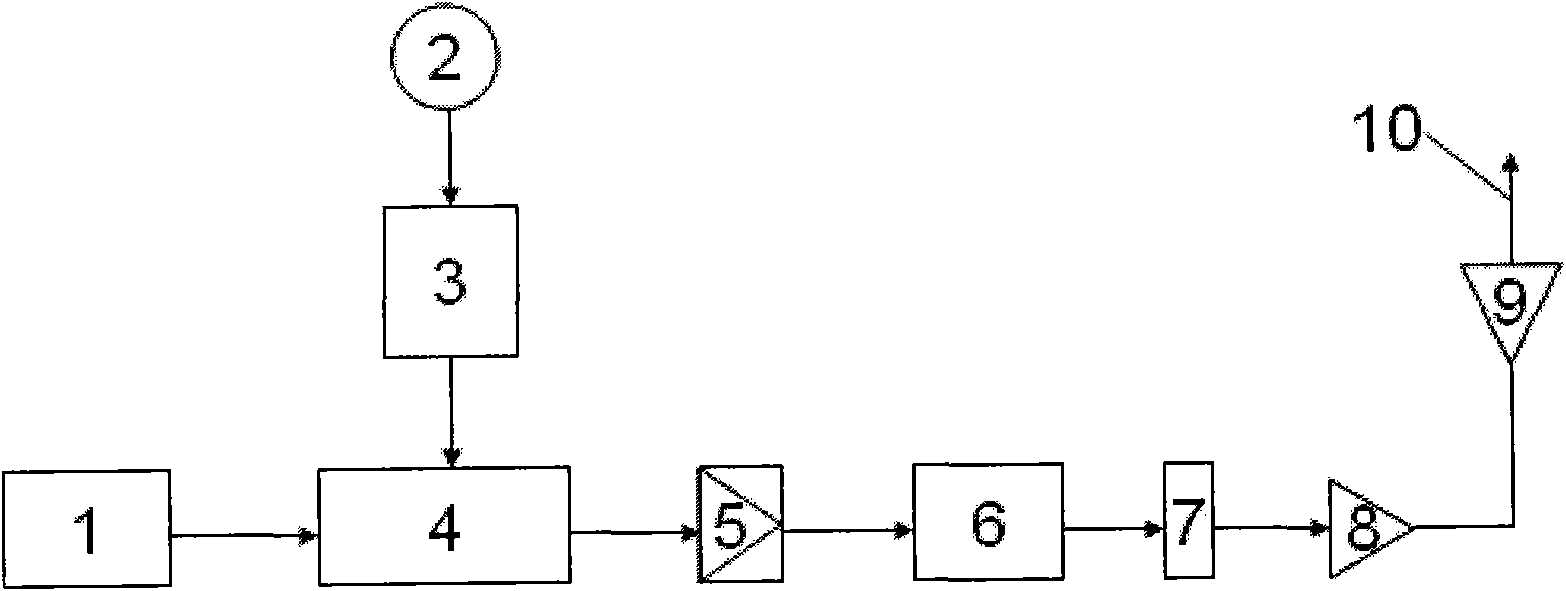
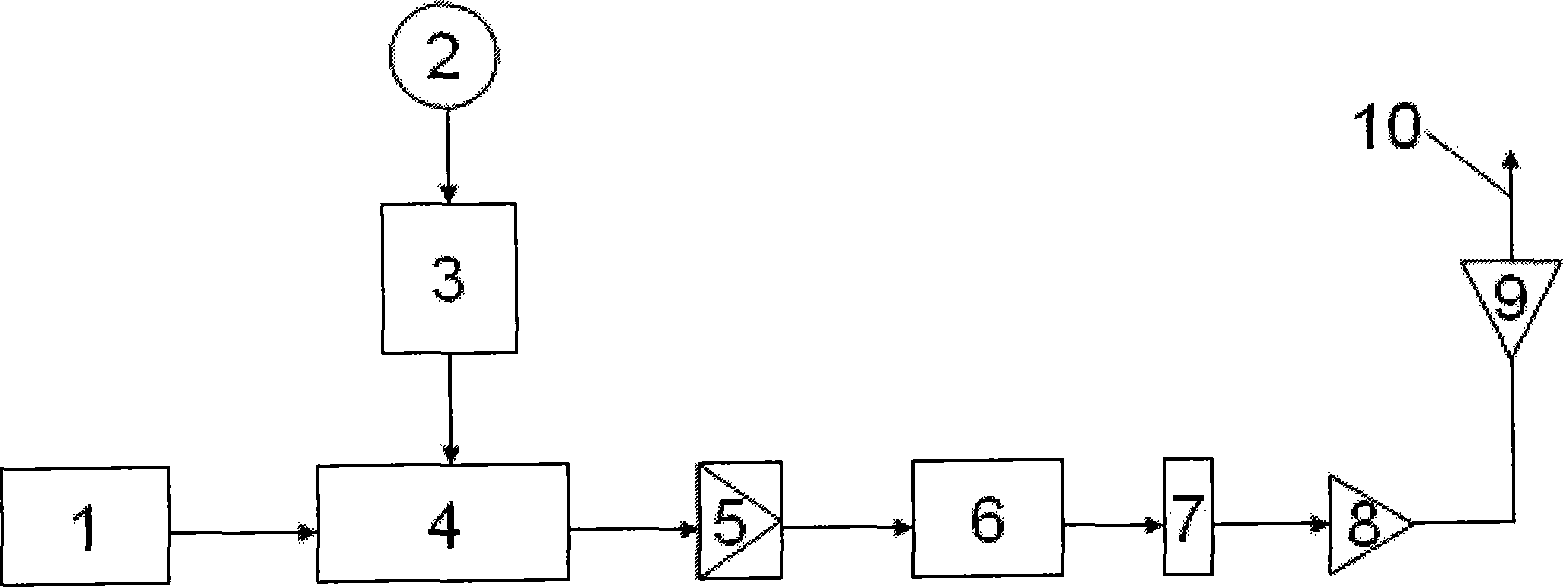
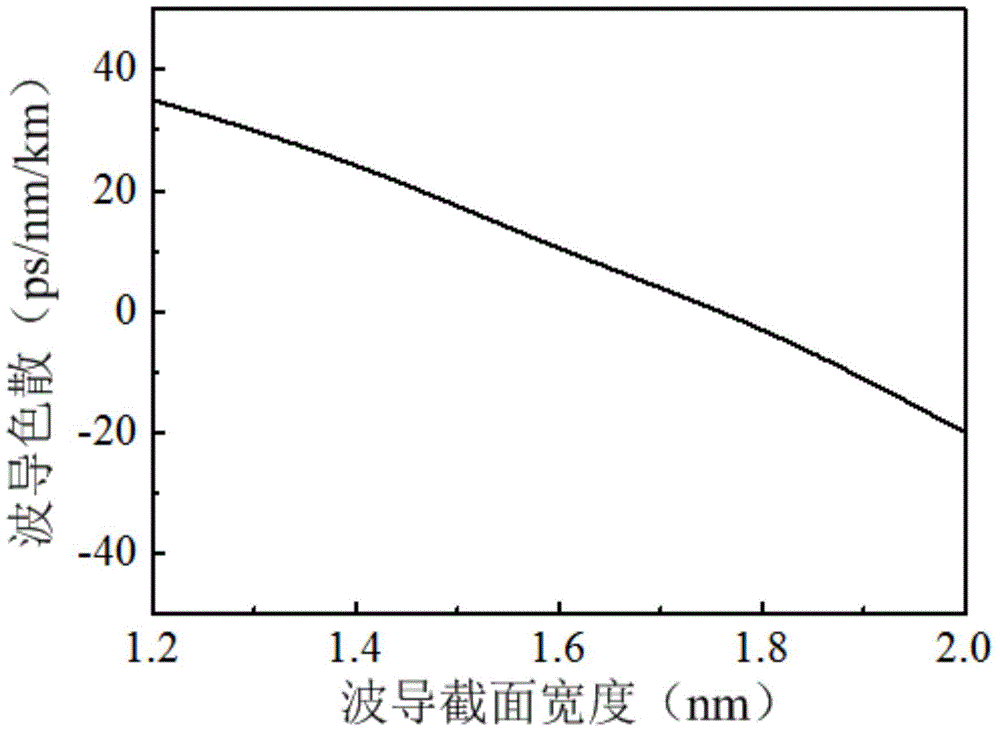
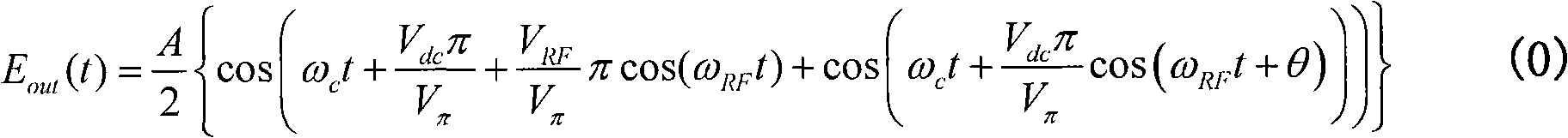Patents
Literature
410 results about "Four-wave mixing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
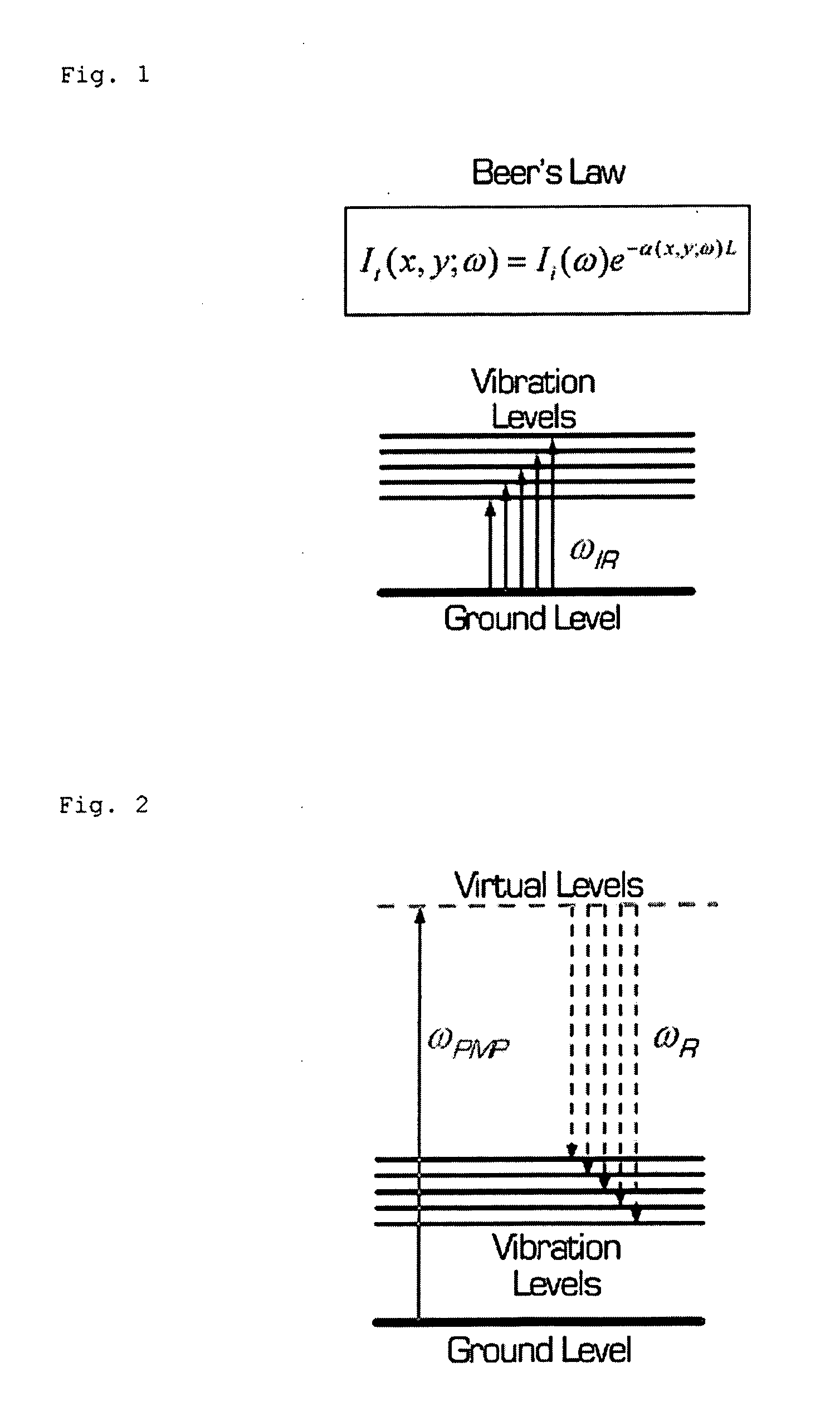
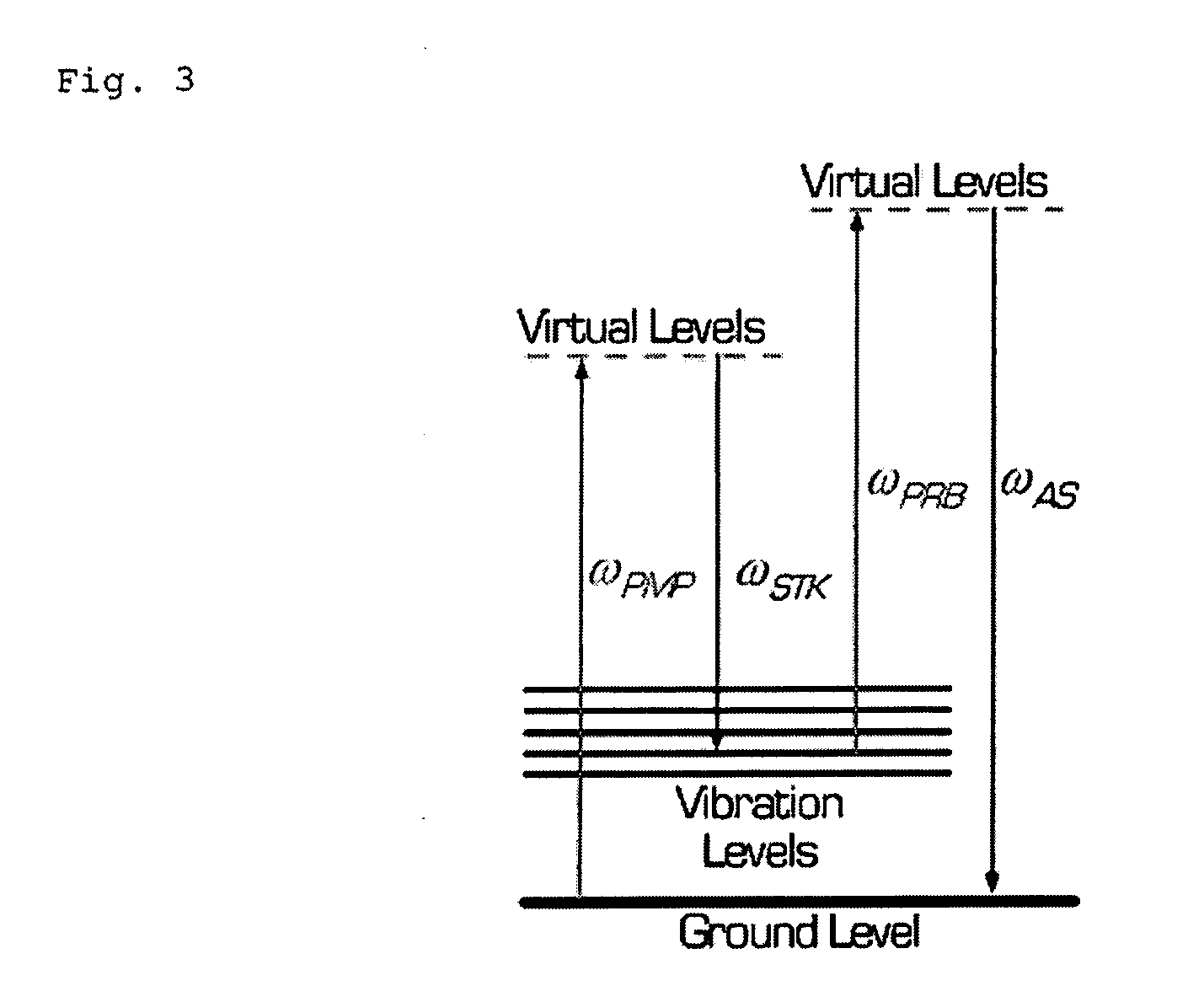
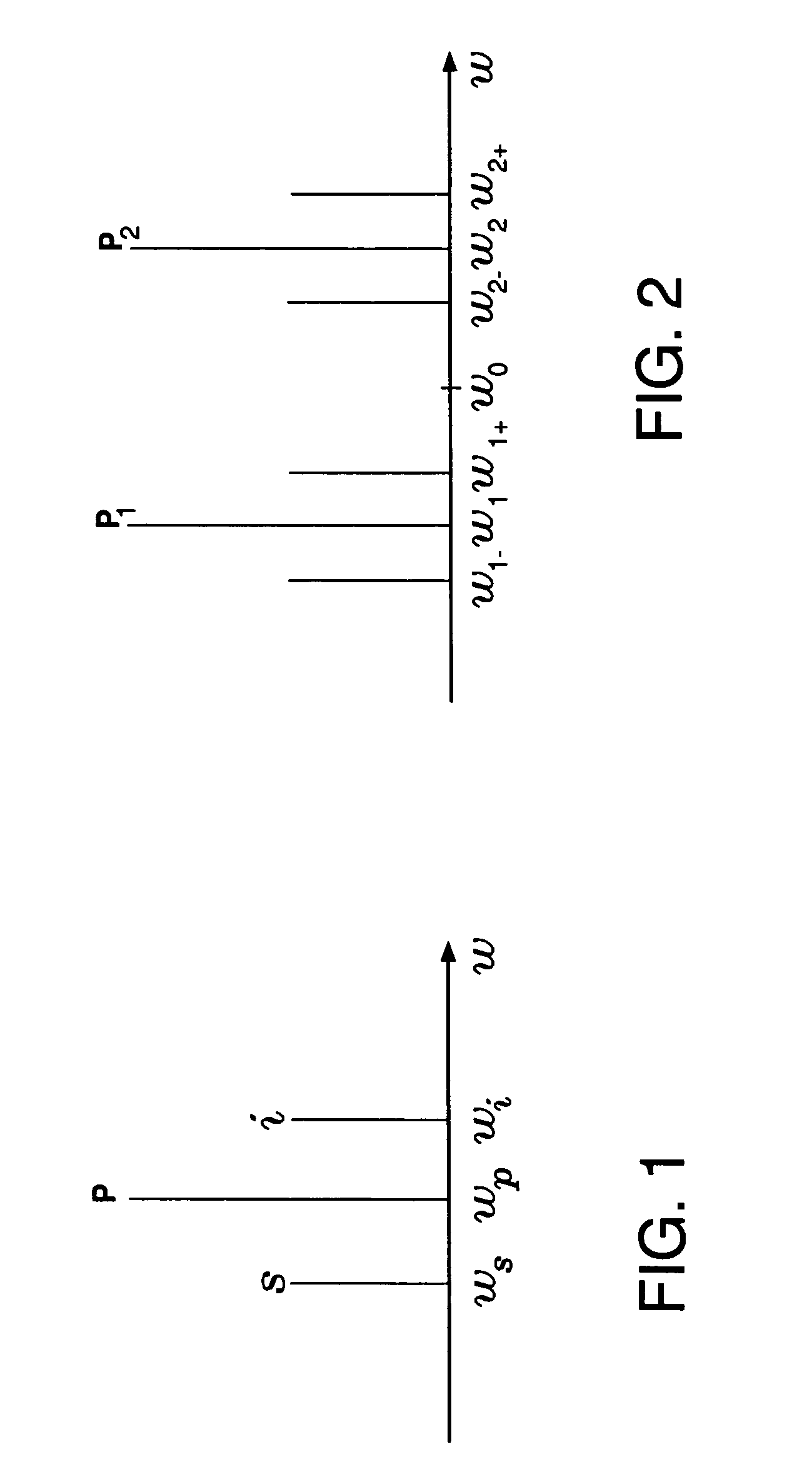
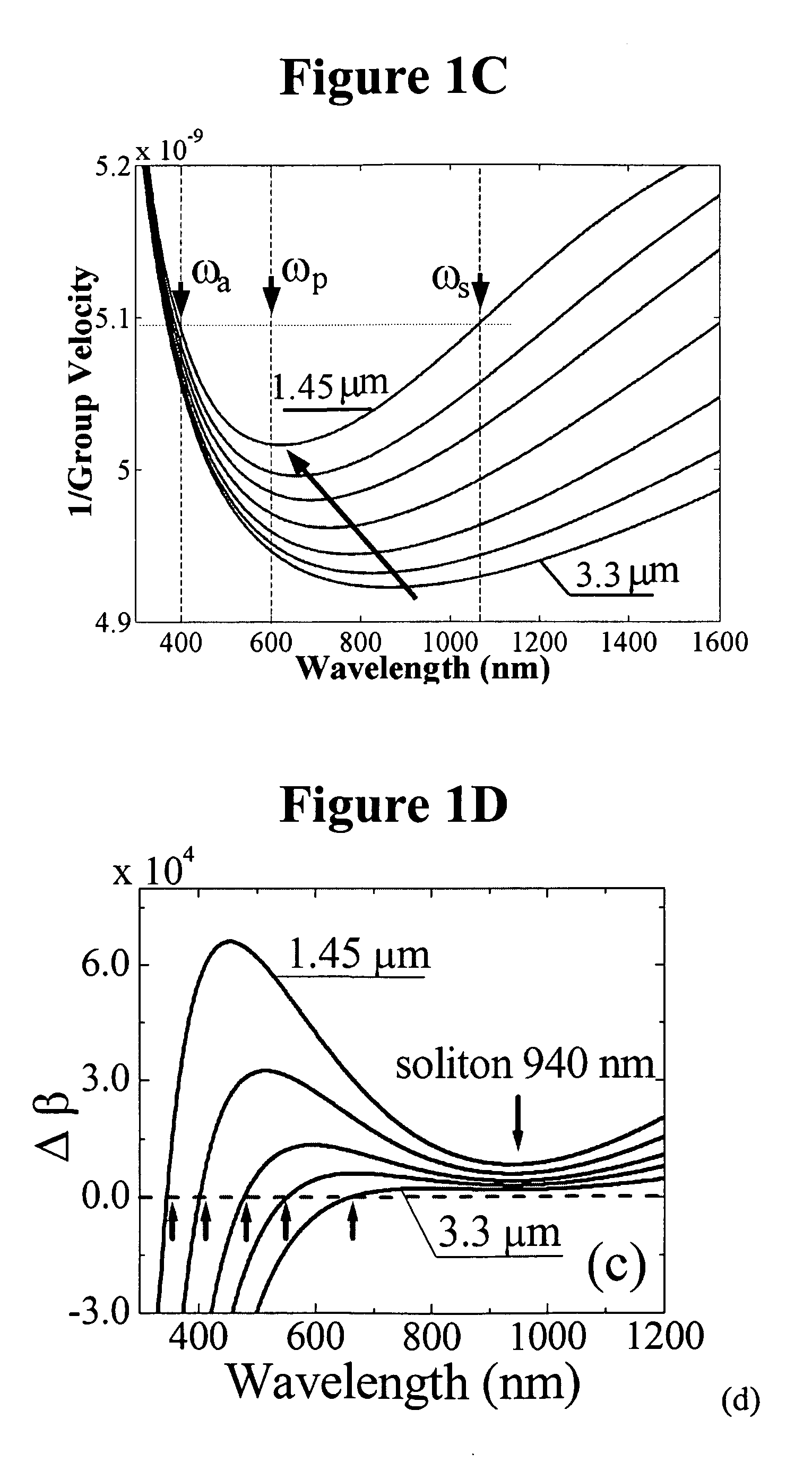
Four-wave mixing (FWM) is an intermodulation phenomenon in non-linear optics, whereby interactions between two or three wavelengths produce two or one new wavelengths. It is similar to the third-order intercept point in electrical systems. Four-wave mixing can be compared to the intermodulation distortion in standard electrical systems. It is a parametric nonlinear process, in that the energy of the incoming photons is conserved. FWM is a phase-sensitive process, in that the efficiency of the process is strongly affected by phase matching conditions.
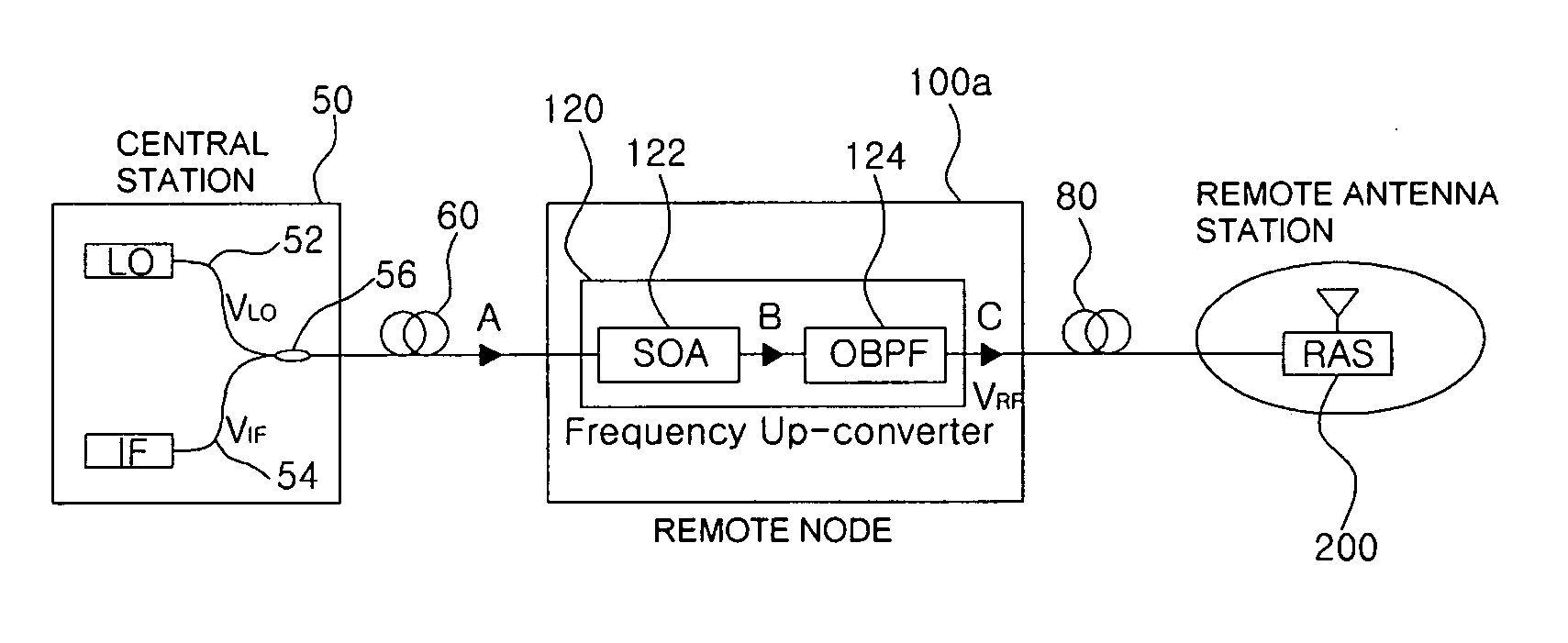
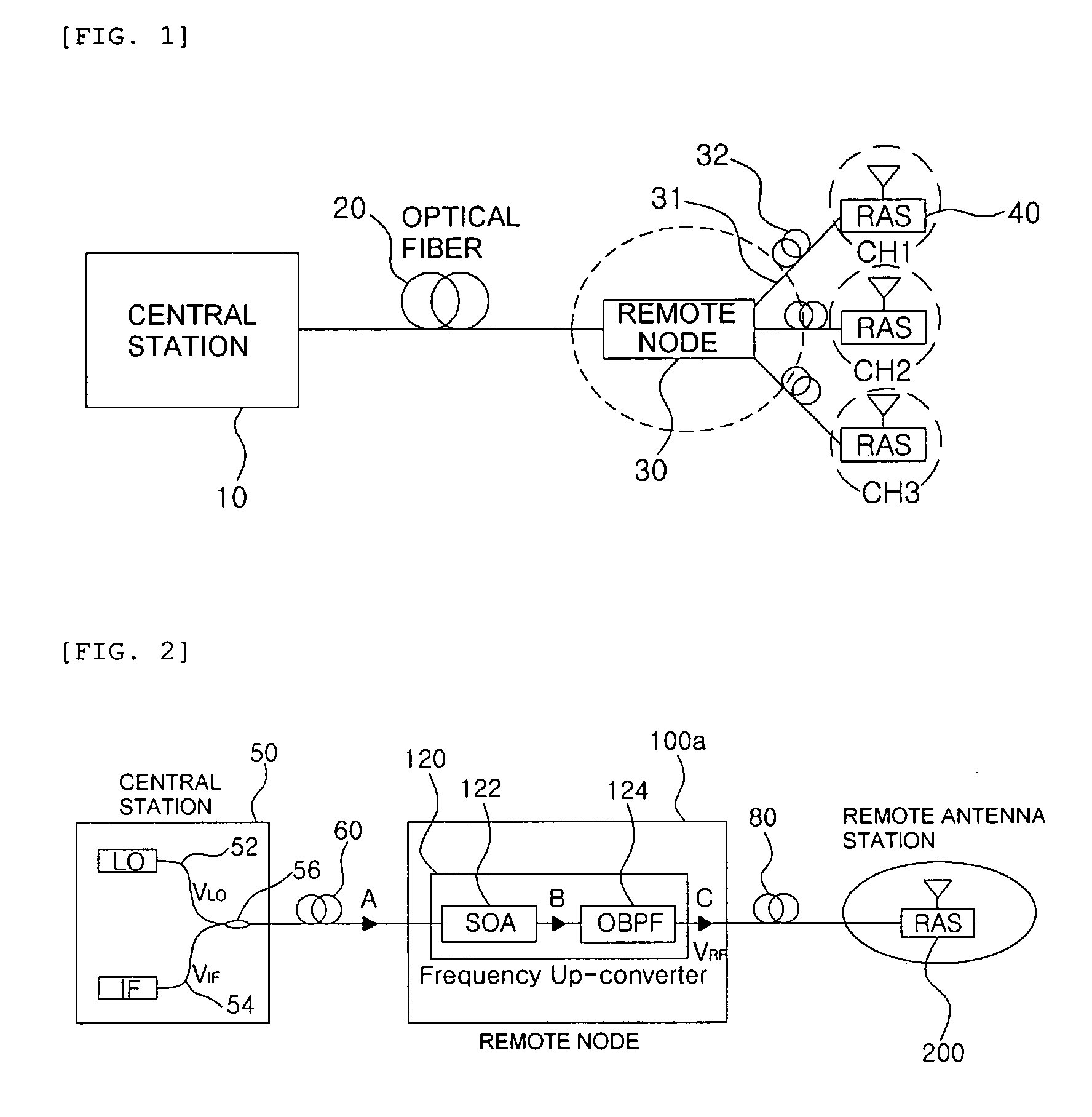
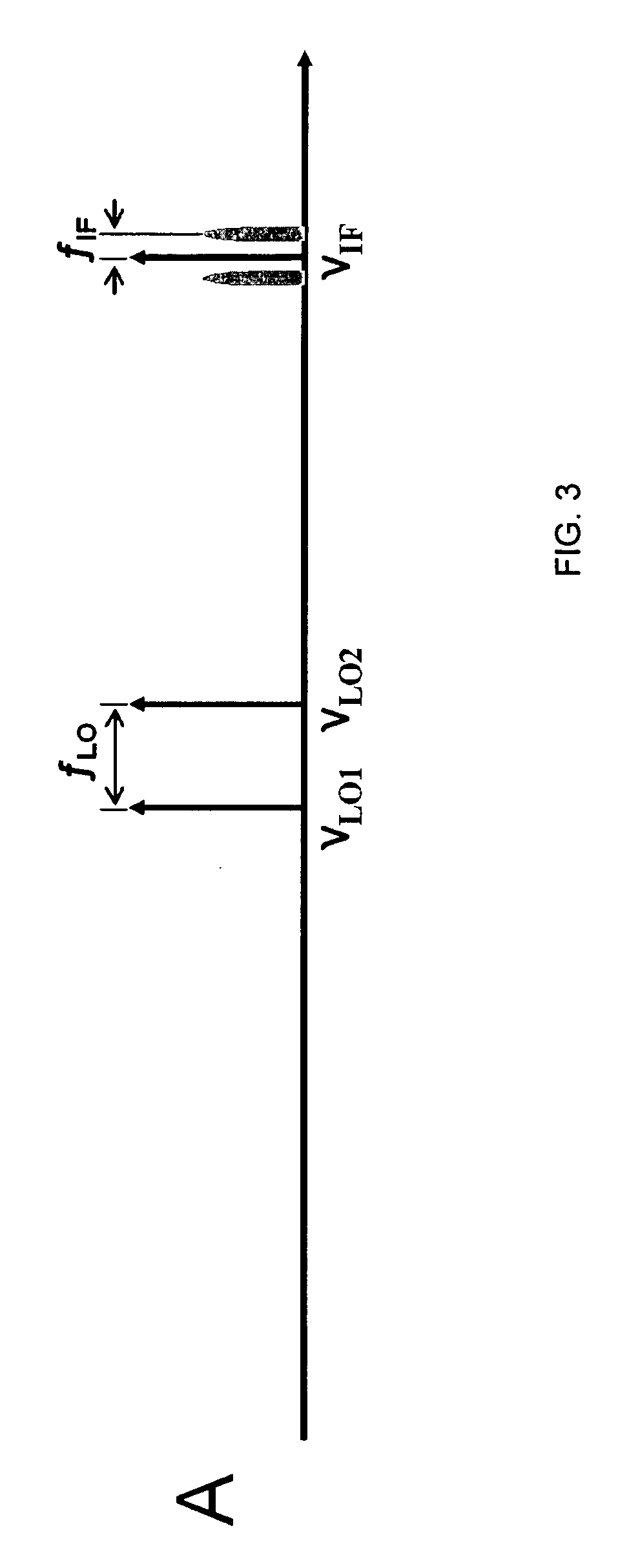
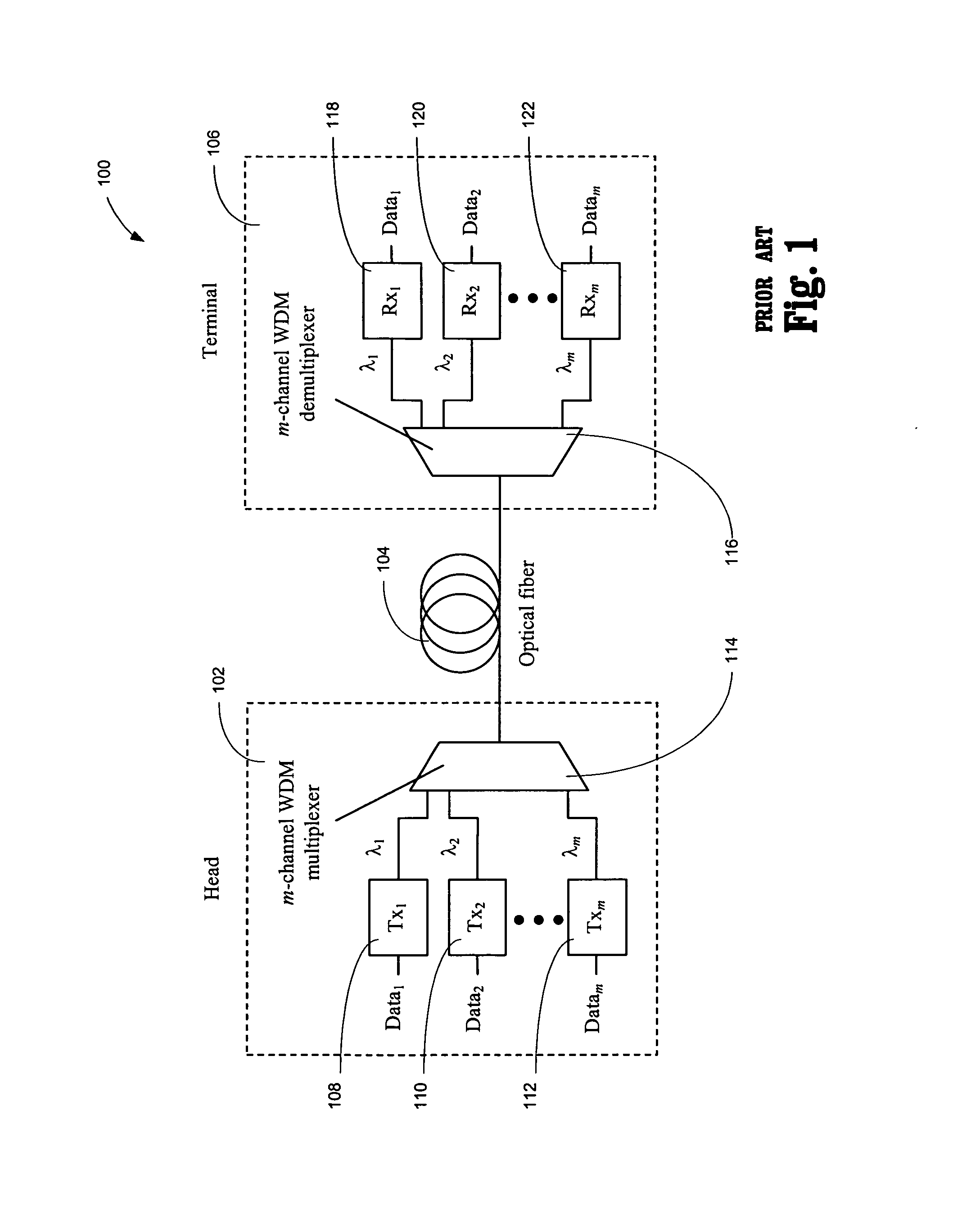
All-optical frequency upconverter and all-optical frequency upconversion method in radio-over-fiber system
InactiveUS20080298813A1Simple configurationRadio-over-fibreElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency changerRadio over fiber
Disclosed is an all-optical frequency upconverter in a radio-over-fiber system that outputs upconverted optical radio frequency (RF) signals using an optical intermediate frequency signal and an optical local oscillation signal. The all-optical frequency upconverter includes a semiconductor optical amplifier that mixes the optical intermediate frequency signal with the optical local oscillation signal through four wave mixing, and an optical filter that filters a plurality of frequency component signals, which are generated through the four wave mixing, to extract optical RF signals. According to the invention the system configuration can be made simple, and wide LO and IF frequency bandwidths can be provided.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
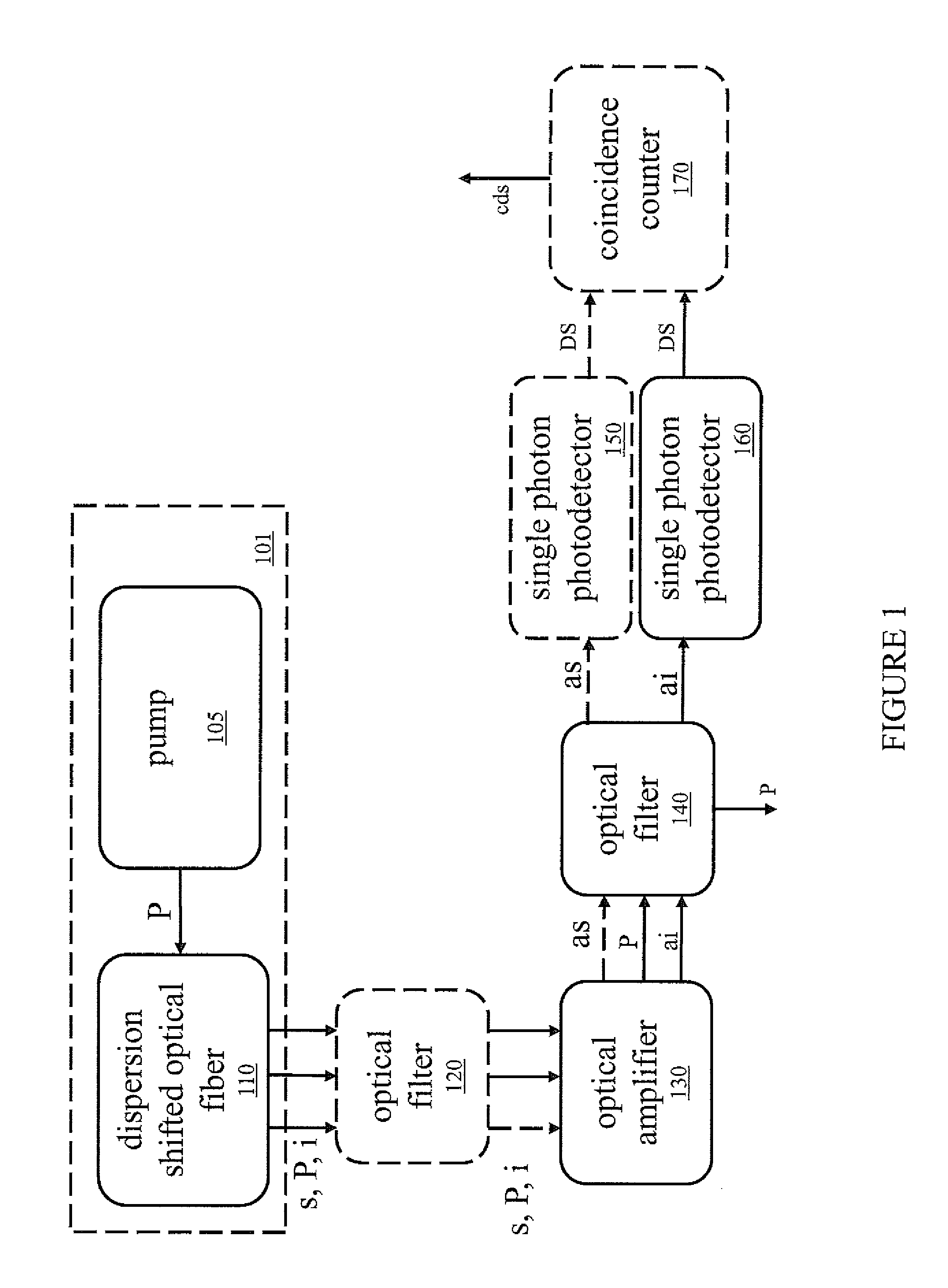
Nonlinear spectroscopic methods for identifying and characterizing molecular interactions
ActiveUS20060063188A1Remarkable effectSmall structureSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNonlinear spectroscopyEquilibrium constant
This invention provides methods and devices for identifying and / or characterizing interactions involving molecules, including, but not limited to, identifying and / or characterizing interactions involving target molecules and candidate molecules. The present invention provides methods using multidimensional infrared spectrographic techniques, such as four wave mixing and pump-probe techniques, for identifying interactions involving biomolecules and therapeutic candidate molecules, and for characterizing such interactions in terms of their binding coefficients and / or equilibrium constants.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
System and method for nonlinear optical devices
InactiveUS9000347B2High sensitivityRadiation pyrometryPhase-affecting property measurementsAudio power amplifierPhoton detection
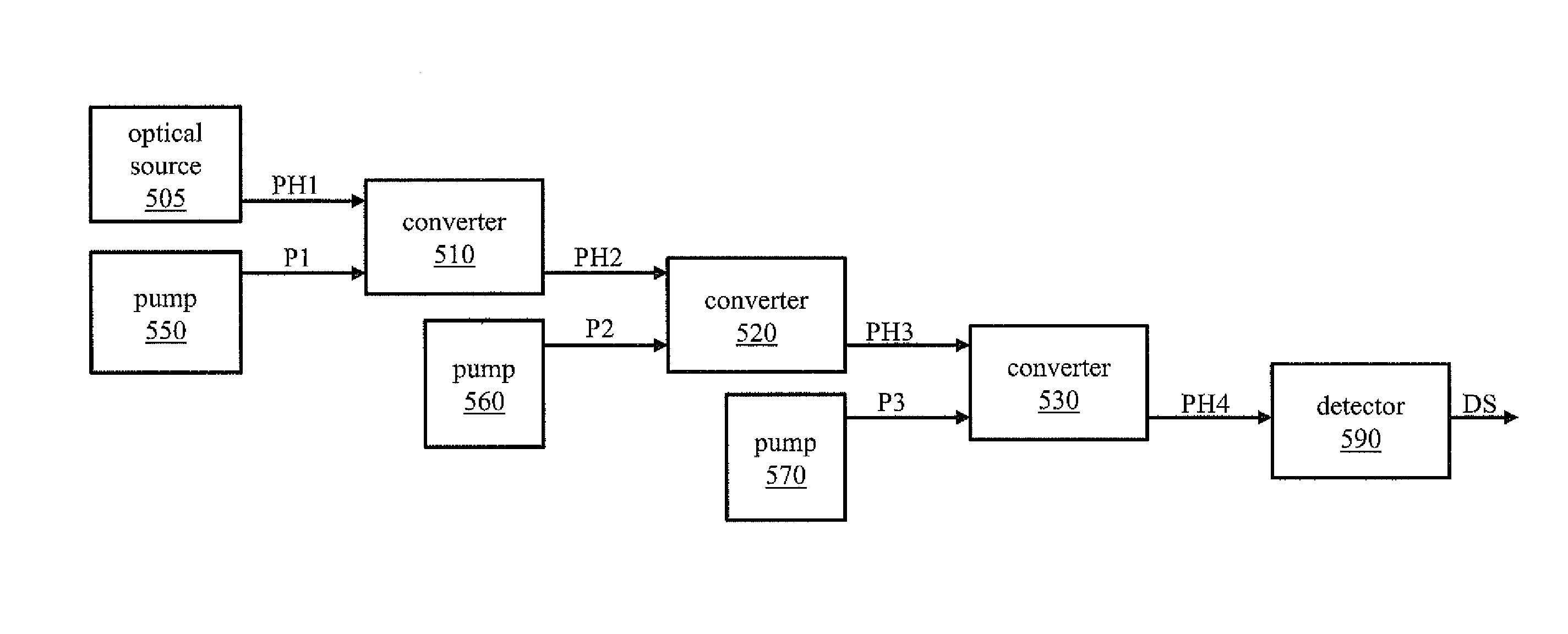
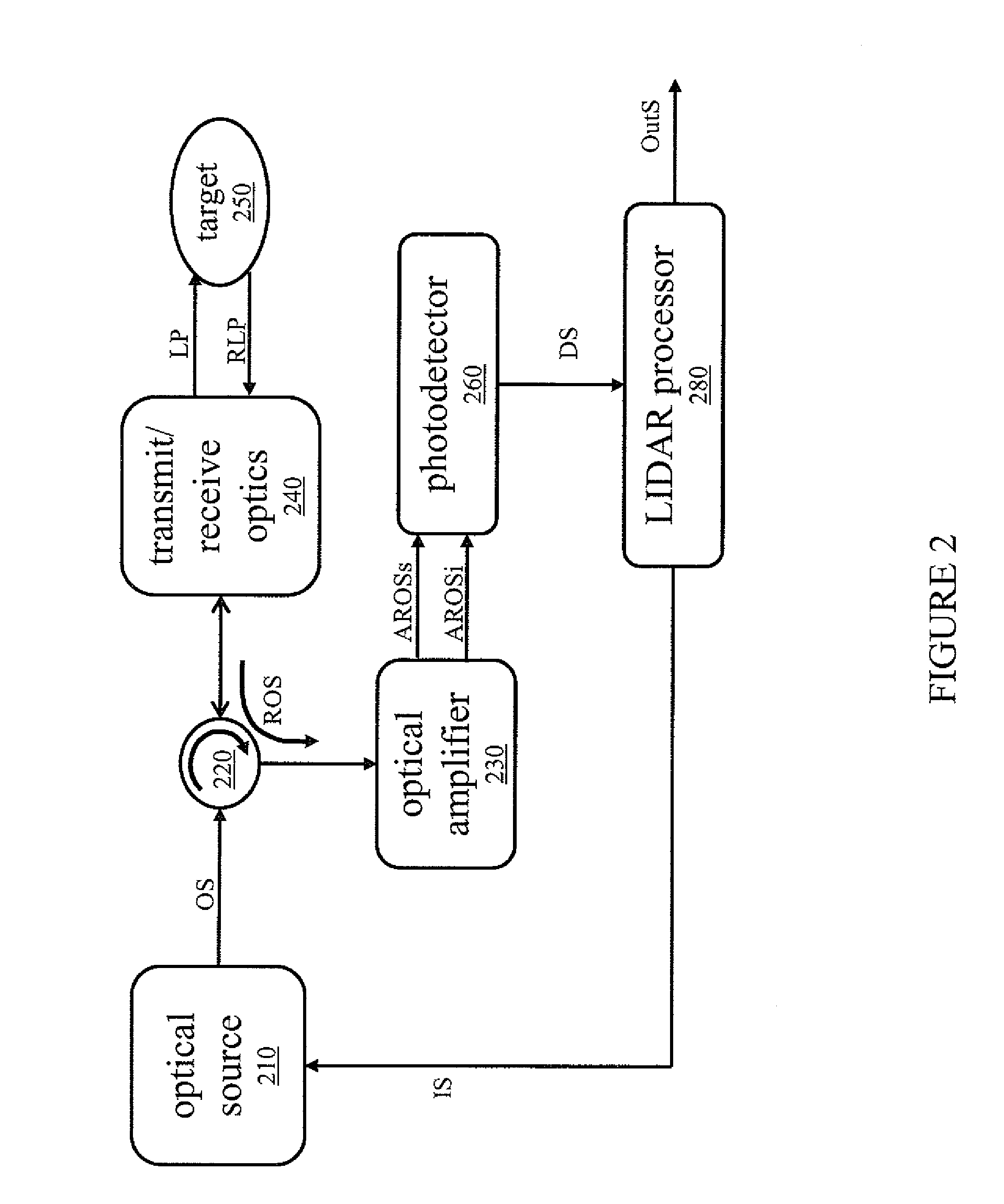
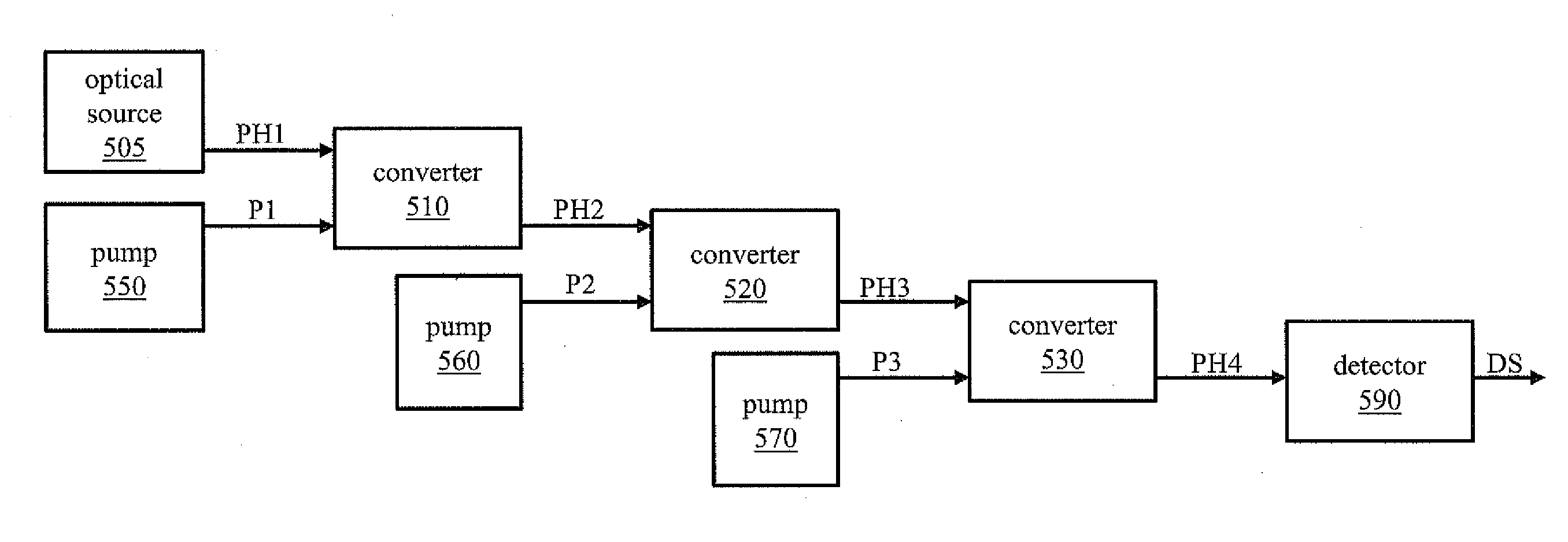
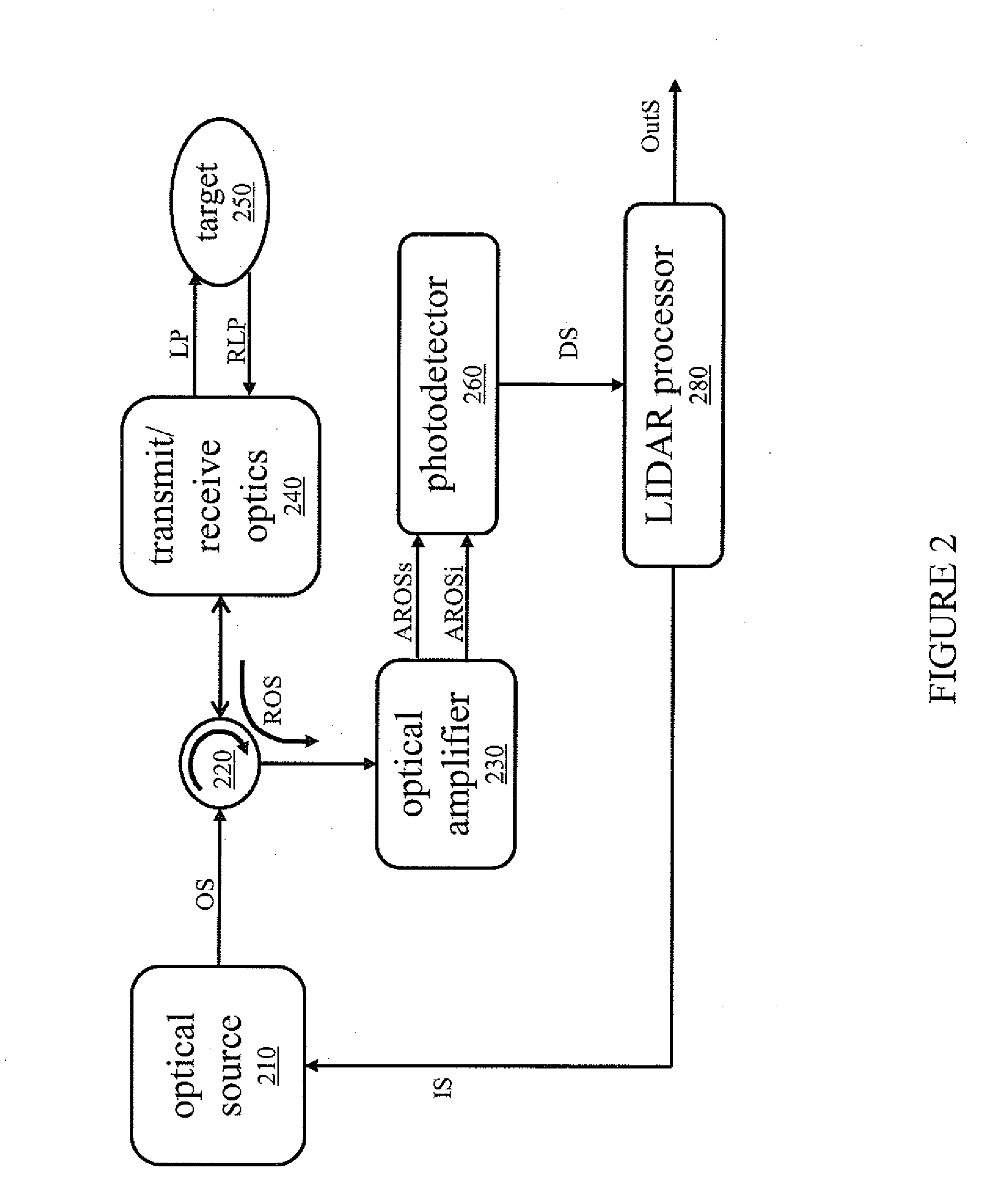
Systems for enhancing the sensitivity of detecting an optical signal using nonlinear optics and method of performing the same. In one embodiment, a single-photon detection system includes an optical amplifier realized in a waveguide, and a photodetector coupled to an output of the optical amplifier. A light detection and ranging system includes the optical amplifier coupled to an optical source and one photodetector. In another embodiment, a photodetection system includes a plurality of optical frequency converters, coupled to an optical source, that sequentially convert a wavelength of photons of the optical source to a final wavelength, and a single-photon photodetector coupled to the optical frequency converters to detect single photons produced by the optical source. In another embodiment, an optical sensor includes an optical pump, and a transducer including an optical ring cavity coupled to the optical pump and configured to utilize optical four-wave mixing to detect an external stimulus.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Arbitrary Optical Waveform Generation Utilizing Optical Phase-Locked Loops
ActiveUS20100085992A1Increase tuning rangeWide bandwidthLaser detailsWave based measurement systemsElectronic systemsOptical frequencies
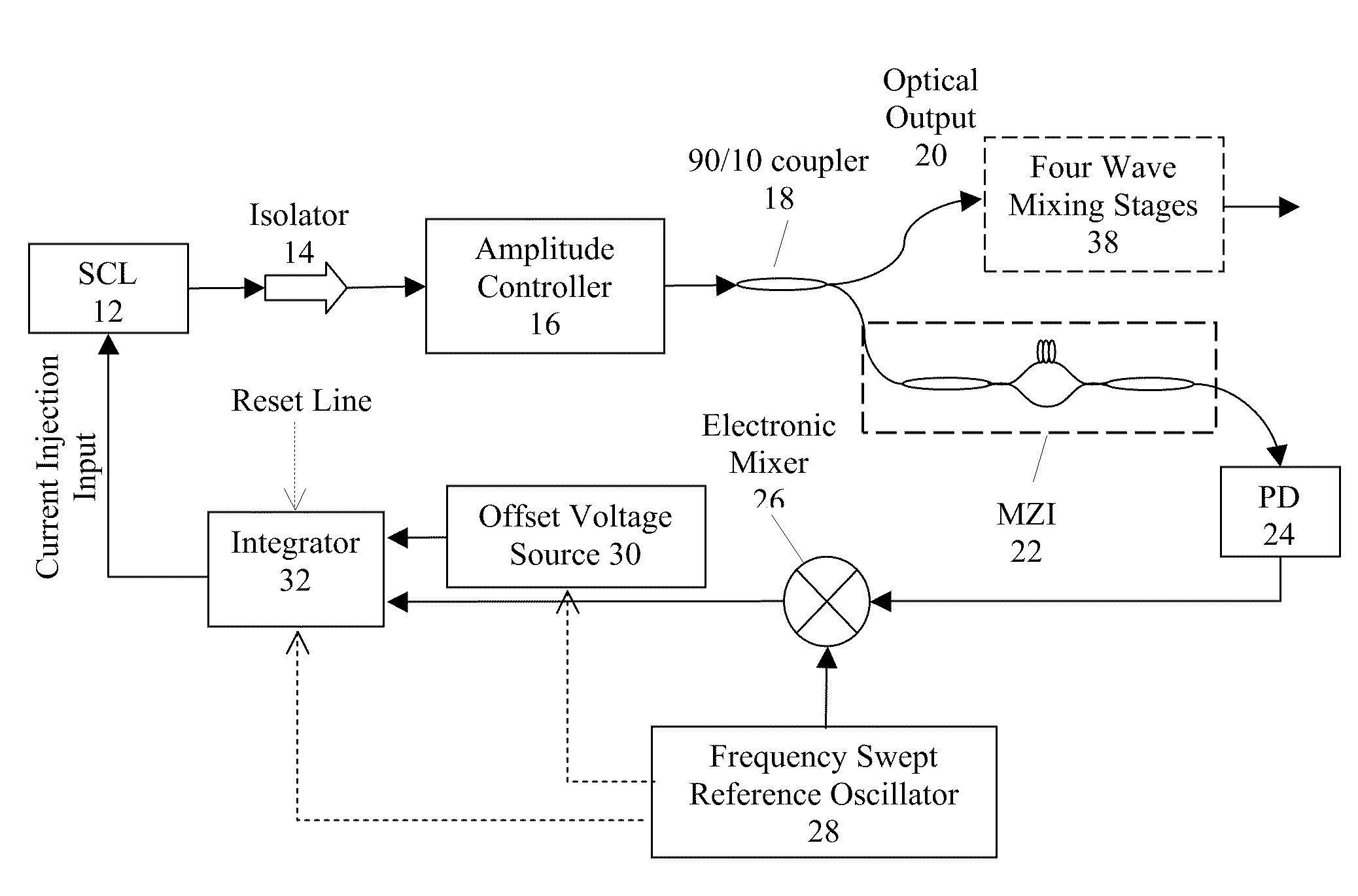
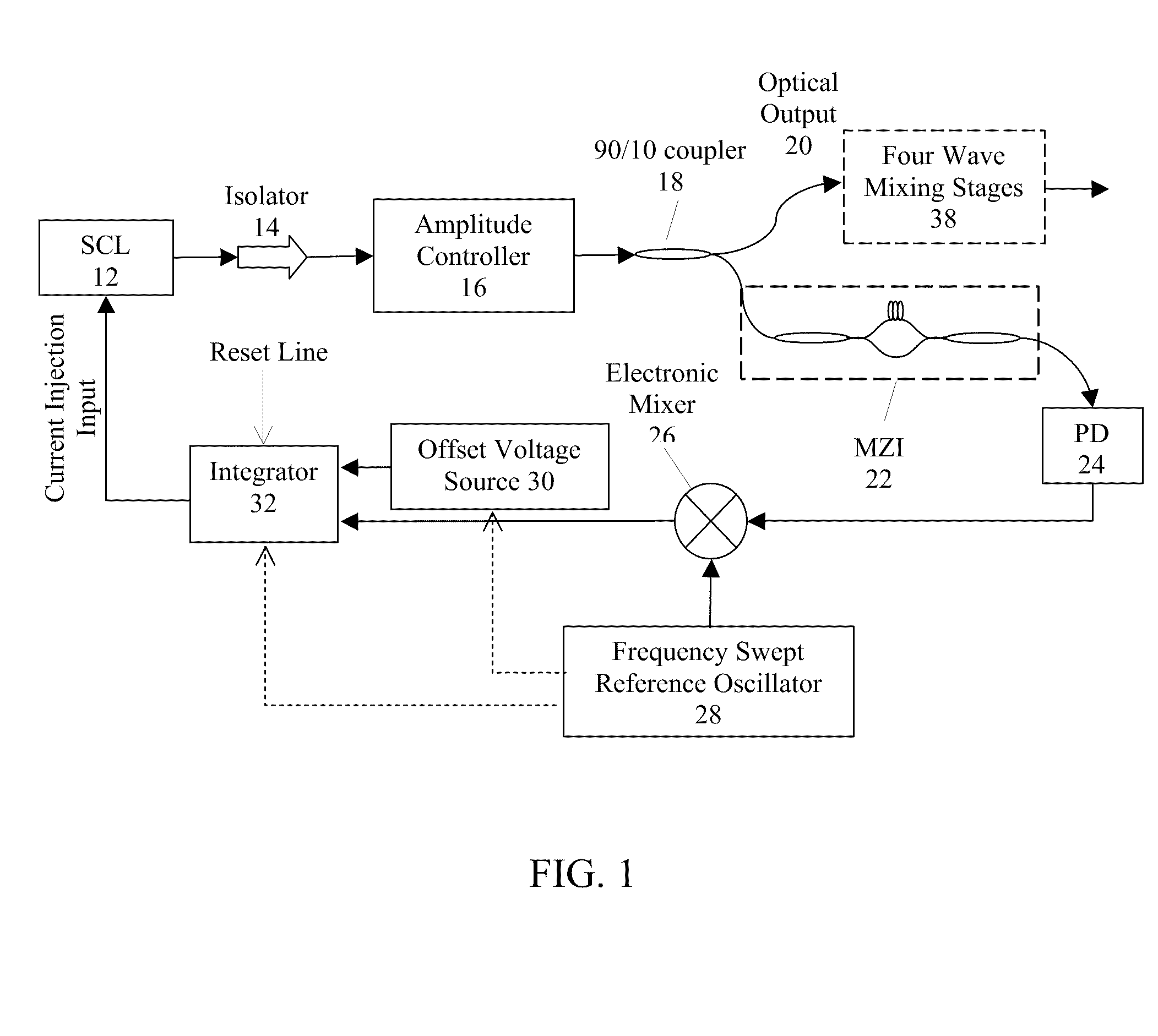
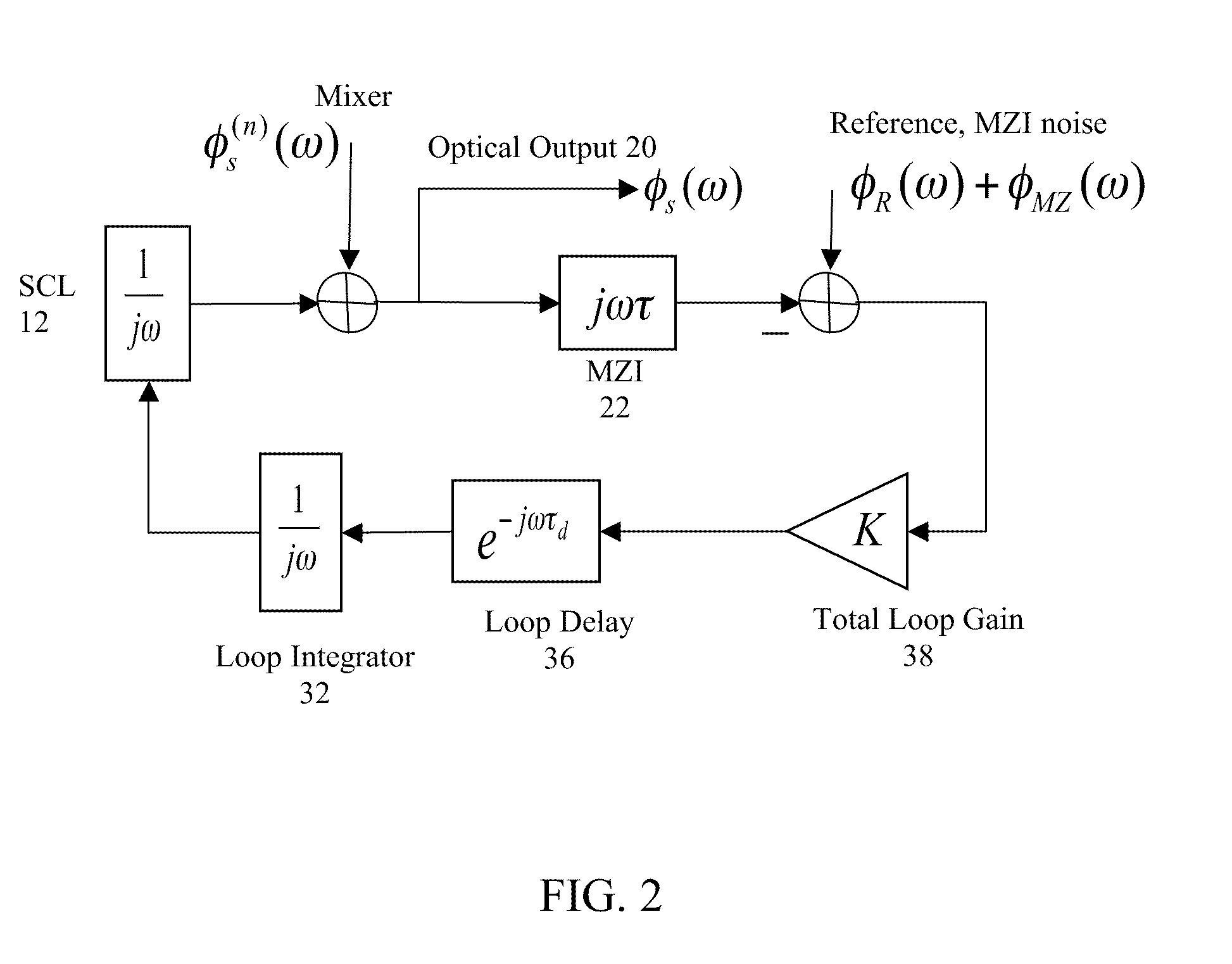
This invention relates to opto-electronic systems using semiconductor lasers driven by optical phase-locked loops that control the laser's optical phase and frequency. Feedback control provides a means for precise, wideband control of optical frequency and phase, augmented further by four wave mixing stages and digitally stitched independent optical waveforms for enhanced tunability.
Owner:INTEL CORP +1
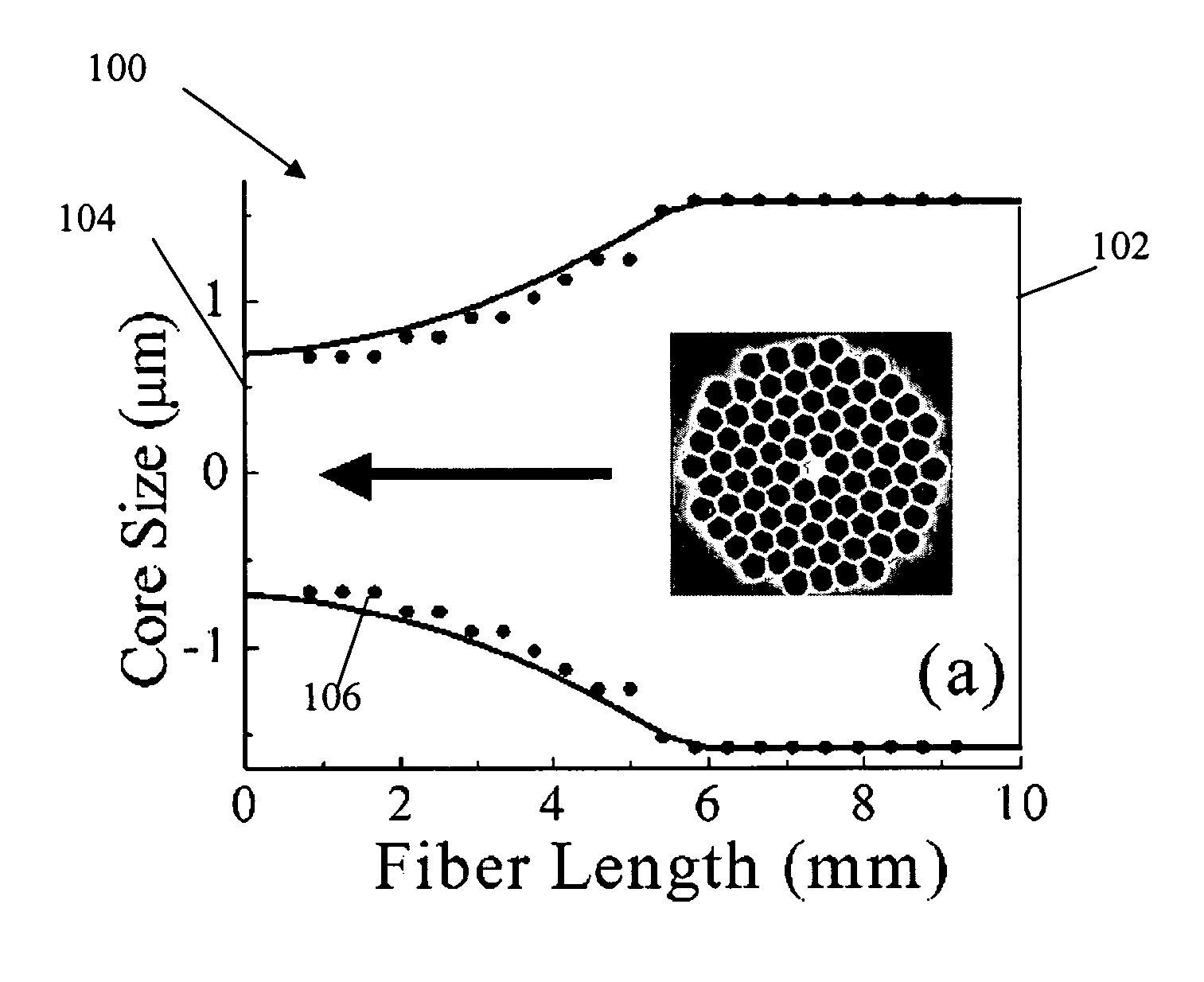
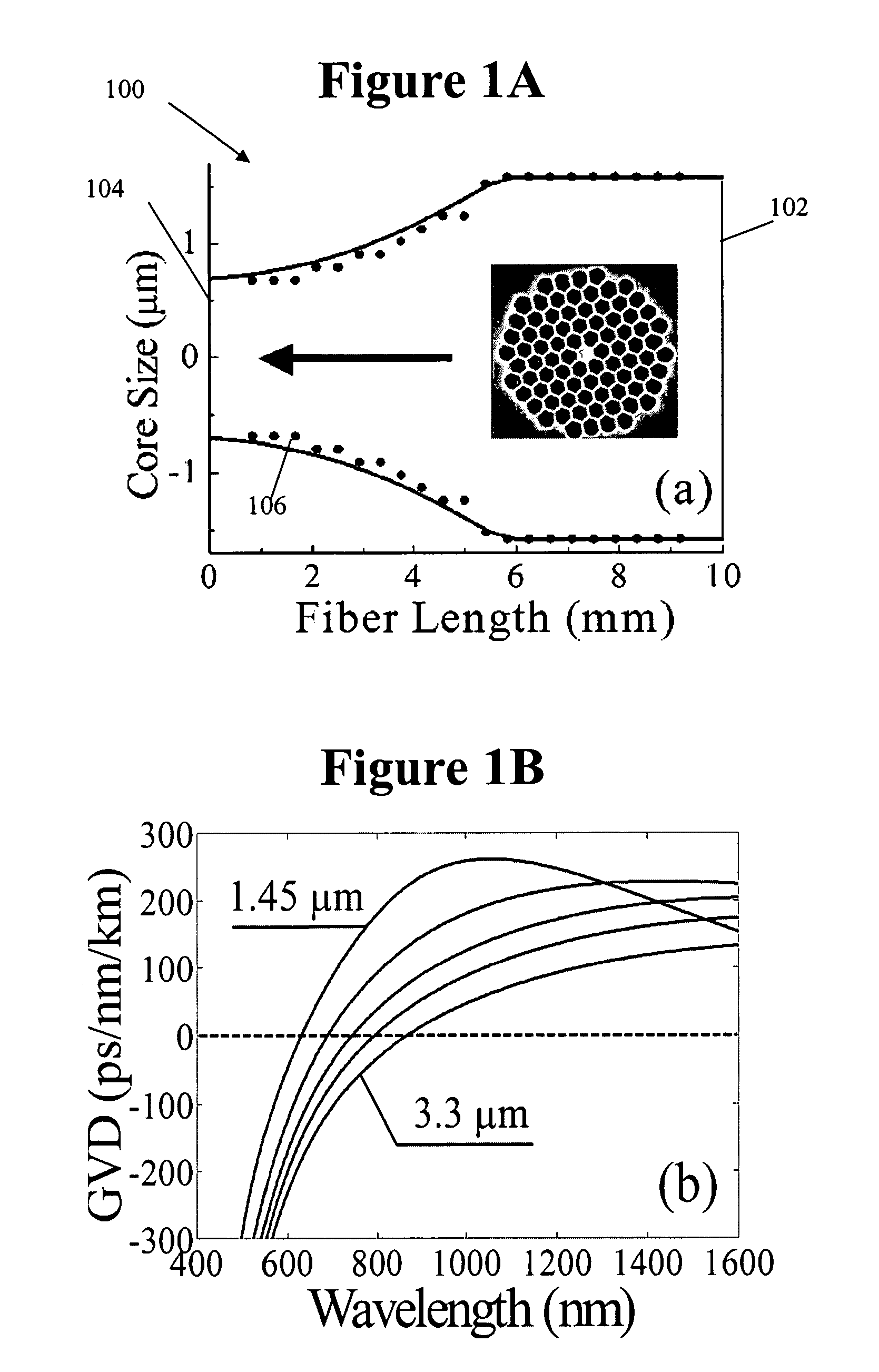
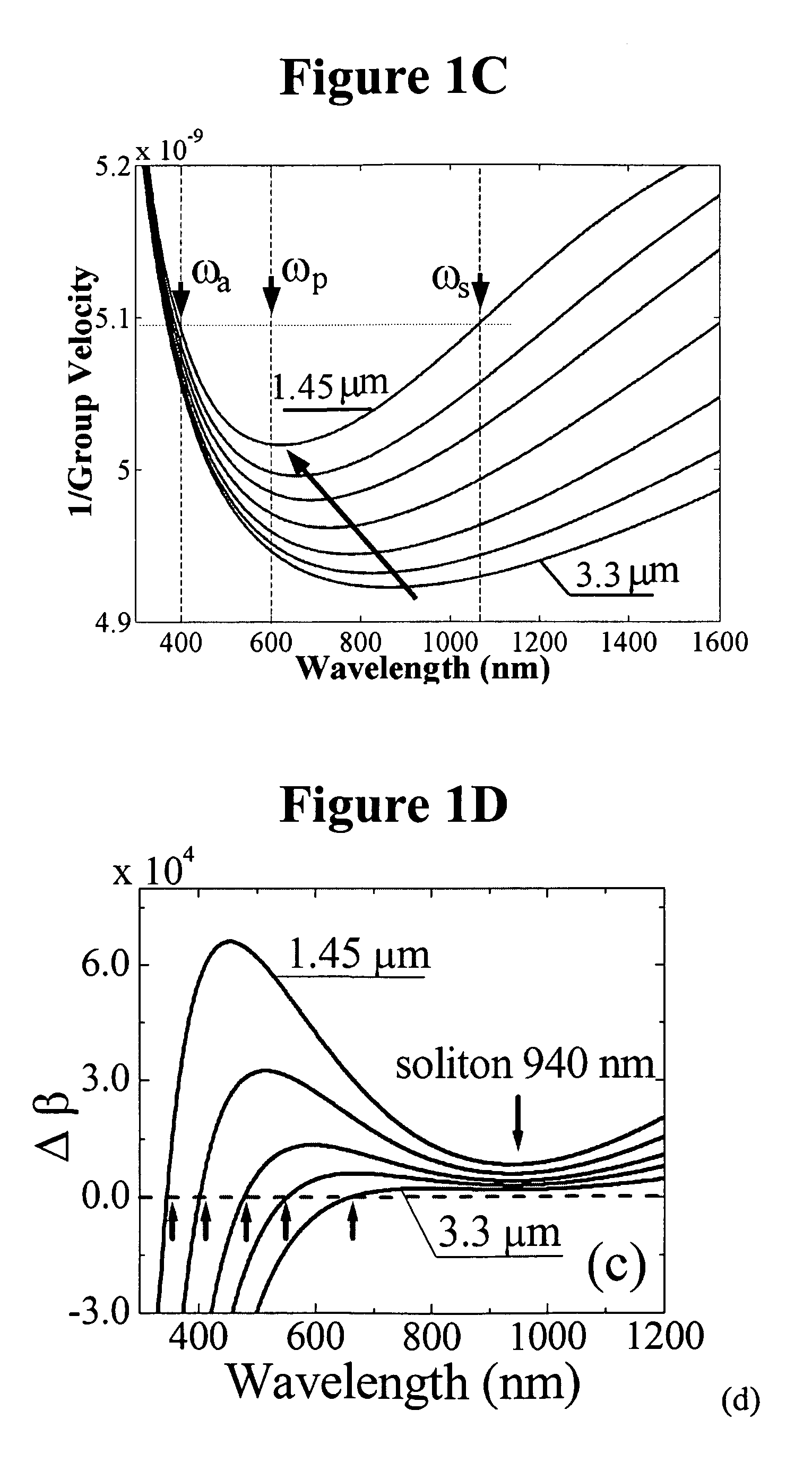
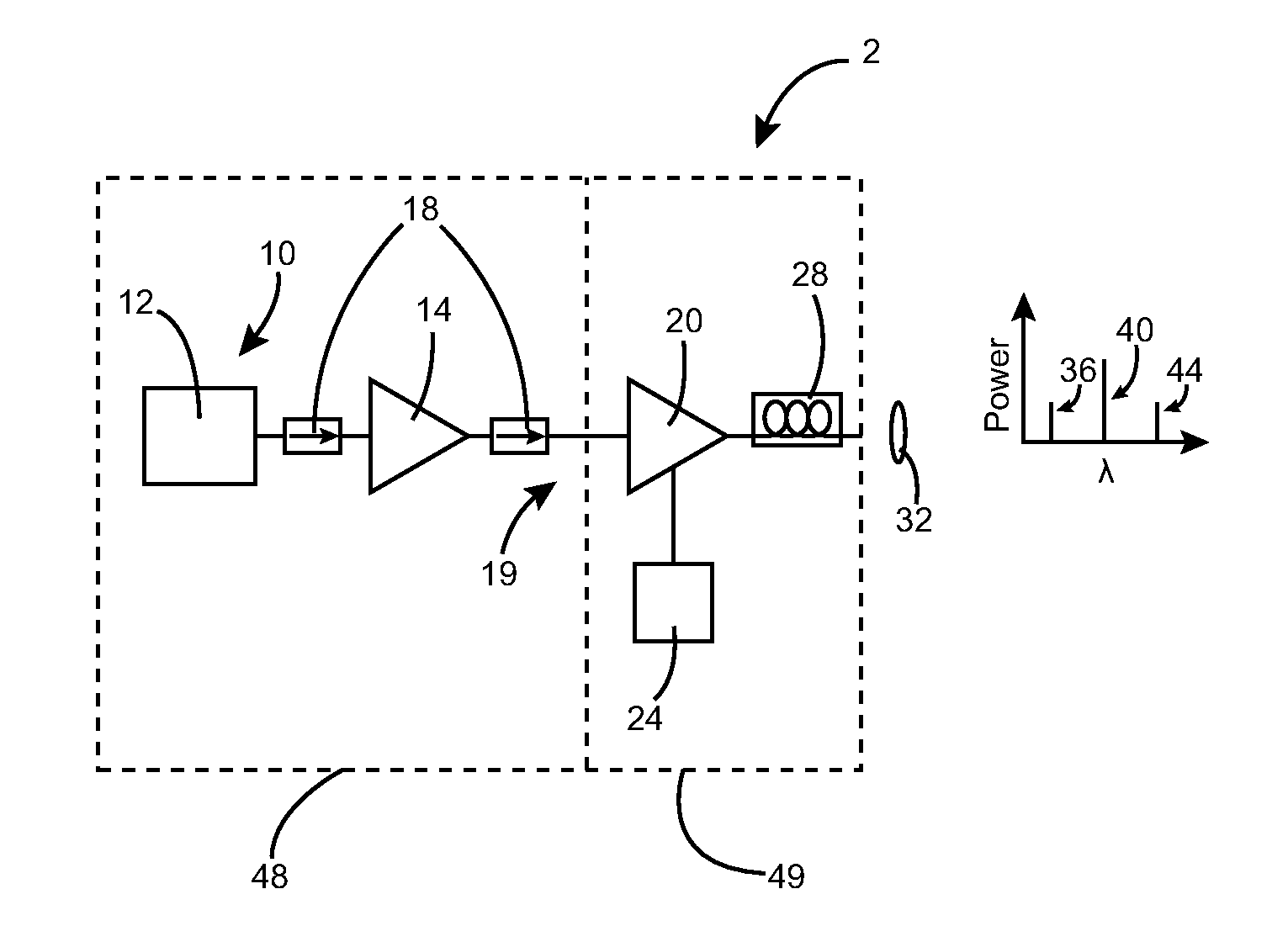
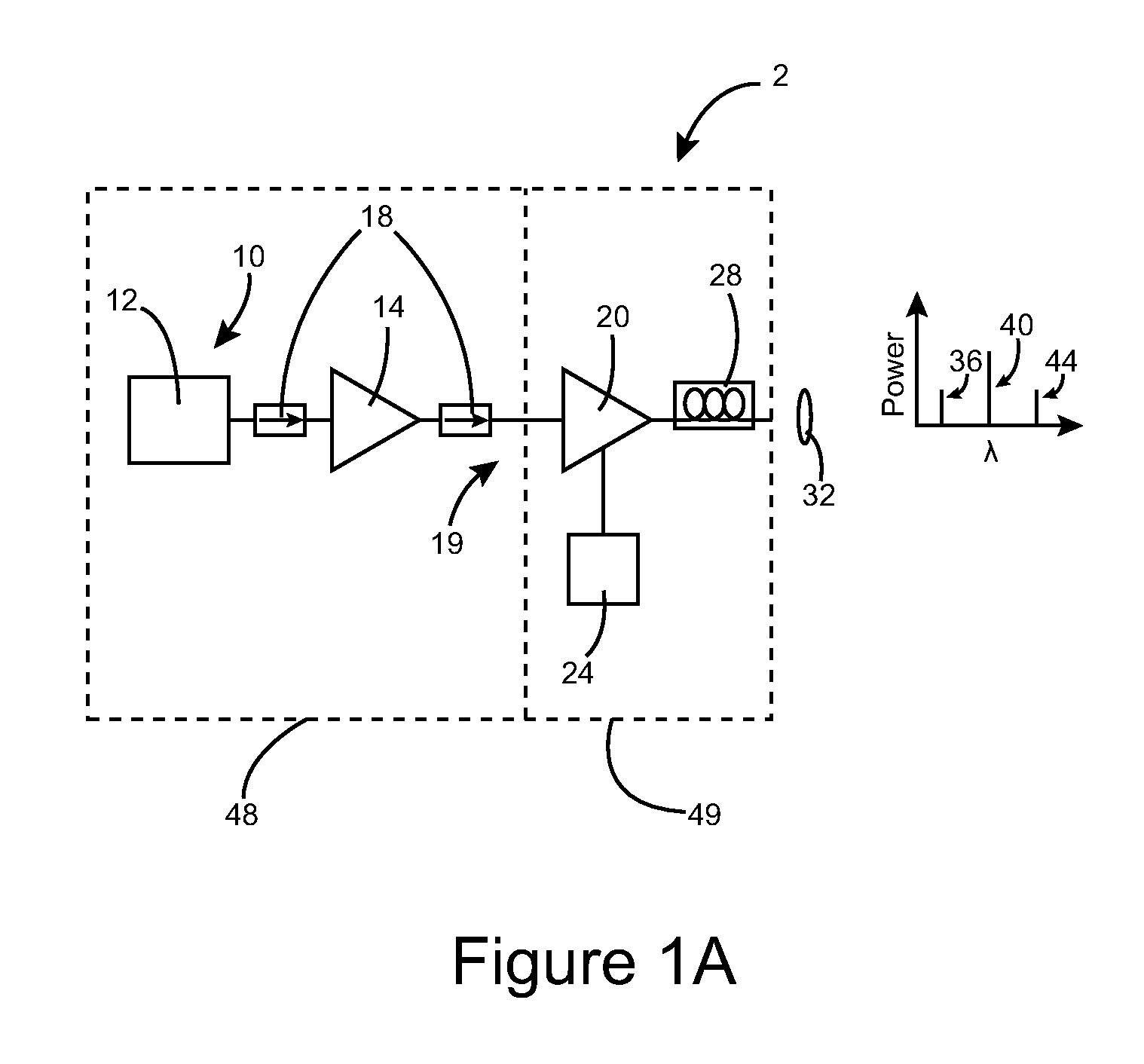
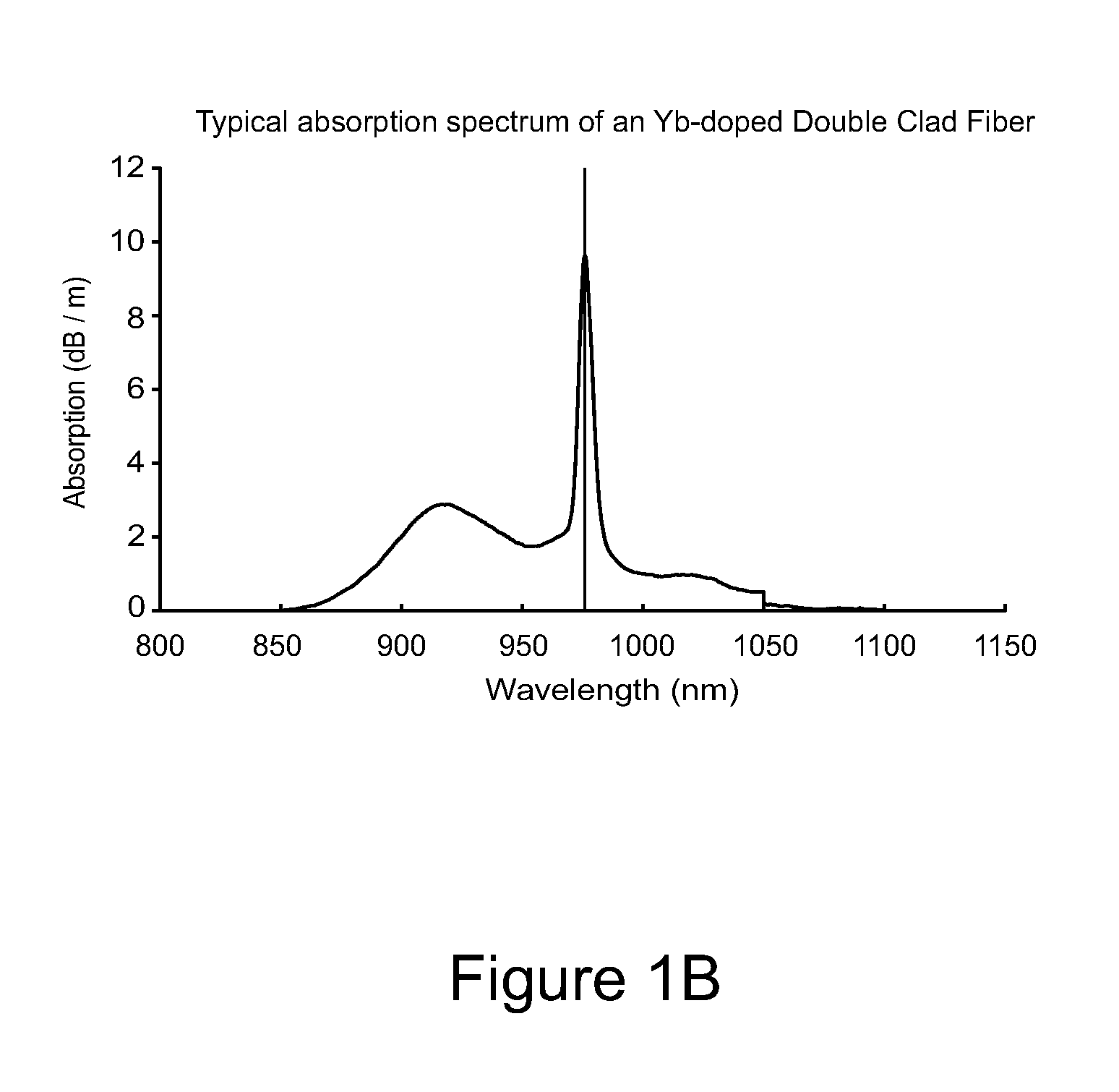
Method and apparatus for optical gain fiber having segments of differing core sizes
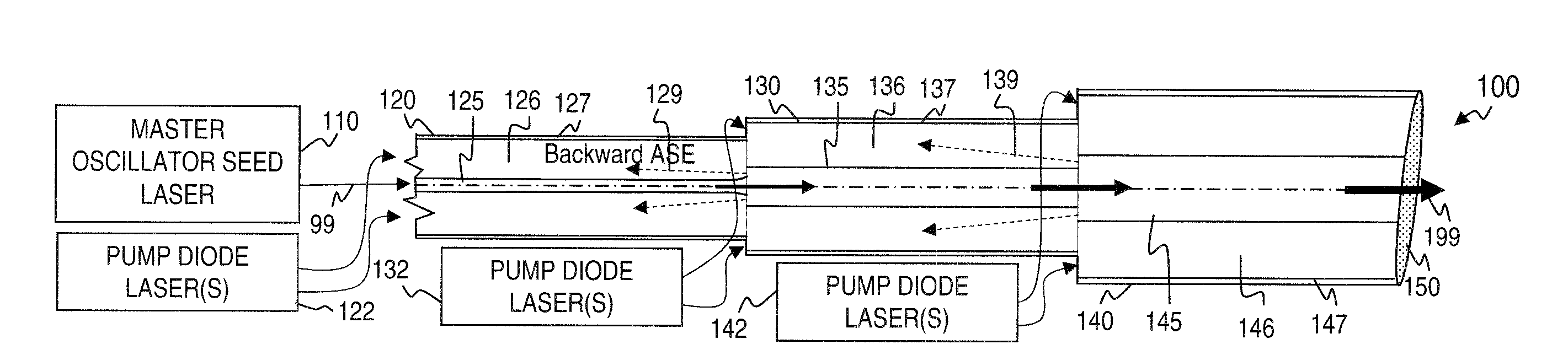
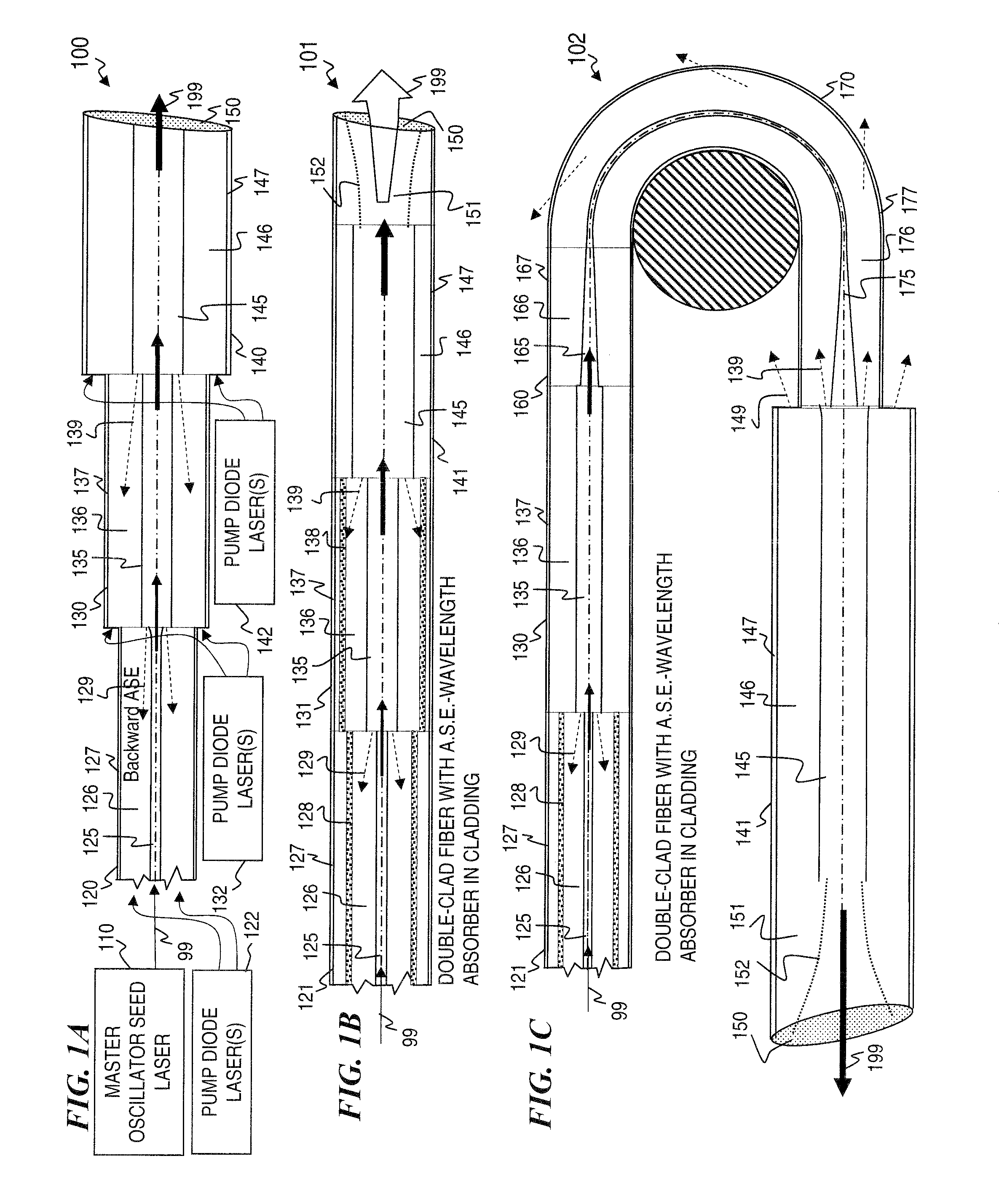
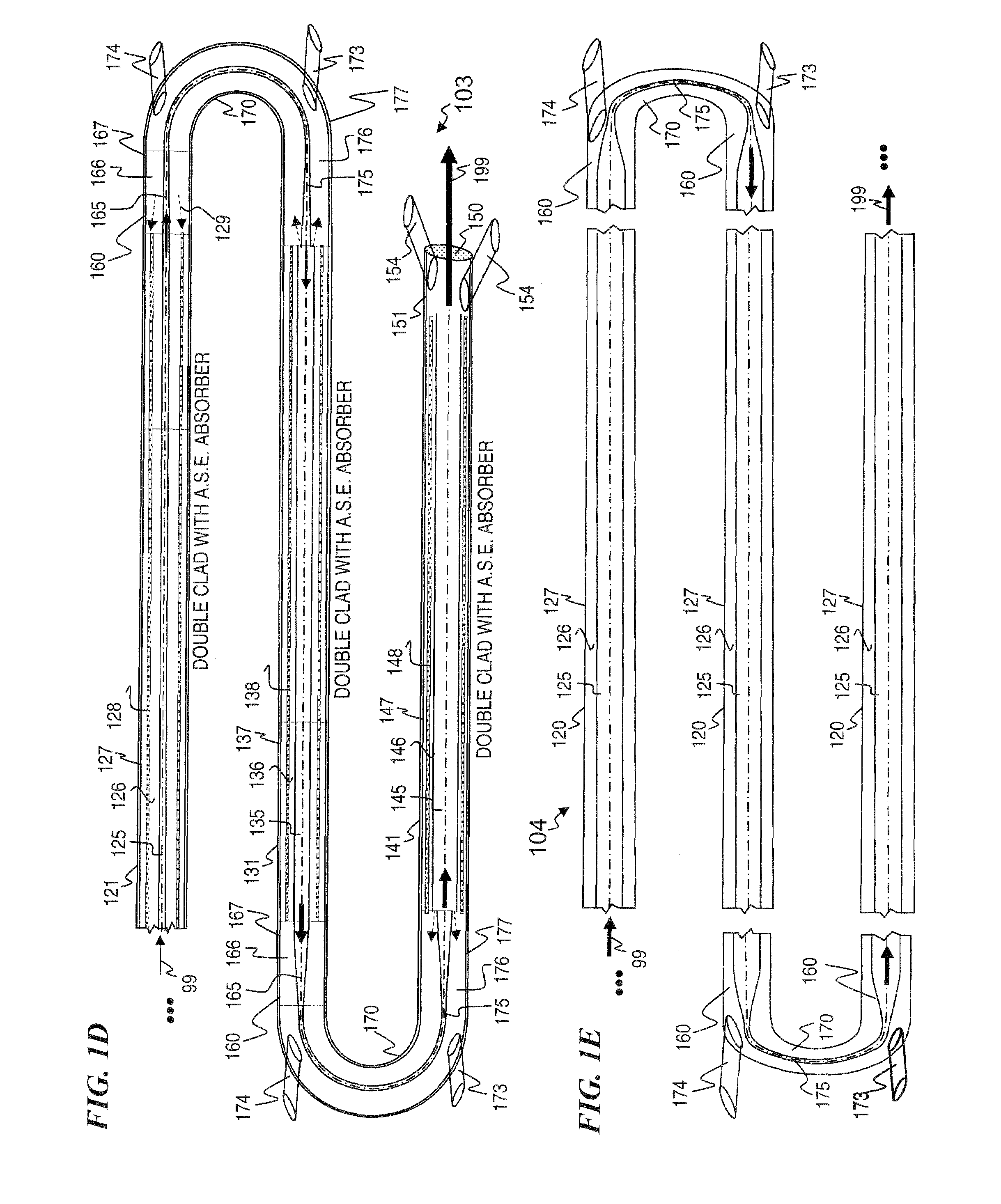
ActiveUS7768700B1Enhanced energy extractionReduce the amount requiredLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionFiberBandpass filtering
Apparatus and method for amplifying laser signals using segments of fibers of differing core diameters and / or differing cladding diameters to suppress amplified spontaneous emission and non-linear effects such as four-wave mixing (FWM), self-phase modulation, and stimulated Brillouin and / or Raman scattering (SBS / SRS). In some embodiments, different core sizes have different sideband spacings (spacing between the desired signal and wavelength-shifted lobes). Changing core sizes and providing phase mismatches prevent buildup of non-linear effects. Some embodiments further include a bandpass filter to remove signal other than the desired signal wavelength and / or a time gate to remove signal at times other than during the desired signal pulse. Some embodiments include photonic-crystal structures to define the core for the signal and / or the inner cladding for the pump. Some embodiments include an inner glass cladding to confine the signal in the core and an outer glass cladding to confine pump light in the inner cladding.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
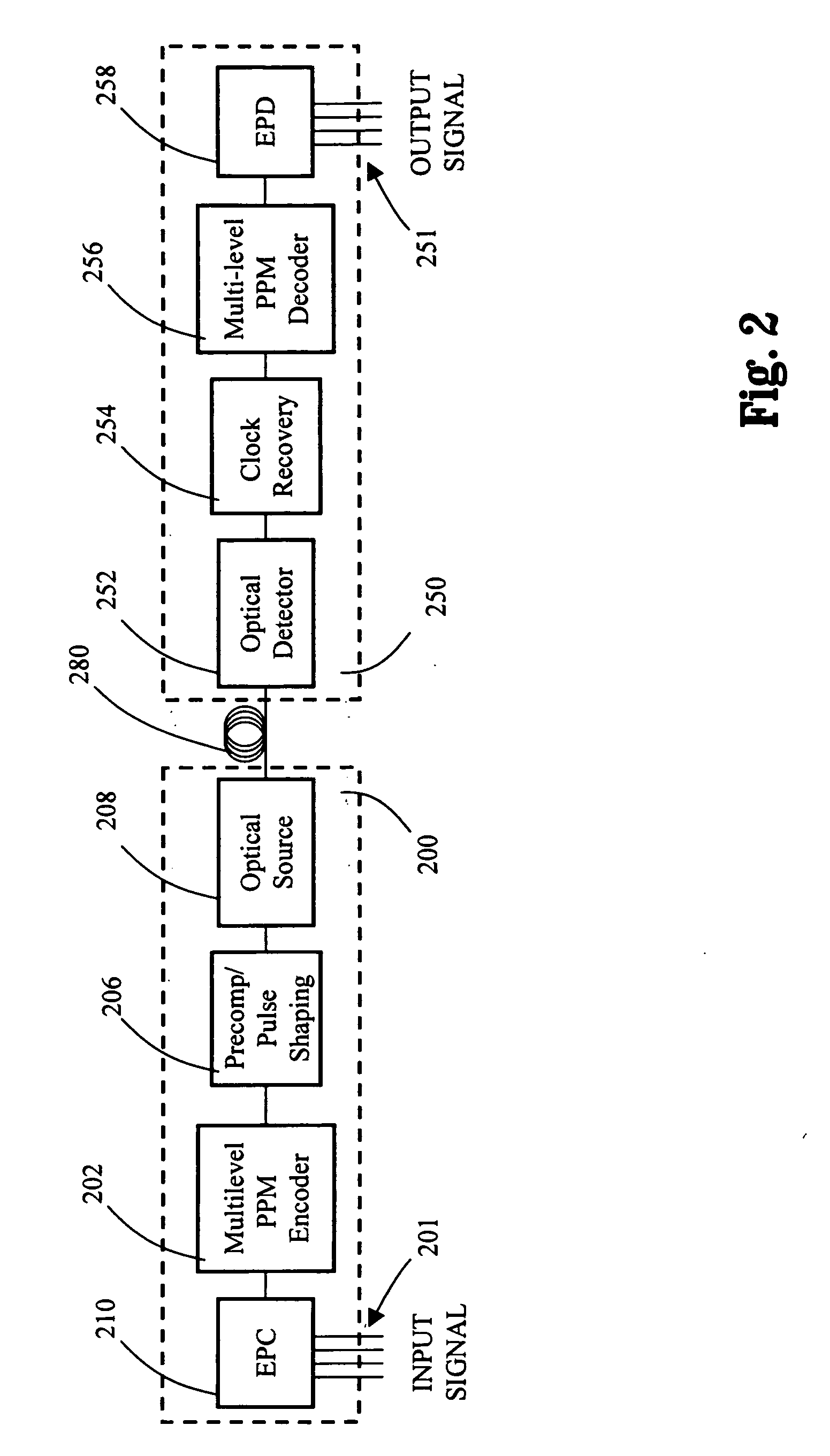
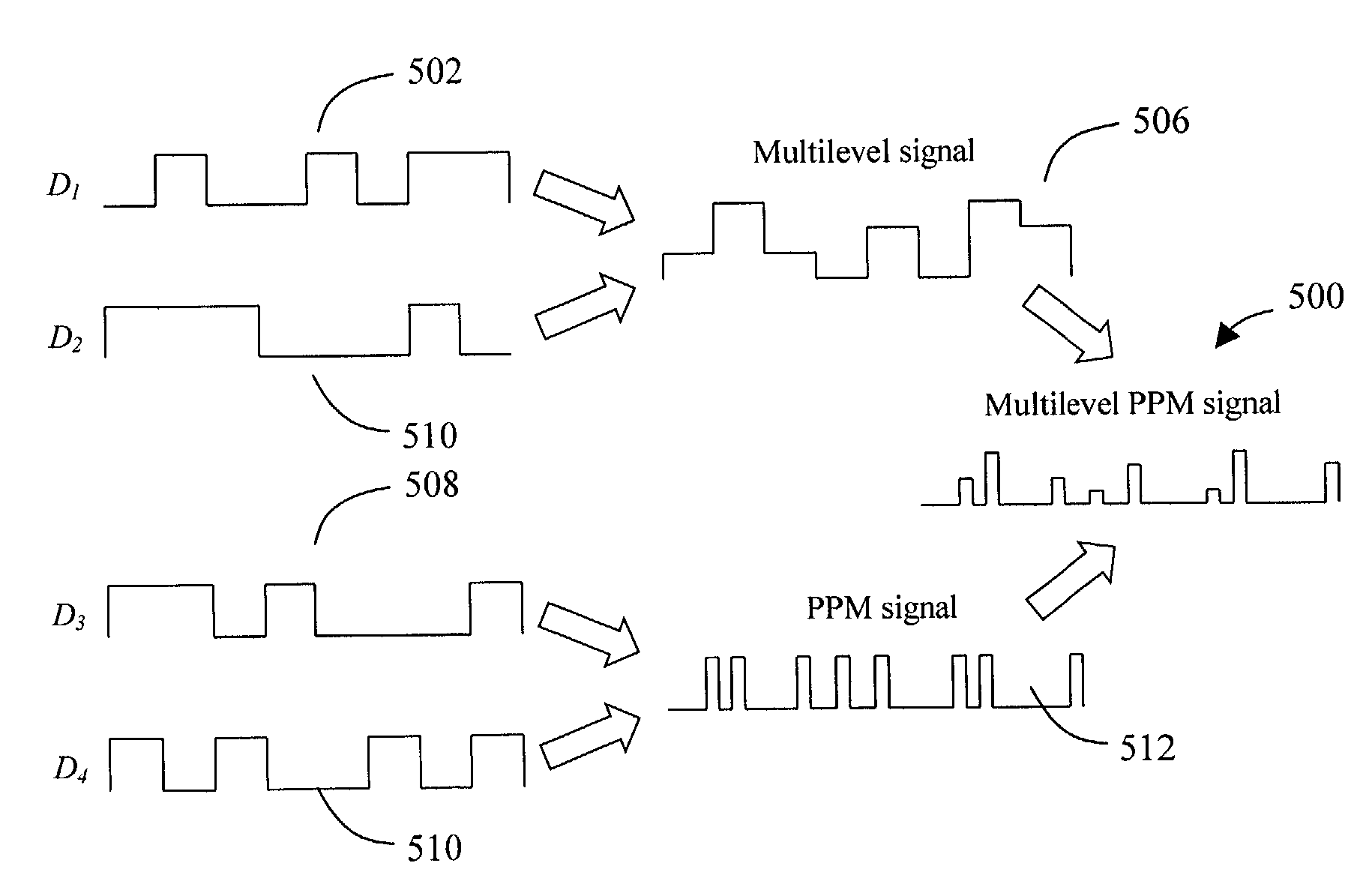
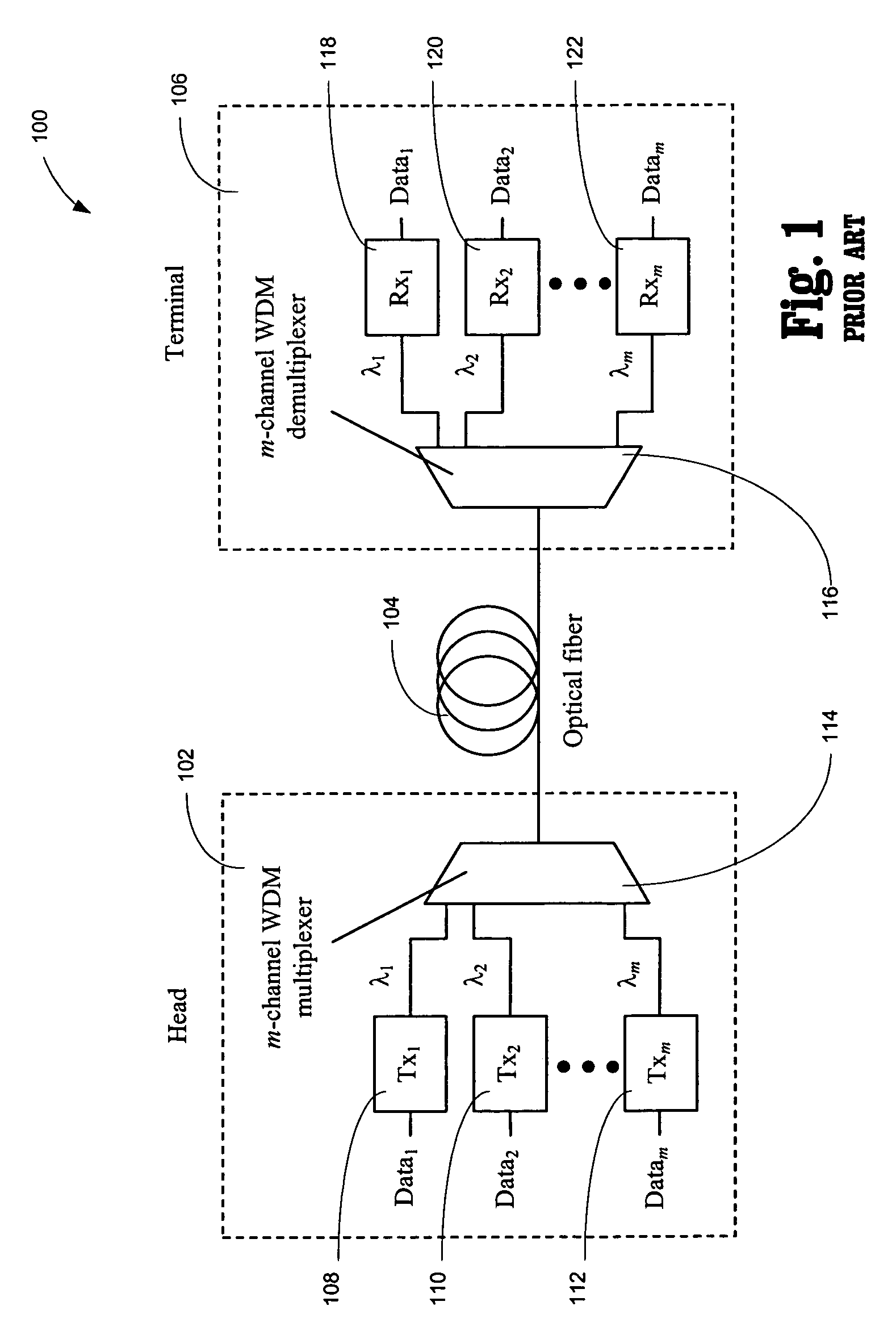
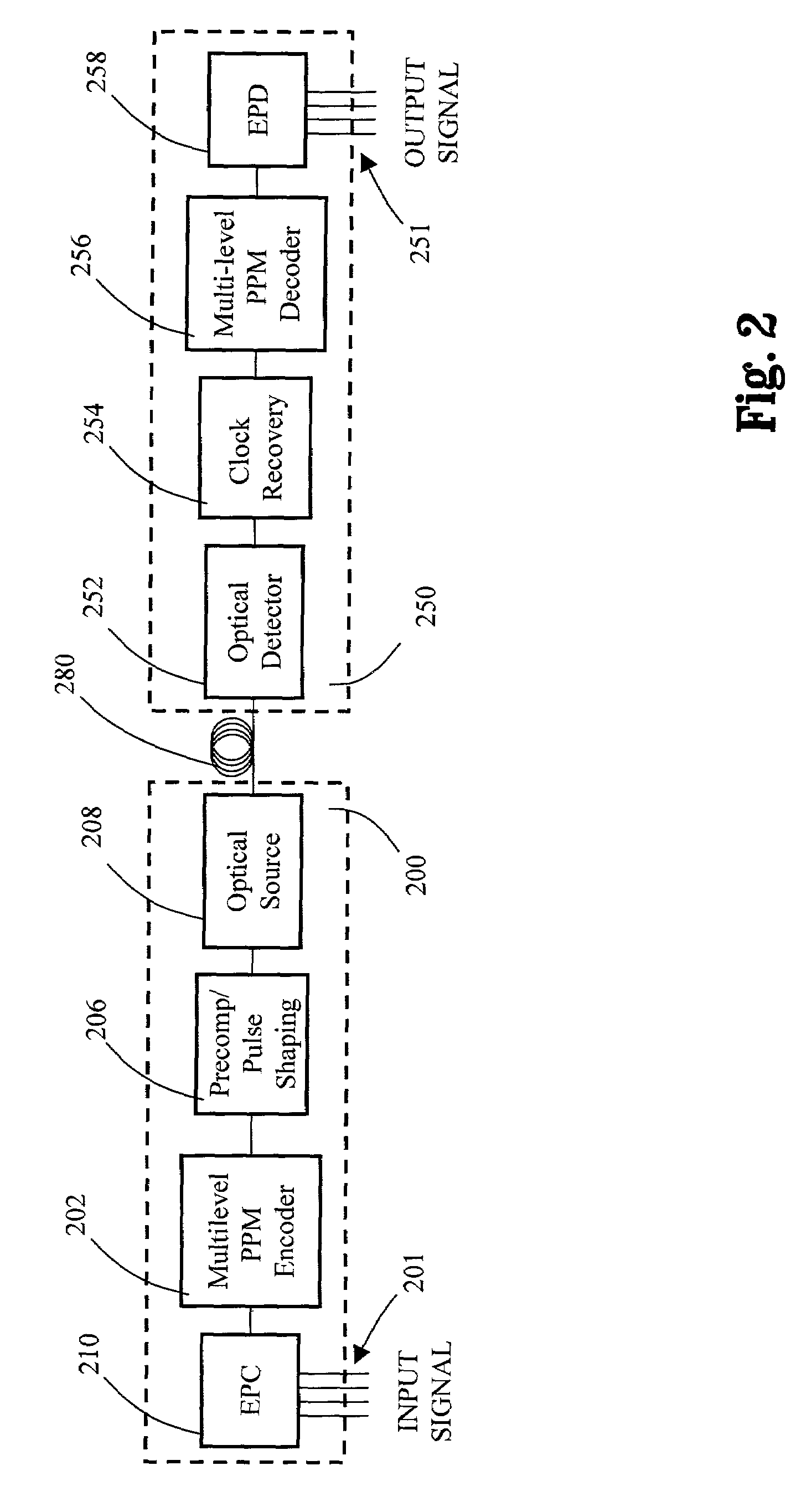
Multilevel pulse position modulation for efficient fiber optic communication
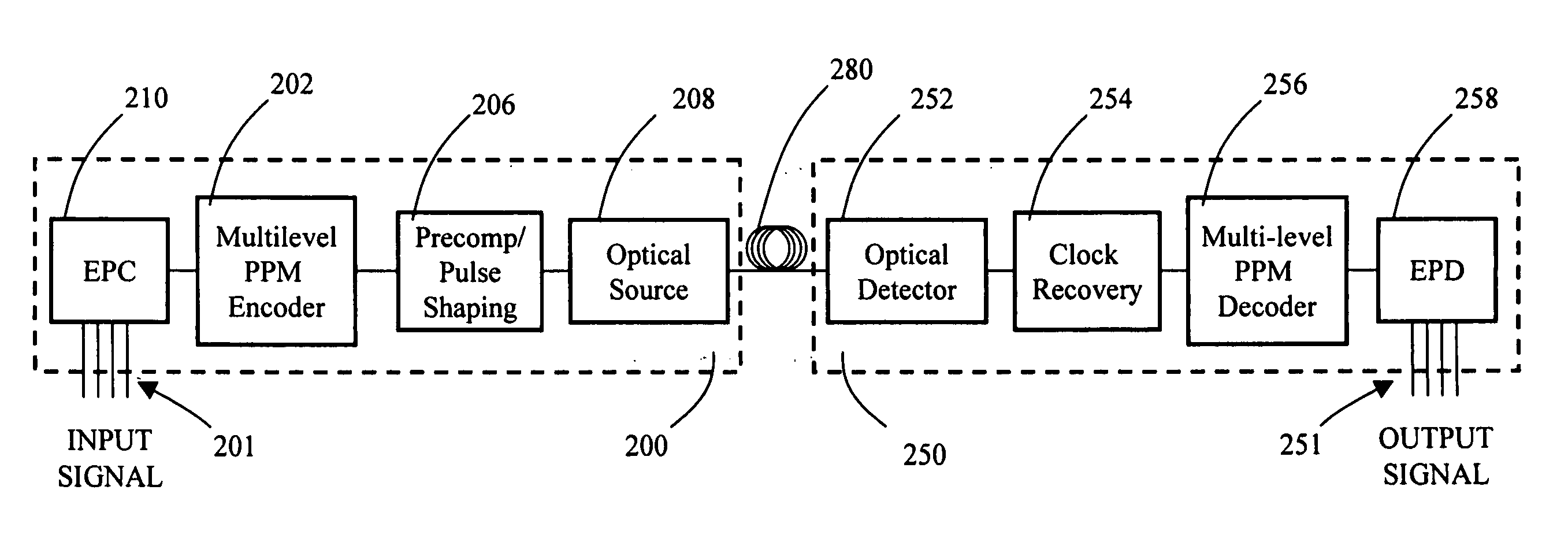
InactiveUS20070092265A1Increasing aggregate data rateReduce transmit powerModulated-carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransmitted powerStimulate raman scattering
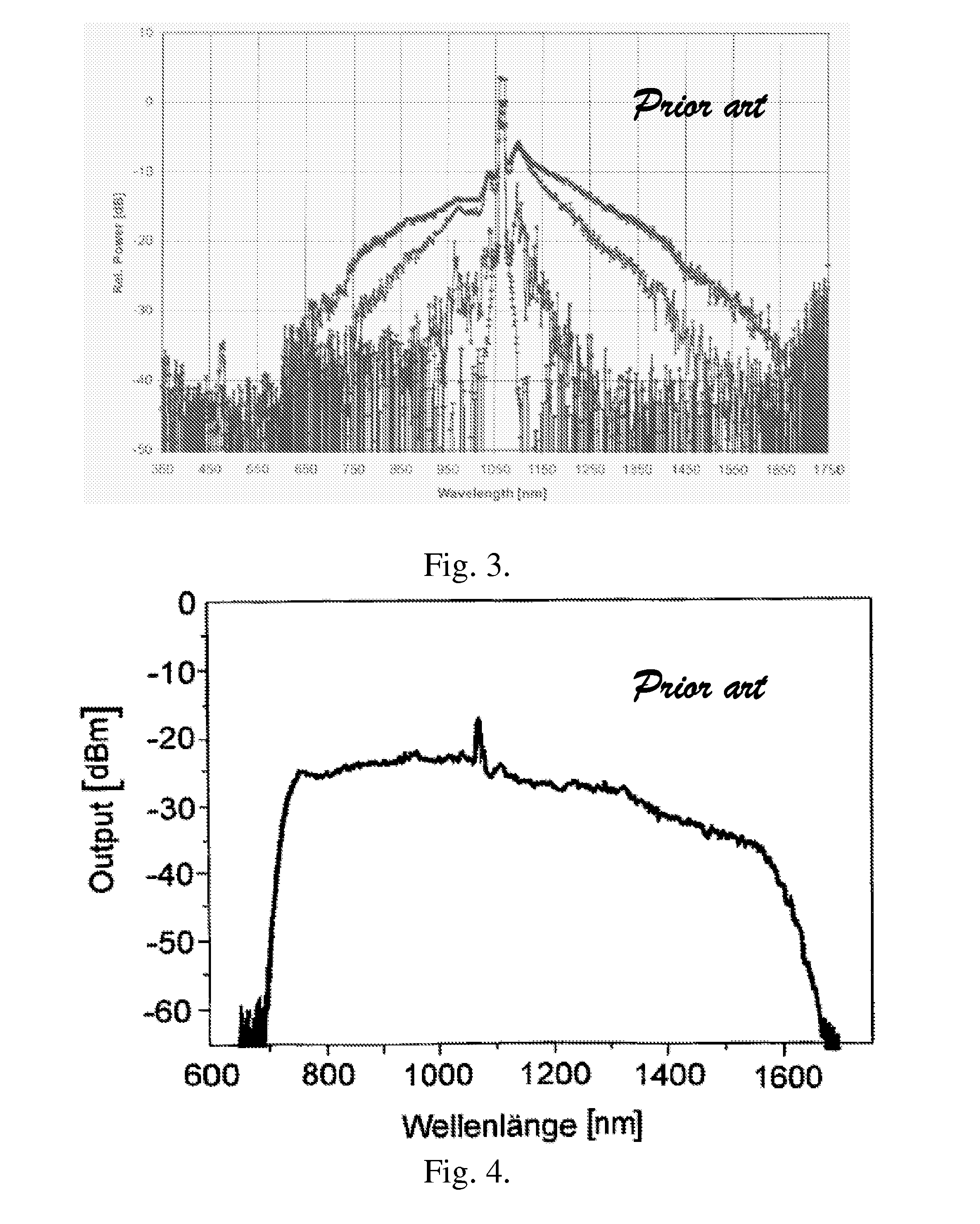
Decreasing the average transmitted power in an optical fiber communication channel using multilevel amplitude modulation in conjunction with Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). This multilevel PPM method does not entail any tradeoff between decreased power per channel and channel bandwidth, enabling a lower average transmitted power compared to On / Off Keying (OOK) with no reduction in aggregate data rate. Therefore, multilevel PPM can be used in high-speed Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) systems where the maximum number of channels is traditionally limited by nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation (SPM), cross-phase modulation (XPM), four-wave mixing (FWM), stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). This modulation technique can enable an increased number of channels in DWDM systems, thereby increasing aggregate data rates within those systems.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
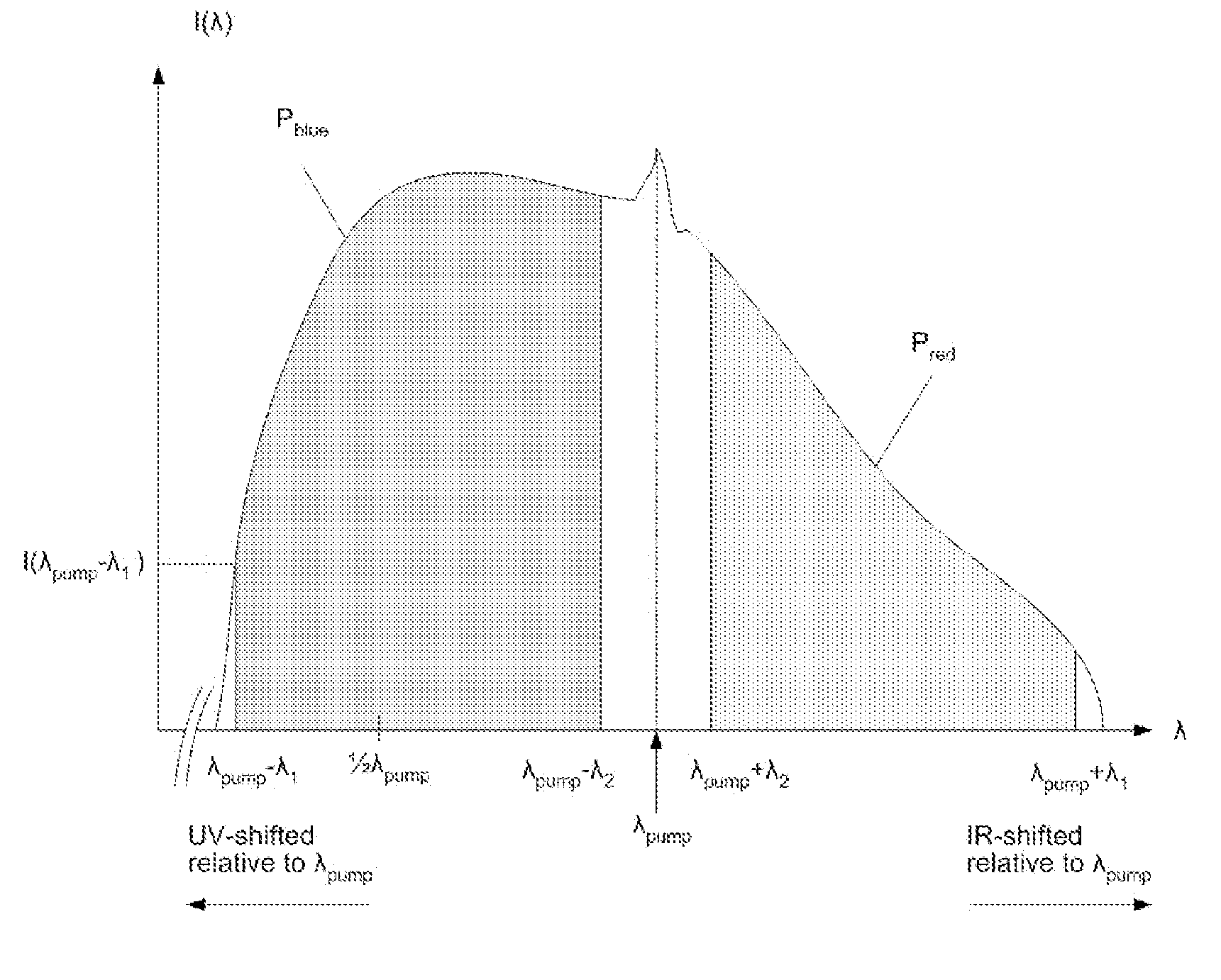
Blue extended super continuum light source
InactiveUS7800818B2Increase powerLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInstabilityRefractive index
In a blue extended super continuum light source, when pulses of partly coherent monochromatic “pump” radiation of essentially constant amplitude are propagating through a microstructure fiber medium within a region of anomalous dispersion of the medium, then, provided the medium has a finite nonlinear coefficient of the index of refraction, the pump pulse is subject to a modulation instability. This results in formation of a train of narrow pulses with Tera Hertz repetition rate. Phase match between red shifted Raman solitons generated by the pump pulse and energy shed by the pump pulse at all frequencies with a group velocity below the pump pulse group velocity may lead to the formation of Cherenkov radiation. The solitons may seed Cherenkov radiation at different wavelengths depending on the actual fiber parameters. This allows extension of generated super continuum light beyond the four wave mixing limit when applying picosecond or nanosecond pump pulses.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Multilevel pulse position modulation for efficient fiber optic communication
InactiveUS7149256B2Reduce transmit powerIncreasing aggregate data rateAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringTransmitted powerStimulate raman scattering
Decreasing the average transmitted power in an optical fiber communication channel using multilevel amplitude modulation in conjunction with Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). This multilevel PPM method does not entail any tradeoff between decreased power per channel and channel bandwidth, enabling a lower average transmitted power compared to On / Off Keying (OOK) with no reduction in aggregate data rate. Therefore, multilevel PPM can be used in high-speed Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) systems where the maximum number of channels is traditionally limited by nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation (SPM), cross-phase modulation (XPM), four-wave mixing (FWM), stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). This modulation technique can enable an increased number of channels in DWDM systems, thereby increasing aggregate data rates within those systems.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
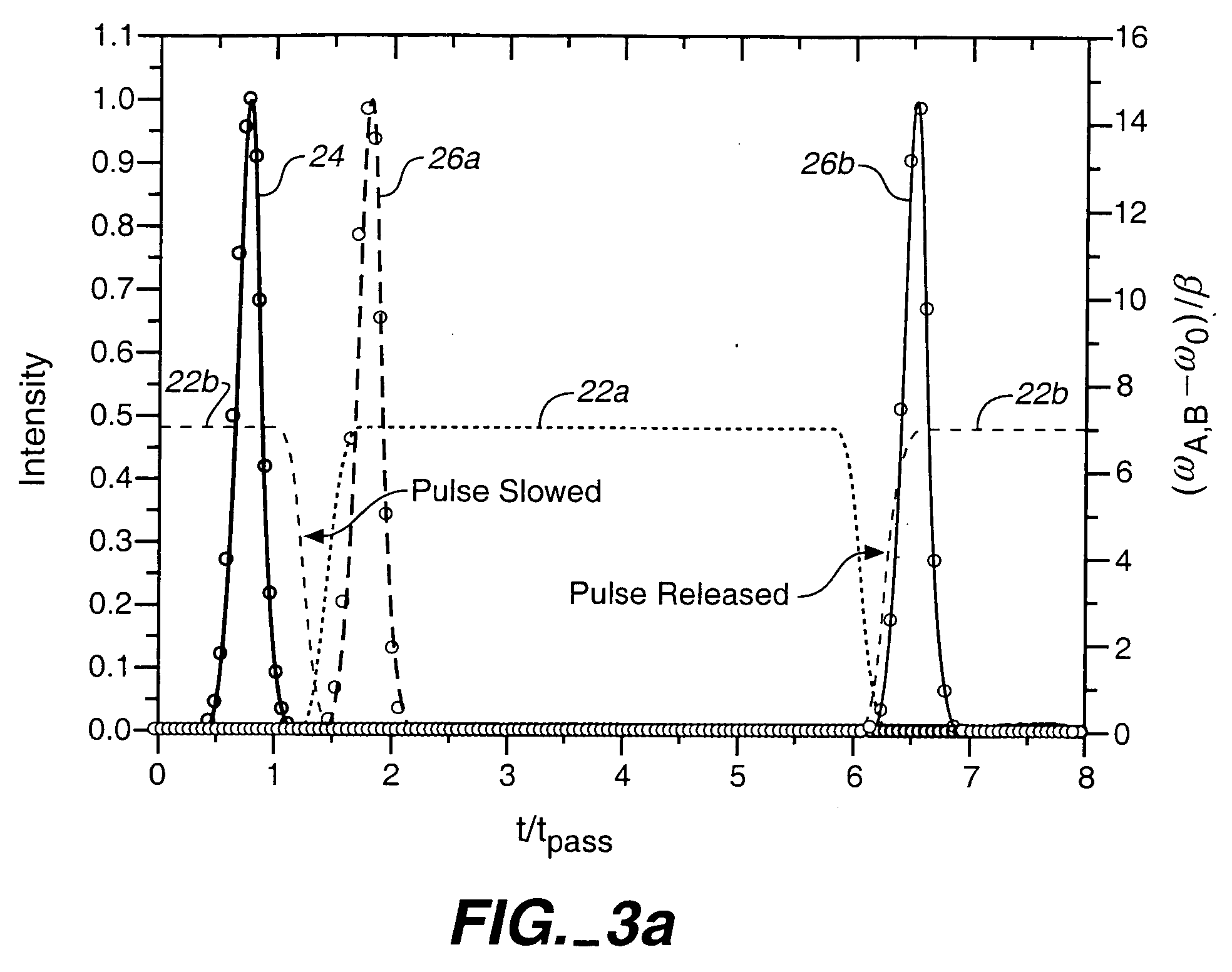
Ultra-slow down and storage of light pulses, and altering of pulse spectrum
Light pulses can be stopped and stored coherently, with an all-optical process that involves an adiabatic and reversible pulse bandwidth compression occurring entirely in the optical domain. Such a process overcomes the fundamental bandwidth-delay constraint in optics, and can generate arbitrarily small group velocities for light pulses with a given bandwidth, without the use of any coherent or resonant light-matter interactions. This is accomplished only by small refractive index modulations performed at moderate speeds and has applications ranging from quantum communications and computing to coherent all-optical memory devices. A complete time reversal and / or temporal / spectral compression and expansion operation on any electromagnetic field is accomplished using only small refractive index modulations and linear optical elements. This process does not require any nonlinear multi-photon processes such as four-wave mixing and thus can be implemented using on-chip tunable microcavity complexes in photonic crystals. The tuning process requires only small refractive index modulations, and moderate modulation speeds without requiring any high-speed electronic sampling.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
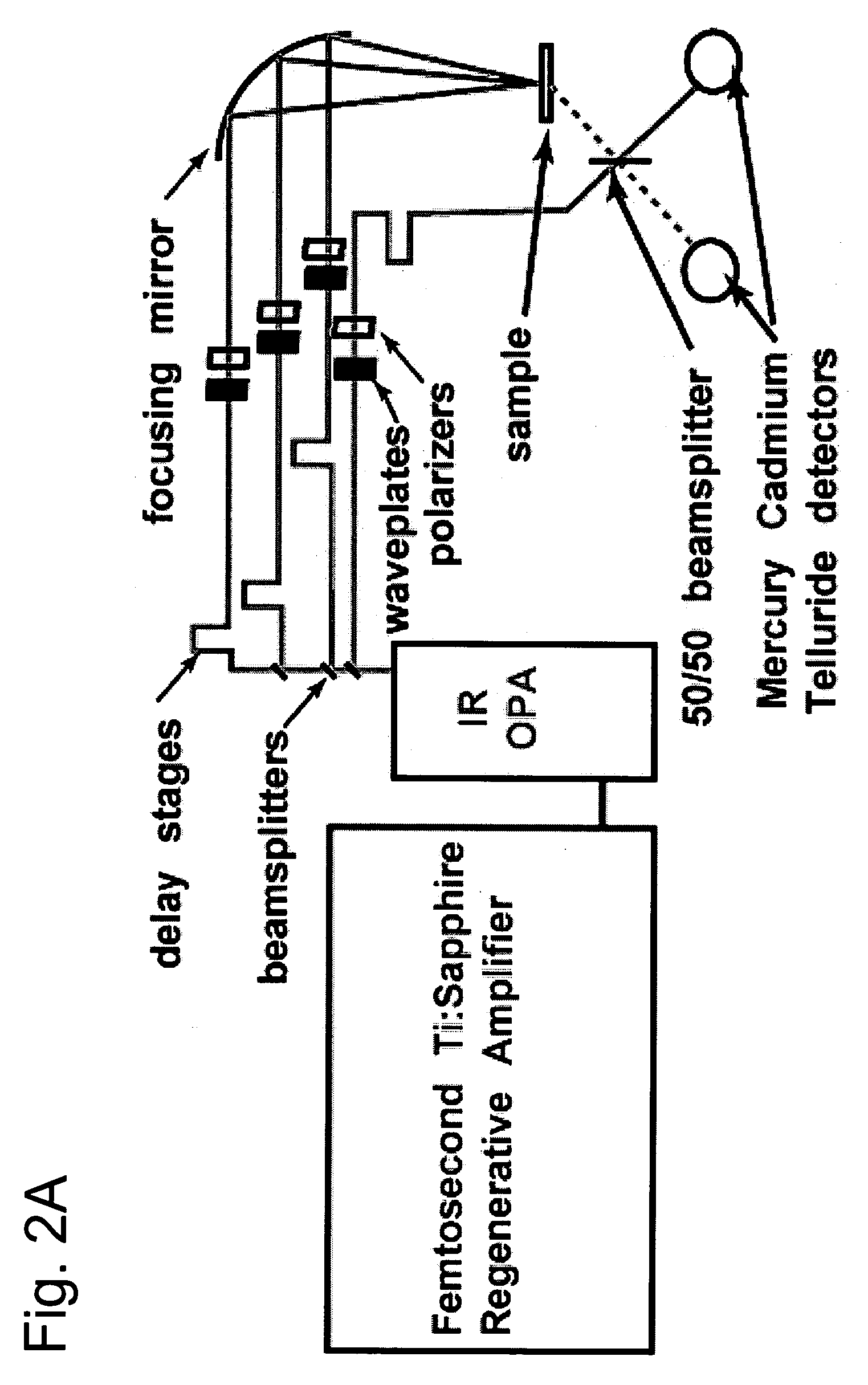
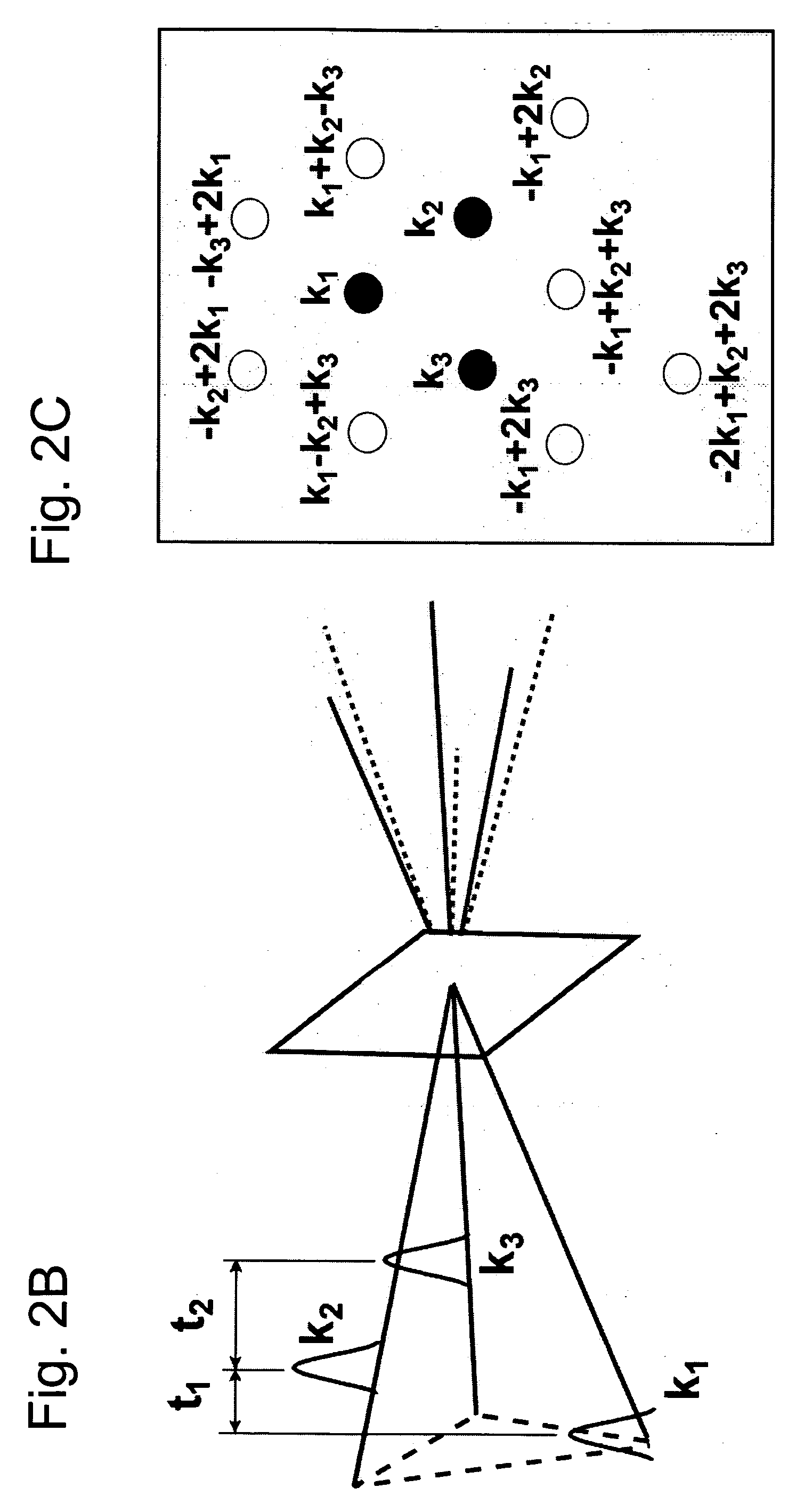
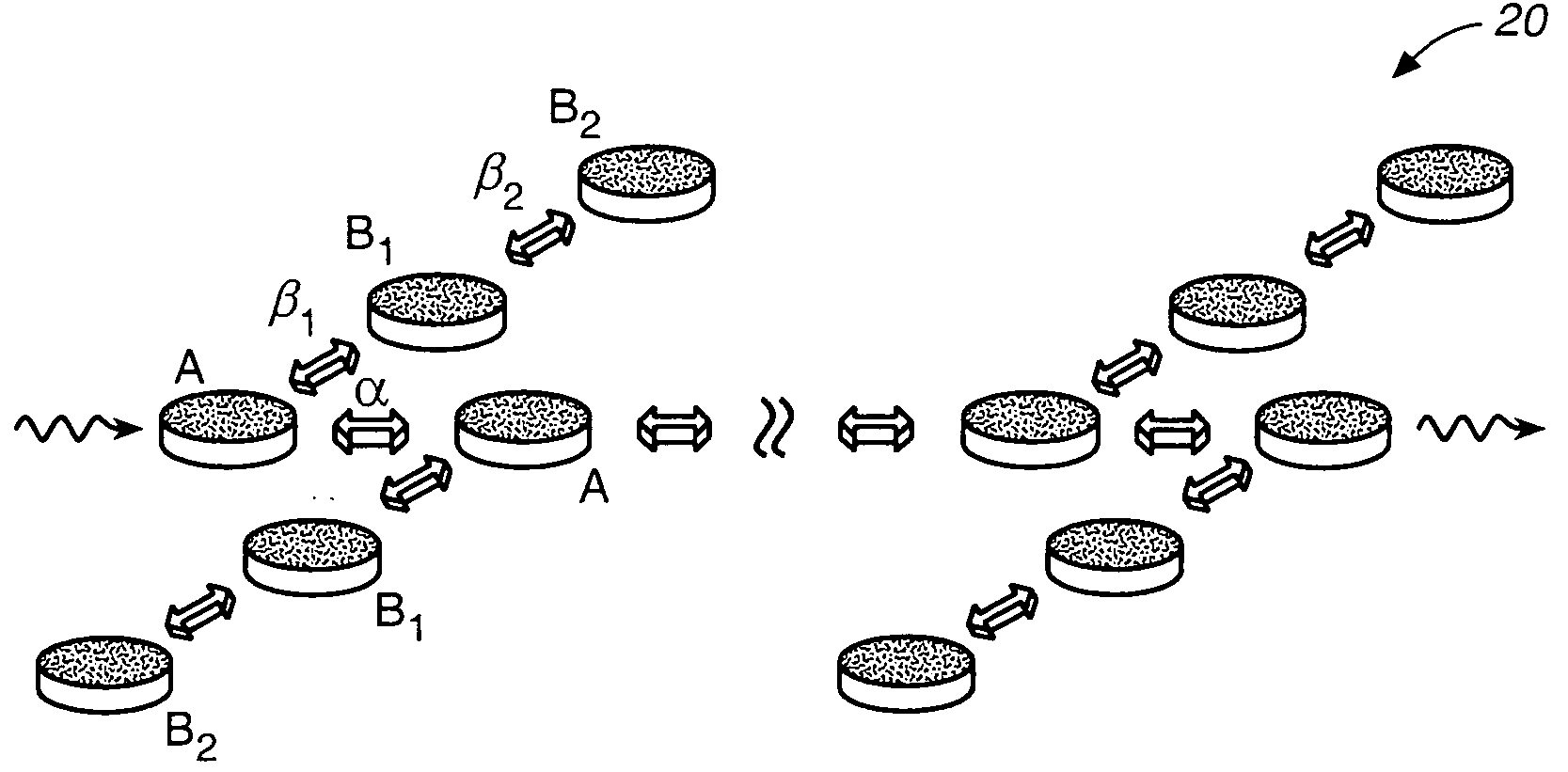
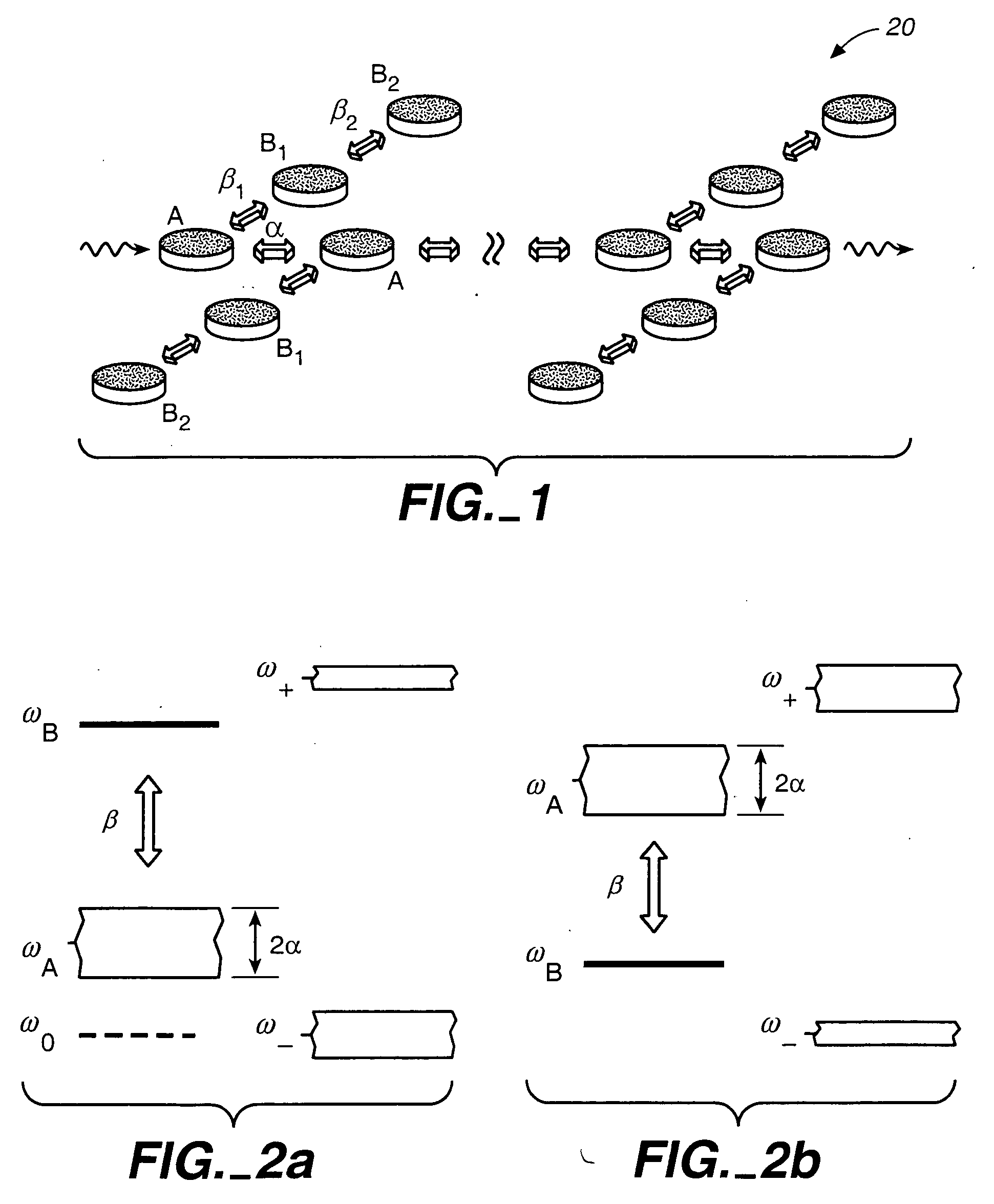
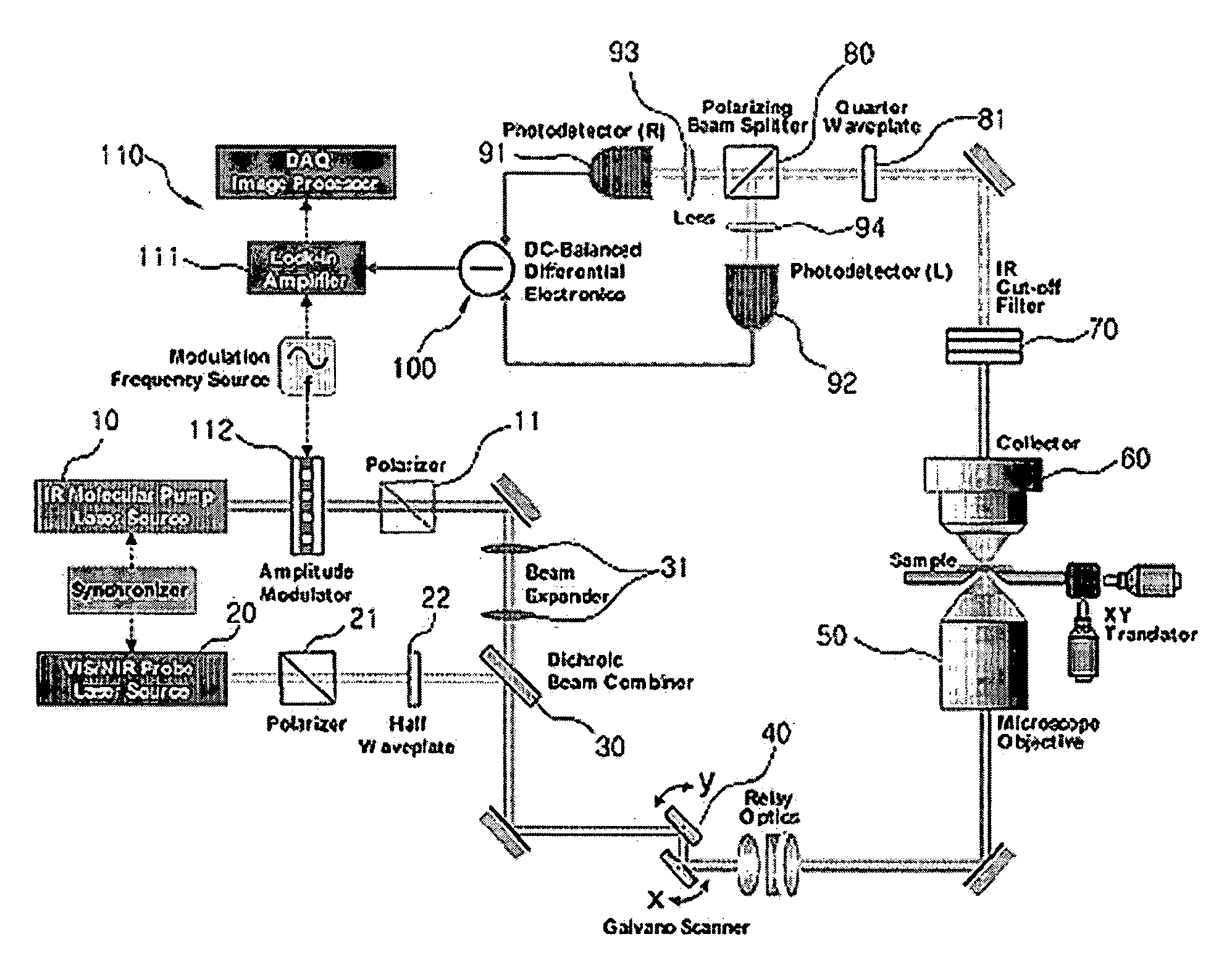
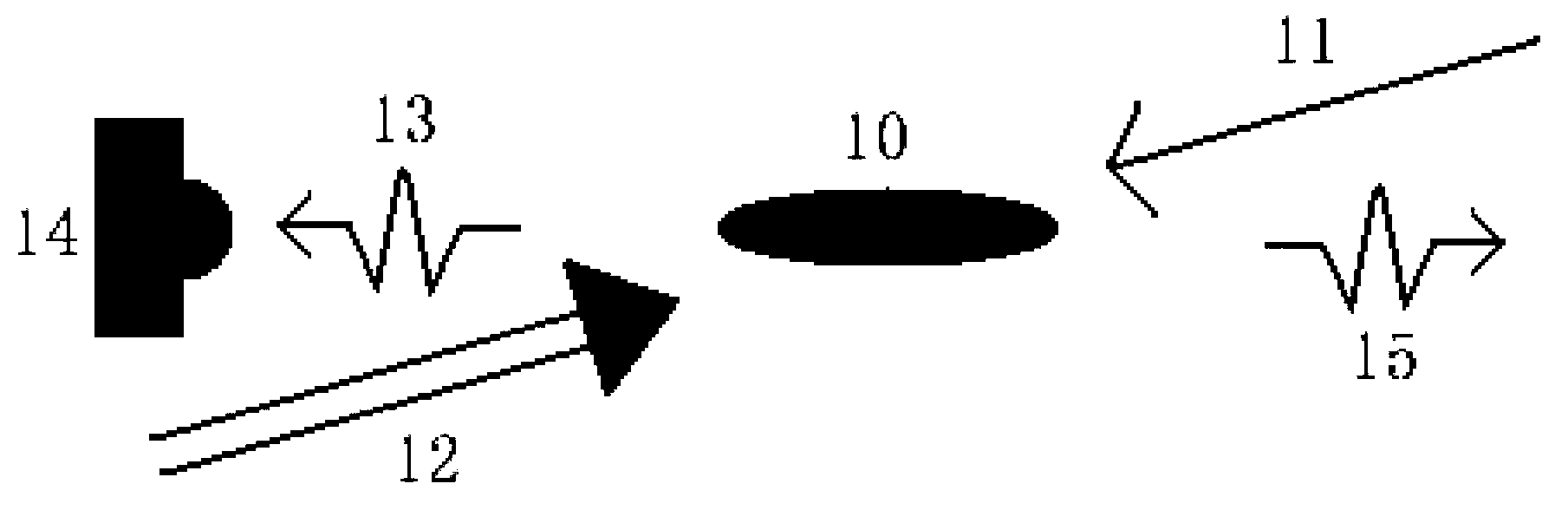
Imaging Apparatus for IR Four-Wave Mixing Polarization Microscopy
InactiveUS20080304047A1Reduce spatial resolutionReduce spacingRadiation pyrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesBeam splitterPhotodetector
The present invention relates to an imaging apparatus for IR four-wave mixing polarization microscopy. The imaging apparatus comprises a pump beam source for generating an infrared pump beam; a probe beam source for generating a probe beam (search beam); a polarizer for linearly polarizing the pump beam and probe beam; a beam combiner which synchronizes temporally and overlaps spatially the polarized pump beam and probe beam on the same axis; a scanner for two-dimensionally scanning the combined pump beam and probe beam; an optical focusing system for focusing the scanned pump beam and probe beam on a local point of the sample; a collecting optical system for collecting the beam which is formed by that the focused beams are interacted with the sample and of which phase is anisotropically retarded by nonlinear birefringence of the sample and forming a parallel beam; a dichroic beam splitter for removing the infrared pump beam out of the parallel beam and splitting the probe beam of which phase is anisotropically retarded; a polarizing beam splitter for converting the split and ansotripically phase-retarded probe beam into linerly polarized beams having their axes perpendicular to each other; a photodetector for detecting an intensity of each of the converted linerly polarized beams; a polarization differential detector for detecting a polarization difference based on the detected intensities of the linerly polarized beams; and a data analyzer for acquiring the detected polarization difference signal and extracting a spectrospcopic information corresponding to the strength of molecular vibrational coherence of the sample.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Phase-sensitive amplification in a fiber
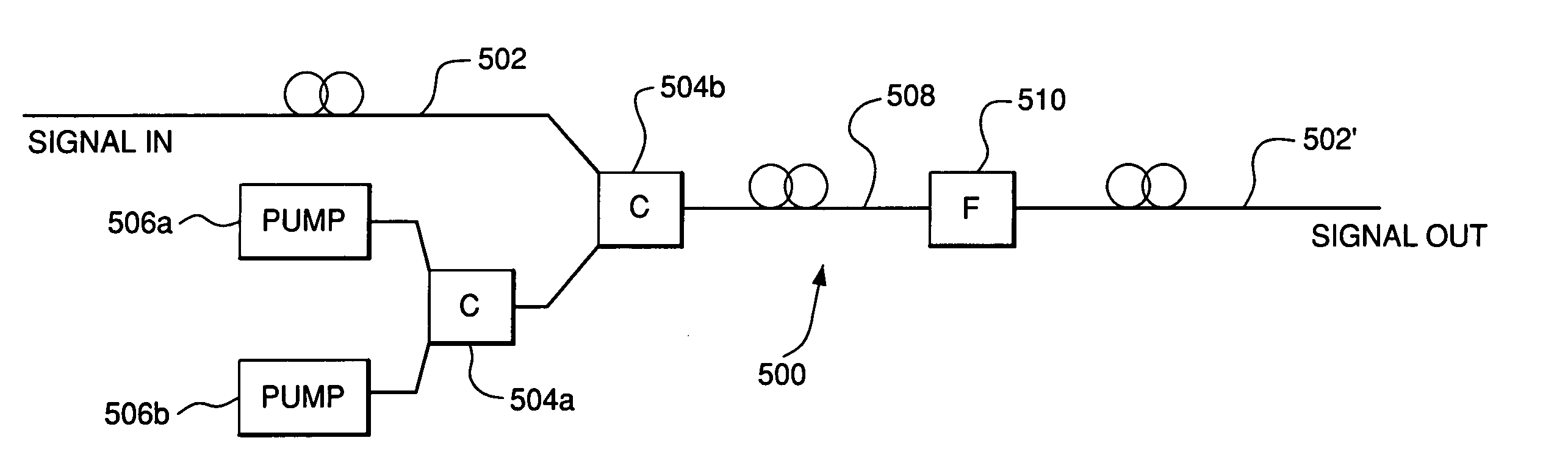
A method of and device for generating an amplified optical signal directly in an optical fiber by way of phase-sensitive amplification based on one or more four-wave mixing (FWM) processes. In one embodiment, an input signal and two pump waves are applied to a highly nonlinear fiber (HNLF). The input signal is amplified in the HNLF due to energy transfer from the pump waves to the input signal via a degenerate phase-conjugation (PC) process. In another embodiment, an input signal and first and second pump waves are applied to a first HNLF to generate, via a Bragg scattering (BS) process, an idler signal corresponding to the input signal. The second pump wave is then filtered out and the first pump wave, a third pump wave, and the input and idler signals are applied to a second HNLF, where they interact via a non-degenerate PC process to produce an amplified output signal.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Coherent Anti-stokes raman holography
InactiveUS20100309465A1Radiation pyrometryHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesLight beamParticle physics
Apparatus and methods of four wave mixing (FWM) holography are described, including illuminating a sample with a first beam, a second beam, and a third beam, and combining the generated FWM signal with a reference beam at a imaging device to obtain holographic image data. In some examples, the first and second beams may be provided by a single pump-probe beam. The third beam may be a Stokes beam or an anti-Stokes beam. A representative example is coherent anti-Stokes Raman holography (CARS holography), which includes illuminating a sample with a pump / probe beam and a Stokes beam to obtain a CARS signal from the sample; and combining the CARS signal with a reference beam to obtain a CARS hologram.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Optical Sources
ActiveUS20120292531A1Reduce noiseImprove efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsRaman scatteringSignal onLength wave
An optical source (10) comprising an optical output (12), a pump optical source (14), an optical splitter arranged to receive an optical signal from the pump optical source and to split the optical signal into a pump signal and a seed pump signal. A seed signal forming apparatus (18) is arranged to receive the seed pump signal at the pump wavelength and to transform the seed pump signal into a seed signal at a seed wavelength. A first microstructured optical fibre (MSF1) (20) is arranged to receive the pump signal and the seed signal. MSF1 is arranged to cause the pump signal to undergo four-wave mixing seeded by the seed signal on transmission through MSF1 such that a first optical signal at a signal wavelength and second optical signal at an idler wavelength are generated. One of the signal wavelength and the idler wavelength are the seed wavelength and one of the first and second optical signals are provided to the optical output.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
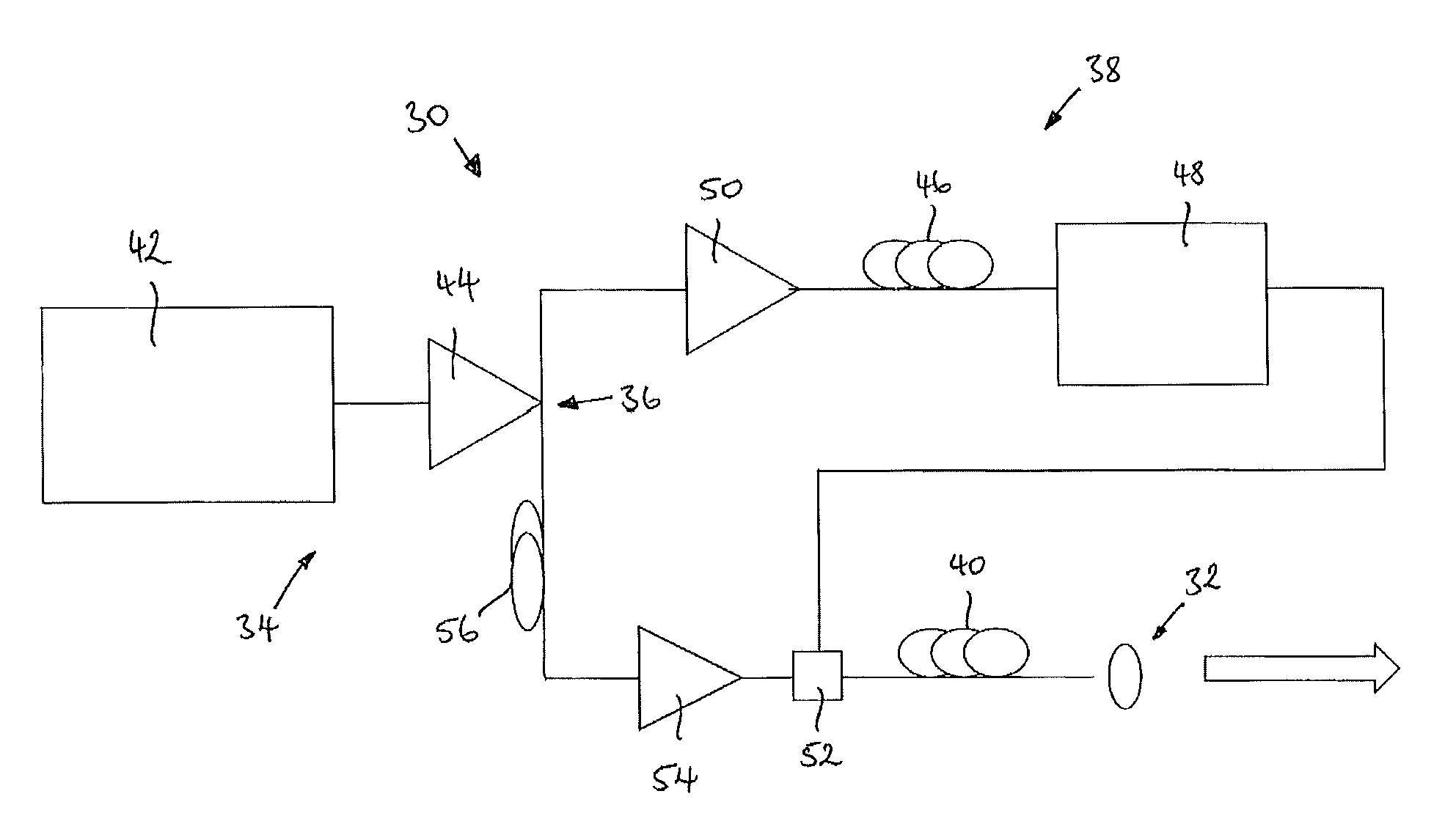
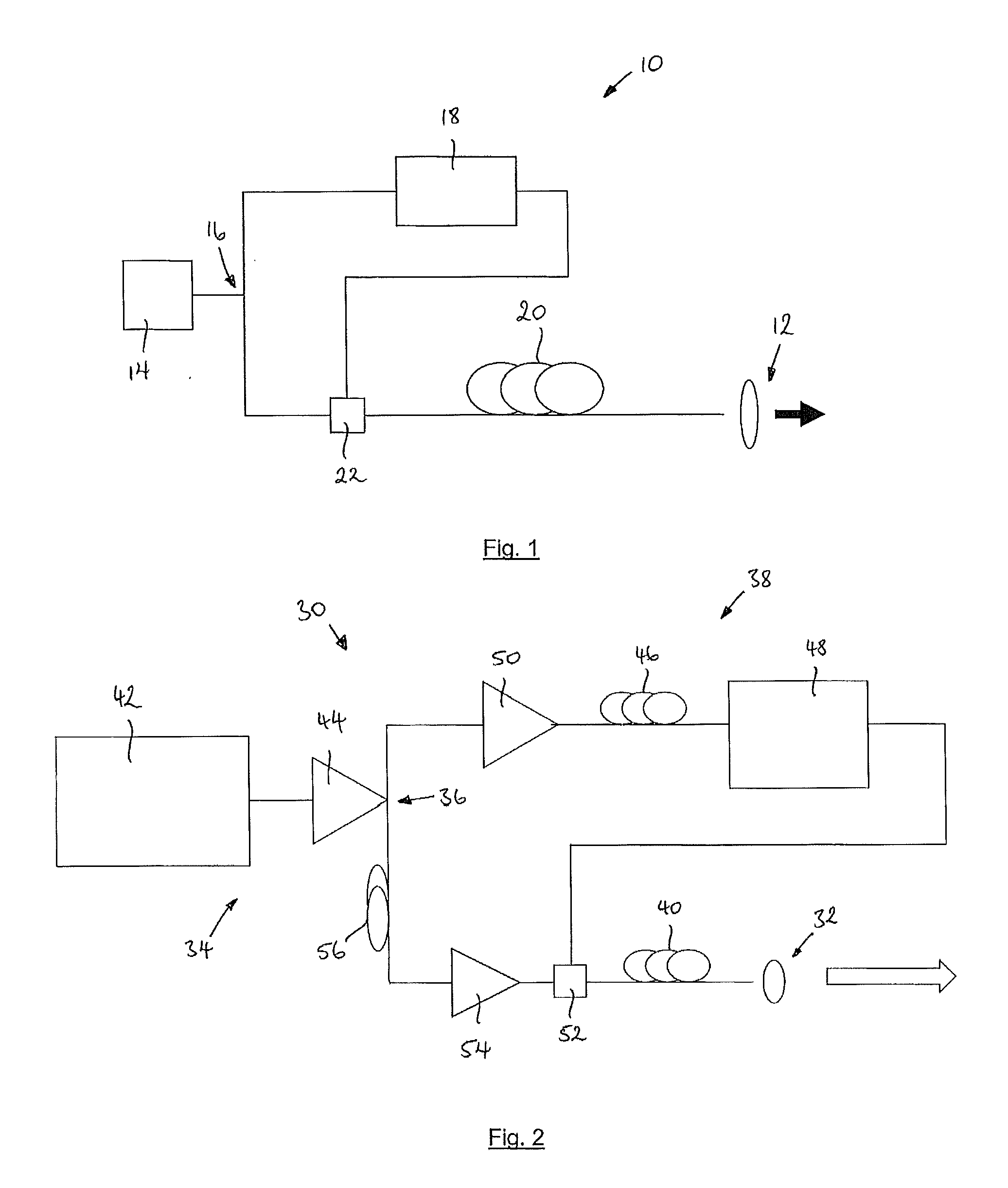
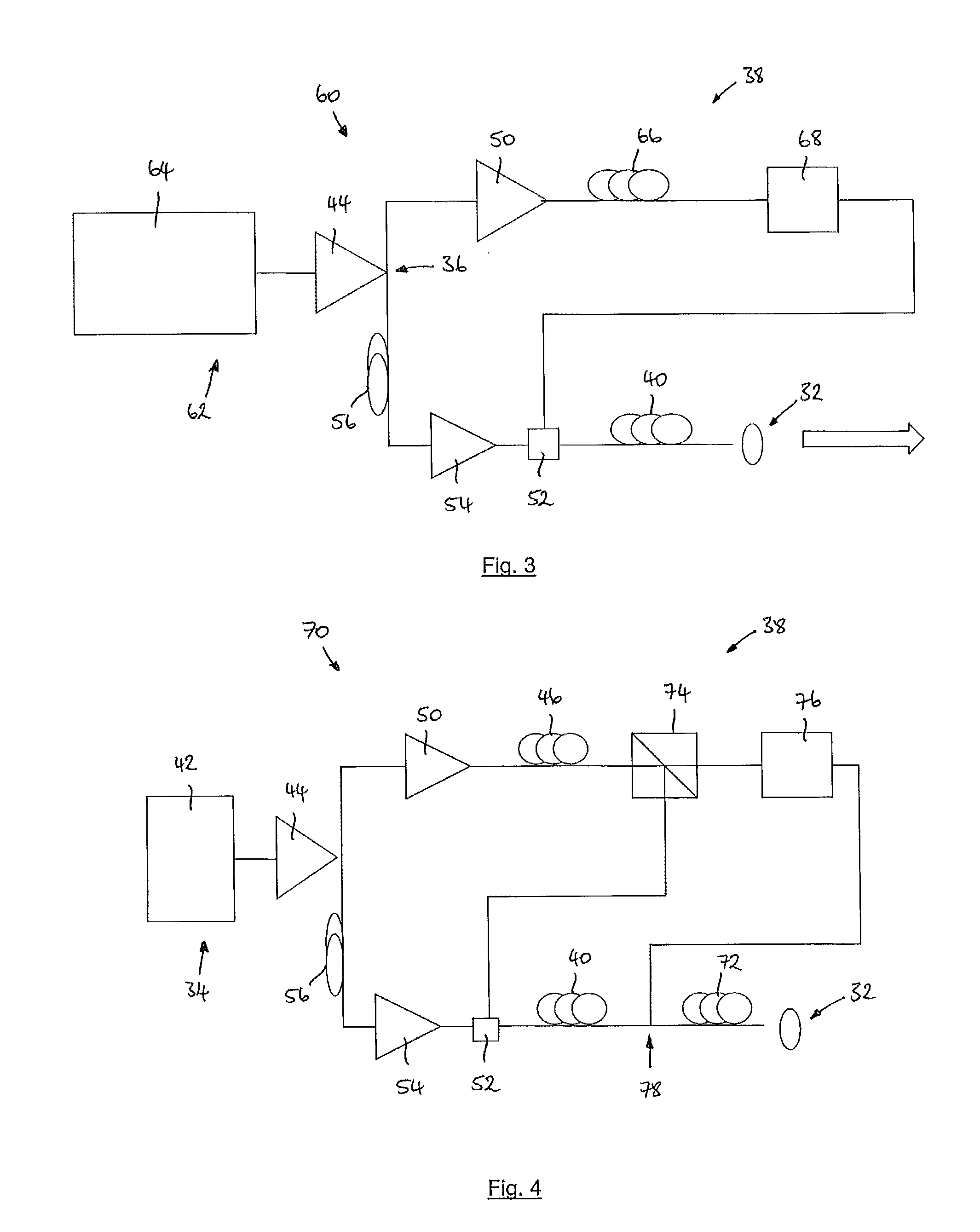
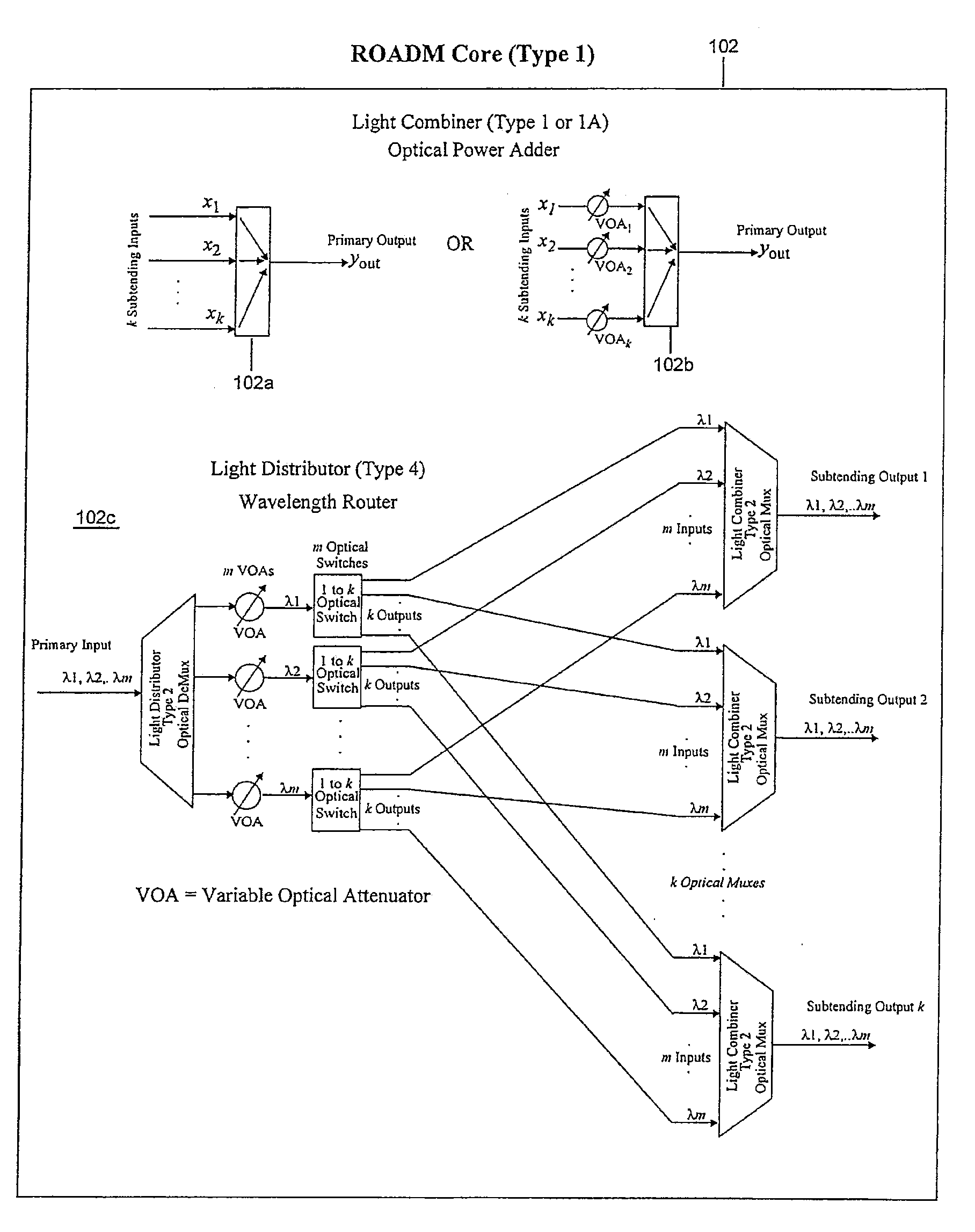
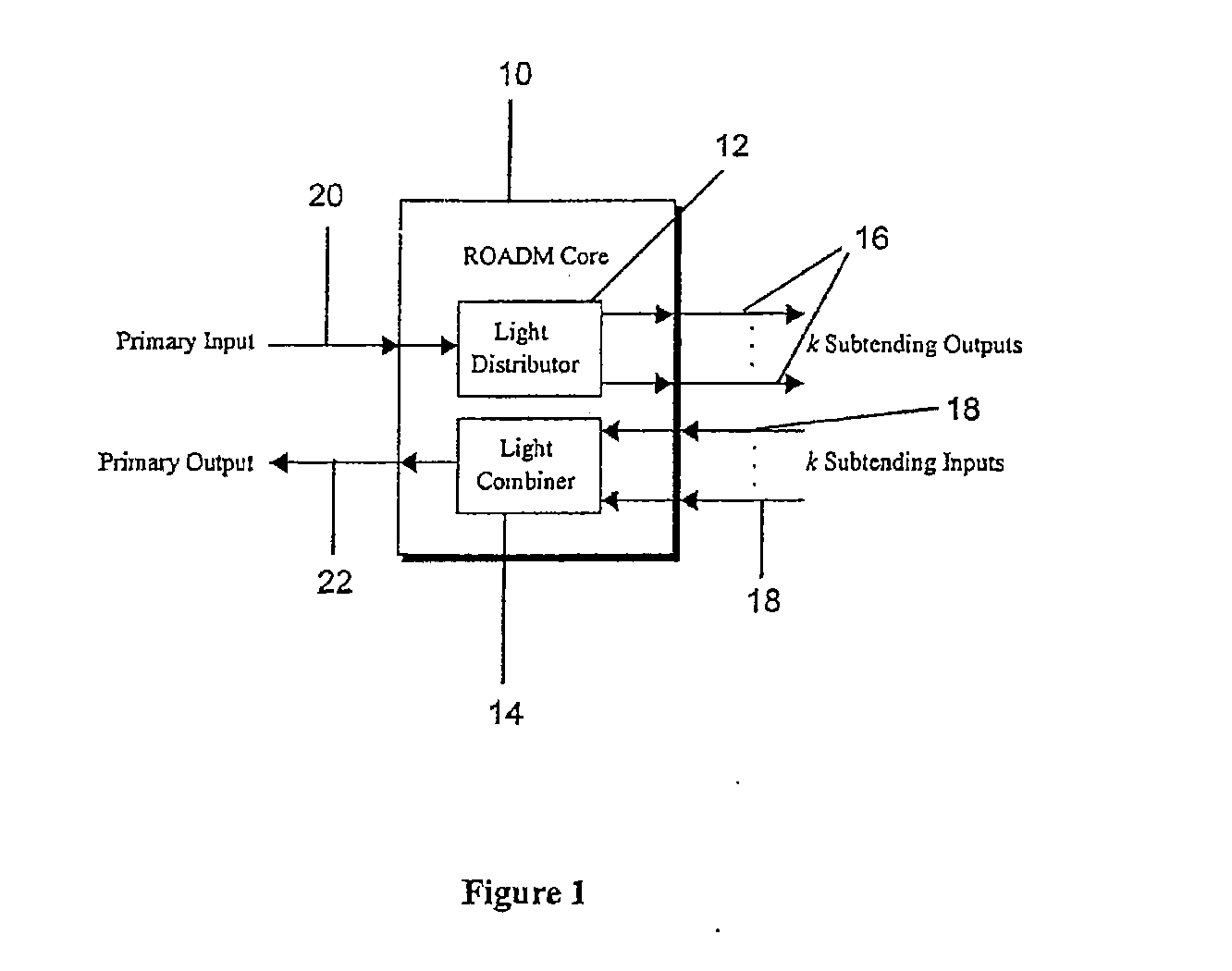
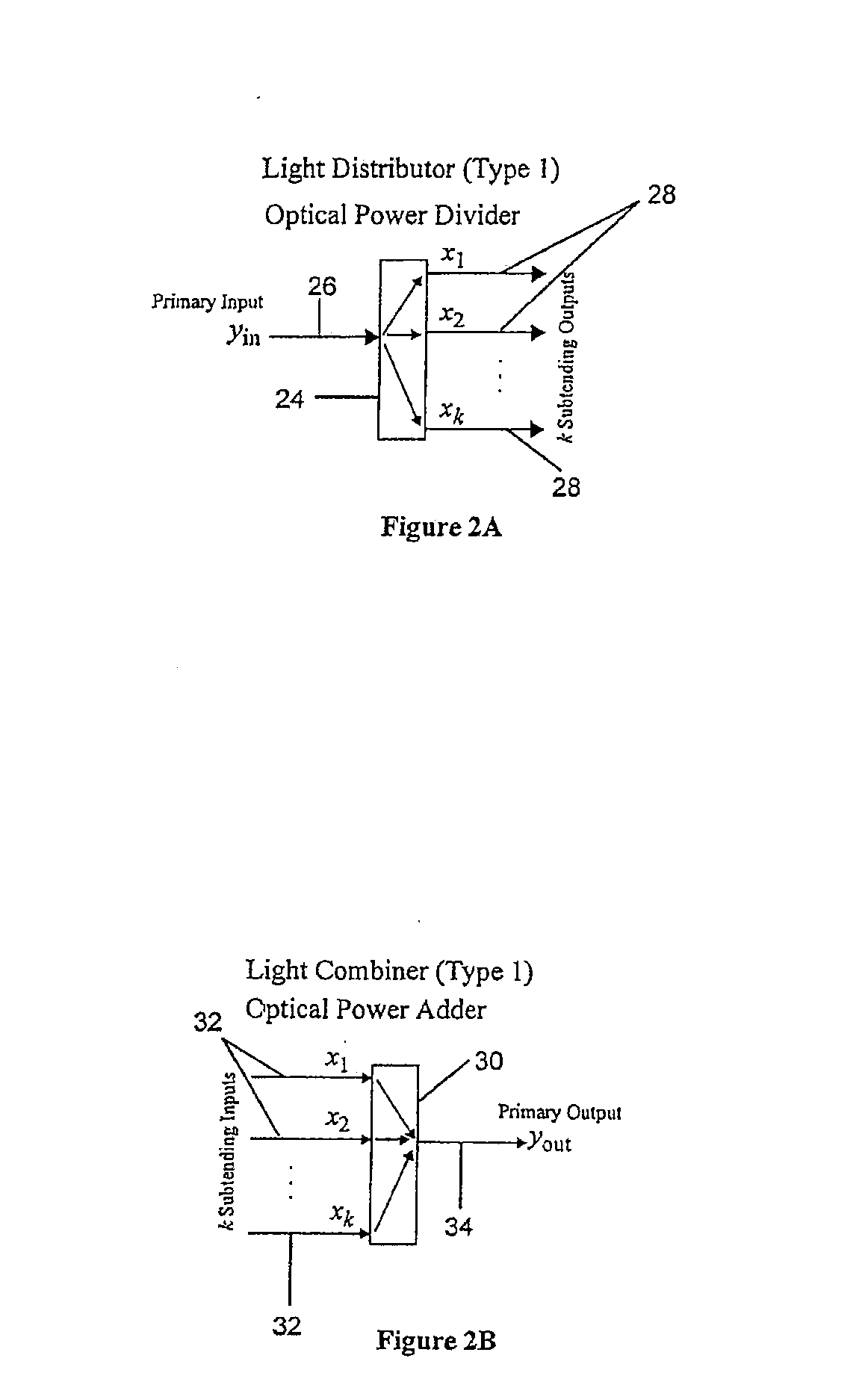
Reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexer and procedure for outputting optical signals from such multiplexer
A reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer (ROADM) includes local interfaces at which optical signals of different wavelengths are locally input into the ROADM, and a network interface configured to connect the ROADM to a network from which multiplexed optical signals of different wavelengths are transmitted to the network. In a first configuration, the ROADM is configured to transmit from the network interface to the network multiplexed signals of different wavelengths having a first minimum frequency difference. In a second configuration, the ROADM is configured to transmit from the network interface to the network multiplexed signals of different wavelengths having a second minimum frequency difference. The second minimum frequency difference is greater than the first minimum frequency difference. This arrangement reduces the power of four wave mixing cross products produced when optical signals of three wavelengths are multiplexed and transmitted from the ROADM to NZDSF or DSF fiber types.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Polarization-entangled quantum light source
ActiveCN102130418AImprove collection efficiencyImprove transmission efficiencyLaser detailsWaveguideNonlinear optical
The invention discloses a polarization-entangled quantum light source which comprises a pumping light generator, a three-order nonlinear optical waveguide and a light-splitting and filtering device, wherein the pumping light generator is used for generating pulse pumping light and inputting the pulse pumping light to the three-order nonlinear optical waveguide; the three-order nonlinear optical waveguide has a characteristic of double refraction and is used for independently exciting a spontaneous scalar four wave mixing process on two polarization shafts, generating a signal with a polarization-entangled characteristic and an idler frequency two-photon and inhibiting a spontaneous vector four wave mixing process; and the light-splitting and filtering device is used for separating the signal and the idler frequency two-photon which are output from the three-order nonlinear optical waveguide from the pulse pumping light to obtain a polarization-entangled two-photon. The polarization-entangled quantum light source in the invention has a simple and compact structure and high efficiency for generating and collecting the polarization-entangled two-photon.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
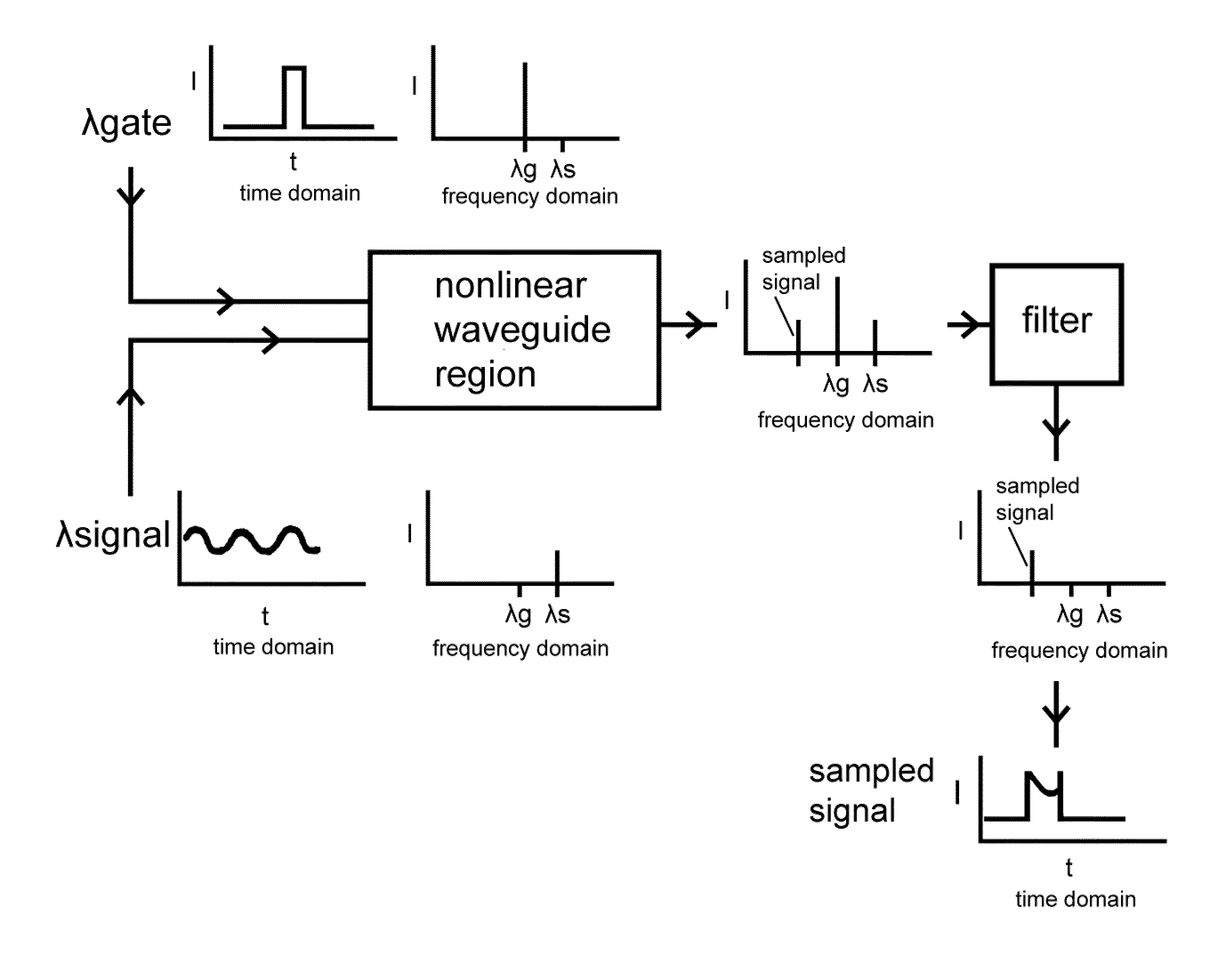
All-optical high bandwidth sampling device based on a third-order optical nonlinearity
An all-optical sampling device using four-wave mixing in third-order optically nonlinear materials is described. The four-wave mixing based sampler comprises a waveguide combiner, which adds a gate optical signal to a signal of interest to be sampled. In a four-wave mixing region, a sampled signal at the output optical frequency is produced. All of the optical signals are sent to a passive optical filter, which preferentially discards the gate and signal optical frequencies, but preserves the sampled signal at the output optical frequency. The sampled signal at the output optical frequency can be observed, displayed, recorded or otherwise manipulated.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
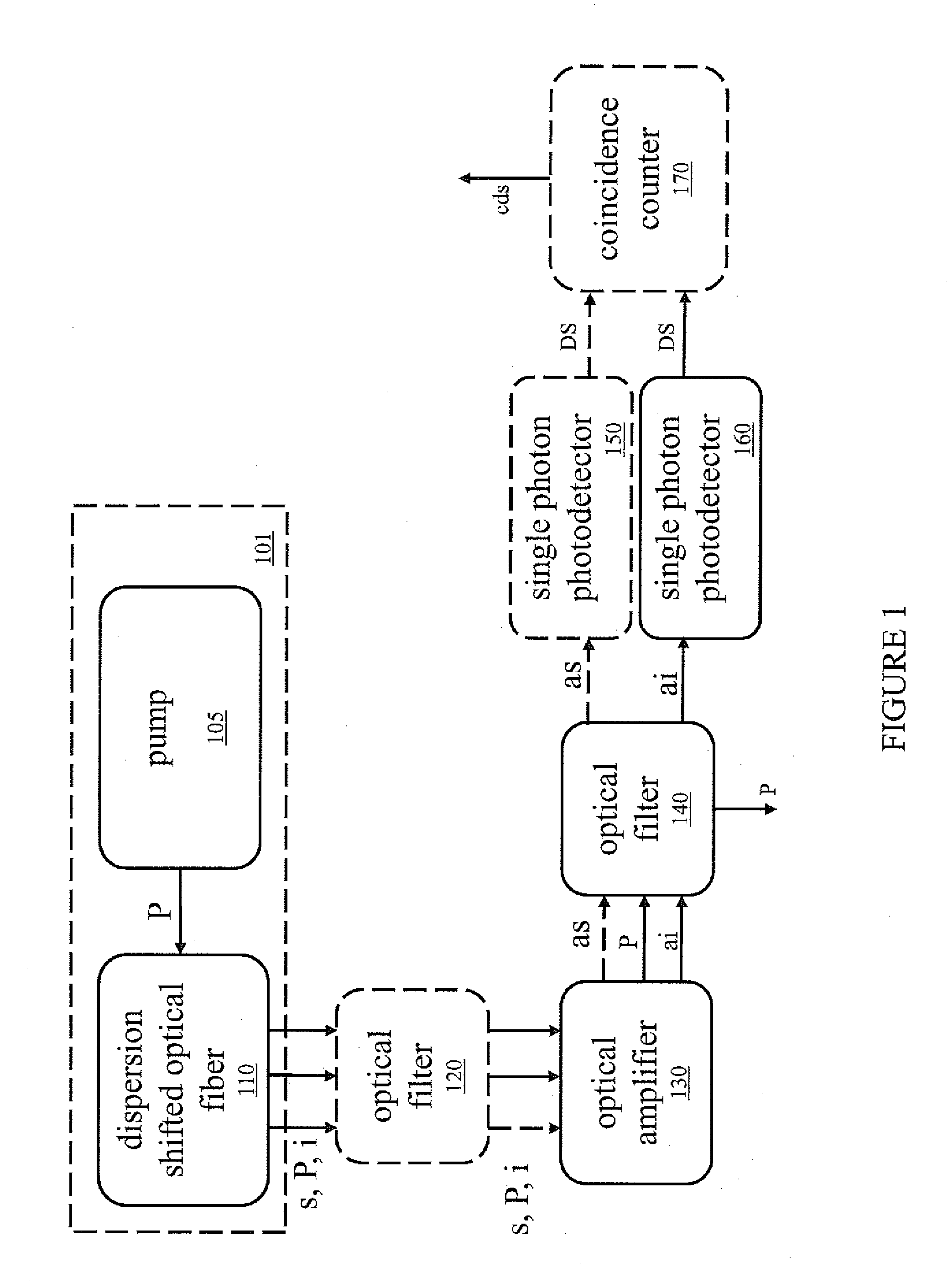
System and method for carrying out CARS (Coherent anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) imaging by using four-wave mixing signals generated by optical fiber
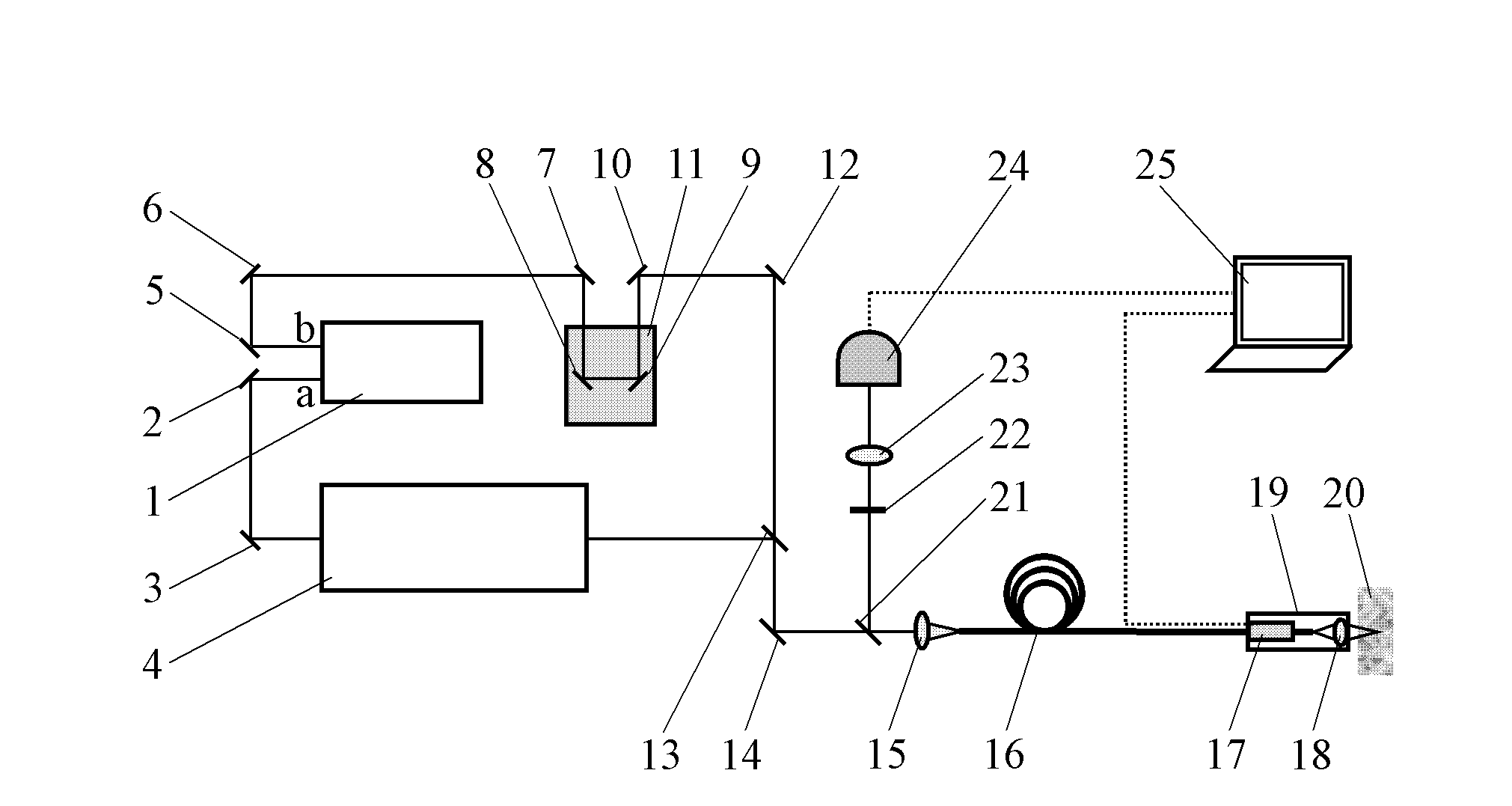
The invention relates to a system and method for carrying out CARS (Coherent anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) imaging by using four-wave mixing signals generated by optical fiber. The system comprises a laser source, multiple reflecting mirrors, an optical parametric oscillator, a precise displacement platform, two long-wave-pass dichroscopes, a coupling objective lens, optical fiber, a two-dimensional scanner, a focusing lens, a supporting sleeve, a sample, a band-pass filter, an imaging lens, a detector and a computer. A light beam which is output after the laser source sends a frequency-doubling light beam for pumping the optical parametric oscillator, and a base-frequency light beam sent by the laser source are respectively pumping light and Stokes light for CARS imaging, and the four-wave mixing signals which are excited after the pumping light and the Stokes light are overlapped on time and space and then transmitted in the optical fiber are probe light for CARS imaging. CARS signal light which is generated after the pumping light and the Stokes light are focused on a sample are not overlapped with the frequency of the pumping light and the frequency of the Stokes light and can be separated by the long-wave-pass dichroscopes. Relative to the standard CARS system, the system disclosed by the invention is not newly provided with any device, has no special requirement on the used devices and is simplified in system and saved in cost.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
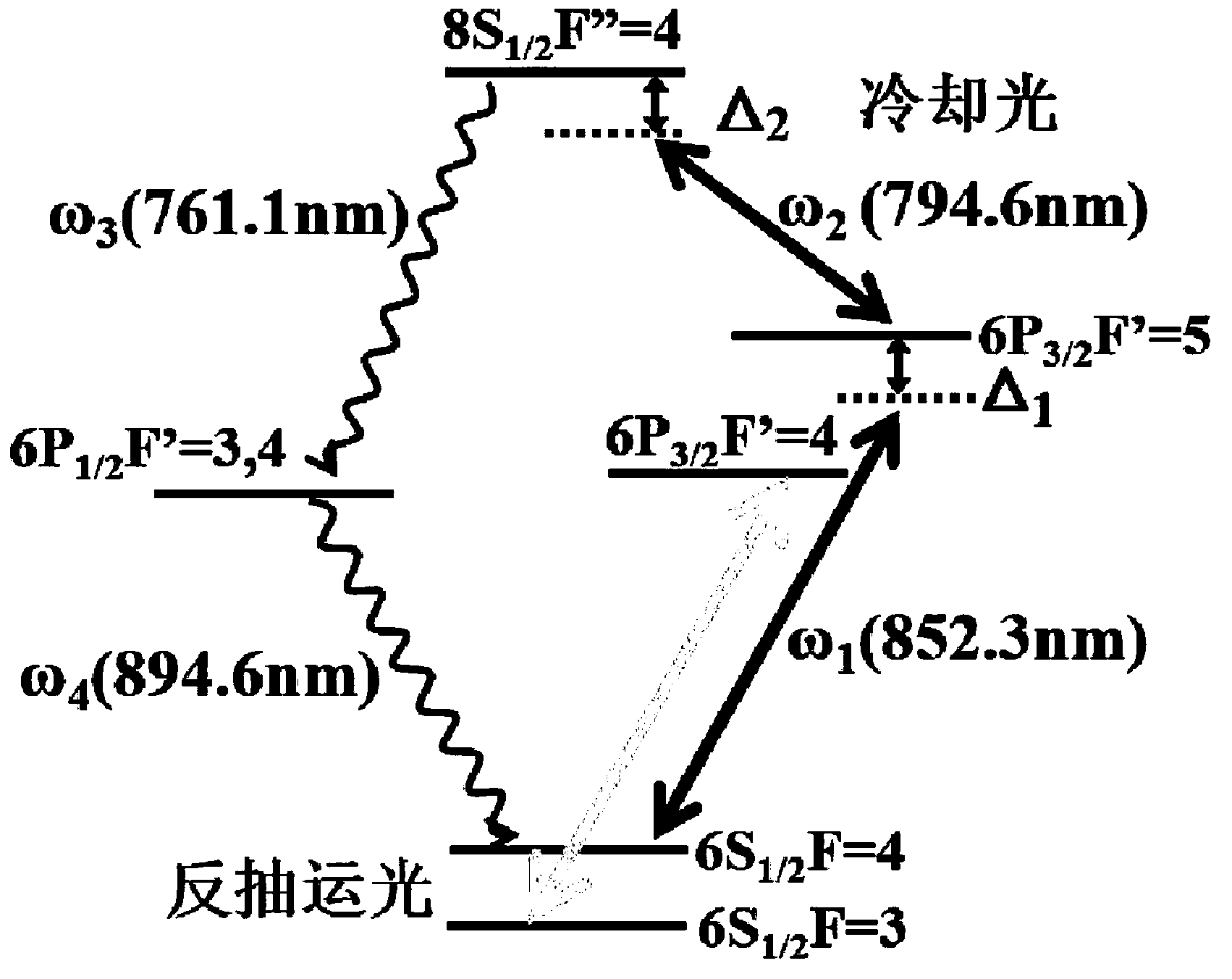
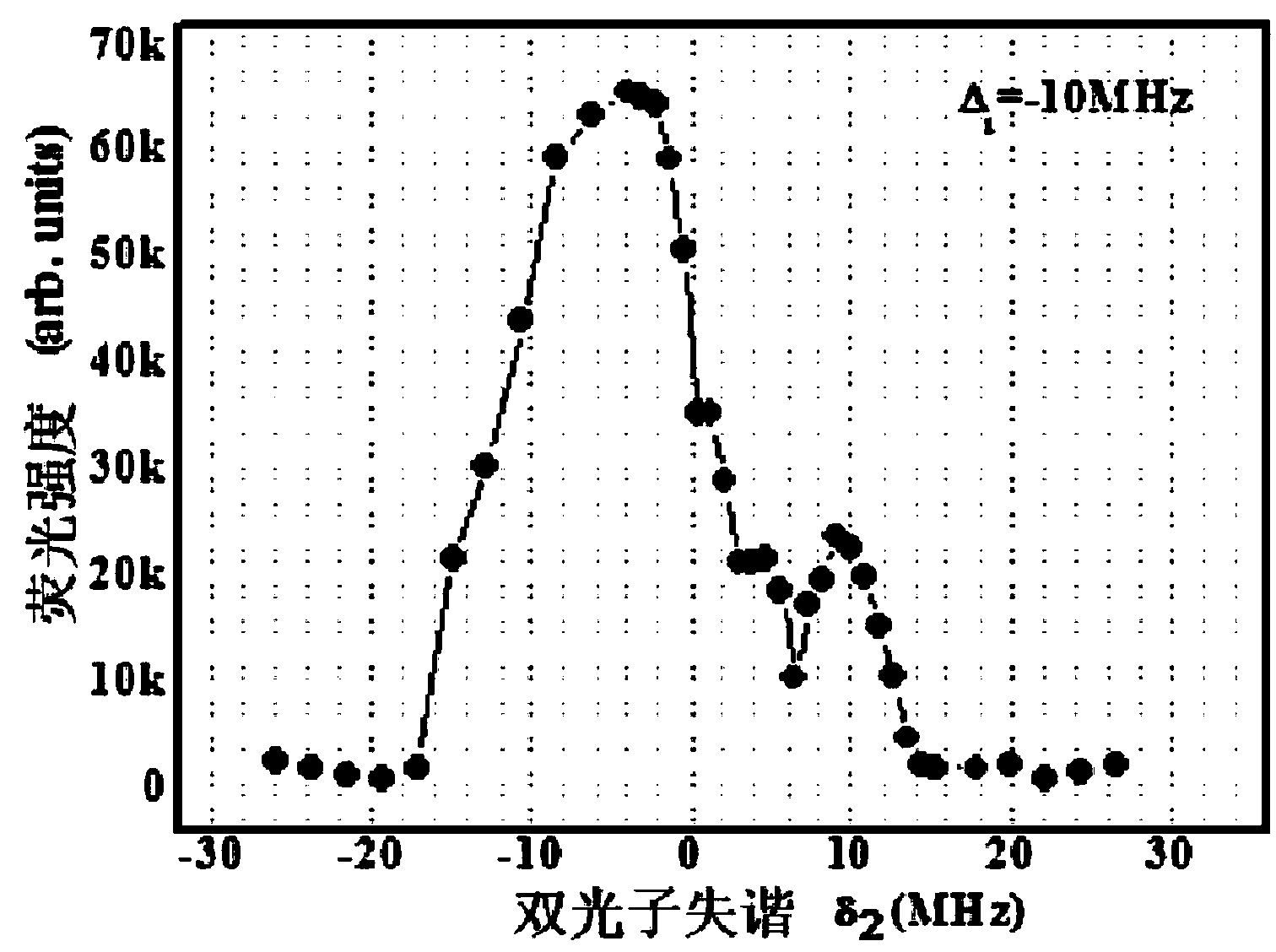
Two-dimensional magnetic optical trap system and narrow line width single photon source preparing method thereof
InactiveCN103258579ADoes not destroy coherenceImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation/particle handlingPhotonic quantum communicationHelmholtz coilAtomic group
The invention discloses a two-dimensional magnetic optical trap system and a narrow line width single photon source preparing method thereof. The system comprises two pairs of reversed Helmholtz coils, a quartz vacuum cavity, an ion pump, a current feed through part with alkali metal releasing agent, a vacuum valve, a six-way connector, a first glass window, a second glass window and a first semiconductor laser. Six openings of the six-way connector are respectively connected with the quartz vacuum cavity, the ion pump, the current feed through part, the vacuum valve, the first glass window and the second glass window. The two pairs of reversed Helmholtz coils are respectively arranged in a horizontal-symmetrical mode and in a vertical-symmetrical mode. According to the method, the two-dimensional magnetic optical trap system obtains a long-strip-shaped cold atomic group through cooling light, then spontaneous radiation four-wave mixing is used, Stokes photons and reversed Stokes photons are generated through pump light and coupling light, and the photons are collected. The line width of a narrow line width single photon source prepared by the two-dimensional magnetic optical trap system is in the megahertz magnitude, and the narrow line width single photon source is suitable for long-distance quantum communication.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
System and Method for Nonlinear Optical Devices
InactiveUS20130087689A1High sensitivityBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhase-affecting property measurementsAudio power amplifierPhoton detection
Systems for enhancing the sensitivity of detecting an optical signal using nonlinear optics and method of performing the same. In one embodiment, a single-photon detection system includes an optical amplifier realized in a waveguide, and a photodetector coupled to an output of the optical amplifier. A light detection and ranging system includes the optical amplifier coupled to an optical source and one photodetector. In another embodiment, a photodetection system includes a plurality of optical frequency converters, coupled to an optical source, that sequentially convert a wavelength of photons of the optical source to a final wavelength, and a single-photon photodetector coupled to the optical frequency converters to detect single photons produced by the optical source. In another embodiment, an optical sensor includes an optical pump, and a transducer including an optical ring cavity coupled to the optical pump and configured to utilize optical four-wave mixing to detect an external stimulus.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Terahertz wave generating device and method based on optical four-wave mixing effect
InactiveCN101794953ALow costReduce bandwidth requirementsSolid masersElectromagnetic transmissionOptical carrier suppressionCarrier signal
The invention discloses terahertz wave generating device and method based on optical four-wave mixing effect, which belong to the technical field of microwave photonics. The method comprises the following steps of: driving an intensity modulator by a microwave source signal through electric frequency multiplication by using optical carrier suppression modulation of the external intensity modulator and the four-wave mixing effect in a nonlinear device, forming a carrier suppression signal with only two first-order side bands, then forming two new side bands through the nonlinear device, filtering the original first-order side bands by an optical filter, only retaining two new side bands and carrying out beat frequency on the two new side bands in a PD (Photo Detector) to generate a terahertz wave frequency with six frequency multiplications. The invention lowers the requirements of the microwave modulation signal frequency and the modulator band width and reduces the cost of a system, the generating device has simple structure and favorable portability and the generated terahertz wave has very high stability.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Micro-annular waveguide optical device used for generating optical frequency comb
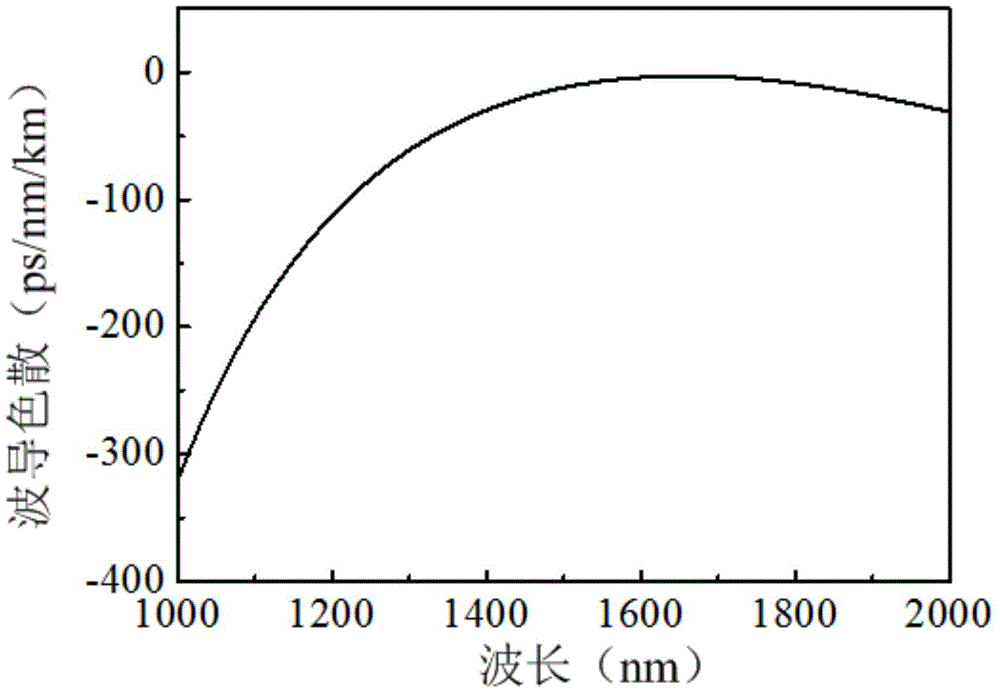
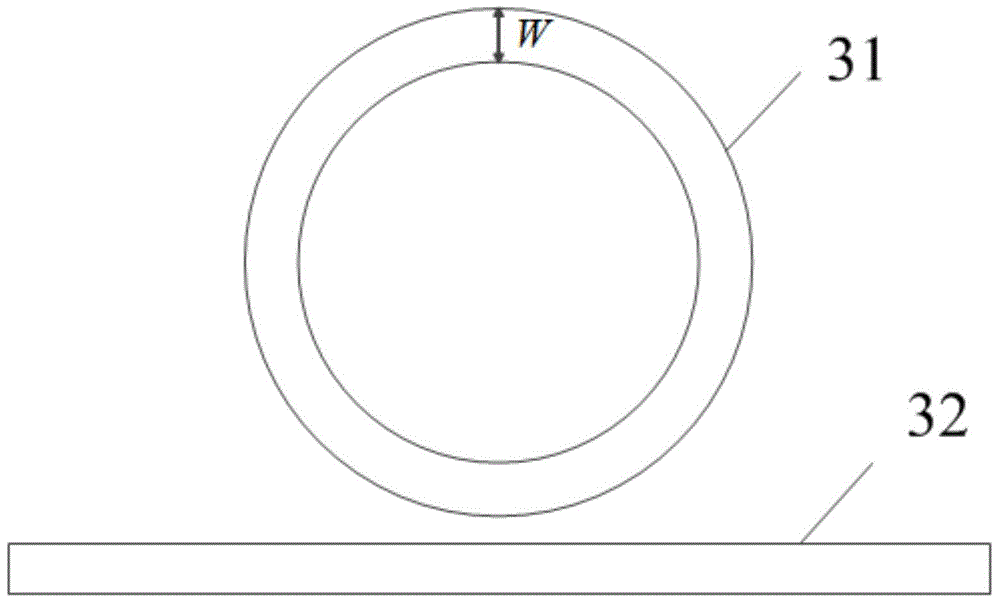
The invention discloses a micro-annular waveguide optical device used for generating an optical frequency comb. The device comprises a straight waveguide and an annular resonant cavity which are coupled together, wherein the annular resonant cavity comprises n first parts with a first section width W1, n second parts with a second section width W2, and conical couplers used for connecting the first parts with the second parts, and the n first parts and the n second parts are alternately coupled to form the annular resonant cavity. By changing the section size of the waveguide, chromatic dispersion within a certain wavelength range can be controlled to vary between positive values and negative values alternately, so that the influences of chromatic dispersion on the four-wave mixing effect are counteracted and tend to be zero, and then the influences of chromatic dispersion on the optical frequency comb are counteracted; in this way, the influence of chromatic dispersion on the optical frequency comb is reduced, the power flatness of the optical frequency comb is improved, and the optical frequency comb with flat power can be obtained.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and optical fiber device for production of low noise continuum
InactiveUS20060159398A1New design degreeCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesLow noisePolarization-maintaining optical fiber
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
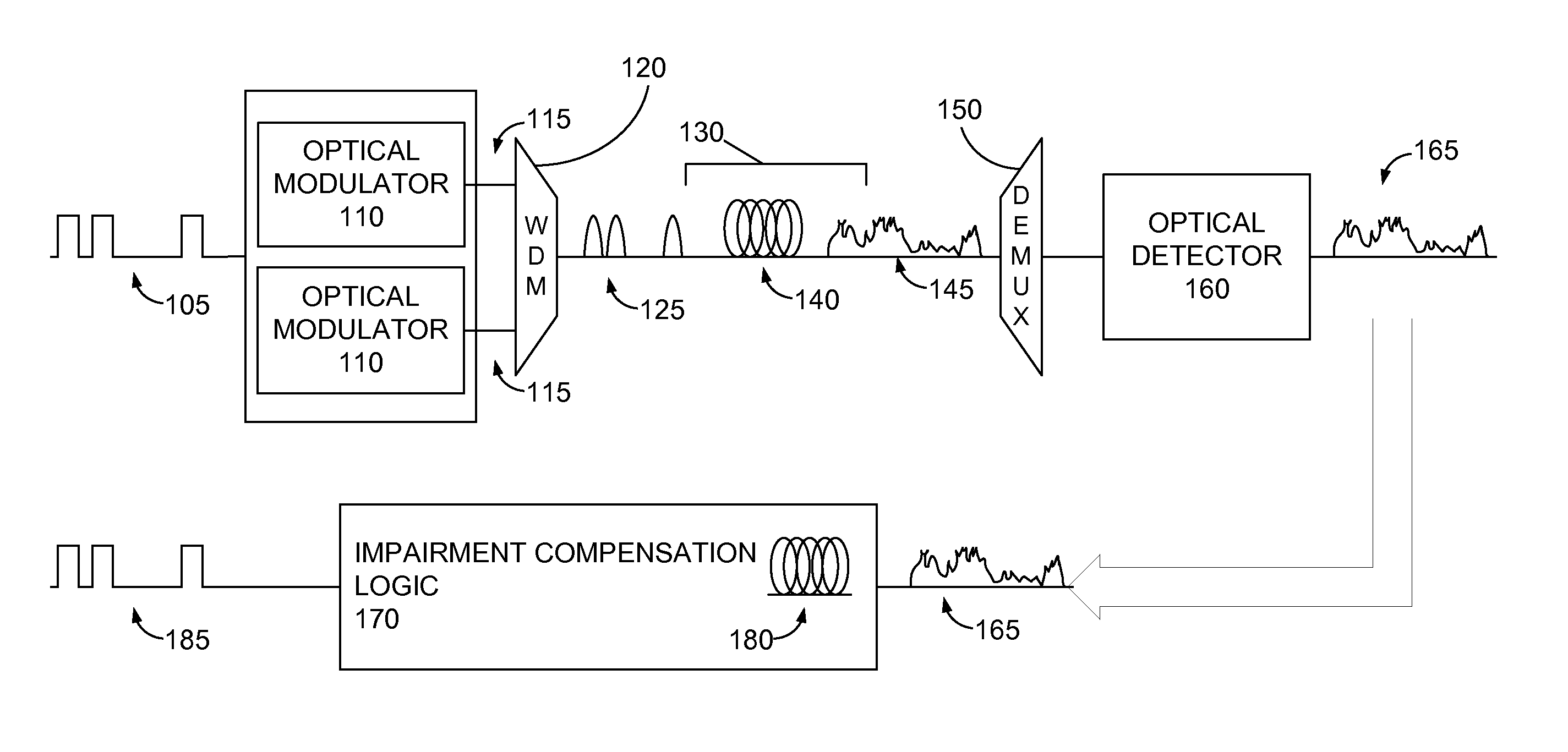
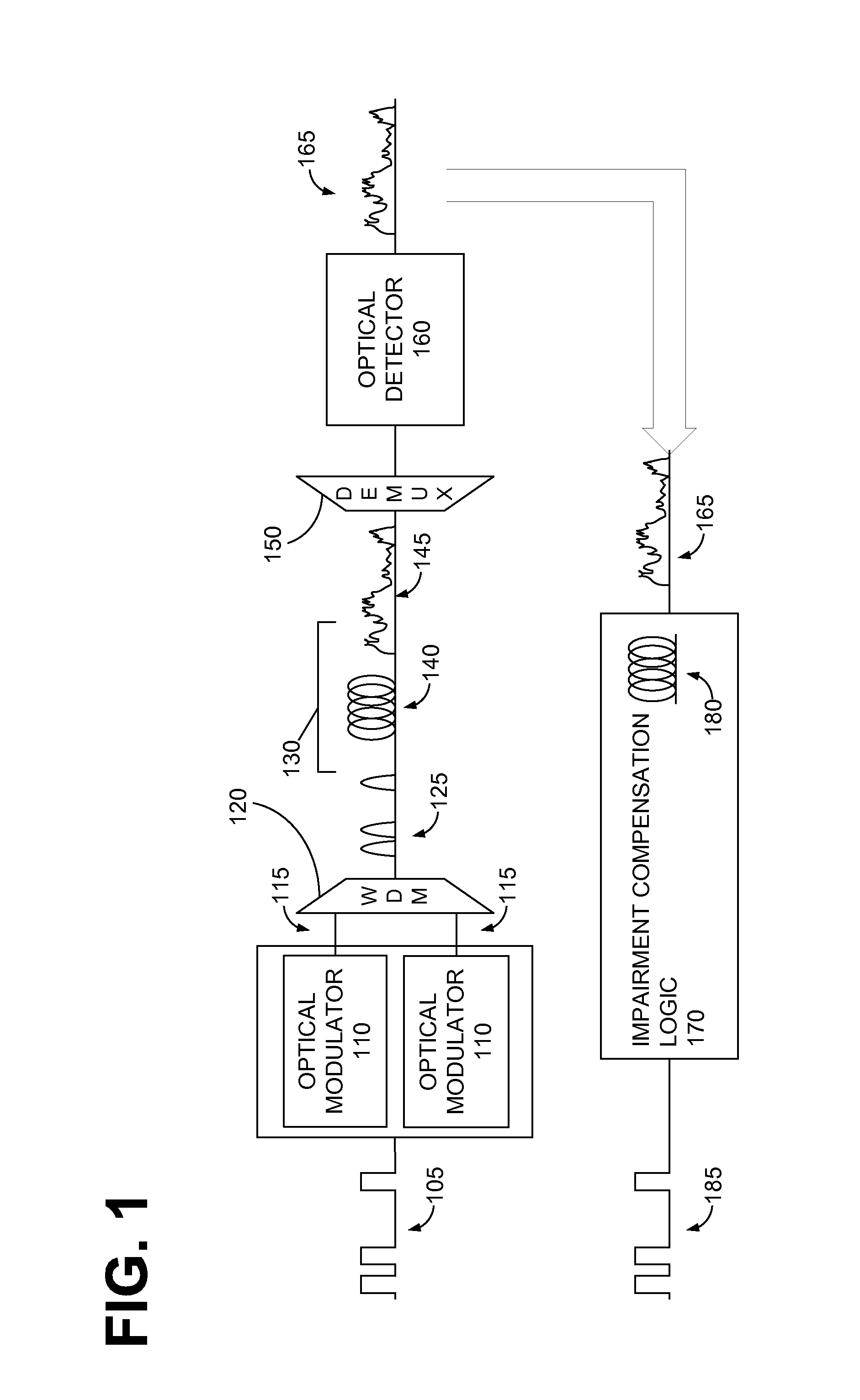
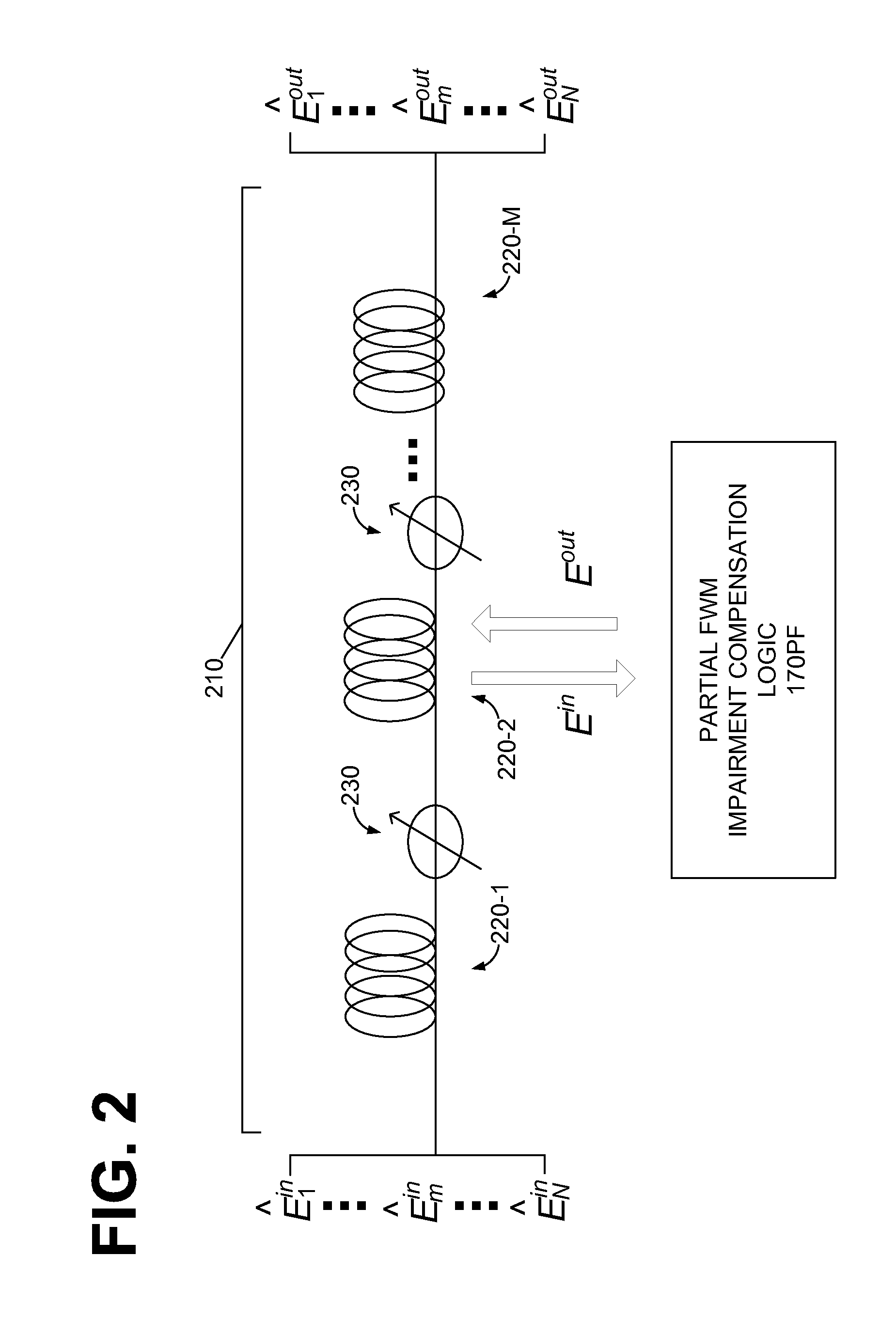
Compensation of Optical Transmission Impairments Using Digital Backward Propagation
ActiveUS20100239262A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingFiber chromatic dispersionTransmission channel
Systems and method of compensating for transmission impairment are disclosed. One such method comprises receiving a wavelength-division multiplexed optical signal. The received optical signal has been distorted in the physical domain by an optical transmission channel. The method further comprises propagating the distorted optical signal backward in the electronic domain in a corresponding virtual optical transmission channel. The backward propagation fully compensates for fiber dispersion, self-phase modulation, and cross-phase modulation (XPM) and partially compensates for four-wave mixing (FWM).
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Method and optical fiber device for production of low noise continuum
InactiveUS7403688B2Reduce noiseCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesLow noisePolarization-maintaining optical fiber
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
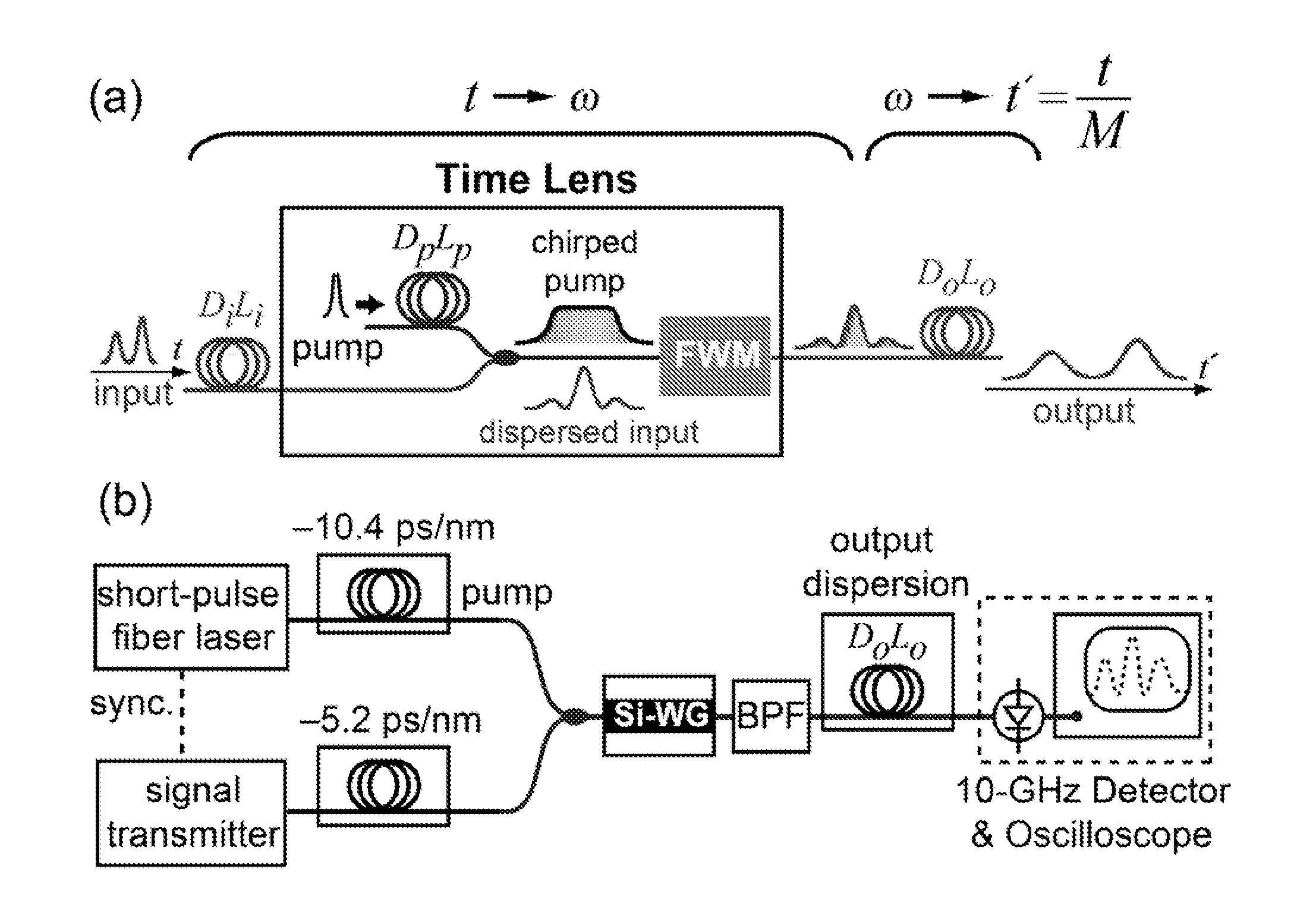
High-speed optical sampling by temporal stretching using four-wave mixing
ActiveUS20120093519A1Electromagnetic transmissionTransmission noise suppressionBandpass filteringOptical frequencies
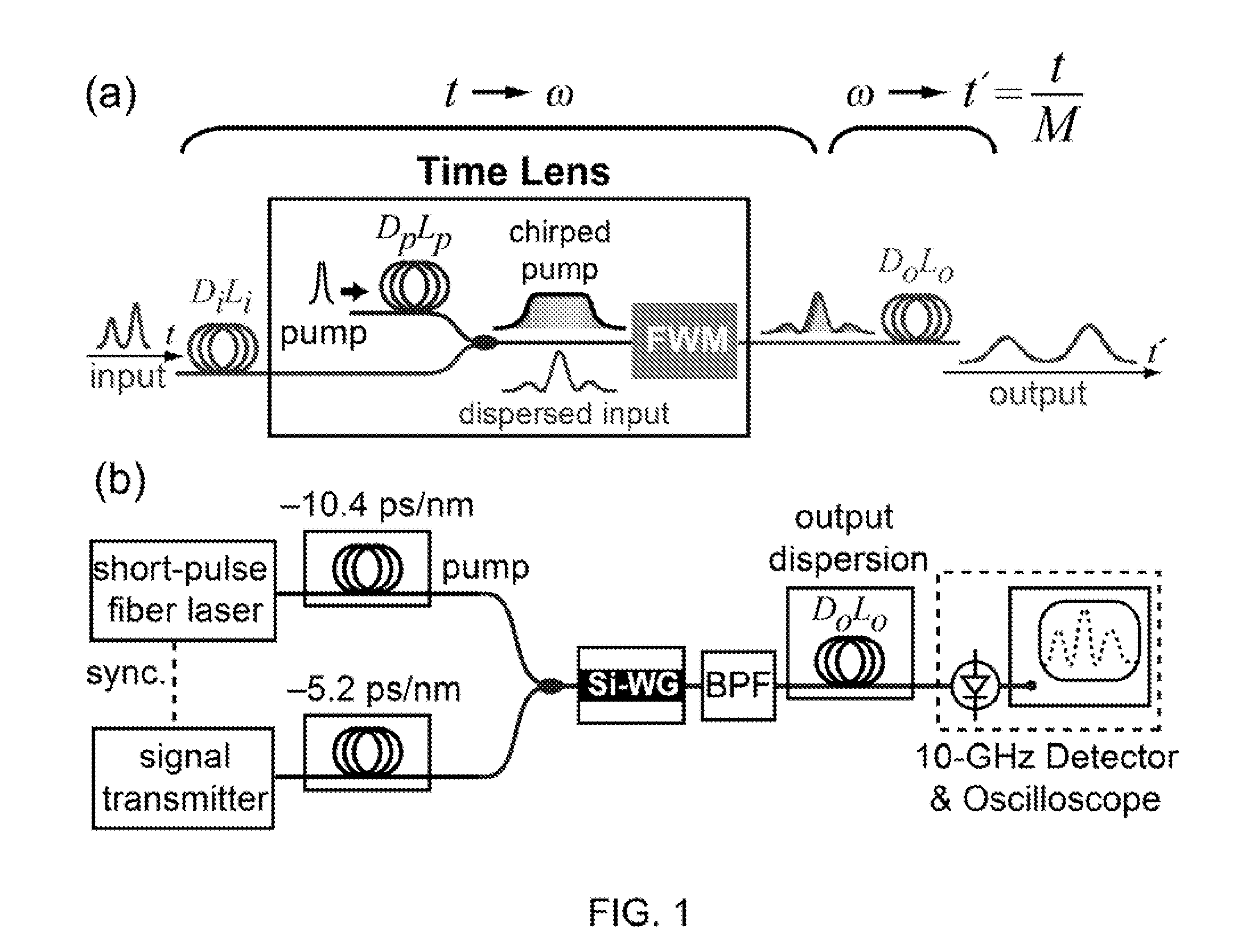
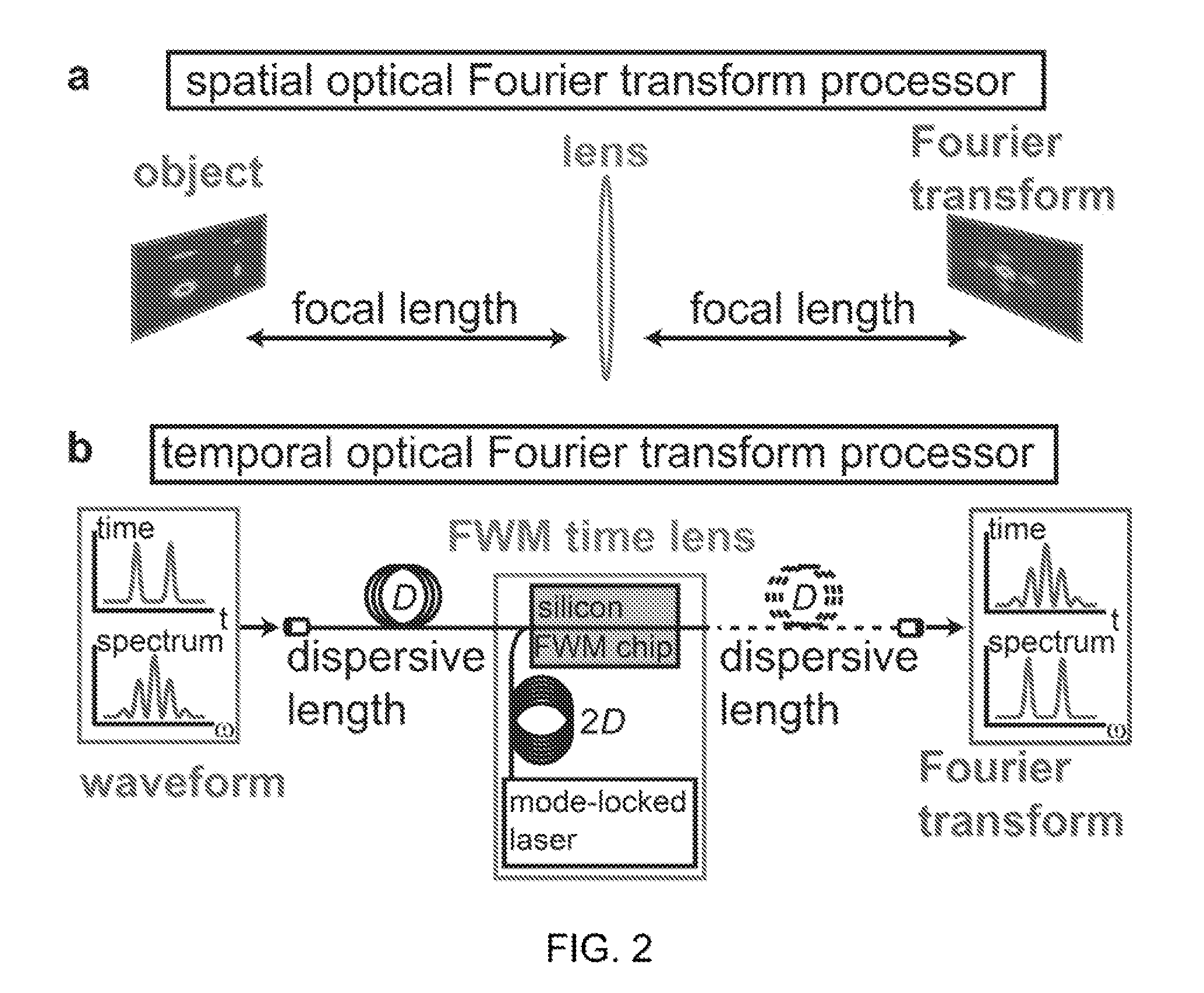
Systems and methods are provided for ultrafast optical waveform sampling based on temporal stretching of an input signal waveform. Temporal stretching is performed using a time lens based on four-wave mixing in a nonlinear medium. The signal is passed through an input dispersive element. The dispersed signal is sent into the time lens, which comprises a chirped pump pulse and a nonlinear medium. The chirped pump pulse is combined with the signal. The four-wave mixing process occurs in the nonlinear device or medium, which results in the generation of a signal at a new optical frequency (idler). The idler is spectrally separated from the signal and pump pulse using a bandpass filter and sent into an output dispersive element. The output dis persive element is longer than the input dispersive element and the temporal stretching factor is given by the ratio between the dispersions of these two elements.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for measuring polarization-mode dispersion
InactiveUS6947129B1Low costShorten the timeMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical apparatus testingFiberAudio power amplifier
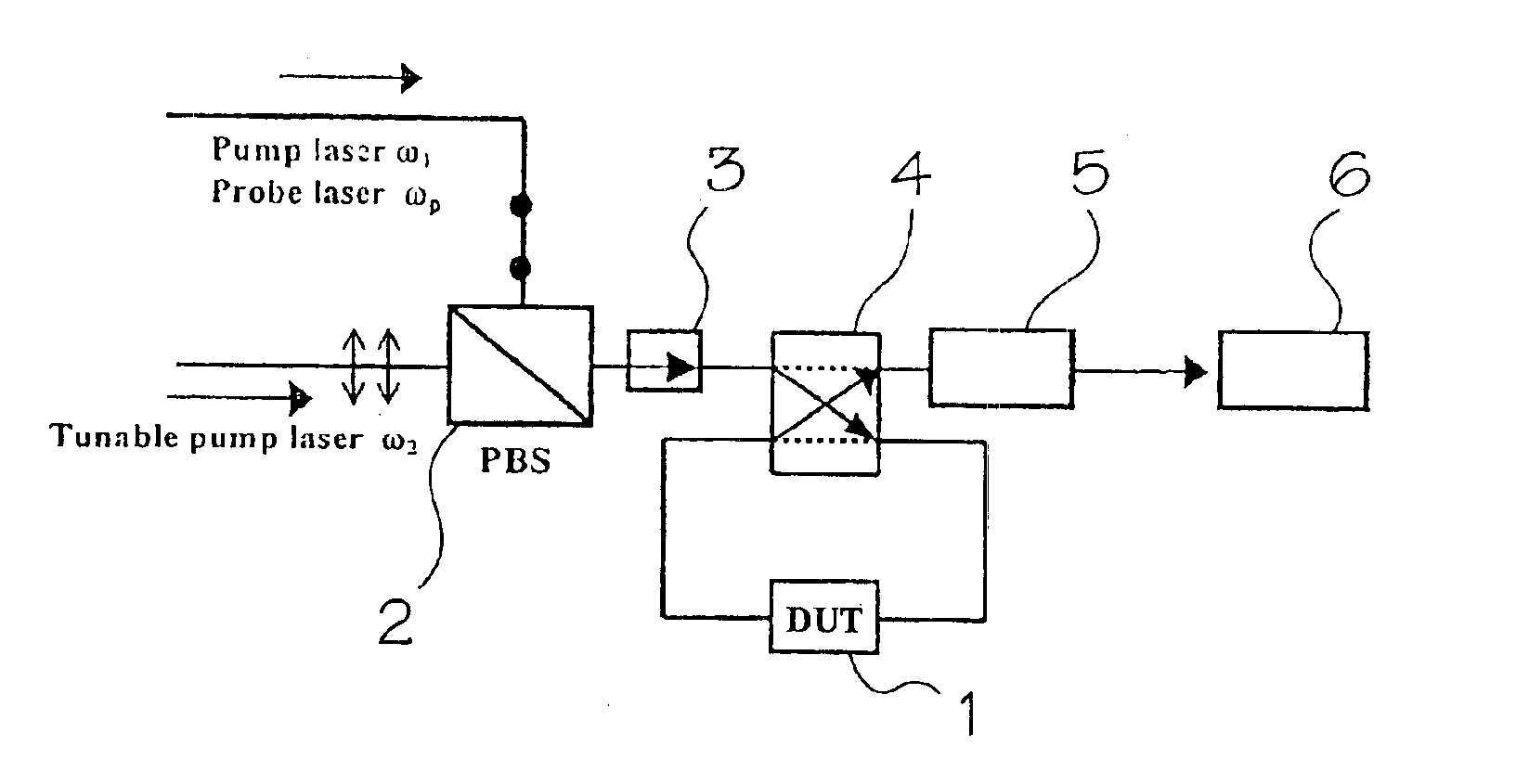
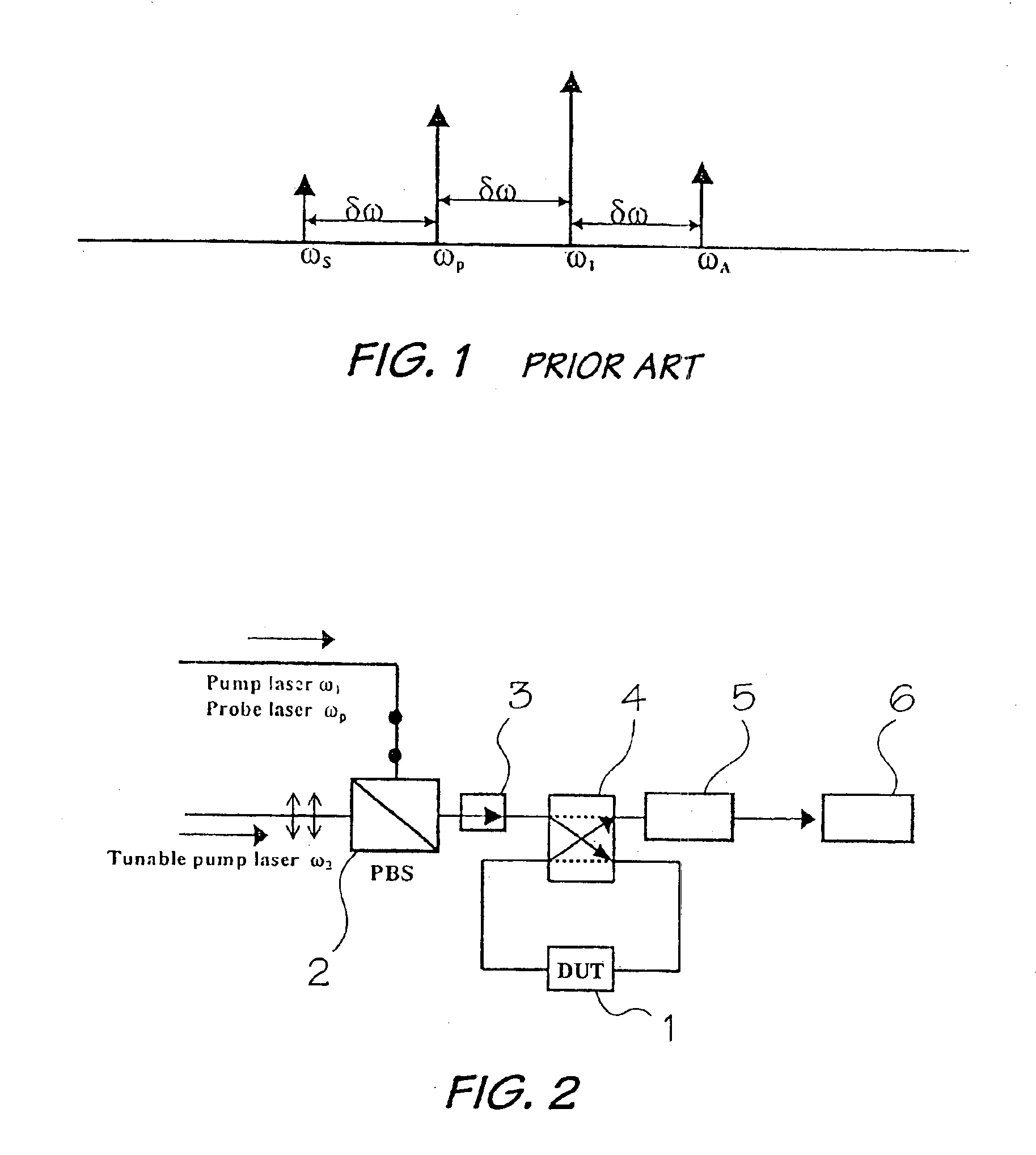
Polarization-mode dispersion (PMD) of an optical device, i.e. fiber or component is effected by launching a first pump laser beam of a fixed wavelength, a probe laser beam with a second fixed wavelength and a second pump laser beam having a variable wavelength and a polarization direction orthogonal to the other two beams into an optical device to generate three output signals which are input into a semiconductor optical amplifier to generate four-wave mixing (FWM) products. The average PMD of the device is computed by measuring the power of the FWM products versus the wavelength of the second pump laser beam.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
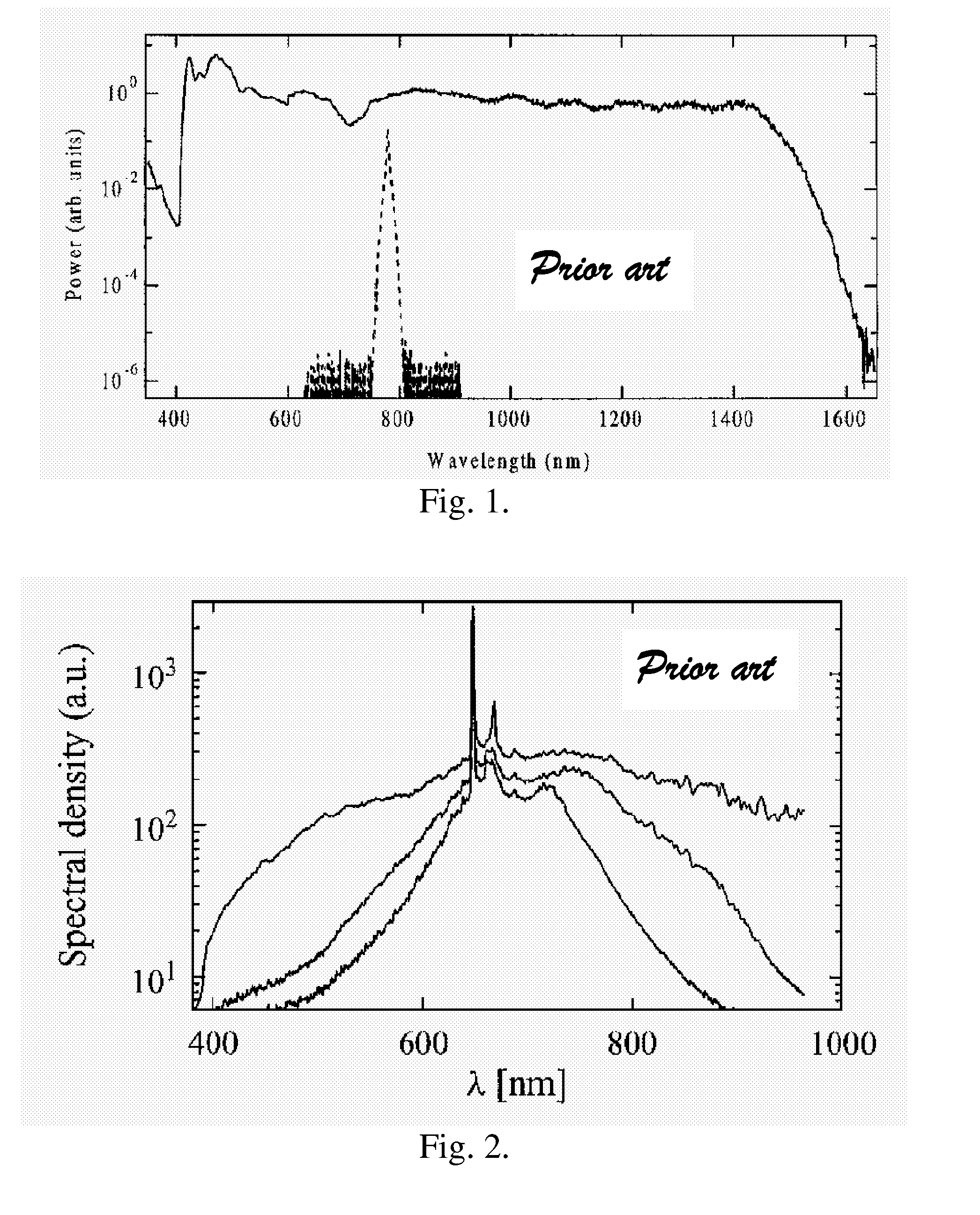
Optical frequency up-conversion of femtosecond pulses into targeted single bands in the visible and ultraviolet
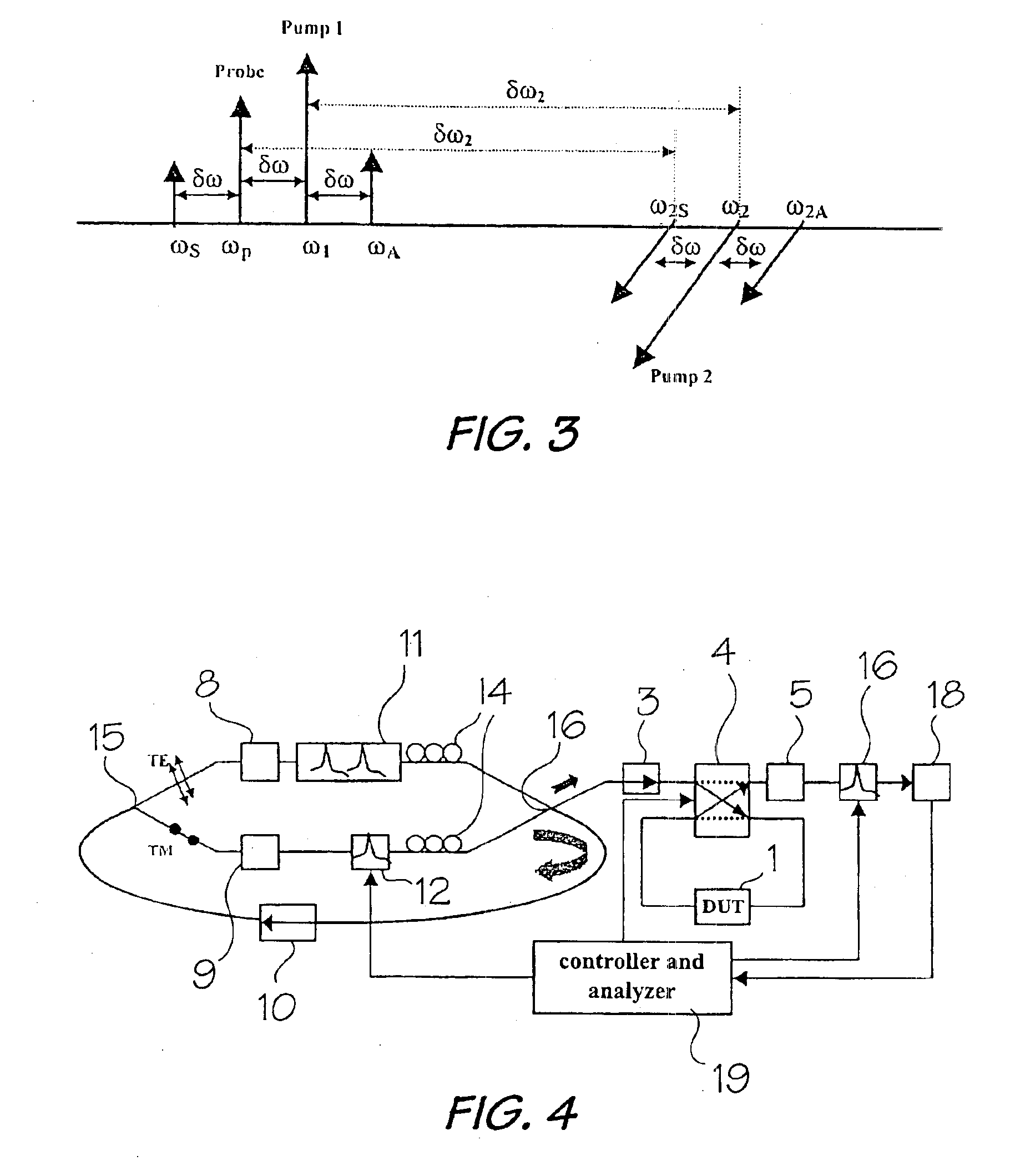
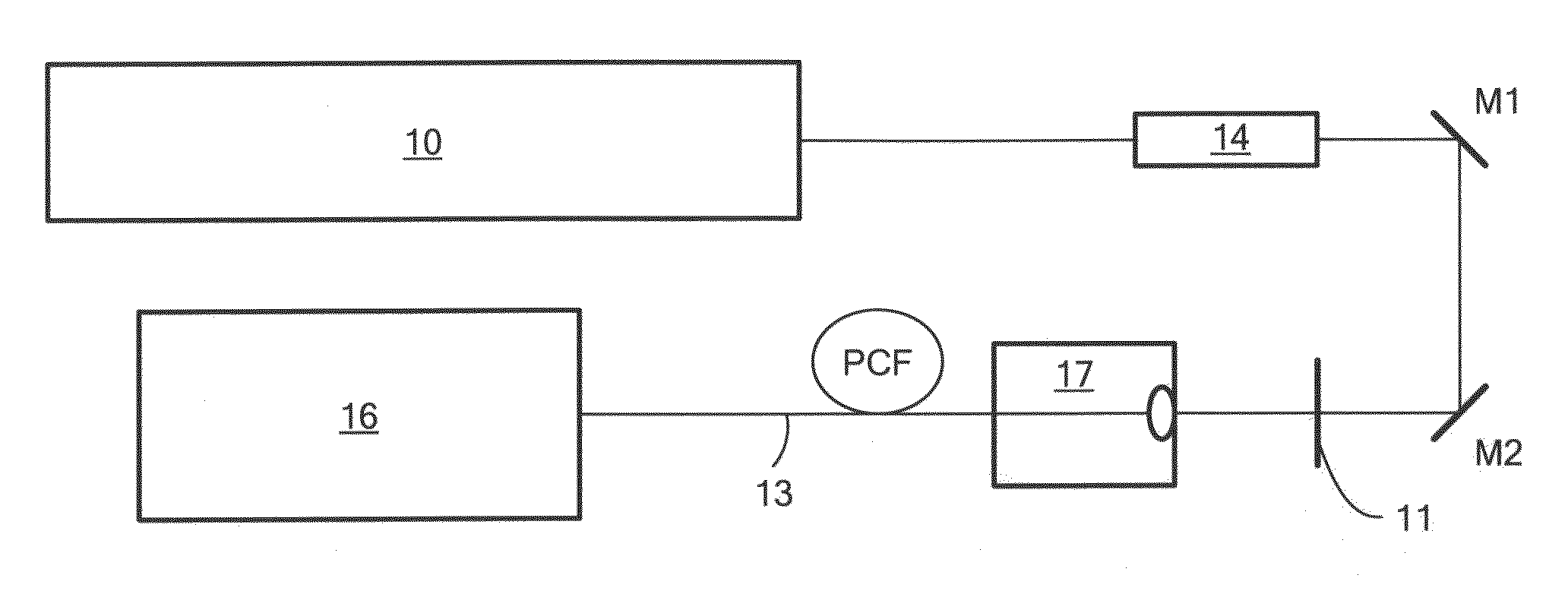
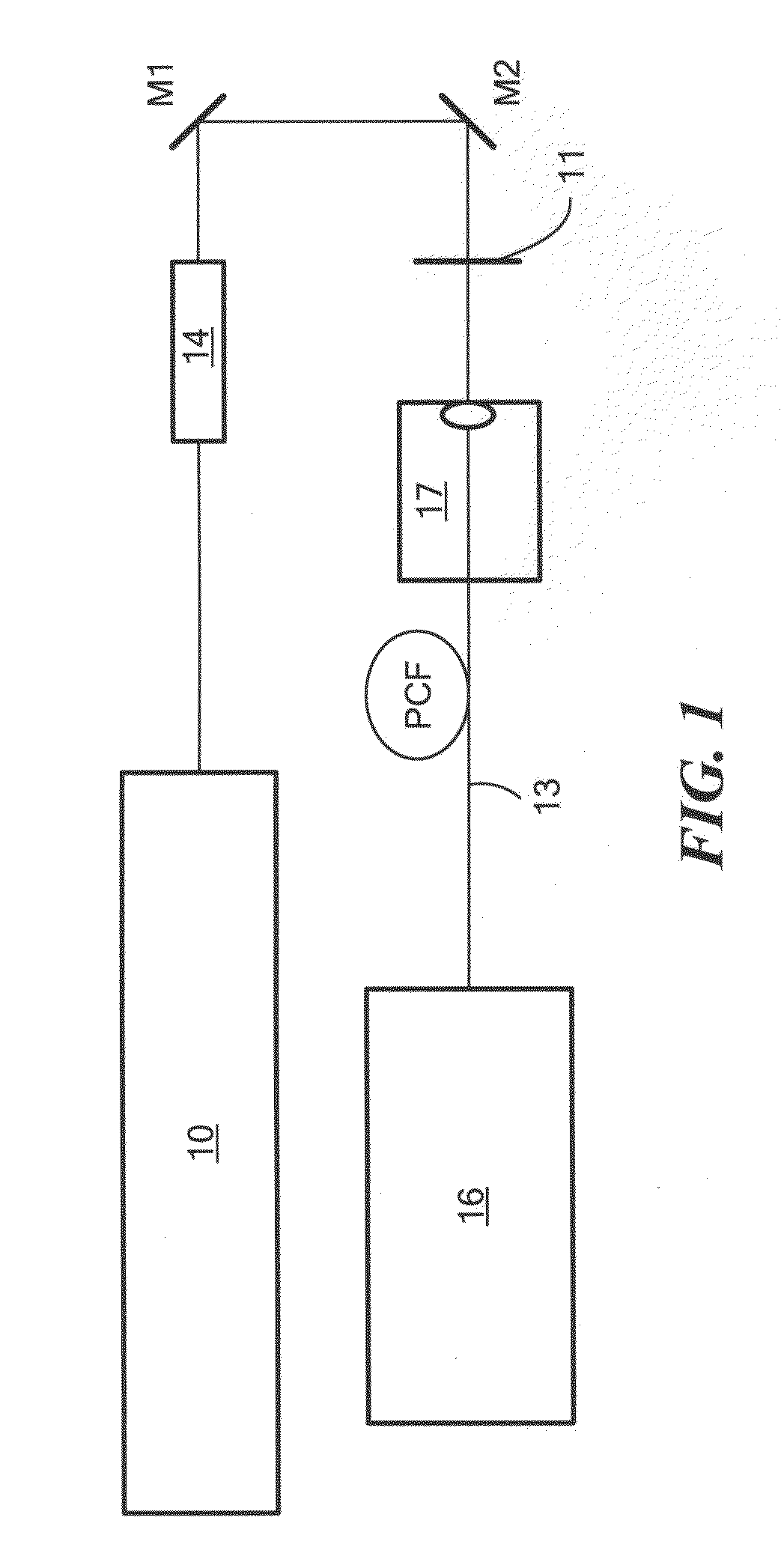
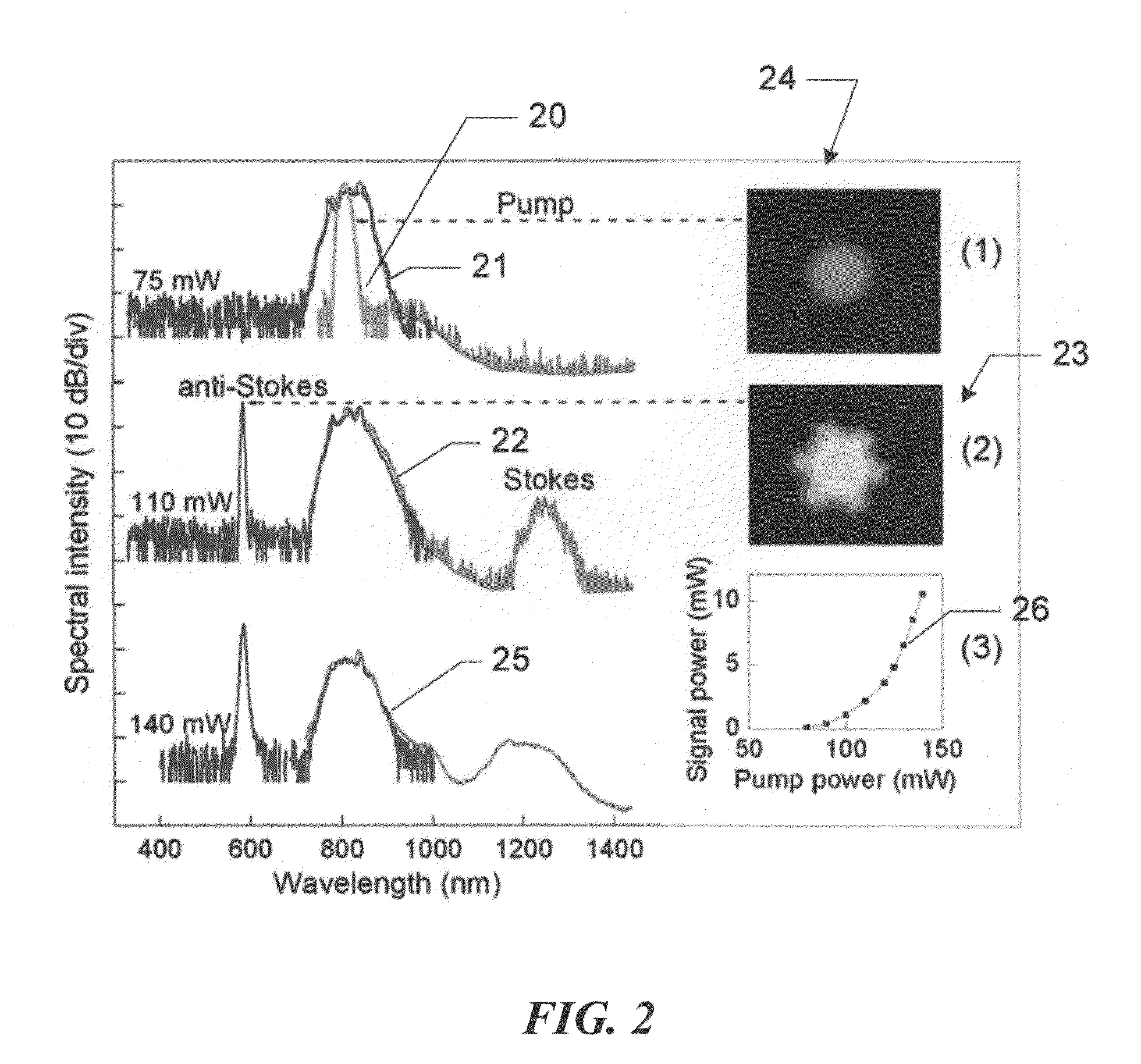
An apparatus and methods for generating a substantially supercontinuum-free widely-tunable multimilliwatt source of radiation characterized by a narrowband line profile. The apparatus and methods employ nonlinear optical mechanisms in a nonlinear photonic crystal fiber (PCF) by detuning the wavelength of a pump laser to a significant extent relative to the zero-dispersion wavelength (ZDW) of the PCF. Optical phenomena employed for the selective up-conversion in the PCF include, but are not limited to, four-wave mixing and Cherenkov radiation. Tunability is achieved by varying pump wavelength and power and by substituting different types of PCFs characterized by specified dispersion properties.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Laser or Amplifier Optical Device Pumped or Seeded with Nonlinearly Generated Light
ActiveUS20130107351A1Reduce repetition rateLaser detailsFibre transmissionAudio power amplifierSignal light
An optical source configured for providing output light for providing input signal light or pump light can comprise pump source for pumping a four wave mixing (FWM) process with light pulses (“FWM pump light”); a FWM element in optical communication with the pump source, the FWM element configured for hosting the FWM process to generate, responsive to the FWM pump light, pulses of FWM signal light and FWM idler light having different wavelengths. The optical source can be configured such that the output light comprises pump light having a pumping wavelength or as input signal light having a gain wavelength for pumping or seeding an amplifying optical device comprising a gain material for providing optical gain. The gain material can have absorption and emission spectra defining gain and pumping wavelengths at which, respectively, the gain material is arranged in the device to provide optical gain via a process of stimulated emission responsive to being pumped.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Bi-color magneto-optical trap method and device for cooling and capturing atoms through lasers
InactiveCN104036841AConvenient researchThe optical path is flexible and changeableRadiation/particle handlingRydberg atomAlkaline earth metal
The invention relates to atom laser cooling and atom laser capturing, in particular to a bi-color magneto-optical trap method and device for cooling and capturing atoms through lasers. According to the bi-color magneto-optical trap method and device, atom cooling and atom capturing are achieved through the bi-color lasers which work in a base-state, middle-excited-state and higher-excited-state cascading energy level, and atom pre-cooling is not needed. A step-type bi-color magneto-optical trap technology is adopted for the bi-color magneto-optical trap device, and the atoms can be directly cooled and captured from a vacuum air chamber. The step-type bi-color magneto-optical trap device can be used for cooling and capturing the alkali metal atoms, the alkaline earth metal atoms and even the rydberg atoms through the lasers; some quantum coherent effects can be directly researched in the cold atoms based on step-type bi-color dual-photon cooling, for example, the problem that correlation photon pairs are directly generated in bi-color magneto-optical traps is researched based on the rhombus-energy-level four-wave mixing effect; as for the experimental device, a bi-color magneto-optical trap experiment idea which is quite flexible and easy to achieve is initiated, and the experimental device can be conveniently applied and popularized.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
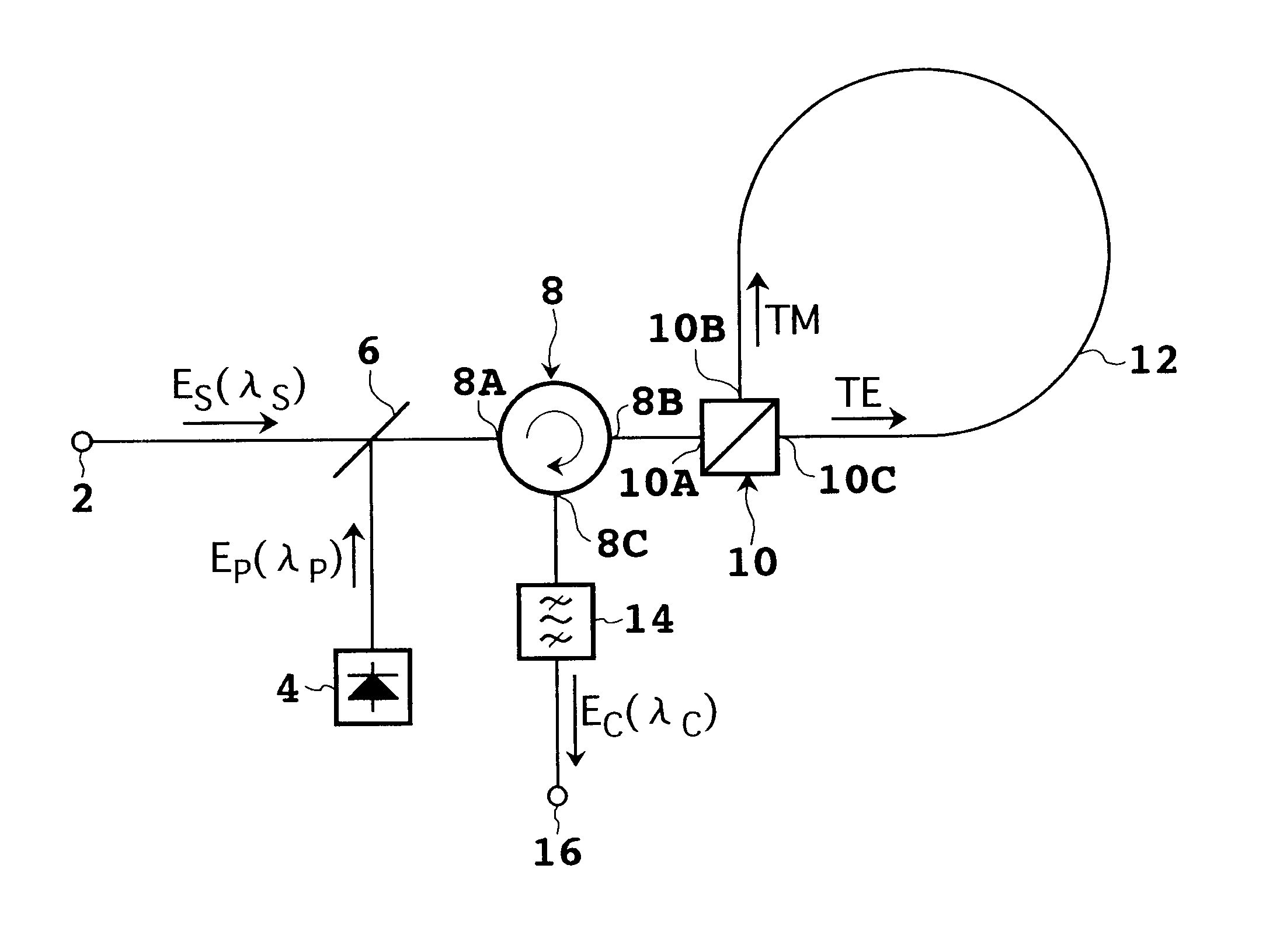
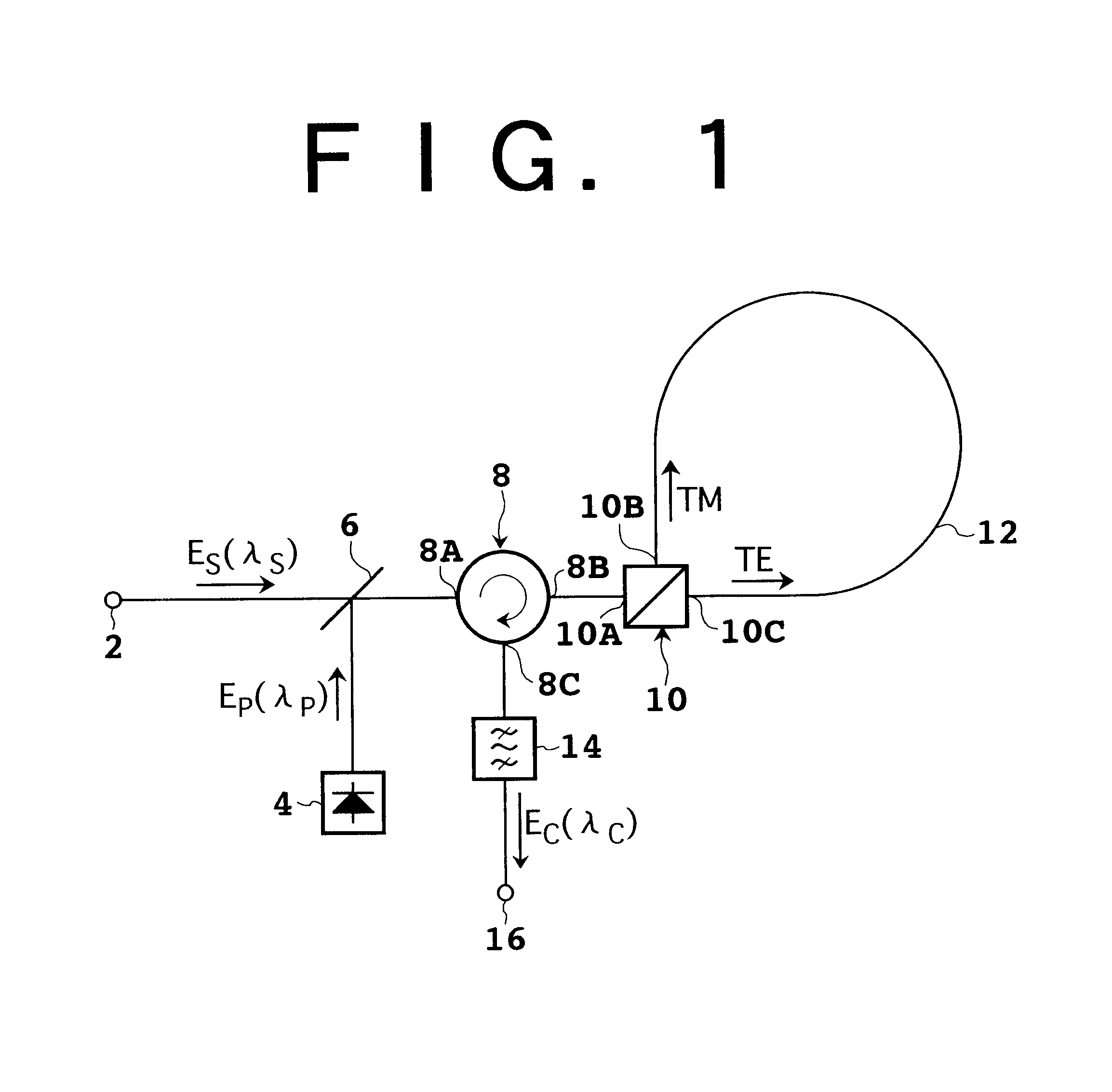
Device and system for phase conjugate conversion and wavelength conversion
InactiveUS7043099B1Broadening conversion bandImprove accuracyCoupling light guidesDistortion/dispersion eliminationFiberOptical circulator
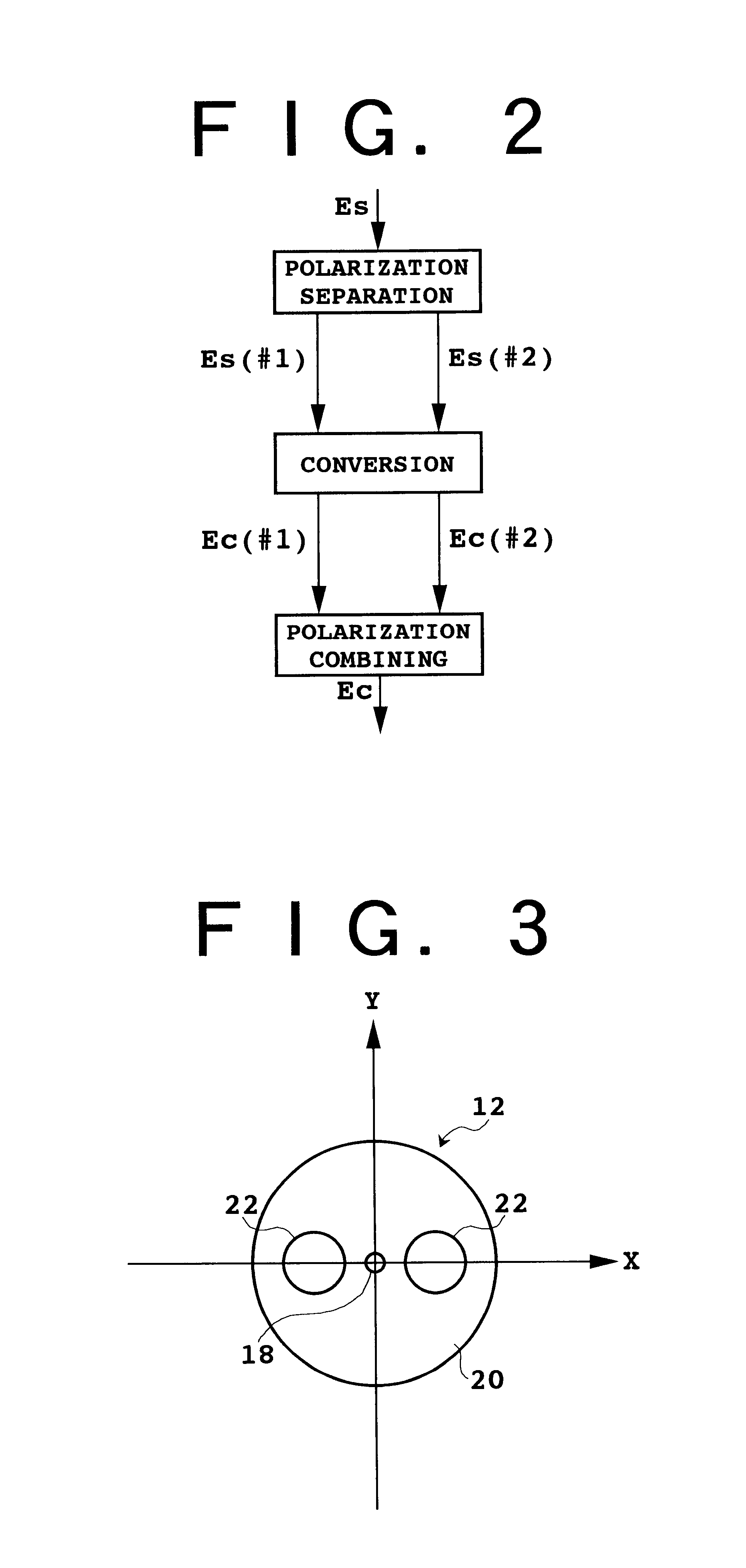
The device according to the present invention relates to phase conjugate conversion and wavelength conversion. This device includes a polarization beam splitter and a polarization maintaining fiber (PMF). The polarization beam splitter has first, second, and third ports. The first port is supplied with signal light including first and second polarization components respectively having first and second polarization planes orthogonal to each other, and with pump light. The first and second ports are coupled by the first polarization plane, and the first and third ports are coupled by the second polarization plane. The PMF has first and second ends, and has a polarization mode to be maintained between the first and second ends. The first end is optically connected to the second port so that the first polarization plane is adapted to the polarization mode, and the second end is optically connected to the third port so that the second polarization plane is adapted to the polarization mode. Converted light generated by four-wave mixing based on the signal light and the pump light in the PMF is output from the first port, so that the converted light can be taken out by an optical circulator.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com