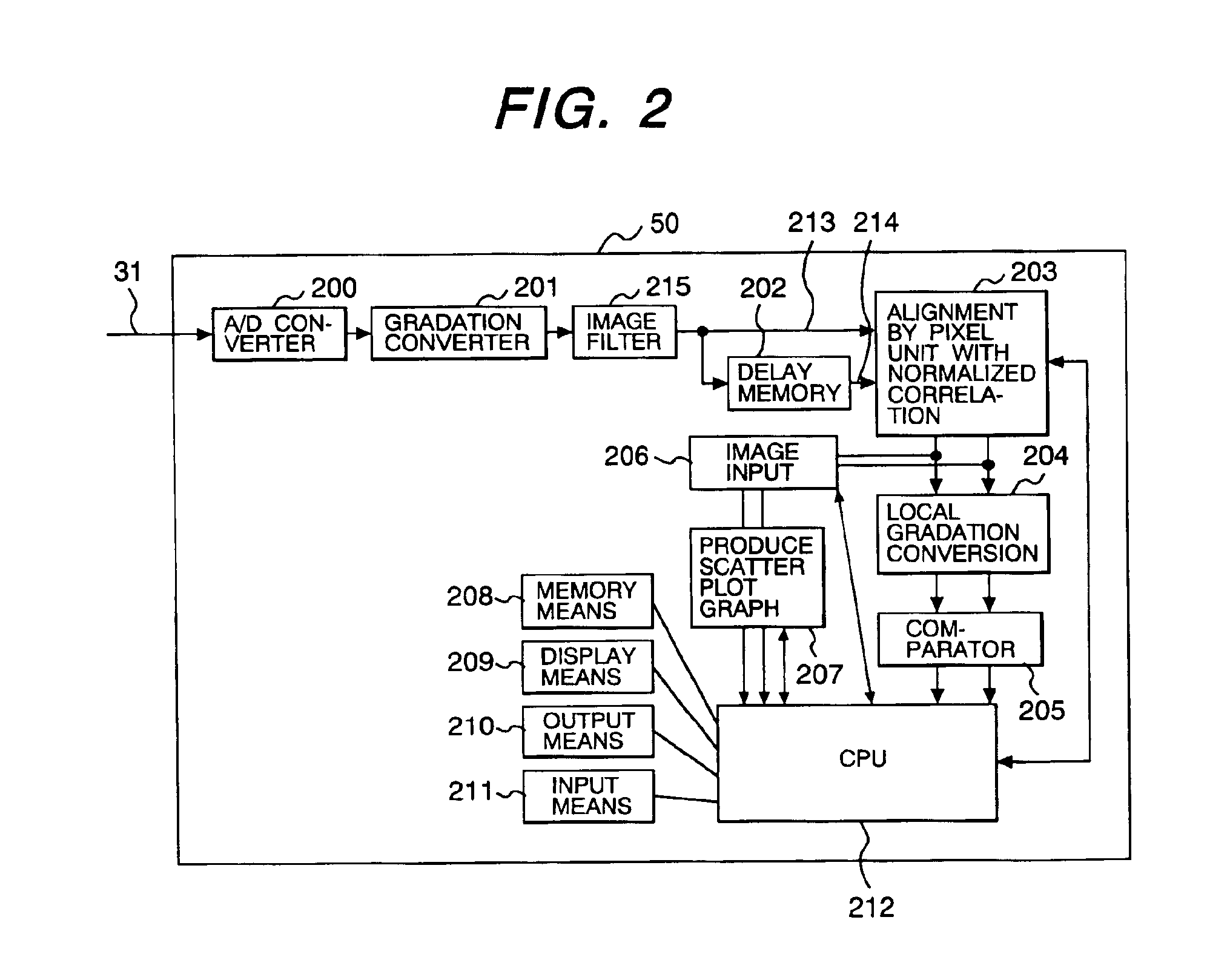
Patents
Literature
689 results about "Laser illumination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
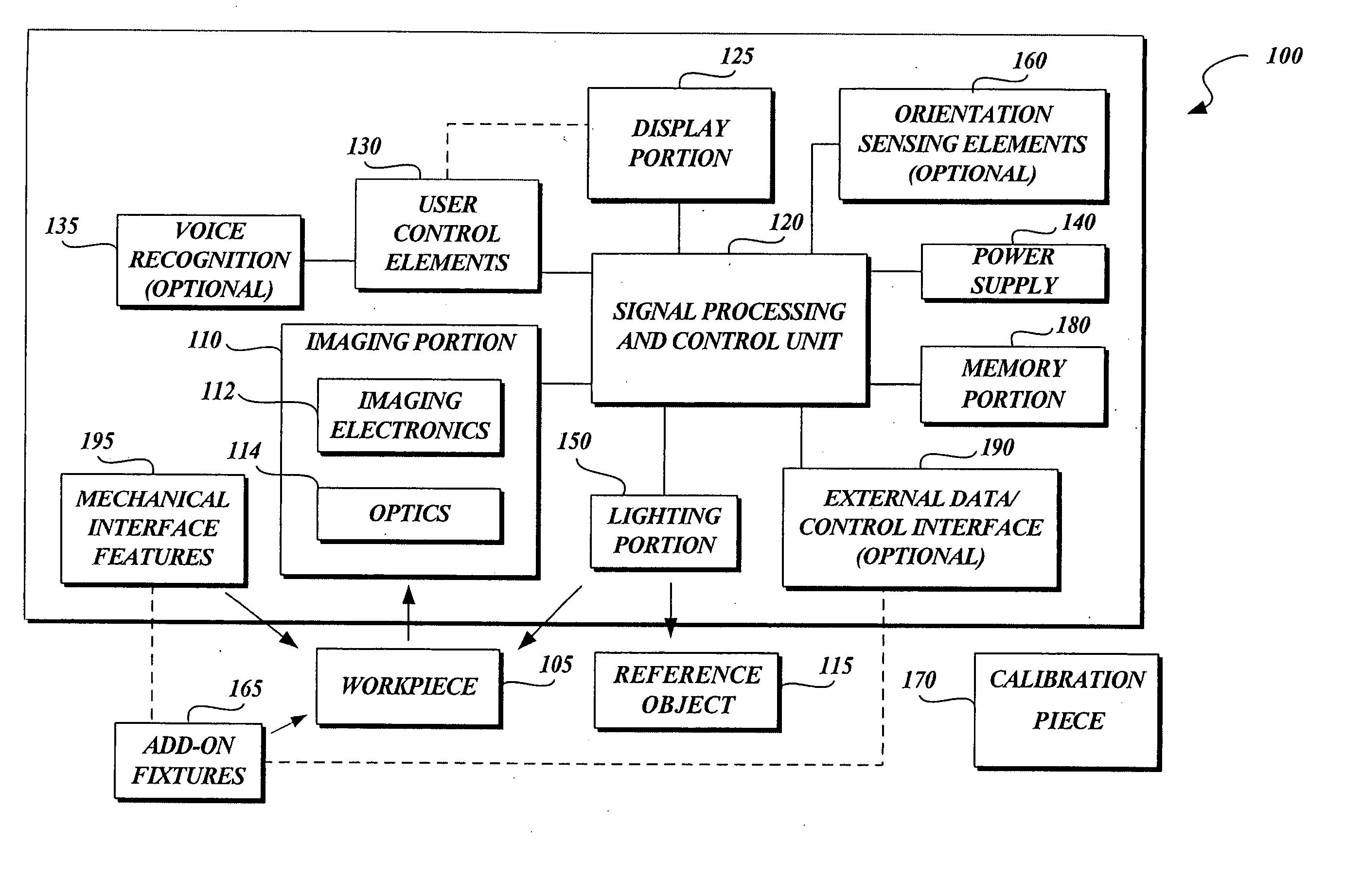
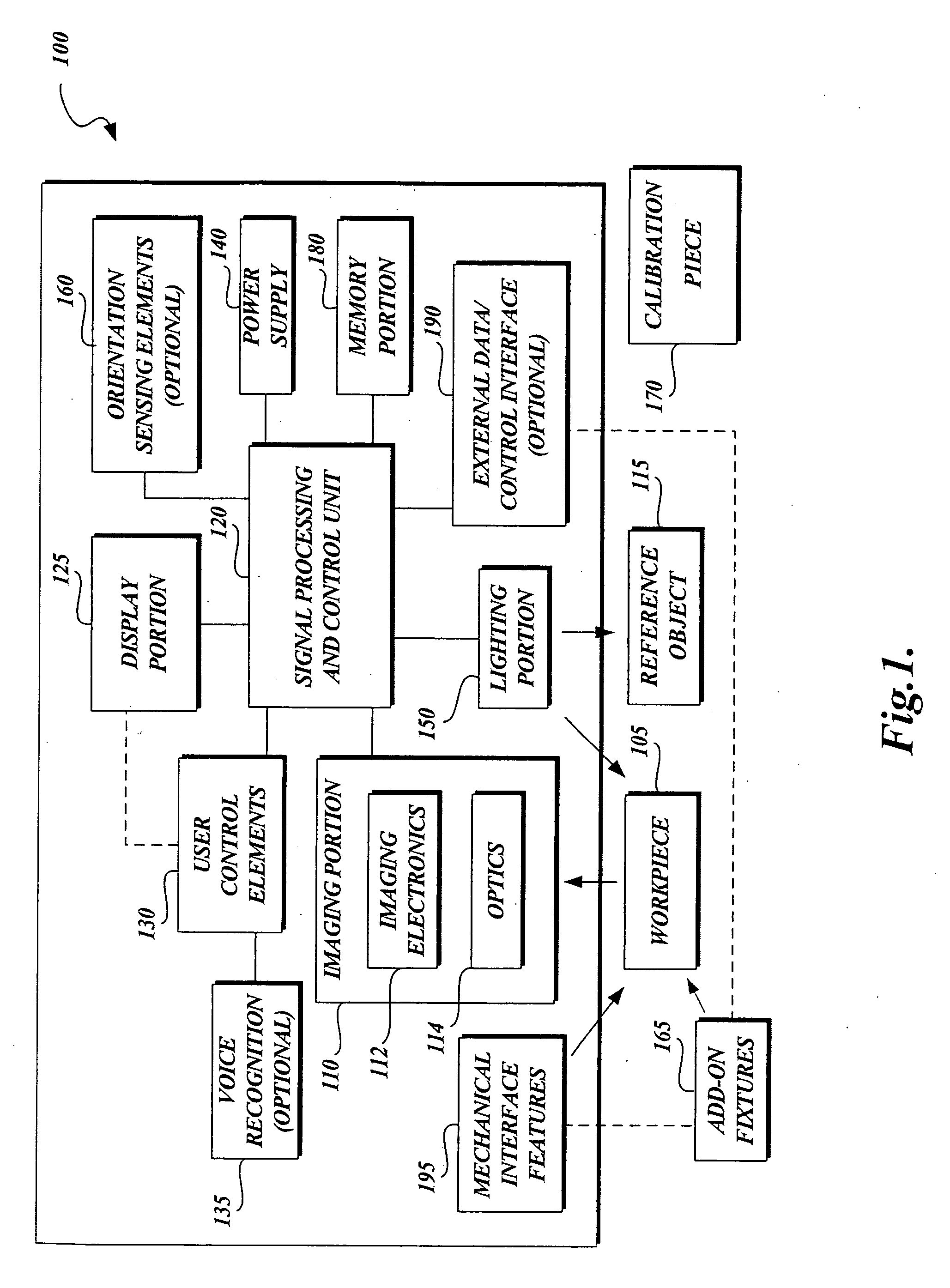
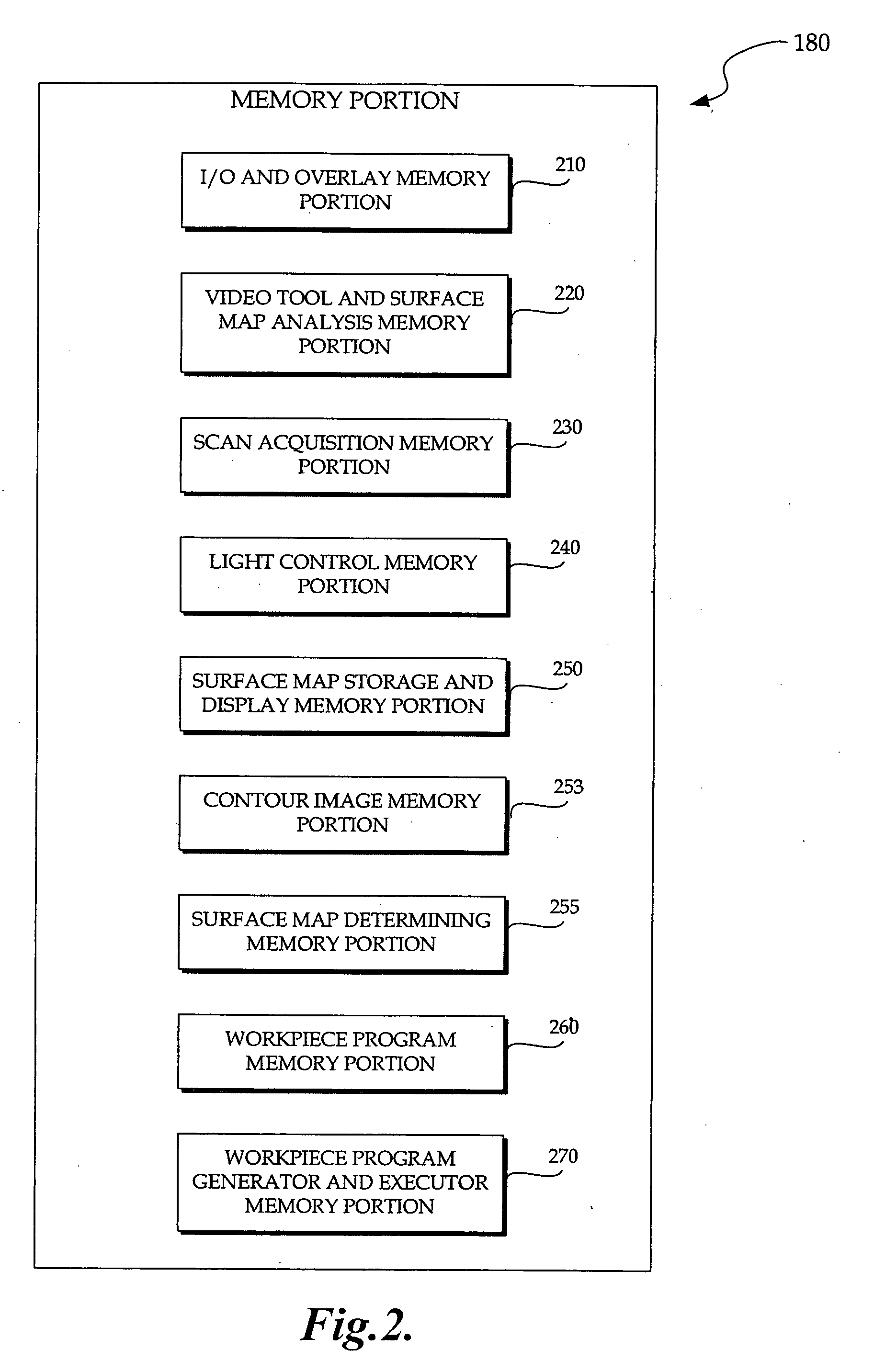
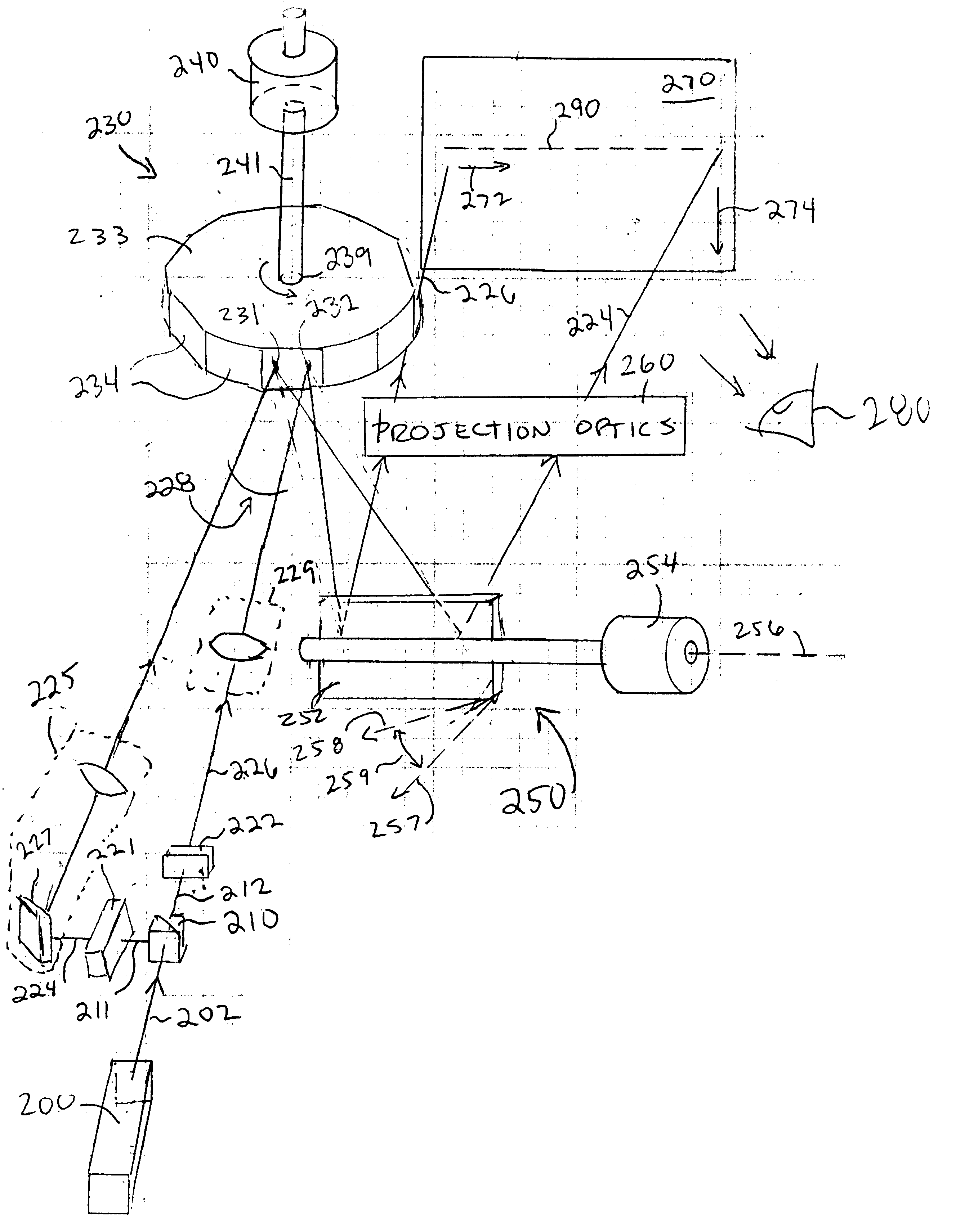
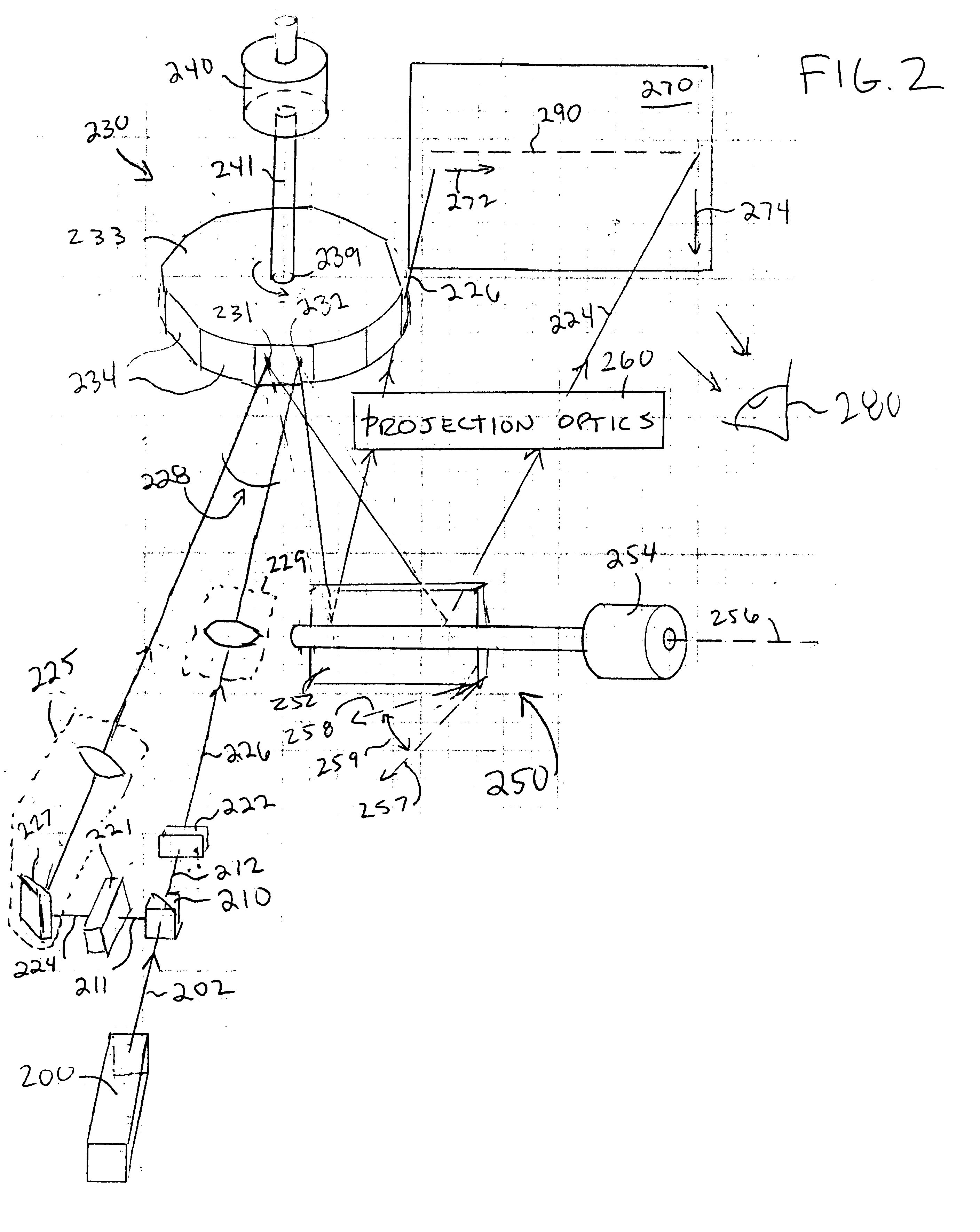
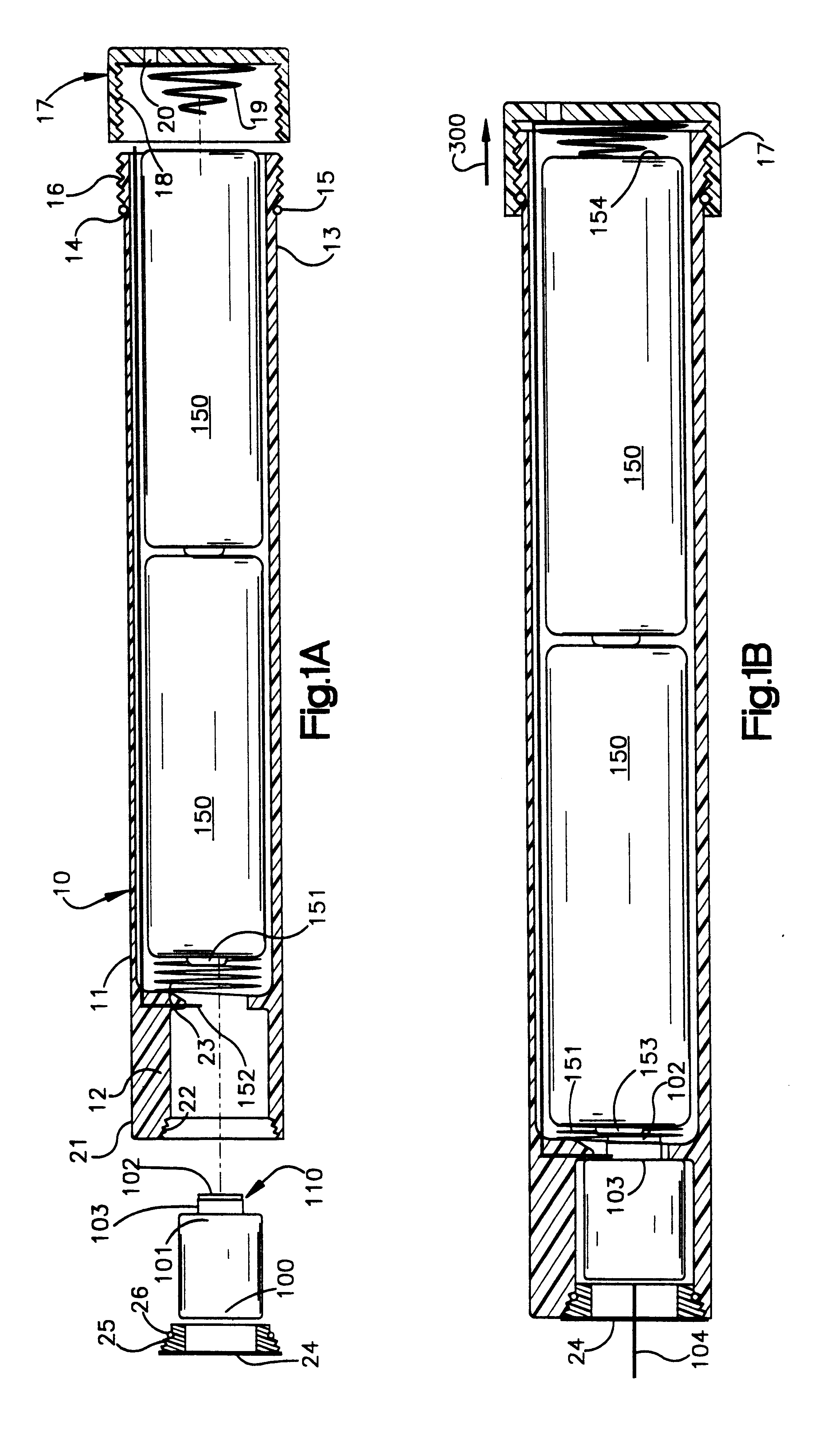
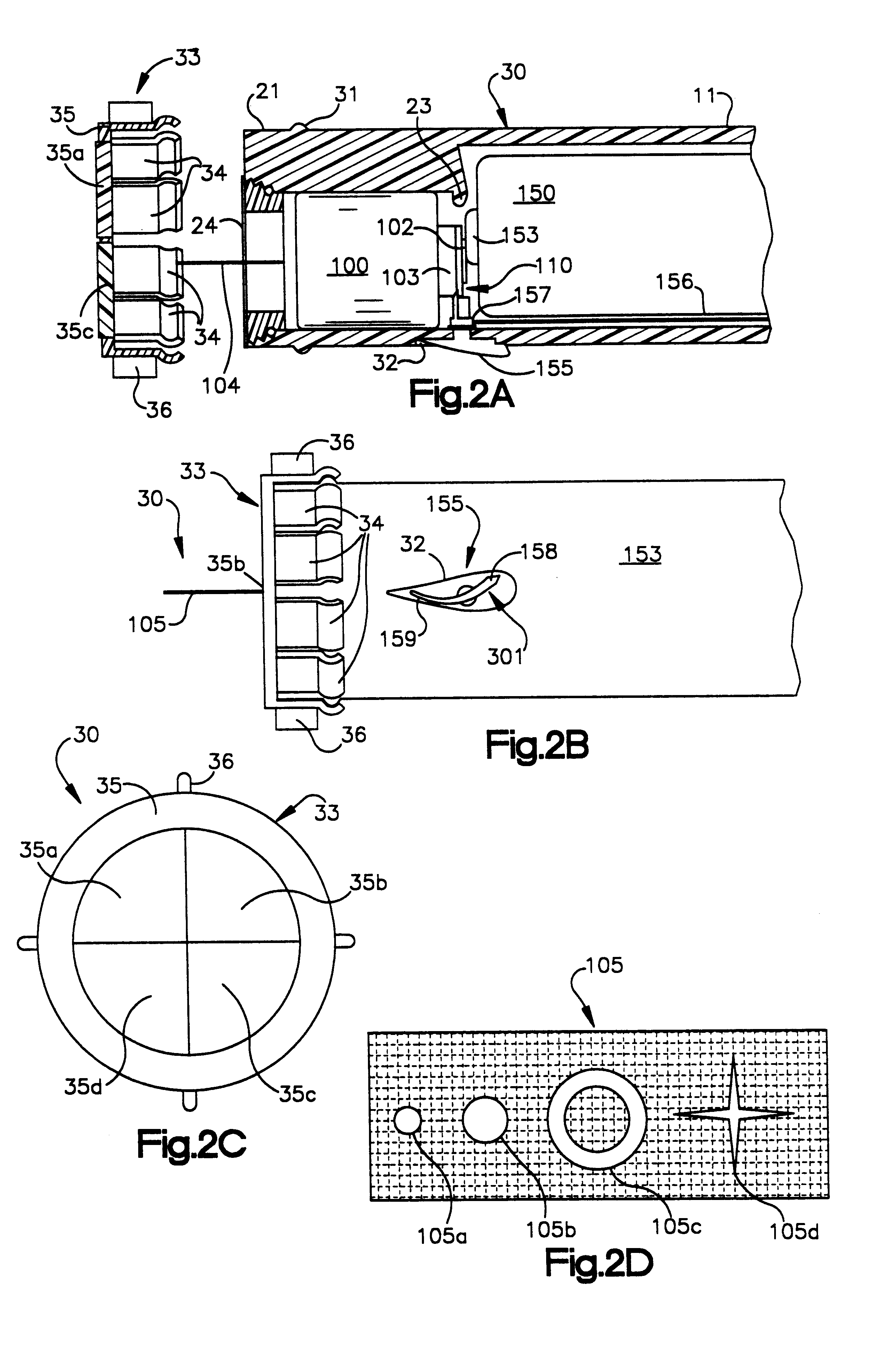
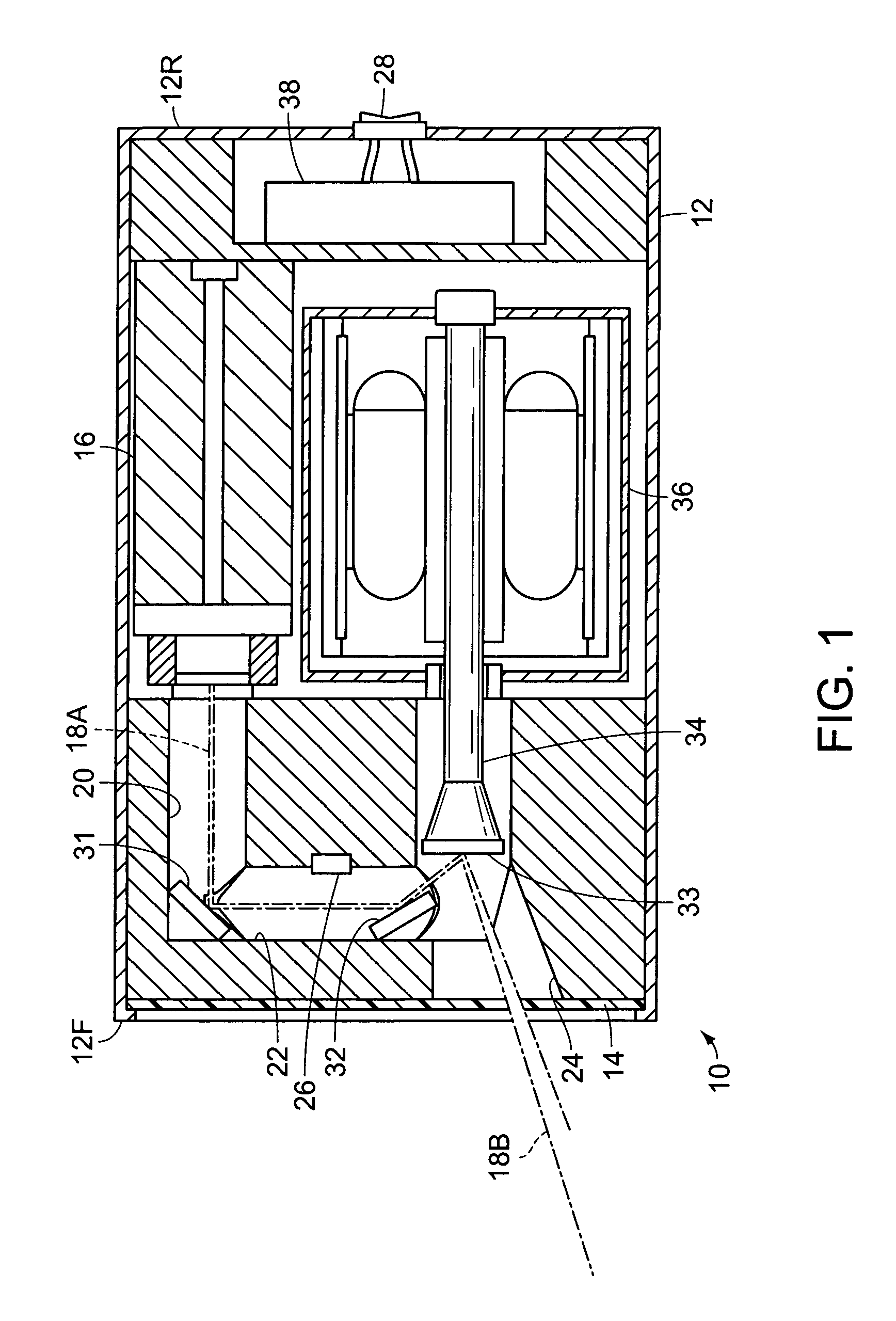
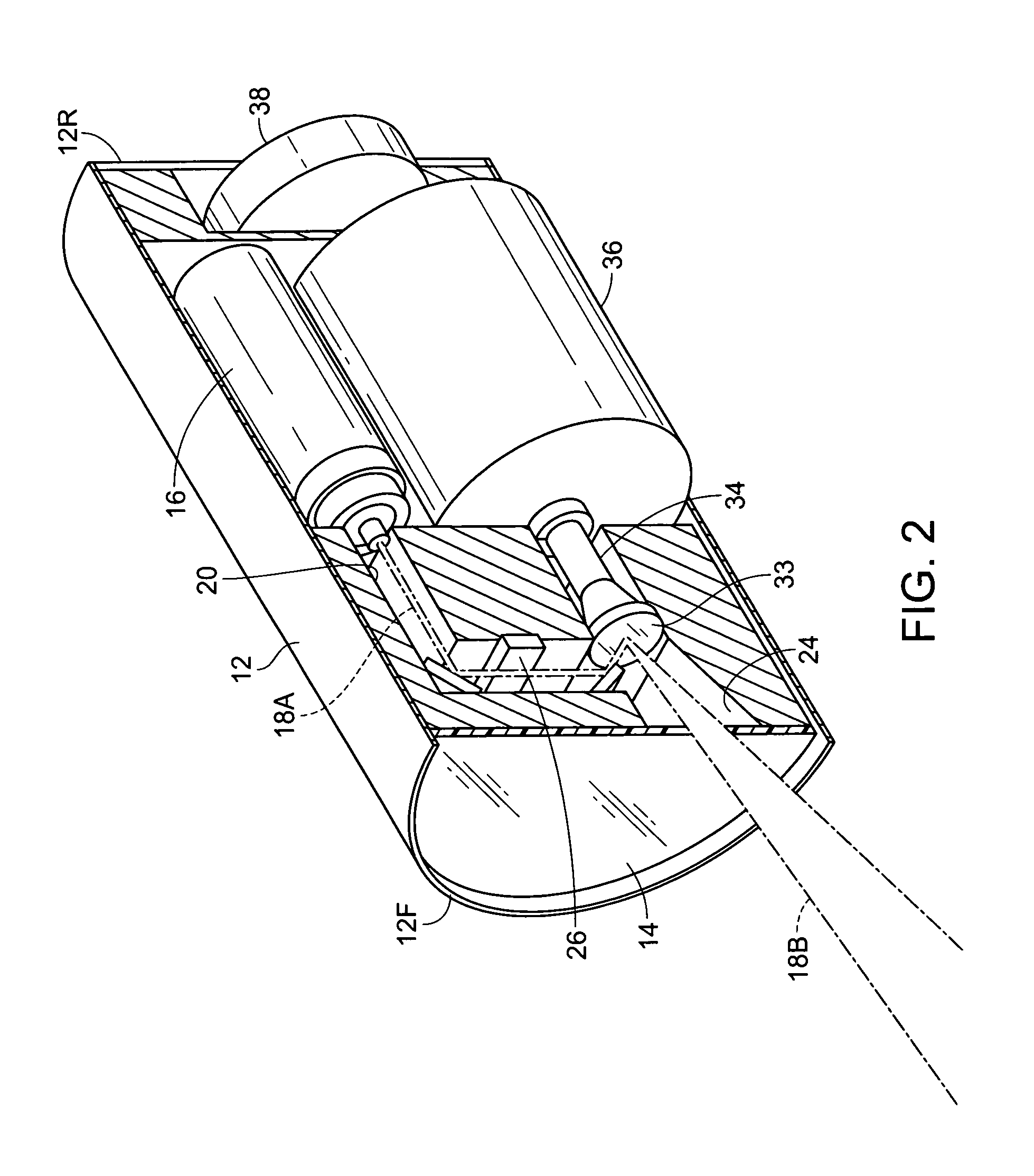
Laser Illuminator System
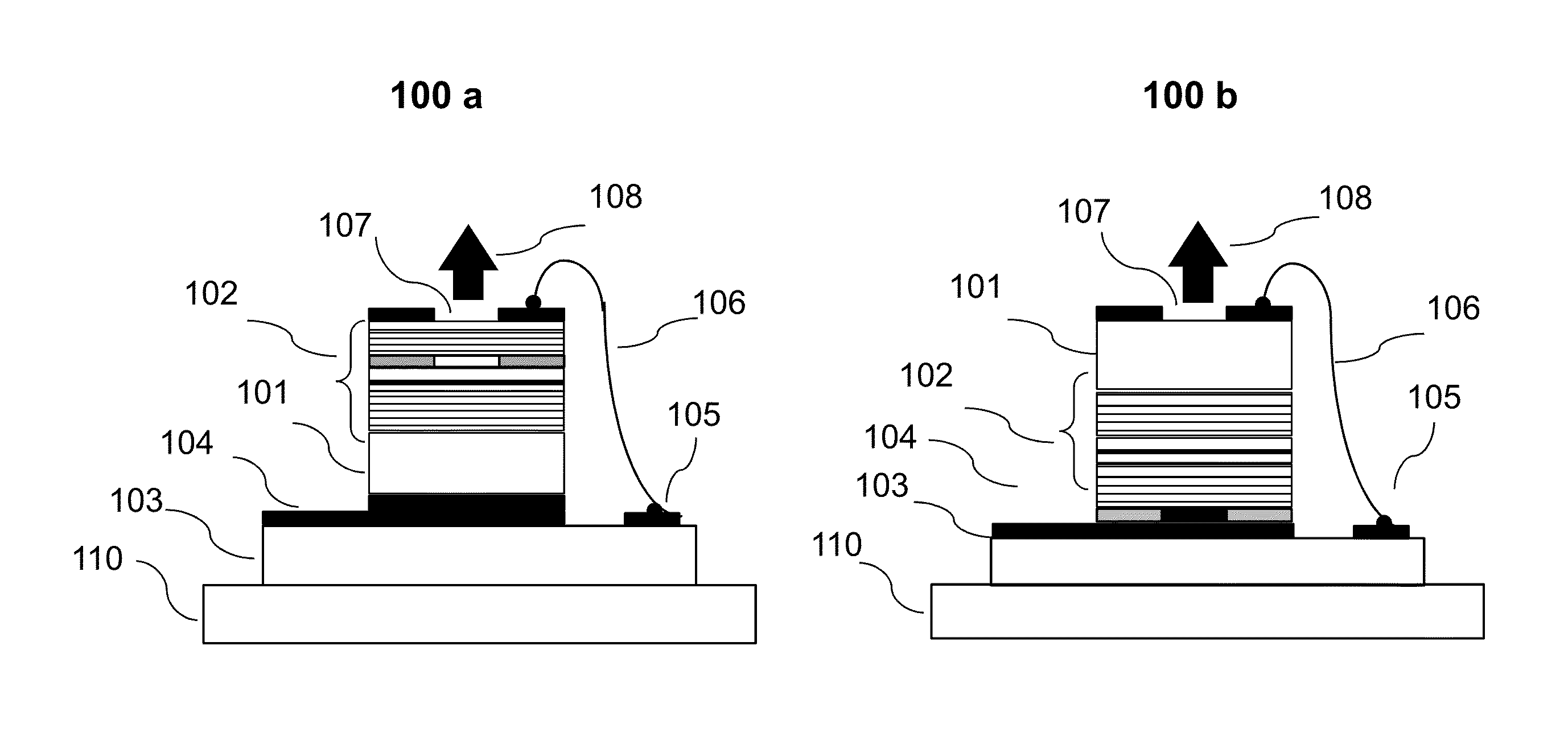
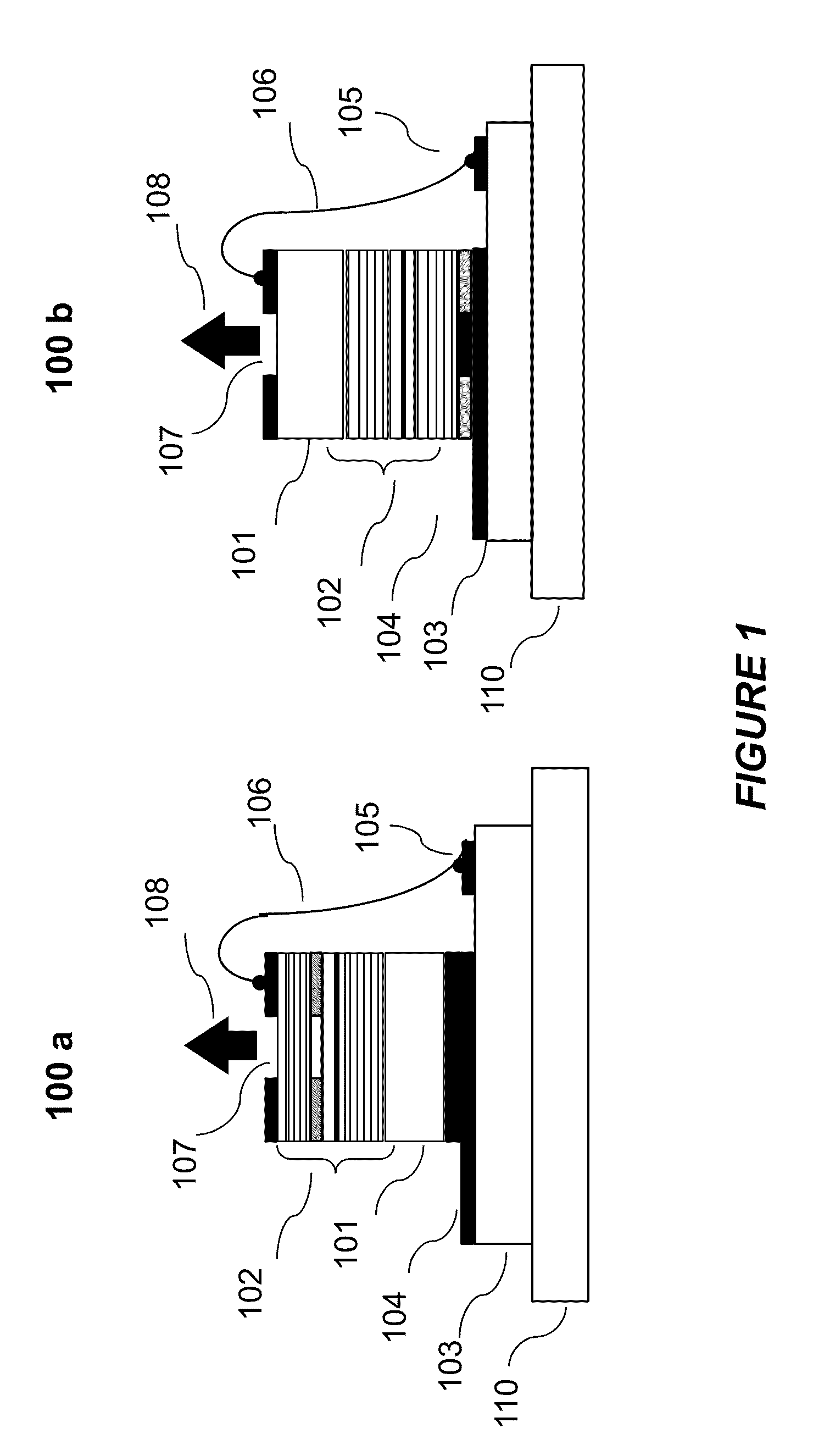
InactiveUS20130163627A1Improve thermal conductivityHeat dissipation fastSolid-state devicesSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLow inductance
An optical illuminator using Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) is disclosed. Optical modules configured using single VCSEL and VCSEL arrays bonded to a thermal submount to conduct heat away from the VCSEL array, are suited for high power and high speed operation. High speed optical modules are configured using single VCSEL or VCSEL arrays connected to a high speed electronic module on a common thermal submount or on a common Printed Circuit Board (PCB) platform including transmission lines. The electronic module provides low inductance current drive and control functions to operate the VCSEL and VCSEL array. VCSEL apertures are designed for a desired beam shape. Additional beam shaping elements are provided for VCSELs or VCSEL arrays, for desired output beam shapes and / or emission patterns. VCSEL arrays may be operated in continuous wave (CW) or pulse operation modes in a programmable fashion using a built-in or an external controller.
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
Laser illumination device
ActiveUS20100202725A1Overcome problemsProjectorsPlanar/plate-like light guidesGratingConductive coating
An Electrically Switchable Bragg Grating (ESBG) despeckler device comprising at least one ESBG element recorded in a hPDLC sandwiched between transparent substrates to which transparent conductive coatings have been applied. At least one of said coatings is patterned to provide a two-dimensional array of independently switchable ESBG pixels. Each ESBG pixel has a first unique speckle state under said first applied voltage and a second unique speckle state under said second applied voltage.
Owner:DIGILENS
Laser illuminating device and image display device
InactiveUS20100053565A1Remove speckle noiseUniform lightDiffusing elementsProjectorsDivergence angleLaser light
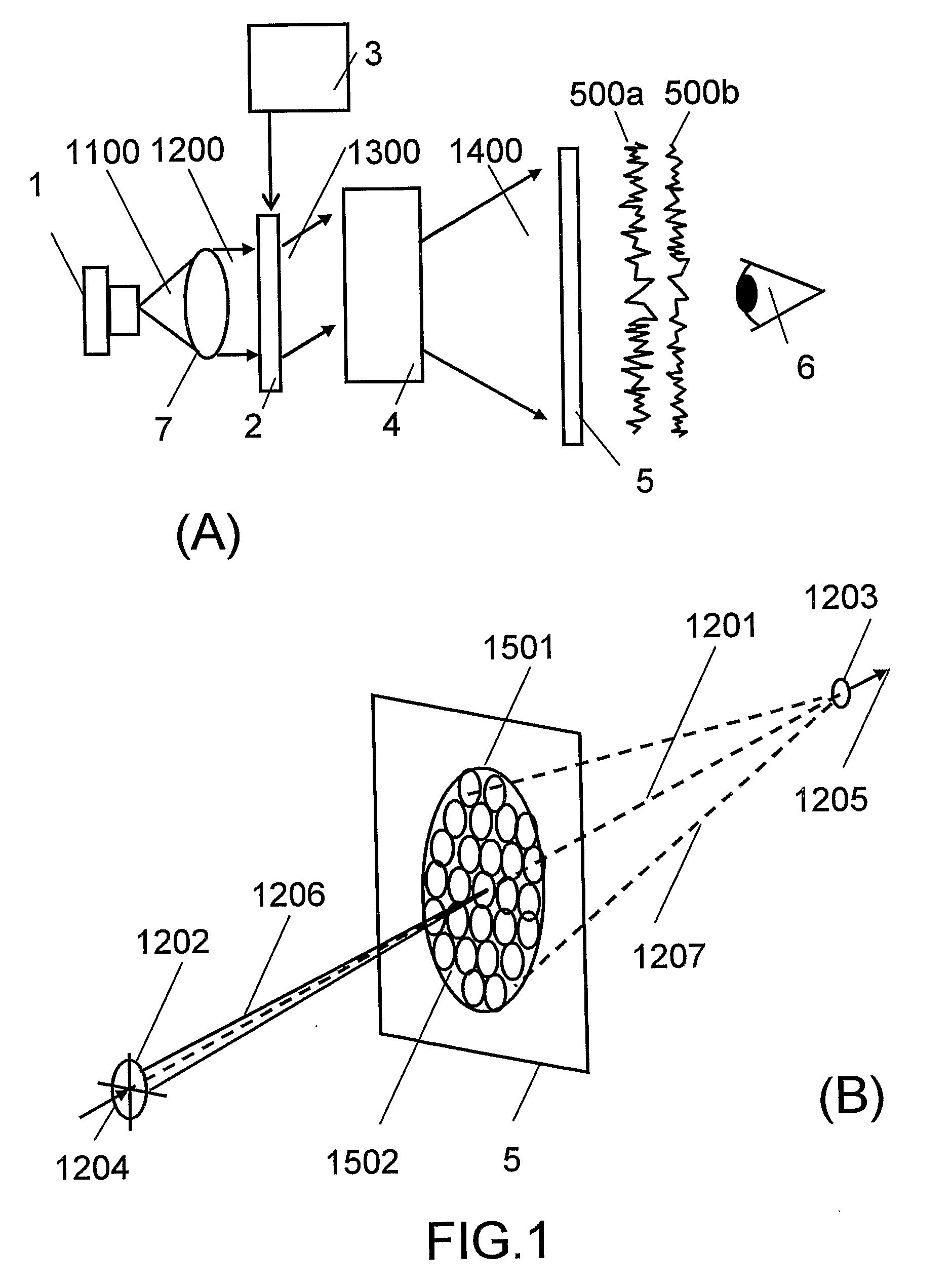
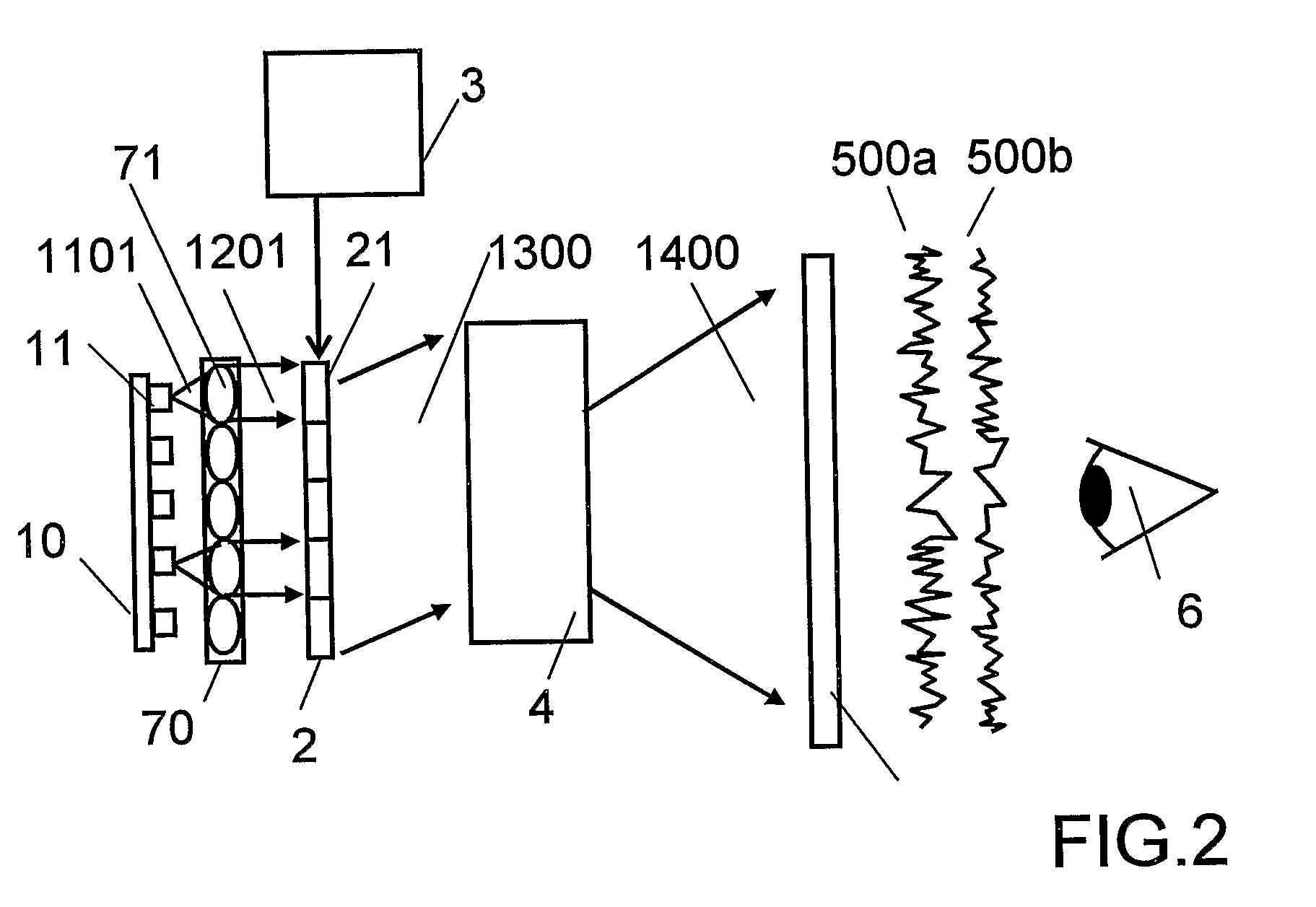
An object of the invention is to provide a laser illuminating device and an image display device that enable to remove speckle noises in a diffraction field and an image field, uniformly illuminate an illumination plane, and realize miniaturization. A laser illuminating device 100 includes a laser light source 3, a first lens 1 including a plurality of microlenses 10 each having a predetermined numerical aperture in an in-plane direction, each of the microlenses 10 being adapted to expand laser light emitted from the laser light source 3 to thereby superimpose the laser light transmitted through each of the microlenses 10; and a second lens 2 having an effective diameter larger than an effective diameter of the first lens 1, and for compensating for a divergence angle of the laser light expanded by each of the plurality of the microlenses 10.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Laser illumination device
An Electrically Switchable Bragg Grating (ESBG) despeckler device comprising at least one ESBG element recorded in a hPDLC sandwiched between transparent substrates to which transparent conductive coatings have been applied. At least one of said coatings is patterned to provide a two-dimensional array of independently switchable ESBG pixels. Each ESBG pixel has a first unique speckle state under said first applied voltage and a second unique speckle state under said second applied voltage.
Owner:DIGILENS
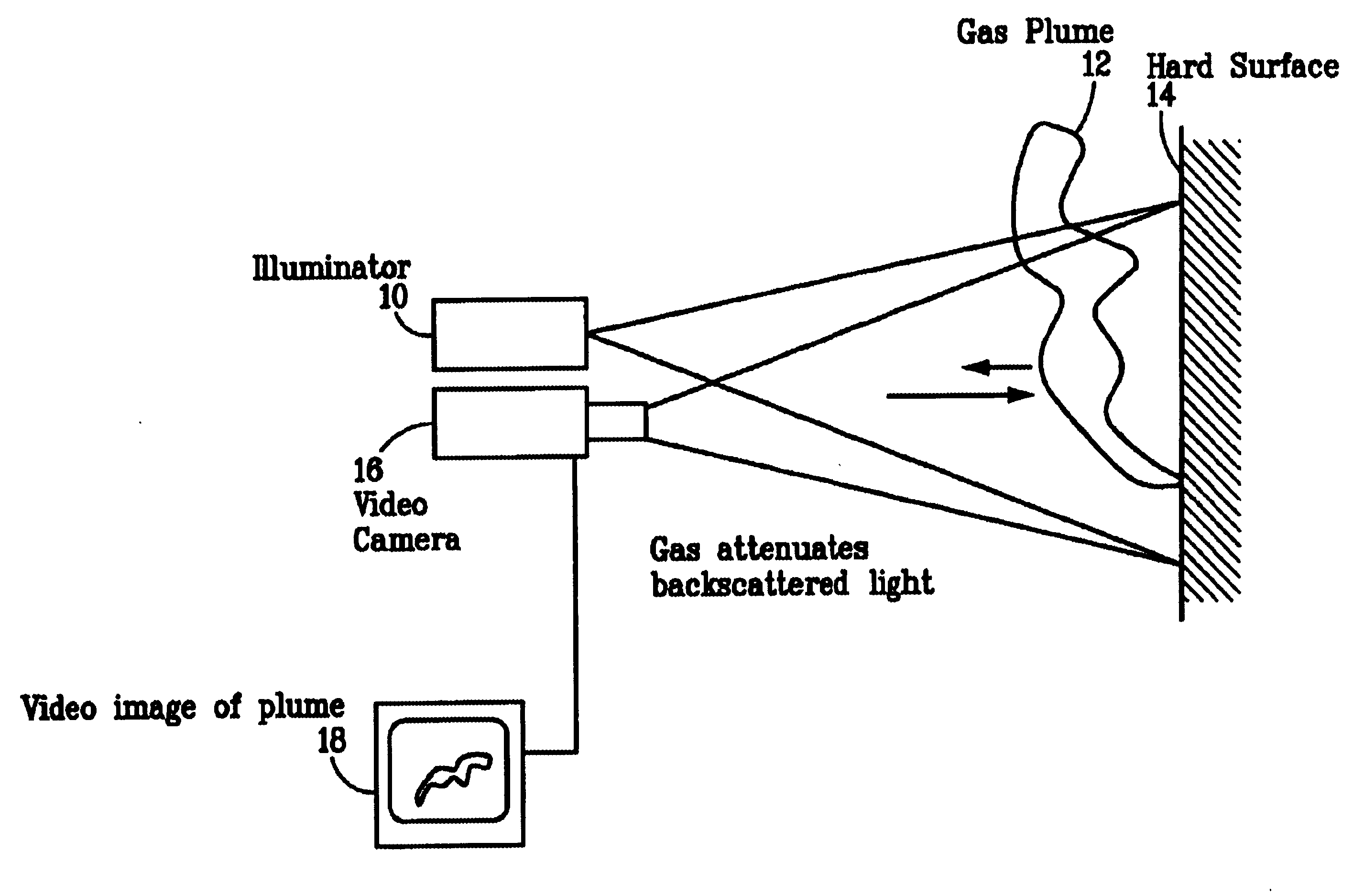
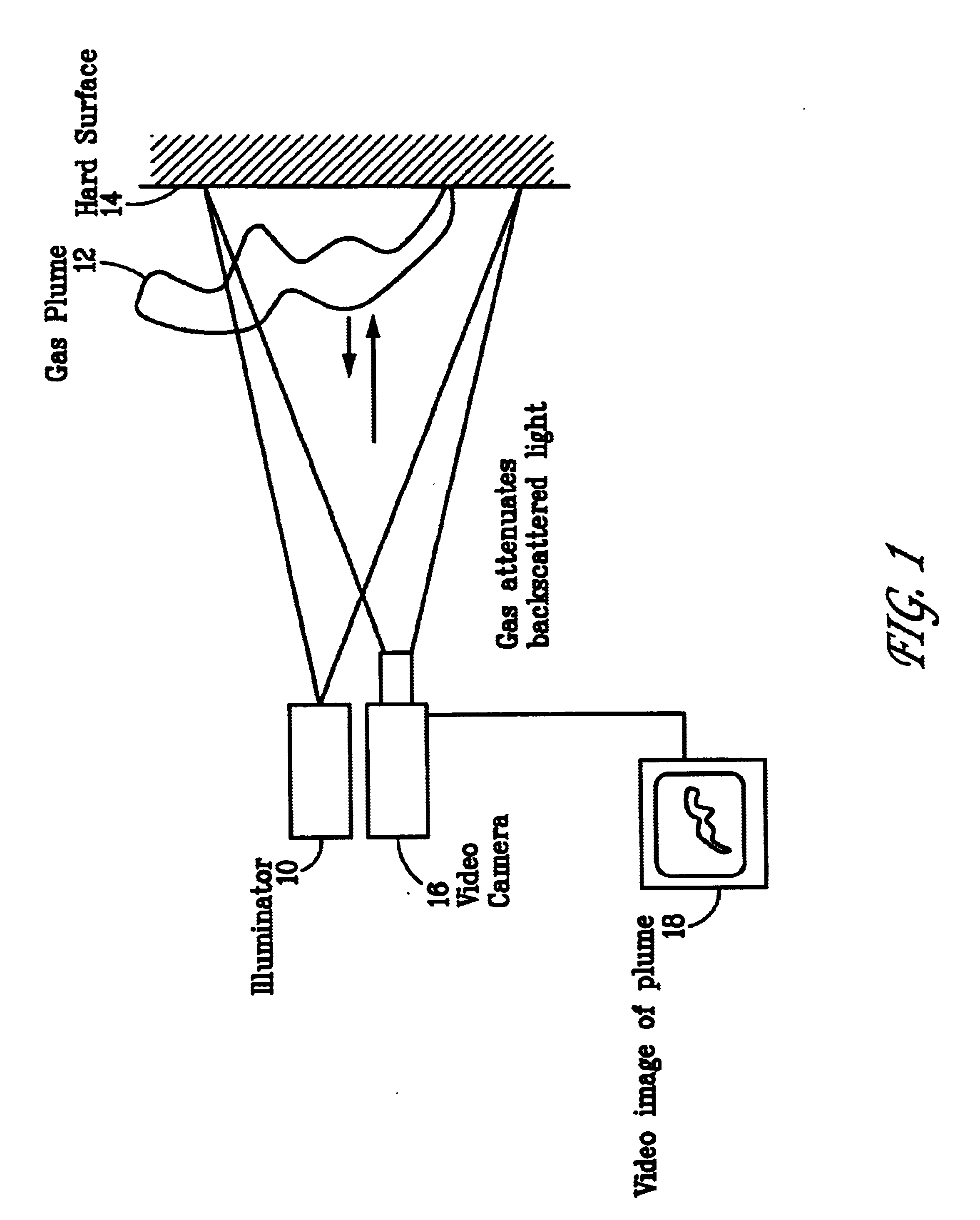
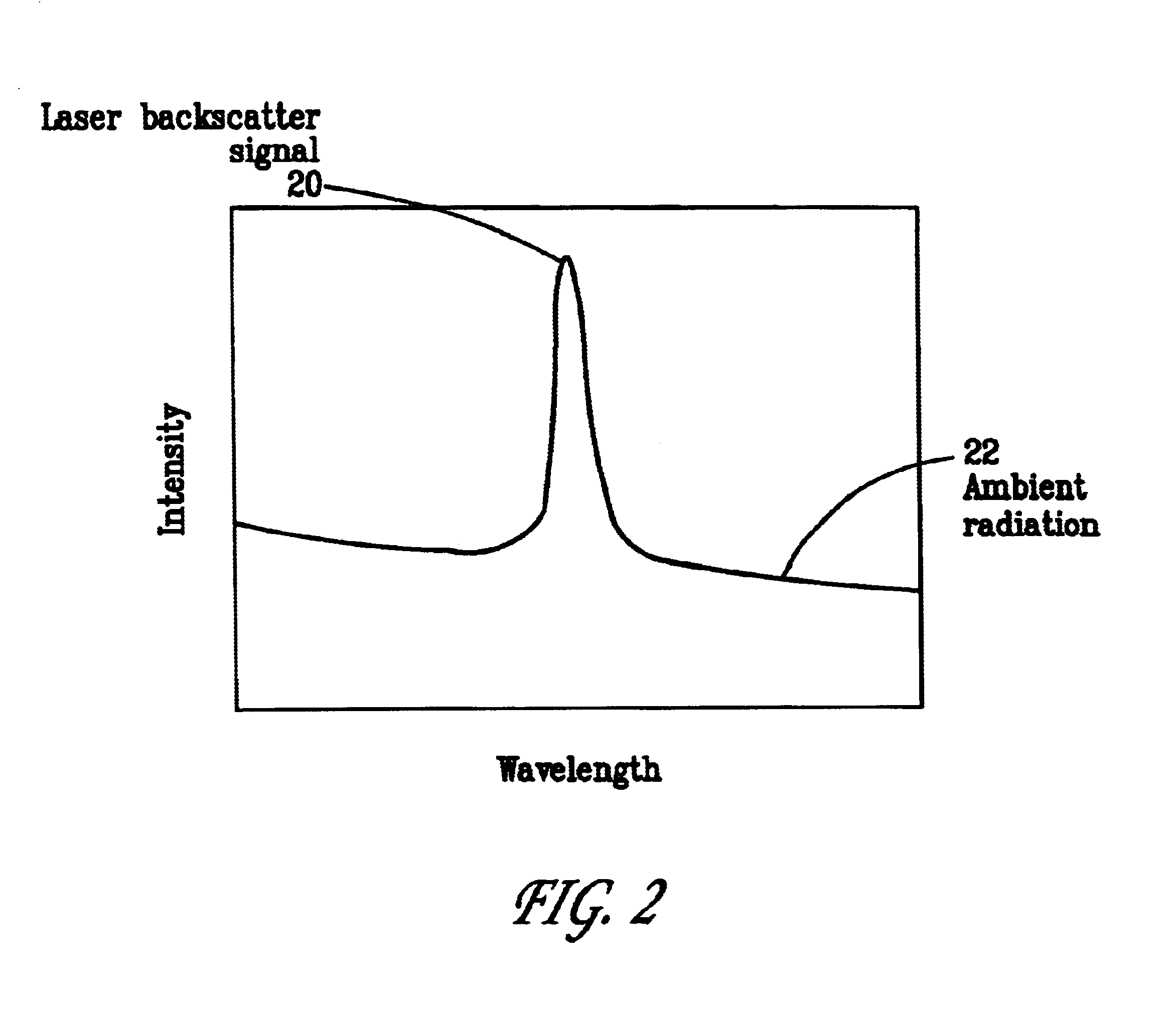
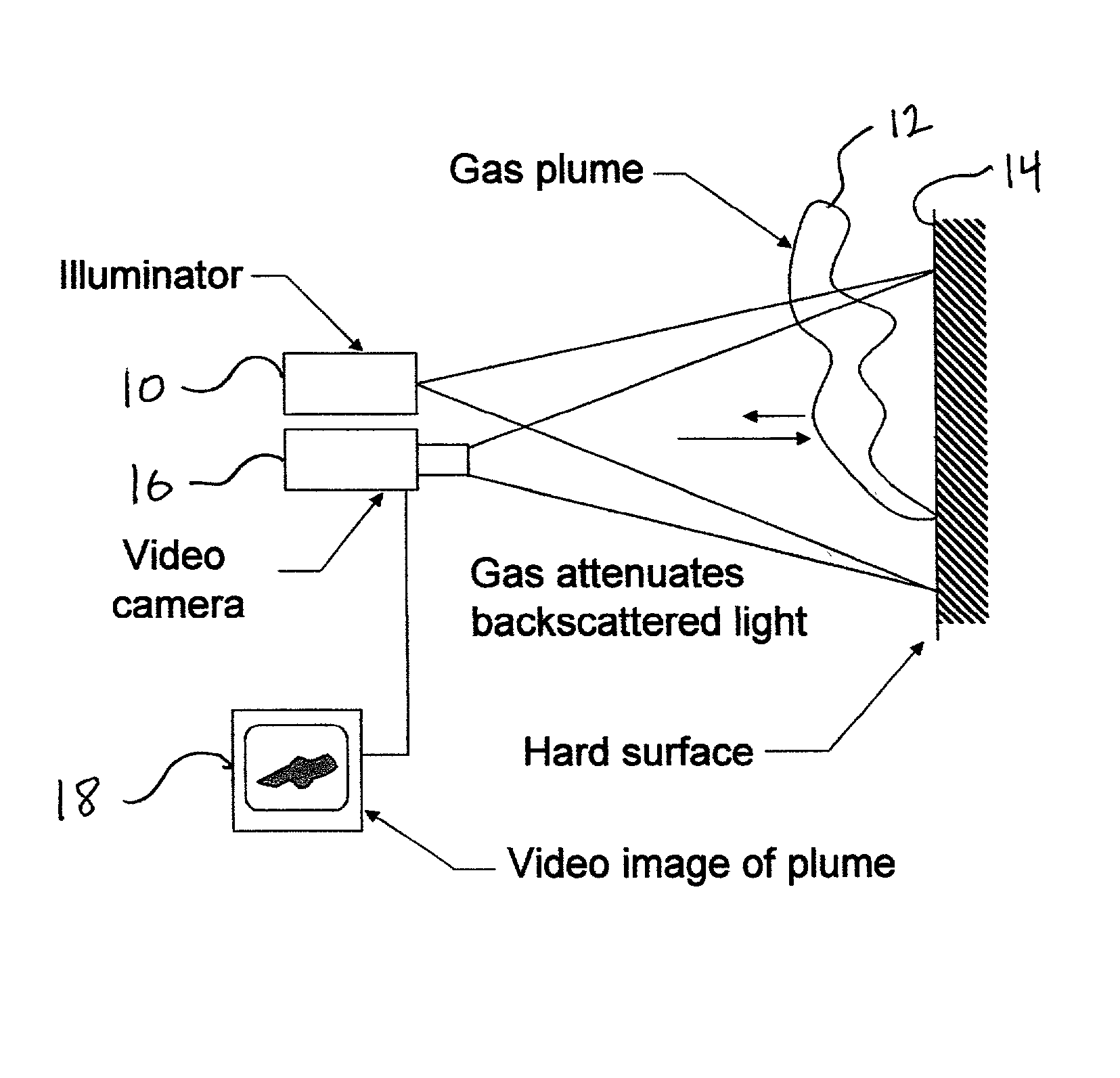
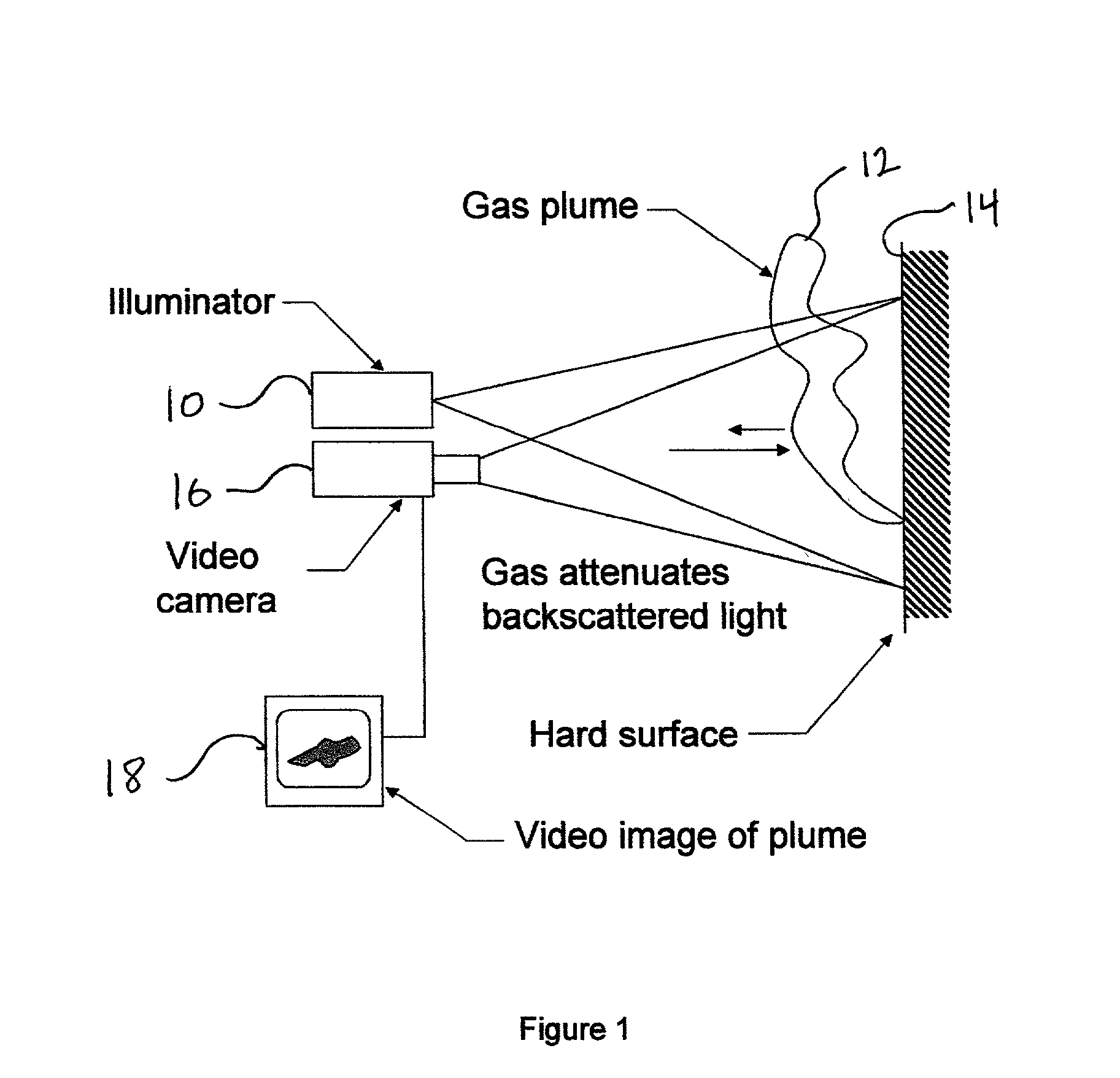
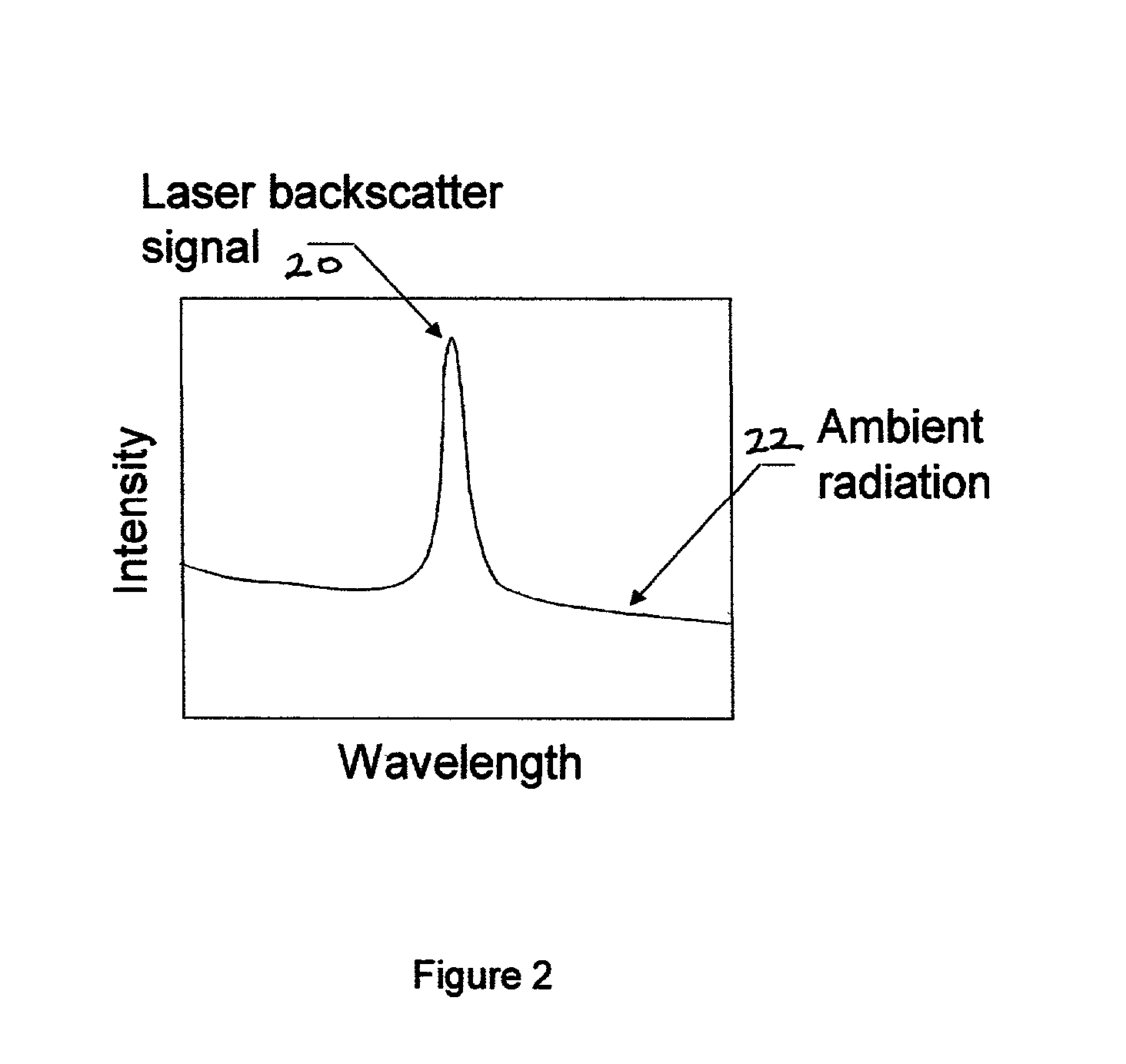
Pulsed laser linescanner for a backscatter absorption gas imaging system
InactiveUS6690472B2Enhanced signalMaximize attenuationScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsMobile vehicleFluence
An active (laser-illuminated) imaging system is described that is suitable for use in backscatter absorption gas imaging (BAGI). A BAGI imager operates by imaging a scene as it is illuminated with radiation that is absorbed by the gas to be detected. Gases become "visible" in the image when they attenuate the illumination creating a shadow in the image. This disclosure describes a BAGI imager that operates in a linescanned manner using a high repetition rate pulsed laser as its illumination source. The format of this system allows differential imaging, in which the scene is illuminated with light at least 2 wavelengths-one or more absorbed by the gas and one or more not absorbed. The system is designed to accomplish imaging in a manner that is insensitive to motion of the camera, so that it can be held in the hand of an operator or operated from a moving vehicle.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Pulsed laser linescanner for a backscatter absorption gas imaging system
InactiveUS20020071122A1Enhanced signalMaximize attenuationScattering properties measurementsTransmissivity measurementsFluenceRadiation
An active (laser-illuminated) imaging system is described that is suitable for use in backscatter absorption gas imaging (BAGI). A BAGI imager operates by imaging a scene as it is illuminated with radiation that is absorbed by the gas to be detected. Gases become "visible" in the image when they attenuate the illumination creating a shadow in the image. This disclosure describes a BAGI imager that operates in a linescanned manner using a high repetition rate pulsed laser as its illumination source. The format of this system allows differential imaging, in which the scene is illuminated with light at least 2 wavelengths-one or more absorbed by the gas and one or more not absorbed. The system is designed to accomplish imaging in a manner that is insensitive to motion of the camera, so that it can be held in the hand of an operator or operated from a moving vehicle.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
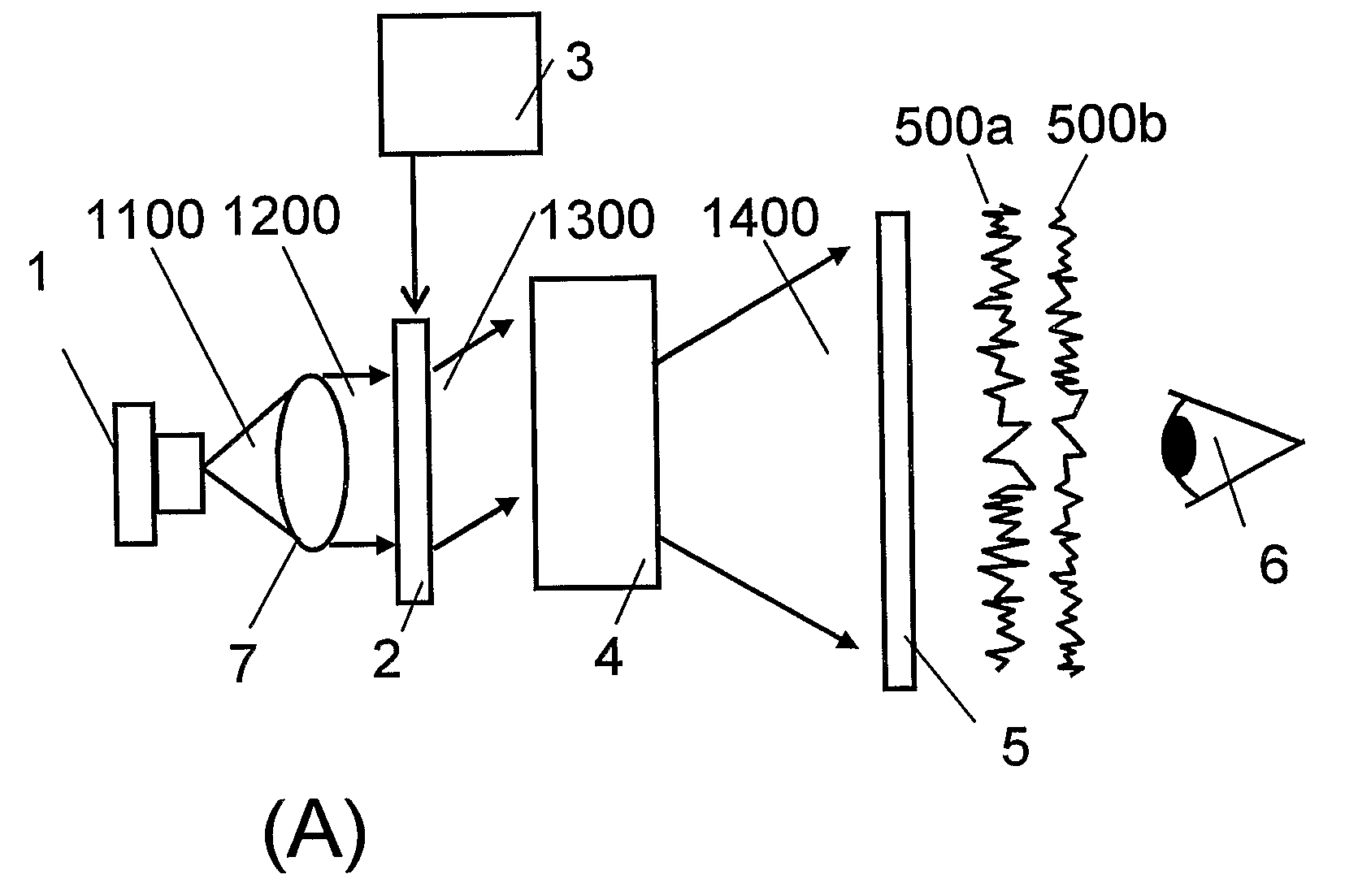
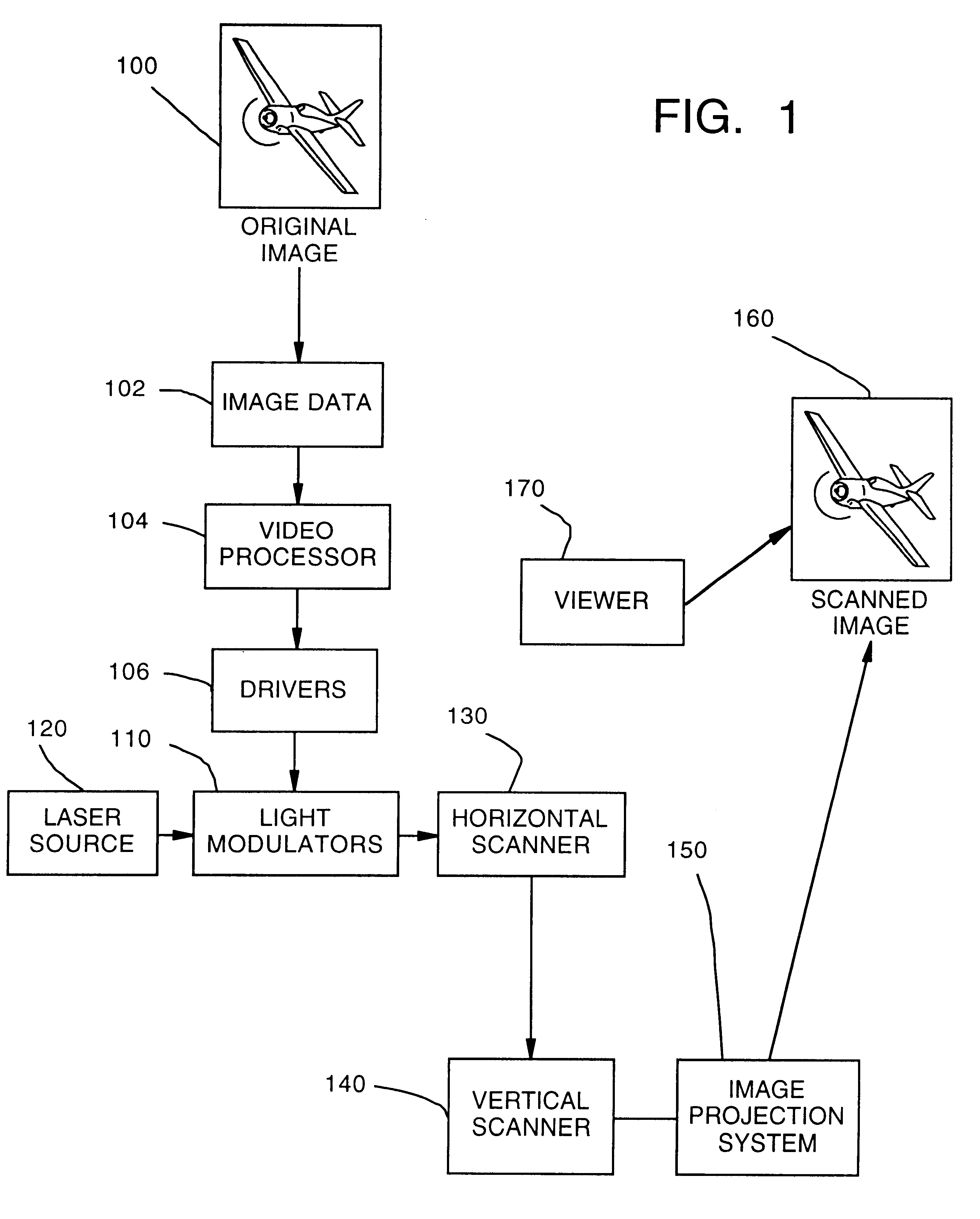
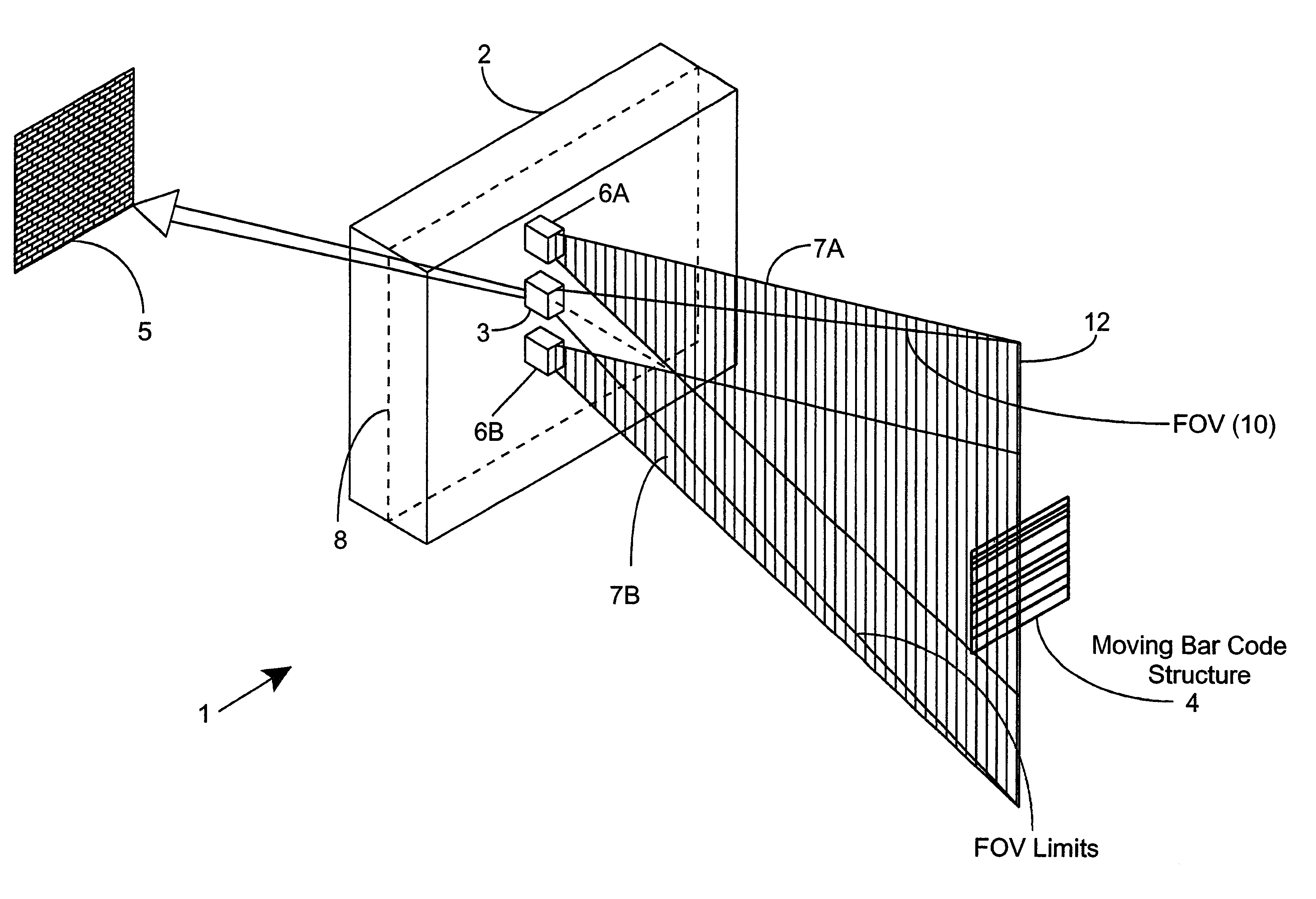
Method of and system for producing digital images of objects with subtantially reduced speckle-noise patterns by illuminating said objects with spatially and/or temporally coherent-reduced planar laser illumination
InactiveUS20020043561A1Reducing speckle-noise patternSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSystems designHand held
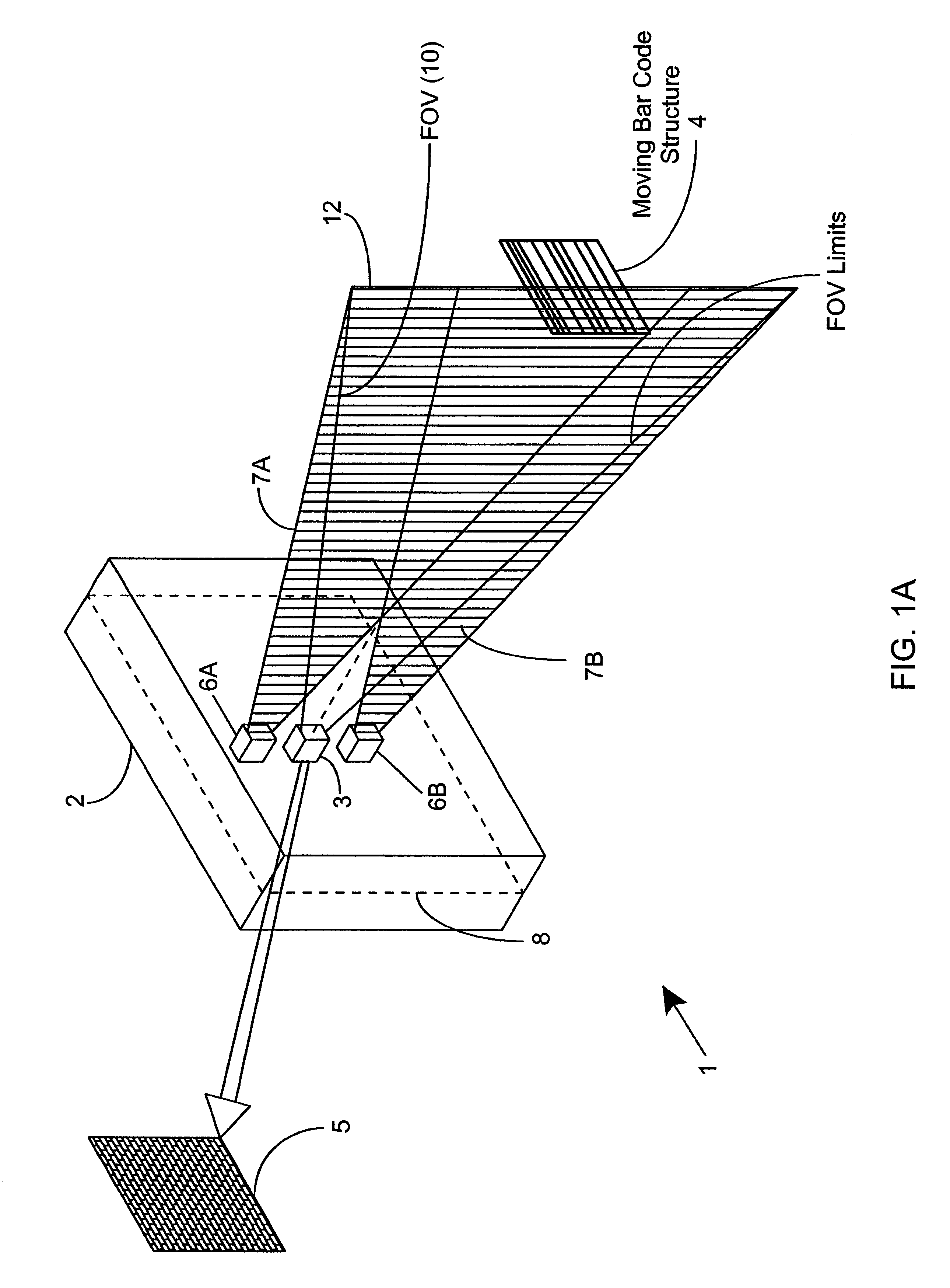
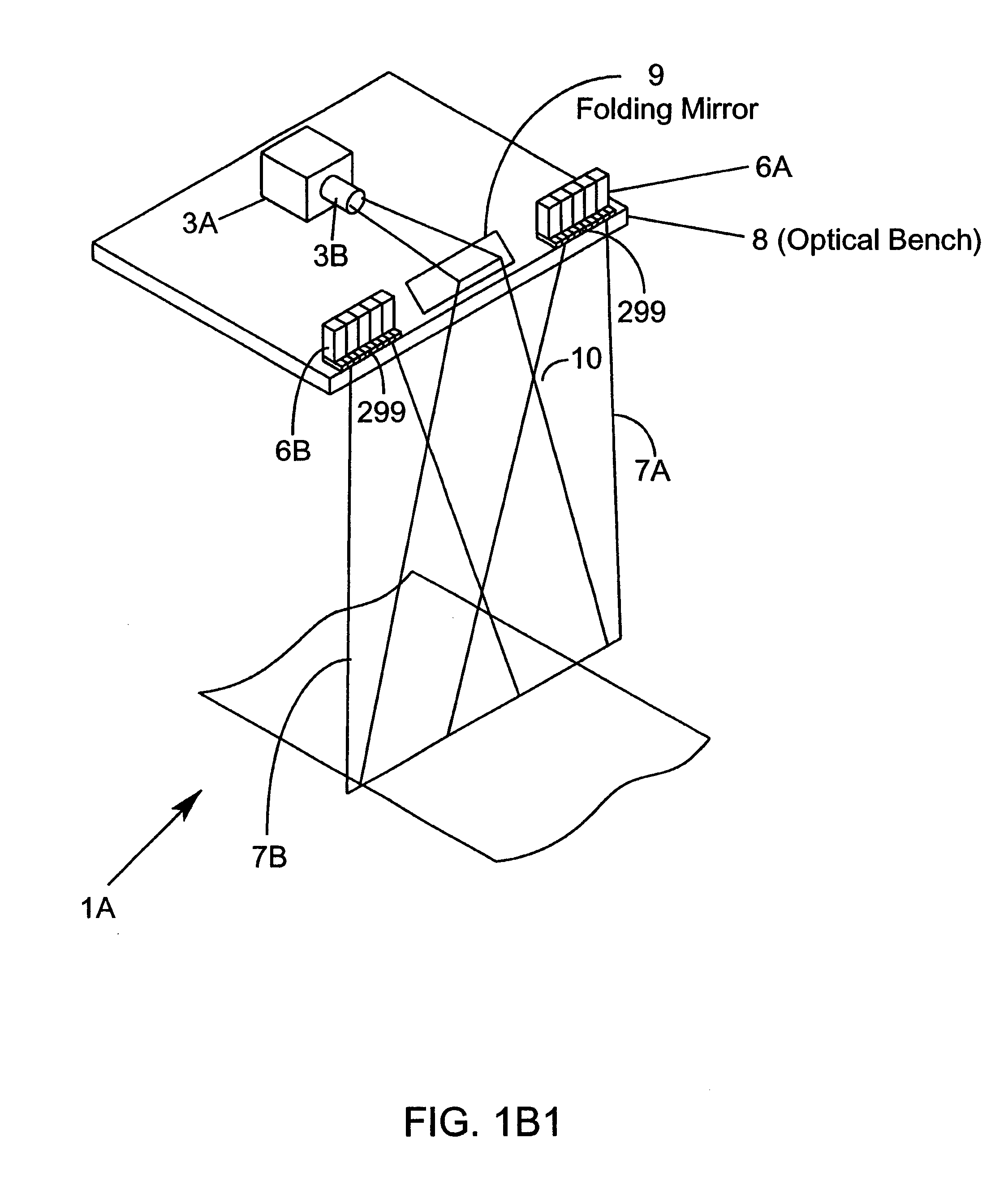
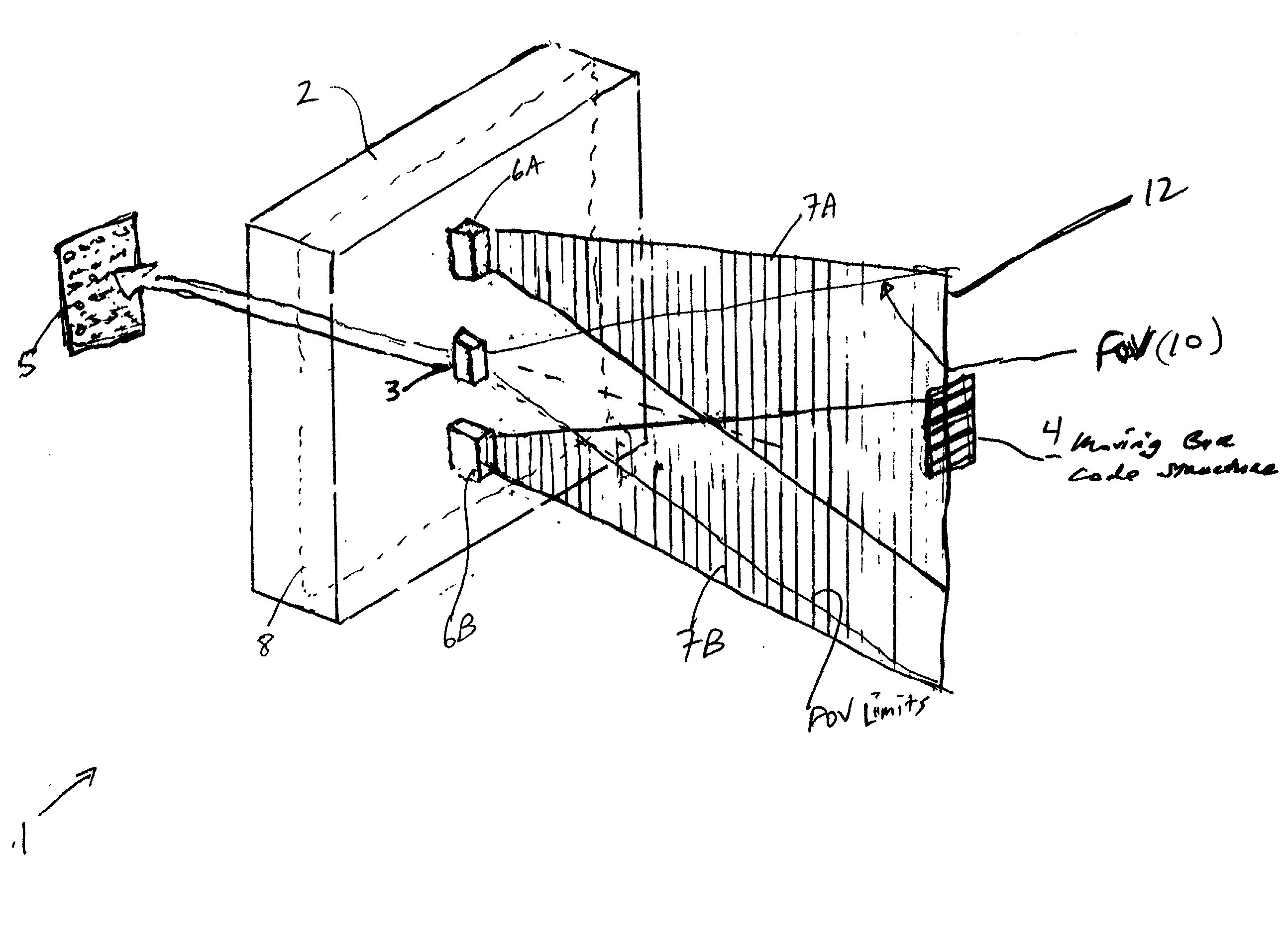
Methods of and systems for illuminating objects using planar laser illumination beams having substantially-planar spatial distribution characteristics that extend through the field of view (FOV) of image formation and detection modules employed in such systems. Each planar laser illumination beam is produced from a planar laser illumination beam array (PLIA) comprising an plurality of planar laser illumination modules (PLIMs). Each PLIM comprises a visible laser diode (VLD, a focusing lens, and a cylindrical optical element arranged therewith. The individual planar laser illumination beam components produced from each PLIM are optically combined to produce a composite substantially planar laser illumination beam having substantially uniform power density characteristics over the entire spatial extend thereof and thus the working range of the system. Preferably, each planar laser illumination beam component is focused so that the minimum beam width thereof occurs at a point or plane which is the farthest or maximum object distance at which the system is designed to acquire images, thereby compensating for decreases in the power density of the incident planar laser illumination beam due to the fact that the width of the planar laser illumination beam increases in length for increasing object distances away from the imaging optics. Advanced high-resolution wavefront control methods and devices are disclosed for use with the PLIIM-based systems in order to reduce the power of speckle-noise patterns observed at the image detections thereof. By virtue of the present invention, it is now possible to use both VLDs and high-speed CCD-type image detectors in conveyor, hand-held and hold-under type imaging applications alike, enjoying the advantages and benefits that each such technology has to offer, while avoiding the shortcomings and drawbacks hitherto associated therewith.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
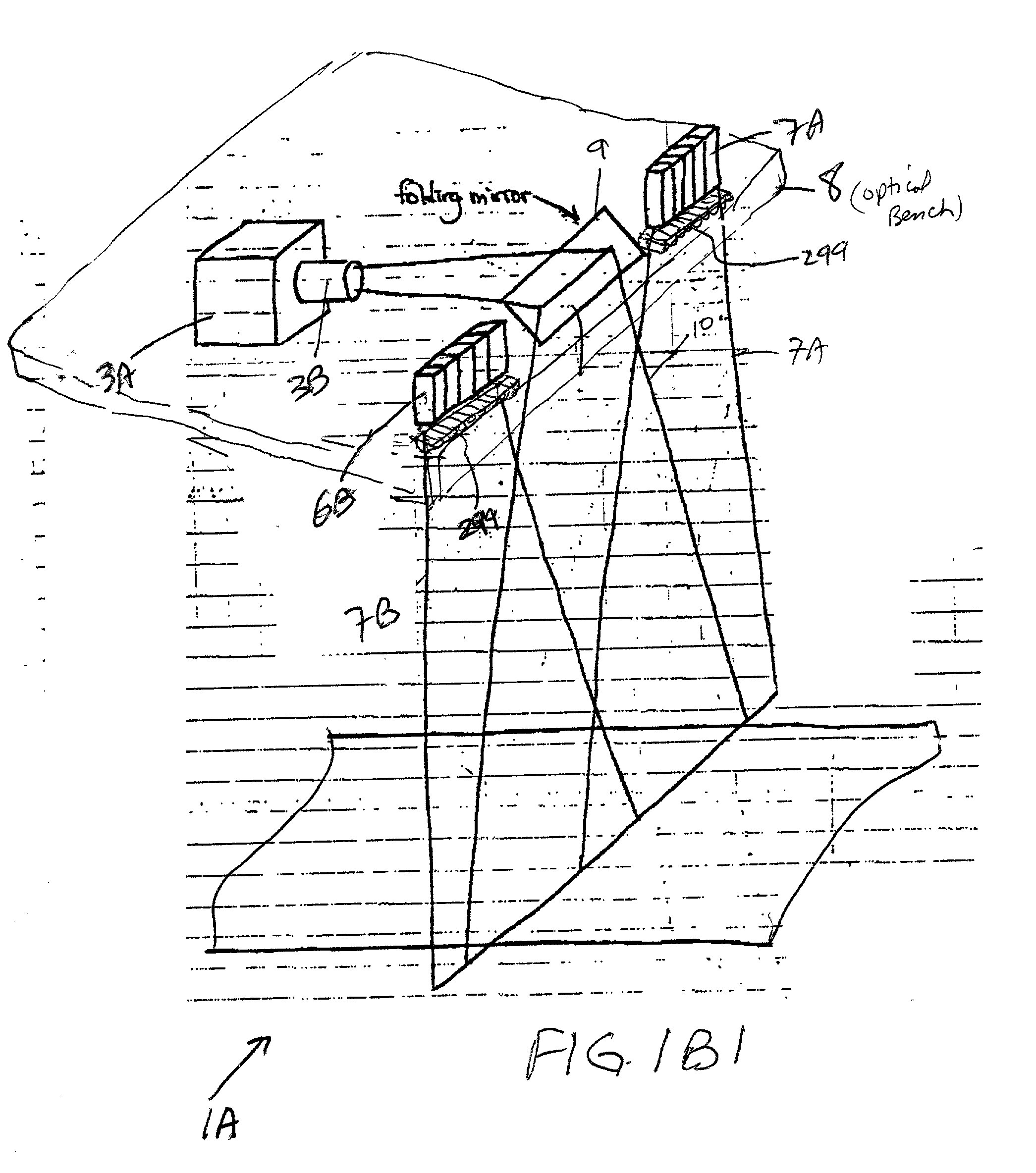
Hand-size structured-light three-dimensional metrology imaging system and method
ActiveUS20070097381A1Enhance the imageImprove measurement resultsImage analysisUsing optical meansDimensional metrologyComputer graphics (images)
A hand-size structured-light three-dimensional metrology imaging system and method. Laser illumination stripes are scanned across a workpiece surface for obtaining z-height and x-coordinate information. A Scheimpflug configuration is used. Utilizing this configuration, a laser illumination stripe across a raised workpiece portion will be shown in a contour image at the image sensor in a focused manner, such that the offsets along the contour image line due to the raised portions of the workpiece surface can be accurately converted to a z-height measurement. The y-axis positions associated with each of the contour images, used for reassembling the information from the contour images into a surface map for the workpiece, may be determined without the need for a position sensor, by including a reference object in the contour images.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Laser imaging system with progressive multi-beam scan architecture
InactiveUS6351324B1Big cost advantageImprove system efficiencyPicture reproducers using projection devicesPicture signal generatorsColor imageBeam scanning
A progressive scan architecture for displaying a two-dimensional image by alternately scanning two or more laser beams, one after the other with a time delay between adjacent beams. The beams are arranged to become incident upon a polygon scanner in a row with an approximately uniform spatial separation and an approximately equal angle between adjacent beams. The polygon scanner scans horizontally and a galvanometer-driven mirror scans vertically. Adjacent lines are progressively scanned in sequence from top to bottom, which advantageously reduces or eliminates psycho-visual effects and is tolerant of non-linearities in the vertical scanner, allowing use of a low-cost galvo mirror. Typically, the beams in the row are arranged in pairs, and only one beam from each pair will be scanning at any one time. Embodiments are described in which the duty cycle is slightly less than 50% and the laser illumination is switched between two interleaved beam scans thereby allowing a single modulator to be used for both beams which provides significant cost advantages and improves system efficiency. For full-color images, each of the beams described can incorporate separate red, green and blue (RGB) components which are individually modulated by separate red, green, and blue modulators. The system can be scaled up with one or more additional pairs of beams to improve resolution and / or increase pixel count without requiring a high-speed polygon scanner or a highly-linear galvo scanner. Furthermore, the height of each facet in the polygon mirror need be only one beam diameter and its length need only be two beam diameters, which allows the system to approach the minimum pixel size attainable, which is useful to provide high efficiency and high brightness in the image.
Owner:PHOTERA TECH
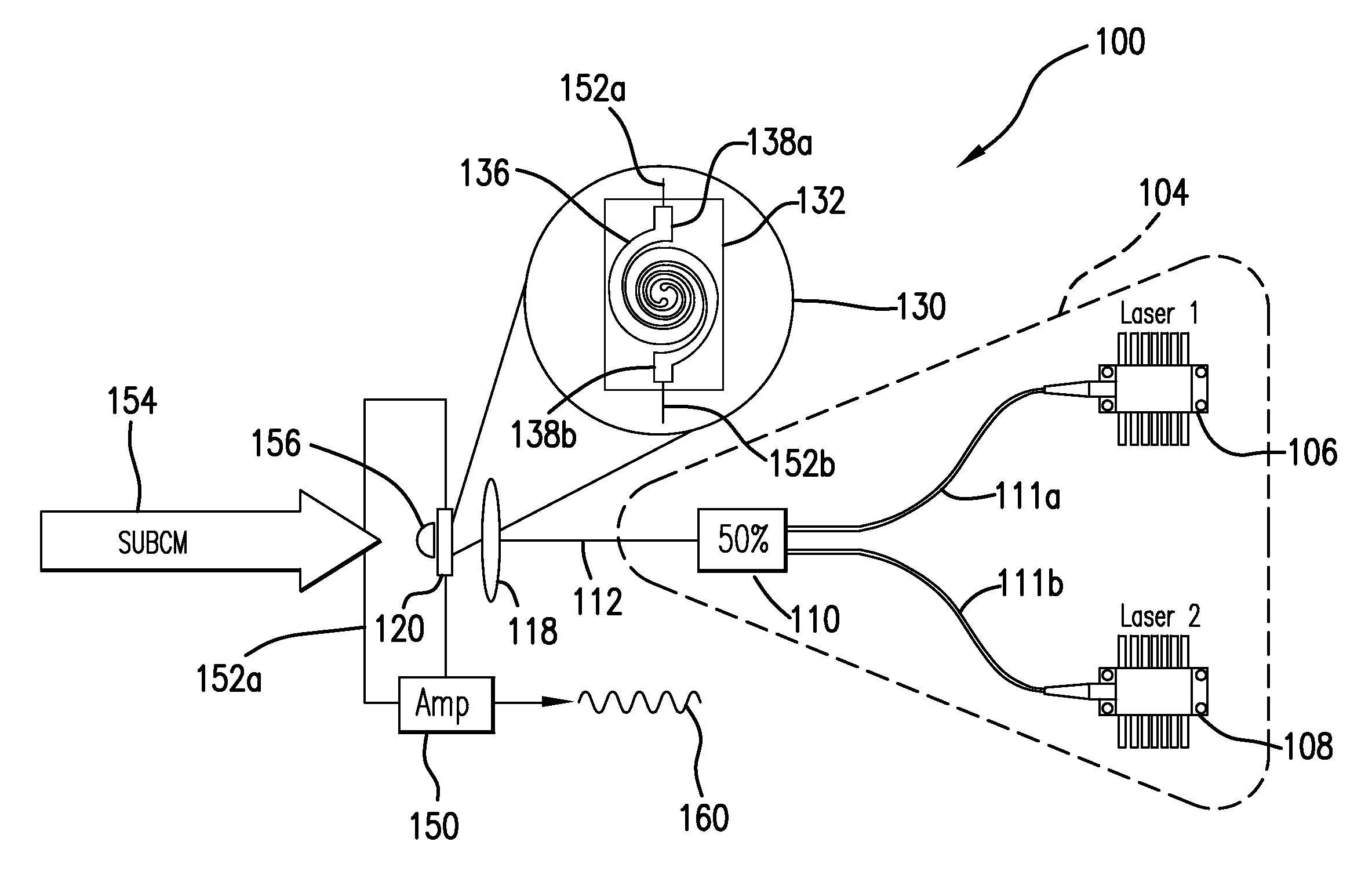
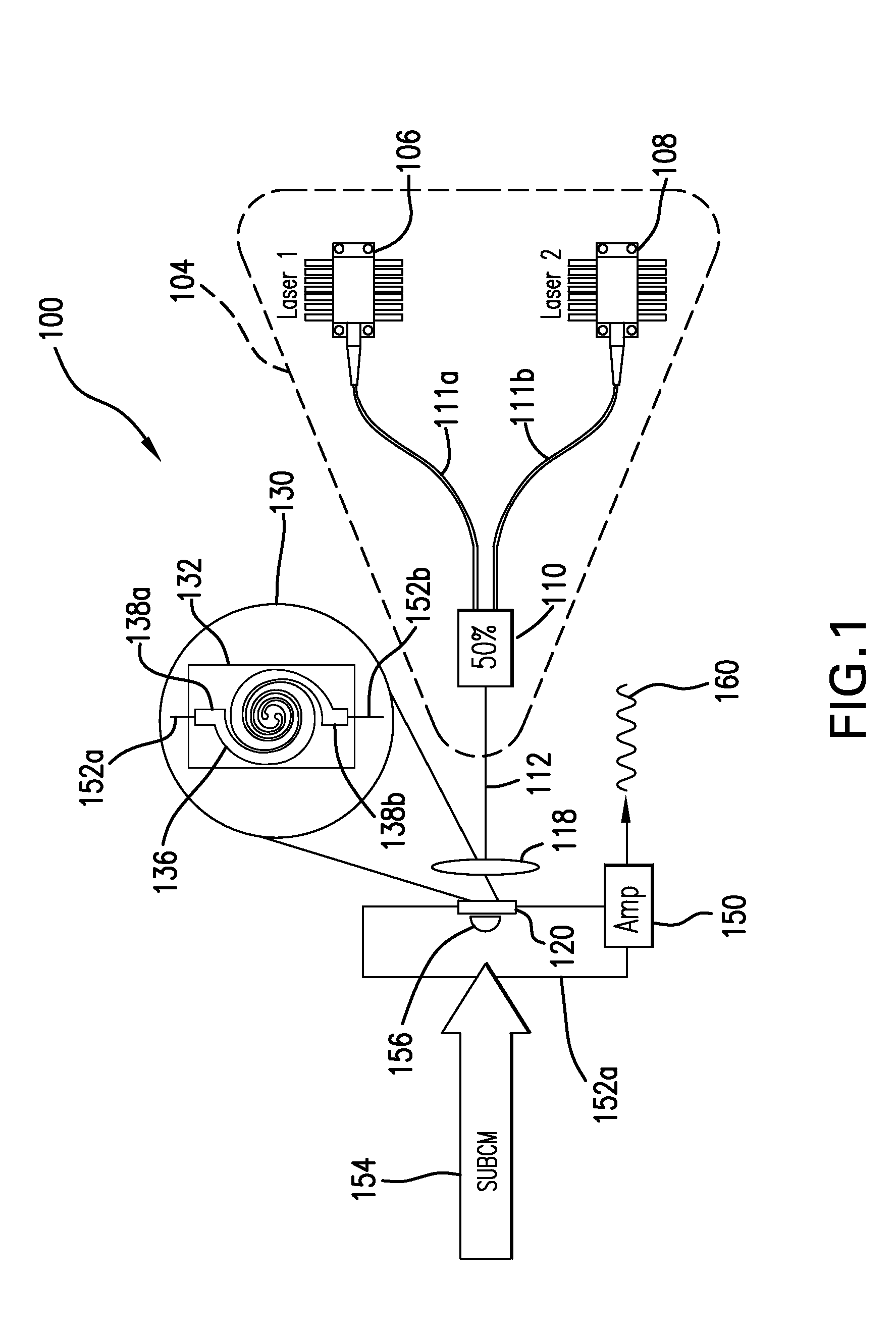
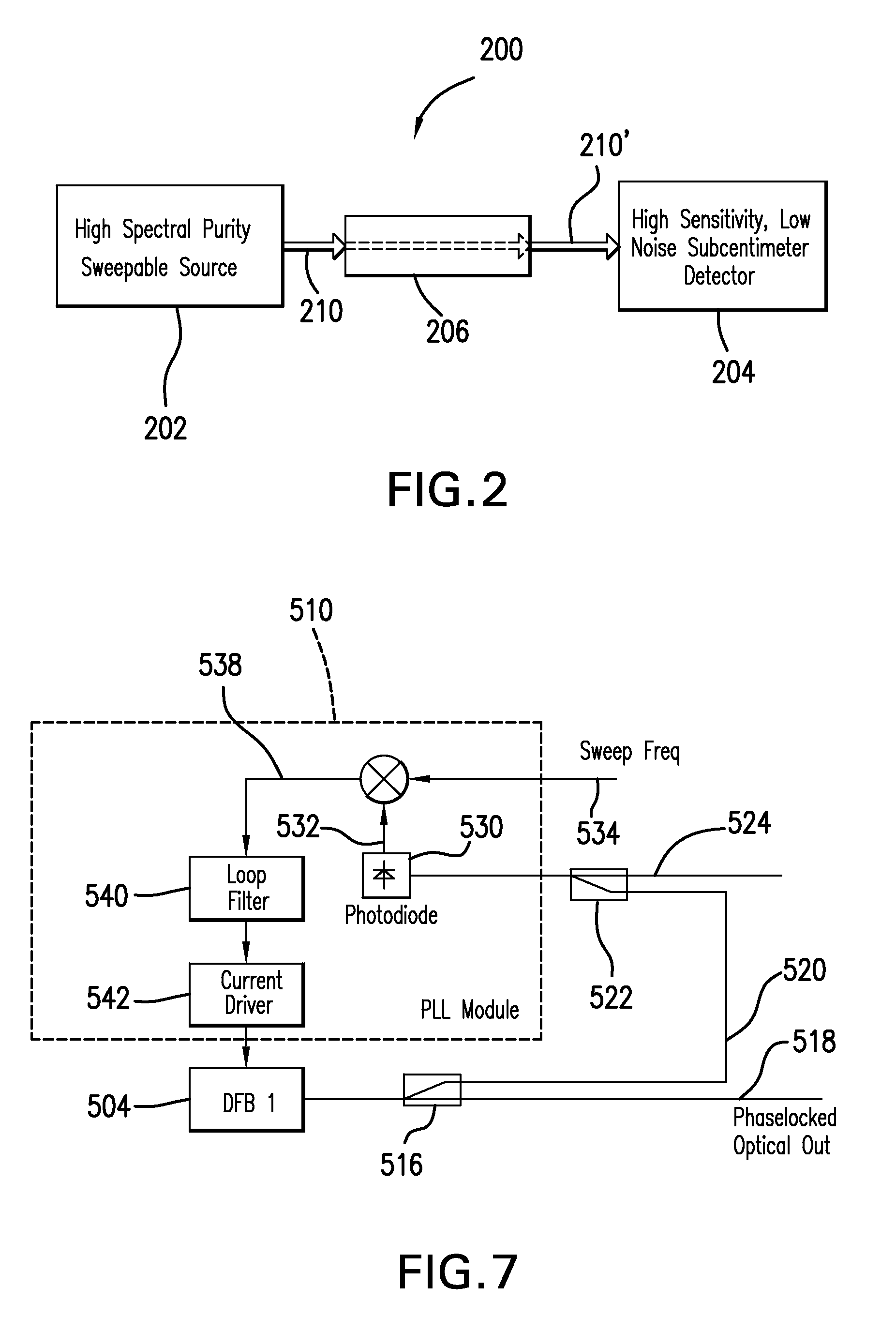
Subcentimeter radiation detection and frequency domain spectroscopy
A system, method and detection arrangement for investigation of a sample are described. A laser illumination arrangement generates (i) a source laser energy that is incident on a source to cause emission of subcentimeter radiation, at least a portion of which interacts with the sample to serve as a sample influenced radiation incident on a detector and (ii) a detector laser energy that is incident on the detector to produce an optical component of the detector laser energy offset with respect to a corresponding optical component of the source laser energy so that the collective energy at the detector generates an electrical output signal responsive to the sample influenced radiation. In another aspect, a detection arrangement is used with at least two continuous wave lasers for causing the detector body to respond in a way which produces a frequency down-converted signal from an incident electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:DEMERS JOSEPH R
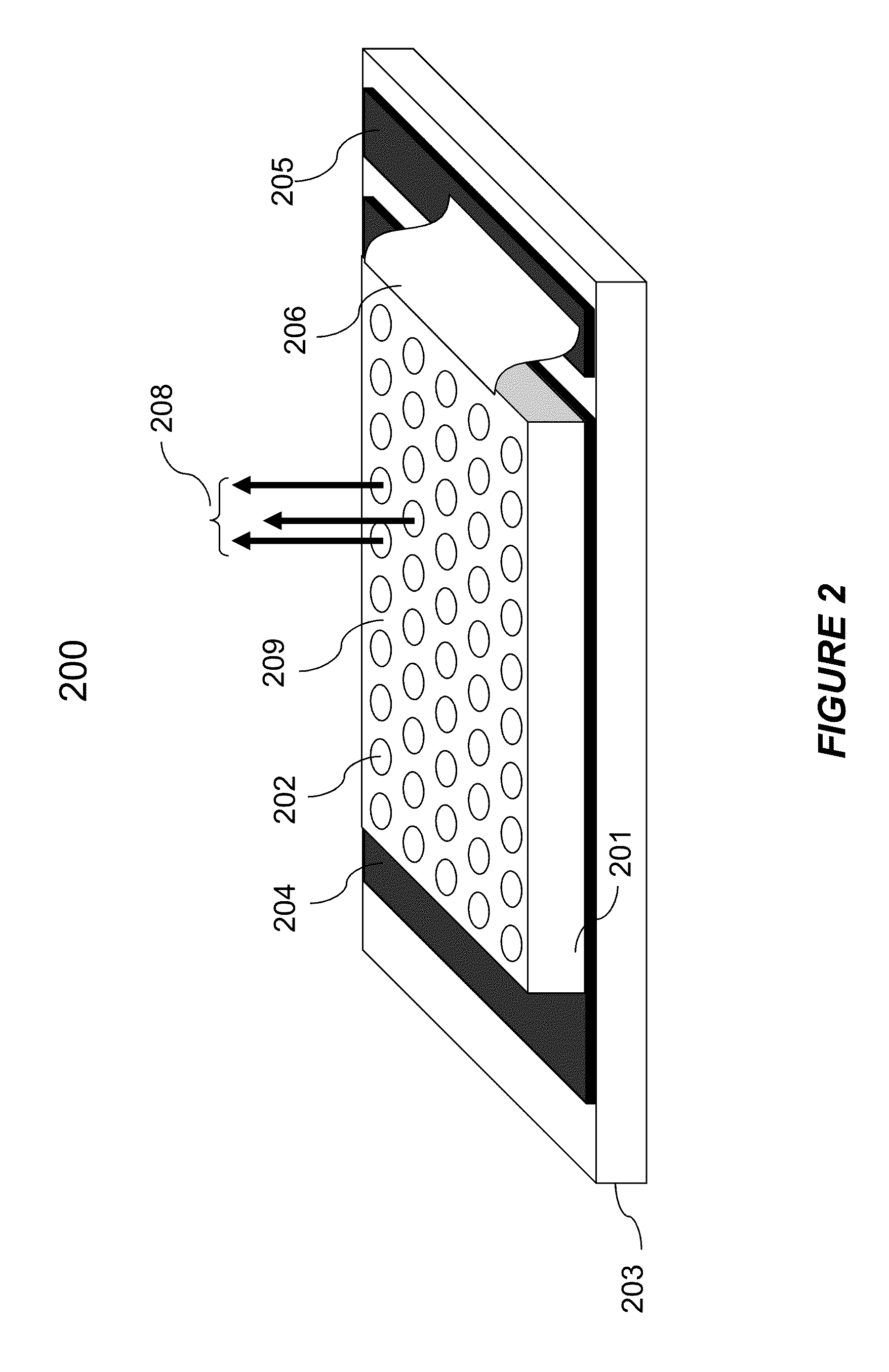
Retarder-based despeckle device for laser illumination systems
ActiveUS20090257106A1Reducing perceived speckleHigh degreeLaser detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionLight beam
A method and apparatus for reducing speckle in a laser illumination system uses a despeckle device including an optical retarder providing an odd integer multiple of substantially half-wave retardation for light emitted from a coherent laser in the laser illumination system. The near half-wave optical retarder has a substantially constant retardance and a spatially varied slow axis. The spatially varied slow axis imposes a phase mask on the beam of light, which provides sub-resolution optical phase modulation to a resolution spot on the detector. The near half-wave optical retarder is actuated mechanically or electrically to vary the sub-resolution optical phase modulation within an integration time of the detector.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Laser illuminated projection displays
InactiveUS7244028B2Reduced coherence radiusMinimizing speckle contrastBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsColor television detailsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
A projection video display includes at least one laser for delivering a light beam. The display includes a beam homogenizer and a condenser lens. A scanning arrangement is provided for scanning the light in beam in a particular pattern over the condenser lens in a manner that effectively increases the beam divergence. The scanned beam is homogenized by a beam homogenizer and a spatial light modulator is arranged to receive the homogenized scanned light beam and spatially modulate the beam in accordance with a component of an image to be displayed. Projection optics are projecting the homogenized scanned light beam onto a screen. The scanning provides that the homogenized scanned light beam at the screen has a coherence radius less than the original coherence radius of the beam. The reduced coherence radius contributes to minimizing speckle contrast in the image displayed on the screen. The screen includes one or more features providing a further contribution to minimizing speckle contrast in the displayed image. In one example, the screen includes a transparent cell containing a liquid having light scattering particles in suspension.
Owner:COHERENT INC
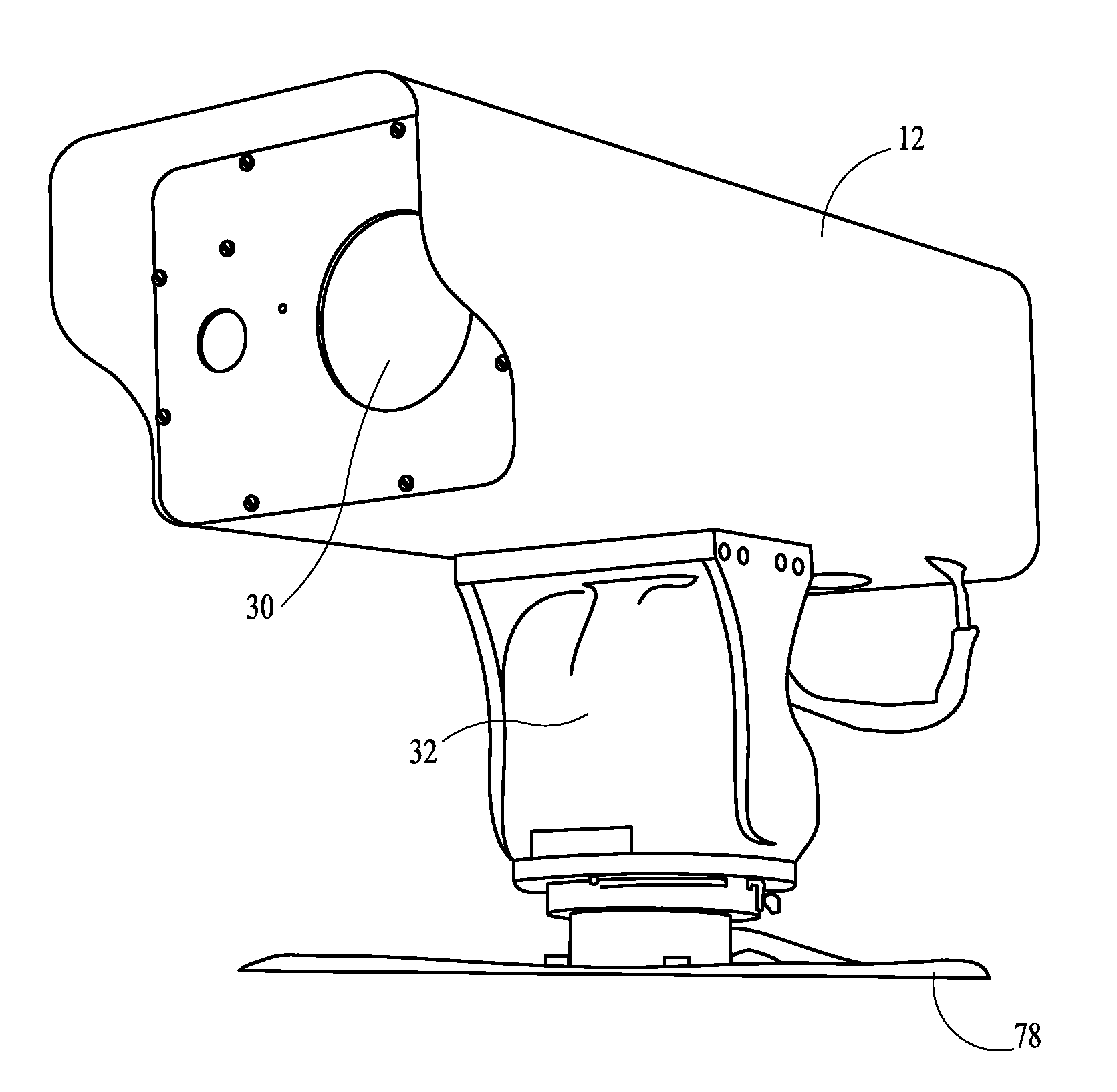
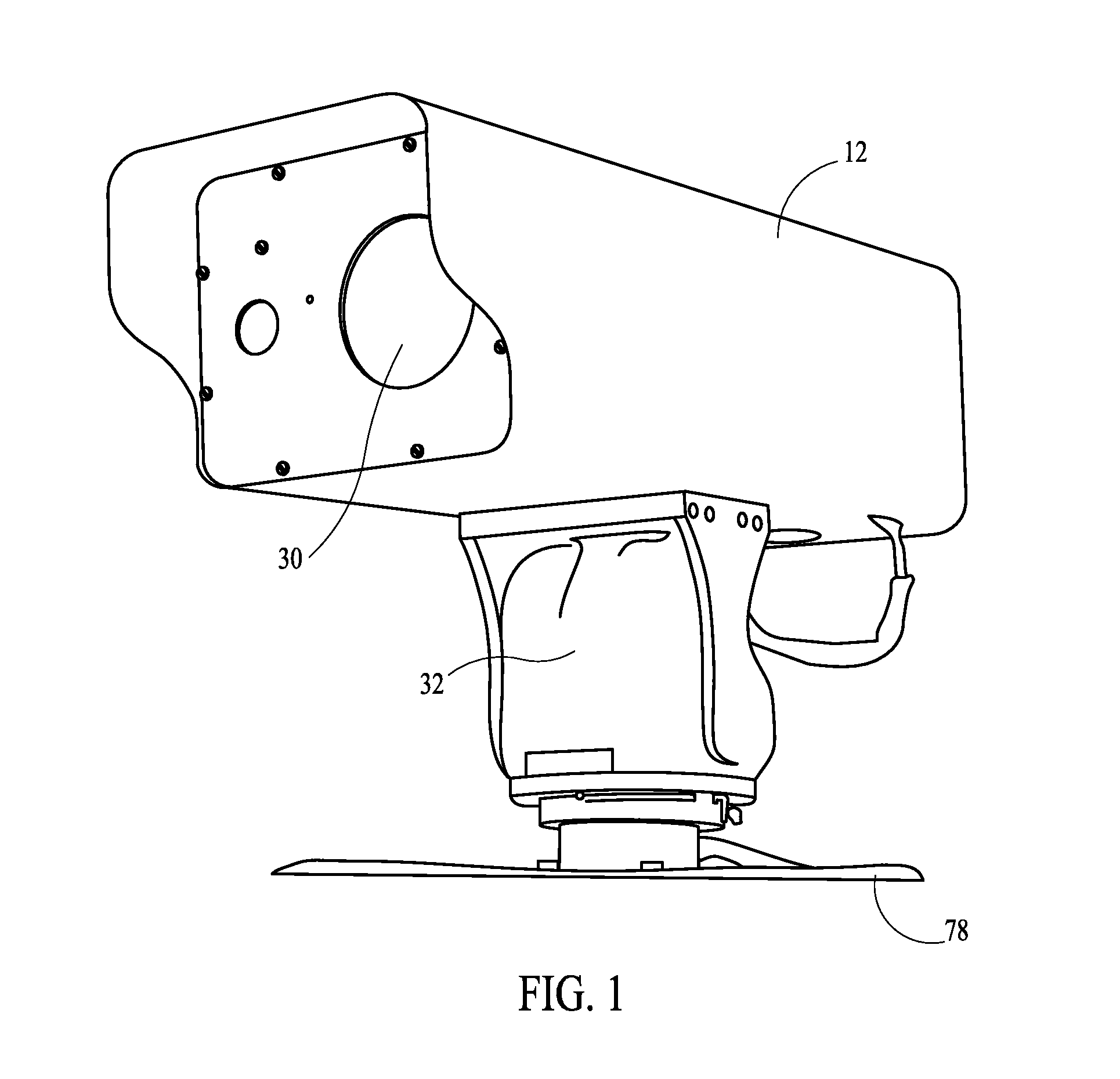
Long Range Day/Night Surveillance Video Camera
InactiveUS20110199482A1Low lightTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPower stationDiode-pumped solid-state laser
This invention relates to video cameras and, more specifically, to a high-resolution day / night video camera with a long lens, fast optics and pan / tilt / zoom electronics, coupled with a diode-pumped solid state laser illuminator for long range low light illumination. Potential applications include ports, borders, pipelines, power stations, communication transmitters and prisons.
Owner:MORGAN ARTHUR C
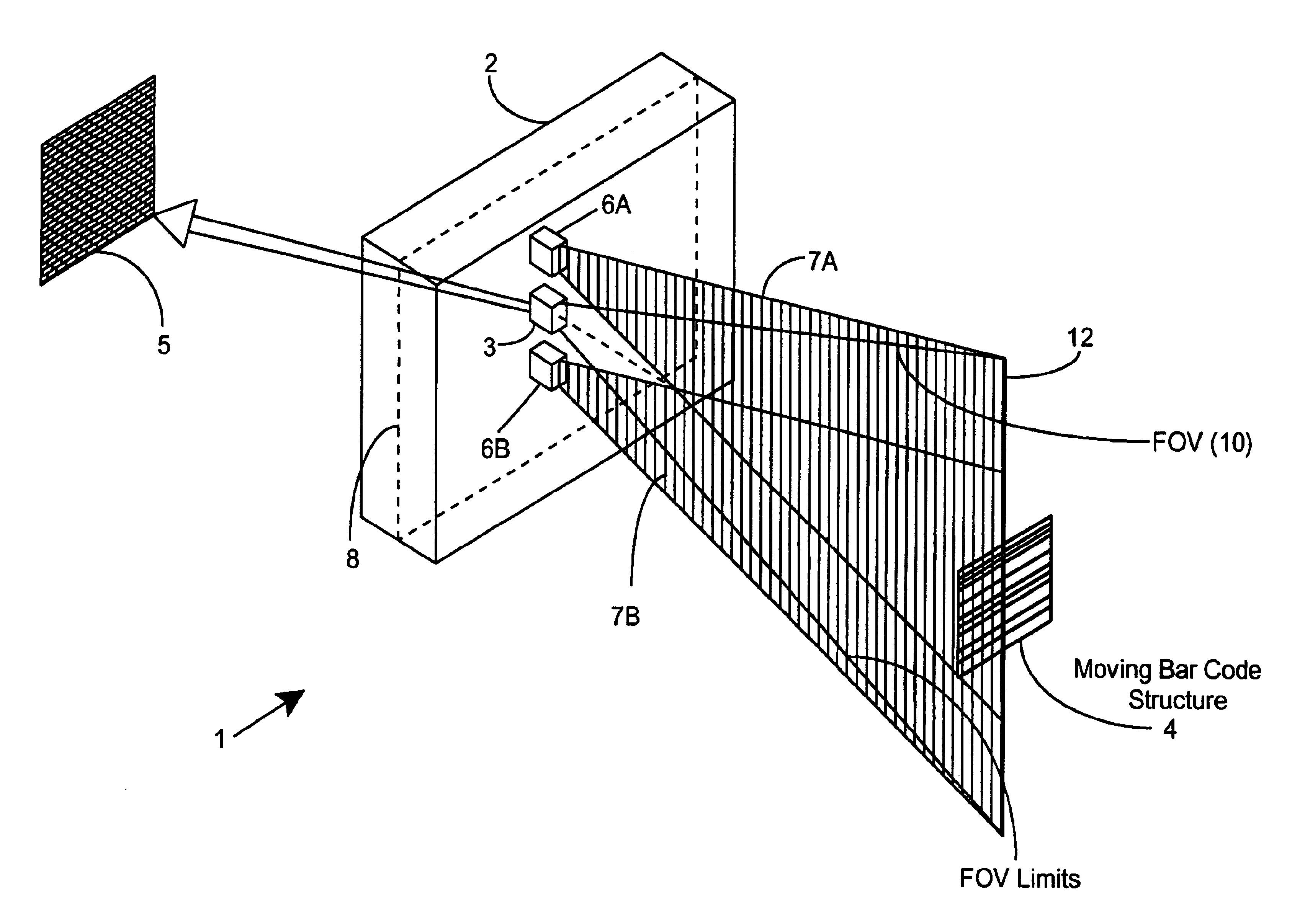
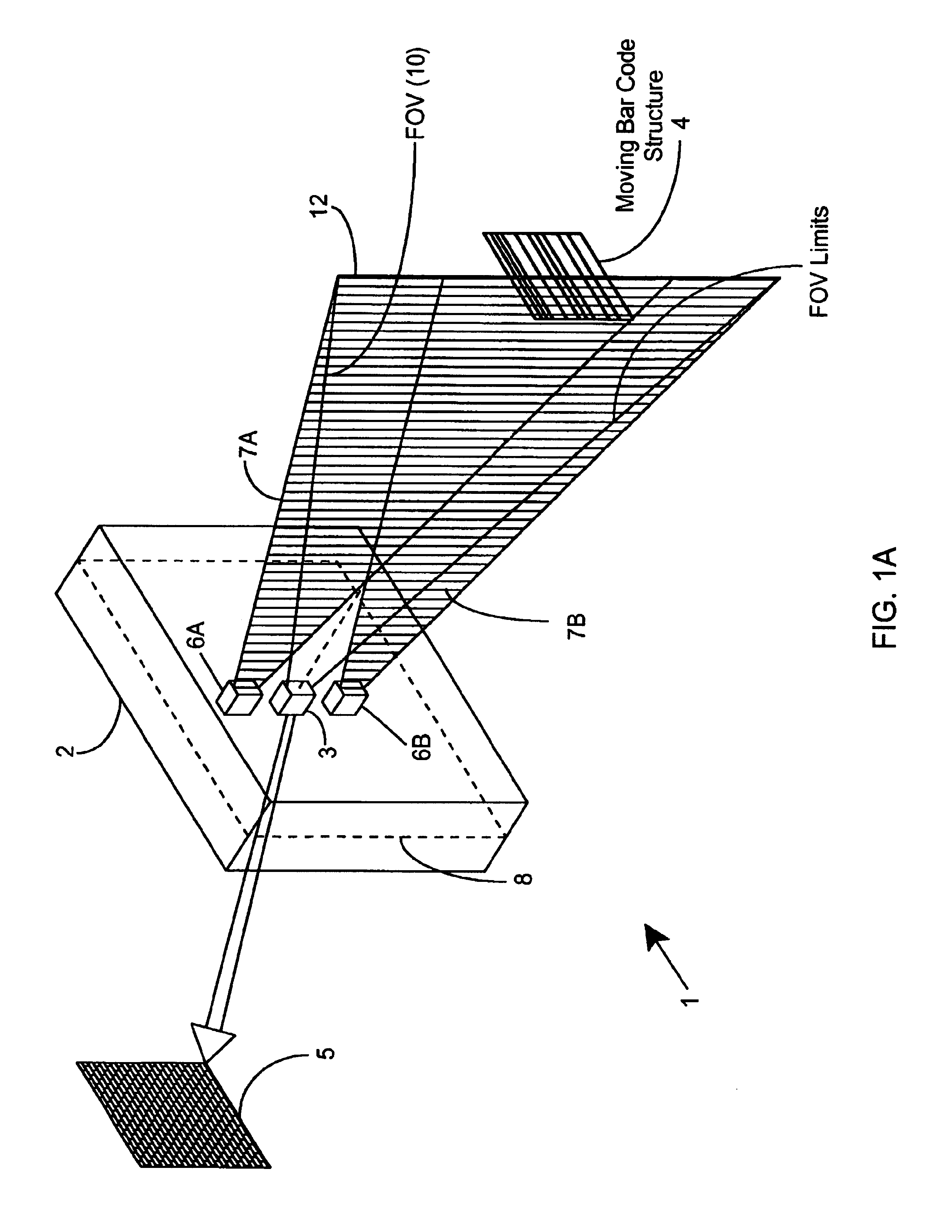
Method of and system for producing images of objects using planar laser illumination beams and image detection arrays
InactiveUS6629641B2Avoid disadvantagesLower Level RequirementsSemiconductor laser arrangementsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage detectionHand held
Methods of and systems for illuminating objects using planar laser illumination beams having substantially-planar spatial distribution characteristics that extend through the field of view (FOV) of image formation and detection modules employed in such systems. Each planar laser illumination beam is produced from a planar laser illumination beam array (PLIA) comprising an plurality of planar laser illumination modules (PLIMs). Each PLIM comprises a visible laser diode (VLD, a focusing lens, and a cylindrical optical element arranged therewith. The individual planar laser illumination beam components produced from each PLIM are optically combined to produce a composite substantially planar laser illumination beam having substantially uniform power density characteristics over the entire spatial extend thereof and thus the working range of the system. Preferably, each planar laser illumination beam component is focused so that the minimum beam width thereof occurs at a point or plane which is the farthest or maximum object distance at which the system is designed to acquire images, thereby compensating for decreases in the power density of the incident planar laser illumination beam due to the fact that the width of the planar laser illumination beam increases in length for increasing object distances away from the imaging optics. By virtue of the present invention, it is now possible to use both VLDs and high-speed CCD-type image detectors in conveyor, hand-held and hold-under type scanning applications alike, enjoying the advantages and benefits that each such technology has to offer, while avoiding the shortcomings and drawbacks hitherto associated therewith.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
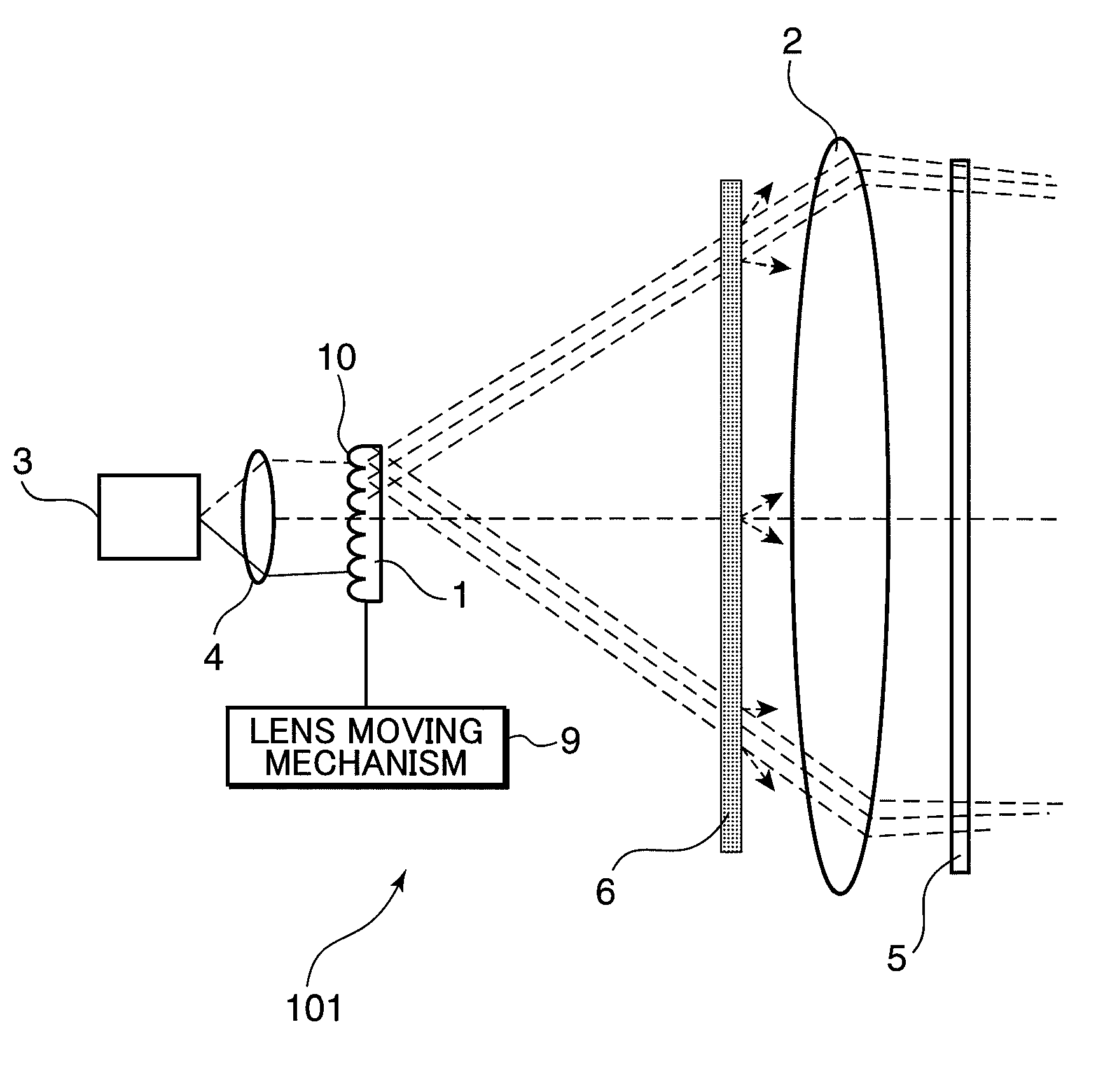
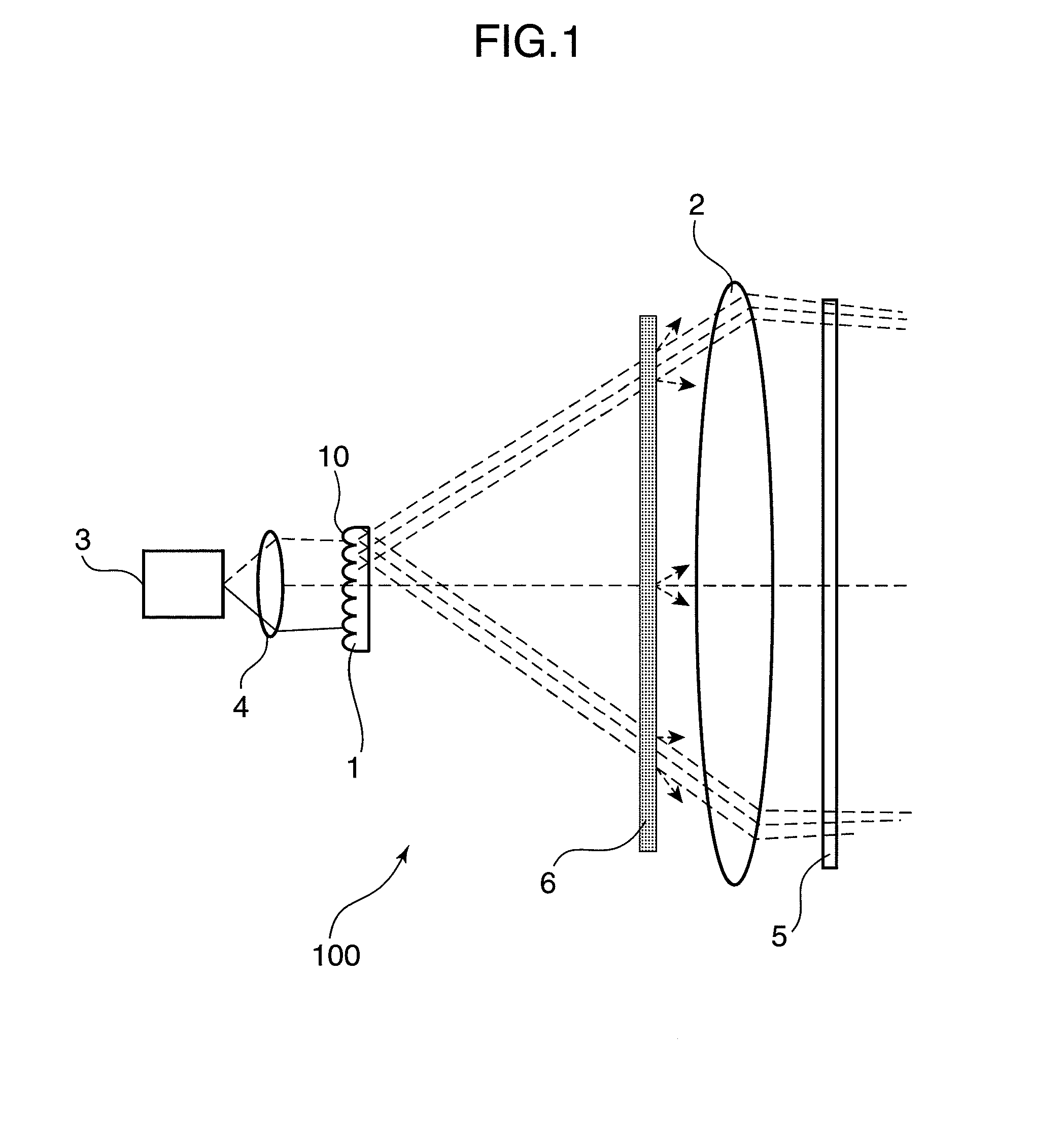
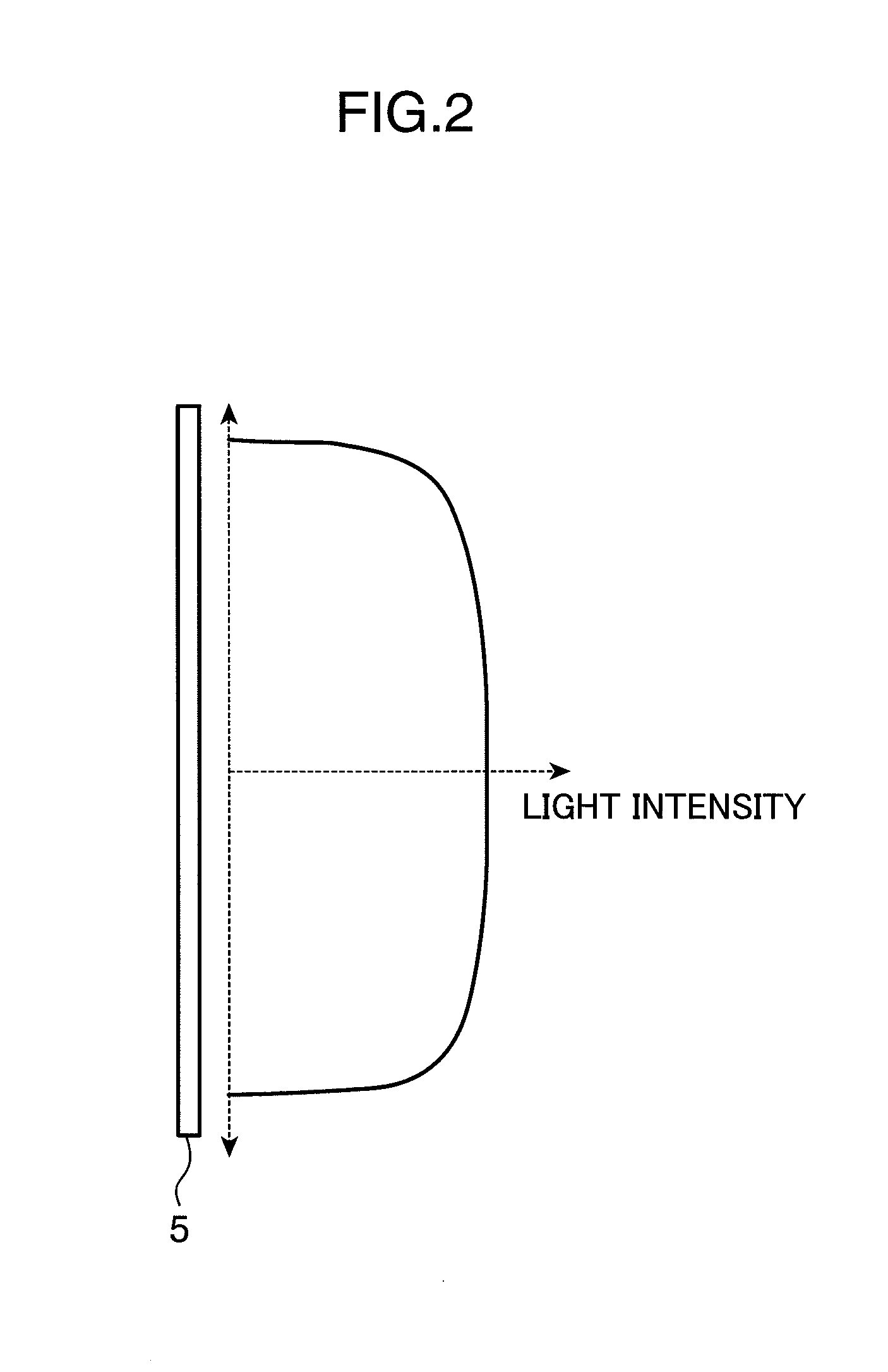
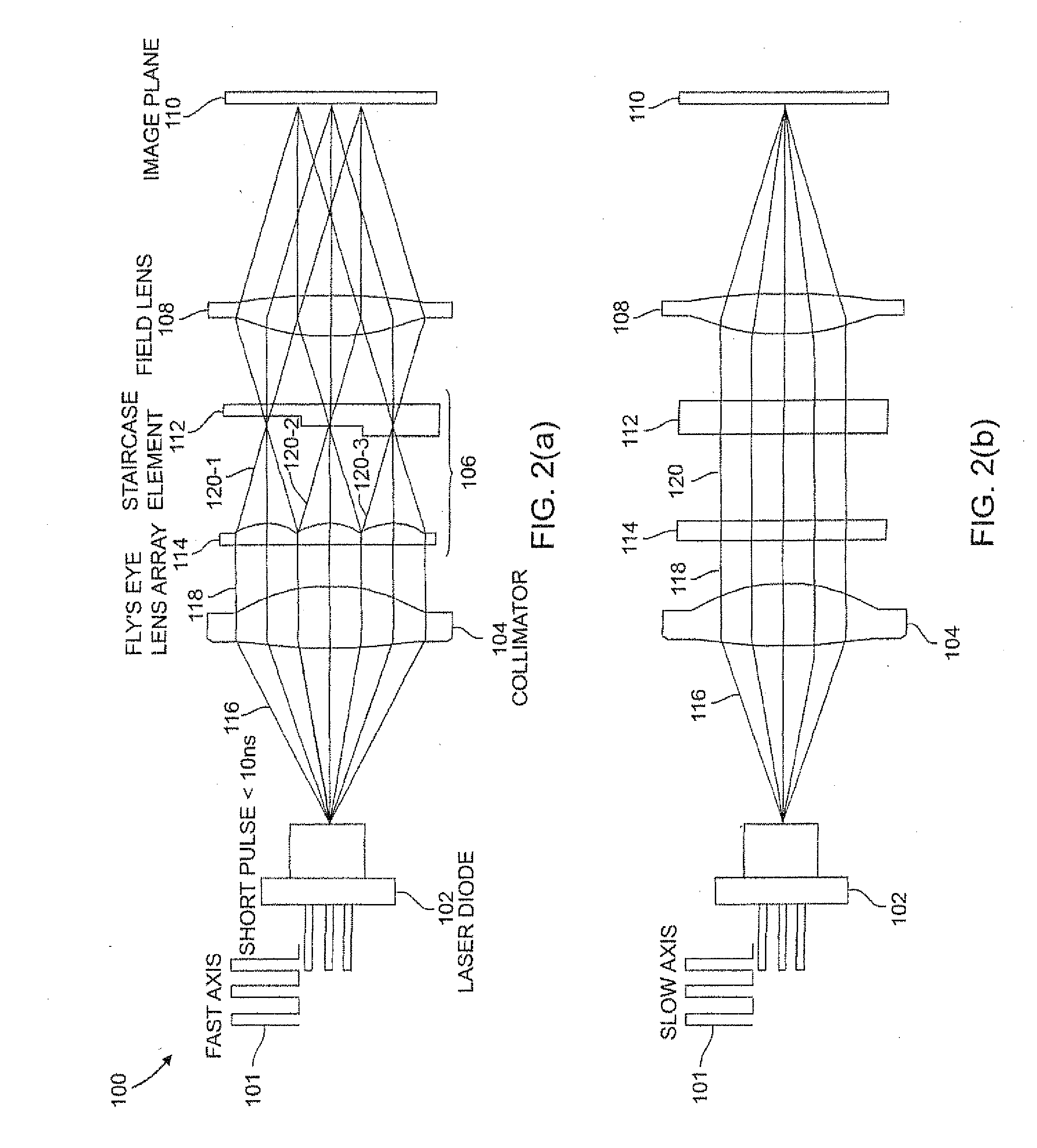
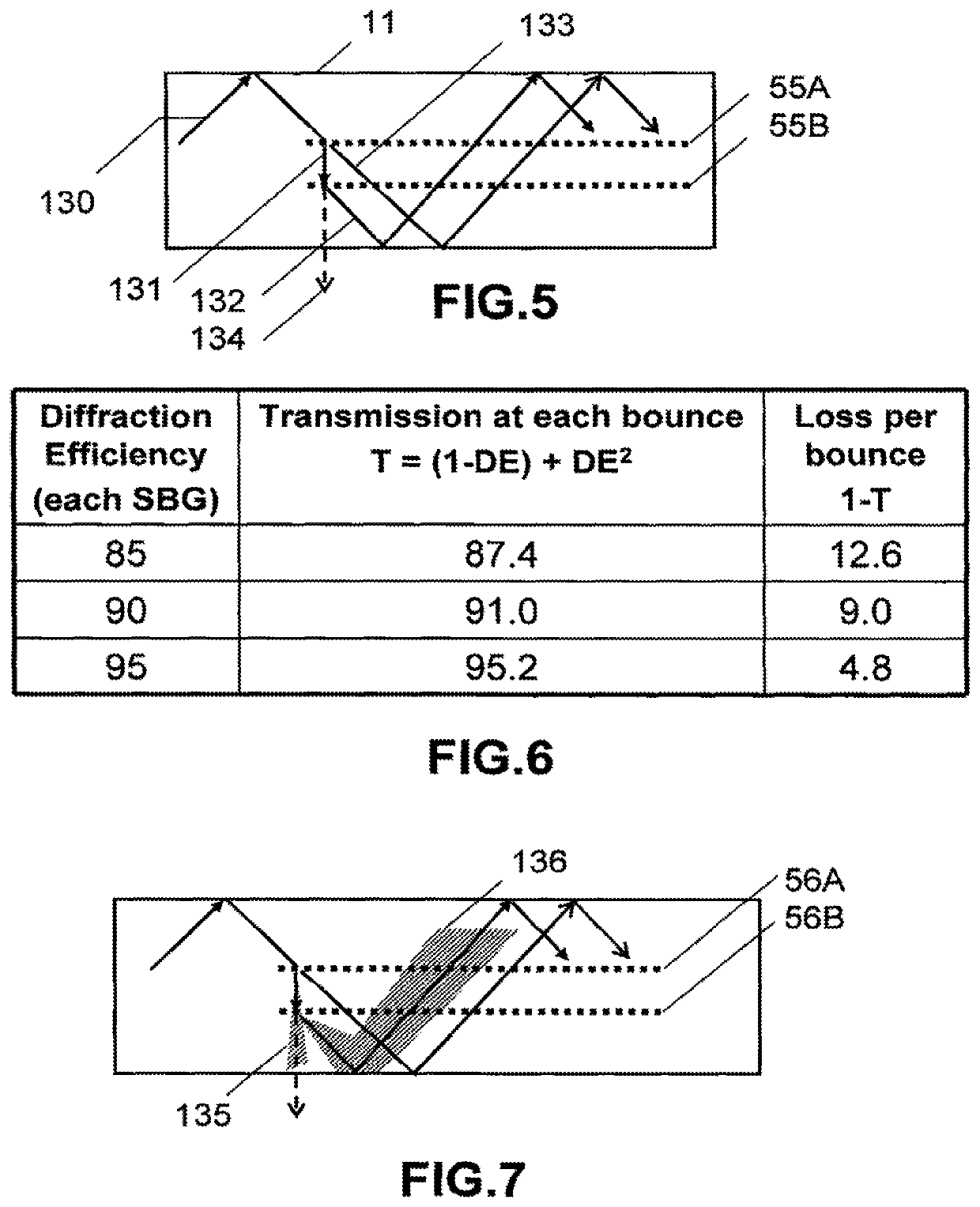
Laser illumination system with reduced speckle
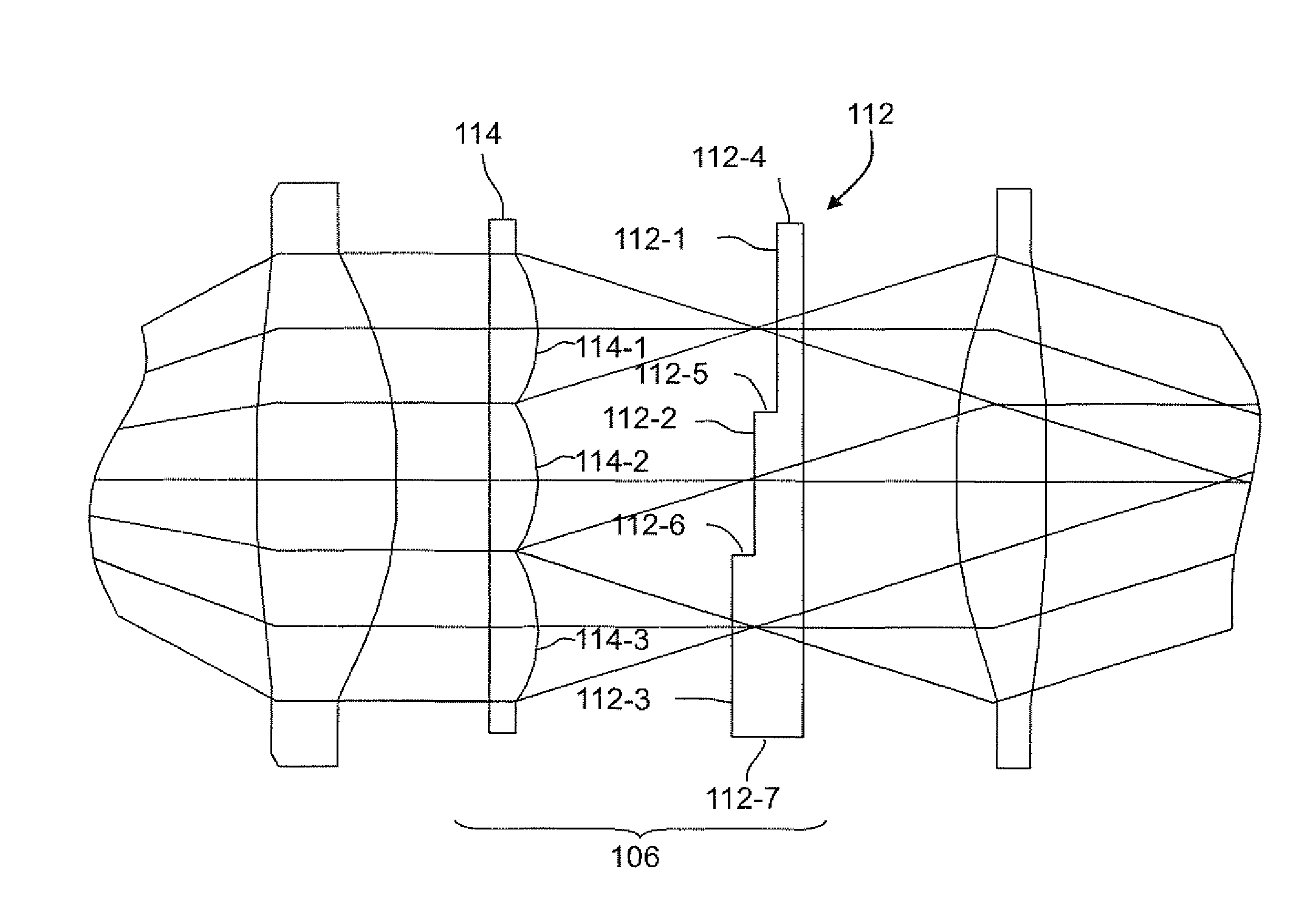
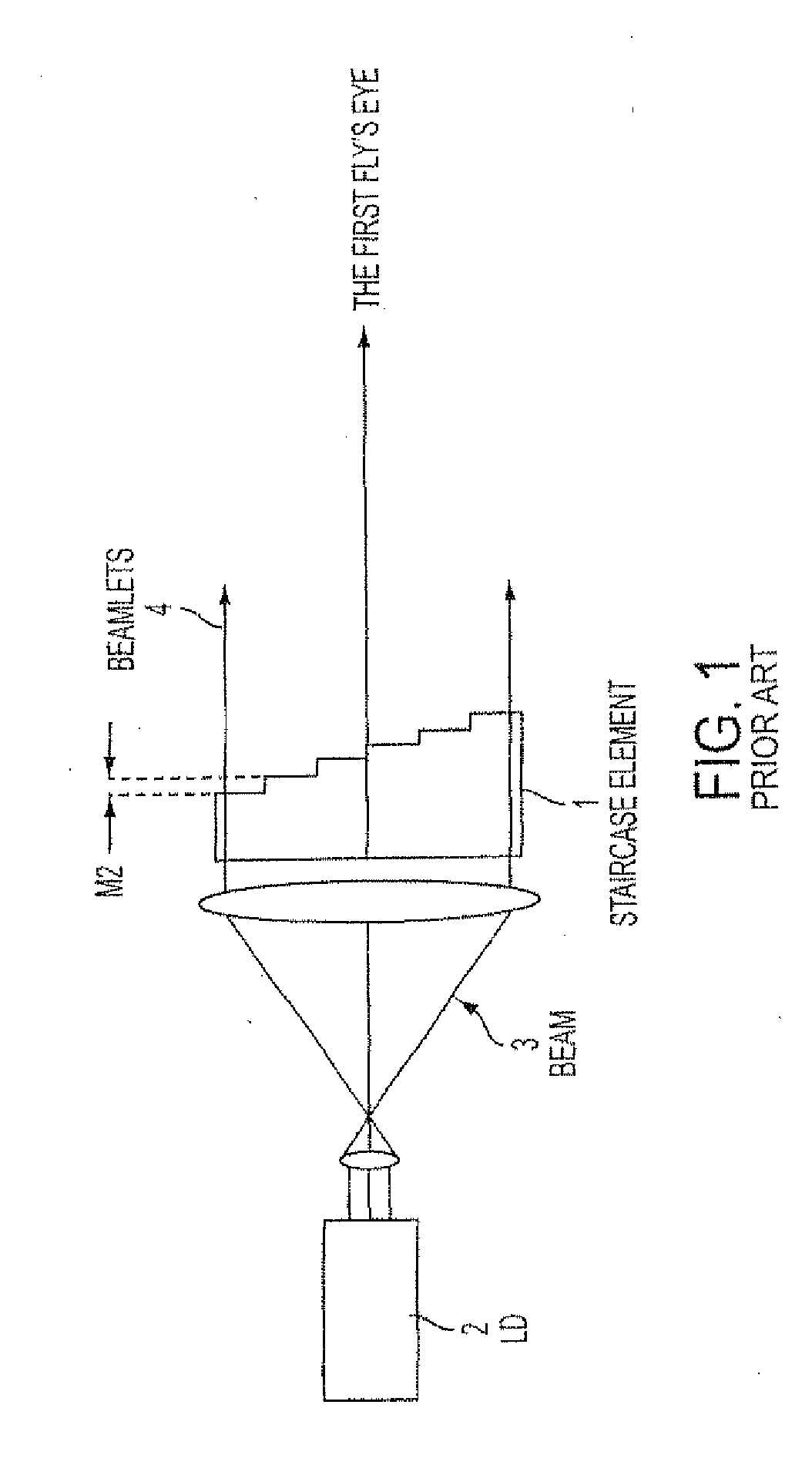
A despeckling device and method in which an optical path difference staircase element is disposed between a fly's eye lens array and the image plane in a position near the focus position of the fly's eye lens array, and a laser generating unit generates and transmits pulsed laser beams to the optical path difference staircase element, wherein the pulsed laser beams are driven at a very short pulsed rate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Laser illuminated projection displays
InactiveUS20060126022A1Reduced coherence radiusMinimizing speckle contrastBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsColor television detailsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
A projection video display includes at least one laser for delivering a light beam. The display includes a beam homogenizer and a condenser lens. A scanning arrangement is provided for scanning the light in beam in a particular pattern over the condenser lens in a manner that effectively increases the beam divergence. The scanned beam is homogenized by a beam homogenizer and a spatial light modulator is arranged to receive the homogenized scanned light beam and spatially modulate the beam in accordance with a component of an image to be displayed. Projection optics are projecting the homogenized scanned light beam onto a screen. The scanning provides that the homogenized scanned light beam at the screen has a coherence radius less than the original coherence radius of the beam. The reduced coherence radius contributes to minimizing speckle contrast in the image displayed on the screen. The screen includes one or more features providing a further contribution to minimizing speckle contrast in the displayed image. In one example, the screen includes a transparent cell containing a liquid having light scattering particles in suspension.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Portable retinal imaging device
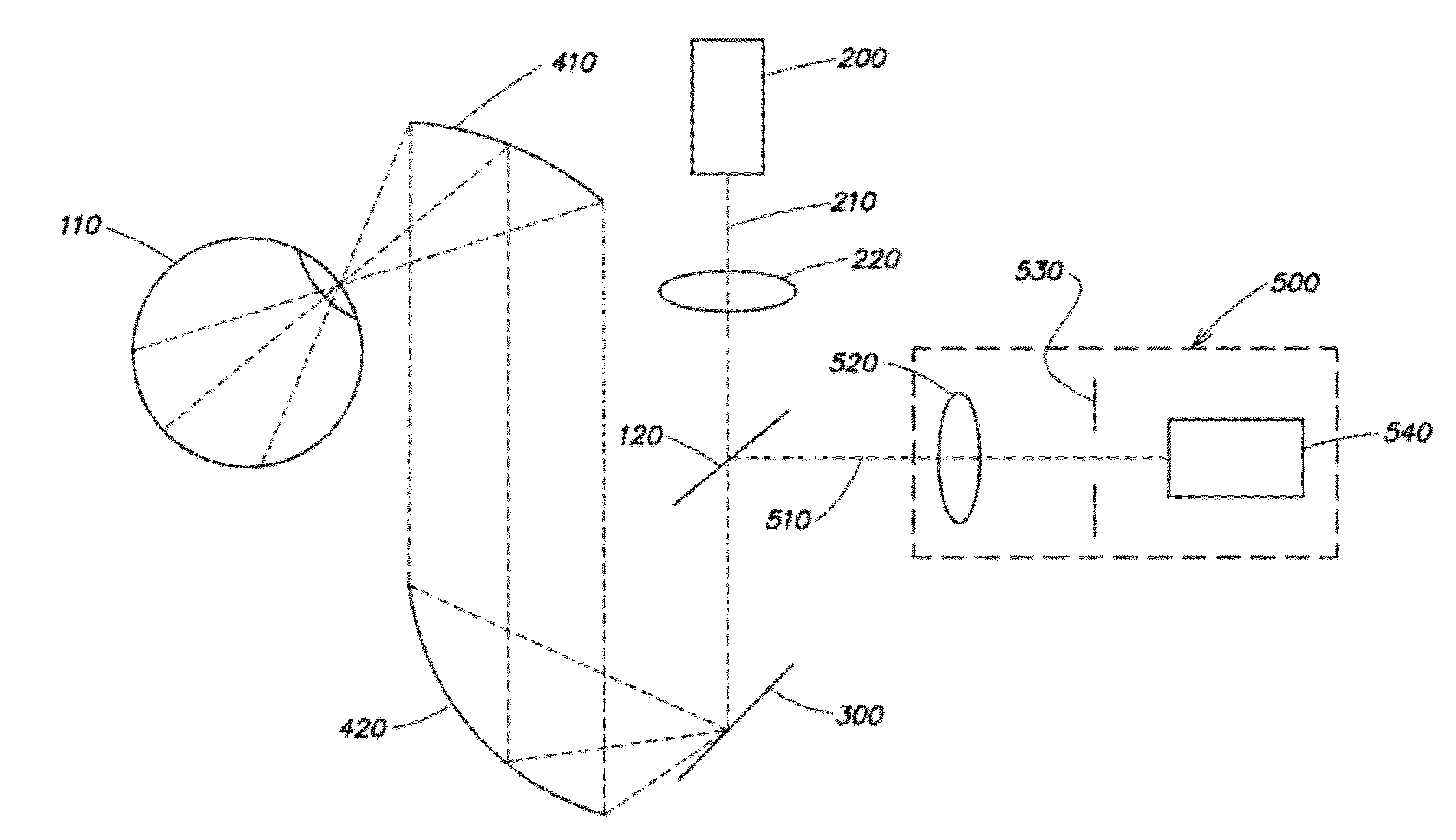
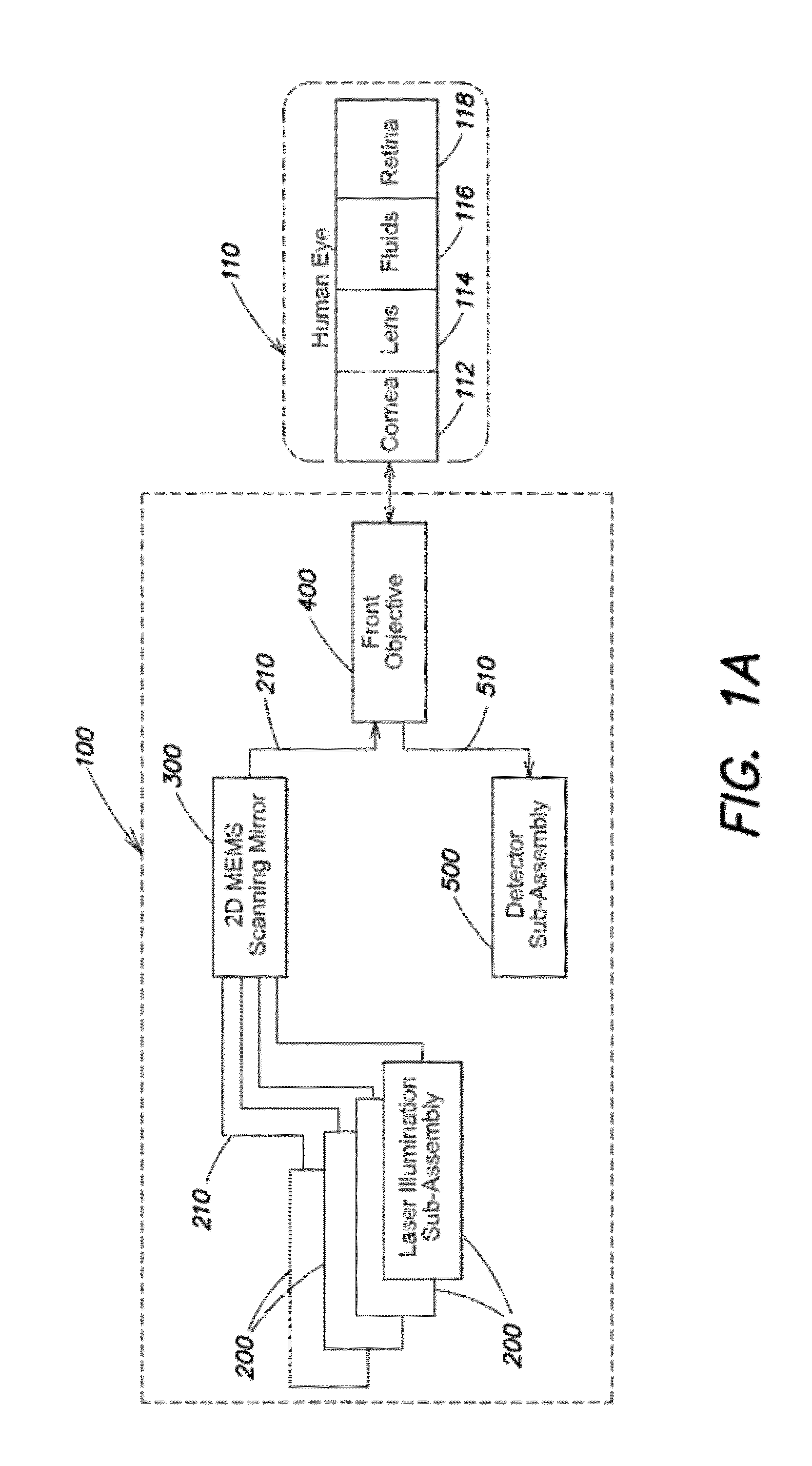
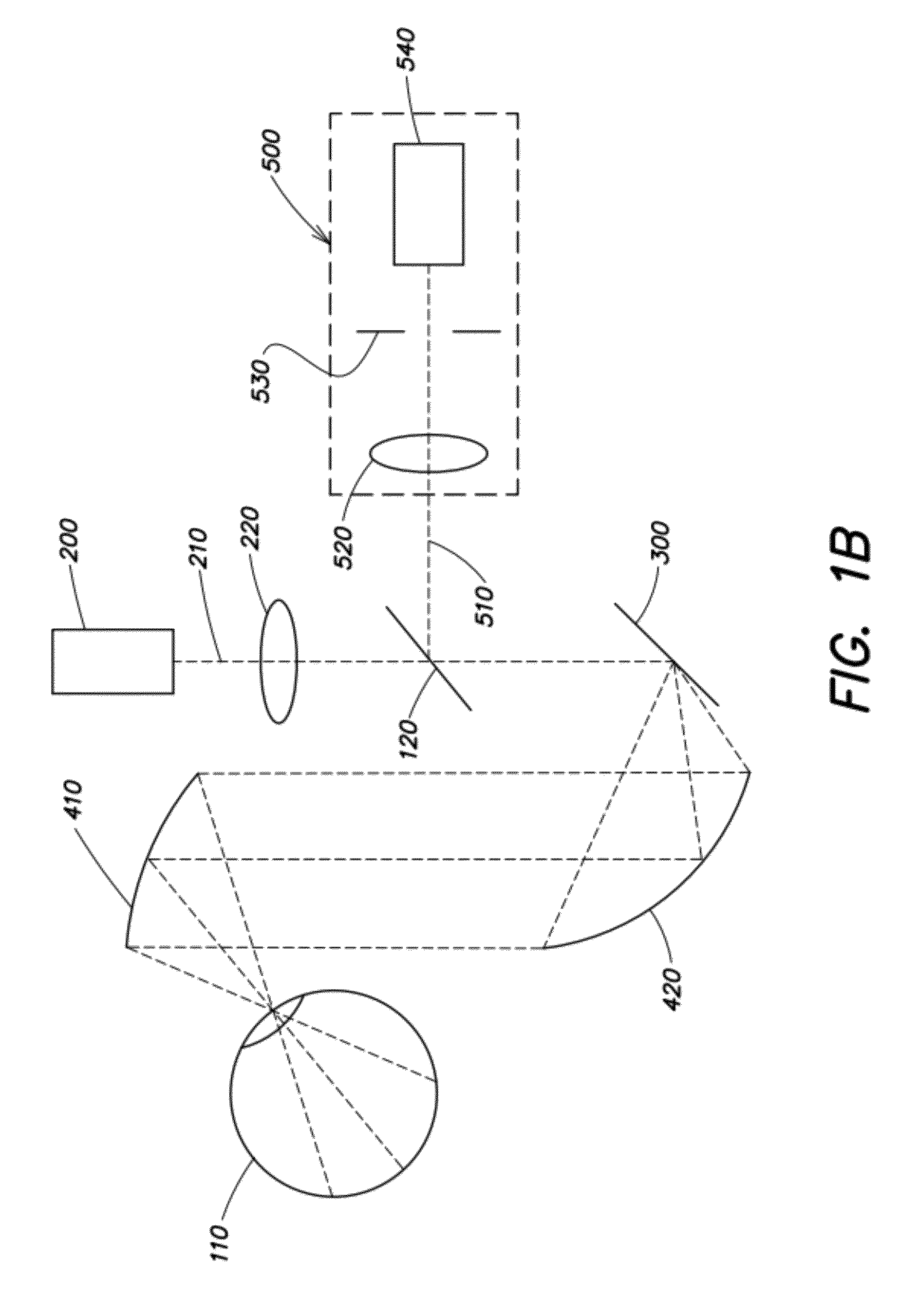
InactiveUS20130194548A1Robust scanningMicroscopesOthalmoscopesOptical radiationScanning laser ophthalmoscope
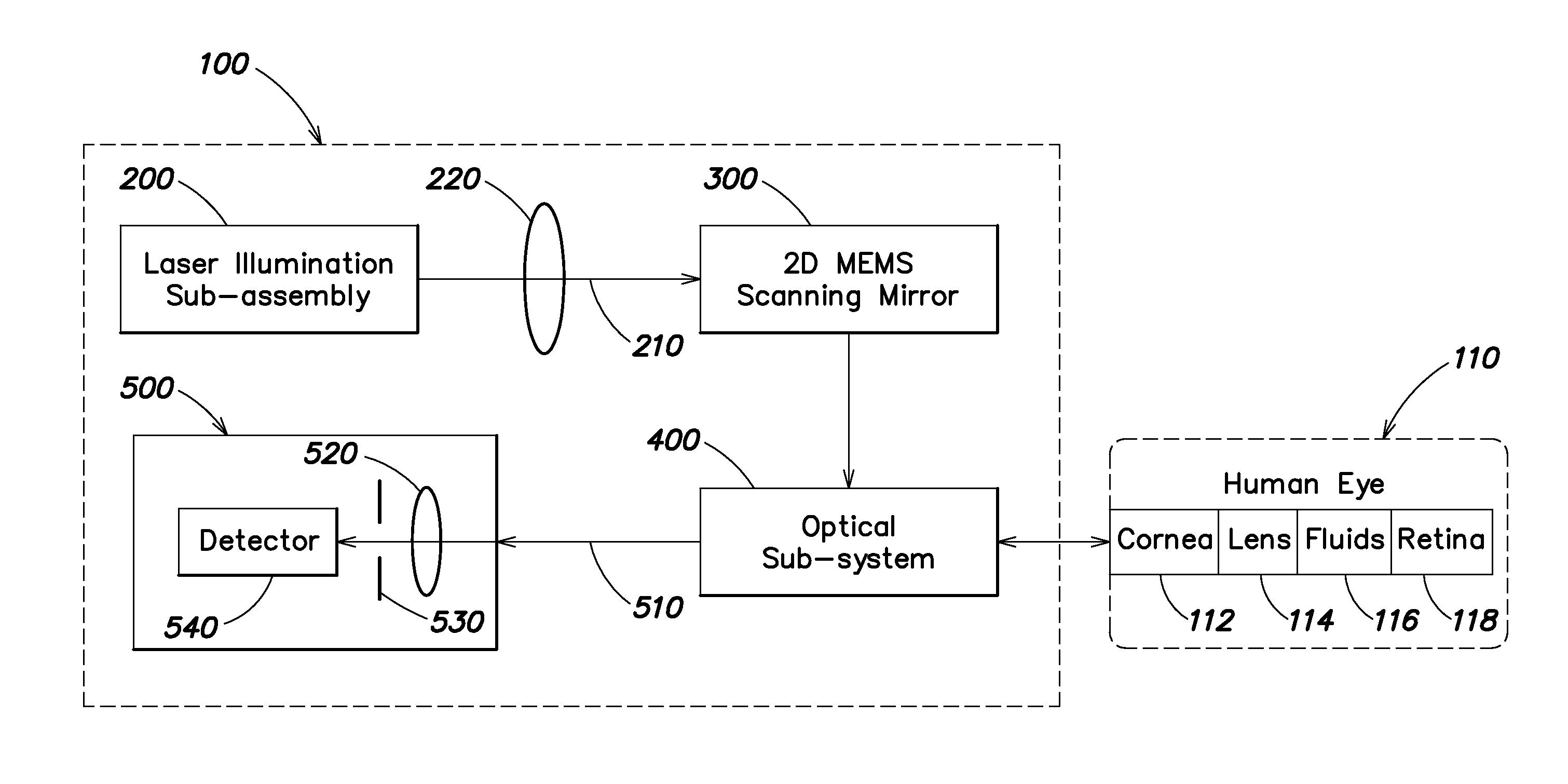
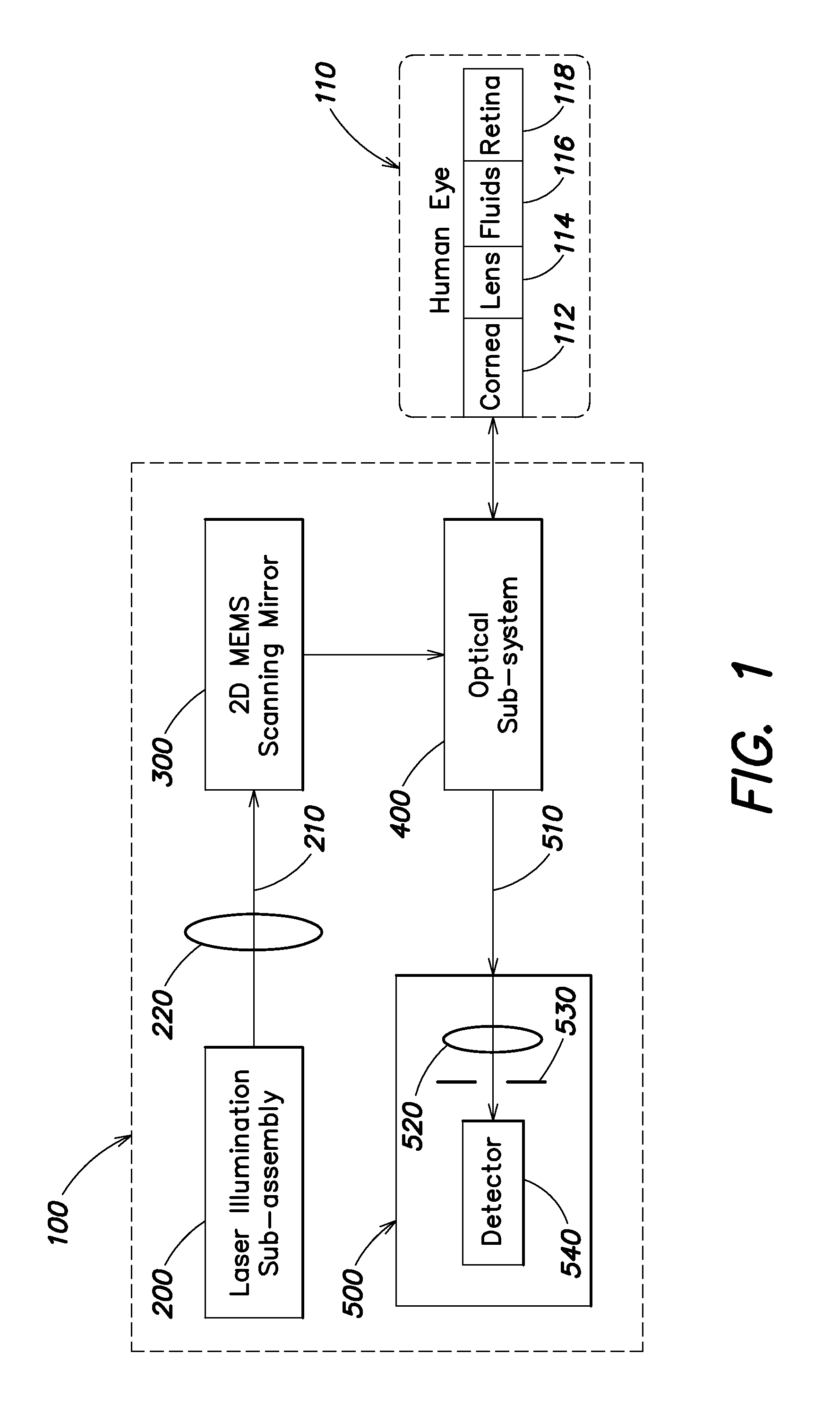
A portable MEMS-based scanning laser ophthalmoscope (MSLO). In one example the MSLO includes a laser illumination sub-assembly that generates a laser illumination beam, a two-dimensional MEMS scan mirror configured to receive and scan the laser illumination beam over at least a portion of the retina of an eye to be imaged, an optical system configured to direct the laser illumination beam from the scan mirror into the eye to illuminate the retina, and a detector sub-assembly configured to intercept optical radiation reflected from the eye to generate an image of the retina. The optical system includes a polarized beamsplitter positioned between the scan minor and the eye and configured to direct the laser illumination beam to into the eye and to direct the optical radiation reflected from the eye to the detector sub-assembly.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method of and system for producing digital images of objects with subtantially reduced speckle-noise patterns by illuminating said objects with spatially and/or temporally coherent-reduced planar laser illumination
InactiveUS6830189B2Semiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSystems designImage detection
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Variable output laser illuminator and targeting device
InactiveUS20020097587A1Increase currentAvoid misuseCosmonautic condition simulationsLaser using scattering effectsOptoelectronicsCurrent switch
A laser illuminator which produces a diffuse coherent output. The energy of the diffuse output may be controlled with a variable current switch and a pinpoint targeting laser may be added to provide illumination and targeting capabilities.
Owner:KRIETZMAN MARK HOWARD +1
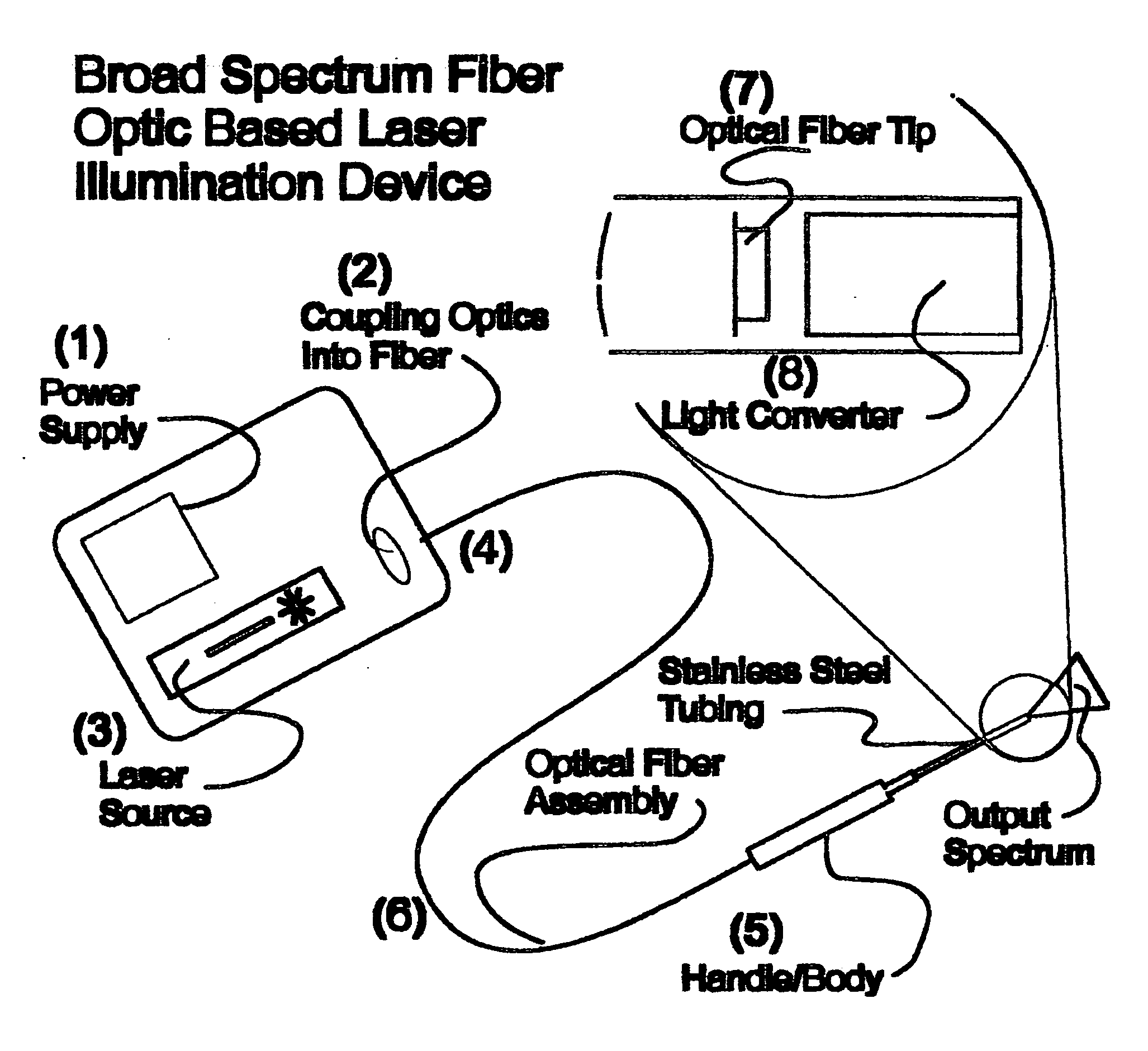
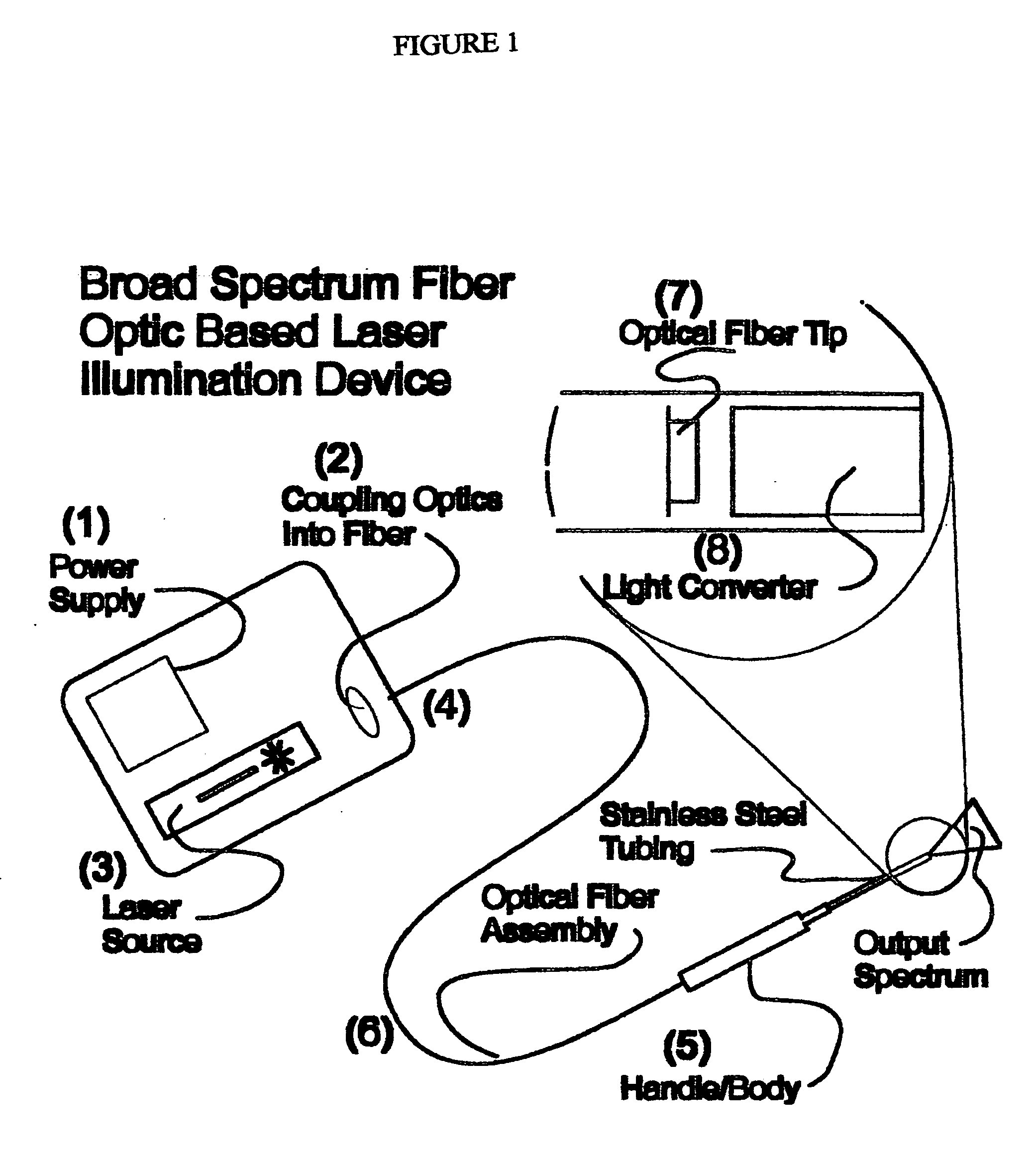
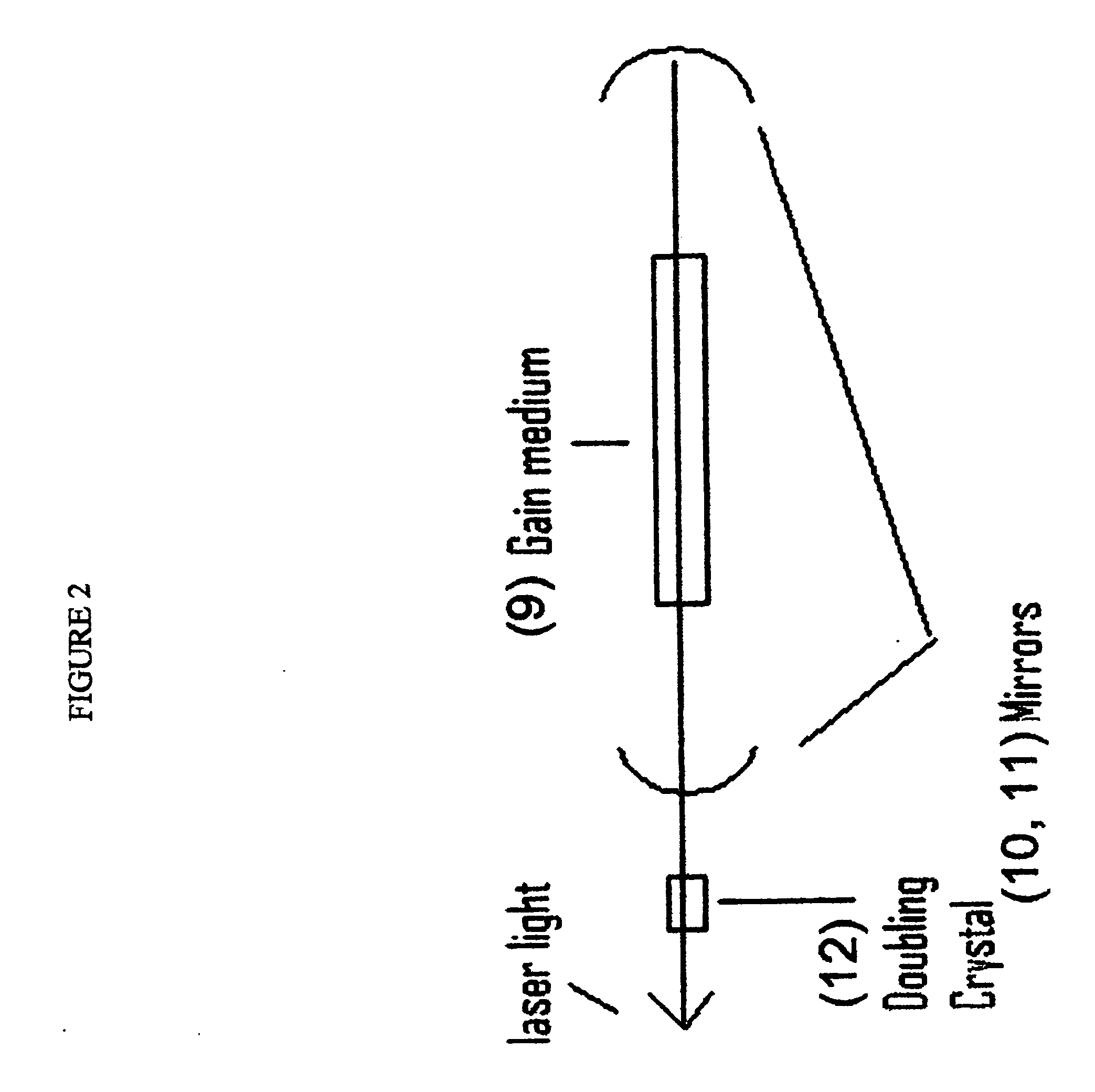
Broad spectrum fiber optic base laser illumination
InactiveUS20090054957A1Easy to useReduced conversion efficiencyCosmonautic condition simulationsOptical articlesFiberLaser light
The present invention is an illumination device designed to provide efficient illumination in confined spaces and methods of using such a device. The devices of the present invention comprise a laser light source of a specifically selected wavelength or wavelengths, optical fiber(s) and one or more light converters to convert the input laser light to broad spectrum white light or a specific desired wavelength. The light converter may be integral / modular with the fiber optic assembly. The light converter may be constructed of phosphors, nanocrystals or other energy converters which are embedded within a transport material such as polymer or glass.
Owner:IRIS
LED device packaging method and LED device
InactiveCN106848043ASimple production processLow costSemiconductor devicesHigh energySemiconductor package
The invention belongs to the field of semiconductor packaging, and is especially suitable for the packaging of light source devices with high luminous flux density, short wavelength and high energy output, such as semiconductor light emitting devices (LEDs) and laser lighting packaging devices. It relates to a packaging method for an LED device. The LED device is composed of a transparent inorganic sealing cover plate, a metal sealing ring, a ceramic substrate, an LED chip, and LED welding wires. Through the transparent inorganic sealing cover plate, the metal sealing ring and the The ceramic substrate is eutectically welded for packaging to form a hermetic LED device.
Owner:光创空间(深圳)技术有限公司
Method and apparatus for inspecting a pattern formed on a substrate
InactiveUS6900888B2Reduce creationIncrease contrastInvestigating moving sheetsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationImage resolutionPupil
The inventive method and apparatus for detecting defects of a microscopic circuit pattern by imaging the pattern at high resolution comprises an objective lens for imaging the subject pattern, a laser illumination means for illuminating the pupil of the objective lens, means of diminishing the coherency of the laser illumination, an accumulative detector, and means of processing the signal detected by the detector. The method and apparatus are capable of imaging the subject pattern at high sensitivity and high speed based on the illumination by a short wavelength, which is indispensable for the enhancement of resolution, particularly based on a laser light source which is advantageous for practicing, with a resulting image being the same or better in quality as compared with an image resulting from the ordinary discharge tube illumination, whereby it is possible to detect microscopic defects at high sensitivity.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Portable self-retinal imaging device
InactiveUS20120257166A1Robust scanningSmall sizeMicroscopesOthalmoscopesCamera lensScanning laser ophthalmoscope
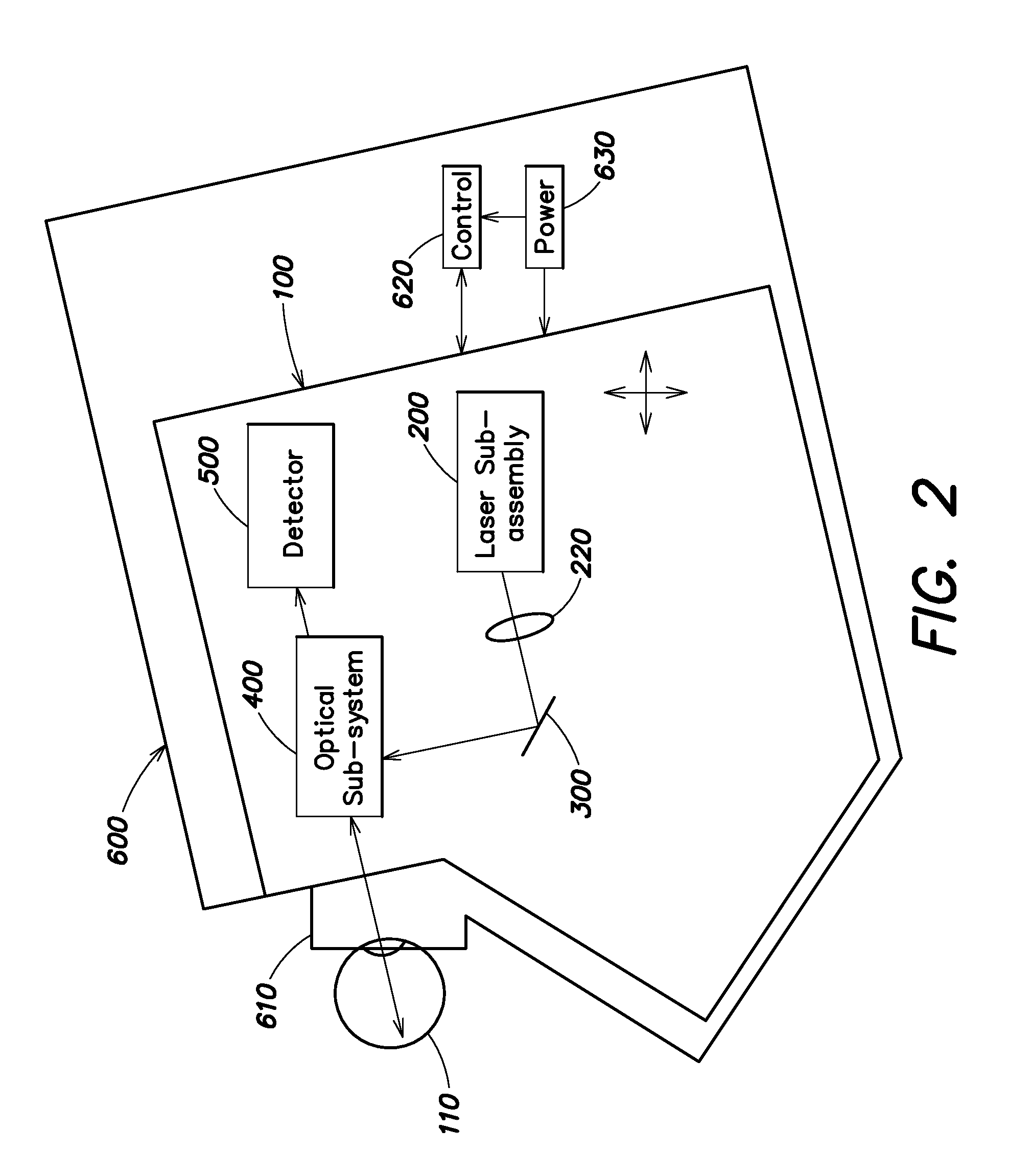
A portable MEMS-based scanning laser ophthalmoscope (MSLO). In one example, the MSLO includes a laser illumination sub-assembly, a two-dimensional MEMS scanning mirror, a conic front objective, and a detector sub-assembly all disposed within a portable housing. A battery configured to provide power to components of the MSLO may also be included within the housing. In one example, the laser illumination sub-assembly includes at least one laser configured to generate in each of two orthogonal dimensions one or more illumination beams separated from one another by a predetermined angle of separation. The MEMS scanning minor and conic front objective are configured to produce a two-dimensional area of illumination from the illumination beam(s) in each dimension and to direct the illumination from the scanning minor to the eye to illuminate the retina.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
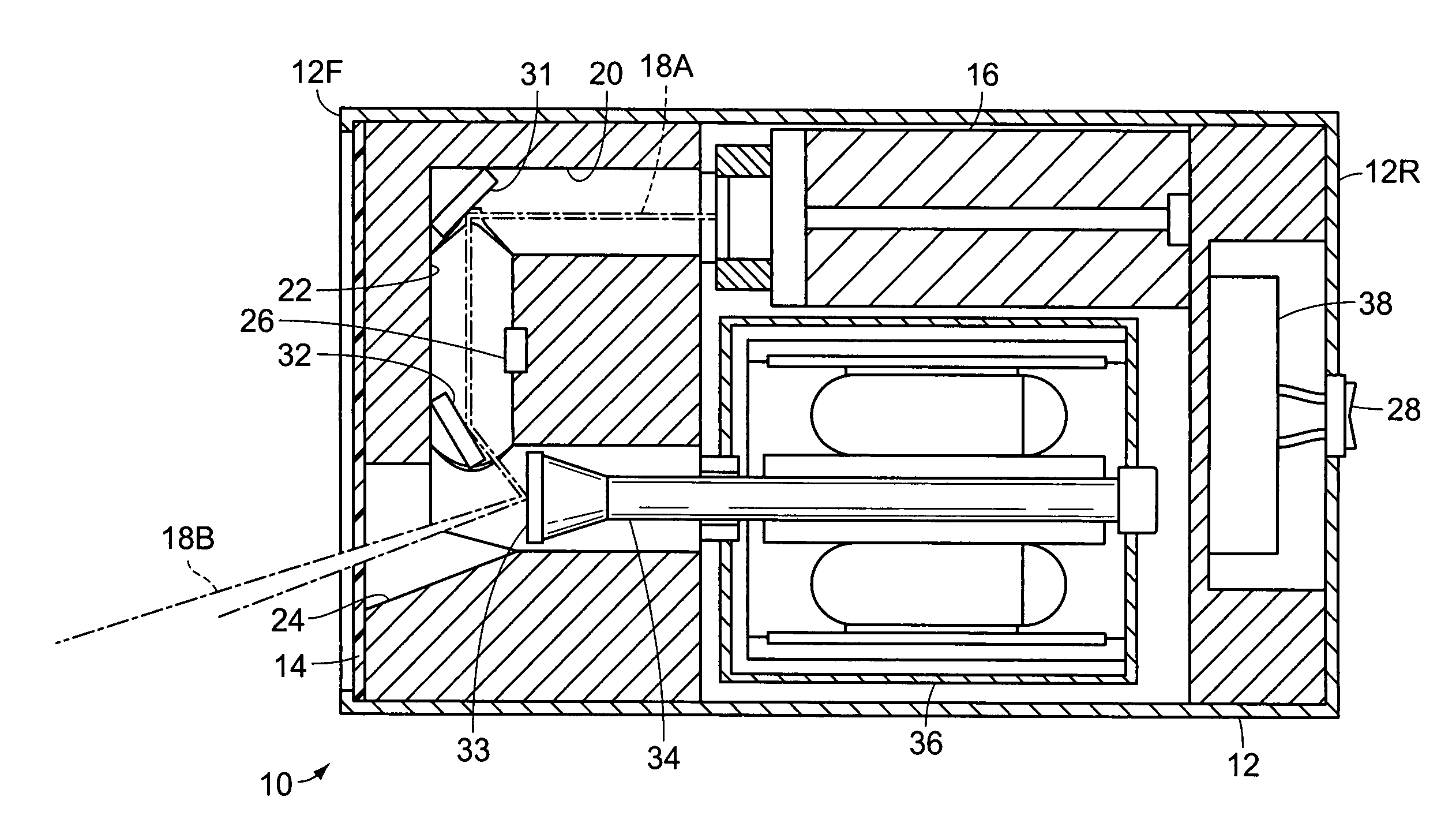
Automotive laser illumination module and system
InactiveUS6883947B1Easy to seeIncrease awarenessPoint-like light sourceOptical signallingLight beamComputer module
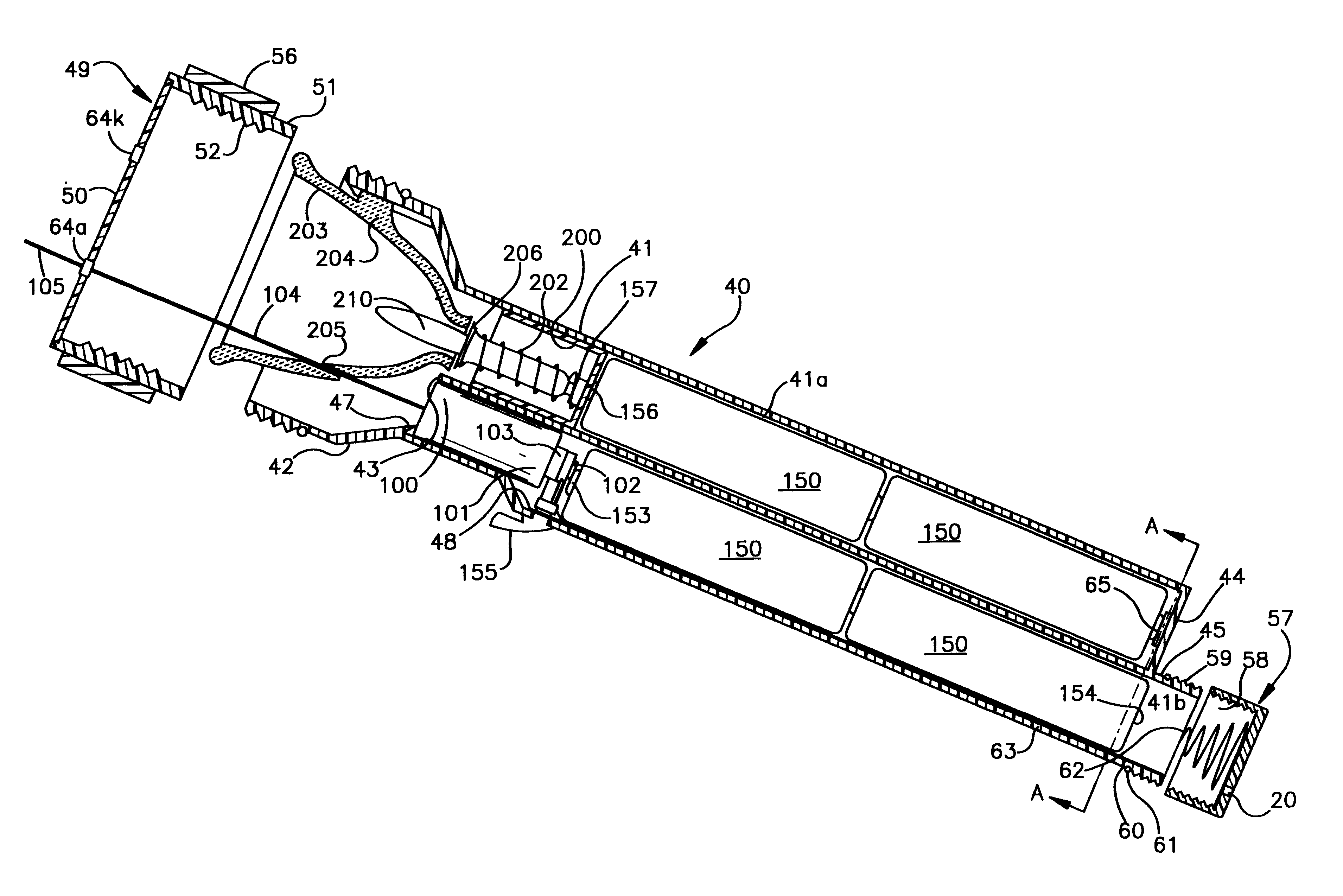
A laser illumination system, for use with an automobile, comprising a plurality of modules. Each module has a housing having a lens, and a mode selection switch for choosing between headlight and taillight modes. Preferably, two modules are mounted at the front of the automobile to function as headlights, and two of the modules are mounted at the rear of the automobile to function as taillights. Each module has a beam emitter which produces an initial beam of laser light and an output mirror which directs an exit beam through the lens, outwardly of the automobile, and ultimately creates a cone of light at the ground surface forwardly or rearwardly of the automobile. When used as a headlight and the mode selection switch is appropriately set, an output mirror rotation motor spreads the output beam so that it creates a larger cone on the ground surface.
Owner:SARABIA MARIBEL
Fluorescent wheel and two-color laser source
ActiveCN106597785AImprove light processing efficiencyPlay a role in dissipating spotsProjectorsFluorescenceOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a fluorescent wheel. A transmission area adopts a diffusion plate, so that while realizing laser transmission, diffusion can also be realized, thereby achieving a speckle removing effect, saving an extra speckle removing component and improving light processing efficiency of the fluorescent wheel. The invention also discloses a two-color laser source using the fluorescent wheel above. Output of three-primary-color light can be realized through the fluorescent wheel part, and transmitting two-color laser can be subjected to speckle removing. The fluorescent wheel and the two-color laser source are applied to the laser illumination and display field.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE LASER DISPLAY CO LTD
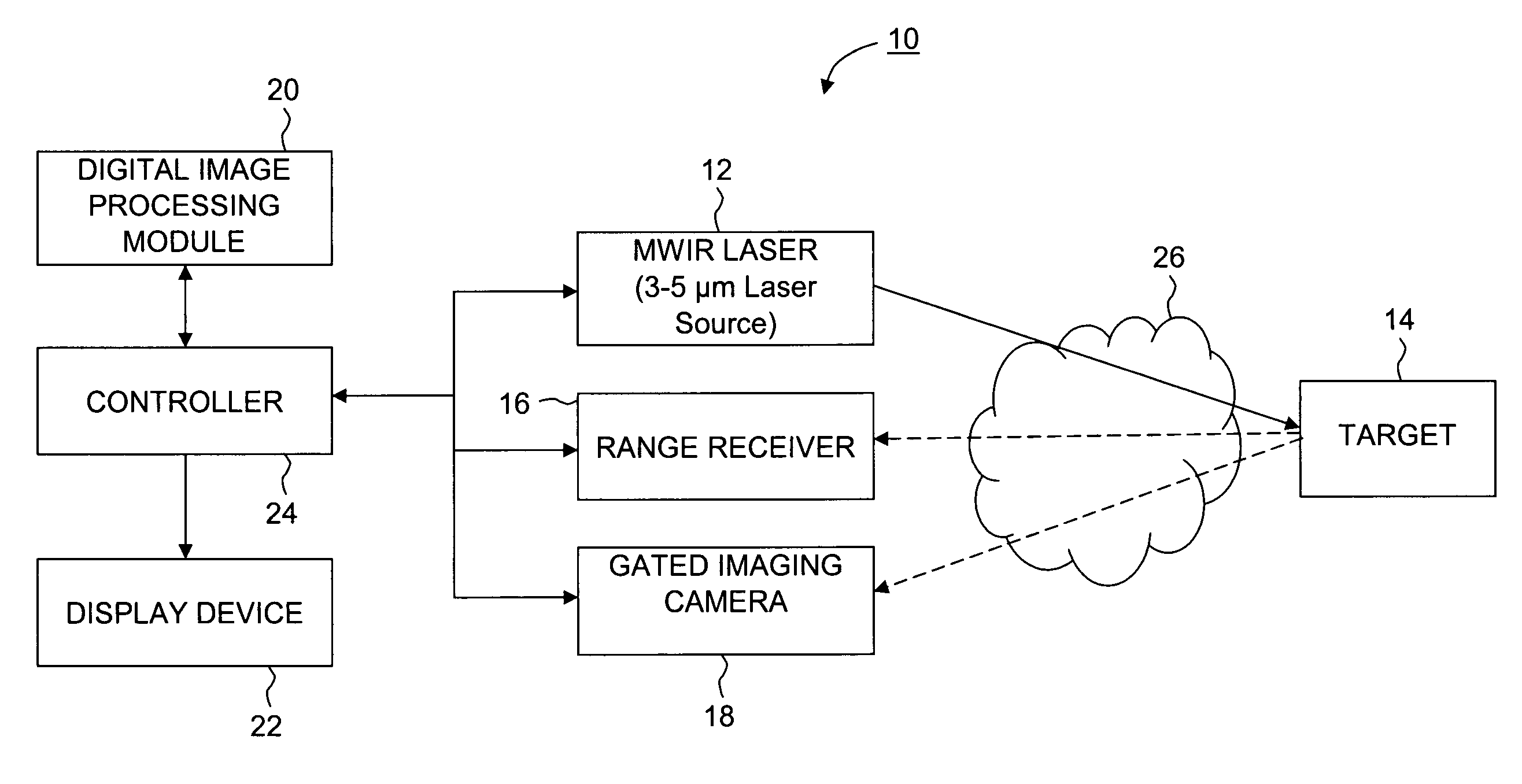
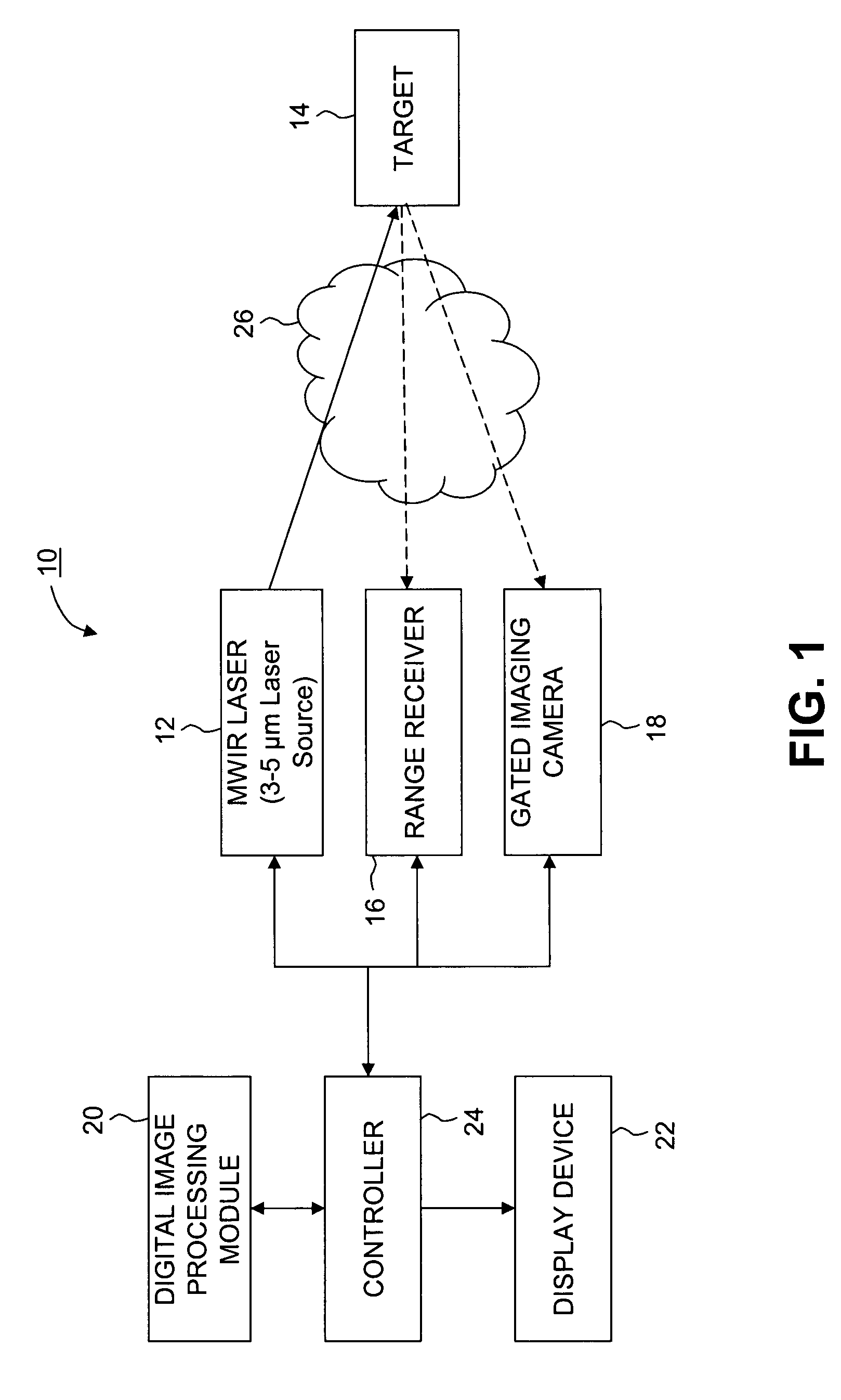
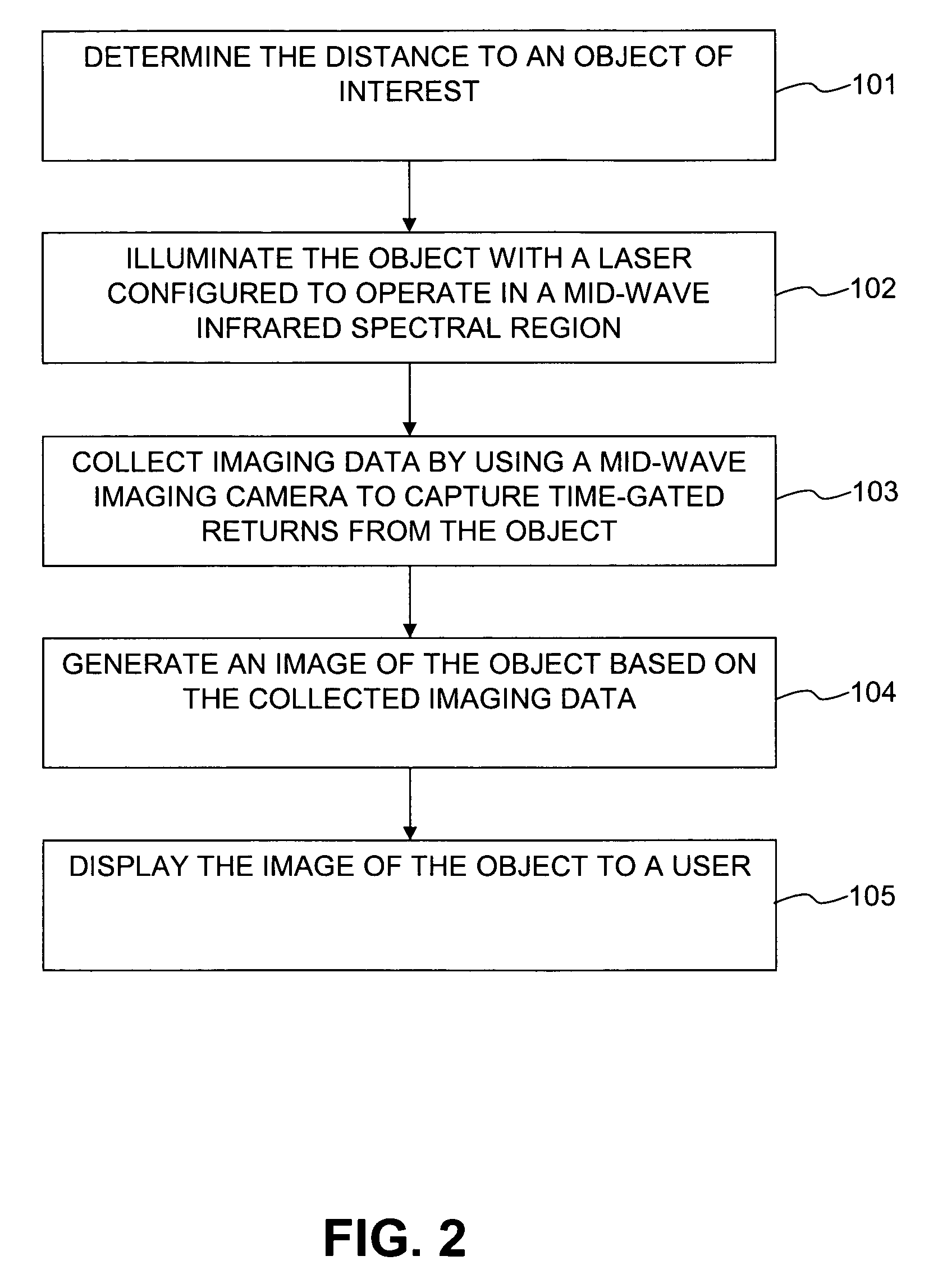
Infrared laser illuminated imaging systems and methods
ActiveUS7541588B2Robust information relatingRadiation pyrometryOptical rangefindersLaser illuminationActive illumination
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
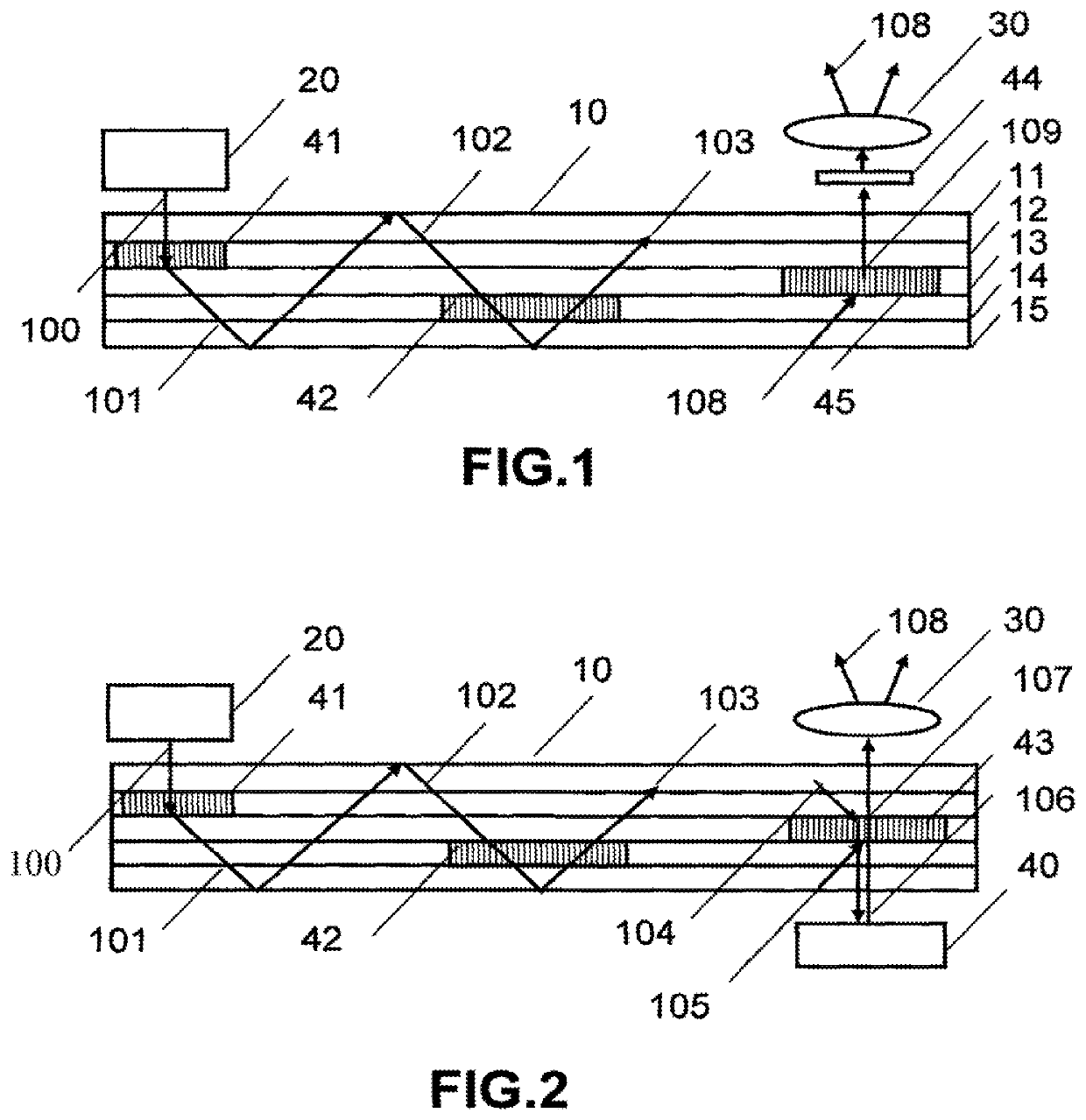
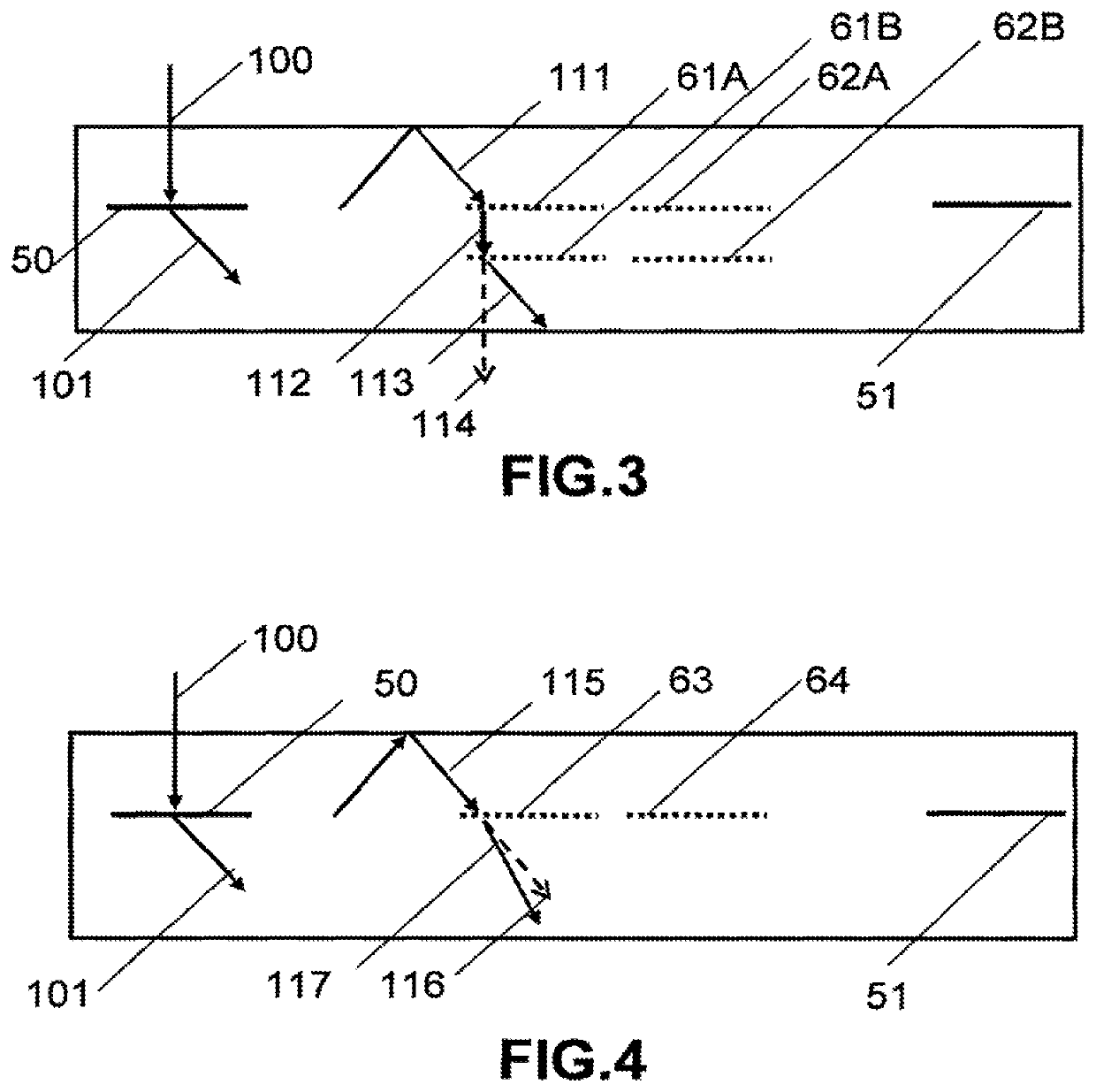
Waveguide laser illuminator incorporating a despeckler
There is provided an illumination device having: a laser; a waveguide including at least first and second transparent lamina; a first grating device for coupling light from the laser into a TIR path in the waveguide; a second grating device for coupling light from the TIR path out of the waveguide; and a third grating device for applying a variation of at least one of beam deflection, phase retardation or polarization rotation across the wavefronts of the TIR light. The first second and third grating devices are each sandwiched by transparent lamina.
Owner:DIGILENS
Method of and system for producing images of objects using planar laser illumination beams and image detection arrays
InactiveUS20020117545A1Avoiding shortcomingSimple methodSemiconductor laser arrangementsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage detectionHand held
Methods of and systems for illuminating objects using planar laser illumination beams having substantially-planar spatial distribution characteristics that extend through the field of view (FOV) of image formation and detection modules employed in such systems. Each planar laser illumination beam is produced from a planar laser illumination beam array (PLIA) comprising an plurality of planar laser illumination modules (PLIMs). Each PLIM comprises a visible laser diode (VLD, a focusing lens, and a cylindrical optical element arranged therewith. The individual planar laser illumination beam components produced from each PLIM are optically combined to produce a composite substantially planar laser illumination beam having substantially uniform power density characteristics over the entire spatial extend thereof and thus the working range of the system. Preferably, each planar laser illumination beam component is focused so that the minimum beam width thereof occurs at a point or plane which is the farthest or maximum object distance at which the system is designed to acquire images, thereby compensating for decreases in the power density of the incident planar laser illumination beam due to the fact that the width of the planar laser illumination beam increases in length for increasing object distances away from the imaging optics. By virtue of the present invention, it is now possible to use both VLDs and high-speed CCD-type image detectors in conveyor, hand-held and hold-under type scanning applications alike, enjoying the advantages and benefits that each such technology has to offer, while avoiding the shortcomings and drawbacks hitherto associated therewith.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com