Patents
Literature
1471 results about "Optical layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
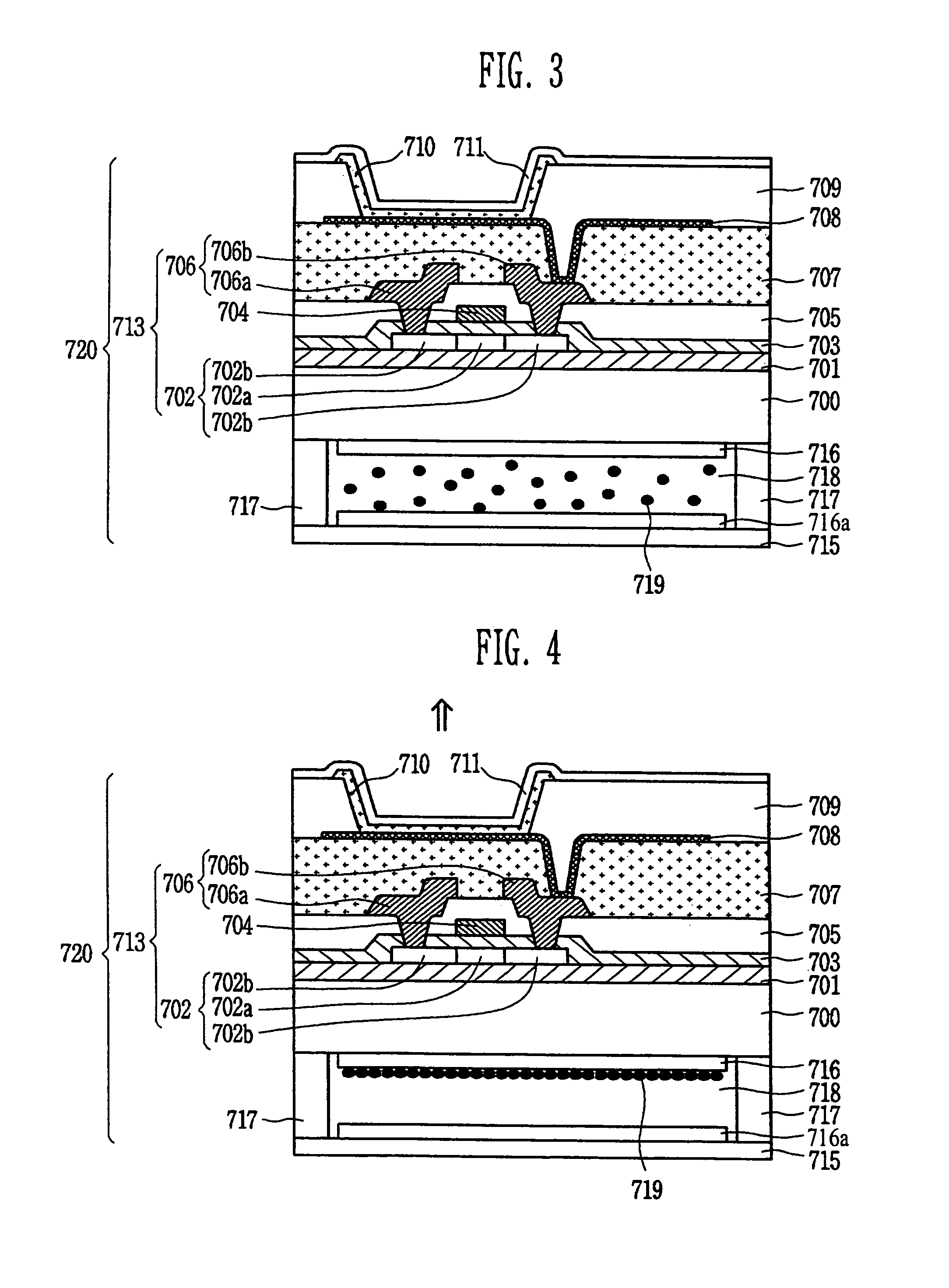
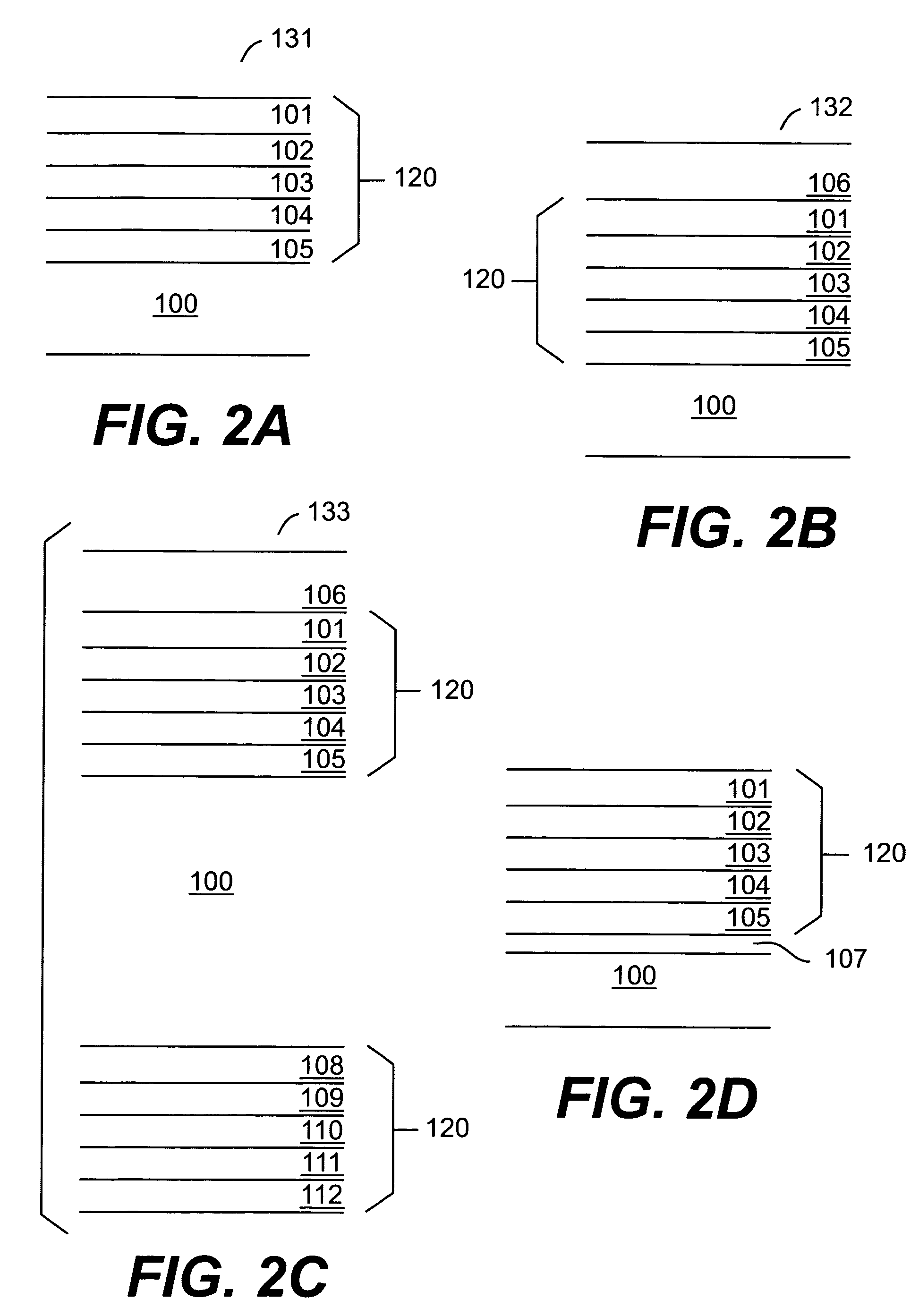
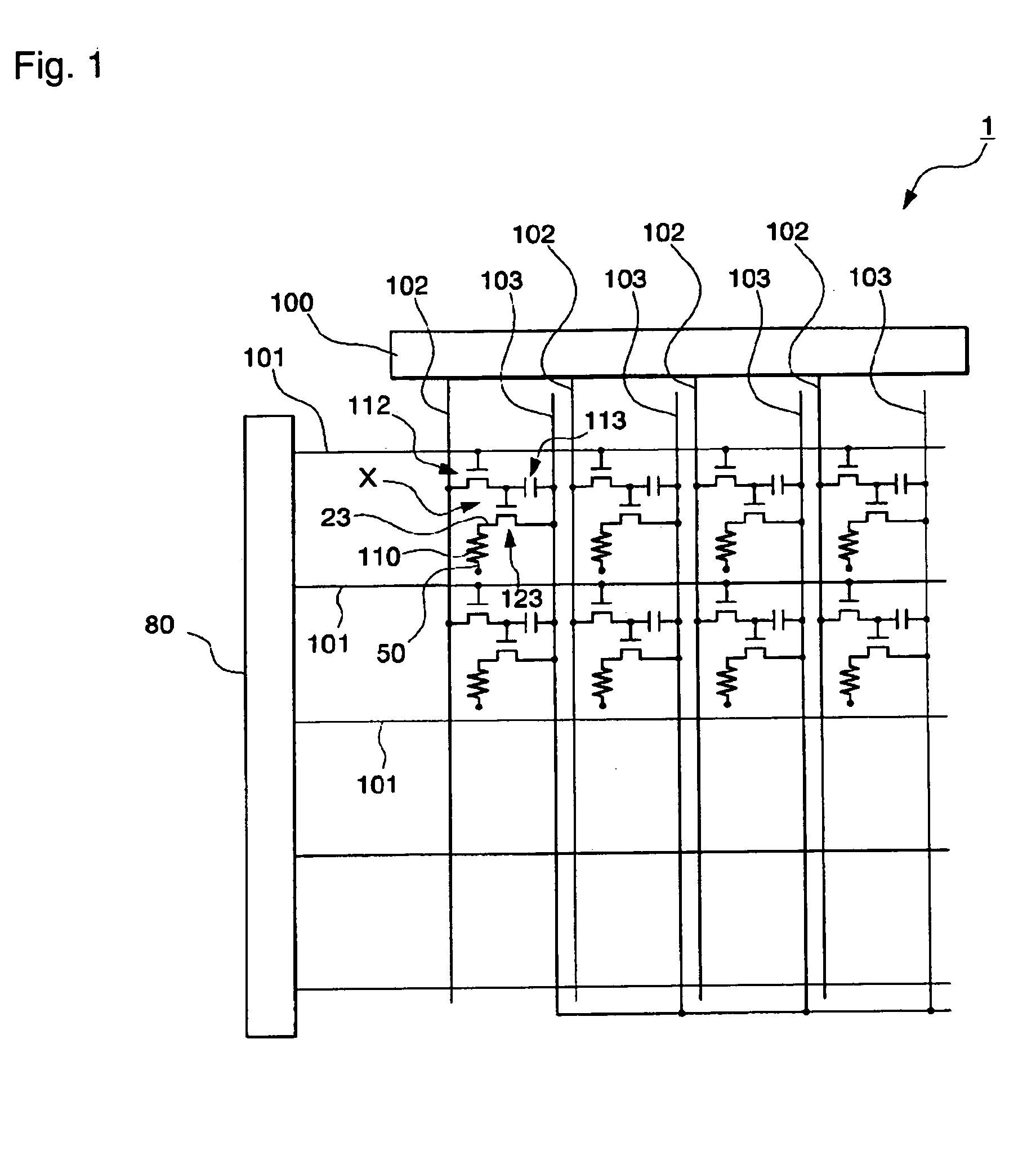
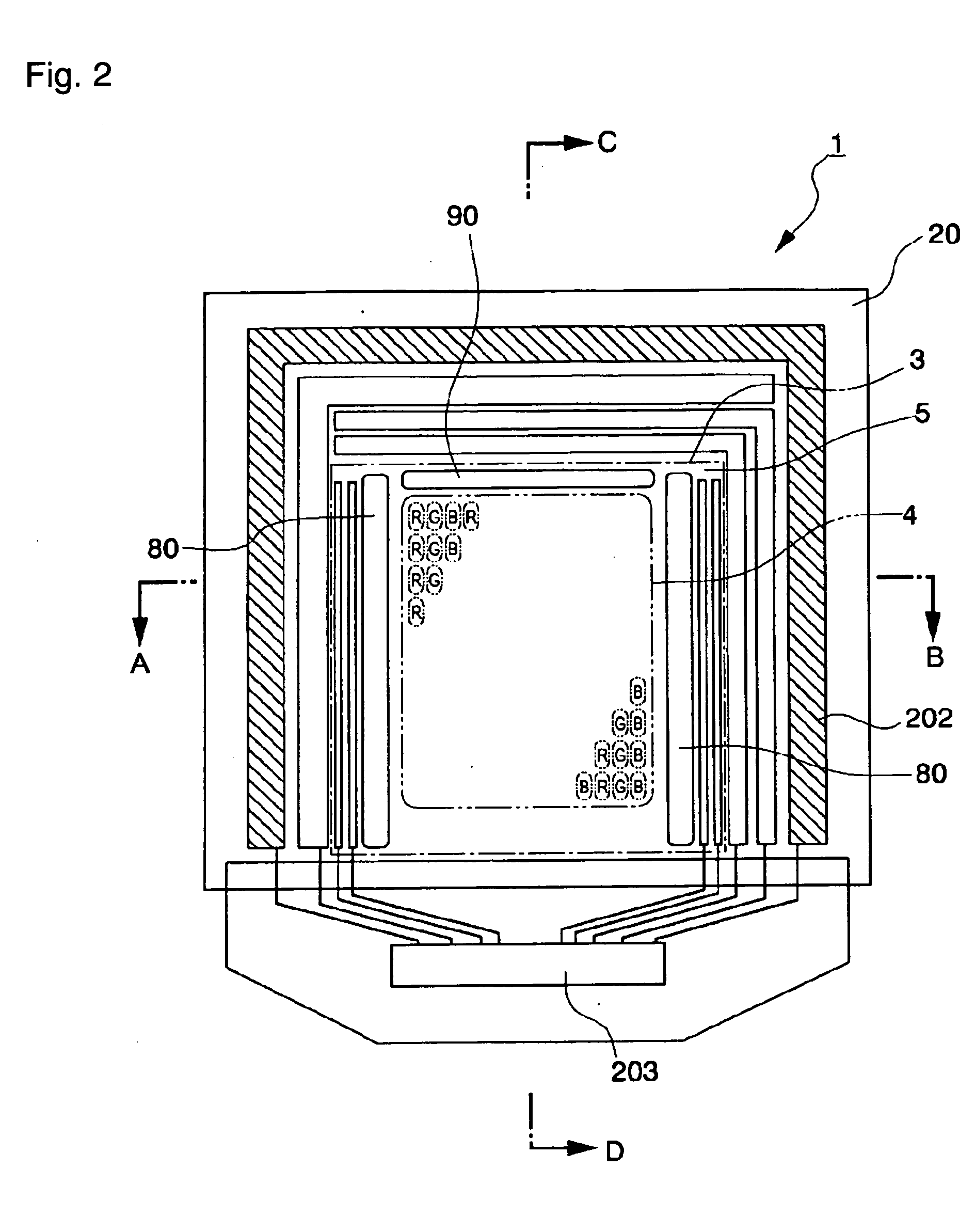
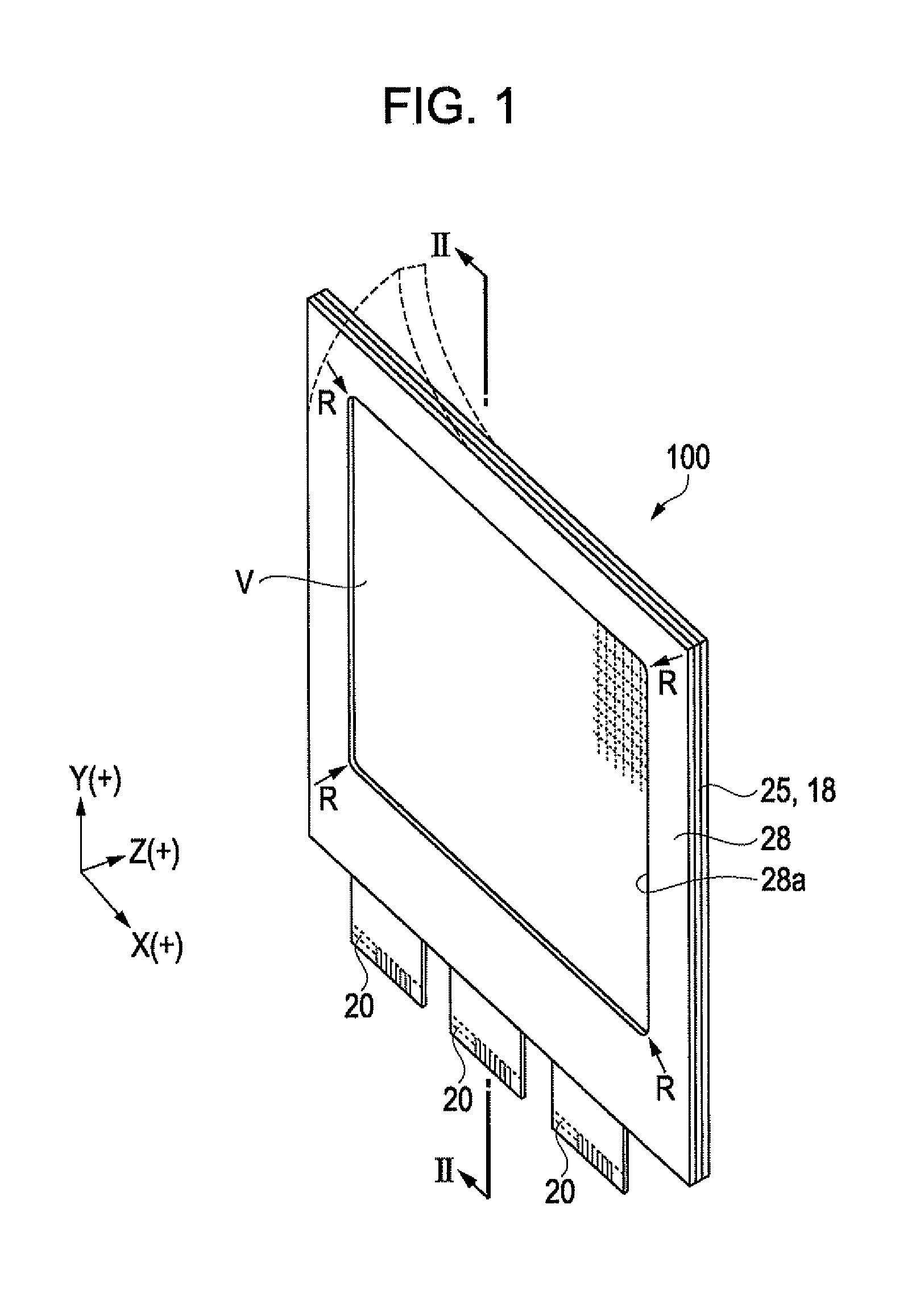
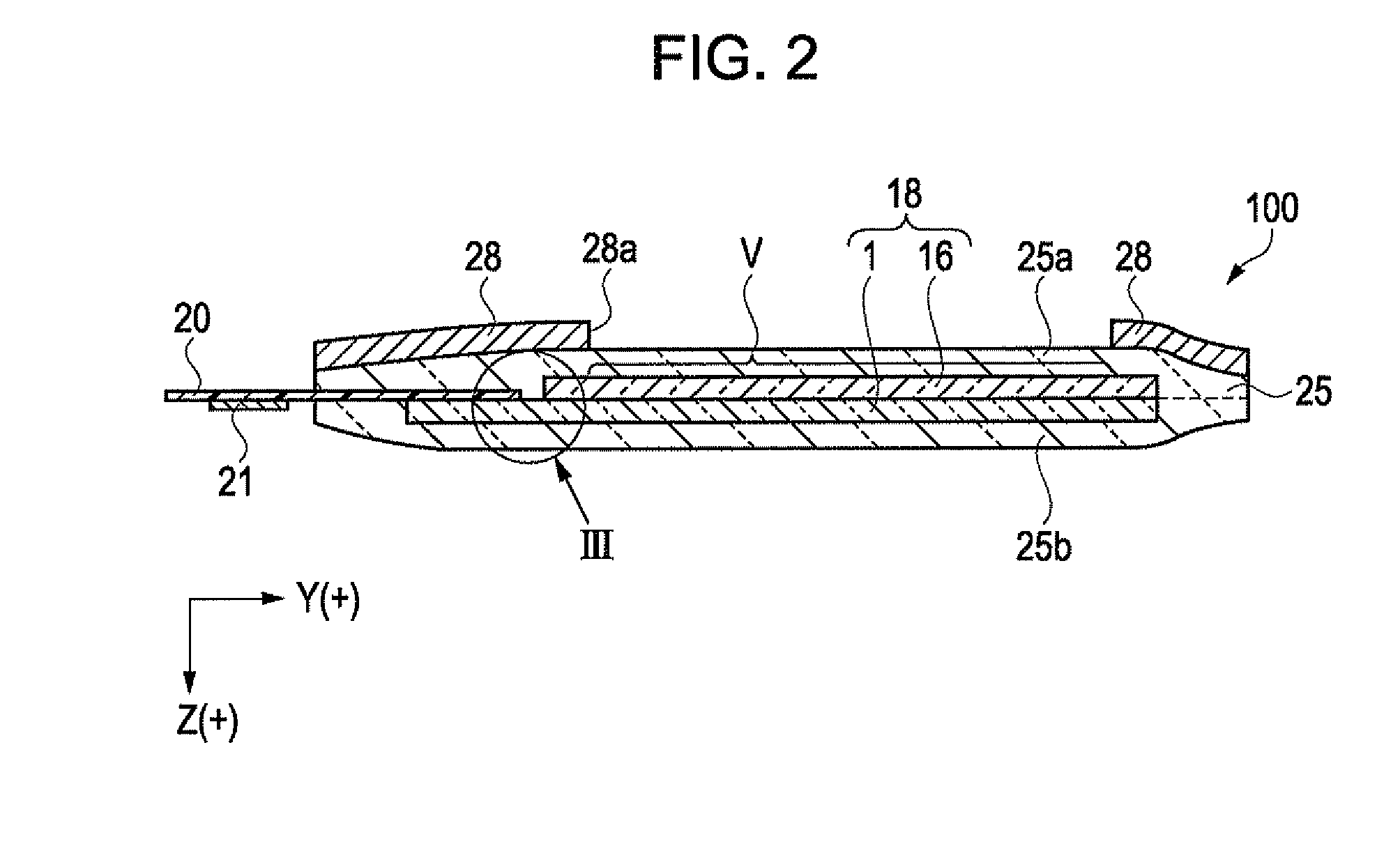
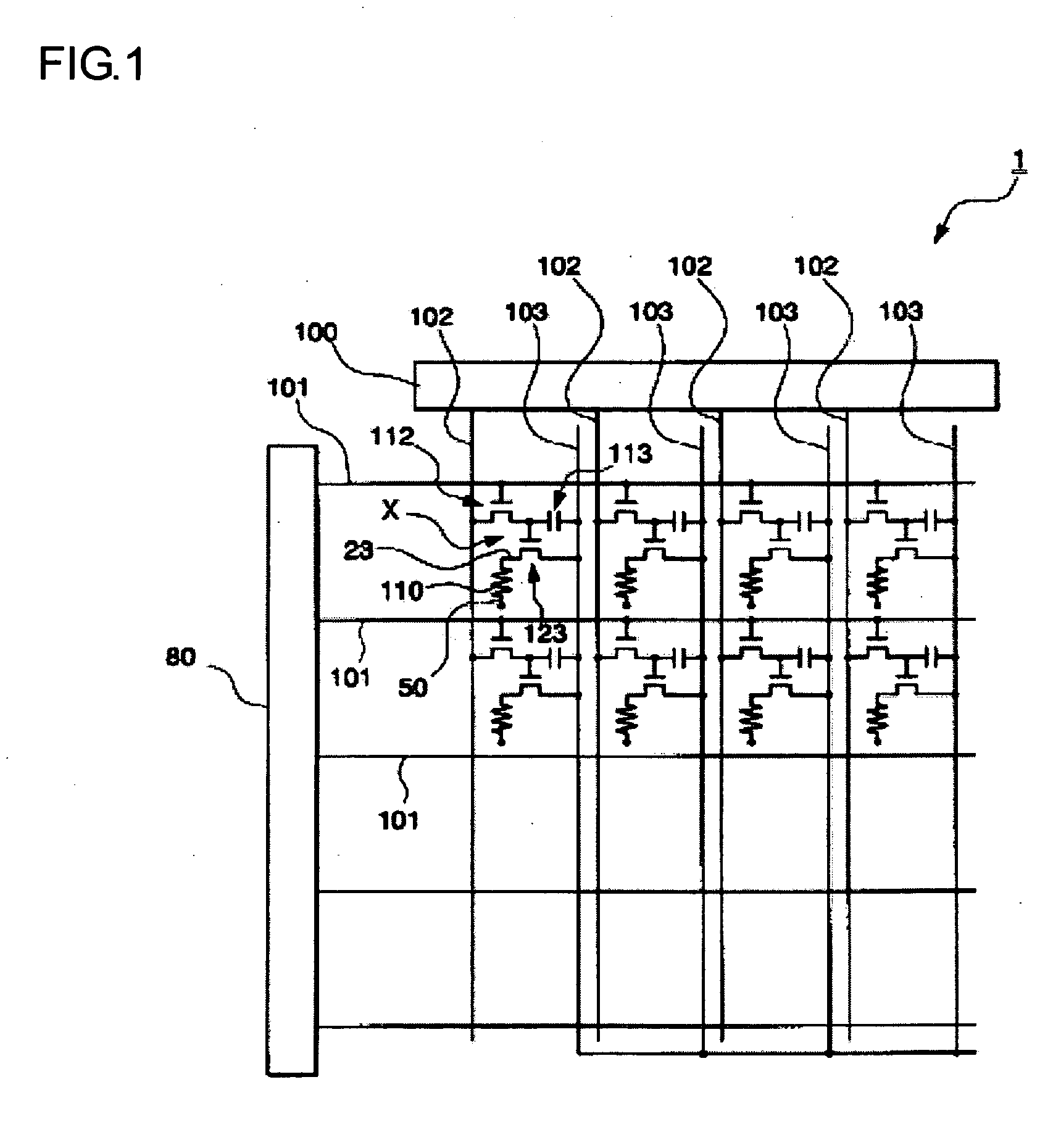
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
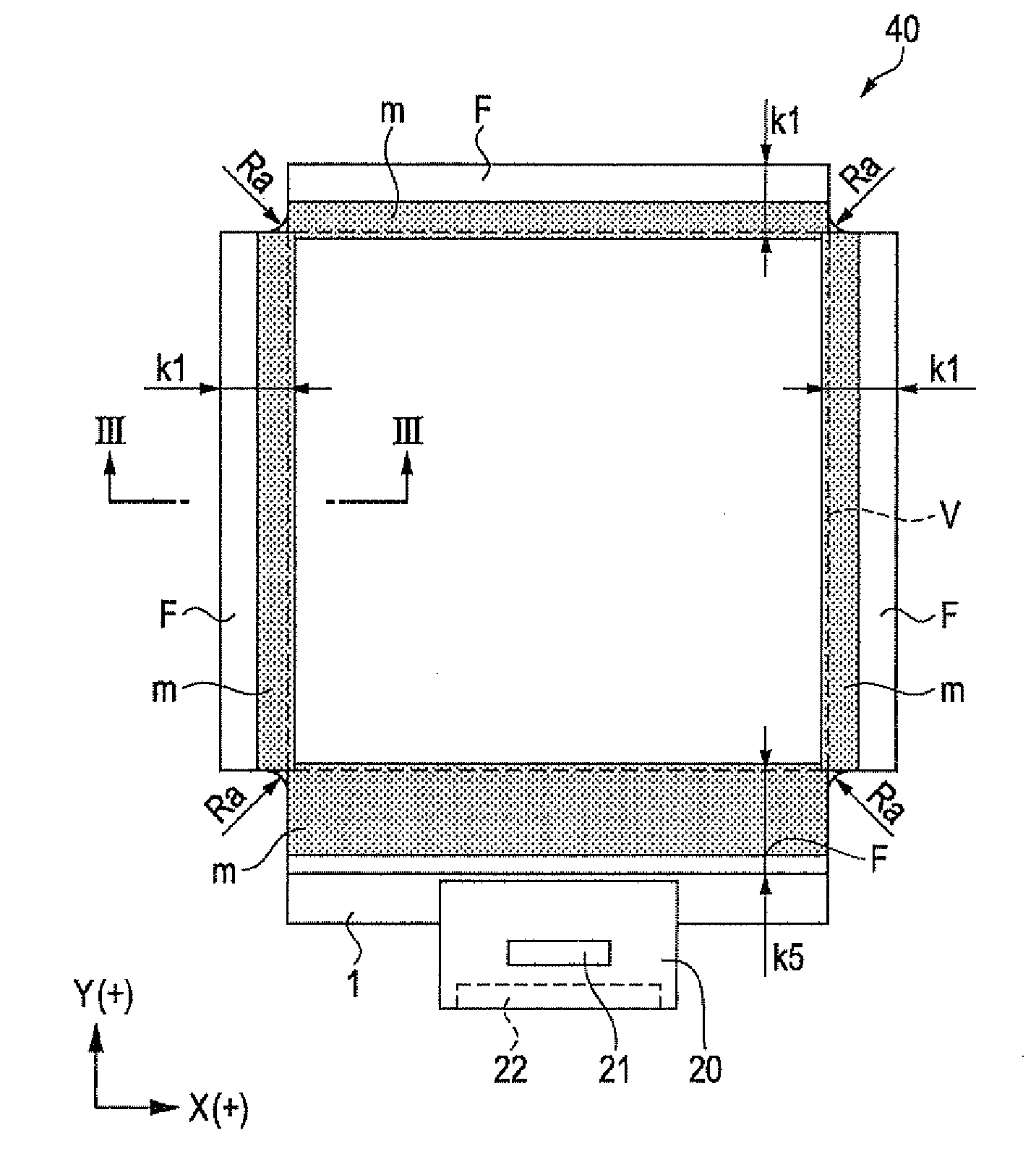
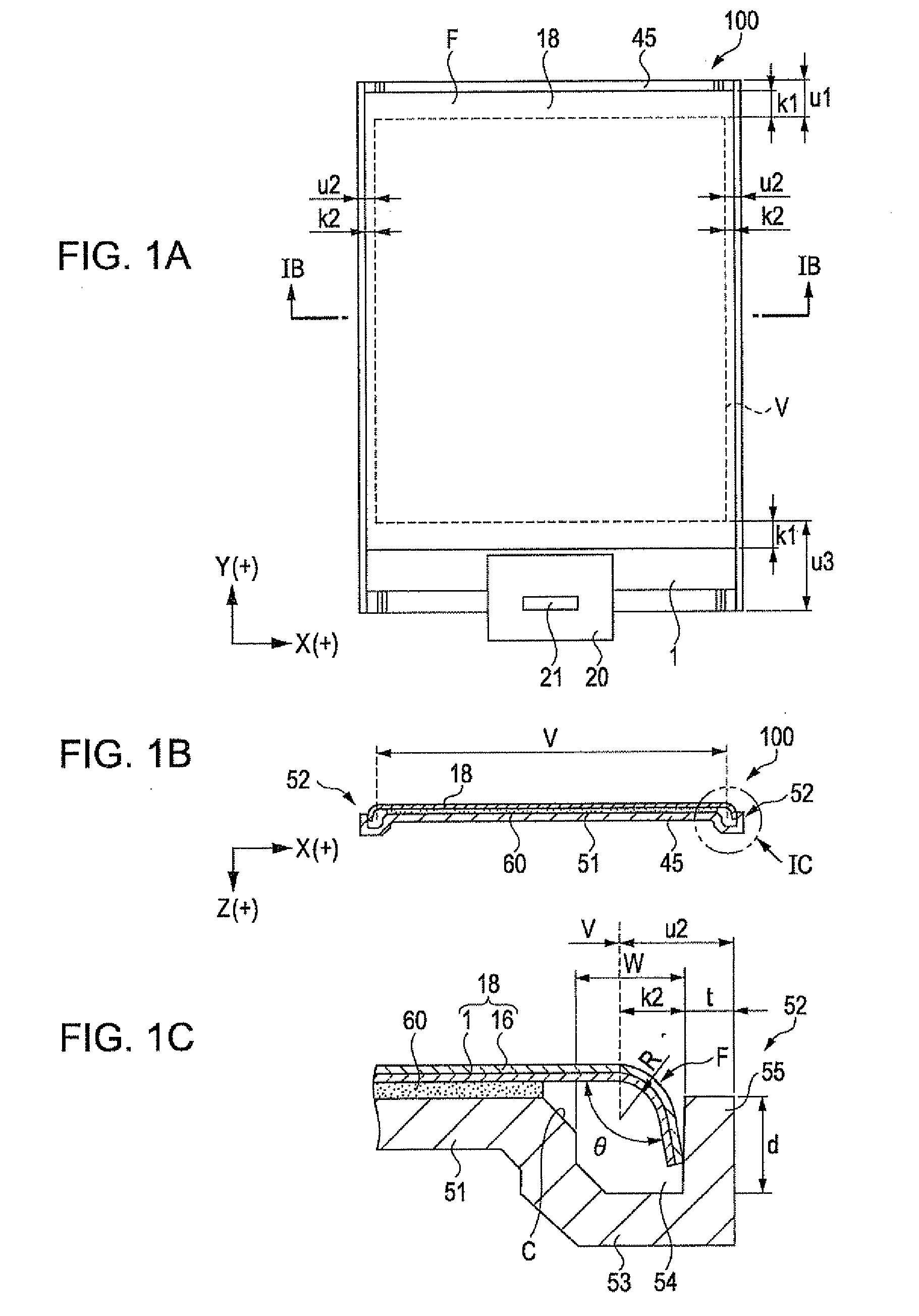
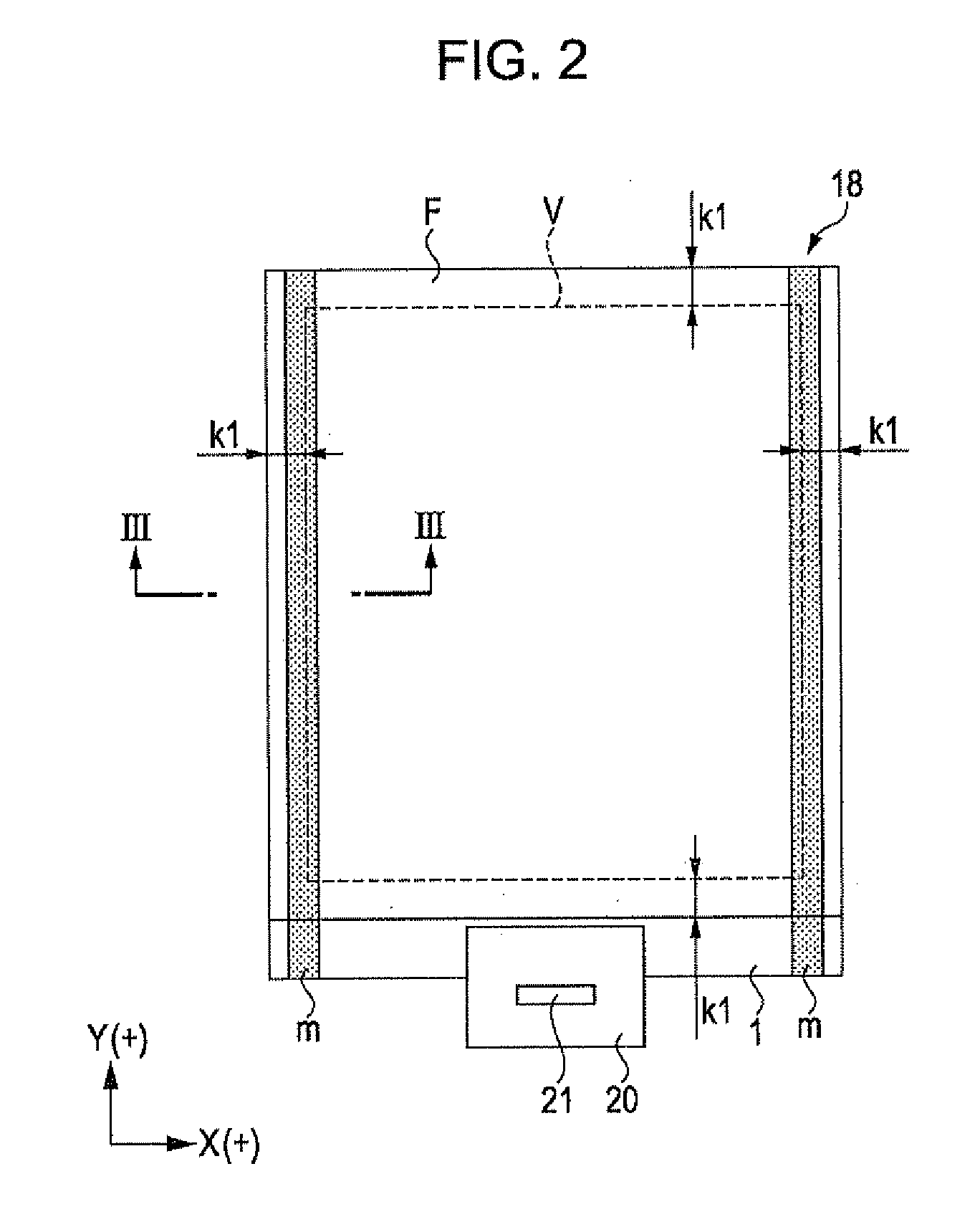
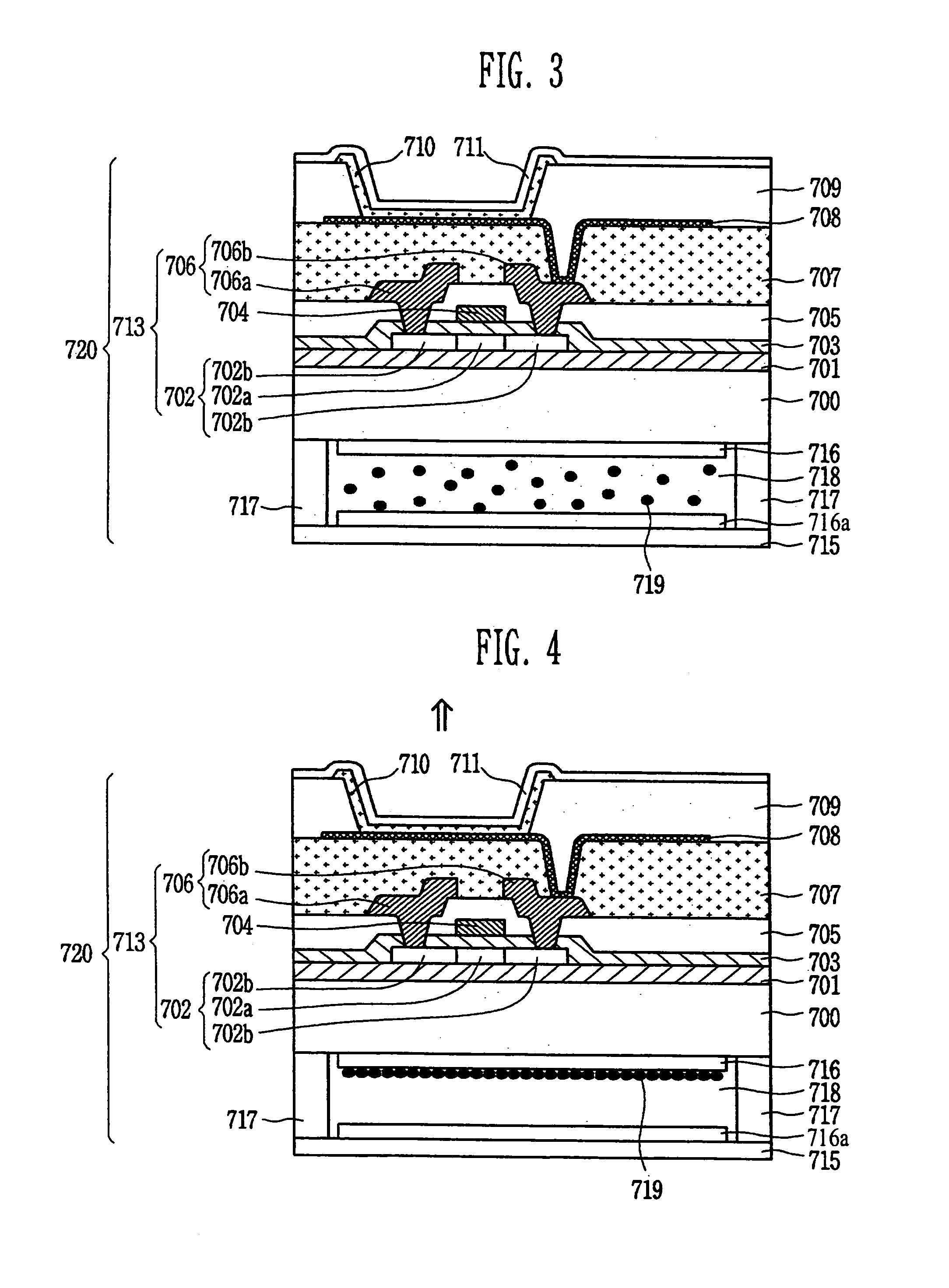
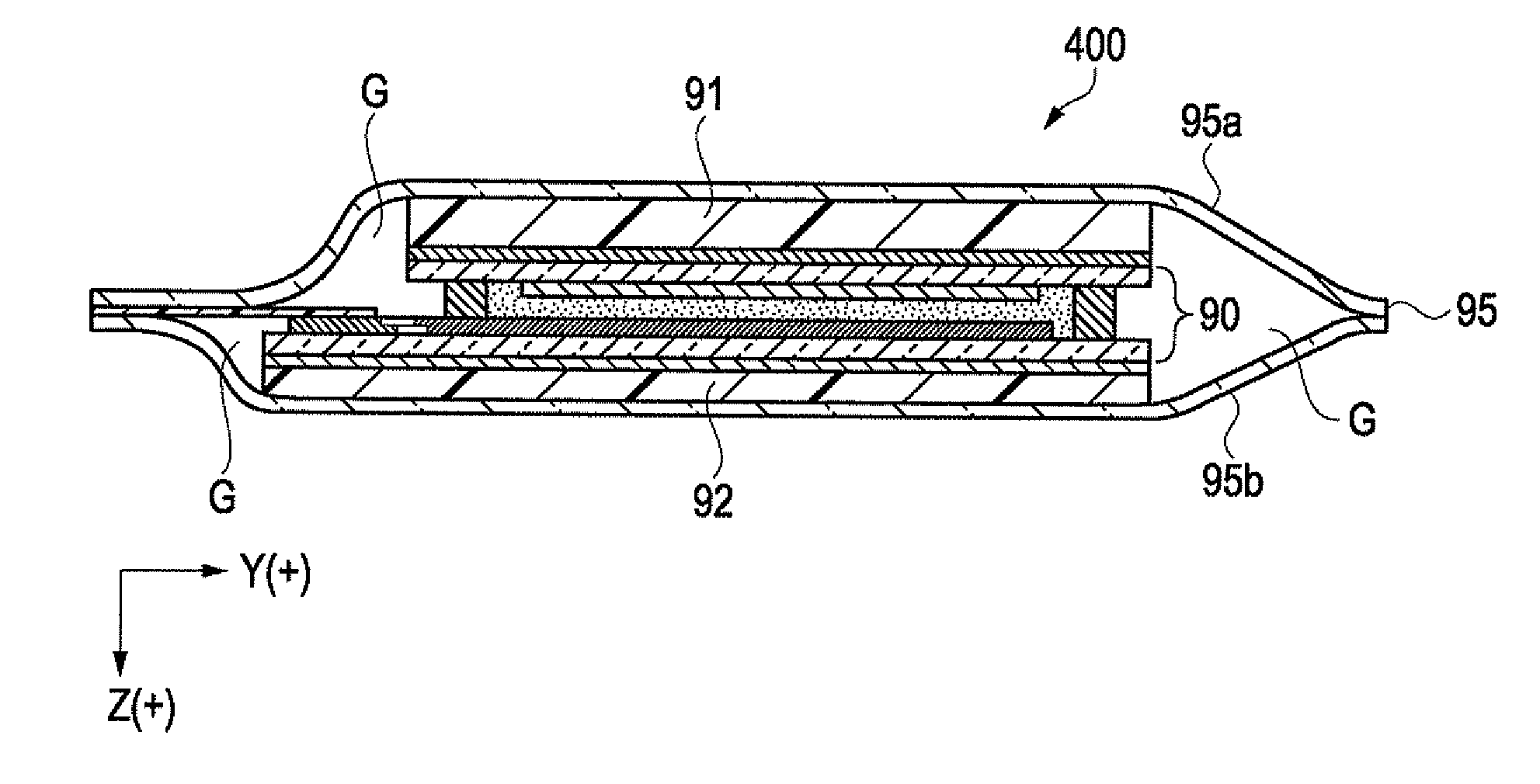
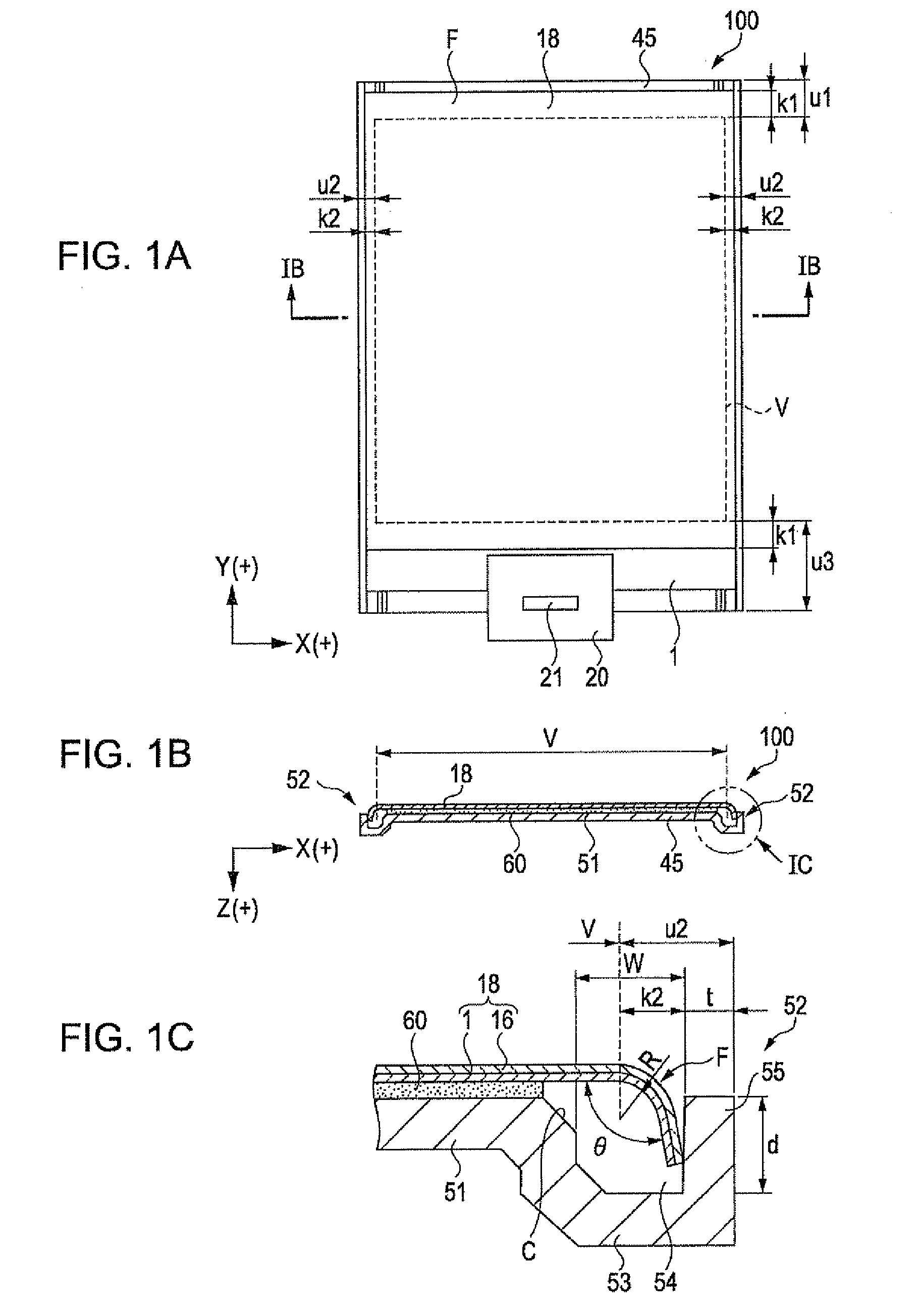
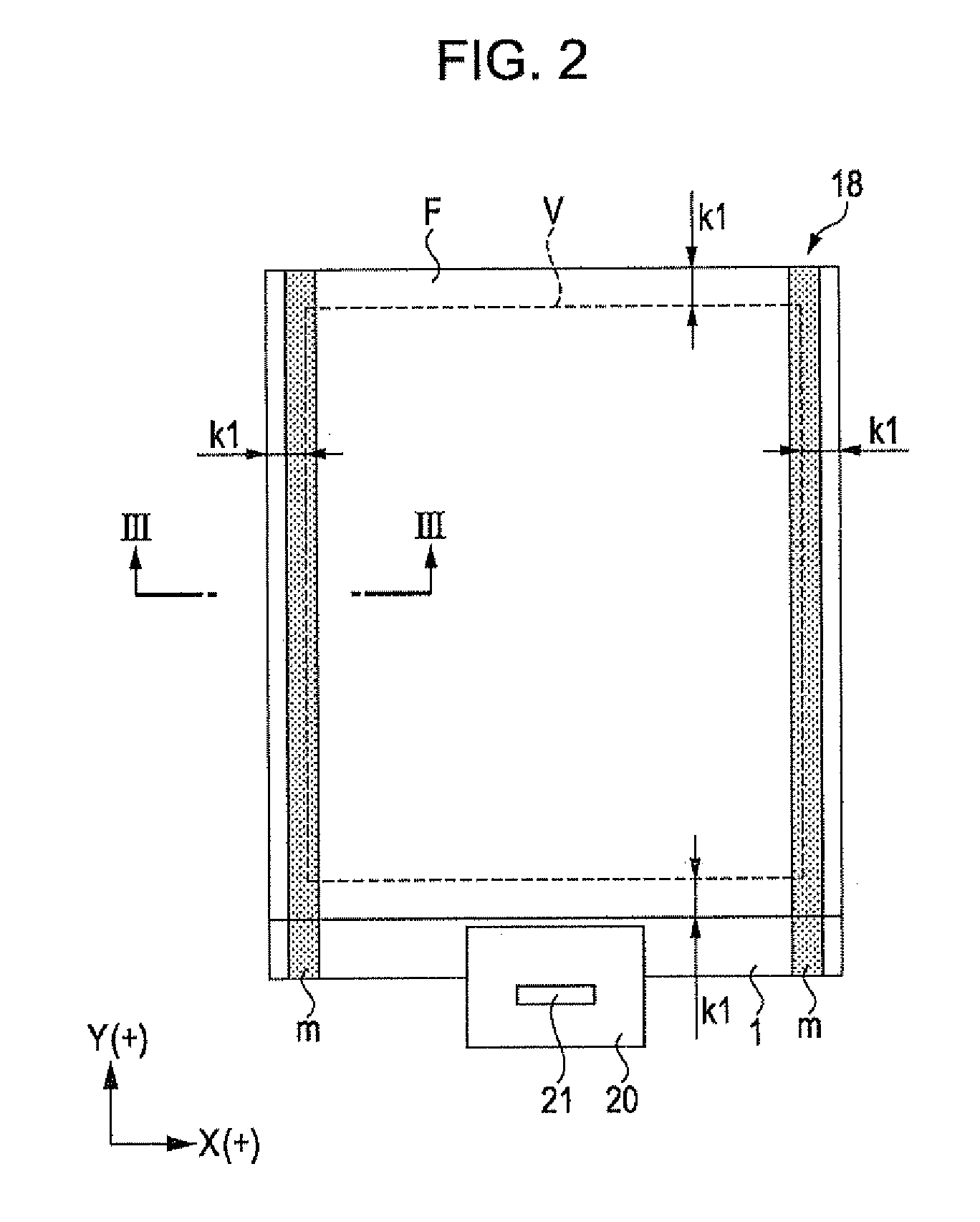
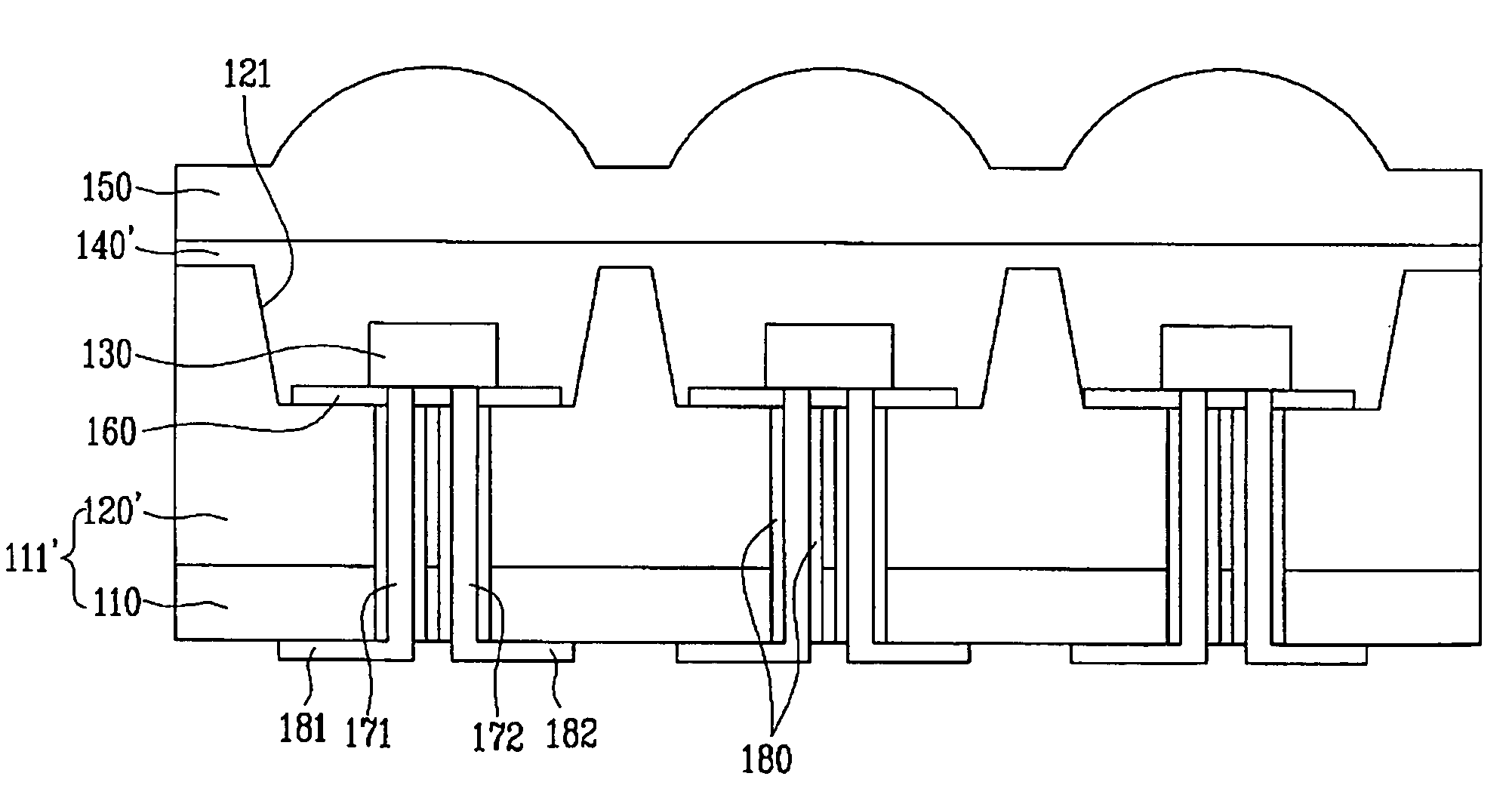
ActiveUS20110050657A1Ensure reliabilityNarrow frameDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsMaterials scienceElectrical and Electronics engineering
An electro-optical device includes a display panel obtained by forming an electro-optical layer, in which a plurality of pixels is formed, on a glass substrate having a thickness of 50 μm or less; and a support frame supporting the display panel, wherein the display panel has at least a display region in which the plurality of pixels is formed and frame regions formed outside the display region, and wherein at least one side of each of the frame regions is bent from the vicinity of a circumference of the display region to the support frame side and is fixed to the support frame.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
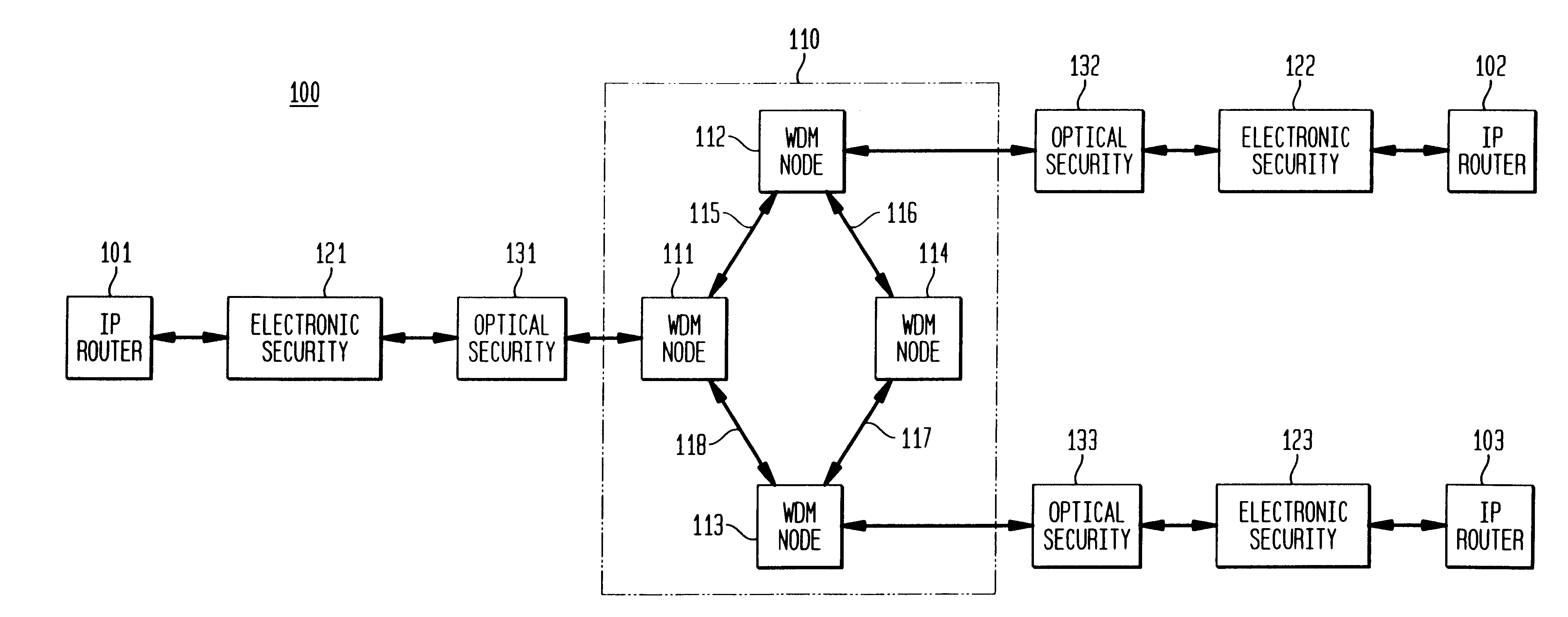
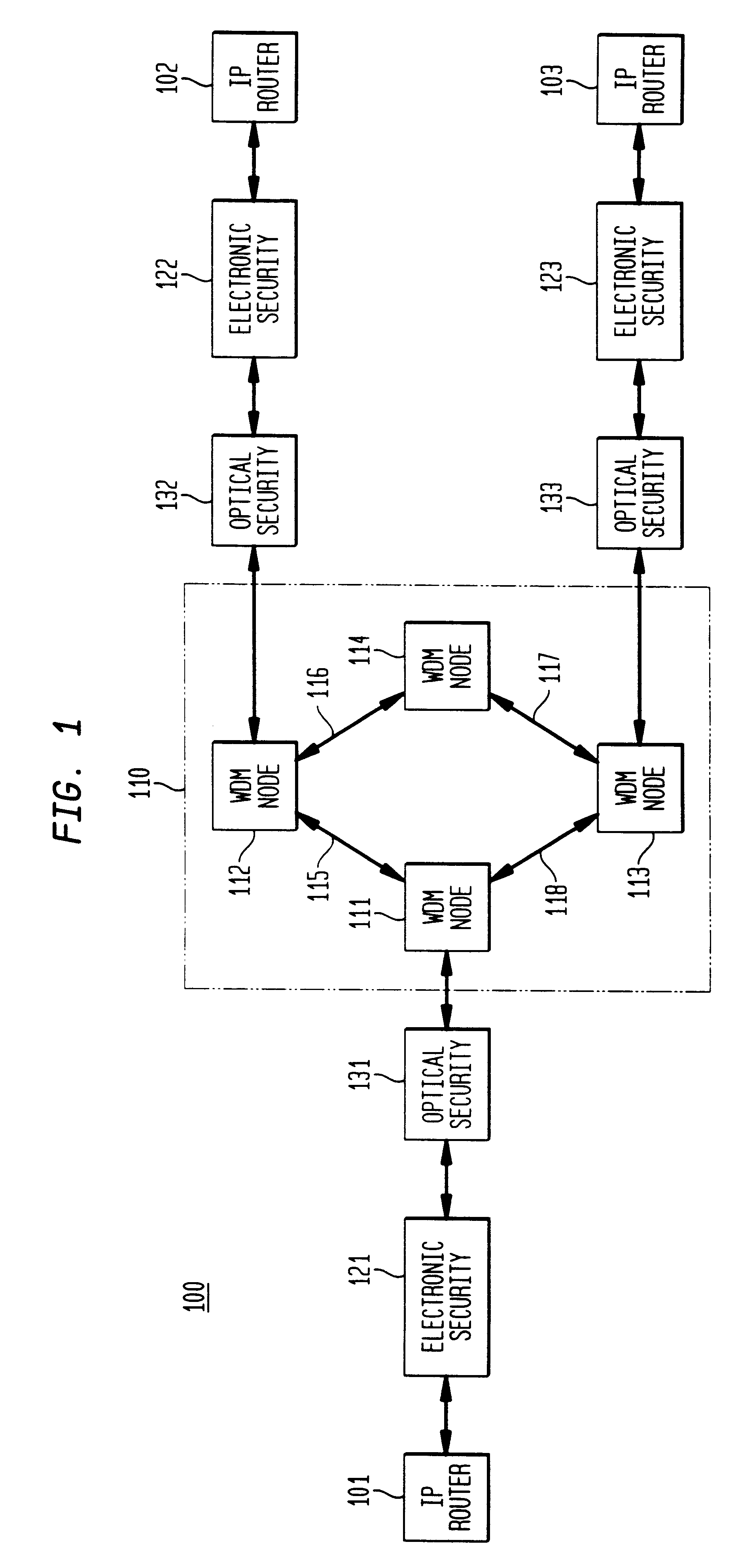
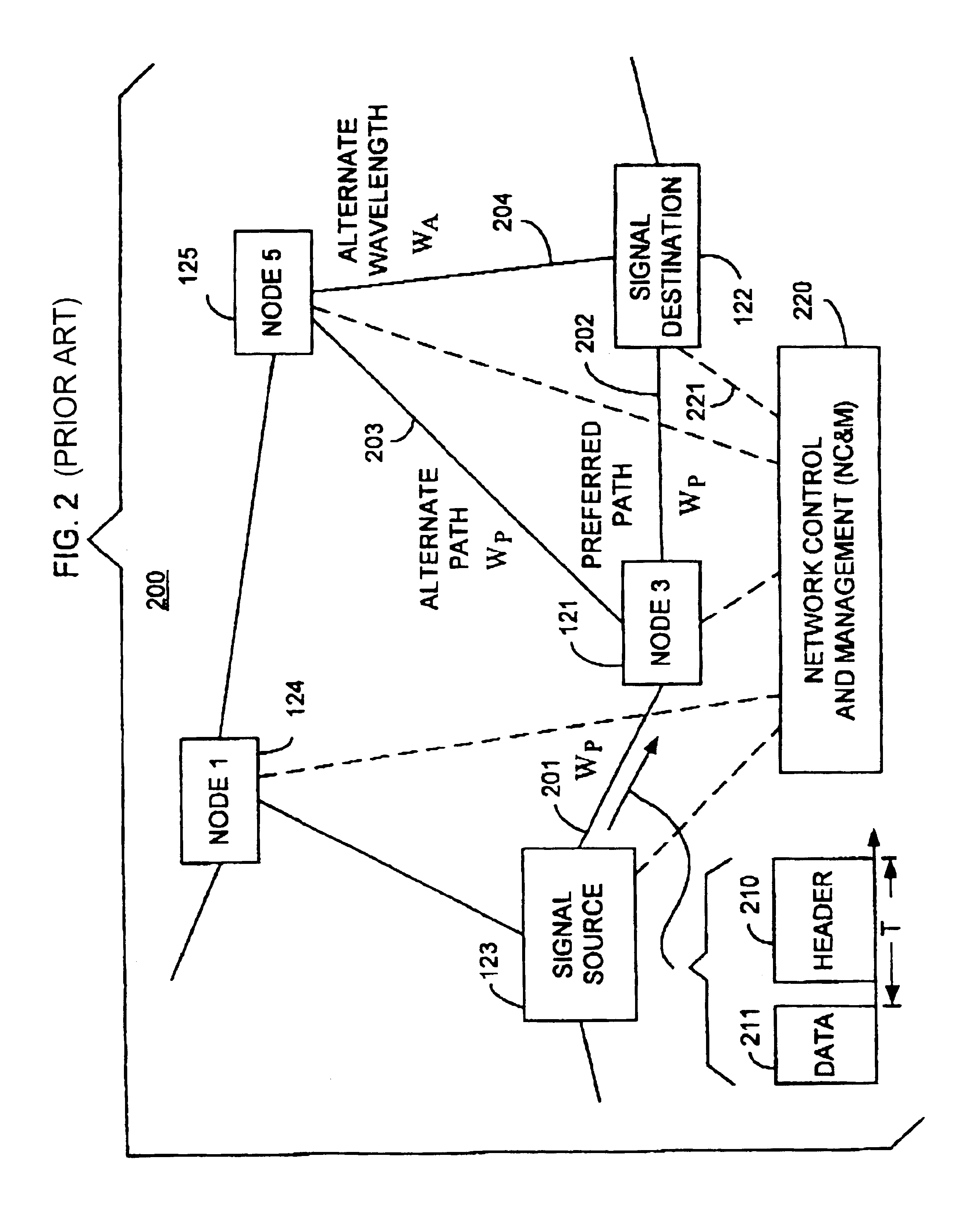
Optical layer survivability and security system using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation and detection
InactiveUS6271946B1Increase probabilityIncrease optical powerMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSurvivabilityOptical burst switching
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The technique effects survivability and security of the optical networks by encompassing conventional electronic security with an optical security layer by generating replicated versions of the input data payload at the input node, and the transmission of each of the replicated versions over a corresponding one of the plurality of links. Moreover, each of the links is composed of multiple wavelengths to propagate optical signals or optical packets, and each of the replicated versions of the data payload may be propagated over a selected one of the wavelengths in each corresponding one of the plurality of links.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical apparatus and method of use for non-invasive tomographic scan of biological tissues
The present invention relates to a non-invasive optical system equipped with optical tomographic scanning method and algorithm for quantifying scattering and absorption properties and chromophore concentrations of highly scattering medium such as biological tissues, for 3D mapping and imaging reconstruction of the spatial and temporal variations in such properties. The invention further relates to a method and an apparatus for simultaneous measurement of concentrations of biochemical substances and blood oxygen saturation inside a biological tissue and arterial blood.
Owner:O2 MEDTECH +1
Touch-sensing display panel
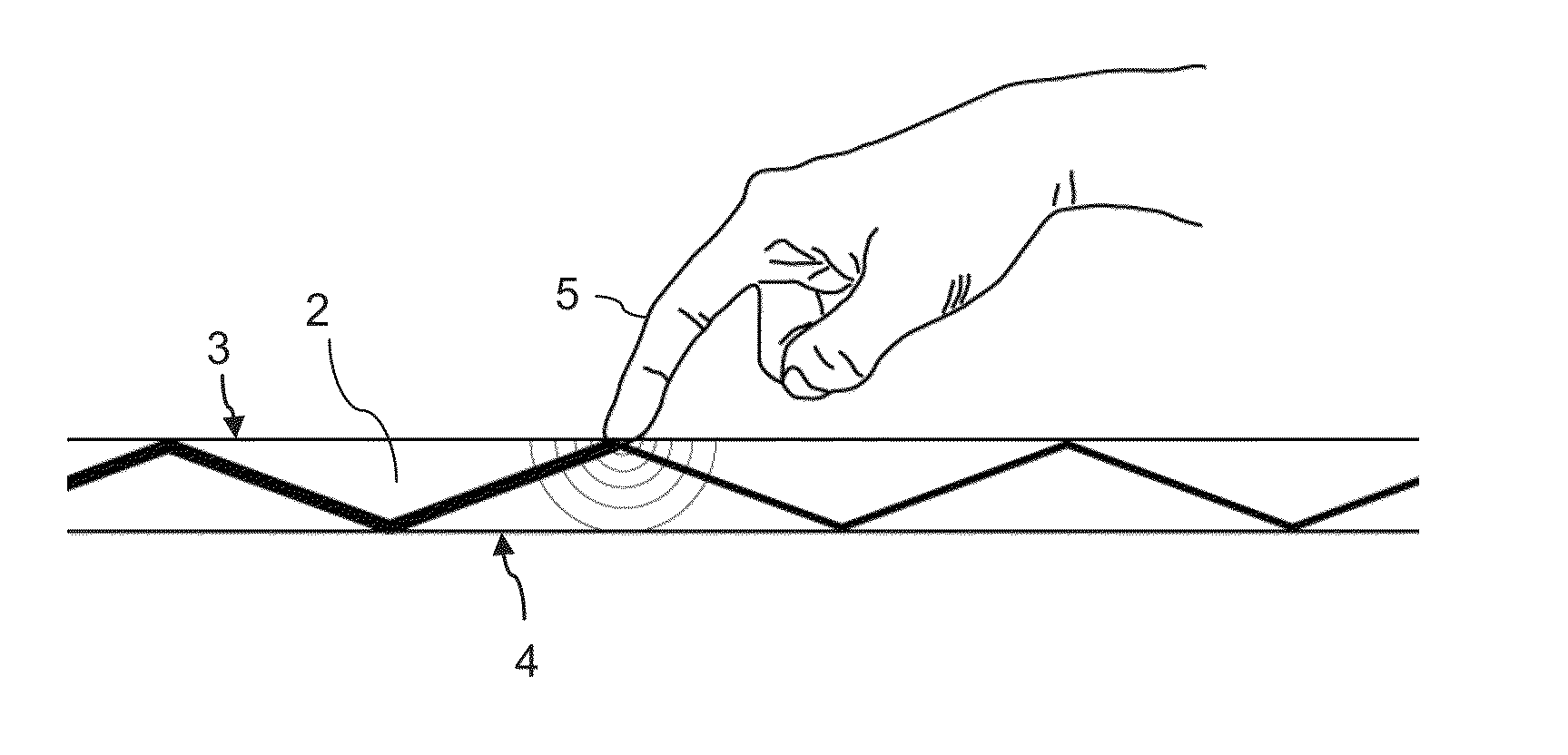
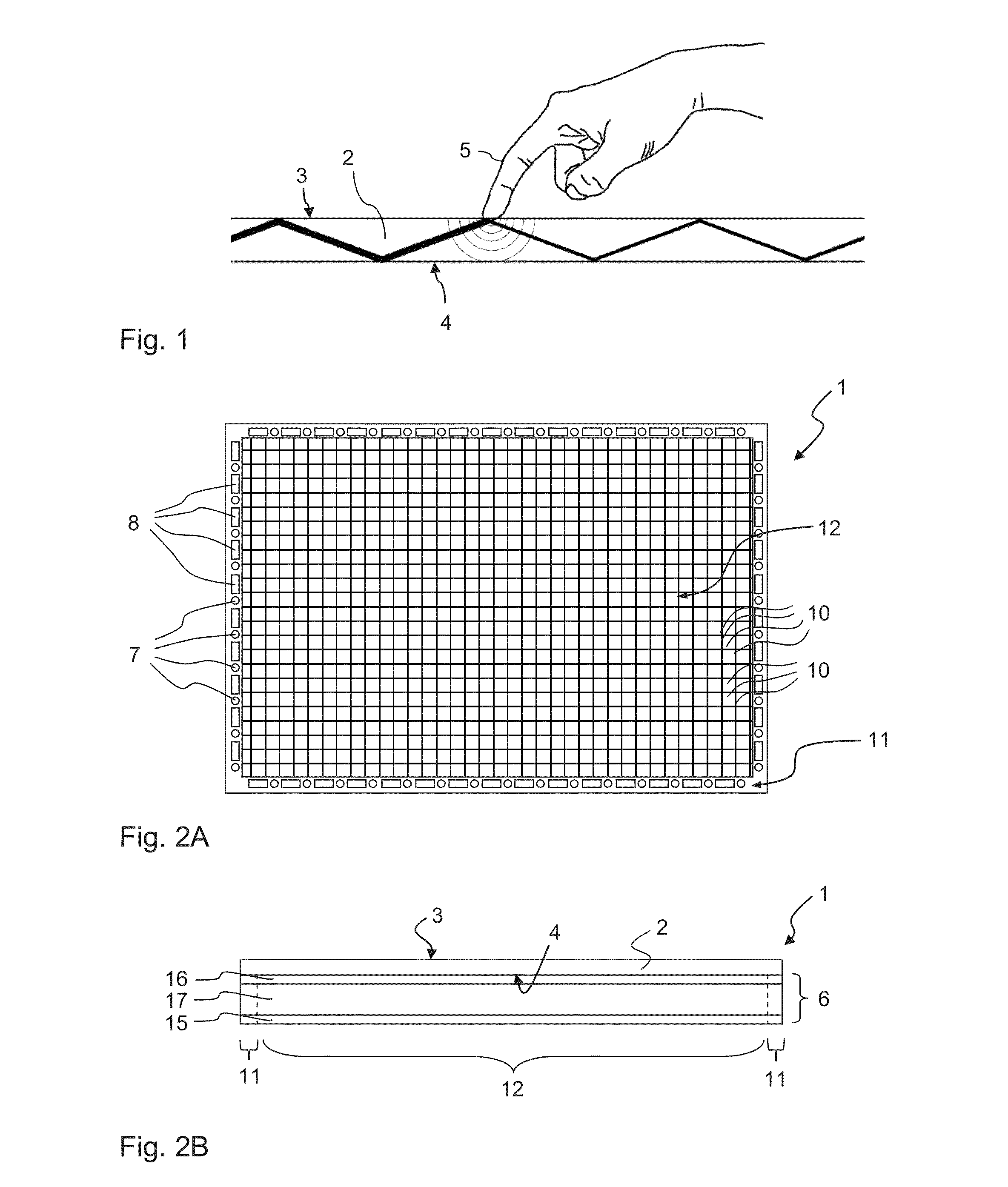
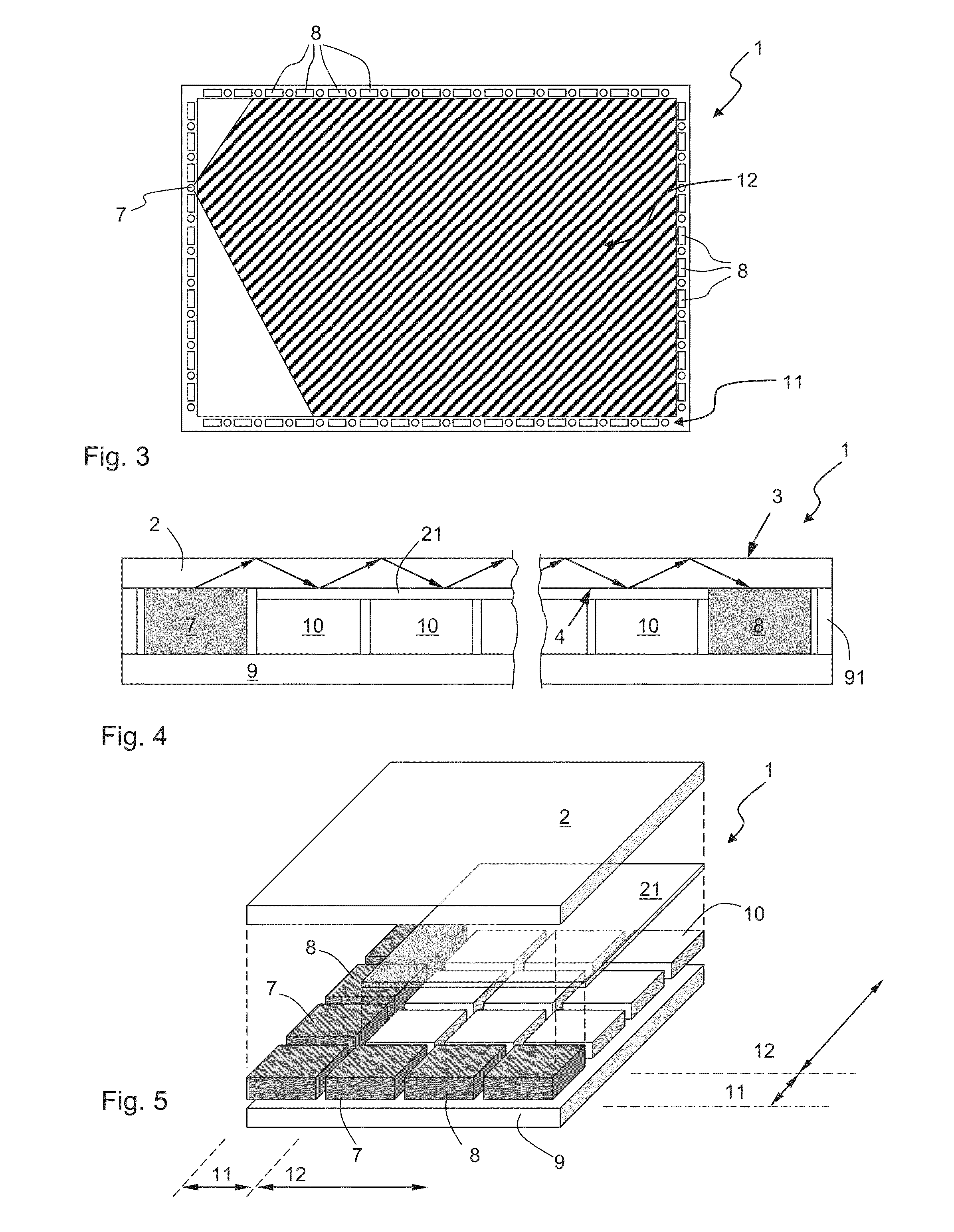
InactiveUS20130127790A1Reduce thicknessNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingTotal internal reflectionTouch Senses
A touch-sensing display panel, comprising a plurality of image-forming pixel elements; a planar light guide with a first refractive index, having a front surface forming a touch-sensing region and an opposite rear surface facing the pixel elements; a plurality of light emitters arranged at a peripheral region of the panel to emit light into the light guide for propagation therein through total internal reflection; a plurality of light detectors disposed at the peripheral region for receiving light from the light guide; and an optical layer disposed at the rear surface of the light guide to cover a plurality of the image-forming pixel elements in at least a central region of the panel, wherein said optical layer is configured to reflect at least a part of the light from the emitters impinging thereon from within the light guide.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
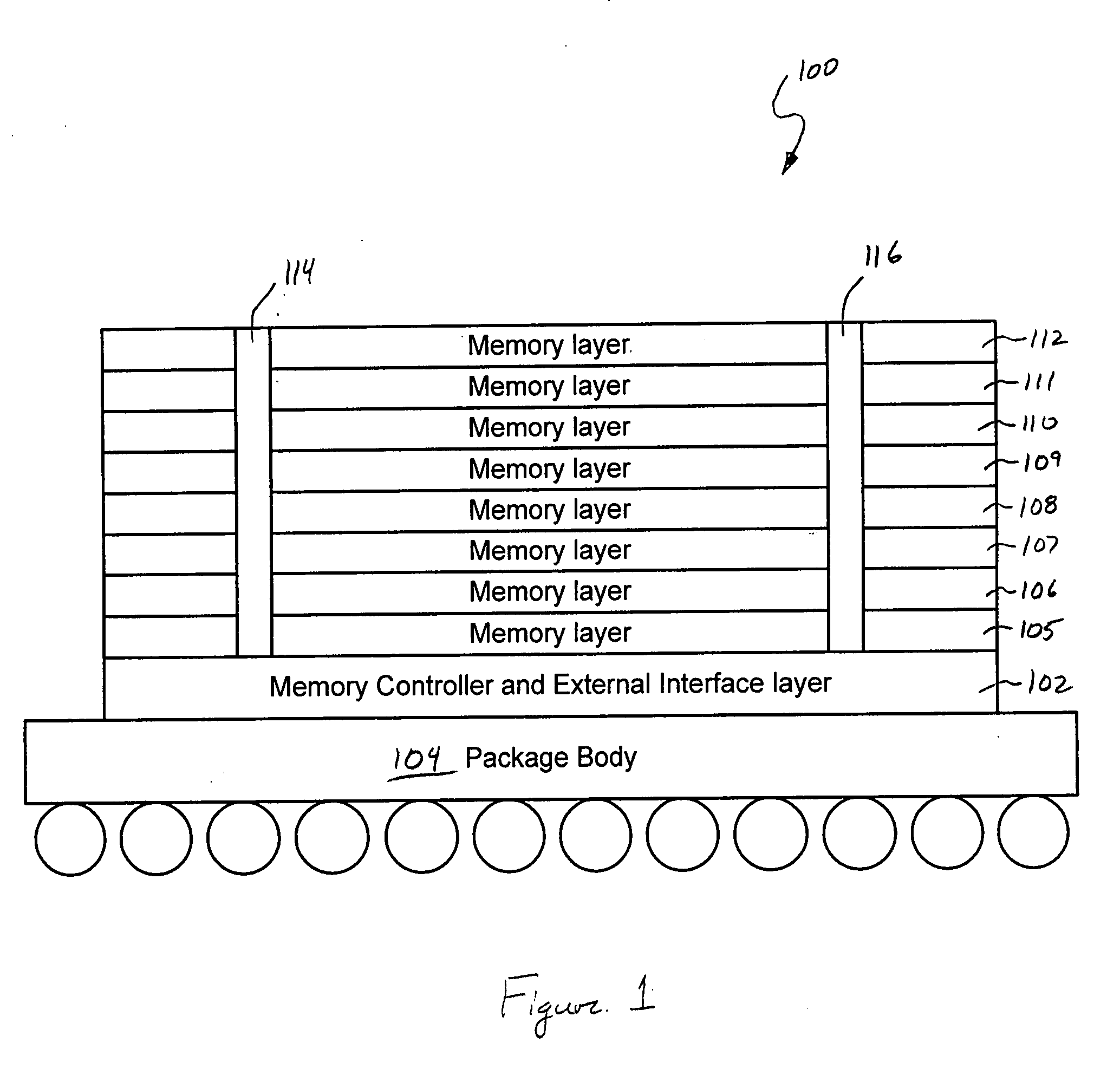
Three-dimensional memory module architectures
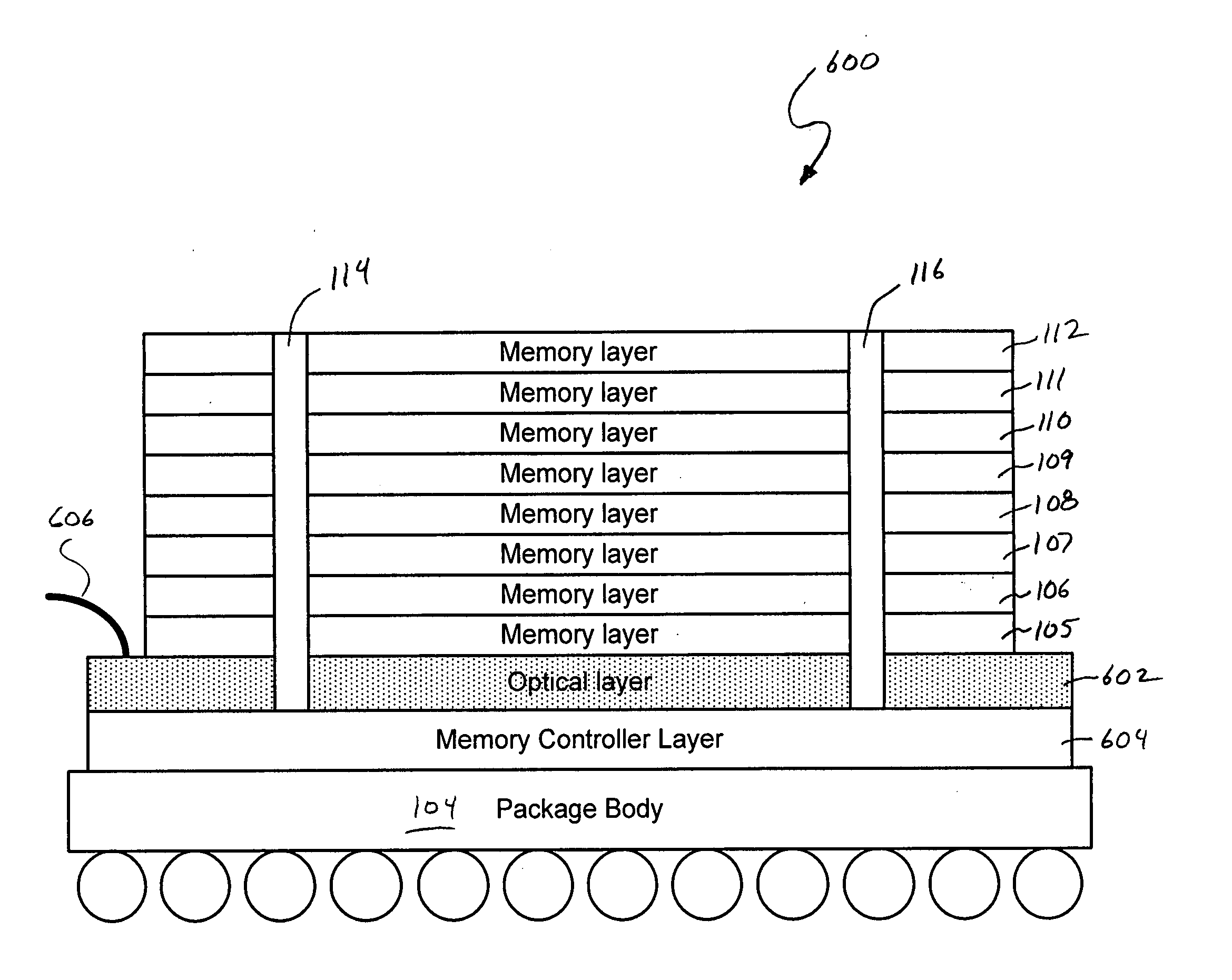
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to stacked memory modules. In one embodiment of the present invention, a memory module comprises at least one memory-controller layer stacked with at least one memory layer. Fine pitched through vias (e.g., through silicon vias) extend approximately perpendicular to a surface of the at least one memory controller through the stack providing electronic communication between the at least one memory controller and the at least one memory layers. Additionally, the memory-controller layer includes at least one external interface configured to transmit data to and from the memory module. Furthermore, the memory module can include an optical layer. The optical layer can be included in the stack and has a bus waveguide to transmit data to and from the at least one memory controller. The external interface can be an optical external interface which interfaces with the optical layer.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
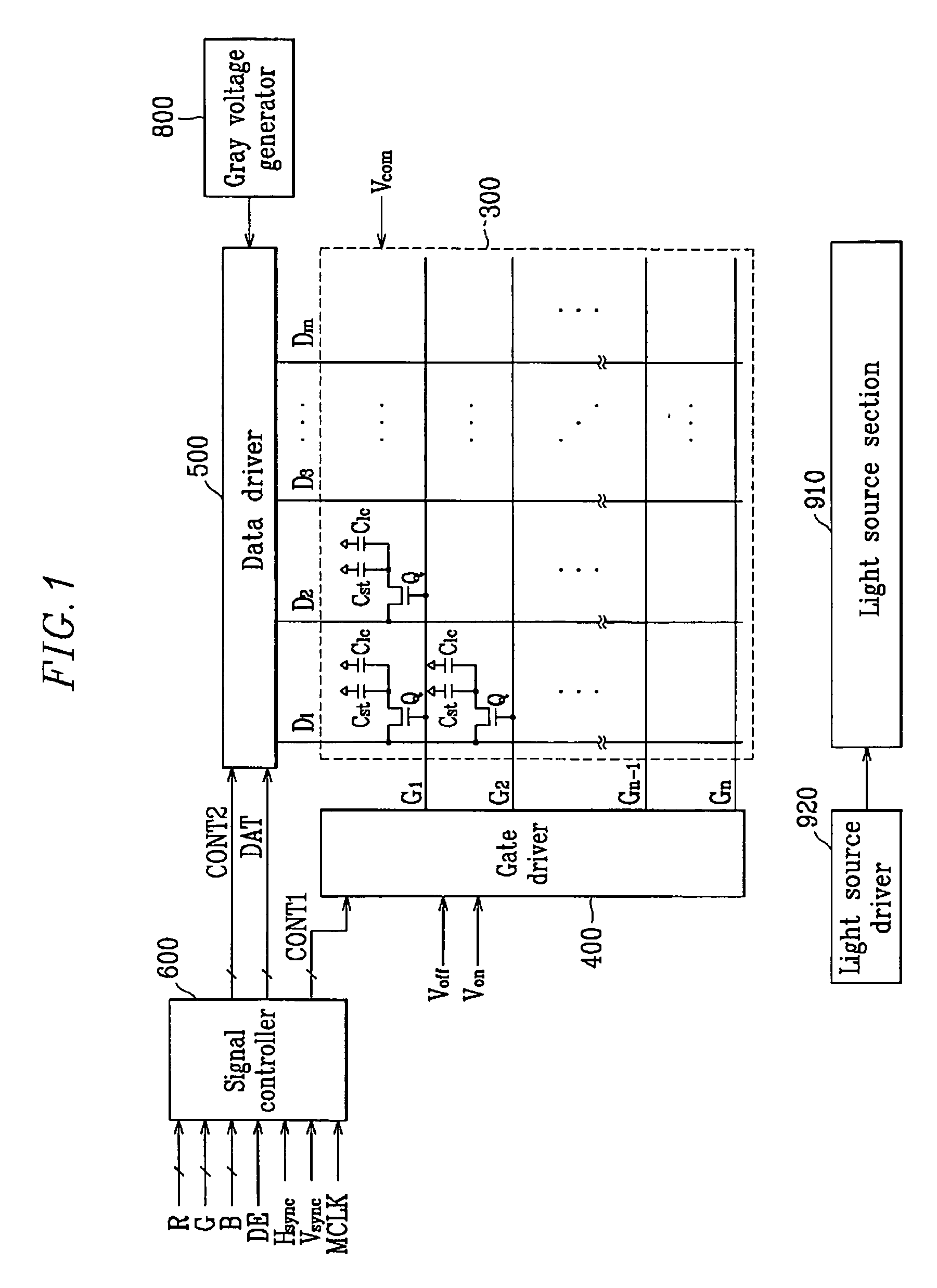
Flat panel display and driving method using the same
ActiveUS7719185B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesAutomatic controlDisplay device
An organic light emitting display (OLED), which includes a display unit and a controlling unit, is provided. The display unit includes an organic light emission layer and a transparent thin film transistor (TFT) to drive the organic light emission layer, and the display unit emits light into two opposite surfaces (upper and lower surfaces). The controlling unit includes an electro-optical layer that is capable of being switched from one state to another state by applying voltage to the layer. The controlling unit controls transmission of light emitted from the display unit. Therefore the flat panel display of the present invention is capable of displaying an image in one surface or in two surfaces. The selection of surface of image display can be manually or automatically controlled by a user. The controlling unit can includes a liquid crystal device, an electrophoretic device, or an electrochromic device.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Substrate mounting for organic, dielectric, optical film
A method for optically coupling a thermoplastic material to an outer surface layer of an organic, dielectric, optical film and the resulting optical filter. Initially, a dielectric film is selected that includes (i) repeating optical layers of at least two polymers having different refractive indexes from each other, (ii) an exterior film surface, (iii) a refractive boundary along the exterior film surface, and (iv) a delamination threshold based on total thermal energy delivered to the film. A thermoplastic material which is miscible with the exterior film surface is fused to the refractive boundary with thermal energy below the delamination threshold to form a polydisperse region having a higher optical transmission than the refractive boundary. Add-on filters in the form of hardcoat layers, anti-reflection layers, holograms, metal dielectric stacks and combinations of these may be combined with the thermoplastic-film construct.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
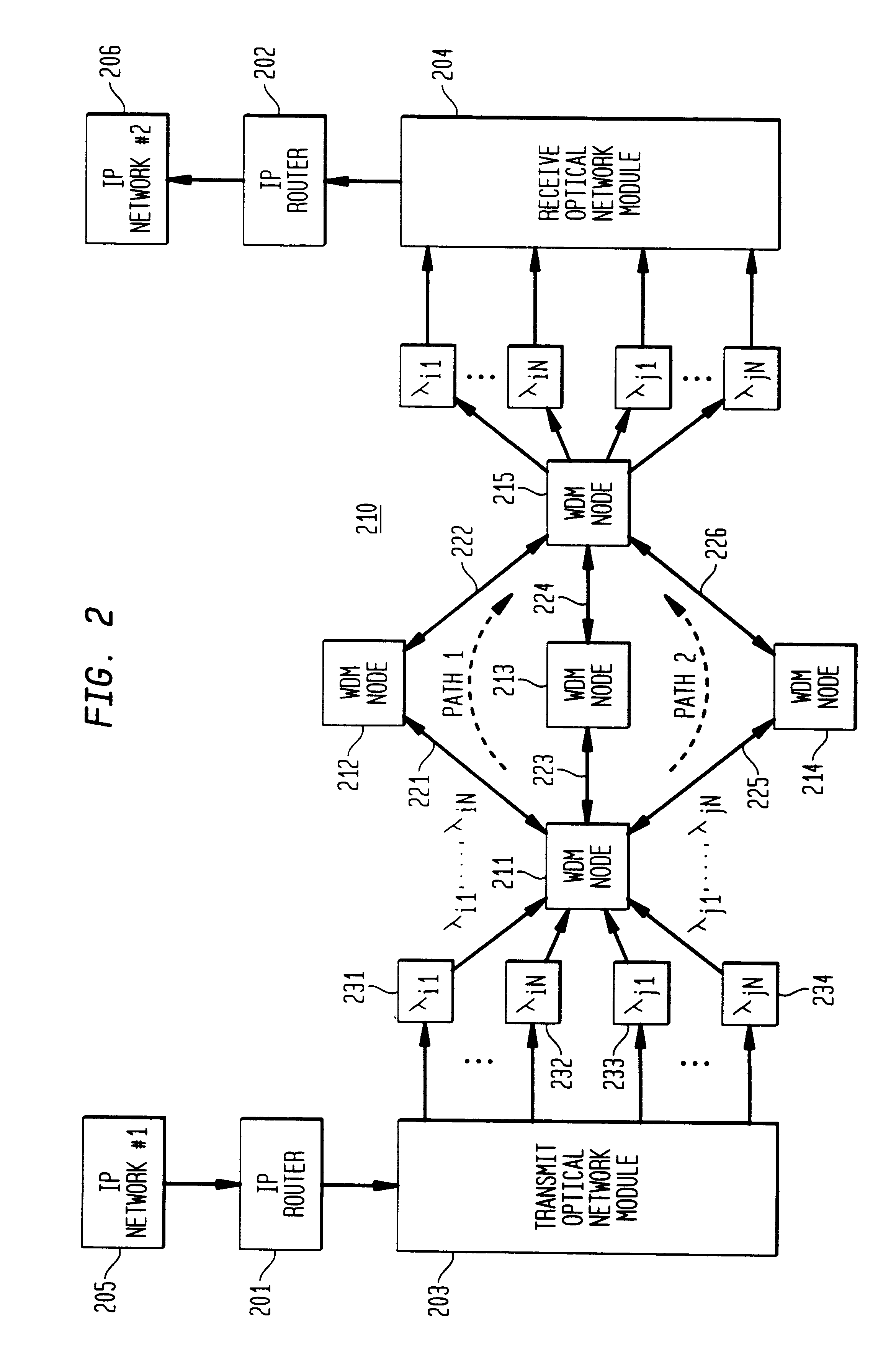
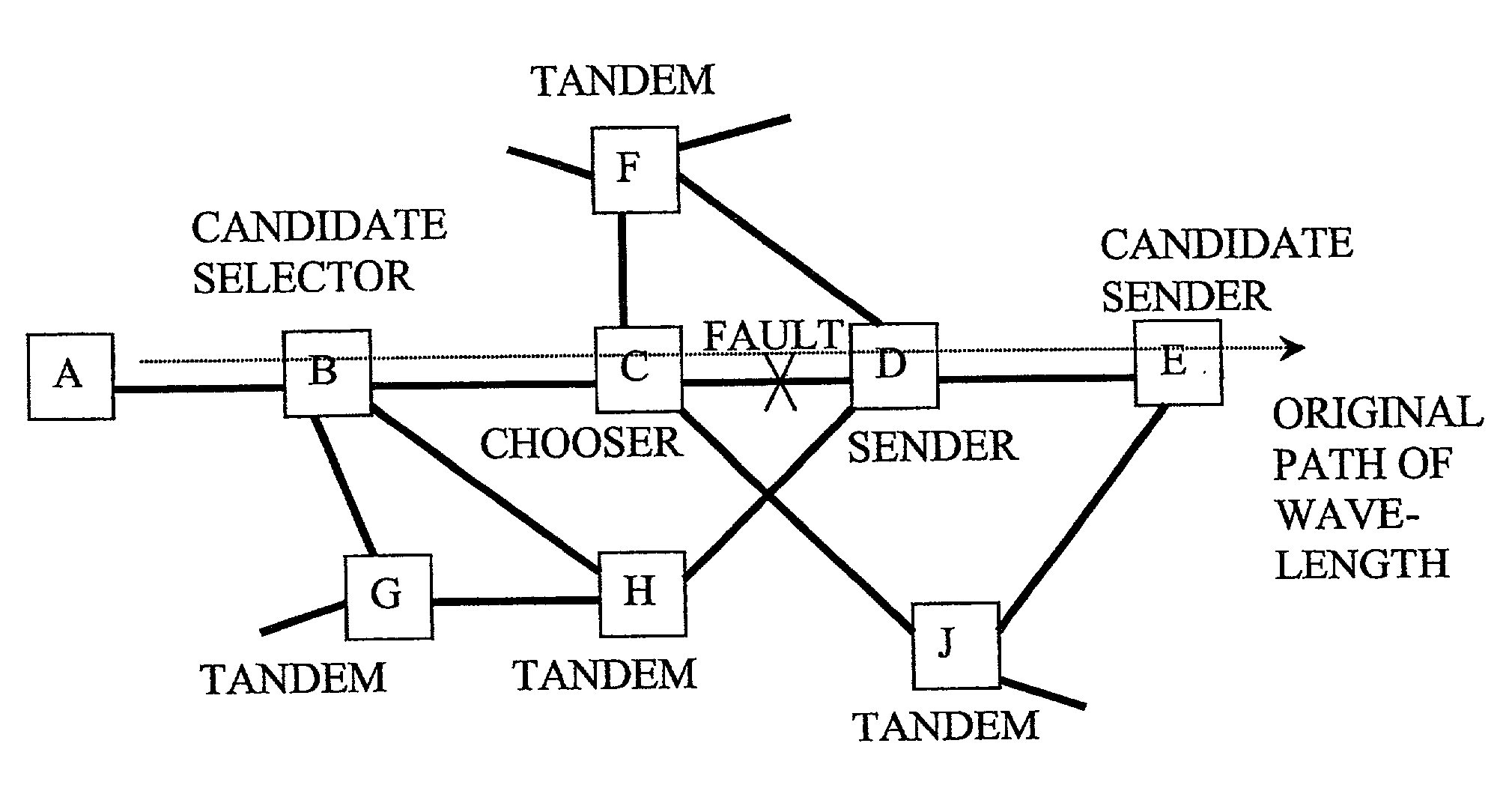
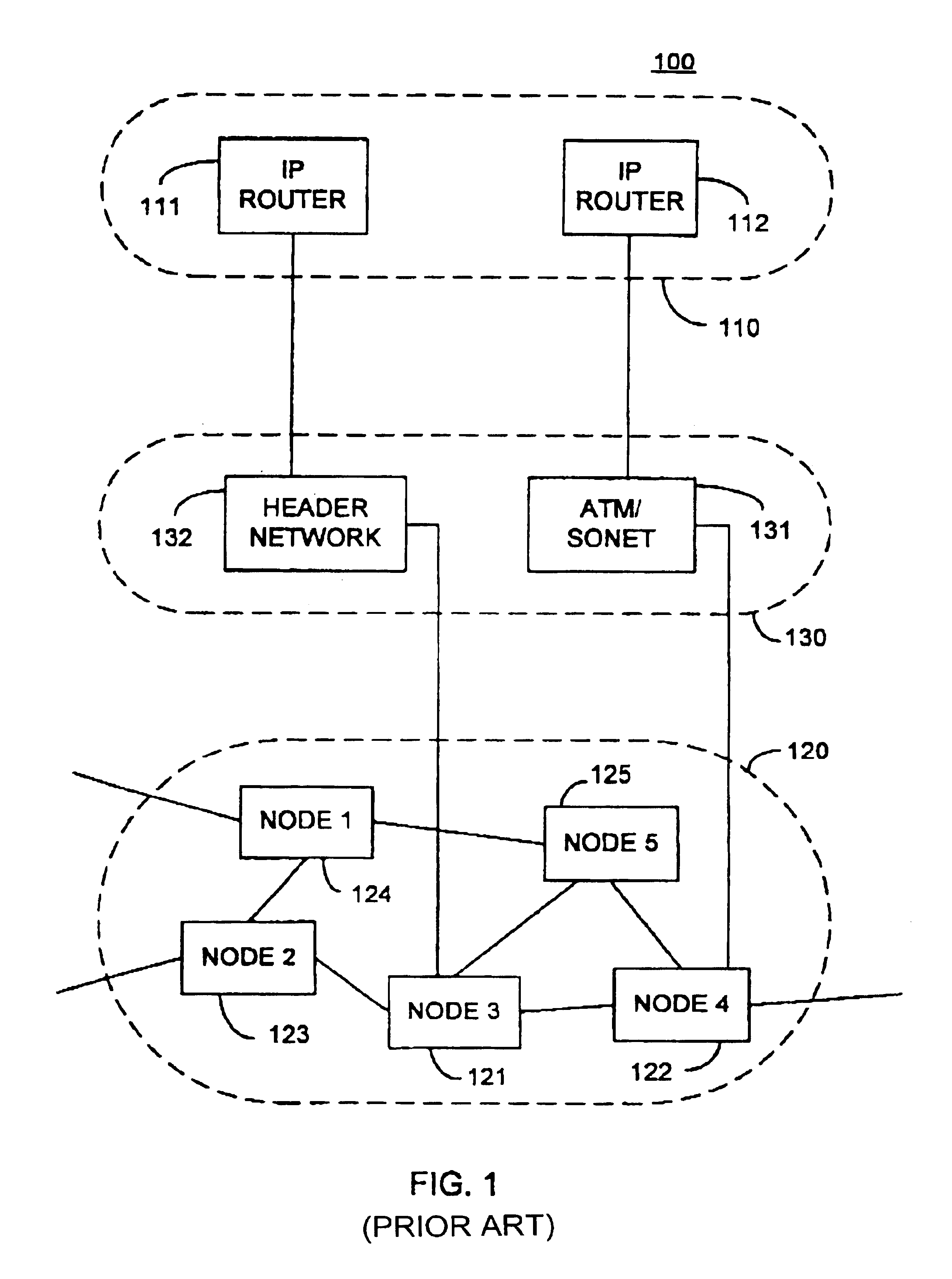
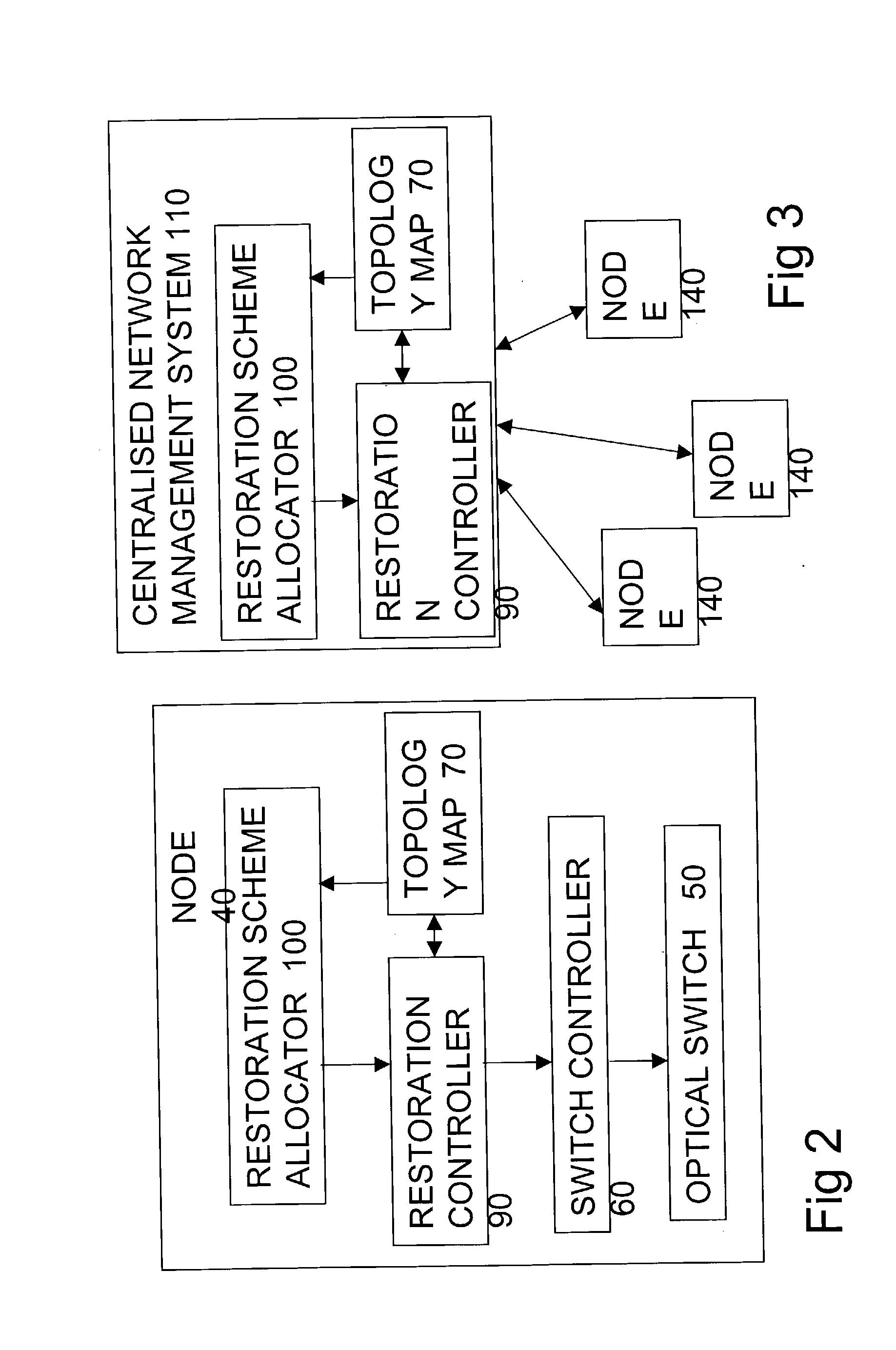
Fast restoration in optical mesh network
InactiveUS20020191247A1Easy to operateImprove good performanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringOptical mesh networkRouting table
A wavelength division multiplexed optical network has a restoration process to re-route one or more of the wavelengths, by dynamically determining possible restoration routes, and re-routing each wavelength along a chosen one of the possible restoration routes. A distributed dynamic search for restoration routes down to the optical layer, for wavelengths, gives faster and more scalable restoration than reconfiguring routing tables and enables much better utilisation of bandwidth than using predetermined restoration paths.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Birefringent reflectors using isotropic materials and form birefringence
Multilayer thin film reflectors, such as mirrors and reflective polarizers, are described in which form birefringent optical layers are incorporated into a plurality of optical repeat units in the film. The form birefringent layers exhibit birefringence as a result of microscopic structures that have a dimension that is small compared to the wavelength of light but large compared to molecular distances. The optical layers within the optical repeat units have out-of-plane indices of refraction that are tailored to produce desired effects as a function of incidence angle for p-polarized light. The multilayer reflectors can be made by conventional vacuum deposition techniques using known inorganic optical materials, but can also be made entirely with polymeric materials by co-extrusion or other processes.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Dielectric barrier layer films
InactiveUS20050006768A1Improve performanceImprove uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical resistance and conductanceGas phase
In accordance with the present invention, a dielectric barrier layer is presented. A barrier layer according to the present invention includes a densified amorphous dielectric layer deposited on a substrate by pulsed-DC, substrate biased physical vapor deposition, wherein the densified amorphous dielectric layer is a barrier layer. A method of forming a barrier layer according to the present inventions includes providing a substrate and depositing a highly densified, amorphous, dielectric material over the substrate in a pulsed-dc, biased, wide target physical vapor deposition process. Further, the process can include performing a soft-metal breath treatment on the substrate. Such barrier layers can be utilized as electrical layers, optical layers, immunological layers, or tribological layers.
Owner:DEMARAY
Two dimensional light source using light emitting diode and liquid crystal display device using the two dimensional light source
ActiveUS20060163596A1Simplify the assembly processSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsLiquid-crystal displayLight-emitting diode
A two-dimensional light source includes a base substrate having holes, wires disposed on a lower surface of the base substrate, a light emitting diode (LED) chip disposed on an upper surface of the base substrate, plugs that connect two electrodes of the LED chip to the wires through the holes, a buffer layer covering the LED chip, and an optical layer that is disposed on the buffer layer and has an optical pattern formed at a portion of the optical layer corresponding to the LED chip.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
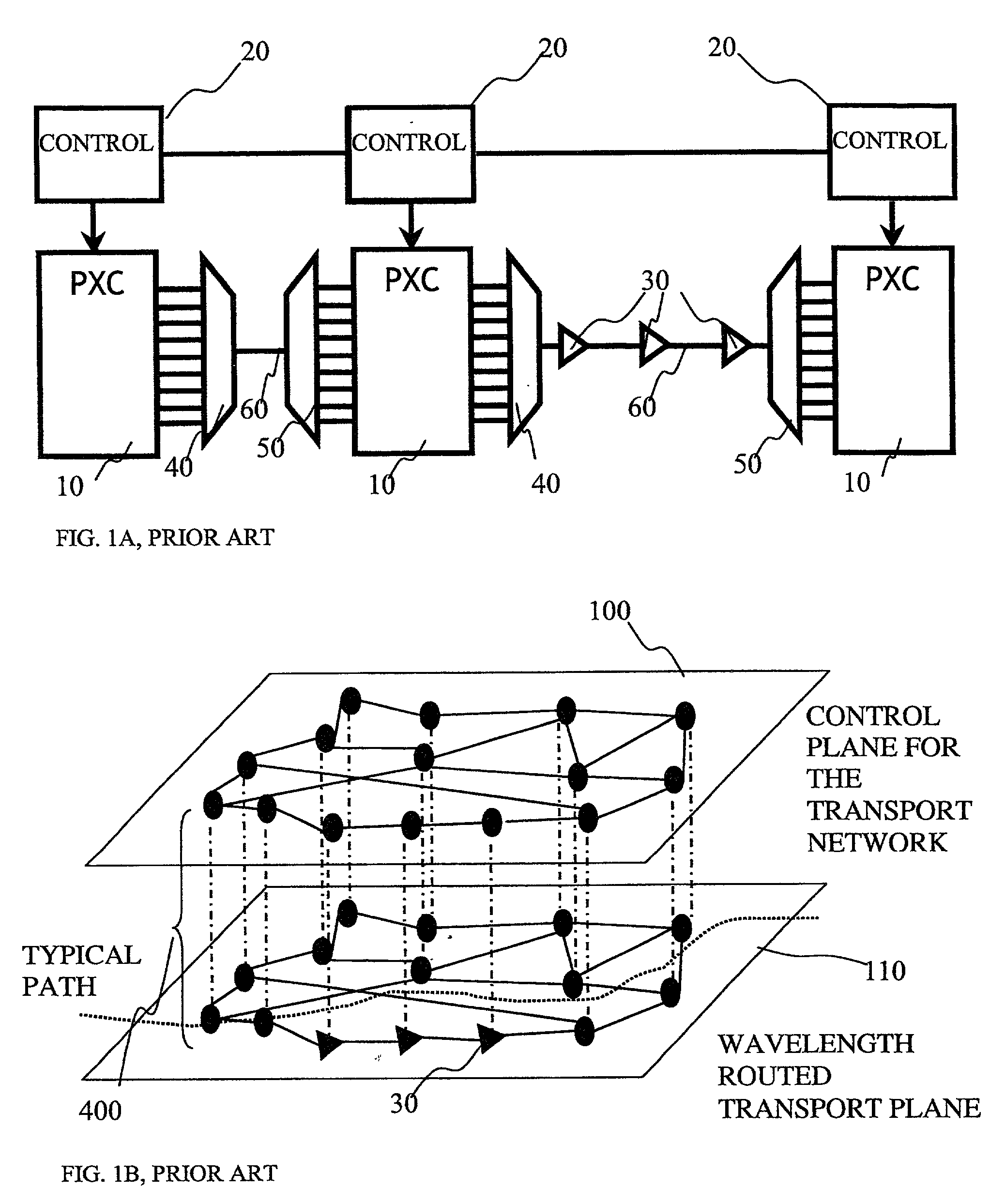
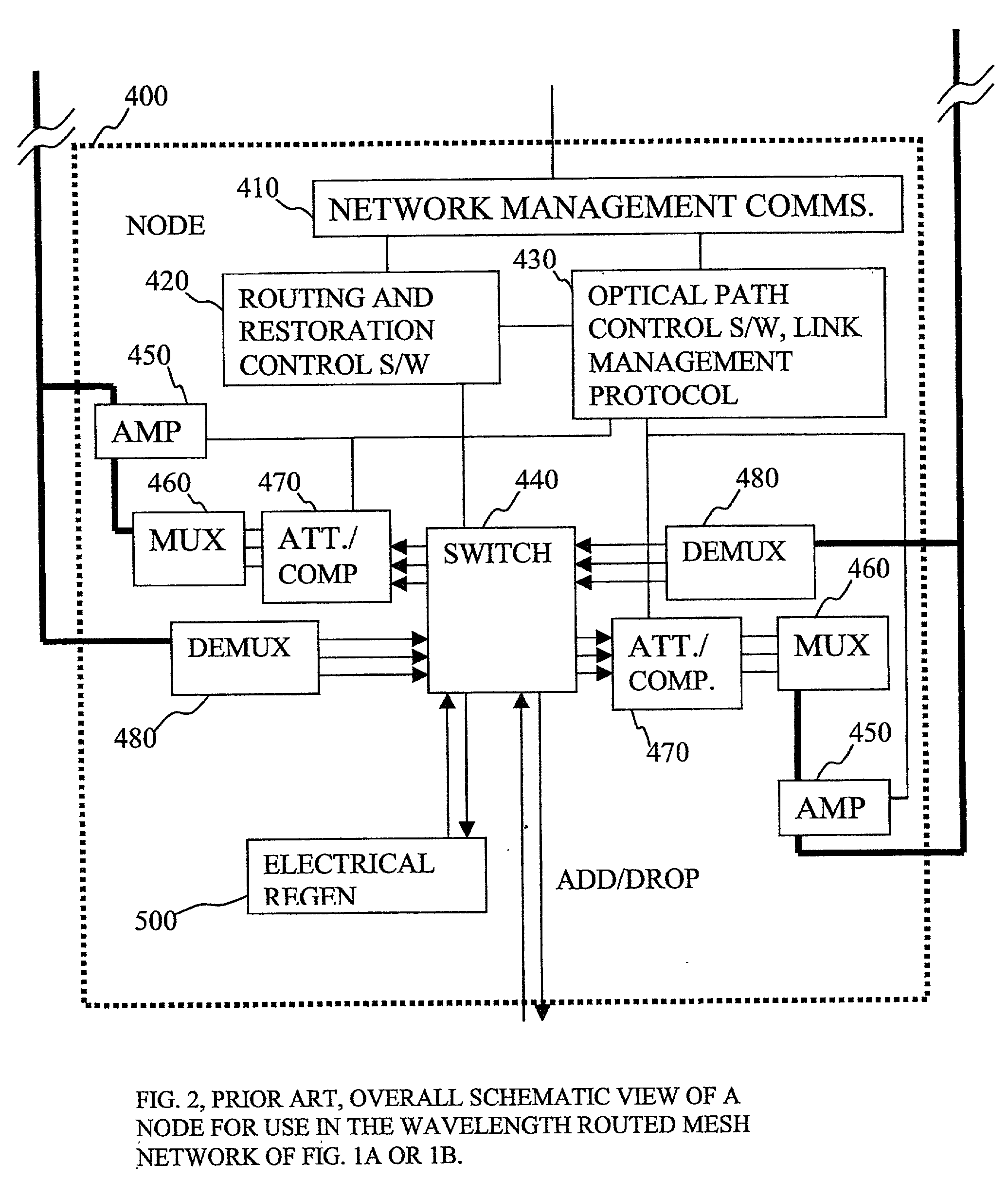
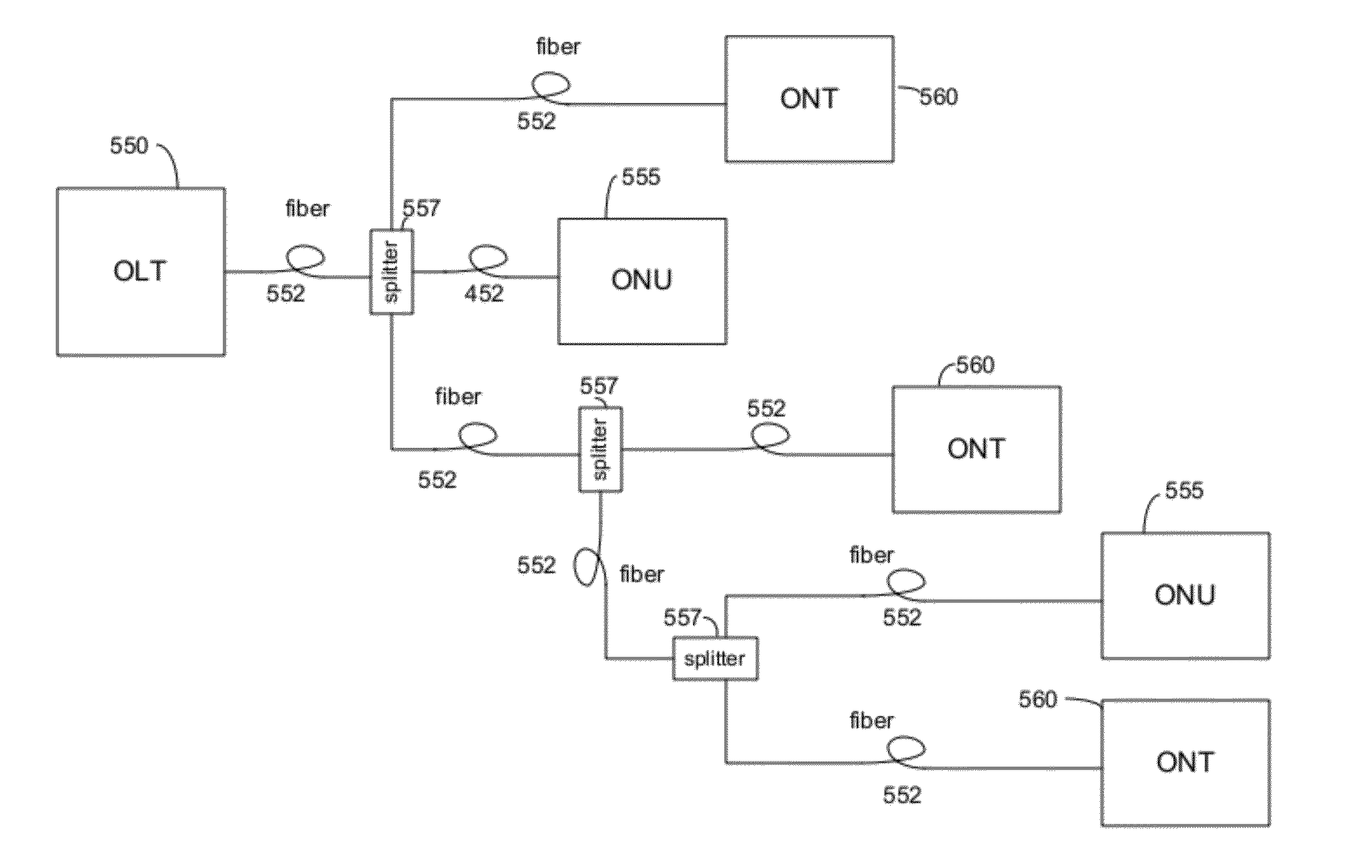
System and Method for Optical Layer Management in Optical Modules and Remote Control of Optical Modules
ActiveUS20120275784A1Low costMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsTransceiverNetwork connection
A system and method for managing the optical layer network data communications of an optical fiber data network by an optical transceiver module is disclosed. The management of the optical layer network data communications comprising data link layer functions or layer 2 functions in an OSI model. Benefits include reduction in reduced cost of network deployments from consolidation of network equipment, such as switches, and reduction in power consumed as well as enabling point-to-multipoint network connections from previously only point-to-point network connection.
Owner:SOTO ALEXANDER I +1
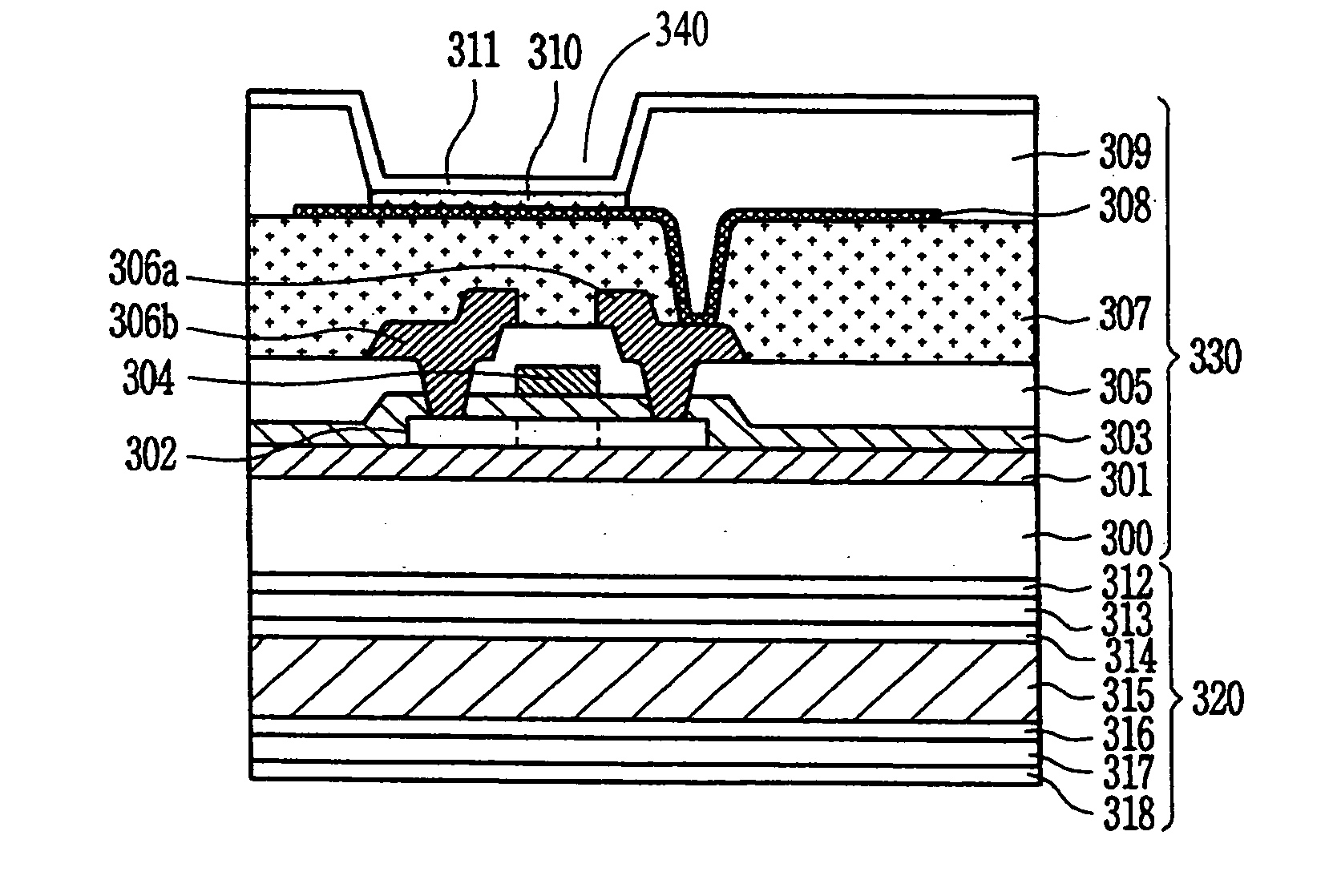
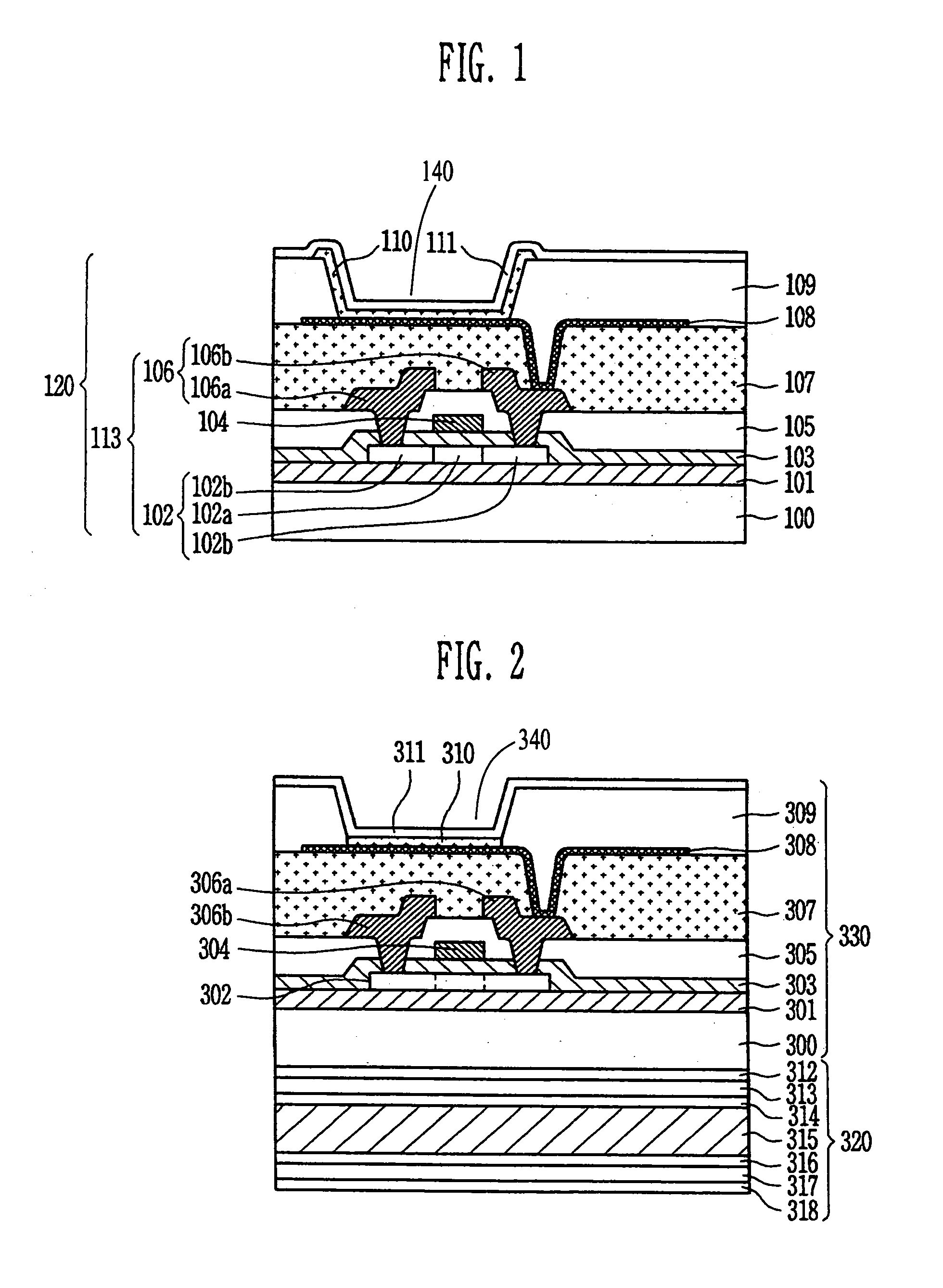
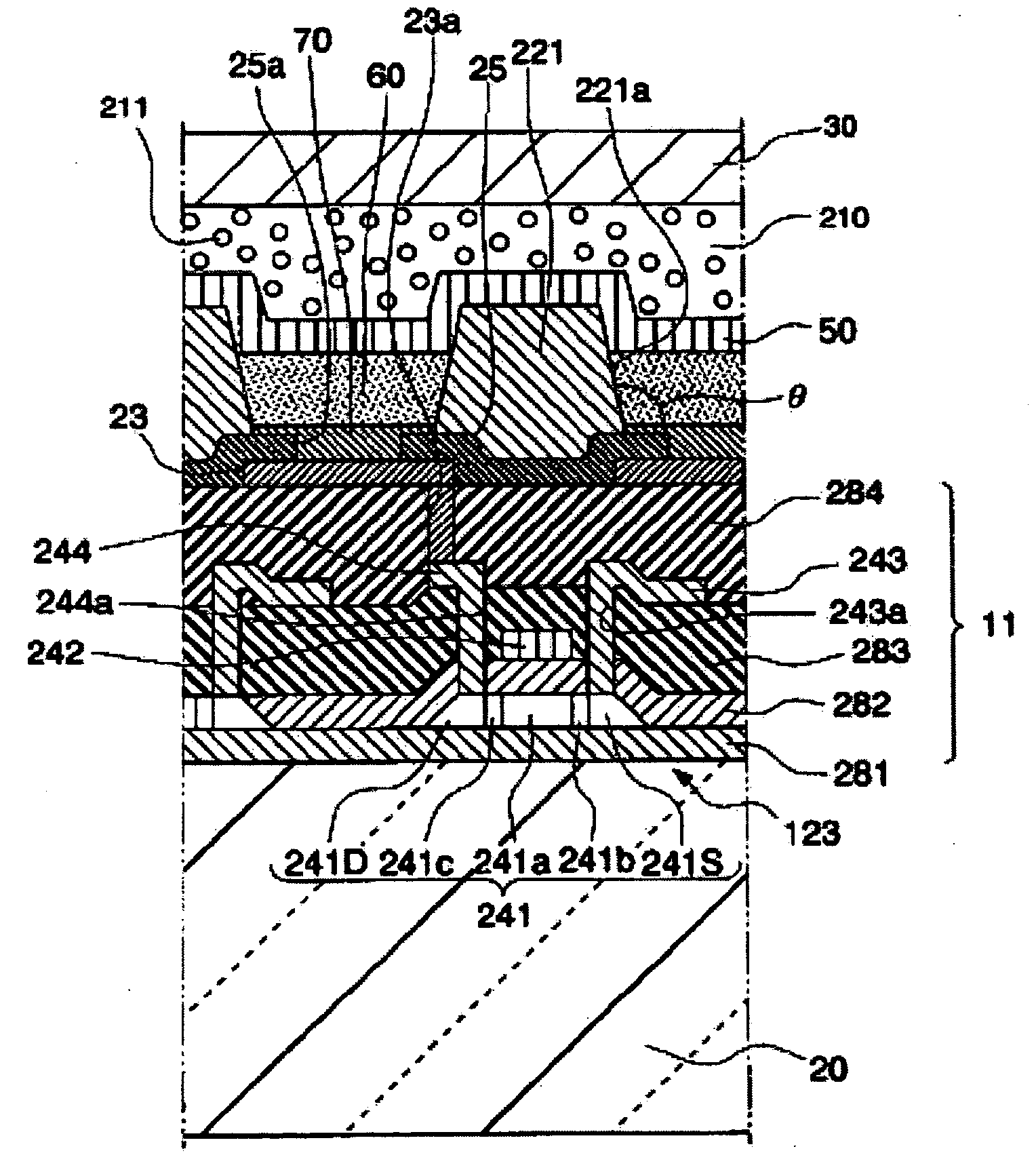
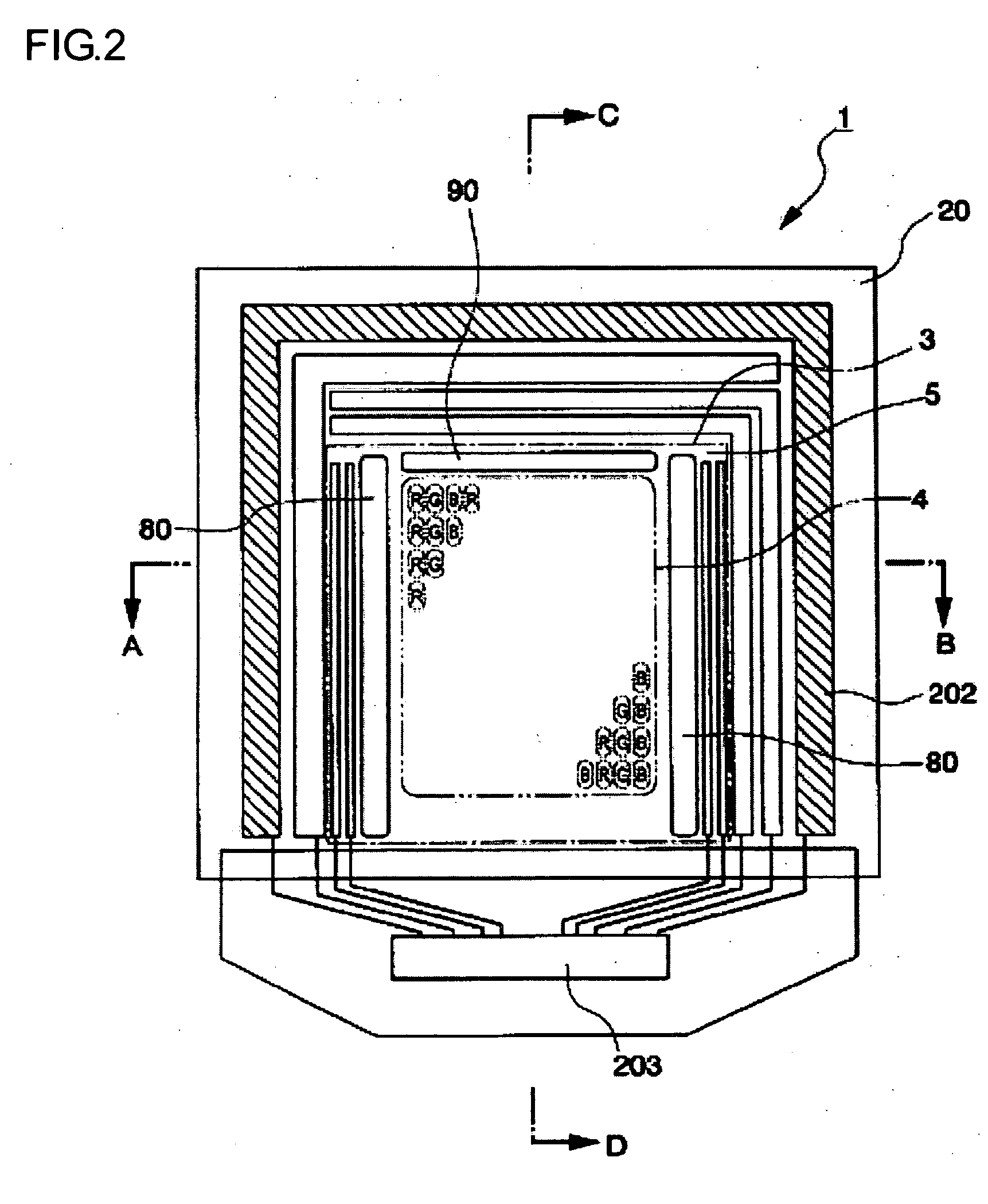
Electro-optical device, method of manufacturing the same, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20040212759A1Reduced or prevented from being deterioratedQuality improvementElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesUltravioletEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Flat panel display and driving method using the same
ActiveUS20070138941A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesAutomatic controlDisplay device
An organic light emitting display (OLED), which includes a display unit and a controlling unit, is provided. The display unit includes an organic light emission layer and a transparent thin film transistor (TFT) to drive the organic light emission layer, and the display unit emits light into two opposite surfaces (upper and lower surfaces). The controlling unit includes an electro-optical layer that is capable of being switched from one state to another state by applying voltage to the layer. The controlling unit controls transmission of light emitted from the display unit. Therefore the flat panel display of the present invention is capable of displaying an image in one surface or in two surfaces. The selection of surface of image display can be manually or automatically controlled by a user. The controlling unit can includes a liquid crystal device, an electrophoretic device, or an electrochromic device.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
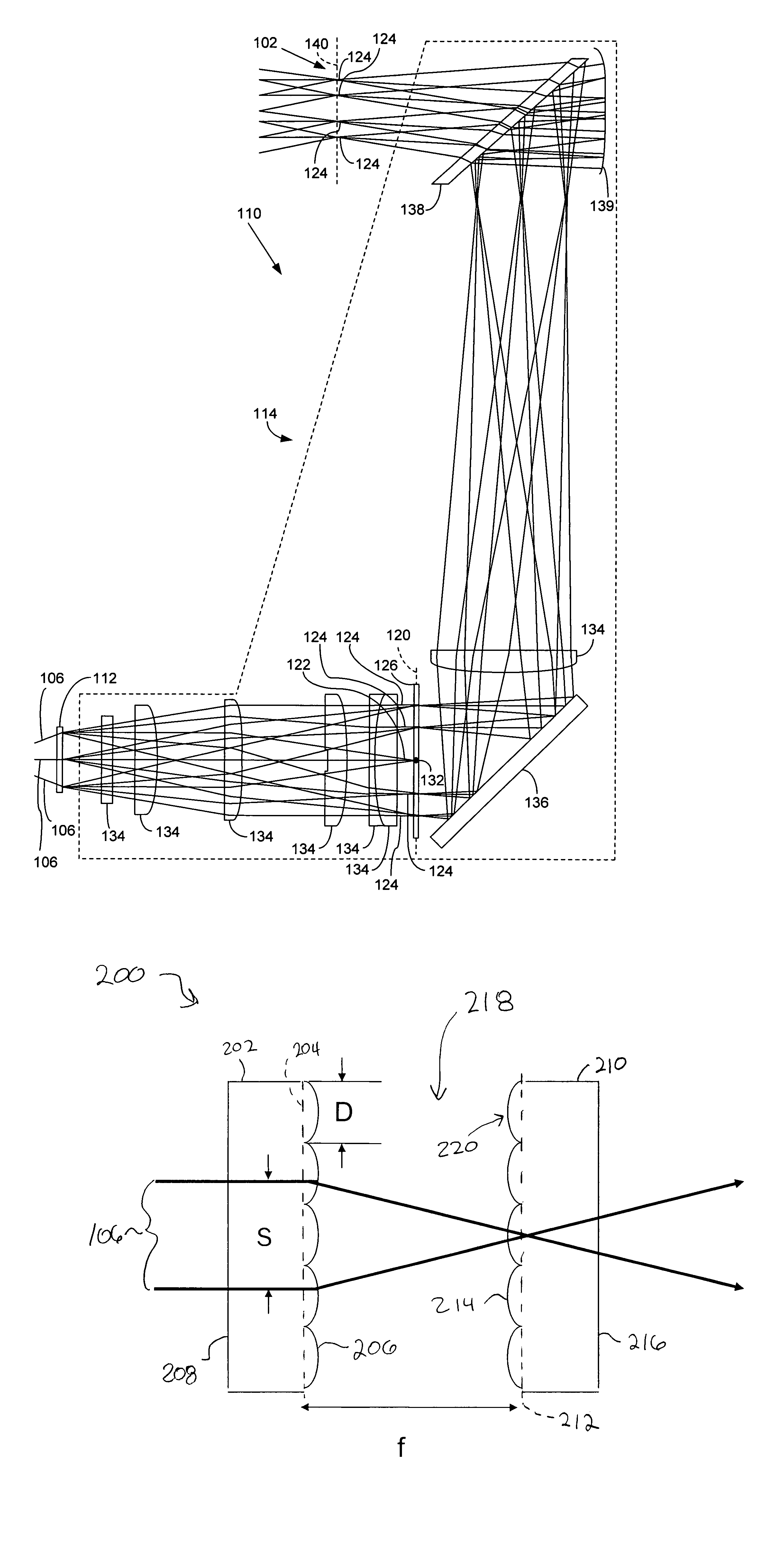
Beam multiplier that can be used as an exit-pupil expander and related system and method
A beam multiplier includes a beam-multiplying layer and an adjacent optical layer. The beam-multiplying layer is operable to generate output beamlets of light from an input beam of light, and the optical layer has an adjustable index of refraction. By switching the index of refraction of the optical layer between first and second values, one can switch the beam multiplier to a first state (e.g., “on”) where it generates the output beamlets of light, and can switch the beam multiplier to a second state (e.g., “off”) where it passes the input beam of light but does not generate the output beamlets. And by using the beam multiplier as an exit-pupil expander, one can switch the exit-pupil expander to a first state where it generates multiple exit-pupil images, and to a second state where it generates only a single exit-pupil image.
Owner:MICROVISION
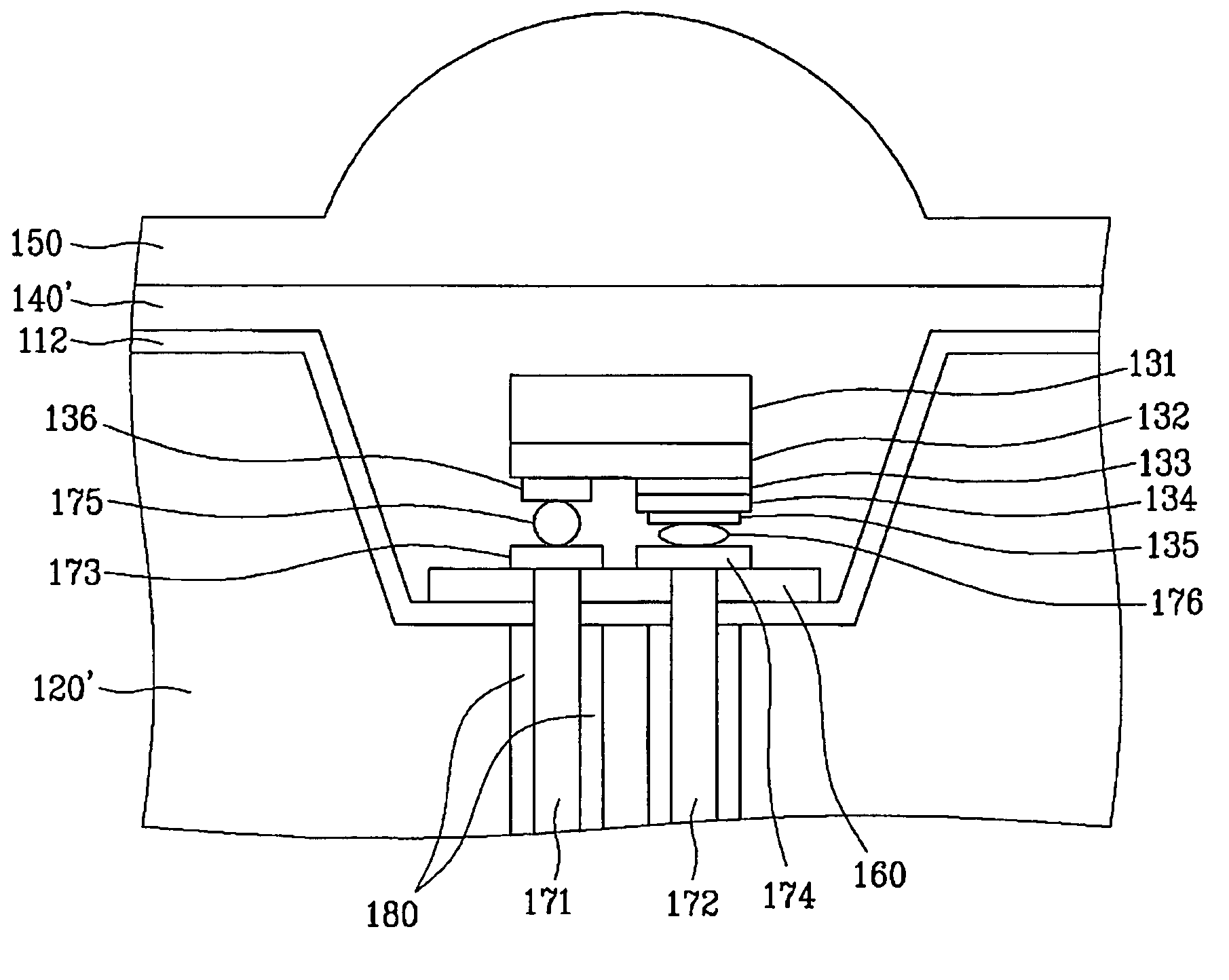
Electro-optical device, electronic device, and illumination apparatus
ActiveUS20100327737A1High tensile strengthReduce deformation rateDischarge tube luminescnet screensSpotlightingEngineeringElectron
An electro-optical device includes a display panel having an electro-optical layer, a first resin film stacked on the display panel to cover a first surface on the side of a display area of the display panel, and a second resin film stacked on the display panel to cover a second surface opposite the first surface, and at least one reinforcing member disposed on at least one of the first resin film and the second resin film.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
Electro-optical device, manufacturing method of the same, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20050110020A1Avoid crackingPrevent peelingTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesStress concentrationEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
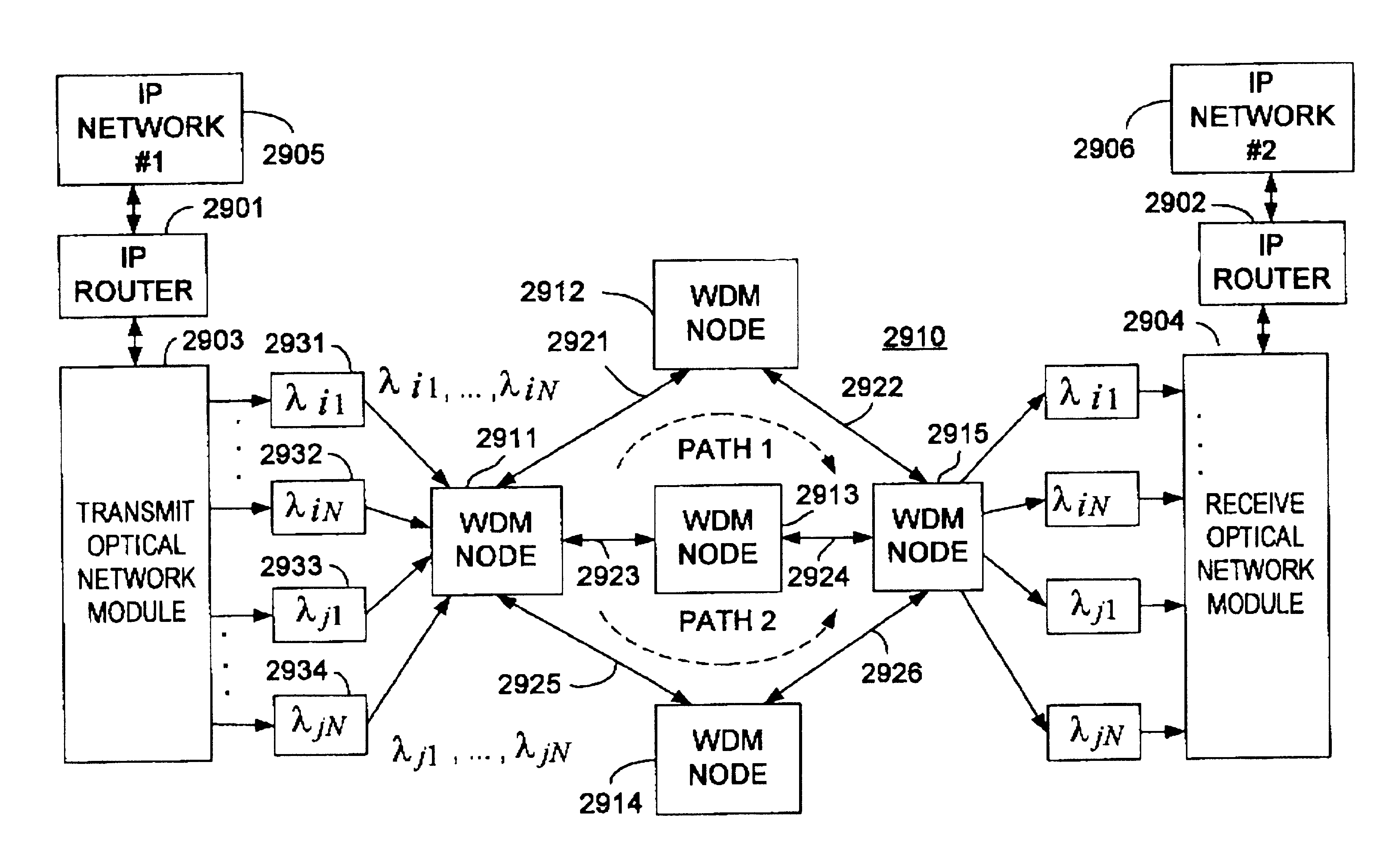
Optical layer multicasting
InactiveUS6873797B2Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical packetEngineering
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The technique effects survivability and security of the optical networks by encompassing conventional electronic security with an optical security layer by generating replicated versions of the input data payload at the input node, and the transmission of each of the replicated versions over a corresponding one of the plurality of links. Moreover, each of the links is composed of multiple wavelengths to propagate optical signals or optical packets, and each of the replicated versions of the data payload may be propagated over a selected one of the wavelengths in each corresponding one of the plurality of links.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC +1
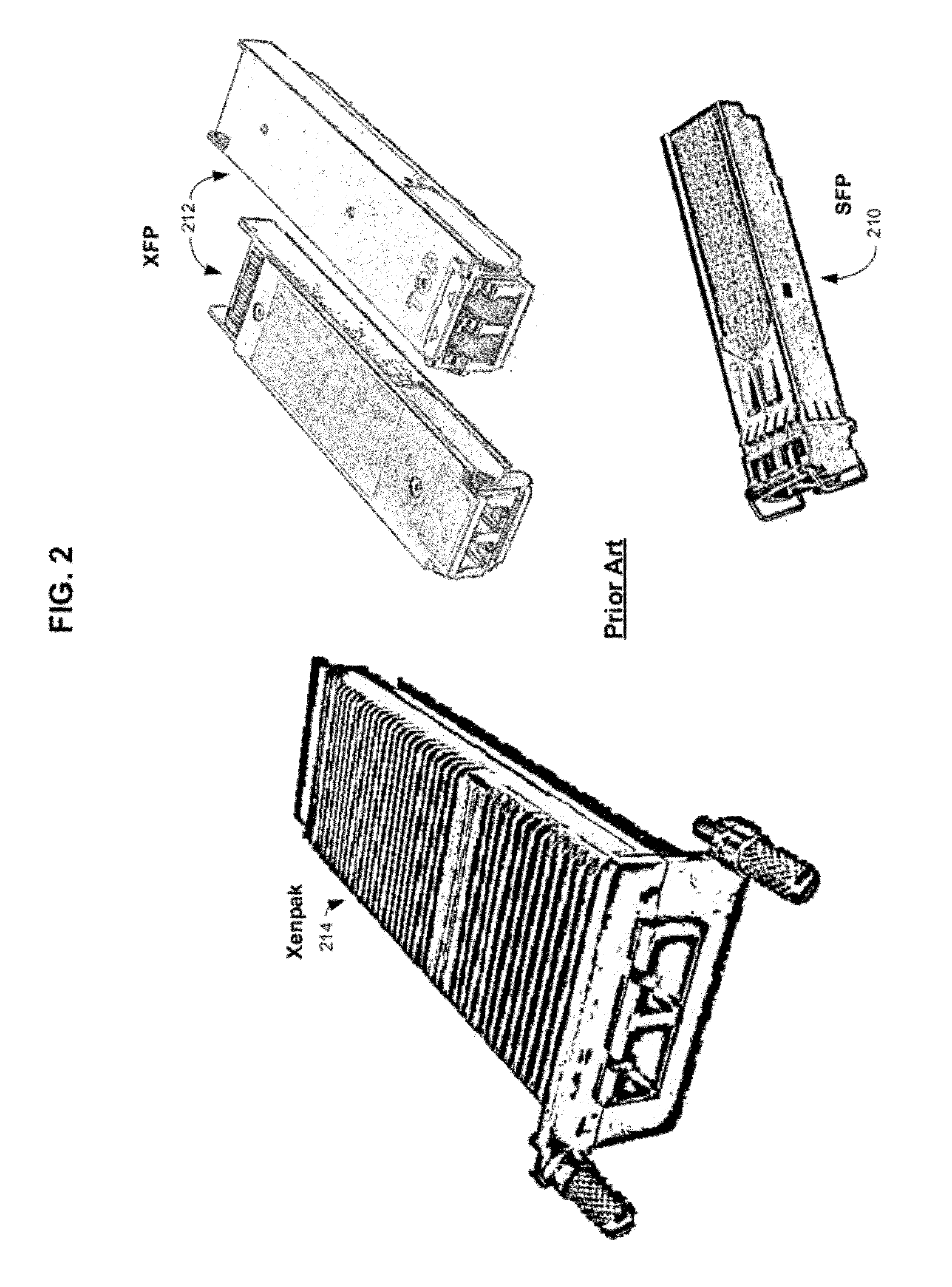
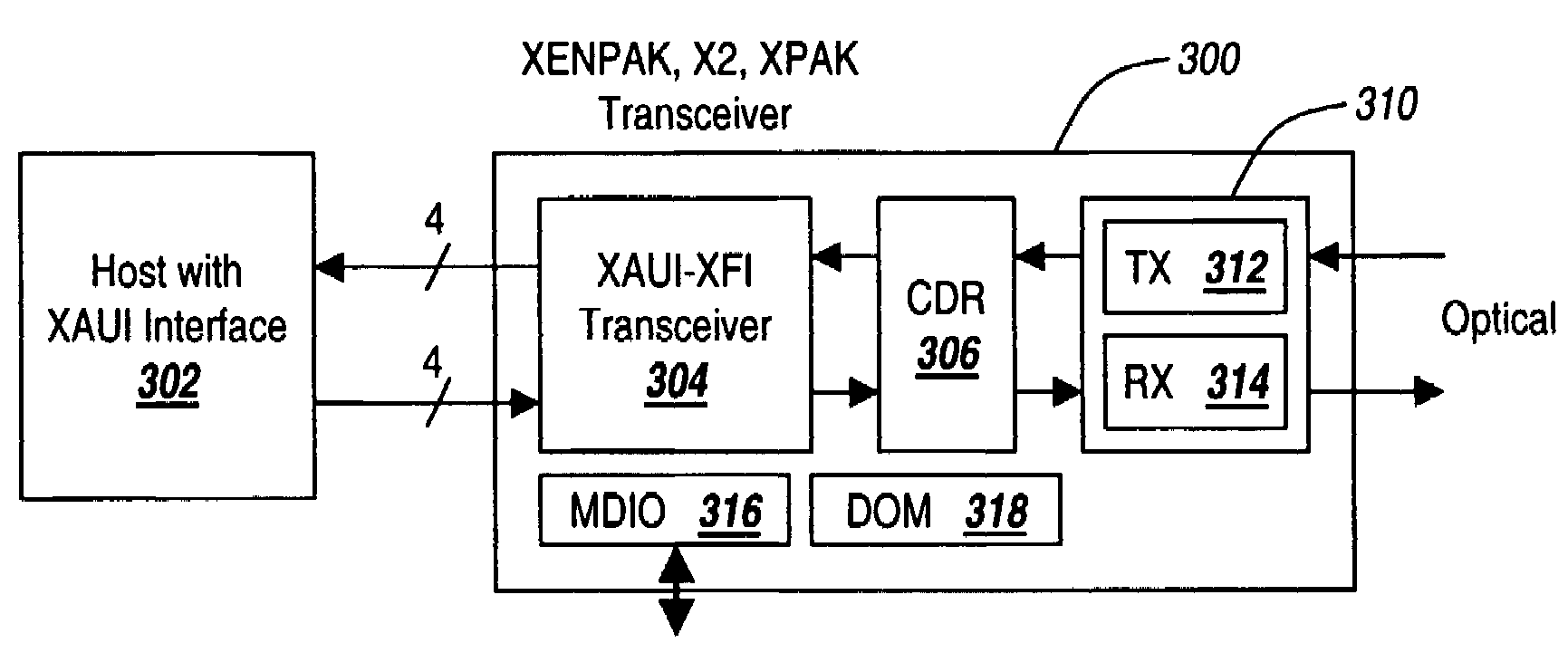
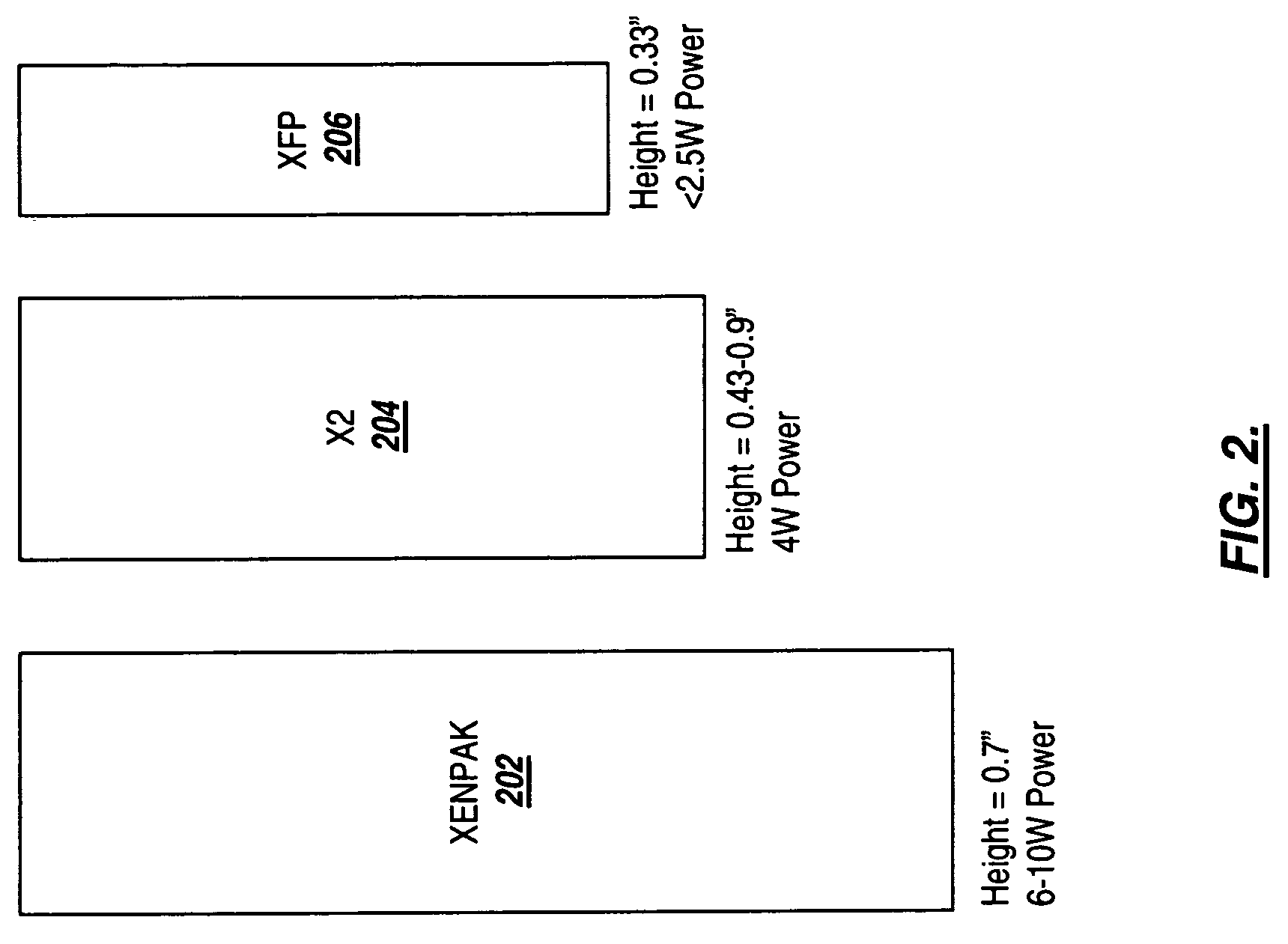
Systems and methods for the integration of framing, OAM&P, and forward error correction in pluggable optical transceiver devices
ActiveUS20080089693A1Extend optical reachEnhance layeringError preventionTime-division multiplexSystems designTransceiver
The present invention provides integrated framing in pluggable optical transceivers to extend the OTN framework into metro, regional, and core applications. Additionally, the present invention provides integrated FEC and optical layer OAM&P features into pluggable optical transceivers. This integration is done with existing pluggable transceivers defined by MSAs such as, but not limited to, XFP, XPAK, XENPAK, X2, XFP-E, and SFP+. Further, the present invention can be extended to new, emerging pluggable transceiver standards and specifications. The integration of framing, FEC, and optical layer OAM&P is done so that the pluggable transceiver preserves the specifications in the MSAs. This allows systems designed for existing pluggable transceivers to realize carrier-grade, robust performance without needed additional equipment such as transponders and without redesigning host equipment such as the line card to support new specifications.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
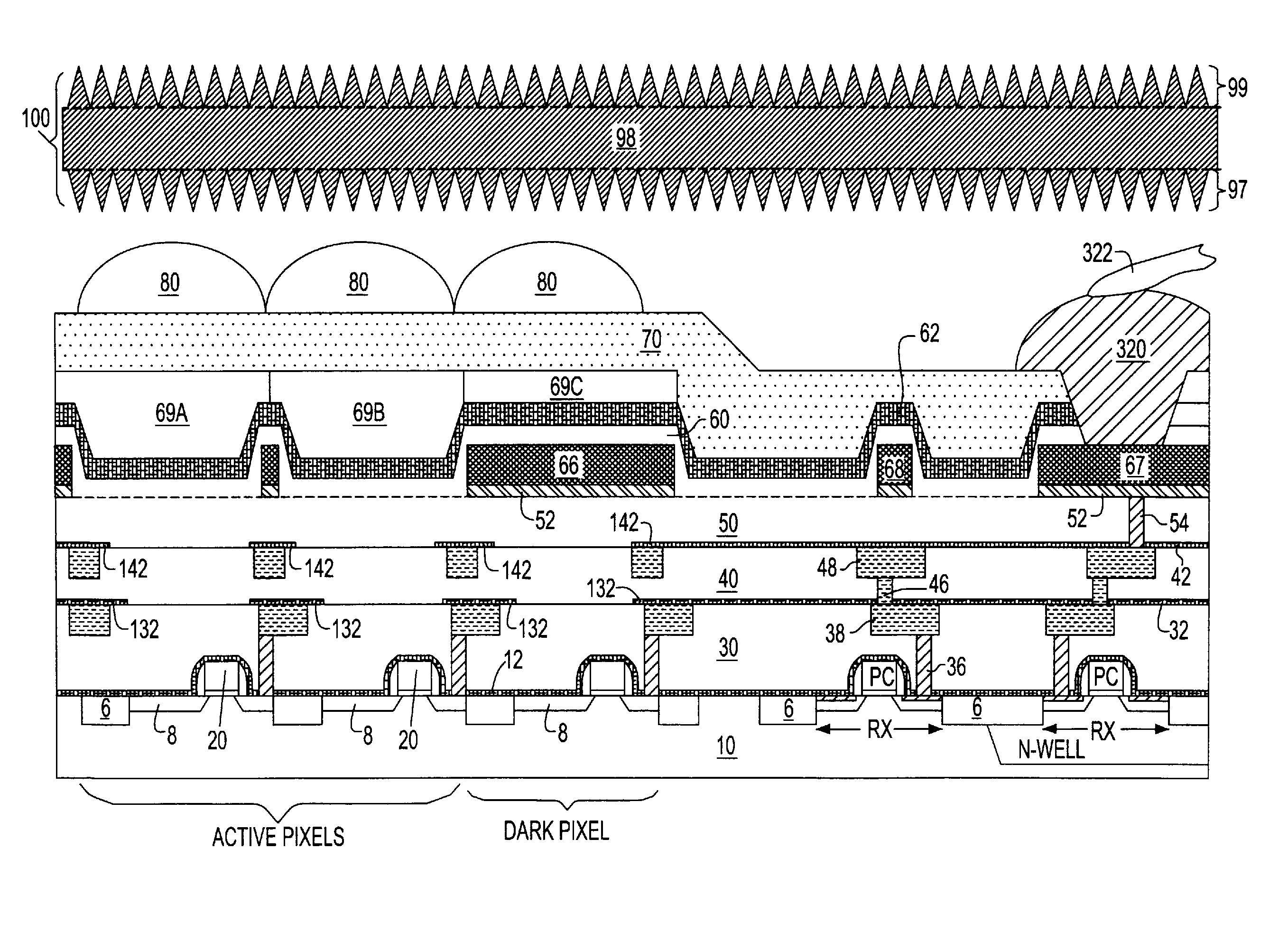
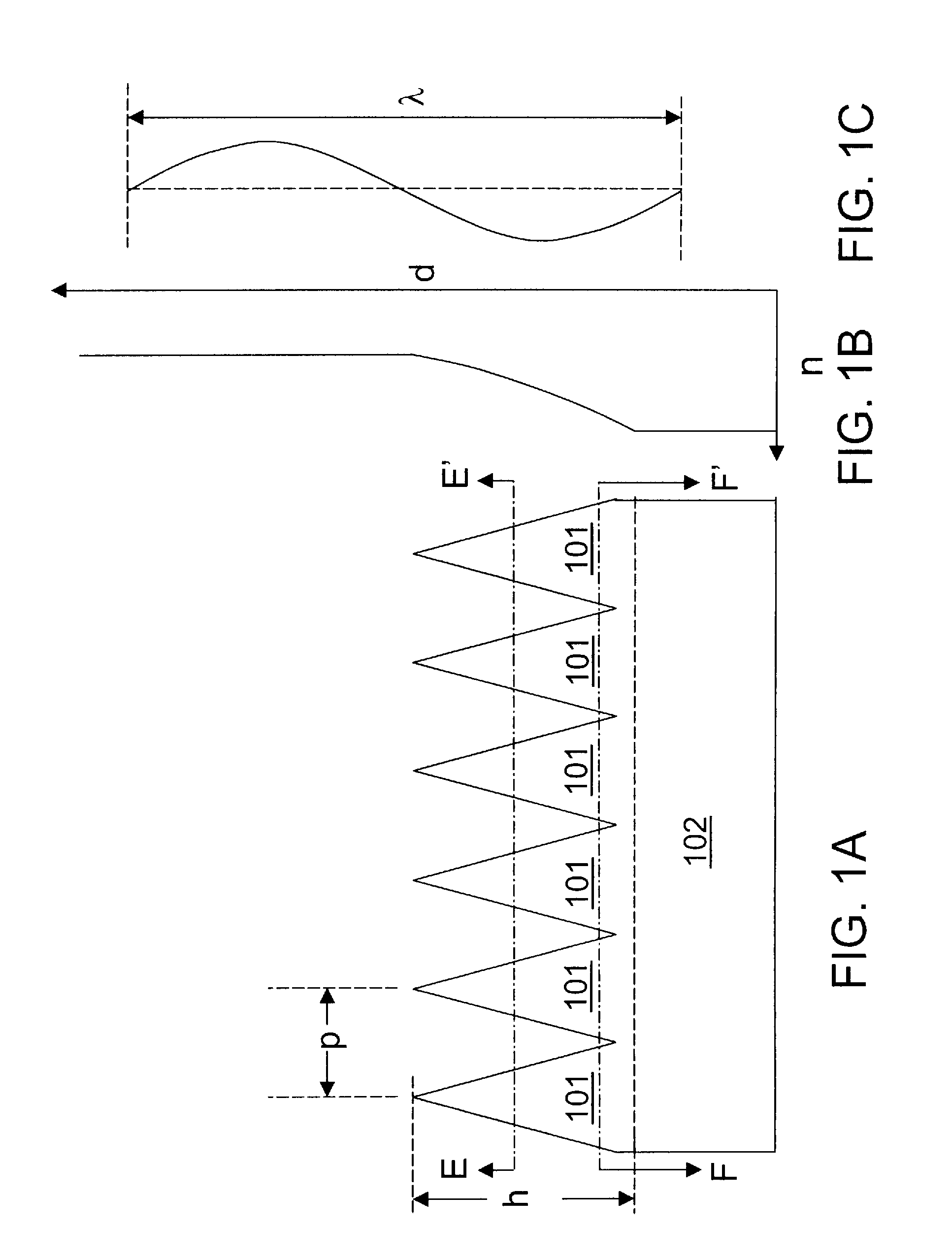
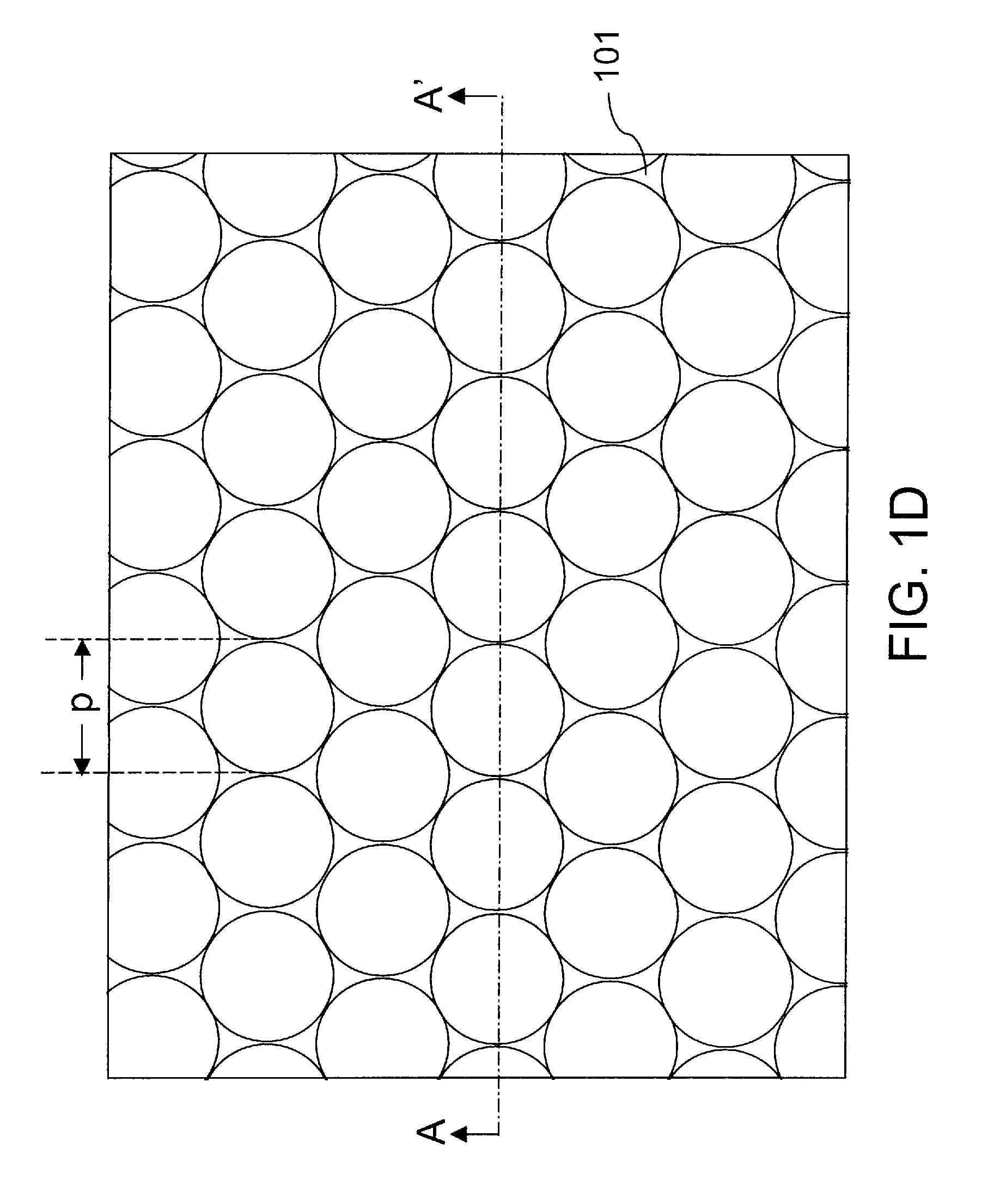
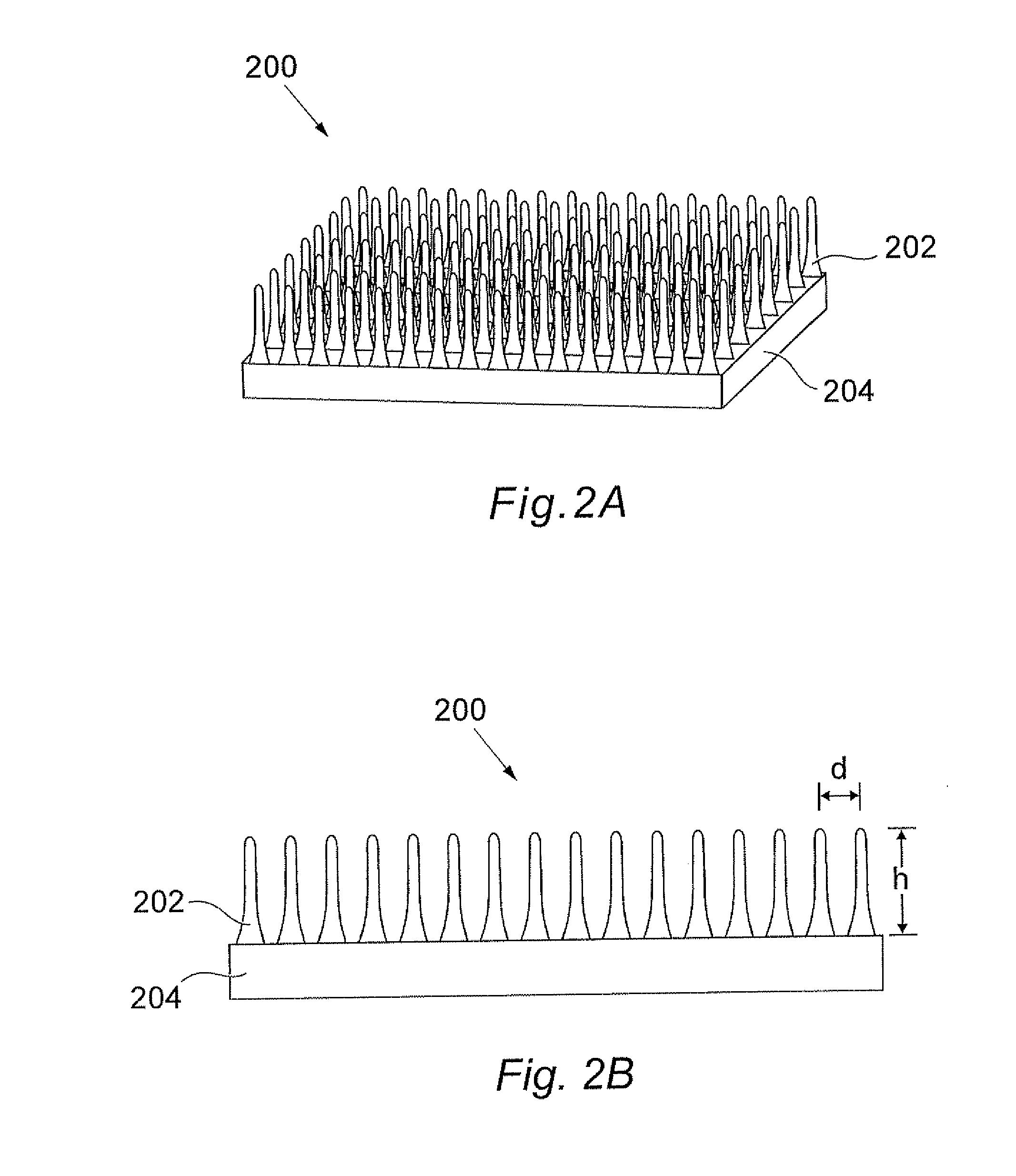
Methods For Forming Anti-Reflection Structures For CMOS Image Sensors
ActiveUS20090286346A1High light transmittanceSmall reflectionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefractive indexPhotodiode
Protuberances, having vertical and lateral dimensions less than the wavelength range of lights detectable by a photodiode, are formed at an optical interface between two layers having different refractive indices. The protuberances may be formed by employing self-assembling block copolymers that form an array of sublithographic features of a first polymeric block component within a matrix of a second polymeric block component. The pattern of the polymeric block component is transferred into a first optical layer to form an array of nanoscale protuberances. Alternately, conventional lithography may be employed to form protuberances having dimensions less than the wavelength of light. A second optical layer is formed directly on the protuberances of the first optical layer. The interface between the first and second optical layers has a graded refractive index, and provides high transmission of light with little reflection.
Owner:SMARTSENS TECH (HK) CO LTD
Optical laminated bodies, lighting equipment and area luminescence equipment
InactiveUS6972813B1Increase brightnessReduce the number of partsMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsLight equipmentEffect light
Lighting devices are disclosed that include optical laminated bodies. An exemplary optical laminated body includes a polarizing layer, a first transparent film disposed closely to a front surface of the polarizing layer and a second transparent film disposed closely to a back surface of the polarizing layer. The polarizing layer includes a reflective polarizing film, and both of the first transparent film and the second transparent film are diffusive films. The lighting devices further include a light source supplying light to the optical laminated body through a light entry surface of the first transparent film of the optical laminated body and a lens film disposed between the light source and the optical laminated body. The lighting device provides diffused-polarized light emitted from a light emitting surface of the second transparent film of the laminated body.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
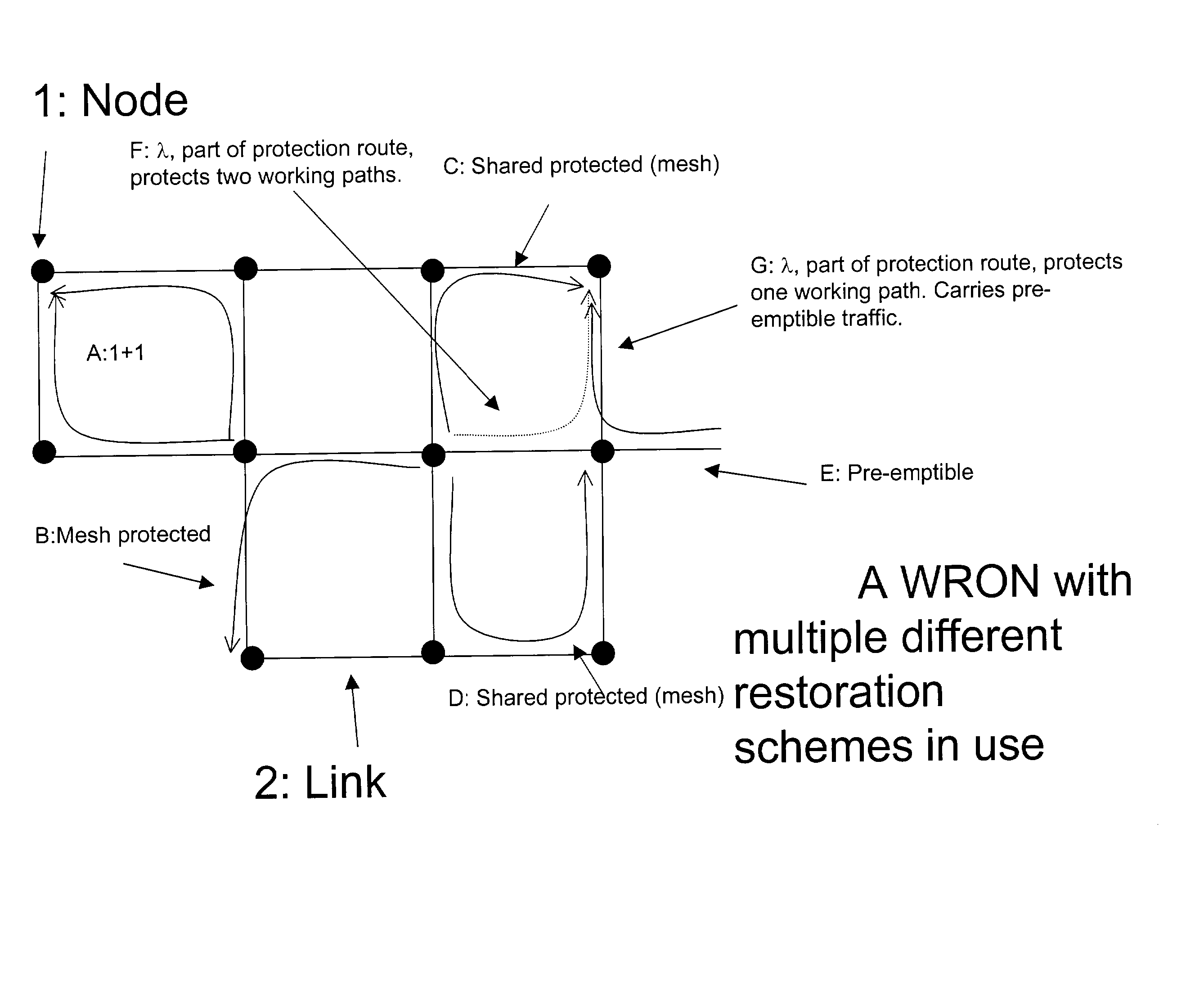
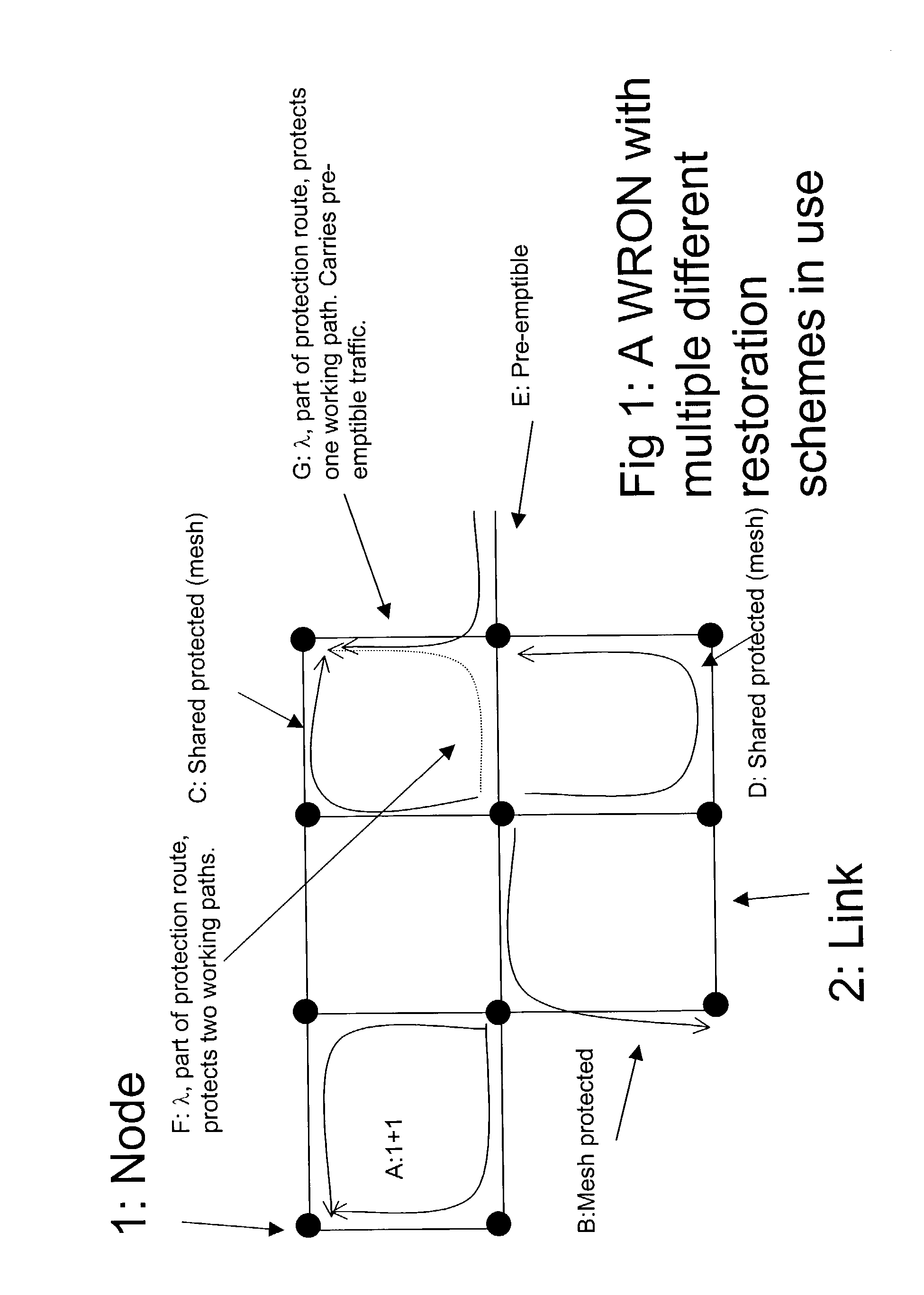
Differentiated resilience in optical networks
InactiveUS20040120705A1Easy to useSame capacityLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTraffic capacityDifferentiated service
A transparent wavelength routed optical network has two or more different optical layer restoration schemes to provide different levels of resilience, and a restoration allocator arranged to allocate the optical layer restoration schemes, to different parts of the traffic. This can enable similar capacity for high resilience traffic as a single resilience level network, and provide additional capacity for lower resilience level traffic, which can reflect the value of the traffic. The allocator can be located centrally in a network manager, or in distributed fashion at each node, and can depend on a translation of a parameter requested by the customer. Nodes have message processors for receiving a message for reserving a path, determining if the path has become unavailable, and if so, sending a second message to collect information about any other paths still available on the same route.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Dielectric barrier layer films
InactiveUS20060071592A1Improve performanceImprove uniformityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical resistance and conductancePulsed DC
In accordance with the present invention, a dielectric barrier layer is presented. A barrier layer according to the present invention includes a densified amorphous dielectric layer deposited on a substrate by pulsed-DC, substrate biased physical vapor deposition, wherein the densified amorphous dielectric layer is a barrier layer. A method of forming a barrier layer according to the present inventions includes providing a substrate and depositing a highly densified, amorphous, dielectric material over the substrate in a pulsed-dc, biased, wide target physical vapor deposition process. Further, the process can include performing a soft-metal breath treatment on the substrate. Such barrier layers can be utilized as electrical layers, optical layers, immunological layers, or tribological layers.
Owner:DEMARAY
Imaging assembly
ActiveUS20100128350A1Improve adhesionRelieve pressureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringWavelength
An image assembly may include a substrate having a face, a first optical layer and at least one spacer member. The imaging assembly may also include an anti-reflection structure. The at least one spacer member may be arranged between the substrate and the first optical layer to define an air gap therebetween. The anti-reflection structure may be coupled to at least part of the face and at least one of the first optical layer and the at least one spacer member. The anti-reflection structure may also include a plurality of projections having dimensions smaller than a wavelength of radiation to be imaged by the imaging assembly.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (RES & DEV) LTD
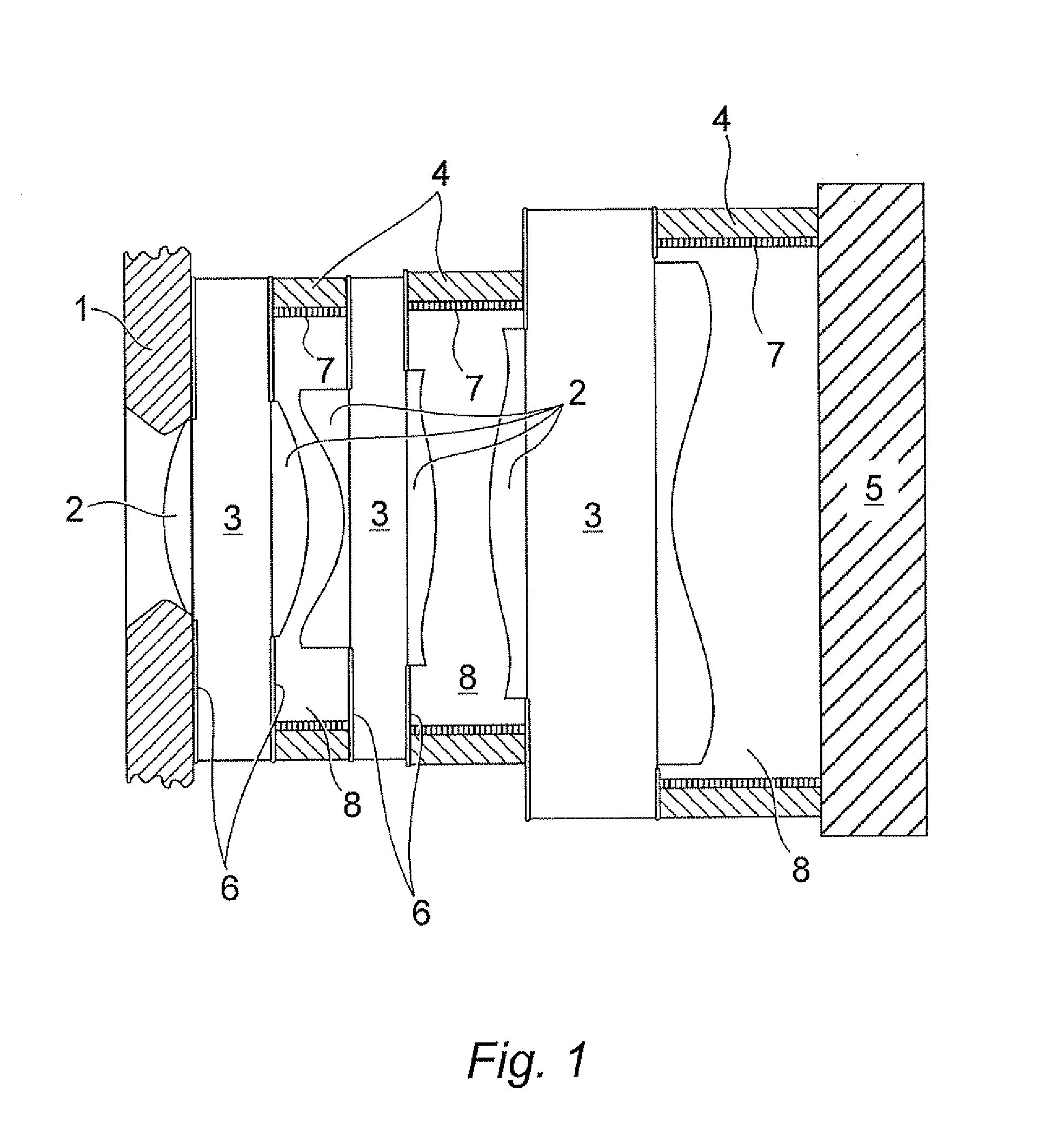
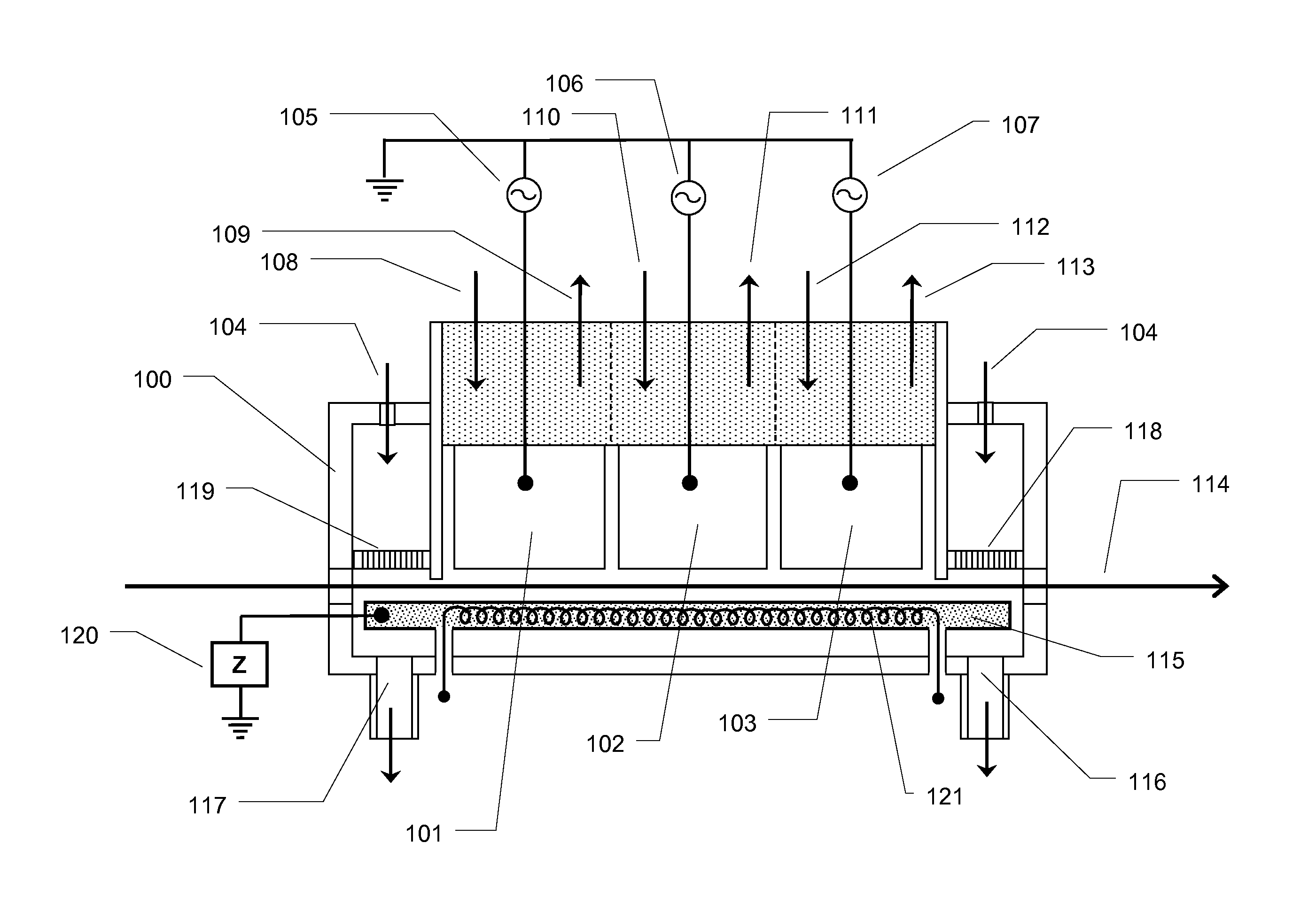
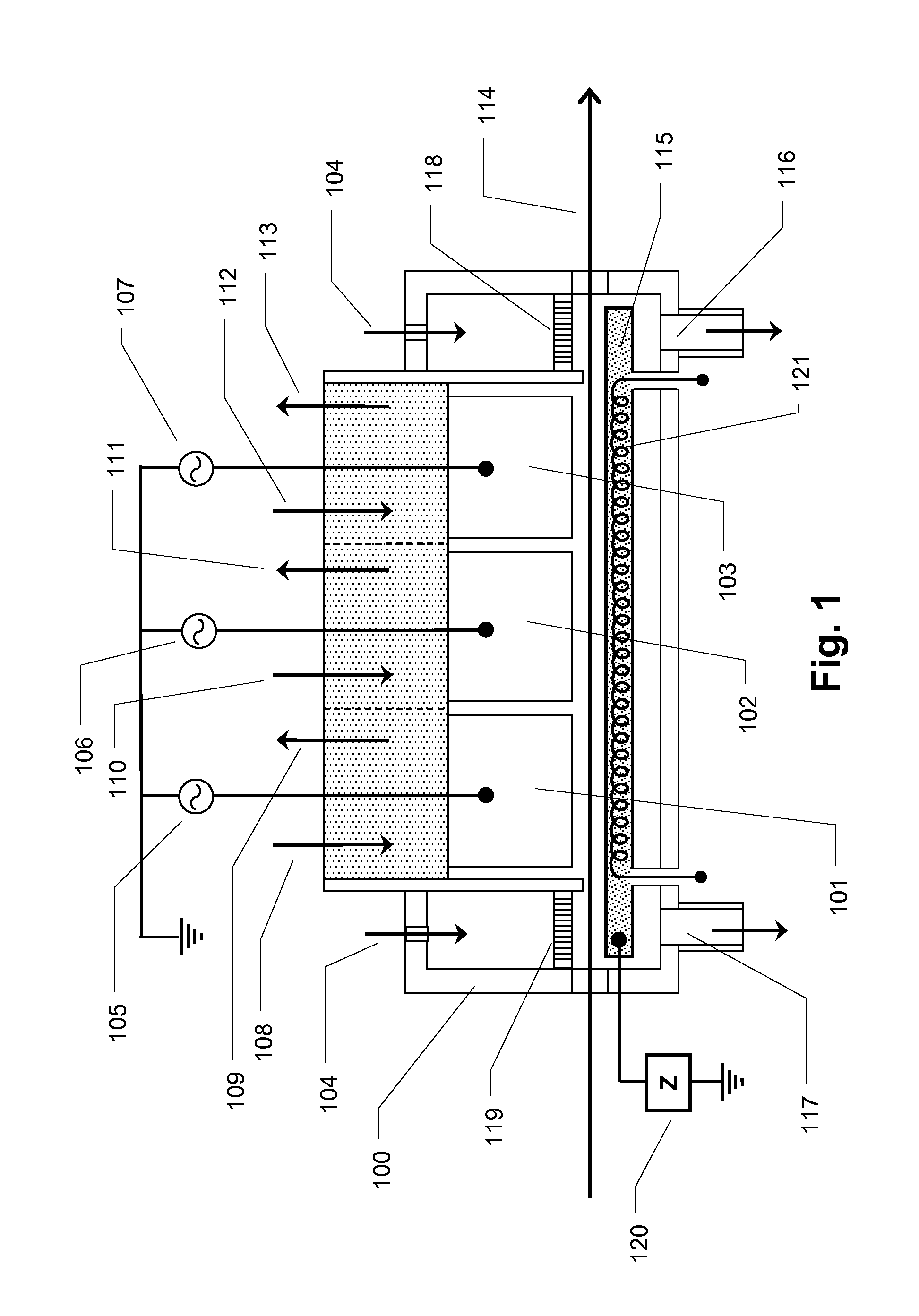
Apparatus and method for forming thin protective and optical layers on substrates
InactiveUS20130337657A1Easy to controlIncreased and reduced plasma power densityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase differenceEngineering
A method and apparatus are provided for plasma-based processing of a substrate based on a plasma source having at least two adjacent electrodes positioned with the long dimensions parallel to define a first gap minimum between the two electrodes of from 5 millimeters to 40 millimeters. A second gap minimum is defined between the two electrodes and the substrate. AC power is provided to the two electrodes through separate electrical circuits from a common supply with the phase difference therebetween. A first gas and a second are injected into the plasma-containing volume between the two electrodes are different positions relative to the substrate. A lower electrode with a lower electrode width that is less than the combined width of the two electrodes is powered from a separately controllable ac power supply at an ac frequency different from that supplied to the two electrodes.
Owner:AIXTRON AG
Optical recording systems
InactiveUS6094413AIncrease contrastImprove signal-to-noise ratioNanoinformaticsOptical beam sourcesOptical storageOptical recording
An optical storage system suitable for optical storage and retrieval of information using a storage medium comprising a substrate, an active layer for retention of the data, and an overlying optical layer, or layers for double-sided. The optical layer serves to produce an evanescent field in or adjacent to the active layer in response to an incident beam of radiation. The evanescent field is frustrated or attenuated by the data in the active layer and produces a signal.
Owner:SENSHIN CAPITAL +1
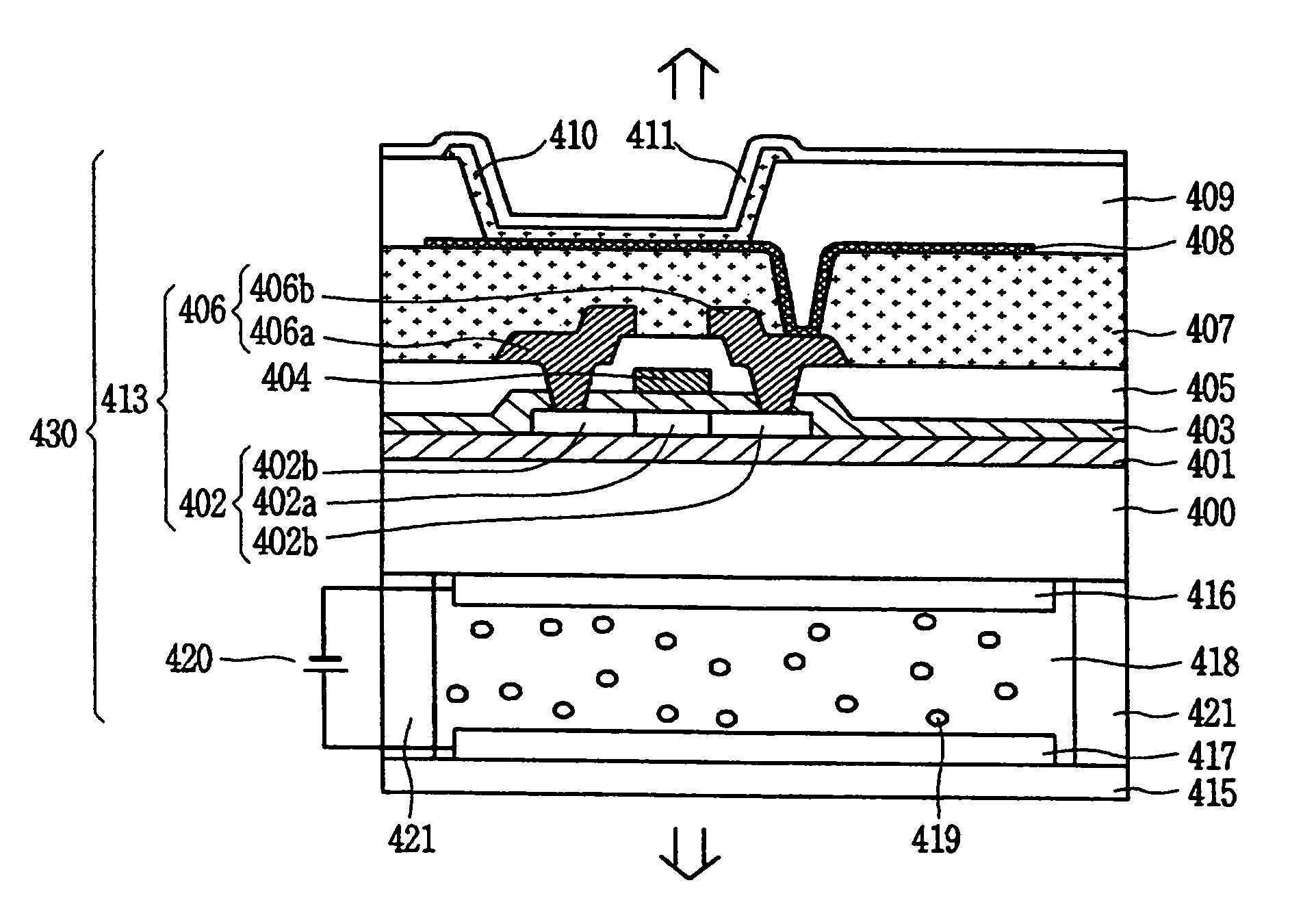
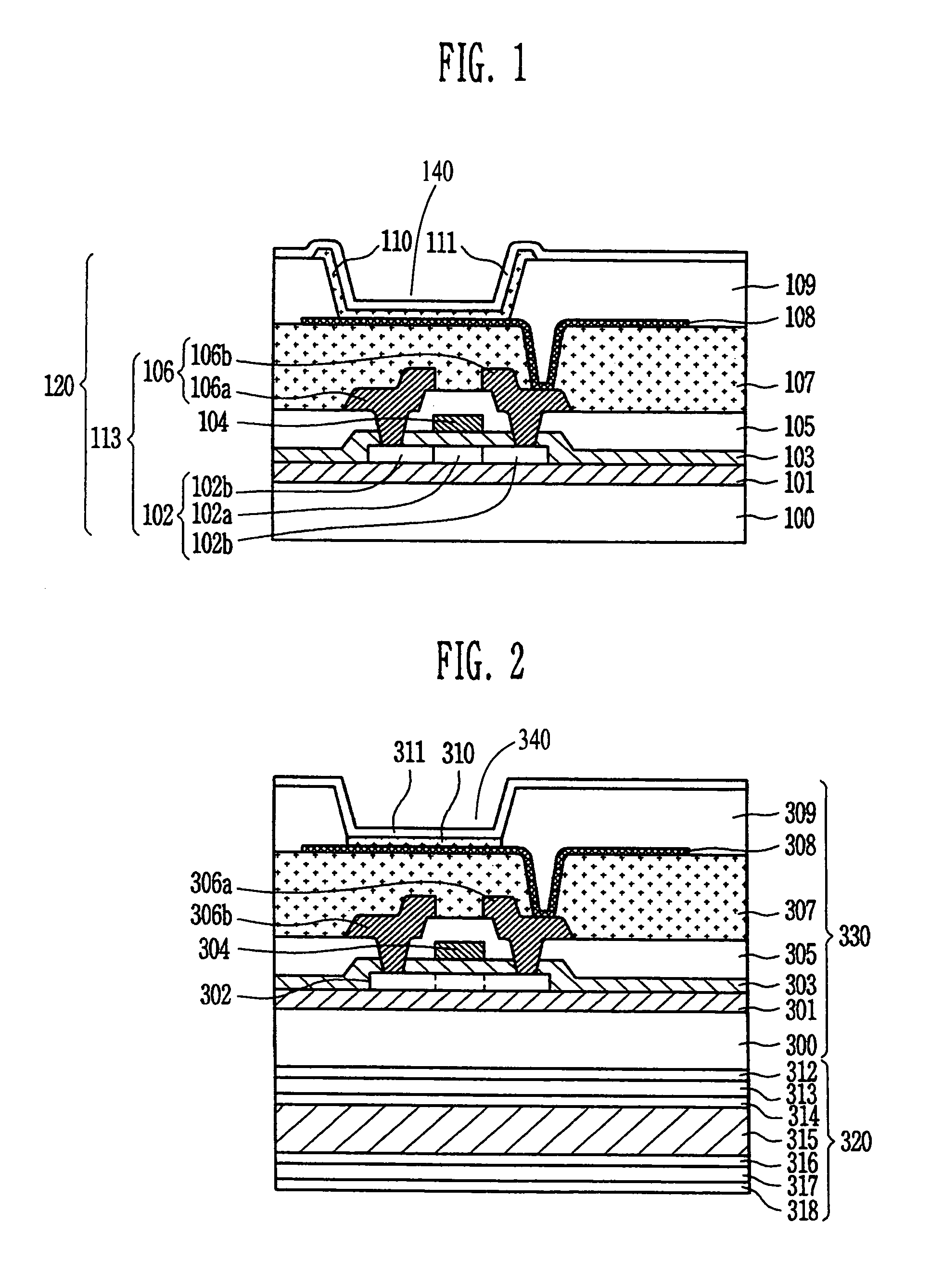
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS8593061B2Shorten planar lengthEnsure reliabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsEngineeringElectron
An electro-optical device includes a display panel obtained by forming an electro-optical layer, in which a plurality of pixels is formed, on a glass substrate having a thickness of 50 μm or less; and a support frame supporting the display panel, wherein the display panel has at least a display region in which the plurality of pixels is formed and frame regions formed outside the display region, and wherein at least one side of each of the frame regions is bent from the vicinity of a circumference of the display region to the support frame side and is fixed to the support frame.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
Multilayer optical bodies
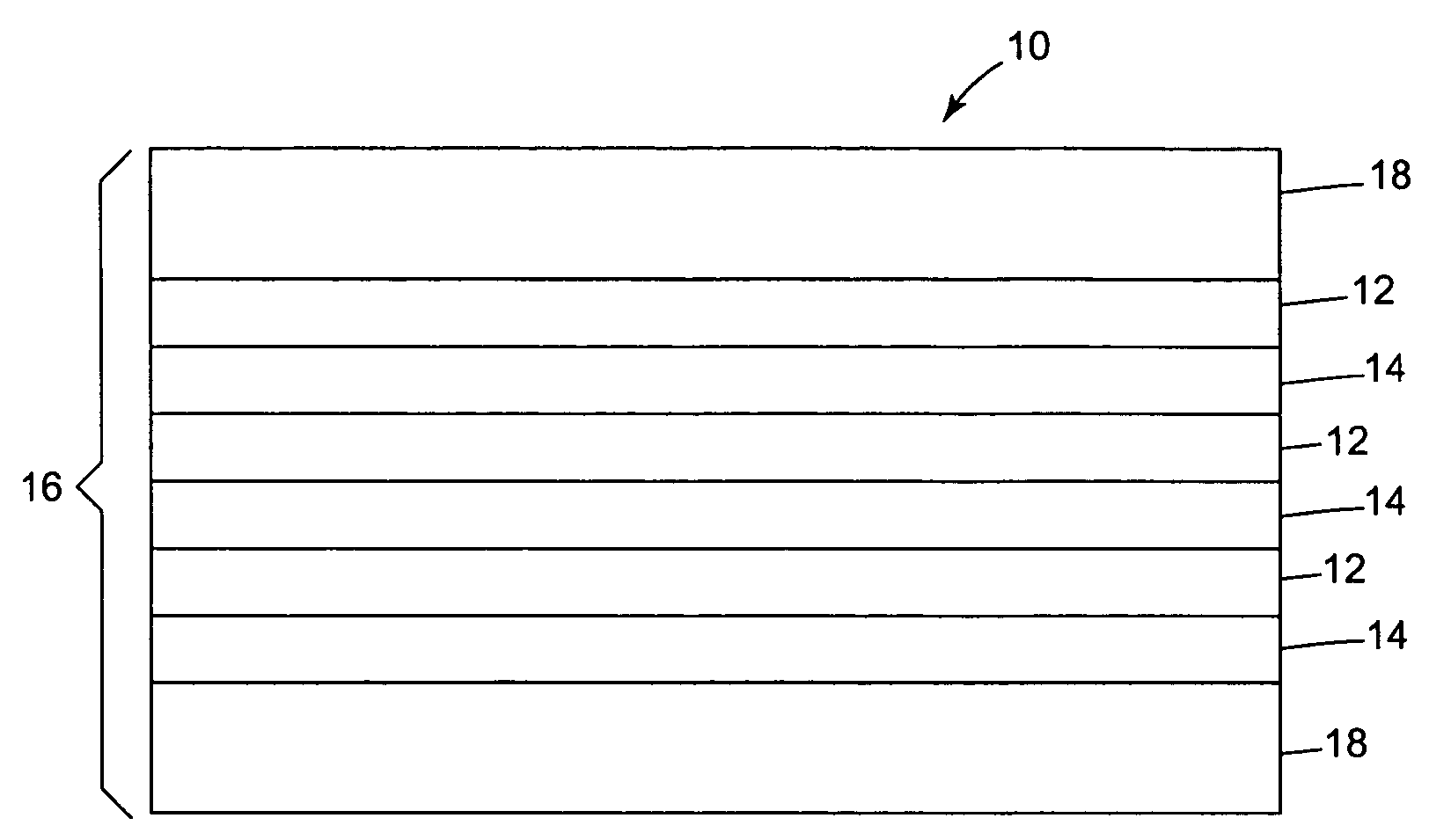
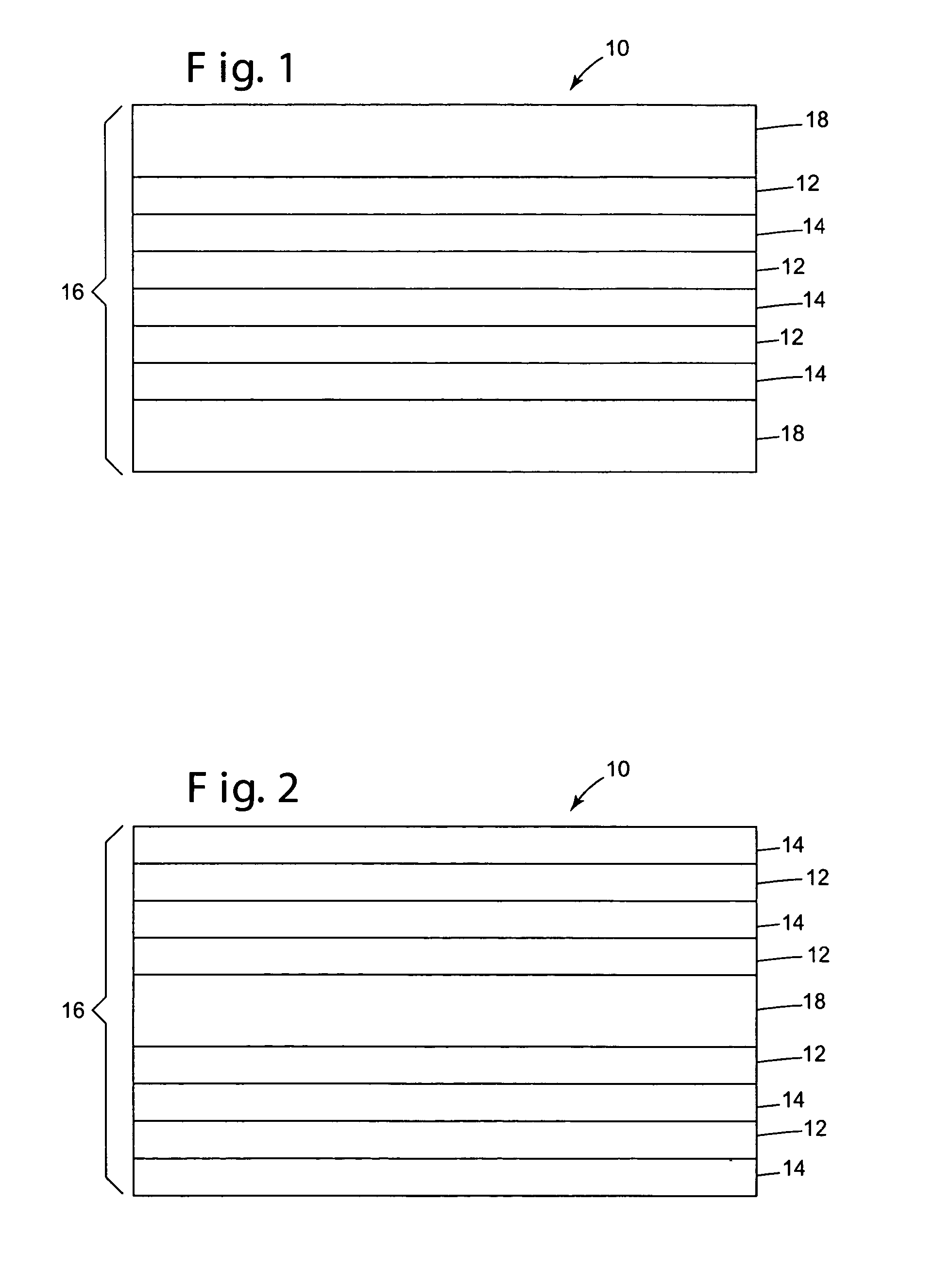
Optical bodies, comprising: a plurality of first optical layers comprising a first polymer composition that comprises (i) a polyester portion having terephthalate comonomer units and ethylene glycol comonomer units; and(ii) a second portion corresponding to a polymer having a glass transition temperature of at least about 130° C.; and a plurality of second optical layers disposed in a repeating sequence with the plurality of first optical layers. Also disclosed are optical bodies comprising: (a) a plurality of first optical layers, each first optical layer being oriented; and (b) a plurality of second optical layers, disposed in a repeating sequence with the plurality of first optical layers, comprising a blend of polymethylmethacrylate and polyvinylidene fluoride. Methods of making the above-described optical bodies, and articles employing such optical bodies are also provided.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Multilayer infrared reflecting film with high and smooth transmission in visible wavelength region and laminate articles made therefrom
InactiveUS7236296B2High visible light transmittanceImprove performanceMirrorsOptical filtersOptical packetLength wave
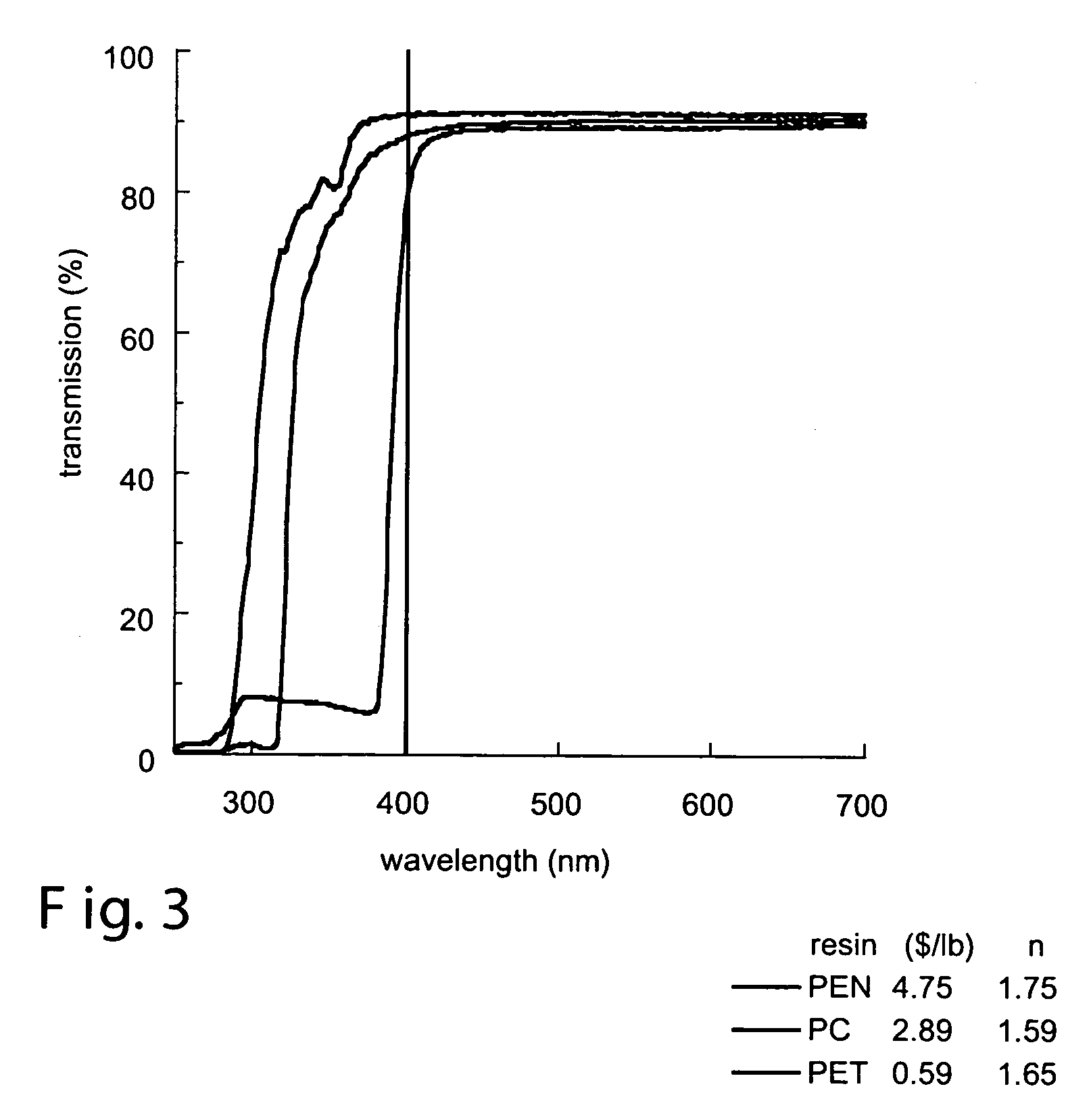
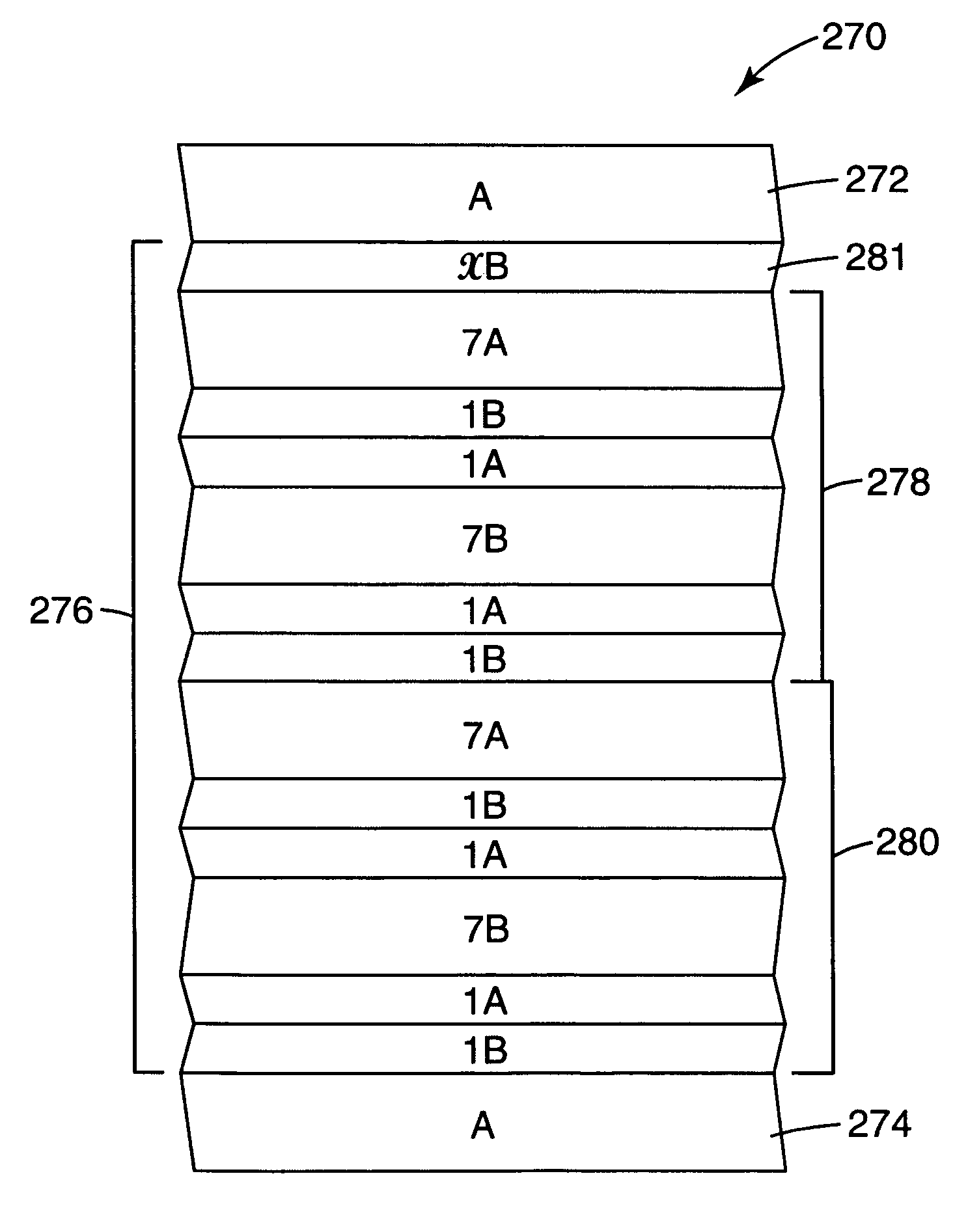
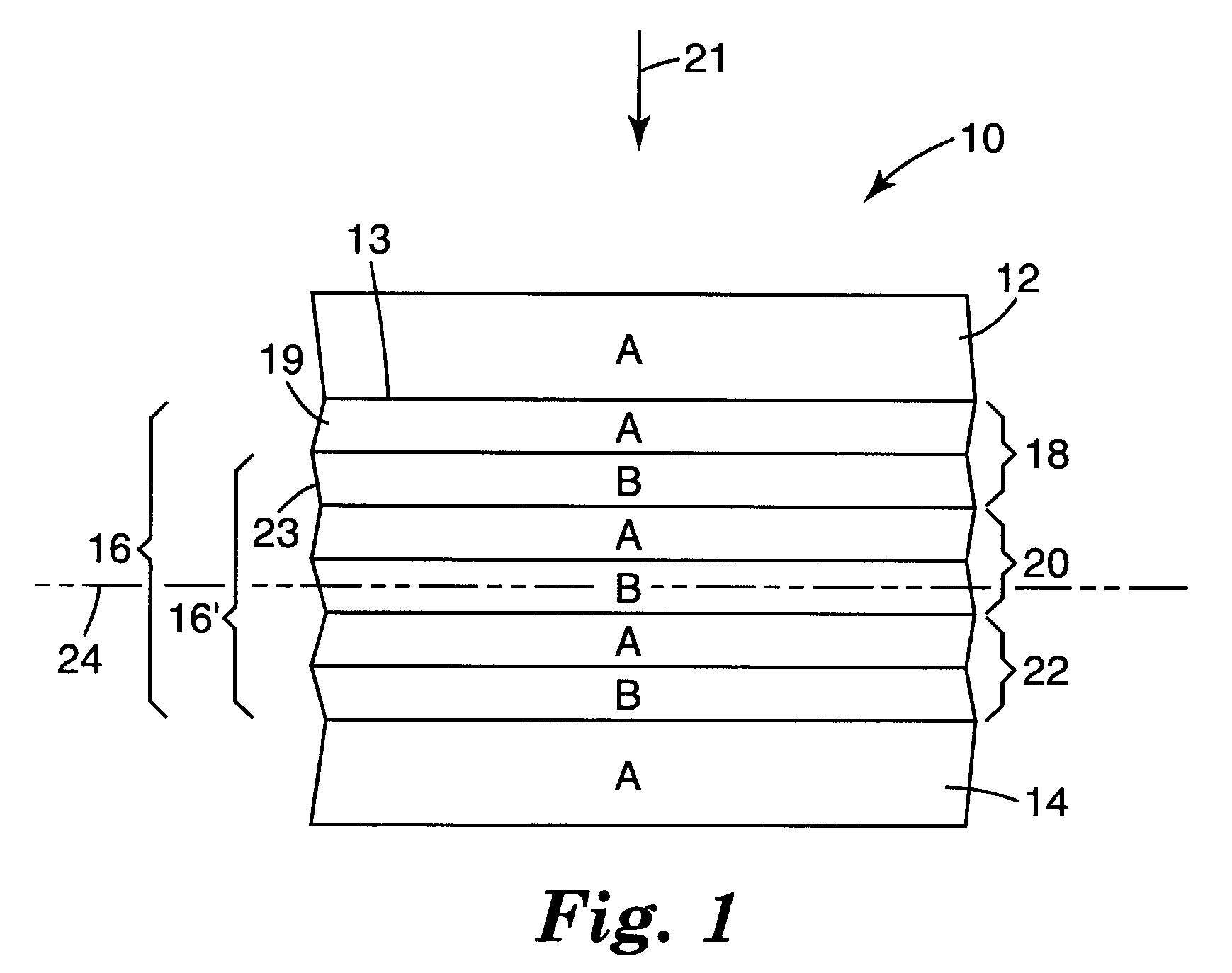
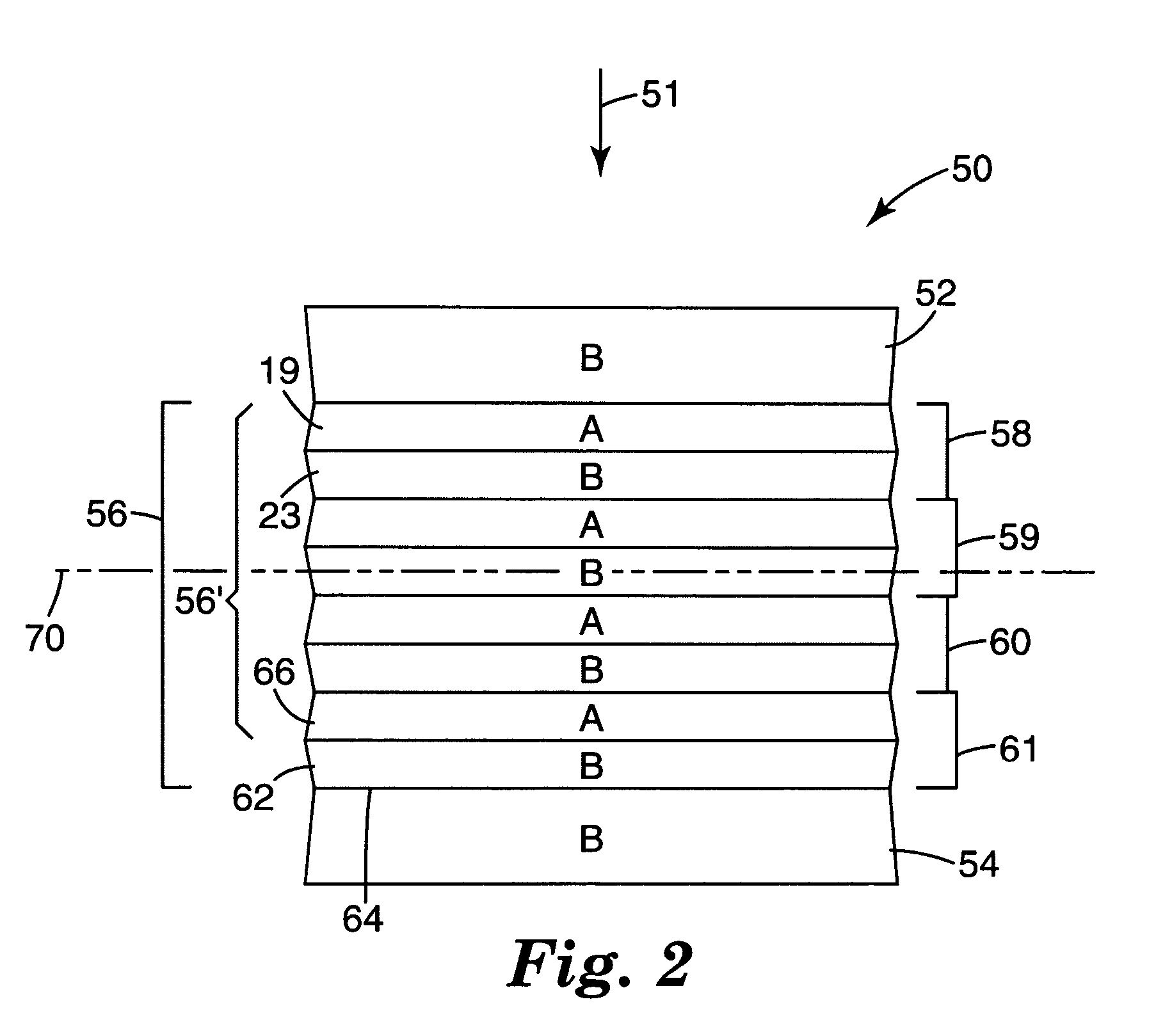
A multilayer film article is disclosed. The film includes an infrared light reflecting multilayer film having alternating layers of a first polymer type and a second polymer type and an infrared light absorbing or reflecting layer adjacent the multilayer film. The film includes a multilayer stack composed of alternating optical layers of first and second diverse polymers A, B. The optical layers when counted from one end of a first effective optical packet form a plurality of unit cells each having six optical layers arranged in relative optical thicknesses in a first cyclic permutation of 7A1B1A7B1A1B. At normal incidence the first effective optical packet provides a reflection band at infrared wavelengths and substantially transmits light at visible wavelengths.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Two dimensional light source using light emitting diode and liquid crystal display device using the two dimensional light source
ActiveUS7436000B2Simplify the assembly processSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsLiquid-crystal displayLight-emitting diode
A two-dimensional light source includes a base substrate having holes, wires disposed on a lower surface of the base substrate, a light emitting diode (LED) chip disposed on an upper surface of the base substrate, plugs that connect two electrodes of the LED chip to the wires through the holes, a buffer layer covering the LED chip, and an optical layer that is disposed on the buffer layer and has an optical pattern formed at a portion of the optical layer corresponding to the LED chip.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com