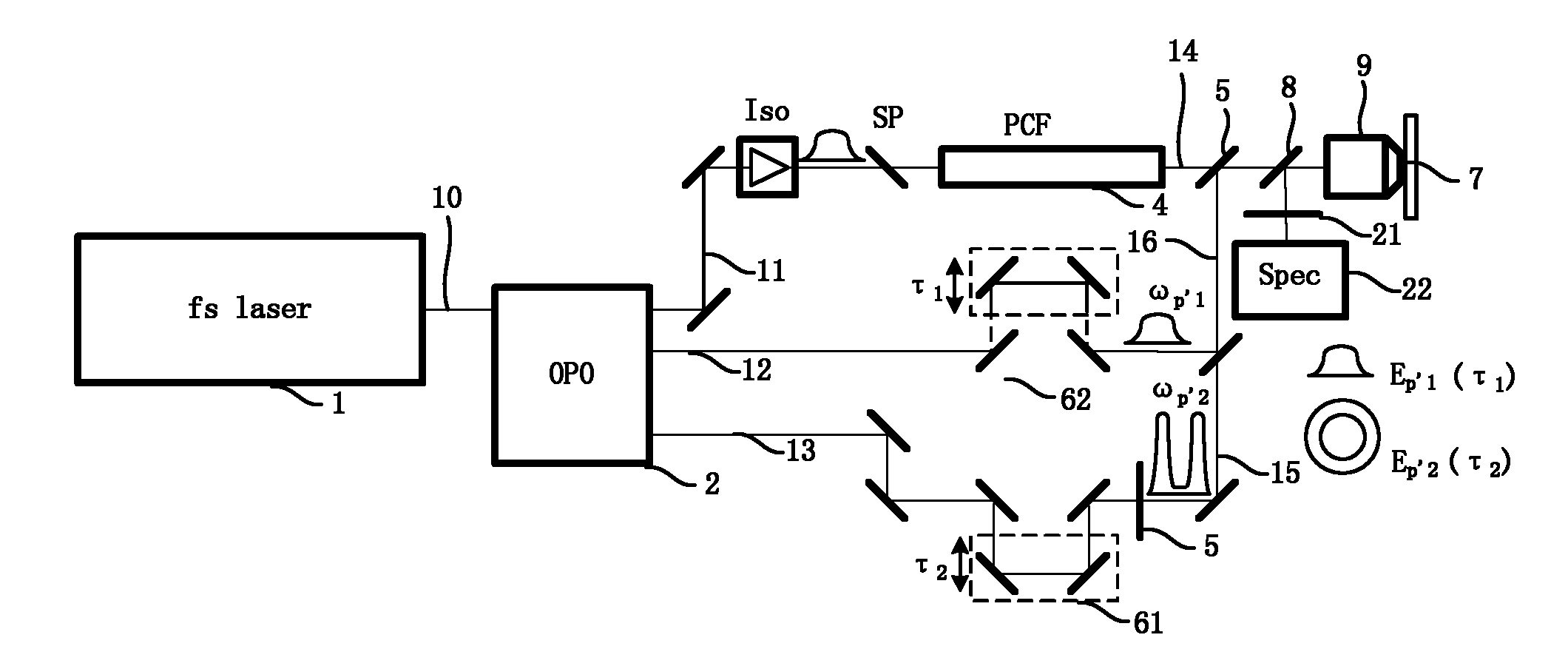
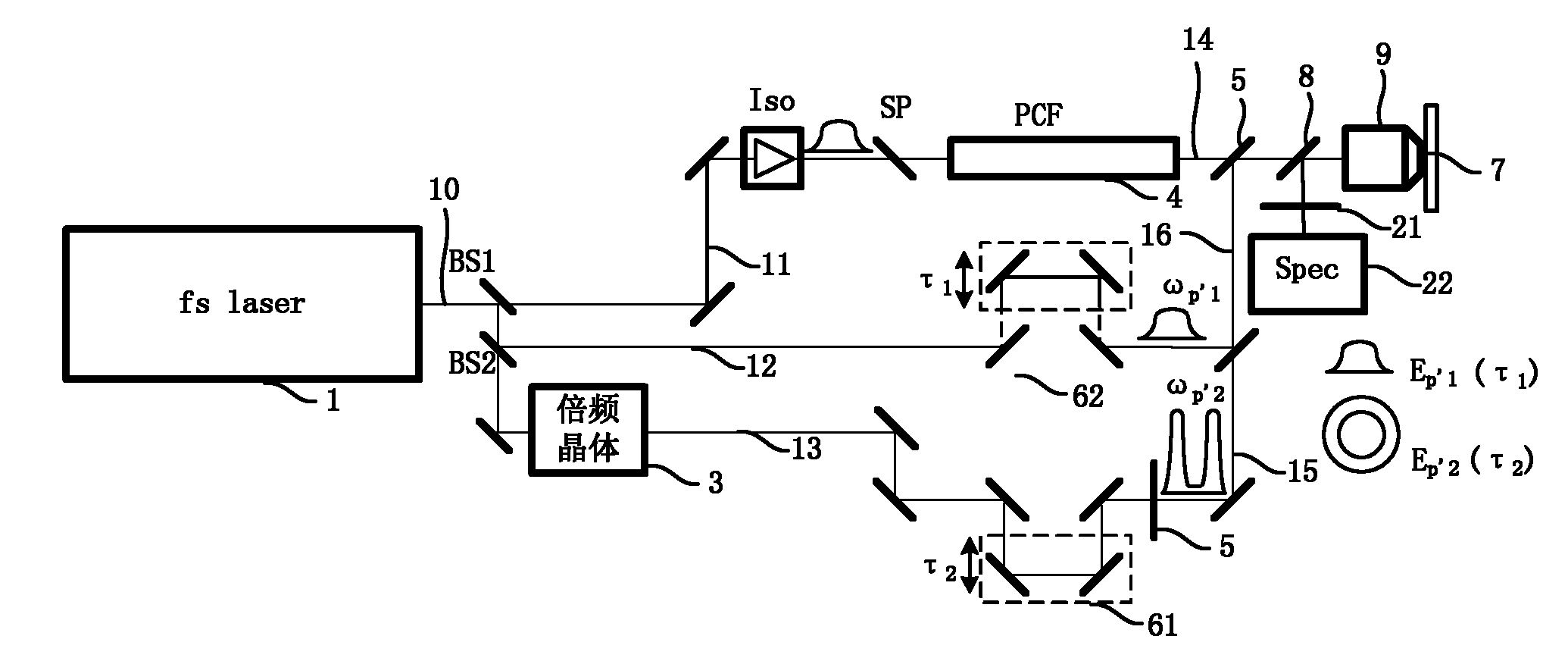
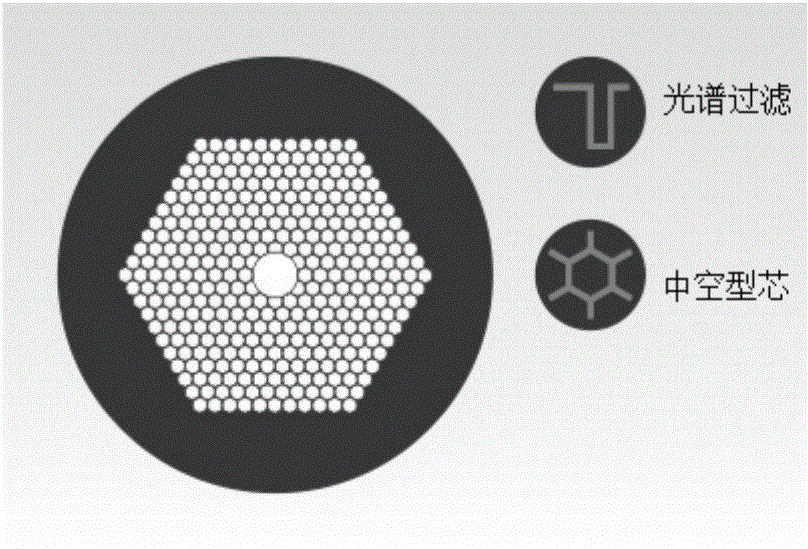
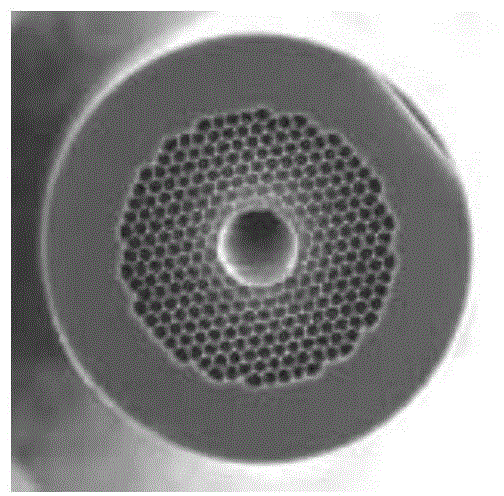
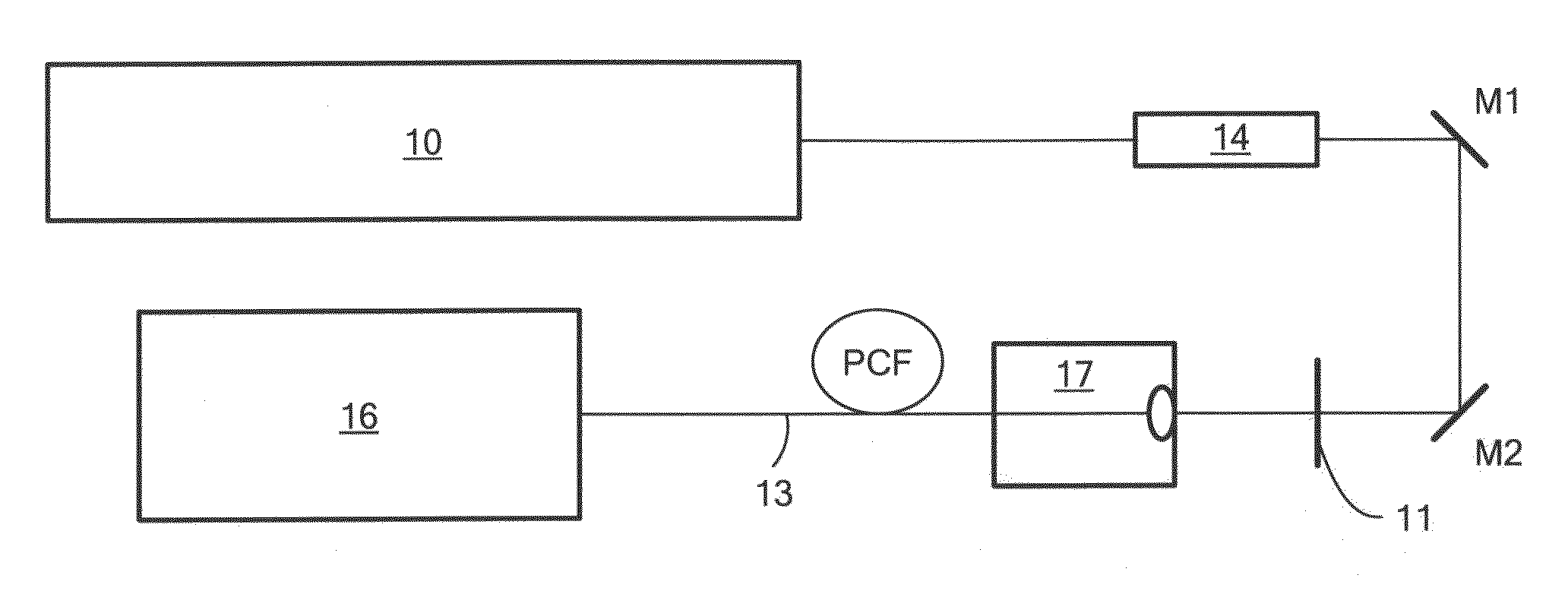
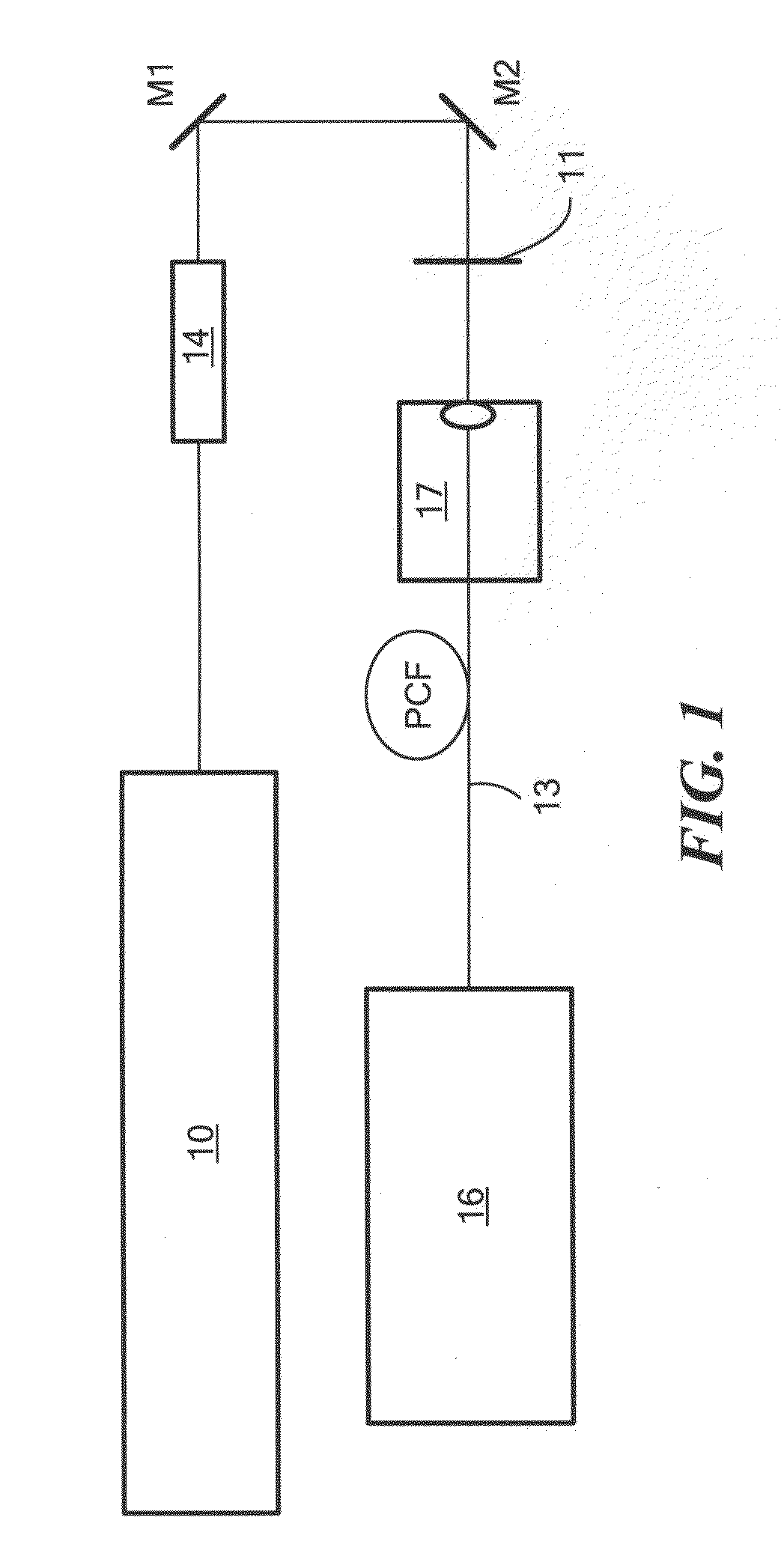
Patents
Literature
323 results about "Supercontinuum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
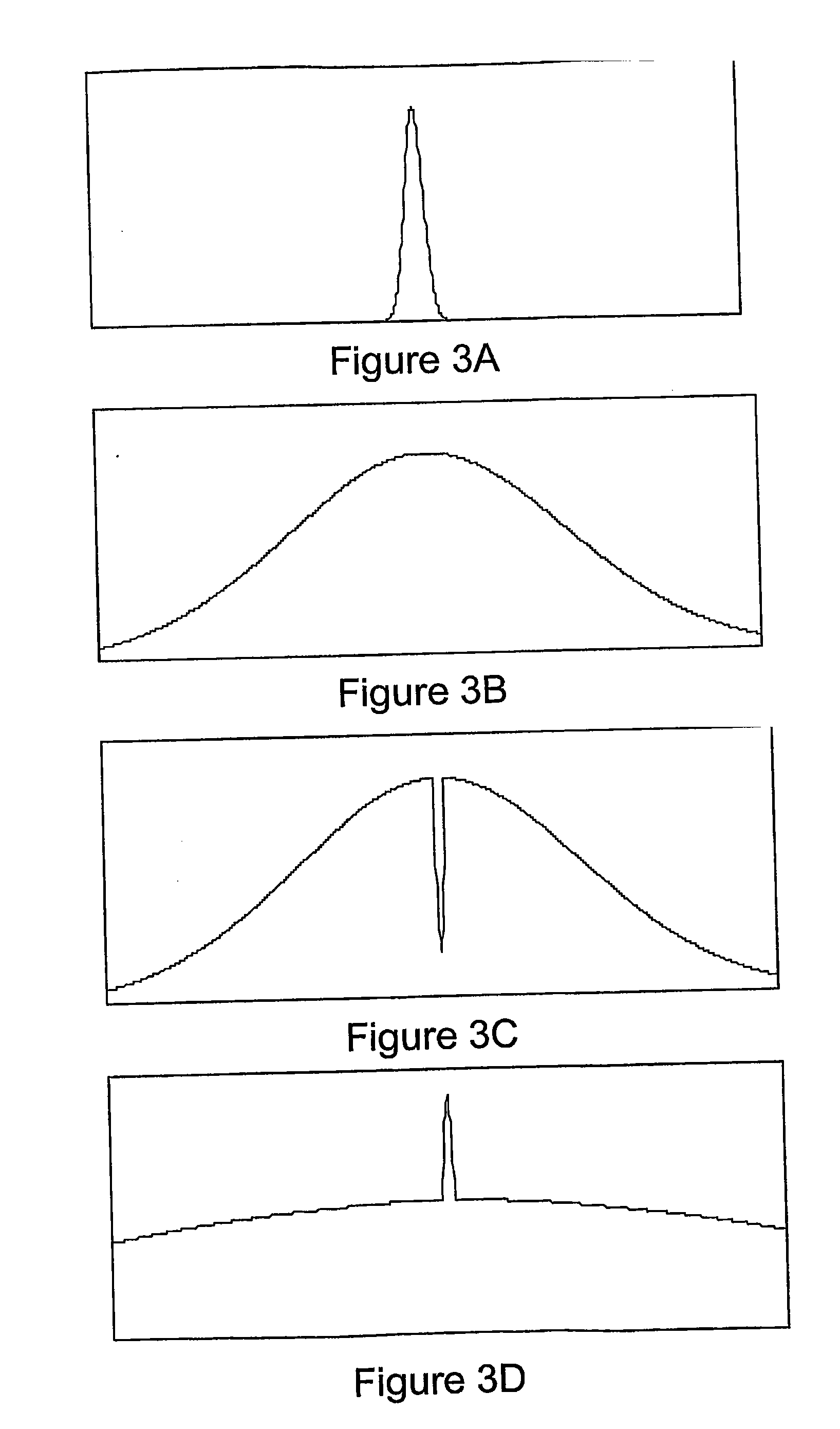
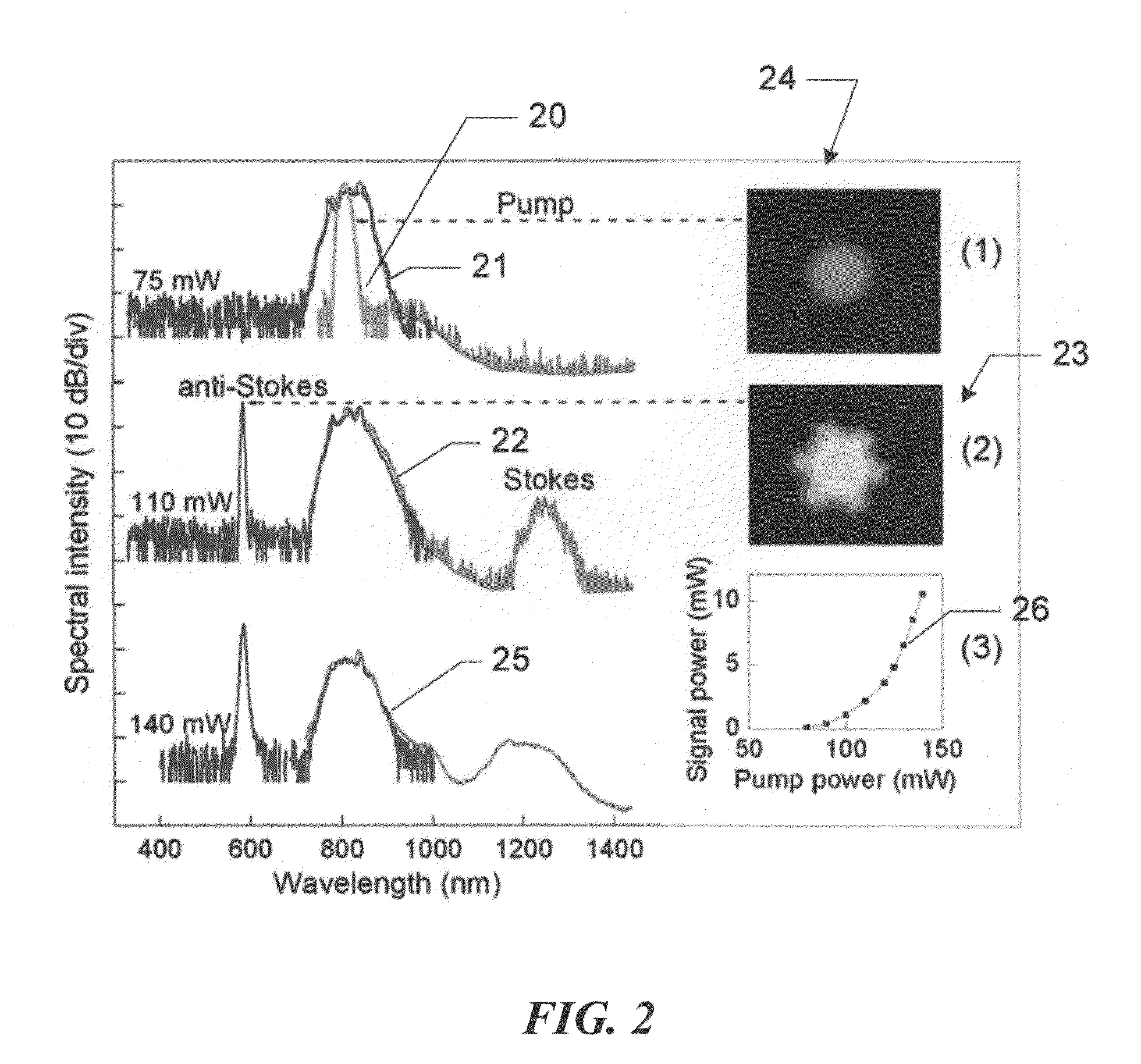
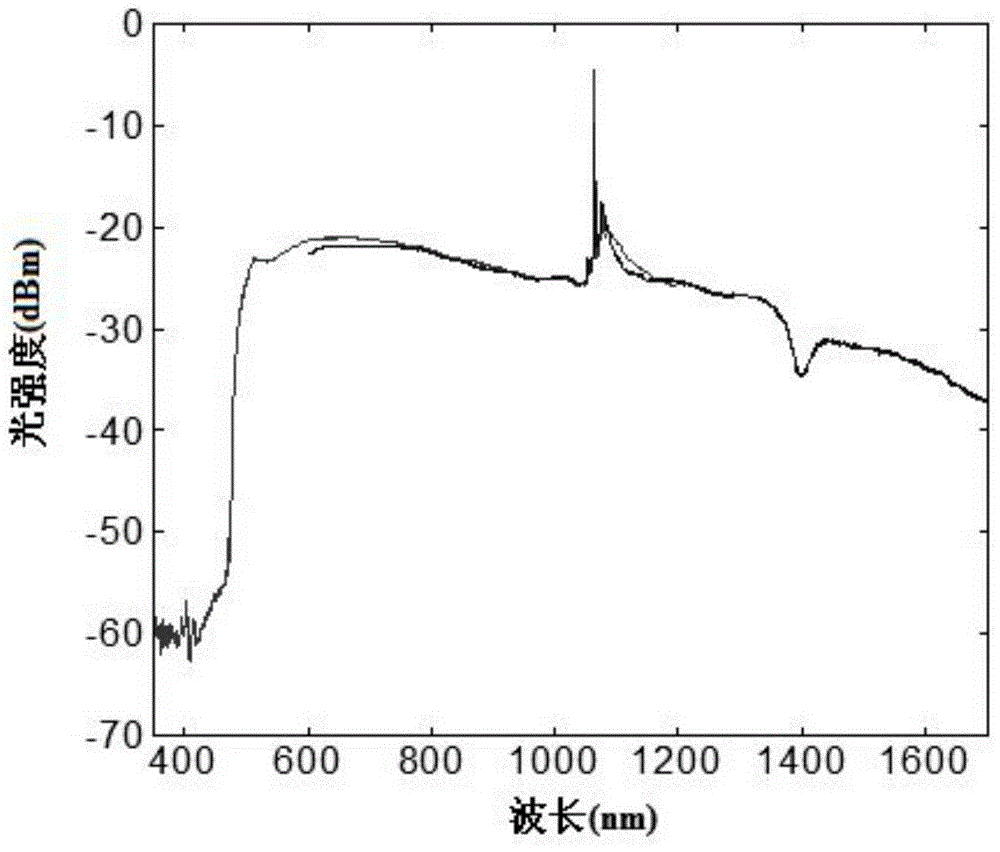
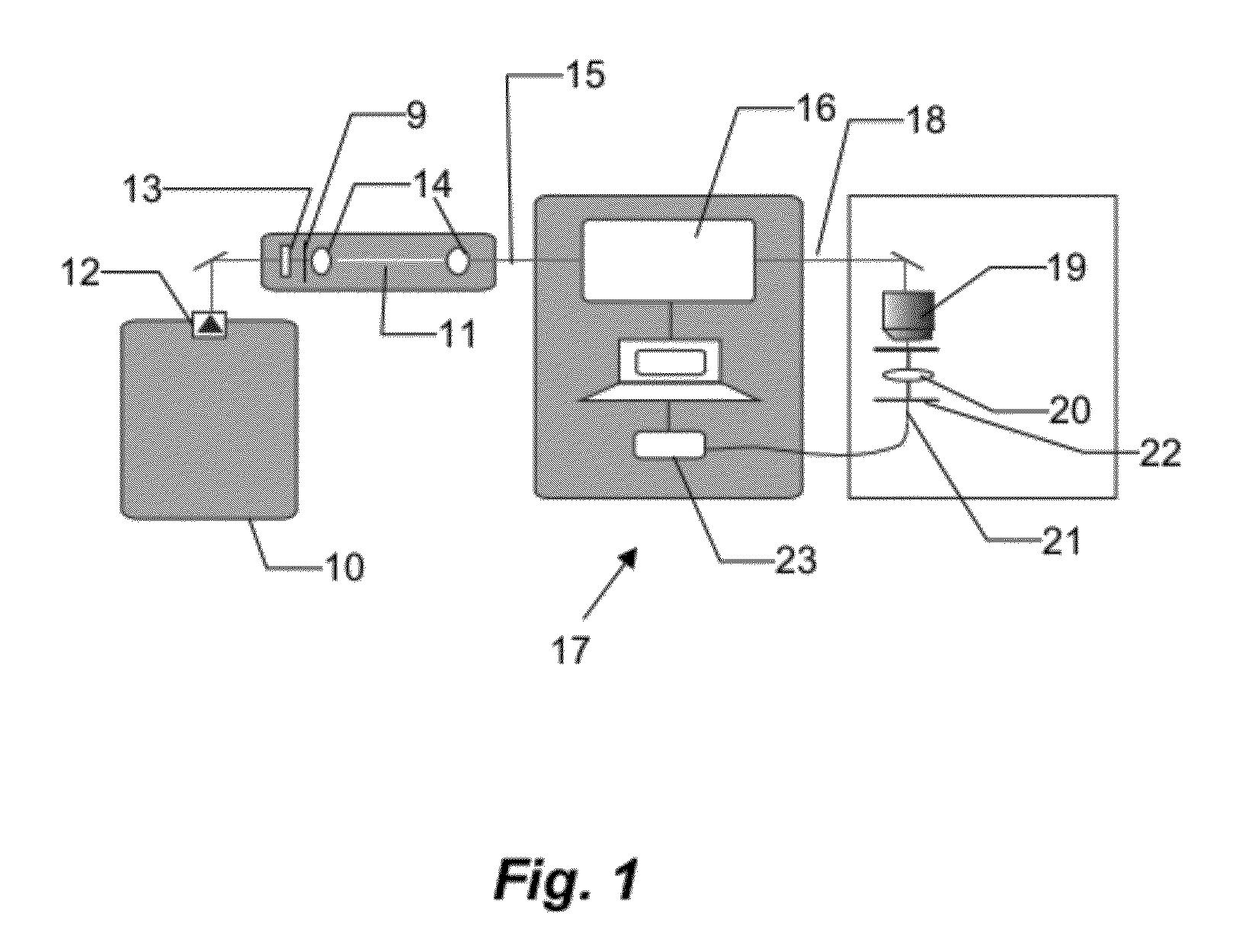
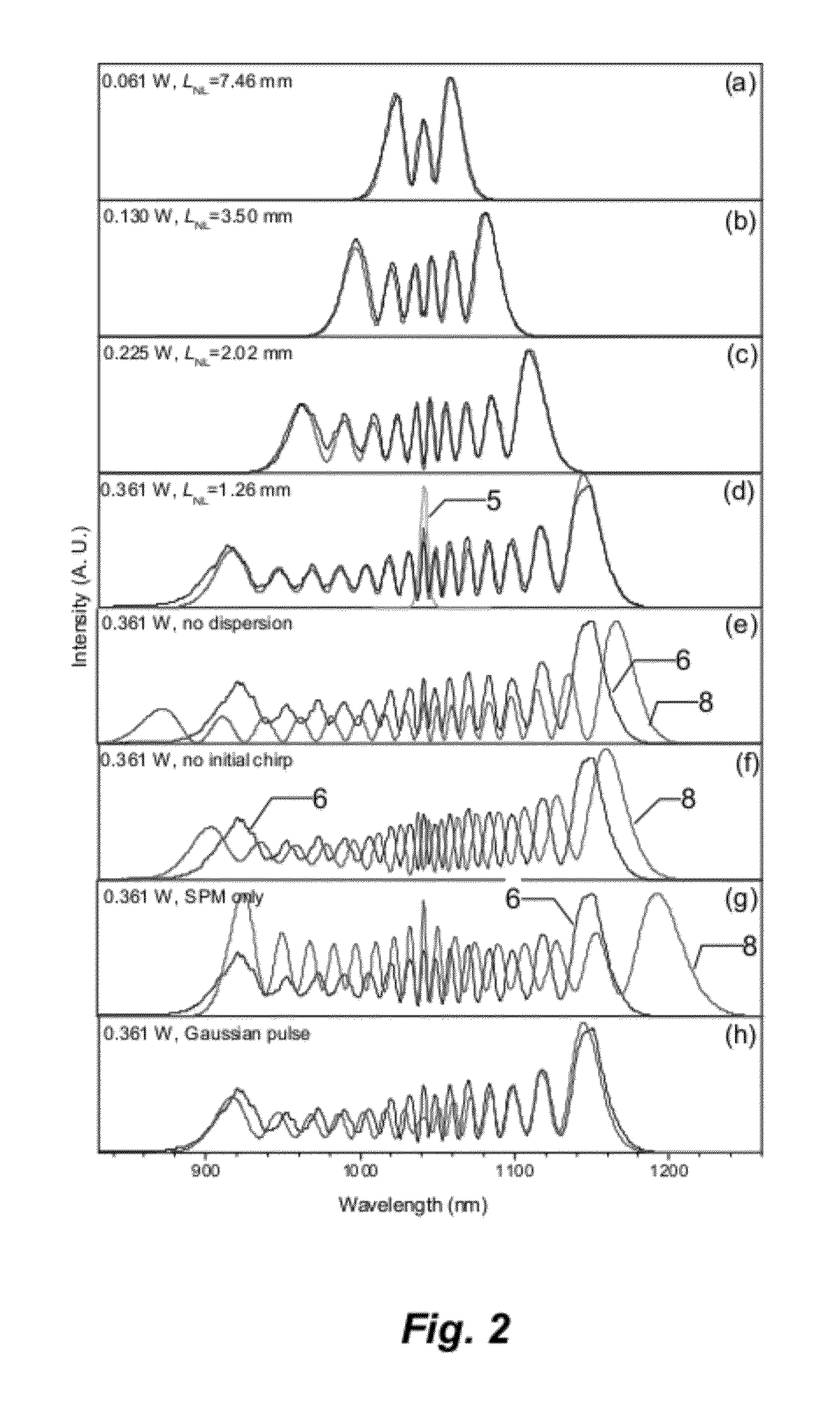
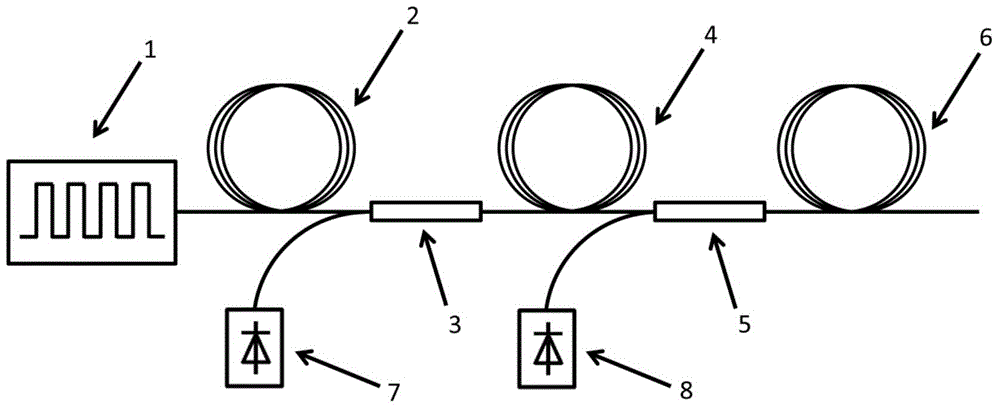
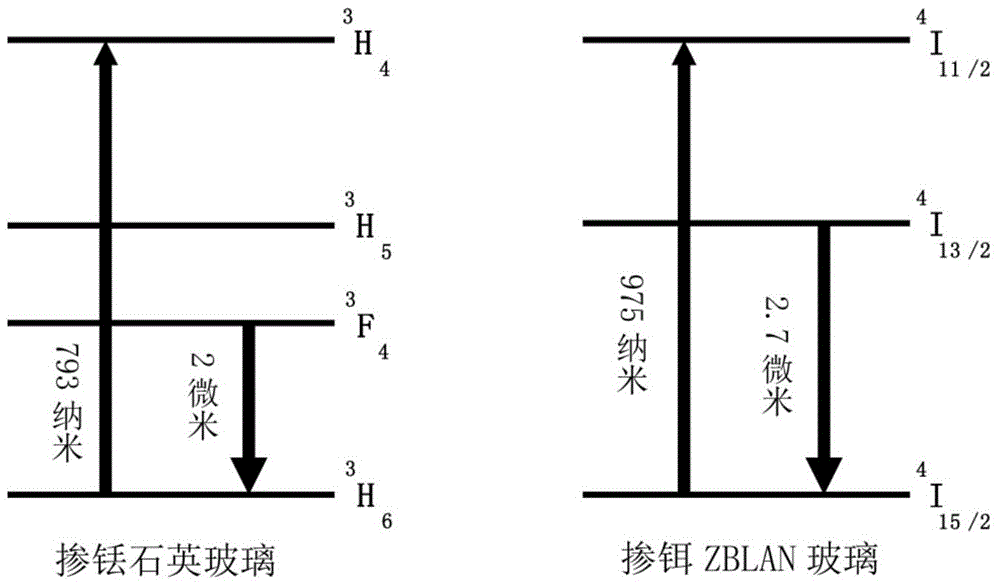
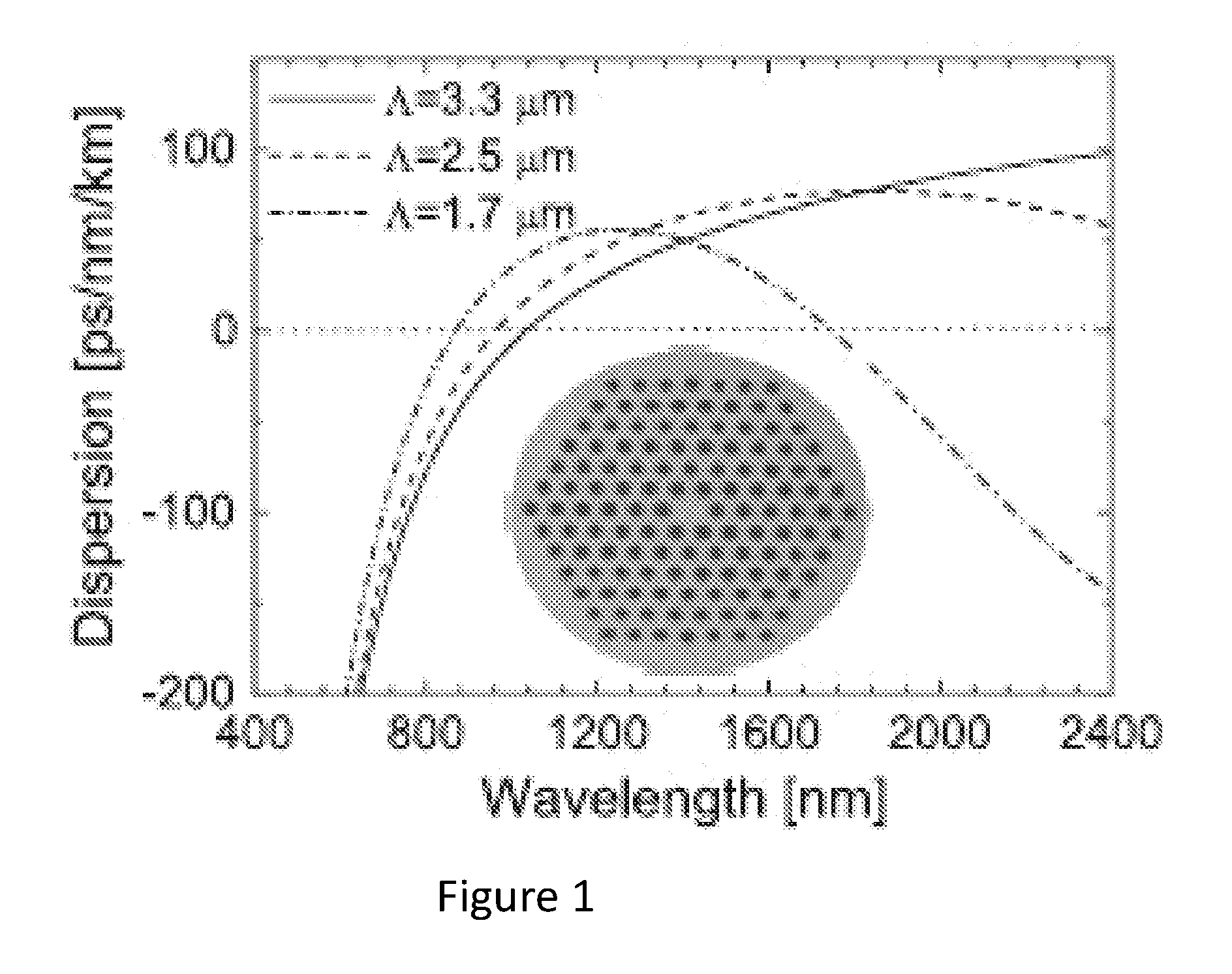
In optics, a supercontinuum is formed when a collection of nonlinear processes act together upon a pump beam in order to cause severe spectral broadening of the original pump beam, for example using a microstructured optical fiber. The result is a smooth spectral continuum (see figure 1 for a typical example). There is no consensus on how much broadening constitutes a supercontinuum; however researchers have published work claiming as little as 60 nm of broadening as a supercontinuum. There is also no agreement on the spectral flatness required to define the bandwidth of the source, with authors using anything from 5 dB to 40 dB or more. In addition the term supercontinuum itself did not gain widespread acceptance until this century, with many authors using alternative phrases to describe their continua during the 1970s, 1980s and 1990s.
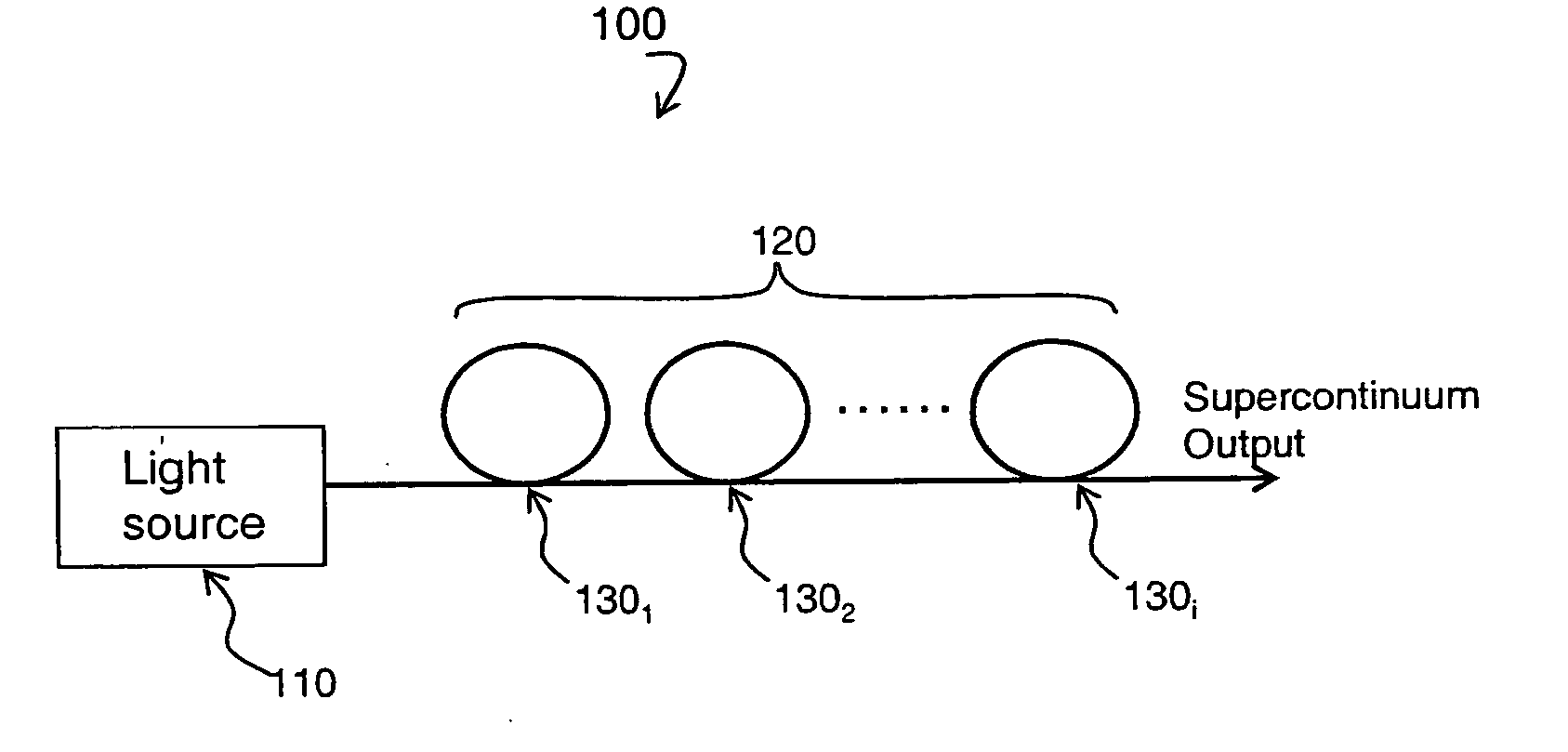
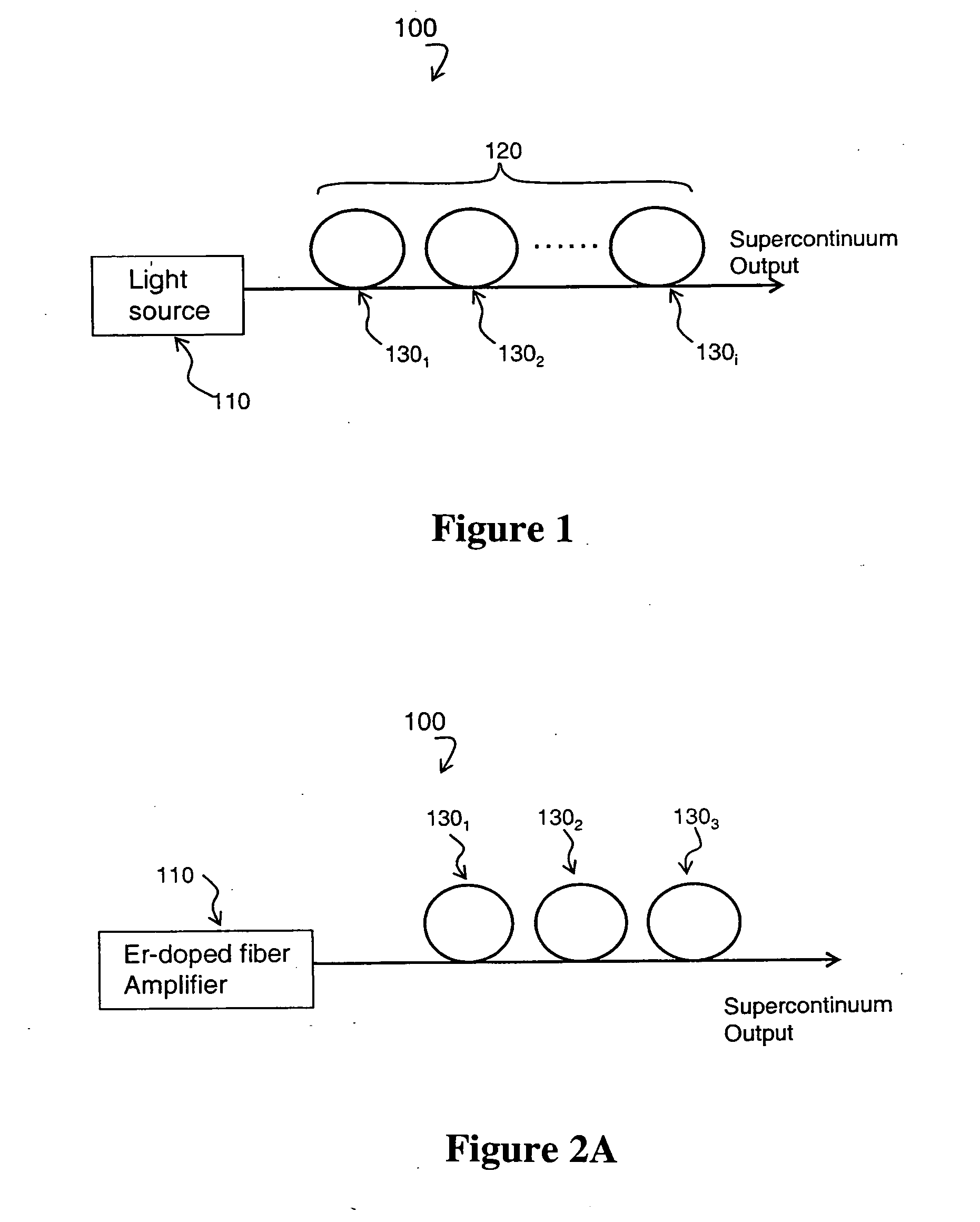
Method and device for creating supercontinuum light pulses
ActiveUS9160137B1Simple controllabilityRemissionLaser using scattering effectsNon-linear opticsGroup velocity dispersionOptoelectronics
A method of spectrally broadening light pulses includes the steps of providing the light pulses with a laser source, said light pulses having a pulse duration below 1 ps, in-coupling the light pulses into a hollow optical waveguide device, and spectrally broadening the light pulses propagating along the pulse guiding medium by subjecting them to a Raman nonlinearity via excitation of a Raman polarization having a first Raman period, wherein the optical waveguide device subjects the light pulses to anomalous group velocity dispersion which combines with the spectral broadening of the light pulses to result in a Raman-enhanced self-compression of the light pulses, and the light pulses further propagate along the optical waveguide device such that the Raman-enhanced self compression results in a further excitation of a Raman polarization having a second Raman period which is faster than the first Raman period.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Optical pulse sources
ActiveUS20090097512A1Low in pulse energyIncrease light intensityLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansFundamental frequencyLength wave
An optical pulse source comprising a DPSS pump laser, a photonic crystal fiber (PCF), and acousto-optic modulator (AOM) gating device is disclosed. The pump pulses are coupled through lenses to the AOM gating device, which is synchronized to the pump laser and is operable to gate the pump pulses to a reduced repetition rate Rr=Rf / N, where Rf is the pump laser fundamental frequency. The pulses from the AOM are injected via optics into the PCF. Propagation through the PCF causes the pulses to broaden spectrally to produce optical supercontinuum pulses. An optical pulse source that further includes an acousto-optical tunable filter (AOTF) operable to convert the optical supercontinuum pulses into wavelength variable output pulses is also provided. A method of scaling the energy of the optical supercontinuum pulses is also disclosed.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Broadband generation of mid ir, coherent continua with optical fibers
ActiveUS20120236314A1Improve fluencyBroad spectral coverageLaser detailsUsing optical meansLow noiseFiber
Coherent and compact supercontinuum light sources for the mid IR spectral regime are disclosed and exemplary applications thereof. The supercontinuum generation is based on the use of highly nonlinear fibers or waveguides. In at least one embodiment the coherence of the supercontinuum sources is increased using low noise mode locked short pulse sources. Compact supercontinuum light sources can be constructed with the use of passively mode locked fiber or diode lasers. Wavelength tunable sources can be constructed using appropriate optical filters or frequency conversion sections. Highly coherent supercontinuum sources further facilitate coherent detection schemes and can improve the signal / noise ratio in lock in detection schemes.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method and apparatus for arbitrary waveform generation using photonics
InactiveUS6724783B2Correction for dispersionLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionLow speedLow-pass filter
An apparatus and method for synthesizing waveforms with arbitrary amplitude, frequency, and phase modulation. Pulses from a broadband (supercontinuum) optical source are filtered into a plurality of wavelength channels, and the intensity of each wavelength channel is adjusted to an appropriate level depending on the desired shape of the envelope of the output pulse. The envelope of the sampling wavelength channels can be stretched, compressed, or inverted in the time domain later using a dispersive medium. After time domain manipulation, the optical pulse train is observed with a combination of high-speed photodetectors and a radio frequency low-pass filter, a low-speed photodetector.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical frequency ruler
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
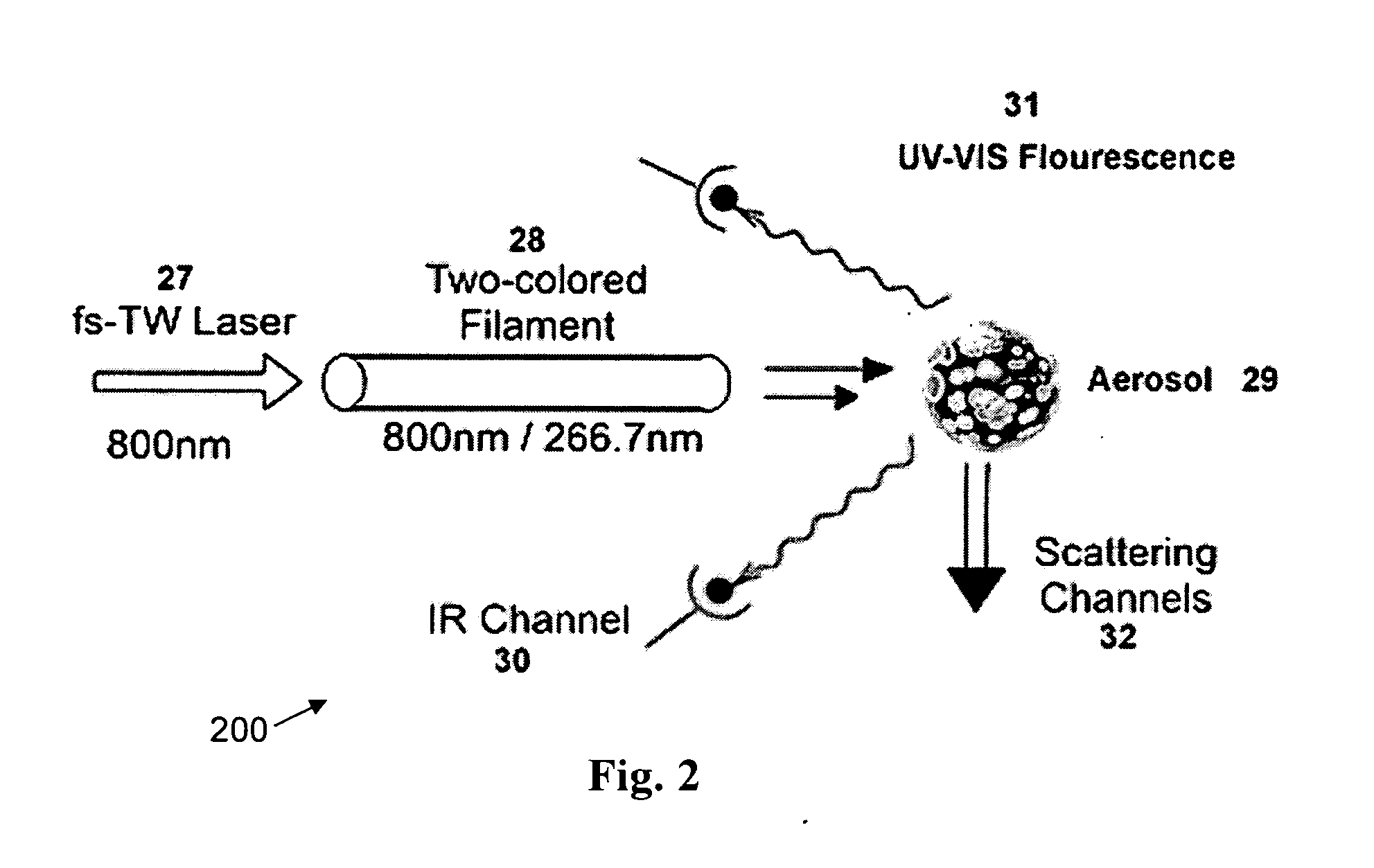
Mobile terawatt femtosecond laser system (MTFLS) for long range spectral sensing and identification of bioaerosols and chemical agents in the atmosphere
InactiveUS7391557B1Reduce probabilitySimultaneous measurementRadiation pyrometryLaser detailsFilamentationUltraviolet
The present invention relates to a system for detection and identification of airborne biological, chemical and / or nuclear threats such as toxins, spores, bacteria, and viruses in real time at distances from a few meters to several kilometers. Compact femtosecond terawatt laser technology is combined with spectroscopic and mathematical methods for spectral sensing of airborne warfare agents such as bio-aerosols. Trigger sensors and standoff devices based on mobile terawatt femtosecond laser systems are provided that may be placed at strategic monitoring locations. Furthermore, the invention relates to the propagation of airborne ultra-short, ultra-intense laser pulses giving rise to plasma channels (filamentation) producing white light supercontinuum ranging from the ultraviolet (UV), visible (VIS), near infra-red (NE) and middle infra-red (MIR). According to this invention, the supercontinuum can be directly produced in a particle cloud and hence is uniquely suitable for multi-spectral long-range atmospheric agent and radioactive isotope detection.
Owner:APPLIED PHOTONICS WORLDWIDE
Solid-state luminescent filament lamps
InactiveUS20090212698A1Improve wavelength conversion efficiencyEliminate thermal quenching lossDischarge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourcePhotonicsPhosphate glass
Traditional incandescent and halogen lamps produce a high CRI warm white light with indirect emission patterns at the cost of poor energy efficiency. This new advancement in solid-state lighting enables the production of a new solid-state filament wherein the tungsten filament is replaced with an array of high efficiency LED emitters which combine through an equiangular spiral, or t-spline / TNURCC lightpipe network to produce a single homogeneous blue light source which then pumps a luminescent filament comprised of a phosphor loaded silicone, phosphor loaded polymer, a lanthanide doped fluoro-phosphate glass, glass ceramic tape, quantum dot filled composite, or super-continuum spectrum producing photonic crystalline structure.
Owner:ILLUMINATION MACHINES
Optical frequency ruler
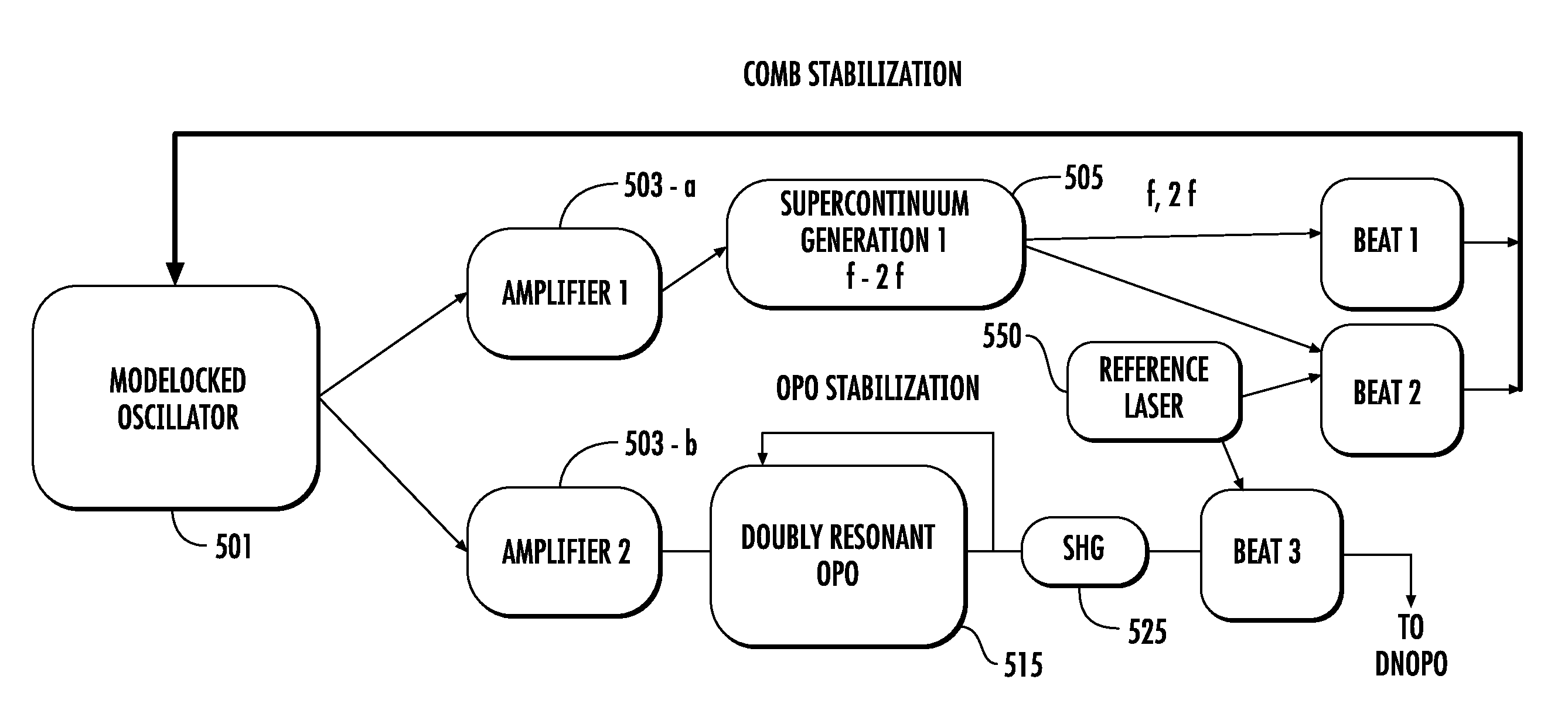
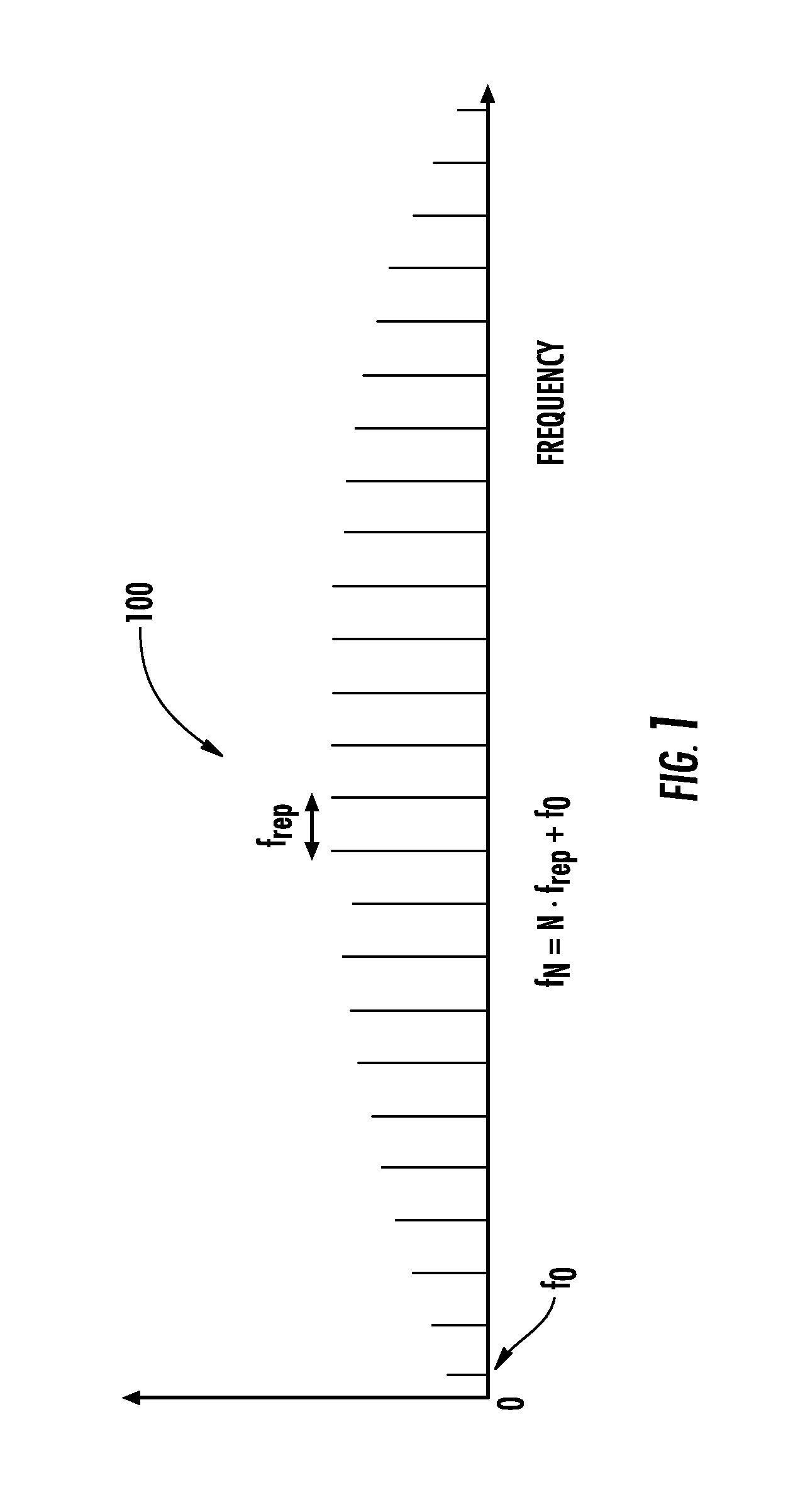
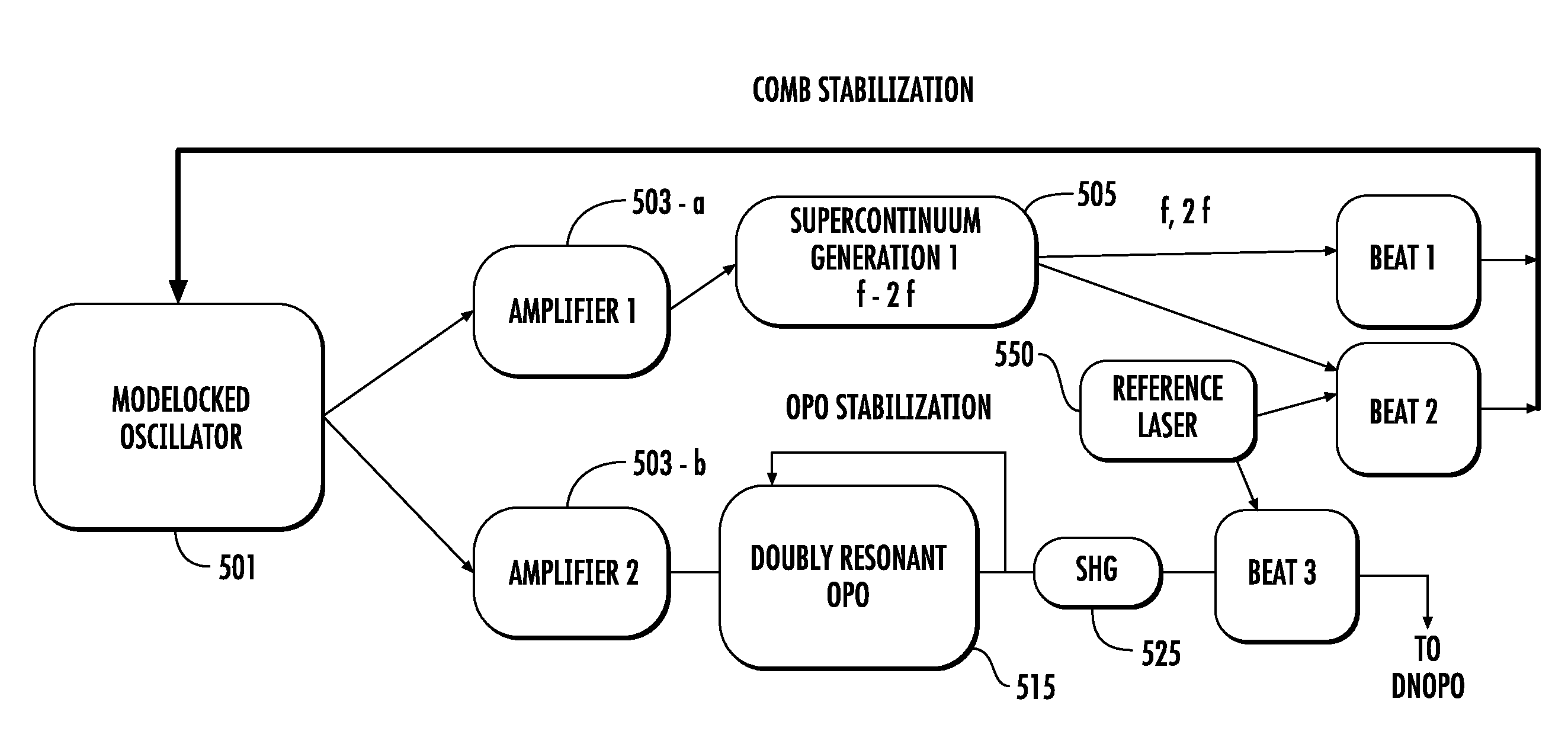
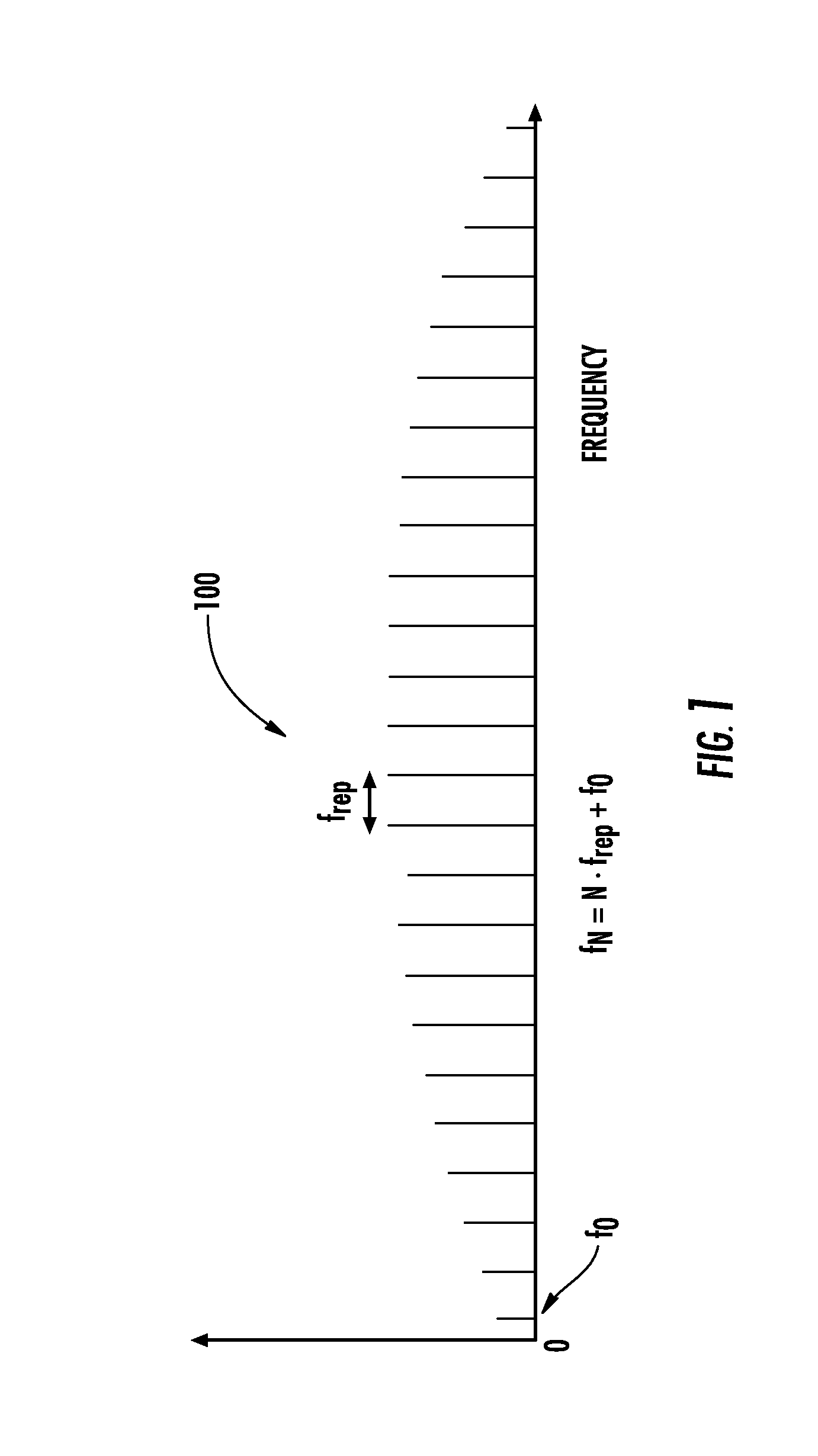
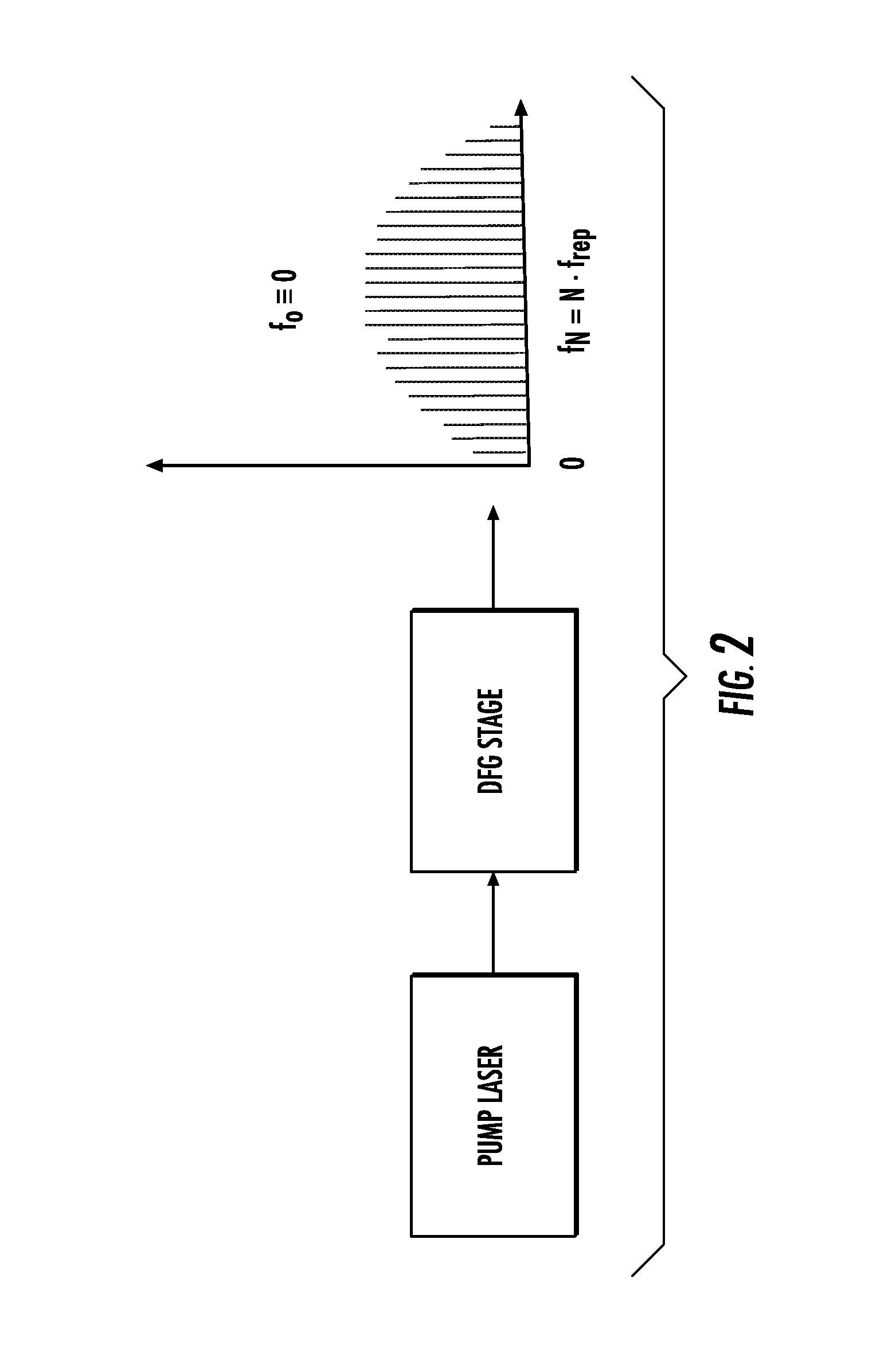
The present invention relates to frequency rulers. At least one embodiment includes a mode locked pump source operated at pulse repetition rate, and a pump output having a pump carrier envelope offset frequency. A nonlinear optical system outputs a frequency ruler spectrum comprising individual frequency modes. The frequency modes may be characterized by a frequency spacing which is an integer multiple of the repetition rate and by distinct ruler carrier envelope offset frequencies which exhibit at least one discontinuity across the frequency output. The ruler carrier envelope offset frequencies are substantially locked to the carrier envelope offset frequency of the pump laser. One preferred embodiment includes a frequency doubled, doubly resonant, non-degenerate OPO (DNOPO), a supercontinuum generation (SC) stage and at least one reference laser arranged downstream from a Tm fiber-based pump source. A plurality of beat signals generated therefrom provide for stabilization of the system.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
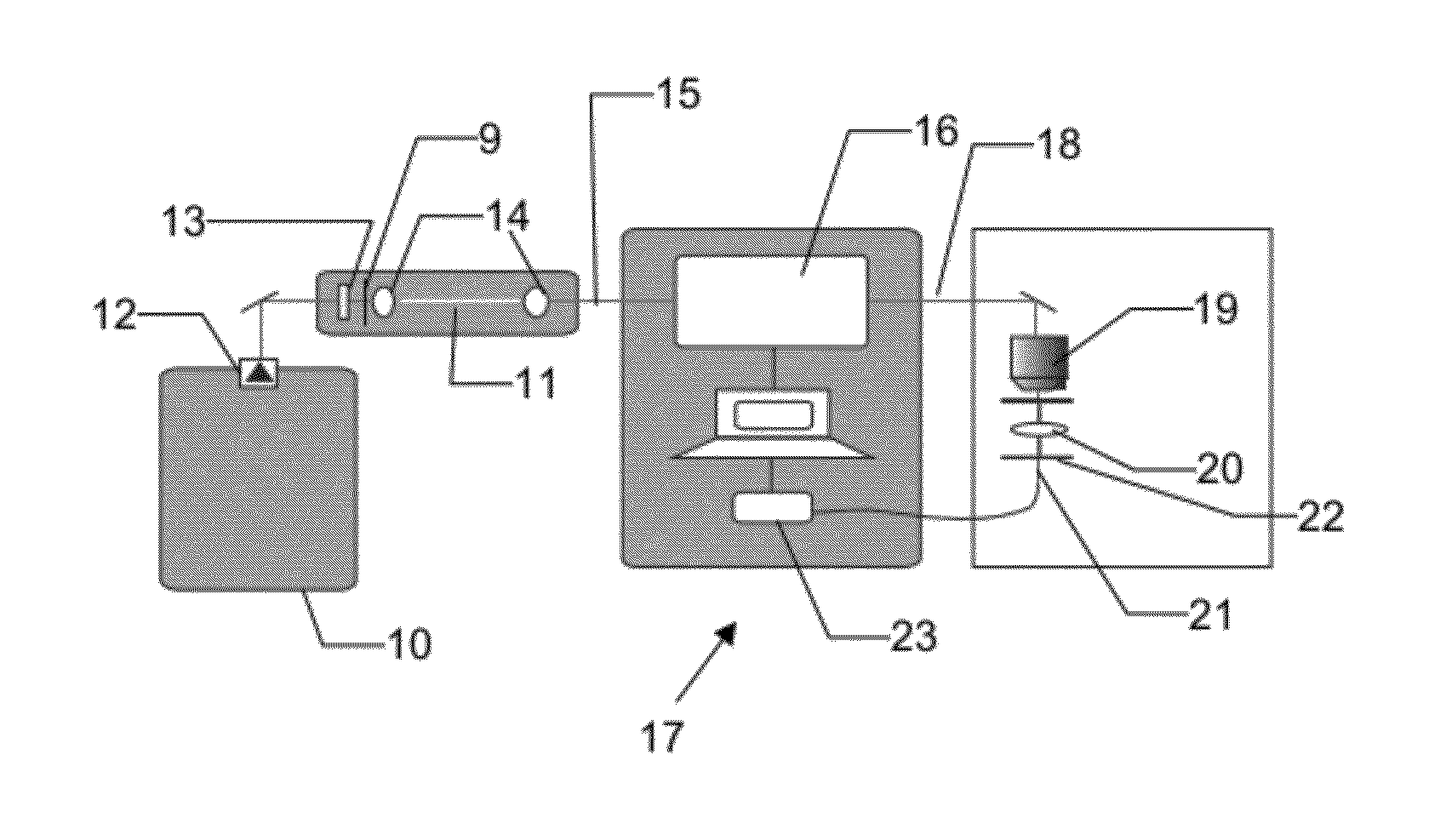
Method of generating supercontinuum optical radiation, supercontinuum optical radiation source, and use thereof
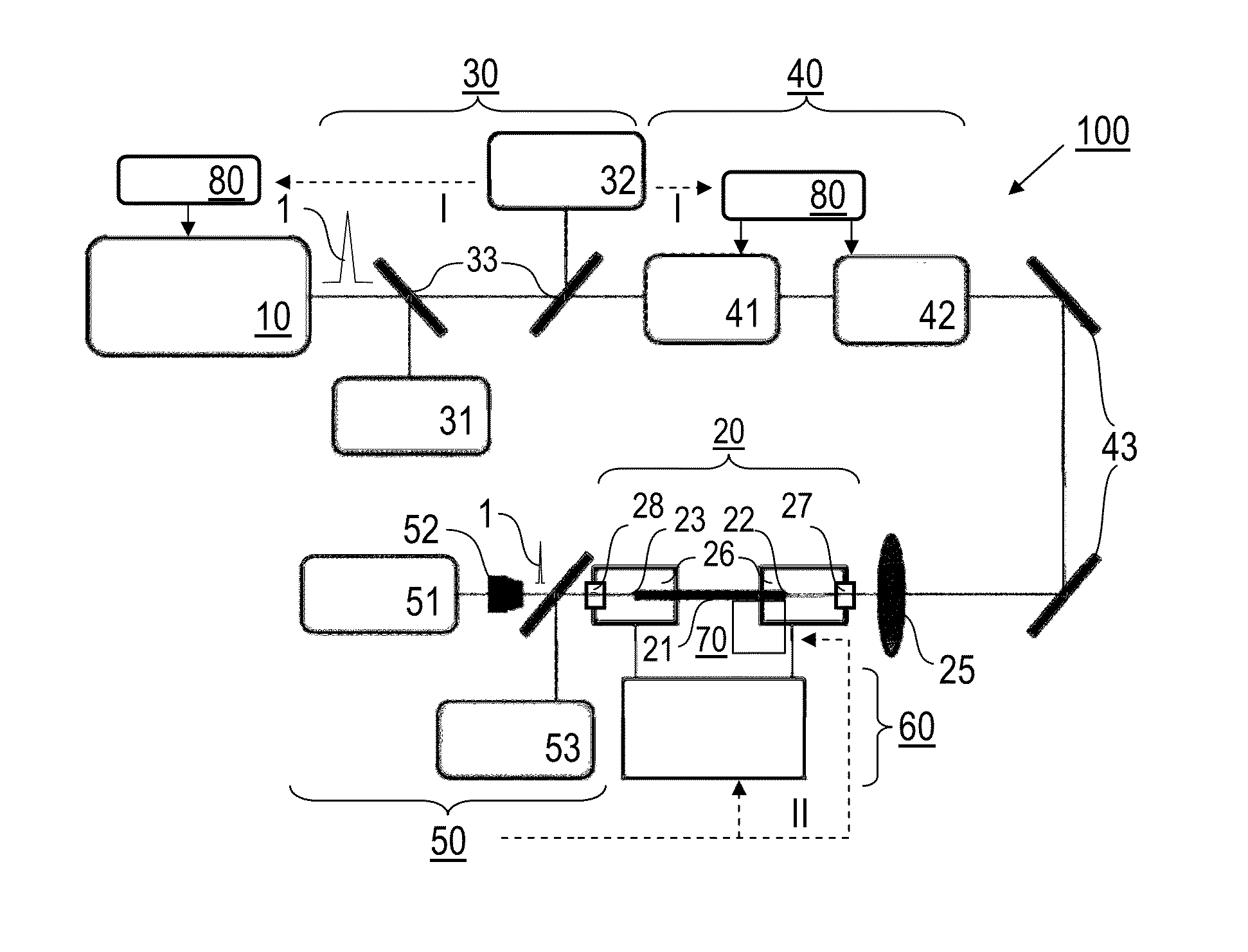
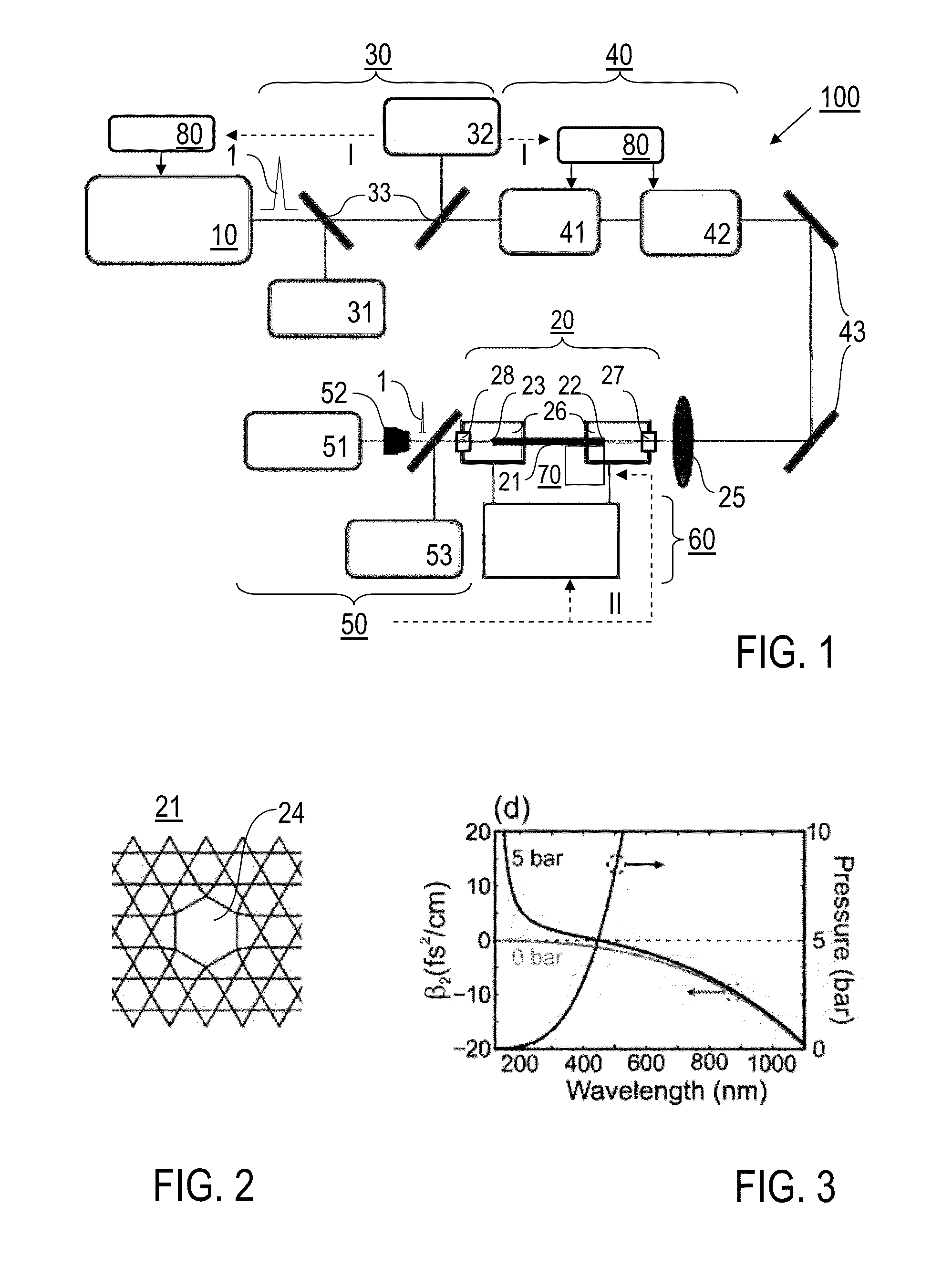
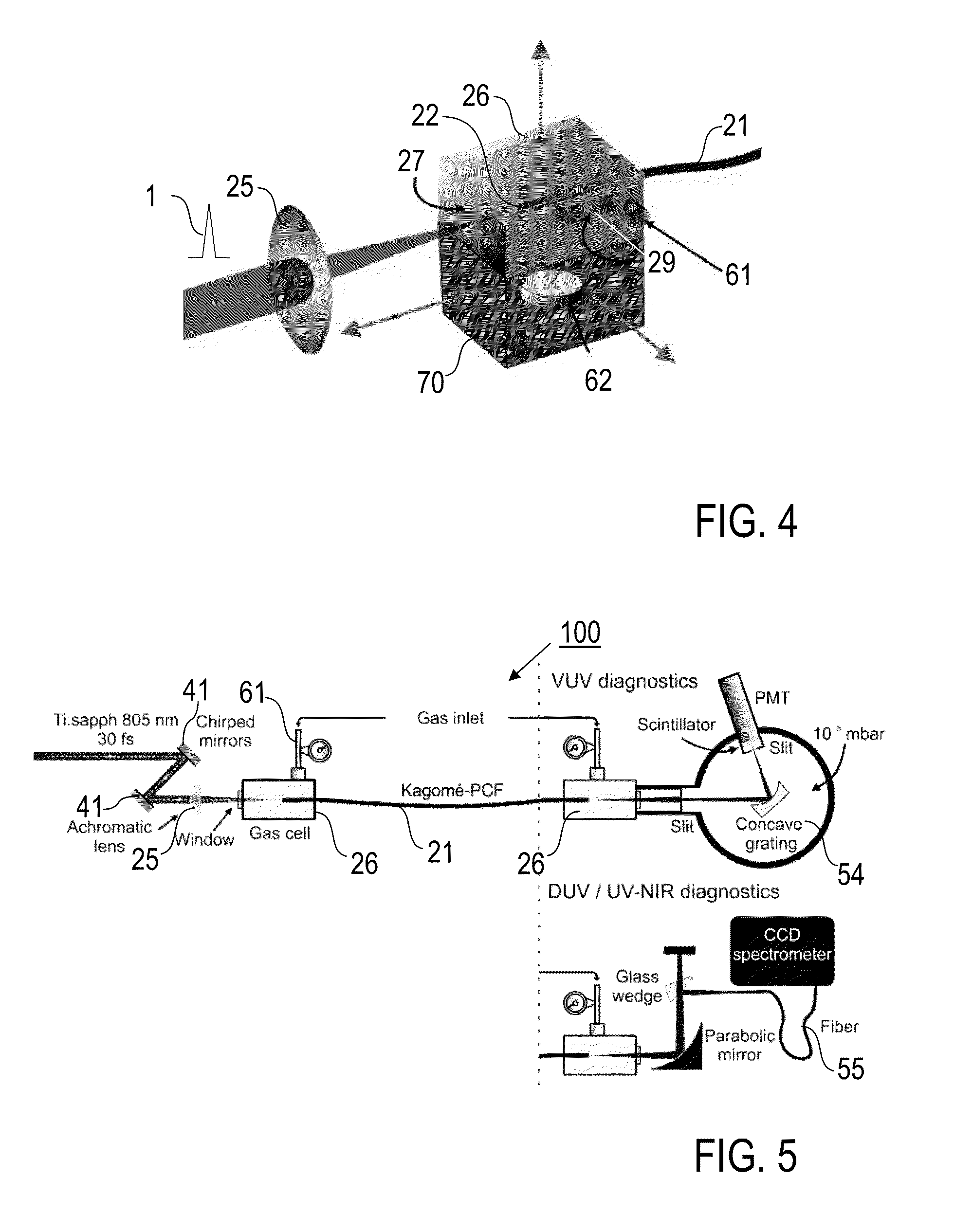
InactiveUS8000574B2Simple and compact supercontinuum optical radiation sourceShort pulseCladded optical fibrePhotometryOptical radiationLength wave
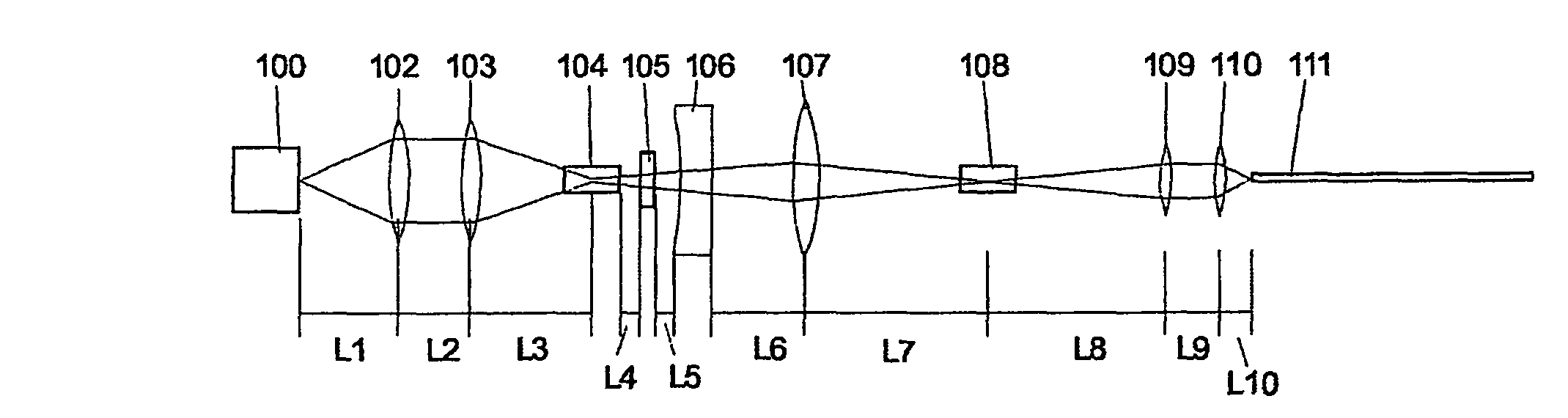
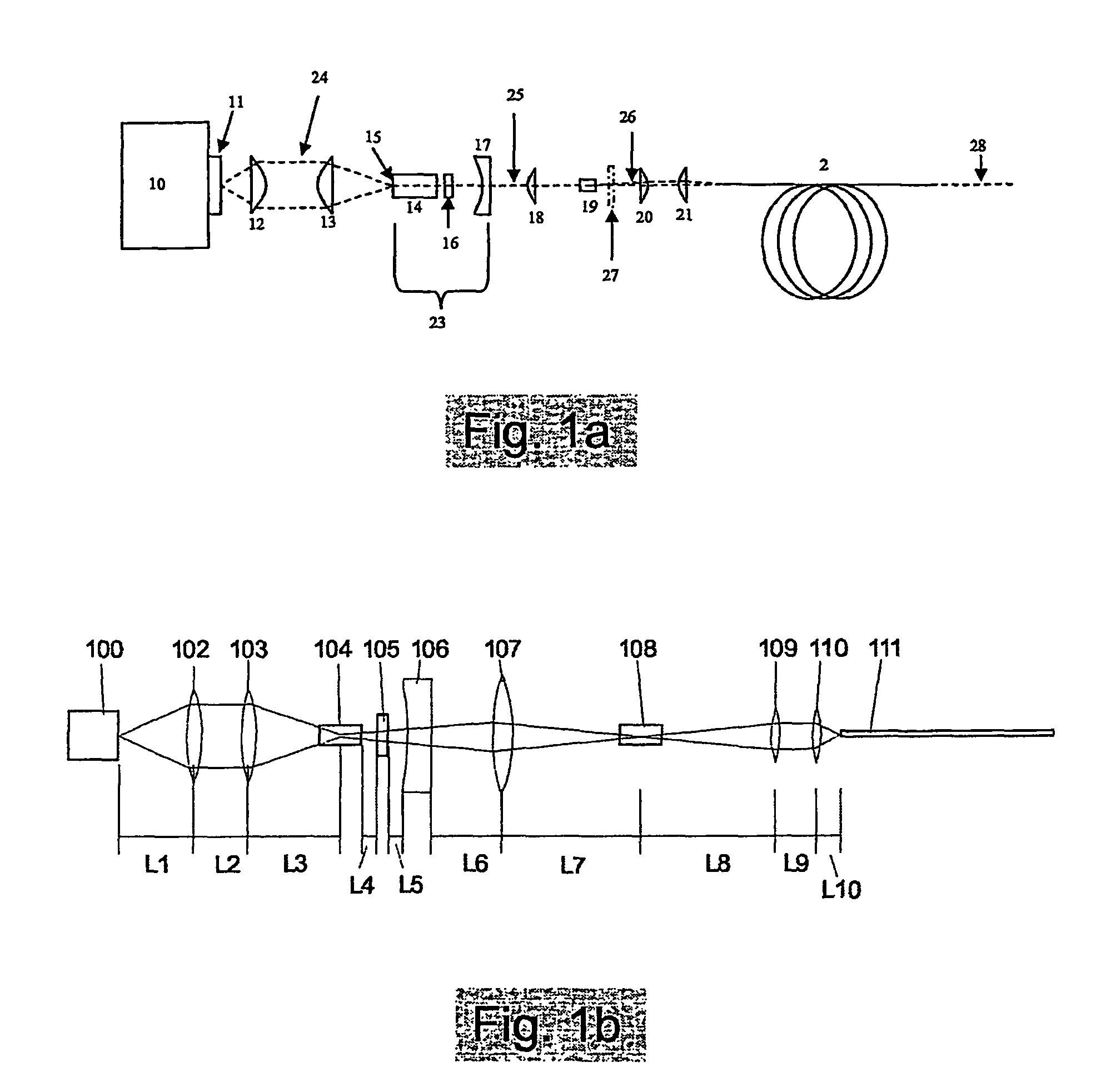
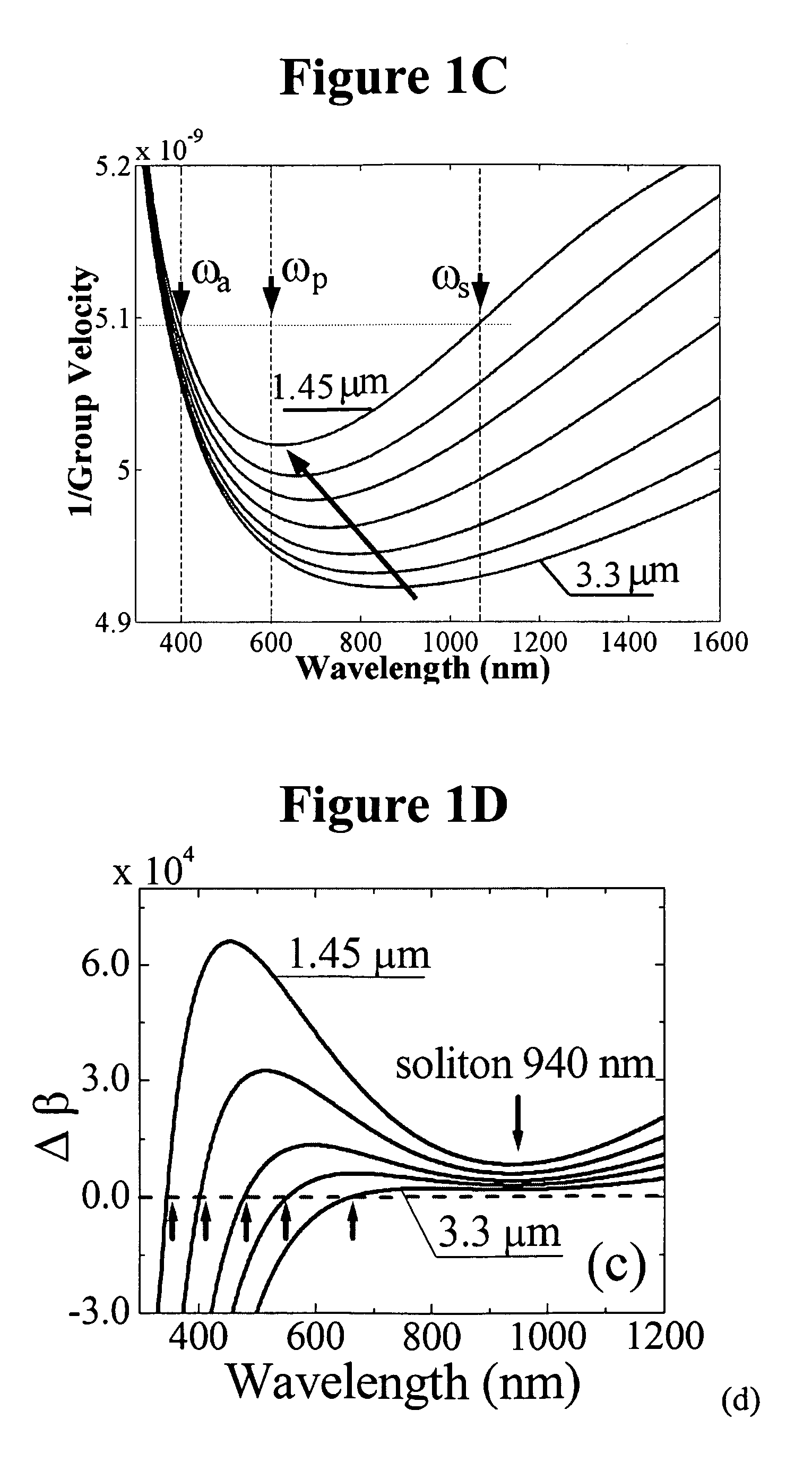
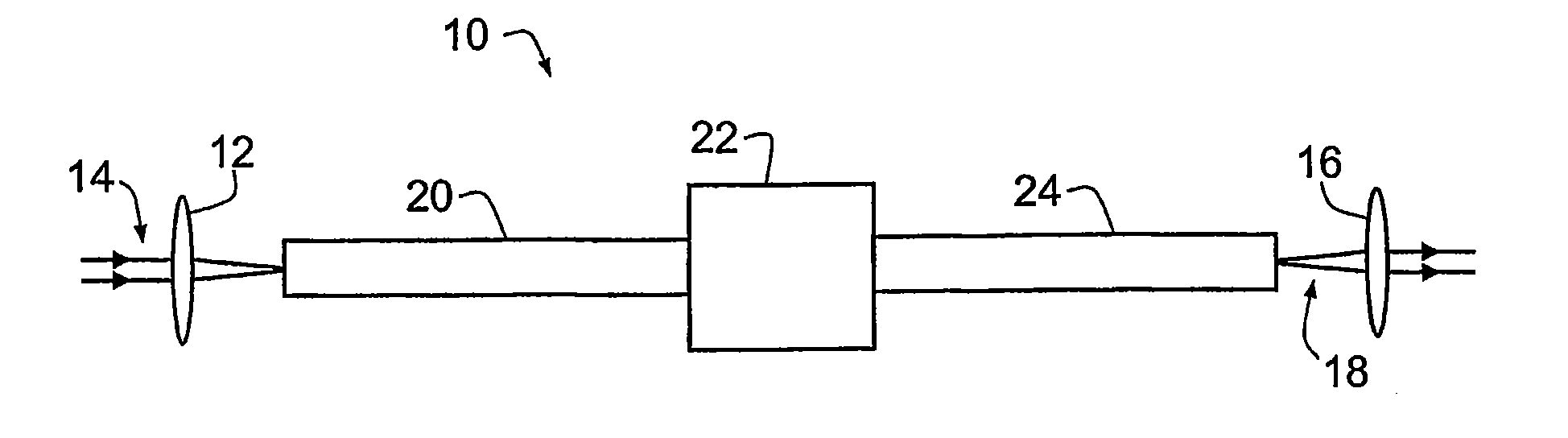
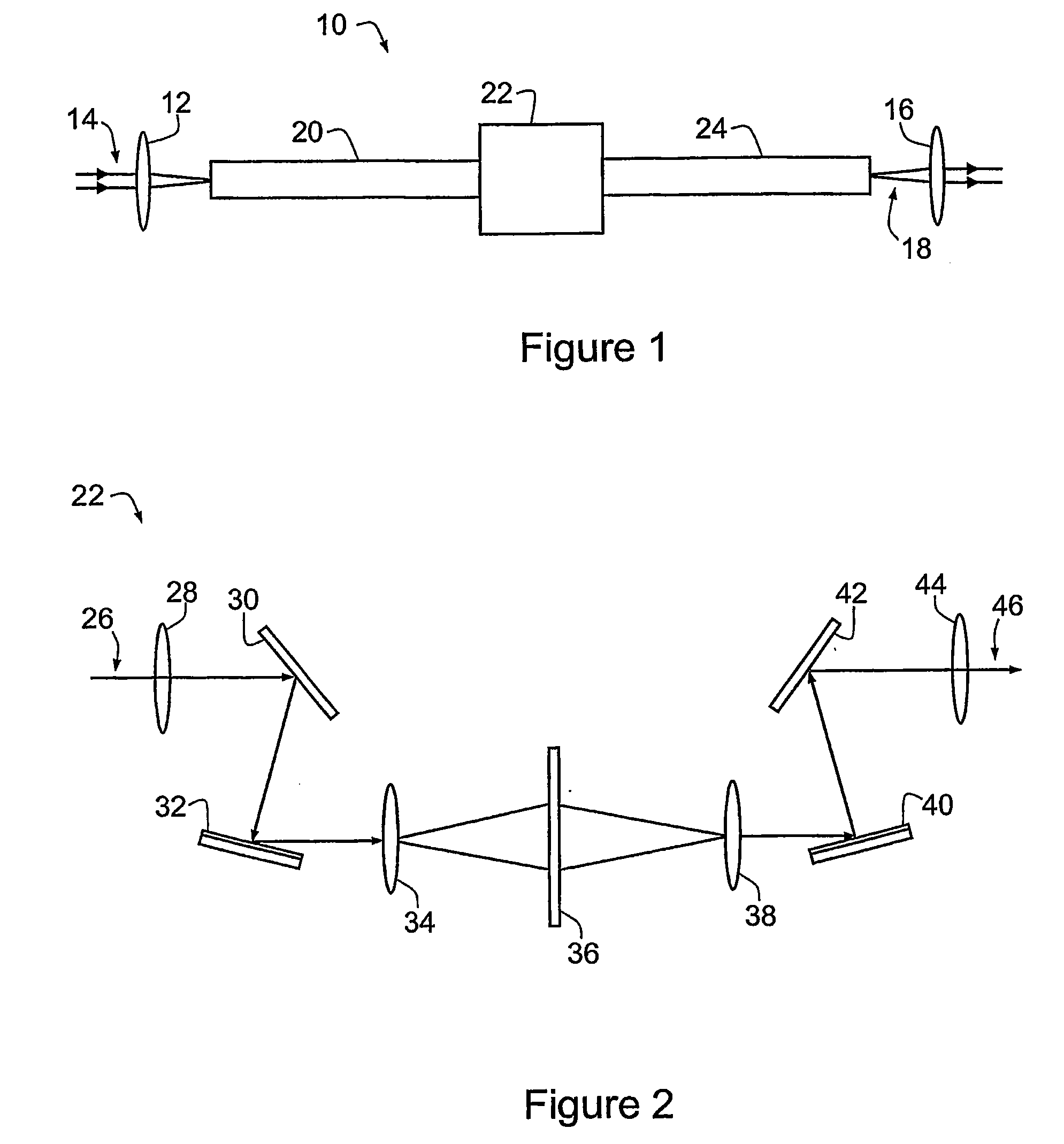
A method of generating supercontinuum optical radiation, the method comprising: (a) providing an optical waveguide (22), said optical waveguide exhibiting a dispersion characteristic of guided optical radiation, said dispersion characteristic comprising: (i) a first dispersion parameter (β21) at a first wavelength (λ1), (ii) a second dispersion parameter (β22) at a second shorter wavelengths (λ2), and (iii) a zero-dispersion parameter at a wavelength in between said first and said second shorter wavelengths; said optical waveguide further comprising at least one entrance for receiving optical radiation, and at least one exit for emitting guided optical radiation; (b) applying at least two laser radiation of said first (25) wavelength, (λ1) at a first power (P1) and applying laser radiation of said second (26) shorter wavelength (λ2) at a second power (P2) into said optical waveguide, said laser radiations at least partially overlapping between said at least one entrance and said at least one exit of said optical waveguide; and (c) phase-matching said applied laser radiations by adjusting said first and second powers; a supercontinuum optical radiation source; and use thereof.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
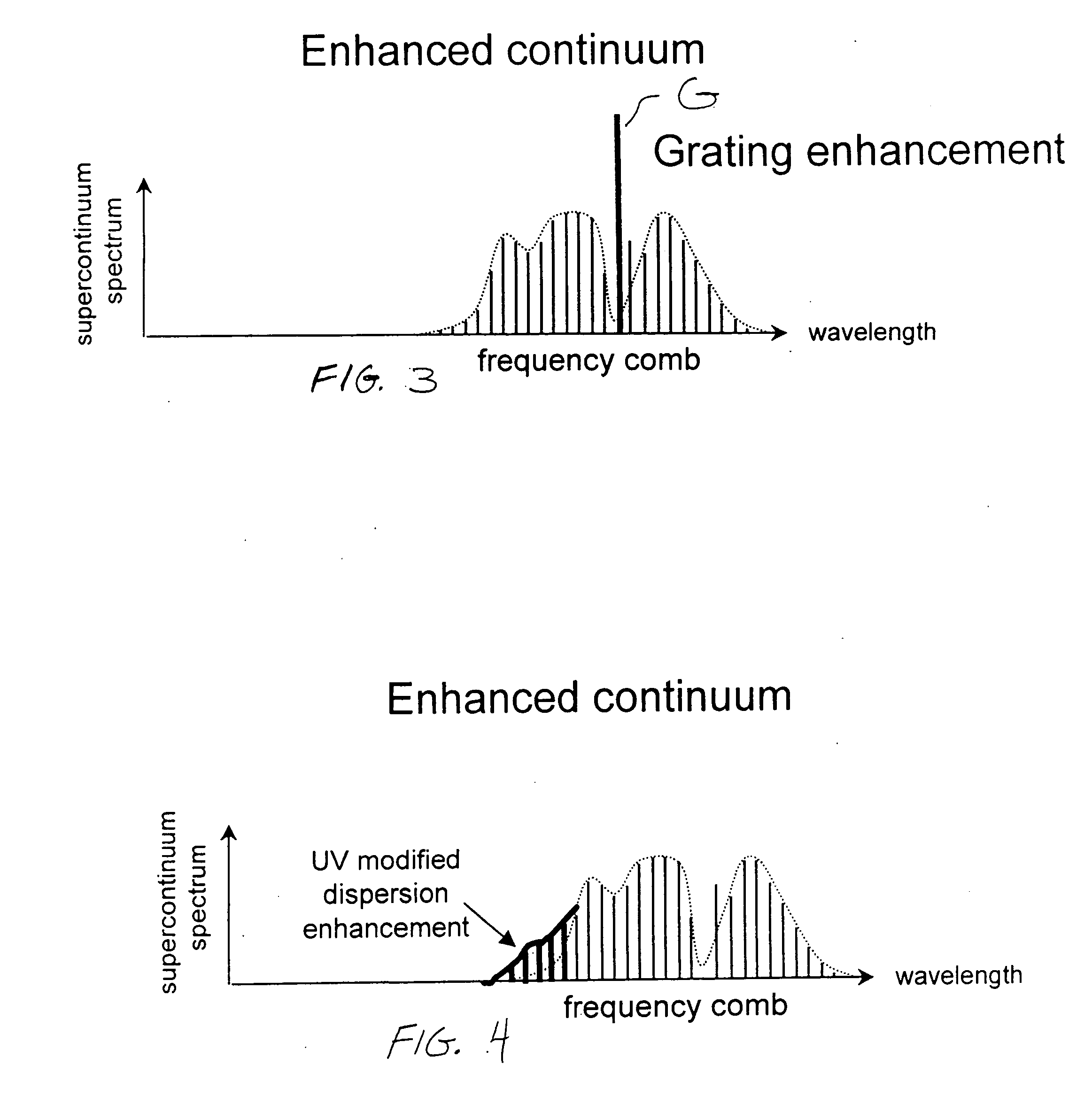
Enhanced supercontinuum generation in highly nonlinear fibers using post-fabrication processing
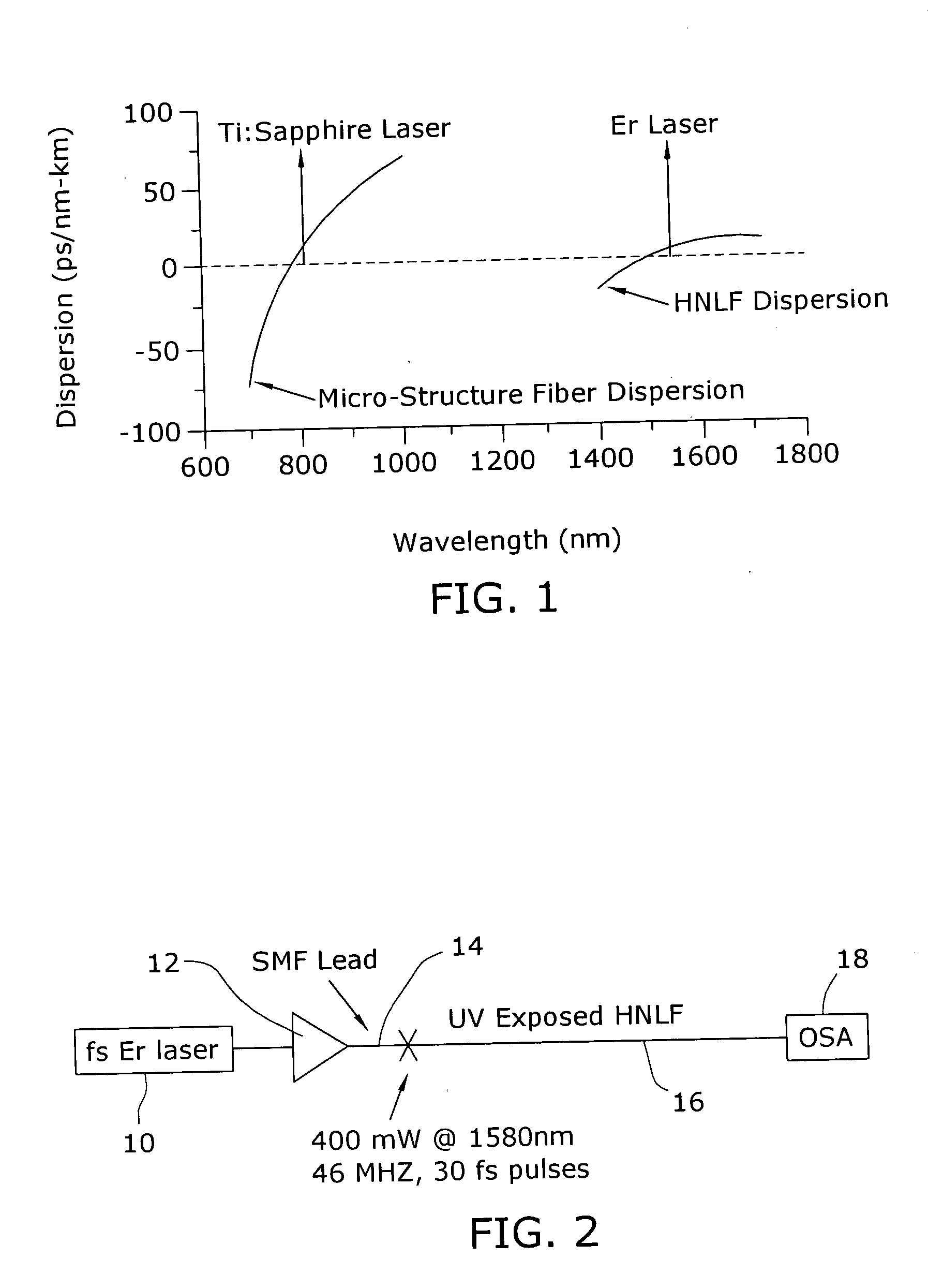
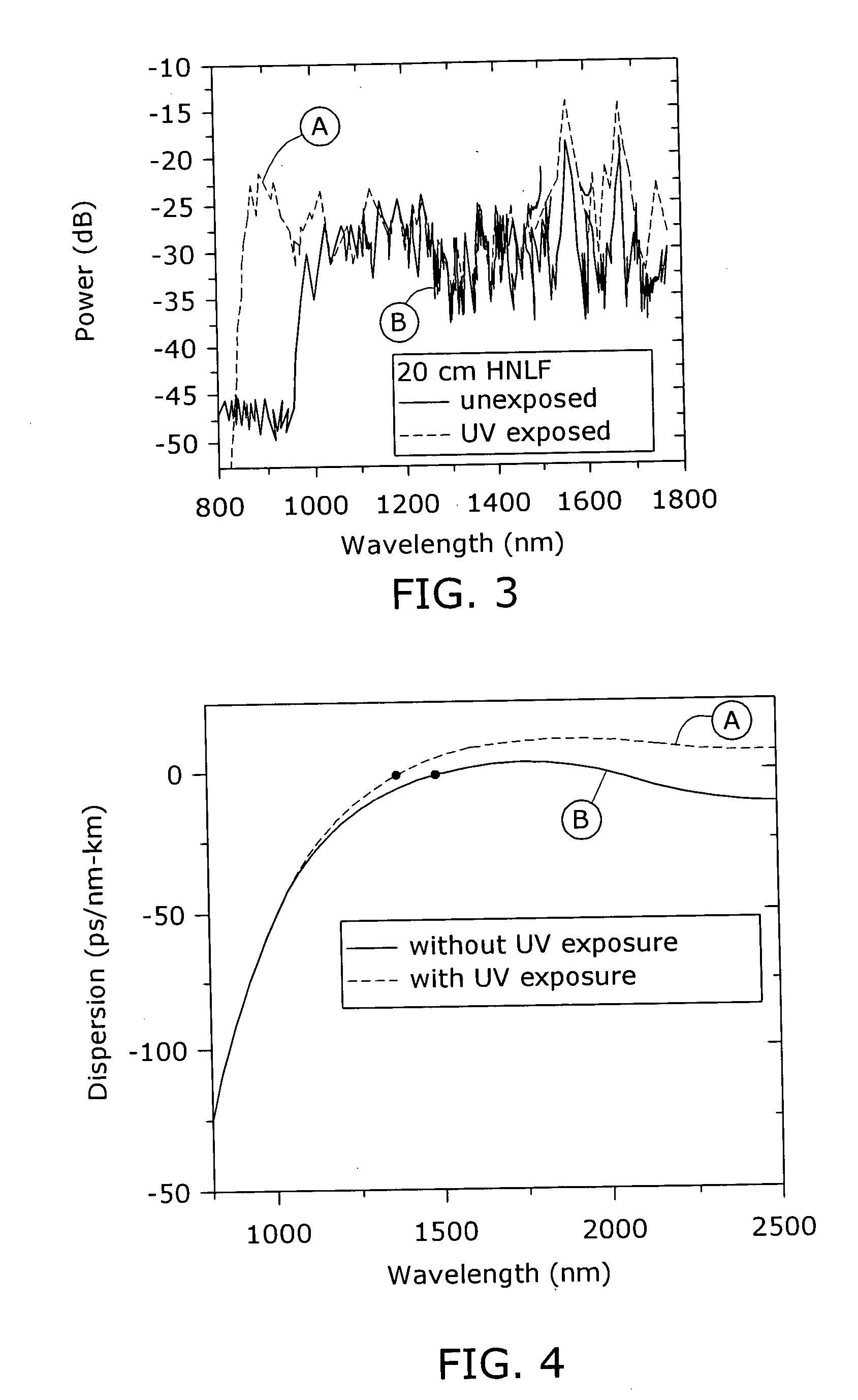
ActiveUS20050226576A1Alteration in dispersionAlteration in effective areaLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringNonlinear fiber
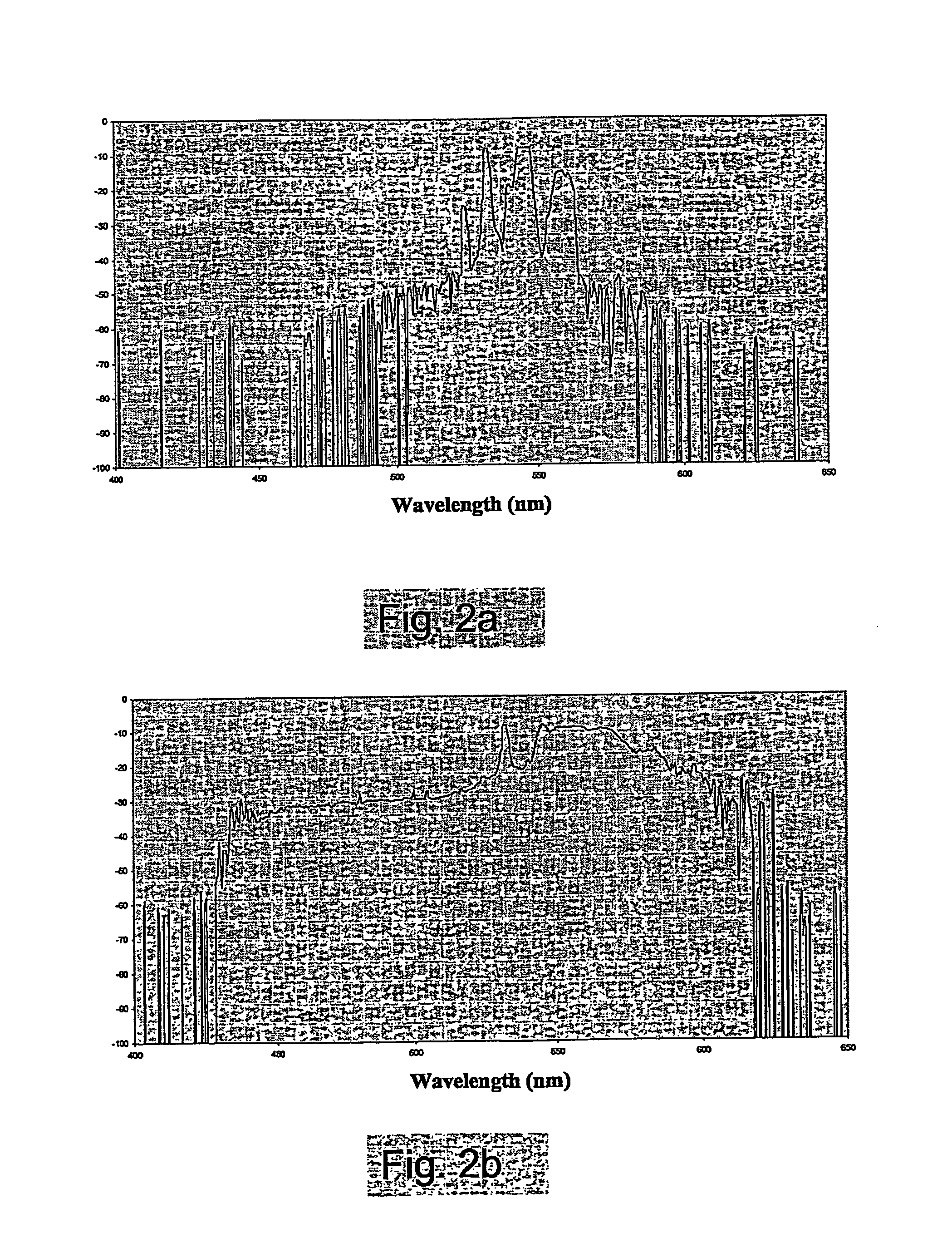
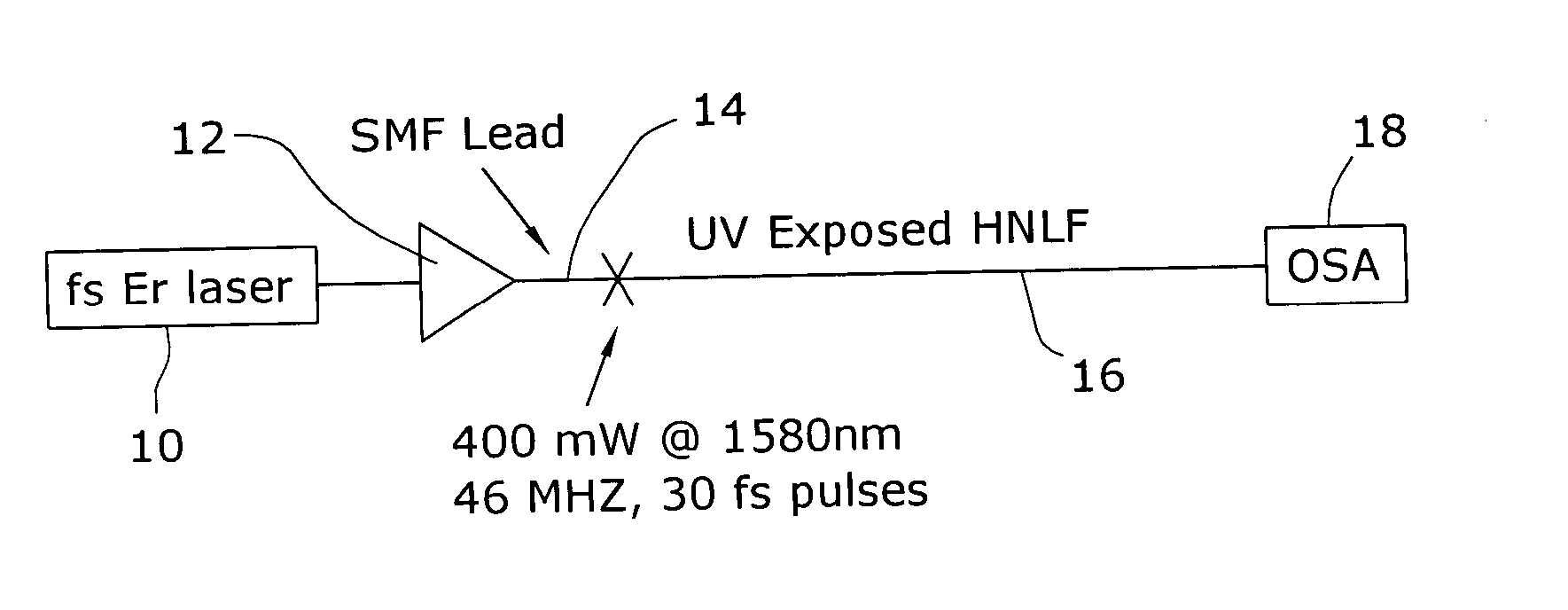
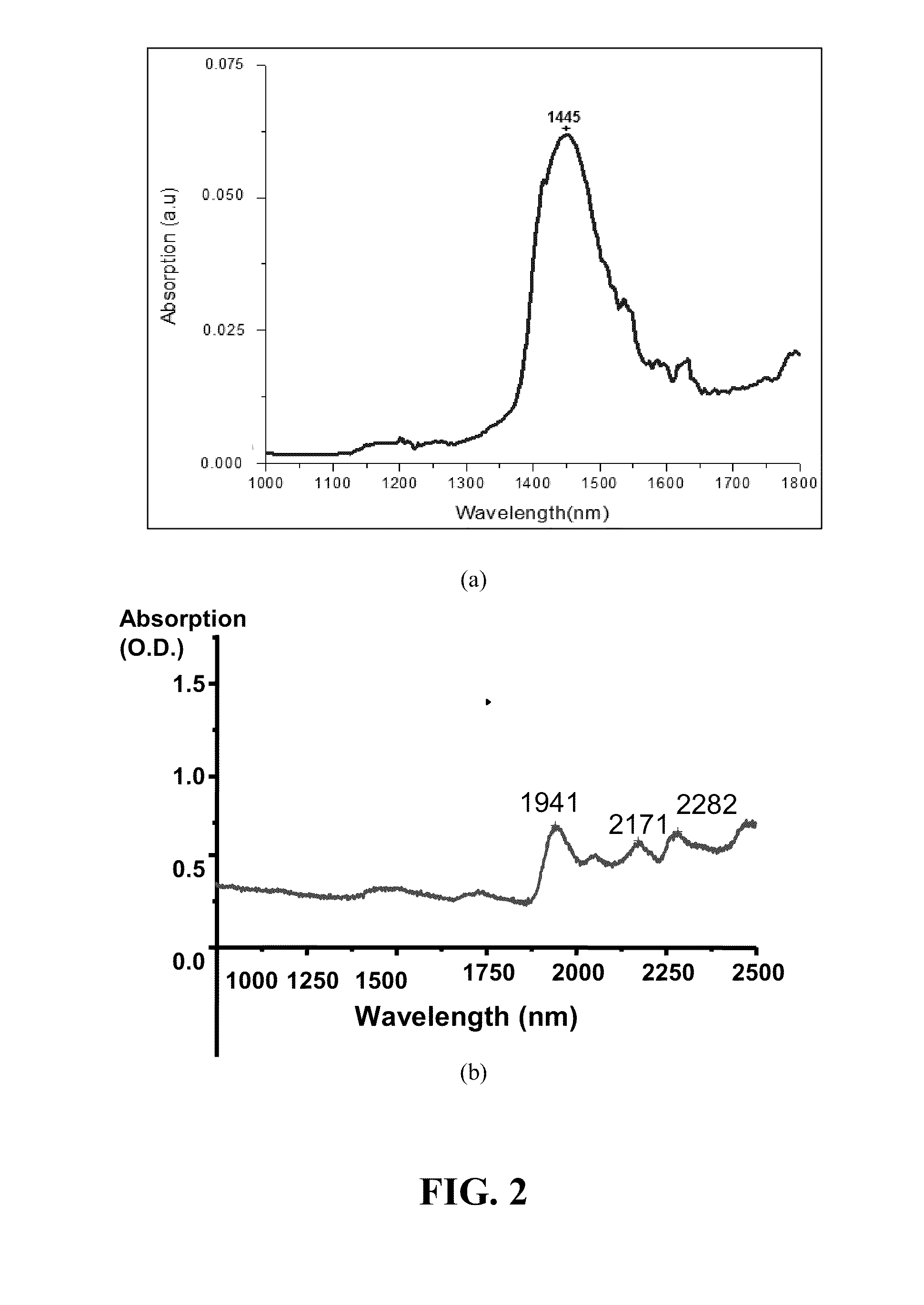
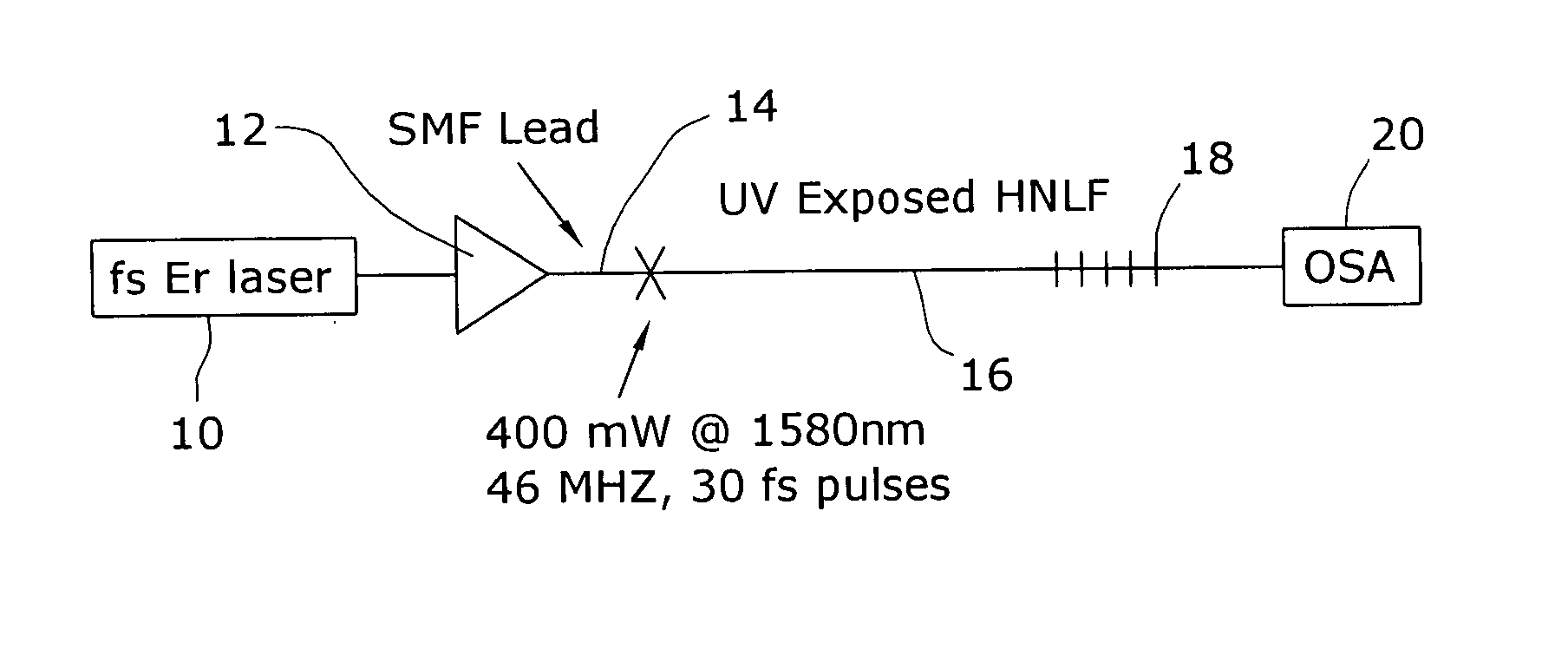
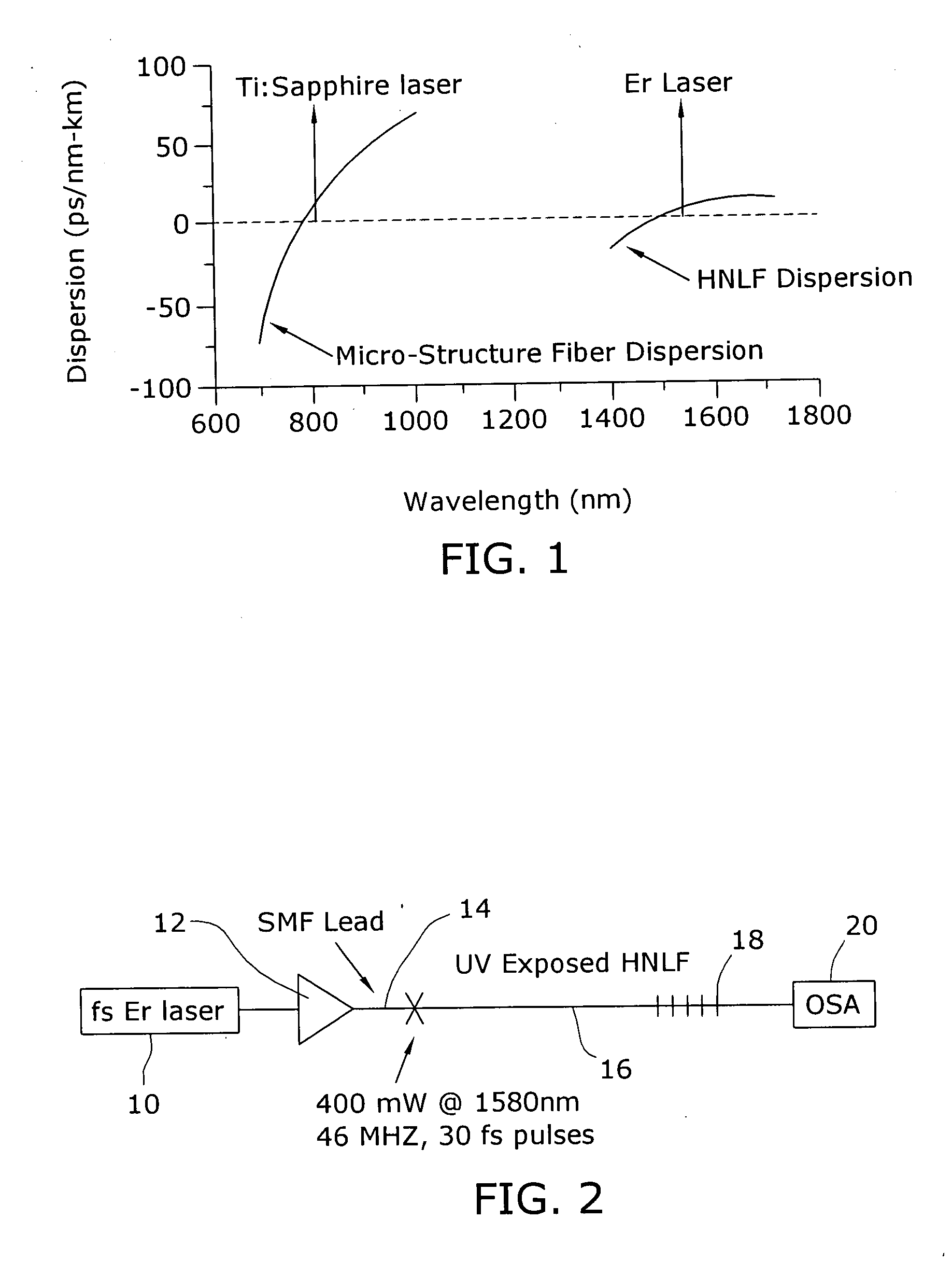
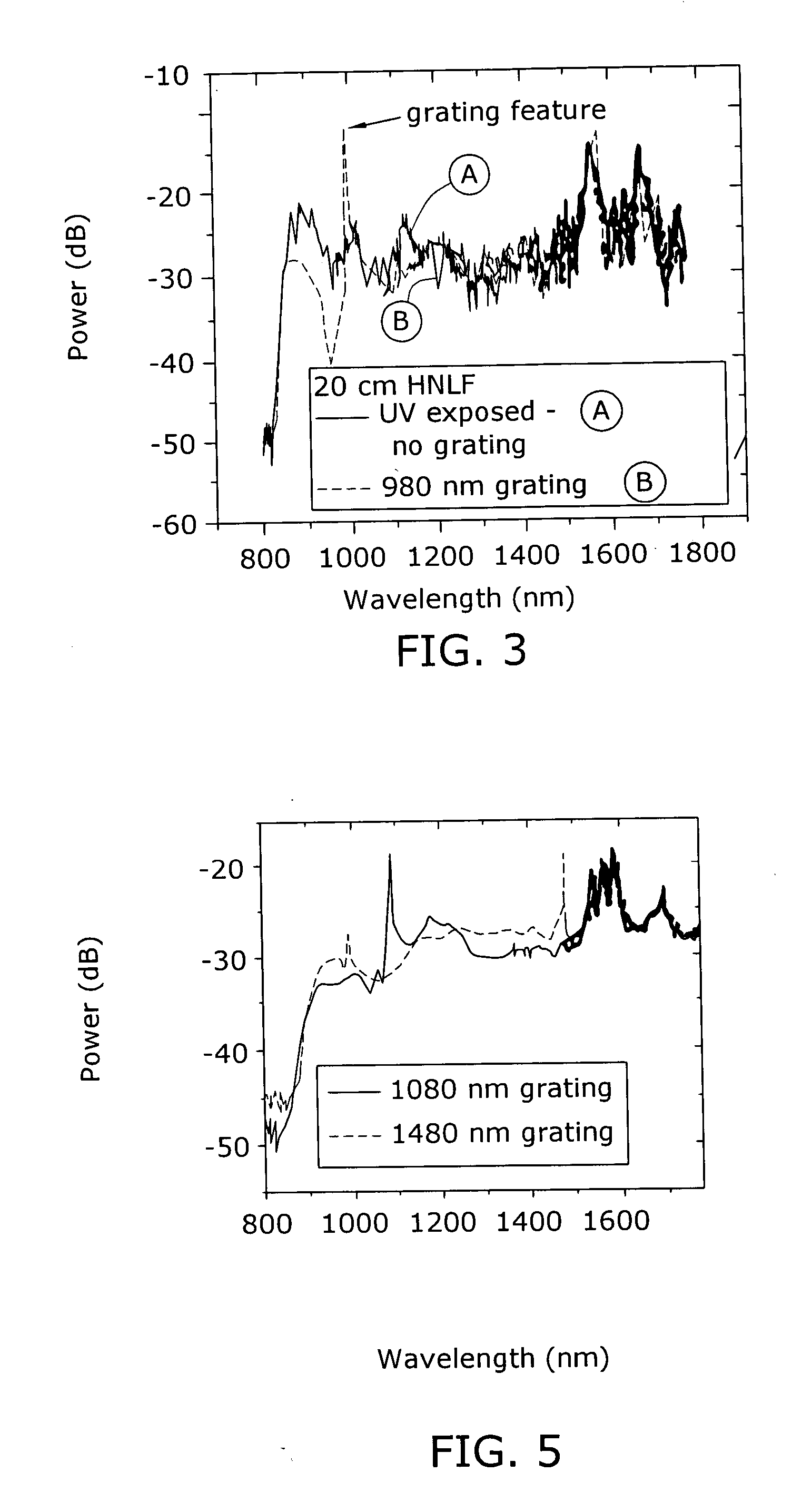
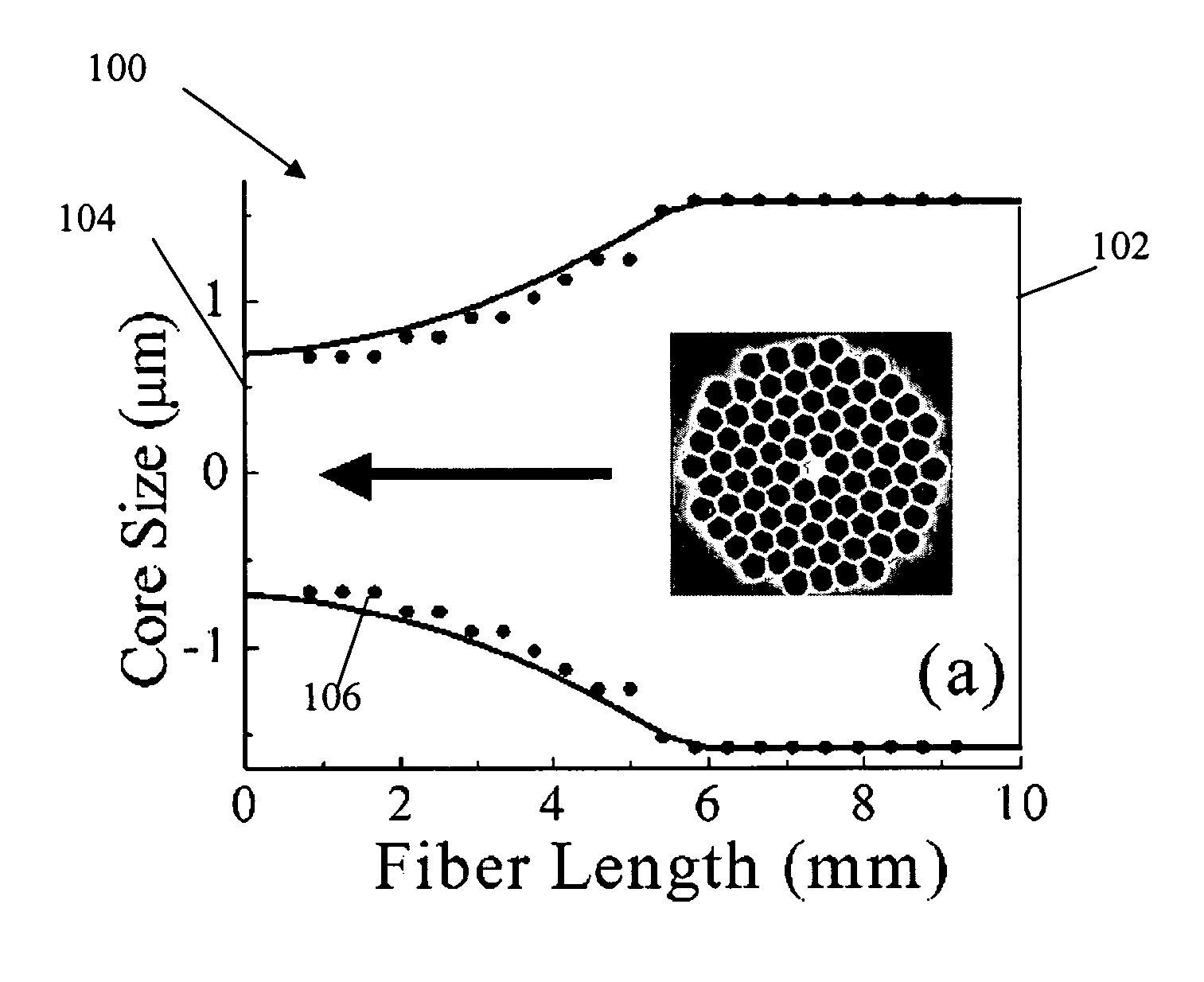
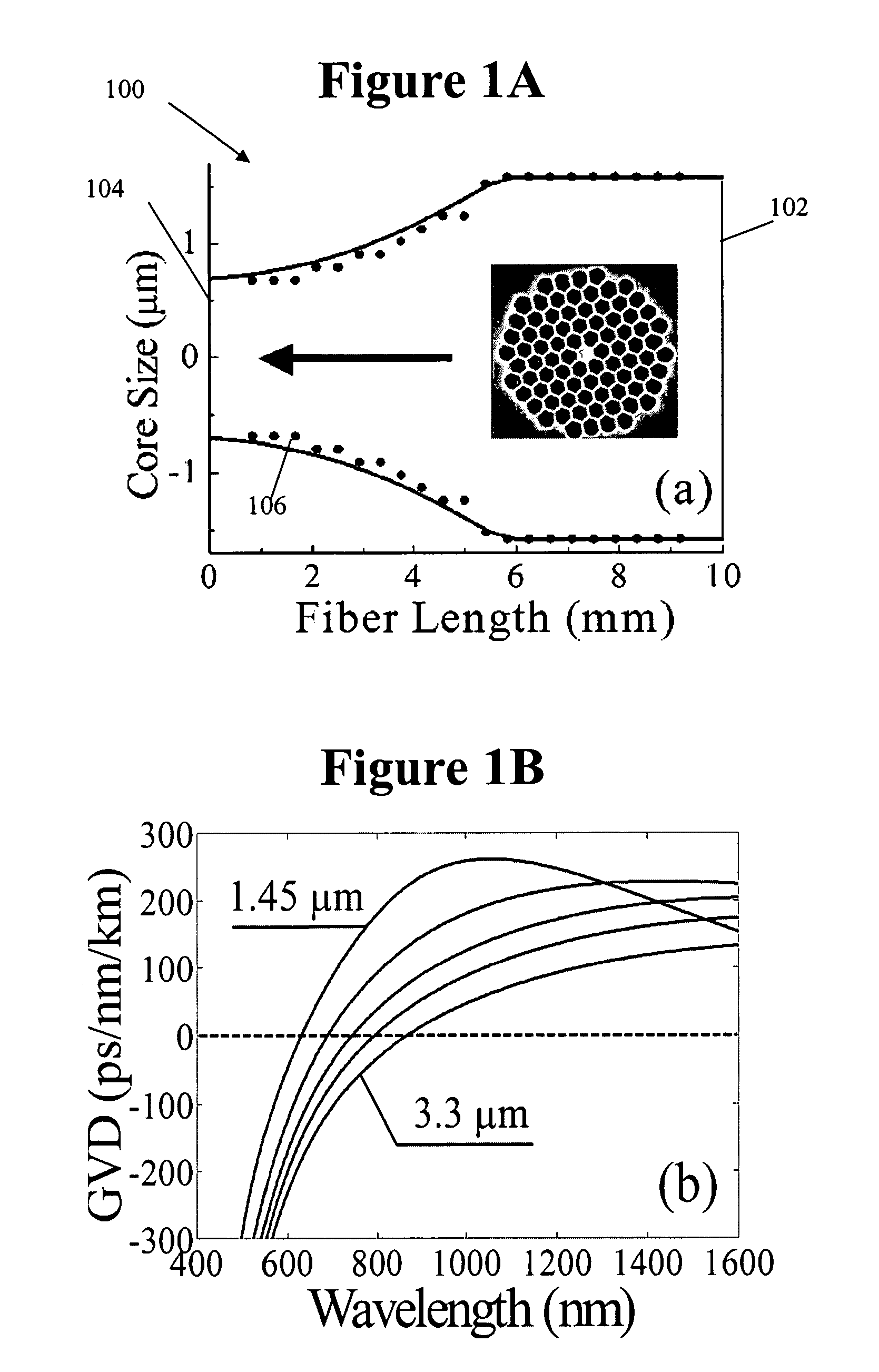
Enhancement of the supercontinuum generation performance of a highly-nonlinear optical fiber (HNLF) is accomplished by performing at least one post-processing treatment on the HNLF. Particularly, UV exposure of the HNLF will modify its dispersion and effective area characteristics so as to increase its supercontinuum bandwidth, without resorting to techniques such as tapering or introducing unwanted reflections into the HNLF. The UV exposure can be uniform, slowly varying or aperiodic along the length of the HNLF, where the radiation will modify the nonlinear properties of the HNLF. Various other methods of altering these properties may be used. The output from the HNLF can be monitored and used to control the post-processing operation in order to achieve a set of desired features in the enhanced supercontinuum spectrum.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Supercontinuum emitting device
A supercontinuum light emitting device comprises an effectively CW light source producing light of wavelength λ1 within a specified bandwidth and a nonlinear fiber optically coupled to the light source. The nonlinear fiber has a plurality of fiber segments with different zero dispersion wavelengths λoi, where each successive fiber segment has zero dispersion wavelength λoi which is larger than the zero dispersion wavelength of the preceding fiber and the zero dispersion wavelength of the first fiber segment is within ±20 nm of λ1.
Owner:CORNING INC
Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopic method and system of super-diffraction limit
The invention is applicable to the field of laser detection and provides a coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopic method and system of a super-diffraction limit. In the method, a spatial resolution of the super-diffraction limit can be obtained through increasing an additional detecting light which is collinearly focused on a sample together with a pump light and a Stokes light at the same time, enabling the additional detecting light to exhaust phonons generated by the pump light and the Stokes light on a periphery of a focal spot so as to form useless CARS (Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) signals, enabling photons in accordance with a phase matching condition in the delayed detecting light to hit phonons at a central area of the focal spot so as to form useful CARS signals, and separating the useless CARS signals. Because supercontinuum laser with a broad band is adopted as the pump light and the Stokes light, a complete CARS spectrum signal of a molecule is obtained to image the whole molecule.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
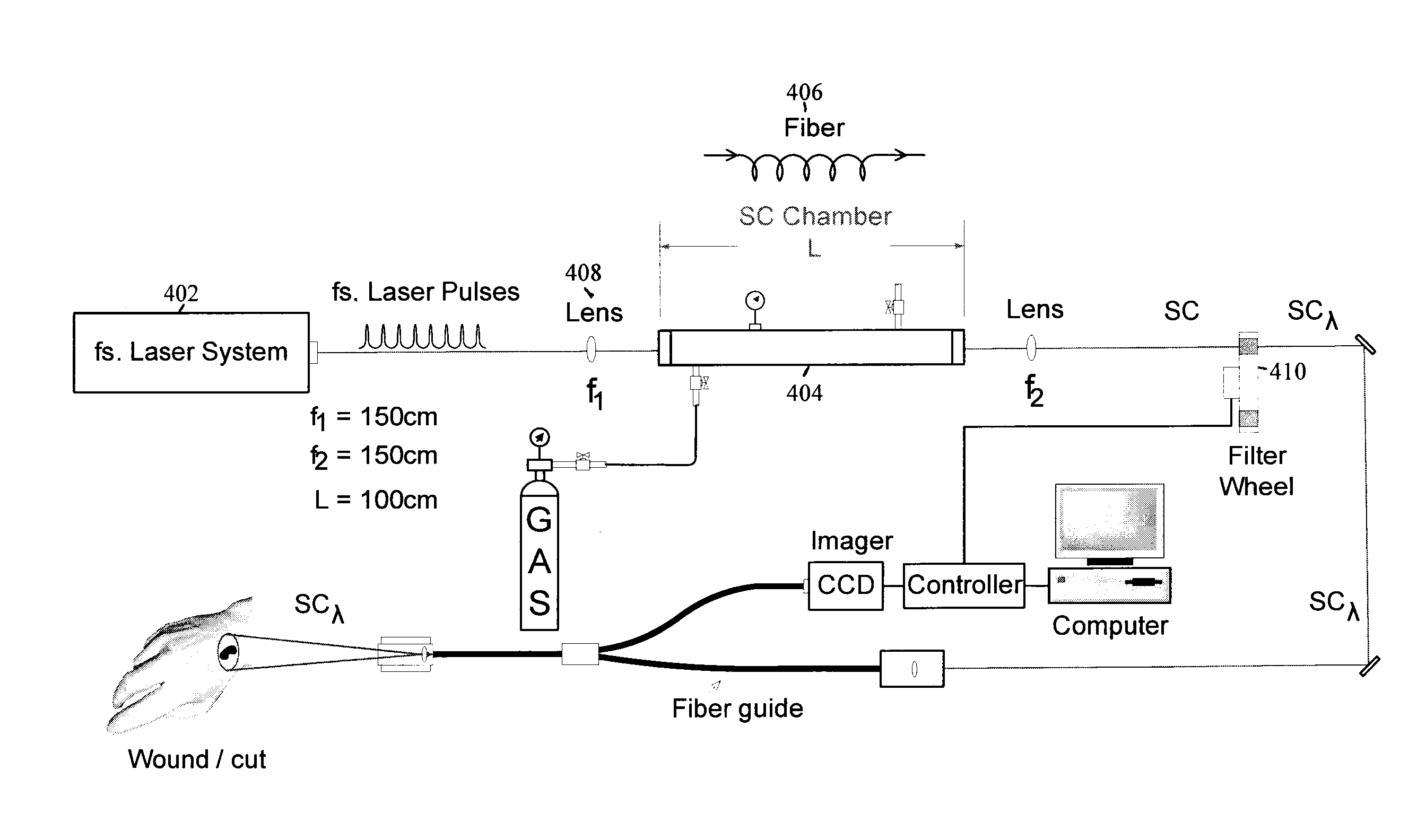
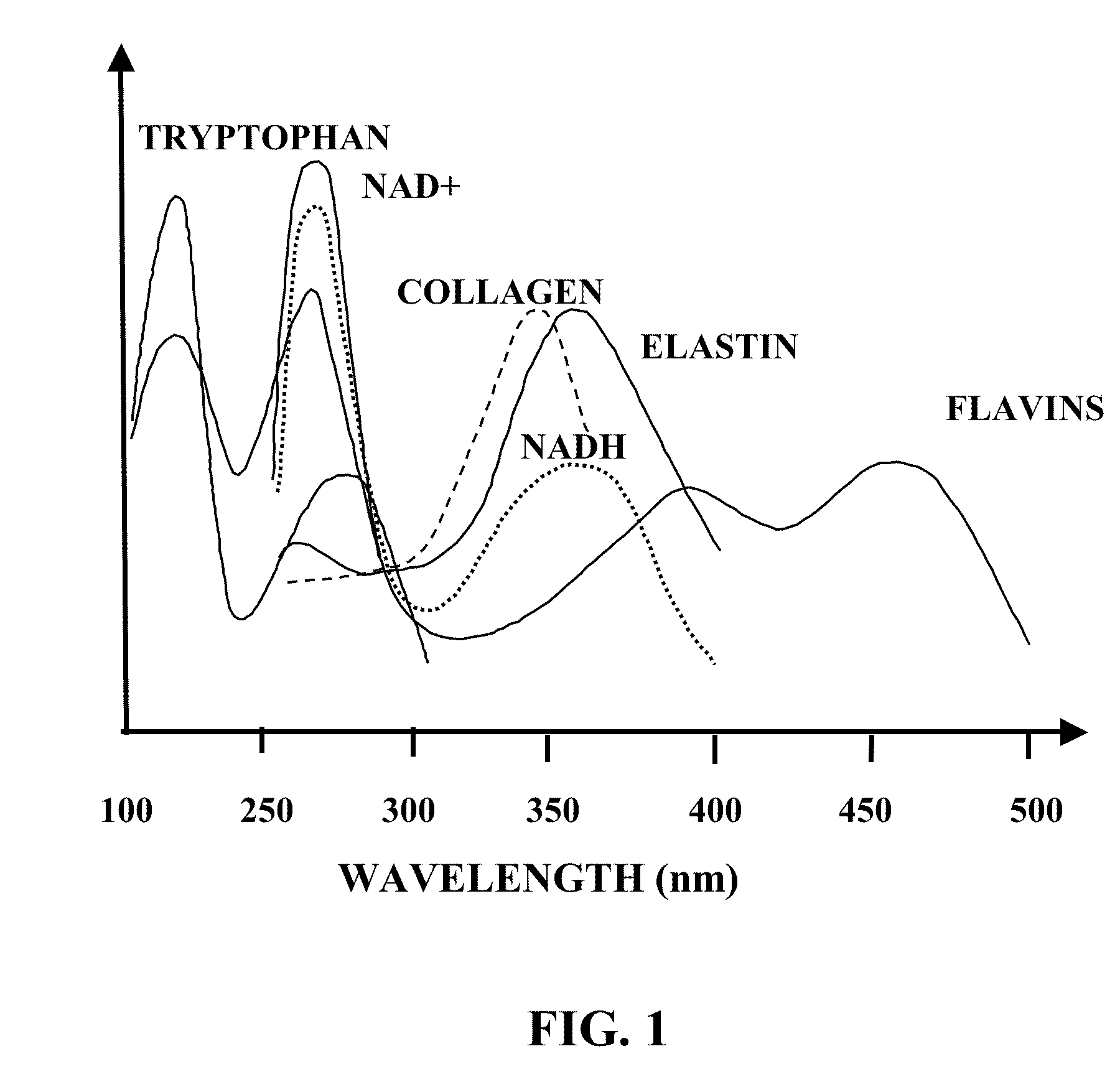
Method and apparatus for producing supercontinuum light for medical and biological applications
A method and an apparatus are provided for producing SuperContinuum (SC) light for medical and biological applications is provided. Pulses are focused from a laser system into at least one of a pressurized cell and one or more fibers. A pump pulse is converted into the SC light at a specified rate of repetition. The SC light is applied at the specified rate of repetition to tissue for medical and biological applications.
Owner:ALFANO ROBERT +1
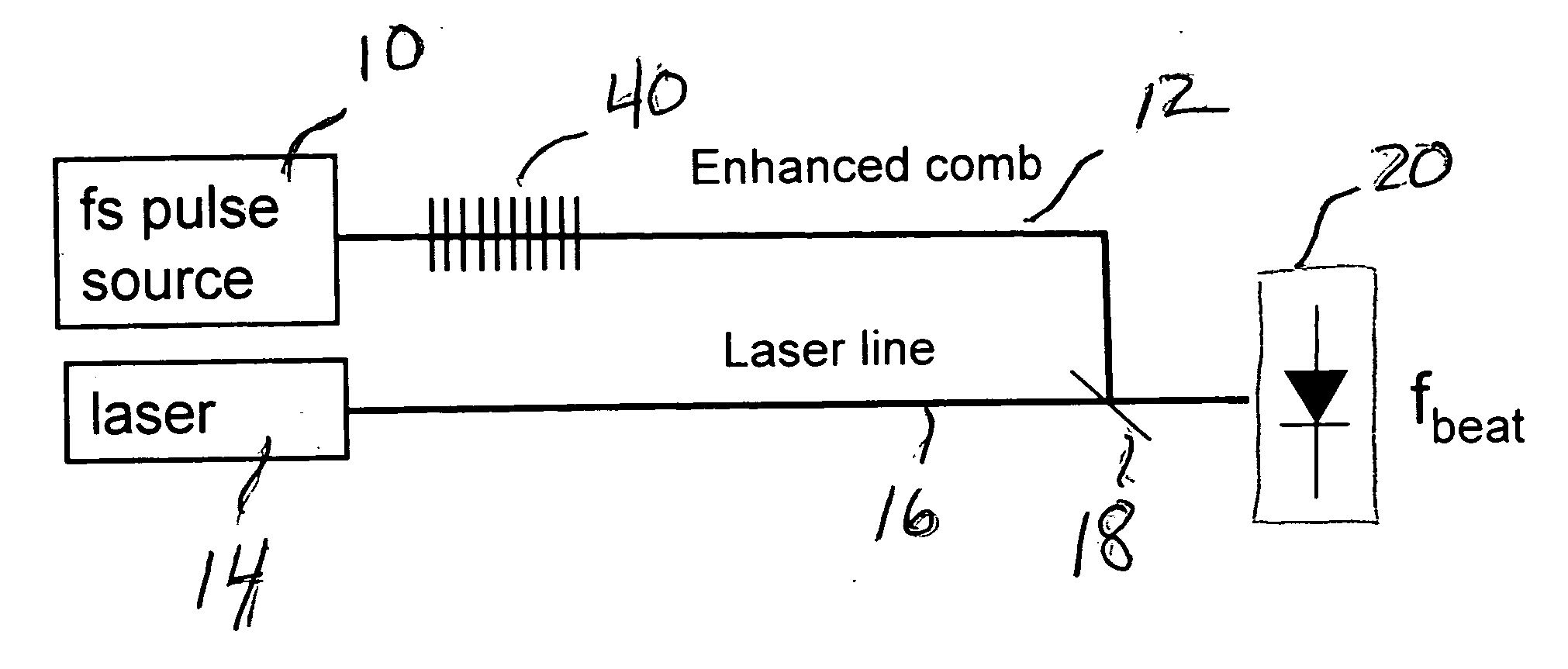
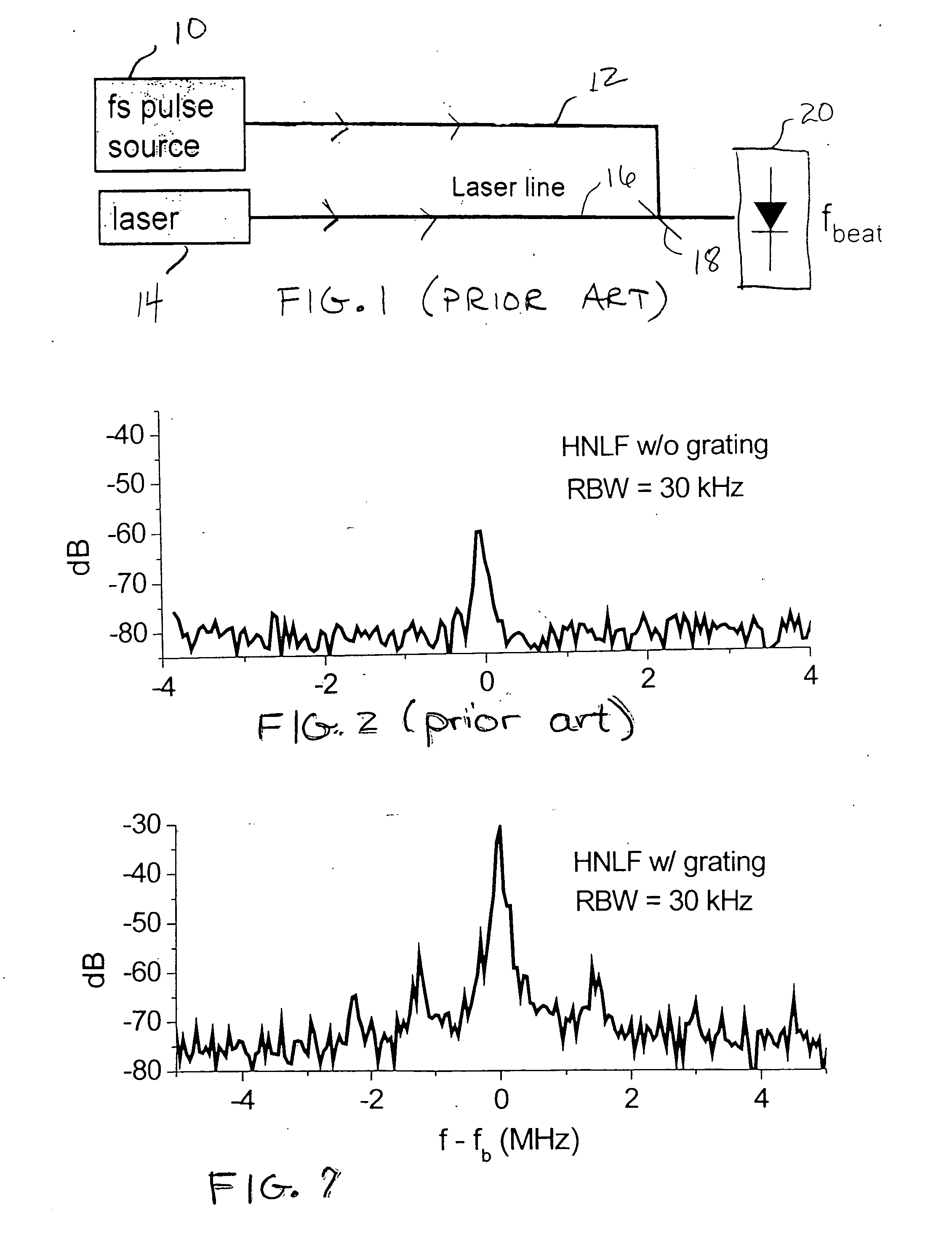
Enhanced supercontinuum generation in highly nonlinear fibers using strong bragg gratings
ActiveUS20050226575A1Enhance generated supercontinuumGenerate and outputWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesGratingResonance
Enhancement of the supercontinuum generation performance of a highly-nonlinear optical fiber (HNLF) is accomplished by incorporating at least one Bragg grating structure in the HNLF. The Bragg grating results in reflecting a core-guided signal into signal which also remains core-guided. The supercontinuum radiation generated by such an arrangement will exhibit a substantial peak in its energy at the grating resonance of the Bragg grating and a region of increased radiation in a narrow wavelength band on the long wavelength side of the peak. A number of such Bragg gratings may be formed so as to “tailor” the enhancements provided in the supercontinuum radiation. Various, well-known Bragg grating modifications (tuning, chirped, blazed, etc.) may also be used in the inventive structure to enhance the generated supercontinuum.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC +1
Mobile terawatt femtosecond laser system (MTFLS) for long range spectral sensing and identification of bioaerosols and chemical agents in the atmosphere
InactiveUS20080180655A1Reduce probabilitySimultaneous measurementLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryFilamentationUltraviolet
The present invention relates to a system for detection and identification of airborne biological, chemical and / or nuclear threats such as toxins, spores, bacteria, and viruses in real time at distances from a few meters to several kilometers. Compact femtosecond terawatt laser technology is combined with spectroscopic and mathematical methods for spectral sensing of airborne warfare agents such as bio-aerosols. Trigger sensors and standoff devices based on mobile terawatt femtosecond laser systems are provided that may be placed at strategic monitoring locations. Furthermore, the invention relates to the propagation of airborne ultra-short, ultra-intense laser pulses giving rise to plasma channels (filamentation) producing white light supercontinuum ranging from the ultraviolet (UV), visible (VIS), near infra-red (NIR) and middle infra-red (MIR). According to this invention, the supercontinuum can be directly produced in a particle cloud and hence is uniquely suitable for multi-spectral long-range atmospheric agent and radioactive isotope detection.
Owner:APPLIED PHOTONICS WORLDWIDE
Method and optical fiber device for production of low noise continuum
InactiveUS20060159398A1New design degreeCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesLow noisePolarization-maintaining optical fiber
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Stabilized optical fiber continuum frequency combs using post-processed highly nonlinear fibers
ActiveUS20060251424A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioMaintain propertiesElectromagnetic transmittersLight demodulationFrequency combNonlinear fiber
An arrangement for generating beat notes with a relatively high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) utilizes a pulsed laser source coupled into a section of post-processed highly-nonlinear optical fiber (HNLF) to generate a frequency comb having one or more regions of enhanced spectral power. A second laser signal source is overlapped with the frequency comb to form one or more “beat notes” at difference frequencies(y) between the second source and the continuum comb. By virtue of the post-processing, areas of spectral enhancement are formed along the comb, and are positioned to interact with the second laser signal to generate optical beat notes. The second laser signal may be from an external source (forming beat notes from a signal “outside” of the comb), or may be a frequency-multiplied version of the generated supercontinuum (forming beat notes from a signal “within” the comb).
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
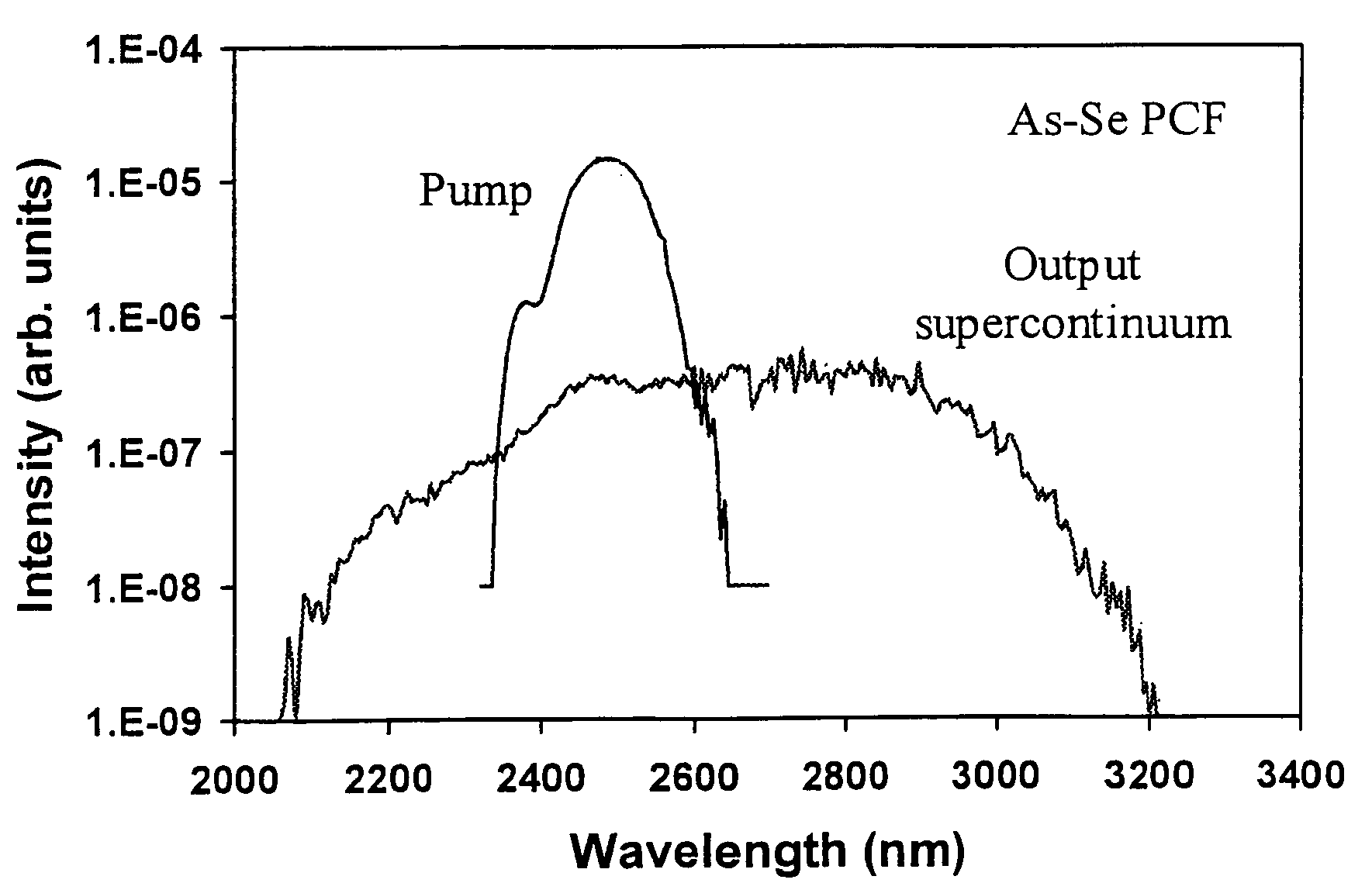
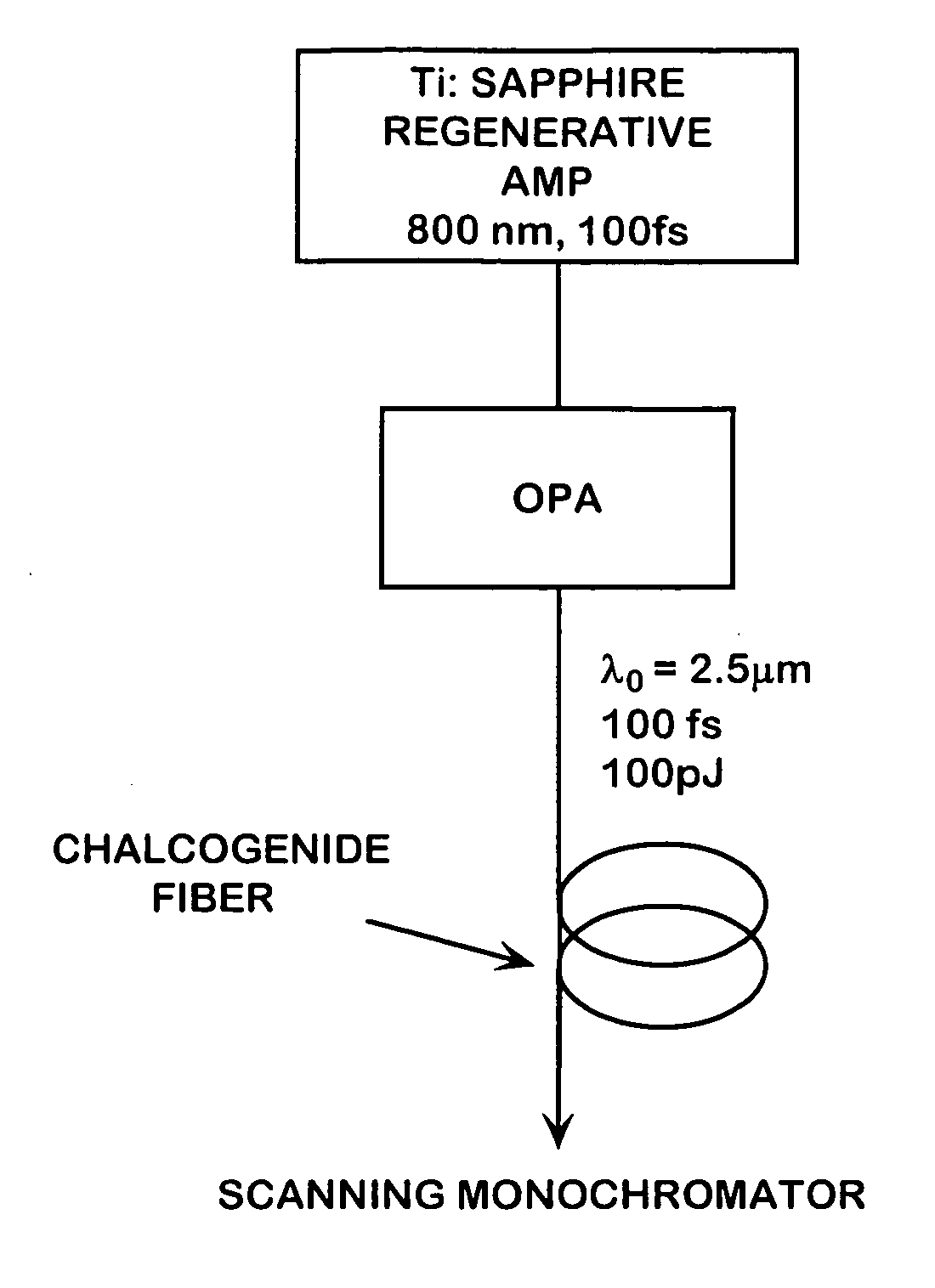
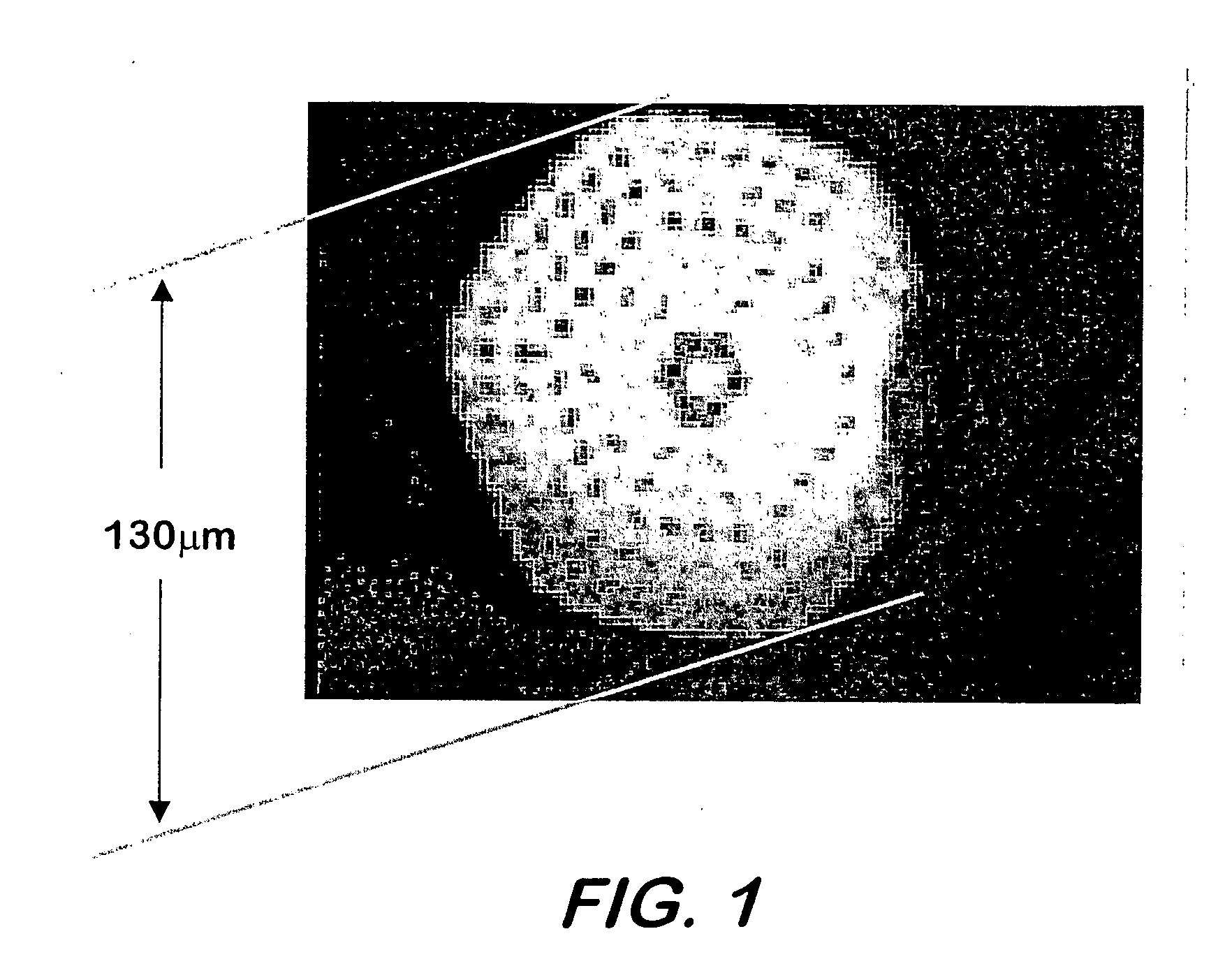
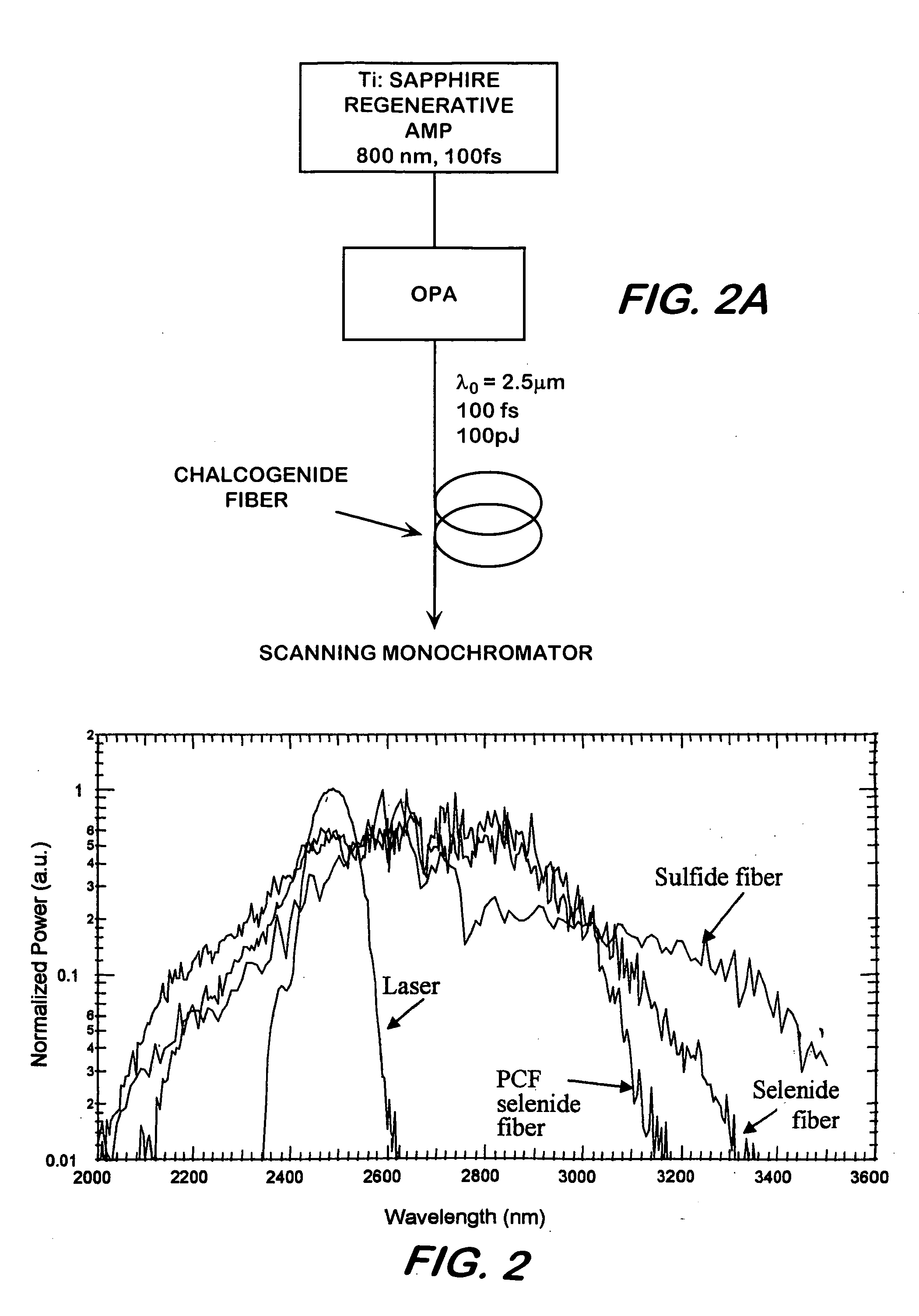
IR supercontinuum source
ActiveUS7133590B2High bandwidthBroaden the spectral widthLaser detailsLight demodulationFiberLight signal
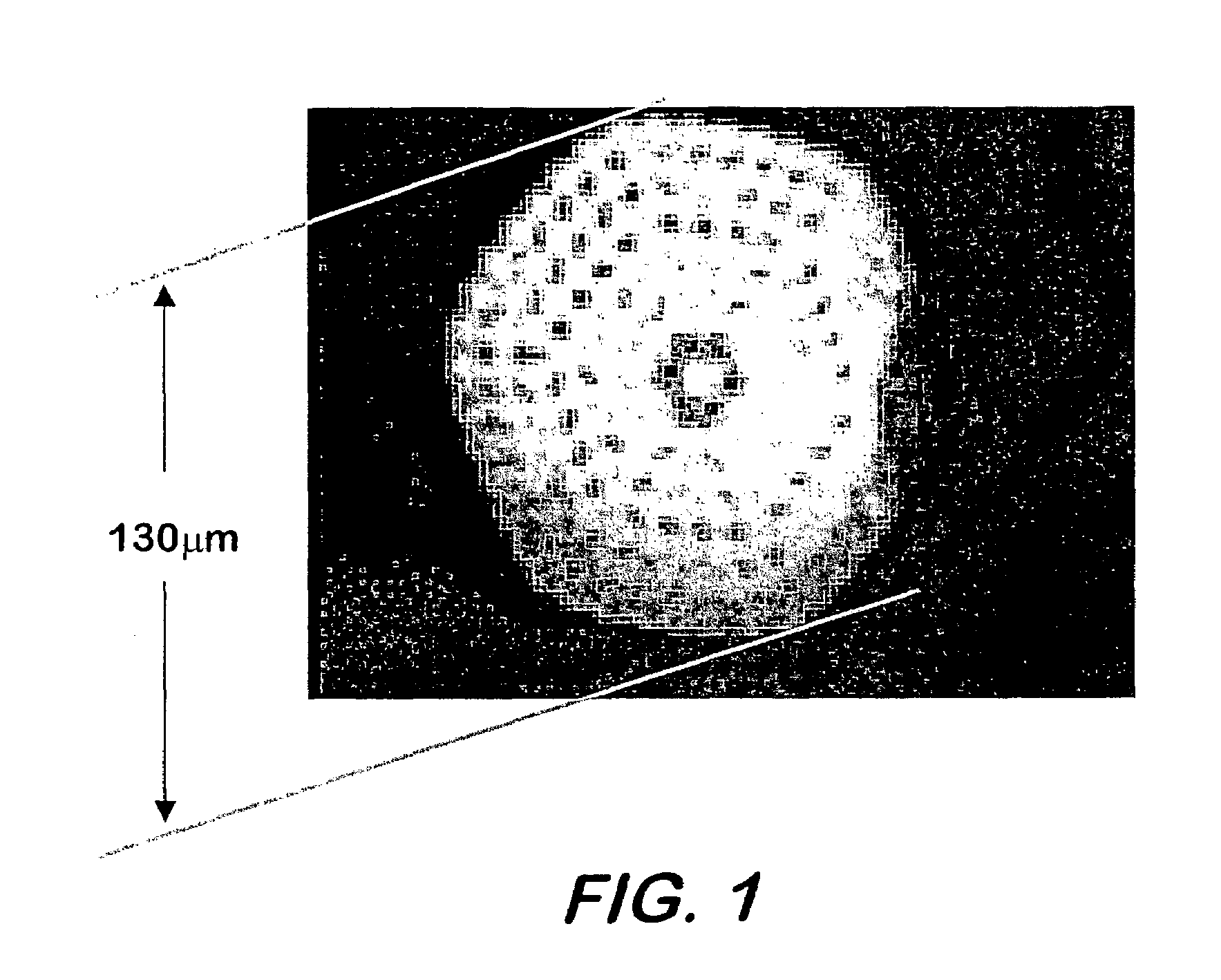
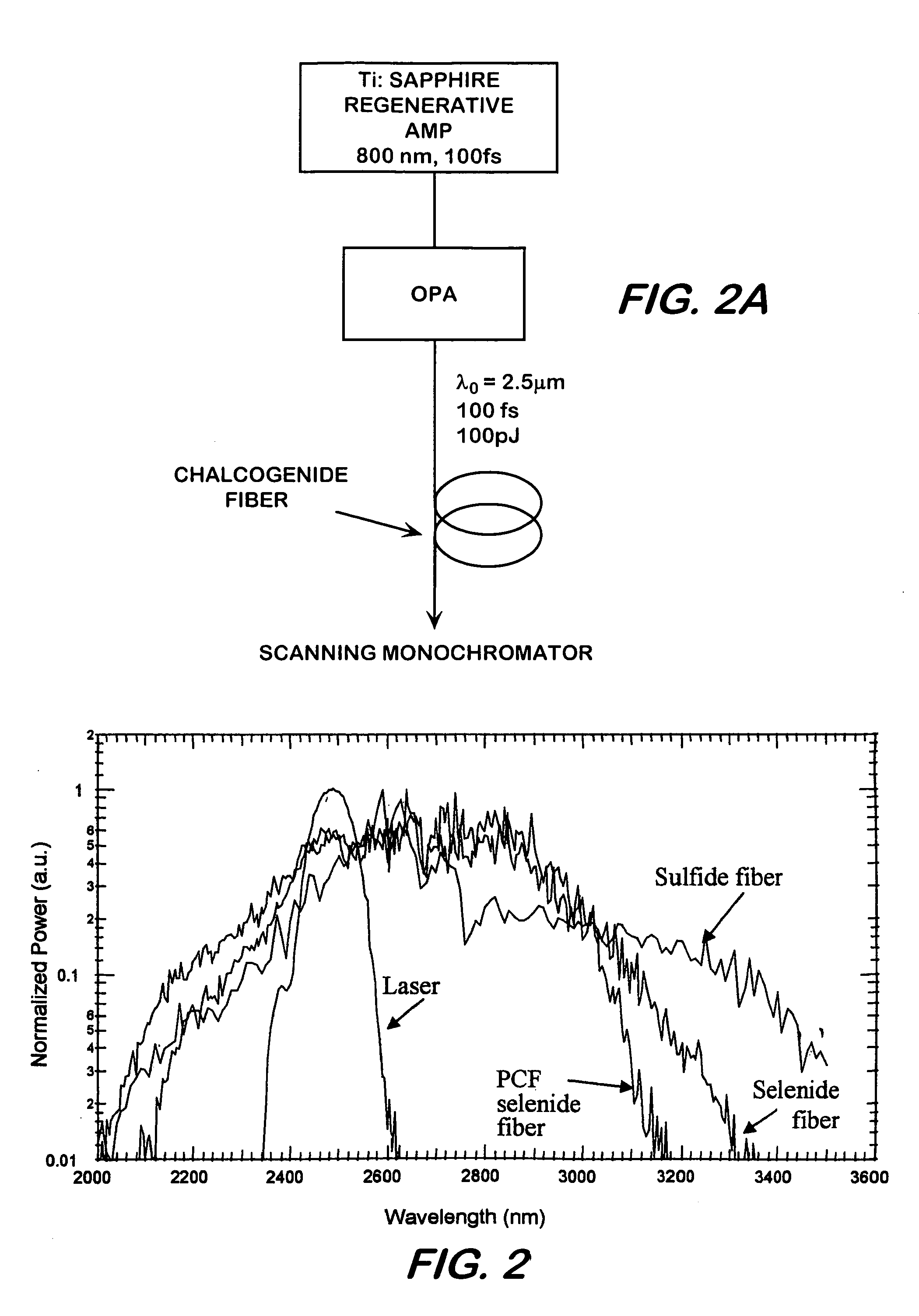
This invention pertains to a device for broadening optical wavelength in the 2–14 μm region comprising a light source and a highly nonlinear chalcogenide fiber associated therewith whereby a light signal is passed from the light source into the fiber wherein and through interactions between the light signal and the material, bandwidth of the light signal is broadened in the 2–14 μm region.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +2
Method and optical fiber device for production of low noise continuum
InactiveUS7403688B2Reduce noiseCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesLow noisePolarization-maintaining optical fiber
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Tunable optical supercontinuum enhancement
InactiveUS20100067555A1Increase intensityImprove accuracyLaser detailsOptical light guidesWaveguideLaser
A method and apparatus for providing optical supercontinuum. The method comprises creating a spectrally narrow phase feature within a supercontinuum spectrum produced from a laser pulse that has been subjected to supercontinuum generation, thereby producing a modified supercontinuum spectrum, and propagating the modified supercontinuum spectrum through an optical waveguide that is suitable for supercontinuum generation, thereby further modifying the modified supercontinuum spectrum. The method may include modifying the modified supercontinuum spectrum by increasing its energy in a vicinity of the phase feature.
Owner:THE UNIV OF SYDNEY
IR supercontinuum source
ActiveUS20060210227A1High bandwidthBroaden the spectral widthLight demodulationOptical light guidesFiberLight signal
This invention pertains to a device for broadening optical wavelength in the 2-14 μm region comprising a light source and a highly nonlinear chalcogenide fiber associated therewith whereby a light signal is passed from the light source into the fiber wherein and through interactions between the light signal and the material, bandwidth of the light signal is broadened in the 2-14 μm region.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +2
Ir fiber broadband mid-ir light source
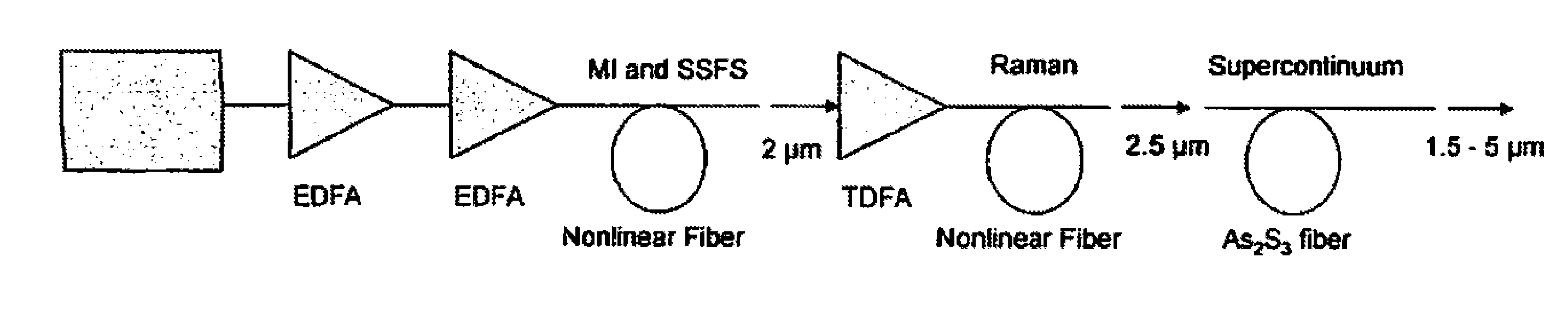
ActiveUS20130188240A1Power scalableCompact and rugged and highly efficientLight demodulationNon-linear opticsBroadbandLength wave
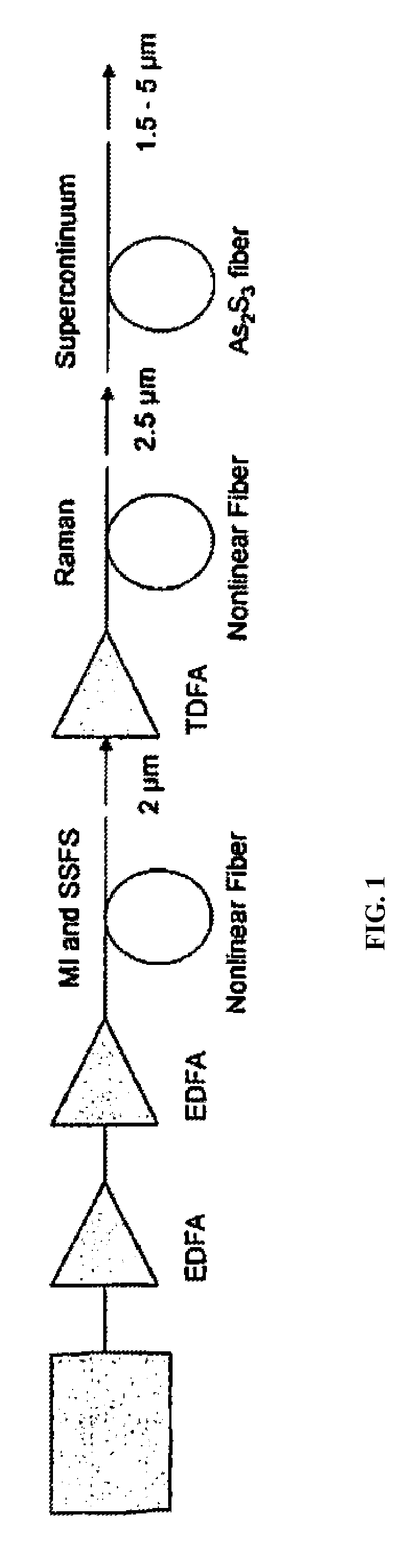
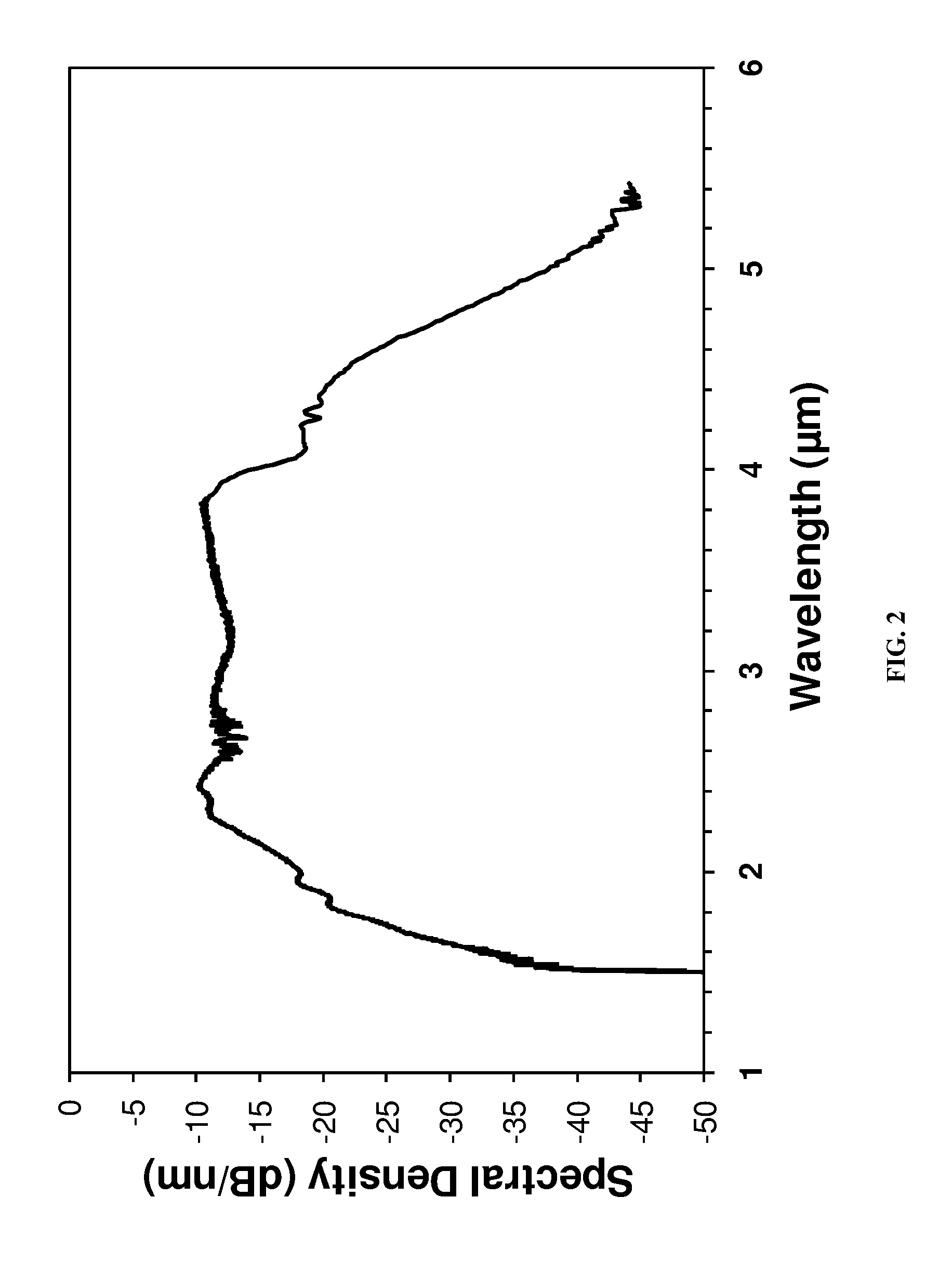
A method of generating a supercontinuum in chalcogenide fiber with a pump light comprising a short pulse fiber laser or diode laser operating with a wavelength of 1.0μm or greater that is wavelength shifted through a nonlinear fiber one or more times and amplified one or more times and launched into a chalcogenide fiber whereby the spectrum is broadened in the chalcogenide fiber through various nonlinear processes to generate a supercontinuum within the mid-IR from 1.5 to greater than 5μm.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
High-power high-efficiency supercontinuum source
InactiveCN103022867AIncrease output powerLow costCladded optical fibreActive medium shape and constructionManufacturing technologyPicosecond
The invention provides a high-power high-efficiency supercontinuum source. By reasonably designing characteristics of photonic crystal fibers, long-pulse pump laser (picosecond, nanosecond laser) acts on a normal dispersion area for the photonic crystal fibers, the central wavelengths of stimulated front stages of Raman-Stokes peaks are positioned in an abnormal dispersion area close to a zero dispersion point of the photonic crystal fibers, and the stimulated Raman-Stokes laser peaks serve as a new pump source for stimulating supercontinuum and meet the requirement of an abnormal dispersion pump mechanism. The supercontinuum source simultaneously has the advantages of a normal dispersion pump mechanism and the abnormal dispersion pump mechanism, and high average output power and continuum output with high optical conversion efficiency and a wider supercontinuum range can be realized. By the aid of mature high-power fiber laser technology, photonic crystal fiber manufacturing technology and photonic crystal fiber post-treatment technology, system cost is reduced, and industrial production and application are facilitated.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Supercontinuum emitting device
A supercontinuum light emitting device comprises an effectively CW light source producing light of wavelength λ1 within a specified bandwidth and a nonlinear fiber optically coupled to the light source. The nonlinear fiber has a plurality of fiber segments with different zero dispersion wavelengths λoi, where each successive fiber segment has zero dispersion wavelength λoi which is larger than the zero dispersion wavelength of the preceding fiber and the zero dispersion wavelength of the first fiber segment is within ±20 nm of λ1.
Owner:CORNING INC
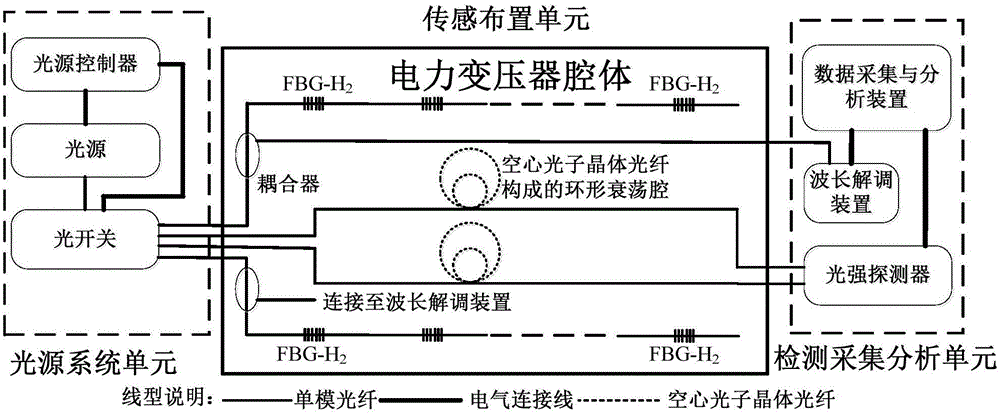
Detection device of dissolved gases in transformer oil based on infrared spectrum absorption
ActiveCN104914066ADoes not consume dissolvedReduce volumeMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberInfrared
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric-power equipment detection, and in particular, relates to a detection device of dissolved gases in transformer oil based on infrared spectrum absorption. The device includes a light source system unit, a sensing arrangement unit and a detection acquisition and analysis unit; the light source system unit is composed of a high-power supercontinuum broadband light source, a light source controller and a photoswitch and is used for realizing output multiplexing control of the light source; the sensing arrangement unit is formed by arranging one sensing path of fiber Bragg grating hydrogen sensor series-connection wavelength division multiplexing and the other one sensing path of hollow photonic crystal optical fiber internal spectrum absorption sensing in a cavity body of an oil-immersed power transformer; the detection acquisition and analysis unit is composed of a wavelength demodulation device, a light intensity detector and a data acquisition and analysis device, the wavelength offset and the spectral absorption intensity of fiber Bragg grating hydrogen sensors are detected, and the data acquisition and analysis device records data and types and contents of corresponding fault gases are obtained by calculation; and on the basis, insulation conditions of the transformer oil are evaluated, positioned, analyzed and forecasted.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +1
Optical frequency up-conversion of femtosecond pulses into targeted single bands in the visible and ultraviolet
An apparatus and methods for generating a substantially supercontinuum-free widely-tunable multimilliwatt source of radiation characterized by a narrowband line profile. The apparatus and methods employ nonlinear optical mechanisms in a nonlinear photonic crystal fiber (PCF) by detuning the wavelength of a pump laser to a significant extent relative to the zero-dispersion wavelength (ZDW) of the PCF. Optical phenomena employed for the selective up-conversion in the PCF include, but are not limited to, four-wave mixing and Cherenkov radiation. Tunability is achieved by varying pump wavelength and power and by substituting different types of PCFs characterized by specified dispersion properties.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
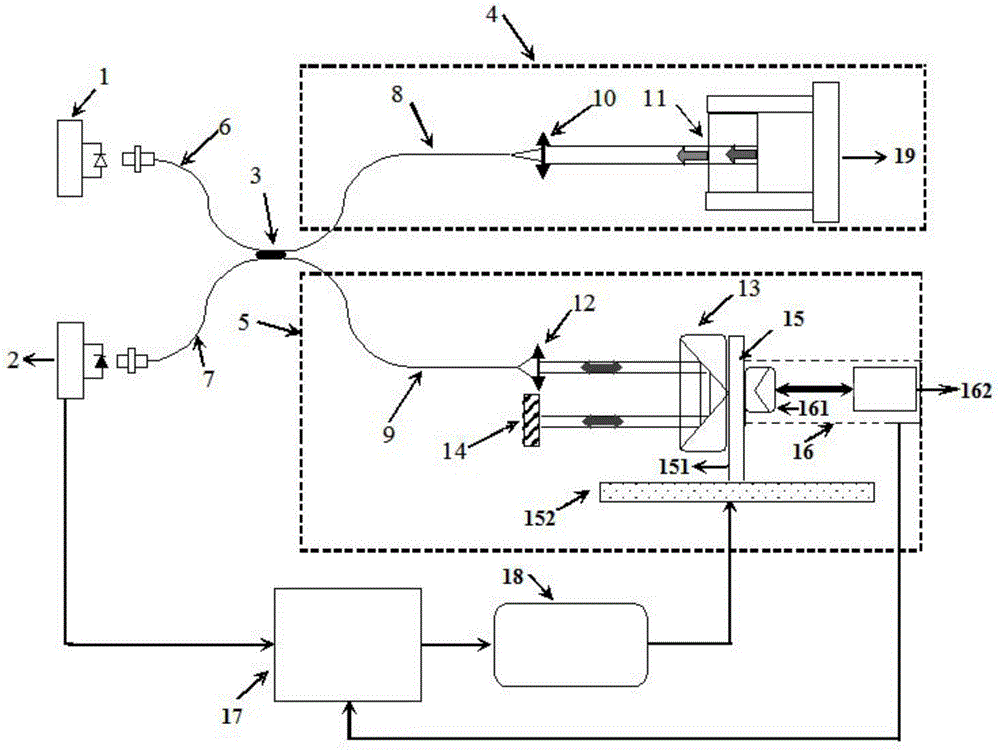
White-light interference lens center thickness measuring system and method
ActiveCN104154869AShort coherence lengthAccurate reading of center positionUsing optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsPlane mirror
The invention discloses a white-light interference lens center thickness measuring system and a method, and belongs to the technical field of optical precise measurement, so as to solve the technical problems that the prior lens center thickness measuring device is low in measuring precision and small in dynamic measuring range. The white-light interference lens center thickness measuring system comprises a supercontinuum source, a photodetector, a 1:1 optical fiber coupler, a measuring arm, a reference arm, a first optical fiber, a second optical fiber and a data processing unit, wherein the measuring arm comprises a third optical fiber and a focusing lens; and the reference arm comprises a fourth optical fiber, a self-focusing lens, a scanning angle reflector, a plane mirror, a displacement mechanism and a length-measuring interferometer system. The precision of the system can reach 0.2 mum(3sigma) and the dynamic range can reach 1.5m.
Owner:BEIJING GUOWANG OPTICAL TECH CO LTD
Compression of Polarized Supercontinuum Pulses Generated in Birefringent All Normal-Dispersion Photonic Crystal Fiber
Methods and apparatus for generating ultrashort optical pulses. Polarized pulses of a near-infrared source are launched substantially along a principle axis of a birefringent photonic crystal fiber characterized by normal dispersion at all wavelengths of transmission of the photonic crystal fiber. Supercontinuum pulses are generated from the photonic crystal fiber and compressed to form compressed pulses. Highly polarized supercontinuum pulses provide for transform-limited compressed pulse durations.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
High average power full optical fiber intermediate infrared supercontinuum light source
InactiveCN103825164AEnhance nonlinear effectsImprove stabilityLaser arrangementsActive medium shape and constructionHigh power lasersFrequency measurements
The invention discloses a high average power full optical fiber intermediate infrared supercontinuum light source. The light source comprises a pulse pumping source with an output pigtail, a single mode passive optical fiber, at least one level of thulium doped optical fiber amplifier, a second optical fiber combiner and an er-doped fluoride optical fiber, wherein the pulse pumping source with the output pigtail, the single mode passive optical fiber, at least one level of thulium doped optical fiber amplifier, the second optical fiber combiner and the er-doped fluoride optical fiber are successively connected along a light path. A second pumping source and the second input end of the second optical fiber combiner are connected. According to the invention, a high power laser diode is used to carry out pumping on the er-doped fluoride optical fiber, thus a spectrum is broadened in the optical fiber due to a nonlinear effect and is strengthened due to high gain produced by pumping near 2.7 microns; the nonlinear effect in an intermediate infrared wave band is further stimulated, thus a eventually acquired supercontinuum has a wide wavelength coverage area and high average power; due to the adoption of a full optical fiber structure, integration and commercialization can be easily carried out; and the light source has a wide application prospect in frequency measurement, wavelength division multiplexing and other fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
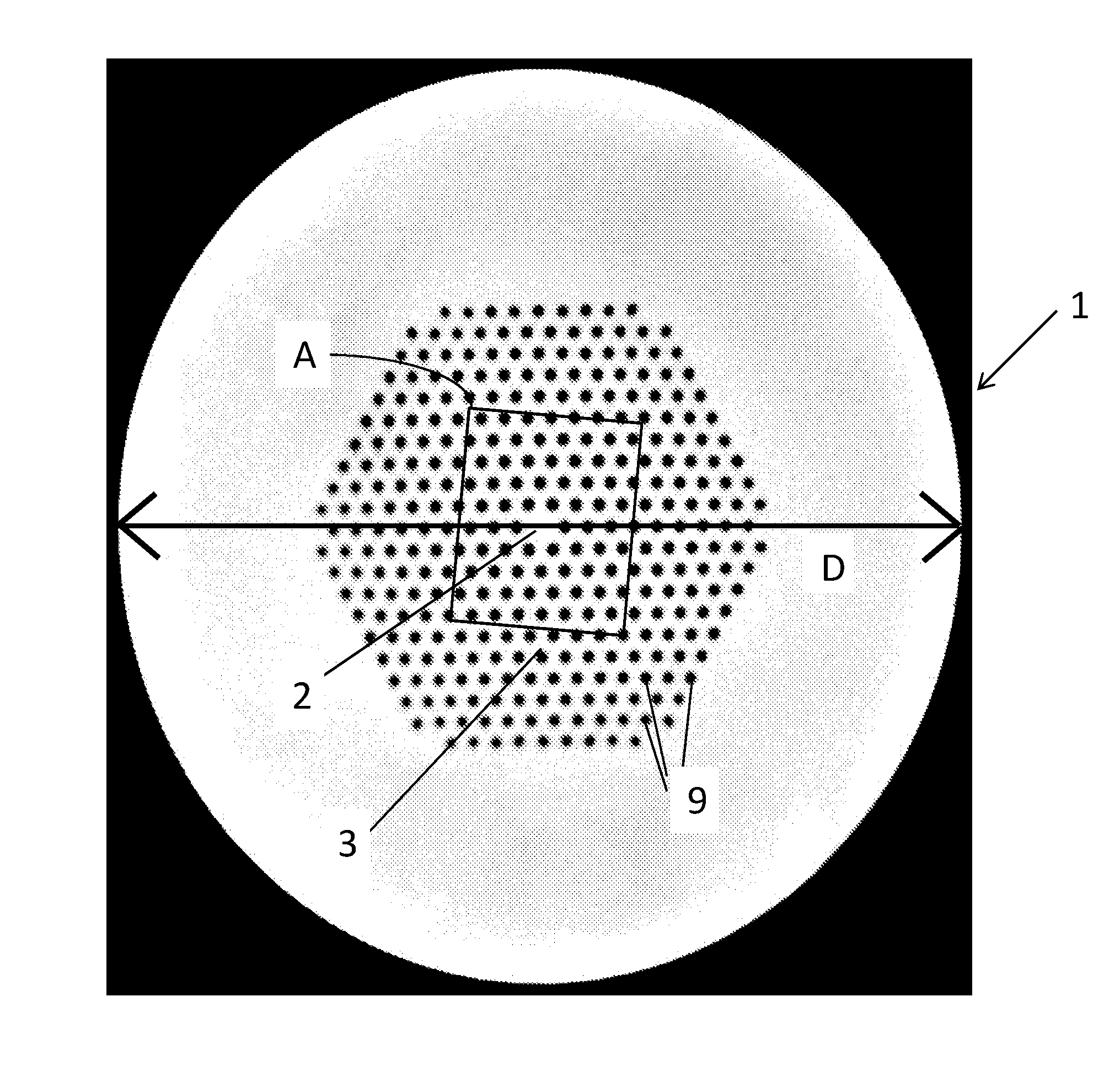
Microstructured optical fiber, supercontinuum light source comprising microstructured optical fiber and use of such light source
ActiveUS20160170136A1Quality improvementReduce noiseLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreFiberOptical fiber cable
The invention relates to a microstructured optical fiber for generating incoherent supercontinuum light upon feeding of pump light. The microstructured optical fiber has a first section and a second section. A cross-section through the second section perpendicularly to a longitudinal axis of the fiber has a second relative size of microstructure elements and preferably a second pitch that is smaller than a blue edge pitch for the second relative size of microstructure elements. The invention also relates to an incoherent supercontinuum source comprising a microstructured optical fiber according to the invention.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com