Patents
Literature
486 results about "Radiofrequency pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
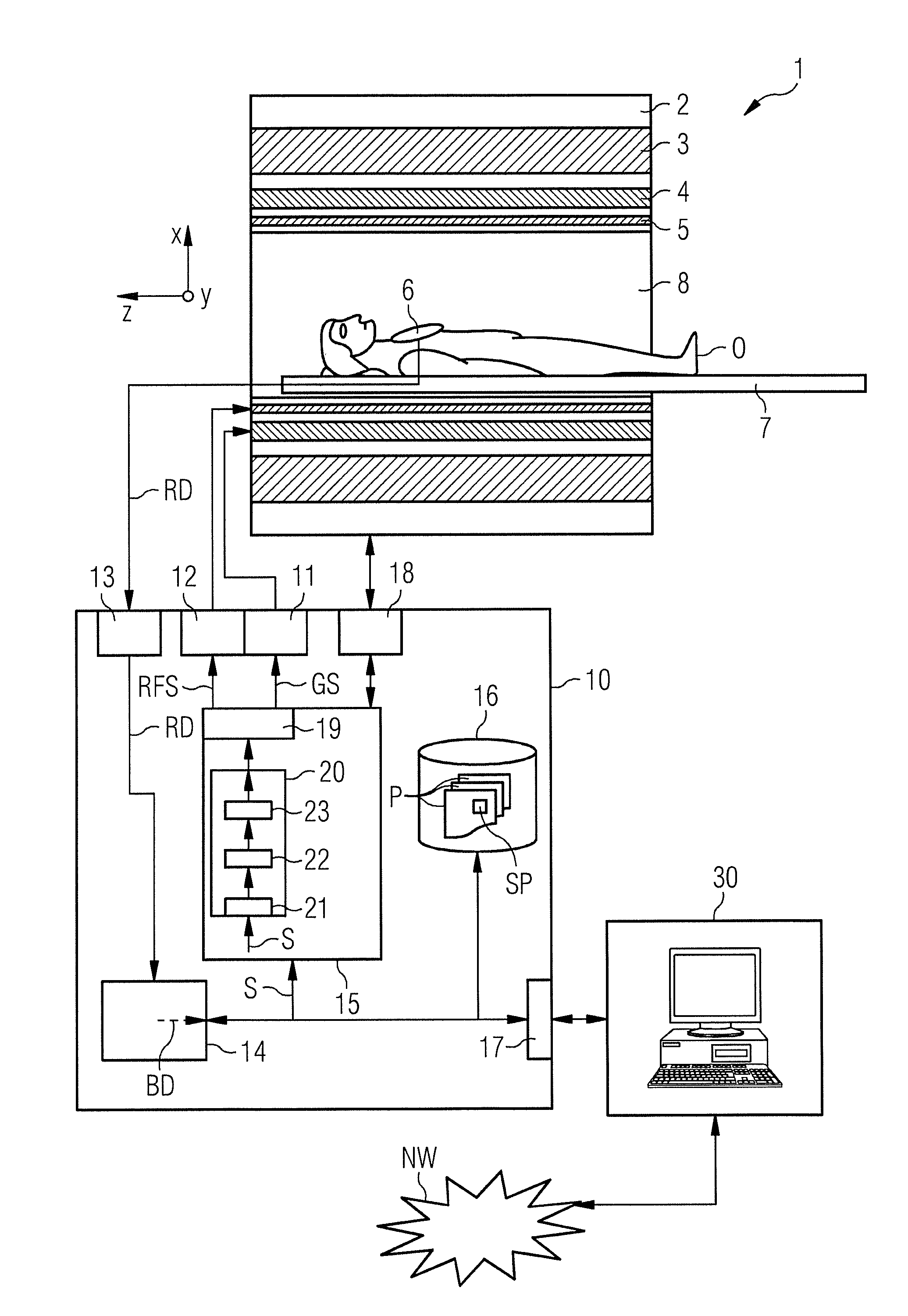
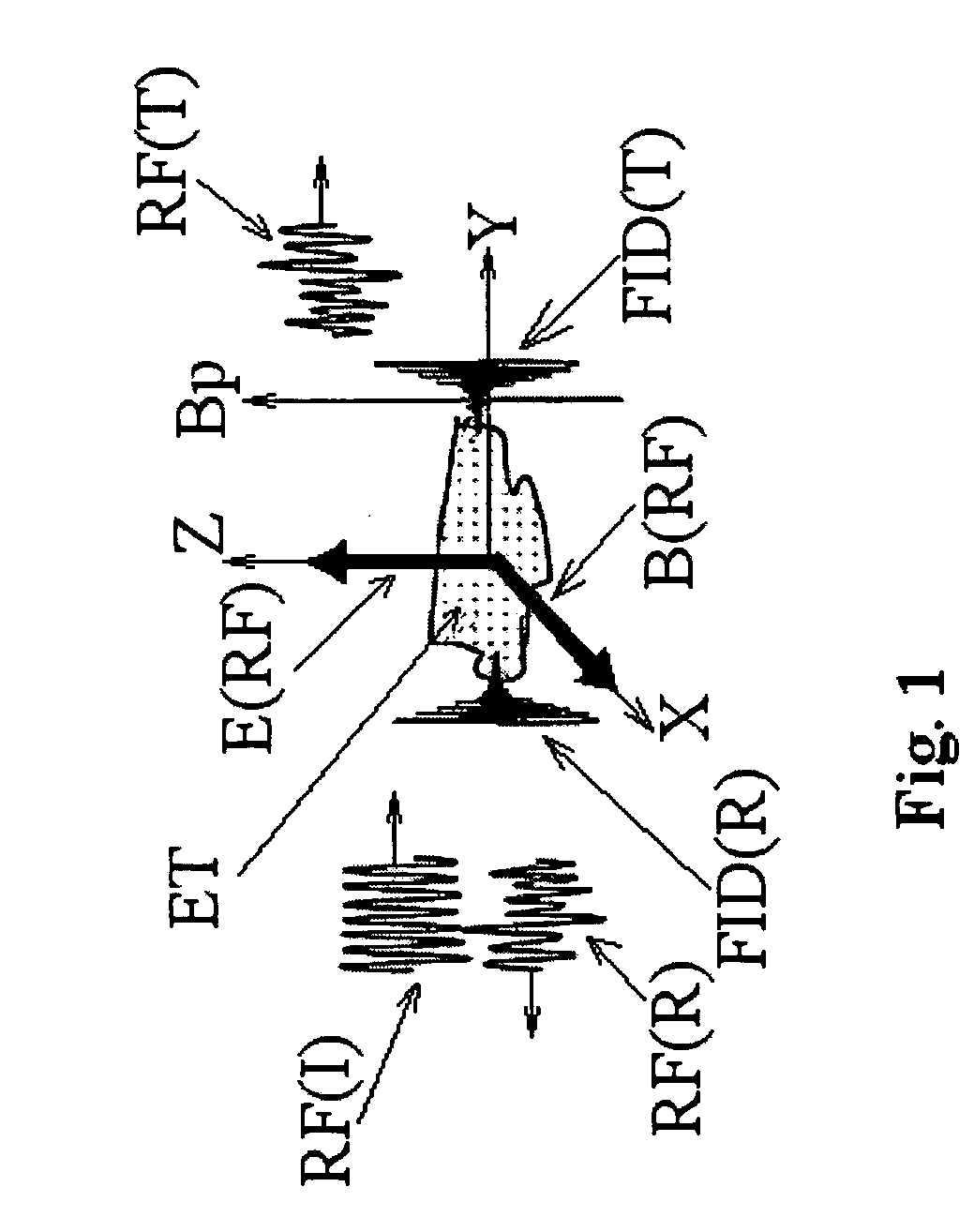
Radiofrequency pulse. a short burst of electromagnetic radiation in the radiofrequency range, used in combination with magnetic gradients to generate a magnetic resonance image.
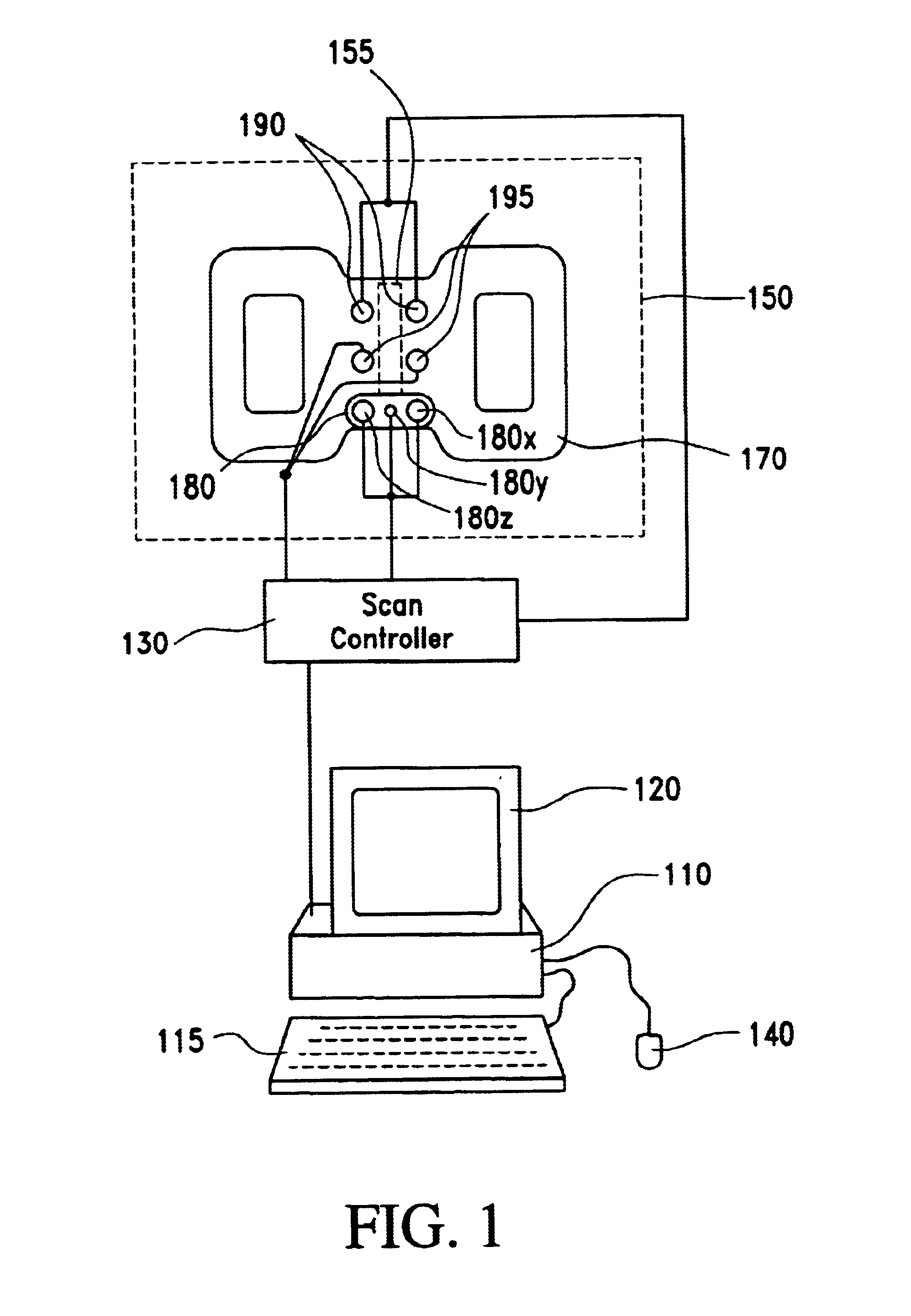
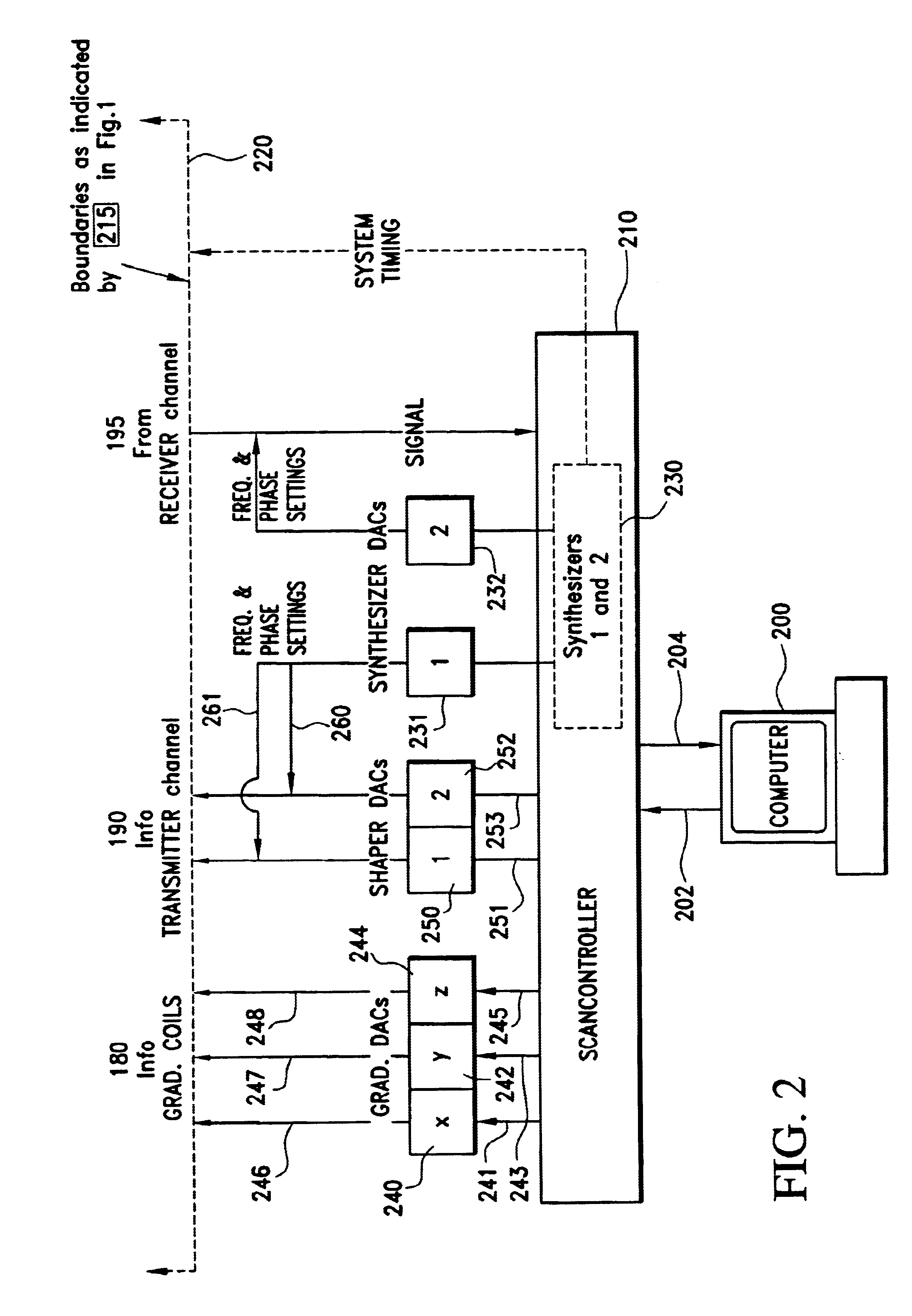
Method of magnetic resonance imaging
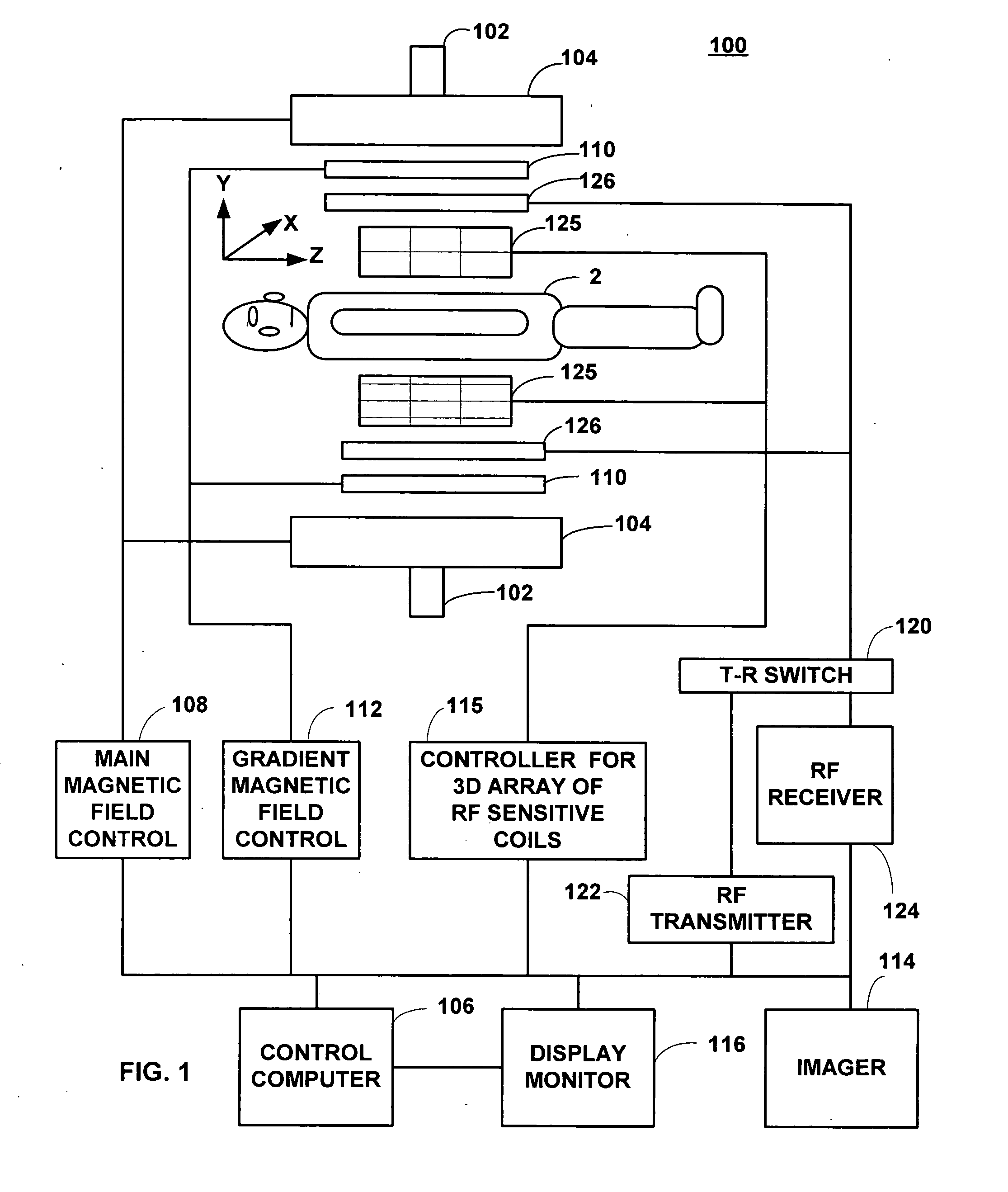
InactiveUS6373250B1Reduce leakageReduce repetitionsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientResonance
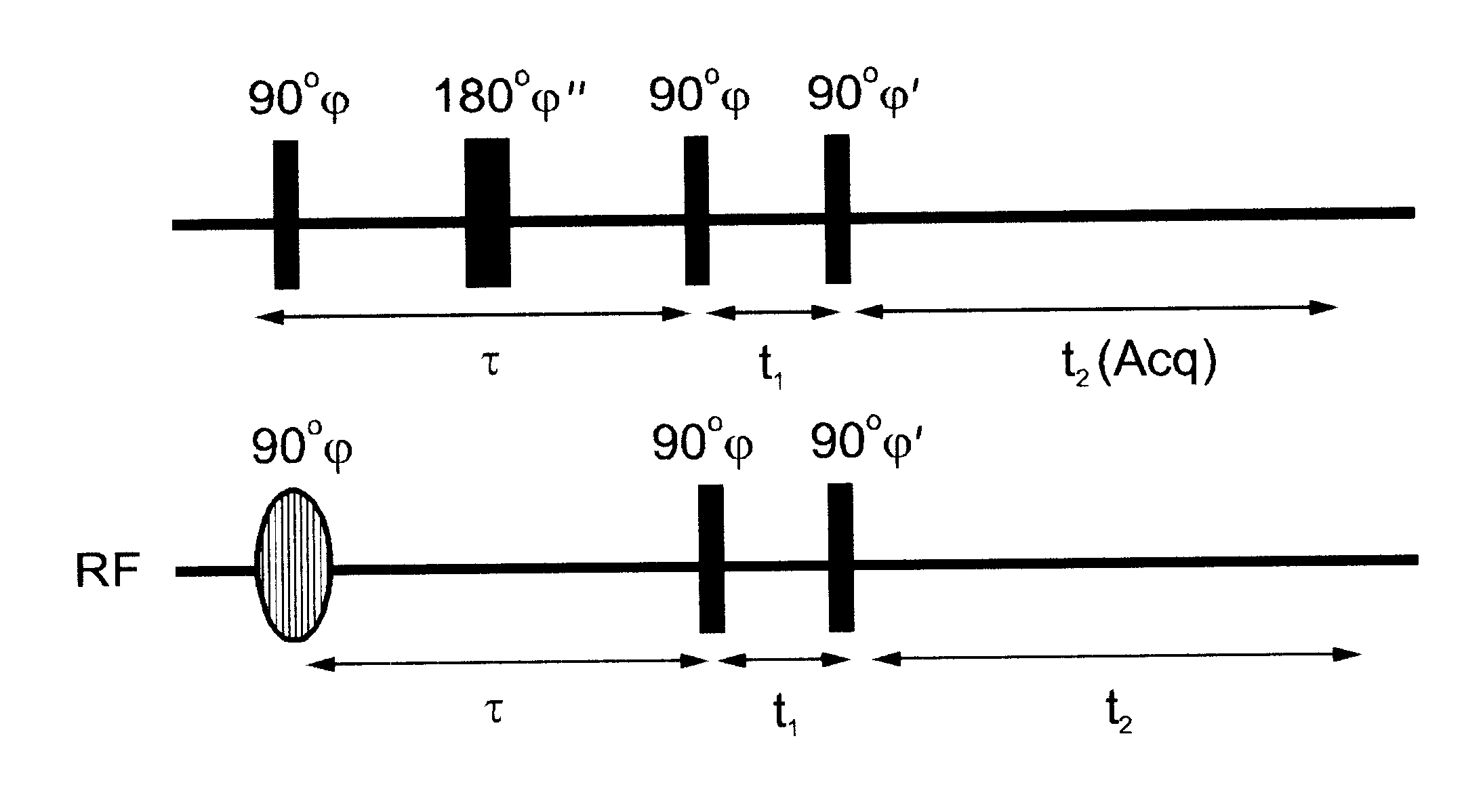
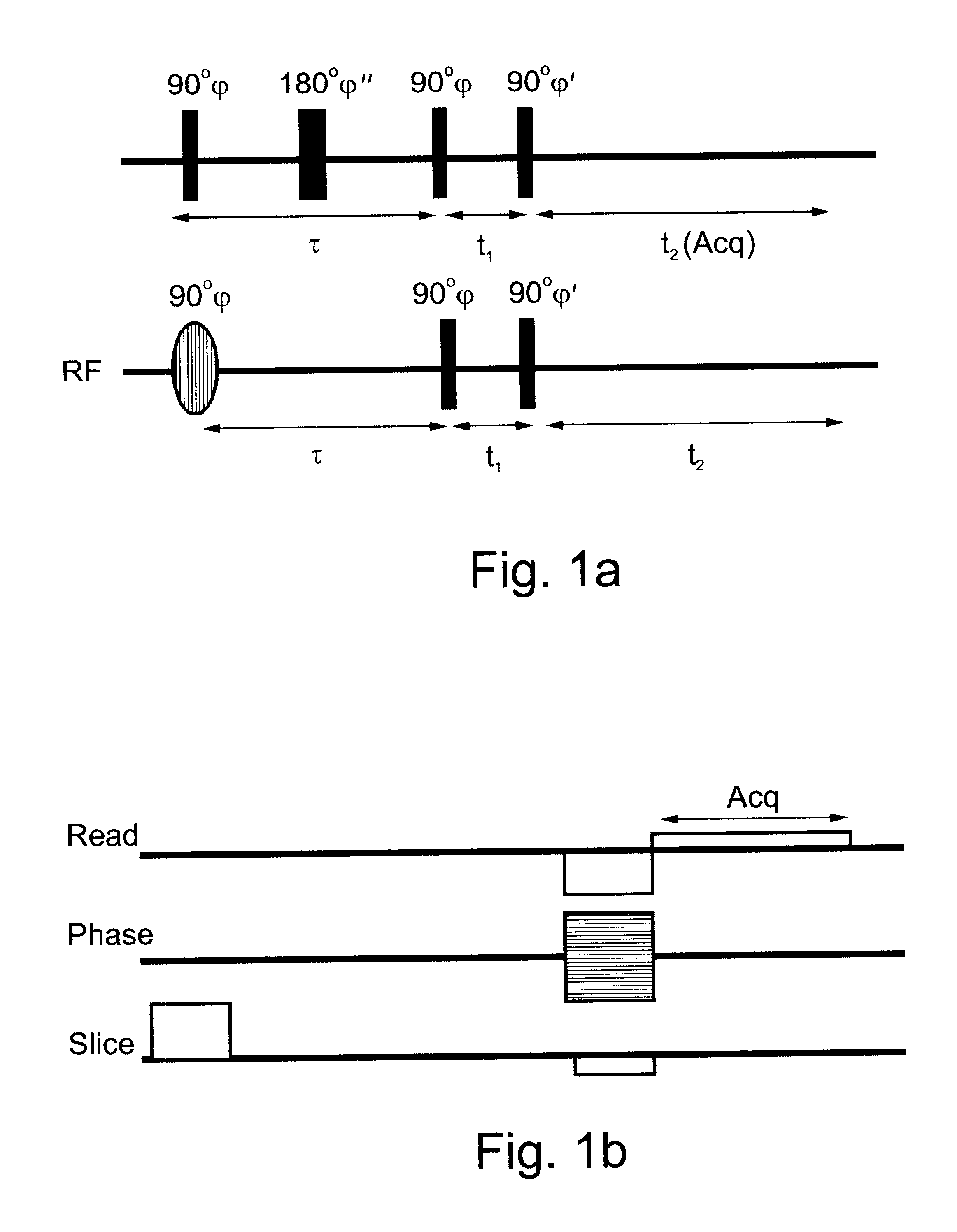
A method of slice selective multiple quantum magnetic resonance imaging of an object is disclosed. The method is effected by implementing the steps of (a) applying a radiofrequency pulse sequence selected so as to select a coherence of an order n to the object, wherein n is zero, a positive or a negative integer other than ±1; (b) applying magnetic gradient pulses, so as to select a slice of the object to be imaged arid to create an image; and (c) acquiring a radiofrequency signal resulting from the object, so as to generate a magnetic resonance slice image of the object. The method provides slice selective multiple quantum magnetic resonance images of yet unprecedented quality in terms of contrast. The method is particularly useful for imaging connective tissues.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA +1
Method and apparatus for examining a substance, particularly tissue, to characterize its type
ActiveUS20050021019A1Easy to implementImprove reliabilitySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsElectrical resistance and conductanceResonance
A method and apparatus for examining a substance volume to characterize its type, particularly useful for examining tissue to characterize it as cancerous or non-cancerous, by: applying a polarizing magnetic field through the examined substance: applying RF pulses locally to the examined substance volume such as to invoke electrical impedance (EI) responses signals corresponding to the electrical impedance of the substance, and magnetic resonance (MR) responses signals corresponding to the MR properties of the substance; detecting the EI and MR response signals; and utilizing the detected response signals for characterizing the examined substance volume type.
Owner:DUNE MEDICAL DEVICES
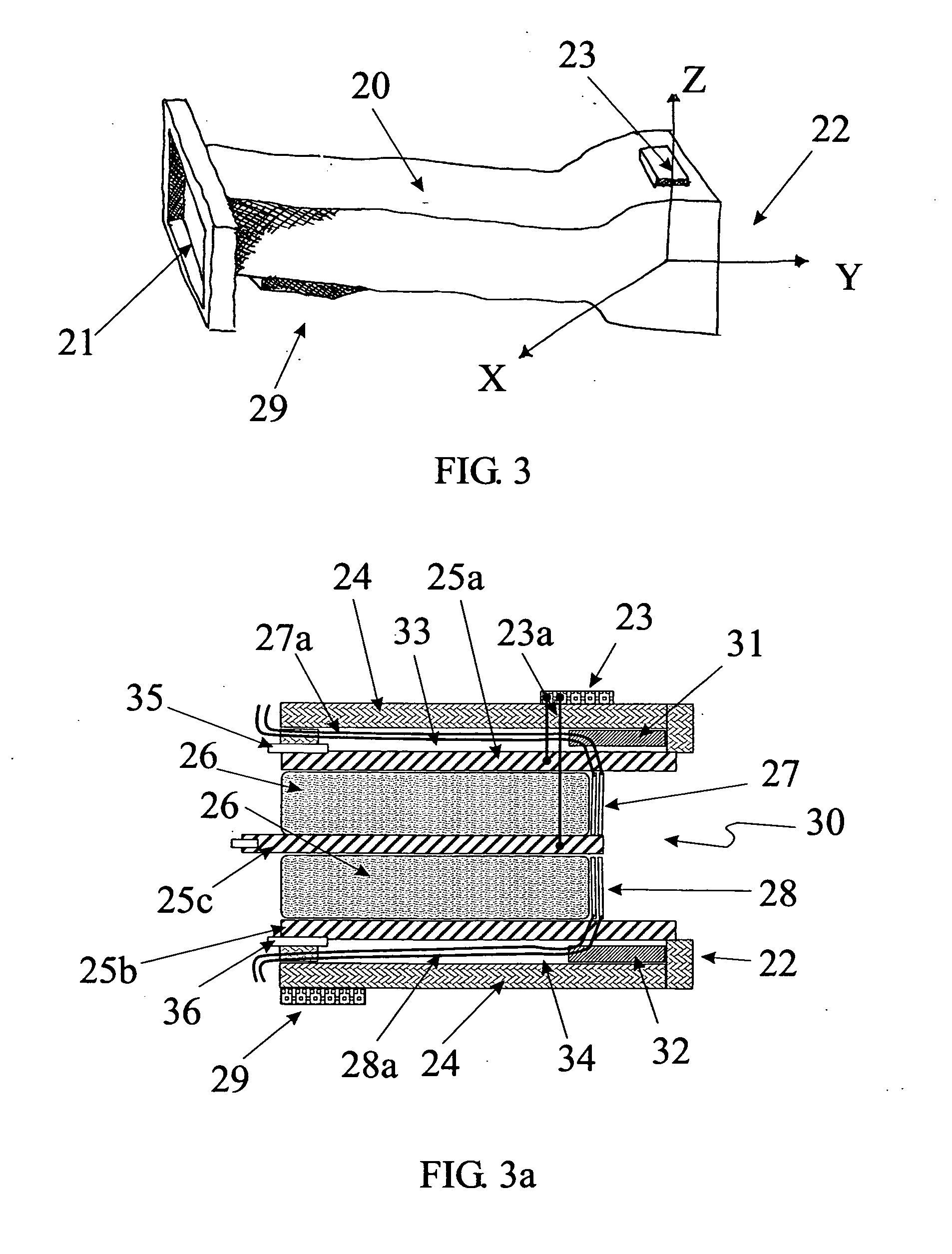
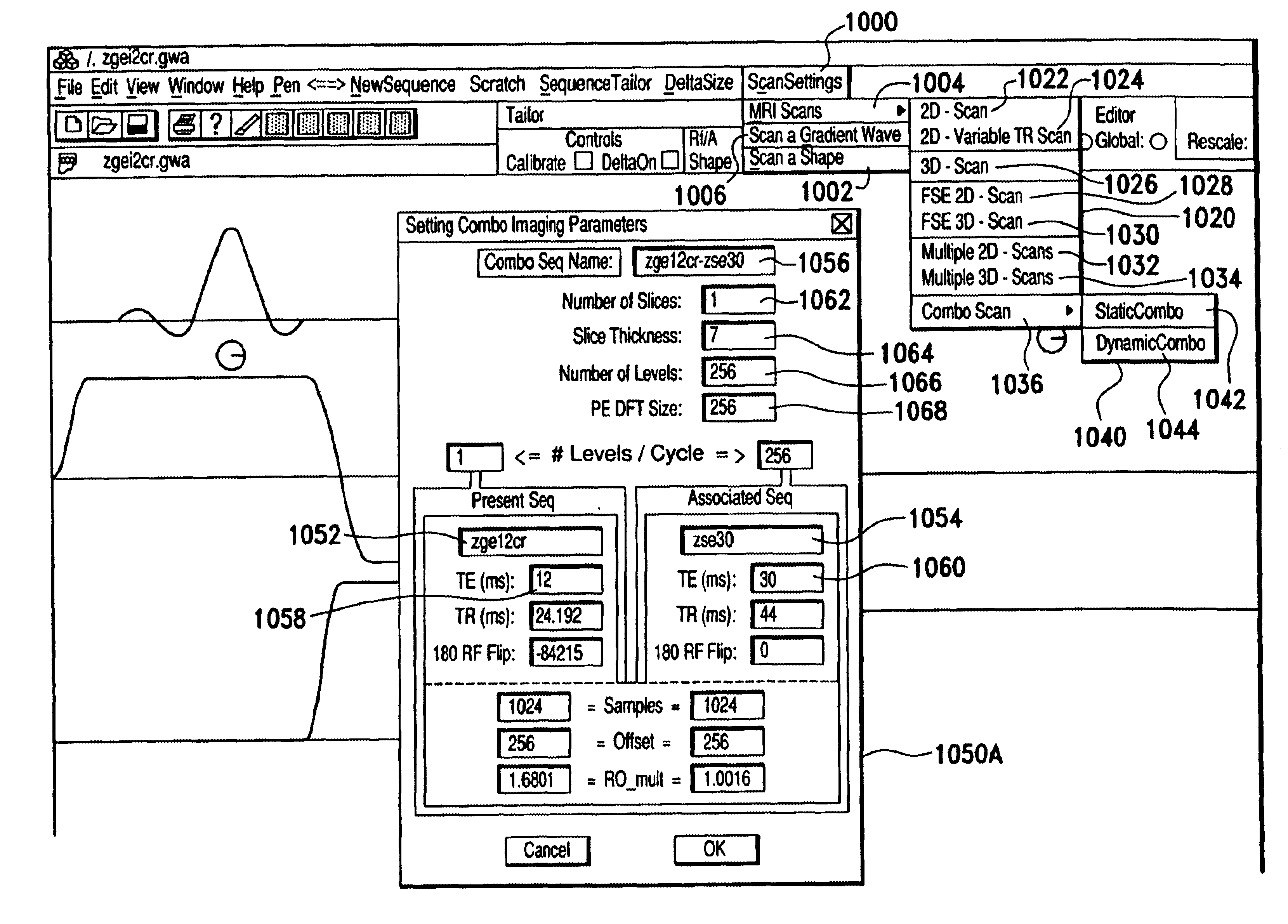
Dynamic real-time magnetic resonance imaging sequence designer
InactiveUS6801037B1Enhanced interactionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTime informationDisplay device
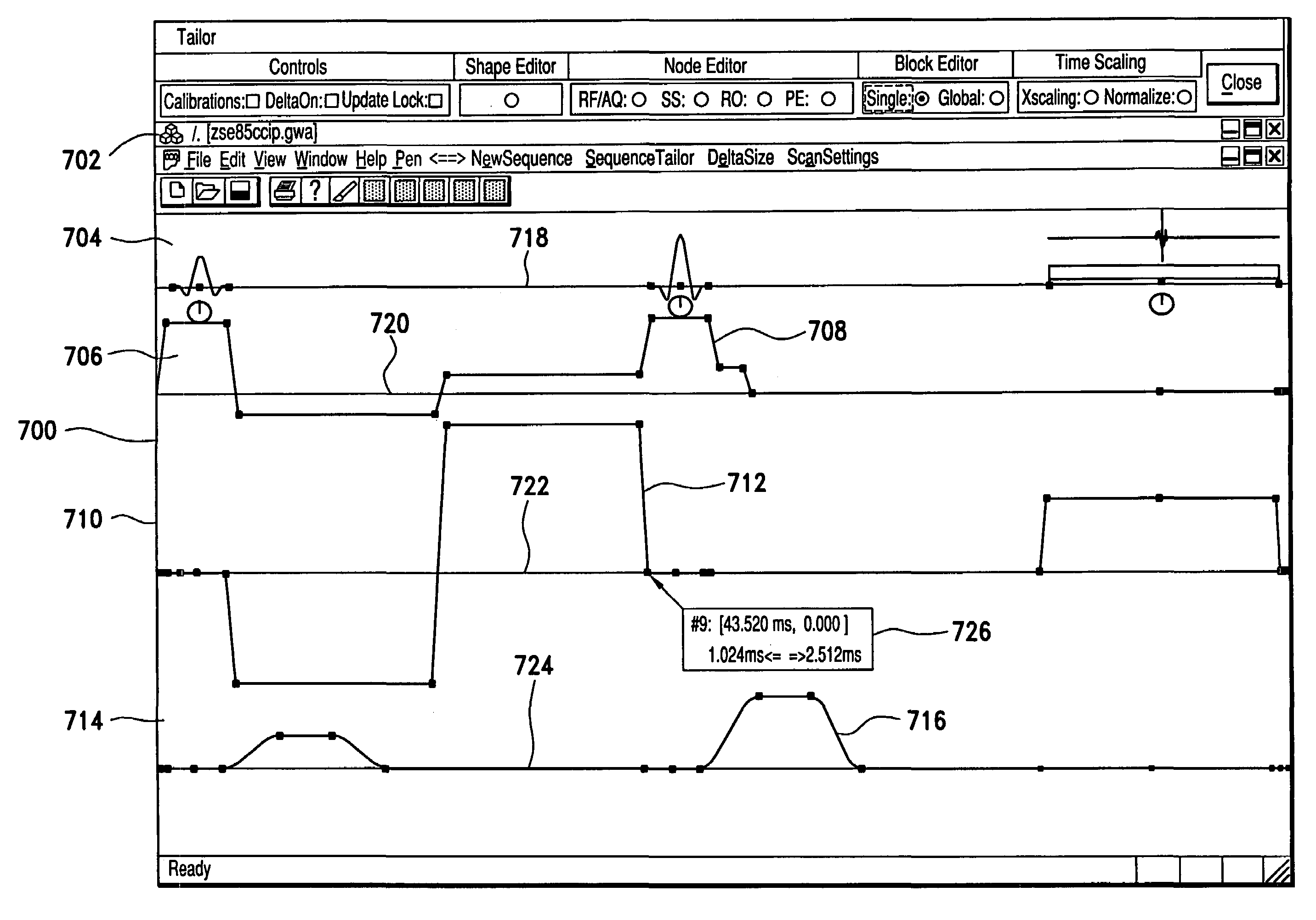
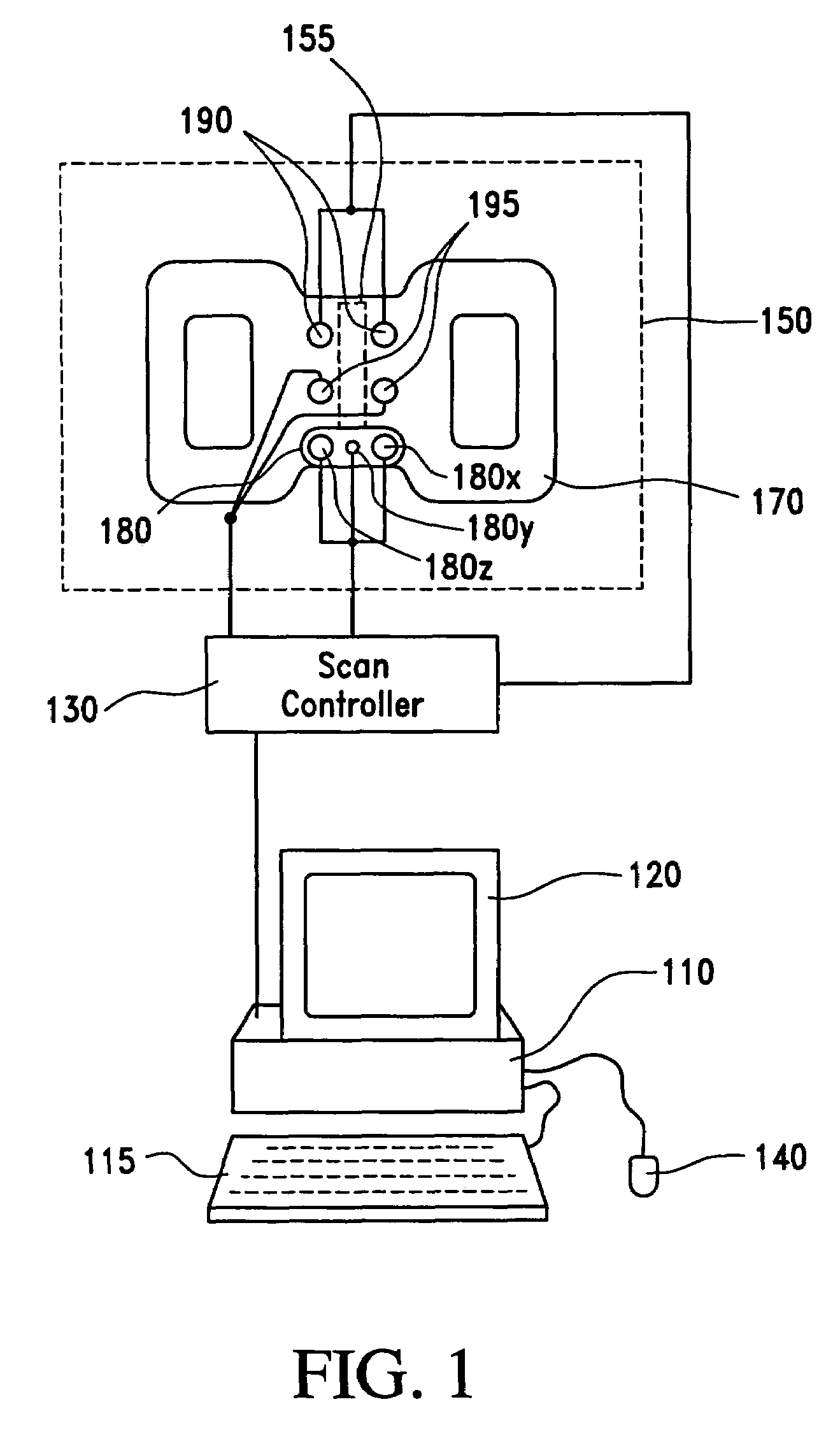
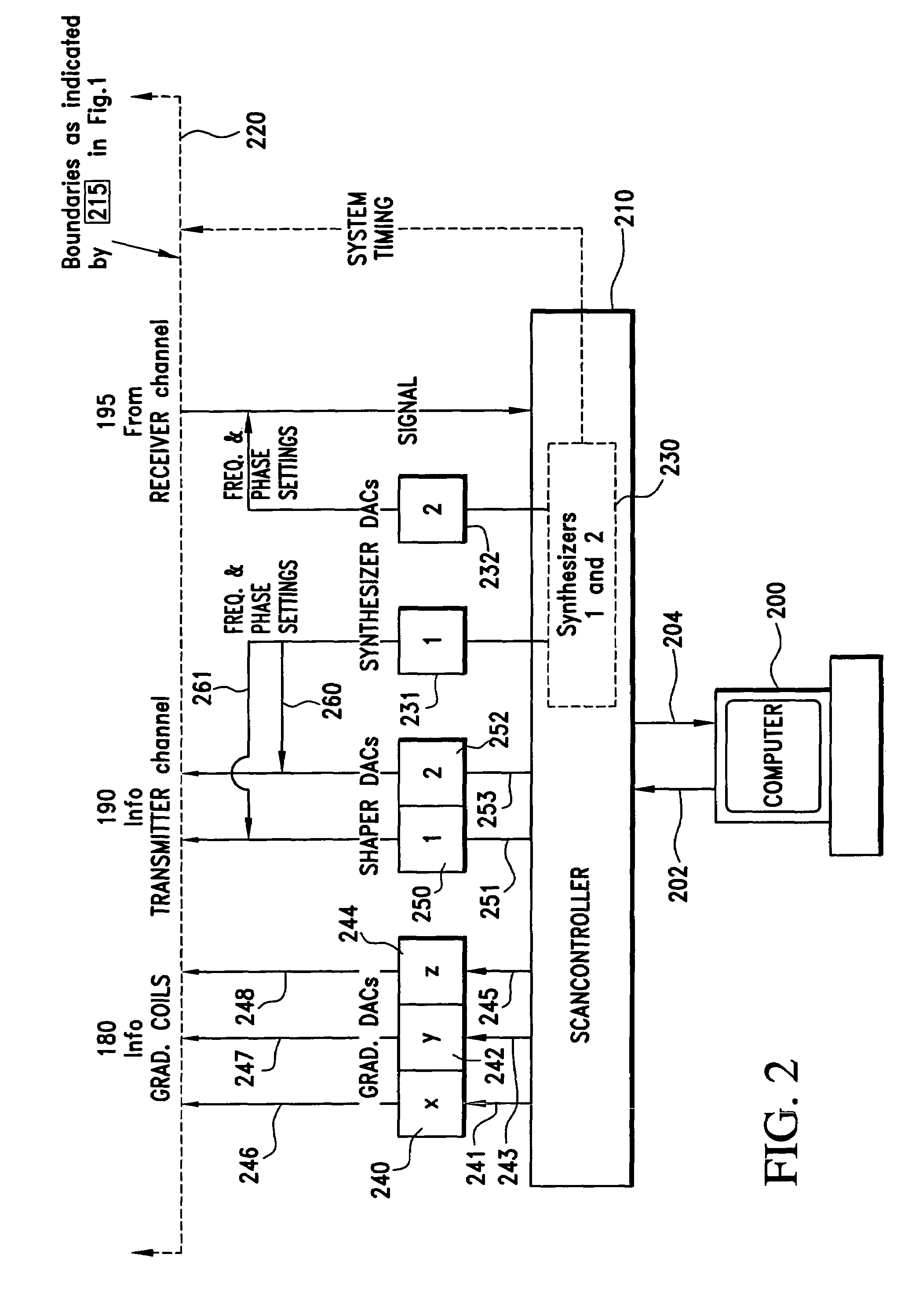
A system and method for facilitating RF pulse sequence generation and modification and for real-time sequence input modification for use in conjunction with magnetic resonance imaging equipment. A graphical user interface is provided through a display coupled to a digital computer operating as the primary control system for a magnetic resonance imaging scanner and associated hardware. Through the graphical user interface, an operator may choose or design sequences of radiofrequency pulses, gradient waveforms and other input parameters for the magnetic resonance imaging apparatus. Real-time information is also communicated to the operator through the graphical user interface allowing for real-time manipulation of the magnetic resonance imaging inputs and for displaying the magnetic resonance response thereto.
Owner:FONAR
Laser pulse picking employing controlled AOM loading
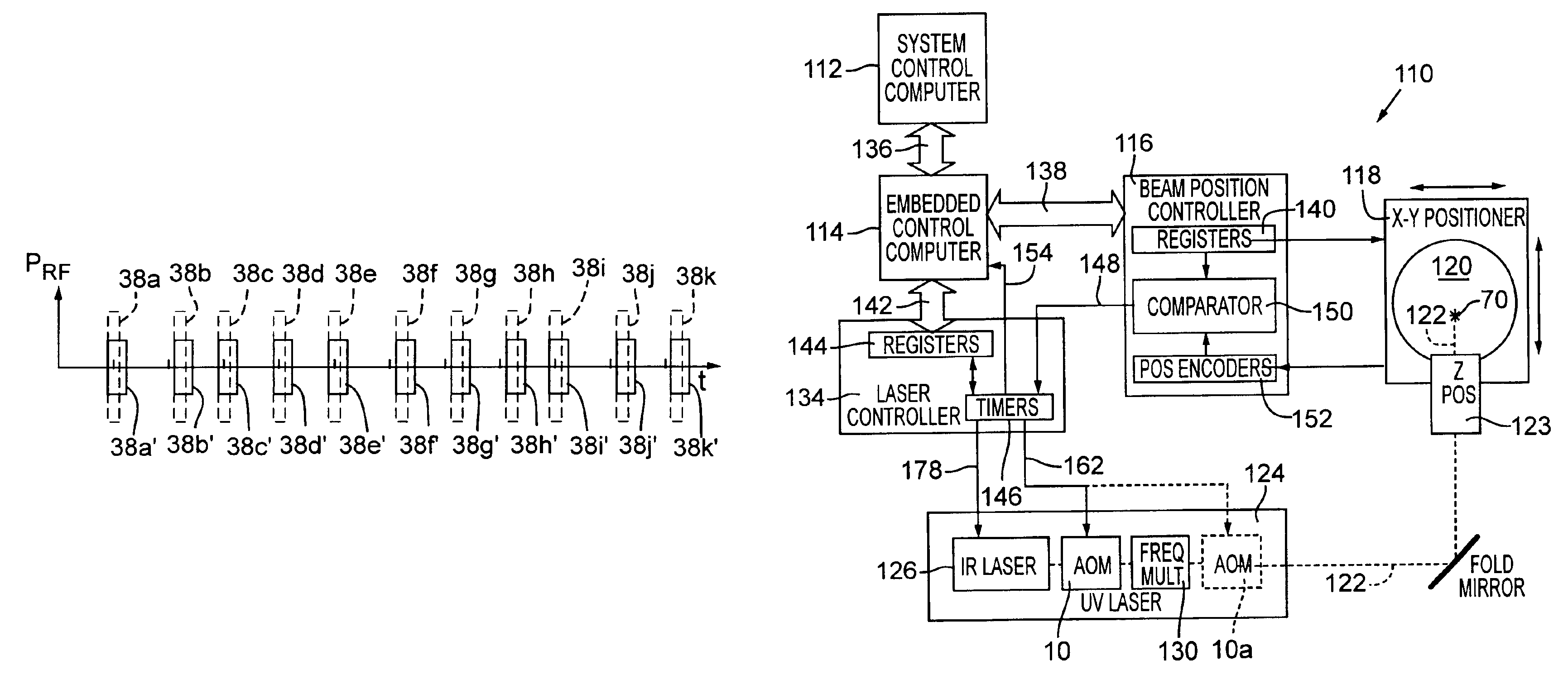
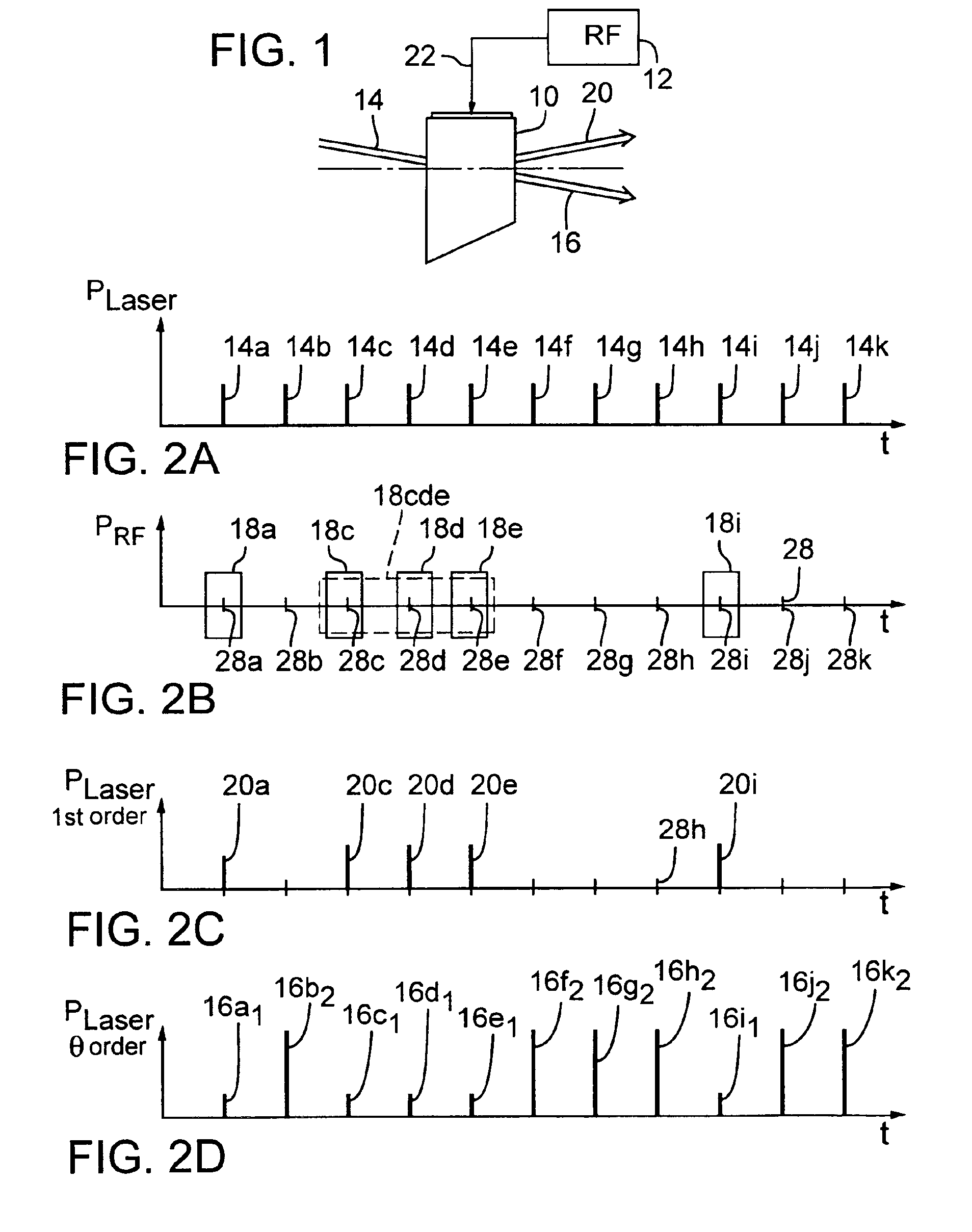
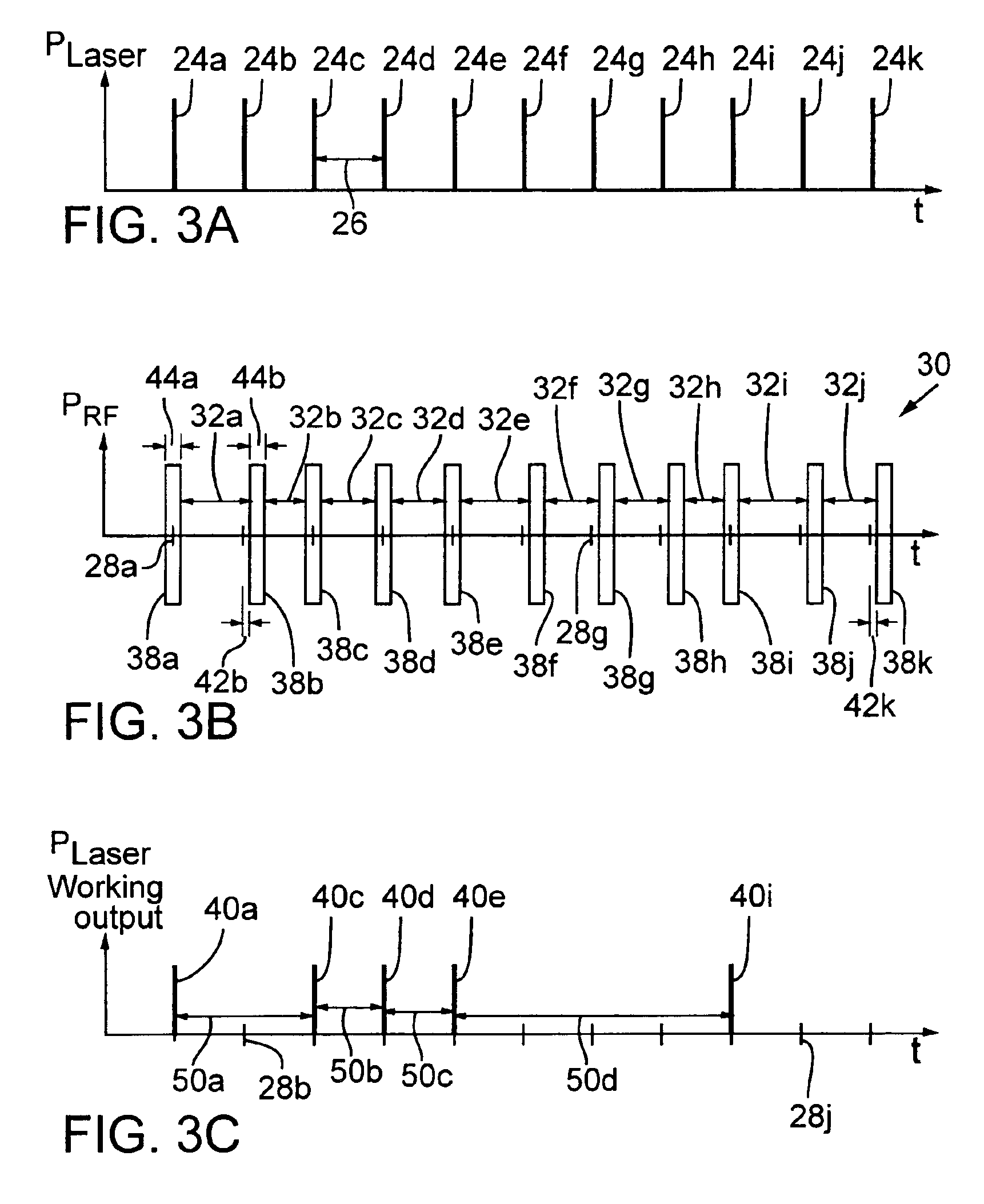
ActiveUS6947454B2Constant RF powerConstant thermal loadingExcitation process/apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPulse energyOptoelectronics
A laser (126) and an AOM (10) are pulsed at substantially regular and substantially similar constant high repetition rates to provide working laser outputs (40) with variable nonimpingement intervals (50) without sacrificing laser pulse-to-pulse energy stability. When a working laser output (40) is demanded, an RF pulse (38) is applied to the AOM (10) in coincidence with the laser output (24) to transmit it to a target. When no working laser output (40) is demanded, an RF pulse (38) is applied to the AOM (10) in noncoincidence with the laser output (24) so it gets blocked. So the average thermal loading on the AOM (10) remains substantially constant regardless of how randomly the working laser outputs (40) are demanded. The AOM (10) can also be used to control the energy of the working laser output (40) by controlling the power of the RF pulse (38) applied. When the RF power is changed, the RF duration (44) of the RF pulse (38) is modified to maintain the constant average RF power. Consistent loading on the AOM (10) eliminates deterioration of laser beam quality and laser beam pointing accuracy associated with thermal loading variation on the AOM (10) and is advantageous for applications such as IC chip link processing where stable working laser outputs (40) with variable output intervals (50) are needed.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Dynamic real-time magnetic resonance imaging sequence designer
InactiveUS7081750B1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsTime informationDisplay device
A system and method for facilitating RF pulse sequence generation and modification and for real-time sequence input modification for use in conjunction with magnetic resonance imaging equipment. A graphical user interface is provided through a display coupled to a digital computer operating as the primary control system for a magnetic resonance imaging scanner and associated hardware. Through the graphical user interface, an operator may choose or design sequences of radiofrequency pulses, gradient waveforms and other input parameters for the magnetic resonance imaging apparatus. Real-time information is also communicated to the operator through the graphical user interface allowing for real-time manipulation of the magnetic resonance imaging inputs and for displaying the magnetic resonance response thereto.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP +1
Multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveUS20060161060A1Faster and accurate perfusion mapImprove time resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac phaseRadio frequency
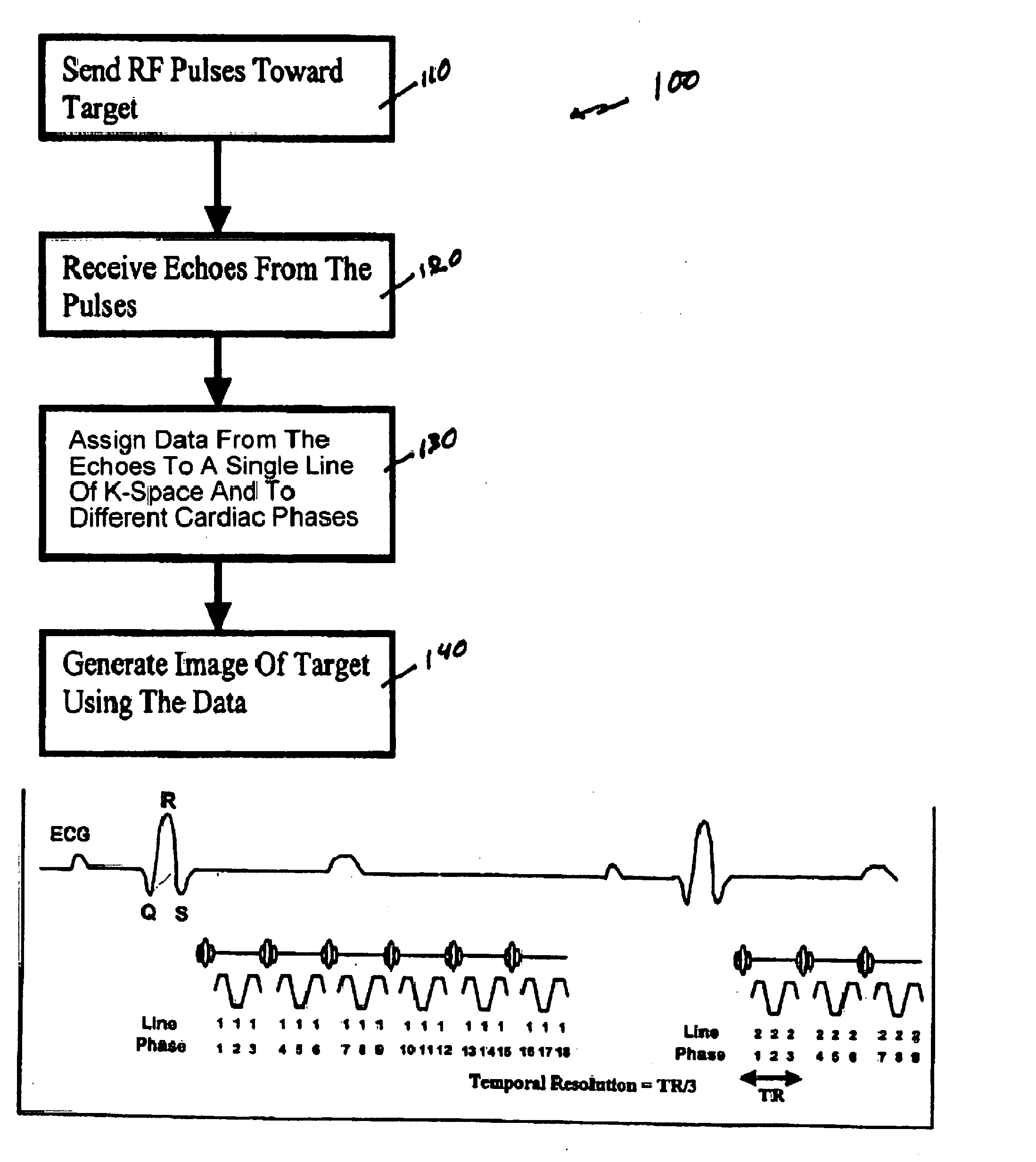
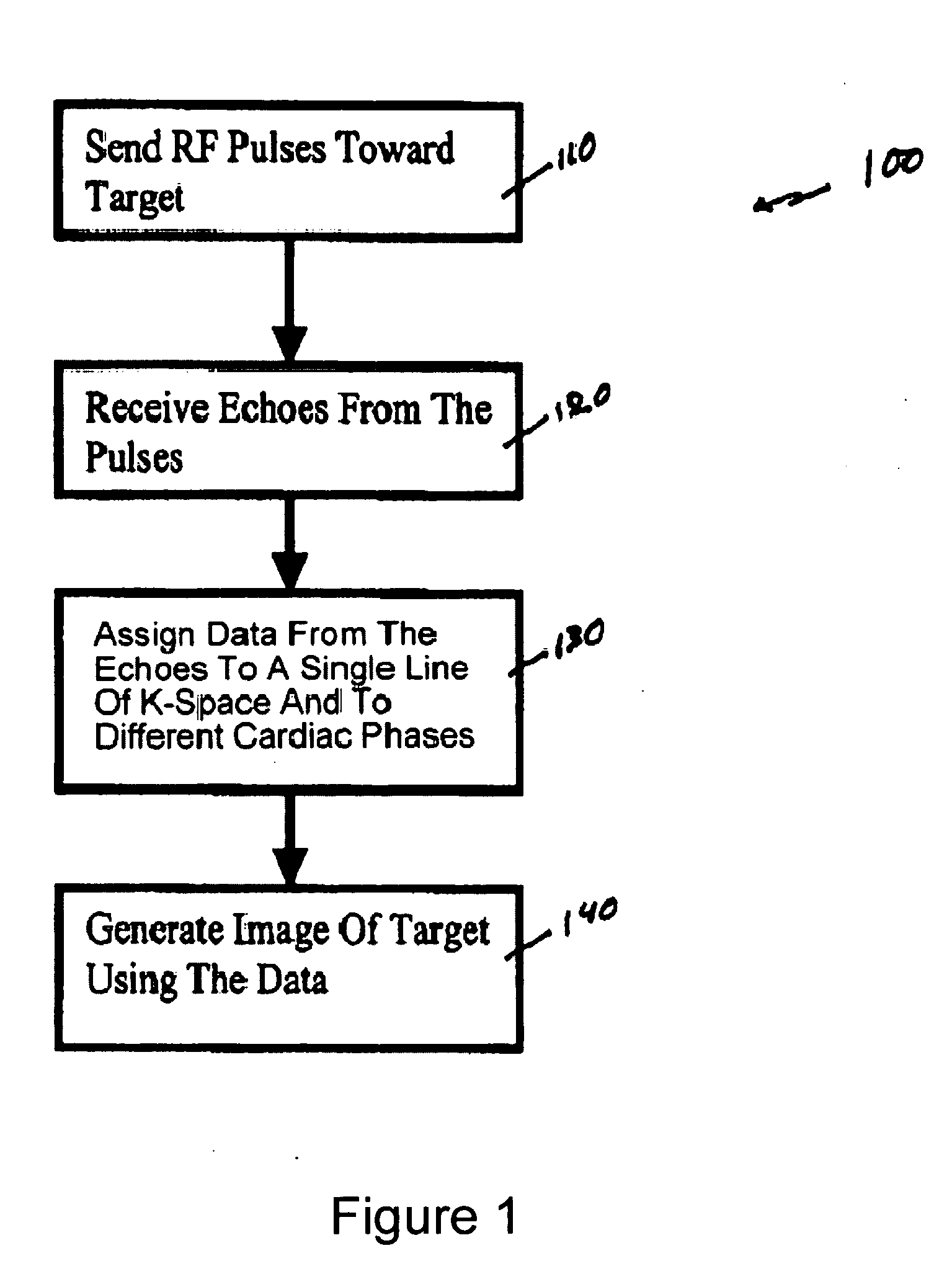
Method, systems and arrangements are provided for creating a high-resolution magnetic resonance image (“MRI”) or obtaining other information of a target, such as a cardiac region of a patient. Radio-frequency (“RF”) pulses can be transmitted toward the target by, e.g., an RF transmitter of an MRI apparatus. In response, multiple echoes corresponding to the plurality of pulses may be received from the target. Data from each of the echoes can be assigned to a single line of k-space, and stored in memory of the apparatus. An image of the target, acceleration data and / or velocity data associated with a target can be generated as a function of the data. In one exemplary embodiment, the data from different echoes may be assigned to the same k-space line, and to different cardiac phases. In one further embodiment, parallel processing may be used to improve the resolution of the image acquired during a single breath-hold duration. In yet another embodiment, utilizing a segmented implementation, multiples lines of k-space are acquired for a given cardiac phase (or time stamp) per trigger signal. The present invention may be utilized for the heart or for any other anatomical organ or region of interest for the evaluation and study of flow dynamics with very high temporal resolution.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
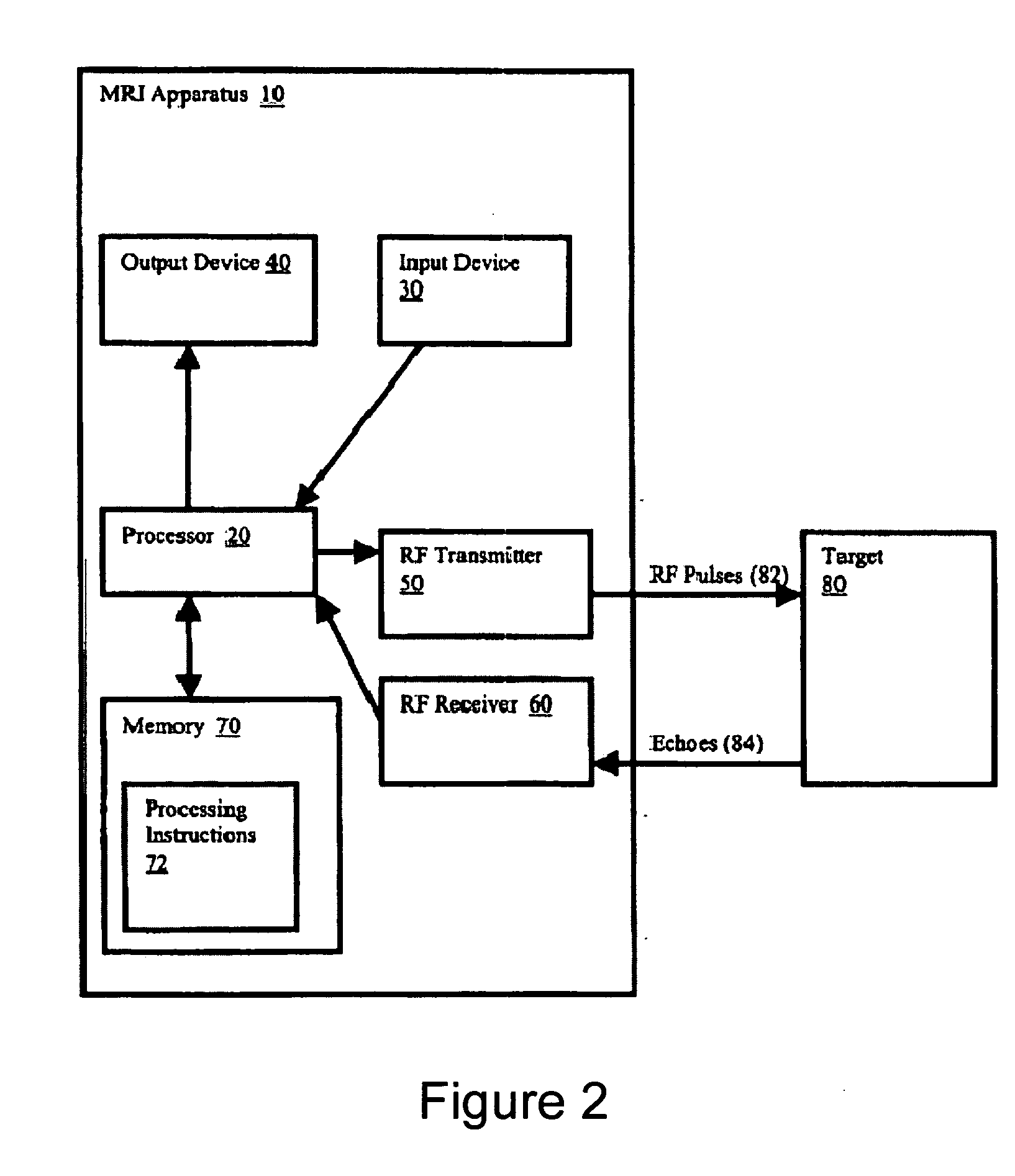
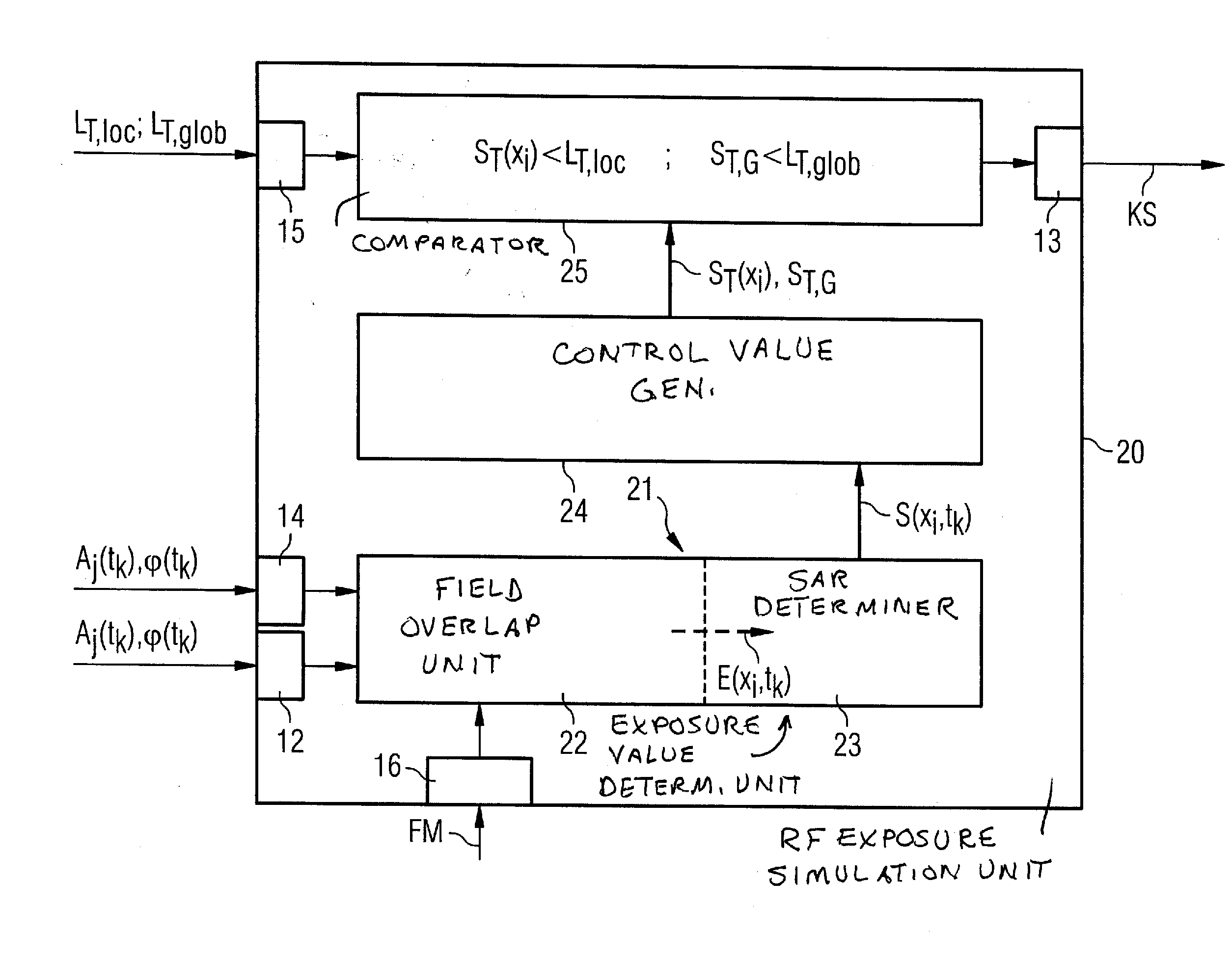
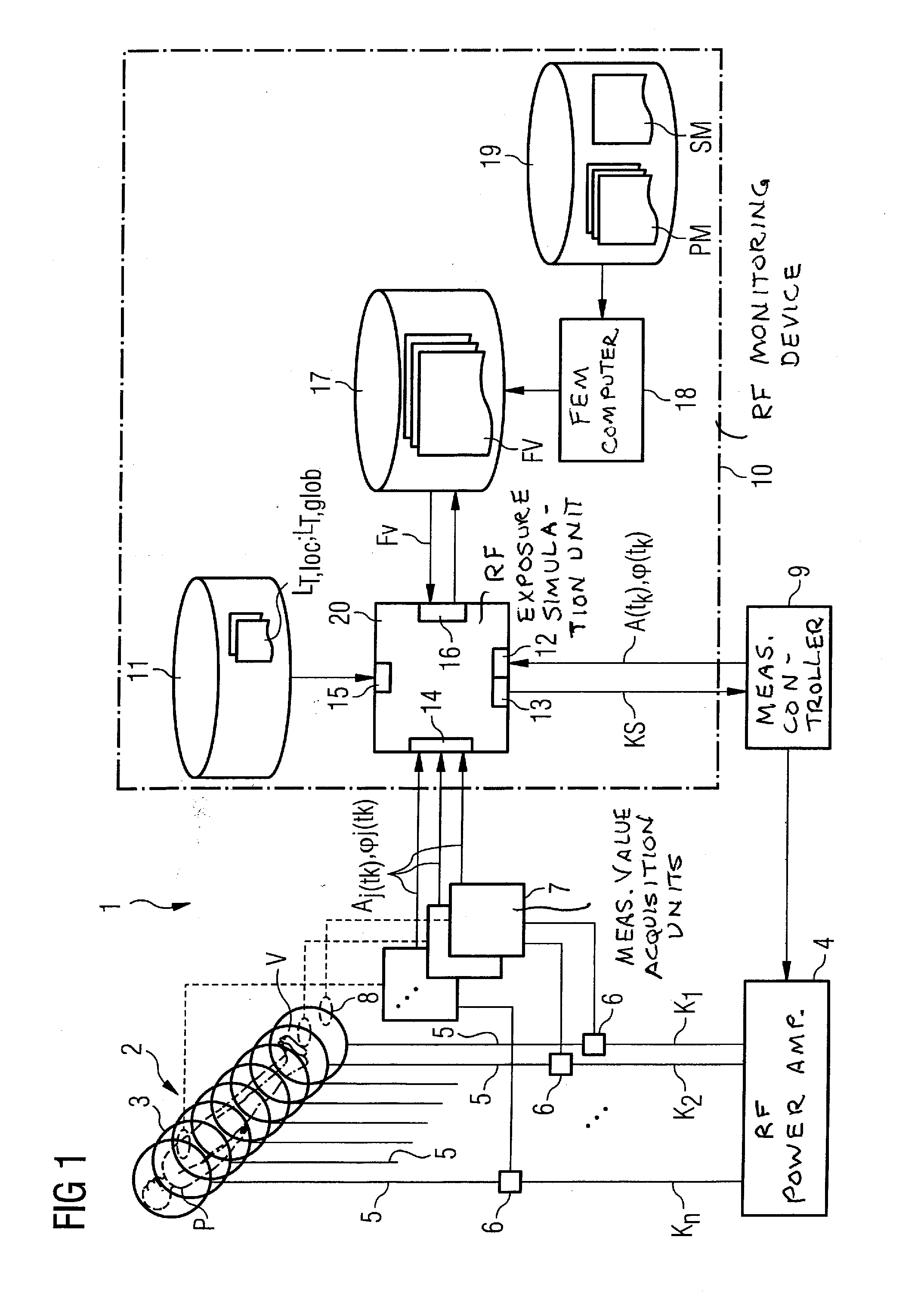
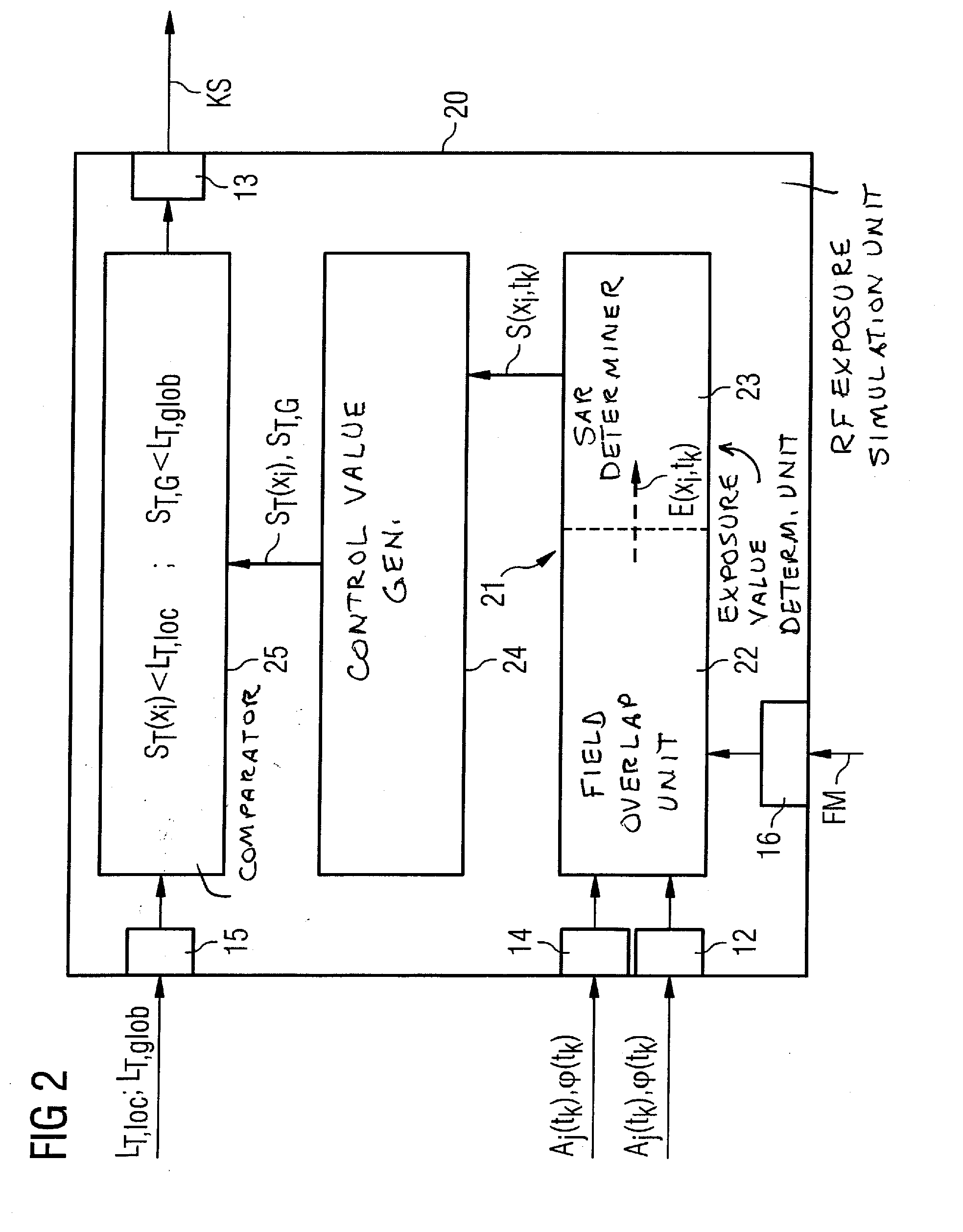
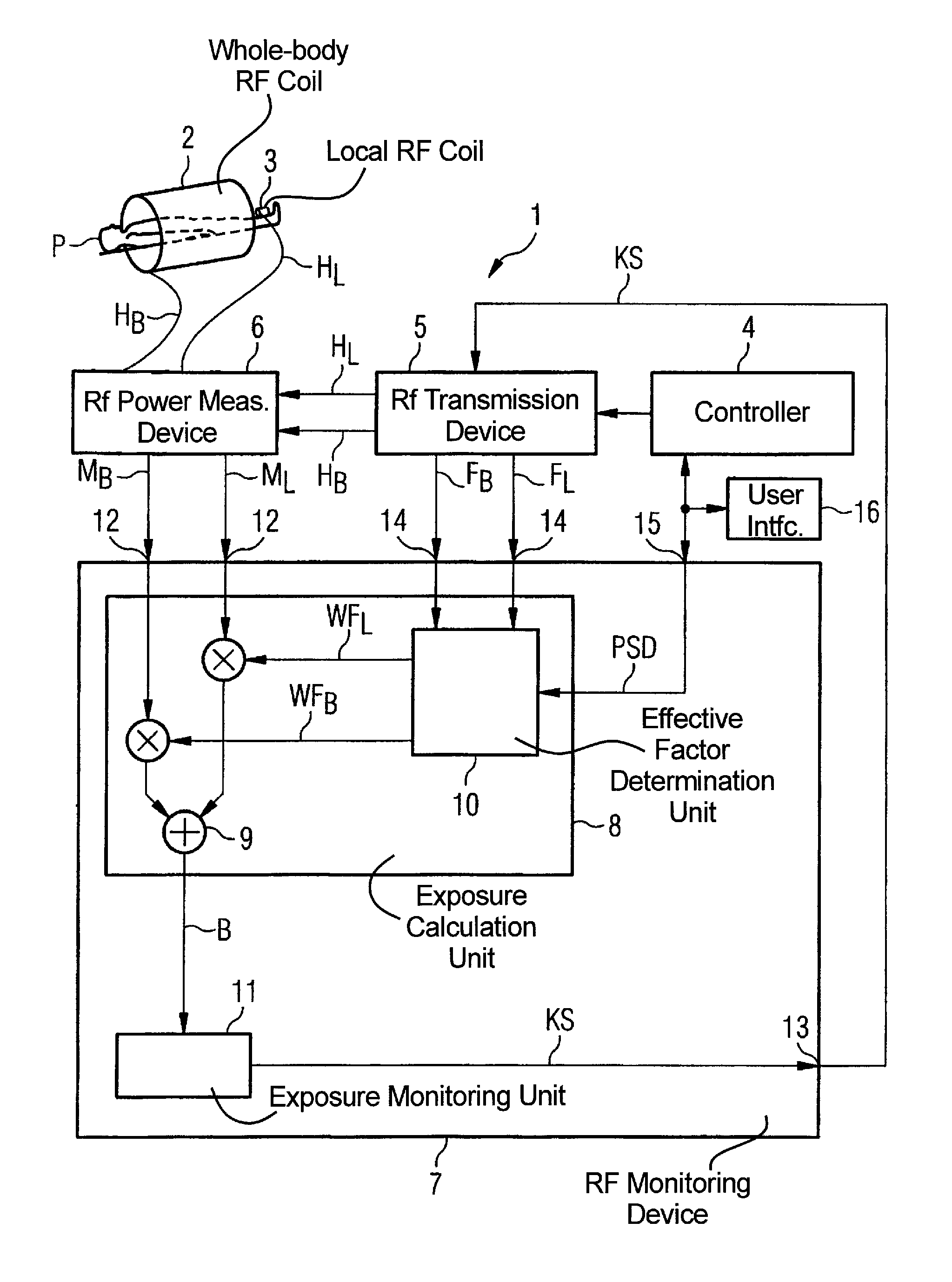
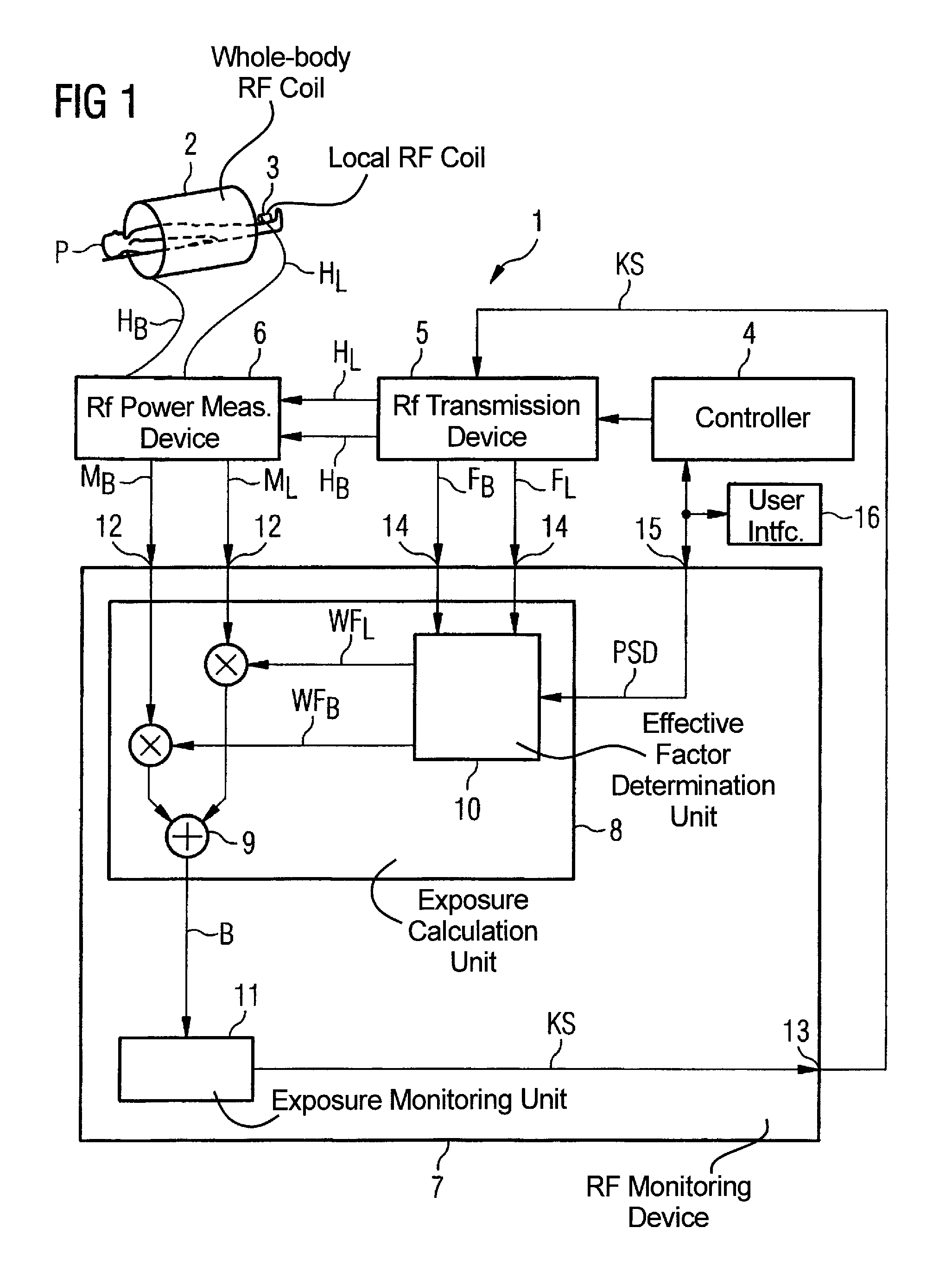
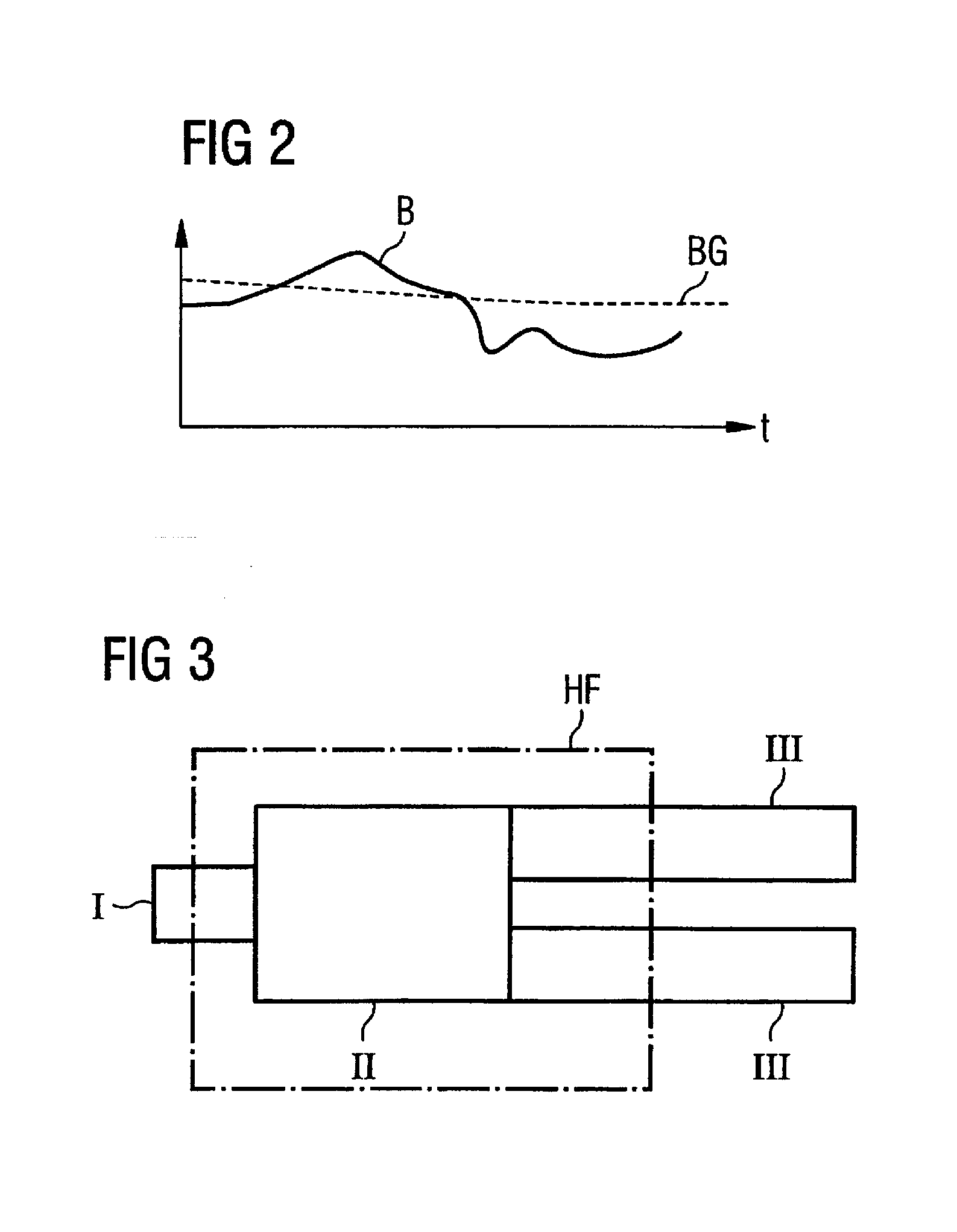
Method and device for monitoring radio-frequency exposure in a magnetic resonance measurement
InactiveUS20080157765A1Fast convergenceHigh transmission powerMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonance measurementControl signal
In a method and device for monitoring the physiologically effective radio-frequency exposure in at least one specific volume region of an examination subject in a magnetic resonance data acquisition scan in a magnetic resonance system, the magnetic resonance system having a radio-frequency antenna structure with a number of individually controllable radio-frequency signal channels for generation of radio-frequency field distributions in an examination volume including the examination subject, amplitude values are acquired that respectively represent, at specific acquisition points in time, a signal amplitude of the radio-frequency signals emitted or to be emitted via the radio-frequency signal channels in the course of the magnetic resonance measurement. Also, phase values are acquired that represent the phases of the appertaining radio-frequency signals at these points in time. Local exposure values are then determined on the basis of the amplitude values and phase values, these local exposure values respectively representing a physiological exposure that the radio-frequency pulses cause at the examination subject at a specific location at a specific time. Based on this, exposure control values are determined that are compared with predetermined exposure limit values. When an exposure limit values is reached or exceeded, a control signal is output.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
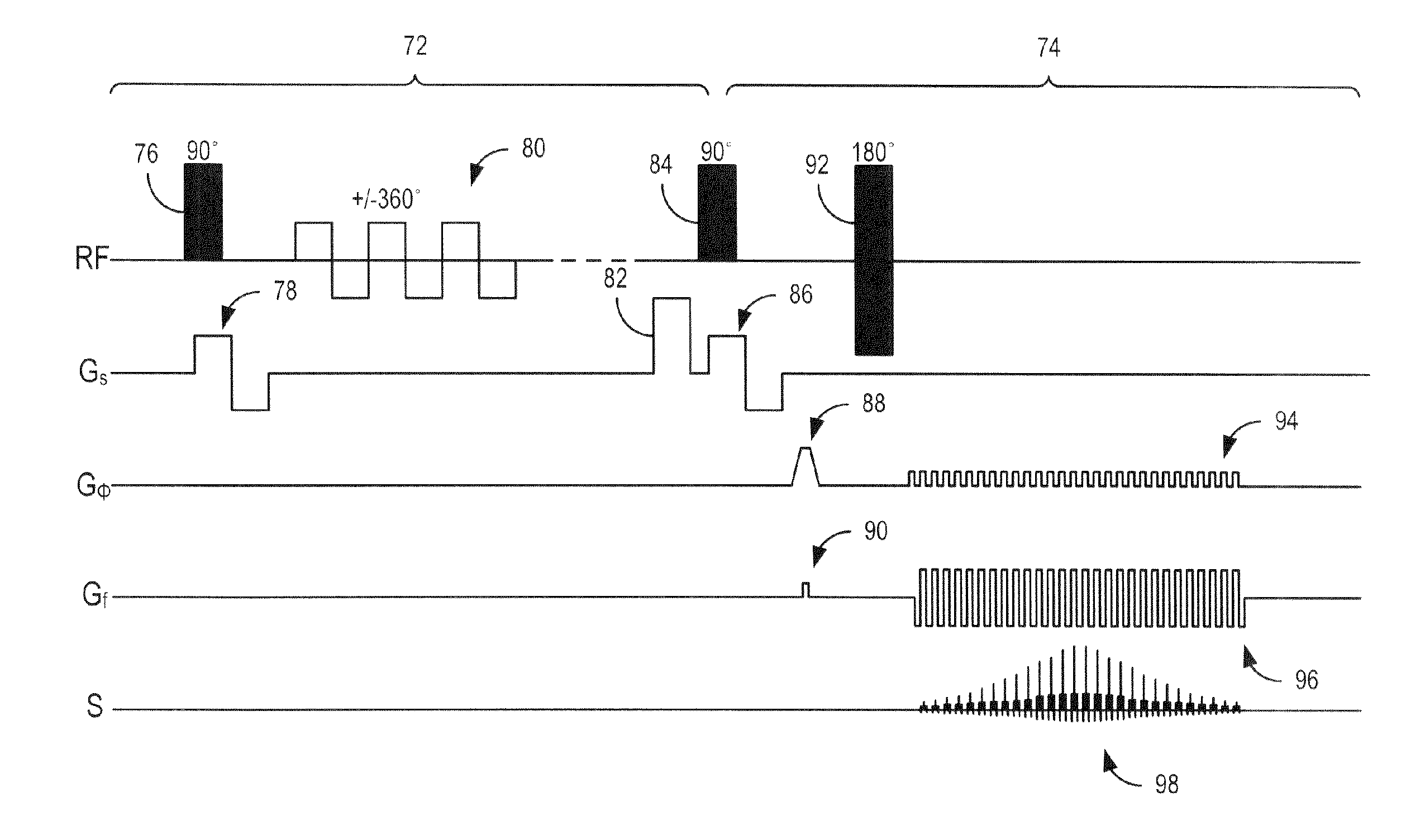
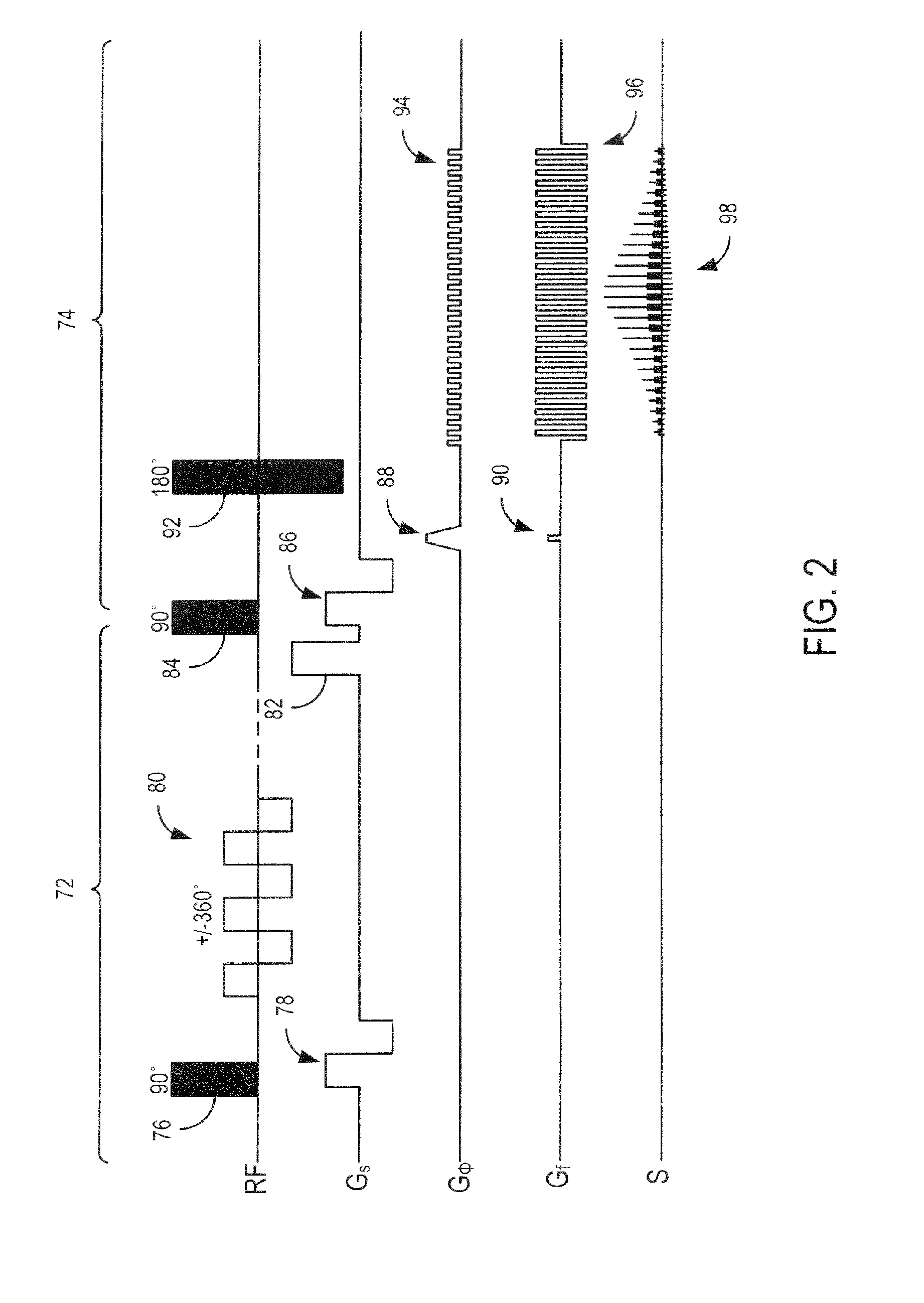
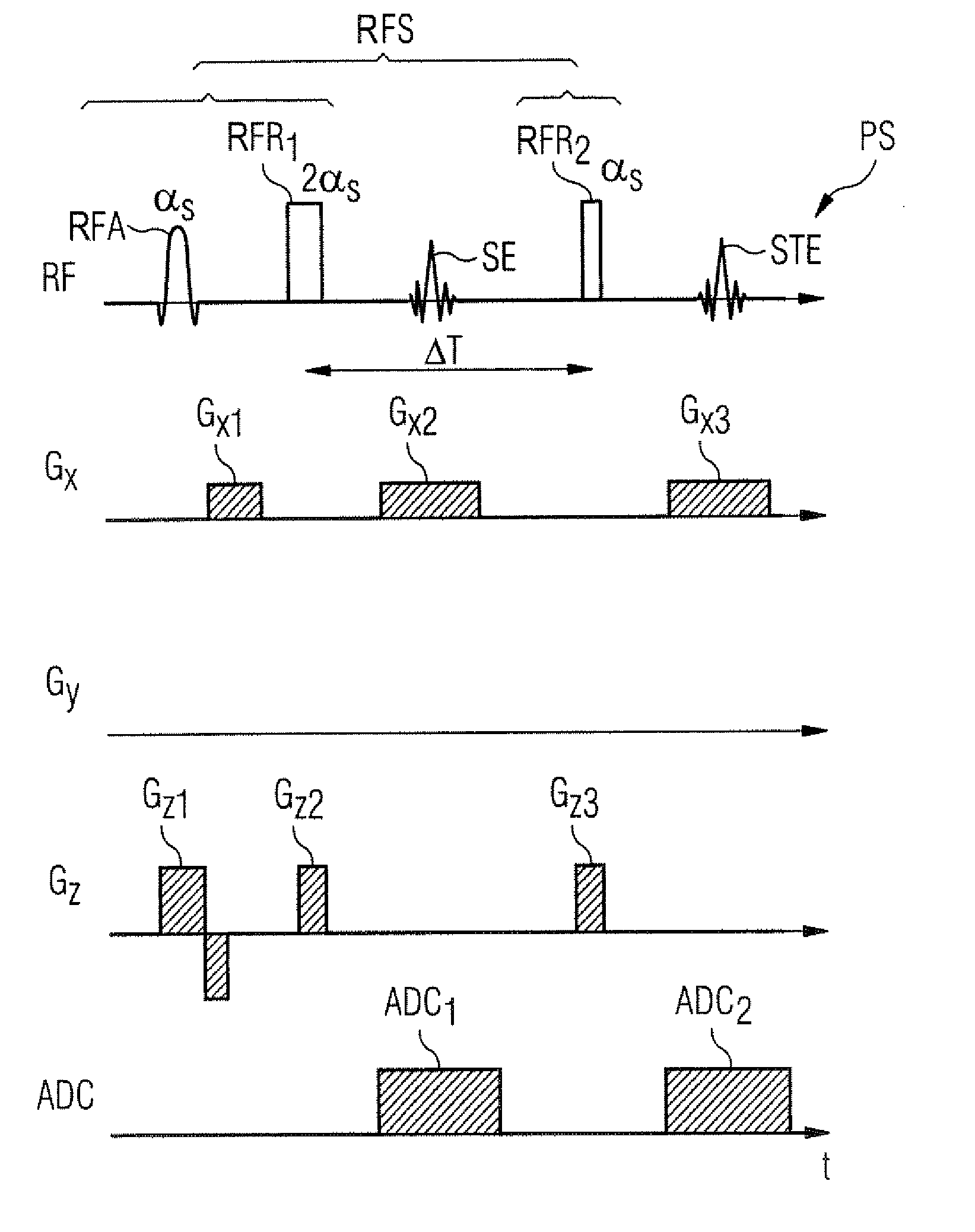
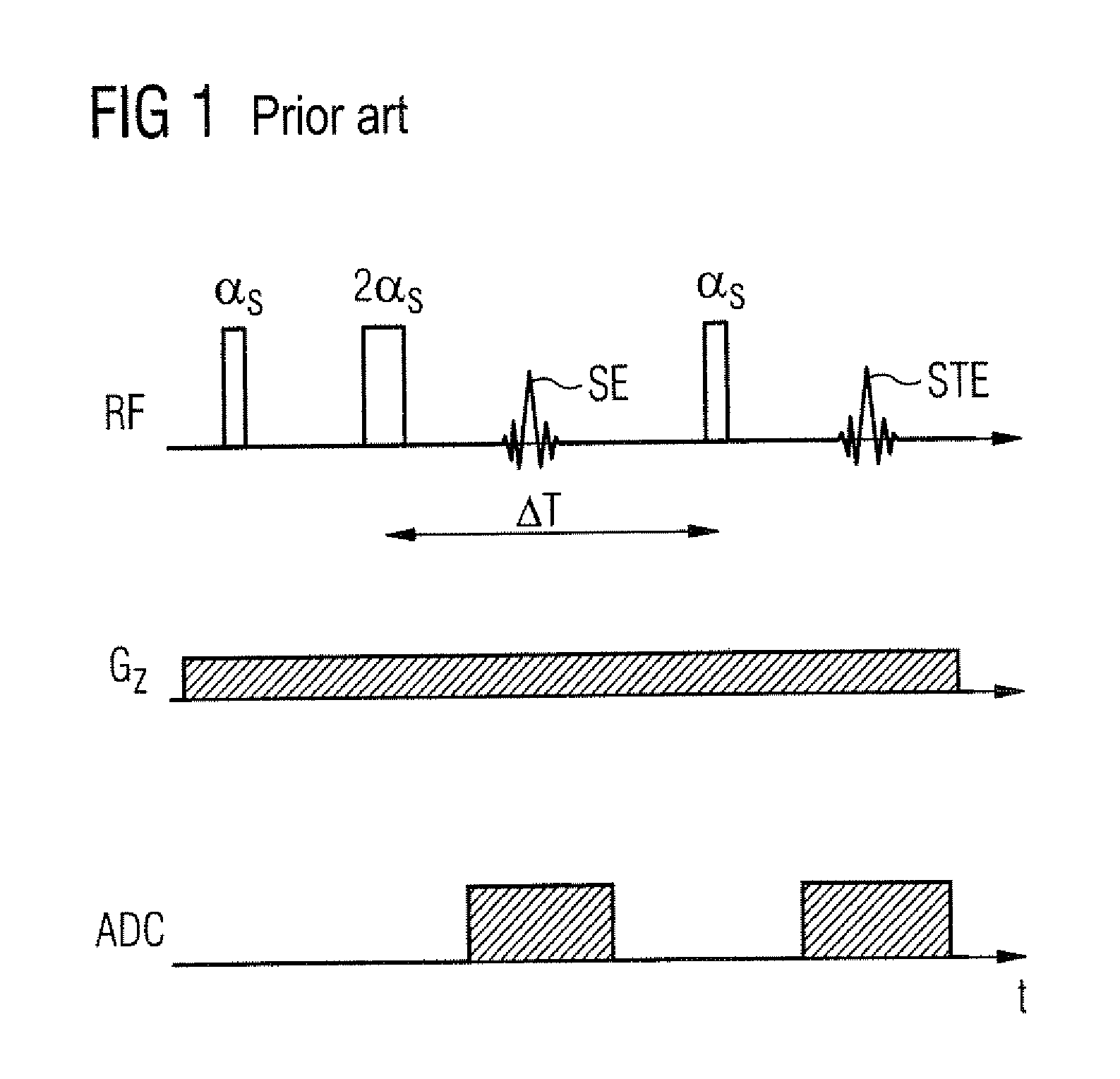
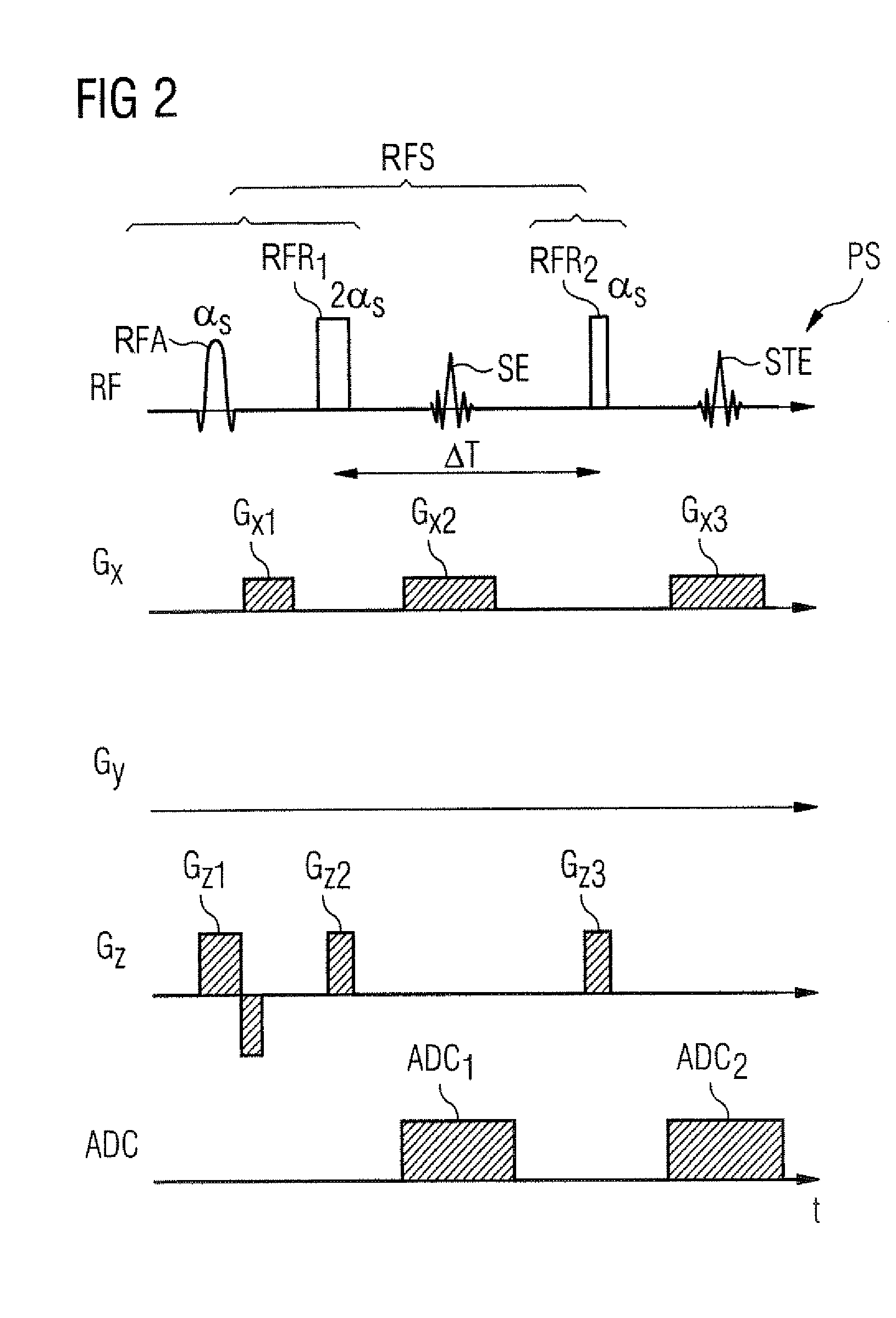
Optimization of a pulse sequence for a magnetic resonance system
ActiveUS20140232396A1Minimize artifactReduced Linearity RequirementsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceChronological time
In a method and a pulse sequence optimization device to determine a pulse sequence for a magnetic resonance system, a pulse sequence is selected for optimization that includes a number of radio-frequency pulses and a number of gradient pulses chronologically coordinated therewith. An automatic analysis of the pulse sequence takes place to identify fixed point / time periods in the pulse sequence that are to be left unmodified, and modifiable time intervals in the pulse sequence that may be optimized. An automatic optimization of gradient pulses in the modifiable time intervals takes place according to a predetermined optimization criterion, while keeping the length of modifiable time intervals constant.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20110115485A1Shorten the length of timeReduce usageMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
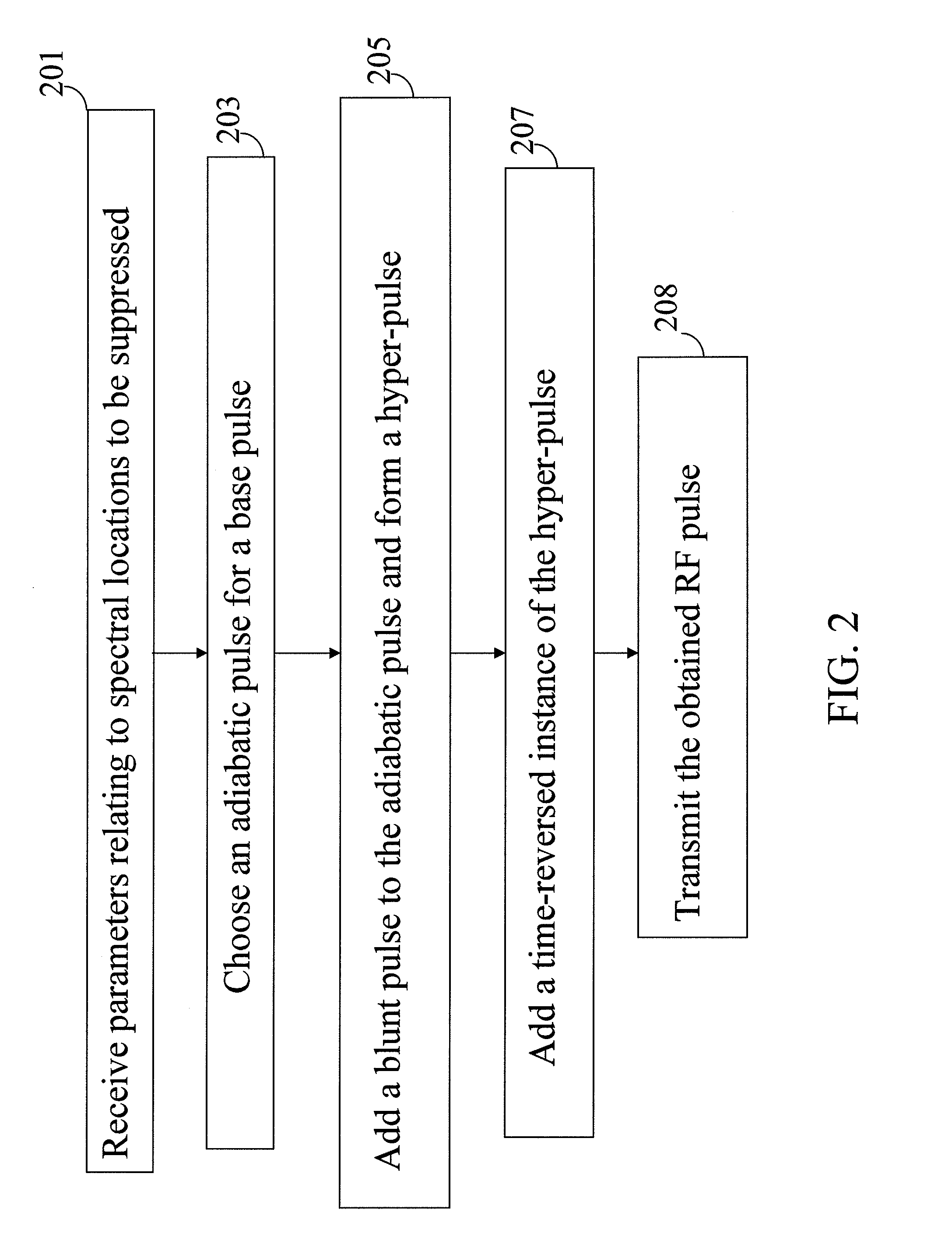
Adiabatic multi-band RF pulses for selective signal suppression in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20110144474A1Suppression problemDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMulti bandChemical composition
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, comprising: a magnetic resonance imaging scanner comprising: a main magnet providing a substantially uniform main magnetic field B0 for a subject under observation; and a radio frequency (RF) coil configured to irradiate a radio frequency (RF) pulse into a region of interest of the subject under observation, wherein the RF pulse comprises a base pulse comprising an adiabatic pulse having a first bandwidth time product (BWTP), wherein the RF pulse selectively suppresses magnetic resonance signals from more than one chemical component or more than one spatial region within the region of interest of the subject under observation, and wherein the adiabatic pulse is characterized by an amplitude modulation function and a frequency modulation function.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
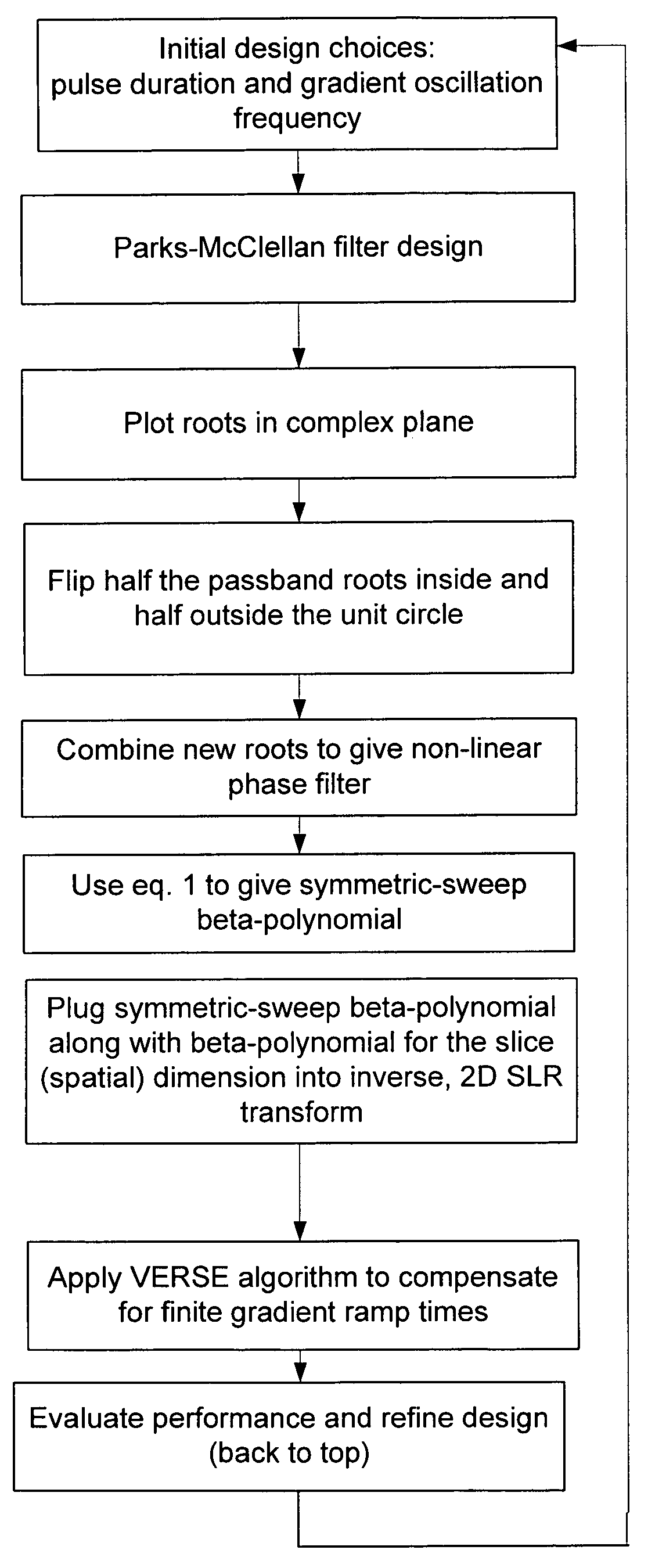
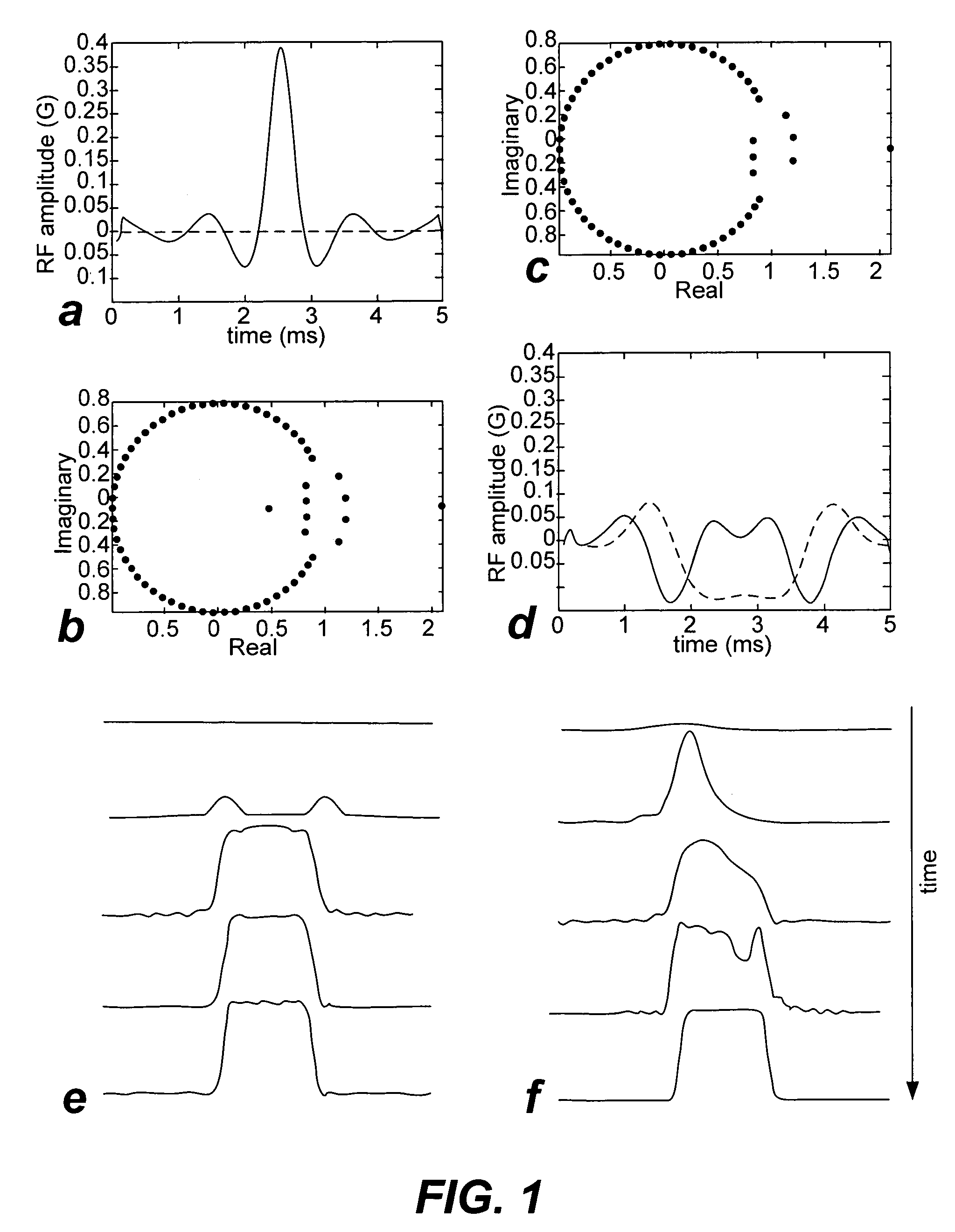
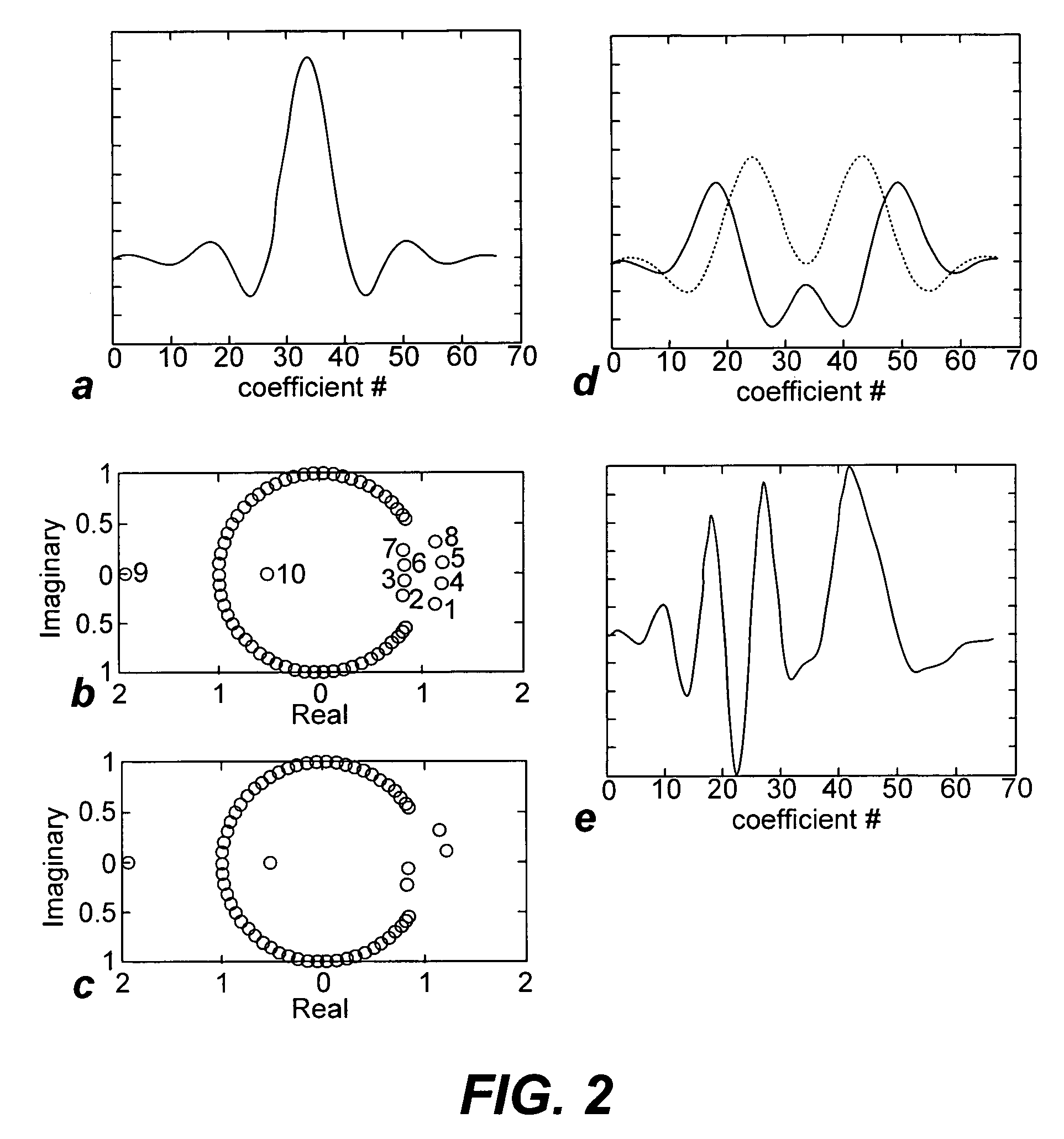
Non-linear symmetric sweep spectral-spatial RF pulses for MR spectroscopy
ActiveUS7042214B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSpectroscopyRadio frequency
A method for designing non-linear phase 180° spectral-spatial radio frequency pulses that can be used for spectral editing in magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. A novel feature of the pulse is a symmetric sweep developed by the spectral profile from the outside edges of the spectral window towards the middle whereby coupled components are tipped simultaneously and over a short interval. Pulses have been designed for lactate editing at 1.5T and 3T. The spectral and spatial spin-echo profiles of the RF pulses can be measured experimentally and altered in an iterative manner. Spectral-spatial radio frequency (SSRF) pulses allow simultaneous selection in both frequency and spatial domains. These pulses are particularly important for clinical and research magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) applications for suppression of large water and lipid resonances.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
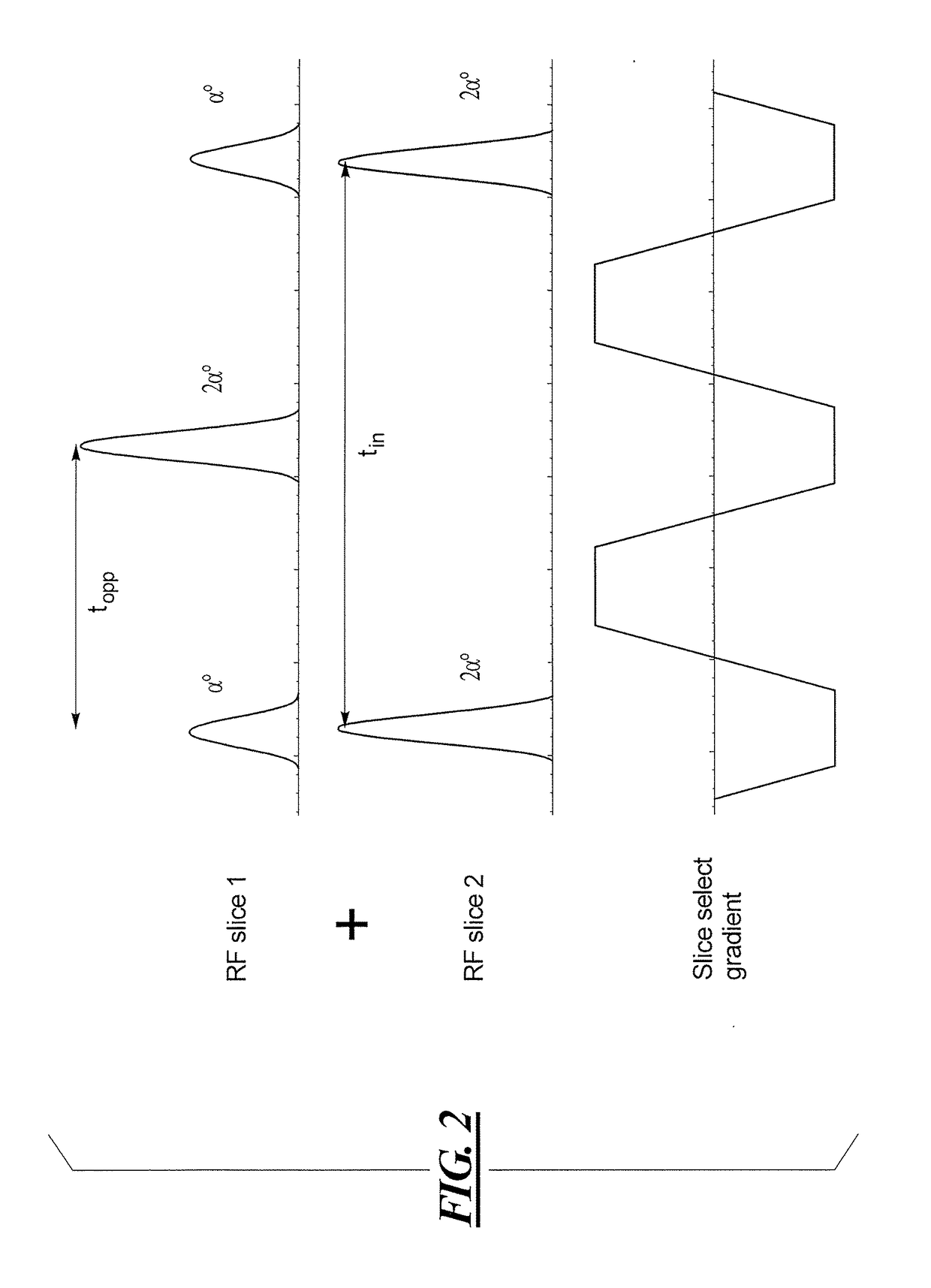
Multi-contrast simultaneous multislice magnetic resonance imaging with binomial radio-frequency pulses
ActiveUS20180024214A1Total acquisition time is halvedImage contrast will not sufferImage enhancementImage analysisMulti bandMulti slice
In a magnetic resonance apparatus and a method for operating the MR apparatus to acquire MR data in a single scan with different contrasts, nuclear spins in multiple slices of an examination subject are simultaneously excited in a single scan, with a simultaneous multi-slice acquisition sequence, in which a radio-frequency multi-band binomial pulse is radiated.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for examining a substance, particularly tissue, to characterize its type
InactiveUS20060264738A1Easy to implementImprove reliabilitySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsElectrical resistance and conductanceResonance
A method and apparatus are disclosed, for examining a substance of a given volume to characterize its type, with an integrated sensing head. The method comprises applying locally to the substance of the given volume a polarizing magnetic field, with a component defining a polarizing axis; applying locally RF pulses to the substance of the given volume, the RF pulses having a B component, orthogonal to the polarizing axis, such as to invoke EI response signals corresponding to the electrical impedance (EI) of the examined substance of the given volume, and magnetic resonance (MR) response signals corresponding to the MR properties of the examined substance of the given volume; detecting locally EI response signals from the substance of the given volume; and detecting locally MR response signals from the substance of the given volume. Two or more sensing heads may be used, both applying locally the RF pulses and detecting. Alternatively, one of the sensing heads may operate as a transmitter, while the other or others may operate as receivers.
Owner:DUNE MEDICAL DEVICES
Method for localizing remote devices, using acoustical and electromagnetic waves
InactiveUS8089827B2Improve reliabilityEasy maintenanceDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationSound sourcesWavefront
Localization of remote devices by: the emission of pulses from acoustic transmitters, whose wavefronts propagate in the space region occupied by the remote devices and finally reach them; the emission of radiofrequency pulses from each remote device at the time of detection of the wavefront by an on-board microphone; the acquisition, by a radio base, of the radiofrequency signals propagating from the remote devices, to evaluate the arrival time delays proportional to the distance between the i-th acoustic source and the j-th remote device; the formation of a reception vector for each emission by the i-th source, this vector having a maximum length M equal to the number of remote devices and consisting of the sequence of distances obtained as the product of the reception times and the estimated sound velocity. These steps are repeated for all acoustic sources, to form N+1 reception vectors, to calculate the position of the device by solving derived matrix equations.
Owner:CAROTENUTO 50 INTEREST RICCARDO
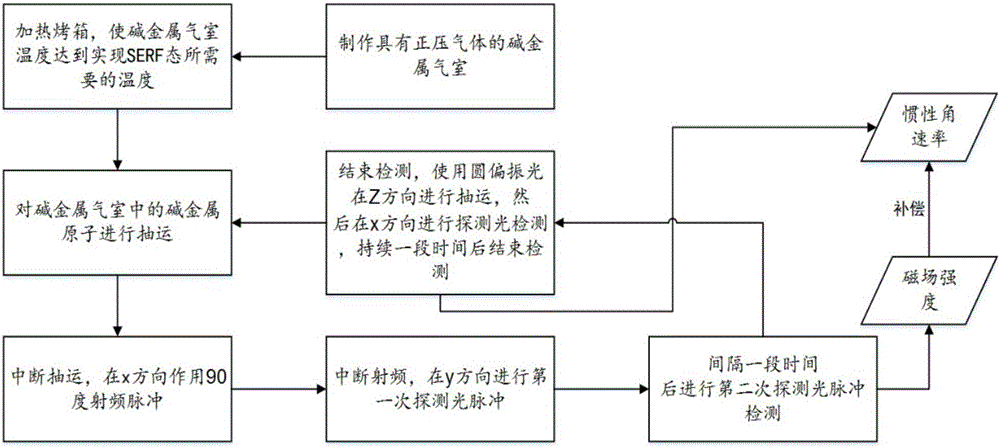
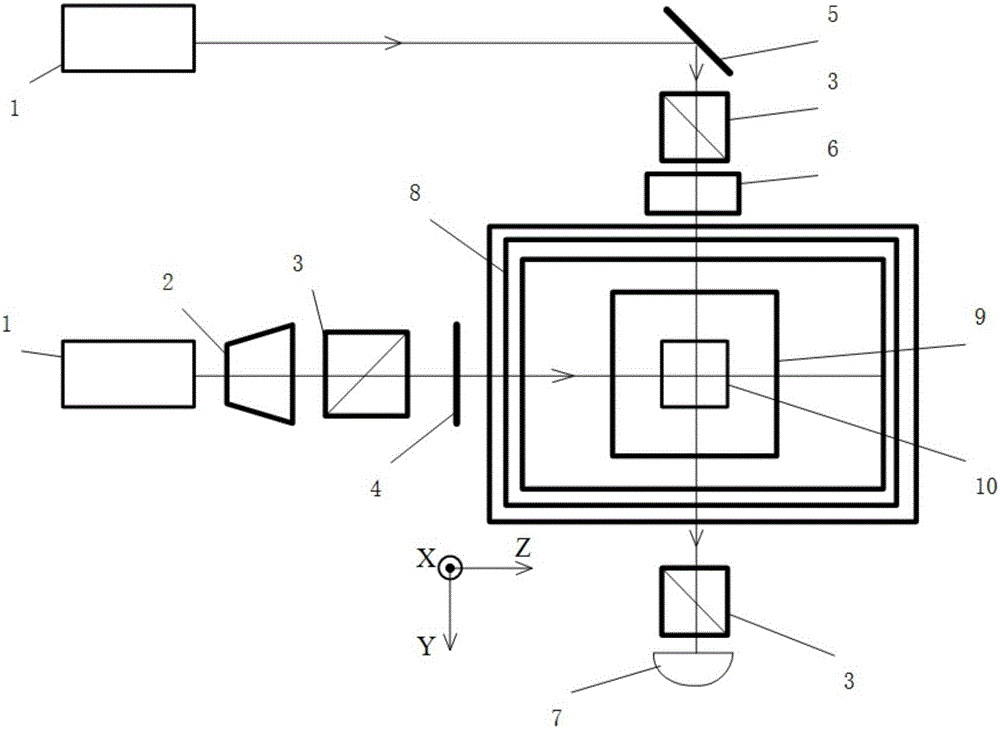
High-precision measurement method for magnetic field compensation inertial angular rate based on of SERF (spin-exchange relaxation free) atomic device
ActiveCN106017451AReduce consumptionSmall footprintNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPositive pressureRadio frequency
The invention provides a high-precision inertial angular rate measurement method based on magnetic field compensation of an SERF (spin-exchange relaxation free) atomic device. The method comprises the steps that a glass gas chamber and a vacuum gas chamber which is filled with positive pressure gas and contains alkali metal are manufactured firstly, an oven is heated to make the temperature in the alkali metal gas chamber reach a temperature required by an SERF state; an operation period begins: pumping is conducted on the alkali metal gas chamber; pumping is interrupted, and 90-degree radio-frequency pulses act in the vertical pumping direction; radio frequency is interrupted, two times of probe light pulse detection are performed in the vertical pumping direction at an interval, and the magnetic field strength can be obtained according to the above measure experimental data; then, pumping is performed for a period of time by using circularly polarized light, then probe light detection is performed in the vertical pumping direction, the experimental data and measured magnetic field strength are compensated so that the high-precision inertial angular rate can be obtained, and pumping and detection are completed. The magnetic field measurement and inertial measurement are performed in the same experimental device under the same conditions, the measured magnetic field is utilized to compensate inertial angular rate errors caused by magnetic field interferences, and the measurement accuracy is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method, device and magnetic resonance tomography system for monitoring emitted RF energy
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus of background suppression in MR imaging using spin locking
ActiveUS7064545B2Efficient magnetizationLongitudinal magnetization regrowth is minimizedMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionBlood flowTransverse magnetization
The present invention is directed to a method and system of tissue or background suppression for the acquisition of image data from blood flow or tissue perfusion. Background suppression with minimal effects upon inflowing spins is achieved through a series of spin locking low level RF pulses that cause adiabatic demagnetization of tissue with a relaxation time T1-rho that is intermediate between T1 and T2 relaxation times. In this regard, the effective transverse magnetization of static tissue resulting from the application of a series of low level RF pulses is reduced and, with the spin locking, longitudinal magnetization regrowth is minimized. As such, inflowing spins to an imaging volume may be directly imaged with significant background tissue suppression. The present invention is particularly applicable to time-of-flight MRA and MR perfusion imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
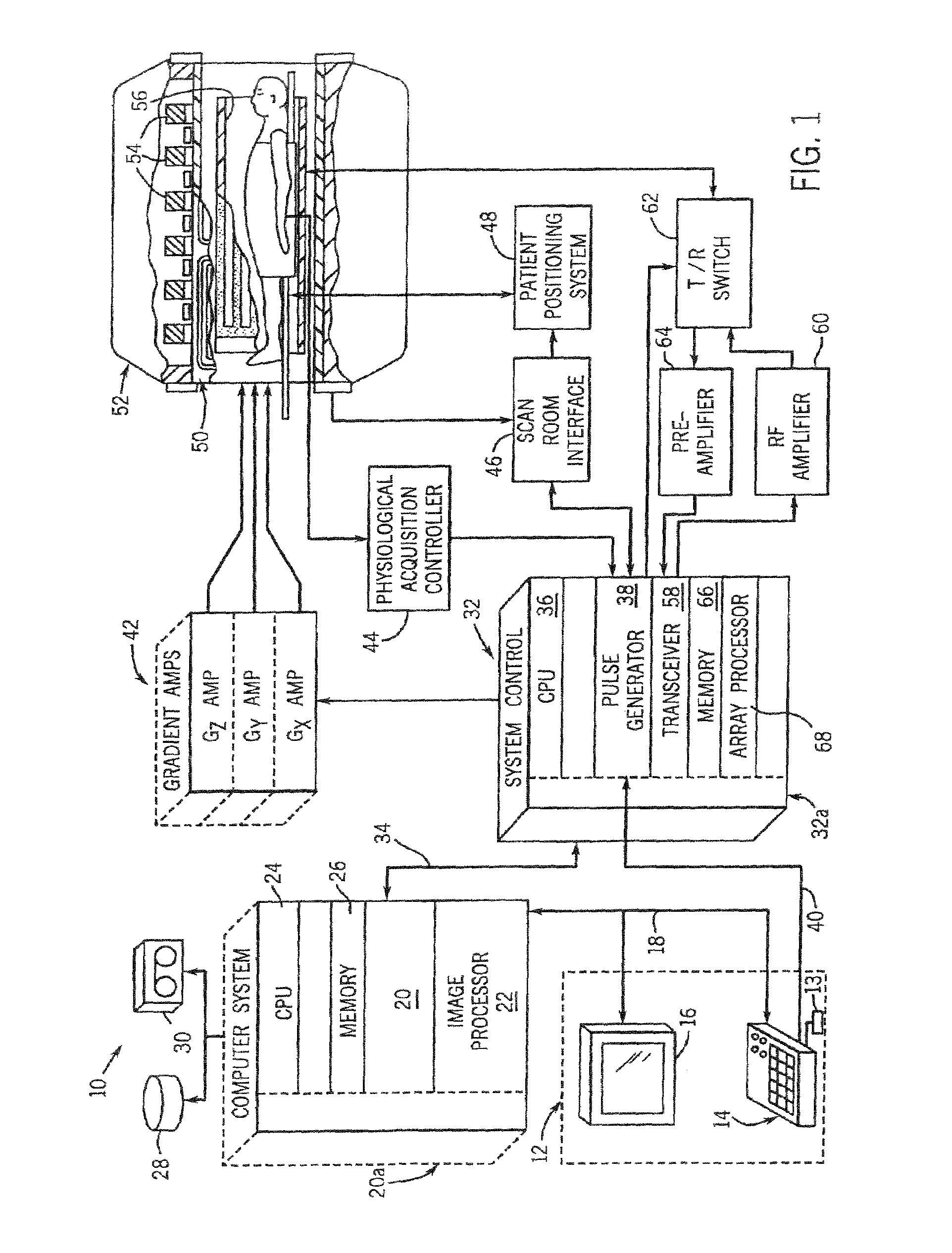
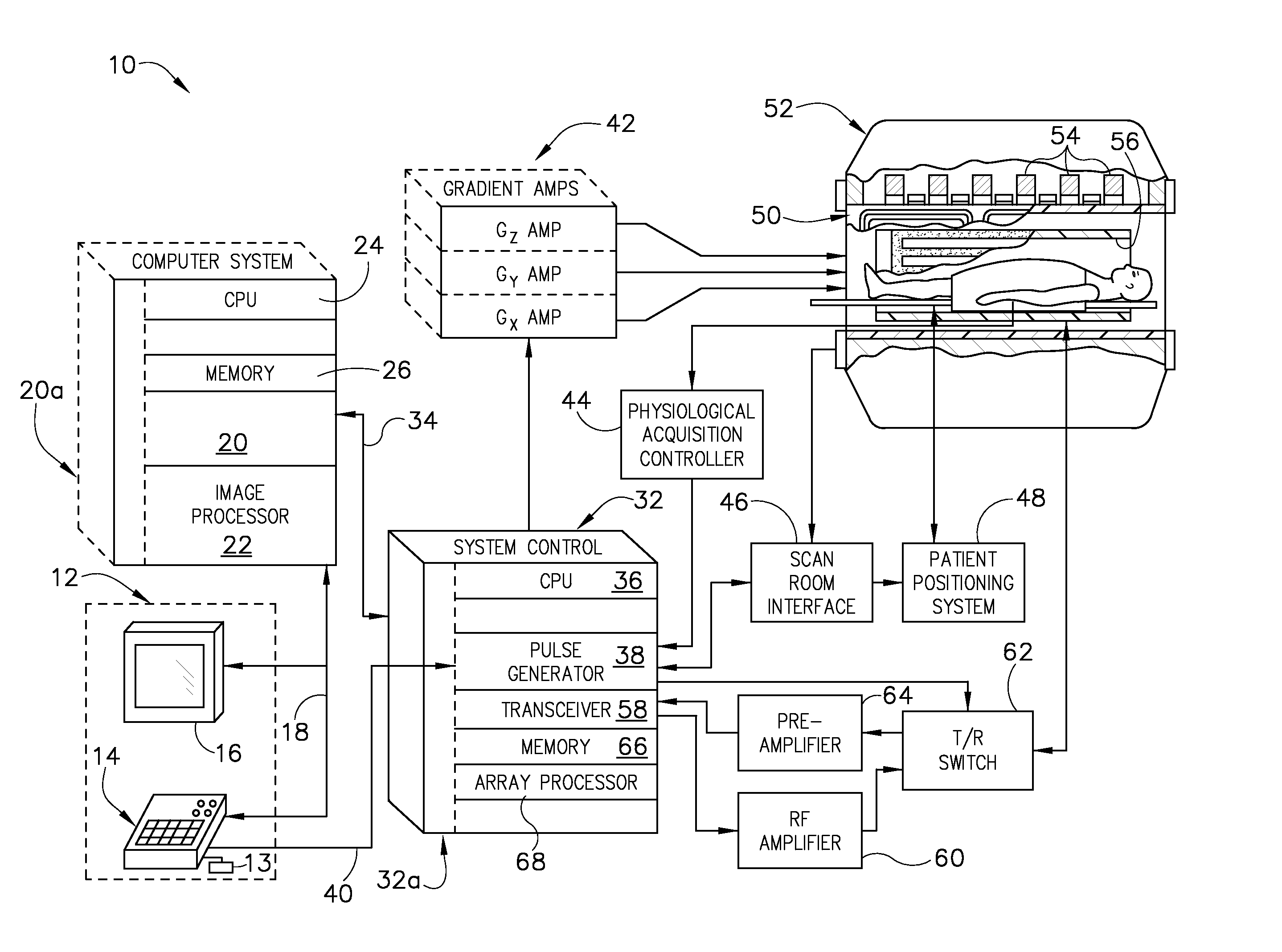
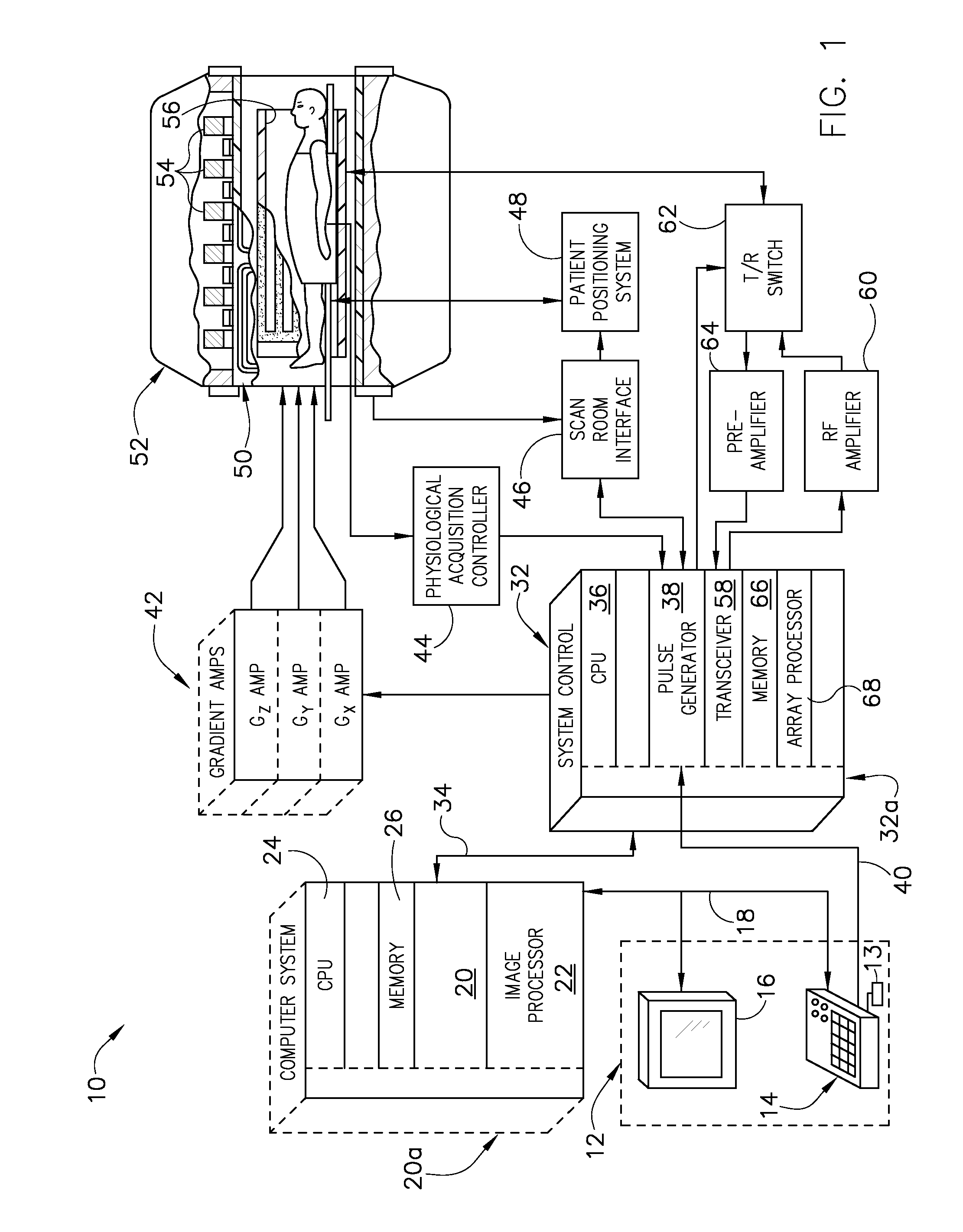
System, method, and apparatus for magnetic resonance rf-field measurement
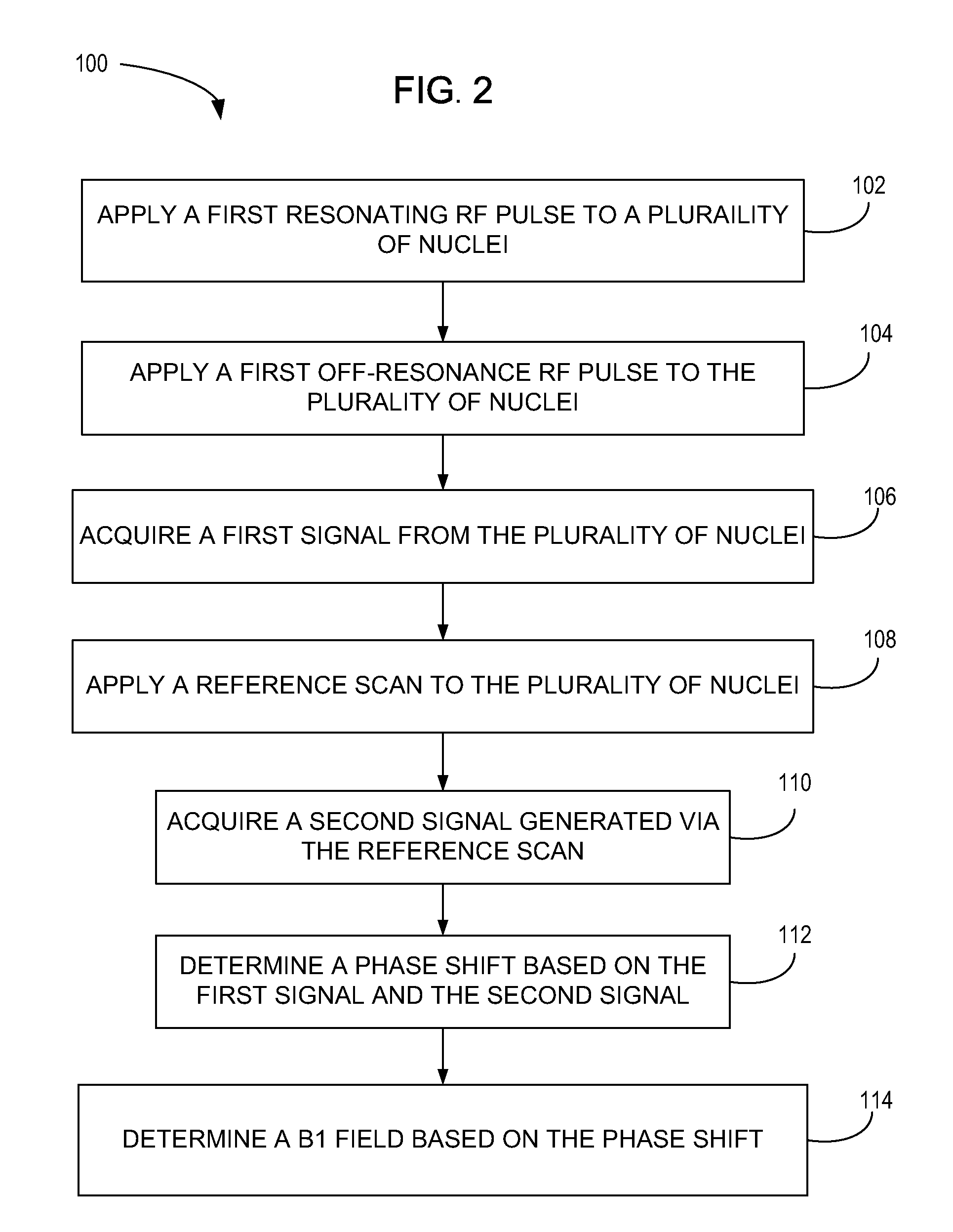
An apparatus, system, and method including a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus includes a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system having a plurality of gradient coils positioned about a bore of a magnet, and an RF transceiver system and an RF switch controlled by a pulse module to transmit RF signals to an RF coil assembly to acquire MR images, and a computer. The computer is programmed to apply a first off-resonant radio frequency (RF) pulse at a first frequency different than the resonant frequency to a plurality of nuclei excited at a resonant frequency, acquire a first signal from the plurality of nuclei after application of the first off-resonant RF pulse, determine a phase shift from the first signal based on the first off-resonant RF pulse, determine a B1 field based on the phase shift, and store the B1 field on a computer readable storage medium.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for obtaining high-resolution two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum
InactiveCN106093099AAvoid signal excitationAvoid applicabilityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDecompositionLine width
The invention provides a method for obtaining a high-resolution two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum, and relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy detection method. The method comprises: loading a sample to be detected into a standard nuclear magnetic test tube, and conveying into the detection chamber of a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; sampling the one-dimensional hydrogen spectrum of the sample to be detected, and obtaining the signal peak distribution area and the spectral line width so as to provide the reference for the spectral width parameter setting, wherein the line width value reflects the magnetic field uniformity condition; measuring the pulse width of a radio frequency pulse required by excitation of the sample to be detected; introducing a compiled pulse sequence on the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, opening the heteronuclear intermolecule multiple quantum coherent signal excitation module, the indirect dimensional evolving module, the spin echo fixed delay module and the J modulating fast sampling module of the pulse sequence, and setting the experiment parameters of various modules; skipping the artificial shimming operation process, and directly executing data sampling; and after completing the data sampling, calling data post-processing codes to carry out related data post-processing so as to obtain the high-resolution two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum being not affected by the inhomogeneous magnetic field.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
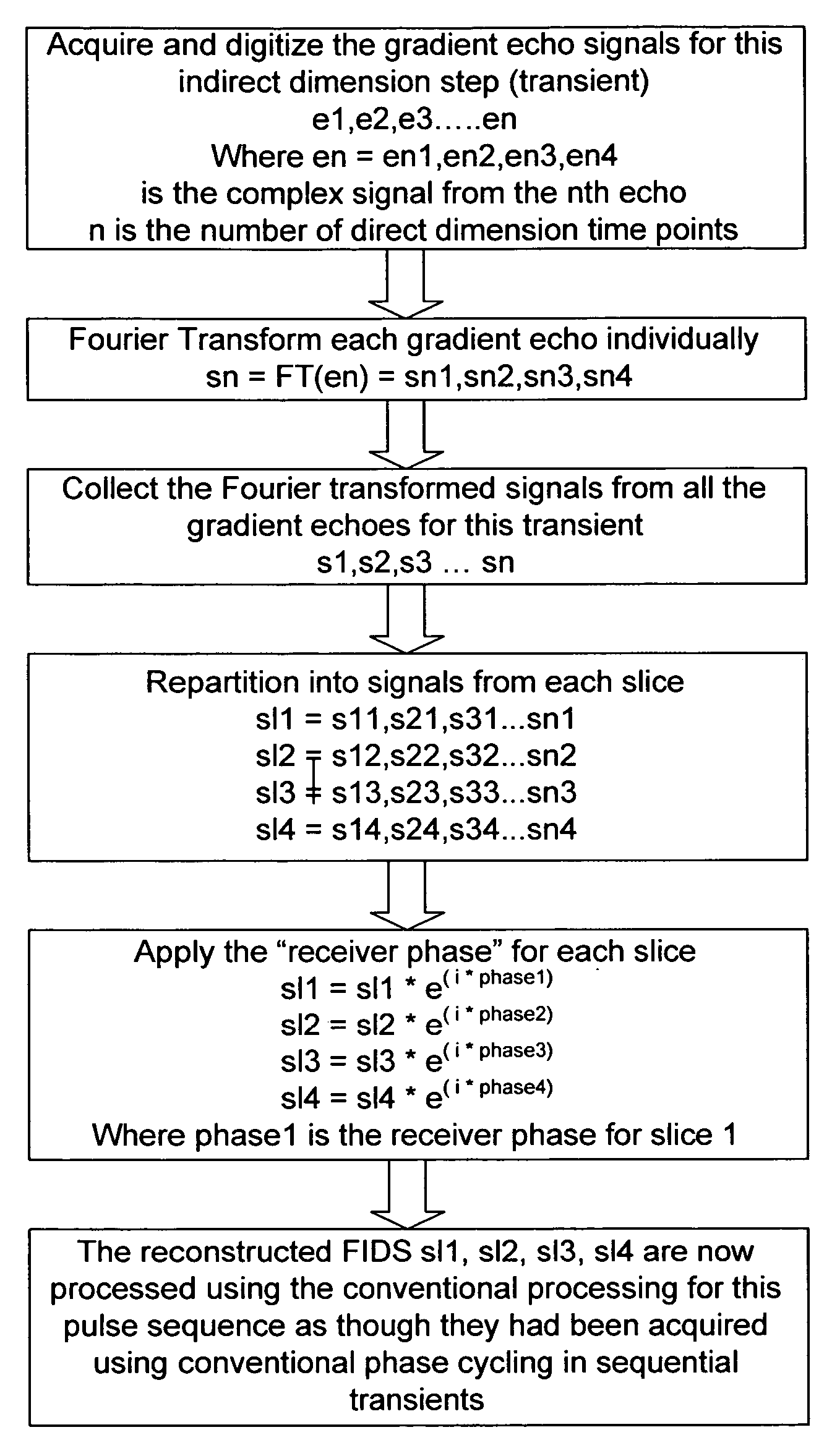
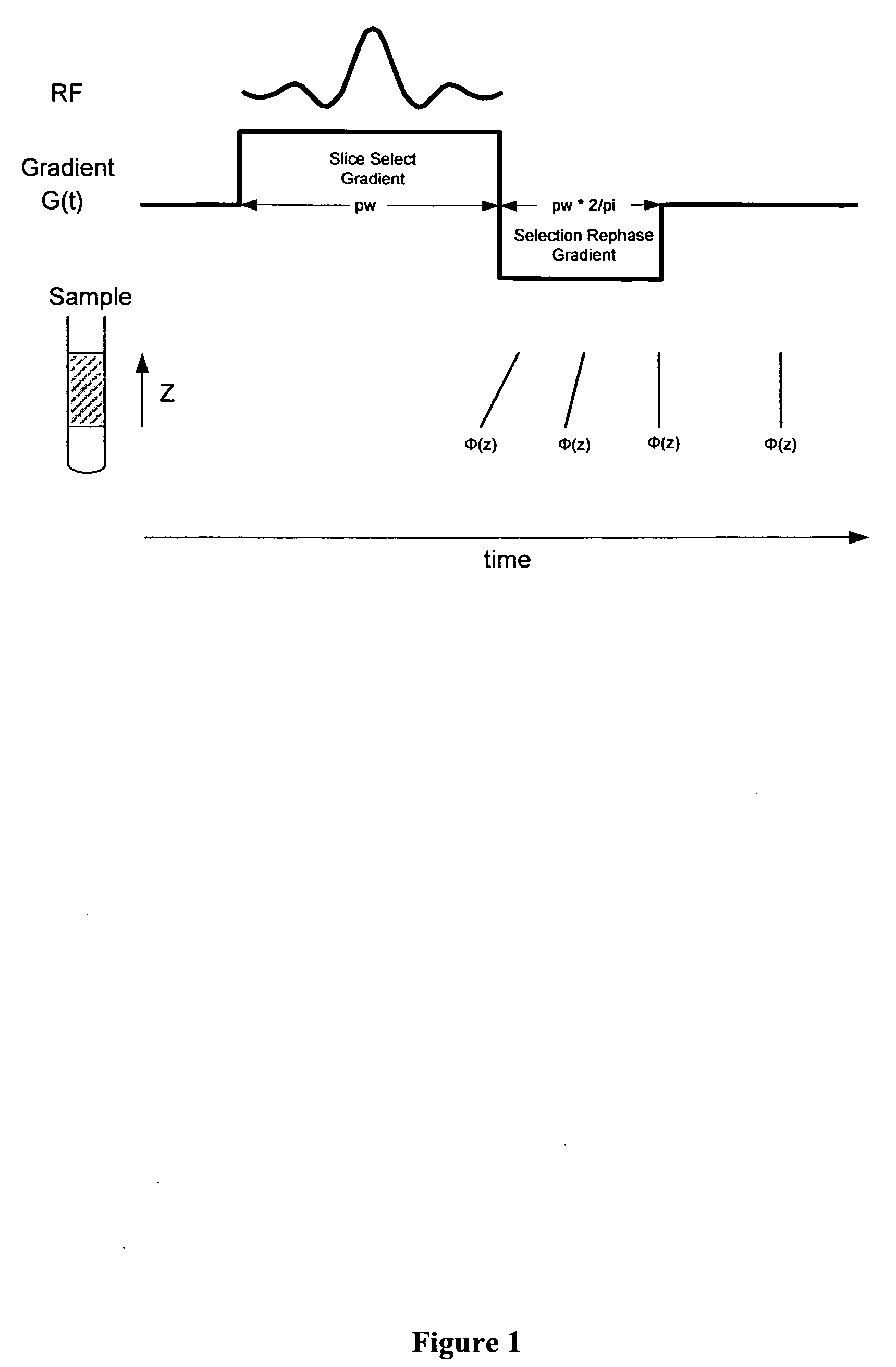
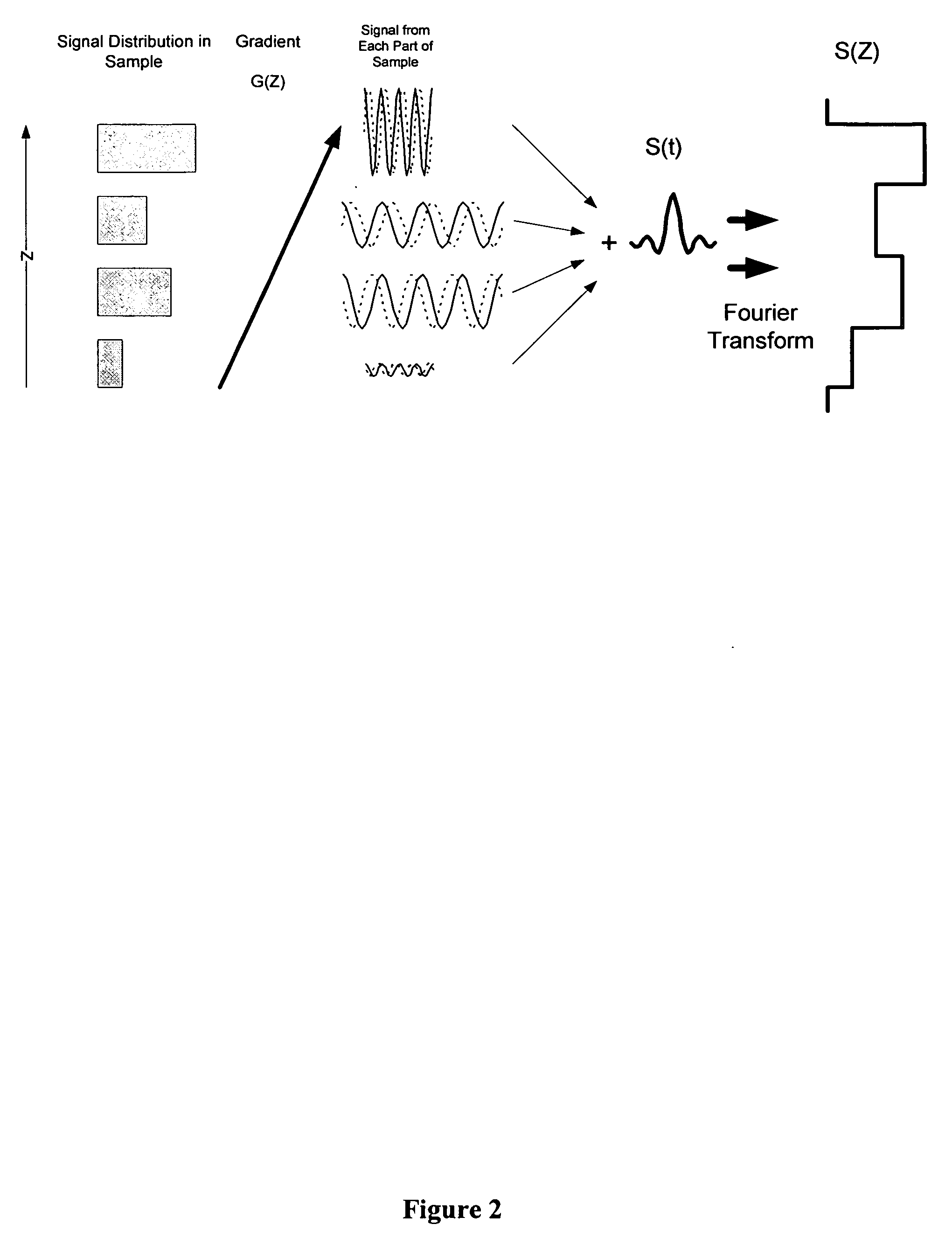
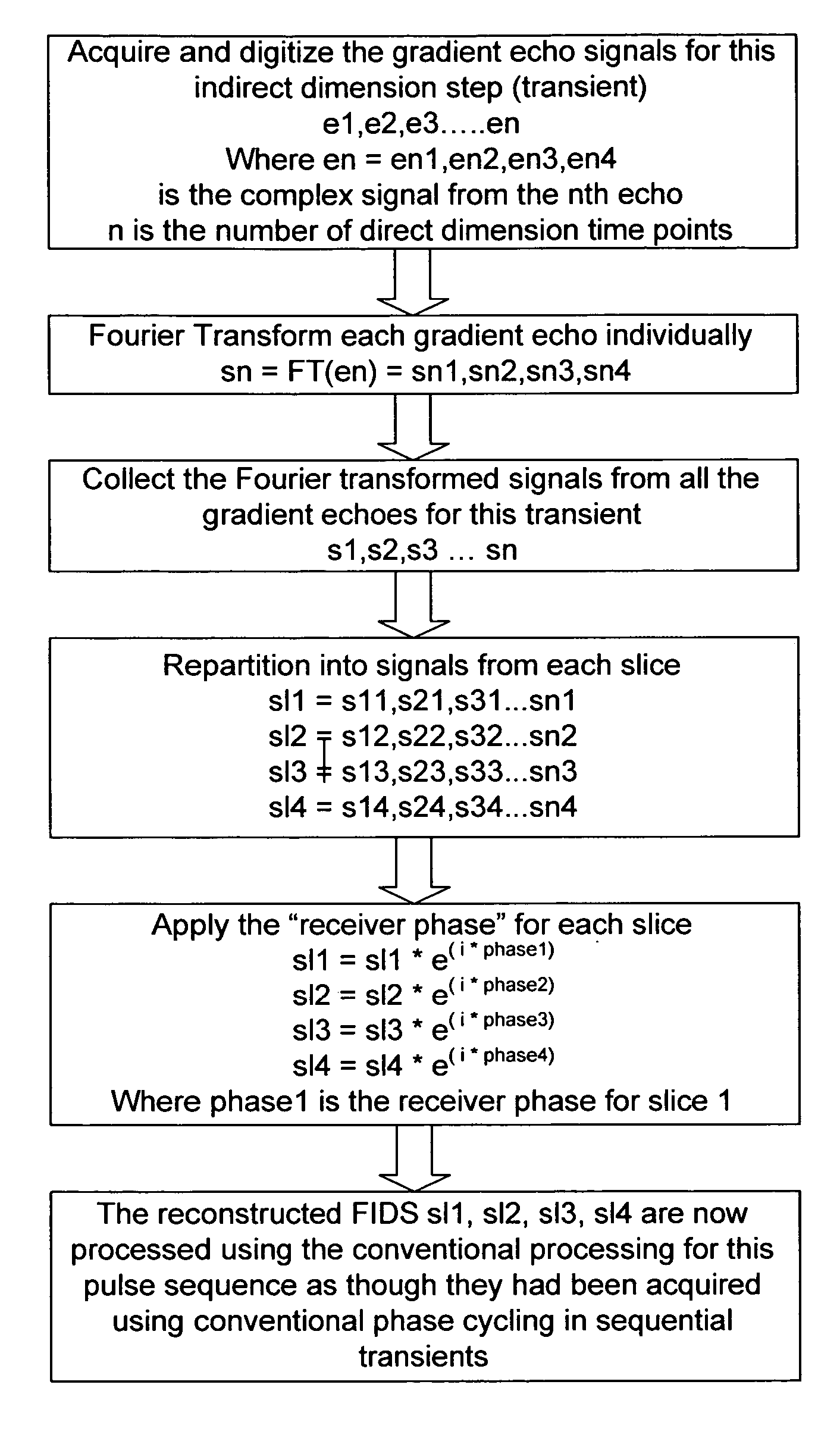
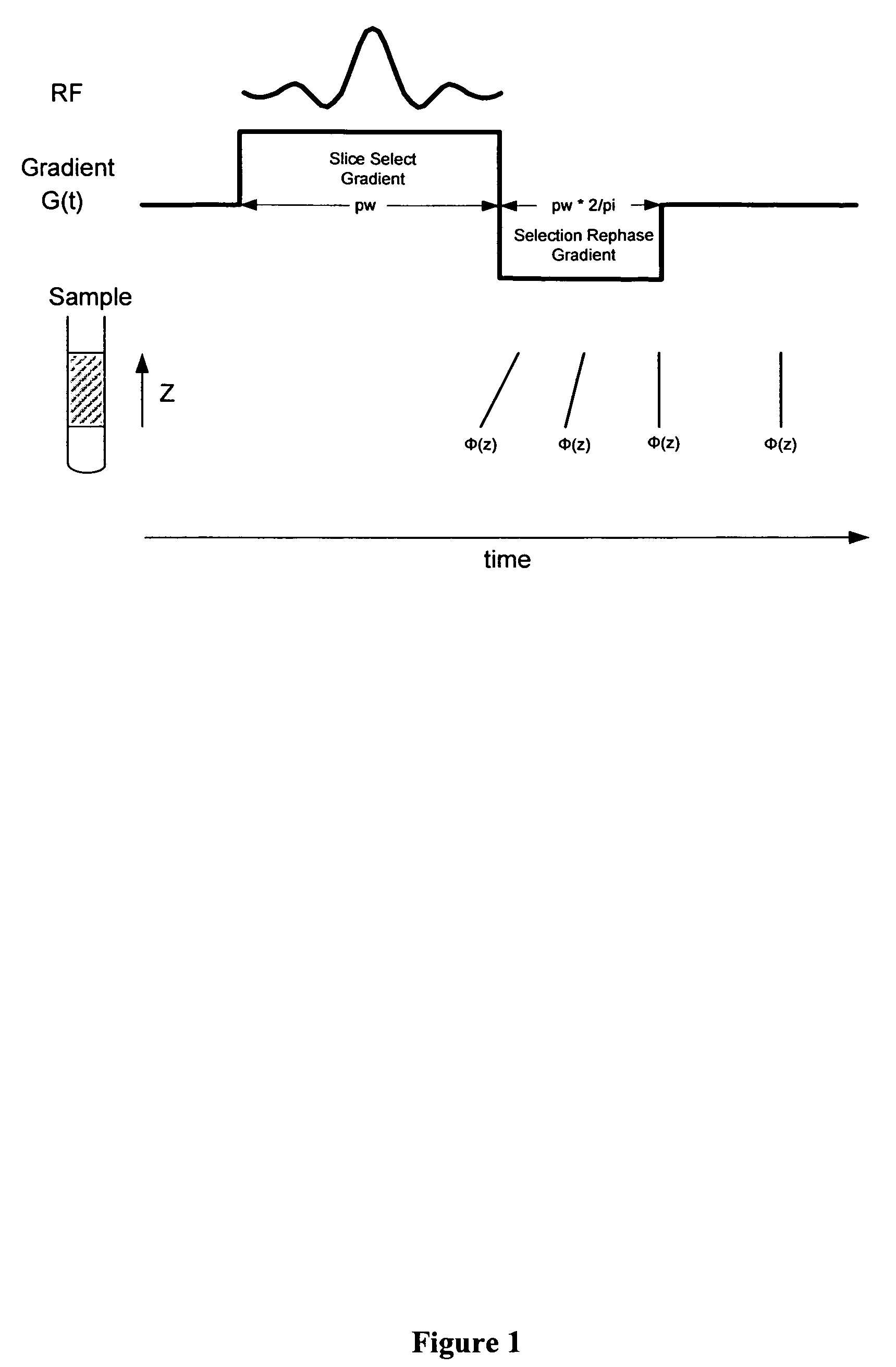
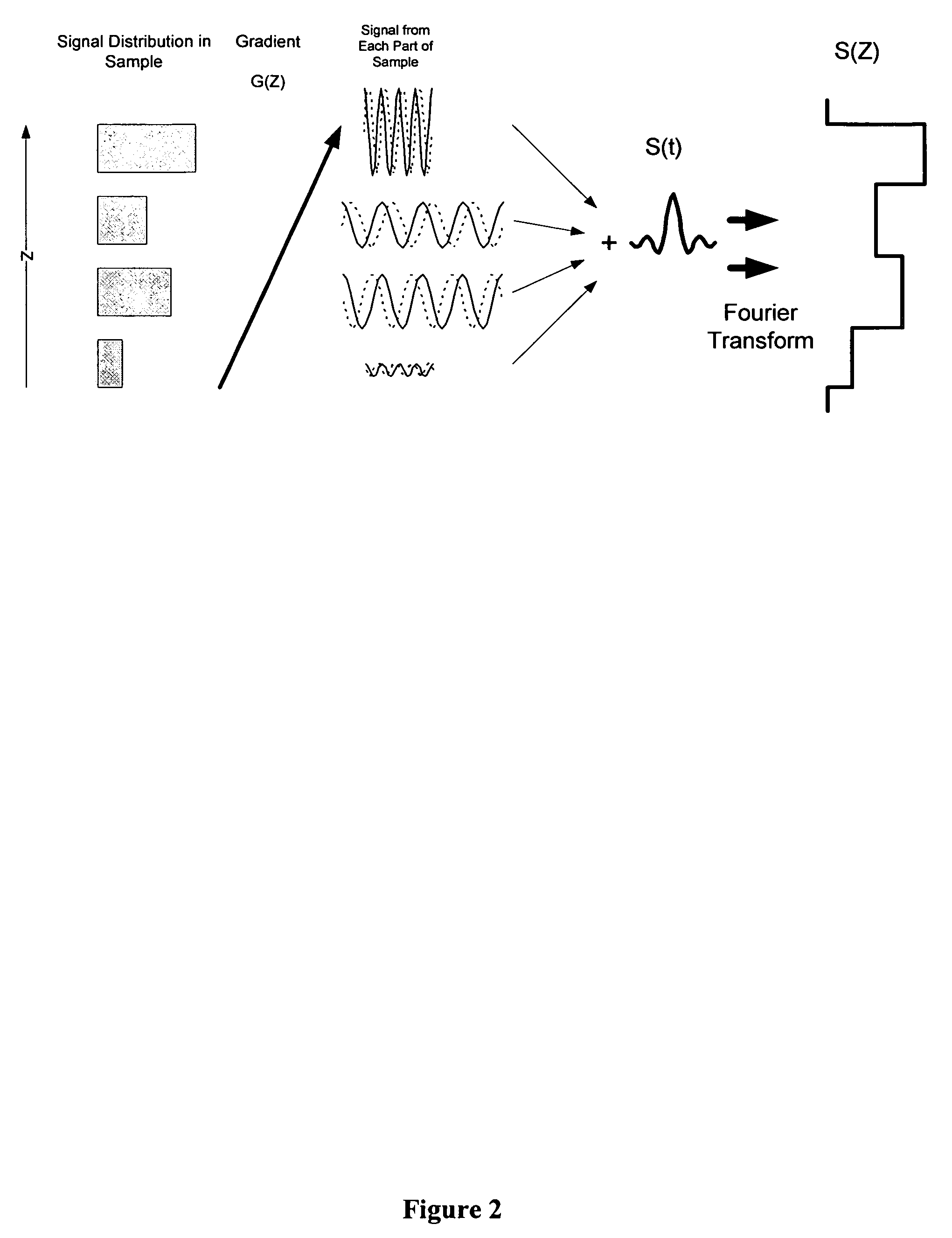
Simultaneous phase cycling for nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS20070007959A1Less timeLimited data is collectedMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRadio frequency
The present invention discloses a method of simultaneously conducting more than one step of a radiofrequency phase cycle in a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiment. The method first involves providing a sample. Next, one or more radiofrequency pulses are applied to a plurality of spatially discrete slices of the sample under conditions effective to simultaneously conduct more than one step of a radiofrequency phase cycle in a single transient. Then, NMR signals generated from the step of applying the radiofrequency pulses are acquired. Finally, the NMR signals are processed to obtain an NMR spectrum.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
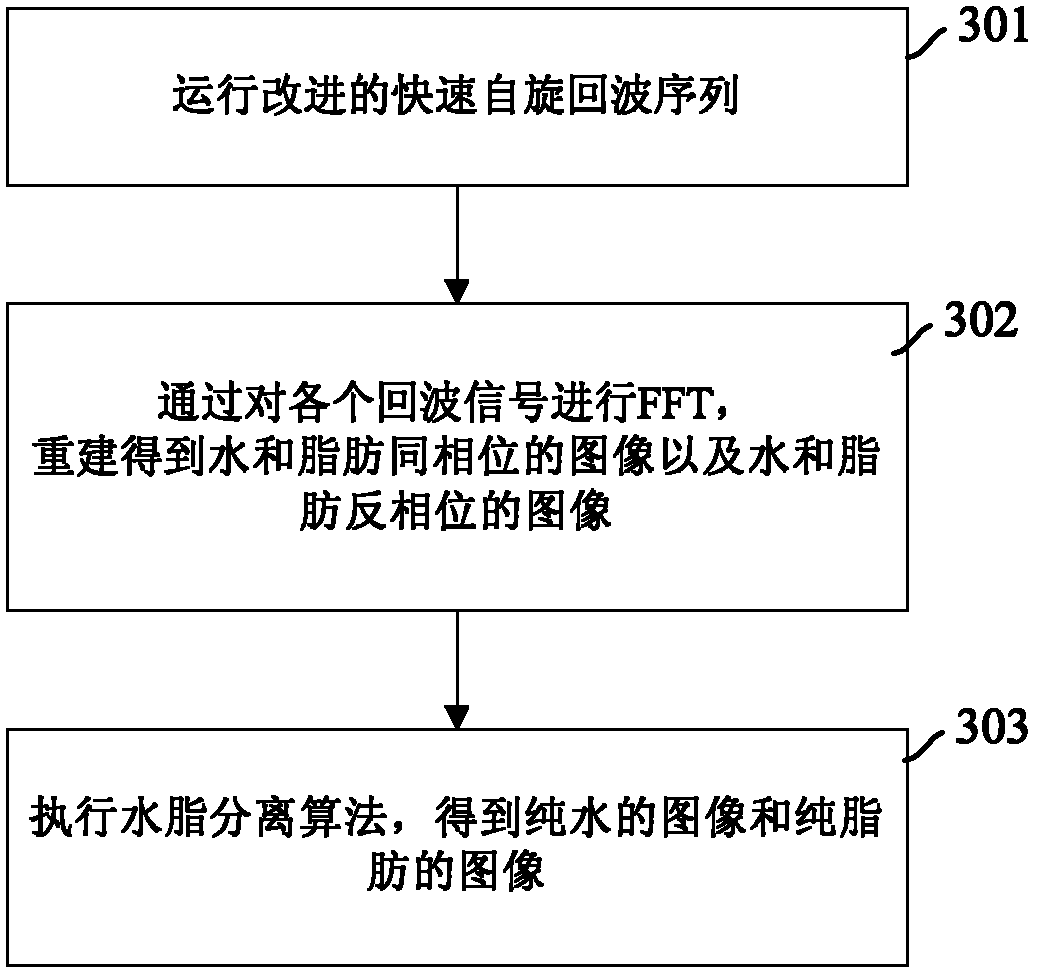
Water and fat separation imaging method and device in magnetic resonance imaging
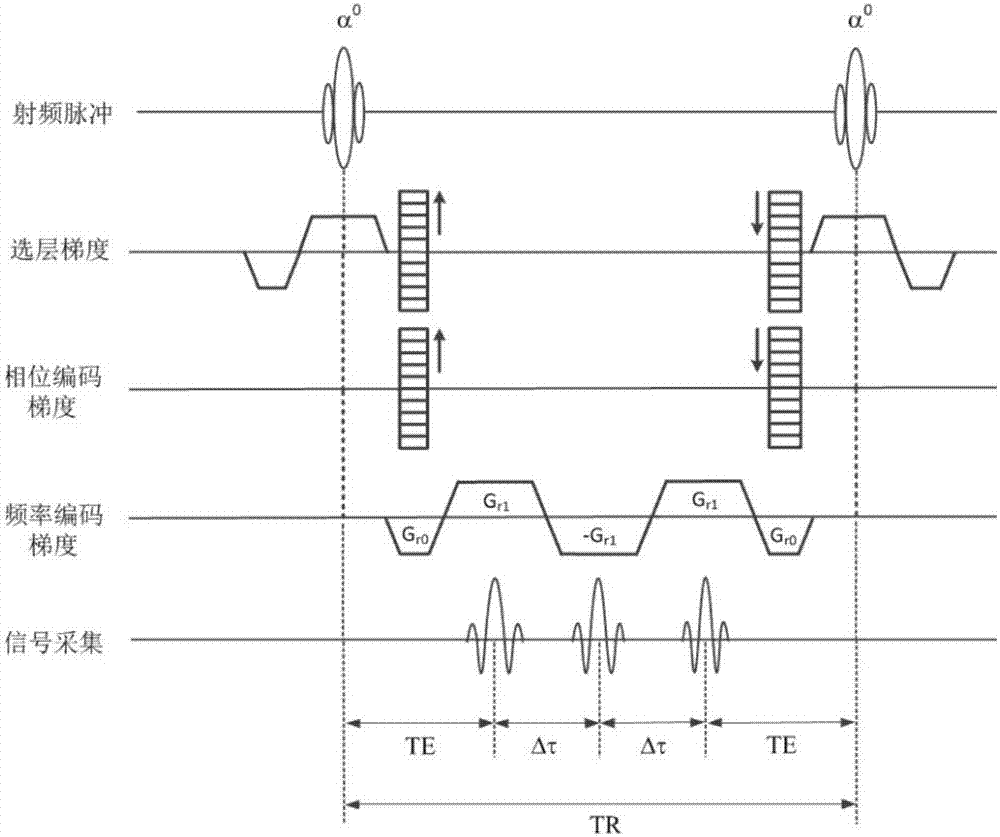
ActiveCN103257333ALower Momentum RequirementsReduce the amplitudeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFast spin echoFourier transform on finite groups
The invention discloses a water and fat separation imaging method in magnetic resonance imaging. A fast spin echo sequence based on a two-point Dixon method is adopted, wherein each refocusing radio-frequency pulse corresponds to two read-out gradients having the same polarity and a rephasing gradient having the opposite polarity, the two read-out gradients corresponding to each refocusing radio-frequency pulse are respectively divided into a front portion and a rear portion through the echo center of each of the two read gradients, the area of the rear portion of the front read gradient is less than that of the front portion of the front read gradient, and the area of the front portion of the rear read gradient is less than that of the rear portion of the rear read gradient. The method comprises operating the fast spin echo sequence; conducting fast Fourier transform (FFT) on each collected echo signal, rebuilding and obtaining water and fat in-phase images and water and fat antiphase images; conducting Fourier transform on the data executing portion of each echo signal; carrying out the water and fat separation algorithm on the water and fat in-phase images and the water and fat antiphase images to obtain pure water images and pure fat images. The invention further provides a corresponding device which can resolve the problem of image artifacts.
Owner:SIEMENS SHENZHEN MAGNETIC RESONANCE
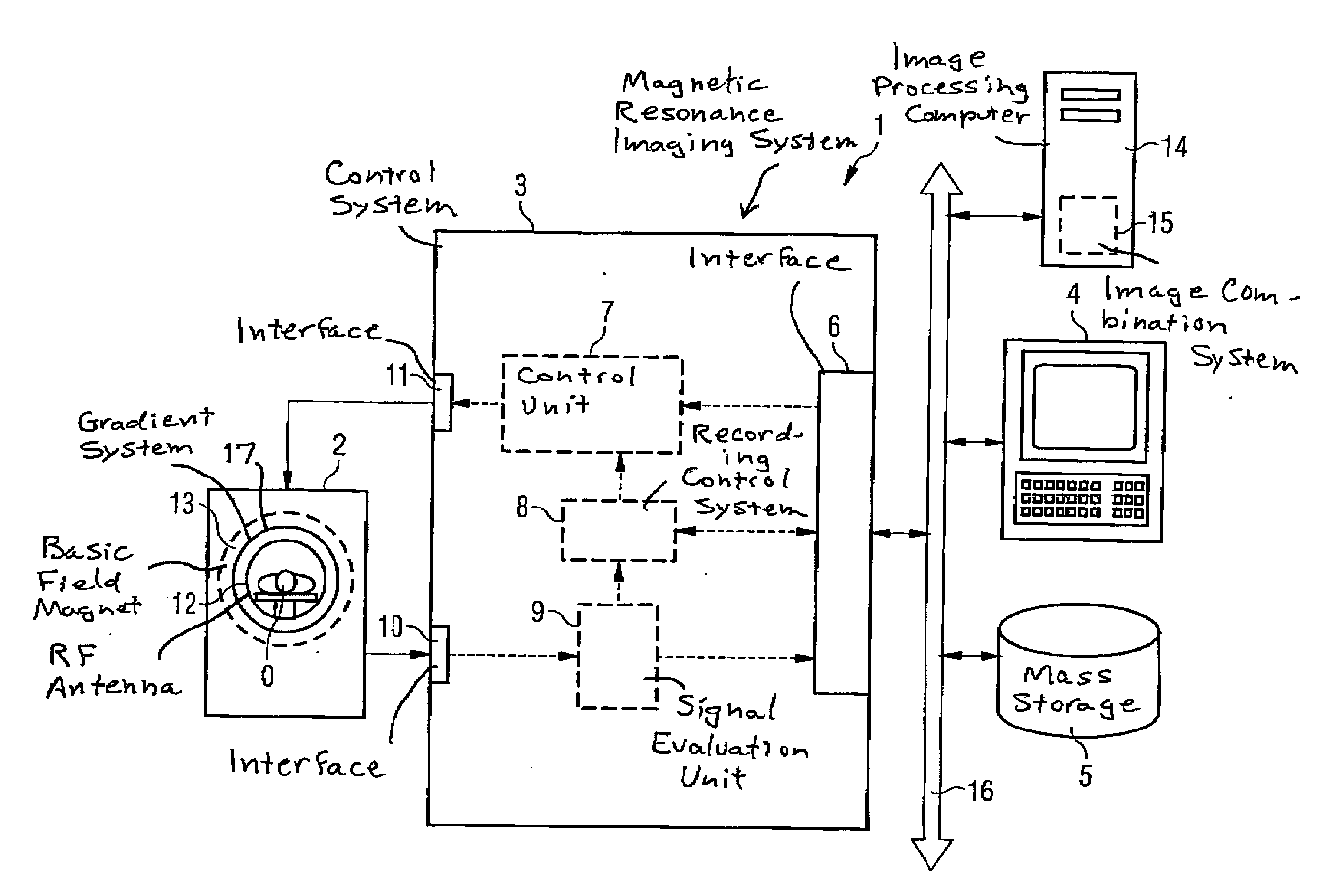
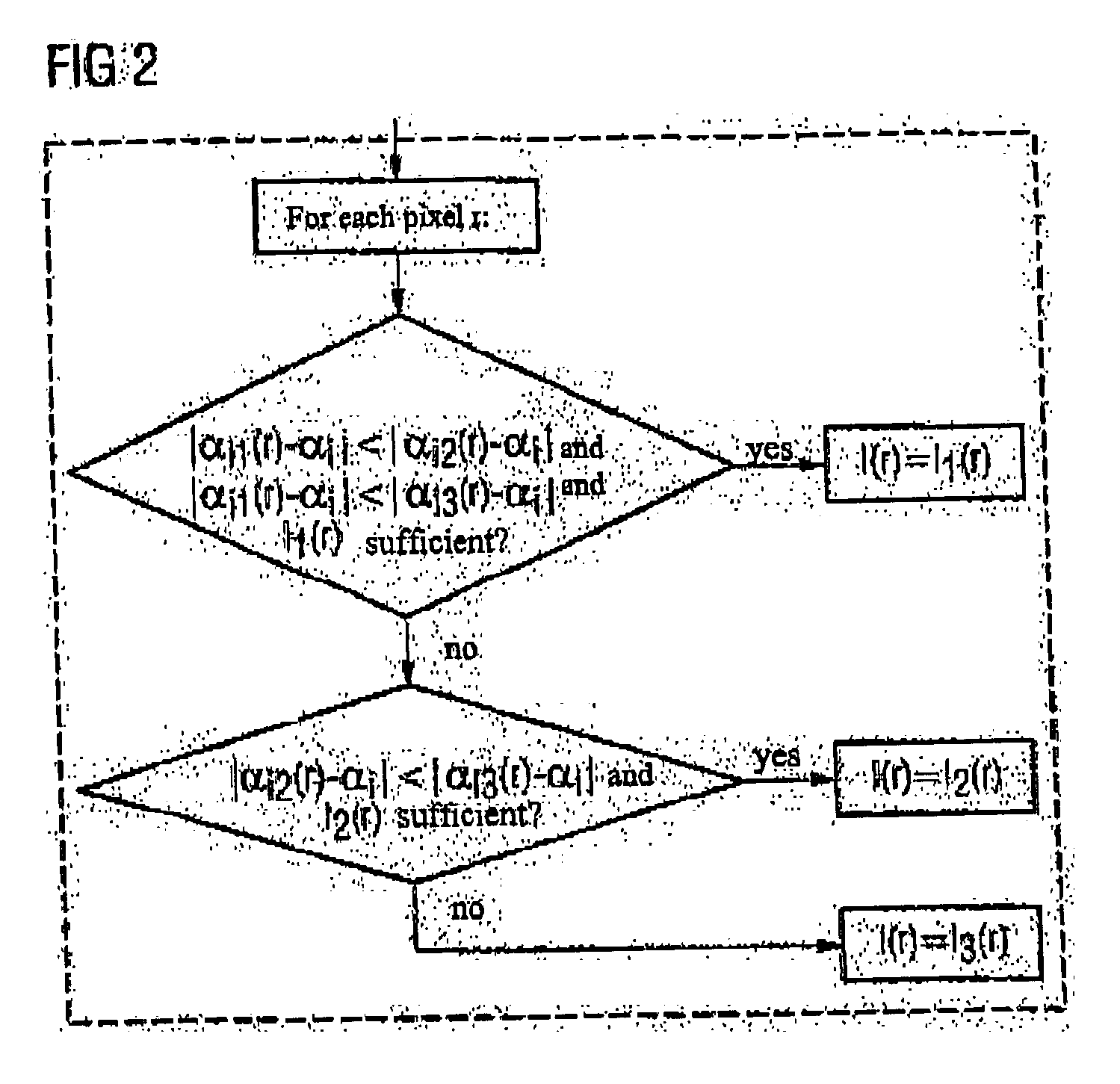
Method and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus for compensating contrast inhomogeneities in magnetic resonance images
InactiveUS20050083054A1Sharp contrastMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionResonancePulse sequence
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus for compensation of contrast inhomogeneities in magnetic resonance images caused by spatial distributions of the radio frequency field associated with the radio frequency pulses that are emitted in order to acquire magnetic resonance (MR) data, multiple individual MR images of a particular region of a subject are recorded with different radio frequency pulse sequences leading to different flip angles. A common contrast-homogenized image for the affected region then is generated based on the different individual images, so that within the contrast-homogenized image, intensity variations due to a distribution of the flip angle are smaller than in the individual images, at least in some areas.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
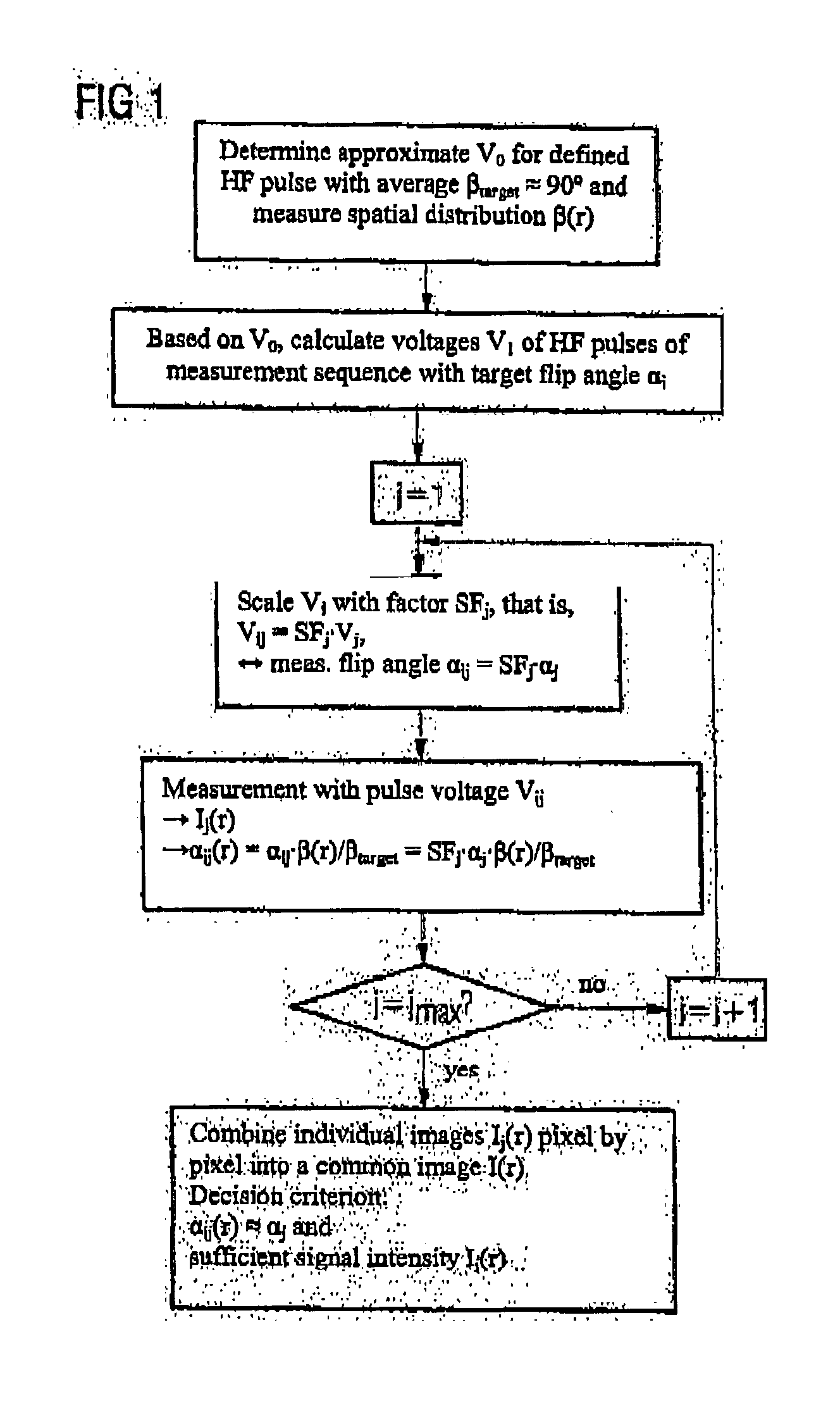
Method and magnetic resonance system for adjustment of the field strength of RF pulses
InactiveUS20070145975A1Equal weightMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSpatially resolvedResonance measurement
In a method for adjustment of the field strength of radio-frequency pulses as well as a magnetic resonance measurement system, radio-frequency pulses are emitted by a radio-frequency antenna of a magnetic resonance measurement system in a magnetic resonance measurement A test volume slice is initially excited by emission of radio-frequency pulses with a defined pulse amplitude by the appertaining radio-frequency antenna and one-dimensional, spatially-resolved characteristic values are determined along an extent direction of the test volume slice. The one-dimensional, spatially-resolved characteristic values respectively represent a local field strength of the B1 field in strips of the test volume slice running perpendicular to the extent direction. An average value of the determined characteristic values is then formed over at least over one determined segment along the extent direction of the test volume slice. A pulse amplitude of the radio-frequency pulses that is to be set for the magnetic resonance measurement to be implemented is determined on the basis of the average value.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
MRI breast image magnet structure
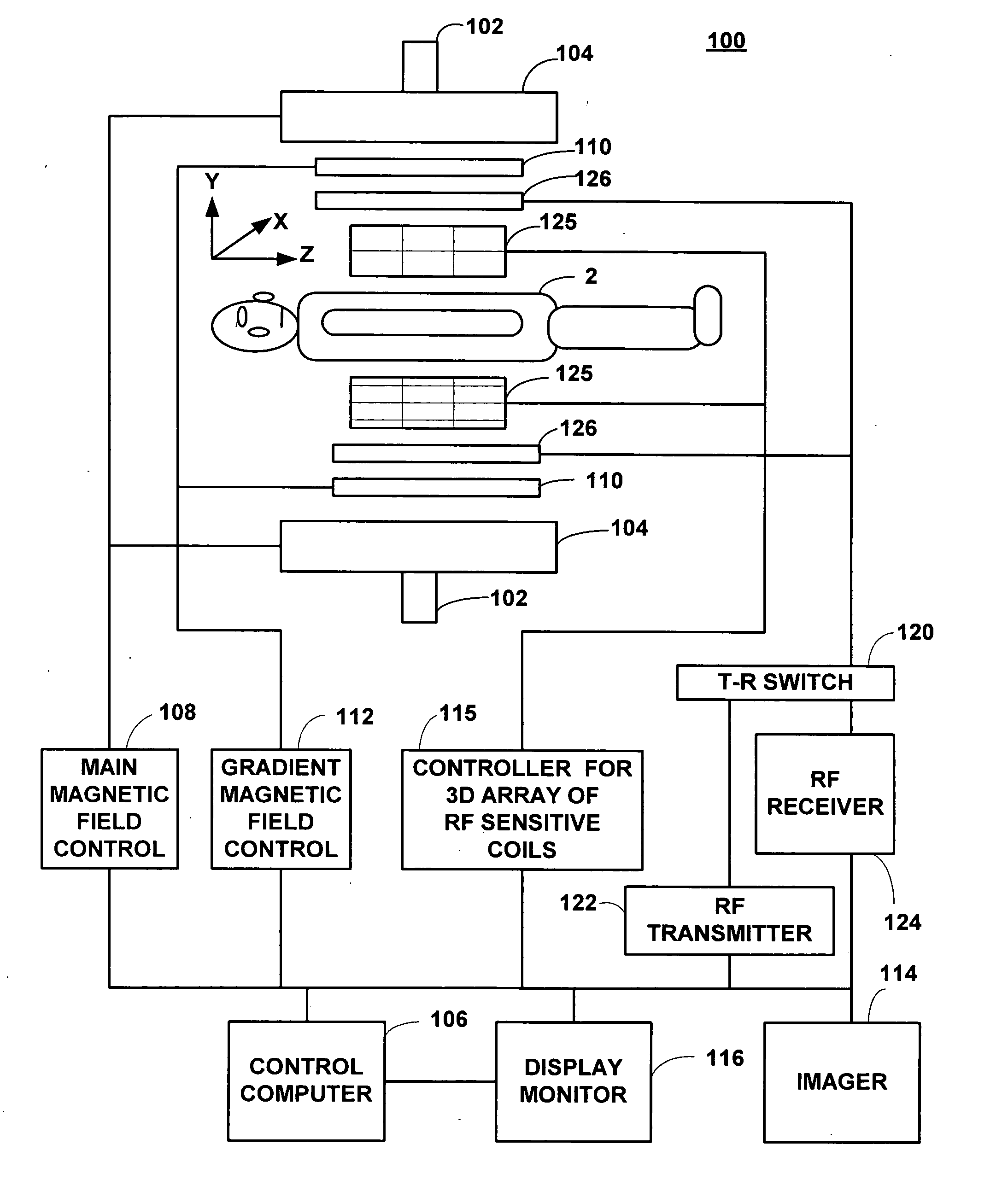
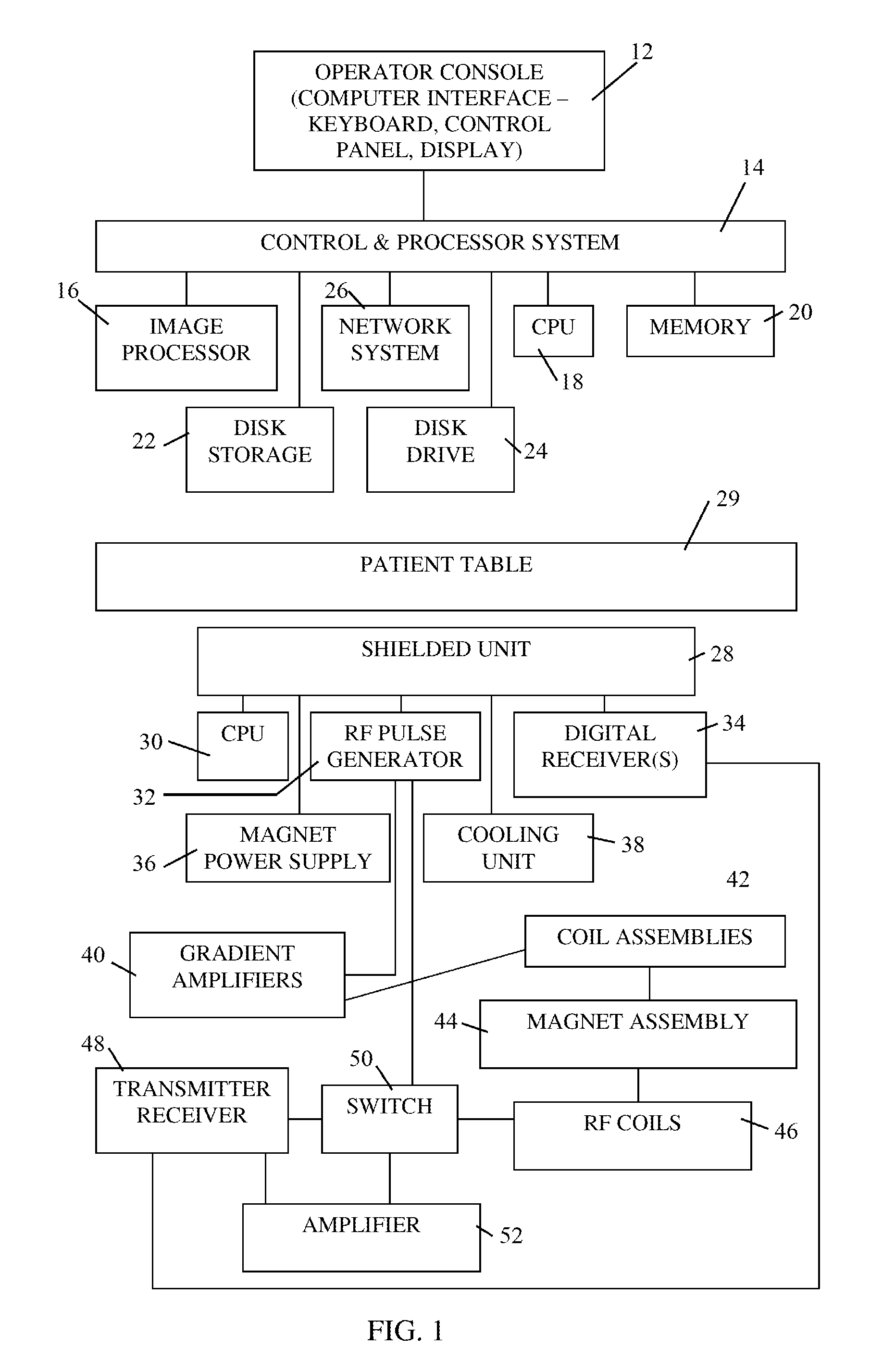
InactiveUS20090082662A1Reduce the impactReduce impactDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic field gradientRf field
Apparatus for producing magnetic resonance (MR) images of a subject over a limited volume, including a patient table, and a shielded unit housed under the patient table, the shielded unit including an RF pulse generator module, a magnet assembly for producing a static magnetic field in magnetic structure including a shaped magnetic “C” core, a gradient field generating assembly for generating magnetic field gradients in two orthogonal planes for producing MR images, a radiofrequency (RF) coil assembly for transmitting a broad band radiofrequency pulse and a RF field matching structure to simulate an infinite volume to the RF coil assembly, wherein the RF coil assembly detects a plurality of MR signals induced from a subject in response to RF pulses from the RF pulse generator.
Owner:ISRAEL HENRY M
Flow Measurement Using NMR
ActiveUS20080174313A1Magnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by using resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) method is used to determine a velocity distribution or velocity image of a flowing fluid in a downhole environment. The method comprises applying a radio frequency pulse sequence; applying a magnetic field gradient magnetic field and a gradient pulse duration; measuring a NMR signal; determining a phase characteristic of the NMR signal; and determining the velocity distribution or image of the fluid using the determined phase characteristic, the magnetic field gradient pulse parameters, and a time delay between gradient pulses.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and magnetic resonance system for acquiring magnetic resonance data
ActiveUS20150084629A1Improve qualitySimple technologyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionImage resolutionResonance
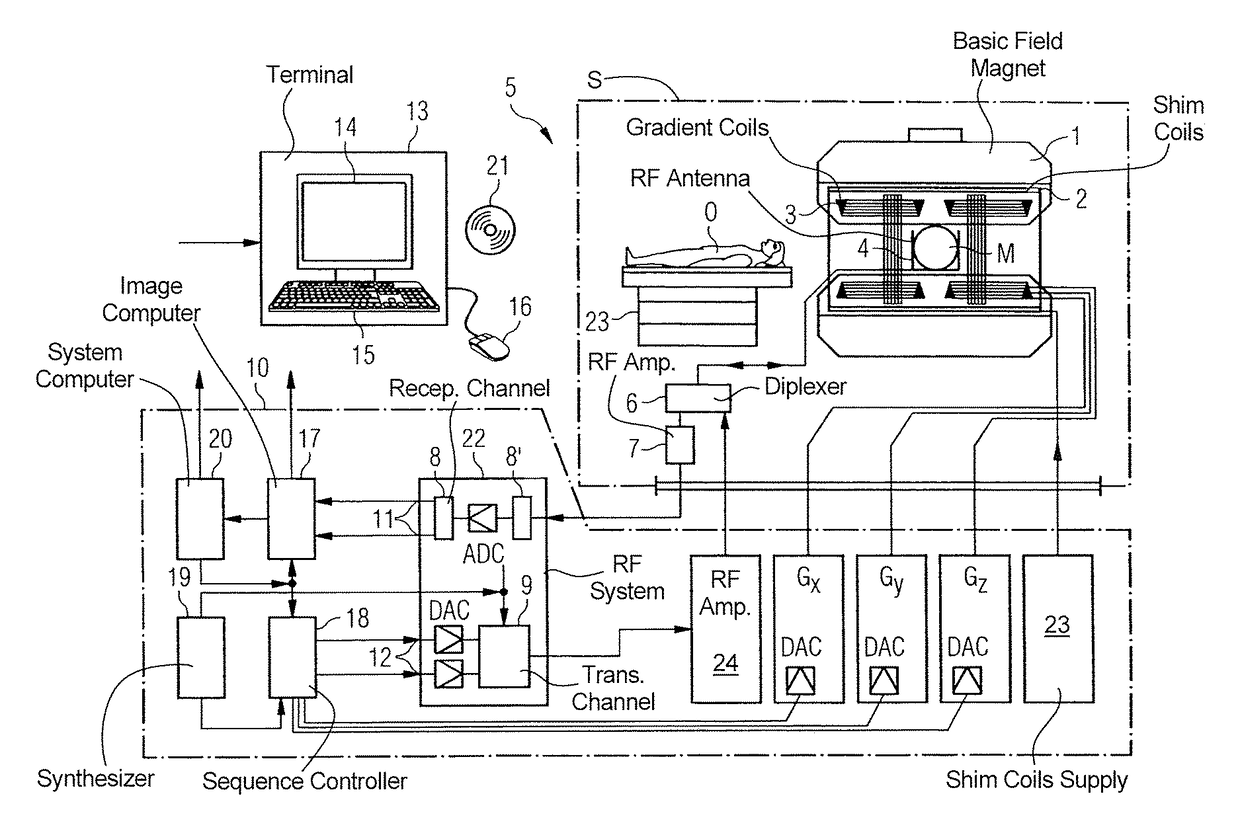
In a method for acquiring magnetic resonance data with a magnetic resonance system using a magnetic resonance sequence, the sequence has a first partial sequence in which magnetic resonance data are acquired for multiple slices that have to be acquired simultaneously, from which image data for the individual slices are calculated by a reconstruction algorithm. The sequence also has a second partial sequence for determining additional data, which are used to evaluate and / or assess the magnetic resonance data, and which have a spatial resolution that is lower than the magnetic resonance data, in which radio-frequency pulses and readout processes take place in a slice-specific manner through a time offset within a single measuring process, in which a single continuous excitation period with the radio-frequency pulses and a single continuous readout period with the readout processes follow one another, so that separate additional data are directly determined for each slice.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Simultaneous phase cycling for nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS7408346B2Less timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopyProton NMR
The present invention discloses a method of simultaneously conducting more than one step of a radiofrequency phase cycle in a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiment. The method first involves providing a sample. Next, one or more radiofrequency pulses are applied to a plurality of spatially discrete slices of the sample under conditions effective to simultaneously conduct more than one step of a radiofrequency phase cycle in a single transient. Then, NMR signals generated from the step of applying the radiofrequency pulses are acquired. Finally, the NMR signals are processed to obtain an NMR spectrum.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
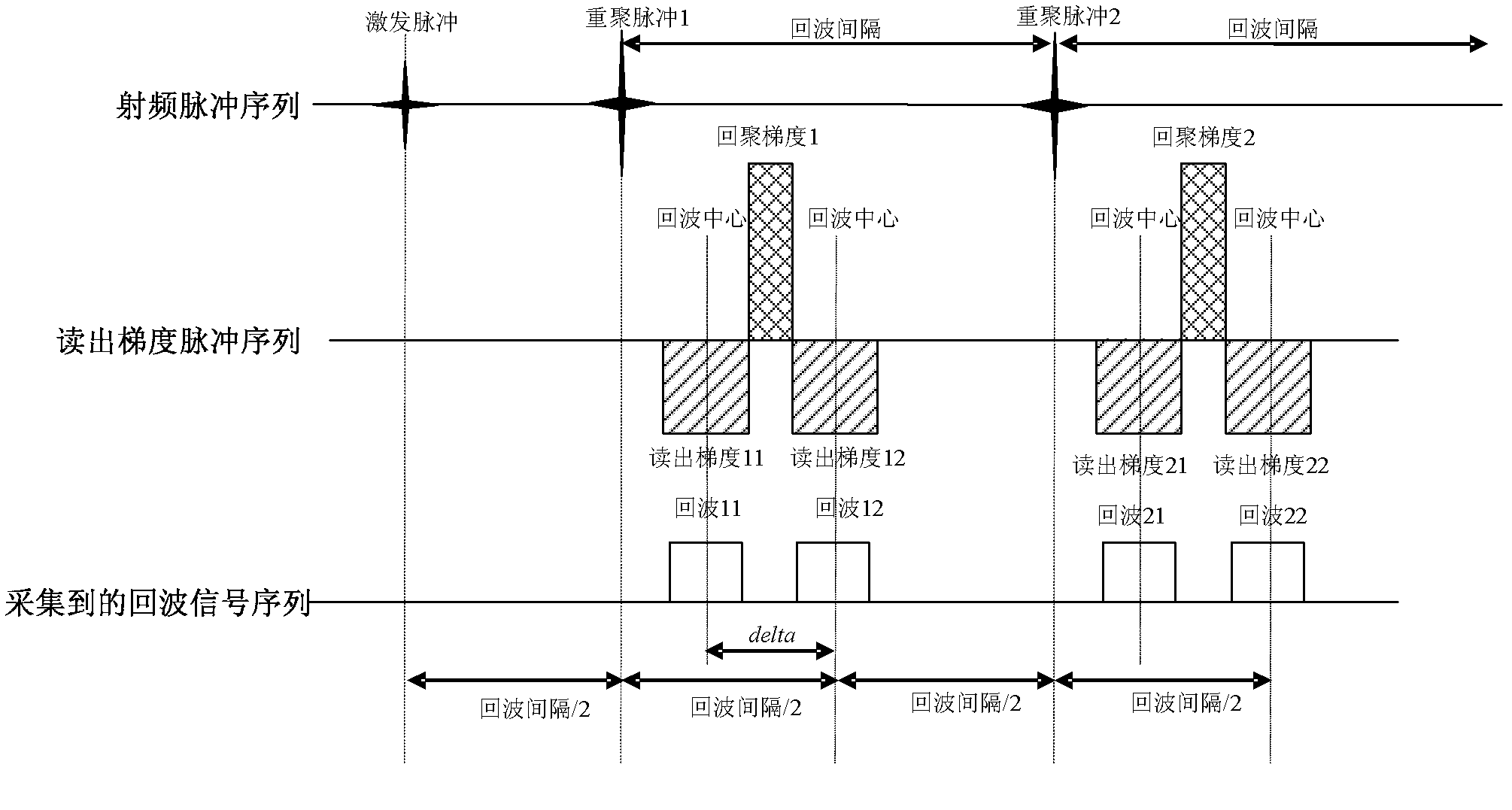
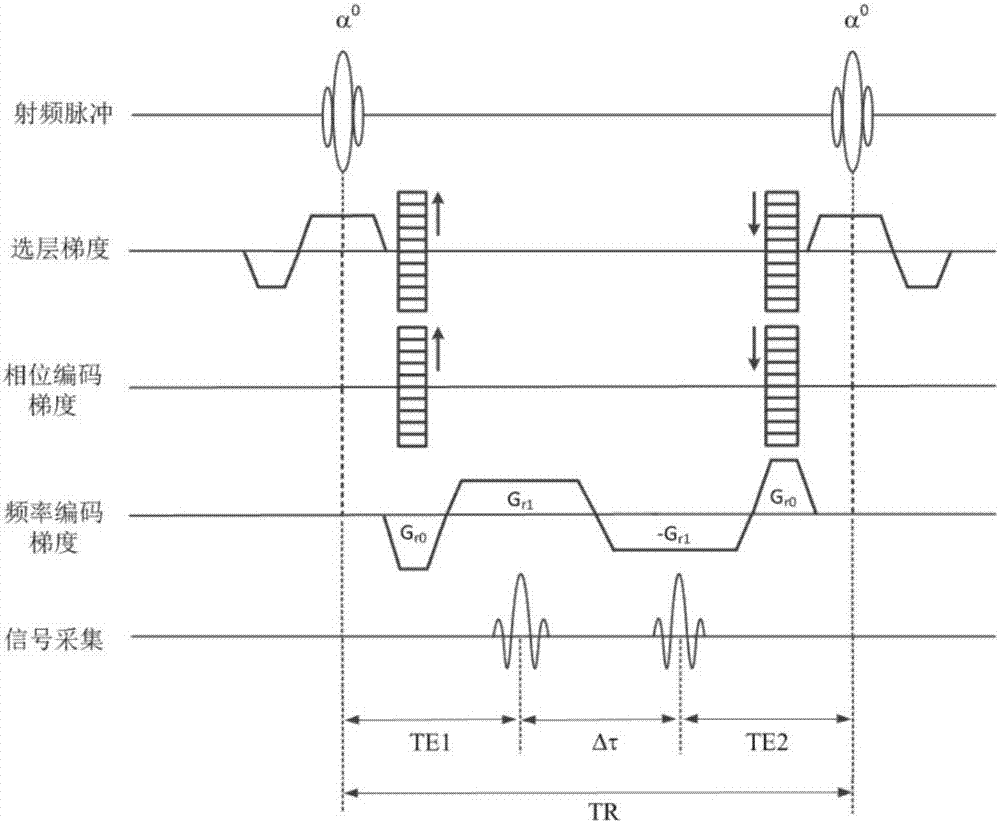
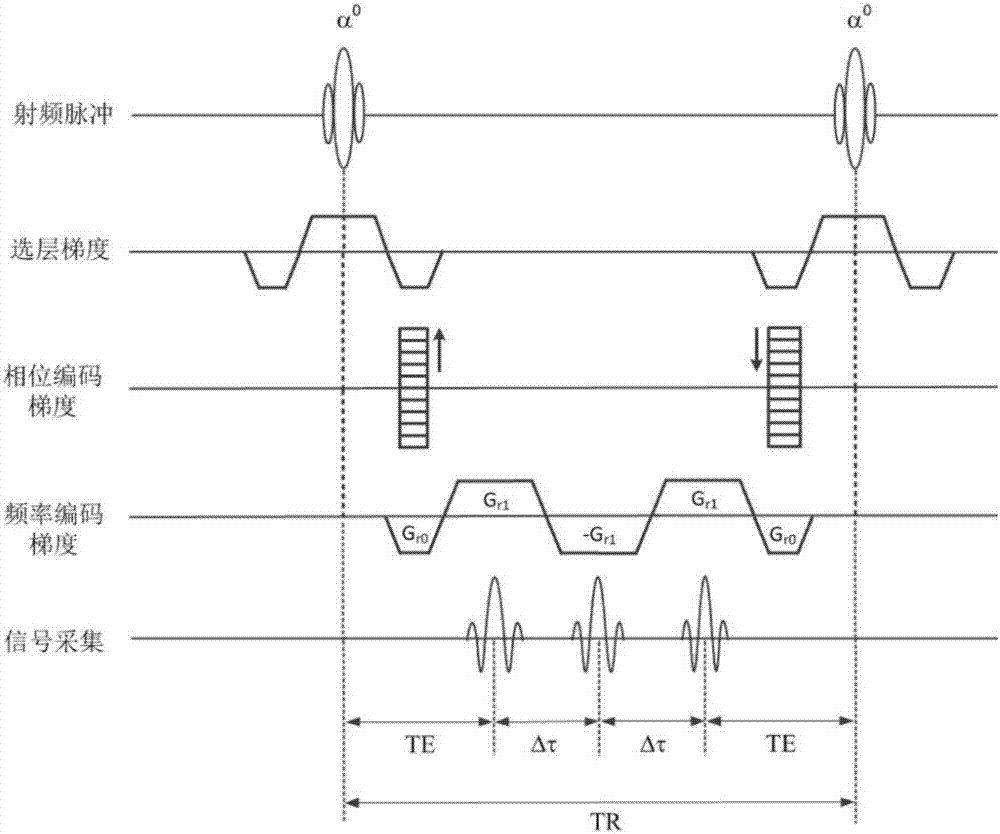
Steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method
ActiveCN107153169AHigh precisionSuppresses Motion ArtifactsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRadio frequencyImage sequence
The invention discloses a steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method. The steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method comprises the following steps of on the basis of a steady-state procession imaging sequence for conventional scanning on a magnetic resonance imaging system, repeatedly exciting the imaging area by a radio frequency pulse at the interval of 10ms magnitude or smaller short cycle TR; setting a pulse flip angle into +alpha / 2 in a first sequence repetition cycle, and eliminating the sampling period; alternatively setting the pulse flip angle into +alpha and -alpha in the subsequent sequence repetition cycle; using the layer selection gradient, phase encoding gradient and frequency encoding gradient to perform three-dimensional encoding, wherein the sum of integral areas of gradients in each bearing is zero, and the proton magnetizing vector procession is approximate to the steady state; enabling the magnetizing vectors to form three or two gradient echoes under the action of three or two positive and negative alternating frequency encoding gradients in each TR period, wherein the integral area of gradients in the frequency encoding direction is zero; performing direct phase encoding on the three or two echoes according to echo peak interval and water and grease chemical displacement difference value.
Owner:谱影医疗科技(苏州)有限公司
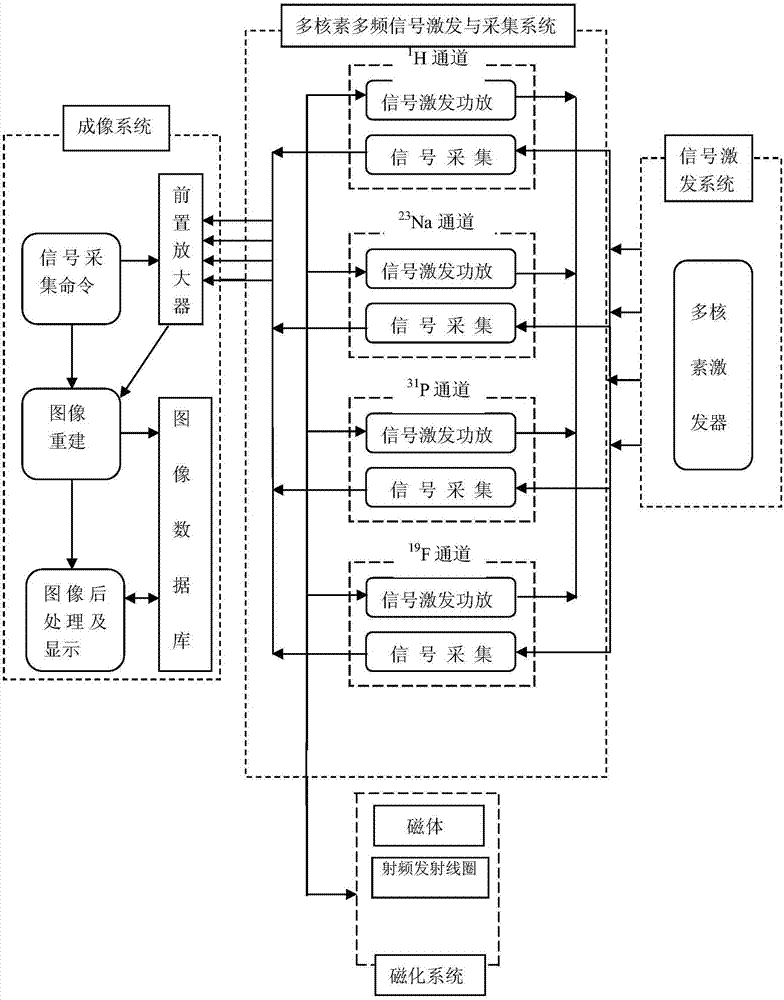
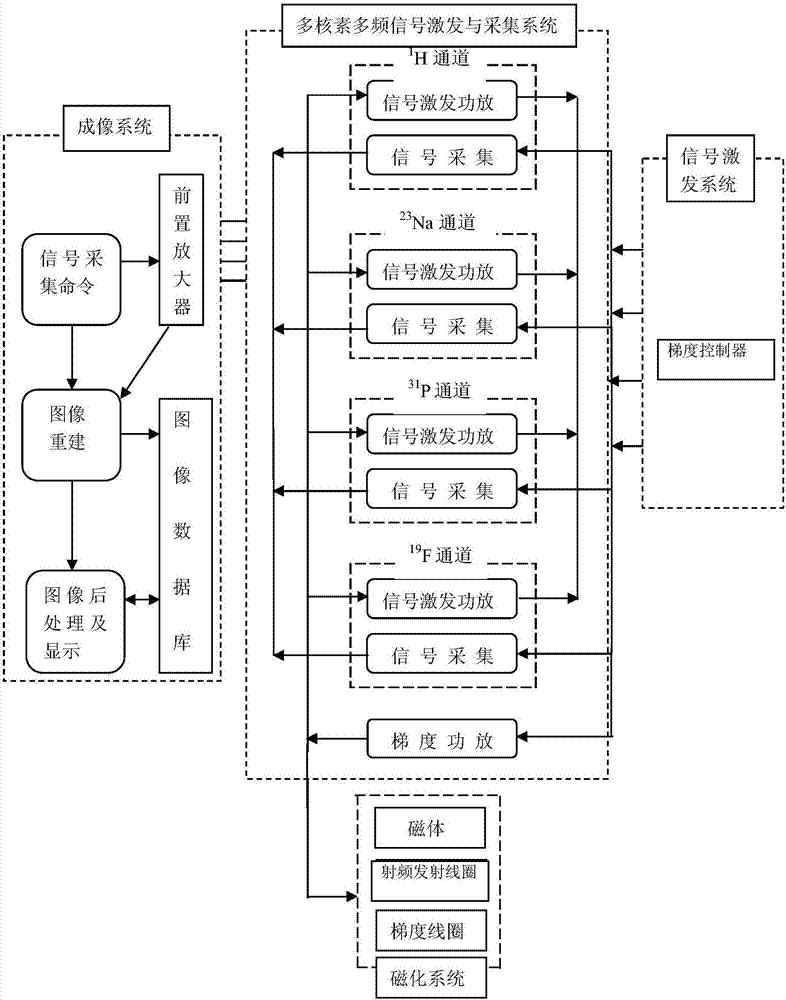
Multi-nuclide multi-frequency resonance synchronous imaging system
ActiveCN107329100AMap SimplificationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringDynamic balanceImage post processing
The invention provides a multi-nuclide multi-frequency resonance synchronous imaging system which is used for detecting the tumor ion dynamic balance, the energy metabolism, the molecular target change and the tumor microenvironment change. The system can simultaneously transmit radio frequency pulse signals corresponding to four nuclides of 1H, 23Na, 31P and 19F and synchronously receive the nuclear magnetic resonance load signals of the four nuclides. The multi-nuclide multi-frequency resonance synchronous imaging system comprises a signal excitation system, a multi-nuclide multi-frequency signal excitation and acquisition system, a magnetization system and an imaging system. The multi-nuclide multi-frequency signal excitation and acquisition system comprises four nuclide channel modules of 1H, 23Na, 31P and 19F, and each nuclide channel module comprises a signal excitation power amplifier submodule and a signal acquisition submodule. The magnetization system comprises magnets and radio frequency transmitting coils. The imaging system comprises a signal preamplifier, a signal acquisition command module, an image reconstruction module, an image post-processing and display module and an image database.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
A Sequence Design Method for Three-Dimensional Spatially Selective Excitation for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
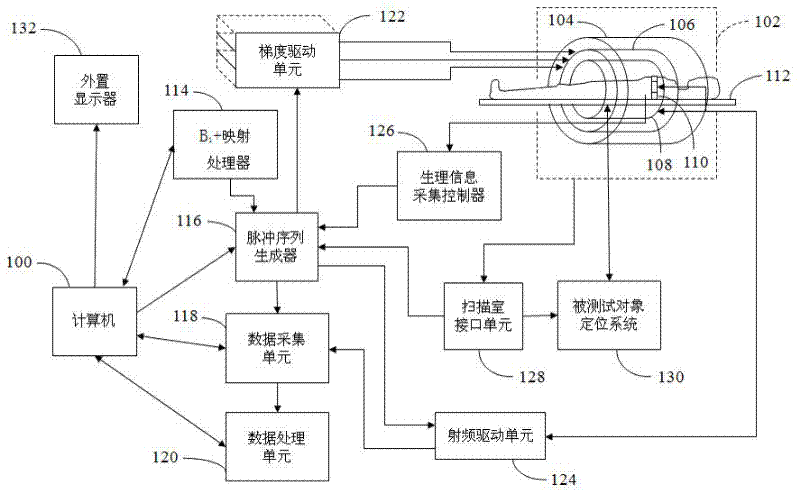
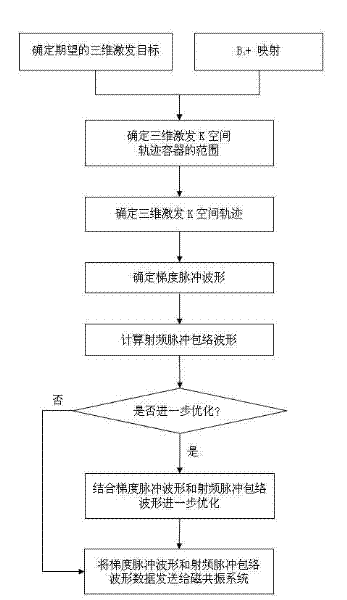
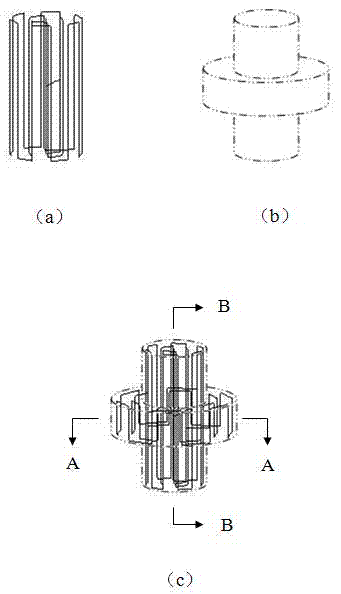
InactiveCN102283649AImprove sampling efficiencyImprove securityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSequence designPulse envelope
The invention discloses a selective excitation sequential design method for magnetic resonance imaging in a three-dimensional space. According to the sequential design method disclosed by the invention, a proper excitation K space track is optimally determined according to space sensitive conditions of an excitation target and a plurality of transmitting channels of a radio-frequency coil, thereby a gradient pulse waveform and a radio frequency pulse envelope waveform corresponding to each transmitting channel are determined. A gradient driving unit and a radio-frequency driving unit in a magnetic resonance system can be used for generating gradient pulse and radio frequency pulse according to the radio frequency pulse envelope waveform and the gradient pulse waveform and driving a gradient coil and the radio frequency coil to apply the gradient pulse and radio frequency pulse in a scanning space, thereby the expected selective excitation target in the three-dimensional space is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com