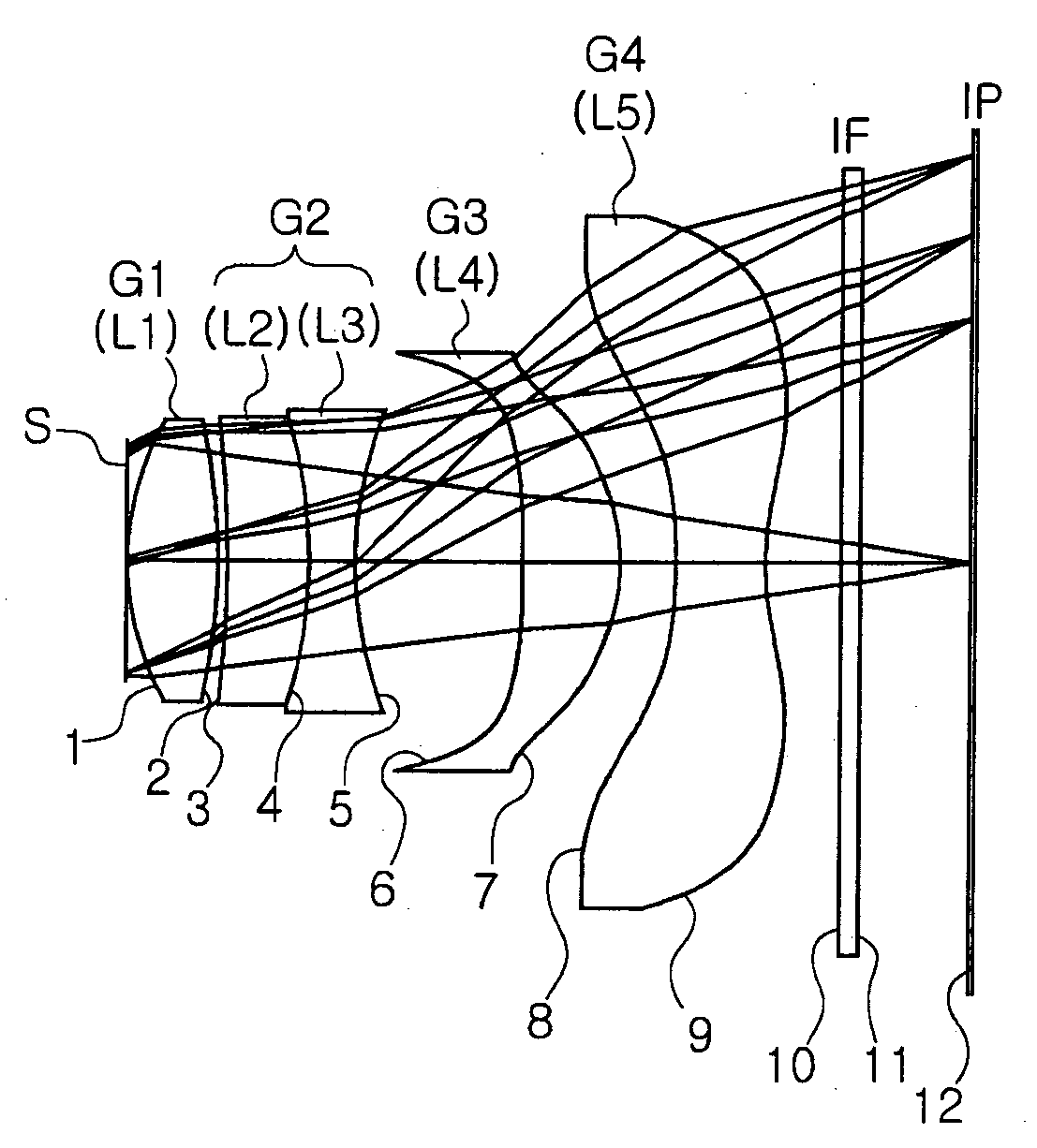
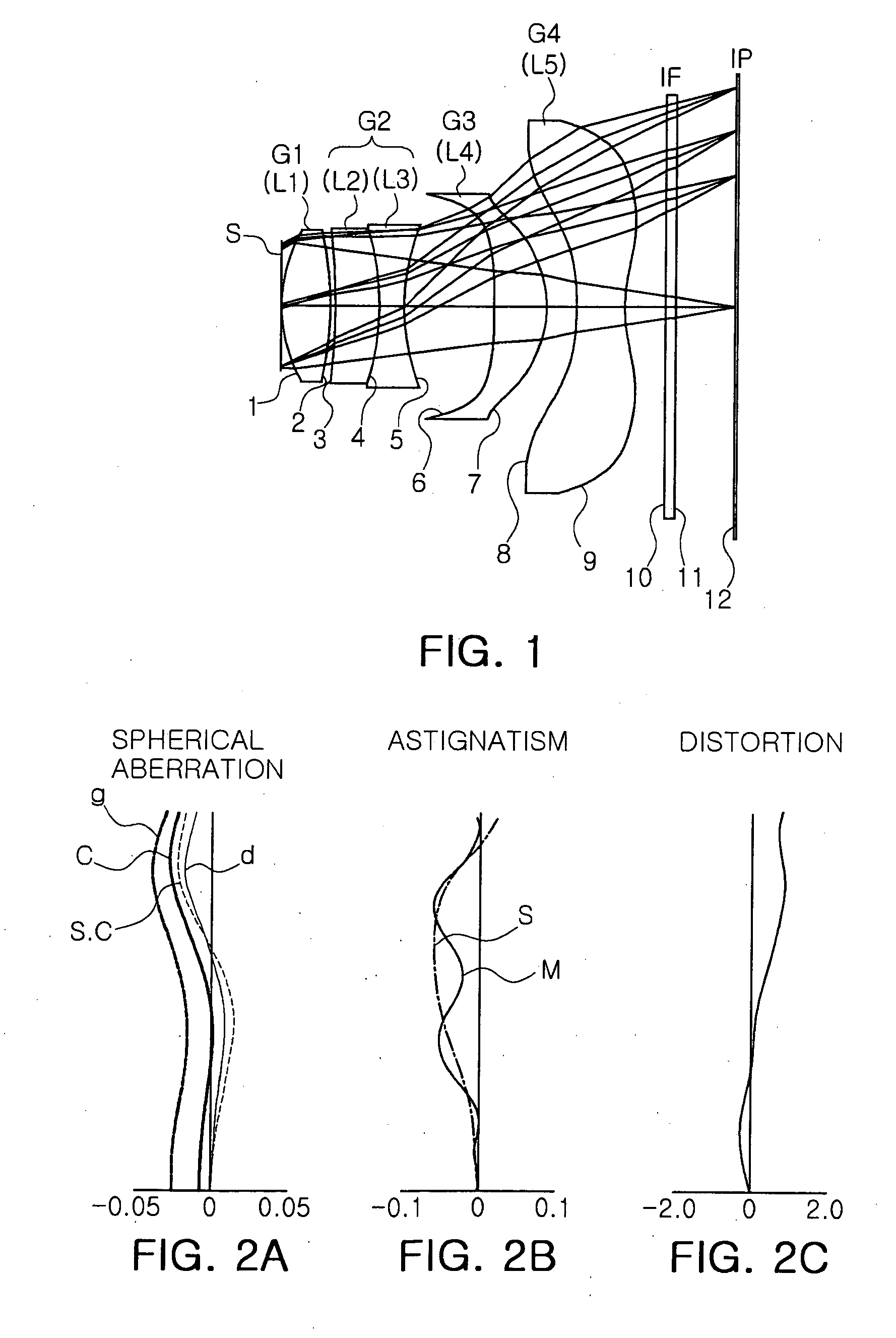
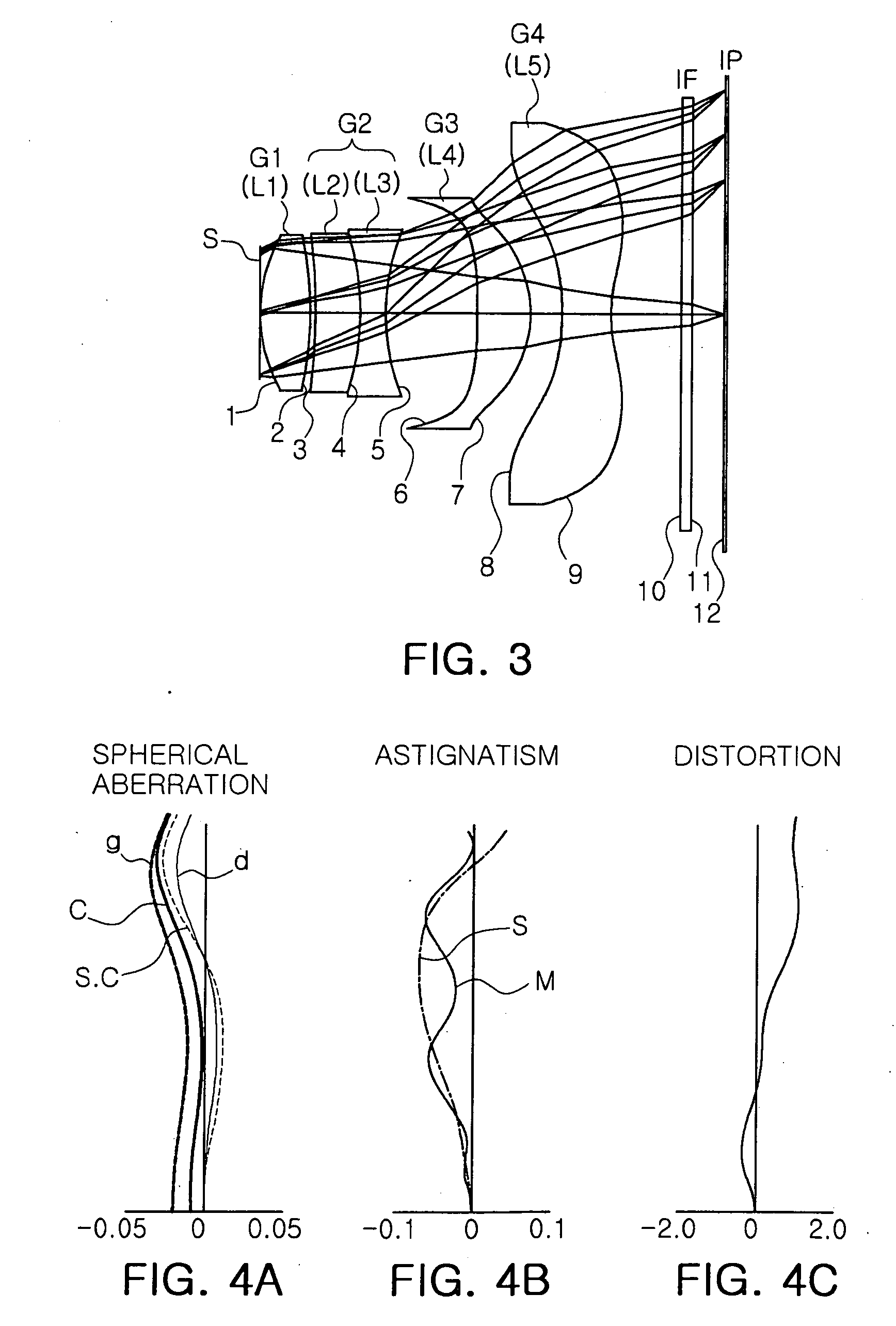
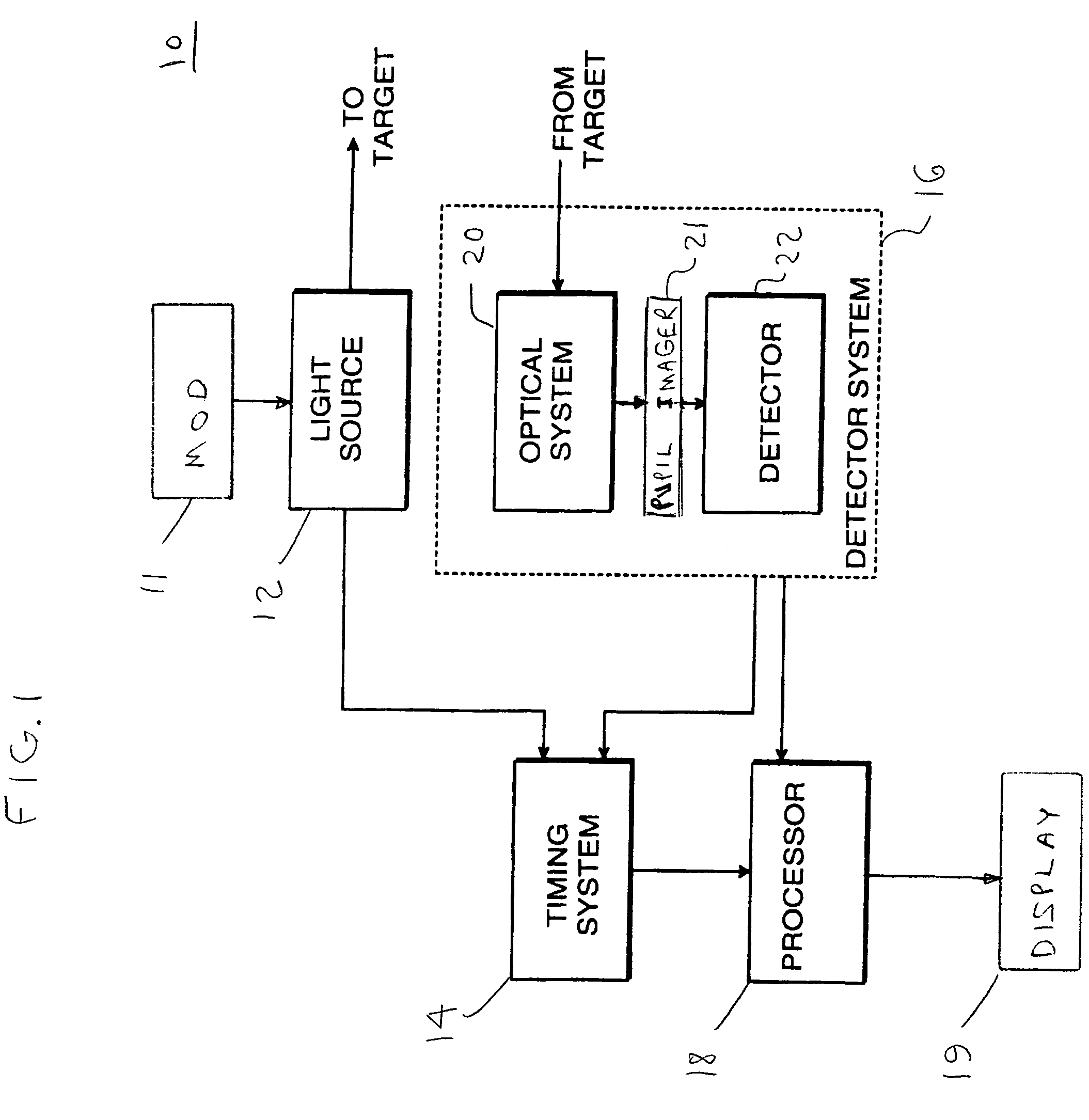
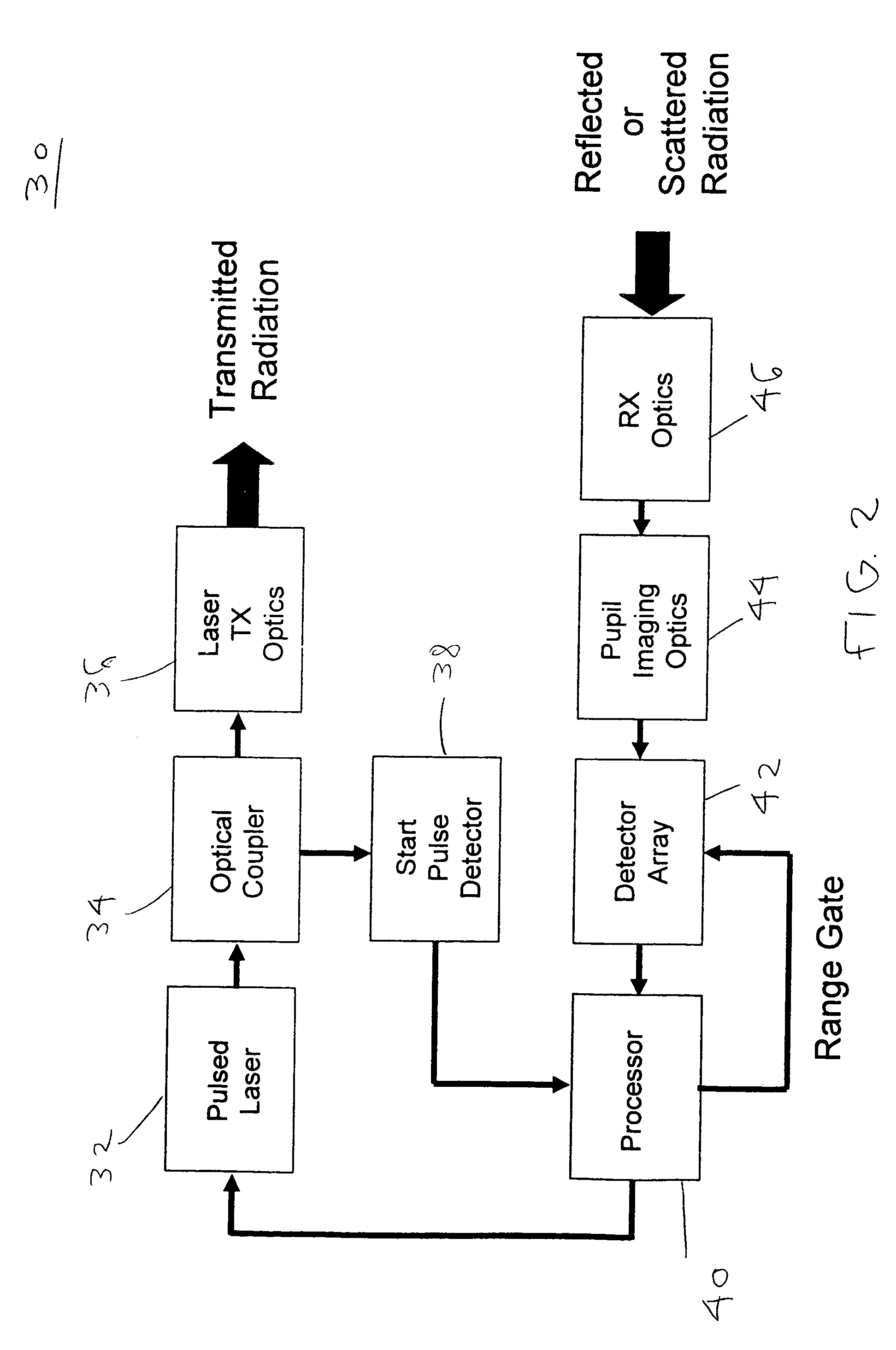
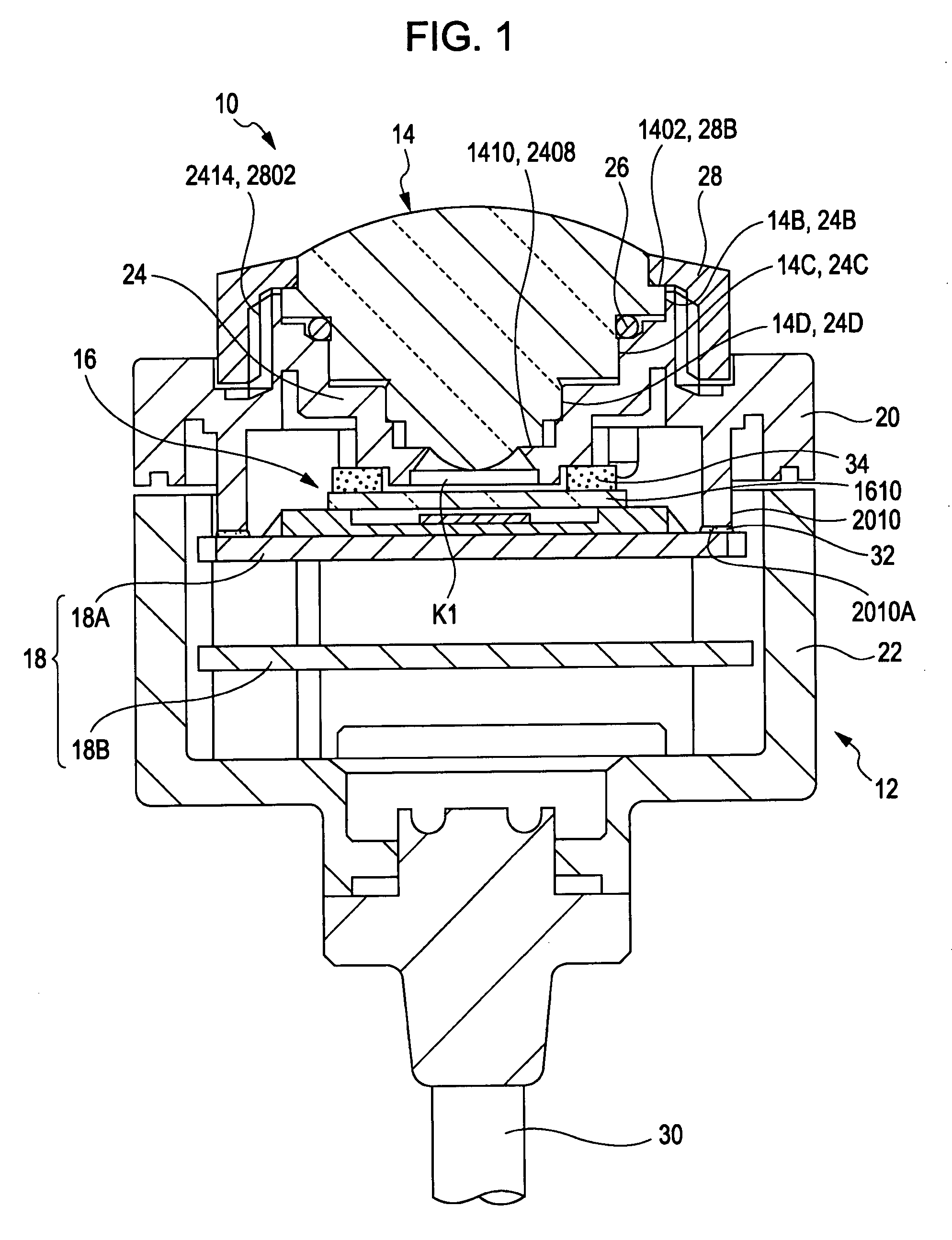
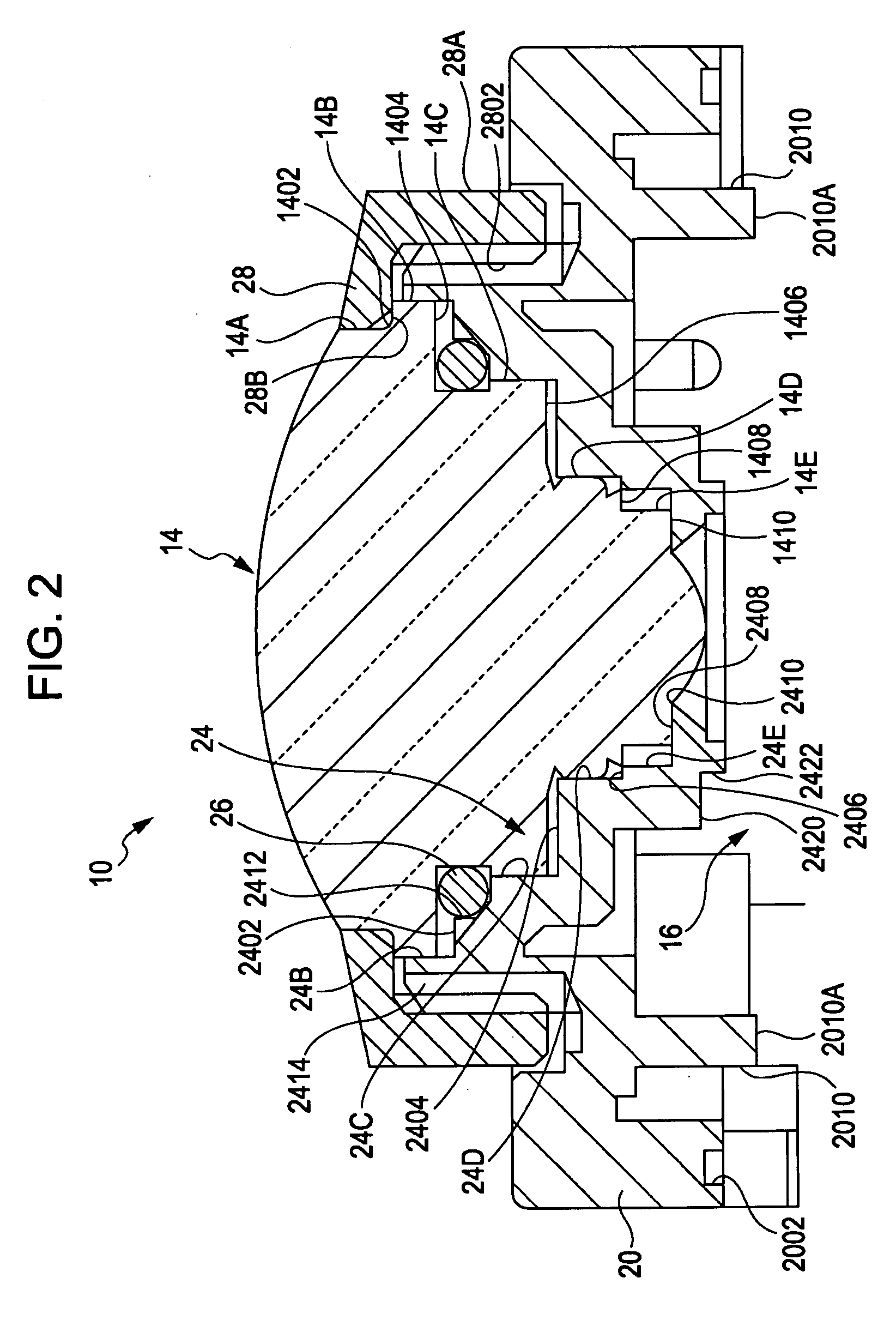
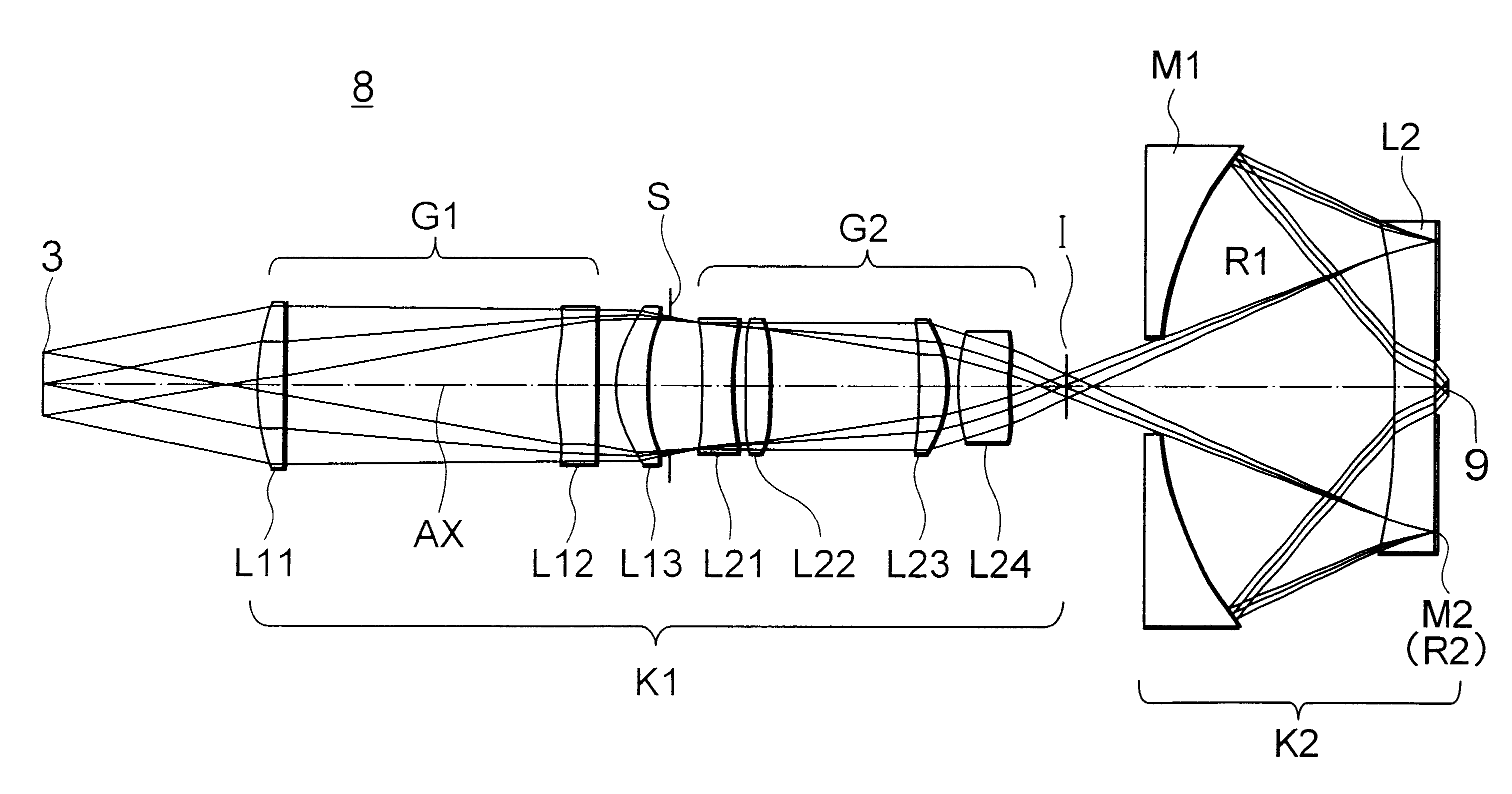
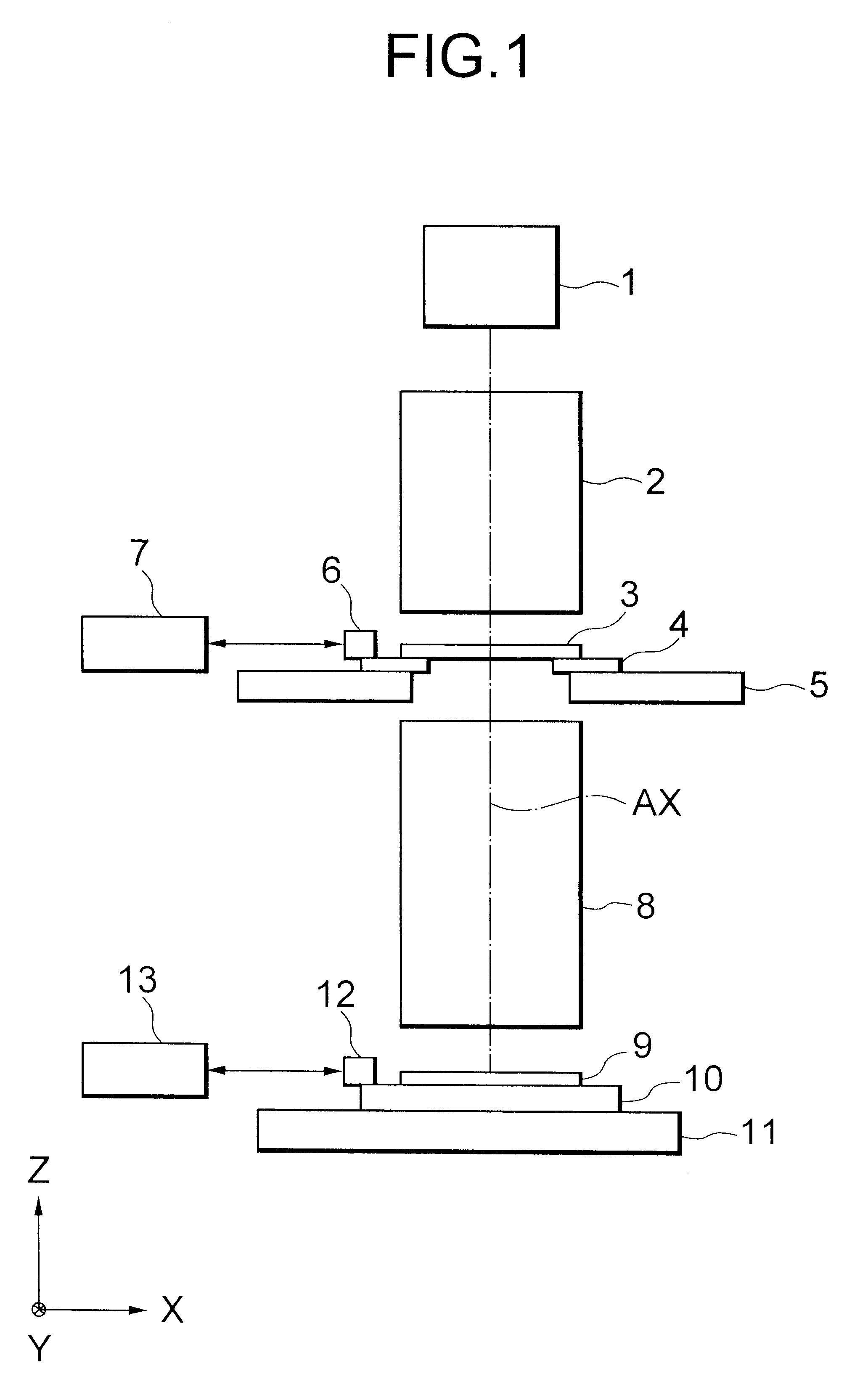
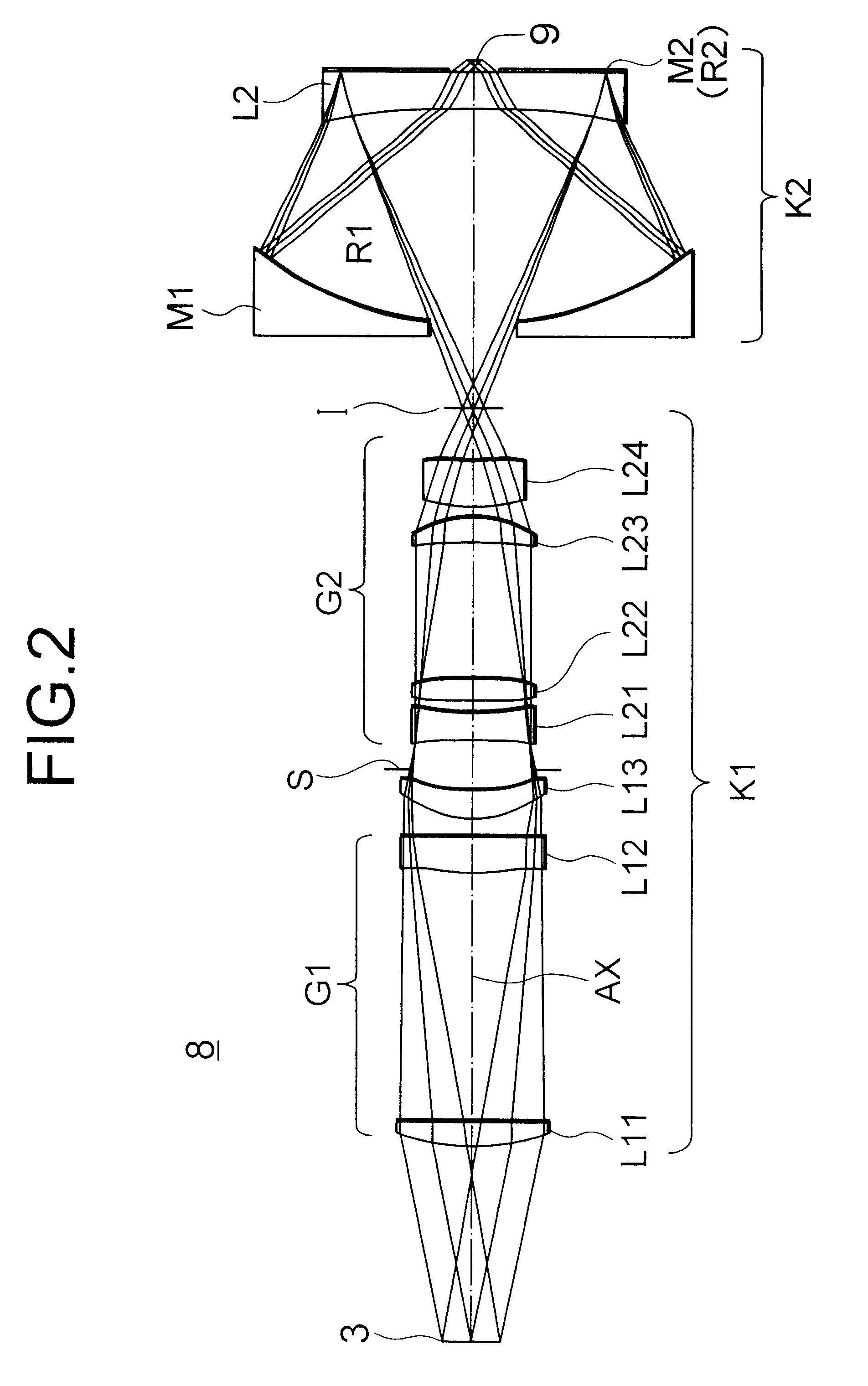
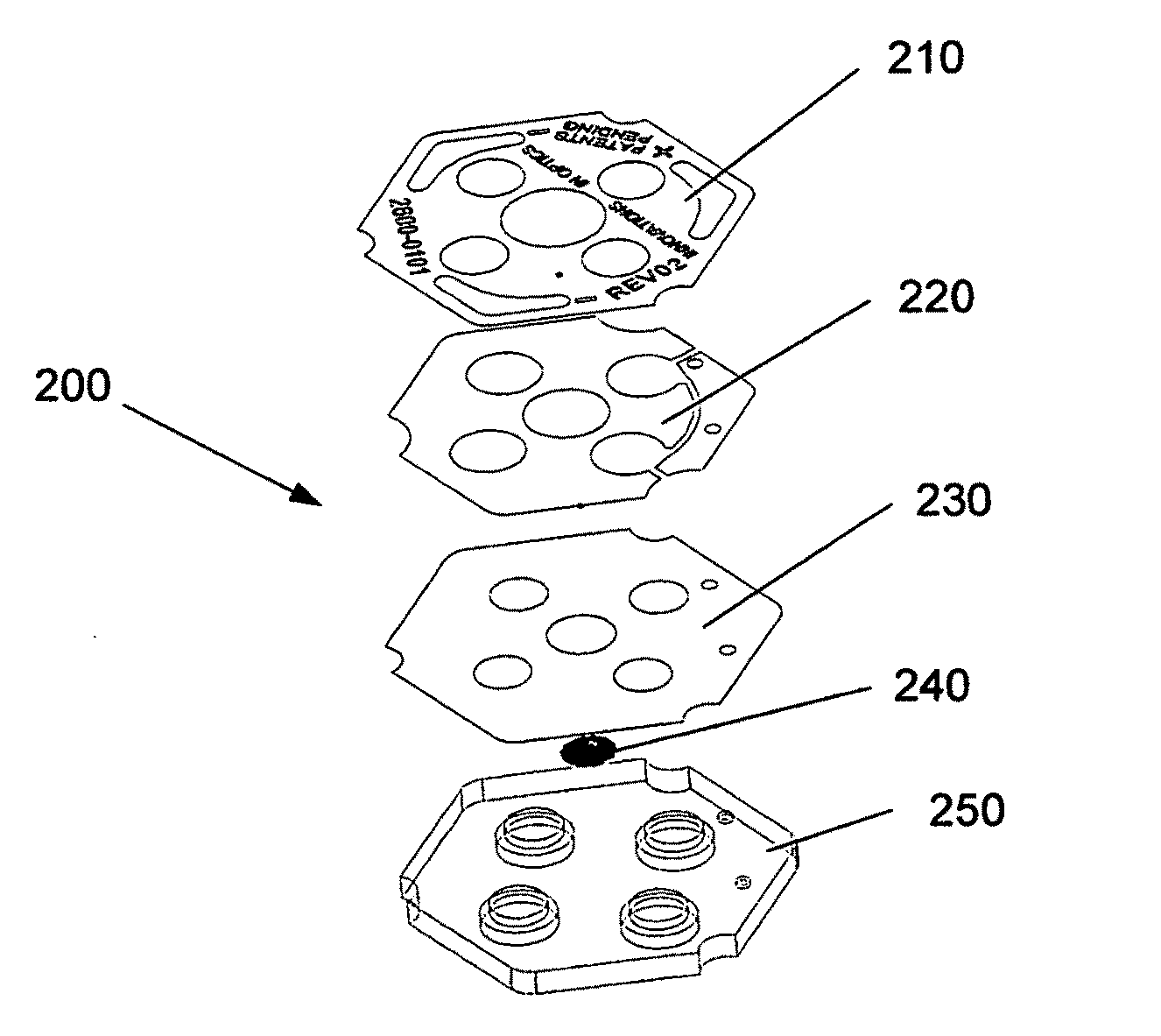
Patents
Literature
2578 results about "Image-forming optical system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In optics, an image-forming optical system is a system capable of being used for imaging. The diameter of the aperture of the main objective is a common criterion for comparison among optical systems, such as large telescopes.
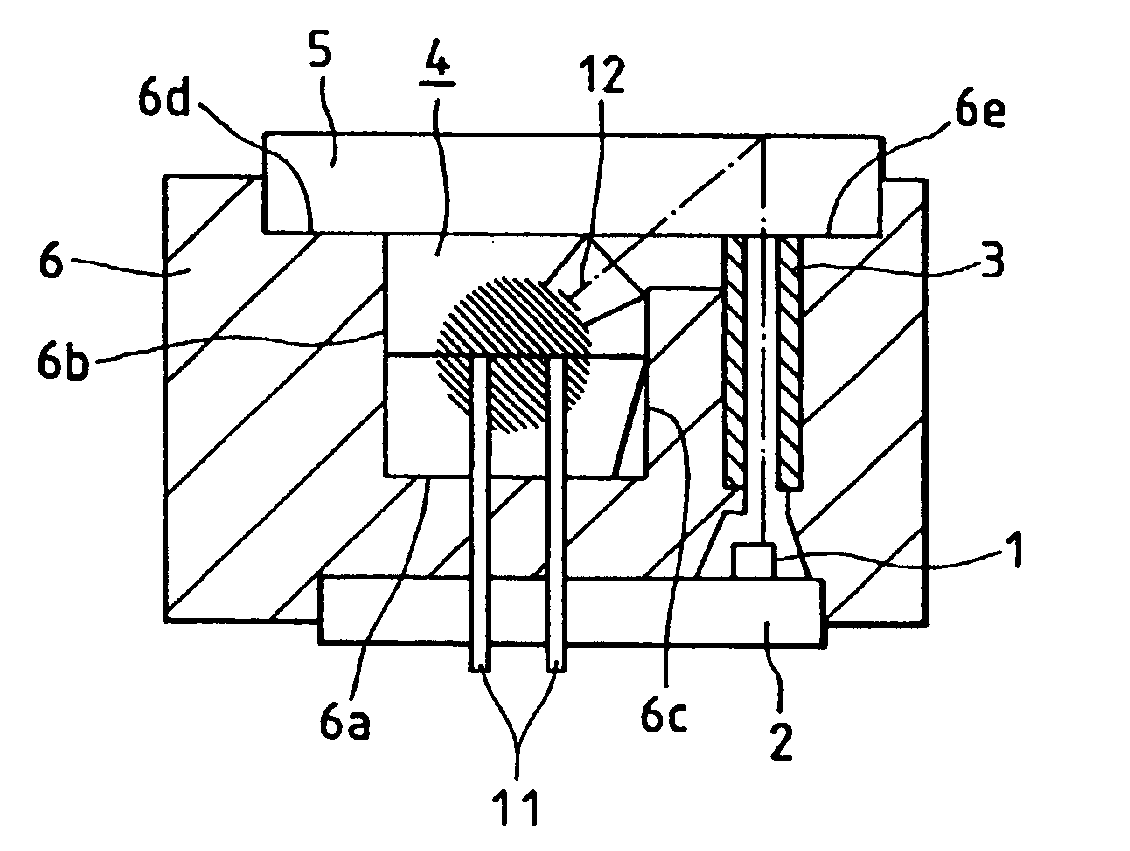
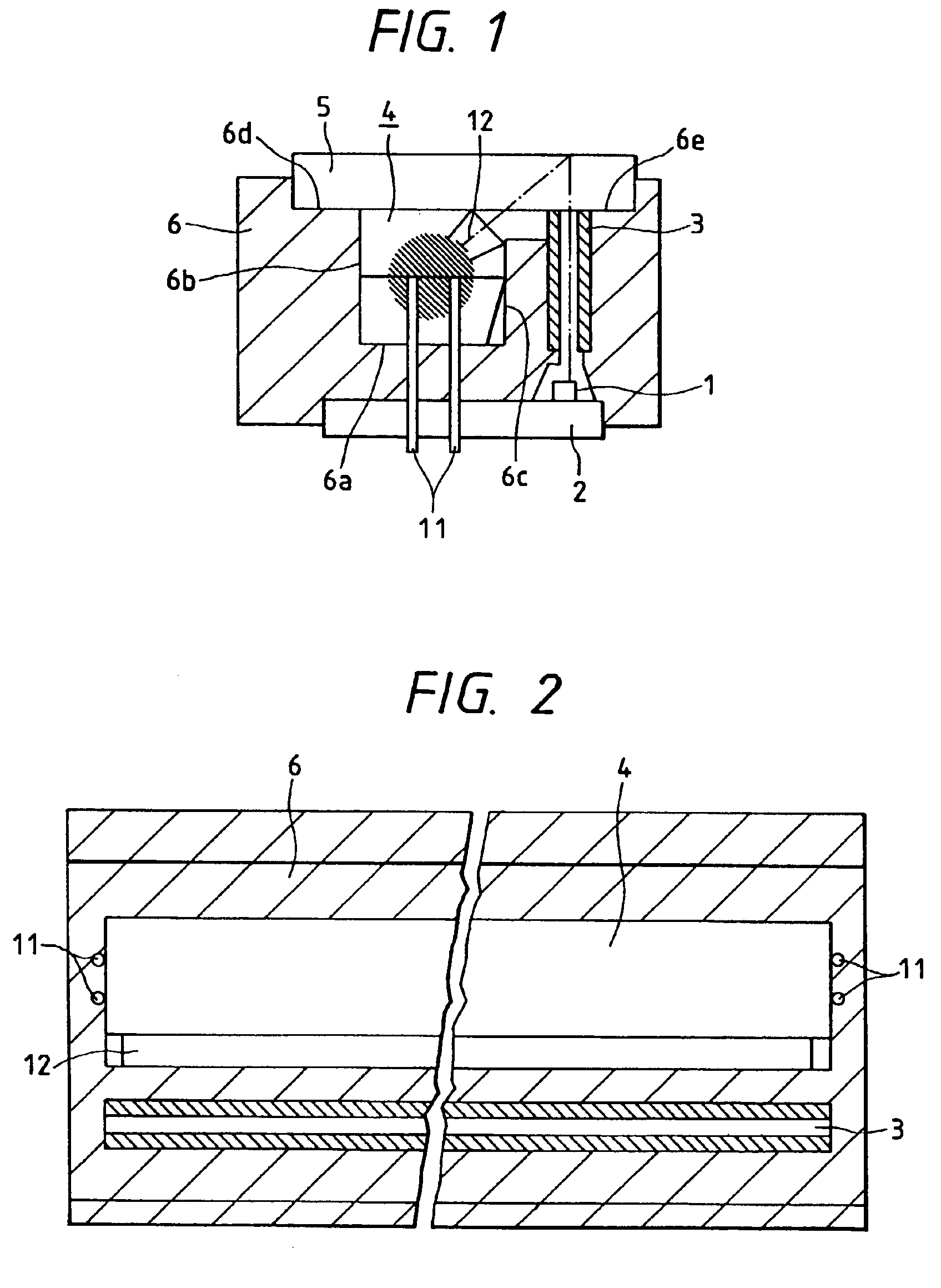
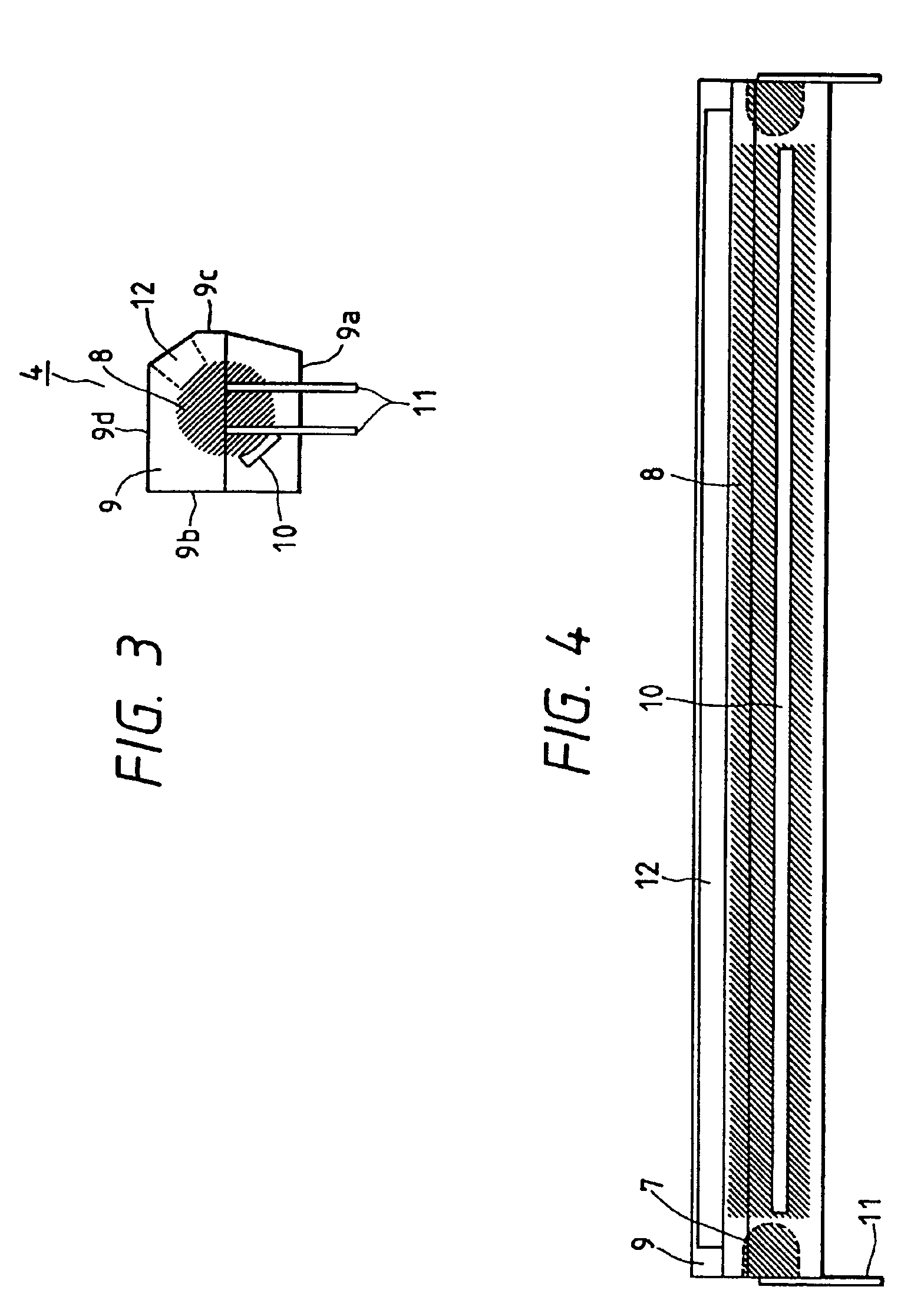
Phosphor screen and displays systems
InactiveUS7733571B1Good optical performanceImprove cooling effectOptical filtersNon-linear opticsPhosphorFluorescence
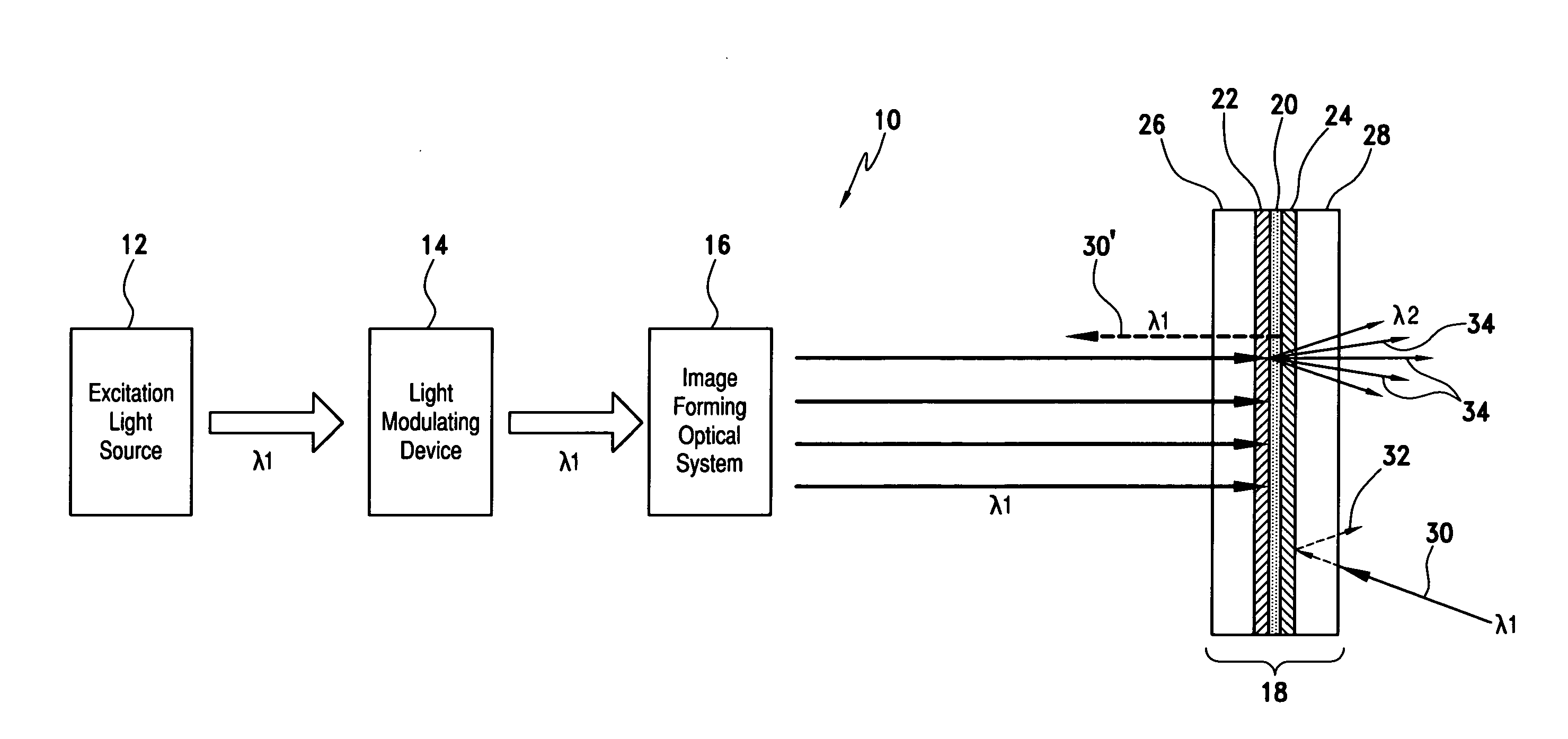
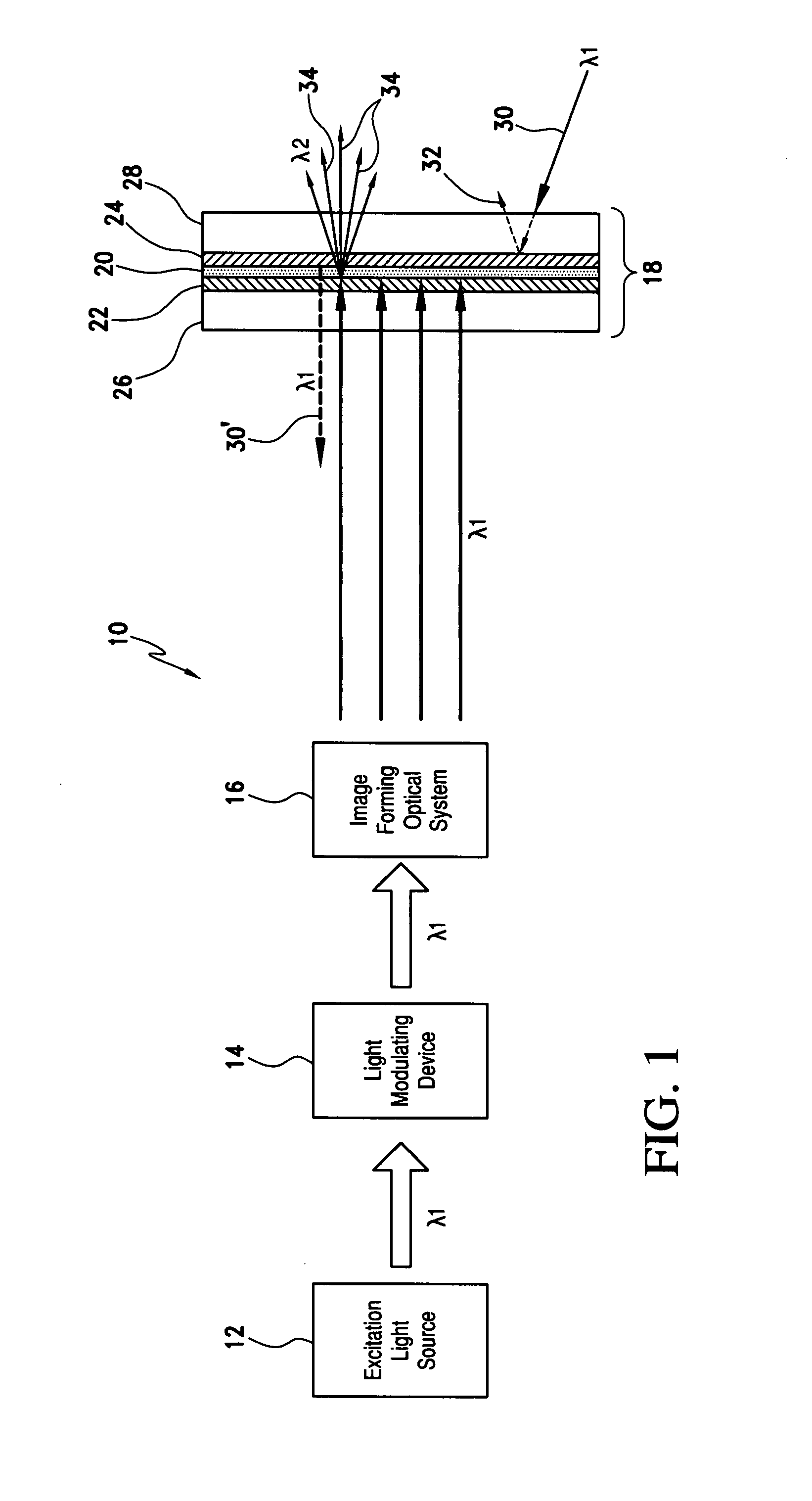
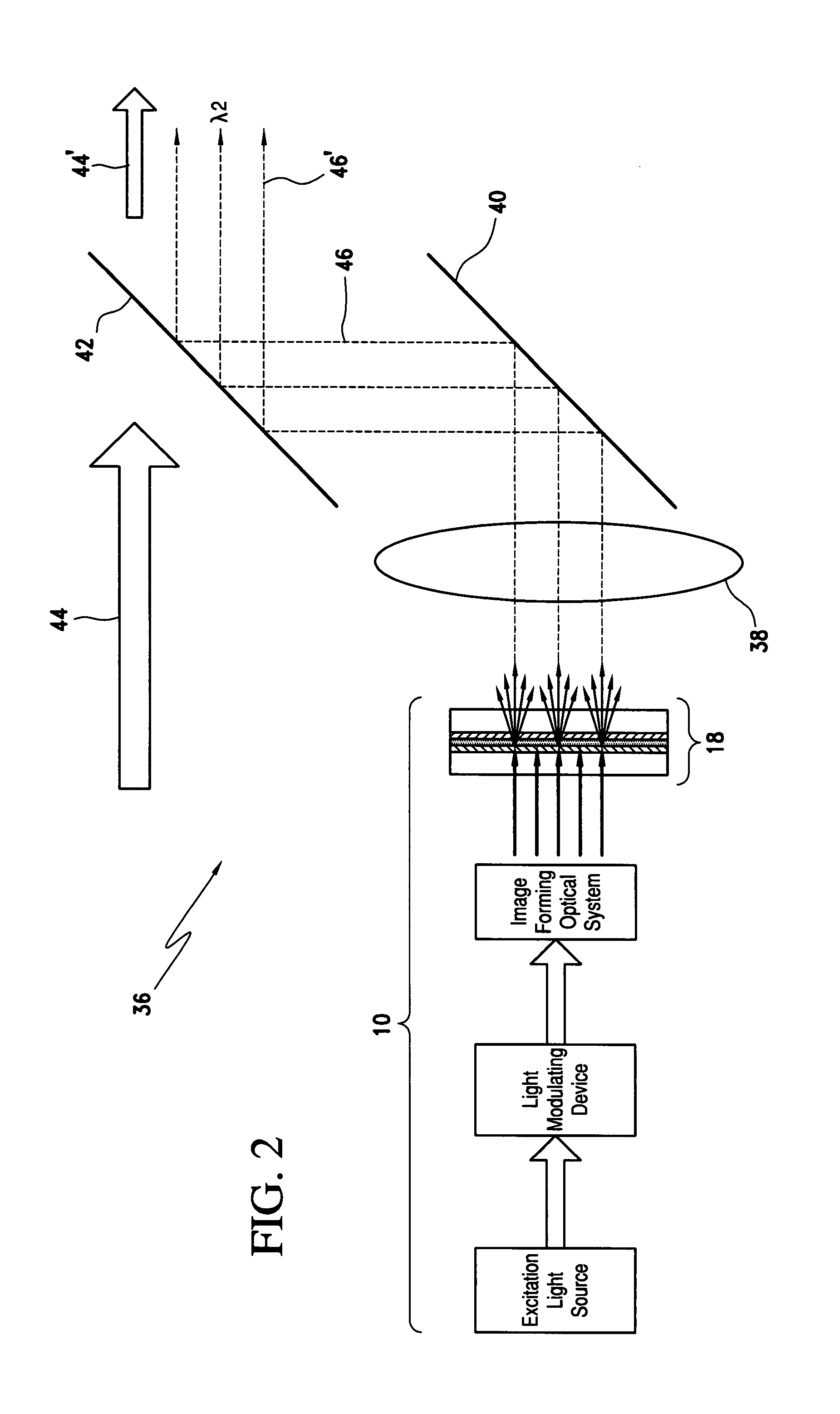
A phosphor screen for image forming including phosphor material being excitable by light in a wavelength λ1. The phosphor screen receives an optical image from an image forming optical system and produces the optical image at a second wavelength λ2. The phosphor screen includes a phosphor layer comprising the phosphor material. A short-pass reflective coating is positioned on a first side of the phosphor layer. The short-pass reflective coating transmits the wavelength λ1 and reflects the wavelength λ2. A long-pass reflective coating is positioned on a second side of the phosphor layer. The long-pass reflective coating transmits the wavelength λ2 and reflects the wavelength λ1. A first substrate is positioned over the short-pass reflective coating. The first substrate is formed of optically clear and thermal conductive material. A second substrate is positioned over the long-pass reflective coating. The second substrate is formed of long-pass absorptive optical filter material that transmits the wavelength λ2 and absorbs wavelength λ1 from ambient light to prevent the phosphor layer from being excited by the ambient light. The phosphor screen may alternatively be used for a direct-view visual display apparatus. These principles can also be utilized for backlighting and general illumination applications.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Holographic Image Display Systems
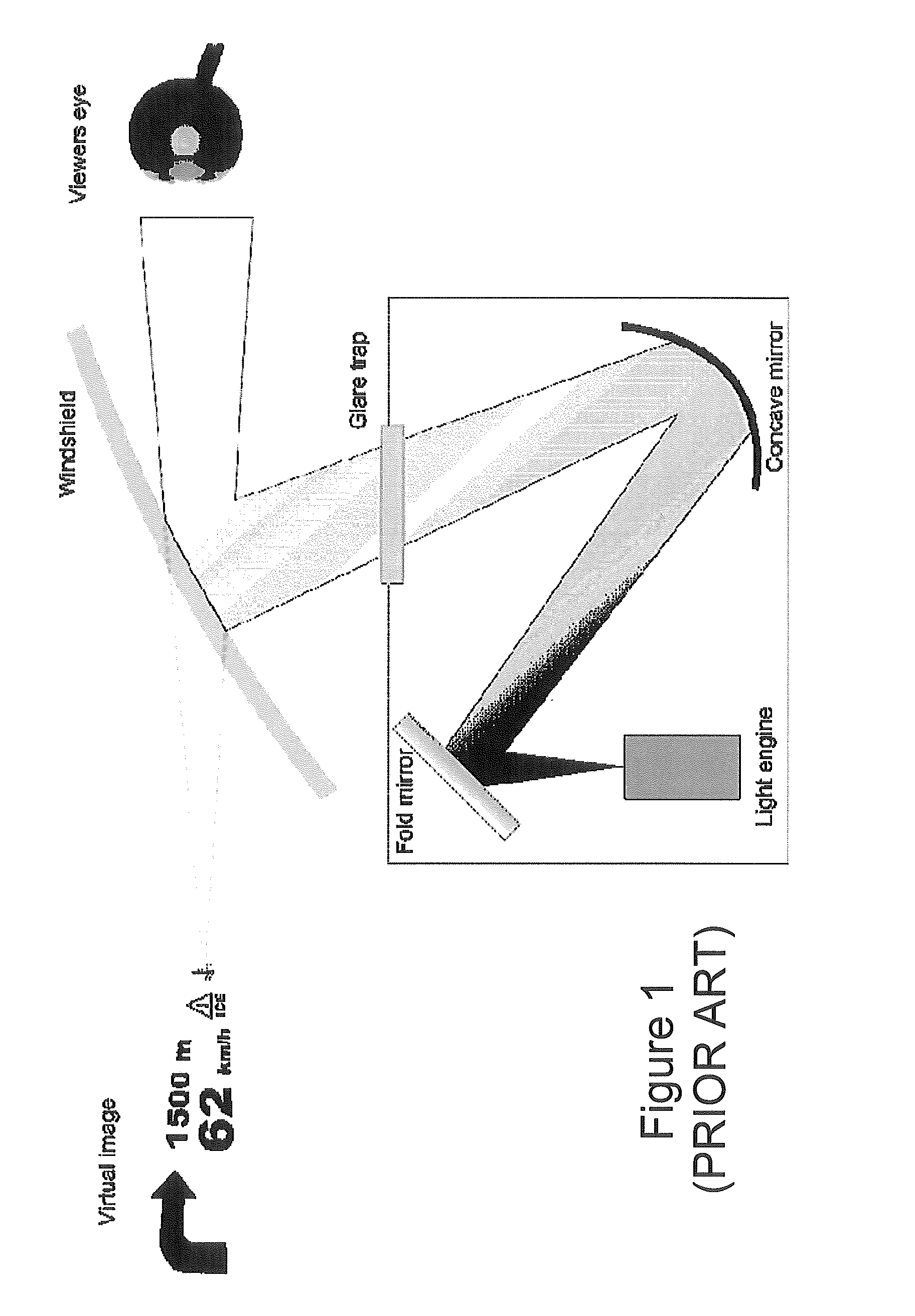
InactiveUS20110157667A1Reduce computing costRealistic effectHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsHead-up displaySpatial light modulator
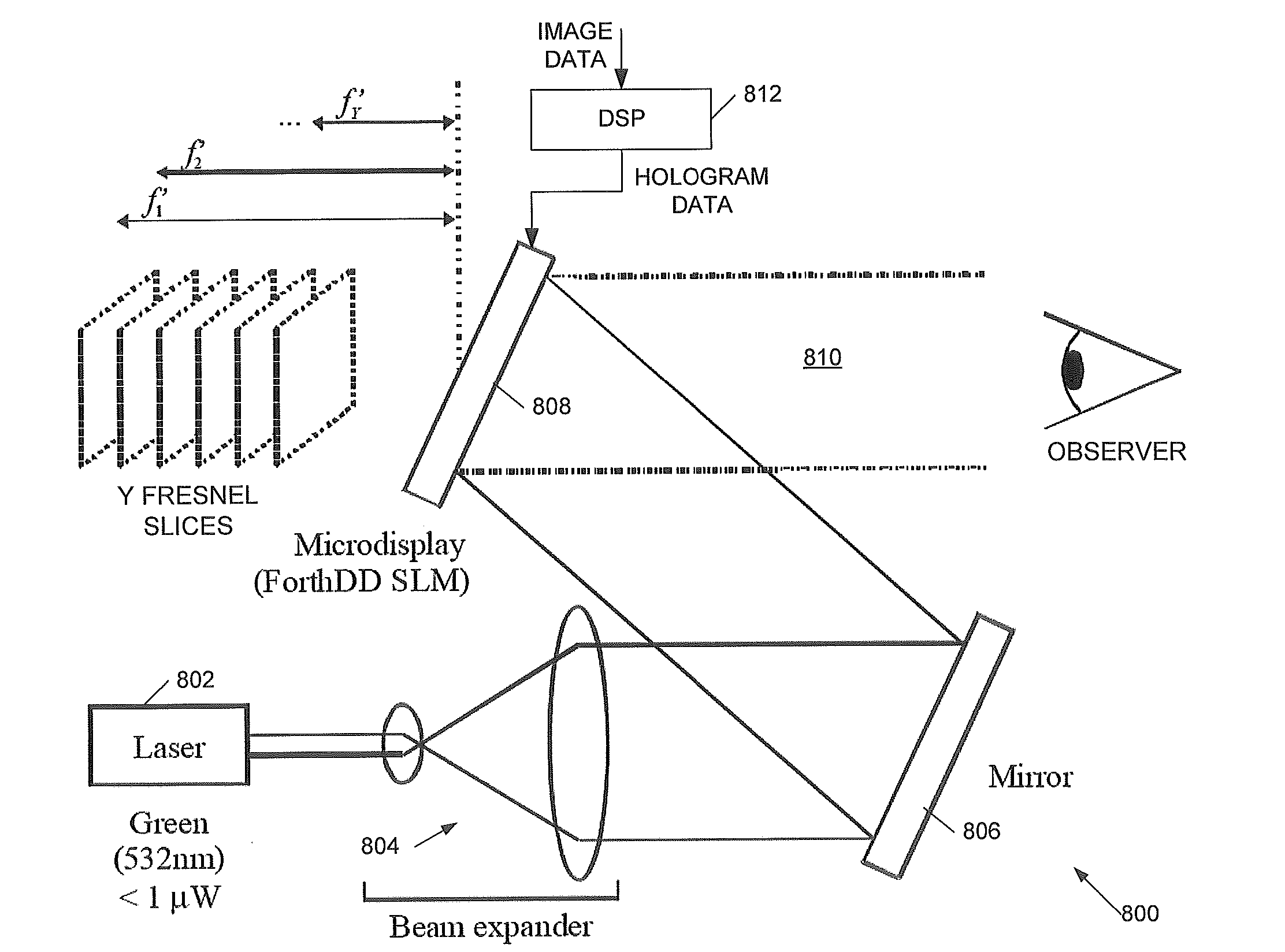
The invention relates to holographic head-up displays, to holographic optical sights, and also to 3D holographic image displays. We describe a holographic head-up display and a holographic optical sight, for displaying, in an eye box of the display / sight, a virtual image comprising one or more substantially two-dimensional images, the head-up display comprising: a laser light source; a spatial light modulator (SLM) to display a hologram of the two-dimensional images; illumination optics in an optical path between said laser light source and said SLM to illuminate said SLM; and imaging optics to image a plane of said SLM comprising said hologram into an SLM image plane in said eye box such that the lens of the eye of an observer of said head-up display performs a space-frequency transform of said hologram on said SLM to generate an image within said observer's eye corresponding to the two-dimensional images.
Owner:LIGHT BLUE OPTICS
Image Acquisition Method and Apparatus
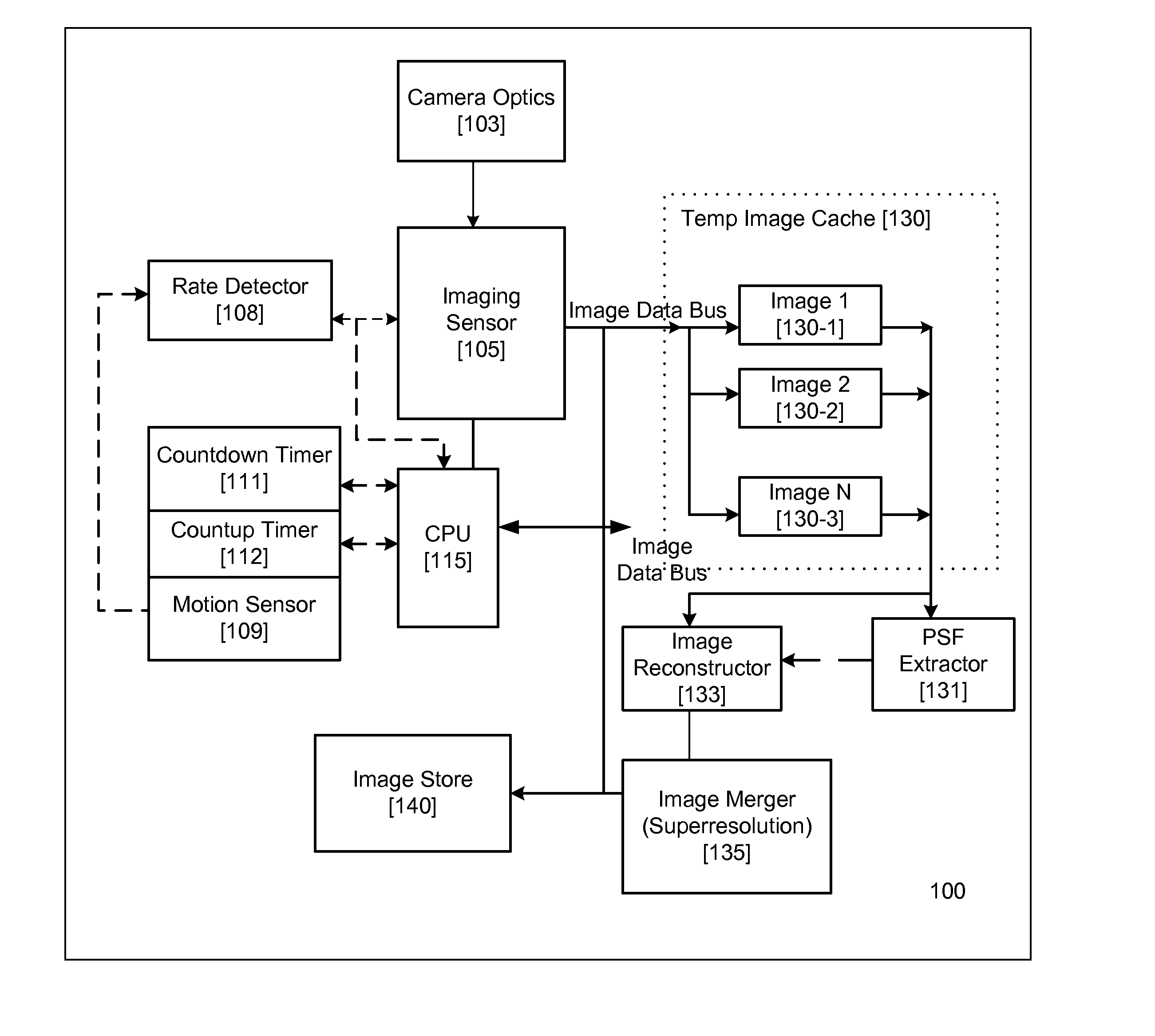
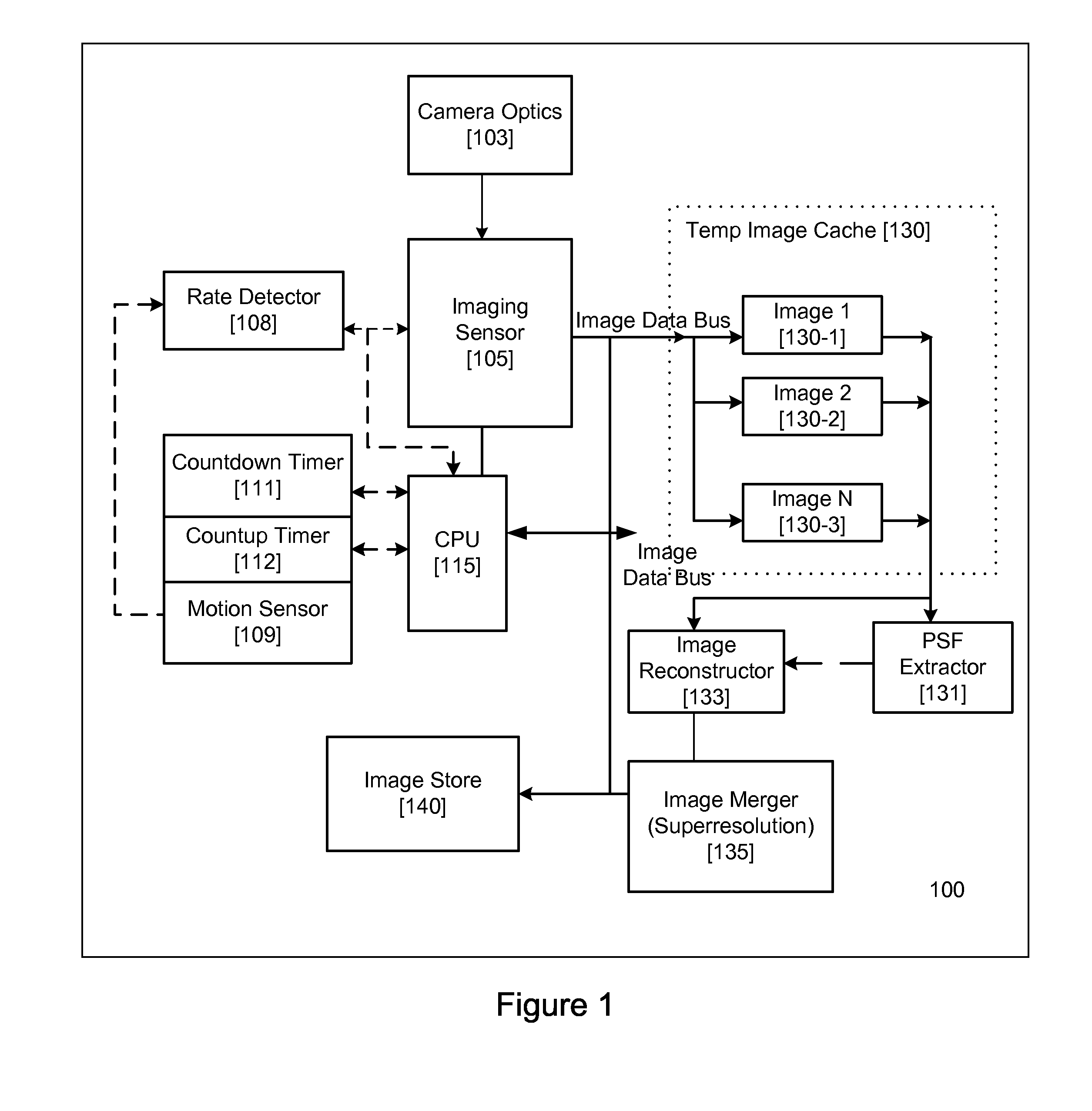
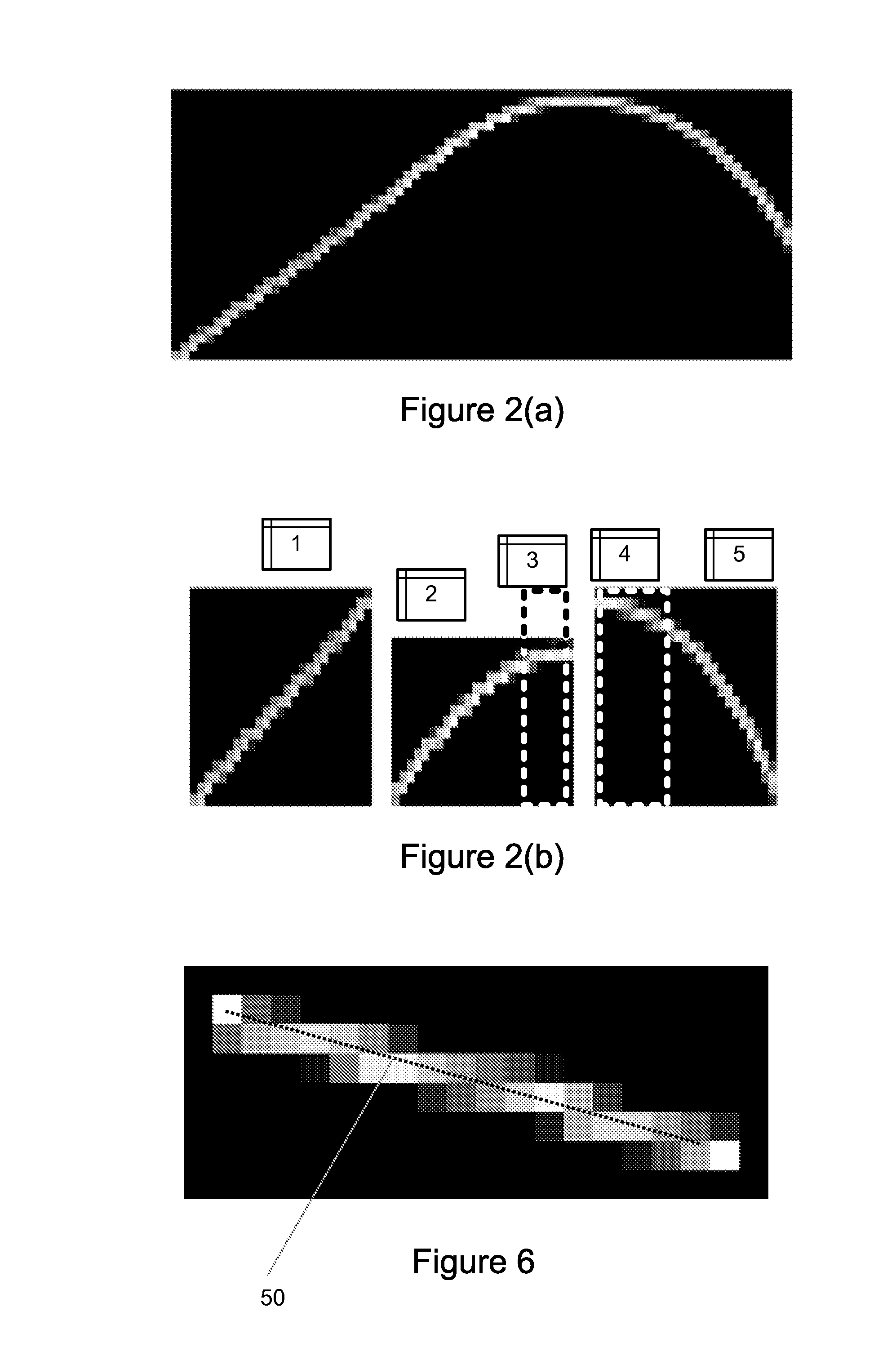
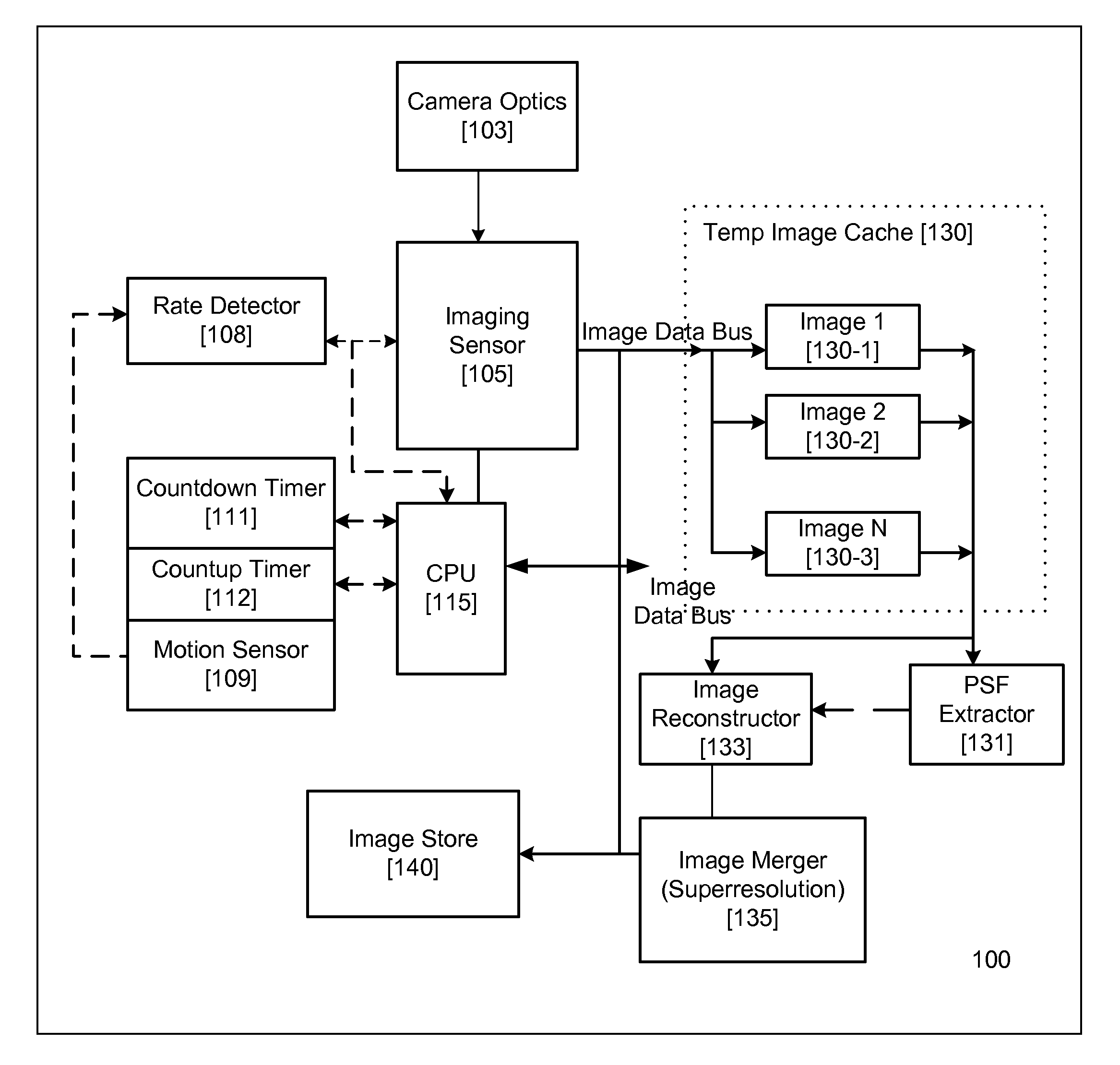
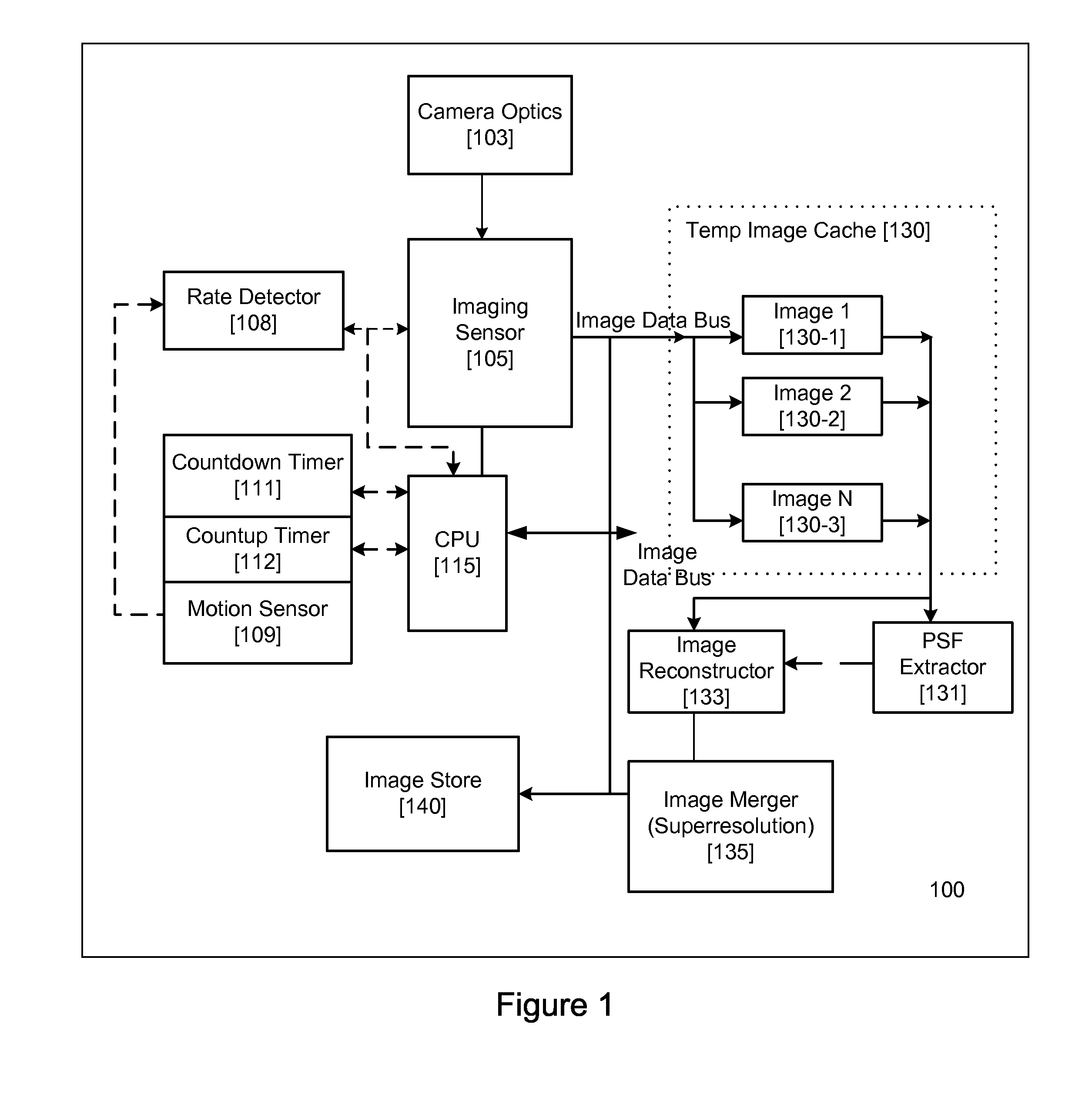
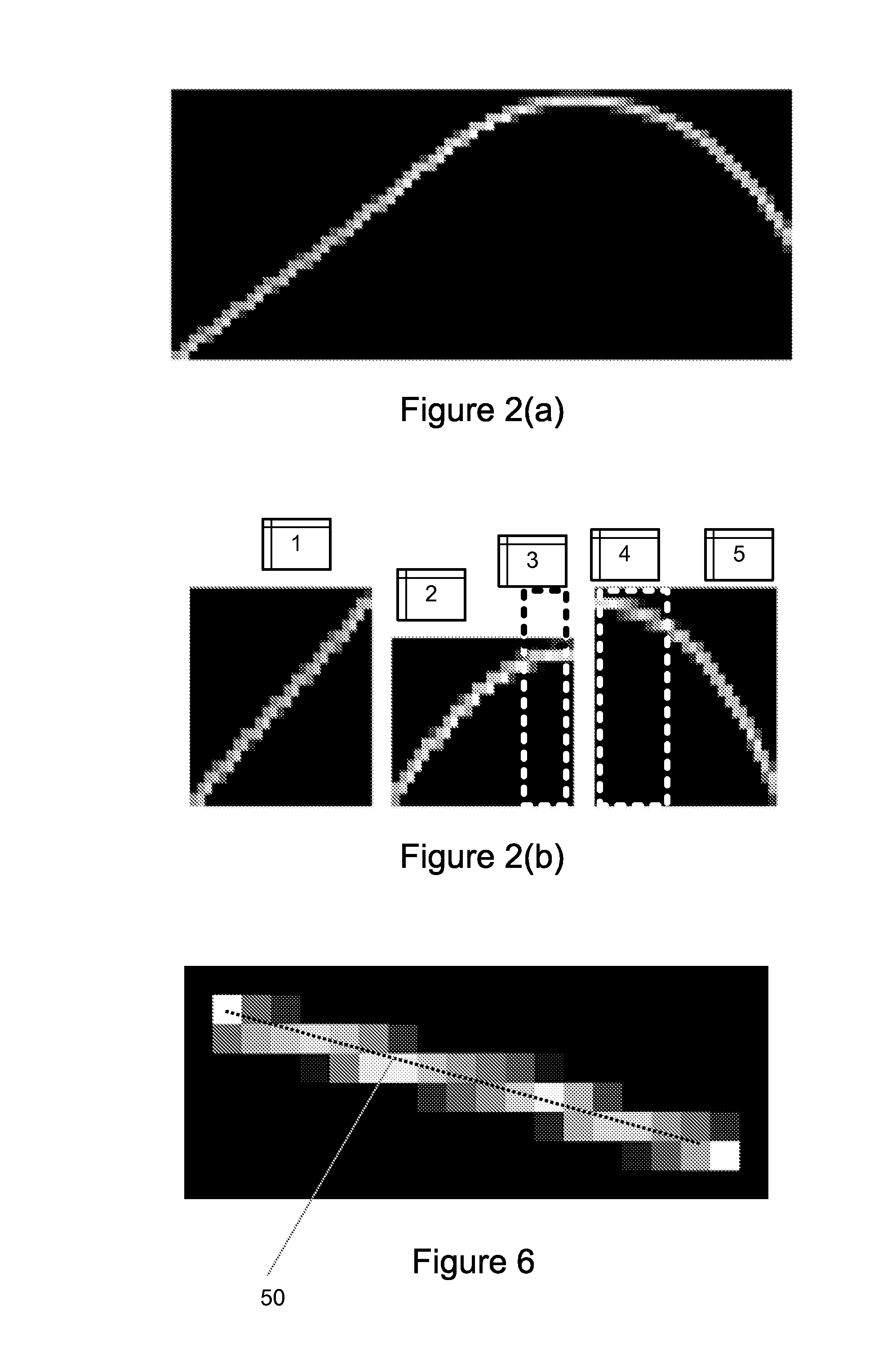
InactiveUS20070296833A1High quality imagingTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMotion detectorAcquisition apparatus
An image acquisition sensor of a digital image acquisition apparatus is coupled to imaging optics for acquiring a sequence of images. Images acquired by the sensor are stored. A motion detector causes the sensor to cease capture of an image when the degree of movement in acquiring the image exceeds a threshold. A controller selectively transfers acquired images for storage. A motion extractor determines motion parameters of a selected, stored image. An image re-constructor corrects the selected image with associated motion parameters. A selected plurality of images nominally of the same scene are merged and corrected by the image re-constructor to produce a high quality image of the scene.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Image acquisition method and apparatus
InactiveUS8169486B2Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMotion detectorAcquisition apparatus
An image acquisition sensor of a digital image acquisition apparatus is coupled to imaging optics for acquiring a sequence of images. Images acquired by the sensor are stored. A motion detector causes the sensor to cease capture of an image when the degree of movement in acquiring the image exceeds a threshold. A controller selectively transfers acquired images for storage. A motion extractor determines motion parameters of a selected, stored image. An image re-constructor corrects the selected image with associated motion parameters. A selected plurality of images nominally of the same scene are merged and corrected by the image re-constructor to produce a high quality image of the scene.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
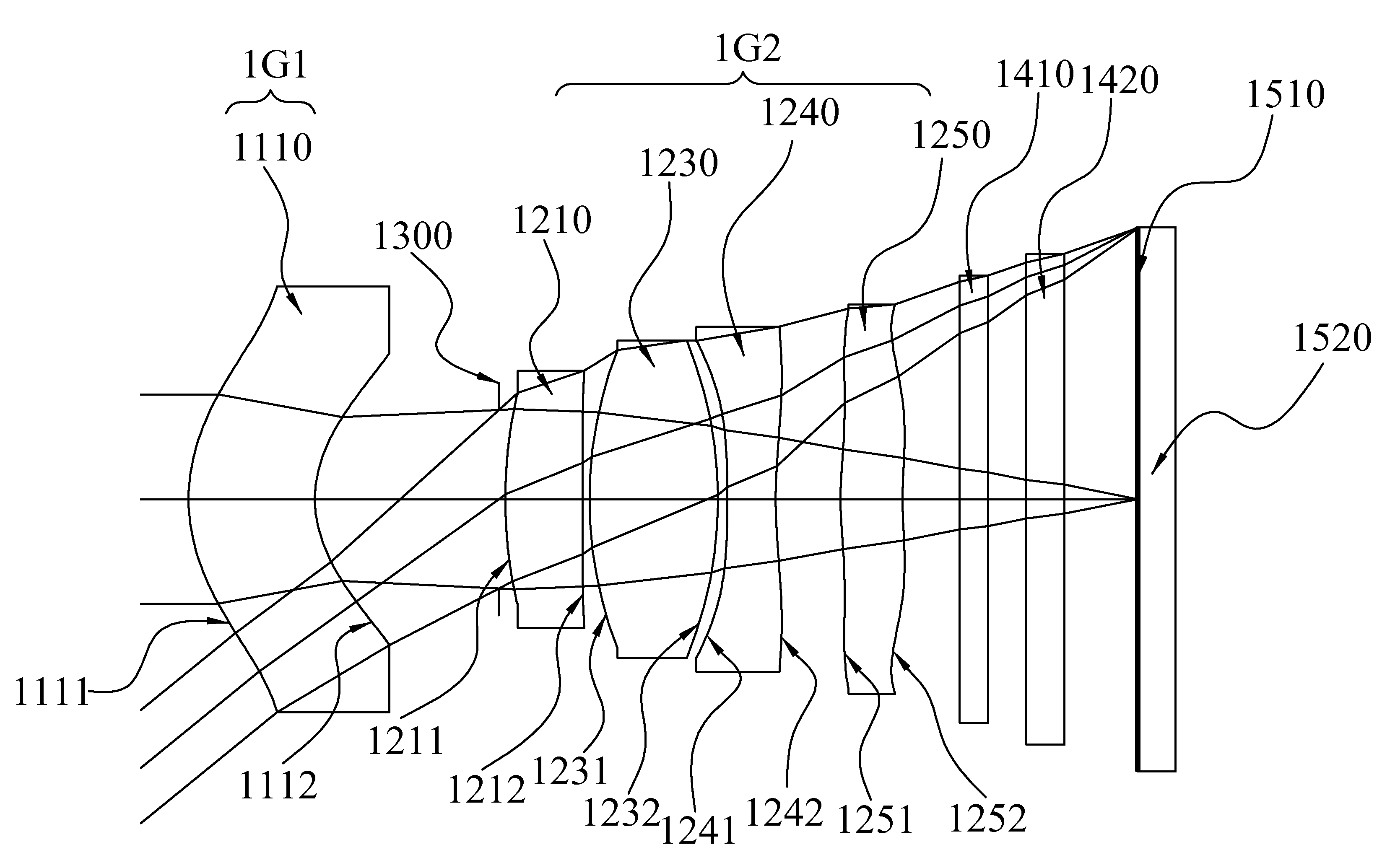
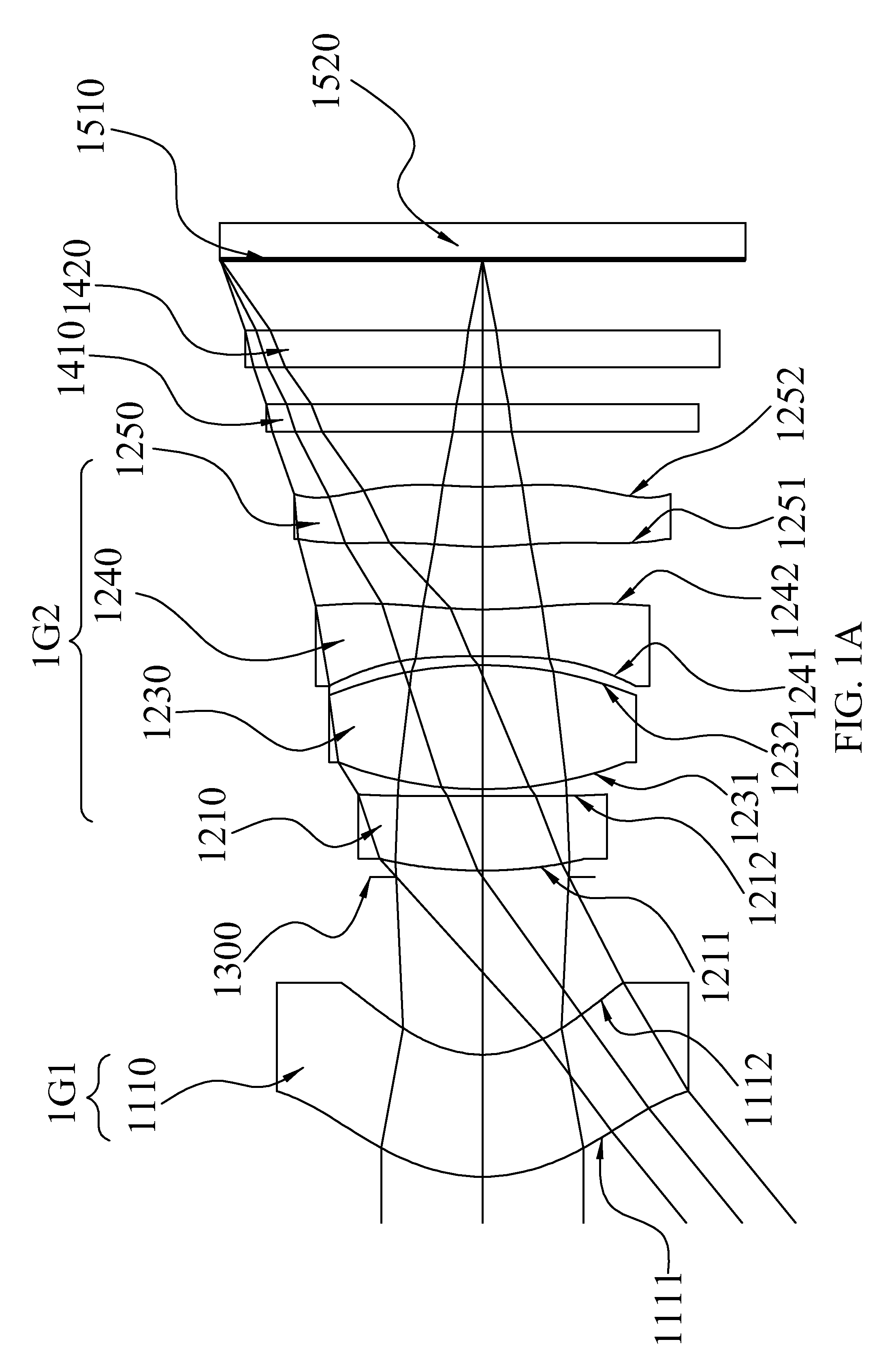
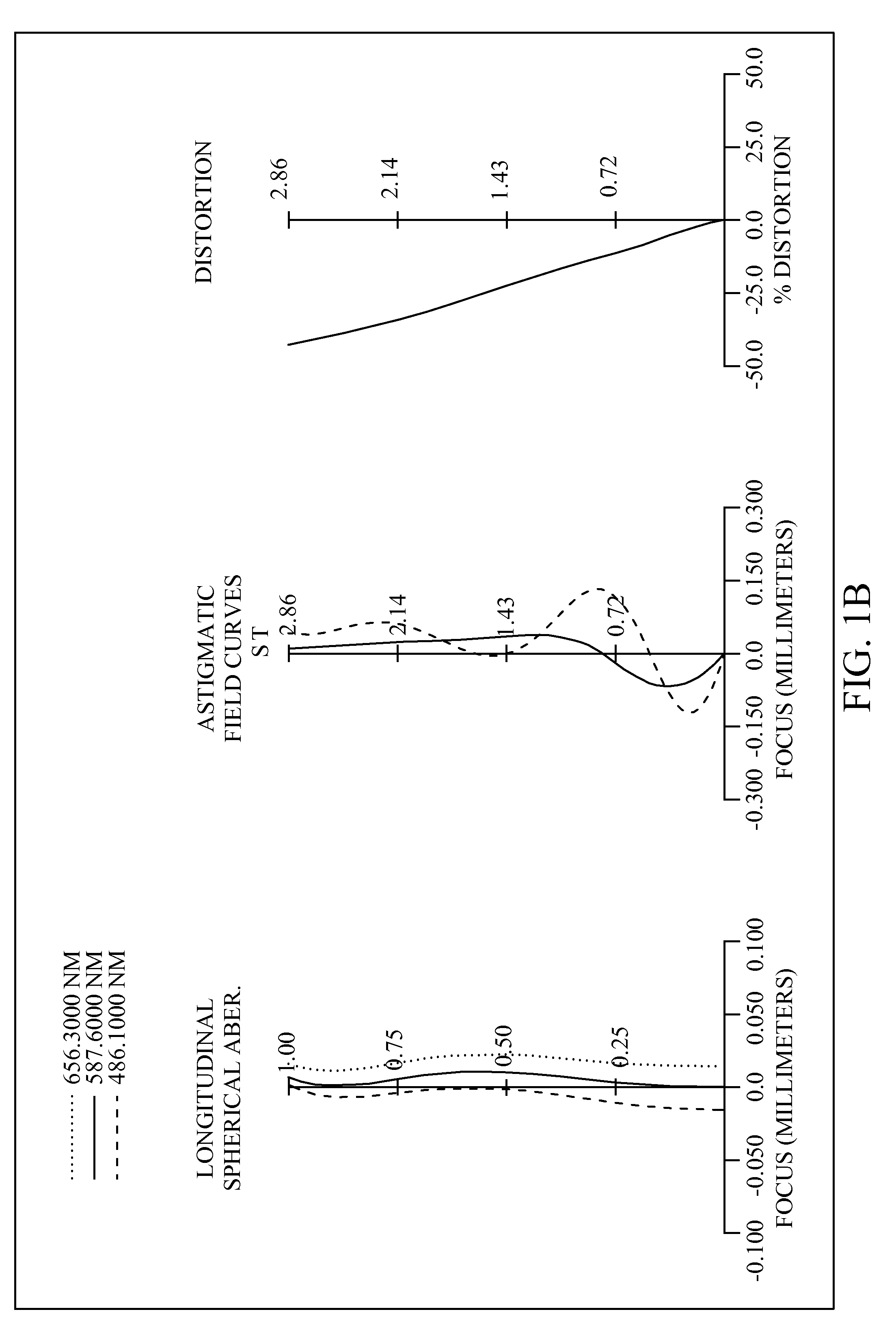
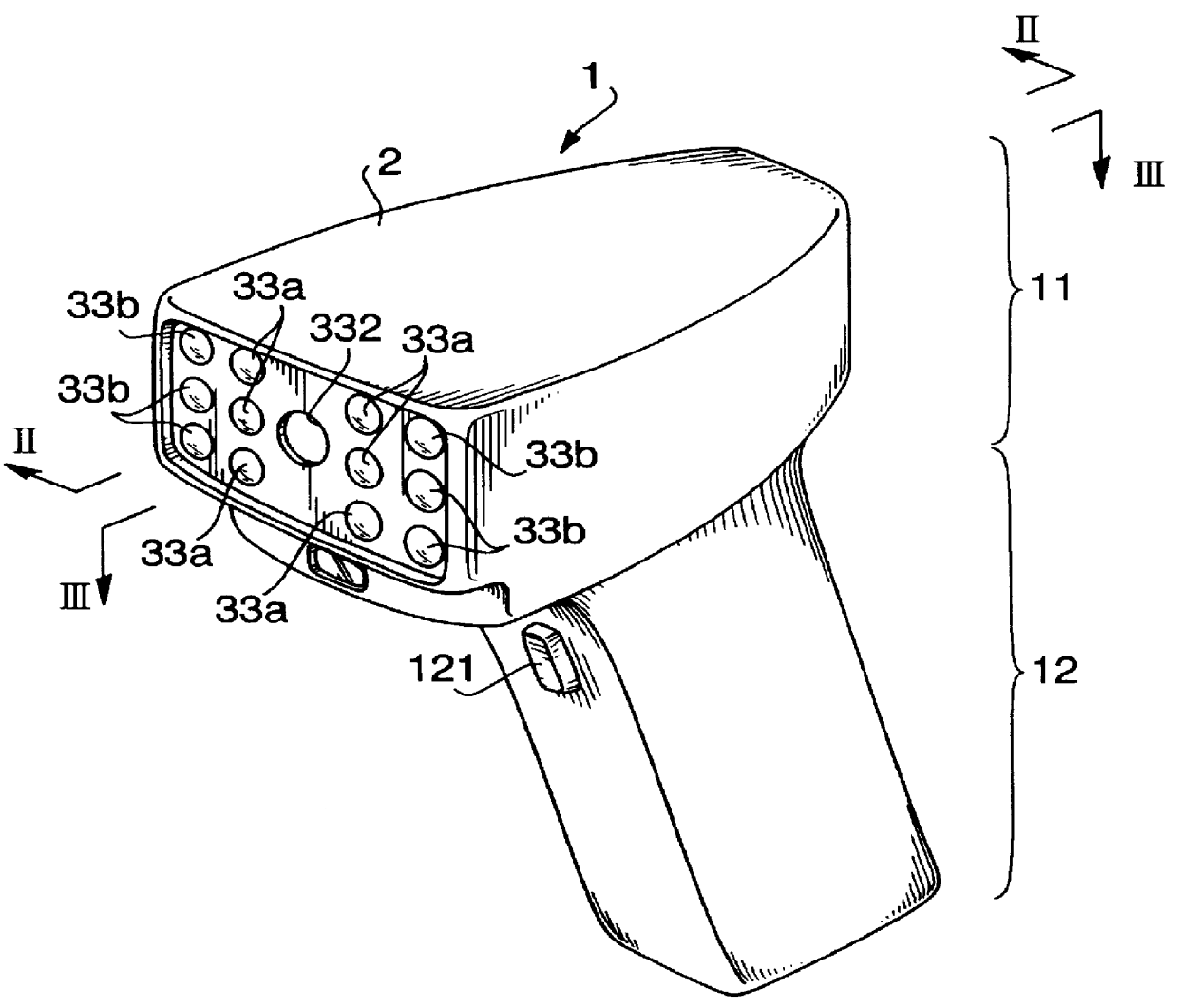
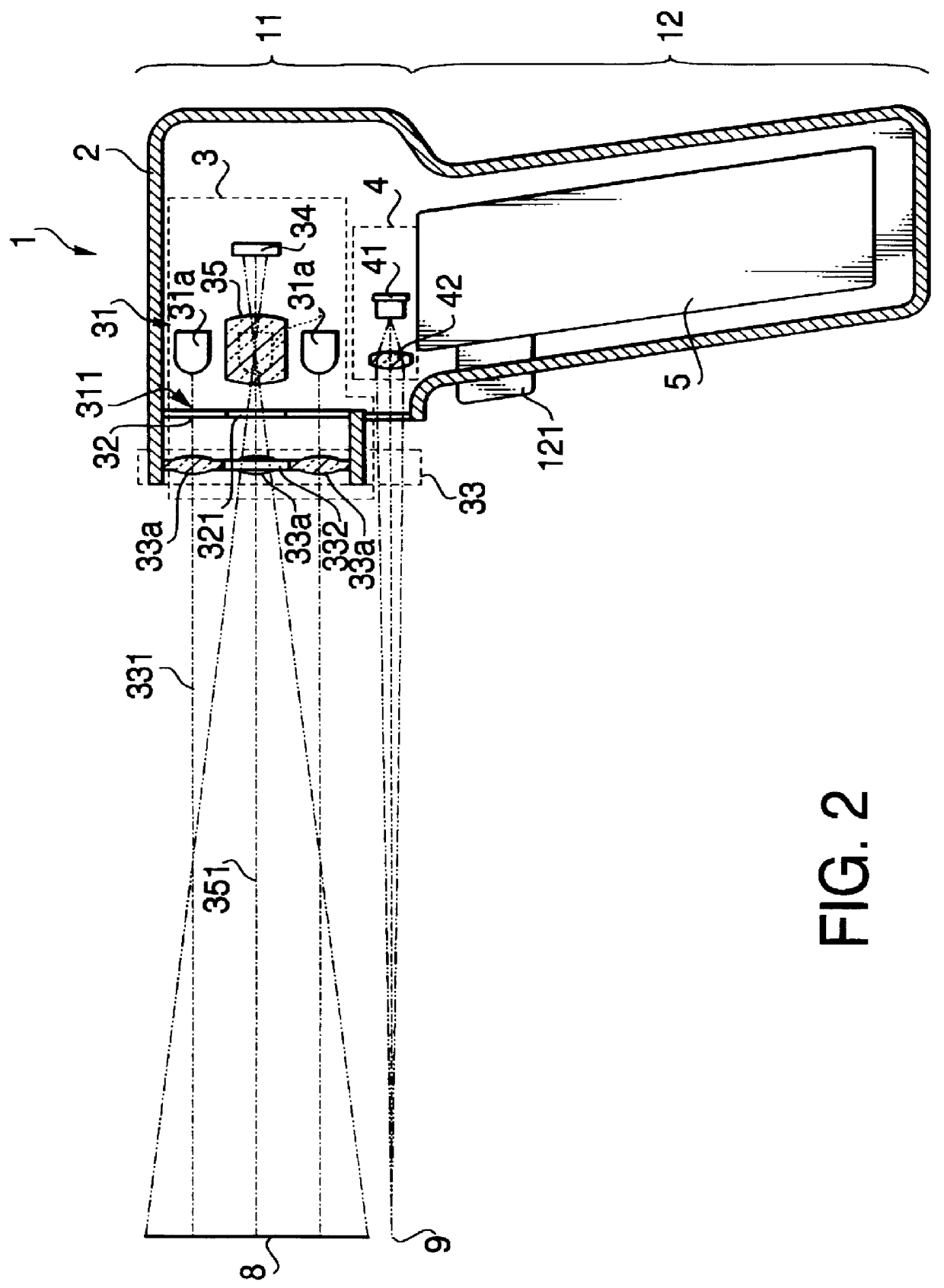
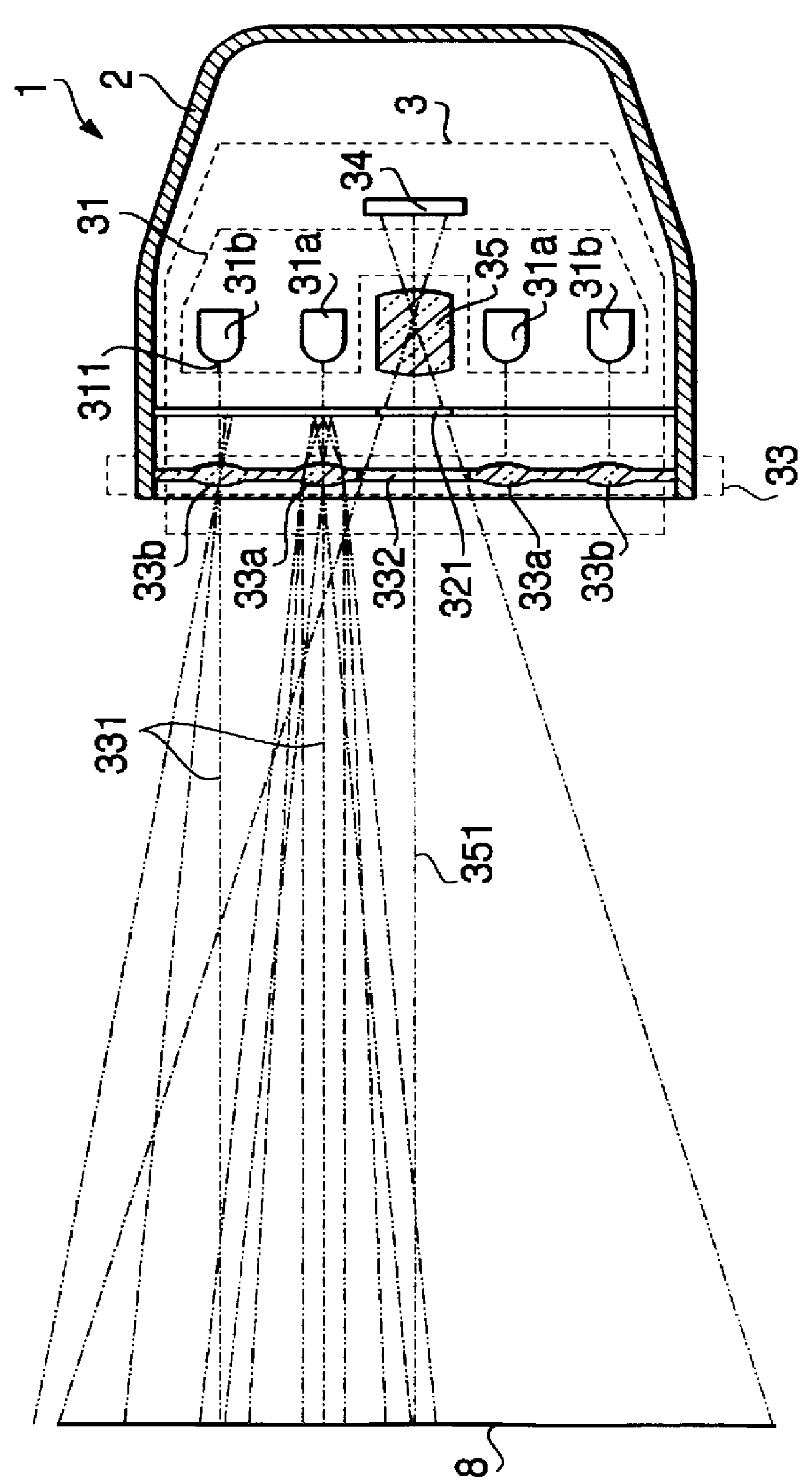
Imaging optical system
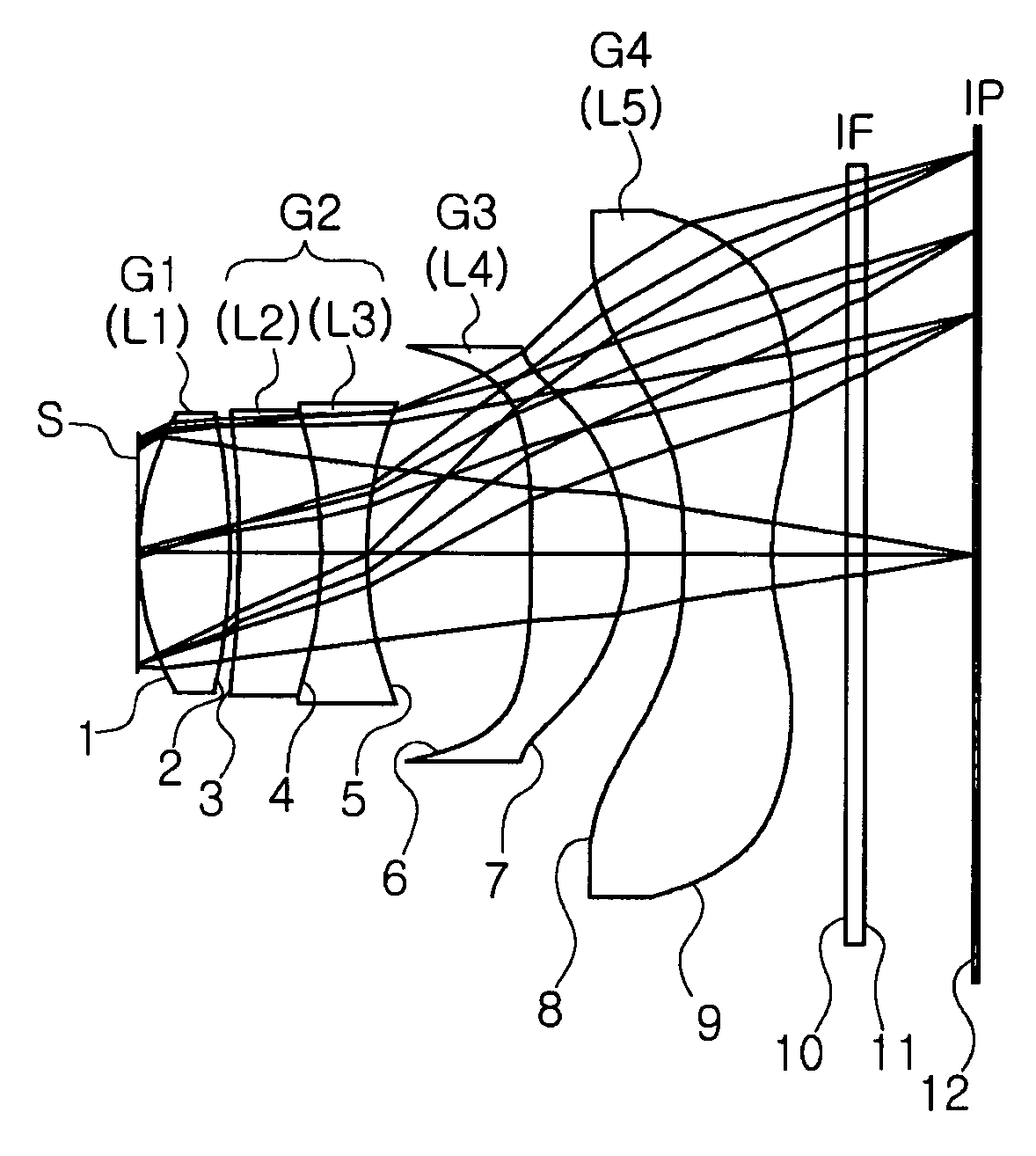
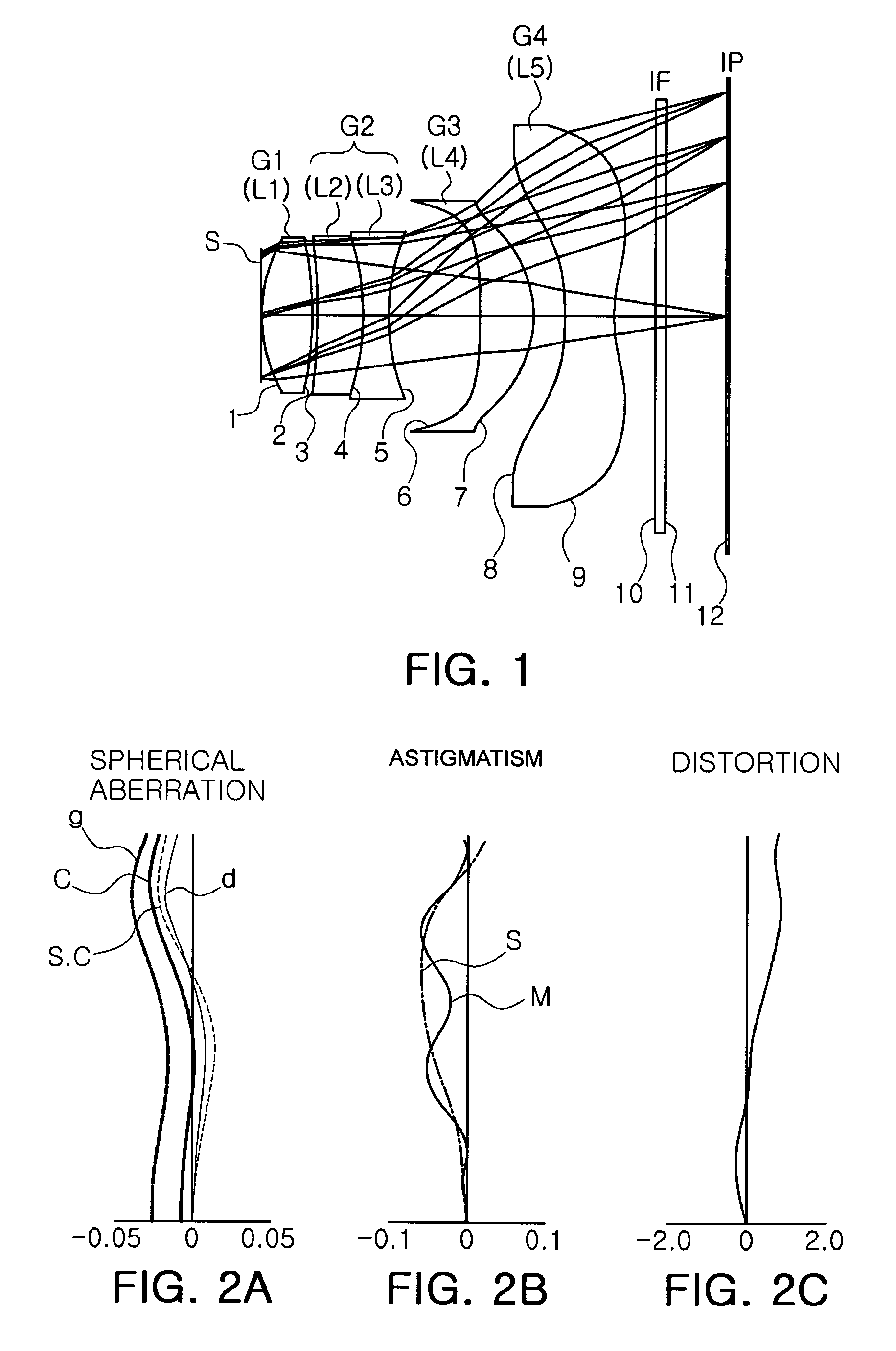
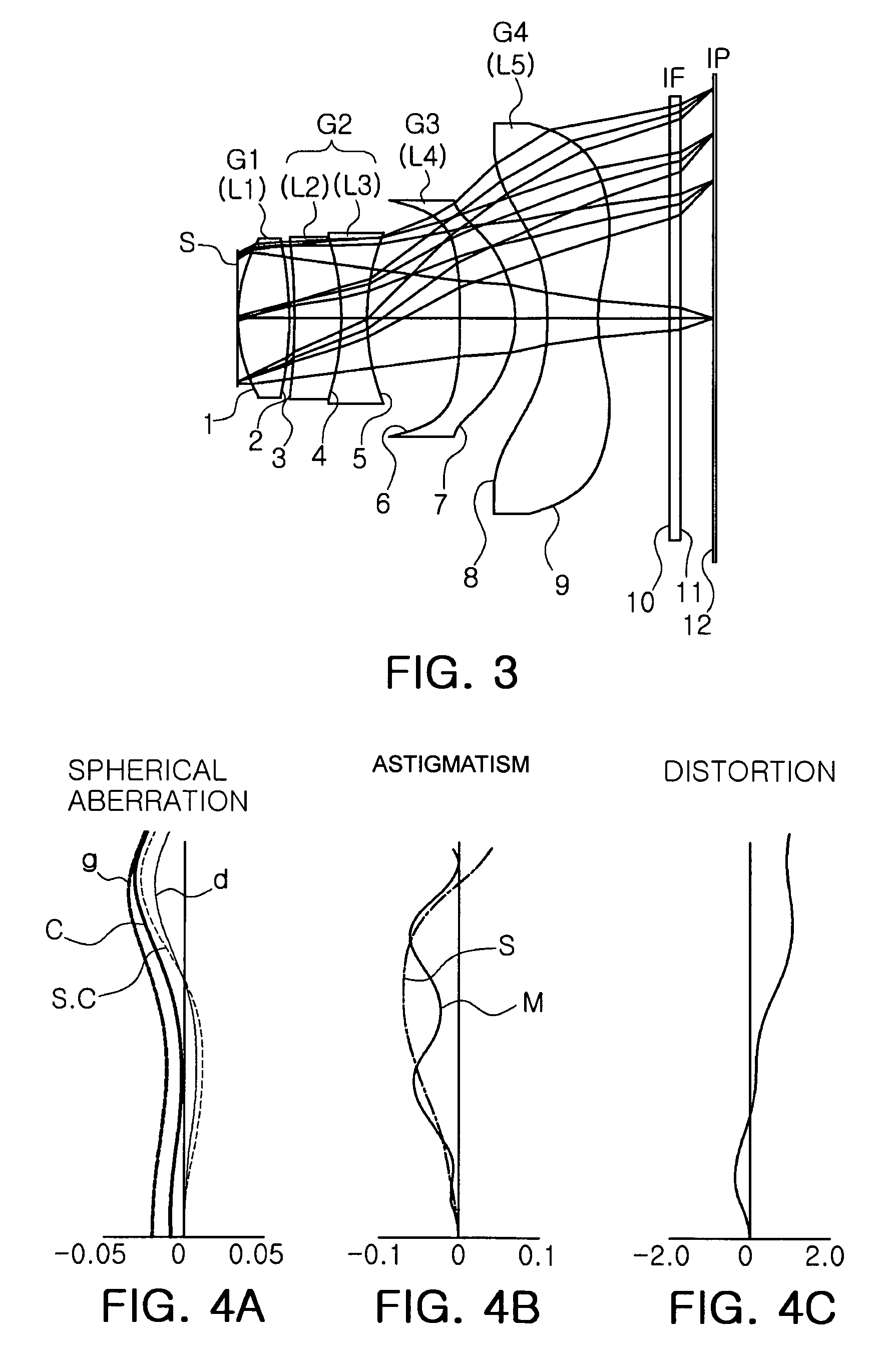
ActiveUS20090122423A1High resolutionCorrect chromatic aberrationLensOptical elementsImage resolutionOptoelectronics
There is provided a high-definition imaging optical system including: an aperture stop; a first lens disposed at an image side of the aperture stop, the first lens having a positive refractive power and having a convex object-side surface; a second lens disposed at an image side surface of the first lens; a third lens disposed at an image side surface of the second lens; a fourth lens having a convex image-side surface and having a positive refractive power; and a fifth lens having a concave image-side surface and having a negative refractive power, wherein a combined refractive power of the second and third lenses is negative. The optical system is high-performing and compact and can be further improved in resolution. Also, the optical system can correct chromatic aberration and improve color fringing in the case of indoor or outdoor photographing.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
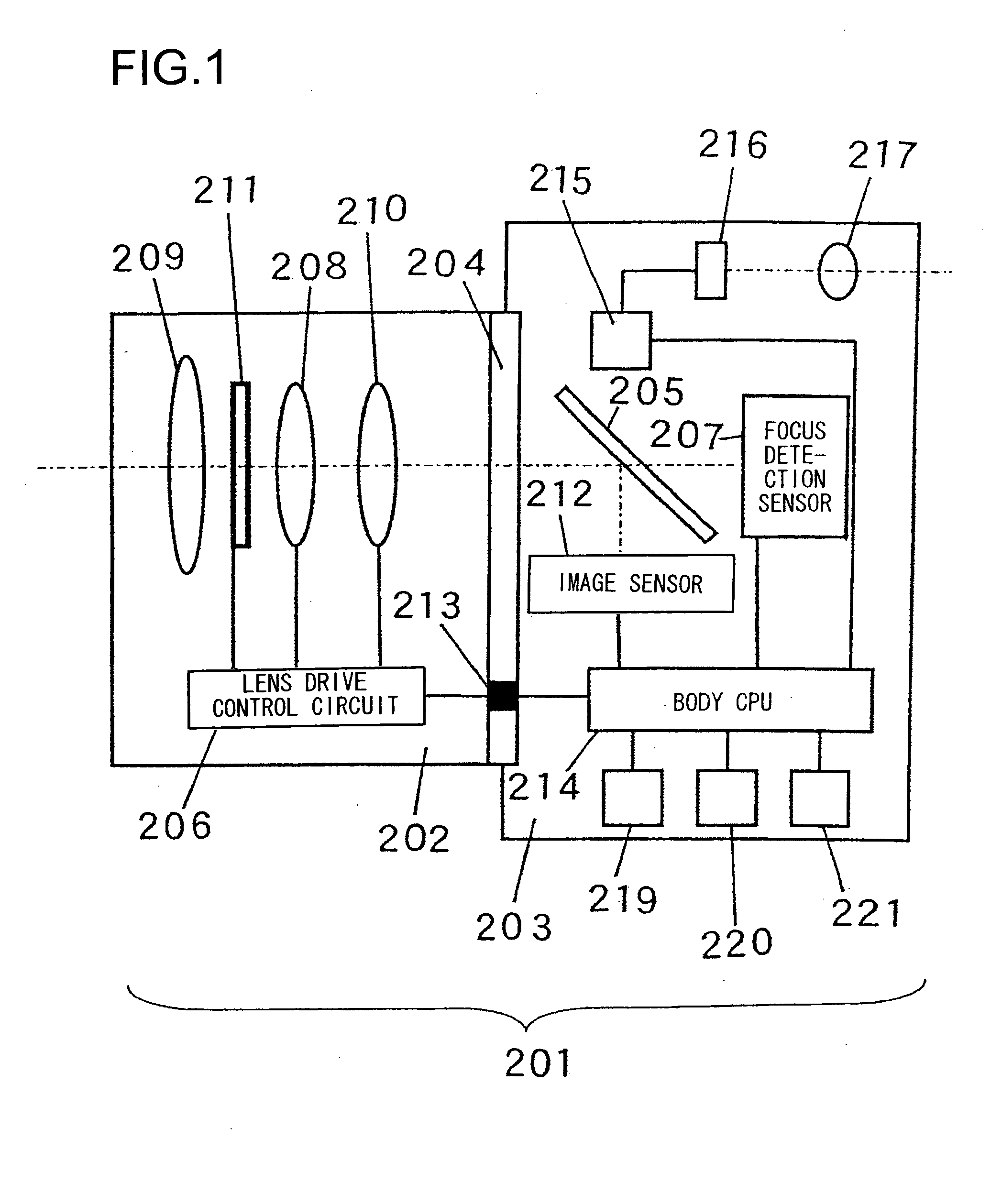
Focus adjustment device, imaging device and focus adjustment method
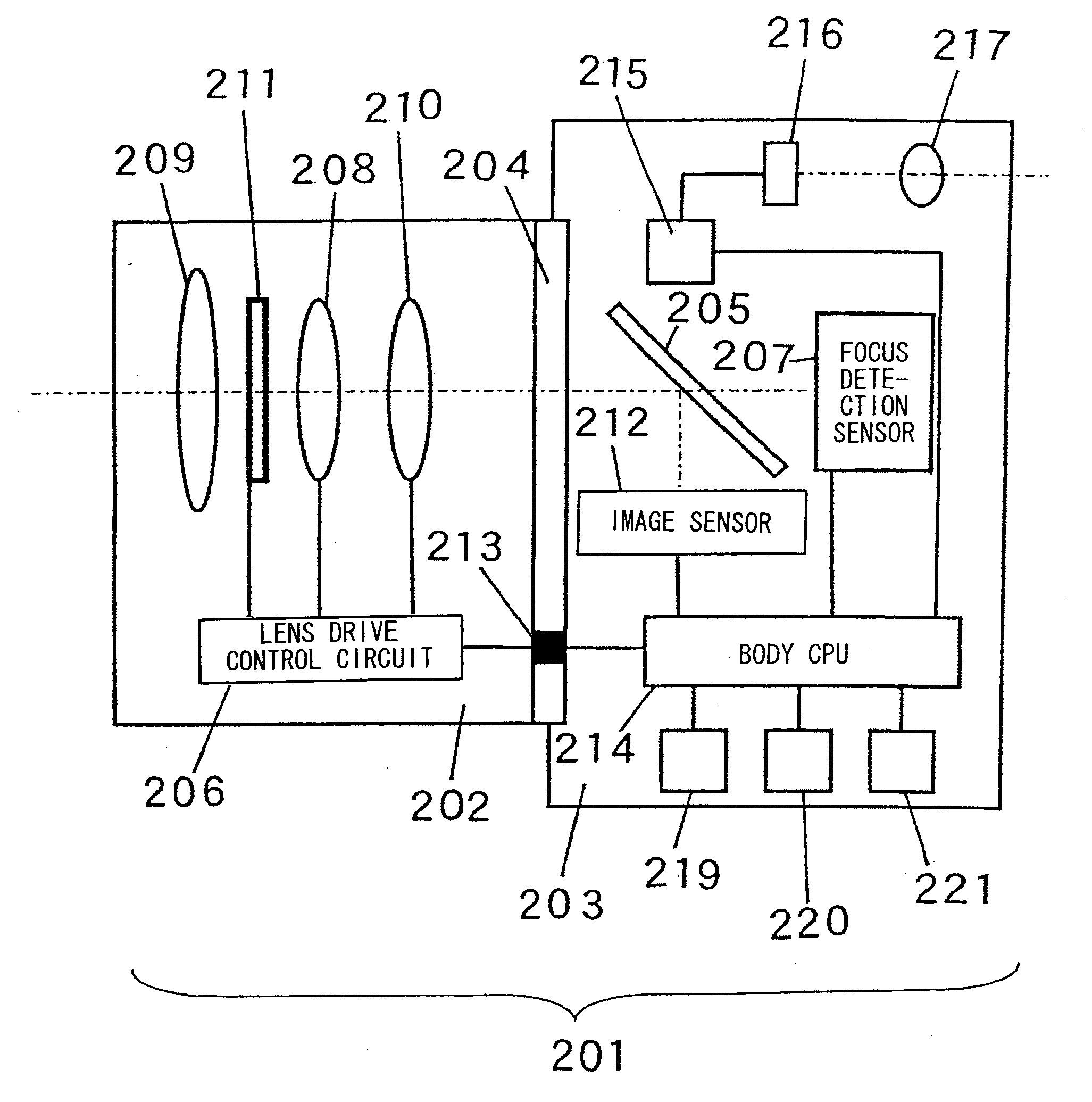
A focus adjustment device includes an image sensor that includes imaging pixels for capturing an image formed via an imaging optical system and focus detection pixels for detecting a focus adjustment state at the imaging optical system through a first pupil division-type image shift detection method, a focus detector that detects a focus adjustment state at the imaging optical system through a second pupil division-type image shift detection method different from the first pupil division-type image shift detection method, and a focus adjustment controller that executes focus adjustment for the imaging optical system based upon the focus adjustment states detected by the image sensor and the focus detector.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Projection optical system and projection exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20020024741A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusProjection opticsOptical axis
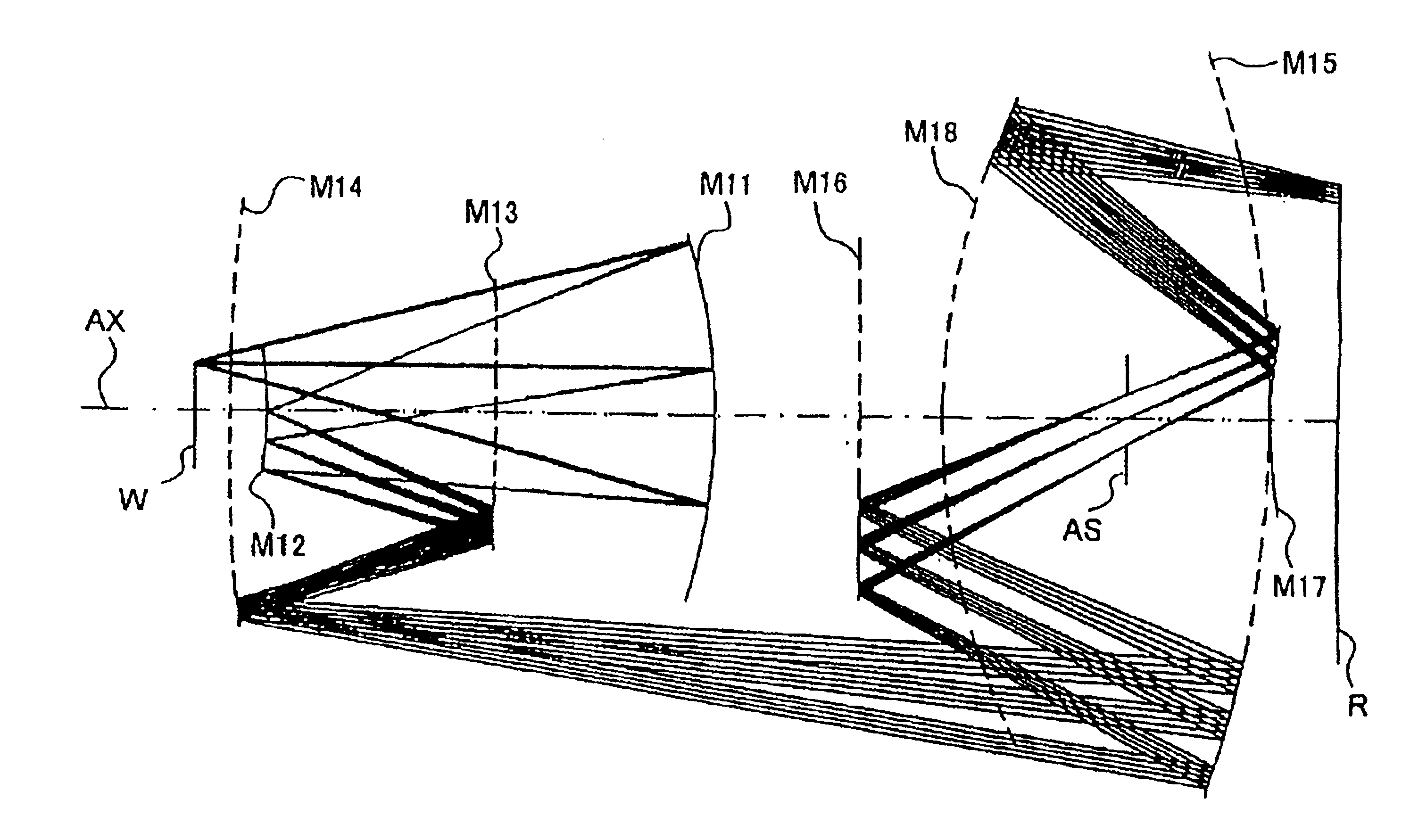
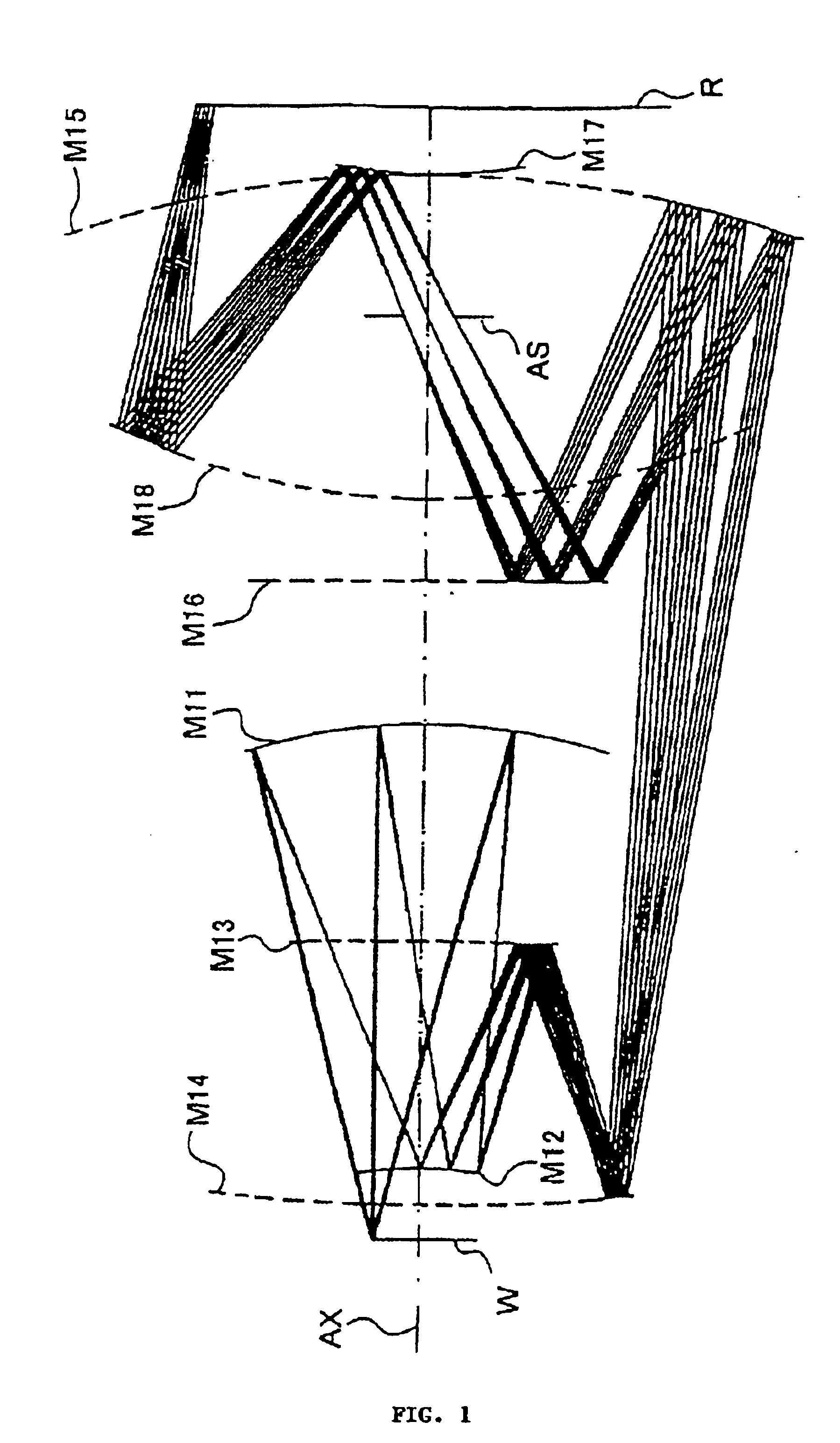
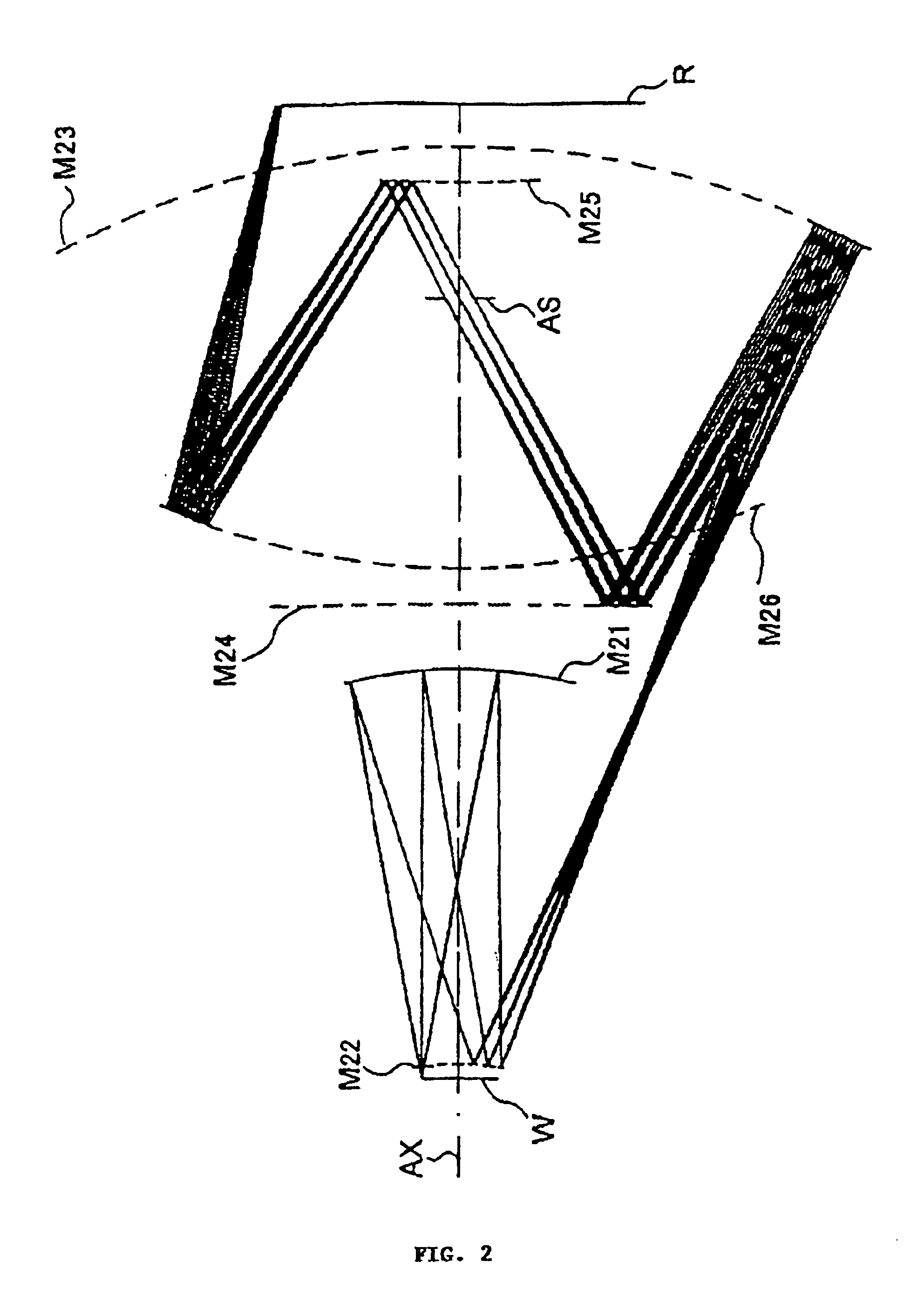
Disclosed is a projection optical system for projecting an image of an object onto an image plane, which includes a first imaging optical system for forming an image of the object, a second imaging optical system for re-imaging the image upon the image plane, wherein the first and second imaging optical systems are disposed in an order from the object side and are disposed along a common straight optical axis, wherein the first imaging optical system includes a first mirror for reflecting and collecting abaxial light from the object, wherein one of the first and second imaging optical systems includes a second mirror for reflecting light from the first mirror to the image plane side, and wherein, with the second mirror, the abaxial light is caused to pass an outside of an effective diameter of the first mirror.
Owner:CANON KK
Disposable Stereoscopic Endoscope System
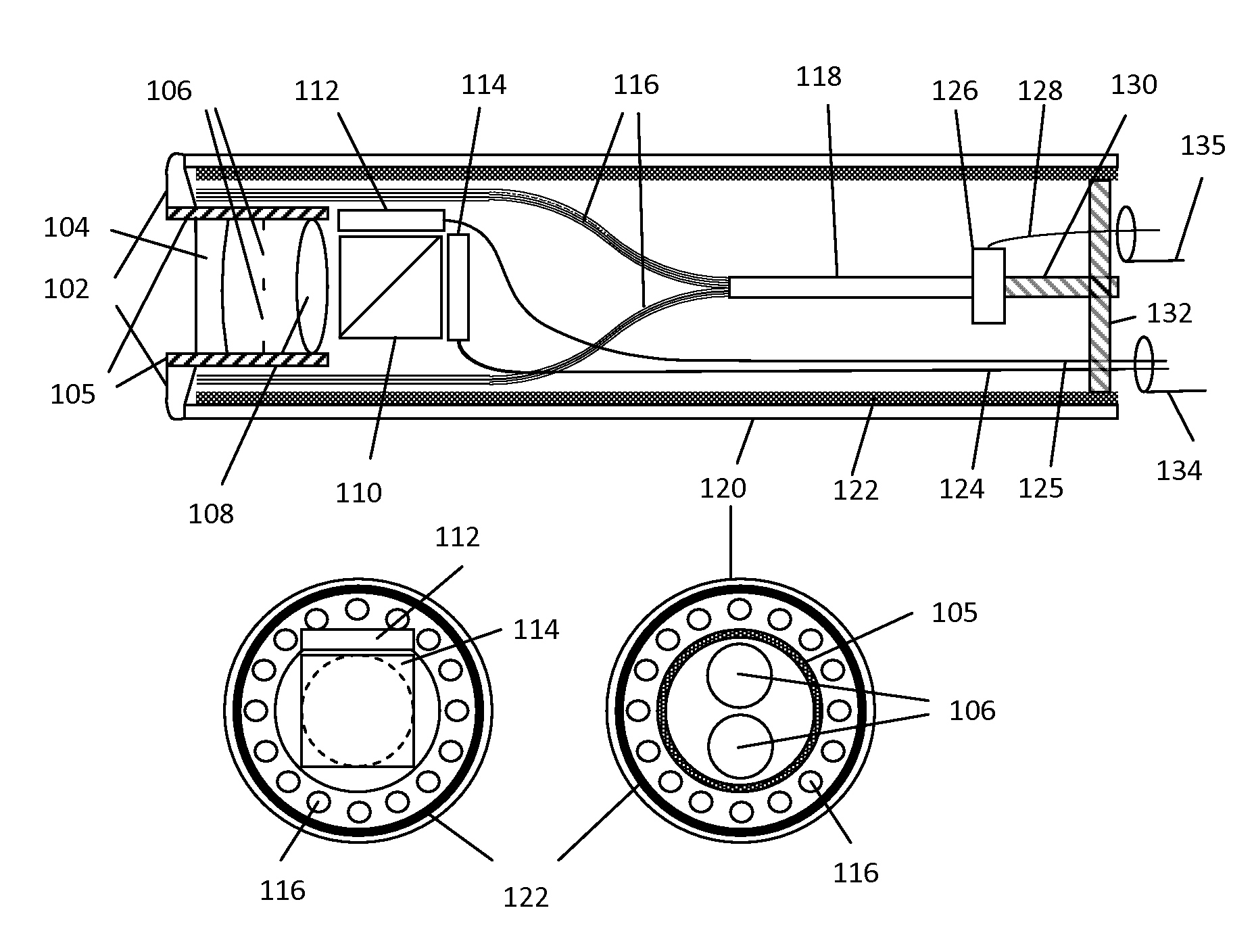
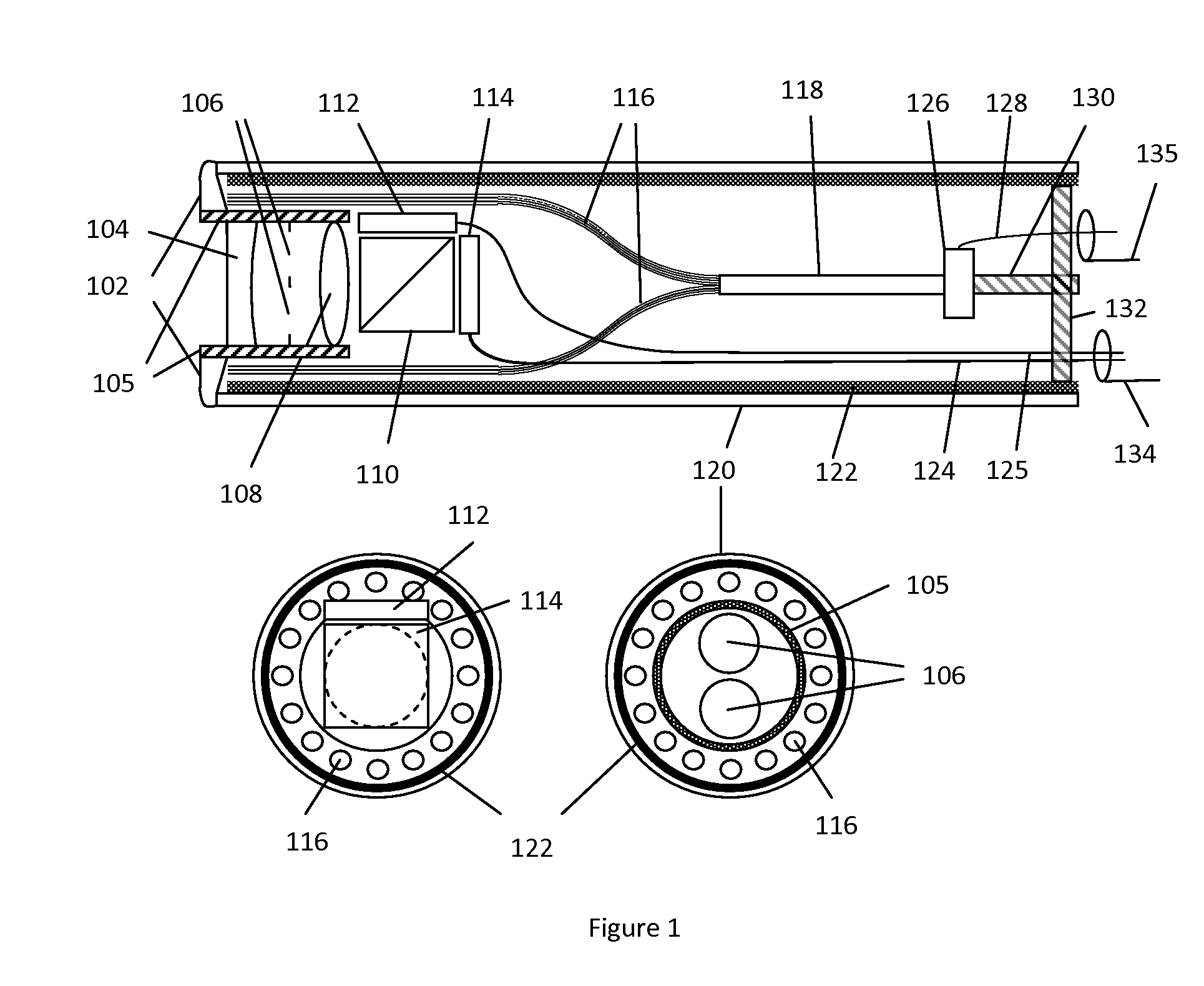
A disposable simultaneous stereo endoscope system is disclosed. The disposable endoscope does not include image relay. Instead, two electronic imaging sensors and solid illumination lighting are arranged inside the endoscope. A demultiplexing beam splitter is used for splitting the two imaging light beams to the two imaging devices. A wedged multi-facet illumination window is used to create an illumination field that is larger than the field of view of the imaging optics. An electrically conductive heat sink is engaged for dissipating the heat generated by the solid light source and also for shielding end side of the endoscope. The disposable endoscope is shielded from electromagnetic interferences. A repeater unit is used to electrically connect the disposable endoscope with a remote receiver and to increase the data transfer rate. An electrical isolation means is provided between the endoscope and an image processing and power conditioning unit to protect the endoscope against electric shock.
Owner:SU WEI +1
Backside illumination image sensor and image-capturing device
ActiveUS20110279727A1Avoid reflectionsTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesExit pupilPhotoelectric conversion
A backside illumination image sensor that includes a semiconductor substrate with a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements and a read circuit formed on a front surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and captures an image by outputting, via the read circuit, electrical signals generated as incident light having reached a back surface side of the semiconductor substrate is received at the photoelectric conversion elements includes: a light shielding film formed on a side where incident light enters the photoelectric conversion elements, with an opening formed therein in correspondence to each photoelectric conversion element; and an on-chip lens formed at a position set apart from the light shielding film by a predetermined distance in correspondence to each photoelectric conversion element. The light shielding film and an exit pupil plane of the image forming optical system achieve a conjugate relation to each other with regard to the on-chip lens.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Photon-counting, non-imaging, direct-detect LADAR
ActiveUS7301608B1Evenly distributedUniform lightOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaserPhoton counting
A light wave rangefinder includes a light transmitting optical system for directing a laser pulse at a target, and a light receiving optical system for receiving reflected light from the target, including a Geiger-mode avalanche photodiode (APD) array and a non-imaging optical device. The non-imaging optical device is positioned between the received reflected light and the APD array, and is configured to uniformly distribute the received reflected light across the APD array. The APD array is uniformly illuminated by a single received reflected laser pulse, producing a plurality of Geiger-mode avalanche events.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS INC
Device and method for measurement of surfaces
ActiveUS7561273B2Freely parametrizableStrongly miniaturizableScattering properties measurementsMicroscopesLight beamLarge distance
Owner:MICRO EPSILON MESSTECHNIK GMBH & CO KG +1
Mobile phone provided with video camera
InactiveUS20020058531A1Reduce usageDevices with rotatable cameraTwo-way working systemsEyepieceDisplay device
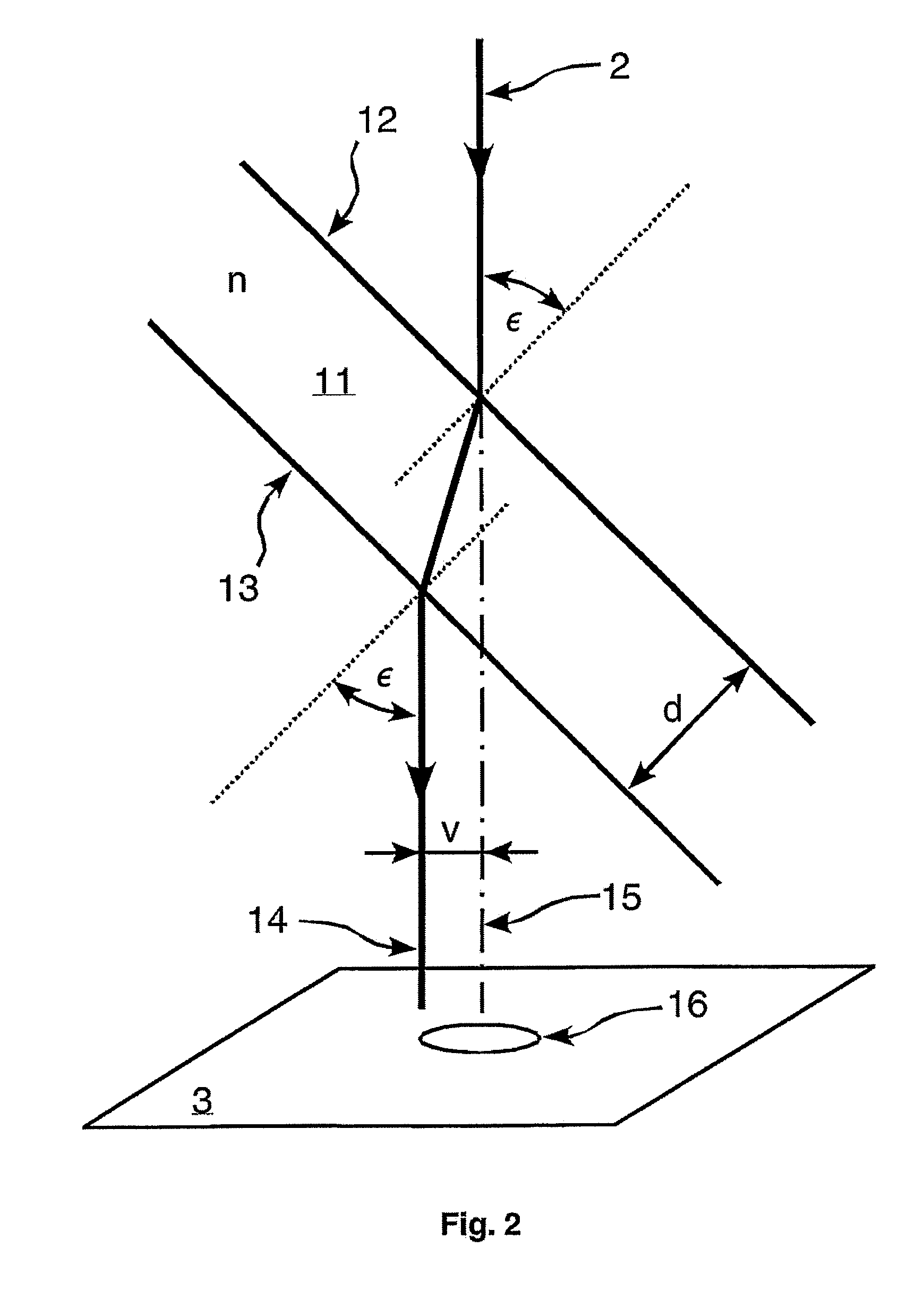
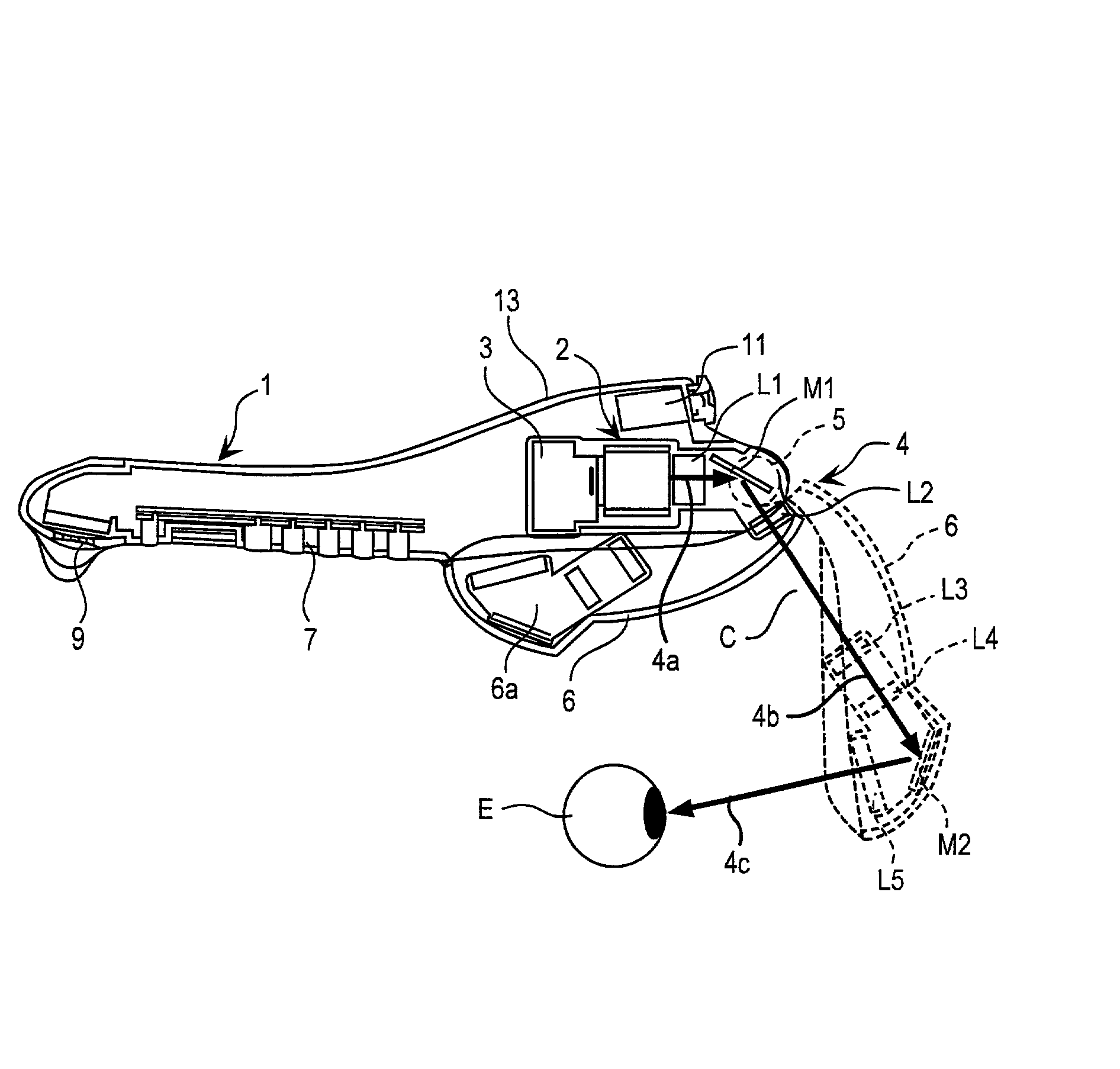
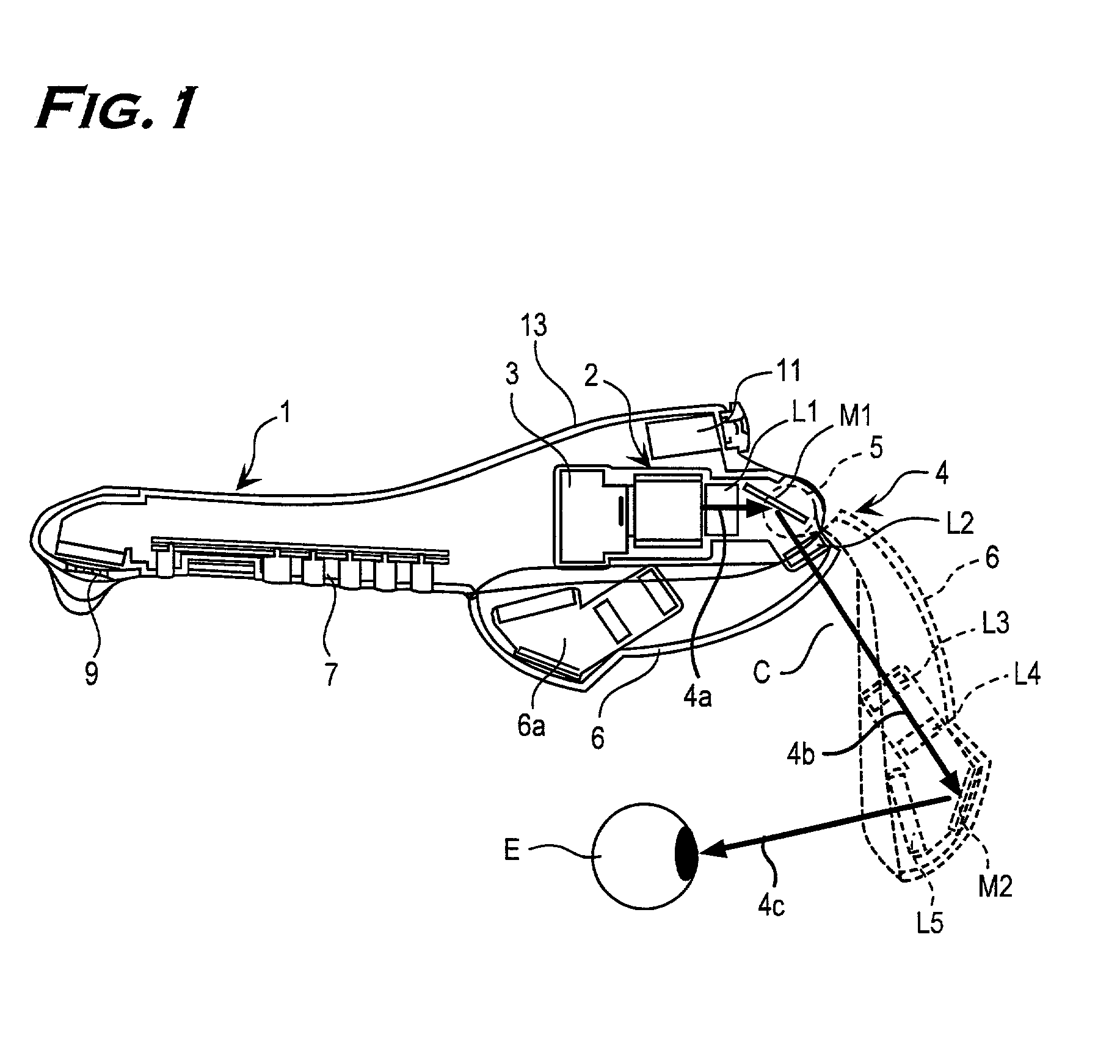
A mobile phone includes a phone body 1 having a wireless transmitting and receiving function of an image and sound and a virtual image optical display device 2 for forming a virtual image on a retina of an eye of a user by passing image information from an image information driving part 3 through an imaging optical system. The virtual image optical display device 2 positioned in front of the eye of the user is made as small as possible to make an eyepiece part of the mobile phone compact. An imaging optical system 4 of the virtual image optical display device 2 is separated into an optical system 4a on an image information driving part side and an optical system 4c on an eyepiece part side via a folding part 4b. The optical system 4c on the eyepiece part side is mounted on the arm 6 attached to the phone body 1 through the hinge 5. A length between a position of the phone body 1 contact with the ear of the user and the hinge 5, an angle of the arm 6 and the phone body 1 in using the phone, and a length of the arm 6 are determined under ergonomically optimum conditions.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Image taking optical system
An image taking optical system, sequentially arranged from an object side to an image side along an optical axis comprising: a front lens group, a stop and a rear lens group. The front lens group comprises at least a meniscus front-group first lens element with a convex object-side surface. The rear lens group comprises at least three lens elements. Through the means of field adjustments that result in desirable distorted images, the image taking optical system may shorten the total length while enhancing the ability to create a larger field of view for panorama usages in compact cameras and mobile phones.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20080024883A1Simple configurationReduce component countTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringAdhesive bonding
An image pickup apparatus includes a housing, a lens incorporated in the front of the housing and configured to constitute an imaging optical system, an image pickup device provided in the housing and configured to capture a subject image guided by the imaging optical system, a printed wiring board provided in the housing and having the image pickup device mounted thereon, a barrel provided integrally with the front of the housing, an annular lens cover configured to push a face of the lens facing forward in a rearward direction, and detachably mounted on the front of the barrel, and a support wall projecting rearward outside a rear end of the barrel in the radial direction and inside the housing, and bonded to the printed wiring board with adhesive.
Owner:SONY CORP
Imaging optical system and imaging lens device
InactiveUS20060017834A1Inexpensive and compactGood optical performanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical powerImaging lens
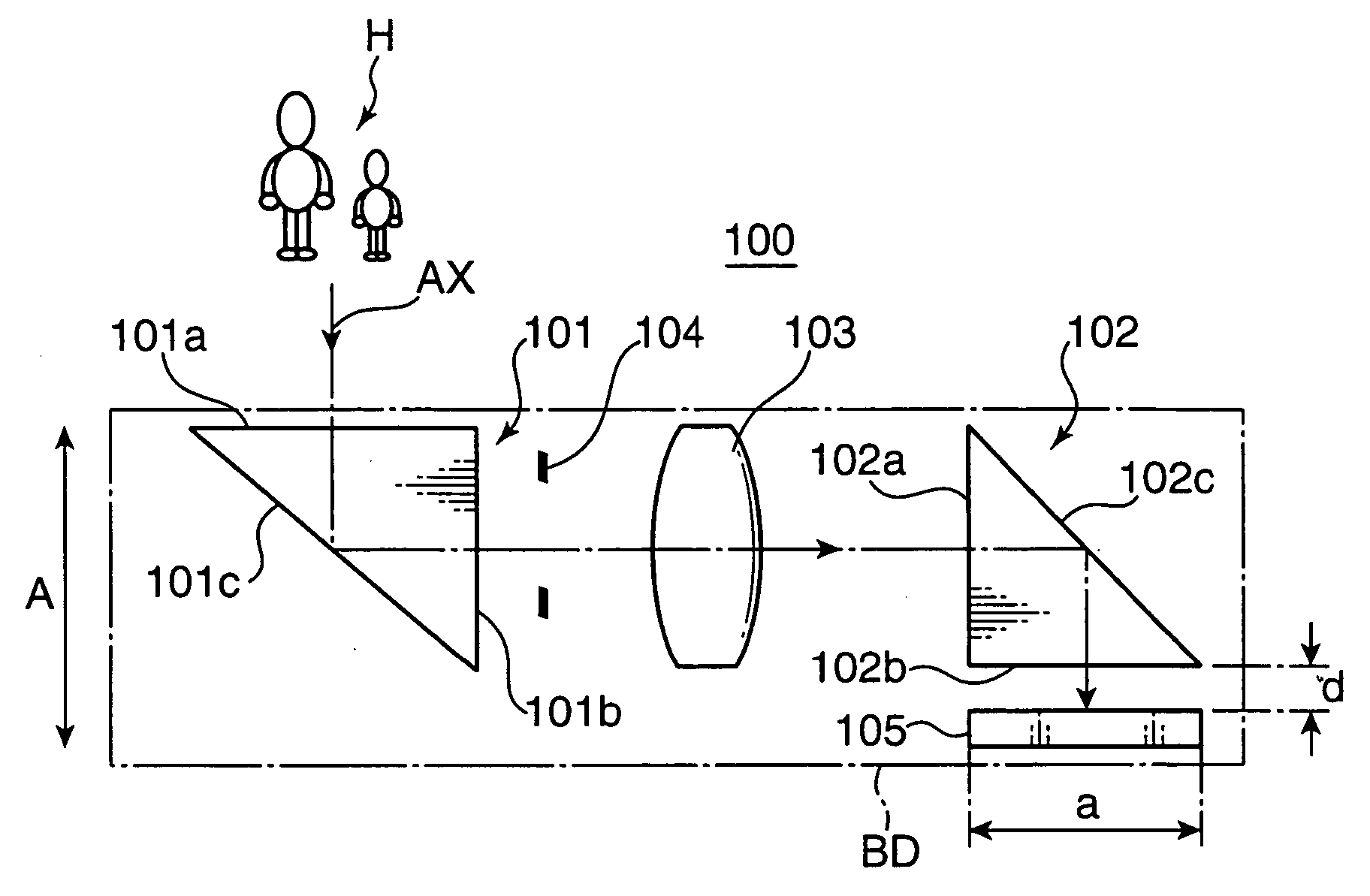
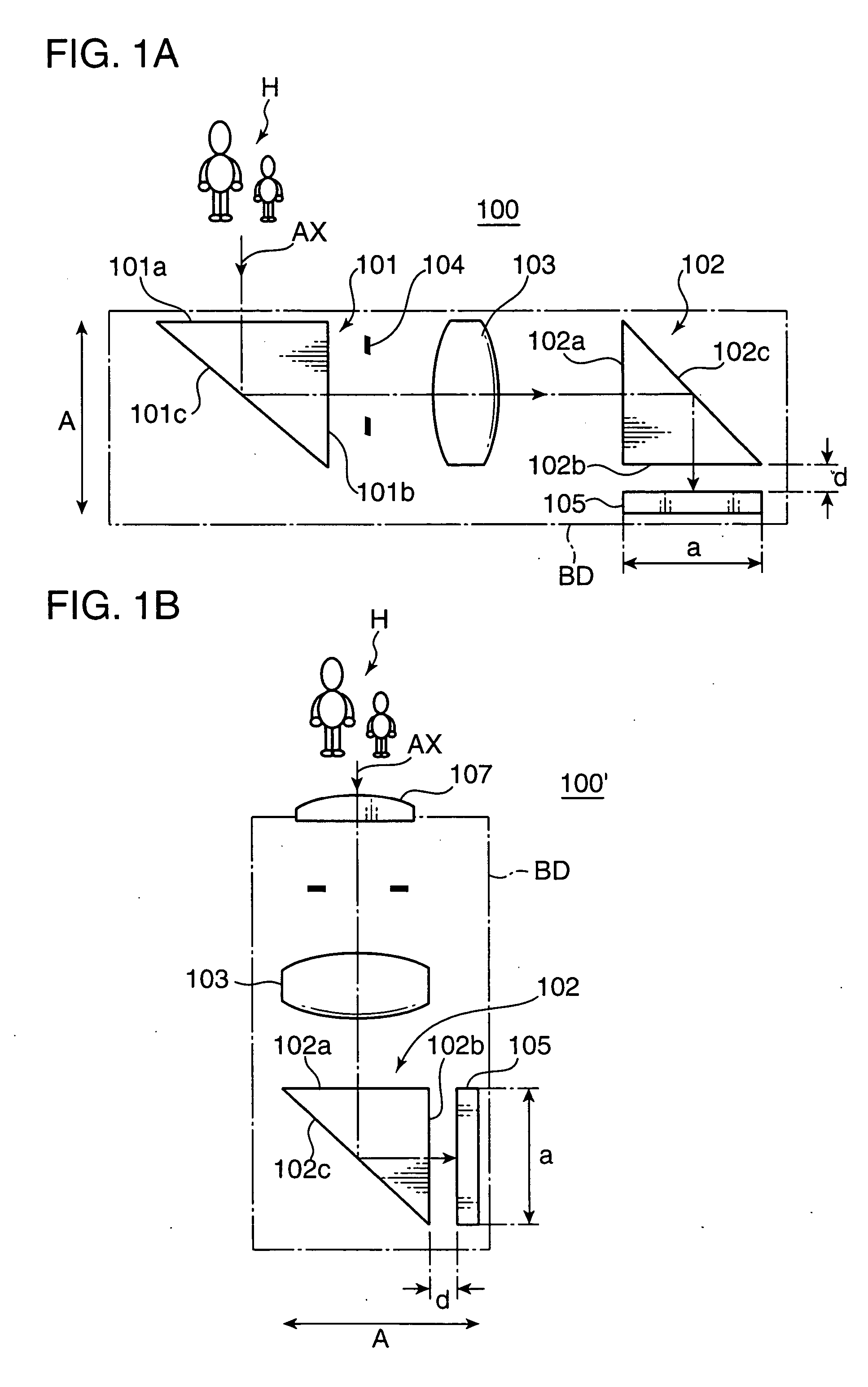
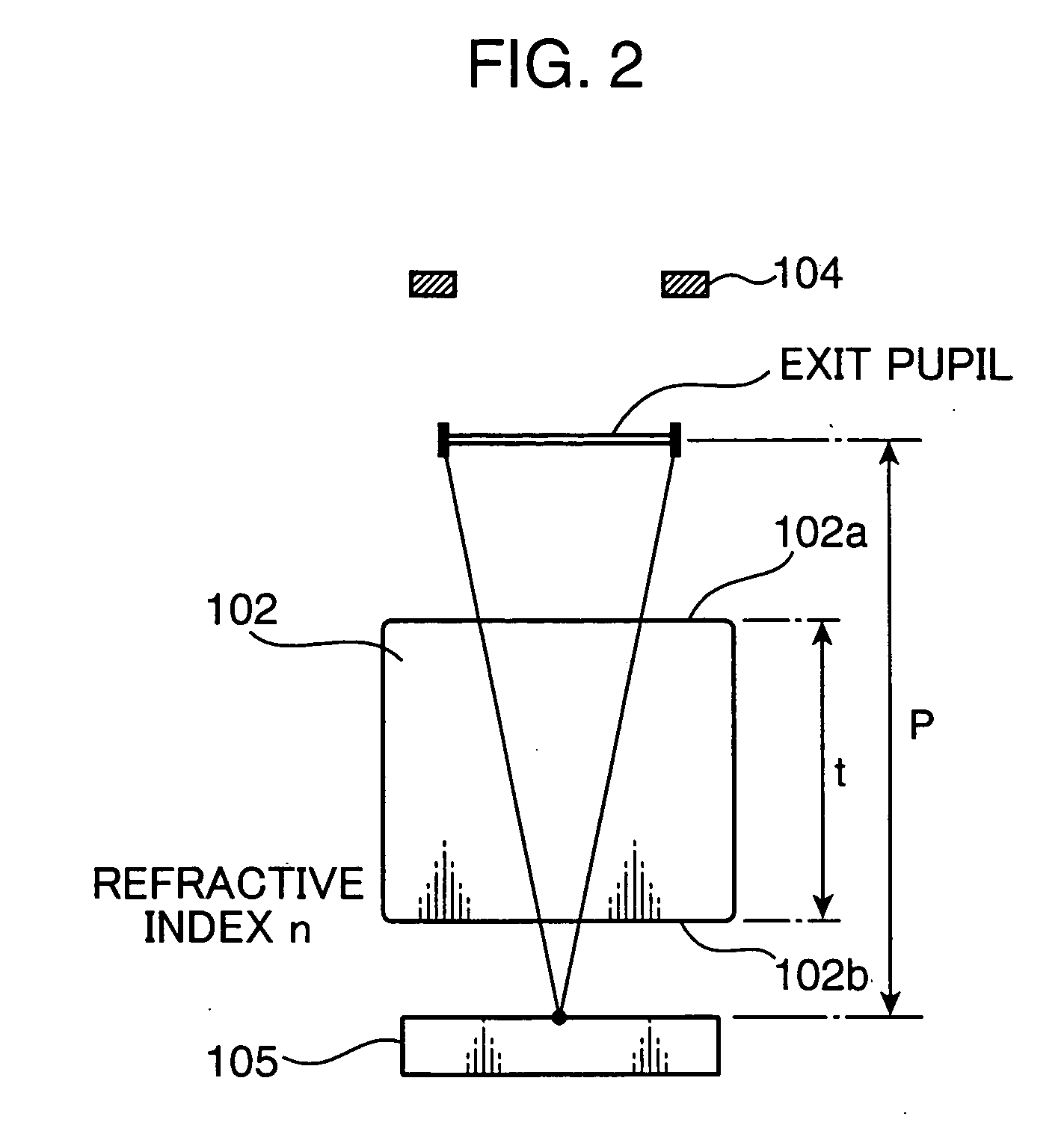
An imaging optical system 100 has an imaging side prism 102 for bending incident light at about 90 degrees for reflection, and an image sensor 105 having a light receiving surface opposing to an exit surface 102b of the imaging side prism 102. At least one of an incident surface 101a of an incident side prism 101 and an incident surface 101a of the imaging side prism 102, or at least one of an exit surface 101b of the incident side prism 101 and the exit surface 102b of the imaging side prism 102 has an optical power. An arrangement relation between the exit surface 102b of the imaging side prism 102 and the image sensor 105 is established to satisfy the conditional formula (1): 0.0≦d / a<0.8 (1) where d represents a distance between the exit surface 102b and the light receiving surface of the image sensor 105, and a represents a height of the light receiving surface of the image sensor 105 on a plane where an optical path of the imaging optical system 100 is folded, e.g., the size of the image sensor 105 in the shorter side direction thereof. This arrangement enables to reduce the thickness of an apparatus housing BD for incorporating the imaging optical system 100.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Imaging optical system
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Illuminating unit having diffusion means
InactiveUS6858837B2High mechanical strengthSuppress mutationMechanical apparatusBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLine sensorDiffusion
There is disclosed an image reading apparatus constructed by an illuminating unit for illuminating an object in a line shape, an image forming optical system for forming a light, as an image, from the object illuminated by the illuminating unit, a line sensor for converting the light formed as an image by the image forming optical system into an image signal, and a frame for holding the illuminating unit and the line sensor, wherein a shape in which vertices of at least a part of the cross section of the illuminating unit are connected by straight lines is set to a polygon of a pentagon or more, so that an image can be stably read at a high quality.
Owner:CANON KK
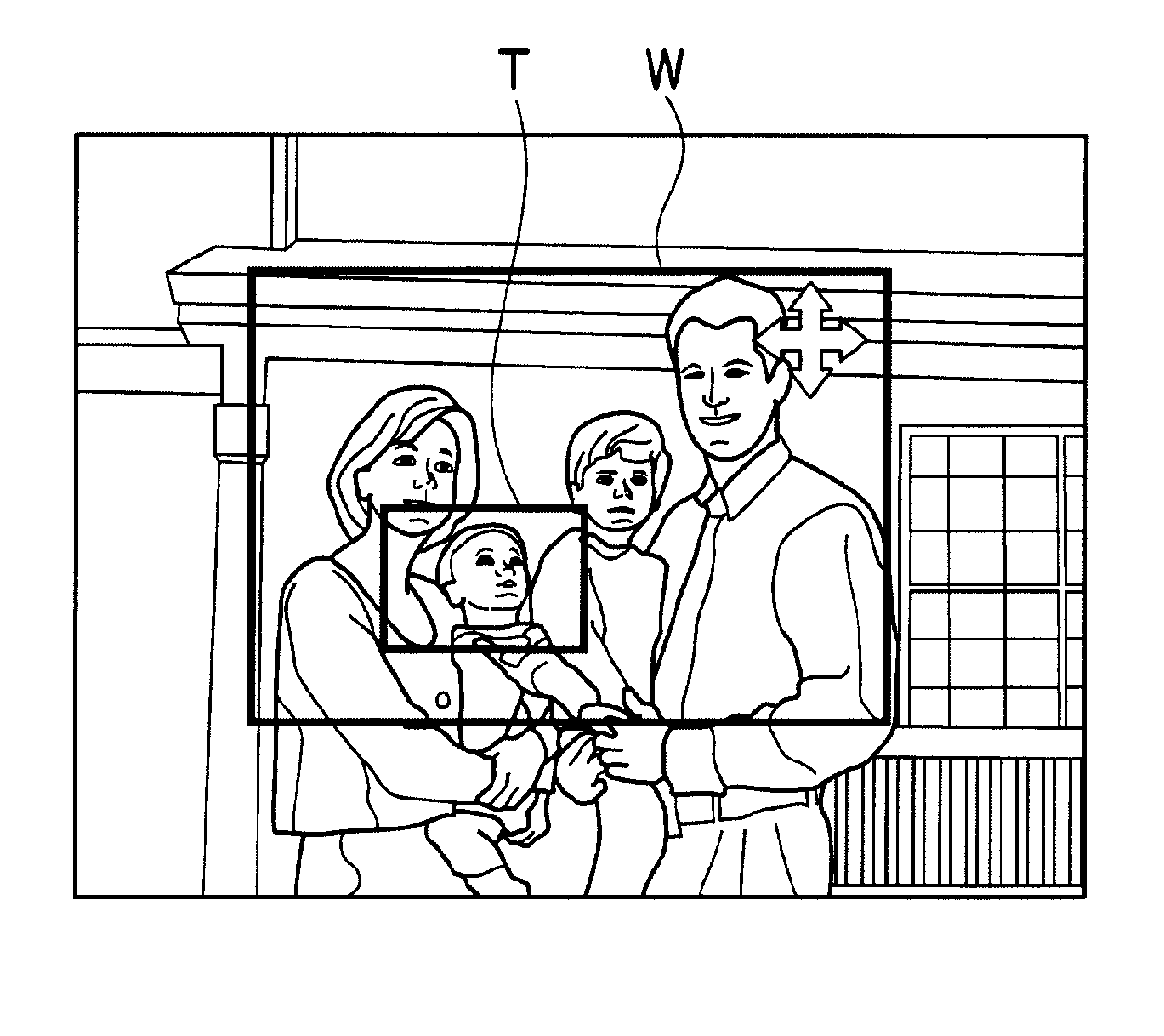
Imaging device and method
ActiveUS20110242369A1Television system detailsColor television detailsStereoscopic imagingMagnification
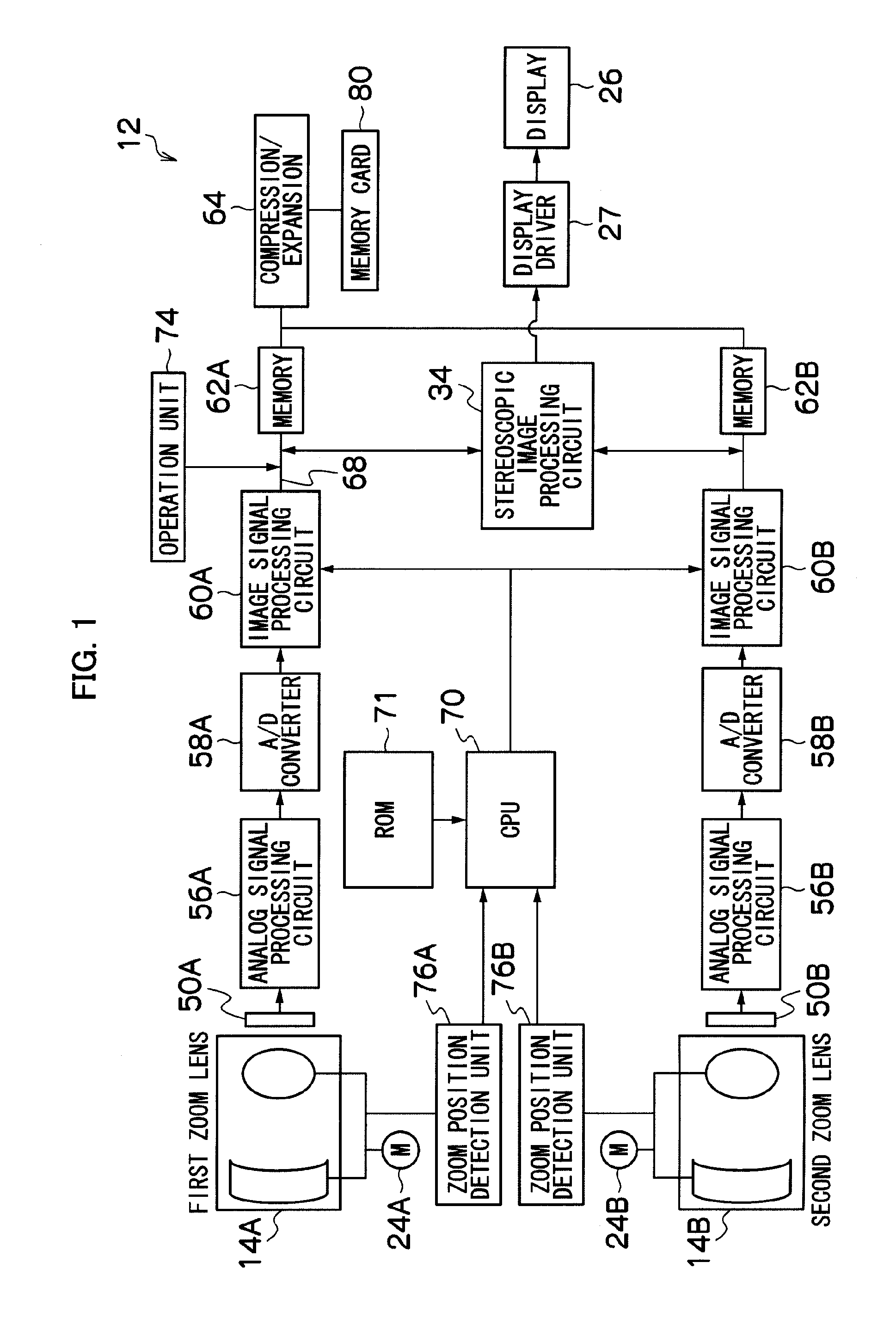
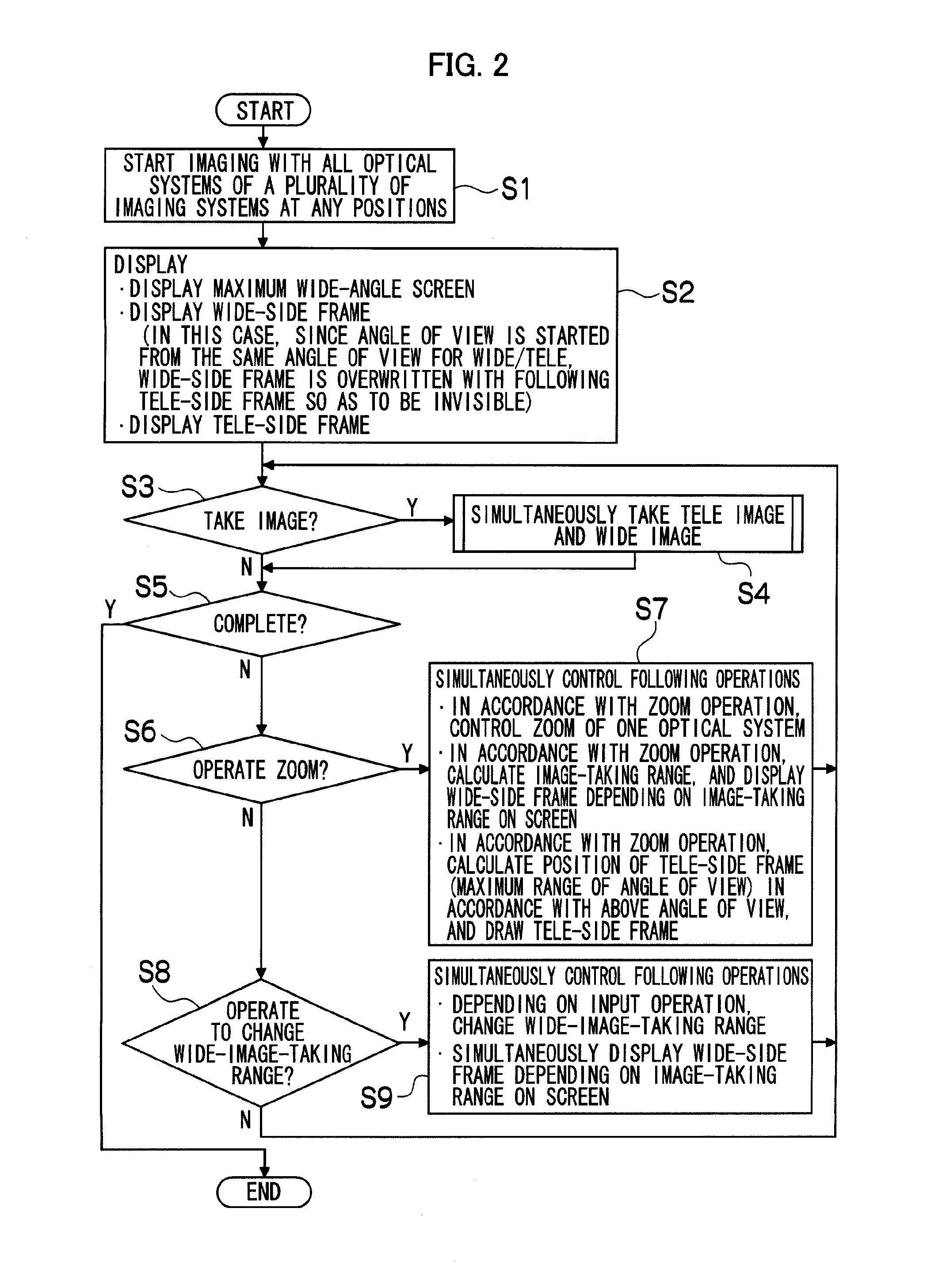
In a stereoscopic imaging device including a plurality of imaging optical systems, a wide-image in which a principal subject is shifted from the center is taken, and also, a tele-image in which the principal subject is enlarged is taken at the same time. A size of a wide-side frame W, that is, a size of an angle of view of a trimming wide-image is decided based on a size of a tele-side frame T, that is, a zoom magnification of a tele-side imaging optical system, a position of the wide-side frame W displayed in the decided size is arbitrarily moved depending on an instruction from an operation unit, an area delimited by the wide-side frame W moved to any position is clipped from a default wide-image, and thereby, the trimming wide-image is obtained. Thereby, the tele-image which is a telephoto image in which a desired subject is zoomed, and the trimming wide-image which is a wide-angle image in which the subject can exist at a position other than the center of the image are simultaneously obtained.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20110298925A1Sufficient heat dissipation effectTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSoft materialsEngineering
An imaging apparatus includes: an electronic circuit unit (30) including an imaging device (31) to acquire an object image formed by an imaging optical system (20); and a housing member (13) housing the electronic circuit unit (30). The electronic circuit unit (30) includes a thermally-conductive heat transfer member (37) in contact with an outer peripheral surface thereof which is in parallel with a fitting direction of the electronic circuit unit (30) into the housing member (13). The heat transfer member (37) includes a soft material portion (37b) in contact with the outer peripheral surface of the electronic circuit unit (37), and a plate portion (37a) in contact with the soft material portion (37b) and an inner peripheral wall surface of the housing member (13). The soft material portion (37b) is made of a shape-conformable member.
Owner:RICOH KK
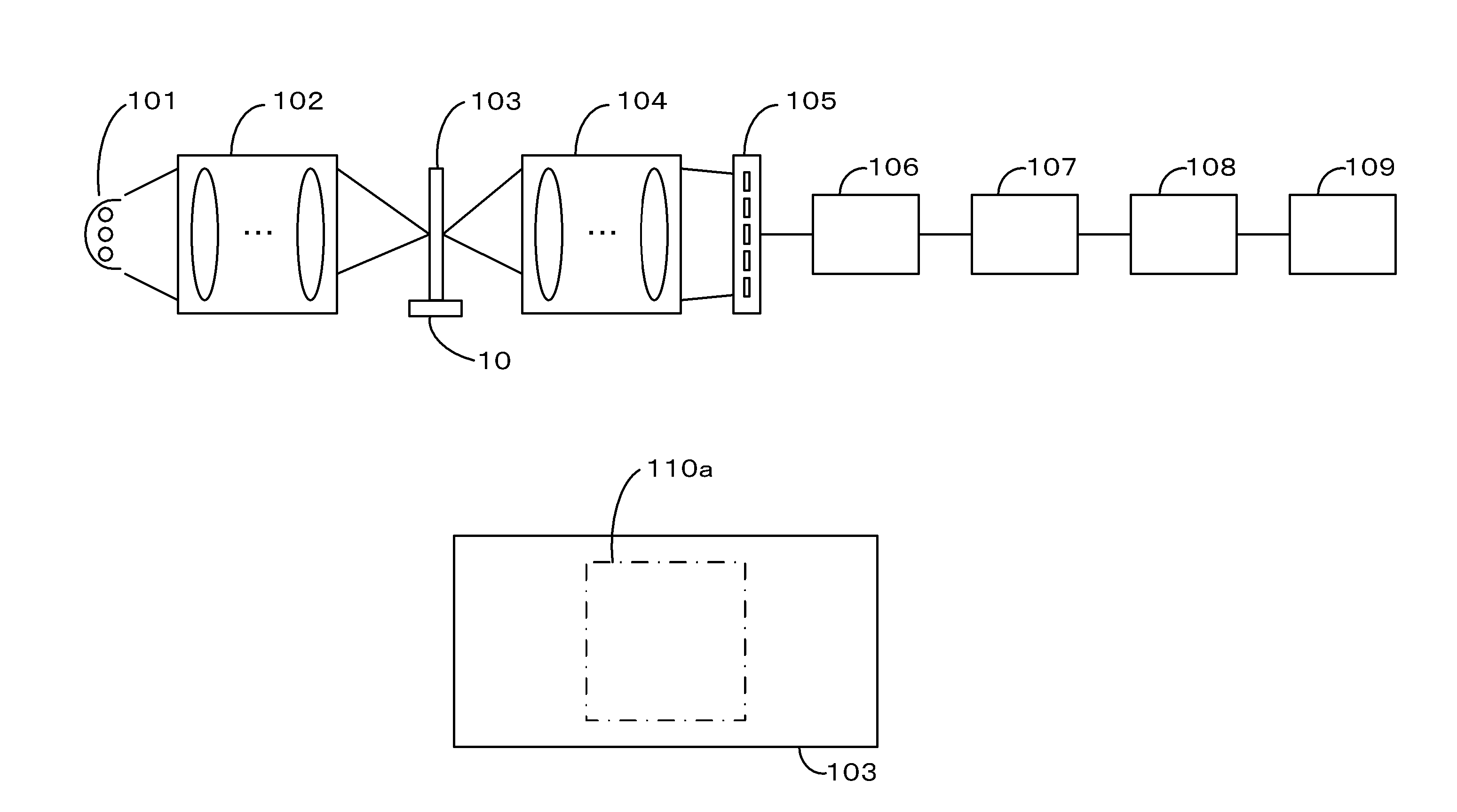
Apparatus and a method for inspection of a mask blank, a method for manufacturing a reflective exposure mask, a method for reflective exposure, and a method for manufacturing semiconductor integrated circuits
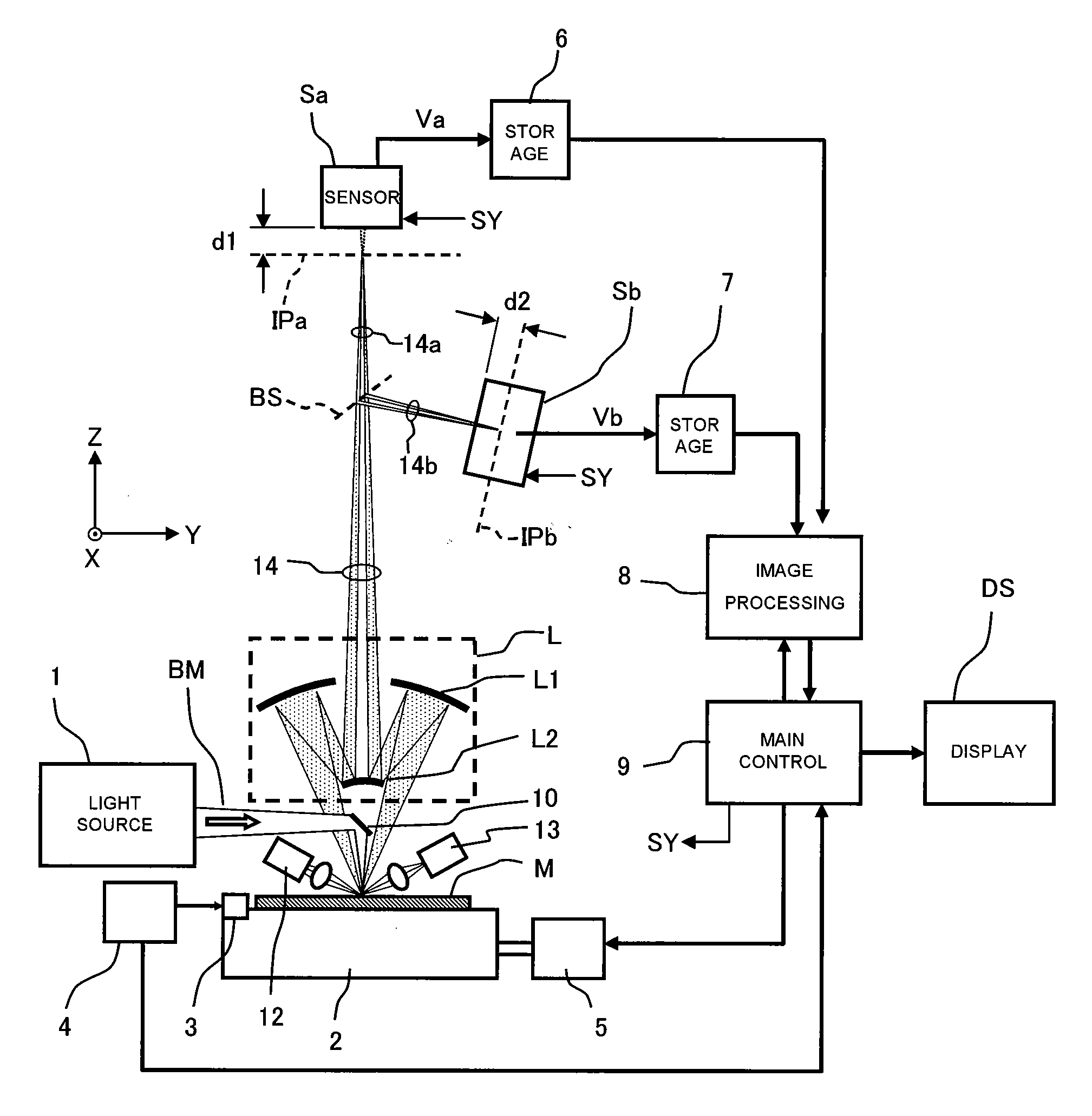
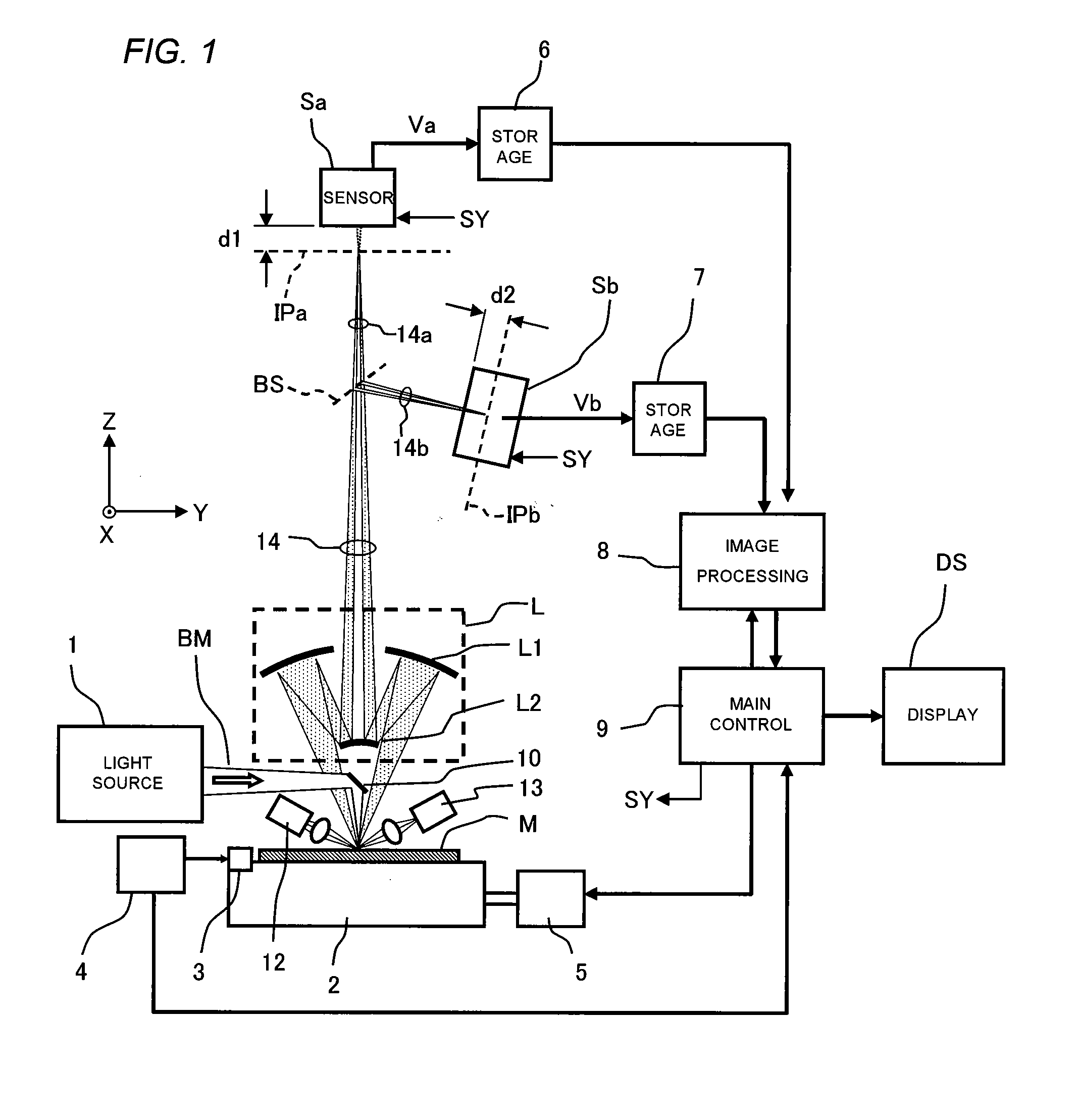
ActiveUS20090091752A1Convenient and accurate inspectionHigh reliability and yieldElectric discharge tubesScattering properties measurementsBeam splitterImaging processing
The mask blank inspection apparatus is constituted of a stage for mounting a reflective mask blank thereon, a light source for generating inspection light, a mirror serving as an illuminating optics, an imaging optical system, a beam splitter, two two-dimensional array sensors, signal storage units, an image processing unit, a main control unit for controlling operation of the whole apparatus, the first sensor being located at a position which is displaced by a predetermined distance from the focal plane of a first light beam, the second sensor being located at a position which is displaced by a predetermined distance from the focal plane of a second light beam along a opposite direction, whereby accurately and conveniently inspecting presence / absence and types of defects in reflective mask blank.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
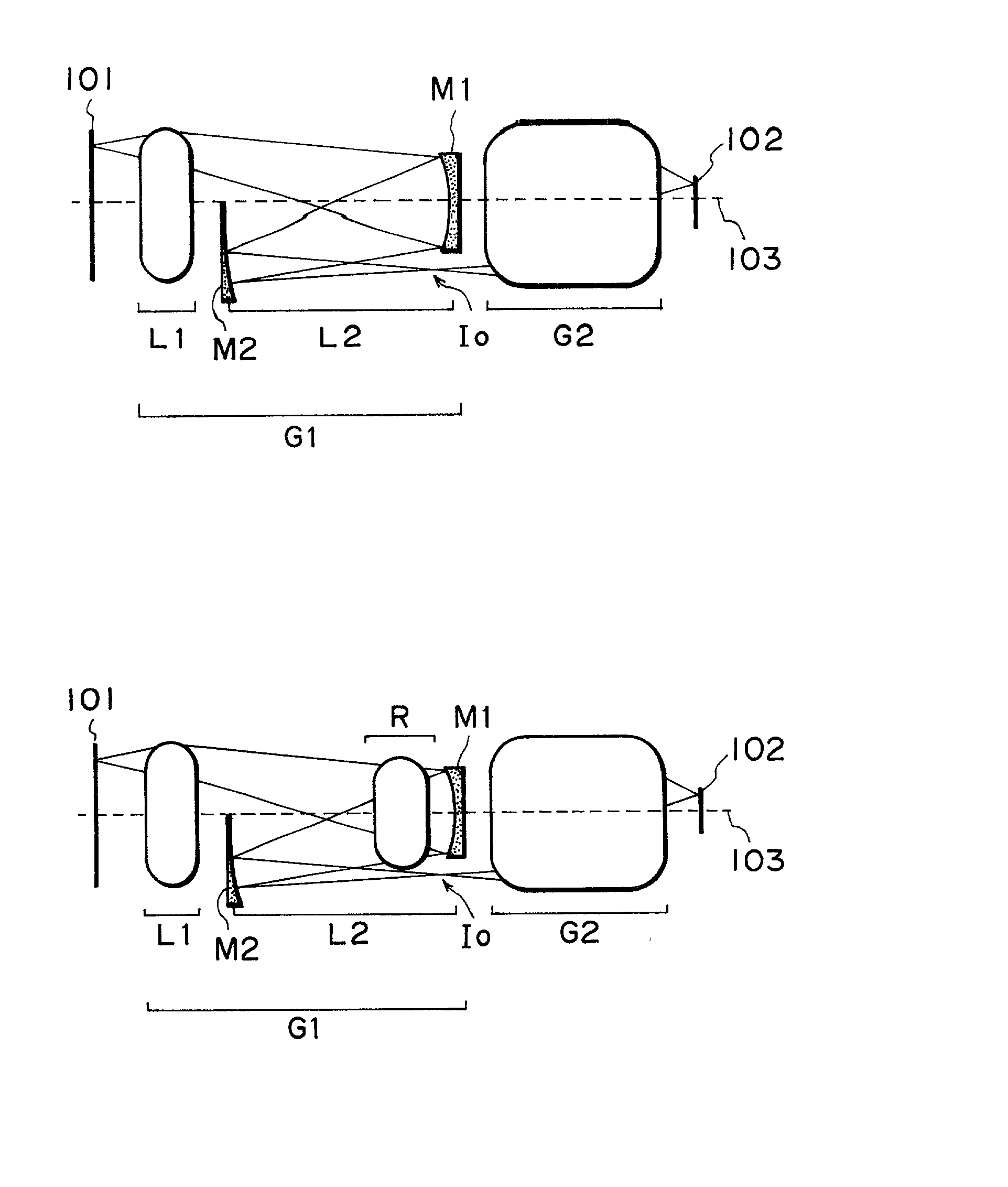
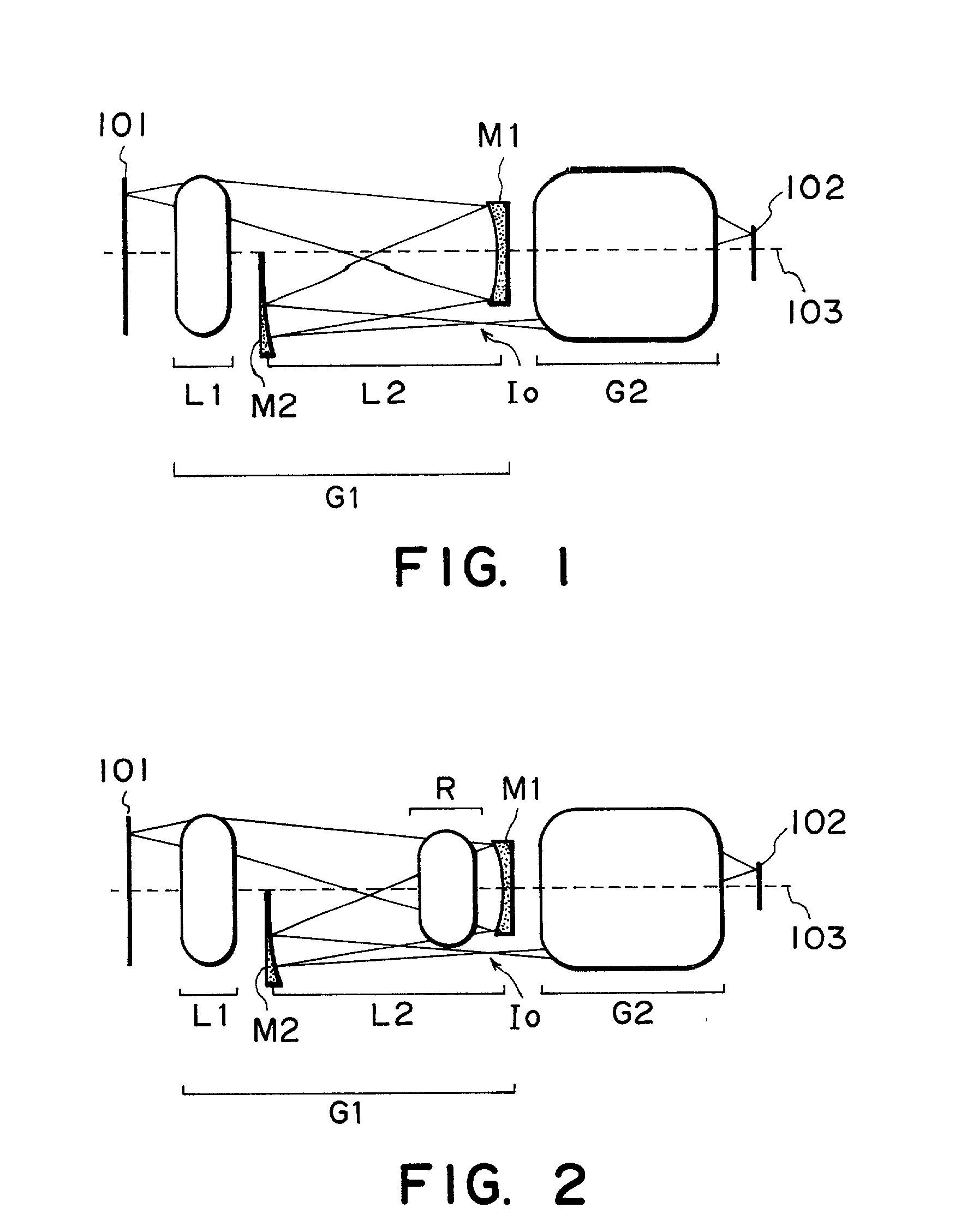
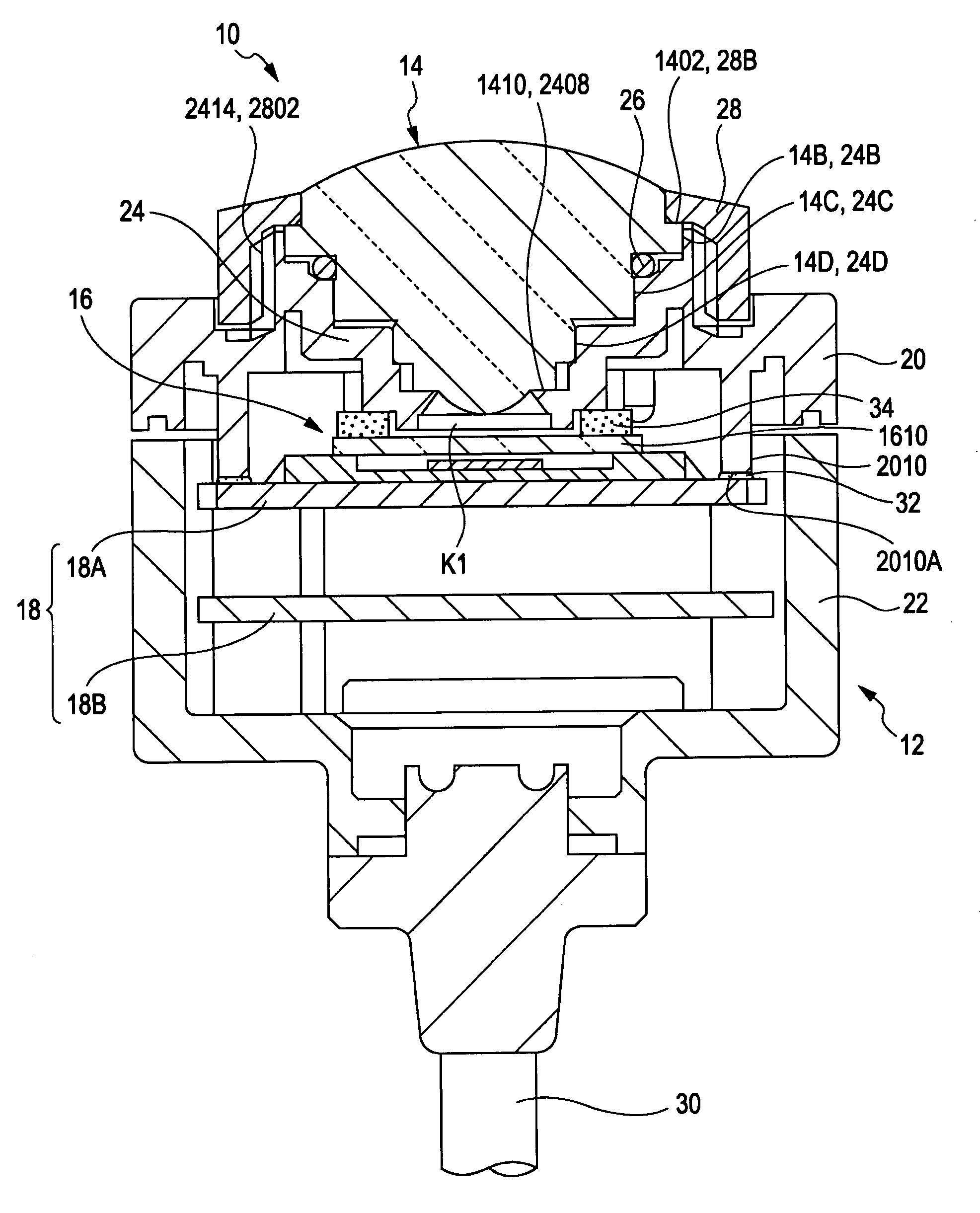
Catadioptric imaging system and a projection exposure apparatus provided with said imaging system
InactiveUS6473243B1Avoiding deterioration of image forming performanceInhibit deteriorationMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusRadiationImage-forming optical system
Owner:NIKON CORP
LED backlighting system with closed loop control
InactiveUS20090122533A1Improve homogeneityReduce intensityNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceOn boardDisplay device
A light emitting diode (LED) based illumination system with particular application to large scale side lighted liquid crystal displays (LCD). The invention uses on board closed loop intensity control in conjunction with red, green and blue (R,G,B) LED die and a hybrid non-imaging optical system to overcome substantial temperature dependence, loss in intensity with time, increased system cost and complexity, and decreased dynamic range. The invention obtains a large color gamut in excess of 110% of the NTSC (National Television System Committee) recommendation. A high performance thermal management design, the use of “chip on board” technology, compact and efficient collection optics, and on board closed loop intensity control increase and maintain luminous performance and decrease cost relative to less efficient RGB LED approaches. One or more line sources can be generated for applications other than in lighting LCD displays.
Owner:INNOVATIONS & OPTICS
Method of and system for producing digital images of objects with subtantially reduced speckle-noise patterns by illuminating said objects with spatially and/or temporally coherent-reduced planar laser illumination
InactiveUS20020043561A1Reducing speckle-noise patternSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSystems designHand held
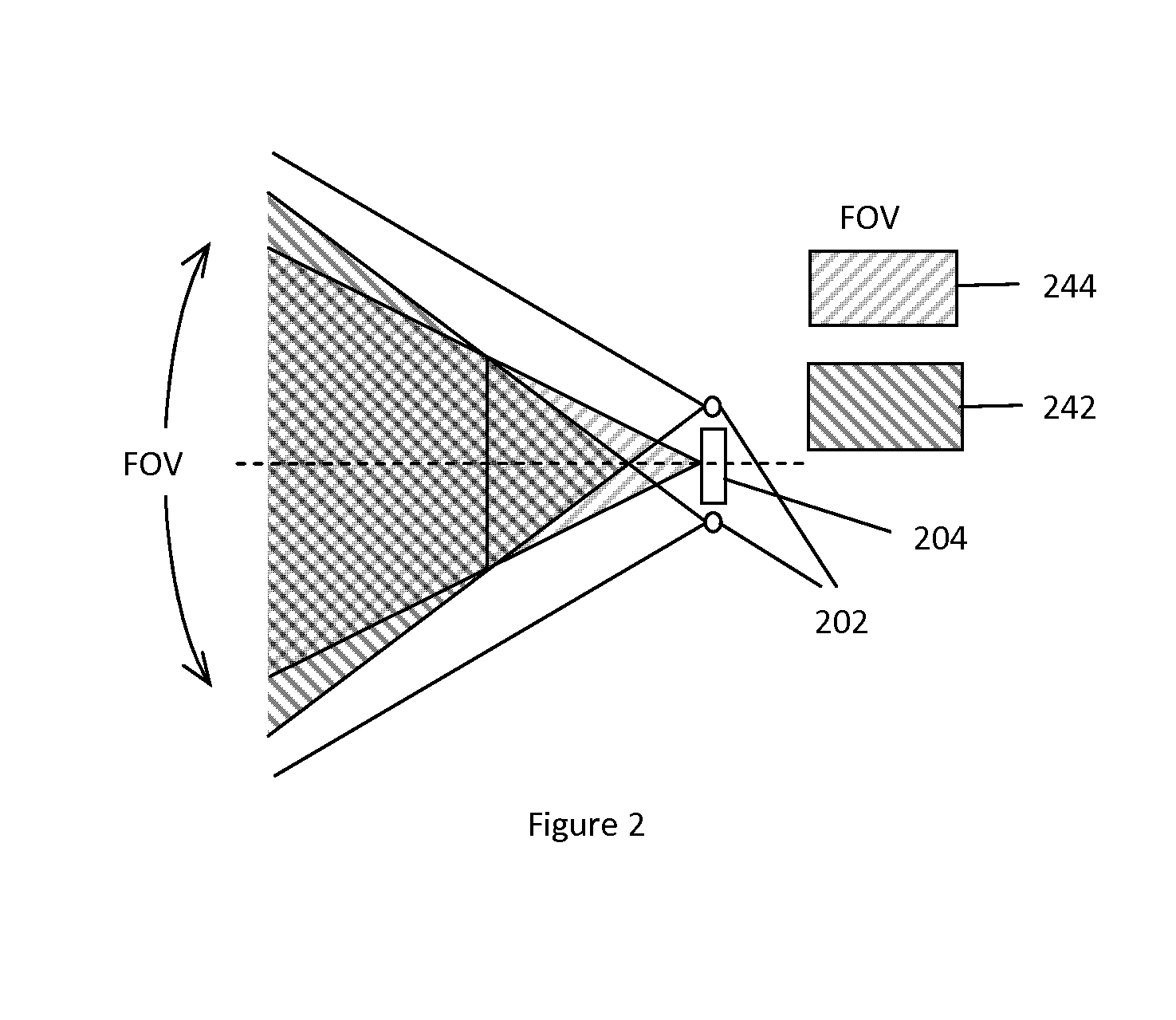
Methods of and systems for illuminating objects using planar laser illumination beams having substantially-planar spatial distribution characteristics that extend through the field of view (FOV) of image formation and detection modules employed in such systems. Each planar laser illumination beam is produced from a planar laser illumination beam array (PLIA) comprising an plurality of planar laser illumination modules (PLIMs). Each PLIM comprises a visible laser diode (VLD, a focusing lens, and a cylindrical optical element arranged therewith. The individual planar laser illumination beam components produced from each PLIM are optically combined to produce a composite substantially planar laser illumination beam having substantially uniform power density characteristics over the entire spatial extend thereof and thus the working range of the system. Preferably, each planar laser illumination beam component is focused so that the minimum beam width thereof occurs at a point or plane which is the farthest or maximum object distance at which the system is designed to acquire images, thereby compensating for decreases in the power density of the incident planar laser illumination beam due to the fact that the width of the planar laser illumination beam increases in length for increasing object distances away from the imaging optics. Advanced high-resolution wavefront control methods and devices are disclosed for use with the PLIIM-based systems in order to reduce the power of speckle-noise patterns observed at the image detections thereof. By virtue of the present invention, it is now possible to use both VLDs and high-speed CCD-type image detectors in conveyor, hand-held and hold-under type imaging applications alike, enjoying the advantages and benefits that each such technology has to offer, while avoiding the shortcomings and drawbacks hitherto associated therewith.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Image capturing apparatus and control method therefor
ActiveUS20080317454A1Easy to detectAccurate detectionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCouplingImage capture
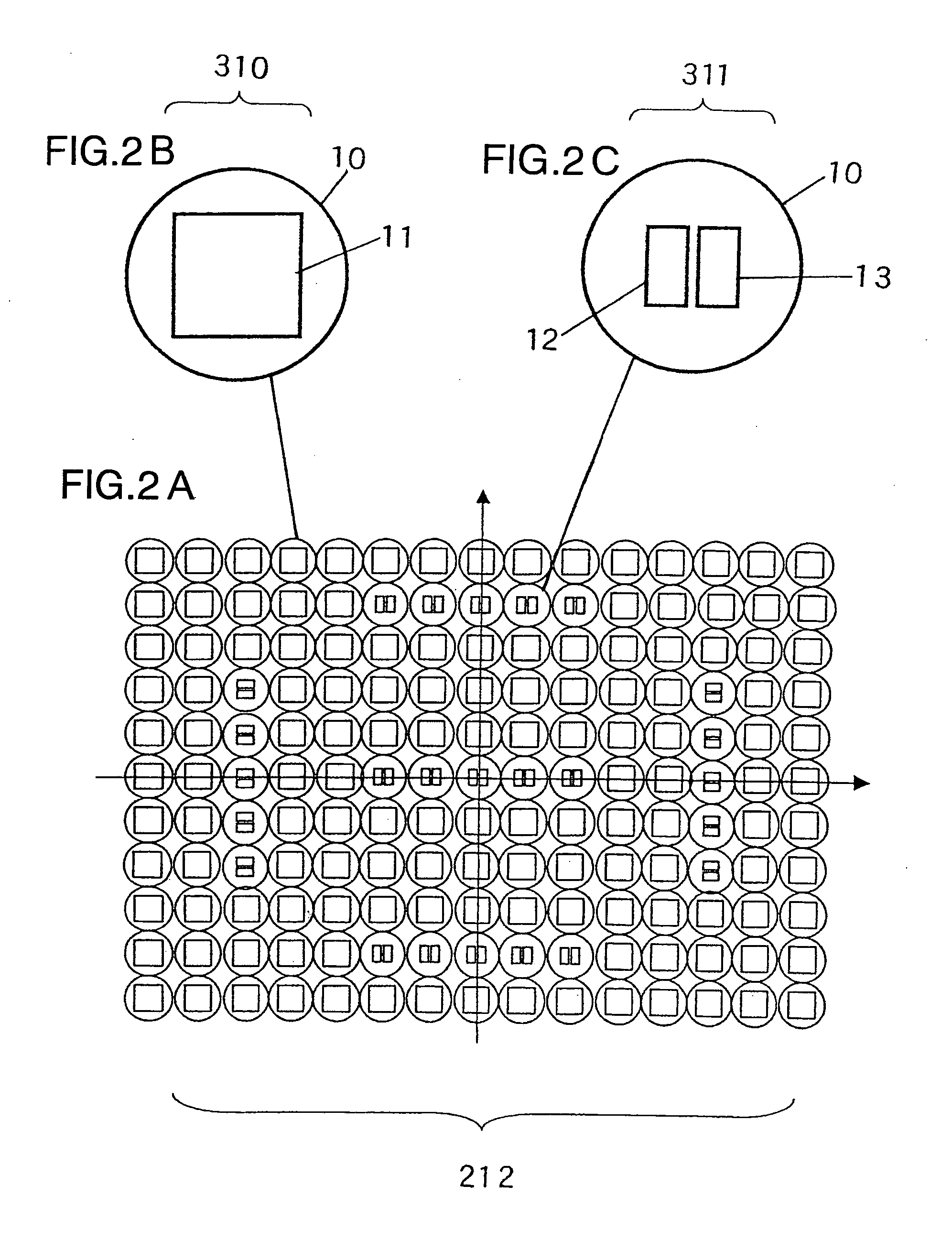
An image capturing apparatus includes an image sensor, composition unit, coupling unit, and arithmetic unit. The image sensor has a plurality of pupil-divided focus detection portions each formed from a first focus detection pixel and second focus detection pixel. The composition unit composites signals output from the first focus detection pixels to obtain a first composite signal, and composites signals output from the second focus detection pixels to obtain a second composite signal in each of sections assigned to the image sensor to include a plurality of focus detection portions. The coupling unit couples first composite signals to obtain a first coupled signal, and couples second composite signals to obtain a second coupled signal in the plurality of sections. The arithmetic unit calculates the defocus amount of an image forming optical system on the basis of the first and second coupled signals.
Owner:CANON KK
Data symbol reading apparatus
InactiveUS6039255ASufficient and uniform illuminationSufficient illuminationMirrorsSensing by electromagnetic radiationDiffusionImage formation
A data symbol reading apparatus, for reading an encoded data symbol, includes: an image pickup element; an image forming optical system for forming an image of the encoded data symbol located within a symbol read area onto a light-receiving surface of the image pickup element; and an illumination system. The illumination system includes a plurality of light sources, a diffusion plate for diffusing light emitted from the light sources, and a lens member for transmitting diffused light diffused by the diffusion plate onto the symbol read area. The plurality of light sources, the diffusion plate, and the lens member are arranged such that a light distribution within the symbol reading area is almost uniform.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20120147224A1Big imageResolution is deterioratedTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImage sensorImage-forming optical system
An imaging apparatus has image sensors, an imaging optical system of which relative position with the image sensors is fixed, and a merging unit which connects images obtained by imaging while changing the relative position between the image sensors and the imaging optical system. Aberration of the imaging optical system in an image obtained by each image sensor is predetermined based on the relative position between the imaging optical system and the image sensor. The merging unit smoothes seams of the two images by setting a correction area in an overlapped area where the two images to be connected overlap with each other, and performing correction processing on pixels in the correction area. A size of the correction area is determined according to the difference in aberrations of the two images, which is determined by a combination of image sensors which have imaged the two images.
Owner:CANON KK
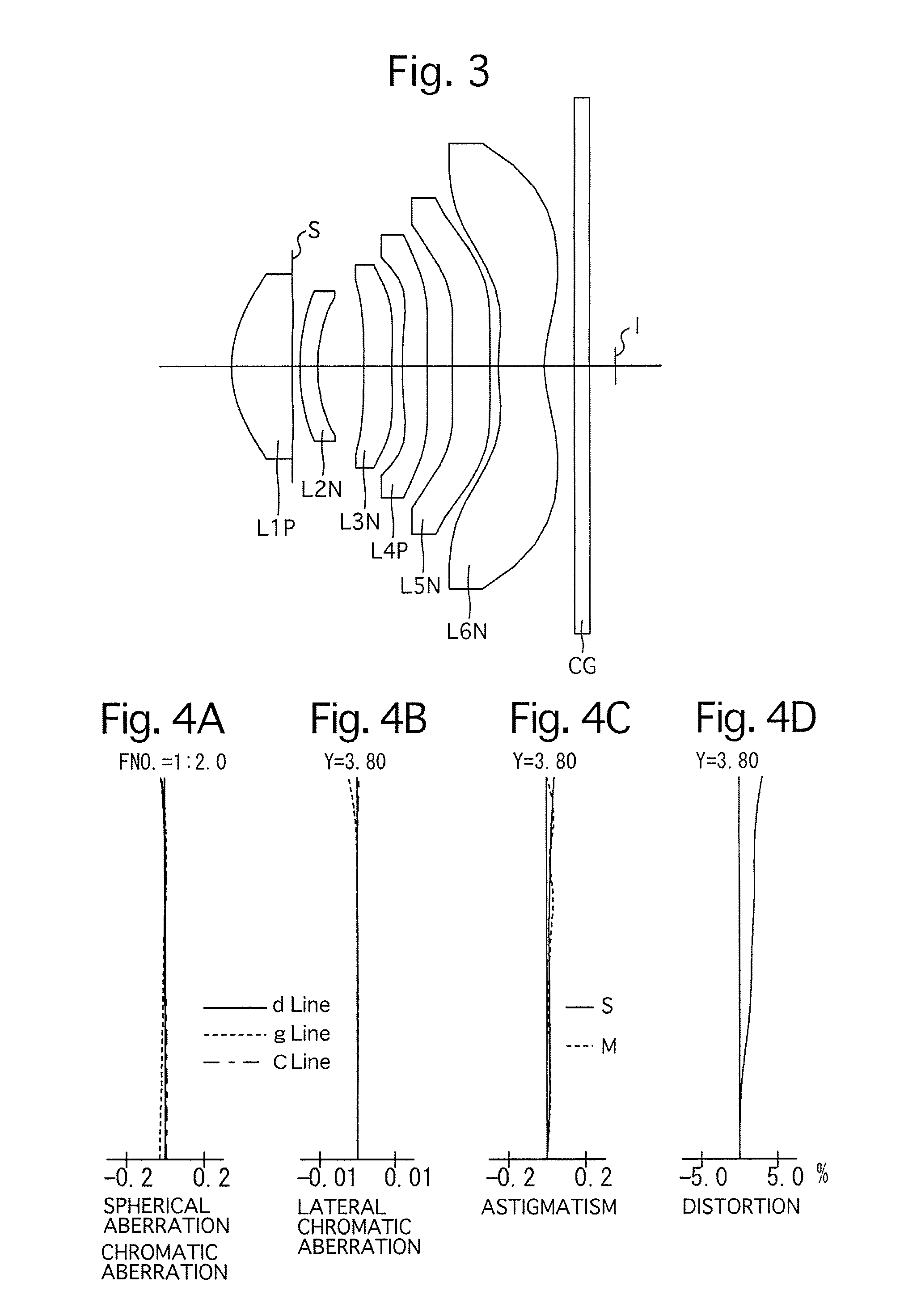
Imaging optical system
InactiveUS20160124192A1Correct abaxial aberrationMinimization requirementsLensOptical axisConvex side
An imaging optical system includes a positive first lens element having a convex surface on the object side, a negative second lens element having a concave surface on the image side, a third lens element, a positive fourth lens element, a fifth lens element, and a negative sixth lens element provided with at least one aspherical surface that has inflection points other than at an optical axis thereof. The following conditions (1) and (2) are satisfied:0.86<f / f12<1.20 (1), and−0.71<(r11−r12) / (r11+r12)<−0.20 (2),wherein f designates the focal length of the imaging optical system, f12 designates the combined focal length of the first and second lens elements, and r11 and r12 designate the radius of curvatures of surfaces on the object side and image side of the first lens element, respectively.
Owner:HOYA CORP
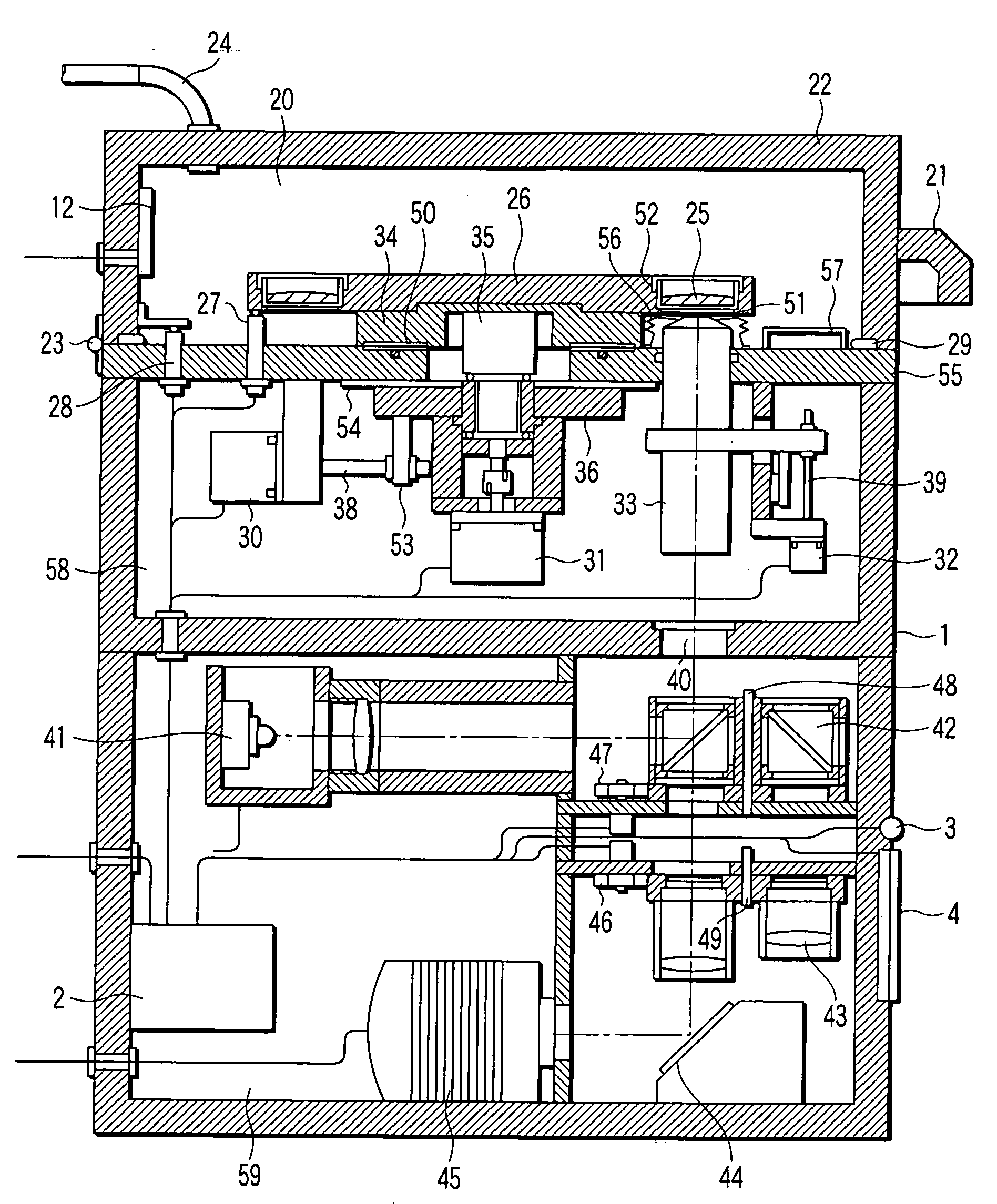
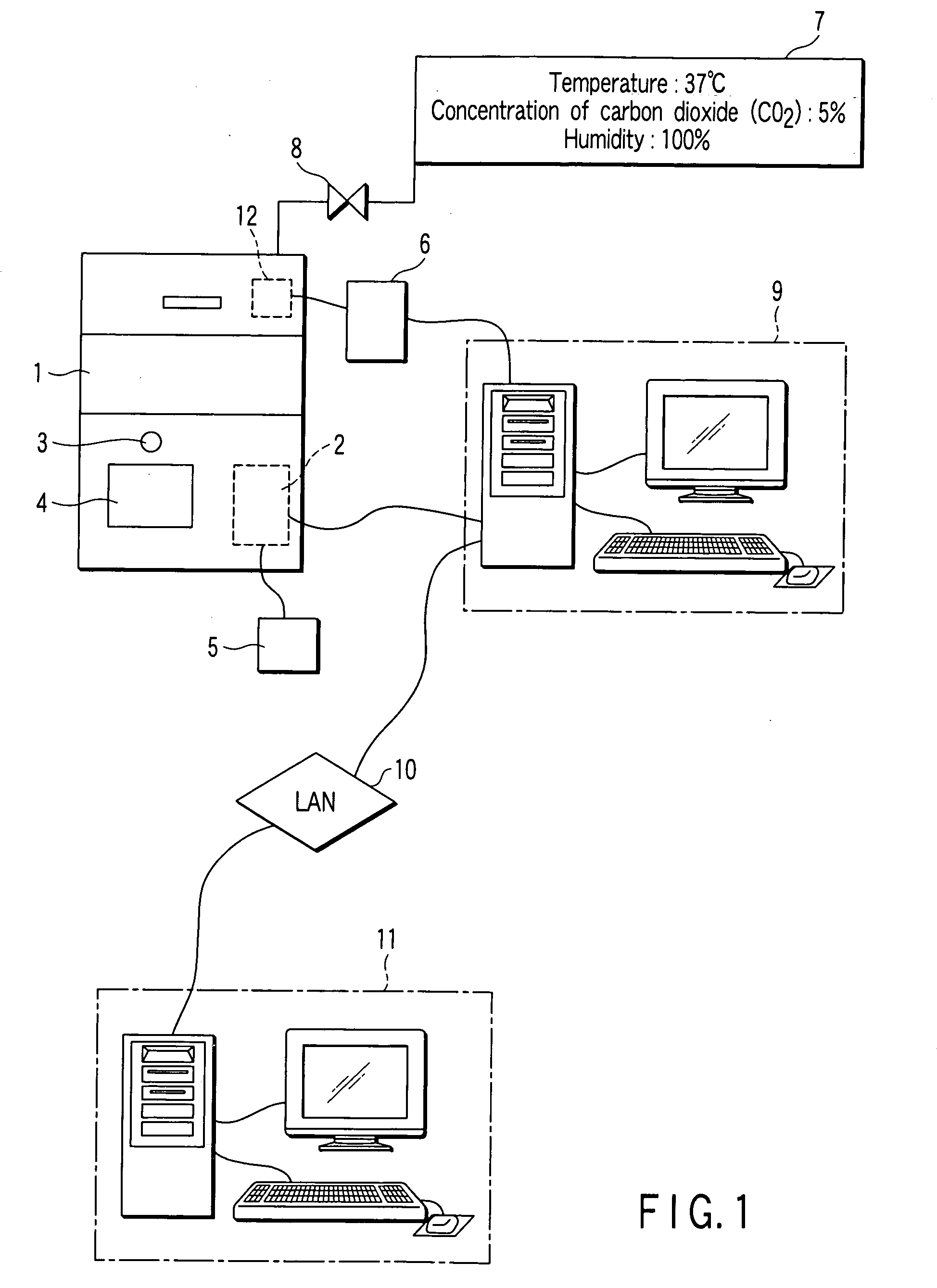
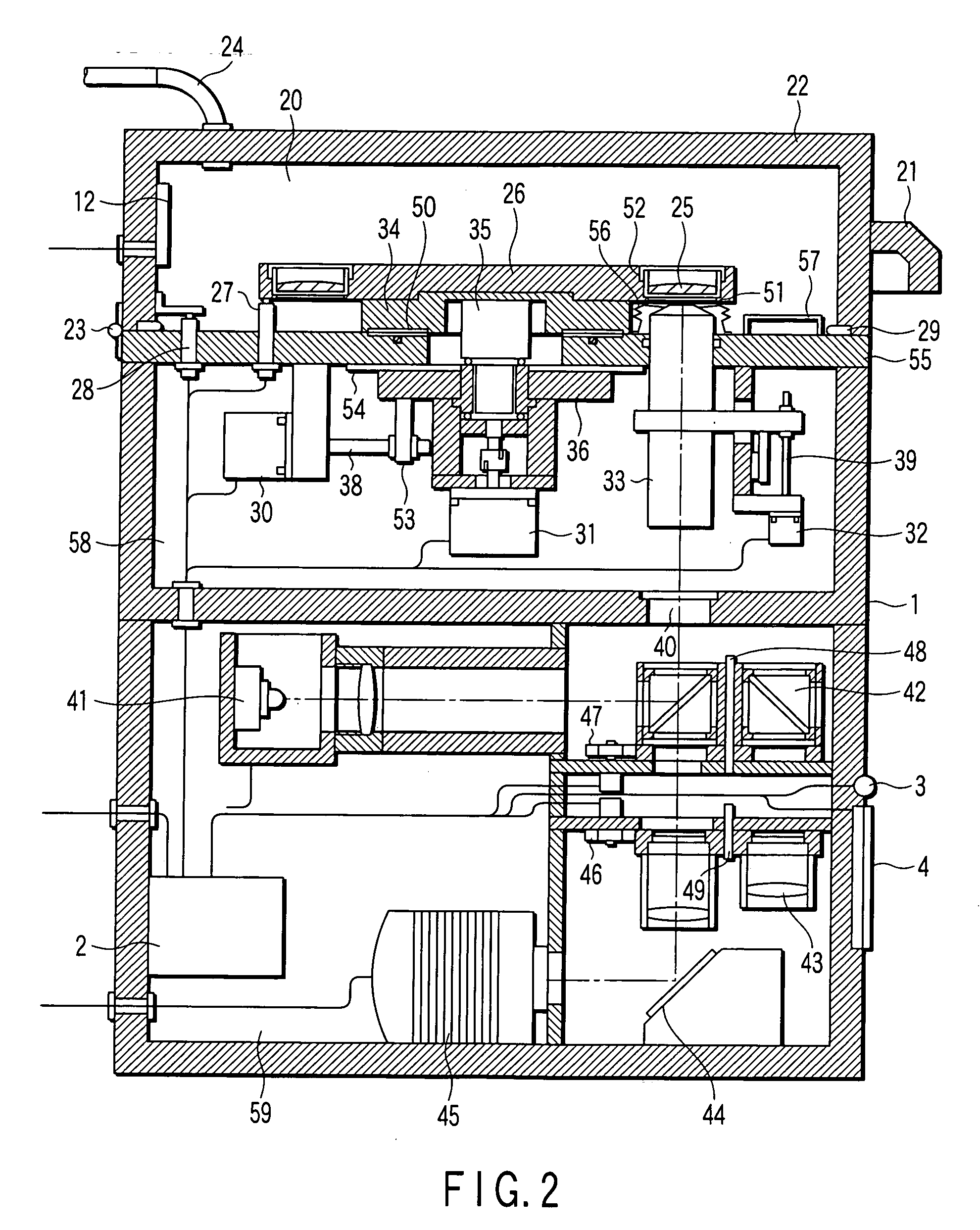
Culture microscope and computer program controlling culture microscope
InactiveUS20050282268A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscopeImage-forming optical system
A culture microscope has an incubator chamber which controls a culture environment in which cells are cultured, an imaging optical system which photographs the cells, and a controller which controls a time-lapse photographing performed by the imaging optical system.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Imaging optical system and exposure apparatus
InactiveUS6781671B2MirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEntrance pupilImage-forming optical system
An imaging optical system may be capable of forming substantially in one or more second planes one or more complete and / or partial images of one or more objects arranged substantially in one or more first planes and may comprise one or more entrance pupils, at least one of which is located substantially on an opposite side of at least one of the first plane or planes from the imaging optical system exclusive of the at least one entrance pupil so located. Such imaging optical system may be constructed so as to be substantially telecentric on at least a same side thereof as at least one of the second plane or planes. Such imaging optical system may be such that all of the reflective surface or surfaces of the imaging optical system are located in one or more spaces substantially between at least one of the first plane or planes and at least one of the second plane or planes, inclusive, and / or such imaging optical system may further comprise one or more locations disposed in one or more optical paths from at least one of the first plane or planes to at least one of the second plane or planes, inclusive, and substantially optically conjugate to at least one of the first plane or planes.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Device, method and program for determining obstacle within imaging range during imaging for stereoscopic display
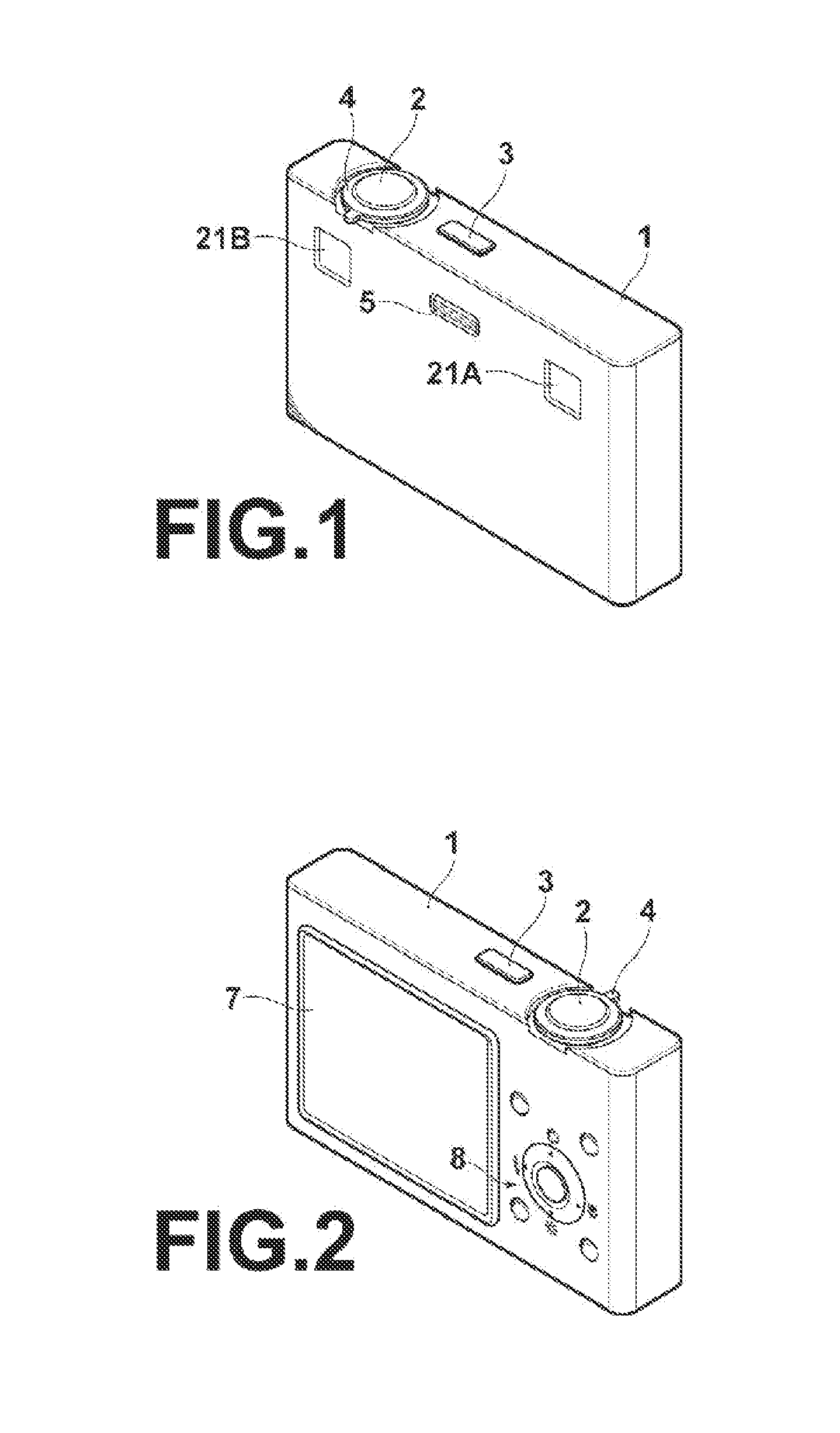
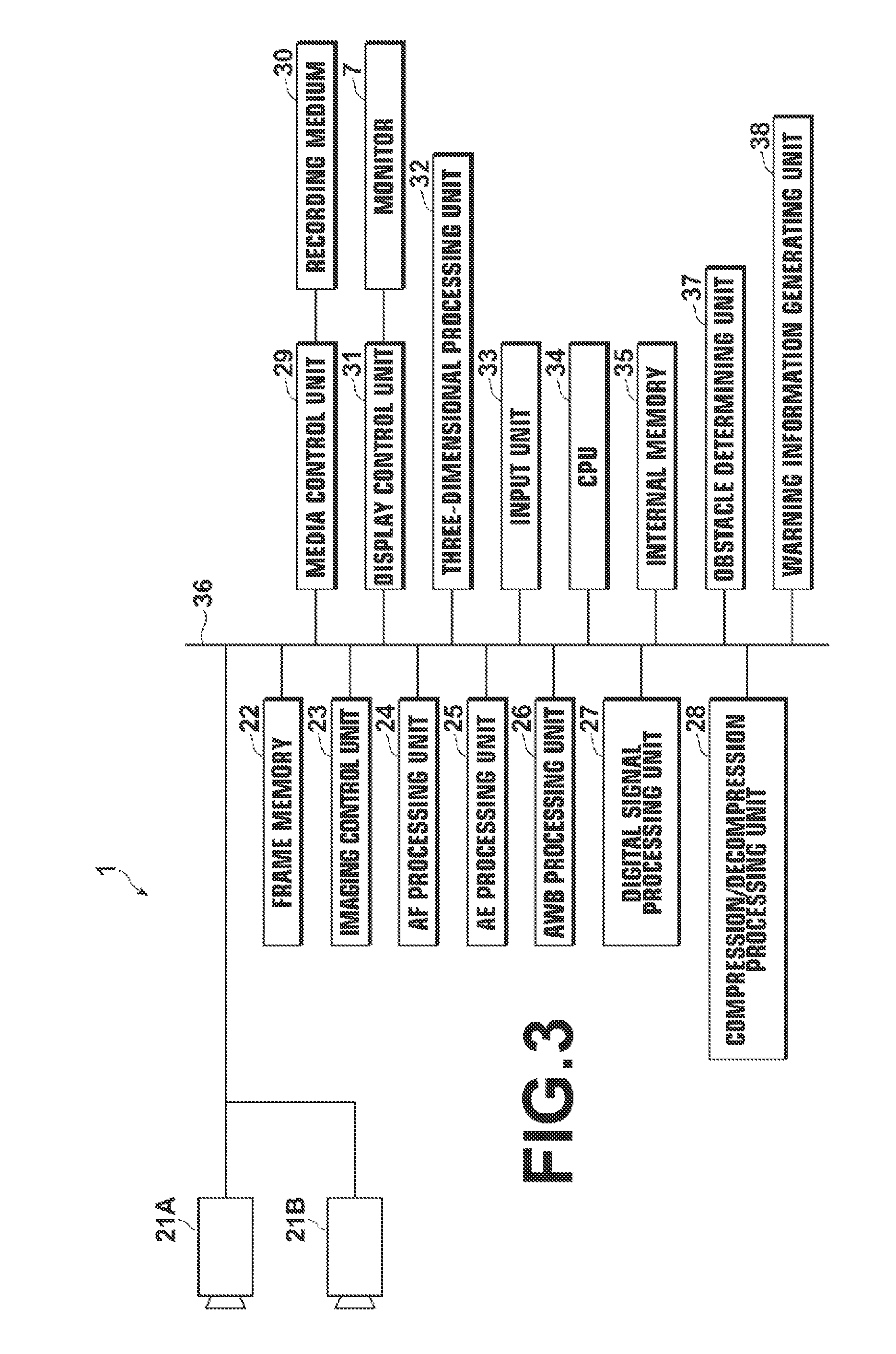
InactiveUS20130113888A1Improve accuracyLow costTelevision system detailsStereoscopic photographyComputer scienceImage-forming optical system
An obstacle determining unit obtains predetermined index values for each of subranges of each imaging range of each imaging unit, compares the index values of the subranges at mutually corresponding positions in the imaging ranges of the different imaging units, and if a difference between the index values in the imaging ranges of the different imaging units is large enough to satisfy a predetermined criterion, determines that the imaging range of at least one of the imaging units contains an obstacle that is close to the imaging optical system of the at least one of the imaging units.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com