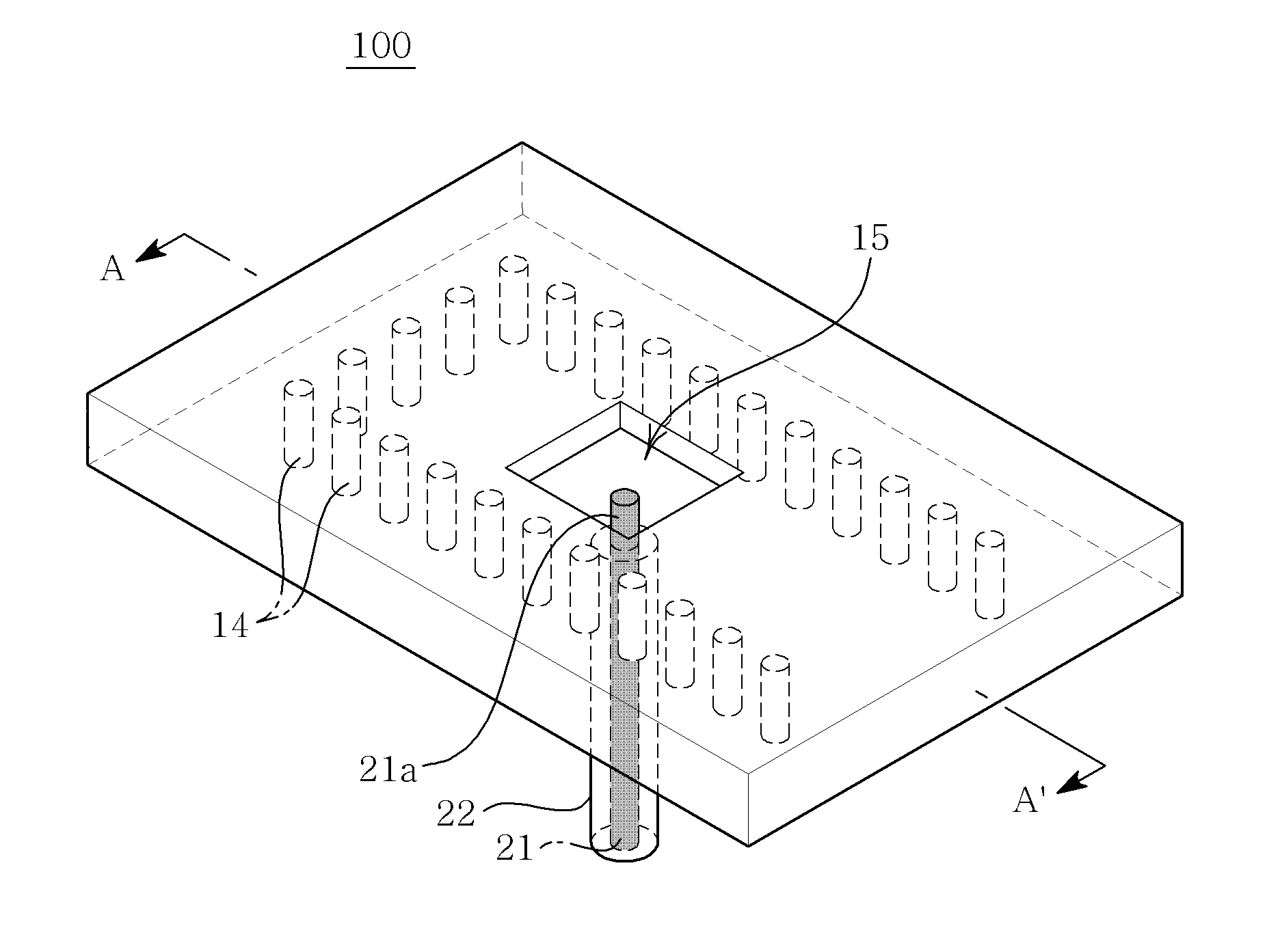
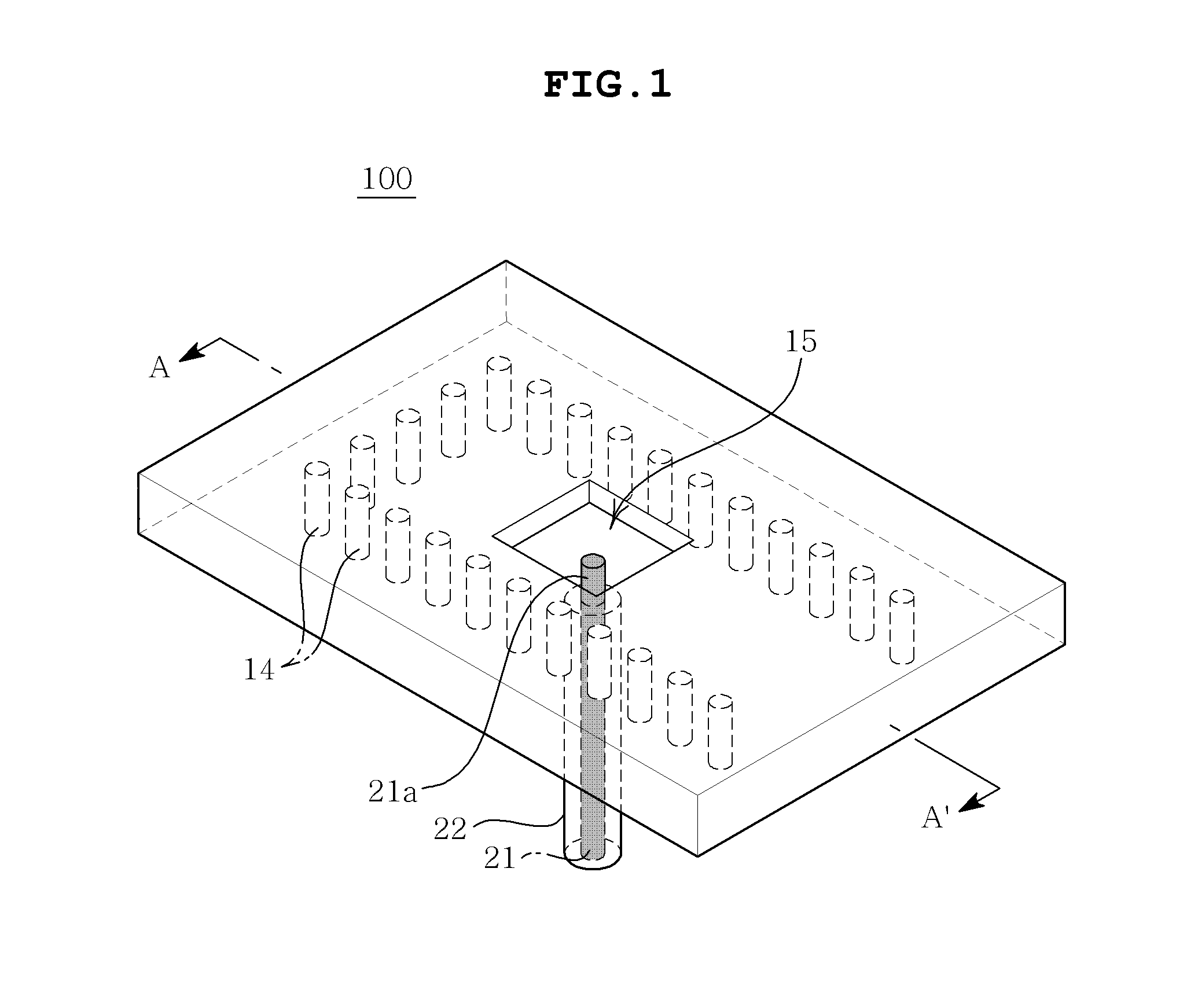
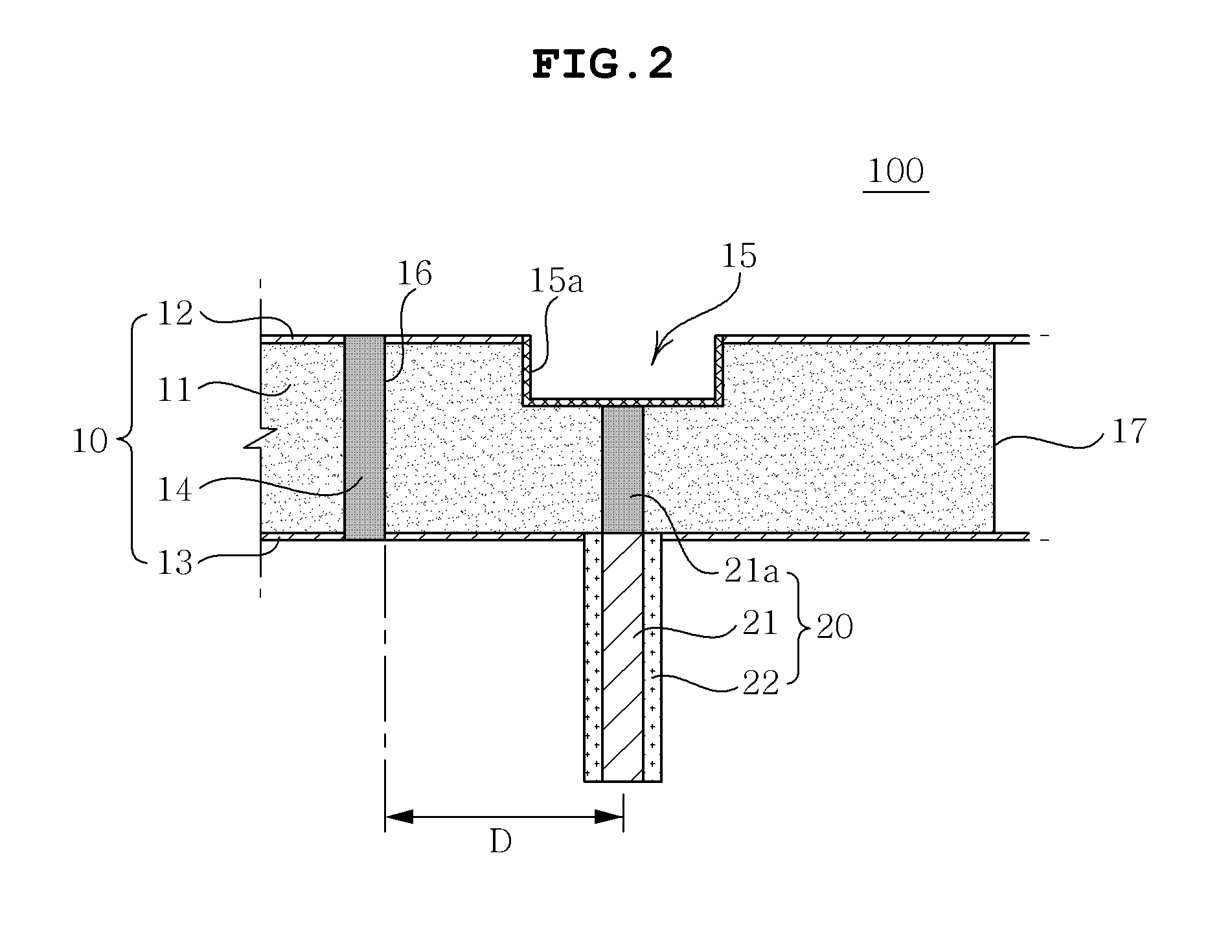
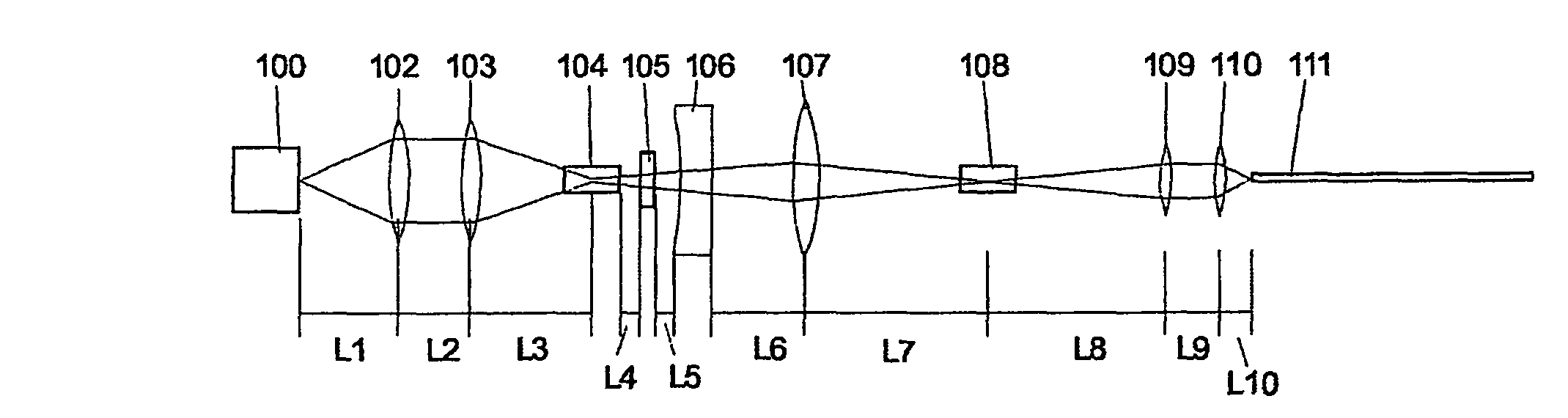
Patents
Literature
1137 results about "Phase matching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
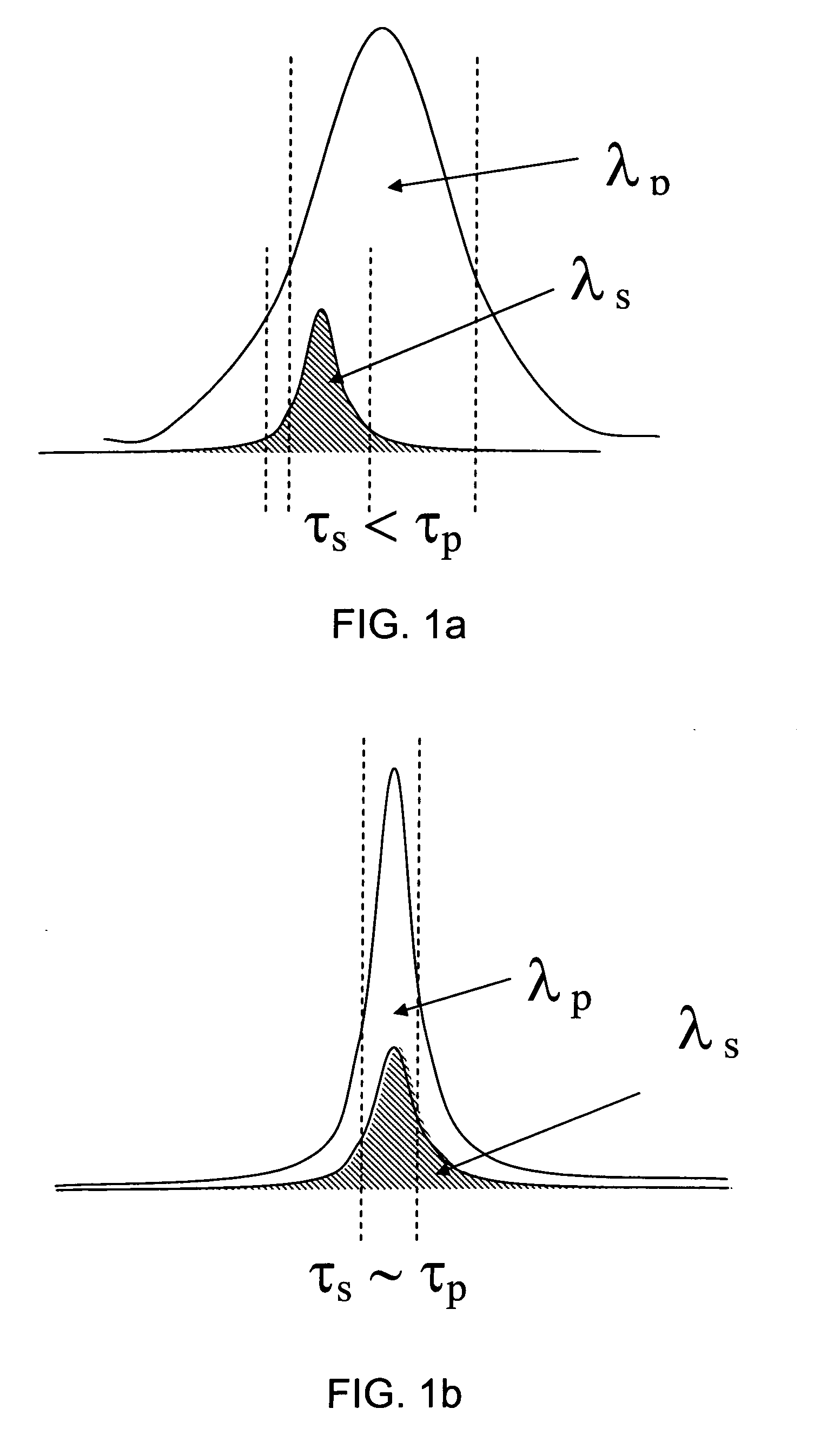
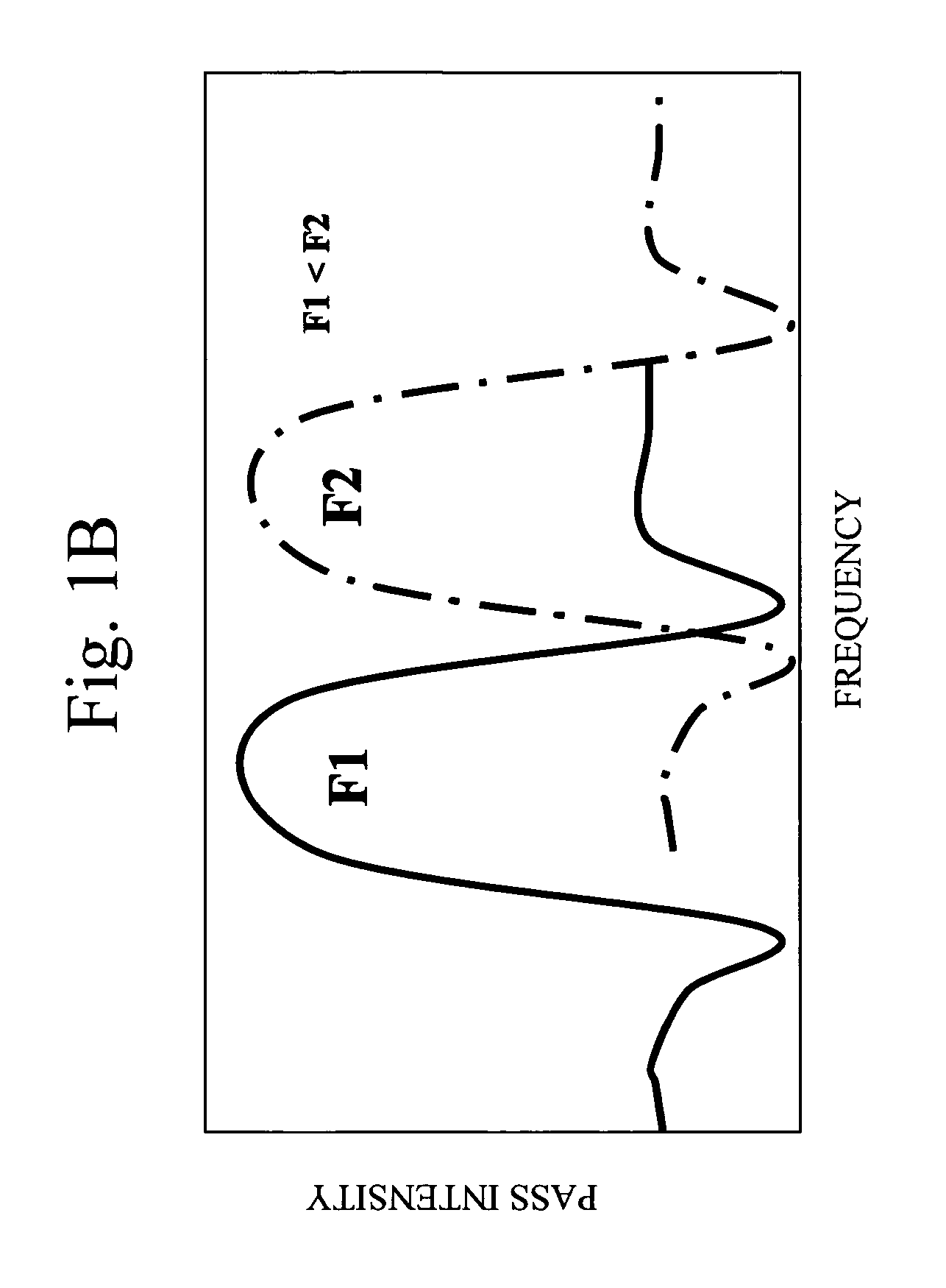
Phase matching. A condition in which the polarization wave produced by two or more beams of incident radiation in a nonlinear medium has the same phase velocity as a freely propagating wave of the same frequency; the amplitude of the polarization wave is then greatly enhanced.
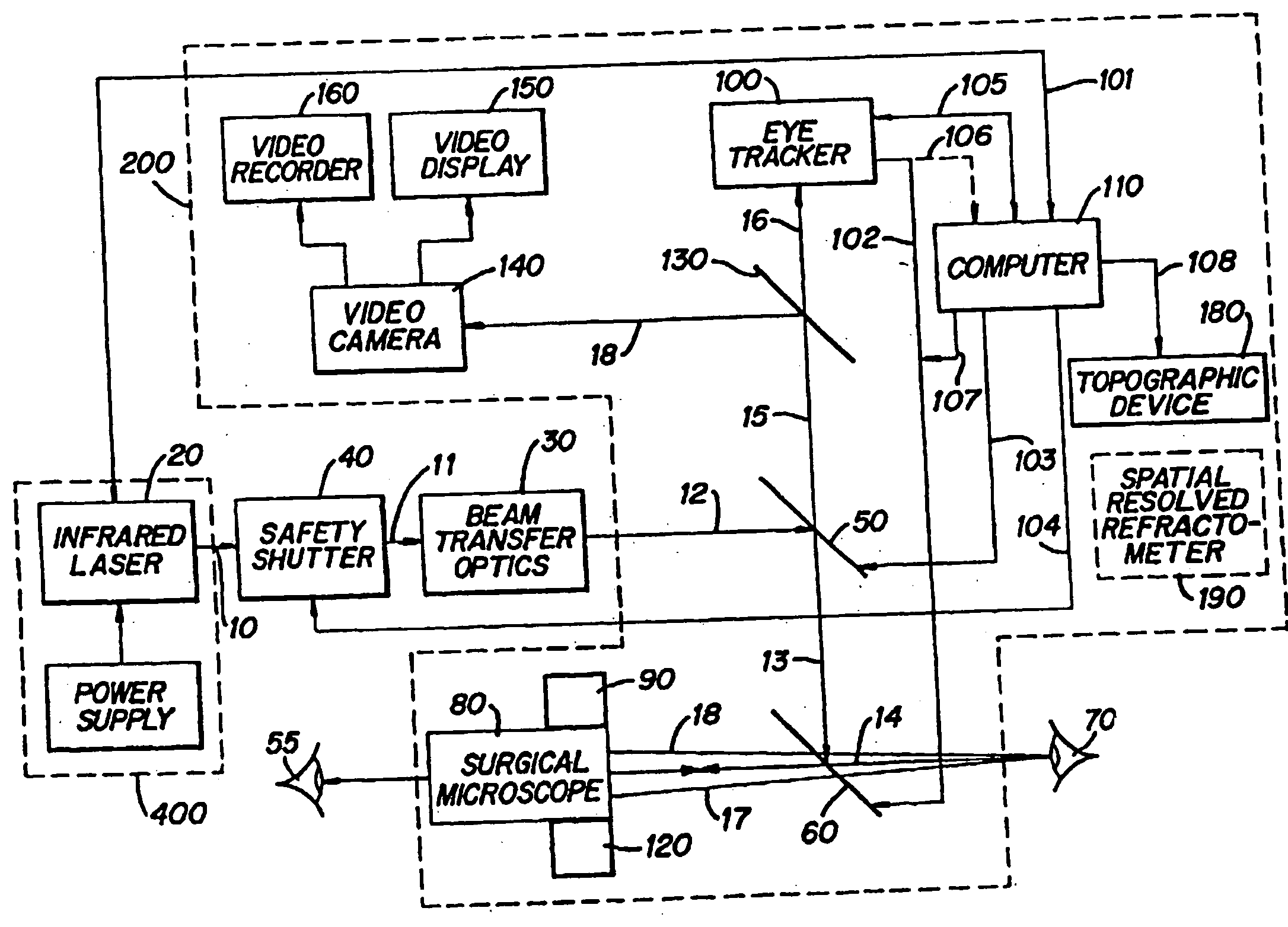
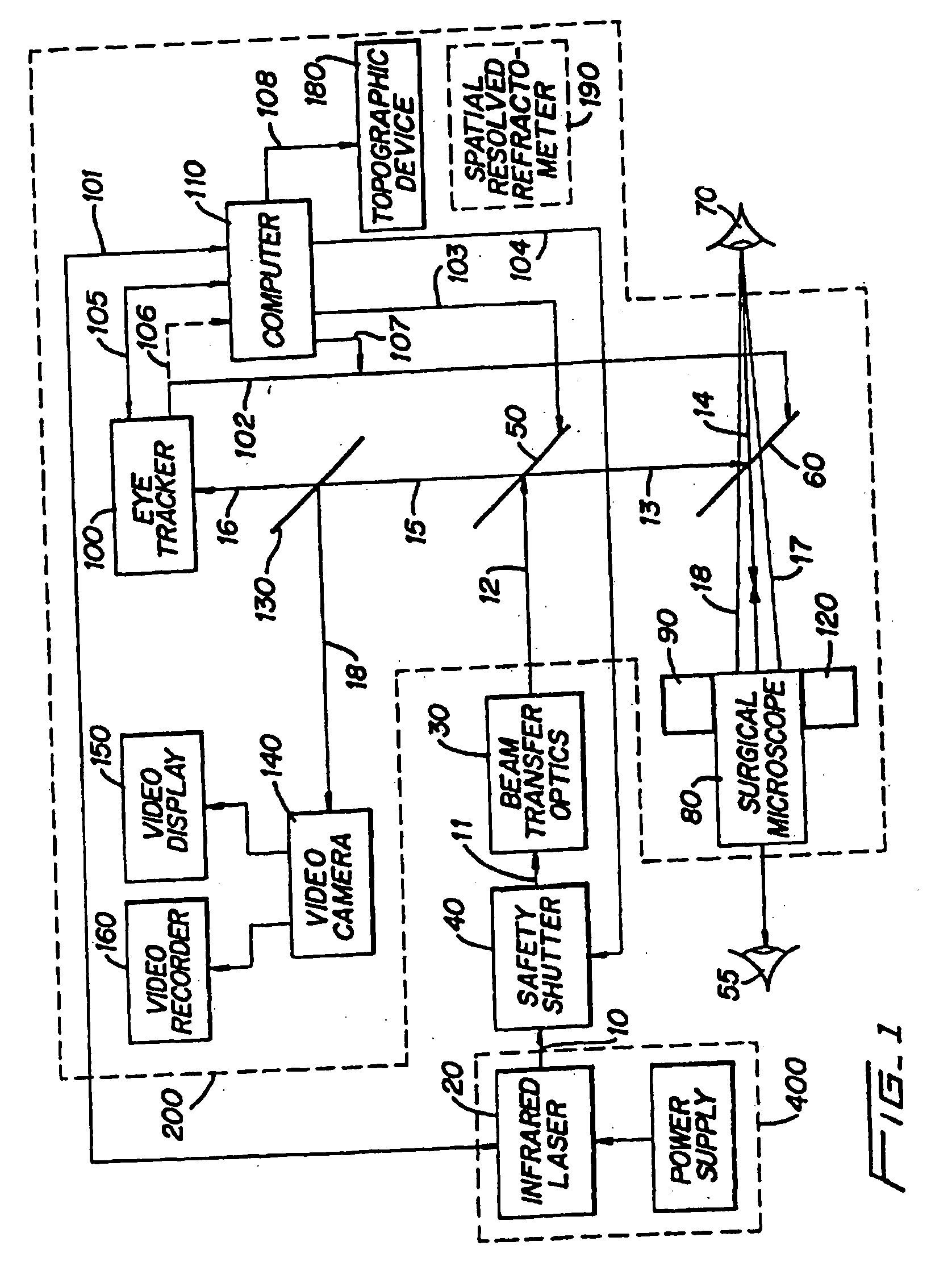
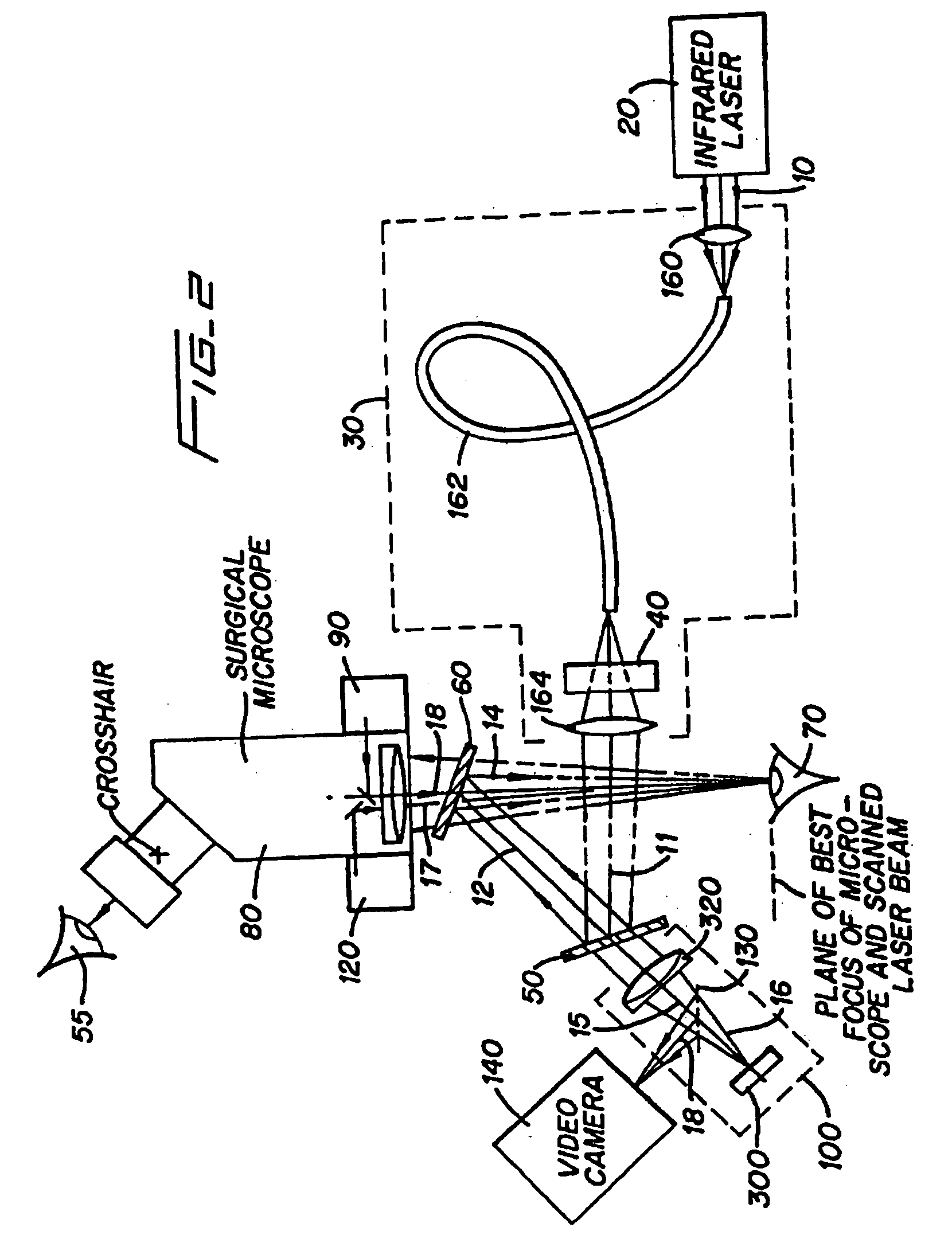
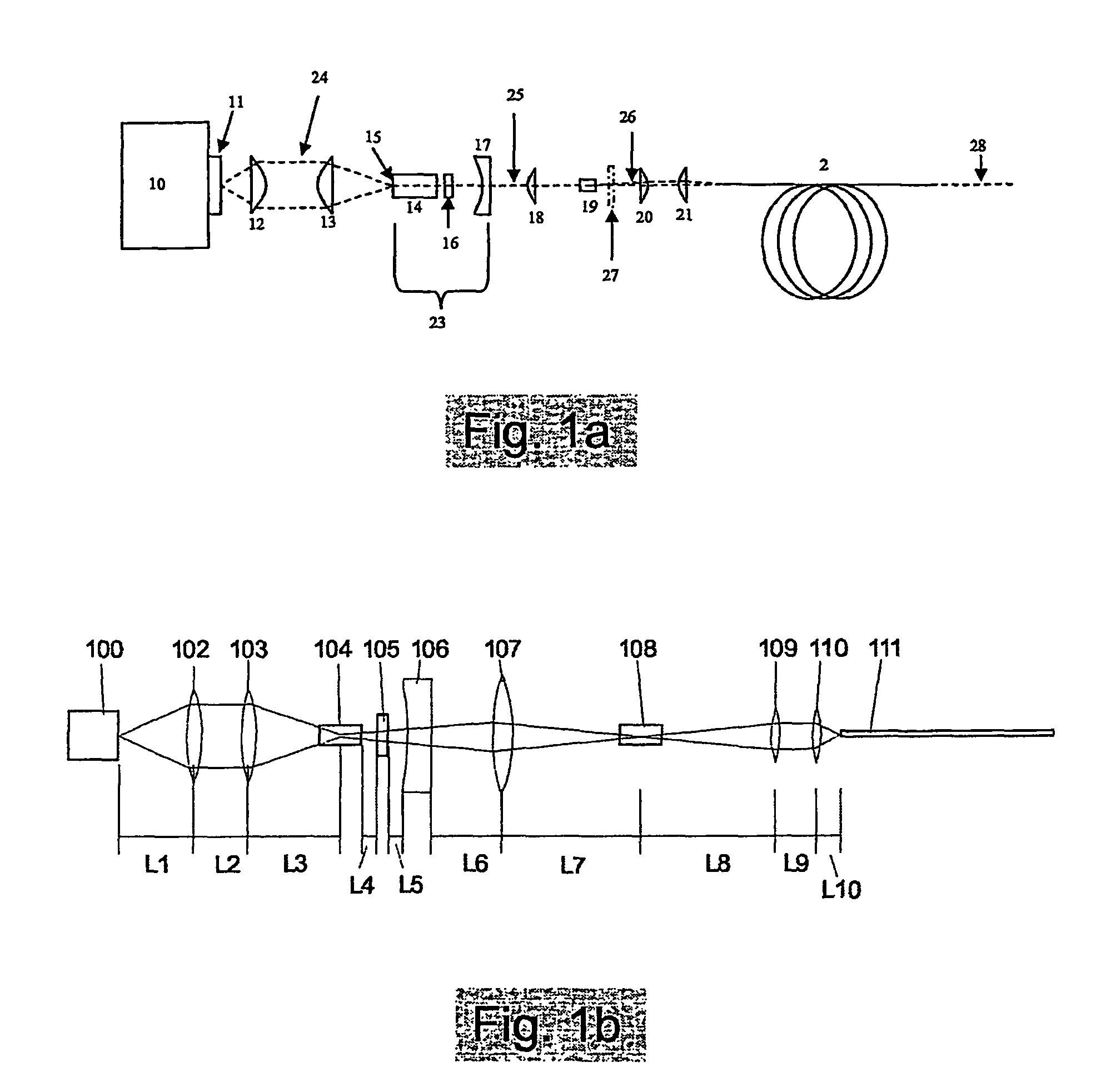
Method and apparatus for removing corneal tissue with infrared laser radiation and short pulse mid-infrared parametric generator for surgery
InactiveUS20050197655A1Reduce undesirable thermal damageMaximum flexibilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLaser scalpelMid infrared laser
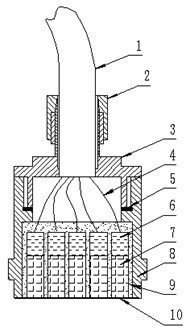
A surgical technique for removing corneal tissue with scanned infrared radiation is disclosed which utilizes short mid-infrared laser pulses to provide a tissue removal mechanism based on photospallation. Photospallation is a photomechanical ablation mechanism which results from the absorption of incident radiation by the corneal tissue. Since photospallation is a mechanical ablation process, very little heat is generated in the unablated adjacent tissue. The disclosed surgical system includes a scanning beam delivery system which allows uniform irradiation of the treatment region and utilizes low energy outputs to achieve controlled tissue removal. A real-time servo-controlled dynamic eye tracker, based on a multiple-detector arrangement, is also disclosed which senses the motion of the eye and provides signals that are proportional to the errors in the lateral alignment of the eye relative to the axis of the laser beam. Temporal and frequency discrimination are preferably utilized to distinguish the tracking illumination from the ambient illumination and the surgical laser beam. A laser parametric generator for surgical applications is disclosed which utilizes short-pulse, mid-infrared radiation. The mid-infrared radiation may be produced by a pump laser source, such as a neodymium-doped laser, which is parametrically down converted in a suitable nonlinear crystal to the desired mid-infrared range. The short pulses reduce unwanted thermal effects and changes in adjacent tissue to potentially submicron-levels. The parametrically converted radiation source preferably produces pulse durations shorter than 25 ns at or near 3.0 microns but preferably close to the water absorption maximum associated with the tissue. The down-conversion to the desired mid-infrared wavelength is preferably produced by a nonlinear crystal such as KTP or its isomorphs. In one embodiment, a non-critically phased-matched crystal is utilized to shift the wavelength from a near-infrared laser source emitting at or around 880 to 900 nm to the desired 2.9-3.0 microns wavelength range. A fiber, fiber bundle or another waveguide means utilized to separate the pump laser from the optical parametric oscillation (OPO) cavity is also included as part of the invention.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
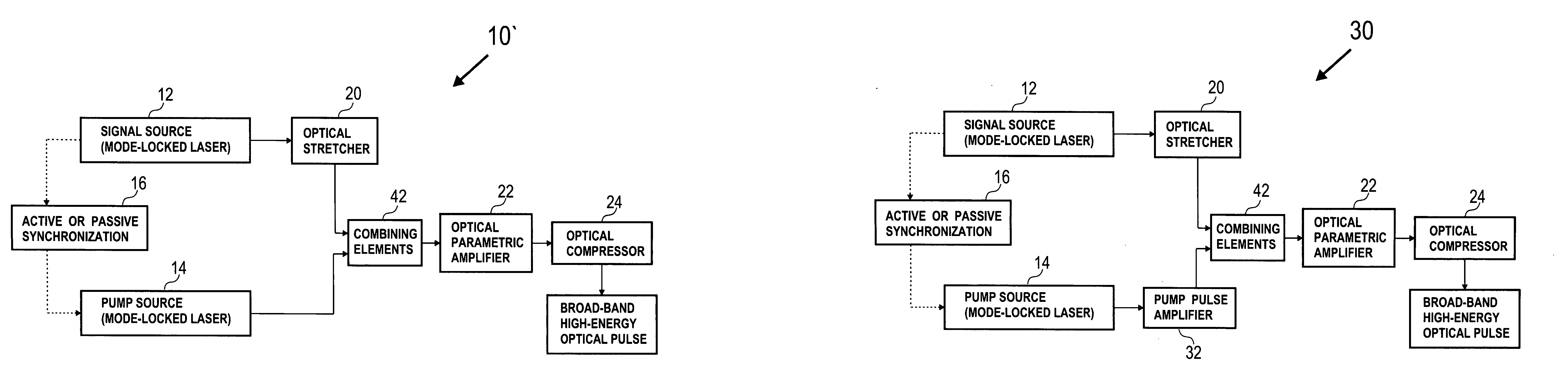
Method and apparatus for high power optical amplification in the infrared wavelength range (0.7-20 mum)
InactiveUS20050271094A1Laser detailsNon-linear opticsAcousto-optic programmable dispersive filterAdemetionine
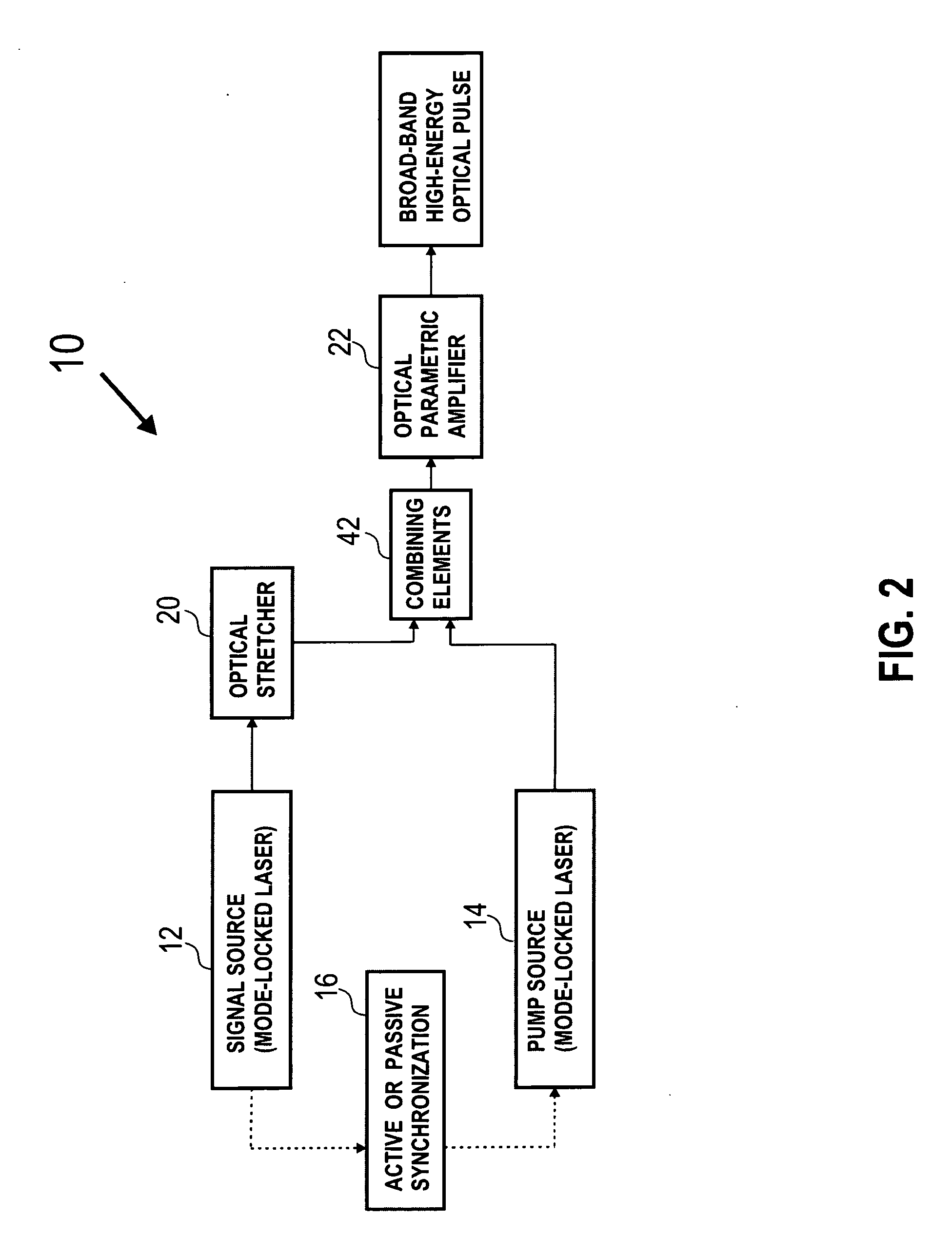
A novel method for high power optical amplification of ultrashort pulses in IR wavelength range (0.7-20 Ãm) is disclosed. The method is based on the optical parametric chirp pulse amplification (OPCPA) technique where a picosecond or nanosecond mode locked laser system synchronized to a signal laser oscillator is used as a pump source or alternatively the pump pulse is created from the signal pulse by using certain types of optical nonlinear processes described later in the document. This significantly increases stability, extraction efficiency and bandwidth of the amplified signal pulse. Further, we disclose five new practical methods of shaping the temporal and spatial profiles of the signal and pump pulses in the OPCPA interaction which significantly increases its efficiency. In the first, passive preshaping of the pump pulses has been made by a three wave mixing process separate from the one occurring in the OPCPA. In the second, passive pre-shaping of the pump pulses has been made by spectral filtering in the pump mode-locked laser or in its amplifier. In the third, the temporal shape of the signal pulse optimized for OPCPA interaction has been actively processed by using an acousto-optic programmable dispersive filter (Dazzler) or liquid crystal light modulators. In the fourth alternative method, the signal pulse intensity envelope is optimized by using passive spectral filtering. Finally, we disclose a method of using pump pulses which interact with the seed pulses with different time delays and different angular orientations allowing the amplification bandwidth to be increased. In addition we describe a new technique for high power IR optical beam delivery systems based on the microstructure fibres made of silica, fluoride or chalcogenide glasses as well as ceramics. Also we disclose a new optical system for achieving phase matching geometries in the optical parametric interactions based on diffractive optics. All novel methods of the ultrashort optical pulse amplification described in this disclosure can be easily generalized to other wavelength ranges.
Owner:MILLER ROBERT JOHN DWAYNE +3
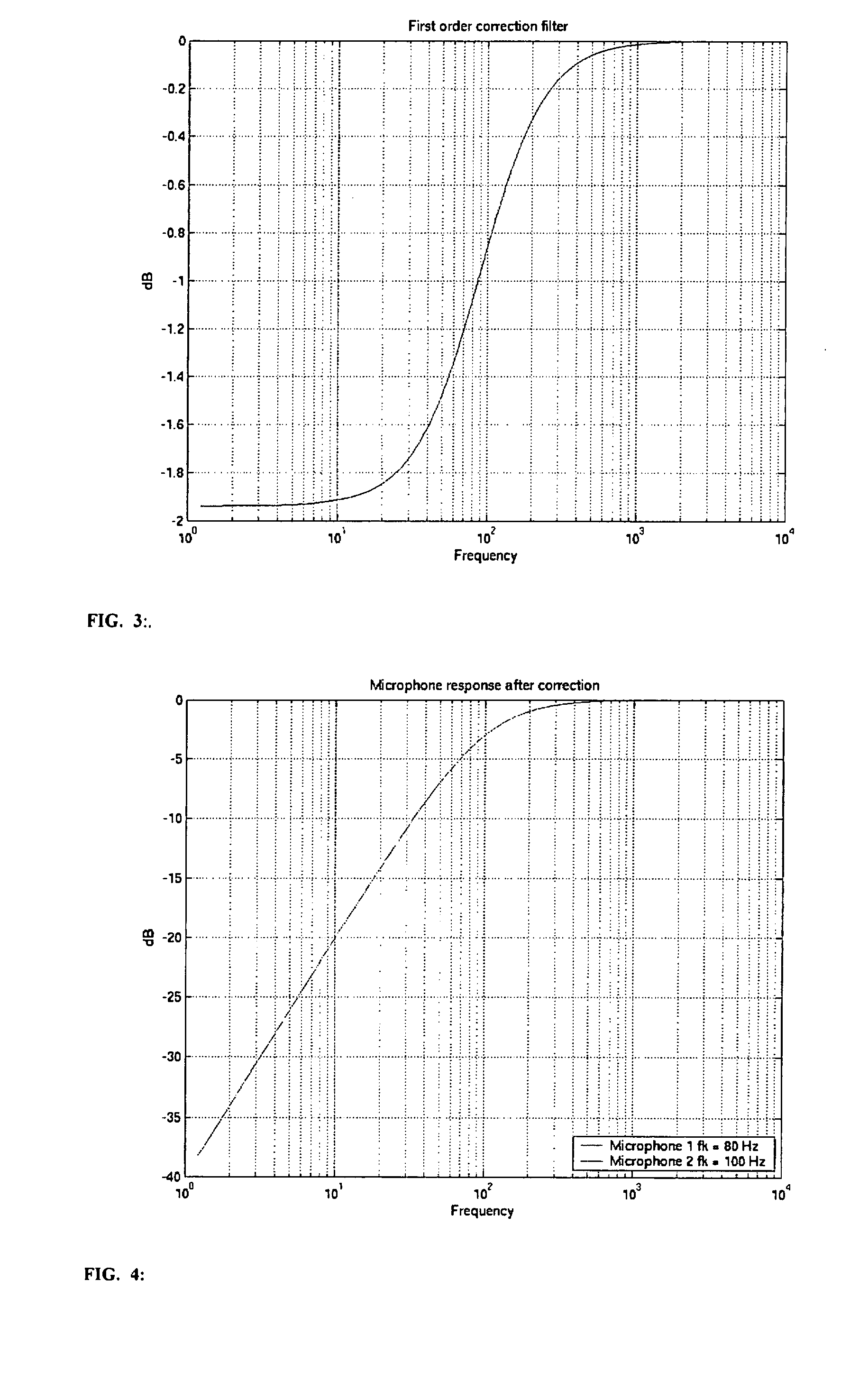
Low Frequency Phase Matching for Microphones
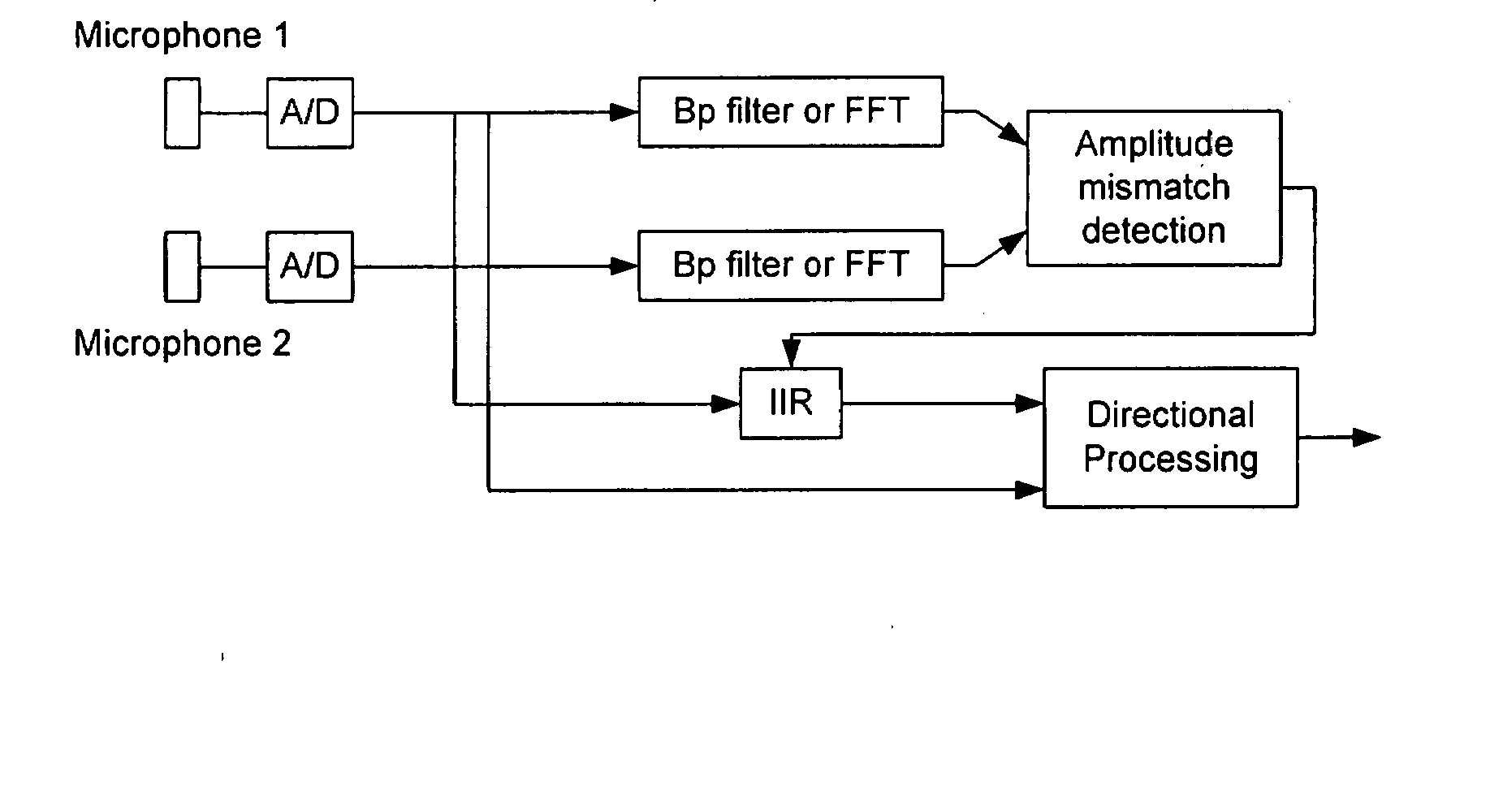
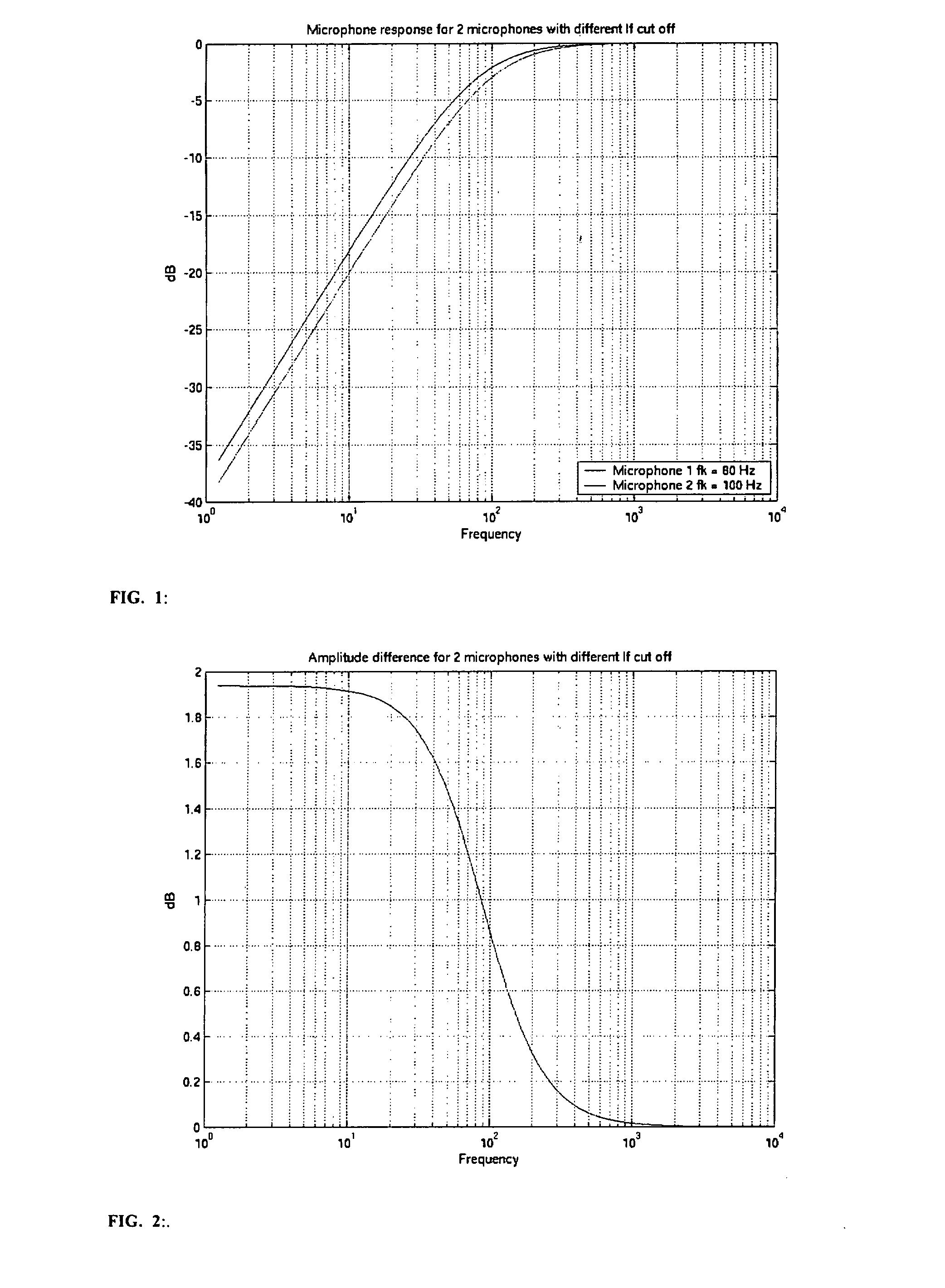
InactiveUS20070258597A1Reliable and adequate correctionStereophonic arrangmentsIir filteringPhase response
The invention relates to a communication device having at least two microphones, where in order to match the microphone performance in respect of the phase response a correction filter in the form of a IIR filter is implemented and where the amplitude of the transfer function for the correction filter is the inverse of the difference between the two microphone amplitudes.
Owner:OTICON
Method and apparatus for phase matching frames in vocoders
In one embodiment, the present invention comprises a vocoder having at least one input and at least one output, an encoder comprising a filter having at least one input operably connected to the input of the vocoder and at least one output, a decoder comprising a synthesizer having at least one input operably connected to the at least one output of the encoder, and at least one output operably connected to the at least one output of the vocoder, wherein the decoder comprises a memory and the decoder is adapted to execute instructions stored in the memory comprising phase matching and time-warping a speech frame.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
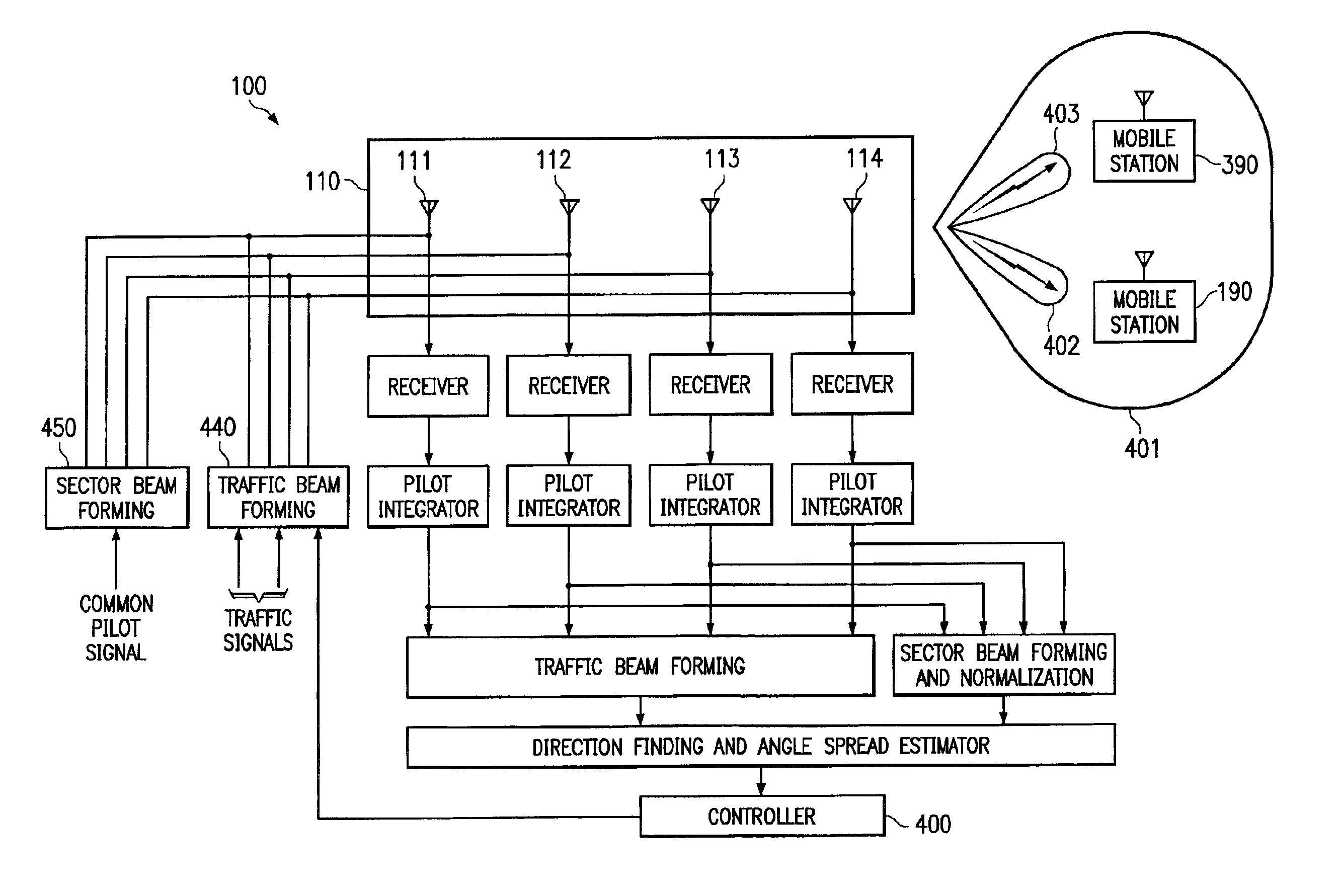
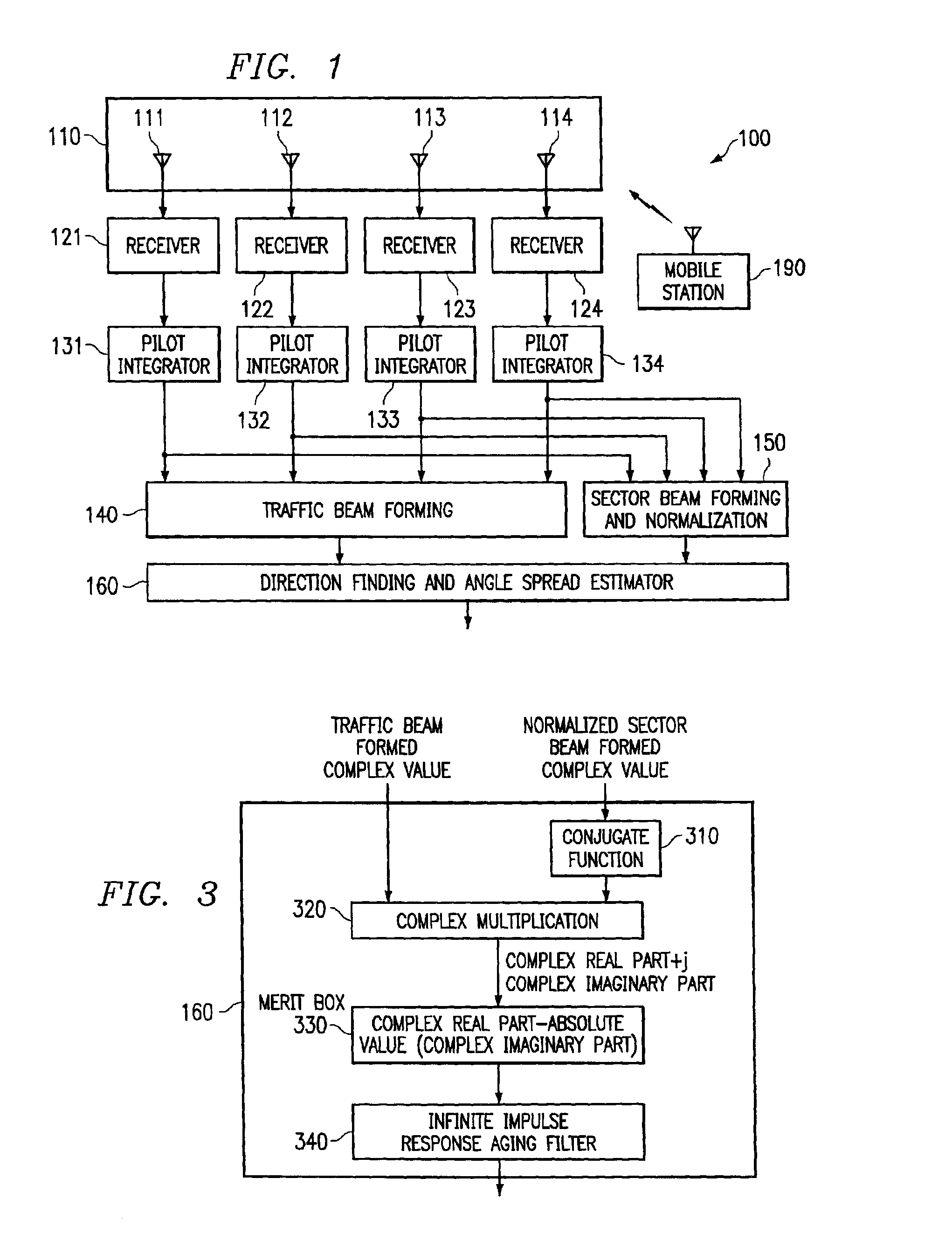
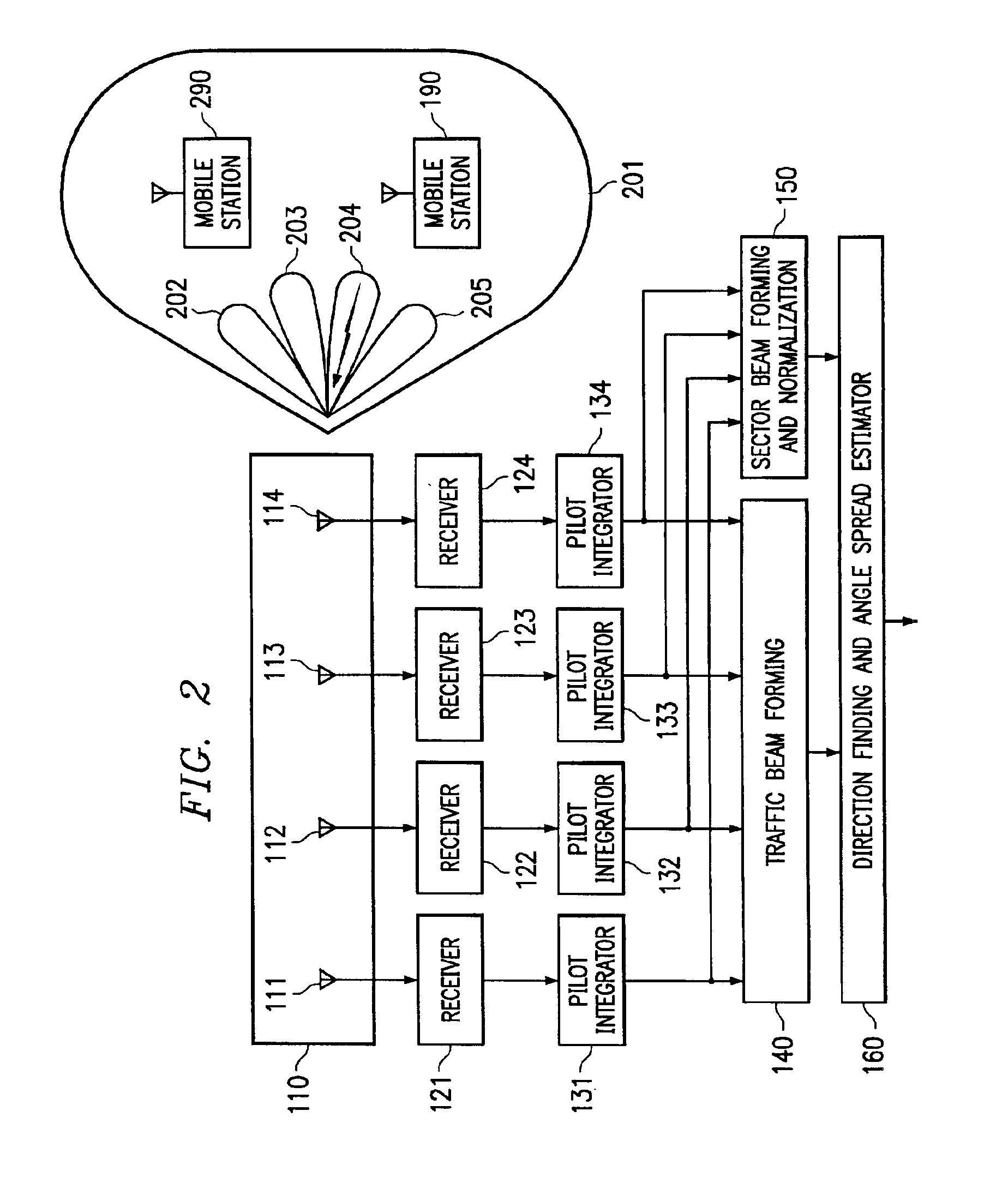
System and method for providing phase matching with optimized beam widths
InactiveUS6847832B2Minimizing interference energySpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentEngineeringPhase matching
Owner:F POSZAT HU
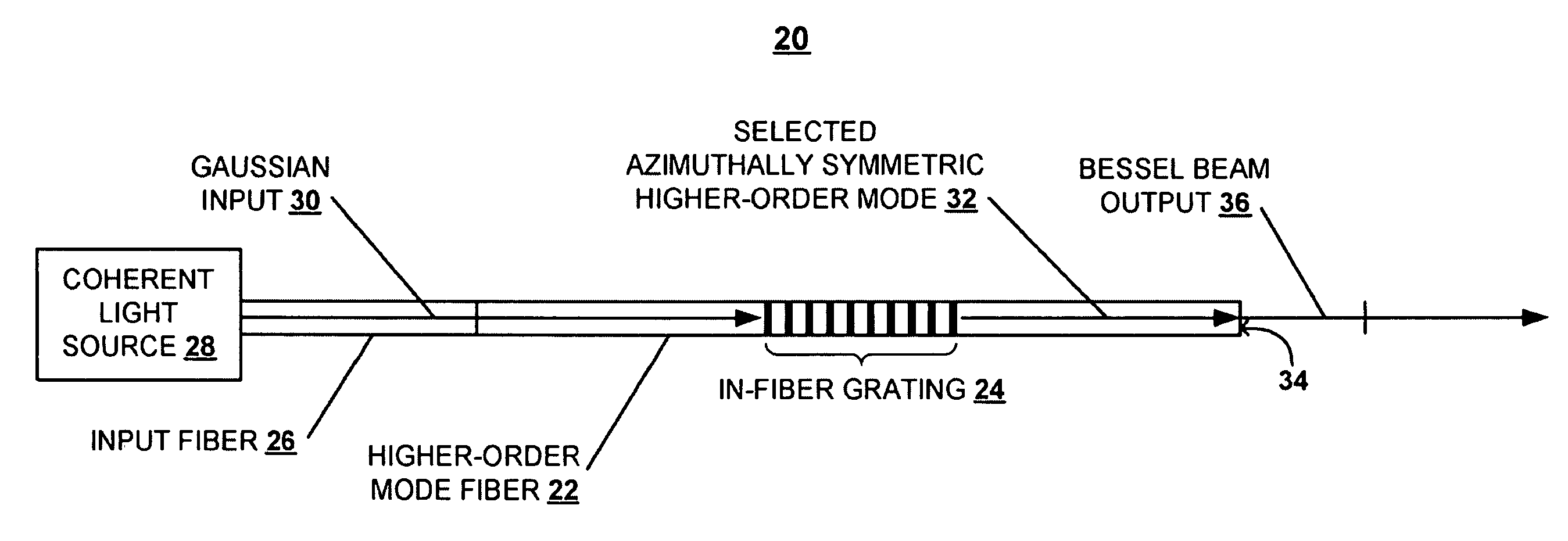
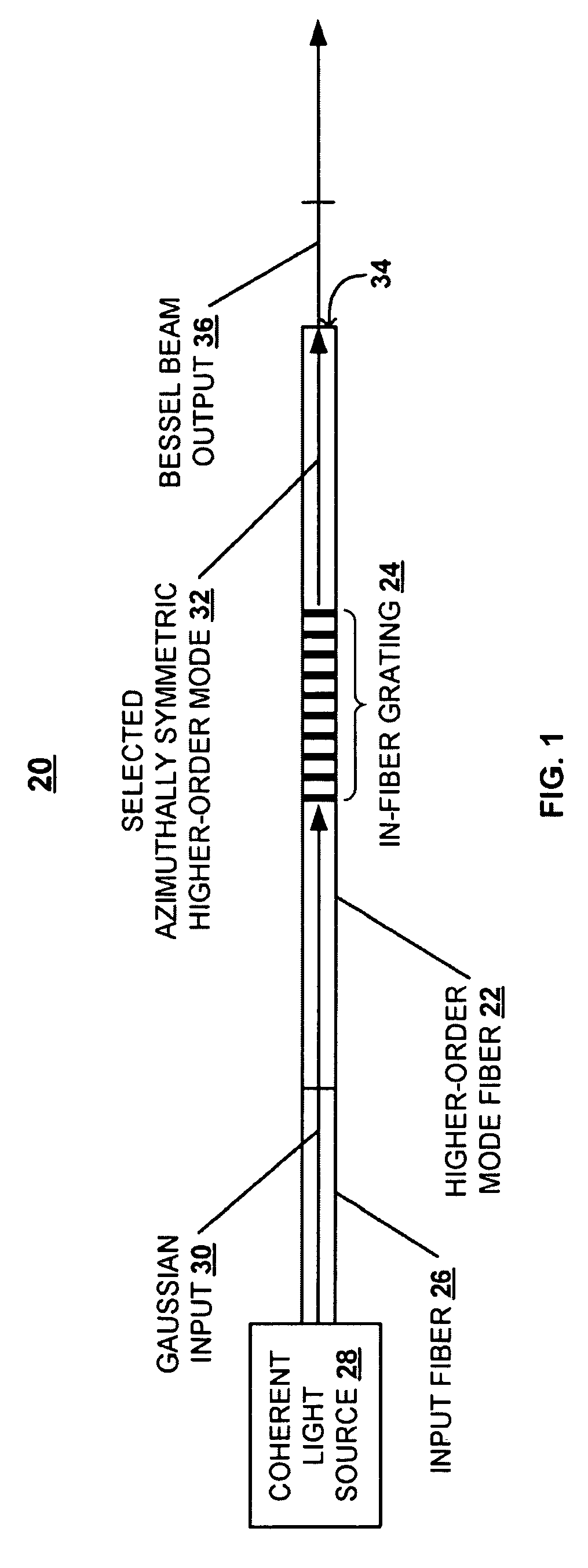
Systems and techniques for generating Bessel beams
A technique is described for generating a Bessel beam. An input optical fiber is provided that supports propagation in the fundamental mode. The input fiber is connected to a fiber mode converting device that provides phase matching, at a predetermined excitation wavelength, between the fundamental mode and a selected azimuthally symmetric higher-order mode. As an input to the fiber mode converting device, a coherent light beam is fed through the input optical fiber to provide a fundamental mode input at the excitation wavelength. The fiber mode converting device resonantly excites the selected azimuthally symmetric mode. The azimuthally symmetric mode is provided as a beam output from an endface of the fiber mode converting device to approximate a Bessel beam.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
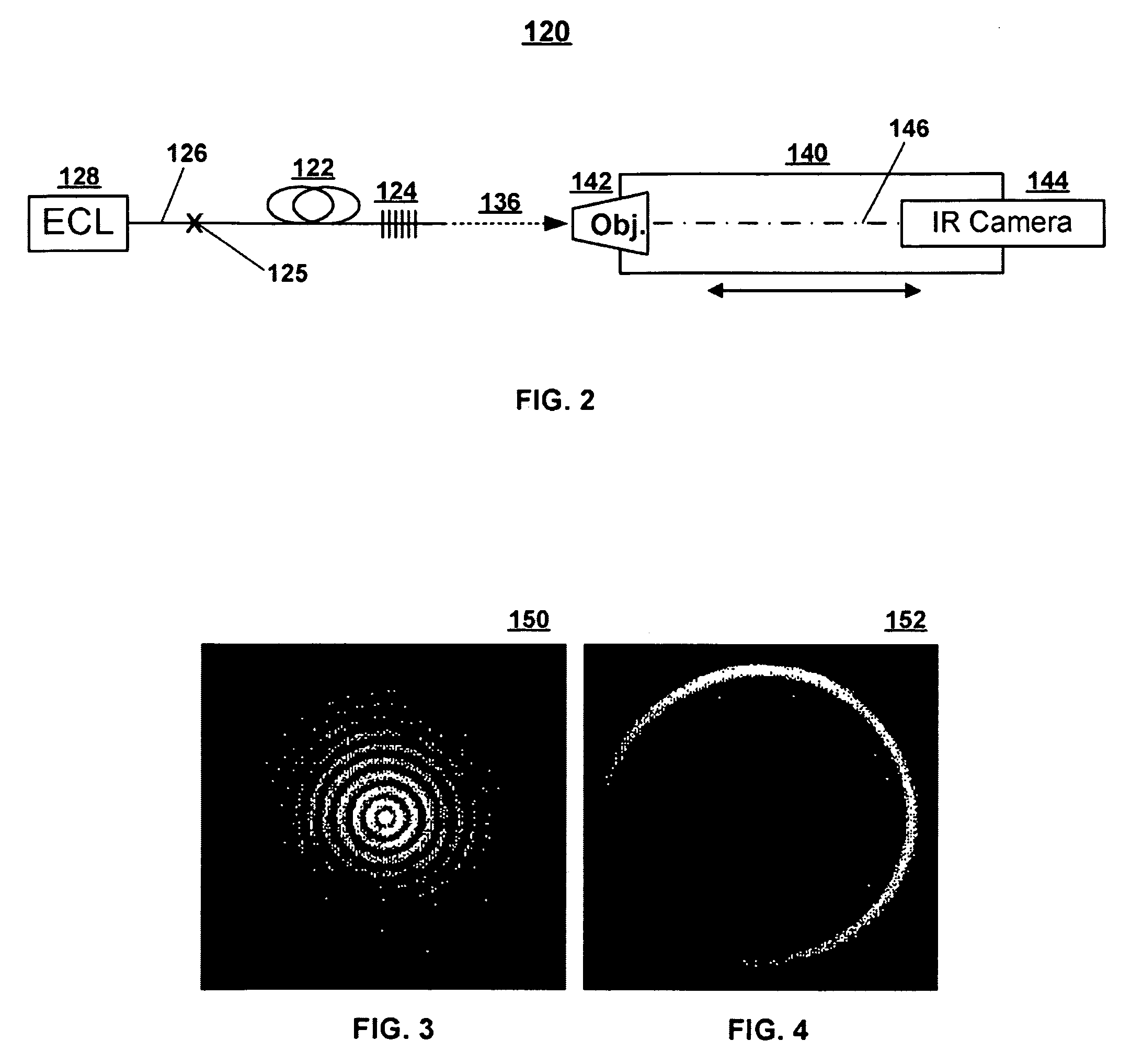
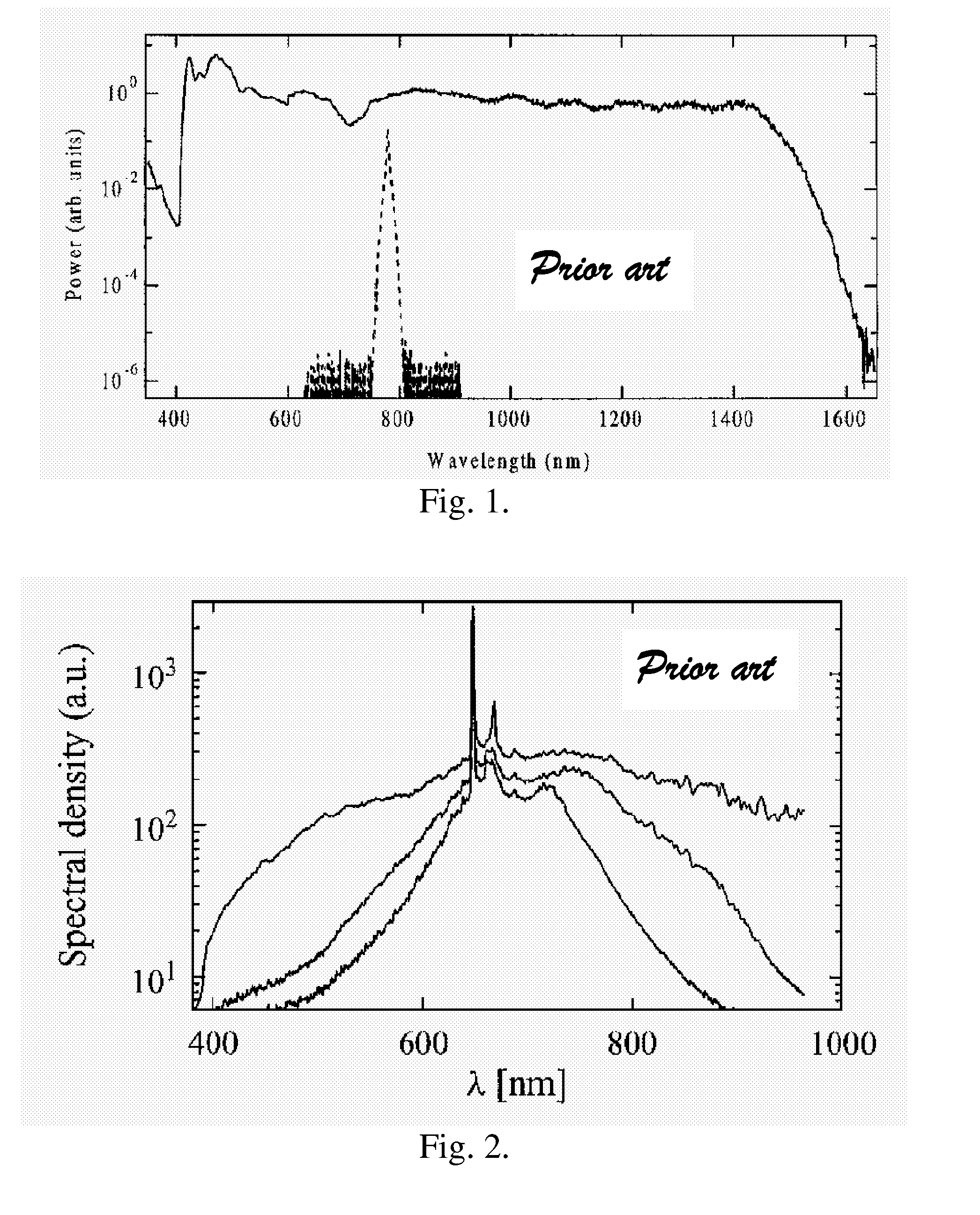
Blue extended super continuum light source
InactiveUS7800818B2Increase powerLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInstabilityRefractive index
In a blue extended super continuum light source, when pulses of partly coherent monochromatic “pump” radiation of essentially constant amplitude are propagating through a microstructure fiber medium within a region of anomalous dispersion of the medium, then, provided the medium has a finite nonlinear coefficient of the index of refraction, the pump pulse is subject to a modulation instability. This results in formation of a train of narrow pulses with Tera Hertz repetition rate. Phase match between red shifted Raman solitons generated by the pump pulse and energy shed by the pump pulse at all frequencies with a group velocity below the pump pulse group velocity may lead to the formation of Cherenkov radiation. The solitons may seed Cherenkov radiation at different wavelengths depending on the actual fiber parameters. This allows extension of generated super continuum light beyond the four wave mixing limit when applying picosecond or nanosecond pump pulses.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
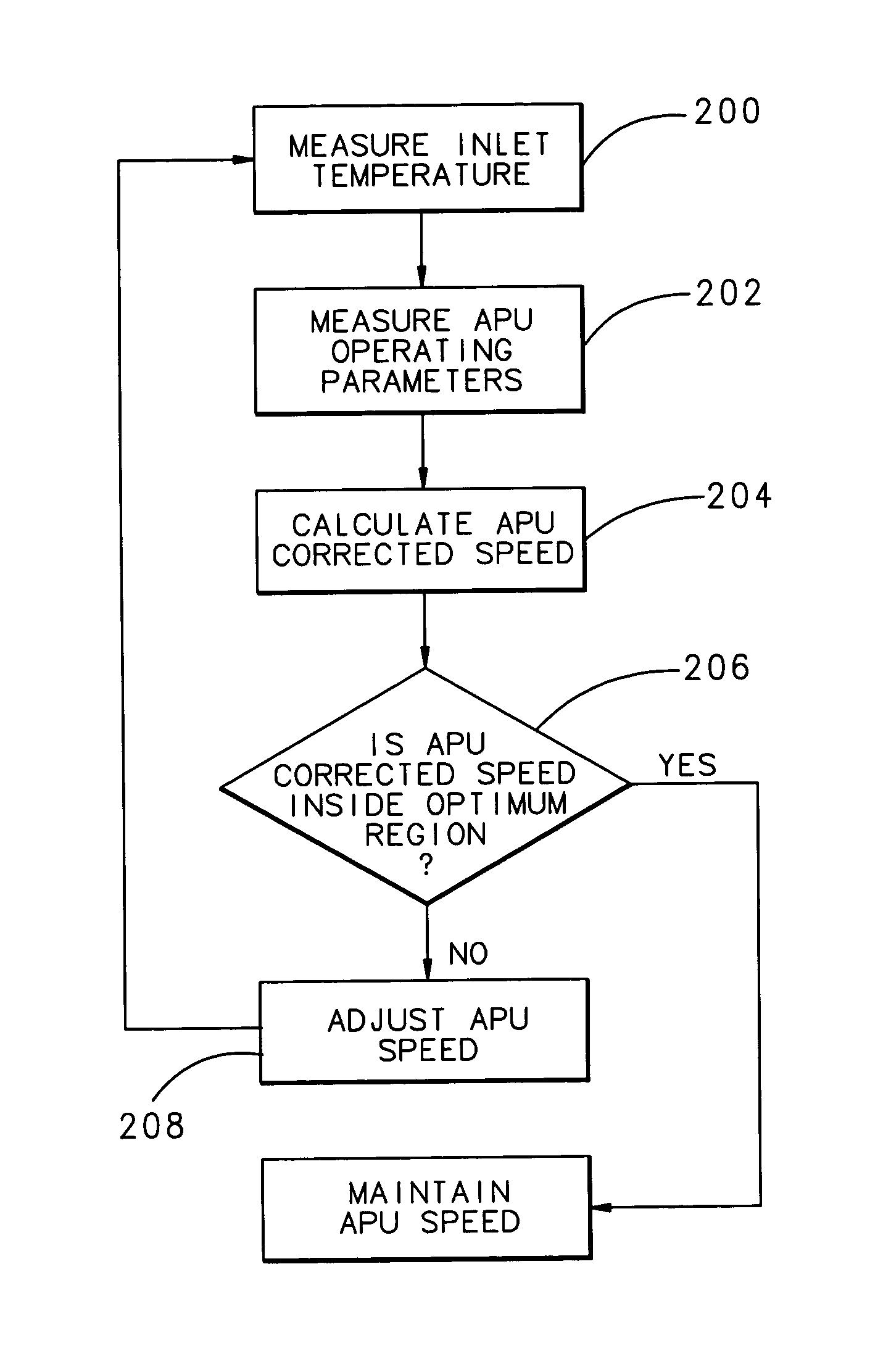
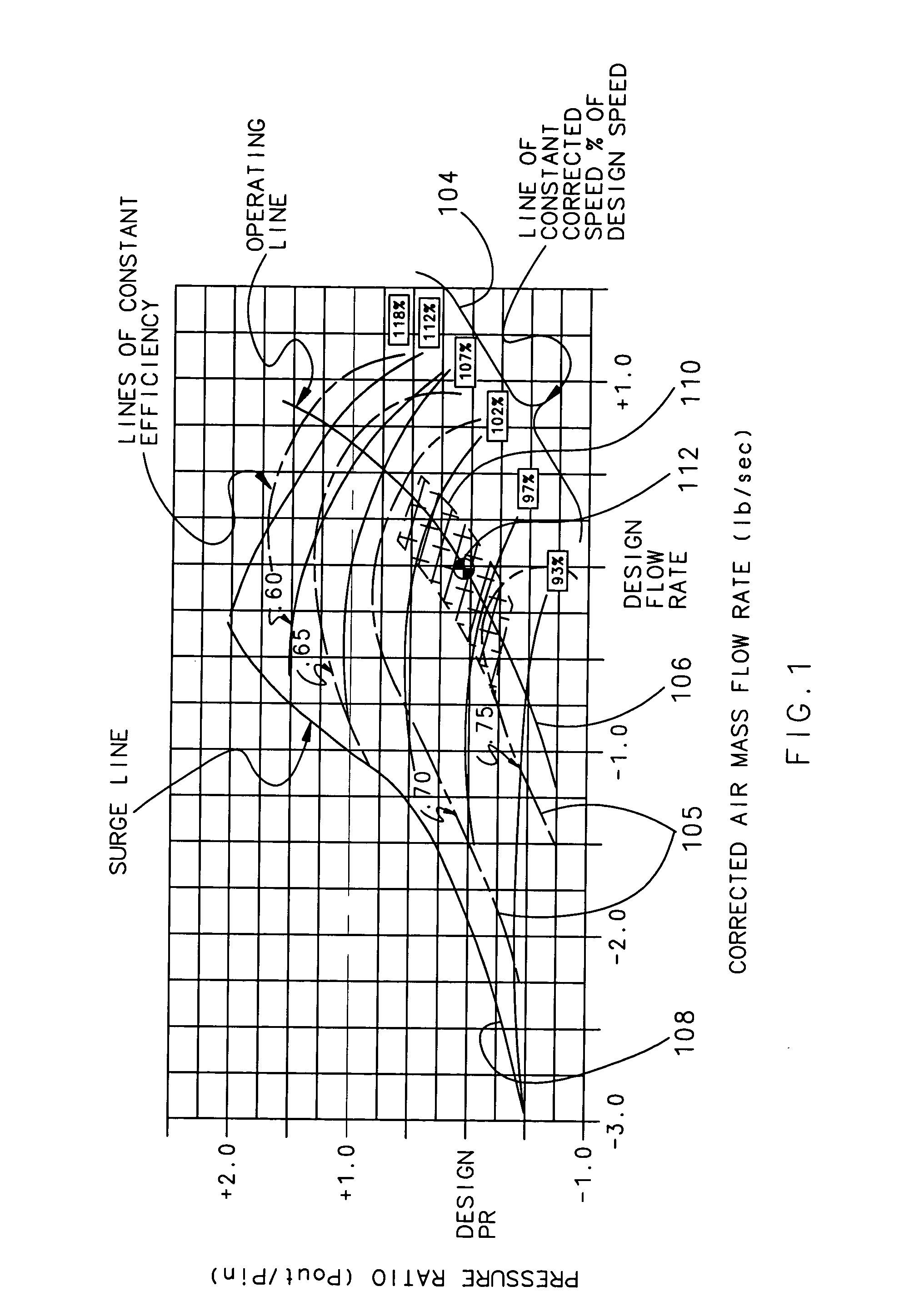
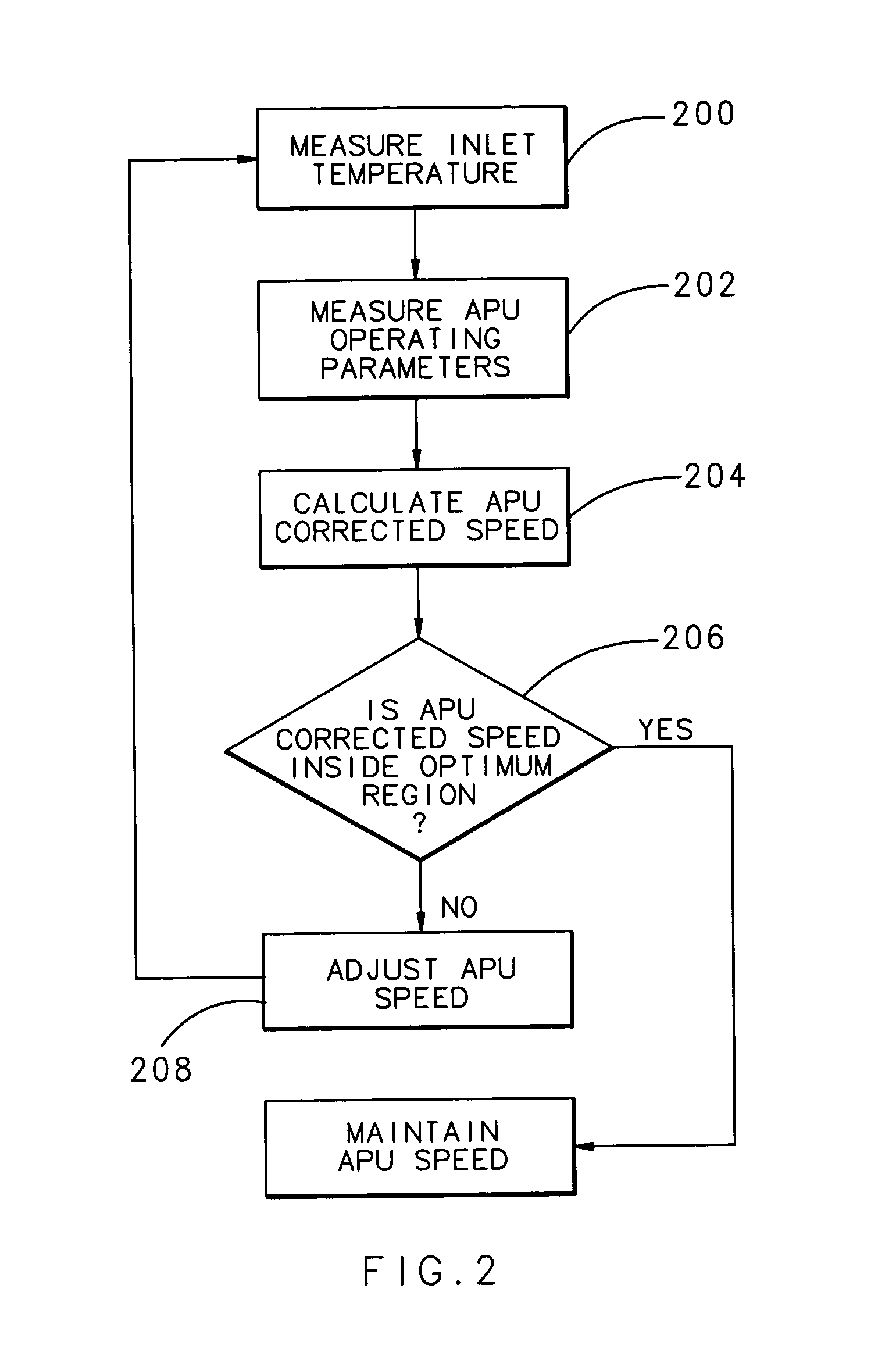
Auxiliary power unit control method and system
ActiveUS7367193B1Smoother transfer of powerSmooth transferExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusEngineeringAuxiliary power unit
An adjustment method and system for an auxiliary power unit (APU) allows the APU speed to vary based on the inlet air temperature to the APU compressor. The APU is controlled by a control law that allows the APU speed to float within a selected range based on speed and electric power generators phase matching criteria that provides smooth power transfer between the APU and a main engine generator. The specific APU mechanical speed for a given temperature may be determined from a compressor map that identifies the optimum combination of pressure ratio, flow rate and efficiency for a given inlet temperature, and avoids running the APU near mechanical resonant vibration conditions.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Wideband transmission line - waveguide transition apparatus
InactiveUS20110267152A1Increase or decrease volumeMultiple-port networksOne-port networksElectricityBroadband transmission
Disclosed herein is a wideband transmission line—waveguide transition apparatus. The wideband transmission line—waveguide transition apparatus includes: a waveguide constituted by a single dielectric substrate; a transmission line applying a signal to the waveguide; and a cavity matching unit in which a cavity of which an inner surface is formed by a metallic surface is formed at a portion of the waveguide to contact with the transmission line and impedance is adjusted through a change of the dielectric constant in the cavity caused by changing the size and shape of the cavity to perform impedance matching between the waveguide and the transmission line, and the position of the cavity is changed to perform phase matching between the waveguide and the transmission line.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
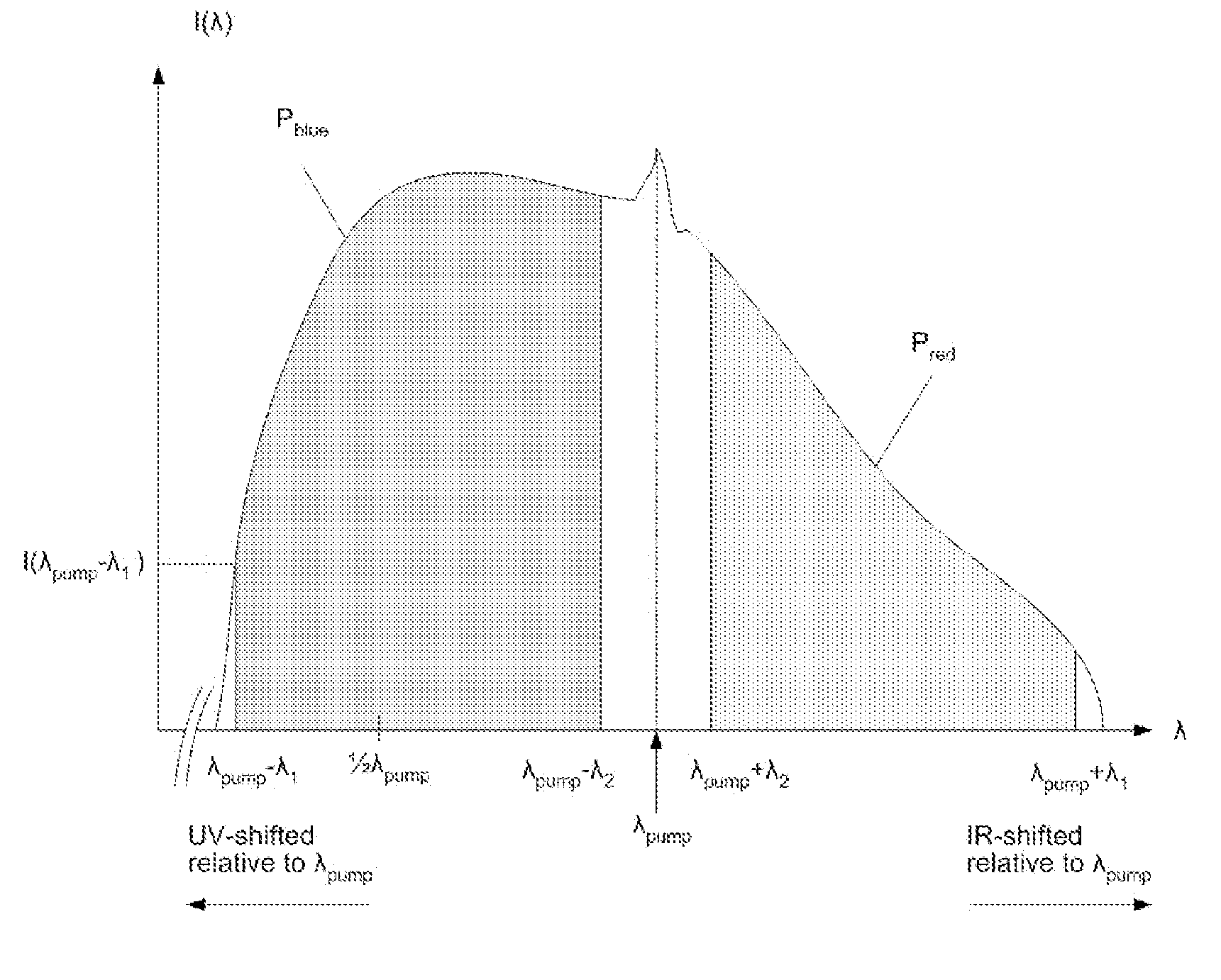
Method of generating supercontinuum optical radiation, supercontinuum optical radiation source, and use thereof
InactiveUS8000574B2Simple and compact supercontinuum optical radiation sourceShort pulseCladded optical fibrePhotometryOptical radiationLength wave
A method of generating supercontinuum optical radiation, the method comprising: (a) providing an optical waveguide (22), said optical waveguide exhibiting a dispersion characteristic of guided optical radiation, said dispersion characteristic comprising: (i) a first dispersion parameter (β21) at a first wavelength (λ1), (ii) a second dispersion parameter (β22) at a second shorter wavelengths (λ2), and (iii) a zero-dispersion parameter at a wavelength in between said first and said second shorter wavelengths; said optical waveguide further comprising at least one entrance for receiving optical radiation, and at least one exit for emitting guided optical radiation; (b) applying at least two laser radiation of said first (25) wavelength, (λ1) at a first power (P1) and applying laser radiation of said second (26) shorter wavelength (λ2) at a second power (P2) into said optical waveguide, said laser radiations at least partially overlapping between said at least one entrance and said at least one exit of said optical waveguide; and (c) phase-matching said applied laser radiations by adjusting said first and second powers; a supercontinuum optical radiation source; and use thereof.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
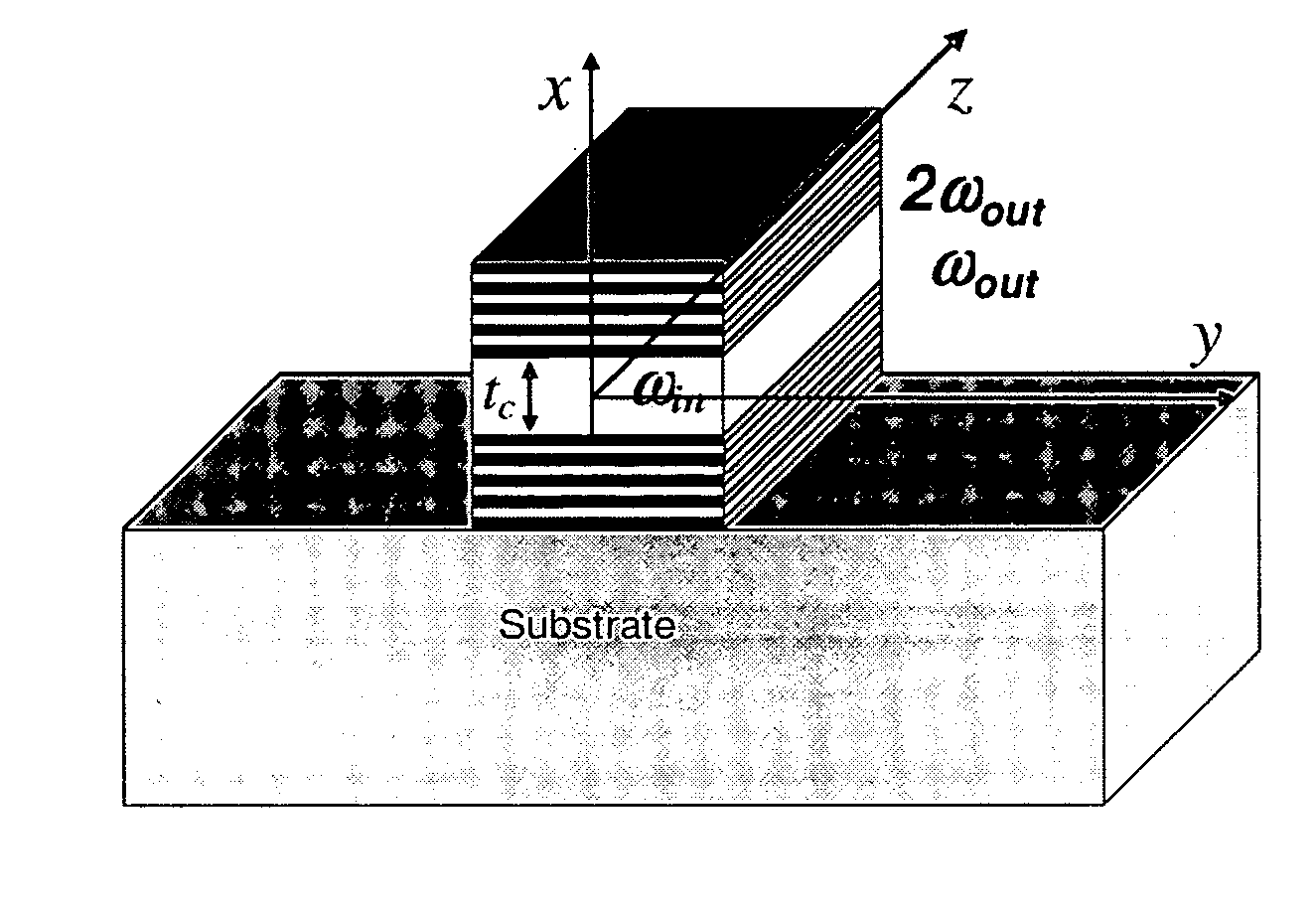
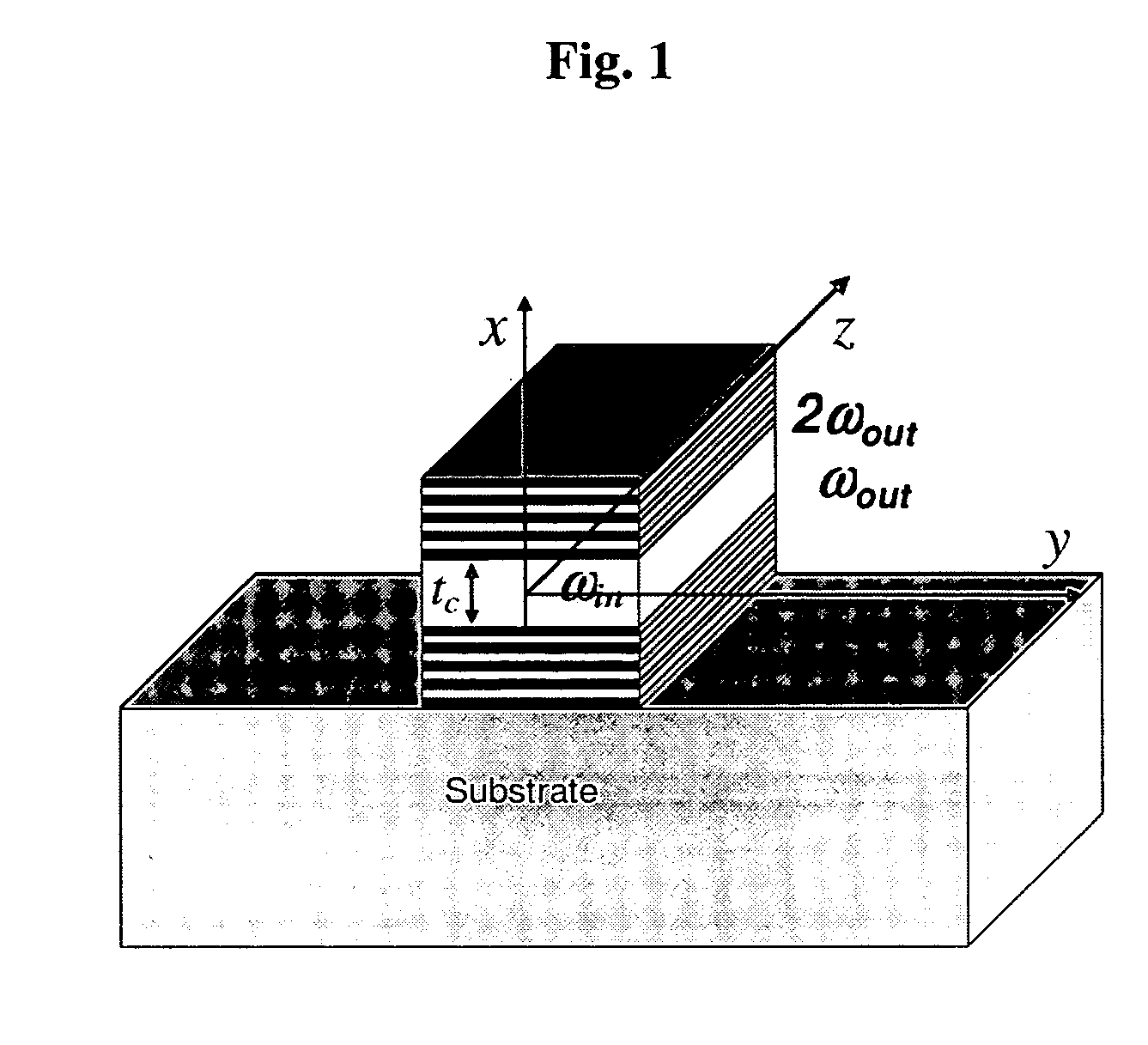
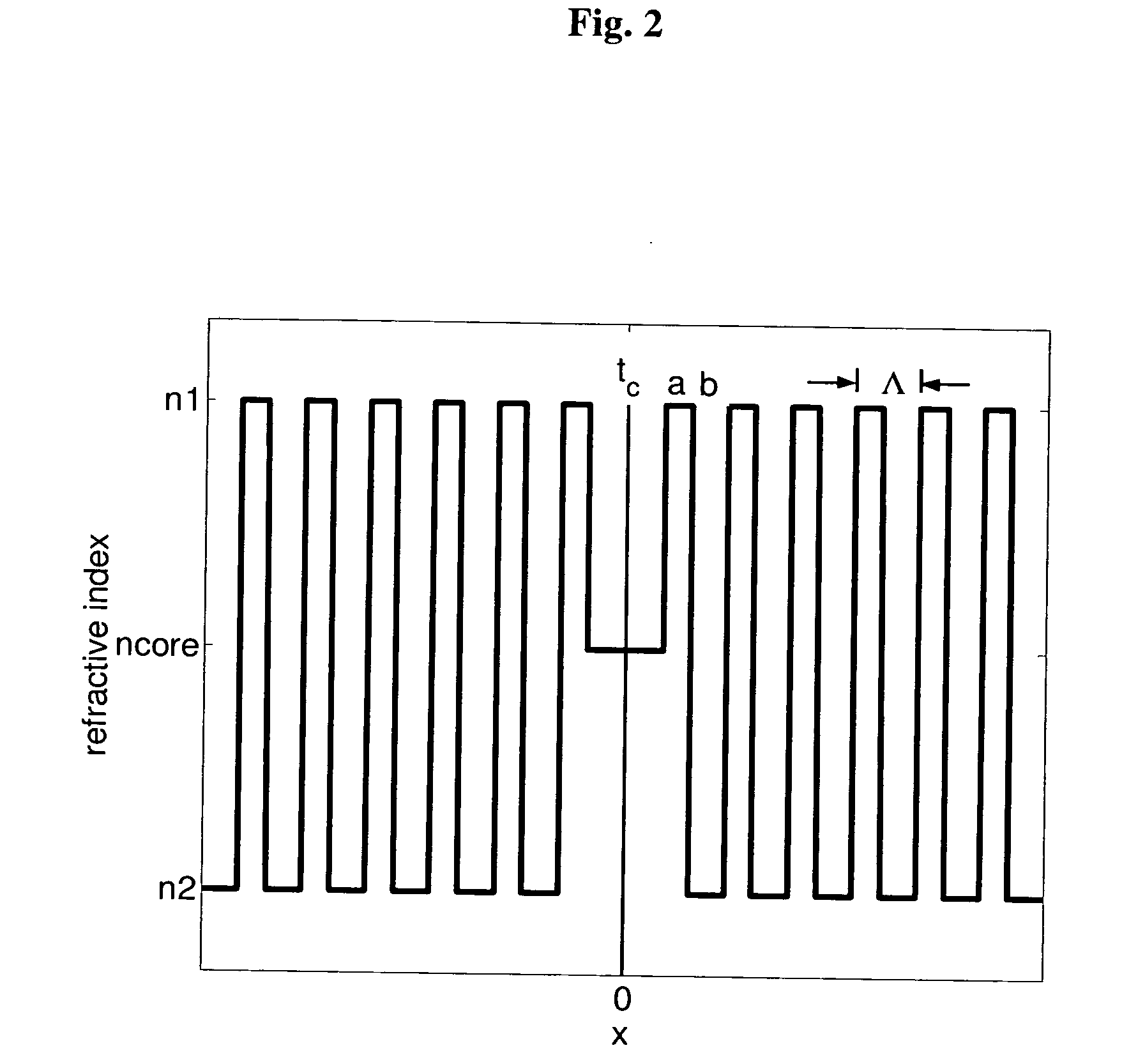
Phase matching for difference frequency generation and nonlinear optical conversion for planar waveguides via vertical coupling
A high index contrast waveguide based source for radiation. In some embodiments, the radiation is in the 0.5-14 Terahertz regime. Waveguides are provided that permit the generation of radiation at the sum and / or difference frequency of two input beams. In order to control the power level within the waveguide, embodiments in which pluralities of similar or identical waveguide are provided, and the input radiation is divided among the plurality of waveguides. The output radiation can be steered by applying phased array methods and principles.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Image forming apparatus, image forming method, and computer program product
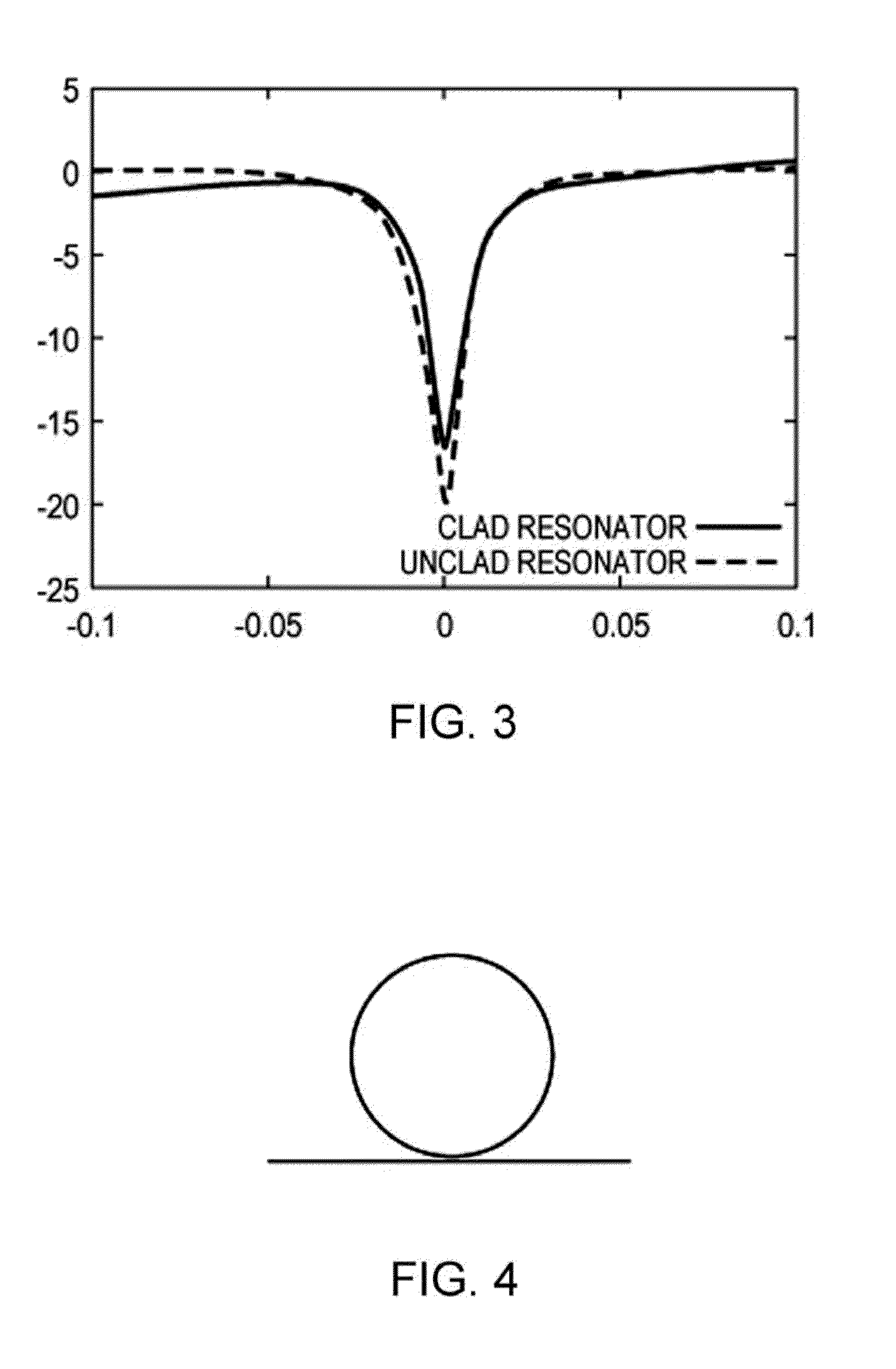
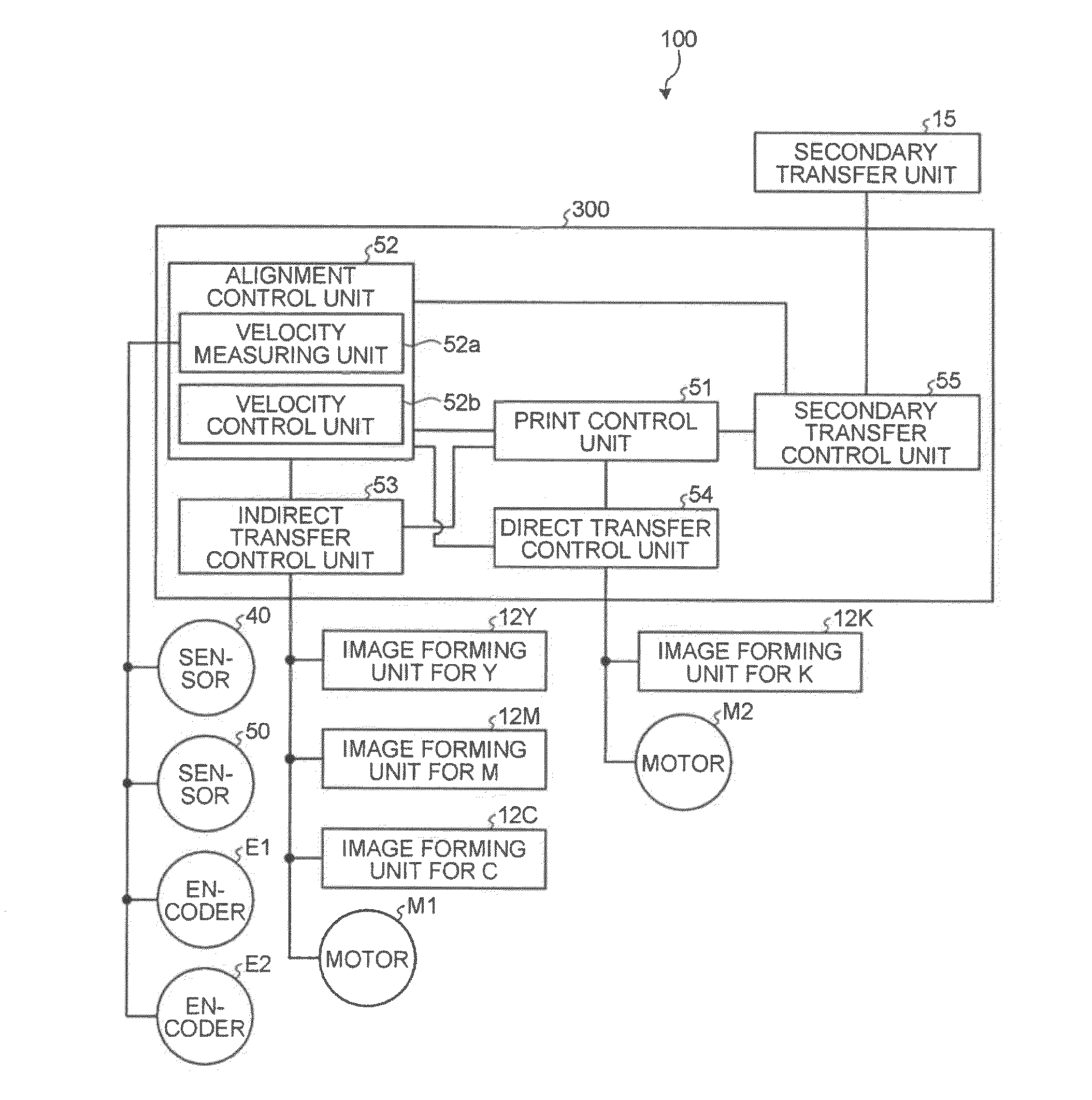
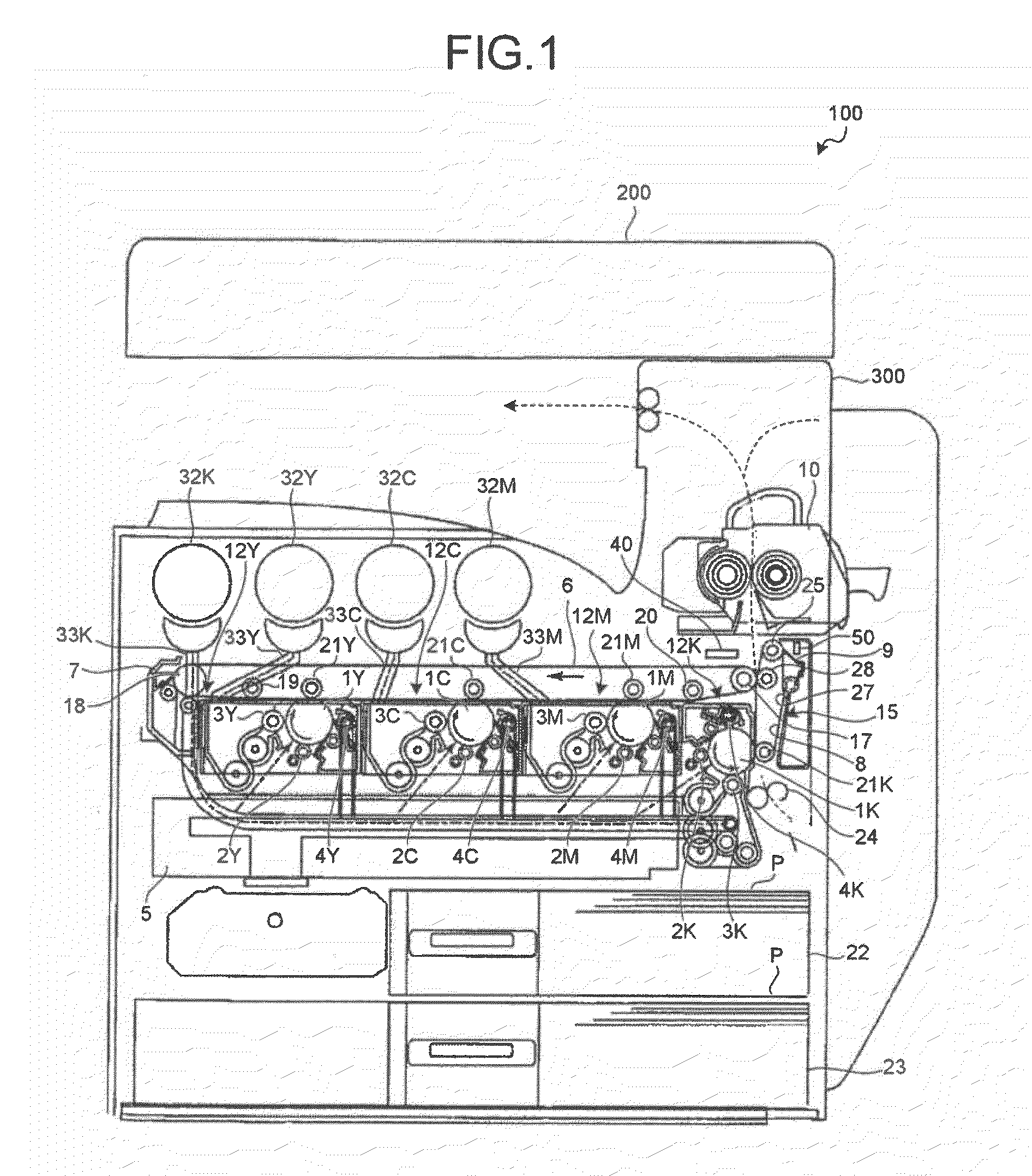
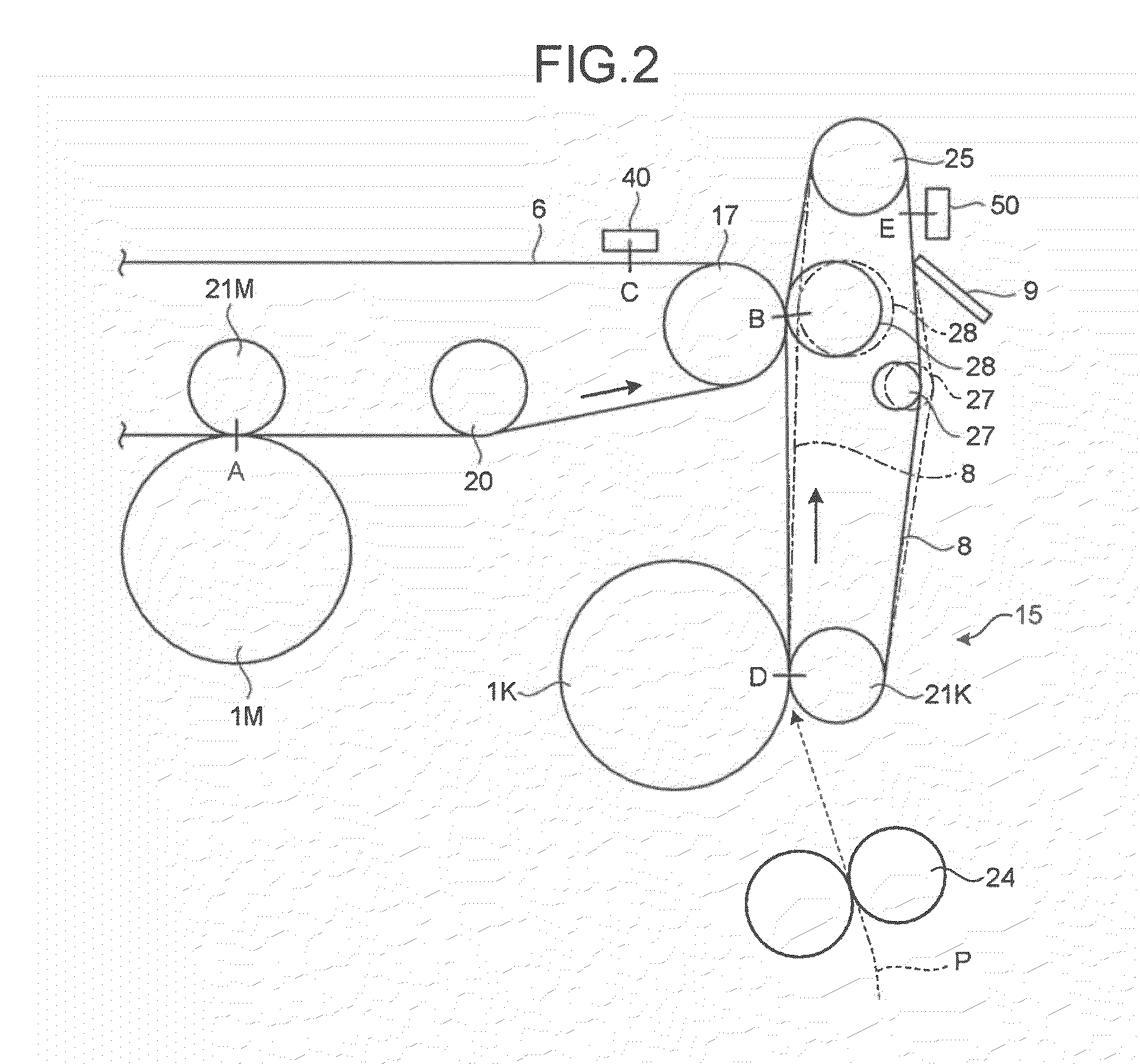
An image forming apparatus includes: a transfer-sheet conveying member that rotates to convey a transfer sheet; a first image forming unit that directly transfers a color image onto the transfer sheet; an intermediate transfer member that rotates while an image is transferred thereon; a second image forming unit that transfers images onto the intermediate transfer member; a secondary transfer unit that transfers the images on the intermediate transfer member onto the transfer sheet; a measuring unit that measures a surface velocity of the transfer-sheet conveying member and the intermediate transfer member; and a control unit that performs phase matching control by accelerating or decelerating the transfer-sheet conveying member or the intermediate transfer member so as to match a phase of fluctuation of the measured surface velocity of the transfer-sheet conveying member and a phase of fluctuation of the measured surface velocity of the intermediate transfer member.
Owner:RICOH KK
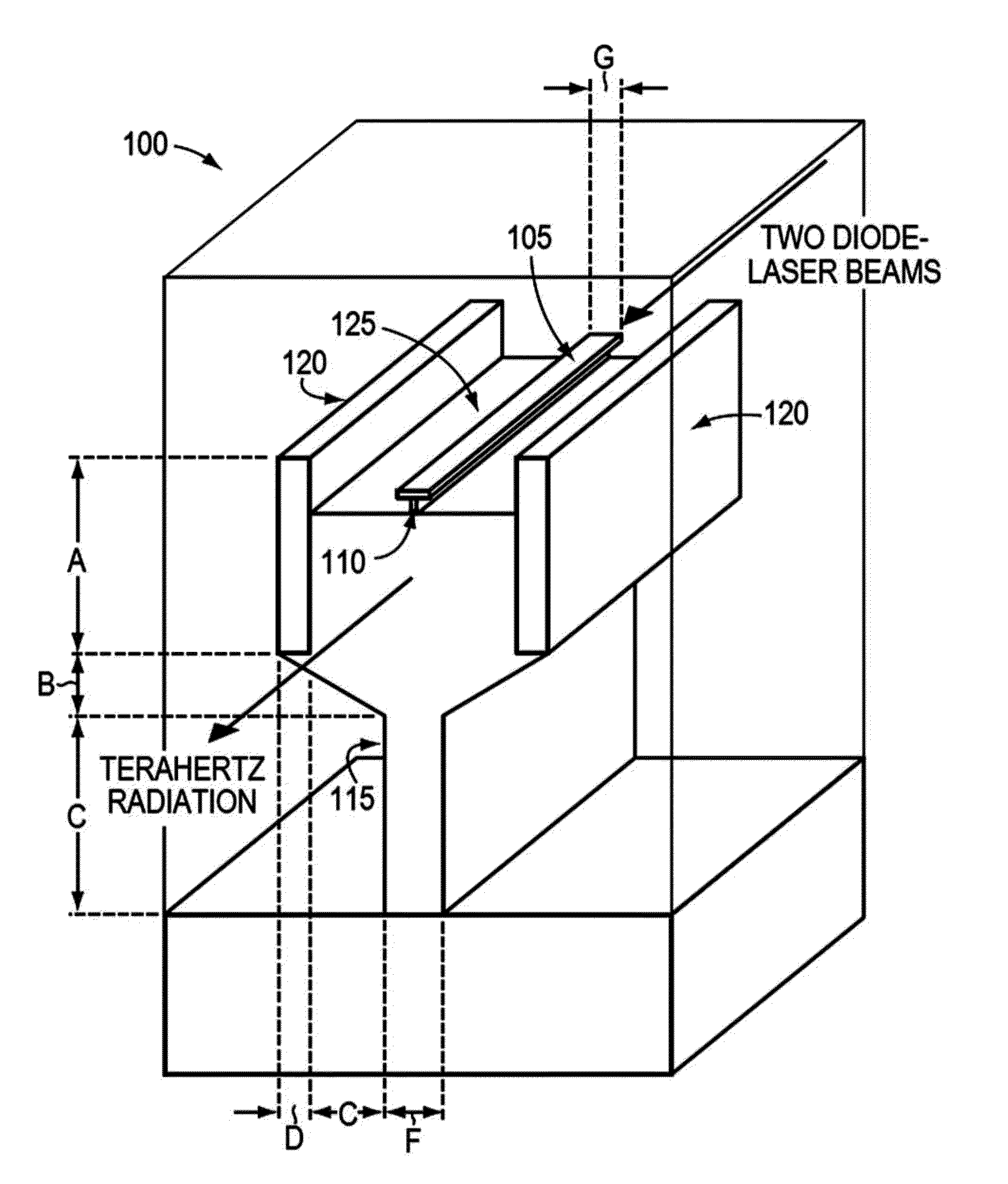
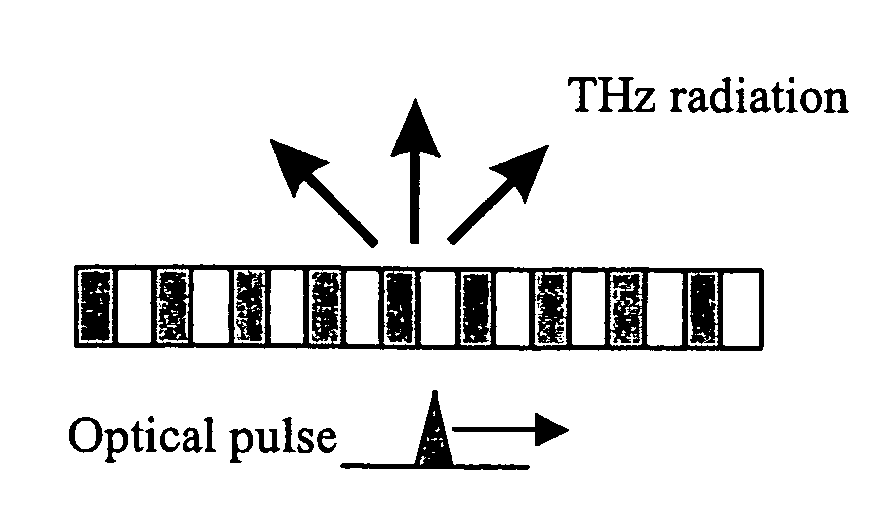
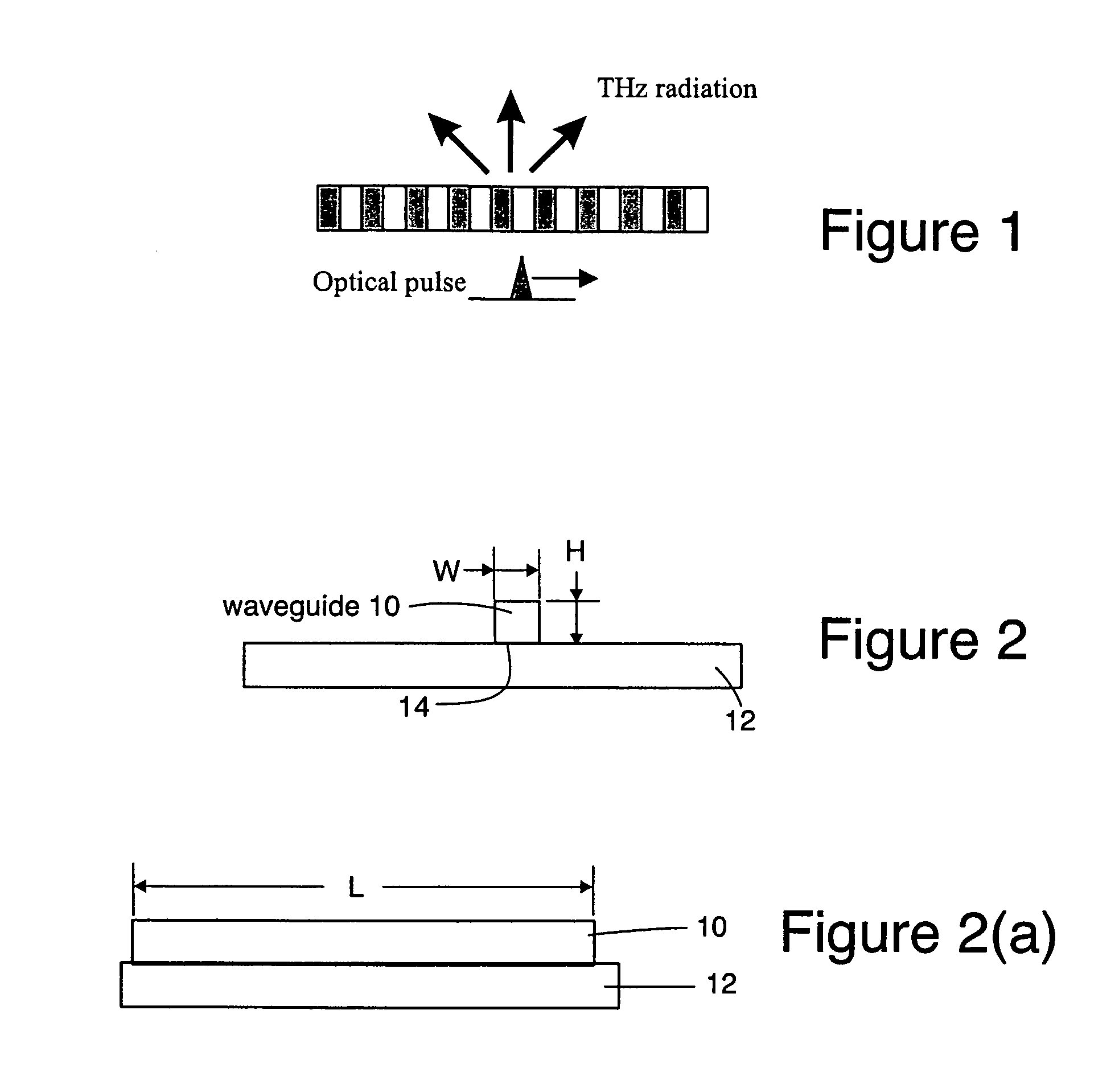
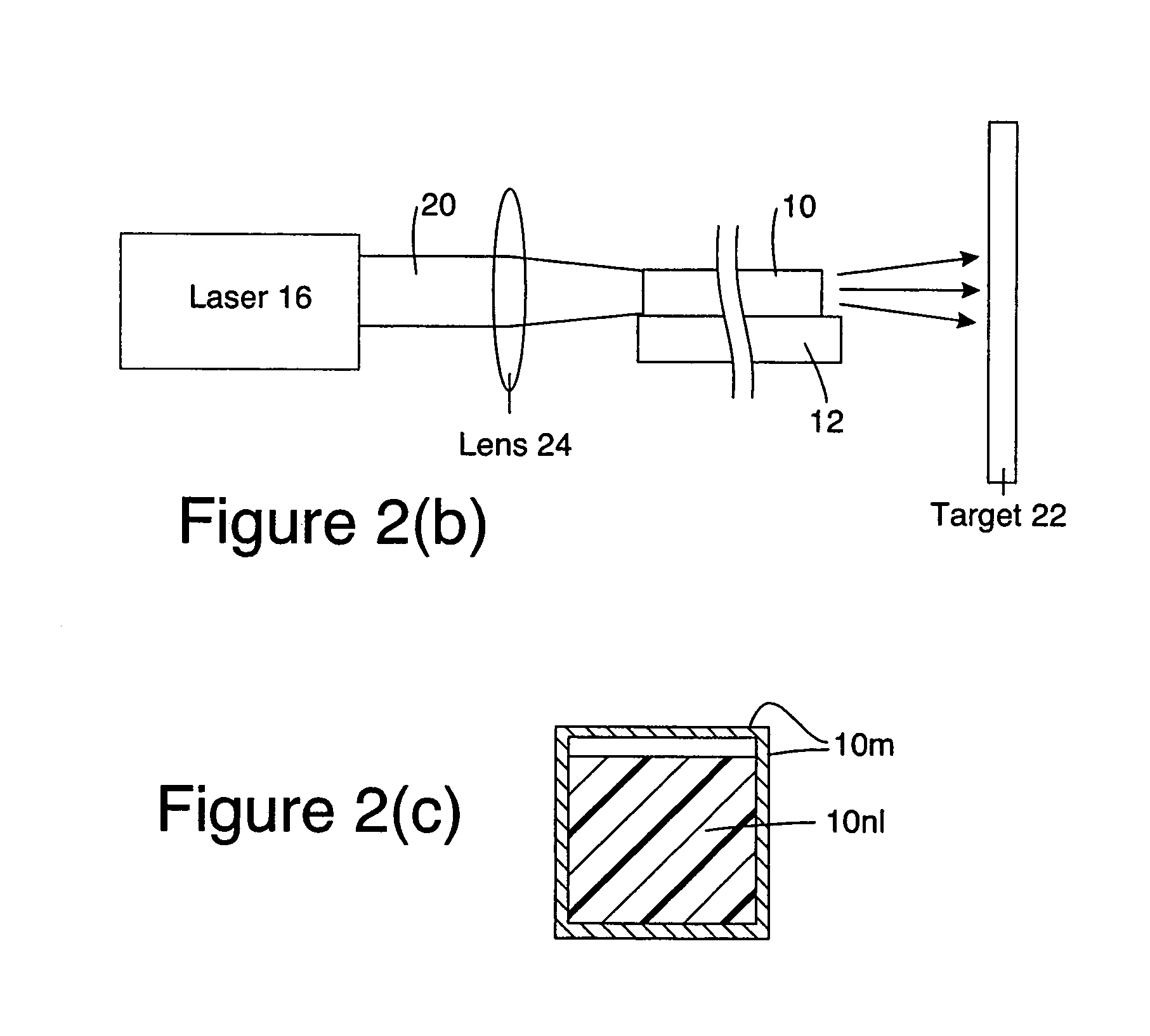
Highly efficient waveguide pulsed THz electromagnetic radiation source and group-matched waveguide THz electromagnetic radiation source
InactiveUS7272158B1Reduce impactReduce travel requirementsCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsNonlinear waveguideOptical power
Electromagnetic radiation sources operating in the Terahertz (THz) region capable of overcoming the Manley-Rowe limits of known optical schemes by achieving phase matching between a THz wave and optical pulse in a nonlinear waveguide, or by achieving both phase and group velocity matching between a THz wave and optical pulse in a nonlinear waveguide to yield even higher efficiencies in converting optical power to the THz region.
Owner:HRL LAB
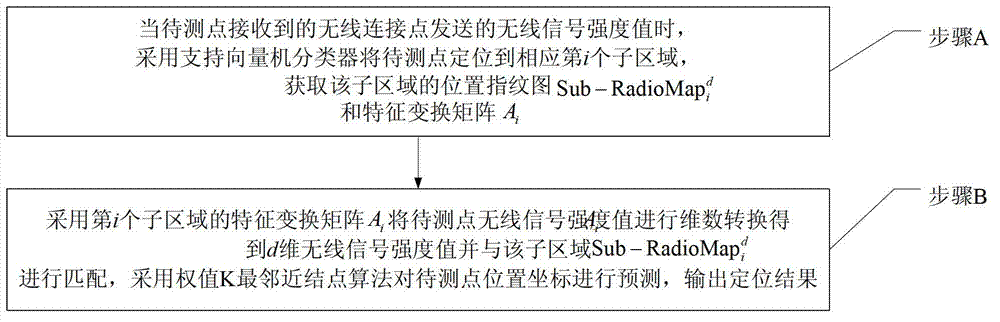
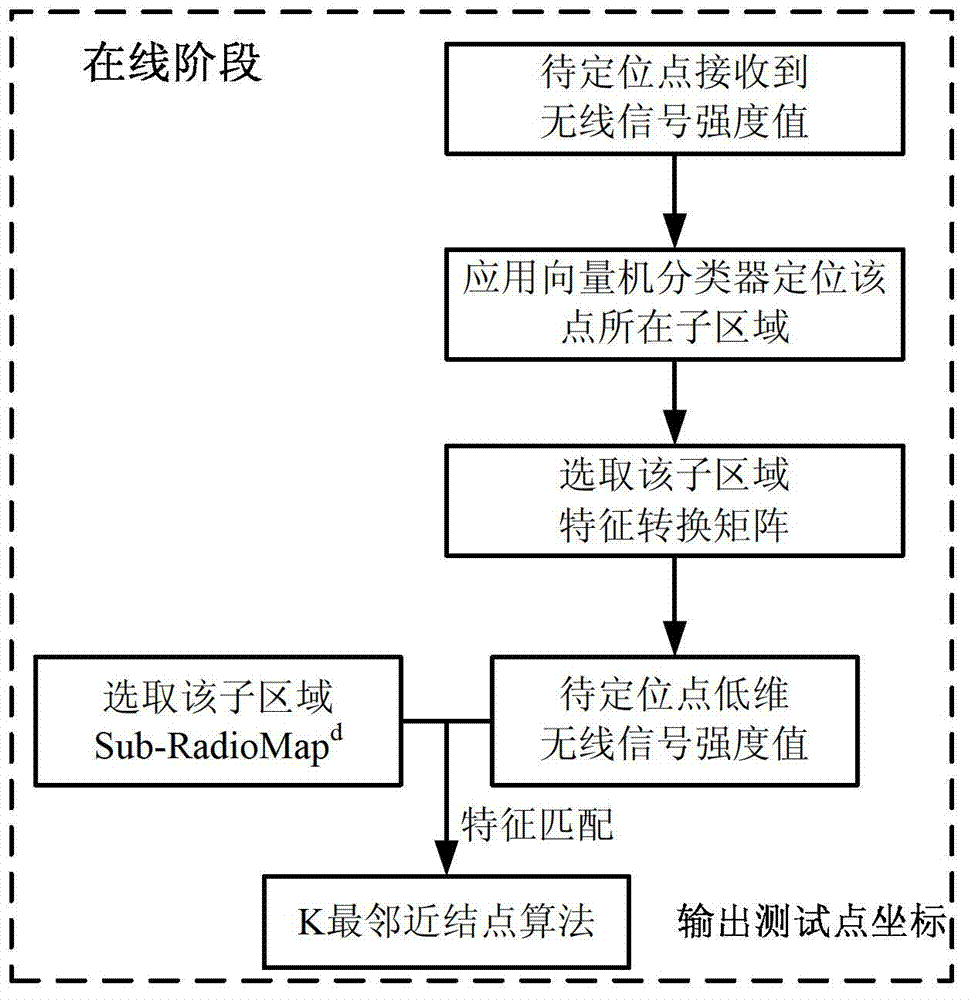
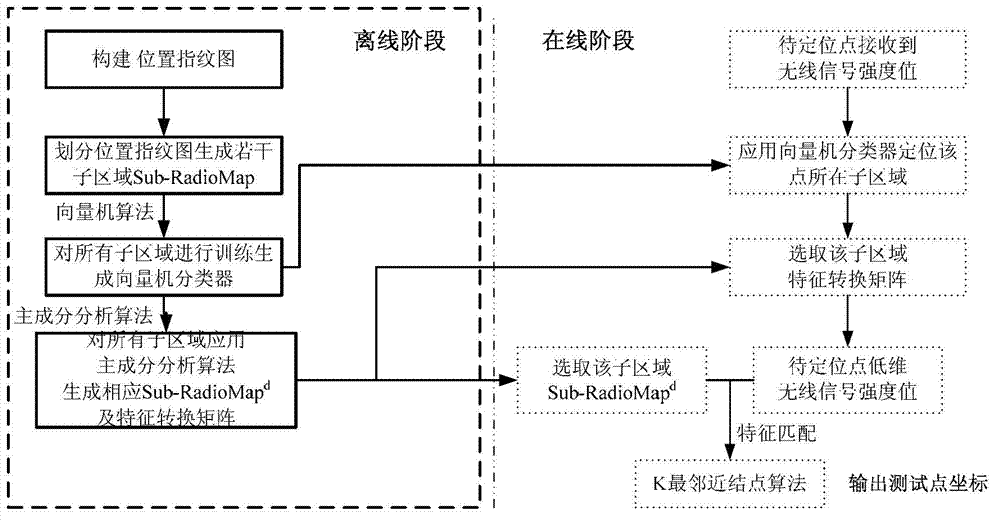
Wireless fidelity (Wi-Fi) indoor positioning method
InactiveCN103096466AReduce operational complexityImprove real-time performanceWireless communicationWi-FiComputation complexity
The invention particularly relates to a wireless fidelity (Wi-Fi) indoor positioning method, and aims at resolving the problems that in a traditional Wi-Fi indoor positioning method, a feature information position fingerprint map data base is too large, computation complexity in an on-line positioning phase matching process is high, instantaneity is poor, and the like. The method includes that when a point to be detected receives a wireless signal strength value sent by a wireless connection point, a support vector machine classifier is adopted to position the point to be detected to a corresponding ith subregion, and a position fingerprint map and a feature transformational matrix Ai of the subregion are obtained; and the feature transformational matrix Ai of the ith subregion is adopted to enable the wireless signal strength value of the point to be detected to achieve shiftdim, a d-dimension wireless signal strength value is obtained and matched with the subregion, the weight K-nearest neighbor node algorithm is adopted to forecast position coordinates of the point to be detected, and positioning results are output. The Wi-Fi indoor positioning method is applied to the communication field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
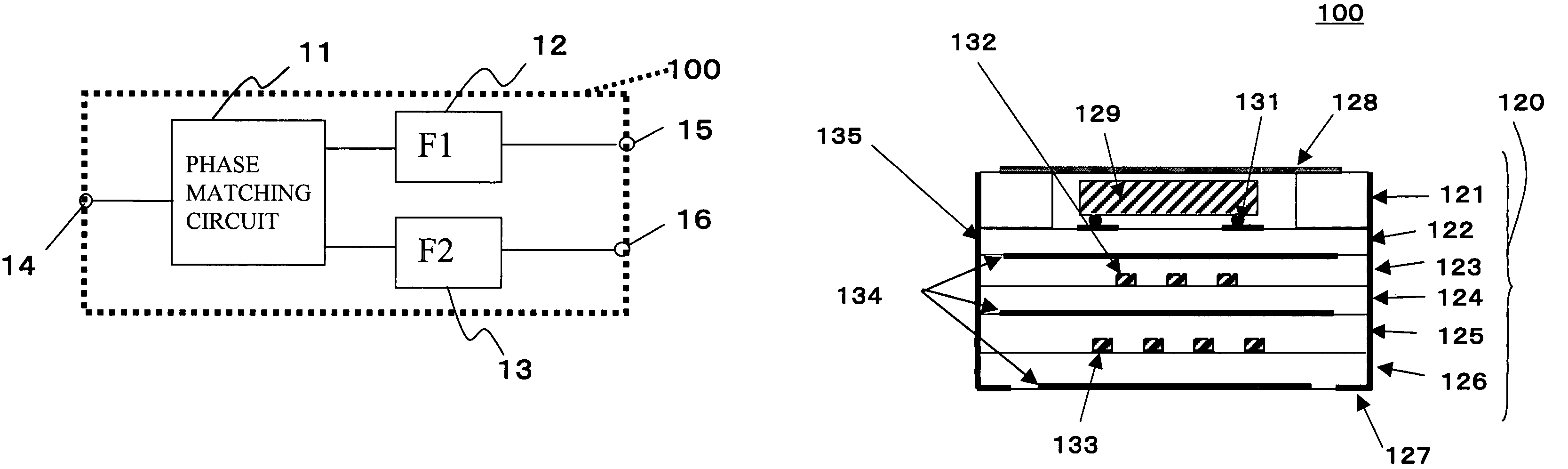
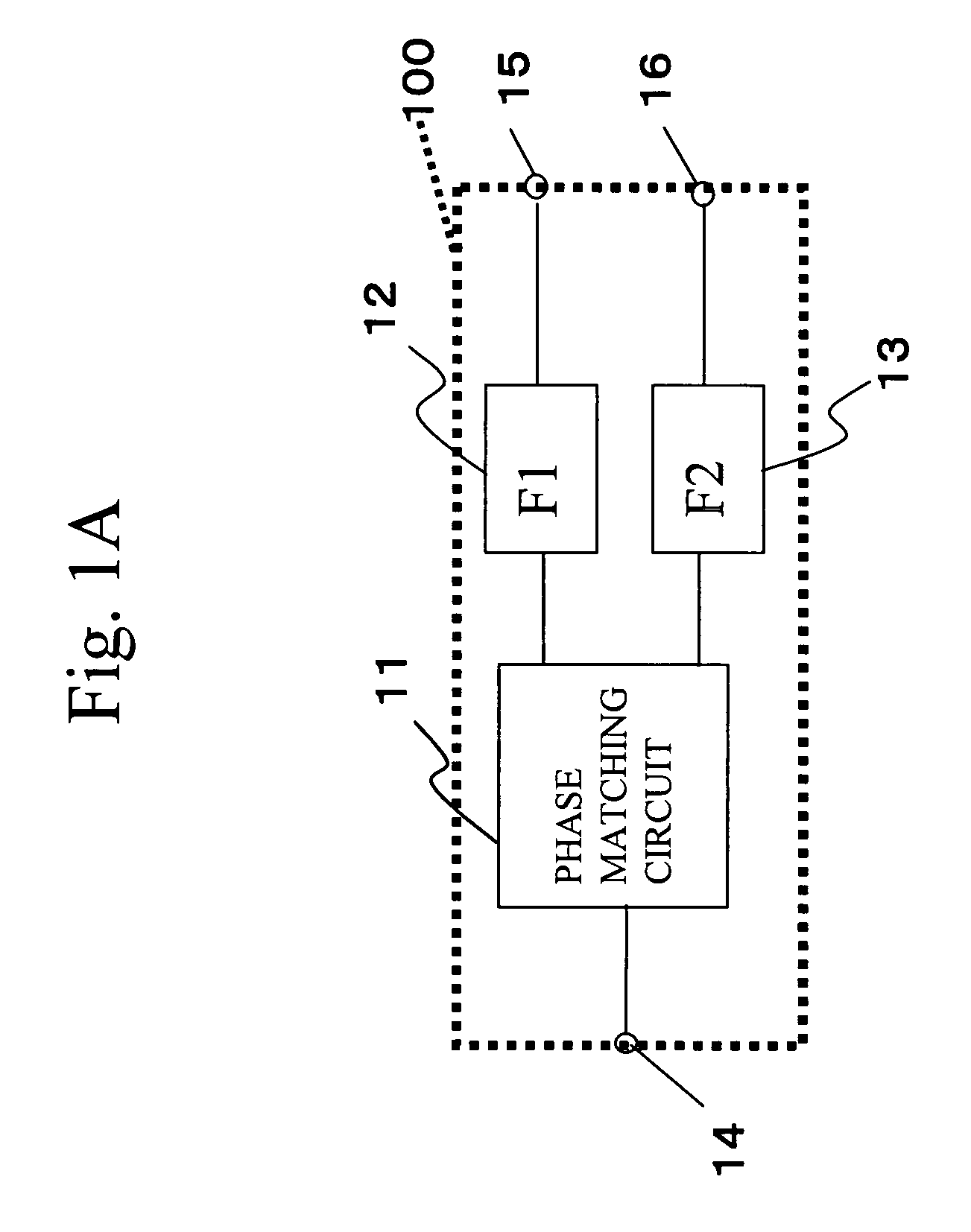
Duplexer using surface acoustic wave filters
ActiveUS7053731B2Improved out-of-band attenuationImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesPhase matchingSurface acoustic wave sensor
A duplexer includes two surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters having different center frequencies, a phase matching circuit that matches phases of the two SAW filters, a package in which the SAW filters and the phase matching circuit are housed, the package having a die-attached layer on which a chip of the SAW filters is facedown mounted, and ground line patterns provided on the die-attached layer and an underlying layer that underlies the die-attached layer, the ground line patterns forming inductances.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
FCSEL that frequency doubles its output emissions using sum-frequency generation
InactiveUS6879615B2Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionPrismWaveguide
A “Folded Cavity Surface Emitting Laser” (FCSEL) sum frequency generating device capable of generating a second harmonic at room temperatures with high efficiency and output power, while having a small size, low energy consumption, and a low manufacturing cost. A FCSEL sum frequency generating semiconductor diode laser has a multilayered structure that comprises a mode discriminating polyhedral shaped prism waveguide, which is located at one end of two light emitting diodes, a partial photon reflecting mirror, which is located at the opposite end of the two light emitting diodes, and a phase-matching sum-frequency generating superlattice, which is located between the polyhedral shaped prism waveguide and the partial photon reflecting mirror.
Owner:HENRICHS JOSEPH REID
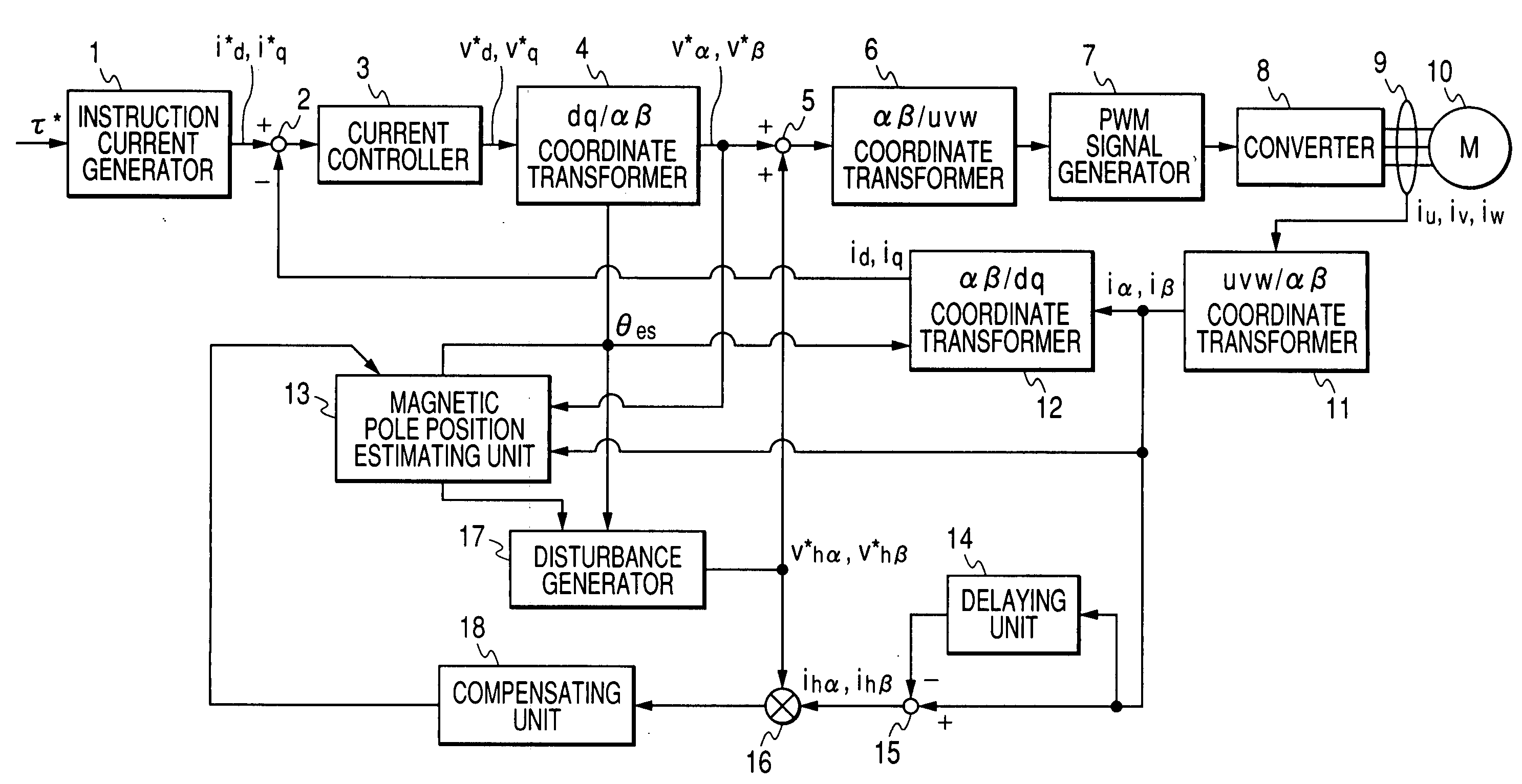
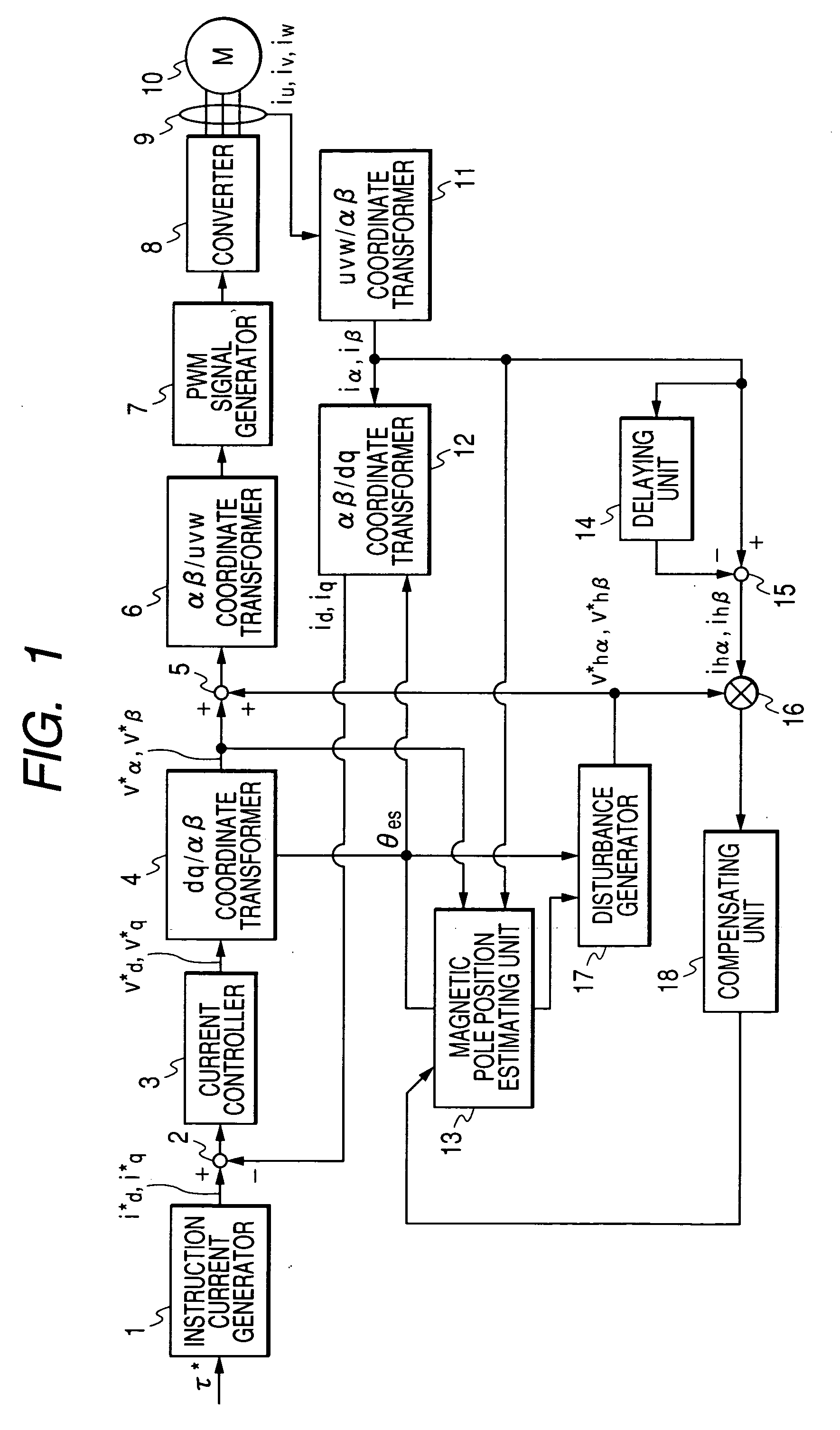
Method of estimating magnetic pole position in motor and apparatus of controlling the motor based on the estimated position
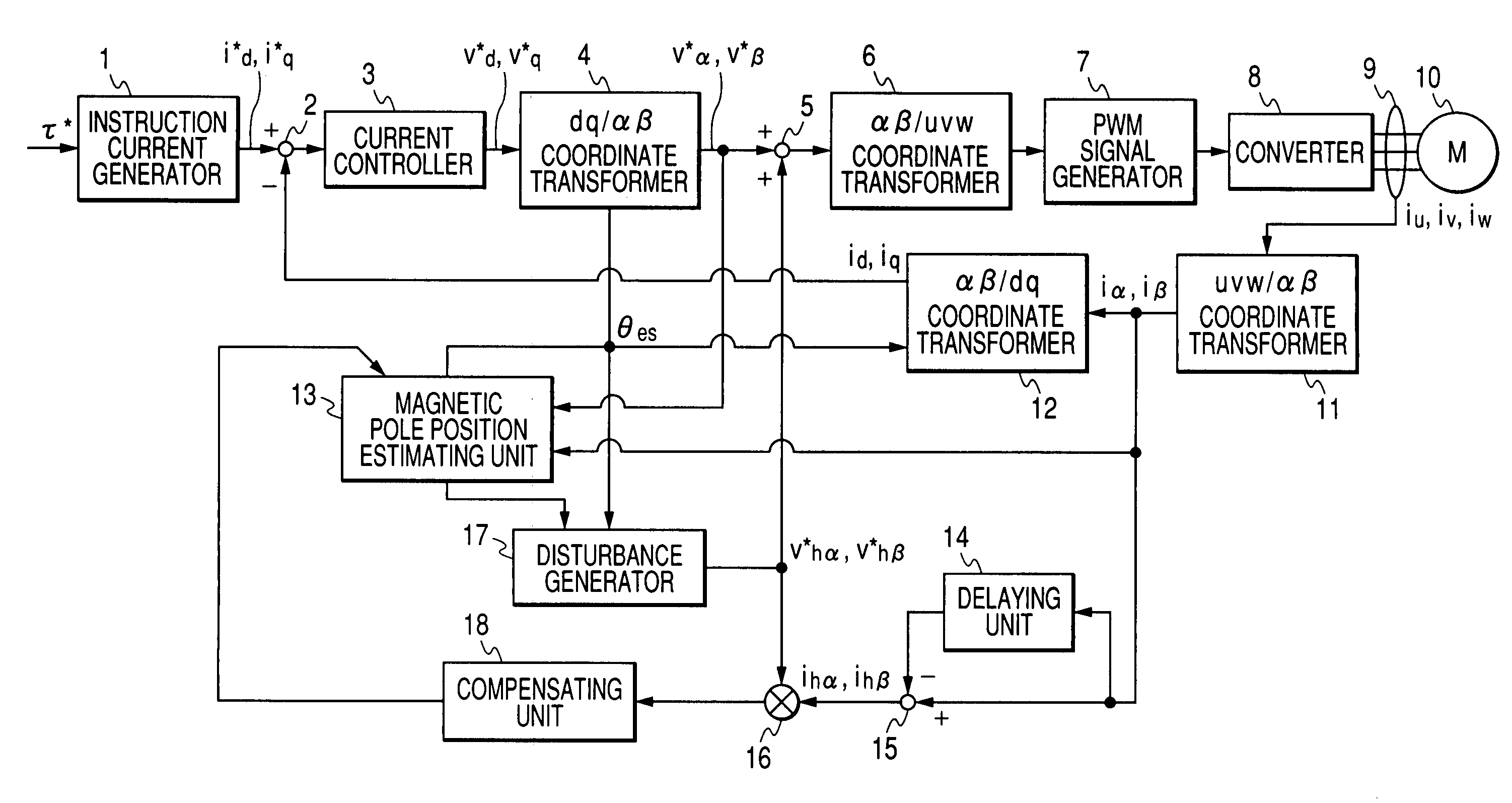
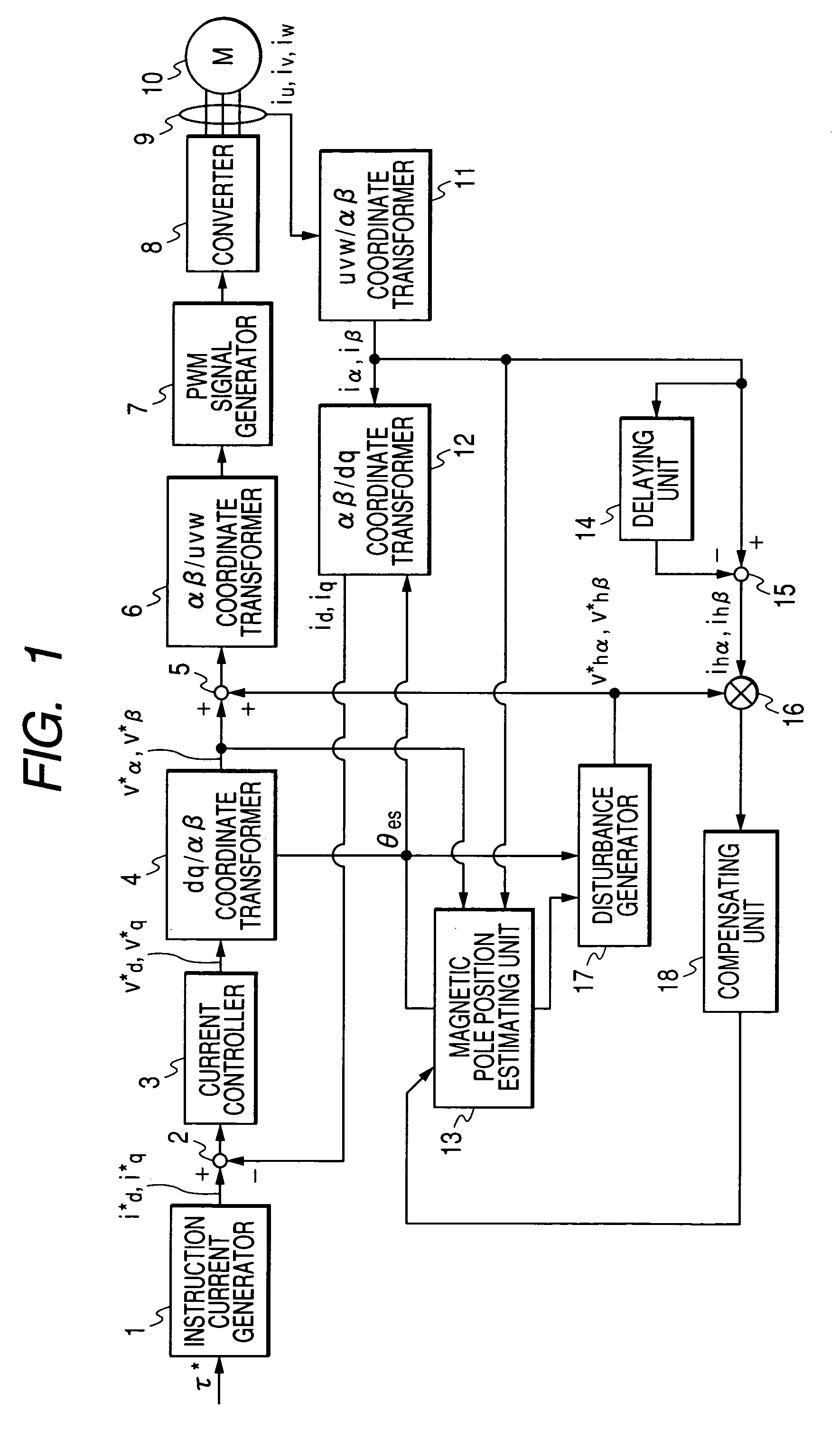
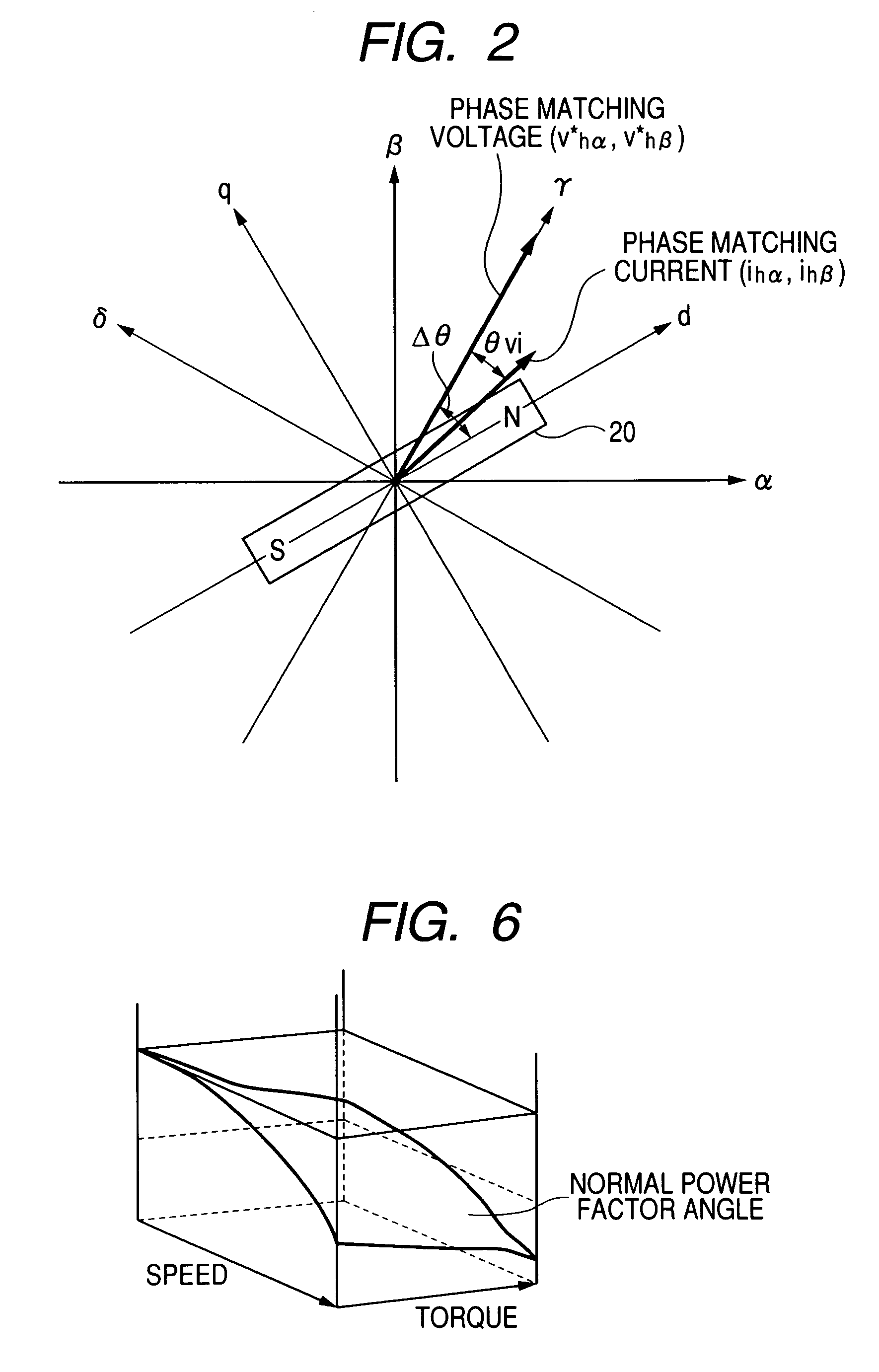
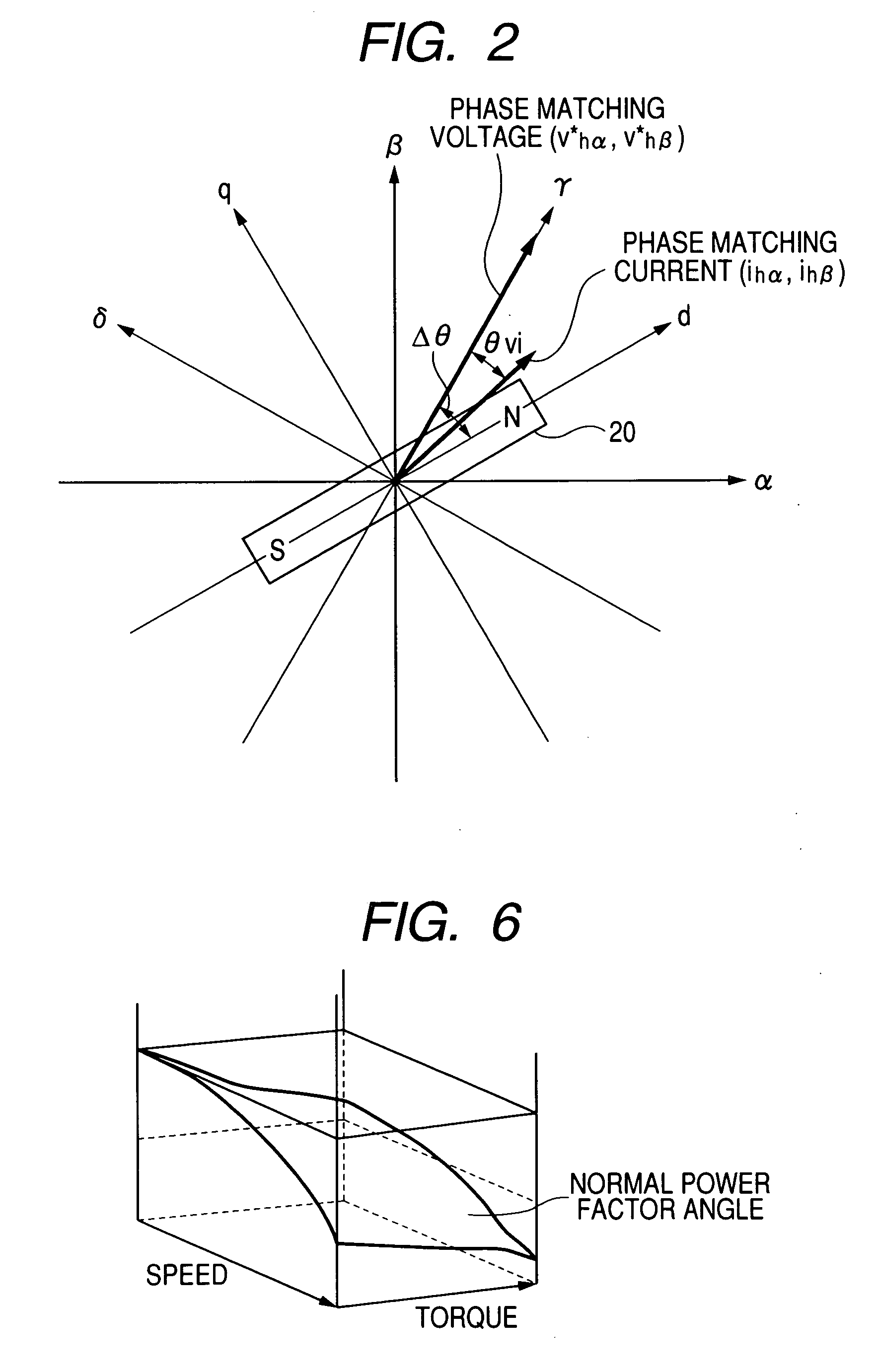
ActiveUS7352151B2Reduce the amount of calculationAccurate estimateSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsSynchronous motorPhase difference
A magnetic pole position in a synchronous motor having salient poles is estimated from an instructed voltage applied to the motor, a current generated from the instructed voltage and parameters. To estimate the position substantially matching with a true magnetic pole position, a phase matching voltage having a phase matching with the estimated magnetic pole position previously obtained is applied to the motor. The phase matching voltage has a harmonic frequency higher than that of the instructed voltage. A phase matching current generated from the phase matching voltage is detected from the motor. A value of at least one of the parameters is corrected such that a difference in phase between the phase matching voltage and the phase matching current substantially becomes zero. An estimated magnetic pole position is calculated from the instructed voltage, the generated current and the parameter having the corrected value.
Owner:DENSO CORP
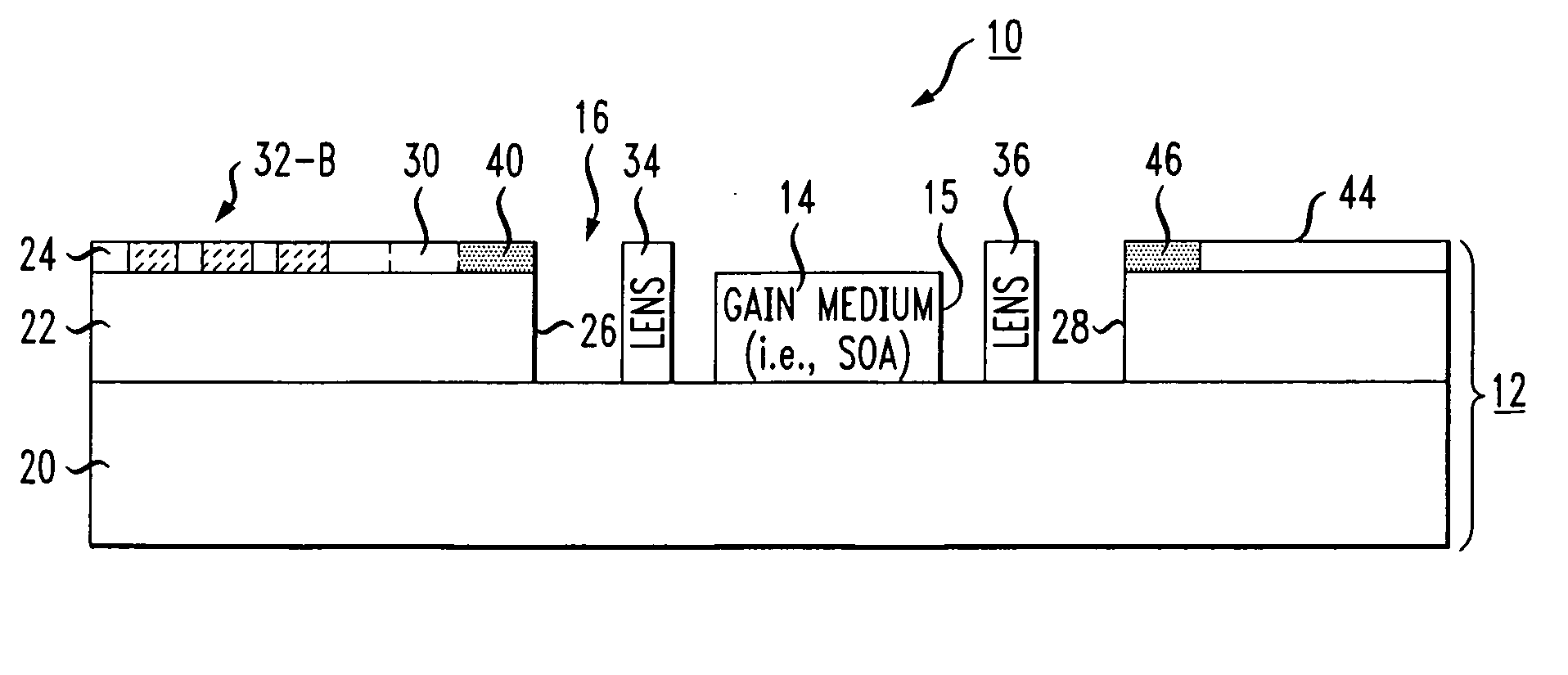
Soi-based tunable laser
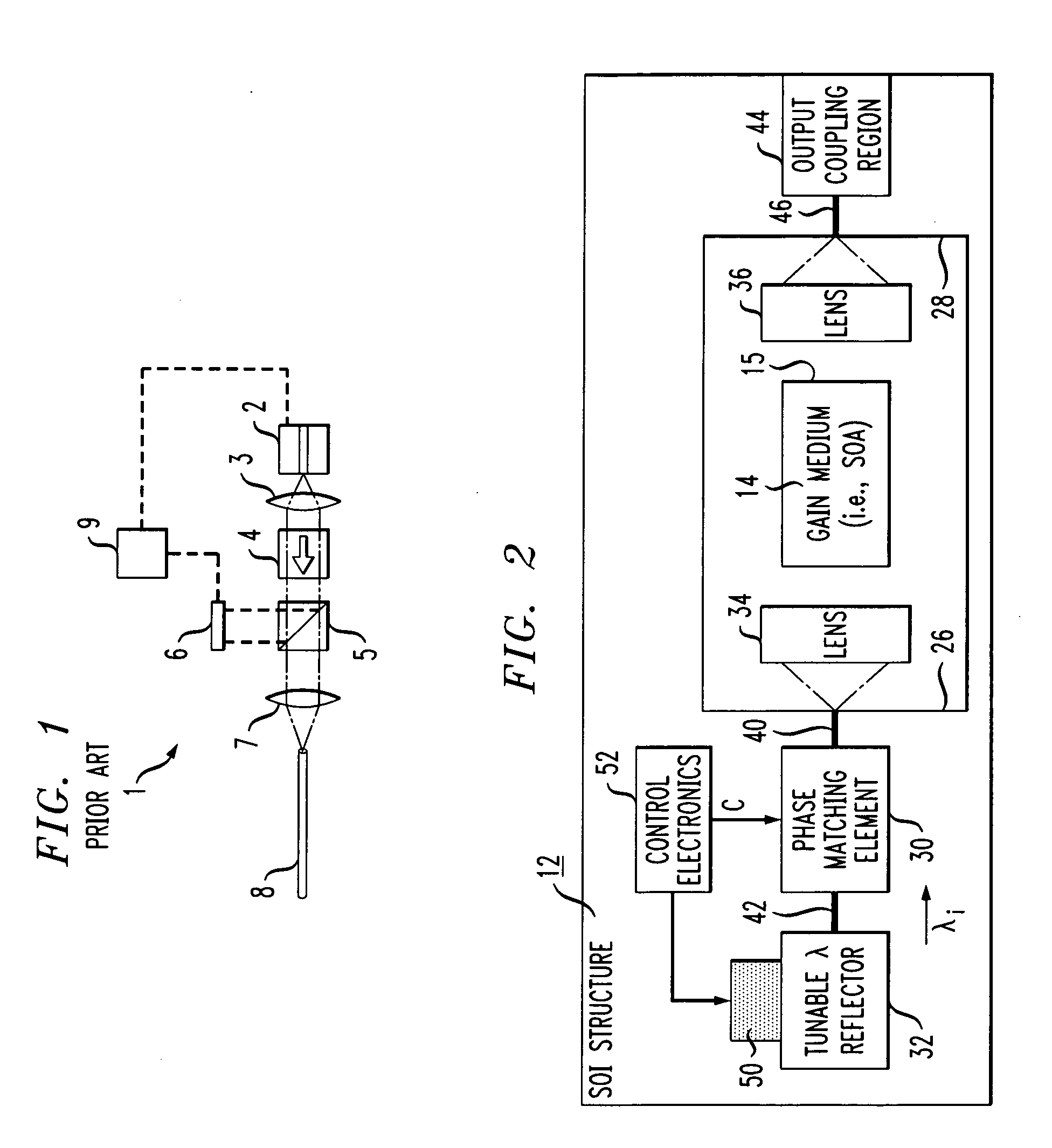
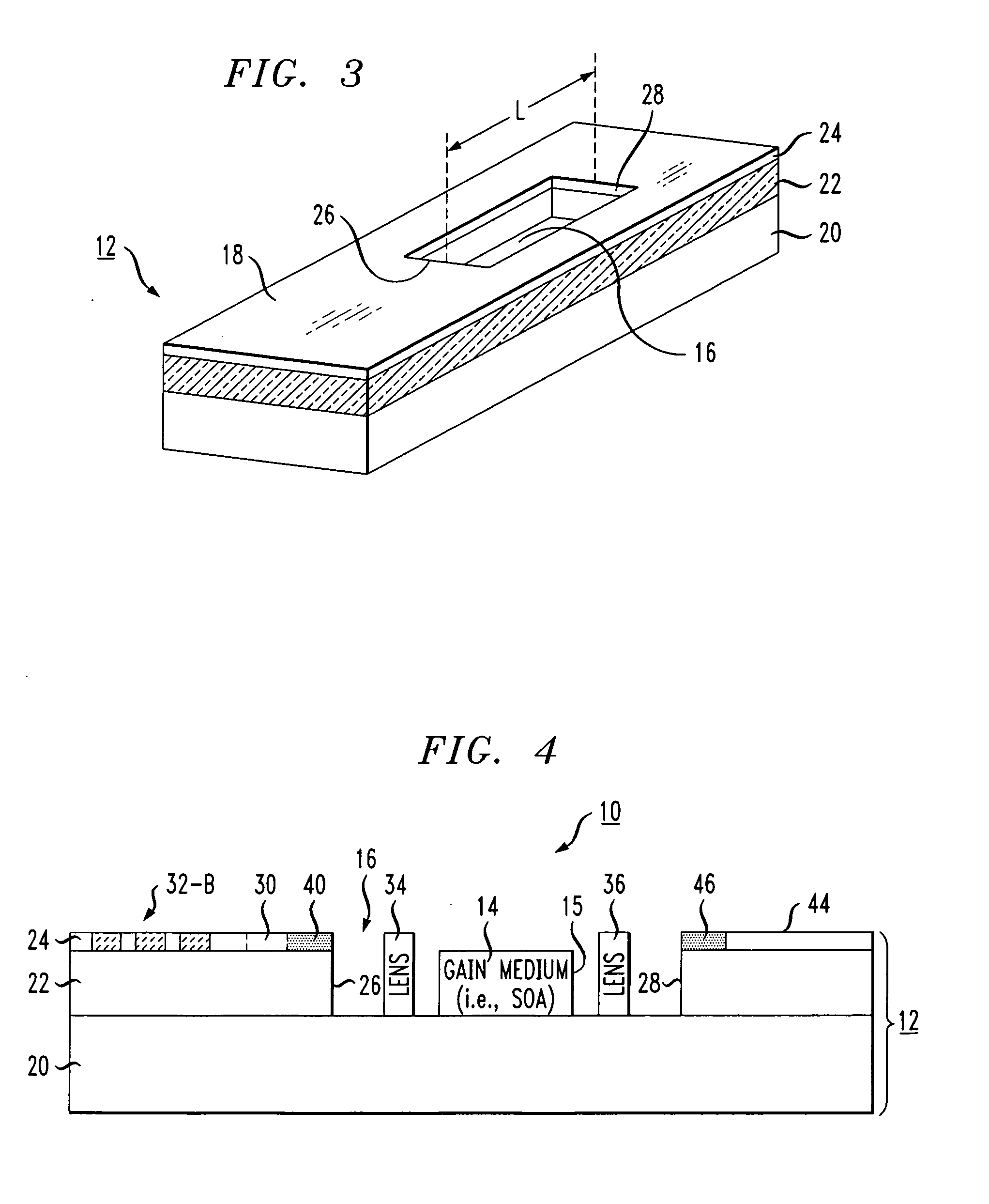
ActiveUS20090135861A1Improve insulation performanceEfficient couplingLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersAudio power amplifierCoupling
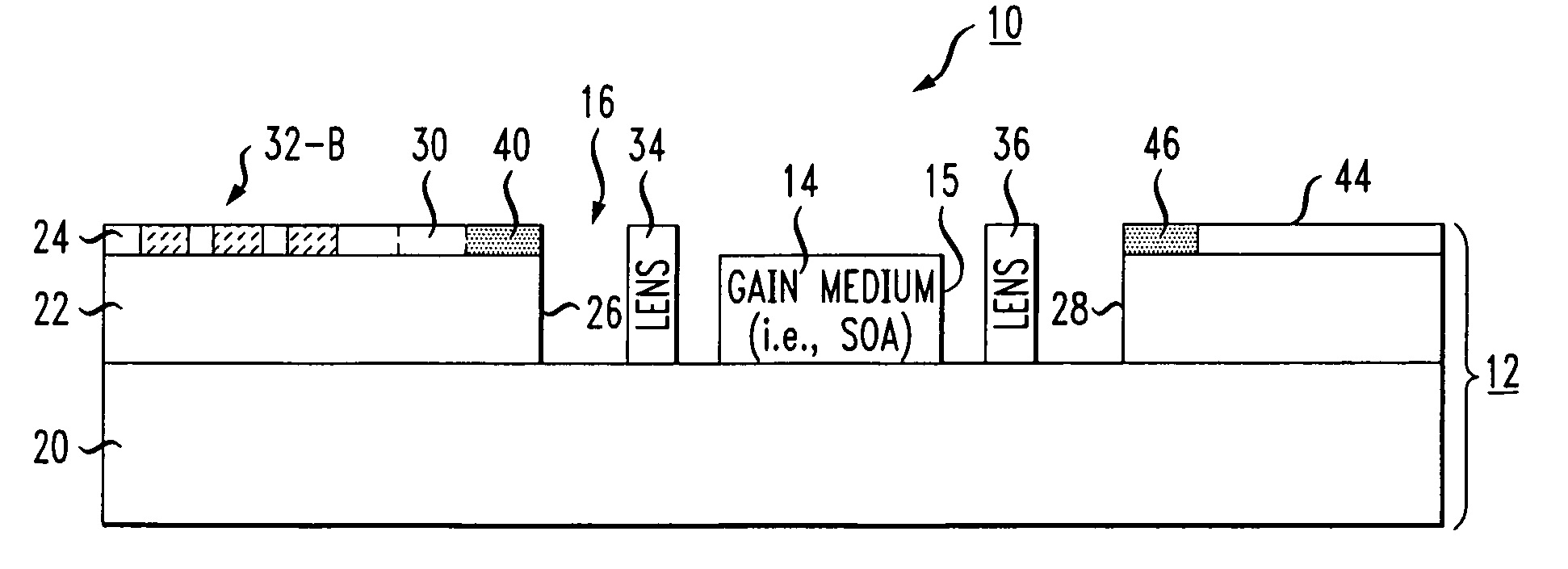
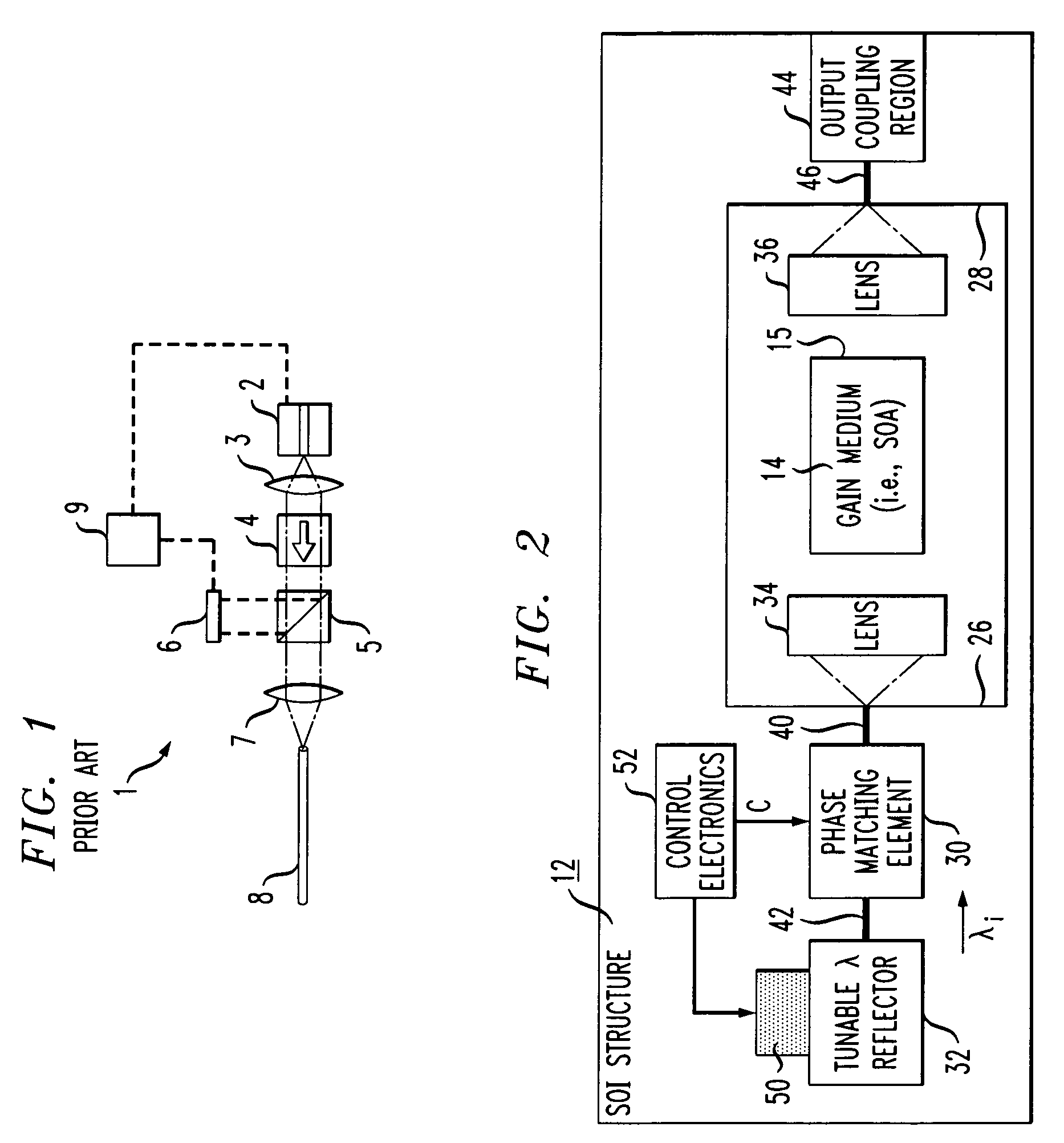
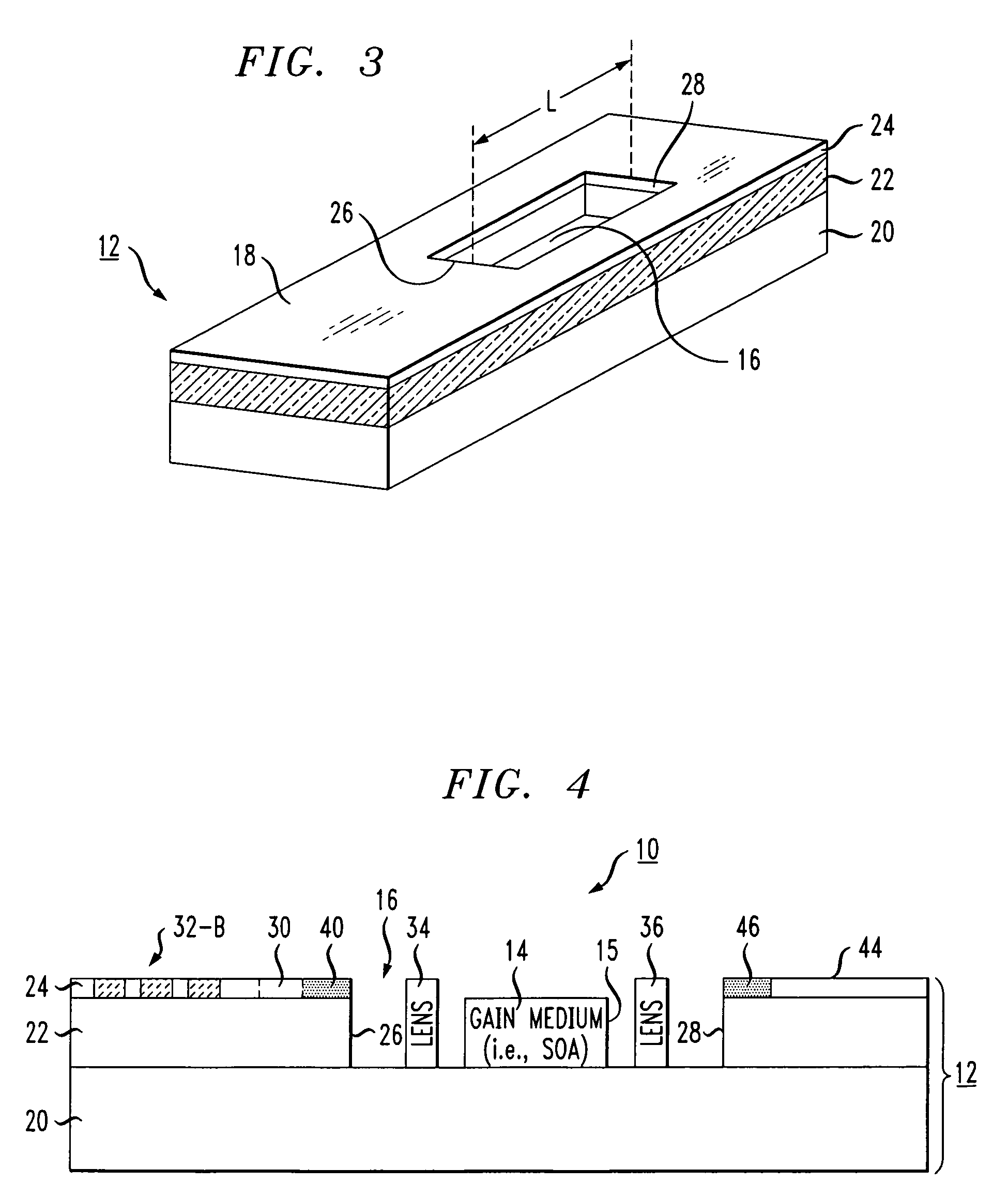
A silicon-on-insulator (SOI)-based tunable laser is formed to include the gain medium (such as a semiconductor optical amplifier) disposed within a cavity formed within the SOI substrate. A tunable wavelength reflecting element and associated phase matching element are formed on the surface of the SOI structure, with optical waveguides formed in the surface SOI layer providing the communication between these components. The tunable wavelength element is controlled to adjust the optical wavelength. Separate discrete lensing elements may be disposed in the cavity with the gain medium, providing efficient coupling of the optical signal into the SOI waveguides. Alternatively, the gain medium itself may be formed to include spot converting tapers on its endfaces, the tapers used to provide mode matching into the associated optical waveguides.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for providing phase matching with optimized beam widths
InactiveUS20020128027A1Minimizing interference energyIncrease system capacitySpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentEngineeringPhase matching
Owner:F POSZAT HU
RF phase modulation technique for performing acousto-optic intensity modulation of an optical wavefront
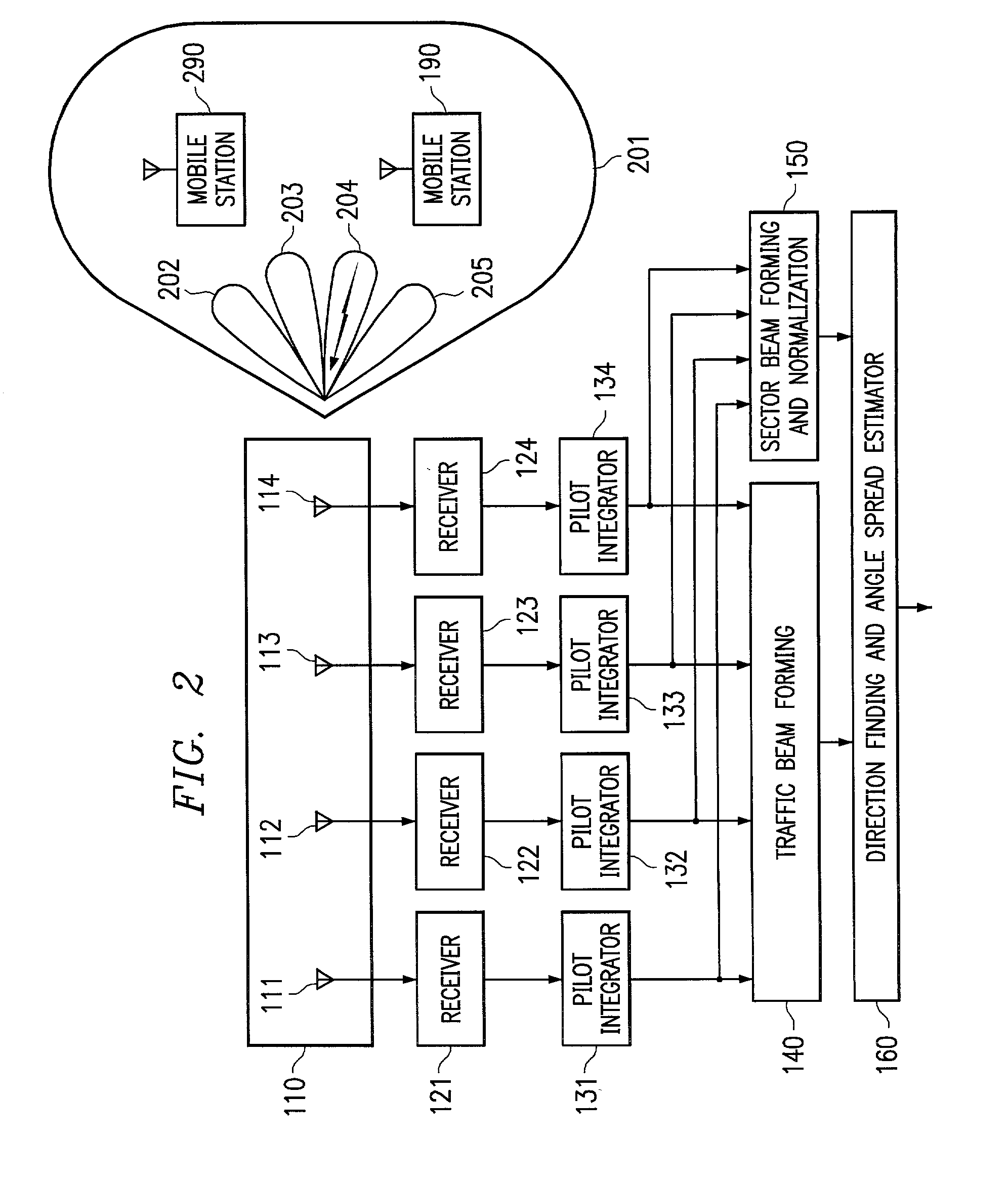
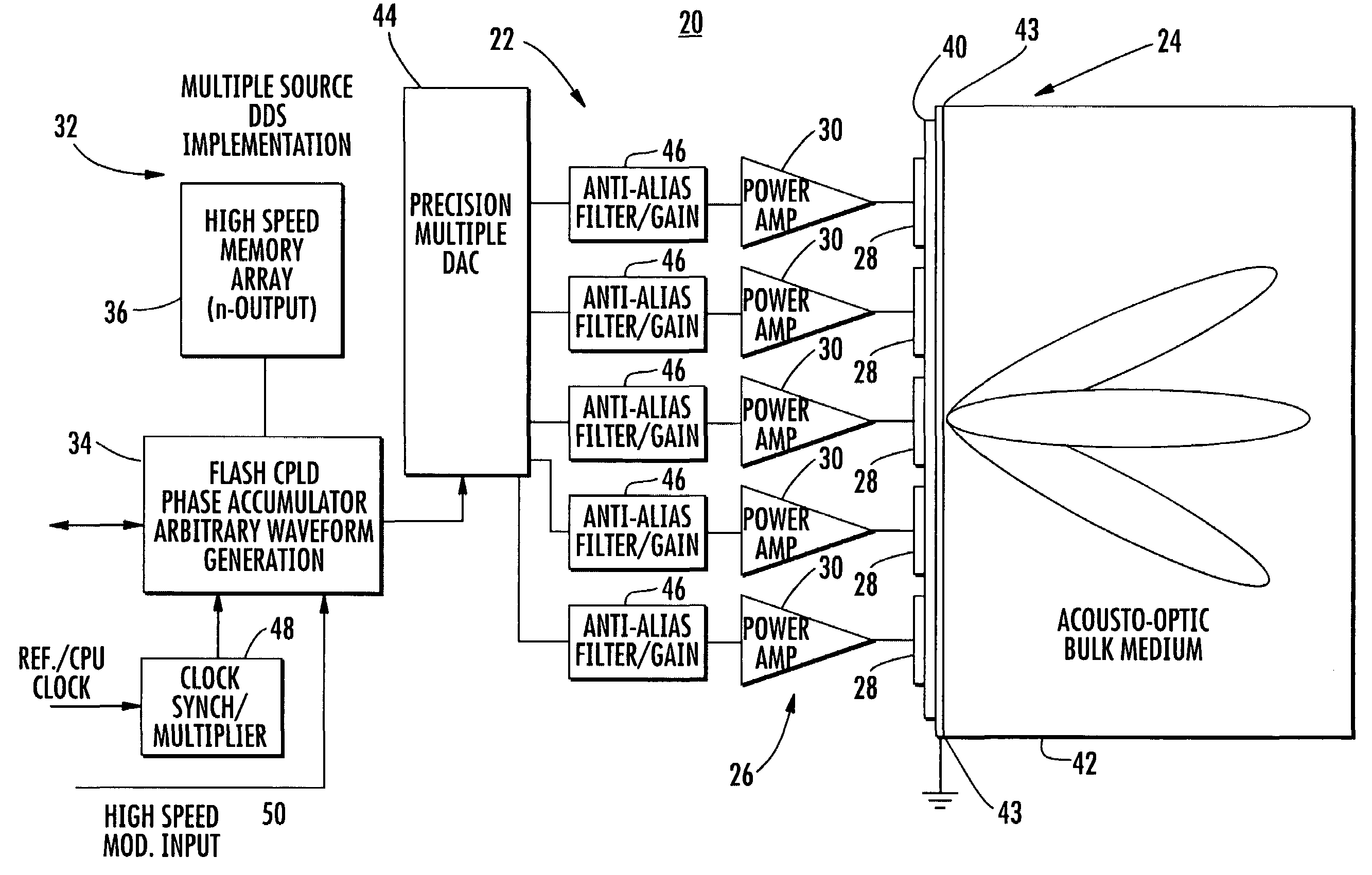
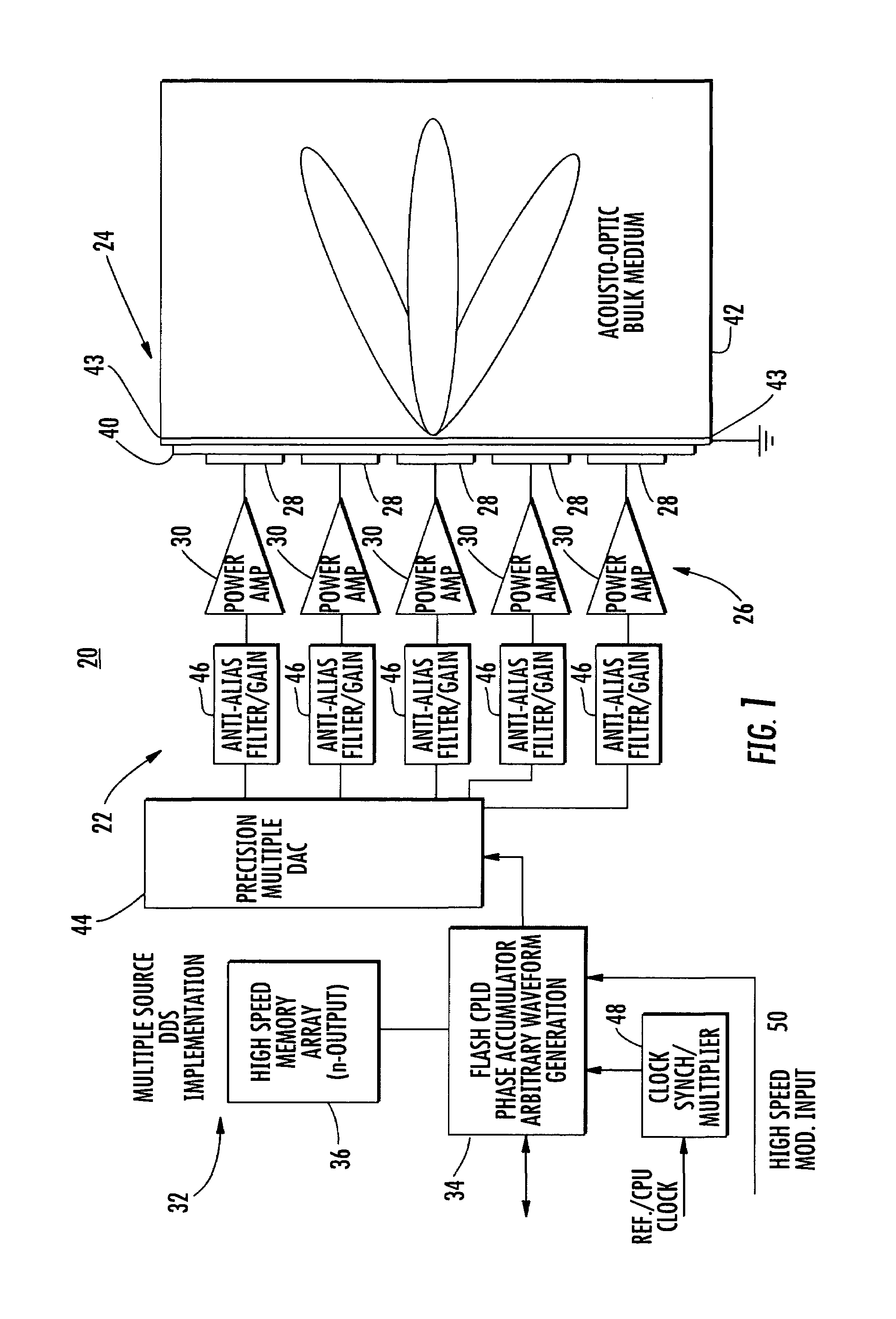
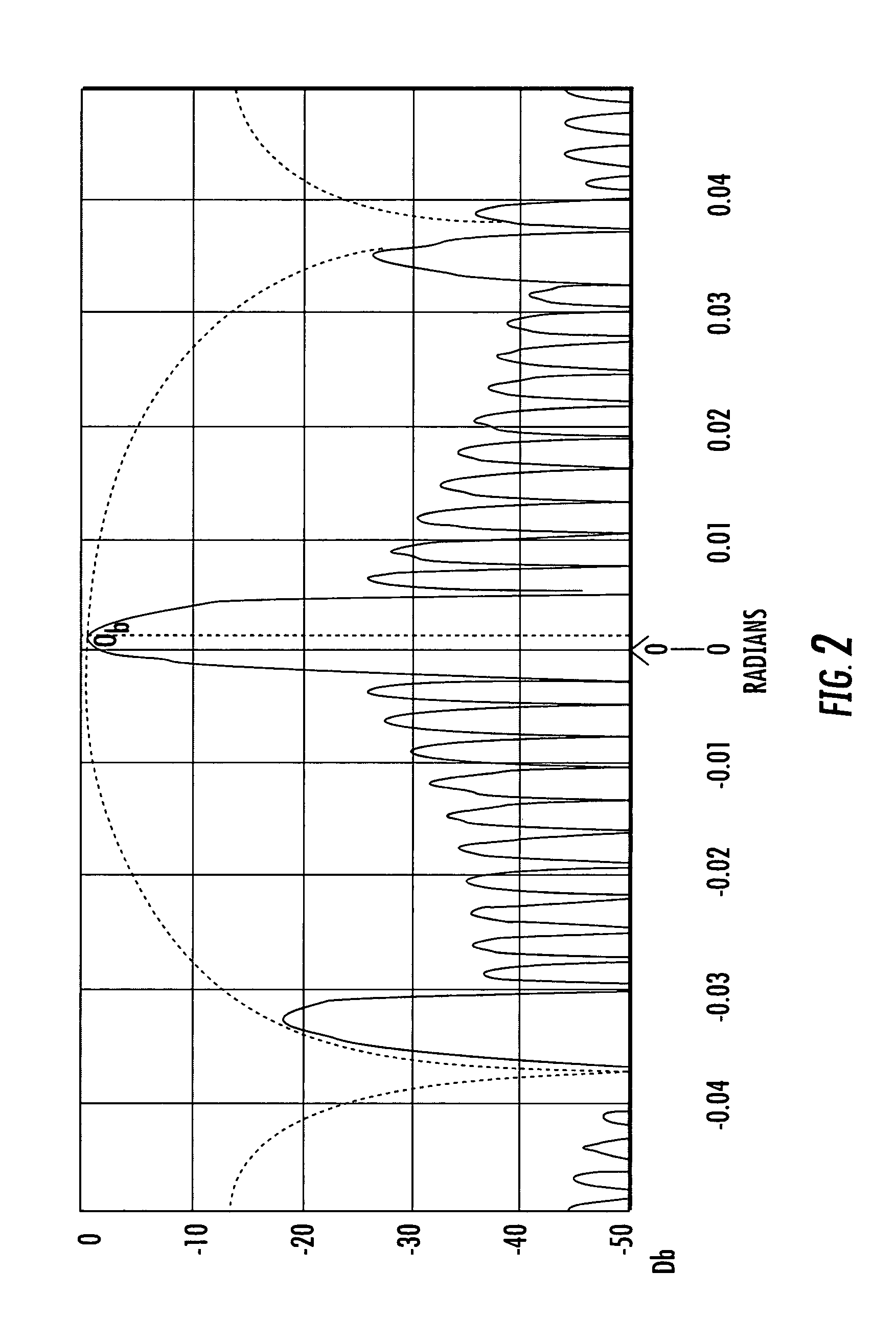
An acousto-optic modulator includes an acousto-optic bulk medium and transducer attached to the acousto-optic bulk medium and formed as a linear array of electrodes. A transducer driver is connected to each electrode and is coherently phase driven to alter the angular momentum distribution of an acoustic field and alternately allow and inhibit phase matching between the optical and acoustic field and produce a desired intensity modulation of an optical wavefront.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
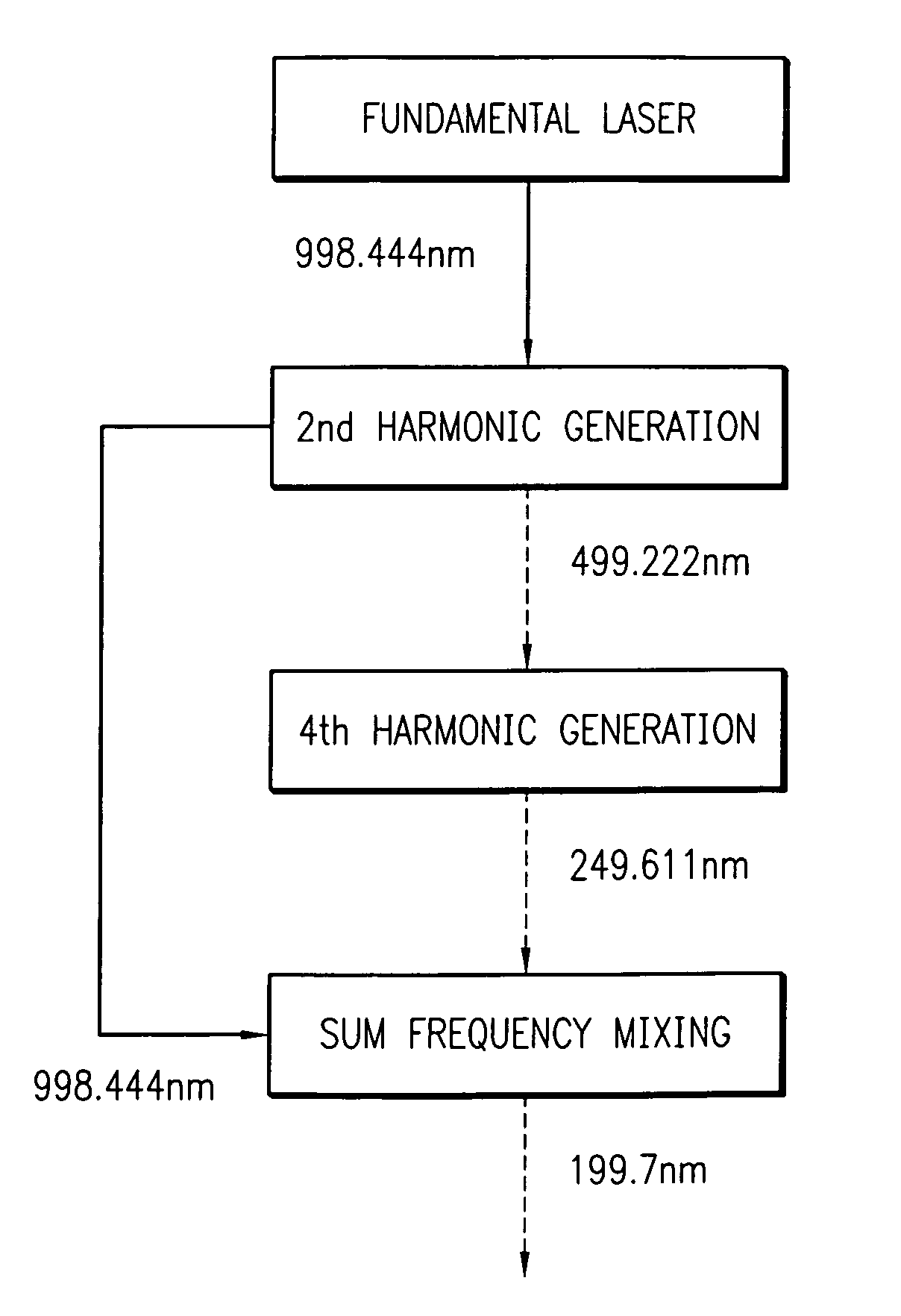
Non-critical phase matching in CLBO to generate sub-213nm wavelengths
A laser illuminator and illumination method for use in an inspection system, such as a semiconductor wafer inspection system or photomask inspection system is provided. The design comprises generating fundamental frequency laser energy at different fundamental wavelengths, such as 998 nm, converting a portion of the fundamental frequency laser energy to 2nd harmonic frequency laser energy, further converting the 2nd harmonic frequency laser energy to 4th harmonic frequency laser energy, and mixing the 4th harmonic frequency laser energy with a portion of the fundamental frequency laser energy to produce laser energy at a sum frequency. Mixing is accomplished by non-critical phase matching in a crystal of Cesium Lithium Borate (CLBO). Alternately, the design may employ shifting a portion of the fundamental frequency laser energy to laser energy at a Raman line and / or mixing the 2nd harmonic frequency laser energy with a portion of the fundamental frequency laser energy to produce 3rd harmonic frequency laser energy.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method and system for locating partial discharge of electrical equipment
ActiveCN102662132AReduce computationImprove direction finding accuracyTesting dielectric strengthElectrical devicesGlobal optimization
A method for locating partial discharge of electrical equipment is used for detecting and locating partial discharge of the electrical equipment. The technical scheme includes the steps: firstly, using three ultrasonic array sensors to receive partial discharge ultrasonic signals at different positions of the electrical equipment and forming an array model; then, converting broadband signals received by the three ultrasonic array sensors into narrow-band signals by applying a TLS (transport layer security)-based broadband focus algorithm, and obtaining azimuth information of partial discharge sources according to a narrow-band direction-finding algorithm combining the phase matching principle and cloud optimization search; and finally, determining specific positions of electrical equipment partial discharge by means of a partial discharge source location algorithm based on global optimization search of a modified genetic algorithm. The invention simultaneously provides an improved system for locating partial discharge. Compared with a traditional method for locating partial discharge, the method has the advantages of small calculation amount, high direction-finding precision, accuracy in location, high convergence rate and the like, and the system for locating partial discharge is simple in structure, low in cost and high in location precision.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +1
Method of estimating magnetic pole position in motor and apparatus of controlling the motor based on the estimated position
ActiveUS20070085508A1Reduce the amount of calculationAccurate estimateSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsSynchronous motorPhase difference
A magnetic pole position in a synchronous motor having salient poles is estimated from an instructed voltage applied to the motor, a current generated from the instructed voltage and parameters. To estimate the position substantially matching with a true magnetic pole position, a phase matching voltage having a phase matching with the estimated magnetic pole position previously obtained is applied to the motor. The phase matching voltage has a harmonic frequency higher than that of the instructed voltage. A phase matching current generated from the phase matching voltage is detected from the motor. A value of at least one of the parameters is corrected such that a difference in phase between the phase matching voltage and the phase matching current substantially becomes zero. An estimated magnetic pole position is calculated from the instructed voltage, the generated current and the parameter having the corrected value.
Owner:DENSO CORP
SOI-based tunable laser
ActiveUS7701985B2Efficient couplingImprove insulation performanceLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersAudio power amplifierCoupling
A silicon-on-insulator (SOI)-based tunable laser is formed to include the gain medium (such as a semiconductor optical amplifier) disposed within a cavity formed within the SOI substrate. A tunable wavelength reflecting element and associated phase matching element are formed on the surface of the SOI structure, with optical waveguides formed in the surface SOI layer providing the communication between these components. The tunable wavelength element is controlled to adjust the optical wavelength. Separate discrete lensing elements may be disposed in the cavity with the gain medium, providing efficient coupling of the optical signal into the SOI waveguides. Alternatively, the gain medium itself may be formed to include spot converting tapers on its endfaces, the tapers used to provide mode matching into the associated optical waveguides.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus and methods for achieving phase-matching using a waveguide
ActiveUS20070104443A1Reduced insertion lossEfficient indexingEnergy efficient ICTSubstation remote connection/disconnectionTotal internal reflectionHarmonic
The present invention relates to an apparatus and methods for achieving phase-matching between various waves and / or modes by operation of a waveguide. Phase-matching between interacting waves is achieved by total internal reflection and transverse Bragg reflection waveguides. Using second harmonic generation in GaAs / AlGaAs as an example, properties are investigated and quantified such as nonlinear coupling efficiency, bandwidth, tunability, and limitations due to dispersion. The technique is advantageous when compared to alternate technologies, where it is particularly attractive as a material independent means to obtain ultra-low-loss nonlinear optical elements for monolithic integration with coherent light source and other active devices.
Owner:HELMY AMR
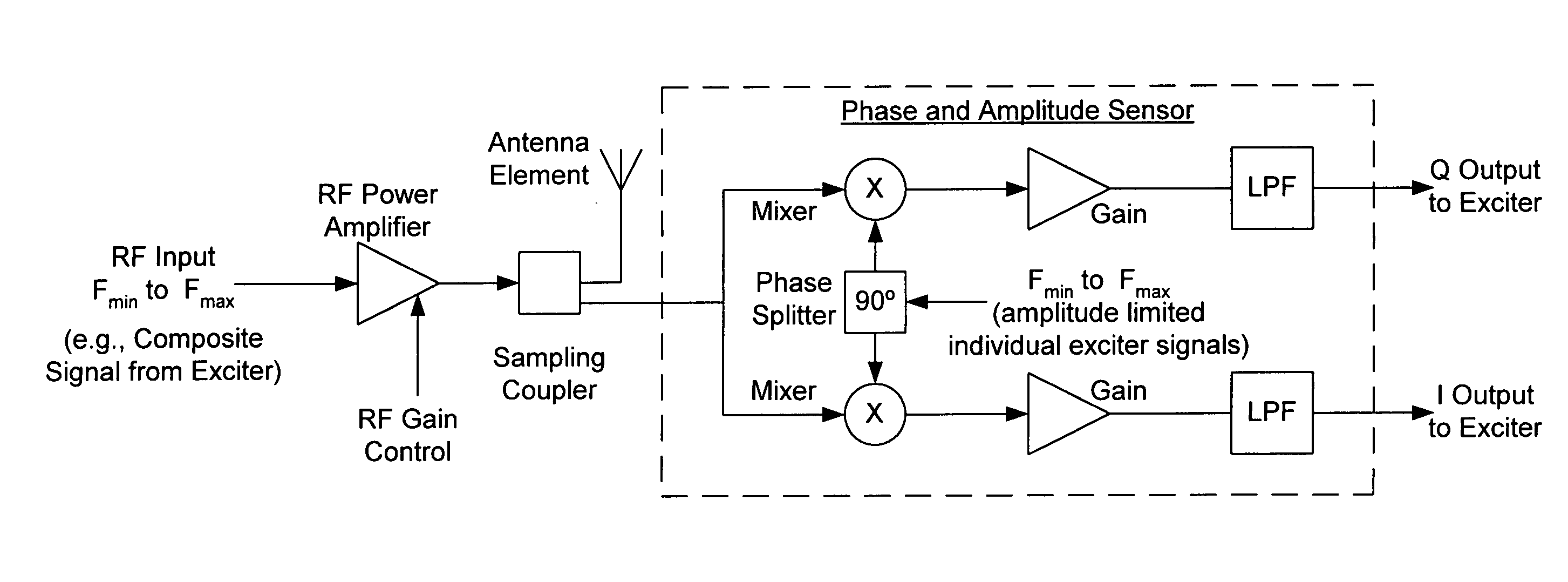
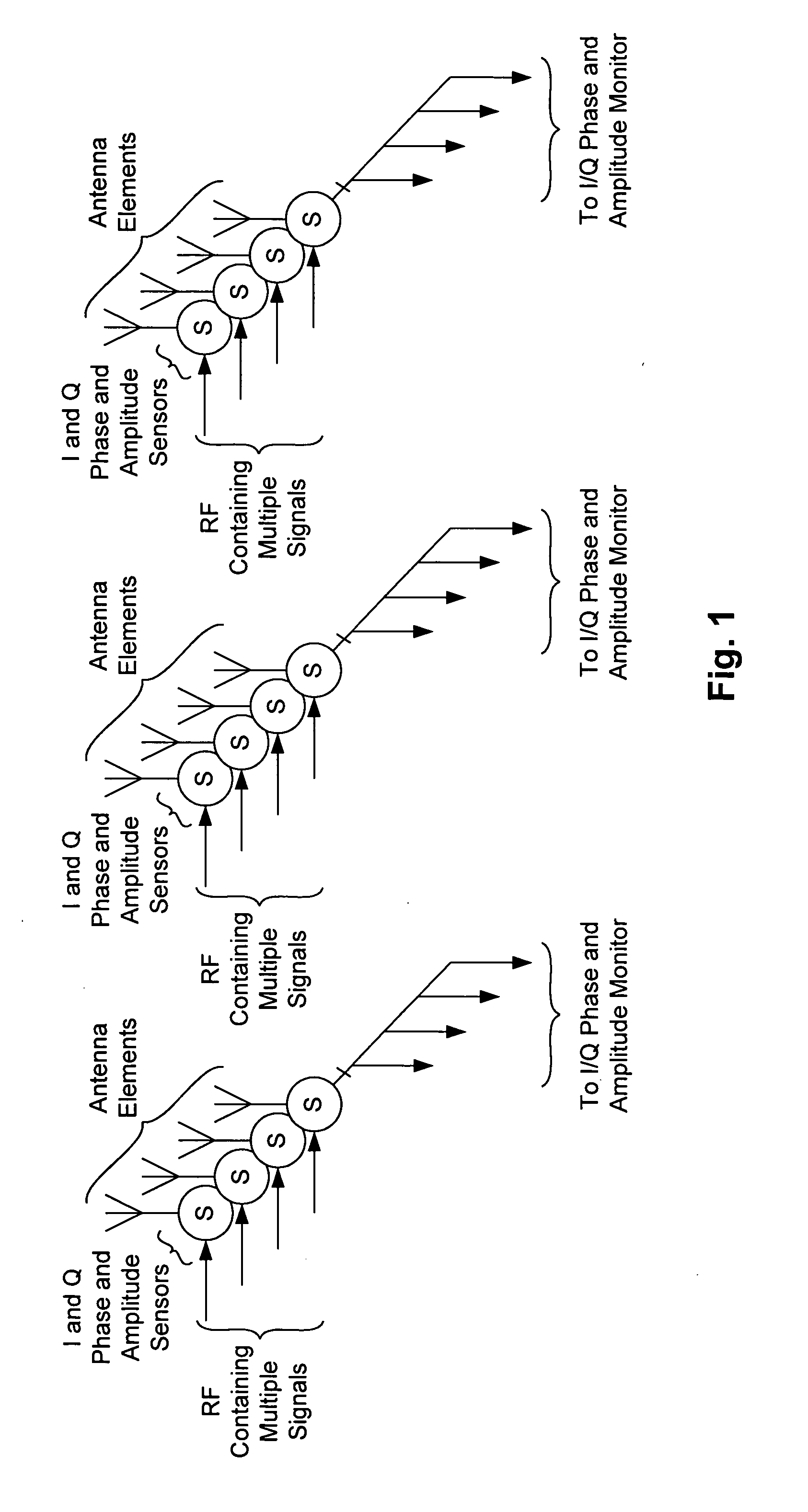
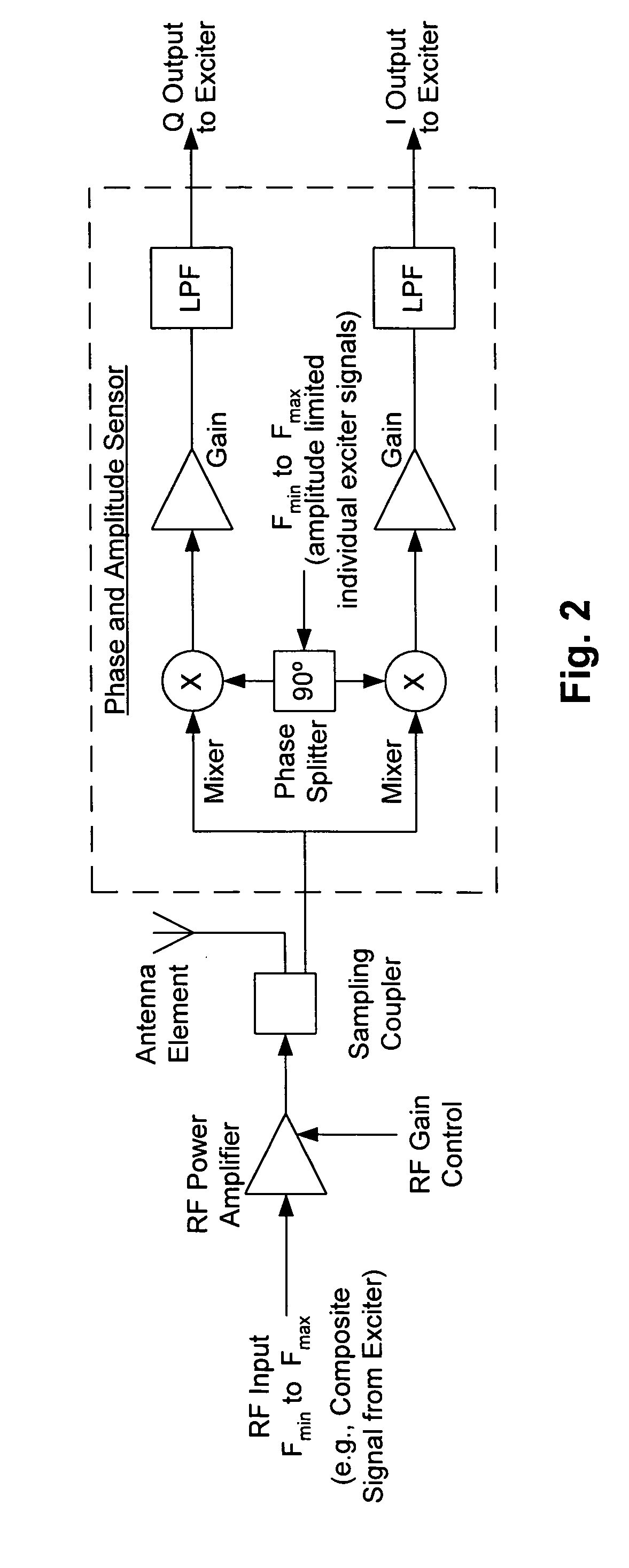
Frequency selective leveling loop for multi-signal phased array transmitters
ActiveUS20060068707A1Radio transmissionTransmission monitoringAudio power amplifierAmplitude control
A frequency selective leveling loop that performs phase and amplitude control of multiple signals within a phased array structure is disclosed. The leveling loop sensor componants are embedded into the array structure. The frequency selective leveling loop can be used with multiple signal amplifiers, and a conventional phase array jamming system can be used to radiate multiple signals simultaneously. The conversion of phase information to baseband eliminates the need for phase matched cables. The frequency selective leveling that is enabled is tolerant of multiple signals and provides the individual signal phase and amplitude feedback by utilizing analytic sampling.
Owner:CAES SYST LLC
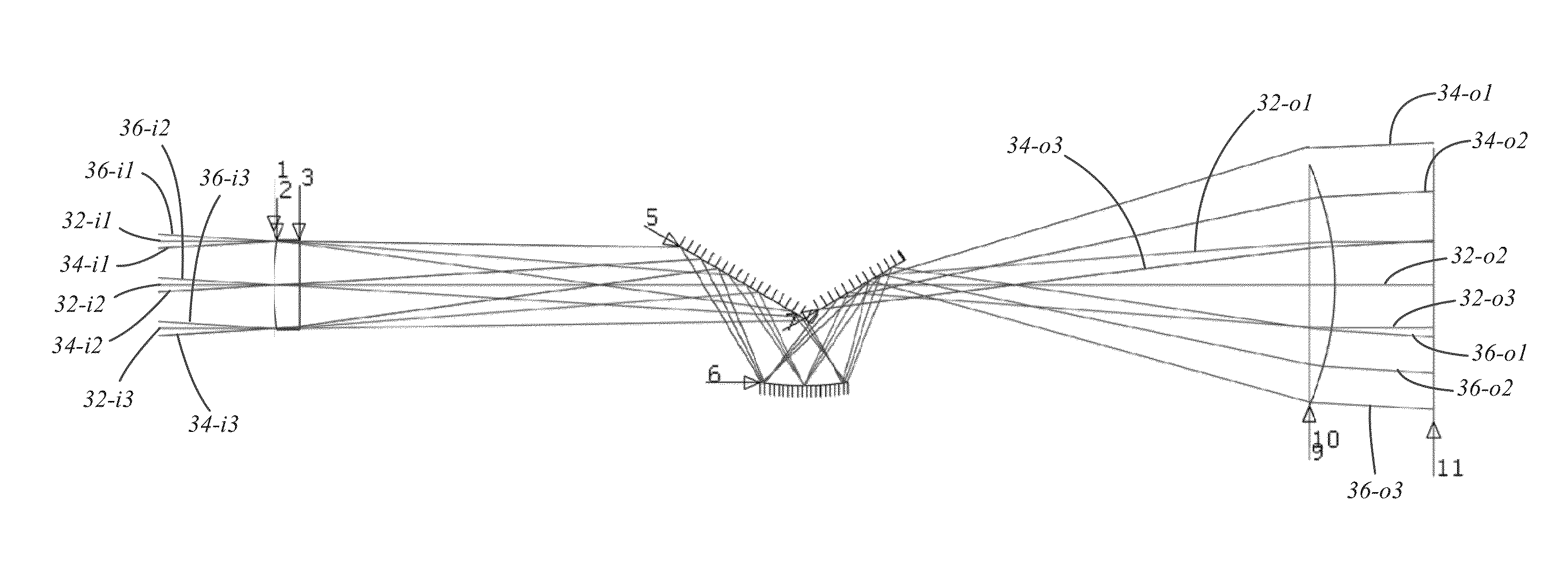
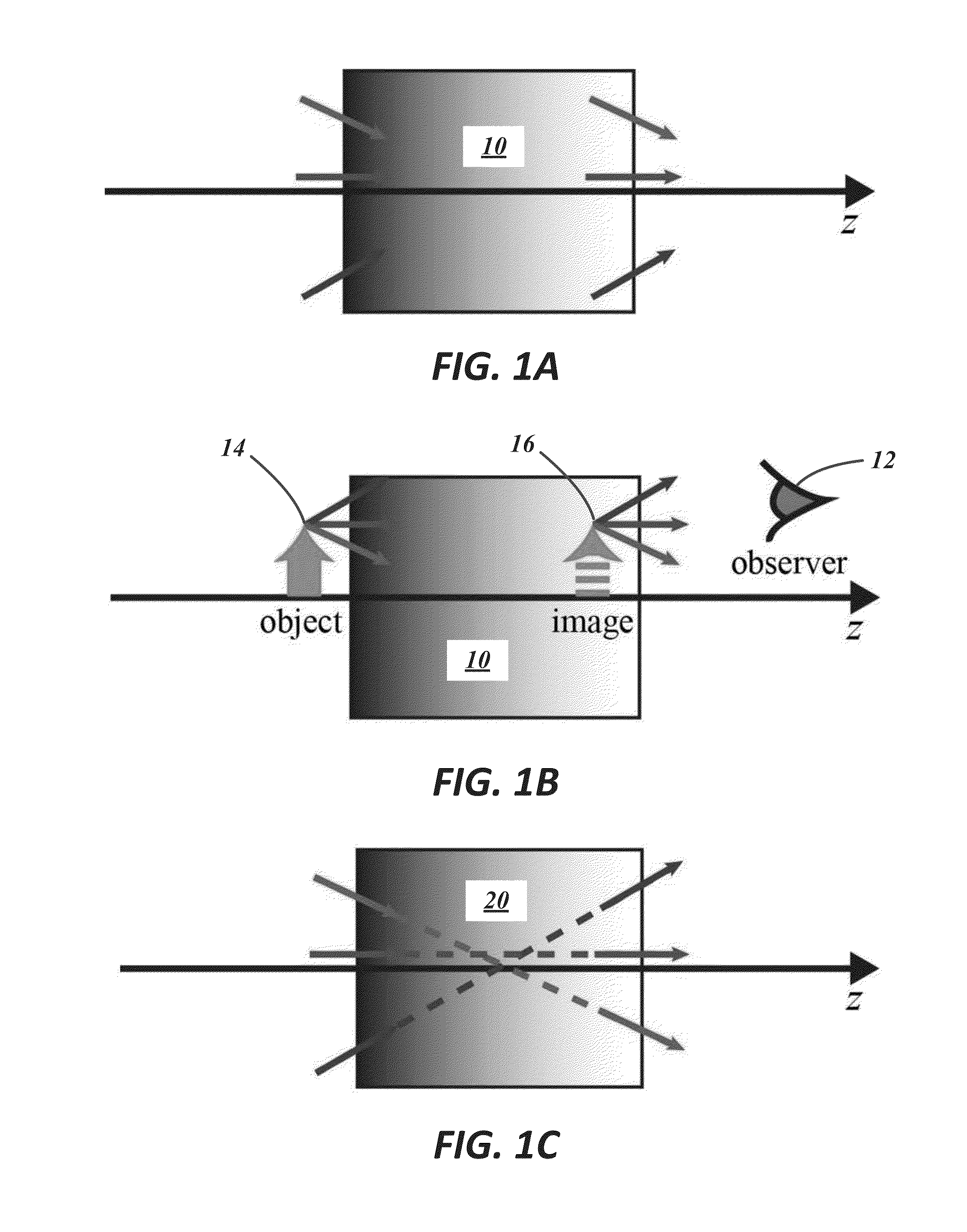
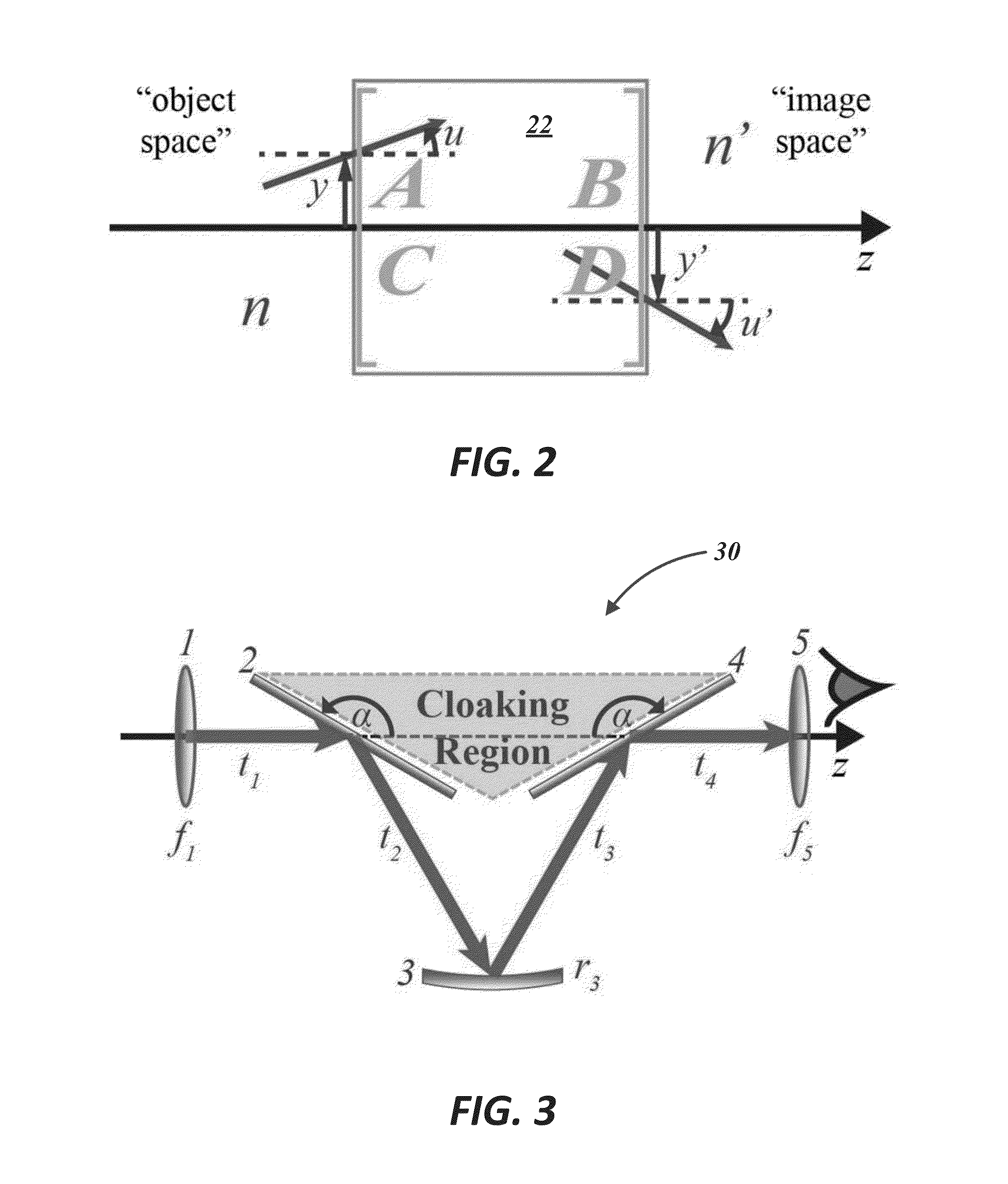
Paraxial cloak design and device
ActiveUS20160025956A1Readily availableNegates needComputation using non-denominational number representationCamouflage devicesOptical axisMagnification
A paraxial cloaking device provides a cloaking volume in which an item can be hid from view. A cloaking device includes an optical input receiving light rays and an optical output from which a continuous range of directions of the received light rays exit the paraxial cloaking device. The cloaking volume being disposed between the optical input and the optical output. For received light rays having incoming directions non-parallel to the reference optical axis up to a first angle, each of the received light rays exits the cloaking device substantially aligned with the respective received light ray and does not pass through the cloaking volume. The paraxial cloaking device has a unity magnification factor. In some instances, the paraxial cloaking device includes a phase matching element.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
High-frequency device, high-frequency module and communications device comprising them
ActiveUS7076216B2Minimizing insertion lossMaximizing harmonic attenuationMultiple-port networksRadio transmissionFundamental frequencyCommunication device
A high-frequency module constituted by an integral laminate for handling a plurality of transmitting / receiving systems having different passbands comprises (a) a switch module part for branching higher-frequency signals and lower-frequency signals and switching connection to the transmitting systems and the receiving systems, (b) a high-frequency amplifying circuit module part, and (c) a phase-adjusting circuit disposed between the switch module part and the high-frequency amplifying circuit module part, wherein the phase matching between the switch module part and the high-frequency amplifying circuit module part via the phase-adjusting circuit is adjusted to conjugate matching in a fundamental frequency band, while it is adjusted in a nonconjugate matching range in n-th frequency bands, wherein n is an integer of 2 or more.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
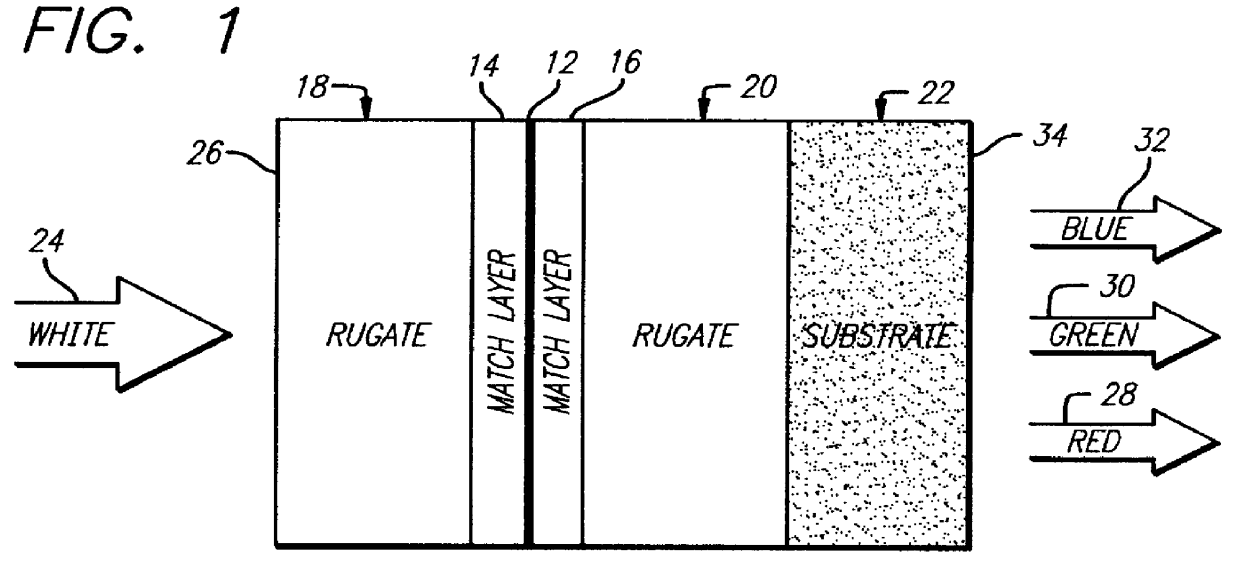
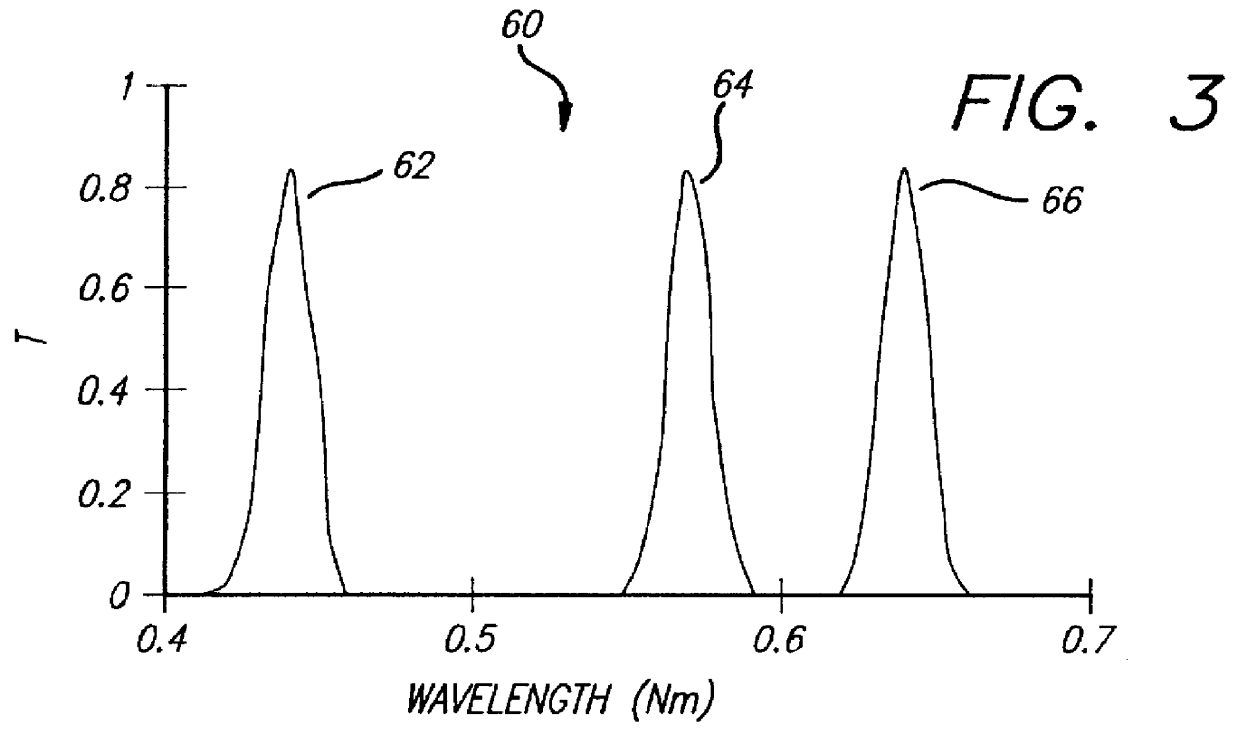
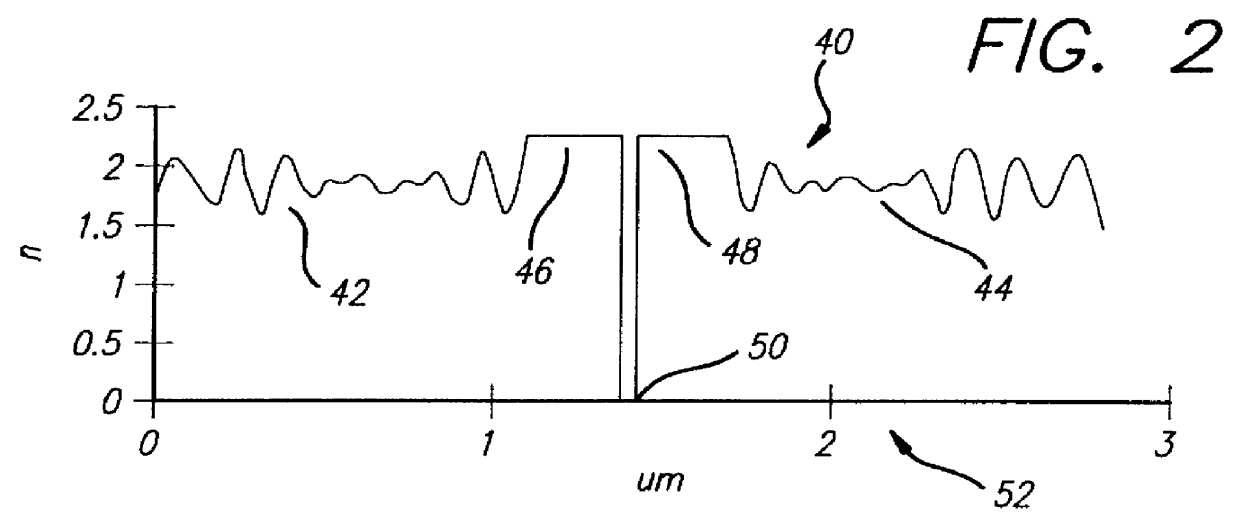
Rugate induced transmission filter
A filter (10) for selectively transmitting electromagnetic energy over a range of frequencies (28, 30, 32) adapted for use with white light (24). The filter (10) includes rugate layers (18, 20) for creating a resonant cavity that resonates at desired bandpass frequencies (28, 30, 32). An absorptive layer (12) absorbs frequencies near the bandpass frequencies (28, 30, 32) and reflects frequencies outside the bandpass frequencies (28, 30, 32). Phase matching layers (14, 16) allow the transmission of electromagnetic energy within the transmission bands (28, 30, 32) through the absorption layer 12. In an illustrative embodiment, the bandpass frequencies (28, 30, 32) comprise the three tristimulus frequencies, i.e., red (28), green (30) and blue (32) frequencies. The rugate layers (18, 20) include first (18) and second (20) rugate layers made of SiO2 and Ta2O5, respectively. Located between the first (18) and second (20) rugate layers is the absorption layer (12) that is surrounded by the first (14) and second (16) phase matching layers. The absorption layer (12) is a silver layer that is approximately 500 angstroms thick. The first rugate layer (18) has a first index of refraction versus layer thickness profile representing a superposition of sinusoids. Each sinusoid has a frequency directly corresponding to tristimulus band frequency. The second rugate layer (20) has a second index of refraction versus layer thickness profile that is a phase-adjusted version of the first index of refraction versus layer thickness profile. Both rugate layers (18, 20) have index or refraction versus layer thickness profiles have several cycles.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
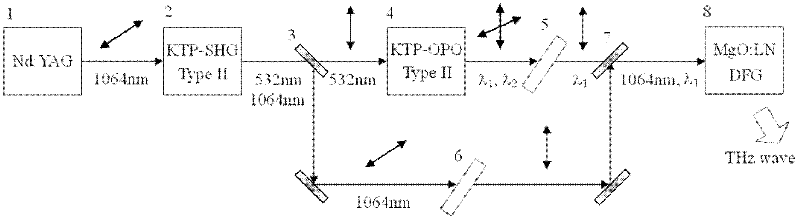
Tunable terahertz radiation source based on difference frequency cherenkov effect and modulation method
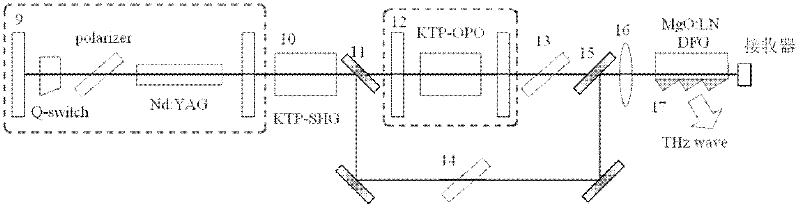
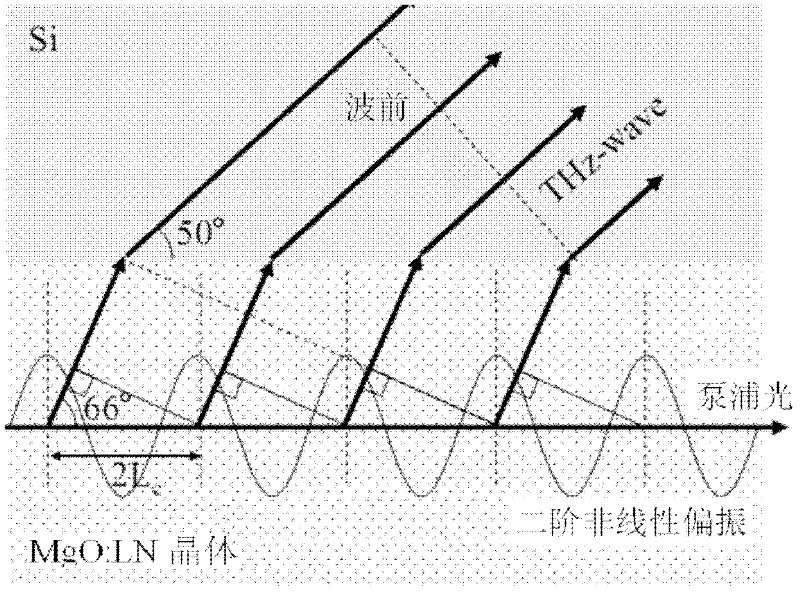
ActiveCN102386549AOvercoming complexityOvercome rangeSolid masersNon-linear opticsOptical frequenciesPrism
The invention relates to the non linear optical frequency conversion. To realize output of high power THz wave which can be continuously tuned, and stable running at room temperature, the technical scheme used by the invention is that: a tunable terahertz radiation source based on difference frequency cherenkov effect is composed of a laser device, a frequency doubling crystal, a double wavelength parametric oscillator, a harmonic mirror, a polarization filter, a combined beam mirror, a column lens and a difference frequency crystal; the harmonic mirror is placed between the frequency doubling crystal and the double wavelength parametric oscillator; the double wavelength parametric oscillator is II type phase matching KTP (Potassium Titanyl Phosphate) crystal OPO (Optical Parametric Oscillator); the polarization filter, the combined beam mirror and the column lens are arranged between the parametric oscillator and the difference frequency crystal; the difference frequency crystal is amagnesium oxide doped lithium niobate crystal with molecular formula of MgO:LiNbO3 or MgO:LN, and the generated THz wave is coupled and output by an Si prism on the side surface of the difference frequency crystal. The tunable terahertz radiation source based on difference frequency cherenkov effect is mainly applied to the optical frequency conversion.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com