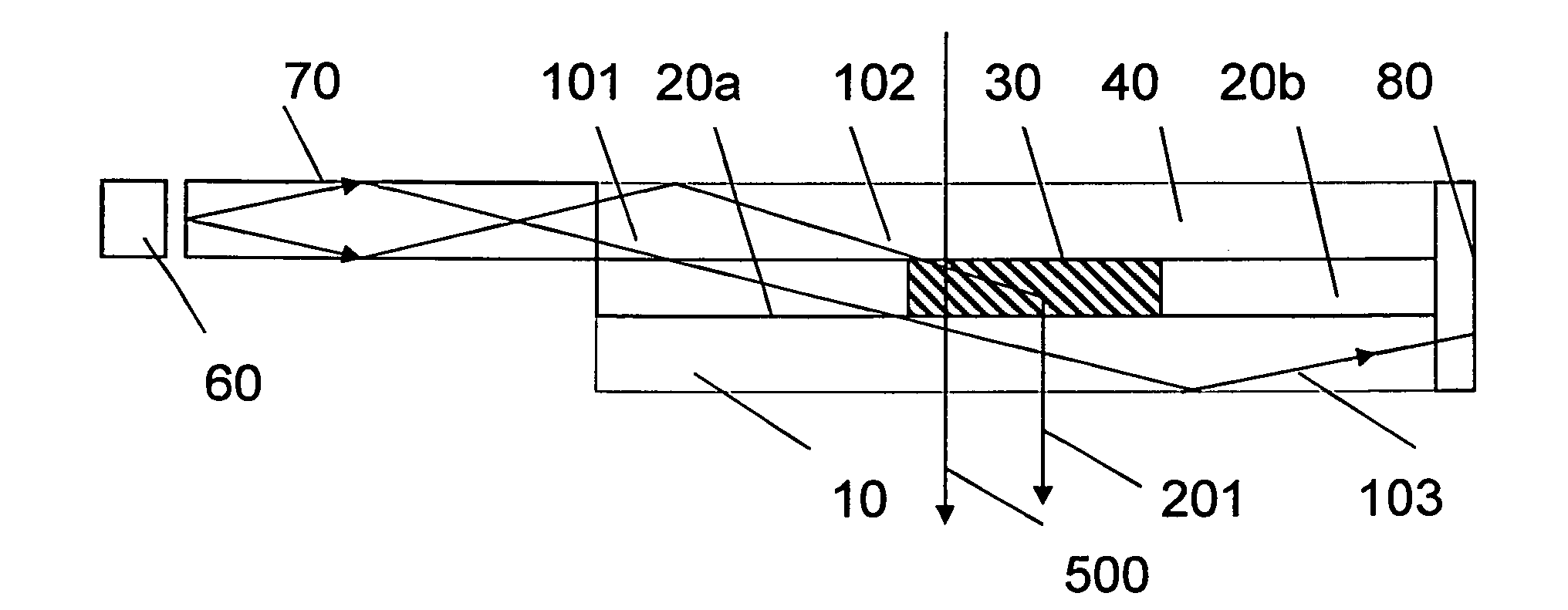
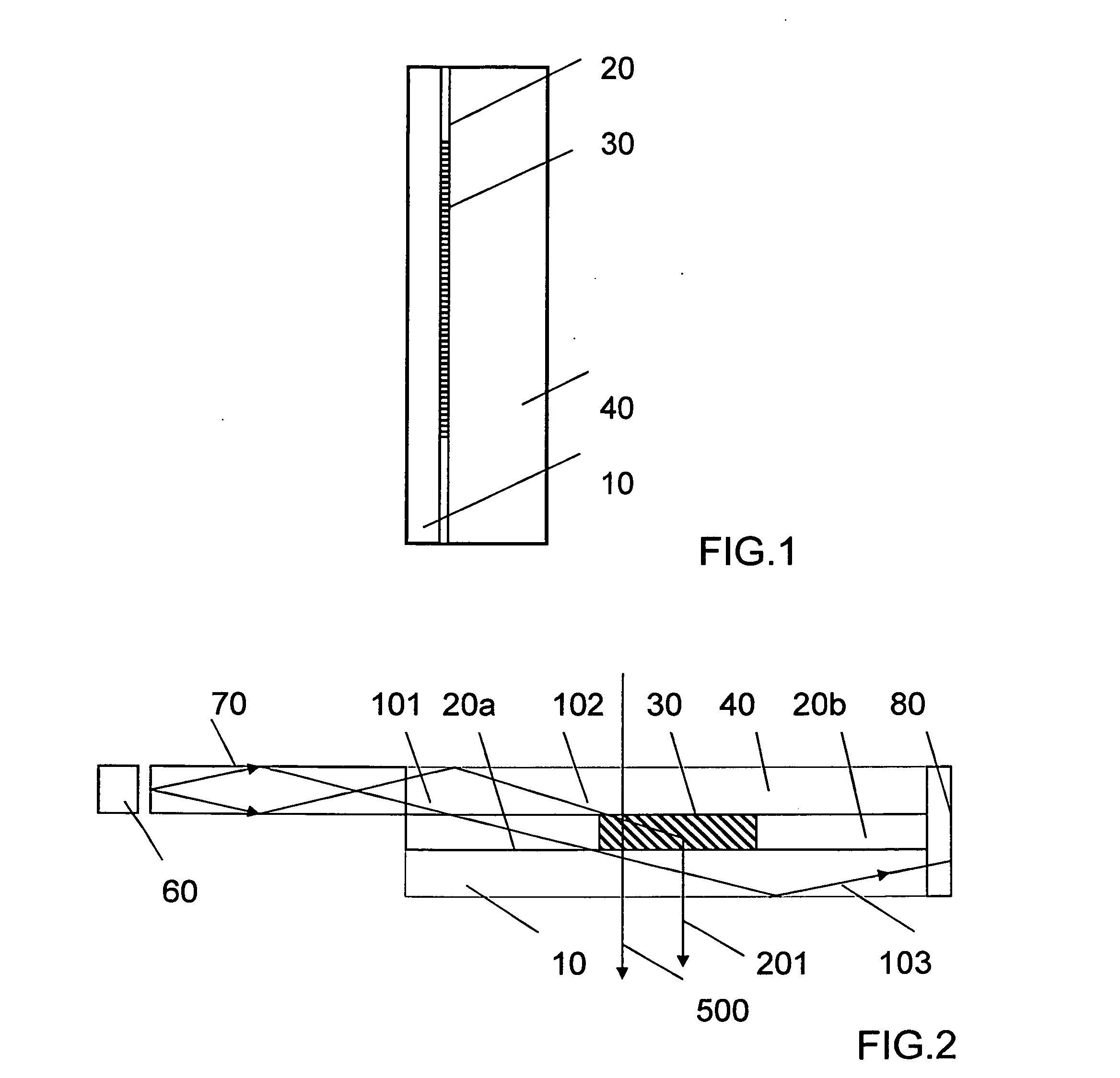
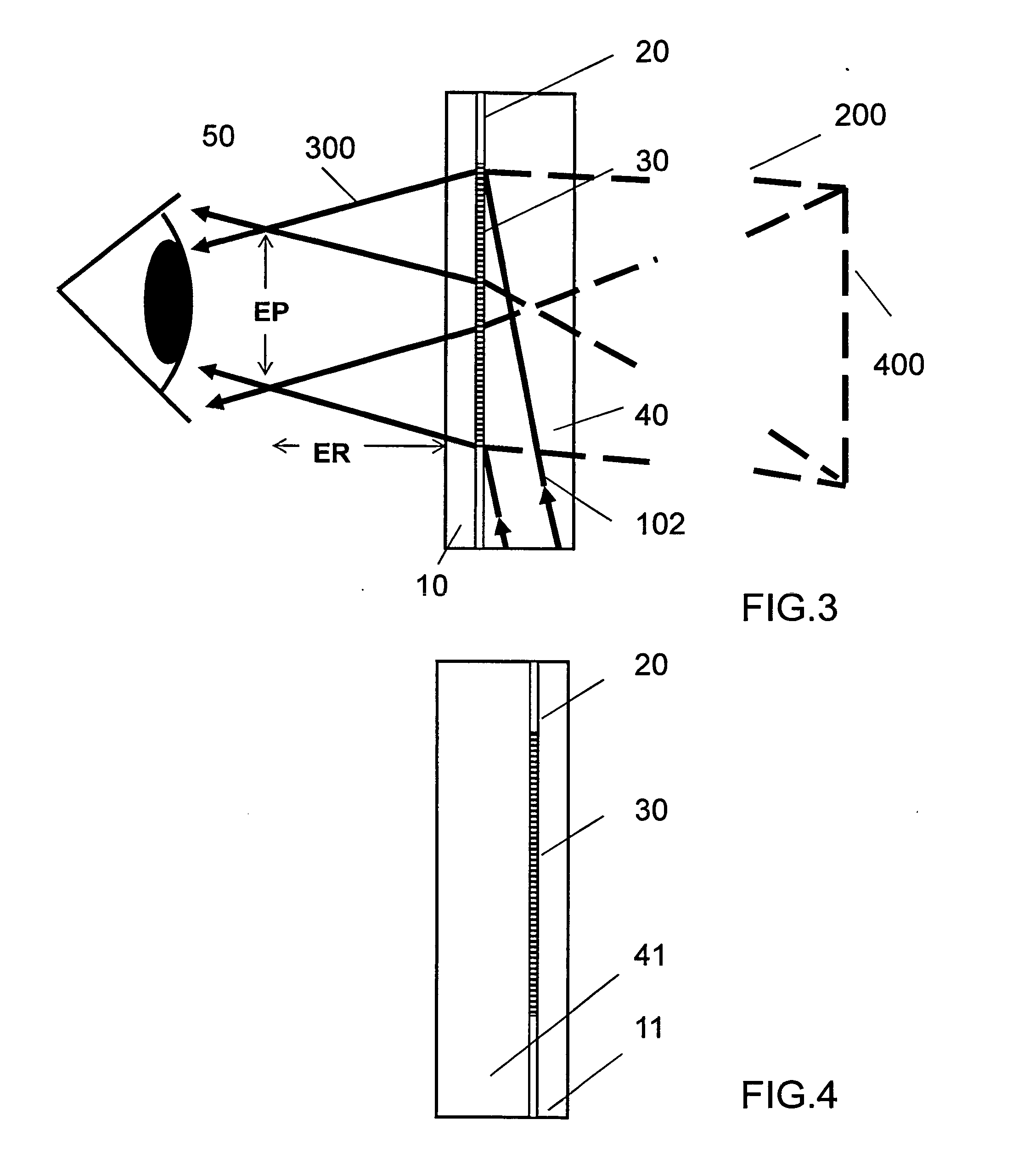
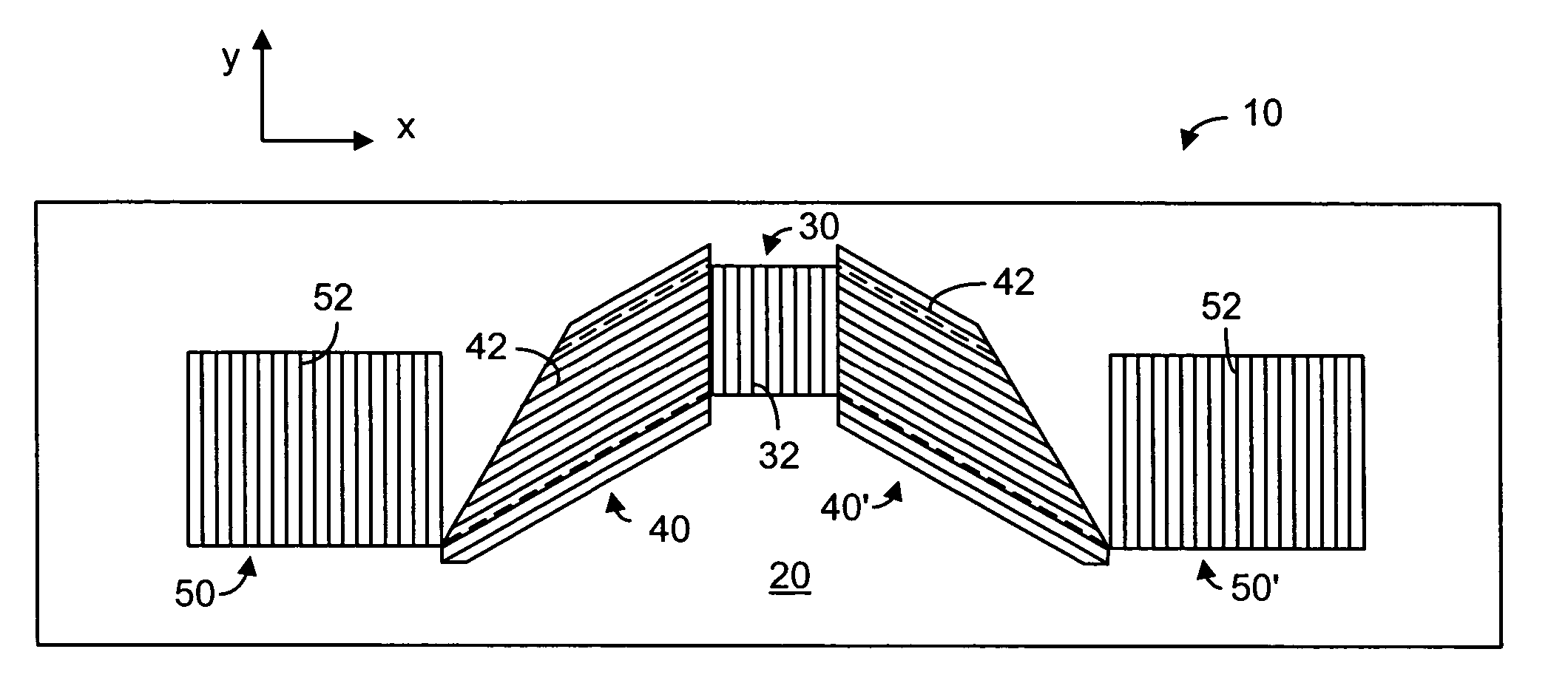
Patents
Literature
1262 results about "Exit pupil" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
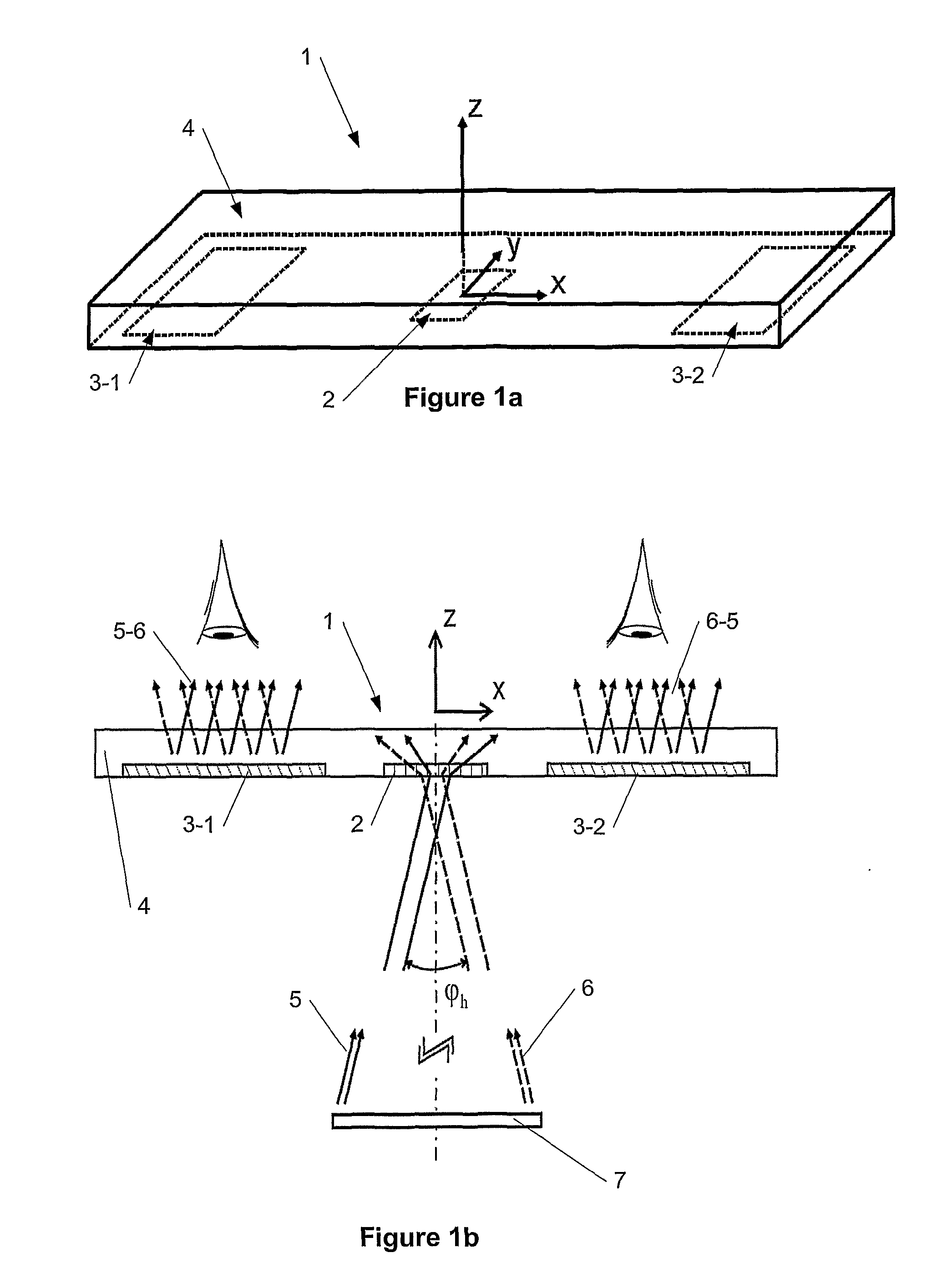
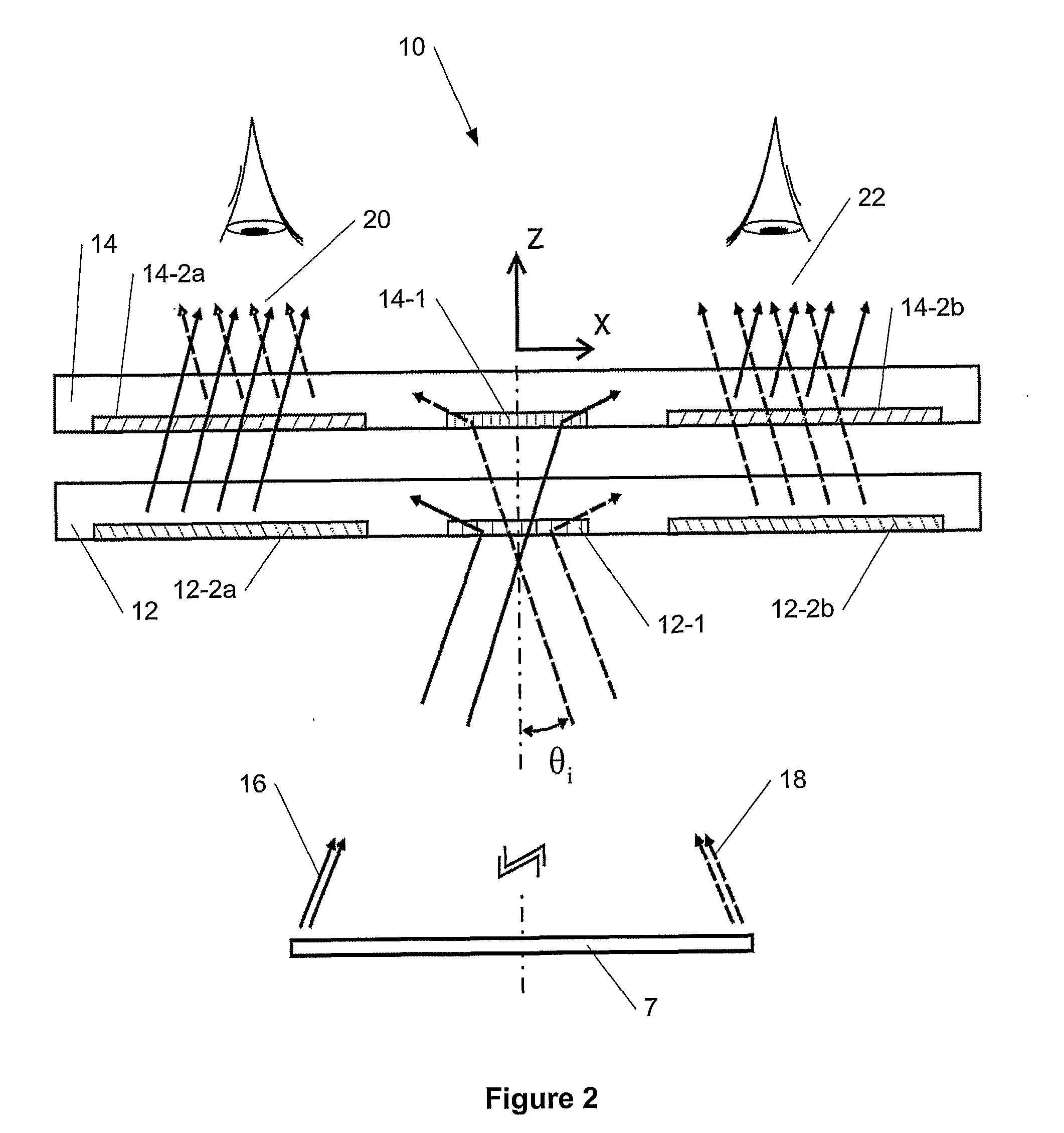
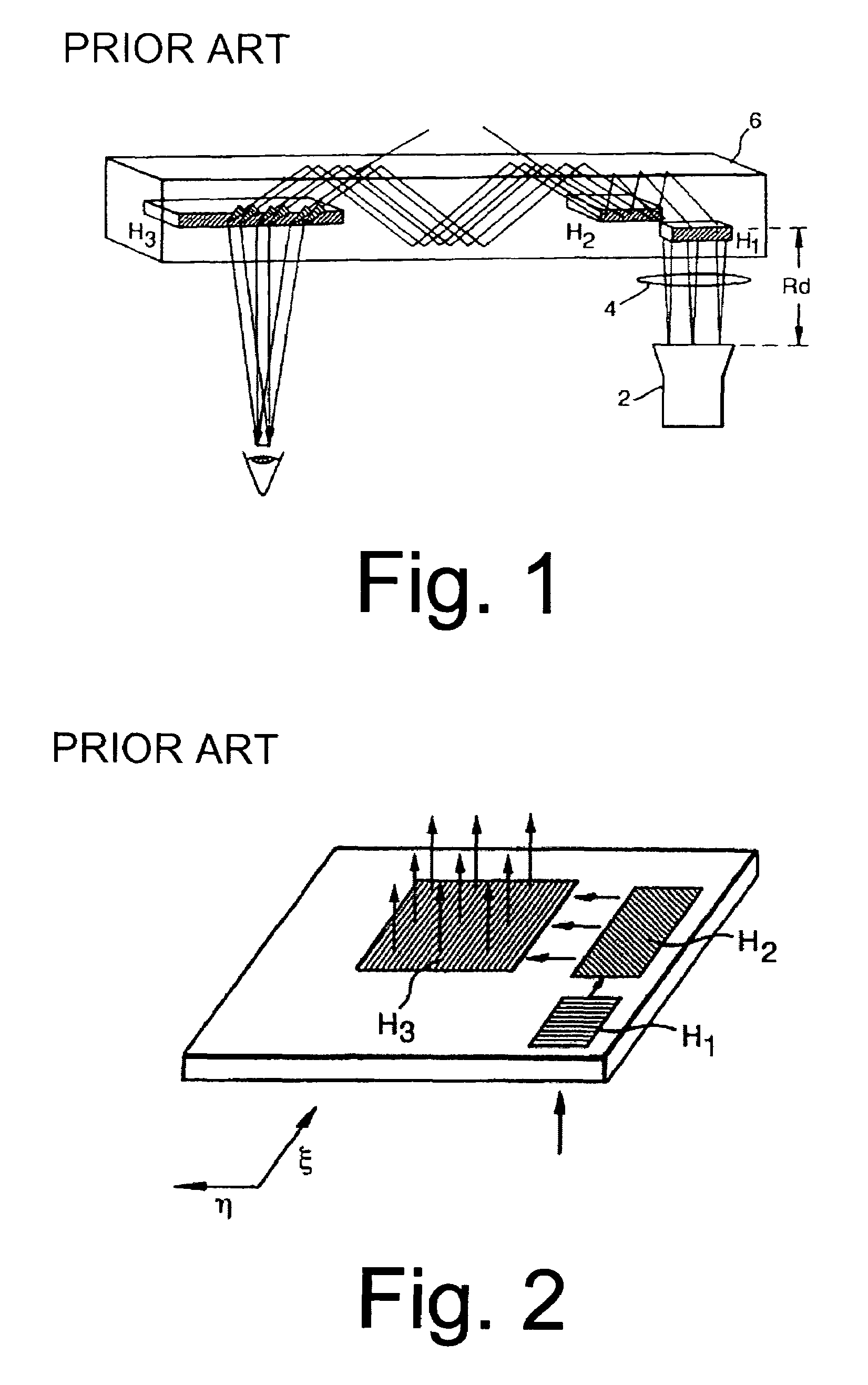
In optics, the exit pupil is a virtual aperture in an optical system. Only rays which pass through this virtual aperture can exit the system. The exit pupil is the image of the aperture stop in the optics that follow it. In a telescope or compound microscope, this image is the image of the objective element(s) as produced by the eyepiece. The size and shape of this disc is crucial to the instrument's performance, because the observer's eye can see light only if it passes through this tiny aperture. The term exit pupil is also sometimes used to refer to the diameter of the virtual aperture. Older literature on optics sometimes refers to the exit pupil as the Ramsden disc, named after English instrument-maker Jesse Ramsden.
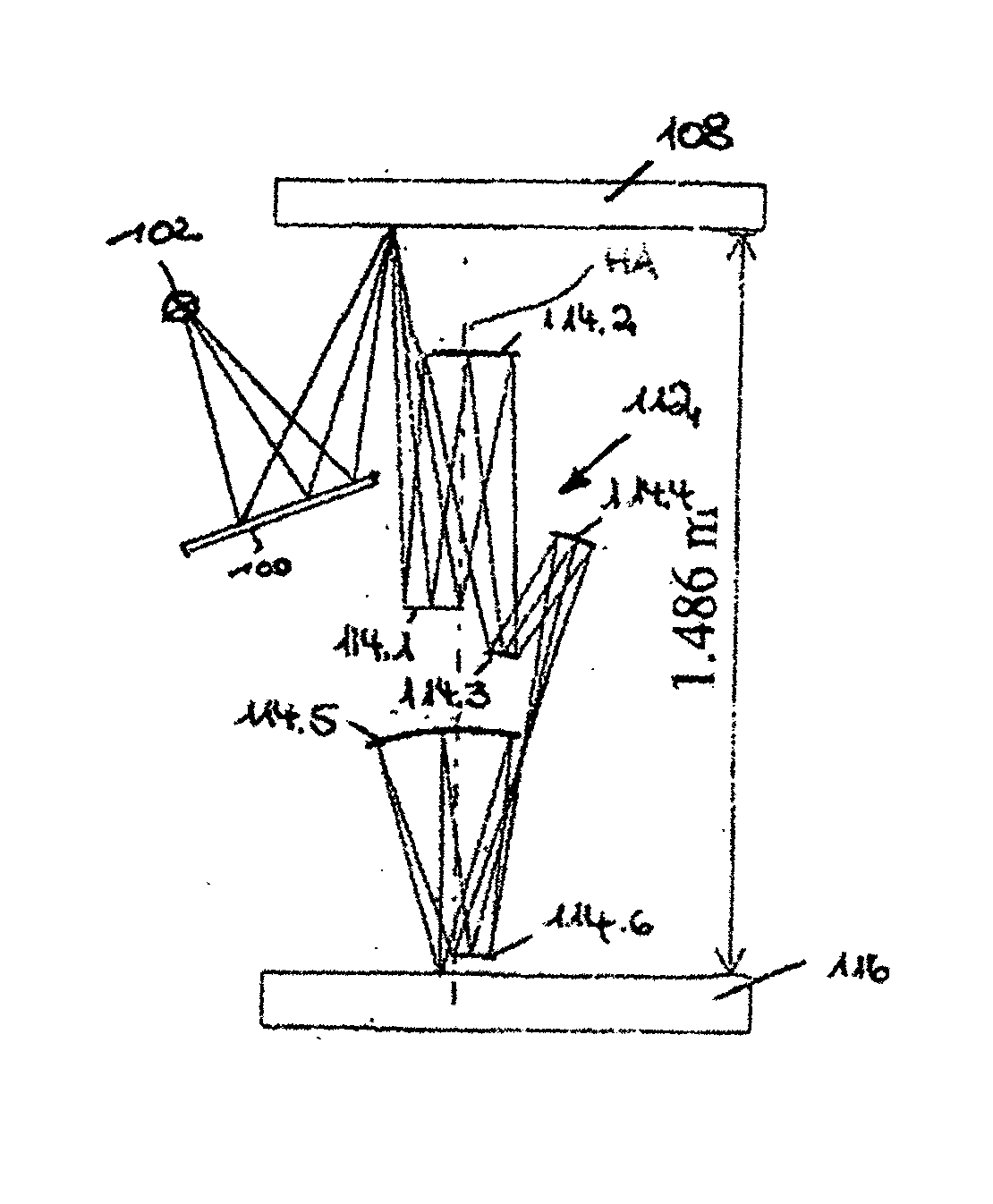
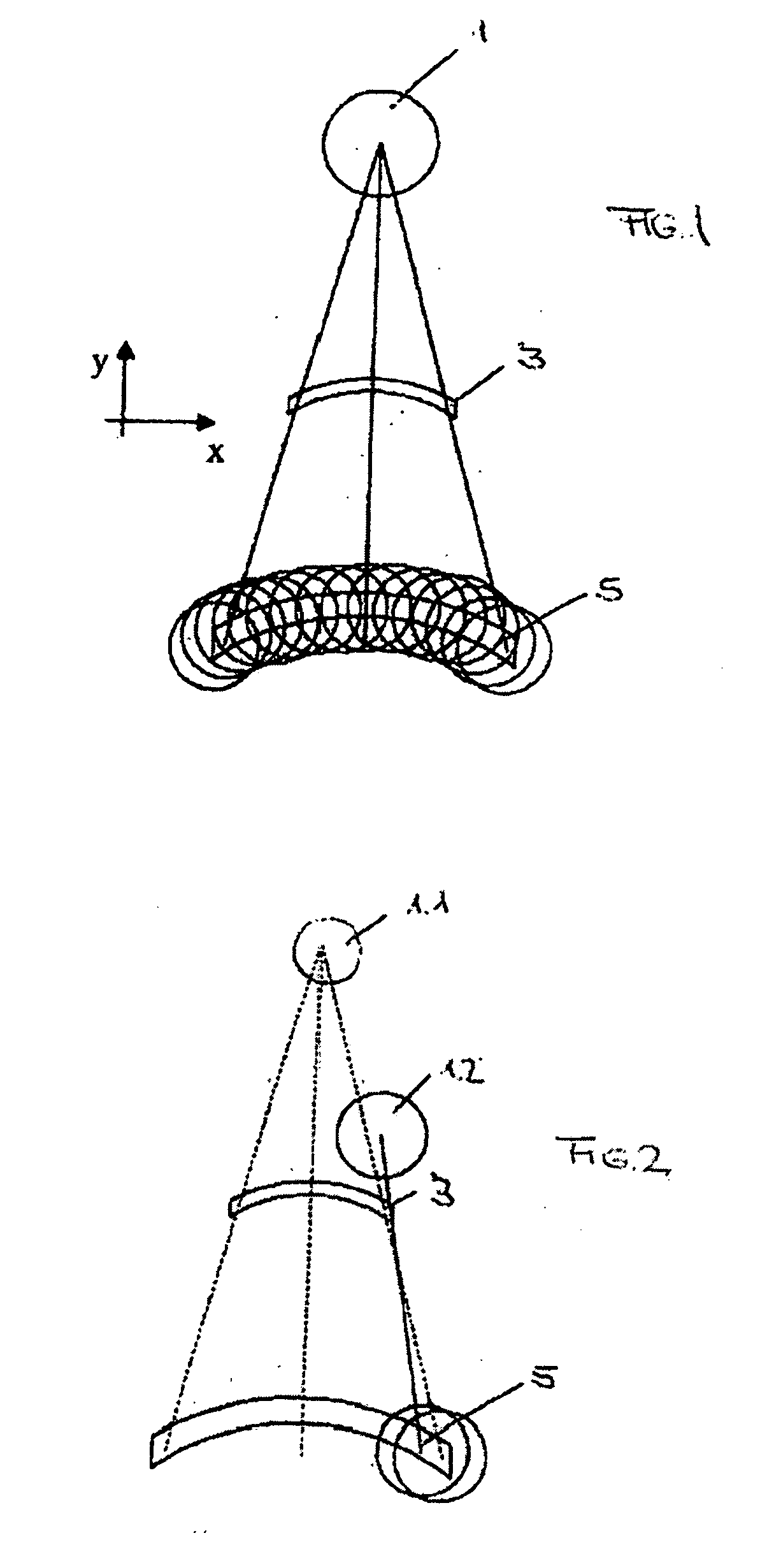
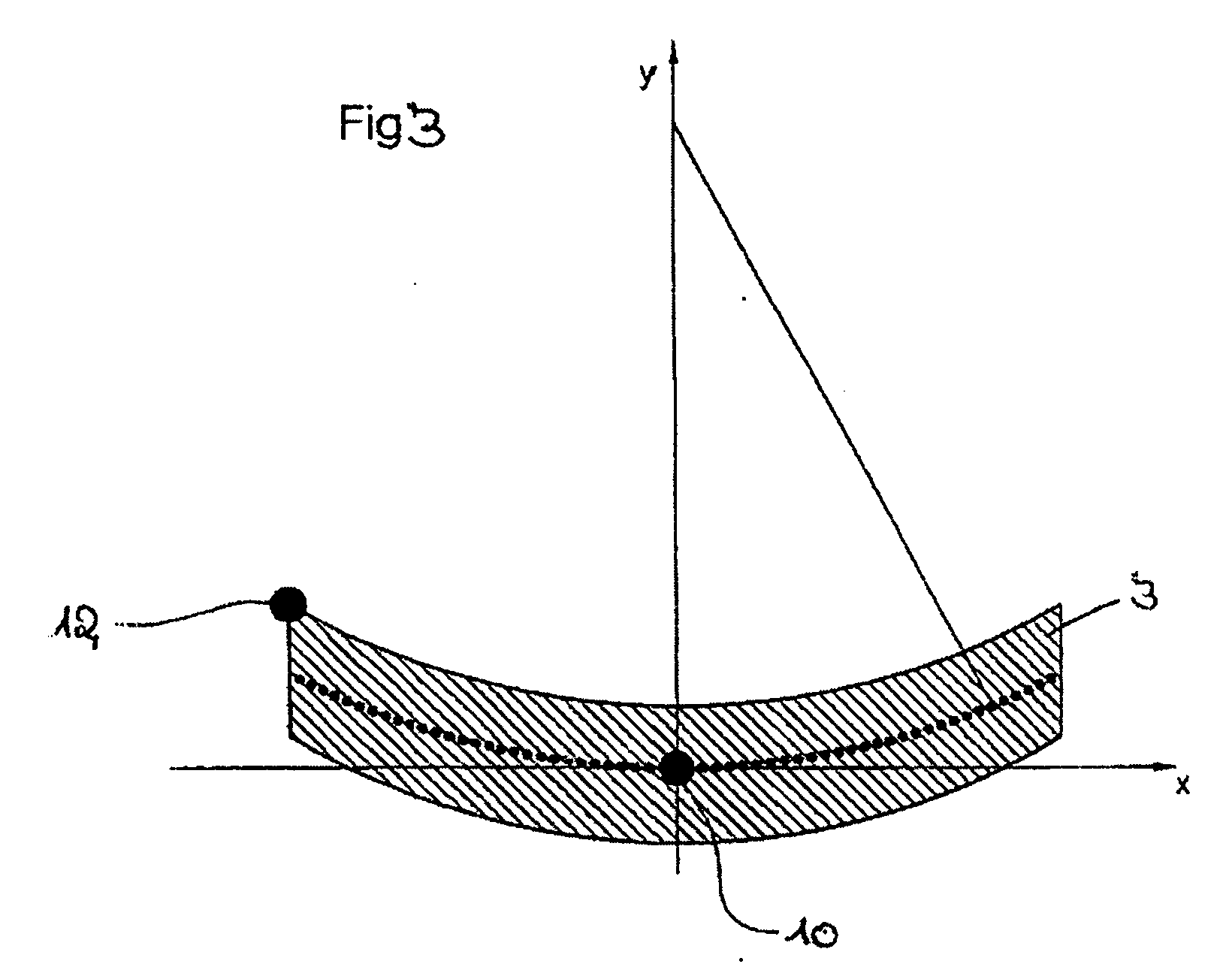
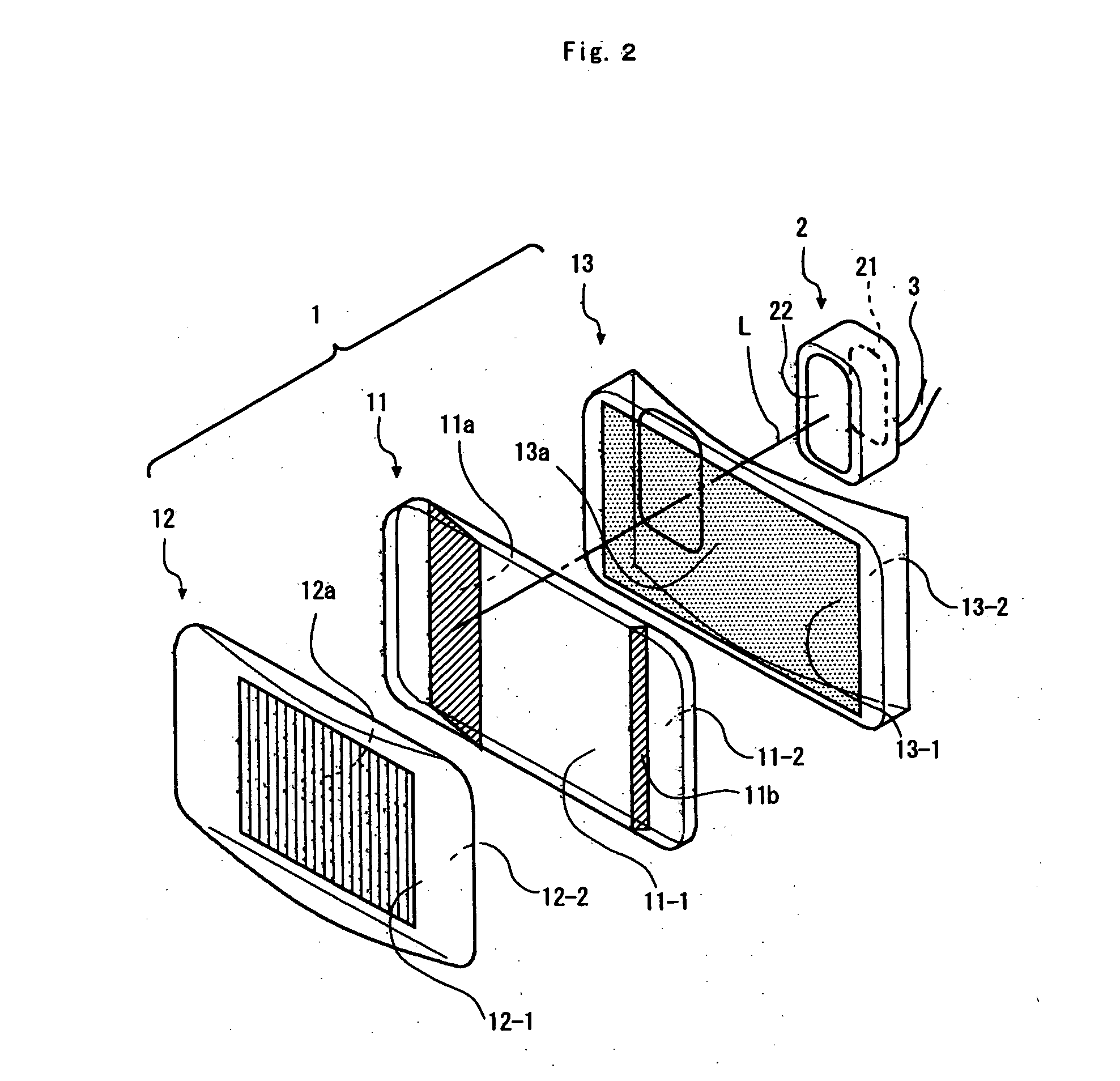
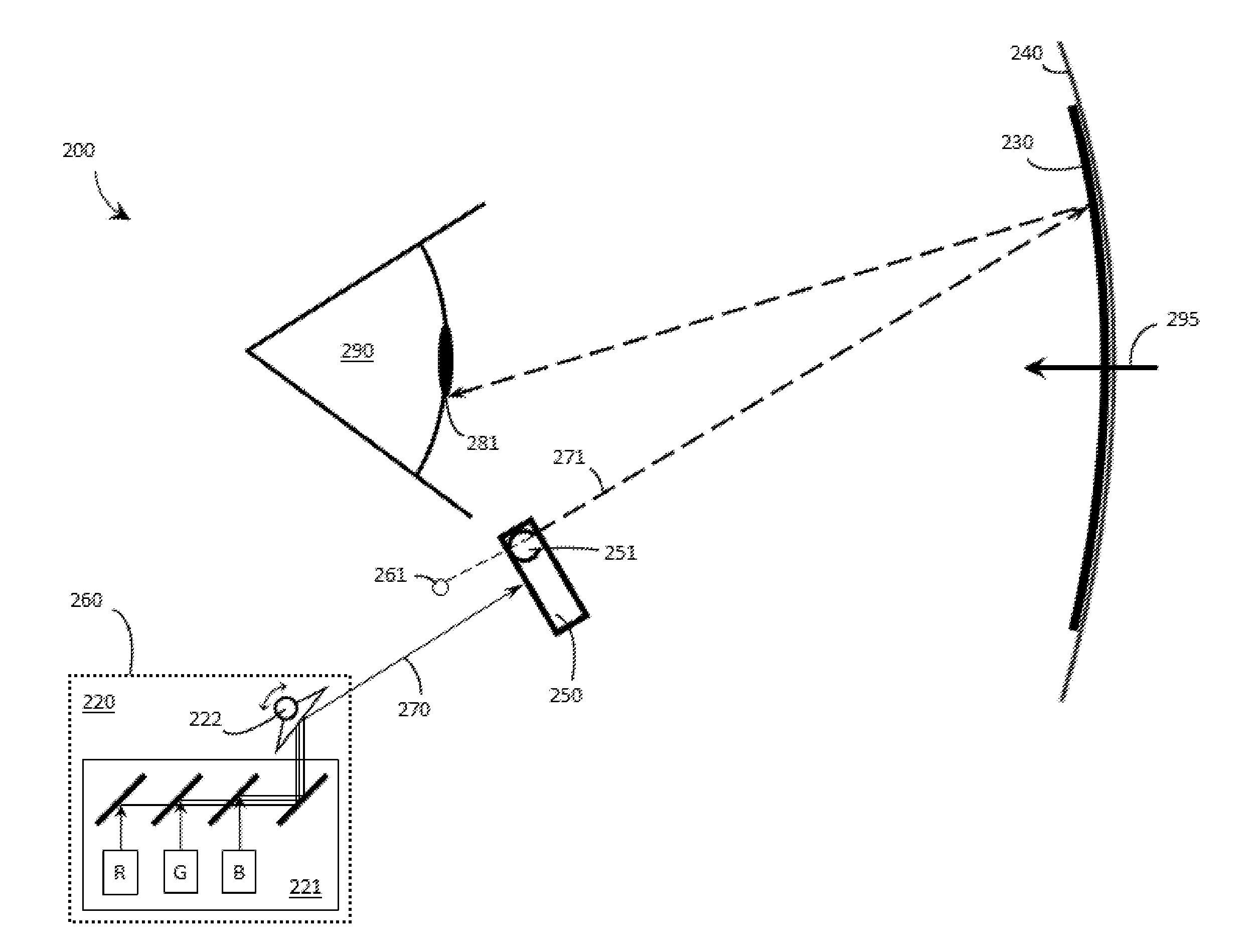
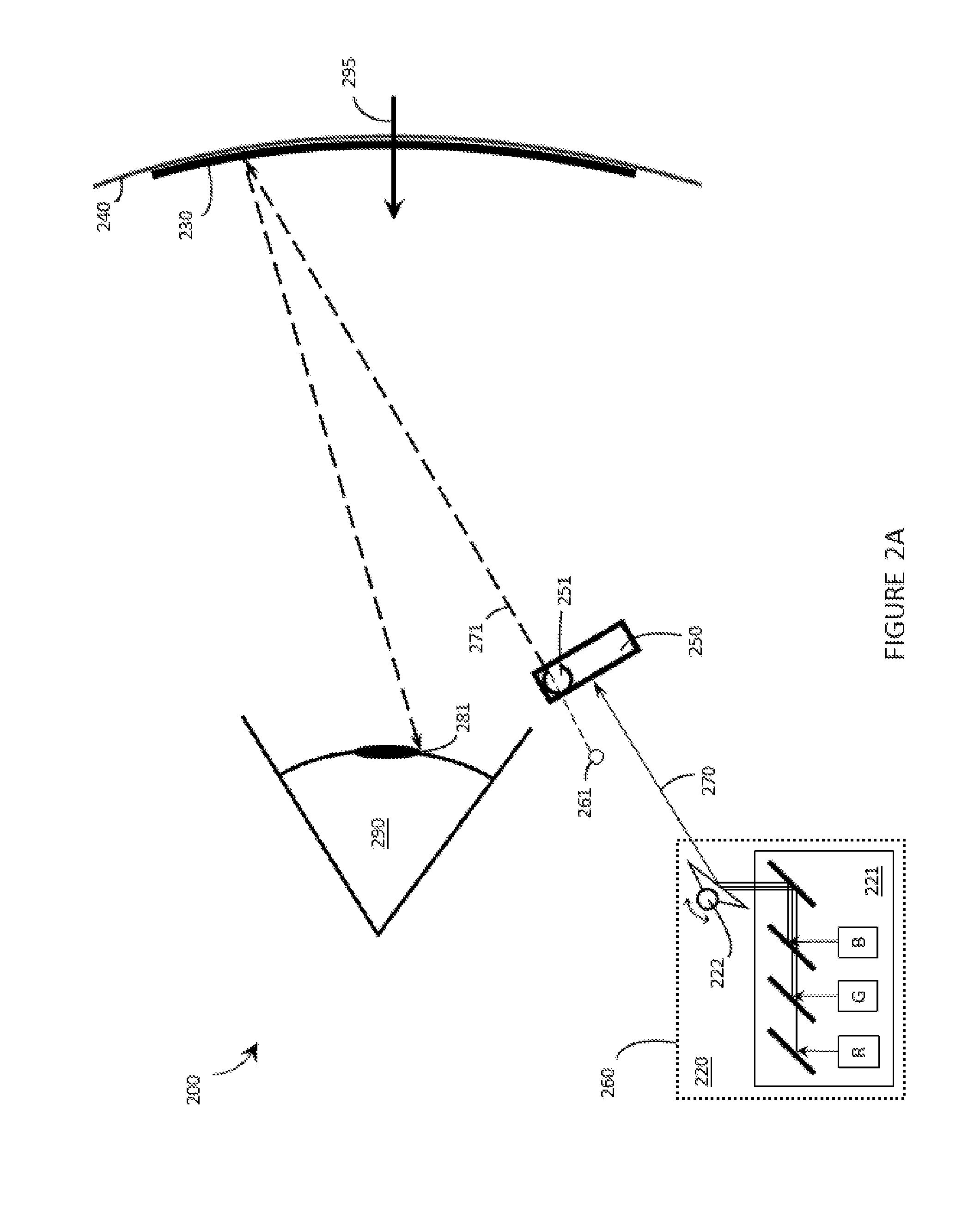
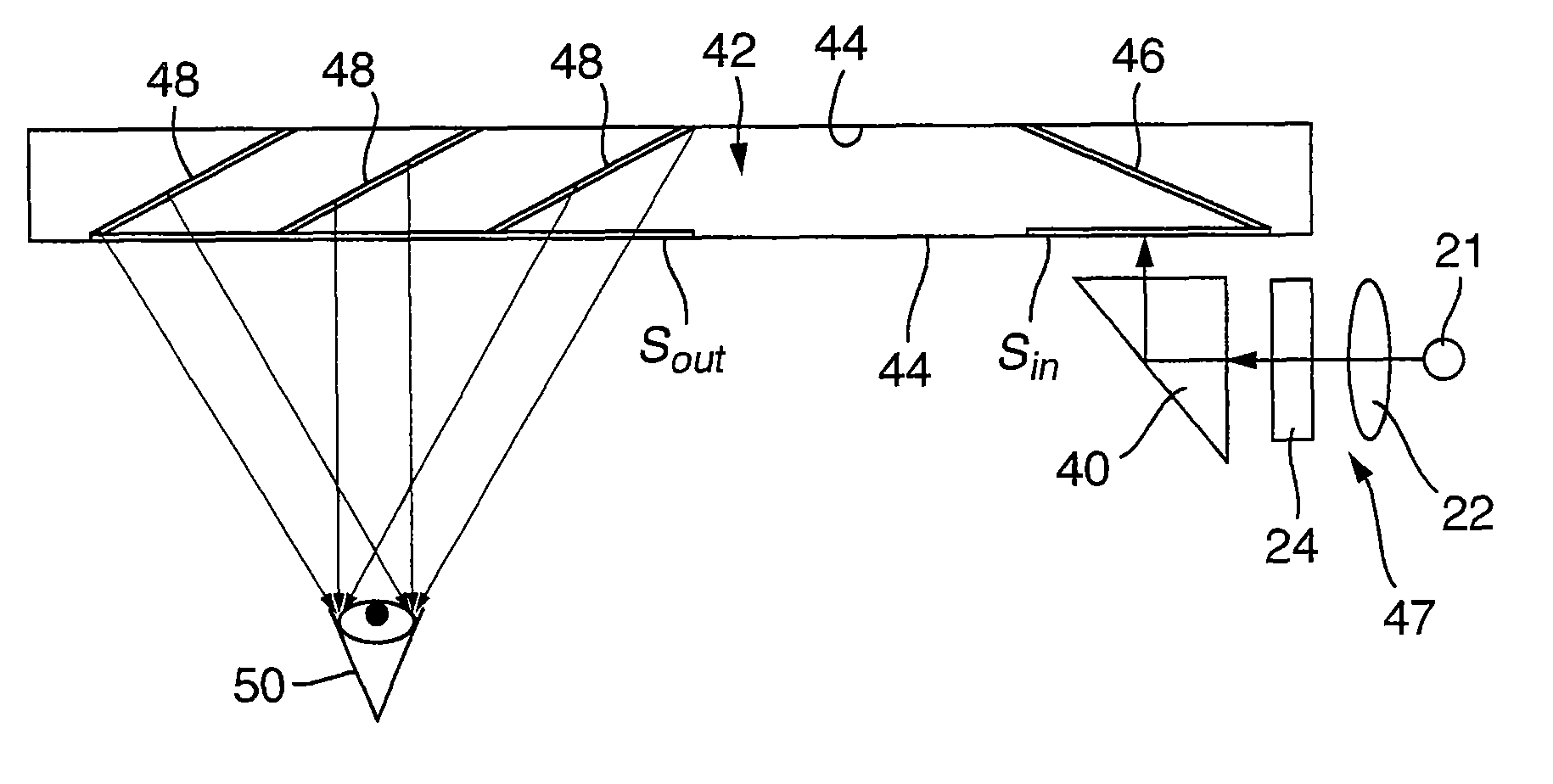
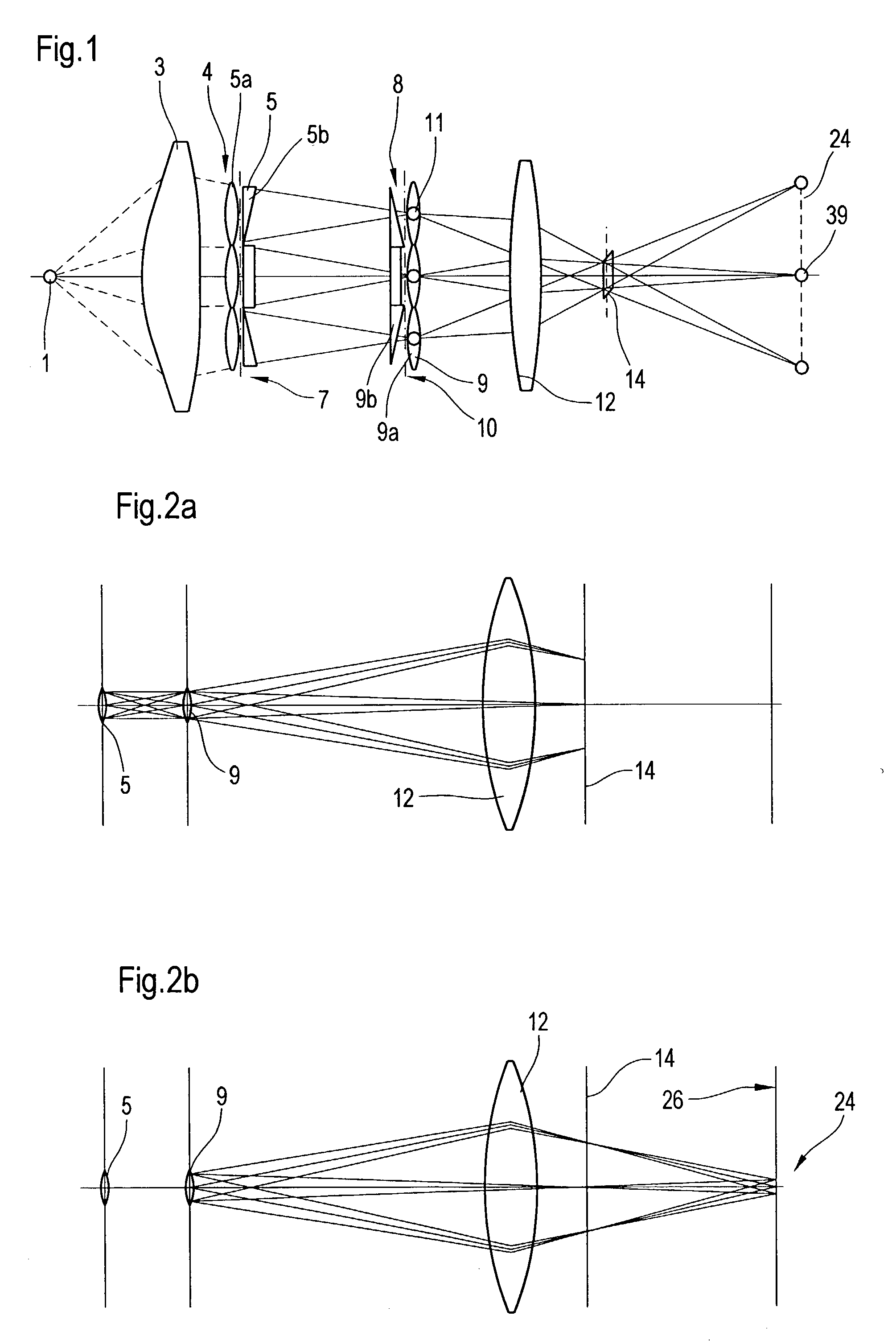
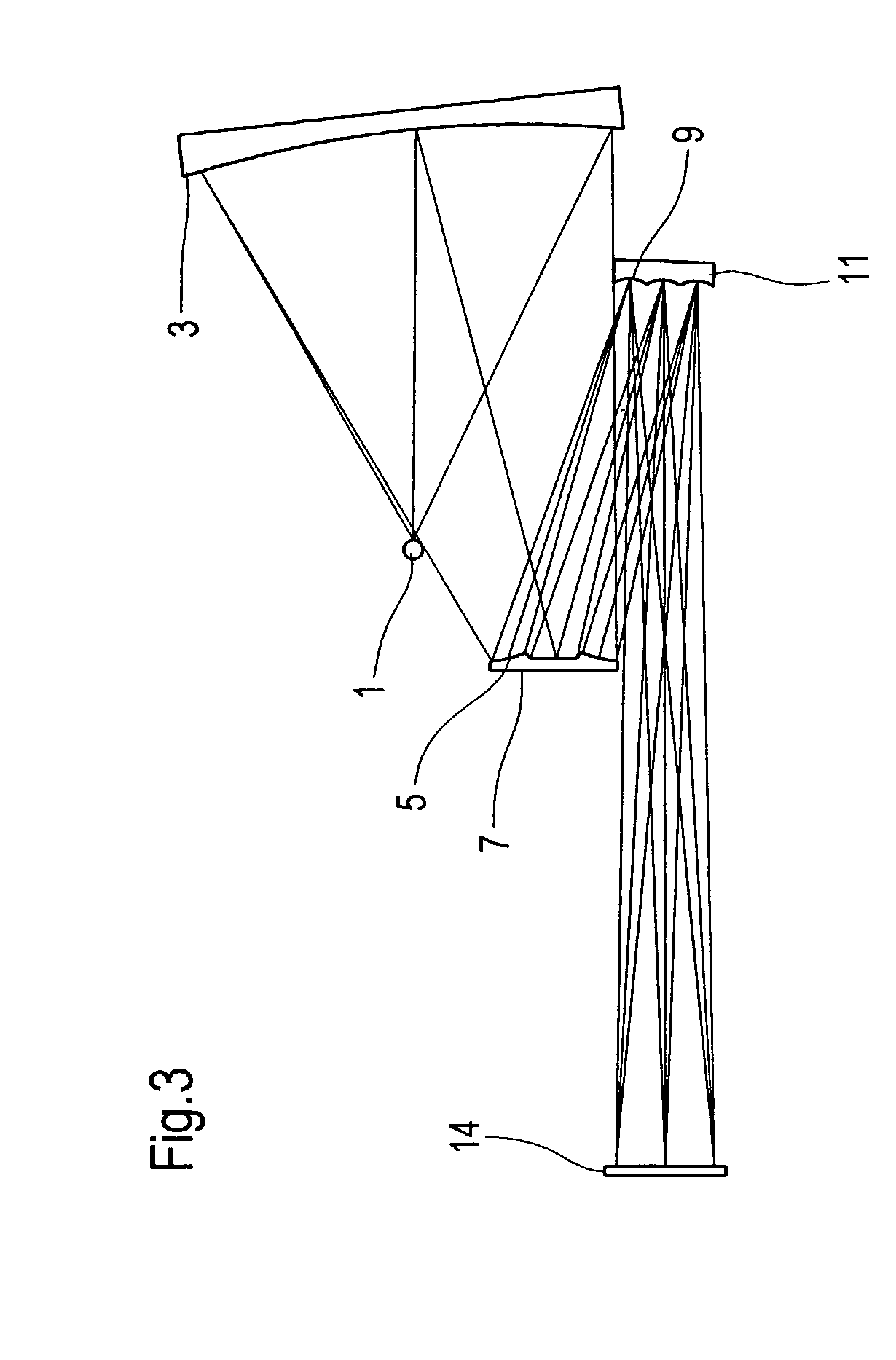
Optical element for an illumination system
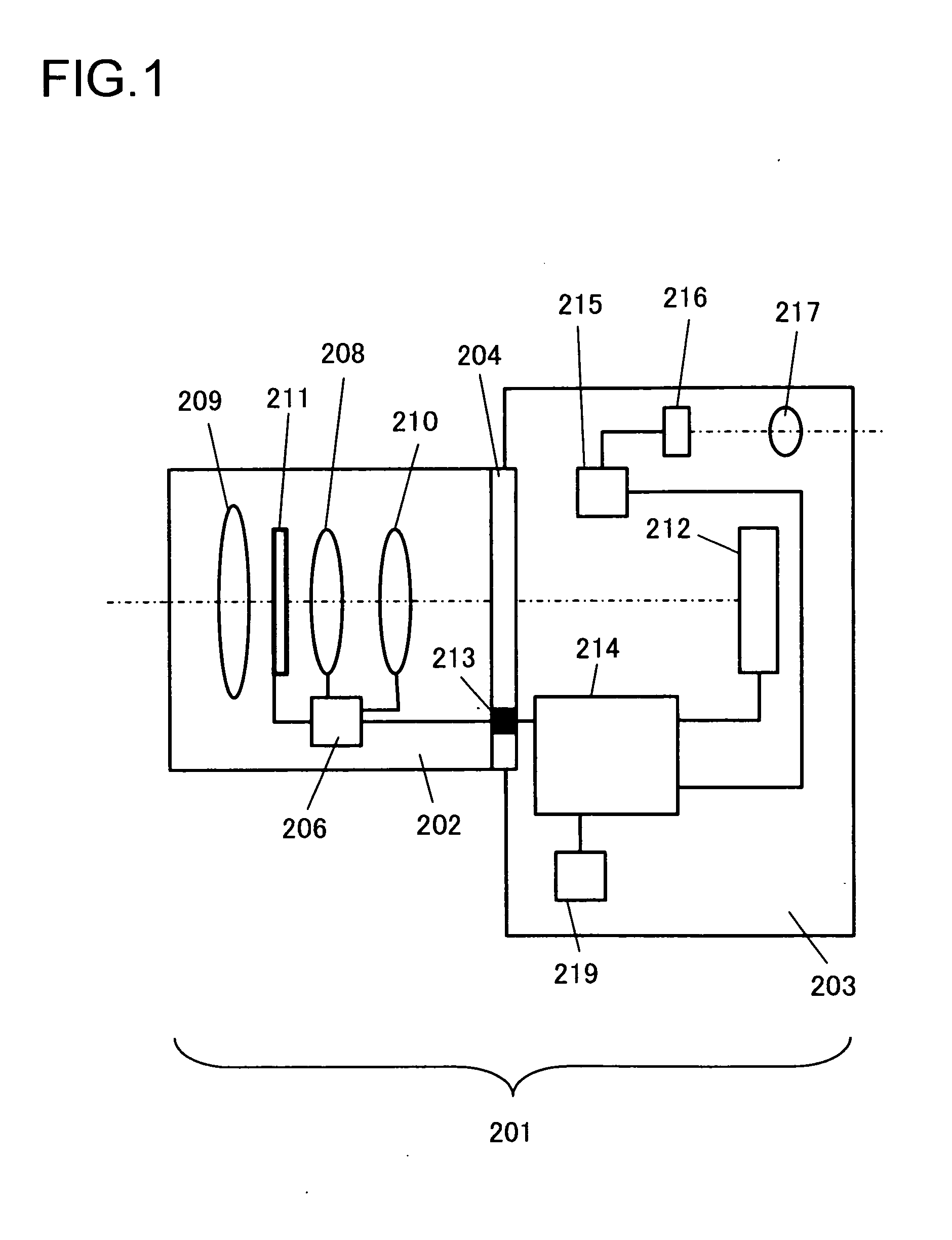
InactiveUS20060132747A1Reduce in quantityReduce light lossPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusExit pupilLength wave
There is provided an optical element for an illumination system for wavelengths of ≦193 nm. The illumination sytem includes a light source, a field plane, an exit pupil, and a plurality of facets. The plurality of facets receives light from the light source and guides the light to a plurality of discrete points in the field plane. The plurality of discrete points collectively illuminate a field in the field plane, and each of the plurality of facets illuminates a region of the exit pupil.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
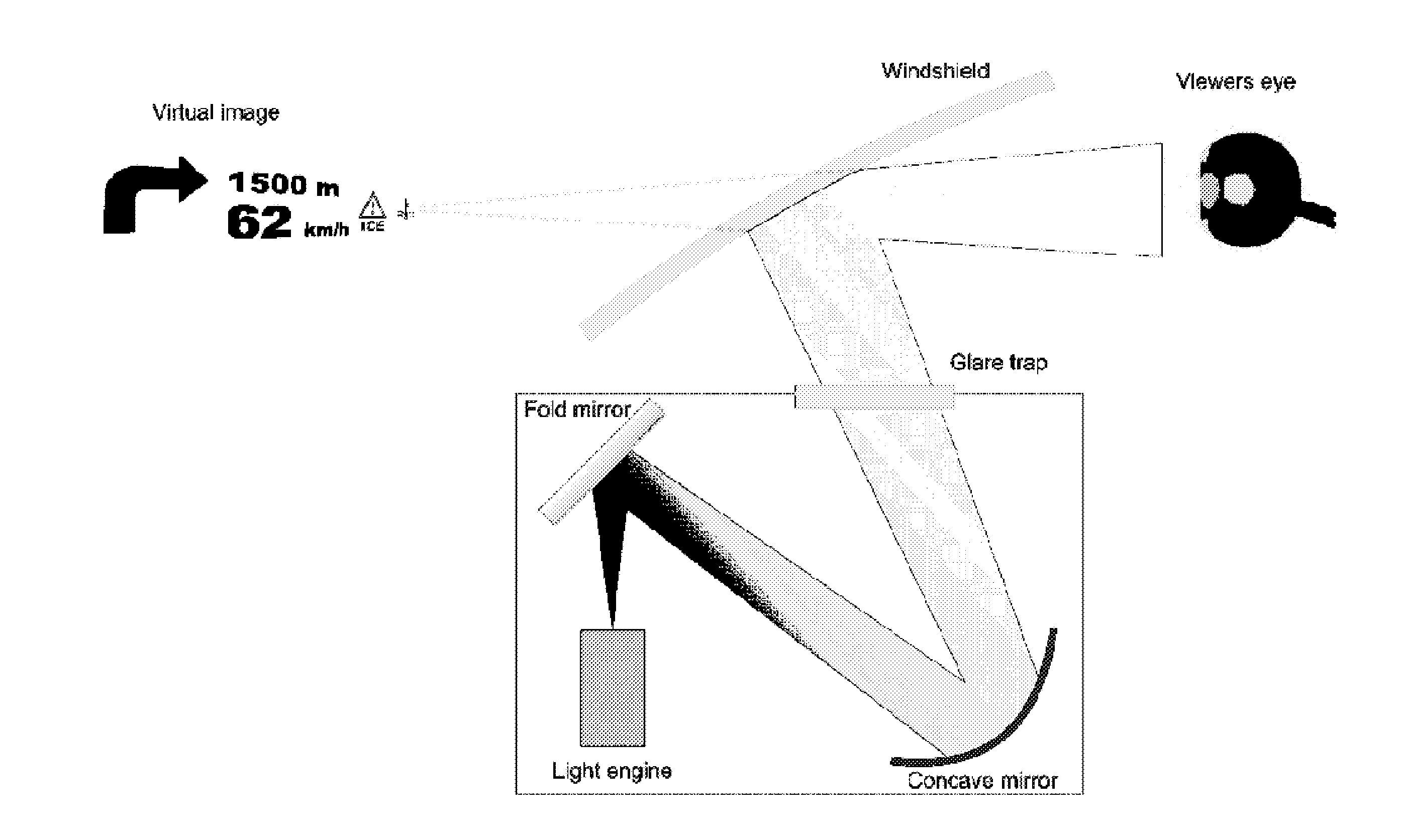
Head up displays
InactiveUS20120224062A1Increase in sizeSmall optical package sizeOptical filtersHolographic optical componentsHead-up displayHorizon
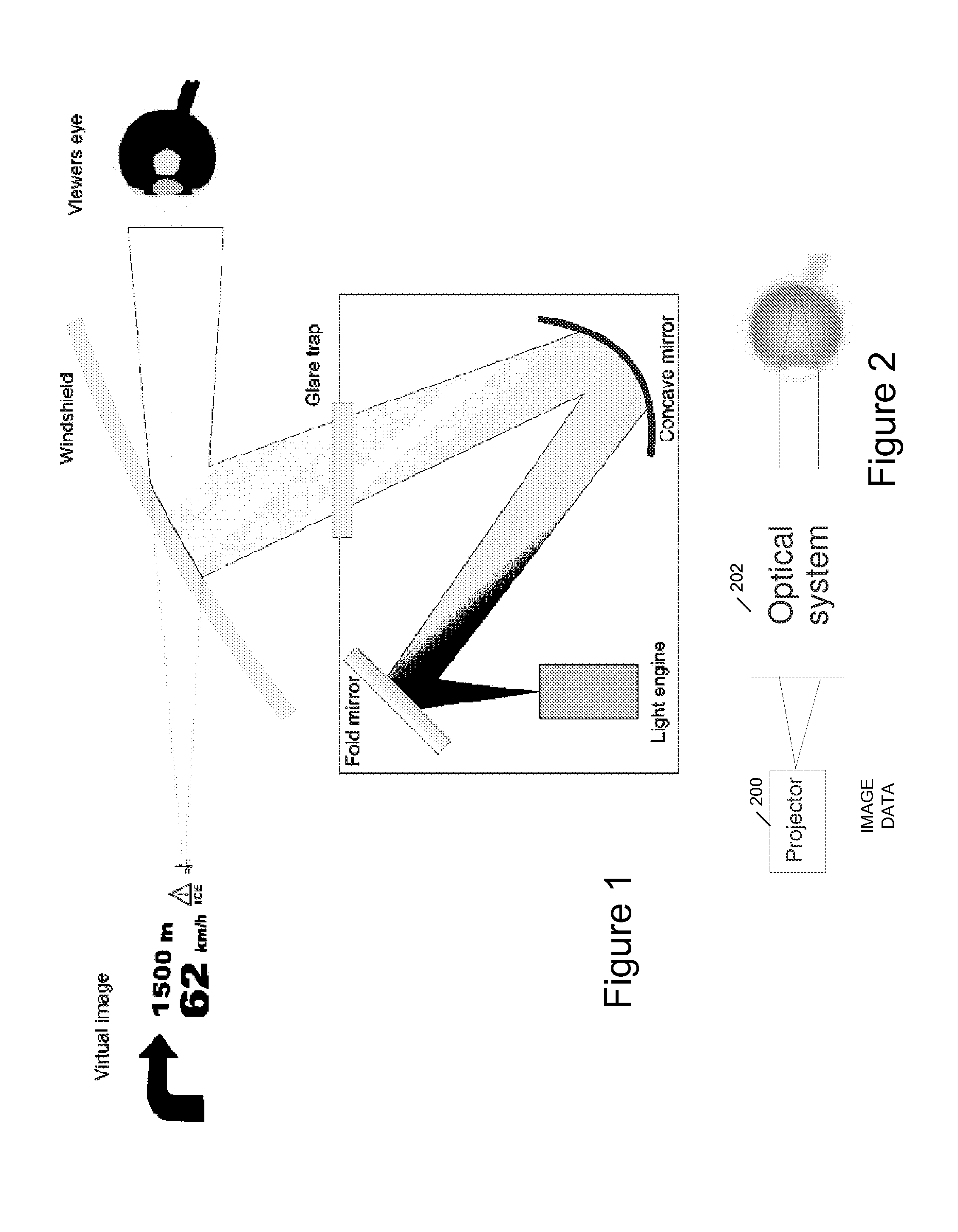
We describe a road vehicle contact-analogue head up display (HUD) comprising: a laser-based virtual image generation system to provide a 2D virtual image; exit pupil expander optics to enlarge an eye box of the HUD; a system for sensing a lateral road position relative to the road vehicle and a vehicle pitch or horizon position; a symbol image generation system to generate symbology for the HUD; and an imagery processor coupled to the symbol image generation system, to the sensor system and to said virtual image generation system, to receive and process symbology image data to convert this to data defining a 2D image for display dependent on the sensed road position such that when viewed the virtual image appears to be at a substantially fixed position relative to said road; and wherein the virtual image is at a distance of at least 5 m from said viewer.
Owner:LIGHT BLUE OPTICS
Method and apparatus for head worn display with multiple exit pupils
ActiveUS20160033771A1Reduce device power consumptionReduce power consumptionMirrorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsExit pupilLight beam
A method for displaying an image viewable by an eye, the image being projected from a portable head worn display, comprises steps of: emitting a plurality of light beams of wavelengths that differ amongst the light beams; directing the plurality of light beams to a scanning mirror; modulating in intensity each one of the plurality of light beams in accordance with intensity information provided from the image, whereby the intensity is representative of a pixel value within the image; scanning the plurality of light beams in two distinct axes with the scanning mirror to form the image; and redirecting the plurality of light beams to the eye using a holographic optical element acting as a reflector of the light beams, whereby the redirecting is dependent on the wavelength of the light beam, to create for each light beam an exit pupil at the eye that is spatially separated from the exit pupils of the other light beams.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Illumination system with variable adjustment of the illumination
InactiveUS6658084B2Avoid lostSimple wayNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionGratingExit pupil
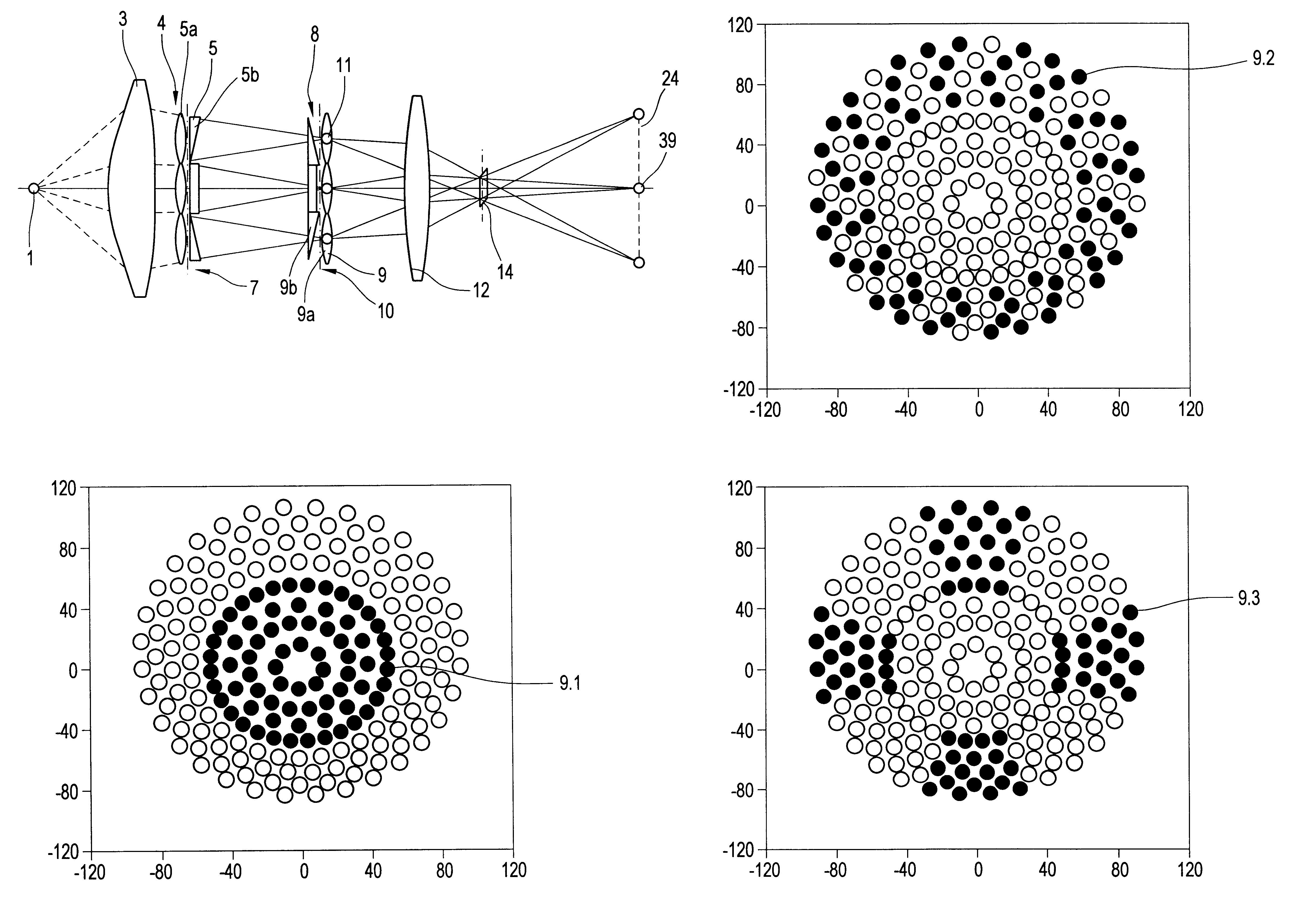
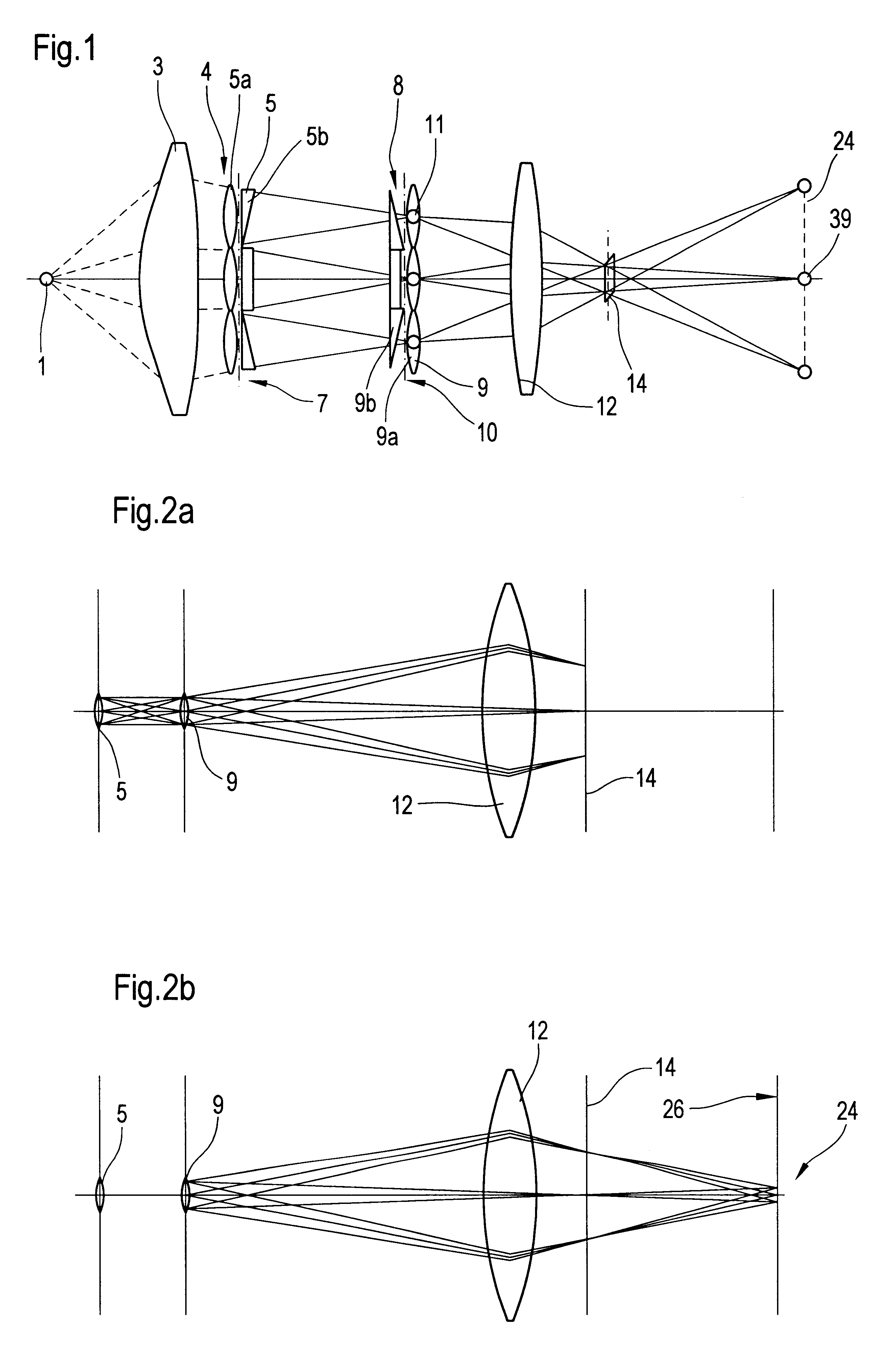
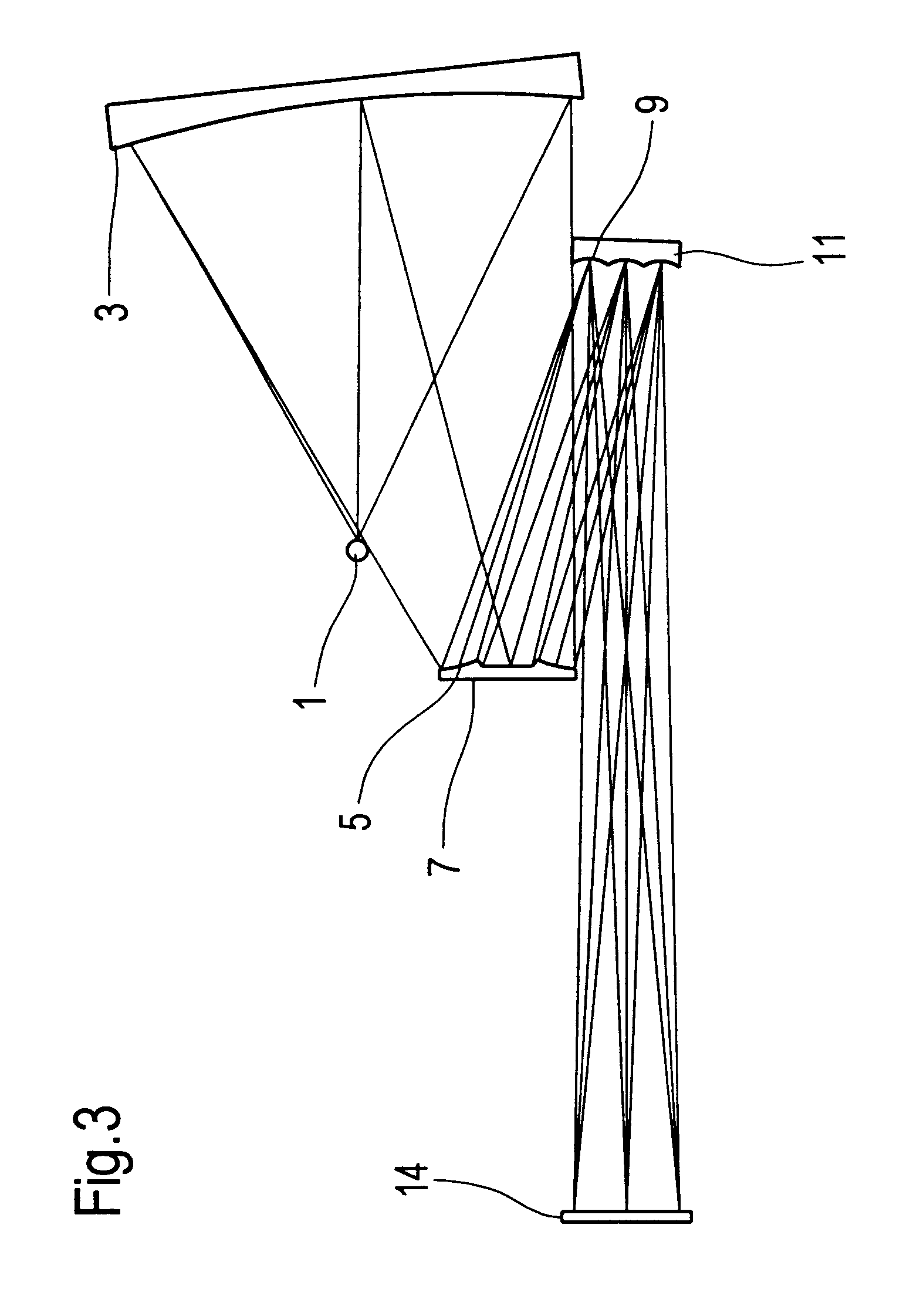
An illumination system comprises (a) a first optical element upon which a light beam impinges, where the first optical element has first raster elements that partition said light beam into light channels; (b) a second optical element that receives said light channels, where the second optical element has a second raster elements; (c) an object plane that receives said light channels via said second optical element; and (d) an exit pupil that is provided with an illumination via said object plane. The system is characterized by an assignment of a member of said first raster elements and a member of said second raster elements to each of said light channels to provide a continuous beam path from said first optical element to said object plane for each of said plurality of light channels. The assignment is changeable to provide an adjustment of said illumination in said exit pupil.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Illumination system particularly for EUV lithography
InactiveUS6198793B1Etendu can be effectively increasedAvoid blurringsNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionCamera lensGrating
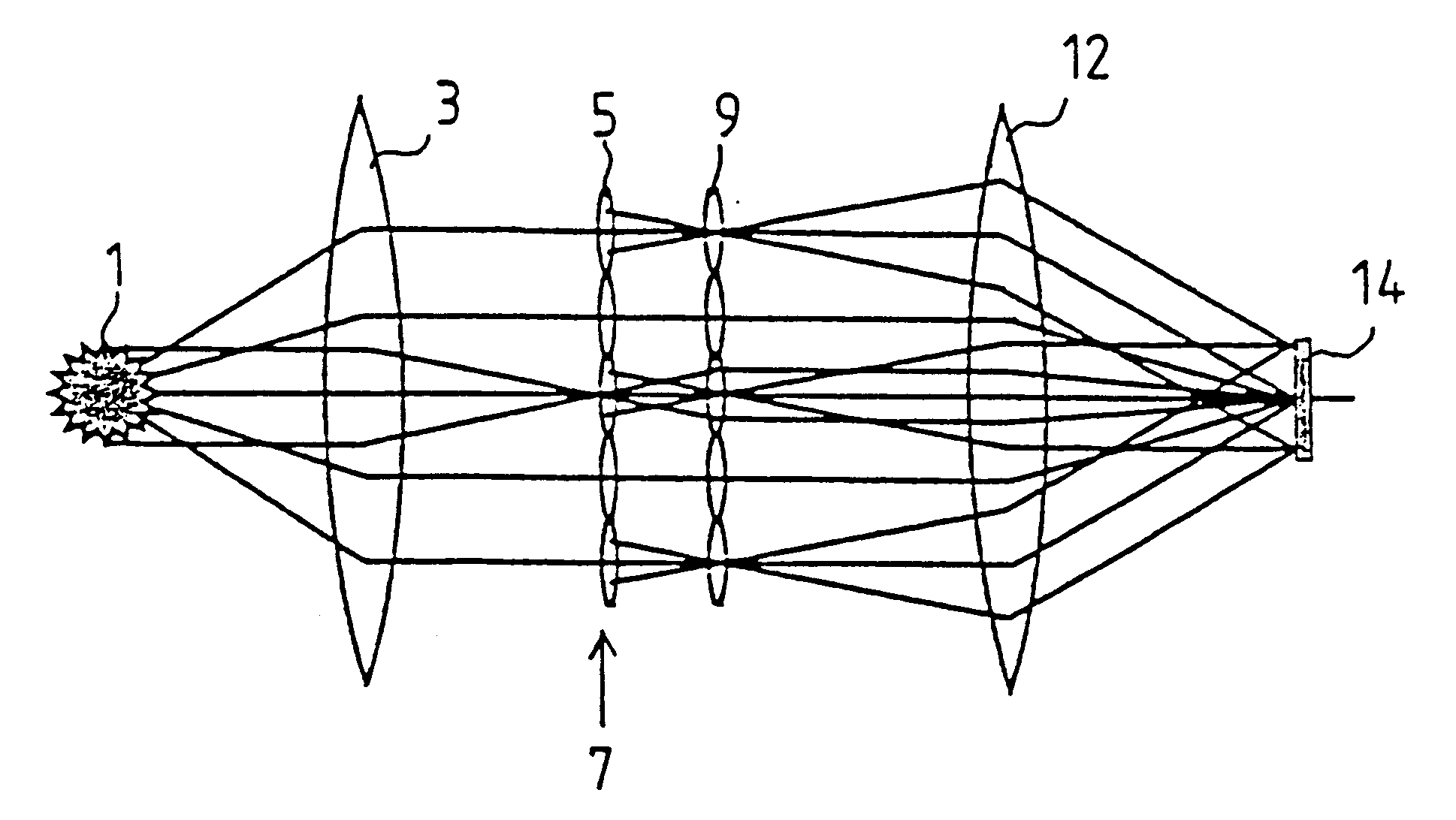
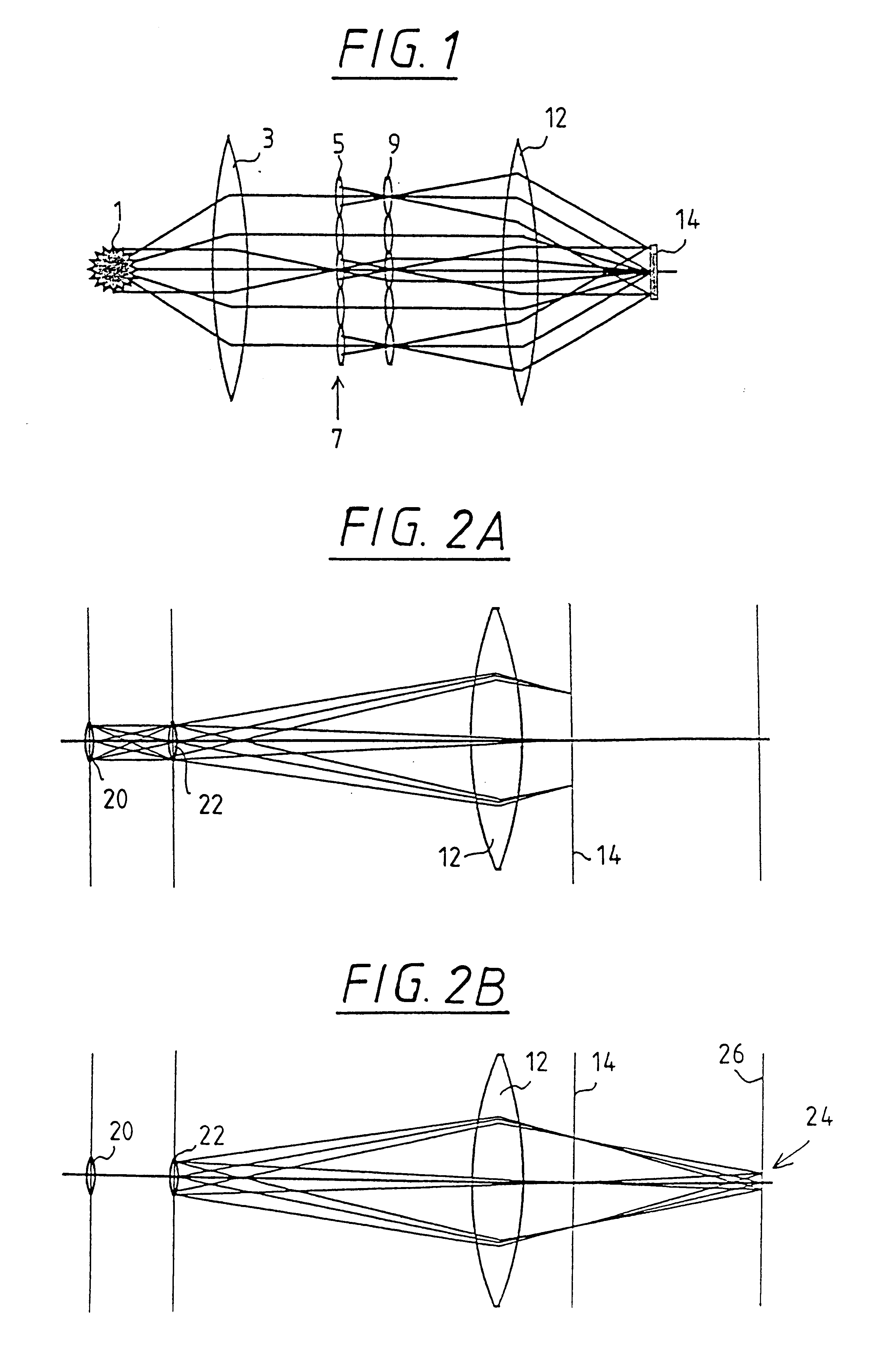
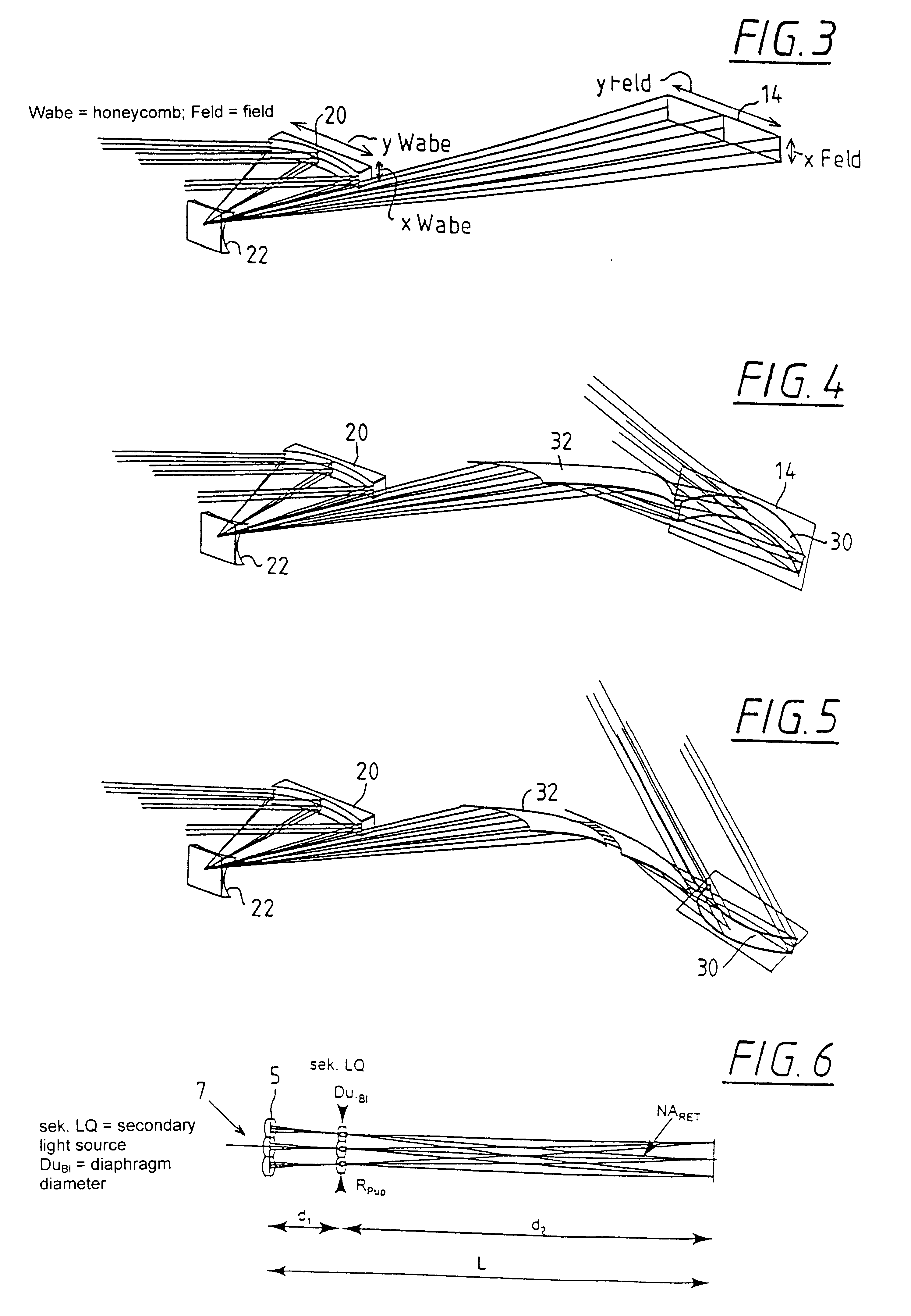
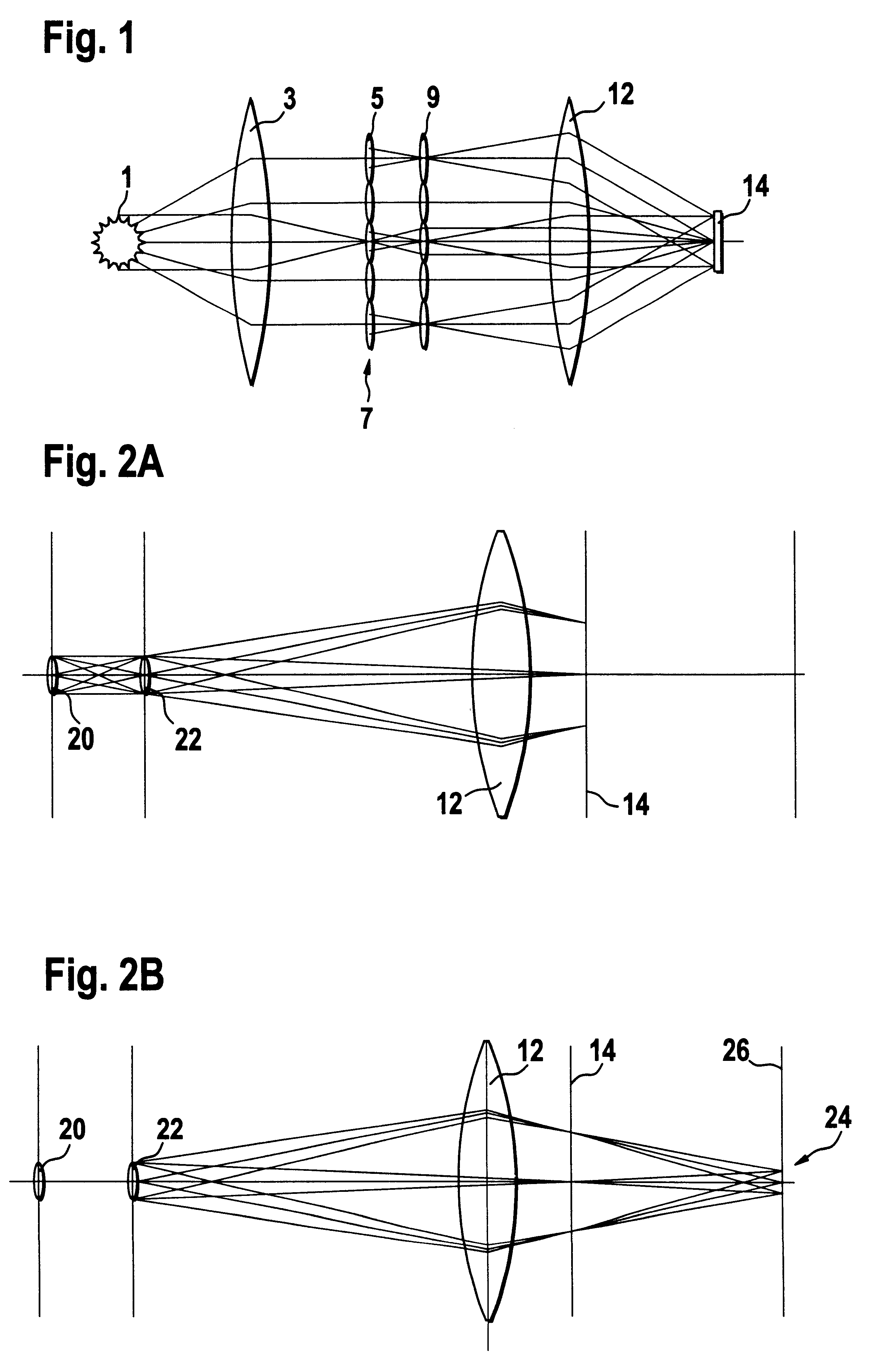
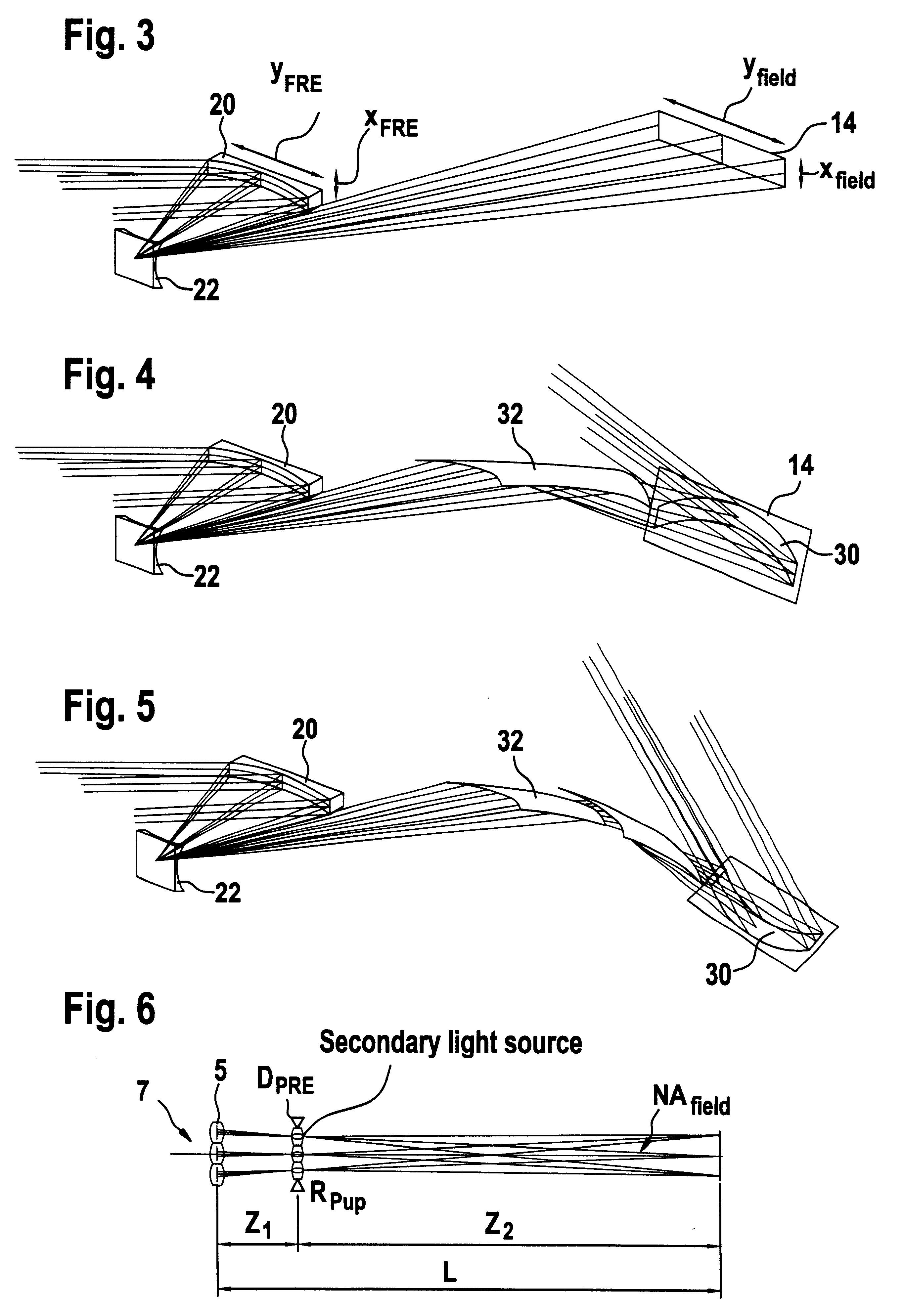
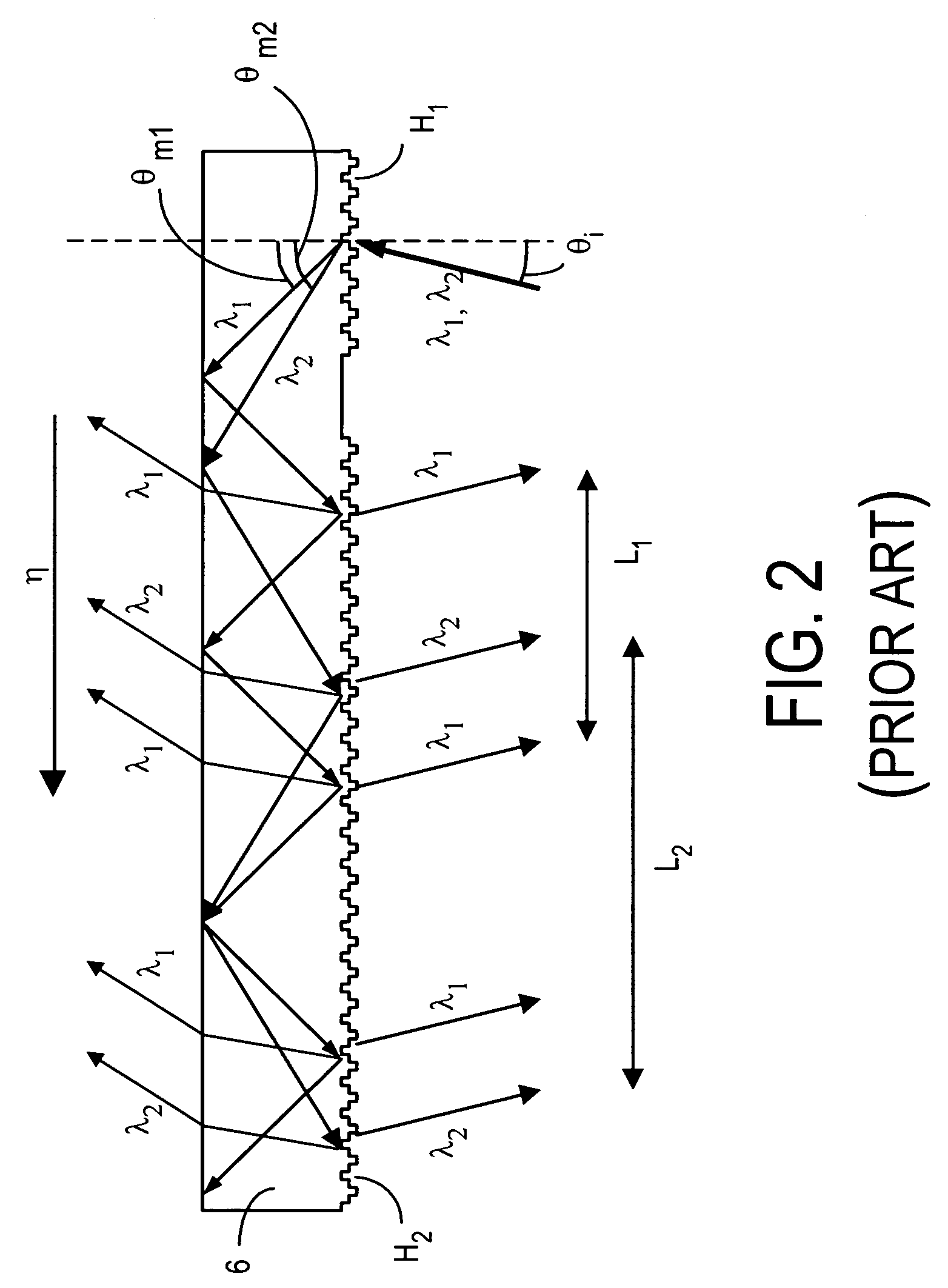
The invention concerns an illumination system for wavelengths <=193 nm, particularly for EUV lithography, with at least one light source, which has an illumination A in a predetermined surface; at least one device for producing secondary light sources; at least one mirror or lens device comprising at least one mirror or one lens, which is or are organized into raster elements; one or more optical elements, which are arranged between the mirror or lens device comprising at least one mirror or one lens, which is or are organized into raster elements and the reticle plane, whereby the optical elements image the secondary light sources in the exit pupil of the illumination system.The illumination system is characterized by the fact that the raster elements of the one or more mirror or lenses are shaped and arranged in such a way that the images of the raster elements cover by means of the optical elements the major portion of the reticle plane and that the exit pupil defined by aperture and filling degree is illuminated.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Illumination system particularly for microlithography
InactiveUS6438199B1Reduced beam diameterReduce the overall diameterNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionExit pupilGrating
The invention concerns an illumination system, particularly for microlithography with wavelengths <=193 nm, comprising a light source, a first optical component, a second optical component, an image plane and an exit pupil. The first optical component transforms the light source into a plurality of secondary light sources being imaged by the second optical component in said exit pupil. The first optical component comprises a first optical element having a plurality of first raster elements, which are imaged into said image plane producing a plurality of images being superimposed at least partially on a field in said image plane. The first raster elements deflect incoming ray bundles with first deflection angles, wherein at least two of the first deflection angles are different. The first raster elements are preferably rectangular, wherein the field is a segment of an annulus. To transform the rectangular images of the first raster elements into the segment of the annulus, the second optical component comprises a first field mirror for shaping the field to the segment of the annulus.
Owner:CARL-ZEISS-STIFTUNG TRADING AS CARL ZEISS
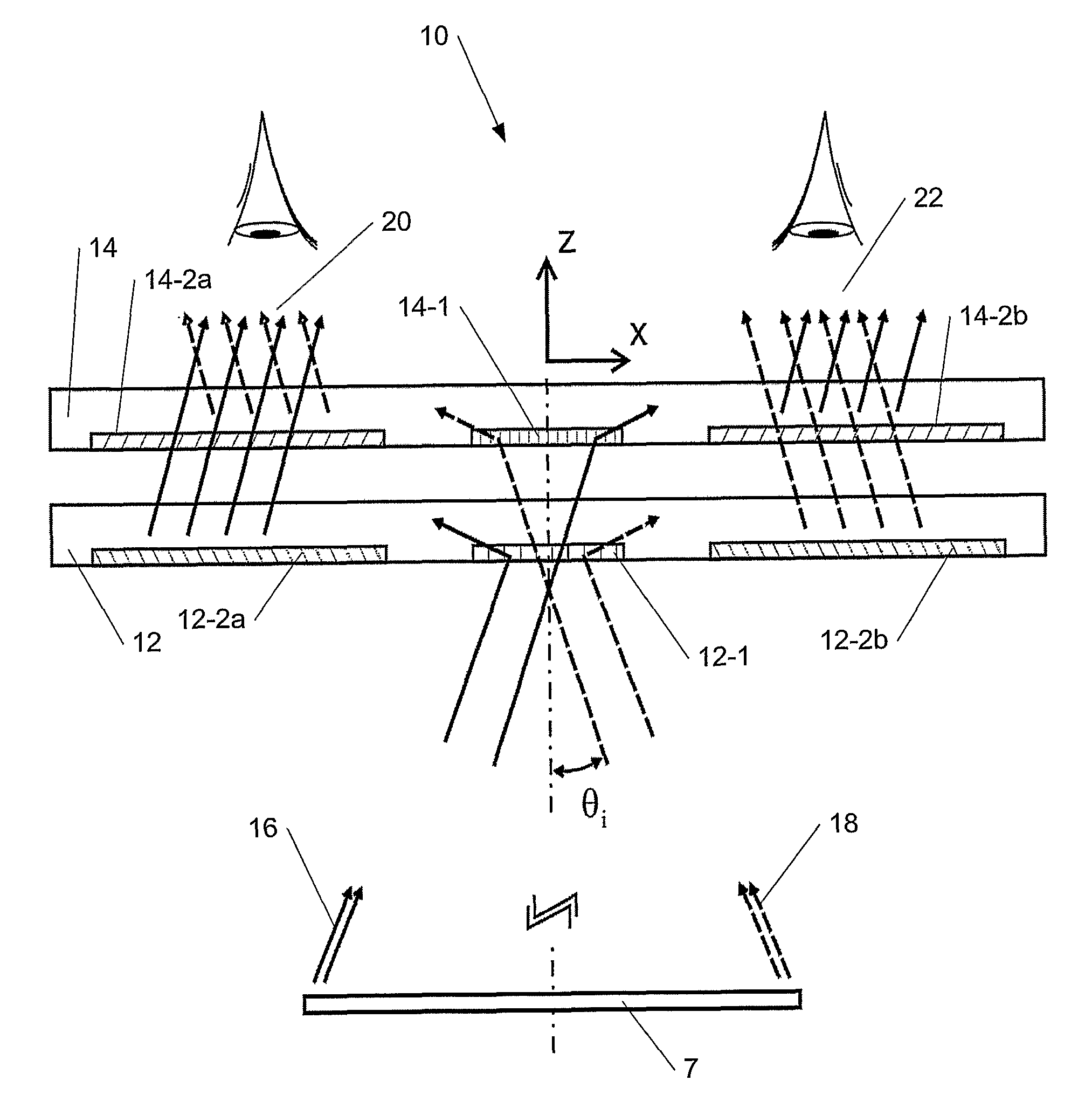
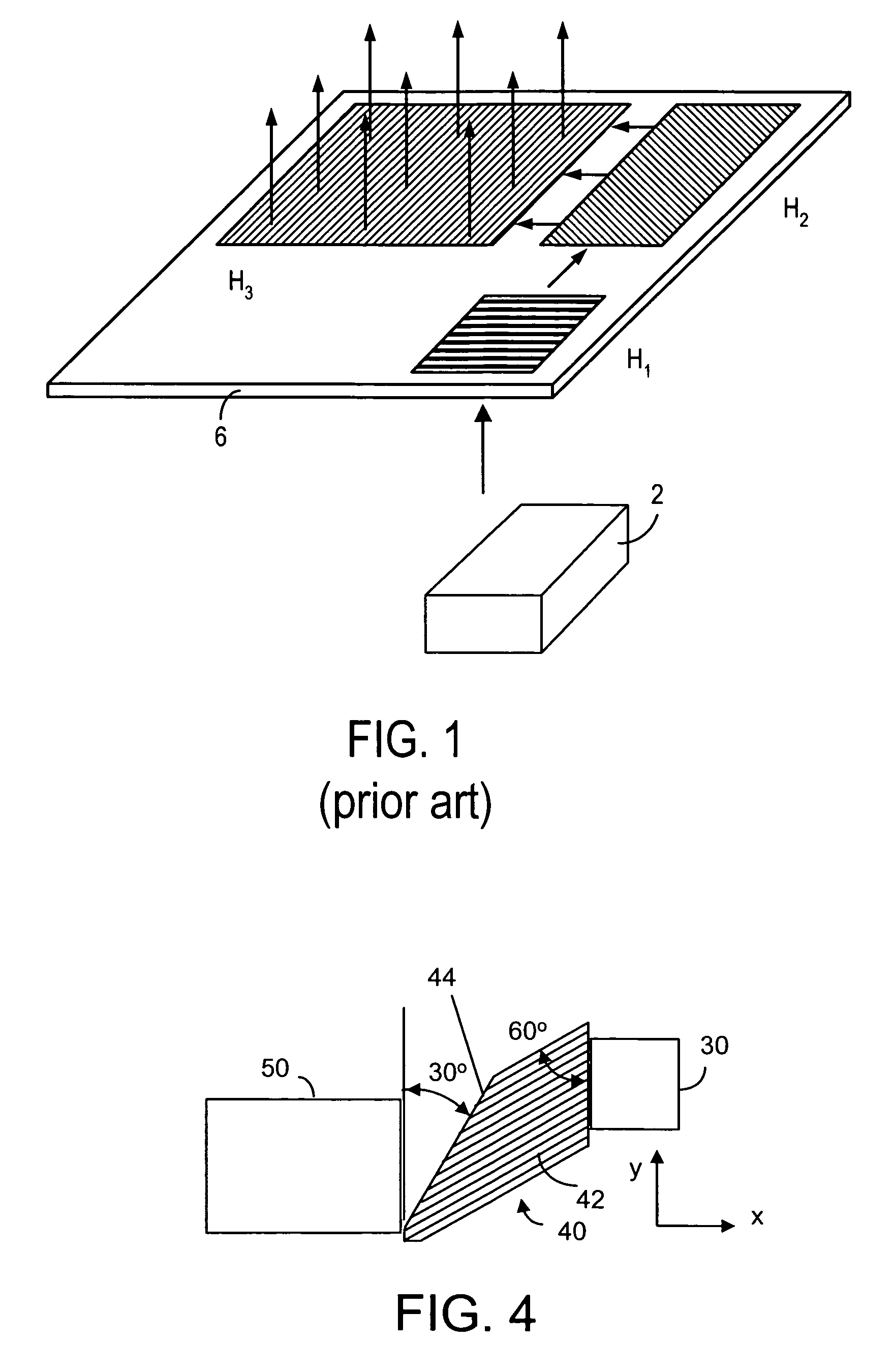
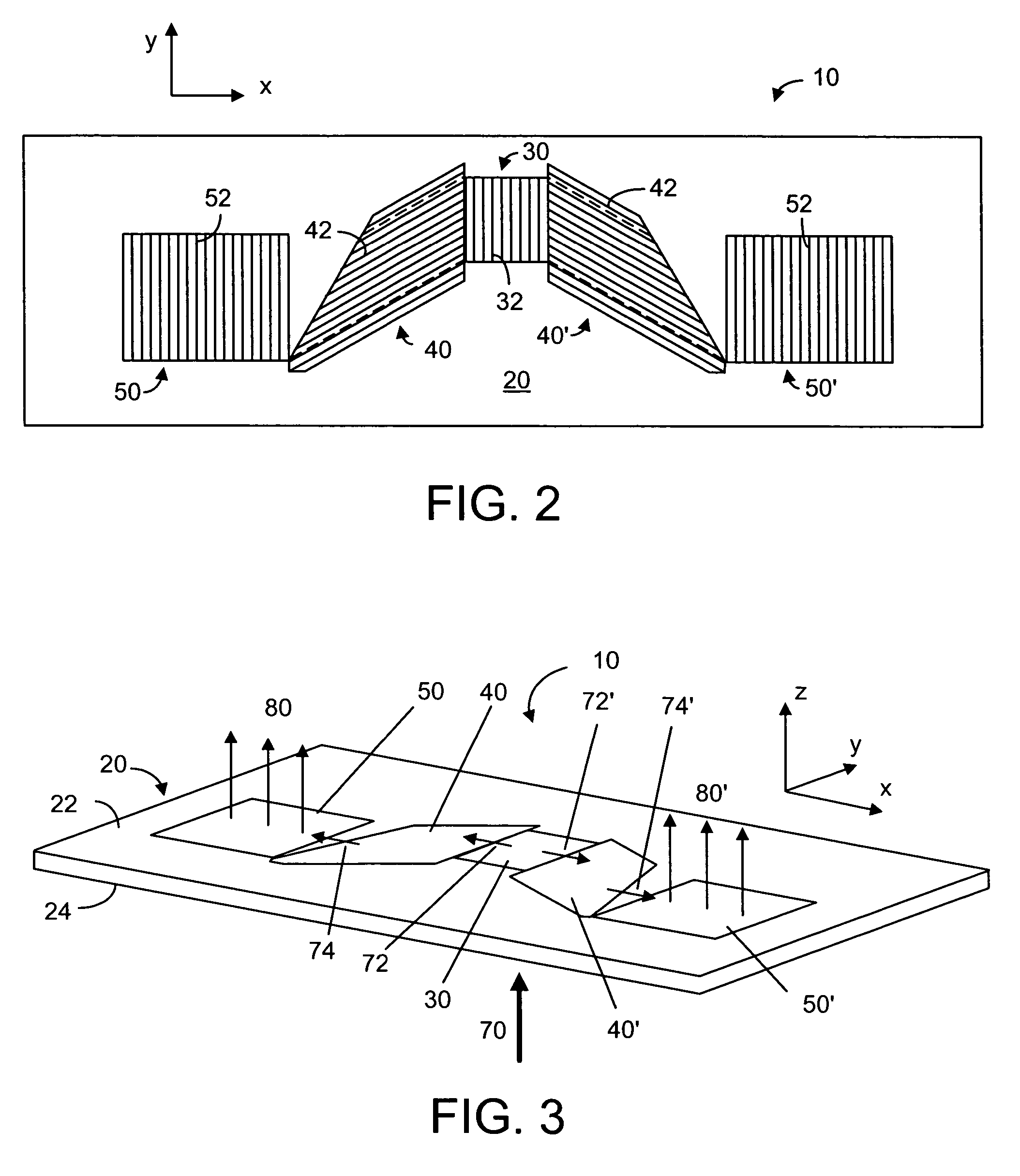
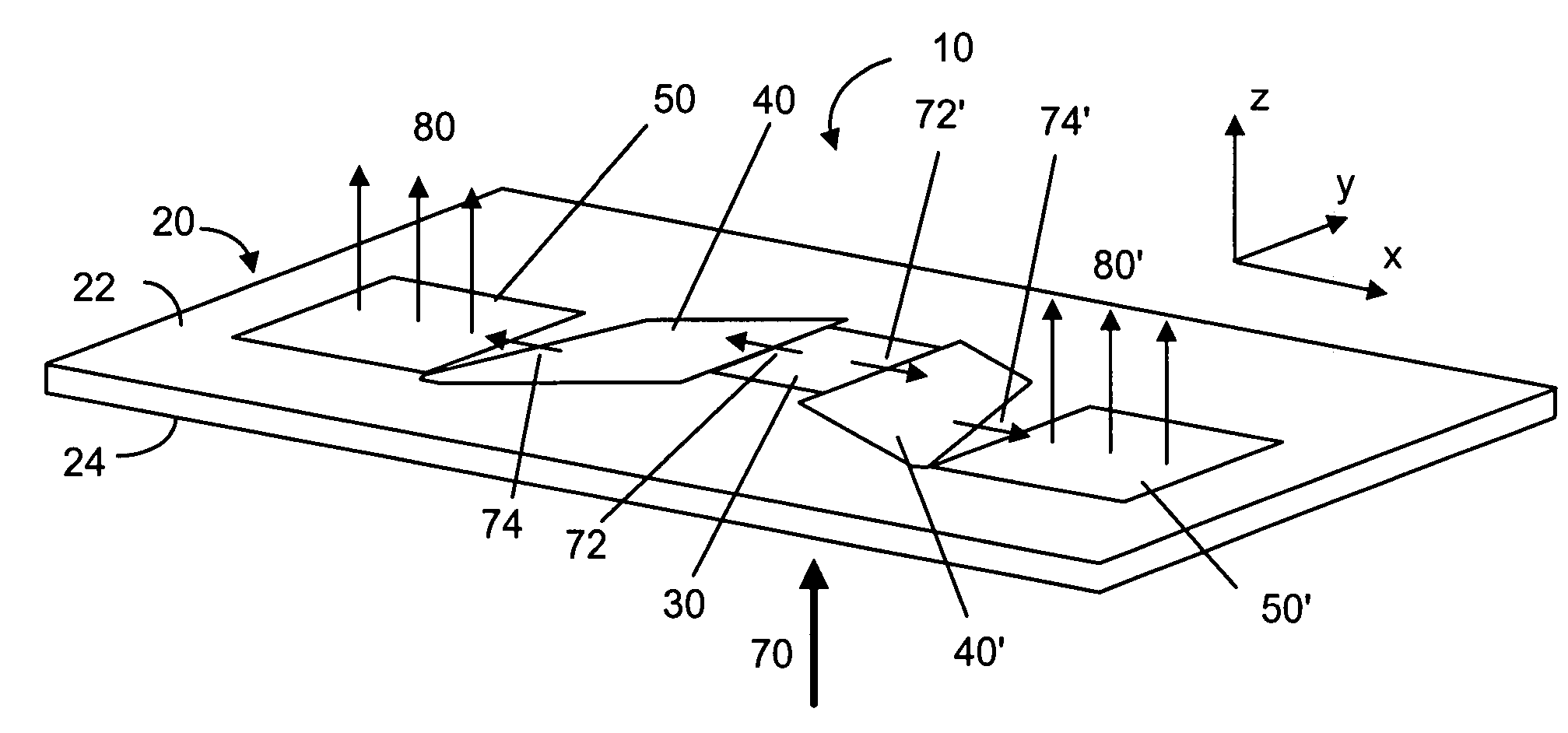
Device for expanding an exit pupil in two dimensions
ActiveUS8160411B2Improve image qualityEfficient couplingDiffraction gratingsCoupling light guidesBeam expanderGrating
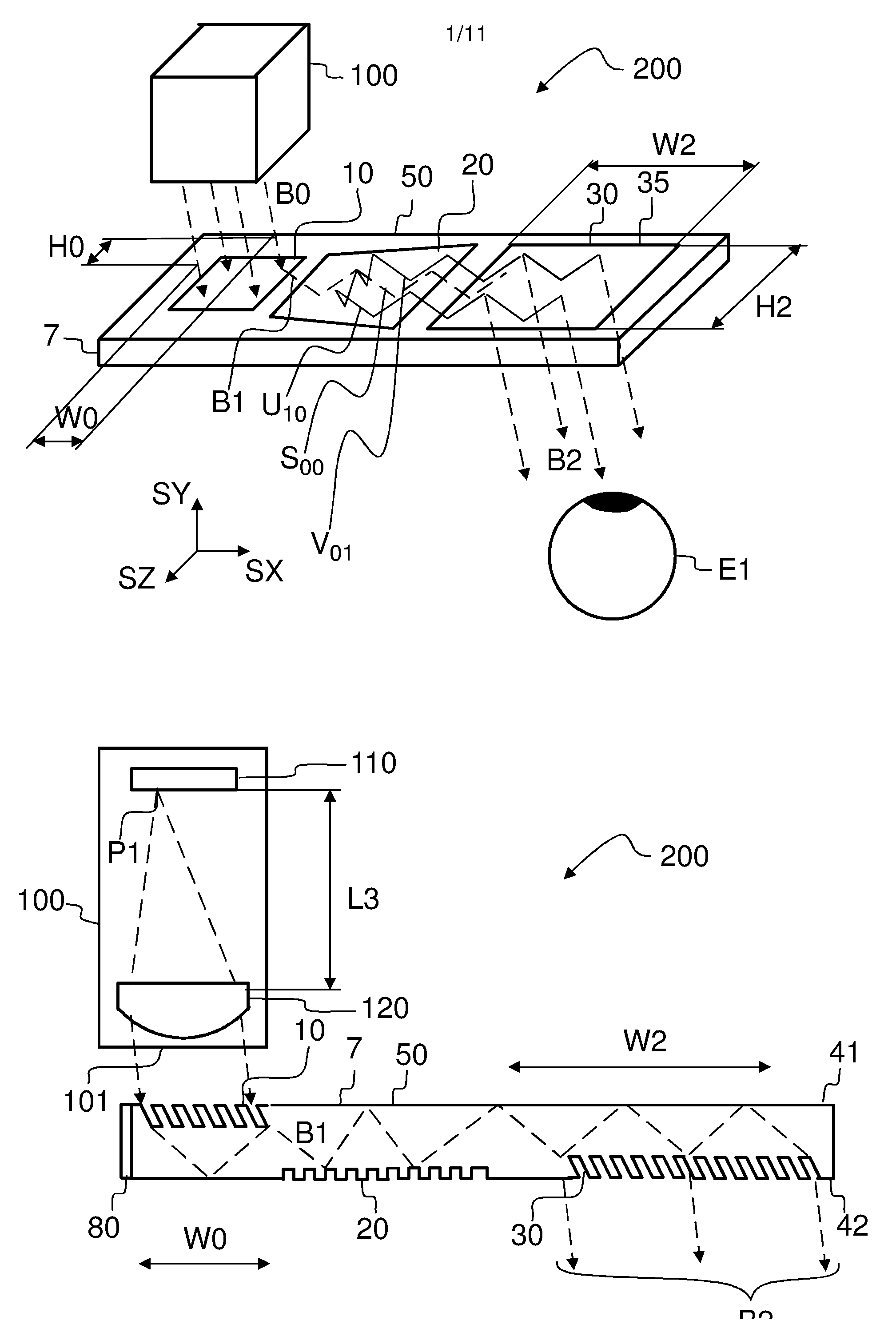
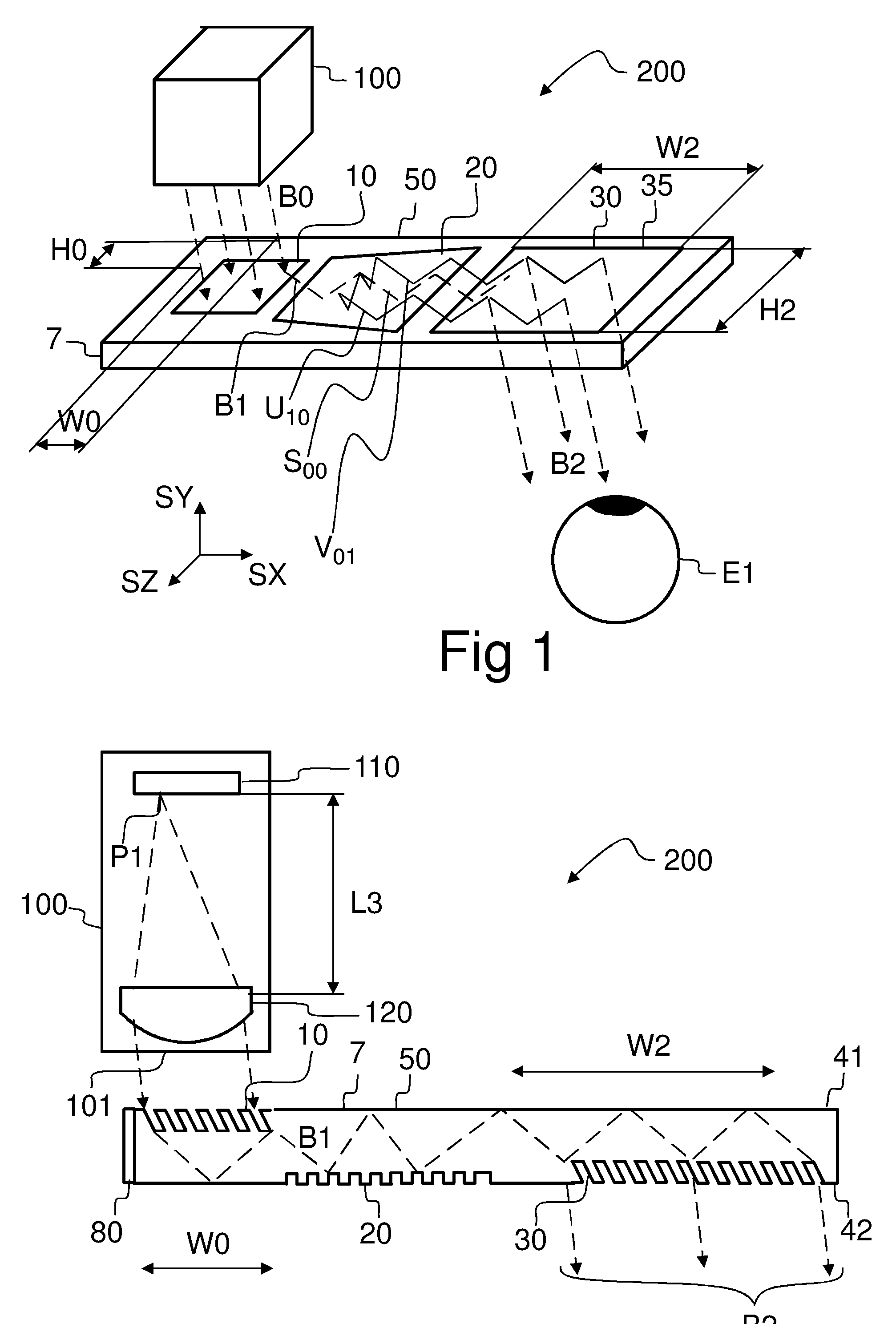
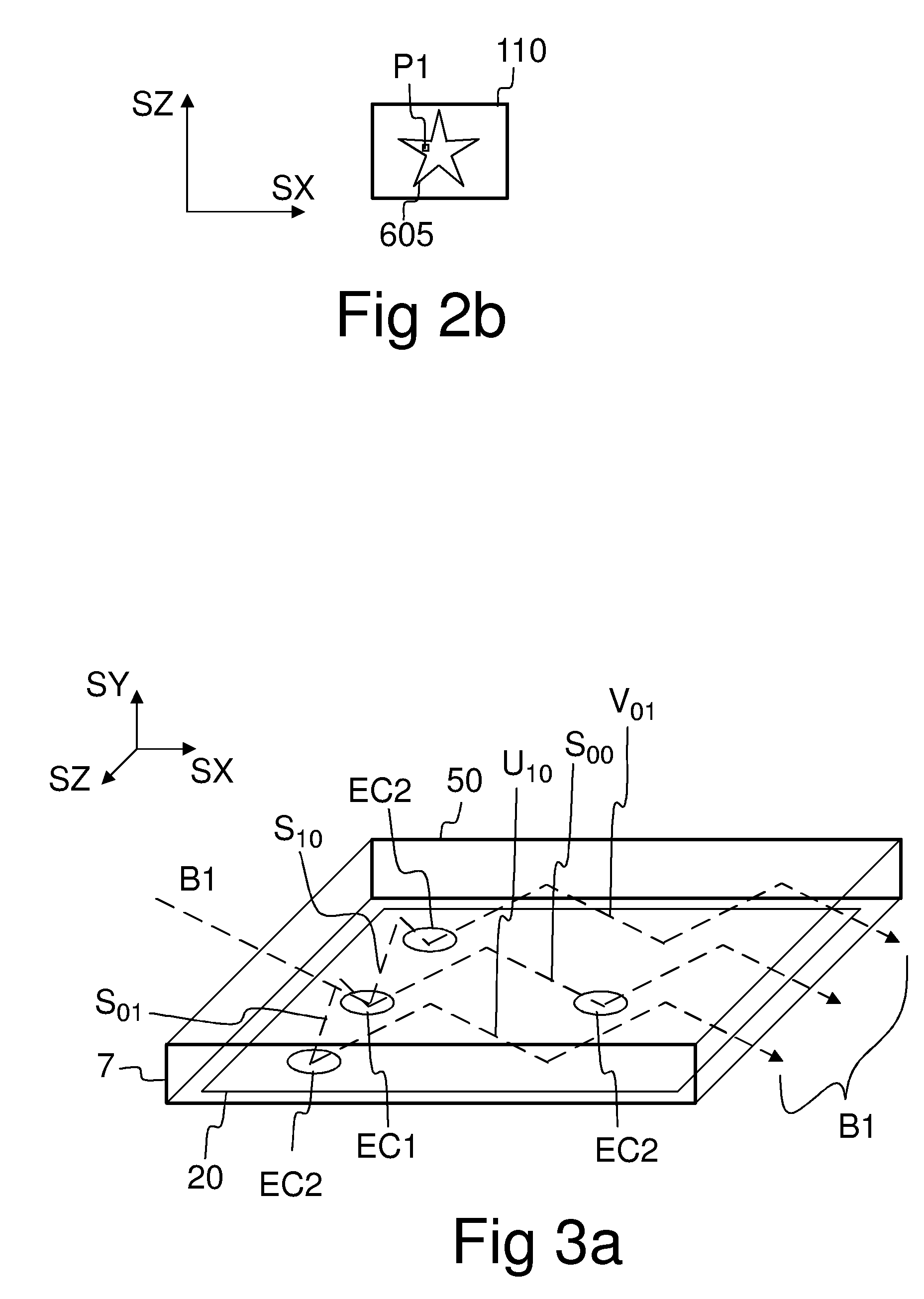
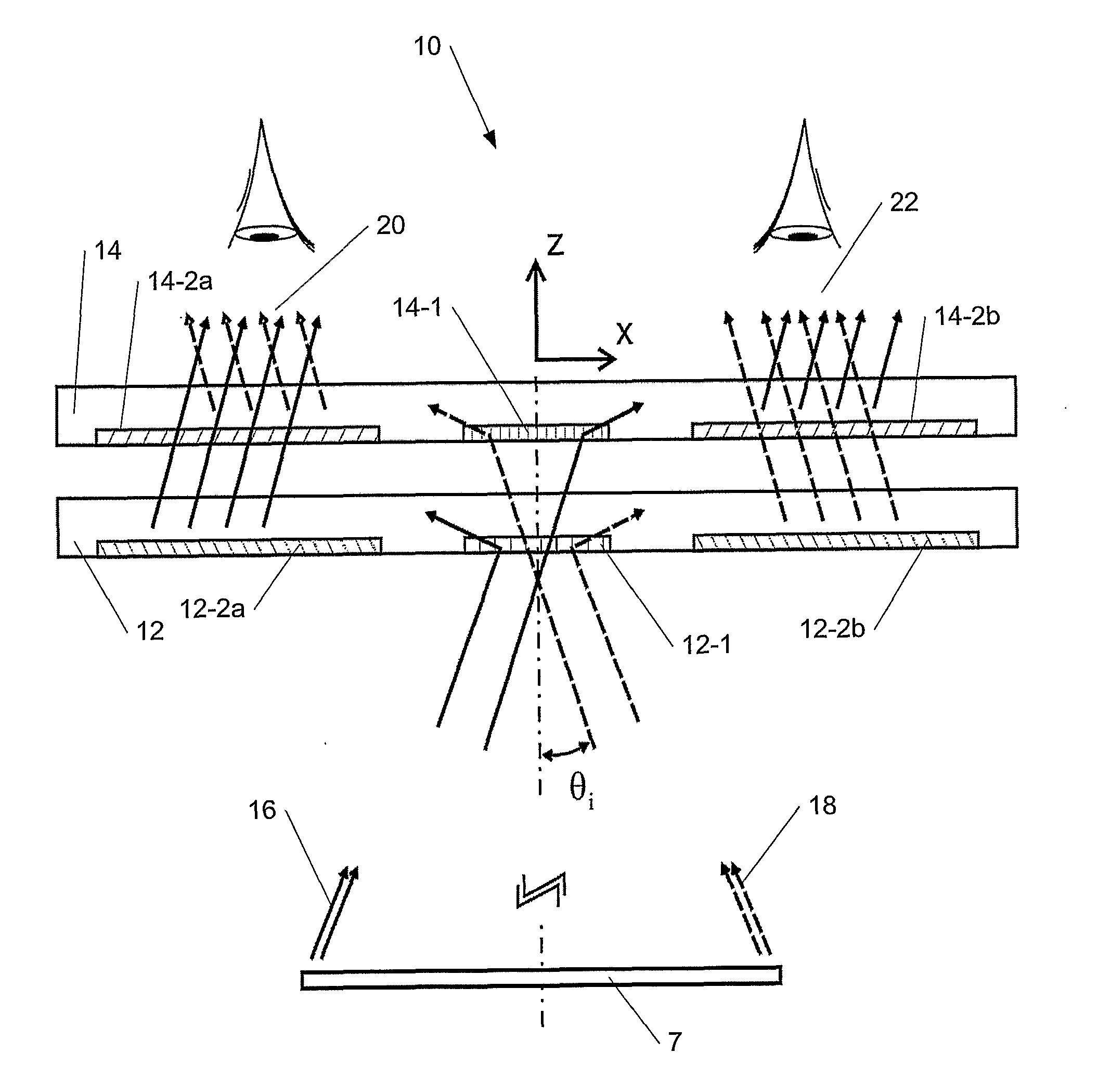
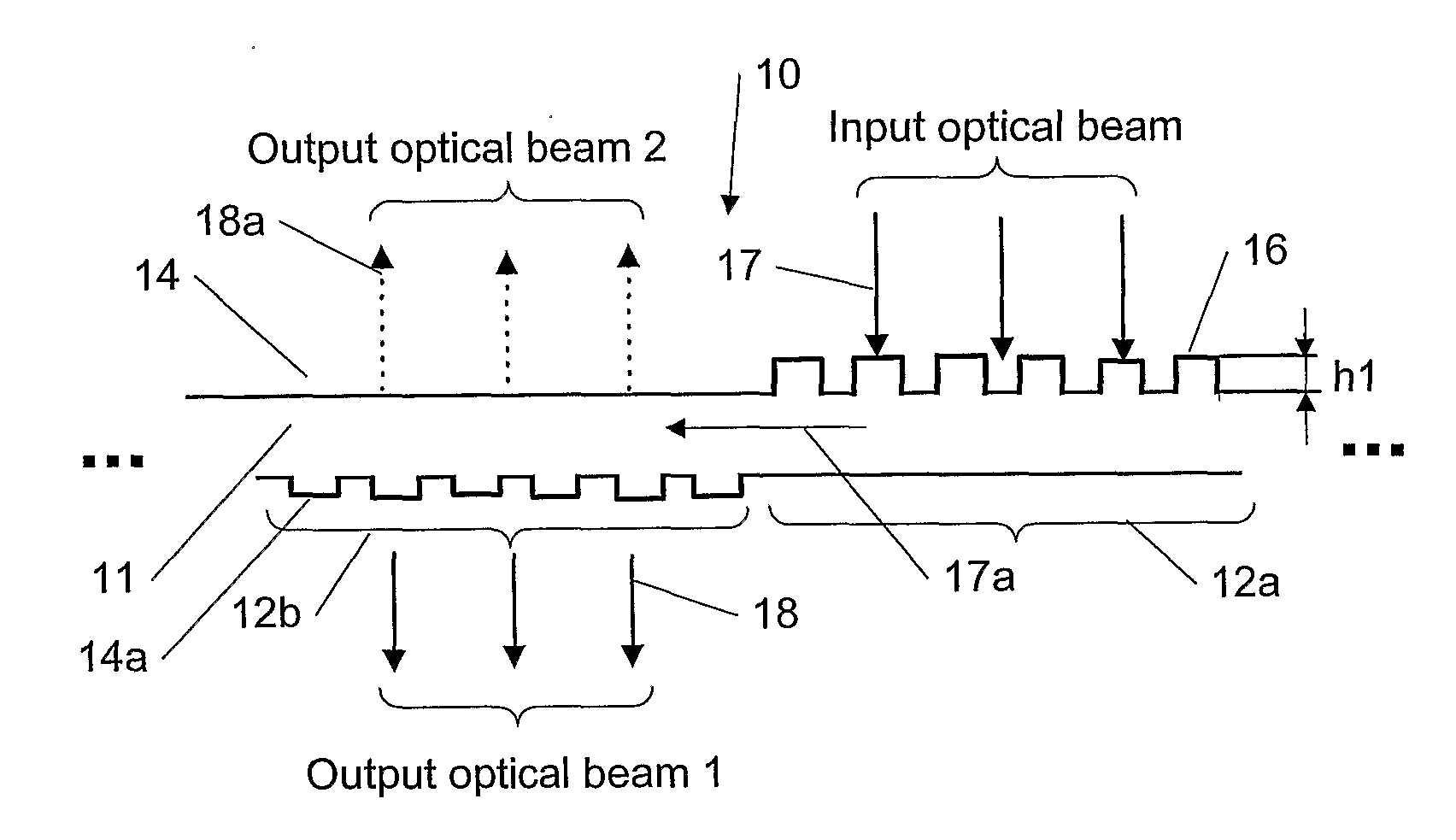
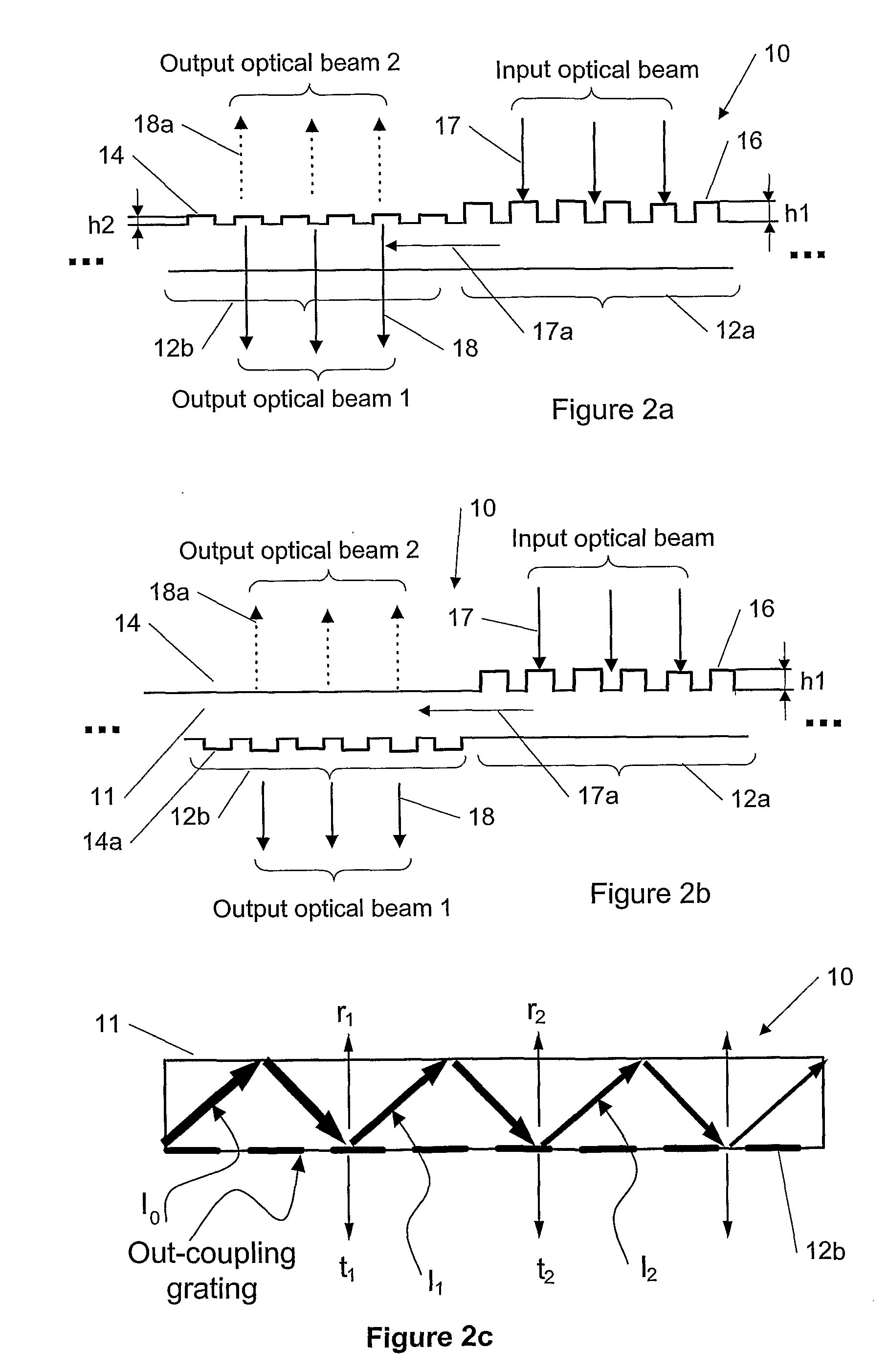
A diffractive beam expander (50) comprises an input grating (10), a crossed grating (20), and an output grating (30) implemented on a planar transparent substrate (7). The crossed grating (20) comprises a plurality of diffractive features (23) arranged along the lines of a first set of parallel lines (25) and along the lines of a second set of parallel lines (26) such that the lines (25) of the first set are parallel to the lines (26) of the second set. The lines of the first set have a first grating period and the lines of the second set have a second grating period. A light beam (B1) coupled into the substrate (7) by the input grating (10) impinges on the crossed grating (20) at a first location (EC1) and further locations (EC2). Interaction at the first location (EC1) provides several sub-beams (S00, S01, S10) which propagate in different directions. Further interactions at second locations (EC2) provide further sub-beams (V01, U10) which propagate in the same direction as the original in-coupled light (B1). Light is subsequently coupled out of the substrate (7) by the output grating (30) to provide a light beam (B2) which is expanded in two directions (SX, SZ) with respect to the beam (B0) impinging on the input grating. A virtual display device (200) may comprise said diffractive beam expander (50).
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Method and system for beam expansion in a display device
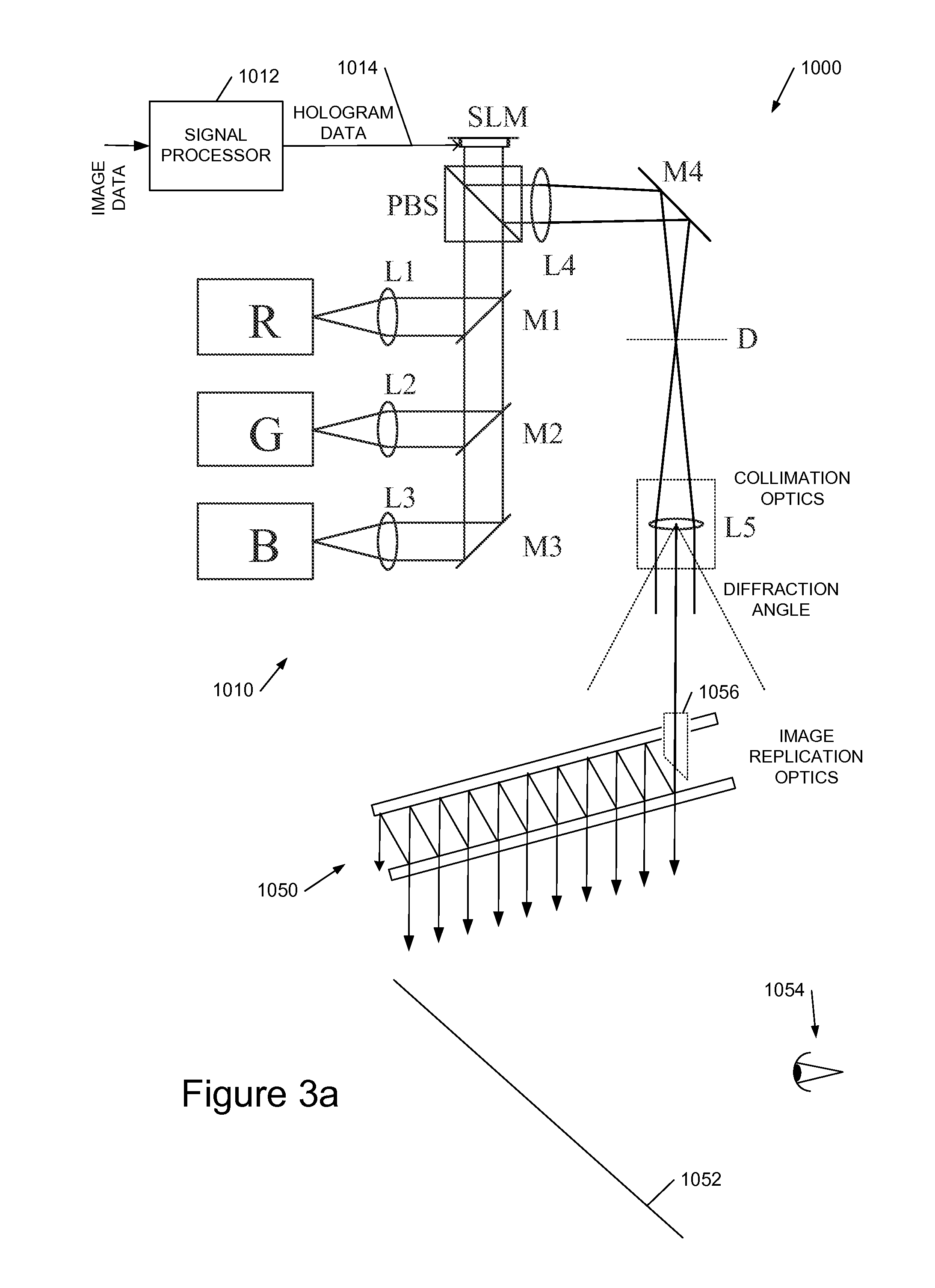
ActiveUS7206107B2Increase volumeReduce the amount requiredDiffraction gratingsPlanar/plate-like light guidesExit pupilDisplay device
An exit pupil extender wherein the relative amount of different color components in the exit beam is more consistent with that of the input beam. In order to compensate for the uneven amount in the diffracted color components in the exit beam, the exit pupil extender, comprises a plurality of layers having additional diffraction gratings so as to increase the amount of diffracted light for those color components with a lower amount. Additionally, color filters disposed between layers to reduce the diffracted light components with a higher amount.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
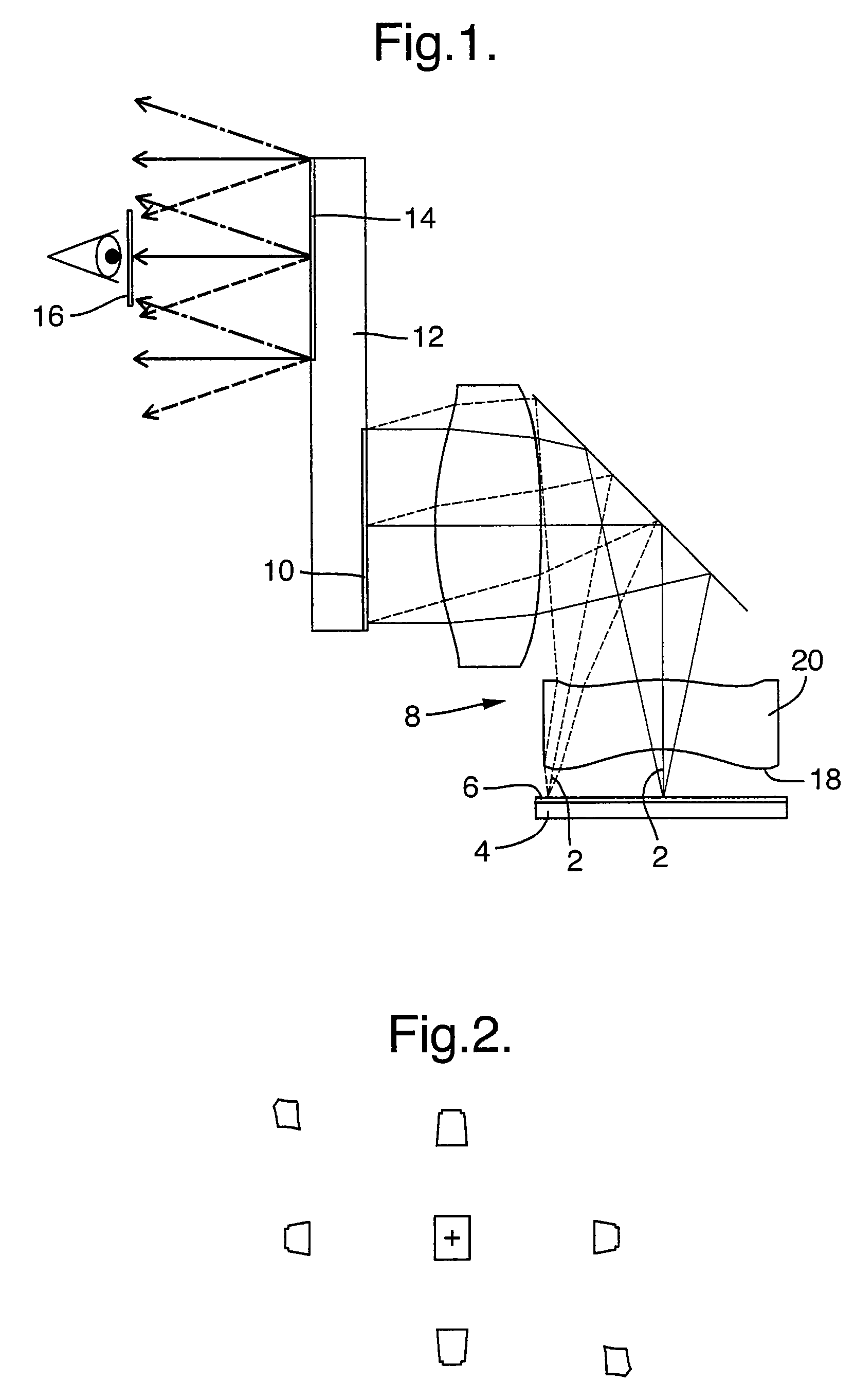
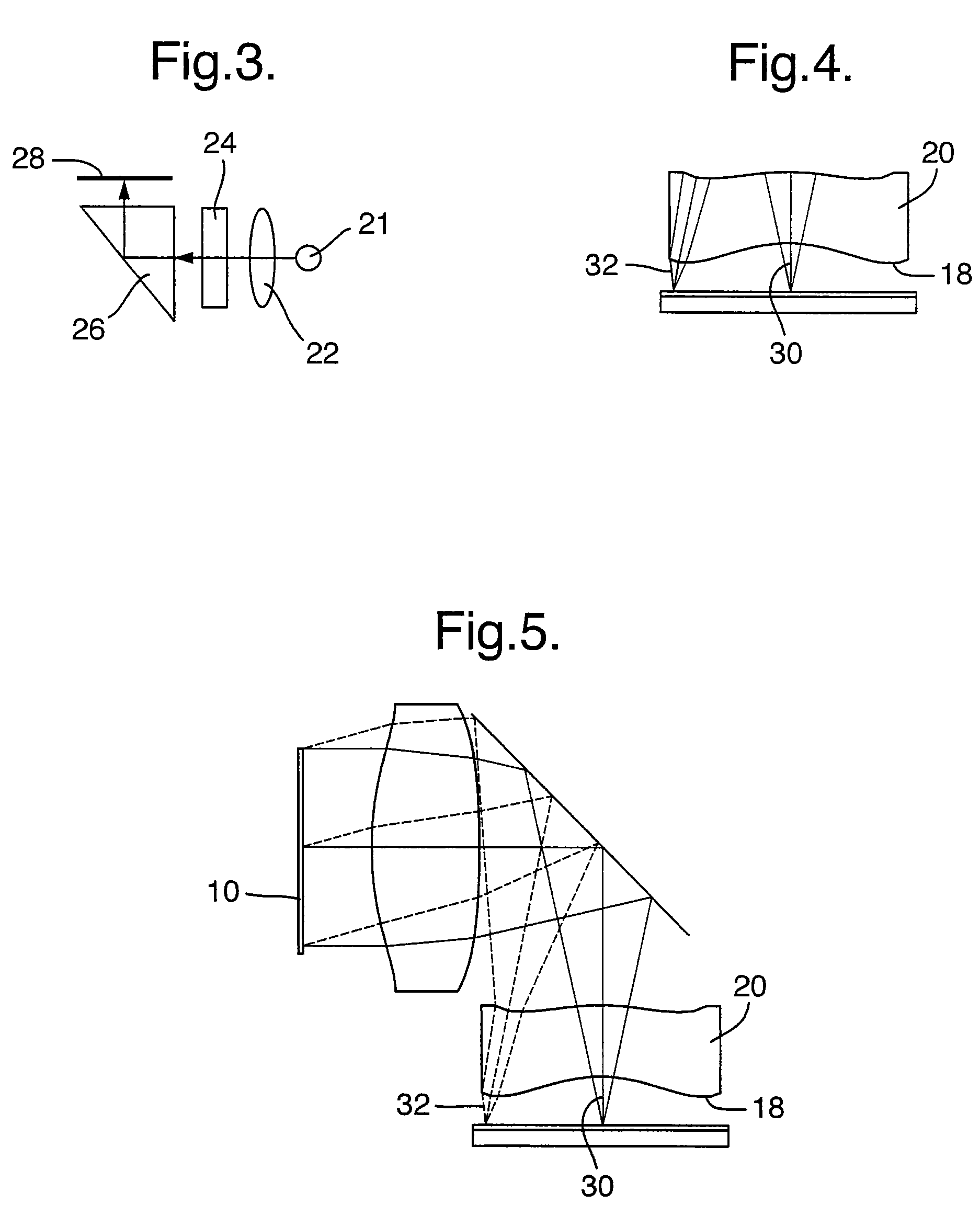
High brightness optical device
ActiveUS20090279180A1Simple designFabrication facilitatedProjectorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical ModuleExit pupil
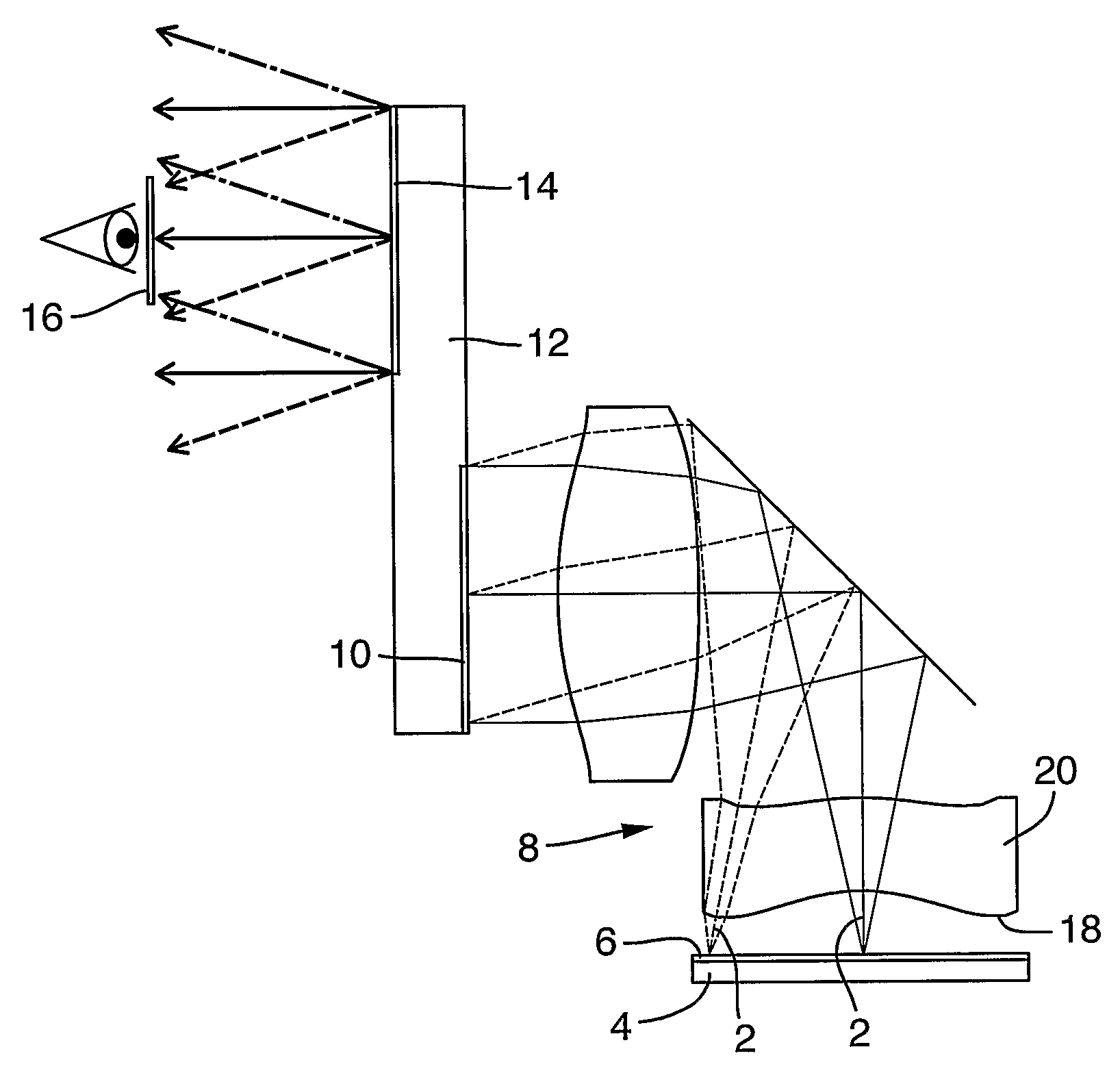
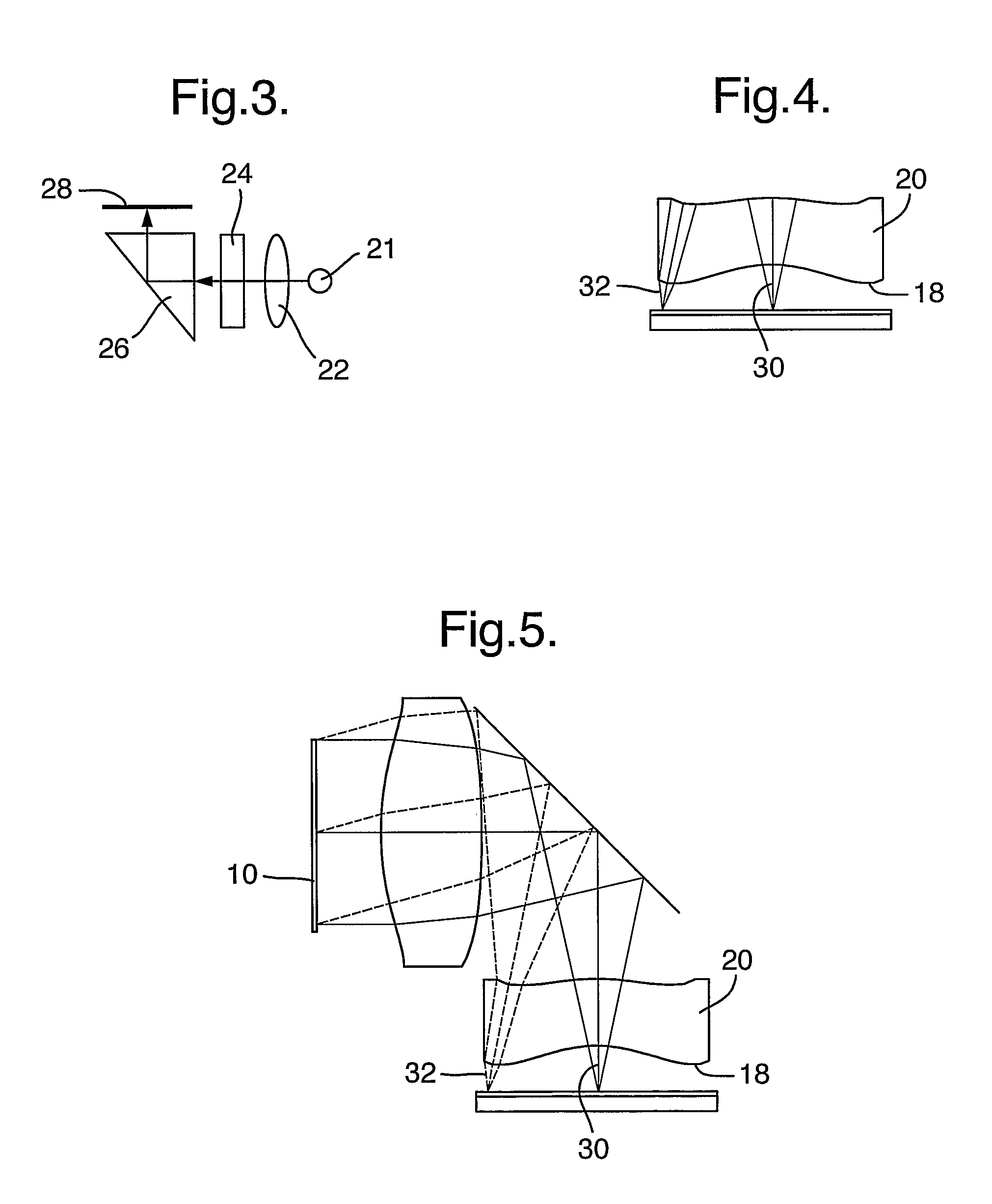
There is provided an optical device, composed of a display source (4), an imaging optical module (8), a projection module (12) having a projection mechanism including an input aperture (10) and output aperture (14) defined by a surface area, and an exit pupil (16). The projection mechanism is non-uniform over the area of the output aperture (14).
Owner:LUMUS LTD
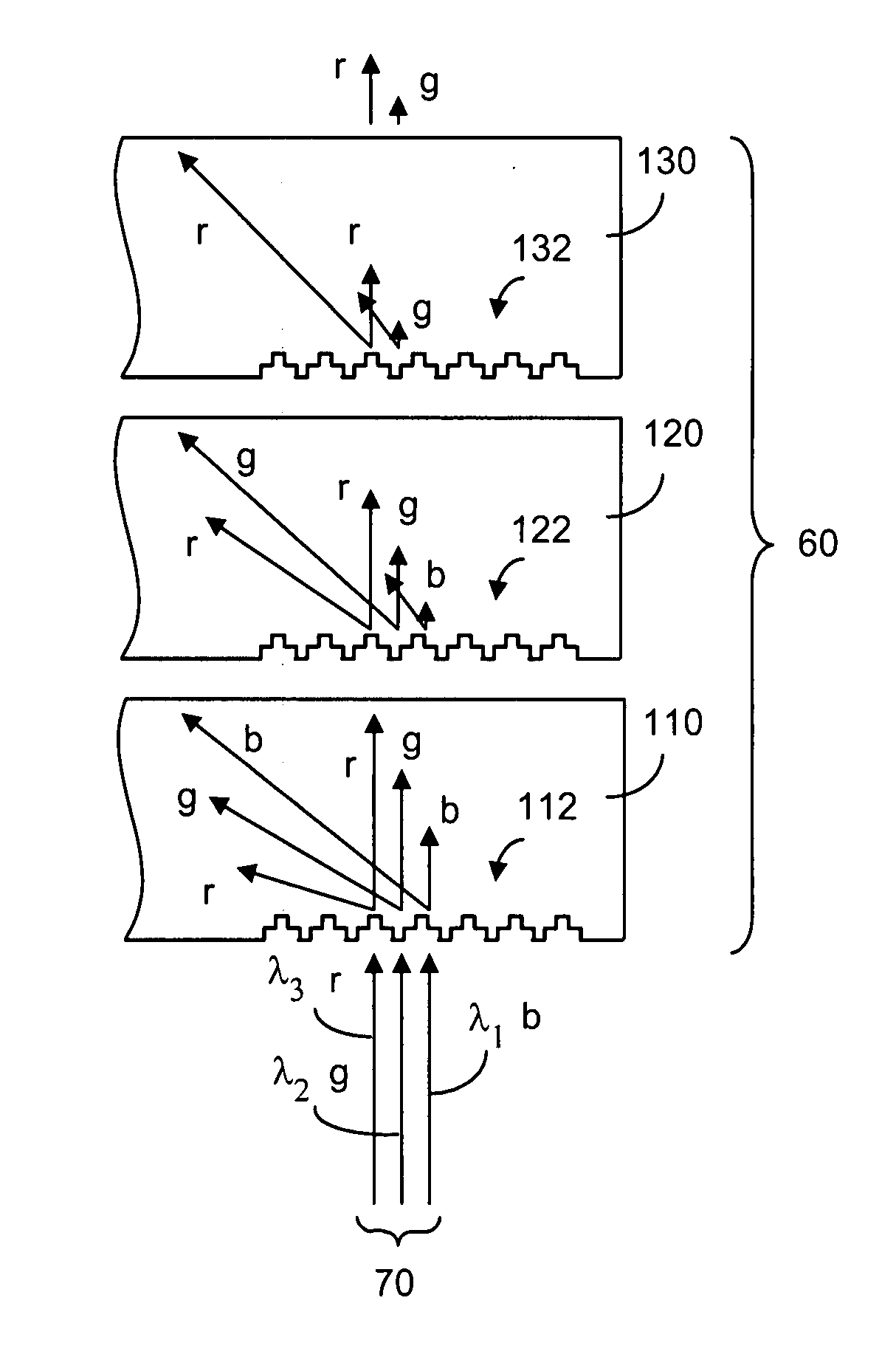
Exit Pupil Expanders with Wide Field-of-View
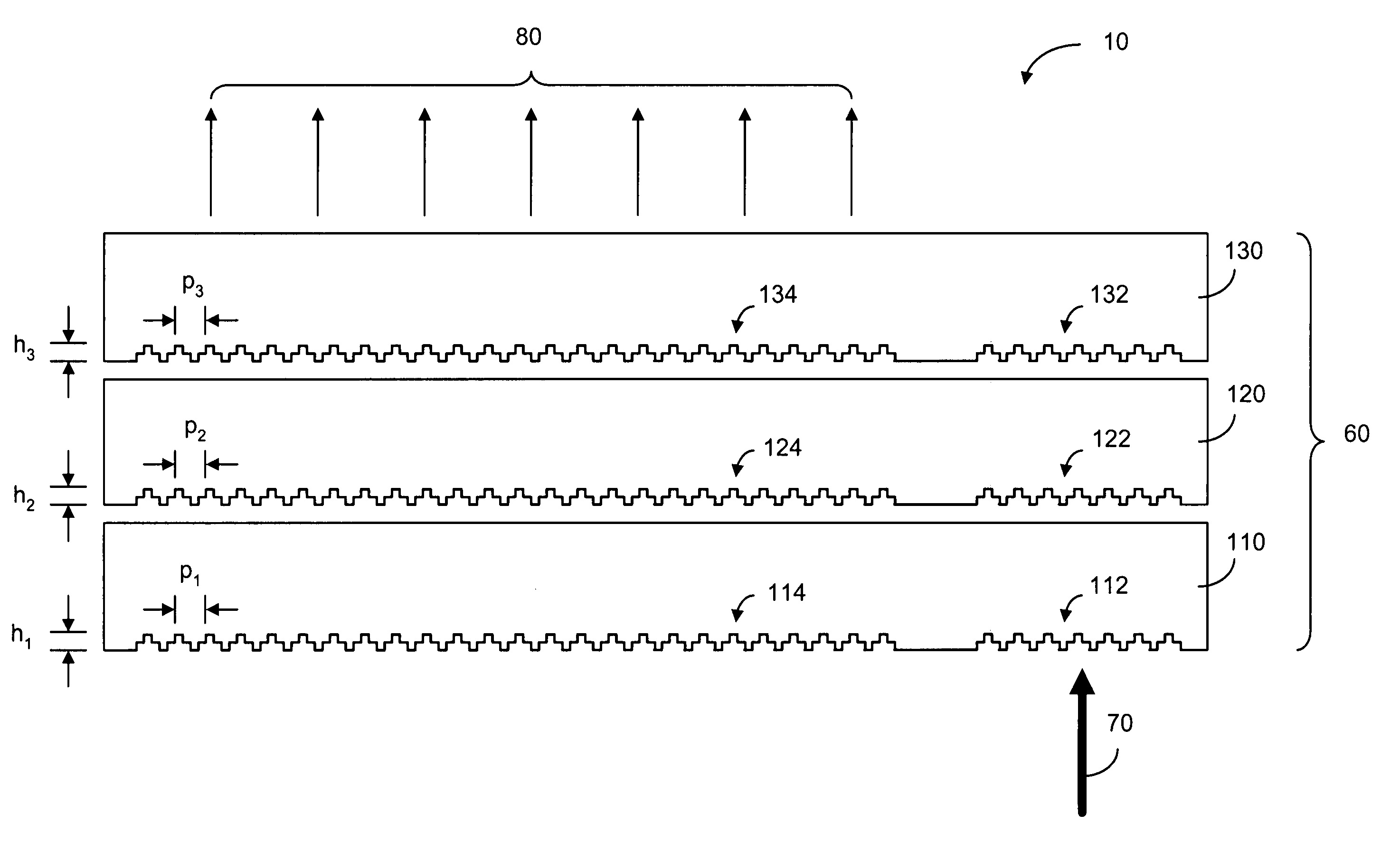
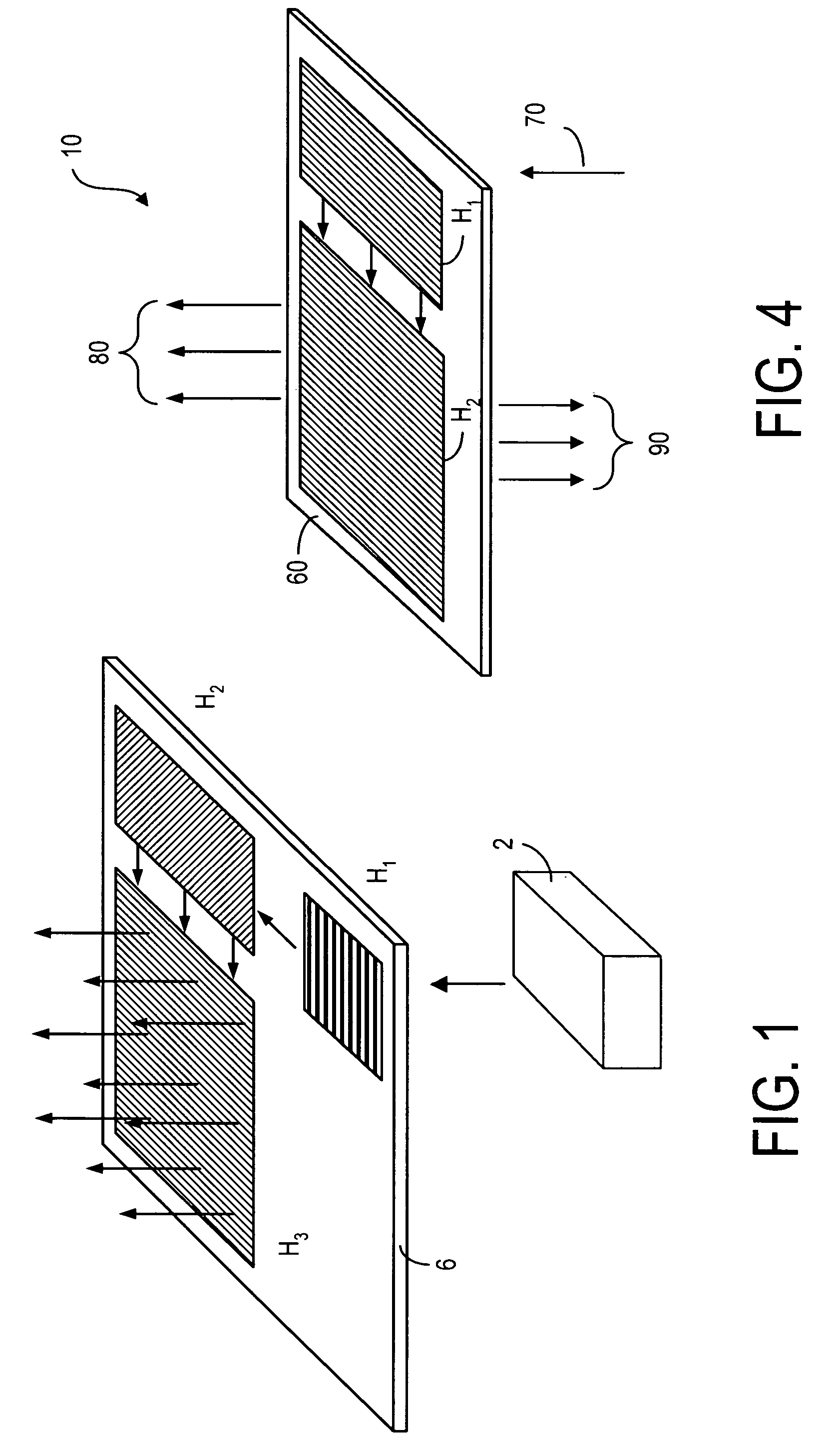
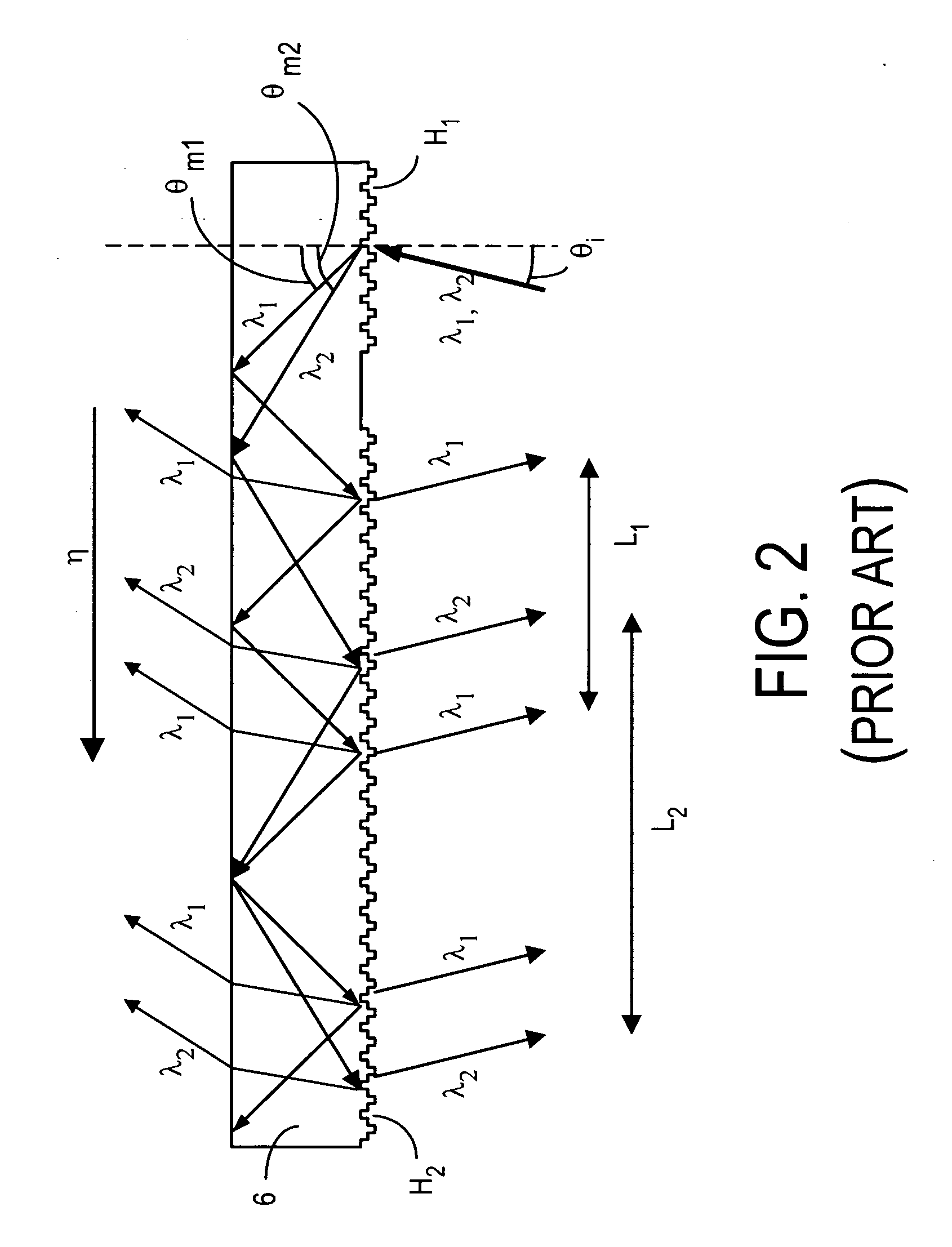
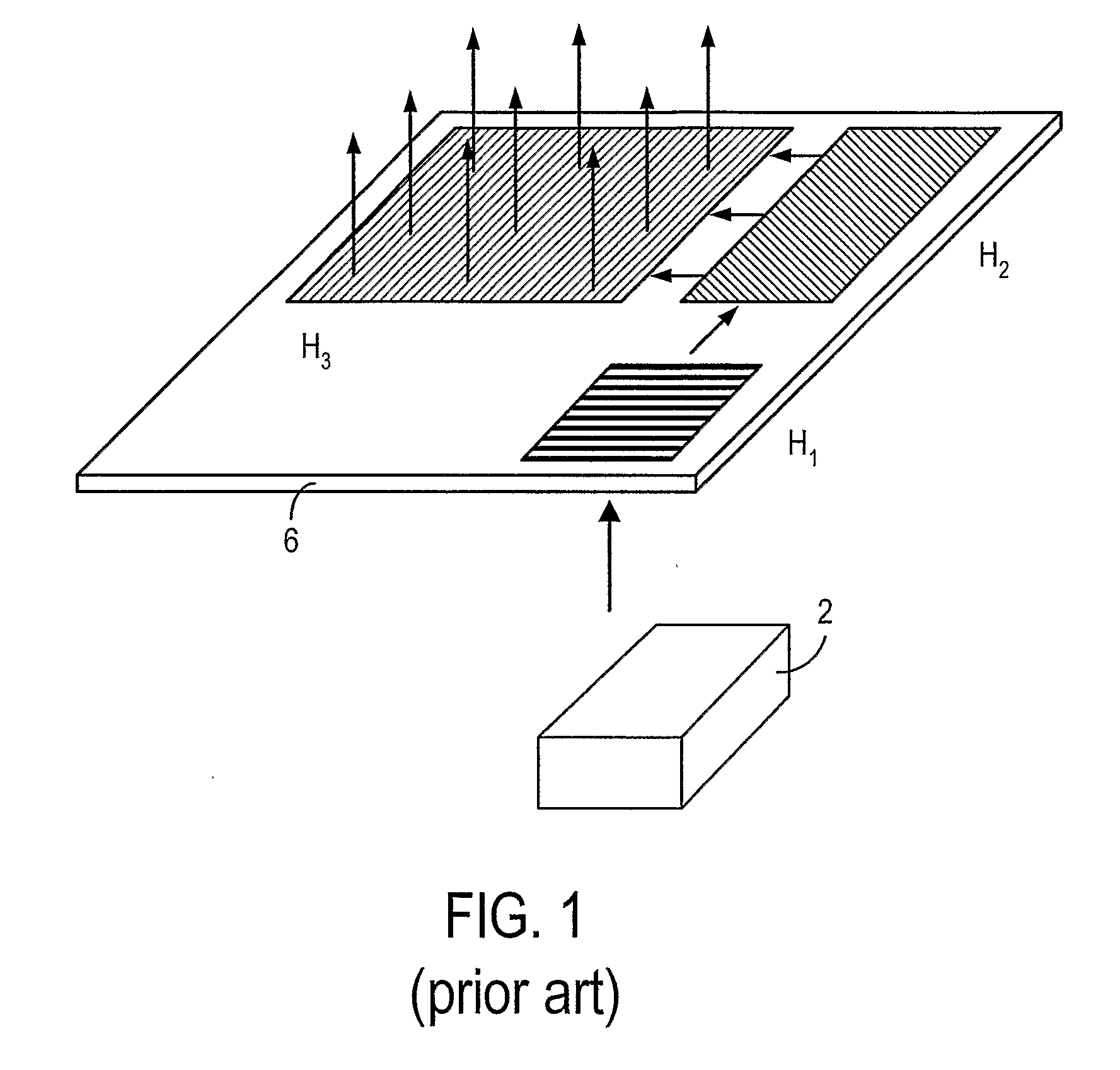
The specification and drawings present a new apparatus and method for providing a wide field-of-view as well as illumination uniformity in exit pupil expanders (EPE) using stacked EPE substrates (or plates) with non-symmetric exit pupil expansion that use a plurality of diffractive elements for expanding the exit pupil of a display for viewing.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Near-to-eye scanning display with exit-pupil expansion
InactiveUS20100079865A1Reduce light lossPolarising elementsDiffraction gratingsExit pupilDisplay device
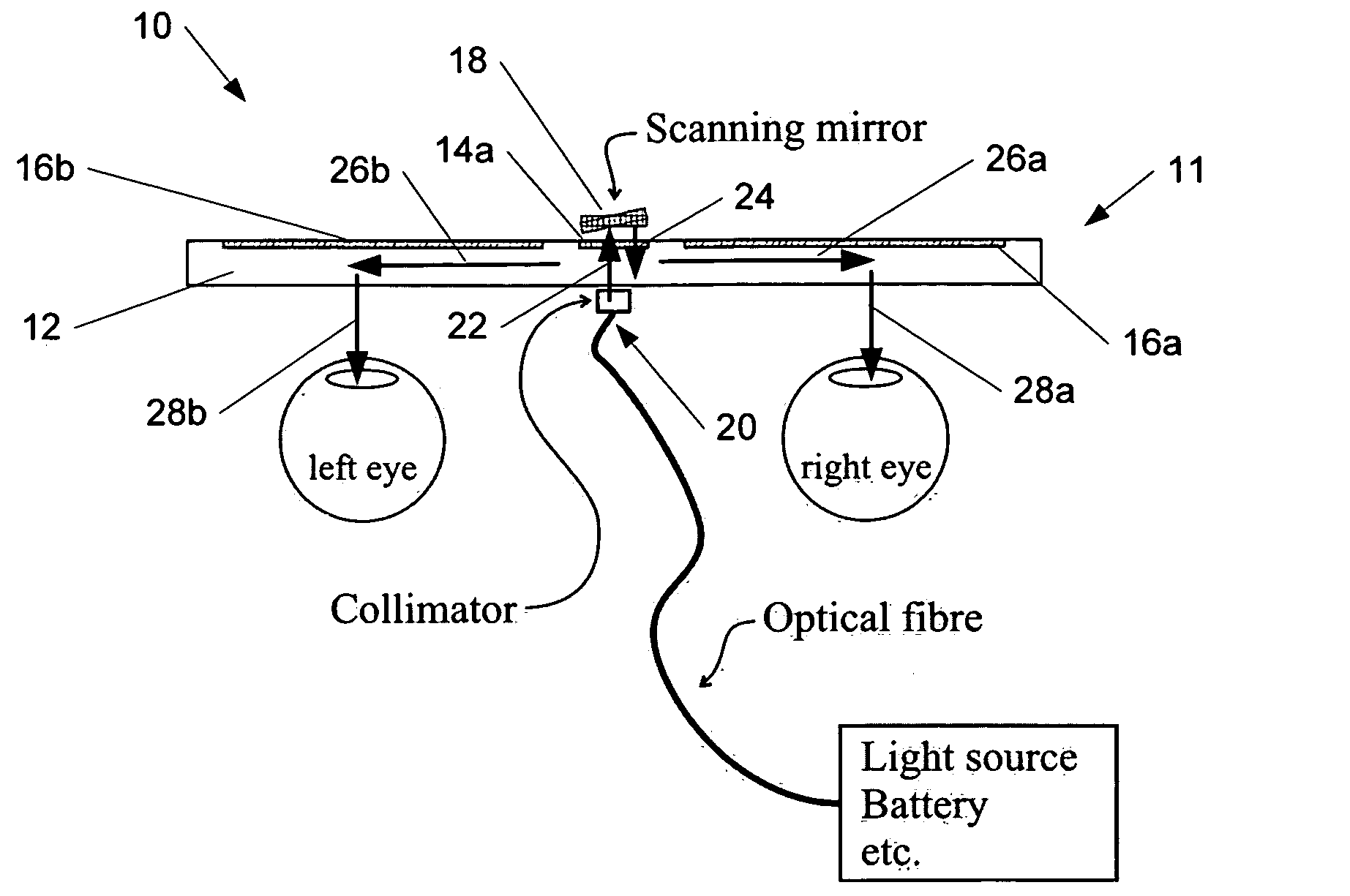
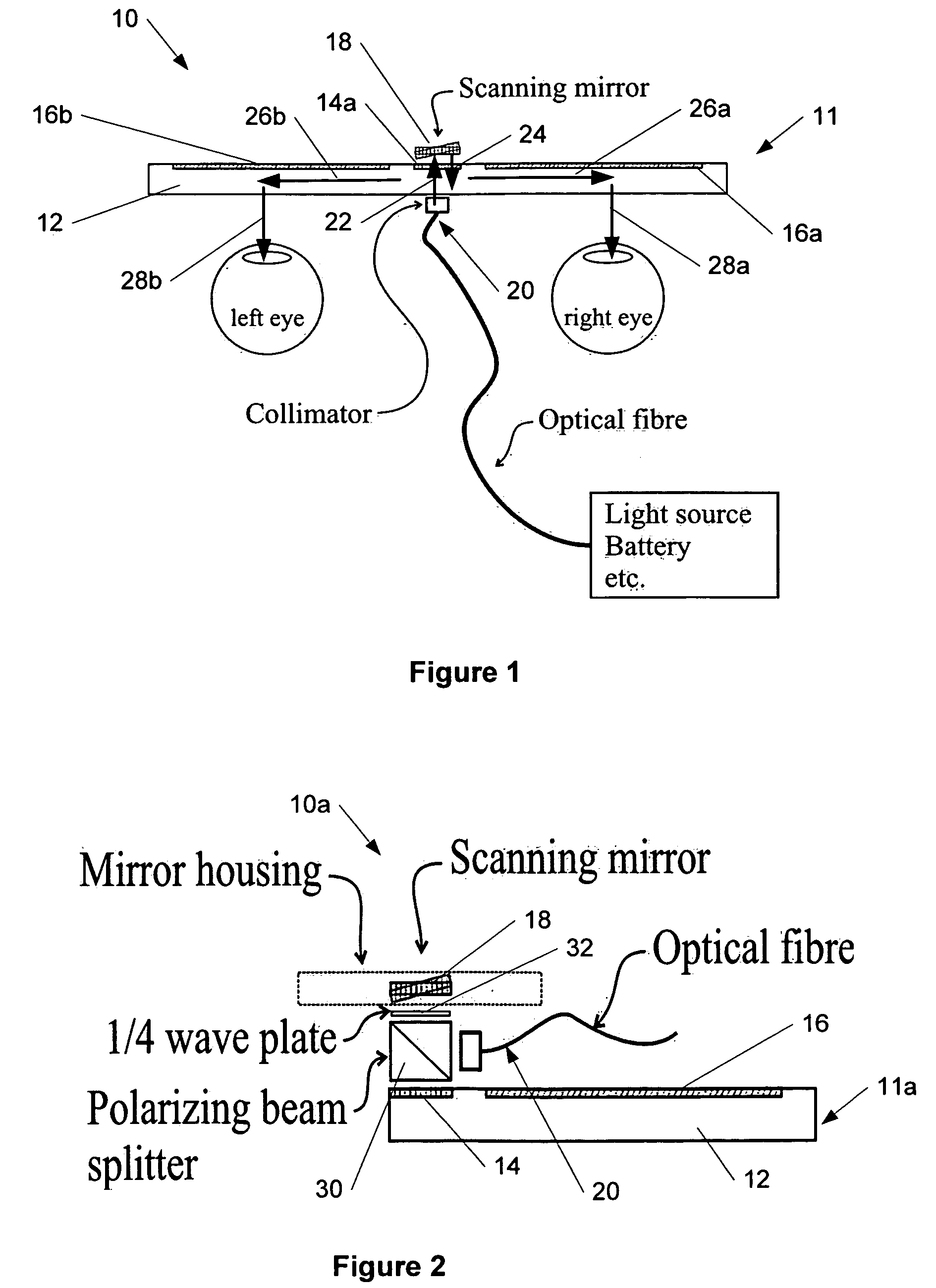
The specification and drawings present a new apparatus and method for near-to-eye (e.g., retinal) displaying with exit-pupil expansion using a scanning component (e.g., a scanning mirror) and an exit-pupil expander (e.g., diffractive exit-pupil expander) for providing a retinal scanning display with a large exit pupil.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Beam expansion with three-dimensional diffractive elements
The specification and drawings present a new apparatus and method for using a three-dimensional (3D) diffractive element (e.g., a 3D diffractive grating) for expanding in one or two dimensions the exit pupil of an optical beam in electronic devices. Various embodiments of the present invention can be applied, but are not limited, to forming images in virtual reality displays, to illuminating of displays (e.g., backlight illumination in liquid crystal displays) or keyboards, etc.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
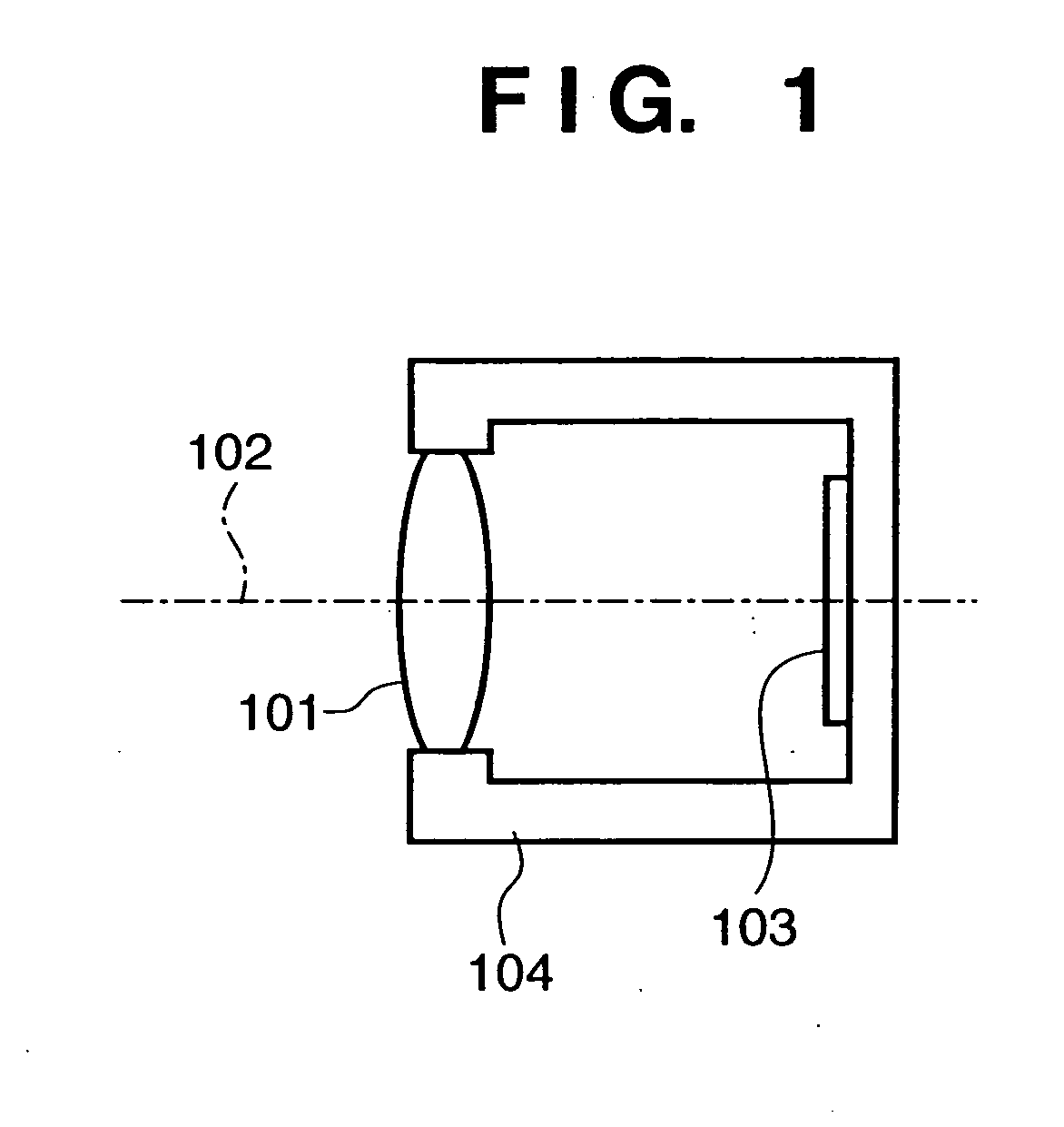
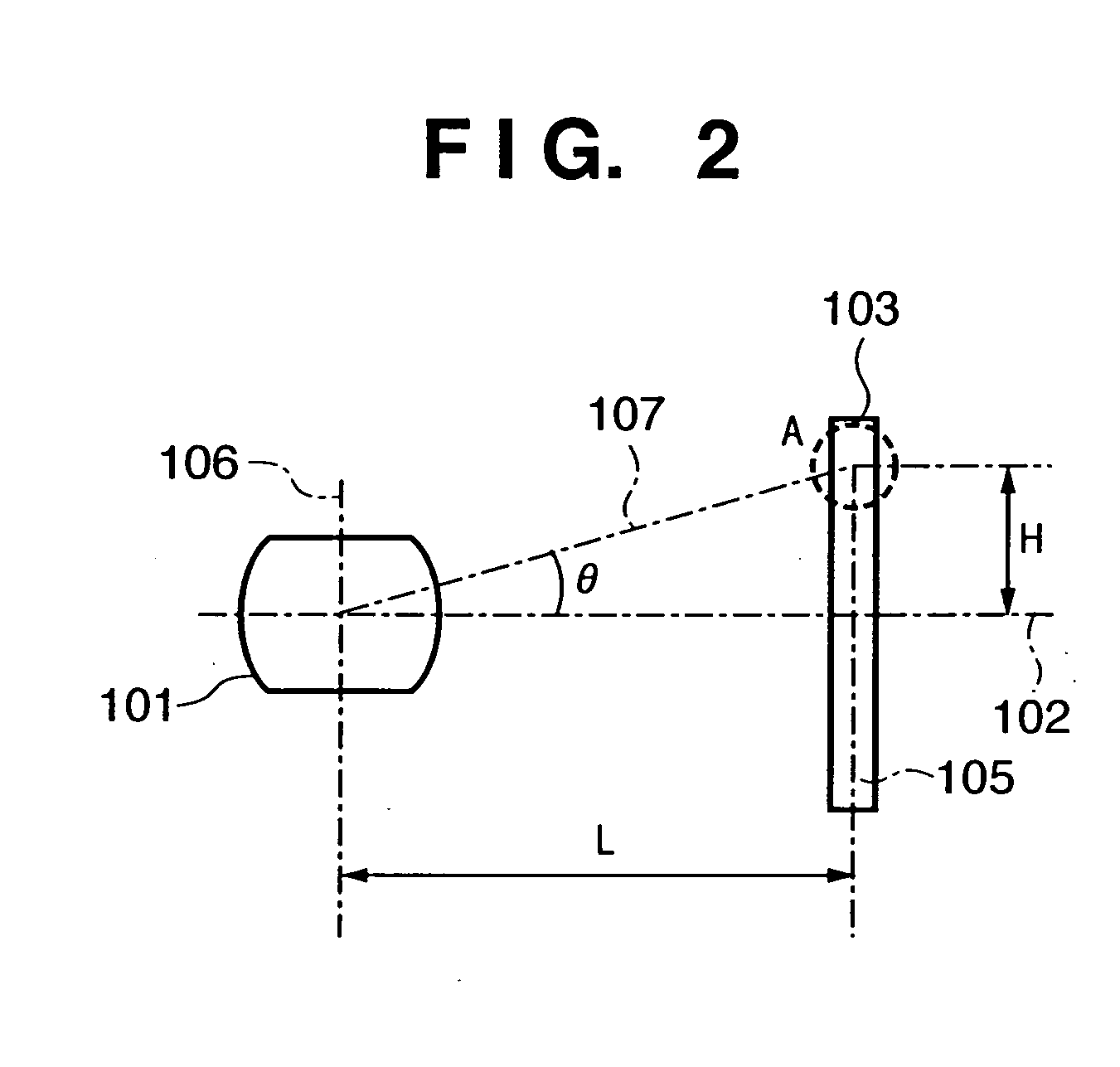
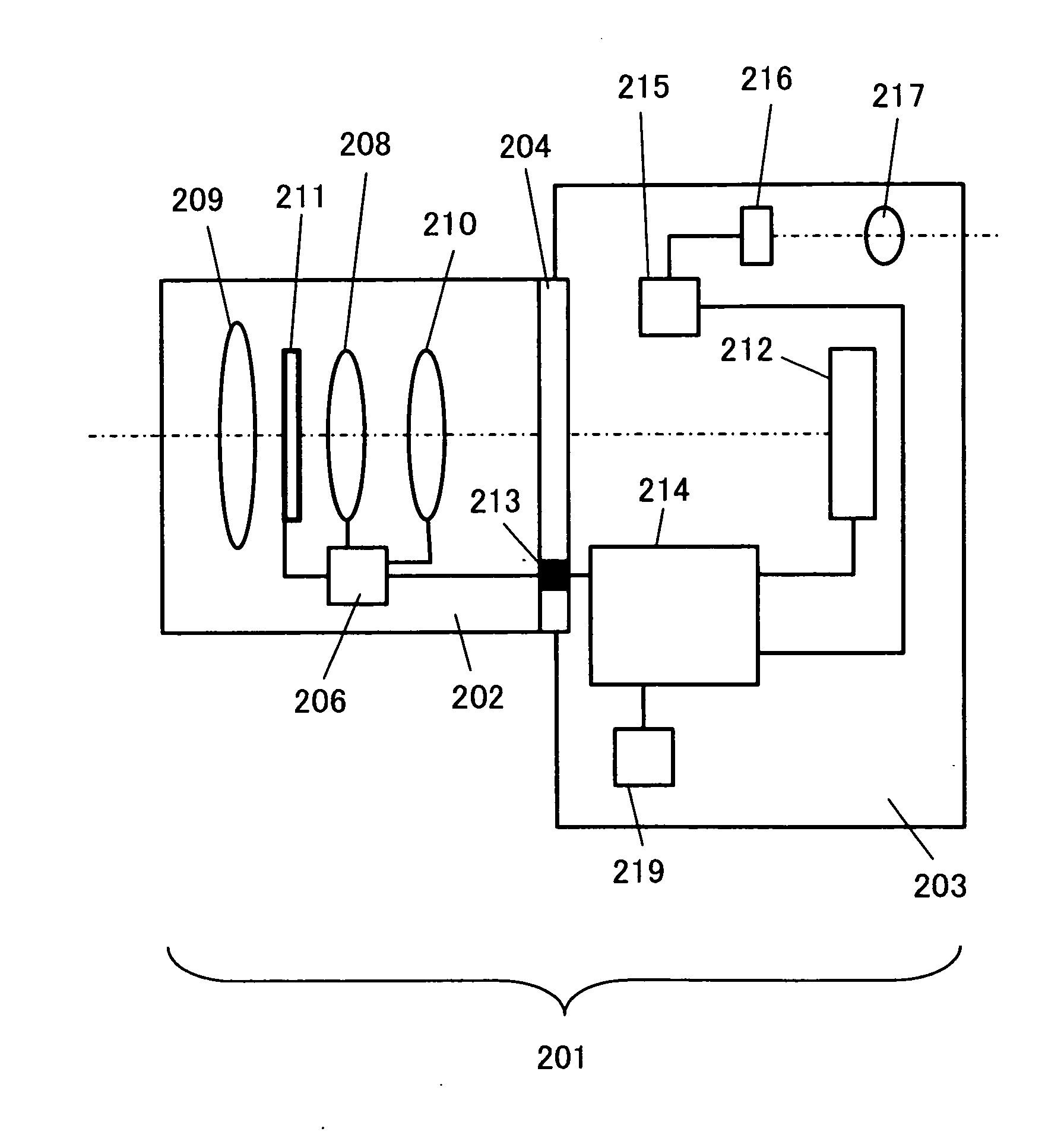
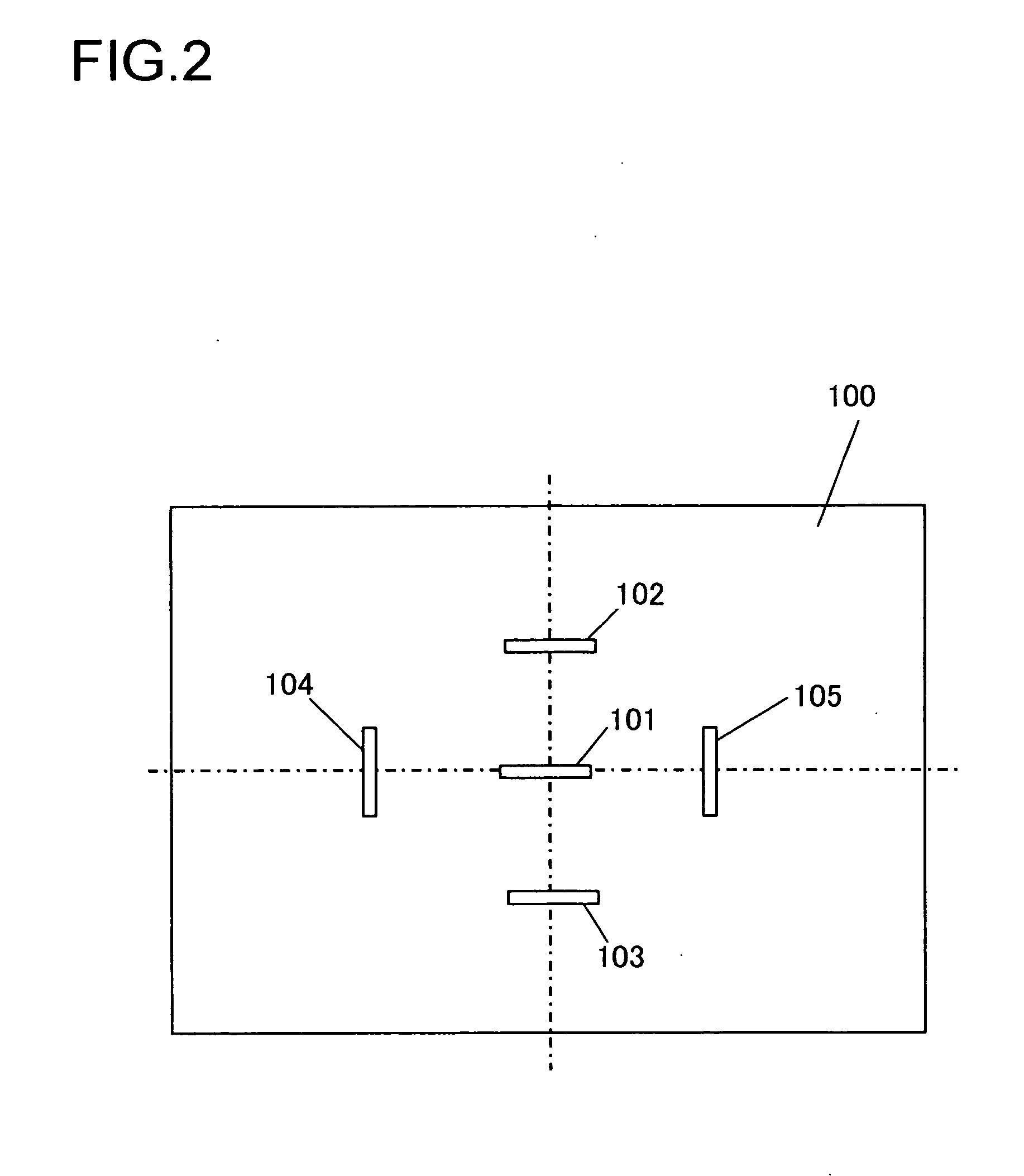
Image sensing apparatus, image sensing system and focus detection method
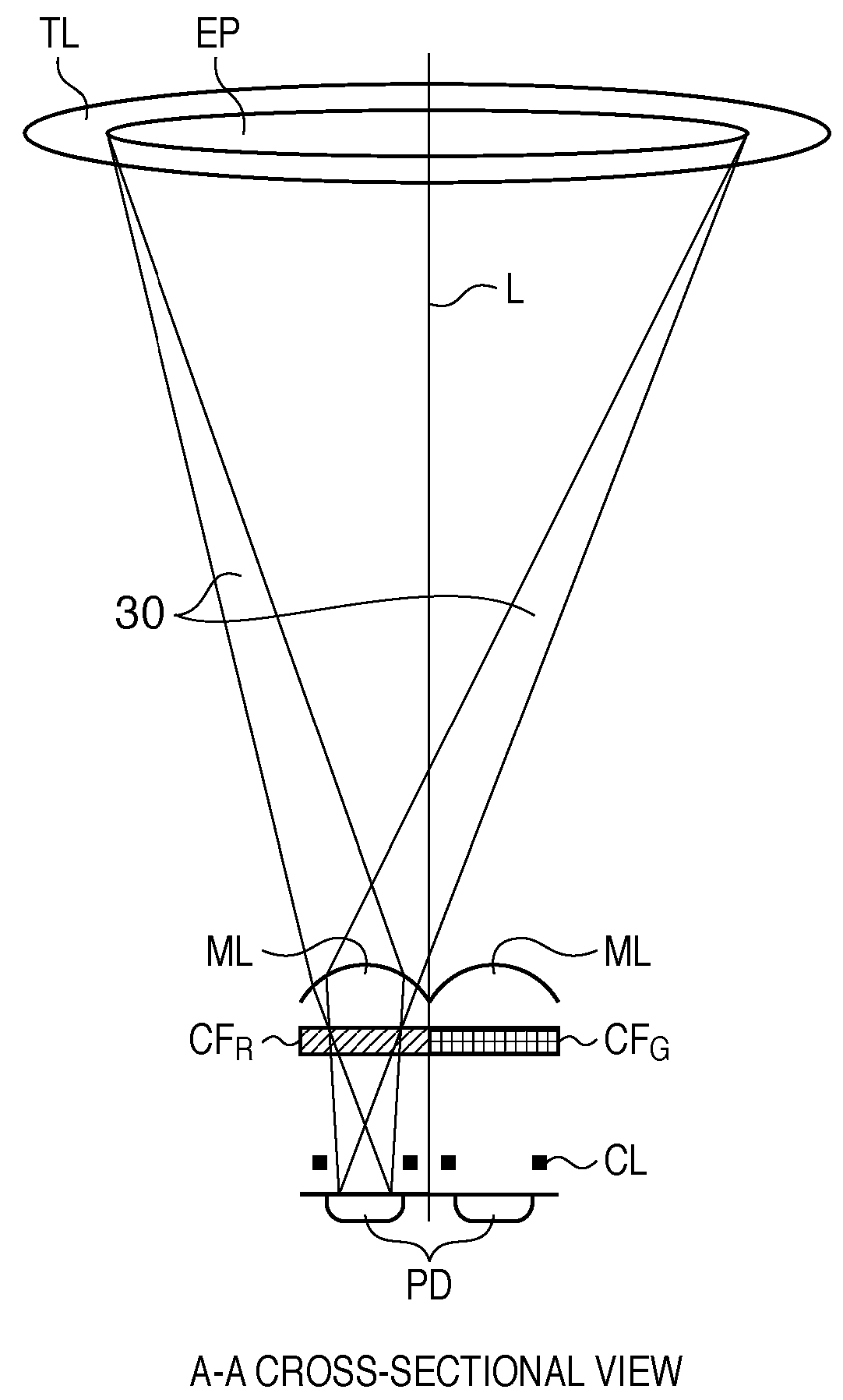
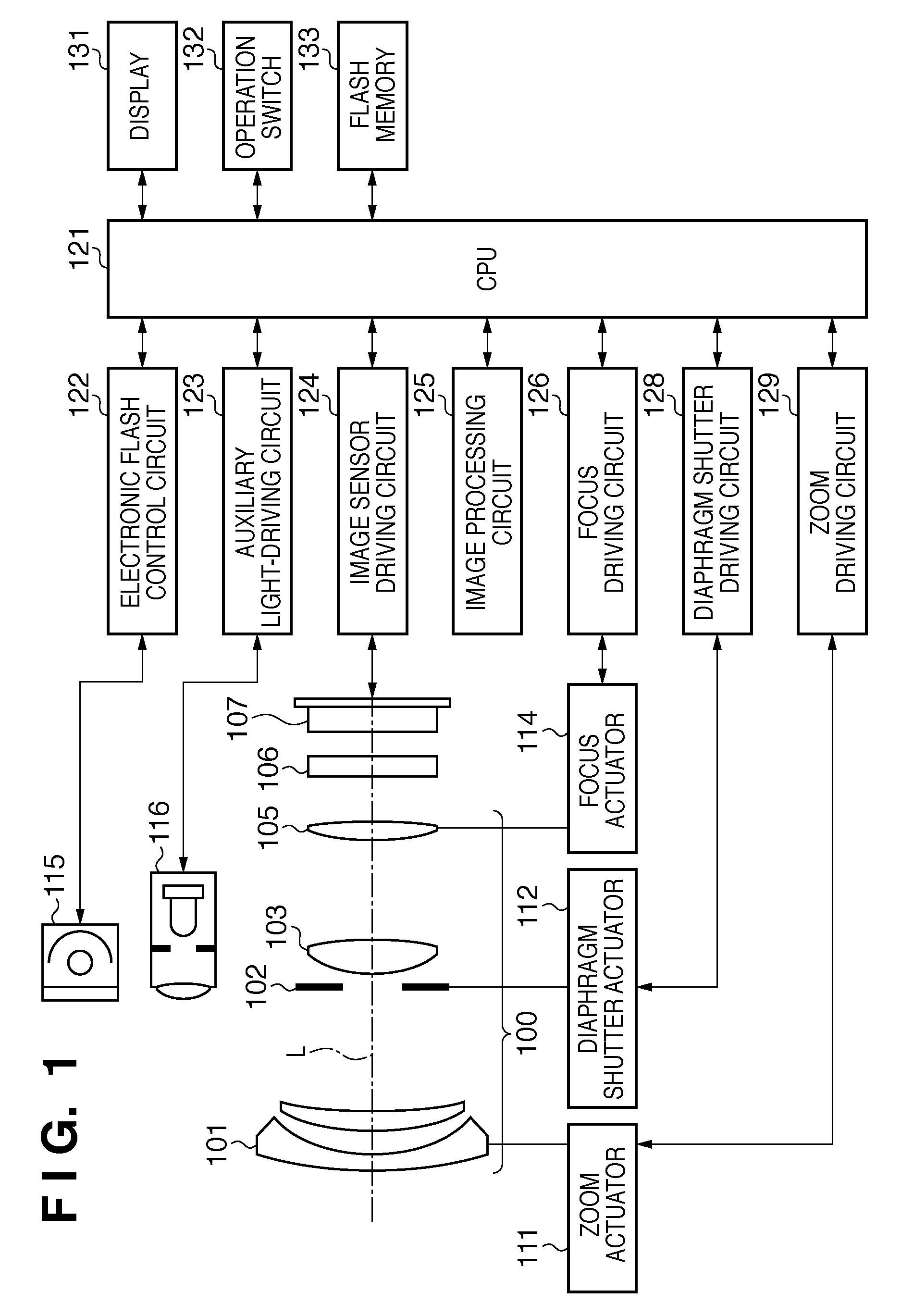
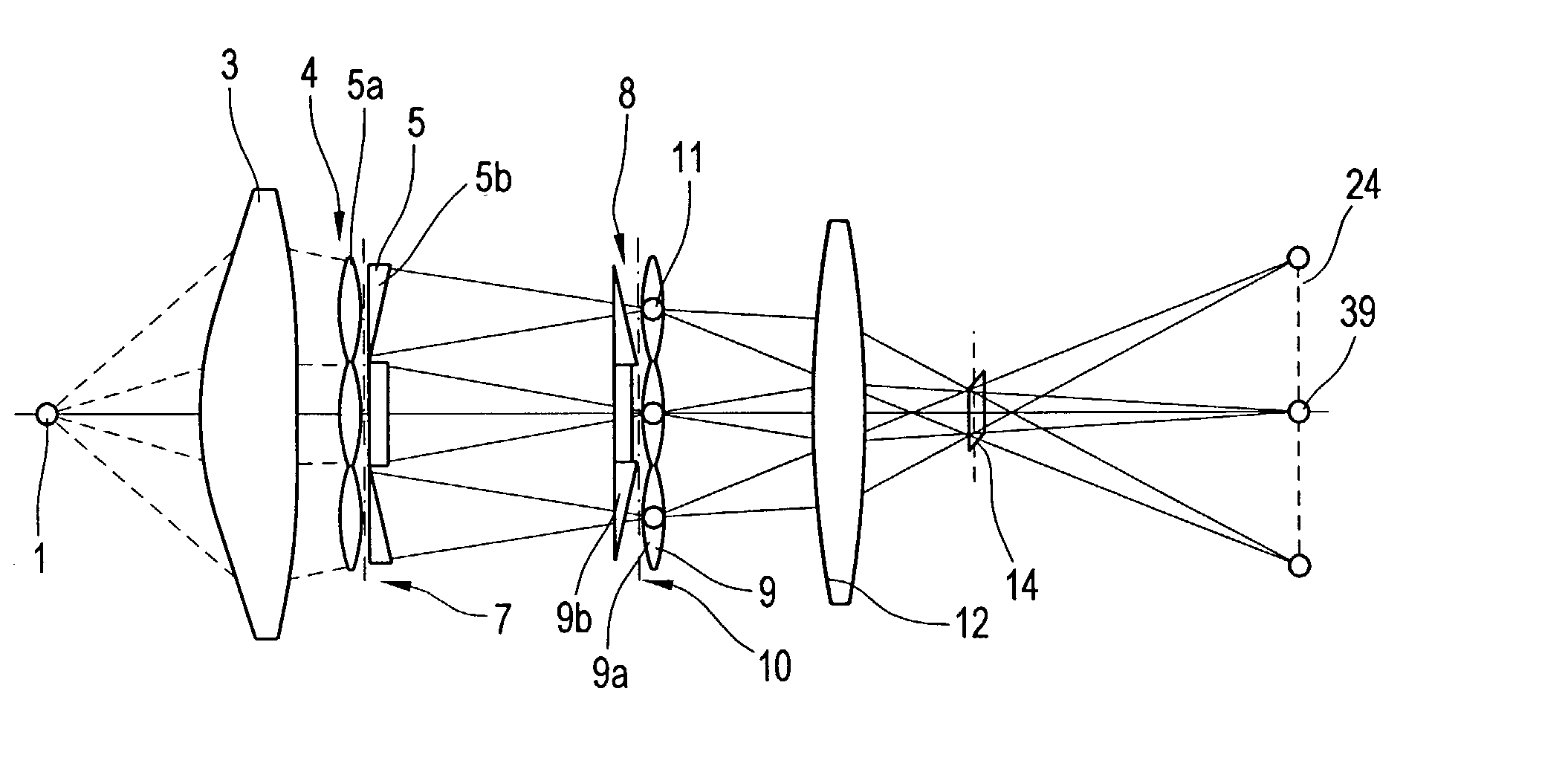
InactiveUS20100045849A1Improve accuracyMethod can be usedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCamera lensRelative shift
An image sensing apparatus including: an image sensor including a plurality of focus detection pixel pairs that perform photoelectric conversion on each pair of light beams that have passed through different regions of a photographing lens and output an image signal pair; a flash memory that stores shift information on relative shift between an optical axis of the photographing lens and a central axis of the focus detection pixel pairs; a correction unit that corrects a signal level of the image signal pair based on the shift information and exit pupil information of the photographing lens so as to compensate for an unbalanced amount of light that enters each of the focus detection pixel pairs; and a focus detection unit that detects a focus of the photographing lens using the image signal pair corrected by the correction unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Exit pupil expanders with wide field-of-view
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Method and system for beam expansion in a display device
ActiveUS20060126179A1Increase volumeReduce the amount requiredDiffraction gratingsPlanar/plate-like light guidesExit pupilDiffraction grating
An exit pupil extender wherein the relative amount of different color components in the exit beam is more consistent with that of the input beam. In order to compensate for the uneven amount in the diffracted color components in the exit beam, the exit pupil extender, comprises a plurality of layers having additional diffraction gratings so as to increase the amount of diffracted light for those color components with a lower amount. Additionally, color filters disposed between layers to reduce the diffracted light components with a higher amount.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
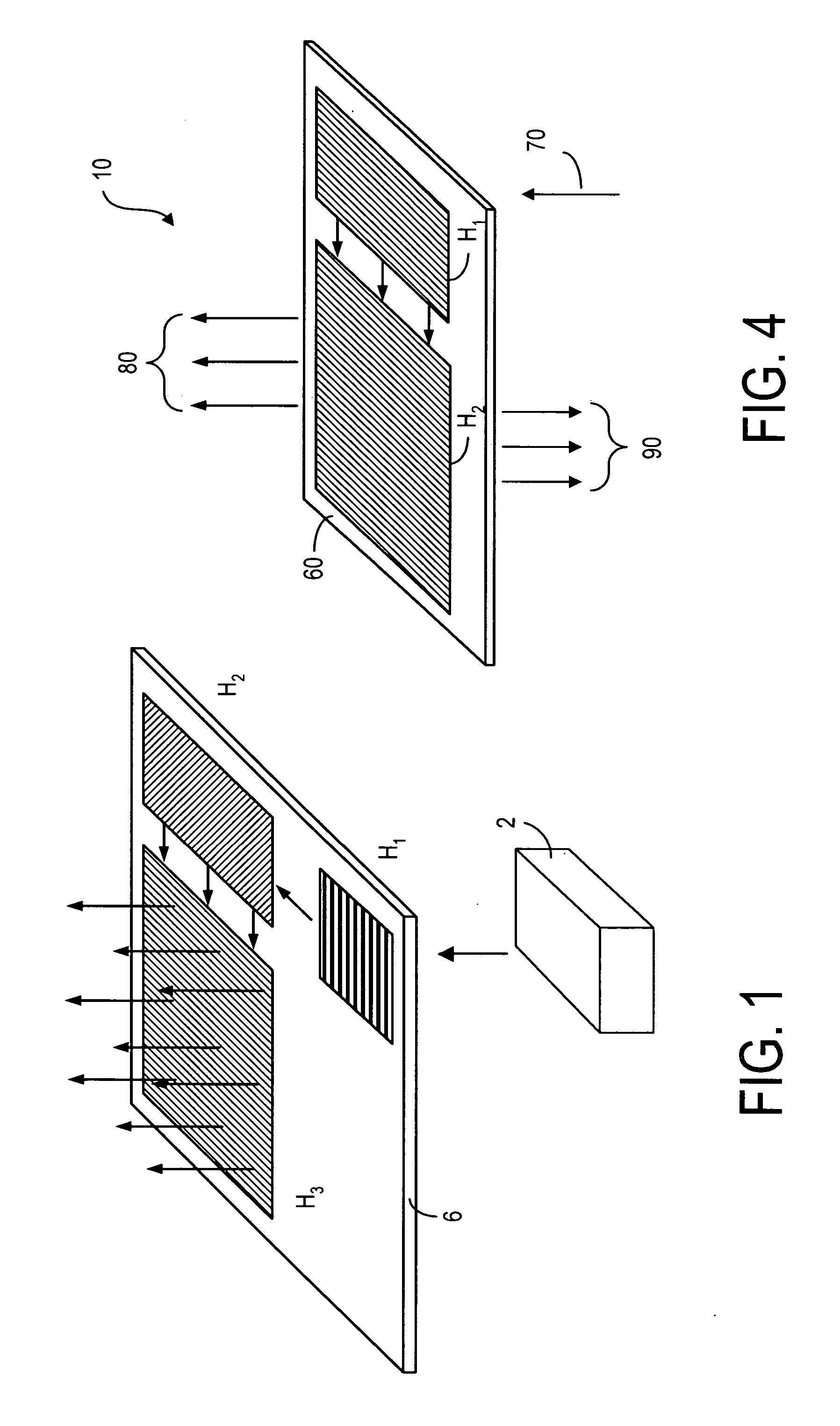
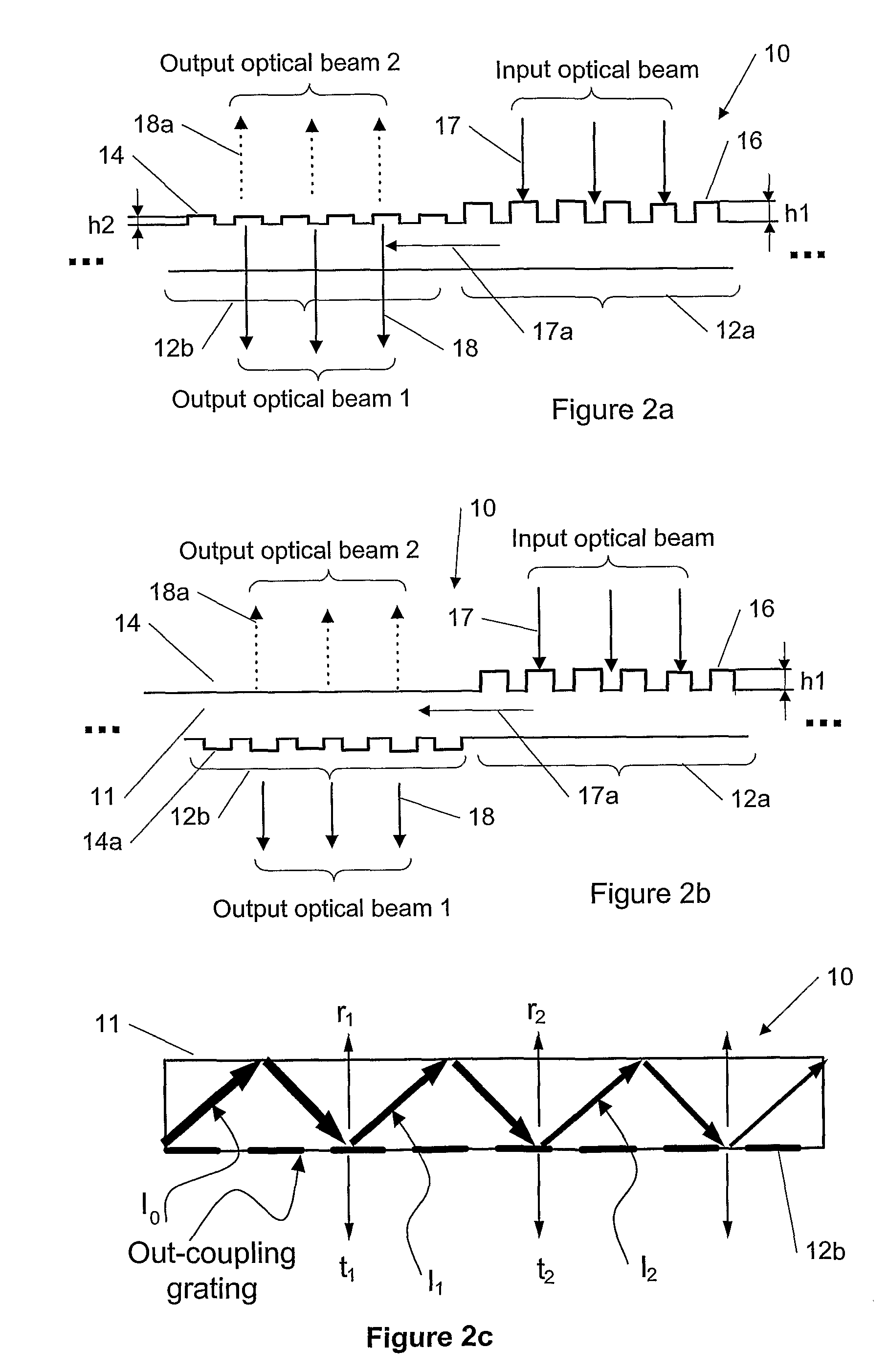
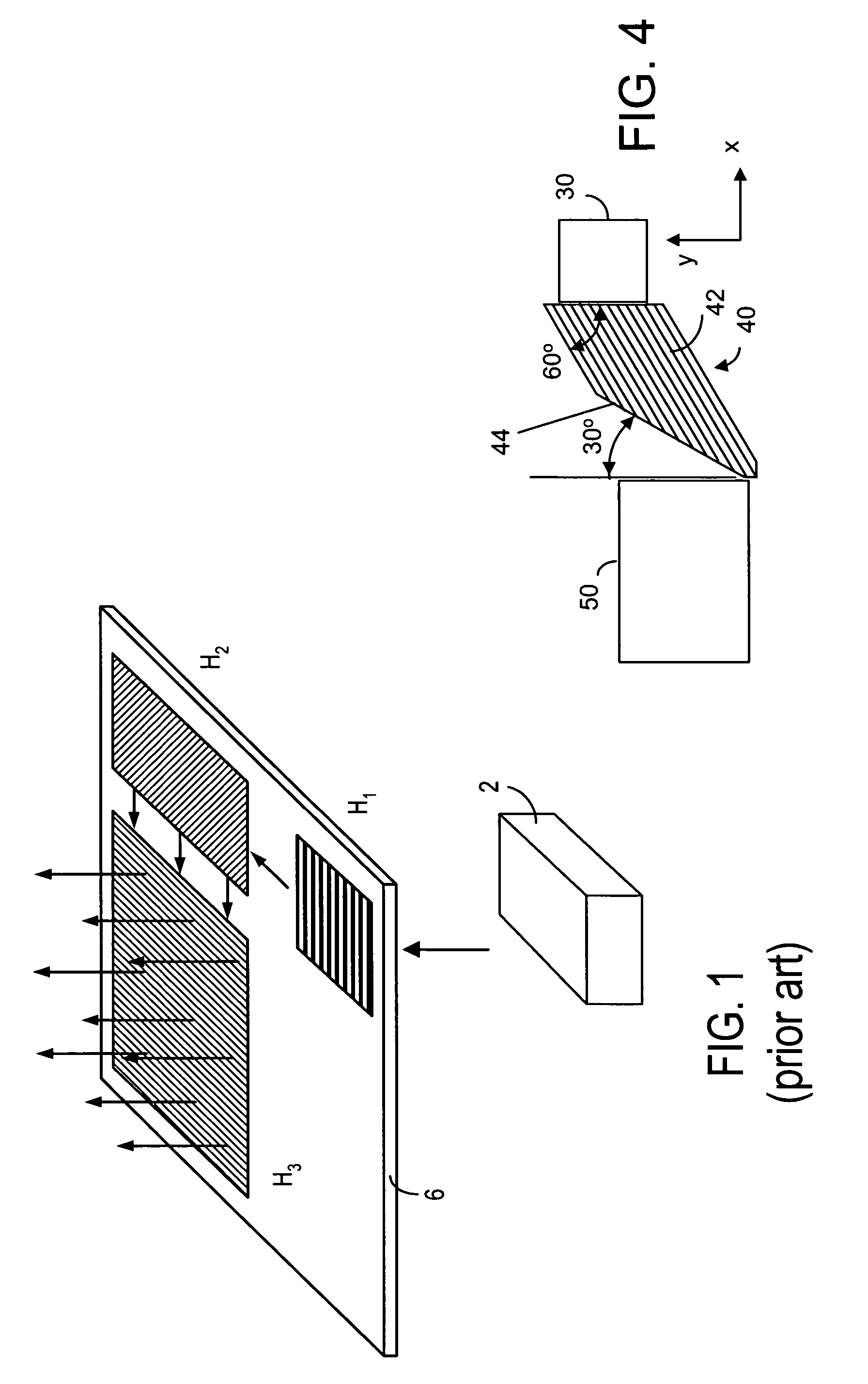
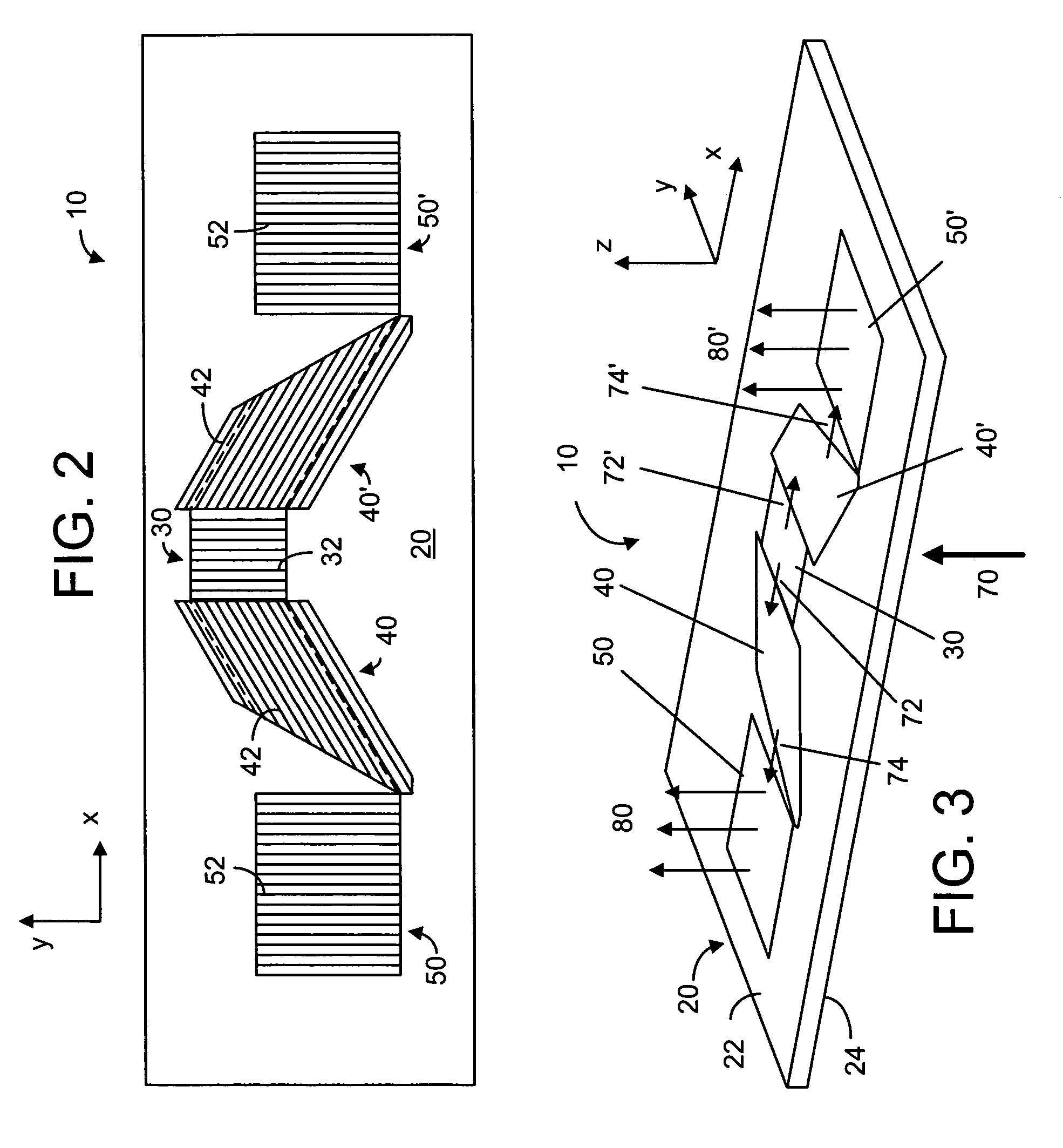
General diffractive optics method for expanding an exit pupil
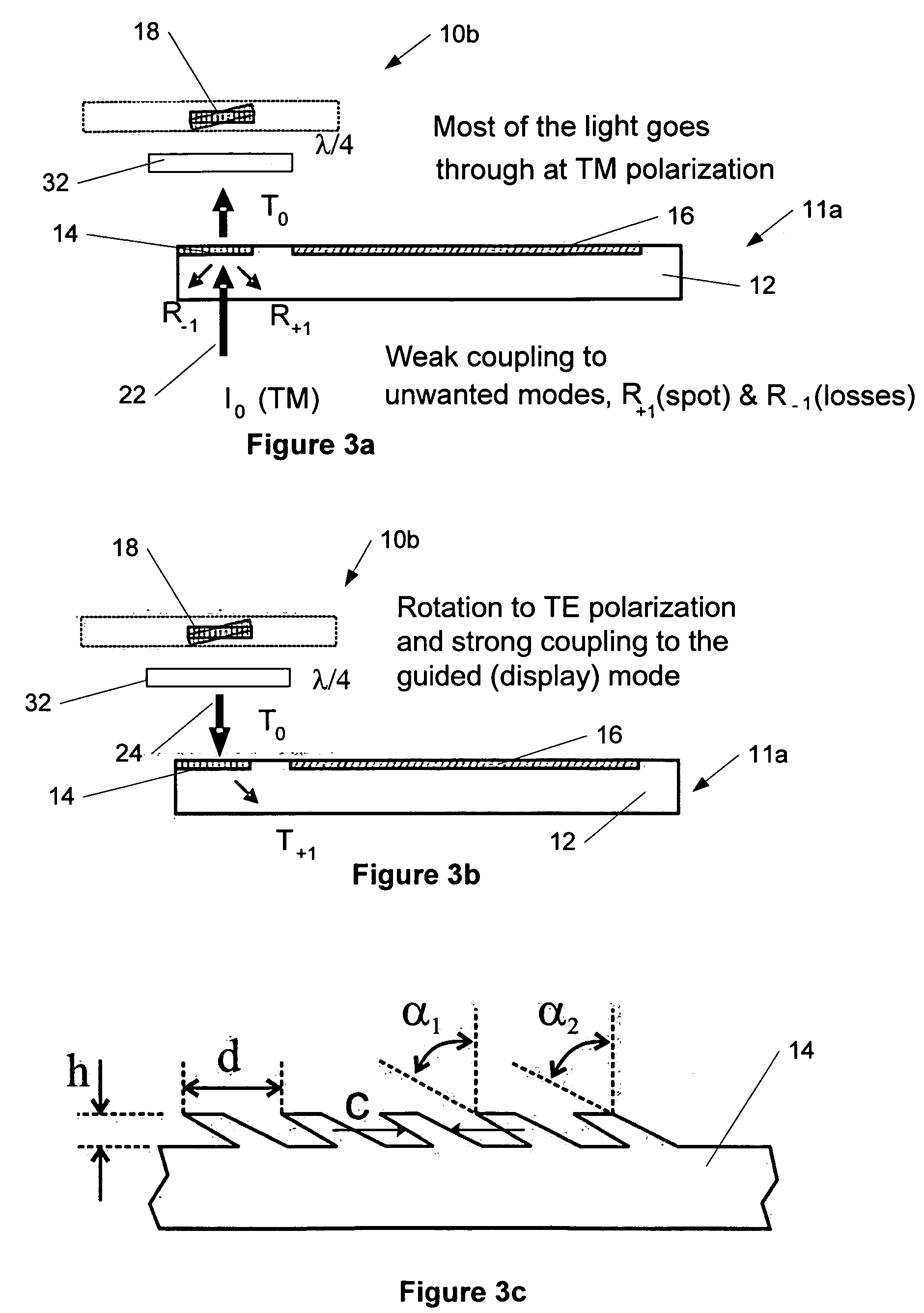
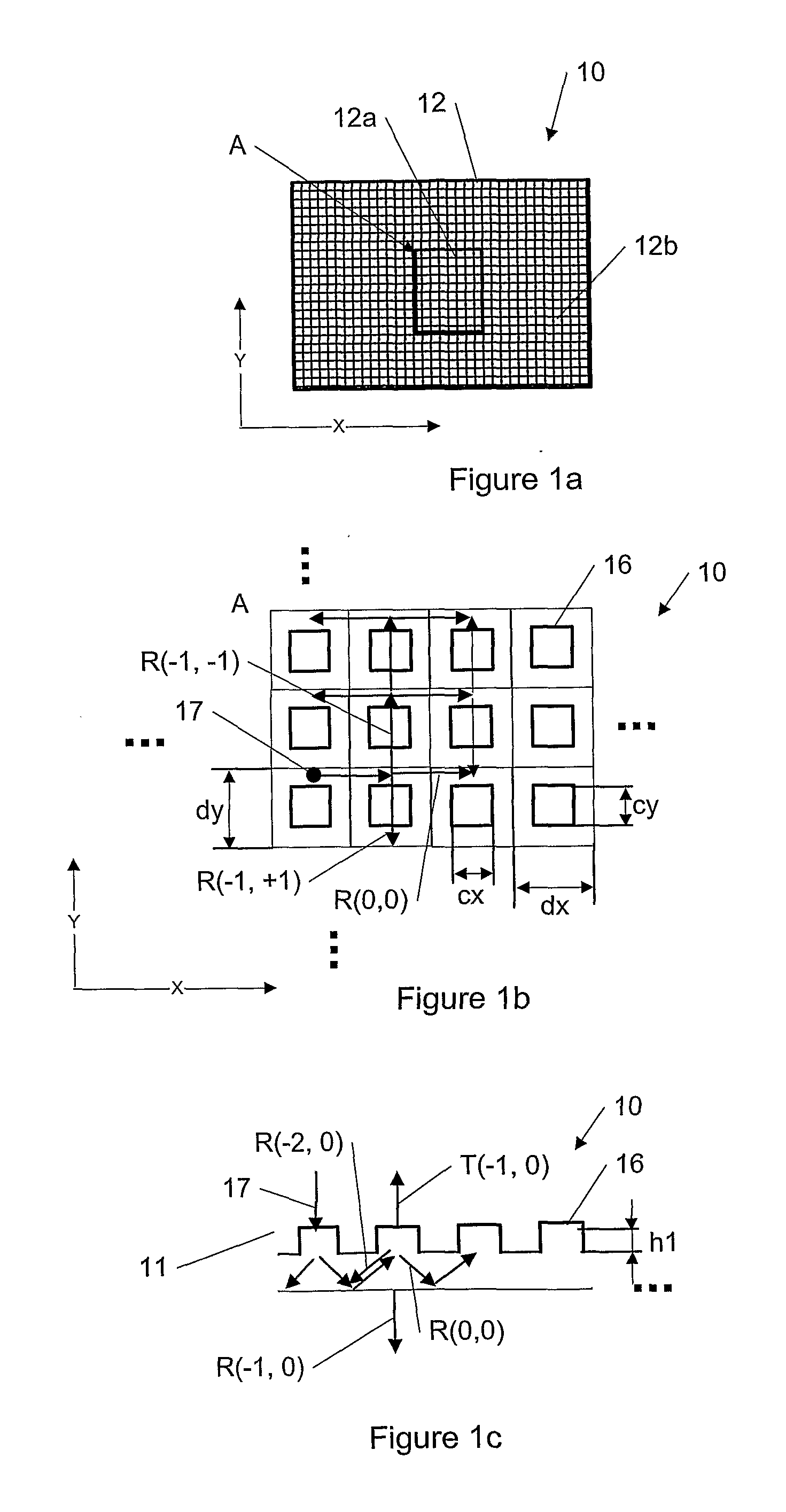
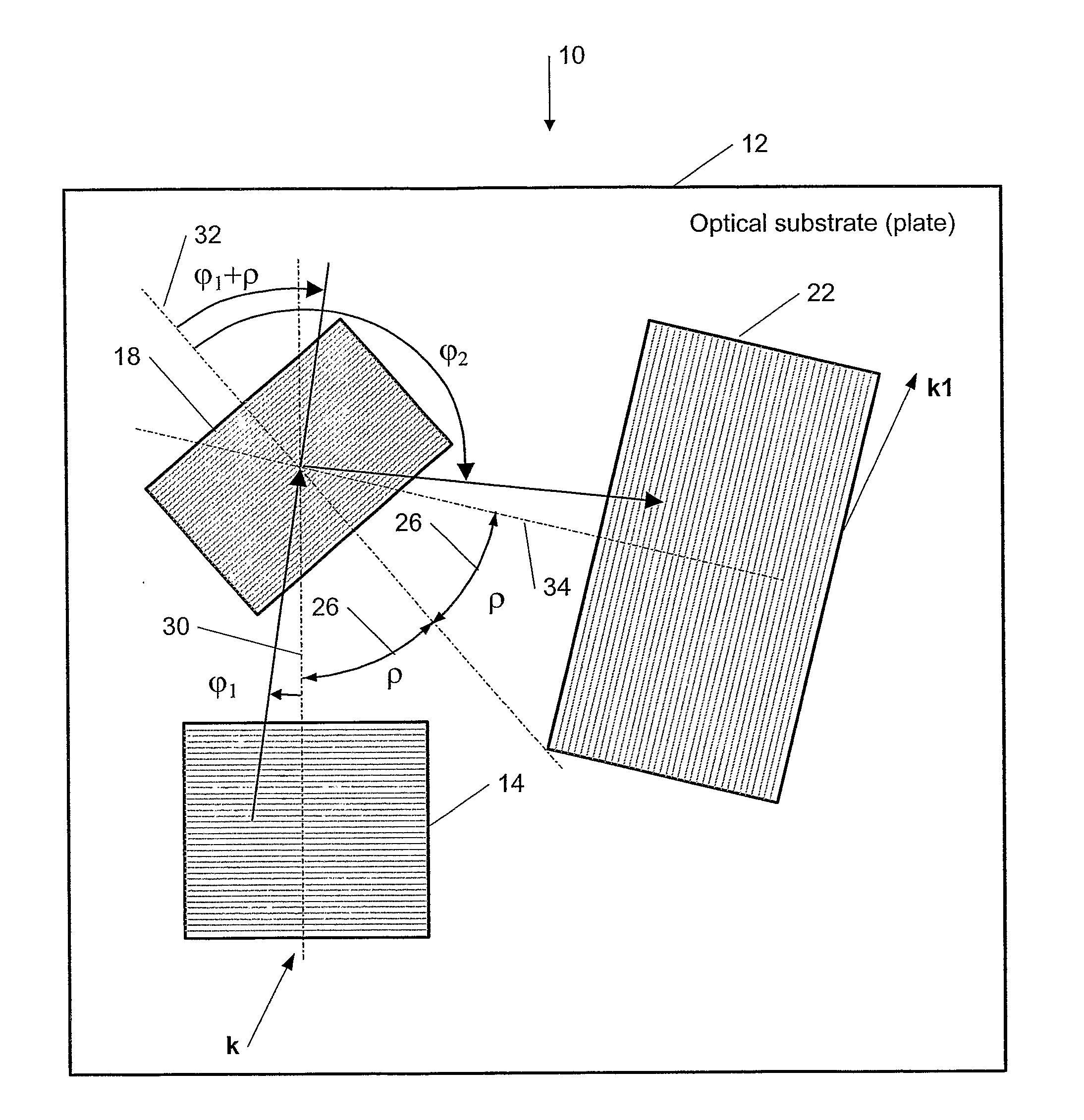
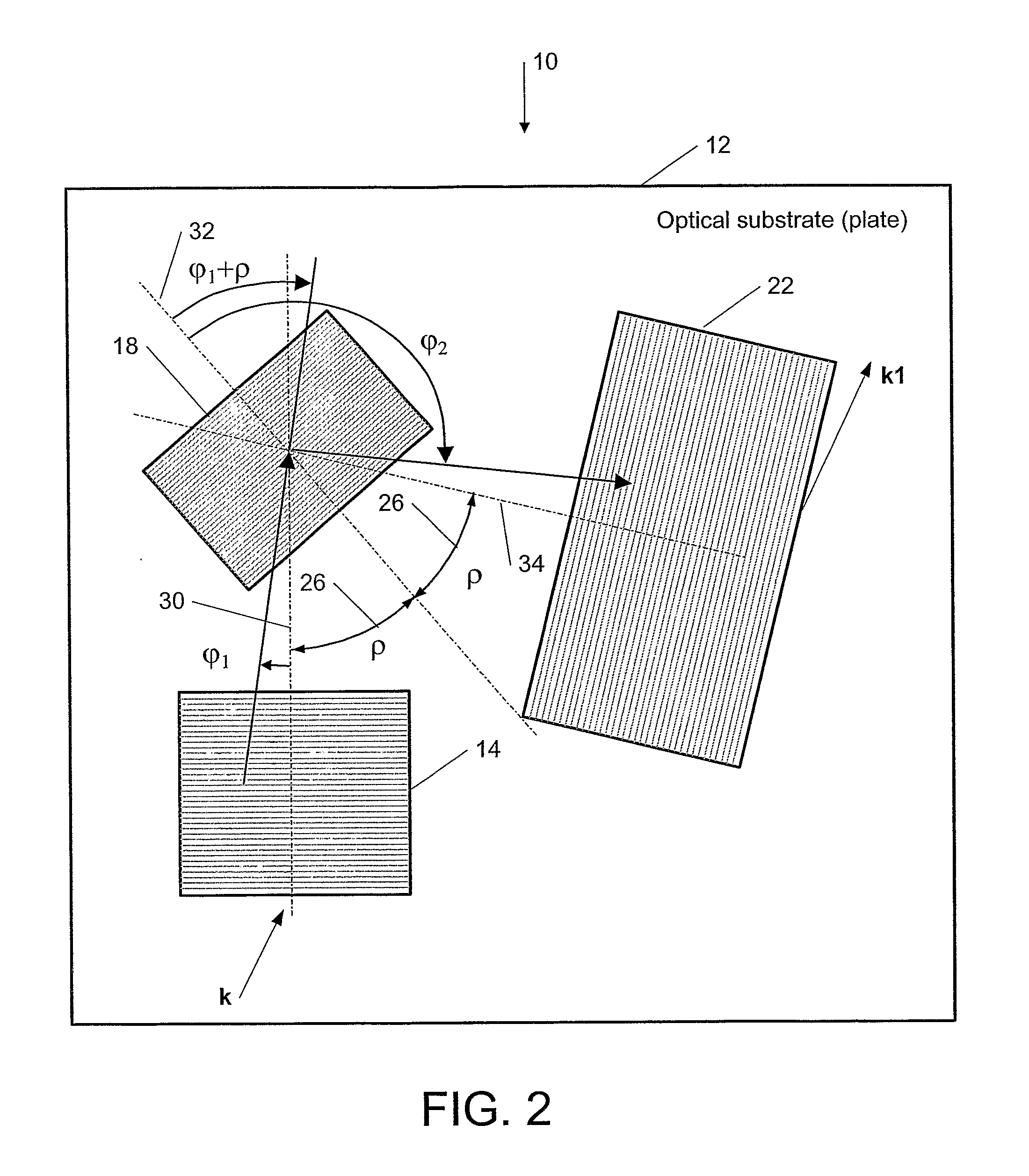
This invention describes a general diffractive optics method that uses a plurality of diffractive elements on an optical substrate for expanding the exit pupil of a display of an electronic device for viewing. The method can be used for optical coupling in an optical device and it is characterized by extending of an exit pupil of an input optical beam in an output optical beam wherein the optical device comprises: an optical substrate and in-coupling, intermediate and out-coupling diffractive element disposed on the optical substrates, wherein periodic lines of the intermediate diffractive element comprise an angle ρ with periodic lines of the in-coupling and of the out-coupling diffractive elements, respectively. The system can support a broad range of rotation angles (e.g., 0<ρ<70°) and corresponding conical angles and remains geometrically accurate.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Holographic Waveguide Display
ActiveUS20150160529A1Minimizing laser speckleBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsPlanar/plate-like light guidesExit pupilGrating
A holographic waveguide display comprises: a source of light; at least one switchable grating layer comprising a multiplicity of grating regions each switchable between a diffracting state and a non diffracting state; means for spatio-temporally modulating light from the source to provide image light comprising at least one beam deflector for scanning the light in at least one of two orthogonal directions and at least one modulator for amplitude modulating the light. A first scanned angular range of light is diffracted through a first area into a first field of view by a first set of grating regions, and through a second area into to the first field of view by a second set of grating regions. Each grating region of the first and second sets has a first grating function. The first and second areas lie within an exit pupil of the display.
Owner:DIGILENS
General diffractive optics method for expanding an exit pupil
An exit pupil extender with one input optical element and two exit optical elements disposed on different sides of the input optical element. The exit pupil extender also comprises two intermediate diffractive optical couplers, each disposed between the input optical element and one exit optical element. The couplers serve as exit pupil extending components. The grating lines of the couplers are at substantially a 60-degree angle from that of the optical elements in order to optimize the exit pupil extending efficiency. This invention further describes a general diffractive optics method that uses a plurality of diffractive elements on an optical substrate for expanding the exit pupil of a display of an electronic device for viewing. The system can support a broad range of rotations angles (e.g., 0<ρ<70°) and corresponding conical angles and remains geometrically accurate.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Optical image display system and image display unit
InactiveUS20070008624A1Simple structureLarge exit pupilTelevision system detailsPolarising elementsExit pupilLight beam
Optical-image display systems are disclosed having simple structure and a large exit pupil. An exemplary system includes a transmissive plate having inside an optical path of light flux from a display at each angular field of view of an image-display element. The light flux is internally reflected repeatedly in the transmissive plate. An optical-deflection member is provided in close contact with a predetermined region of one surface of the plate used for internal reflection. The optical-deflection member emits to the outside of the plate a portion of each of the light fluxes from the display having reached the predetermined region, and deflects a portion of each light flux in a predetermined direction by reflection. Thus, a virtual image is formed of the display screen of the image-display element.
Owner:NIKON CORP
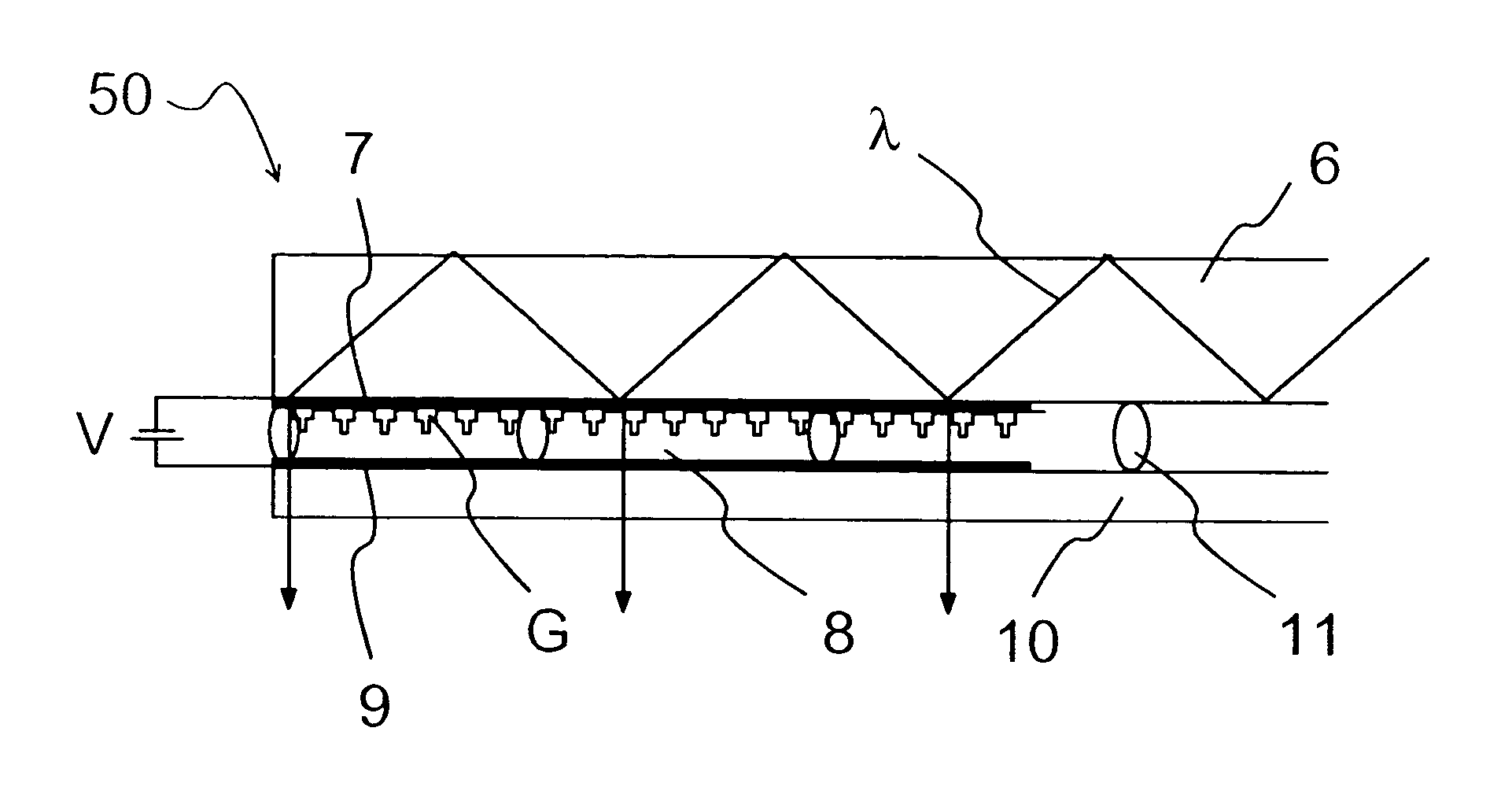
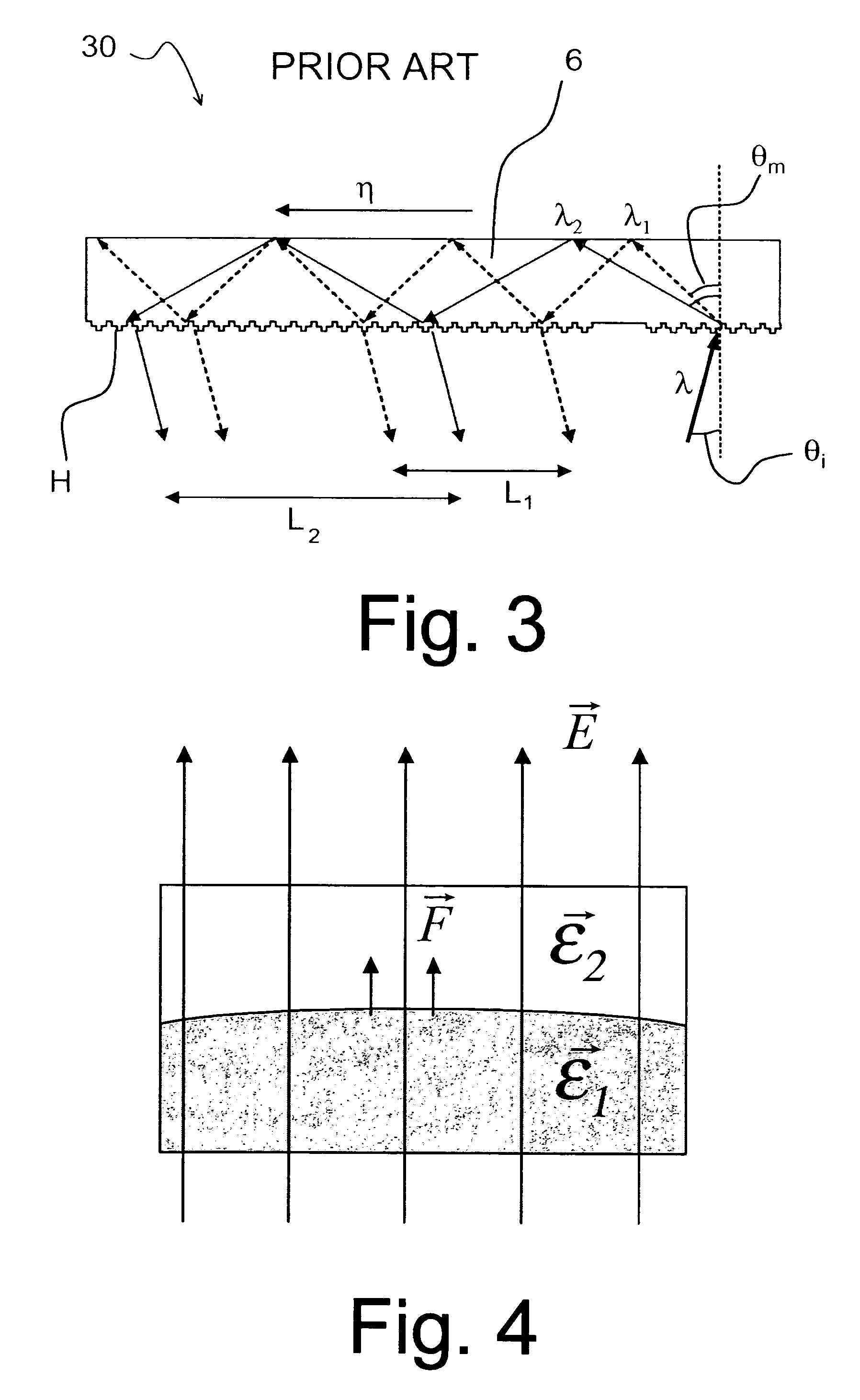
Electrically tunable diffractive grating element
ActiveUS7184615B2Improve color uniformityImprove image qualityDiffraction gratingsCoupling light guidesElectricityExit pupil
The invention relates to an optical device (50) for manipulating a light wave (λ) using a diffractive grating structure (G). According to the basic idea behind the invention a prior art type diffractive grating structure having a permanently shaped surface relief is substituted with an electrically deformable diffractive grating structure (G), where a preformed, basic surface relief of the grating is composed of dielectric and deformable viscoelastic material, which can be electrically and sequentially fine tuned in shape to adjust the diffraction properties of said grating individually for different wavelengths. The invention permits manufacture of virtual display devices with a significantly larger exit pupil diameter than prior art solutions without degrading the color uniformity of the display device.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
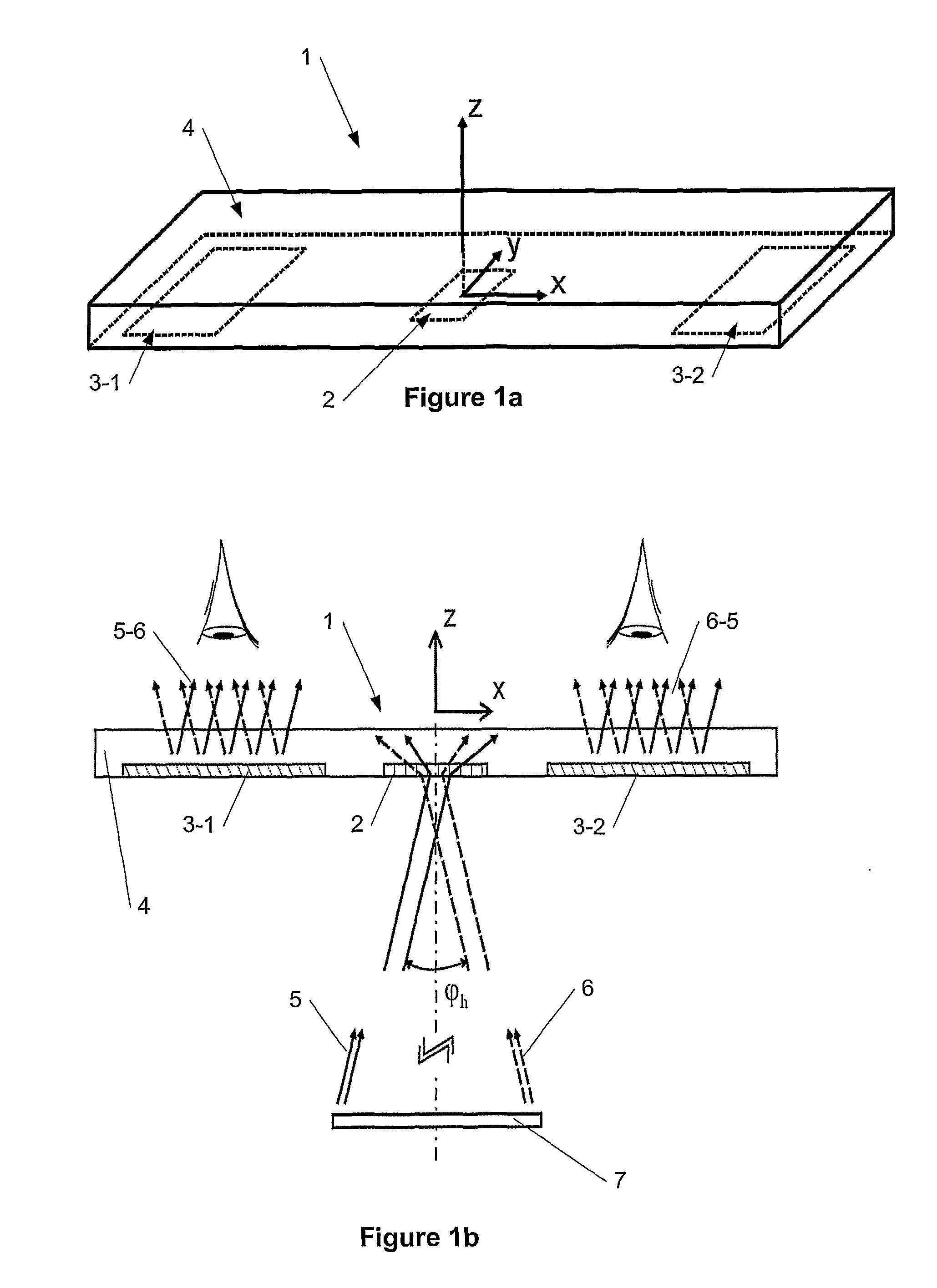
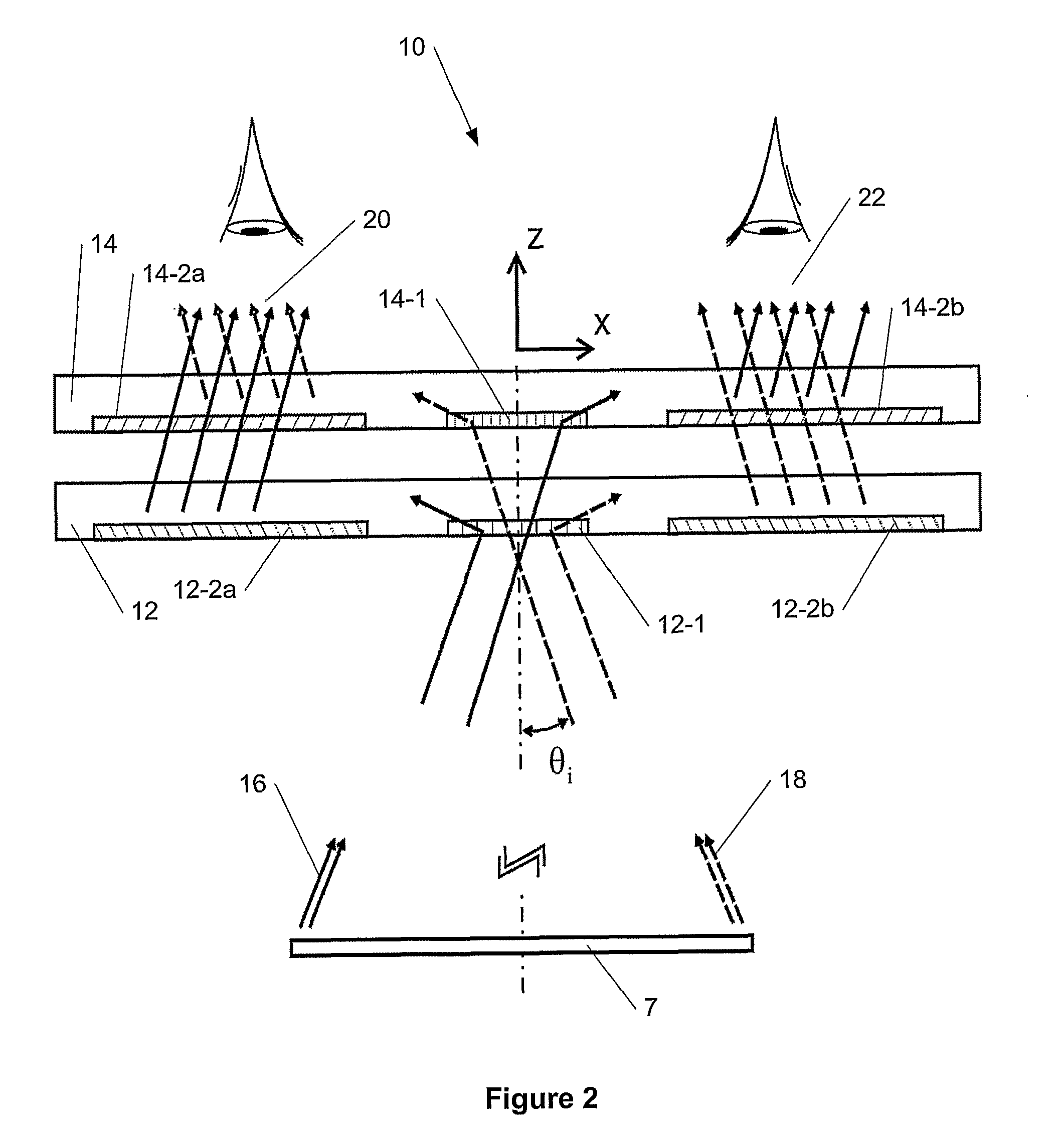
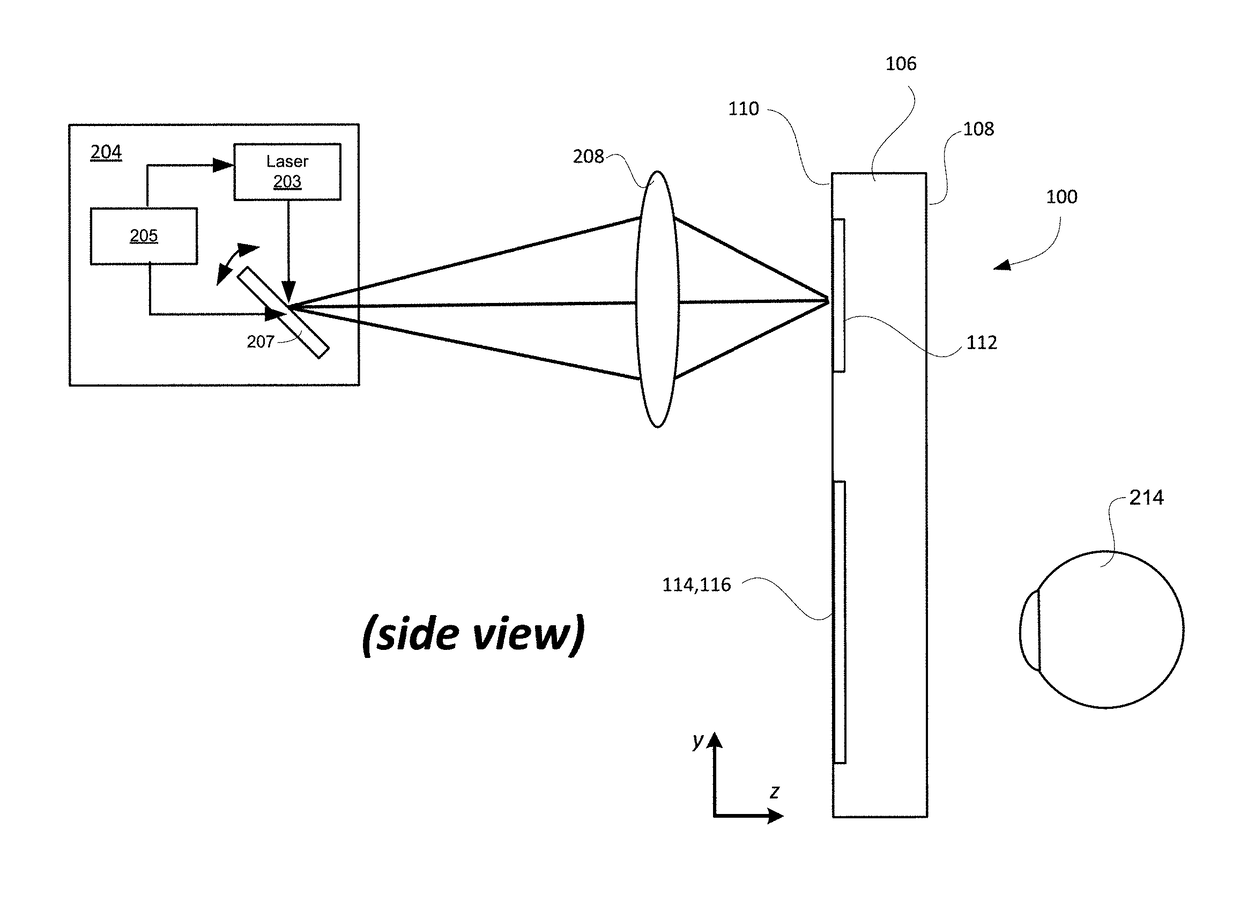
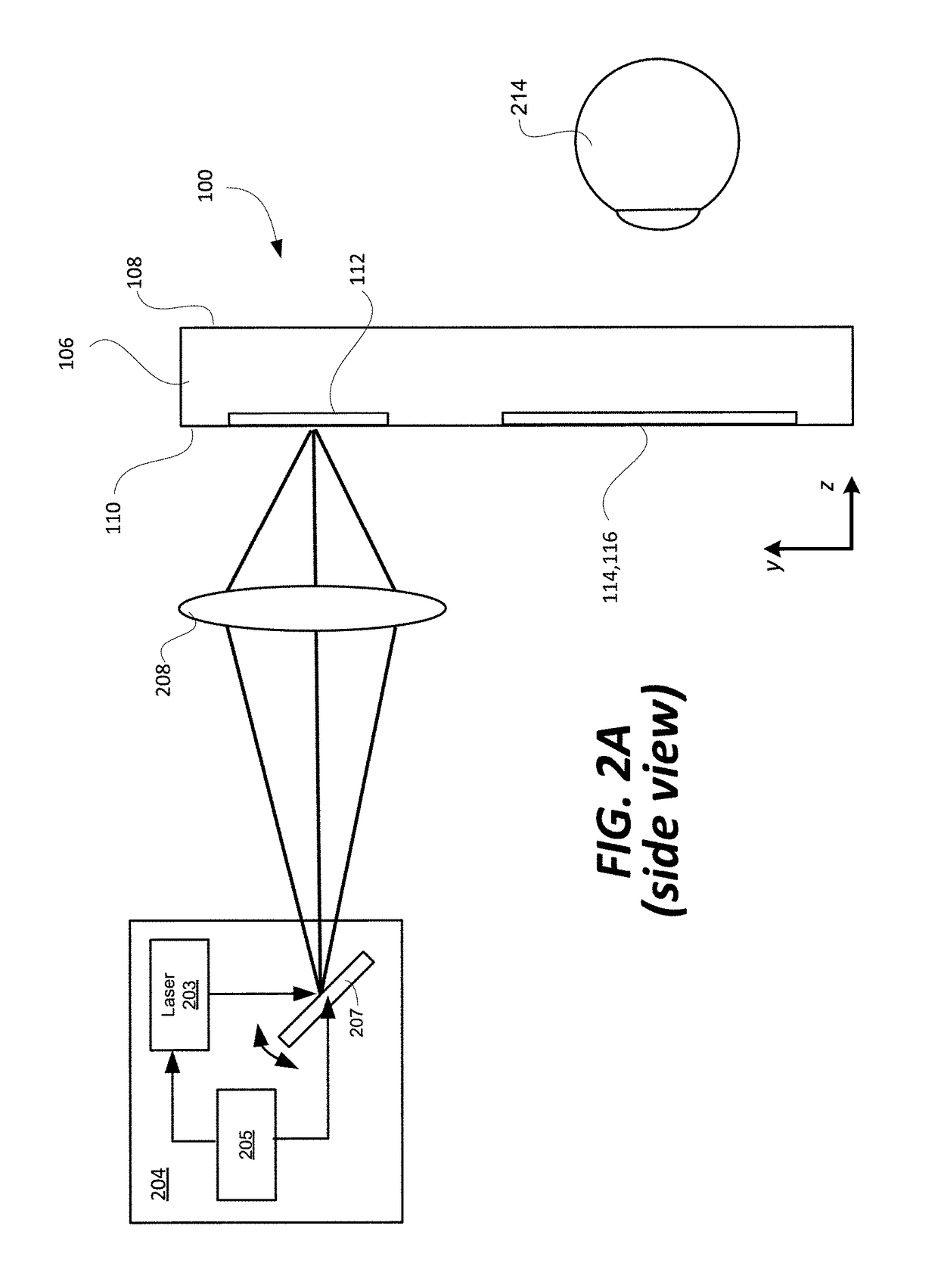
Systems, devices, and methods for eyebox expansion in wearable heads-up displays
ActiveUS20160238845A1Input/output for user-computer interactionStatic indicating devicesHead-up displayExit pupil
Systems, devices, and methods for eyebox expansion by exit pupil replication in wearable heads-up displays (“WHUDs”) are described. A WHUD includes a scanning laser projector (“SLP”), a holographic combiner, and an exit pupil selector positioned in the optical path therebetween. The exit pupil selector is controllably switchable into and between N different configurations. In each of the N configurations, the exit pupil selector receives a light signal from the SLP and redirects the light signal towards the holographic combiner effectively from a respective one of N virtual positions for the SLP. The holographic combiner converges the light signal to a particular one of N exit pupils at the eye of the user based on the particular virtual position from which the light signal is made to effectively originate. In this way, multiple instances of the exit pupil are distributed over the eye and the eyebox of the WHUD is expanded.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
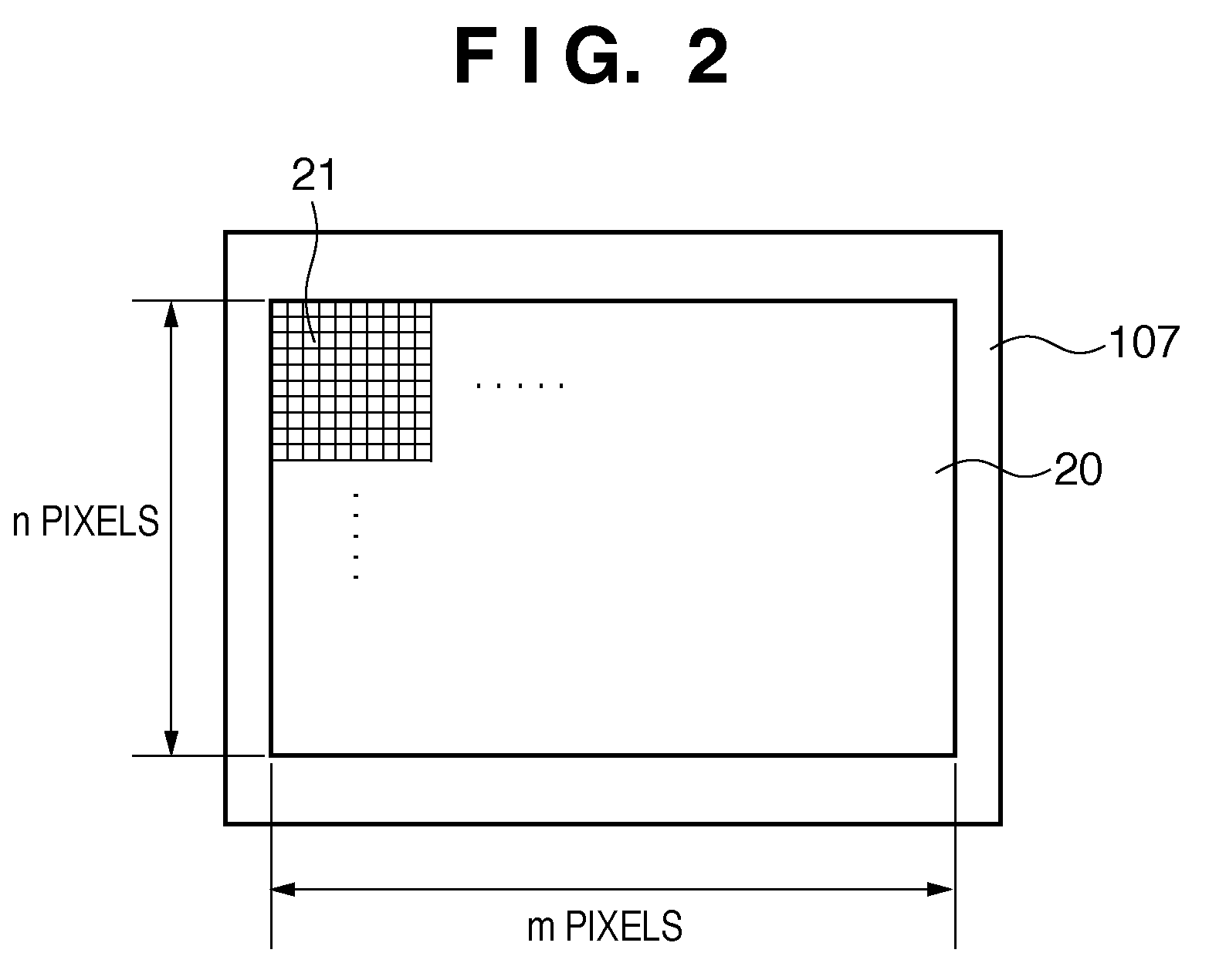
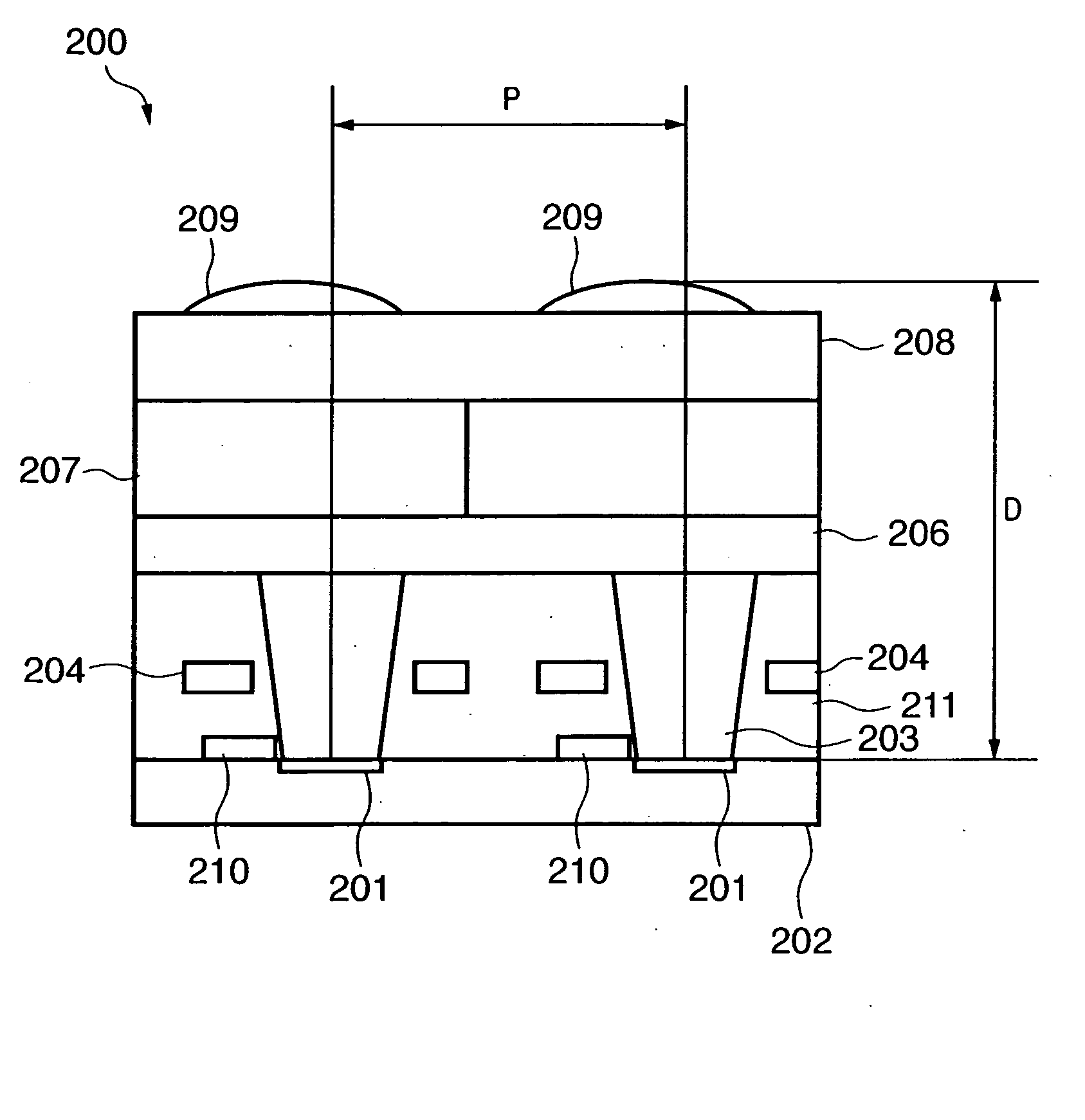
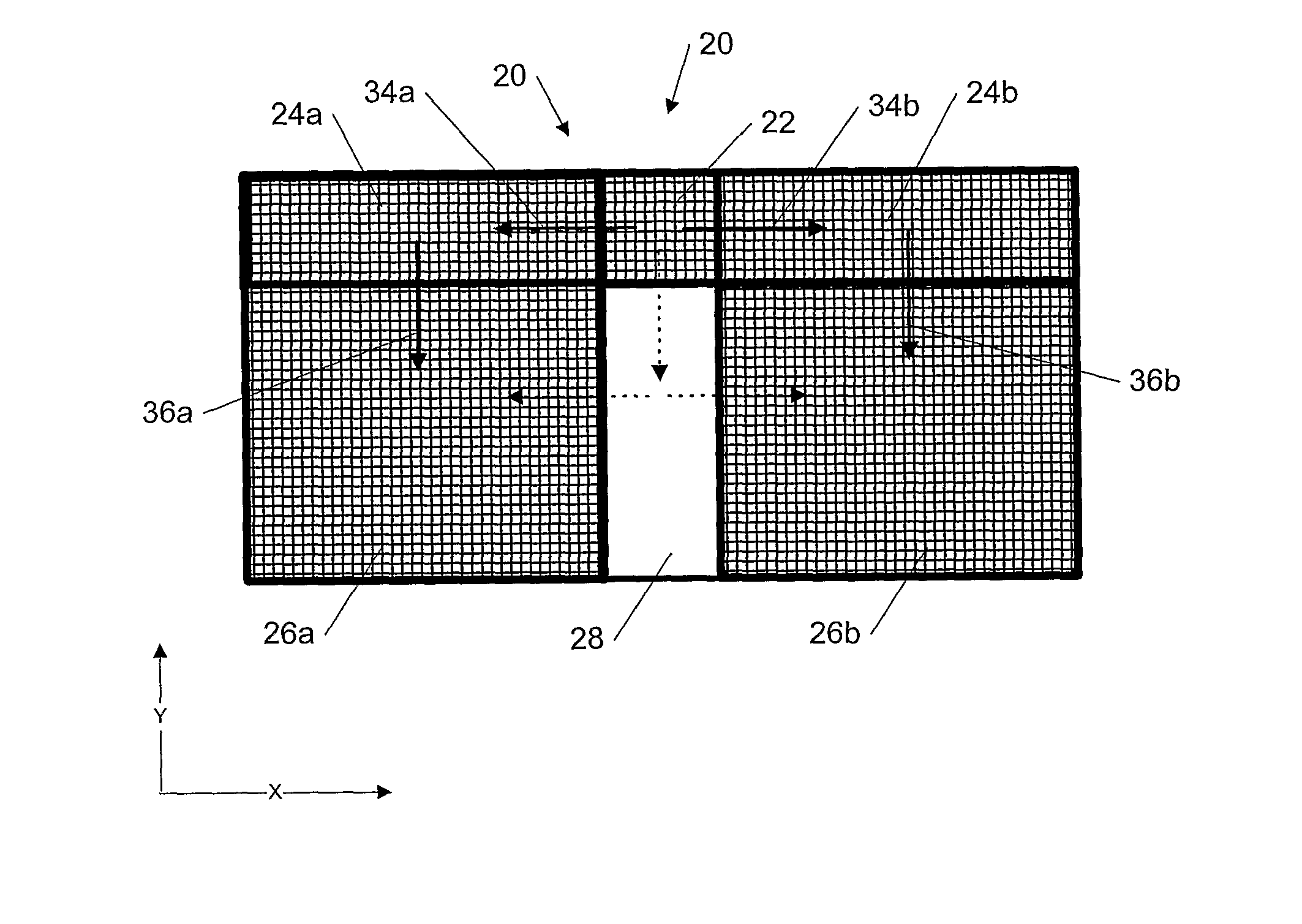
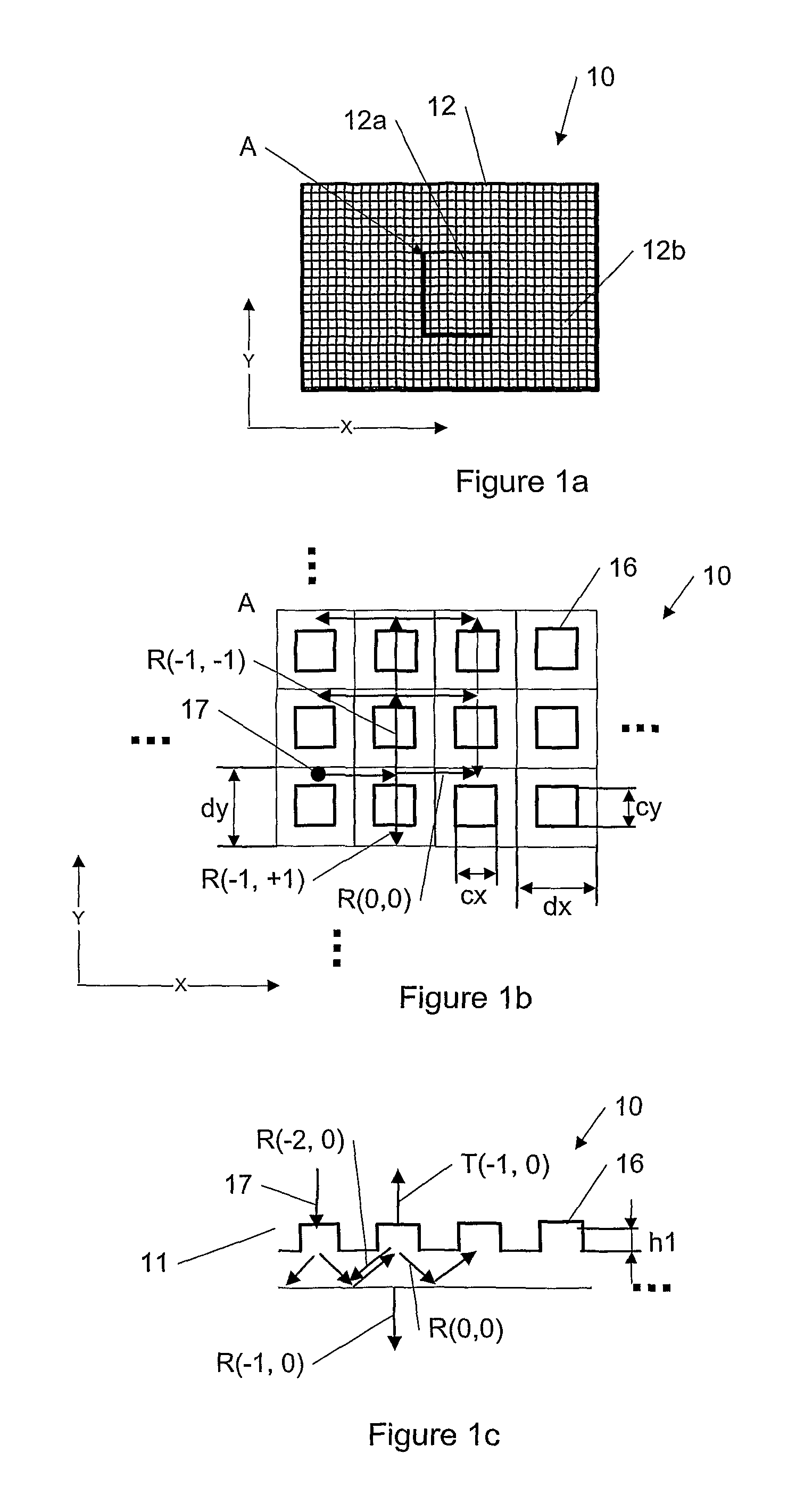
Solid-state image sensing element and its design support method, and image sensing device
ActiveUS20050236553A1Increase freedomImprove light collection efficiencyTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesExit pupilLight guide
A solid-state image sensing element has a photoelectric conversion element which converts incoming light into an electrical signal in accordance with an amount of the light, a microlens which is arranged on an incident surface, a light guide which is arranged between the photoelectric conversion element and the microlens, and an insulating interlayer which is arranged around the light guide. The solid-state image sensing element located at a distance (H) satisfies: H·DL·P<a·NHNL for 0<a<1where L is the distance from an exit pupil of an image sensing optical system of an image sensing device, which mounts an image sensor formed by two-dimensionally arranging a plurality of the solid-state image sensing elements, H is the distance from a center of the image sensor to a position of the solid-state image sensing element on the image sensor, D is the height from the photoelectric conversion element to an apex of the microlens, P is the spacing between the plurality of solid-state image sensing elements, NH is the refractive index of the light guide, and NL is the refractive index of the insulating interlayer.
Owner:CANON KK
Beam expansion with three-dimensional diffractive elements
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Waveguide-Based Displays With Exit Pupil Expander
ActiveUS20170299860A1Good optical performanceMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesHead-up displayExit pupil
A near eye or heads up display system includes a scan beam projector engine, an optical waveguide, and an exit pupil expander (EPE) optically coupled between the scan beam projector engine and the optical waveguide. The EPE improves the optical performance of the display system. The EPE could include a diffusive optical element, diffractive optical element, micro-lens array (MLA), or relay of aspherical lenses. A dual MLA EPE may have cells that prevent cross-talk between adjacent pixels. A dual MLA EPE may have a non-periodic lens array. The optical power of one MLA may be different from the other MLA.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
High brightness optical device
ActiveUS8098439B2Design and fabrication is facilitatedEasy to useProjectorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsExit pupilOptical Module
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Backside illumination image sensor and image-capturing device
ActiveUS20110279727A1Avoid reflectionsTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesExit pupilPhotoelectric conversion
A backside illumination image sensor that includes a semiconductor substrate with a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements and a read circuit formed on a front surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and captures an image by outputting, via the read circuit, electrical signals generated as incident light having reached a back surface side of the semiconductor substrate is received at the photoelectric conversion elements includes: a light shielding film formed on a side where incident light enters the photoelectric conversion elements, with an opening formed therein in correspondence to each photoelectric conversion element; and an on-chip lens formed at a position set apart from the light shielding film by a predetermined distance in correspondence to each photoelectric conversion element. The light shielding film and an exit pupil plane of the image forming optical system achieve a conjugate relation to each other with regard to the on-chip lens.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Exit pupil expanders with spherical and aspheric substrates
The specification and drawings present a new apparatus and method for using exit pupil expanders (EPE) with spherical or aspheric non-flat substrates and a plurality of diffractive elements for expanding the exit pupil of a display for viewing in order to reduce image spreading. This can also enable improved image resolution and utilization of shorter focus distances.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Wide angle and high resolution tiled head-mounted display device
ActiveUS20130187836A1Avoiding pupil aberrationAvoid distortionPrismsCathode-ray tube indicatorsWide fieldExit pupil
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
Method and system for beam expansion in a display device
An exit pupil extender with one input optical element and two exit optical elements disposed on different sides of the input optical element. The exit pupil extender also comprises two intermediate optical couplers, each disposed between the input optical element and one exit optical element. The couplers serve as exit pupil extending components. All optical elements and couplers are diffractive optical elements having grating lines. The grating lines of one optical element are substantially parallel to that of other optical elements, but the grating lines of the couplers are at substantially a 60-degree angle from that of the optical elements in order to optimize the exit pupil extending efficiency.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Illumination system with variable adjustment of the illumination
InactiveUS20020136351A1Avoid lostSimple wayNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionGratingExit pupil
An illumination system comprises (a) a first optical element upon which a light beam impinges, where the first optical element has first raster elements that partition said light beam into light channels; (b) a second optical element that receives said light channels, where the second optical element has a second raster elements; (c) an object plane that receives said light channels via said second optical element; and (d) an exit pupil that is provided with an illumination via said object plane. The system is characterized by an assignment of a member of said first raster elements and a member of said second raster elements to each of said light channels to provide a continuous beam path from said first optical element to said object plane for each of said plurality of light channels. The assignment is changeable to provide an adjustment of said illumination in said exit pupil.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com