Patents
Literature
549 results about "Optical focusing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
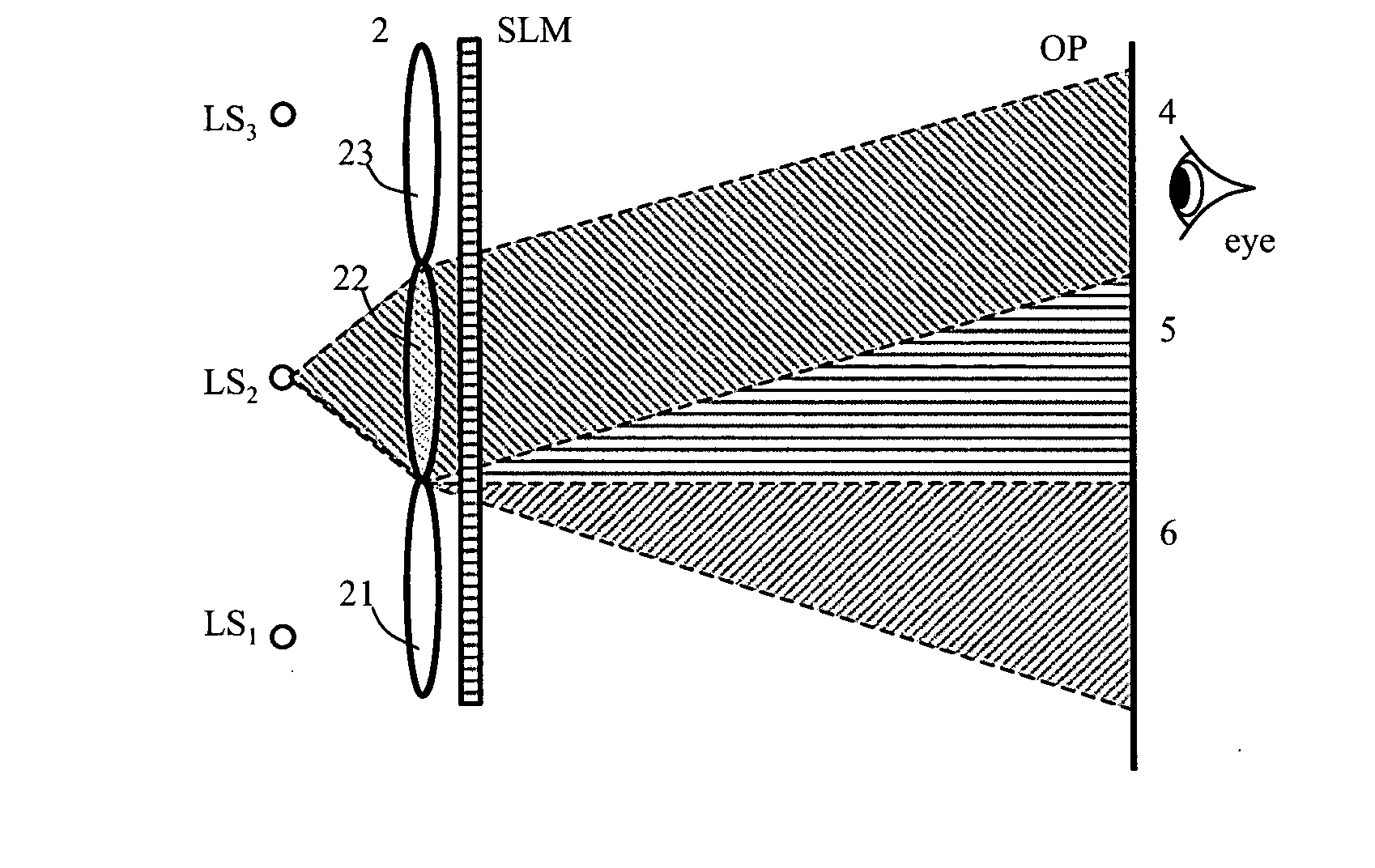
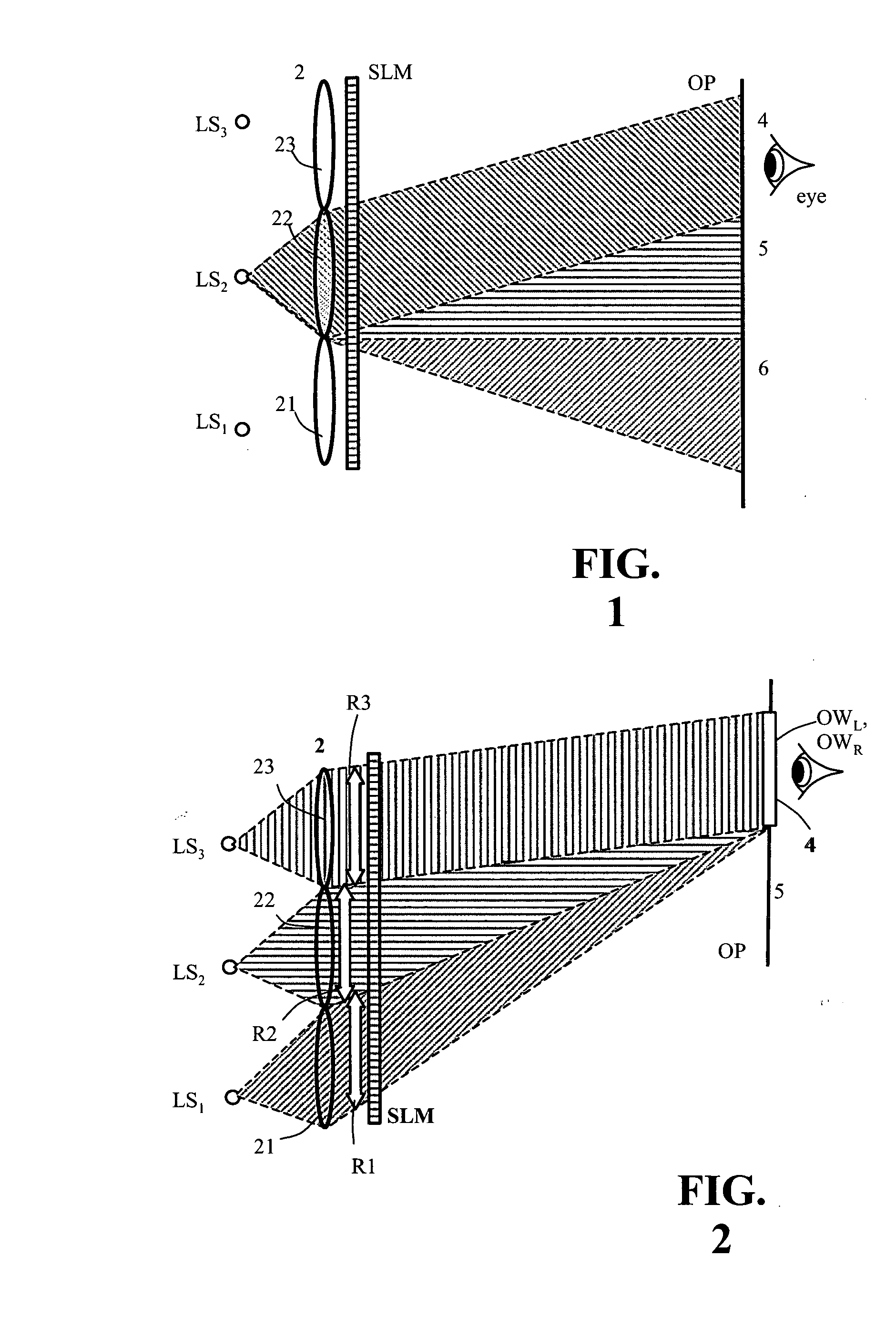
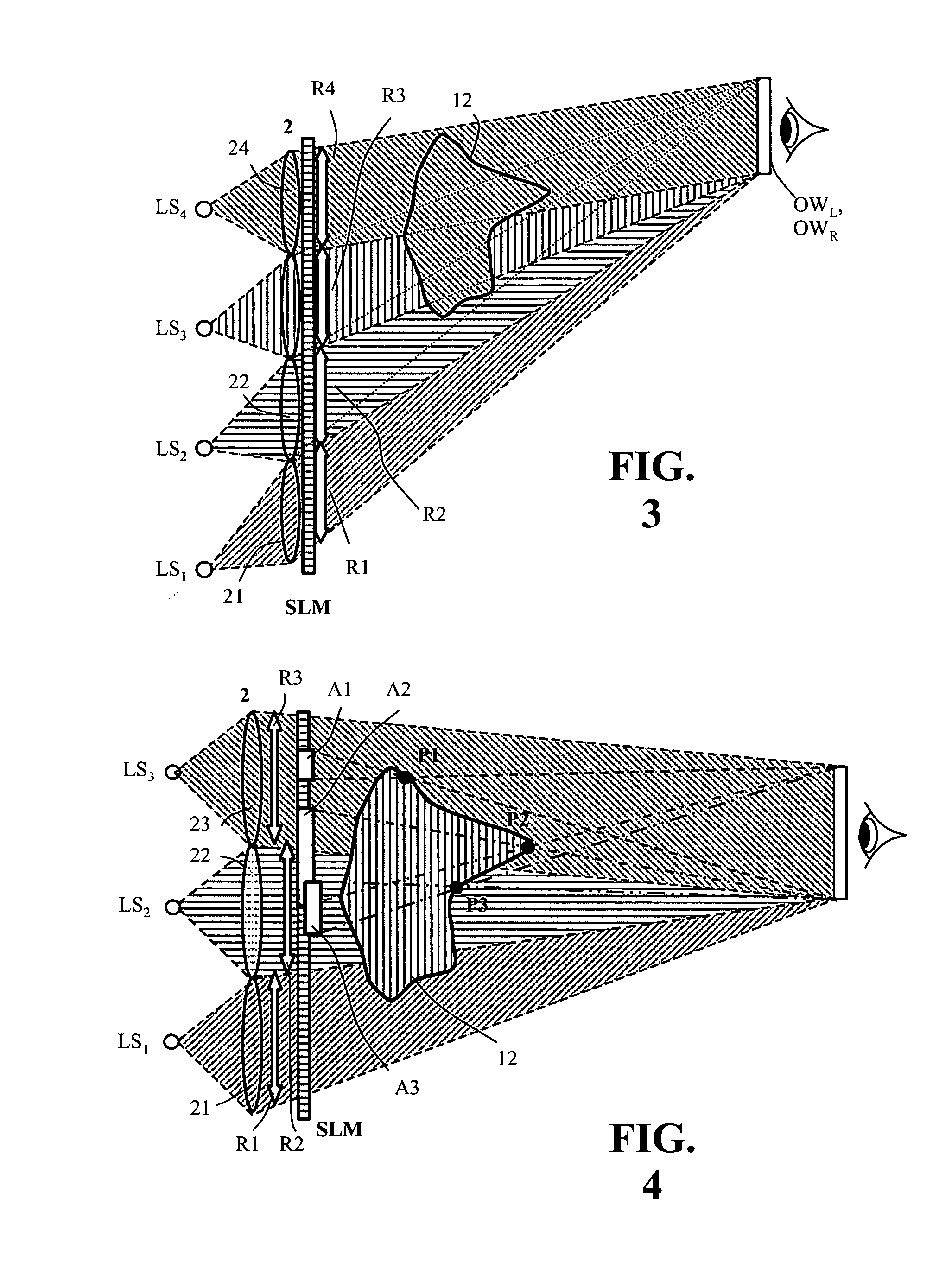
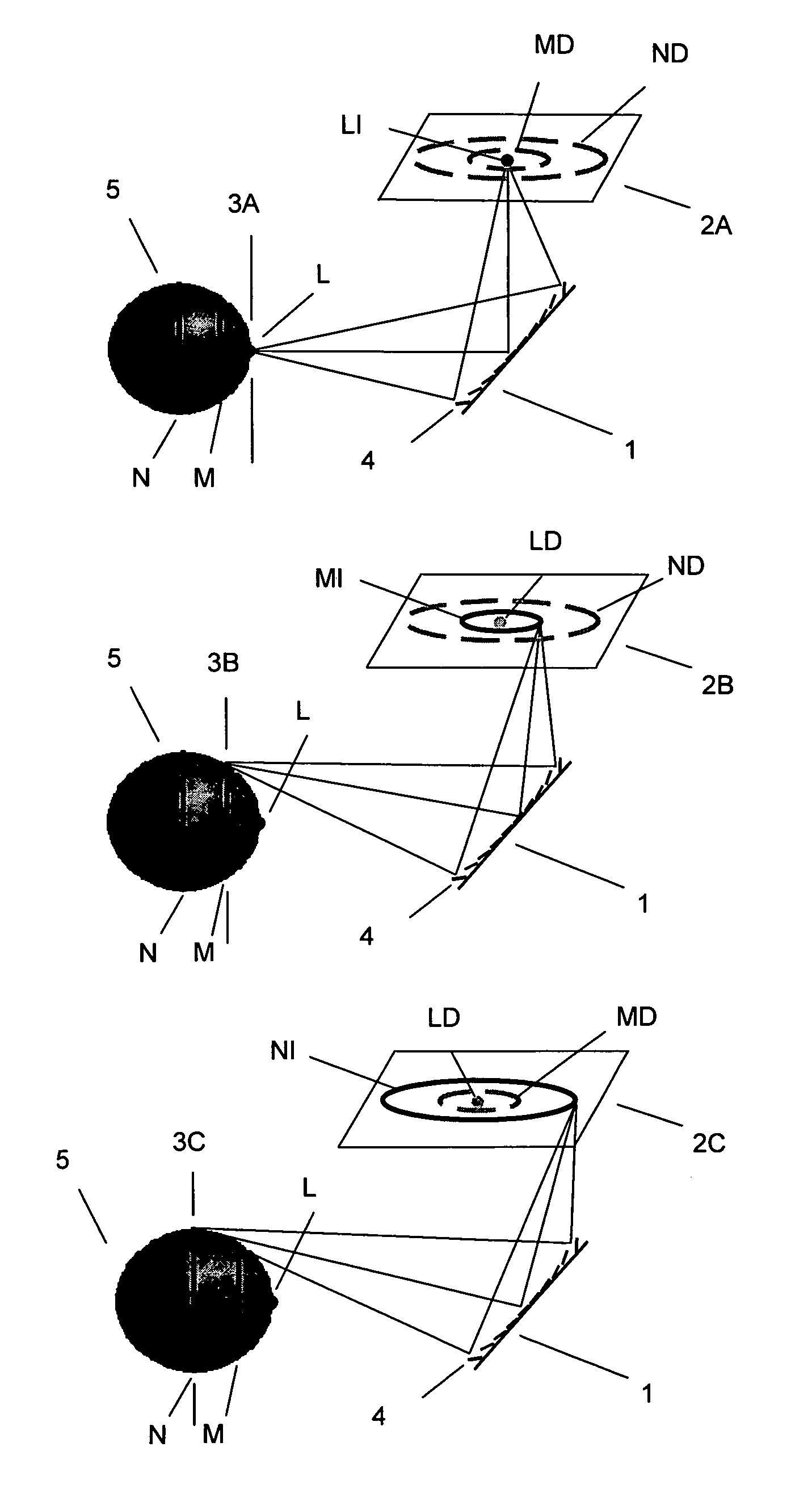
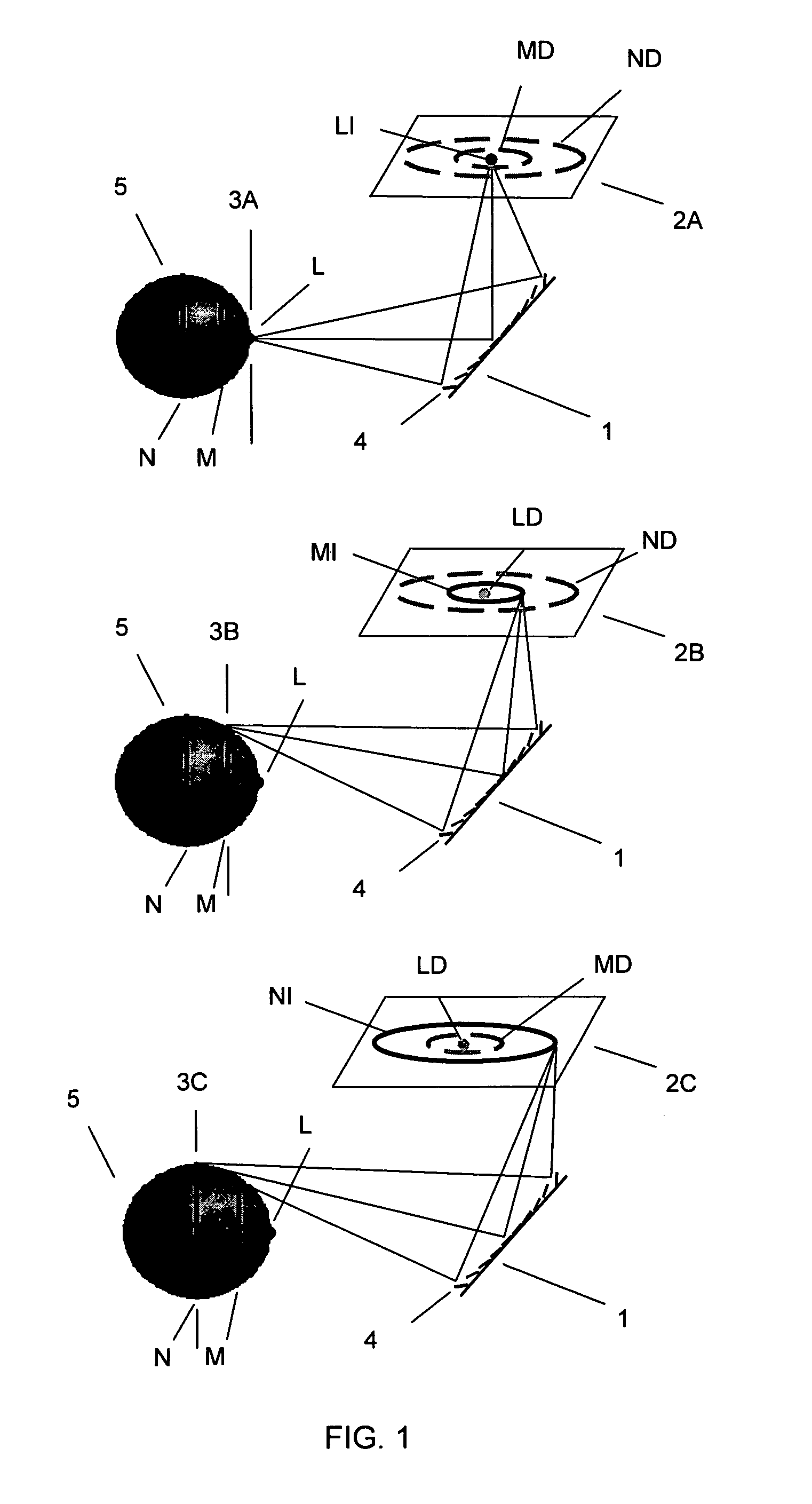
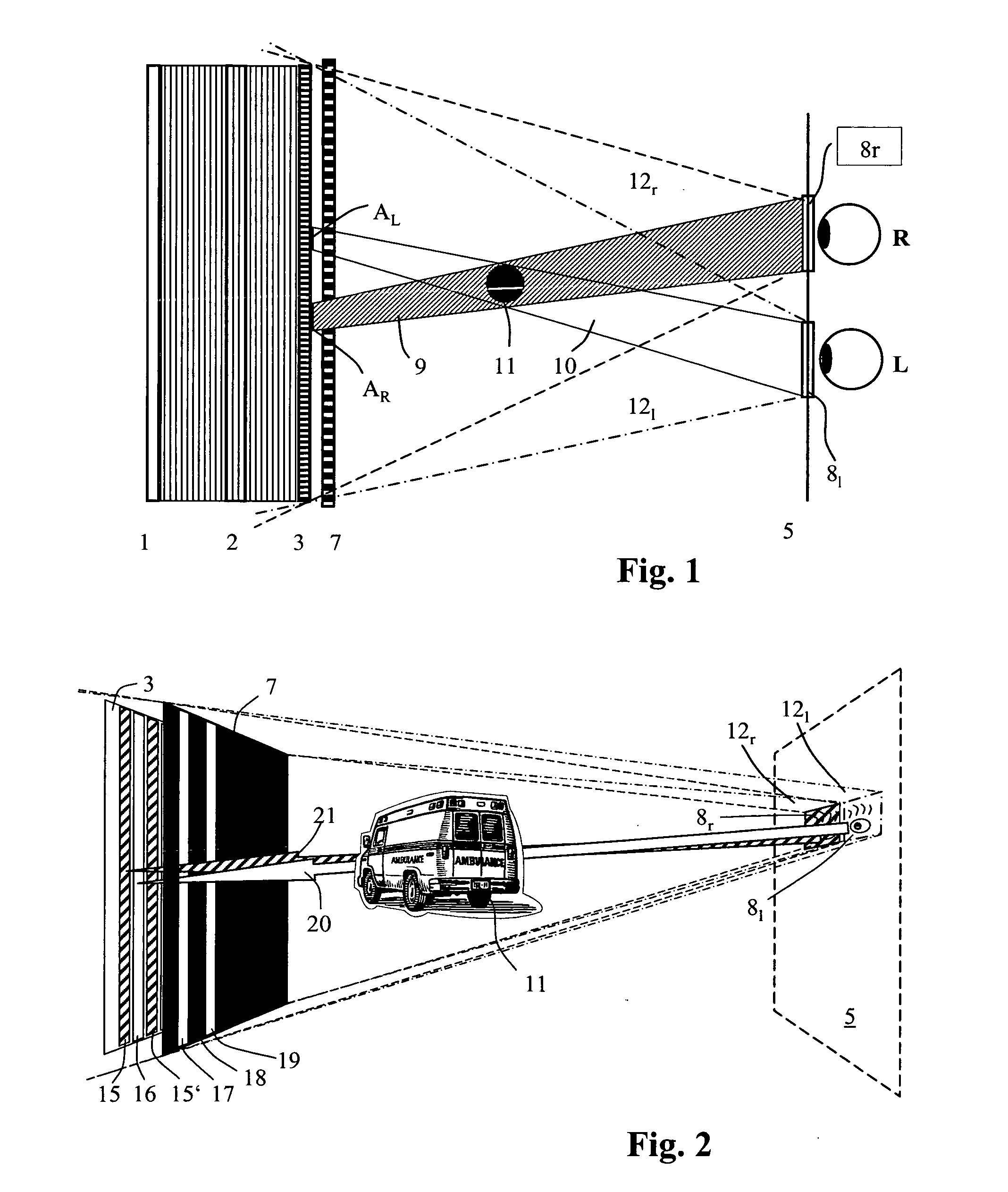
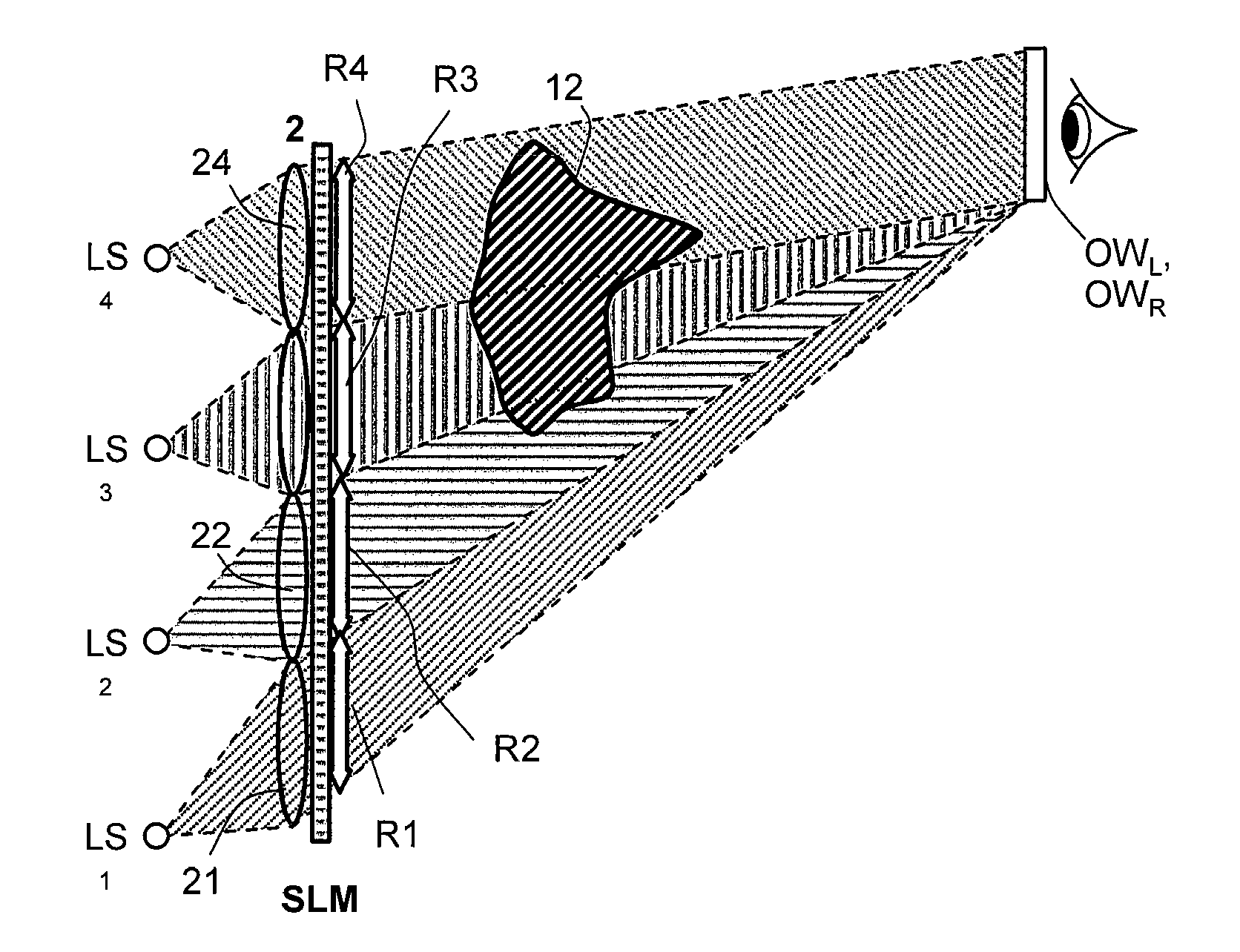
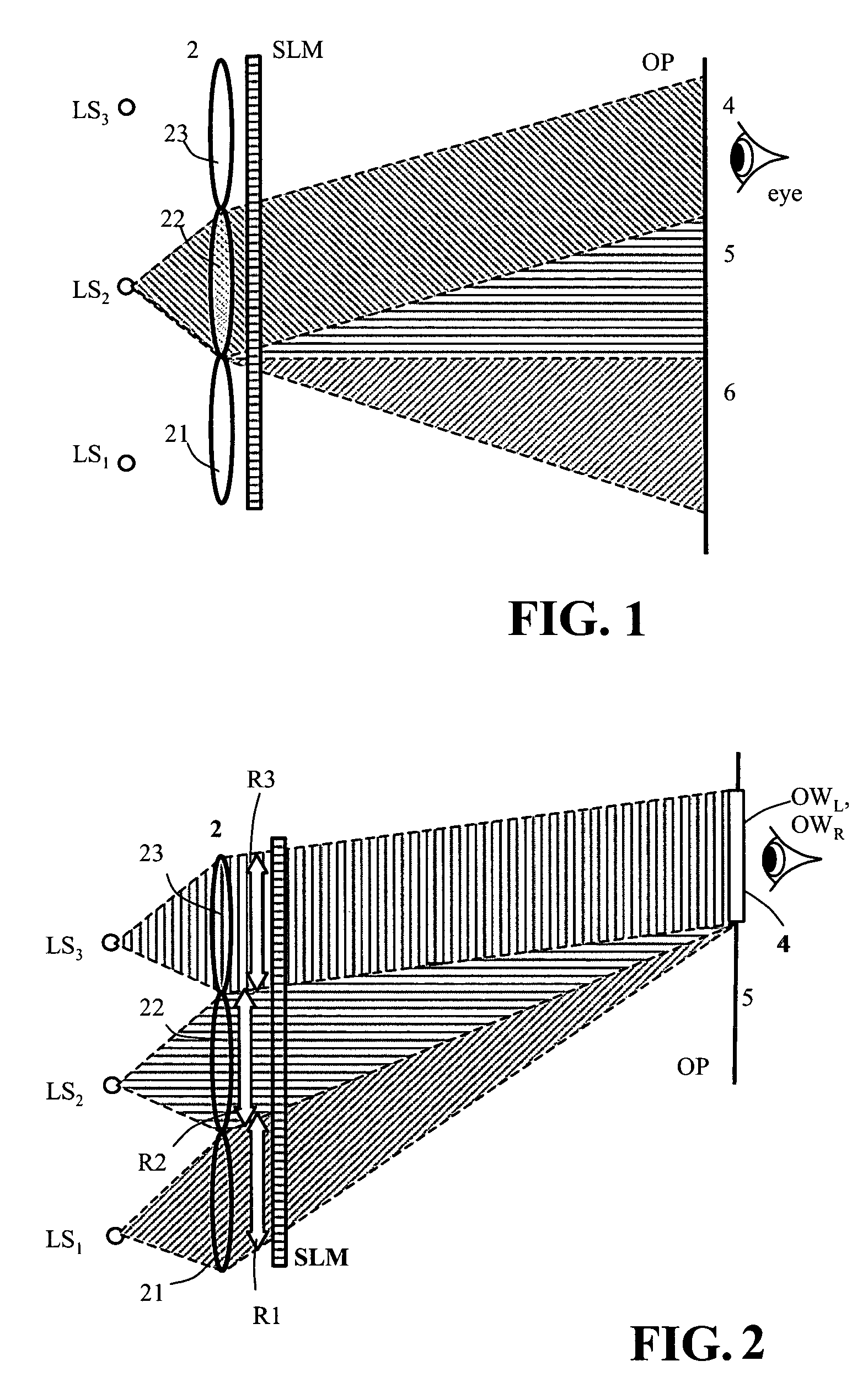
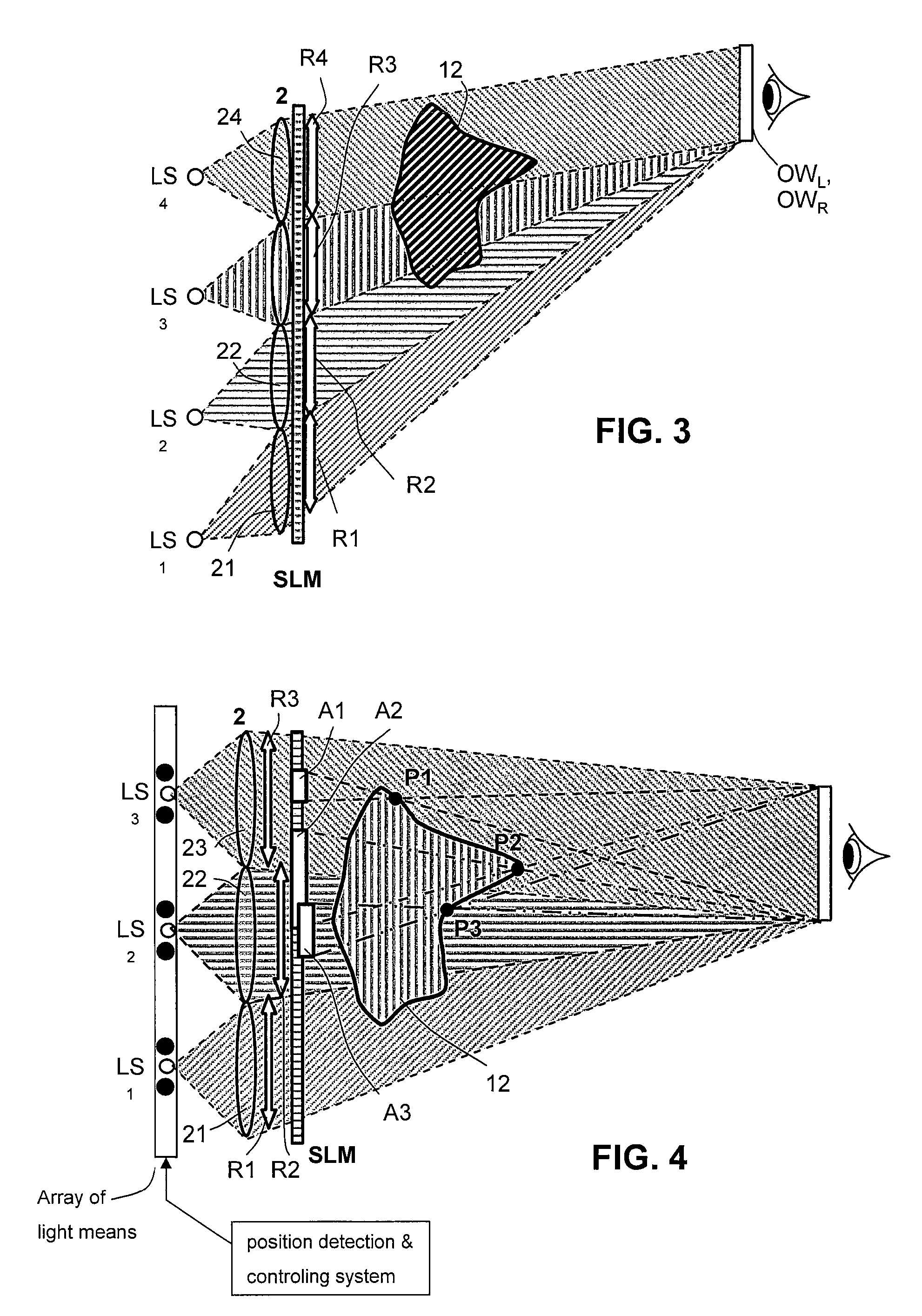
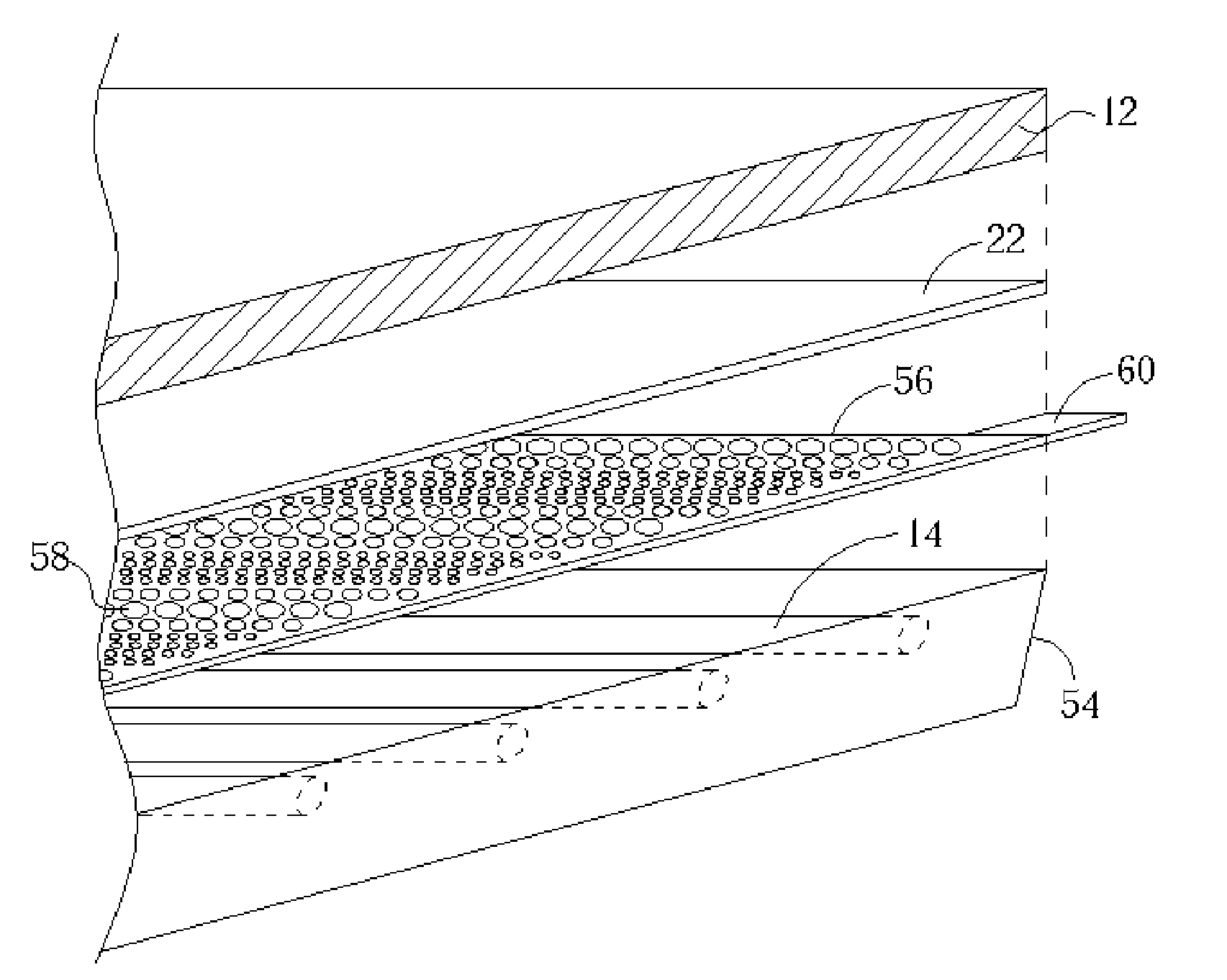
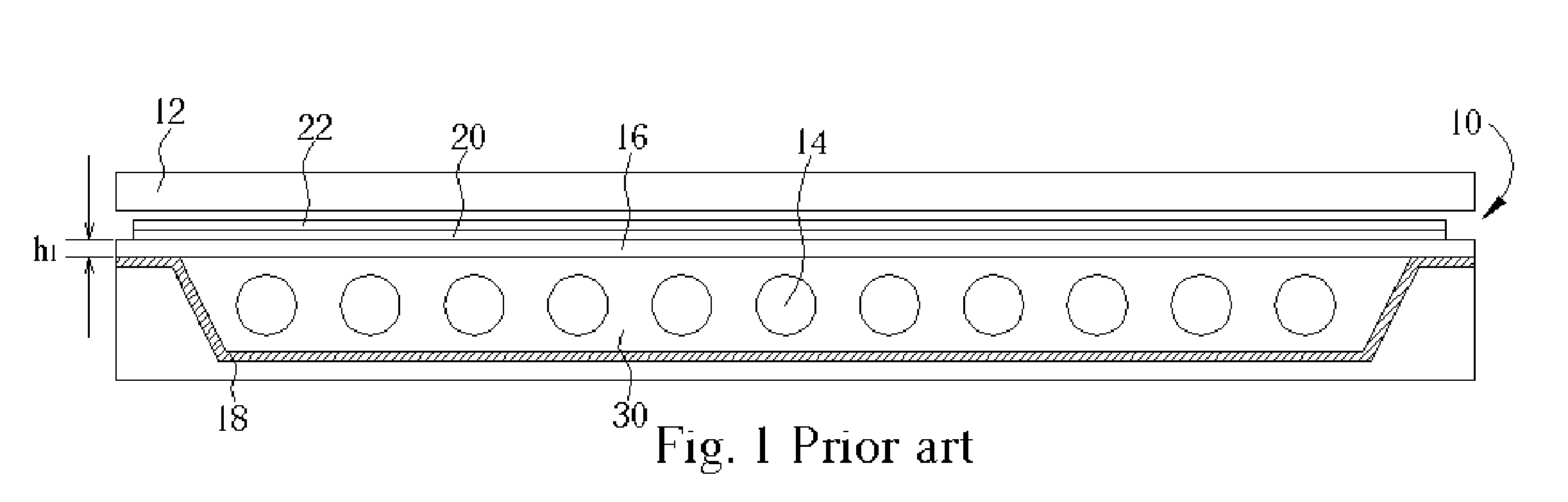
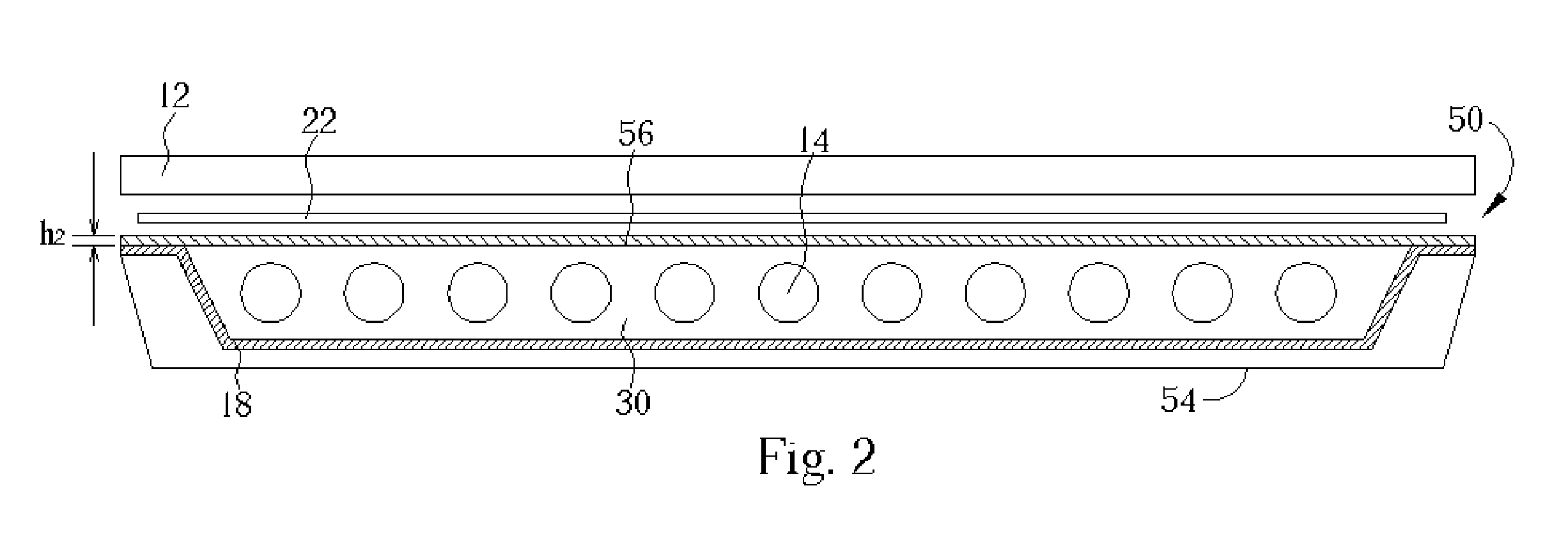
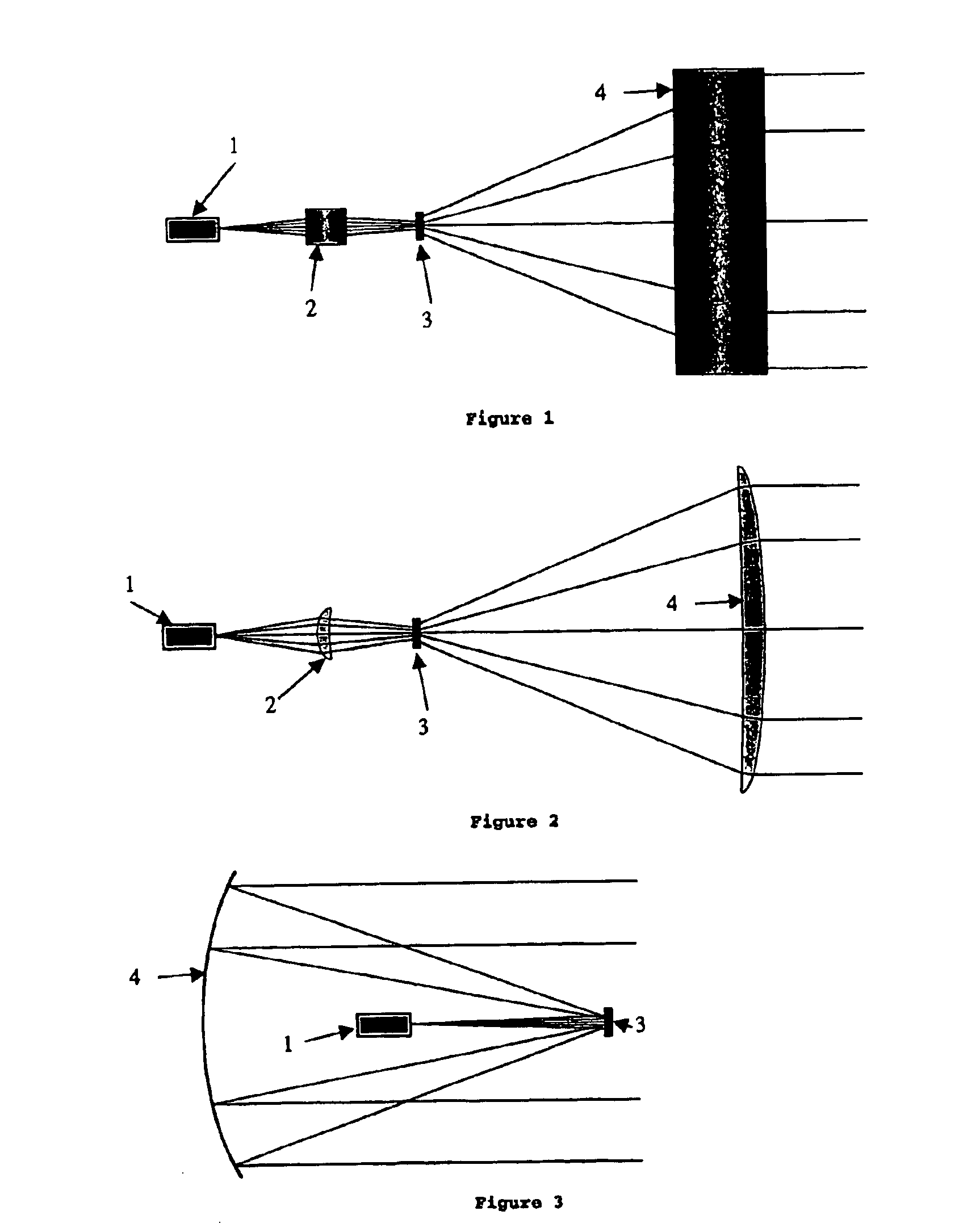
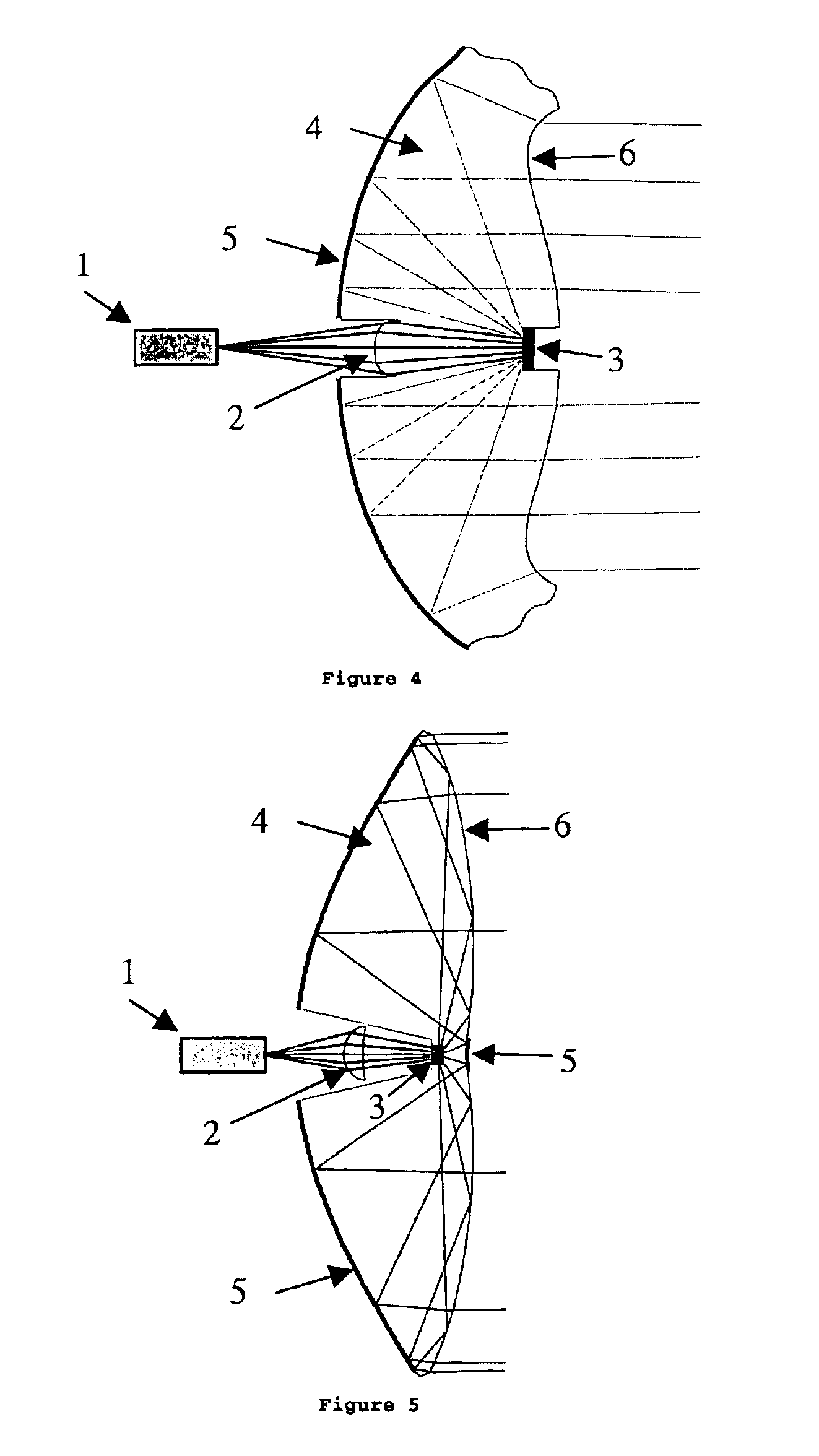
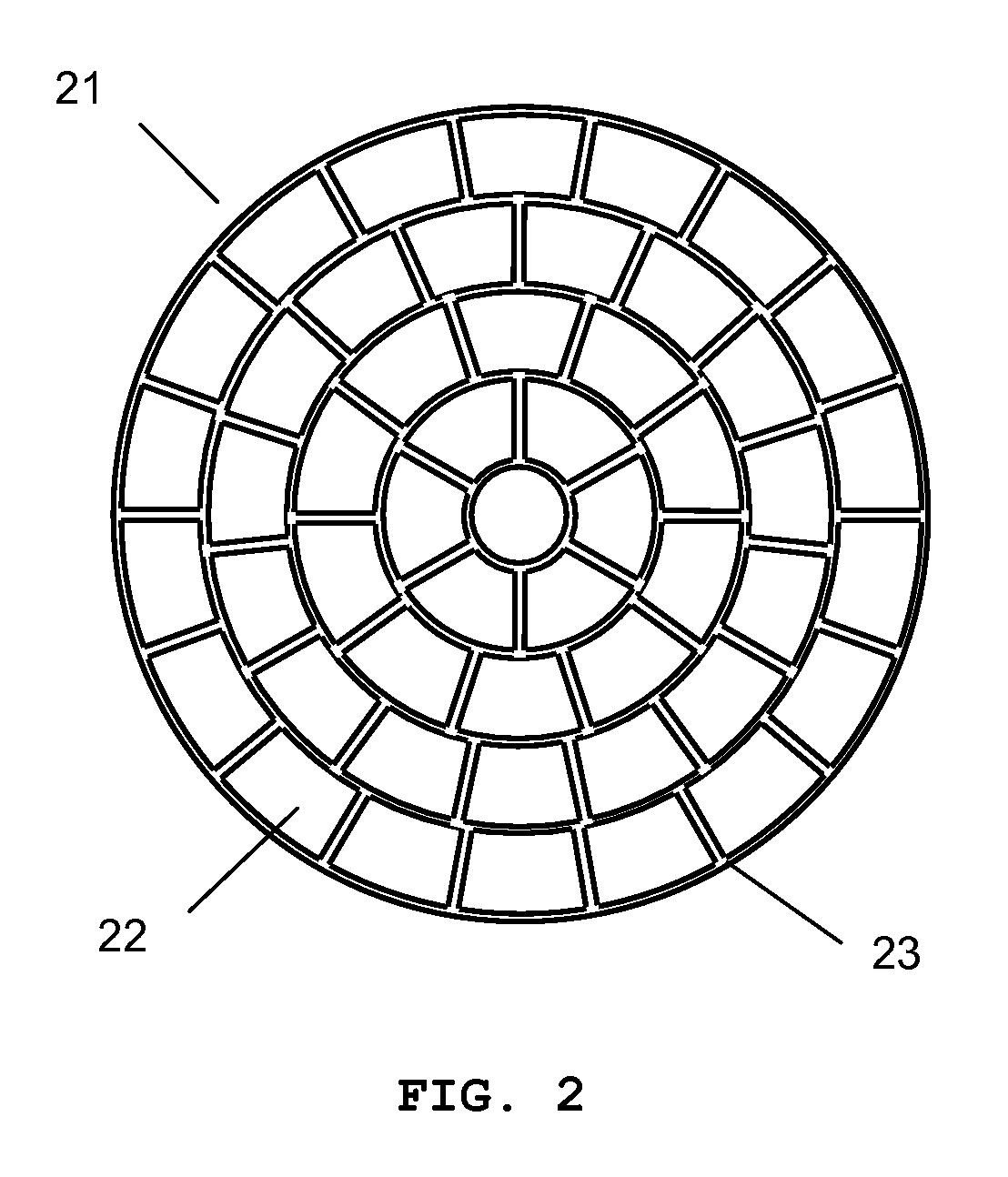
Device for holographic reconstruction of three-dimensional scenes
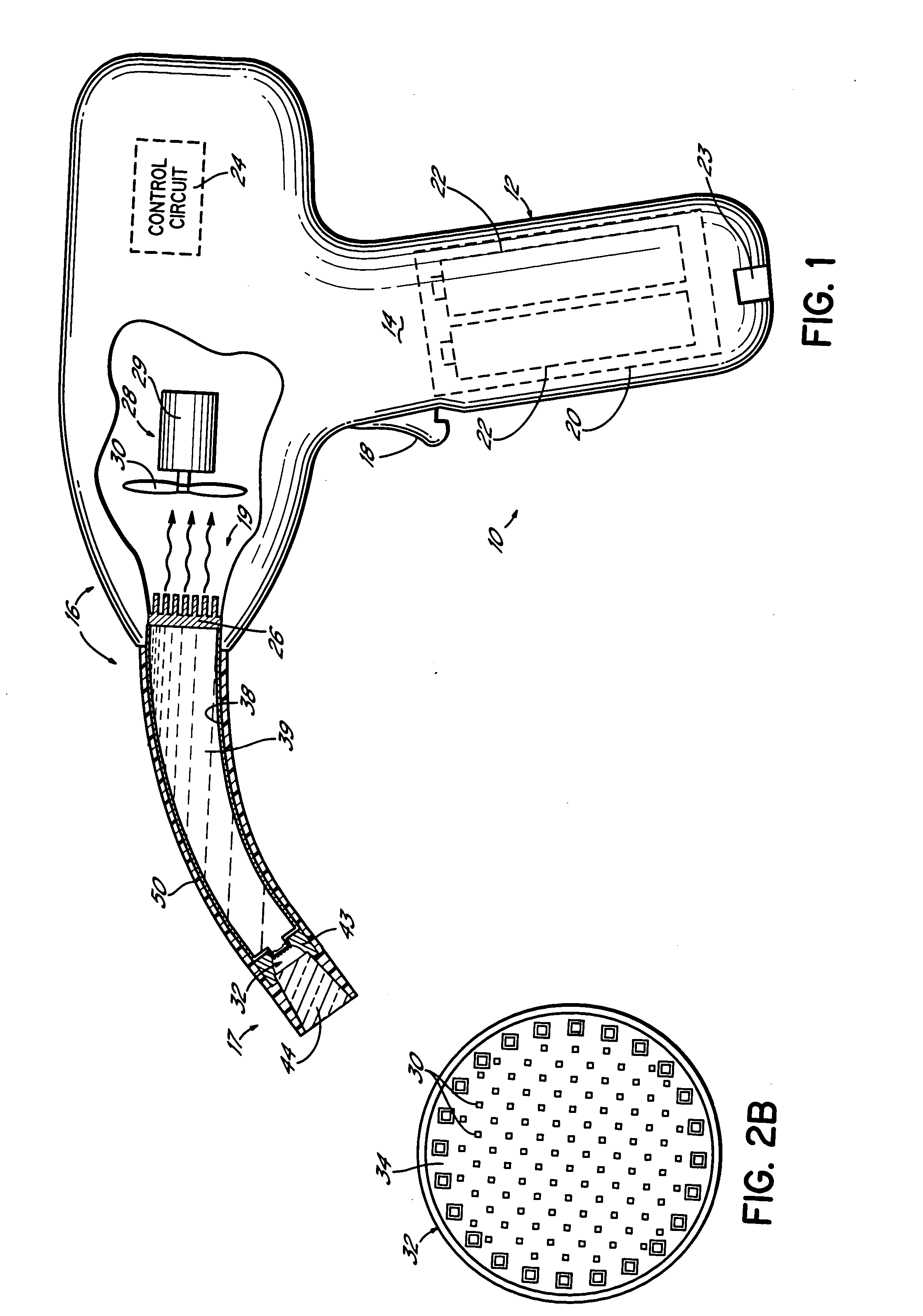
ActiveUS20060250671A1Reasonable effortLarge cell pitchHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsSpatial light modulatorOptical focusing
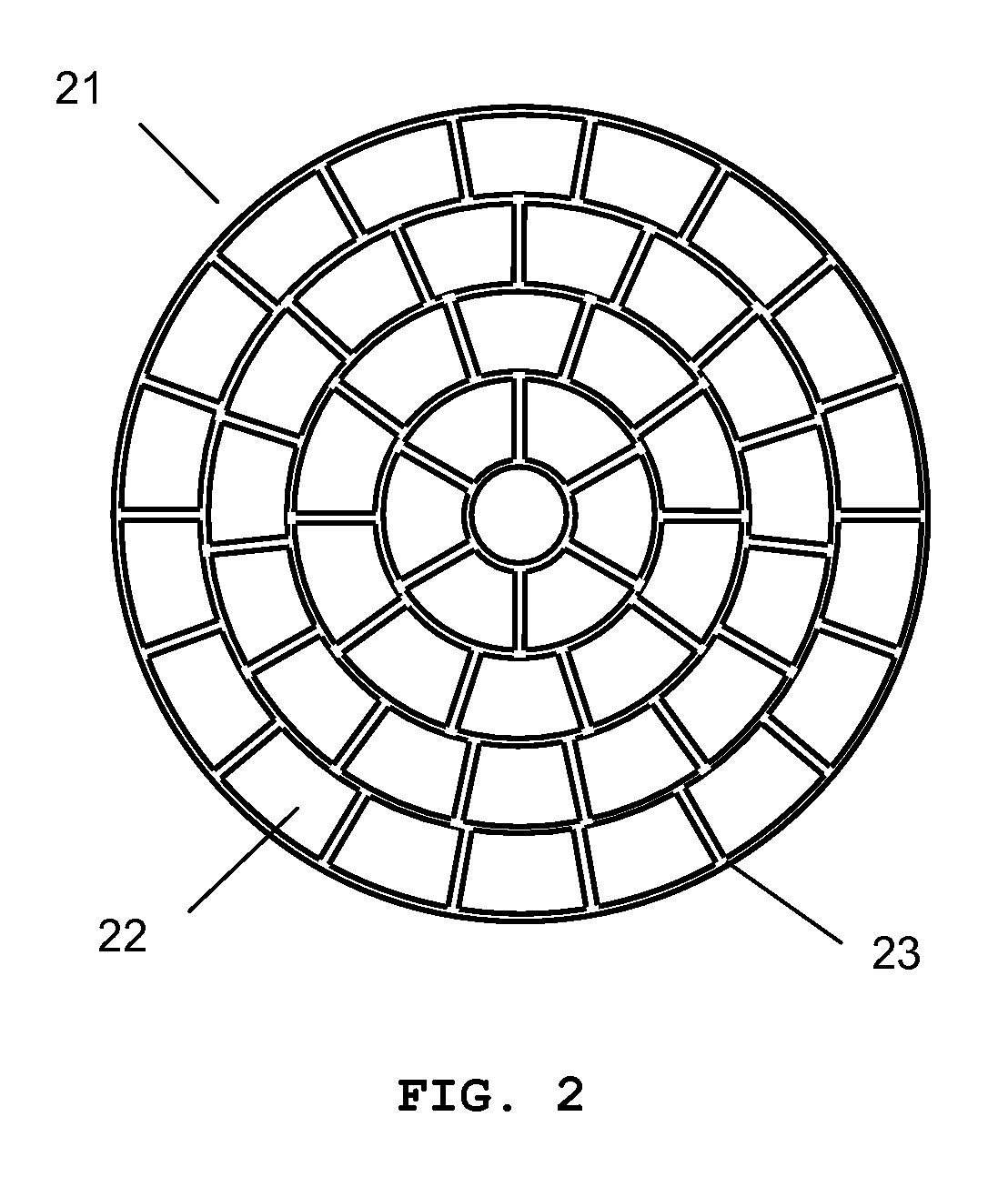
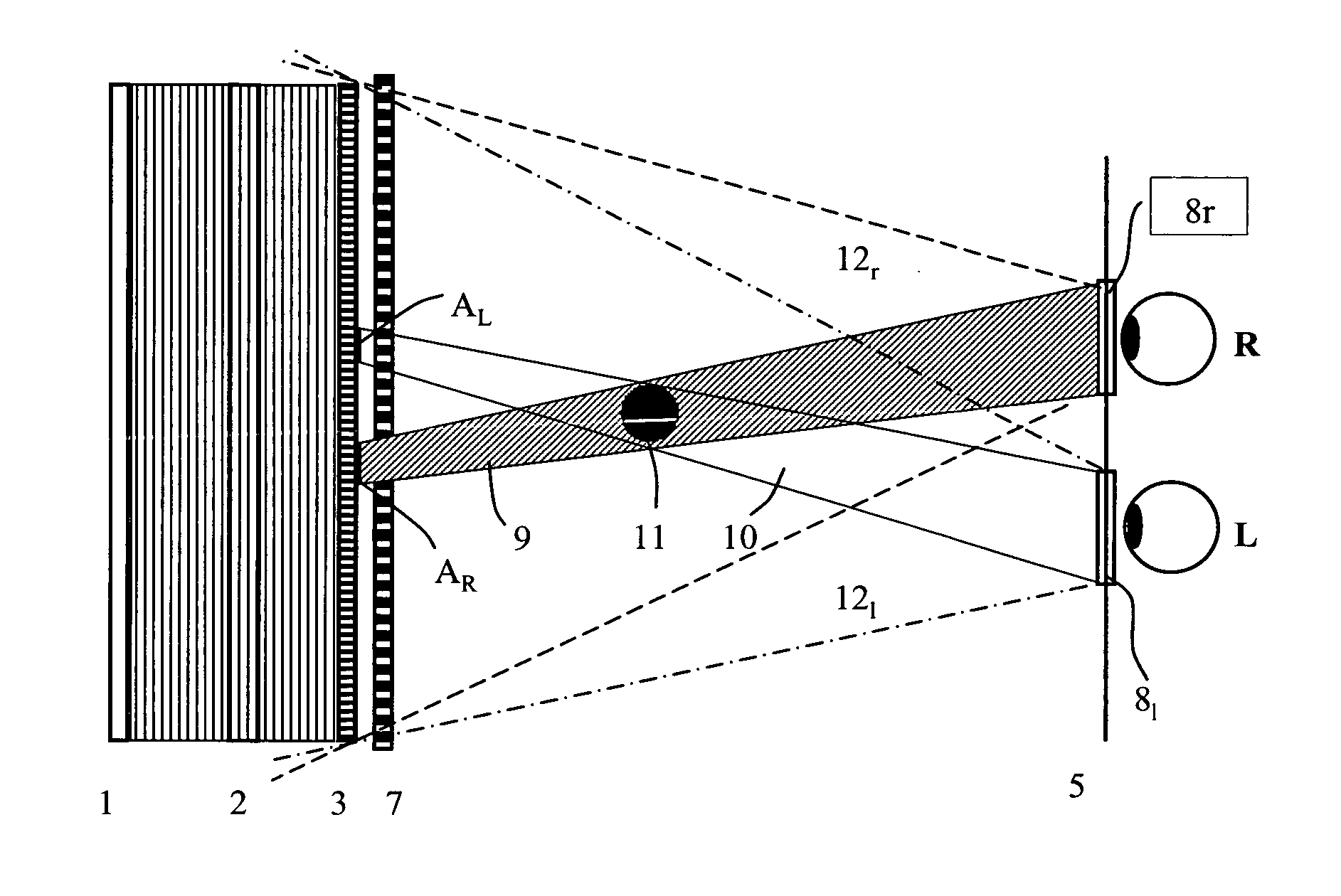
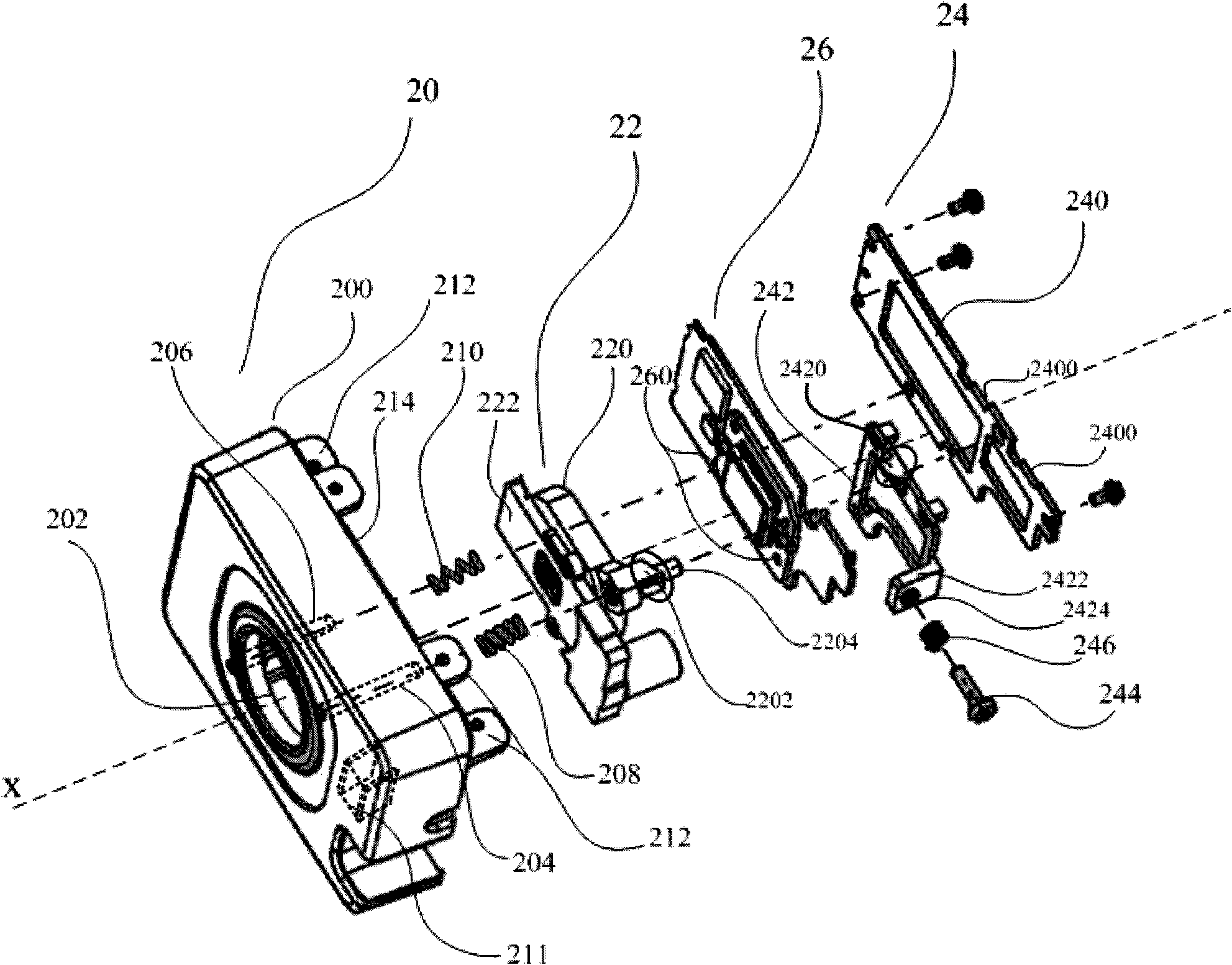
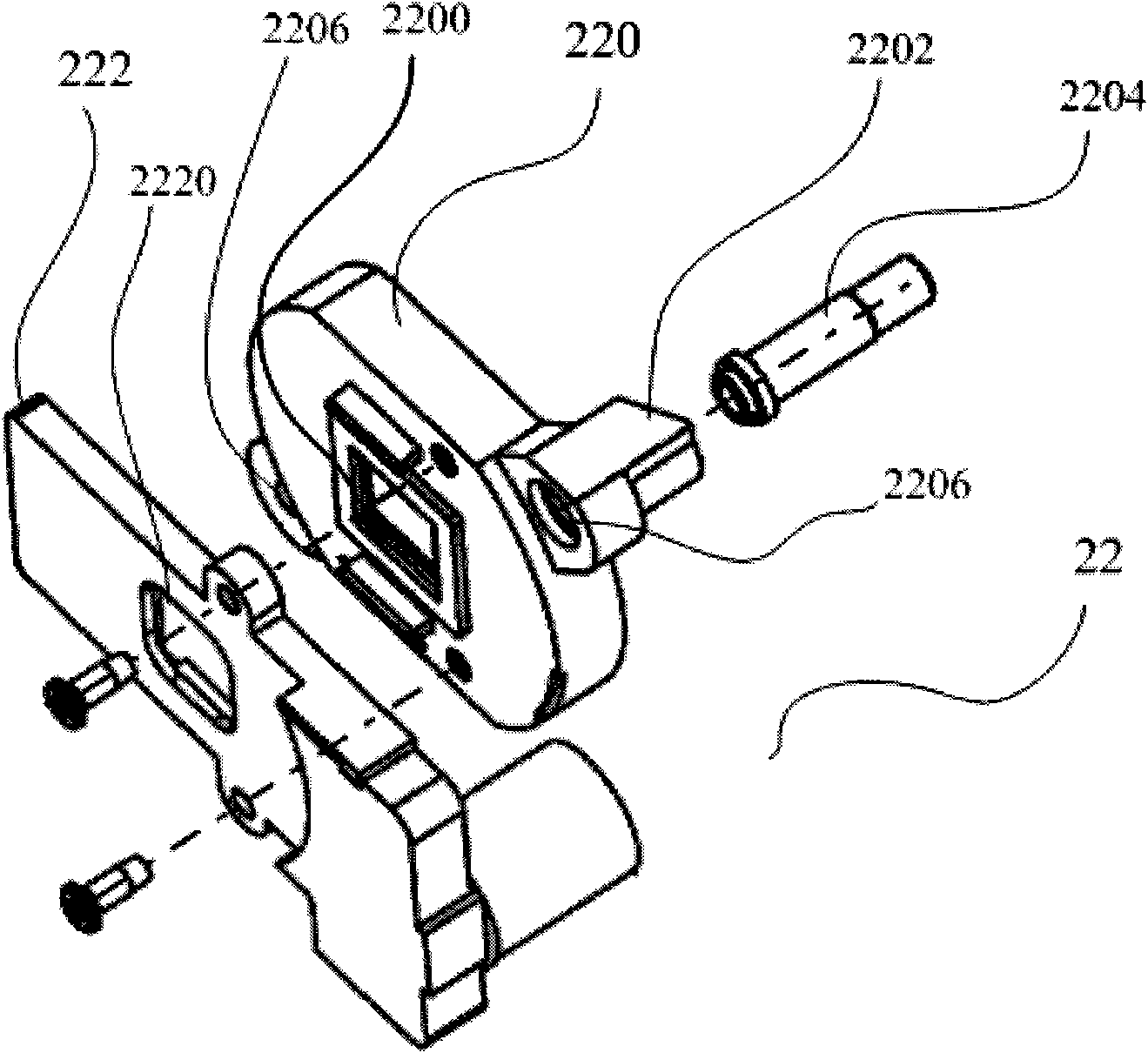
A device for holographic reconstruction of three-dimensional scenes includes optical focusing means which directs sufficiently coherent light from light means to the eyes of at least one observer via a spatial light modulator that is encoded with holographic information. The device has a plurality of illumination units for illuminating the surface of the spatial light modulator (SLM); each unit comprises a focusing element (21 / 22 / 23 or 24), and a light means (LS1 / LS2 / LS3 or LS4) that emits sufficiently coherent light such that each of these illumination units illuminates one separate illuminated region (R1 / R2 / R3 or R4) of the surface, whereby the focusing element and the light means are arranged such that the light emitted by the light means (LS1-LS4) coincides close to or at the observer eyes.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
Three-dimensional imaging device
A new three-dimensional imaging device has been needed to overcome the problems of the prior arts that the used variable focal length lenses that are still slow, have small focal length variation and low focusing efficiency, and requires a complex mechanism to control it. The invented three-dimensional imaging system uses the variable focal length micromirror array lens. Since the micromirror array lens has lots of advantages such as very fast response time, large focal length variation, high optical focusing efficiency, large size aperture, low cost, simple mechanism, and so on, the three-dimensional imaging device can get a real-time three-dimensional image with large depth range and high depth resolution.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Selecting autofocus area in an image
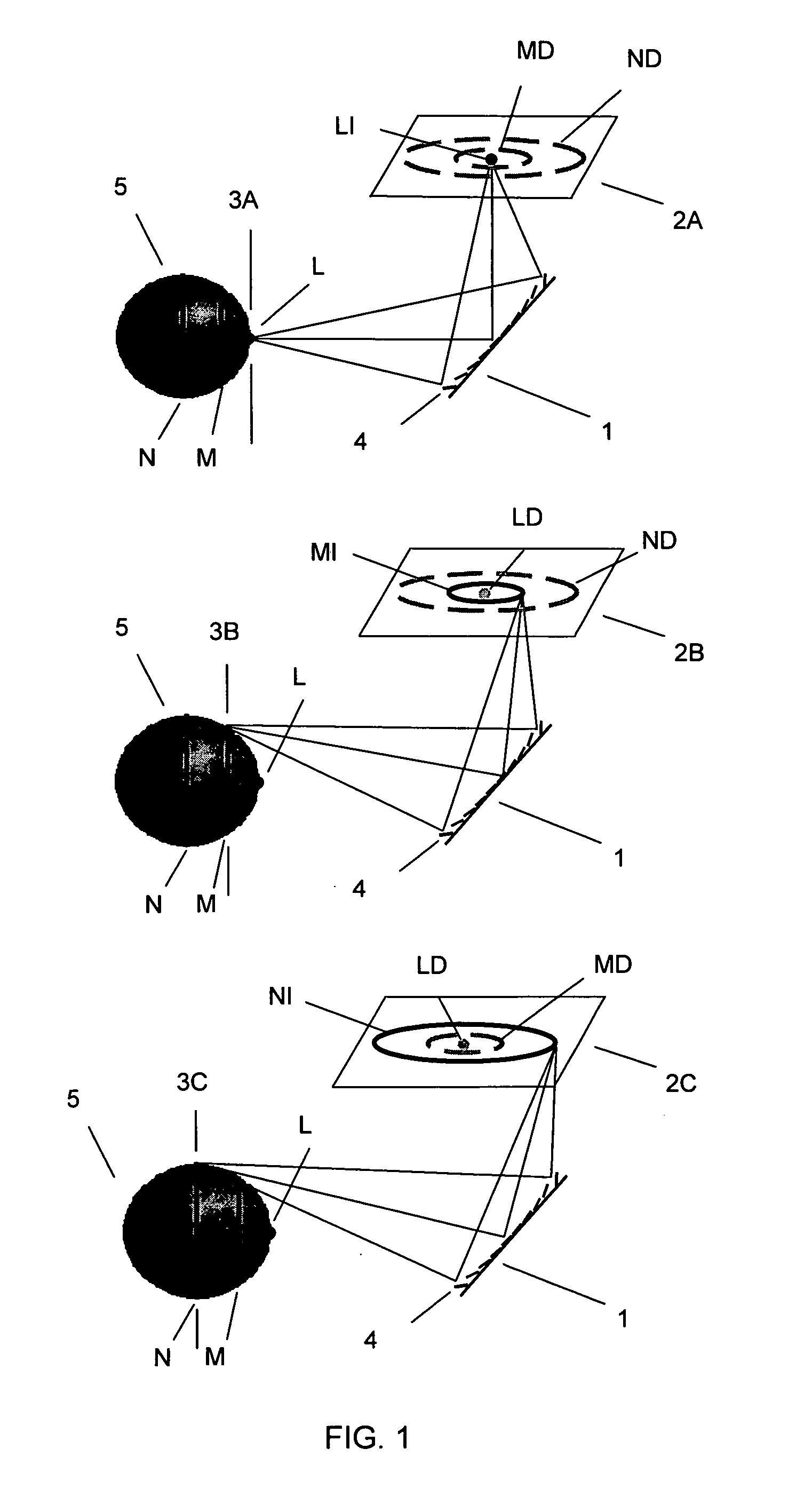
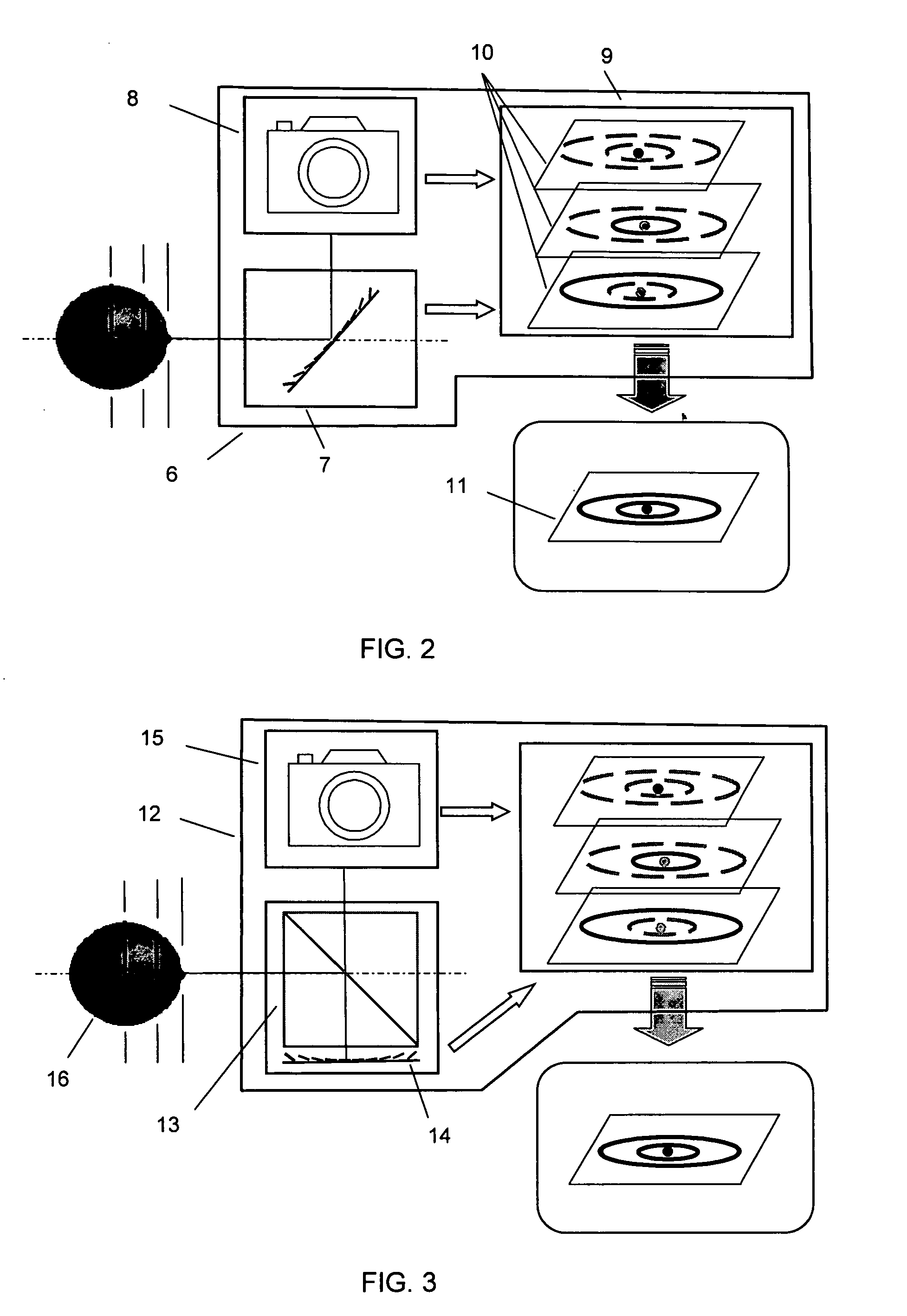
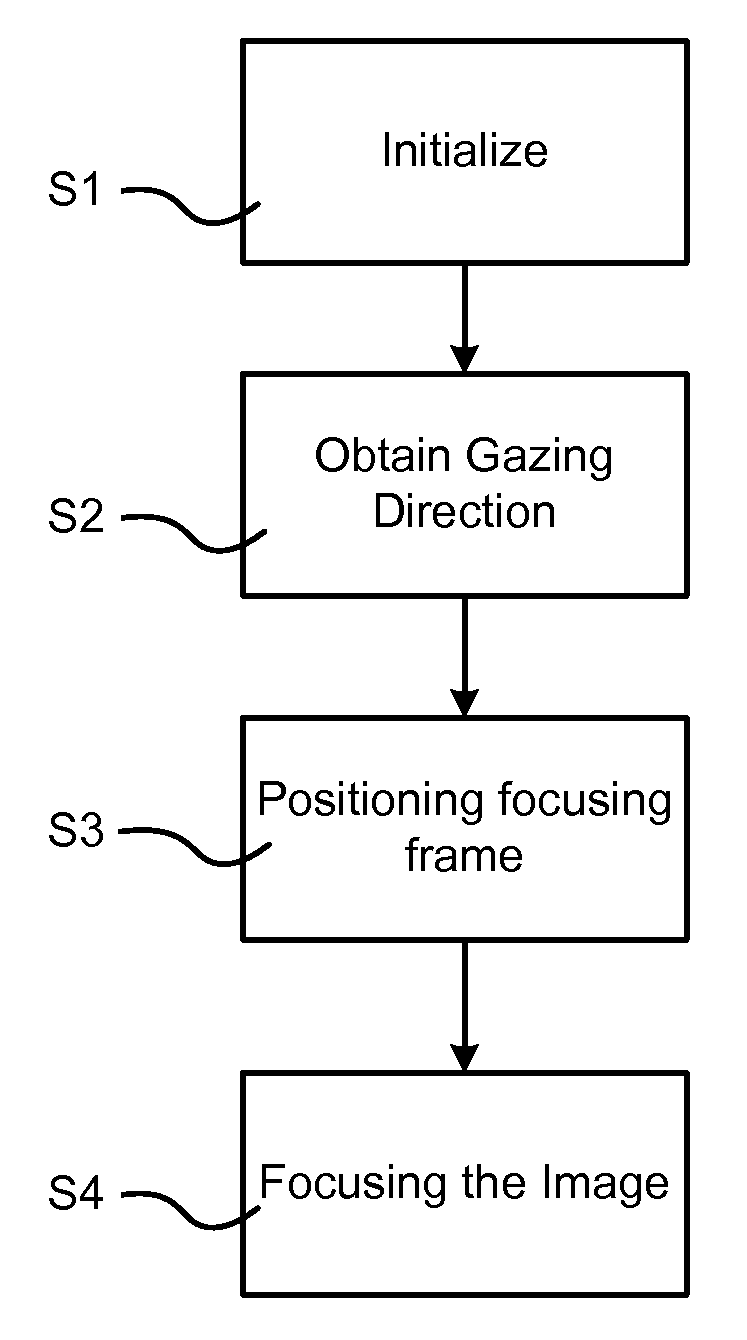
ActiveUS20080080846A1Efficient and flexible procedureLess actionTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementAutofocusGaze directions
A system and method are provided for obtaining a gazing direction of a user of an image-capturing device relative to an image of an object to be captured; identifying an area of the image based on the obtained gazing direction; and performing optical focusing for the identified area using an autofocus arrangement of the image-capturing device.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus and method for curing materials with light radiation
InactiveUS7066733B2Effective lightingEliminate requirementsDental toolsSpannersLength waveHigh pressure
An instrument and method for curing light-curable compounds in the mouth of a patient, the instrument comprising a housing and a plurality of solid state, light-emitting elements on a substrate supported by the housing. The elements form a collective array on the substrate operable for collectively emitting light having wavelengths within a narrow band of wavelengths.An optical focusing device is positioned to intercept the light emitted by the array of elements and includes a non-imaging optical device which is operable for collimating the light from the array into a beam to be directed onto a compound for curing the compound. A disposable sleeve covers the housing and array and may incorporate the optical focusing device. The sleeve is removed and discarded after use to eliminate the need to autoclave the instrument.
Owner:THE KERR
Three-dimensional imaging device
A new three-dimensional imaging device has been needed to overcome the problems of the prior arts that the used variable focal length lenses that are still slow, have small focal length variation and low focusing efficiency, and requires a complex mechanism to control it. The invented three-dimensional imaging system uses the variable focal length micromirror array lens. Since the micromirror array lens has lots of advantages such as very fast response time, large focal length variation, high optical focusing efficiency, large size aperture, low cost, simple mechanism, and so on, the three-dimensional imaging device can get a real-time three-dimensional image with large depth range and high depth resolution.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
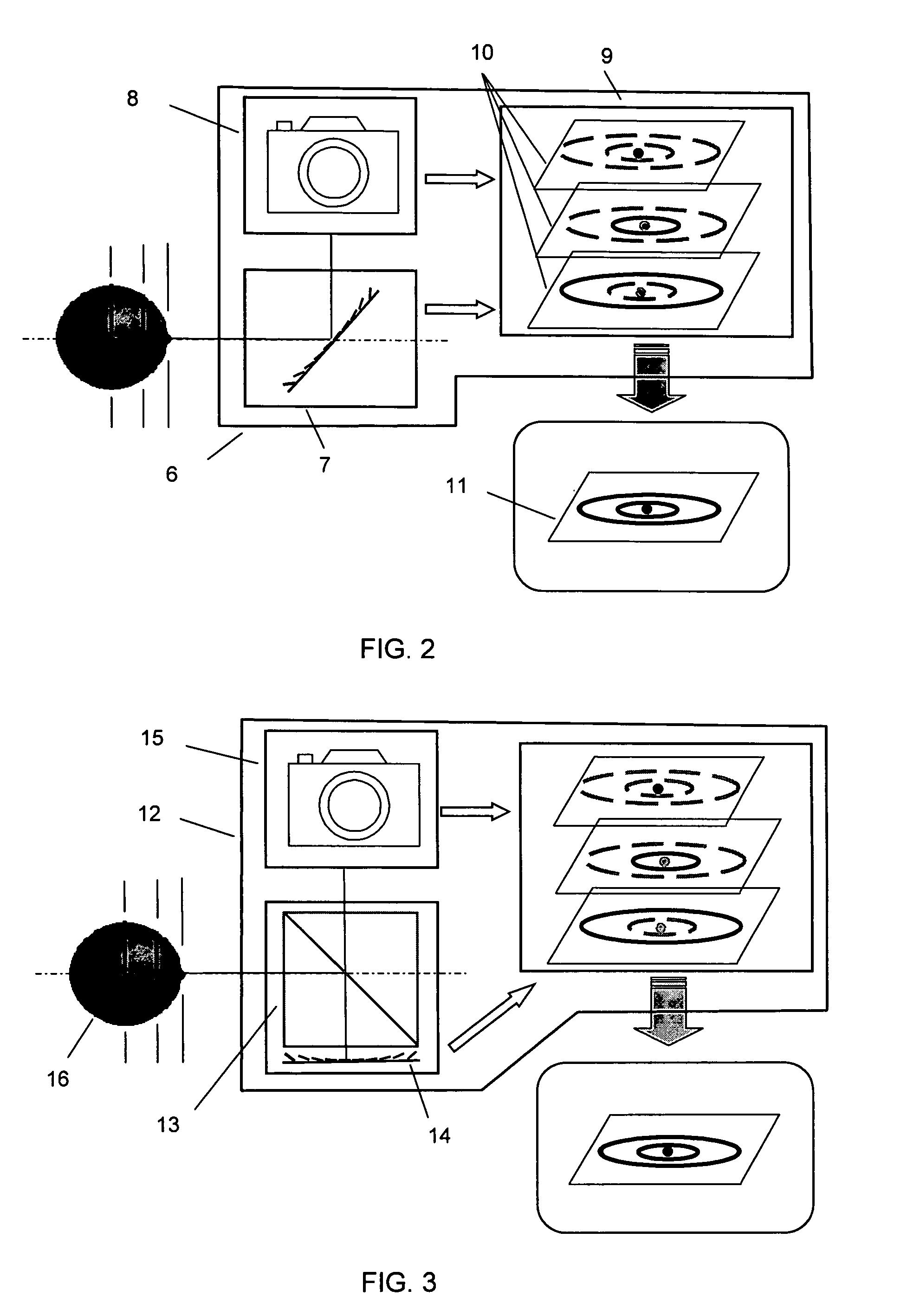
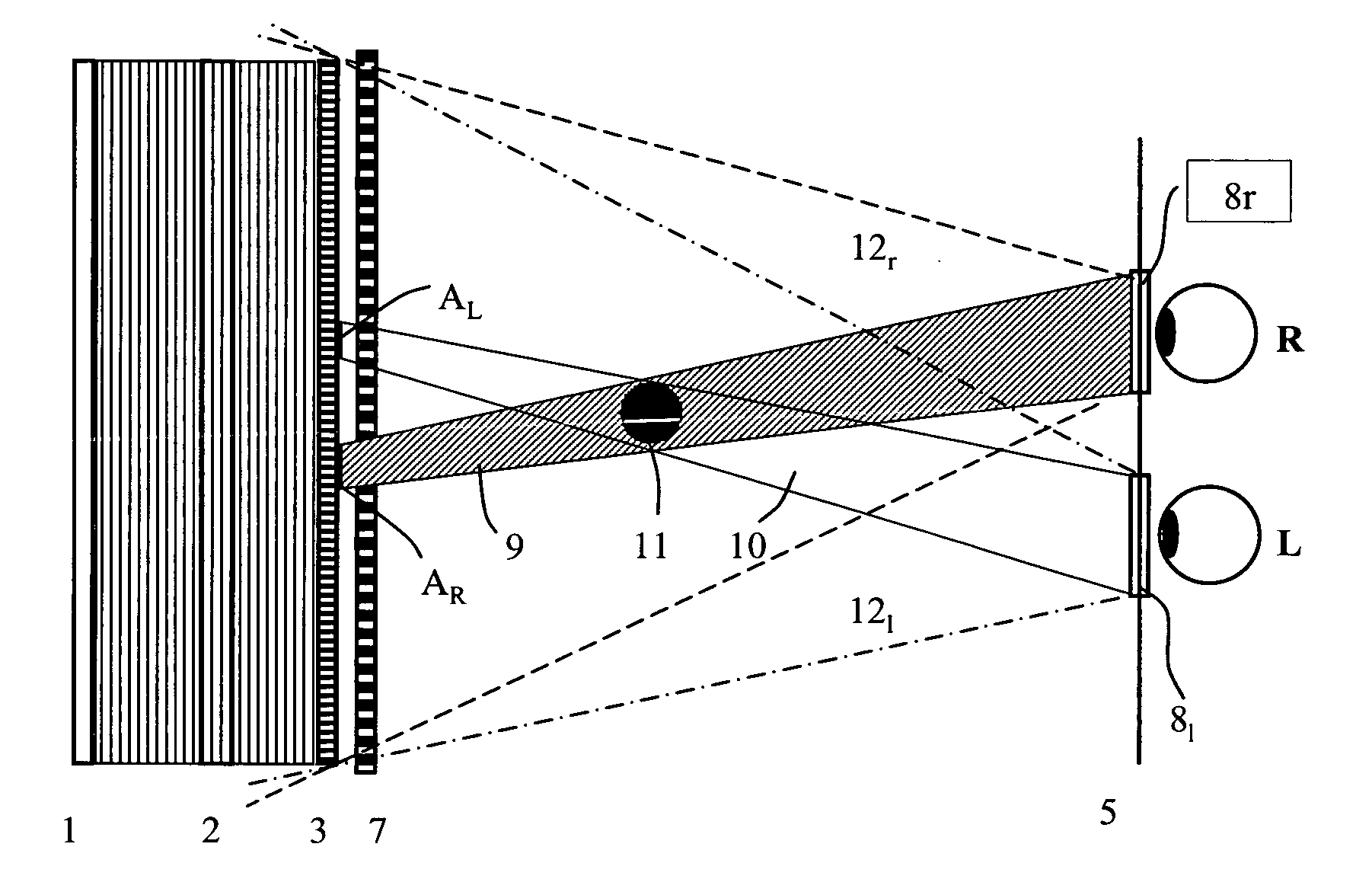
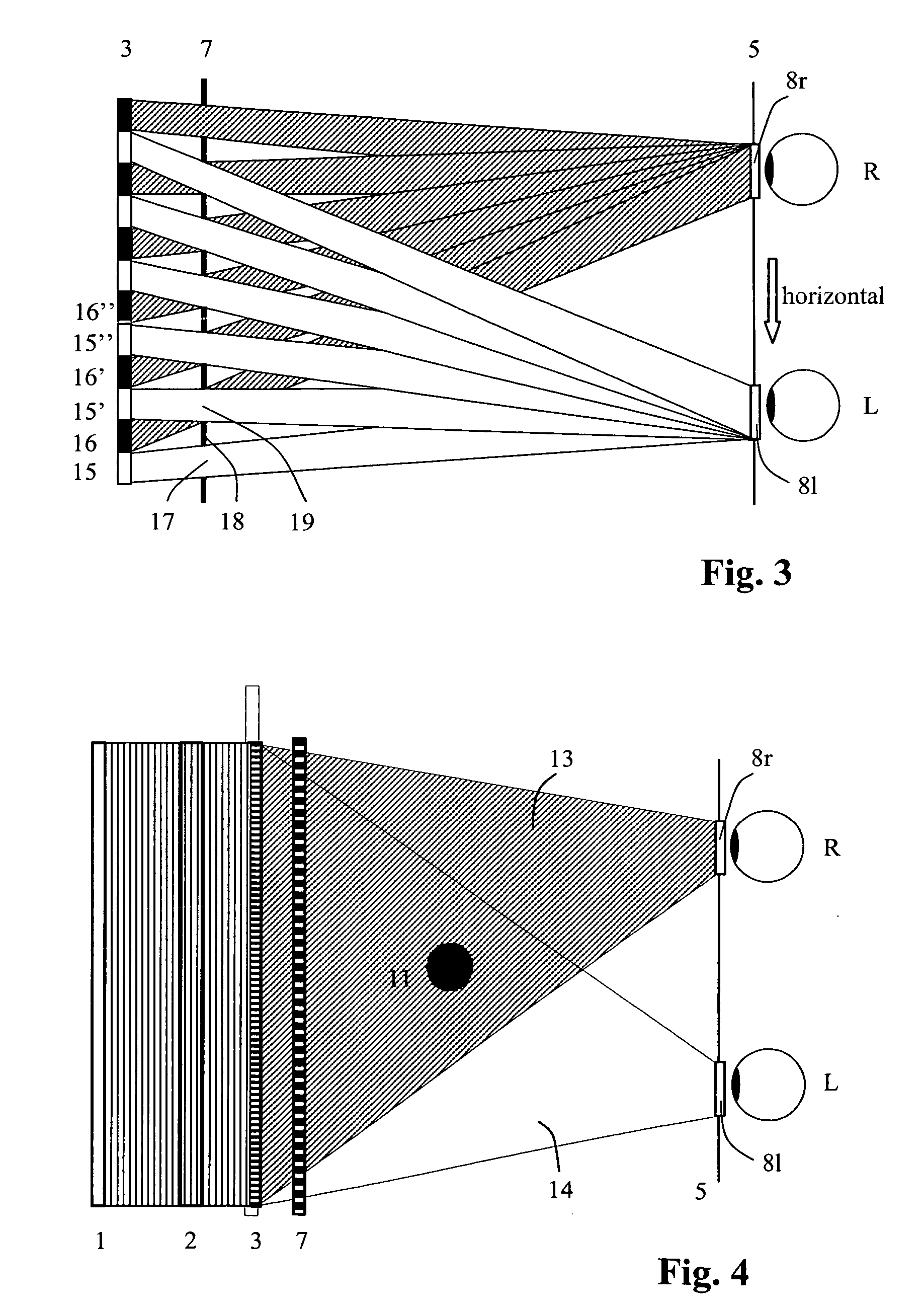
Method and device for encoding and reconstructing computer-generated video holograms
ActiveUS20060050340A1Lower refresh rateAvoids costly heavyHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsLiquid-crystal displayImage resolution
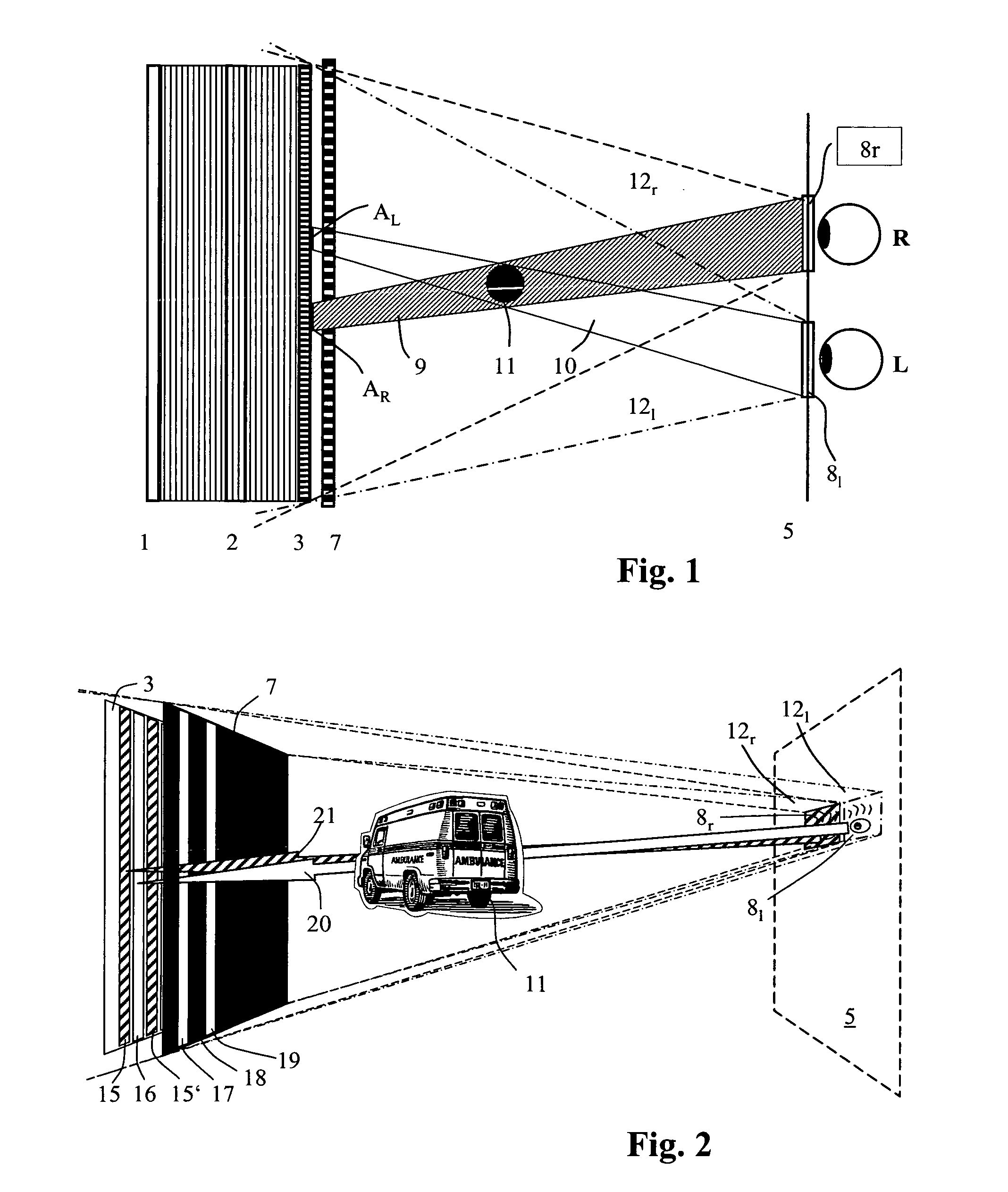
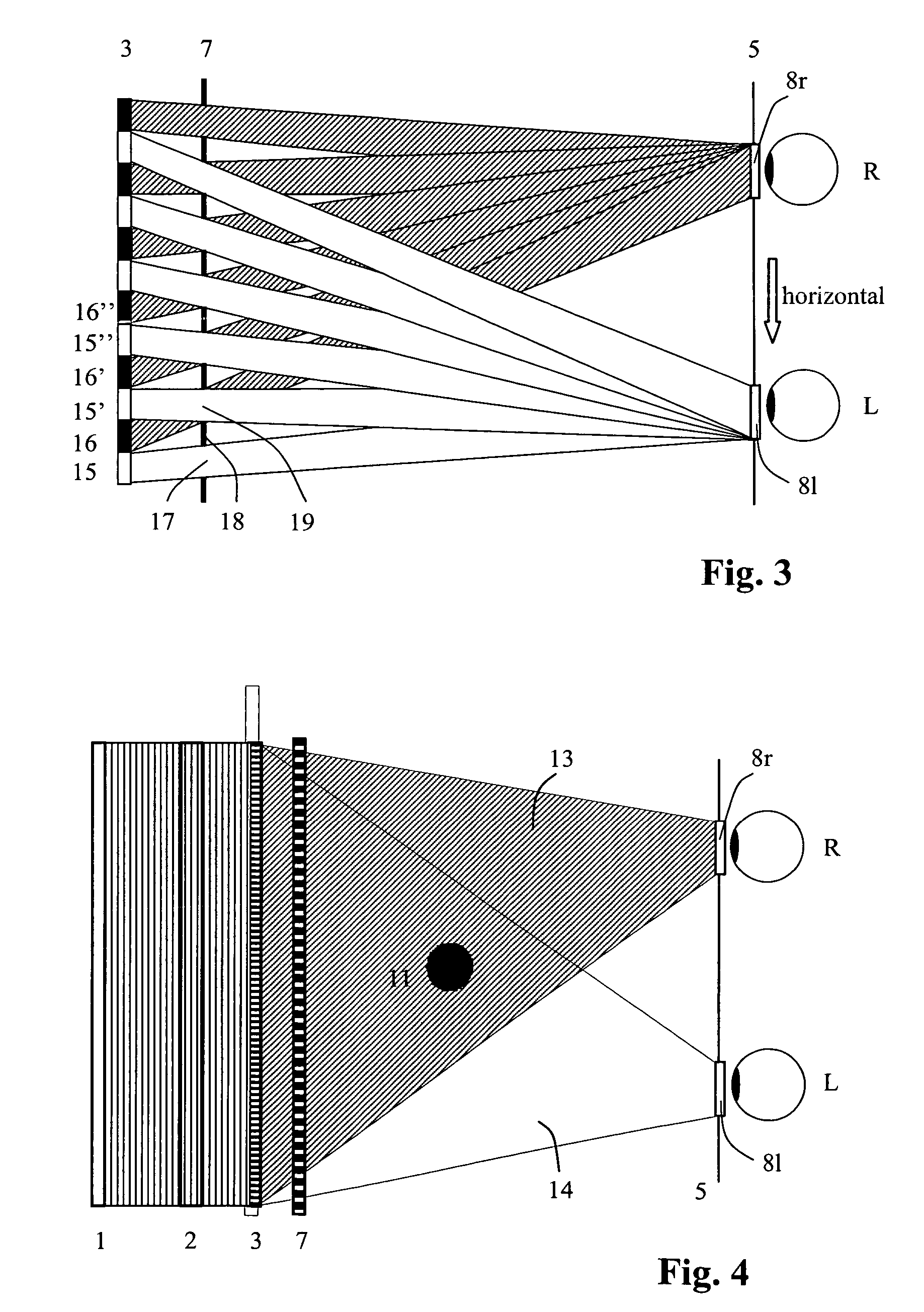
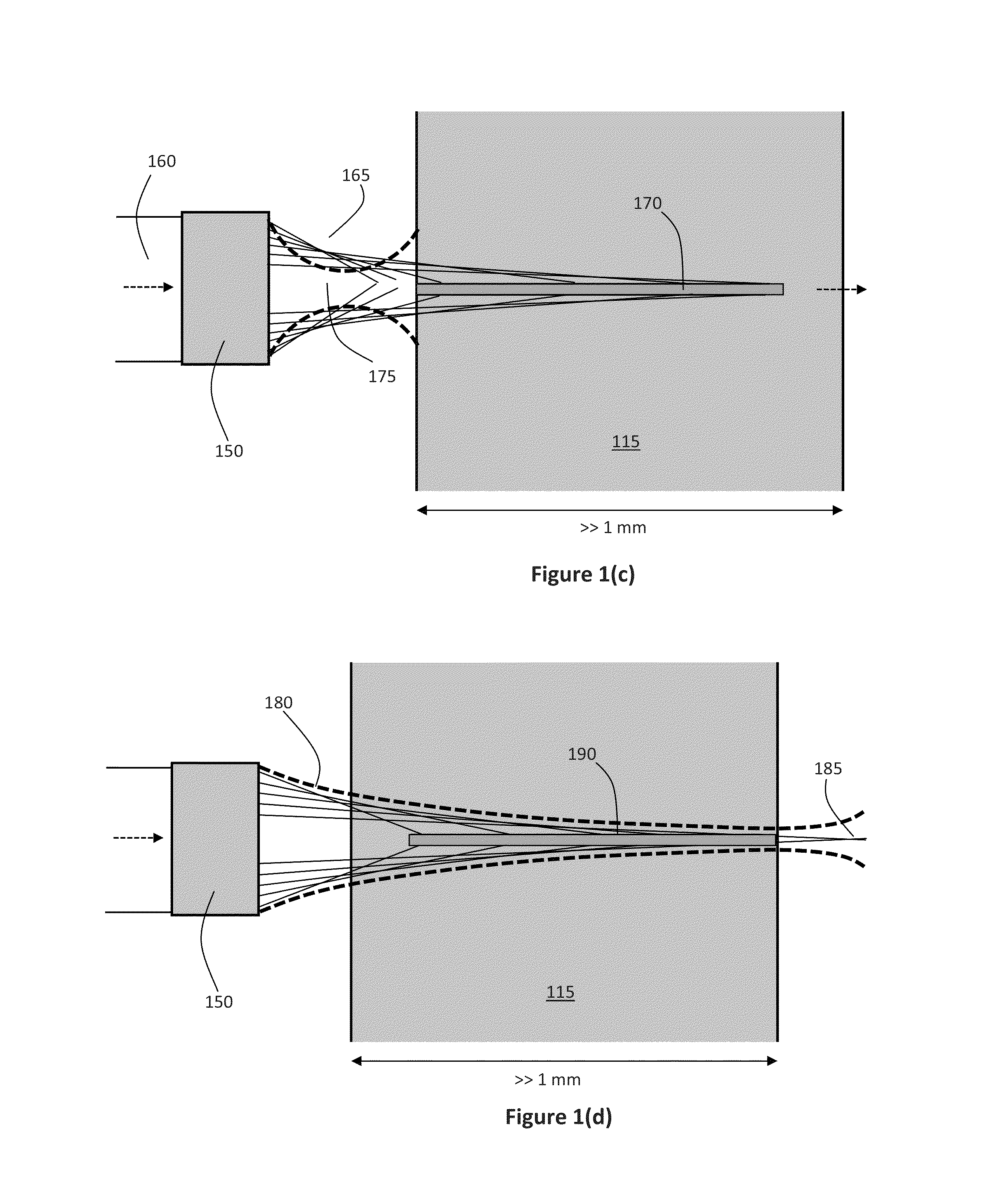
A method and a device for encoding and reconstructing computer-generated video holograms using a conventional LC display: it provides holographic reconstruction of three-dimensional scenes using electronically controllable pixel in a holographic array (3) with a conventional resolution, and is reasonably free from flickering and cross-talk. Reconstruction is in real time, and for both eyes at the same time, over a large viewing zone. The method takes advantage of an optical focusing means (2) in order to image vertically coherent light emitted by a line light source (1) into viewing windows (8R, 8L) after modulation by the pixel array (3). The holographic reconstruction (11) of the scene is rendered visible from viewing windows (8R, 8L) for both eyes of an observer by way of diffraction at the pixels. According to the invention, the controllable pixels are disposed in vertical pixel columns (15, 16), which encode separate holograms of the same scene for each of the viewer's eyes (R, L), where said holograms are one-dimensional in the vertical direction and horizontally interleaved. An image separation means (7) with separating elements arranged parallel to the pixel columns reveals the respective pixel columns (15, 15′ or 16, 16′) for one eye and covers them for the other eye.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
Micromirror arry lens with optical surface profiles
A Micromirror Array Lens comprises a plurality of micromirrors arranged on a flat or a curved surface to reflect incident light. Each micromirror in the Micromirror Array Lens is configured to have at least one motion. The Micromirror Array Lens forms at least one optical surface profile reproducing free surfaces by using the motions of the micromirrors. The free surface can be any two or three-dimensional continuous or discrete reflective surface. The Micromirror Array Lens having the corresponding optical surface profile provides optical focusing properties substantially identical to those of the free surface. The Micromirror Array Lens can forms various optical elements such as a variable focal length lens, a fixed focal length lens, an array of optical switches, a beam steerer, a zone plate, a shutter, an iris, a multiple focal length lens, other multi-function optical elements, and so on.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Heatsink for concentrating or focusing optical/electrical energy conversion systems
InactiveUS20070089777A1Dissipate energyPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationThermal energyEngineering
The present invention relates to heatsink technology for helping to dissipate thermal energy generated or absorbed with respect to optical focusing and / or concentrating systems such as projectors and spotlights as well as trough or dish reflectors. More specifically, the present invention relates to heat sink technology for helping to dissipate thermal energy generated by or absorbed in the proximity of the focus of optical concentrating elements of solar concentrator modules, wherein the heat sink includes a plurality of heat dissipating fins.
Owner:SOLIANT ENERGY INC
Laser micro/nano processing system and method
ActiveCN102000912AHigh processing resolutionPrecise Control of ResolutionNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsLaser lightMobile station
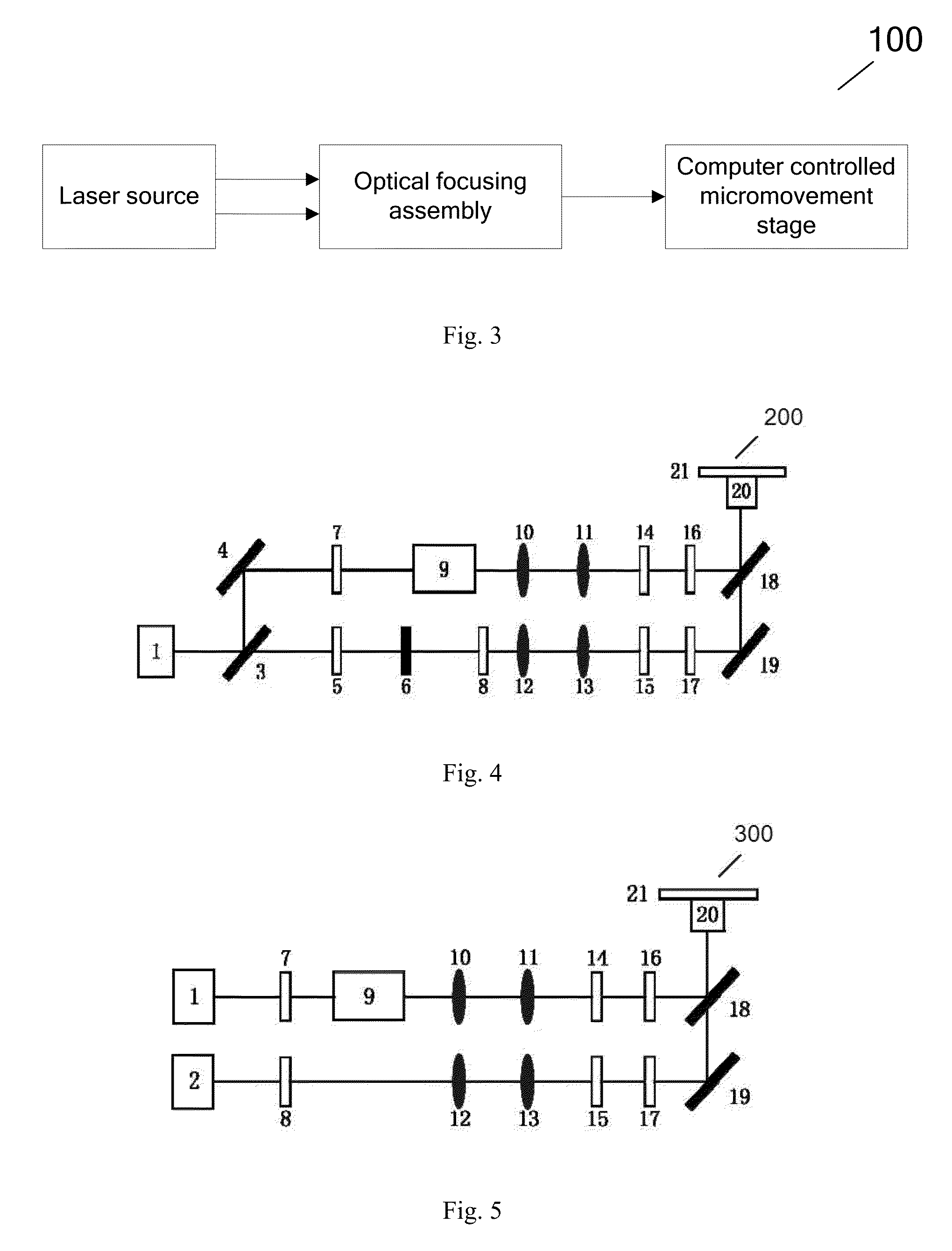
The invention provides a laser micro / nano processing system and a laser micro / nano processing method. The system of the invention comprises a laser light source, an optical retardation component, an optical focusing component and a computer-controlled micro mobile station, wherein the laser light source is used for providing a first laser beam having a first wavelength and a second laser beam having a second wavelength, the pulse widths of the first laser beam and the second laser beam range from femtosecond to nanosecond and the first wavelength is different from the second wavelength; the optical retardation component is used for regulating the optical path of the first laser beam or the second laser beam so that the difference between the arrival times of the first laser beam and the second laser beam at a focus is not greater than the level life time for a photochromic material to be processed to be excited to an excited state; the optical focusing component is used for focusing the first laser beam and the second laser beam onto the same focus; and the computer-controlled micro mobile station is used for regulating a photochromic material on the computer-controlled micro mobile station to the focus.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus and method for curing materials with light radiation
InactiveUS20050003322A1Effective lightingEliminate requirementsDental toolsSpannersLight beamCompound (substance)
An instrument and method for curing light-curable compounds in the mouth of a patient, the instrument comprising a housing and a plurality of solid state, light-emitting elements on a substrate supported by the housing. The elements form a collective array on the substrate operable for collectively emitting light having wavelengths within a narrow band of wavelengths. An optical focusing device is positioned to intercept the light emitted by the array of elements and includes a non-imaging optical device which is operable for collimating the light from the array into a beam to be directed onto a compound for curing the compound. A disposable sleeve covers the housing and array and may incorporate the optical focusing device. The sleeve is removed and discarded after use to eliminate the need to autoclave the instrument.
Owner:THE KERR
System for performing laser filamentation within transparent materials
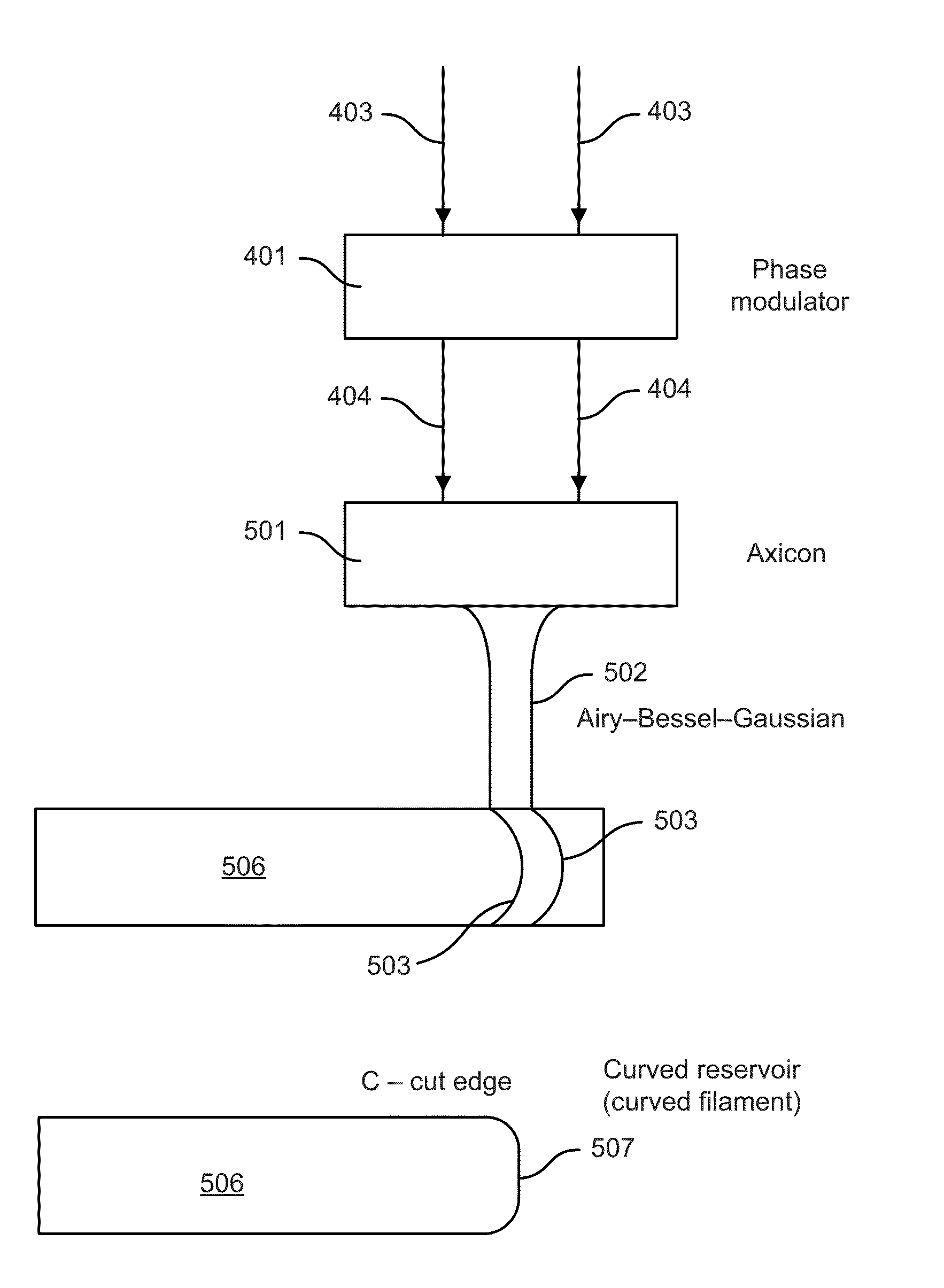
InactiveUS20150034613A1Promote formationEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGlass severing apparatusFilamentationLight beam
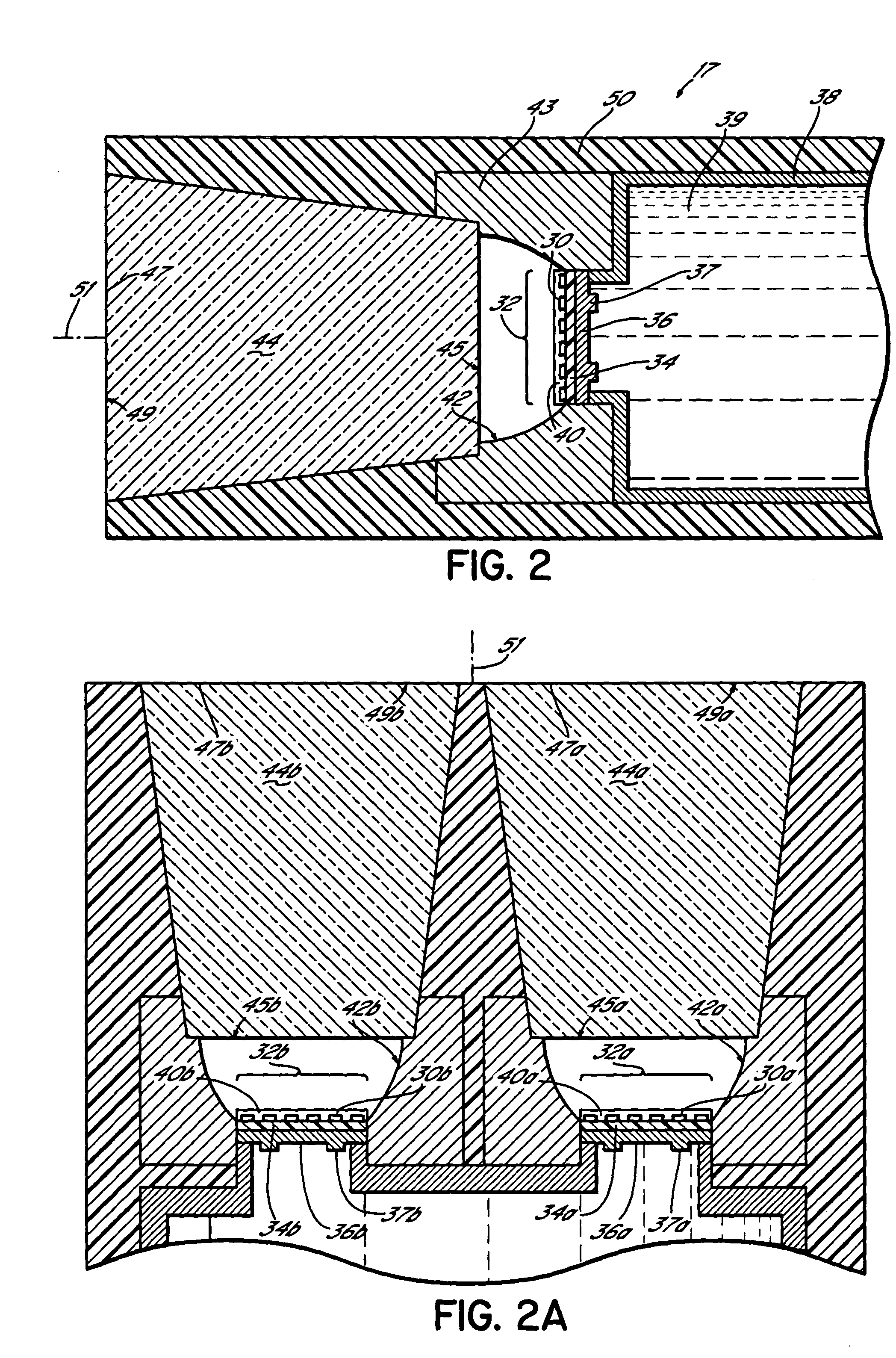
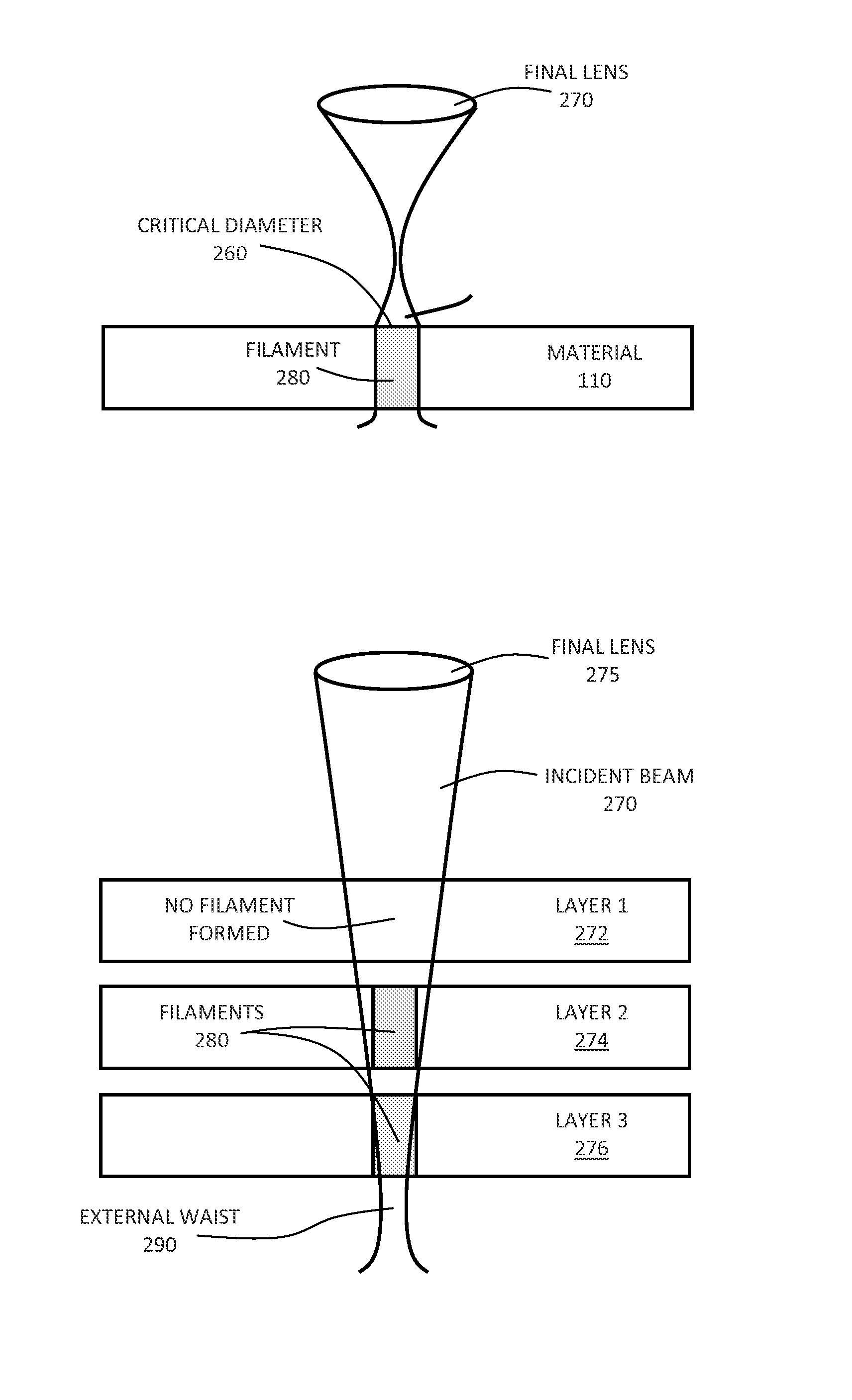
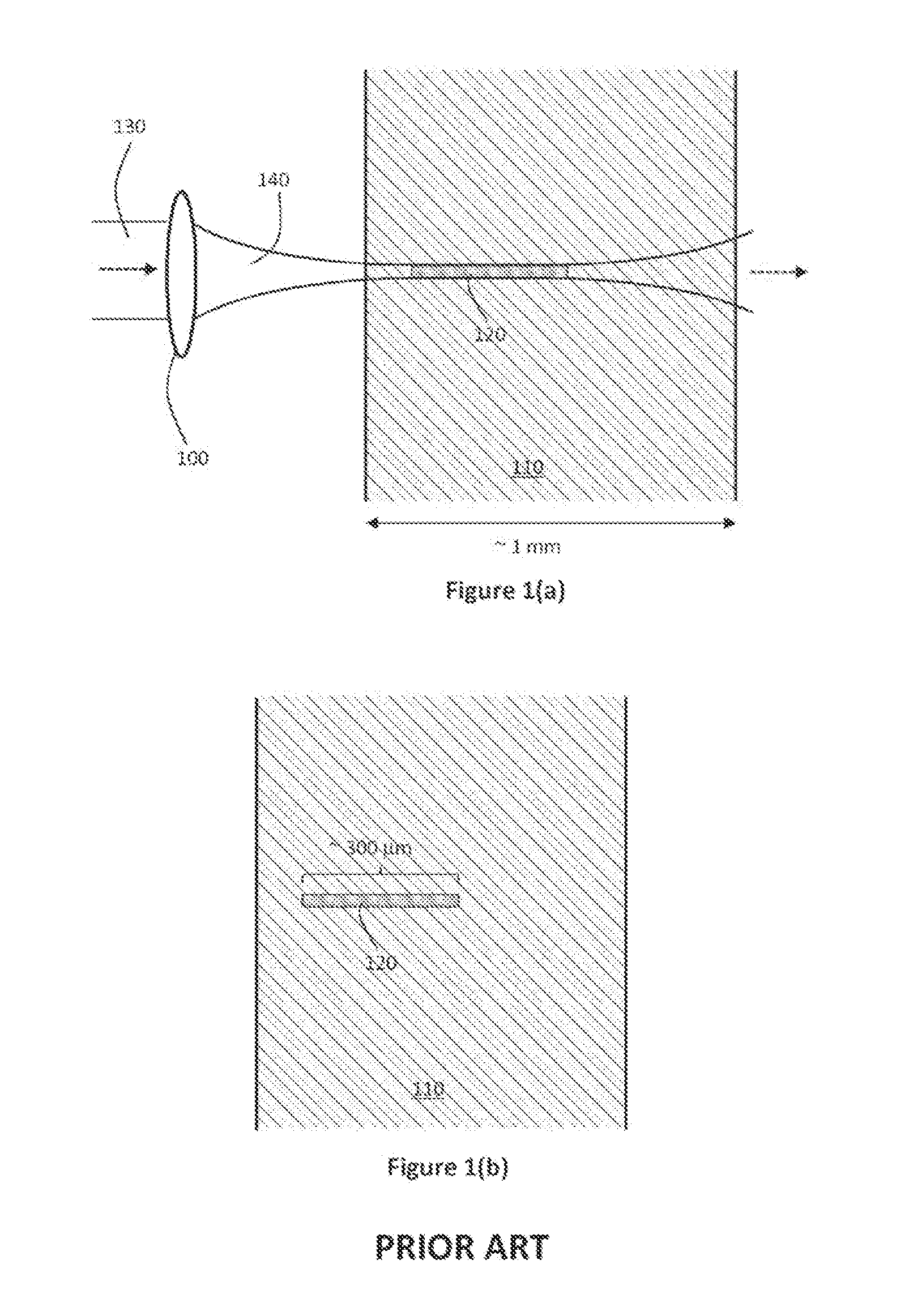
Systems and methods are described for forming continuous laser filaments in transparent materials. A burst of ultrafast laser pulses is focused such that a beam waist is formed external to the material being processed without forming an external plasma channel, while a sufficient energy density is formed within an extended region within the material to support the formation of a continuous filament, without causing optical breakdown within the material. Filaments formed according to this method may exhibit lengths exceeding up to 10 mm. In some embodiments, an aberrated optical focusing element is employed to produce an external beam waist while producing distributed focusing of the incident beam within the material. Various systems are described that facilitate the formation of filament arrays within transparent substrates for cleaving / singulation and / or marking. Optical monitoring of the filaments may be employed to provide feedback to facilitate active control of the process.
Owner:ROFIN SINAR TECH
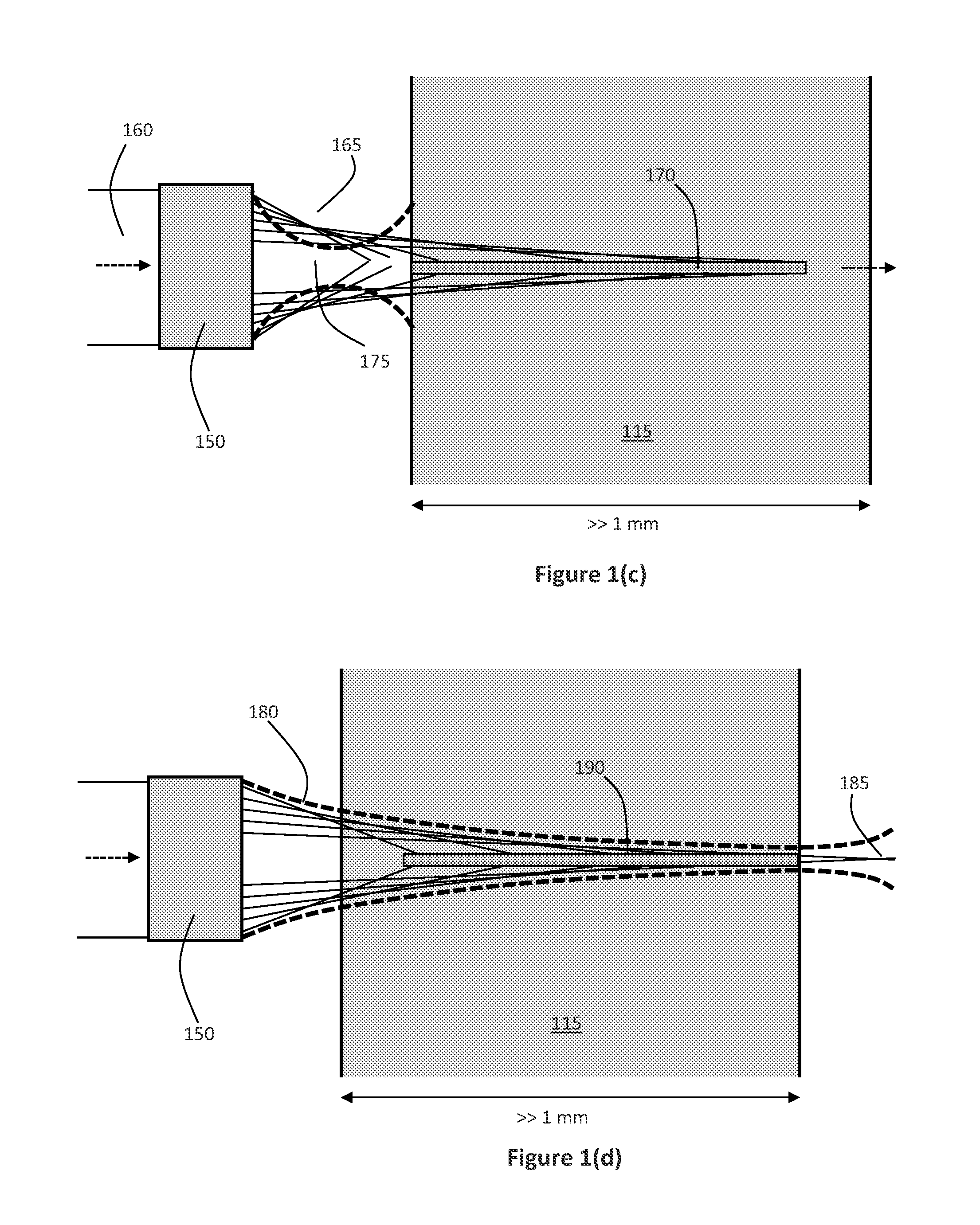
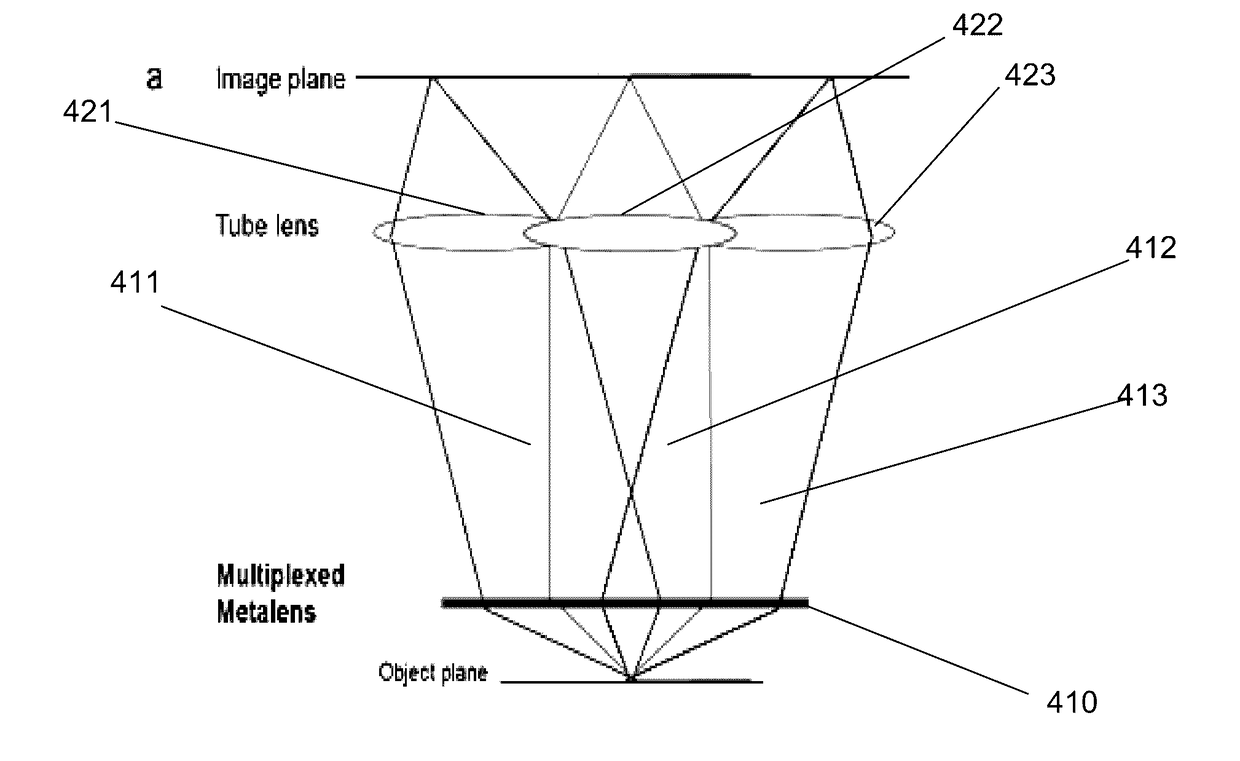
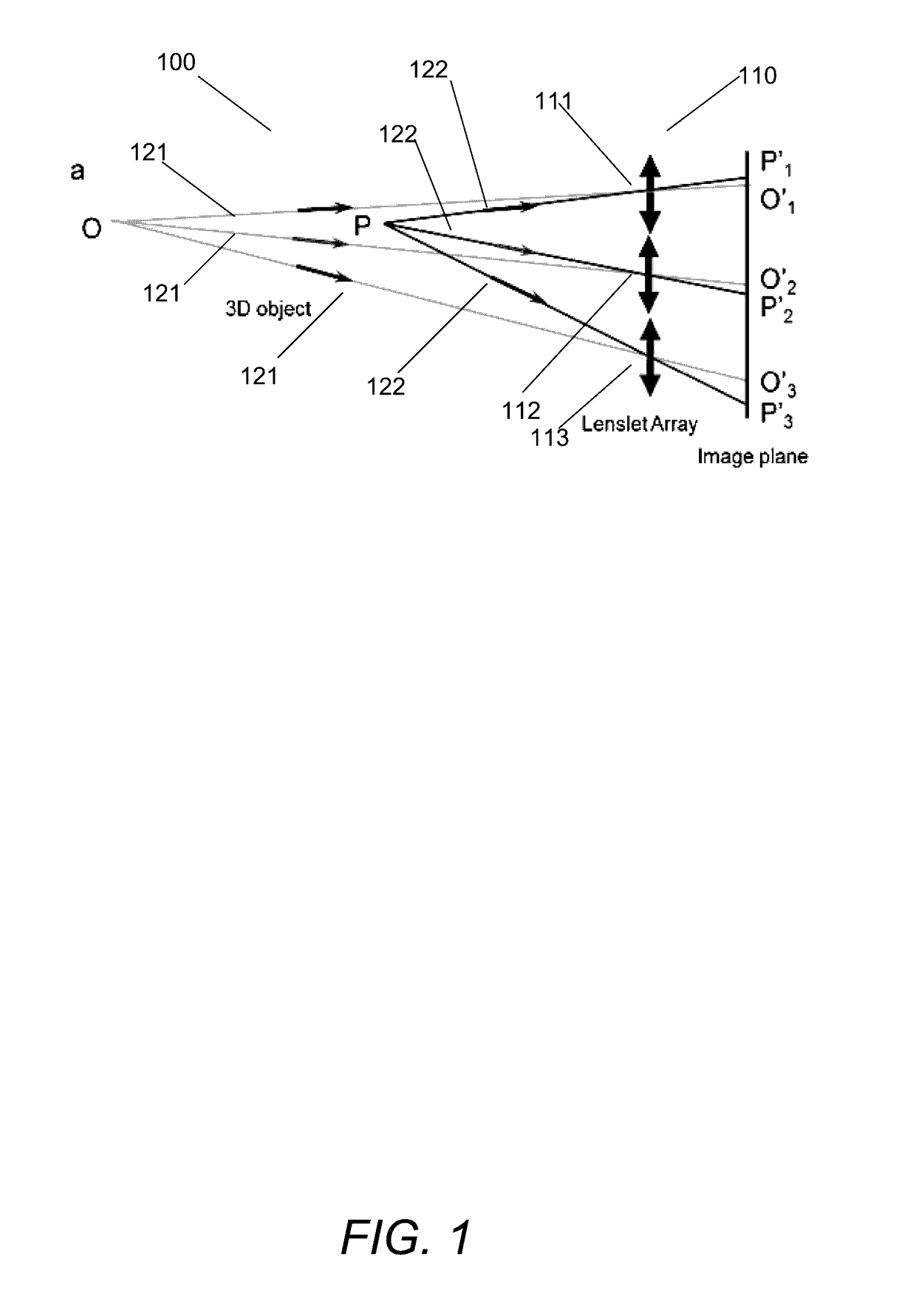
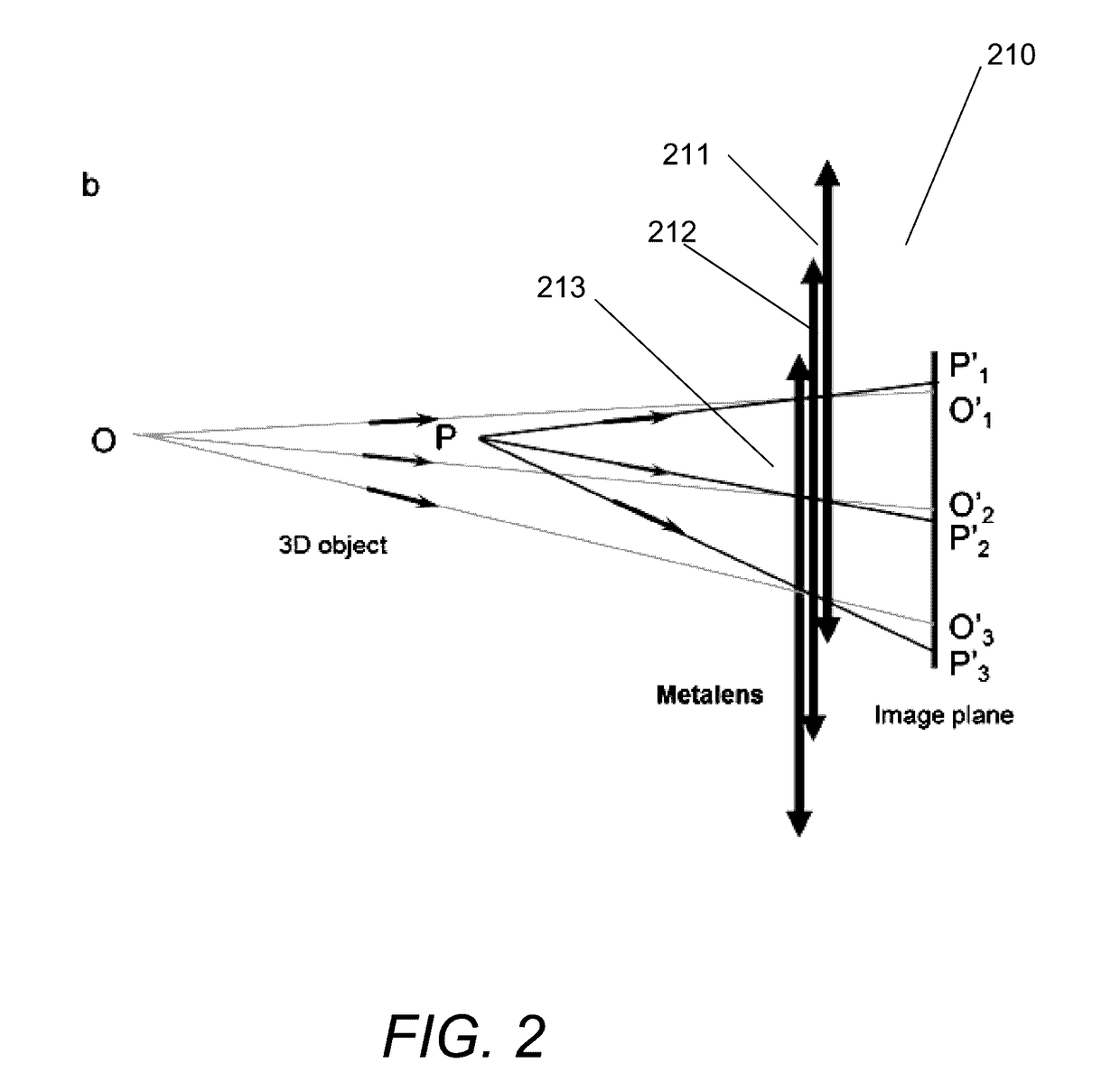
Light-field Imaging Using a Gradient Metasurface Optical Element
Embodiments of 3D imaging systems that use a multifunctional, nano structured metalens to replace the conventional microlens array in light field imaging are disclosed. The optical focusing properties of the metalenses provided by gradient metasurface optical elements. The gradient metasurfaces allow the properties of the elements of the metalens array to be changed by tuning the gradient metasurfaces.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and apparatus for performing laser curved filamentation within transparent materials
ActiveUS20160016257A1Improve bending strengthInhibition formationGlass drawing apparatusGlass transportation apparatusFilamentationPlasma channel
Systems and methods are described for forming continuous curved laser filaments in transparent materials. The filaments are preferably curved and C-shaped. Filaments may employ other curved profiles (shapes). A burst of ultrafast laser pulses is focused such that a beam waist is formed external to the material being processed without forming an external plasma channel, while a sufficient energy density is formed within an extended region within the material to support the formation of a continuous filament, without causing optical breakdown within the material. Filaments formed according to this method may exhibit lengths in the range of 100 μm-10 mm. An aberrated optical focusing element is employed to produce an external beam waist while producing distributed focusing of the incident beam within the material. Optical monitoring of the filaments may be employed to provide feedback to facilitate active control of the process.
Owner:ROFIN SINAR TECH
Method for encoding video holograms for holographically reconstructing a scene
ActiveUS7400431B2Lower refresh rateAvoids costly heavyHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsImage resolutionDisplay device
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
Optical packet header identifier, optical router incorporating the same therein, and optical routing method using the router
InactiveUS6892001B2Simple configurationReduce power consumptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsGratingOptical packet
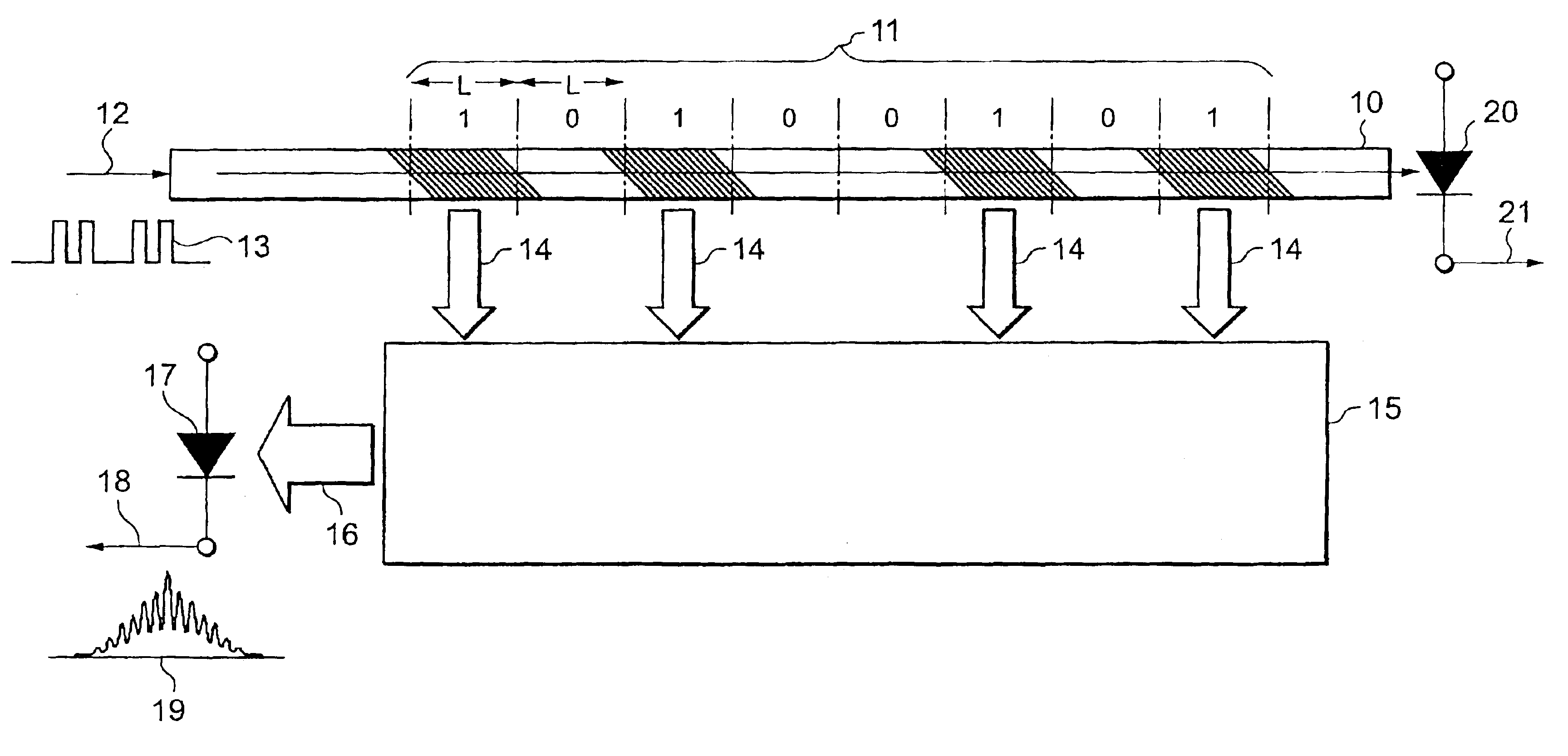
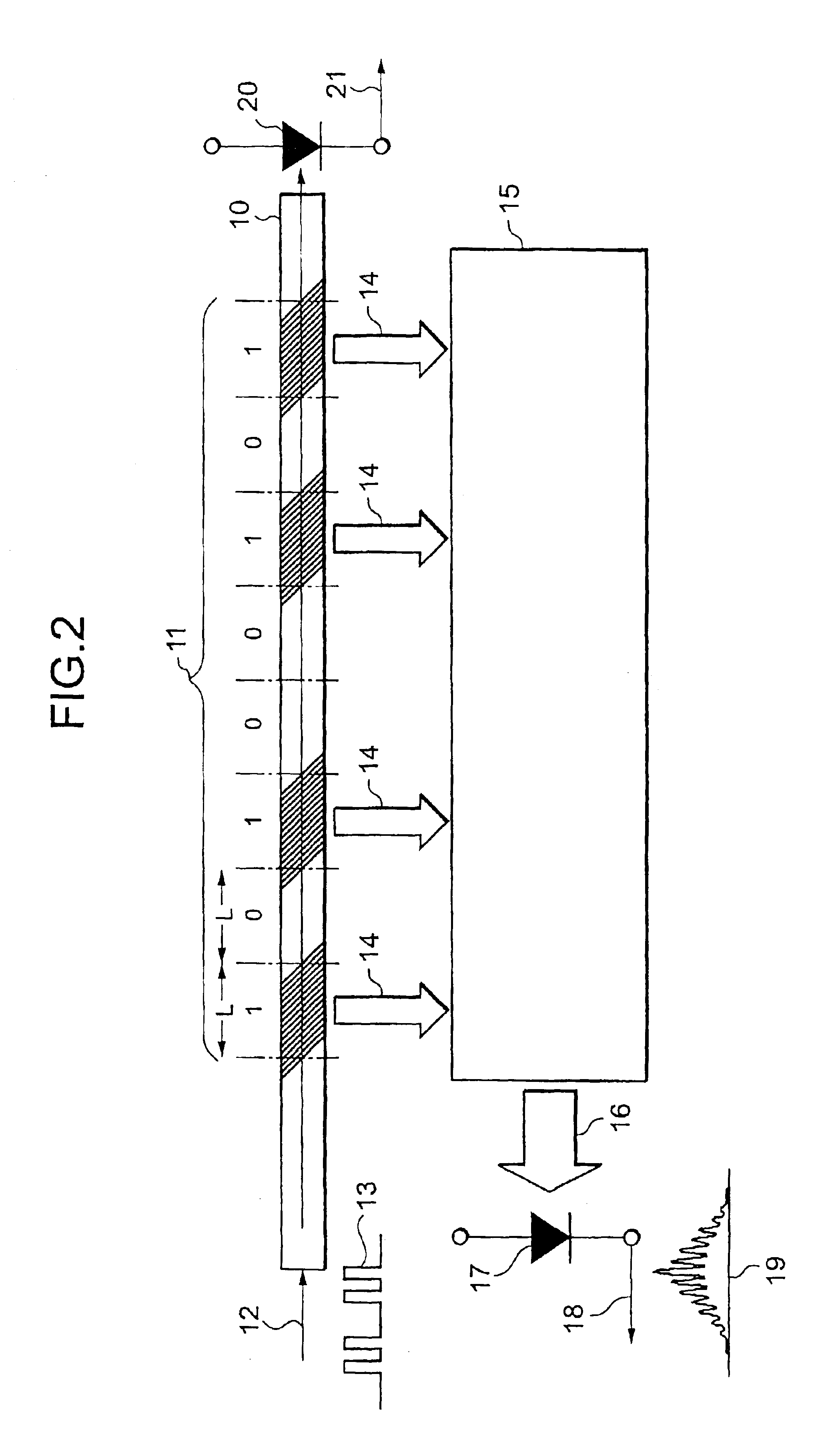
An optical packet header identifier having a simplified configuration and being superior in reliability, stability, and economical efficiency, an optical router incorporating the identifier therein, and a routing method using the optical router are provided. The optical packet header identifier includes an optical waveguide, optical focusing elements, and a photo receiver. Tilted gratings for diffracting an incident optical beam and emitting the beams as diffracted optical beams to the outside of the waveguide are formed within the optical waveguide. The tilted gratings are not formed uniformly in a longitudinal direction of a core of the optical waveguide, but are arranged at intervals. The length of a portion containing a set of gratings and the length of a portion containing no gratings can be defined in increments of length “L”. “L” equals to the spatial length which 1 bit in an optical signal occupies.
Owner:LASERFRONT TECH
Column simultaneously focusing a partilce beam and an optical beam
InactiveUS7045791B2Reducing output electrode aberrationThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersParticle beamComputational physics
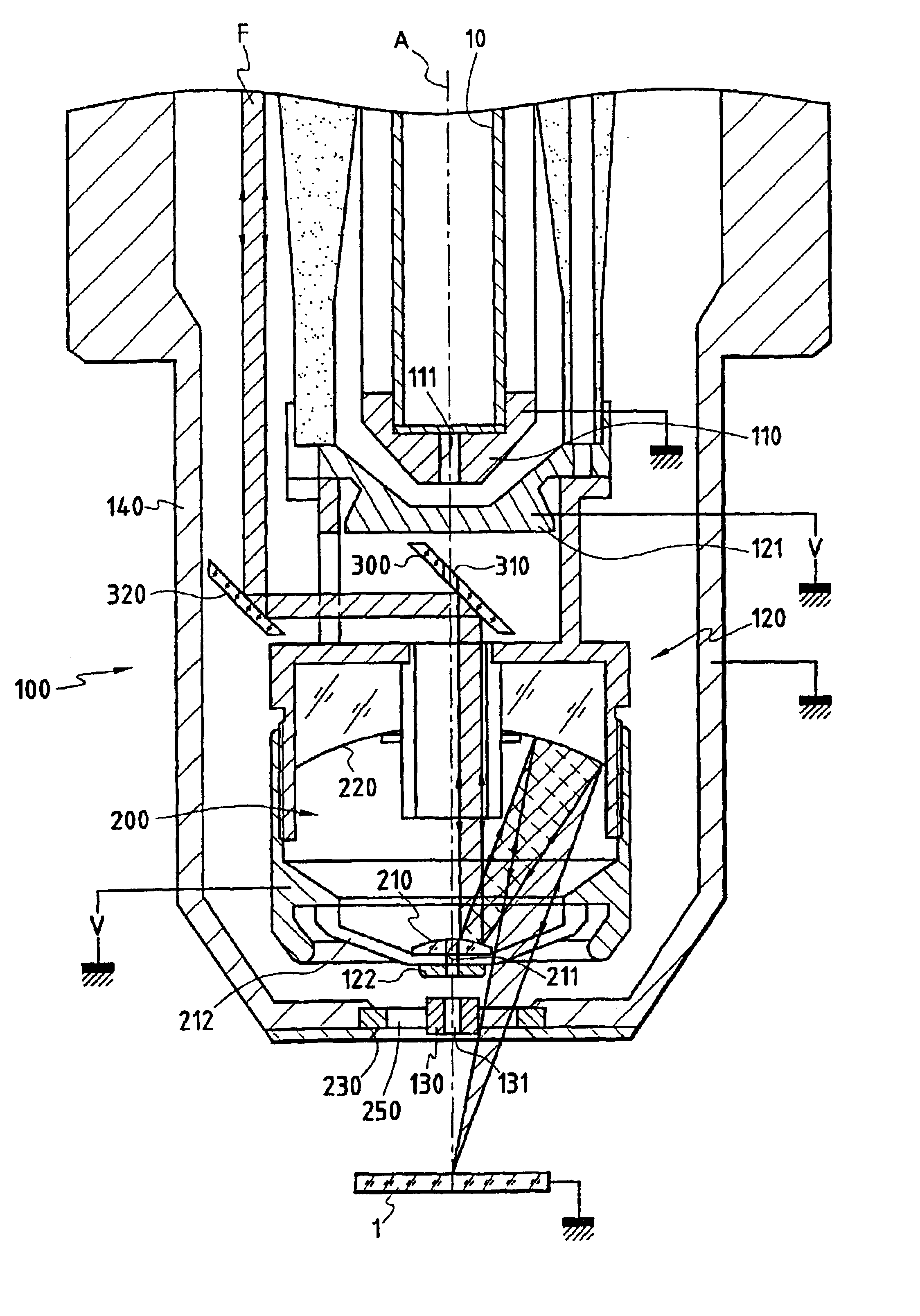
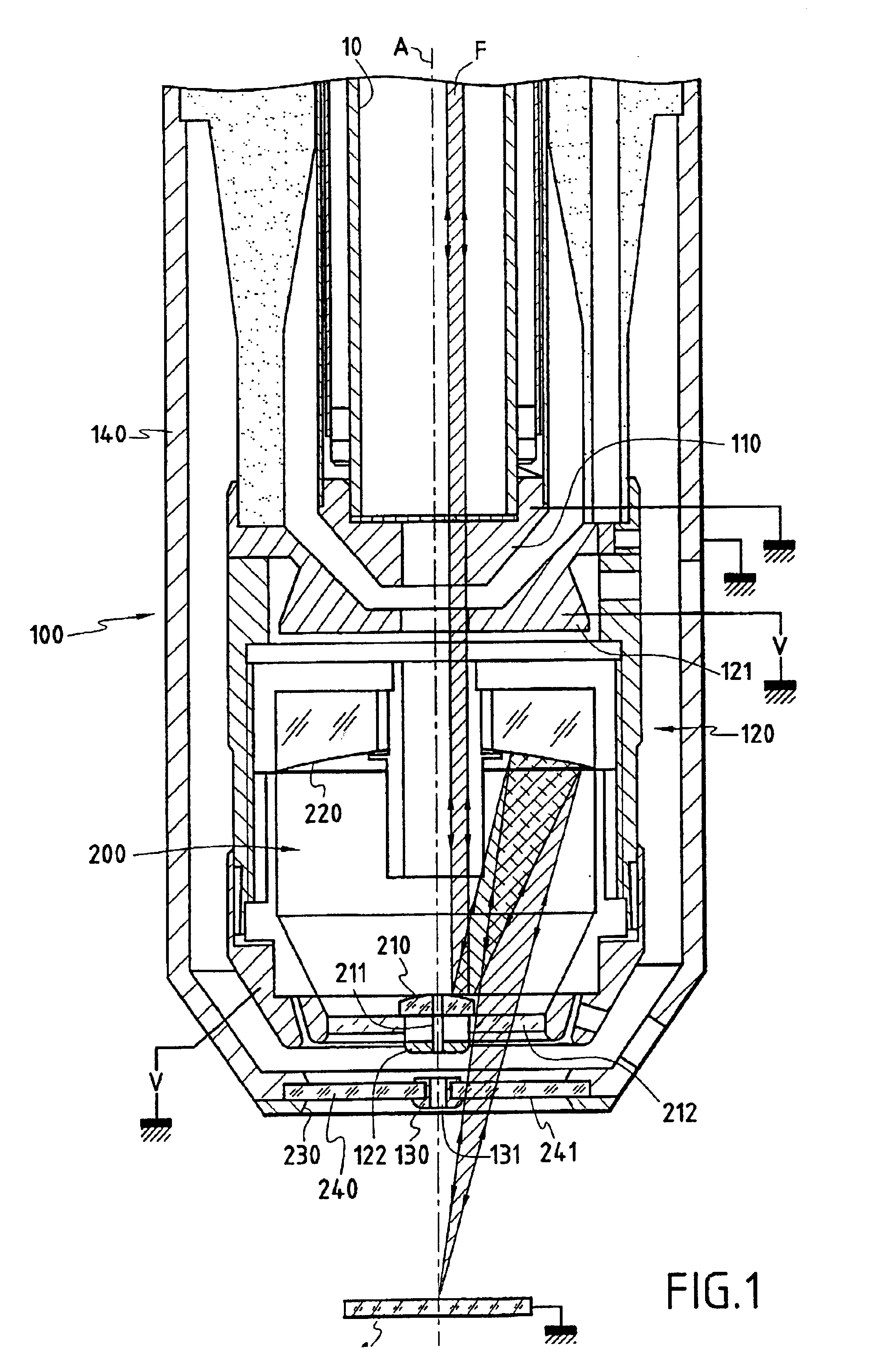
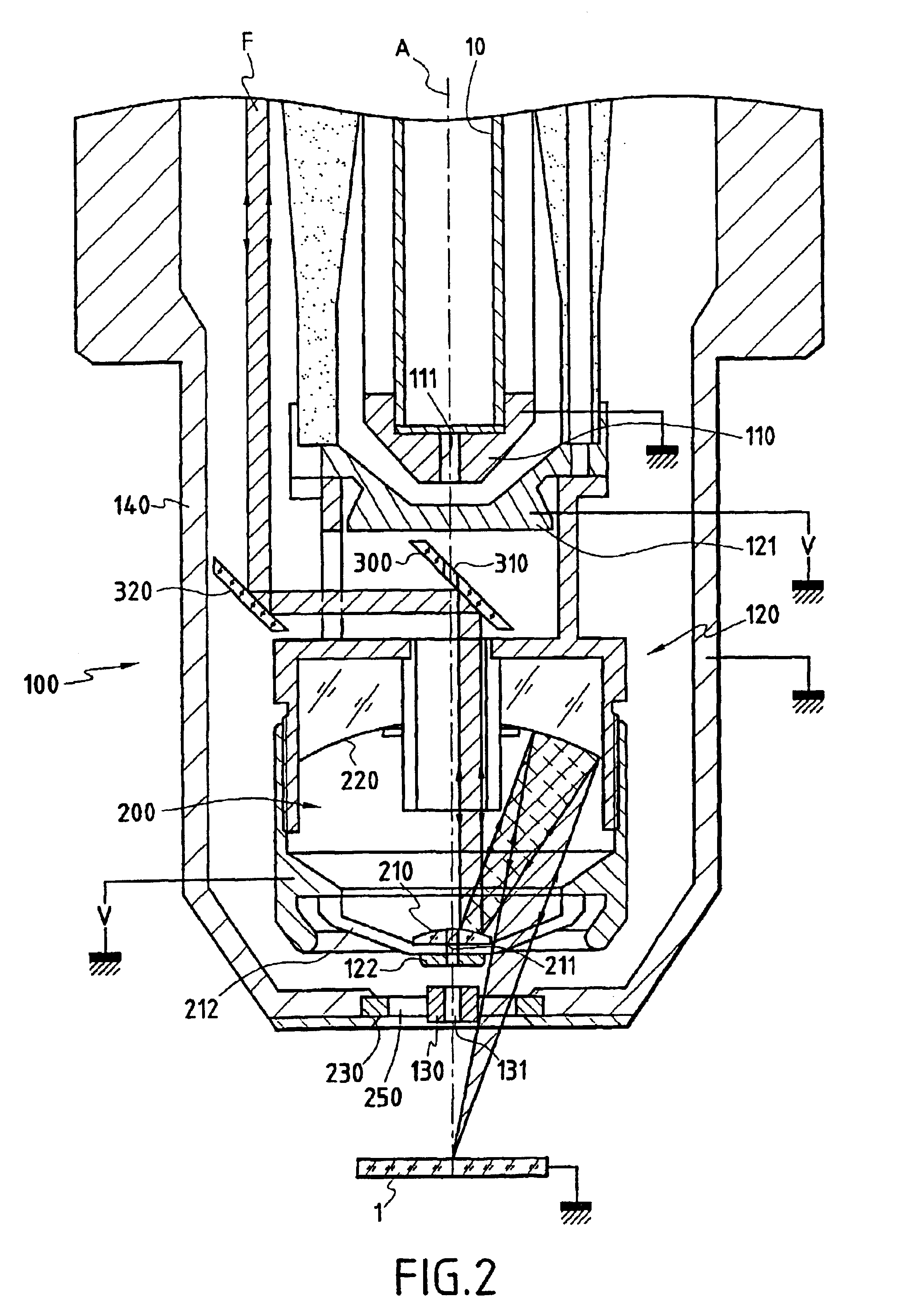
The invention concerns a column for producing a focused particle beam comprising: a device (100) focusing particles including an output electrode (130) with an output hole (131) for allowing through a particle beam (A); an optical focusing device (200) for simultaneously focusing an optical beam (F) including an output aperture (230). The invention is characterized in that said output aperture (230) is transparent to the optical beam (F), while said output electrode (130) is formed by a metallic insert (130) maintained in said aperture (230) and bored with a central hole (131) forming said output orifice.
Owner:ORSAY PHYSICS +1
Device for holographic reconstruction of three-dimensional scenes
ActiveUS7535607B2Reasonable effortLarge cell pitchHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsSpatial light modulatorOptical focusing
A device for holographic reconstruction of three-dimensional scenes includes optical focusing means which directs sufficiently coherent light from light means to the eyes of at least one observer via a spatial light modulator that is encoded with holographic information. The device has a plurality of illumination units for illuminating the surface of the spatial light modulator (SLM); each unit comprises a focusing element (21 / 22 / 23 or 24), and a light means (LS1 / LS2 / LS3 or LS4) that emits sufficiently coherent light such that each of these illumination units illuminates one separate illuminated region (R1 / R2 / R3 or R4) of the surface, whereby the focusing element and the light means are arranged such that the light emitted by the light means (LS1-LS4) coincides close to or at the observer eyes.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
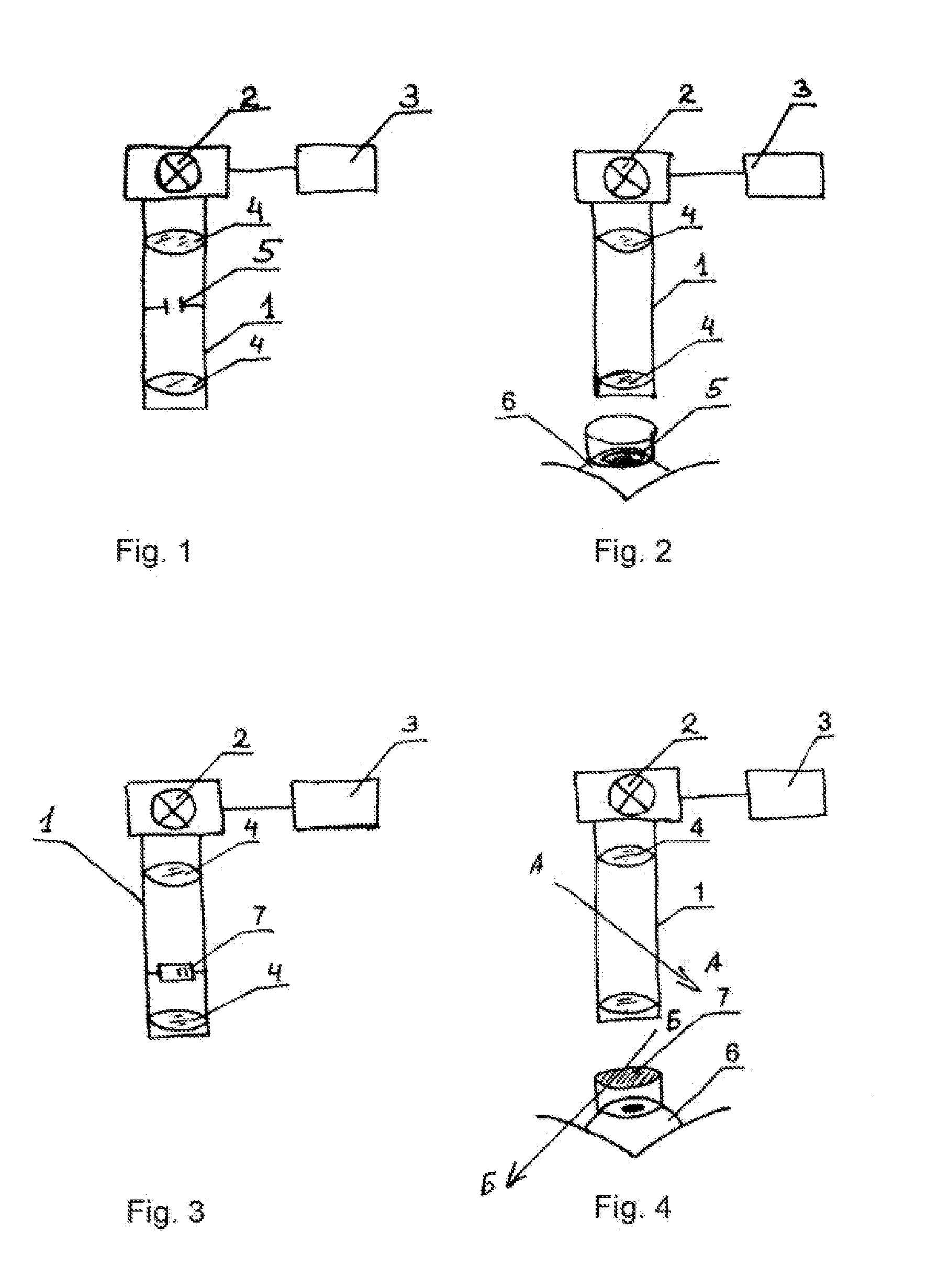
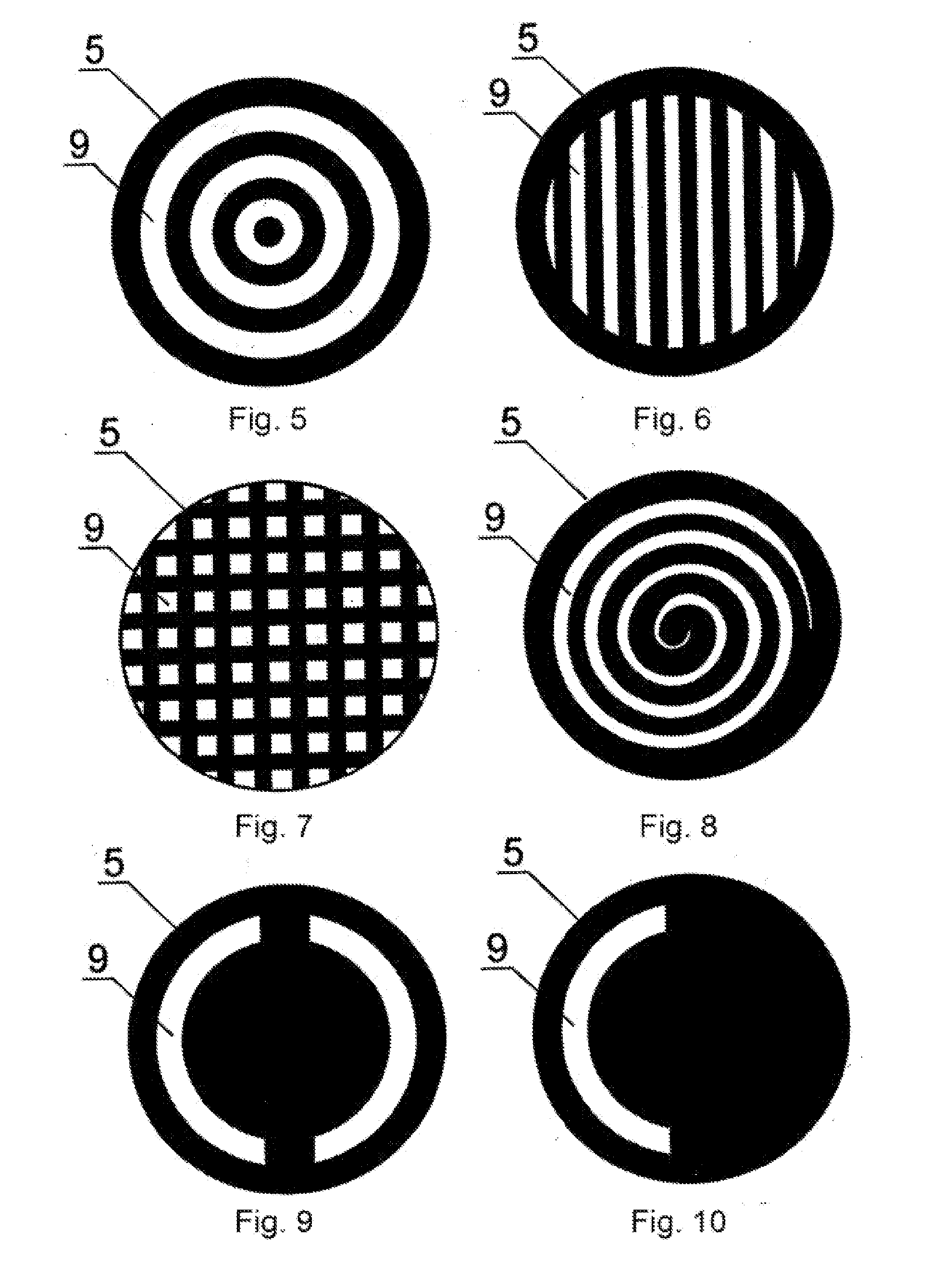
Method for treating keratoconus by UV radiation and a device for carrying out said method (variants)
InactiveUS20110190742A1Reduce adverse effectsEfficacy of treatmentLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsOptical axisUltraviolet
The invention relates to ophthalmology and is used for treating keratoconus. The inventive method comprises forming one or more radiation areas of different shape, comprising concentric circles, arcs, parallel lines, cells, grids, spirals or other geometrical figures. In the other variant, the method comprises polarizing UV radiation and adjusting the depth of the UV radiation action by directing the UV radiation polarization plane at an angle of 1-180° to the plane of light polarization by the cornea, thereby using the effect of light polarization by the cornea. The device for treating keratoconus comprises, positioned on the optical axis common with an UV radiation source optical focusing elements and a diaphragm. The diaphragm is situated on the optical axis common with the UV radiation source and is made in the form of a mask with alternating transparent and shaded elements in the form of concentric circles, arcs, parallel lines, cells, grids, spirals or other geometrical figures. In the other variant, the device comprises, situated on the optical axis common with the UV radiation source, the optical focusing elements, the diaphragm and a polarisor.
Owner:ANISIMOV SERGEY IGOREVICH
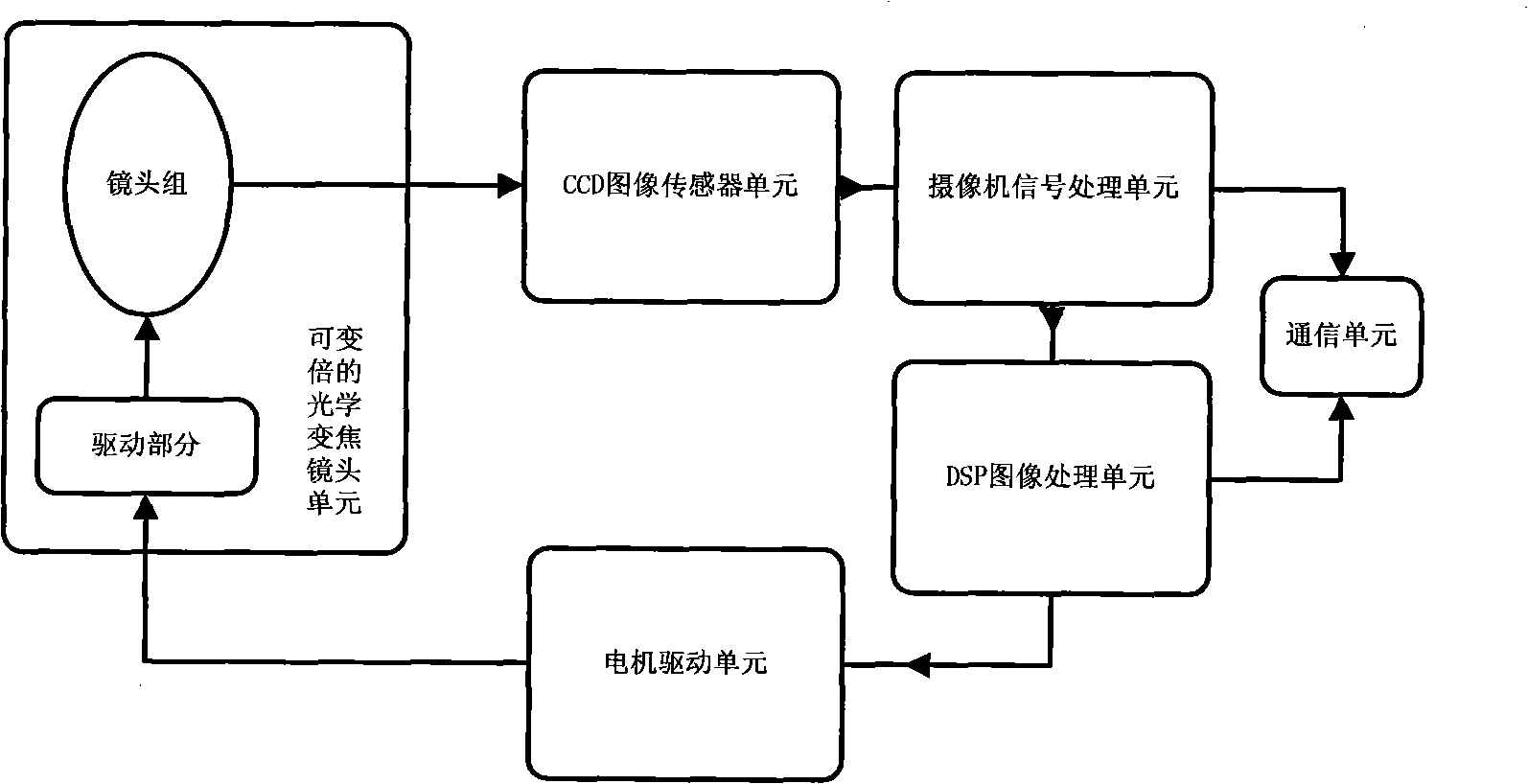
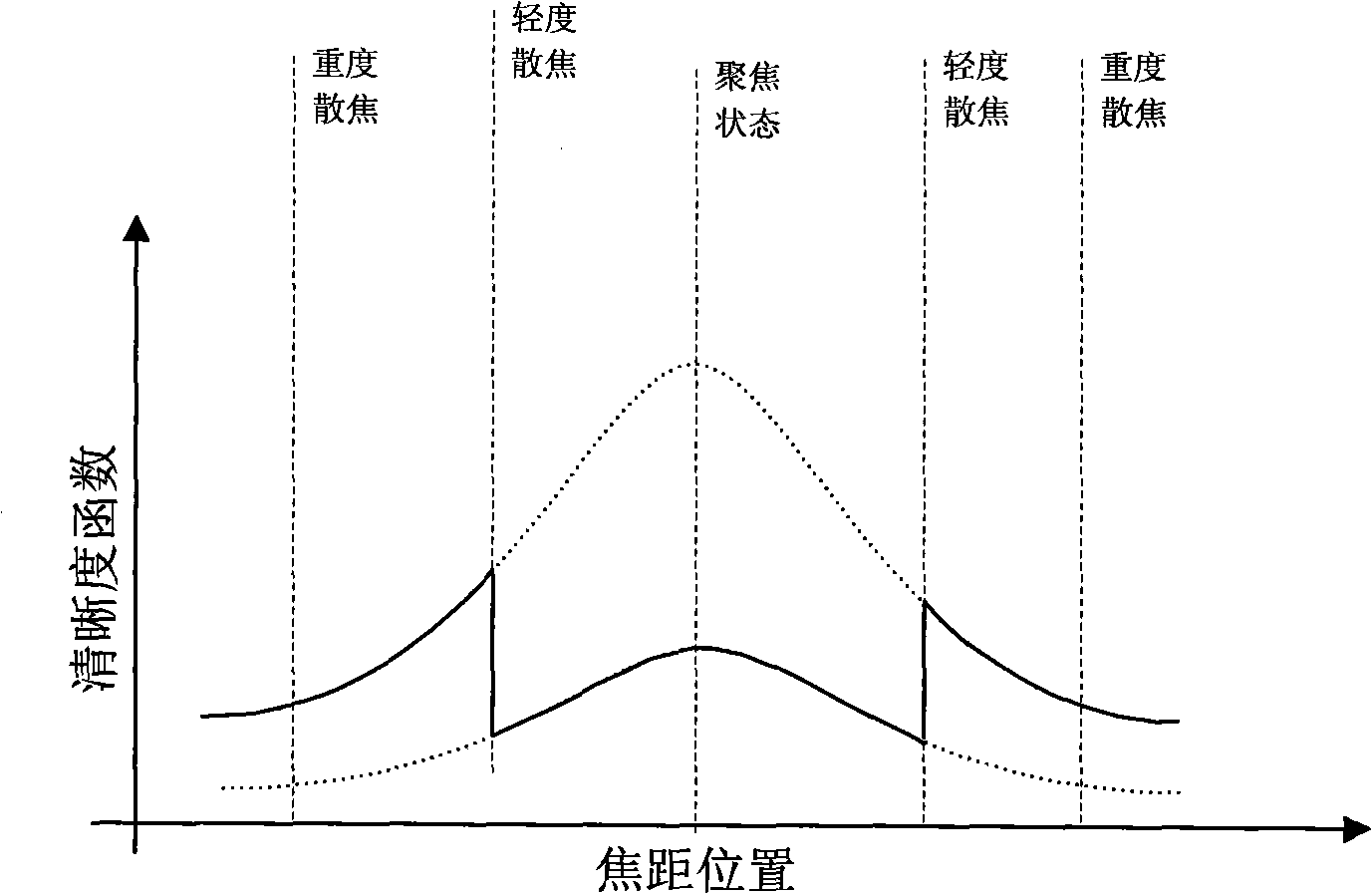
Integrated automatic focusing camera device and definition evaluation method
InactiveCN101943839ARealize all-in-one imaging functionSatisfy real-timeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital signal processorStepper motor
The invention discloses an integrated automatic focusing camera device and a definition evaluation method. The reliable evaluation of the focusing definition is guaranteed by taking the high-frequency component of an image signal as a feature estimation value of the focusing definition and by adopting a spatial domain and frequency domain combined algorithm method. The automatic focusing device realizes the calculation of the definition evaluation value and the control over the back and forth movement of an optical focusing lens by controlling a stepper motor, makes an image formed at a most definite focusing position by adopting a spatial domain and frequency domain multi-feature climbing search strategy and ensures quick focusing by adopting a digital signal processor for acceleration. By combining a communication interface and a control protocol, an integrated camera device is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
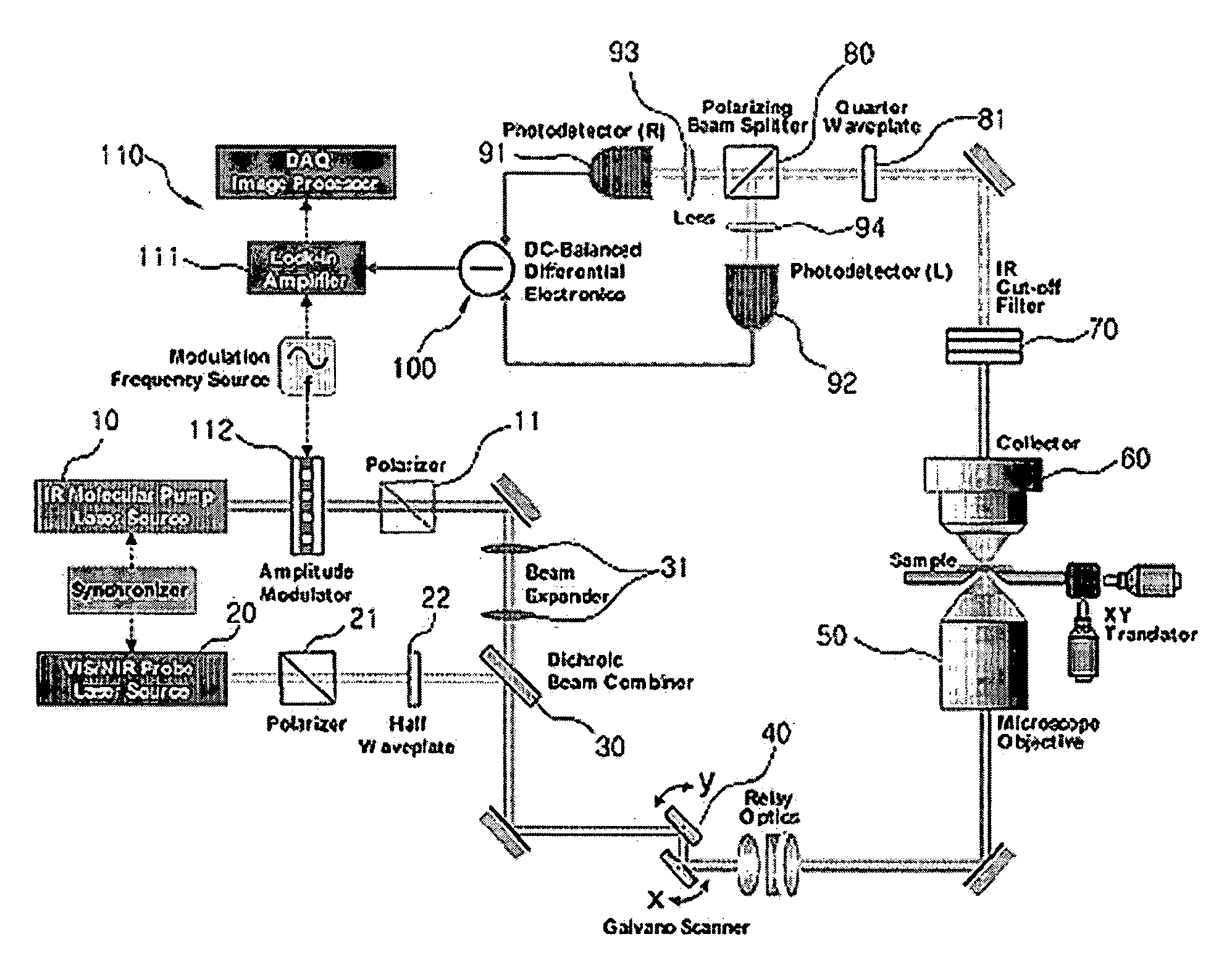
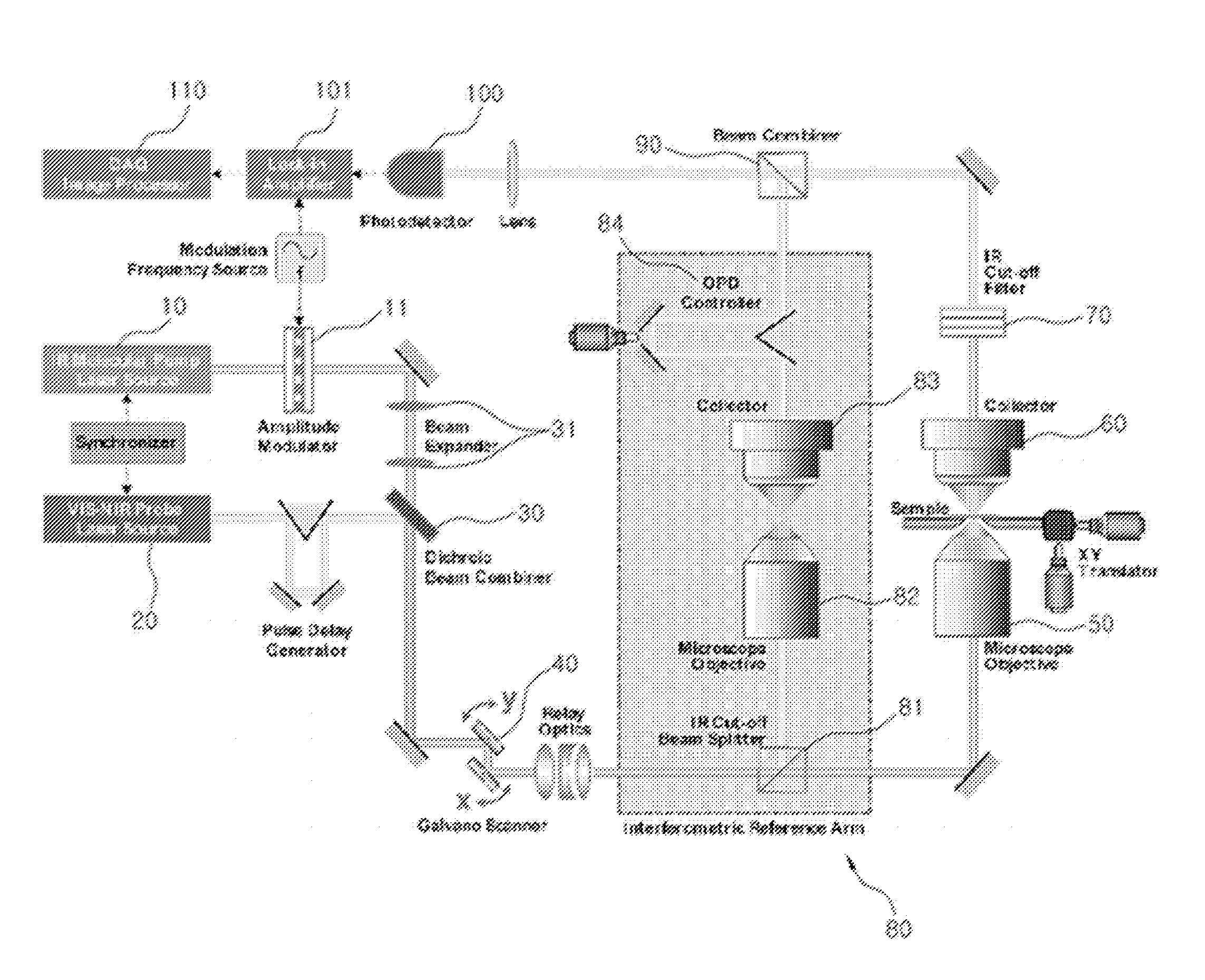
Imaging Apparatus for IR Four-Wave Mixing Polarization Microscopy
InactiveUS20080304047A1Reduce spatial resolutionReduce spacingRadiation pyrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesBeam splitterPhotodetector
The present invention relates to an imaging apparatus for IR four-wave mixing polarization microscopy. The imaging apparatus comprises a pump beam source for generating an infrared pump beam; a probe beam source for generating a probe beam (search beam); a polarizer for linearly polarizing the pump beam and probe beam; a beam combiner which synchronizes temporally and overlaps spatially the polarized pump beam and probe beam on the same axis; a scanner for two-dimensionally scanning the combined pump beam and probe beam; an optical focusing system for focusing the scanned pump beam and probe beam on a local point of the sample; a collecting optical system for collecting the beam which is formed by that the focused beams are interacted with the sample and of which phase is anisotropically retarded by nonlinear birefringence of the sample and forming a parallel beam; a dichroic beam splitter for removing the infrared pump beam out of the parallel beam and splitting the probe beam of which phase is anisotropically retarded; a polarizing beam splitter for converting the split and ansotripically phase-retarded probe beam into linerly polarized beams having their axes perpendicular to each other; a photodetector for detecting an intensity of each of the converted linerly polarized beams; a polarization differential detector for detecting a polarization difference based on the detected intensities of the linerly polarized beams; and a data analyzer for acquiring the detected polarization difference signal and extracting a spectrospcopic information corresponding to the strength of molecular vibrational coherence of the sample.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Direct-type backlight unit with diffusion film for flat panel liquid crystal display
InactiveUS7068332B2Lighting heating/cooling arrangementsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A direct-type backlight unit for flat panel liquid crystal display is provided. The direct-type backlight unit includes a plurality of lamps installed within a housing. A reflection plate is installed under the plurality of lamps in the housing. A diffusion film with a plurality of apertures thereon is installed above the plurality of lamps for diffusing light generated by the plurality of lamps. An optic focusing film is located on the diffusion film. The flat panel liquid crystal display is located above the optic focusing film.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for performing laser filamentation within transparent materials
ActiveUS9102007B2Promote formationFor active controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGlass severing apparatusPlasma channelOptical breakdown
Systems and methods are described for forming continuous laser filaments in transparent materials. A burst of ultrafast laser pulses is focused such that a beam waist is formed external to the material being processed without forming an external plasma channel, while a sufficient energy density is formed within an extended region within the material to support the formation of a continuous filament, without causing optical breakdown within the material. Filaments formed according to this method may exhibit lengths exceeding 10 mm. In some embodiments, an aberrated optical focusing element is employed to produce an external beam waist while producing distributed focusing of the incident beam within the material. Various systems are described that facilitate the formation of filament arrays within transparent substrates for cleaving / singulation and / or marking. Optical monitoring of the filaments may be employed to provide feedback to facilitate active control of the process.
Owner:KINESTRAL TECH
Illuminated optical enlargement device
InactiveUS6384988B1Sharp contrastEnhance the imageOperating tablesLighting device detailsLight-emitting diodeDiode
An illuminated optical magnifying device with an optical focusing unit that can produce a magnified image of an object to be observed and with an illumination device whose light is at least partially applicable for illuminating the object to be observed, whereby the illumination device is composed of at least one luminous diode, which is arranged in the magnifying device in such a way that its light can emerge from the magnifying device essentially straight toward the direction of the object to be observed.
Owner:LIFATEC GMBH FASEROPTIK & OPTOELEKTRONIK
Imaging Apparatus for Infrared Rays Nonlinear Molecular Vibrational Microscopy
InactiveUS20080304046A1Reduce spatial resolutionReduce spacingRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBeam splitterBeam source
The present invention relates to an imaging apparatus for infrared rays nonlinear molecular vibrational microscopy. The imaging apparatus comprises a pump beam source for generating an infrared pump beam; a probe beam source for generating a probe beam; a beam combiner which synchronizes temporally and overlaps spatially the pump beam and probe beam on the same axis; a scanner for two-dimensionally scanning the combined pump beam and probe beam; a first optical focusing system for focusing the scanned pump beam and probe beam on a local point of the sample; a first collecting optical system for collecting the beam of which phase is shifted by interaction with the sample and forming a parallel beam; a first dichroic beam splitter for removing the infrared pump beam out of the parallel beam and splitting the probe beam of which phase is shifted; a reference interferometer for splitting a part of the probe beam out of the beams scanned by the scanner and generating a reference probel beam; an interferometric beam combiner for combining the probe beam having the shifted phase and the reference probe beam; a photodetector for detecting an intensity of a molecular vibrational beam signal from the combined probe beam; and a data analyzer for acquiring the detected signals and extracting a spectrospcopic information corresponding to the strength of molecular vibrational coherence of the sample.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Light source device
InactiveUS6867929B2Reduce widthNo longer be switchedDiffusing elementsPhotometryLight beamOptoelectronics
The present invention provides a light source device that is safe for human eyes and whose switching is performed at high speed. The light source device comprises one or more laser light sources (1) for emitting a monochromatic or polychromatic light beam, a diffuser (3), which may be transmissive, reflective, or a mixture thereof, for diffusing the light beam received directly from the laser light source or via an optical focusing system (2), and an optical collimator (4), which collimates the diffused light bundle emitted from the diffuser (3).
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Laser micro/nano processing system and method
ActiveUS20130183833A1Improve accuracyLimited resolutionDecorative surface effectsPhotomechanical apparatusNano structuringNanosecond
A laser micro / nano processing system (100, 200, 300, 400) comprises: a laser light source used to provide a first laser beam having a first wavelength and a second laser beam having a second wavelength different from the first wavelength, with the pulse width of the first laser beam being in the range from a nanosecond to a femtosecond; an optical focusing assembly used to focus the first laser beam and the second laser beam to the same focal point; and a micro mobile platform (21) controlled by a computer. Also disclosed are a method for micro / nano-processing photosensitive materials with a laser and a method for fabricating a device with a micro / nano structure using laser two-photon direct writing technology. In the system and methods, spatial and temporal overlapping of two laser beams is utilized, so as to obtain a micro / nano structure with a processing resolution higher than that of a single laser beam, using an average power lower than that of a single laser beam.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
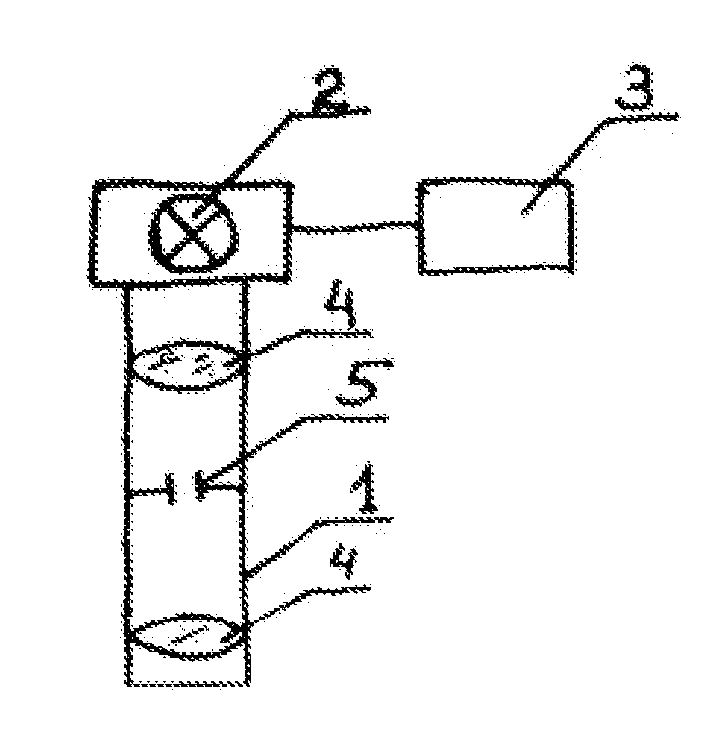
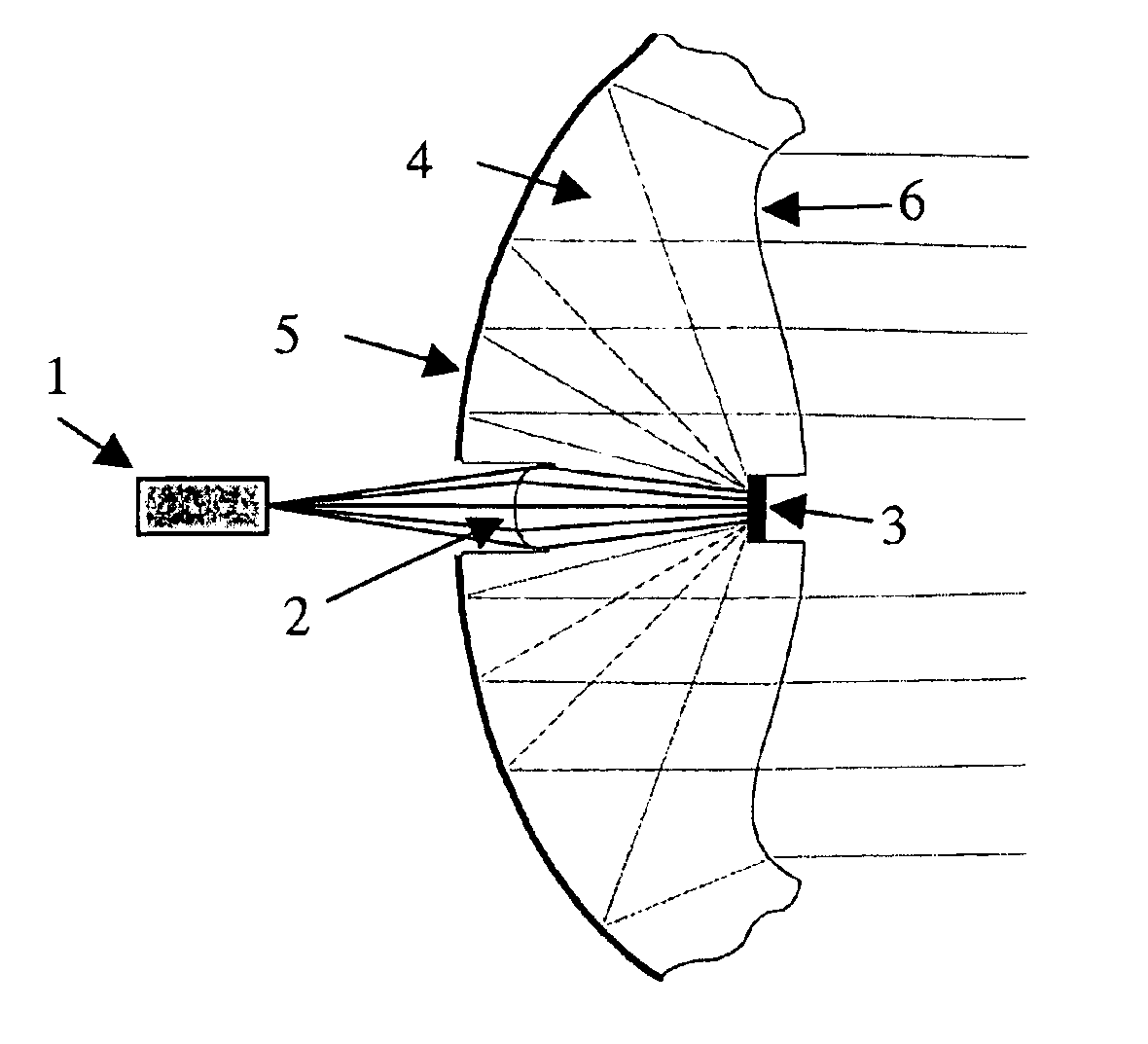
Optical focusing device
The invention provides an optical focusing device, which comprises a shell, an image sensor component and an actuating component. The actuating component actuates to drive an image sensor panel provided with an image sensor in the image sensor component to move along an axis direction of an aperture so as to adjust the distance between the image sensor panel and a lens, thereby realizing the optical focusing. The optical focusing device of the invention has the advantages of improving the adjustment precision and the stability of focusing, along with simple structure and convenient operation.
Owner:SONY CORP
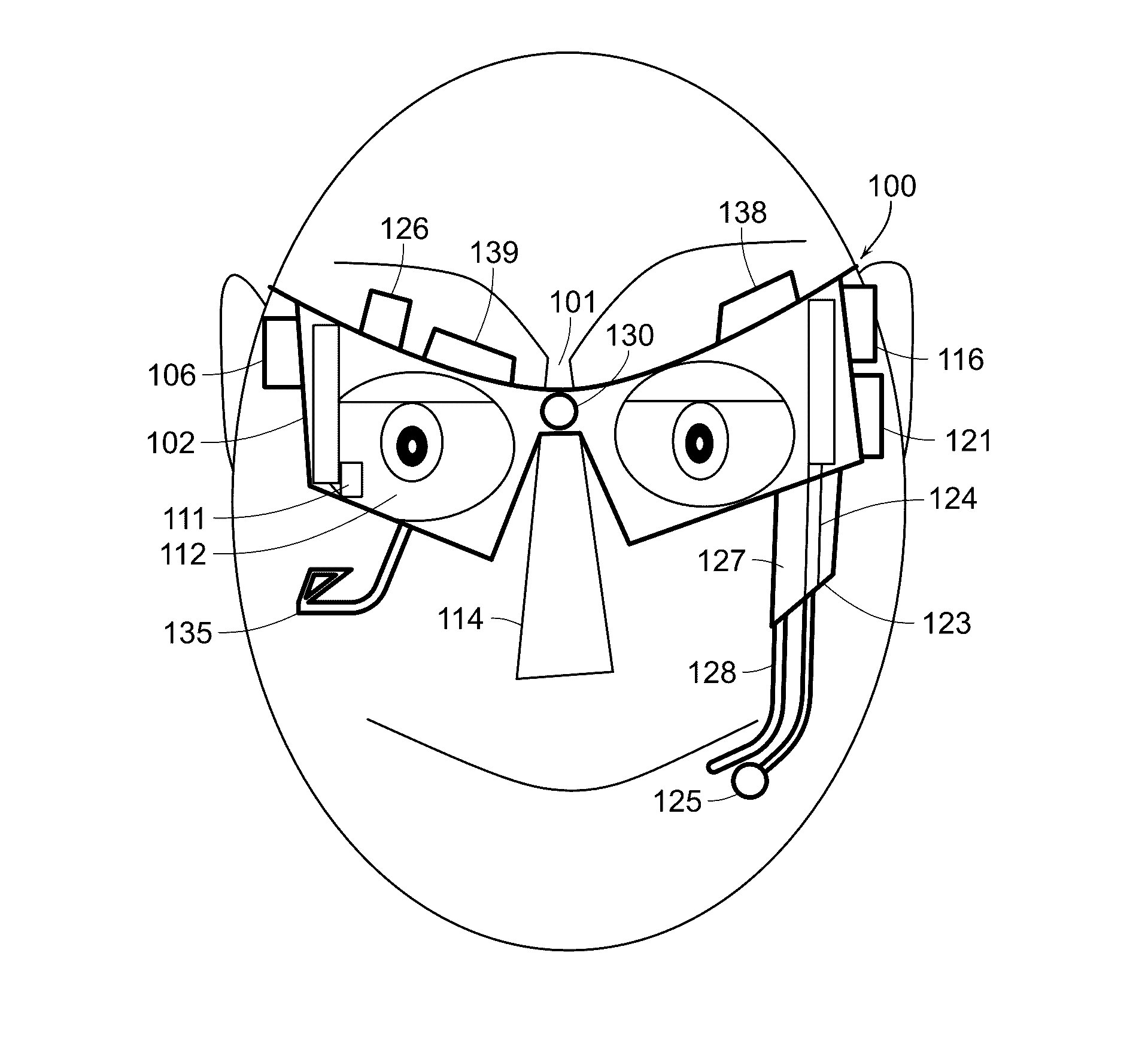
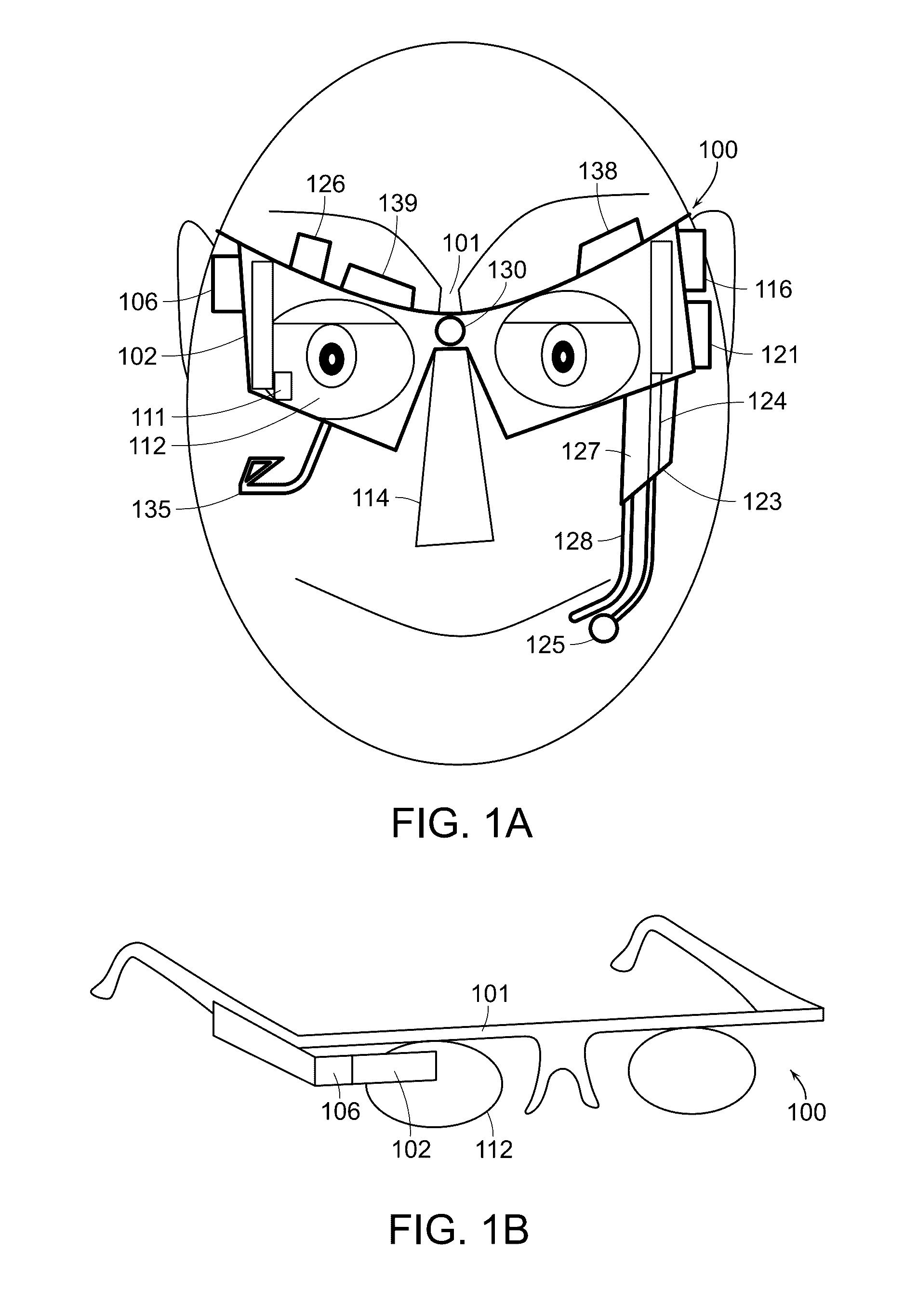
Eye and head tracking device
ActiveUS20160342206A1Improve accuracyInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementSensor arrayHead movements
An apparatus and method of use for tracking eye and head movement comprising (1) at least one optoelectronic array sensor or optical flow sensor formed of a plurality of optoelectronic sensor cells; (2) a body configured to support the optoelectronic array sensor with focusing means along with a source of light with collimating means in front of and in proximity to an eye of a user; (3) an optical focusing means to focus an image of the ocular surface of the user on the optoelectronic array sensor; (4) a focusing lens with a source of light; (5) a means to detect blinking; (6) a driver configured to receive signals from the sensor array to generate coordinate signals corresponding to changes in the position of the ocular surface relative to the sensor array; and (7) a means to detect user's additional input and gestures.
Owner:SHAZLY TAREK A +1
Micromirror array lens with optical surface profiles
A Micromirror Array Lens comprises a plurality of micromirrors arranged on a flat or a curved surface to reflect incident light. Each micromirror in the Micromirror Array Lens is configured to have at least one motion. The Micromirror Array Lens forms at least one optical surface profile reproducing free surfaces by using the motions of the micromirrors. The free surface can be any two or three-dimensional continuous or discrete reflective surface. The Micromirror Array Lens having the corresponding optical surface profile provides optical focusing properties substantially identical to those of the free surface. The Micromirror Array Lens can forms various optical elements such as a variable focal length lens, a fixed focal length lens, an array of optical switches, a beam steerer, a zone plate, a shutter, an iris, a multiple focal length lens, other multi-function optical elements, and so on.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
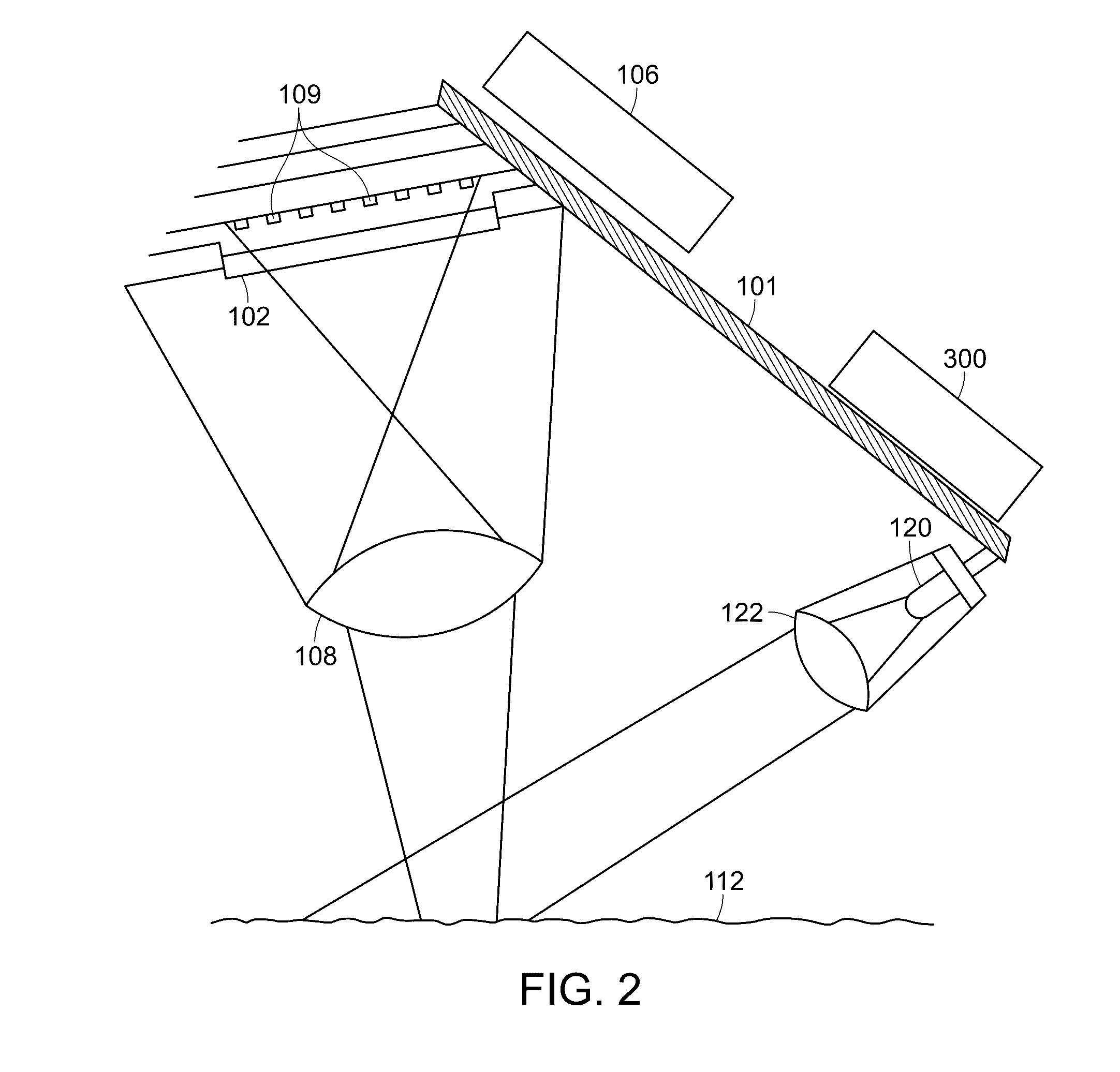
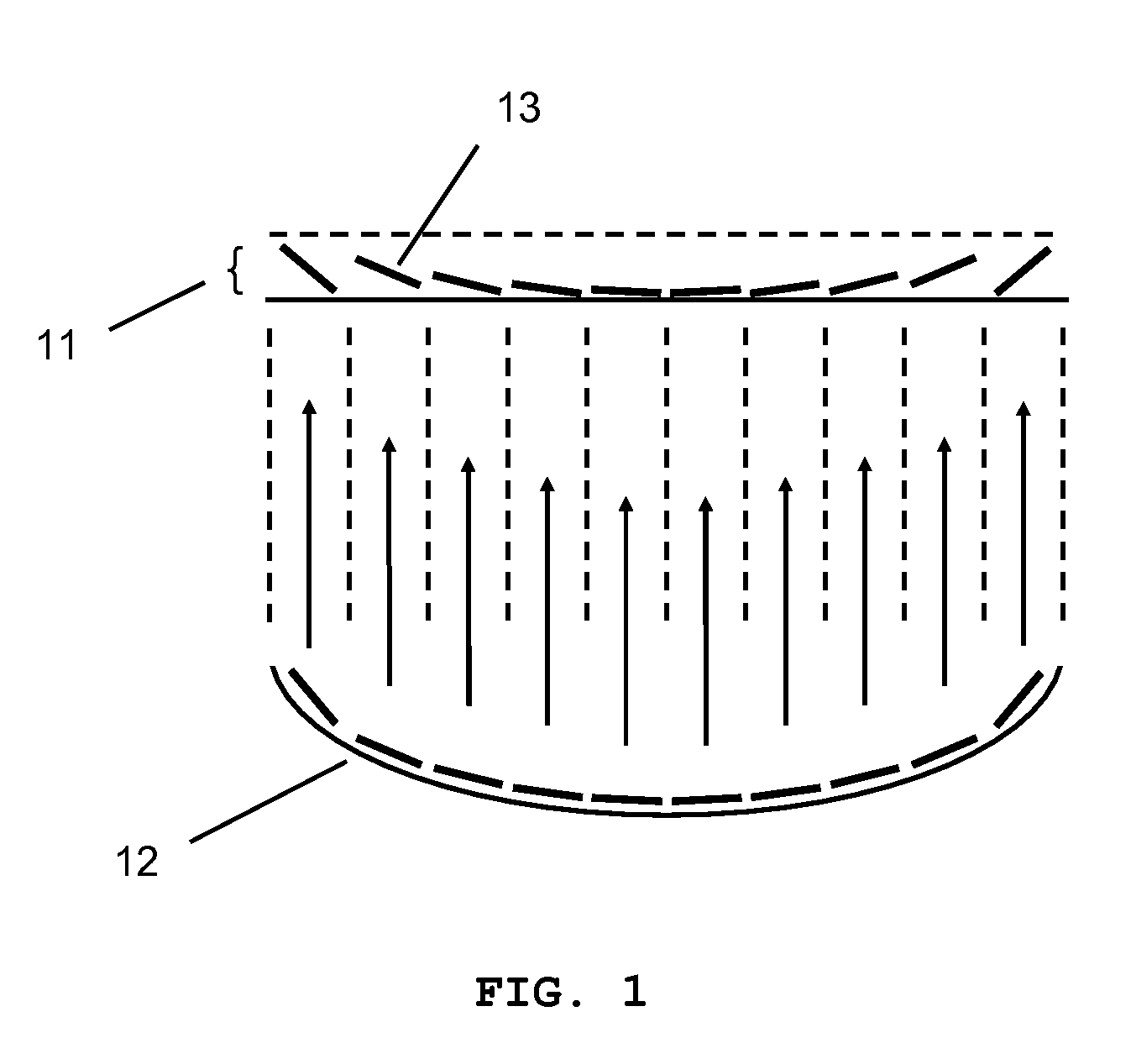
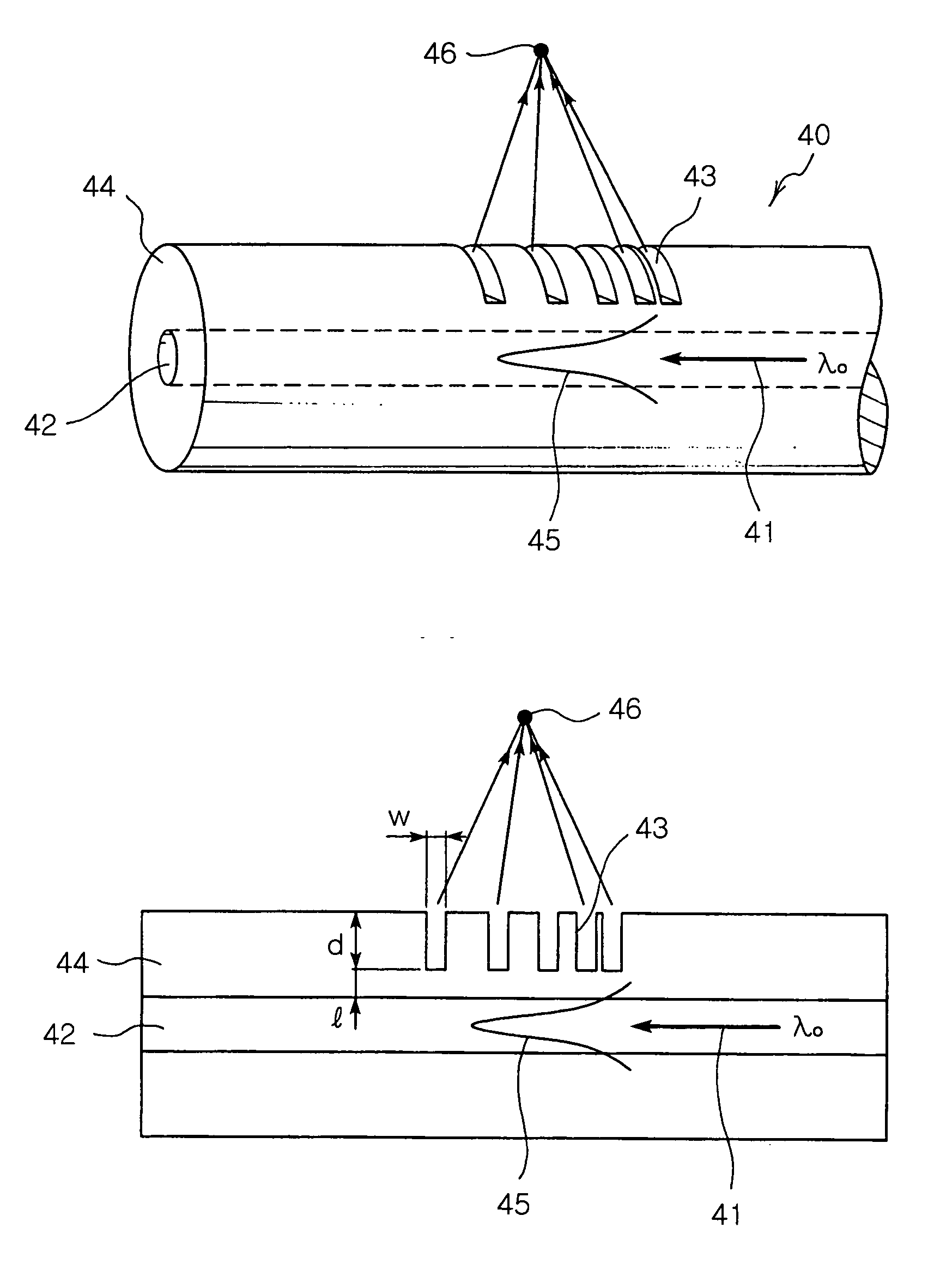
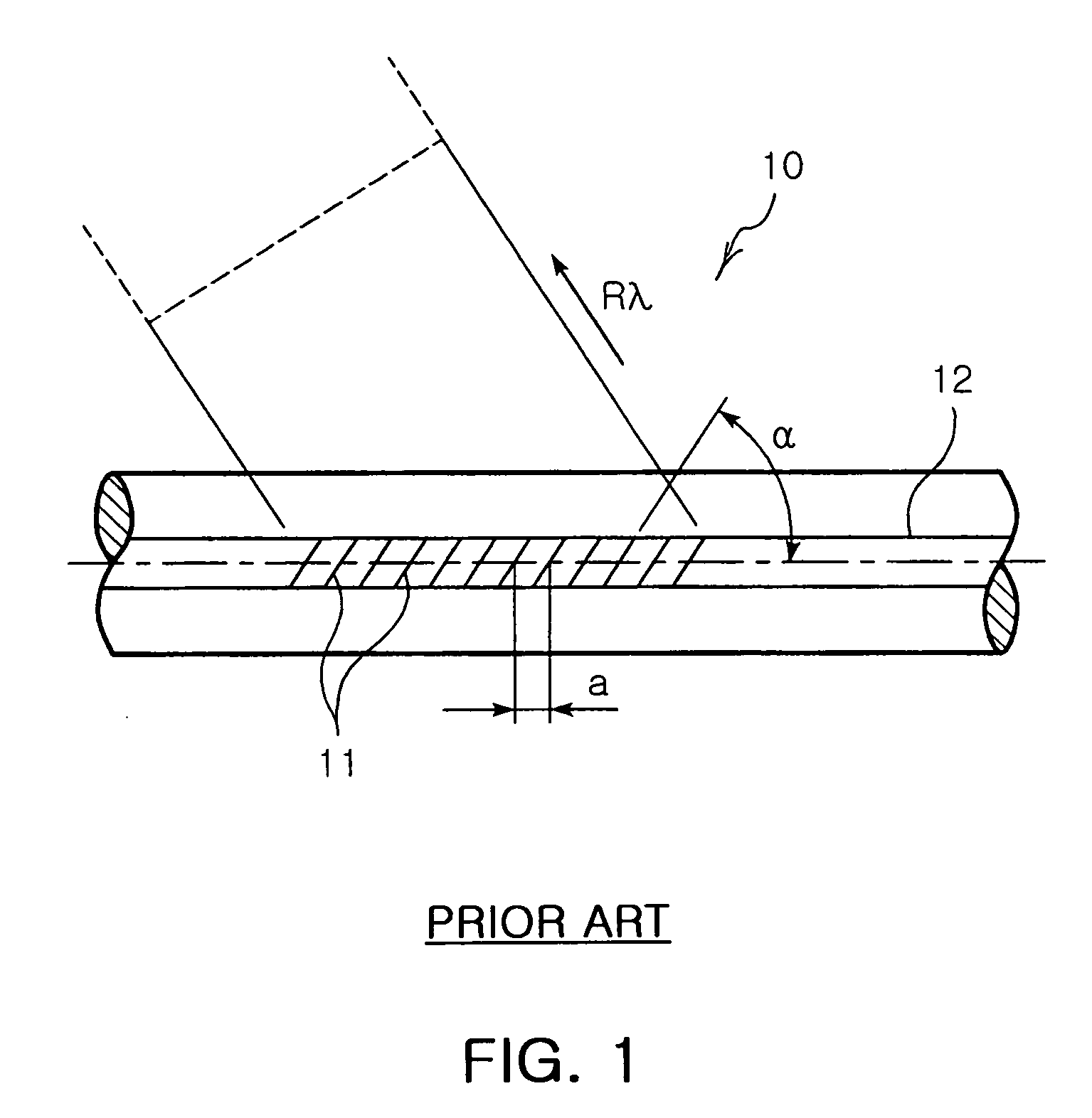
Wavelength selective optical focusing device using optical fiber and optical module using the same
InactiveUS20070071389A1Excellent reproducibility in manufacturingPrevent agingCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesOptical ModuleEtching
The present invention provides a wavelength selective optical focusing device using the cladding-etching of an optical fiber and an optical module using the same. The wavelength selective optical focusing device includes a core for transmitting an optical signal therethrough; and a cladding layer surrounding the core and having a plurality of grooves formed in the outer circumferential surface thereof such that the grooves are changed at a designated rate, wherein an optical signal having a designated wavelength guided by the core is focused to the outside of the cladding layer by the grooves.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com