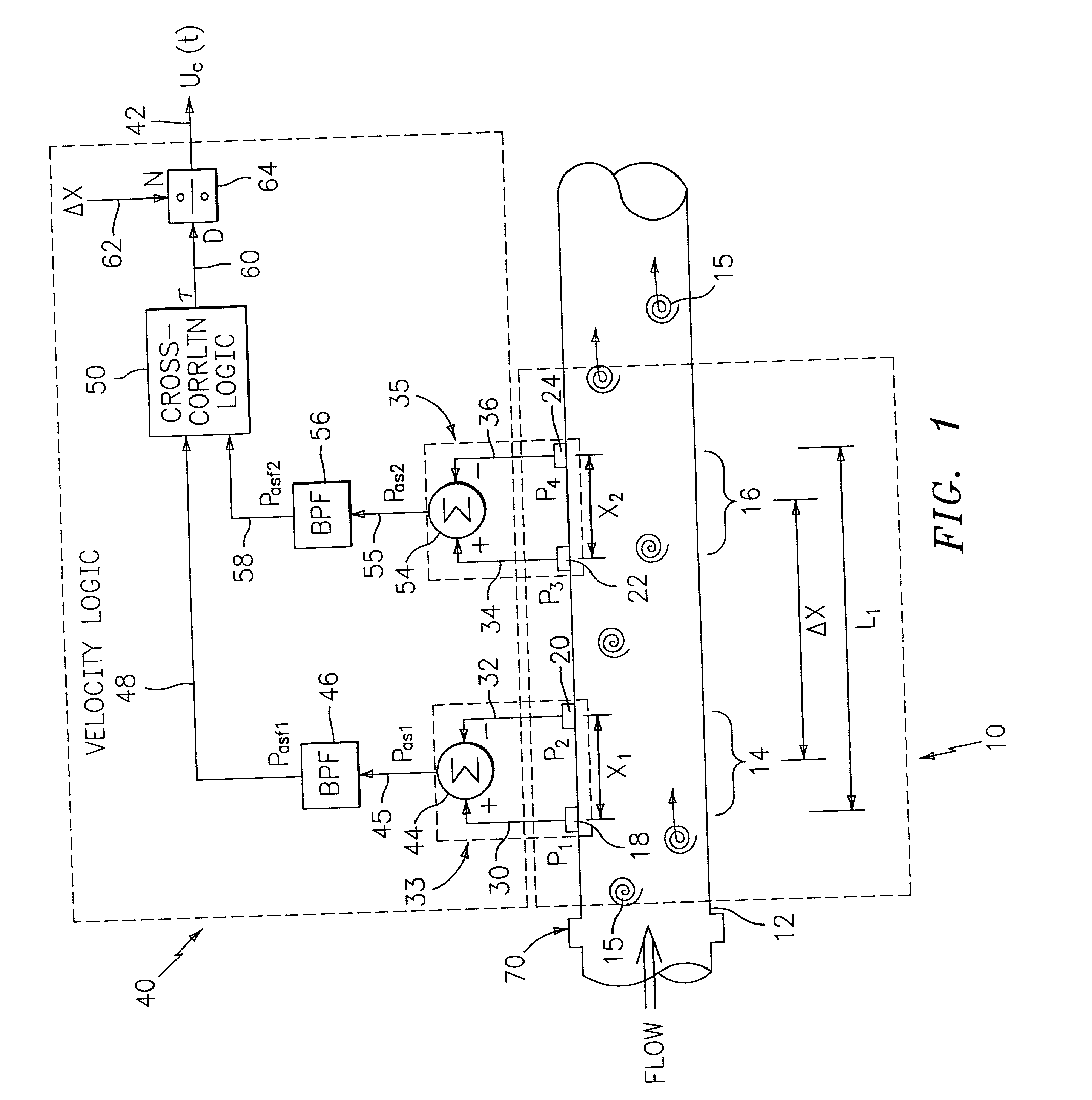Patents
Literature
913 results about "Rate measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
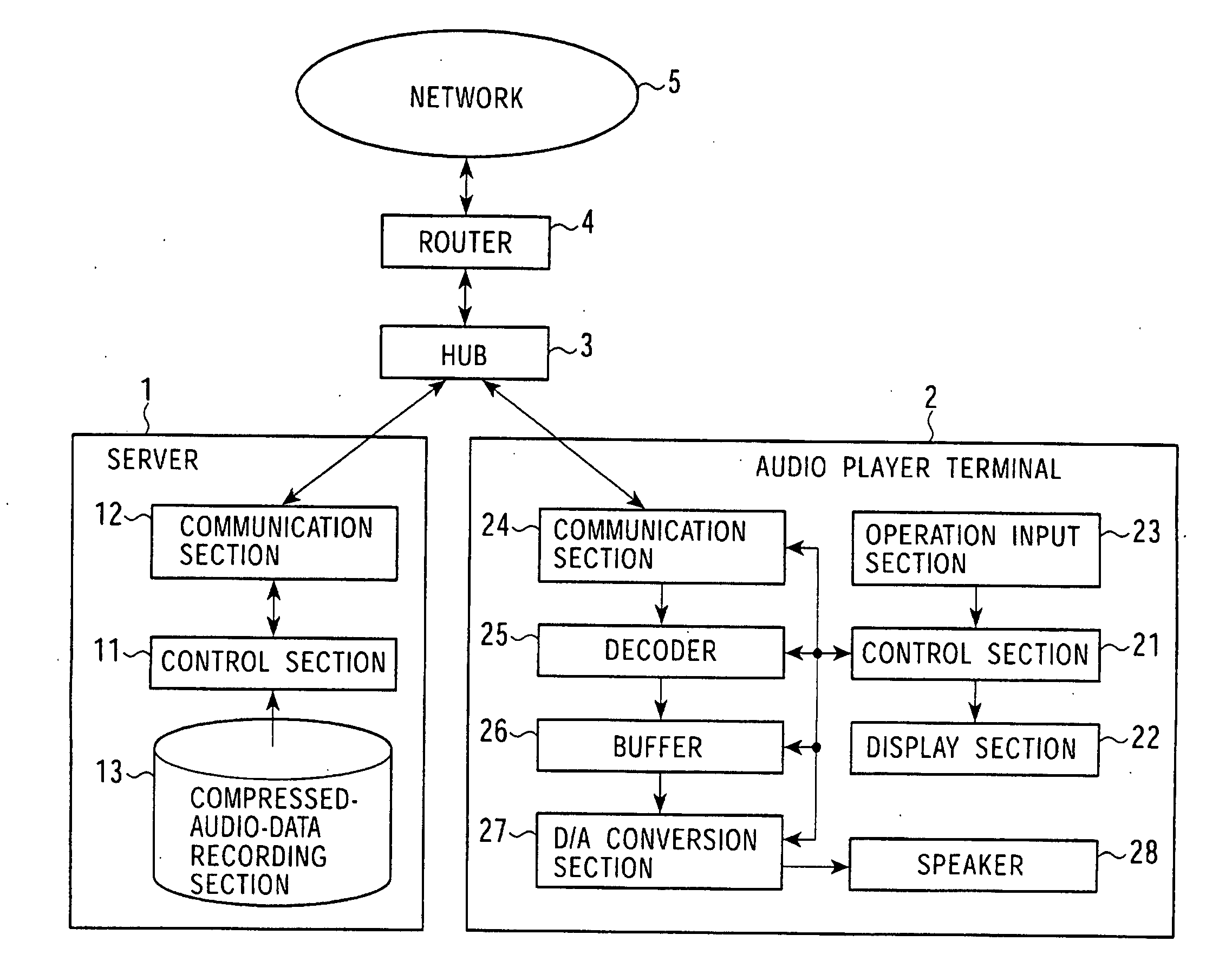
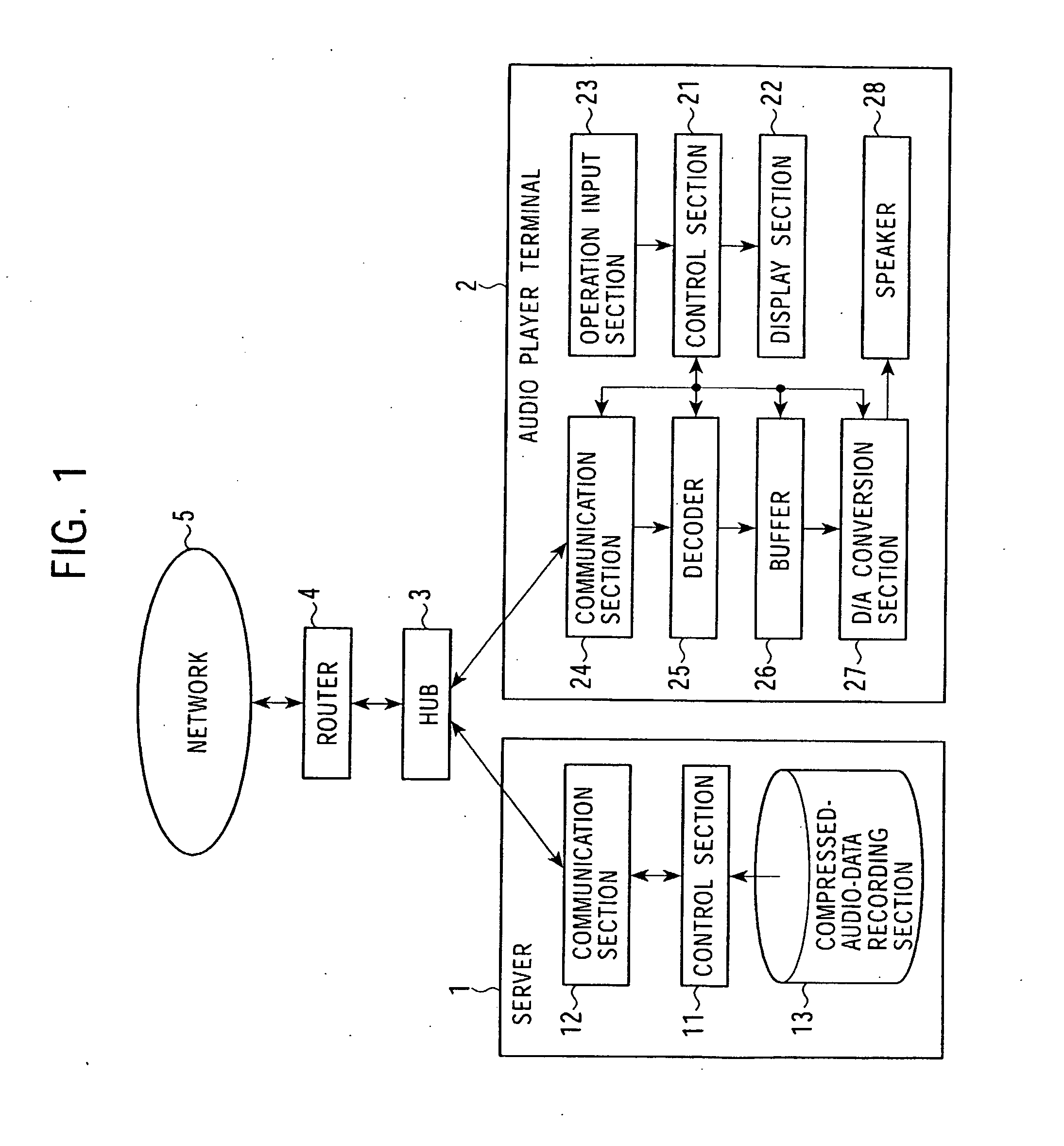
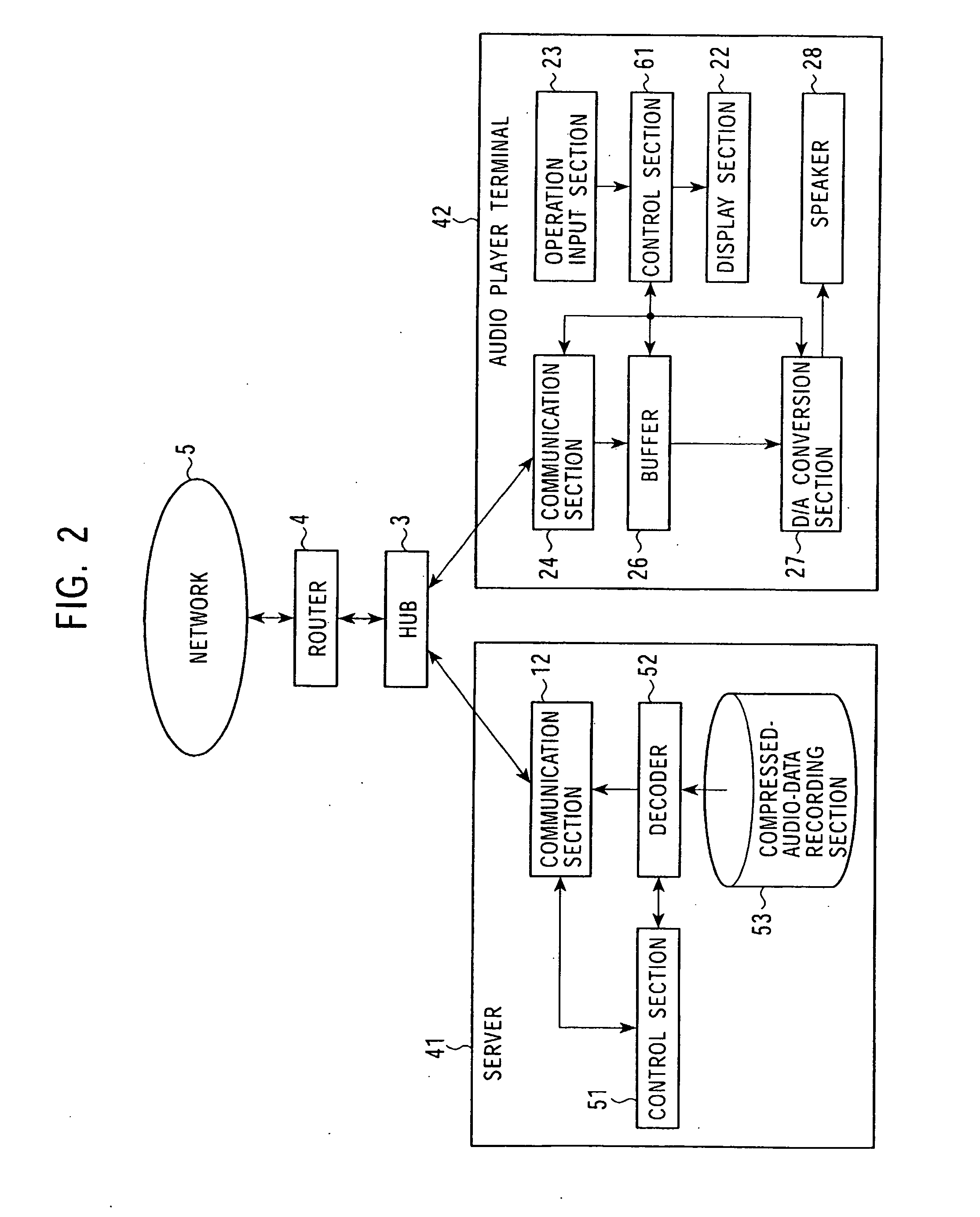
Data stream-distribution system and method therefor
InactiveUS20080147874A1Low data rateReproducing dataSpeech analysisData switching by path configurationData streamDistribution system
A mutual recognition process is performed in step S1. When it is determined in step S2 that a request for sending a list of musical pieces has been received, the list of musical pieces is sent in step S3. When a request for sending audio data has been received in step S4, a transfer-rate measurement process is executed in step S5. When it is determined according to the transfer rate in step S6 that the audio can be transmitted, the corresponding compressed audio data is extracted in step S7, the compressed audio data is decoded to generate linear PCM data suited to the transfer rate in step S8, and transmitted in step S9. When the audio data cannot be transmitted, an error message is transmitted in step S10. The present invention can be applied, for example, to a server for distributing audio data and an audio player terminal for reproducing the distributed audio data.
Owner:SONY CORP
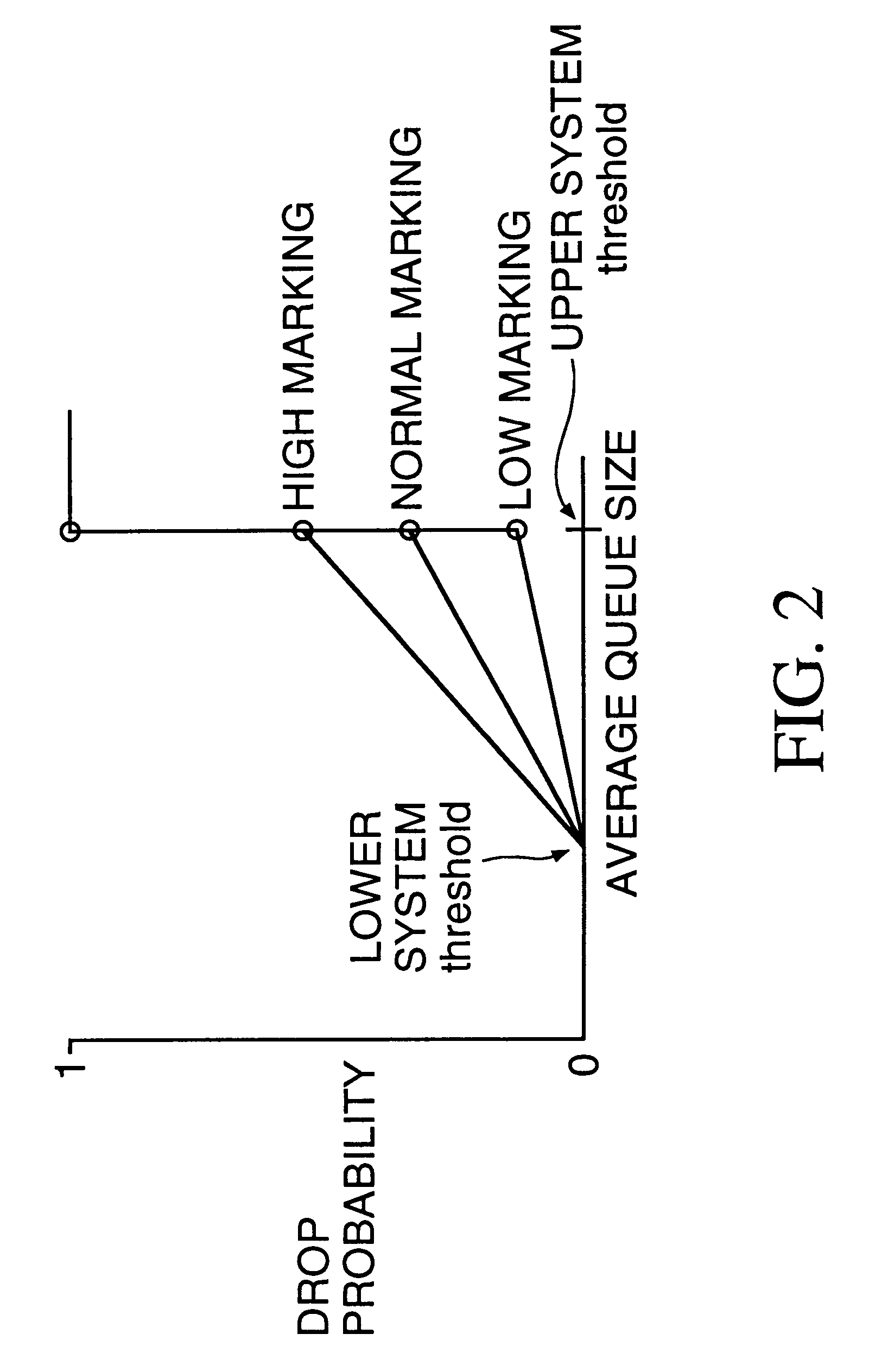
System performance in a data network through queue management based on ingress rate monitoring
InactiveUS6252848B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityQueue management system
A method optimizes performance in a data network including a plurality of ingress ports and output queues. Ingress rates of a plurality of flows are monitored, where each flow includes a sequence of packets passing from an ingress port to an output queue and each flow has a profile related to flow characteristics. Each packet is marked with a marking based on criteria including the ingress flow rate and the flow profile. A drop probability of each packet is adjusted at an output queue according to a value of a drop function taken as a function of a queue size. The drop function is selected according to the marking on the packet. The drop functions are zero for queue sizes less than a lower threshold range and positive for queue sizes greater than the lower threshold range. By selecting drop functions according to ingress flow rate measurements and flow profiles, the data network can be optimized for overall system performance.
Owner:PLURIS
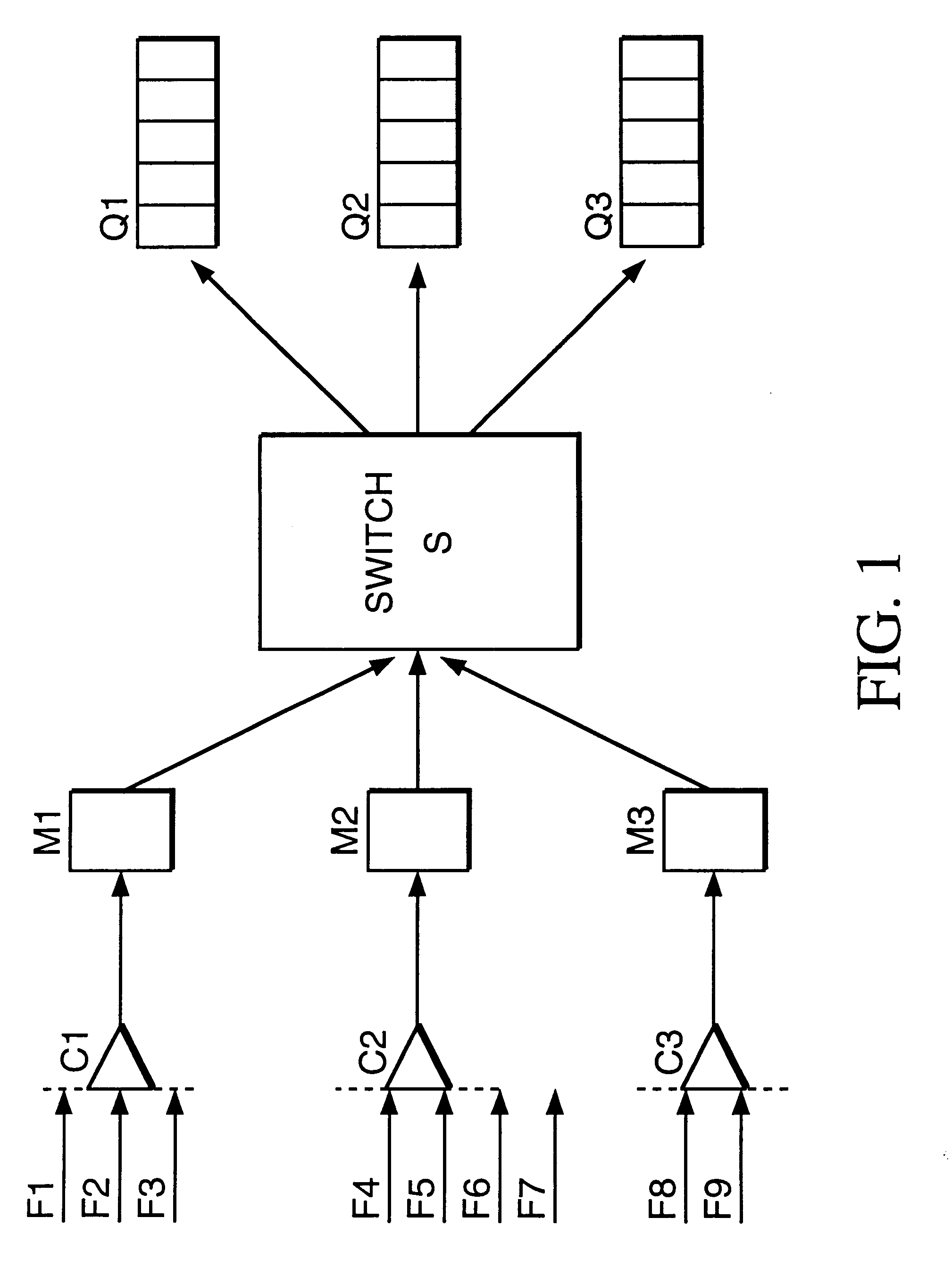
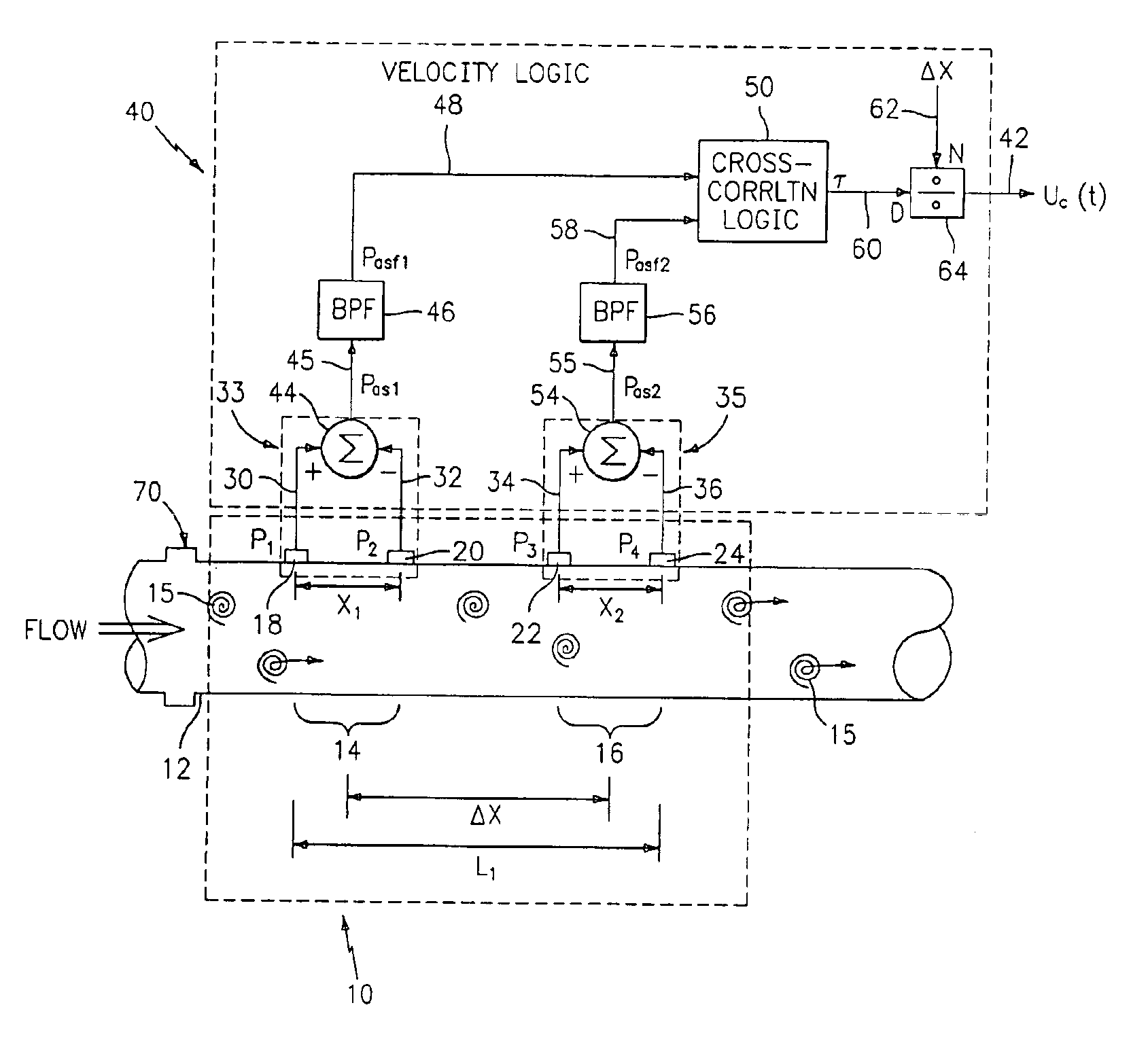
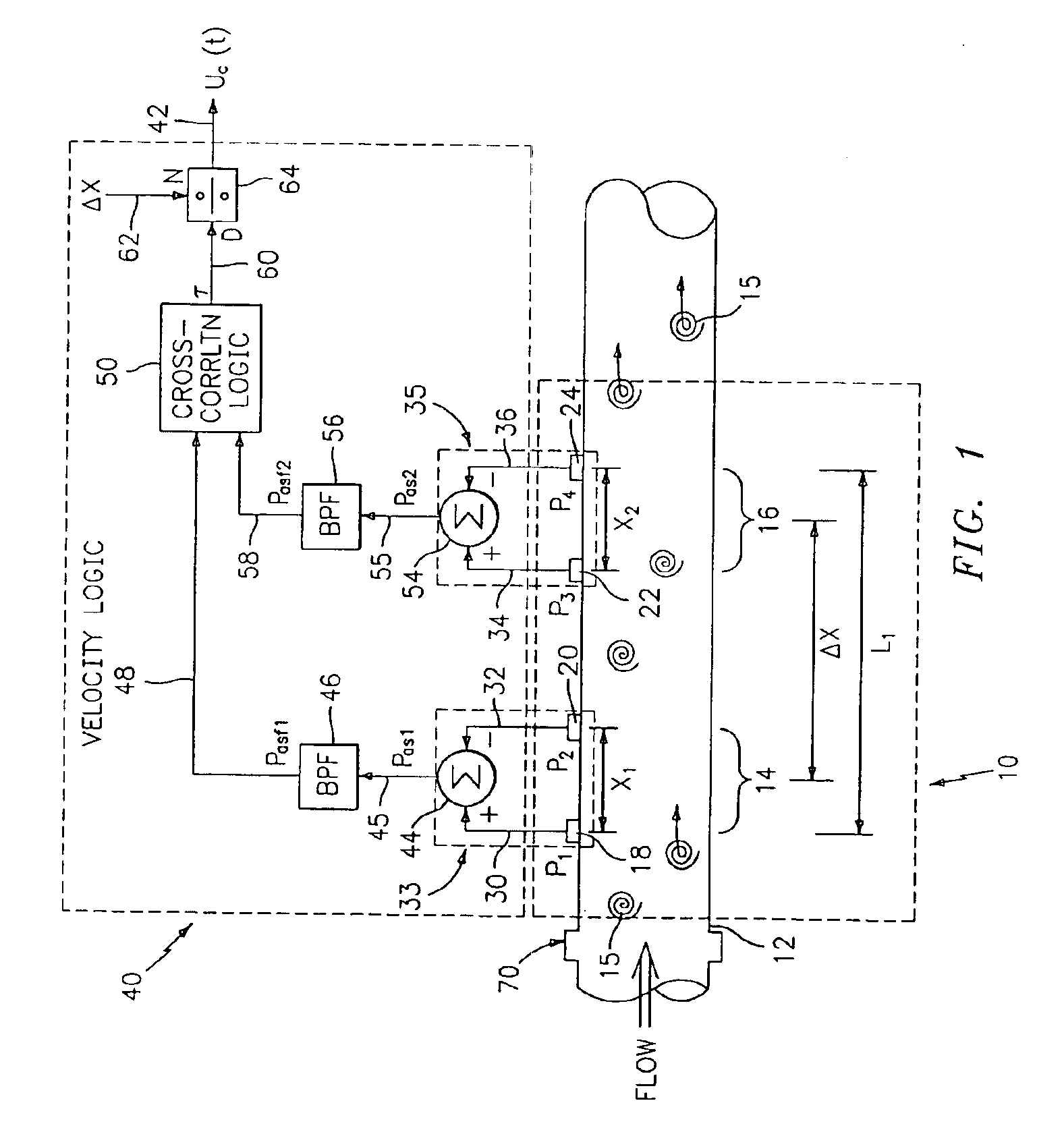
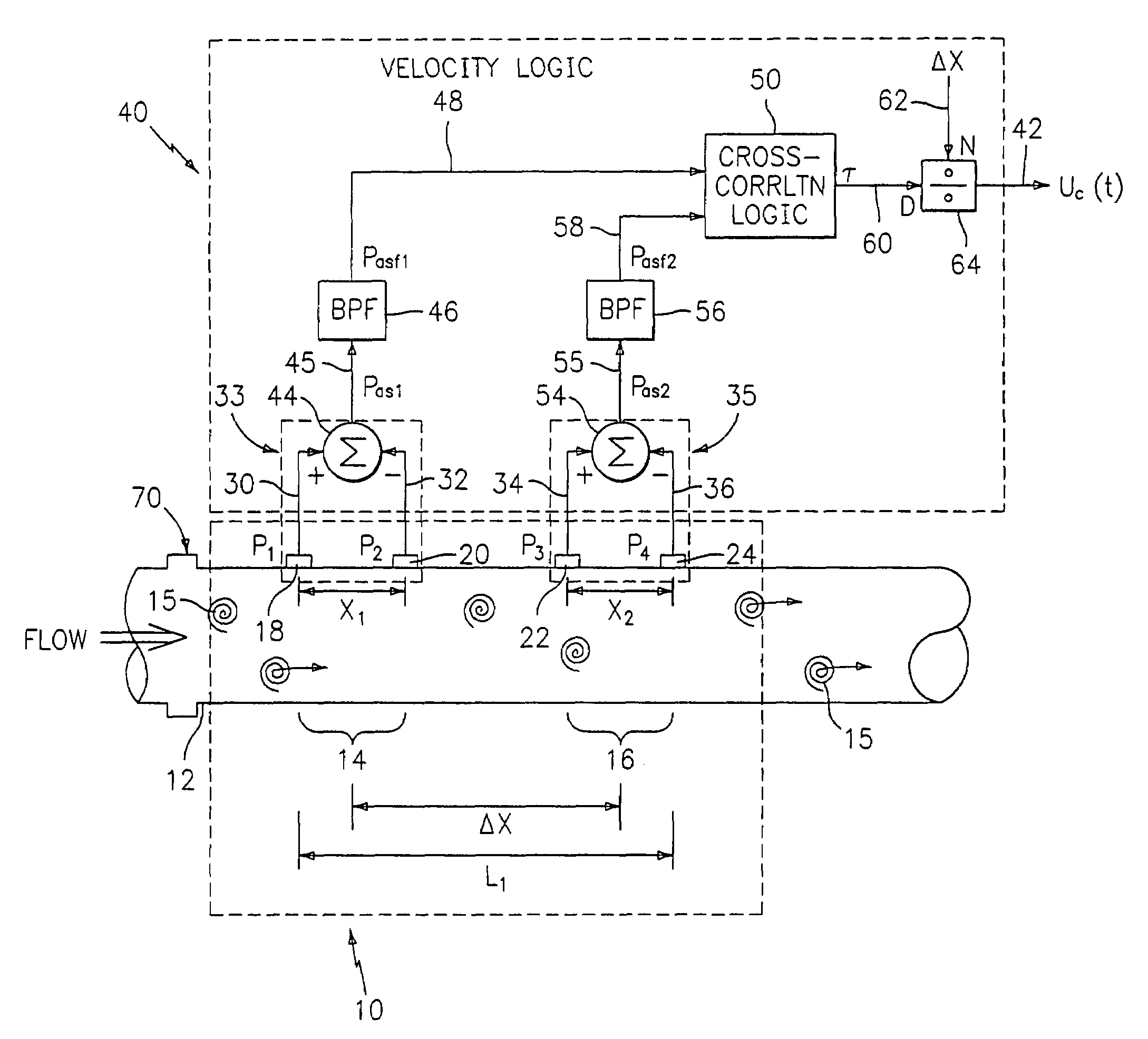
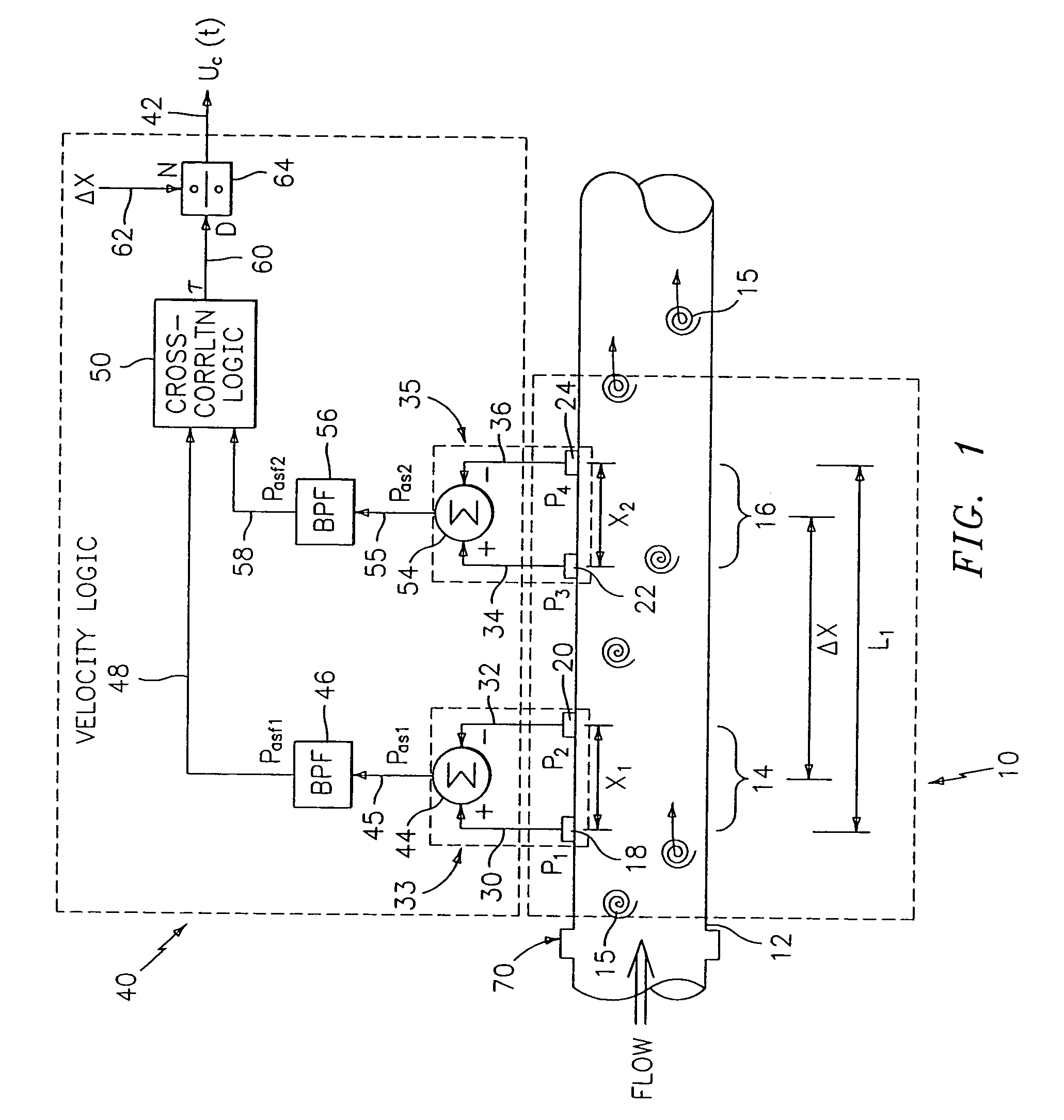
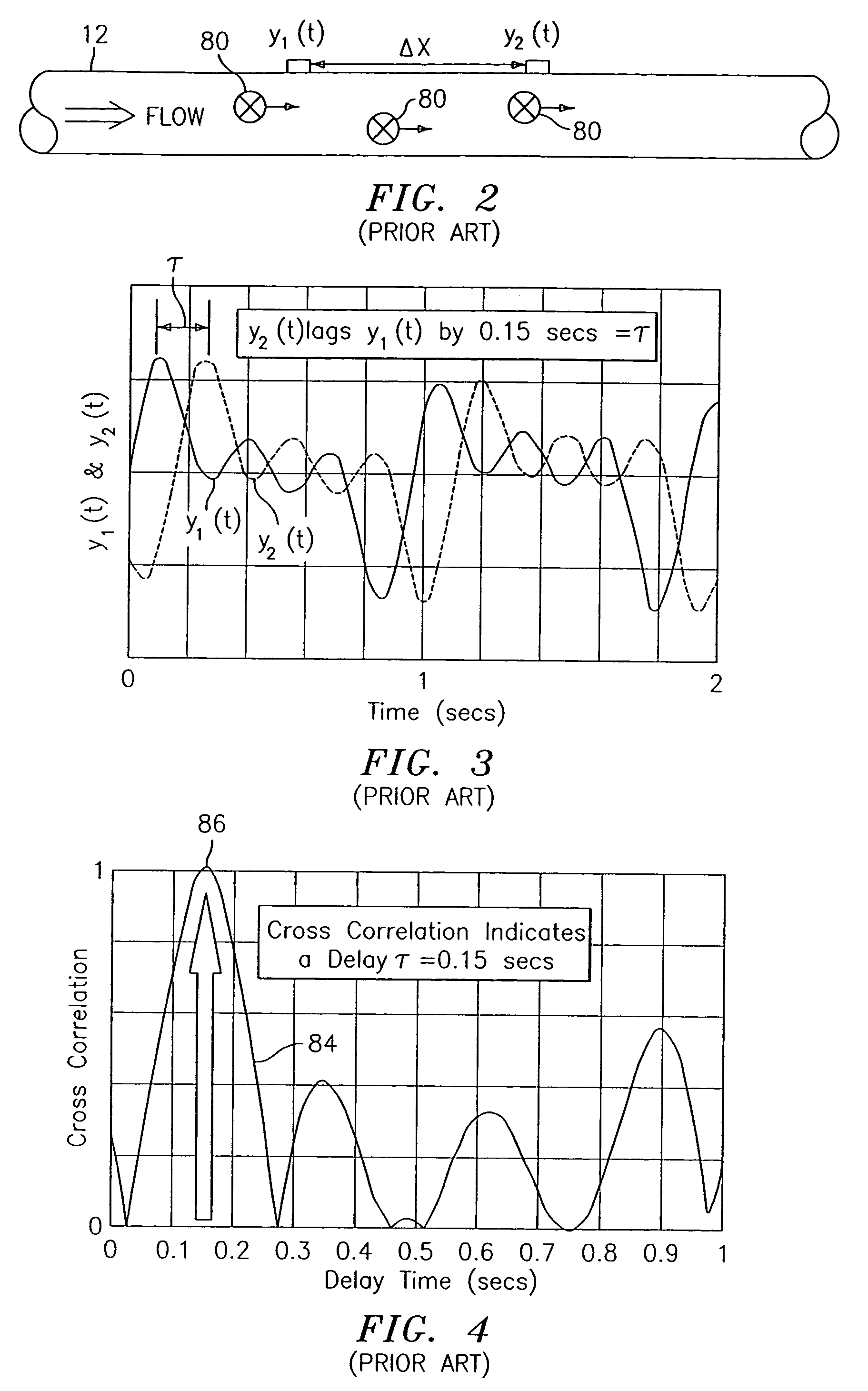
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
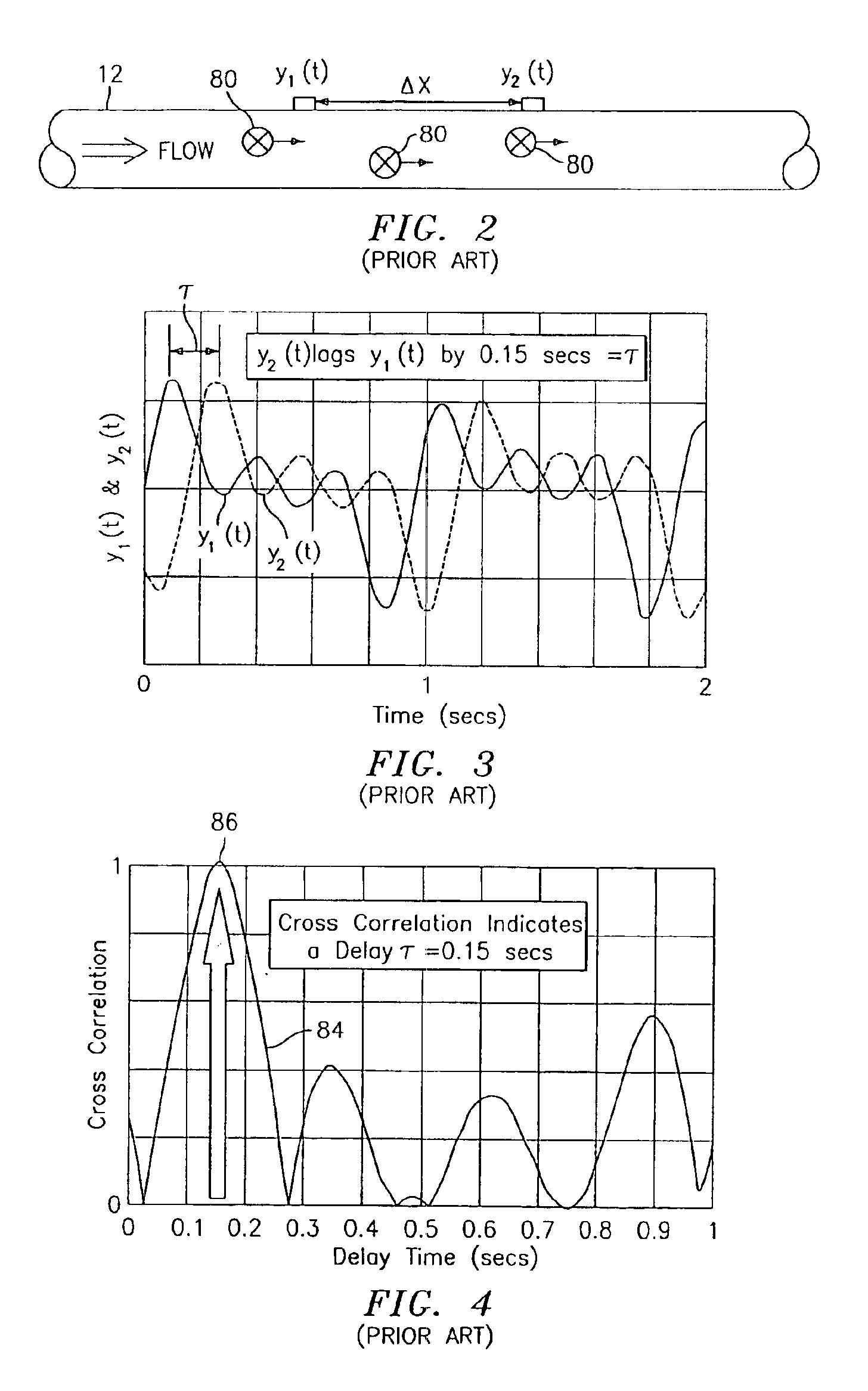
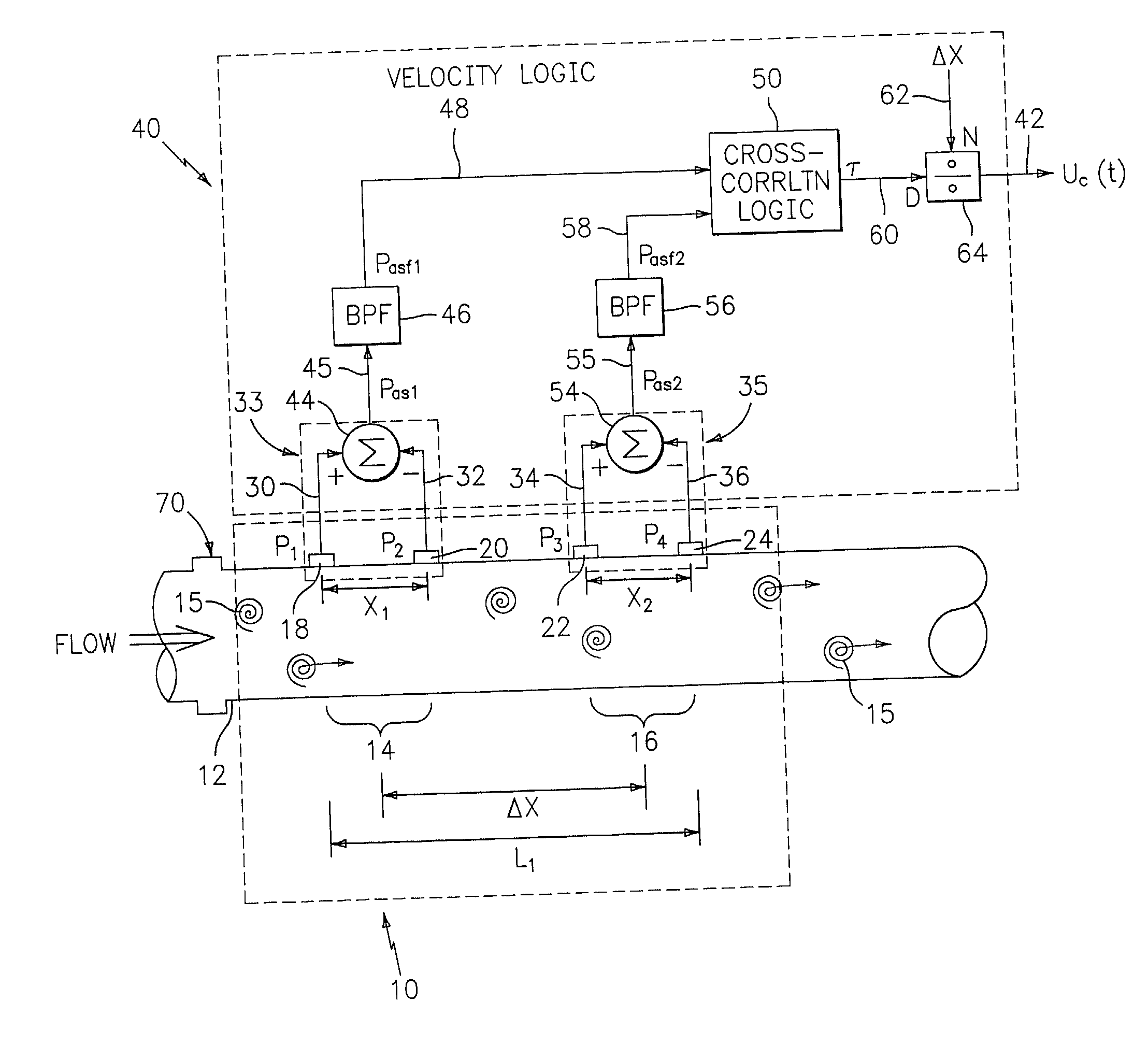
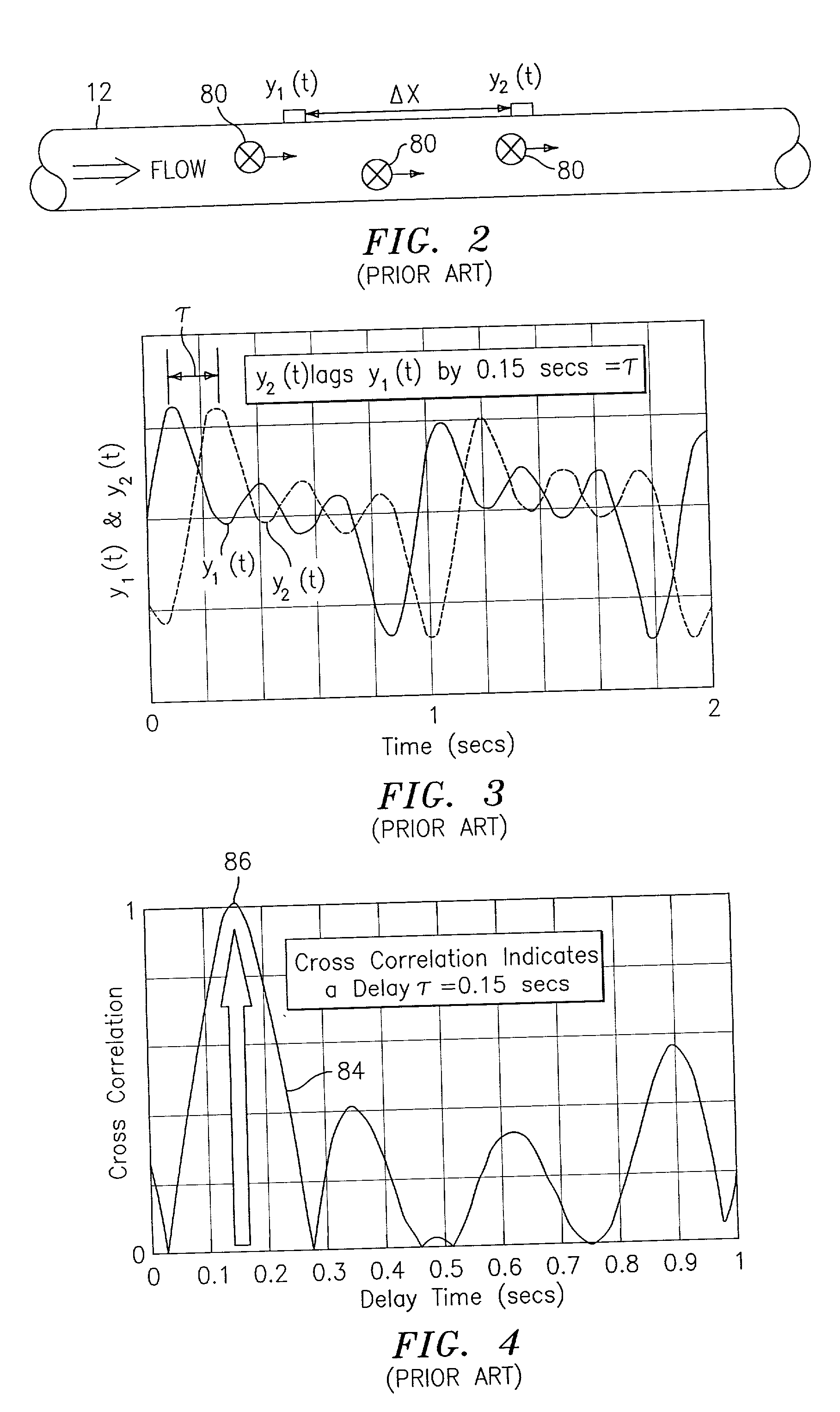
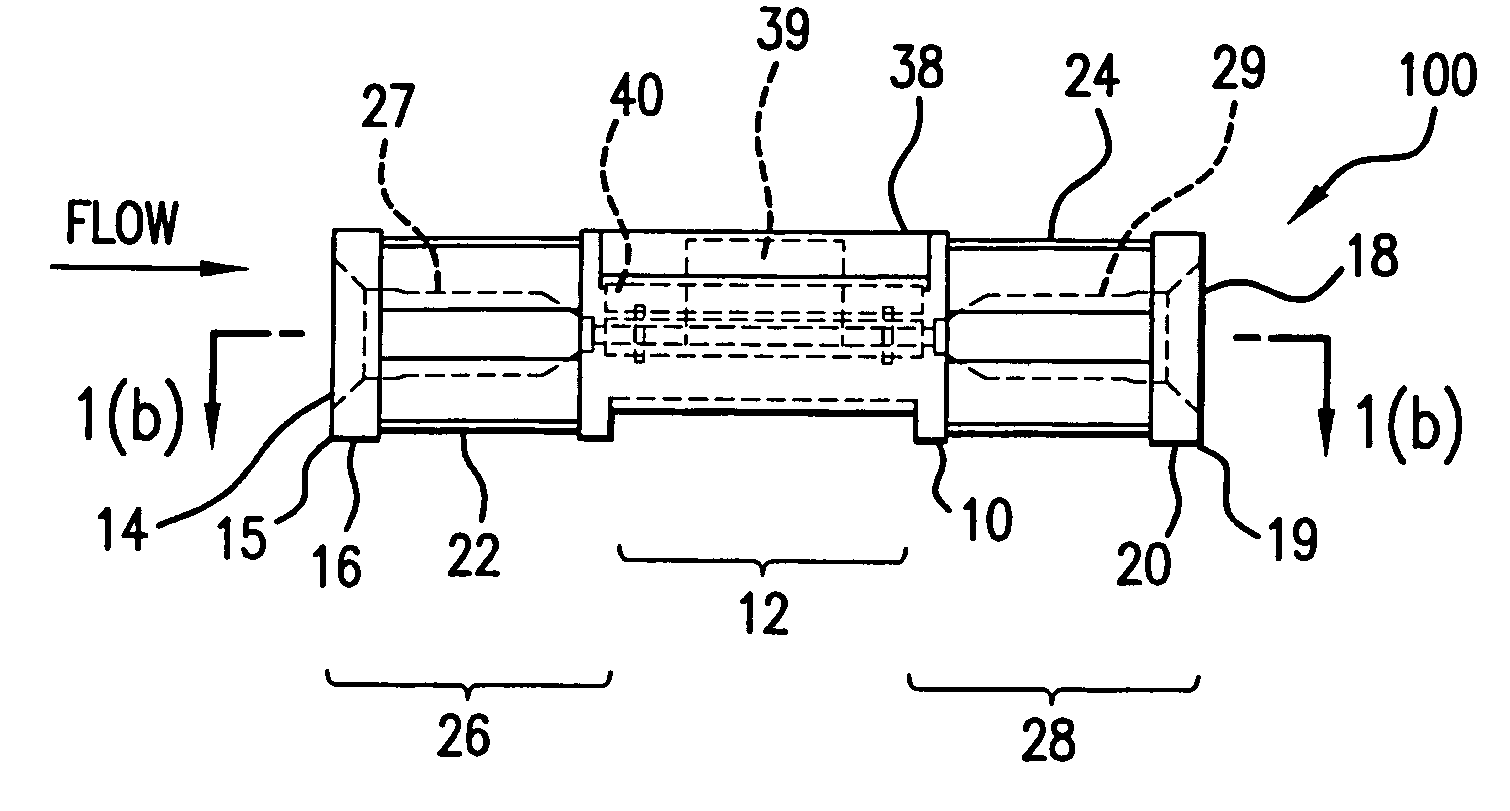
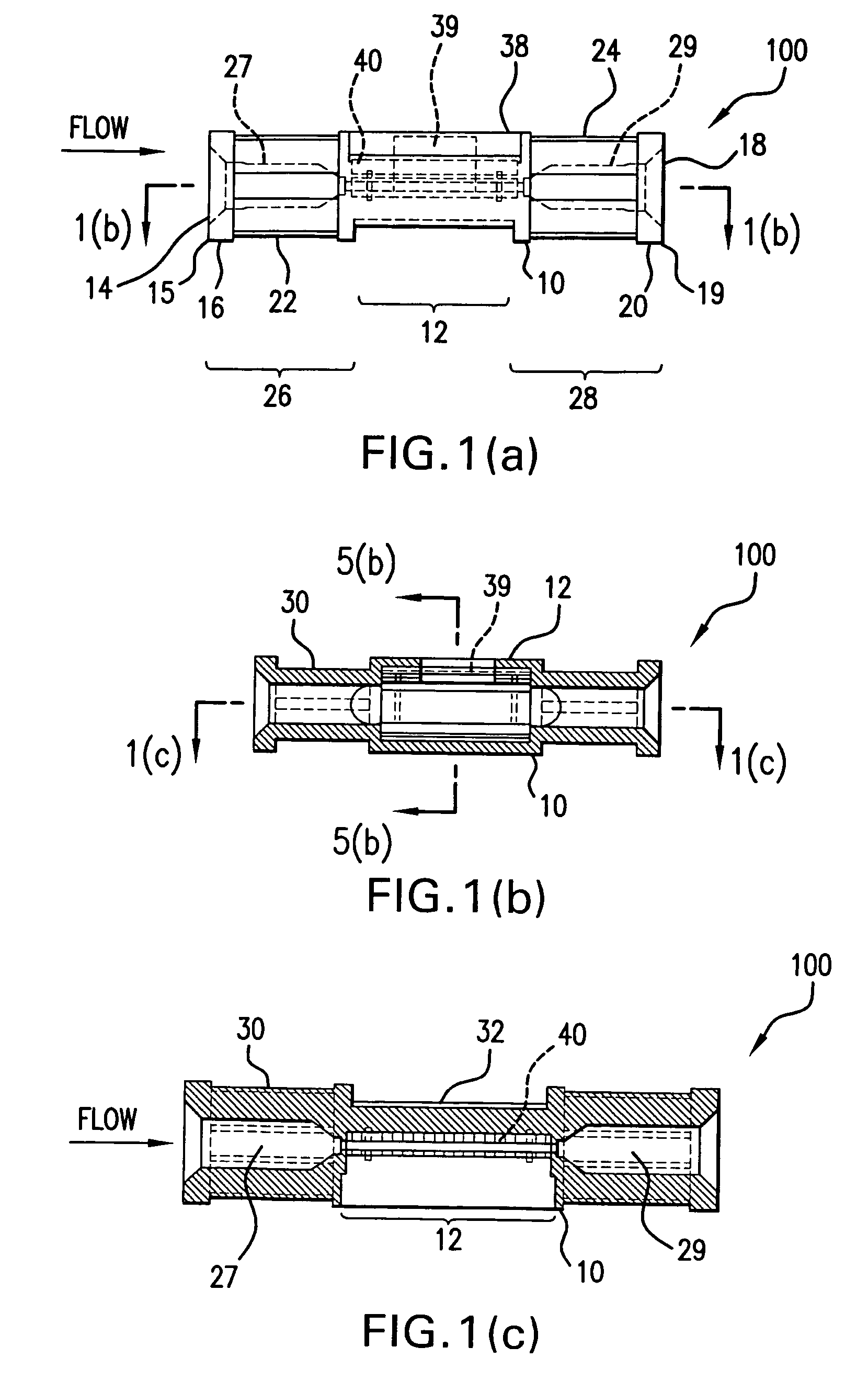
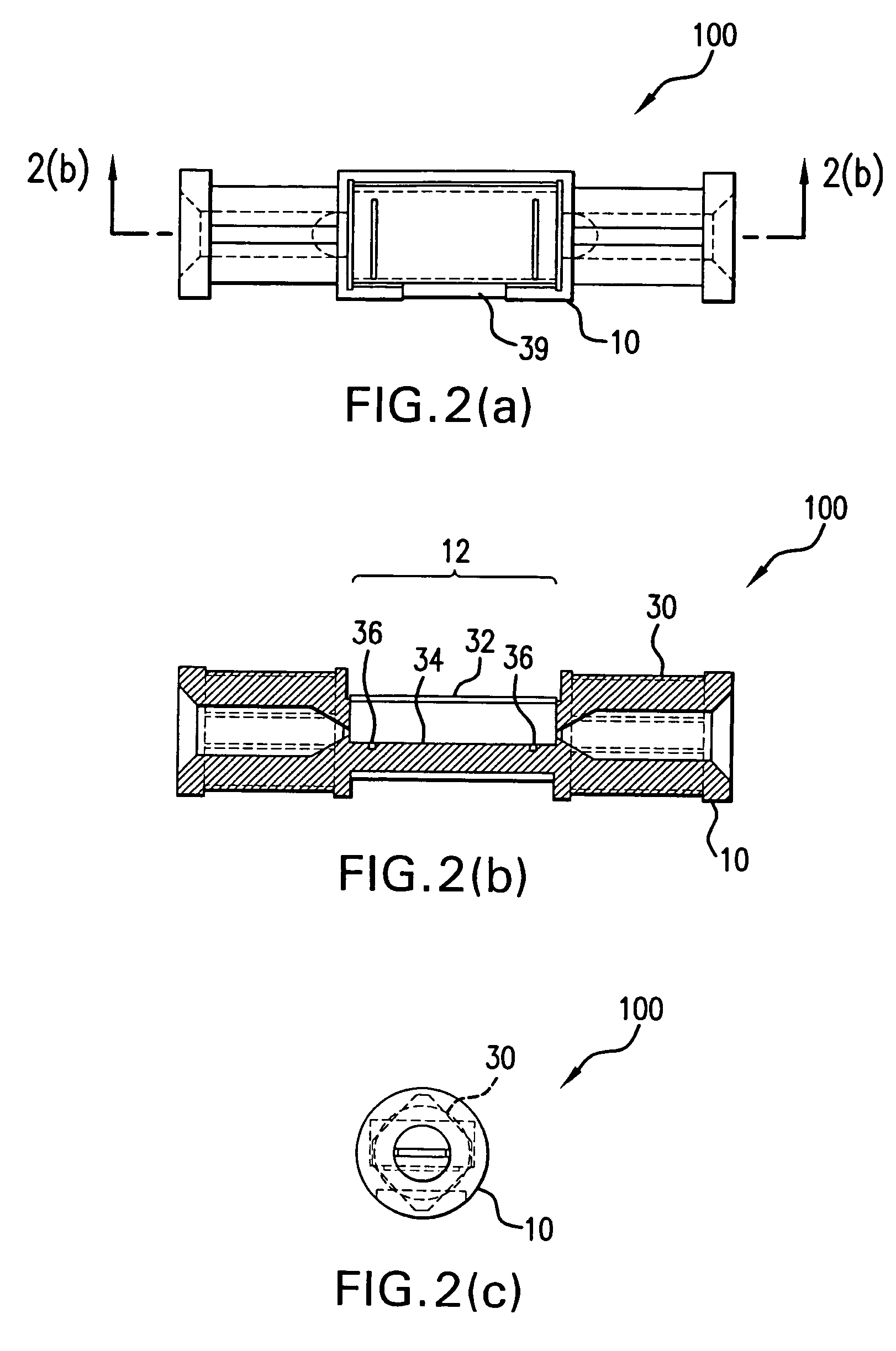
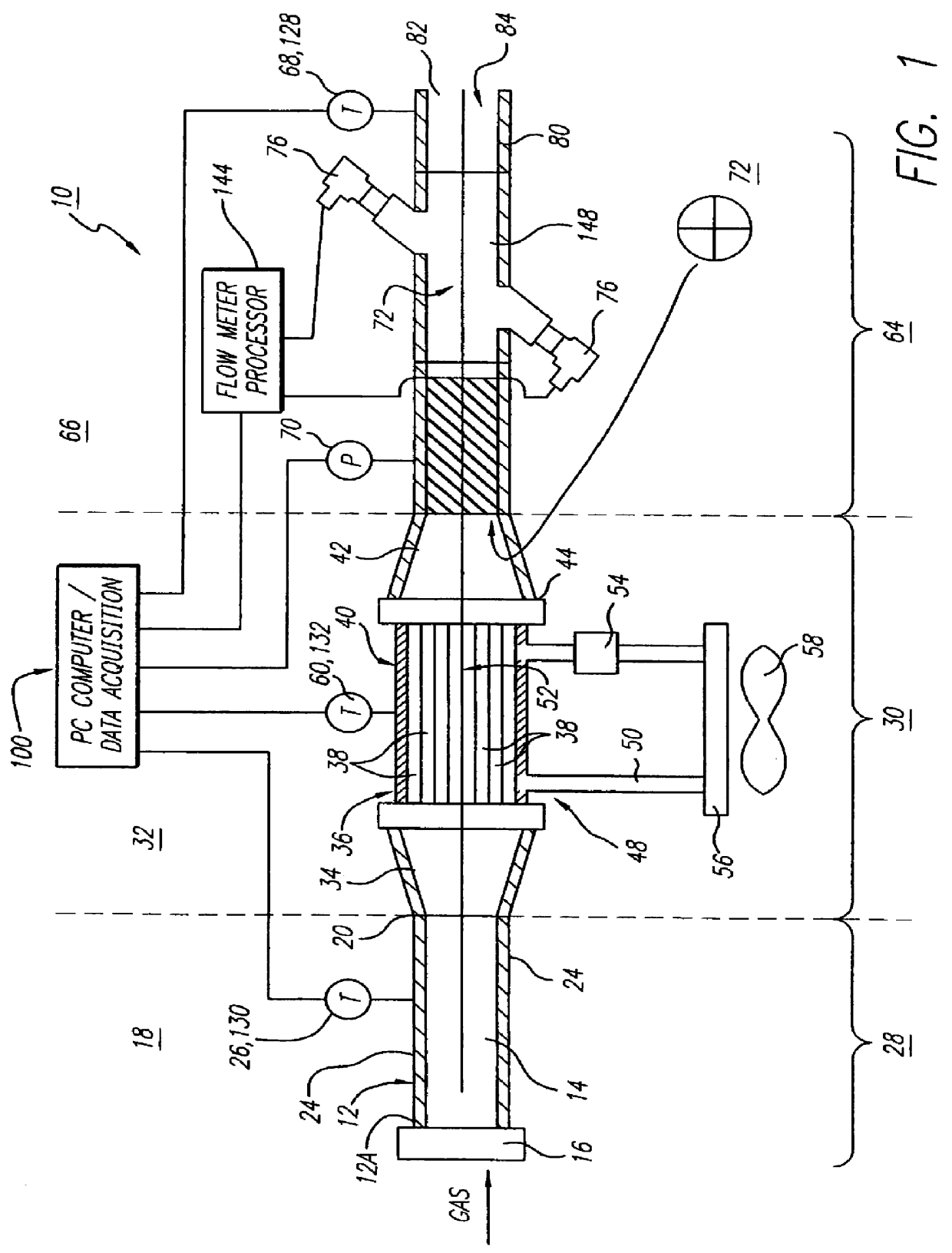
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance ΔX apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35 filters out acoustic pressure disturbances Pacoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances Pvortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals Pas1,Pas2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The Pvortical -dominated filtered signals Pasf1,Pasf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay τ between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance ΔX to obtain a convection velocity Uc(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance .DELTA.X apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X.sub.1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X.sub.2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35 filters out acoustic pressure disturbances P.sub.acoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances P.sub.vortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals P.sub.as1,P.sub.as2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The P.sub.vortical -dominated filtered signals P.sub.asf1,P.sub.asf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay .tau. between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance .DELTA.X to obtain a convection velocity U.sub.c(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
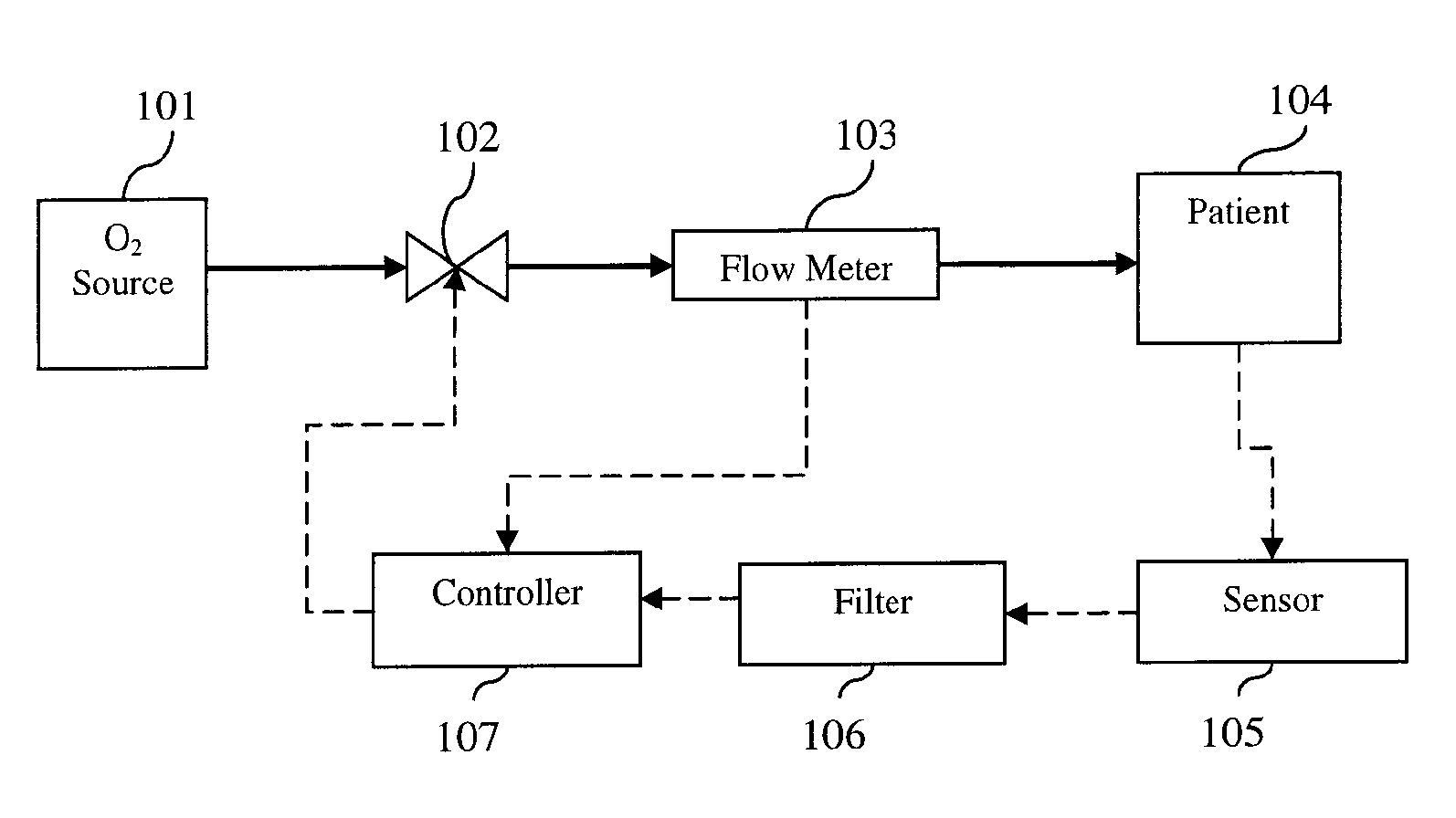
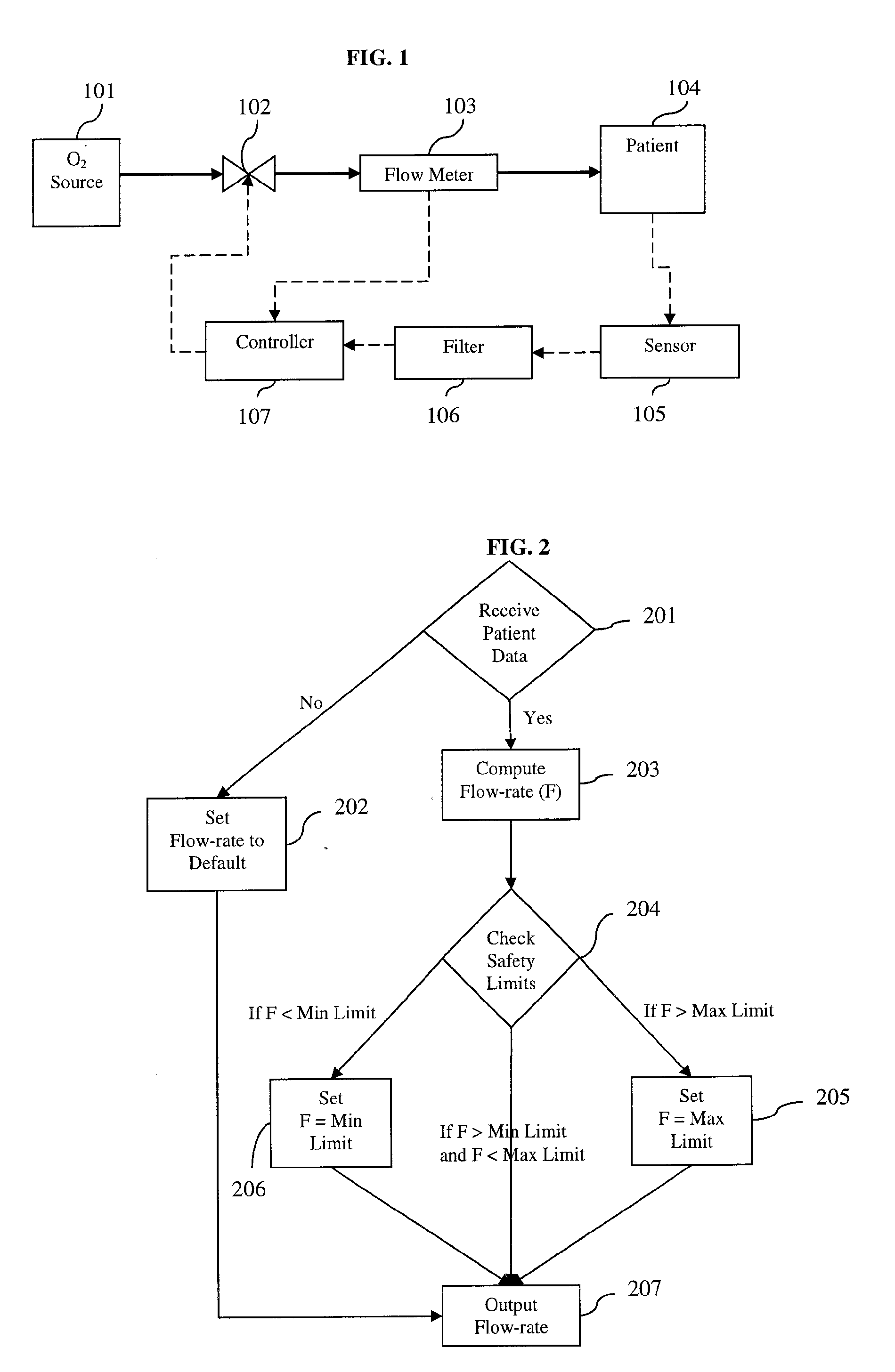
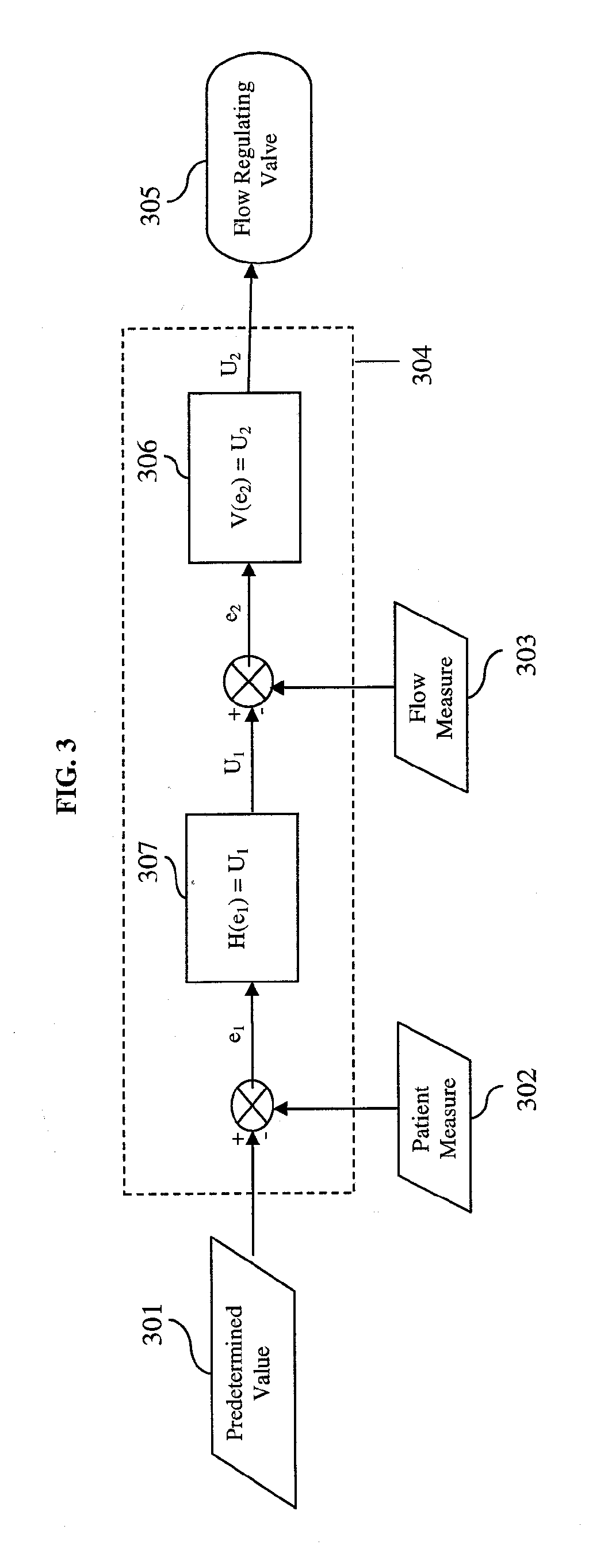
Device and method for automatically regulating supplemental oxygen flow-rate
InactiveUS20060225737A1Minimize biasPrevent adverse eventsRespiratorsElectrocardiographySupplemental oxygen therapyClosed loop
Device and method for limiting adverse events during supplemental oxygen therapy are disclosed. In the present invention, the oxygen flow between a patient and an oxygen source is controlled with a valve such as a proportional solenoid capable of constraining flow-rates within a continuous range. The flow-rate of oxygen is accurately controlled in a closed-loop with flow-rate measurements. Measures of a patient's vital physiological statistics are used to automatically determine optimum therapeutic oxygen flow-rate. Controller signal filtering is disclosed to improve the overall response and stability. The control algorithm varies flow-rates to minimize disturbances in the patient feedback measurements.
Owner:IOBBI MR MARIO
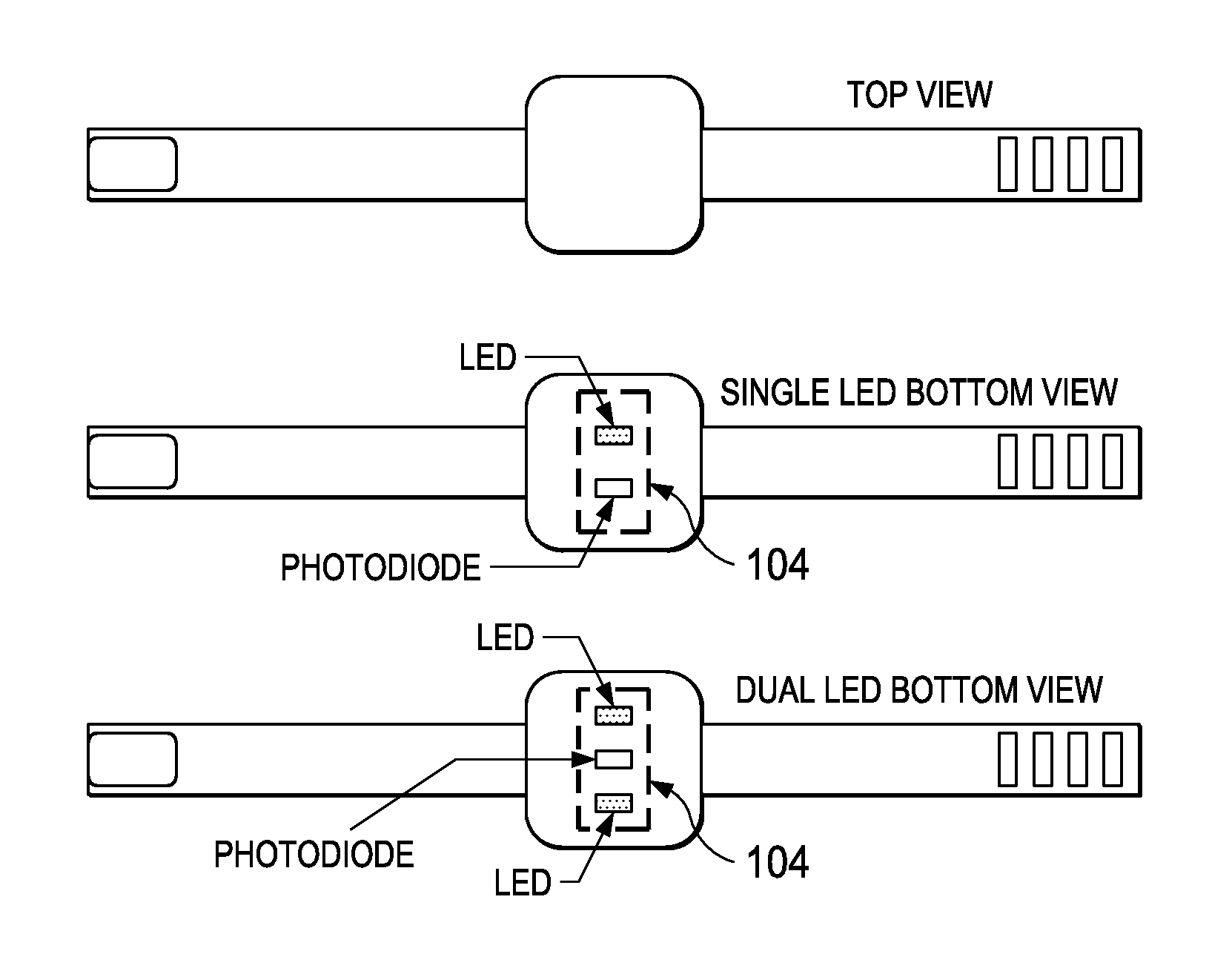
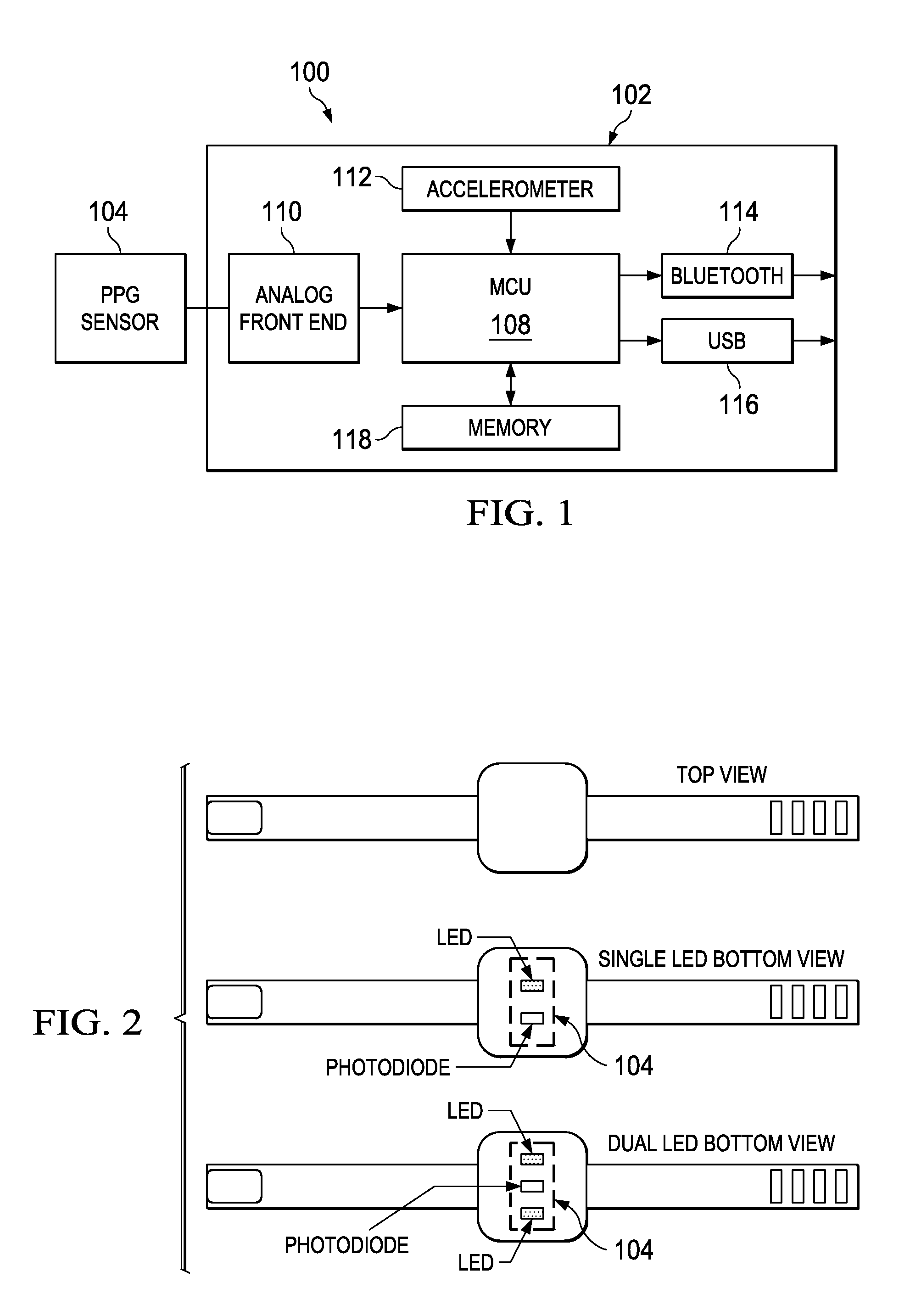
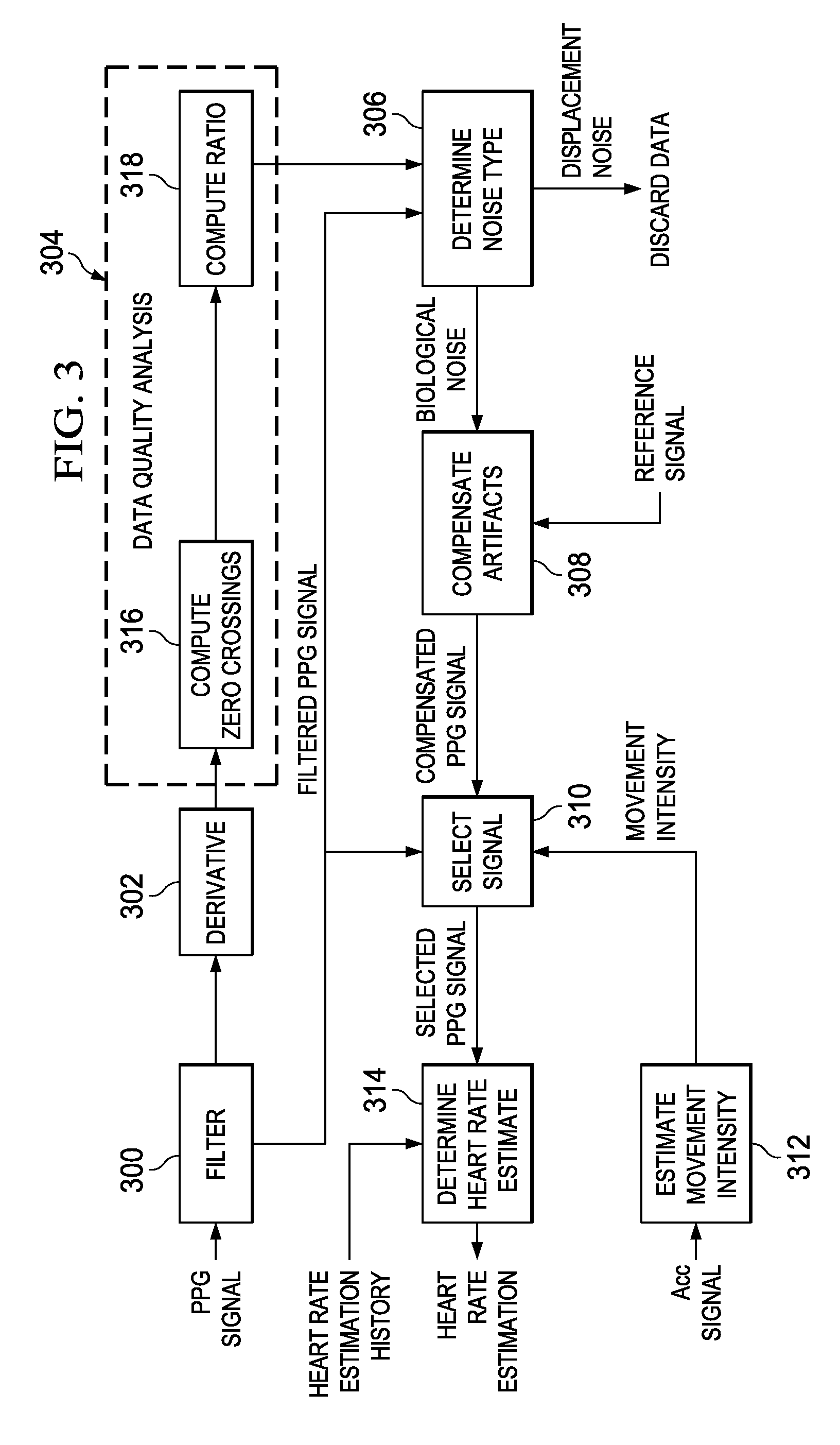
Low-Complexity Sensor Displacement Tolerant Pulse Oximetry Based Heart Rate Measurement
ActiveUS20140213863A1SensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateRelative displacementHeart rate measurement
Methods for heart rate measurement based on pulse oximetry are provided that can tolerate some degree of relative displacement of a photoplethysmograph (PPG) heart rate monitor device. In some methods, artifact compensation based on a reference signal is performed on the PPG signal data to remove artifacts in the signal that may be caused, for example, by changes in ambient light and / or motion of a person wearing the monitor device. The reference signal used for artifact compensation may be generated using an LED of a complementary wavelength to that of the LED used to generate the PPG signal, or by driving an LED at a lower current than the current applied to generate the PPG signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
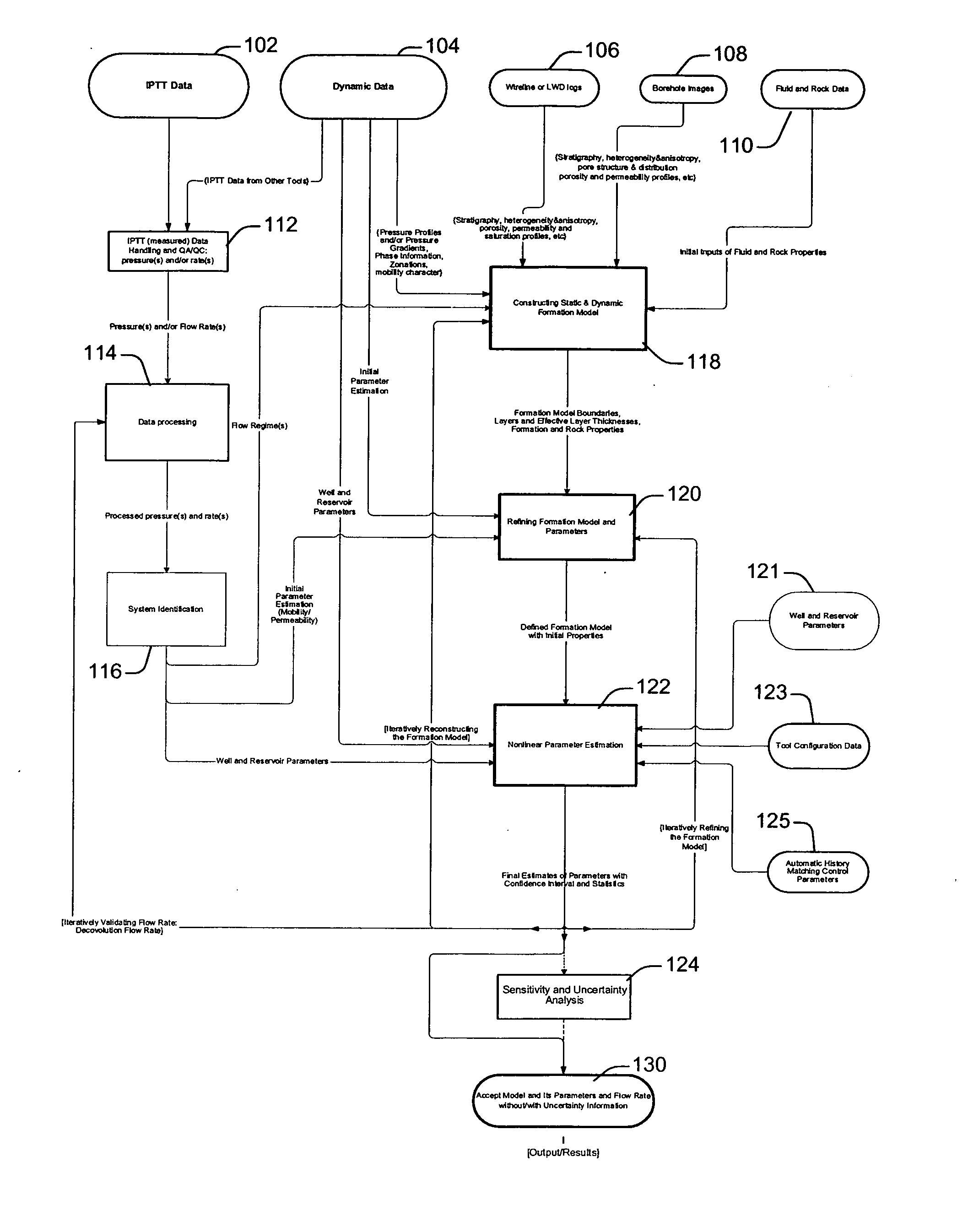
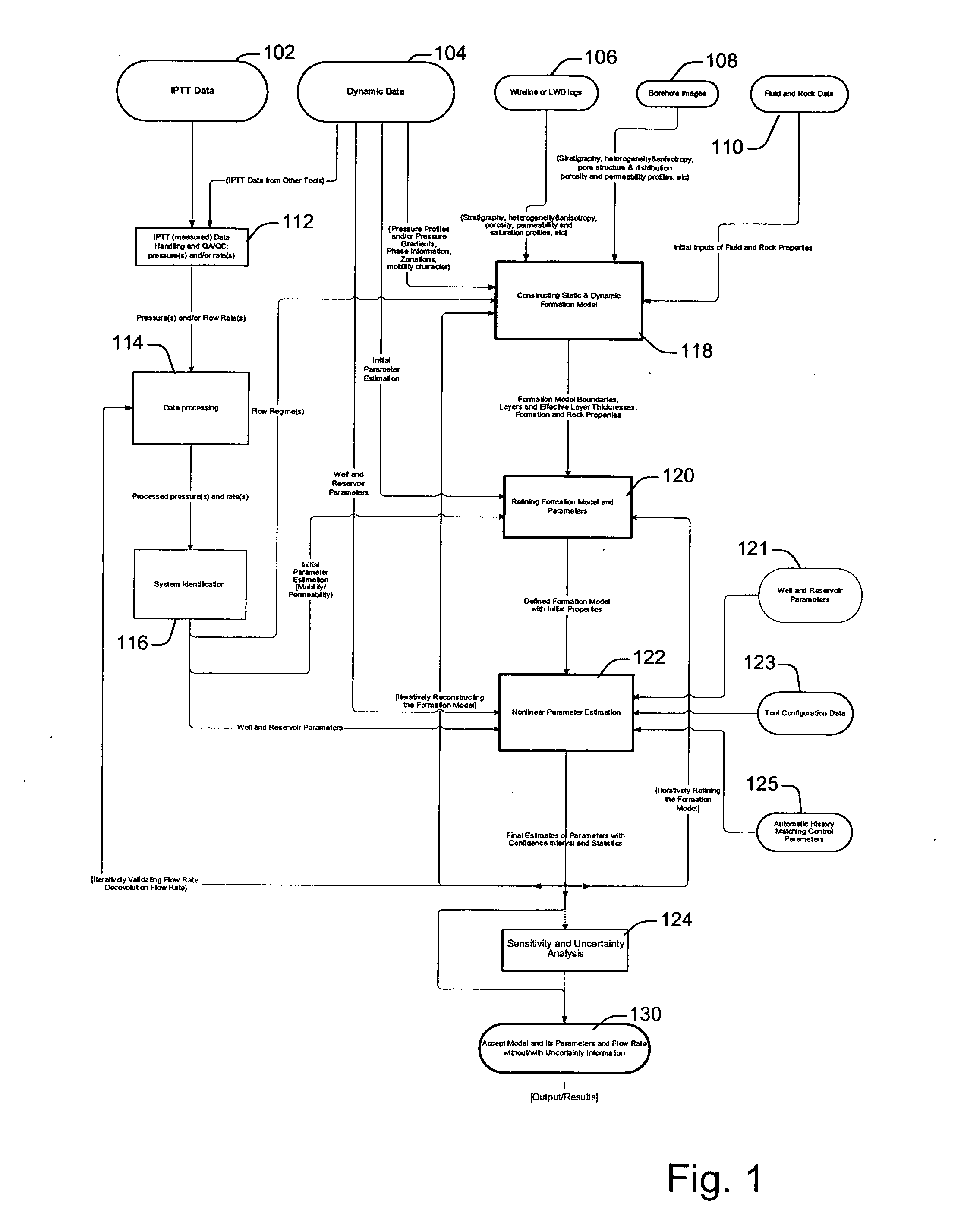
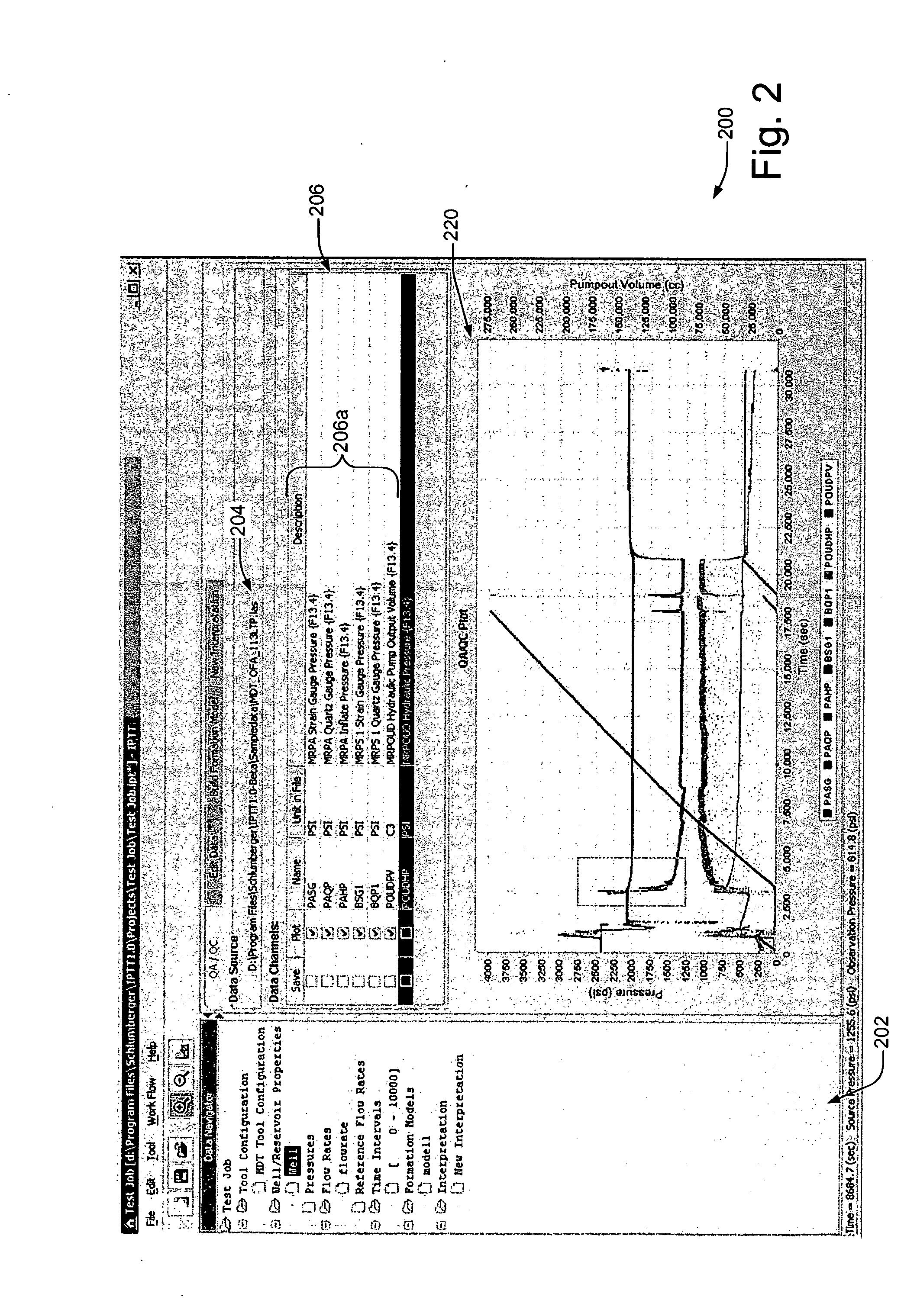
System and methods of characterizing a hydrocarbon reservoir
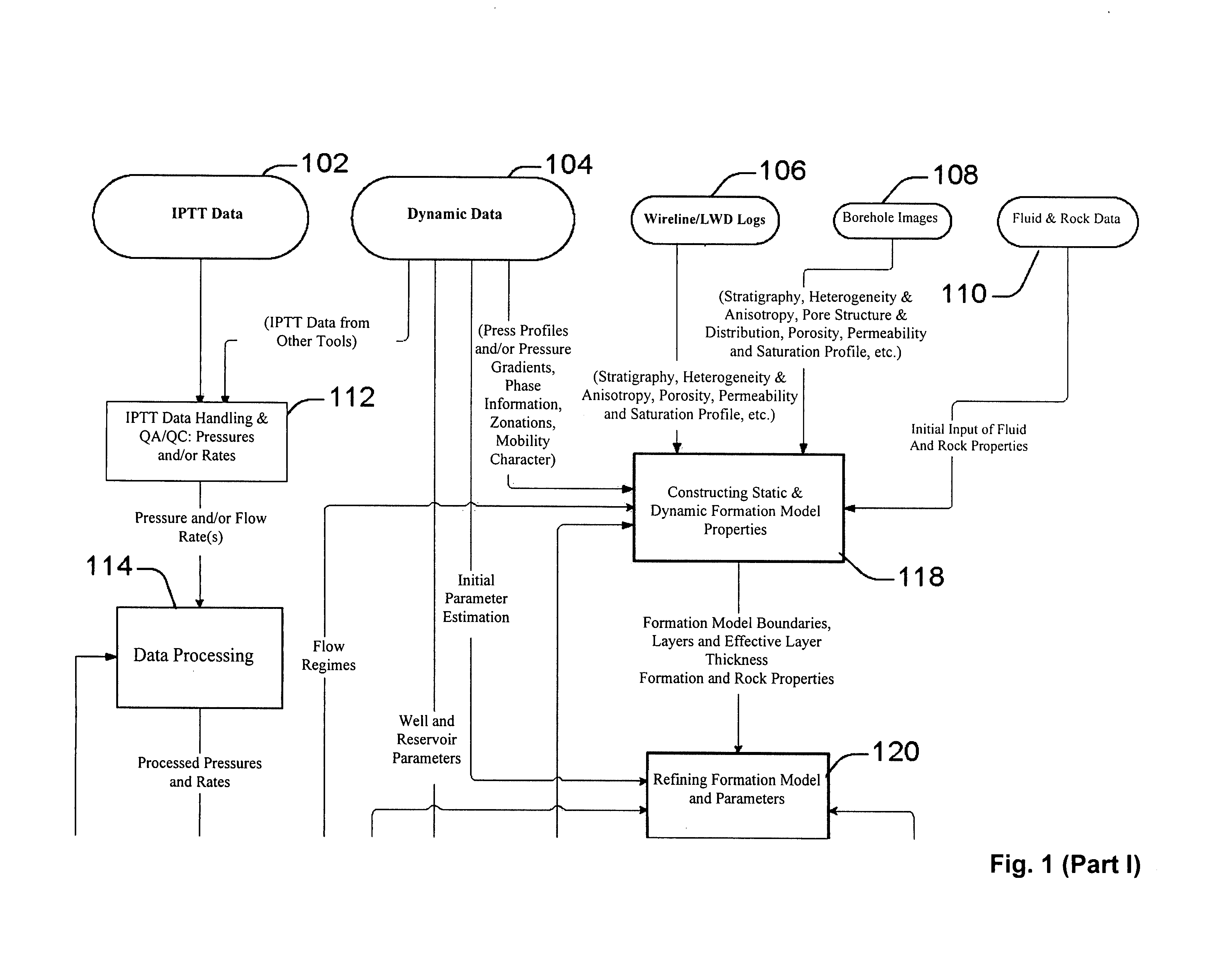
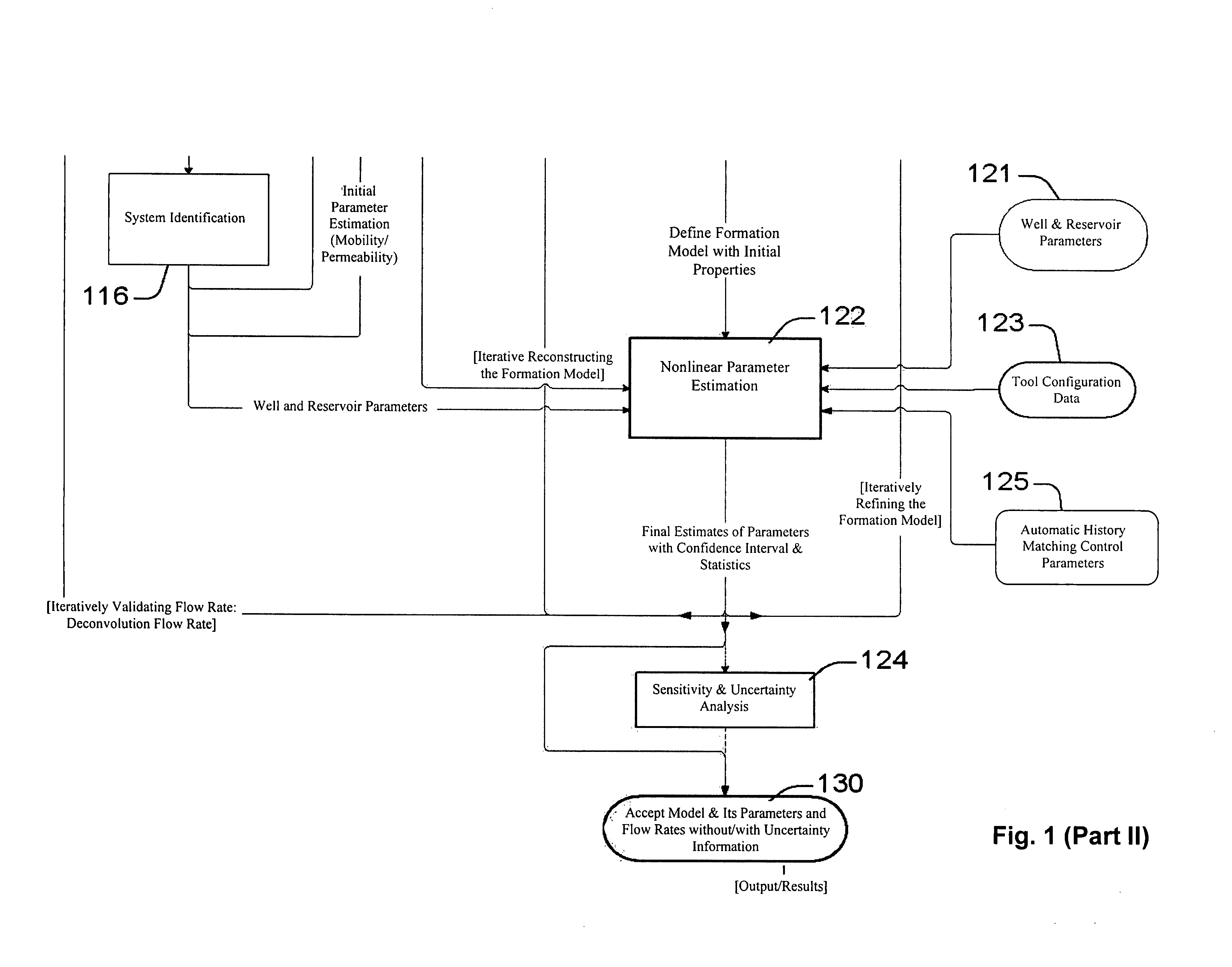
ActiveUS20060241867A1Facilitating in performing data processing operationEasy to operateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisCompressibilityWork flow
A technique is described for interpretation of IPTT tests. In one implementation, the technique may be configured or designed to standardize the complete interpretation procedure of IPTT in a heterogeneous reservoir, using if available, modern wireline logs (such as, for example, nuclear magnetic resonance and imaging), dynamic data from wireline formation testers and / or any other relevant information (such as, for example, geological description, core data and local knowledge) as constraints on the interpretation. Additionally, an iterative method may be used to define formation layering. An advanced regression technology may also be used to obtain optimized horizontal and vertical permeabilities of reservoir layers. Further a graphical user interface (GUI) based IPTT workflow technique of the present invention provides an integrated user-friendly interpretation platform for analyzing formation testing pressures and flow rate measurements in order to estimate the values and associated uncertainties of local characteristics of a hydrocarbon reservoir such as, for example, local permeability, local reservoir pressure, local compressibility, etc.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
In VIVO sensor and method of making same
InactiveUS20060074479A1Easy to detectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryIn vivoRadio frequency
Implantable in vivo sensors used to monitor physical, chemical or electrical parameters within a body. The in vivo sensors are integral with an implantable medical device and are responsive to externally or internally applied energy. Upon application of energy, the sensors undergo a phase change in at least part of the material of the device which is then detected external to the body by conventional techniques such as radiography, ultrasound imaging, magnetic resonance imaging, radio frequency imaging or the like. The in vivo sensors of the present invention may be employed to provide volumetric measurements, flow rate measurements, pressure measurements, electrical measurements, biochemical measurements, temperature, measurements, or measure the degree and type of deposits within the lumen of an endoluminal implant, such as a stent or other type of endoluminal conduit. The in vivo sensors may also be used therapeutically to modulate mechanical and / or physical properties of the endoluminal implant in response to the sensed or monitored parameter.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
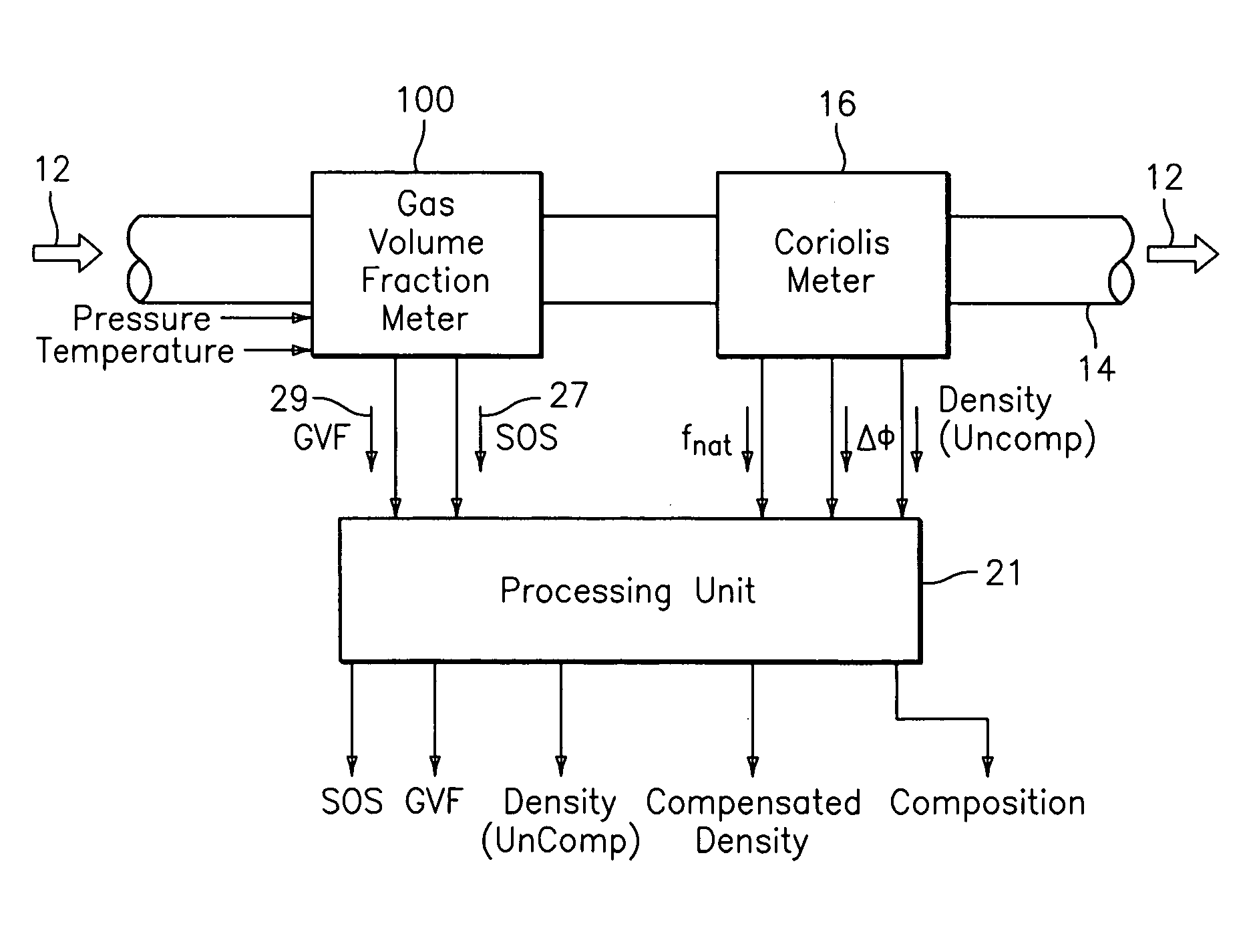
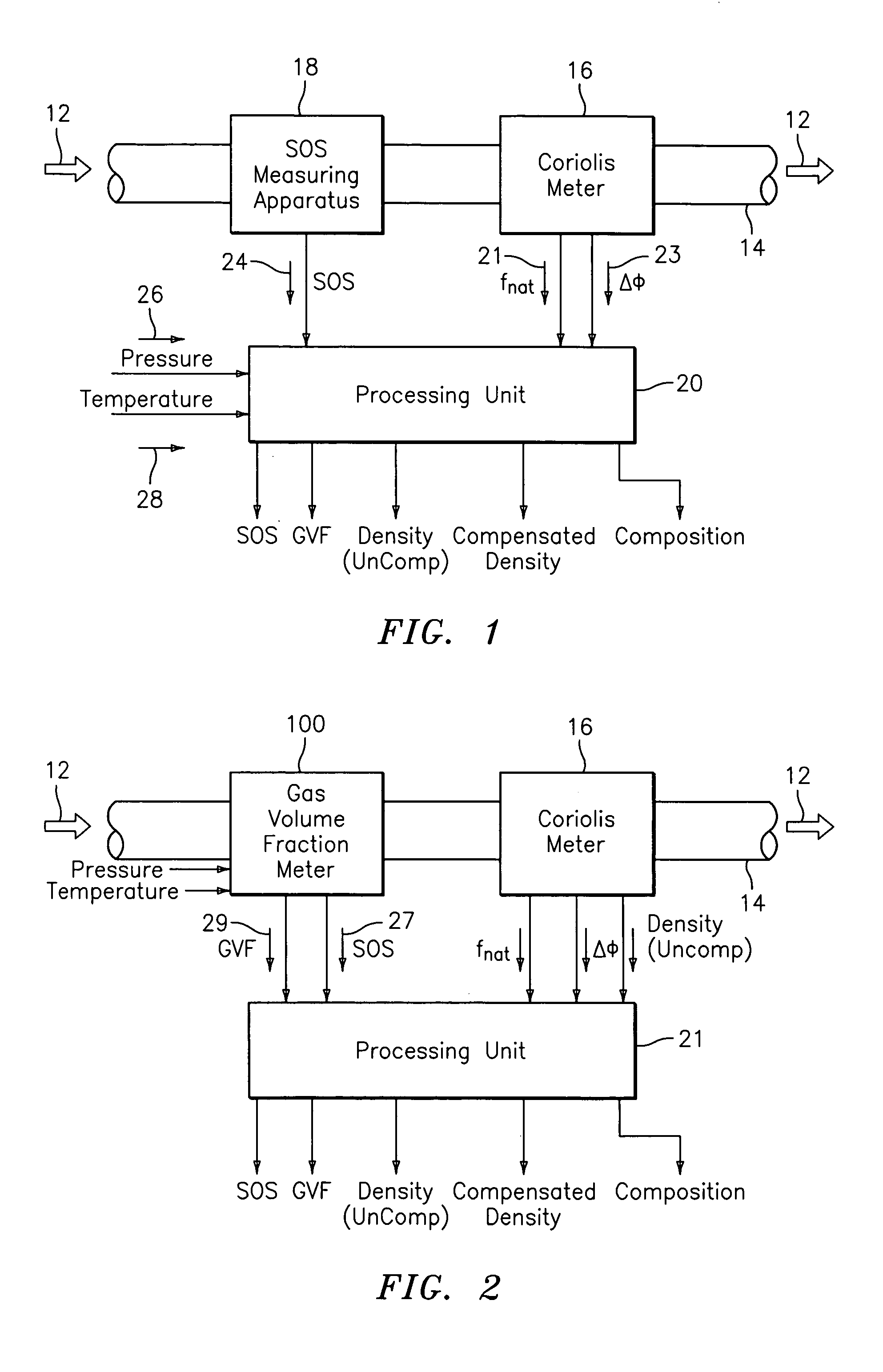
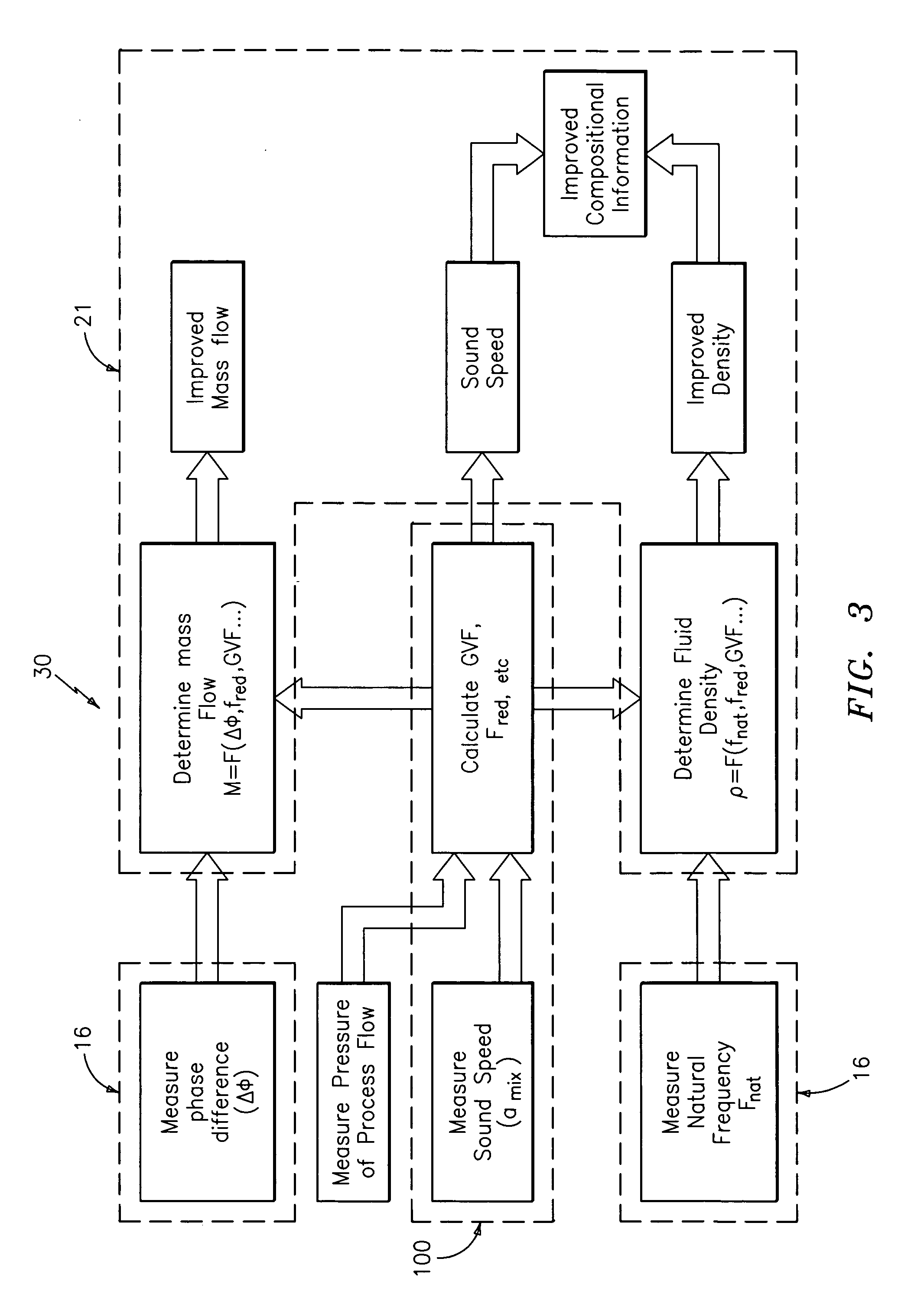
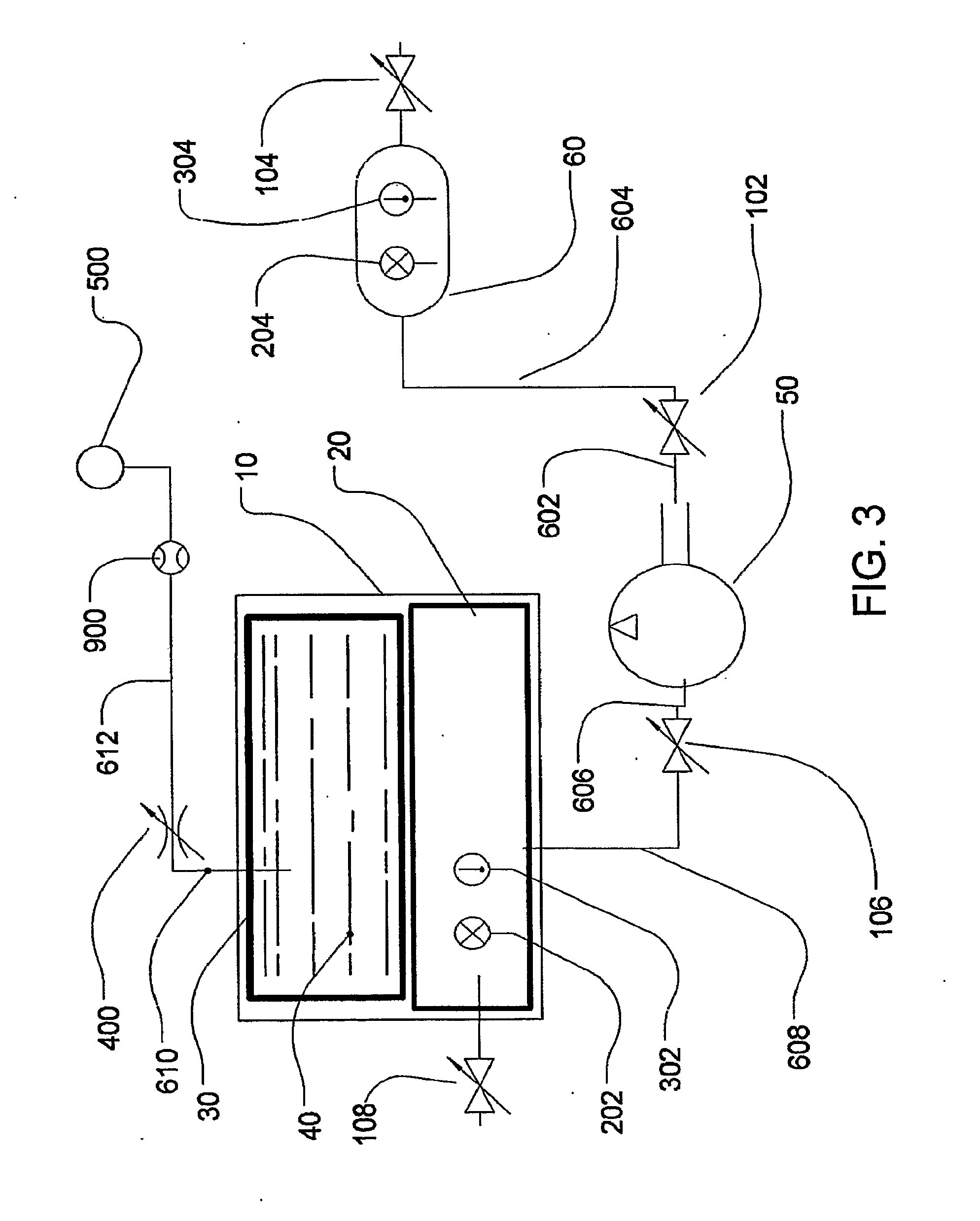
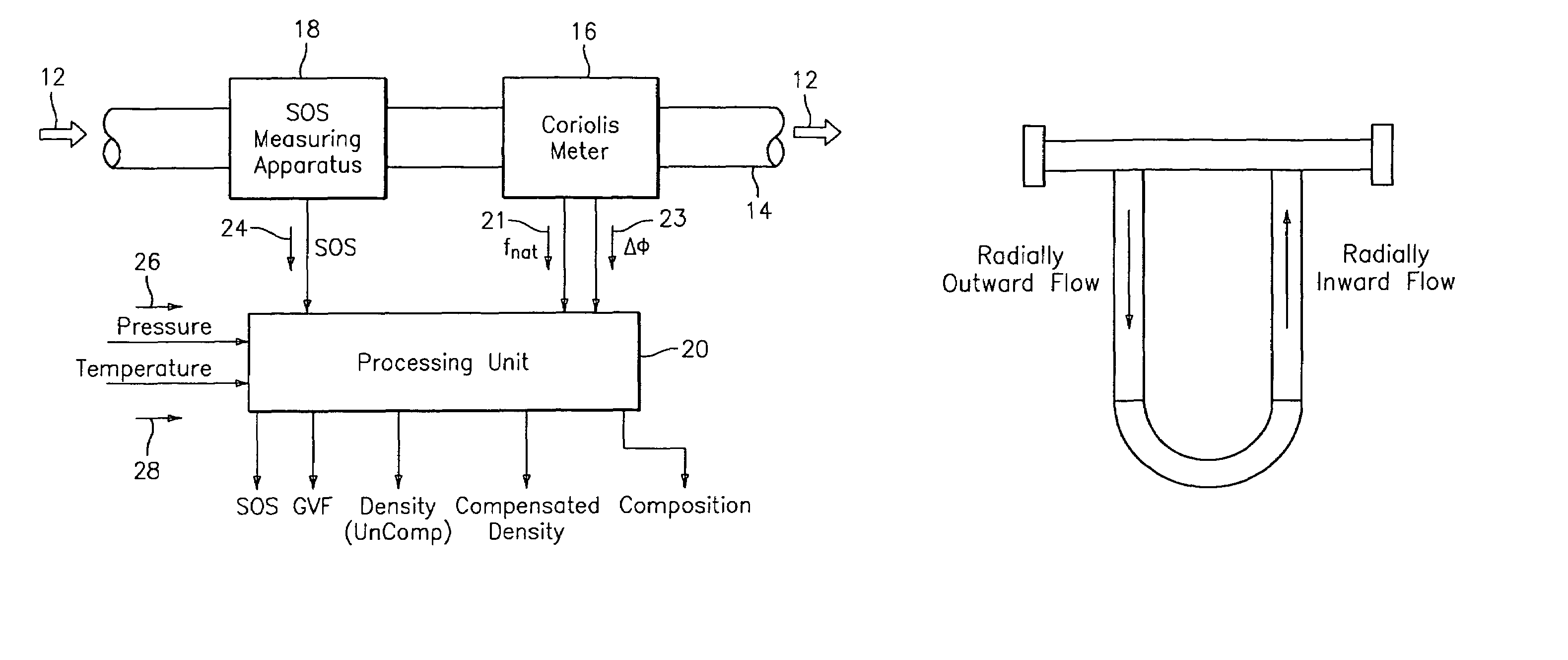
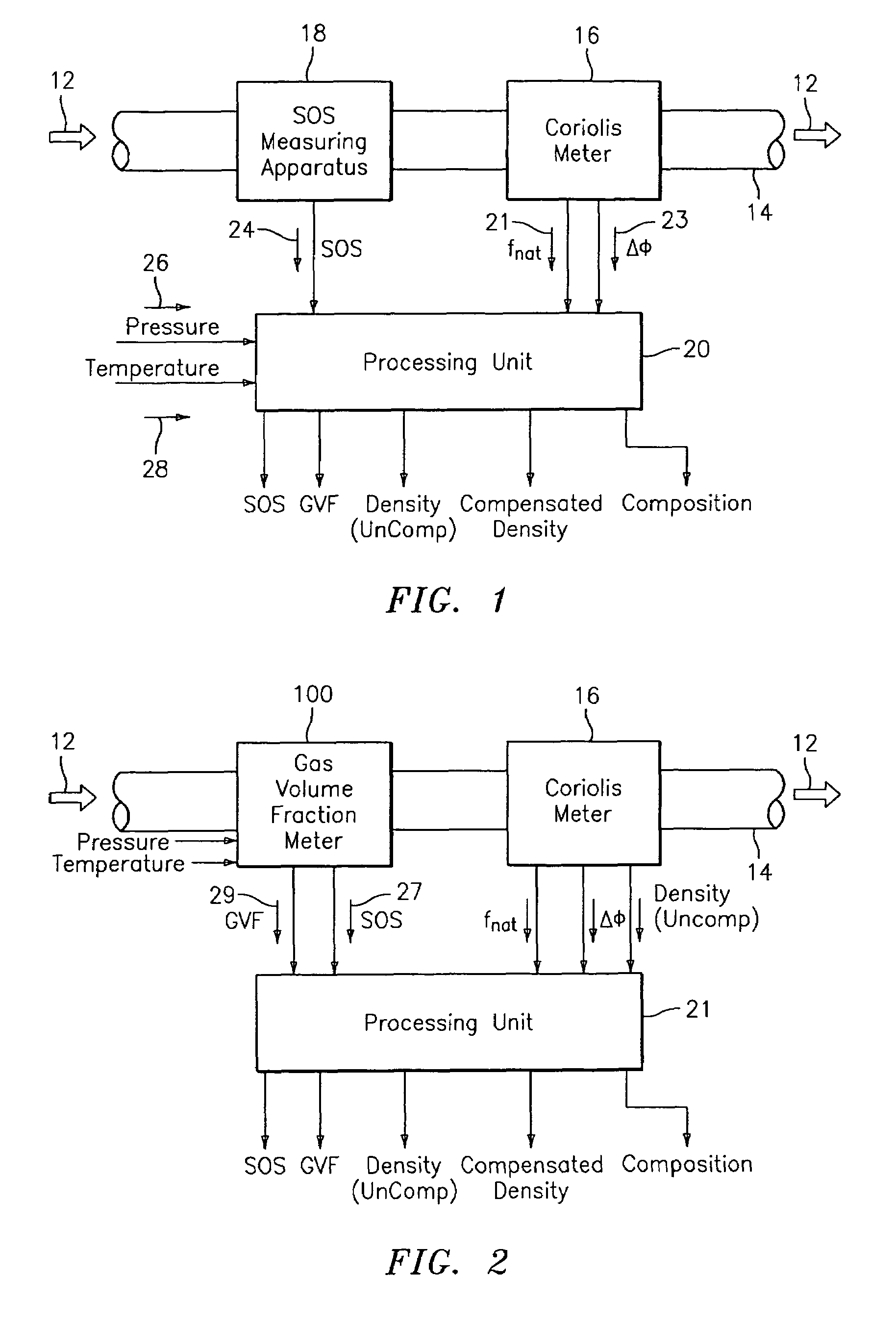
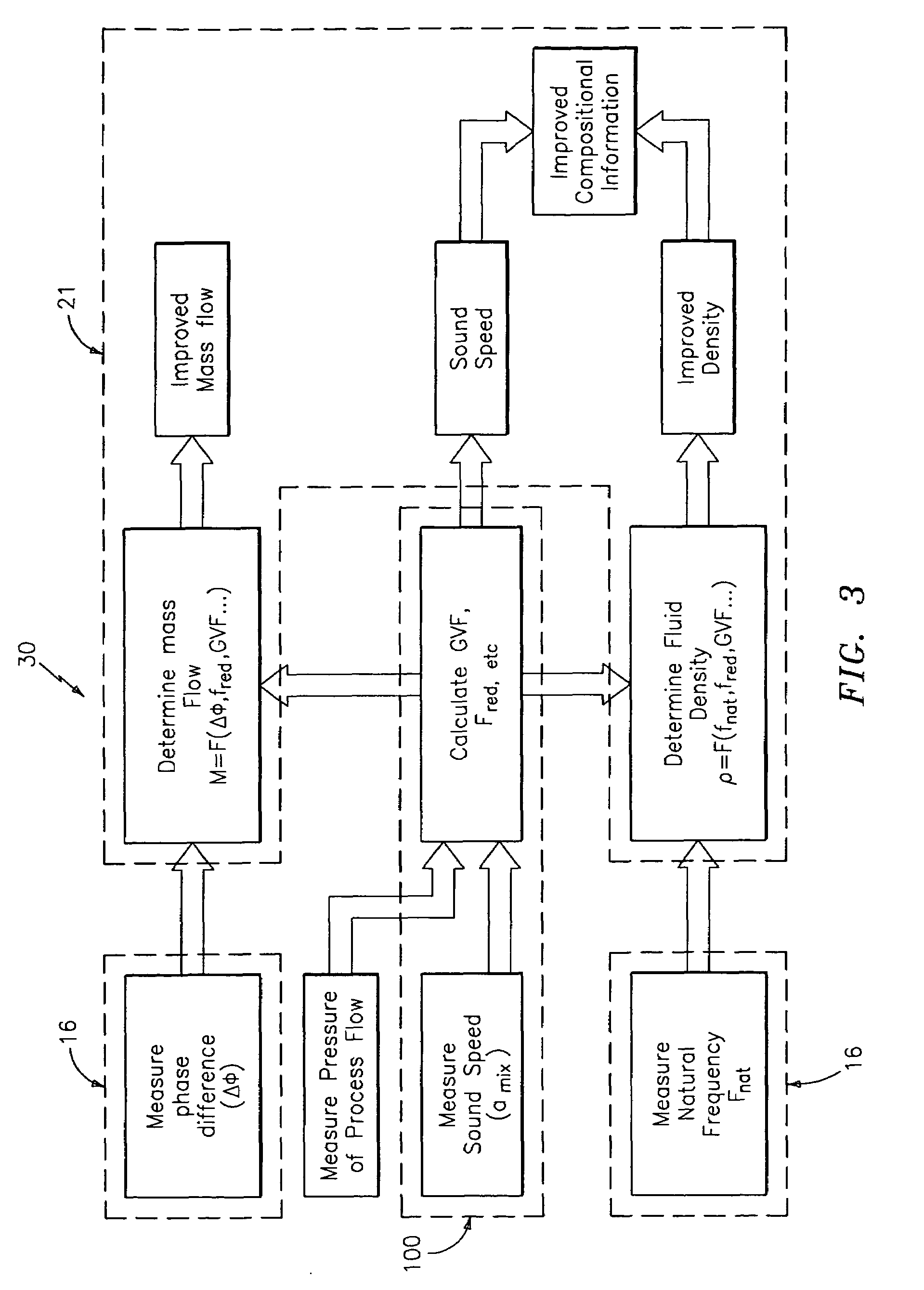
Apparatus and method for compensating a coriolis meter
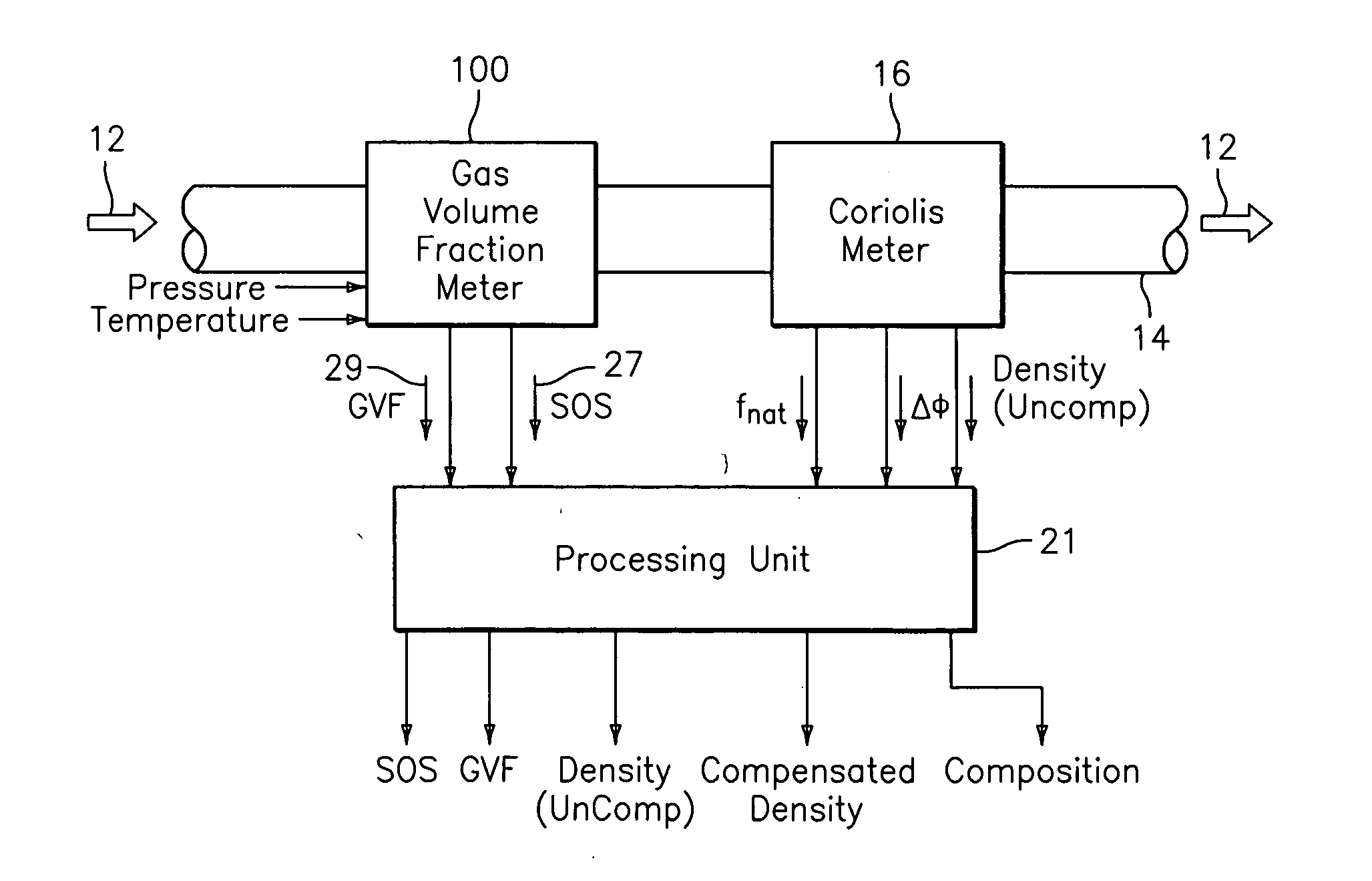
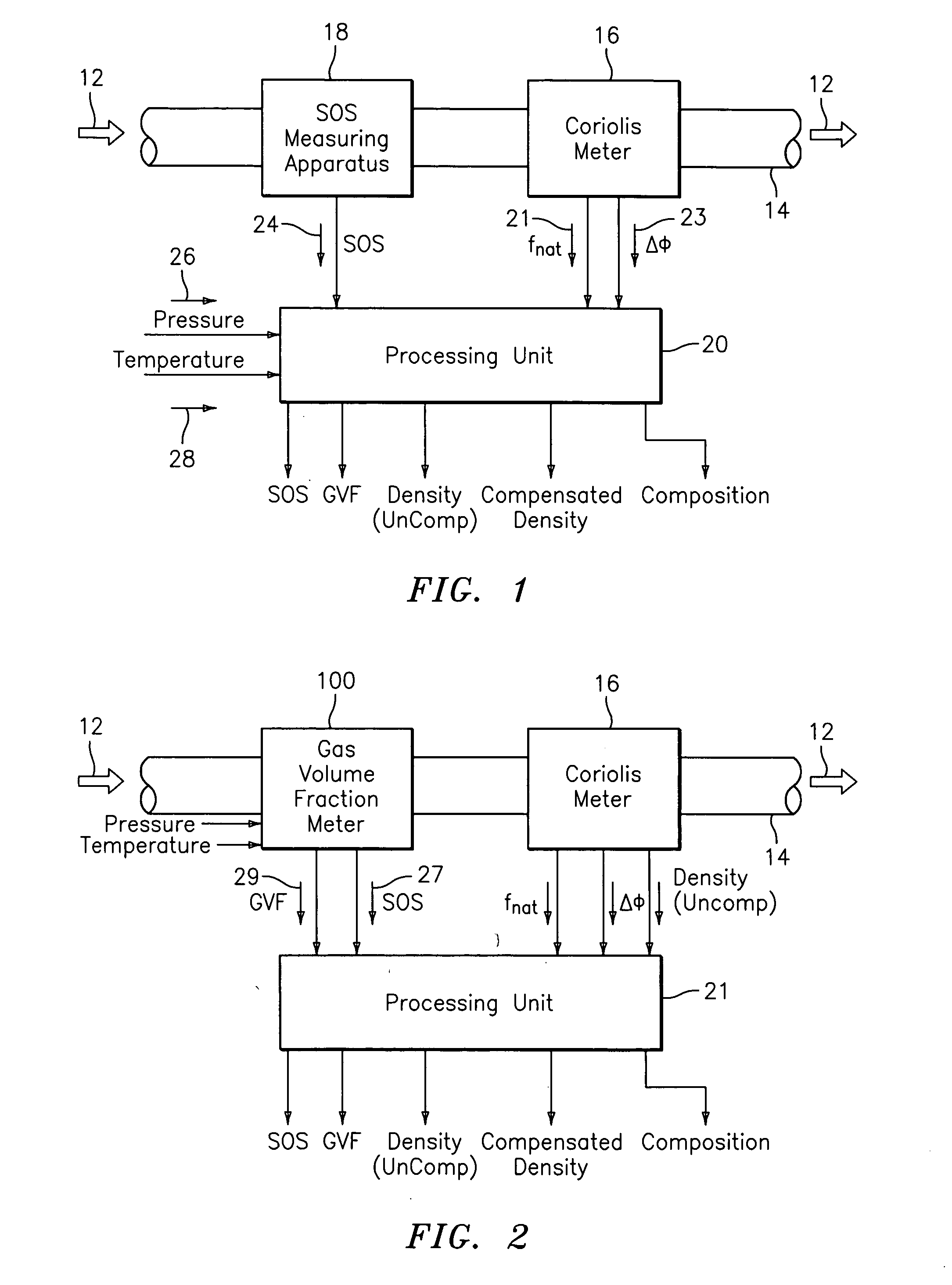
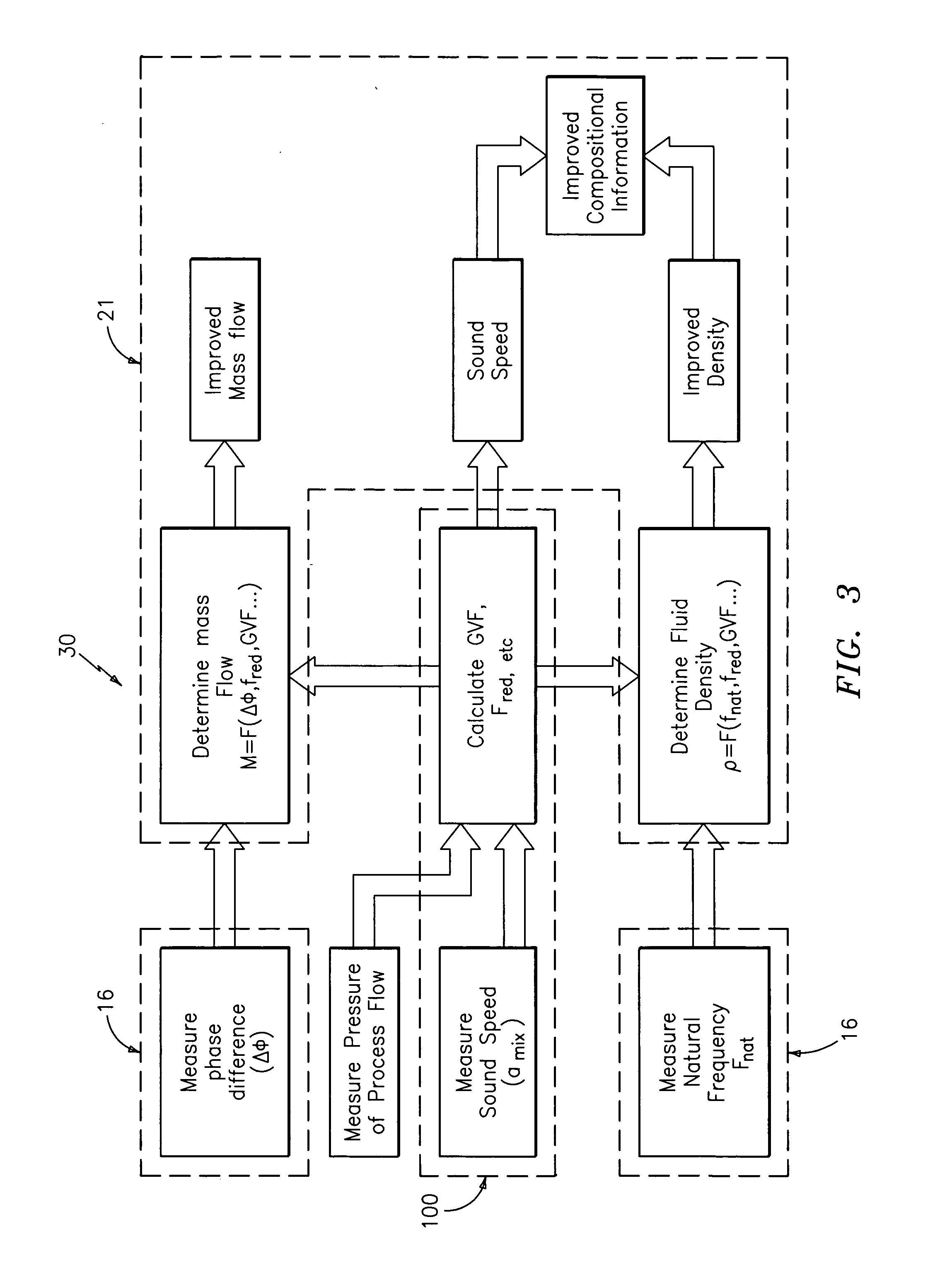
ActiveUS20050044929A1High densityAdd additional massVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectVolume meteringVolumetric Mass DensityDischarge measurements
A flow measuring system is provided that provides at least one of a compensated mass flow rate measurement and a compensated density measurement. The flow measuring system includes a gas volume fraction meter in combination with a coriolis meter. The GVF meter measures acoustic pressures propagating through the fluids to measure the speed of sound αmix propagating through the fluid to calculate at least gas volume fraction of the fluid and / or the reduced natural frequency. For determining an improved density for the coriolis meter, the calculated gas volume fraction and / or reduced frequency is provided to a processing unit. The improved density is determined using analytically derived or empirically derived density calibration models (or formulas derived therefore), which is a function of the measured natural frequency and at least one of the determined GVF, reduced frequency and speed of sound, or any combination thereof. The gas volume fraction (GVF) meter may include a sensing device having a plurality of strain-based or pressure sensors spaced axially along the pipe for measuring the acoustic pressures propagating through the flow.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
System and methods of characterizing a hydrocarbon reservoir
ActiveUS7277796B2Facilitating in performing data processing operationEasy to operateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisCompressibilityIterative method
A technique is described for interpretation of IPTT tests. In one implementation, the technique may be configured or designed to standardize the complete interpretation procedure of IPTT in a heterogeneous reservoir, using if available, modern wireline logs (such as, for example, nuclear magnetic resonance and imaging), dynamic data from wireline formation testers and / or any other relevant information (such as, for example, geological description, core data and local knowledge) as constraints on the interpretation. Additionally, an iterative method may be used to define formation layering. An advanced regression technology may also be used to obtain optimized horizontal and vertical permeabilities of reservoir layers. Further a graphical user interface (GUI) based IPTT workflow technique of the present invention provides an integrated user-friendly interpretation platform for analyzing formation testing pressures and flow rate measurements in order to estimate the values and associated uncertainties of local characteristics of a hydrocarbon reservoir such as, for example, local permeability, local reservoir pressure, local compressibility, etc.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Flow rate measurement for industrial sensing applications using unsteady pressures
Flow rate measurement system includes two measurement regions 14,16 located an average axial distance ΔX apart along the pipe 12, the first measurement region 14 having two unsteady pressure sensors 18,20, located a distance X1 apart, and the second measurement region 16, having two other unsteady pressure sensors 22,24, located a distance X2 apart, each capable of measuring the unsteady pressure in the pipe 12. Signals from each pair of pressure sensors 18,20 and 22,24 are differenced by summers 44,54, respectively, to form spatial wavelength filters 33,35, respectively. Each spatial filter 33,35filters out acoustic pressure disturbances Pacoustic and other long wavelength pressure disturbances in the pipe 12 and passes short-wavelength low-frequency vortical pressure disturbances Pvortical associated with the vortical flow field 15. The spatial filters 33,35 provide signals Pas1,Pas2 to band pass filters 46,56 that filter out high frequency signals. The Pvortical-dominated filtered signals Pasf1,Pasf2 from the two regions 14,16 are cross-correlated by Cross-Correlation Logic 50 to determine a time delay τ between the two sensing locations 14,16 which is divided into the distance ΔX to obtain a convection velocity Uc(t) that is related to an average flow rate of the fluid (i.e., one or more liquids and / or gases) flowing in the pipe 12. The invention may also be configured to detect the velocity of any desired inhomogeneous pressure field in the flow. The invention may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Apparatus and method for compensating a coriolis meter
ActiveUS7152460B2High densityAdd additional massMaterial analysis using microwave meansVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectDischarge measurementsVolumetric Mass Density
A flow measuring system is provided that provides at least one of a compensated mass flow rate measurement and a compensated density measurement. The flow measuring system includes a gas volume fraction meter in combination with a coriolis meter. The GVF meter measures acoustic pressures propagating through the fluids to measure the speed of sound αmix propagating through the fluid to calculate at least gas volume fraction of the fluid and / or the reduced natural frequency. For determining an improved density for the coriolis meter, the calculated gas volume fraction and / or reduced frequency is provided to a processing unit. The improved density is determined using analytically derived or empirically derived density calibration models (or formulas derived therefore), which is a function of the measured natural frequency and at least one of the determined GVF, reduced frequency and speed of sound, or any combination thereof. The gas volume fraction (GVF) meter may include a sensing device having a plurality of strain-based or pressure sensors spaced axially along the pipe for measuring the acoustic pressures propagating through the flow.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Fluid flow measurement device
InactiveUS6964204B2Easy to compressVolume/mass flow by differential pressureFlow monitorsMeasurement deviceBiomedical engineering
Owner:ICU MEDICAL INC
Gas flow rate measurement apparatus and method
InactiveUS6053054AHigh measurement sensitivityShort response timeVolume meteringIndirect mass flowmetersMeasurement deviceState variable
A gas flow rate measurement apparatus for obtaining a normalized flow rate of a gas having at least one liquid component. The gas travels from an upstream position and in a downstream direction. The gas flow rate measurement apparatus comprises a gas inlet conduit in the upstream position for receiving the gas; a gas flow conditioning section in fluid communication with the gas inlet conduit and in a first downstream position for conditioning the gas to vaporize substantially all of the at least one liquid component without adding any other gas; a flow rate measurement section in fluid communication with the gas flow conditioning section and in a second downstream position more distant from the upstream position than the first downstream position, the flow rate measurement section including at least one sensor for sensing at least one state variable for the gas and generating at least one gas state signal, and a flow rate sensor for measuring an actual flow rate of the gas and generating a flow rate signal, and a processing device operatively coupled to the flow rate measurement section for using the at least one gas state signal and the flow rate signal to obtain the normalized mass flow rate. A related method also is provided.
Owner:FLOW TECH
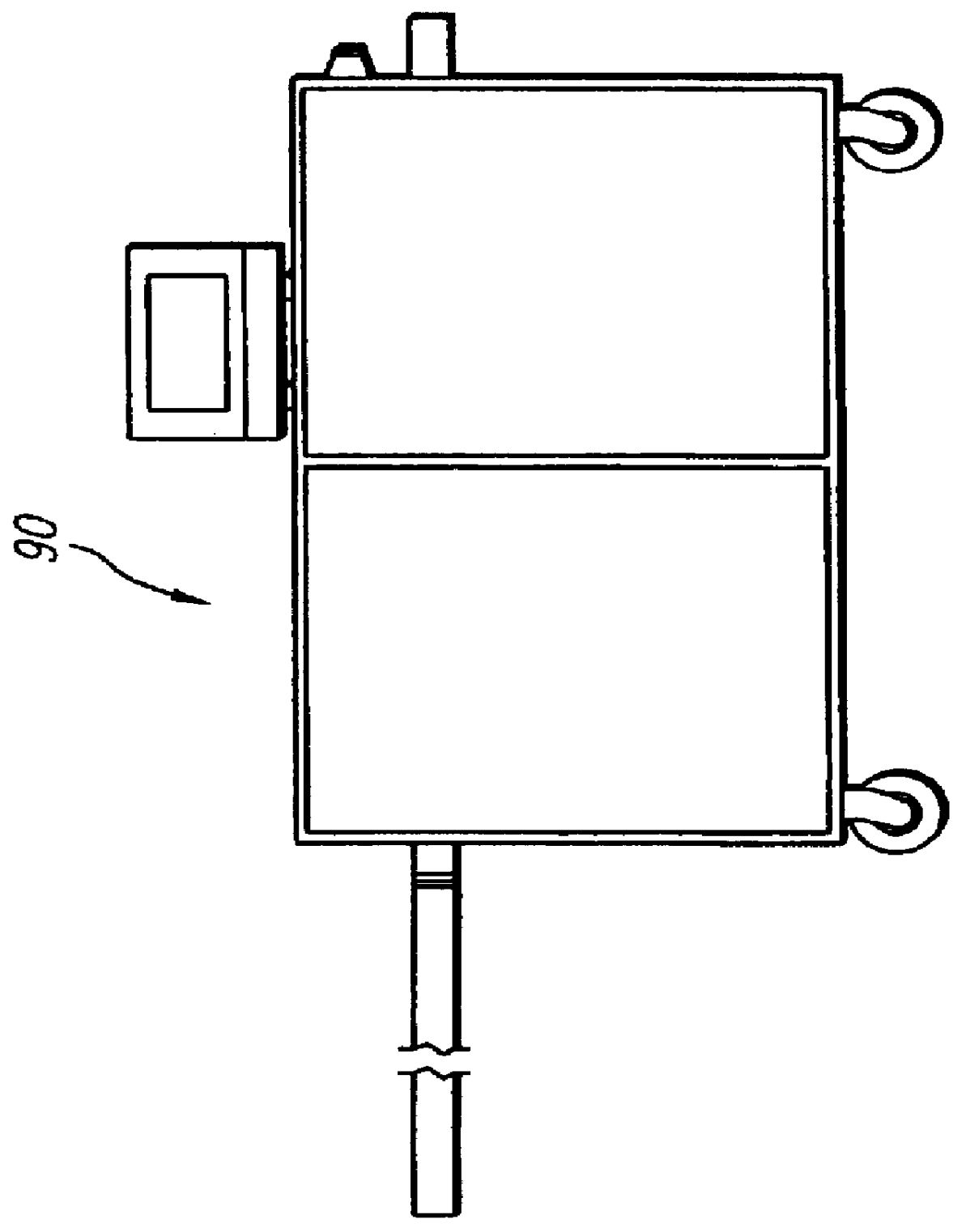
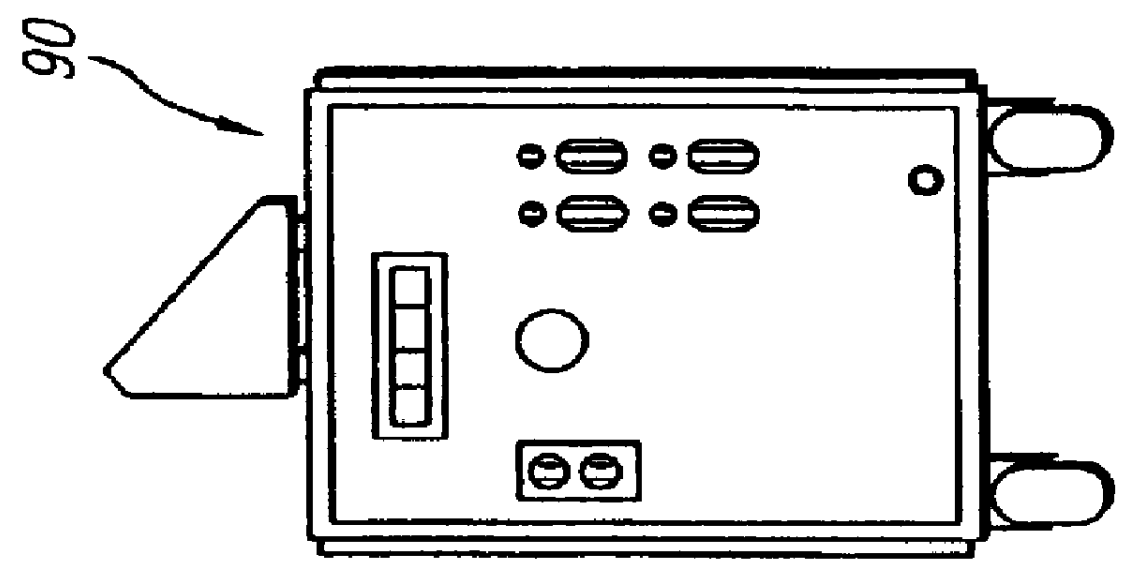
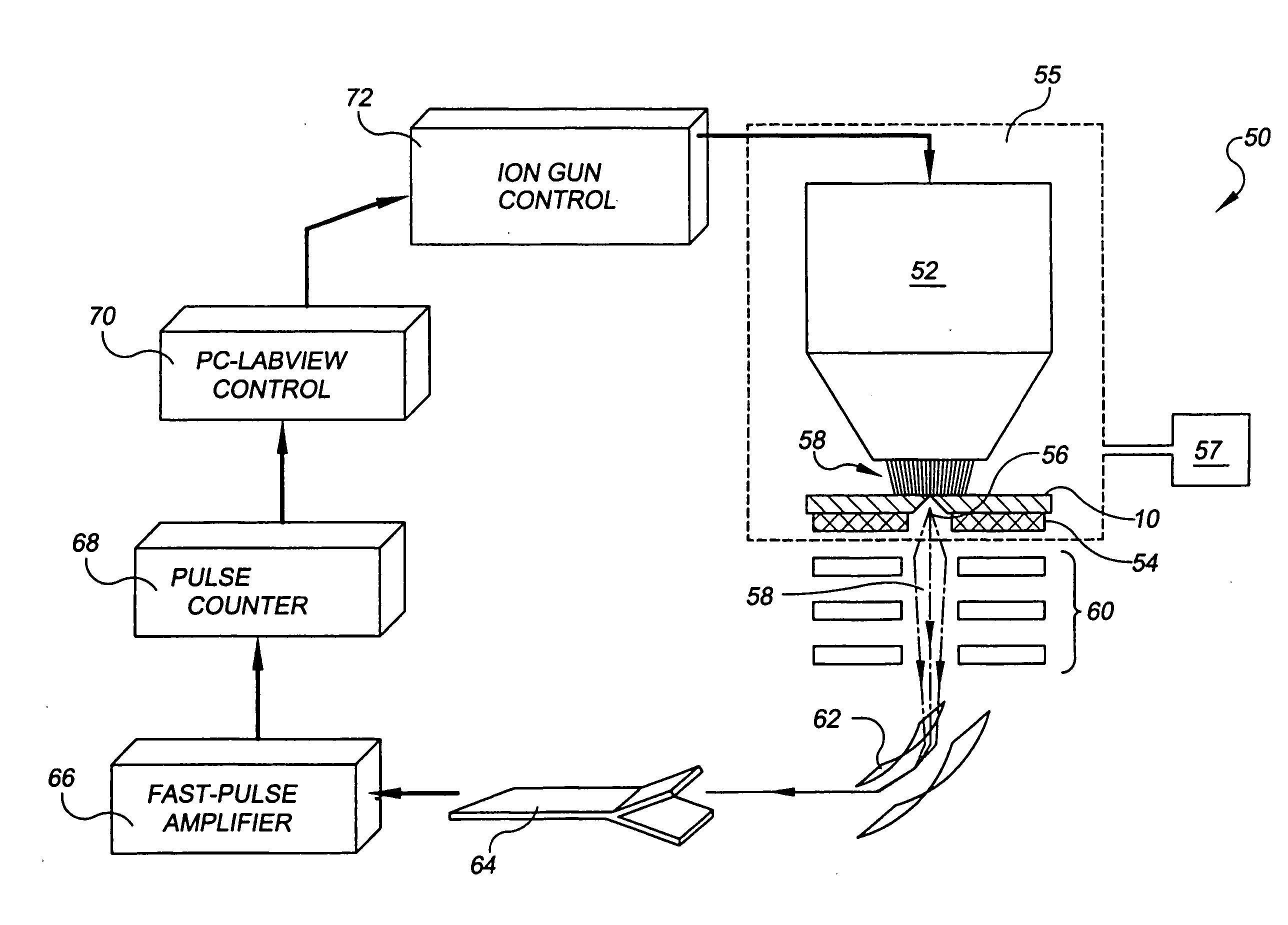
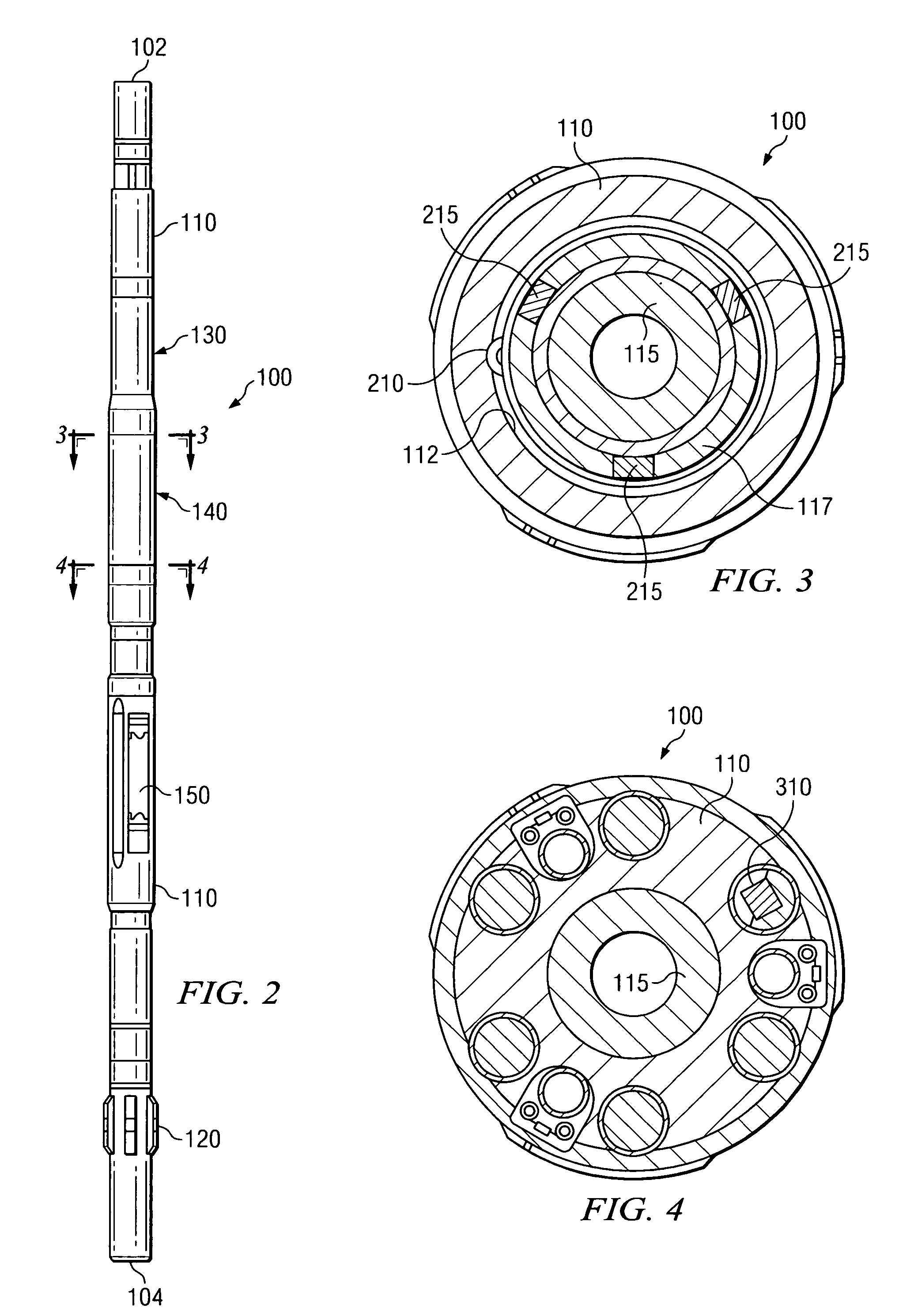
High-precision feedback control for ion sculpting of solid state features
InactiveUS20050126905A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementFixed microstructural devicesSolid-stateRate measurement
The invention provides a method for controlled fabrication of a solid state structural feature. In the method, a solid state structure is provided and the structure is exposed to an ion beam, under fabrication process conditions for producing the structural feature. A physical detection species is directed toward a designated structure location, and the rate at which the detection species proceeds from the designated structure location is measured. Detection species rate measurements are fit to a mathematical model, and the fabrication process conditions are controlled, based on the fitted detection species rate measurements, to fabricate the structural feature.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC +1
Device for measuring the mass rate of flow
ActiveUS20070151368A1Easy to produceImprove accuracyDirect mass flowmetersMeasurement deviceStream flow
A mass flow rate measurement device which works according to the coriolis principle, and has two measurement tubes (1) and a vibration converter. It is provided that a carrier (2) is mounted on each of the measurement tubes (1) as a pair of carriers, and the vibration converter is made and arranged such that it acts between the pair carriers (2). In this way, a coriolis mass flow rate measurement device which is simple to produce is attained, with measurement tubes (1) which can be located extremely close to one another.
Owner:KRONE GMBH
Method and system for pointing and stabilizing a device
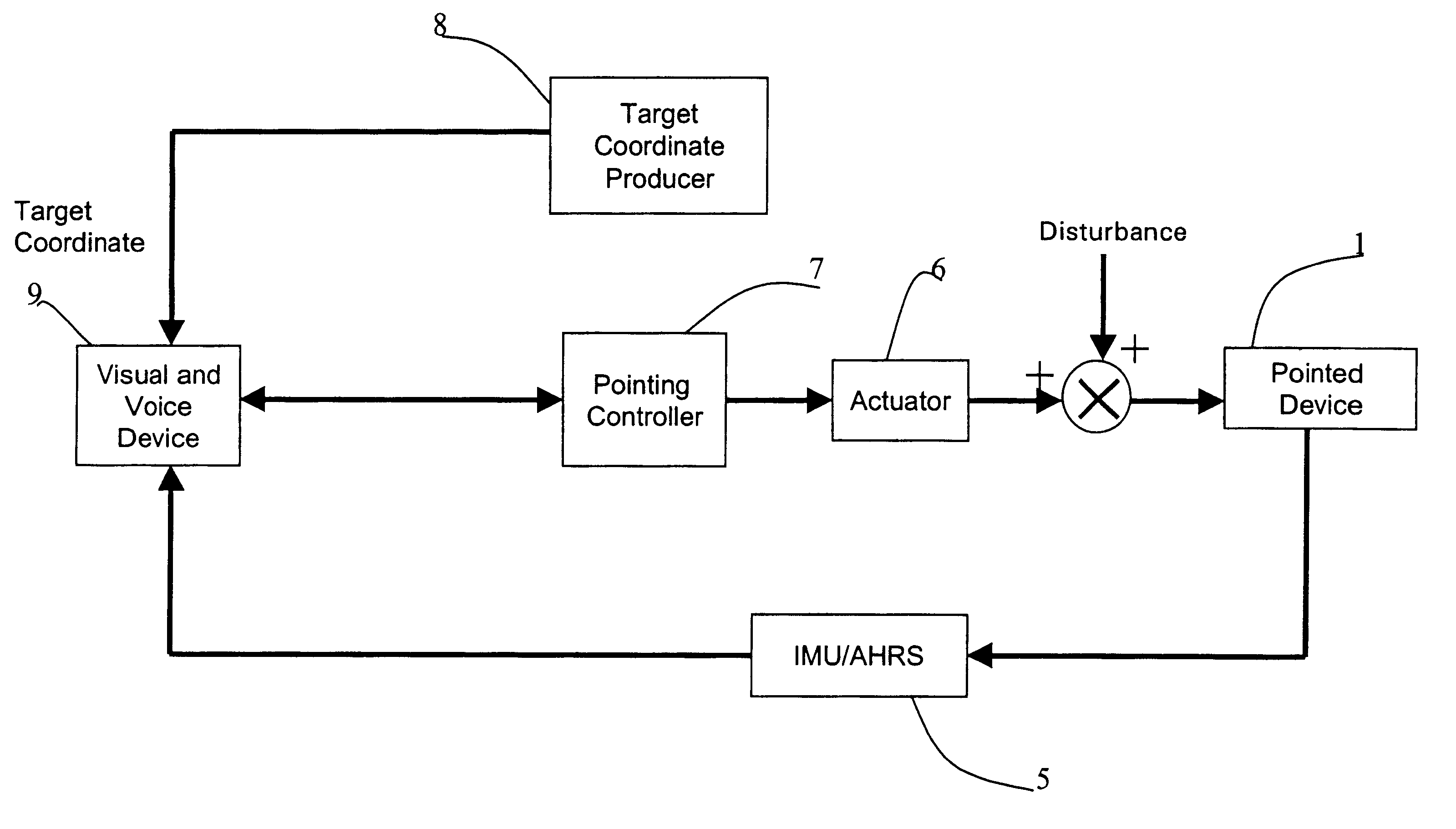
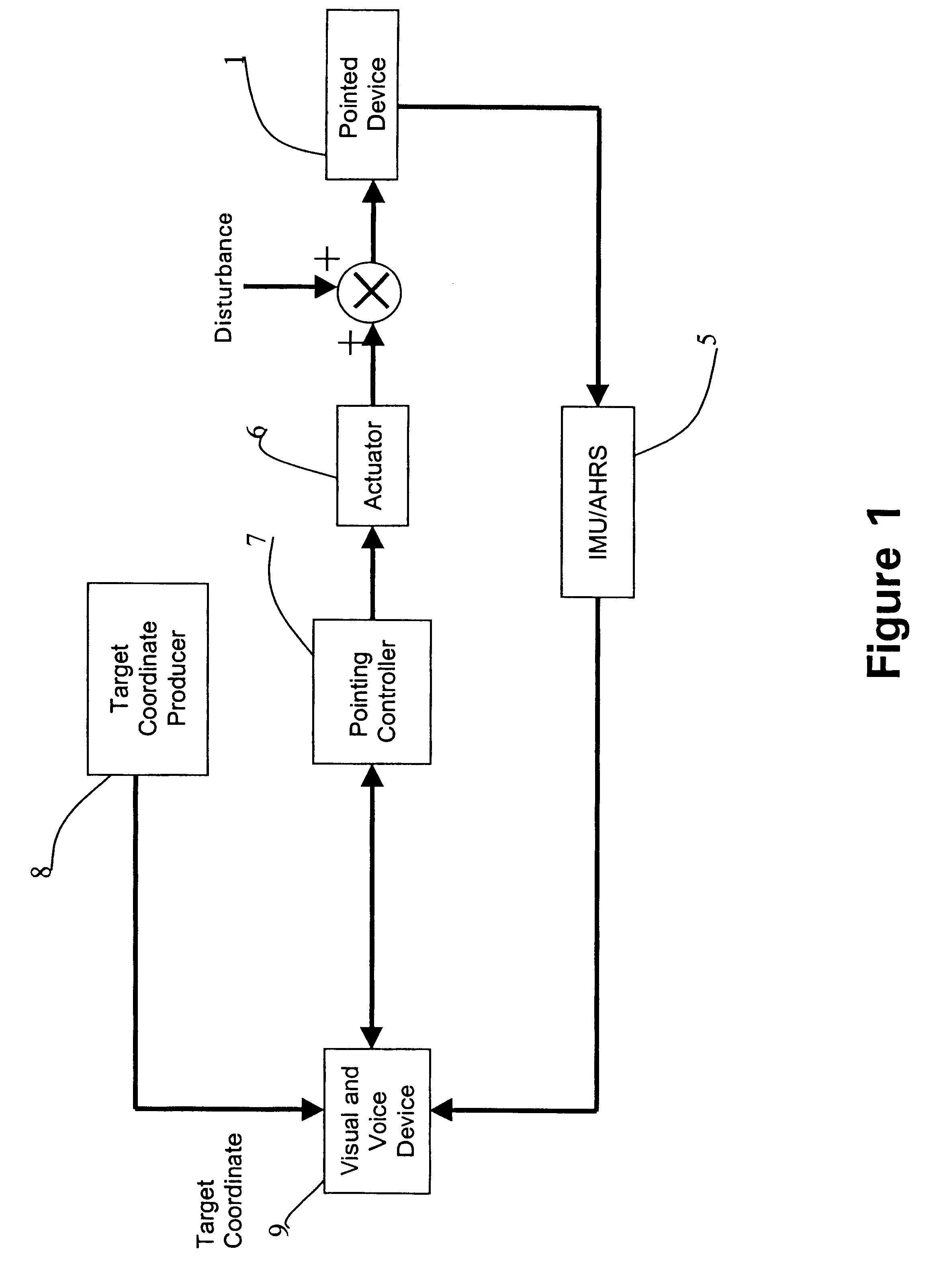
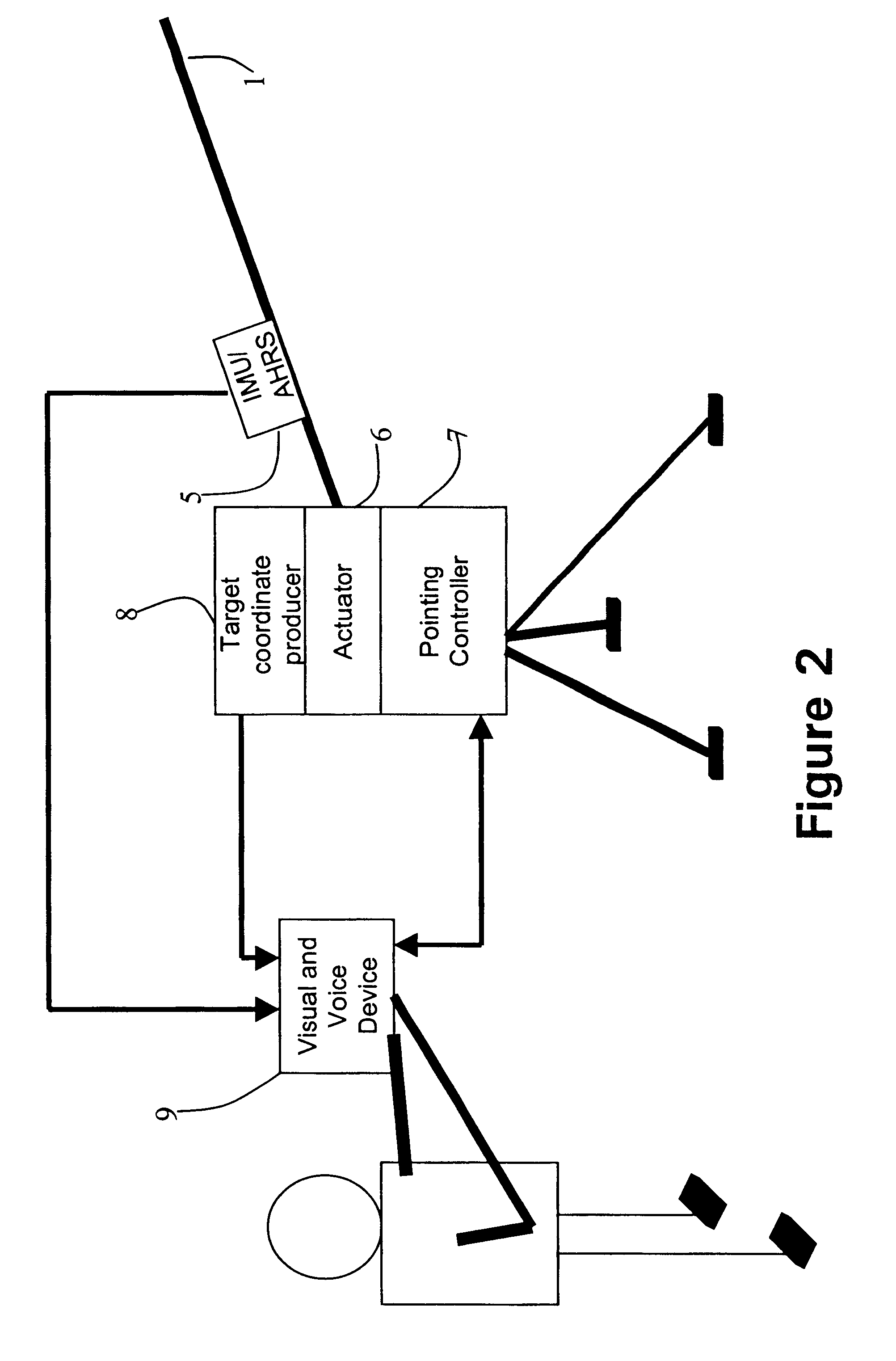
InactiveUS6596976B2Improve accuracyReduce sensitivityDirection controllersAiming meansEngineeringActuator
A method and system for pointing and stabilizing a device that needs to be pointed and stabilized with a desired direction, are disclosed, wherein current attitude measurement and attitude rate measurement of the device measured by an attitude producer, which includes an inertial measurement unit, and the desired direction information measured by a target coordinates producer are processed by a pointing controller to compute rotation commands to an actuator. An actuator rotates and stabilizes the device at the desired direction according to the rotation commands in the presence of disturbances and parametric uncertainties to account for the undesired vibration due to disturbances. A visual and voice device provide an operator with visualization and voice indication of the pointing and stabilization procedure of the device.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
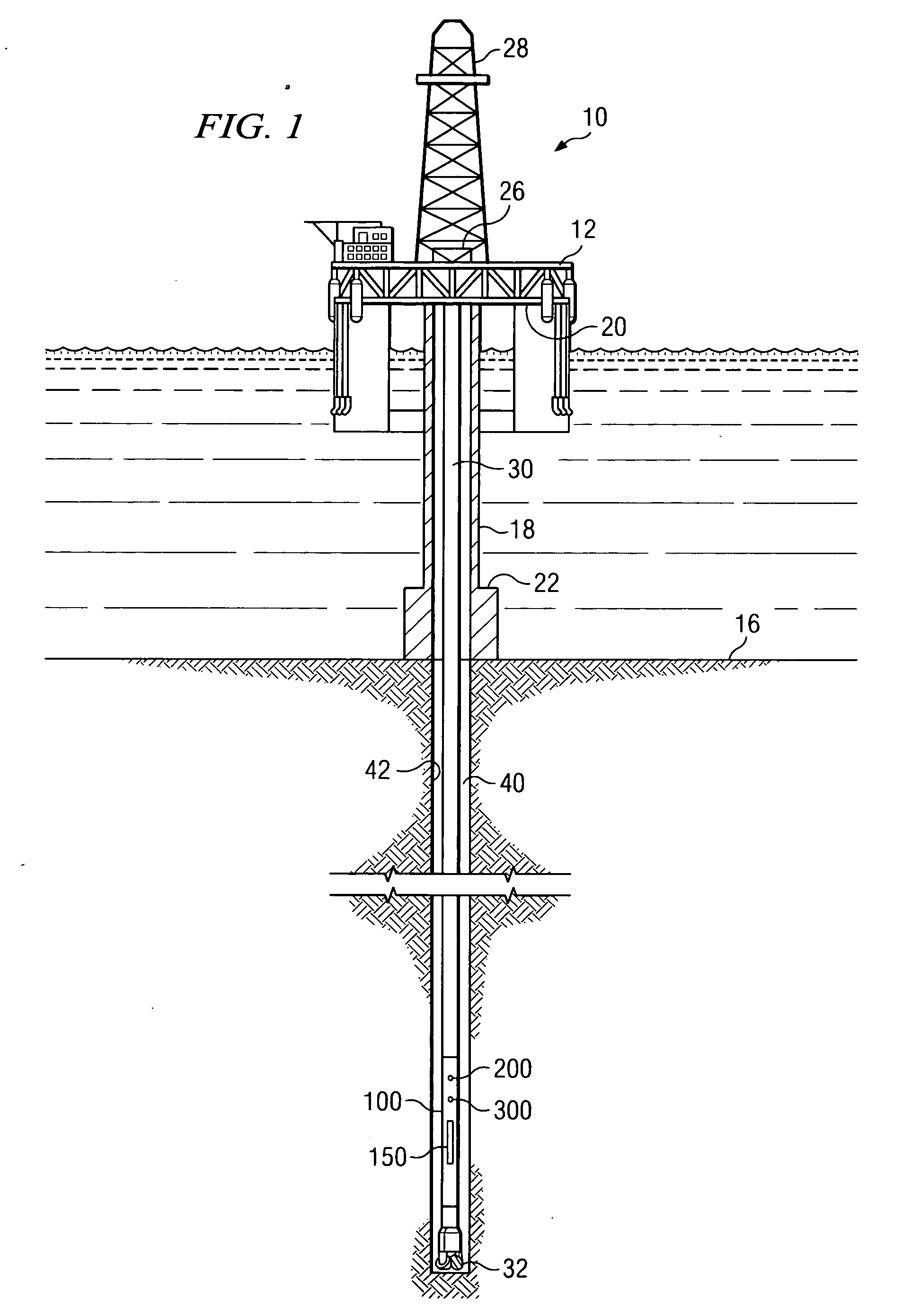
Apparatus and method for downhole dynamics measurements
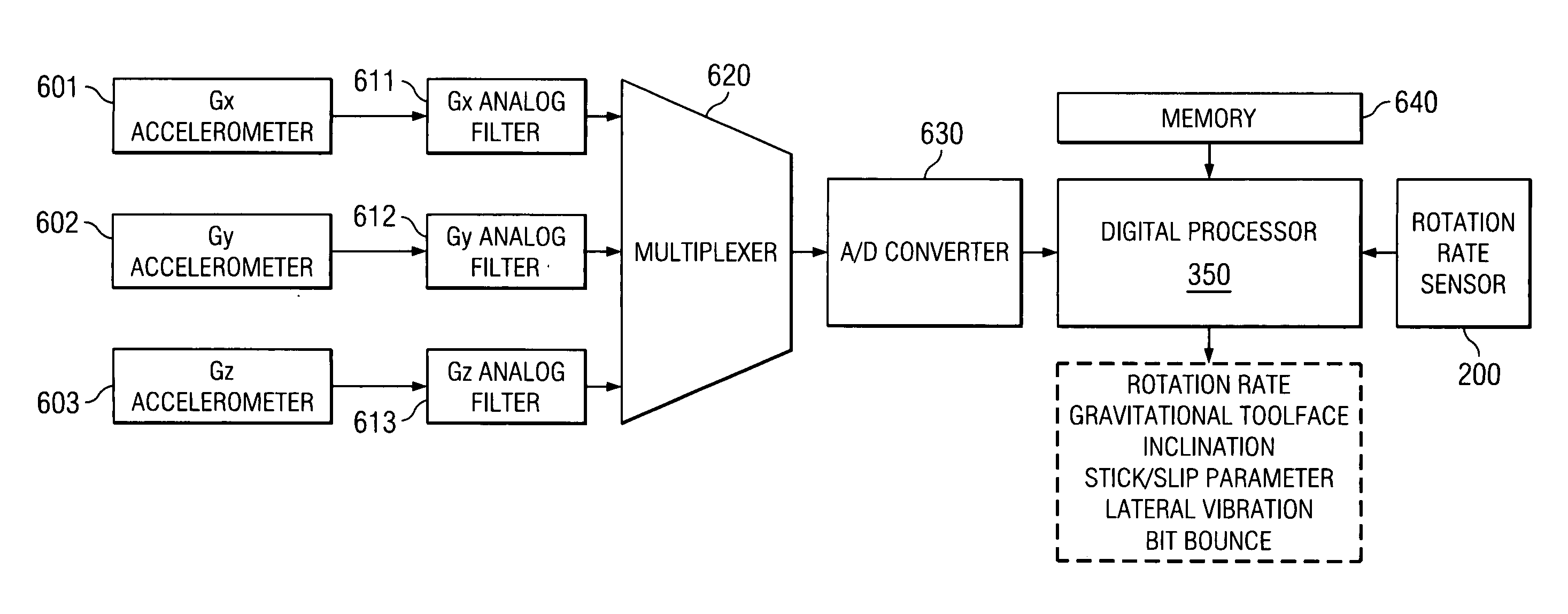
InactiveUS20070289373A1Improve reliabilityReduce component countSurveyMeasurement devices for drillingAccelerometerMeasurement device
Aspects of this invention include a rotary steerable steering tool having a sensor arrangement for measuring downhole dynamic conditions. Rotary steerable tools in accordance with this invention include a rotation rate measurement device disposed to measure a difference in rotation rates between a drive shaft and an outer, substantially non-rotating housing. A controller is configured to determine a stick / slip parameter from the rotation rate measurements. Exemplary embodiments may also optionally include a tri-axial accelerometer arrangement deployed in the housing for measuring lateral vibrations and bit bounce. Downhole measurement of stick / slip and other vibration components during drilling advantageously enables corrective measures to be implemented when dangerous dynamic conditions are encountered.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
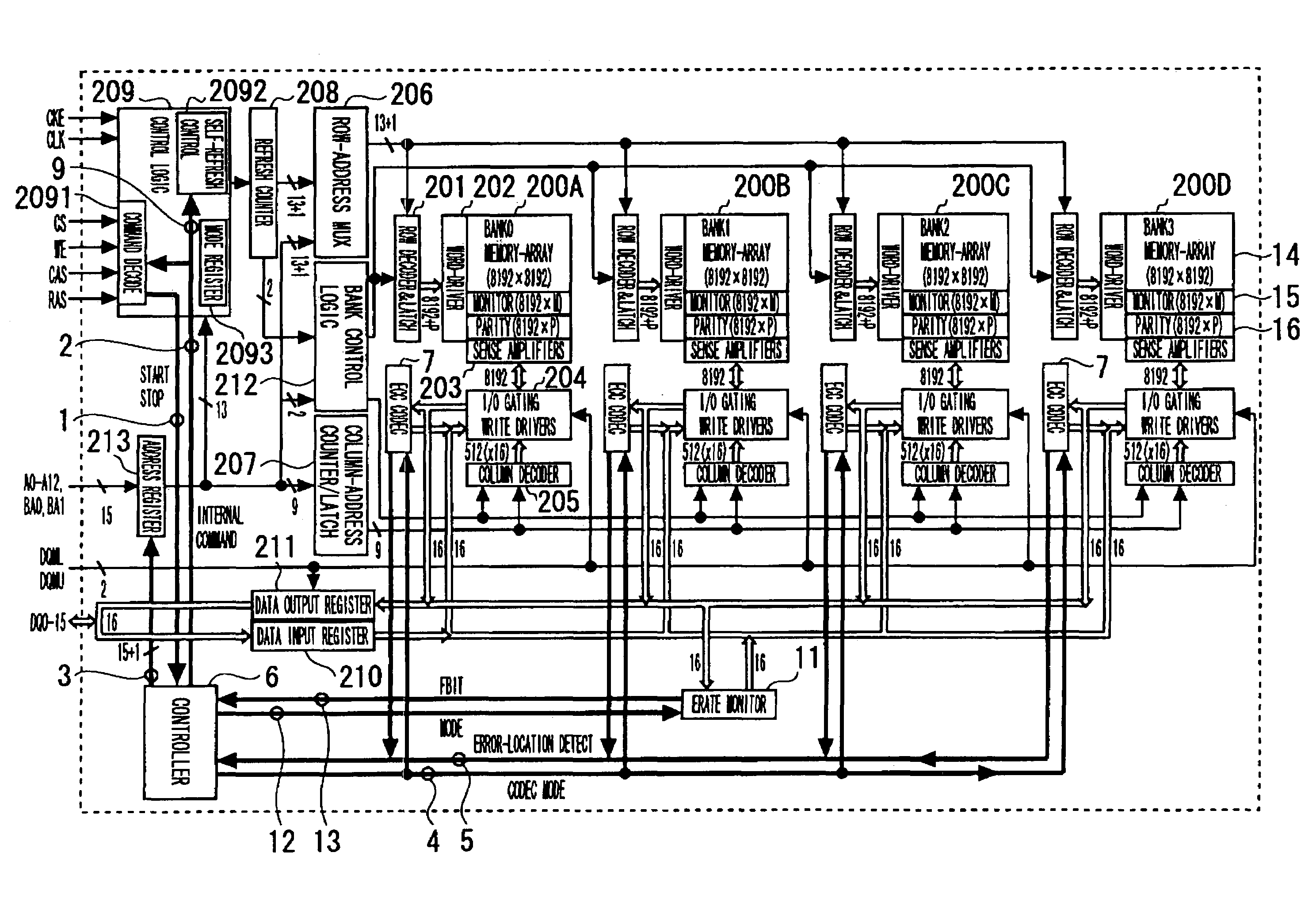
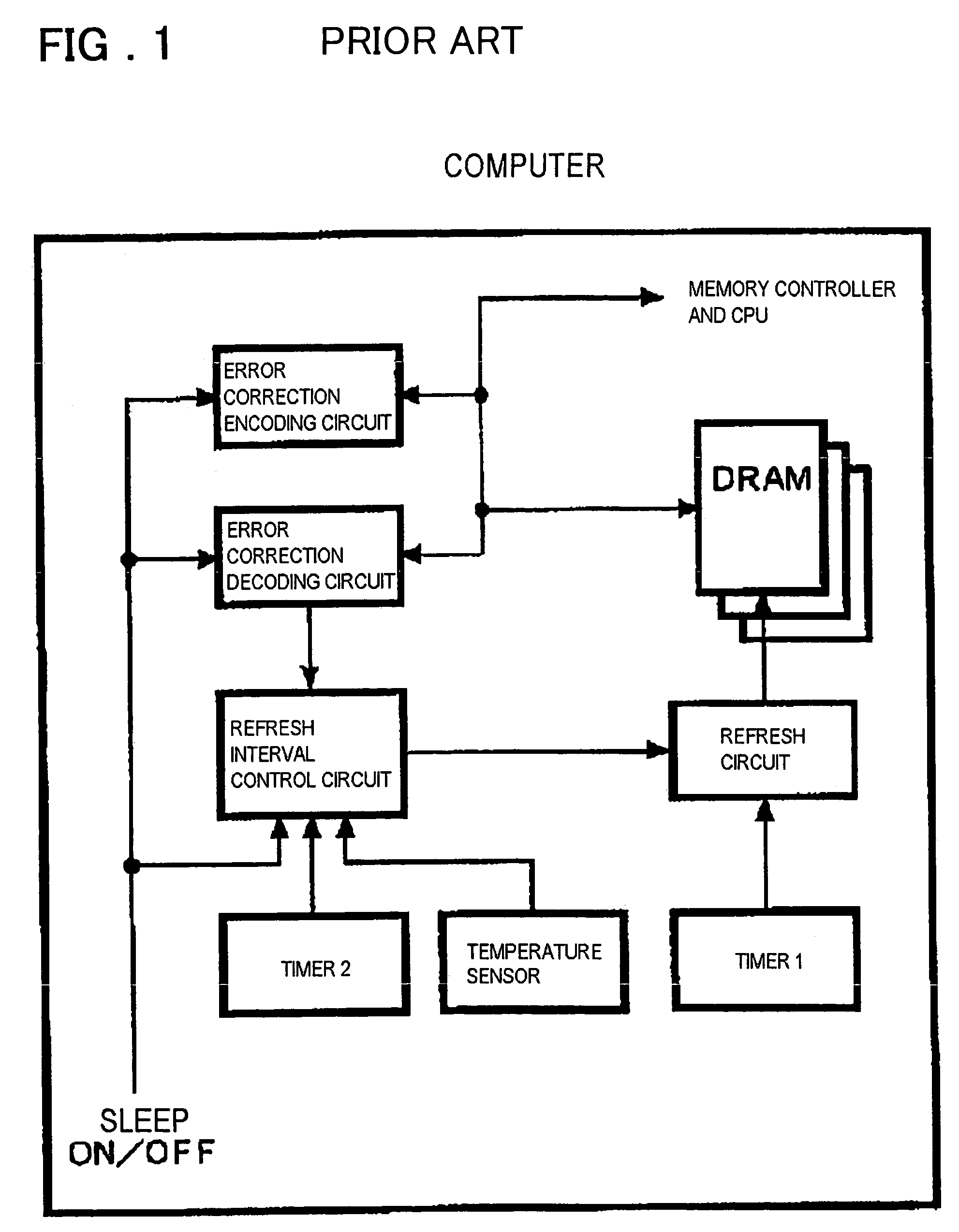
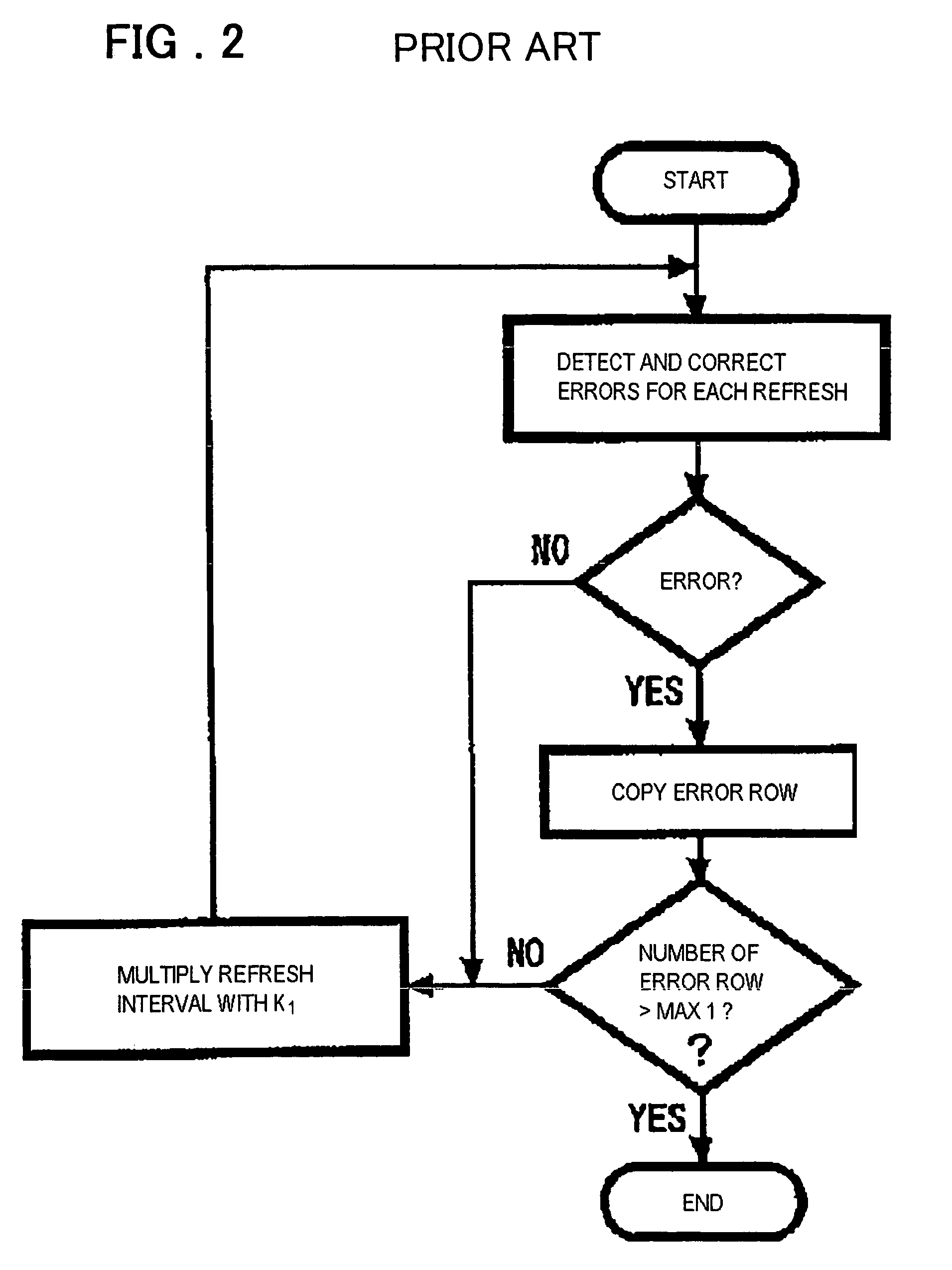
Semiconductor memory device and refresh period controlling method
InactiveUS7493531B2Reduce dataFacilitates temperature compensationError detection/correctionCode conversionControl circuitSemiconductor
Disclosed is a memory device including an error rate measurement circuit and a control circuit. The error rate measurement circuit, carrying a BIST circuit, reads out and writes data for an area for monitor bits every refresh period to detect an error rate (error count) with the refresh period. The control circuit performs control for elongating and shortening the refresh period so that a desired error rate will be achieved. The BIST circuit issues an internal command and an internal address and drives the DRAM from inside. The BIST circuit writes and reads out desired data, compares the monitor bits to expected values (error decision) and counts the errors.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
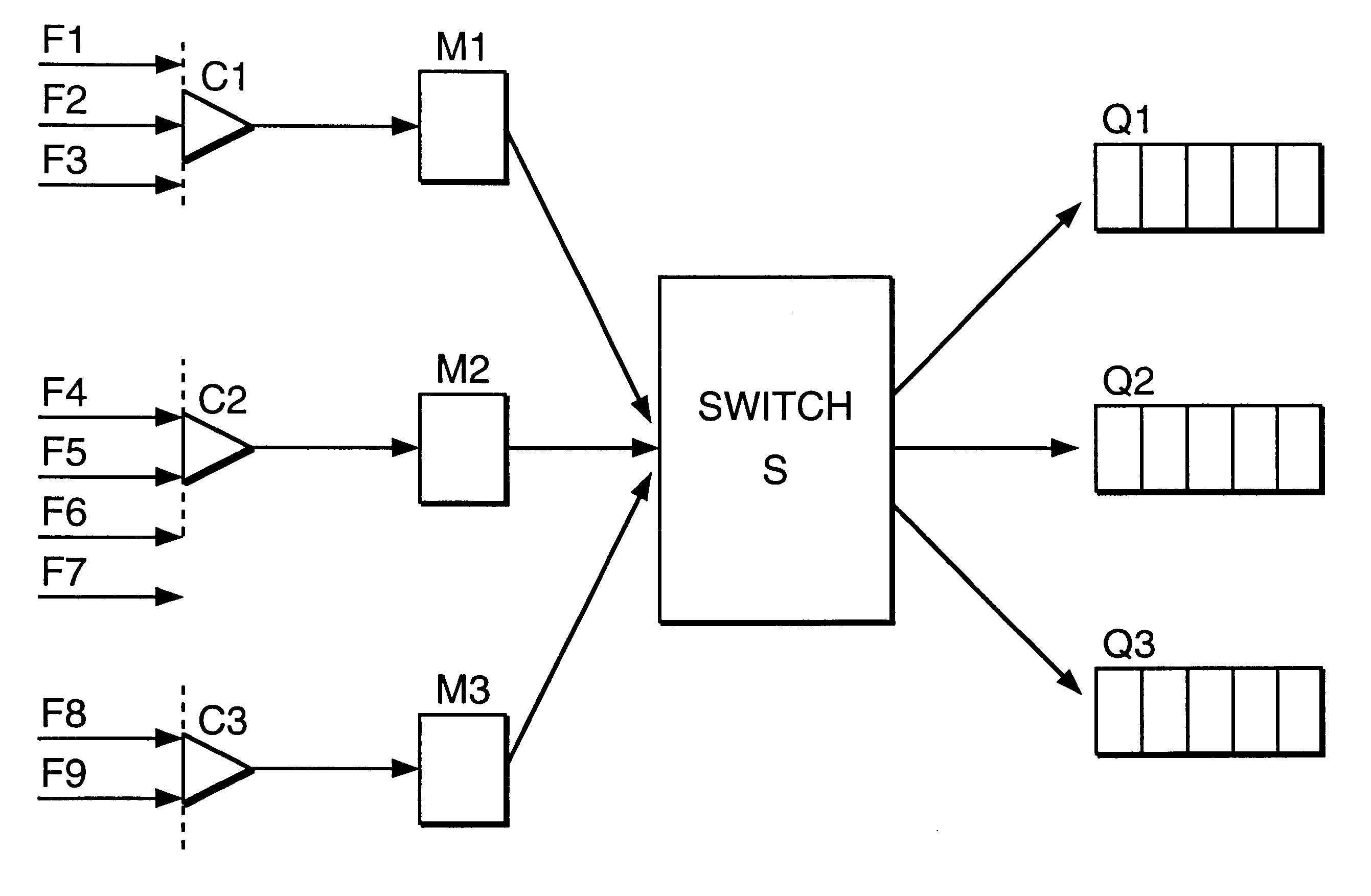
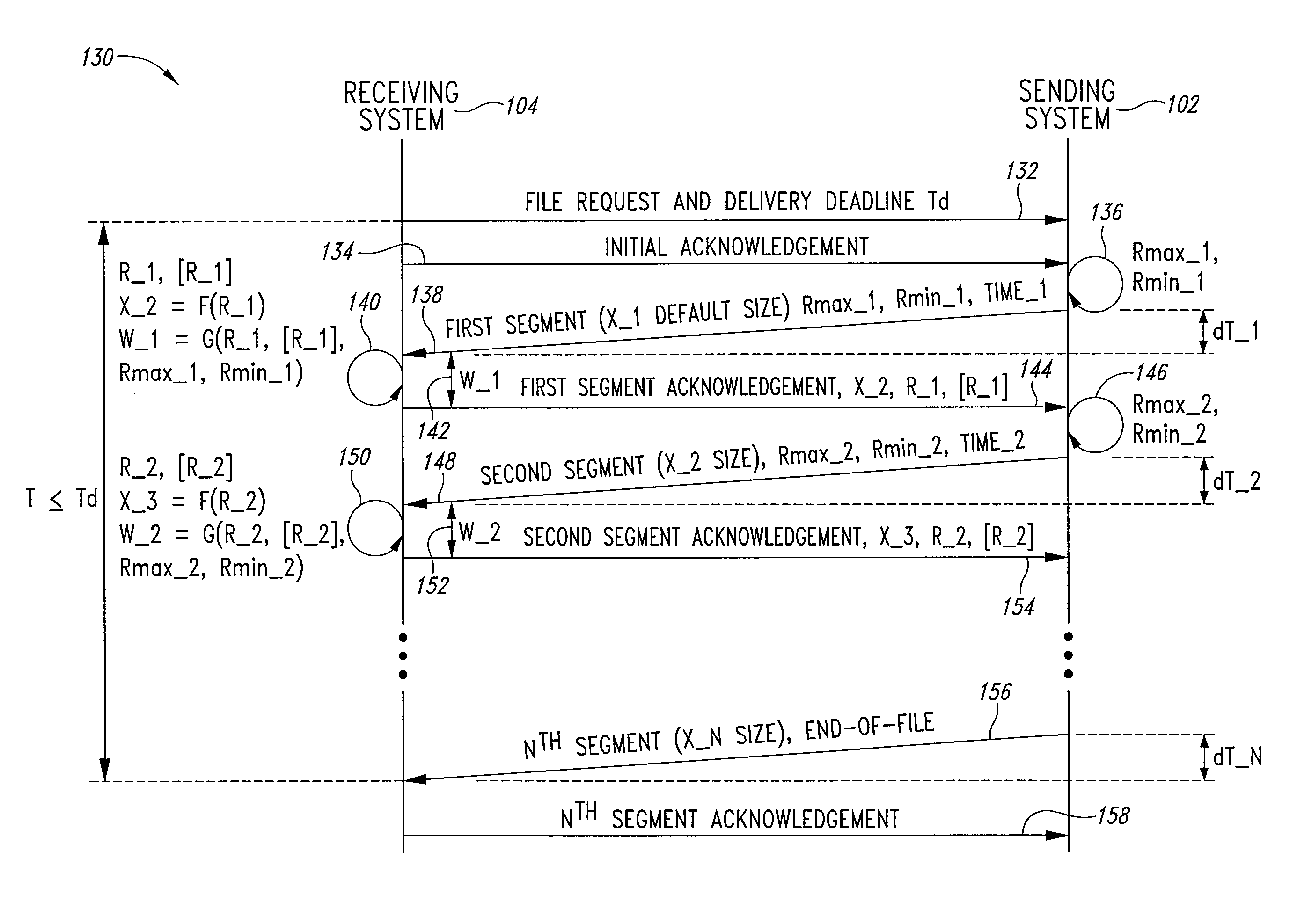
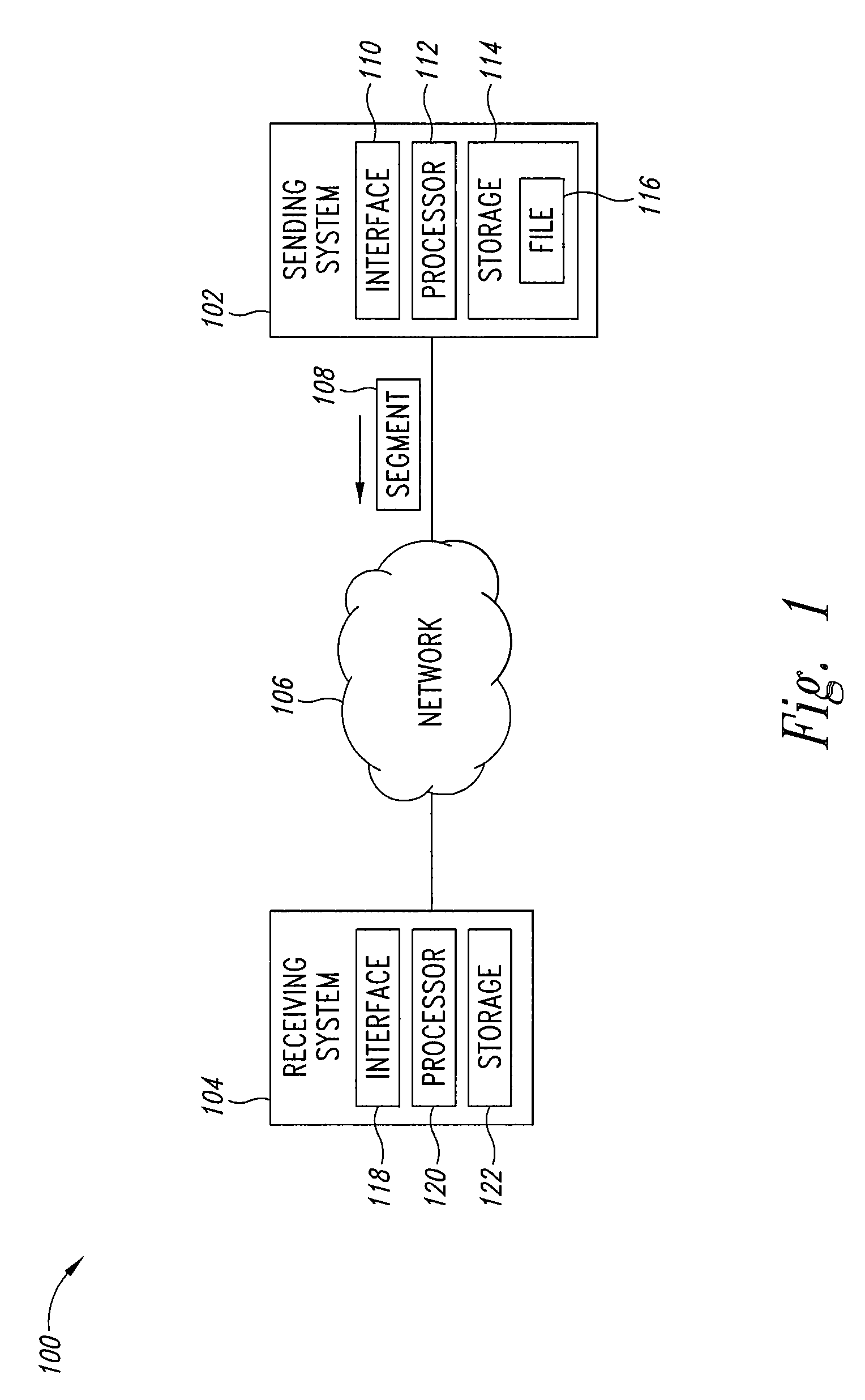
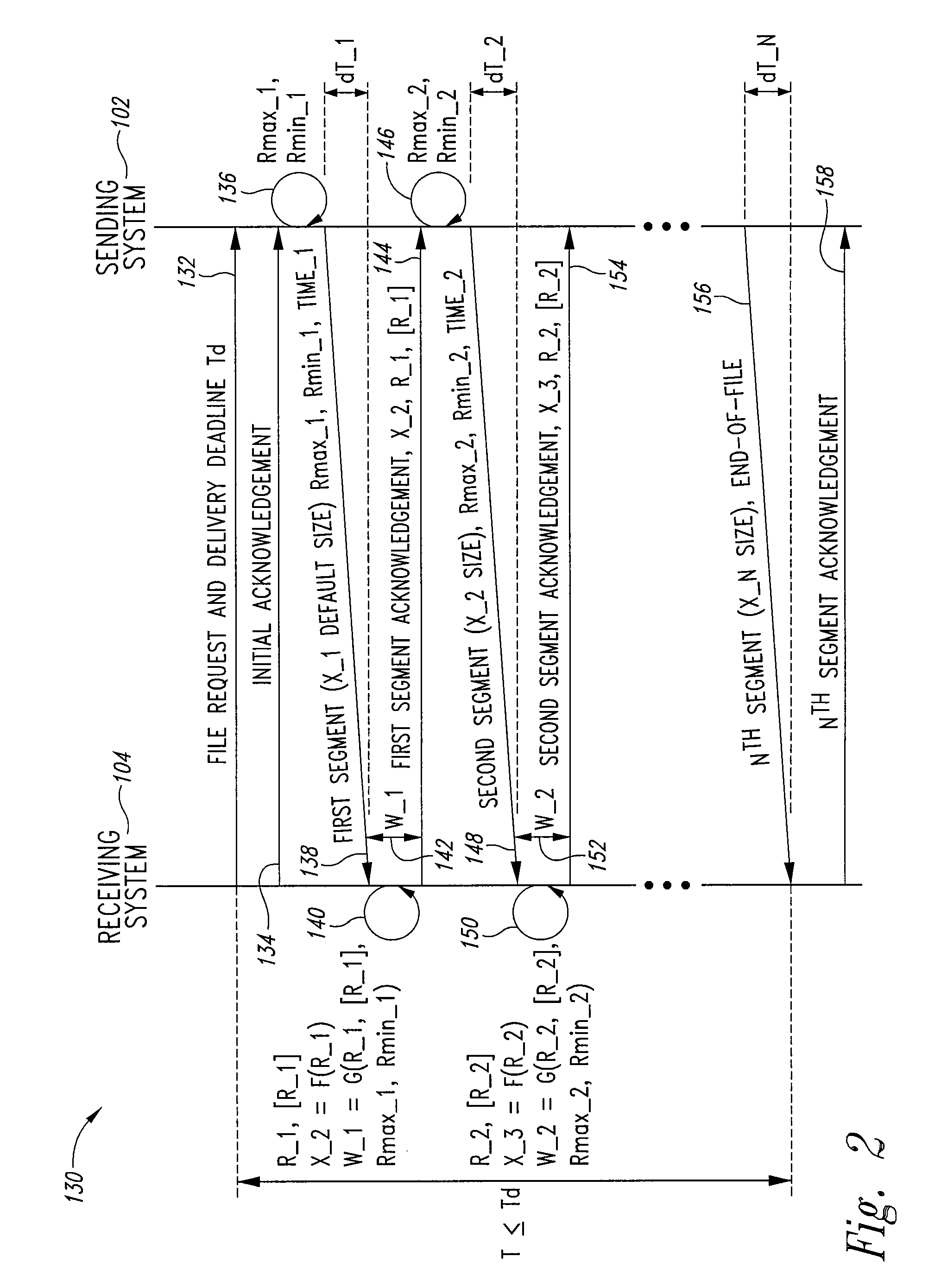
Adaptive file delivery system and method
ActiveUS7500010B2Transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityTime segment
An adaptive file delivery system and method transmits a data file, such as an audio-video file, over a network or collection of networks in segments, each segment transmitted during a different time period. Each time period has a transmission portion to transmit its associated file segment and a wait portion in which no further interaction with the network occurs regarding the transmitted segment. In some implementations, the duration of the transmission portion of each time period is sufficient to reach a steady-state throughput condition, which allows the traffic load status of the network or networks to be determined from rate measurements of file segment transmissions. The duration of the wait portion of each time period is at least long enough to limit the average rate of file segment transmission to adapt to network traffic load variations while causing the entire file to be delivered in a predetermined delivery deadline.
Owner:OPANGA NETWORKS
Statistical reservoir model based on detected flow events
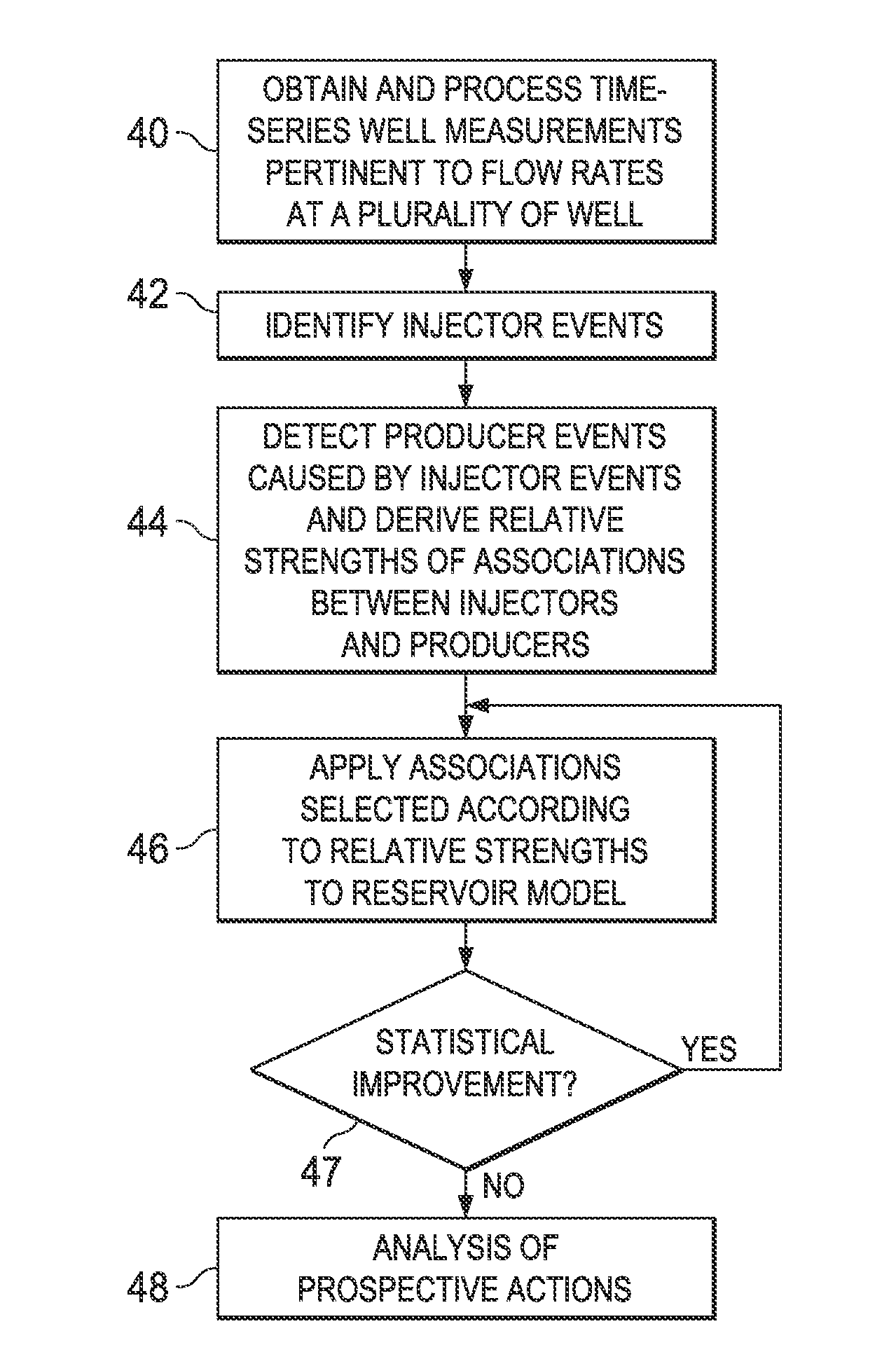
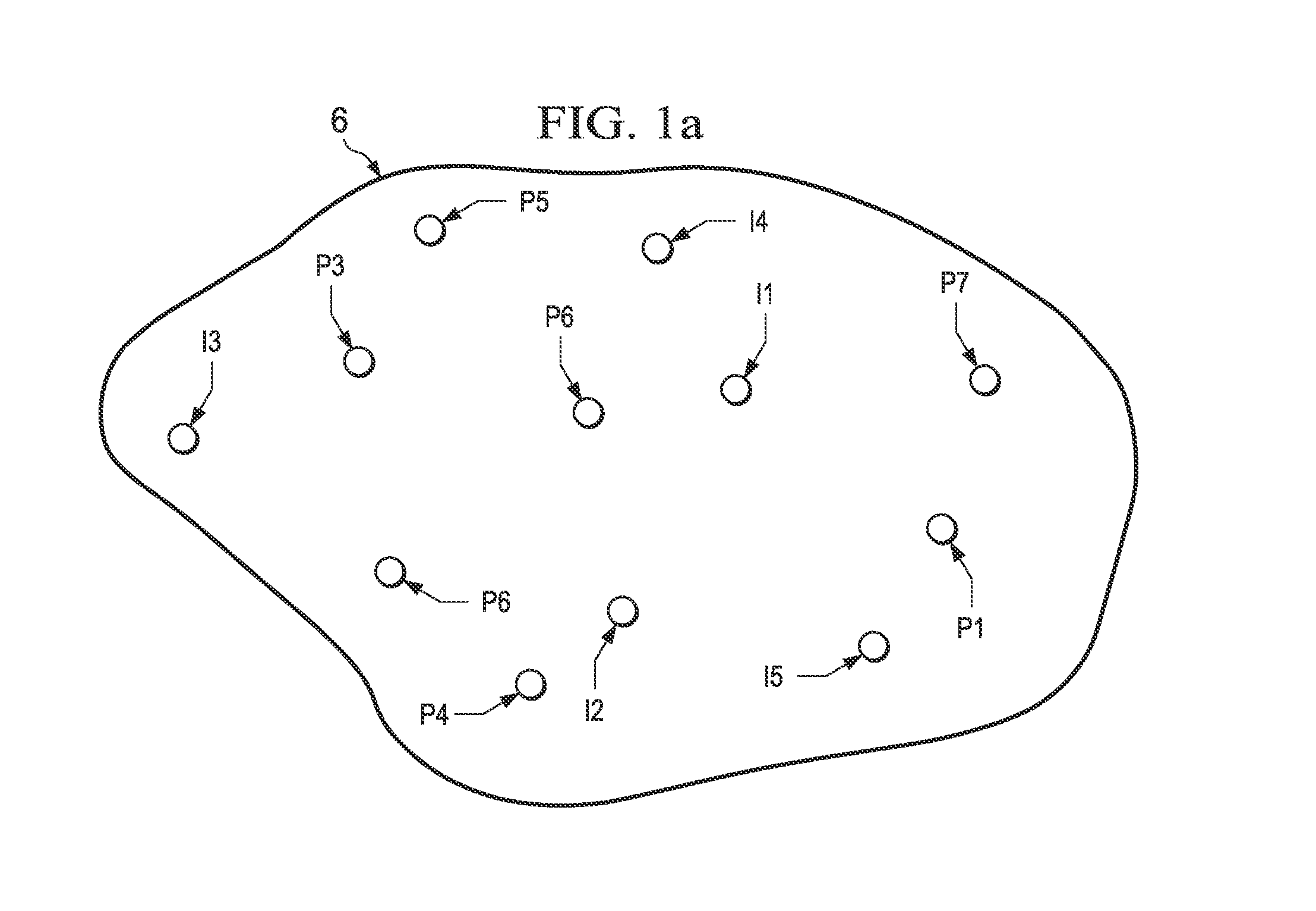
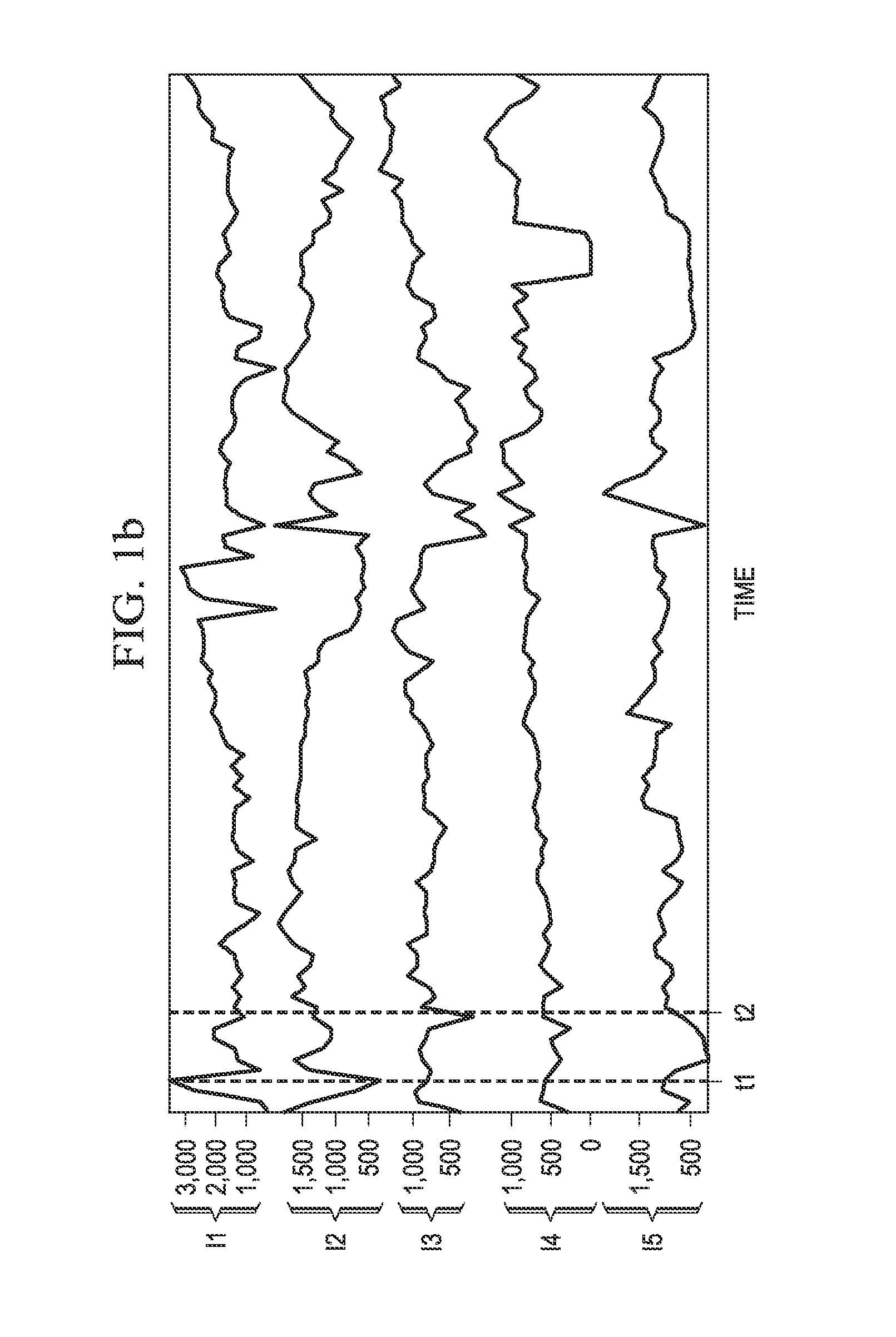
ActiveUS20130116998A1Efficiently derivedEfficient analysisFluid removalAnalogue processes for specific applicationsCapacitanceTime over threshold
Computerized method and system for deriving a statistical reservoir model of associations between injecting wells and producing wells. Potential injector events are interactively identified from time series measurement data of flow rates at the wells, with confirmation that some response to those injector events appears at producing wells. Gradient analysis is applied to cumulative production time series of the producing wells, to identify points in time at which the gradient of cumulative production changes by more than a threshold value. The identified potential producer events are spread in time and again thresholded. An automated association program rank orders injector-producer associations according to strength of the association. A capacitance-resistivity reservoir model is evaluated, using the flow rate measurement data, for the highest-ranked injector-producer associations. Additional associations are added to subsequent iterations of the reservoir model, until improvement in the uncertainty in the evaluated model parameters is not statistically significant.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC +1
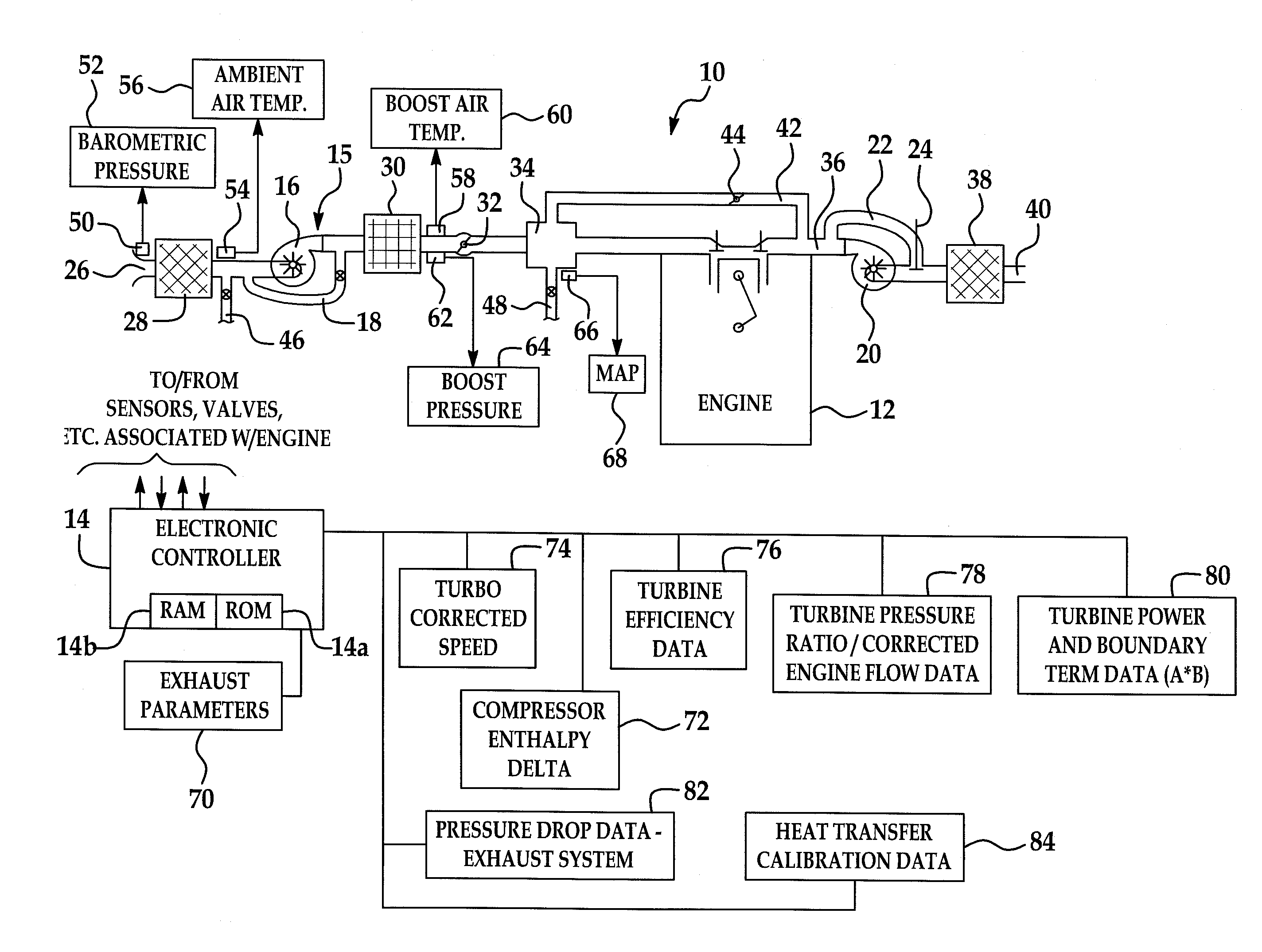
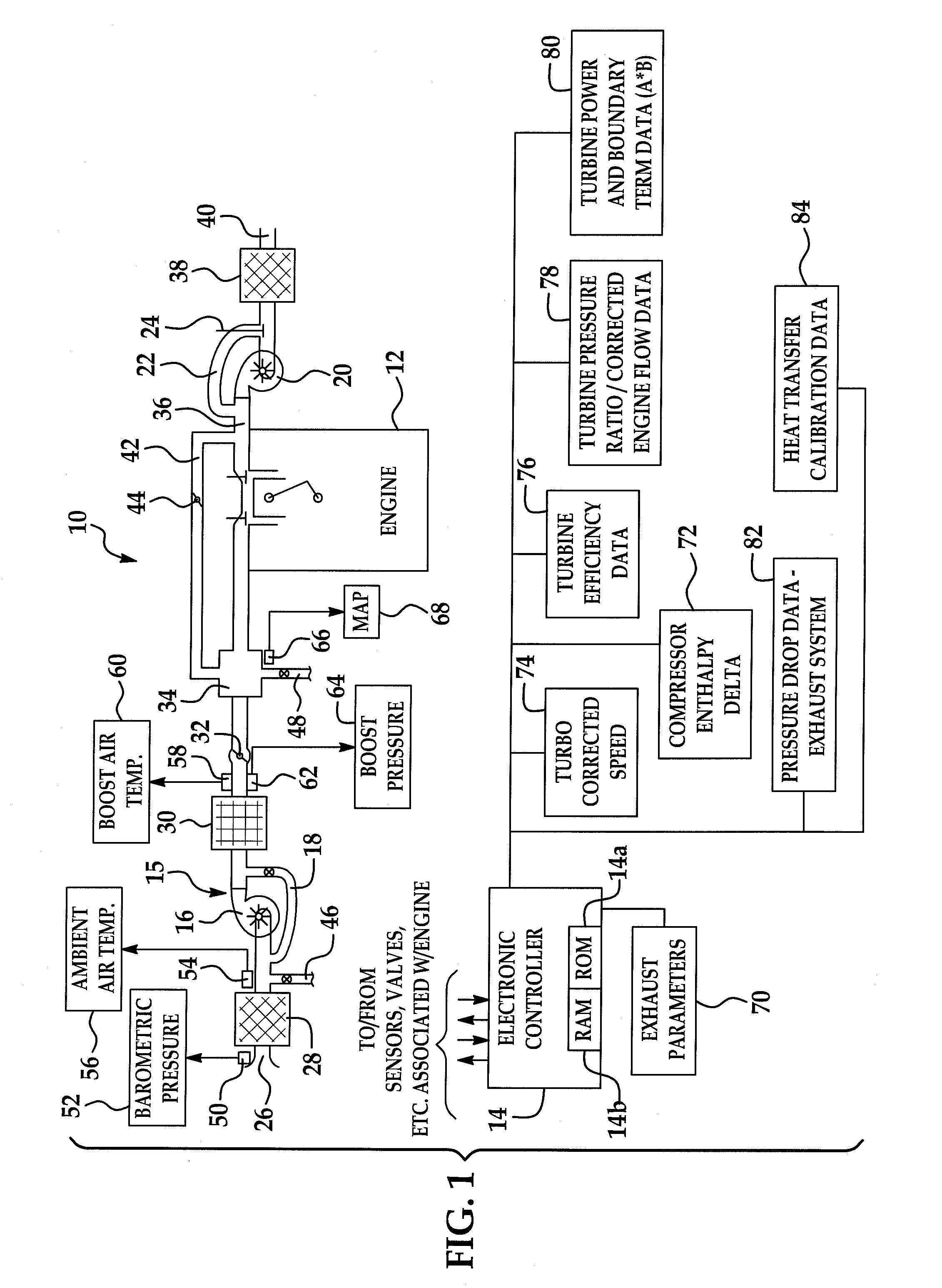
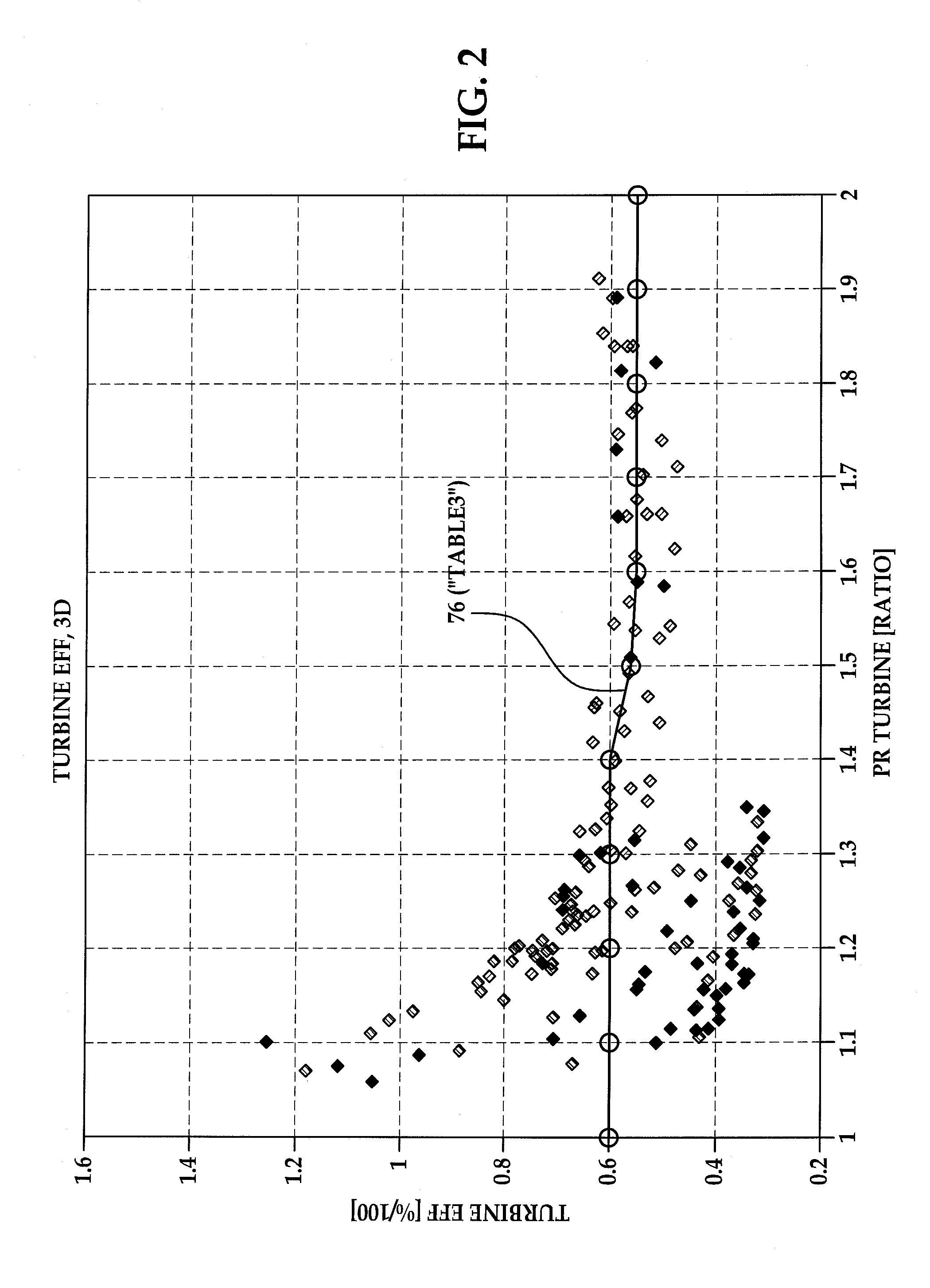
System and method for modeling of turbo-charged engines and indirect measurement of turbine and waste-gate flow and turbine efficiency
InactiveUS20090094009A1Easy to implementSuitable for implementationGeometric CADElectrical controlInlet temperatureRate measurement
A real-time system for modeling a turbo-charged engine includes a model configured to estimate various exhaust states such as turbine inlet pressure, turbine outlet pressure, turbine outlet temperature, turbine mass flow rate and waste-gate valve mass flow rate. The model is dependent only on the availability of normal operating values available in a conventionally-configured automotive controller and one or more measured intake side parameters such as ambient pressure, boost pressure, ambient temperature and compressor mass flow rate. The model is constructed to reflect a high-level application of energy conservation between the turbine (generated power) and compressor (absorbed power). A method for the indirect measurement of turbine and waste-gate flow uses turbine inlet and outlet pressure, inlet temperature and engine mass air flow rate measurements. A method for the indirect measurement of turbine efficiency avoids the need for manufacturer's turbine data.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Flow Sensor Calibrated by Volume Changes
InactiveUS20100063765A1High precisionIncrease opportunitiesVolume measurement apparatus/methodsTesting/calibration apparatusVolume variationInfusion pump
An infusion pump and method are provided which combine flow rate measurements calibrated by accurate volume measurements over time.
Owner:IVENIX
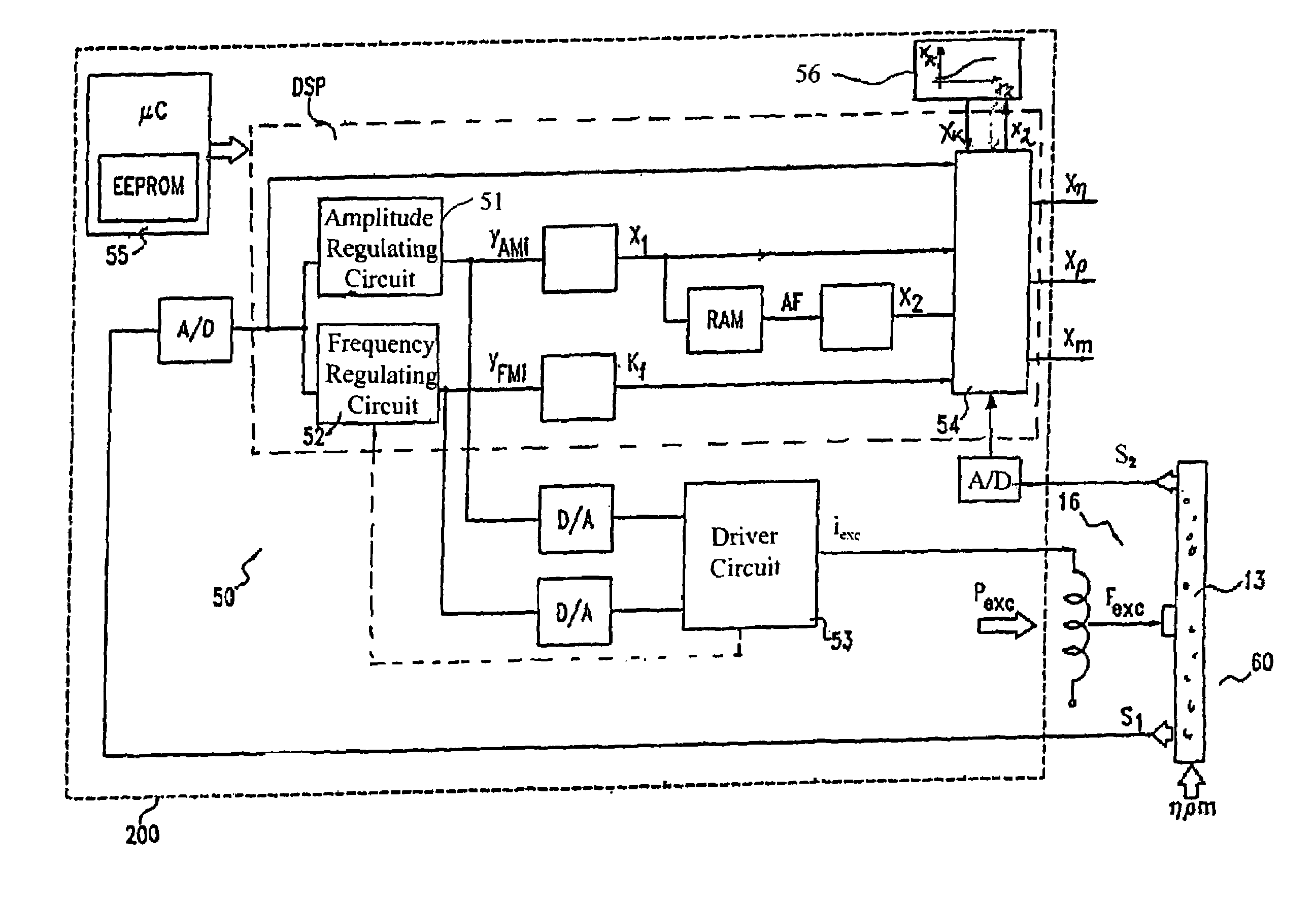
Coriolis mass measuring device
ActiveUS7040181B2Accurate measurementImprove accuracyFlow propertiesVolume meteringMeasurement deviceApparent viscosity
A Coriolis mass flow measuring device includes a vibratory measuring transducer having at least one measuring tube, which has medium flowing through it during operation. In operation, the measuring tube is caused by an exciter arrangement to undergo mechanical oscillations, especially bending oscillations. Additionally, the Coriolis mass flow measuring device includes a sensor arrangement for producing oscillation measurement signals (s1, S2) representing the inlet-end and outlet-end oscillations of the measuring tube. Measuring device electronics controlling the exciter arrangement produces an exciter current (iexc) and an intermediate value (X′m) derived from the oscillation measurement signals (s1, s2). This intermediate value represents an uncorrected mass flow. Derived from the exciter current and / or from a component of the exciter current (iexc), an intermediate value (X2) is produced, which corresponds to a damping of the oscillations of the measuring tube. This damping is especially a function of an apparent viscosity, and / or a viscosity-density product, of the medium guided in the measuring tube. Furthermore, a correction value (XK) is produced for the intermediate value (X′m) utilizing the intermediate value (X2) and a viscosity measurement value (Xη) determined initially or during operation. The viscosity measurement value (Xη) corresponds to a viscosity of the medium guided in the measuring tube and / or to a predetermined reference viscosity. On the basis of the intermediate value (X′m) and the correction value (XK), the measuring device electronics then produces an exact mass flow rate measurement value (Xm).
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
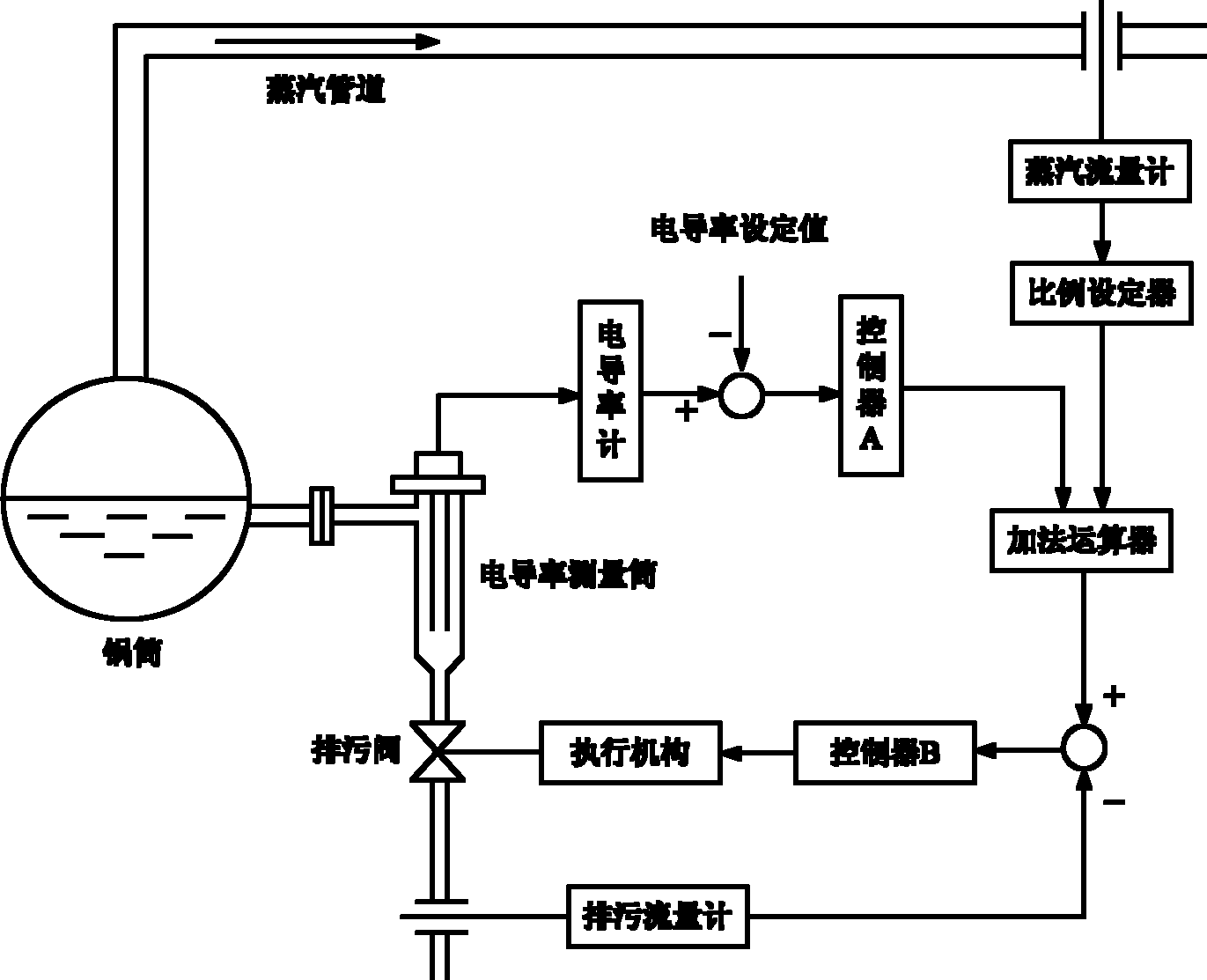
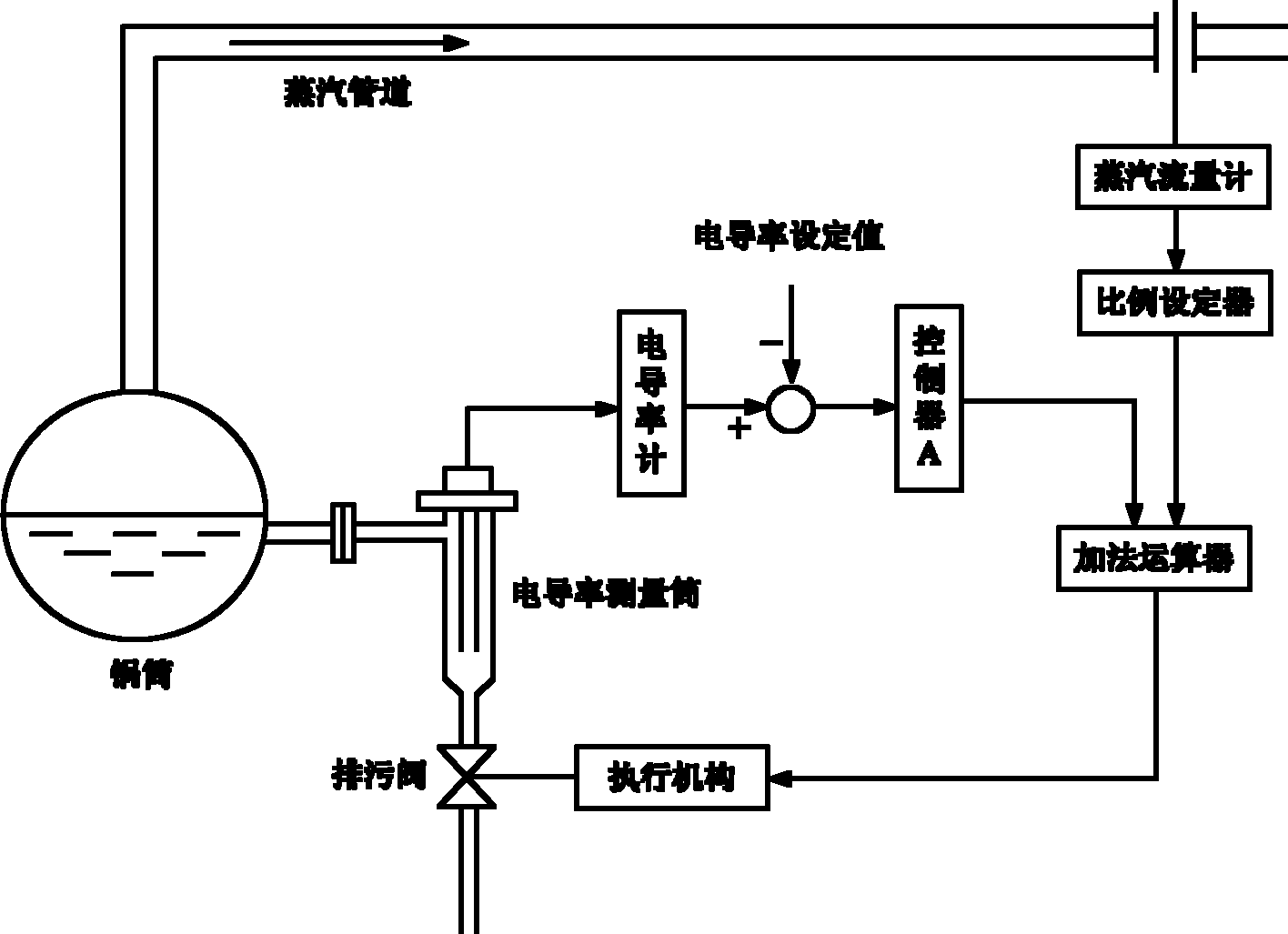
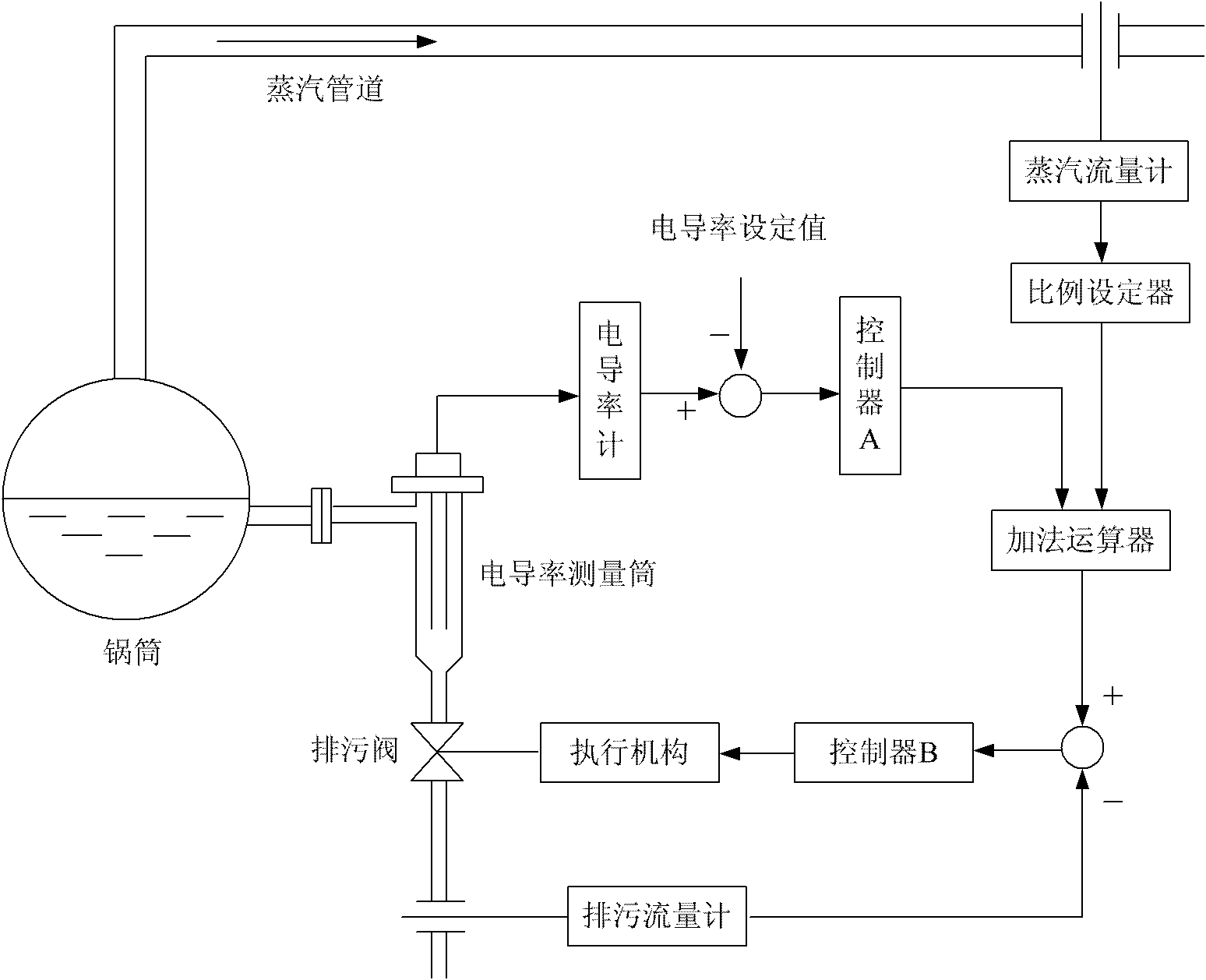
Optimal energy-saving method for controlling surface pollutant discharge of steam boiler
The invention discloses an optimal energy-saving method for controlling the surface pollutant discharge of a steam boiler. The method comprises the steps of firstly controlling the flow of pollutant discharge according to the steam flow proportionally, and continuously diluting water in the steam boiler as required; on this basis, configuring a conductivity close loop control circuit to prevent the influences, such as water supply salinity fluctuation, flow rate measurement error, boiler bottom periodic pollutant discharge and the like, and coupling the both by an addition logic unit so as to form a feedforward-feedback complex control system. The invention can prevent various interferences, stably keep the salinity of the water in the steam boiler above the desired level, and realize the optimal energy-saving and emission-reducing effects by the least pollutant discharge amount.
Owner:西安交大思源科技股份有限公司 +2
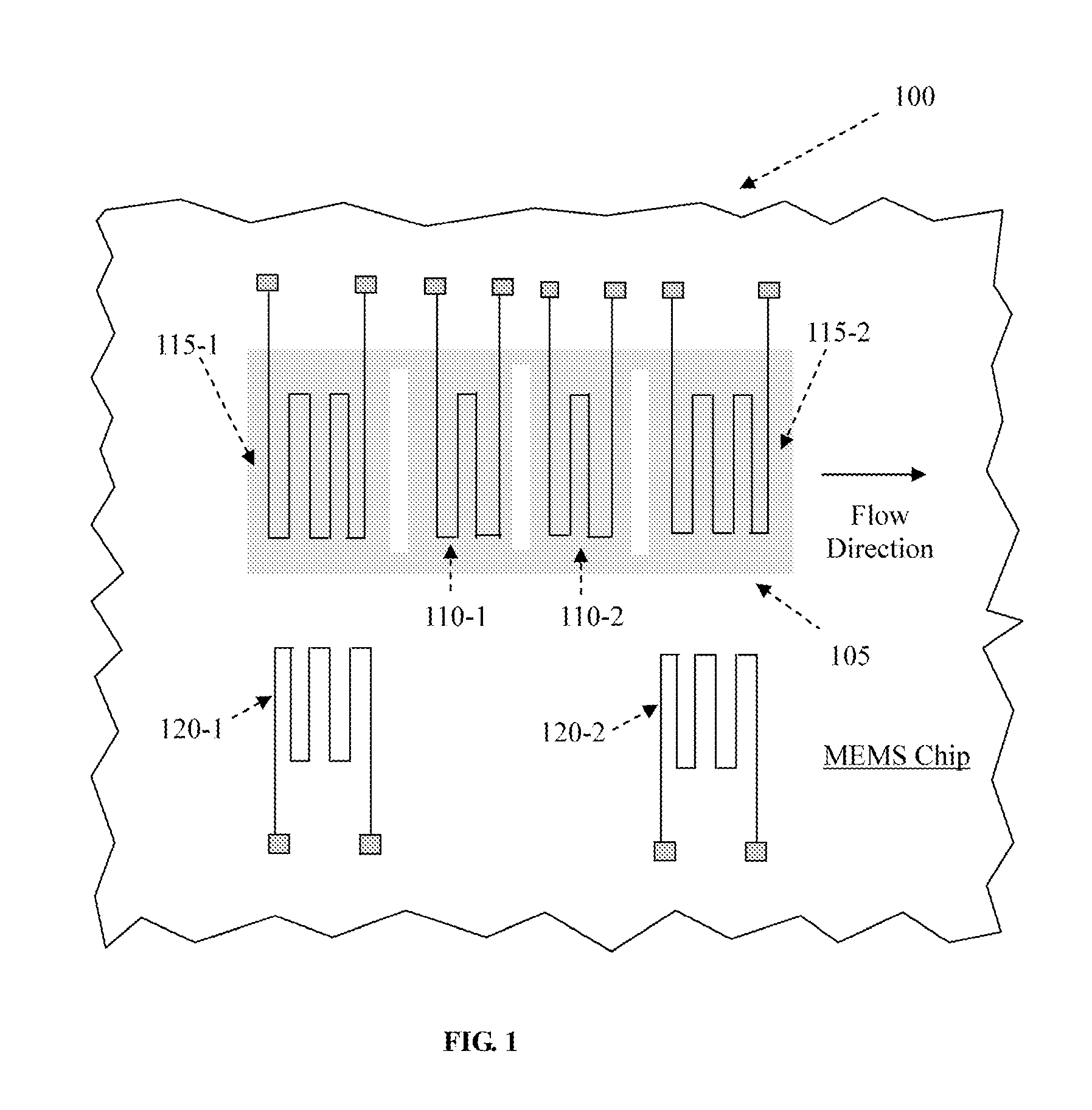
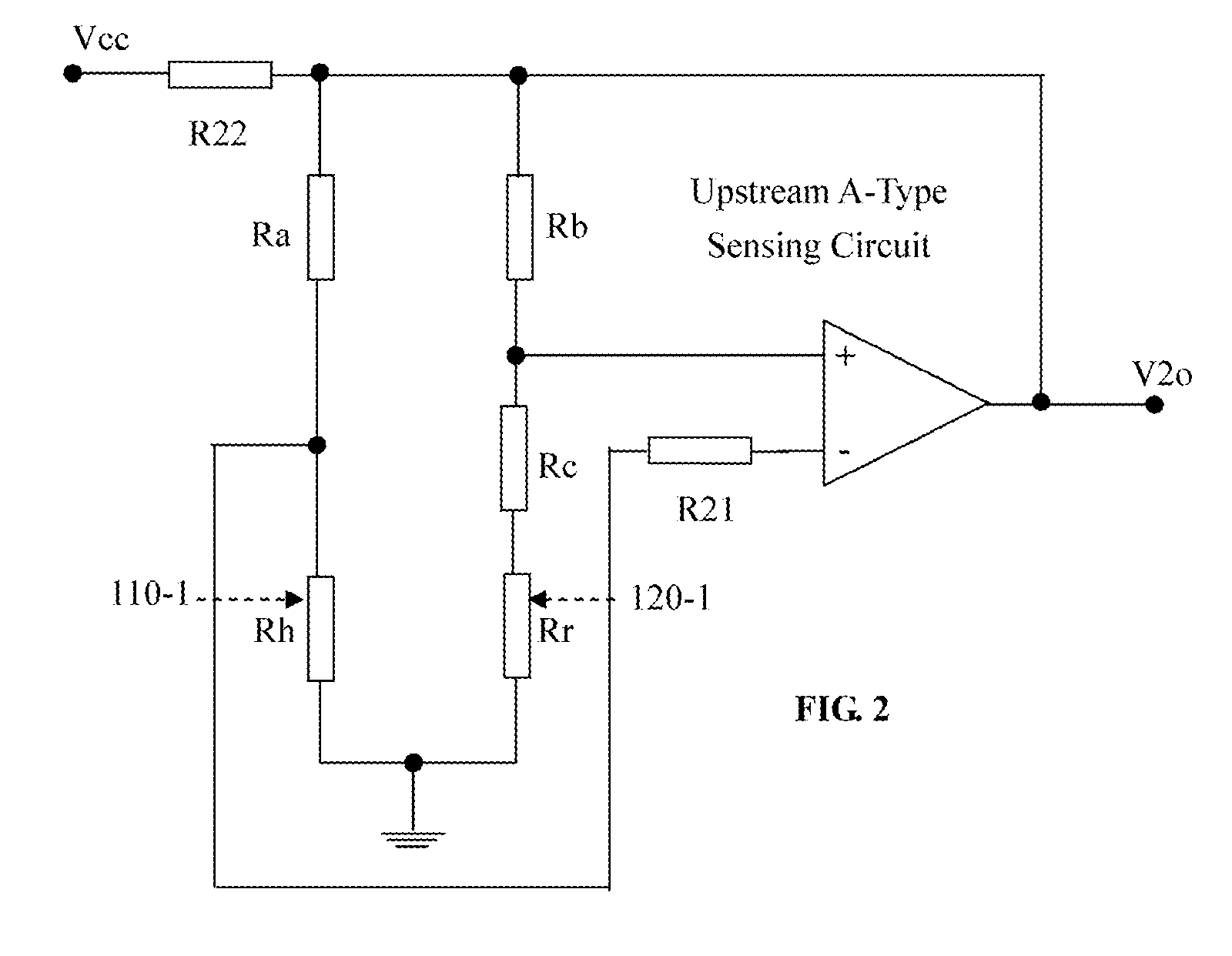
Integrated micromachined thermal mass flow sensor and methods of making the same
ActiveUS20090164163A1Accurate flowIncrease speedTesting/calibration apparatusVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsEngineeringP type silicon
An integrated mass flow sensor is manufactured by a process of carrying out a micro-machining process on an N or P-type silicon substrate with orientation <100>. This mass flow sensor comprises an upstream thin-film heater, an downstream thin-film heater, and a pair of thin-film heat sensing elements, and a thermally isolated membrane for supporting the heaters and the sensors out of contact with the substrate base. This mass flow sensor is operated with three sets of circuits, a first circuit for measuring a flow rate in a first range of flow rates, a second circuit for measuring a flow rate in a second range of flow rates, and a third circuit in a differential configuration for measuring a flow rate in said first range of flow rates or said second range of flow rates, to significantly increase range of flow rate measurements and provide an optional for concentration measurement, while maintains a high degree of measurement accuracy.
Owner:M TECH INSTR HLDG
Apparatus and method for augmenting a Coriolis meter
ActiveUS7299705B2High densityAdd additional massMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume meteringDischarge measurementsUsage analysis
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Compact flow meter
InactiveUS20040244501A1Material analysis using microwave meansVolume/mass flow by differential pressureDifferential pressureEngineering
Apparatus for measuring the composition and flow rate of a fluid (1) comprising a mixture of e.g. oil and water in a pipe (2), wherein an integrated mechanical structure (3) serves as a microwave resonator sensor for providing permittivity measurements and where the mechanical structure also functions as a differential pressure element for providing flow rate measurements.
Owner:ROXAR FLOW MEASUREMENT
Full self-determination type underground pipeline measuring systems based on inertia technology
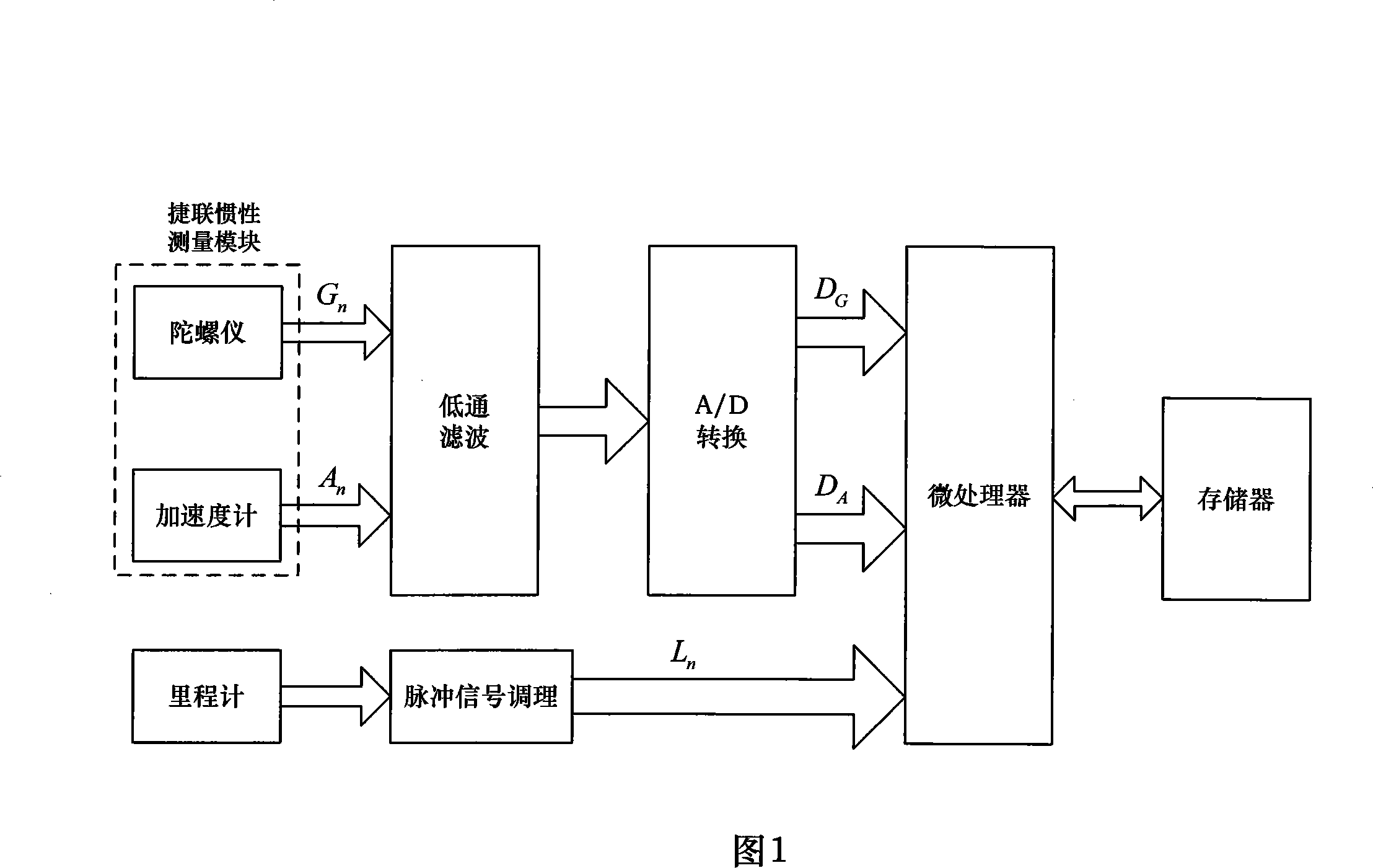
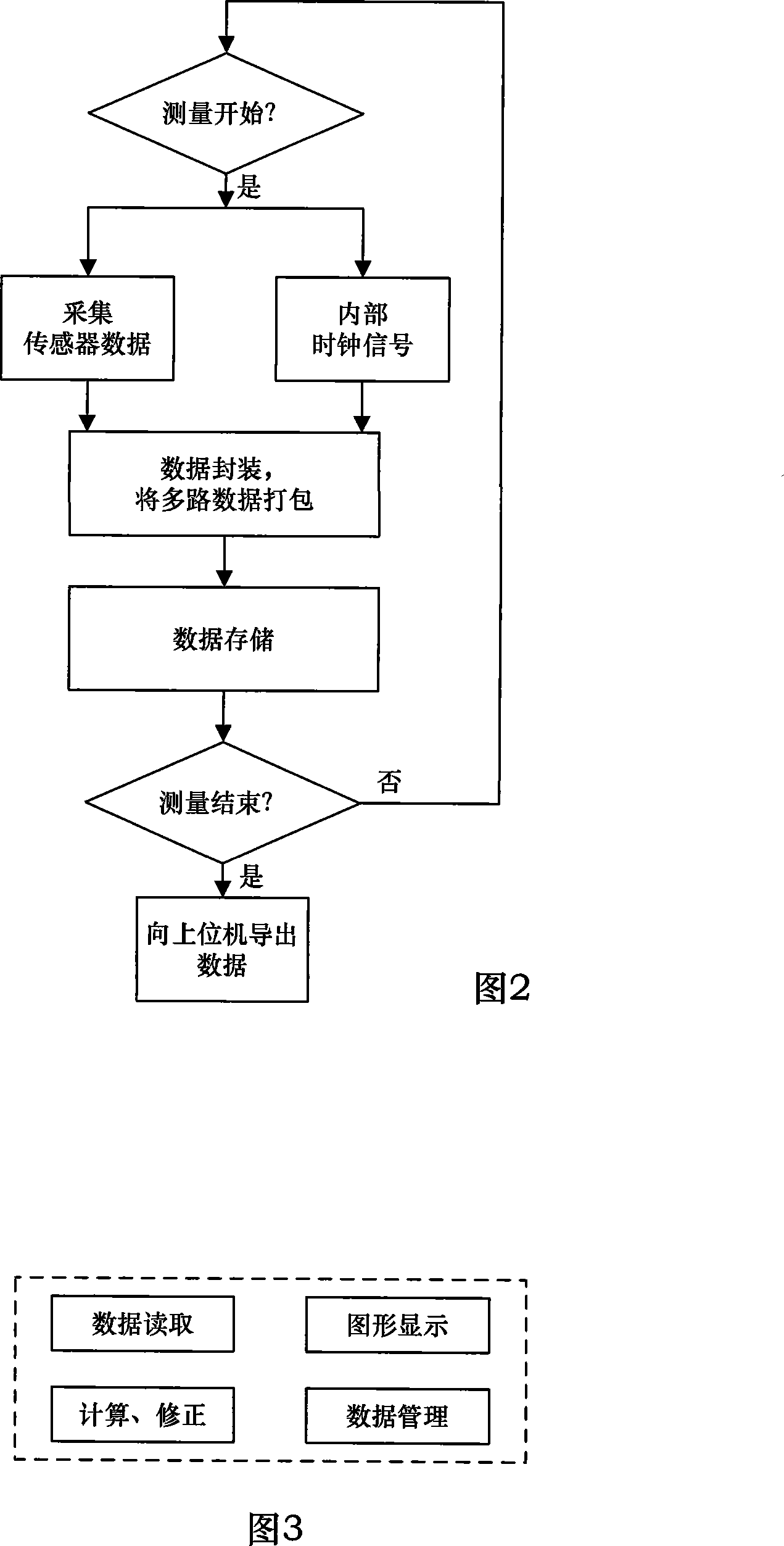
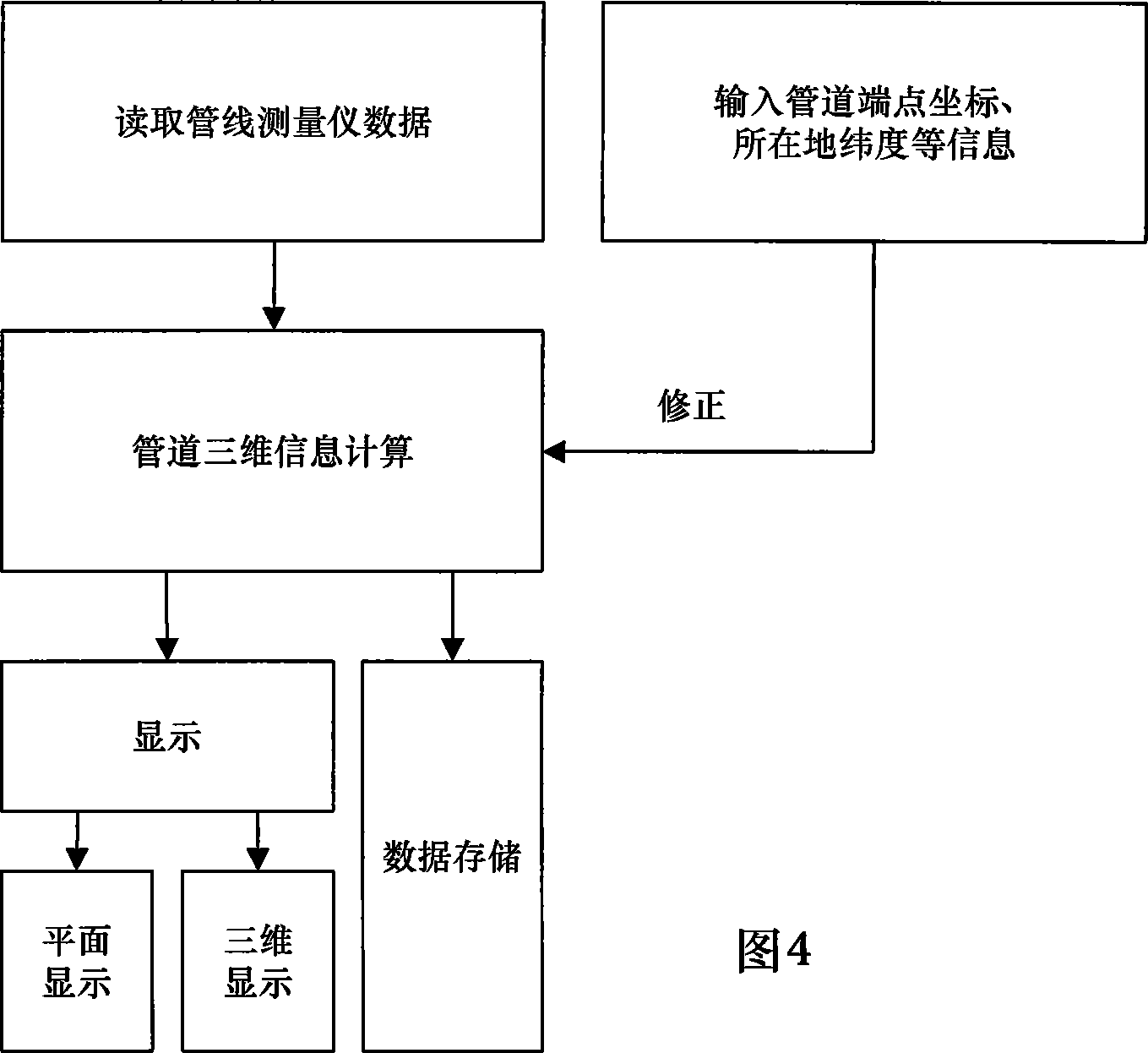
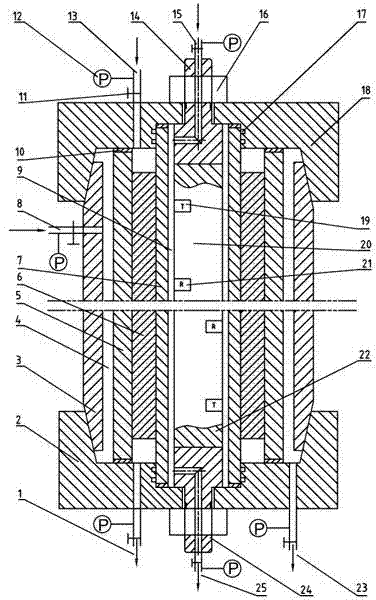
InactiveCN101118159ANot affectedBeacon systems using radio wavesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeLine tubing
The present invention discloses a full-autonomous underground pipeline measurement system based on an inertia technology, and the system consists of an in-pipe measurement unit, an external control unit, and a data information processing unit. The in-pipe measurement unit is arranged into a pipeline being measured and is caused to move along the central axle line of the pipeline, the three dimensional information of the pipeline can be completely gotten through measuring the moving track of the in-pipe measurement unit. The system adopts a strapped-down inertial navigation technology to measure the course heading and the attitude angle of the in-pipe measurement unit (carrier), the angular motion information of the carrier is measured according to the gyro output angle rate, each instant accurate location of the carrier can be analyzed according to the integrated angle and the displacement information, thereby the three dimensional information of the pipeline can be obtained. The operation of the in-pipe measurement unit is irrelevant to the external factor such as depth, location, peripheral electromagnetic field, etc., not limited by other conditions, the integrated course angle, the attitude angle, and the instant location information of a navigation principle are applied to any depth, and the three dimensional information of the pipeline waiting for measuring can be independently measured.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Device and method for evaluating influence of pressure change on completeness of cement sheath
The invention provides a device and a method for real simulation of underground environments, completeness maintaining of experiment equipment, and accurate and omnibearing evaluation of completeness of a cement sheath. The device mainly comprises an upper end cap, a lower end cap, an outer pipe, a middle pipe, the cement sheath, a sleeve pipe, a long source distance sector cement bond logging instrument (SBT (segmented bond tool)) and a high-temperature and high-pressure kettle. The method comprises the following steps of utilizing the high-temperature and high-pressure kettle to simulate the stratum temperature pressure of the curing and forming of the cement sheath; loading and unloading an inner annulus and an outer annulus, so as to simulate the actions of change of well shaft pressure and stratum pressure on the cement sheath under the actual working condition; utilizing a transmitting probe and a receiving probe of the SBT to continuously transmit and receive acoustic wave signals, and performing the omnibearing and high-resolution compensation type attenuation rate measurement, so as to obtain the bonding qualities of a first interface and a second interface of the cement sheath of the well cementing cement sheath under the actual stratum environment, and the amounts, sizes and bearings of cracks and channeling in the cement sheath. The device and the method have the advantage that the underground environment can be really simulated in the omnibearing way, so as to accurately and efficiently evaluate the completeness of the well cementing cement sheath, provide the new method and basis for indoor cement slurry evaluation systems and sites to take the targeted measures, and improve the well cementing quality.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com