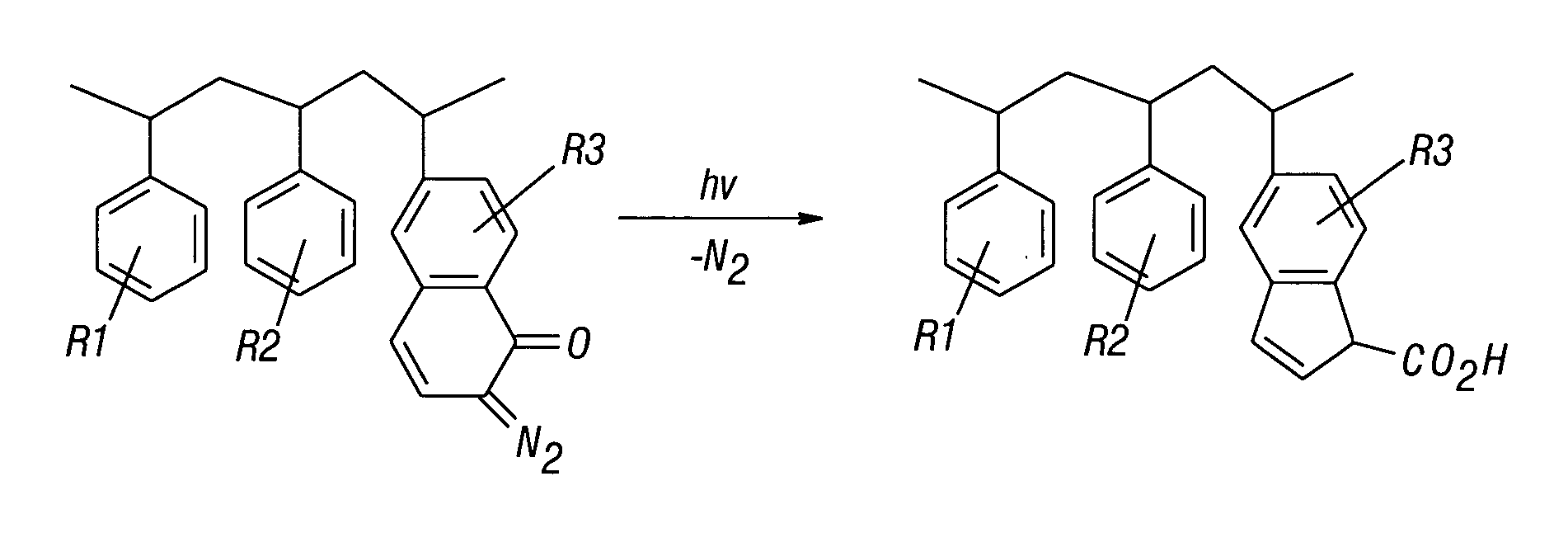
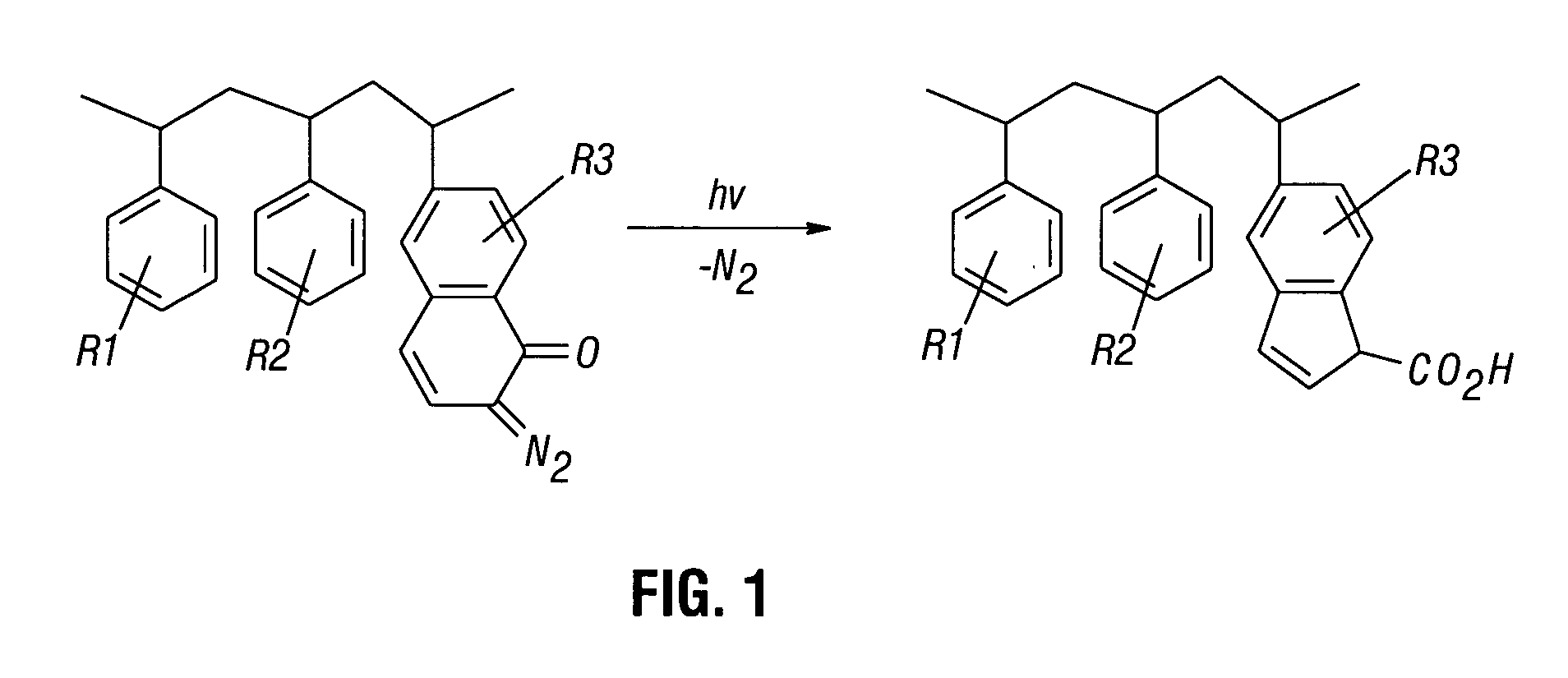
Patents
Literature
18660 results about "Contrast ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The contrast ratio is a property of a display system, defined as the ratio of the luminance of the brightest color (white) to that of the darkest color (black) that the system is capable of producing. A high contrast ratio is a desired aspect of any display. It has similarities with dynamic range.
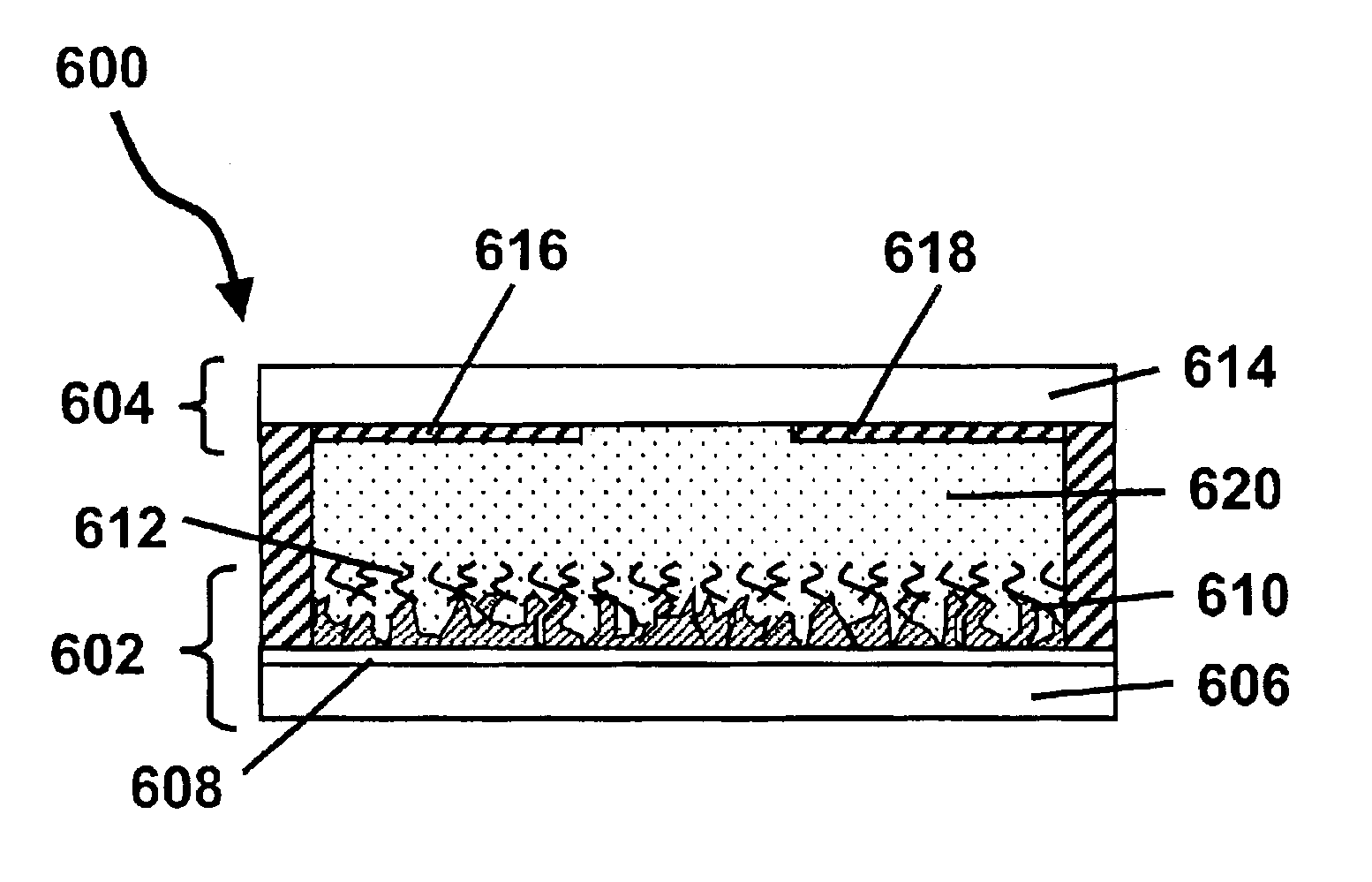
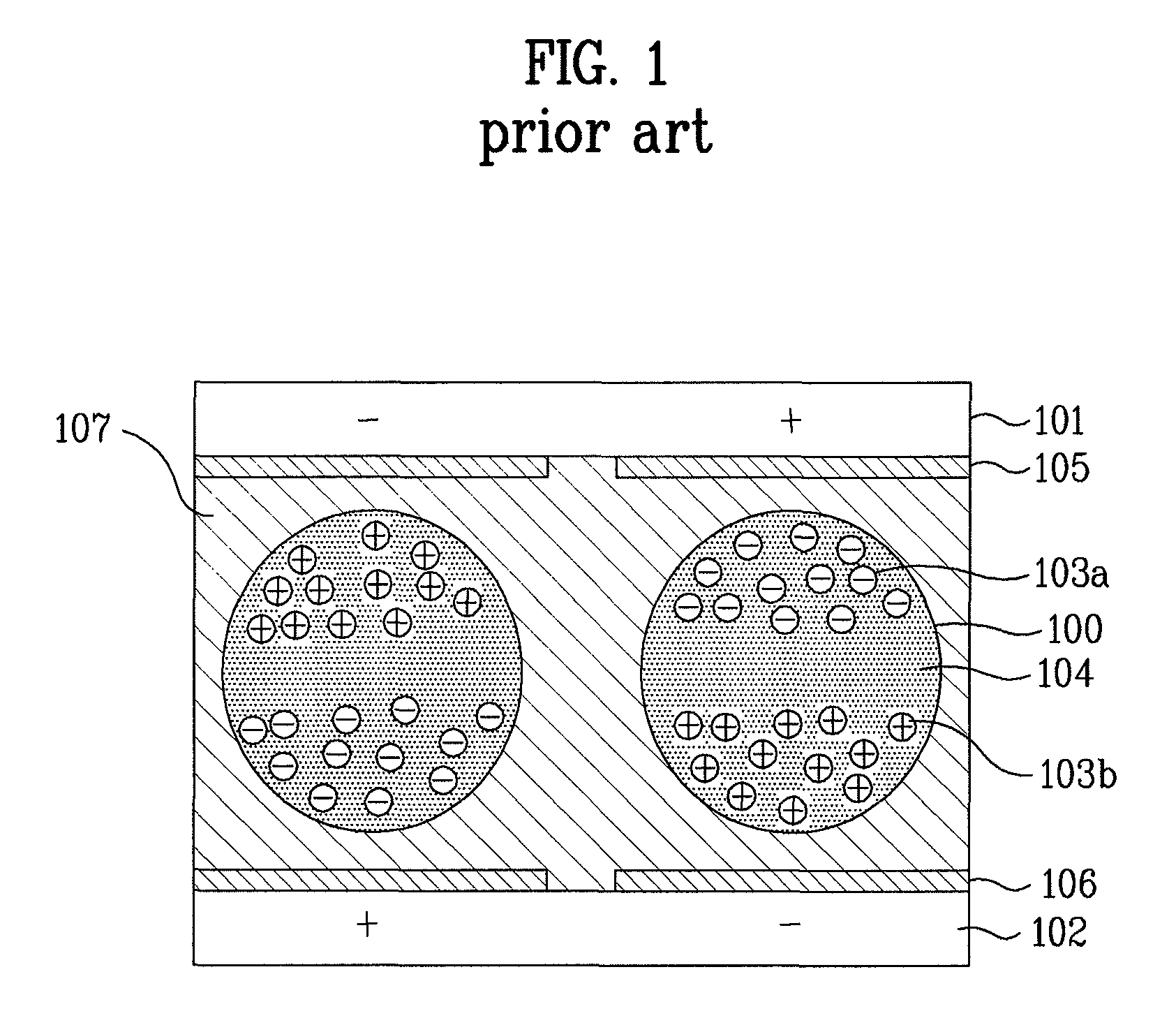
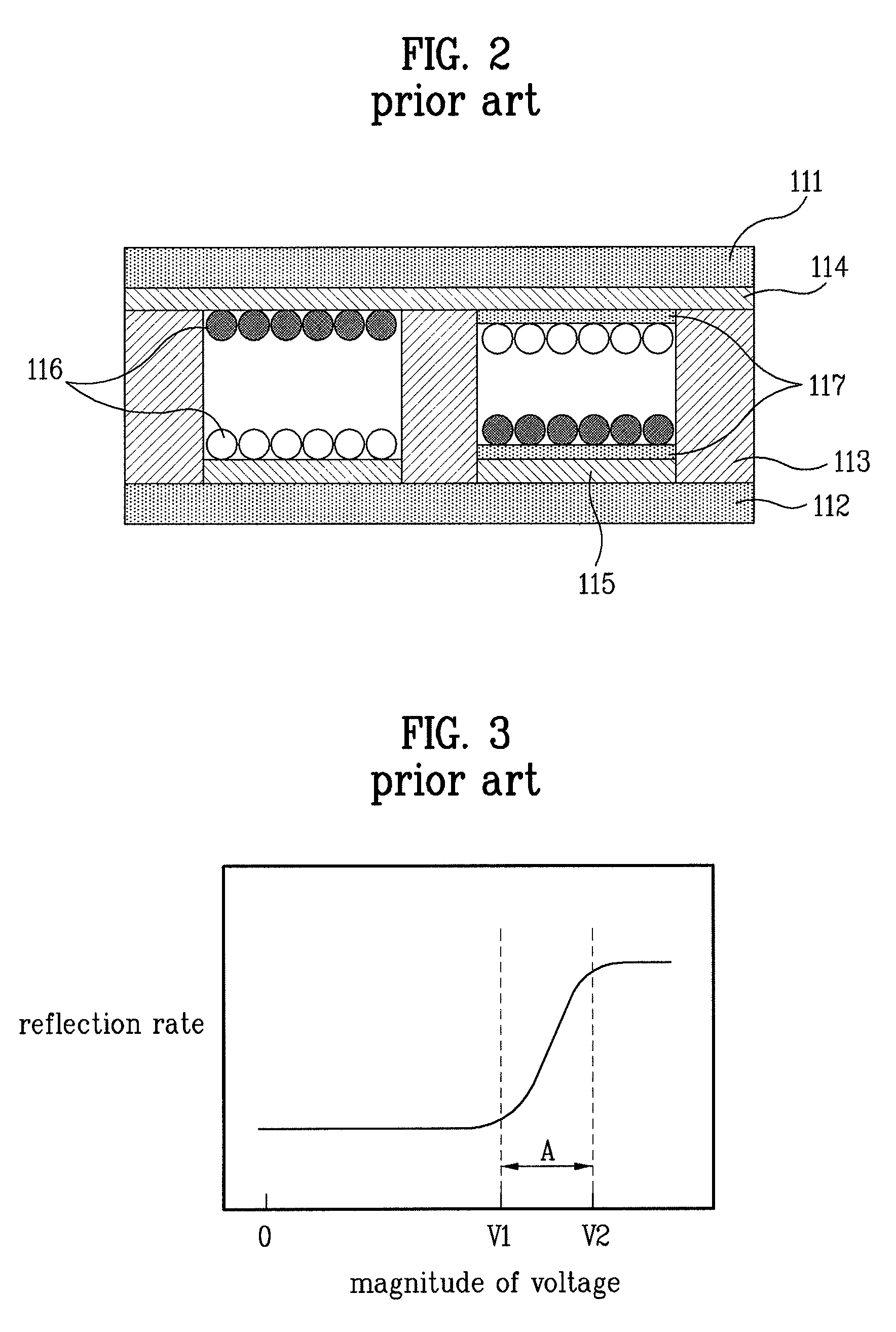
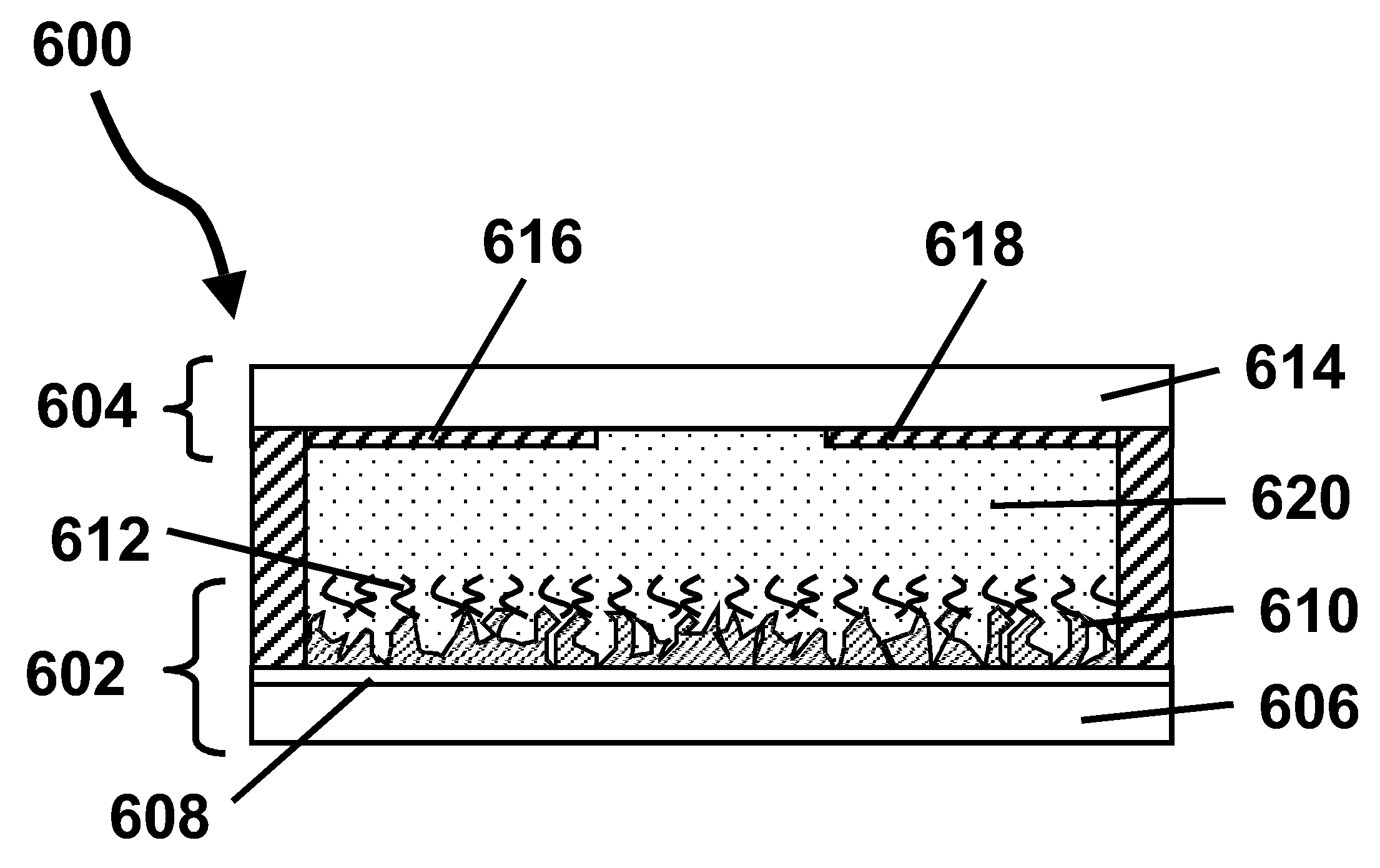
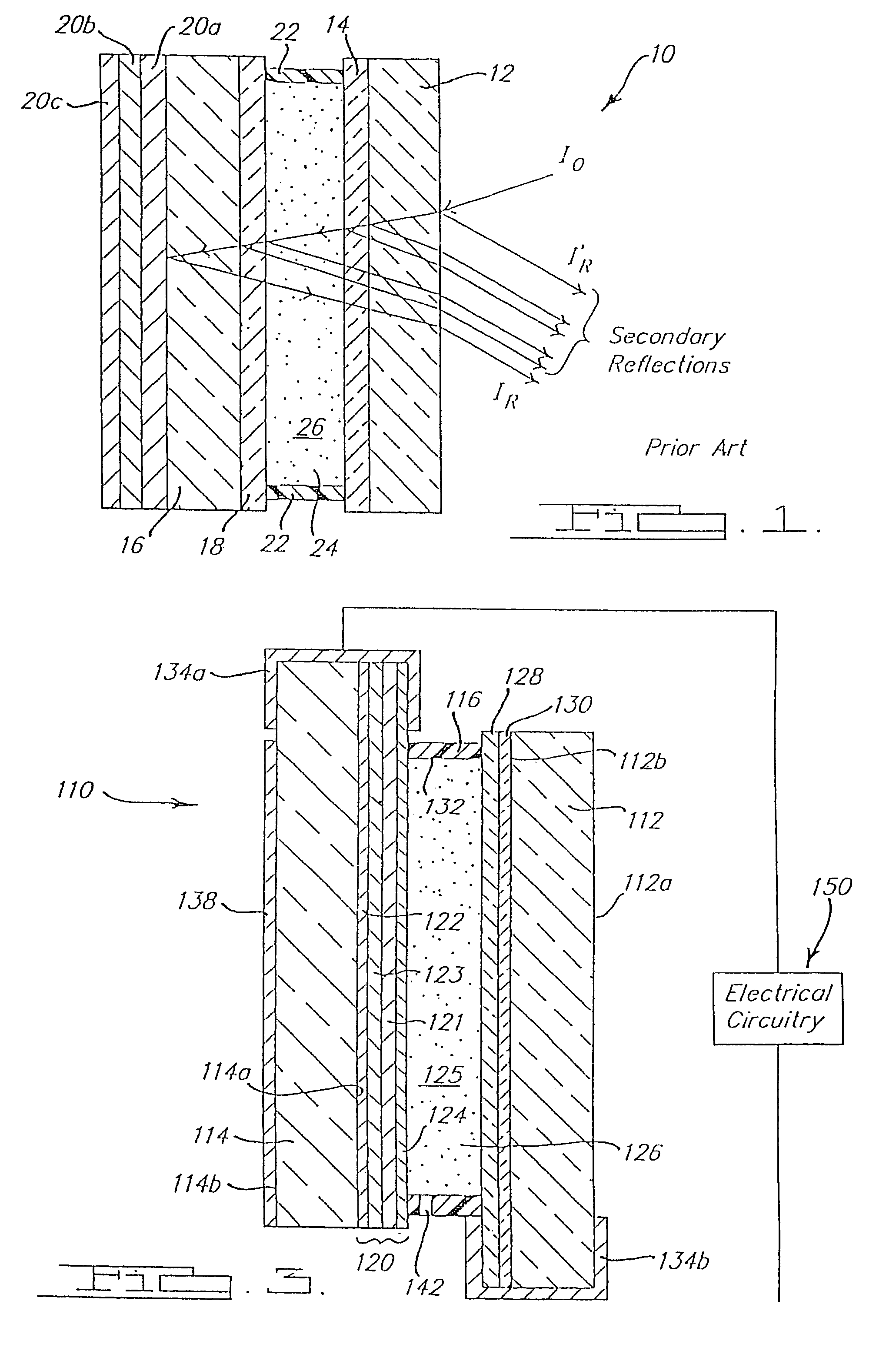
Electro-optic displays, and methods for driving same
InactiveUS6950220B2Reduce and eliminate exposureReducing and eliminating light degradationNon-linear opticsElectricityTransport layer
The invention relates to electro-optic displays and methods for driving such displays. The invention provides (i) electrochromic displays with solid charge transport layers; (ii) apparatus and methods for improving the contrast and reducing the cost of electrochromic displays; (iii) apparatus and methods for sealing electrochromic displays from the outside environment and preventing ingress of contaminants into such a display; and (iv) methods for adjusting the driving of electro-optic displays to allow for environmental and operating parameters.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
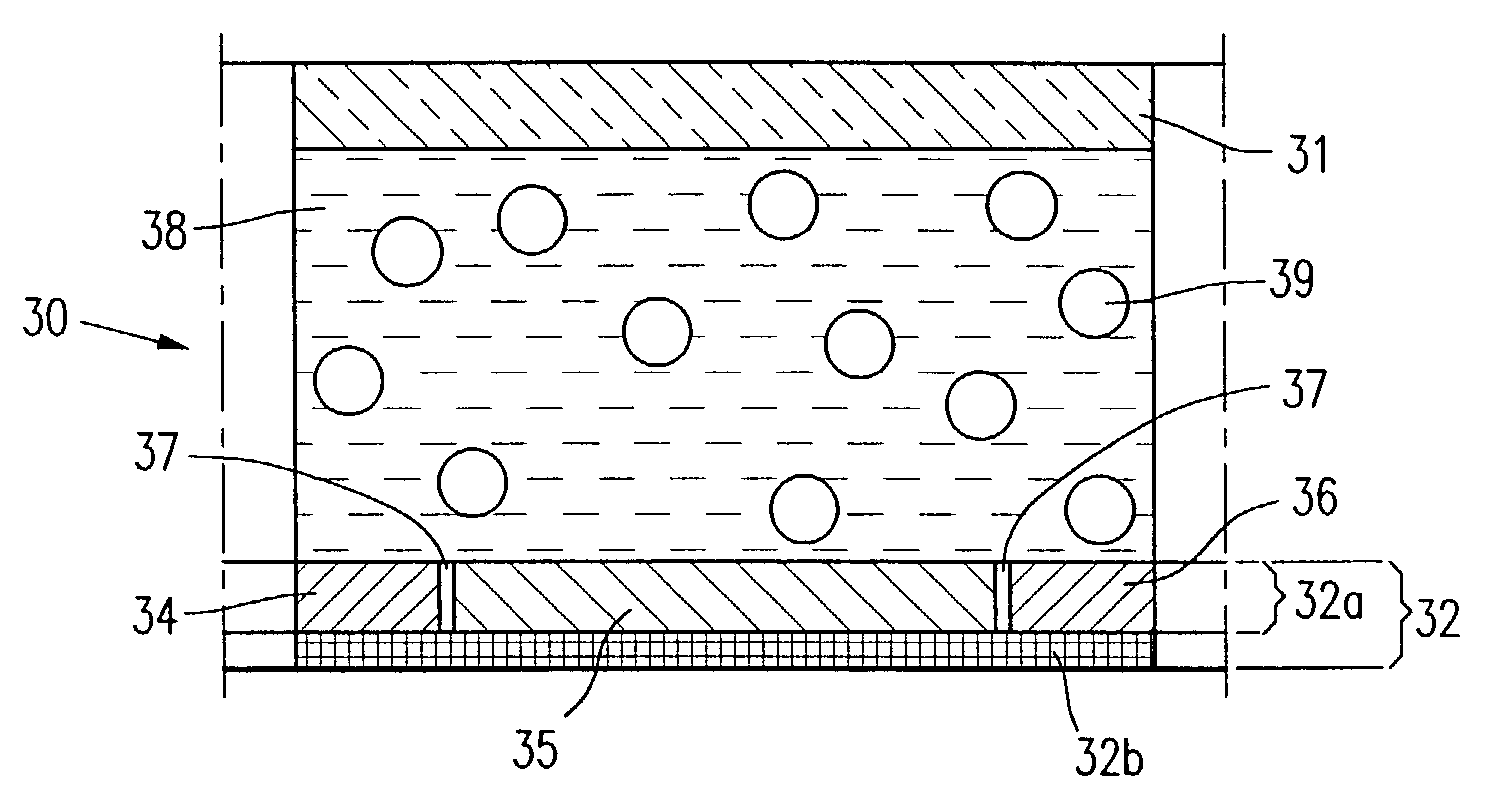
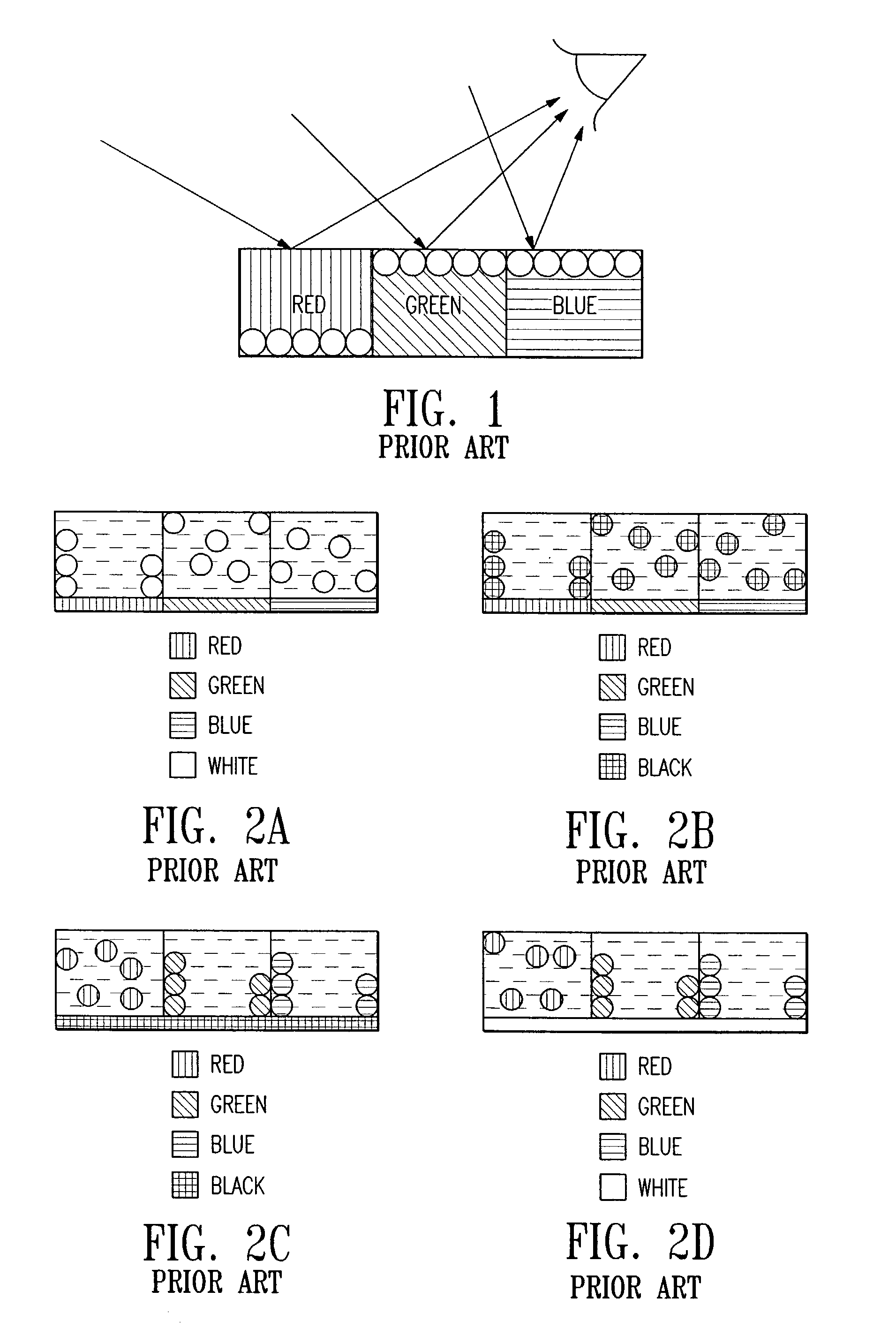
Particle use for image display media, image display panel using the particles, and image display device
InactiveUS7236291B2Increase brightness factorImprove reflectivityStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsComputer graphics (images)Display device
An image display device, in which image display media are sealed between opposed substrates, at least one of two substrates being transparent, and in which the image display media, to which an electrostatic field is applied, are made to move so as to display an image. A construction of particles used as the image display media is improved (the first, second, fourth, fifth, sixth, eighth and ninth aspects of the invention), and a material of the particles used as the image display media is improved (the third, seventh and tenth aspects of the invention). Whiteness of the particles and a liquid powder using the particles is improved, particle agglutination is prevented, and the charge property is controlled. Moreover, durability is improved such that a contrast of the image display during a repetition display is not decreased. As a result, an excellent image display can be achieved.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Liquid crystal display device and method of manufacture of the same
InactiveUS20060103804A1Improve reliabilityLittle and no tendency to exhibit white lineLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayReduced contrast volume
A liquid crystal composition, comprising a liquid crystal and a polymerizable compound capable of polymerization by means of light, heat, or a combination thereof, is placed in the gap between two parallel substrates on which are formed a pair of electrodes, and the polymerizable compound is polymerized to form a liquid crystal layer and a resin film. A liquid crystal display device is manufactured accordingly. The polymerizable compound comprises a monofunctional polymerizable compound, and the dipole moment of the monofunctional polymerizable compound is 4 debyes or lower. Thus, a liquid crystal display device, with high reliability, and of excellent quality with little or no contrast reduction due to white lines, is provided.
Owner:SHARP KK
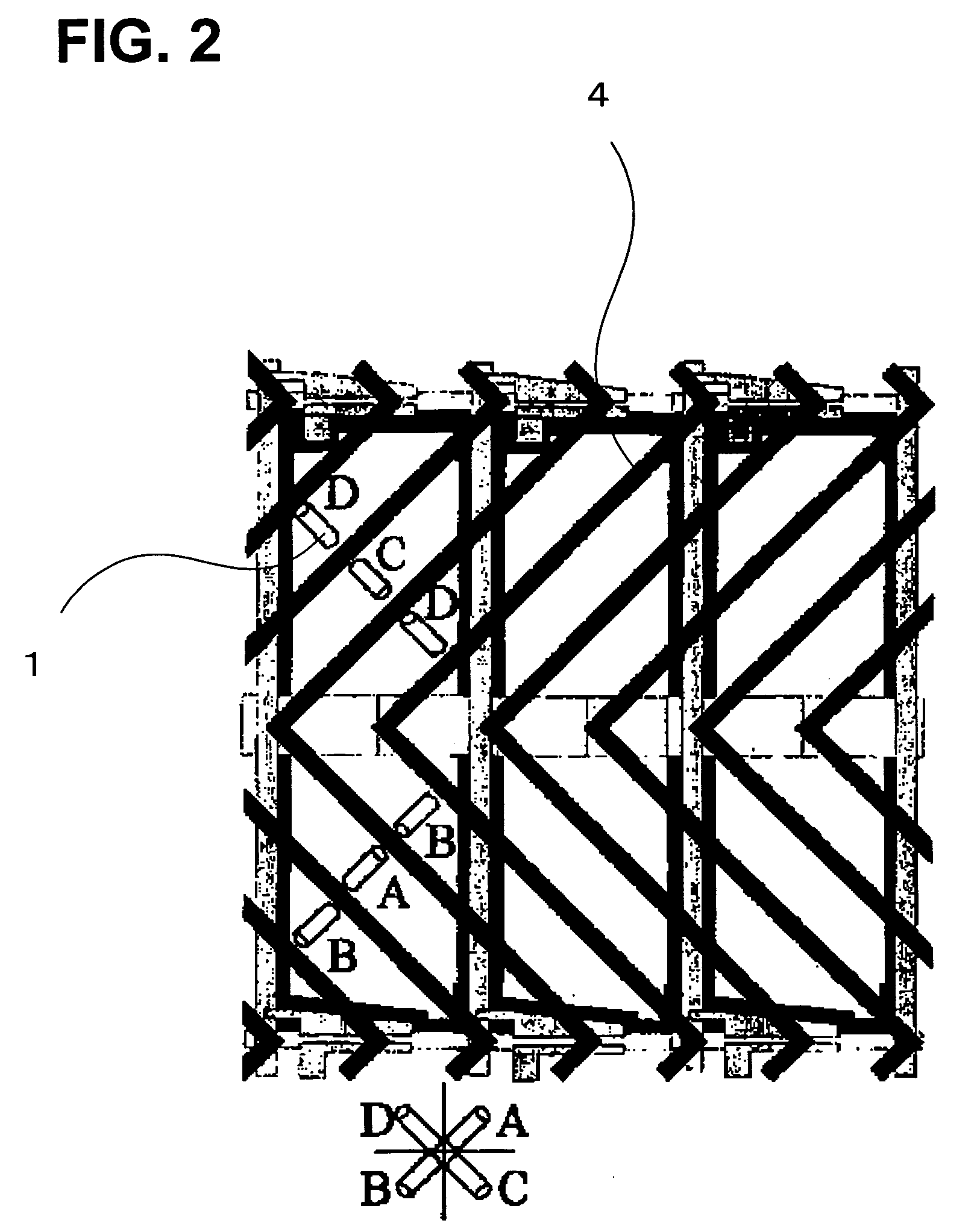
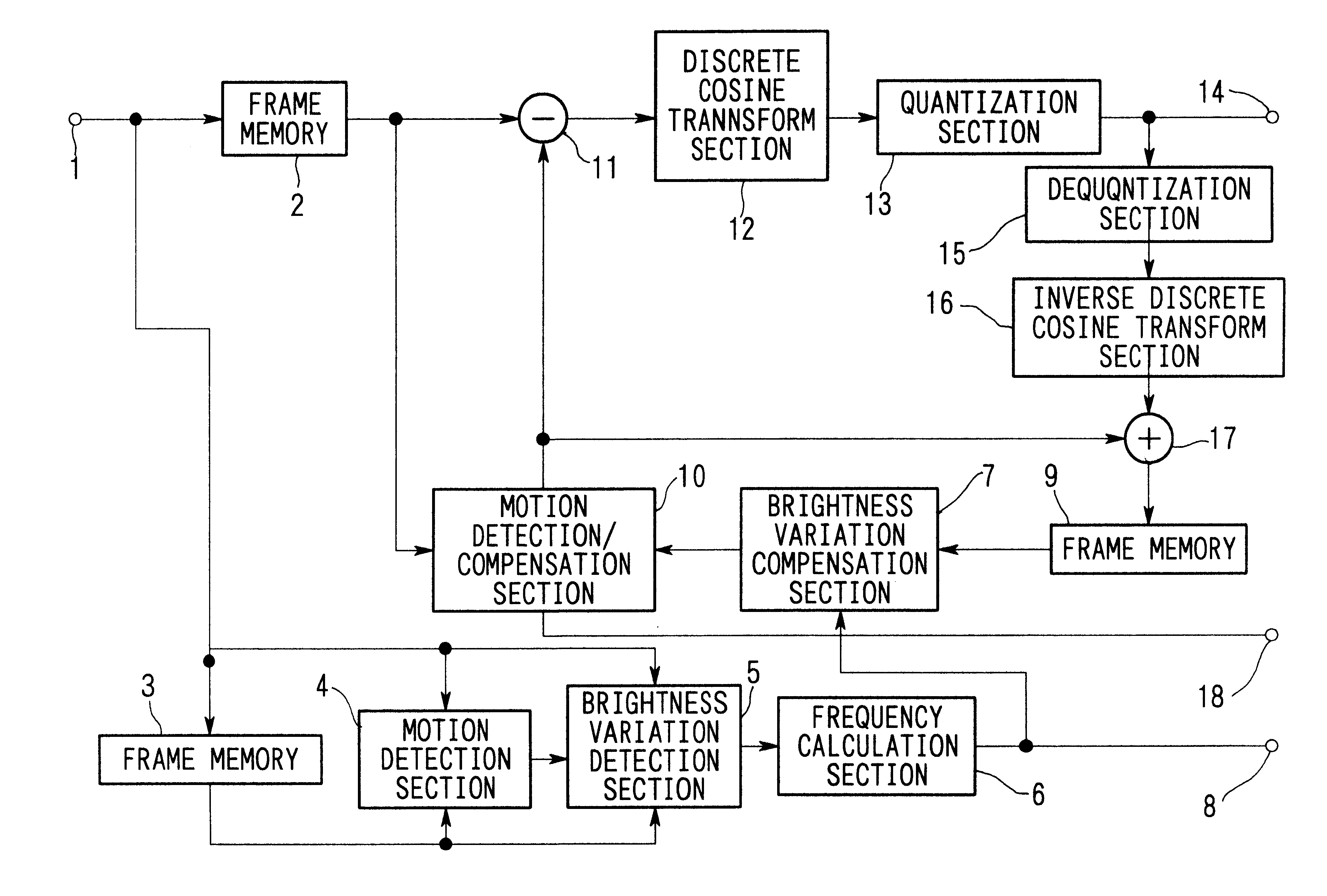
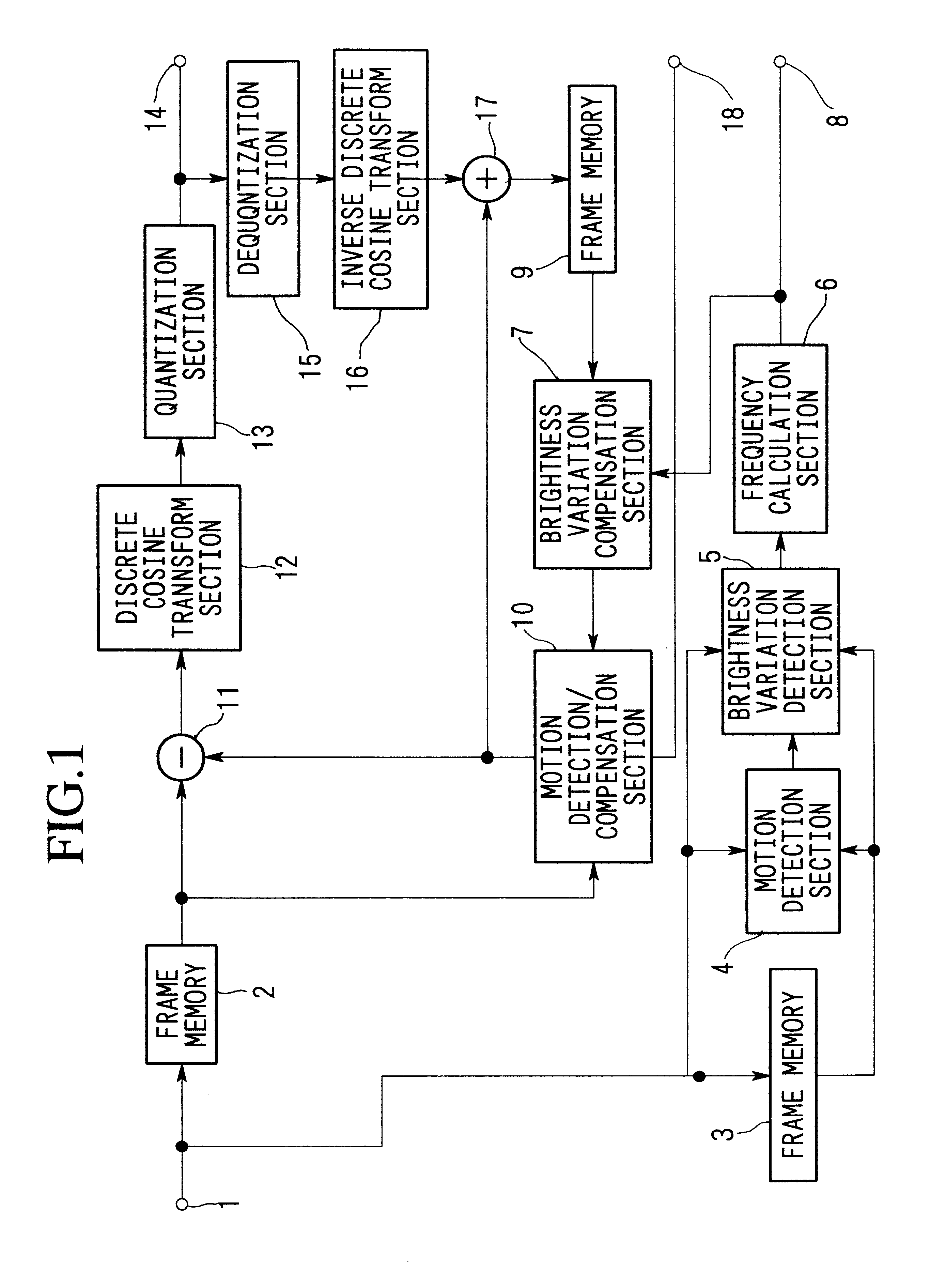
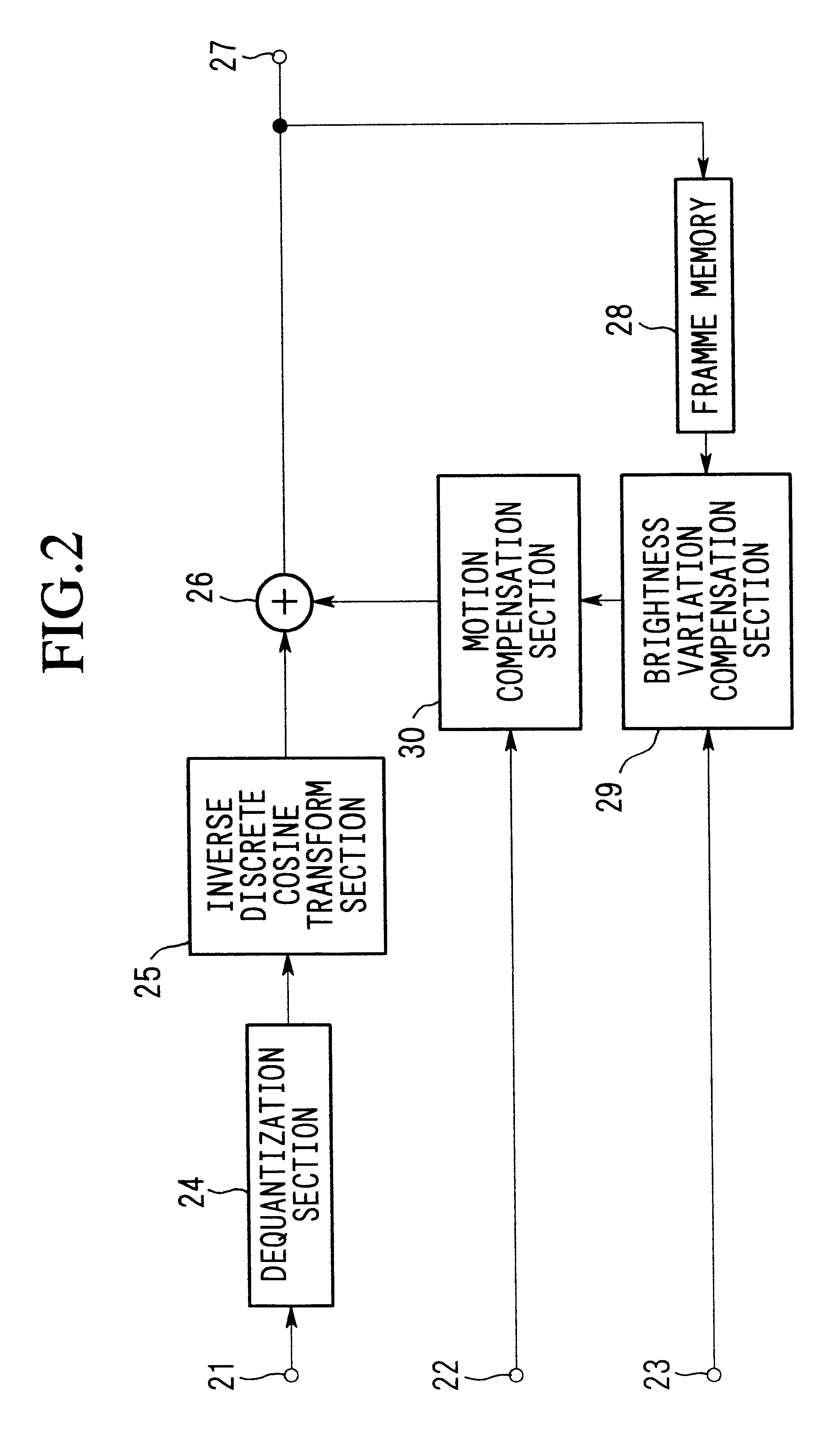
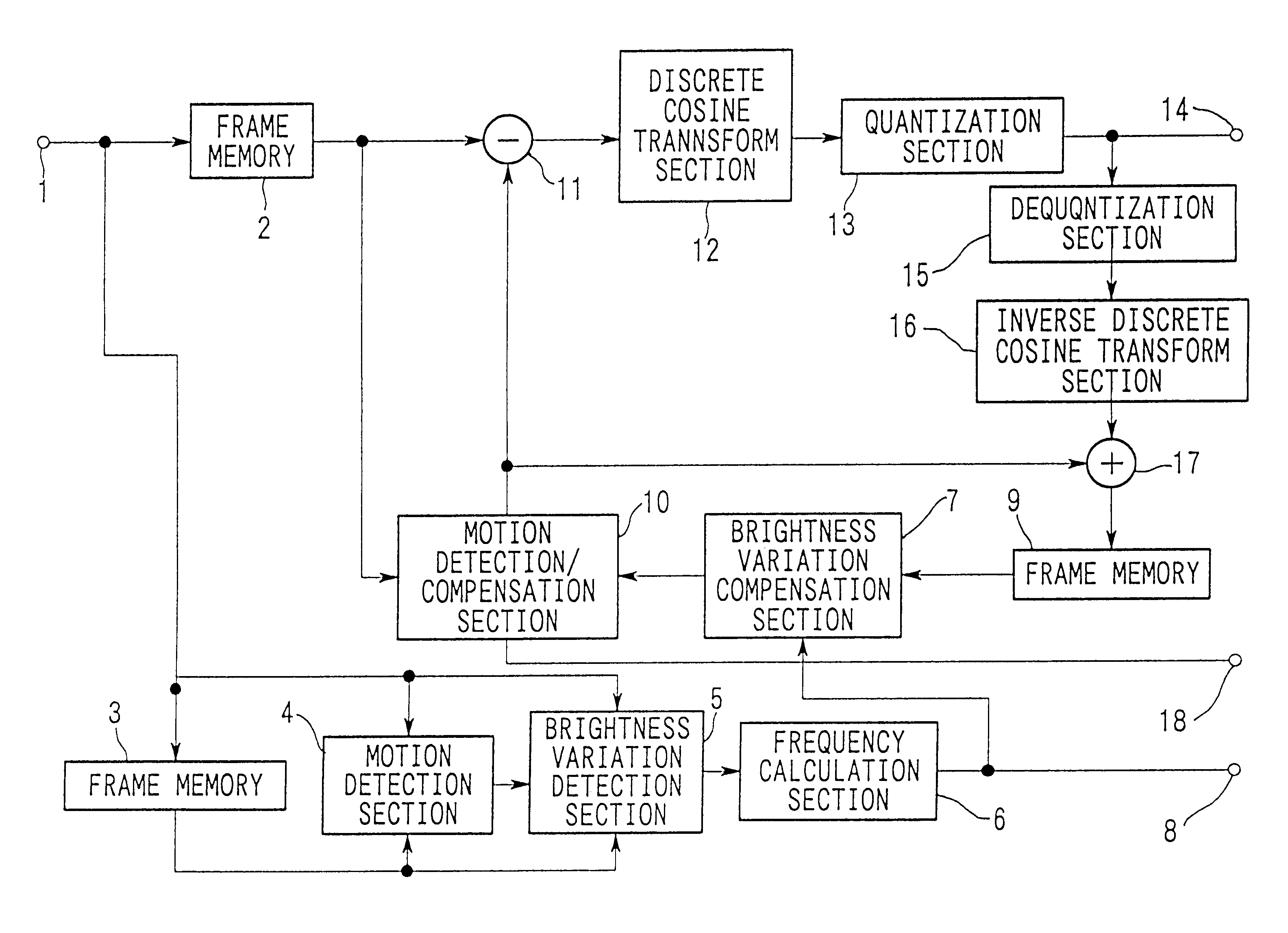
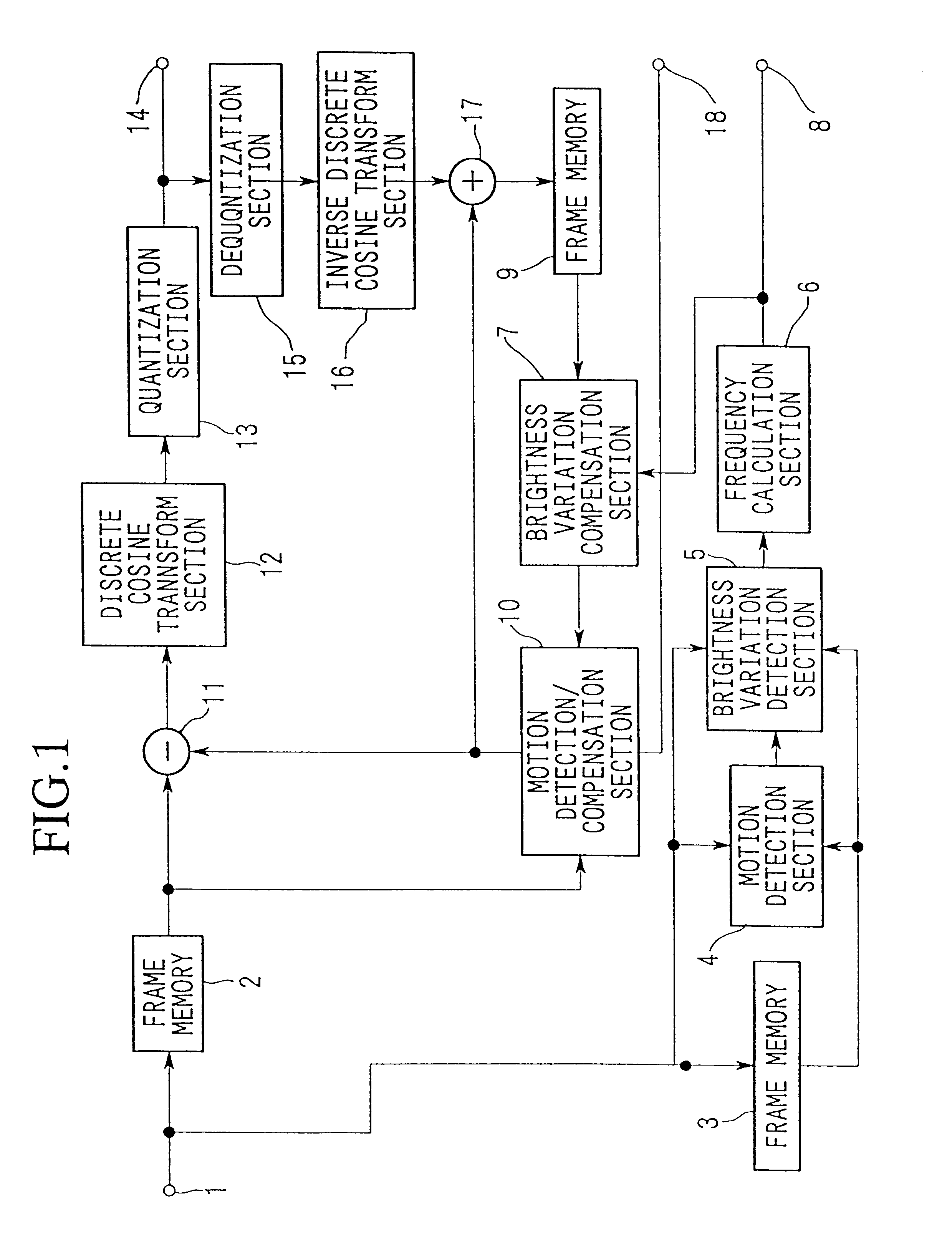
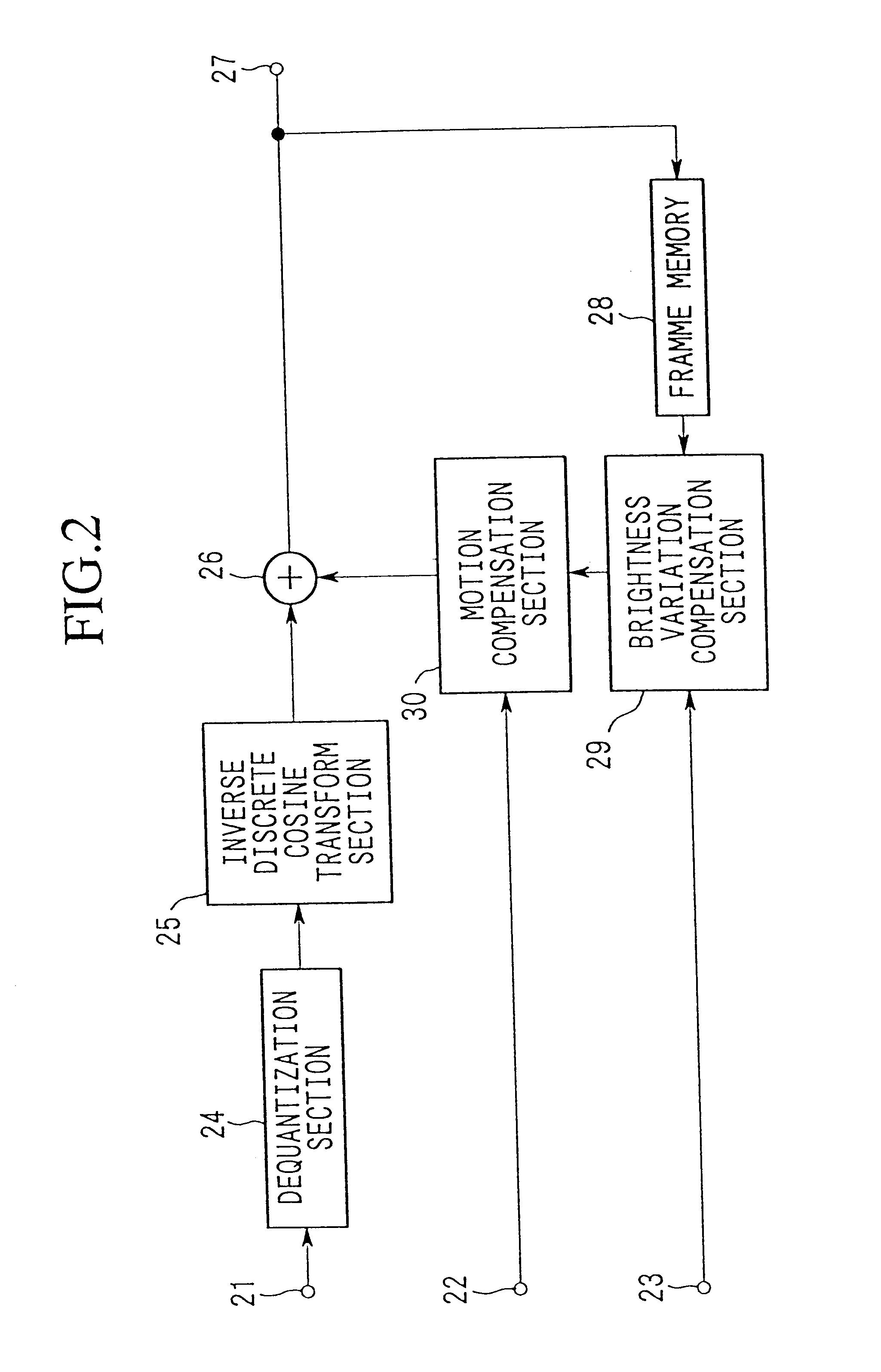
Brightness-variation compensation method and coding/decoding apparatus for moving pictures
InactiveUS6266370B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImaging processingReference image
A moving image brightness variation compensation method for encoding digital moving images for transmission and storage, and for image processing when editing moving images, the moving image brightness variation compensation method comprising a step of compensating for overall brightness variations by correcting a luminance value x of each pixel according to the formula DC.x+DB, wherein DB is a parameter indicating a gain change and DC is a parameter indicating a contrast change, the parameters representing overall luminance changes between a reference image plane and an image plane being processed.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Brightness-variation compensation method and coding/decoding apparatus for moving pictures
InactiveUS6456658B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImaging processingReference image
A moving image brightness variation compensation method for encoding digital moving images for transmission and storage, and for image processing when editing moving images, the moving image brightness variation compensation method comprising a step of compensating for overall brightness variations by correcting a luminance value x of each pixel according to the formula DC.x+DB, wherein DB is a parameter indicating a gain change and DC is a parameter indicating a contrast change, the parameters representing overall luminance changes between a reference image plane and an image plane being processed.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Electronic paper display device, manufacturing method and driving method thereof
InactiveUS7751115B2Quick responseReduce voltageStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsVoltage pulseElectrophoresis
An electronic paper display device, a manufacturing method and a driving method thereof are disclosed. Micro protrusion members are formed at electrodes or at insulating layers. Consequently, the electrophoretic particles are prevented from being securely attached to an upper or the lower structure, and therefore, the quality of pictures is improved, and the contrast ratio of the pictures is increased. The relative sizes and the injection amounts of two kinds of electrophoretic particles are changed such that the relative sizes and the injection amounts of the electrophoretic particles are different from each other. Consequently, the driving voltage is lowered by excessively electrifying the electrophoretic particles of one kind. Protrusions are formed at the corresponding electrode such that a relatively large electric field is distributed around the electrode at which electrophoretic particles are located in the initial stage of voltage application. Consequently, the electrophoretic particles are easily separated from the electrode and moved even at low driving voltage. As such, the voltage level of the driving voltage pulse is lowered. Consequently, it is possible to further increase the response speed of the driving devices and to lower the internal voltage of the devices, thereby reducing the costs related to the driving devices.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
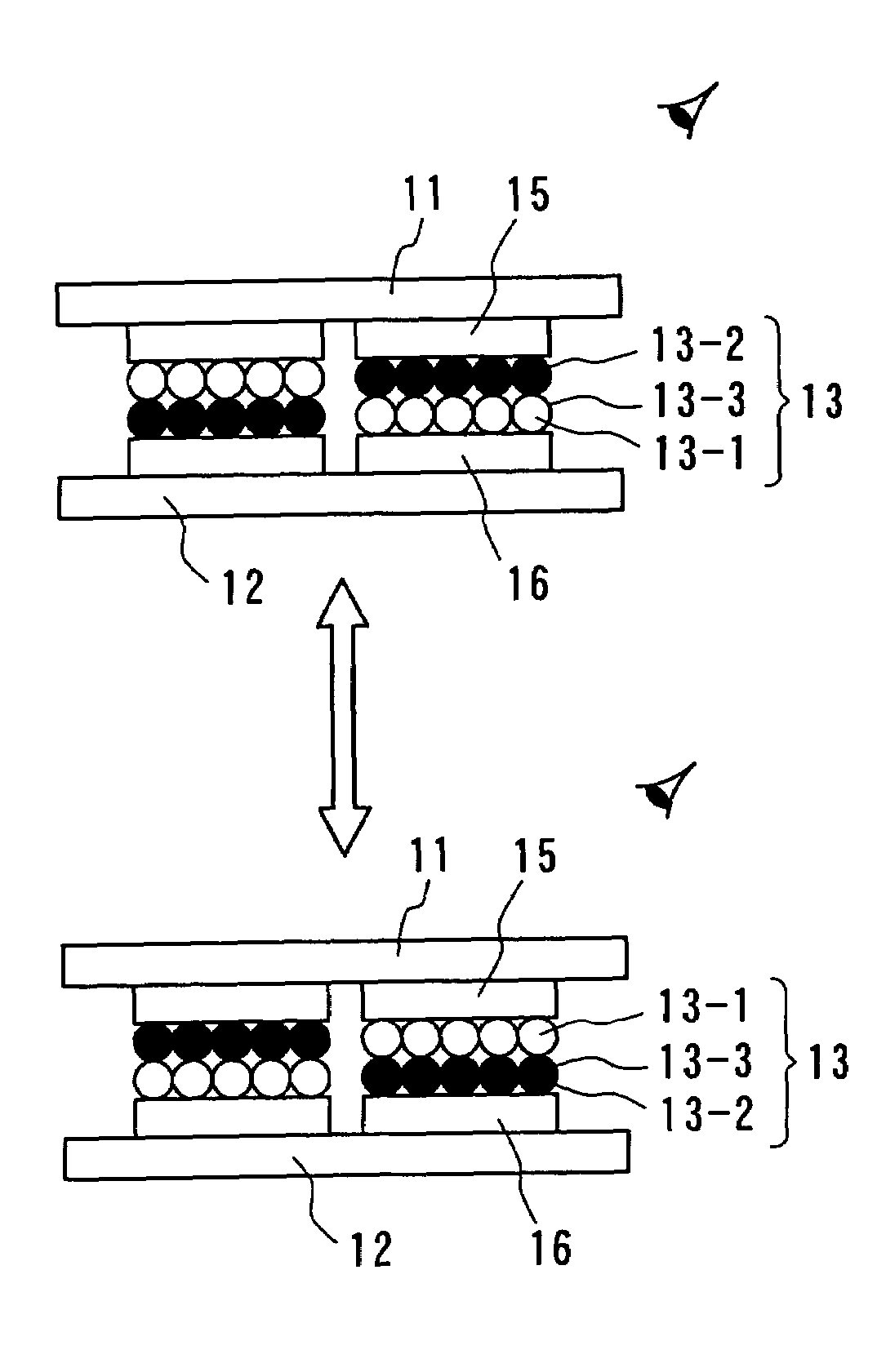
Electrophoretic display with dual mode switching
InactiveUS7046228B2Low costIncrease contrastStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsIn planeDual mode
The present invention relates to an improved EPD which comprises both the traditional up / down switching and the in-plane switching modes. In other words, the improved EPD has dual switching modes.The monochrome EPDs of the present invention are capable of displaying highlight color of choice which is different from the text. For example, white background, blue text, and red highlight can be shown in any selected areas of the display. Furthermore, the full color EPDs of the present invention are capable of displaying high contrast images of high color saturation. Both high quality black and white states are possible in the full color displays of the present invention. The EPDs of the present invention do not need complex circuitry design, and are compatible with low cost and high yield roll-to-roll manufacturing processes.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
High performance selective light wavelength filtering providing improved contrast sensitivity
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
One component EUV photoresist
In one embodiment, a photoactive compound may be attached to a polymer backbone. This embodiment may be more resistant to the generation of reactive outgassing components and may exhibit better contrast.
Owner:INTEL CORP
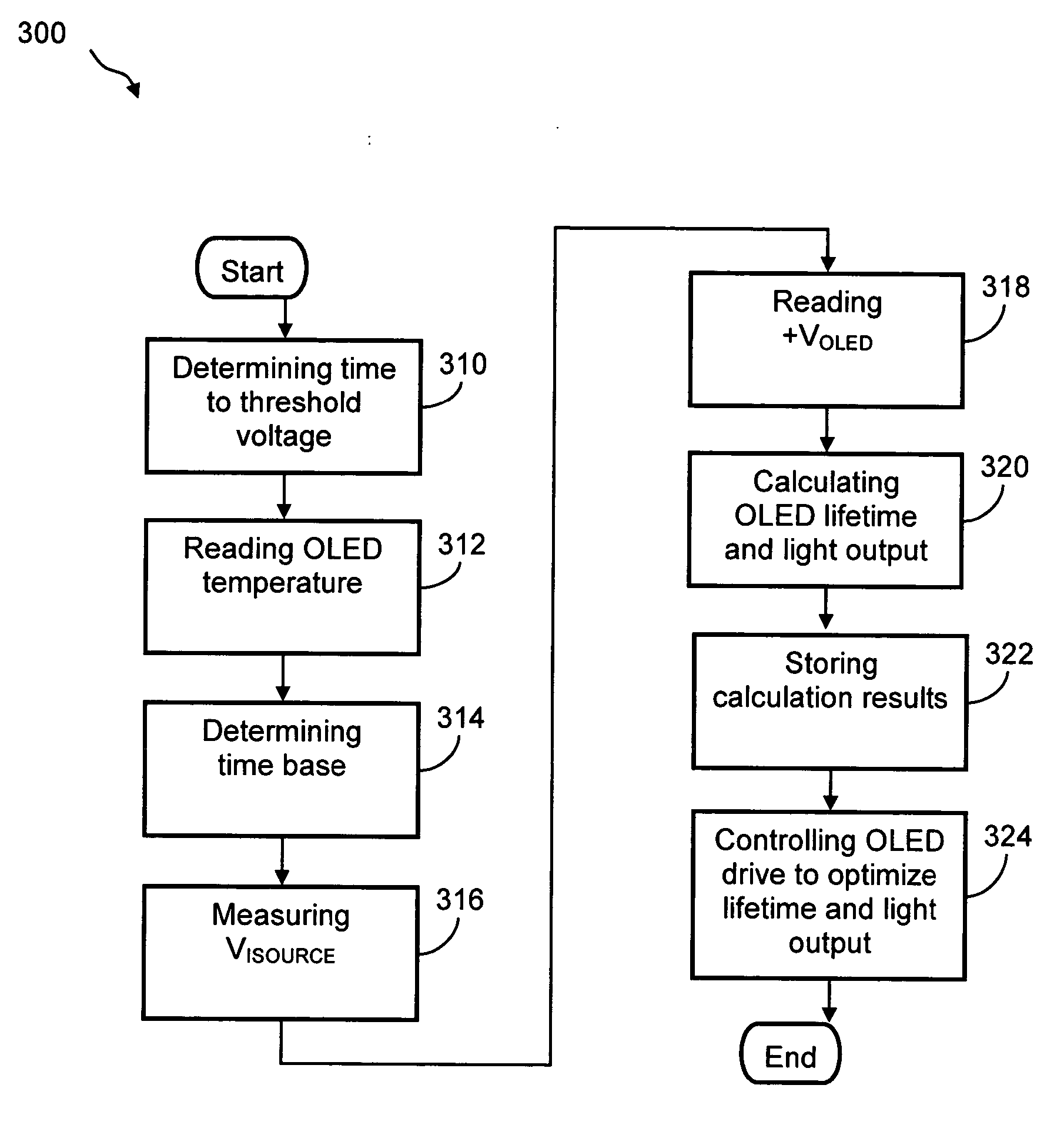
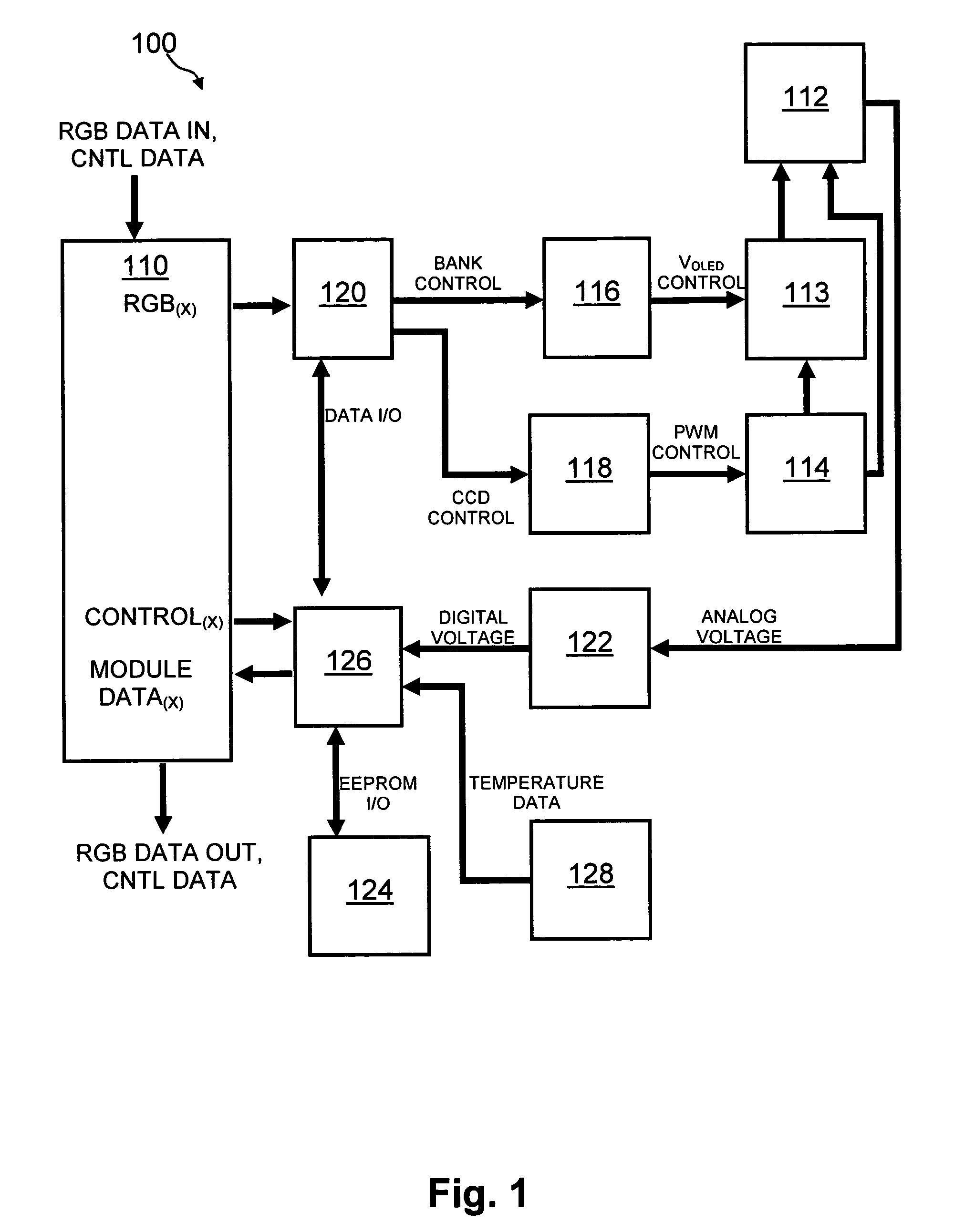
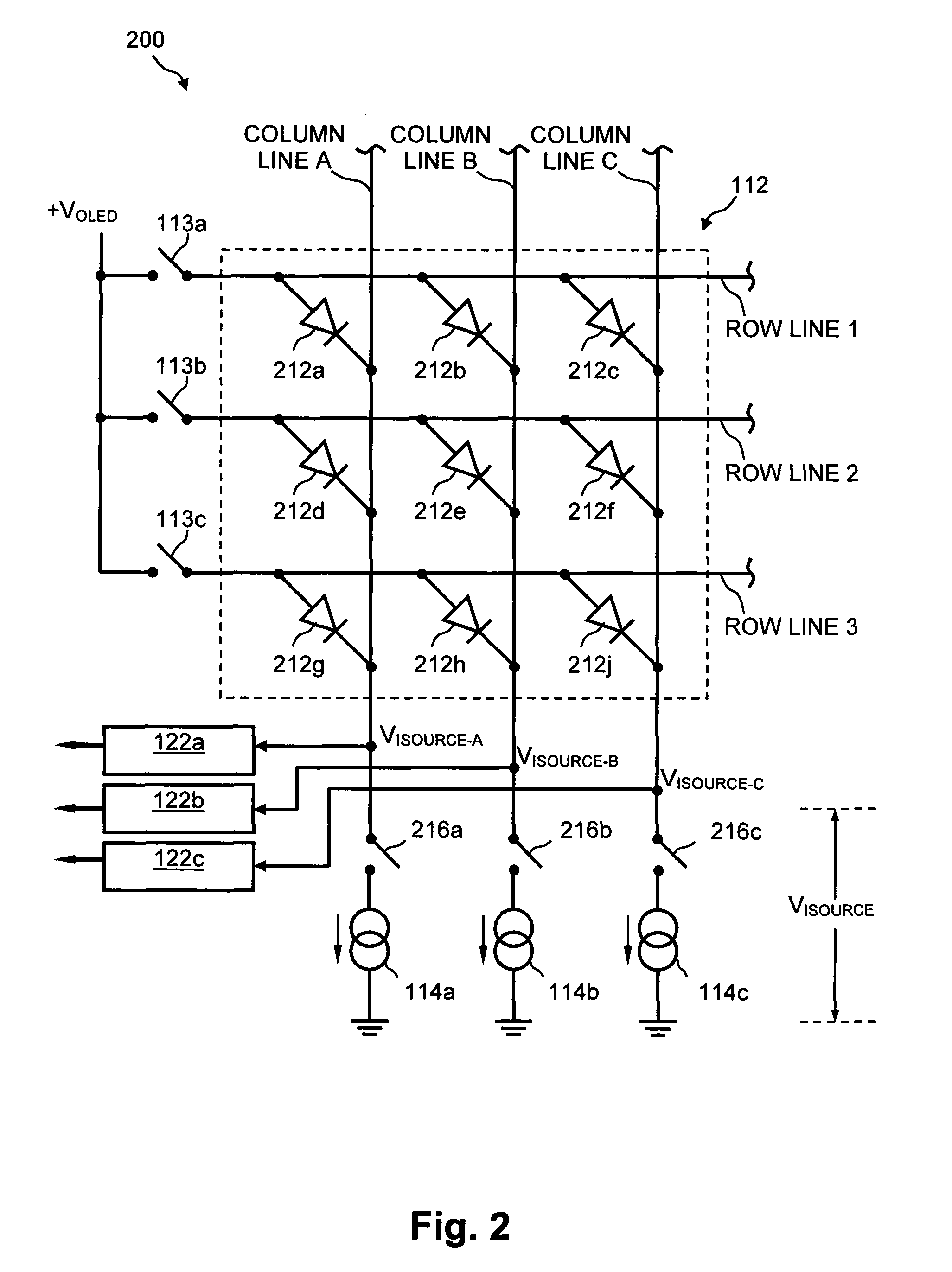
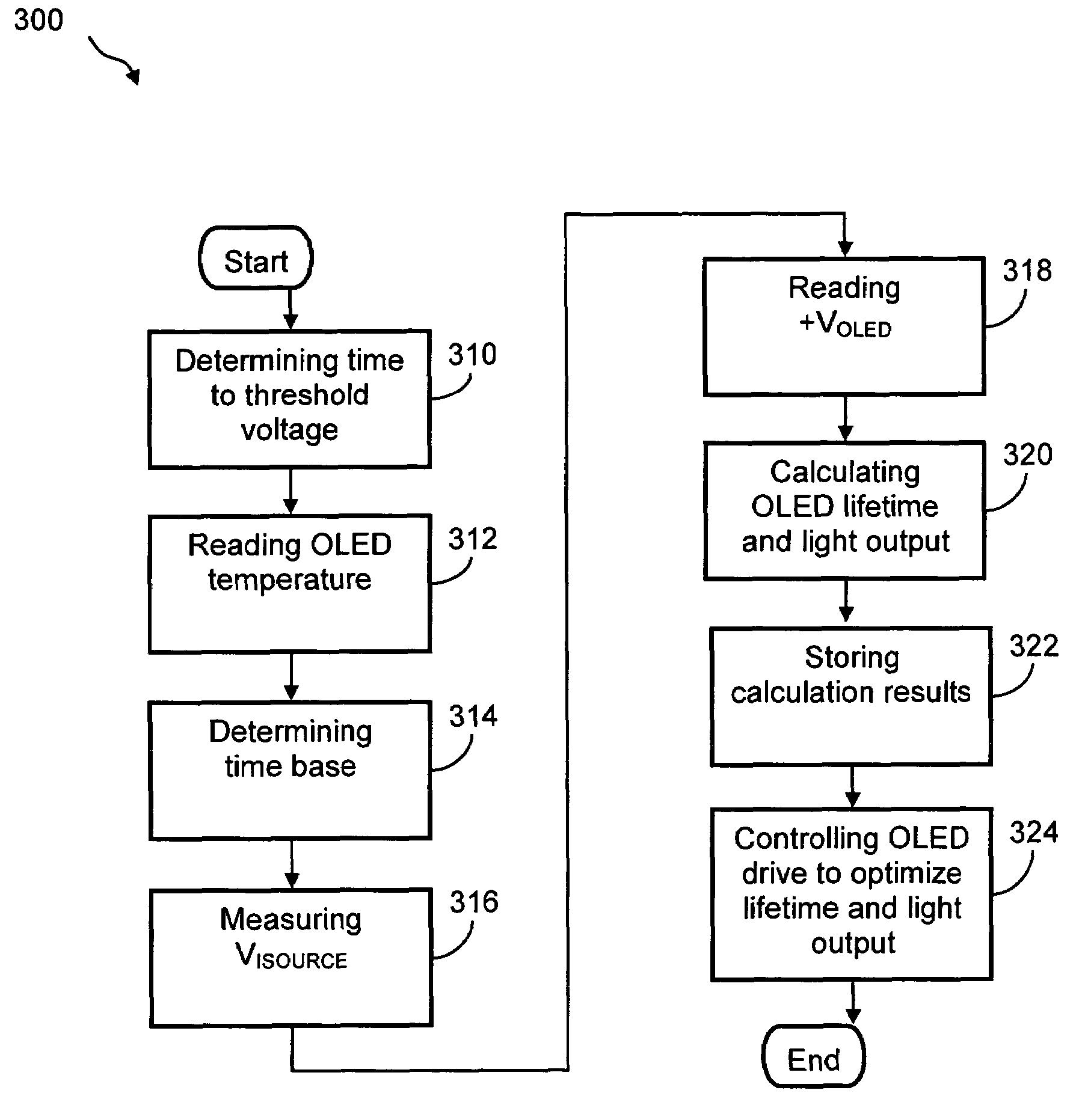
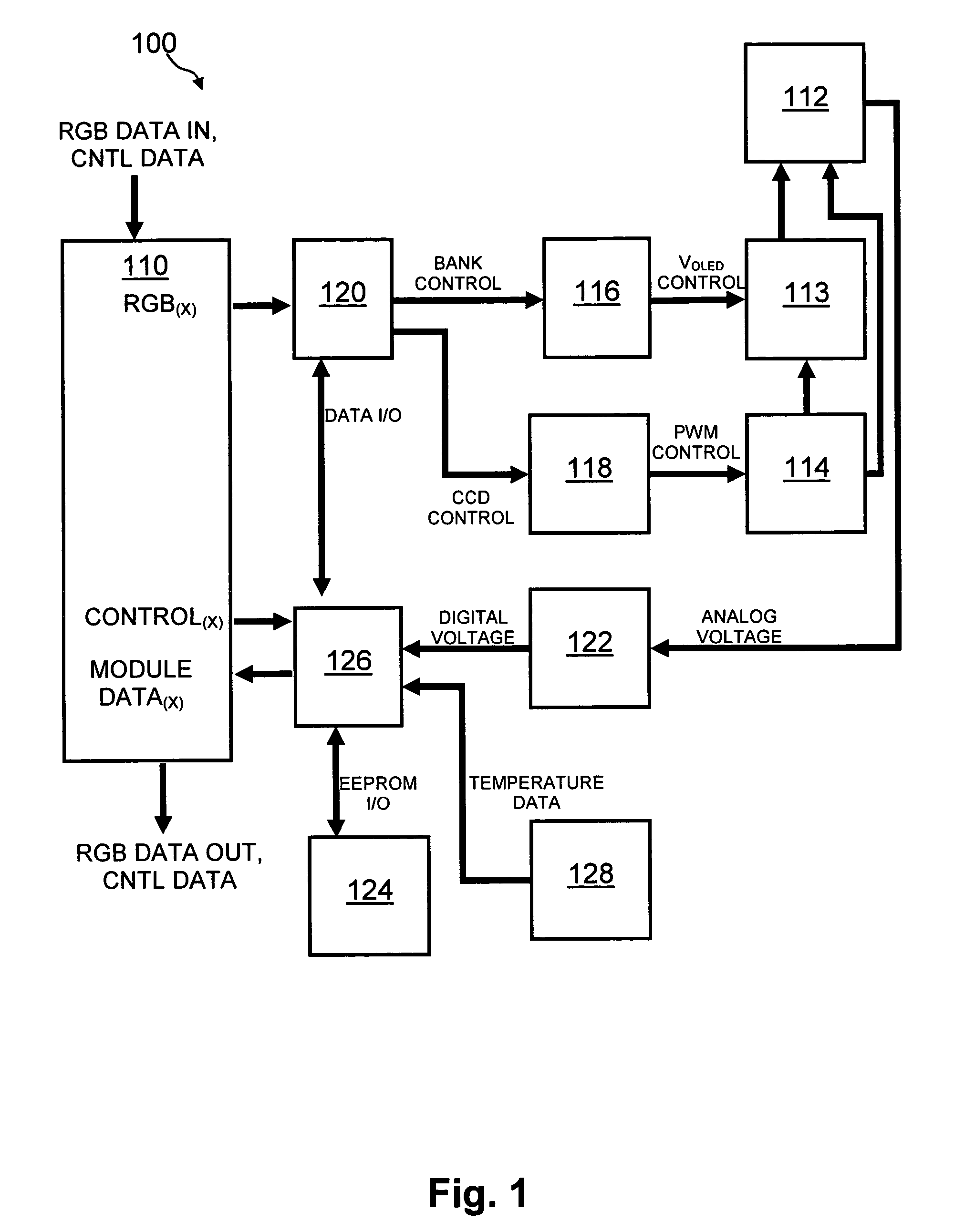
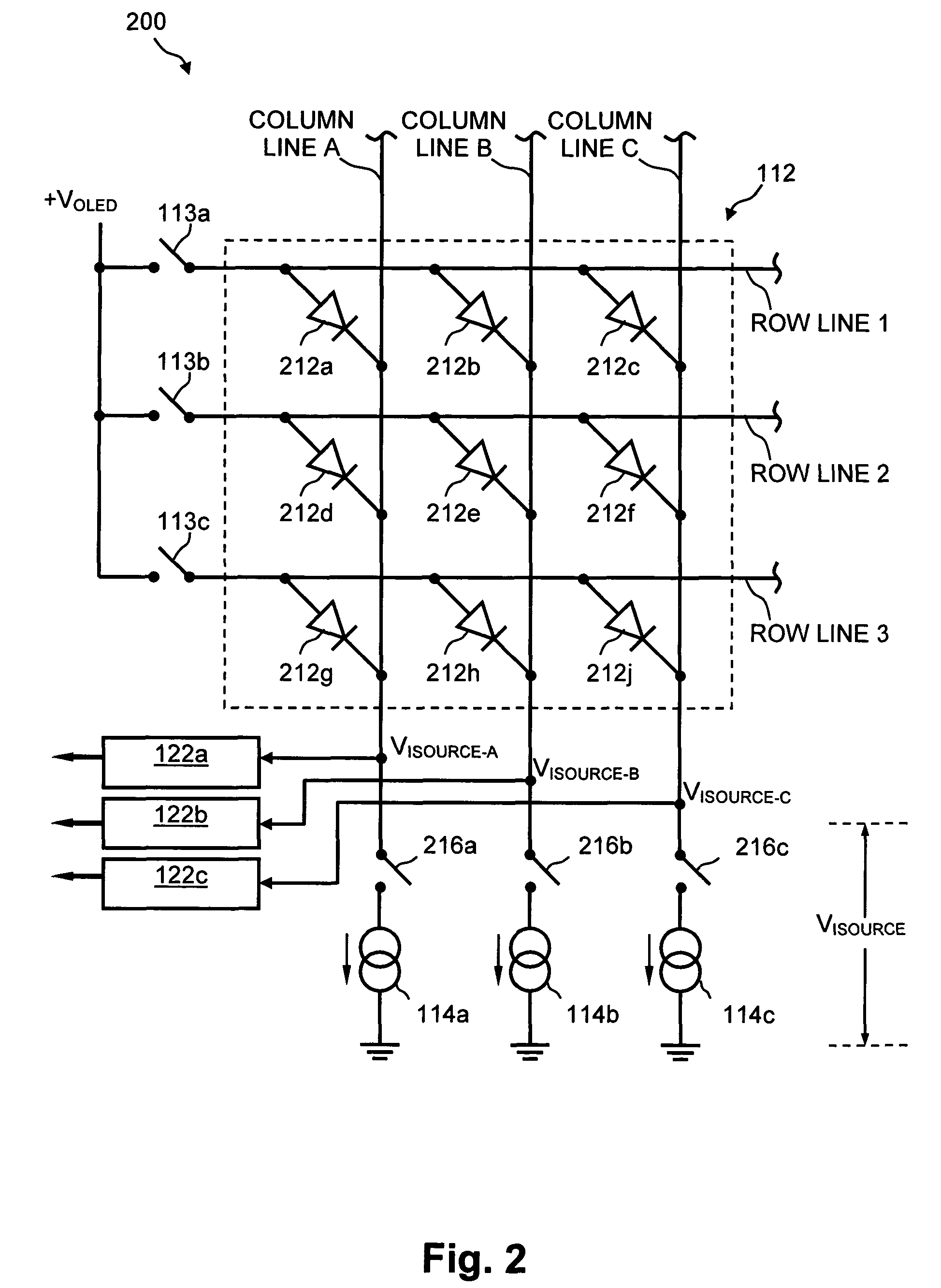
Method and system for measuring and controlling an OLED display element for improved lifetime and light output
InactiveUS20050030267A1Delay agingImprove the display effectCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPre-chargeDisplay device
A method of optimizing lifetime of an OLED display element and an OLED display element with optimized lifetime for possible use in a tiled display, while maintaining light output are described. It compensates an OLED operating parameter such as supply voltage and / or on-time of the operating current based on at least one environmental factor which affects aging and on at least one operating factor which is indicative of aging, e.g. by determining the brightness of an OLED display element. To optimize the light output, pre-charge of the aged OLED display elements can be optimized. The knowledge of the working temperature of OLED tiles may be used to regulate the cooling and thus the working temperature, thus improving the lifetime of the display. Furthermore the intensity and contrast of the display illumination may be set within predefined limits to reduce the aging.
Owner:BARCO NV
Particles and device for displaying image
InactiveUS20050001810A1Improve stabilityEnhance the imageStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsBreaking strengthUltrasound attenuation
The present invention intends to provide particles for displaying images used in an image display device capable of displaying and eliminating repeatedly accompanied by flight and movement of particles utilizing Coulomb force, being superior in stability, particularly in repetition durability, memory characteristic stability, adaptability for temperature change, having capability of regulating charge amount, and accordingly, favorable images with sufficient contrast should be stably obtained. The present invention provides particles coated with a resin; specifying Span of particle diameter distribution, charge attenuation property, thermal change of the surface hardness, tensile break strength, Izod impact strength (with a notch), abrasion loss (Taber), tensile elastic modulus, flexural elastic modulus, or tear strength. The present invention also proposes about the structure of the particles.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Methods and Systems for Determining Image Processing Operations Relevant to Particular Imagery
ActiveUS20110244919A1Improve performanceImprove the usefulnessCustomer communicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging processing
Image data, such as from a mobile phone camera, is analyzed to determine a colorfulness metric (e.g., saturation) or a contrast metric (e.g., Weber contrast). This metric is then used in deciding which of, or in which order, plural different image recognition processes should be invoked in order to present responsive information to a user. A great number of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
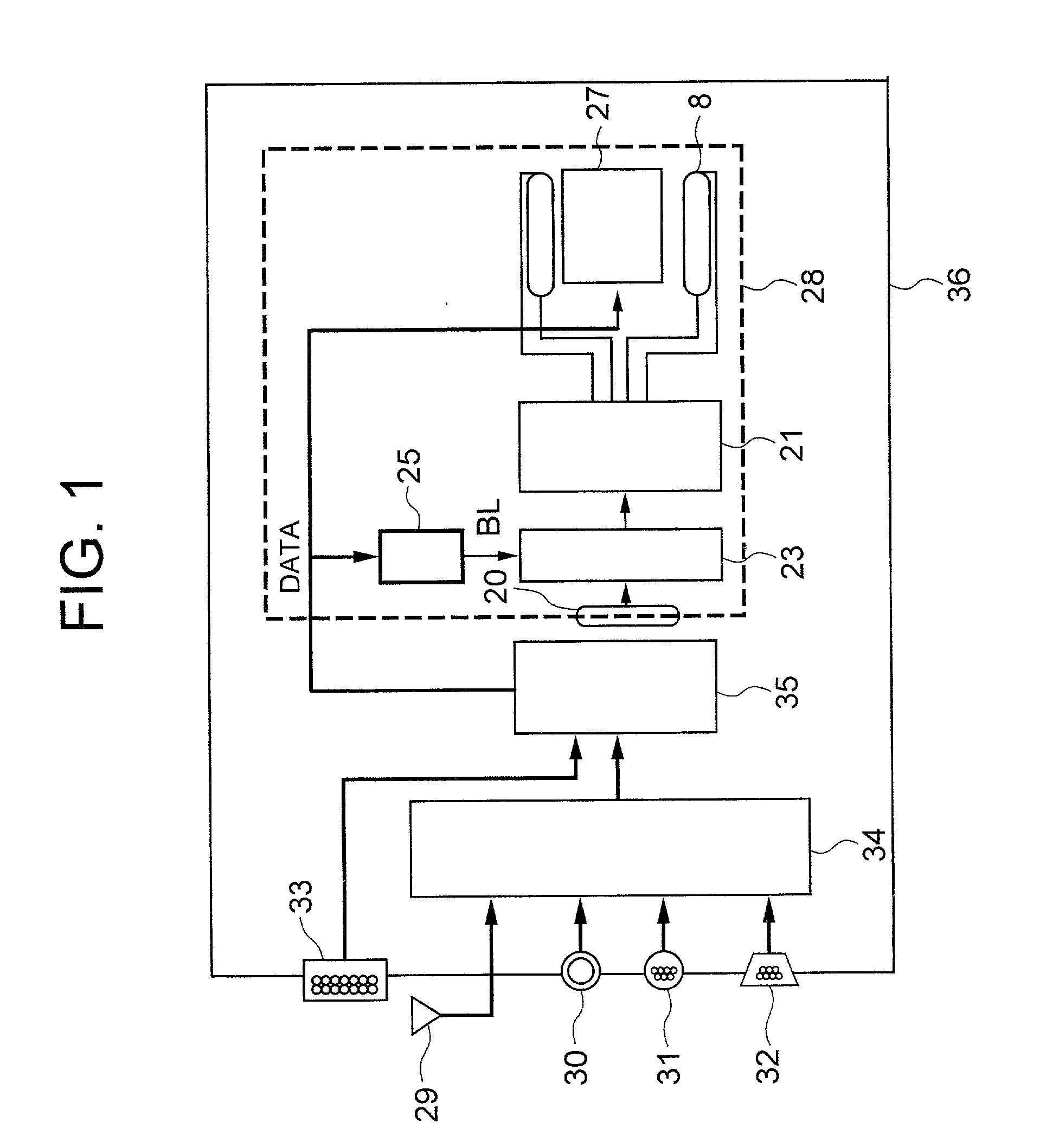
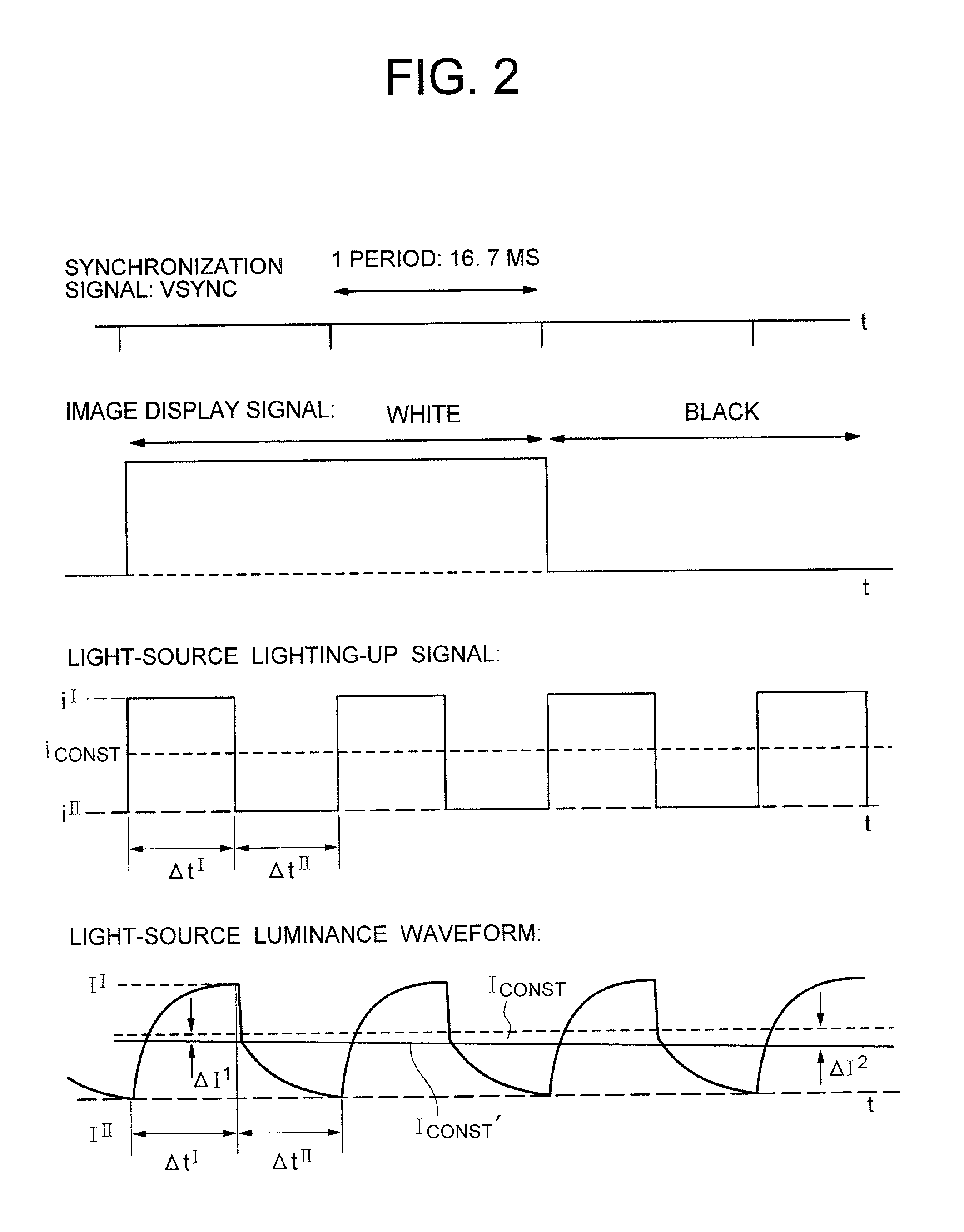
Liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS20020057238A1Static indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayControl circuit
The present invention includes a panel on which a plurality of pixels are located, a light-source for visualizing an image displayed on the plurality of pixels, a controlling circuit for controlling the light-source, and an image-signal tone characteristic controlling circuit. Moreover, the light-source controlling circuit has a function of repeating a period. Here, the period includes a 1st time-period during which an electric current having a 1st intensity is fed to the light-source, and a 2nd time-period during which an electric current having a 2nd intensity differing from the 1st intensity is fed to the light-source. The light-source controlling circuit controls the 1st time-period and the 2nd time-period in accordance with display information. Also, in accordance with the display information as well, the tone characteristic controlling circuit is controlled so that the excellent contrast will be always available.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS +1
Electrophoretic display and novel process for its manufacture
ActiveUS7072095B2Improve contrast ratioImprove switching performanceStatic indicating devicesElectrographic processes using photoelectrophoresisElectrophoresisDisplay device
This invention relates to an electrophoretic display with improved contrast ratio, switching performance, reflectivity at the Dmin state and structural integrity, and methods for its manufacture.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
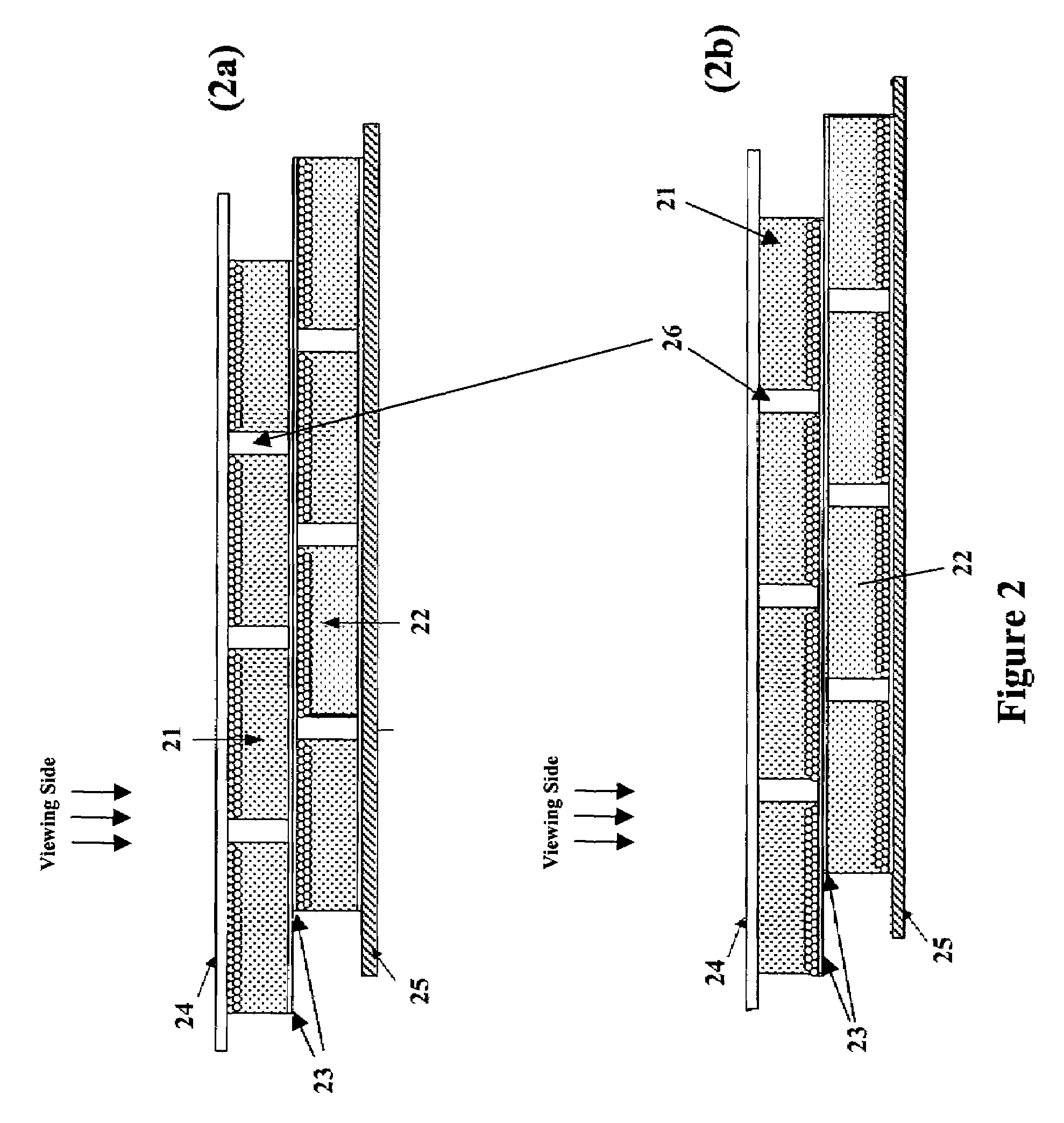
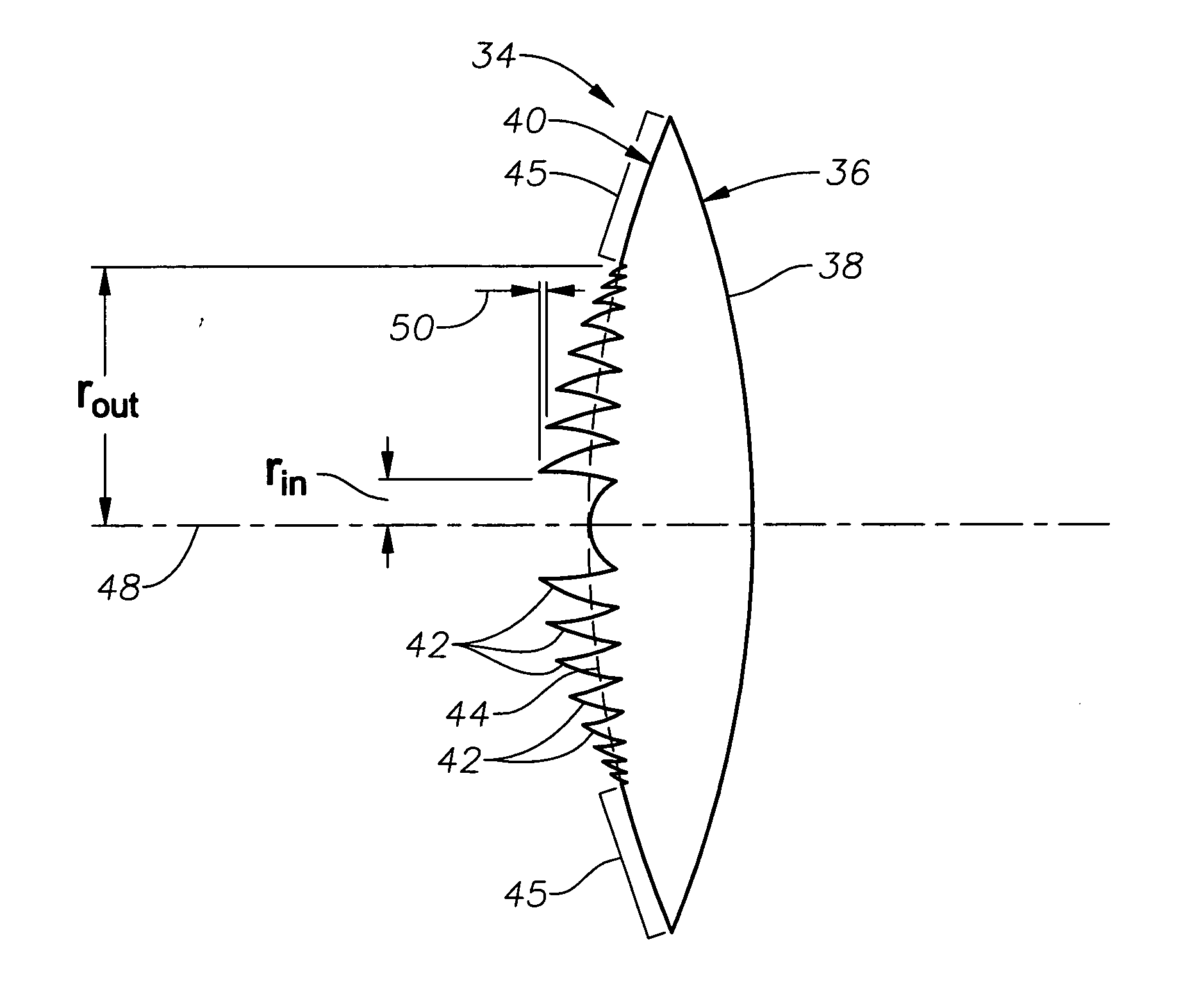
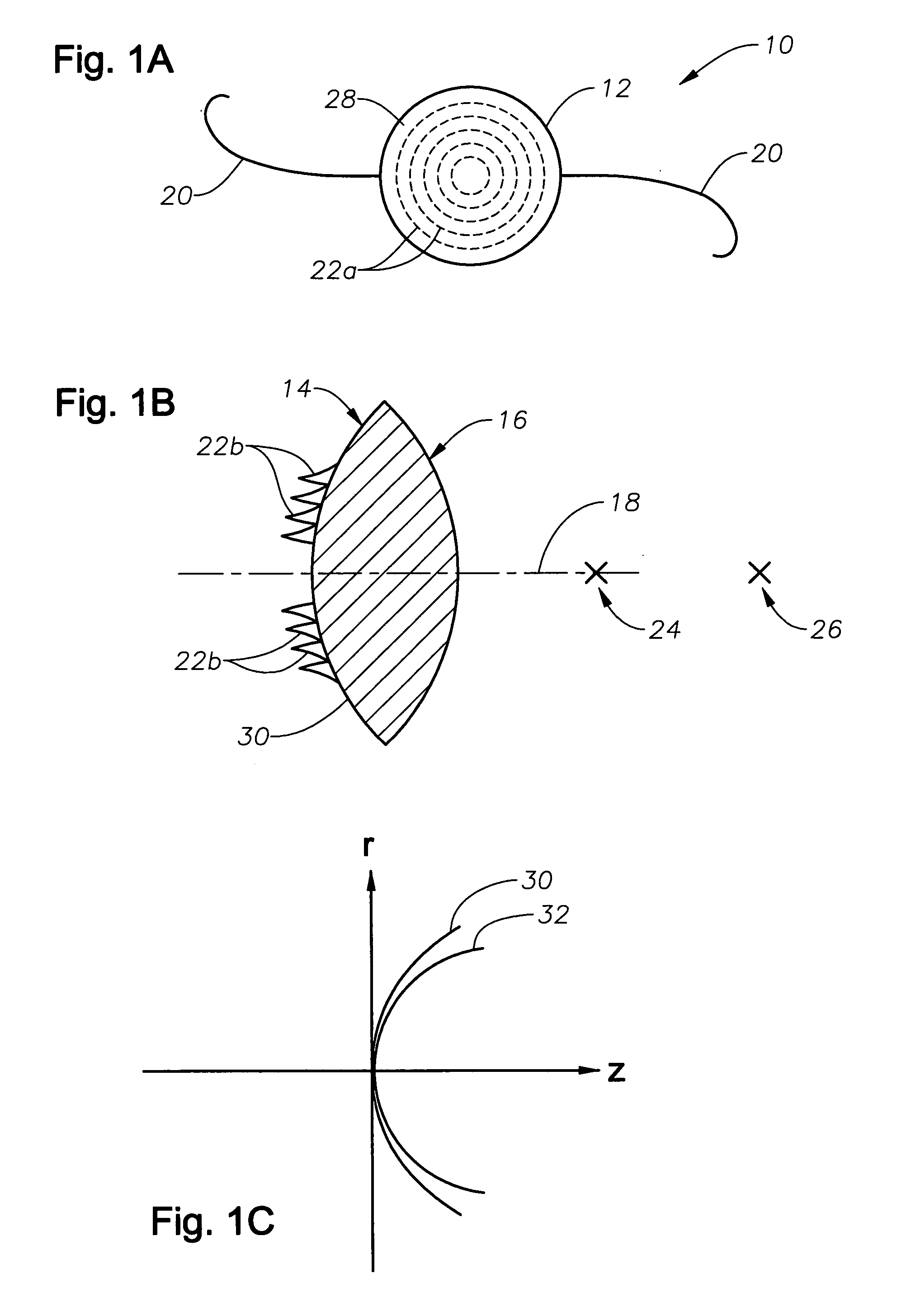
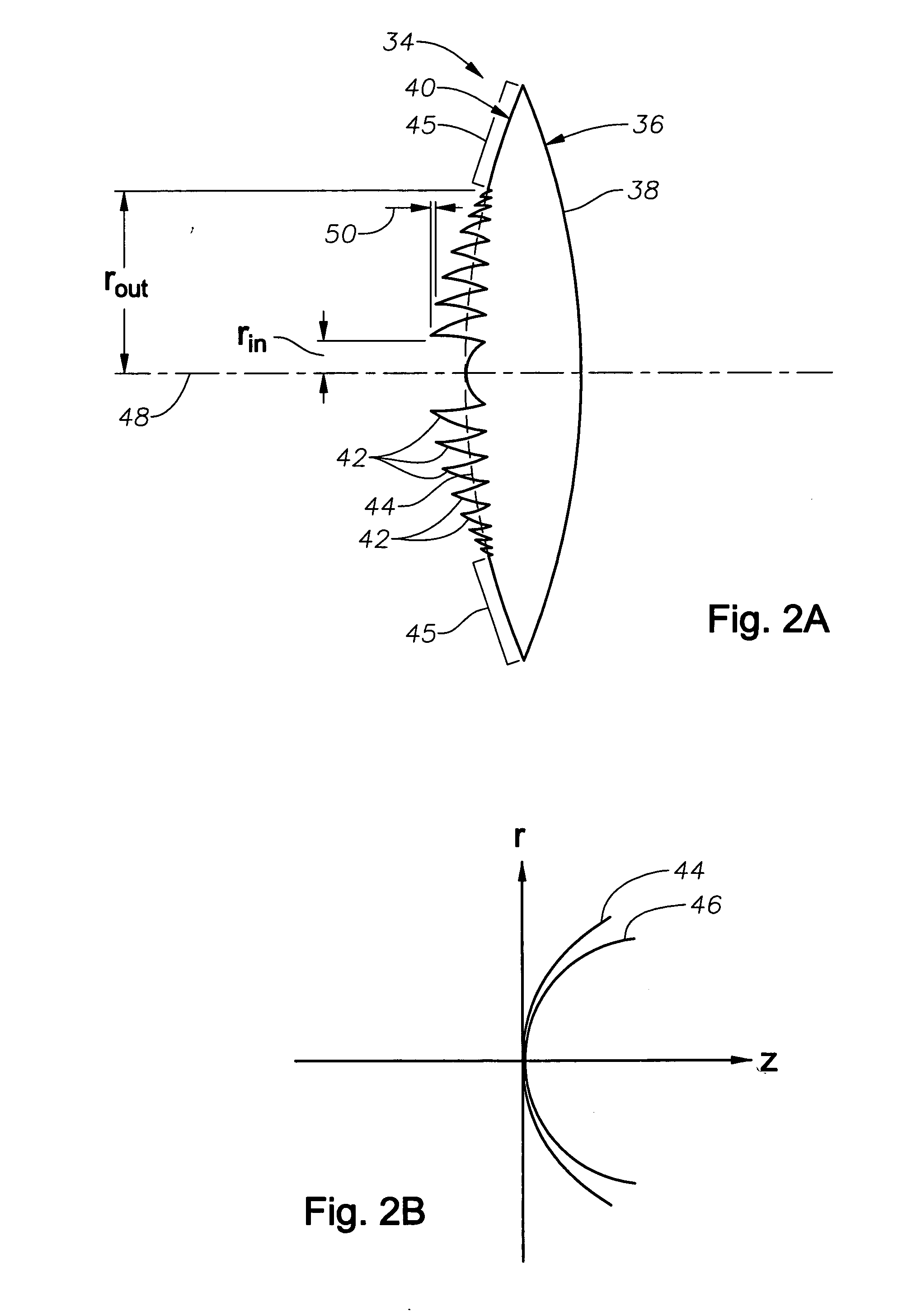
Apodized aspheric diffractive lenses
InactiveUS20060116764A1Improve image contrastSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryCamera lensImage contrast
Aspheric diffractive lenses are disclosed for ophthalmic applications. For example, multifocal intraocular lens (IOLs) are disclosed that include an optic having an anterior surface and a posterior surface, at least one of which surfaces includes an aspherical base profile on a portion of which a plurality of diffractive zones are disposed so as to generate a far focus and a near focus. The aspherical base profile enhances image contrast at the far focus of the lens relative to that obtained by a substantially identical IOL in which the respective base profile is spherical.
Owner:ALCON INC
Optical imaging device
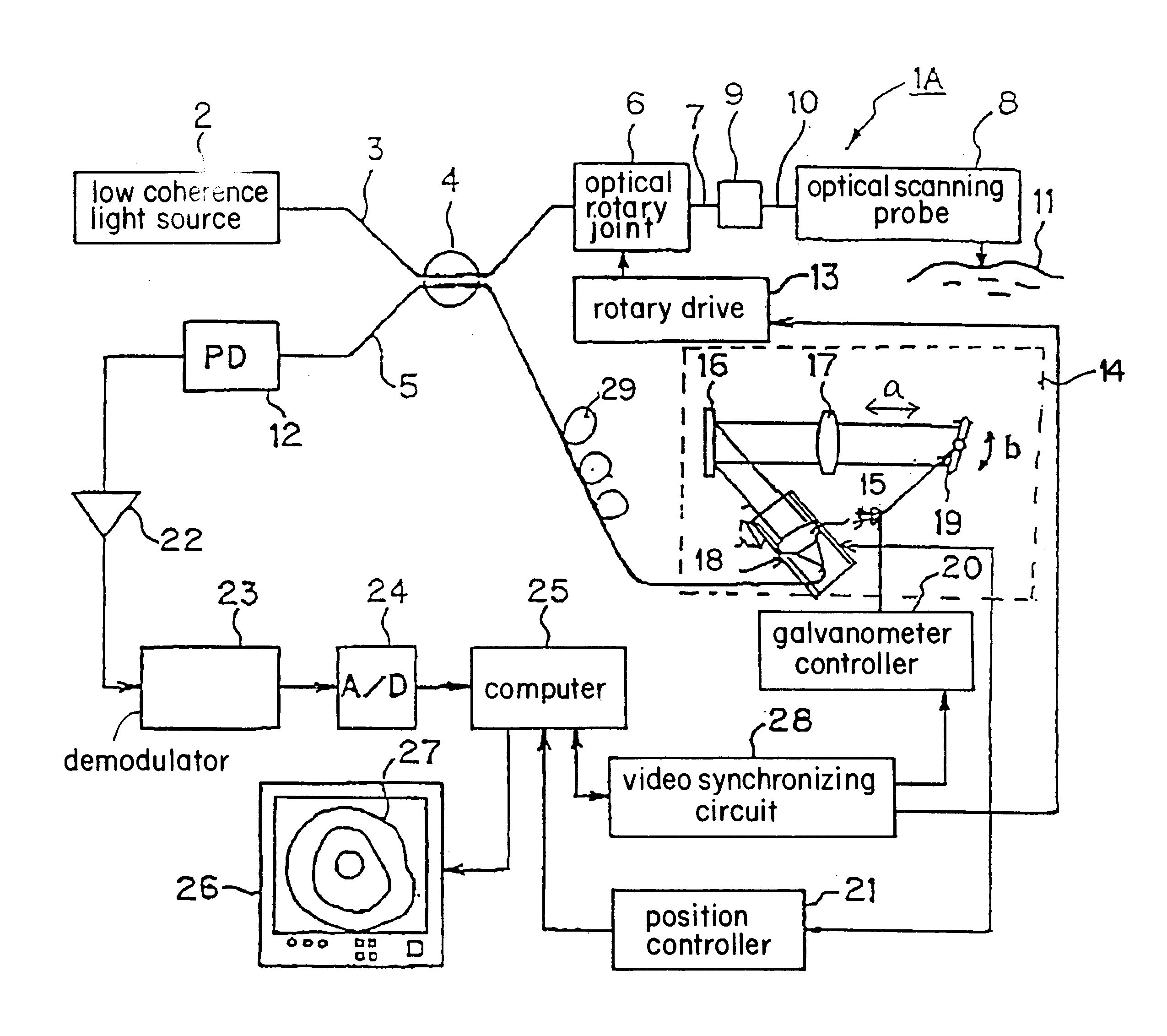
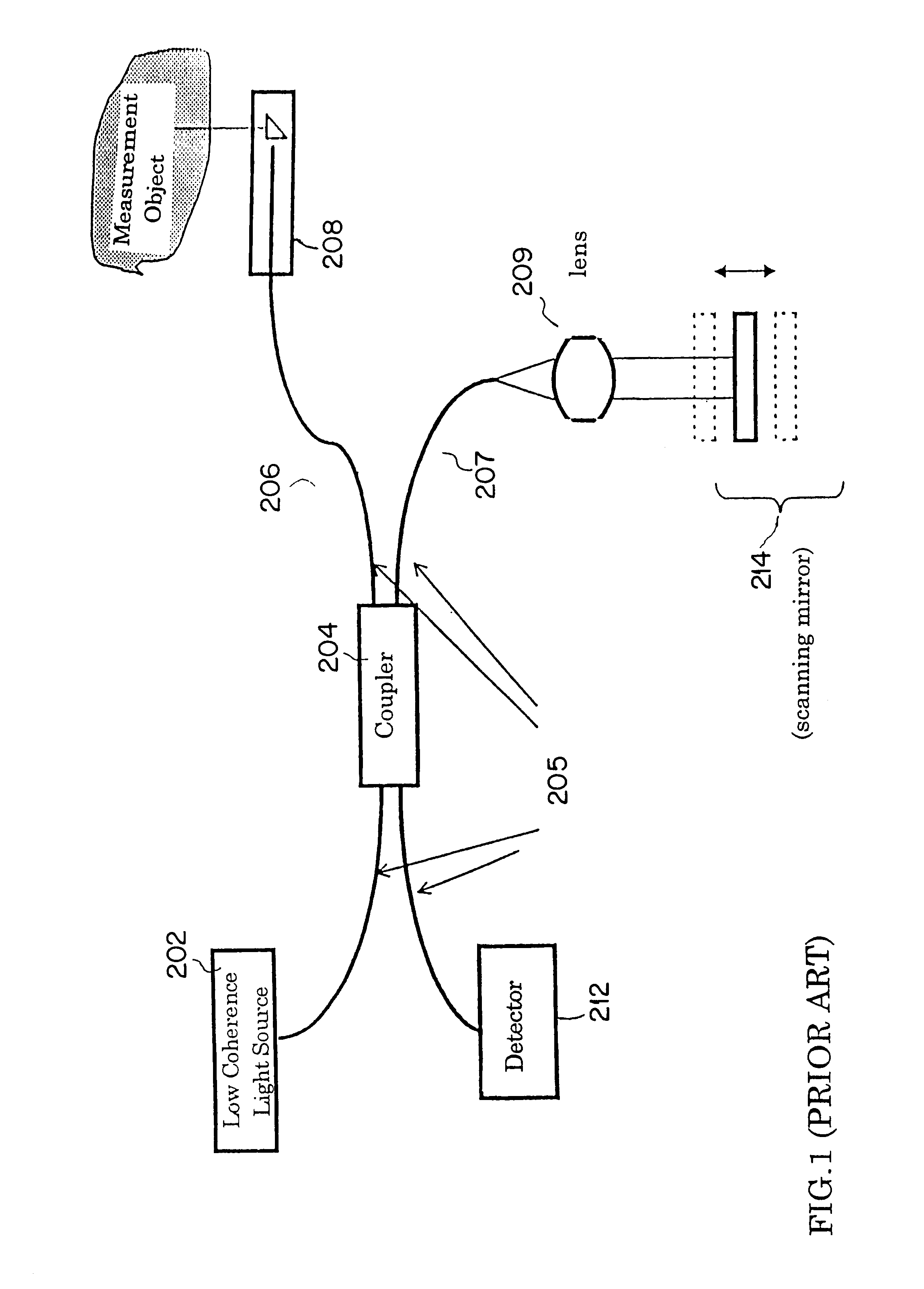
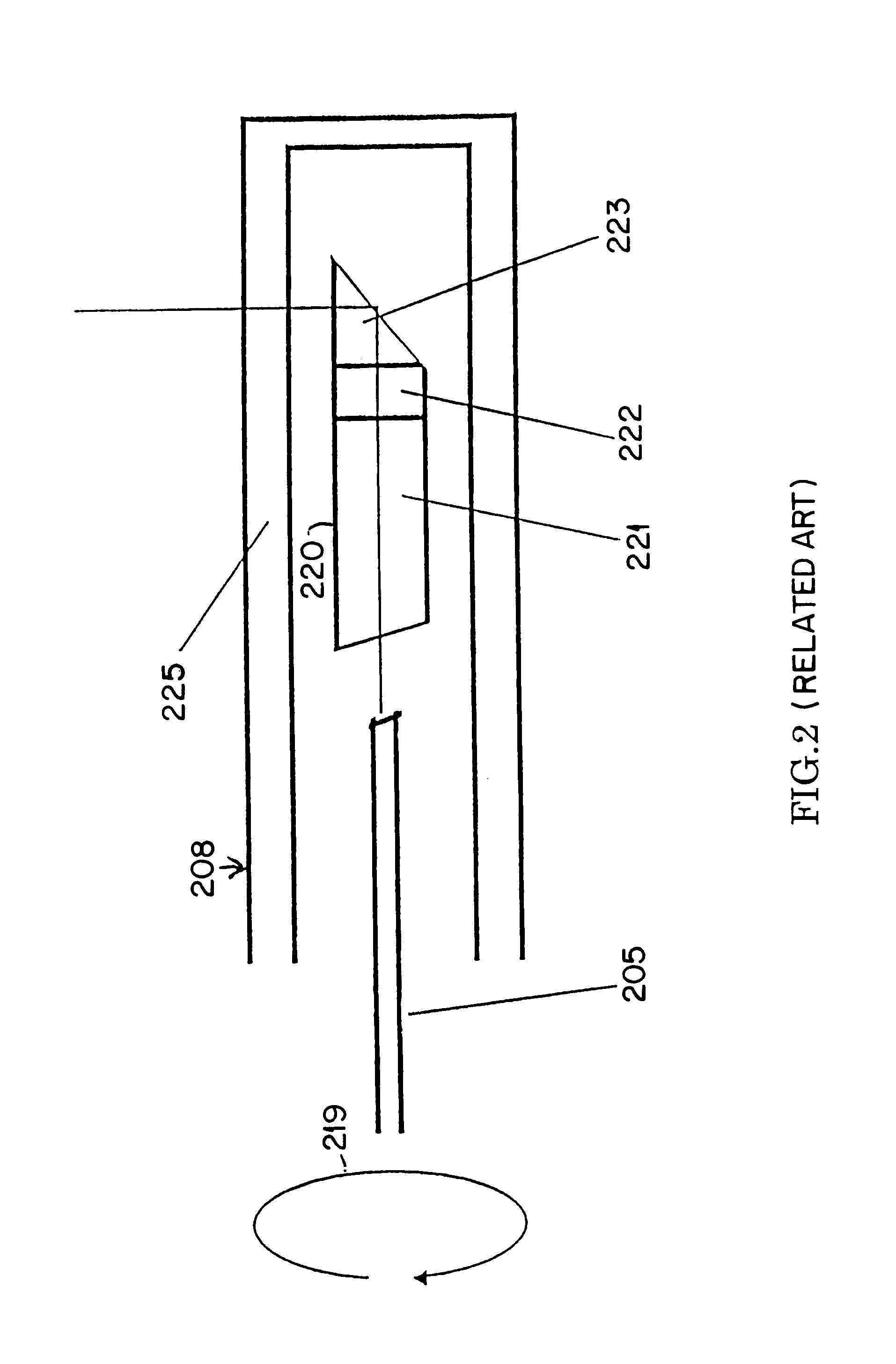
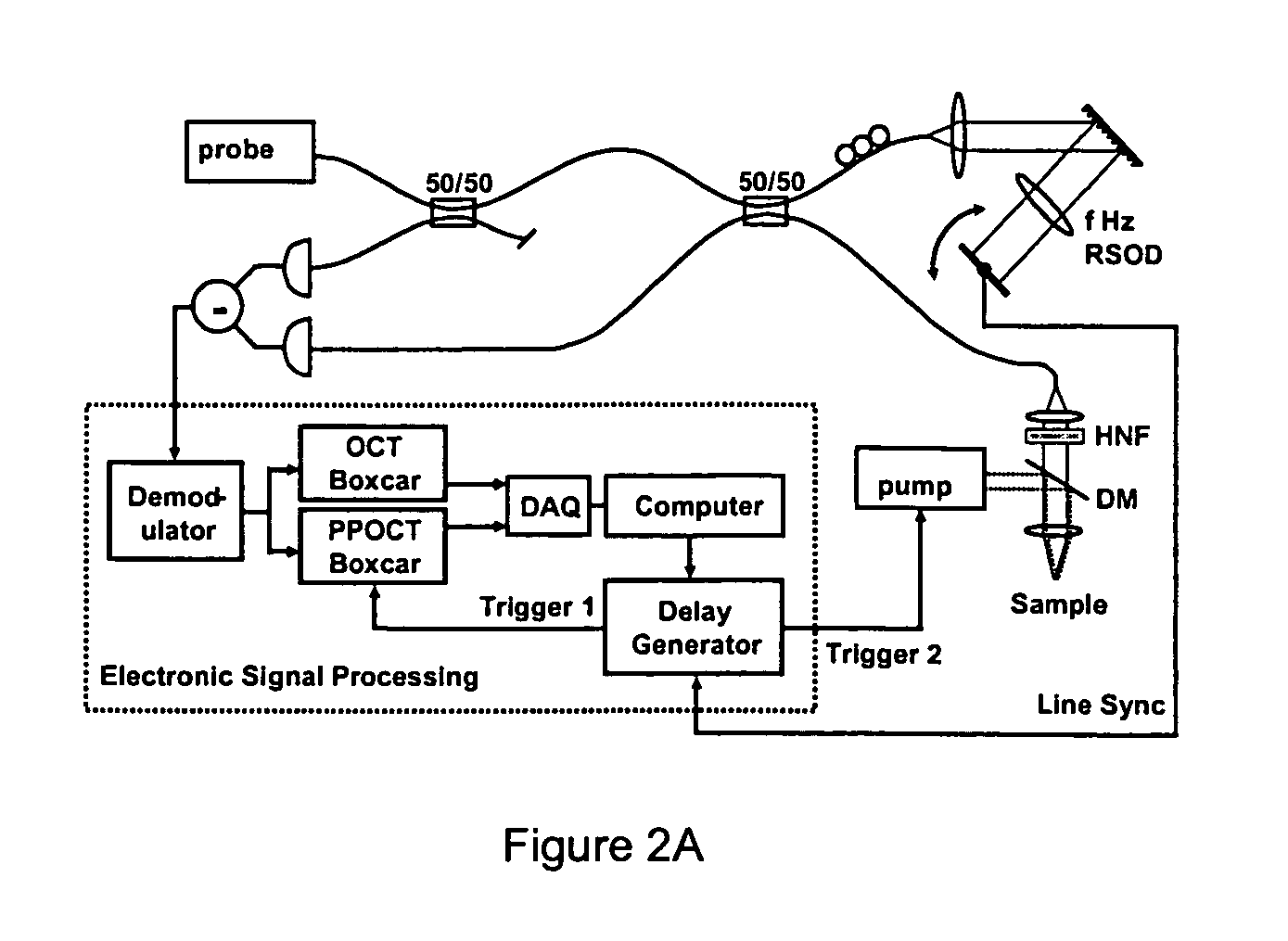
An Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) device irradiates a biological tissue with low coherence light, obtains a high resolution tomogram of the inside of the tissue by low-coherent interference with scattered light from the tissue, and is provided with an optical probe which includes an optical fiber having a flexible and thin insertion part for introducing the low coherent light. When the optical probe is inserted into a blood vessel or a patient's body cavity, the OCT enables the doctor to observe a high resolution tomogram. In a optical probe, generally, a fluctuation of a birefringence occurs depending on a bend of the optical fiber, and this an interference contrast varies depending on the condition of the insertion. The OCT of the present invention is provided with polarization compensation means such as a Faraday rotator on the side of the light emission of the optical probe, so that the OCT can obtain the stabilized interference output regardless of the state of the bend.
Owner:UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS OF CLEVELAND CLEVELAND +1
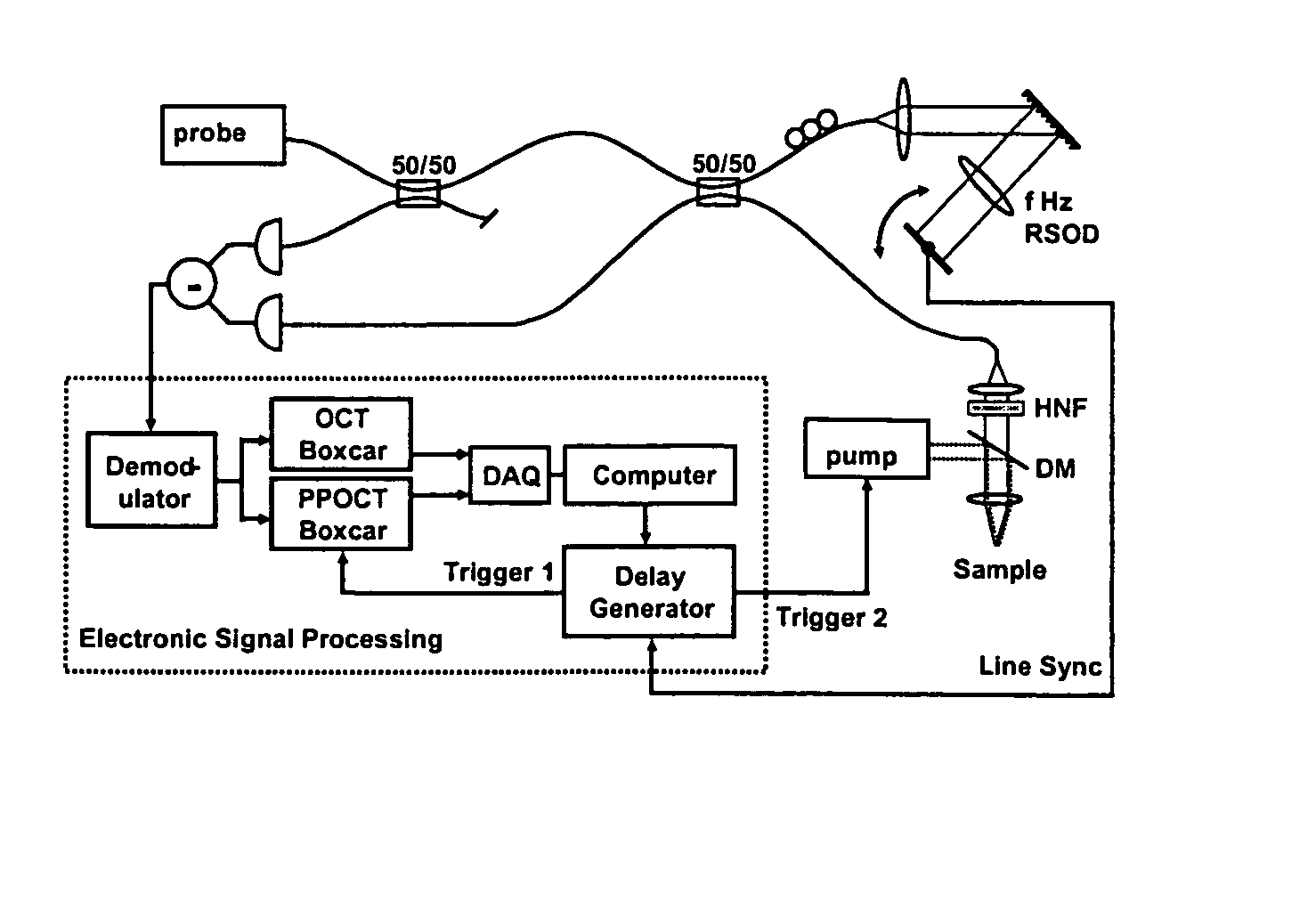
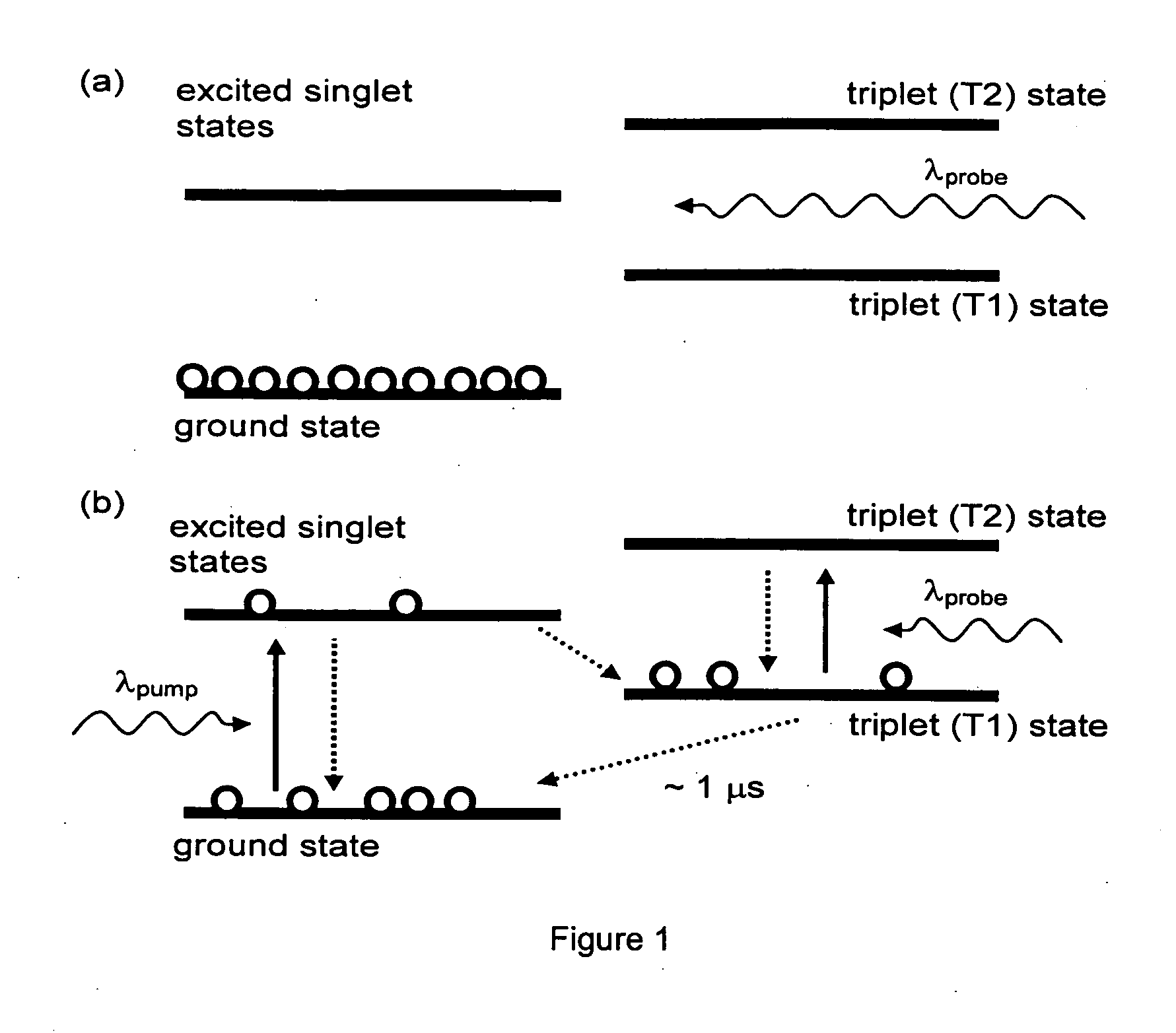
Method for optical coherence tomography imaging with molecular contrast
Spatial information, such as concentration and displacement, about a specific molecular contrast agent, may be determined by stimulating a sample containing the agent, thereby altering an optical property of the agent. A plurality of optical coherence tomography (OCT) images may be acquired, at least some of which are acquired at different stimulus intensities. The acquired images are used to profile the molecular contrast agent concentration distribution of the sample.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
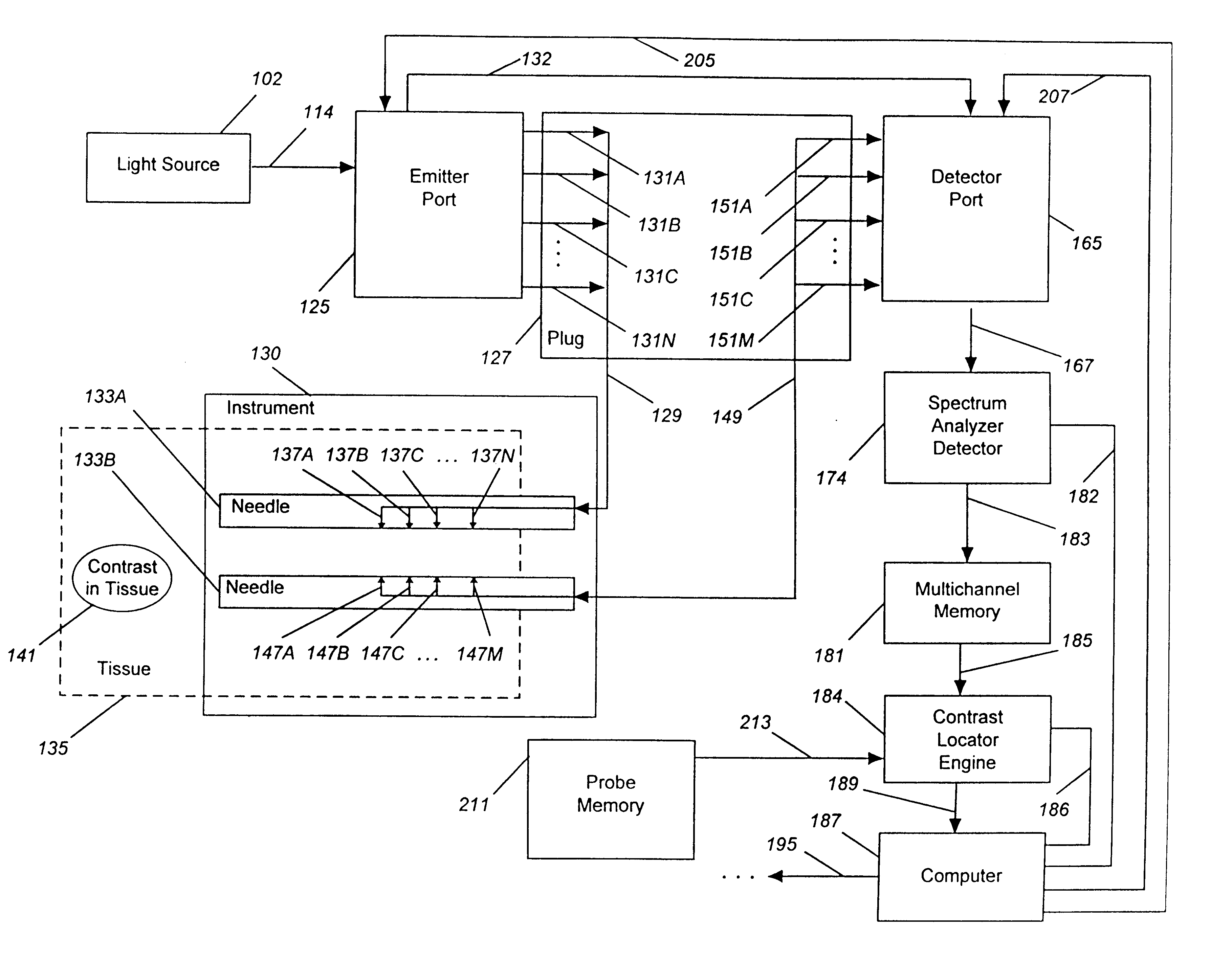
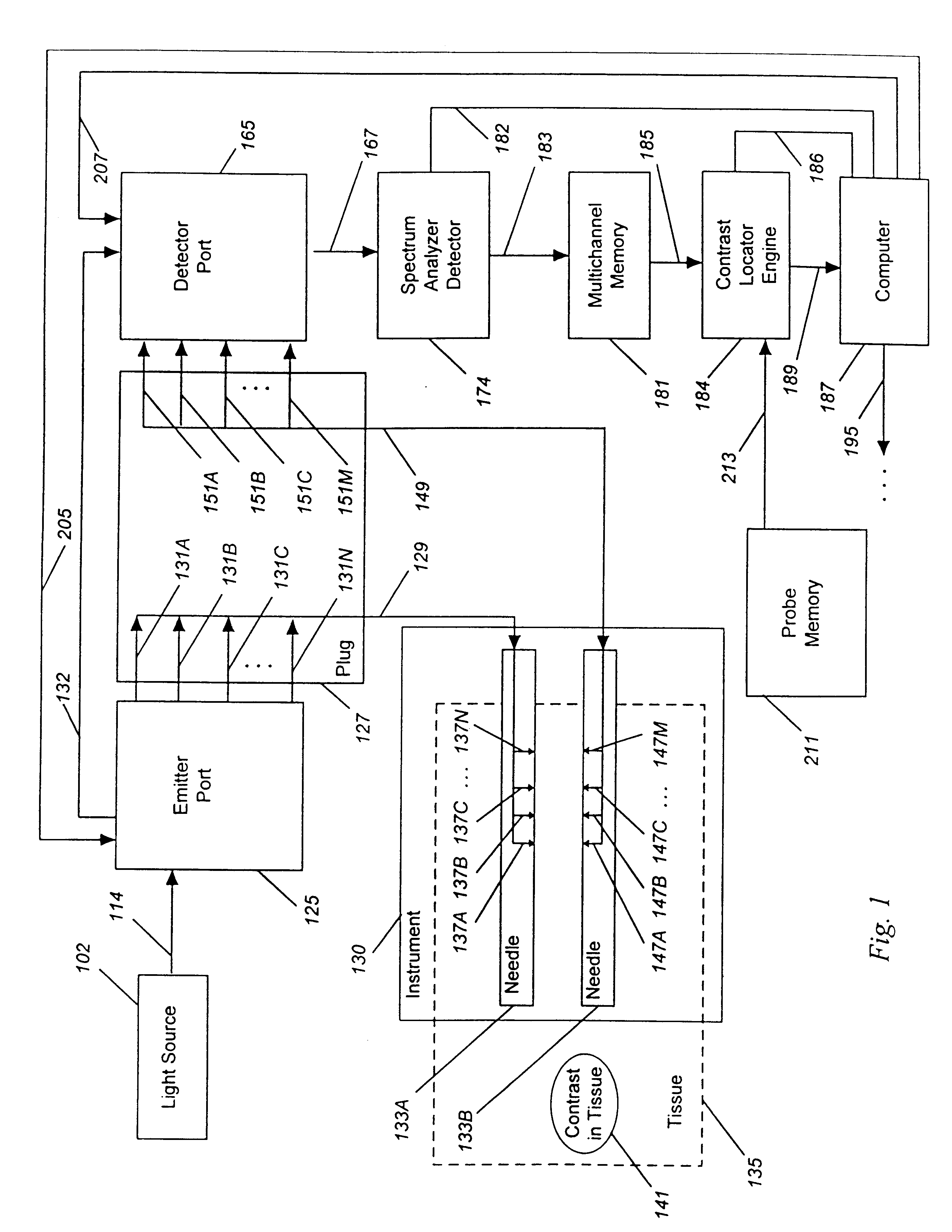
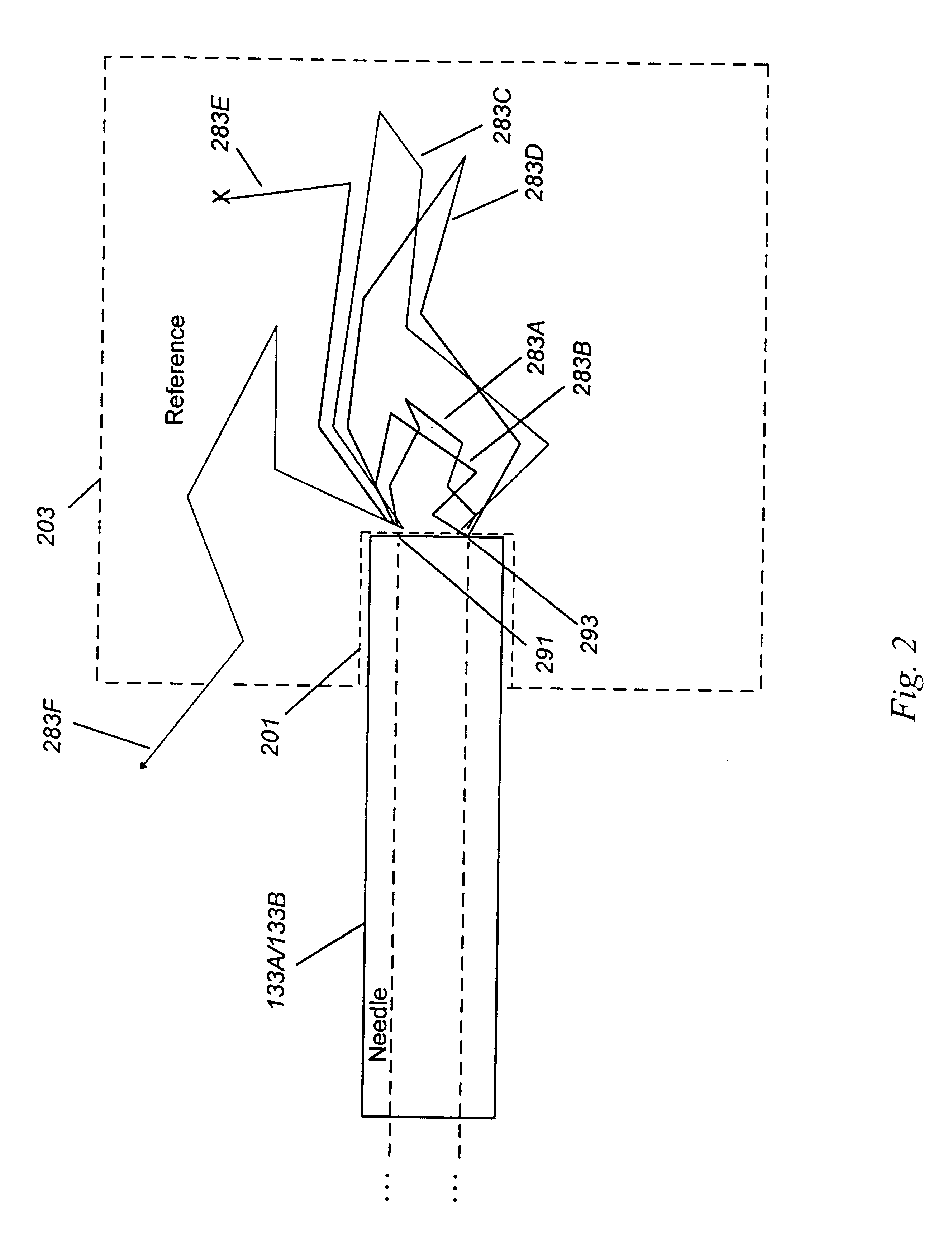
Detecting, localizing, and targeting internal sites in vivo using optical contrast agents
InactiveUS6246901B1Rapid imaging and localization and positioning and targetingNanoinformaticsDiagnostics using spectroscopyIn vivoOptical contrast
Owner:J FITNESS LLC
Multifocal imaging systems and method
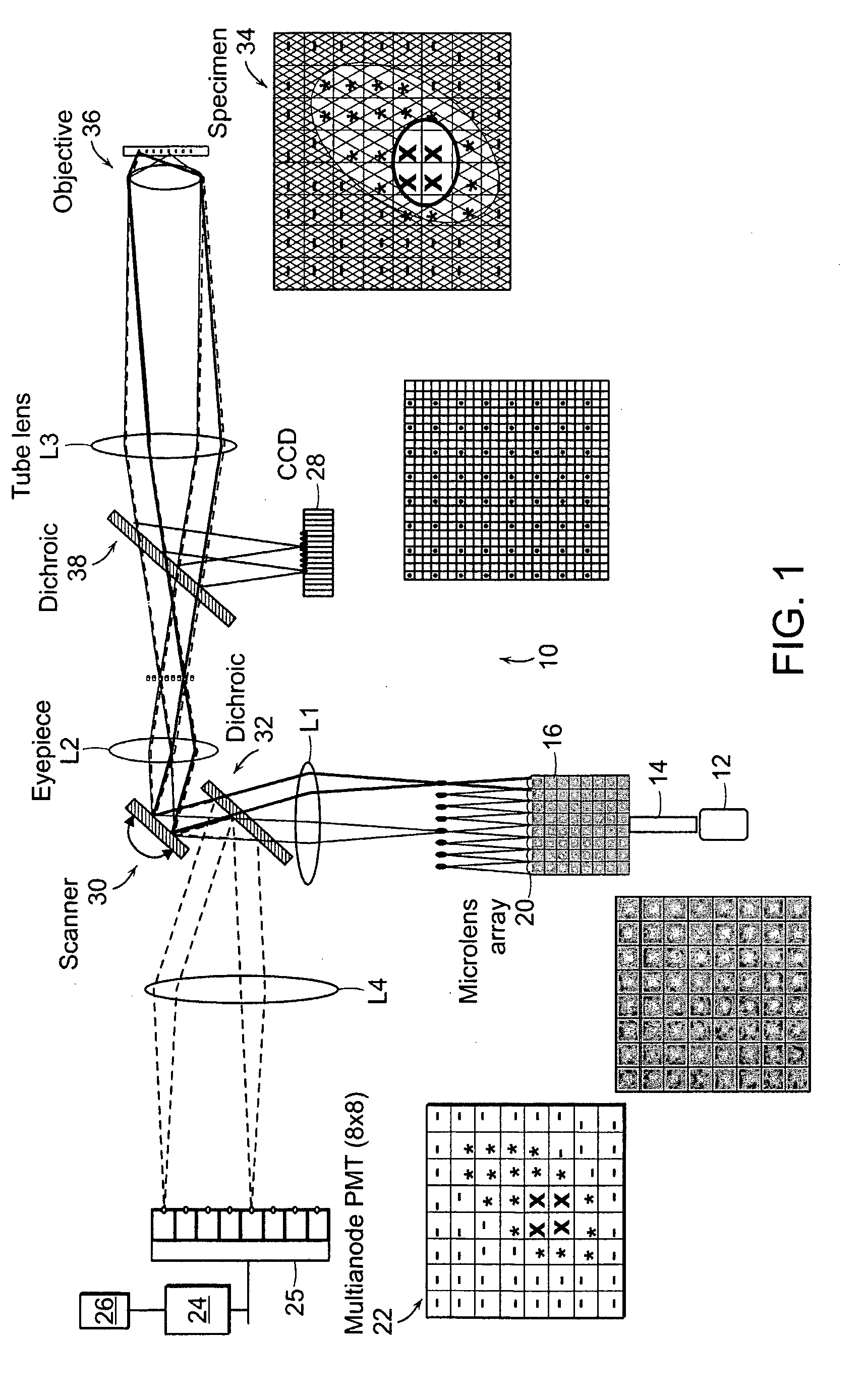
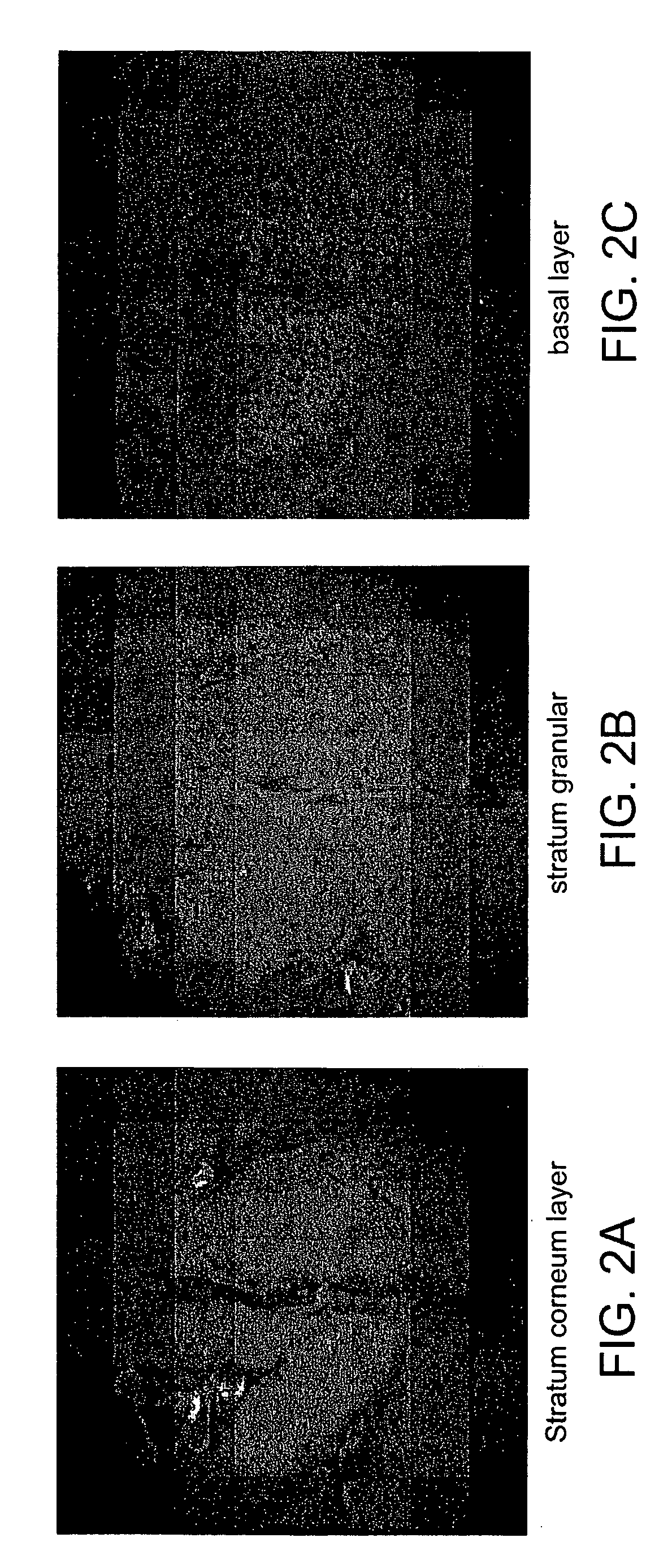
InactiveUS20070057211A1Fast imagingEfficient collectionMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsLow noiseGrating
In the systems and methods of the present invention a multifocal multiphoton imaging system has a signal to noise ratio (SNR) that is reduced by over an order of magnitude at imaging depth equal to twice the mean free path scattering length of the specimen. An MMM system based on an area detector such as a multianode photomultiplier tube (MAPMT) that is optimized for high-speed tissue imaging. The specimen is raster-scanned with an array of excitation light beams. The emission photons from the array of excitation foci are collected simultaneously by a MAPMT and the signals from each anode are detected using high sensitivity, low noise single photon counting circuits. An image is formed by the temporal encoding of the integrated signal with a raster scanning pattern. A deconvolution procedure taking account of the spatial distribution and the raster temporal encoding of collected photons can be used to improve decay coefficient. We demonstrate MAPMT-based MMM can provide significantly better contrast than CCD-based existing systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Electro-optic displays, and methods for driving same
InactiveUS7787169B2Reduce and eliminate exposureReducing and eliminating light degradationNon-linear opticsOptical elementsElectricityTransport layer
The invention relates to electro-optic displays and methods for driving such displays. The invention provides (i) electrochromic displays with solid charge transport layers; (ii) apparatus and methods for improving the contrast and reducing the cost of electrochromic displays; (iii) apparatus and methods for sealing electrochromic displays from the outside environment and preventing ingress of contaminants into such a display; and (iv) methods for adjusting the driving of electro-optic displays to allow for environmental and operating parameters.
Owner:E INK CORP
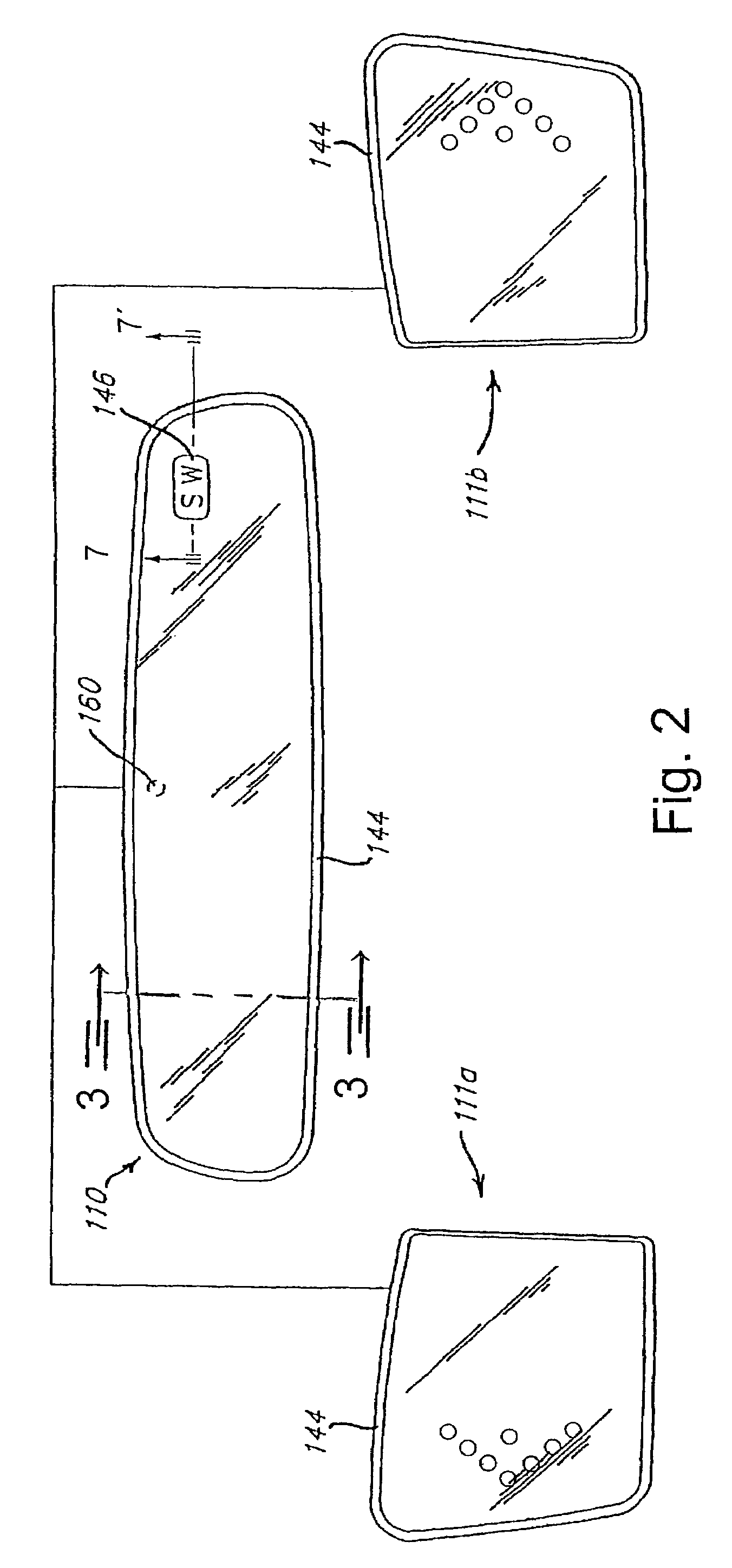
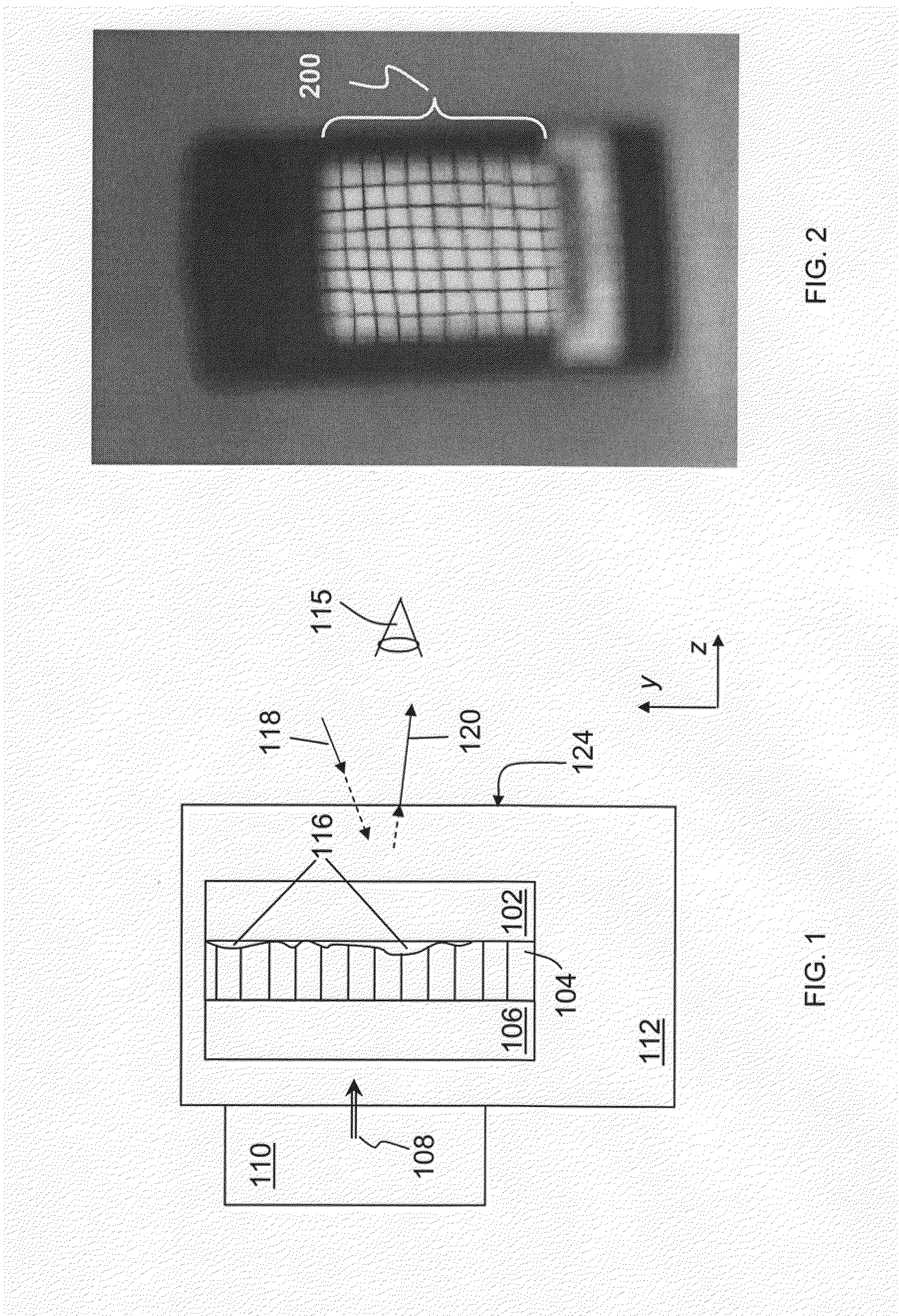
Electrochromic rearview mirror assembly incorporating a display/signal light
According to one embodiment of the present invention, an electrochromic rearview mirror assembly for a vehicle includes an electrochromic mirror having a variable reflectivity, a glare sensor for sensing levels of light directed towards the front element from the rear of the vehicle, an ambient sensor for sensing levels of ambient light, a display positioned behind the partially transmissive, partially reflective portion of the reflector for displaying information therethrough; and a control circuit coupled to the sensors and the display. The control circuit determines whether daytime or nighttime conditions are present as a function of the ambient light level sensed by the ambient sensor. During daytime conditions, the control circuit responds to light levels sensed by the glare sensor to control a contrast ratio of light originating from the display and light reflecting from the partially transmissive, partially reflective area of the reflector.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Rearview Mirror Assemblies With Anisotropic Polymer Laminates
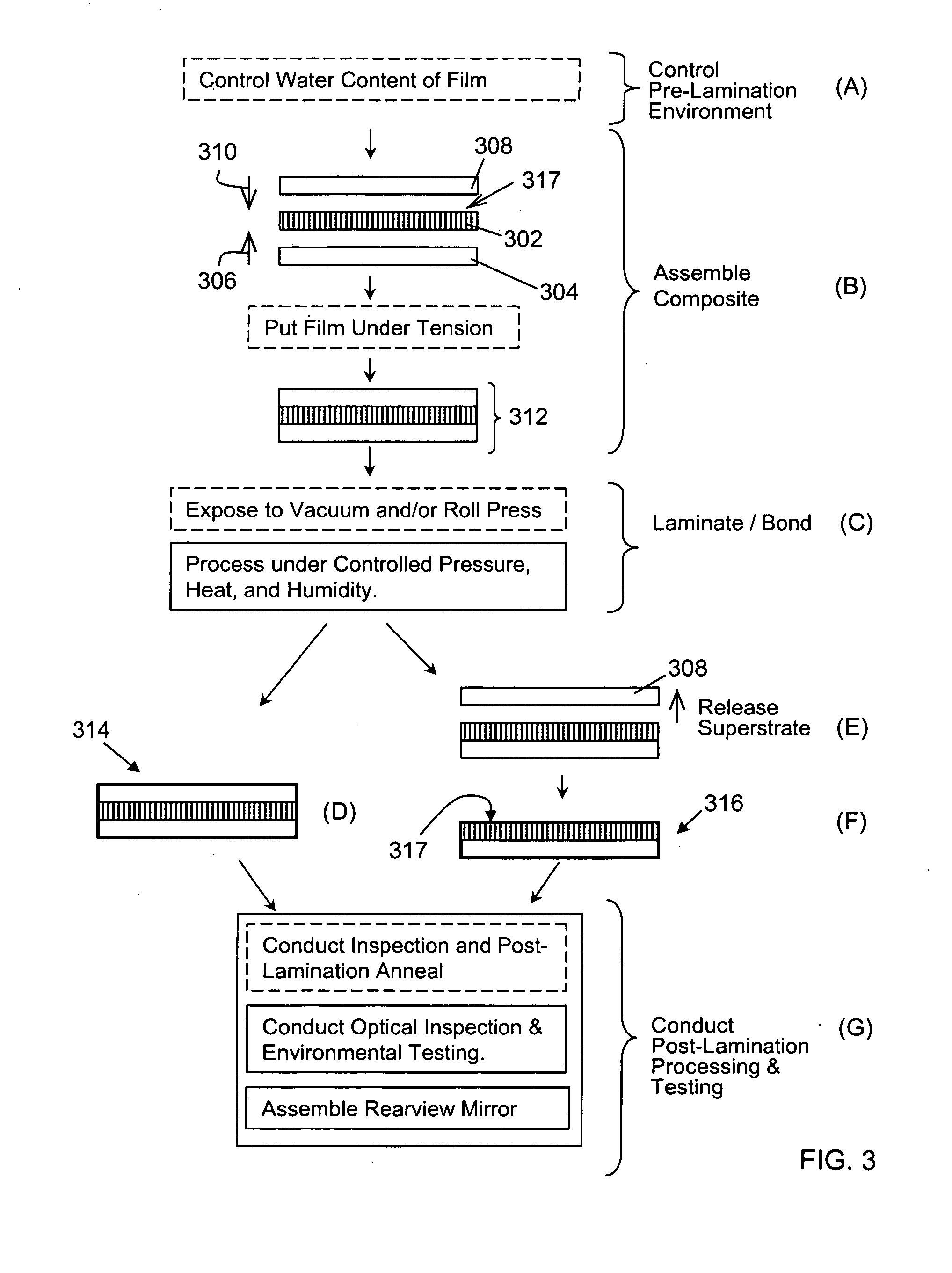
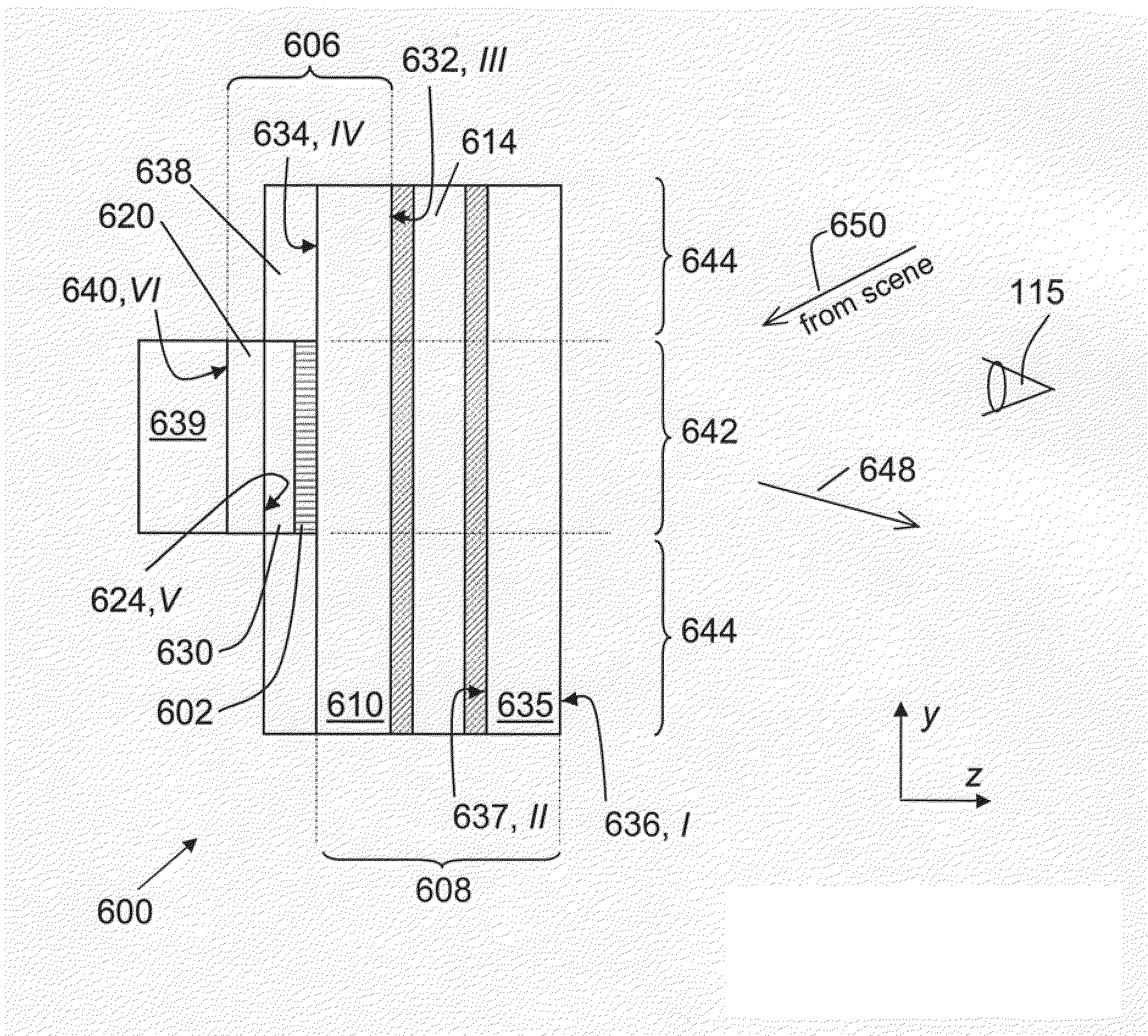
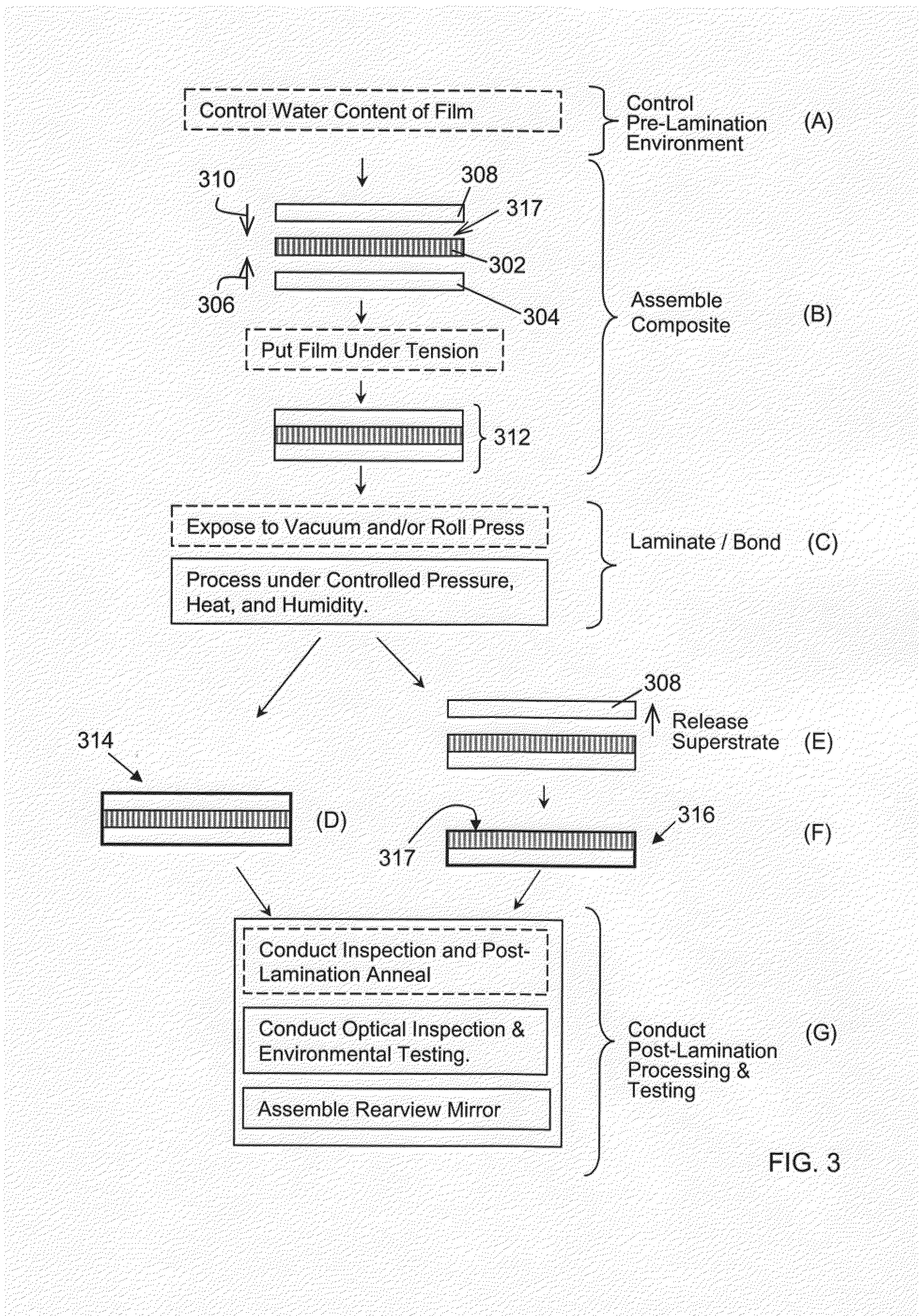
ActiveUS20100277786A1High strengthAdequate flatness of filmPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsLower limitGlass transition
Anisotropic film laminates for use in image-preserving reflectors such as rearview automotive mirror assemblies, and related methods of fabrication. A film may comprise an anisotropic layer such as a light-polarizing layer and other functional layers. The film having controlled water content is heated under omnidirectional pressure and vacuum to a temperature substantially equal to or above a lower limit of a glass-transition temperature range of the film so as to be laminated to a substrate. The laminate is configured as part of a mirror structure so as to increase contrast of light produced by a light source positioned behind the mirror structure and transmitted through the mirror structure towards a viewer. The mirror structure is devoid of any extended distortion and is characterized by SW and LW values less than 3, more preferably less than 2, and most preferably less than 1.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
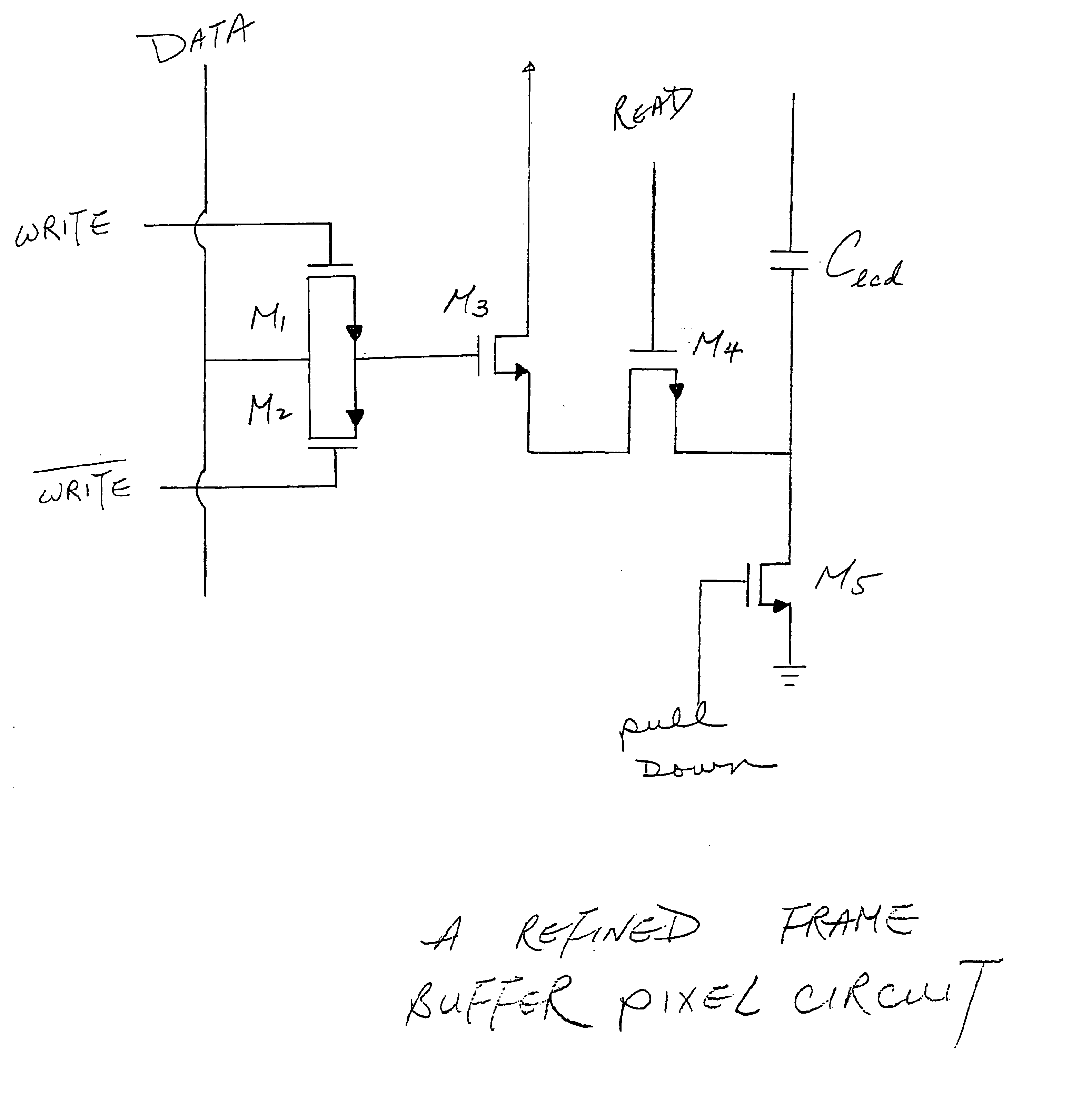
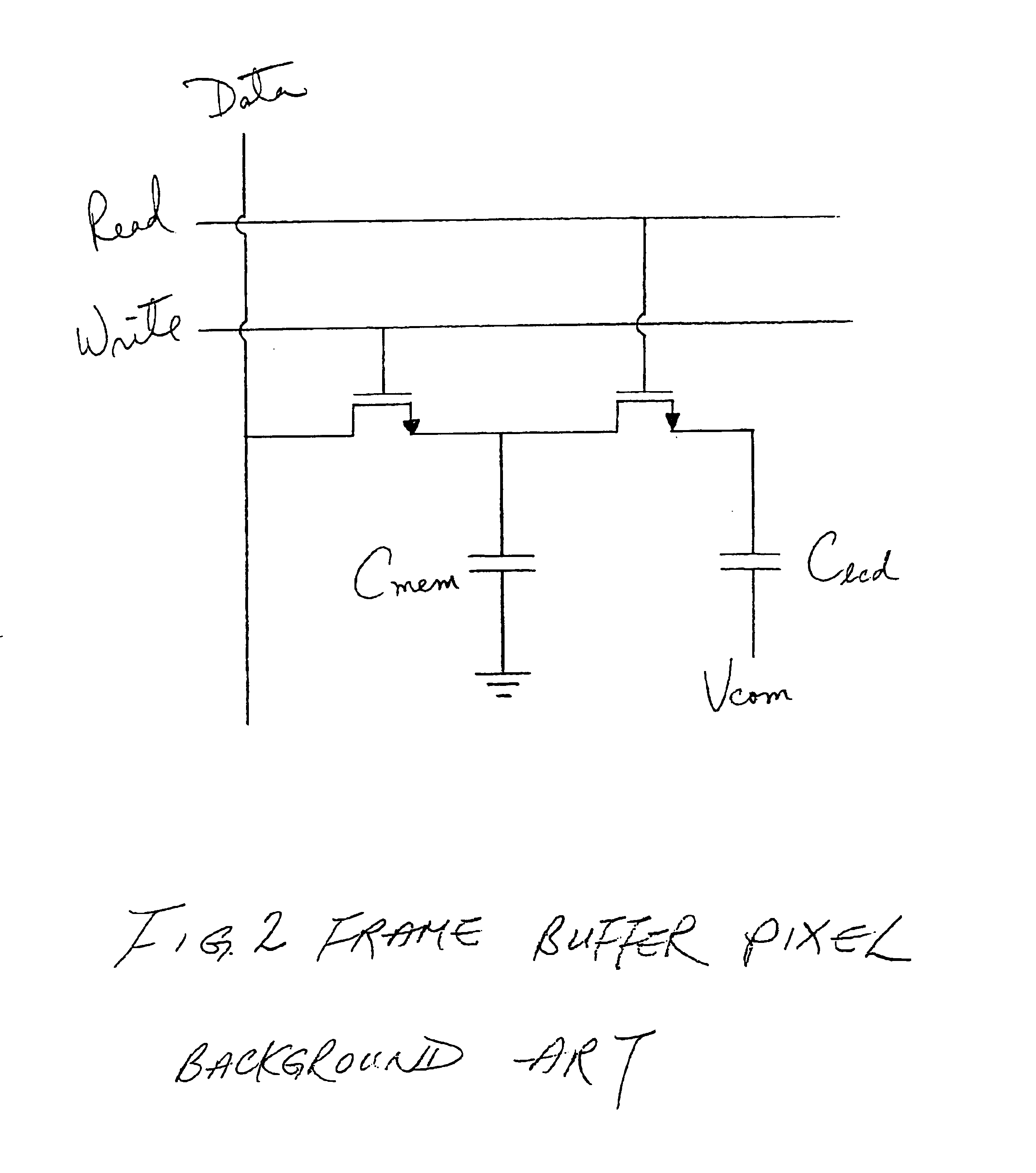
Frame buffer pixel circuit for liquid crystal display
InactiveUS6911964B2Enhanced frame buffer pixelIncrease contrastStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsCMOSLiquid-crystal display
An enhanced frame buffer pixel circuit with two control transistors and a separate capacitor put in as a memory capacitor before the memory transistor yields a high contrast ratio by removing induced charge and solving a charge sharing problem between the memory capacitor and the liquid crystal display (LCD) capacitor. The memory transistor may be made of either CMOS or PMOS. The frame buffer pixel can be used to drive binary displays which expresses ON and OFF only if a comparator is put in after the pixel electrode circuit to represent gray levels with reduced sub-frame frequency.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Method and system for measuring and controlling an OLED display element for improved lifetime and light output
InactiveUS7262753B2Delay agingImprove the display effectCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingPre-chargeDisplay device
A method of optimizing lifetime of an OLED display element and an OLED display element with optimized lifetime for possible use in a tiled display, while maintaining light output are described. It compensates an OLED operating parameter such as supply voltage and / or on-time of the operating current based on at least one environmental factor which affects aging and on at least one operating factor which is indicative of aging, e.g. by determining the brightness of an OLED display element. To optimize the light output, pre-charge of the aged OLED display elements can be optimized. The knowledge of the working temperature of OLED tiles may be used to regulate the cooling and thus the working temperature, thus improving the lifetime of the display. Furthermore the intensity and contrast of the display illumination may be set within predefined limits to reduce the aging.
Owner:BARCO NV
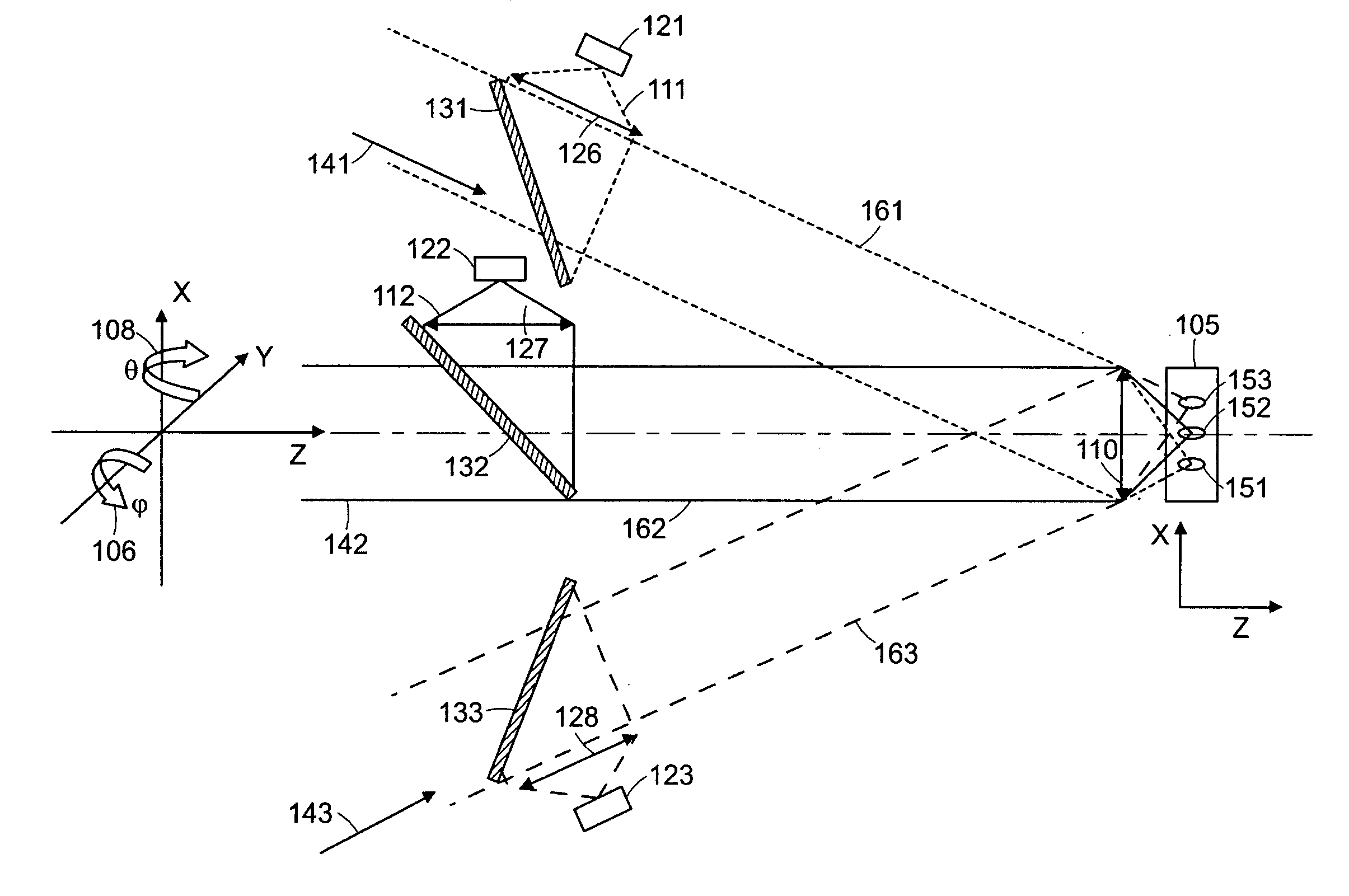
Optical arrangements for use with an array camera
A variety of optical arrangements and methods of modifying or enhancing the optical characteristics and functionality of these optical arrangements are provided. The optical arrangements being specifically designed to operate with camera arrays that incorporate an imaging device that is formed of a plurality of imagers that each include a plurality of pixels. The plurality of imagers include a first imager having a first imaging characteristics and a second imager having a second imaging characteristics. The images generated by the plurality of imagers are processed to obtain an enhanced image compared to images captured by the imagers. In many optical arrangements the MTF characteristics of the optics allow for contrast at spatial frequencies that are at least as great as the desired resolution of the high resolution images synthesized by the array camera, and significantly greater than the Nyquist frequency of the pixel pitch of the pixels on the focal plane, which in some cases may be 1.5, 2 or 3 times the Nyquist frequency.
Owner:FOTONATION CAYMAN LTD
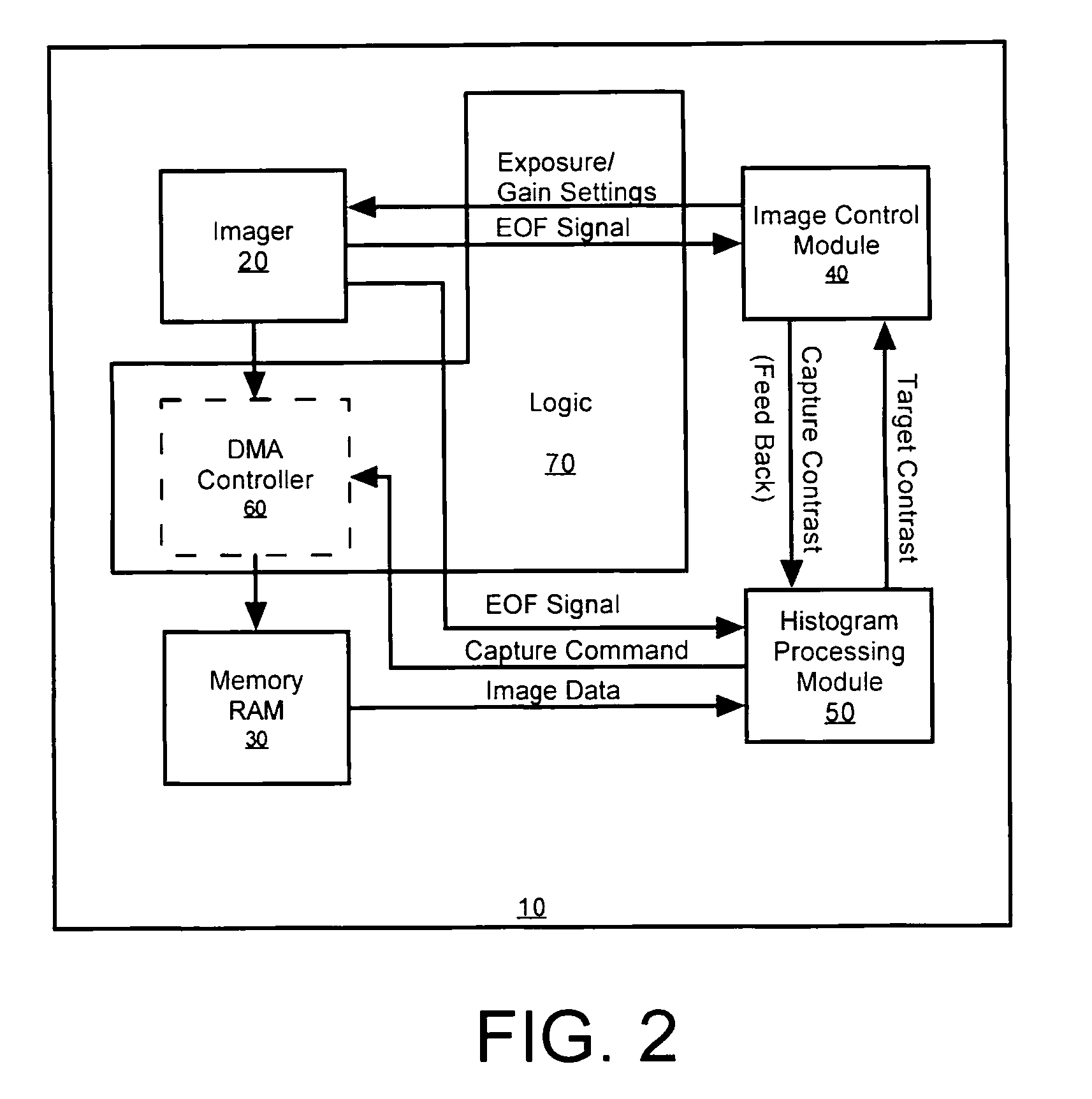
Methods and apparatus for automatic exposure control
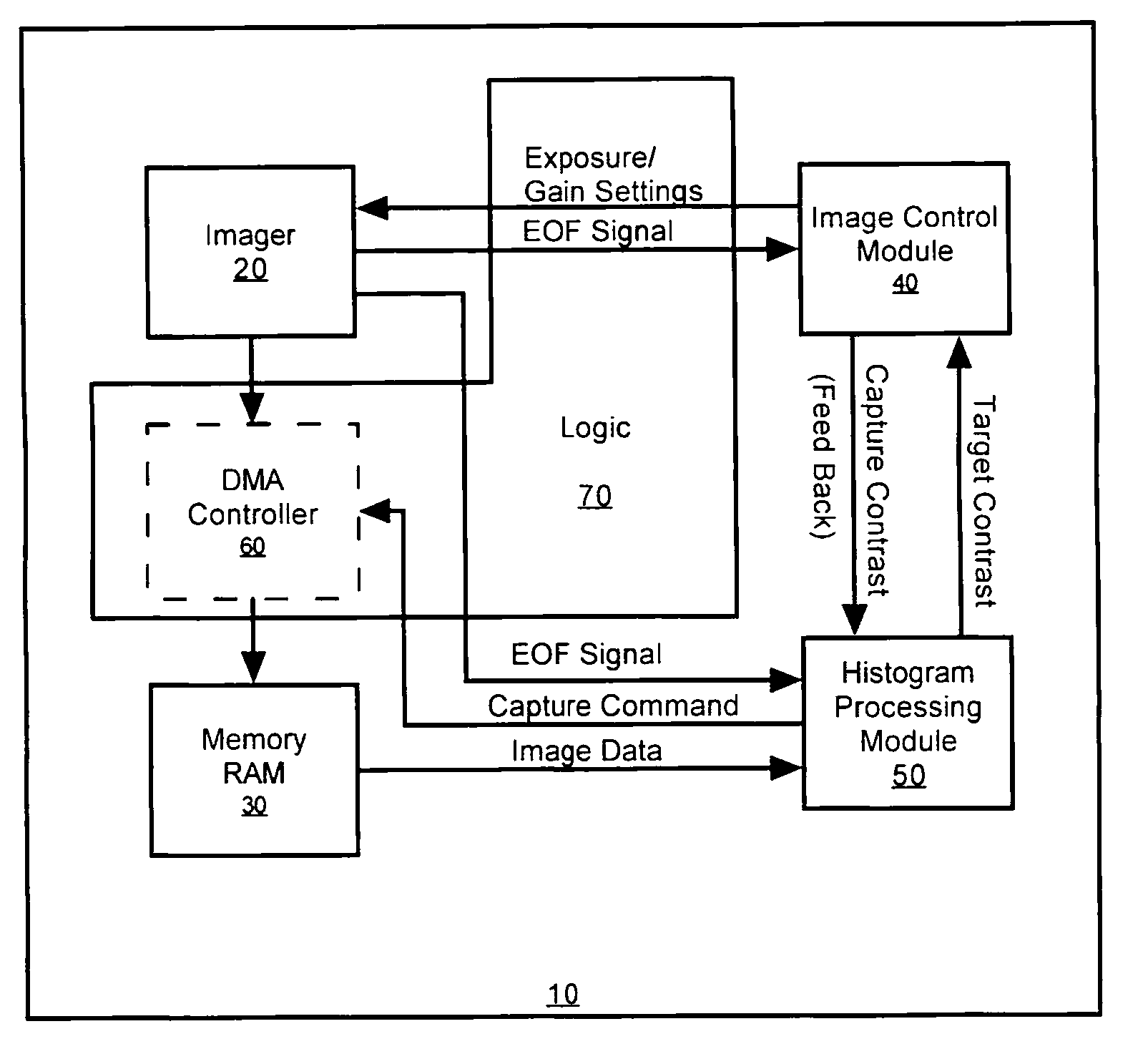
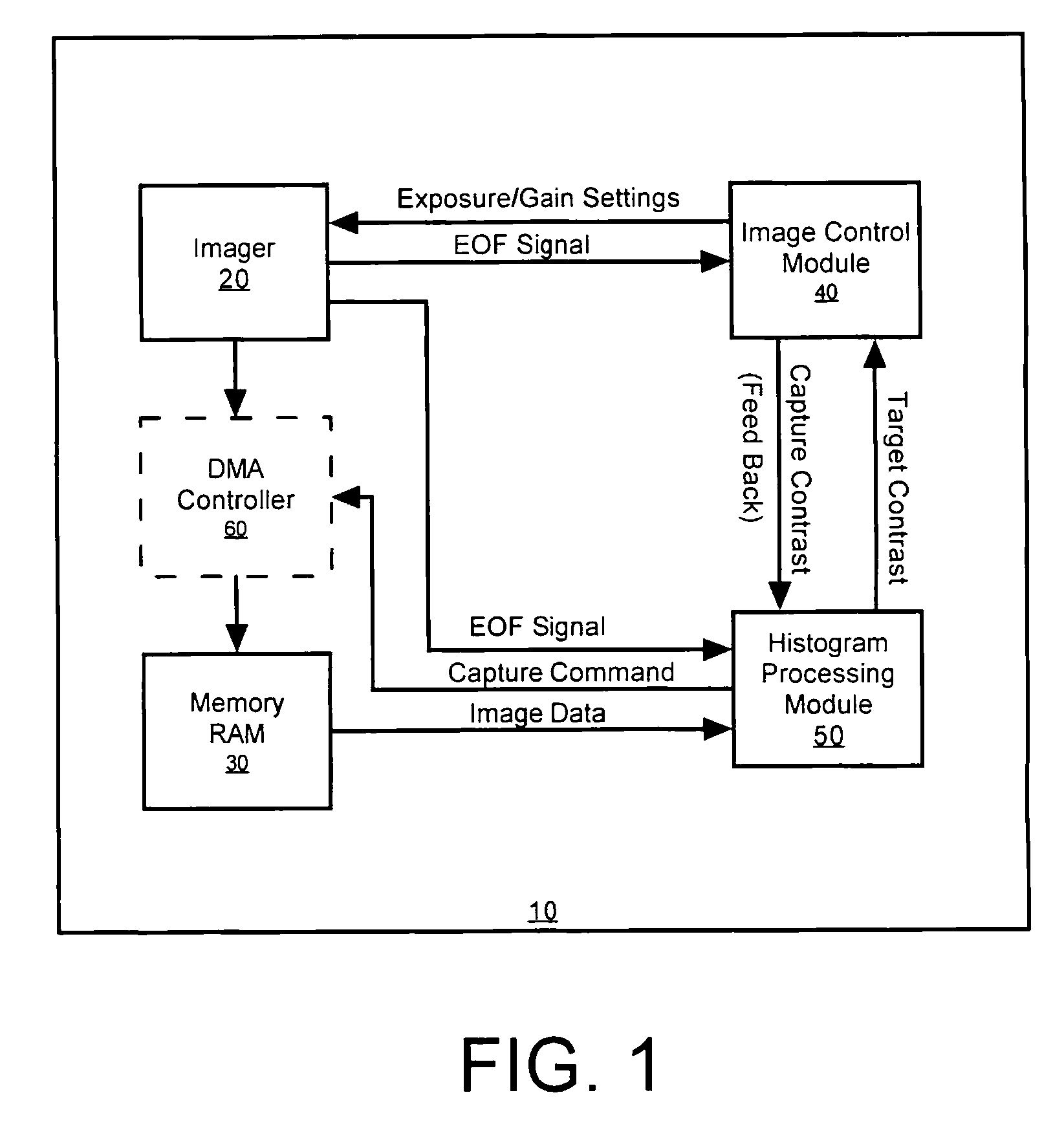
A multi-dimensional imaging device and method for automated exposure control that implement two distinct modules to control the exposure and gain settings in the imager so that processing can occur in a multi-tasking single CPU environment. The first module, referred to herein as the imager control module, controls the exposure and gain settings in the imager. The first module is typically implemented in a high priority routine, such as an interrupt service routine, to insure that module is executed on every captured frame. The second module, referred to herein as the histogram processing module, calculates a target contrast (the product of the targeted exposure and gain settings) based on feedback data from the first module and image data from memory. The second module is typically implemented in a low priority routine, such as a task level routine, to allow for the routine to be executed systematically in accordance with priority.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
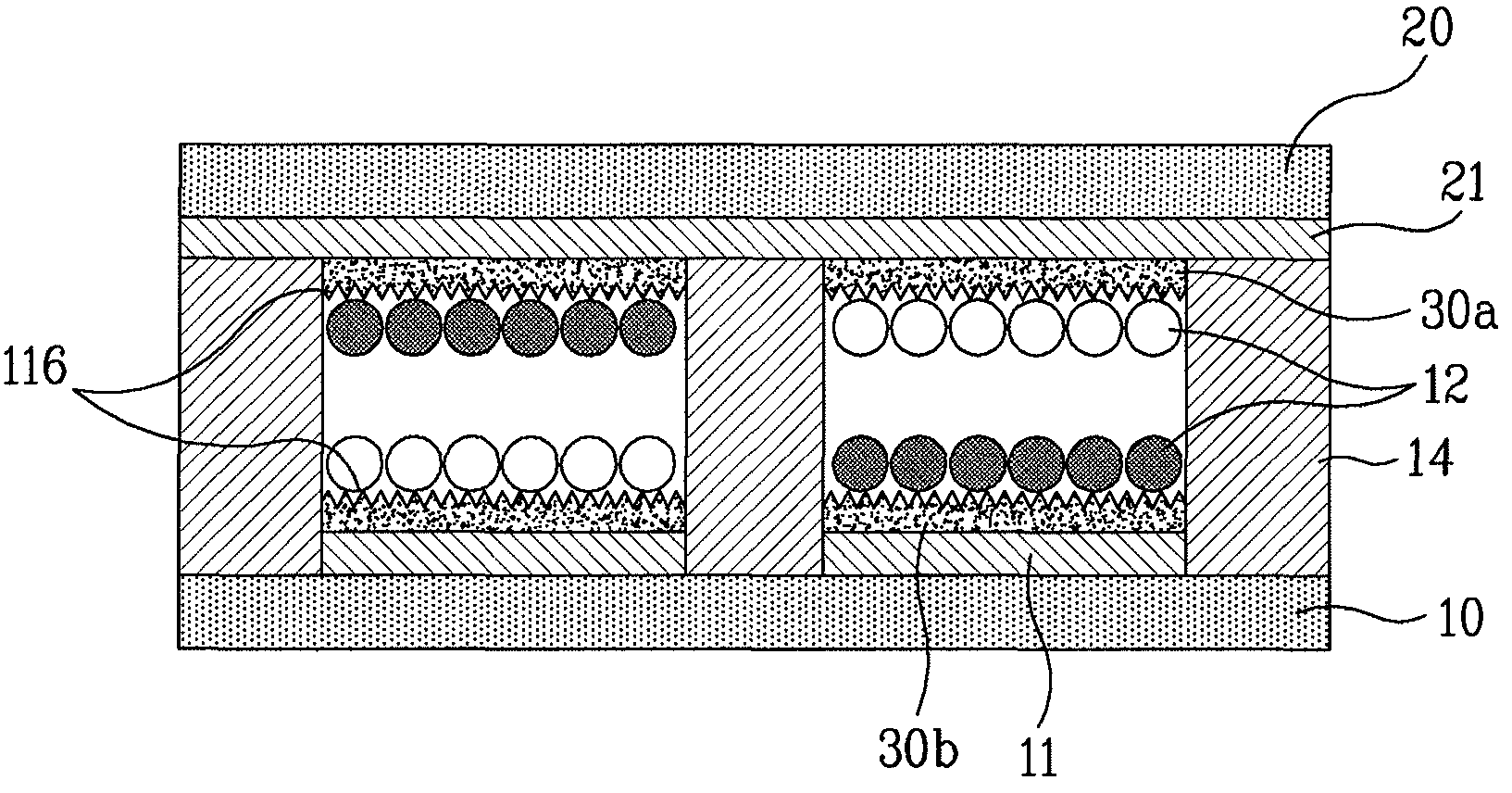
Overlapped image display type information input/output apparatus
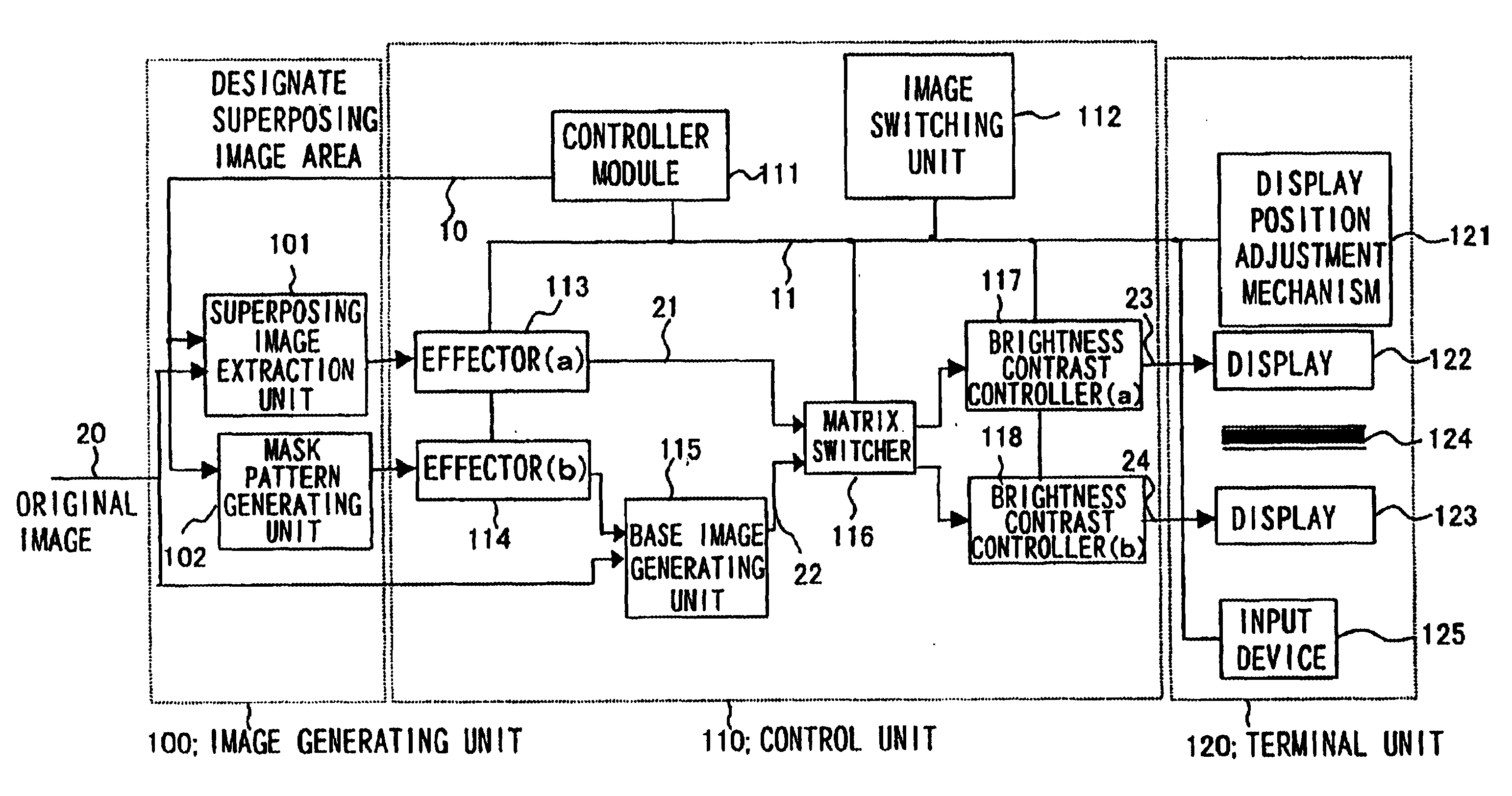
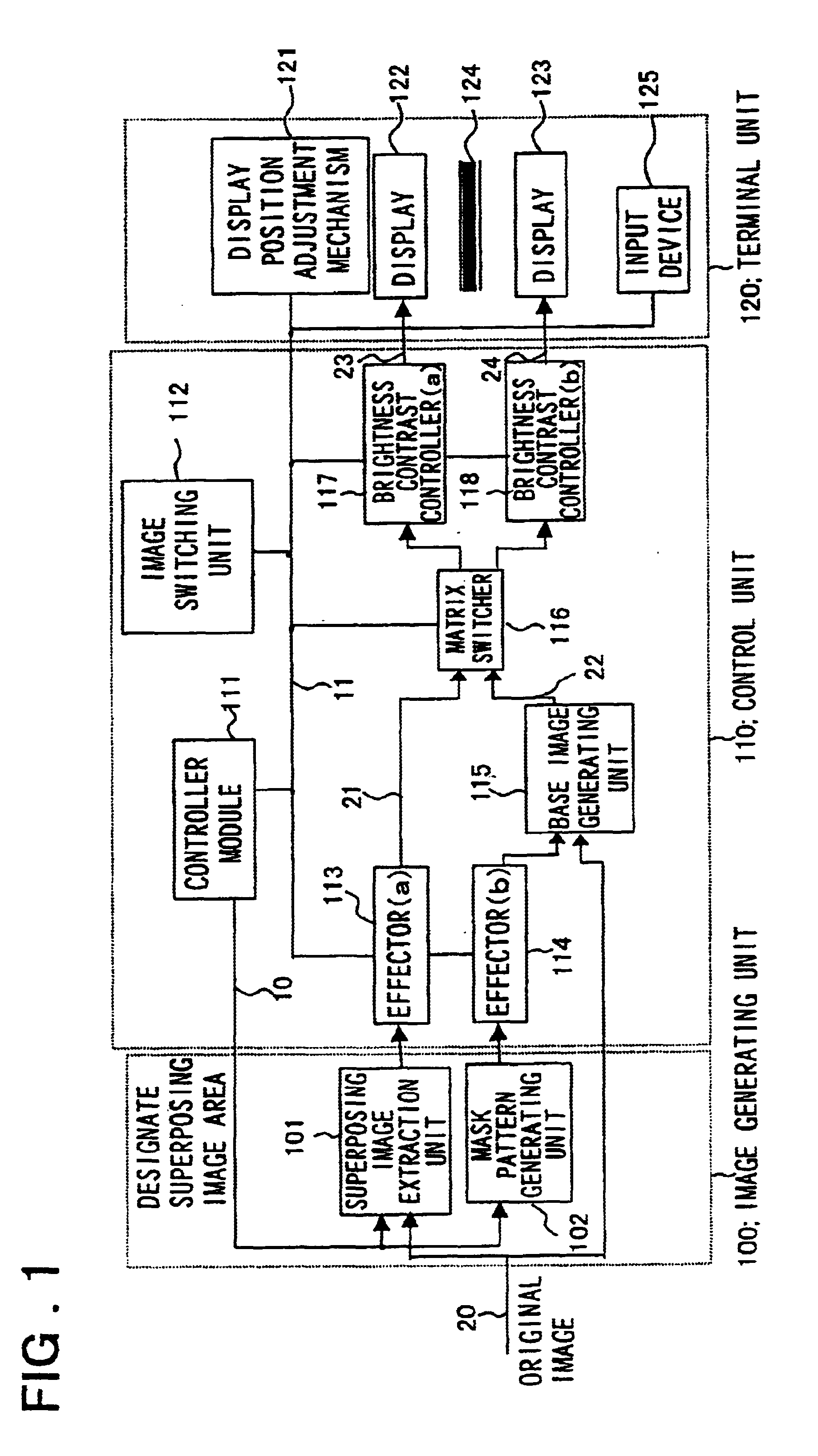
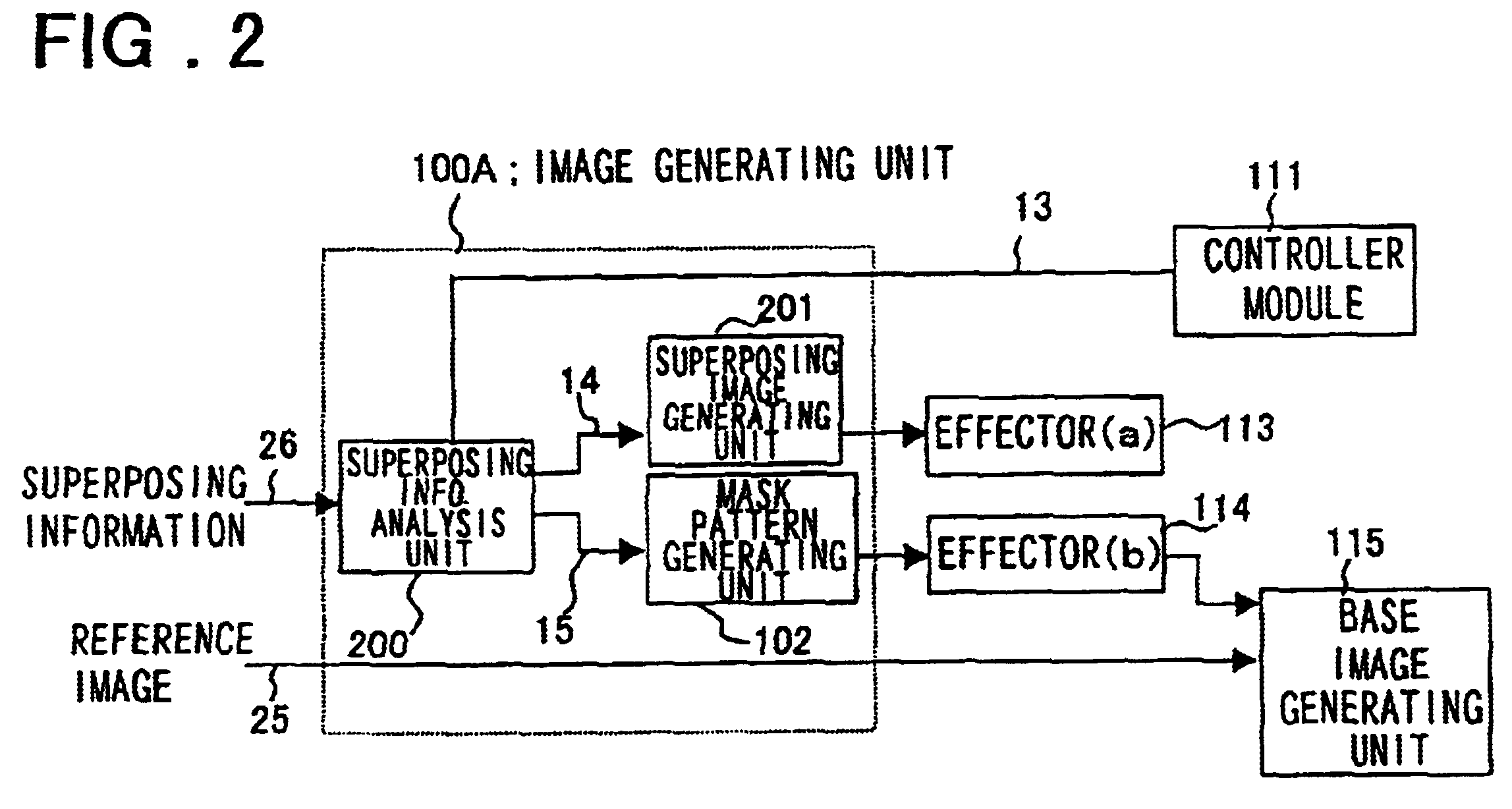
InactiveUS6661425B1Lower the volumeCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital output to display deviceImage extractionComputer graphics (images)
An information input / output device having an intuitive operating feeling and improved information viewing and discriminating properties. The device comprises an superposing image extraction unit 101 extracting a portion for superpositional display from an image to output the extracted image portion as an superposing image, a mask pattern generating unit 102 generating a mask pattern, effectors 113, 114 processing the superposing image, and the mask pattern based on the effect designation information, and a base image generating unit 115 synthesizing the mask pattern image and the original image to generate a base image. The device also comprises a switcher 116, brightness / contrast controllers 117, 118 adjusting the brightness or contrast of the display image switching means 112, a control unit 111, superpositional image display unit 124 for superposed demonstration of display image planes of the displays 122, 123 and a display position adjustment mechanism 121. The display information of the image for display in superposition is demonstrated at a position which appears to be floated or recessed from the basic display plane.
Owner:NEC CORP
Rearview Mirror Assemblies With Anisotropic Polymer Laminates
ActiveUS20090296190A1High strengthAdequate flatness of filmMirrorsSynthetic resin layered productsLower limitWing mirror
Anisotropic film laminates for use in image-preserving reflectors such as rearview automotive mirror assemblies, and related methods of fabrication. A film may comprise an anisotropic layer such as a light-polarizing layer and other functional layers. The film having controlled water content is heated under omnidirectional pressure and vacuum to a temperature substantially equal to or above a lower limit of a glass-transition temperature range of the film so as to be laminated to a substrate. The laminate is configured as part of a mirror structure so as to increase contrast of light produced by a light source positioned behind the mirror structure and transmitted through the mirror structure towards a viewer. The mirror structure is devoid of any extended distortion and is characterized by SW and LW values less than 3, more preferably less than 2, and most preferably less than 1.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
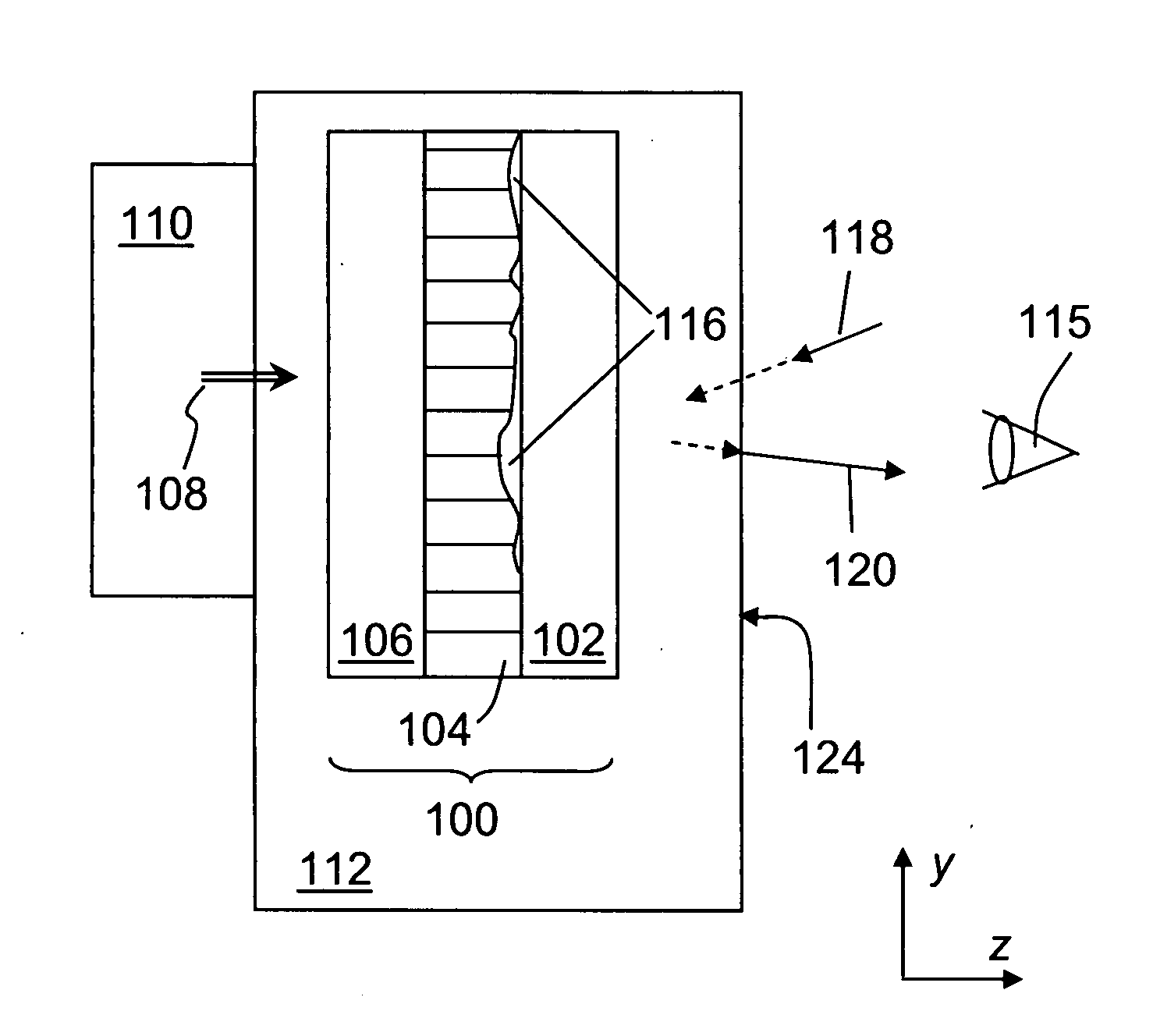
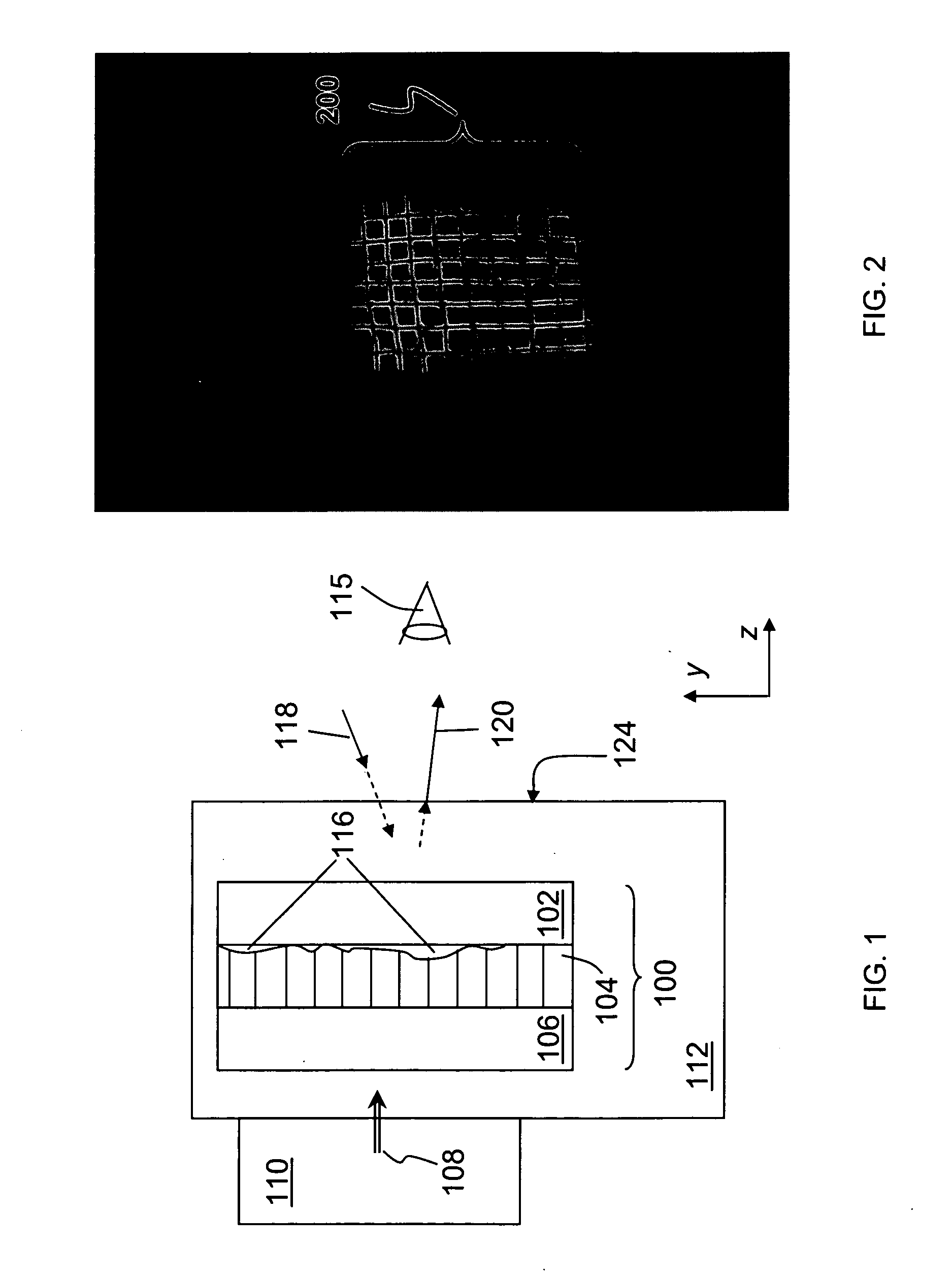
Systems and methods for displaying changes in biological responses to therapy
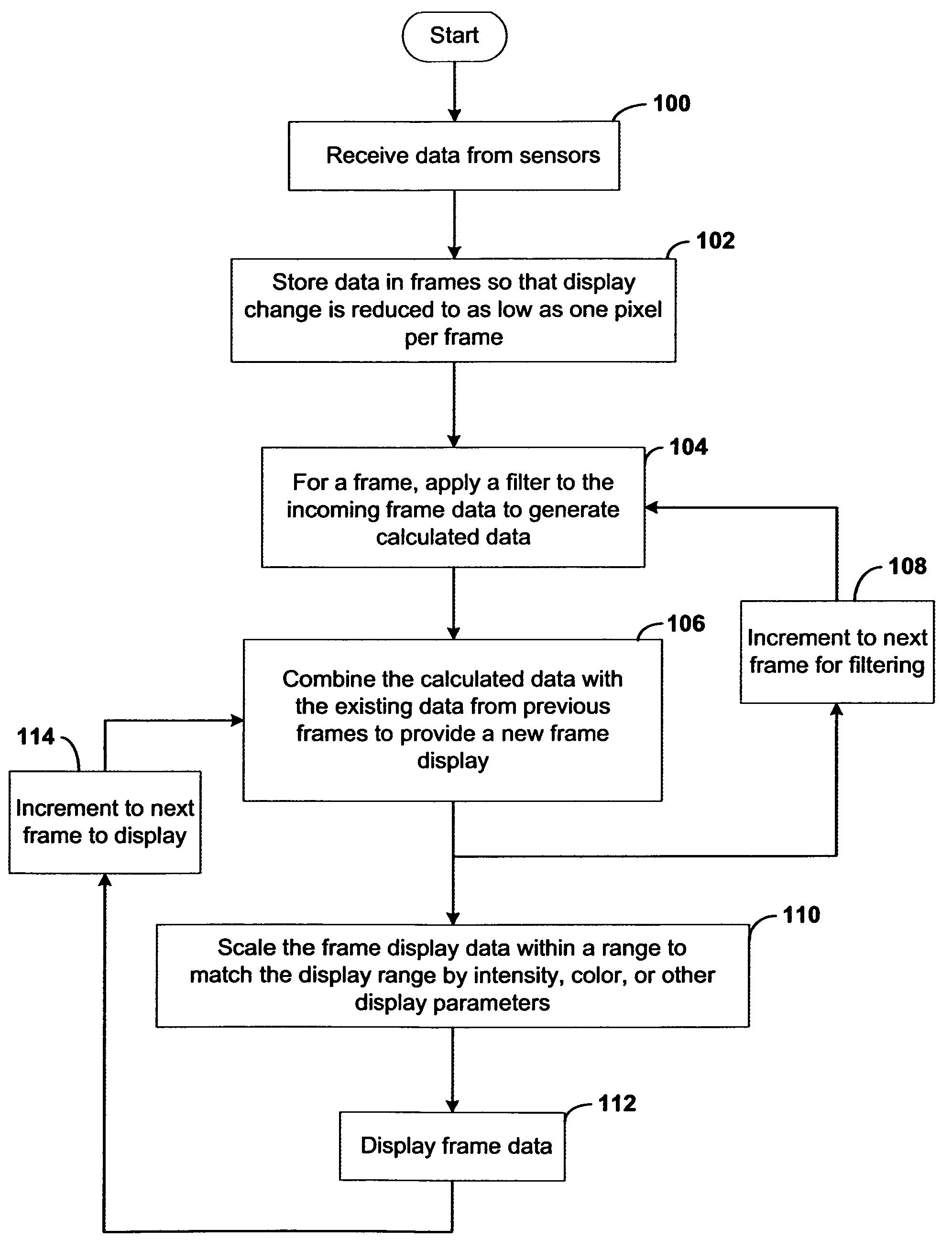
InactiveUS7720306B2Better convey information to the viewerImprove visibilityDrawing from basic elementsPerson identificationCorrelation functionDisplay device
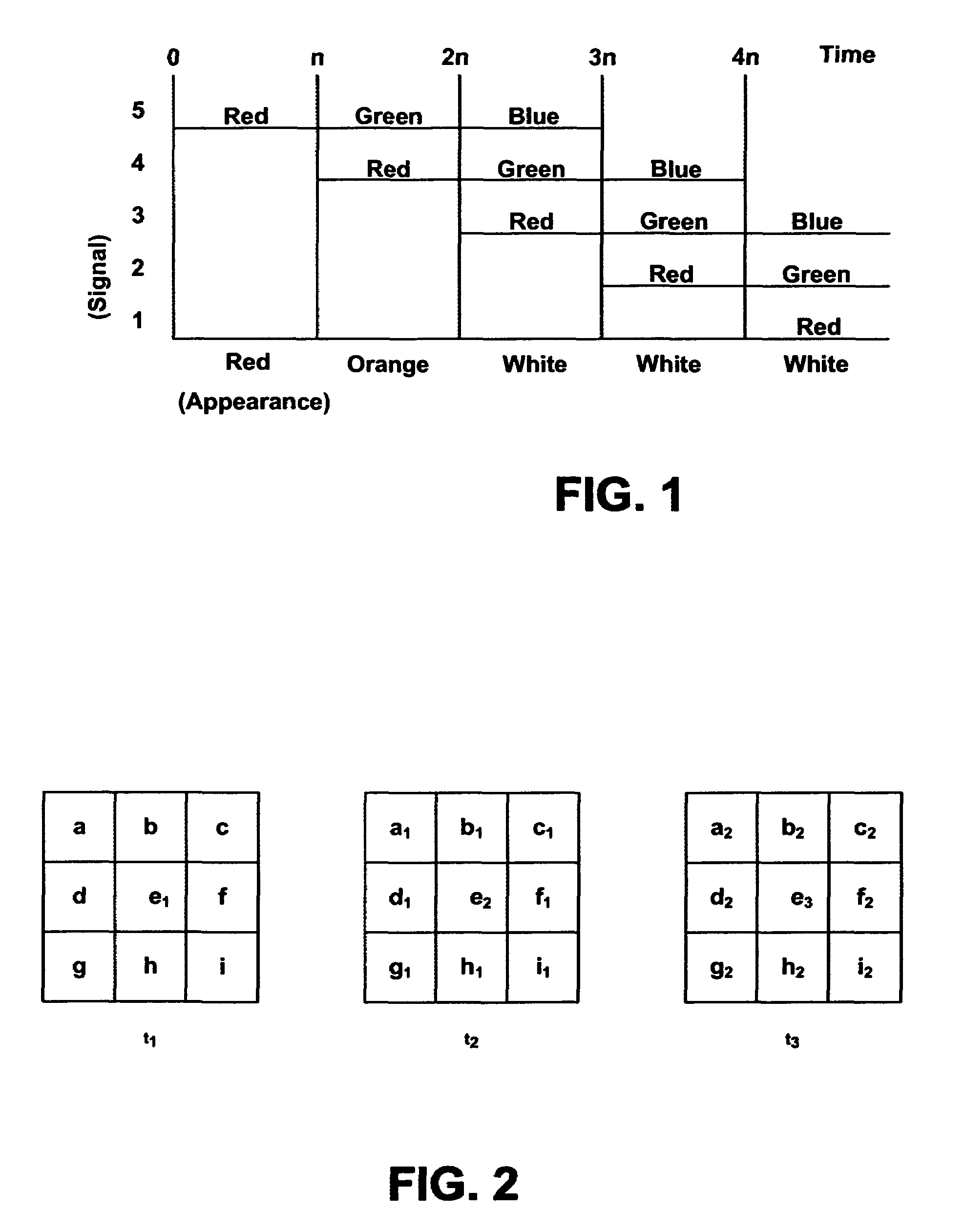
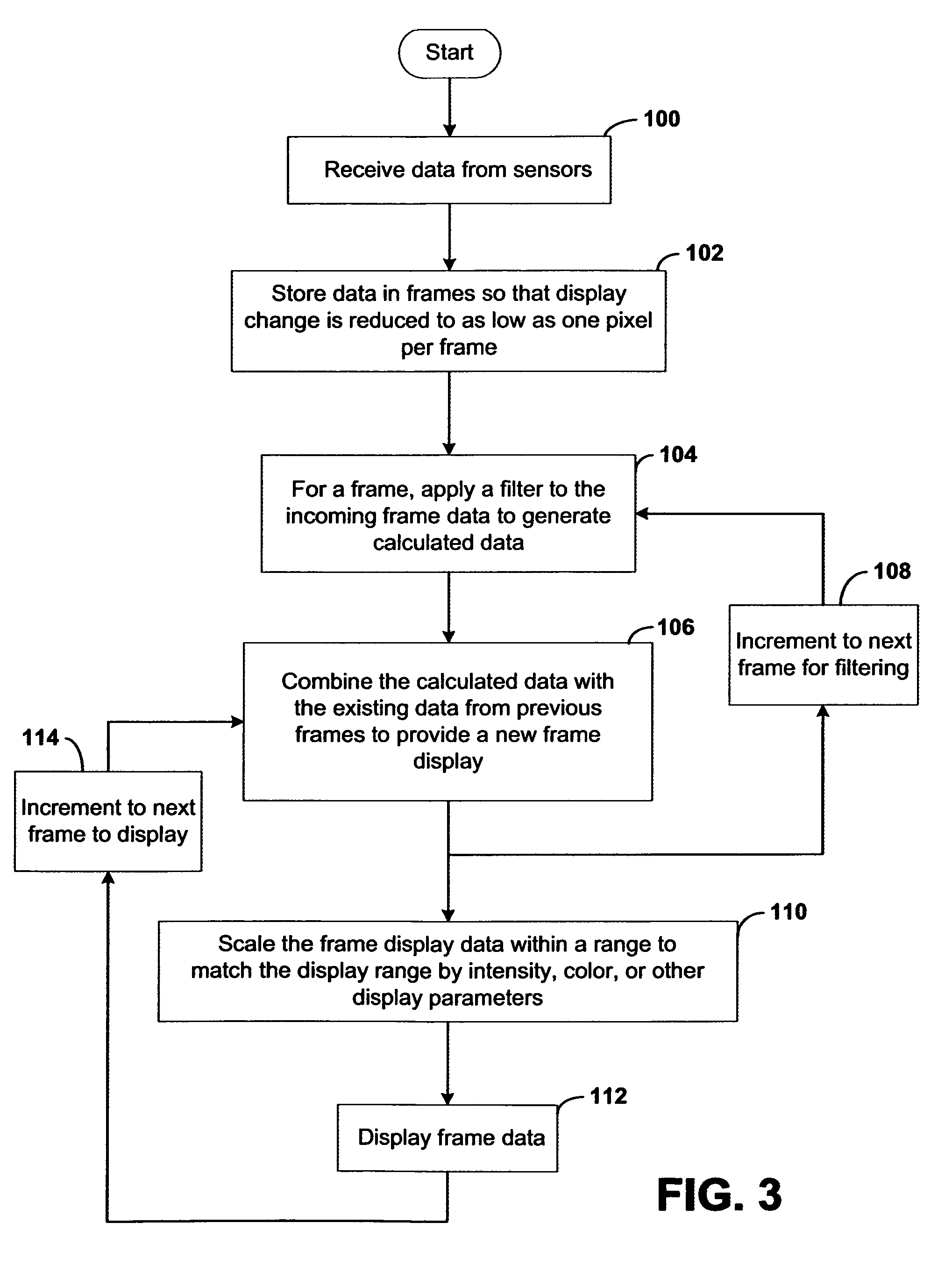
Systems and methods of this invention display data using pixels with information indicated by color and intensity changes, particularly used for monitoring of physiological variables in real time. For certain methods, physiological data can be acquired by sensors, acquired data can be stored in data frames, data frames can be processed using computer-implemented methods, and processed data frames can be scaled to a display frame for display on a display device. Using such methods, a spot made up of a group of pixels can be updated during a time frame, or cycle using a computer-implemented method, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division or a time dependent function. Newly received data can be combined with prior received data to indicate time-dependent changes. In this way, each spot contains a cumulative history of data starting at some initial time. In other embodiments, visual contrast can be enhanced between desired data and other data. In further embodiments, two or more different types of data can be plotted together to indicate relationships between variables. Real time monitoring of signals during therapeutic treatment using light, electricity or other nerve or muscle stimuli can allow a user to monitor physiological responses during stimulation and to make rapid decisions about medical treatment.
Owner:PHOTOMED TECH
Method of magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6373250B1Reduce leakageReduce repetitionsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientResonance
A method of slice selective multiple quantum magnetic resonance imaging of an object is disclosed. The method is effected by implementing the steps of (a) applying a radiofrequency pulse sequence selected so as to select a coherence of an order n to the object, wherein n is zero, a positive or a negative integer other than ±1; (b) applying magnetic gradient pulses, so as to select a slice of the object to be imaged arid to create an image; and (c) acquiring a radiofrequency signal resulting from the object, so as to generate a magnetic resonance slice image of the object. The method provides slice selective multiple quantum magnetic resonance images of yet unprecedented quality in terms of contrast. The method is particularly useful for imaging connective tissues.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com