Patents
Literature
671 results about "Phase retardation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
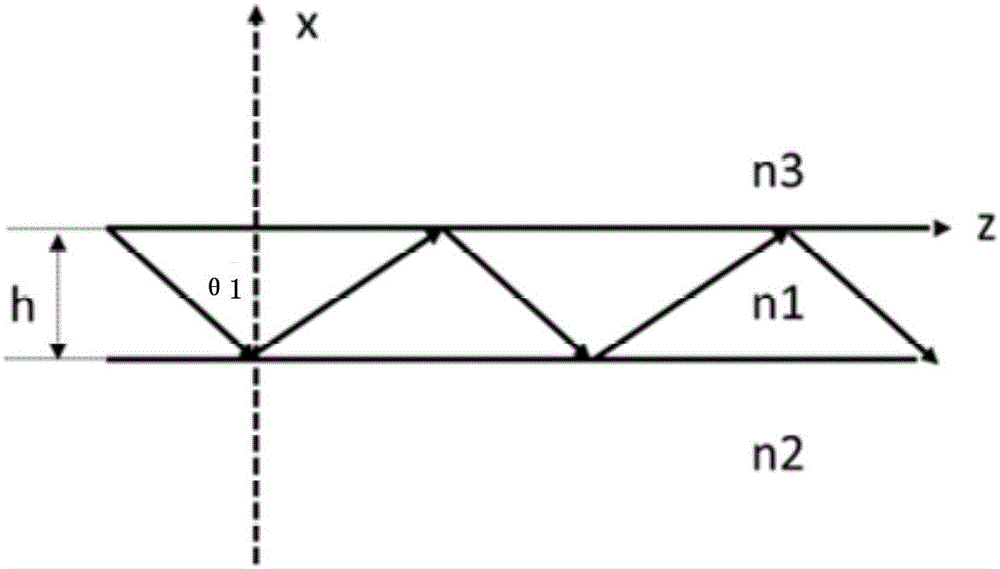
Retardation of Phase. The fractional lagging behind of waves or alternating currents; by lagging behind a portion of a wave length the corresponding phases, as of full amplitude, are kept back or retarded.
Microwave antenna and outer cover thereof
ActiveCN101958461AImproved radiation F/B performanceHigh gainRadiating element housingsPhase retardationMicrowave
The invention discloses a microwave antenna and an outer cover thereof. The outer cover is a rotational symmetric element which comprises a plurality of homocentrically arranged parts as below: a compensation part arranged at the middle of the outer cover and used for compensating the phase delay of the electric field distribution at the middle of an antenna aperture surface caused by the shielding of a feed source, a main reflection part arranged at the periphery of the compensation part and used for reflecting the electromagnetic wave emitted from the microwave antenna feed source to a specific direction deviating from the feed source, and an assistant reflection part arranged at the periphery of the main reflection part and used for carrying out reflex bunching on the edge diffraction electromagnetic wave of the microwave antenna. All the parts of the outer cover are especially designed and shaped, therefore the microwave antenna has the characteristics of excellent electrical properties, stable structure, low cost and the like.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST (GUANGZHOU) LTD
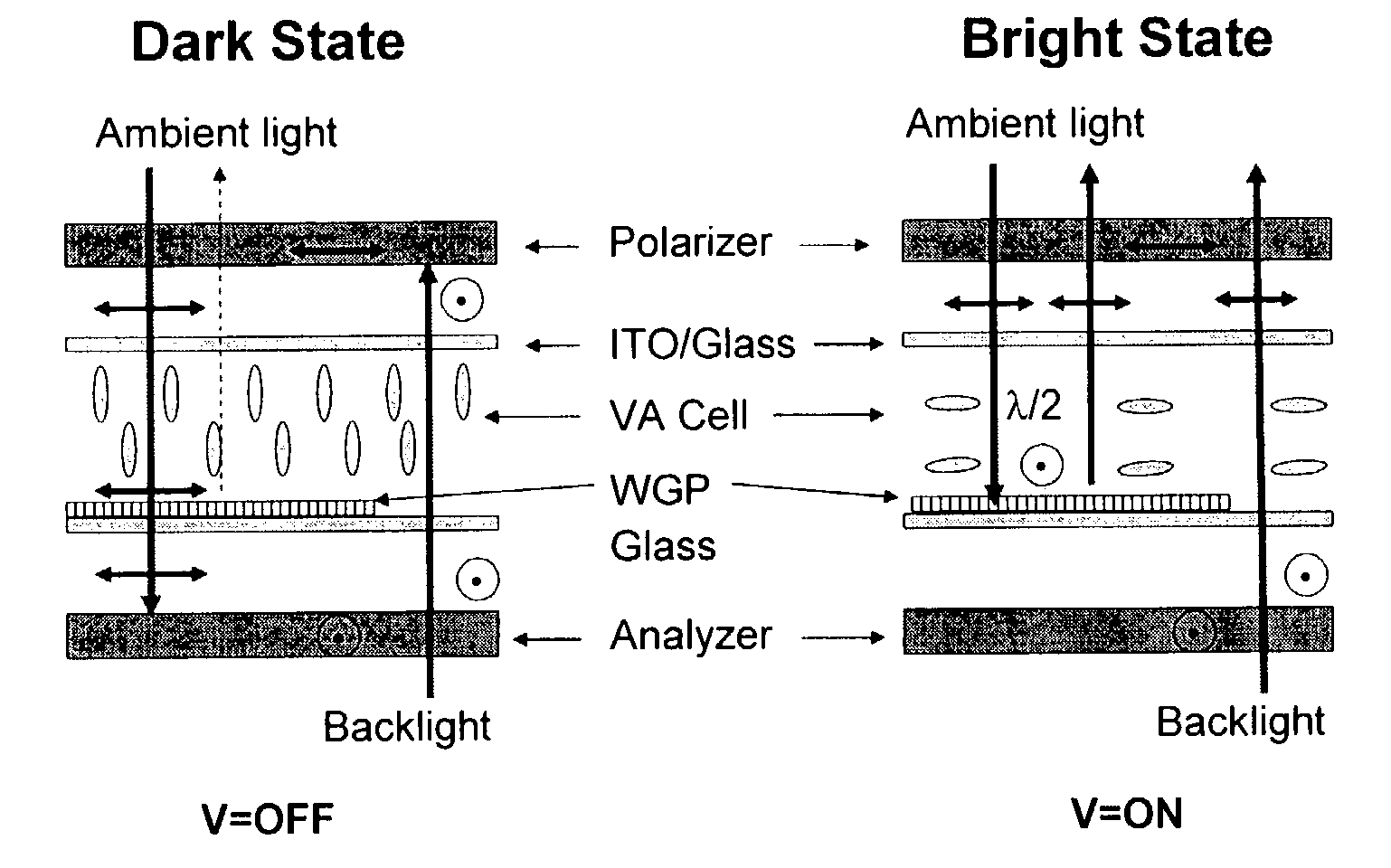
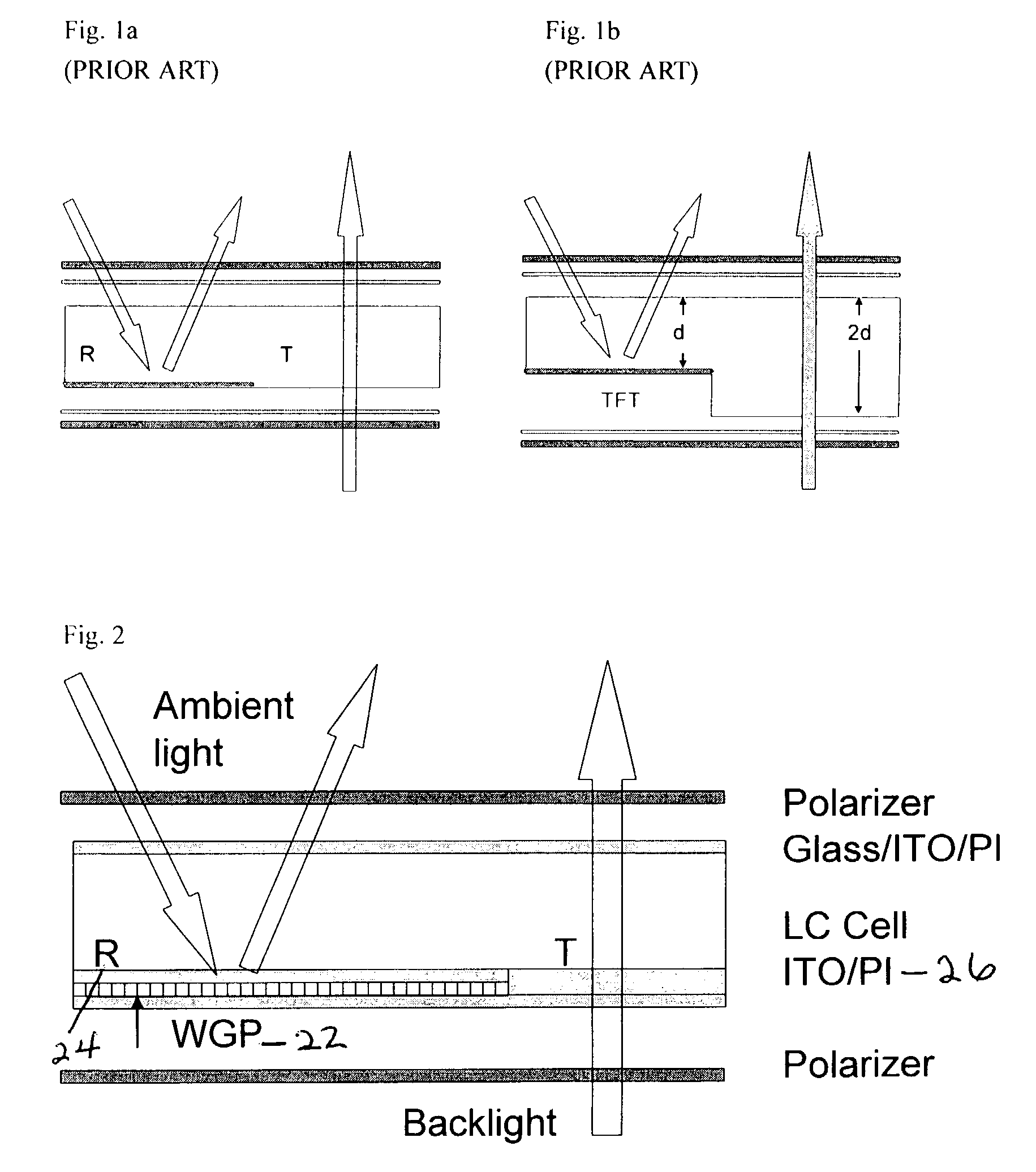
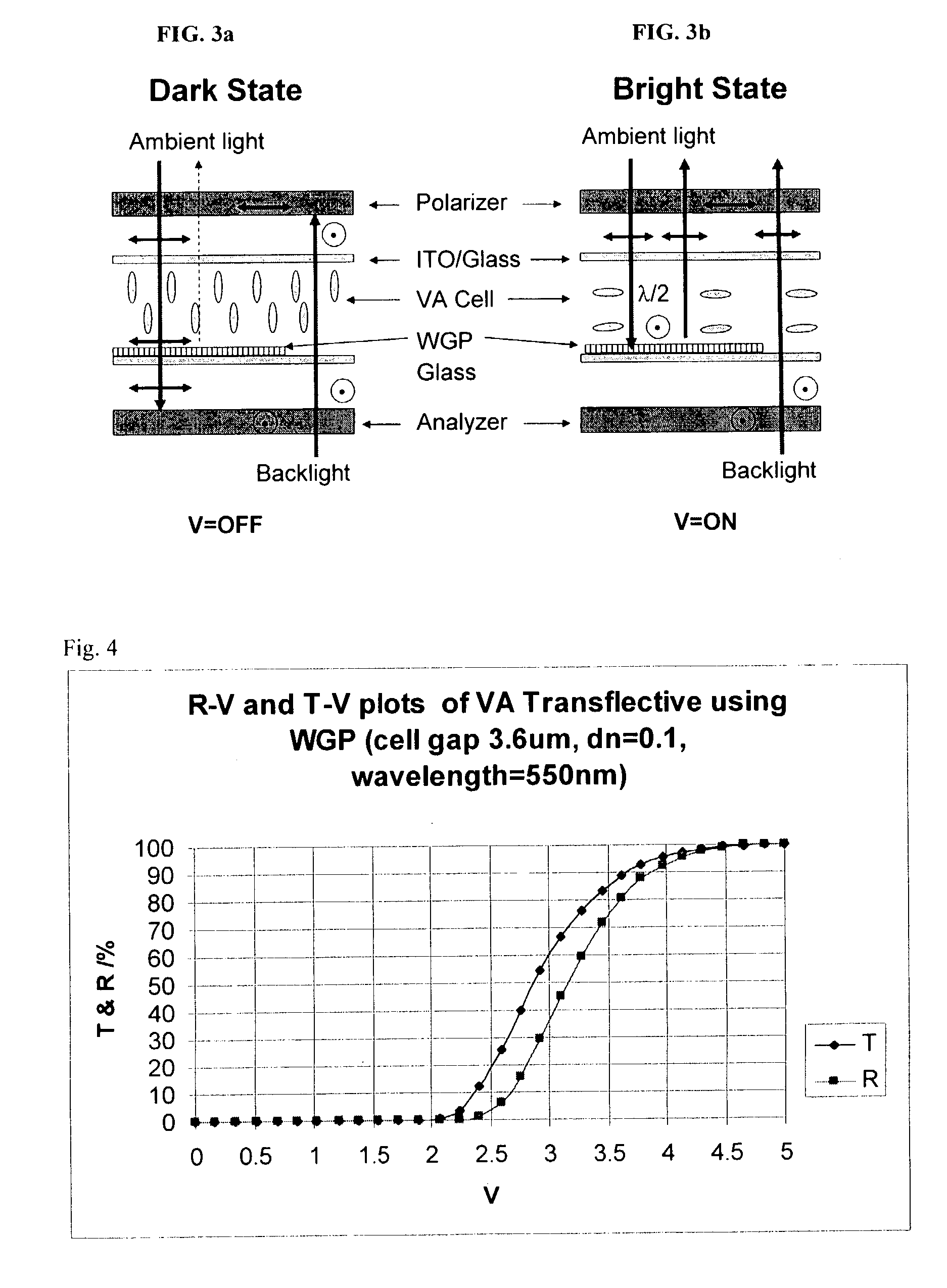
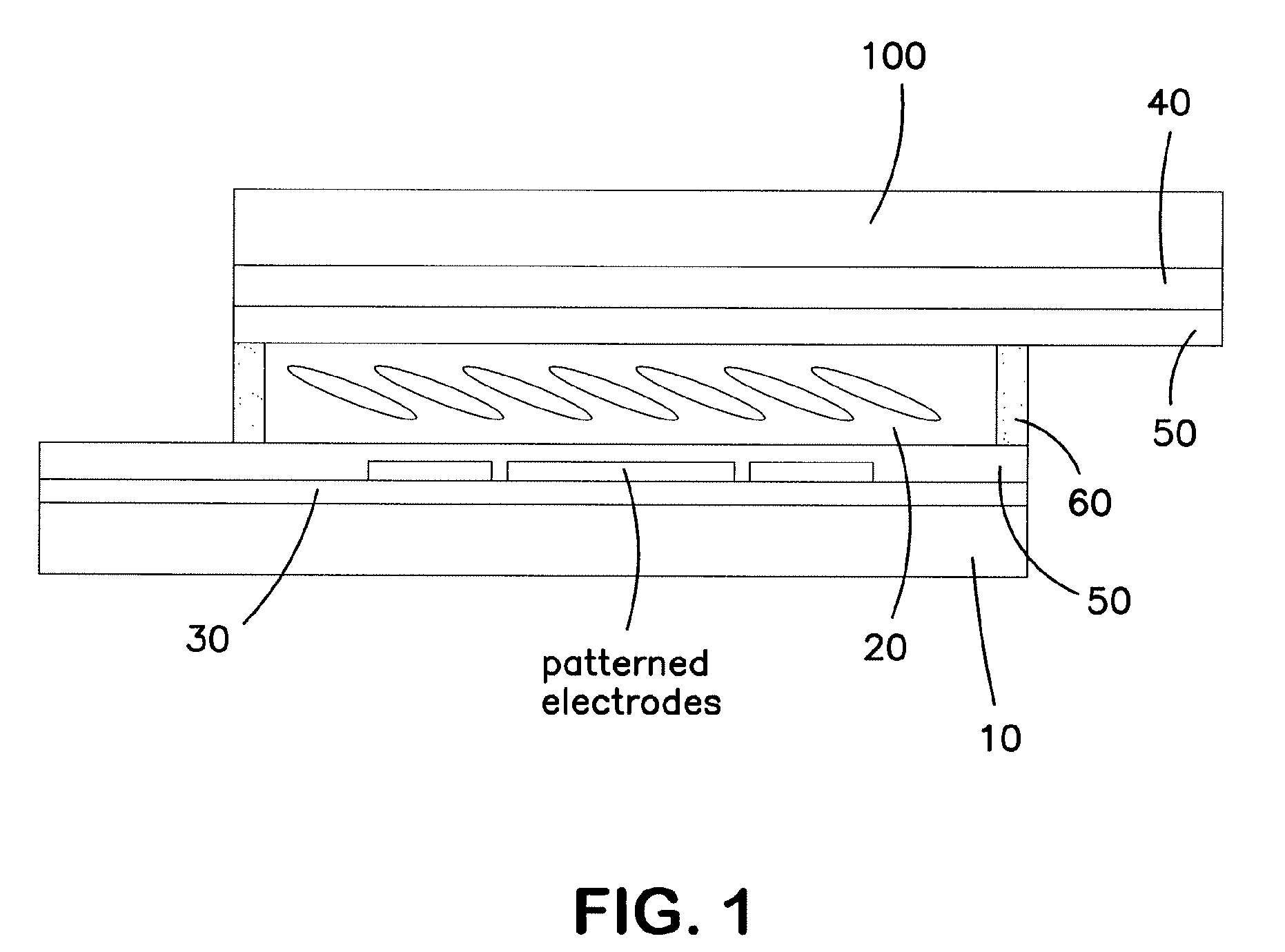
Reflective and transflective liquid crystal display using a wire grid polarizer
A device structure for single cell gap reflective and transflective liquid crystal displays (TF-LCDs). For an entirely reflective LCD, the imbedded wire-grid polarizer (WGP) serves as a polarization-dependent for the ambient light. For a transflective TF-LCD, the WGP only covers the reflective pixels. The disclosure also includes a method of using single cell gap liquid crystal displays (LCDs) without phase retardation films by providing a single cell gap LCD having reflective pixels and transmissive pixels, covering solely the reflective pixels, with at least one of: a wire grid polarizer and a broadband cholesteric reflector (BCR), reflecting ambient light off the reflective pixels; and passing back light through the transmissive pixels whereby the cell gap LCD obtains high contrast ratios without using phase retardation films.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Microwave antenna and outer cover thereof
ActiveCN101958461BImproved radiation F/B performanceHigh gainRadiating element housingsMicrowavePhase retardation
A microwave antenna radome used for covering a microwave antenna and of rotatablely symmetrical includes the following components all of which are arranged concentrically; a compensation portion located at a central portion of the radome and used for compensating phase delay of electrical field at the central portion of an antenna aperture plane caused by blocking of a feed; a main reflective portion located on a periphery of the compensation portion and used for reflecting electromagnetic wave originating from the feed of the microwave antenna at a specific direction biased from the feed; and an auxiliary reflective portion located on a periphery of the main reflective portion and used for bunching and reflecting diffraction electromagnetic wave at edge of the microwave antenna. All components of the radome are specifically shaped. The microwave antenna thus formed has good electrical performance, stable structure and low cost.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST (GUANGZHOU) LTD
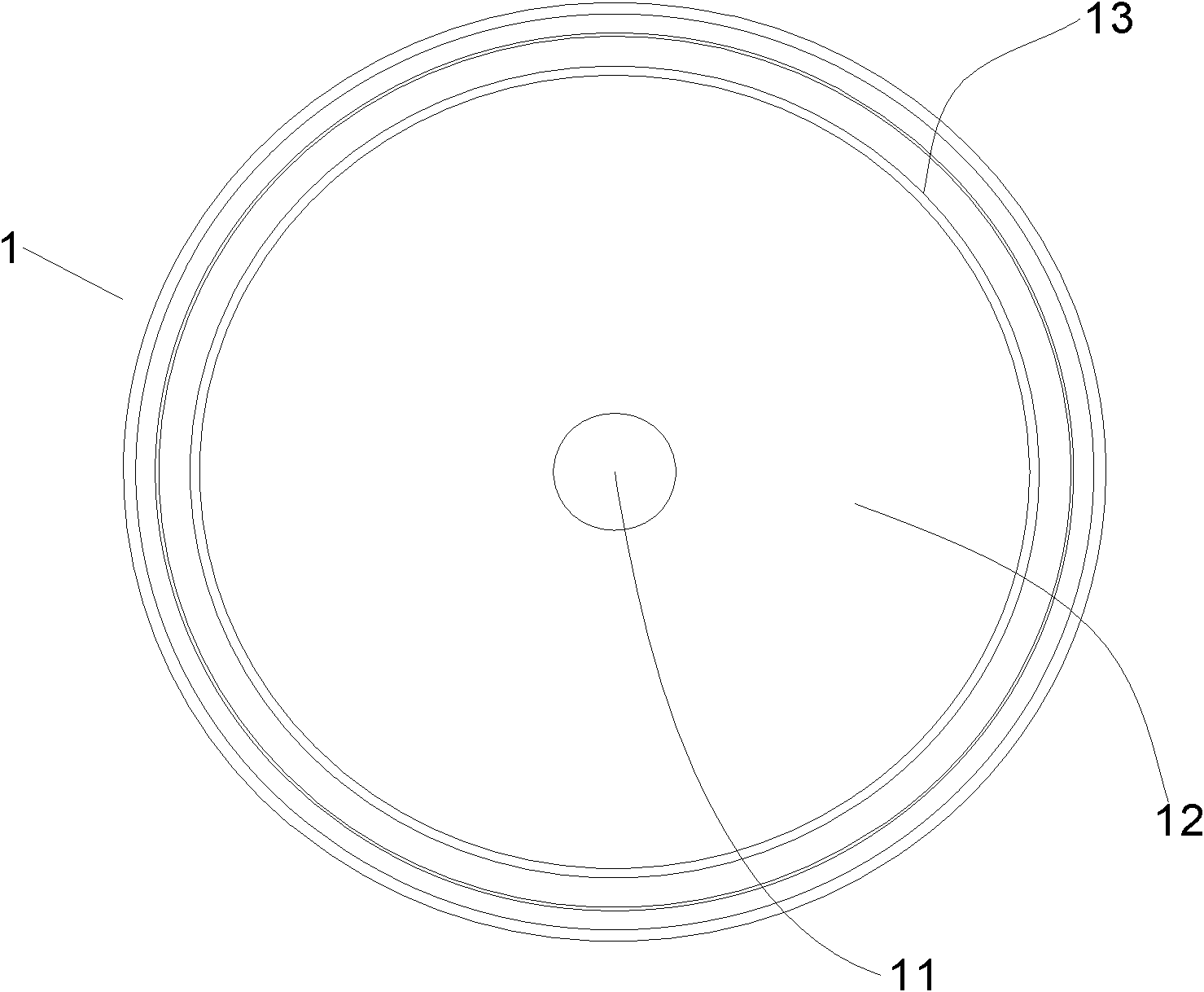
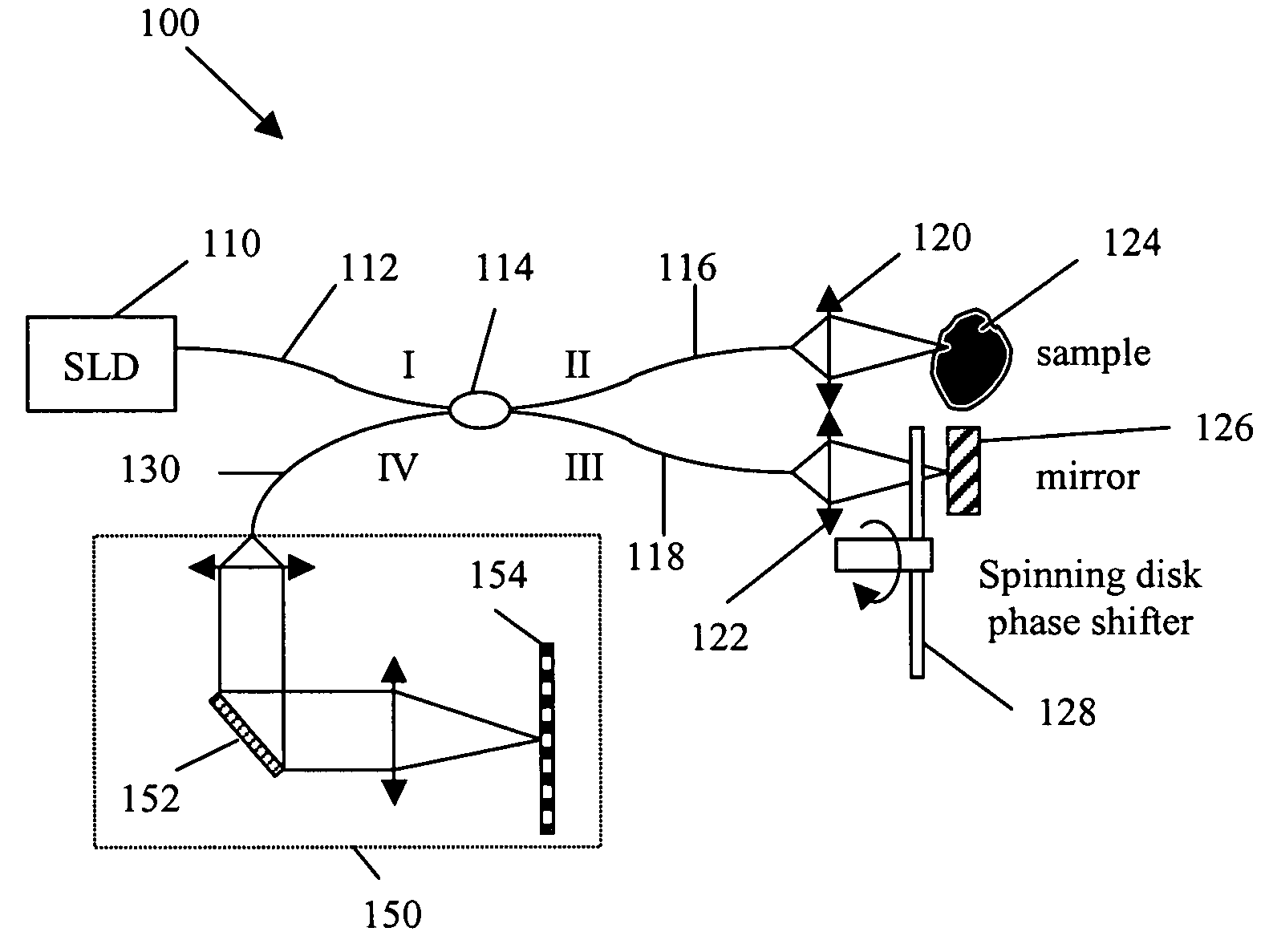
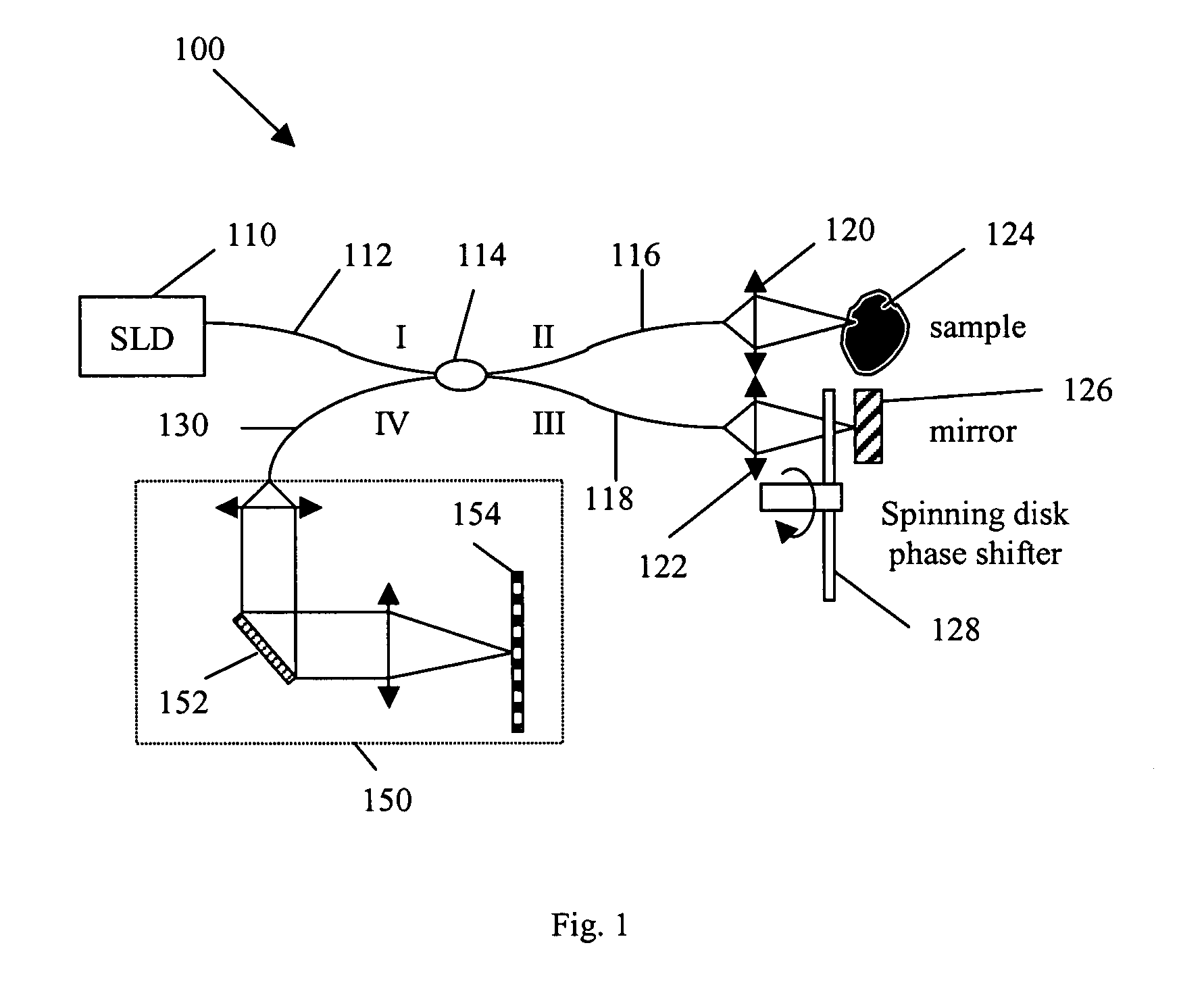
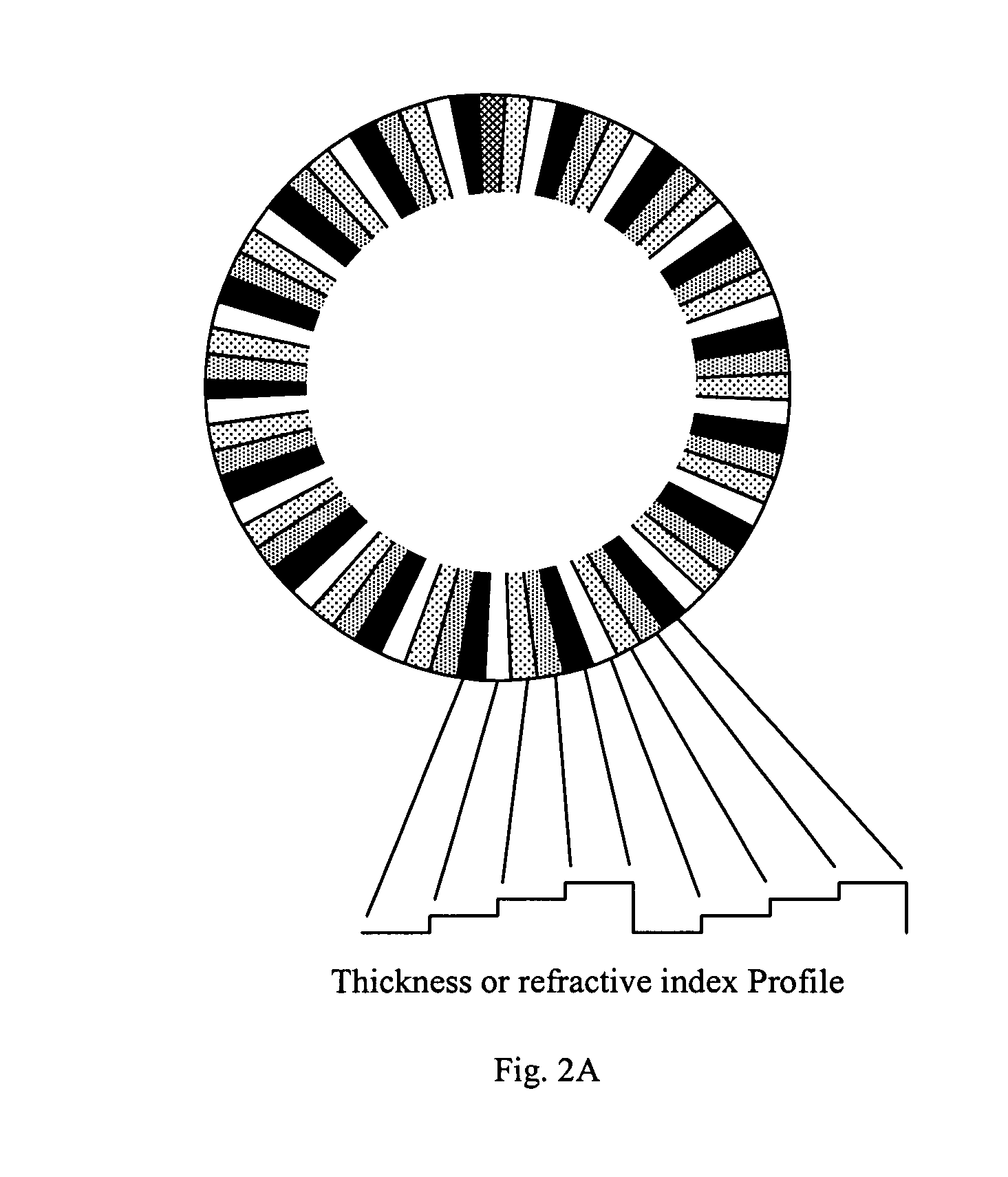
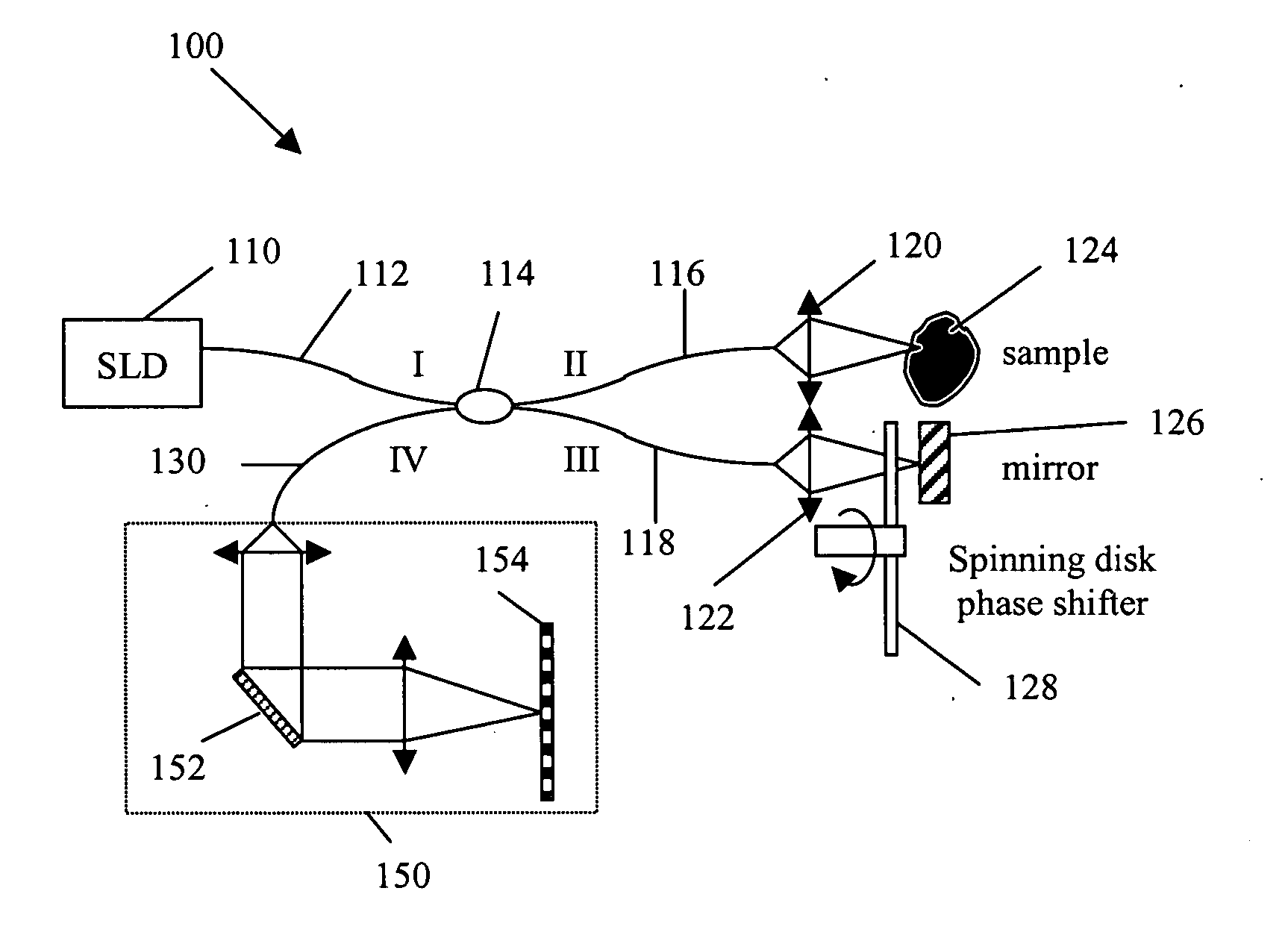
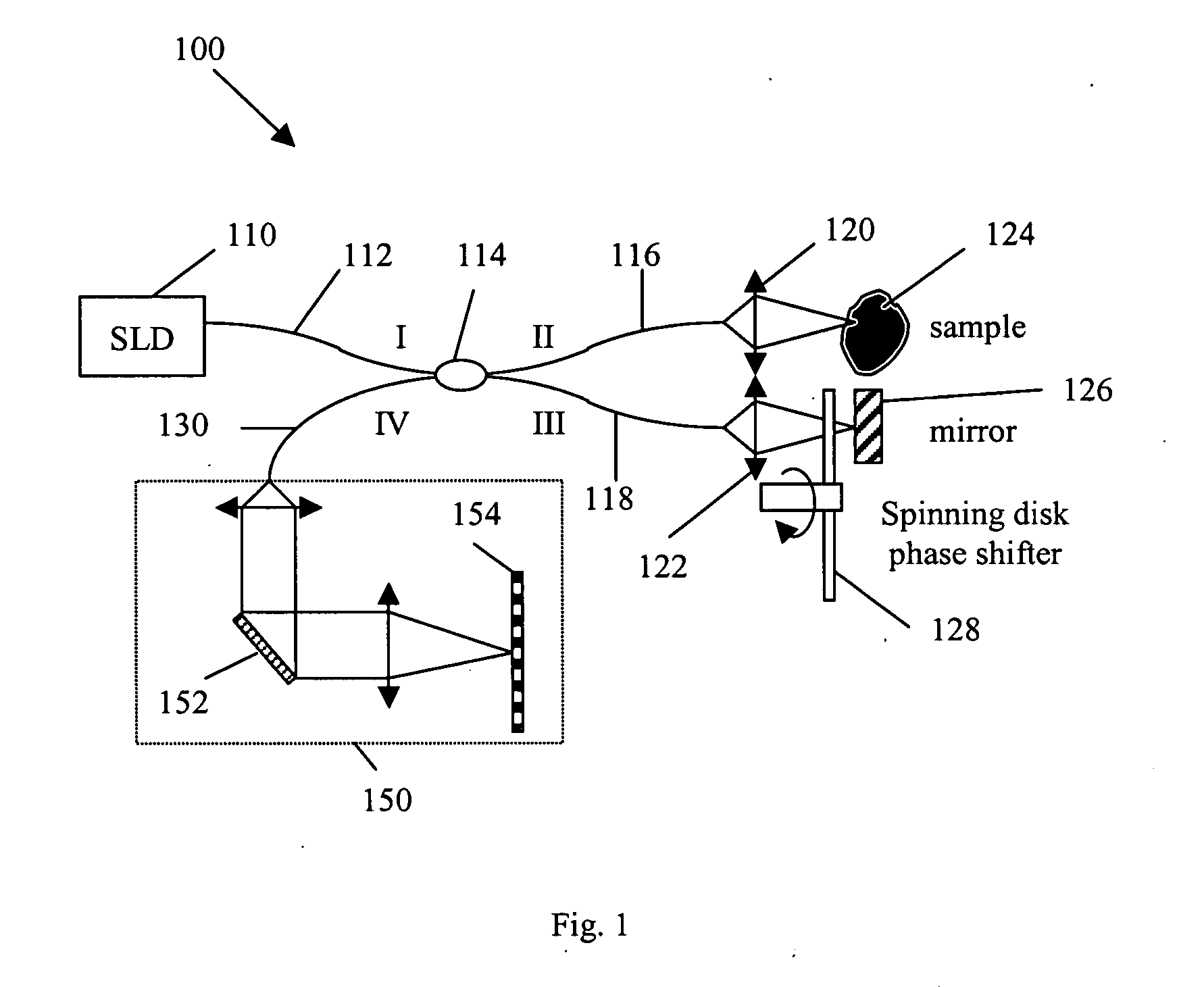
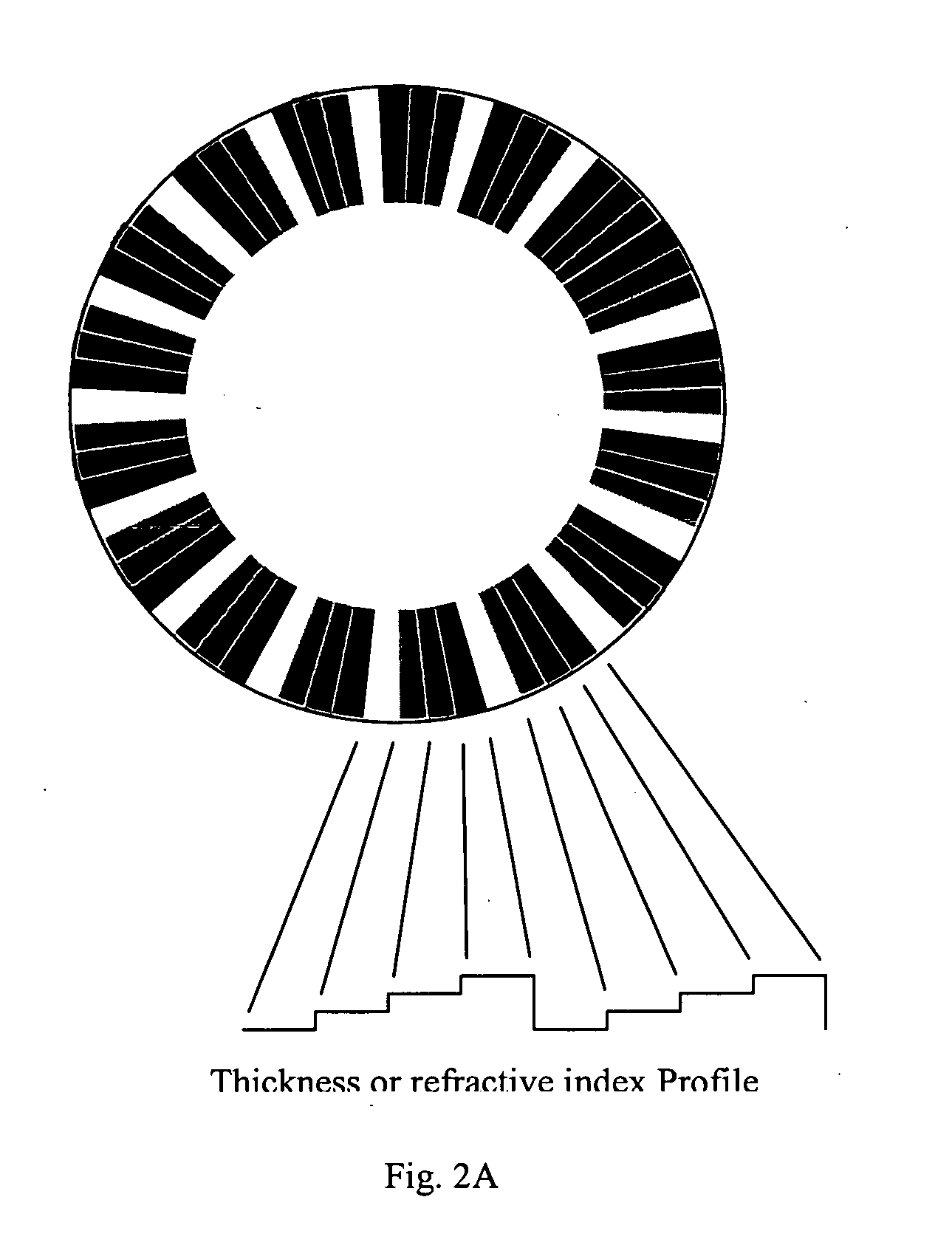
Patterned spinning disk based optical phase shifter for spectral domain optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS7433046B2Low costSolve the slow scanning speedInterferometersEye diagnosticsPhase shiftedPhase retardation
A low cost patterned spinning disk is disclosed for achieving relatively rapid discrete optical phase shifts for an optical beam. The invention is particularly useful in a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system. The disk contains stepped patterns of different heights and / or refractive index distribution such that as it spins, an optical beam passing through or being reflected by the disk will experience different discrete optical phase delays. The disk can be operated as a phase shifter or it can be operated in synchronization with an intensity modulating chopper disk or a direct intensity modulation of the light source. The disk can also contain intensity modulating patterns such that both phase shifting and intensity modulation can be achieved at the same time. Various possible methods are also disclosed for the fabrication of the disk.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Liquid crystal display having a narrow viewing mode
InactiveUS20150346532A1High light transmittanceReduce thicknessNon-linear opticsPhase retardationLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display includes a liquid crystal display panel having a first substrate and a second substrate. An upper polarizer is disposed on an outer surface of the first substrate. A viewing angle control film is disposed on the upper polarizer. The viewing angle control film includes a polarizing layer having a transmission axis substantially parallel to a transmission axis of the upper polarizer and a phase retardation layer including a birefringence material having an optical axis with a poloidal angle of about 40 degrees to about 75 degrees.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
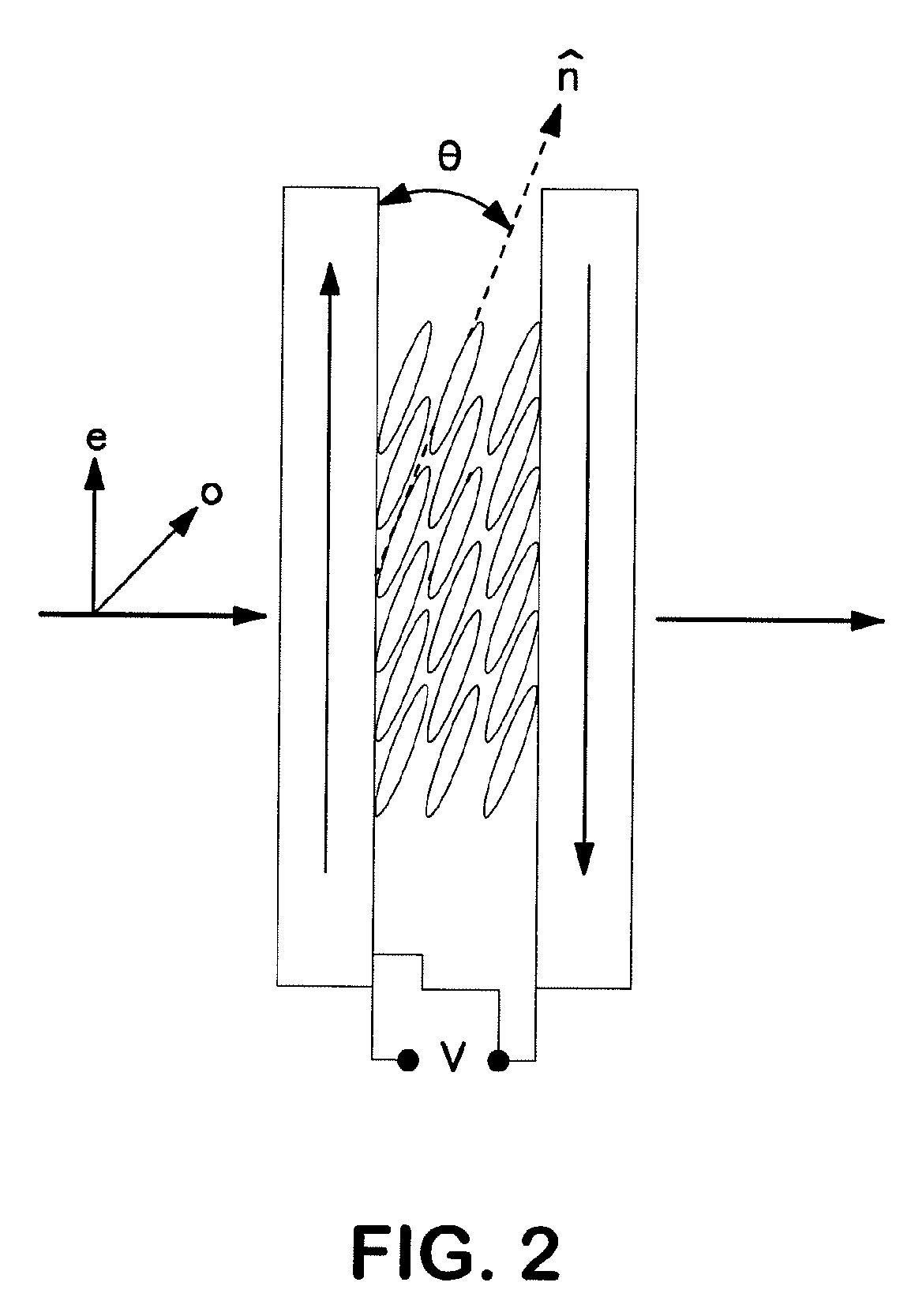
Electro-Optic Lenses Employing Resistive Electrodes
InactiveUS20080212007A1Easy to adaptSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsElectricityPhase retardation
Provided is an electro-optic device comprising: a liquid crystal layer between a pair of opposing transparent substrates; a resistive patterned electrode set positioned between the liquid crystal layer and the inward-facing surface of the first transparent substrate; and a conductive layer between the liquid crystal layer and the inward-facing surface of the second transparent substrate, wherein the conductive layer and resistive patterned electrode set are electrically connected, and wherein said resistive patterned electrode set comprises one or more electrically-separated electrodes, wherein the desired voltage drop is applied across each electrode to provide the desired phase retardation profile.
Owner:MEREDITH GERALD
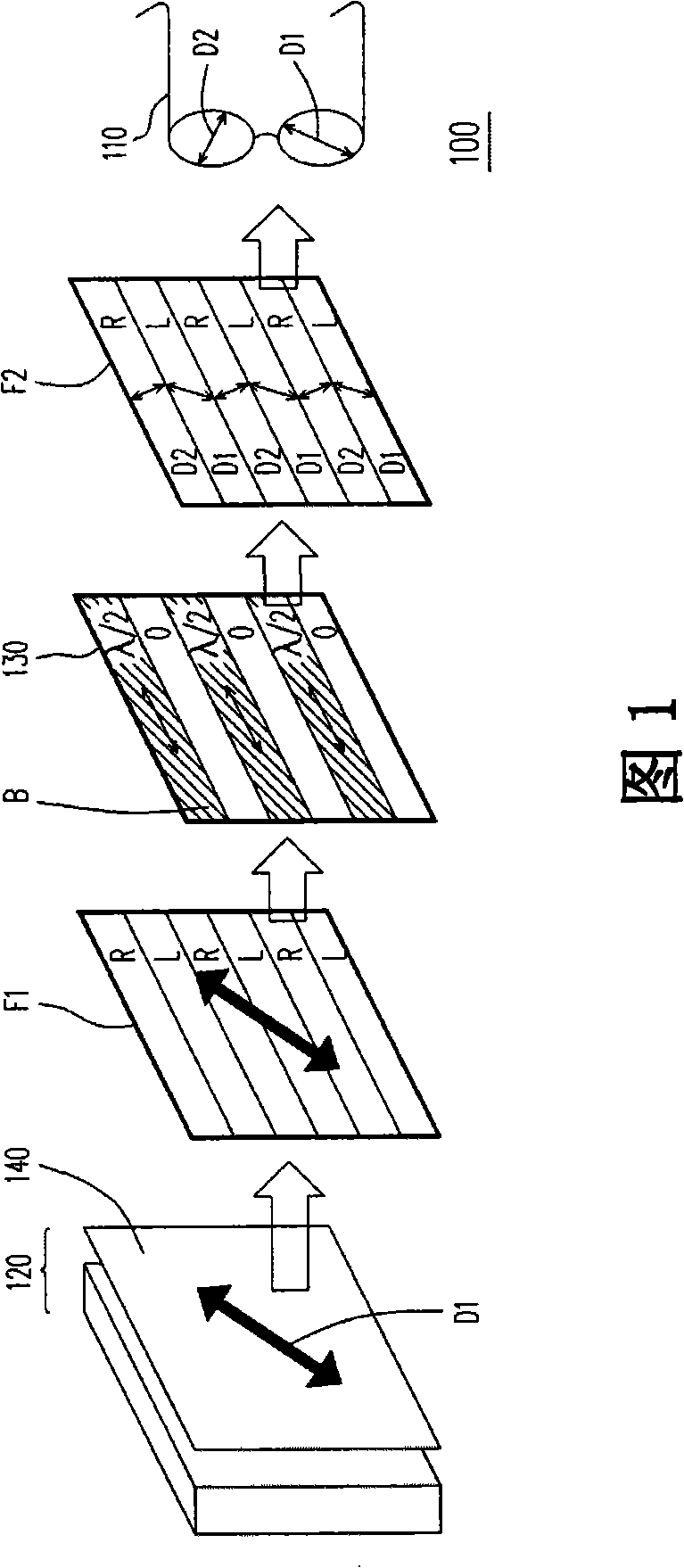
Solid display, manufacturing method thereof and control method
ActiveCN101359099AWiden perspectiveImprove display qualityStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayPhase retardation
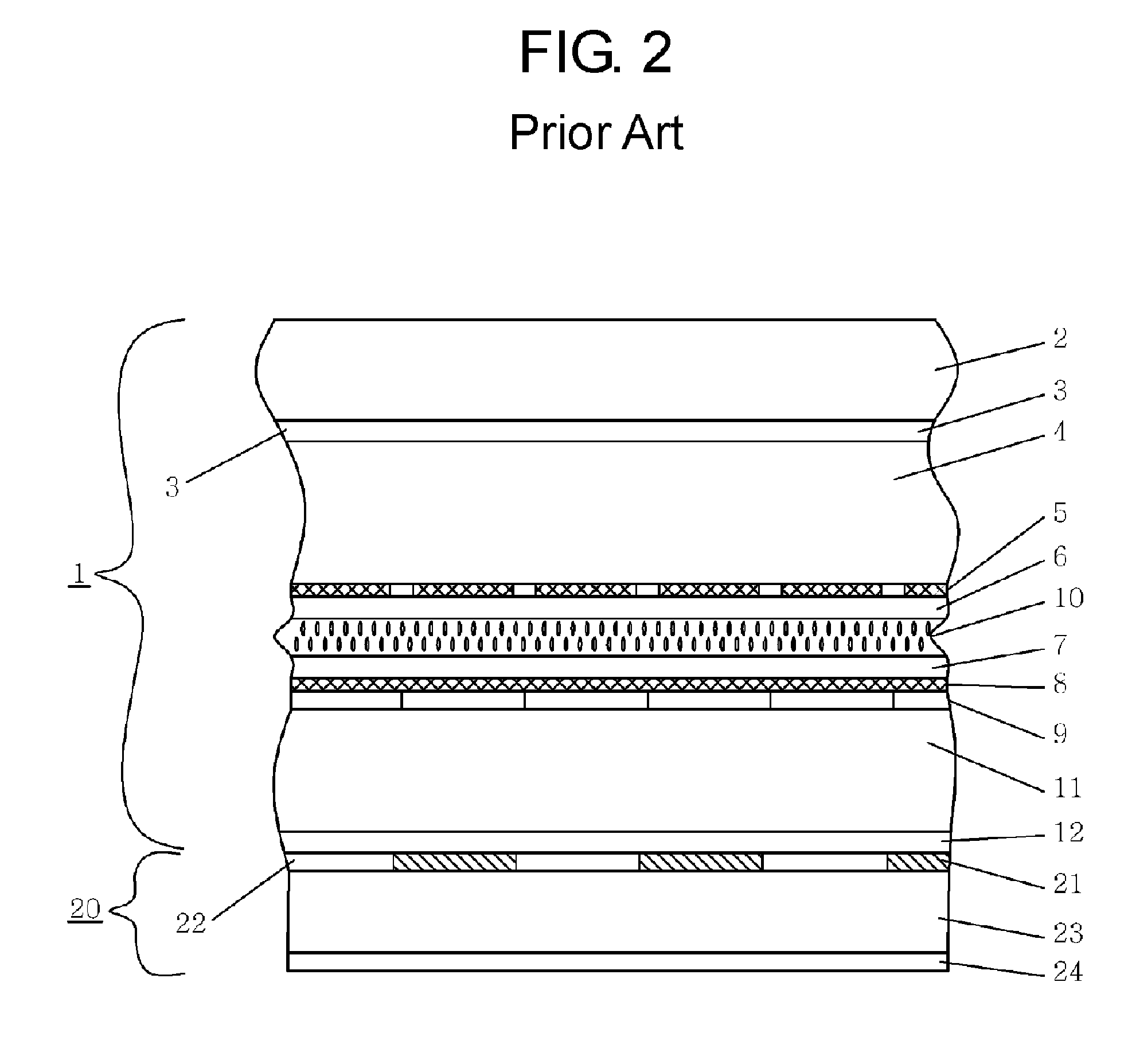
The invention provides a three-dimensional display, a production method and a control method thereof; the three-dimensional display is suitable for an observer to watch when wearing glasses which are provided with two lenses orthogonalized in the polarization direction; and the three-dimensional display comprises a display panel and a liquid crystal phase modulation panel. The display panel is provided with pixels and a polarizing plate between the pixels and the glasses; the polarizing plate is provided with a penetration shaft; and the display panel is suitable for displaying images. The liquid crystal phase modulation panel is located between the polarizing plate and glasses and provided with a liquid crystal layer and an alignment layer adjacent to the display panel; wherein, the angle formed between the alignment direction of the alignment layer and the penetration shaft is actually n multiplying 45 degrees; the absolute value of n is an integer; the liquid crystal phase modulation panel is suitable for providing the phase retardation; by adjusting the phases of images, the liquid crystal phase modulation panel outputs the images with three-dimensional information; and the liquid crystal phase modulation panel does not have any polarizing plate.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Fringe field switching mode transflective liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20060256268A1High quality imagingWide viewing angleNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayPhase retardation
Disclosed is a fringe field switching mode transflective liquid crystal display capable of displaying high quality images. The transflective liquid crystal display includes a lower substrate having a counter electrode and a pixel electrode, an upper substrate aligned in opposition to the lower substrate by interposing a liquid crystal layer therebetween, an upper polarizing plate, a lower polarizing plate, a reflective plate provided at an inner portion of the lower substrate, a lower λ / 2 plate, and an upper λ / 2 plate. An inclination angle, a slit width and a slit interval of the pixel electrode of the reflective area are different from those of the pixel electrode of the transmissive area. The liquid crystal layer presents a phase delay of about 0 to λ / 4 in the reflective area and presents a phase delay of about 0 to λ / 2 in the transmissive area.
Owner:HYDIS TECH
Retardation compensator and single-panel type color liquid crystal projector
InactiveUS20040141122A1Increased durabilityReduce manufacturing costPolarising elementsColor television detailsPhase retardationRefractive index
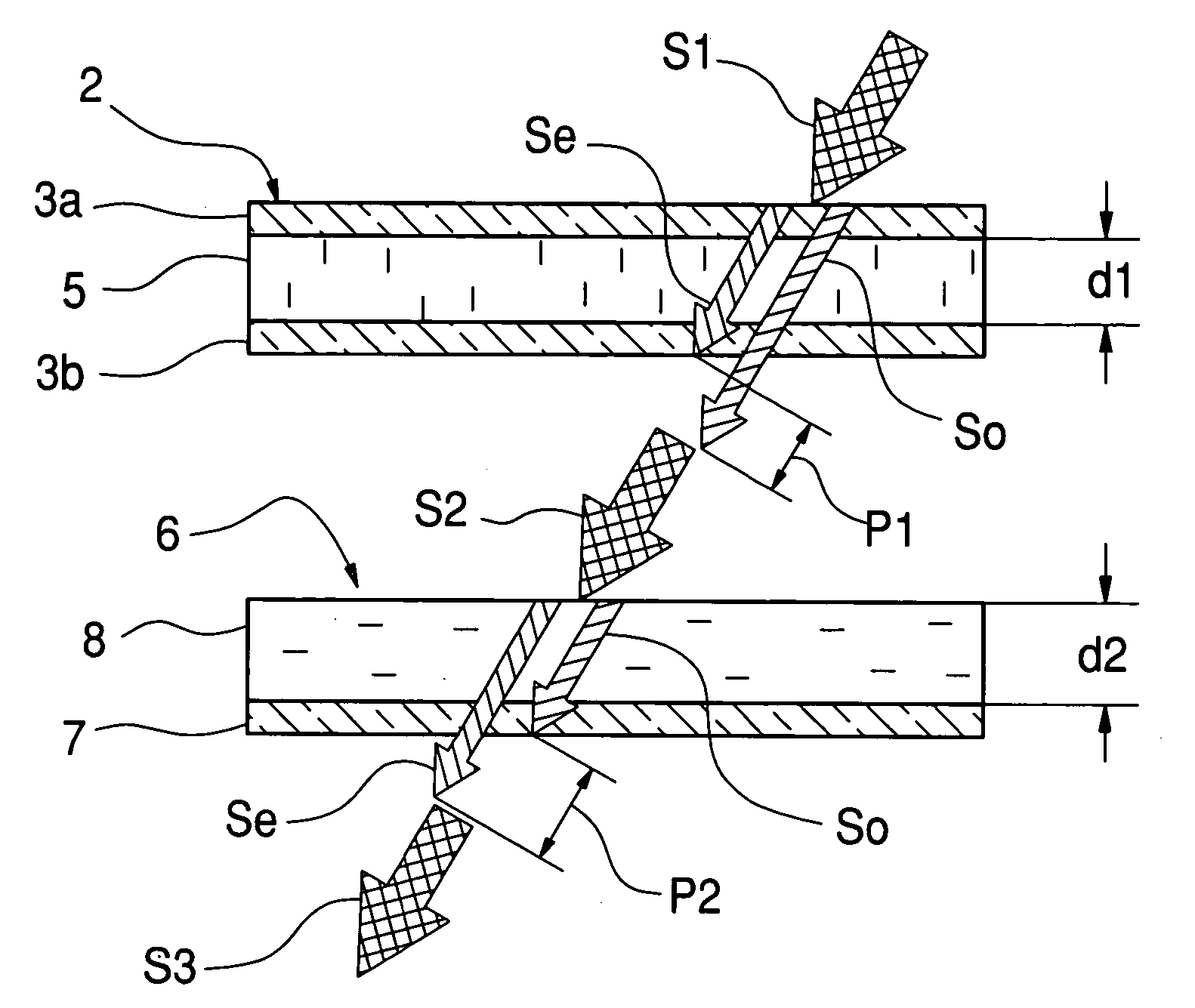
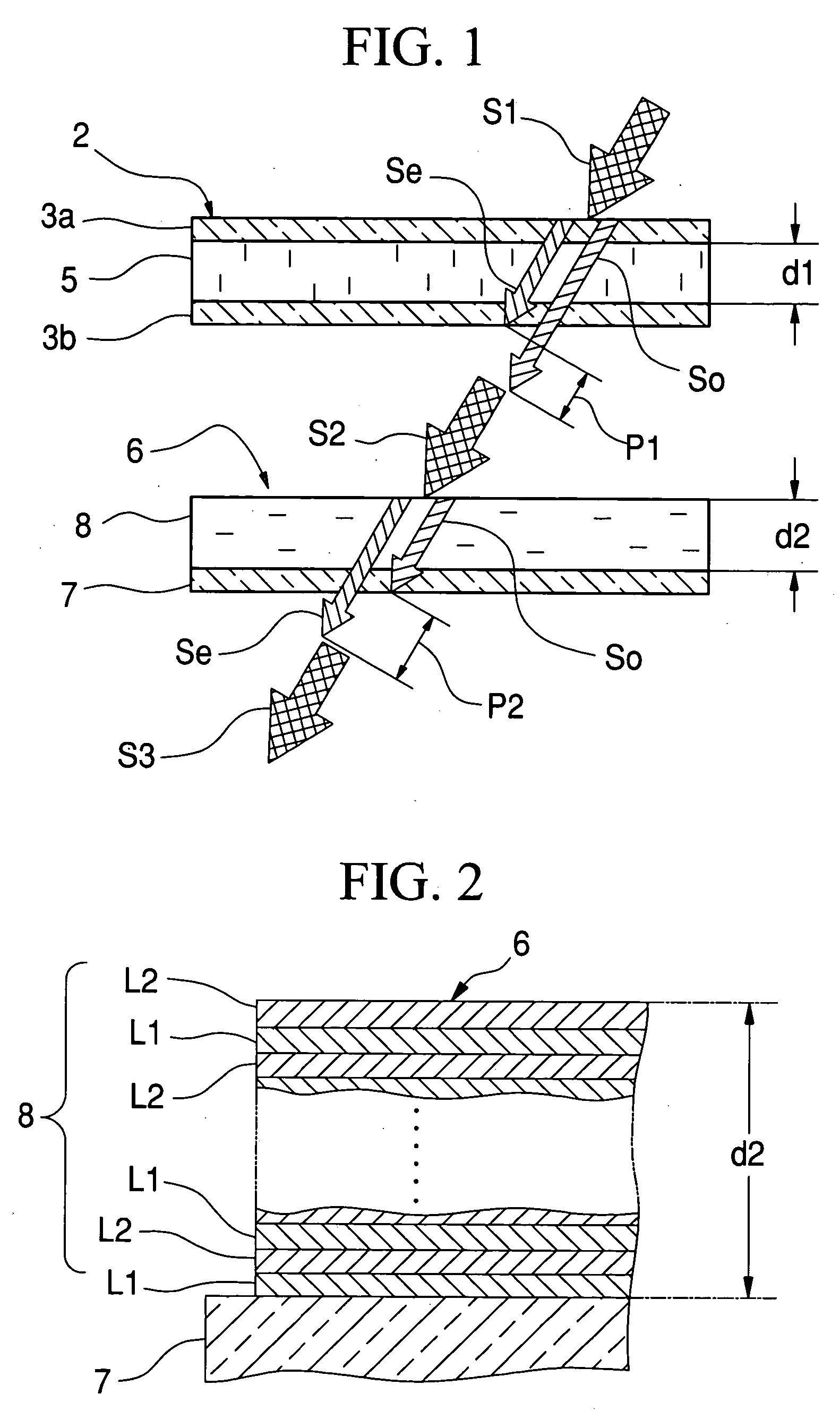
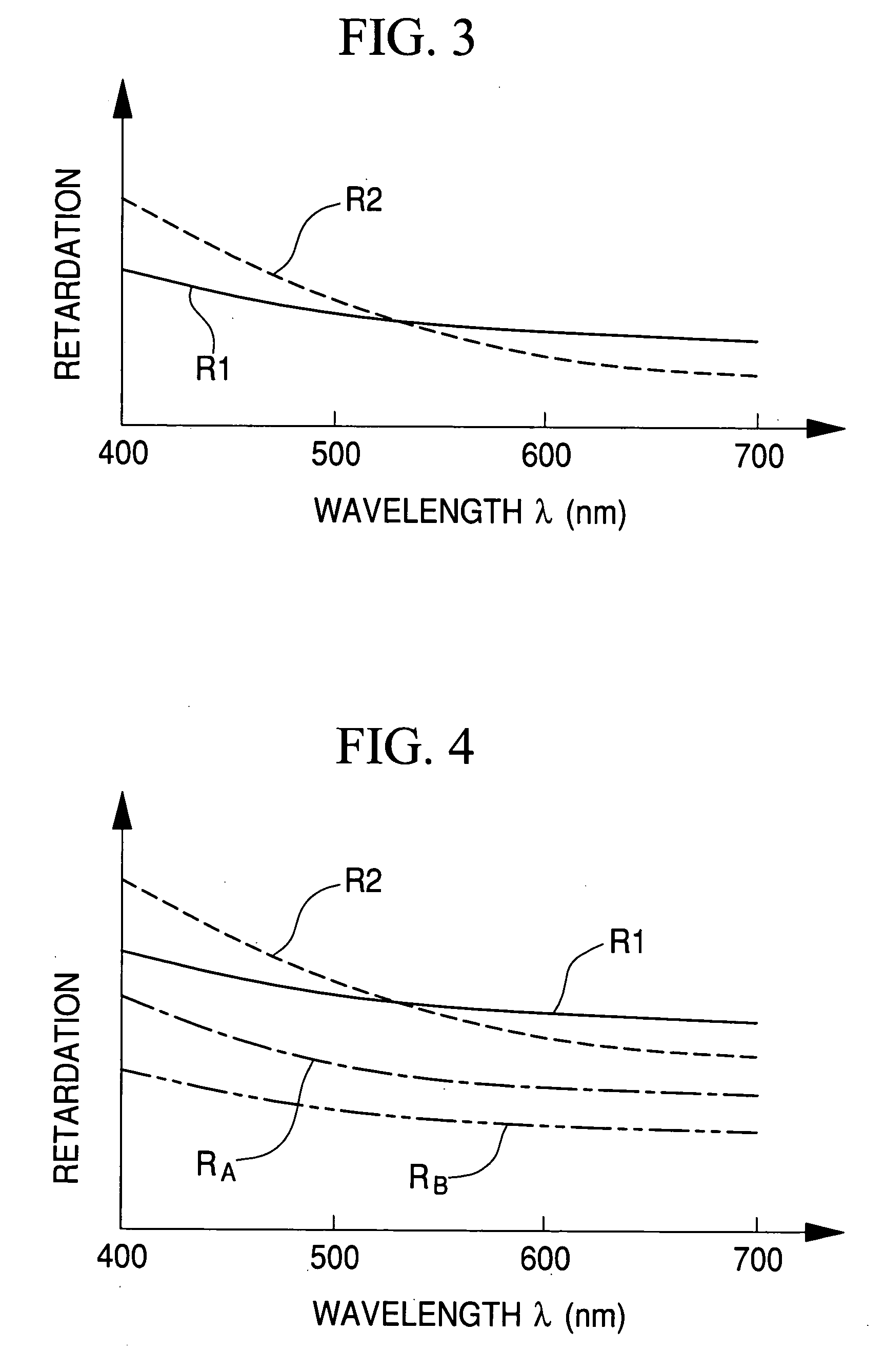
A form birefringence to compensate the phase retardation caused by a liquid crystal device has a retardation compensation film that is composed of alternately deposited high and low refractive index layers. The retardation compensation film is provided in at least one of the incident side and the emanation side of the liquid crystal device. The birefringence value Deltan and the total thickness d of the retardation compensation film are adjusted such that the retardation of the retardation compensation film agrees with the retardation of the liquid crystal device at least at one wavelength in the visible band.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
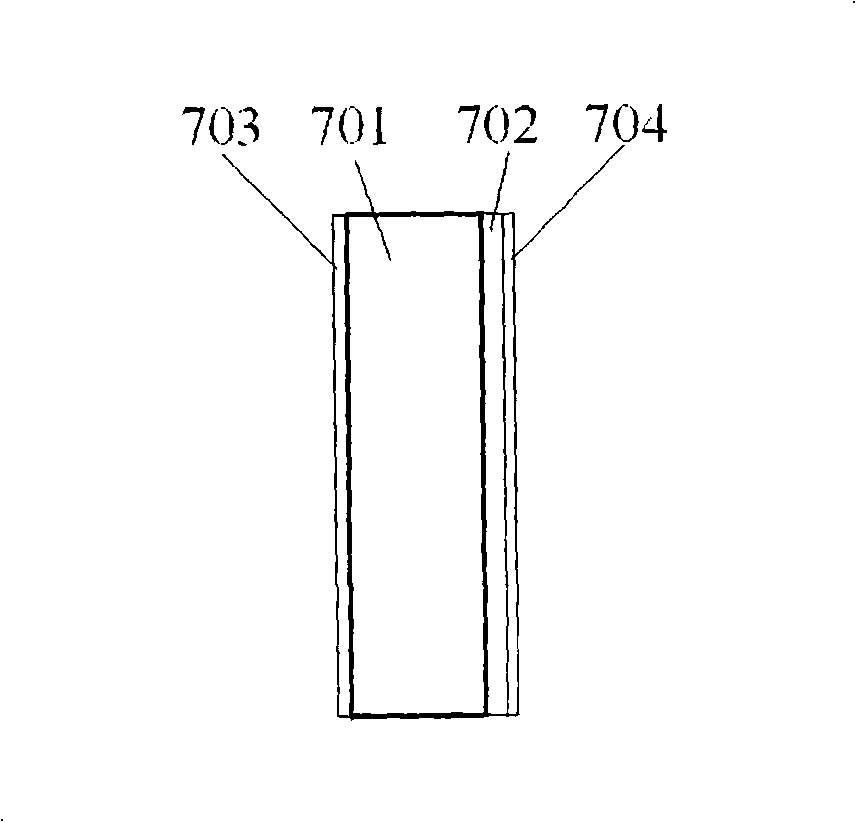
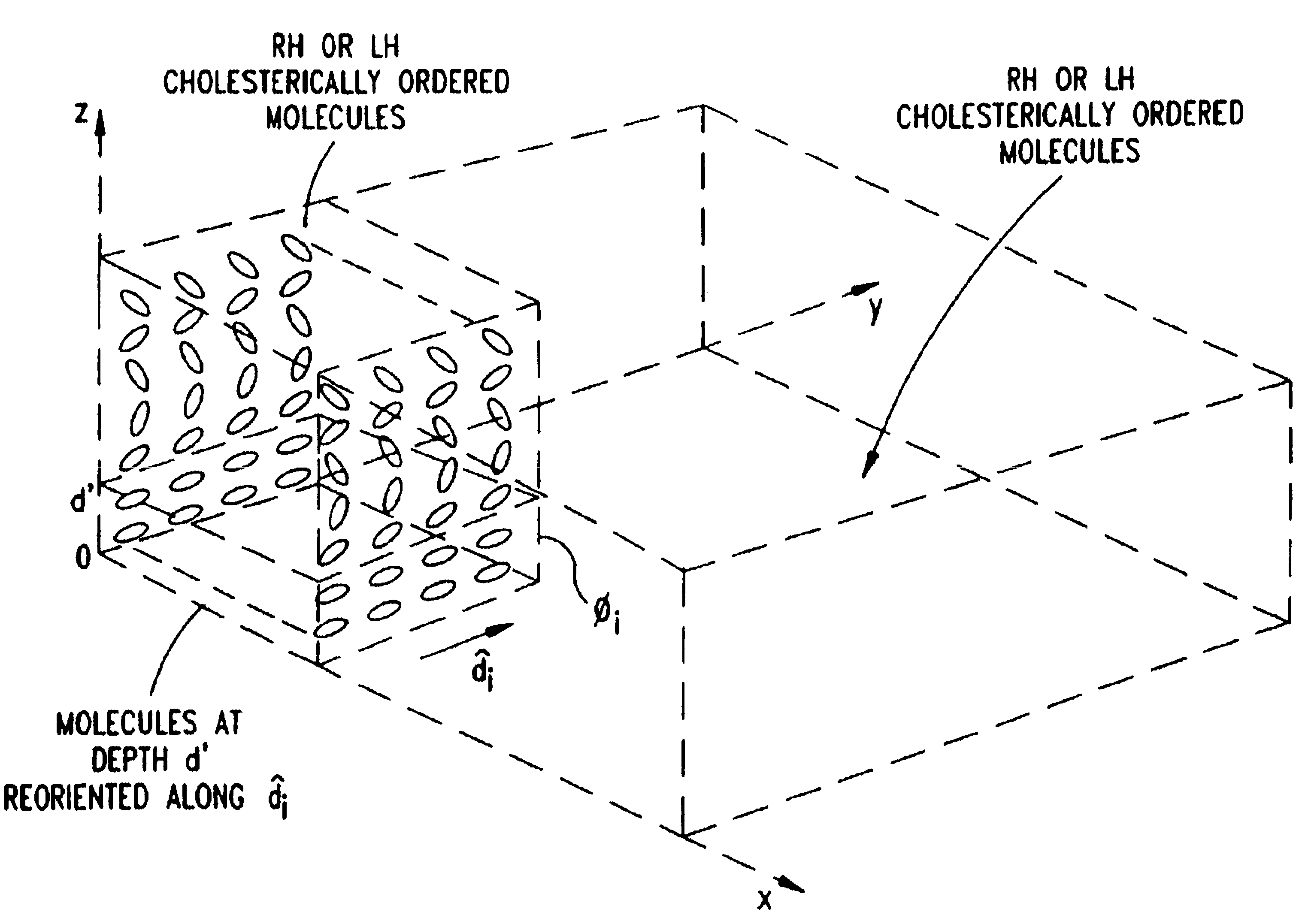
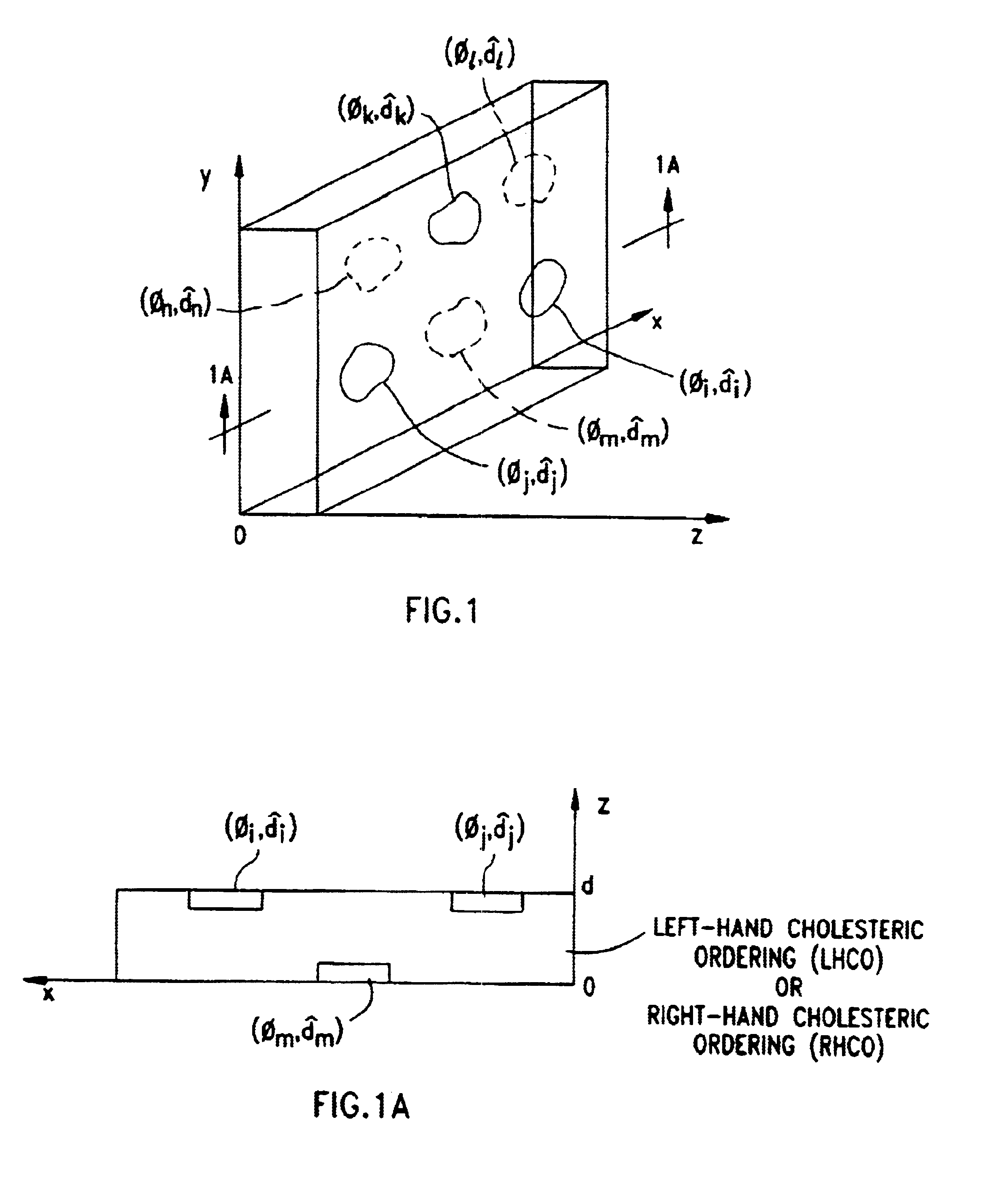
Liquid crystal film structures with phase-retardation surface regions formed therein and methods of fabricating the same
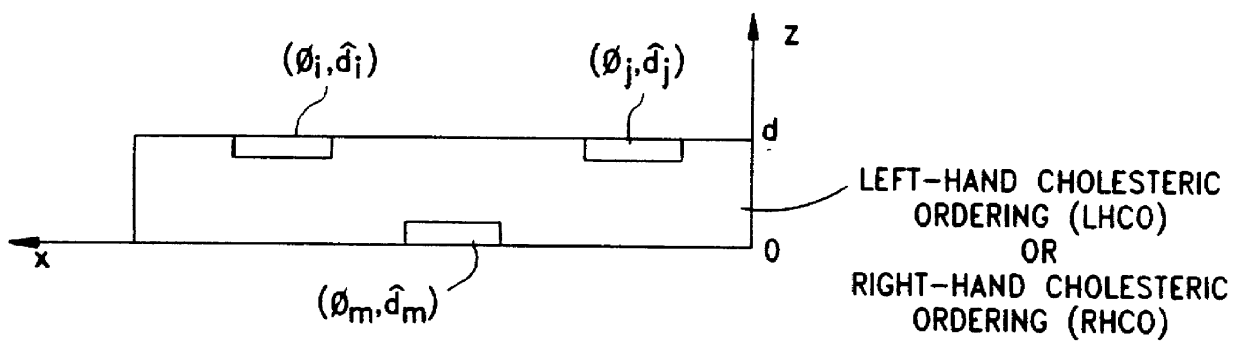
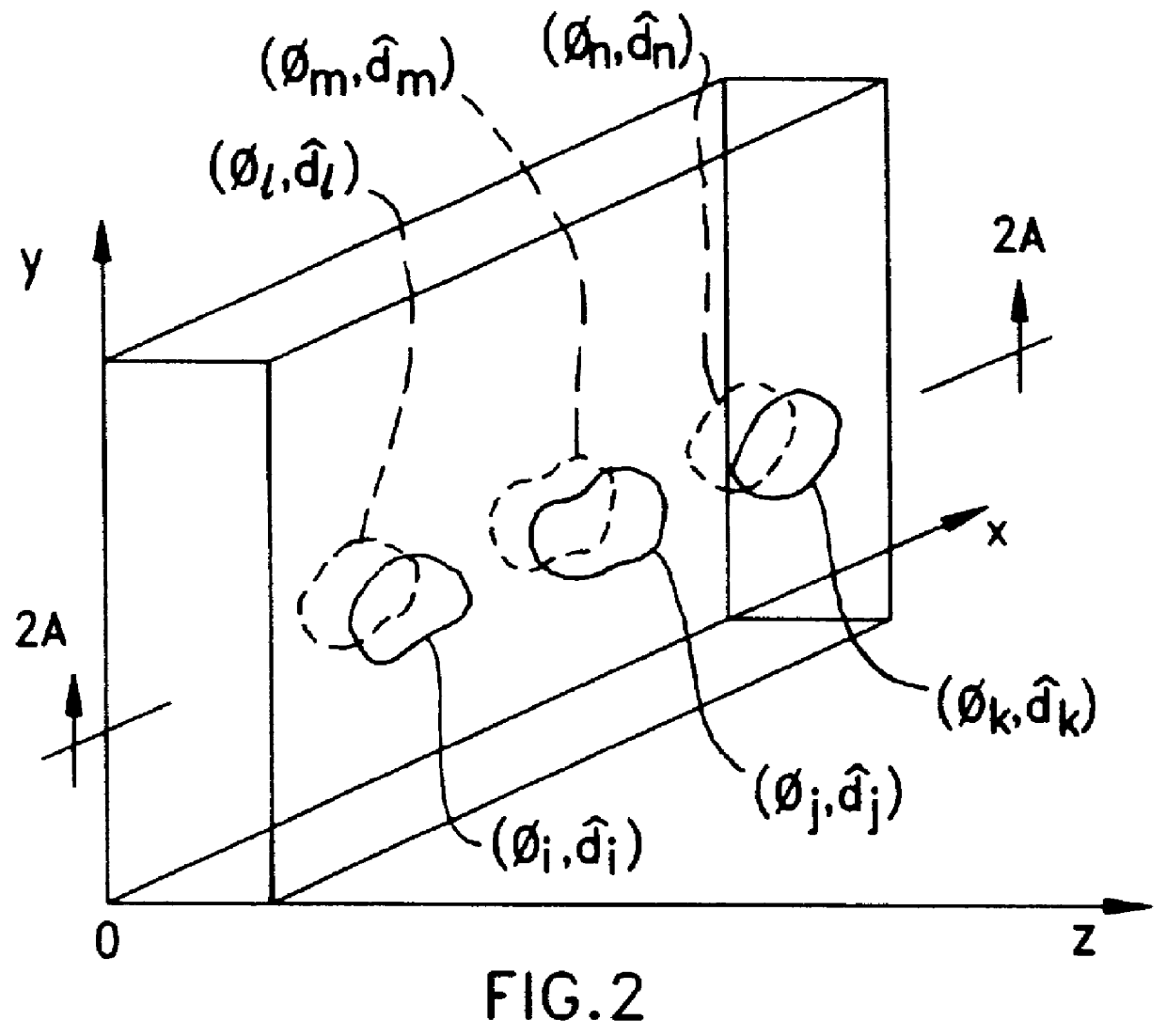
Disclosed are liquid crystal (LC) phase-retarders and linear polarizers and methods and apparatus for making the same. The liquid crystal phase-retarder is realized by a liquid crystal film structure having one or more phase retardation regions formed therein. Each phase retardation region has an optical axis specified by the direction and depth of orientation of liquid crystal molecules along the surface of the liquid crystal film structure. The liquid crystal linear polarizer is realized by a liquid crystal film structure having a chiral phase region within which liquid crystal molecules are cholesterically ordered. One or more nematic phase regions are formed along the surface of the liquid crystal film structure within which liquid crystal molecules are oriented along a direction and to a surface depth sufficient to realize one or more phase retardation regions therein having optical axes along the direction of liquid crystal molecule orientation.
Owner:REVEO
Liquid crystal display device having thin polarizing film and thin phase retardation film
InactiveUS20060023143A1Fabrication process can be shortenedReduce manufacturing costSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsPhase retardationLiquid-crystal display
A LCD device having a thin phase retardation film is disclosed, which is achieved using a thin film polarizing film formed by accurately processing a thin aluminum film, a polarizing film of a nano imprint lithography method that uses polymer, and a polarizing film and a liquid crystal material that form a polarizing nano material thin film by uniformly coating a polarizing nano material (TCF).
Owner:PAVONINE
Optical film
ActiveUS20130044286A1Effectively and constantly manufacturedEffective controlElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPhase retardationDisplay device
An optical film, a circular polarizing plate, and a display device are provided. The optical film may exhibit a desired phase retardation property in a wide wavelength range even when it is relatively thin. The optical film may exhibit the 1 / 4 wavelength phase retardation property. The optical film may be manufactured by a simple process. The optical film may be used in LCDs such as a reflective LCD, or OLEDs.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Patterned spinning disk based optical phase shifter for spectral domain optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS20060072424A1Low costSolve the slow scanning speedInterferometersRecord information storageCircular discIntensity modulation
A low cost patterned spinning disk is disclosed for achieving relatively rapid discrete optical phase shifts for an optical beam. The invention is particularly useful in a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system. The disk contains stepped patterns of different heights and / or refractive index distribution such that as it spins, an optical beam passing through or being reflected by the disk will experience different discrete optical phase delays. The disk can be operated as a phase shifter or it can be operated in synchronization with an intensity modulating chopper disk or a direct intensity modulation of the light source. The disk can also contain intensity modulating patterns such that both phase shifting and intensity modulation can be achieved at the same time. Various possible methods are also disclosed for the fabrication of the disk.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Display panel and display device
ActiveCN106324897AImprove transmittanceFast response timeStatic indicating devicesOptical light guidesGratingRefractive index
The invention discloses a display panel and a display device. The display panel comprises a first substrate, a liquid crystal layer, a waveguide layer, a grating layer, a first electrode and a second electrode, the liquid crystal layer, the first electrode and the second electrode are positioned between the waveguide layer and the first substrate, the first electrode and the second electrode are used for adjusting the refractive index of the liquid crystal layer, the liquid crystal layer is used for controlling light emission from the waveguide layer in a coupling manner, the coupling light emission quantity of the waveguide layer is determined according to the difference between the refractive index of the waveguide layer and the refractive index of the liquid crystal layer, and the grating layer is used for controlling light with a special wavelength among the light coupled from the waveguide layer to be emitted in a special direction. A polarizing film and a color resistor set in the display panel are omitted, so that transmittance of the display panel is improved. As the polarizing film set in the display panel is omitted, the overall phase retardation quantity of the liquid crystal layer is not required, a liquid crystal box can be thin, and the response time of liquid crystals is prolonged.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
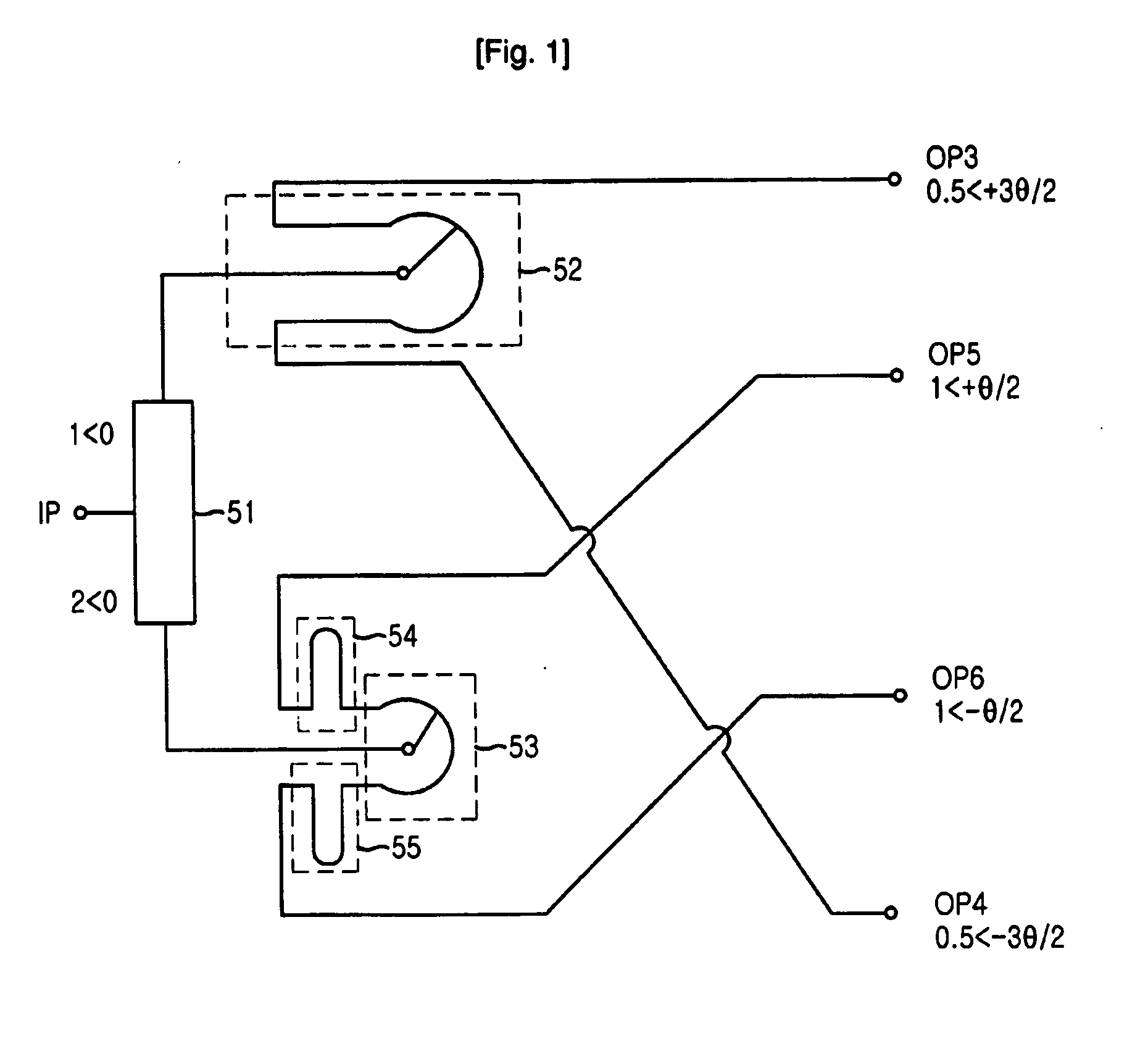
Phase shifter having power dividing function
ActiveUS20060164185A1Preventing modulation of signalWide rangeAntenna supports/mountingsDelay linesPath lengthPhase shifted
Disclosed is a phase shifter having a power dividing function. The phase shifter includes: an input port for receiving a radio frequency (RF) signal; a power dividing unit for dividing the RF signal into a first divided signal of which phase is to be varied and a second divided signal having a fixed phase value; a first output port for outputting the second divided signal having the fixed phase value; a phase shift unit for dividing the first divided signal into a third divided signal and a fourth divided signal wherein the third divided signal and the fourth divided signal move in opposite directions; a phase delay unit for shifting phase of the third divided signal and the fourth divided signal based on a difference in a path length of the third divided signal and the fourth divided signal, to thereby generate phase-shifted signals; and at least two second output ports connected to the phase delay unit, for outputting the phase-shifted signals.
Owner:ACE TECH
Liquid crystal waveguide having two or more control voltages for controlling polarized light
A waveguide and method for controllably altering an optical phase delay (OPD) of light traveling along a propagation direction through the waveguide. Many embodiments are disclosed, and in one example, a waveguide may include a core for guiding the light through the waveguide; at least one cladding adjacent the core, wherein the at least one cladding has liquid crystal molecules disposed therein; at least one electrode for receiving a first voltage for controllably altering the optical phase delay of the TE polarized light traveling through the waveguide; and at least one electrode for receiving a second voltage for controllably altering the optical phase delay of the TM polarized light traveling through the waveguide.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
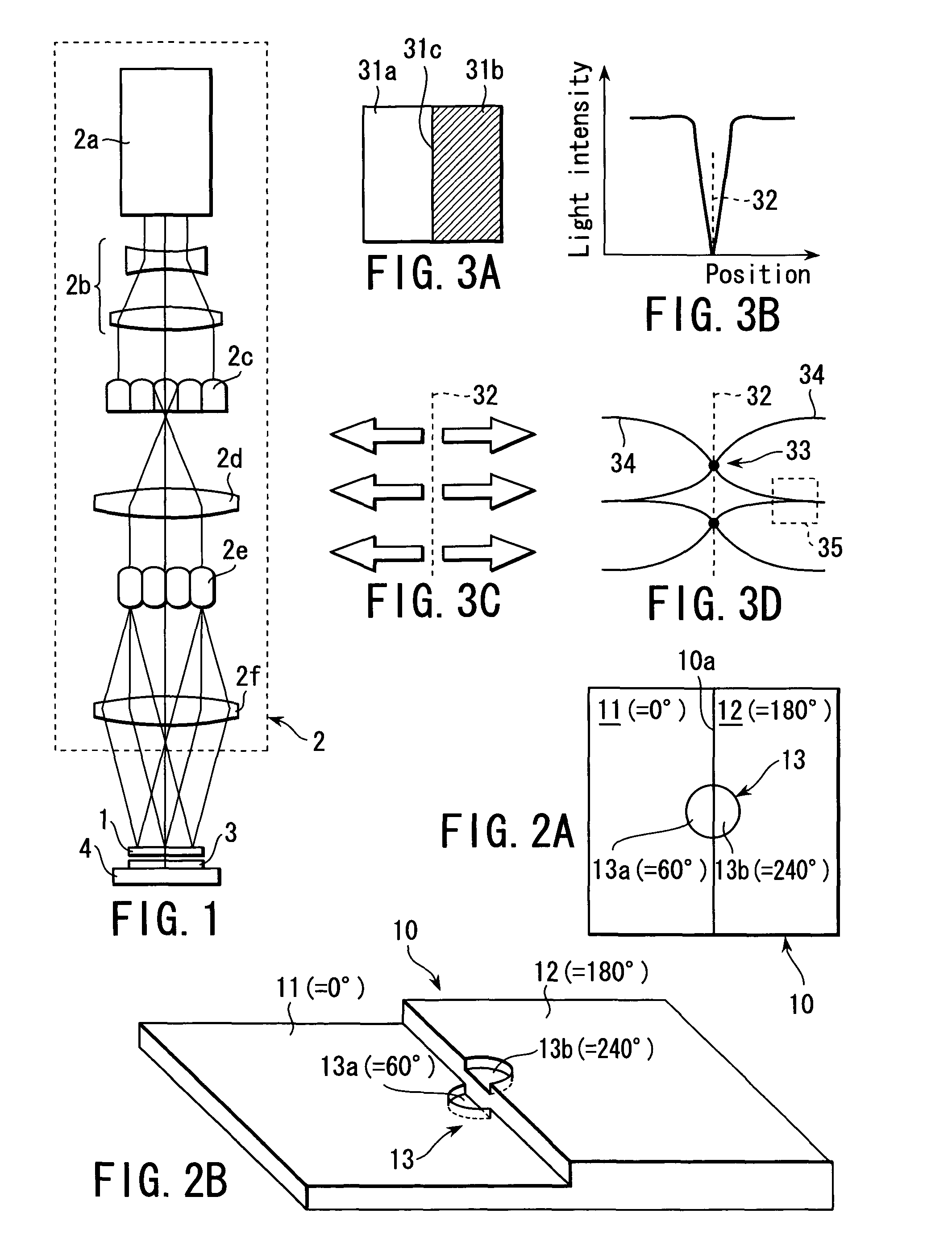
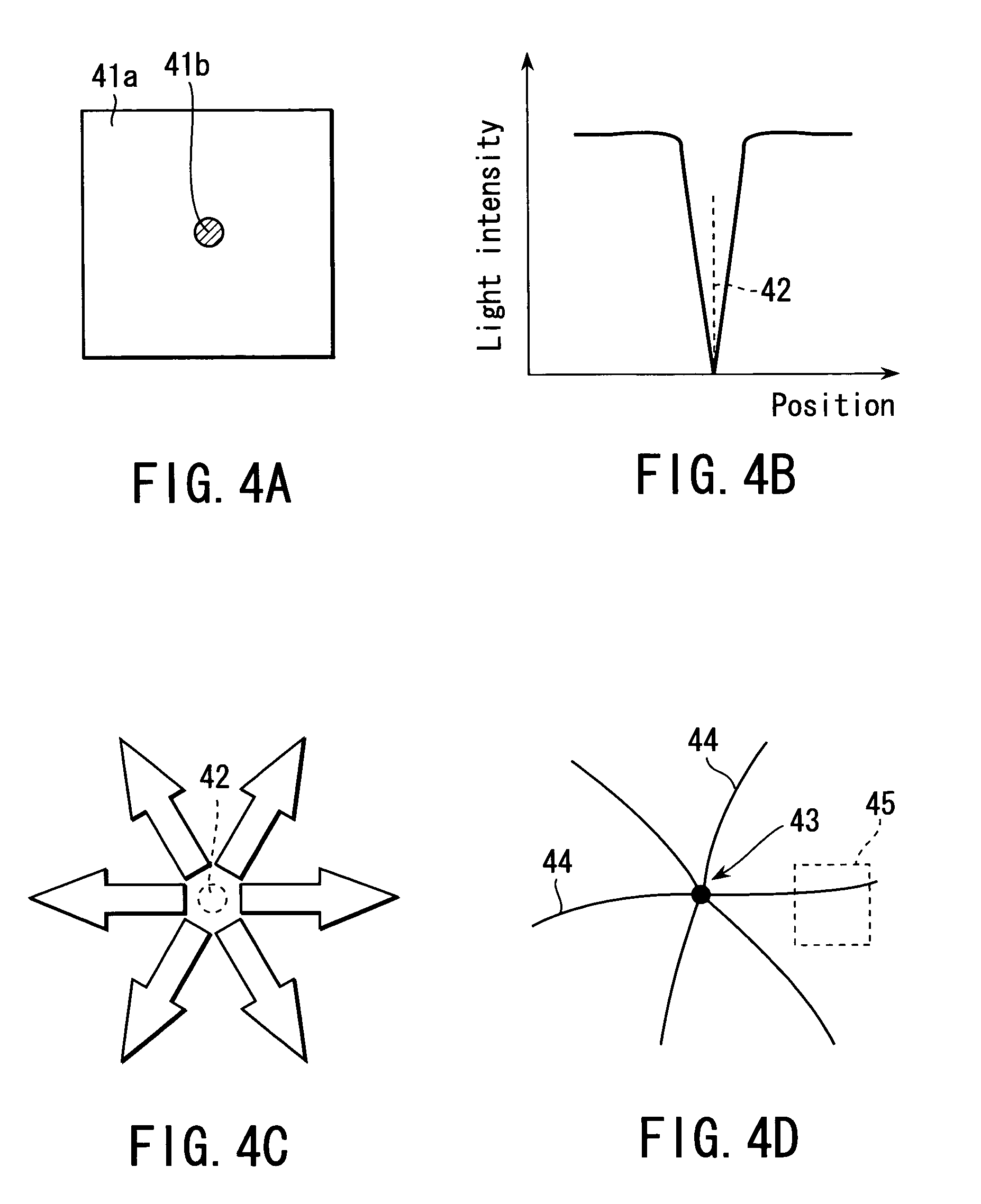
Crystallization apparatus, crystallization method, and phase shifter
A crystallization apparatus includes an illumination system which applies illumination light for crystallization to a non-single-crystal semiconductor film, and a phase shifter which includes first and second regions disposed to form a straight boundary and transmitting the illumination light from the illumination system by a first phase retardation therebetween, and phase-modulates the illumination light to provide a light intensity distribution having an inverse peak pattern that light intensity falls in a zone of the non-single-crystal semiconductor film containing an axis corresponding to the boundary. The phase shifter further includes a small region which extends into at least one of the first and second regions from the boundary and transmits the illumination light by a second phase retardation with respect to the at least one of the first and second regions.
Owner:ADVANCED LCD TECH DEVMENT CENT
Touch panels and display devices having touch panels
ActiveUS20130194205A1Reduce optical lossReduce thicknessSolid-state devicesPolarising elementsPhase retardationTouch Senses
A display device including a touch panel arranged on a display panel, the touch panel including at least one phase retardation layer, a polarization plate arranged on the at least one phase retardation layer, a touch sensing structure including at least one sensing pattern arranged directly on at least one of at least one face of the phase retardation layer and at least one face of the polarization plate, an adhesion layer arranged on the polarization plate and a window arranged on the adhesion layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Optical compensation films based on stretched polymer films
The present invention provides uniaxially stretched polymer films that have a refractive index profile suitable for use as negative A-plates or biaxial birefringent plates in a liquid crystal display (LCD) device. These wave plates can be used to compensate for the phase retardations existing in various modes of LCDs including TN (twisted nematic), VA (vertically aligned), IPS (in-plane switching), and OCB (optically compensated bend), and therefore improving the viewing quality of the displays.
Owner:AKRON POLYMER SYST
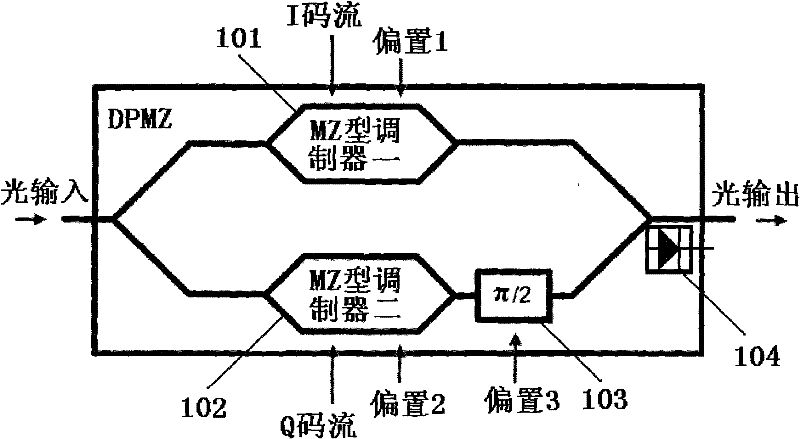
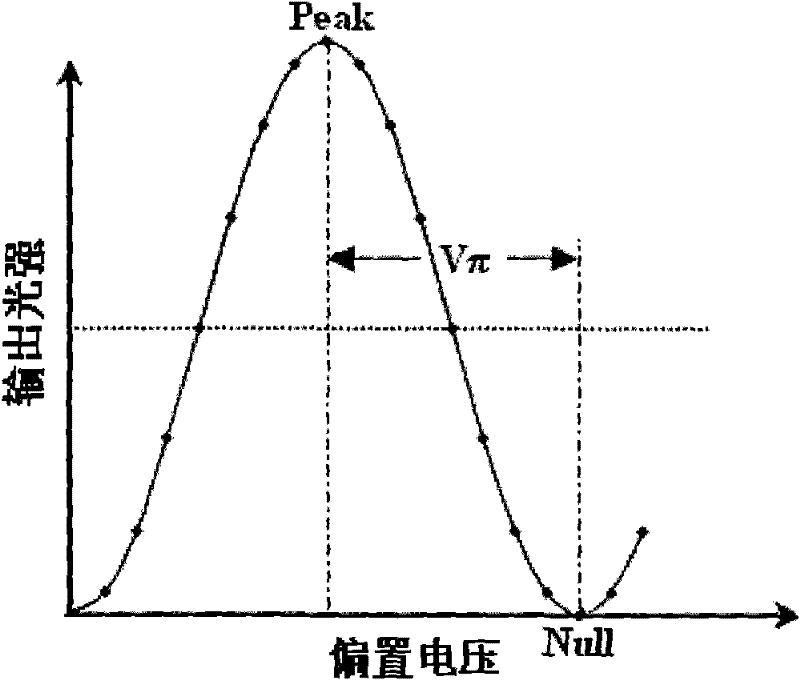
Method and device for offset control of DPMZ (dual parallel Mach-Zehnder) modulator
ActiveCN102201868AReduce complexityLow costElectromagnetic transmittersNon-linear opticsPhase retardationEngineering
The invention discloses a method and device for offset control of a DPMZ (dual parallel Mach-Zehnder) modulator. The method comprises the following steps: converting a light current output by the DPMZ modulator into two paths of voltage signals, and carrying out LPF (Lowpass filtering) and highpass filtering to obtain the average light intensity output by the DPMZ and LF (low frequency) RF (radio frequency) components of the output light intensity; dividing time into continuous multiple groups of TSs (time slots), wherein each group of TSs comprises TS1, TS2 and TS3; controlling the bias 1 and bias 2 of two MZ modulators in the TS1 and the TS2 so as to obtain the maximum average light intensity output by the DPMZ modulator, thus the bias 1 and bias 2 are in an optimal state; adopting a logarithmic RF detector to detect power of the LF RF components of the light intensity output by the DPMZ modulator, representing the power in a DC (direct-current) voltage Vrf form; and changing phase delay by bias 3 of a control bit delayer in the TS3 so as to minimize the Vrf, thus the bias 3 is in an optimal state. The method and device are used to improve the bias control accuracy of the two MZ modulators and a phase delayer in the DPMZ modulator and reduce the complexity and the cost of a circuit.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
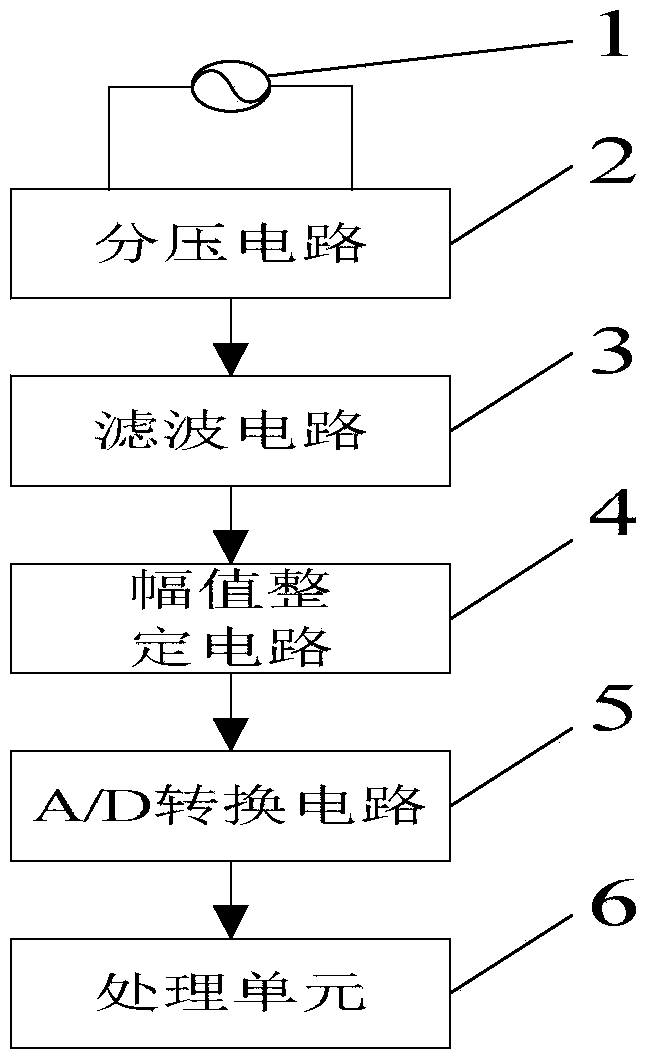
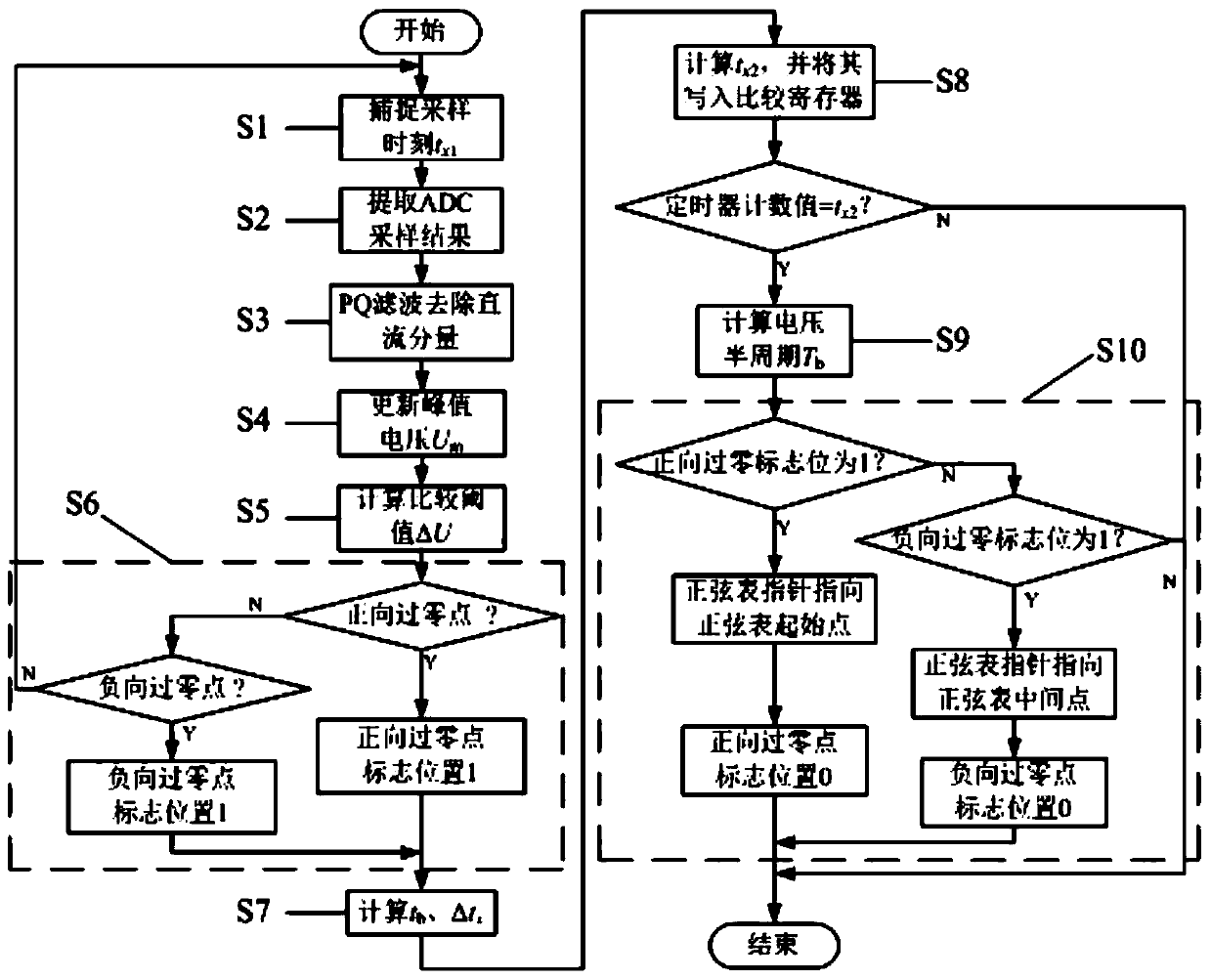
Zero-crossing-point accurate detection method for AC power-grid voltage signals
InactiveCN104090151AImprove anti-interference abilityPrecise phase lockMeasurement using digital techniquesMicrocontrollerPhase retardation
The invention discloses a zero-crossing-point accurate detection method for AC voltage signals. The method includes the following steps: firstly selecting a comparatively large hardware filtering time constant to ensure that harmonic waves and random noises which may be included in the AC voltage signals can be filtered comparatively well; using large-time-constant software PQ filtering to extract and eliminate DC drift generated by software and hardware; setting a software judgment advancing quantity so as to offset zero-crossing-point delay caused by hardware filtering; accurately calculating random errors t caused by sampling intervals; and at last, using capture and comparison functions of an embedded microcontroller to realize accurate information of an AC voltage frequency and phase so that accurate phase locking of the AC signals can be realized. The detection method solves a problem of zero drift and phase delay caused by a hardware detection circuit and a software algorithm when zero-crossing-point detection is carried out on the AC voltage signals.
Owner:XI'AN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Dynamic diffractive optical transform
InactiveUS20050017925A1High diffraction efficiencyStatic indicating devicesHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesFresnel lensPhase retardation
A dynamic diffractive optical transform. An electric field pattern is created across a body of material, the material being characterized in that it has an optical transmission property which varies in response to of an electric potential applied across a portion thereof. The electric field pattern is created such that the resulting profile of the transmission property is an arbitrary shape which produces a desired diffraction pattern that may not be physically realizable in conventional refractive optics or is a Fresnel lens-like construct derived from a refractive optical element. This is done by selectively applying electric potentials to transparent electrode pairs having liquid crystal material therebetween and preferably relatively small proportions in relation to the relevant wavelength of light, so as to create variations in phase delay that are aperiodic, have other than fifty percent spatial duty factor or have multiple levels of phase delay. The transform is embodied in an optical scanner, an adaptive lens, and an optical switch.
Owner:BIRDWELL WILLIAM A
Waveguide laser illuminator incorporating a despeckler
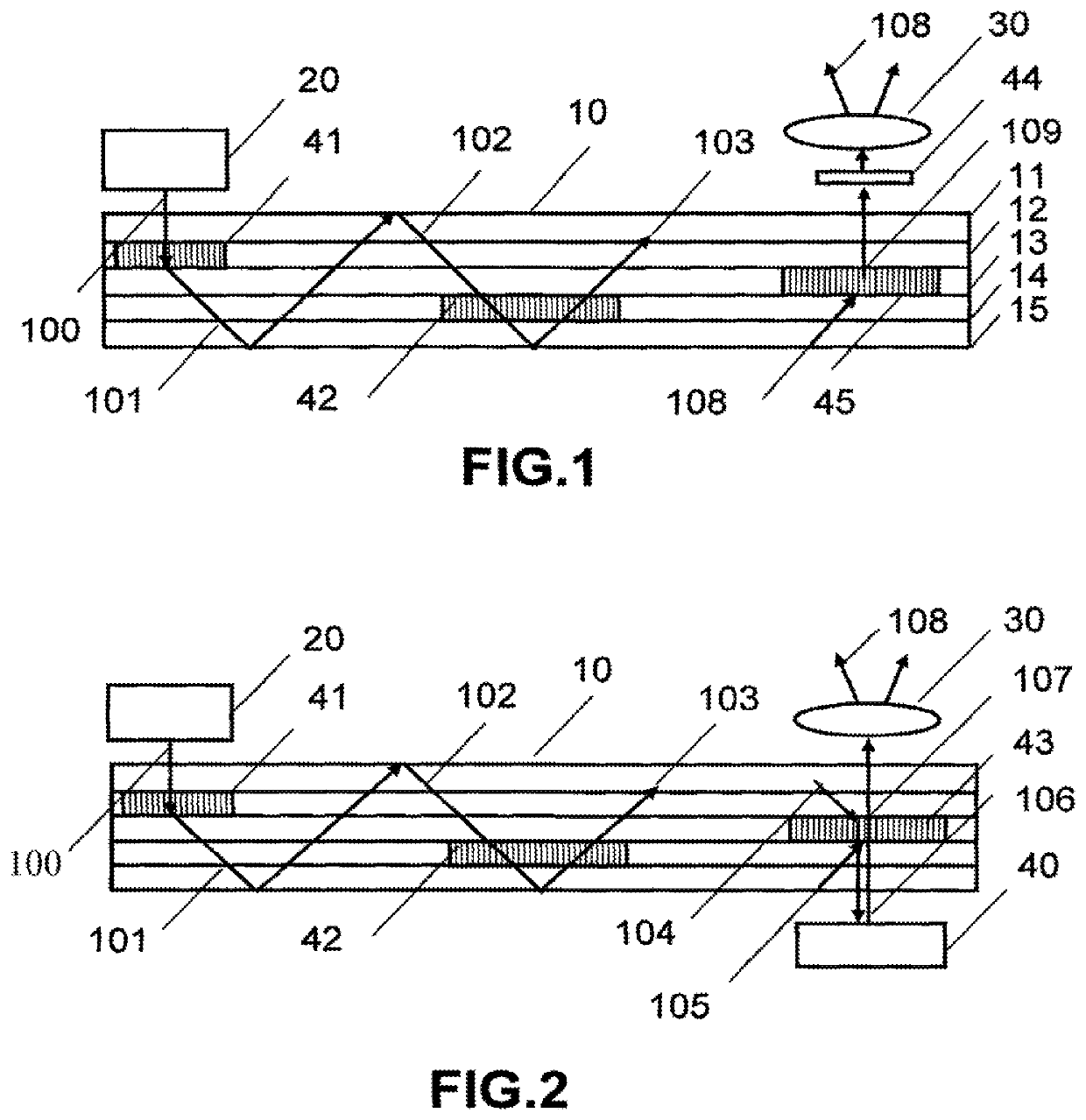
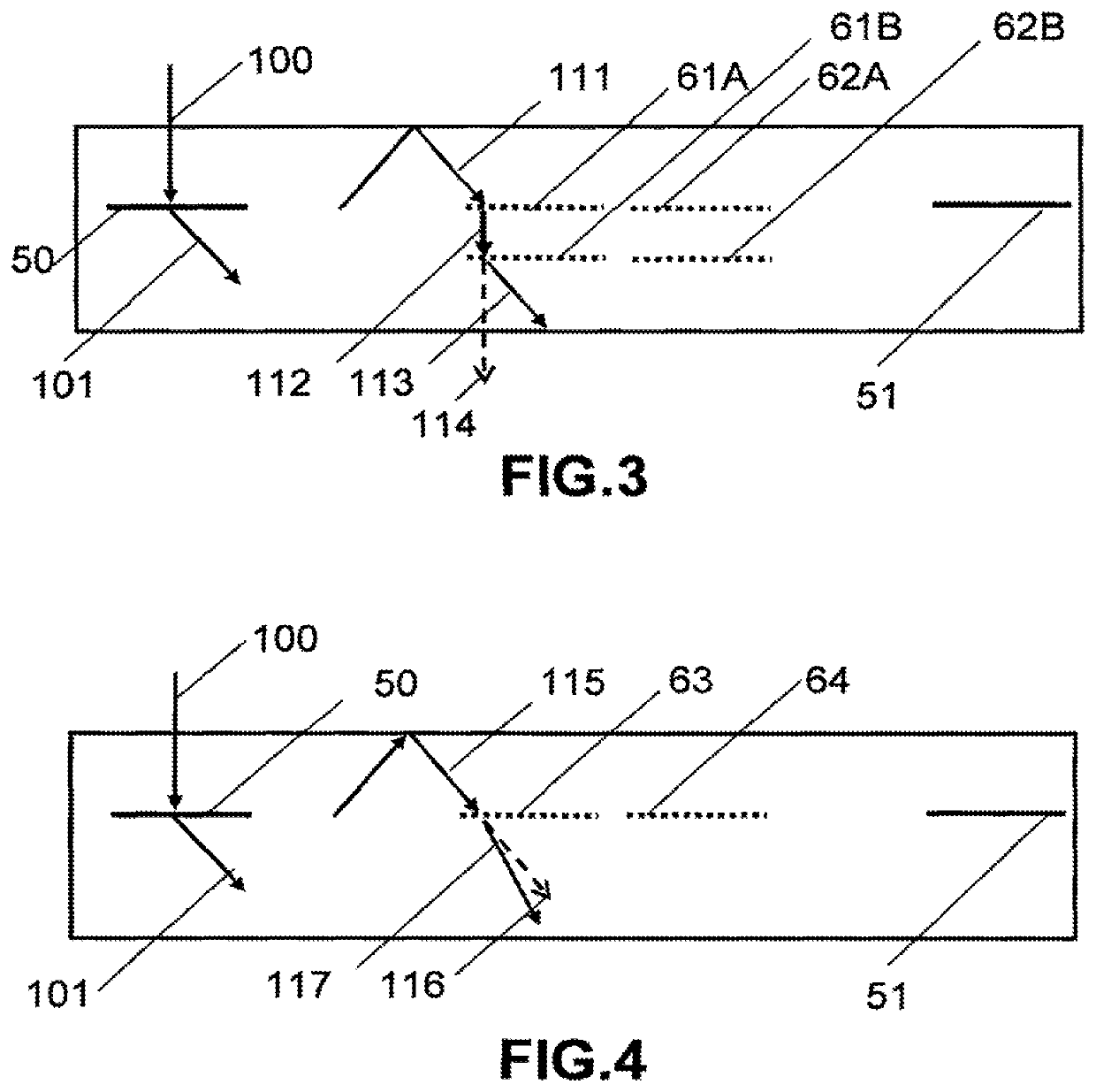
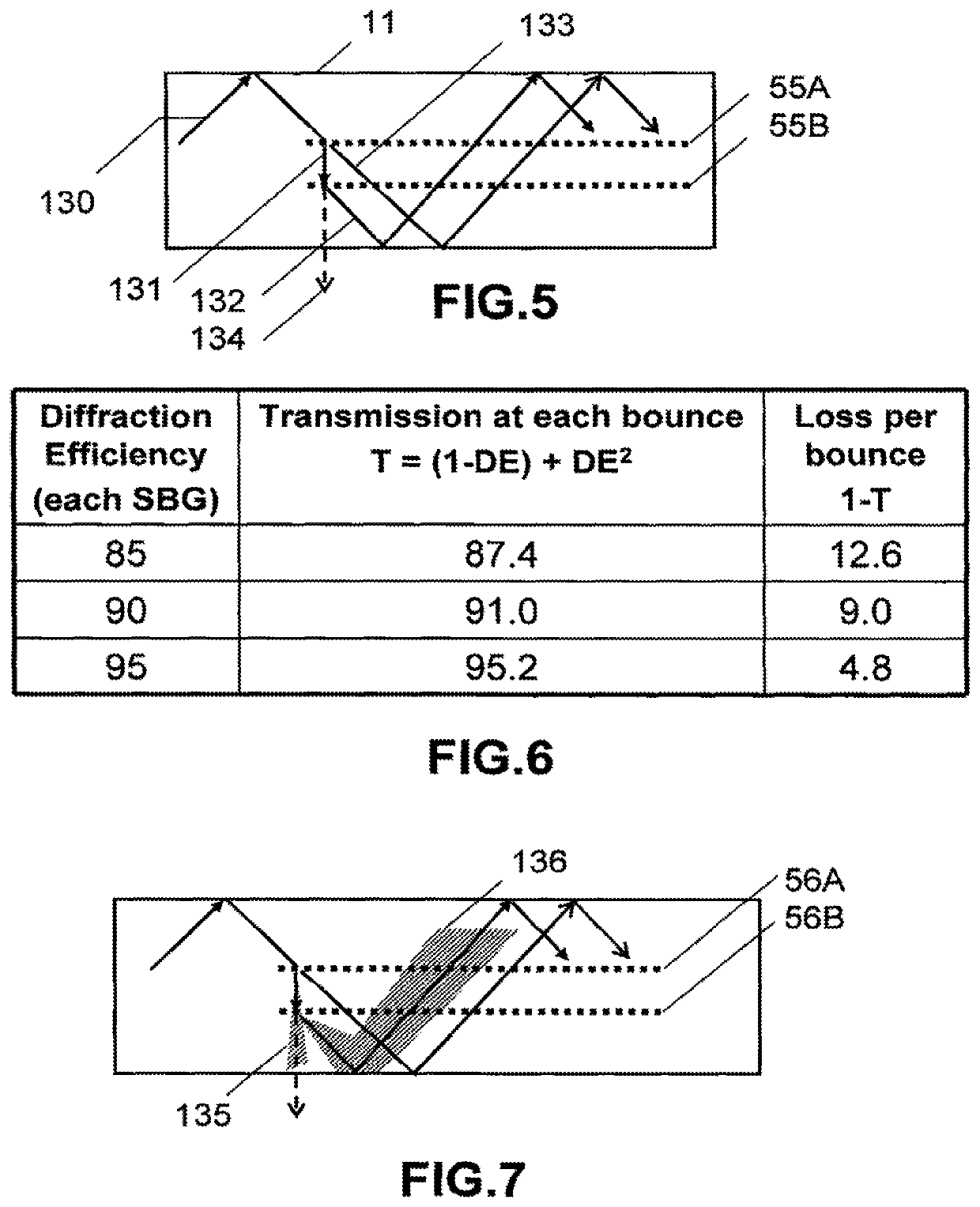
There is provided an illumination device having: a laser; a waveguide including at least first and second transparent lamina; a first grating device for coupling light from the laser into a TIR path in the waveguide; a second grating device for coupling light from the TIR path out of the waveguide; and a third grating device for applying a variation of at least one of beam deflection, phase retardation or polarization rotation across the wavefronts of the TIR light. The first second and third grating devices are each sandwiched by transparent lamina.
Owner:DIGILENS
Organic light emitting diode display with a mirror function
The present disclosure relates to an organic light emitting diode (OLED) display having a mirror function to reflect external light for when the OLED display does not emit light. The organic light emitting diode display includes a substrate member, an organic light emitting element formed on the substrate member, a phase retardation plate formed on the organic light emitting element, and a selective reflective layer formed on the phase retardation plate. The selective reflective layer selectively passes some light from outside and reflects the rest.
Owner:SAMSUNG MOBILE DISPLAY CO LTD
Stereoscopic tft-lcd with wire grid polarizer affixed to internal surfaces substrates
InactiveUS20090310044A1Simple structureReduce manufacturing costSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsLithographic artistWire grid
A stereoscopic TFT-LCD with a wire grid polarizer affixed to internal surfaces substrates, applies to a LCD device having a thin polarizing film and a thin phase retardation film to display a 2D image and a 3D image, a thin film polarizing film formed by accurately processing a thin aluminum film, a polarizing film of a nano imprint lithography method that uses polymer, and a polarizing film and a liquid crystal material that form a polarizing nano material thin film by uniformly coating a polarizing nano material (TCF).
Owner:PAVONINE
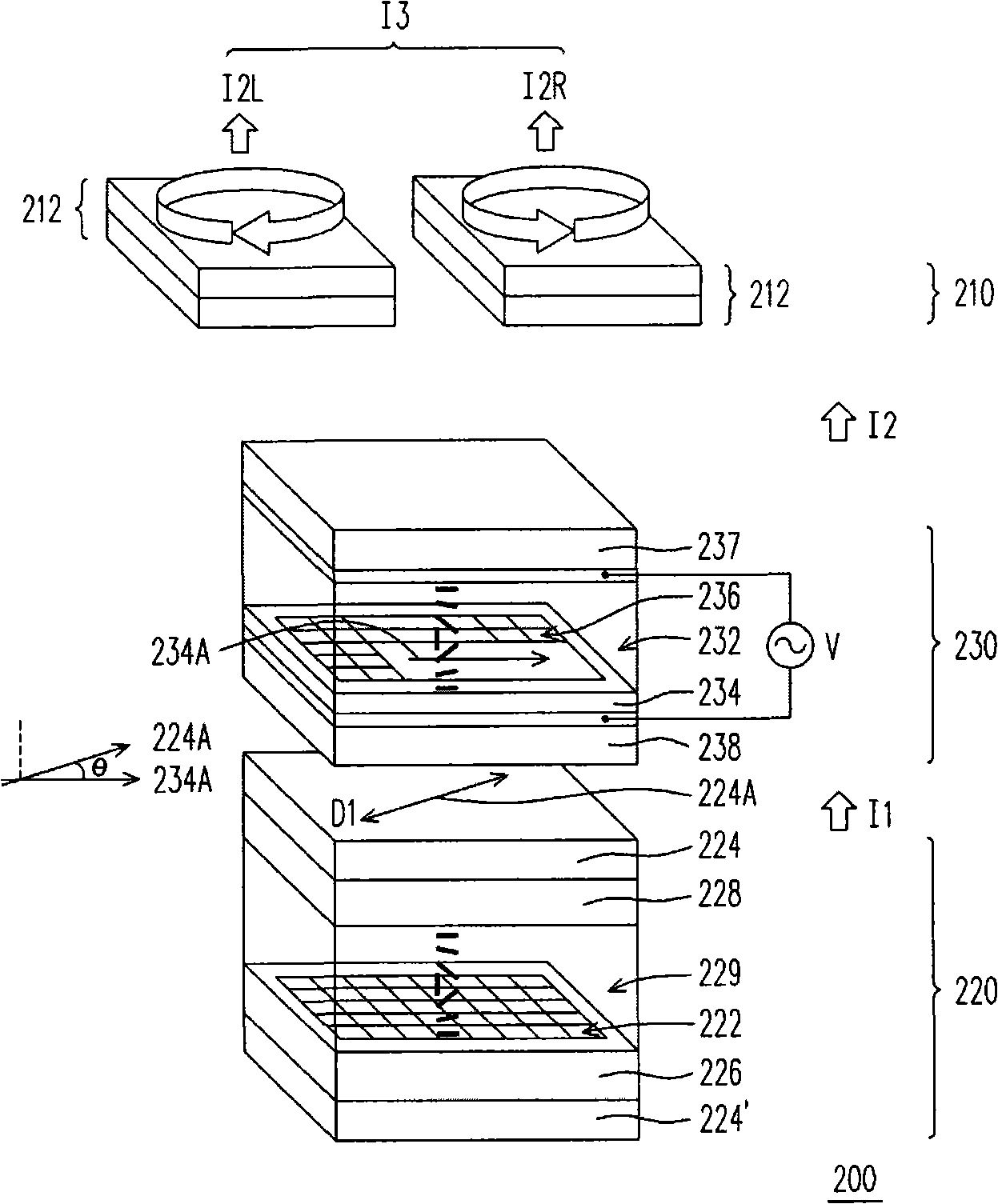
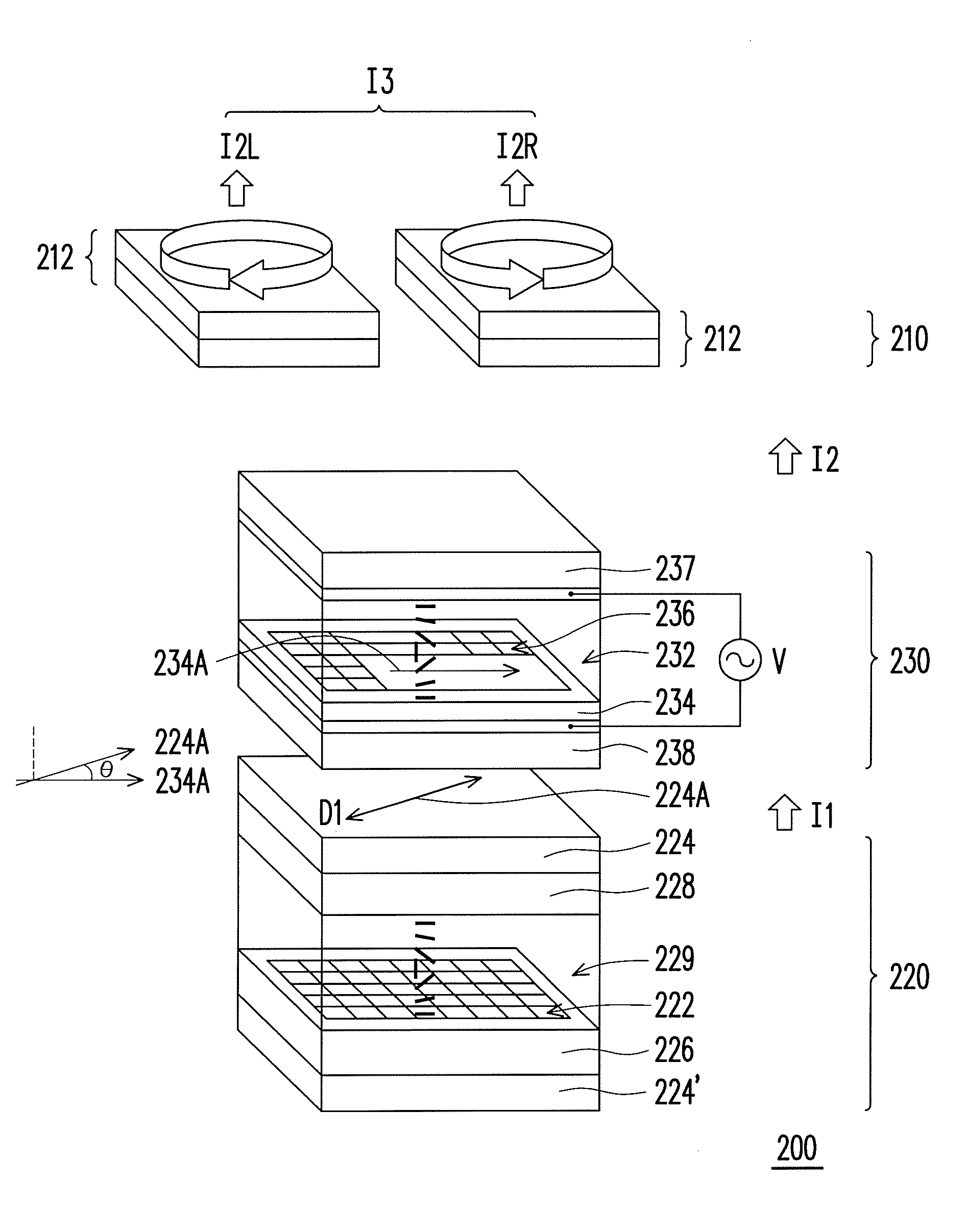
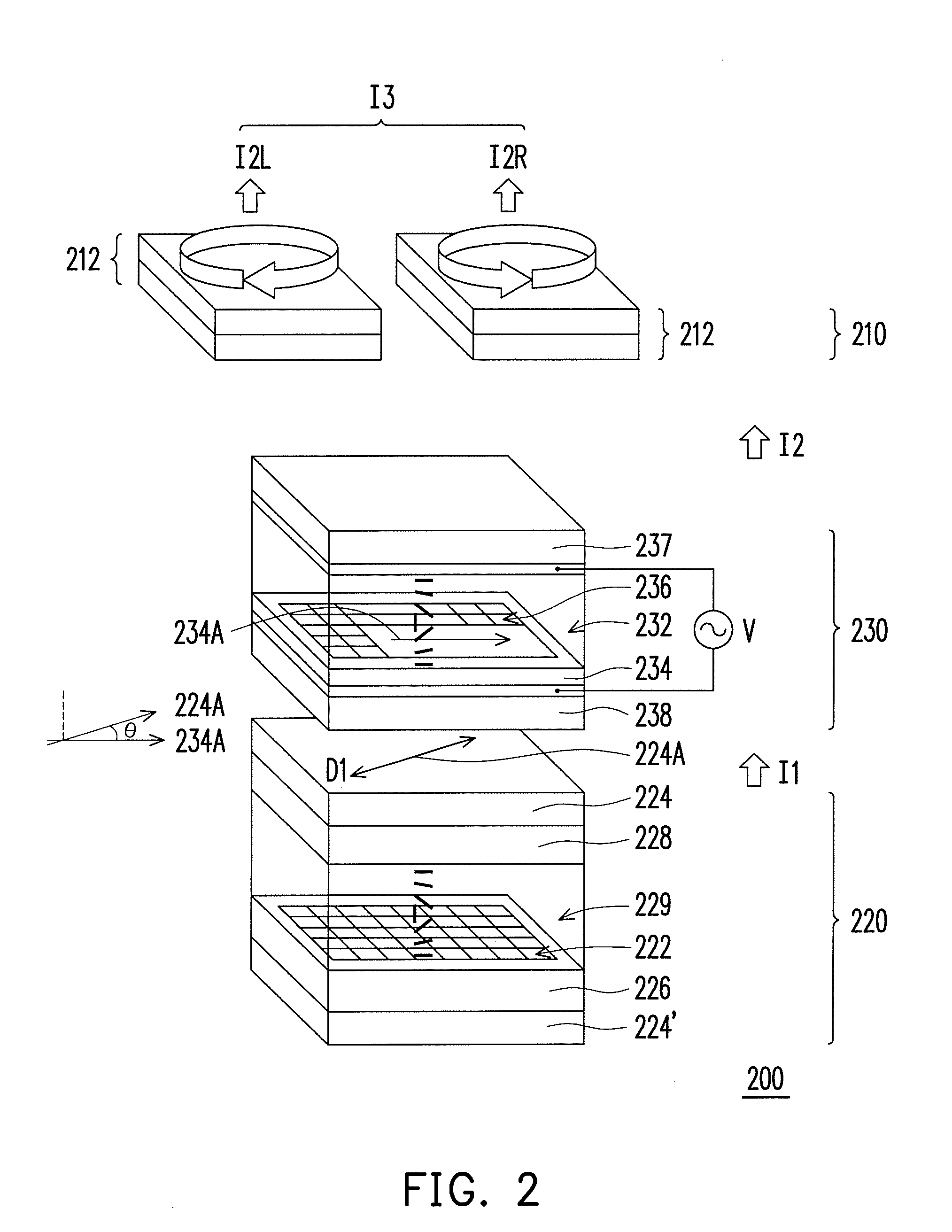
Three-dimensional display, fabricating method and controlling method thereof
ActiveUS20100060721A1Maintain resolutionAvoid flickeringSteroscopic systemsOptical elementsPhase retardationPolarizer
A three-dimensional display for the viewer to watch through glasses is provided, wherein the glasses have two lenses and the polarized directions thereof are perpendicular to each other. The three-dimensional display includes a display panel and a liquid crystal phase modulator. The display panel, suitable for displaying an image, has a plurality of pixels arranged in array and a polarizer having a transmission axis, wherein the polarizer disposed between the pixels and the glasses. The liquid crystal phase modulator suitable for providing phase retardation includes a liquid crystal layer and an alignment layer adjacent to the display panel. An included angle between an alignment direction of the alignment layer and the transmission axis is substantially equal to n×45 degrees, wherein an absolute value of n is an integer. The liquid crystal phase modulator adjusts a phase of the image and then outputs an image with three-dimensional information.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Synchronous phase-shift fiso interferometer
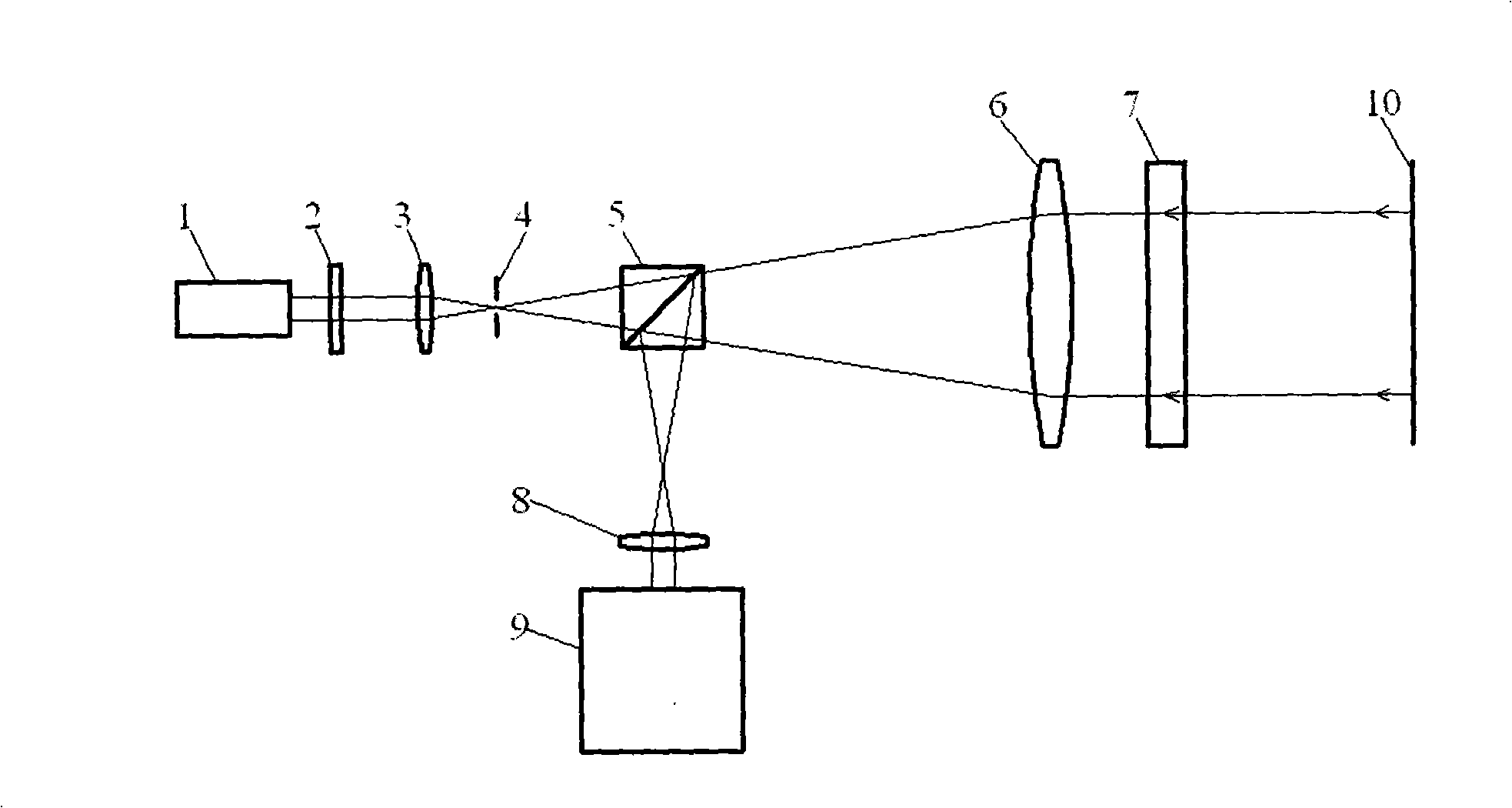
InactiveCN101324421AUnprincipled backhaul errorNo principle return errorOptical measurementsPolarising elementsBeam splitterPhase shifted
A synchronous phase-shifting Fizeau interferometer comprises a half-wave plate, a focusing lens, a diaphragm, a beam splitter, a first collimating lens, and a birefringent thin-film standard lens, which are arranged sequentially along the beam advancing direction of a linearly polarized laser source, wherein the diaphragm is positioned on the back focus and the front focus of the first collimating lens; a second collimating lens and a synchronous phase shifter are sequentially arranged in a direction perpendicular to the beam advancing direction of the beam splitter; the beam having a surface to be detected on the linearly polarized laser source passes through the emergent direction of the birefringent thin-film standard lens; the birefringent thin-film standard lens is a standard flat panel and has an antireflection film on the incident surface of the standard flat panel and a birefringent thin film and an antireflection film on the emergent surface; and the birefringent thin film has a phase delay of 90 DEG. The synchronous phase-shifting Fizeau interferometer has the advances of no principle return error, long measurement distance, simple structure and easy operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Liquid crystal film structures with phase-retardation surface regions formed therein
Disclosed are liquid crystal phase-retarders and linear polarizers and methods and apparatus for making the same. The liquid crystal phase-retarder is realized by a liquid crystal film structure having one or more phase retardation regions formed therein. Each phase retardation region has an optical axis specified by the direction and depth of orientation of liquid crystal molecules along the surface of the liquid crystal film structure. The liquid crystal linear polarizer is realized by a liquid crystal film structure having a chiral phase region within which liquid crystal molecules are cholesterically ordered (FIG. 3). One or more nematic phase regions are formed along the surface of the liquid crystal film structure within which liquid crystal molecules are oriented along a direction and to a surface depth sufficient to realize one or more phase retardation regions therein having optical axes along the direction of liquid crystal molecules orientation.
Owner:REVEO
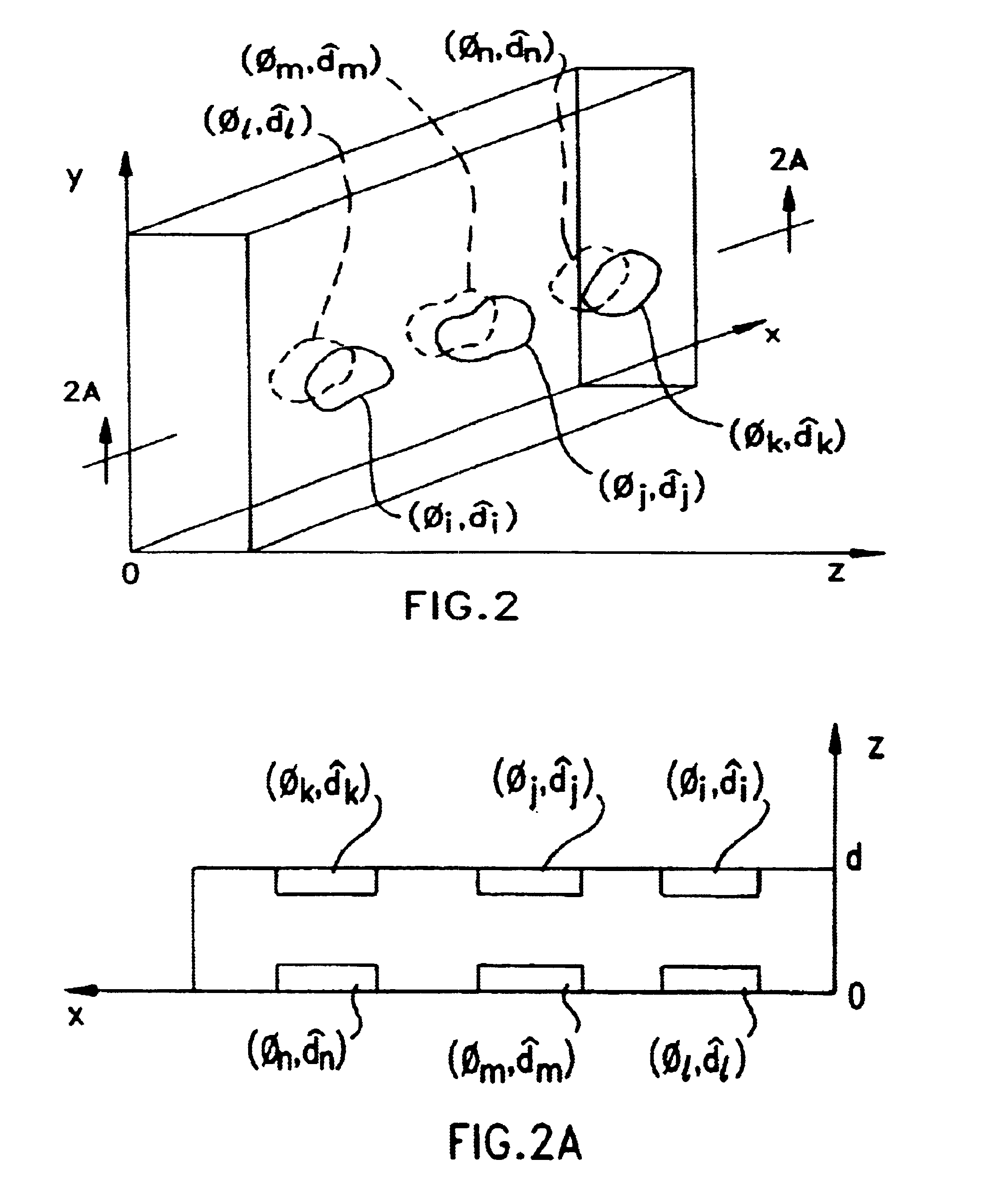
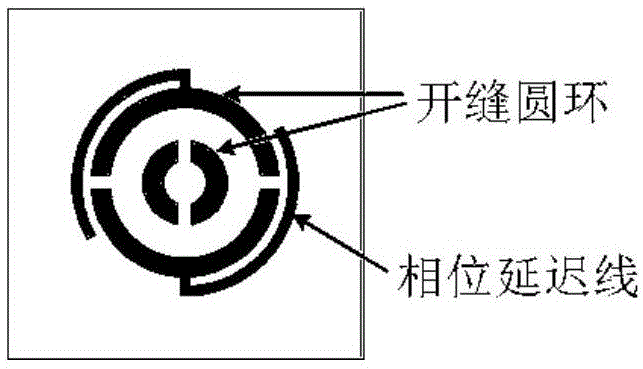
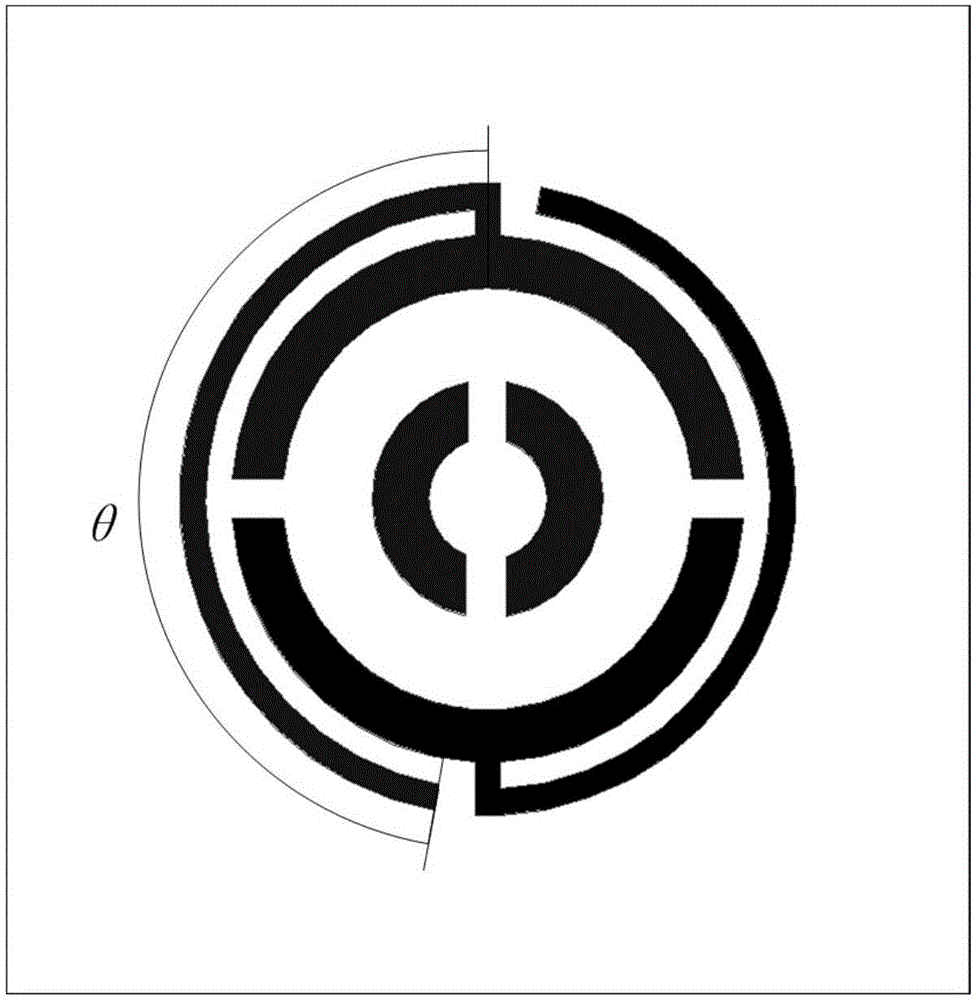
Phase delay linetype reflector element based reflective array antenna
ActiveCN105140655ASuppression of cross-polarization componentsAntennasUltra wideband antennasPhase retardation
The invention provides a phase delay linetype reflector element based reflective array antenna. The reflective array antenna comprises a pyramid horn feed source and a reflector array, wherein the reflector array is formed by periodically arranging a plurality of phase delay linetype reflector elements in a mirror symmetry manner; and the phase delay linetype reflector element structure comprises two slotting circular ring nests and two phase delay lines that are in opposite in positions. The gain bandwidth of the reflector array antenna is greatly increased, an ultra wide band antenna is realized, and cross polarization is effectively restrained as well; and in addition, the reflection array antenna provided by the invention adopts a single-layer dielectric substrate structure, so that the reflector array is simple in structure, easy to process, low in cost and light in weight.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Multilayered optical film, manufacturing method thereof, and display device
ActiveUS20130301129A1Lamination ancillary operationsPolarising elementsPhase retardationOptical axis
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com