Patents
Literature
298 results about "Optical packet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
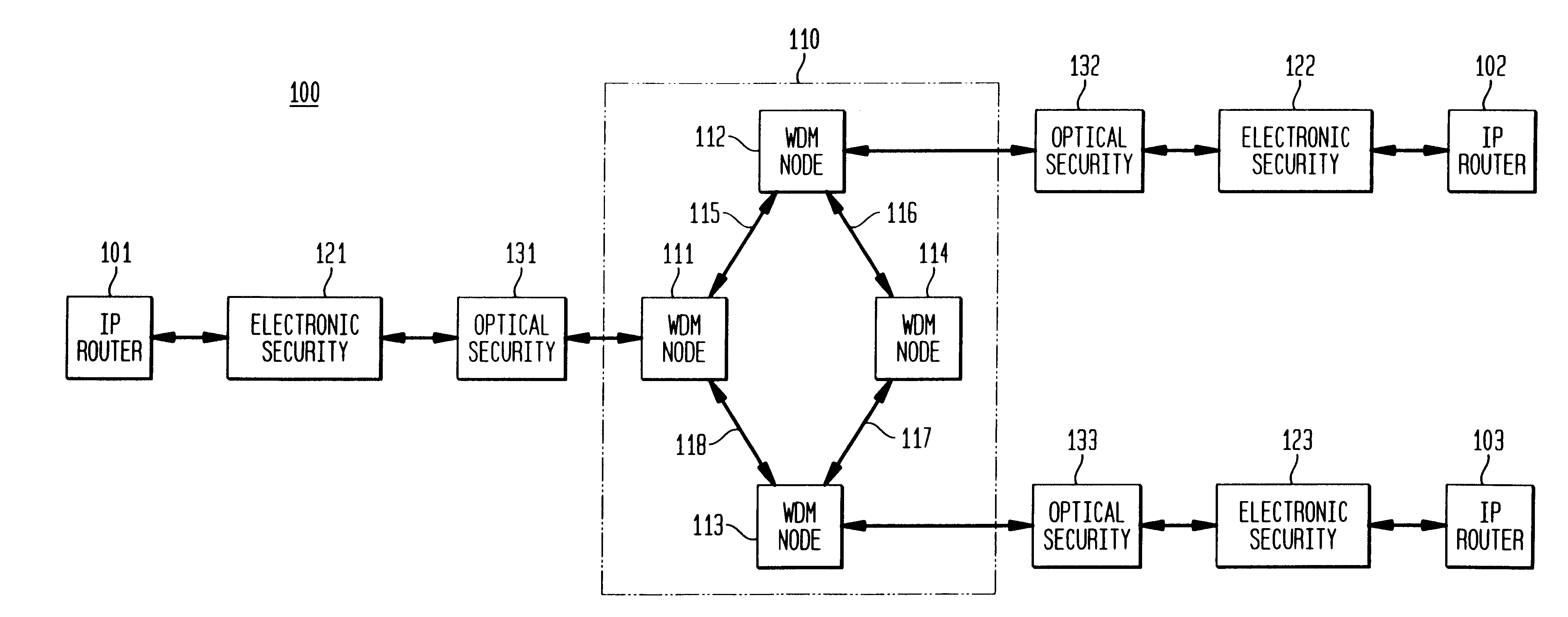
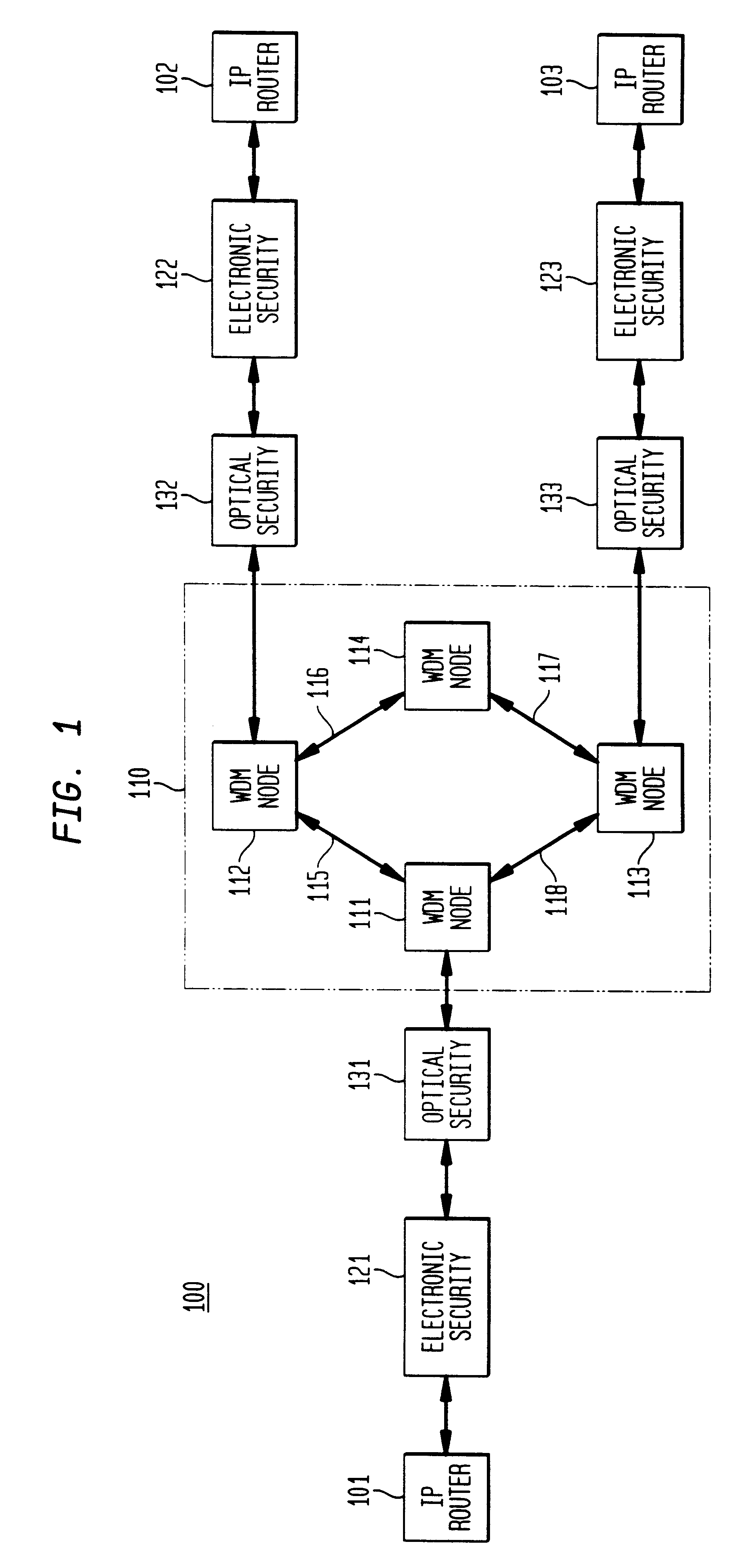
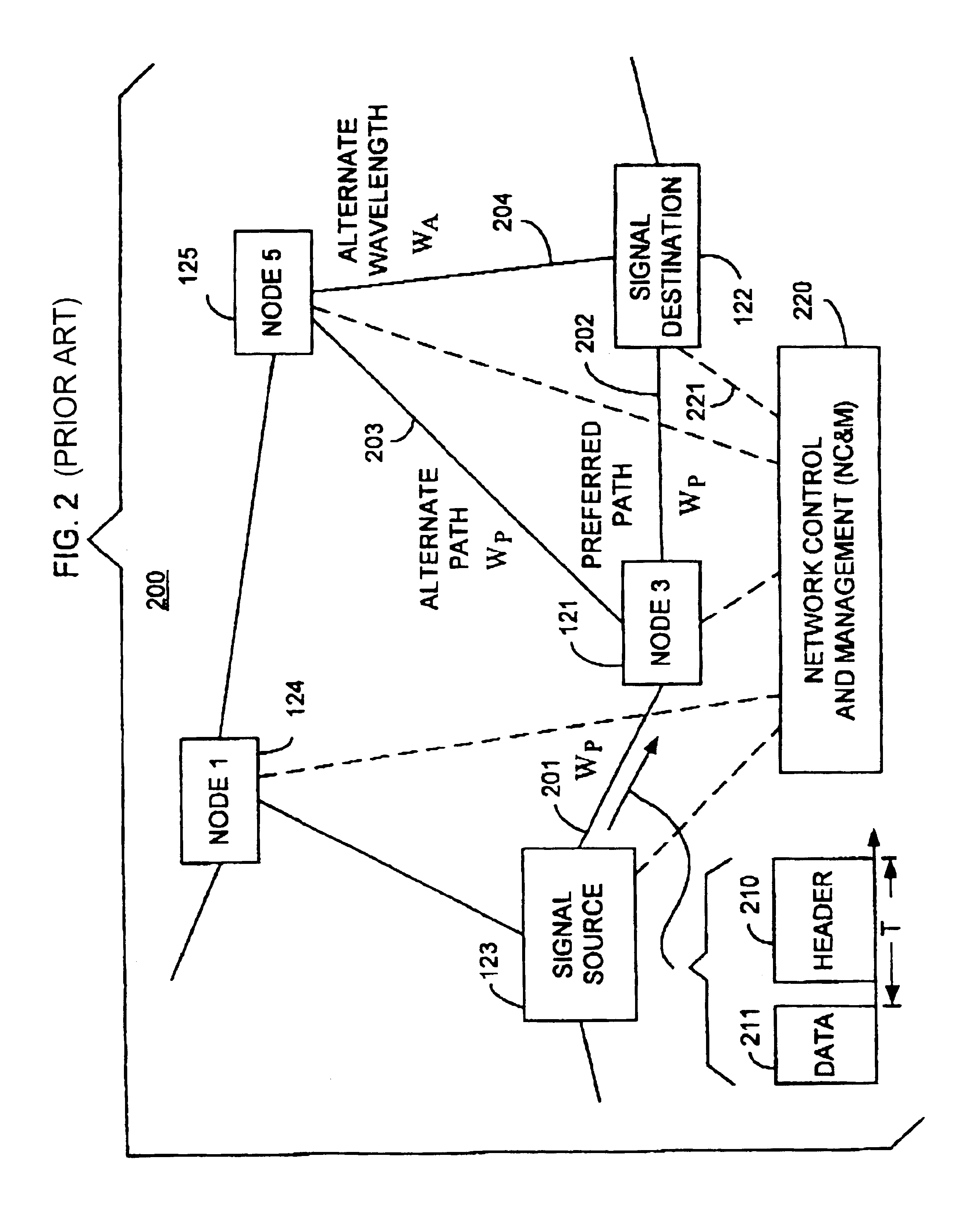
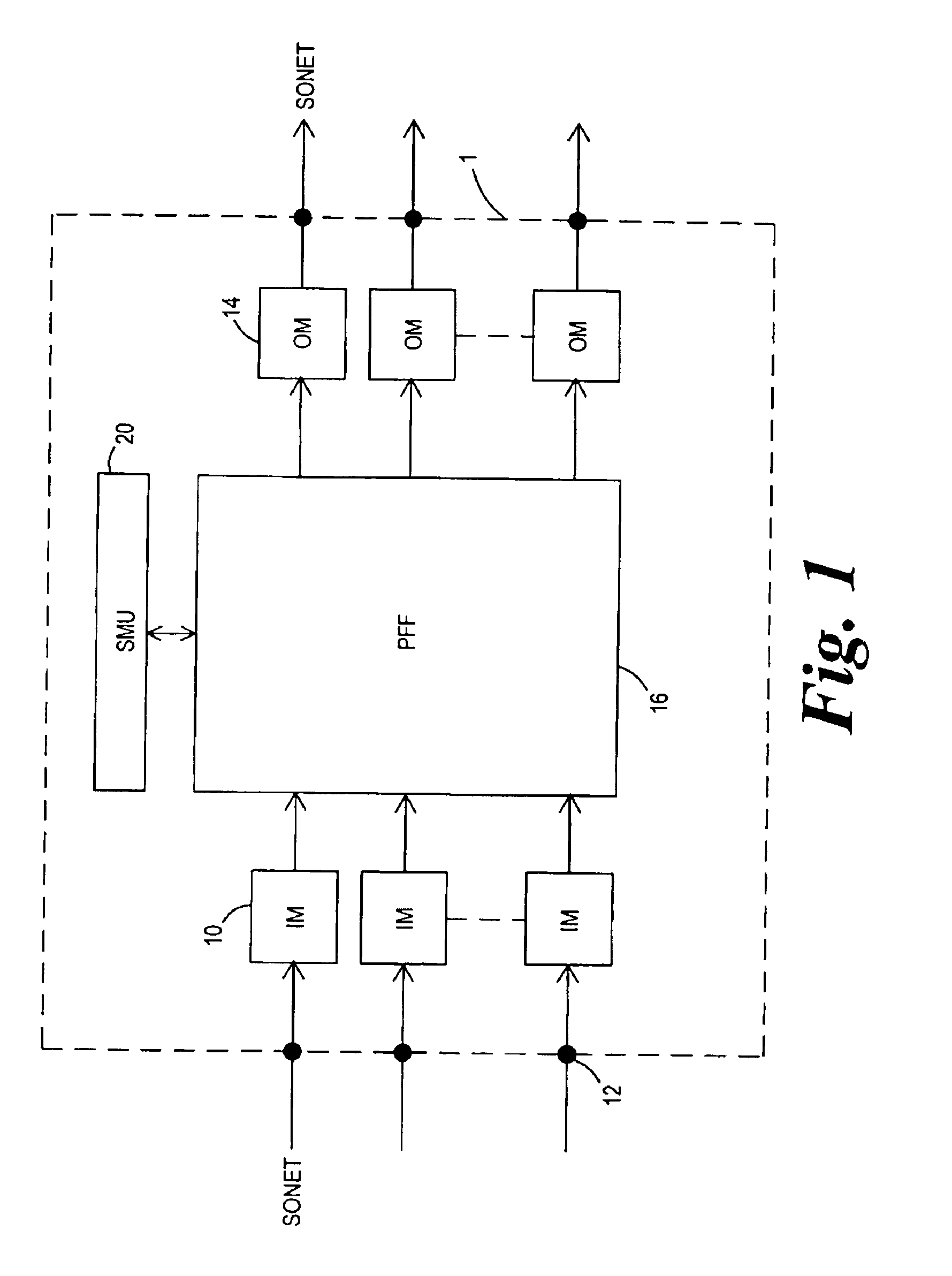
Optical layer survivability and security system using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation and detection
InactiveUS6271946B1Increase probabilityIncrease optical powerMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSurvivabilityOptical burst switching
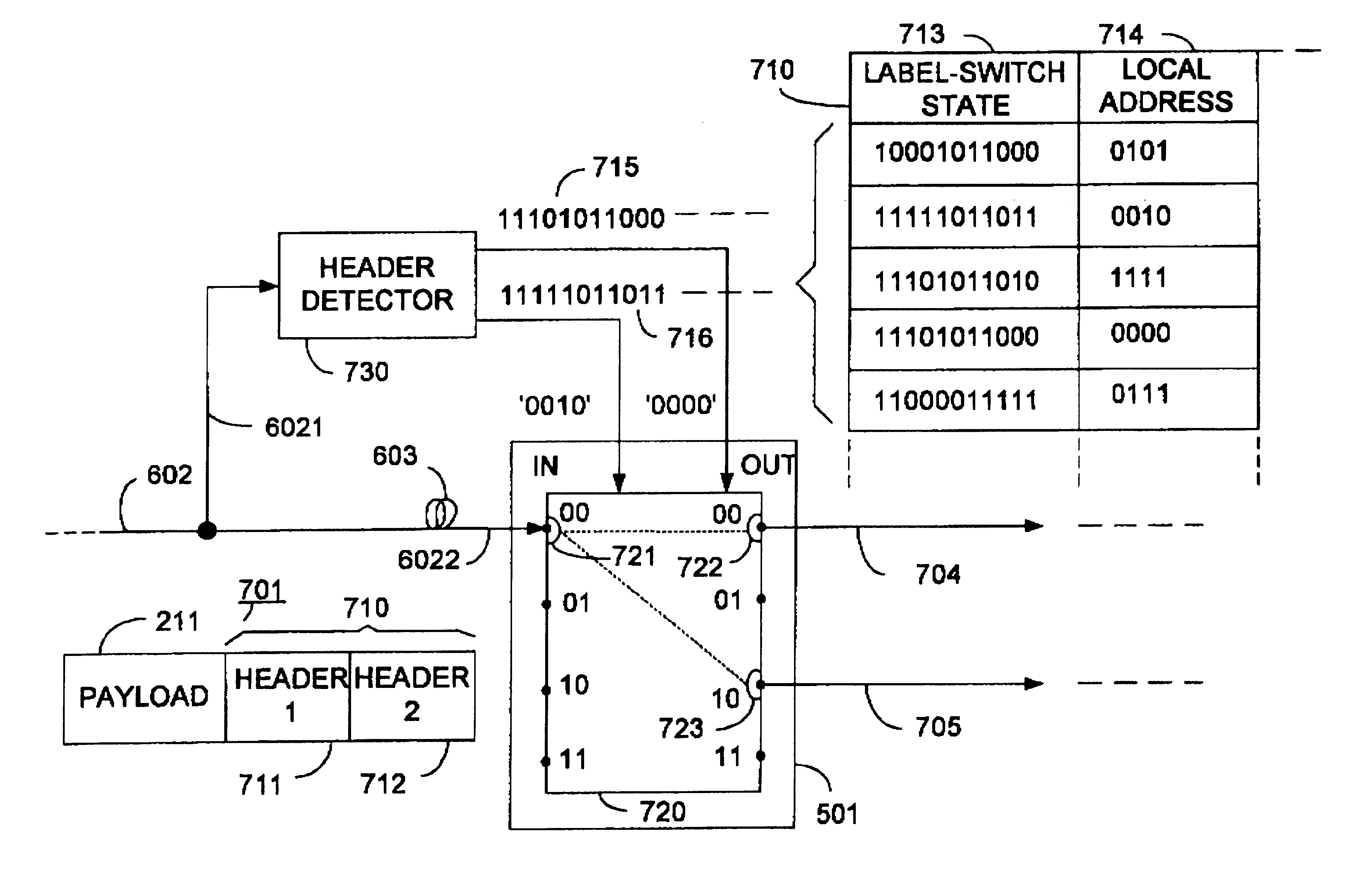
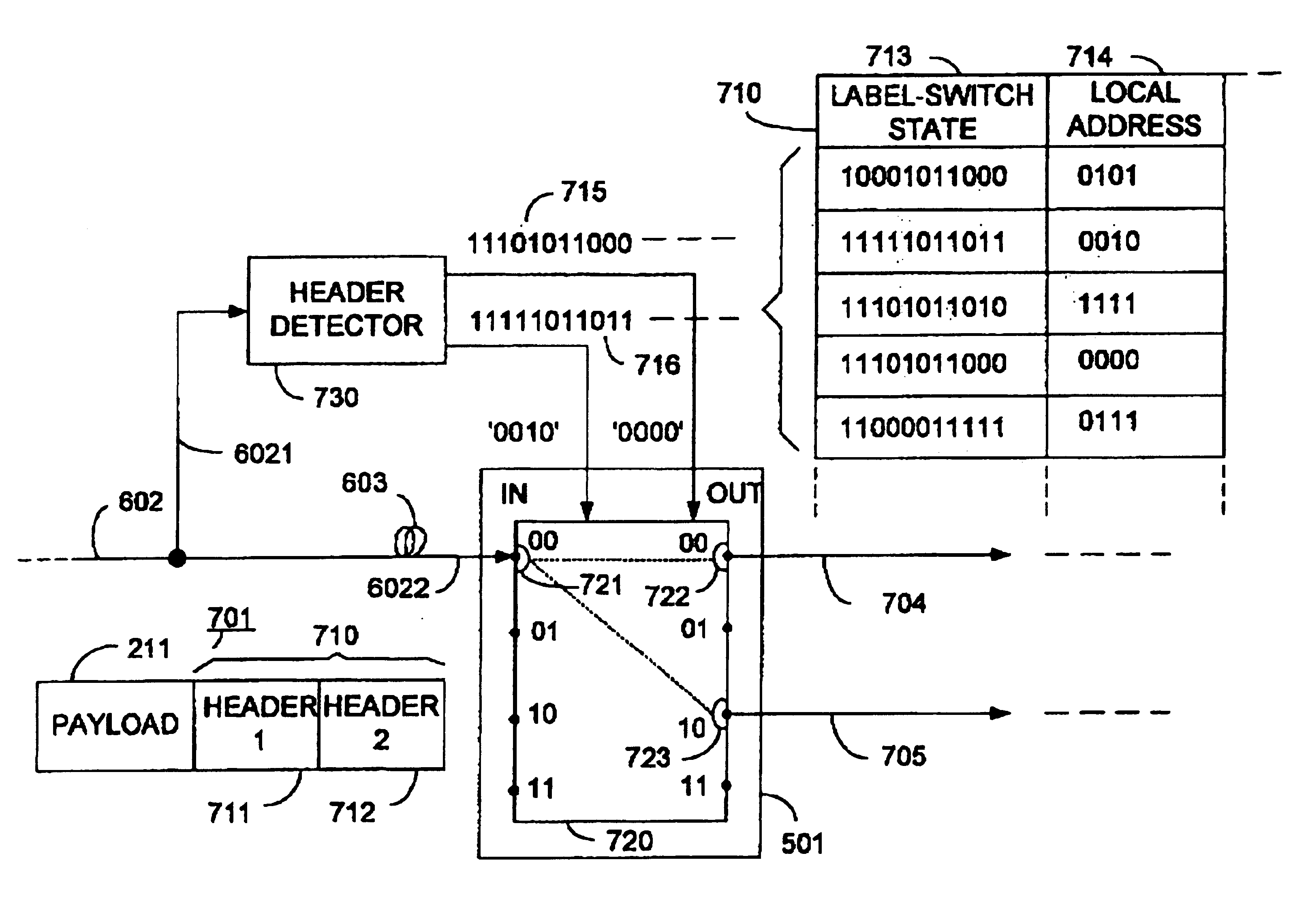
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The technique effects survivability and security of the optical networks by encompassing conventional electronic security with an optical security layer by generating replicated versions of the input data payload at the input node, and the transmission of each of the replicated versions over a corresponding one of the plurality of links. Moreover, each of the links is composed of multiple wavelengths to propagate optical signals or optical packets, and each of the replicated versions of the data payload may be propagated over a selected one of the wavelengths in each corresponding one of the plurality of links.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Communications network
InactiveUS6714552B1Efficient routingSimple processTime-division optical multiplex systemsData switching by path configurationOptical packetNetwork routing
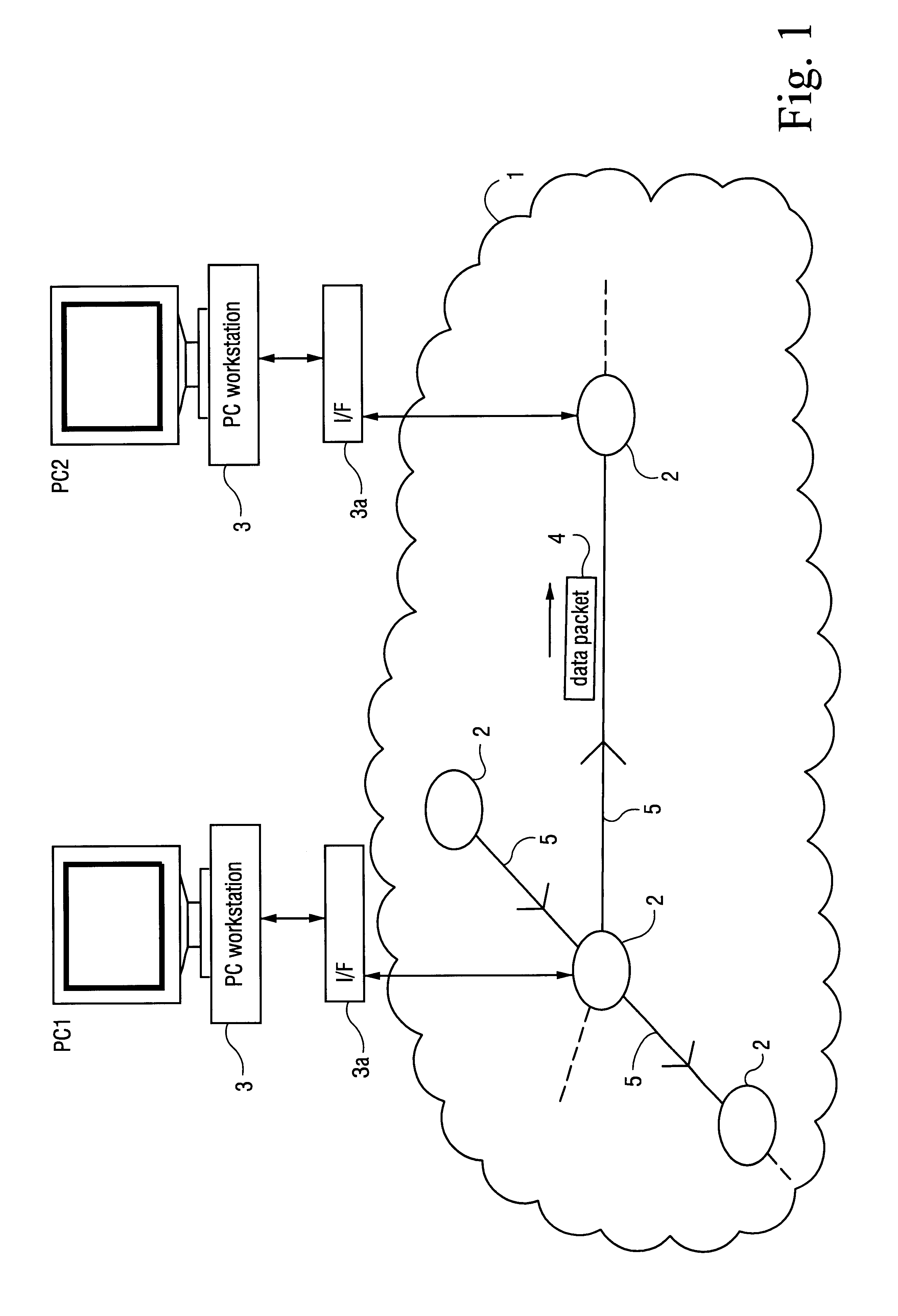
A communications network, suitable, for example, for linking computer processors, is formed from a number of nodes and links. The nodes and links are configured as a multiplicity of directed trails. Each directed trail spans some only of the nodes, but in combination the directed trails span every node of the network. Packets are routed through the network by selecting the appropriate one of the directed trails which links the source node and destination node, and by outputting the packet at the source node onto the selected trail. The nodes throughout the network may switch between predetermined and prescheduled switching states, and a given trail may be selected by choosing appropriately the time slot in which the packet is put onto the network. The network may be a photonic network carrying optical packets.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
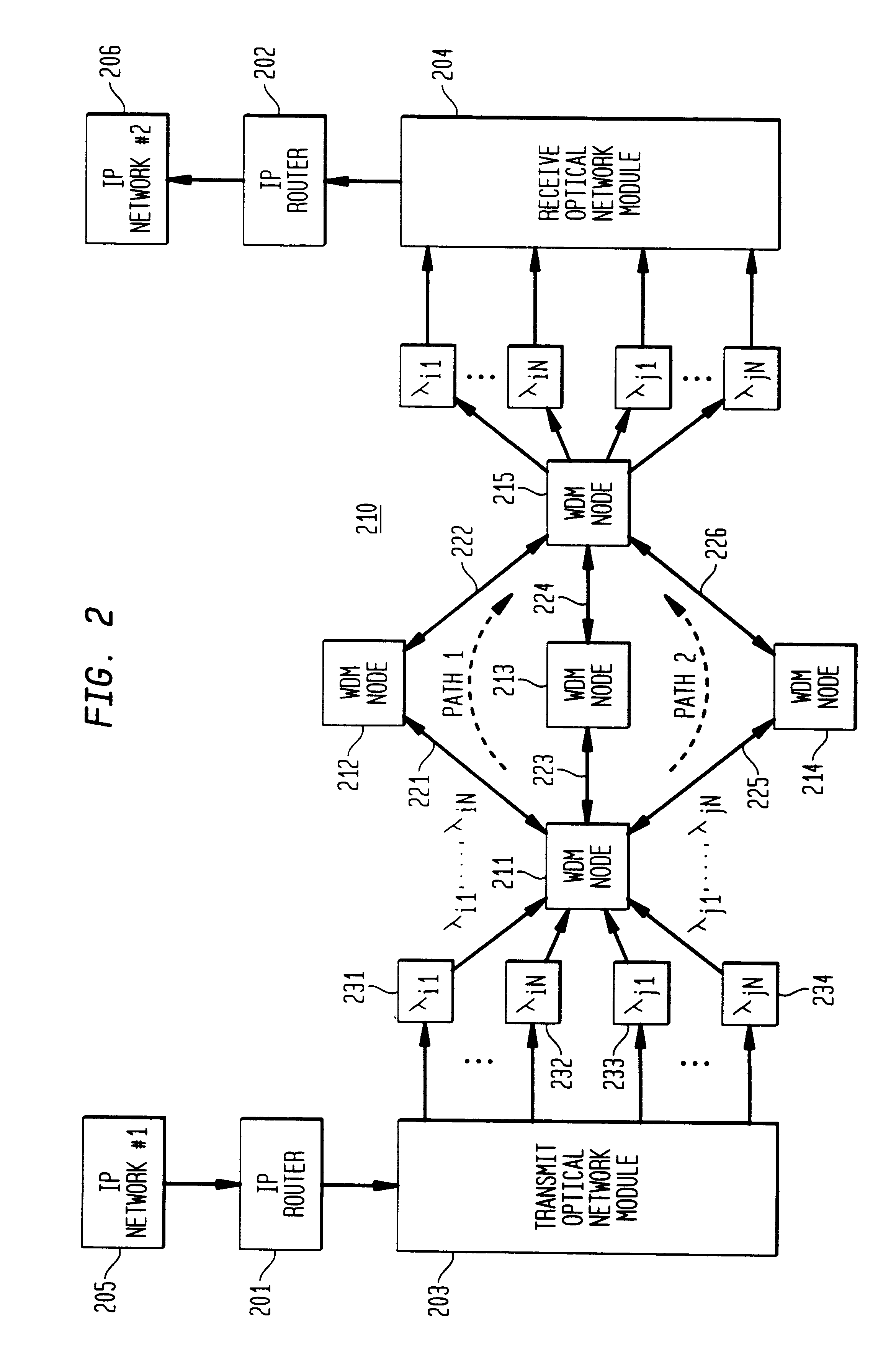
Optical layer multicasting
InactiveUS6873797B2Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical packetEngineering
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The technique effects survivability and security of the optical networks by encompassing conventional electronic security with an optical security layer by generating replicated versions of the input data payload at the input node, and the transmission of each of the replicated versions over a corresponding one of the plurality of links. Moreover, each of the links is composed of multiple wavelengths to propagate optical signals or optical packets, and each of the replicated versions of the data payload may be propagated over a selected one of the wavelengths in each corresponding one of the plurality of links.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC +1
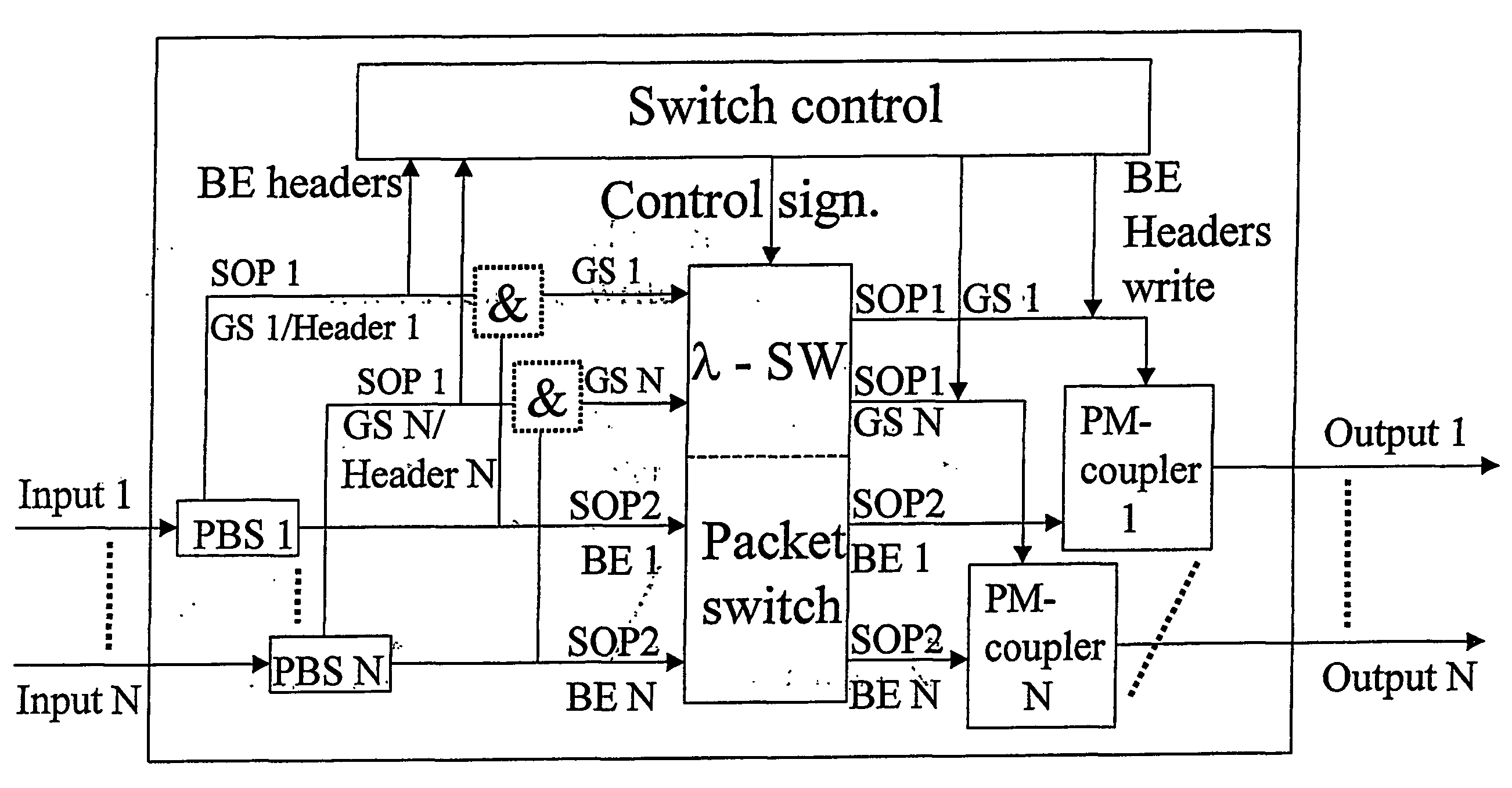
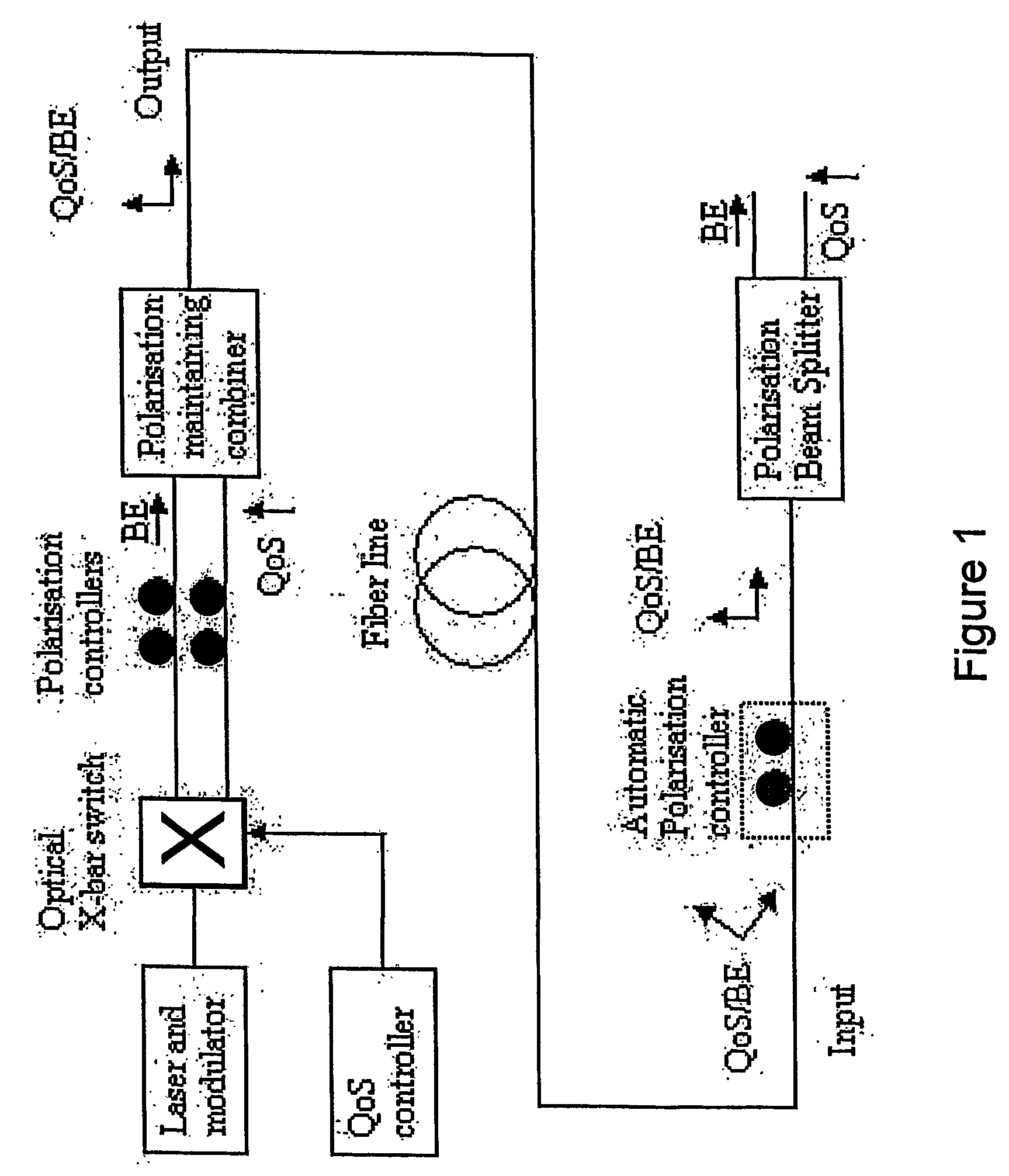
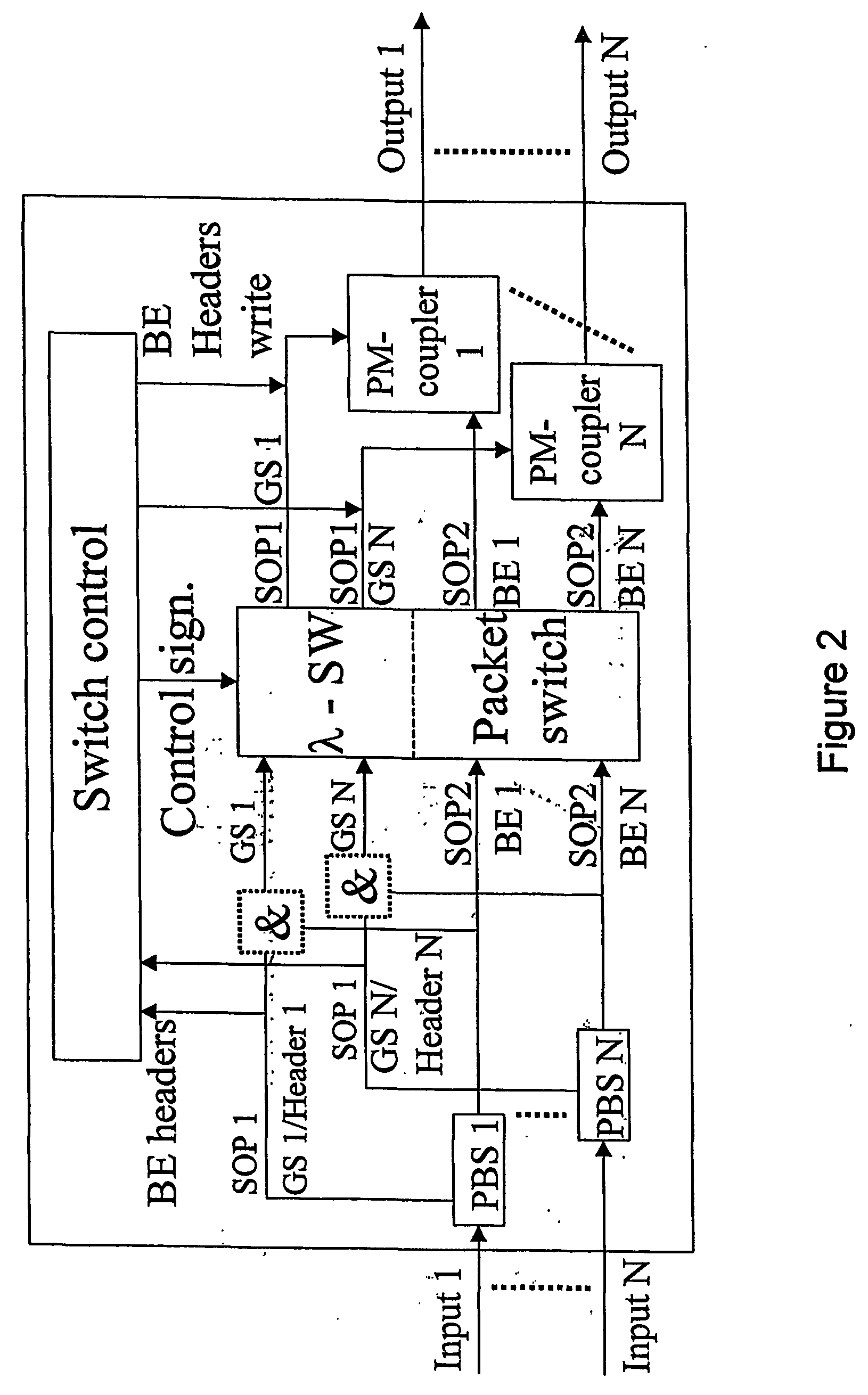
Use of polarization for differentiation of information
ActiveUS20060159454A1Reduce complexityLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsPolarization multiplexedElectronic network
The present invention discloses a system for signalling within optical or combined optical / electronic networks wherein a first transmission node executes polarization multiplexing on transmitted traffic, and at one or more intermediate nodes one or more of the following processes are carried out on the sent traffic: demultiplexing by polarization and / or polarization and / or SOP-alignment. Further a method for packet handling within optical packet switched networks where, at a first transmission node carries out polarisation demultiplexing of transmitted traffic, and at one or a number of intermediate nodes carries out one or more of the following processes on the transmitted traffic; demultiplexing by polarisation, and / or polarisation and / or SOP-alignment. Said separation into states of polarisation is used in separation of QoS-classes.
Owner:TRANSPACKET
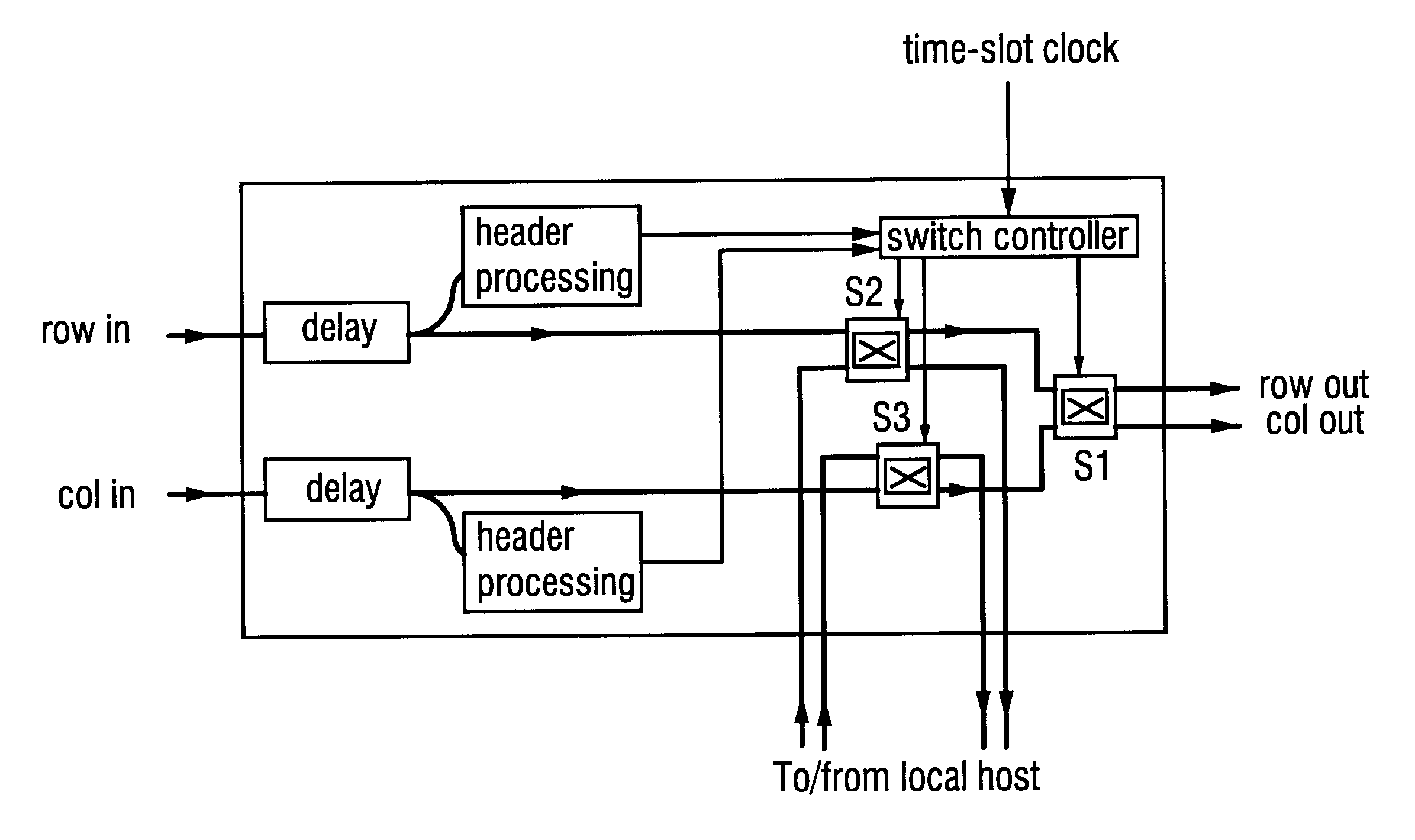
Optical packet switch
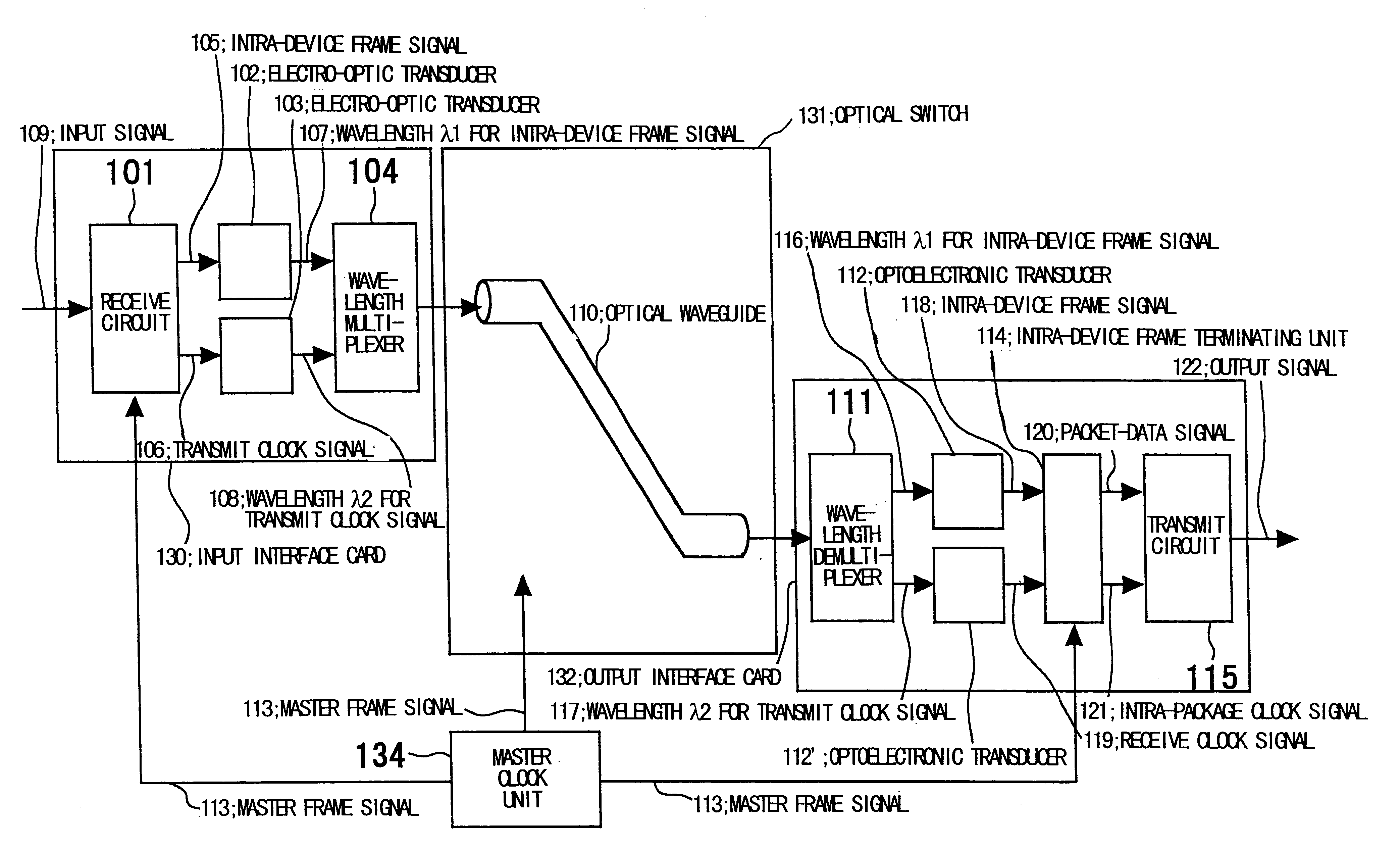
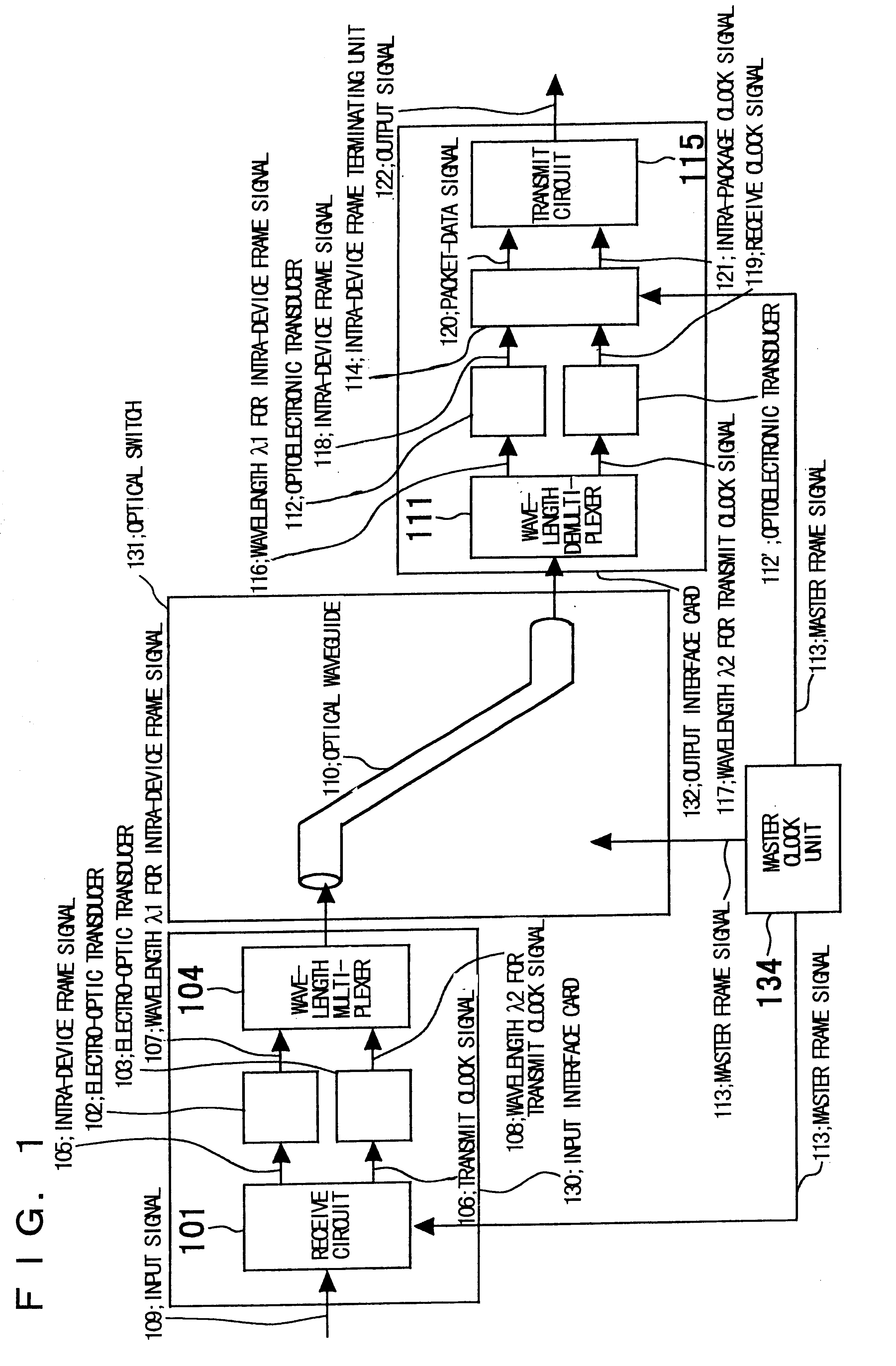
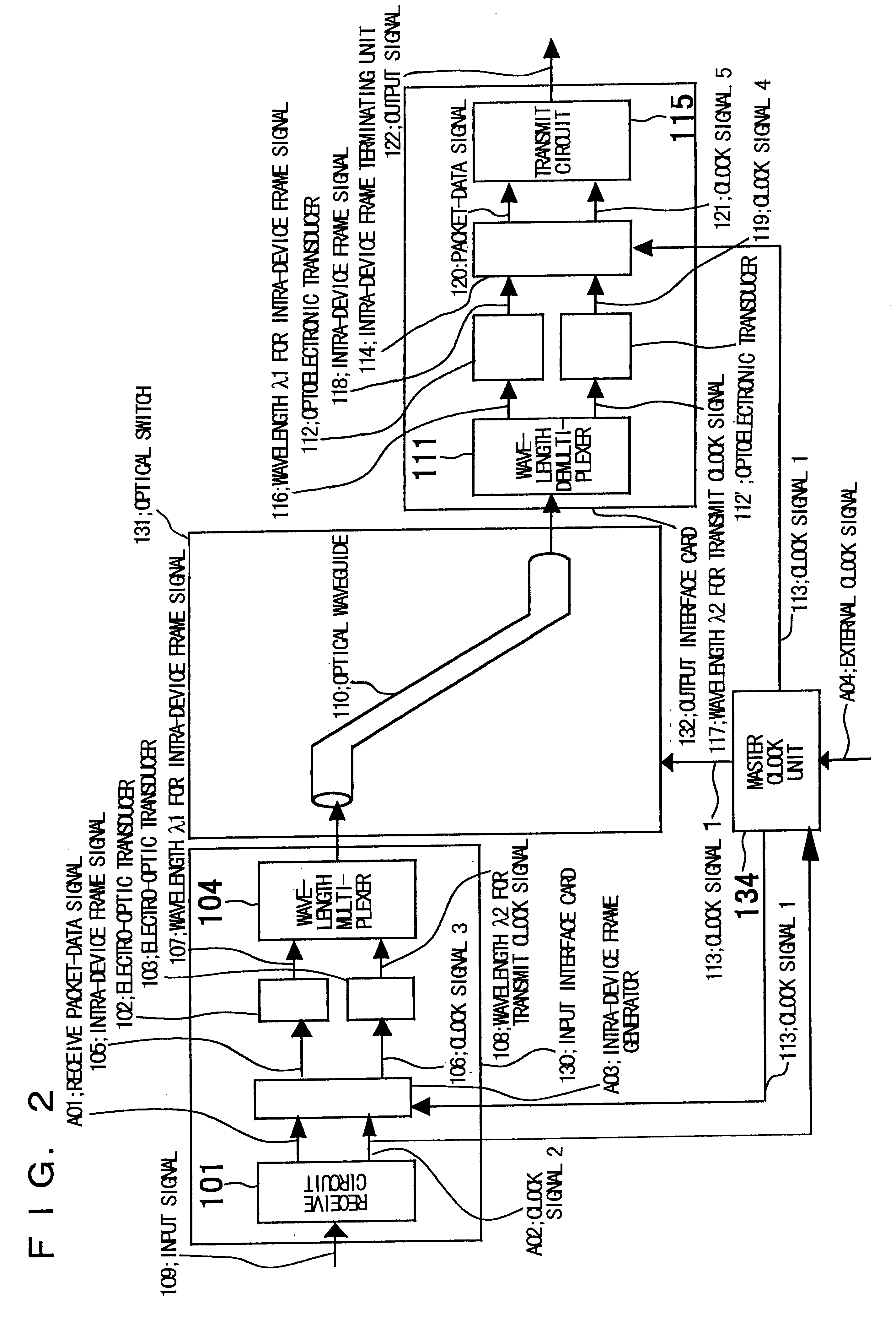
InactiveUS6512616B1Increase in sizeDevice is bulkyMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical packetData field
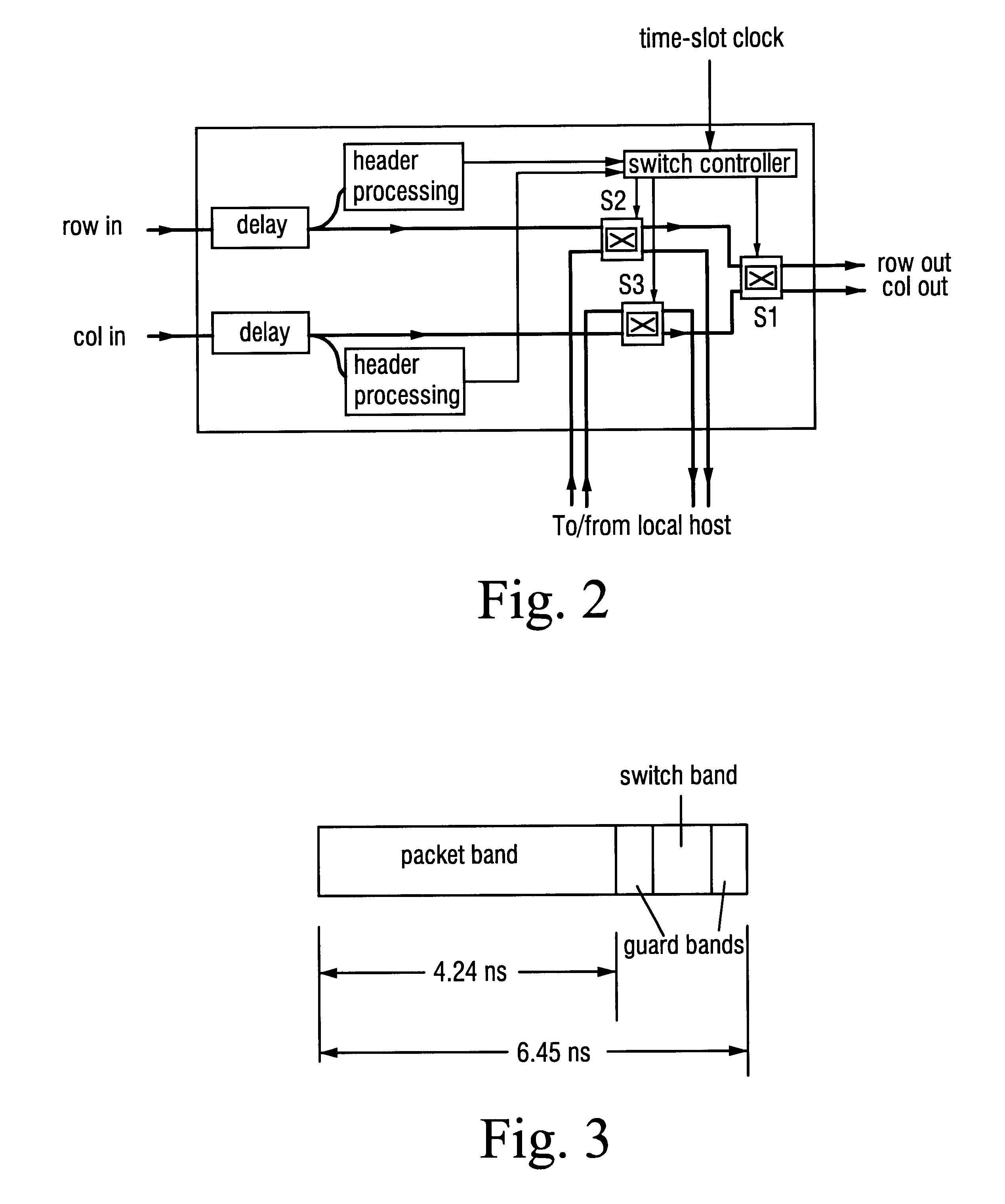
An optical packet switch uses electric circuits to implement input and output sections of an optical switch that performs packet switching. Retiming of packet data in the output section is facilitated to reduce the scale of the circuitry. In the input section a packet-data signal and a clock signal for retiming the packet data are wavelength multiplexed by a wavelength multiplexer and transferred over the same optical waveguide of the optical switch. In the output section the packet-data signal and the clock signal, which have been transferred from the same optical waveguide in the packet switch, are demultiplexed by a wavelength demultiplexer, and retiming of the packet-data signal is performed by an intra-device frame terminating unit. A frame format comprises, in addition to a flag pattern and a data field, a preamble and dummy data at the beginning and end thereof, respectively, for accommodating skew caused by transfer through the optical switch as well as a period of signal instability produced by switching of the optical switch. The packet data is transferred upon being placed in the data field of the frame format.
Owner:NEC CORP
Multilayer infrared reflecting film with high and smooth transmission in visible wavelength region and laminate articles made therefrom
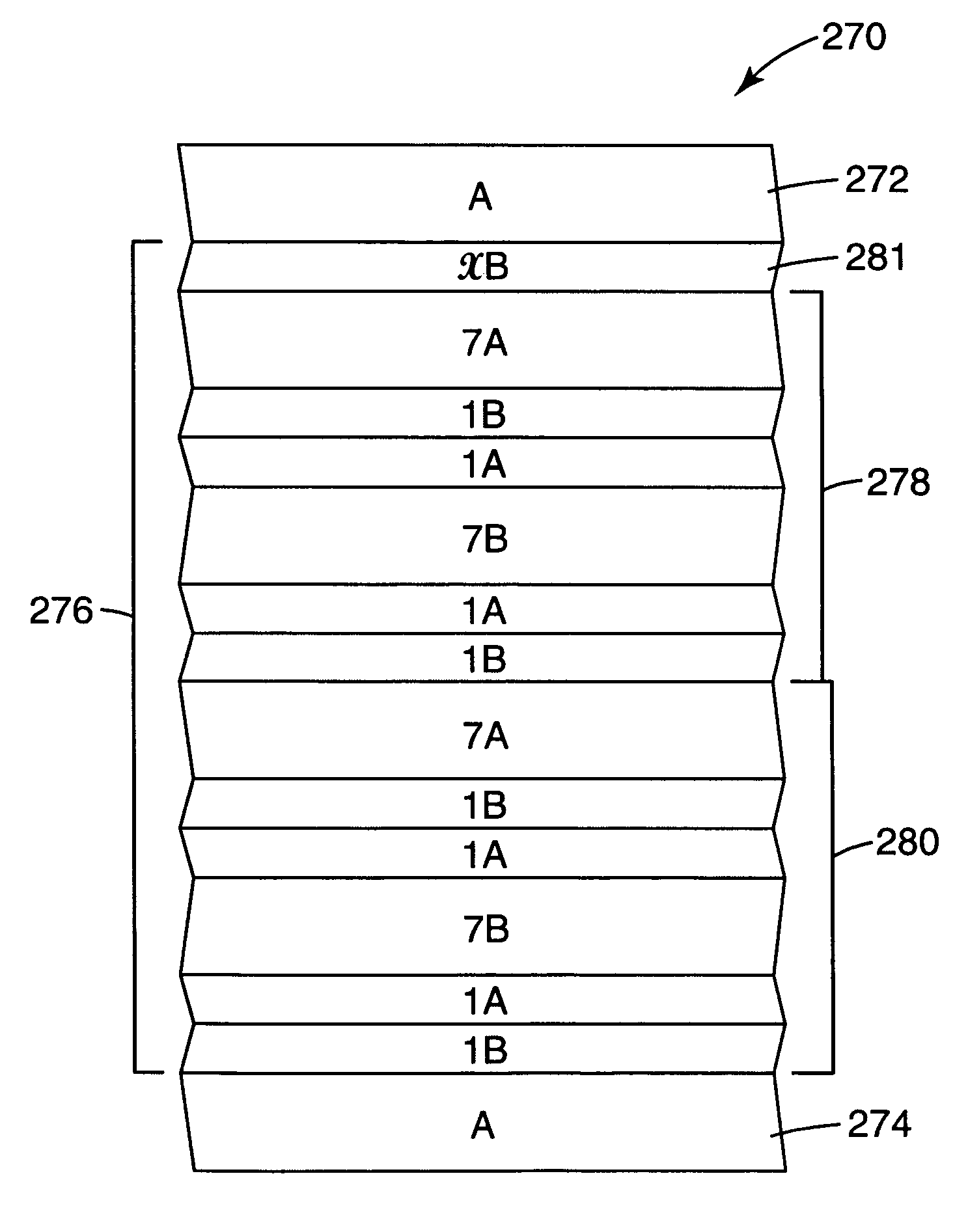
InactiveUS7236296B2High visible light transmittanceImprove performanceMirrorsOptical filtersOptical packetLength wave
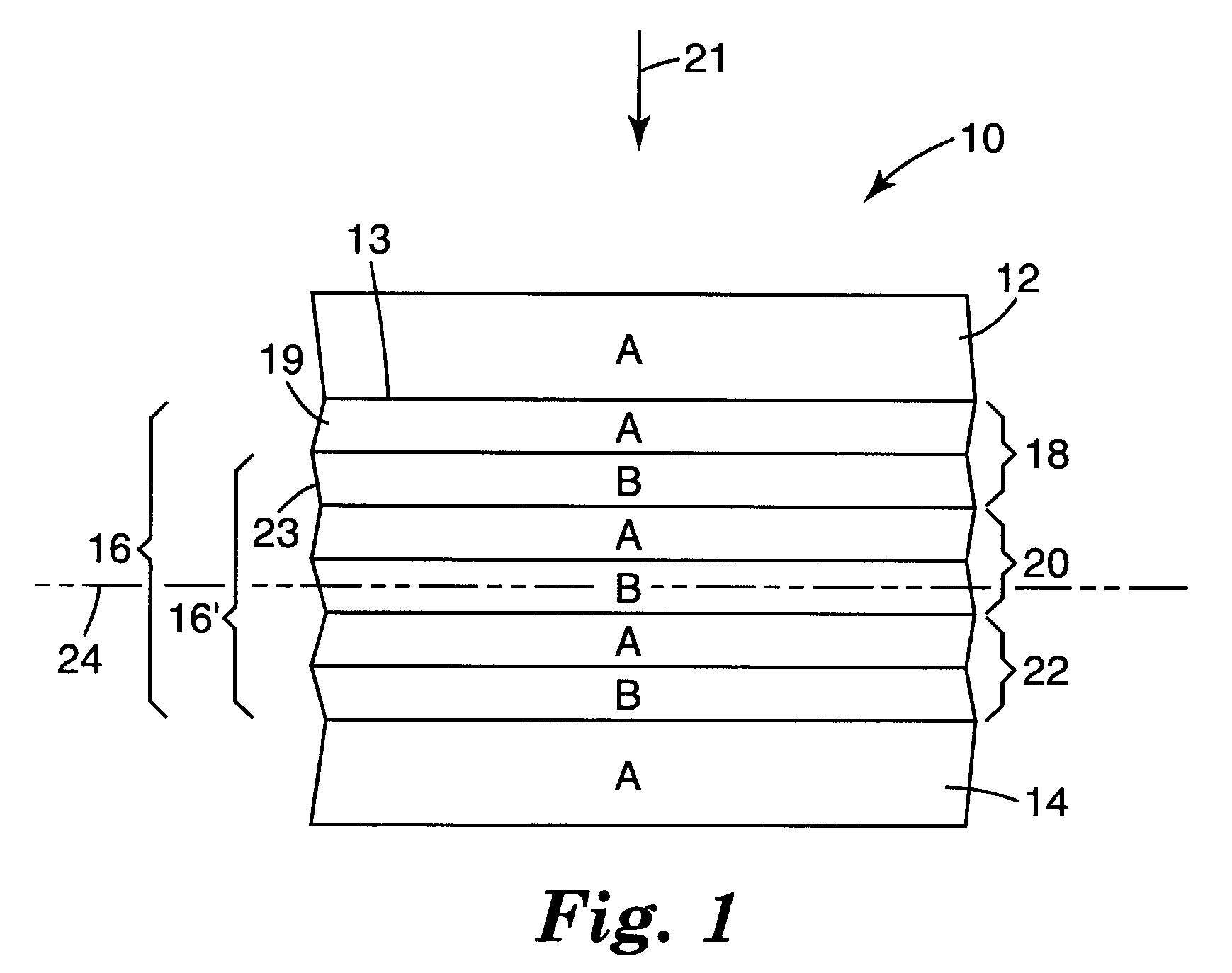
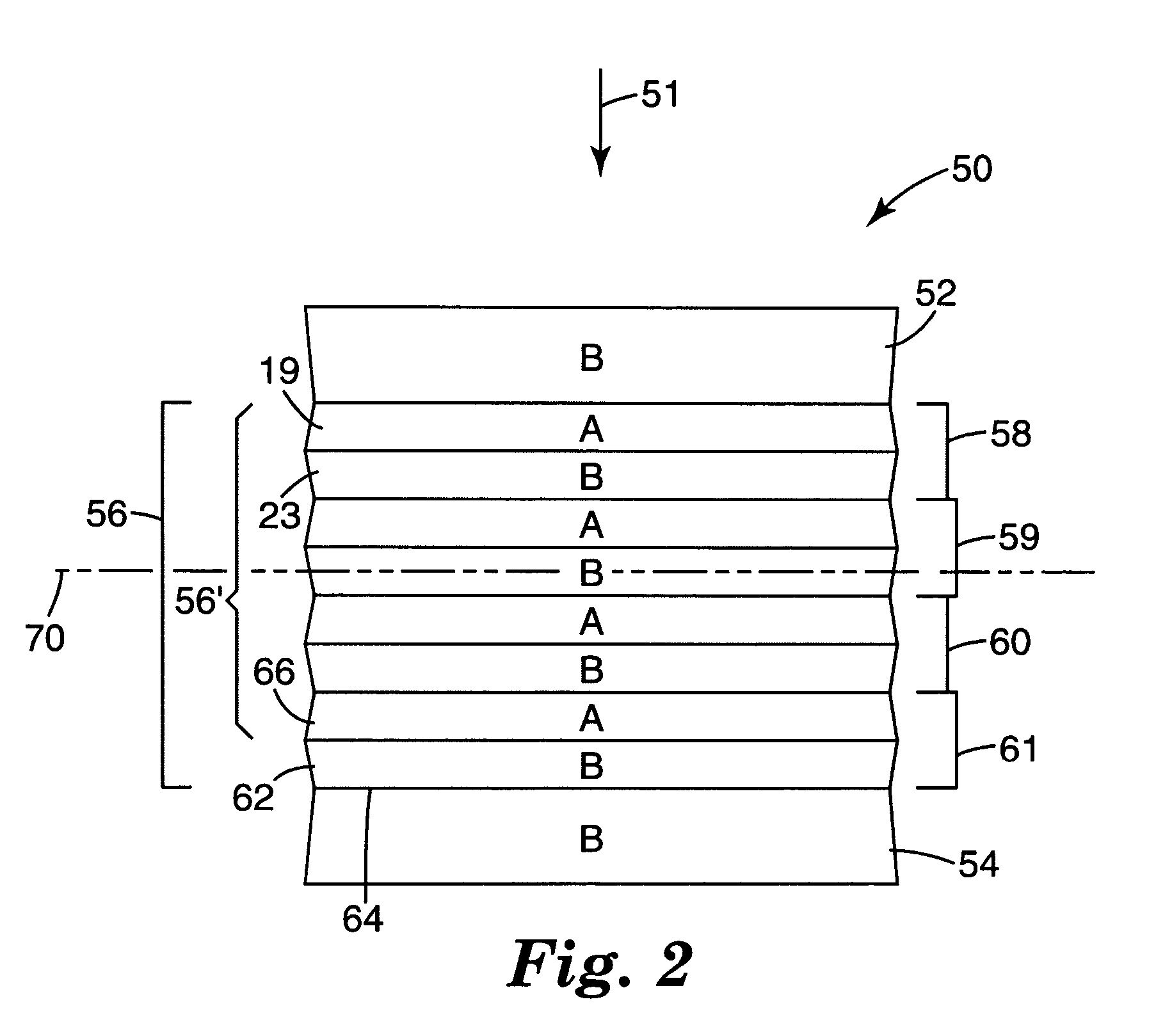
A multilayer film article is disclosed. The film includes an infrared light reflecting multilayer film having alternating layers of a first polymer type and a second polymer type and an infrared light absorbing or reflecting layer adjacent the multilayer film. The film includes a multilayer stack composed of alternating optical layers of first and second diverse polymers A, B. The optical layers when counted from one end of a first effective optical packet form a plurality of unit cells each having six optical layers arranged in relative optical thicknesses in a first cyclic permutation of 7A1B1A7B1A1B. At normal incidence the first effective optical packet provides a reflection band at infrared wavelengths and substantially transmits light at visible wavelengths.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
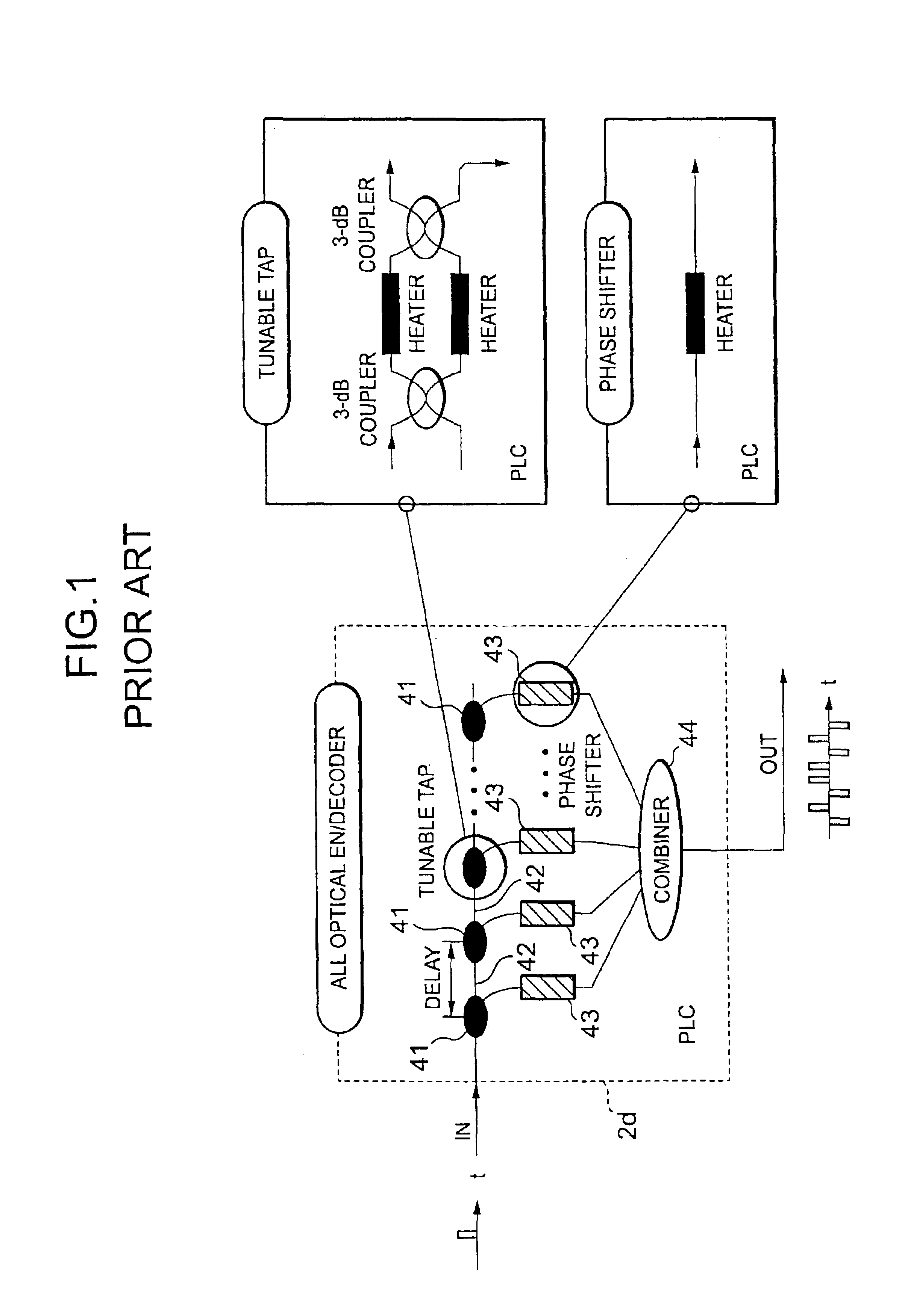
Optical processor
Method and apparatus are disclosed for optical packet decoding, waveform generation and wavelength multiplexing / demultiplexing using a programmed holographic structure. A configurable programmed holographic structure is disclosed. A configurable programmed holographic structure may be dynamically re-configured through the application of control mechanisms which alter operative holographic structures.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
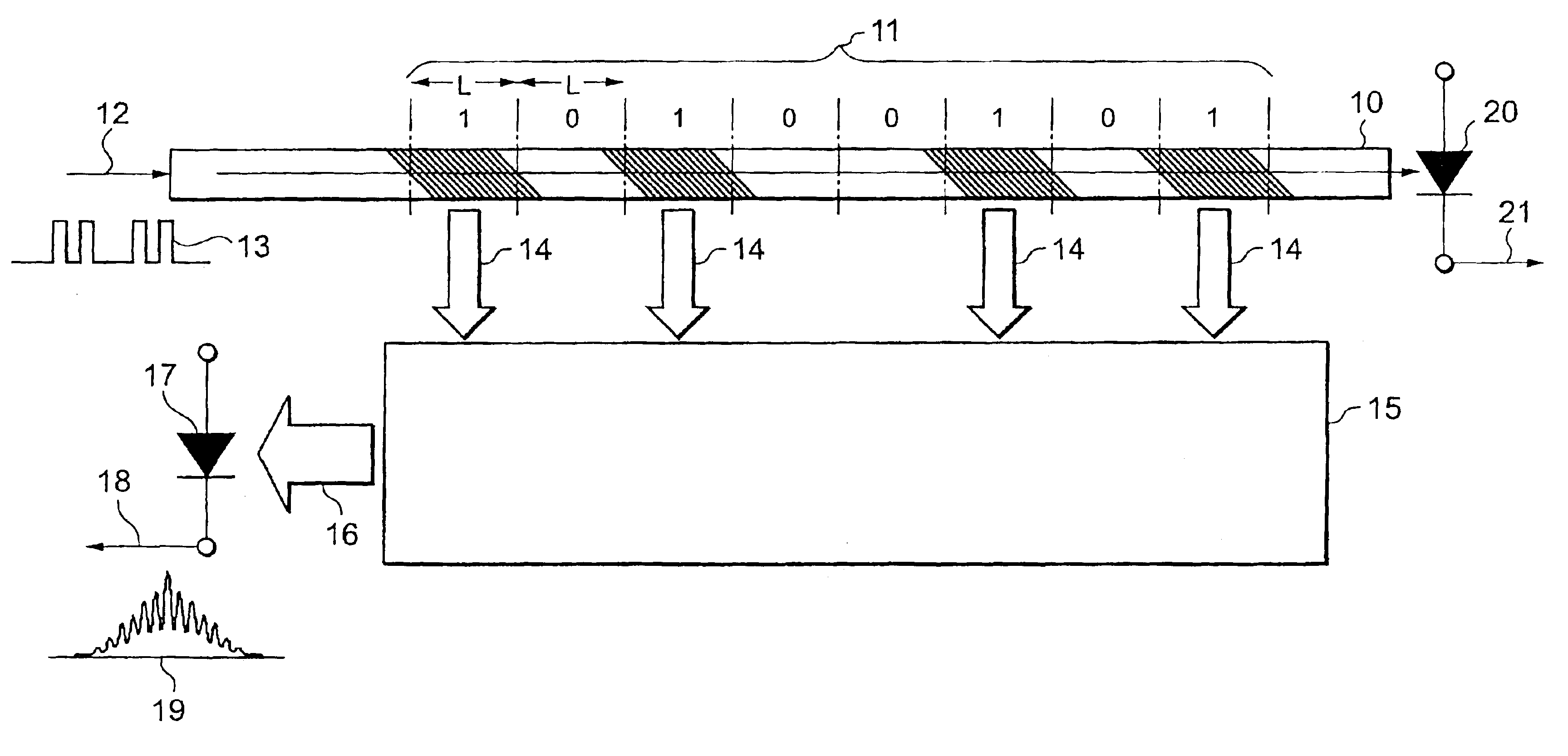
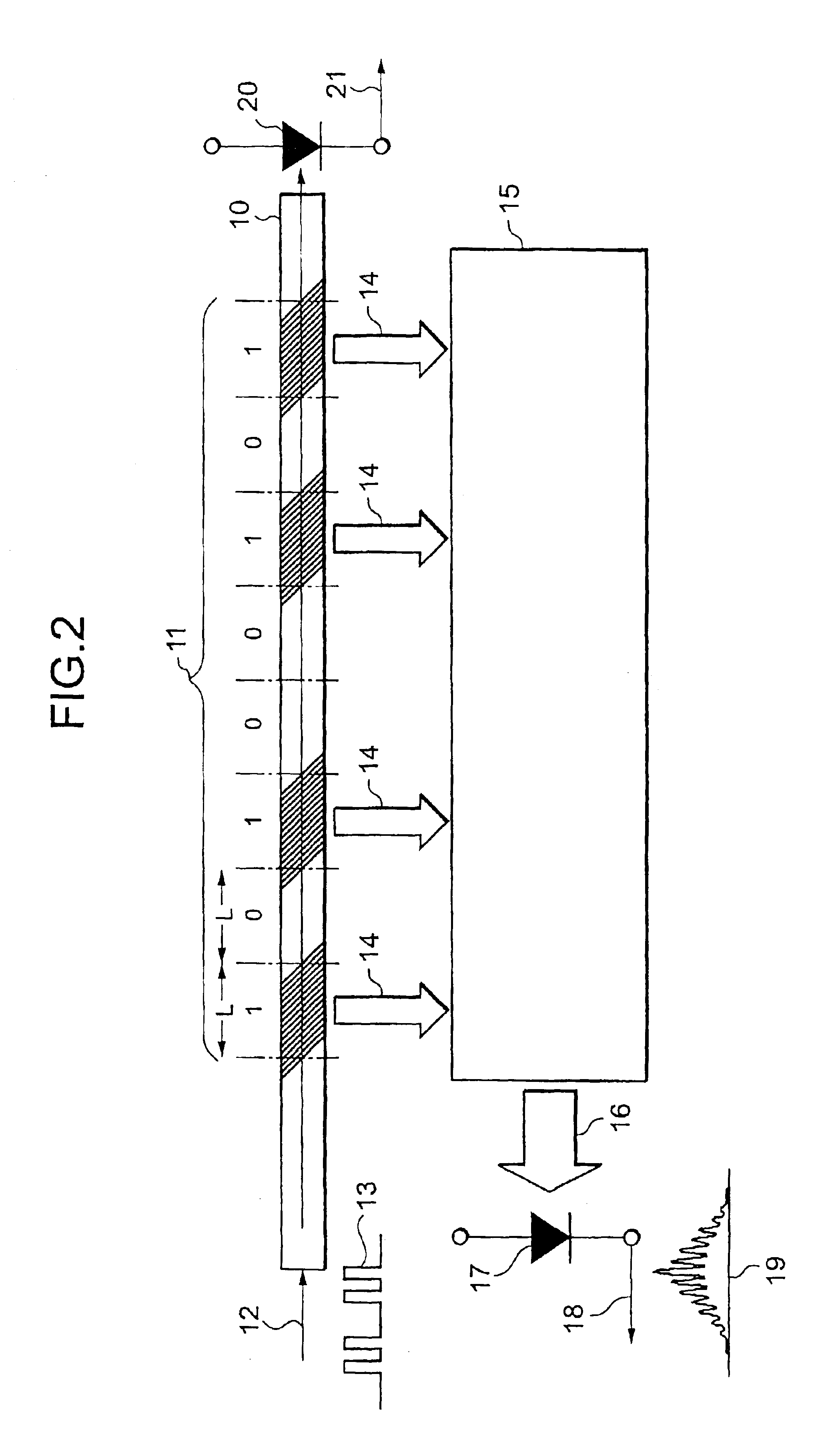
Optical packet header identifier, optical router incorporating the same therein, and optical routing method using the router
InactiveUS6892001B2Simple configurationReduce power consumptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsGratingOptical packet
An optical packet header identifier having a simplified configuration and being superior in reliability, stability, and economical efficiency, an optical router incorporating the identifier therein, and a routing method using the optical router are provided. The optical packet header identifier includes an optical waveguide, optical focusing elements, and a photo receiver. Tilted gratings for diffracting an incident optical beam and emitting the beams as diffracted optical beams to the outside of the waveguide are formed within the optical waveguide. The tilted gratings are not formed uniformly in a longitudinal direction of a core of the optical waveguide, but are arranged at intervals. The length of a portion containing a set of gratings and the length of a portion containing no gratings can be defined in increments of length “L”. “L” equals to the spatial length which 1 bit in an optical signal occupies.
Owner:LASERFRONT TECH
Secure optical layer multicasting to effect survivability
InactiveUS6850707B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer hardwareSurvivability
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The technique effects survivability and security of the optical networks by encompassing conventional electronic security with an optical security layer by generating replicated versions of the input data payload at the input node, and the transmission of each of the replicated versions over a corresponding one of the plurality of links. Moreover, each of the links is composed of multiple wavelengths to propagate optical signals or optical packets, and each of the replicated versions of the data payload may be propagated over a selected one of the wavelengths in each corresponding one of the plurality of links.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
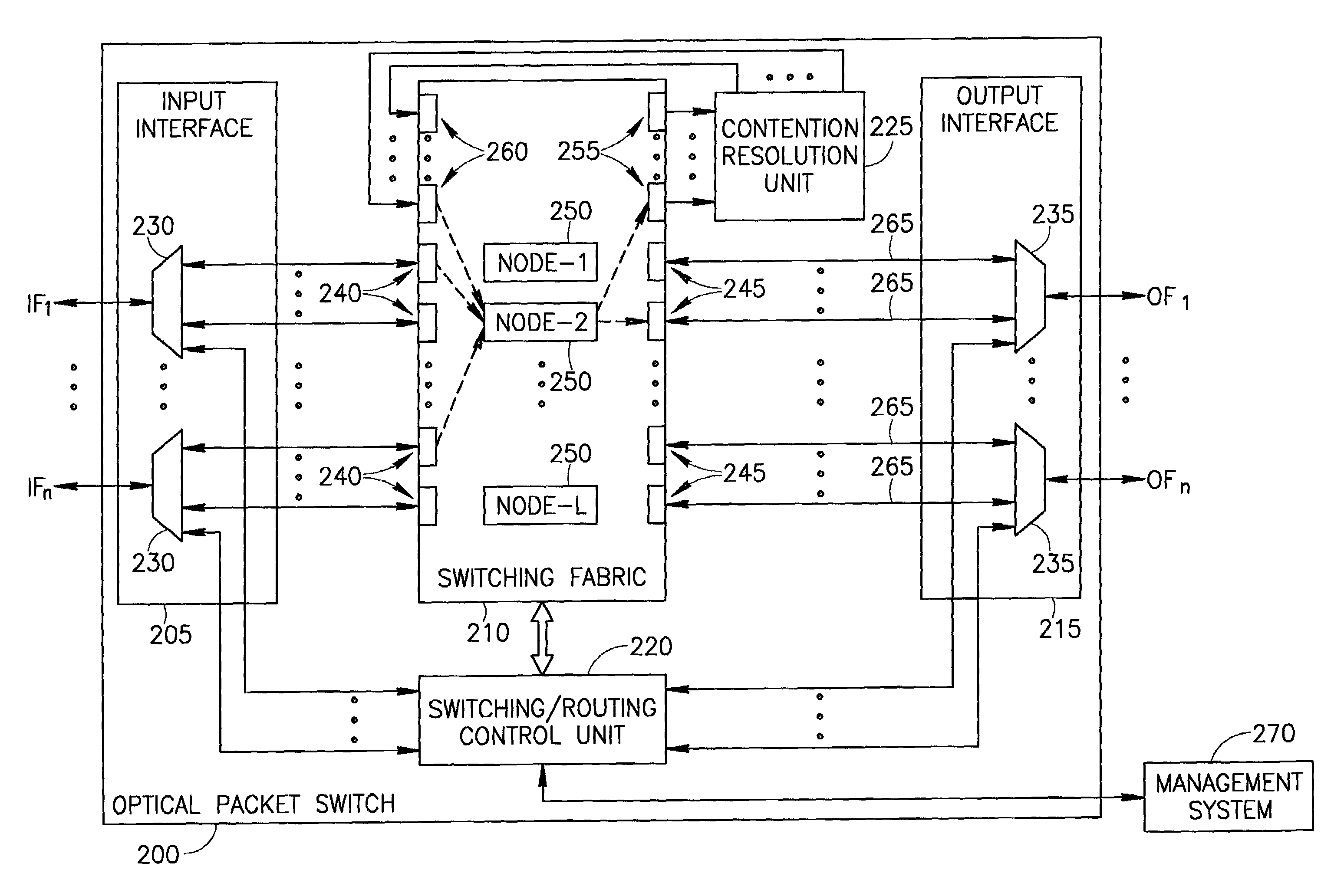
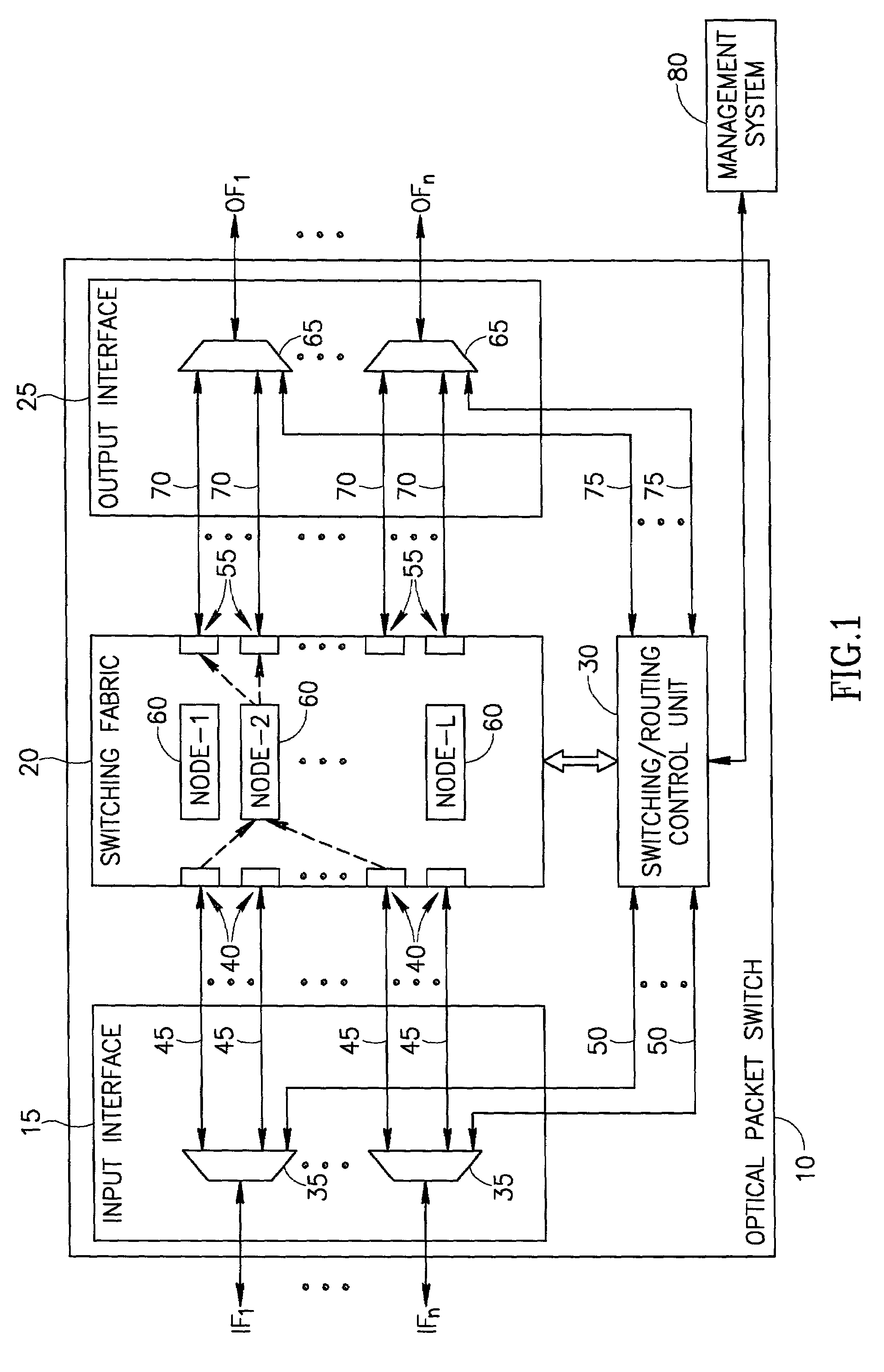
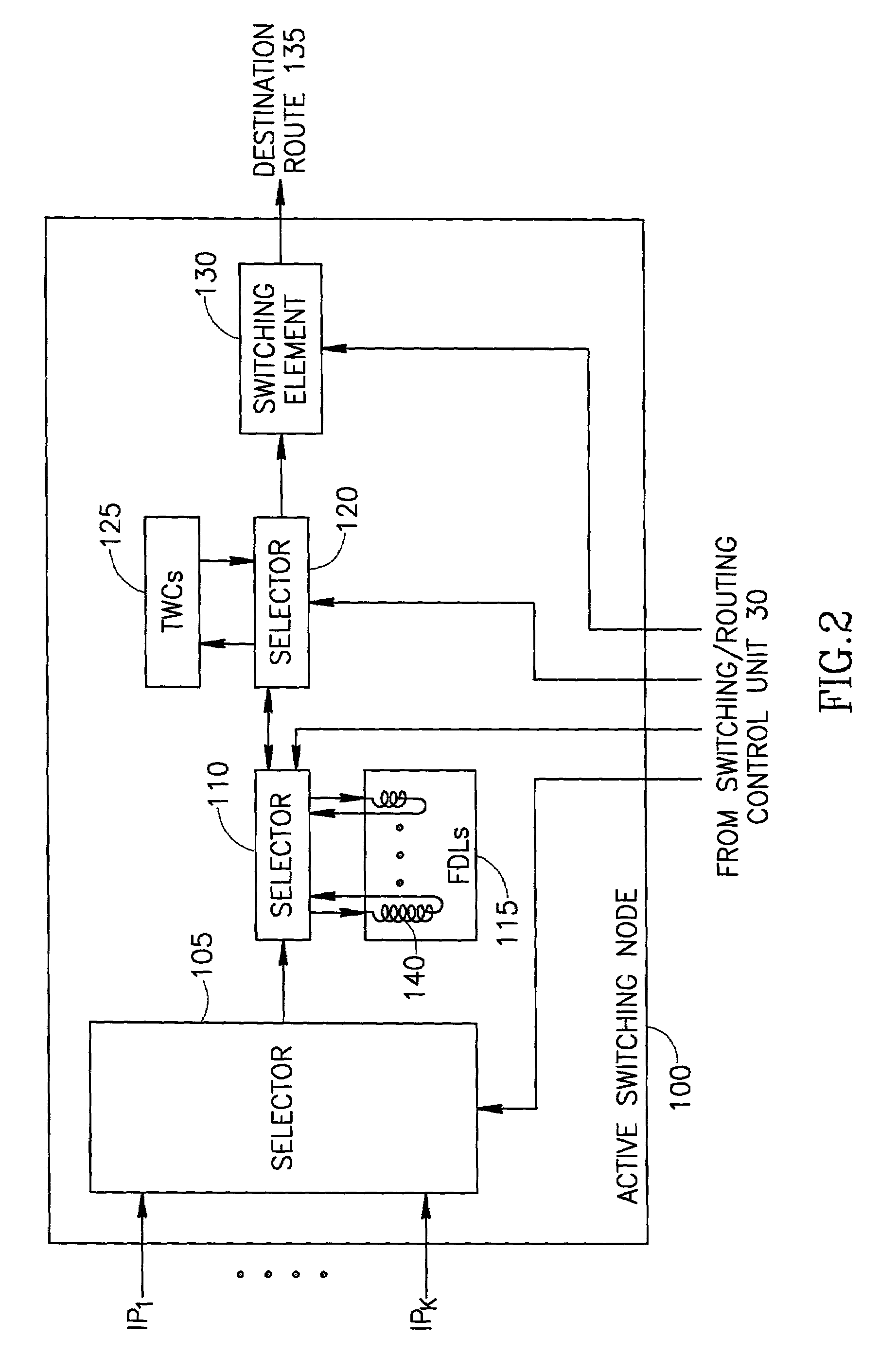
Optical packet switching apparatus and methods
ActiveUS7106967B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionComputer networkOptical packet
An optical packet switch switches optical packets according to bit-rates at which the optical packets are provided. For example, optical packets that are received at similar bit-rates may be routed to a destination at separate time slots over a single channel wavelength, and optical packets that are received at different bit-rates may be routed to the destination over separate channel wavelengths. When optical packets are provided at different bit-rates on a plurality of input paths, optical packets provided at low bit-rates may be compacted before switching to the destination. Alternatively or additionally, the bit-rates of the optical packets may be balanced before switching to the destination. Bandwidth contention among optical packets may be resolved by polarizing optical packets originating from separate input paths in different polarization directions, and merging optical packets having different polarization directions onto a single switched channel wavelength. Compaction of optical packets may alternatively be employed for resolution of bandwidth contention. Related apparatus and methods are also described.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
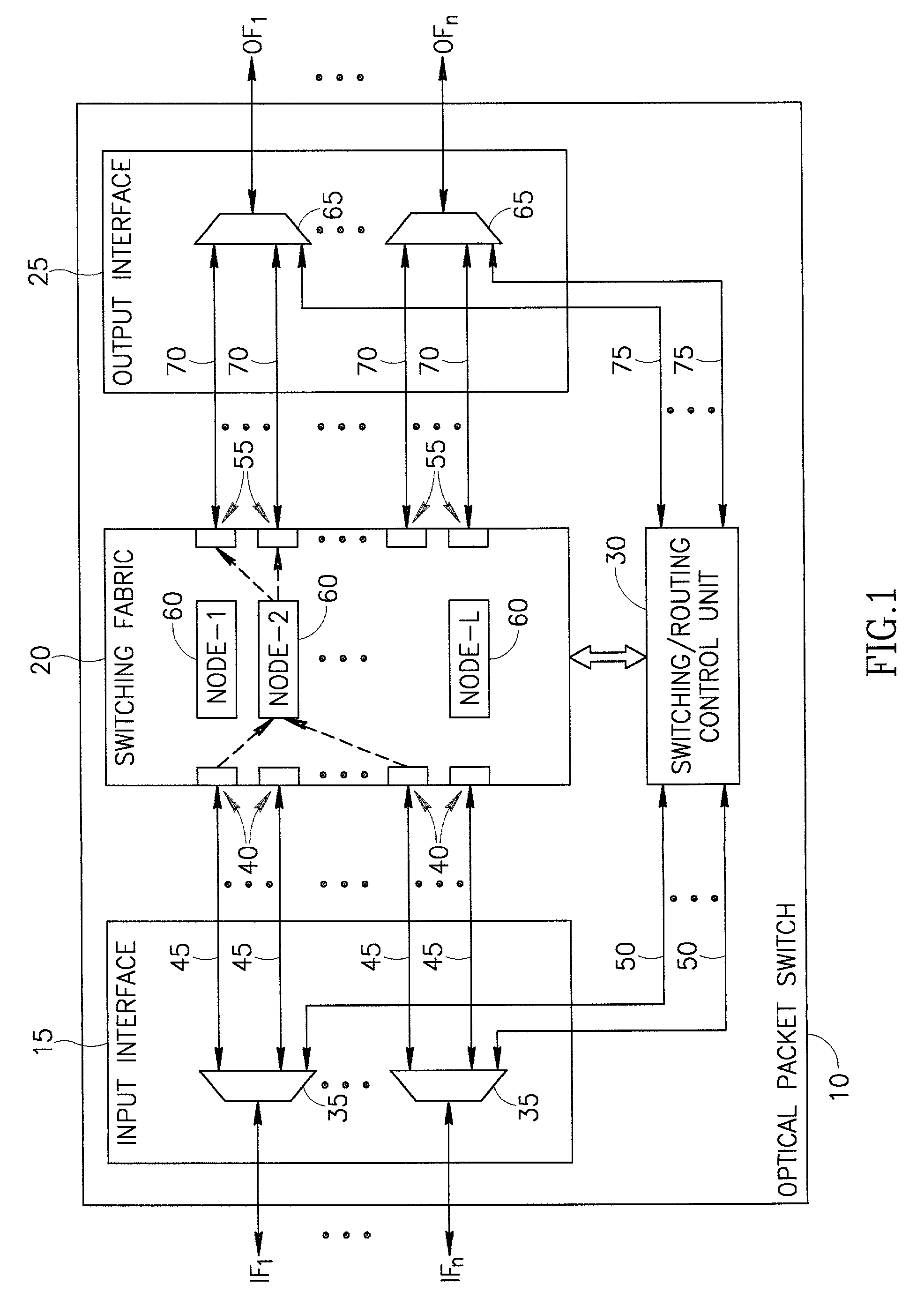
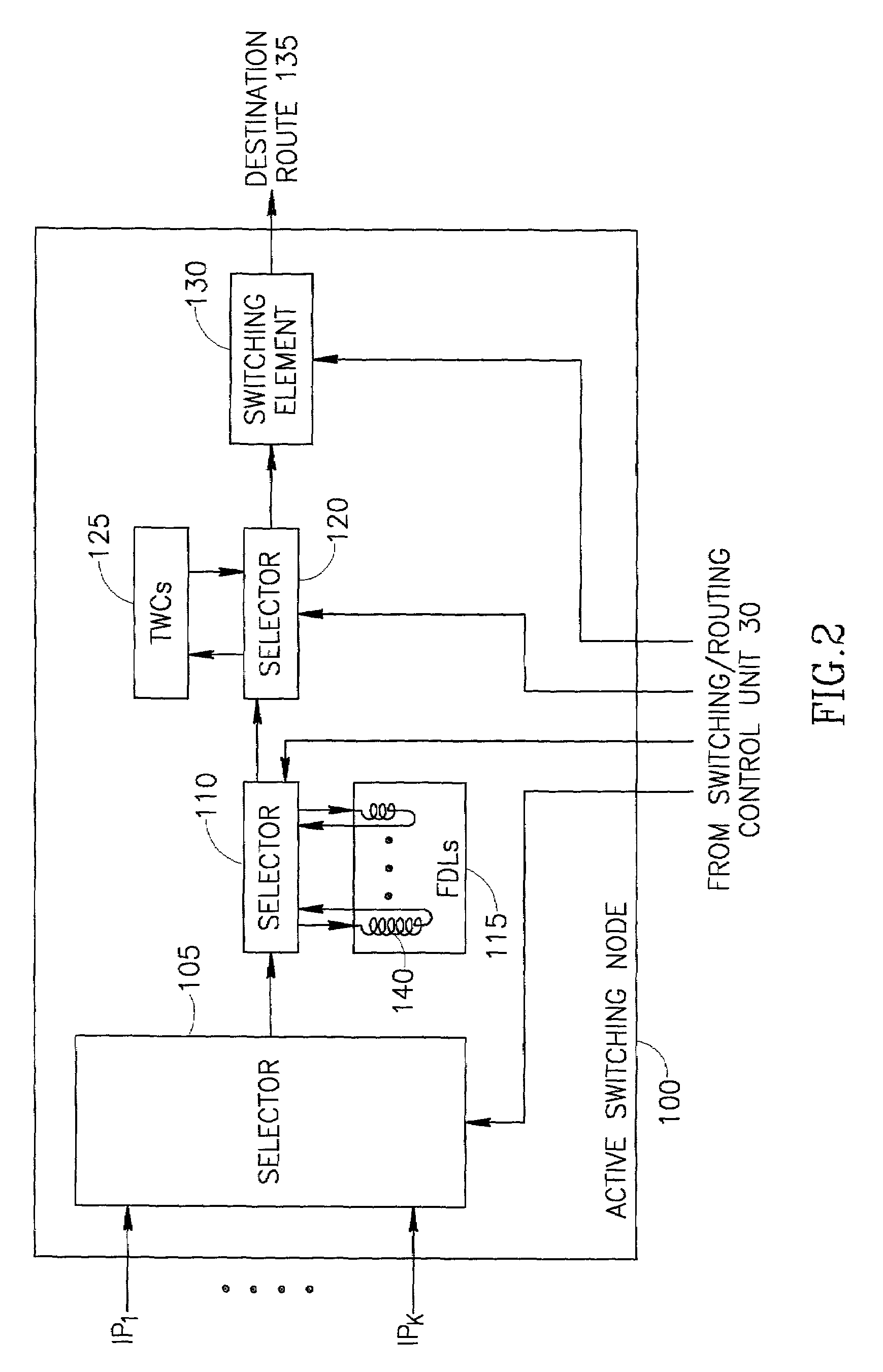
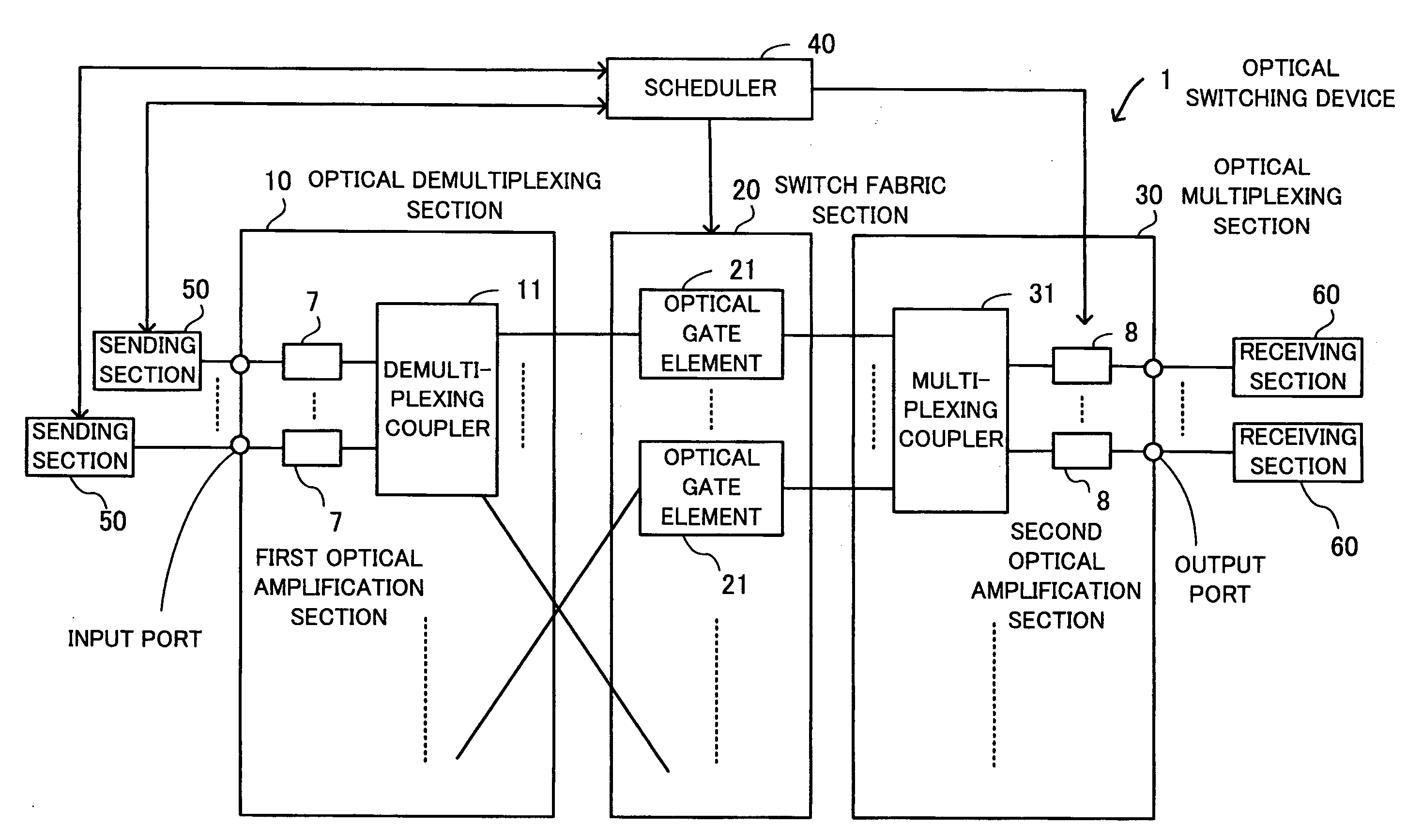
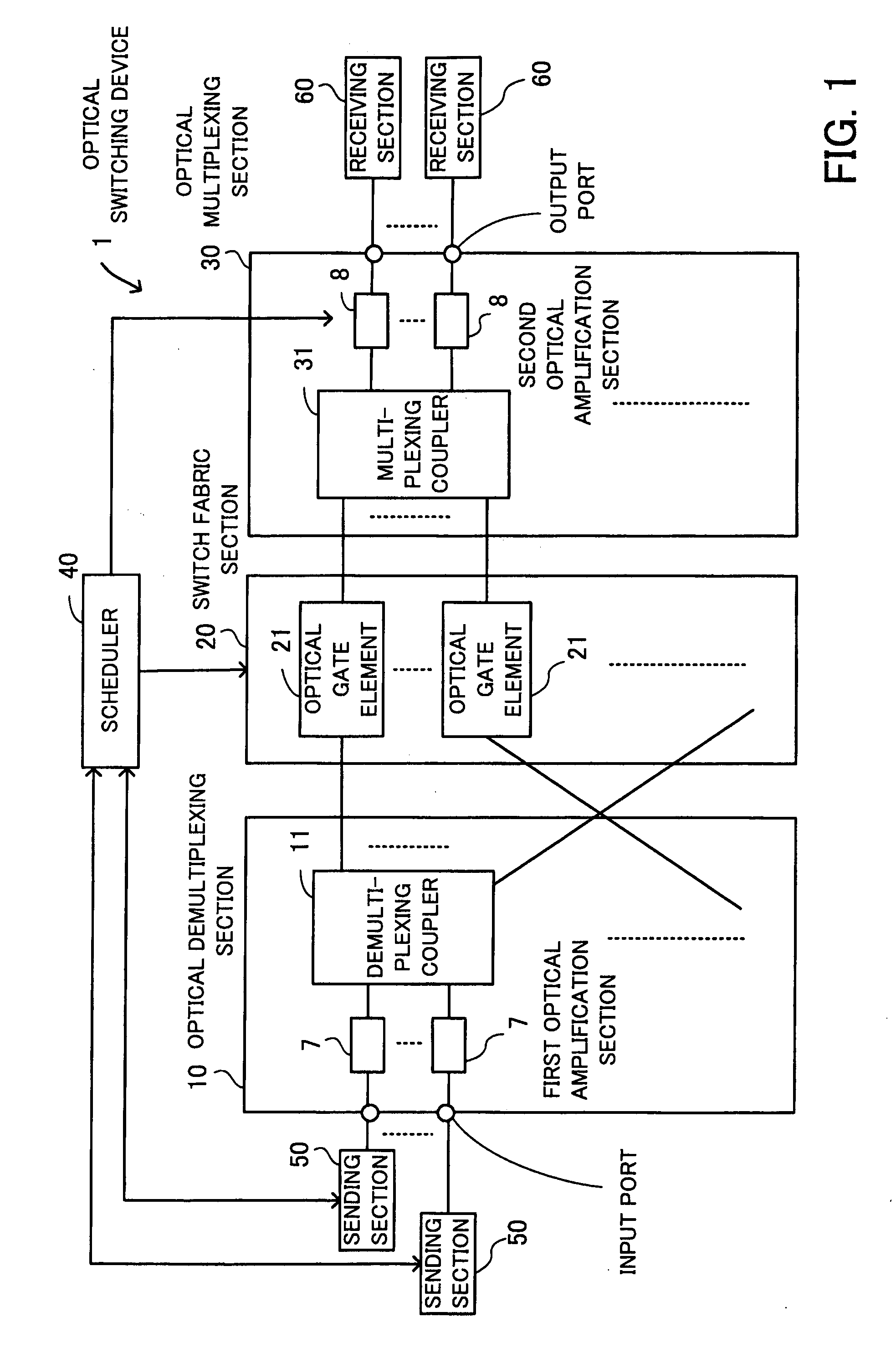
Optical switching device
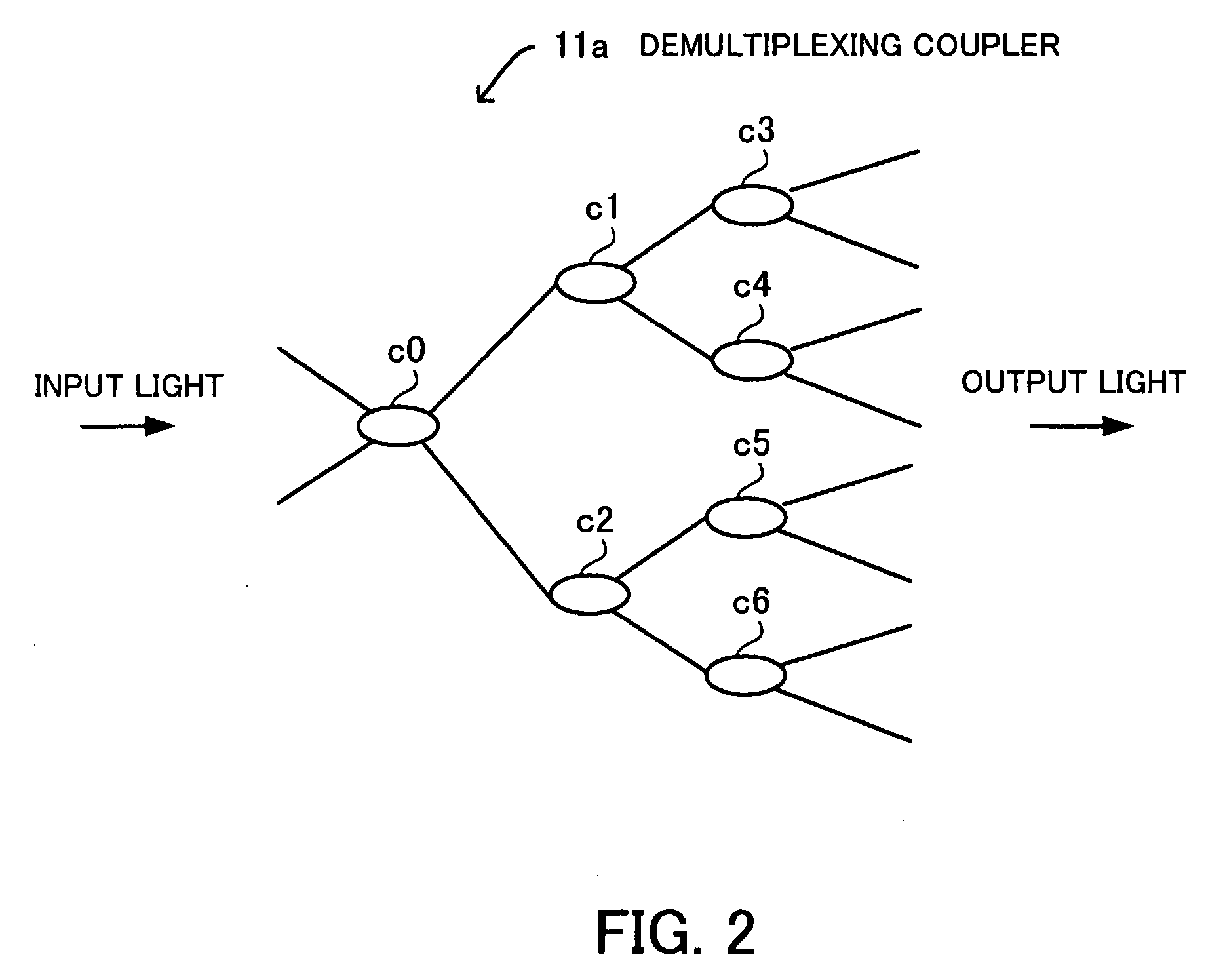
ActiveUS20090003827A1Low coatScale upMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexMultiplexingOptical packet
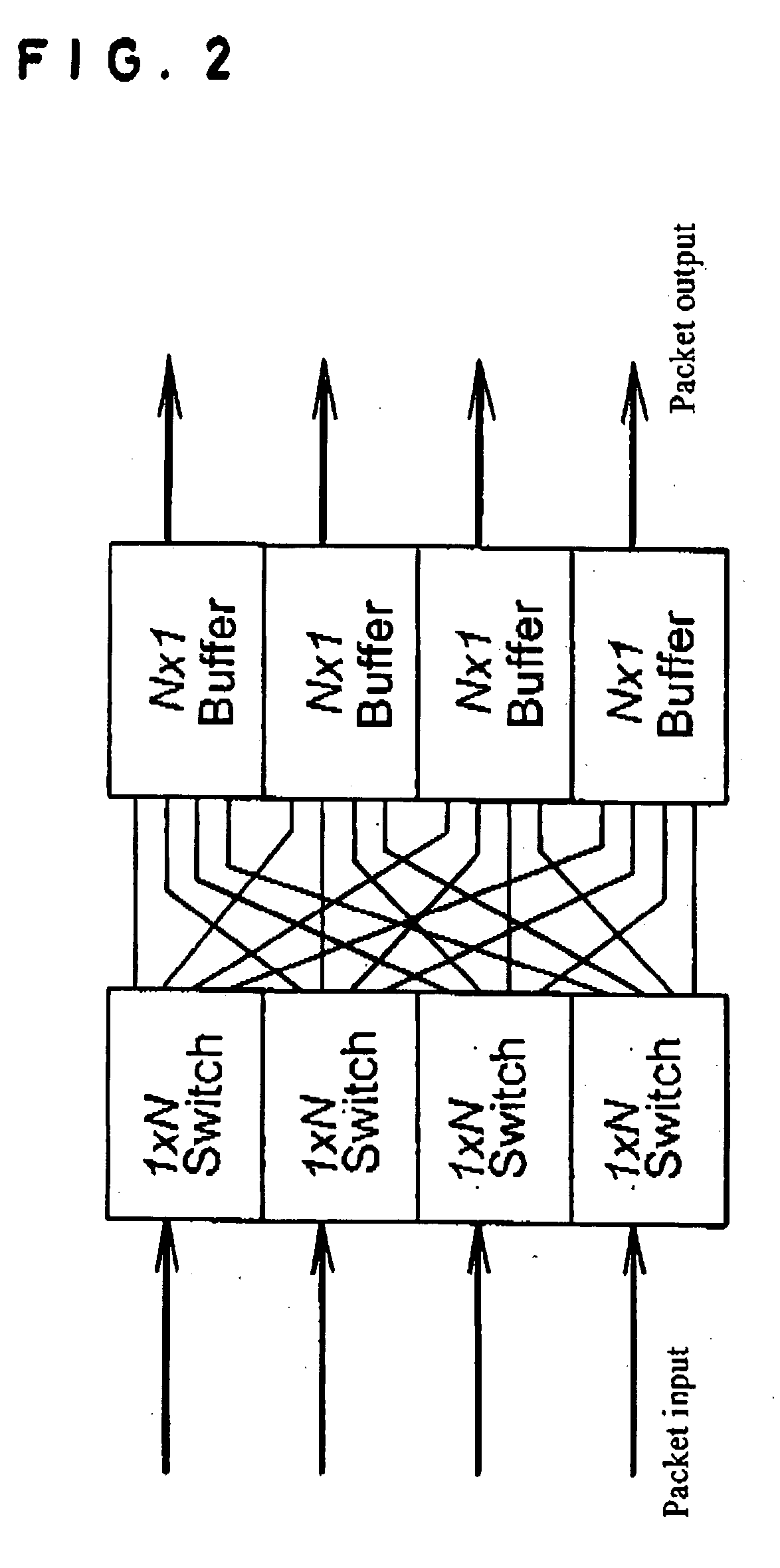
An optical switching device the size and costs of which are reduced by decreasing the number of switching elements and which can flexibly accommodate the expansion of the number of ports. An optical demultiplexing section has 2n (n=1, 2, 3, . . . ) input ports and 2m (m>n) output ports and includes demultiplexing couplers for demultiplexing input optical packets. A switch fabric section includes optical gate elements for switching optical packets outputted from the optical demultiplexing section by switch drive control. An optical multiplexing section has 2m input ports and 2n output ports and includes multiplexing couplers for multiplexing the optical packets which pass through the optical gate elements. A scheduler exercises control over an entire optical packet switching process.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
On-Chip Optical Router for Hybrid Switching
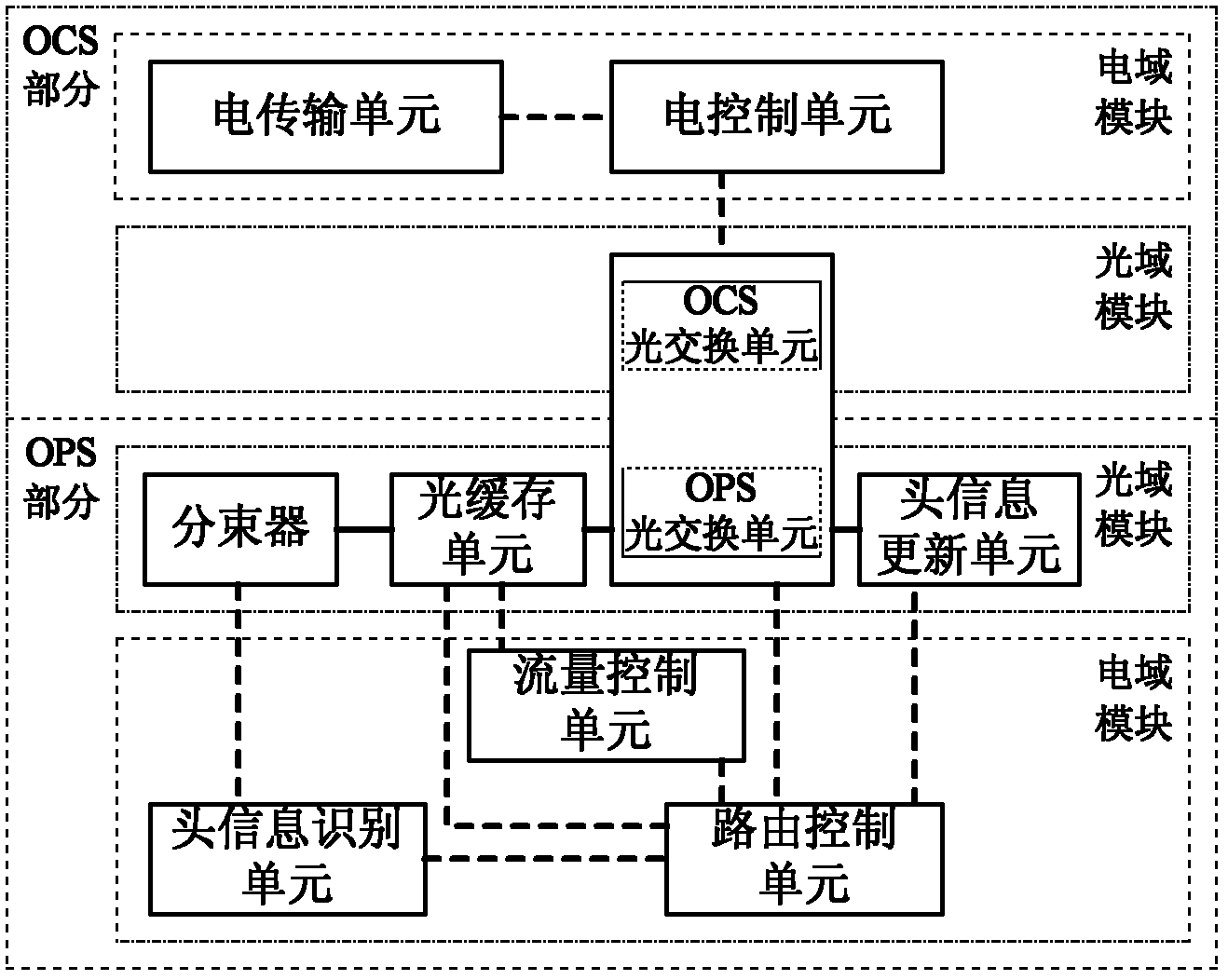
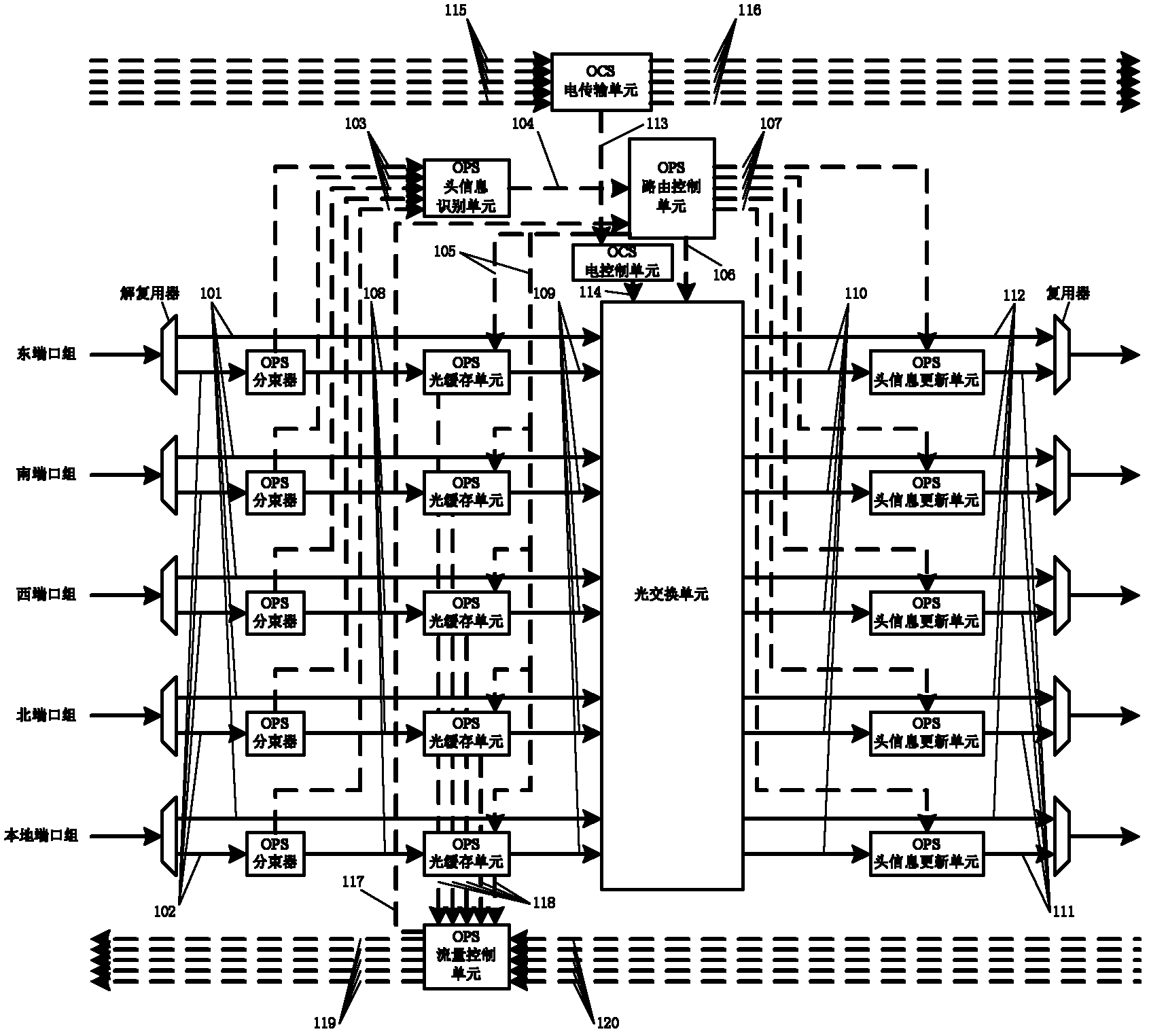
InactiveCN102281478AImprove resource utilizationReduce communication delayMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksResource utilizationOptical packet
The invention discloses an on-chip optical router for hybrid switching, which mainly solves the problems of high communication delay, low network transmission efficiency and low resource utilization rate facing a single exchange mechanism in the existing on-chip optical router. The router comprises an OCS (Optical Circuit Switching) part and an OPS (Optical Packet Switching) part, wherein each part is composed of an electric field module and an optical field module, the OCS electric field module establishes an optical link for the OCS optical field module according to electric link establishing information before transmitting messages, and the OPS electric field module provides control information for the OPS optical field module in a transmitting and switching process of optical packets. The OCS part is used for transmitting the messages for using an OCS switching mechanism, and the OPS part is used for transmitting the messages for using an OPS switching mechanism. The on-chip optical router respectively optimizes performances of different types of messages, has the advantages of less communication delay, high network transmission efficiency and high resource utilization rate, and is suitable for interconnections and communications in an on-chip optical network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
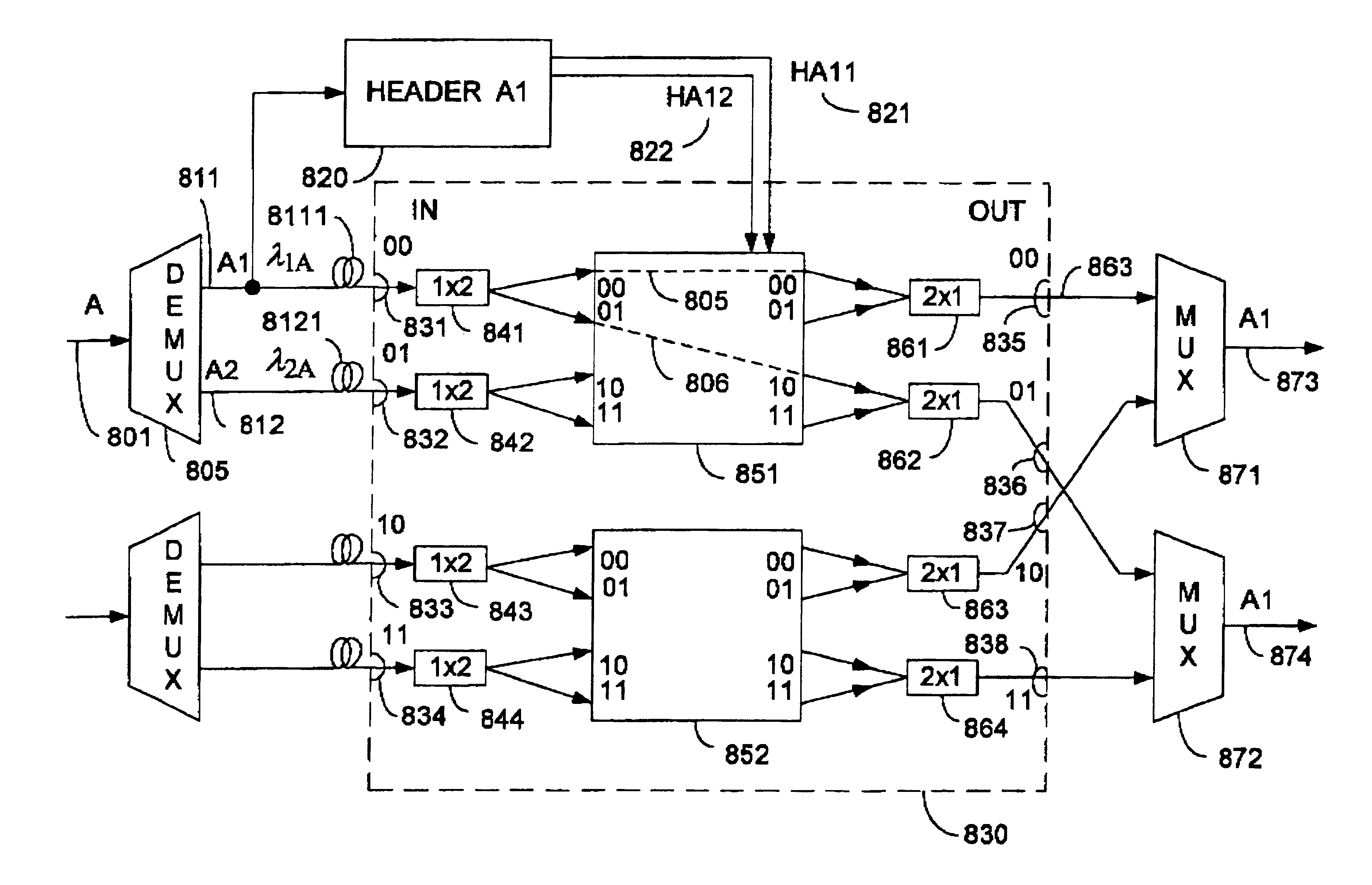
Time slot tunable all-optical packet data demultiplexer
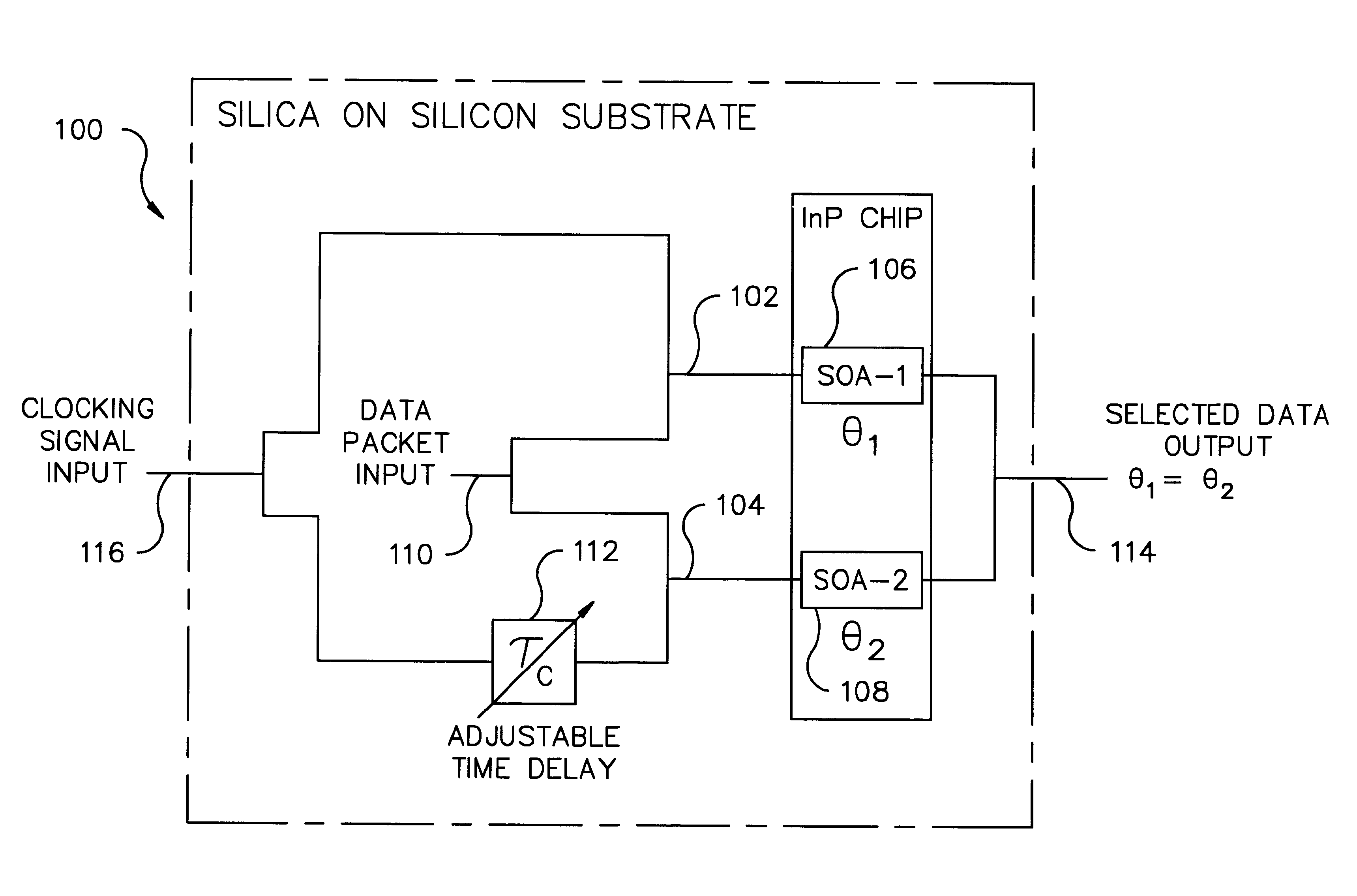
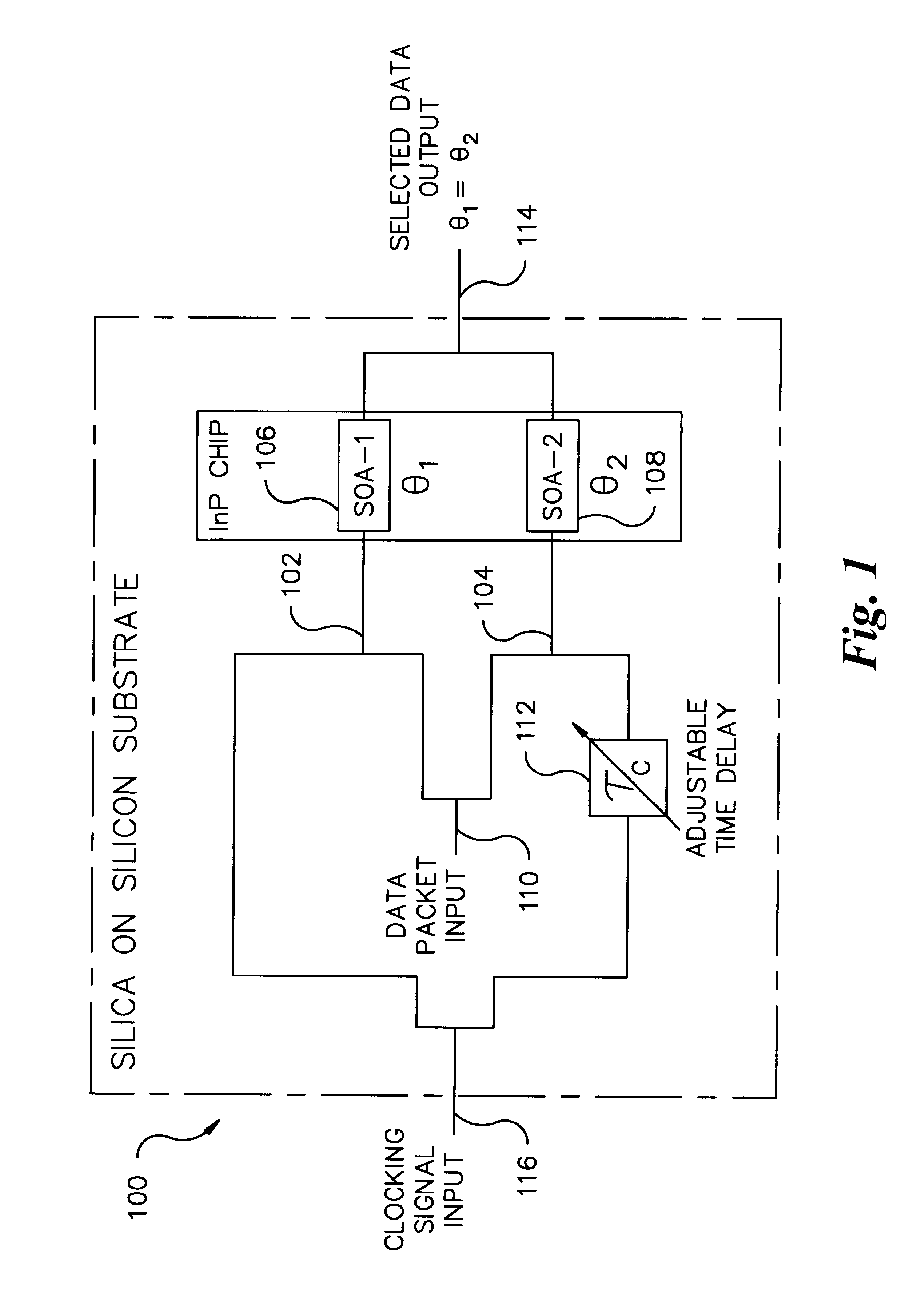
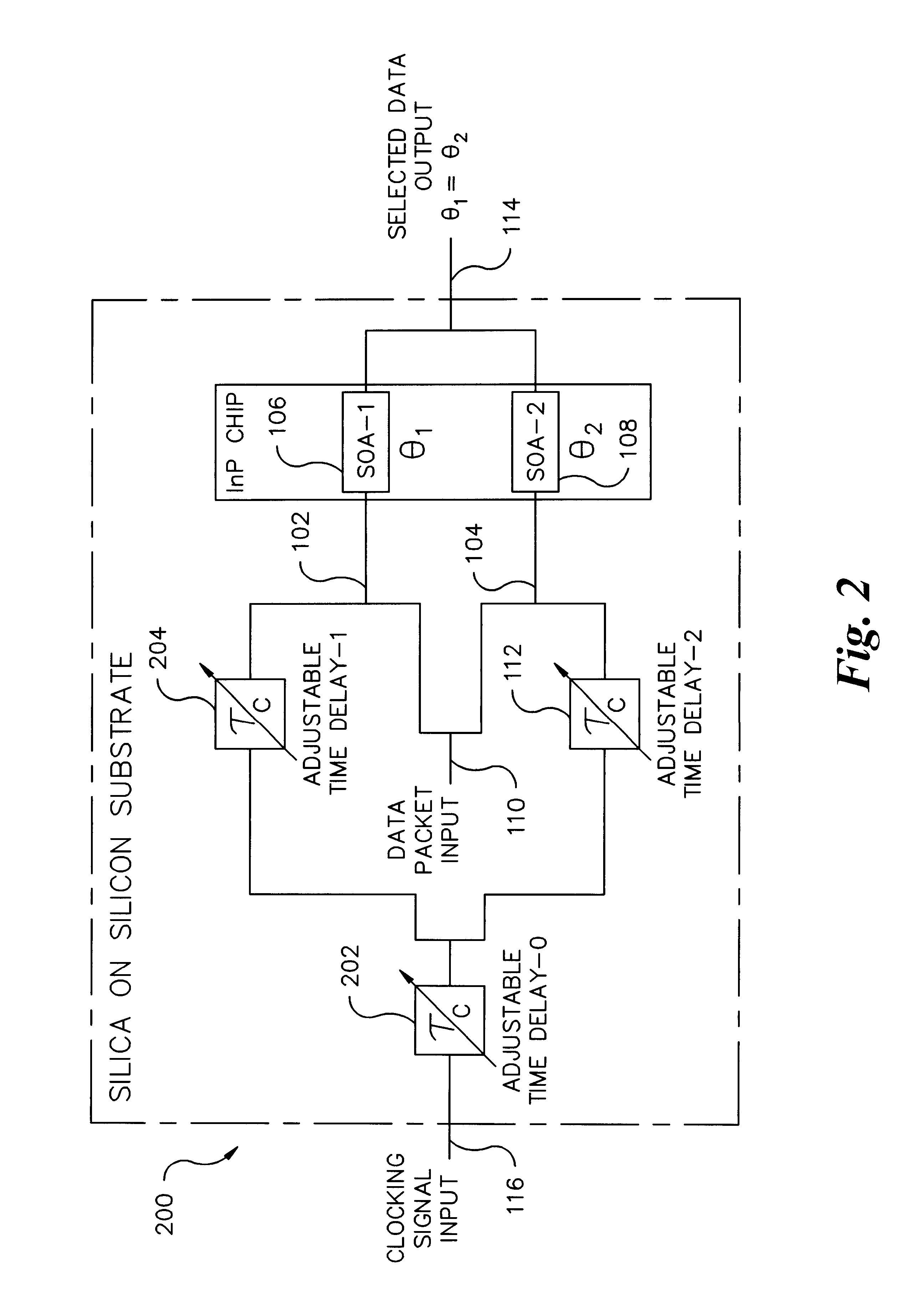
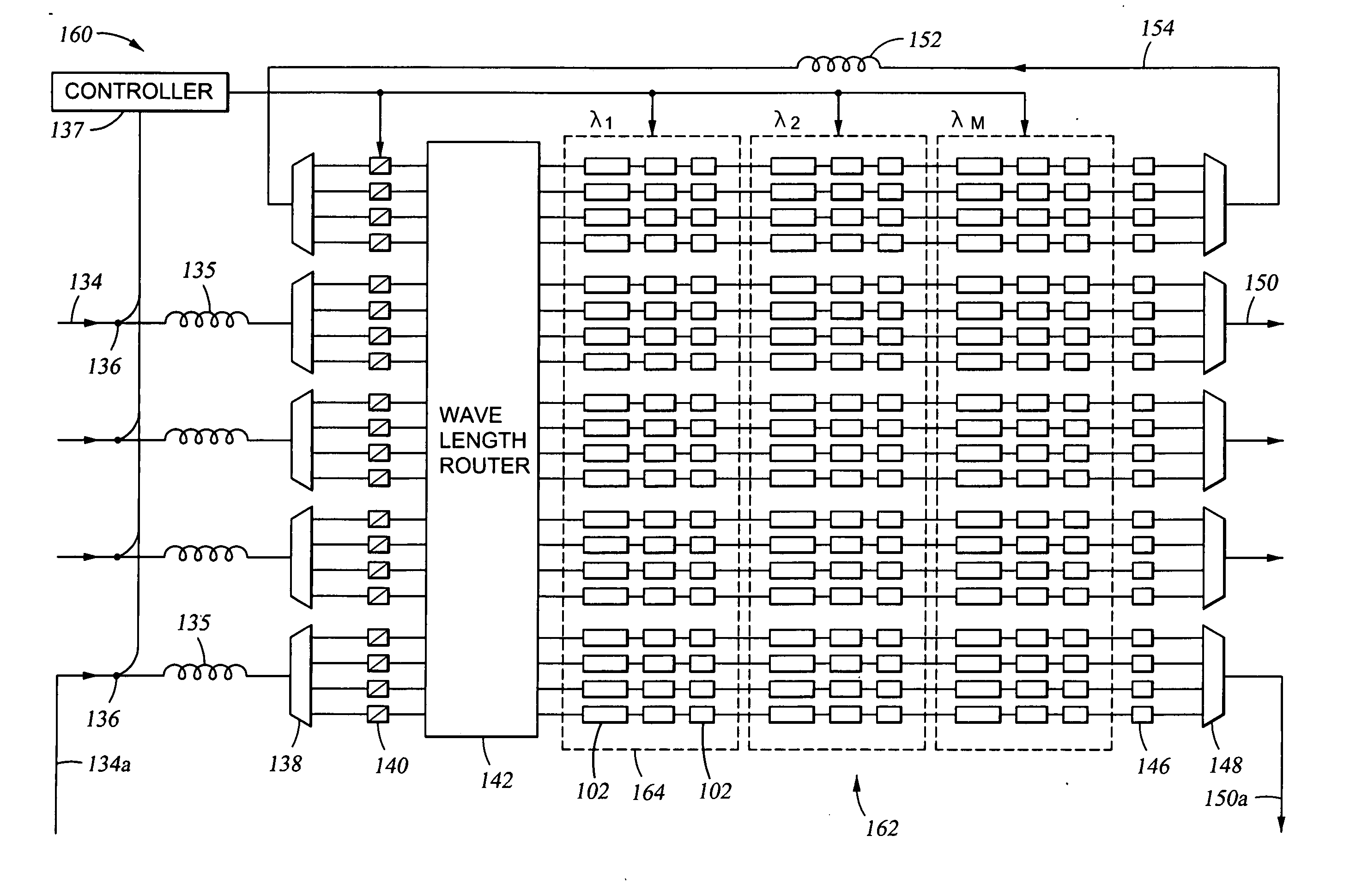
InactiveUS6650800B2Improve performanceIncrease profitTime-division optical multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesTime delaysSoftware engineering
A fully "time tunable" all-optical demultiplexer selects which digital bits or groups of bits in an all-optical data packet or all-optical data burst are to be read / demultiplexed. The all-optical demultiplexer is implemented in either a semiconductor hybrid or in a completely monolithic form. The all-optical demultiplexer is formatted in either a "normally on" or "normally off" configuration. Variable time delay elements adjust the time delay of a clocking signal input and a data packet input. The clocking signal determines the state of two nonlinear optical elements, such as semiconductor optical amplifiers, incorporated in the upper and lower arms of a Mach-Zehnder configuration. Only desirable digital bits or groups of bits are outputted from the demultiplexer. All other undesirable bits are suppressed.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
All optical variable buffer queue useful in optical packet networks
InactiveUS20050053375A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical packetLength wave
A variable optical buffer queue, particularly useful either as an input or an output queue in an optical packet router in a wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) communication network. An input queue includes plural separately controllable optical delay units disposed on wavelength channels between a demultiplexer and tunable wavelength converters controlling switching through a wavelength router. An output queue includes for each output port of a wavelength router plural separately controllable optical delay units tuned to different wavelengths. The delay units may induce selective amounts of delay and may be implemented as a series of controlled microresonators coupled to waveguide. Such a structure is usable as a controllably accessible optical memory.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cross-layer route optimization method and device for wireless Mesh network
ActiveCN102387559AReduce negative impactImprove throughputWireless communicationRouting decisionPacket loss
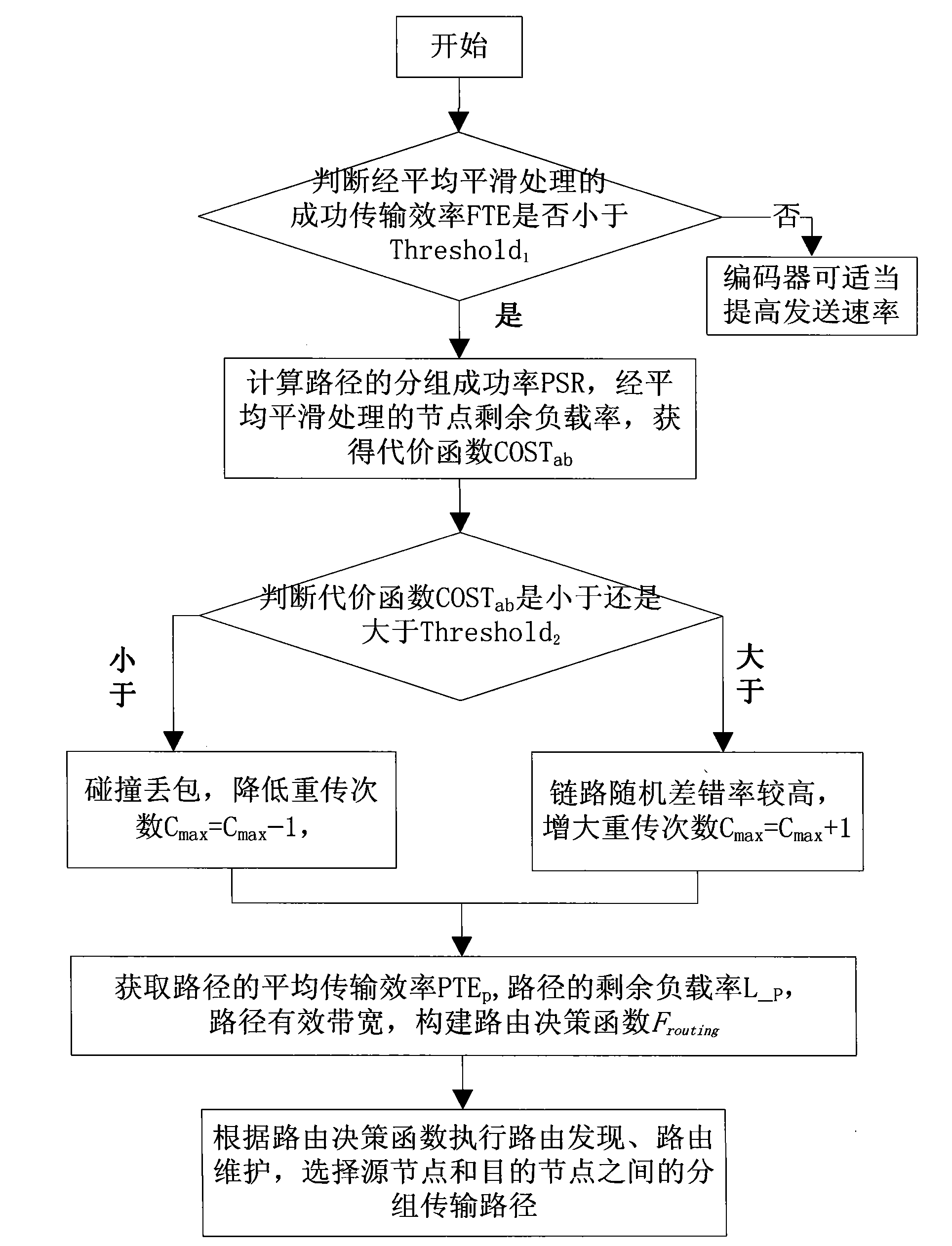
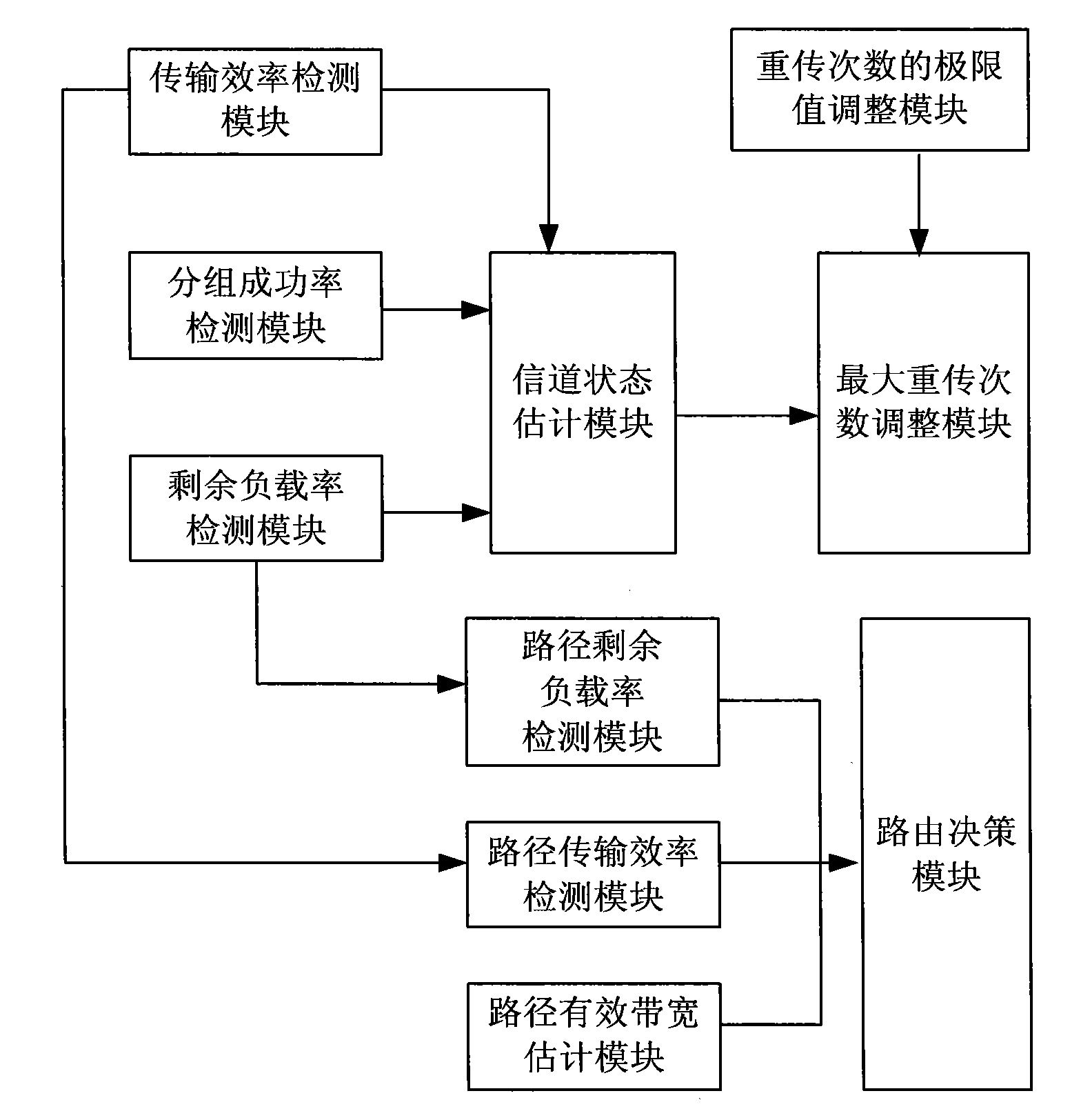
The invention discloses a cross-layer route optimization method and a cross-layer route optimization device for a wireless Mesh network. The method comprises the following steps of: estimating the channel state of a current network according to the transmission efficiency parameter of a wireless link, judging the major cause of current packet loss according to a packet success ratio and a residual load rate when the channel state is poor, and adjusting the maximum retransmission time according to the packet loss cause; and acquiring the transmission efficiency PTEP of an entire route according to the transmission efficiency parameter of the wireless link, acquiring the residual load rate L-P of the route from which a source node and a target node are removed, computing the effective bandwidth etaB(c) of the route, constructing a route decision function according to the transmission efficiency PTEP of the route, the residual load rate L-P of the route and the effective bandwidth etaB(c) of the route, performing route discovery and route maintenance operation by using the route decision function, and selecting an optical packet transmission route between the source node and the target node. According to the invention, the route quality of an MAC (Media Access Control) layer can be sensed more accurately, and the error judgment times of the route are reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Optical packet switching system
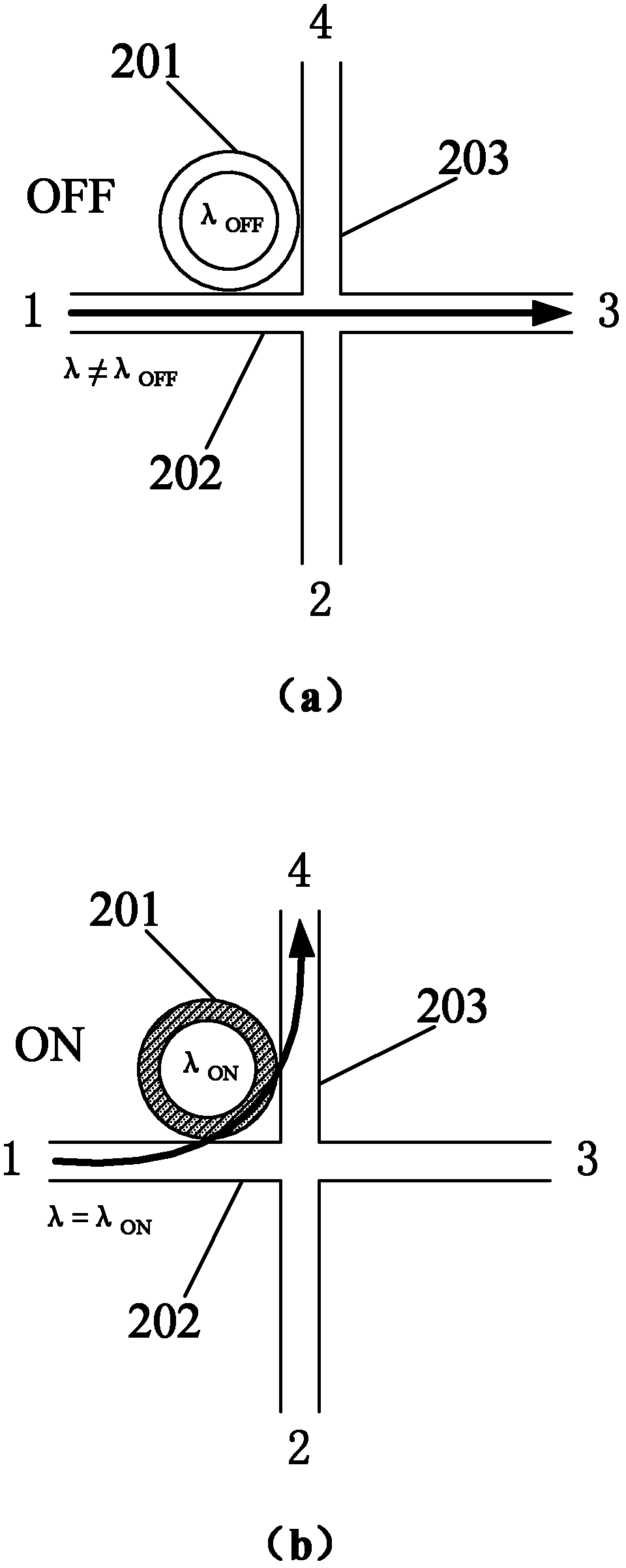
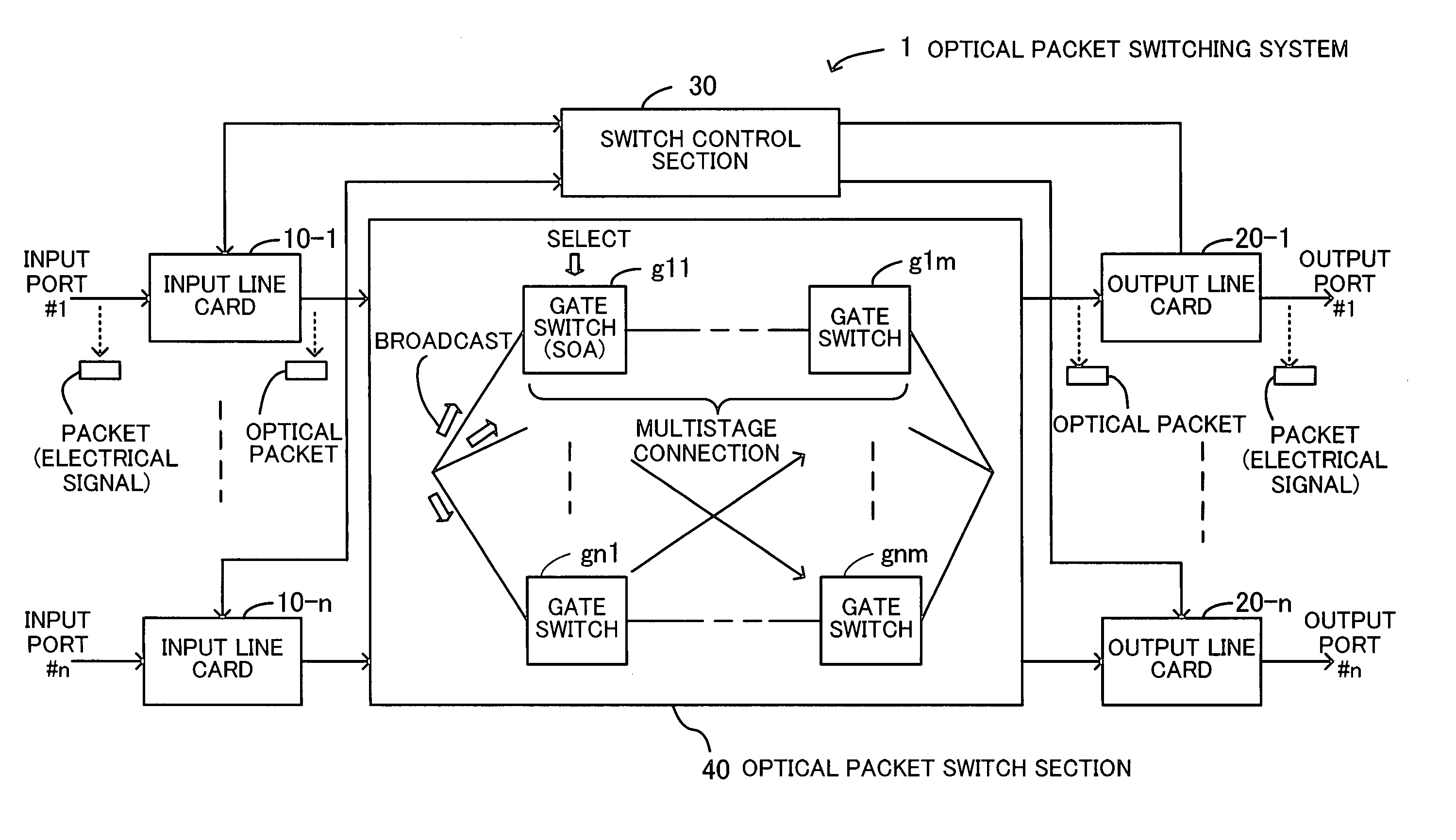
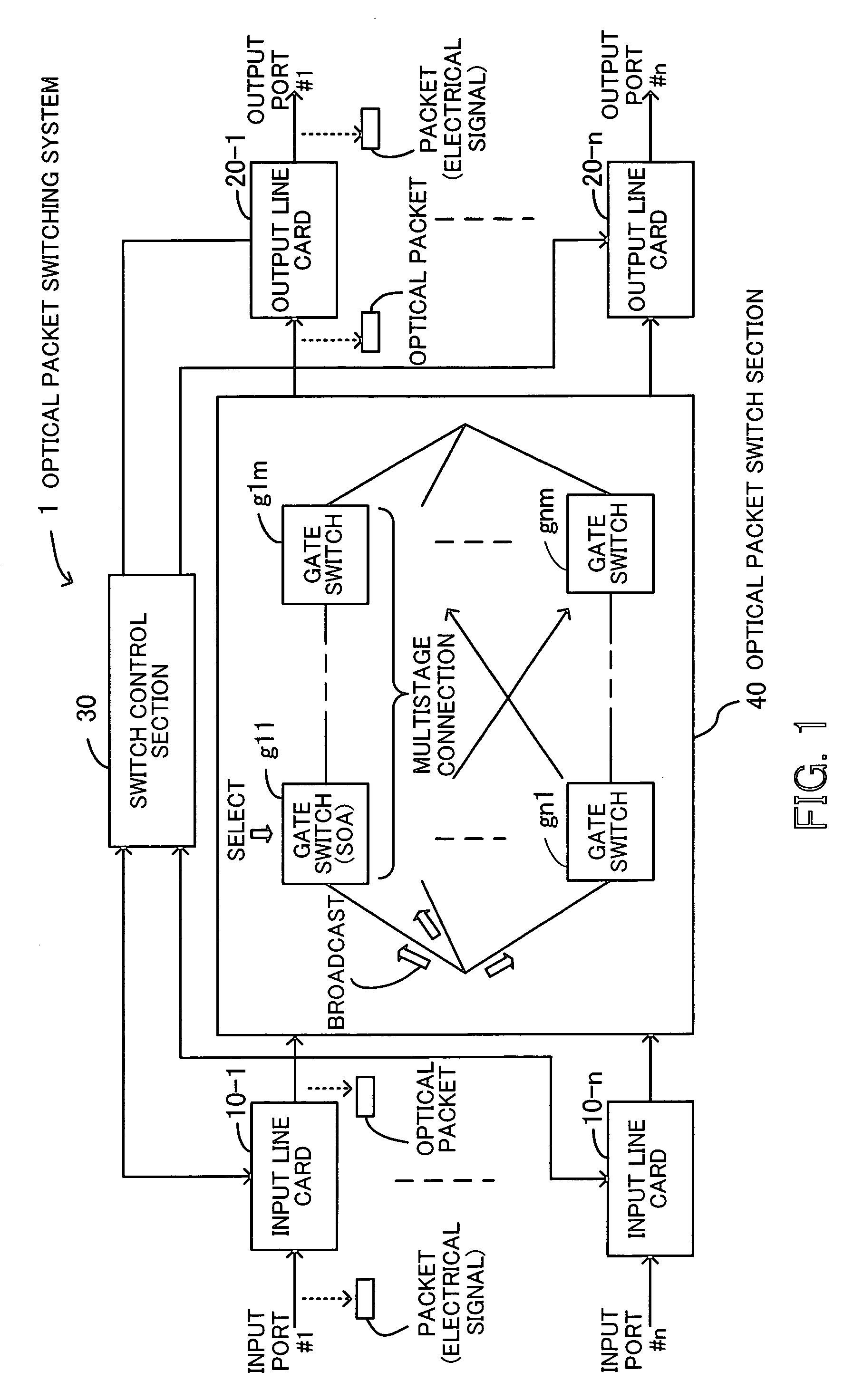
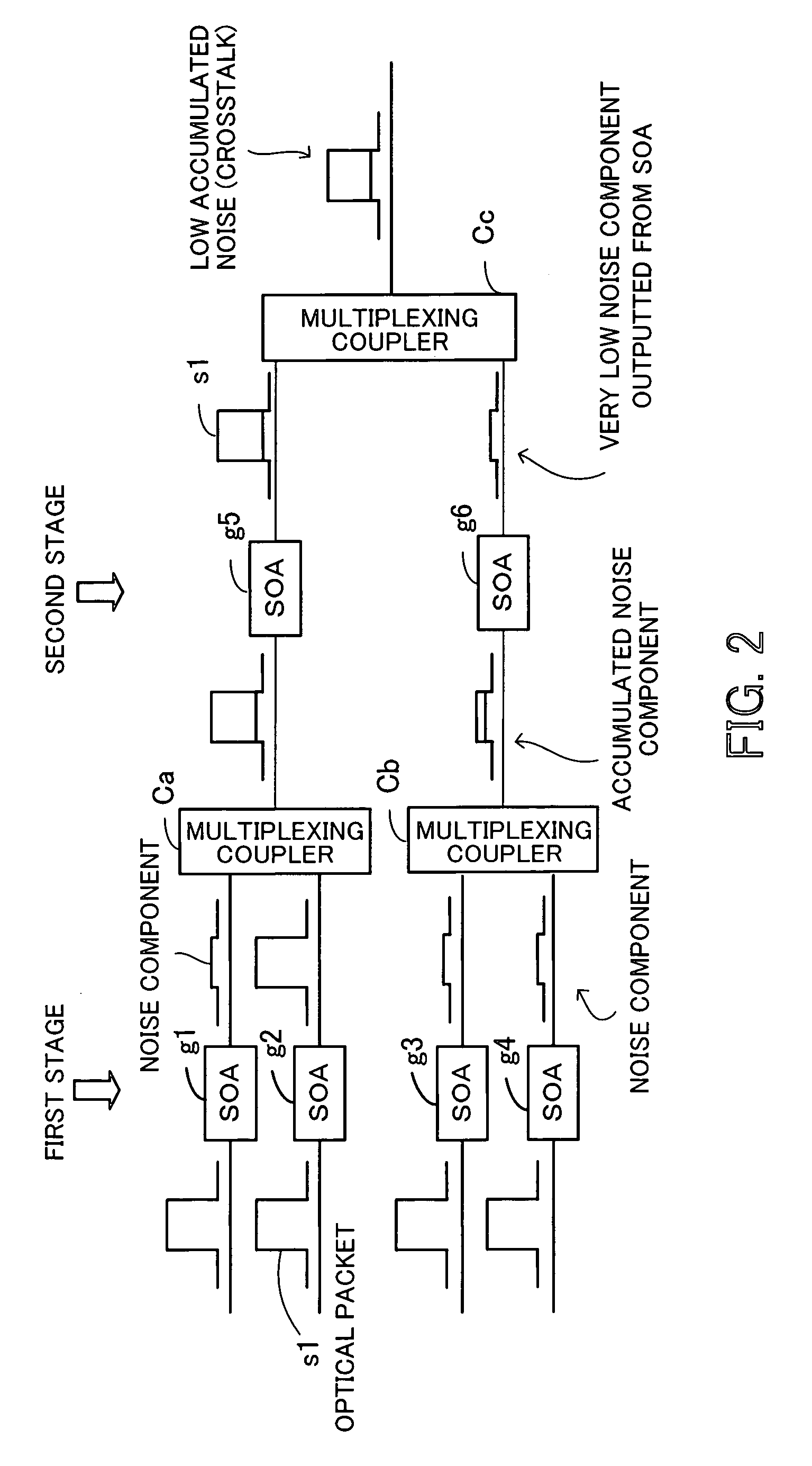
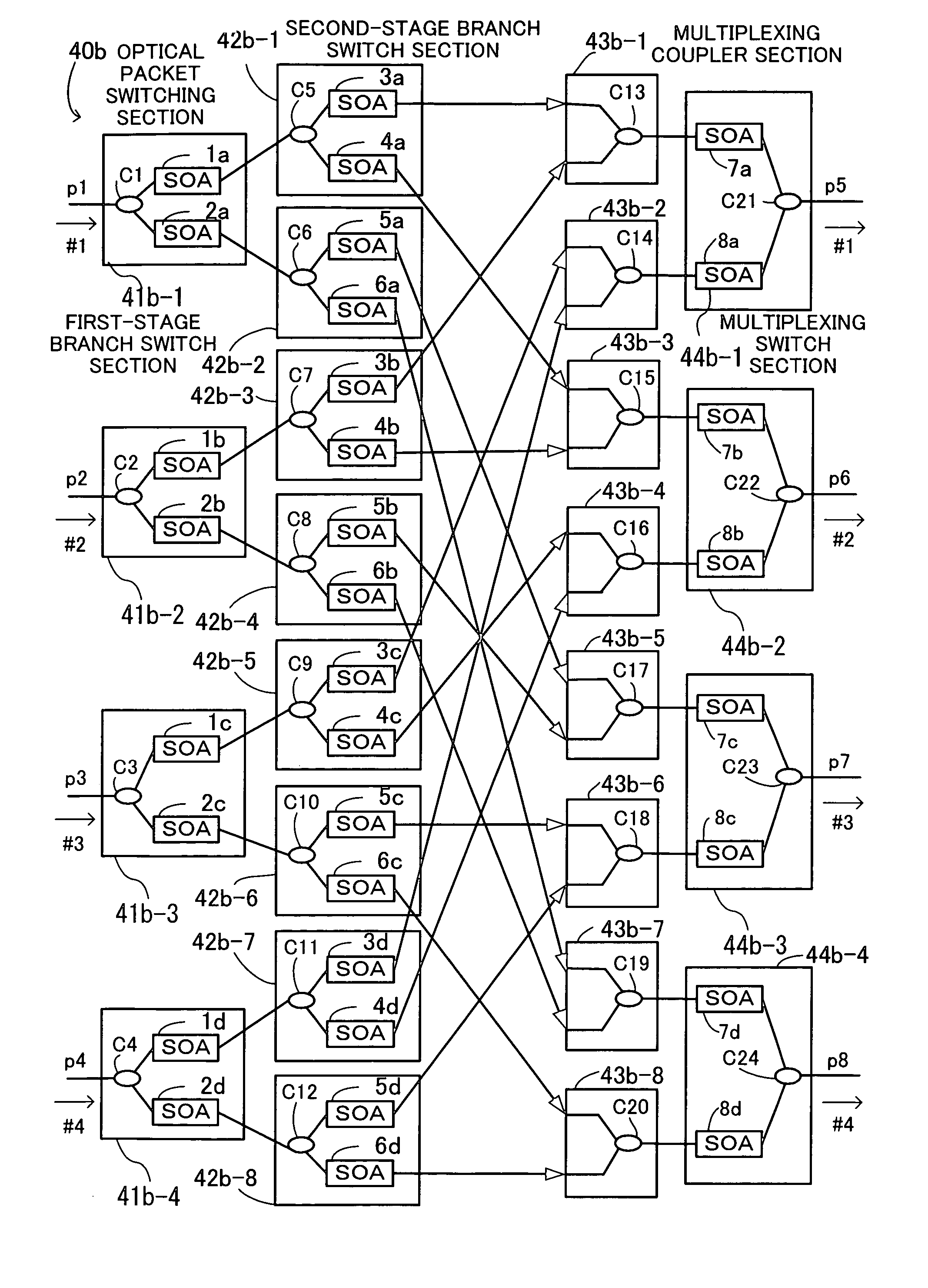
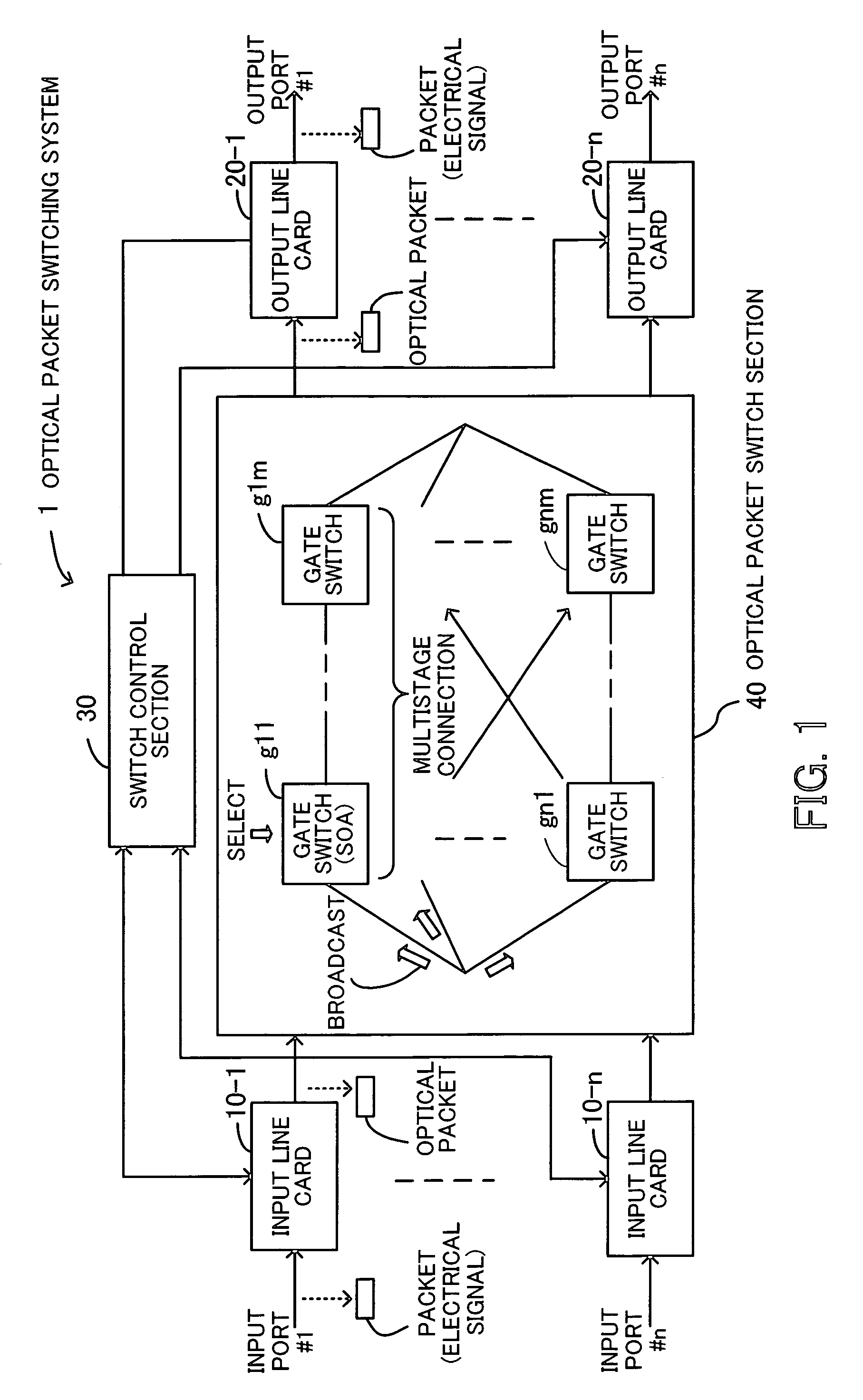
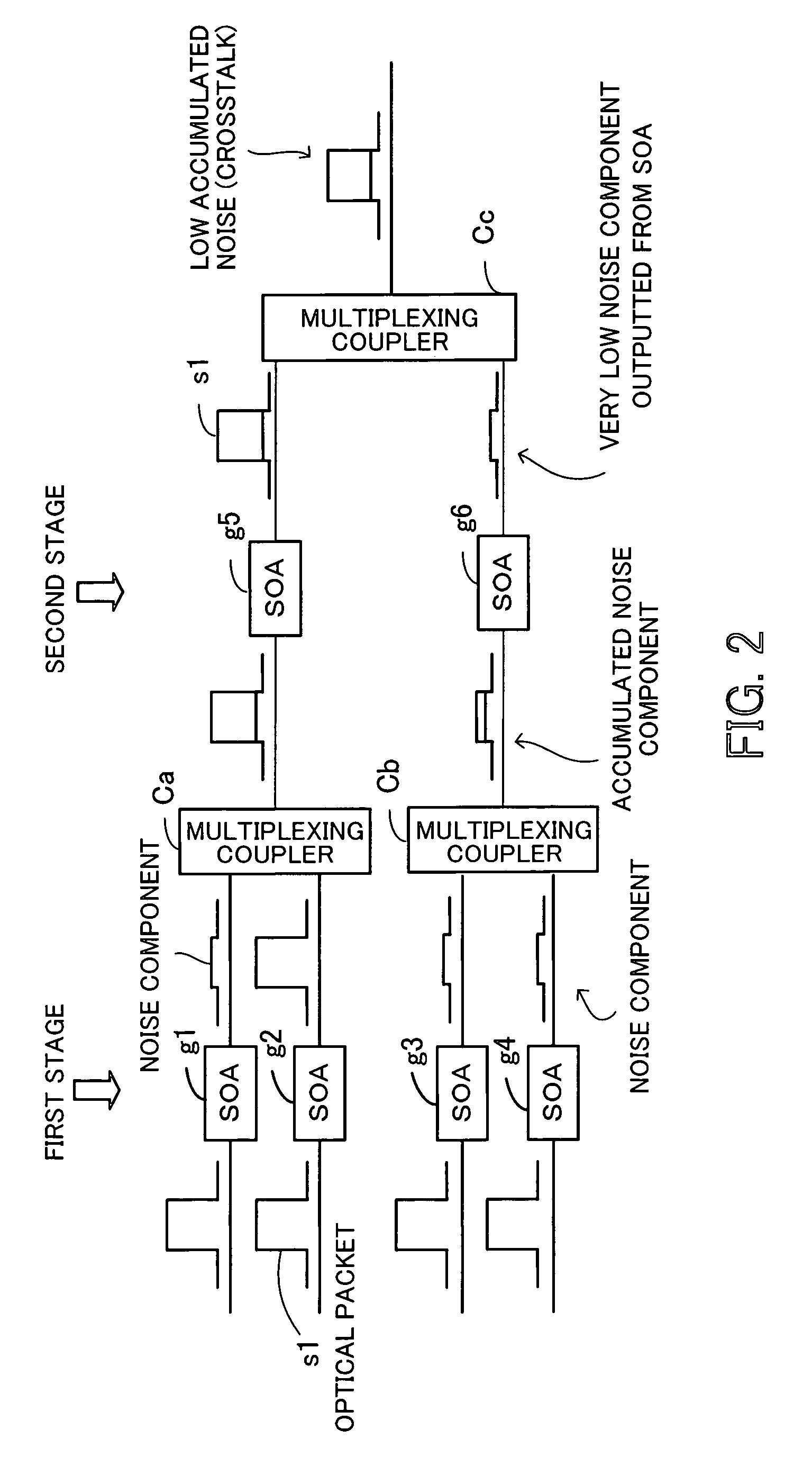
InactiveUS20060222361A1Improve OSNRQuality improvementMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic network arrangementsAudio power amplifierSystems management
An optical packet switching system in which transmission quality, reliability, and system management in optical packet switching control are improved. An optical packet switch section includes semiconductor optical amplifiers as gate switches multistage-connected on paths along which optical packets sent from a plurality of input line cards are transmitted and performs optical packet switching by broadcasting the optical packets to a plurality of gate switches, by selecting the optical packets by ON / OFF gating operation of the gate switches, and by absorbing noise signals which flow along non-selected paths by putting gate switches at a final stage into the OFF state. A switch control section exercises ON / OFF drive control over the gate switches in the optical packet switch section on the basis of port connection requests from the plurality of input line cards so as to generate requested paths.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical packet switching system
InactiveUS7317873B2Easy to controlQuality improvementMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic network arrangementsSystems managementLine card
An optical packet switching system in which transmission quality, reliability, and system management in optical packet switching control are improved. An optical packet switch section includes semiconductor optical amplifiers as gate switches multistage-connected on paths along which optical packets sent from a plurality of input line cards are transmitted and performs optical packet switching by broadcasting the optical packets to a plurality of gate switches, by selecting the optical packets by ON / OFF gating operation of the gate switches, and by absorbing noise signals which flow along non-selected paths by putting gate switches at a final stage into the OFF state. A switch control section exercises ON / OFF drive control over the gate switches in the optical packet switch section on the basis of port connection requests from the plurality of input line cards so as to generate requested paths.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical packet buffering device and buffering method thereof
InactiveUS20050041970A1Simple calculationSimplicity of implementationMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic network arrangementsOptical packetVariable length
A device that accepts input of asynchronously-arriving variable-length optical packets transmitted over a plurality of lightpaths, and outputs same to a single optical path, comprising: in order to prevent the optical packets from overlapping in the output lightpath, a controller that uses the delay times of the delay elements and the optical packet length and arrival gap time thus read to determine by computation the delay element used for temporary storage, where a plurality of stages of processors is provided. Thus, the processing required to determine the delay time is performed by parallel processing with the results of processing the prefix-sum operation used in parallel pipelined processing along with the queue length, optical packet length and arrival gap time of the buffering device.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Optical layer multicasting using a single sub-carrier header and a multicast switch with active header insertion
InactiveUS6934472B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsSurvivabilityOptical packet
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The technique effects survivability and security of the optical networks by encompassing conventional electronic security with an optical security layer by generating replicated versions of the input data payload at the input node, and the transmission of each of the replicated versions over a corresponding one of the plurality of links. Moreover, each of the links is composed of multiple wavelengths to propagate optical signals or optical packets, and each of the replicated versions of the data payload may be propagated over a selected one of the wavelengths in each corresponding one of the plurality of links.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical packet exchange system and optical switch
InactiveUS20020131120A1Fast executionNetwork speedMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical packetOptical switch
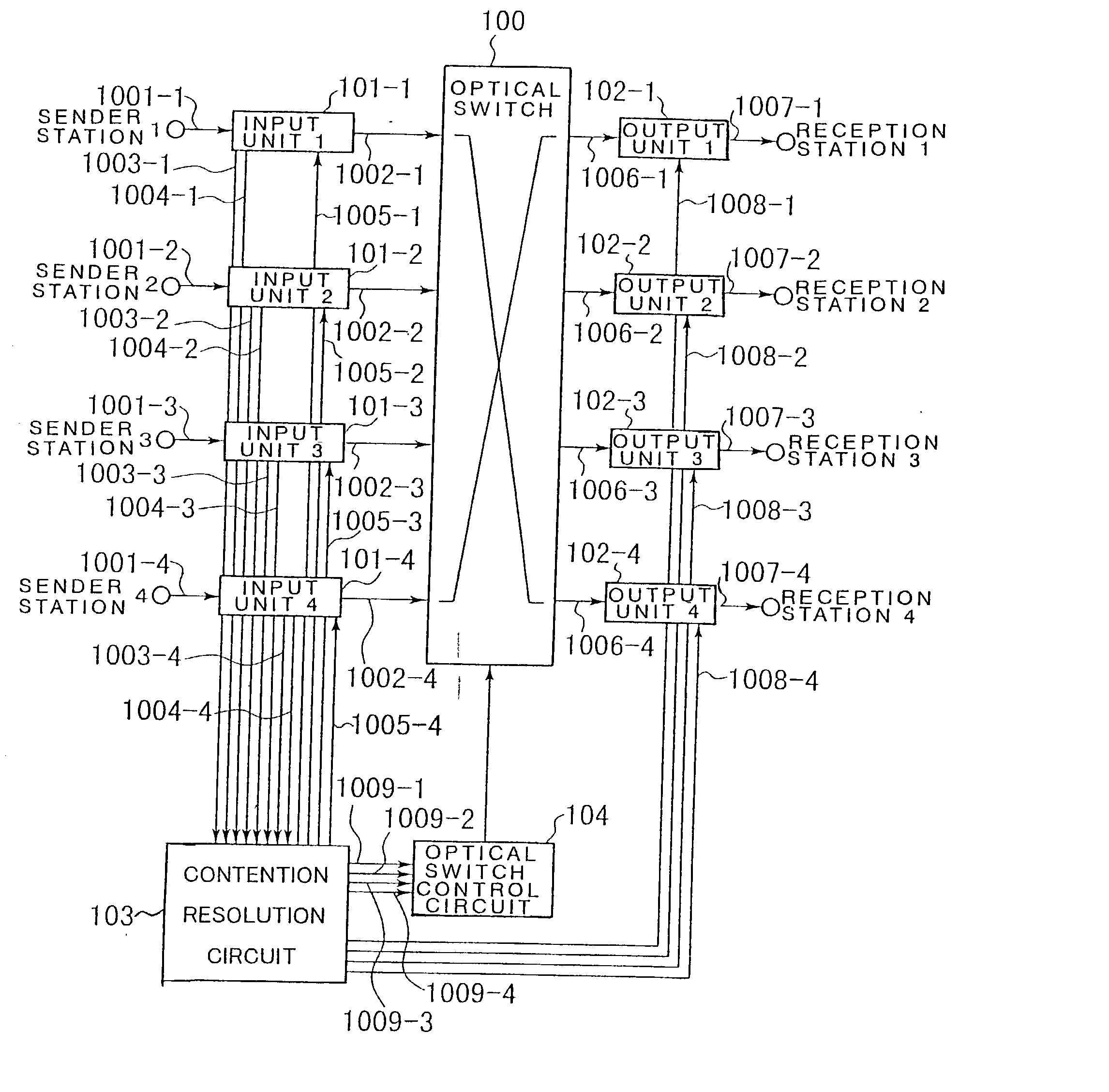
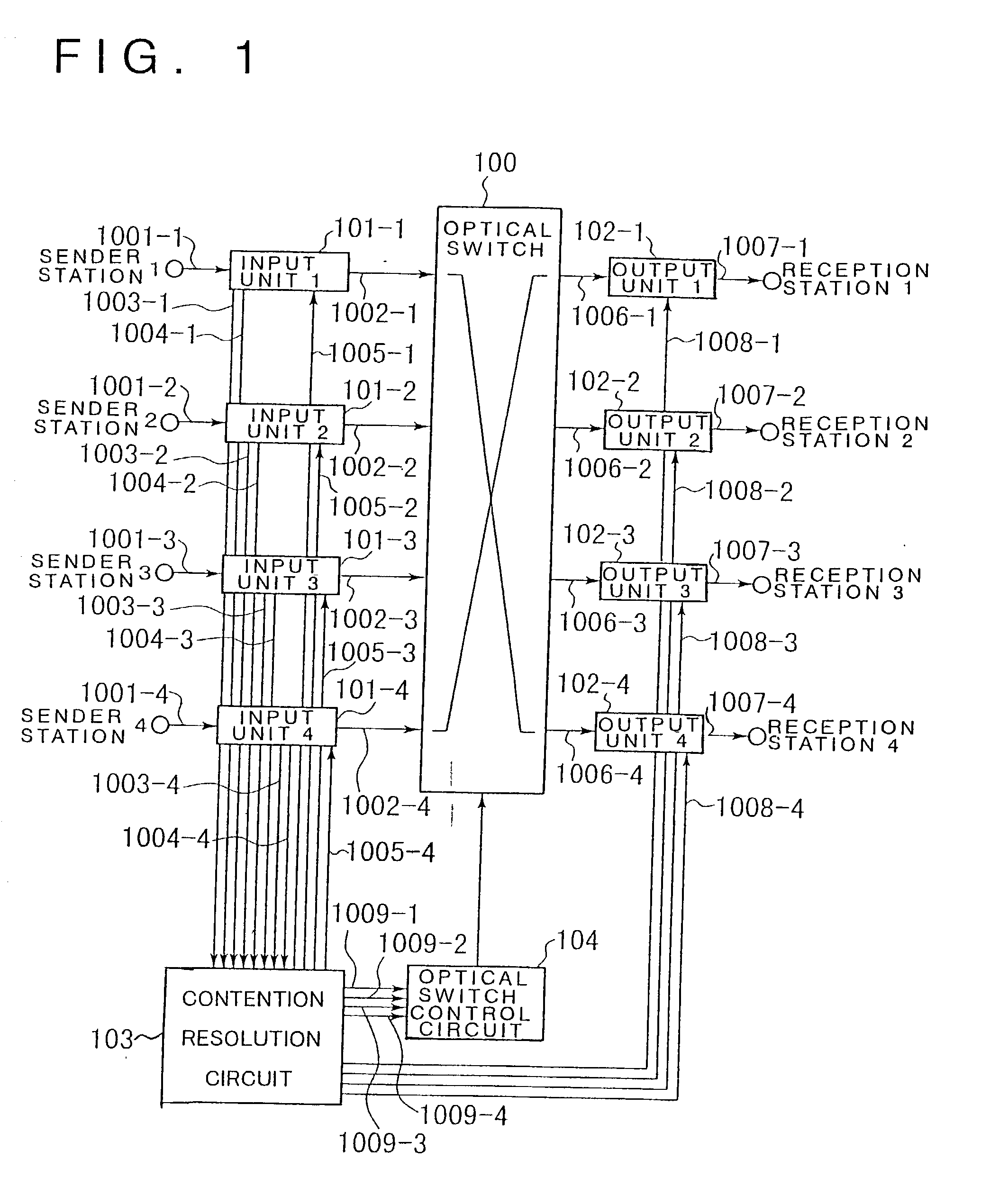
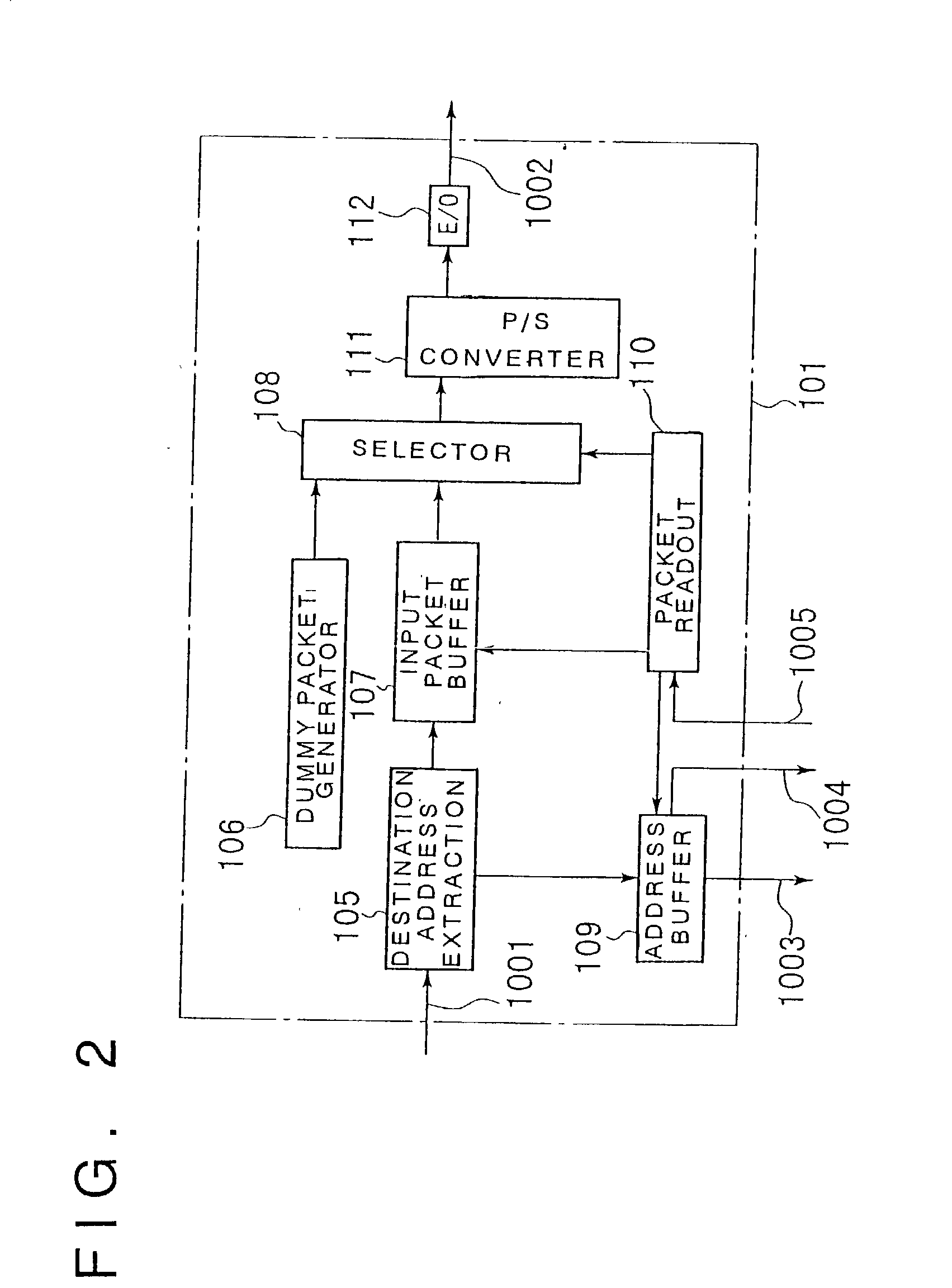
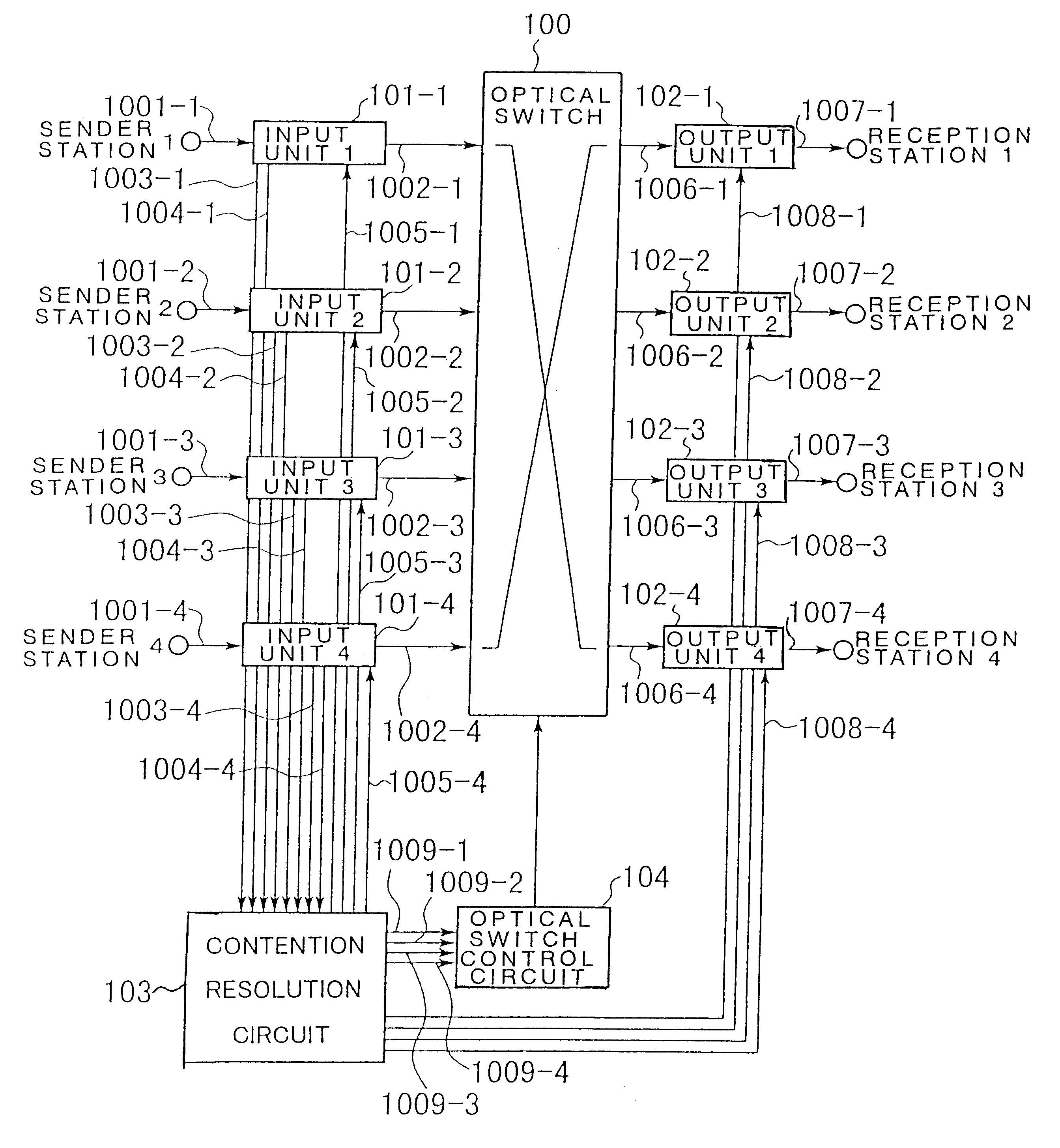
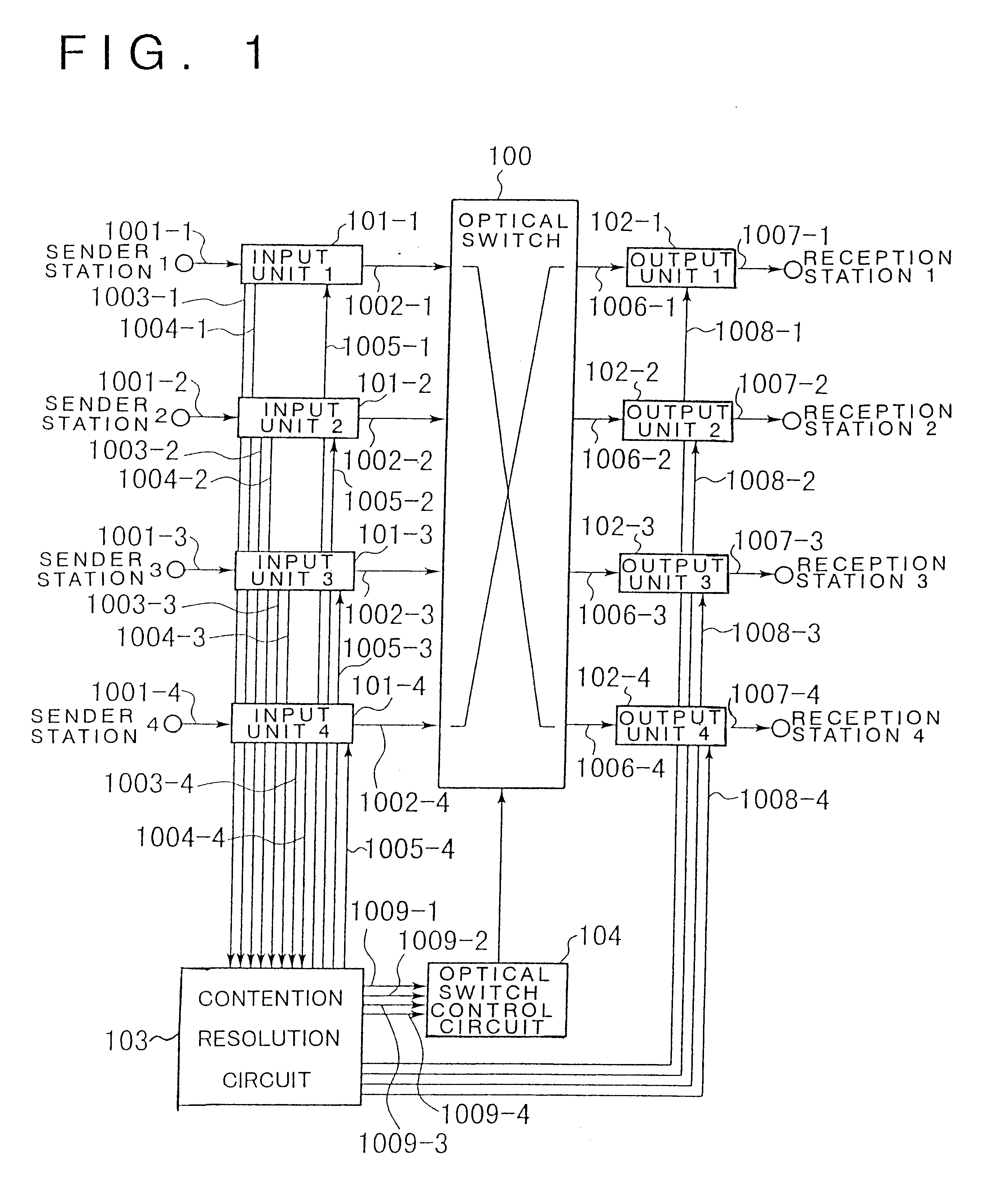
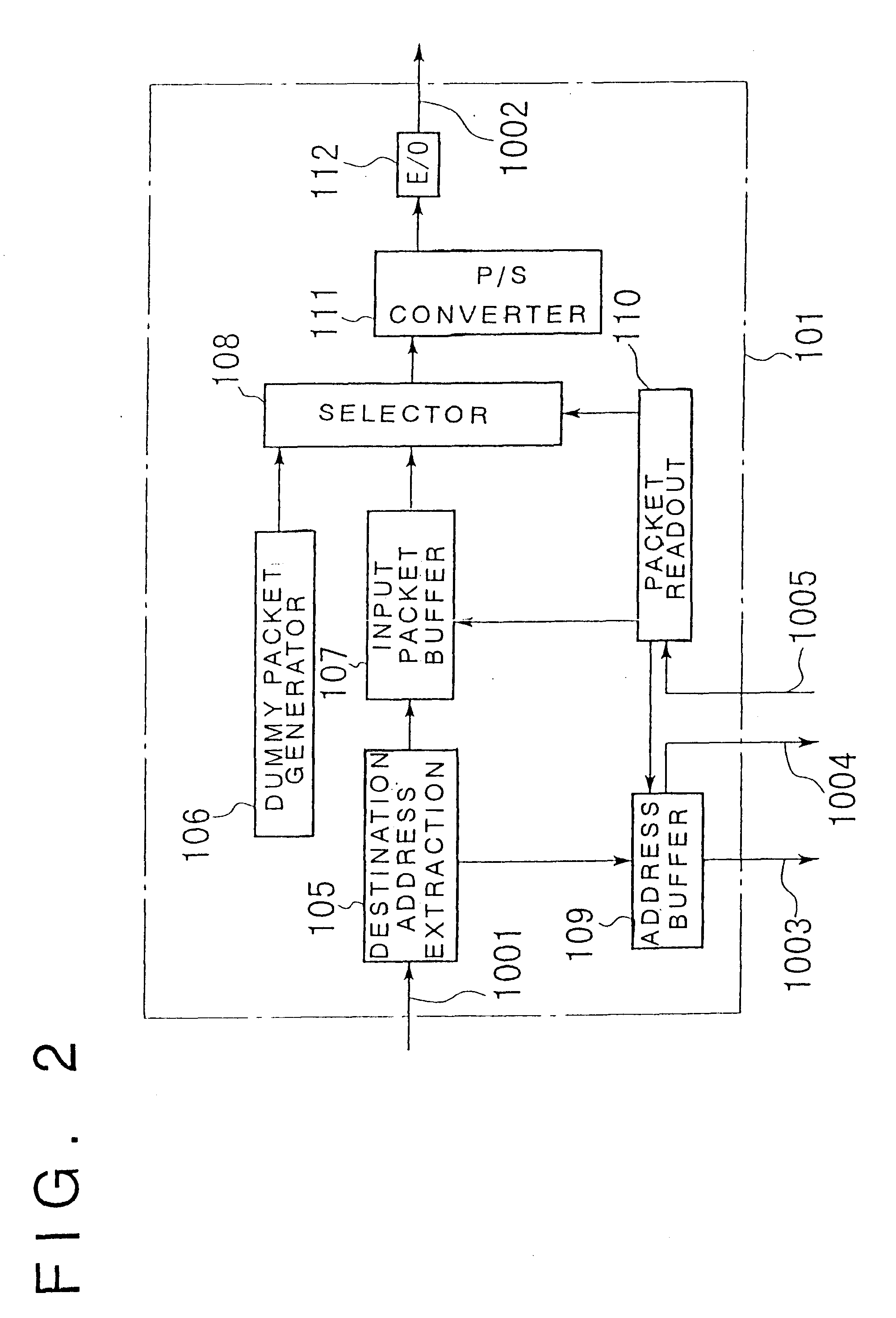
An optical packet exchange apparatus and an optical switch in which search for a connection pattern between an input unit devoid of a packet to be transmitted and an output unit devoid of a packet to be received is reduced to enable fast switch control even in cases wherein the number of channels of the exchange apparatus is increased or network speed is higher. A plurality of input units, a plurality of output units and an optical switch are provided. Each input unit includes an input buffer unit, a parallel / serial conversion unit, an electrical / optical conversion unit, and a dummy packet insertion unit for sending a dummy packet if there is no packet to be transmitted. Each output unit includes an exchange counterpart contention resolution unit for controlling the exchange counterpart, an optical / electrical conversion unit, a serial / parallel conversion unit, and a packet eliminating unit. The exchange counterpart contention resolution unit controls the packet eliminating unit to eliminate a dummy packet.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical packet exchange system and optical switch
InactiveUS6441935B1Fast executionNetwork speedMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical packetOptical switch
An optical packet exchange apparatus and an optical switch in which search for a connection pattern between an input unit devoid of a packet to be transmitted and an output unit devoid of a packet to be received is reduced to enable fast switch control even in cases wherein the number of channels of the exchange apparatus is increased or network speed is higher. A plurality of input units, a plurality of output units and an optical switch are provided. Each input unit includes an input buffer unit, a parallel / serial conversion unit, an electrical / optical conversion unit, and a dummy packet insertion unit for sending a dummy packet if there is no packet to be transmitted. Each output unit includes an exchange counterpart contention resolution unit for controlling the exchange counterpart, an optical / electrical conversion unit, a serial / parallel conversion unit, and a packet eliminating unit. The exchange counterpart contention resolution unit controls the packet eliminating unit to eliminate a dummy packet.
Owner:NEC CORP
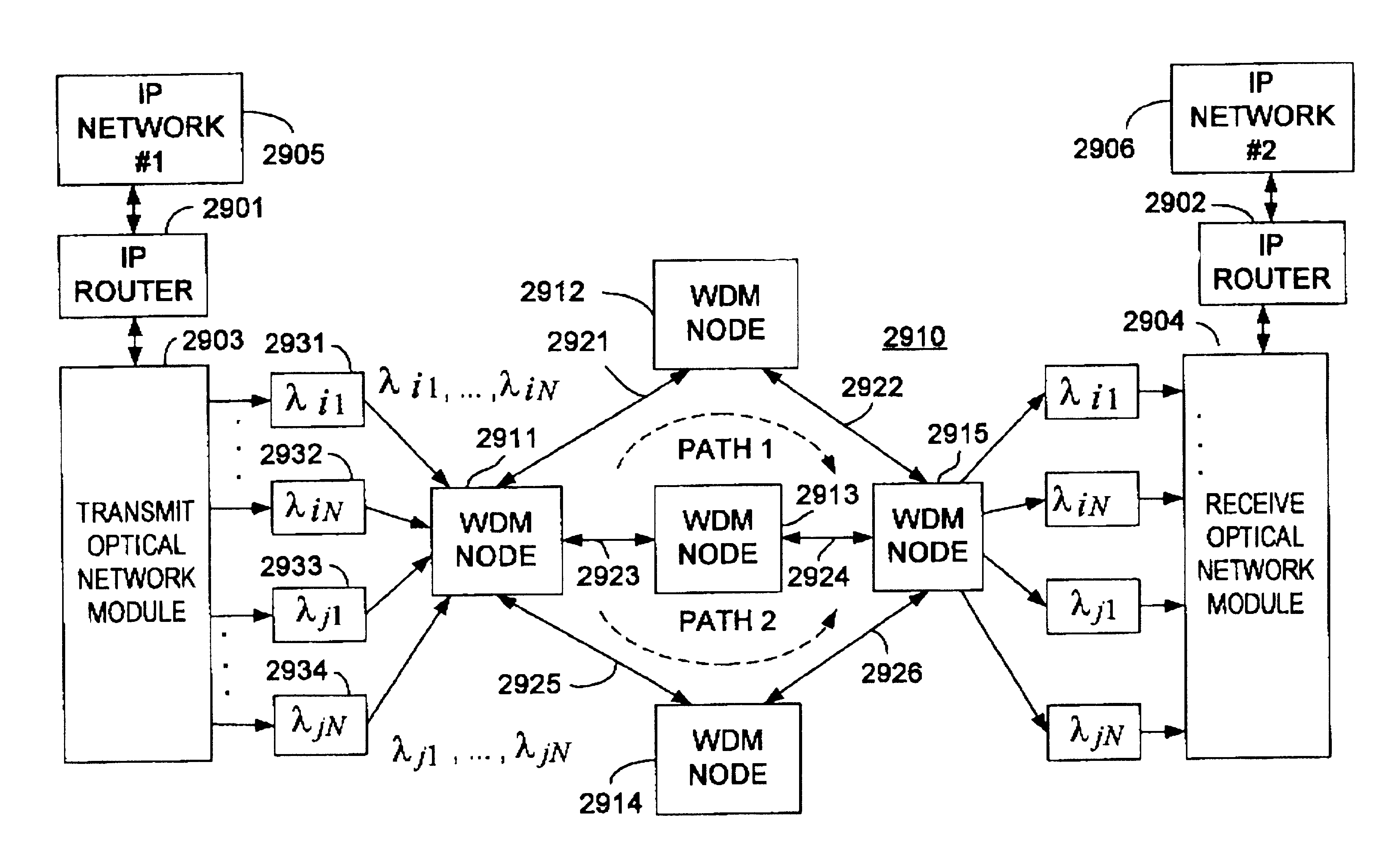
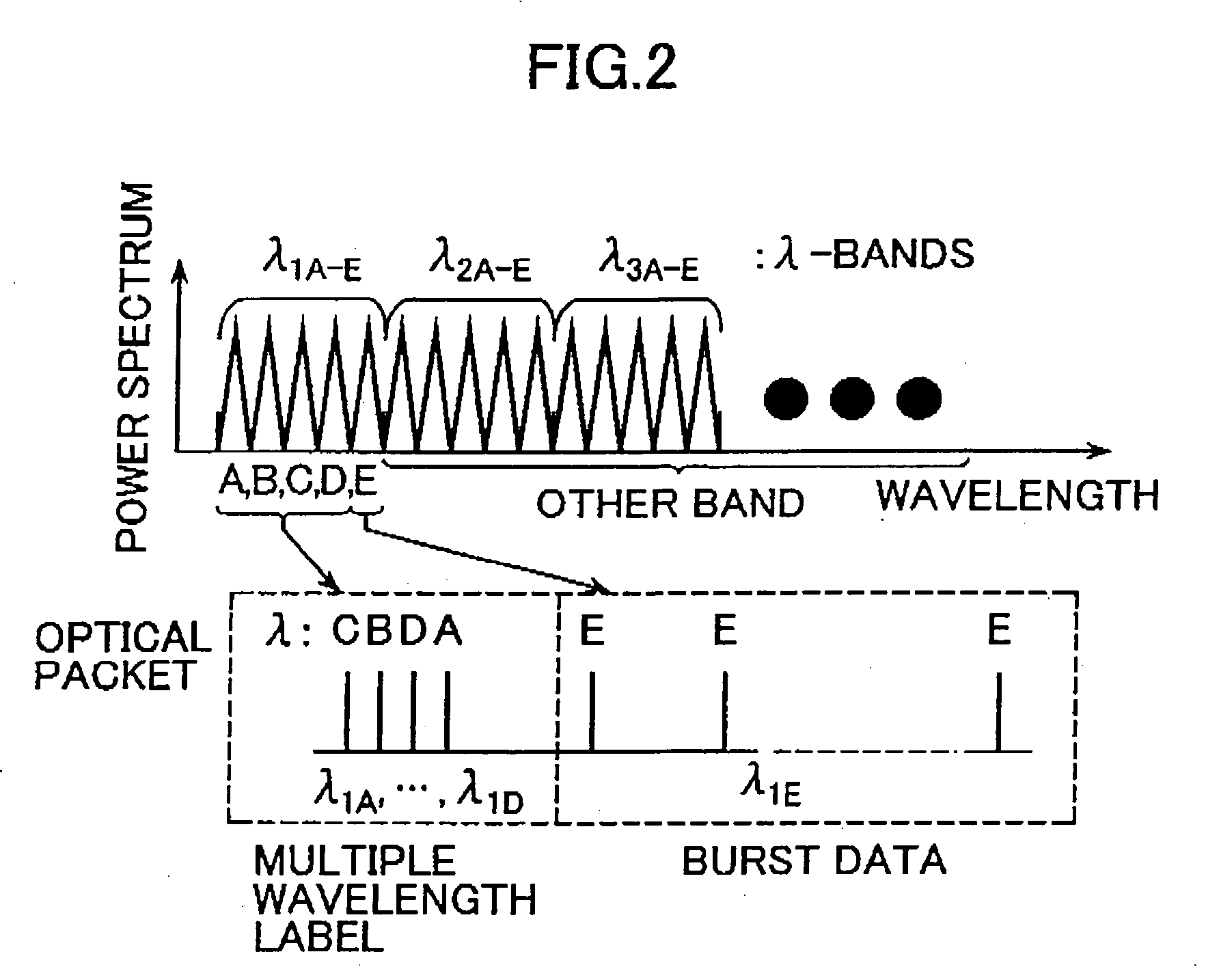
Method for routing optical packets using multiple wavelength labels, optical packet router using multiple wavelength labels, and optical packet network that uses multiple wavelength labels
InactiveUS20050180750A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsDelayed timeOptical packet
A method for routing optical packets using multiple wavelength labels includes converting optical packet address signals to a plurality of optical pulses having different time-deviated wavelengths by executing a first operation to impart a wavelength dependent delay time with respect to a plurality of optical pulses having different wavelengths at a same time axis position. When the optical pulses are transmitted along a predetermined optical path having dispersion the dispersion is compensated for by executing a second operation on the optical pulses corresponding to a reverse process of the operation to impart a wavelength dependent delay time. This second operation results in the generation of a plurality of optical pulses having different wavelengths at a given point on the time axis. The pulse signals thus generated are used to determine the packet transmission route.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Optical packet switching apparatus and methods
ActiveUS7162155B2Improve optical packet switchingExtended routeMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionOptical packetLength wave
In an optical packet switch, NW wavelengths, over which inputted optical packets may be switched, are grouped into KG groups of wavelengths, where NW and KG are integers greater than one. The KG groups of wavelengths are characterized in that each of the KG groups of wavelengths is allocated to optical packets distinguished from other optical packets by at least one attribute of at least one packet characteristic. Each one inputted optical packet is switched over a wavelength having an available transmission resource selected from among wavelengths in one of the KG groups of wavelengths that is matched to the one inputted optical packet by correspondence of attributes of the at least one packet characteristic. Related apparatus and methods are also described.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
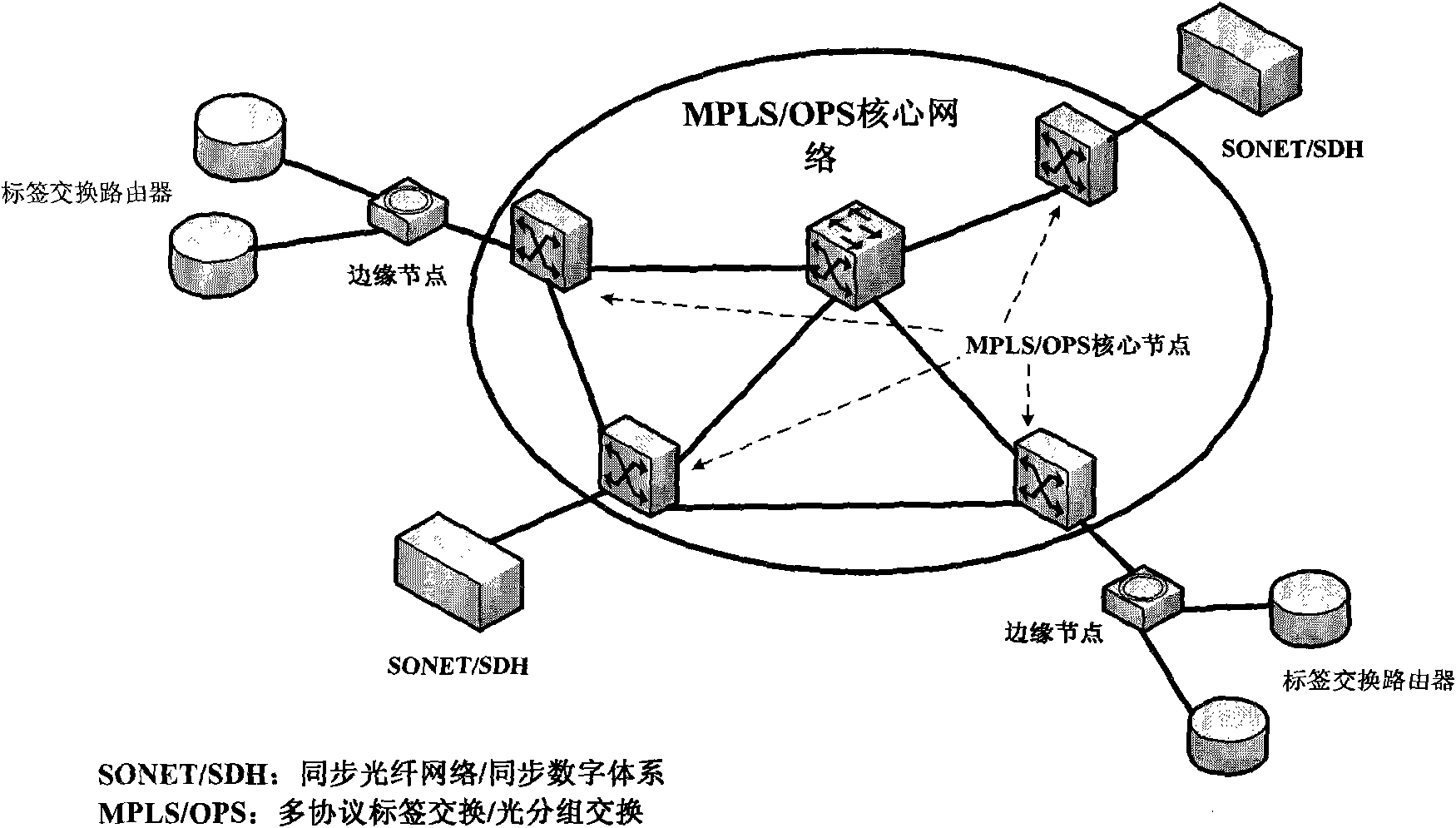
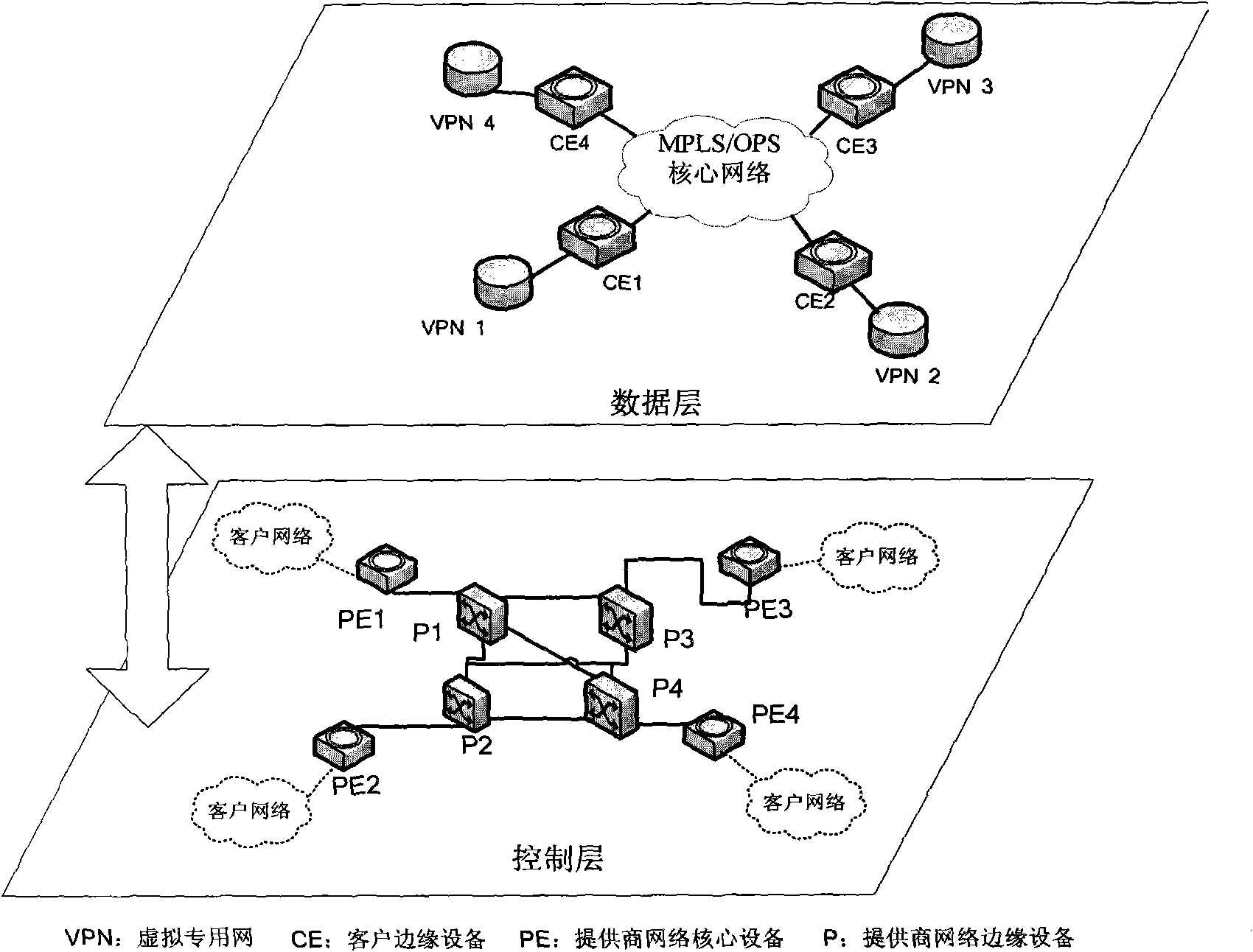
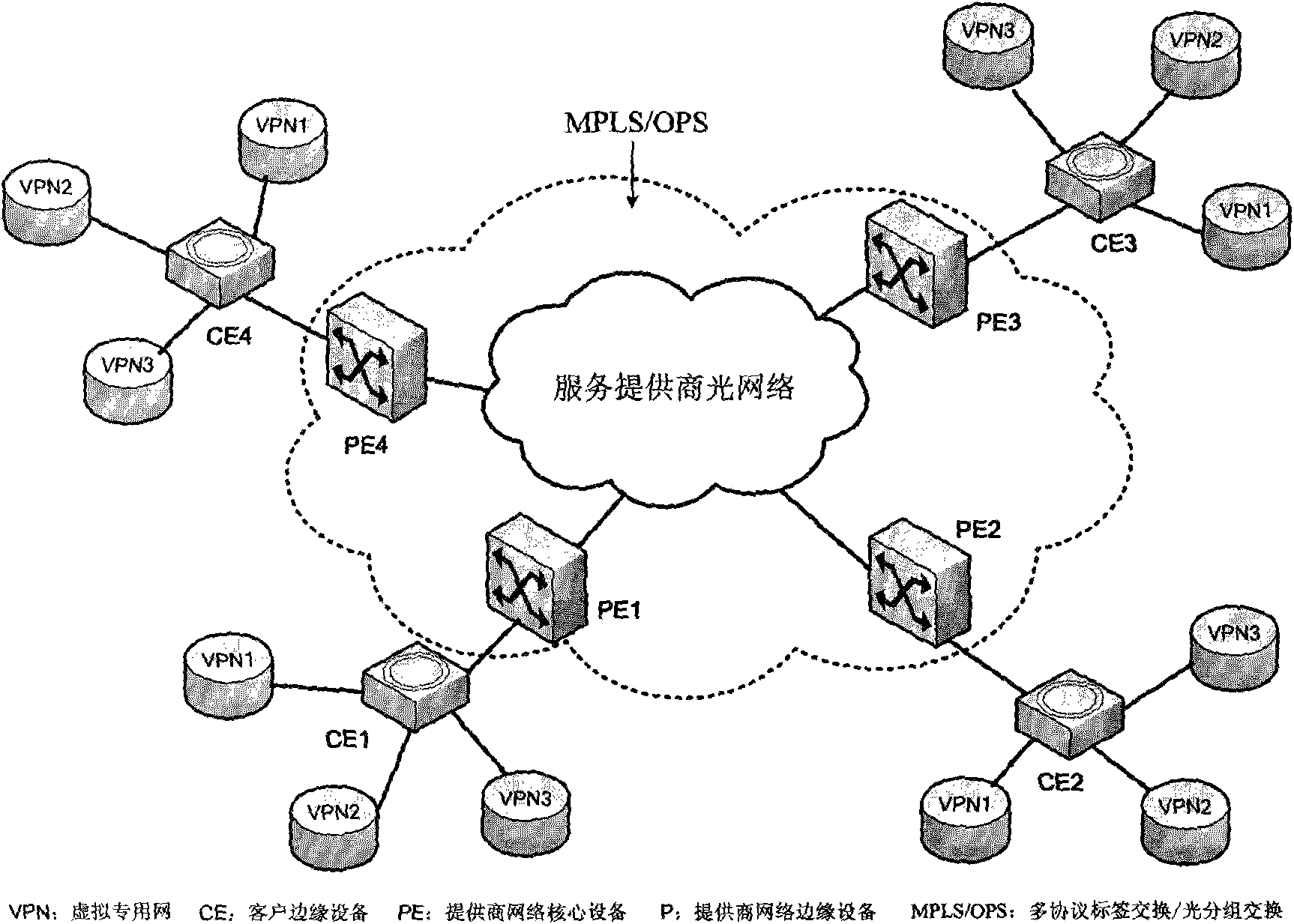
Virtual private network implementation method based on MPLS/OPS
InactiveCN101834793ARealize transmissionElectromagnetic transmissionNetworks interconnectionOriginal dataPrivate network
The invention relates to a virtual private network (VPN) implementation method based on multi-protocol label switching / optical packet switching (MPLS / OPS), combining the multi-protocol label switching (MPLS), the optical packet switching (OPS) and the virtual private network (VPN). The scheme is based on three-layer VPN, and the structure mainly includes a data plane and a control plane. The method is characterized in that a network tunnel protocol encrypts and encapsulates user data into VPN data, the VPN data is packed into optical packet (OPS) by a client edge device (CE) and is transmitted into a core network, the strong function of MPLS is utilized to carry out classifying mapping, and hierarchy label stack structure of MPLS is utilized to erasure old label and write in new label for forwarding in label switching route (LSP) forwarding process. Optical packet OPS dismounting process is realized at an exit border node, so as to obtain VPN data, a receiving terminal utilizes a corresponding key to carry out decryption authentication, thus obtaining the original data and realizing the whole data transmission process.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Optical layer multicasting using a single sub-carrier header and a multicast switch with active header insertion via light circulation
InactiveUS6850515B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexSurvivabilityOptical packet
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The technique effects survivability and security of the optical networks by encompassing conventional electronic security with an optical security layer by generating replicated versions of the input data payload at the input node, and the transmission of each of the replicated versions over a corresponding one of the plurality of links. Moreover, each of the links is composed of multiple wavelengths to propagate optical signals or optical packets, and each of the replicated versions of the data payload may be propagated over a selected one of the wavelengths in each corresponding one of the plurality of links.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
MAC protocol for optical packet-switched ring network
InactiveUS6925259B2Ring-type electromagnetic networksTime-division optical multiplex systemsRing networkOptical packet
A flexible, credit-based MAC protocol along with an admission algorithm enhance the throughput capacity of a packet switched WDMA ring network utilizing packet wavelength stacking and unstacking.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
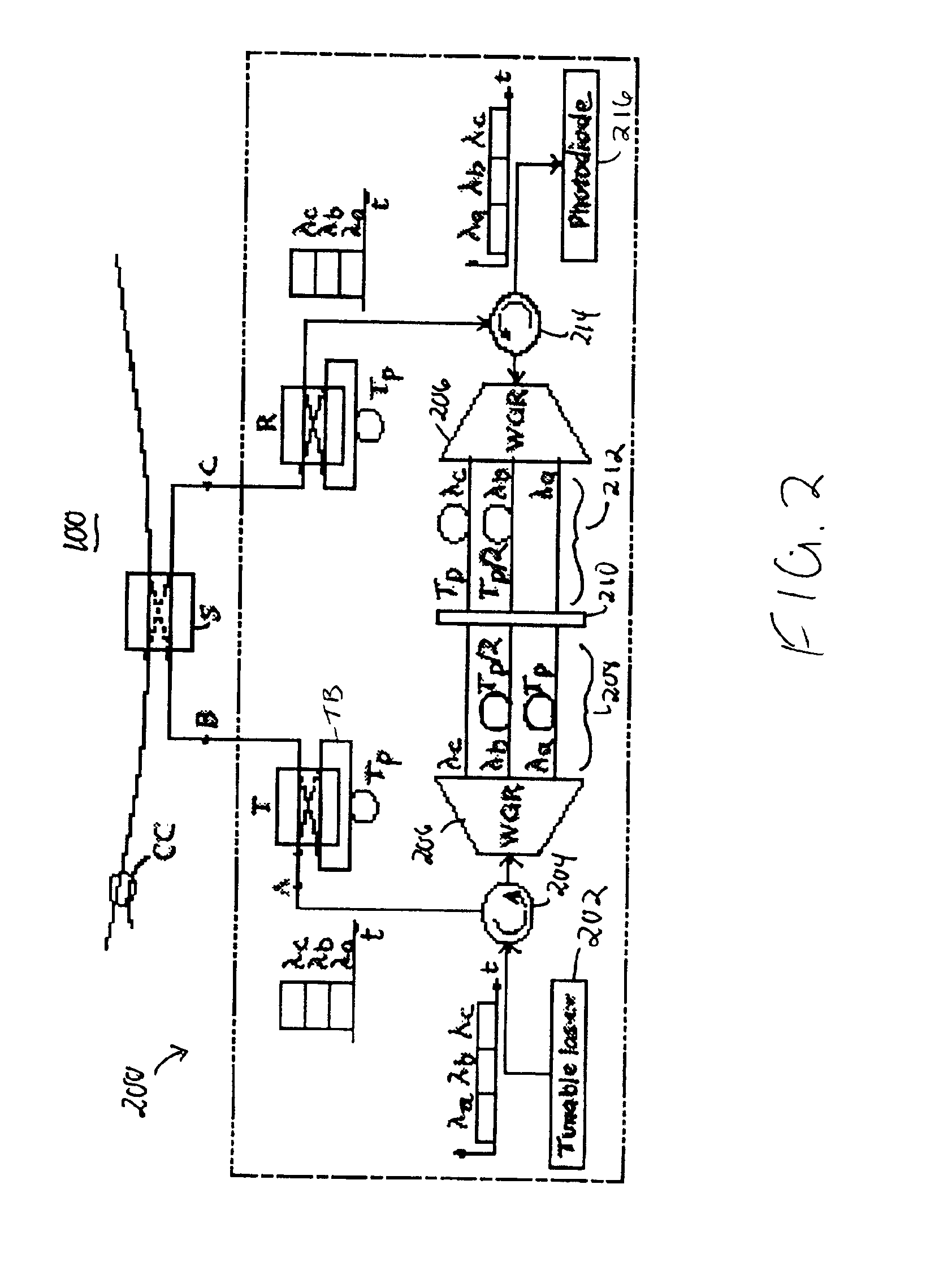
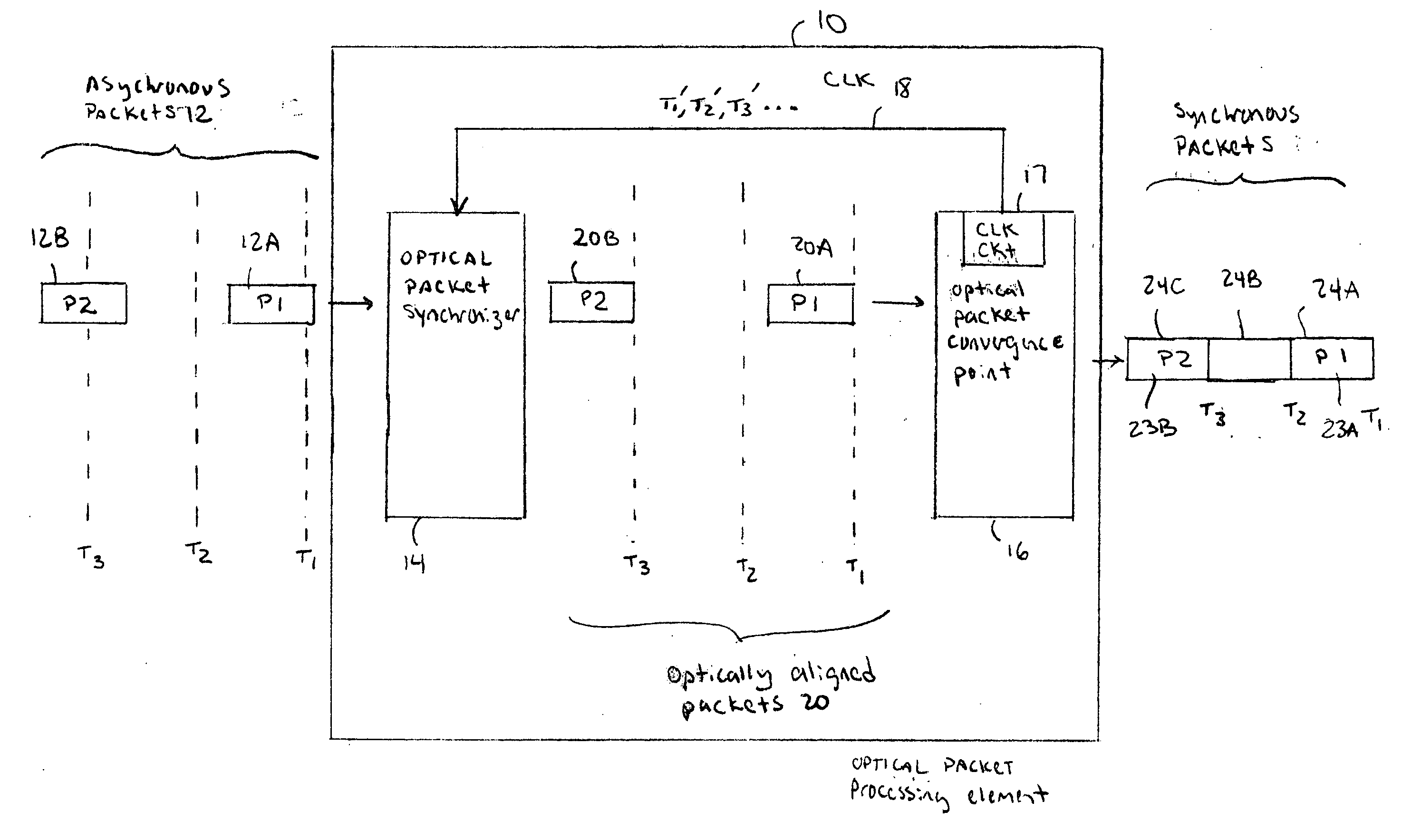
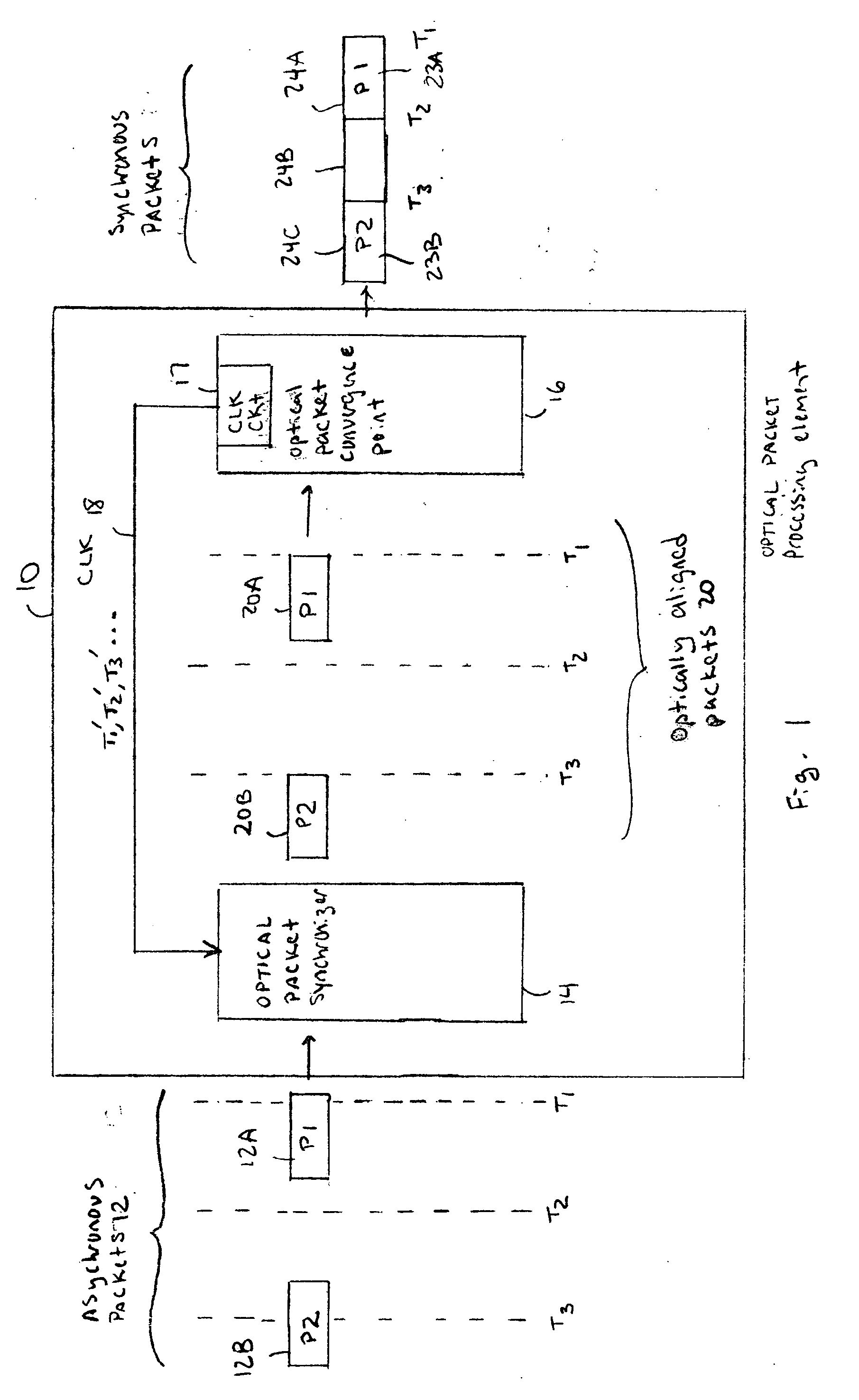
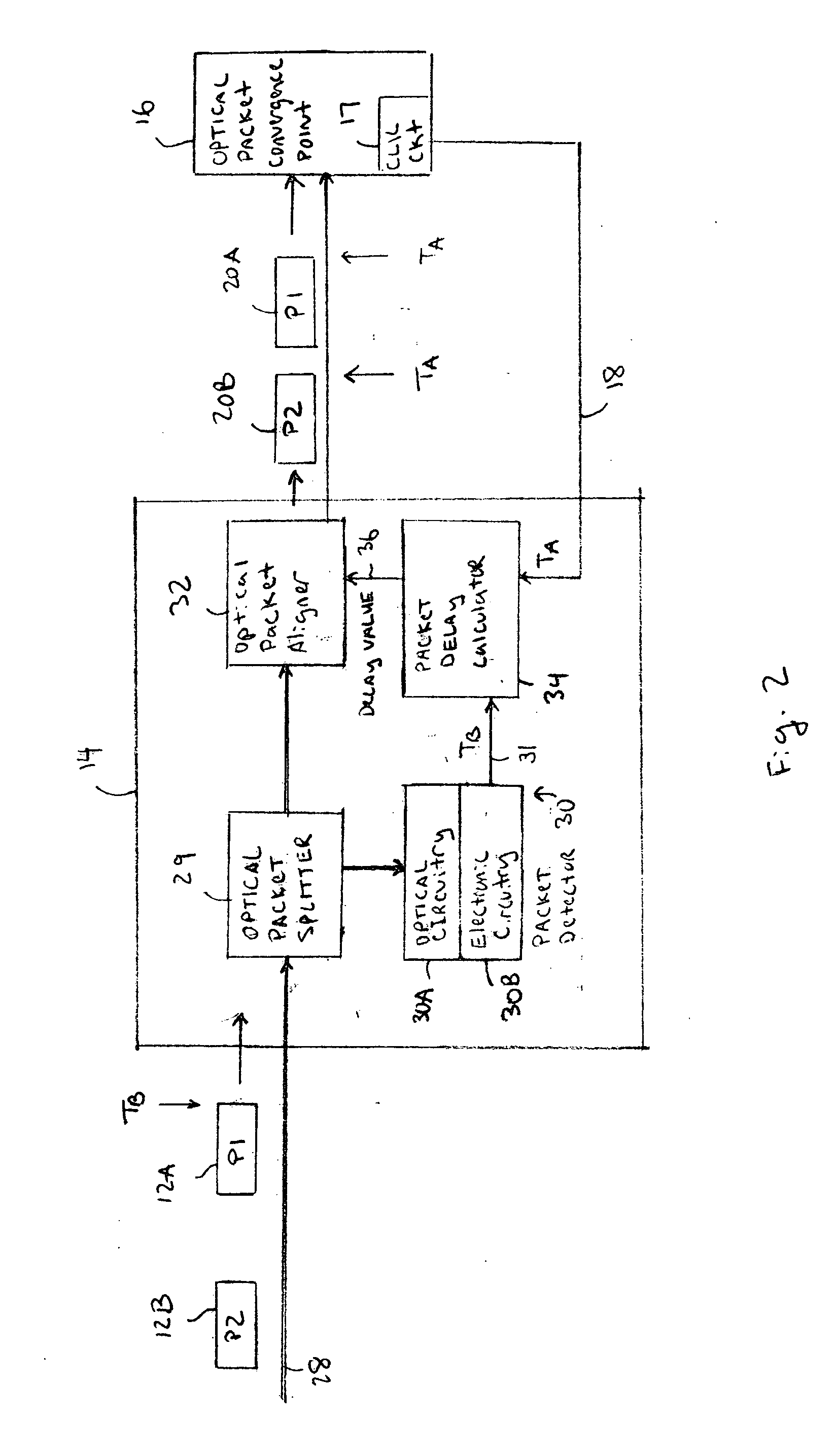
Optical data synchronization scheme
ActiveUS20070201877A1Readily apparentMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexData synchronizationOptical burst switching
Asynchronous optical data is aligned with synchronous convergence points in an optical packet switching system. The convergence points can be any place where data enters an optical packet switching element, buffer stage, switch fabric, etc. The arrival time for data approaching the convergence point is compared with a reference signal associated with the upcoming convergence point. The comparison is used to identify the amount of time-shift required to align the approaching data with the reference signal. Control information is derived according to the comparison and used to control an optical data aligner that synchronizes the data with the convergence point.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
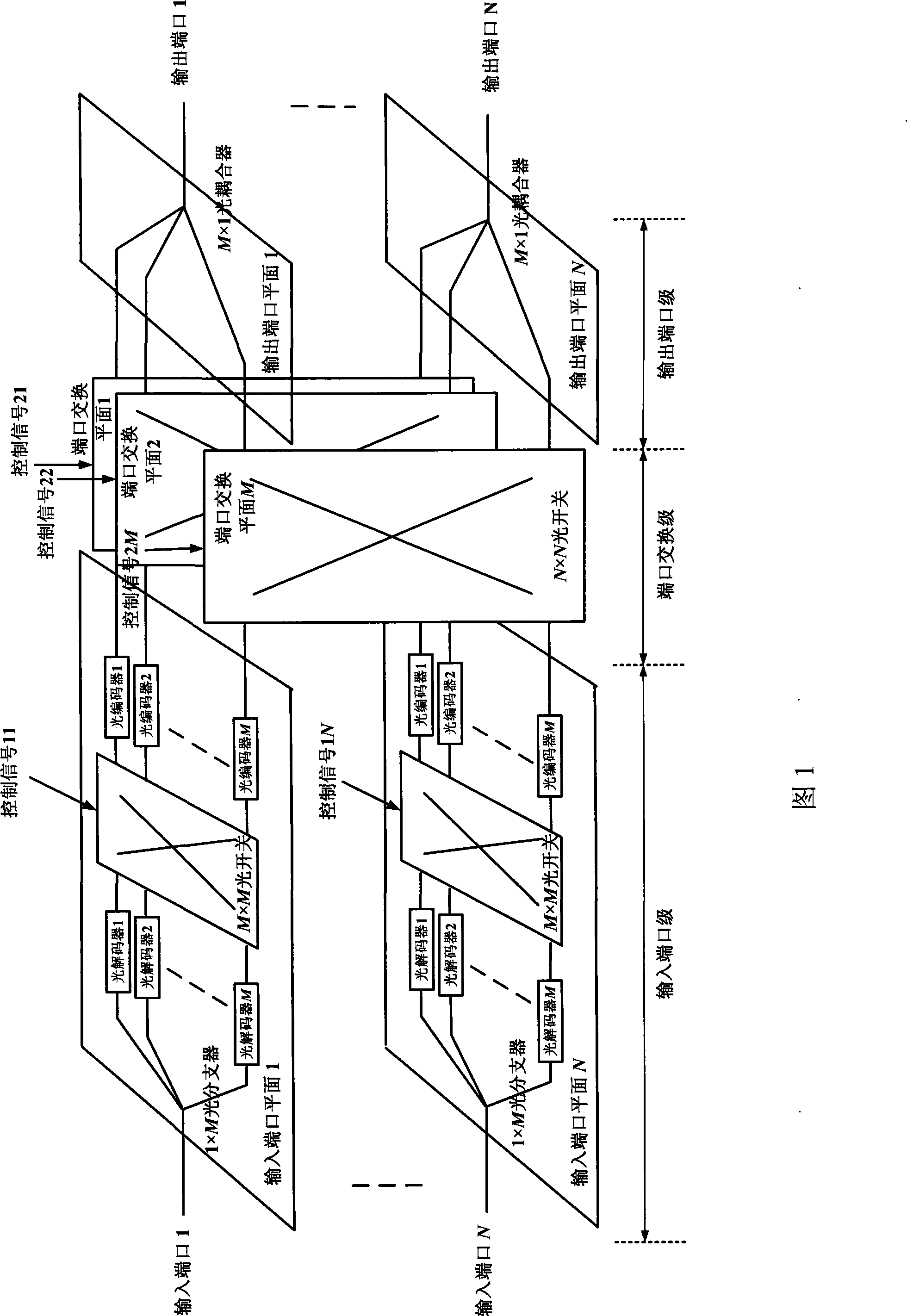
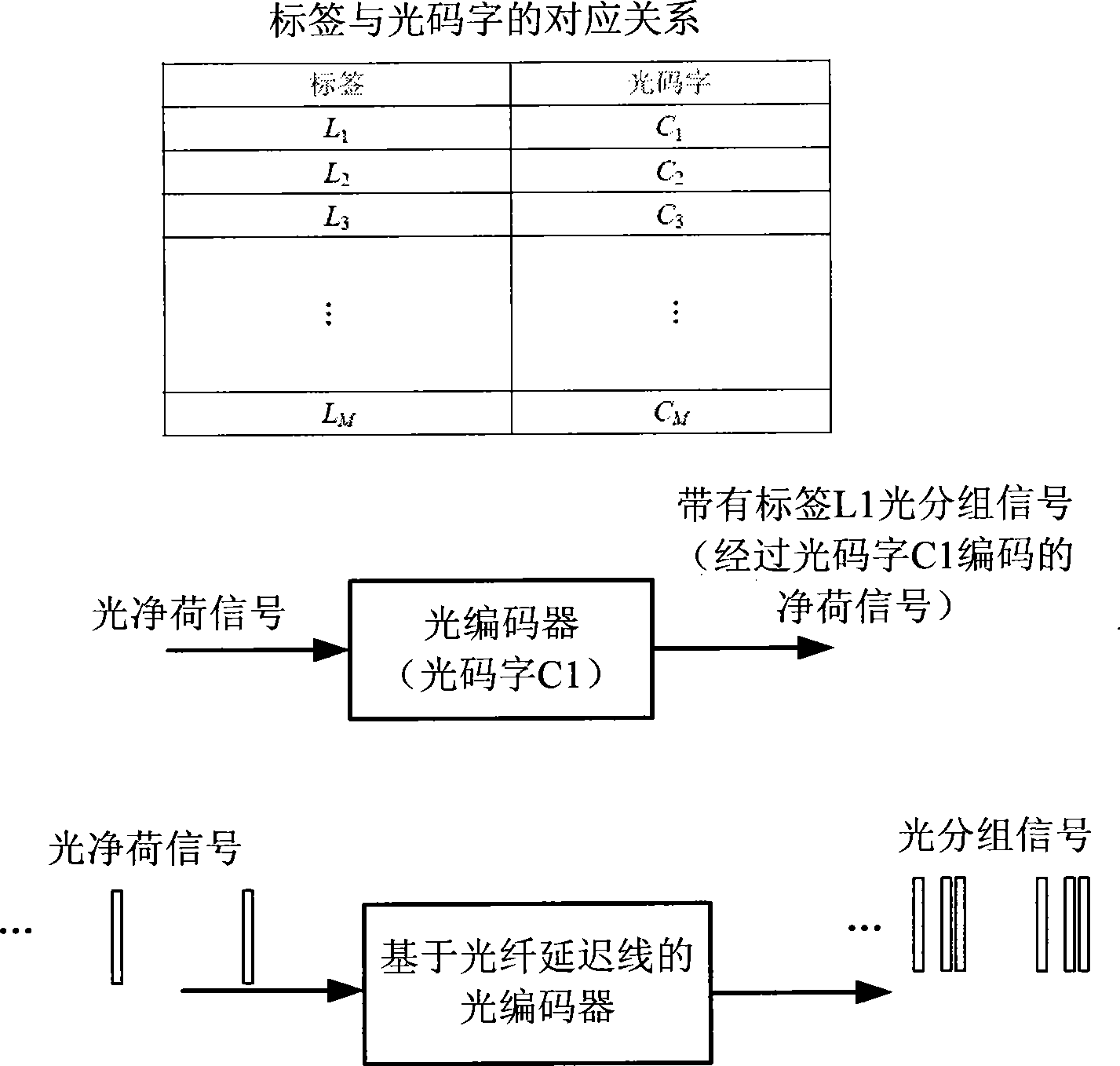
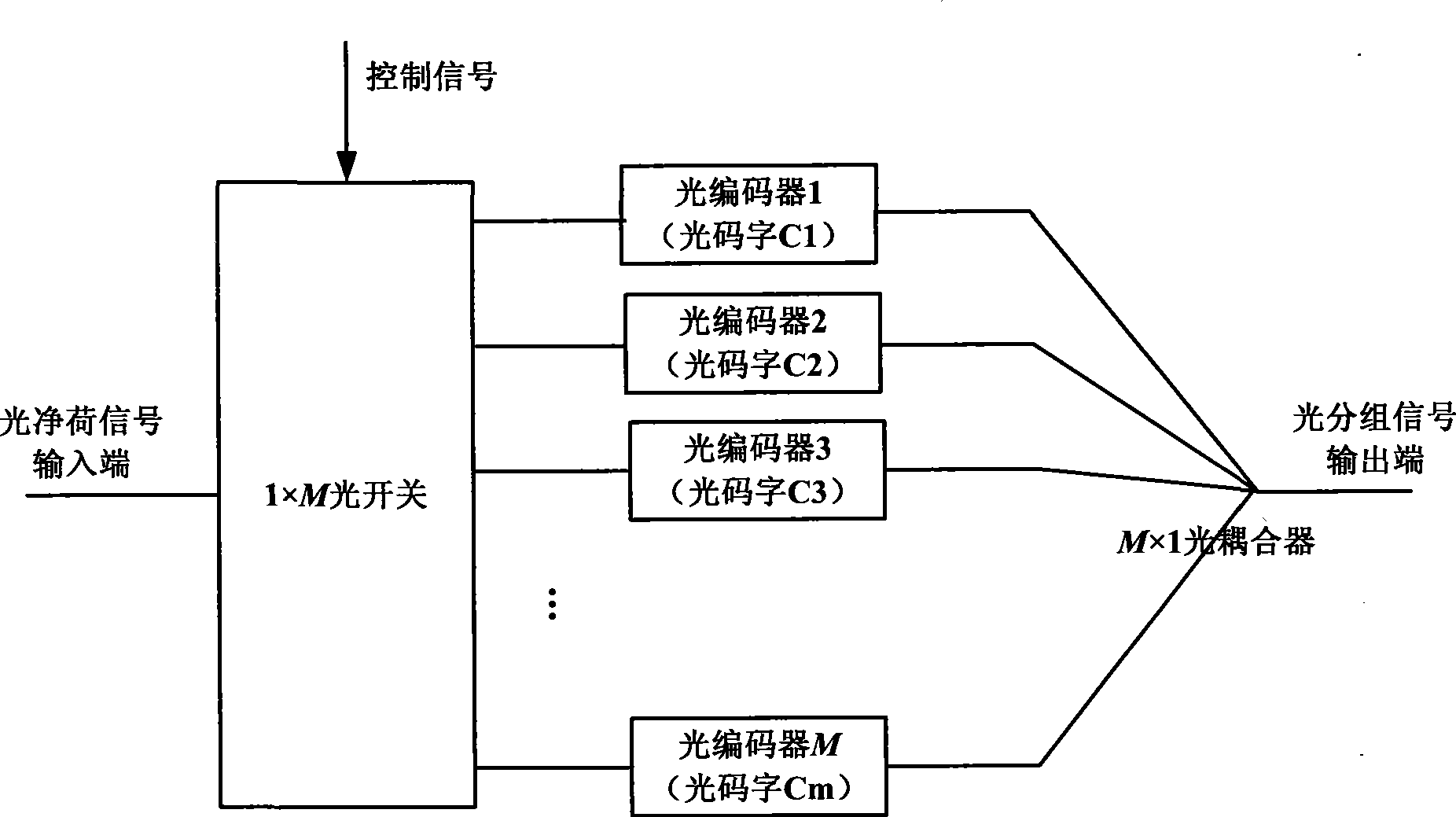
Light packet switching structure based on light code division multiplexing
InactiveCN101437178AMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsControl signalOptical packet
The invention discloses an optical packet switching structure on the basis of optical code division multiplexing, which adopts two stages of optical switches to perform interconnection, wherein the first stage optical switch, namely the optical switch in an input port plane, is connected with optical decoders and optical coders to achieve label update; and the second stage optical switch, namely the optical switch in a port exchange plane, is connected with different input / output ports to achieve port exchanges. According to the corresponding relation between an input label and an output label in certain input port in a label forwarding table, the connection relation between each optical coder and each optical decoder is determined, and the connection relation is achieved through driving the optical switch in the input port plane by a control signal. The connection relation between the output ports of the optical coder is determined according to the input port in the label forwarding table and the output port corresponding to the input label, and the connection relation is achieved through driving the optical switch in the port exchange plane by the control signal. Therefore, the optical packet label update and the port exchange are achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Full optical packet switching node structure for supporting burst or non-burst businesses
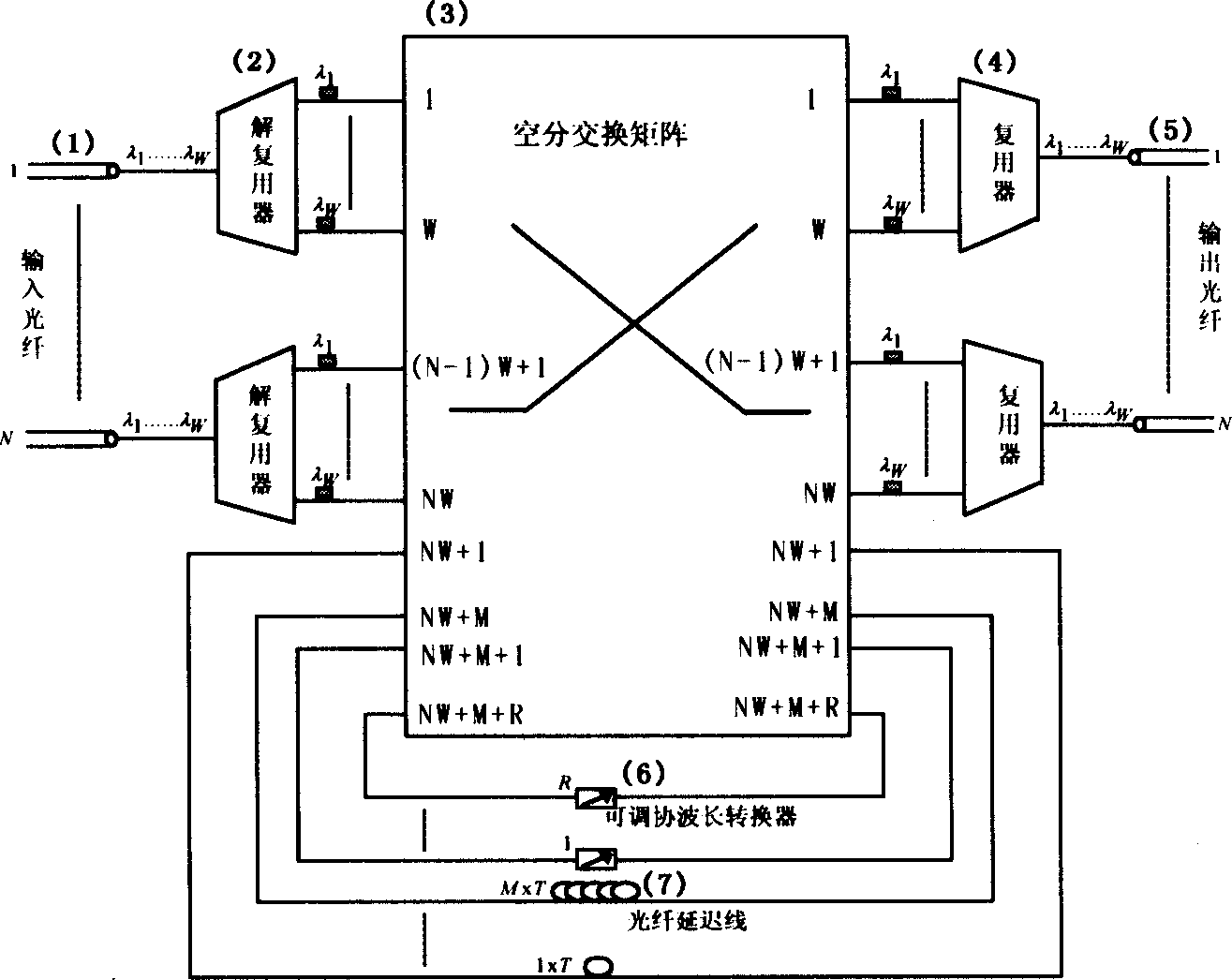
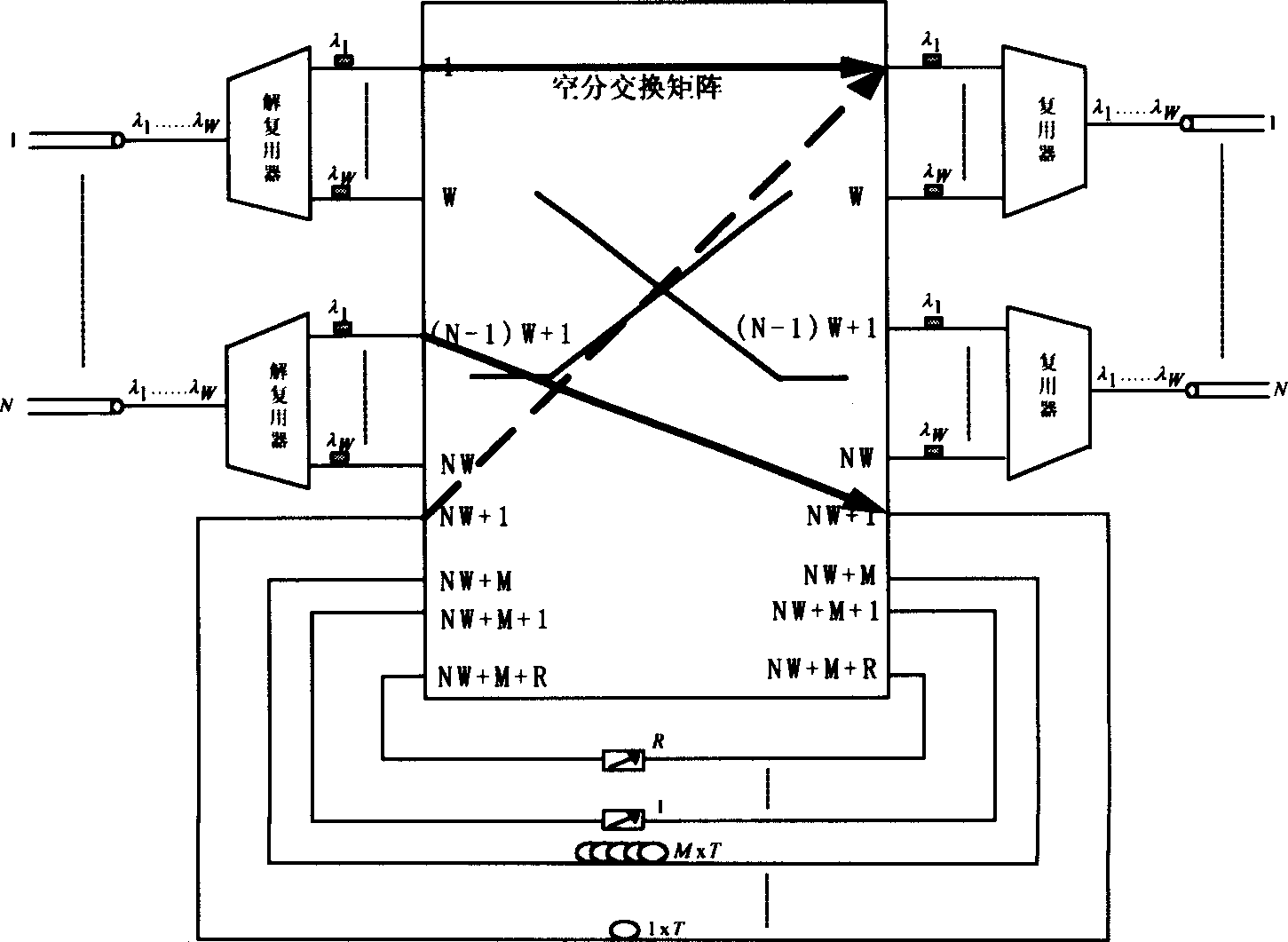
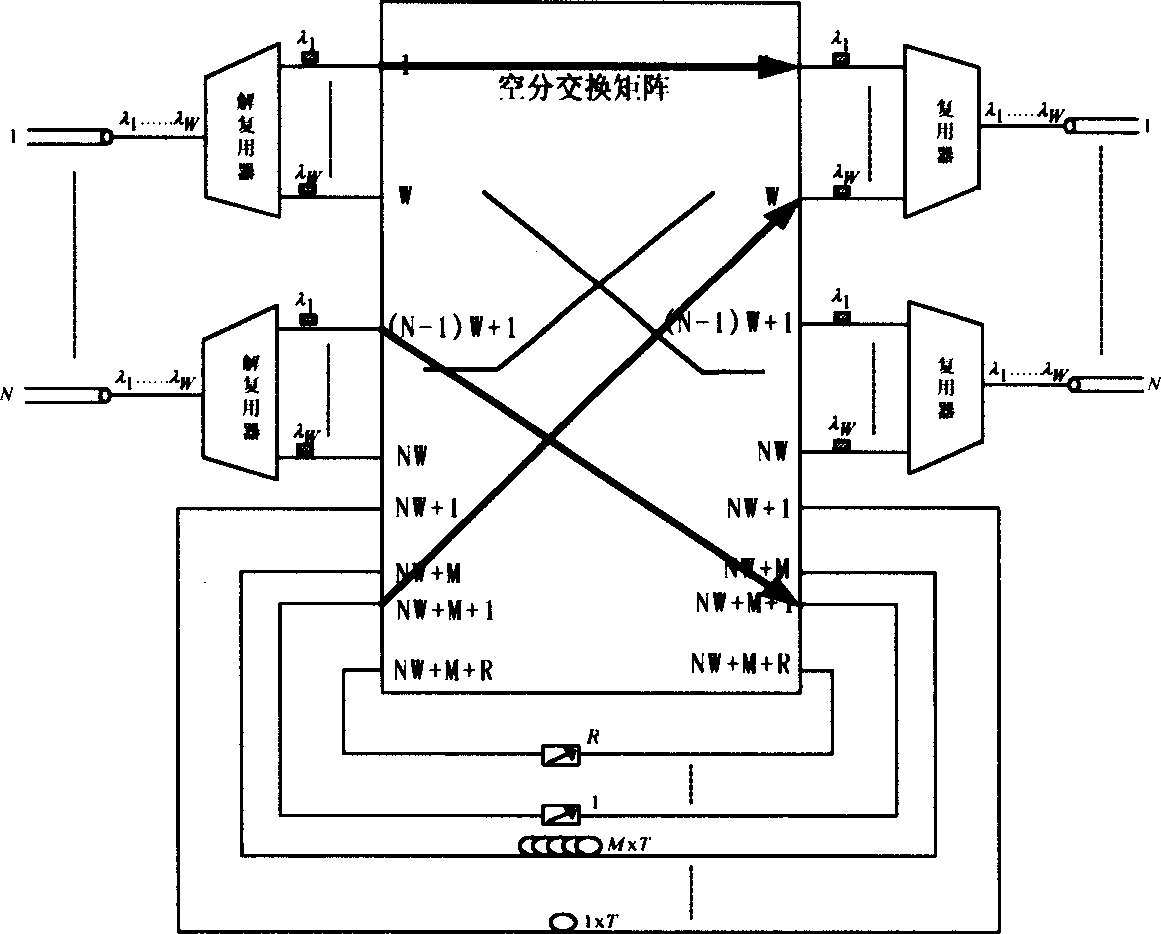
InactiveCN1472969AReduce the numberReduce volumeMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFull waveMultiplexer
A full optical structure for exchanging nodes in grouping, which supports the abrupt and non-abrupt business is a symmetric structure consisting of N numbers of 1XW light-wave decomposing multiplexer, N numbers of Wx1 light-wave decomposing multiplexer, one of (WN+R+M)x(WN+R+M) full optical unblocking exchanging matrix module, R numbers of full wave-length converter and M numbers of optical fiber delaying line, wherein N is the number of input / output optical fiber port, W is the number of wave-length channel which can be transmitted at each port, M number of delaying line constitute a structure of degenerate form, the shortest or the longest delaying line provides the buffer-storing time T or MT to the grouping respectively.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
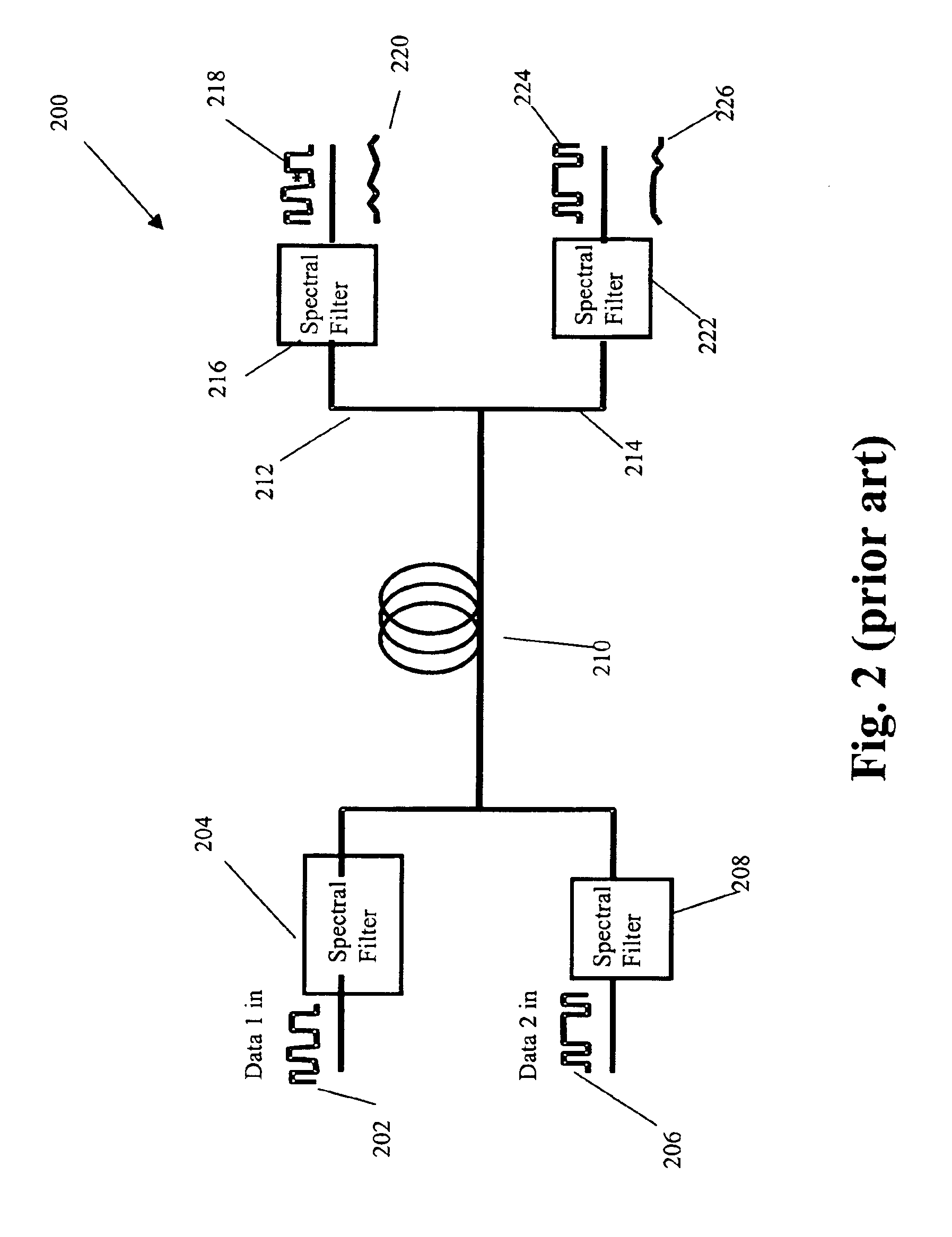
Packet-based optical communications networks
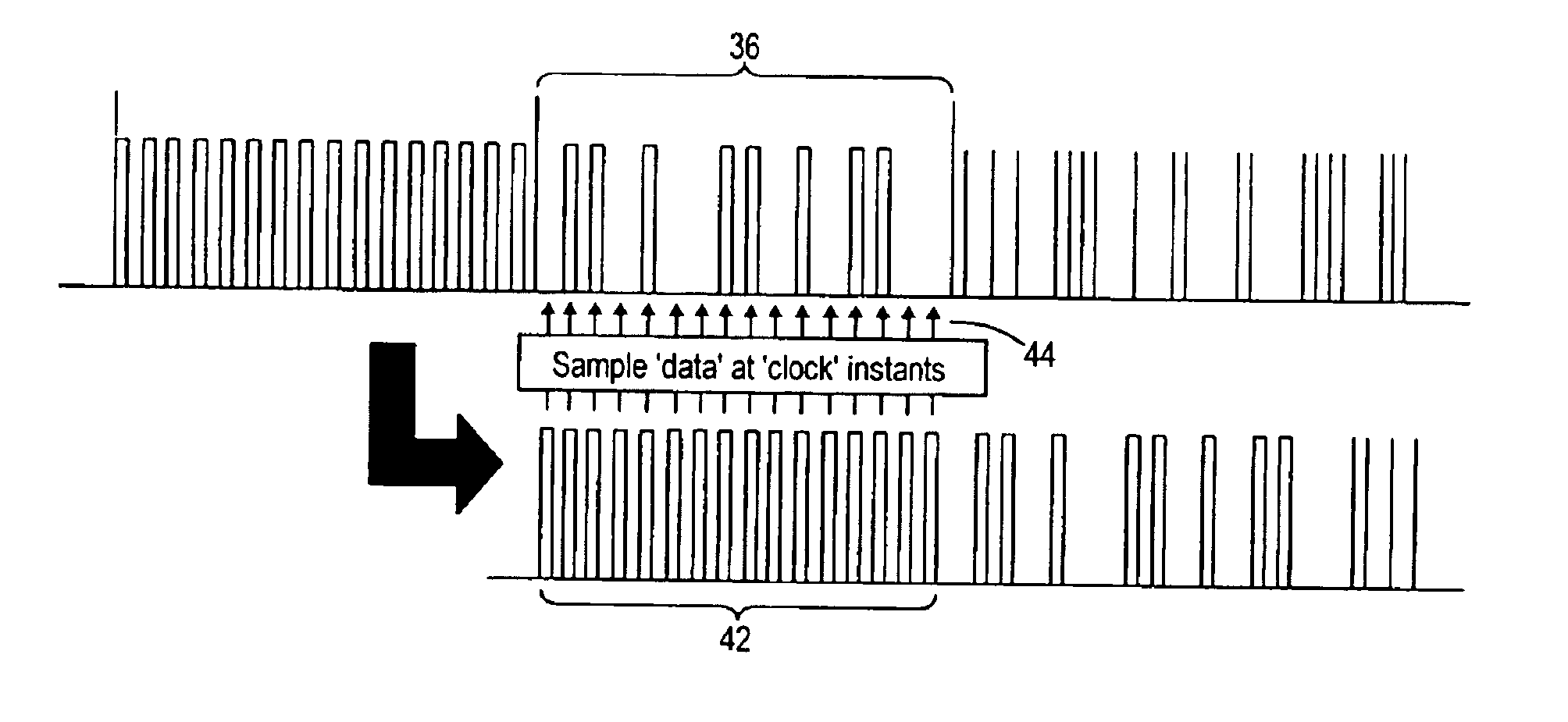
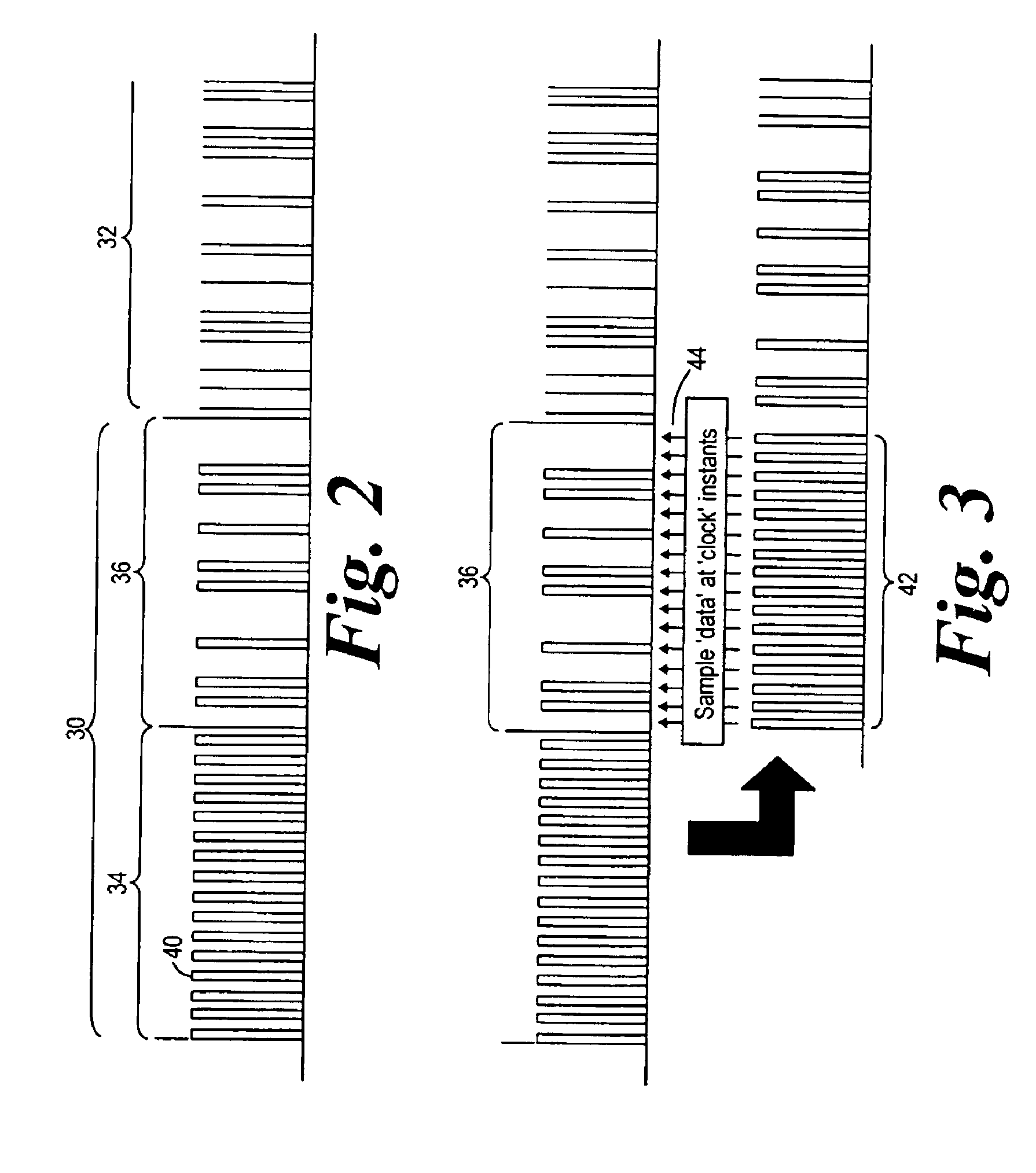
InactiveUS6895023B2Reduce overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexStructure of Management InformationData rate
A structure for an optical packet for transmission over an optical network comprises a packet header (30) and a packet payload (32). The header comprises first and second sections (34, 36). The first section (34) comprises a series of clock pulses (40) at the data rate of the second section of the packet header, or a multiple or sub-multiple thereof. This header structure enables the clock pulses in the first section (34) to be used to control the timing instants when the header information in the second section (36) is read. The header information can thus be read using the data in the header alone, without needing to alter the structure of the packet payload. The clock pulses can be delayed in order to enable them to be used to control the reading of data in the second section of the packet header. The invention ca be used in optical communications networks.
Owner:CIENA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com