Patents
Literature
1035results about "Indirect mass flowmeters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
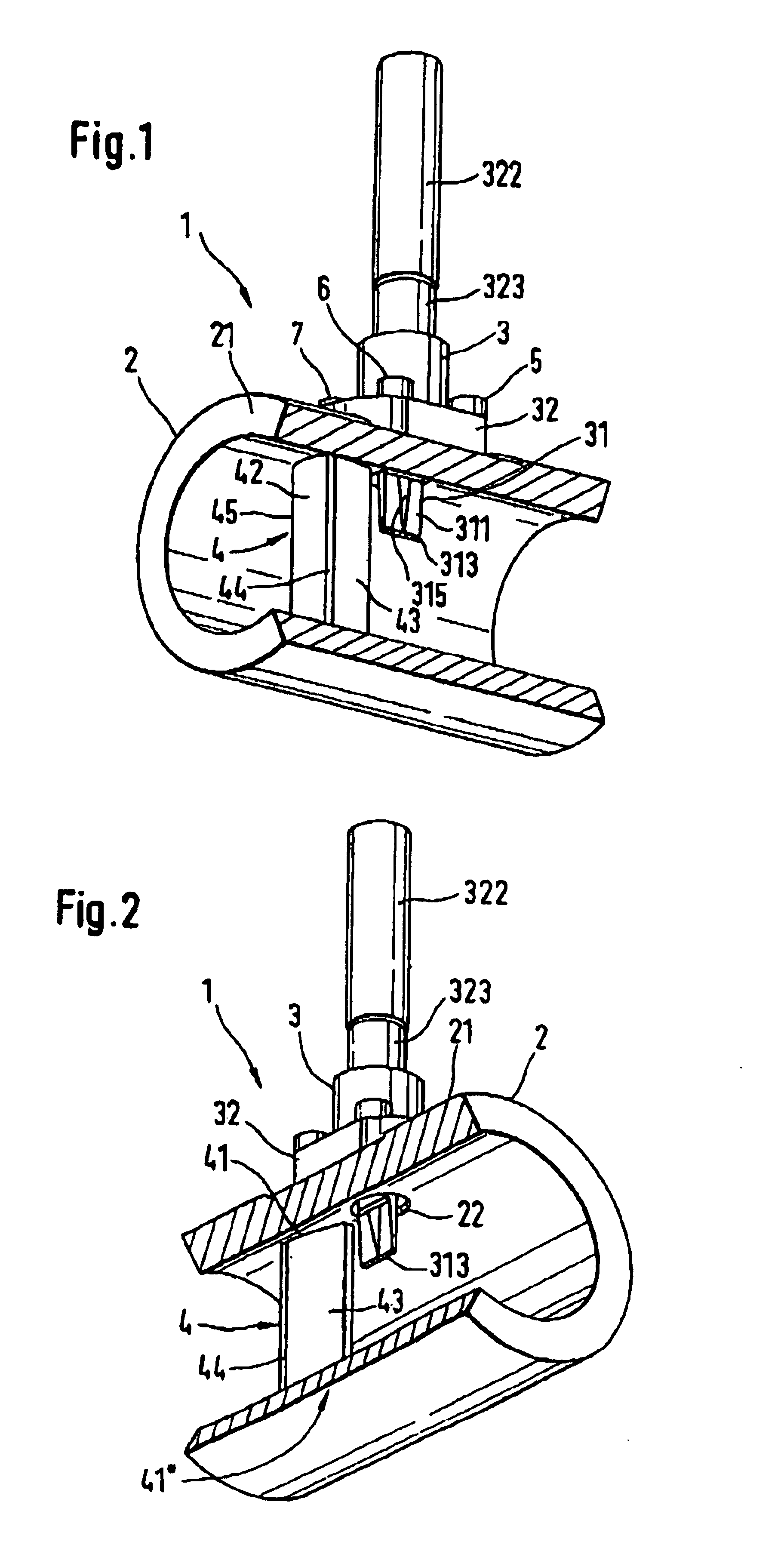
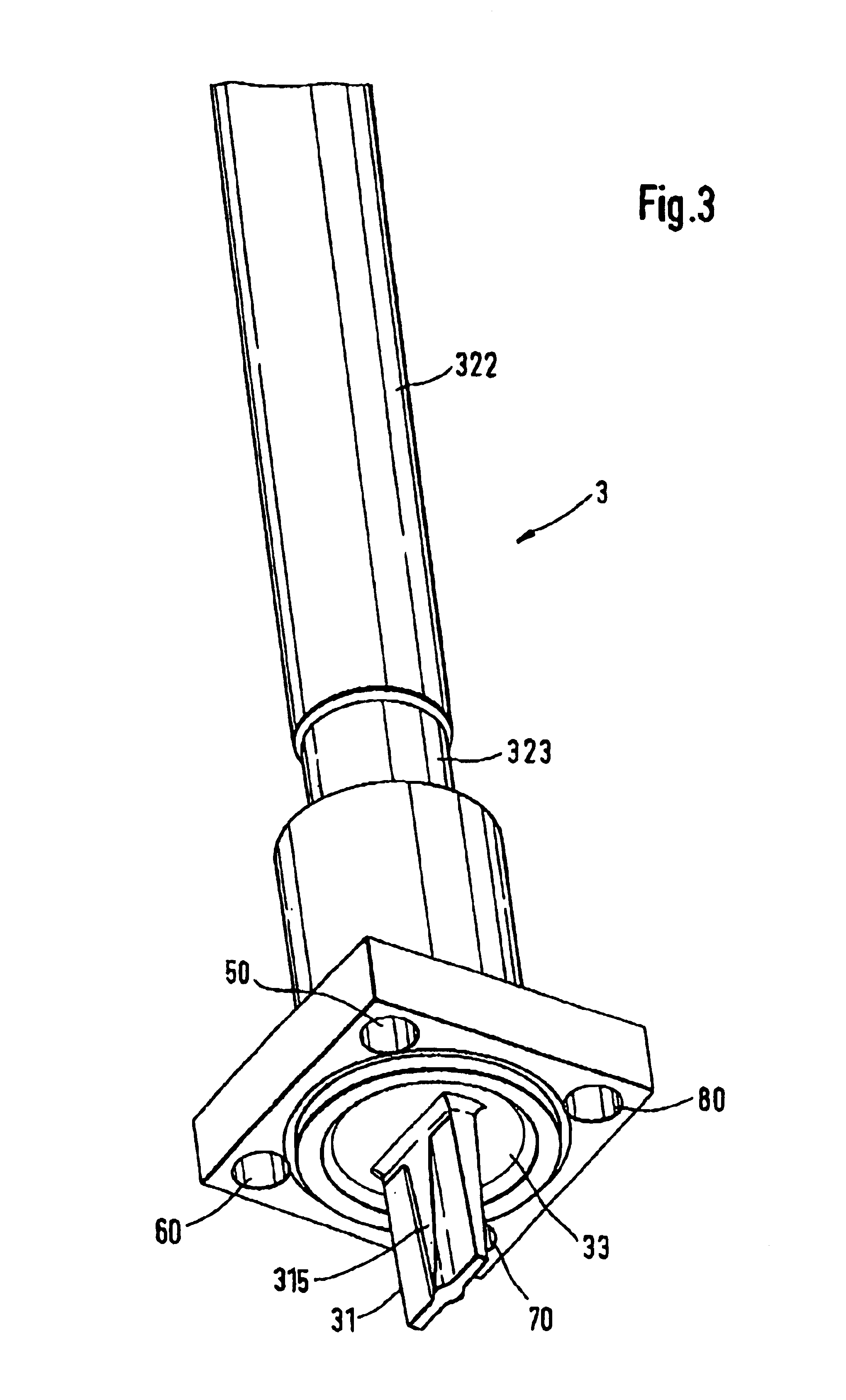
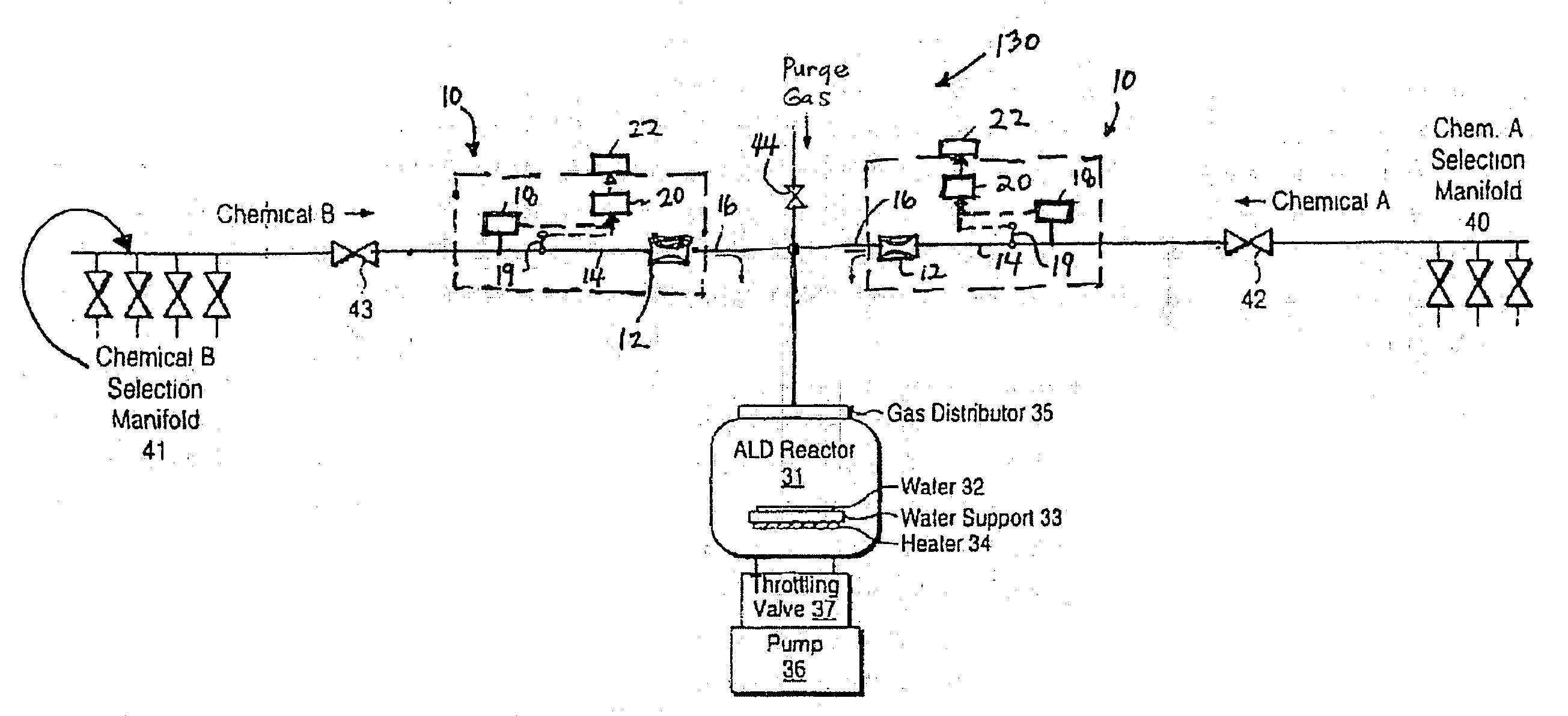
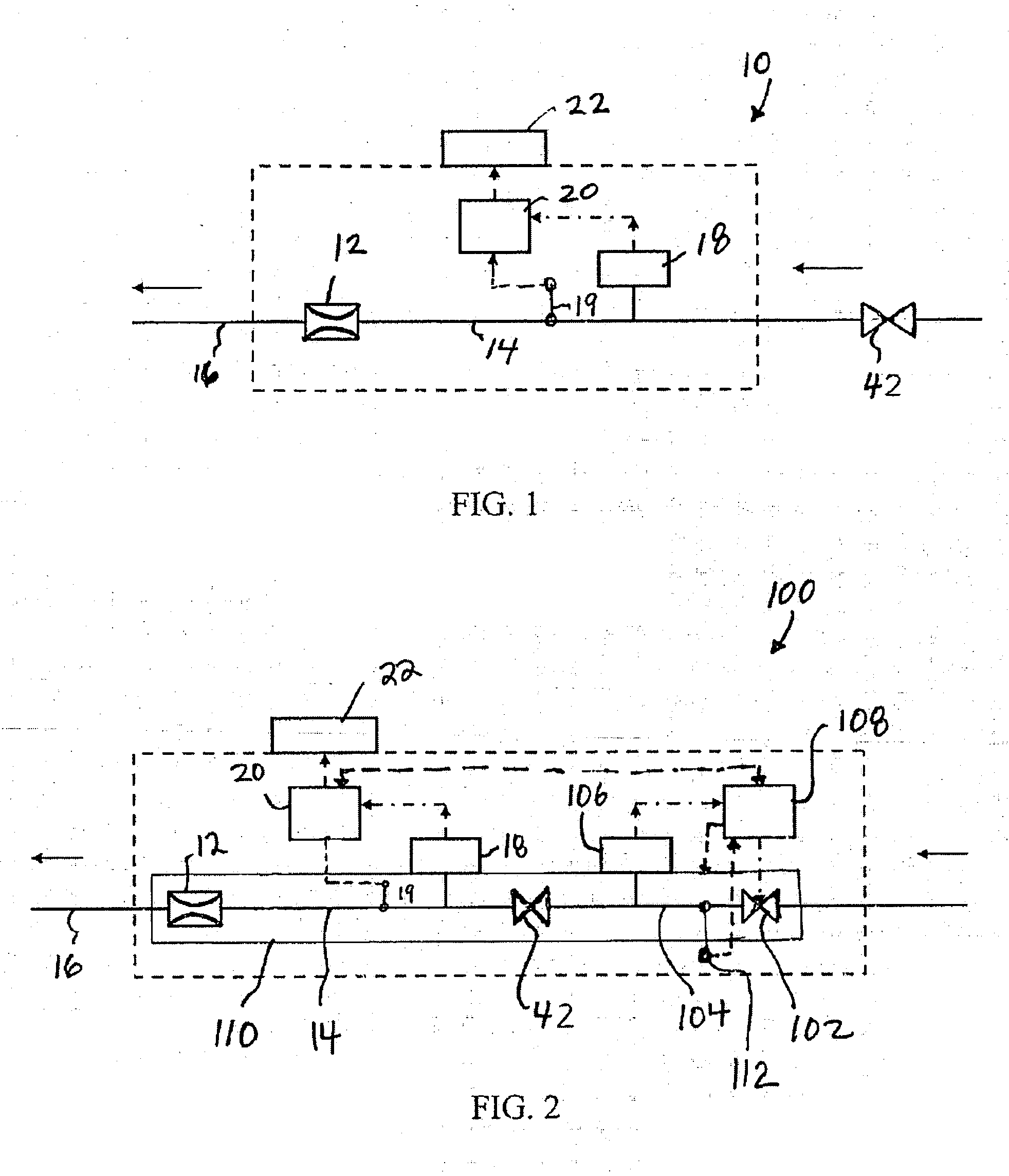
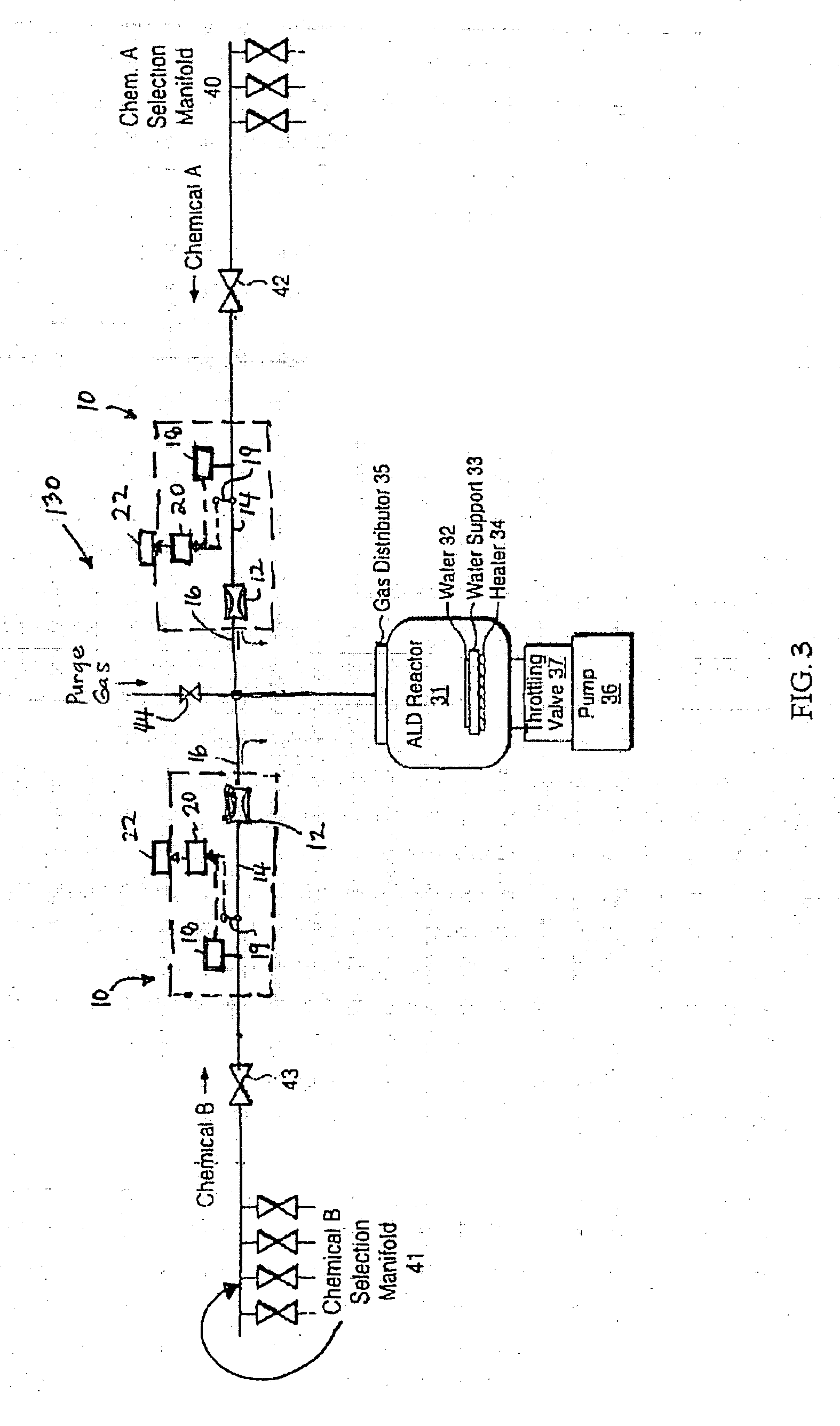
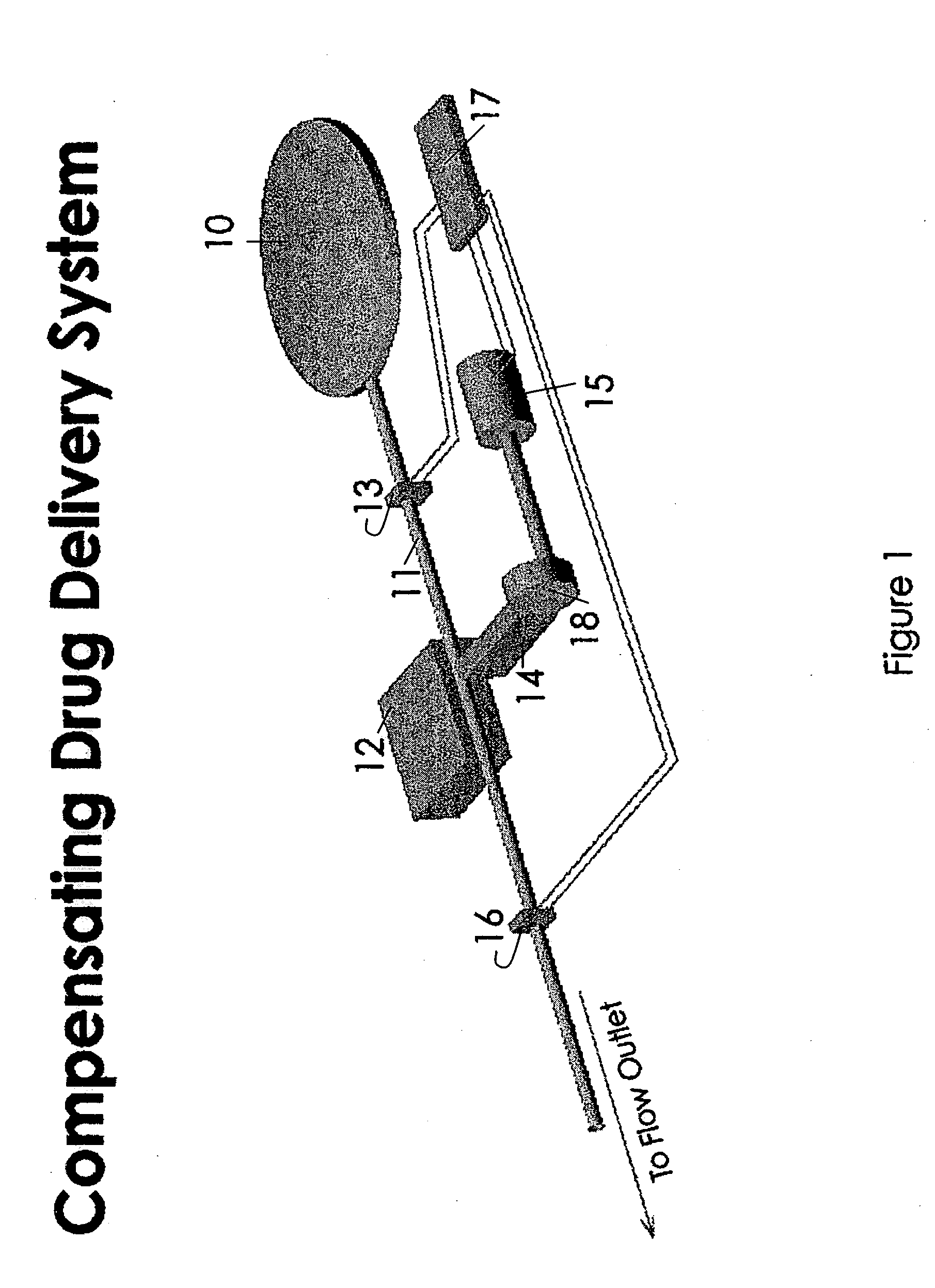
Method for wide range gas flow system with real time flow measurement and correction
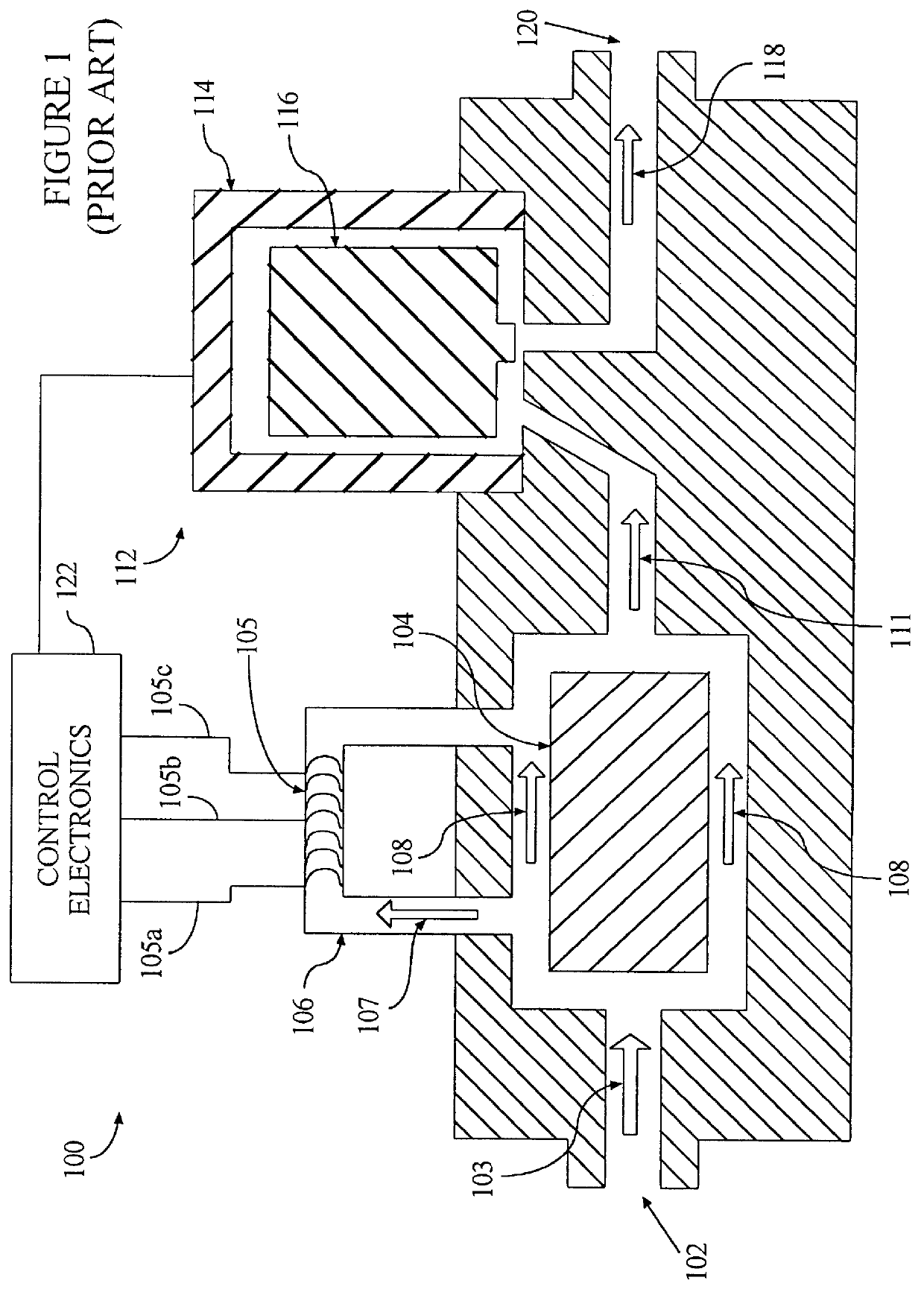
InactiveUS6119710AAccurate measurementAccurate flowOperating means/releasing devices for valvesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsDifferential pressureInlet valve
A gas delivery system accurately measures and optionally regulates mass flow rate in real time. A fluid conduit connects an inlet valve, calibration volume, flow restrictor, and outlet valve in series. Pressure and temperature sensors are coupled to the calibration volume. One or more pressure sensors may be attached across the flow restrictor. Alternatively, an absolute pressure sensor may be attached upstream of the flow restrictor. One embodiment of differential pressure sensors comprises a floating reference differential pressure sensor, including a first transducer attached to the fluid conduit upstream of the flow restrictor and a second transducer attached to the conduit downstream of the flow restrictor. In this embodiment, each transducer receives a reference pressure from a reference source, and optionally, after the calibration volume is charged, the floating reference differential pressure transducers are calibrated. When gas flow is initiated, differential and / or absolute pressure measurements are repeatedly taken, and a measured mass flow rate calculated thereon. Gas flow is adjusted until the measured mass flow rate reaches a target mass flow. Using the temperature / pressure sensors at the calibration volume, repeated calculations of actual flow rate are made to uncover any discrepancy between actual and measured mass flow rates. Whenever a discrepancy is found, the manner of calculating measured mass flow is conditioned to account for the discrepancy; thus, the measured mass flow rate more accurately represents the actual mass flow rate thereby providing an actual mass flow rate more accurately achieving the target mass flow rate.
Owner:CYBER INSTR TECH LLC AN ARIZONA LIMITED LIABILITY +1
Flow meter
Various embodiments of the present invention provide a flow meter device having a laser Doppler anemometer (LDA) which measures the instantaneous center line velocity of fluid flow in a pipe. The flow meter may process the instantaneous velocity so obtained to compute the volumetric flow rate, mass rate, and / or other flow characteristics (e.g., as instantaneous quantities and / or integrated over a time interval) The flow meter may use an electronic processing method. The electronic processing method may provide essentially an exact solution to the Navier-Stokes equations for any periodically oscillating flow.
Owner:COMBUSTION DYNAMICS
Ultrasonic flow metering system
InactiveUS6487916B1EliminateAvoid missing signalAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalEngineeringSystem usage
A system for determining the density, flow velocity, and mass flow of a fluid comprising at least one sing-around circuit that determines the velocity of a signal in the fluid and that is correlatable to a database for the fluid. A system for determining flow velocity uses two of the inventive circuits with directional transmitters and receivers, one of which is set at an angle to the direction of flow that is different from the others.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
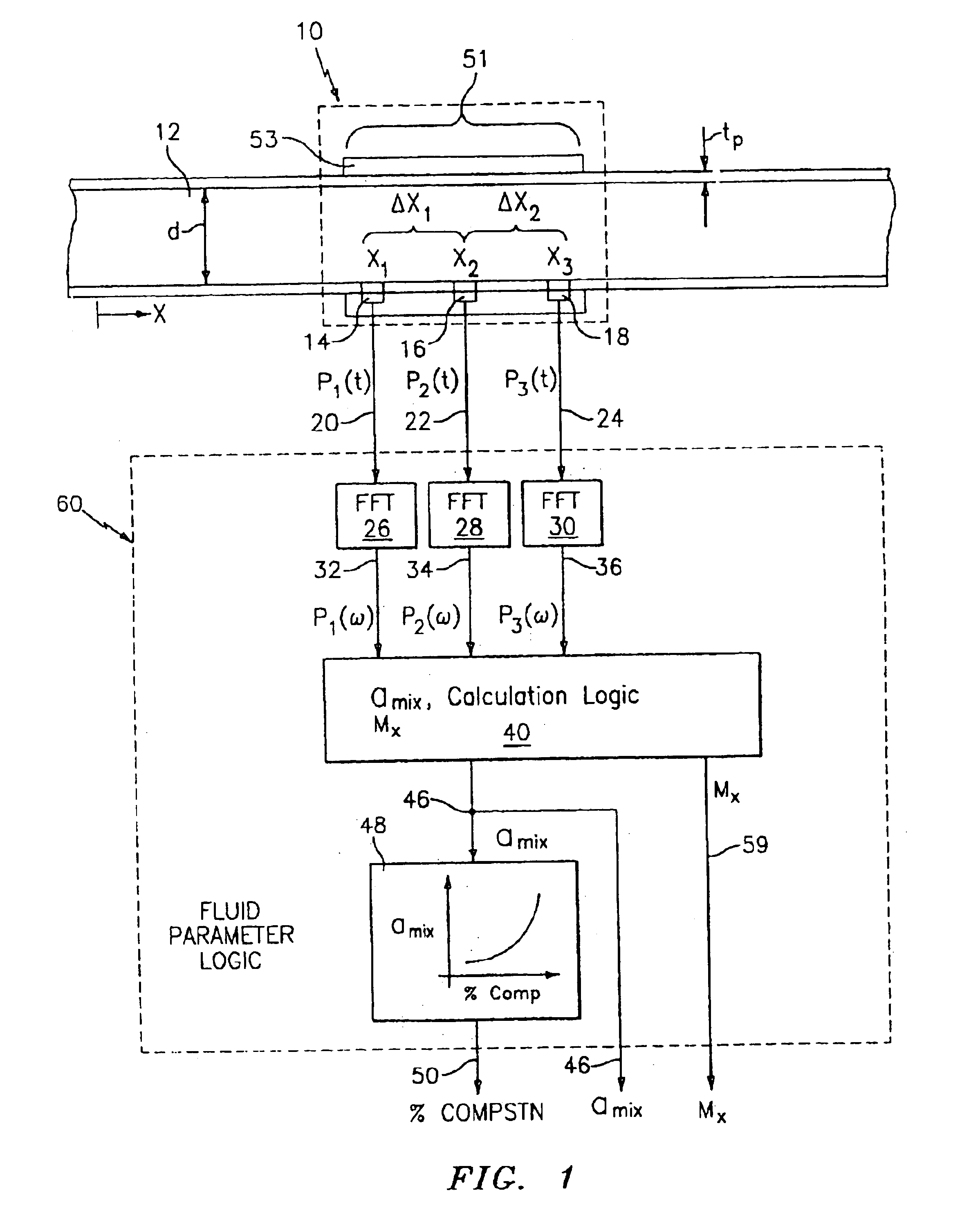
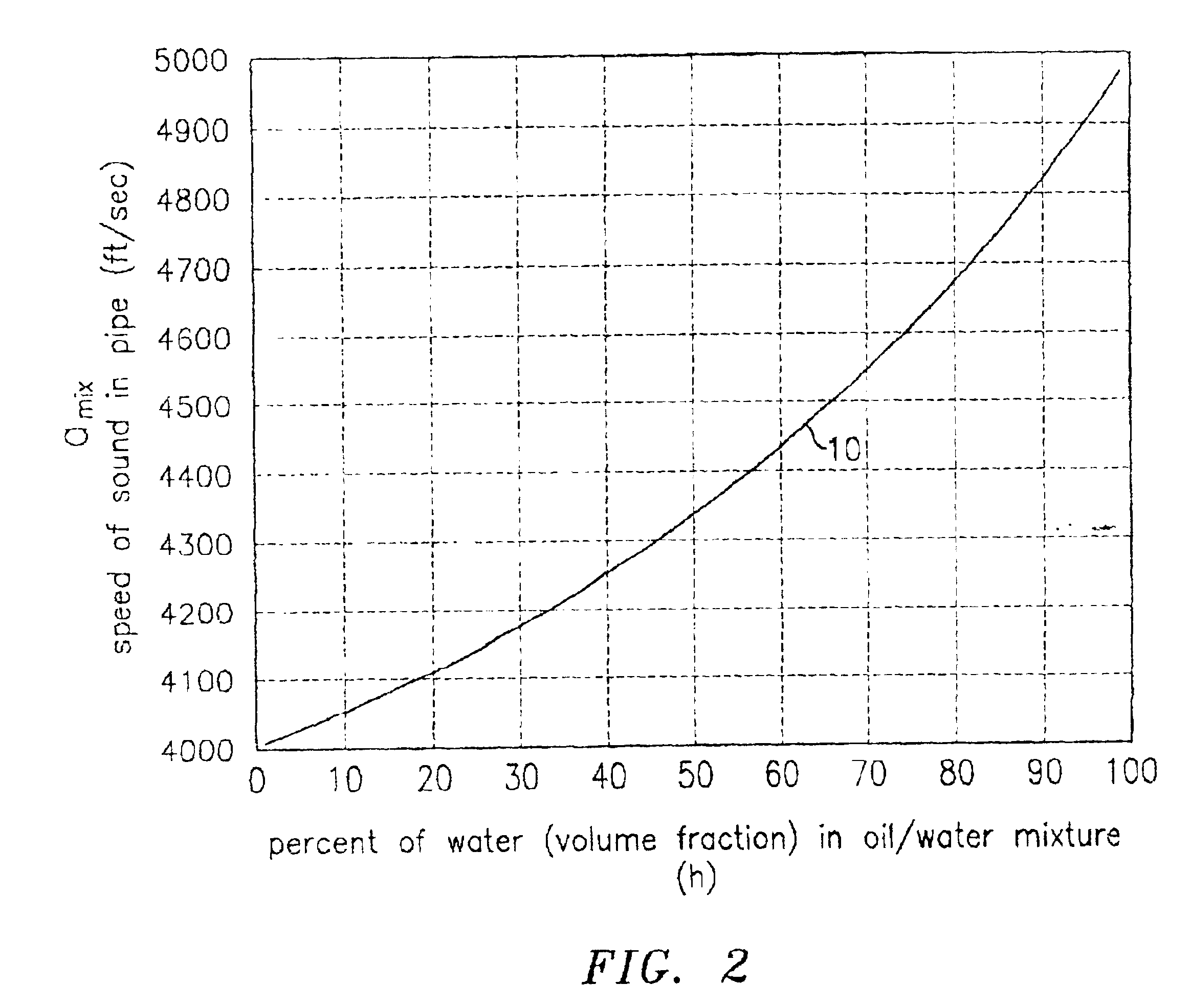
Fluid parameter measurement in pipes using acoustic pressures
InactiveUS6862920B2Less sensitive to static shifts (or errors) in sensingImprove measurement reliabilityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringWater fraction
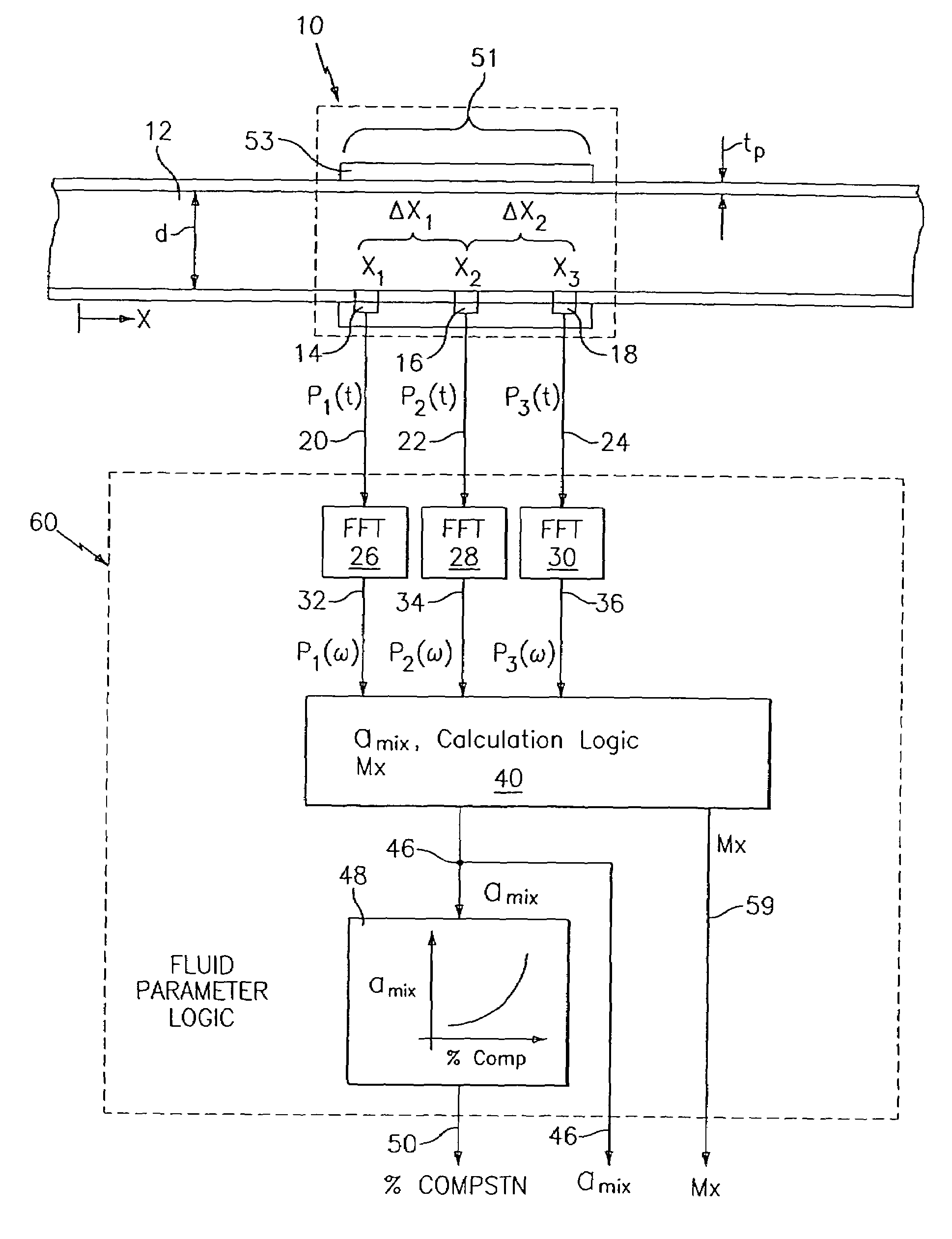
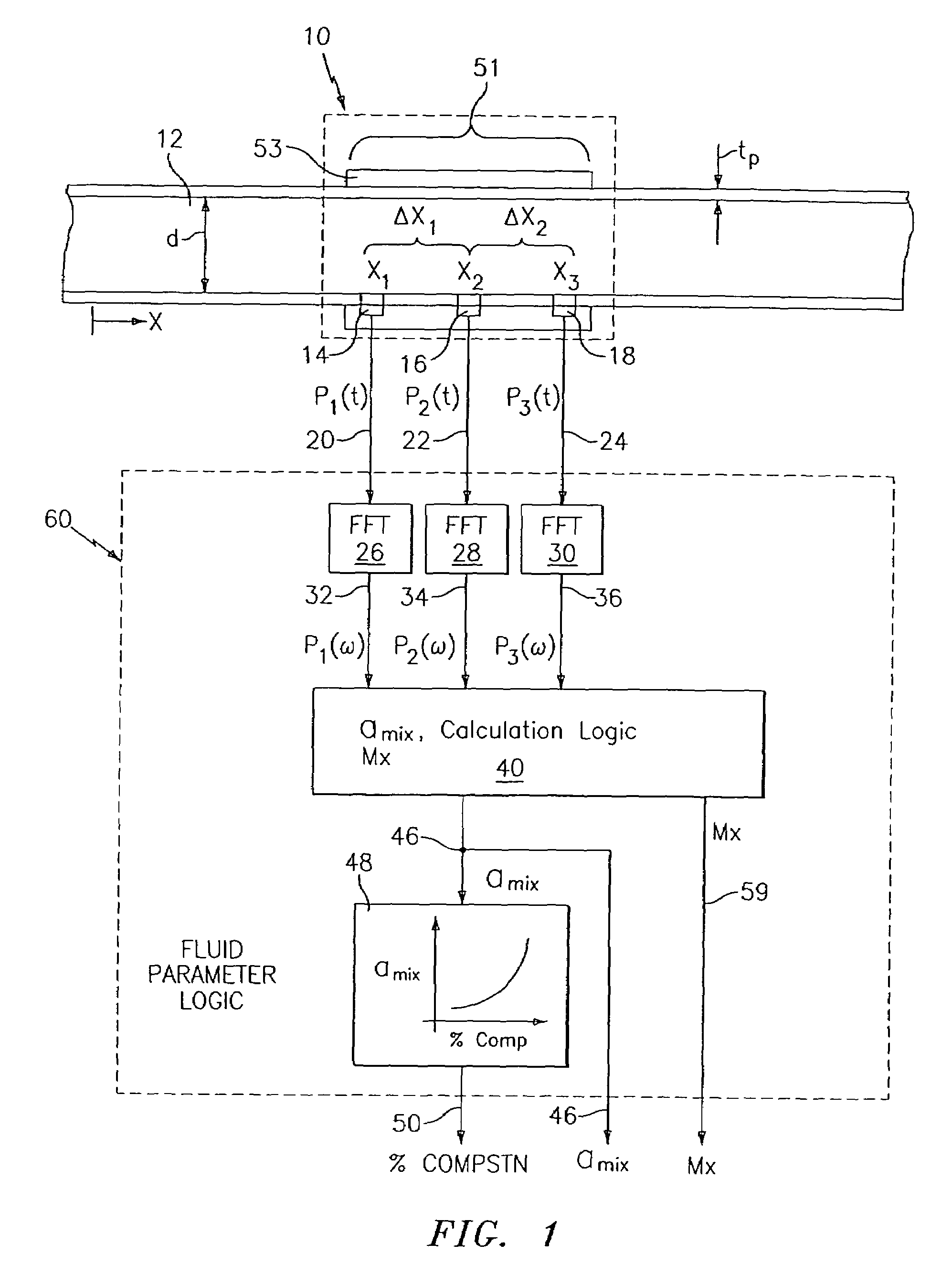
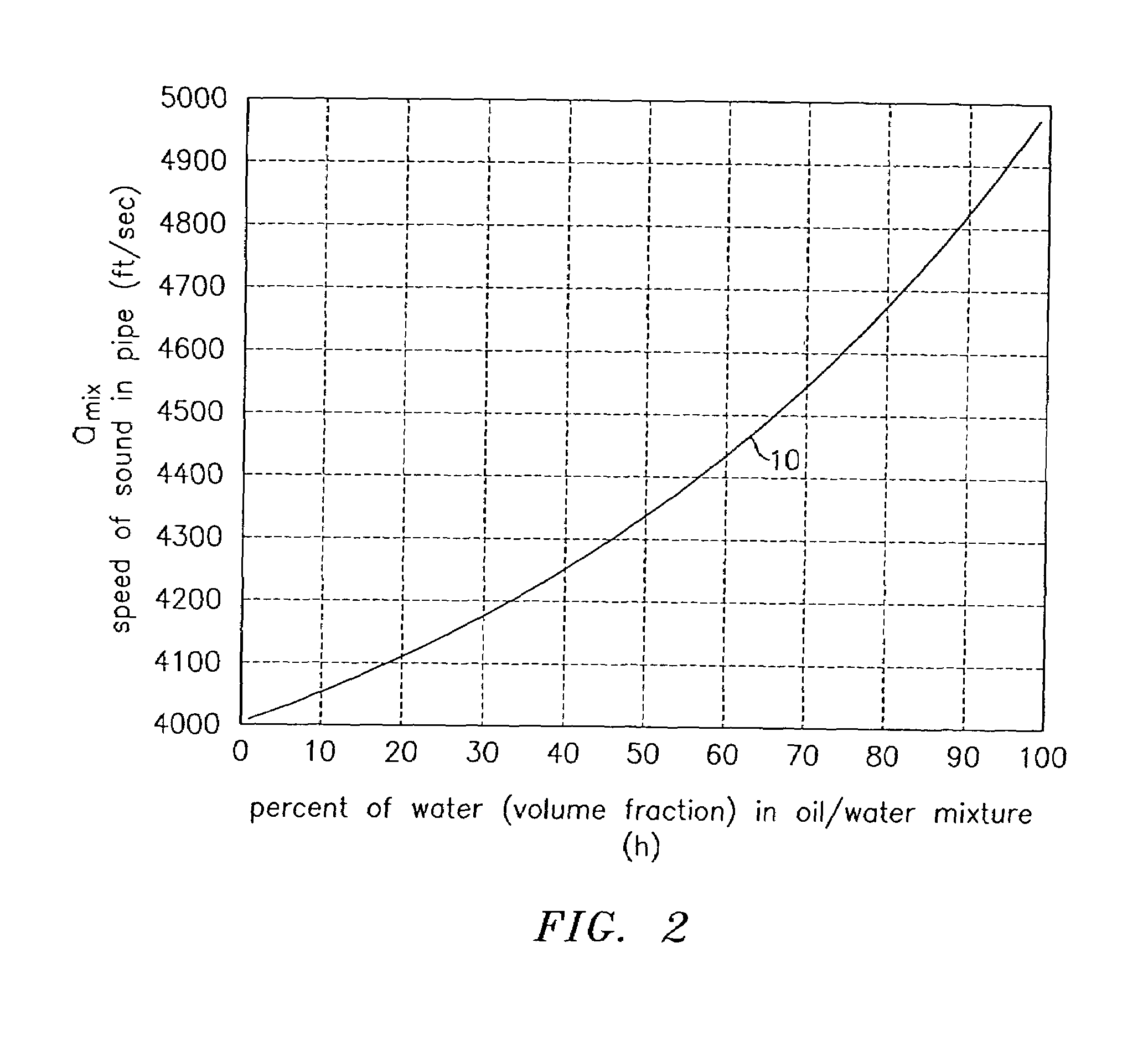
At least one parameter of at least one fluid in a pipe is measured using a spatial array of acoustic pressure sensors placed at predetermined axial locations along the pipe 12. The pressure sensors provide acoustic pressure signals, which are provided to a signal processing system that determines the speed of sound amix of the fluid (or mixture) in the pipe 12 using acoustic spatial array signal processing techniques. Numerous spatial array processing techniques may be employed to determine the speed of sound amix. The speed of sound amix is provided to another logic system that calculates the percent composition of the mixture, e.g., water fraction, or any other parameter of the mixture or fluid which is related to the sound speed amix. The signal processing system may also determine the Mach number Mx of the fluid. The acoustic pressure signals measured are lower frequency (and longer wavelength) signals than those used for ultrasonic flow meters, and thus are more tolerant to inhomogeneities in the flow. No external source is required and thus may operate using passive listening. The invention will work with arbitrary sensor spacing and with as few as two sensors if certain information is known about the acoustic properties of the system.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Flow measuring apparatus
ActiveUS20110271769A1Reliable and accurate measurementImprove energy transferFlow propertiesVolume flow measuring devicesPropagation timeUltrasonic radiation
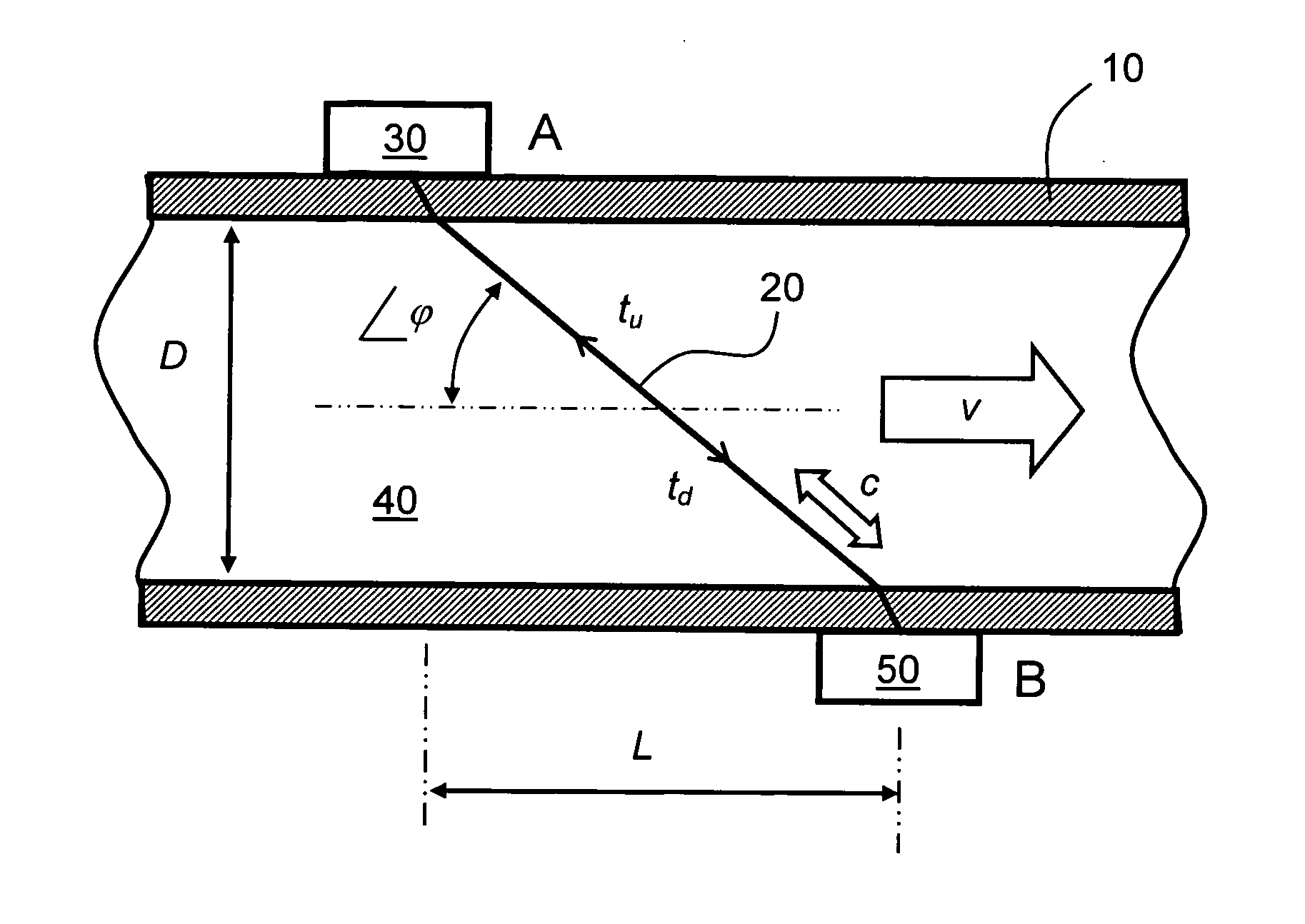
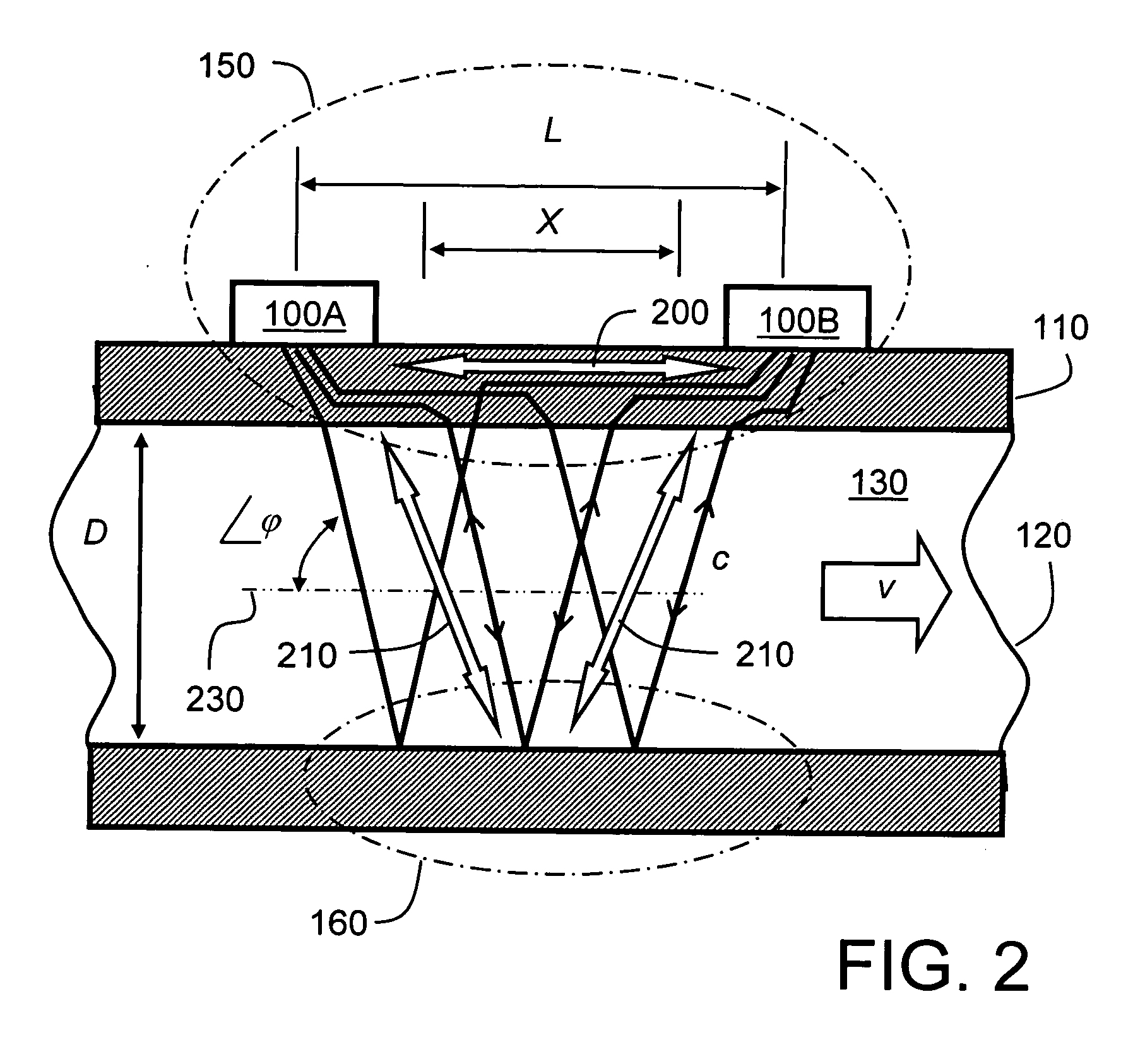
A flow measuring apparatus (300, 500) measures a fluid flow (130) within a conduit (120) including a wall (110). The apparatus (300, 500) includes a transducer arrangement including at least two transducers (100A, 100B) for alternately emitting and receiving ultrasonic radiation through the conduit wall (110) and the flow (130). The apparatus (300, 500) also includes a signal processing arrangement (310) for generating signals to excite the transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) and for processing received signals provided by the transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) for generating output signals from the signal processing arrangement (310) indicative of properties of the flow. The transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) in cooperation with the conduit (120) provides a first path (200) for Lamb-wave ultrasonic radiation coupling directly from a first of the at least two transducers (100A, 100B), to a second of said at least two transducers to generate a first received signal. The transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) in cooperation with the conduit (120) provides at least one second path (210) for ultrasonic propagation along the wall (100) via Lamb waves coupling to at least a portion of the flow (130) from a first of the at least two transducers (100A, 100B) to a second of the at least two transducers (100A, 100B) to generate a second received signal. The signal processing arrangement (310) determines from said first and second received signals ultrasonic radiation propagation time periods through the first path (200) and through the at least one second path (210), and to perform computational operations on the propagation time periods to determine properties of the flow including, but not limited to, at least one of: fluid flow velocity (v) in the conduit (120), a sound velocity (c) through the fluid (130).
Owner:XSENS
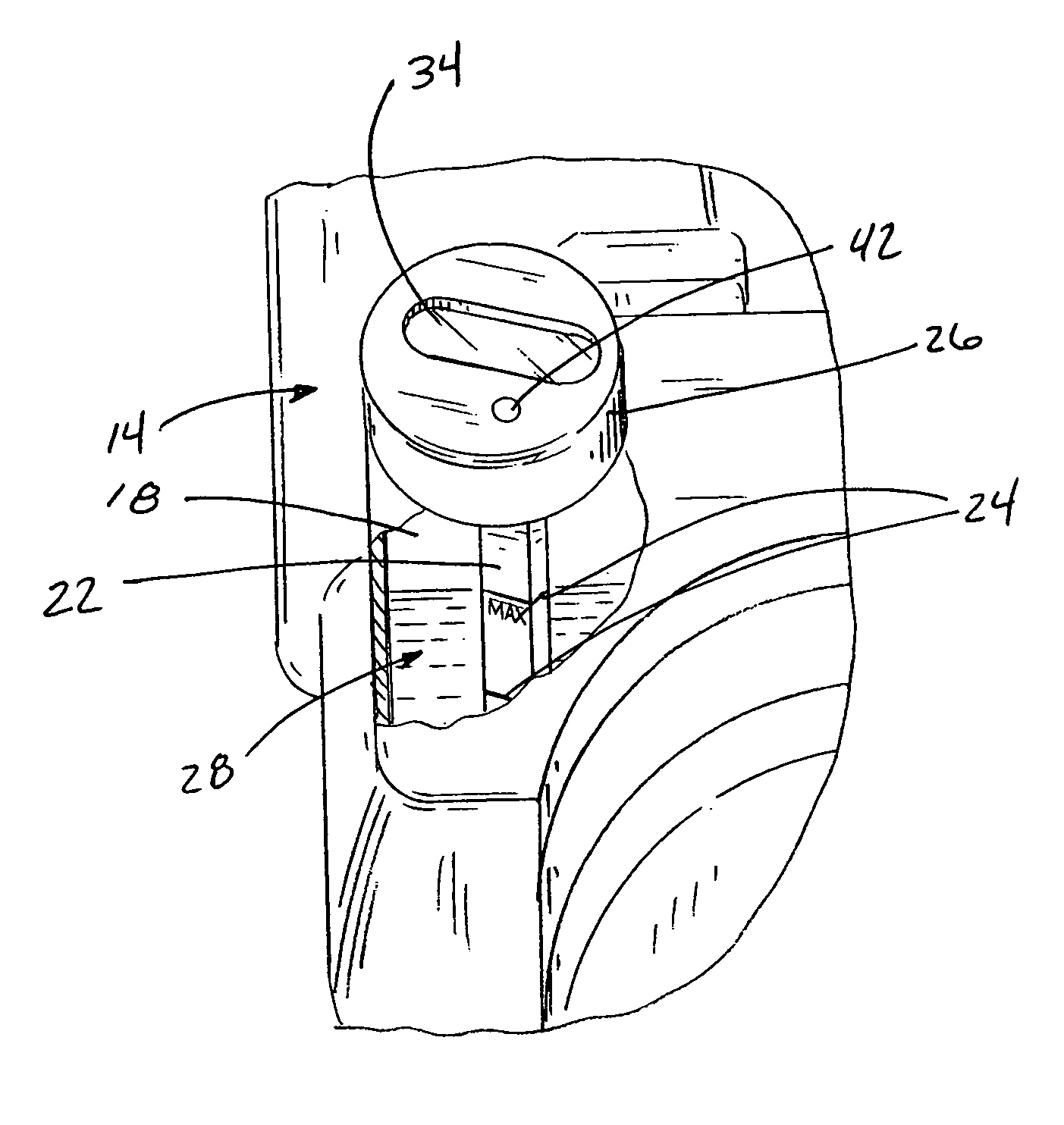
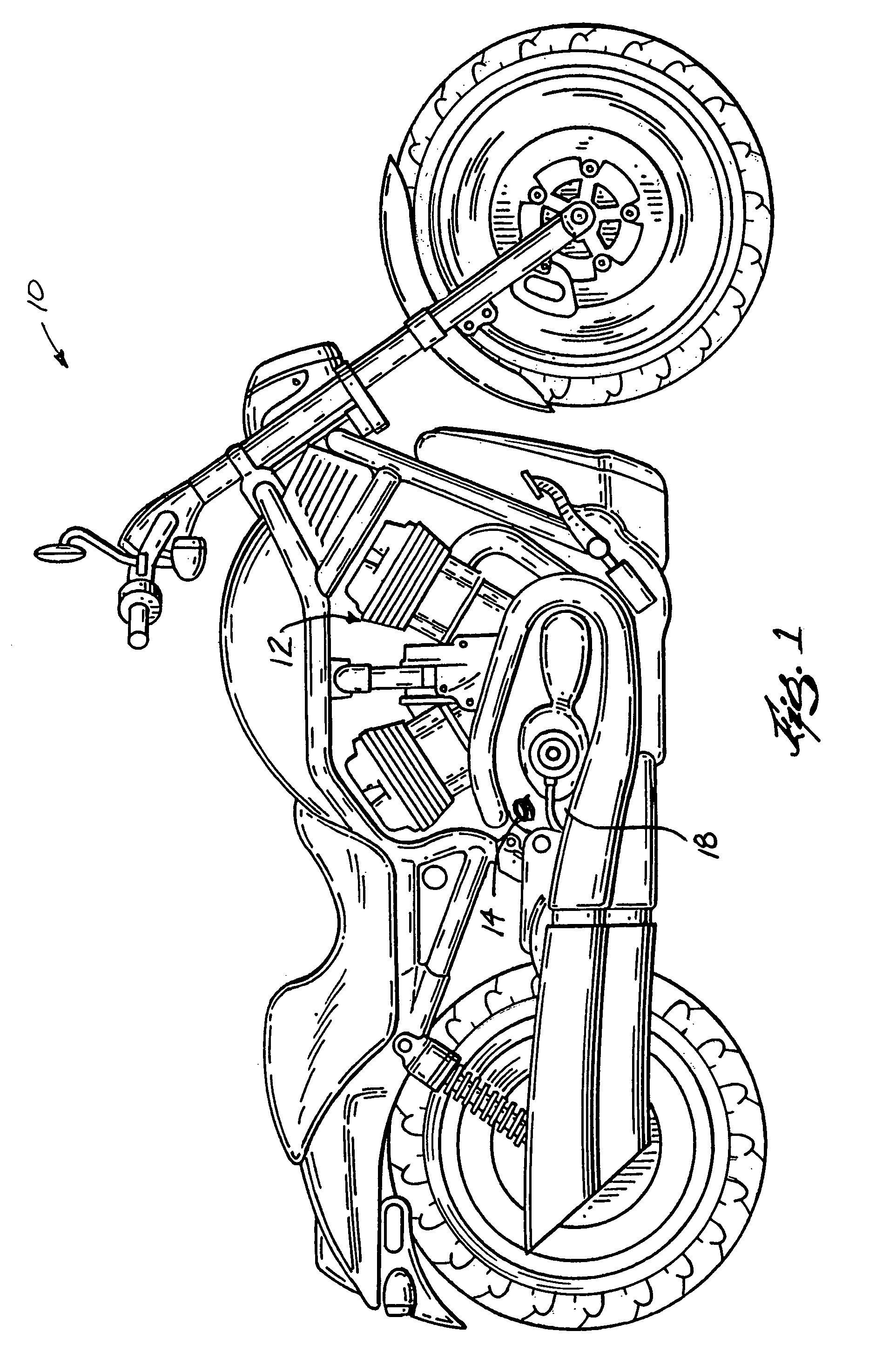
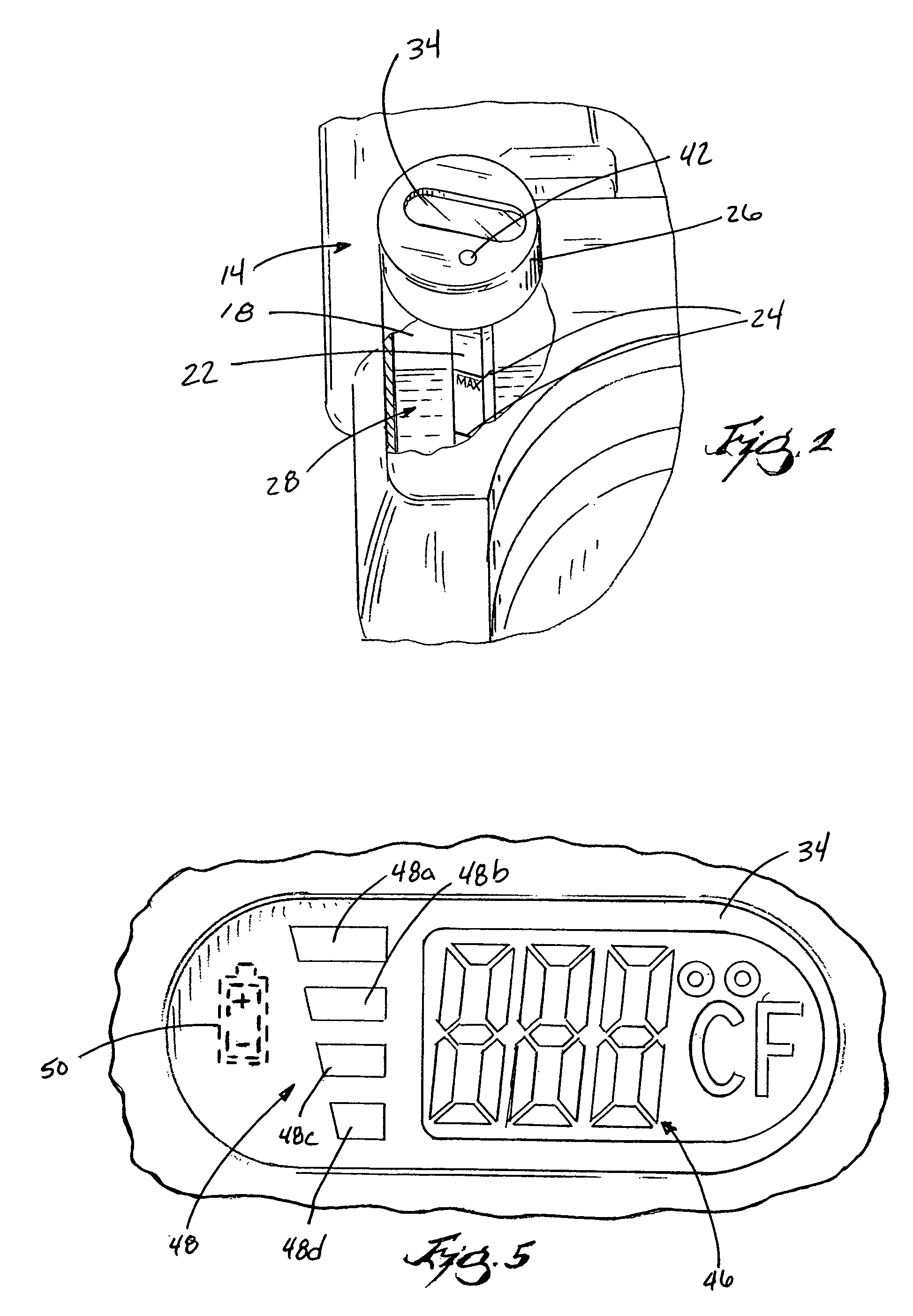
Apparatus for indicating oil temperature and oil level within an oil reservoir
Owner:HARLEY DAVIDSON MOTOR COMPANY GROUP INC
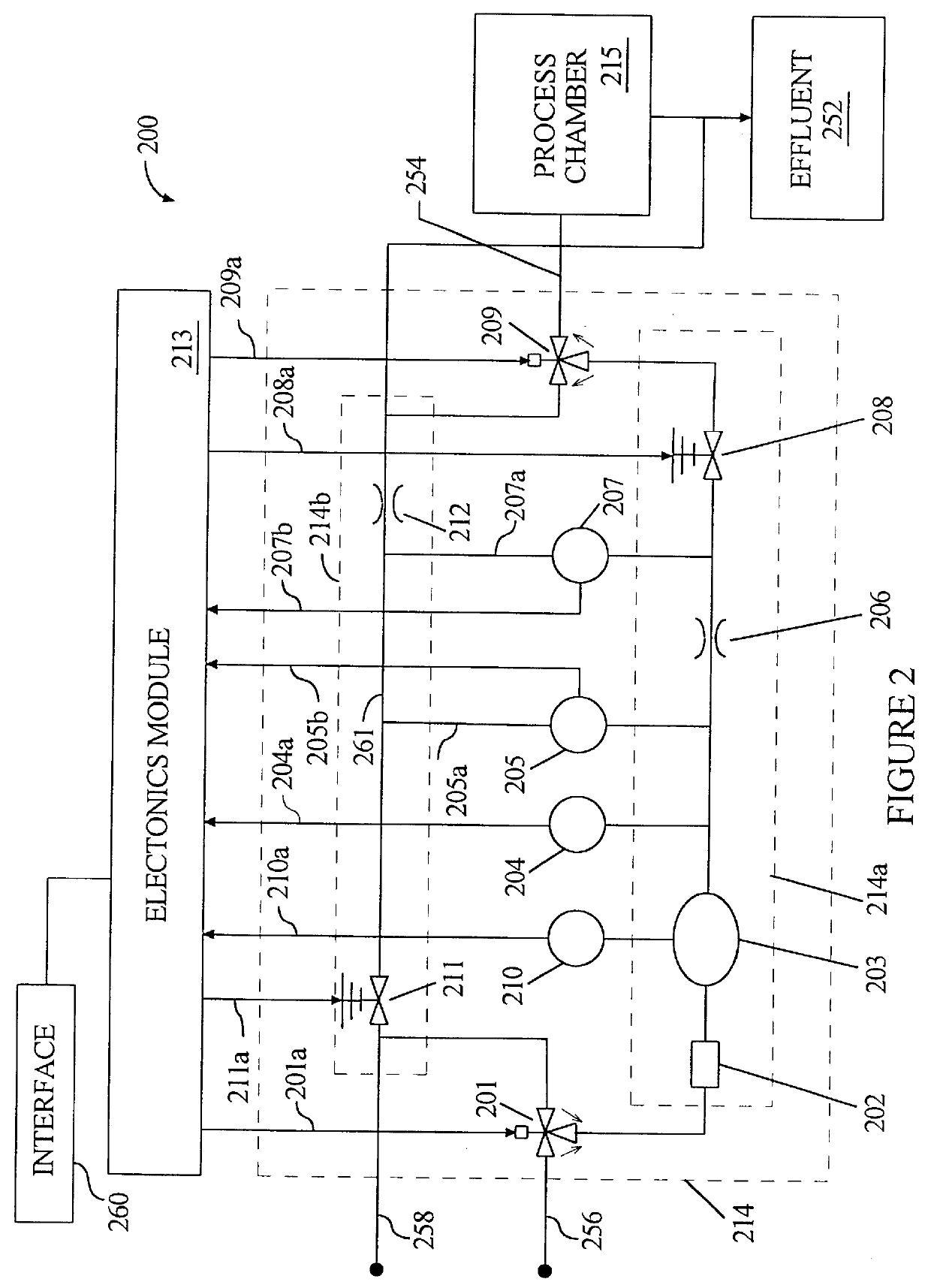
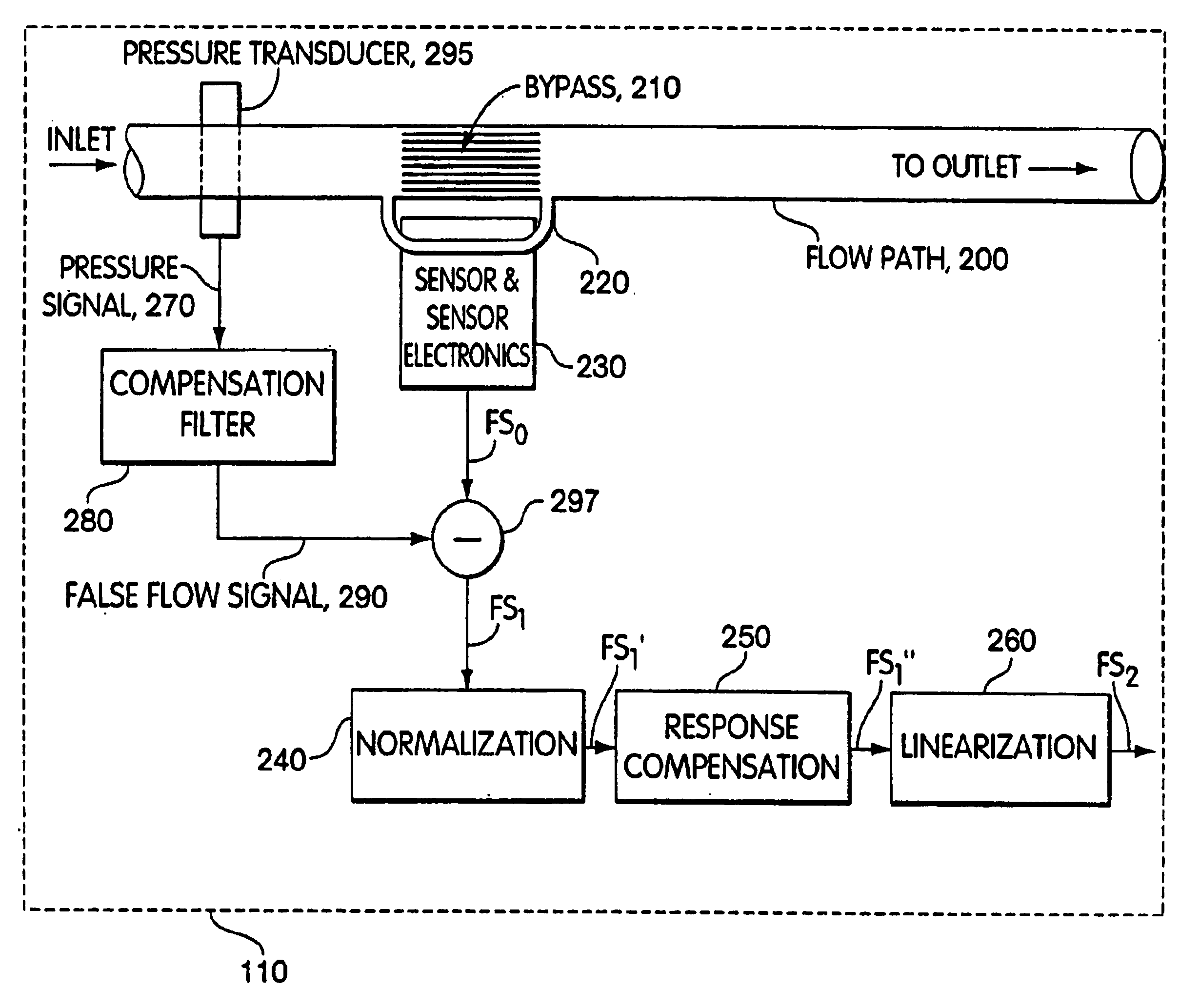
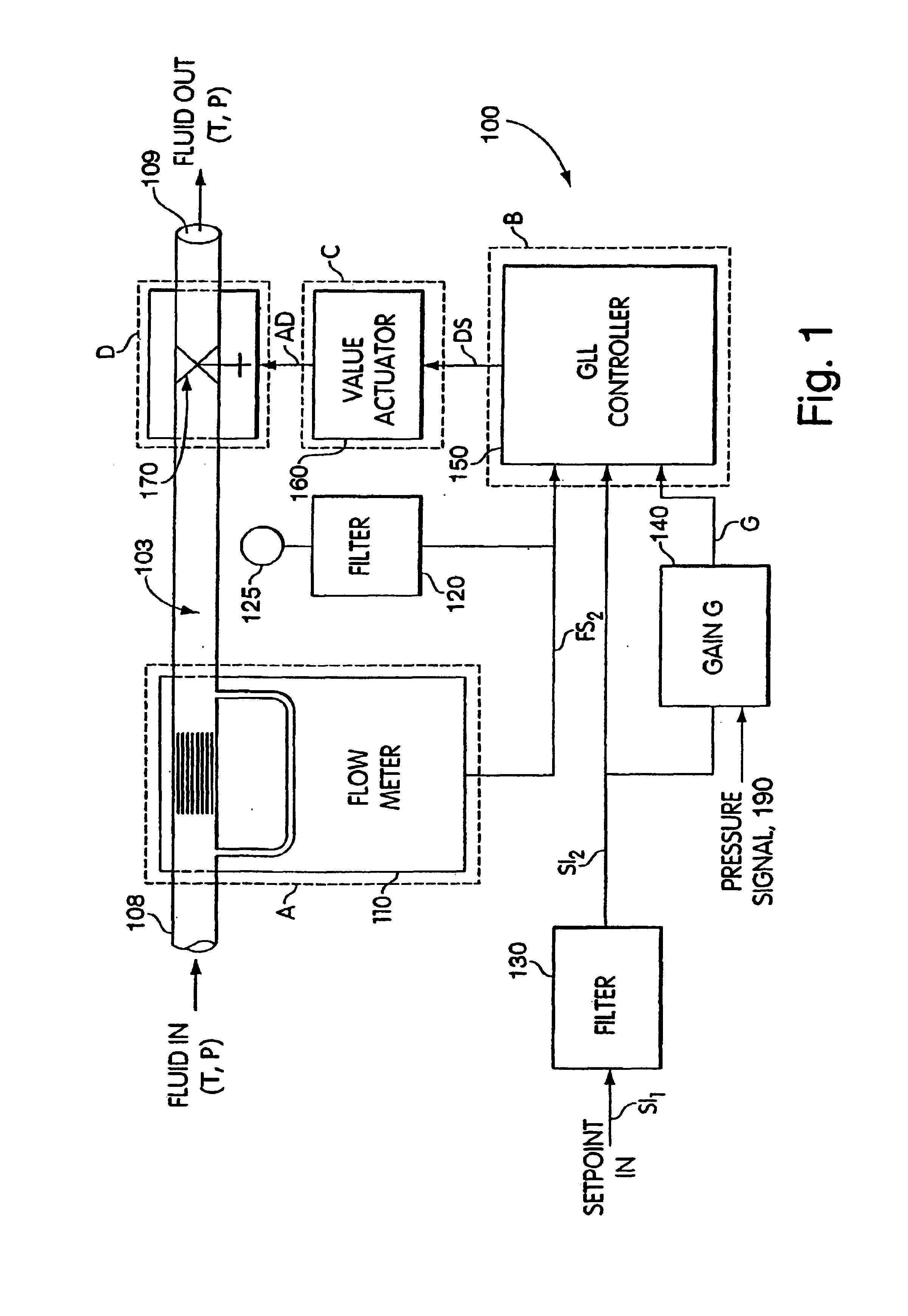
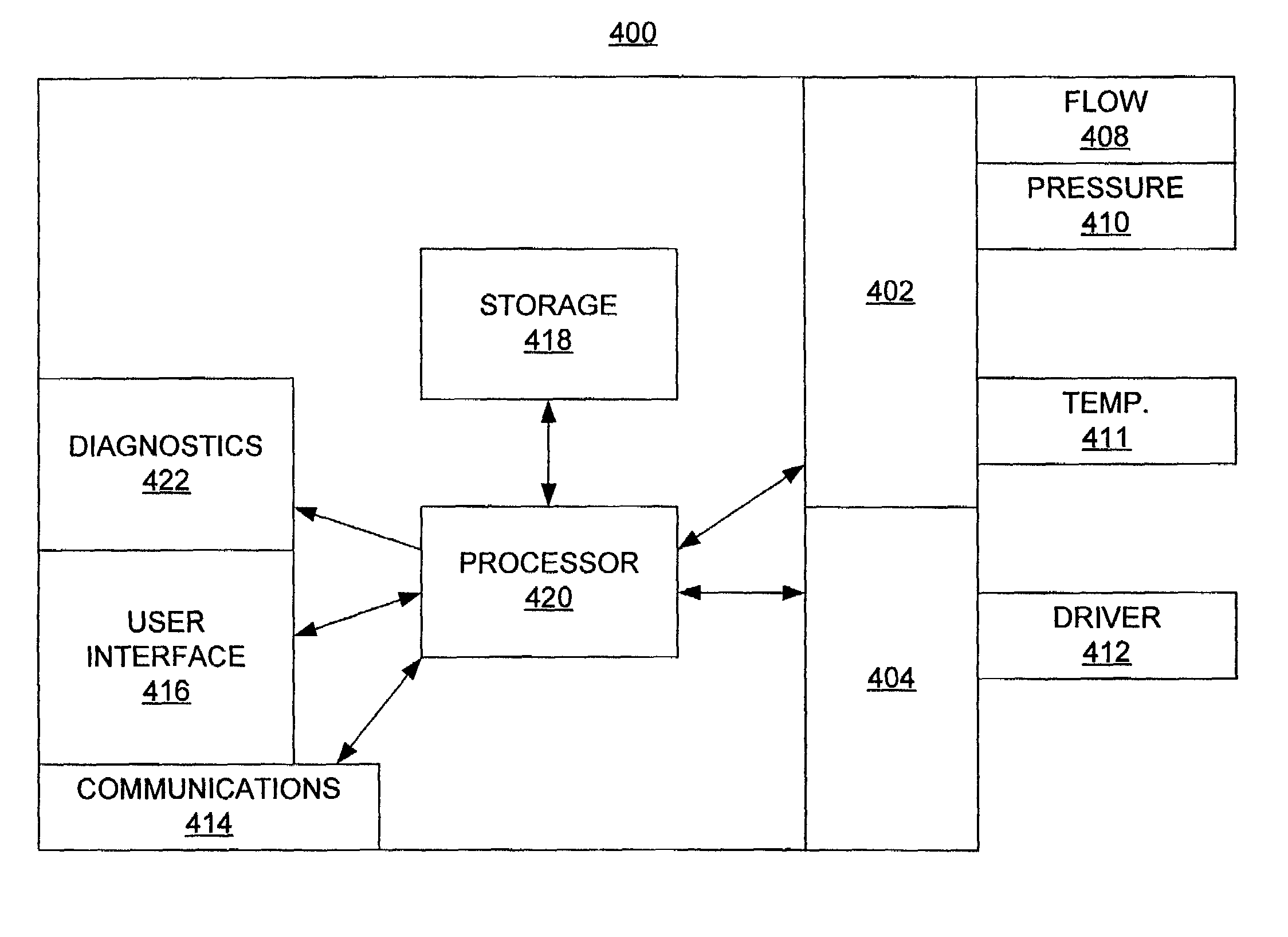
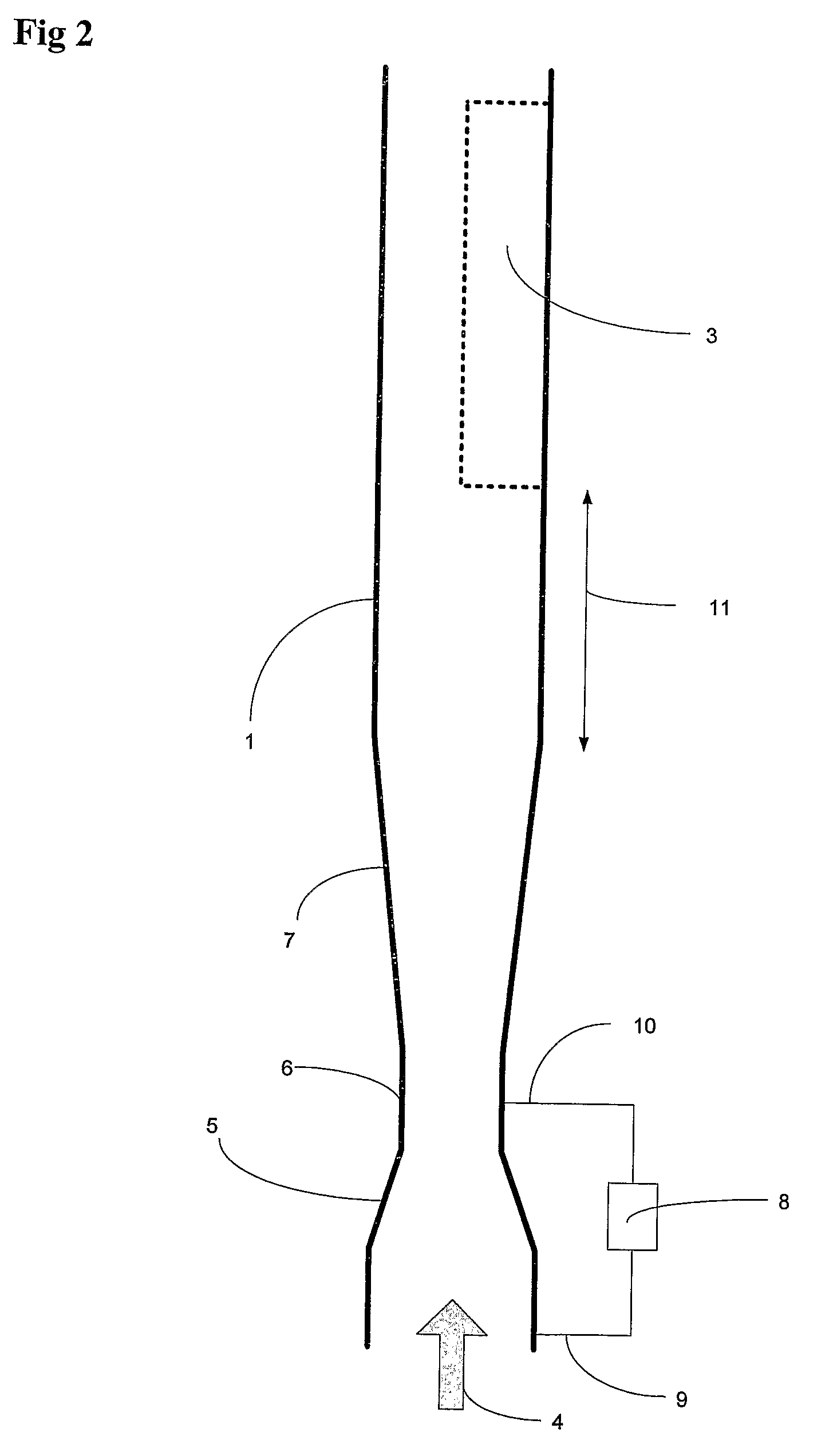
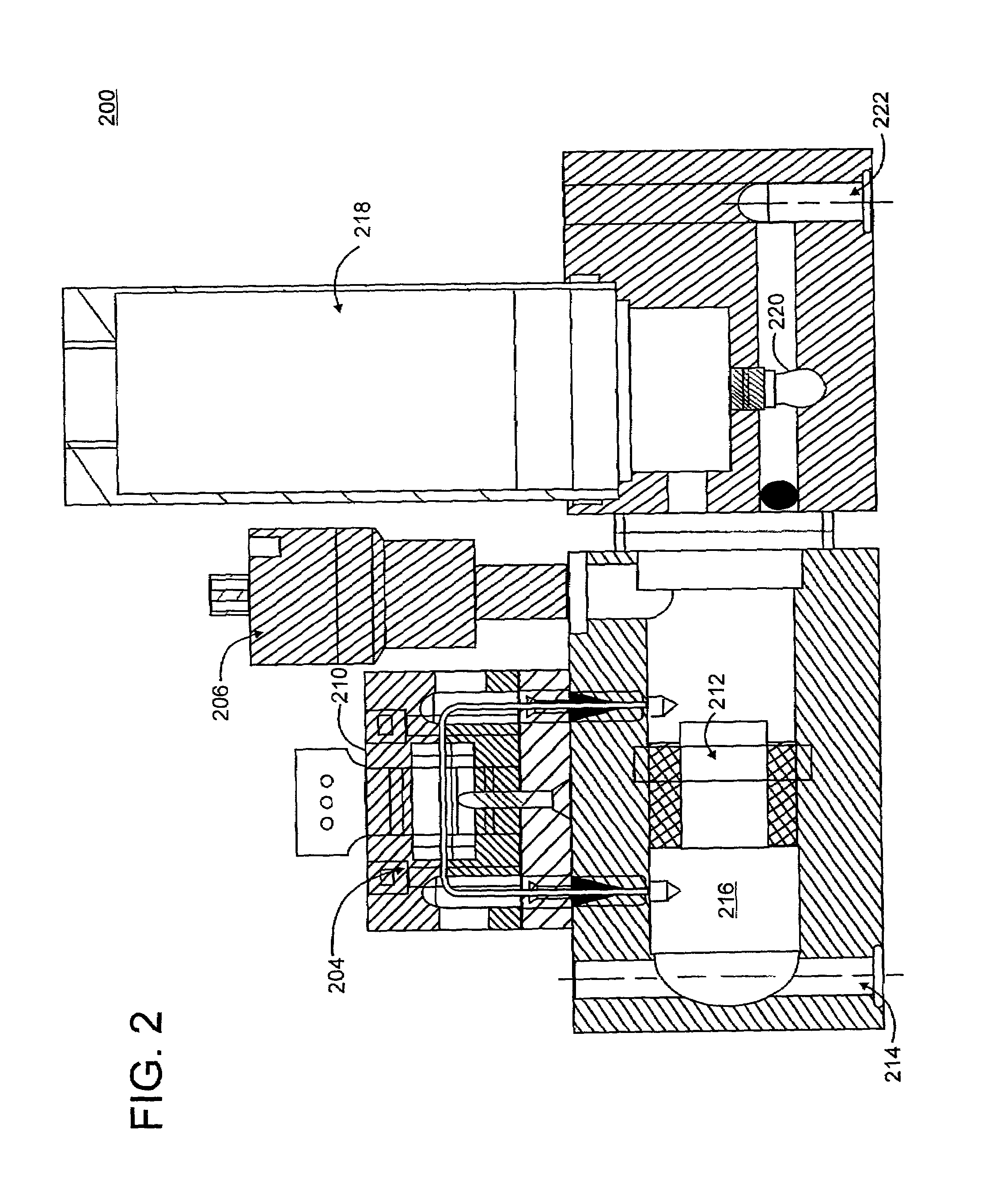
Methods and apparatus for pressure compensation in a mass flow controller
Performance of mass flow controller may be vulnerable to pressure transients in a flow path to which the controller is coupled for the purpose of controlling the fluid flow. A system and method are provided for reducing or eliminate performance degradations, instabilities, and / or inaccuracies of a mass flow controller caused by changes in the pressure environment. In particular, a method and system are provided for compensating for pressure transients in the pressure environment of a flow path and mass flow controller.
Owner:BROOKS INSTRUMENT
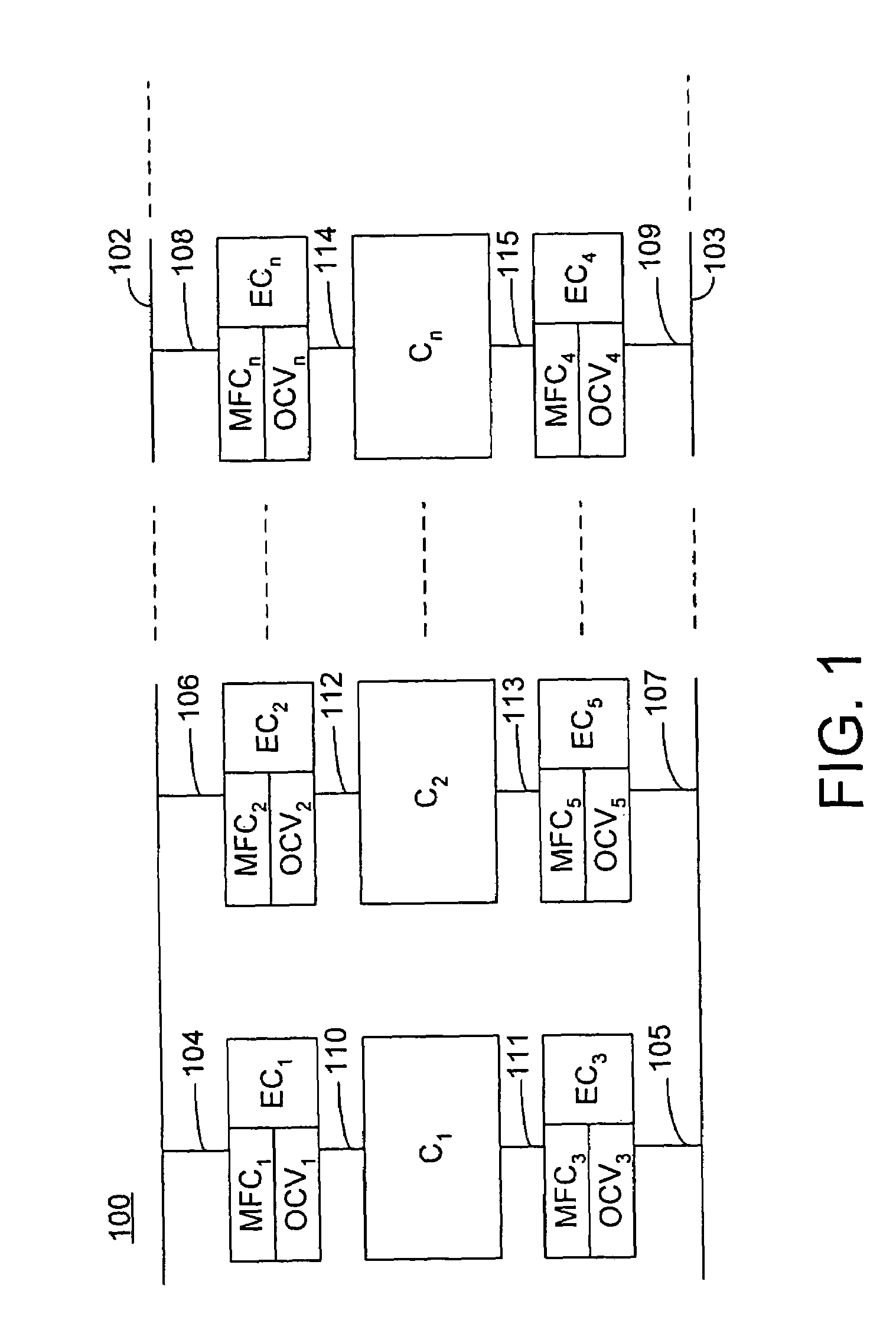
Gas flow rate measurement apparatus and method
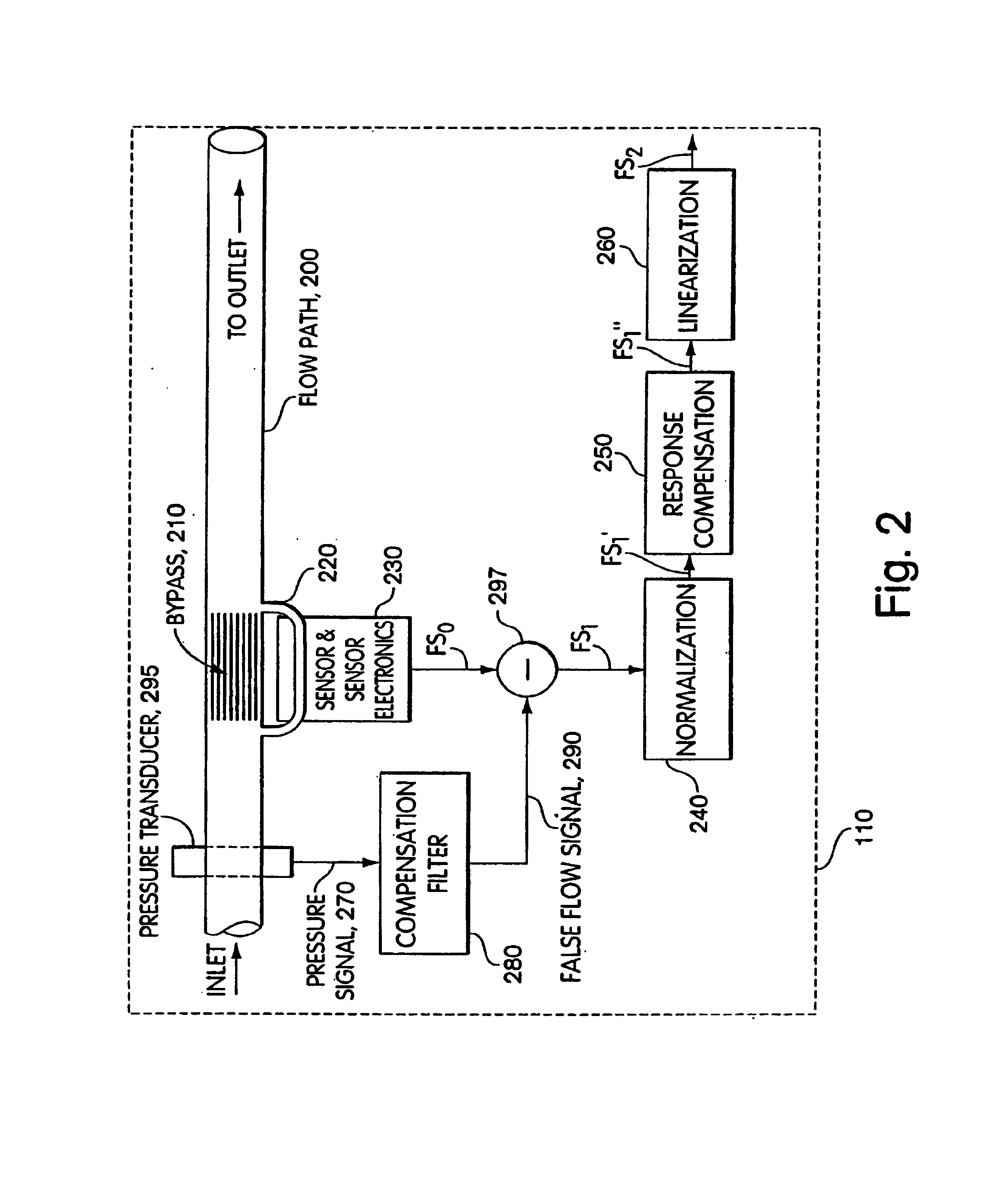
InactiveUS6053054AHigh measurement sensitivityShort response timeVolume meteringIndirect mass flowmetersMeasurement deviceState variable
A gas flow rate measurement apparatus for obtaining a normalized flow rate of a gas having at least one liquid component. The gas travels from an upstream position and in a downstream direction. The gas flow rate measurement apparatus comprises a gas inlet conduit in the upstream position for receiving the gas; a gas flow conditioning section in fluid communication with the gas inlet conduit and in a first downstream position for conditioning the gas to vaporize substantially all of the at least one liquid component without adding any other gas; a flow rate measurement section in fluid communication with the gas flow conditioning section and in a second downstream position more distant from the upstream position than the first downstream position, the flow rate measurement section including at least one sensor for sensing at least one state variable for the gas and generating at least one gas state signal, and a flow rate sensor for measuring an actual flow rate of the gas and generating a flow rate signal, and a processing device operatively coupled to the flow rate measurement section for using the at least one gas state signal and the flow rate signal to obtain the normalized mass flow rate. A related method also is provided.
Owner:FLOW TECH
System to measure density, specific gravity, and flow rate of fluids, meter, and related methods
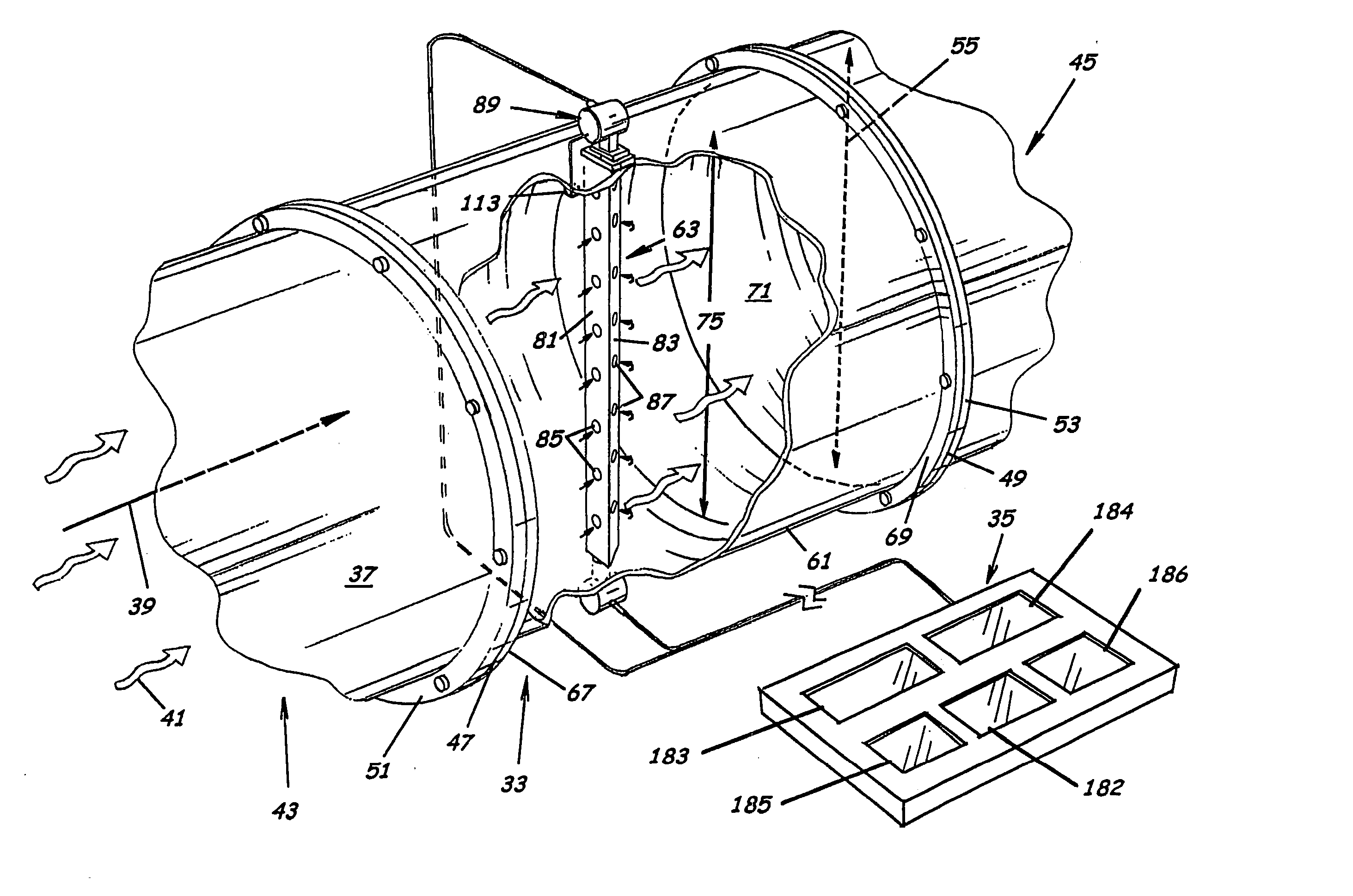
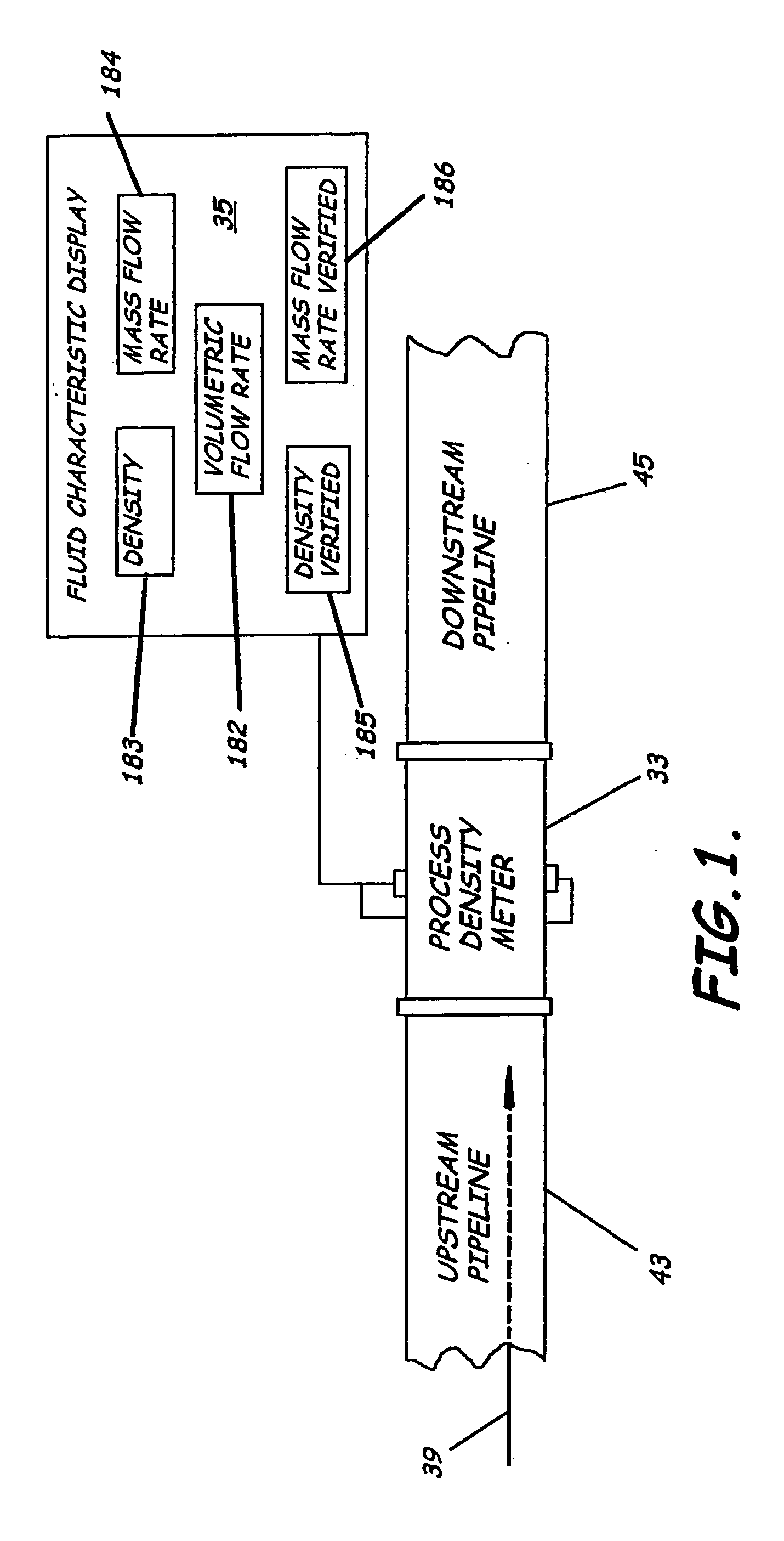
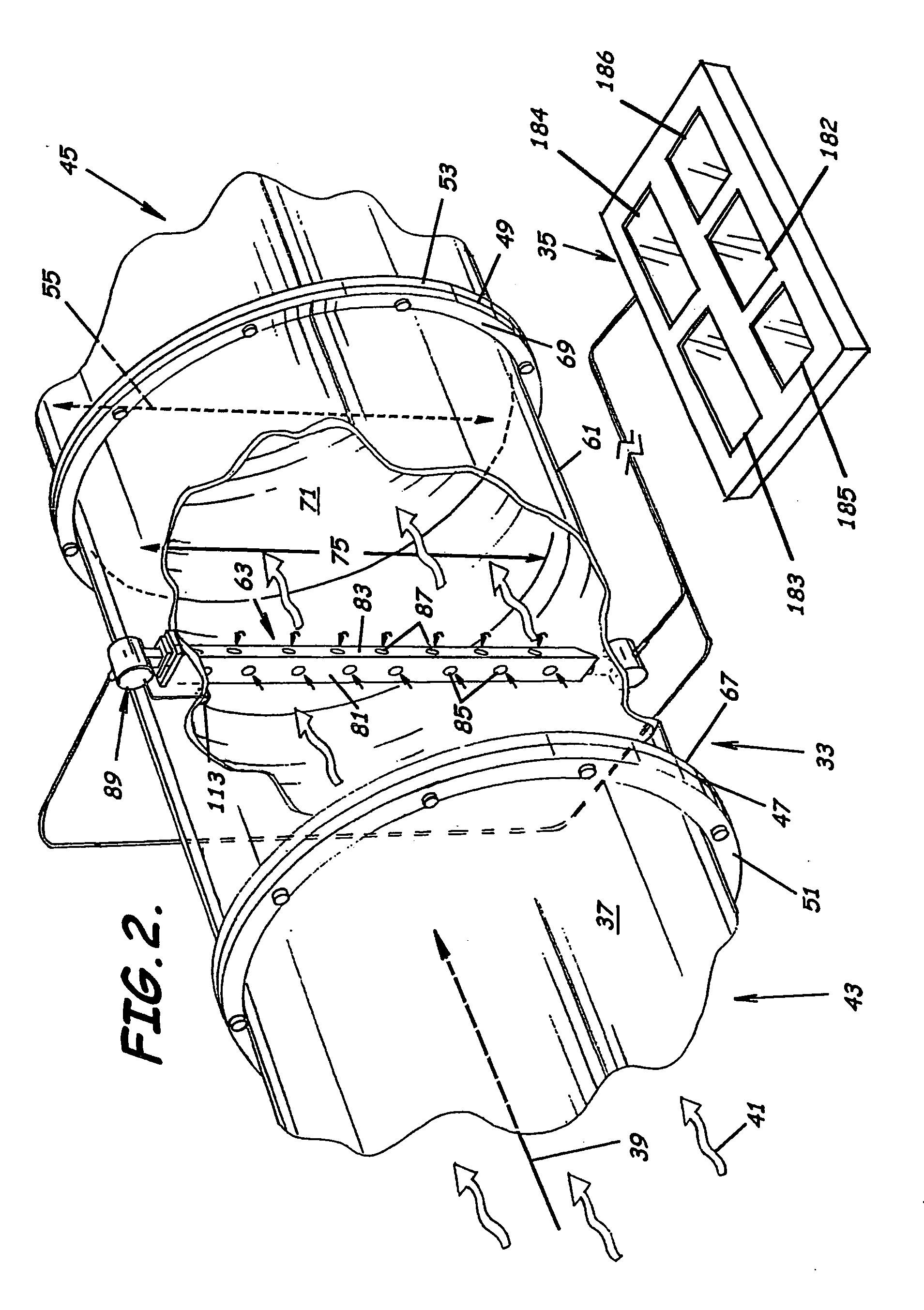
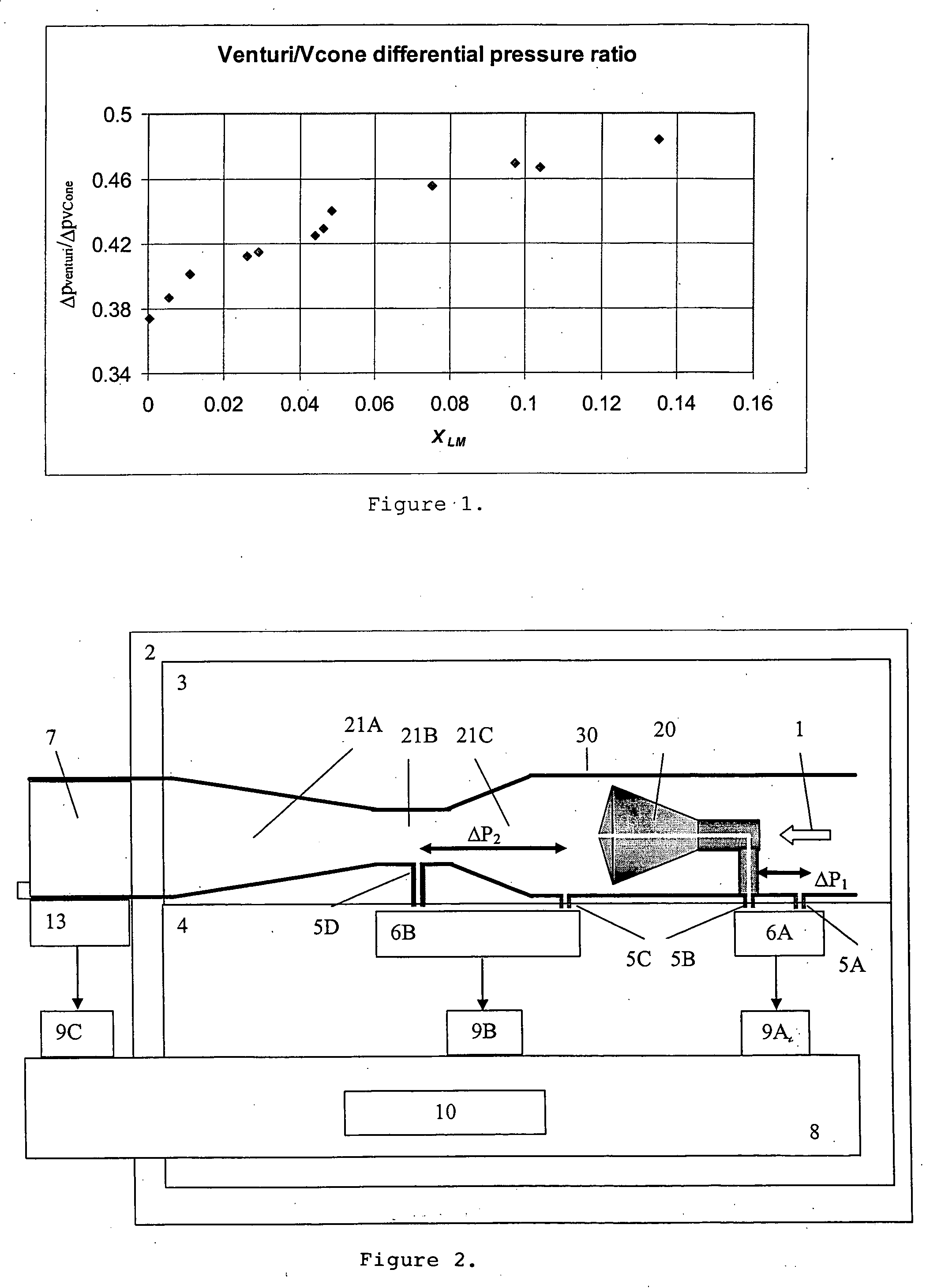
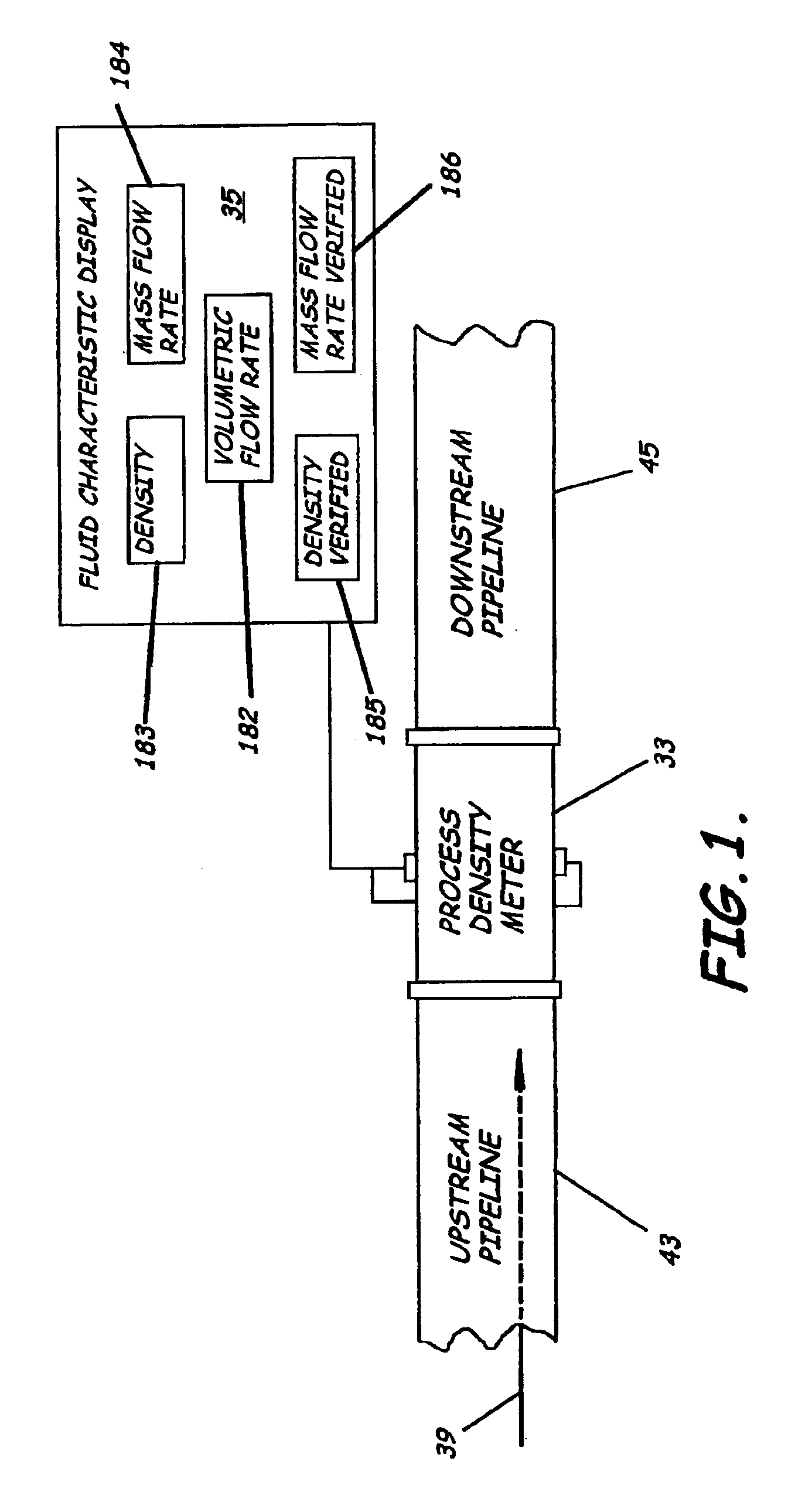
ActiveUS20050034535A1Little maintenanceMinimization needsVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectDifferential pressureDisplay device
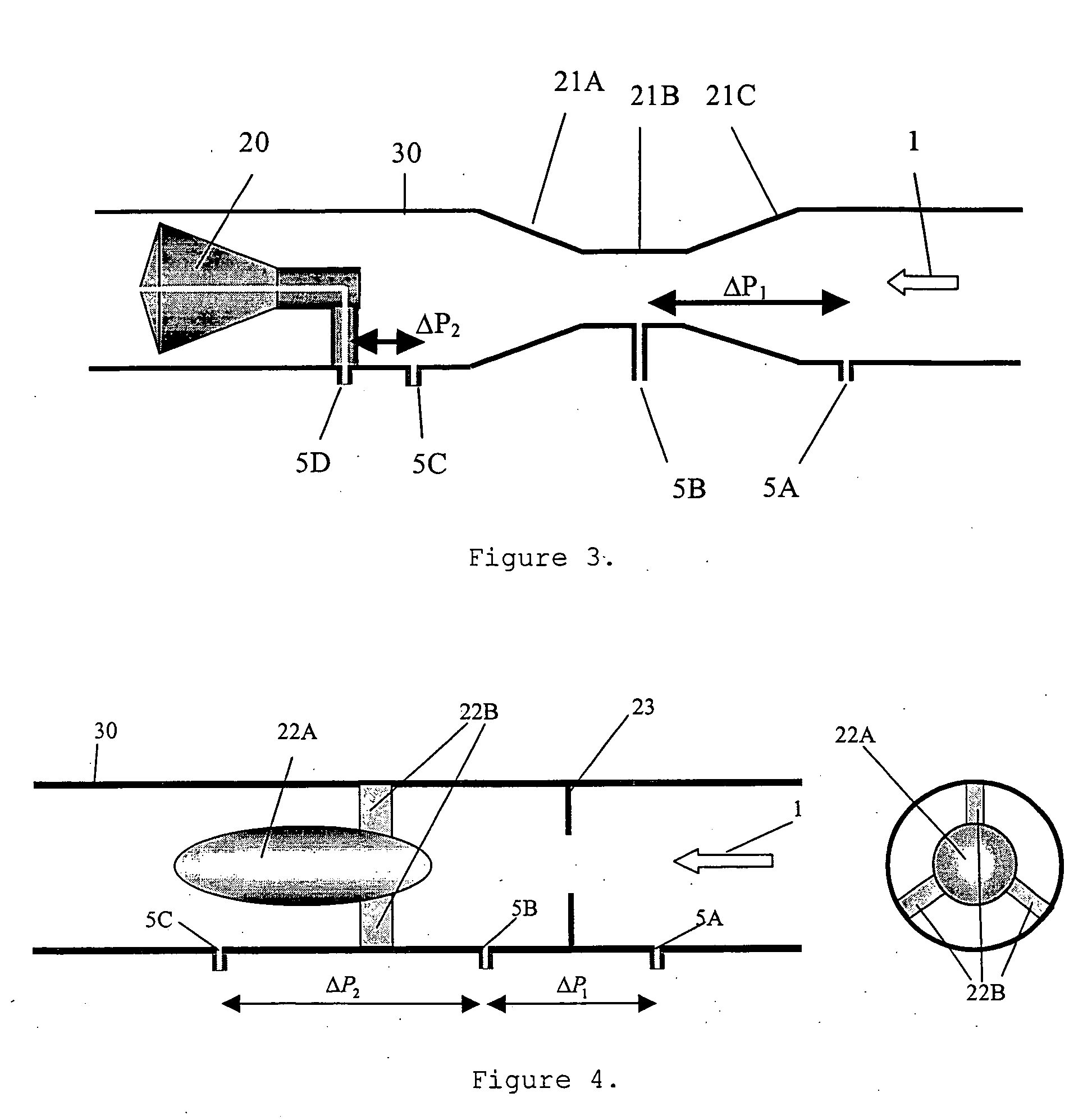
A system to measure fluid flow characteristics in a pipeline, meter, and methods includes a pipeline having a passageway to transport flowing fluid therethrough, a process density meter including at least portions thereof positioned within the pipeline to provide flowing fluid characteristics including volumetric flow rate, fluid density, and mass flow rate of the flowing fluid, and a fluid characteristic display to display the fluid characteristics. The process density meter includes a vortex-shedding body positioned within the pipeline to form vortices and a vortex meter having a vortex frequency sensor to measure the frequency of the vortices and to determine the volumetric flow rate. The process density meter further includes a differential pressure meter positioned adjacent the vortex-shedding body to produce a differential pressure meter flow rate signal indicative of the density of fluid when flowing through the pipeline. The process density meter also includes a thermal flow meter positioned adjacent the vortex-shedding body to produce a mass flow rate signal indicative of the mass flow rate of fluid when flowing through the pipeline. The process density meter produces an output of a volumetric flow rate, a flowing fluid density, and a mass flow rate to be displayed by the fluid characteristic display.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Flow meter
ActiveUS20050188771A1Specific gravity by measuring pressure differencesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLiquid stateDifferential pressure
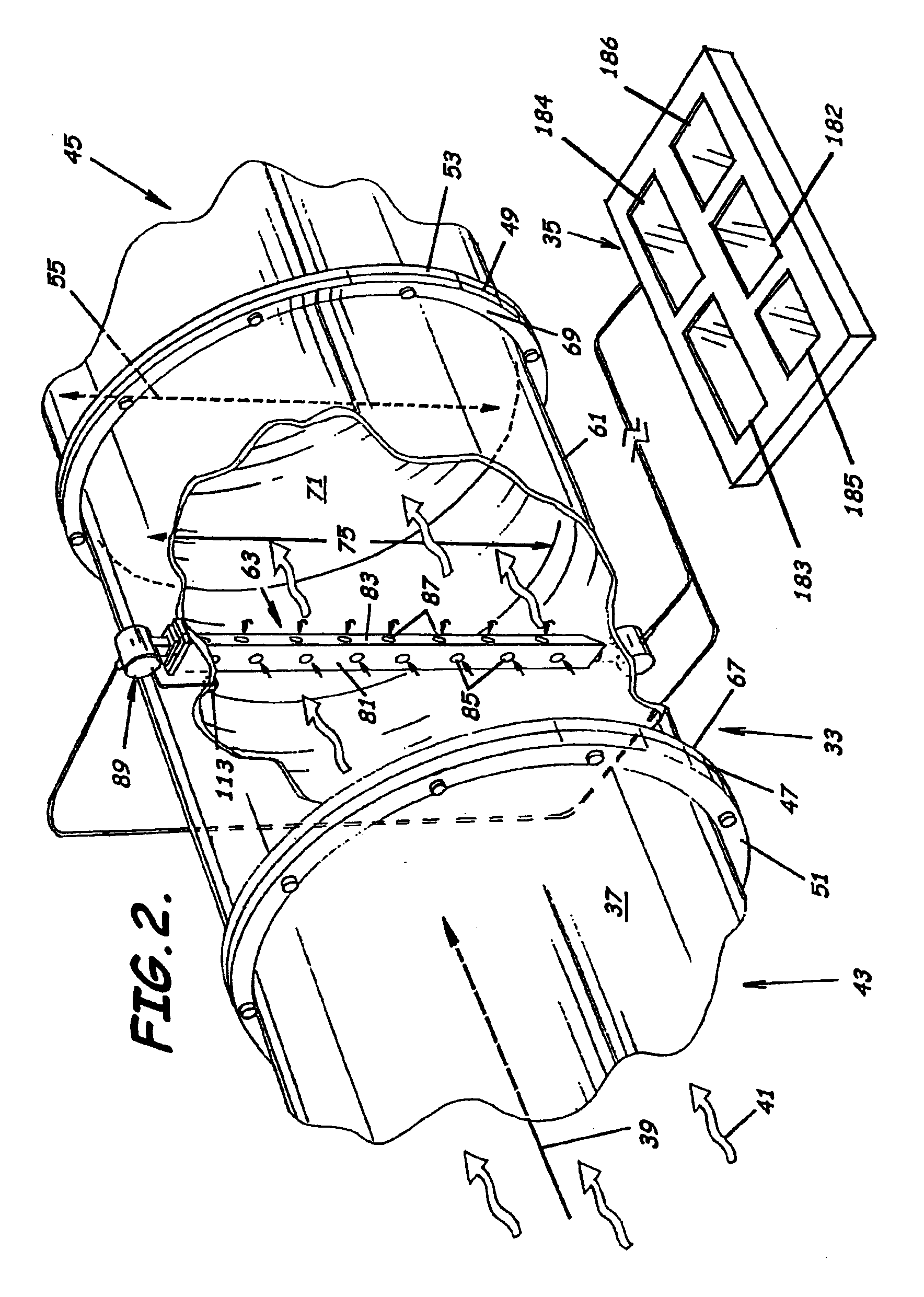
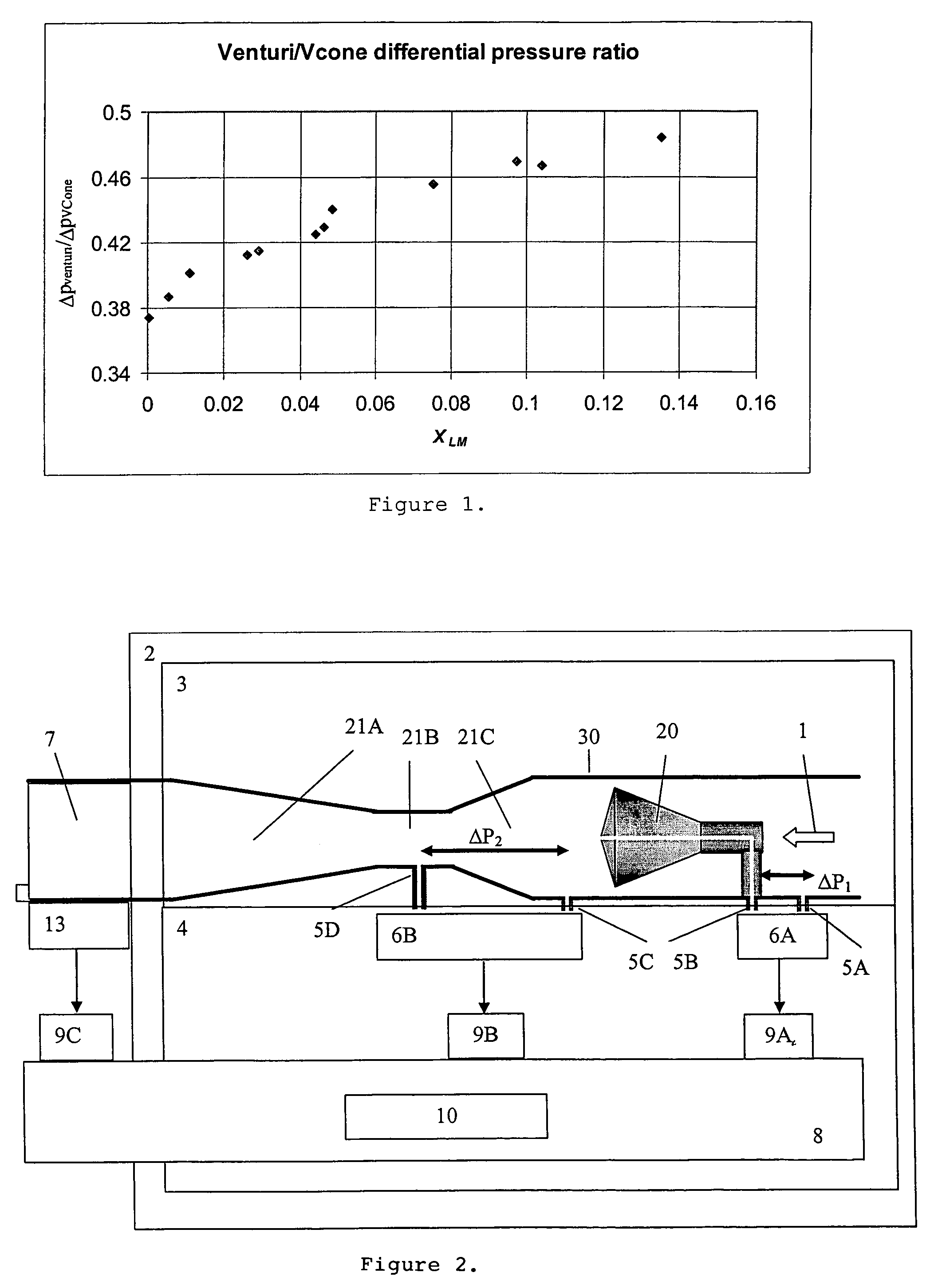
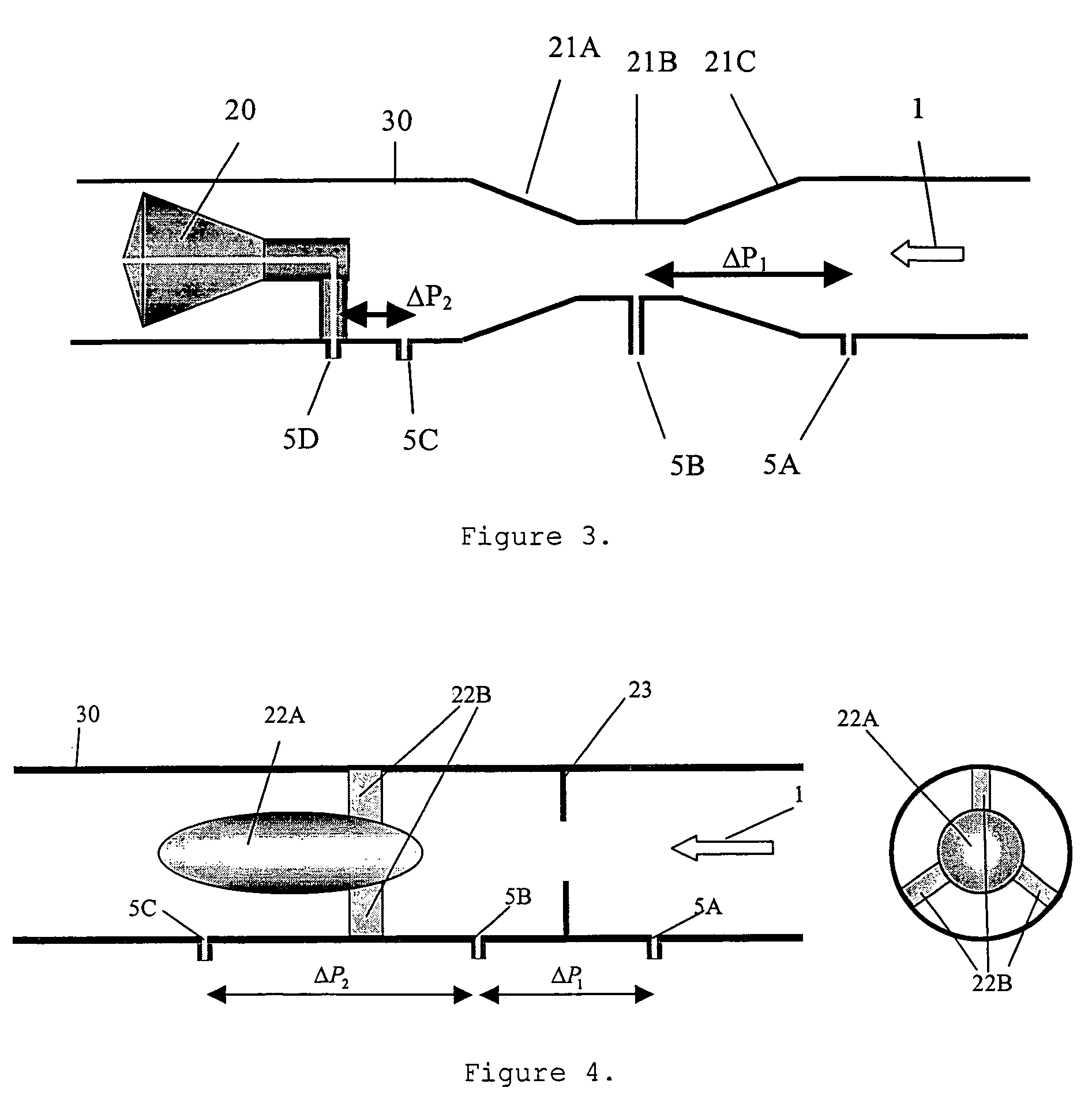
A flow meter obtains the individual flow rates of gas, liquid hydrocarbons, and water in a predominantly gas-containing flowing fluid mixture. The flow meter comprises a water content meter (7) provides a signal representing a measure of the water content of said fluid. It also comprises a double differential pressure generating (3) and measuring (4) structure, denoted a DDP-unit (2), that provides two measurement signals (6A and 6B) representing two independent values of differential pressure (DP) in said fluid (1). In addition to the above, the meter also comprises a signal processing unit (8) having inputs (9A-C) for receiving the measurement signals and the water content signal, and a calculation module (10) which calculates values representing the volumetric flow rates of said gas, liquid hydrocarbons and water in said fluid.
Owner:ROXAR FLOW MEASUREMENT
System to measure density, specific gravity, and flow rate of fluids, meter, and related methods
ActiveUS6957586B2Little maintenanceMinimization needsVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsSpecific gravity using flow propertiesDifferential pressureDisplay device
A system to measure fluid flow characteristics in a pipeline, meter, and methods includes a pipeline having a passageway to transport flowing fluid therethrough, a process density meter including at least portions thereof positioned within the pipeline to provide flowing fluid characteristics including volumetric flow rate, fluid density, and mass flow rate of the flowing fluid, and a fluid characteristic display to display the fluid characteristics. The process density meter includes a vortex-shedding body positioned within the pipeline to form vortices and a vortex meter having a vortex frequency sensor to measure the frequency of the vortices and to determine the volumetric flow rate. The process density meter further includes a differential pressure meter positioned adjacent the vortex-shedding body to produce a differential pressure meter flow rate signal indicative of the density of fluid when flowing through the pipeline. The process density meter also includes a thermal flow meter positioned adjacent the vortex-shedding body to produce a mass flow rate signal indicative of the mass flow rate of fluid when flowing through the pipeline. The process density meter produces an output of a volumetric flow rate, a flowing fluid density, and a mass flow rate to be displayed by the fluid characteristic display.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Flow meter for measuring fluid mixtures
ActiveUS7293471B2Specific gravity by measuring pressure differencesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDifferential pressureLiquid hydrocarbons
Owner:ROXAR FLOW MEASUREMENT
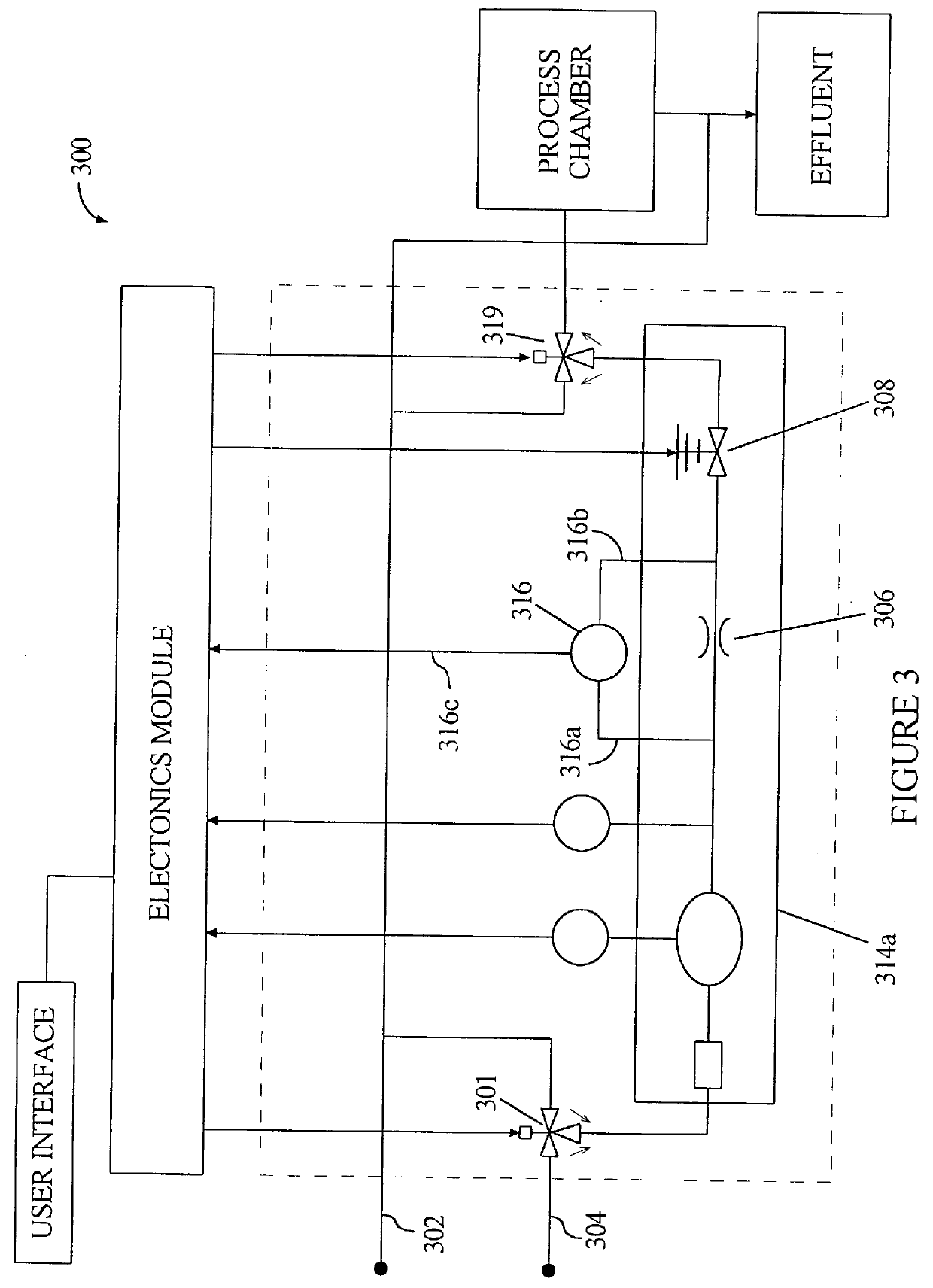
Apparatus and method for self-calibration of mass flow controller
InactiveUS6948508B2Testing/calibration apparatusFluid pressure measurementEngineeringMass flow sensor
A mass flow controller includes a mass flow sensor and a calibrator configured to perform a self-calibration on the mass flow controller. The calibrator generates flow measurements that are used as “standards” and flow measurements from the mass flow sensor are correlated to flow measurements from the calibrator.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Vortex flow sensor for measuring fluid flow through a flow tube
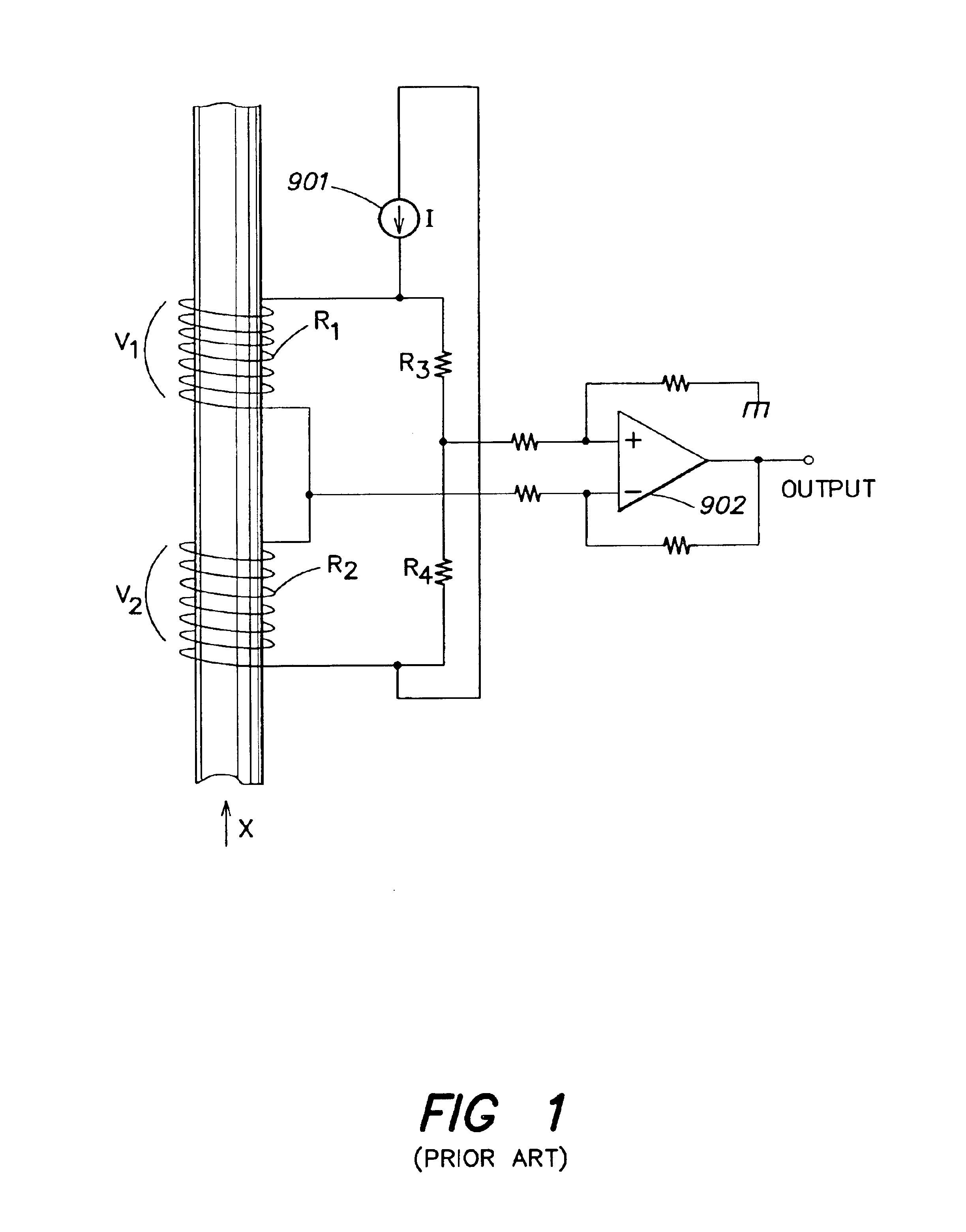
InactiveUS6910387B2Improve thermal conductivityEasy to measureVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectIndirect mass flowmetersTwo temperatureEngineering
The vortex flow sensor is designed to measure the mass flow rate, the volumetric flow rate, or the flow velocity of a fluid flowing in a flow tube having a tube wall, and has two temperature sensors arranged in such a way that the vortex flow sensor may also be used with fluids which would corrode the temperature sensors. A bluff body in the flow tube sheds vortices and thus causes pressure fluctuations. A vortex sensor device responsive thereto is fitted downstream of the bluff body in a hole provided in the wall of the flow tube. The vortex sensor device comprises a sensor vane extending into the fluid. The temperature sensors are disposed in a blind hole of the sensor vane. Alternatively, the temperature sensor may be disposed in blind hole of the bluff body.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Apparatus and method for calibration of mass flow controller
InactiveUS7136767B2Testing/calibration apparatusVolume flow proportion measurementDifferentiatorEngineering
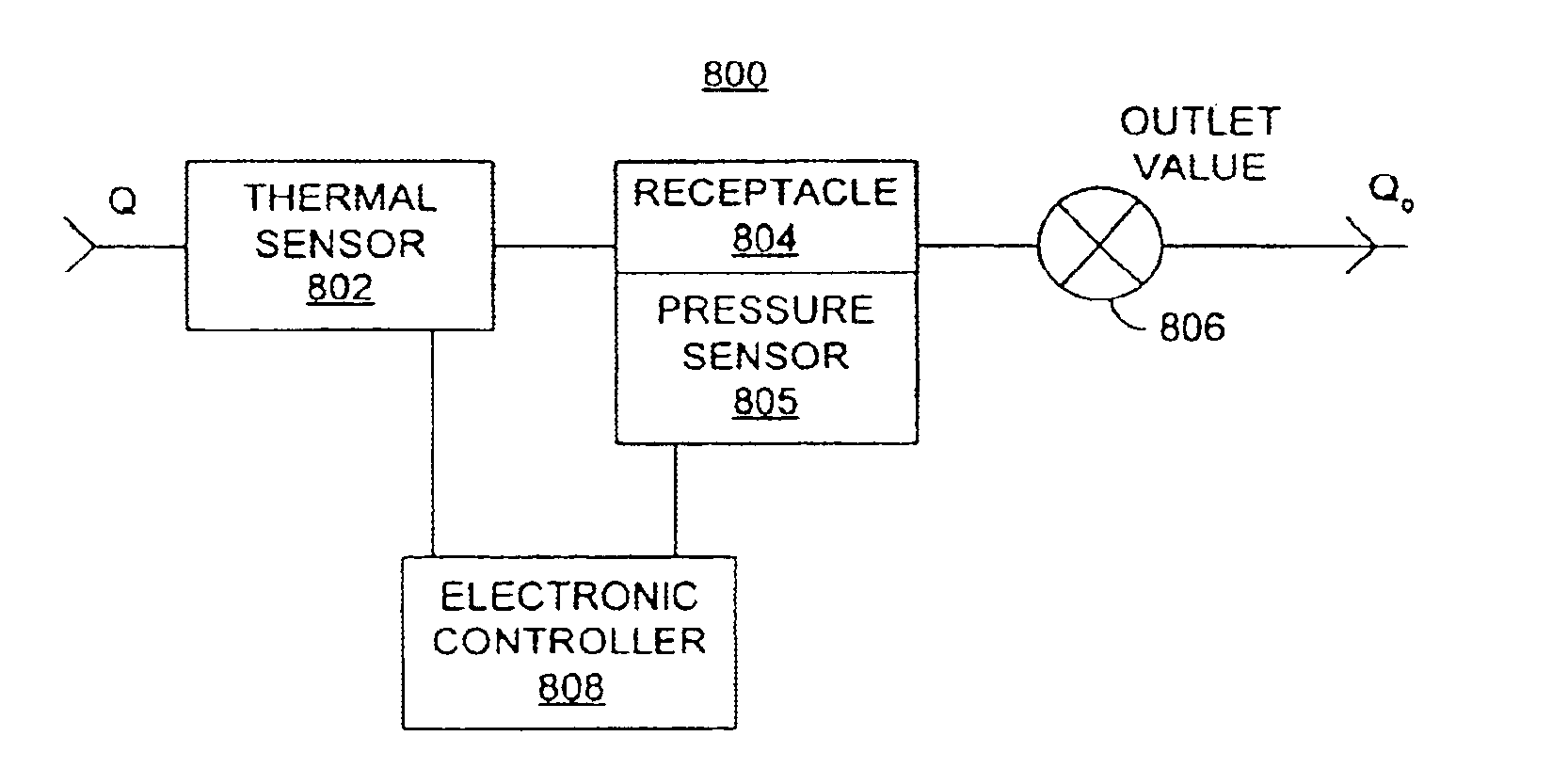
A mass flow sensor calibrator employs a variable-flow fluid source, a receptacle of known volume, and a pressure differentiator. The variable-flow fluid source supplies gas at varying rates to the mass flow sensor being calibrated and at proportional rates to a receptacle of known volume. A pressure differentiator computes the time derivative of gas flow into the receptacle of known volume and, from that, the actual flow into the receptacle. Given the actual flow, the proportionate flow into the mass flow sensor may be determined and the flow signal from the mass flow sensor correlated to the actual flow.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
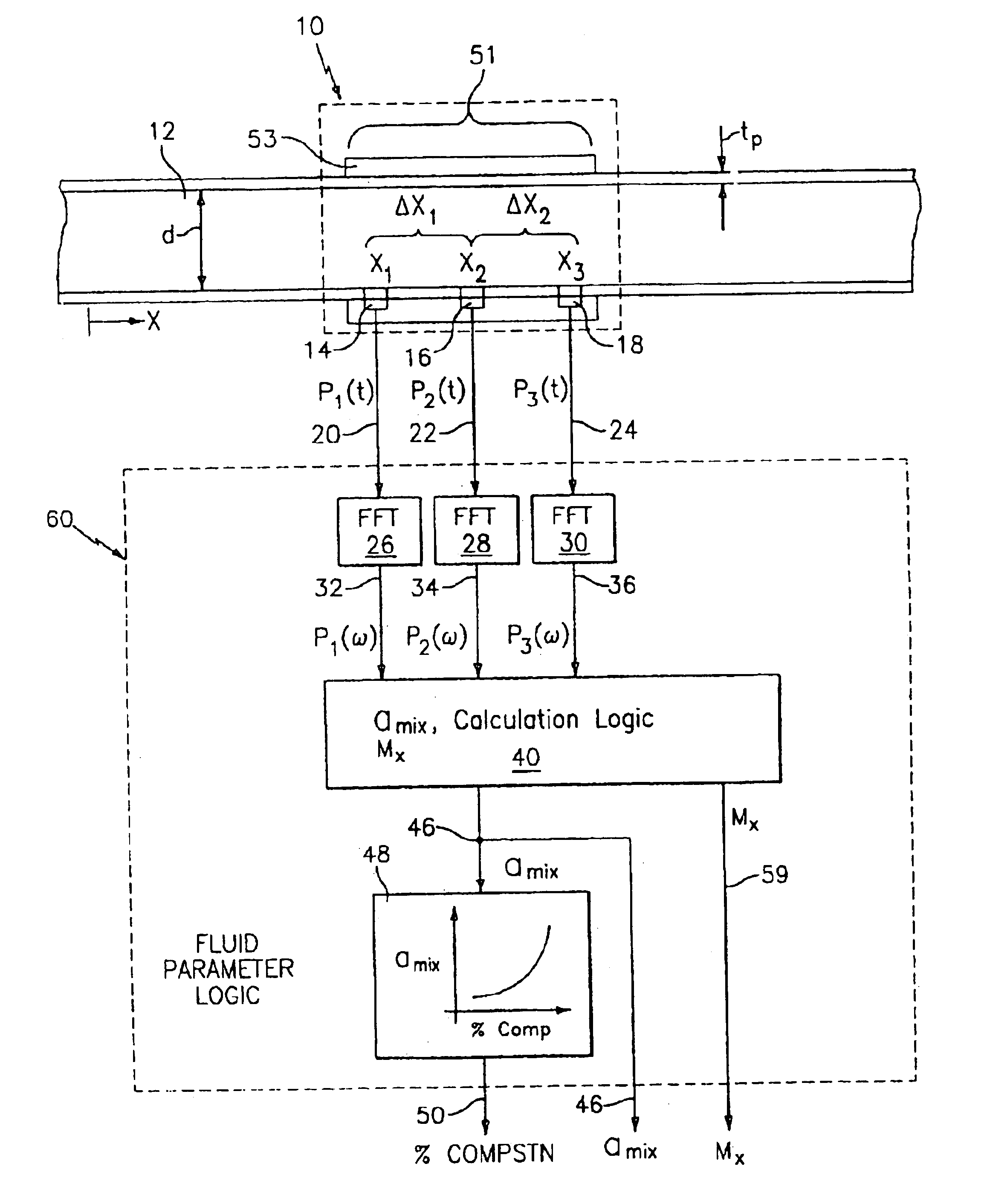
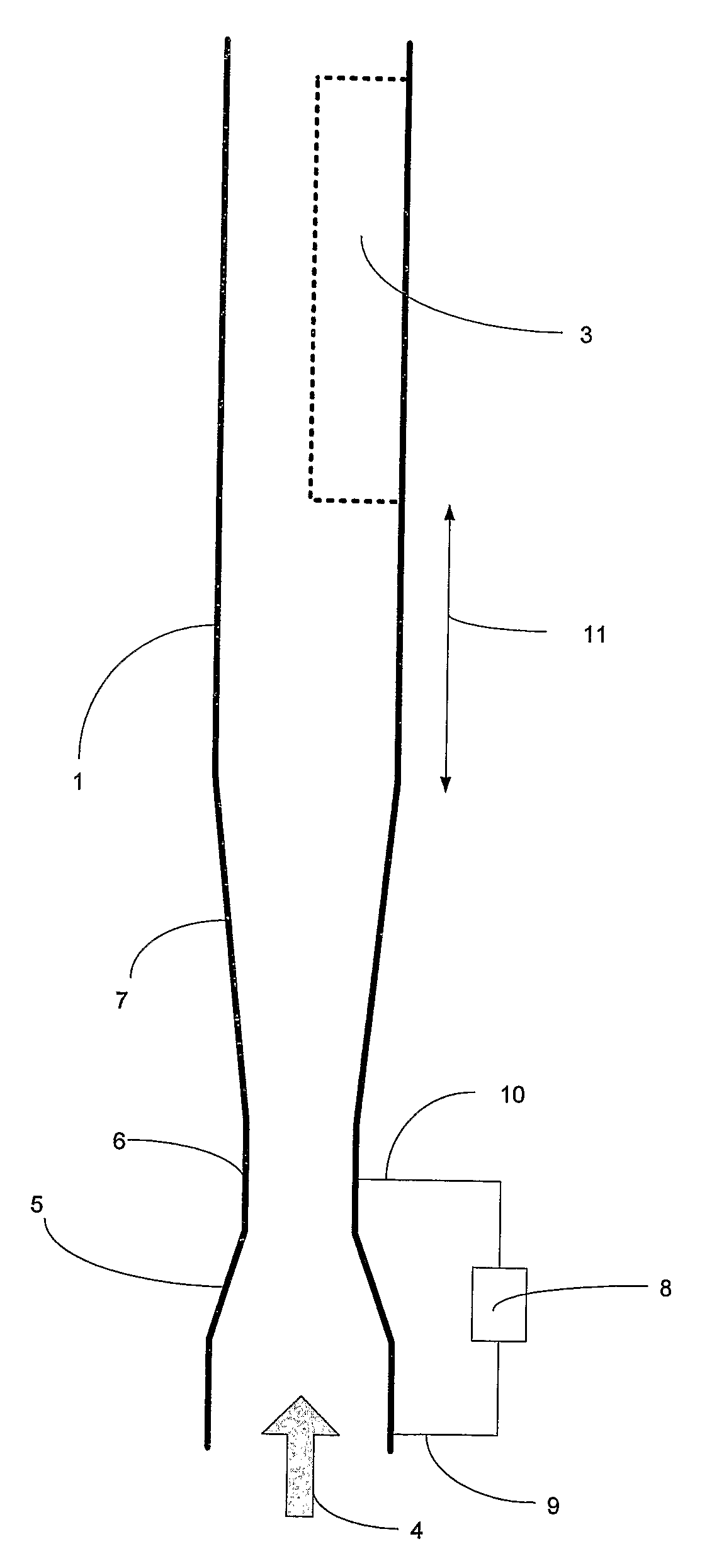
Fluid parameter measurement for industrial sensing applications using acoustic pressures
InactiveUS6988411B2Less sensitive to static shifts (or errors) in sensingImprove measurement reliabilityVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringSound pressure
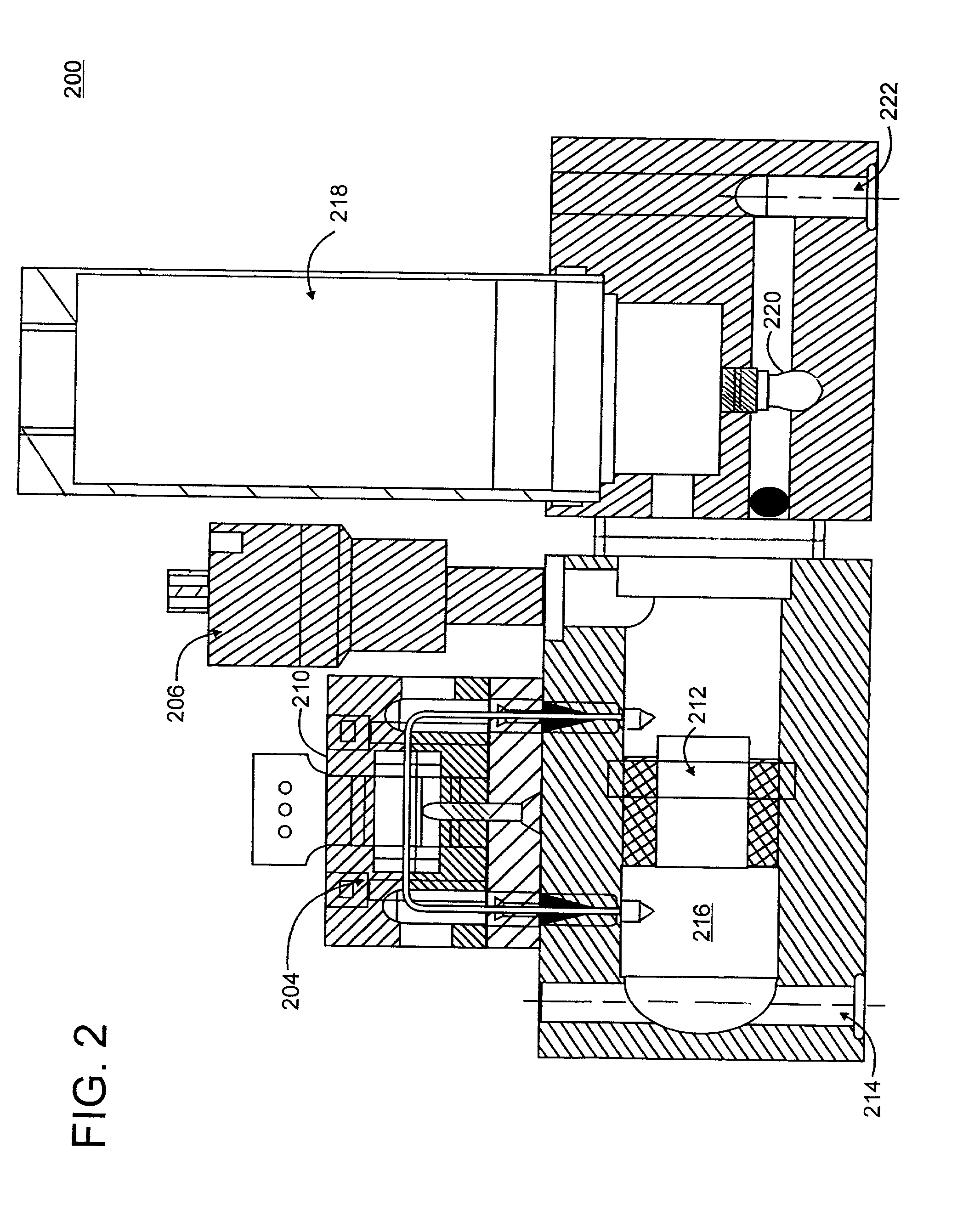
In industrial sensing applications at least one parameter of at least one fluid in a pipe 12 is measured using a spatial array of acoustic pressure sensors 14,16,18 placed at predetermined axial locations x1, x2, x3 along the pipe 12. The pressure sensors 14,16,18 provide acoustic pressure signals P1(t), P2(t), P3(t) on lines 20,22,24 which are provided to signal processing logic 60 which determines the speed of sound amix of the fluid (or mixture) in the pipe 12 using acoustic spatial array signal processing techniques with the direction of propagation of the acoustic signals along the longitudinal axis of the pipe 12. Numerous spatial array-processing techniques may be employed to determine the speed of sound amix. The speed of sound amix is provided to logic 48, which calculates the percent composition of the mixture, e.g., water fraction, or any other parameter of the mixture, or fluid, which is related to the sound speed amix. The logic 60 may also determine the Mach number Mx of the fluid. The acoustic pressure signals P1(t), P2(t), P3(t) measured are lower frequency (and longer wavelength) signals than those used for ultrasonic flow meters, and thus is more tolerant to inhomogeneities in the flow. No external source is required and thus may operate using passive listening. The invention will work with arbitrary sensor spacing and with as few as two sensors if certain information is known about the acoustic properties of the system. The sensor may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Pulsed mass flow measurement system and method
InactiveUS20060130755A1Highly repeatable and precise quantityChemical vapor deposition coatingIndirect mass flowmetersTransducerGas passing
A system for measuring a pulsed mass flow rate of gas passing from an upstream source of gas to a downstream process chamber through an on / off type valve of the source of gas. The system includes a passageway for connecting the source of gas to the process chamber, a flow restrictor device dividing the passageway into an upstream portion and a downstream portion, a pressure transducer providing measurements of pressure within the upstream portion of the passageway, a temperature probe providing measurements of temperature within the upstream portion of the passageway, and a CPU connected to the pressure transducer and the temperature probe. The CPU is programmed to receive pressure measurements from the pressure transducer, temperature measurements from the temperature probe, and calculate a mass flow rate through the passageway using the pressure measurements and the temperature measurements.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
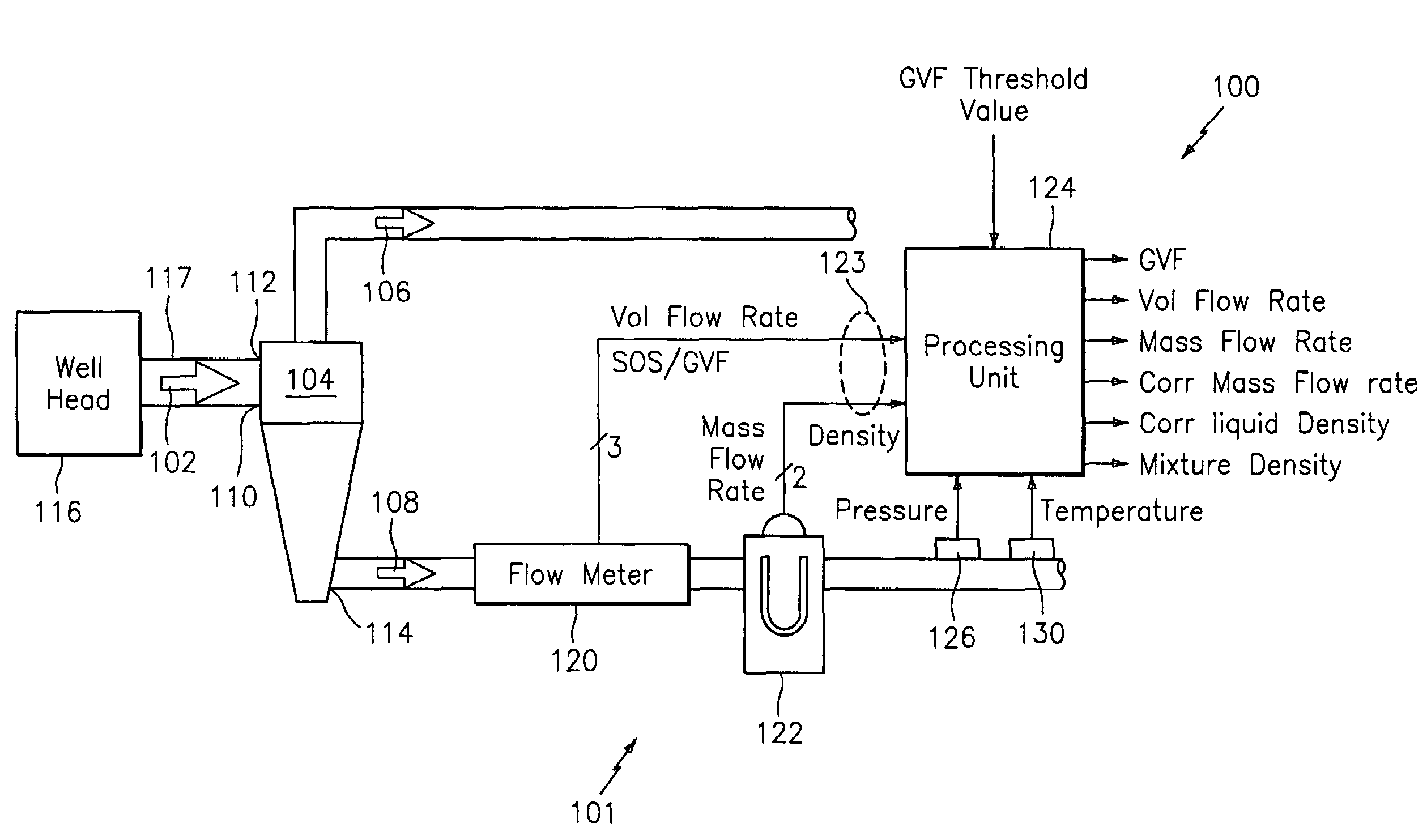
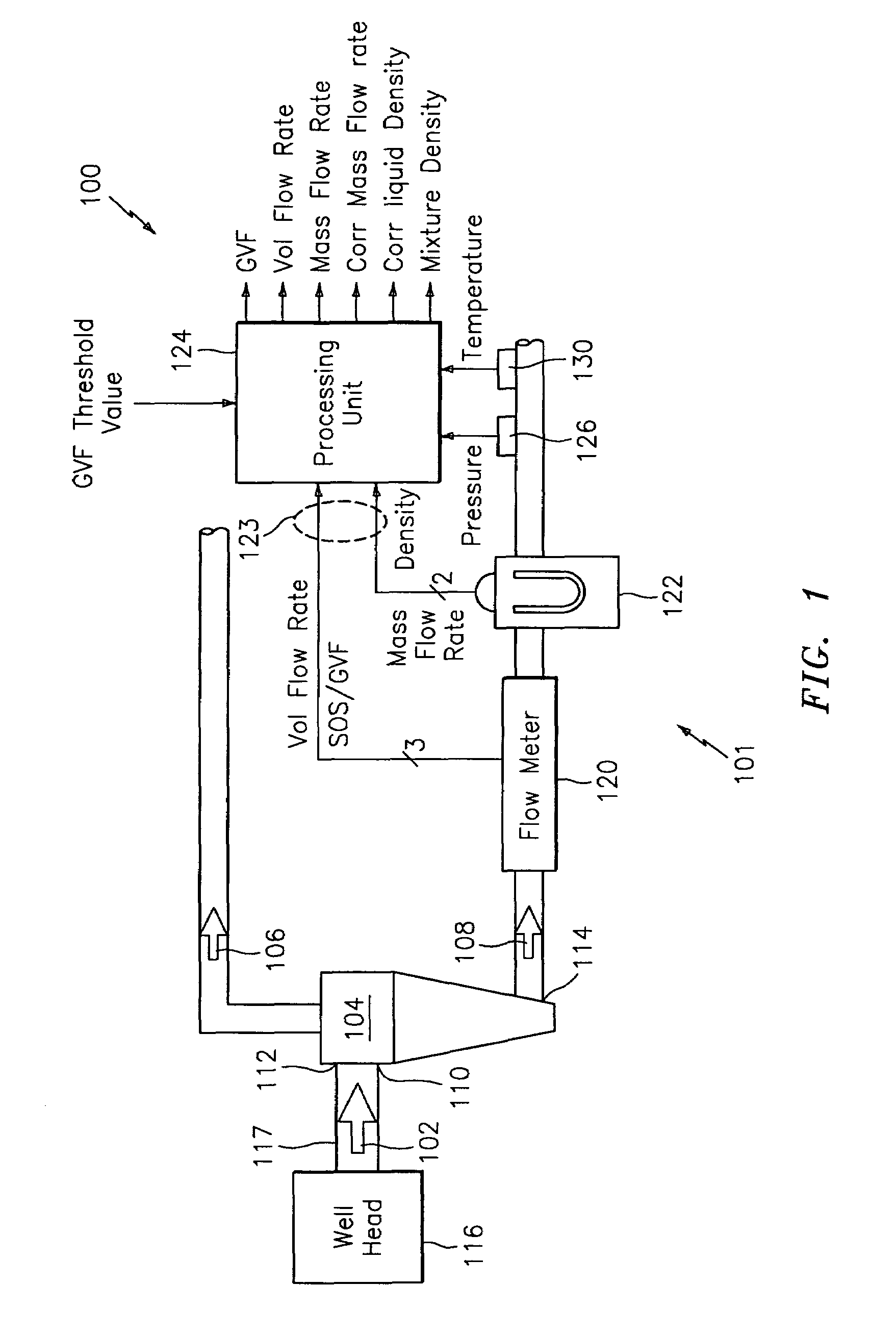
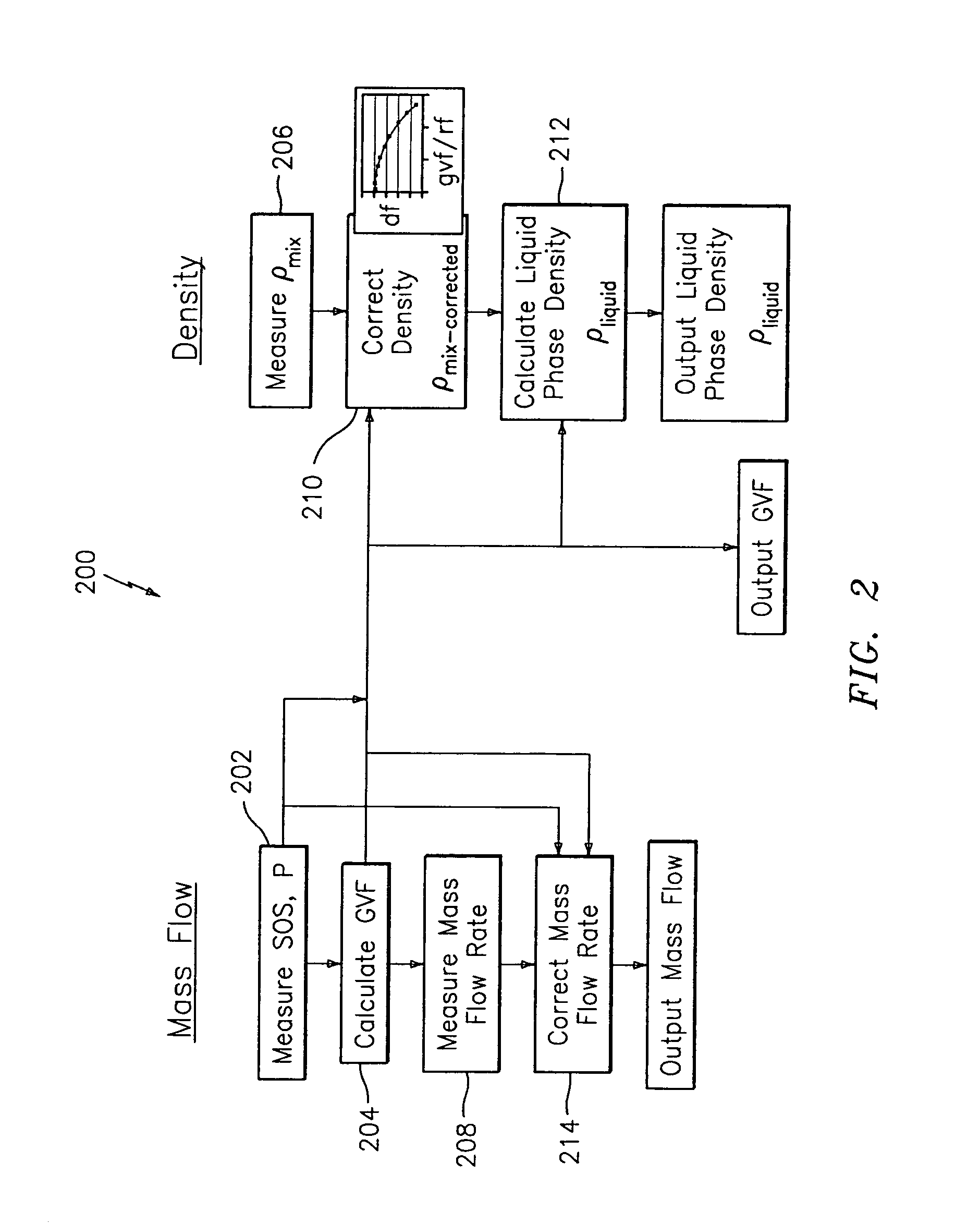
System for measuring a parameter of an aerated multi-phase mixture flowing in a pipe
A method and apparatus for measuring at least one characteristic of an aerated fluid flowing within a pipe is provided, wherein the method includes generating a measured sound speed, a measured density, a pressure and a gas volume fraction for the aerated fluid. The method also includes correcting the measured density responsive to the measured sound speed, the pressure and the gas volume fraction to generate a corrected density. The method further includes calculating a liquid phase density, determining whether the gas volume fraction is above a predetermined threshold value and generating a mass flow rate responsive to whether the gas volume fraction is above the predetermined threshold value.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Method and Apparatus for Tomographic Multiphase Flow Measurements
ActiveUS20090126502A1High measurement accuracyImprove component rangeVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectVolume meteringElectricityDensity distribution
A method for determining the flow rates of a fluid comprising a multi-component mixture of a gas and at least one liquid in a pipe, the method comprising the following steps: a) the multi-component mixture flow is conditioned to create a symmetrical annular gas concentration flow condition, b) the density distribution and / or dielectric constant distribution in said symmetrical flow within a cross-section of the pipe is determined, c) a function describing the radial distribution of density and / or radial distribution of dielectric constant is determined, d) the velocity of the multi-component mixture is determined, e) the temperature and pressure are obtained, and, f) based on the knowledge of densities and / or dielectric constants of the components of the fluid mixture, and the result from the above steps a-e, the volume and / or mass flow rates of the gas and liquid components of the fluid mixture are calculated. An apparatus for performing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:FMC KONGSBERG SUS
Apparatus and method for mass flow controller with a plurality of closed loop control code sets
InactiveUS6868862B2Testing/calibration apparatusFluid pressure measurementTraffic capacityElectronic controller
A mass flow controller includes an electronic controller for which a plurality of closed loop control codes sets may be uploaded. In a dual processor embodiment, one processor may upload a plurality of codes sets for another, with the selection of codes sets determined by the uploading processor either autonomously or through user interaction.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Mass flow meter and mass flow controller
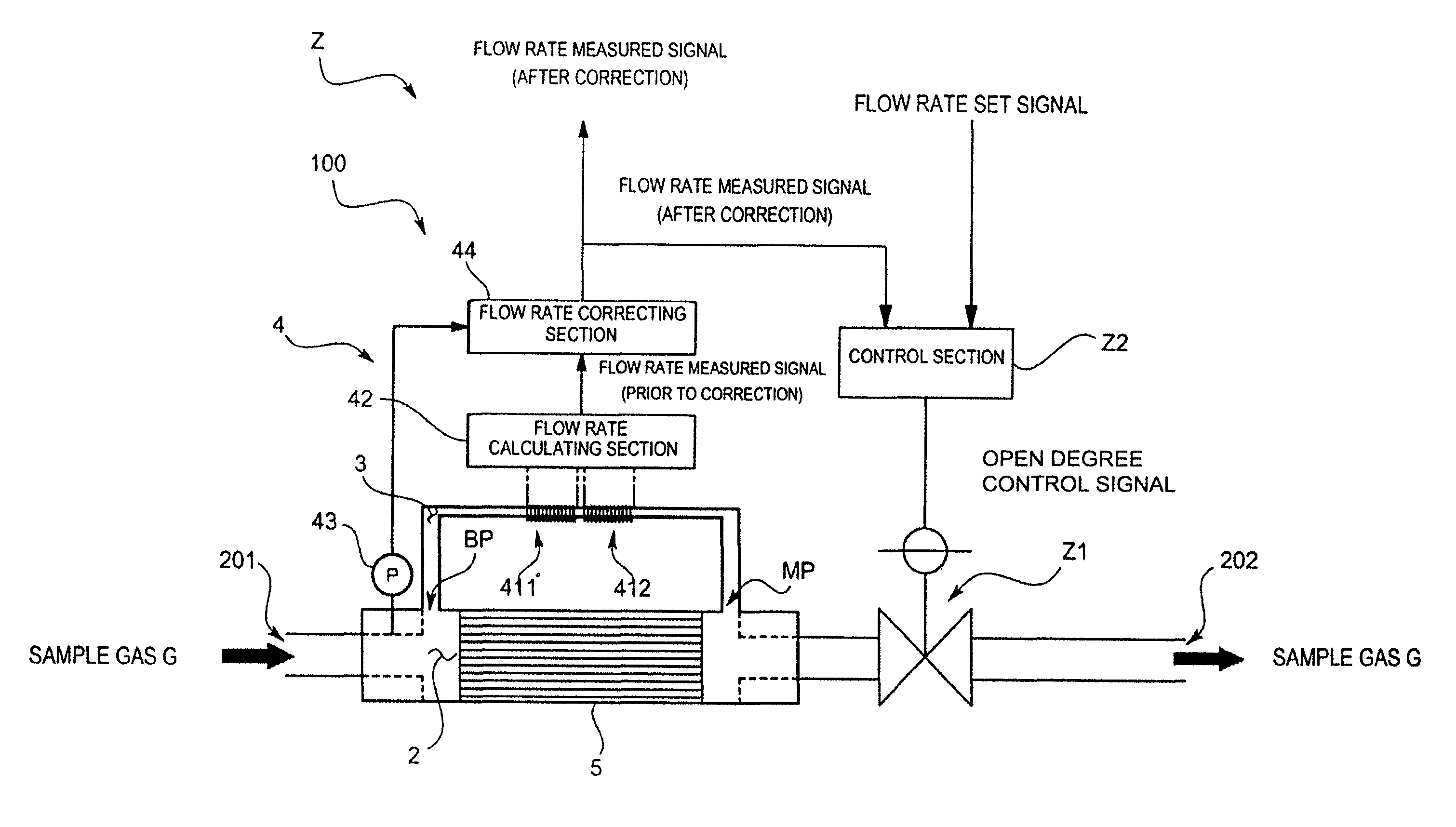
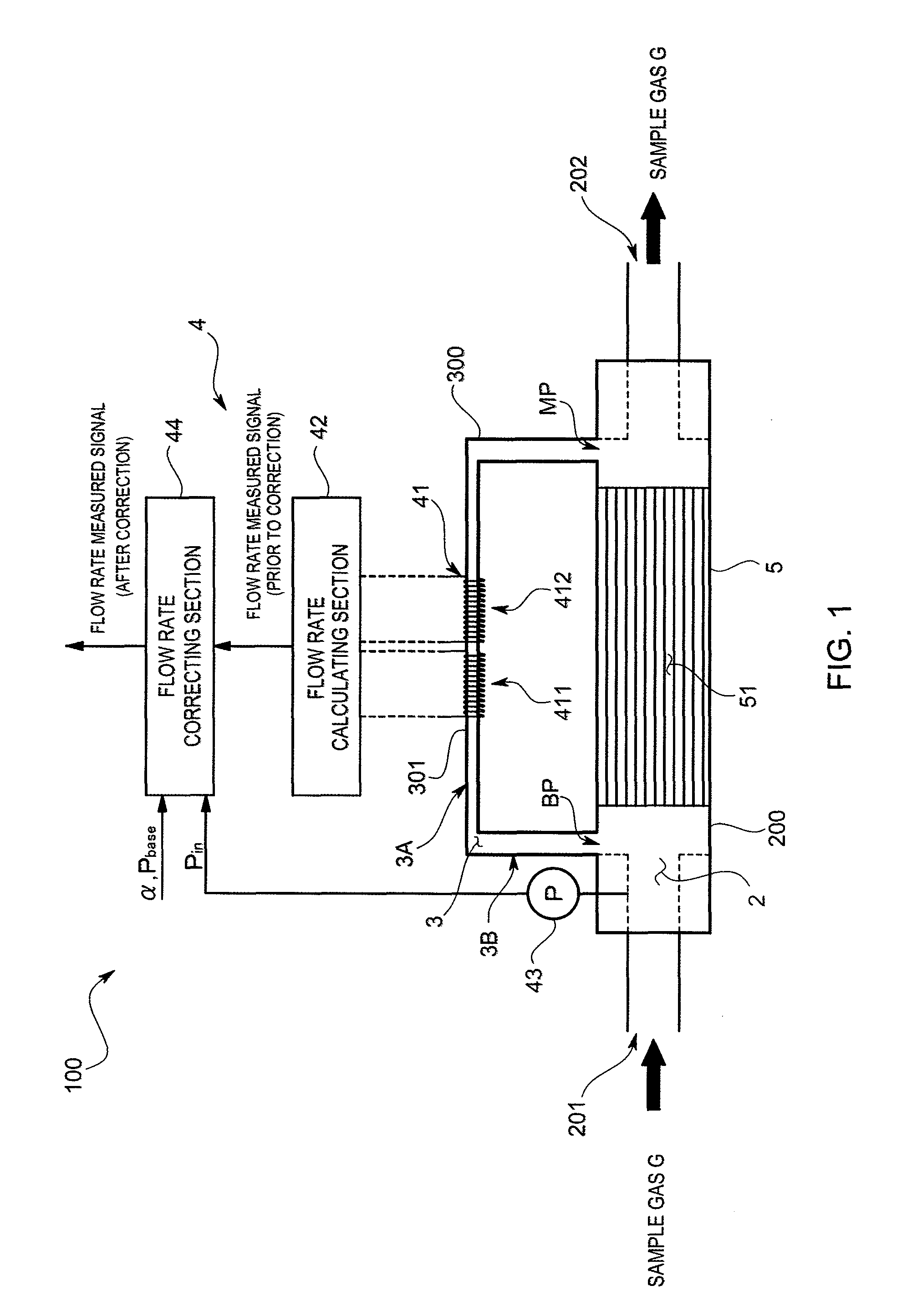
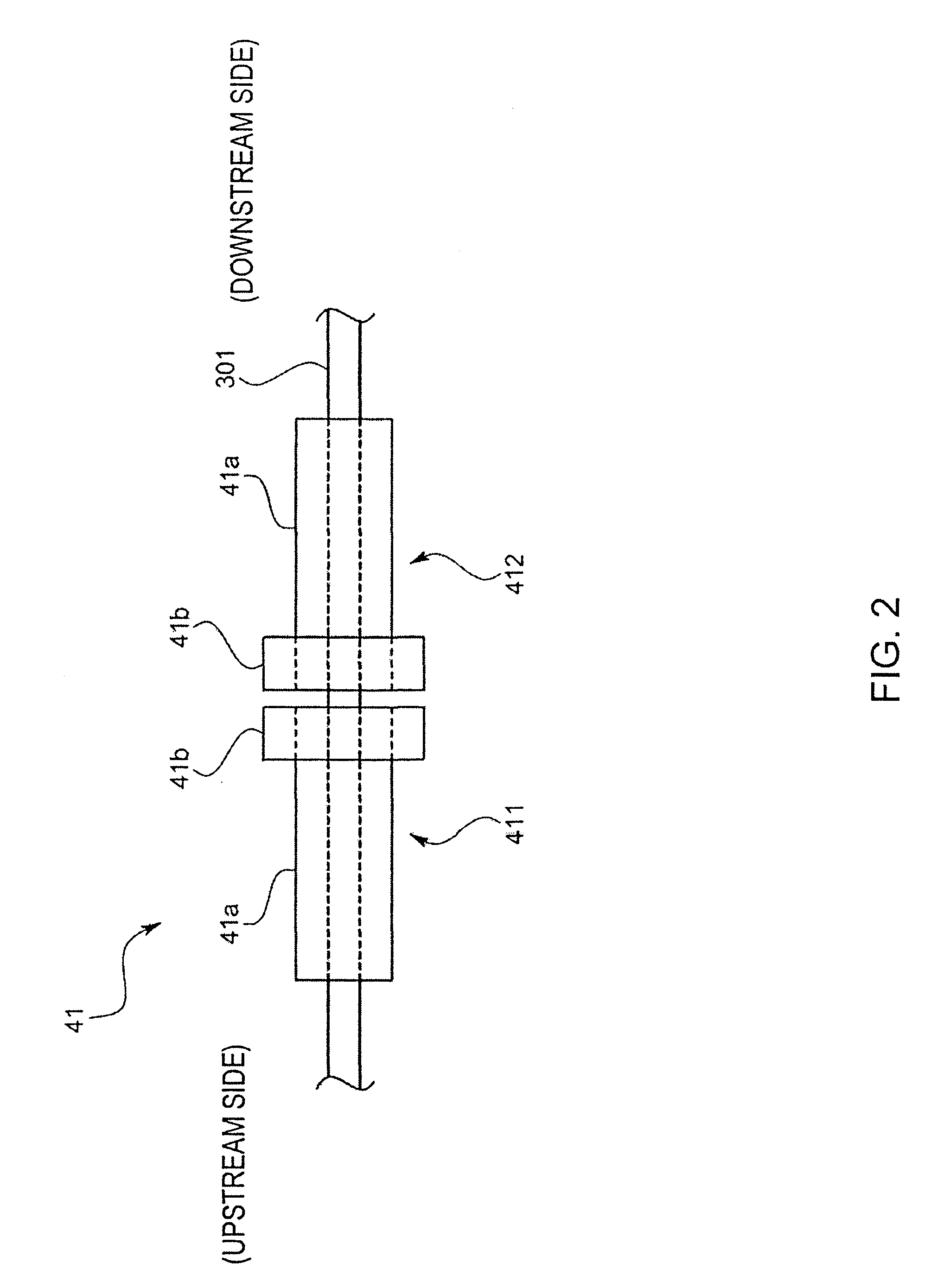
ActiveUS8356623B2Reduce measurement errorHigh flow accuracyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsEngineeringStreamflow
In order to improve a measurement accuracy of a mass flow meter, the mass flow meter comprises a flow rate calculating section that obtains an output signal from a sensor section having a thermosensitive resistive element arranged in a flow channel where a sample gas flows and that calculates a flow rate of the sample gas, a pressure measuring section that measures a primary side pressure in the flow channel, and a flow rate correcting section that corrects the measured flow rate obtained by the flow rate calculating section by the use of the primary side pressure obtained by the pressure measuring section and a gas coefficient determined by an isobaric specific heat of the sample gas.
Owner:HORIBA STEC CO LTD
Simplified fluid property measurement
ActiveUS7258024B2Volume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectIndirect mass flowmetersDifferential pressureEngineering
A process fluid measurement system provides a first measurement relative to process fluid flowing in a pipe. An additional measurement of process fluid flow velocity in the pipe is combined with the first measurement to provide a simplified indication of mass fluid flow and / or density or other fluid parameter. In some embodiments, the first measurement is a differential pressure measurement. Additionally, one embodiment provides a vortex flowmeter having configurable terminations for coupling to a variety of pressure or differential pressure sensors or transmitters for advanced process fluid measurements or calculations.
Owner:MICRO MOTION INC
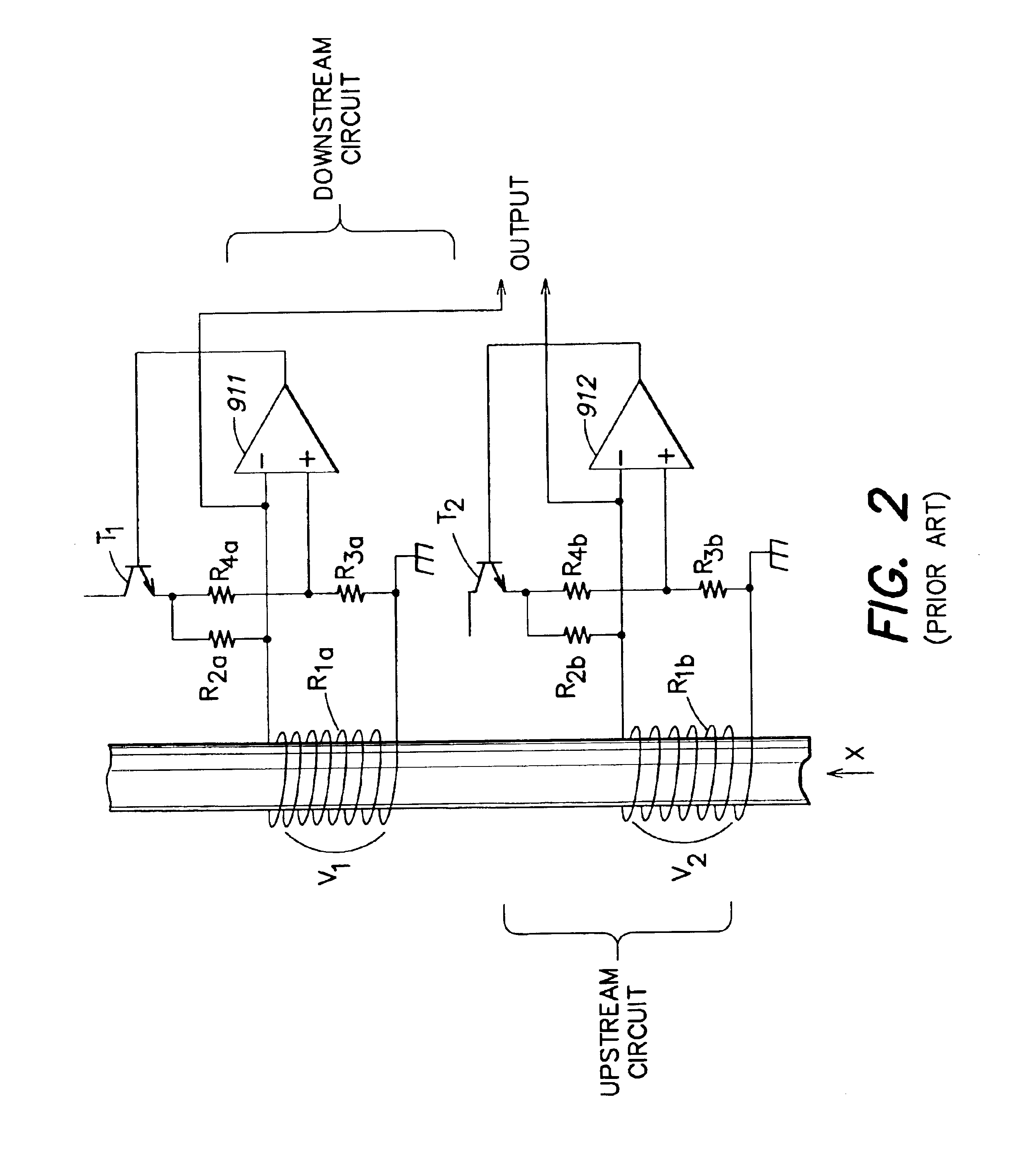
Vortex flow pickup
InactiveUS6938496B2Better heat conductorAccurate temperature measurementVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectIndirect mass flowmetersEngineeringEddy-current sensor
A vortex flow pickup serves for measuring mass flow, volume flow or flow velocity of a fluid which is flowing in a measuring tube having a tube wall, and has a temperature sensor arranged in such a way that the vortex flow pickup may also be used together with those fluids which corrode the temperature sensor. A bluff body which produces vortices, and consequently pressure fluctuations, is arranged in the measuring tube. A vortex sensor responding to these pressure fluctuations is fitted downstream of the bluff body in a bore of the tube wall of the measuring tube. The vortex sensor comprises a diaphragm which covers the bore and on which a sensor vane protruding into the fluid is fastened. The temperature sensor is fixed on the bottom of a blind hole of the sensor vane. On the side of the diaphragm lying opposite the sensor vane, a sensor element is fastened. The temperature sensor may alternatively be arranged in a longitudinal bore of the bluff body.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
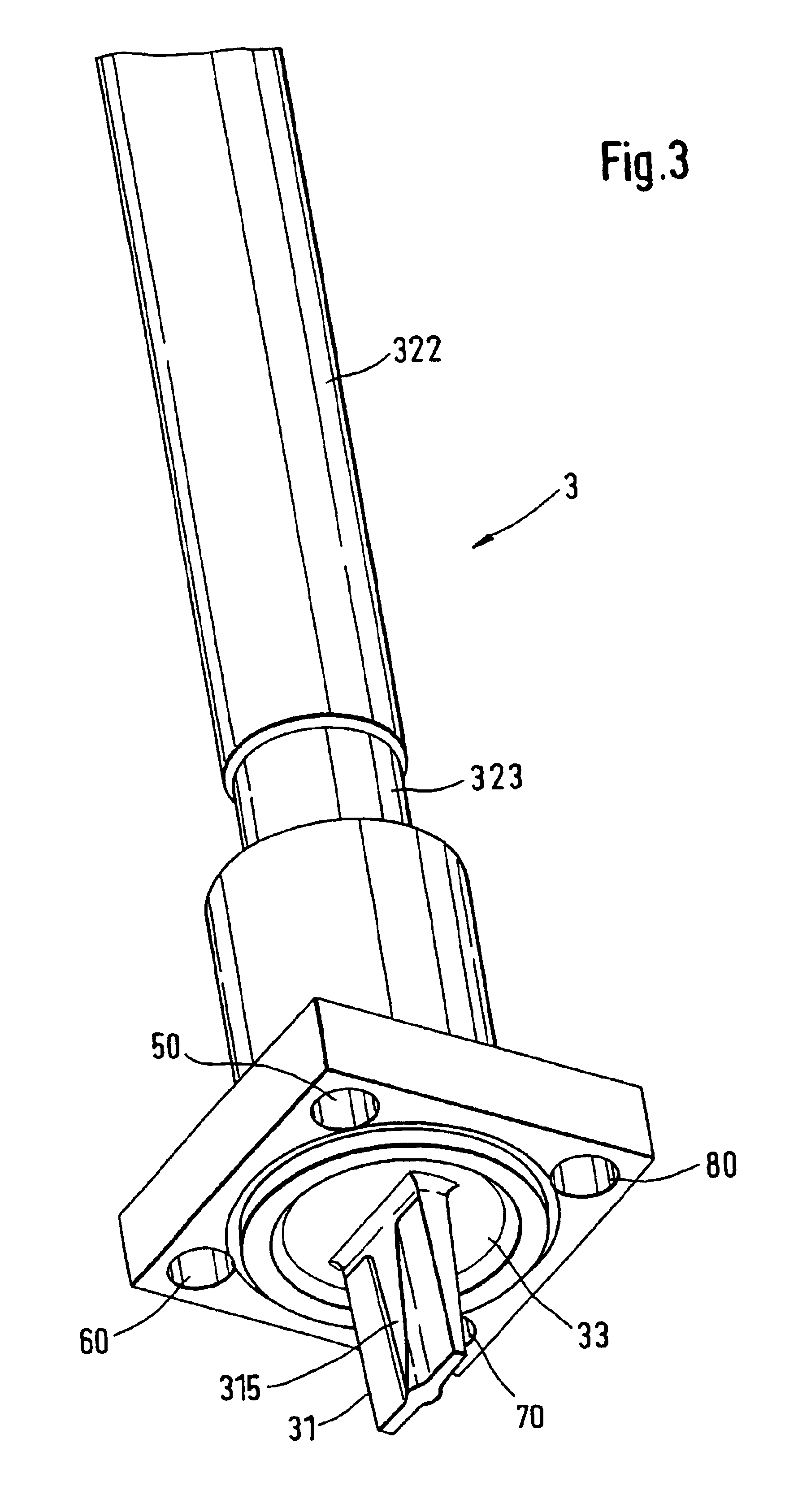
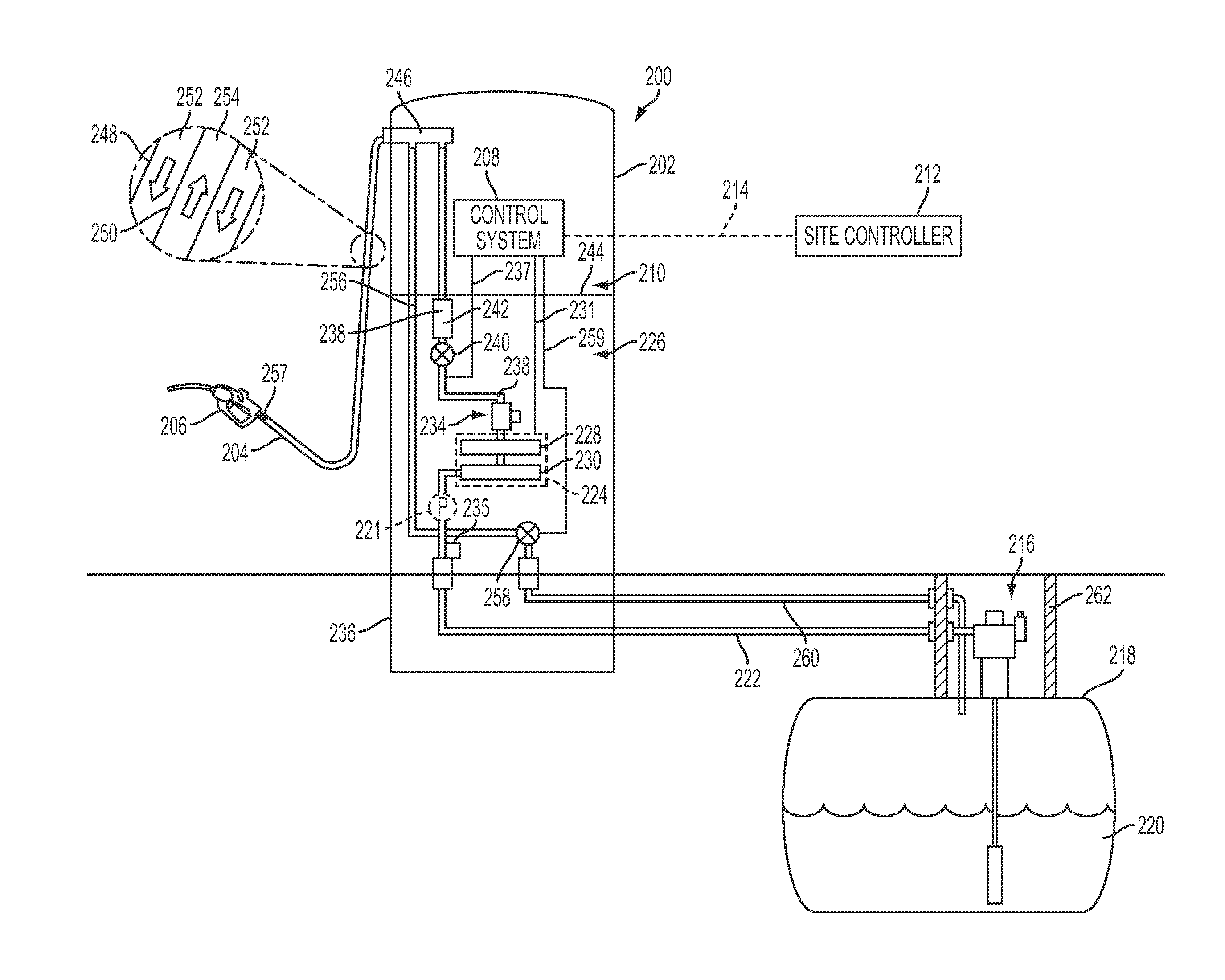
Fuel or def dispenser having fluid temperature conditioning and control system
ActiveUS20120024892A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesUsing liquid separation agentControl systemEngineering
A fluid dispenser comprising a housing in which fluid flow control components are located and a fluid conduit completing a fluid flow path between a fluid storage tank and a nozzle coupled to the housing. The fluid dispenser further comprises a control system, at least one controllable valve in and a fluid flow meter located along the fluid flow path. The fluid dispenser further comprises a fluid temperature conditioning subsystem located along the fluid flow path upstream of the flow meter. The control system is selectively operates the fluid temperature conditioning subsystem upon detection of a predetermined temperature. At least one controllable recirculation valve may also be provided, and the control system may selectively actuate the controllable recirculation valve such that the fluid flows back to the fluid storage tank. A method of measuring the flow rate of a fluid in the fluid dispenser is also disclosed.
Owner:GILBARCO
Ultrasonic gas flowmeter as well as device to measure exhaust flows of internal combustion engines and method to determine flow of gases
ActiveUS20050066744A1Minimize impactHigh precisionVolume variation compensation/correction apparatusIndirect mass flowmetersCombustionUltrasonic sensor
An ultrasonic gas flowmeter includes a measuring pipe with flowing gas, transmitting and receiving sound transducers, transmission and reception electronics, and evaluation electronics. The sound transducers (7, 8, 9, 10) are designed as capacitive electro-acoustic ultrasonic transducers to construct a flowmeter with improved capacity, especially in view of temperature stability and the reduction and consideration of a temperature profile. Devices (5, 6) are provided to level the gas temperature profile and to minimize the influence of the temperature profile on the flow measurement. A more accurate and dependable detection of the volume flow or the mass flow of gases is to be achieved, especially in highly dynamic flows, for the method of determining the flow of gases whereby the mean flow velocity is determined and the flowing gas quantity is determined with highly synchronized resolution from the two transit times of two acoustic signals. In addition, an assessed value is computed (35) for the flow after the determination of the transit times and the assessed value is corrected at least by means of a characteristic temperature of the gas and the temperature of the wall of the measuring pipe (36).
Owner:AVL LIST GMBH
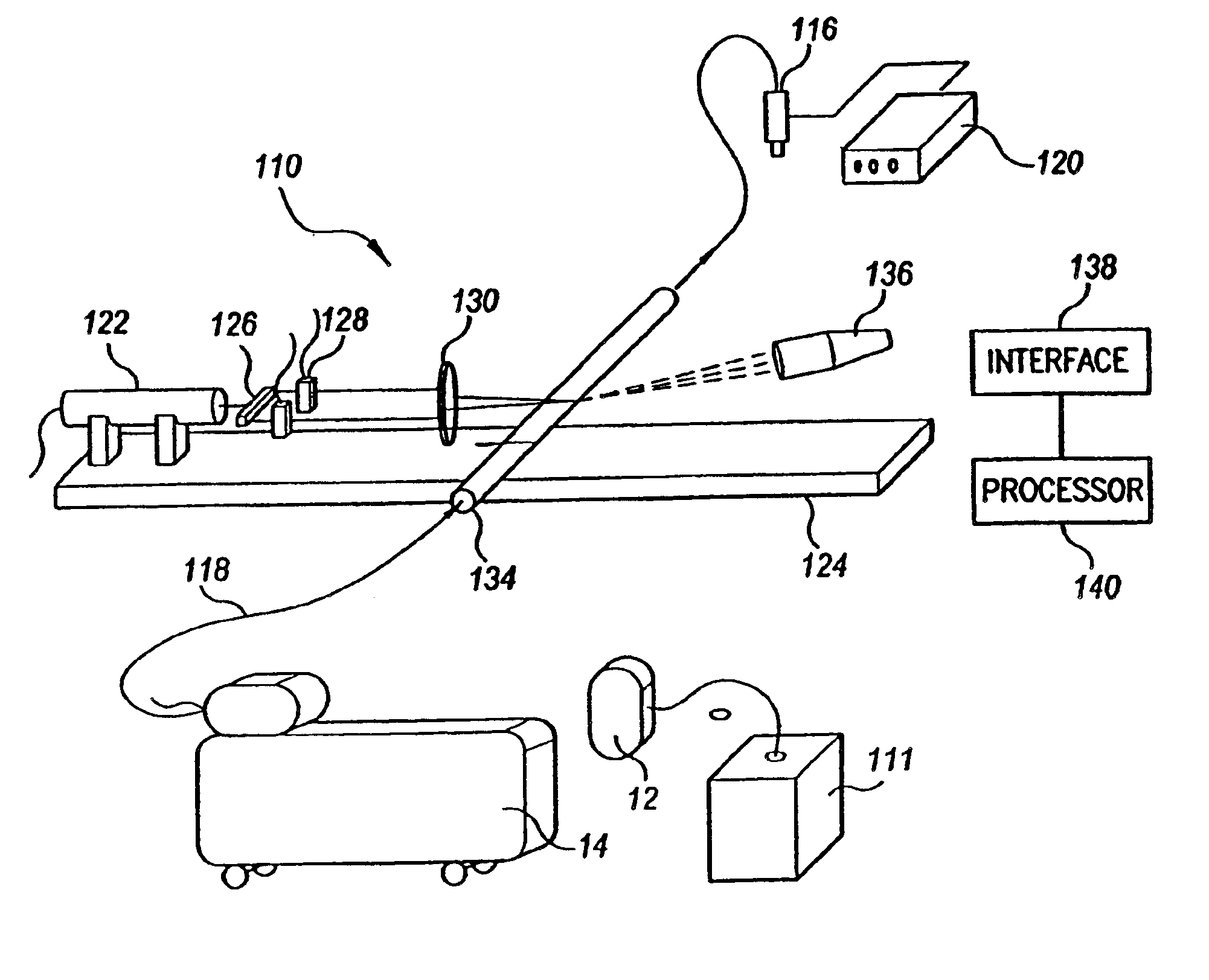
Liquid metering system
InactiveUS20050005710A1Volume variation compensation/correction apparatusIndirect mass flowmetersThermal energyEngineering
Systems and methods for measuring the flow of a fluid along a passageway are disclosed. A heat source applies thermal energy to a portion of the fluid thereby elevating its temperature and decreasing its density. An optical sensing means measures a change in a property of illumination directed through the passageway caused by the change in the density of the heated portion of fluid. The time required for the heated portion of the liquid to move from the point of application of thermal energy to the point of optical sensing is measured. This measured time, and the distance of separation of the source of heat and the optical sensor permits calculation of the fluid velocity in the passageway.
Owner:THERAFUSE
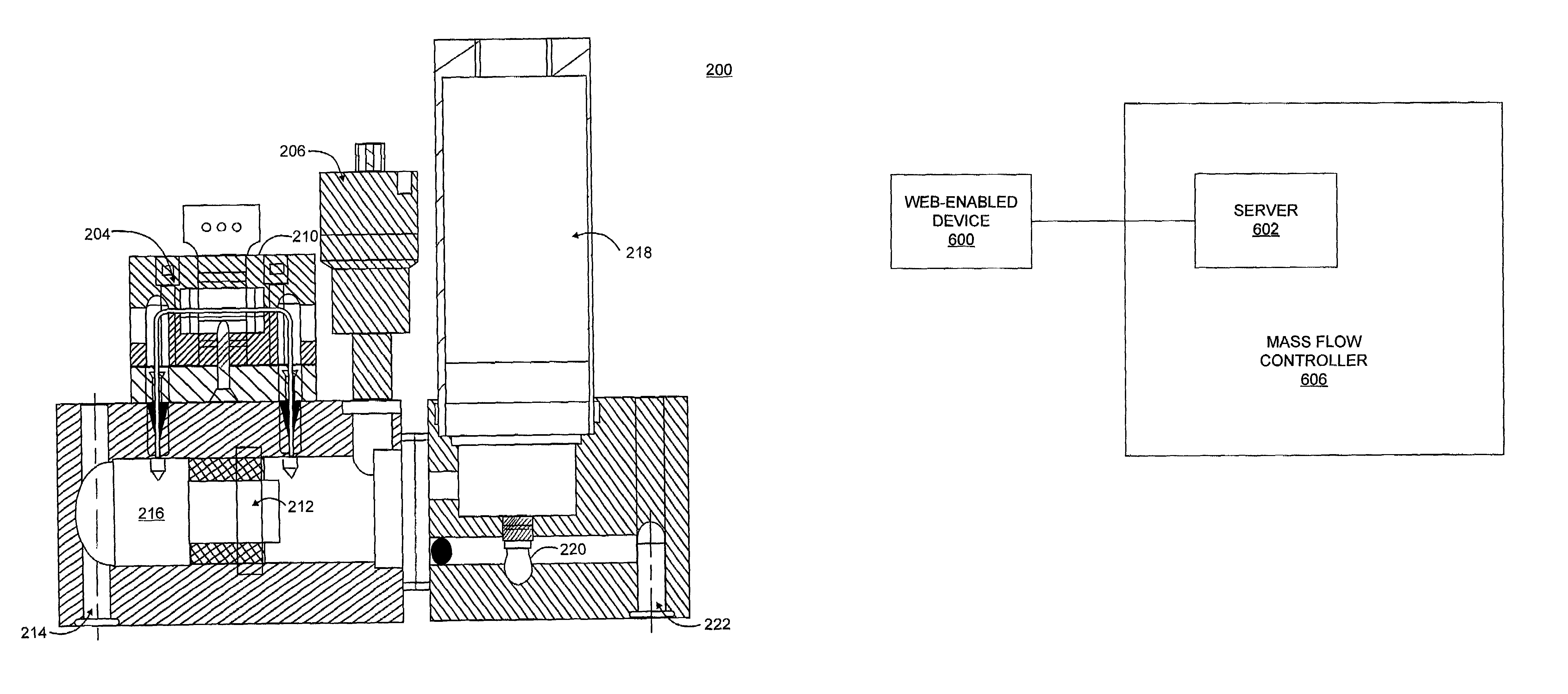
Apparatus and method for mass flow controller with embedded web server
InactiveUS7004191B2Testing/calibration apparatusFluid pressure measurementTraffic capacityElectronic controller
A mass flow controller includes an electronic controller that provides a web server that allows access to the web server through such interworking networks as the Internet.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
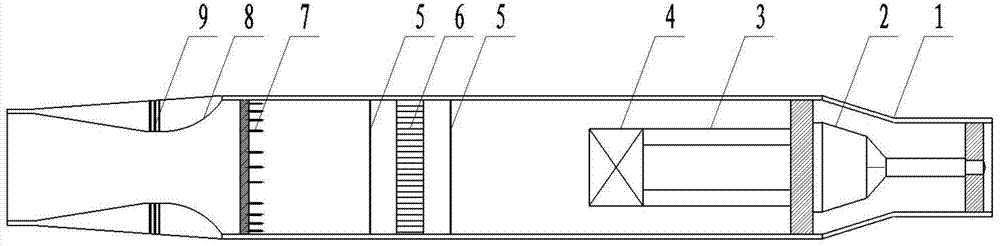
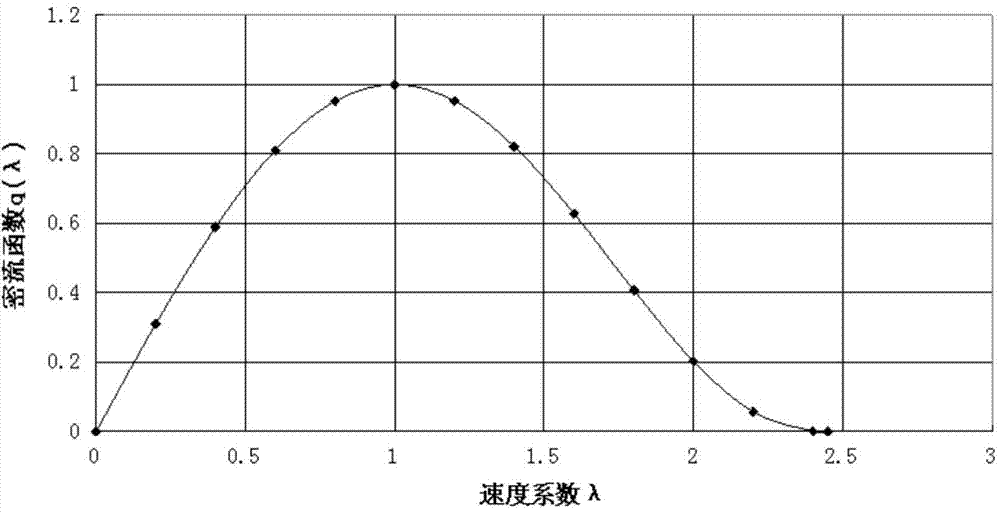
Air duct flow measuring system
ActiveCN104848904AAccurate measurementEasy to assemble and disassembleAerodynamic testingIndirect mass flowmetersSpecific testAirway flow measurement
The invention discloses an air duct flow measuring system. The air duct flow measuring system comprises a shell, a reverse pressure adjusting device, a rectifying device, a total pressure measurement rake, a Laval spraying tube and a static pressure measuring device, wherein the shell is cylindrical; a connector is arranged at the front end of the shell; an expansion section is arranged at the rear end of the connector and is used for reducing the speed of incoming flow; a straight section is arranged behind the expansion section; the reverse pressure adjusting device comprises a throttling cone and a driving control mechanism; the throttling cone is arranged in the expansion section; the driving control mechanism is arranged in the straight section; the rectifying device, the total pressure measurement rack and the Laval spraying tube are sequentially arranged in the straight section and behind the driving control mechanism; an outlet of the Laval spraying tube is parallel and level to a rear end opening of the shell; and the static pressure measuring device is arranged at the throat of the Laval spraying tube. By the air duct flow measuring system, reverse pressure of an outlet of the double-spraying air duct can be adjusted in real time, the flow of air flowing into the double-spraying air duct can be measured accurately, and the air flowing in the air duct can be sucked according to specific test conditions so as to increase the flow of the air and meet requirements of a test on the air duct.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Variable resistance sensor with common reference leg
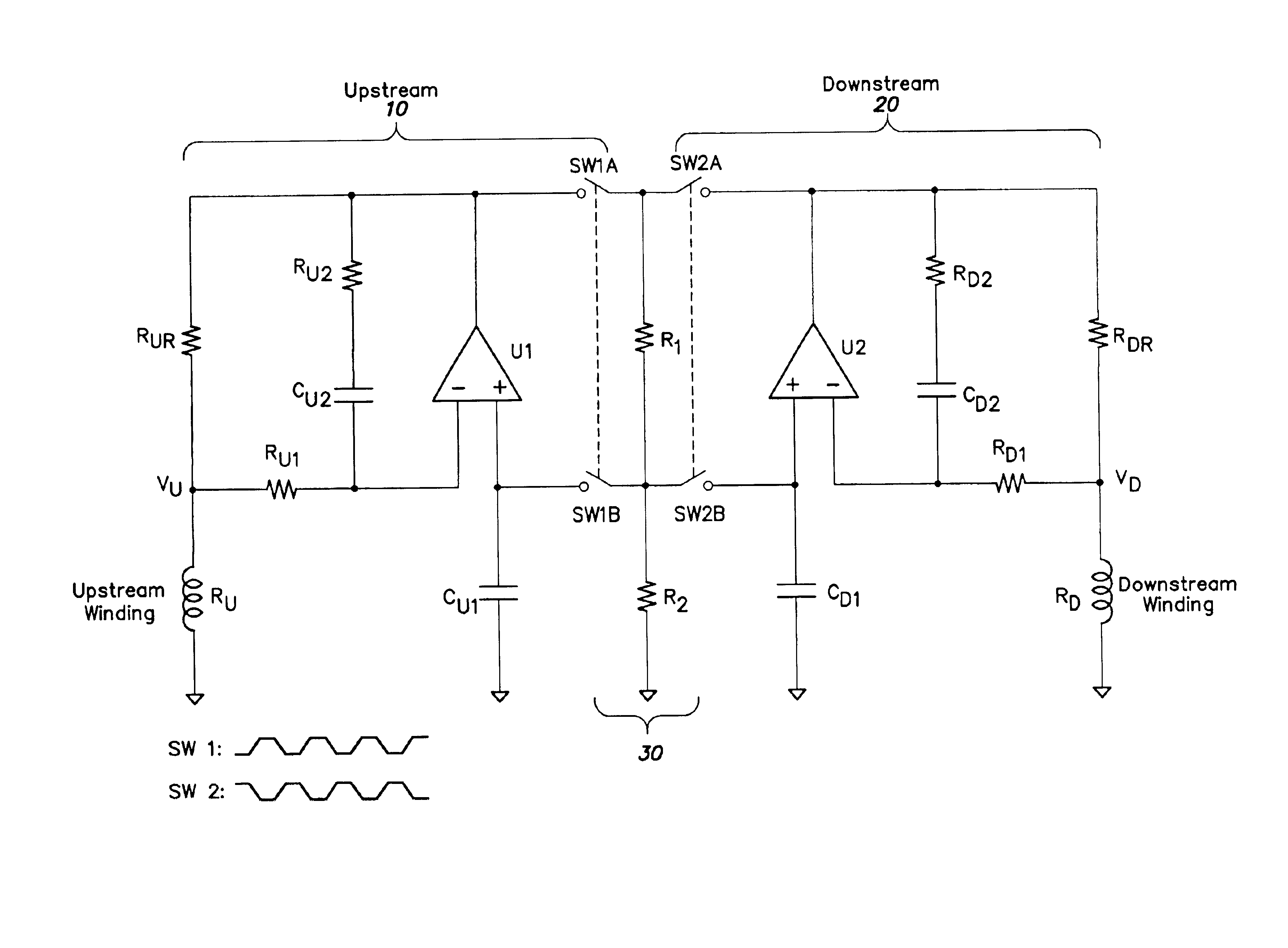
InactiveUS6845659B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsEngineeringResistor
A resistive bridge sensor circuit that includes a first resistive bridge circuit having a first variable resistance resistor and a second resistive bridge circuit having a second variable resistance resistor. The first and second resistive bridge circuits share at least a portion of a common reference leg that sets a resistance of a first and second variable resistors. The common reference leg or a portion of the common reference leg is alternately switchably connected to one of the first and second resistive bridge circuits.
Owner:BROOKS INSTRUMENT
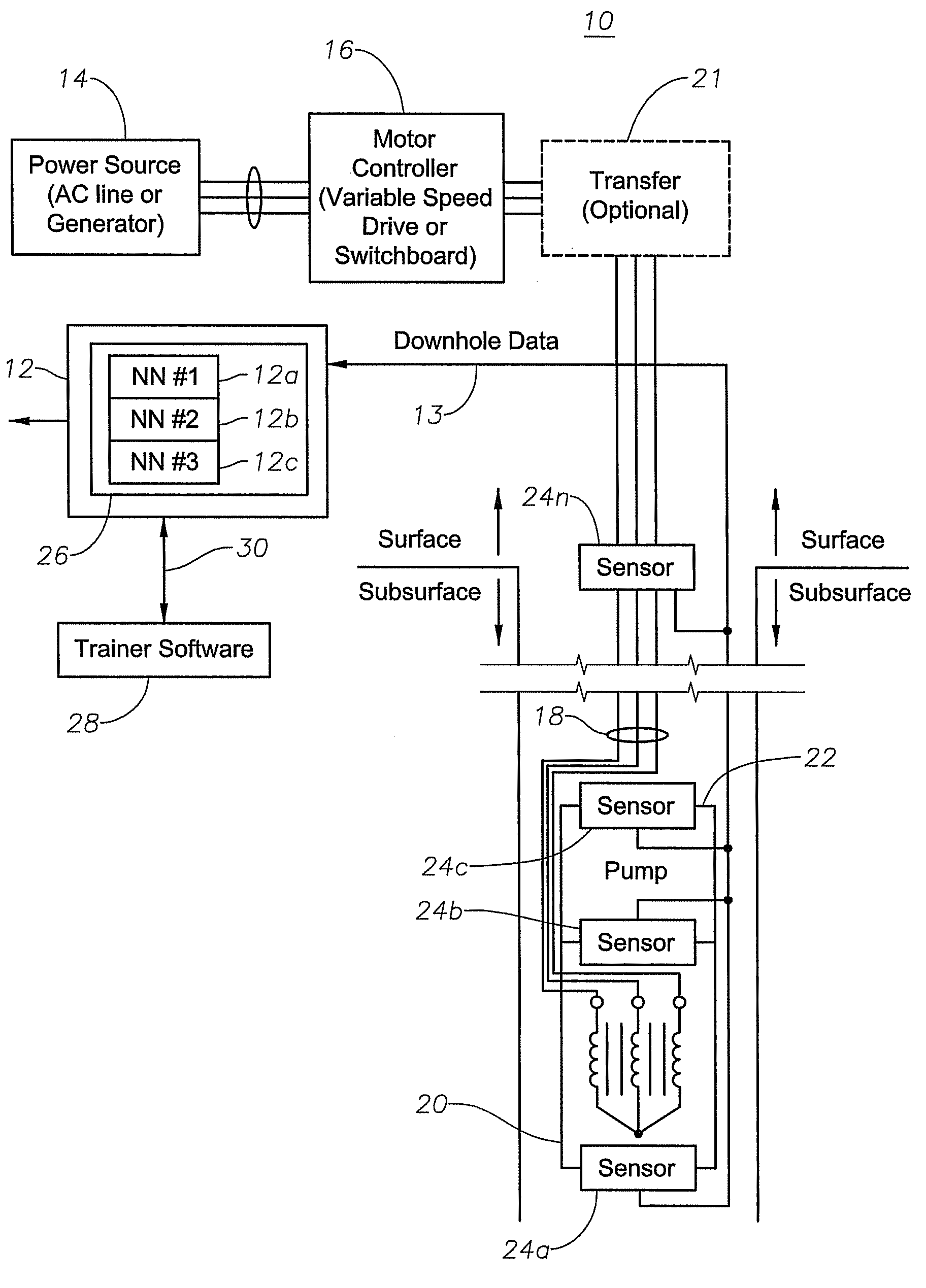
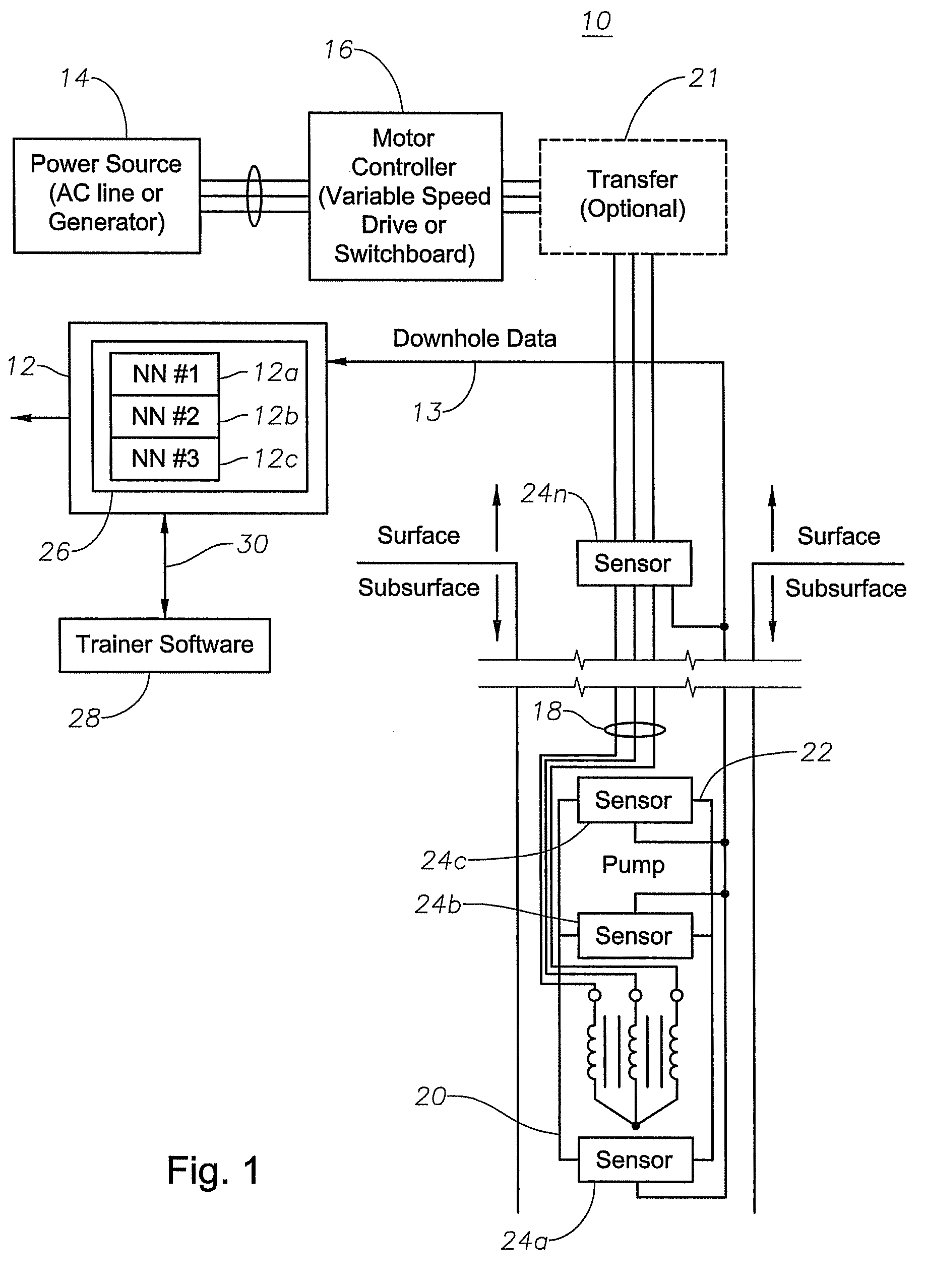
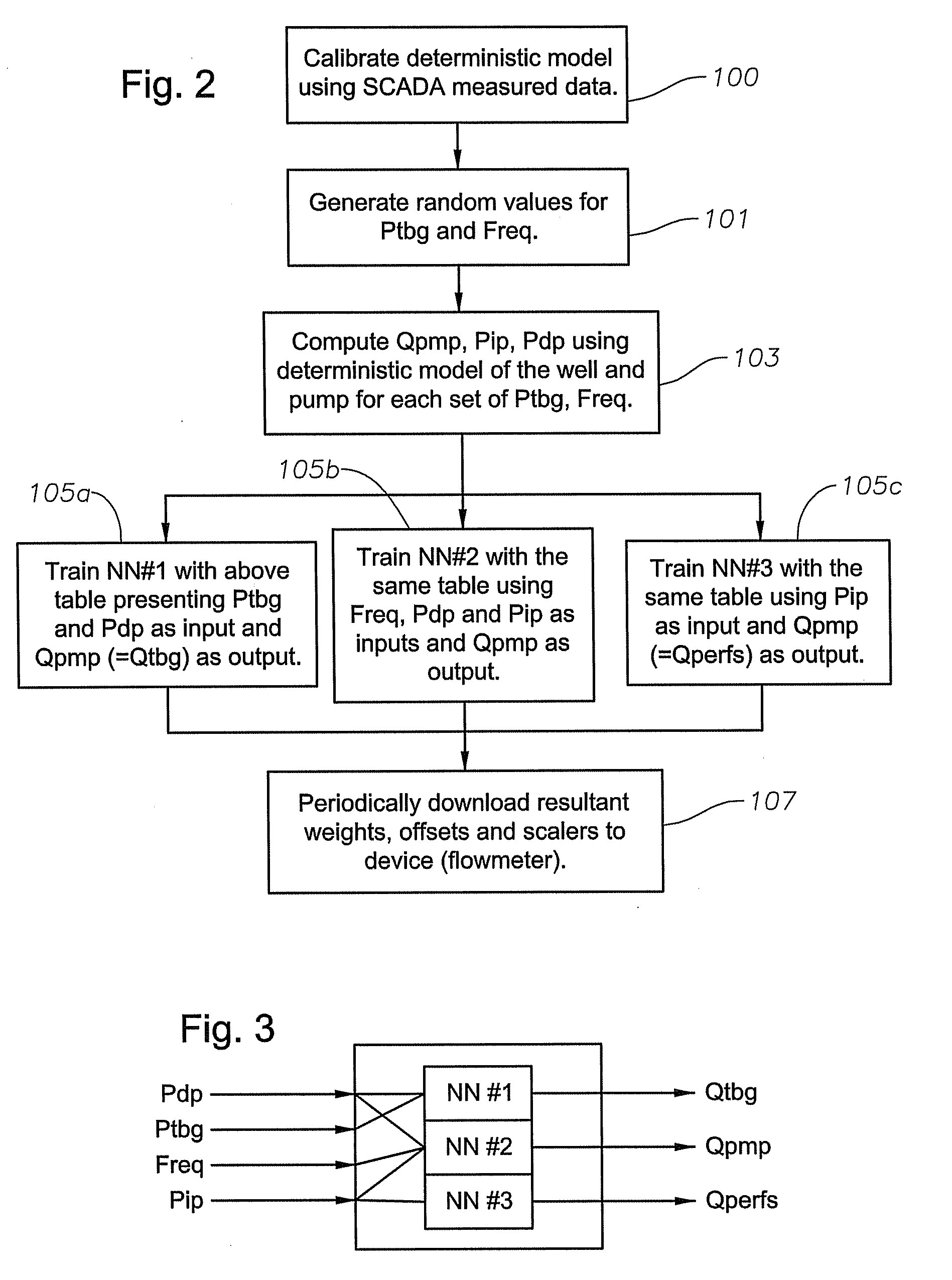
Multiphase flow meter for electrical submersible pumps using artificial neural networks
A multiphase flow meter used in conjunction with an electrical submersible pump system in a well bore includes sensors to determine and transmit well bore pressure measurements, including tubing and down hole pressure measurements. The multiphase flow meter also includes at least one artificial neural network device to be used for outputting flow characteristics of the well bore. The artificial neural network device is trained to output tubing and downhole flow characteristics responsive to multiphase-flow pressure gradient calculations and pump and reservoir models, combined with standard down-hole pressure, tubing surface pressure readings, and the frequency applied to the electrical submersible pump motor.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com