Patents
Literature
86 results about "Gas volume fraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
There are several quantitative terms: gas volume fraction (GVF) is the volume of the gas flow divided by the total volume of fluid flowing.
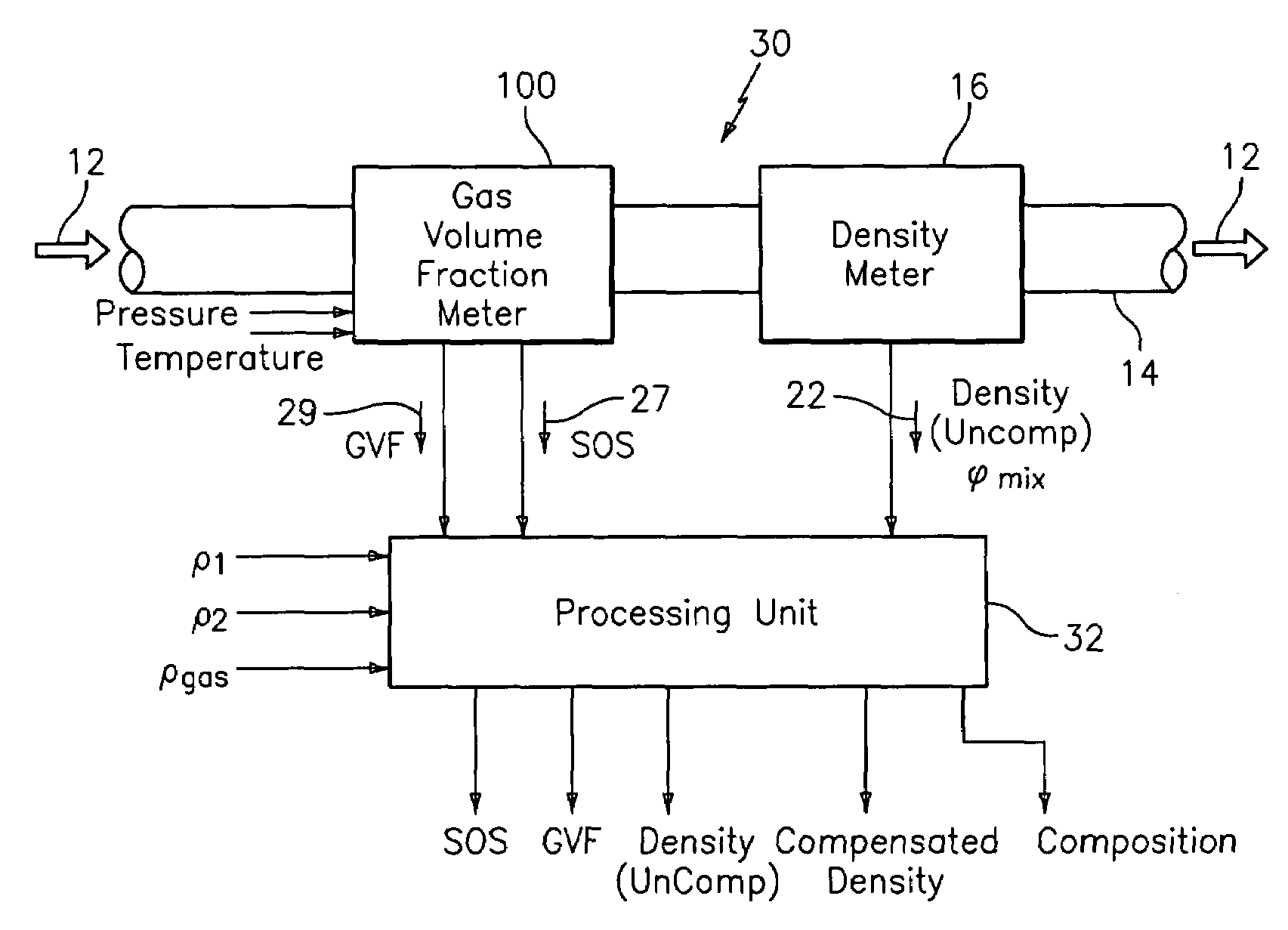
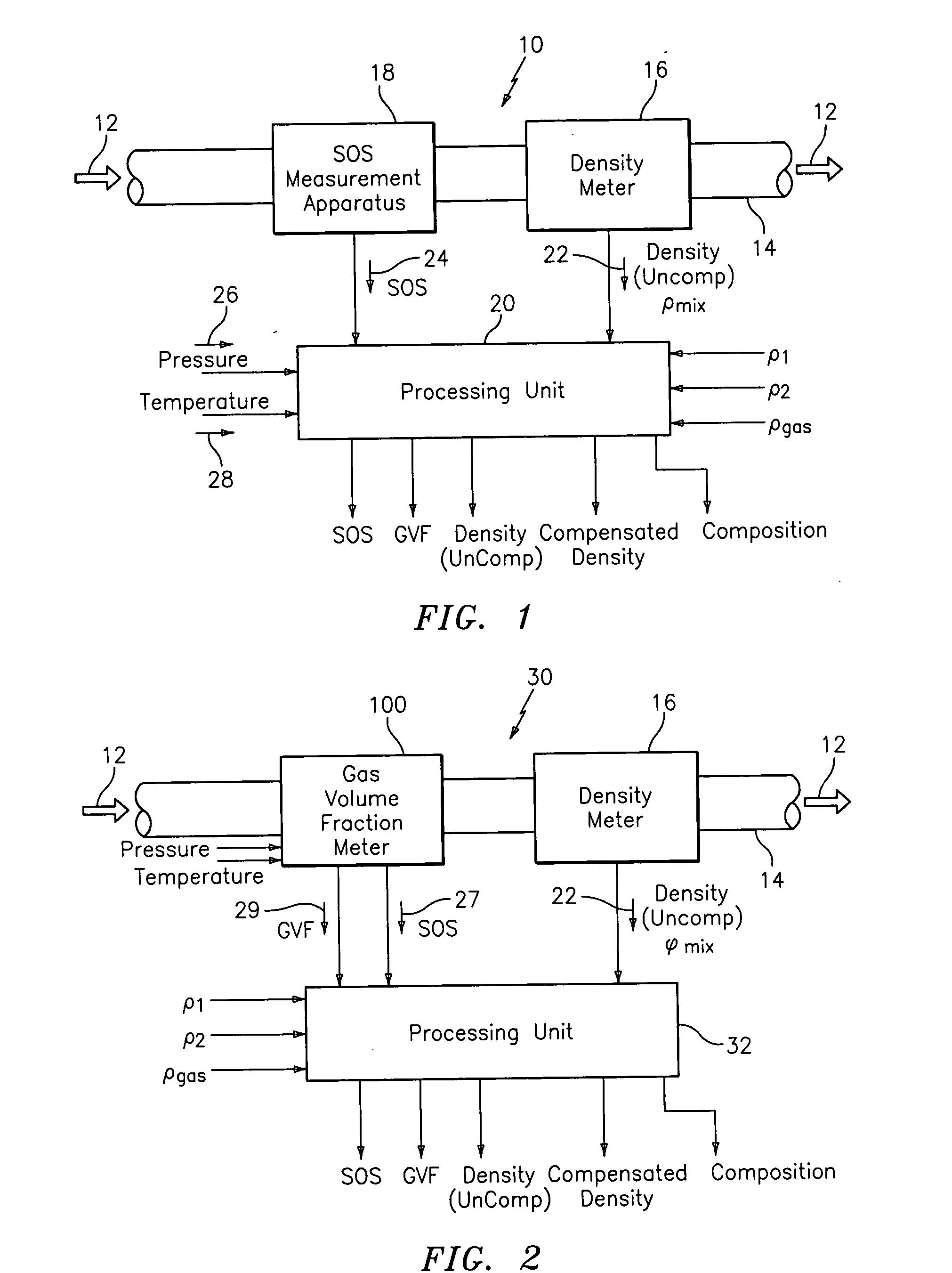
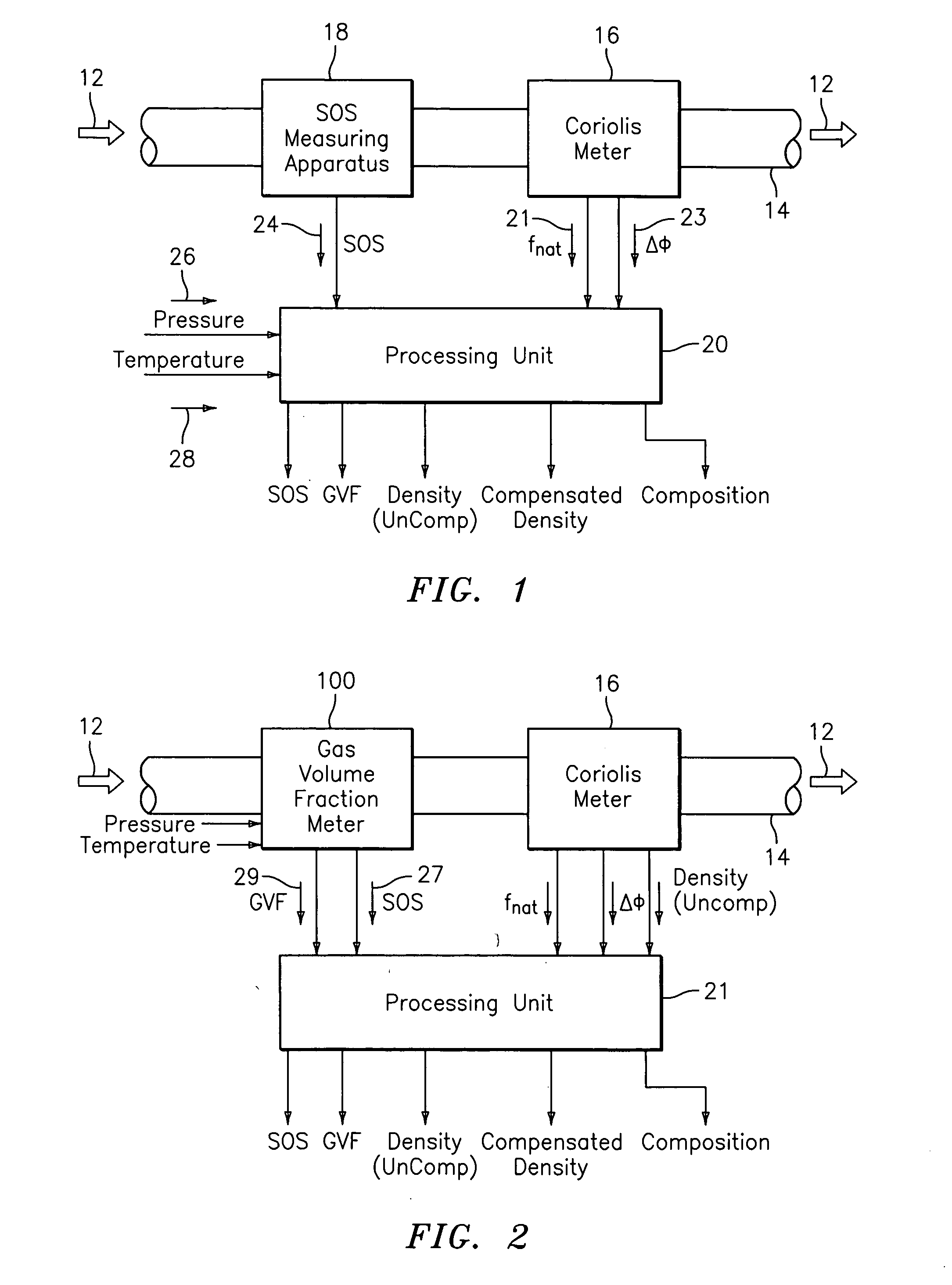
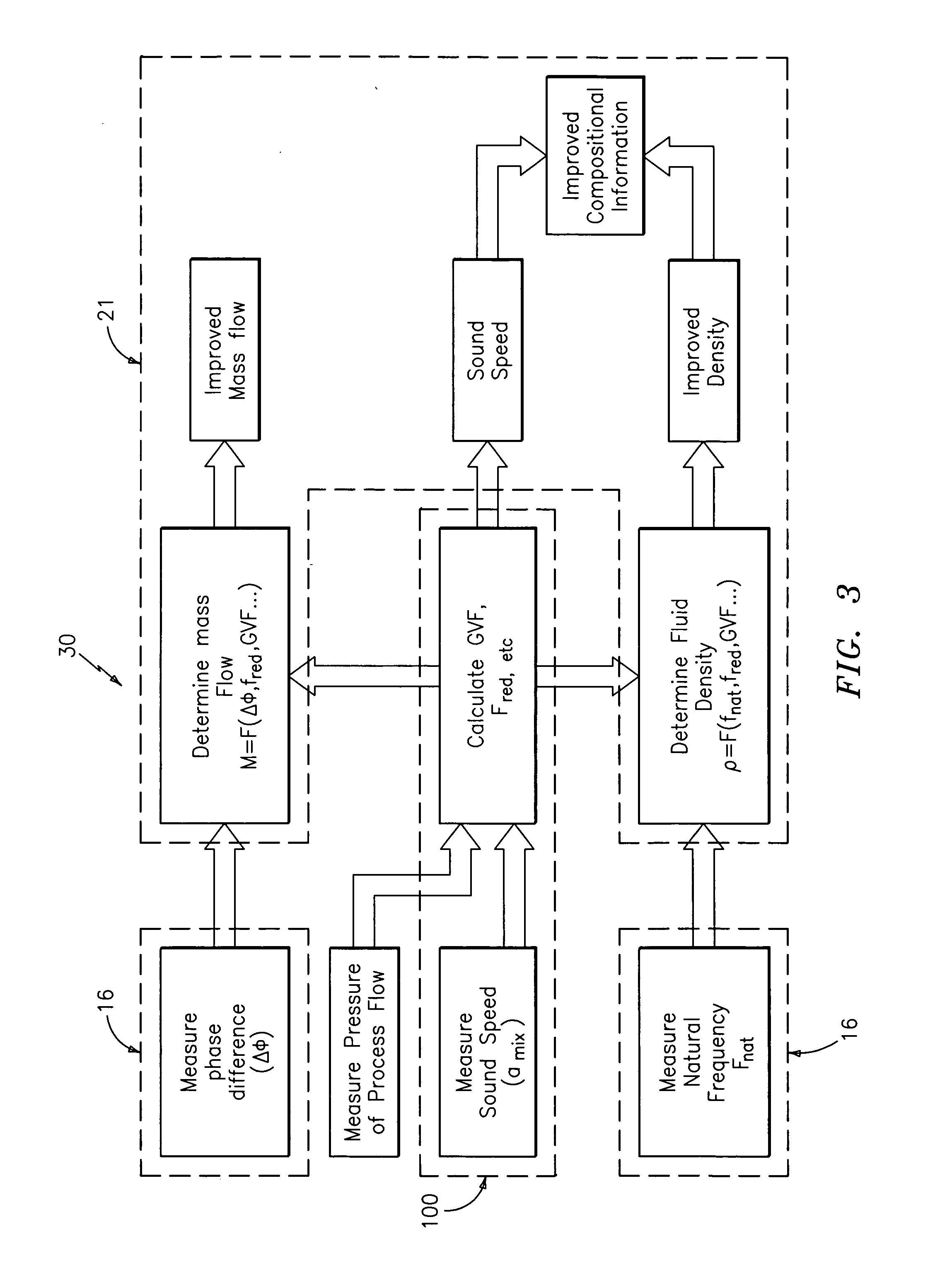
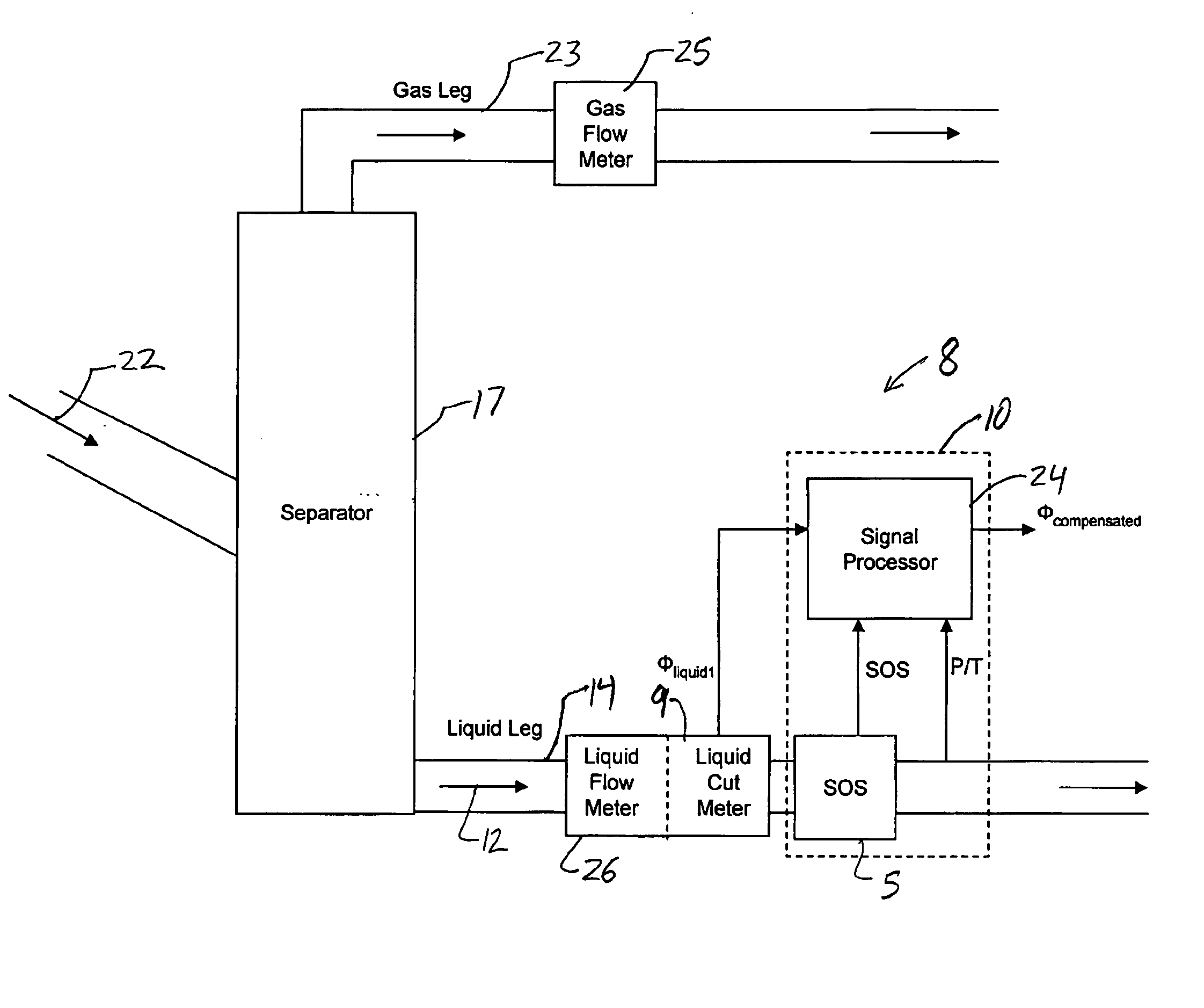
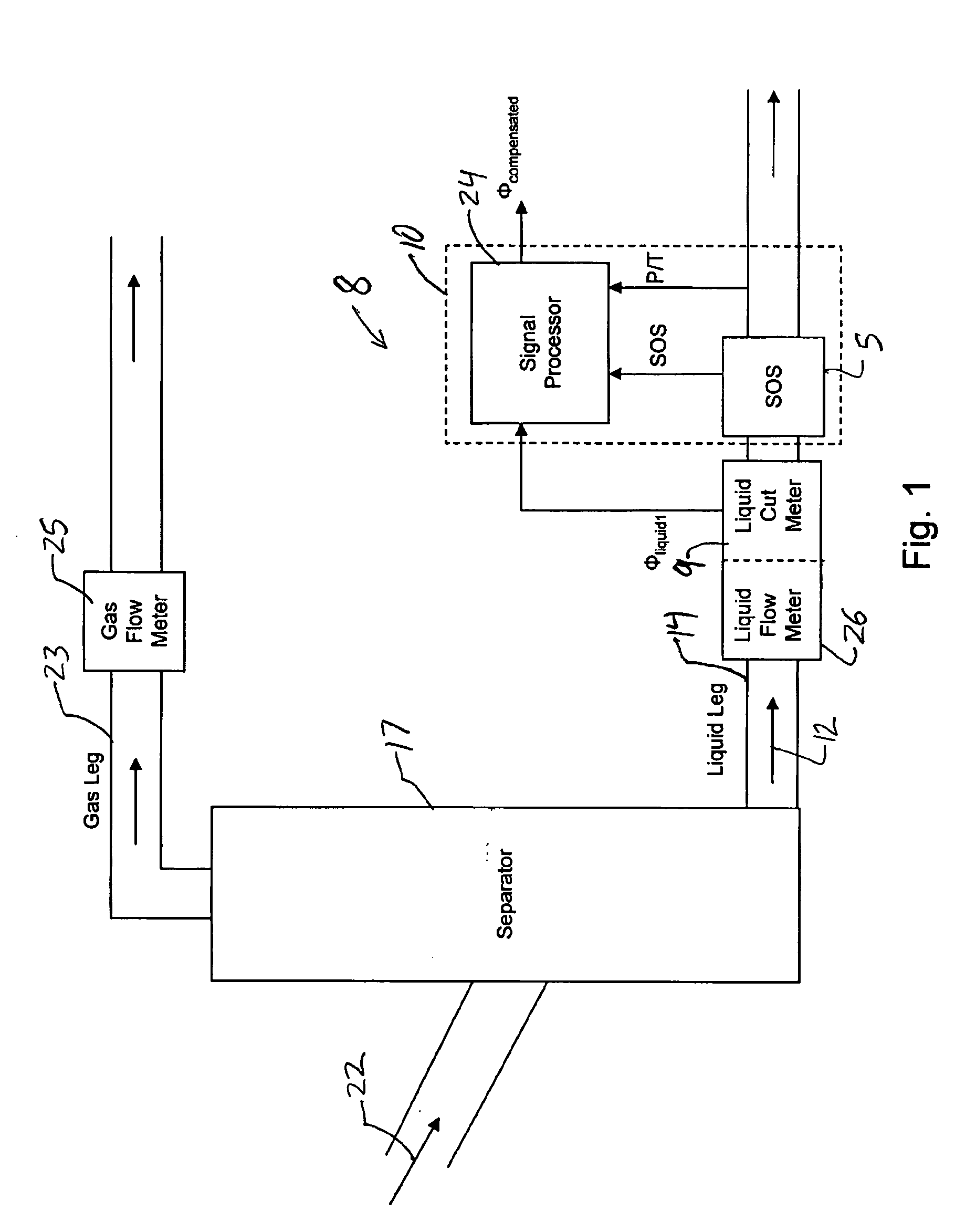
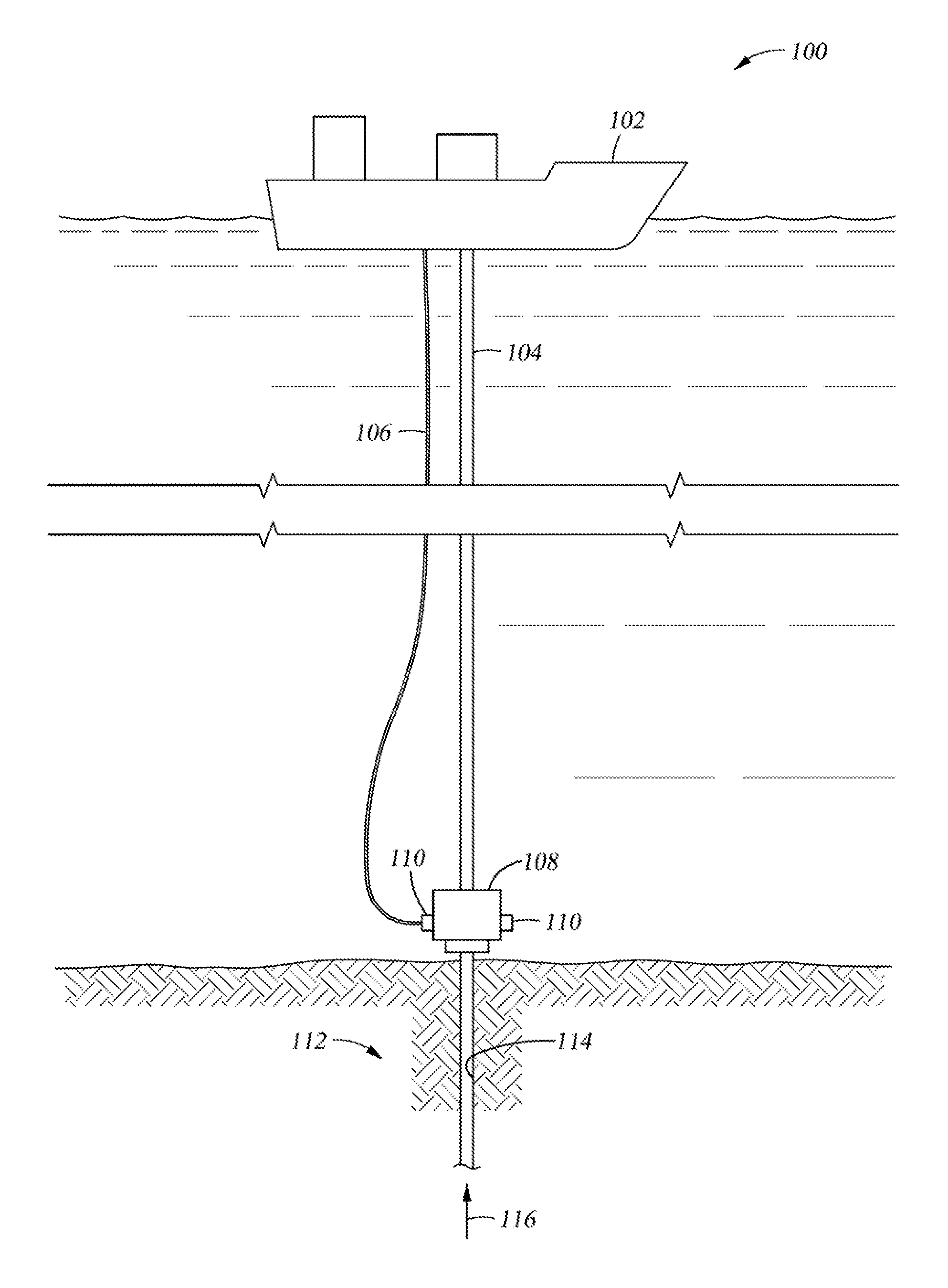
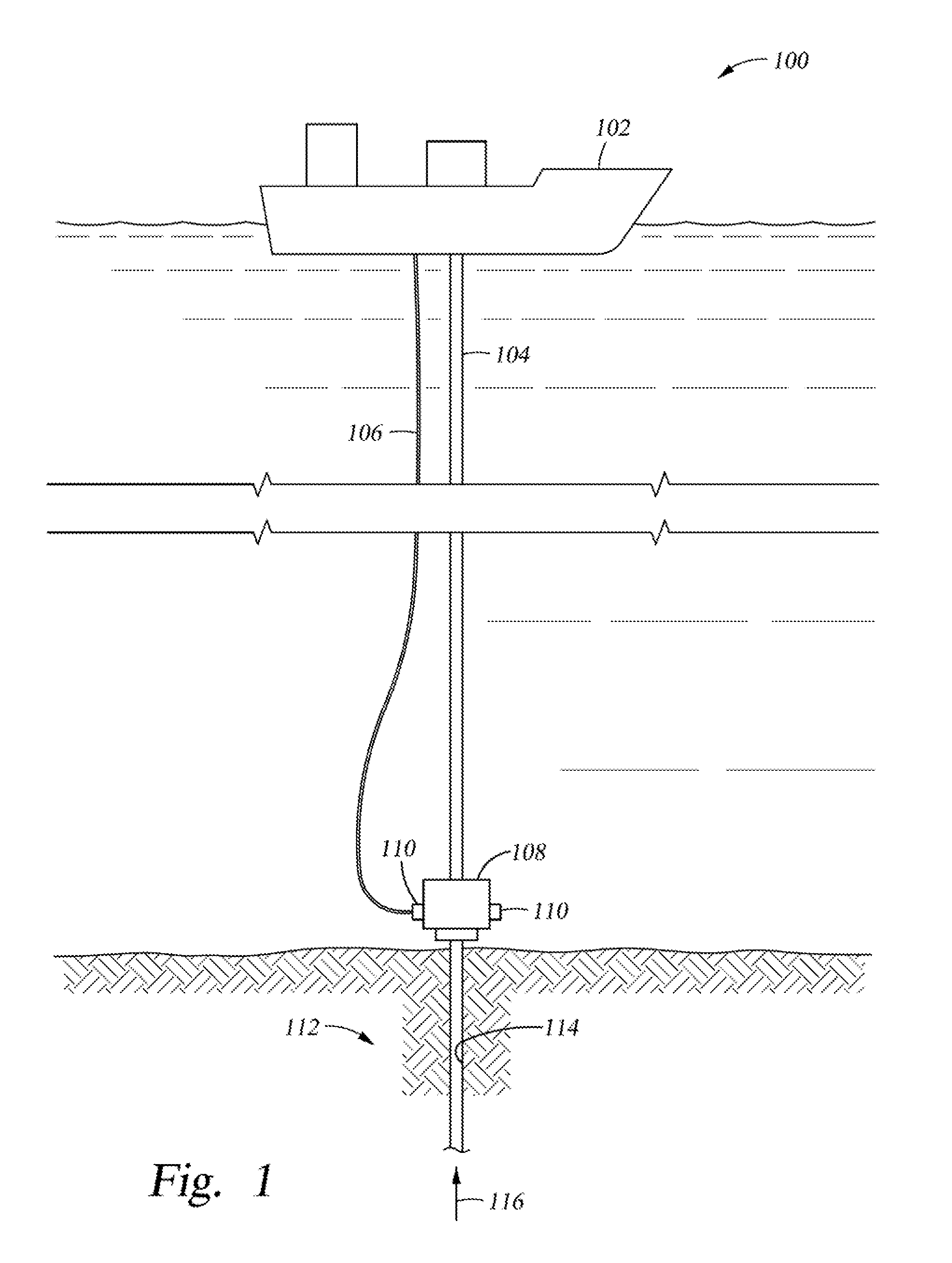
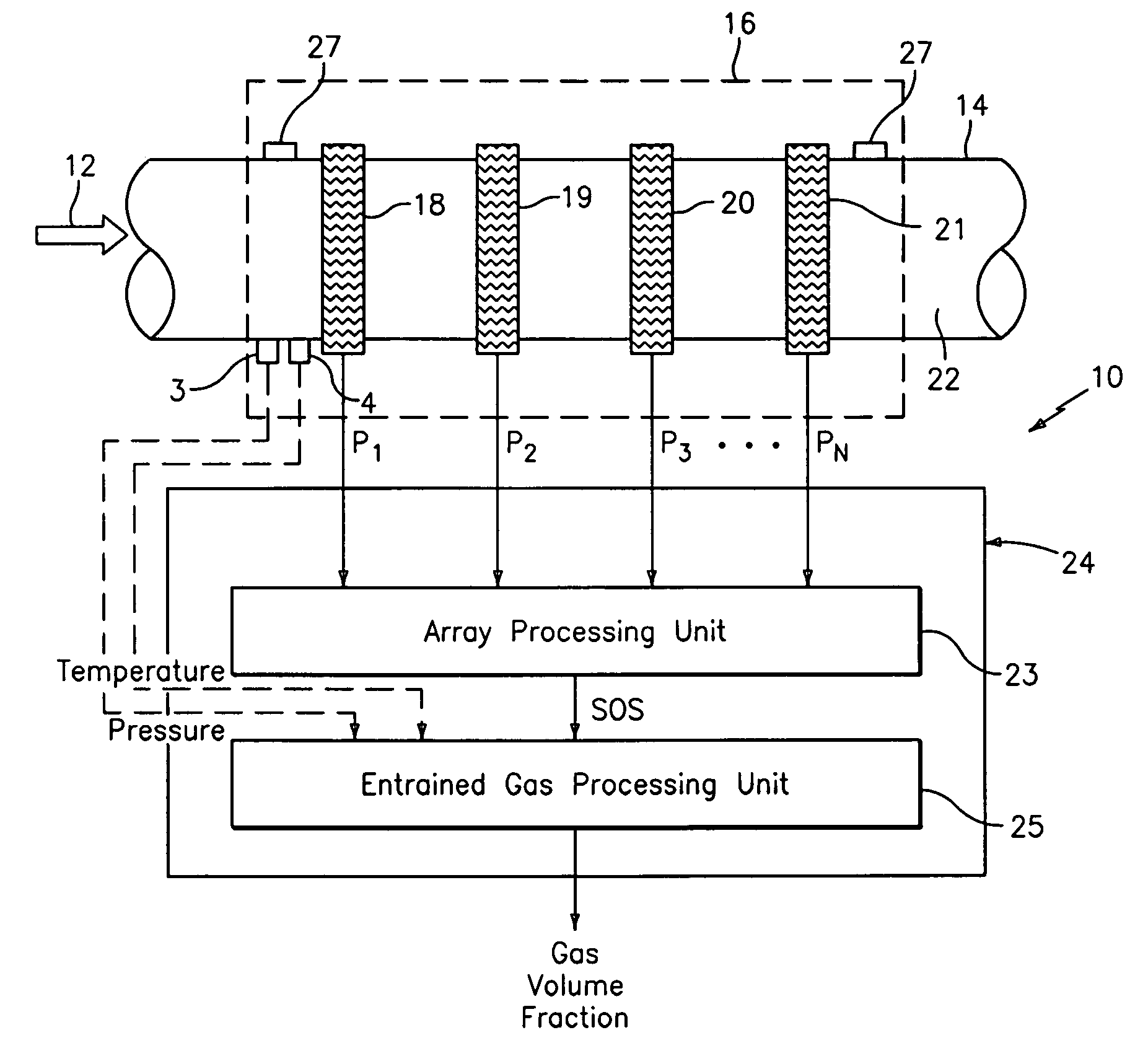
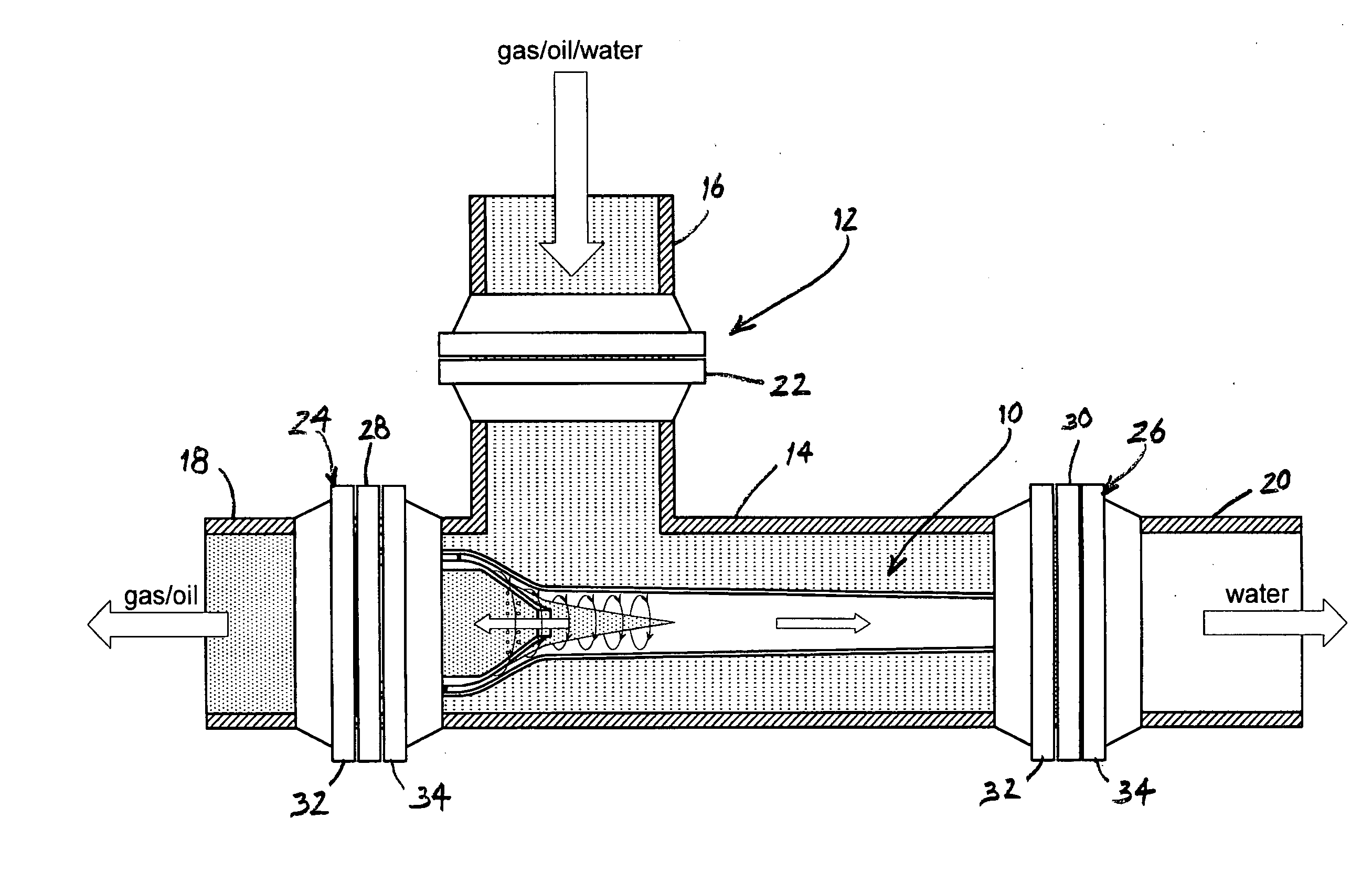
Apparatus and method for providing a density measurement augmented for entrained gas
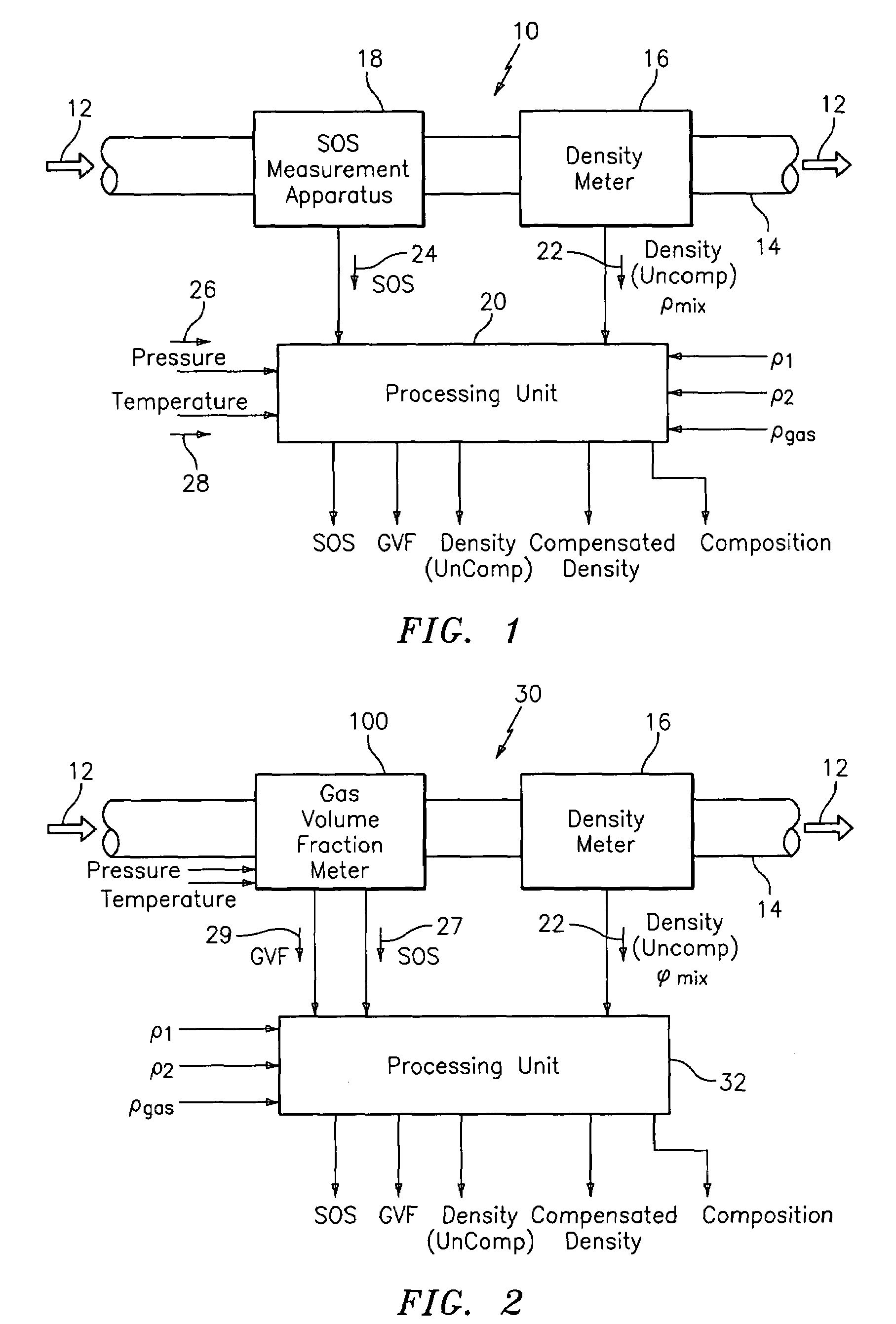
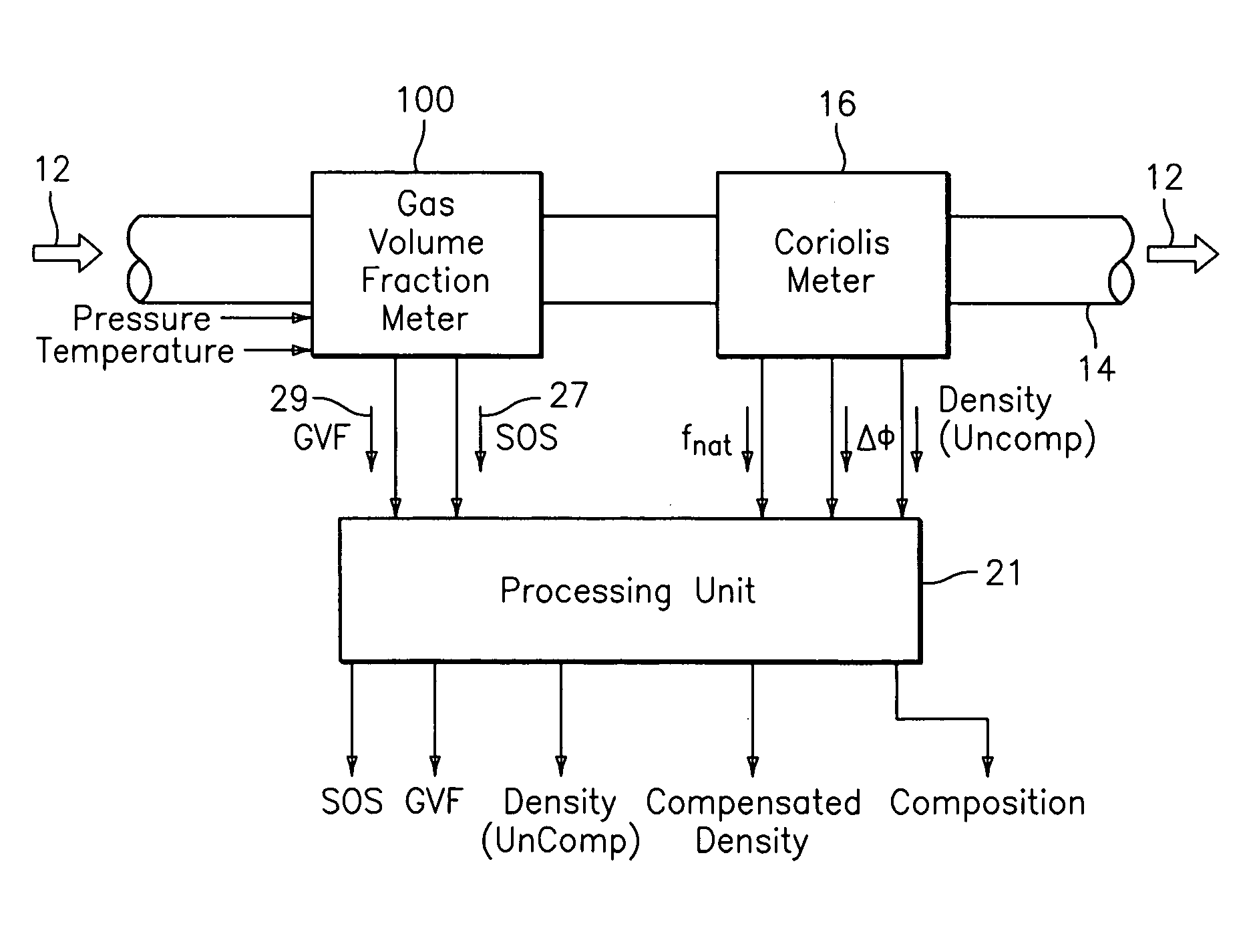
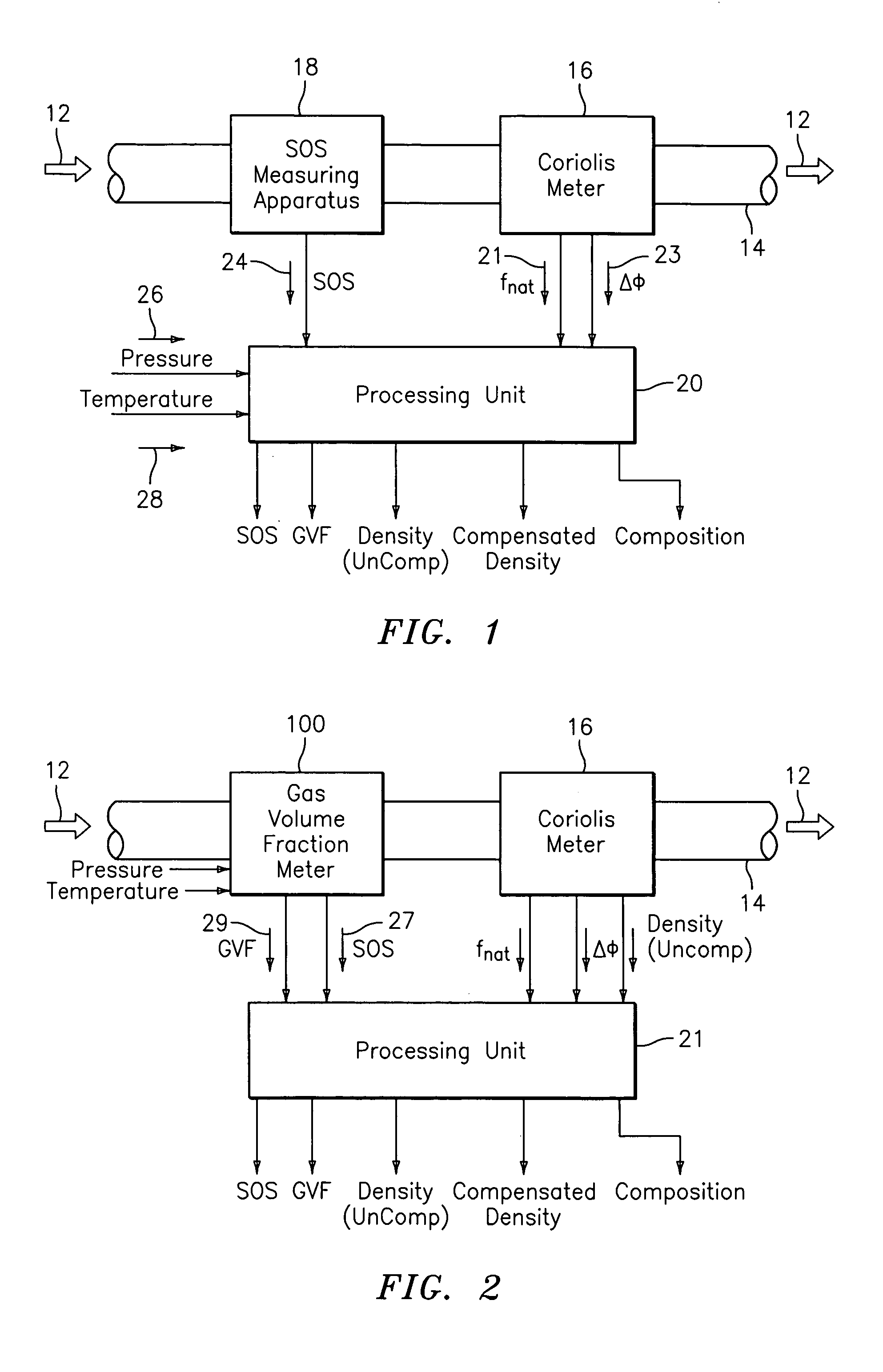
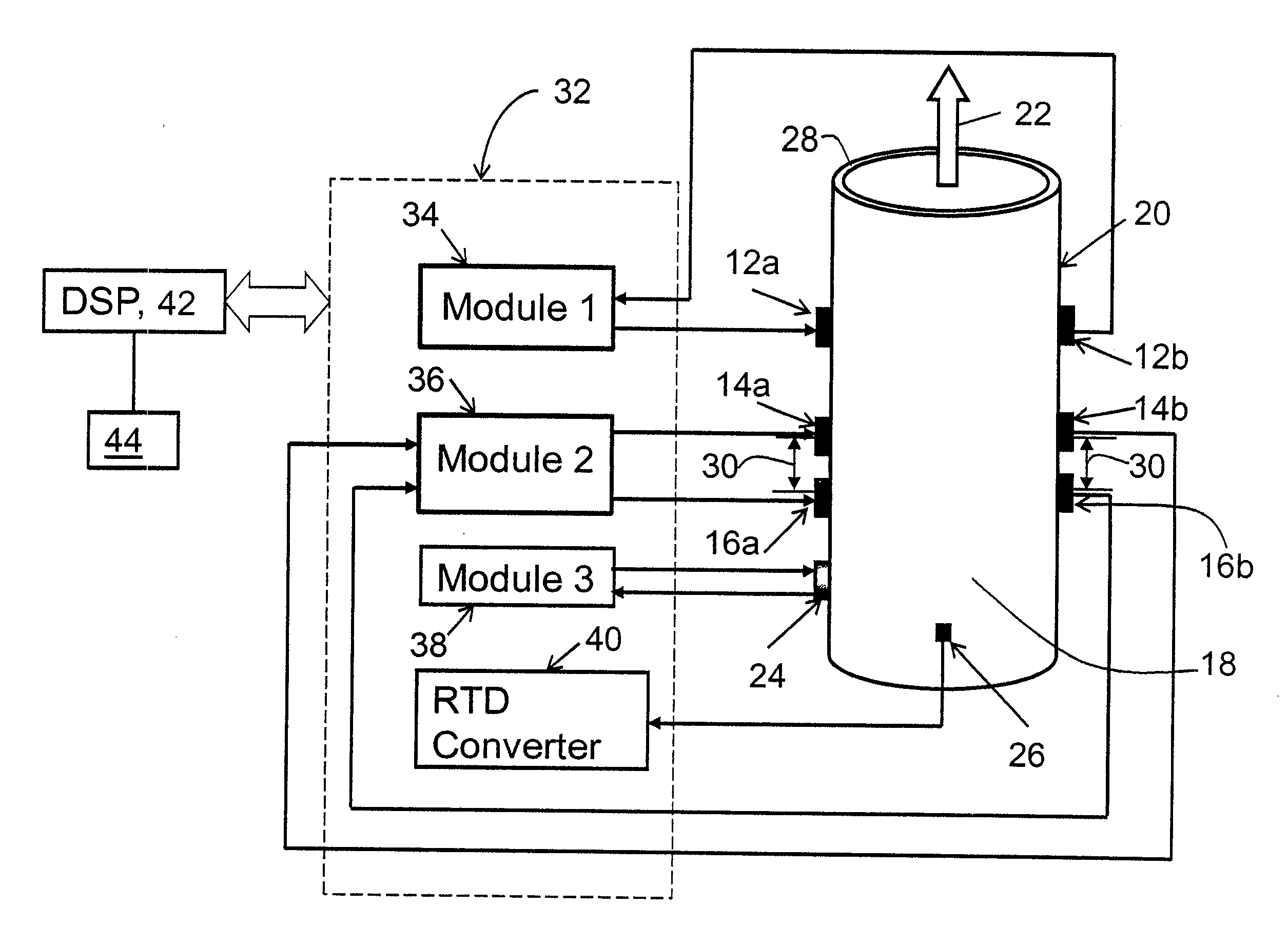
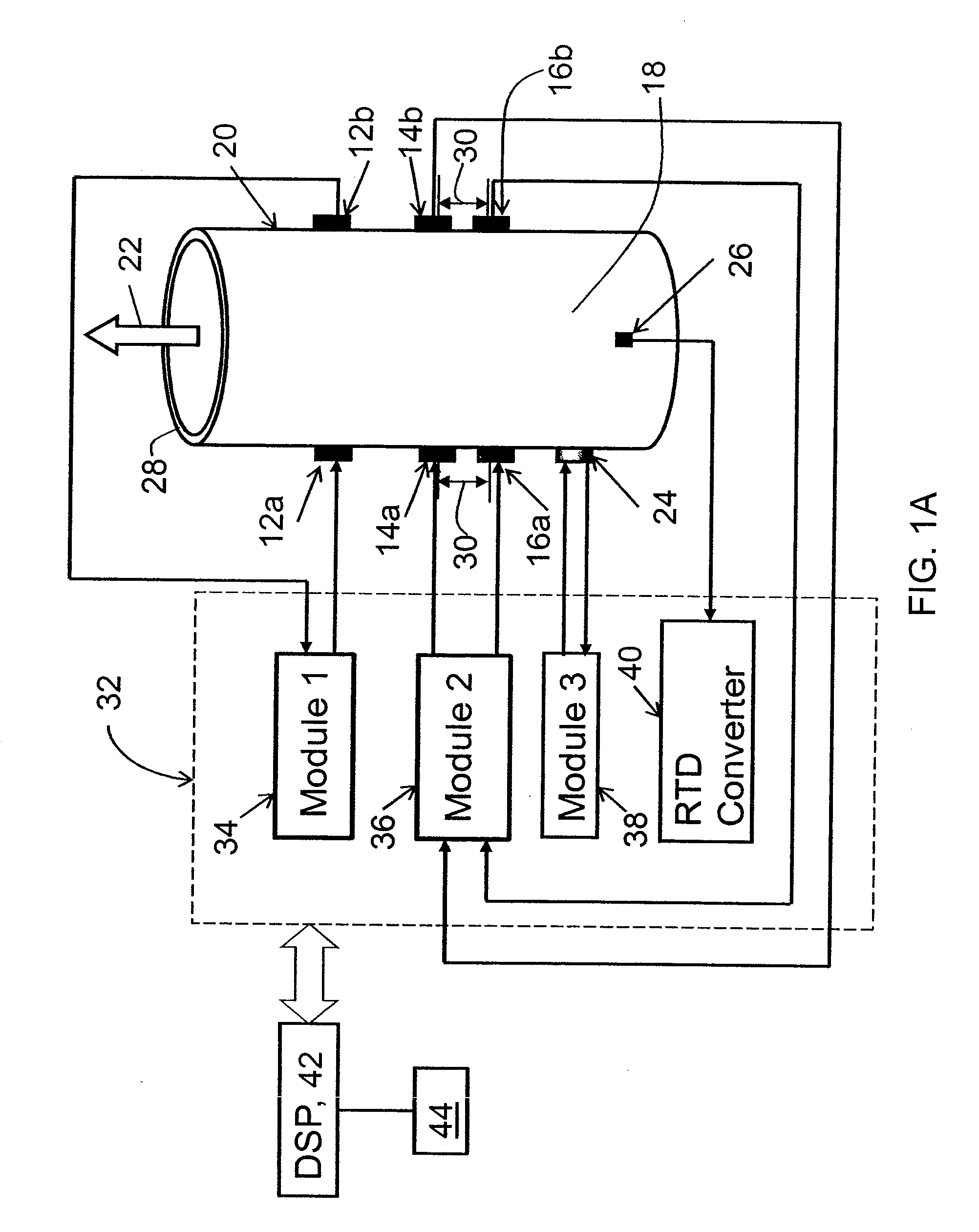
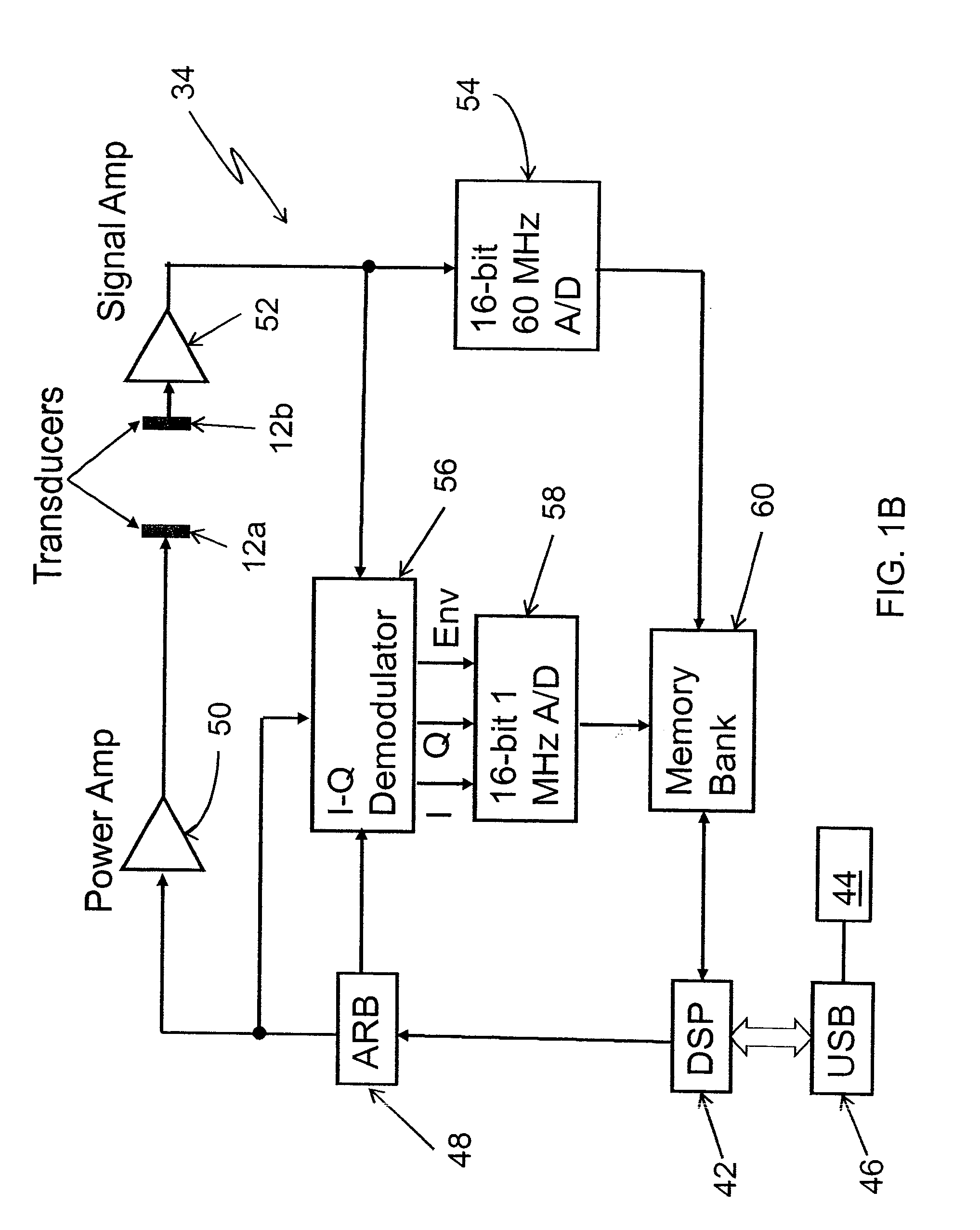
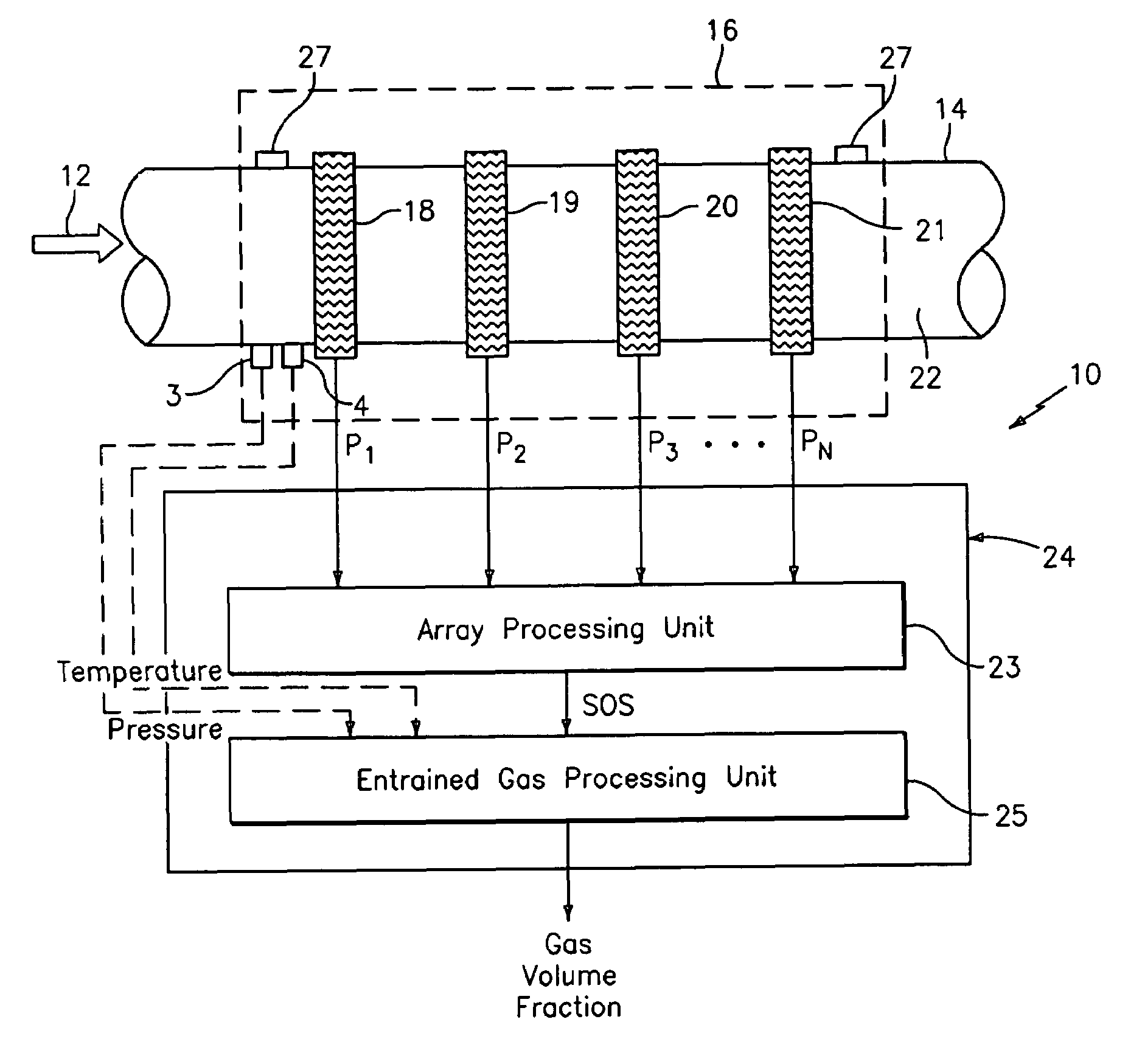
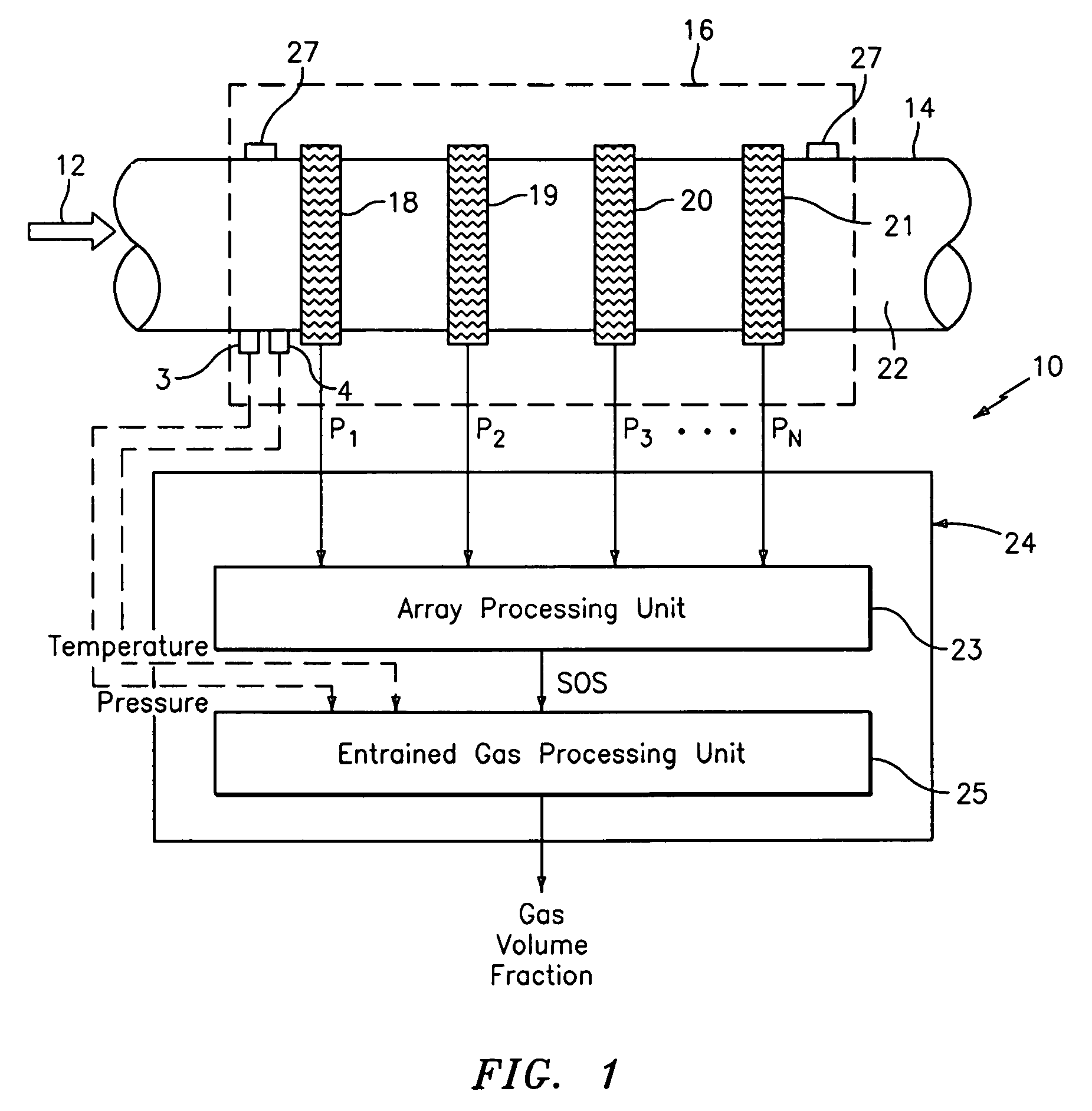
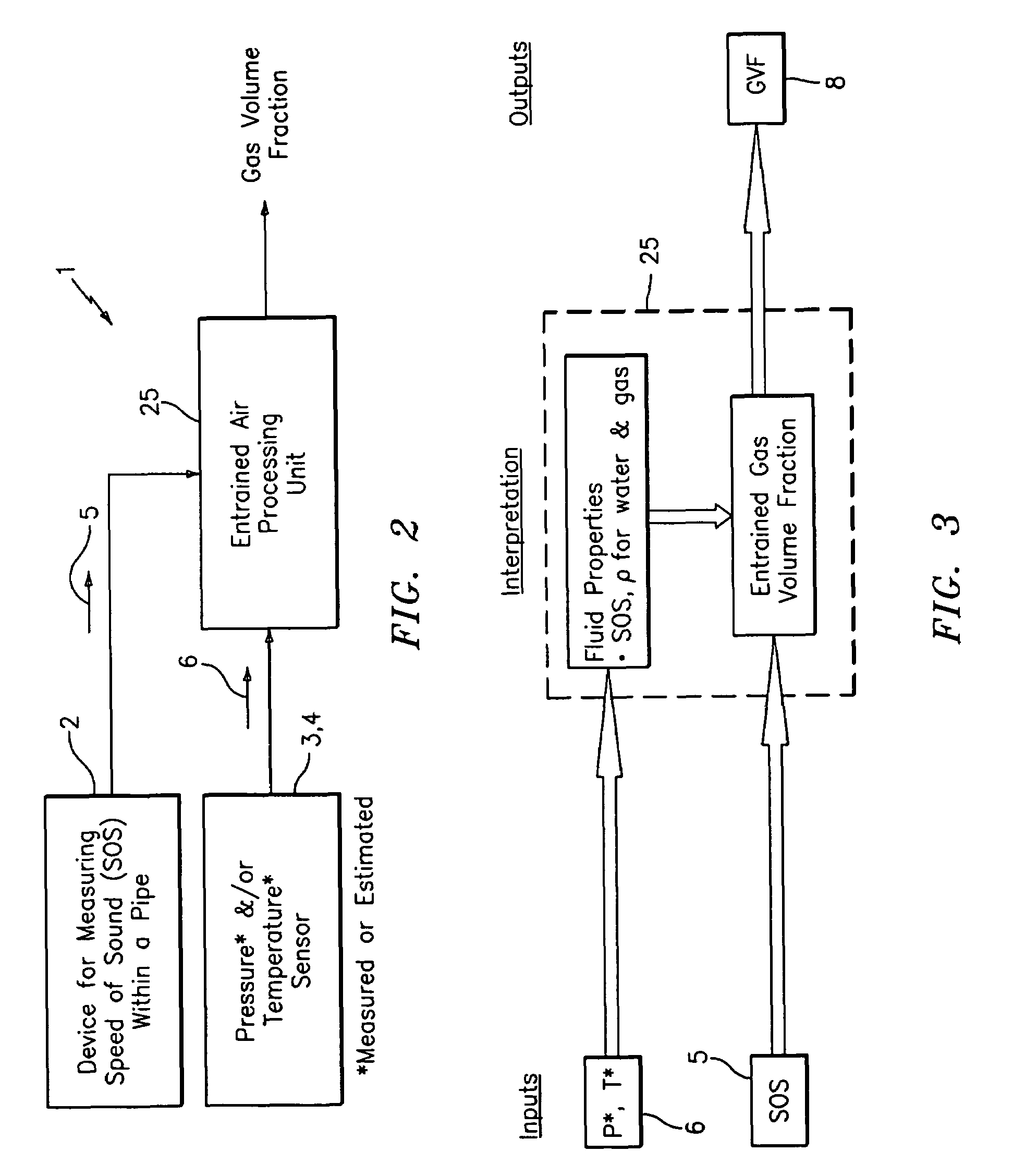
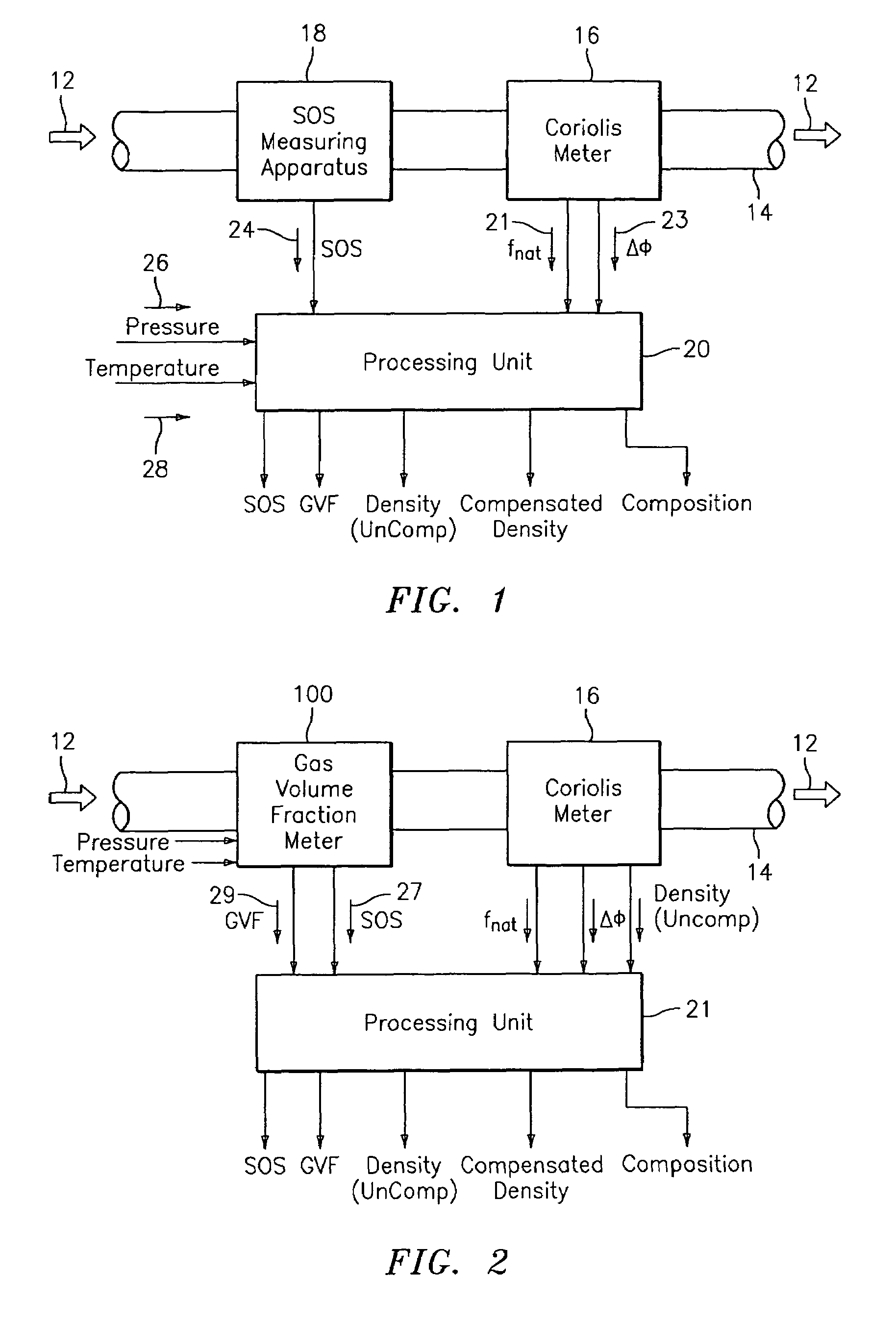
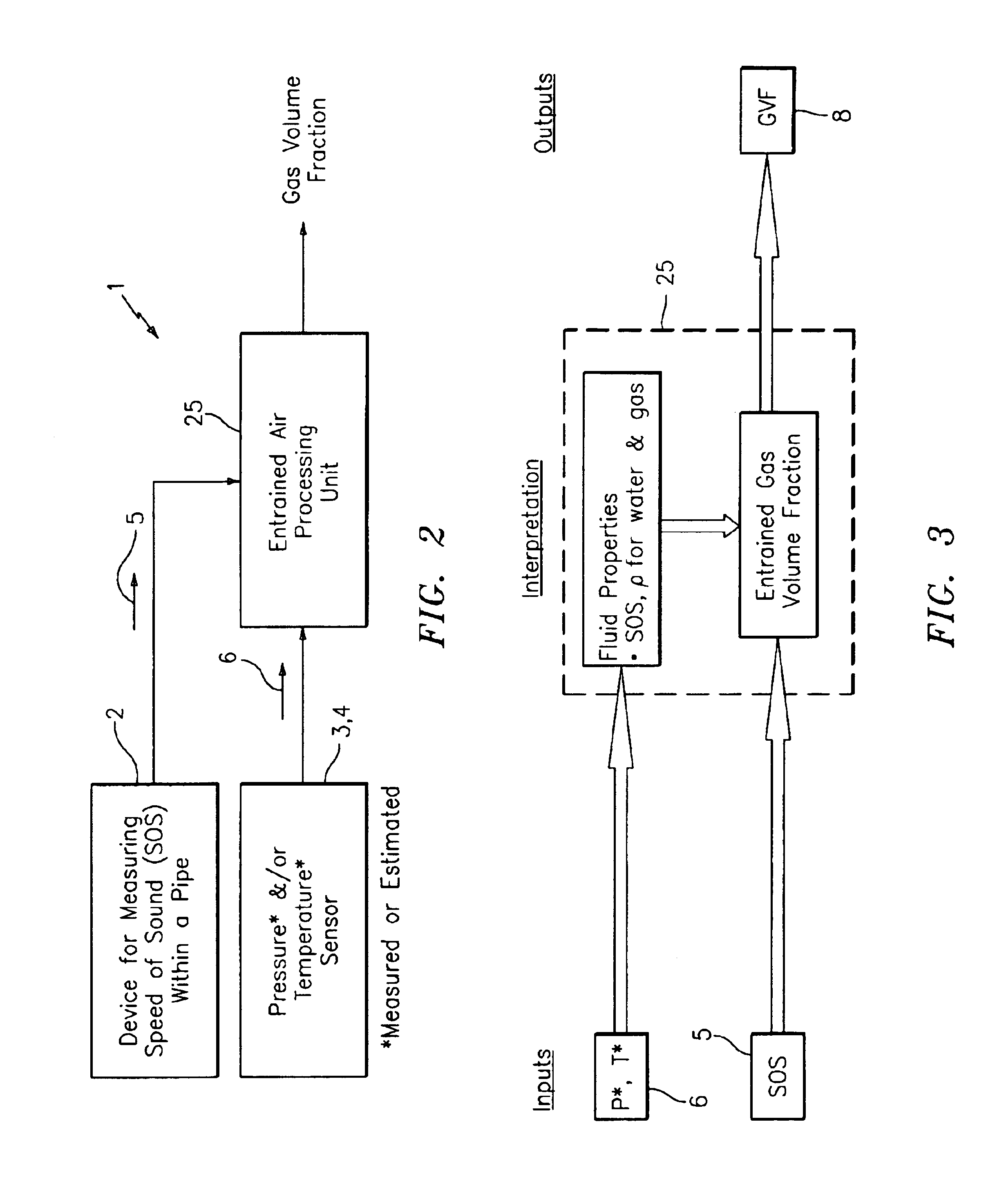
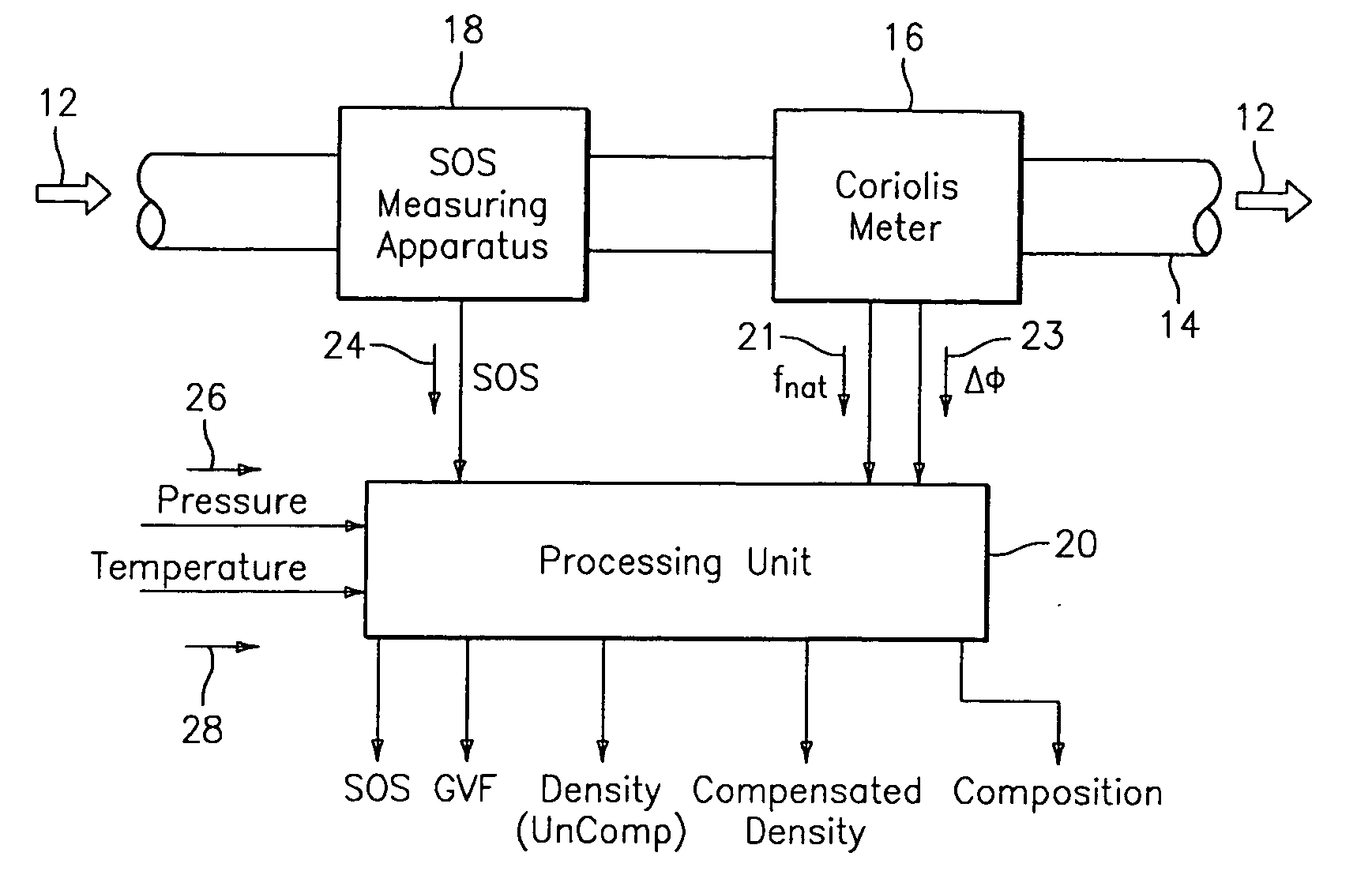
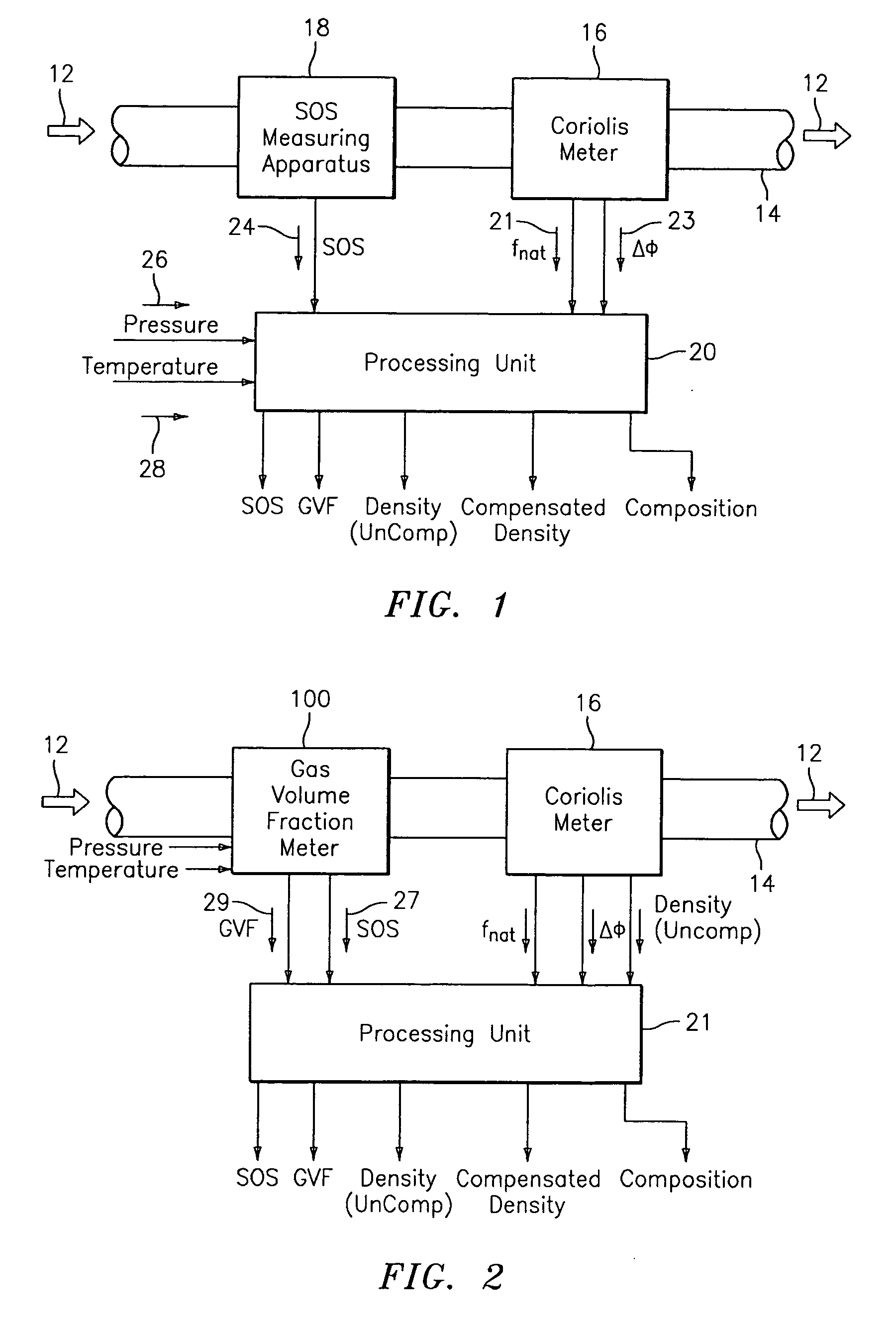
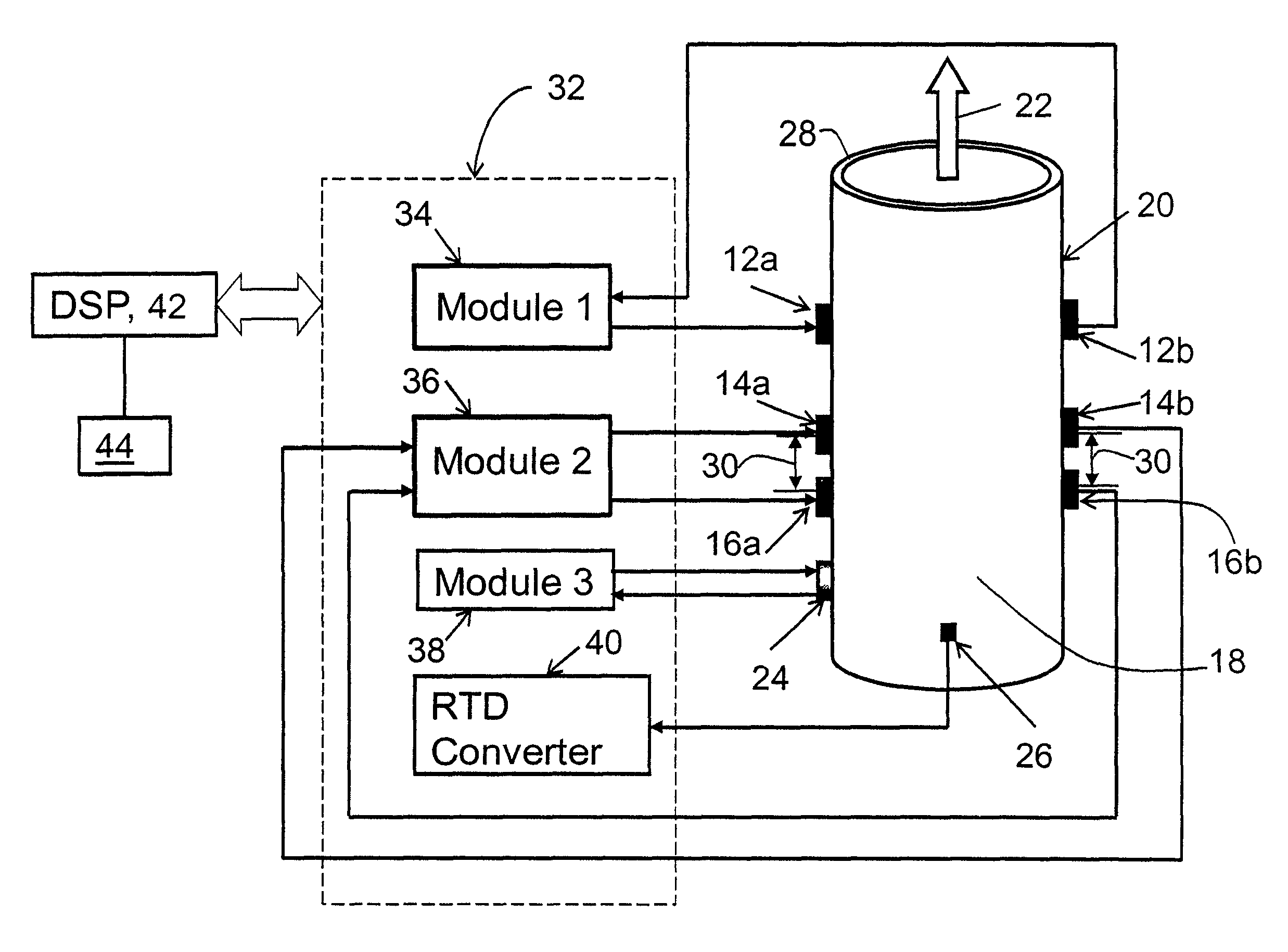
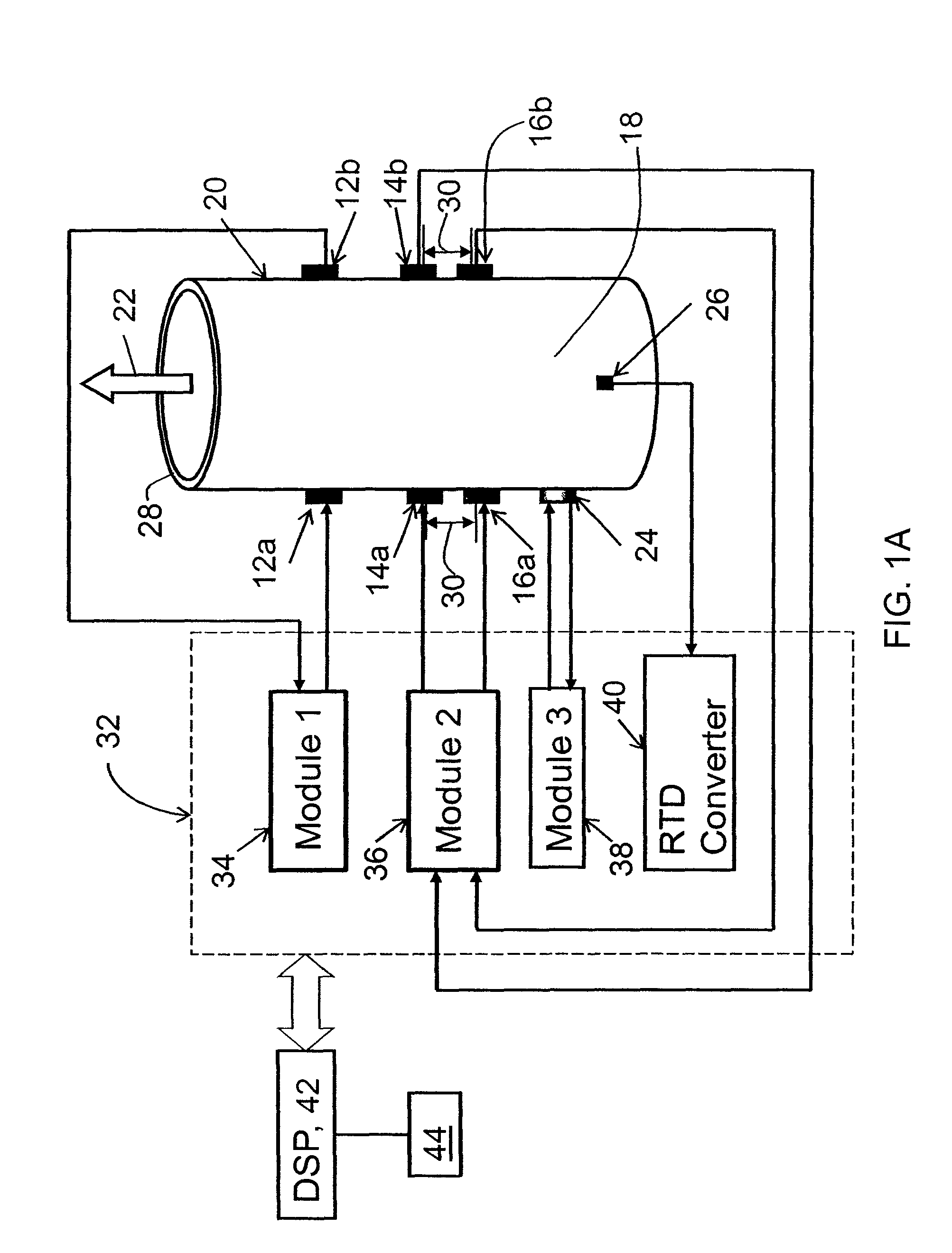
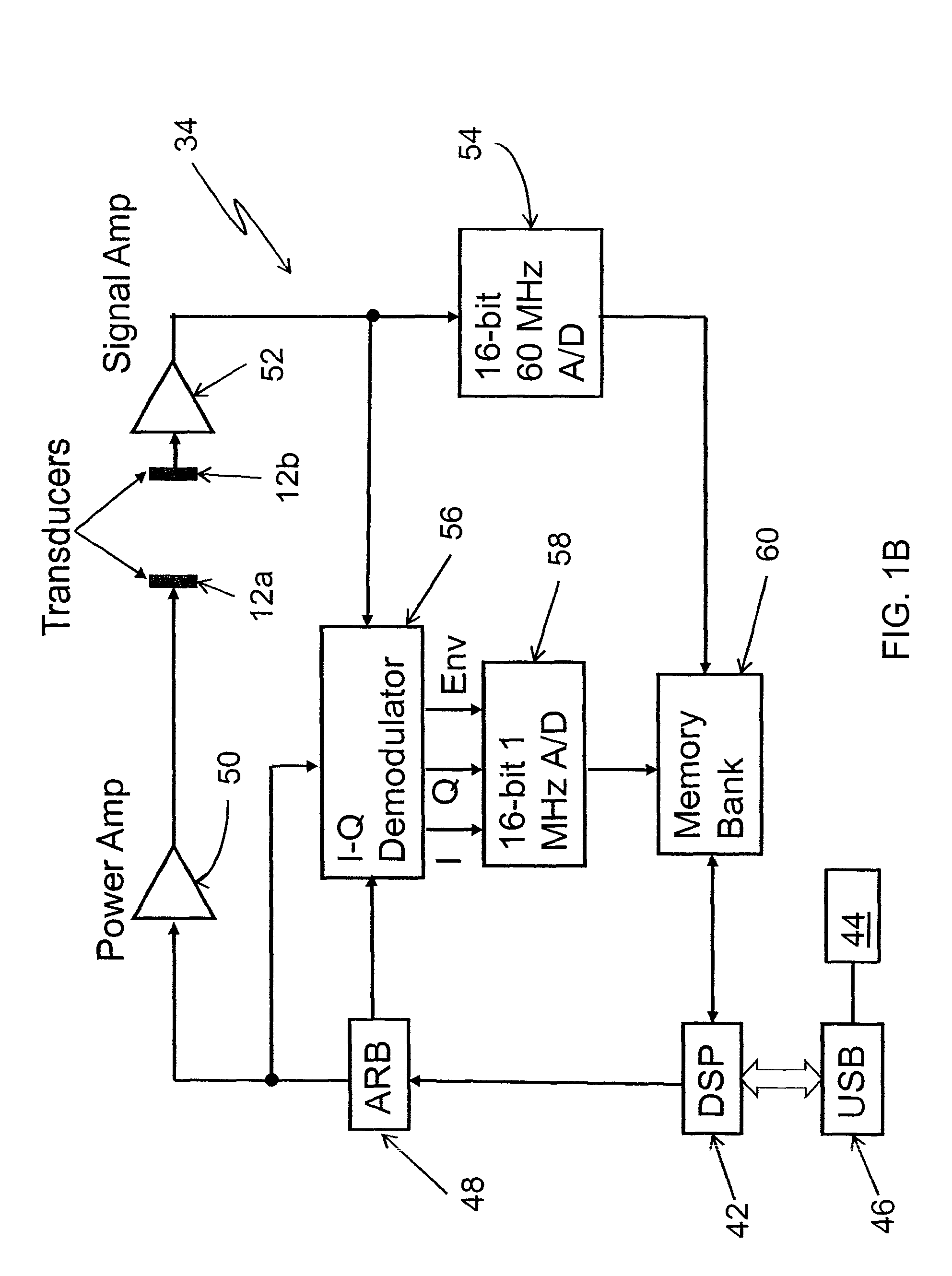
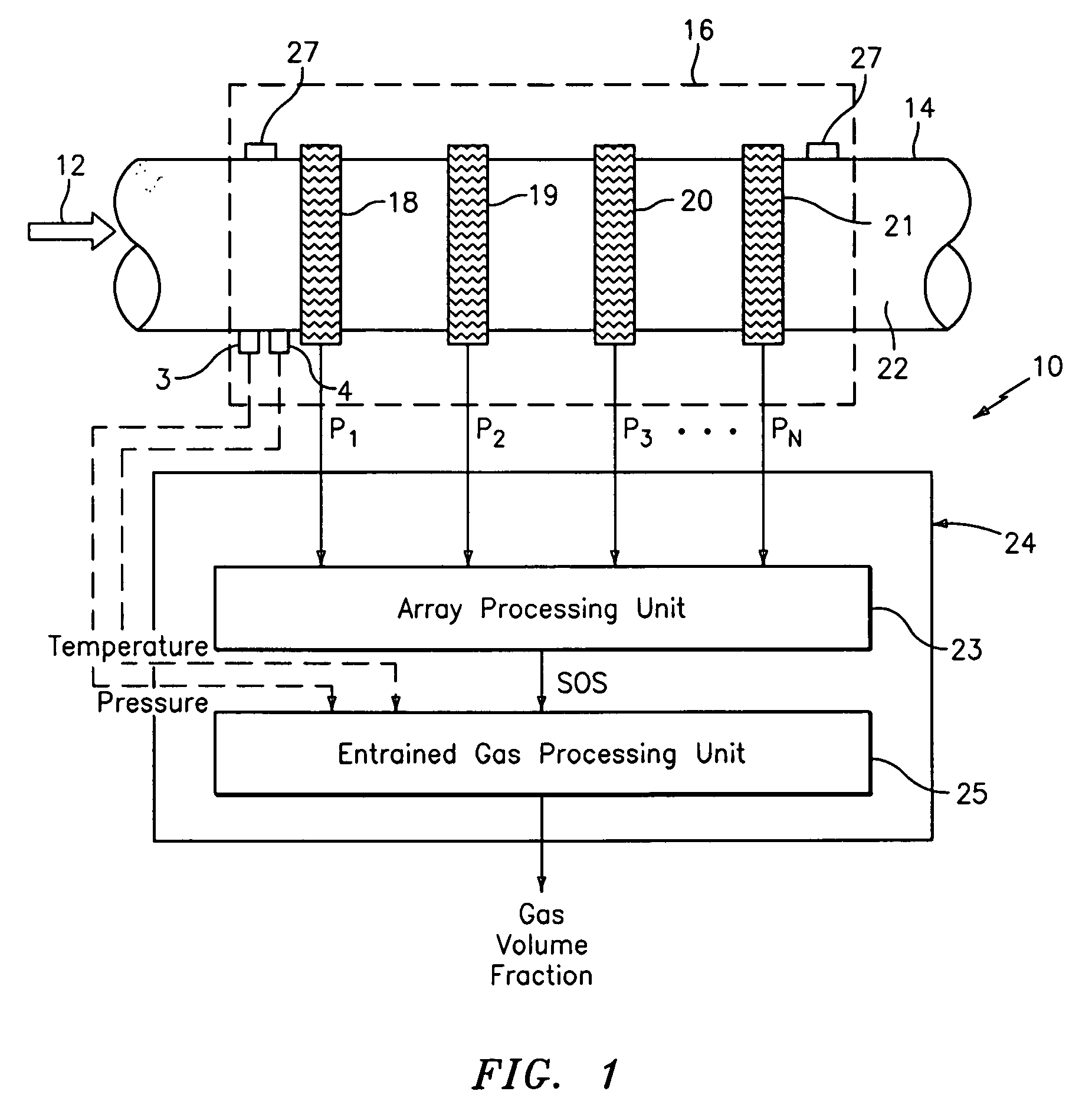
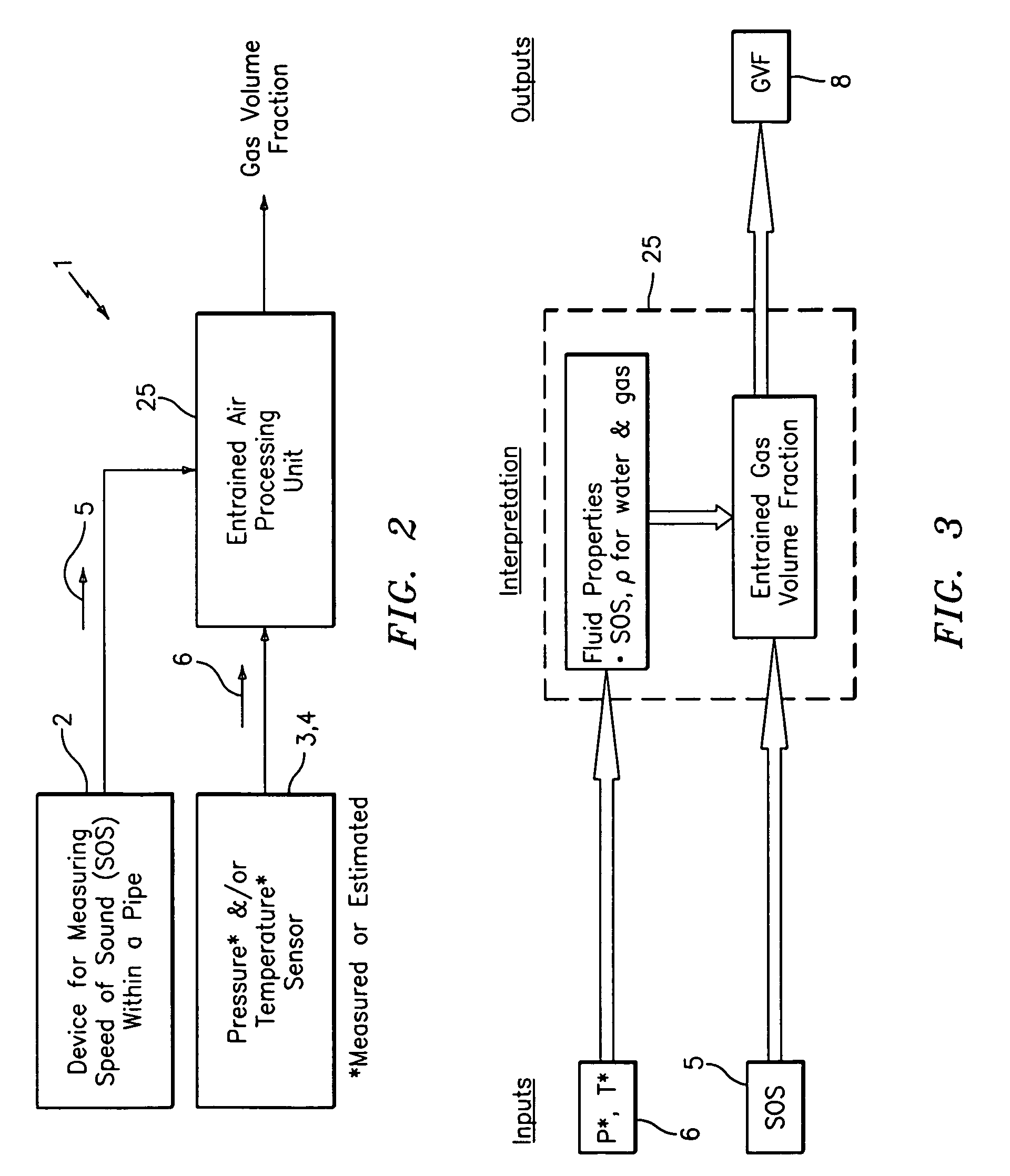
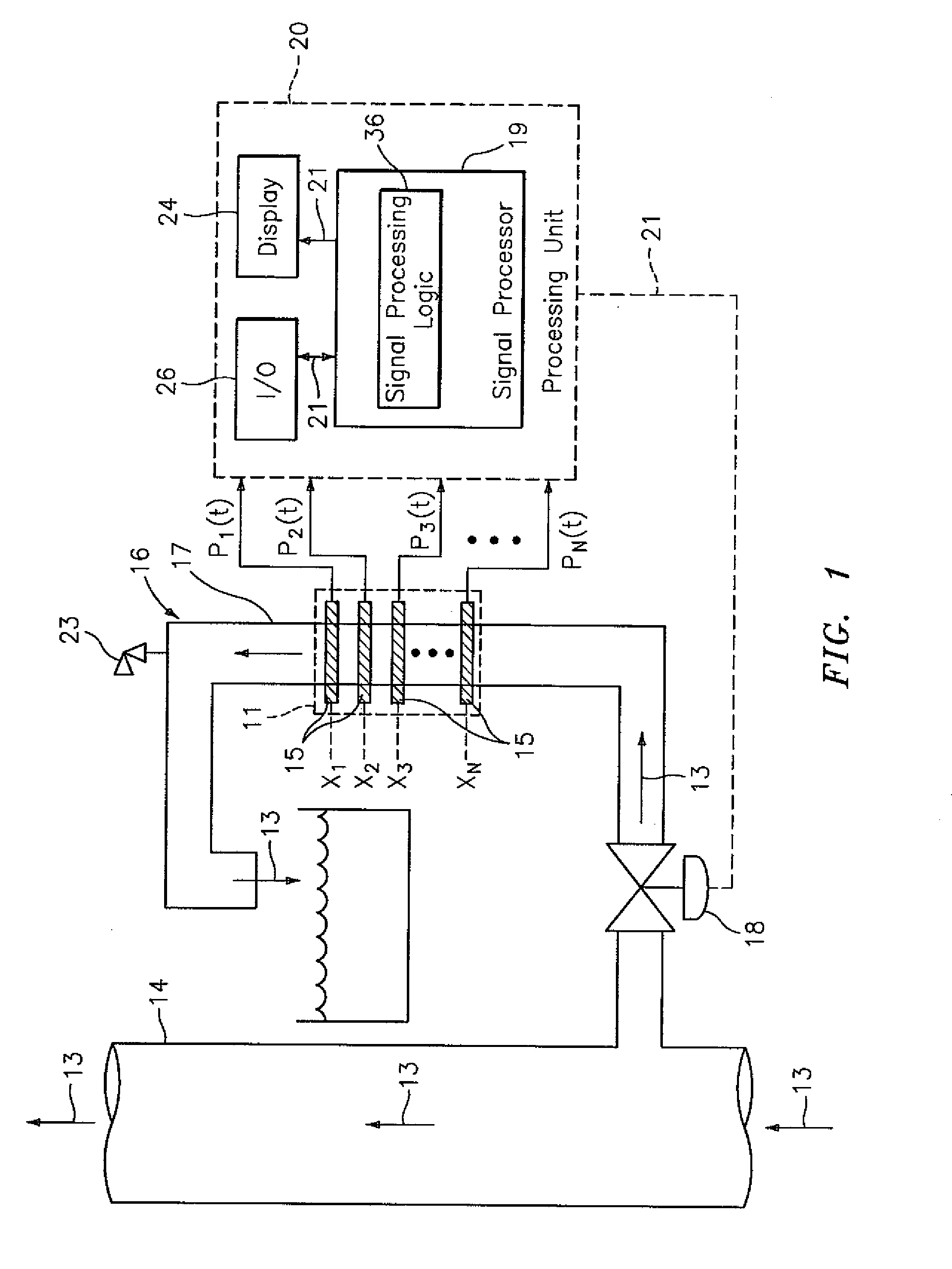
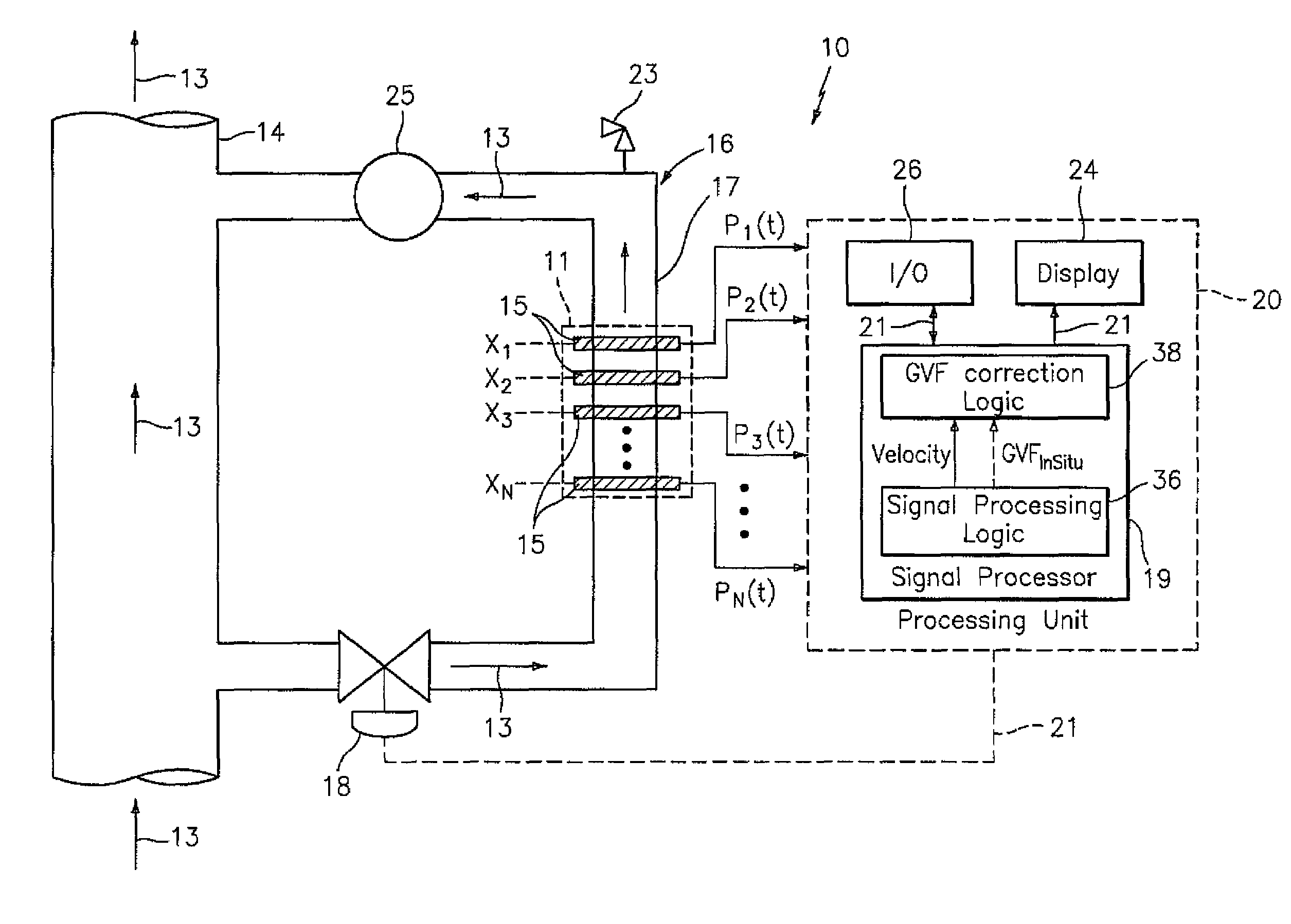
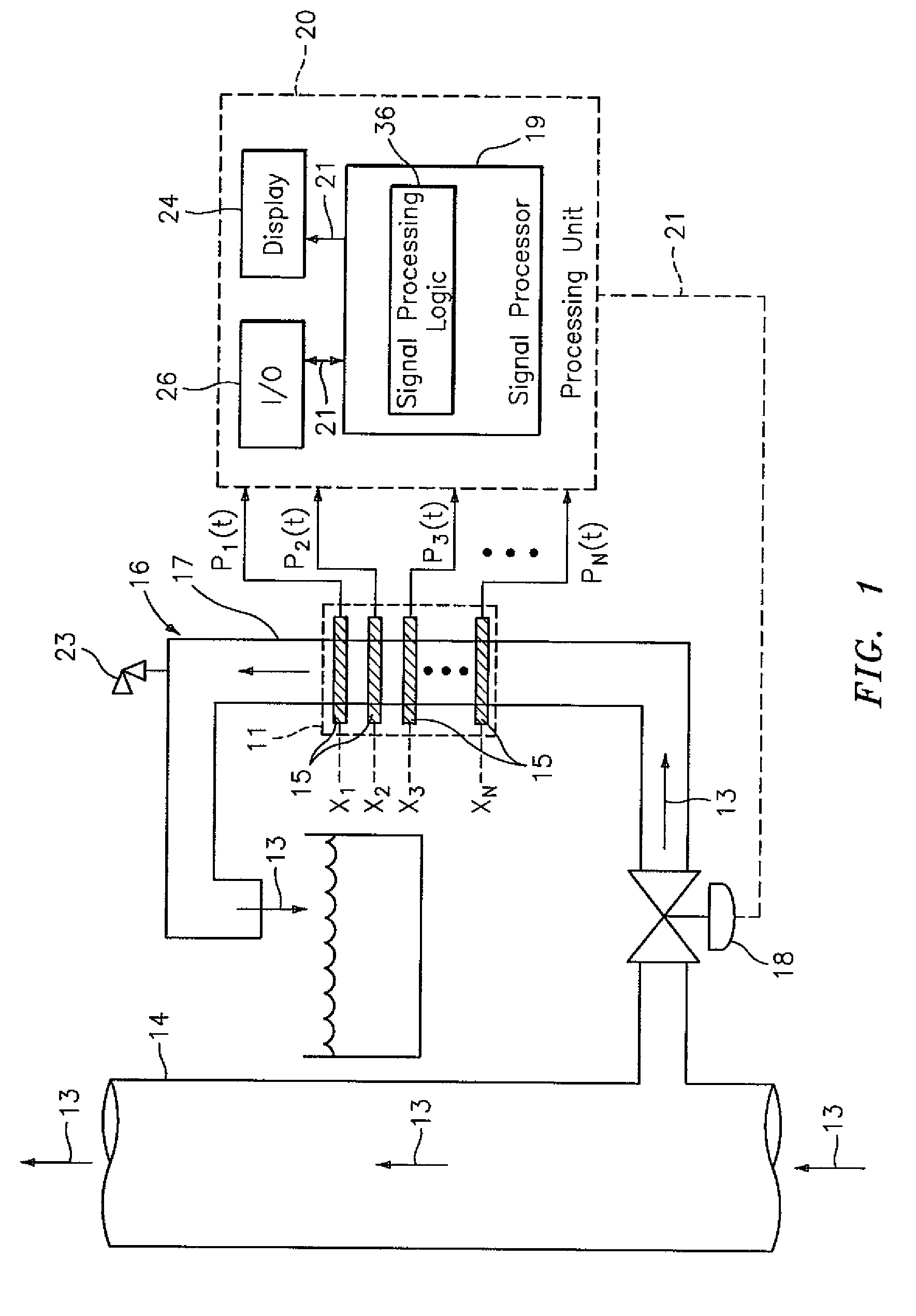
A flow measuring system combines a density measuring device and a device for measuring the speed of sound (SOS) propagating through the fluid flow and / or for determining the gas volume fraction (GVF) of the flow. The GVF meter measures acoustic pressures propagating through the fluids to measure the speed of sound αmix propagating through the fluid to calculate at least gas volume fraction of the fluid and / or SOS. In response to the measured density and gas volume fraction, a processing unit determines the density of non-gaseous component of an aerated fluid flow. For three phase fluid flows, the processing unit can determine the phase fraction of the non-gaseous components of the fluid flow. The gas volume fraction (GVF) meter may include a sensing device having a plurality of strain-based or pressure sensors spaced axially along the pipe for measuring the acoustic pressures propagating through the flow.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Apparatus and method for providing a density measurement augmented for entrained gas
ActiveUS20050061060A1Improve accuracySpecific gravity using flow propertiesVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectThree-phaseDischarge measurements
A flow measuring system combines a density measuring device and a device for measuring the speed of sound (SOS) propagating through the fluid flow and / or for determining the gas volume fraction (GVF) of the flow. The GVF meter measures acoustic pressures propagating through the fluids to measure the speed of sound αmix propagating through the fluid to calculate at least gas volume fraction of the fluid and / or SOS. In response to the measured density and gas volume fraction, a processing unit determines the density of non-gaseous component of an aerated fluid flow. For three phase fluid flows, the processing unit can determine the phase fraction of the non-gaseous components of the fluid flow. The gas volume fraction (GVF) meter may include a sensing device having a plurality of strain-based or pressure sensors spaced axially along the pipe for measuring the acoustic pressures propagating through the flow.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
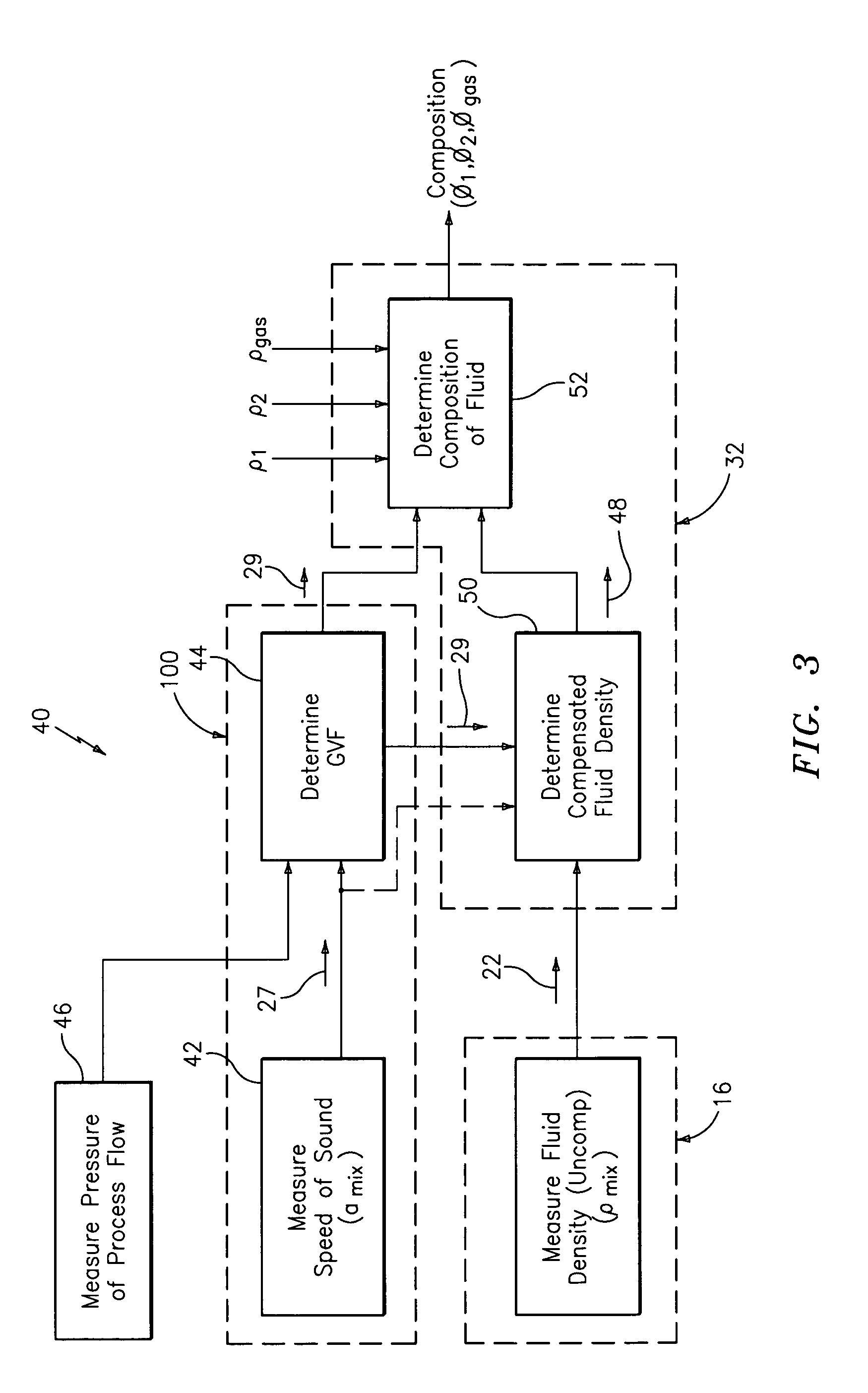
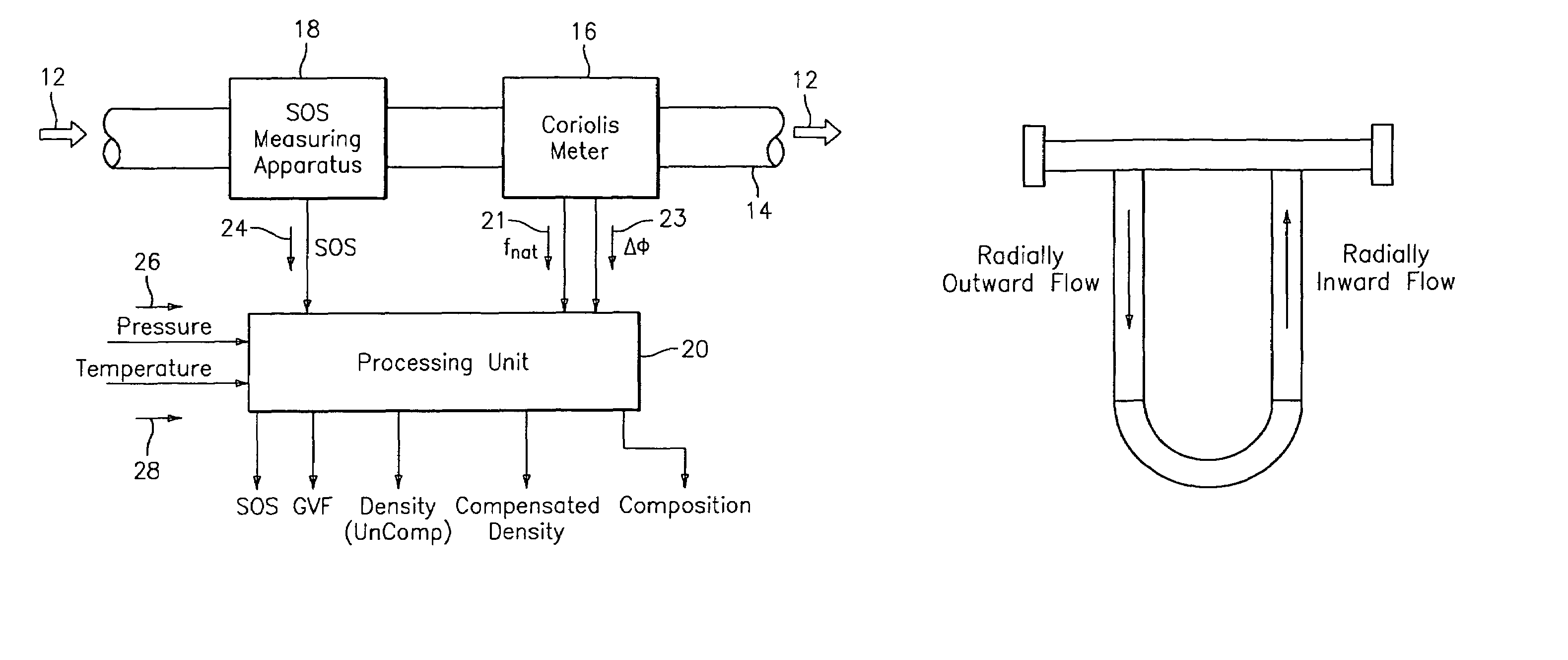
Apparatus and method for compensating a coriolis meter
ActiveUS20050044929A1High densityAdd additional massVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectVolume meteringVolumetric Mass DensityDischarge measurements
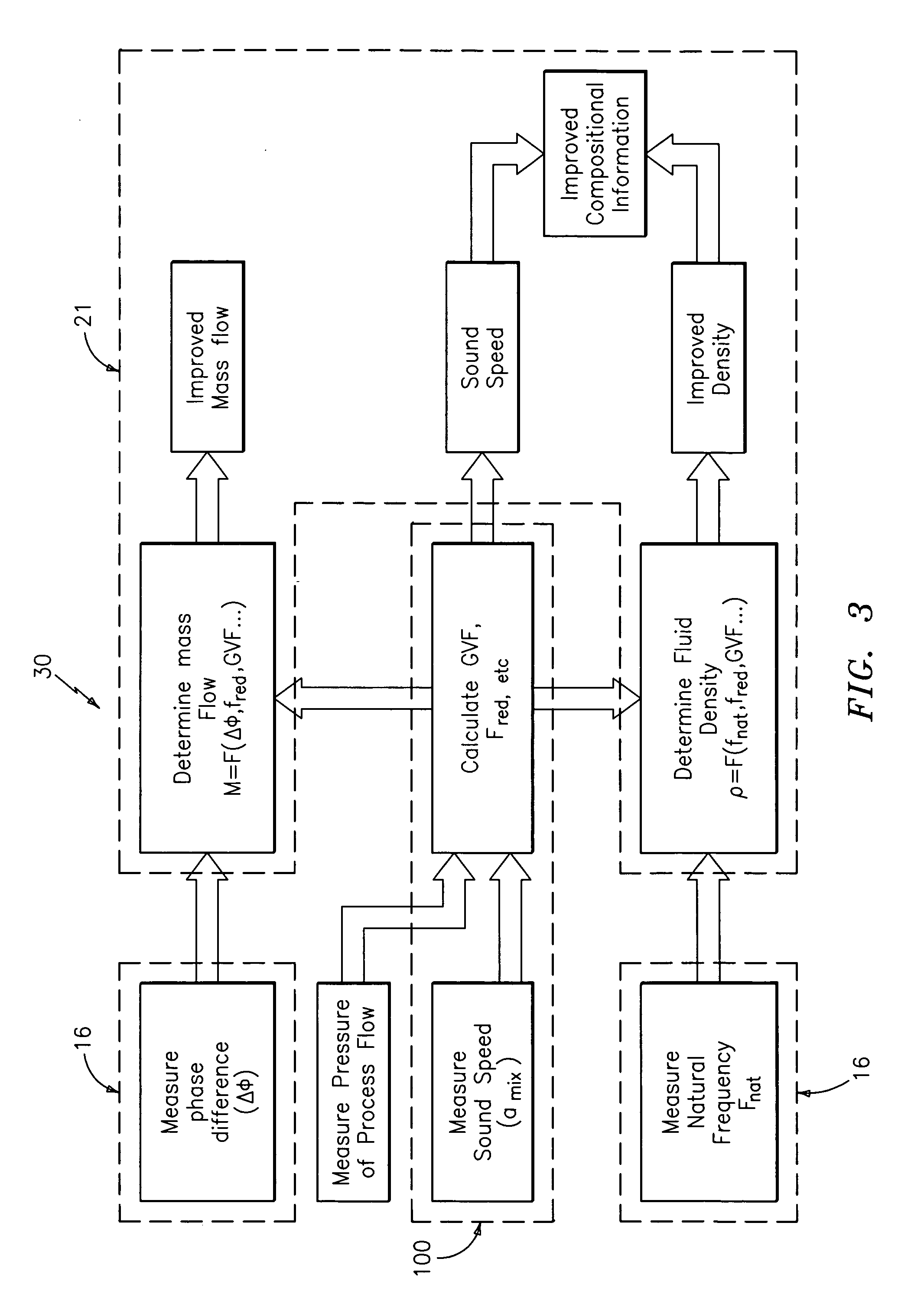
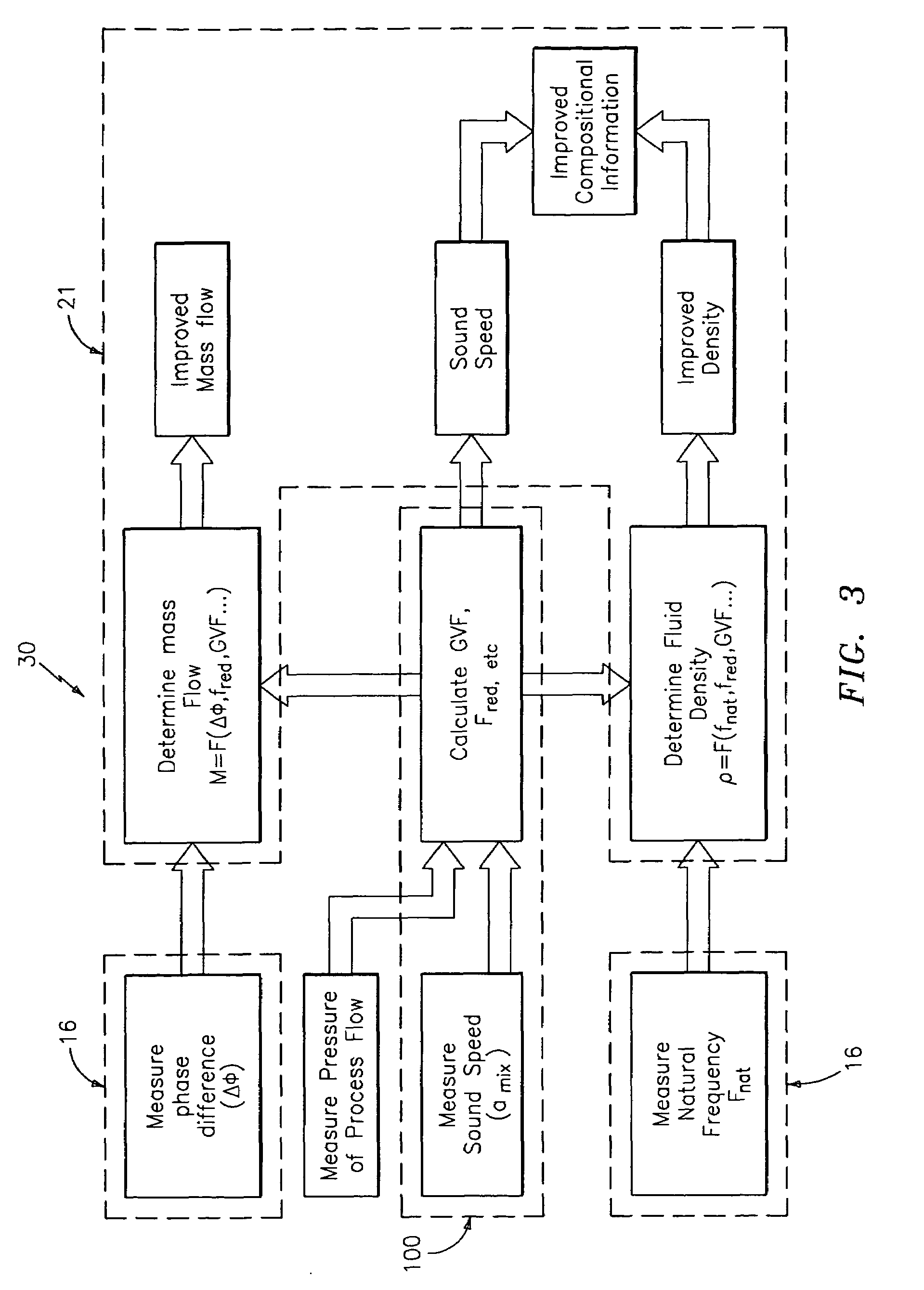
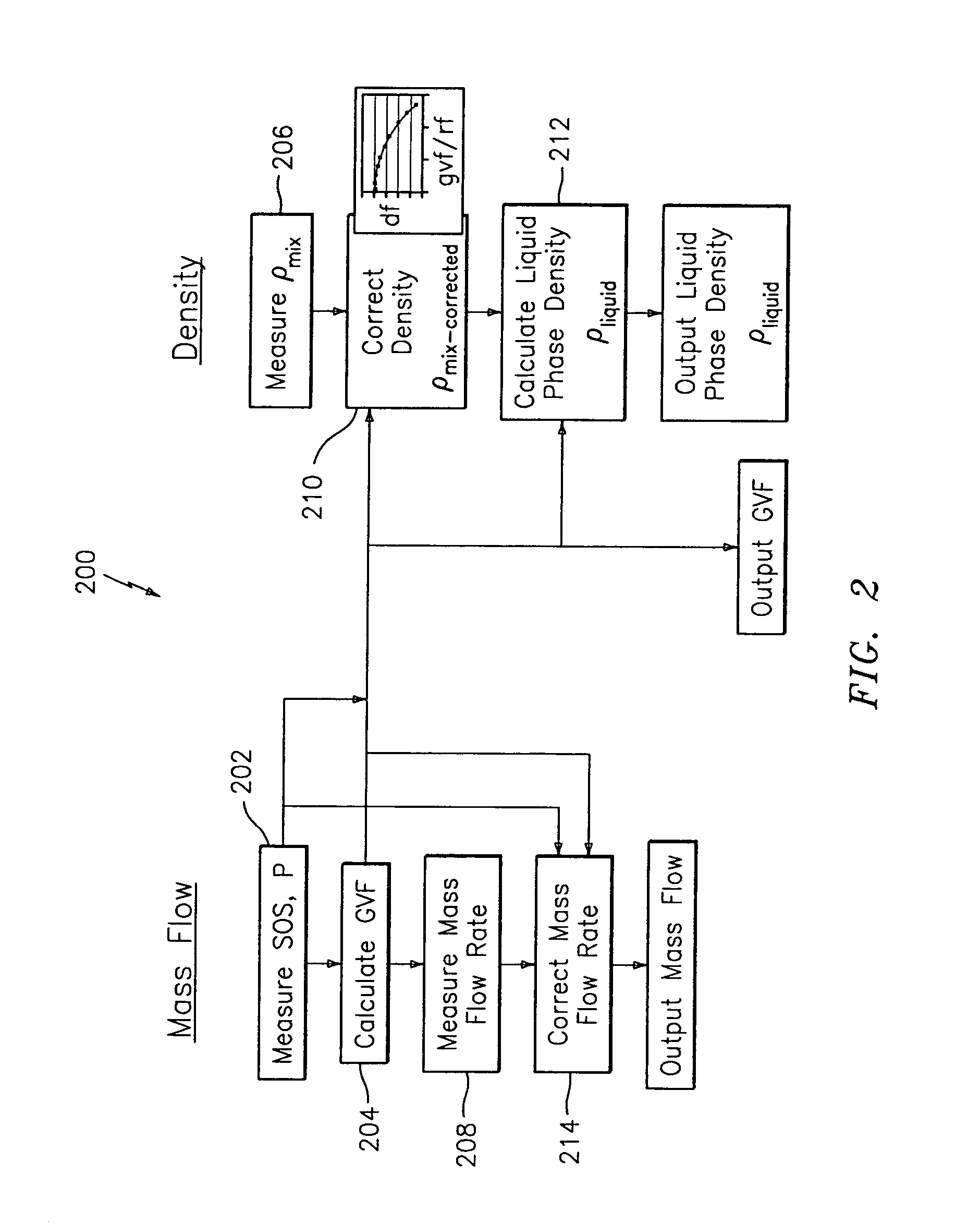
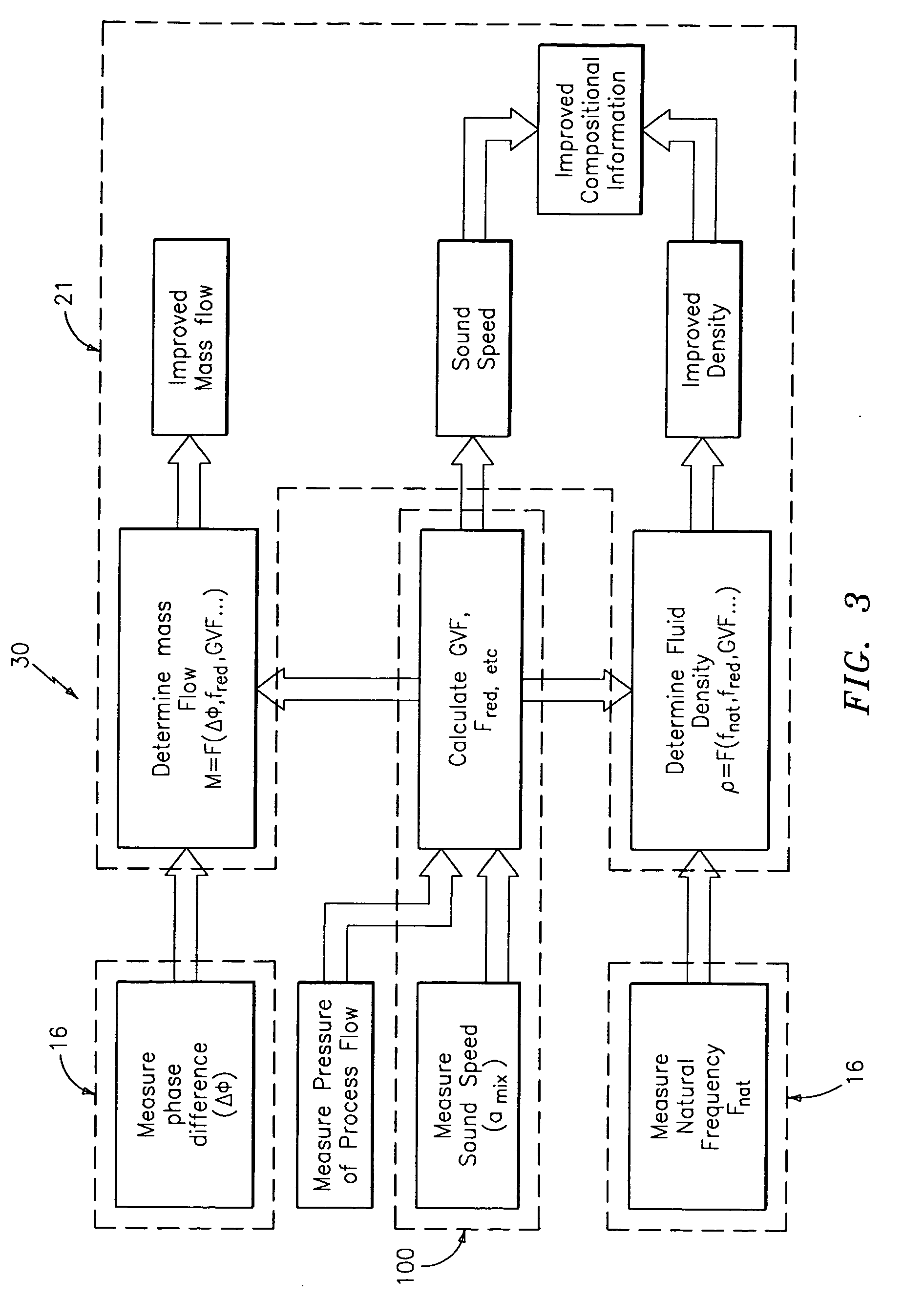
A flow measuring system is provided that provides at least one of a compensated mass flow rate measurement and a compensated density measurement. The flow measuring system includes a gas volume fraction meter in combination with a coriolis meter. The GVF meter measures acoustic pressures propagating through the fluids to measure the speed of sound αmix propagating through the fluid to calculate at least gas volume fraction of the fluid and / or the reduced natural frequency. For determining an improved density for the coriolis meter, the calculated gas volume fraction and / or reduced frequency is provided to a processing unit. The improved density is determined using analytically derived or empirically derived density calibration models (or formulas derived therefore), which is a function of the measured natural frequency and at least one of the determined GVF, reduced frequency and speed of sound, or any combination thereof. The gas volume fraction (GVF) meter may include a sensing device having a plurality of strain-based or pressure sensors spaced axially along the pipe for measuring the acoustic pressures propagating through the flow.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
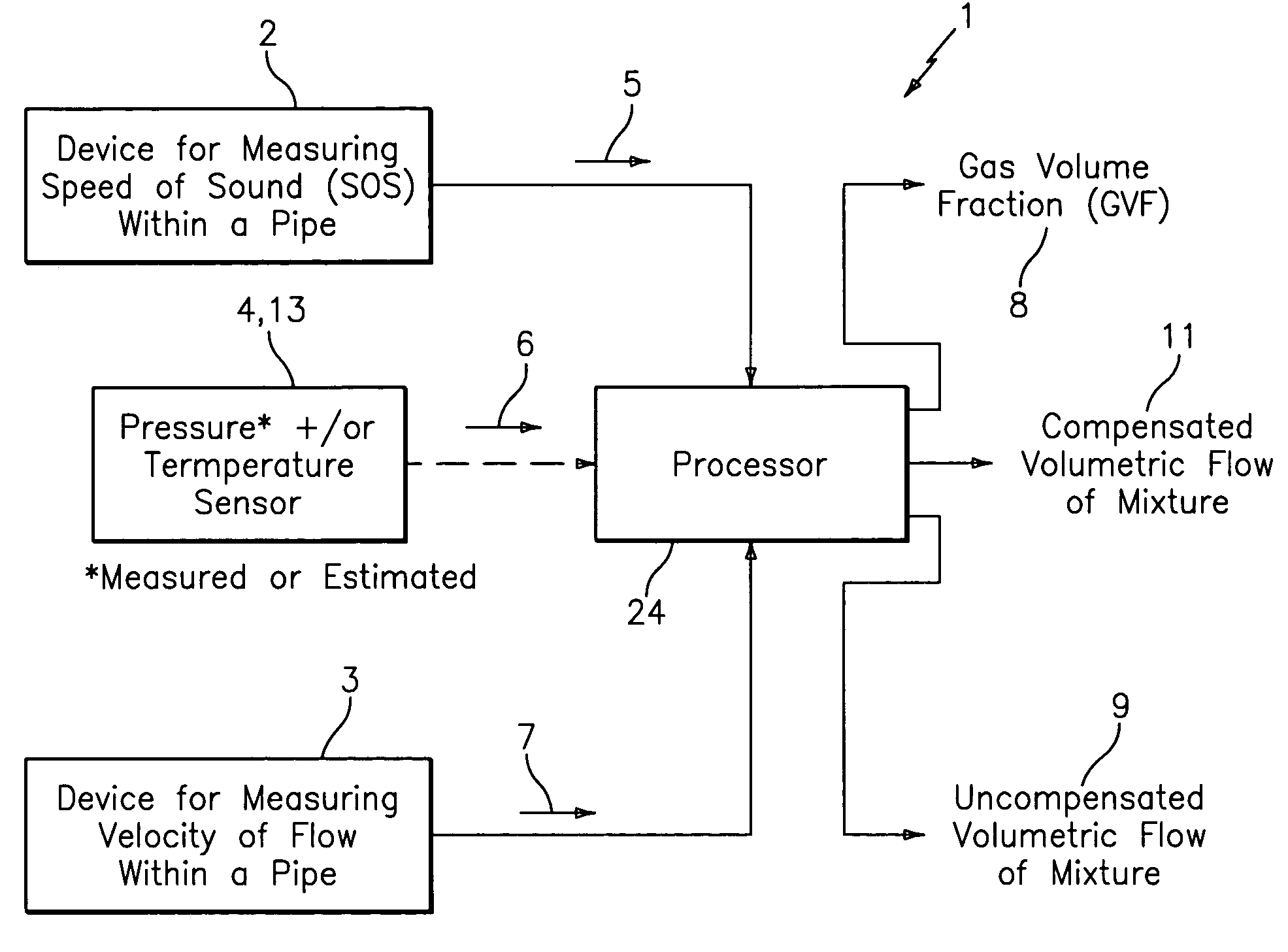
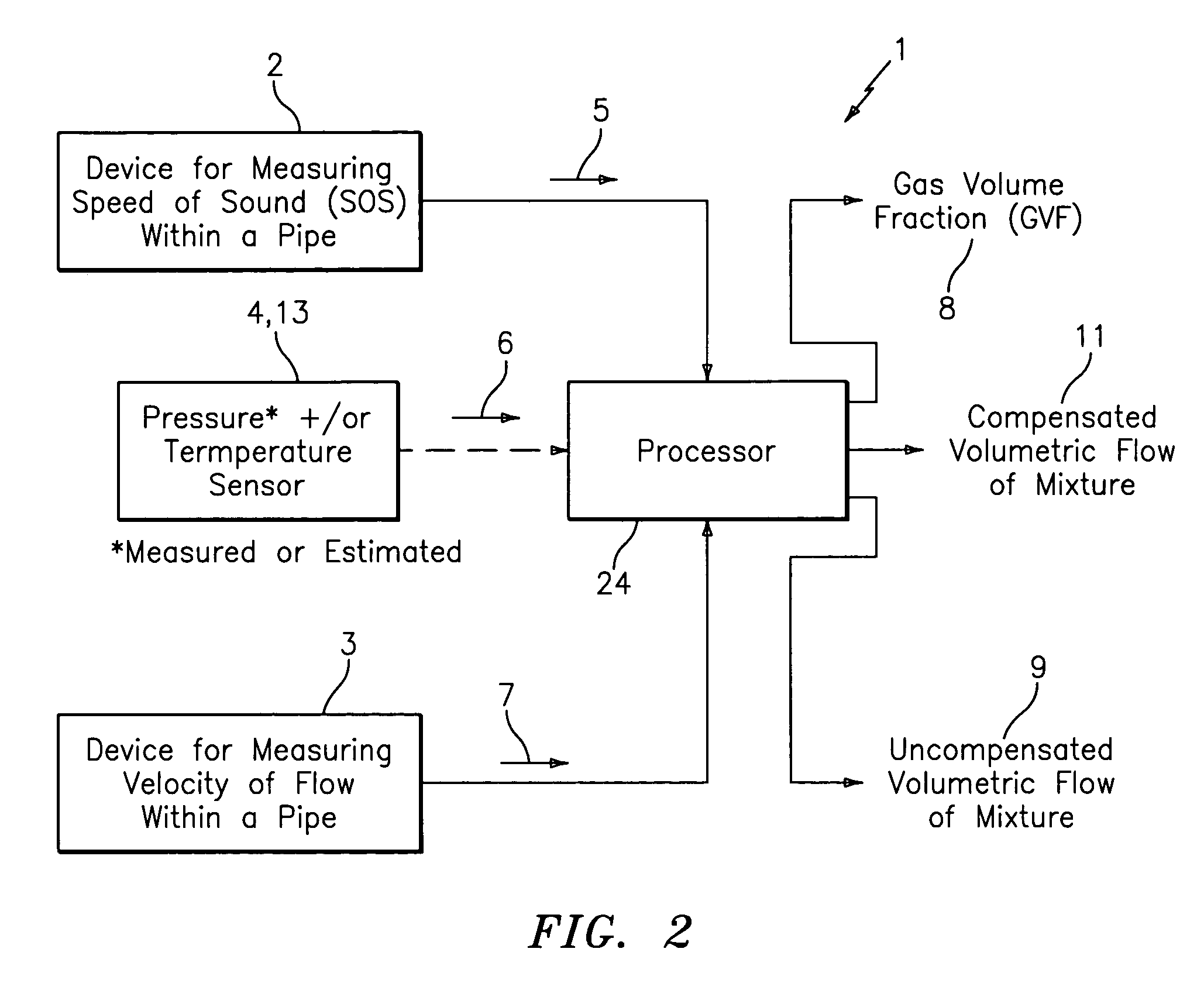
Apparatus and method for providing a flow measurement compensated for entrained gas
ActiveUS7165464B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using microwave meansSensor arrayAir entrainment
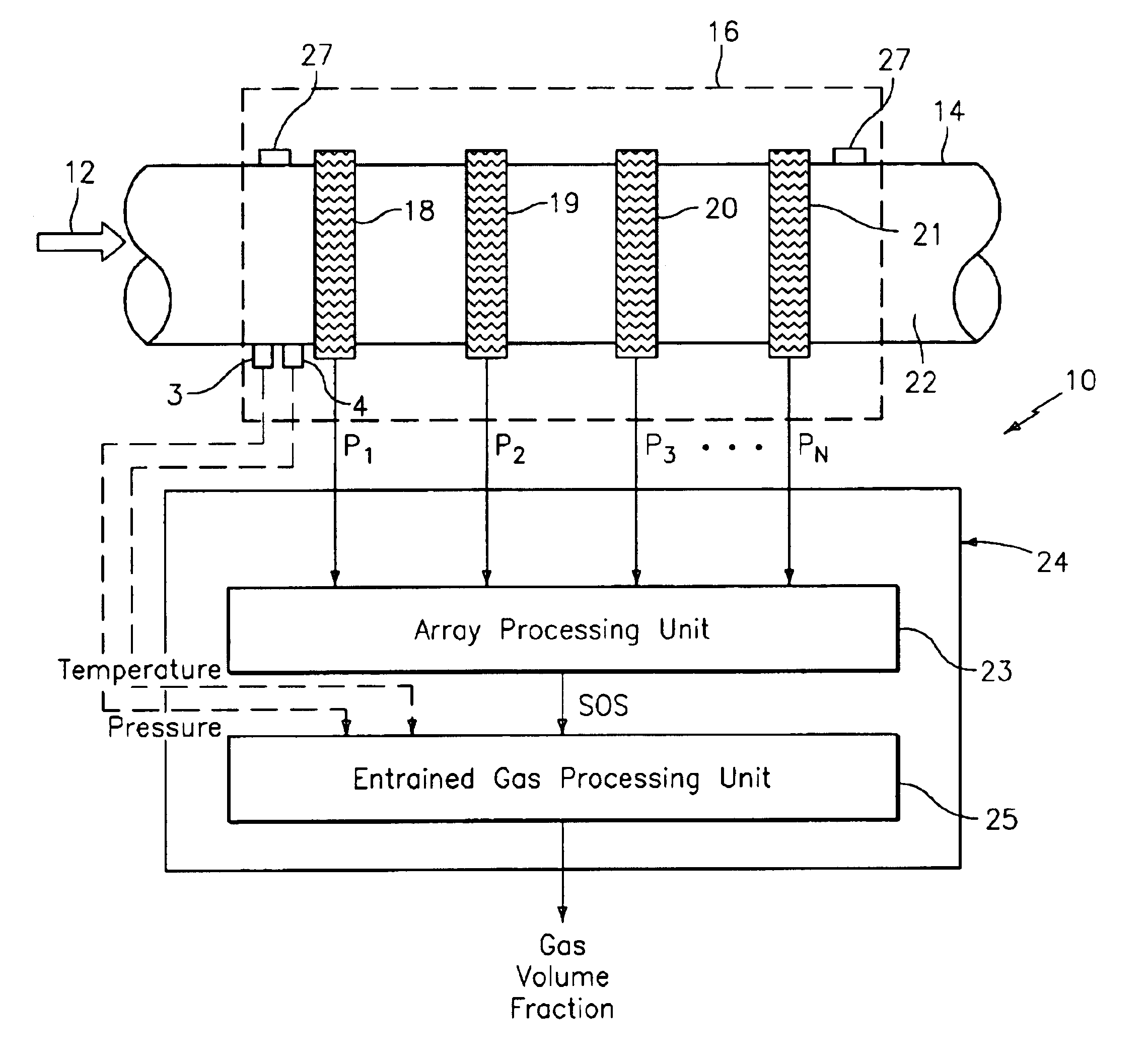
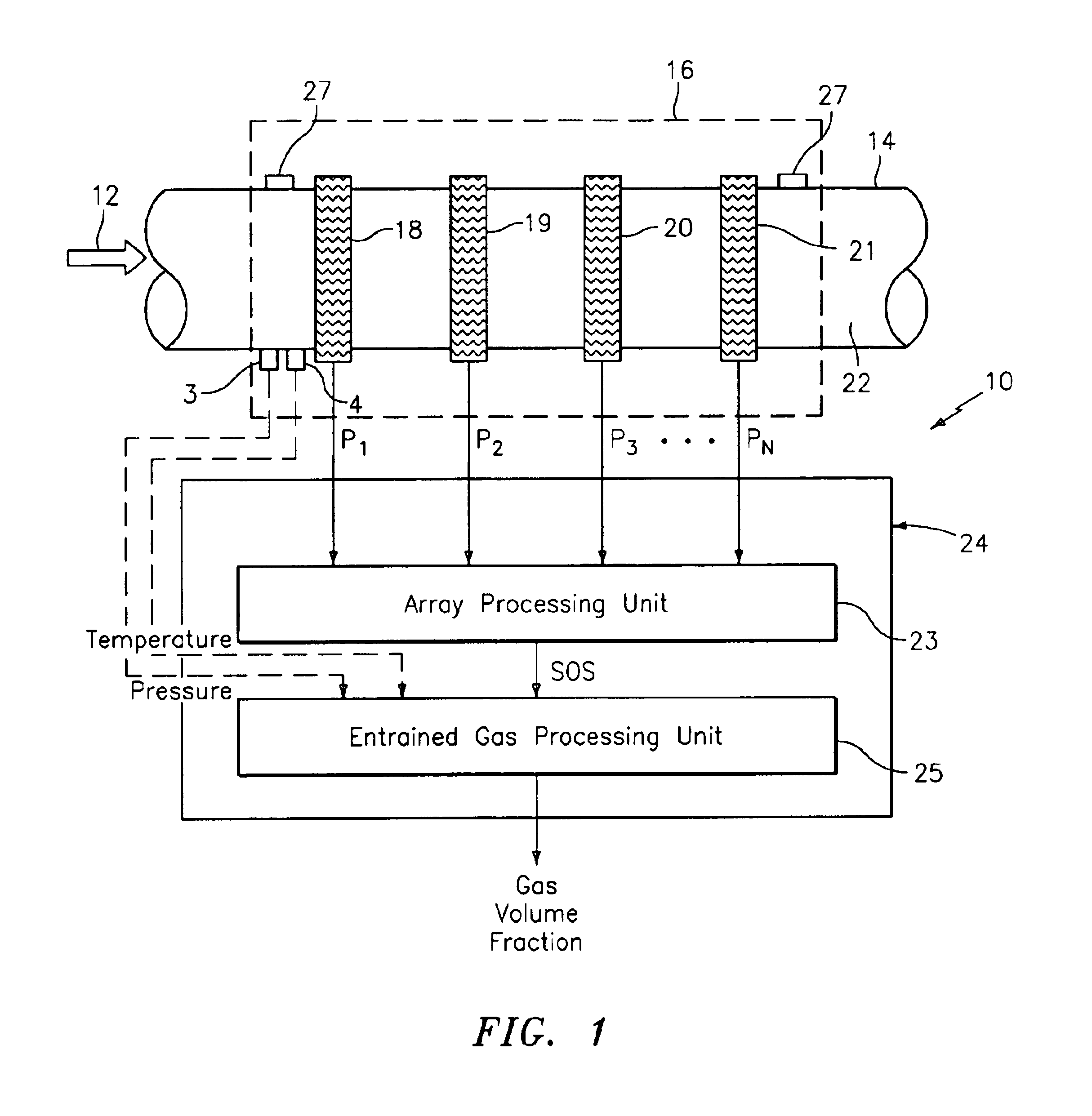
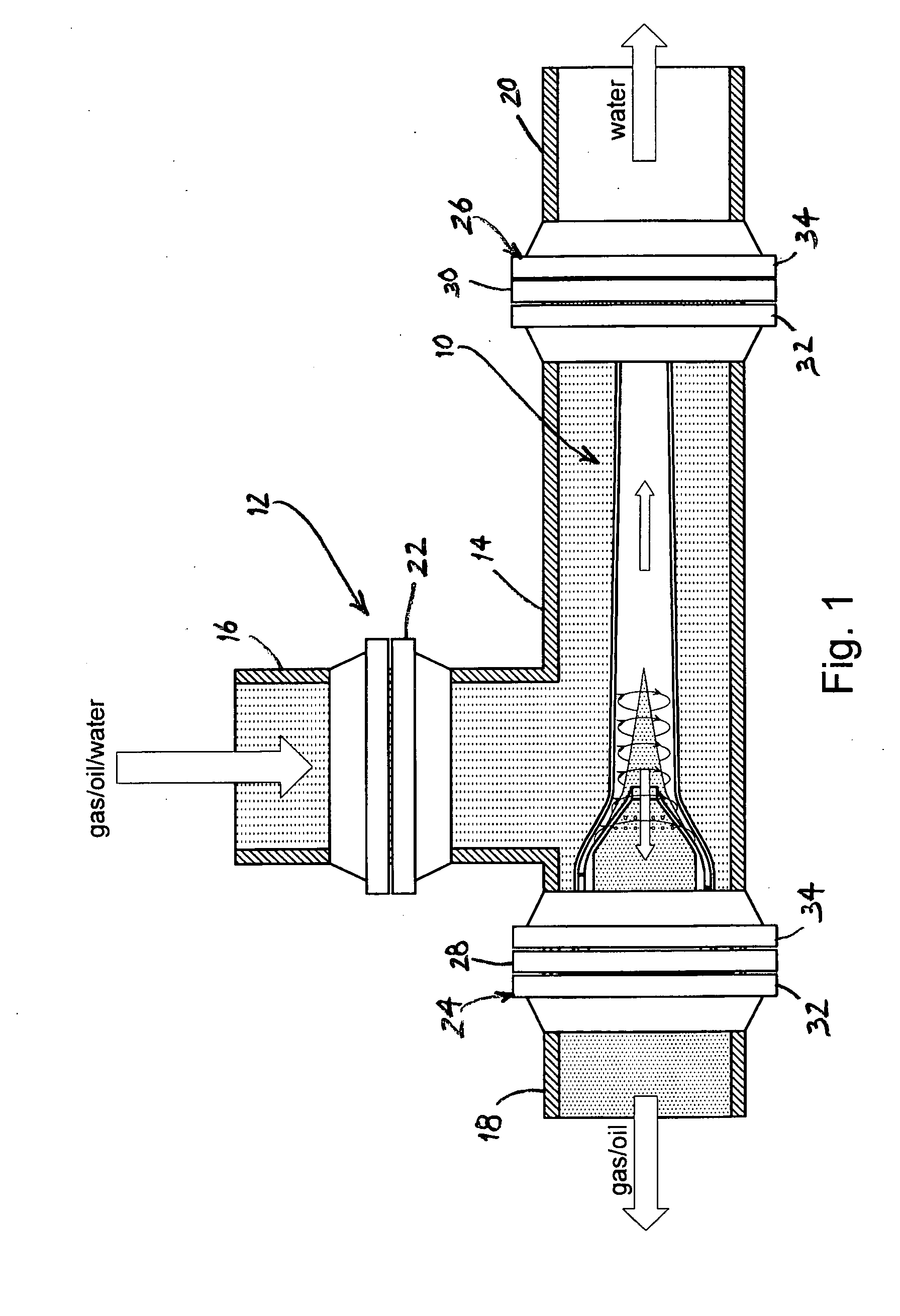
A apparatus 10,110 is provided that measures the speed of sound and / or vortical disturbances propagating in a fluid or mixture having entrained gas / air to determine the gas volume fraction of the flow 12 propagating through a pipes and compensating or correcting the volumetric flow measurement for entrained air. The GVF meter includes and array of sensor disposed axially along the length of the pipe. The GVF measures the speed of sound propagating through the pipe and fluid to determine the gas volume fraction of the mixture using array processing. The GVF meter can be used with an electromagnetic meter and a consistency meter to compensate for volumetric flow rate and consistency measurement respective, to correct for errors due to entrained gas / air.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Apparatus and method for compensating a coriolis meter
ActiveUS7152460B2High densityAdd additional massMaterial analysis using microwave meansVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectDischarge measurementsVolumetric Mass Density
A flow measuring system is provided that provides at least one of a compensated mass flow rate measurement and a compensated density measurement. The flow measuring system includes a gas volume fraction meter in combination with a coriolis meter. The GVF meter measures acoustic pressures propagating through the fluids to measure the speed of sound αmix propagating through the fluid to calculate at least gas volume fraction of the fluid and / or the reduced natural frequency. For determining an improved density for the coriolis meter, the calculated gas volume fraction and / or reduced frequency is provided to a processing unit. The improved density is determined using analytically derived or empirically derived density calibration models (or formulas derived therefore), which is a function of the measured natural frequency and at least one of the determined GVF, reduced frequency and speed of sound, or any combination thereof. The gas volume fraction (GVF) meter may include a sensing device having a plurality of strain-based or pressure sensors spaced axially along the pipe for measuring the acoustic pressures propagating through the flow.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Multiphase fluid characterization system
ActiveUS20120055239A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTesting/calibration for volume flowUltrasound attenuationResonance
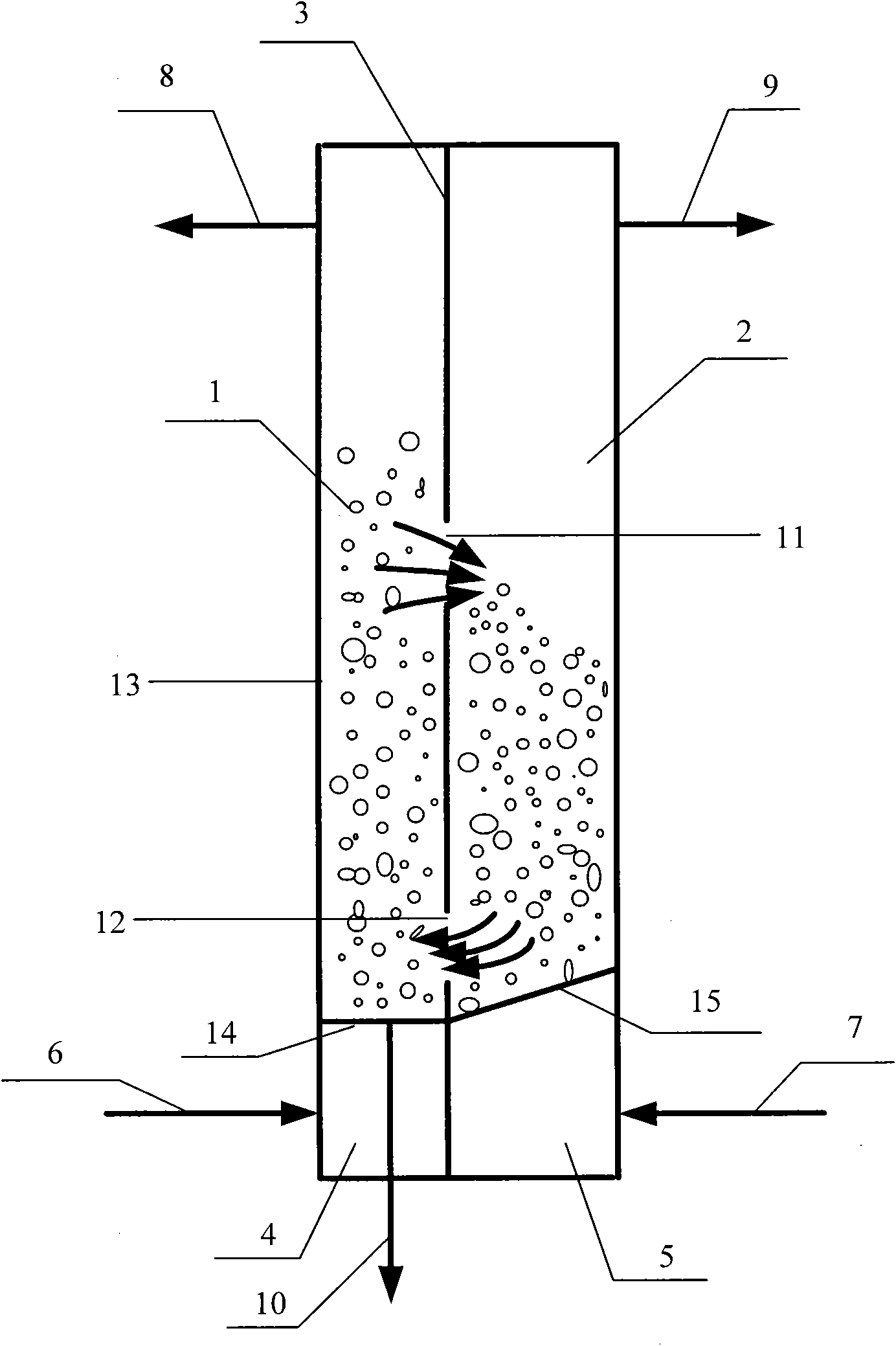
A measurement system and method for permitting multiple independent measurements of several physical parameters of multiphase fluids flowing through pipes are described. Multiple acoustic transducers are placed in acoustic communication with or attached to the outside surface of a section of existing spool (metal pipe), typically less than 3 feet in length, for noninvasive measurements. Sound speed, sound attenuation, fluid density, fluid flow, container wall resonance characteristics, and Doppler measurements for gas volume fraction may be measured simultaneously by the system. Temperature measurements are made using a temperature sensor for oil-cut correction.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
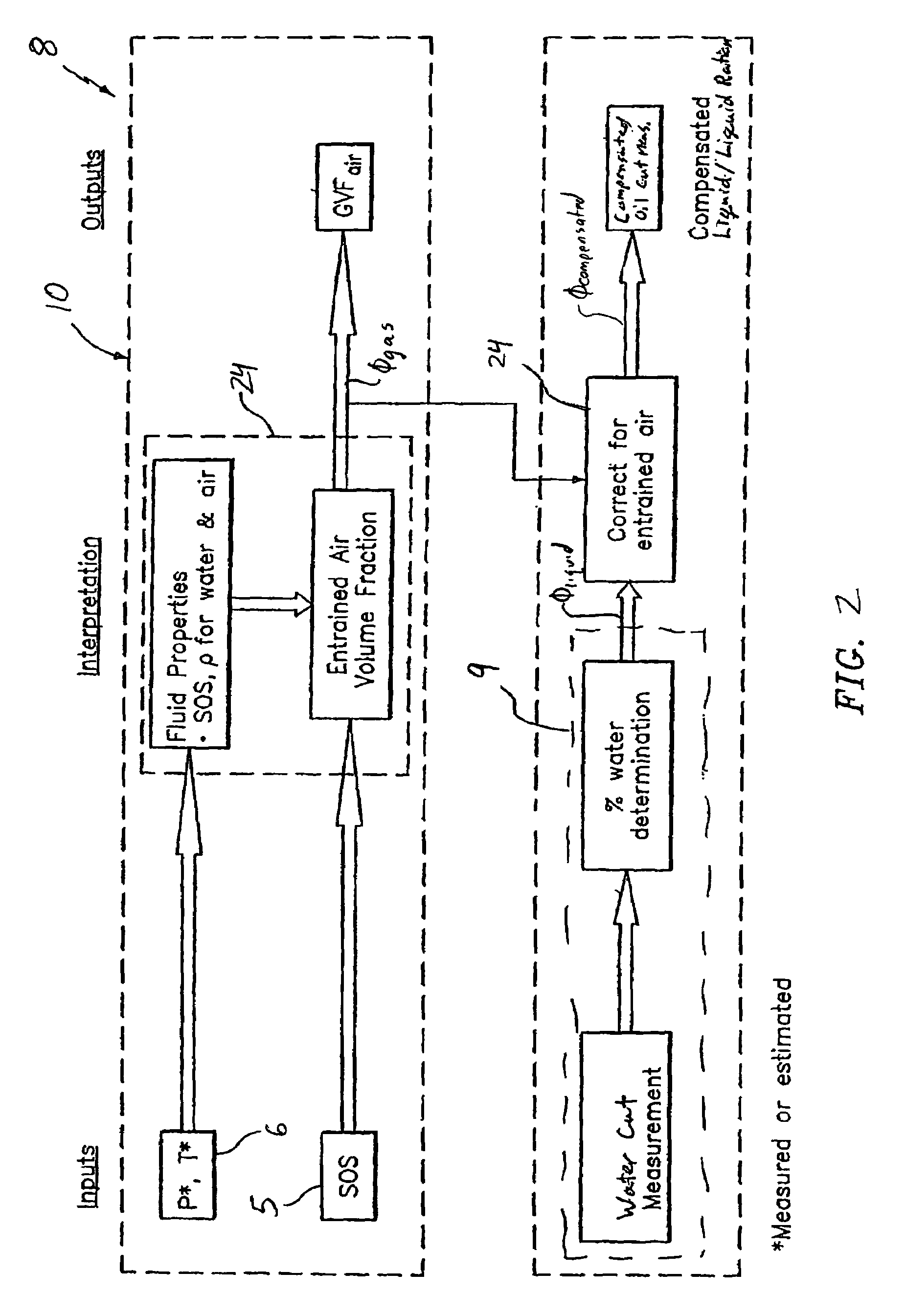
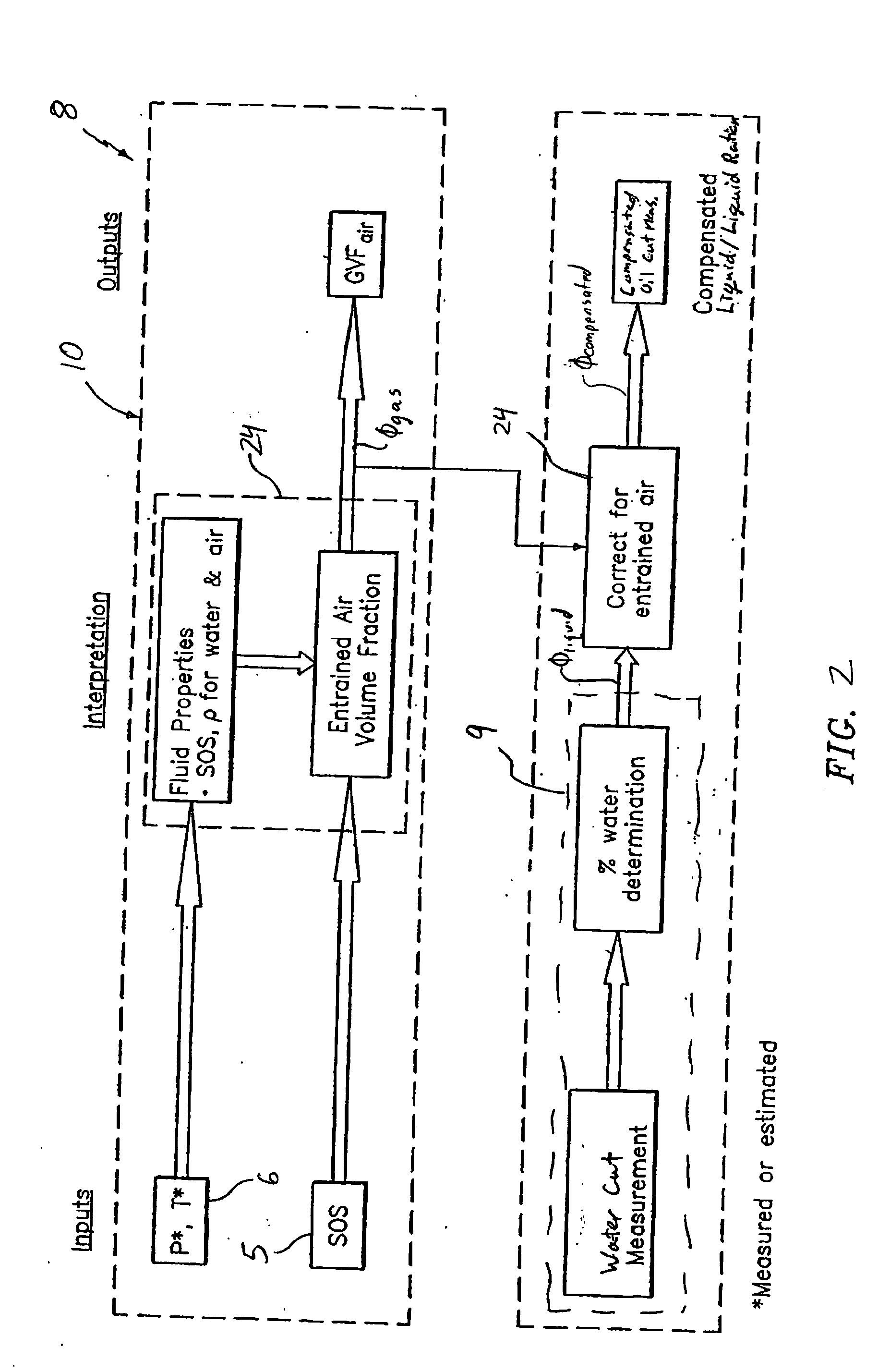
Apparatus and method for providing a fluid cut measurement of a multi-liquid mixture compensated for entrained gas
ActiveUS7380438B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTesting/calibration apparatusEngineeringPermittivity
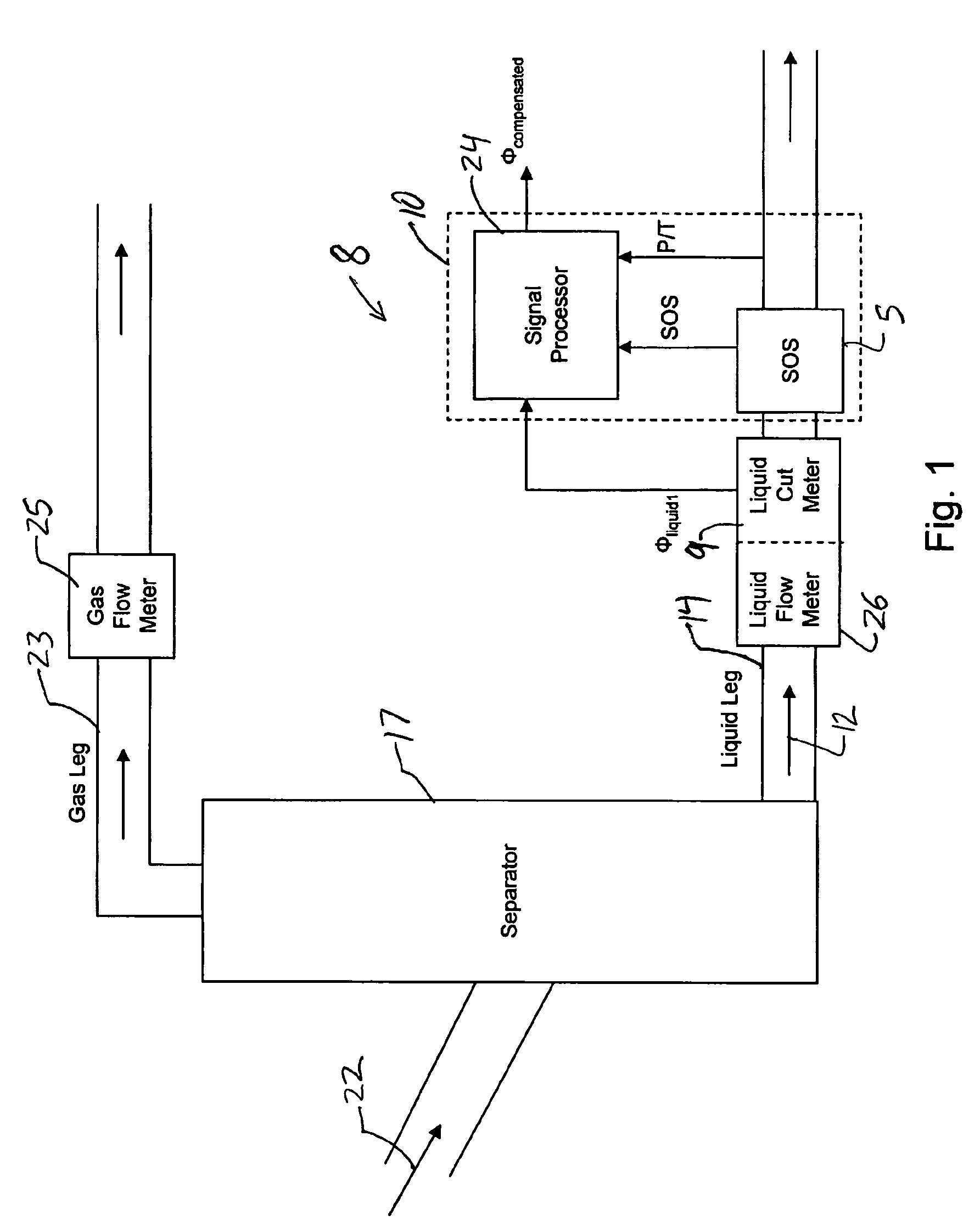
An apparatus for determining a fluid cut measurement of a multi-liquid mixture includes a first device configured to sense at least one parameter of the mixture to determine a fluid cut of a liquid in the mixture. A second device is configured to determine a concentration of gas in the mixture in response to a speed of sound in the mixture; and a signal processor is configured to adjust the fluid cut of the liquid using the concentration of the gas to determine a compensated fluid cut of the liquid. The parameter of the mixture sensed by the first device may include a density of the mixture (e.g., by way of a Coriolis meter), a permittivity of the mixture (e.g., by way of a resonant microwave oscillator), or an amount of microwave energy absorbed by the mixture (e.g., by way of a microwave absorption watercut meter). The signal processor may employ different correction factors depending on the type of fluid cut device used. The second device may include a gas volume fraction meter.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
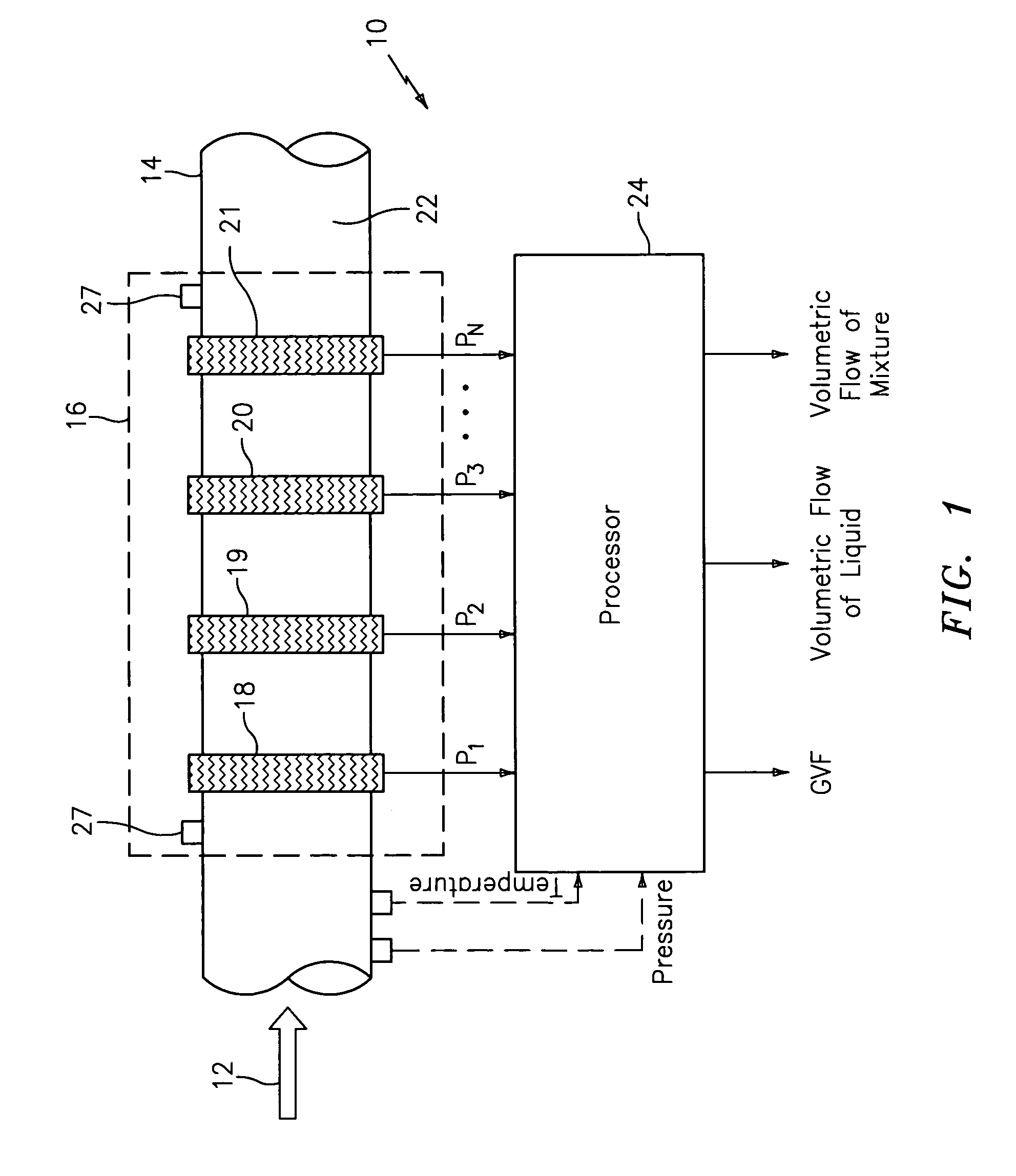
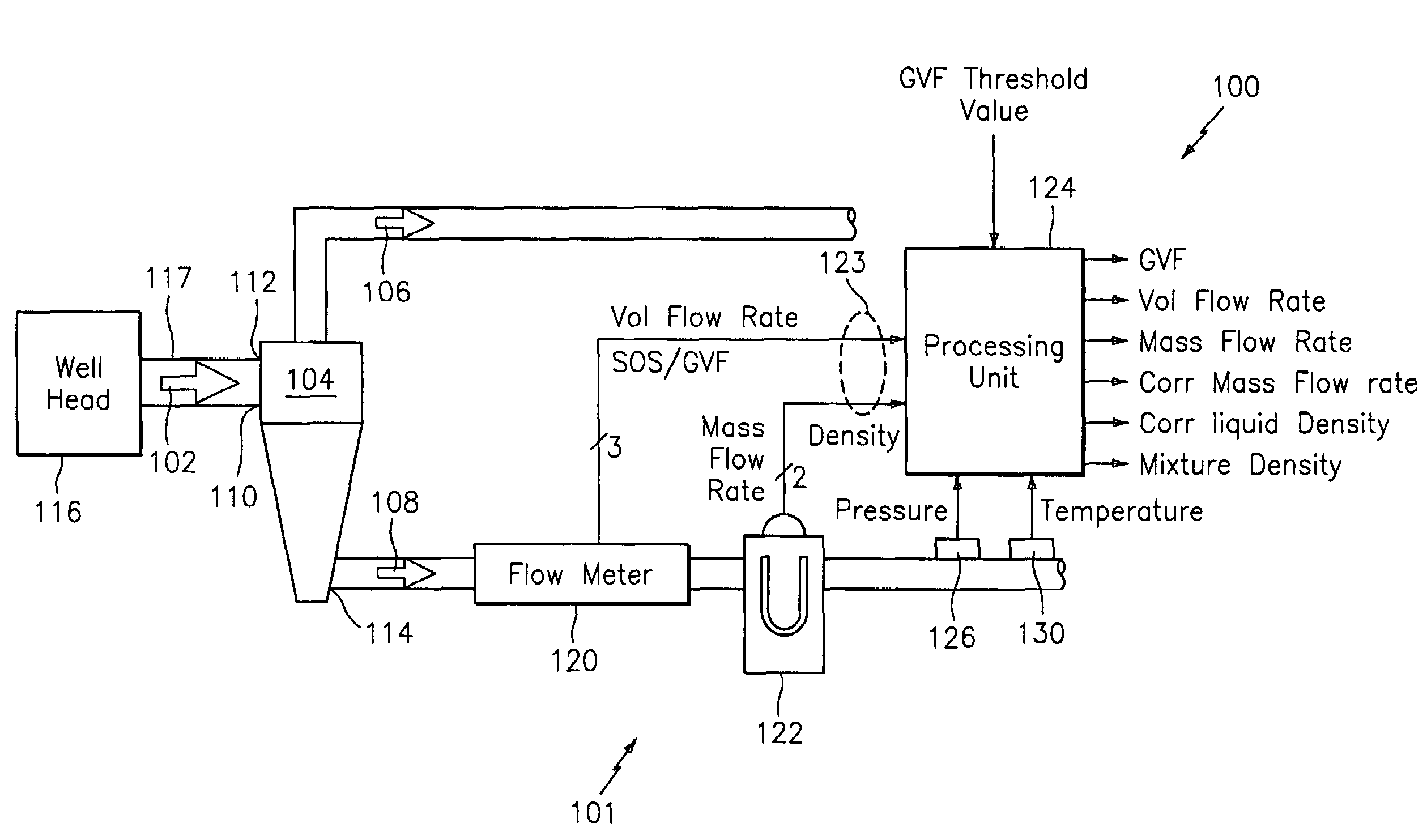
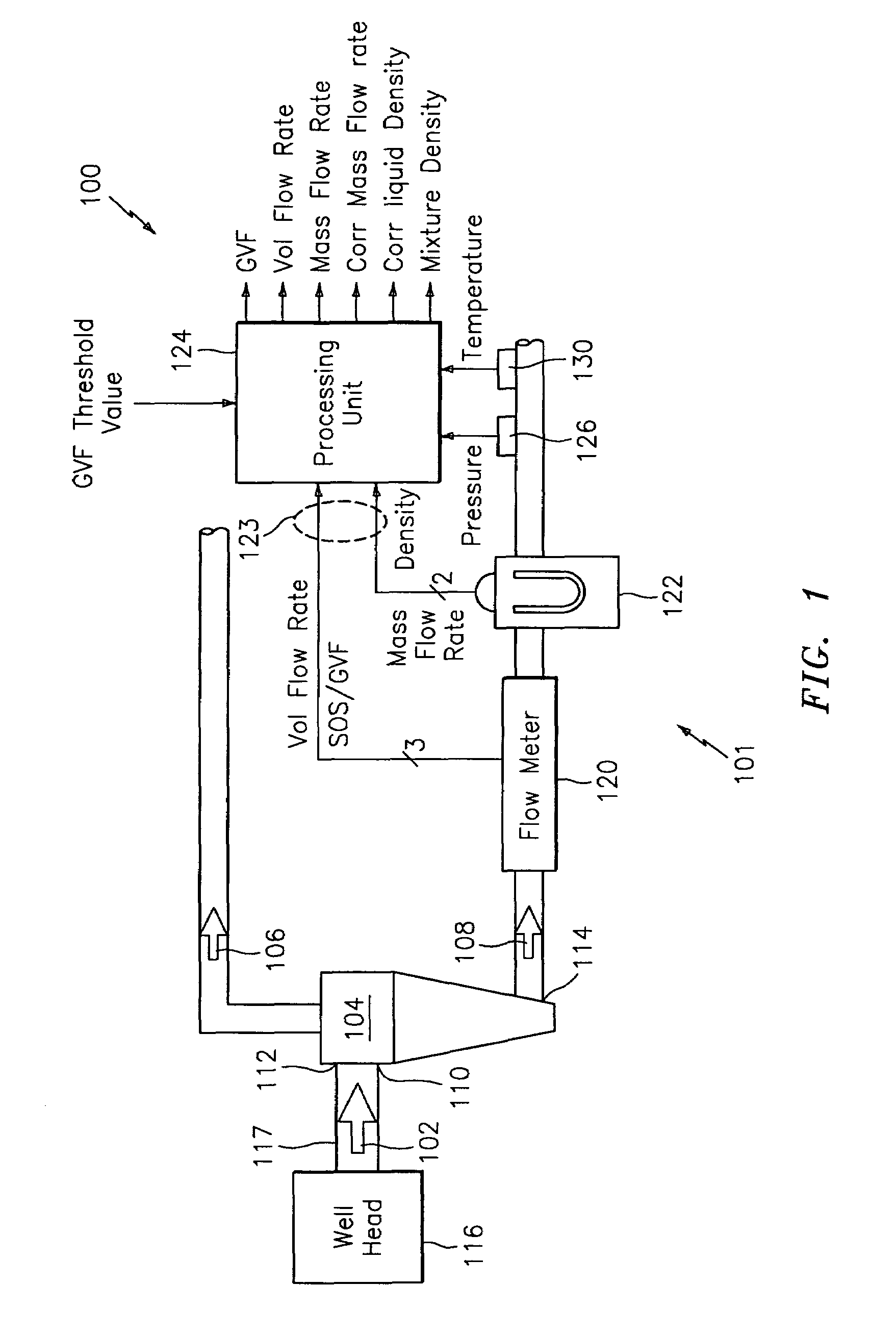
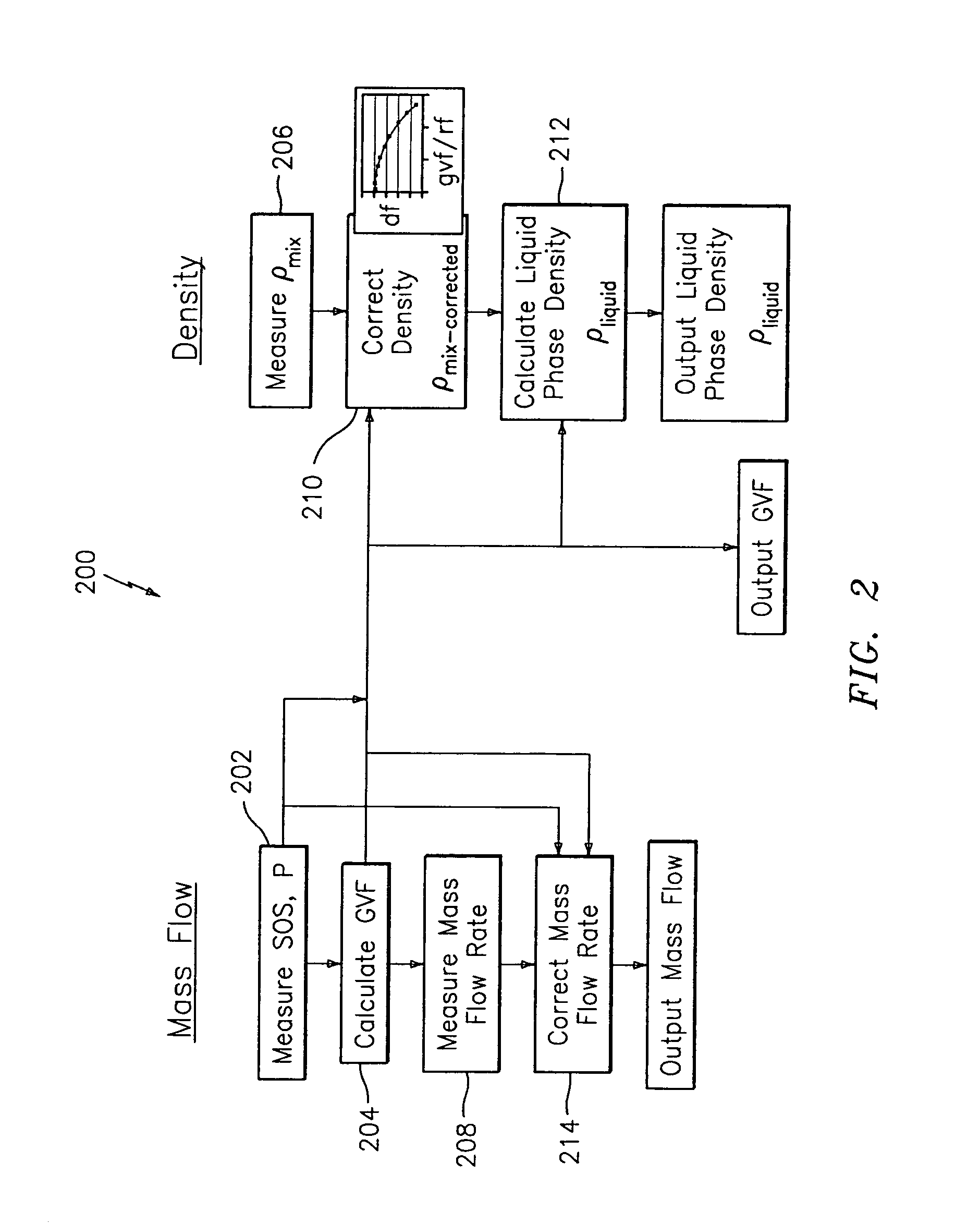
System for measuring a parameter of an aerated multi-phase mixture flowing in a pipe
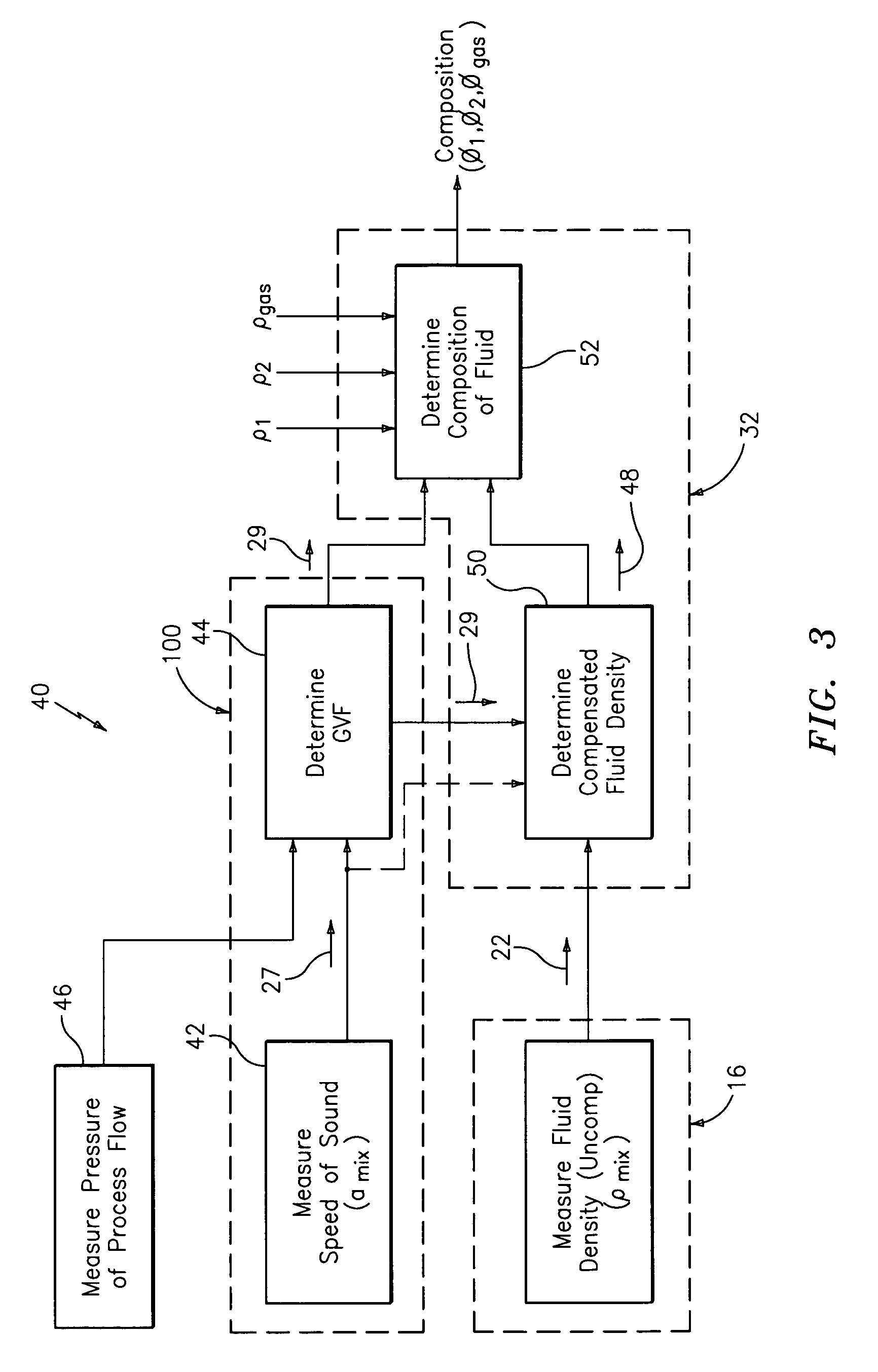
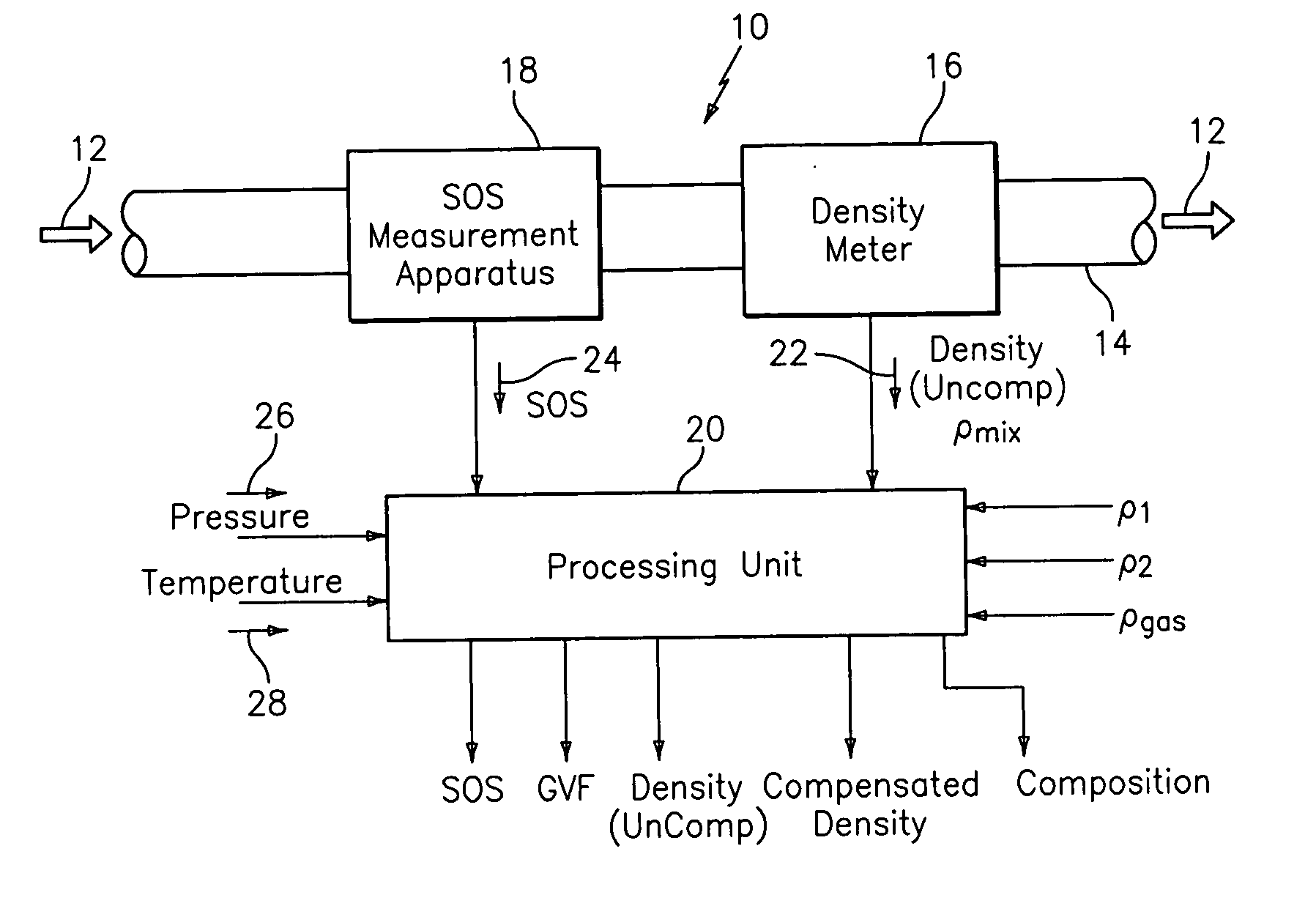
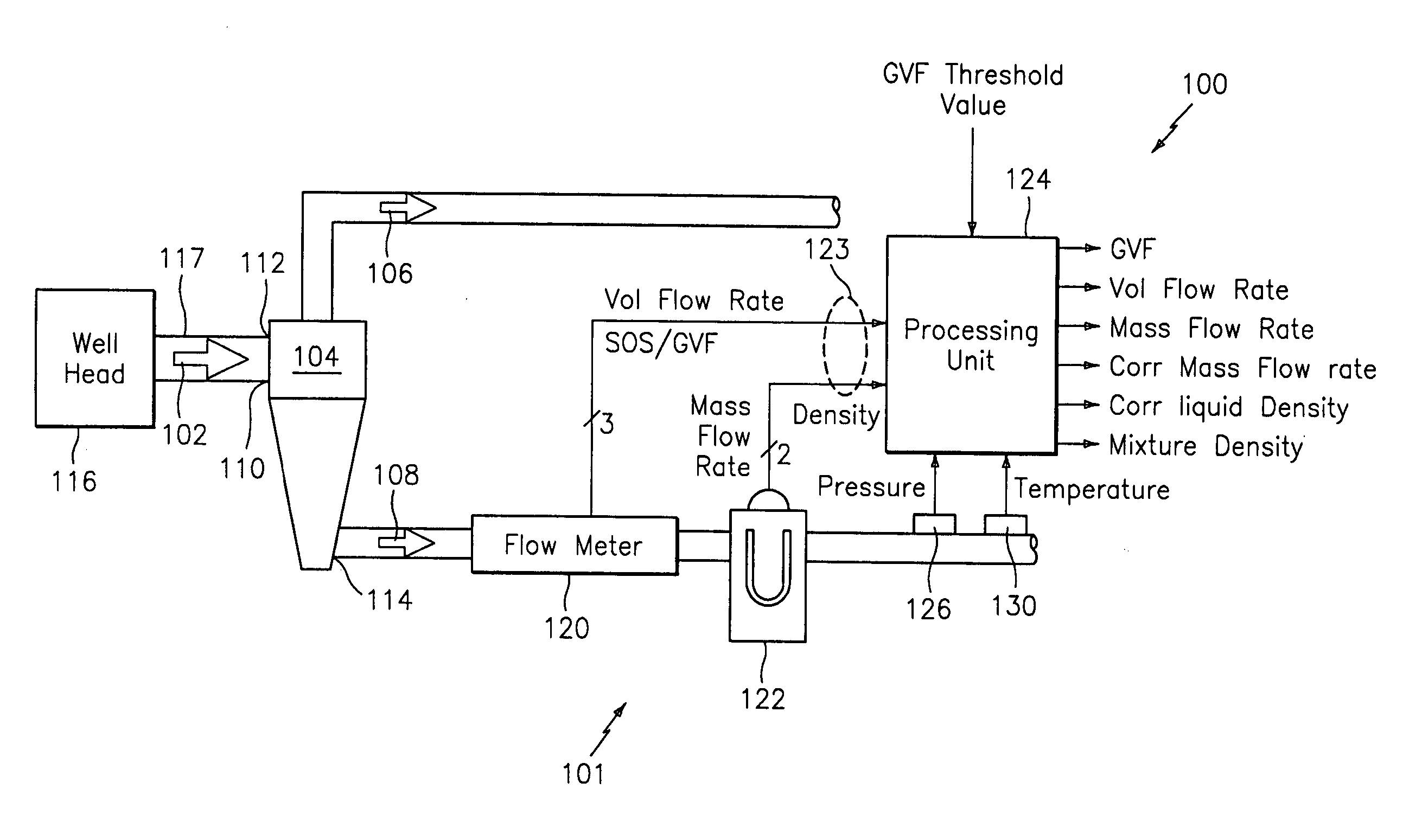
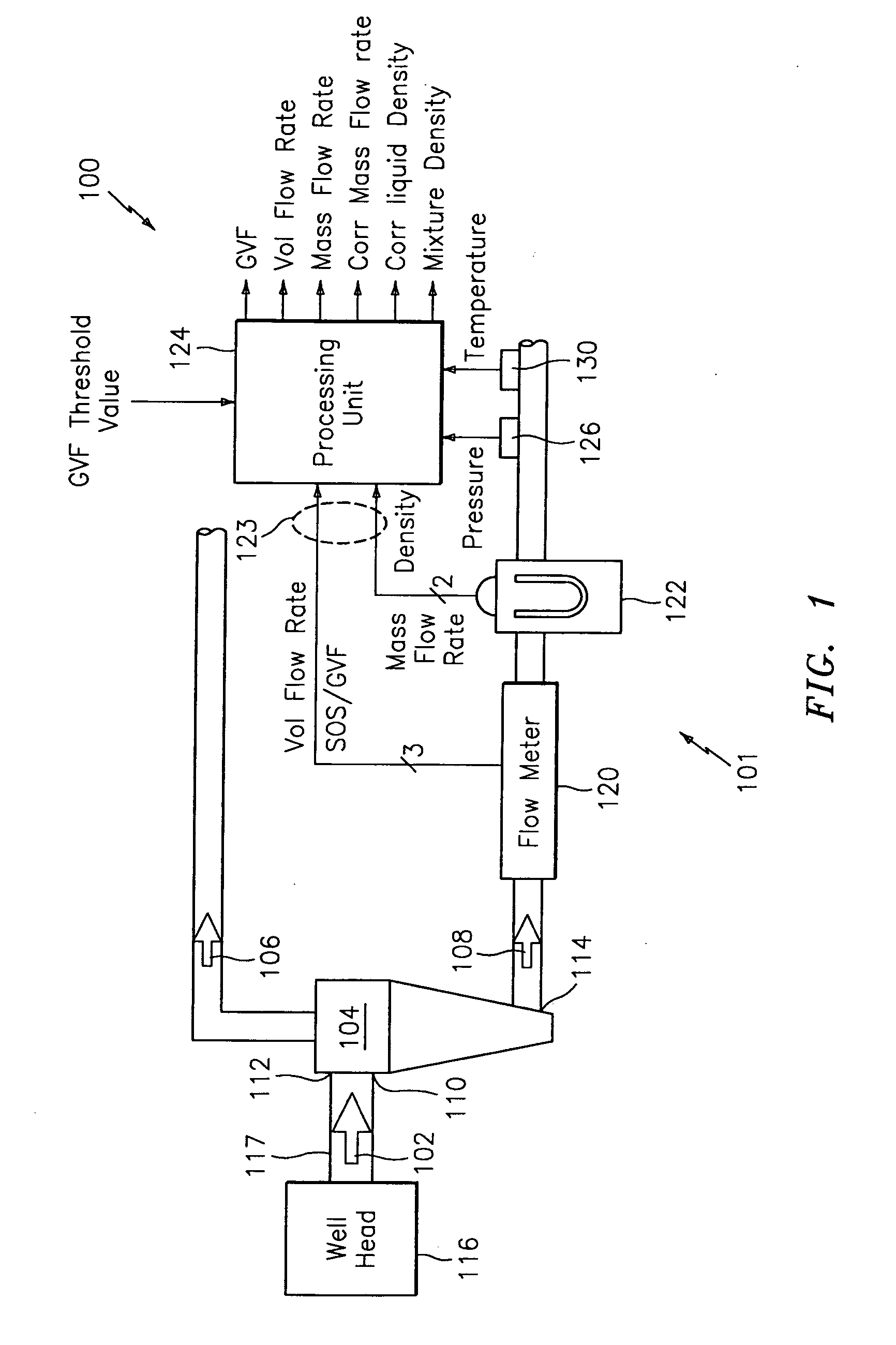
A method and apparatus for measuring at least one characteristic of an aerated fluid flowing within a pipe is provided, wherein the method includes generating a measured sound speed, a measured density, a pressure and a gas volume fraction for the aerated fluid. The method also includes correcting the measured density responsive to the measured sound speed, the pressure and the gas volume fraction to generate a corrected density. The method further includes calculating a liquid phase density, determining whether the gas volume fraction is above a predetermined threshold value and generating a mass flow rate responsive to whether the gas volume fraction is above the predetermined threshold value.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
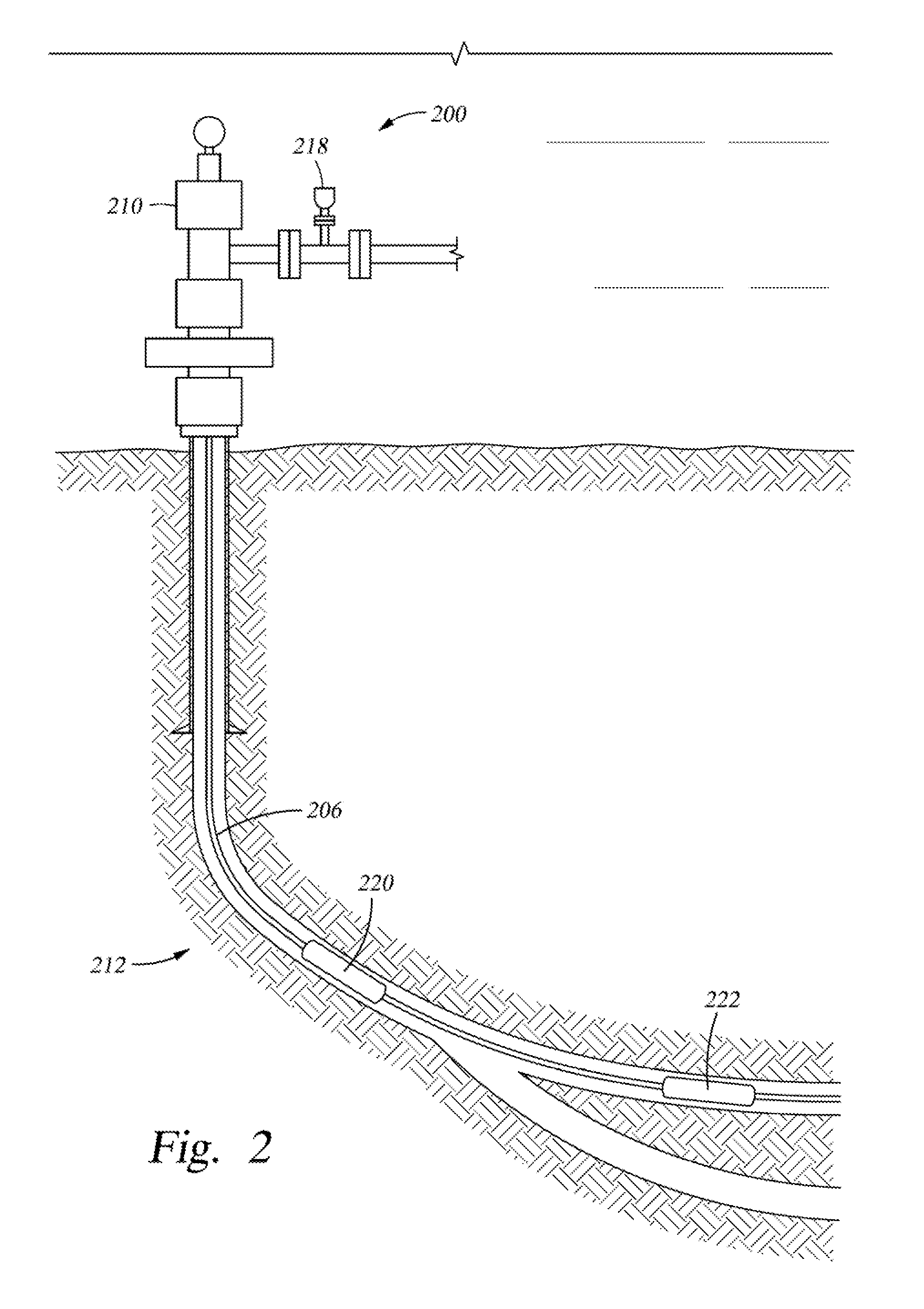
Apparatus and method of measuring gas volume fraction of a fluid flowing within a pipe
ActiveUS7343818B2Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesEngineeringProduct gas
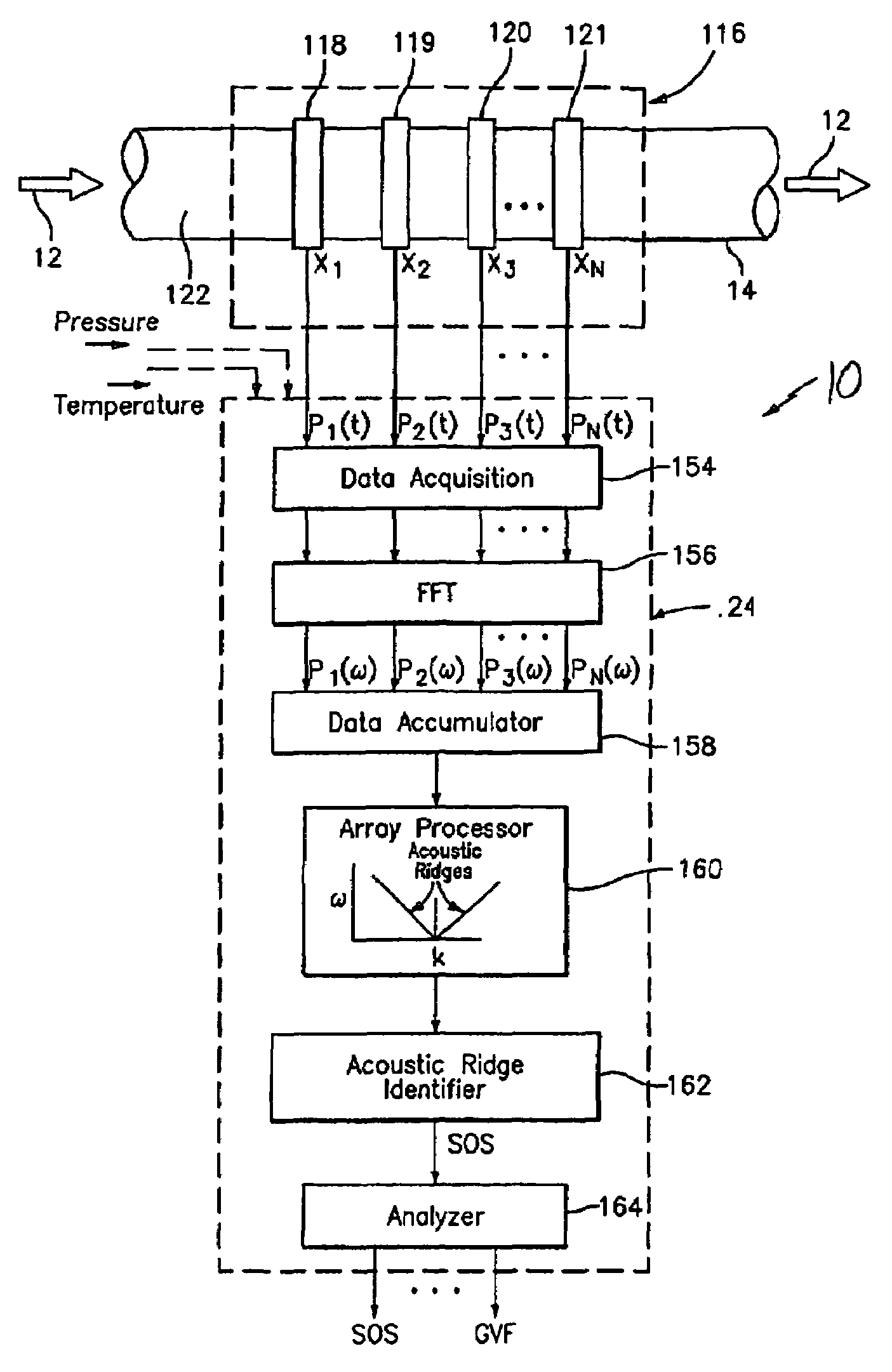
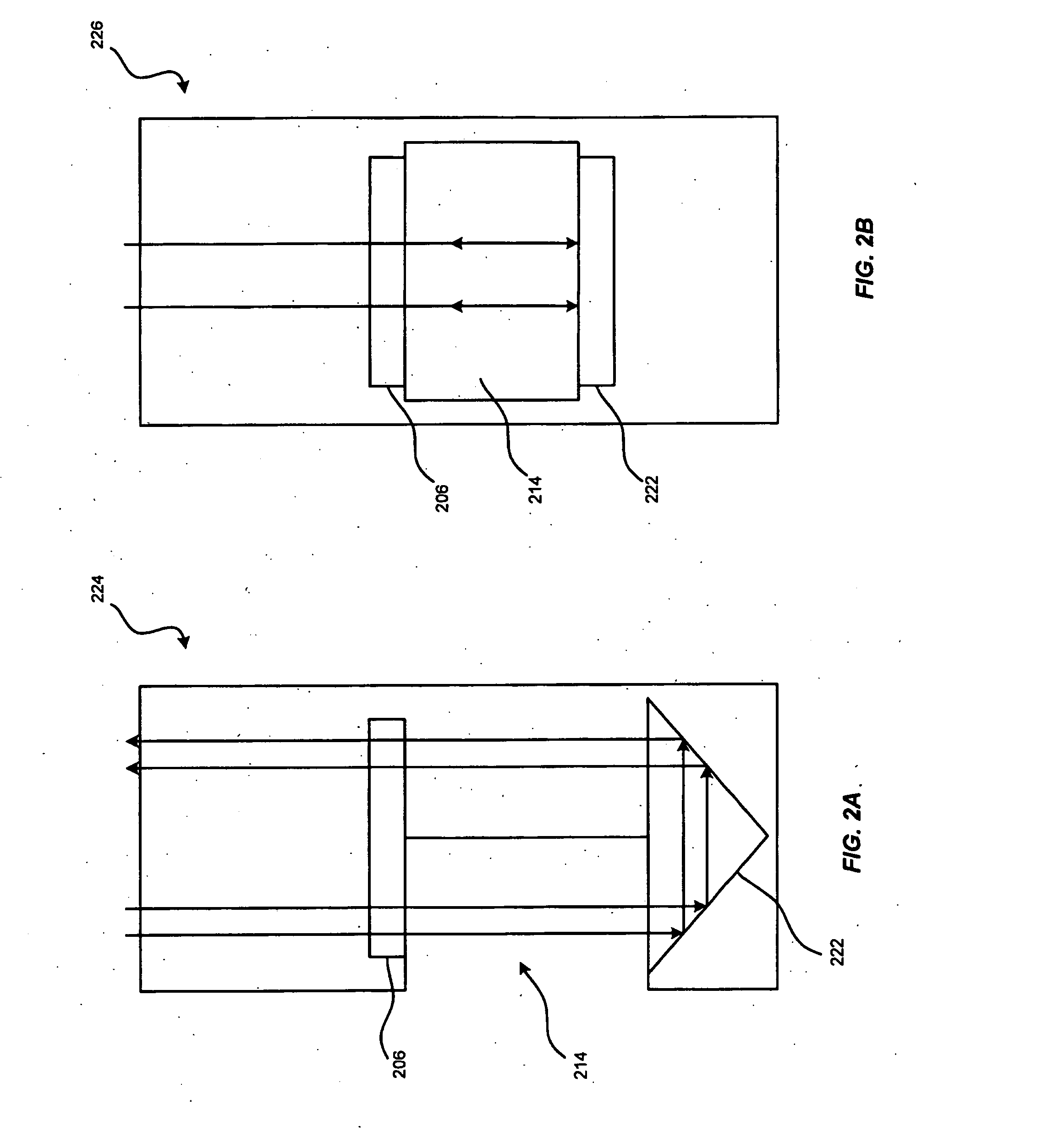
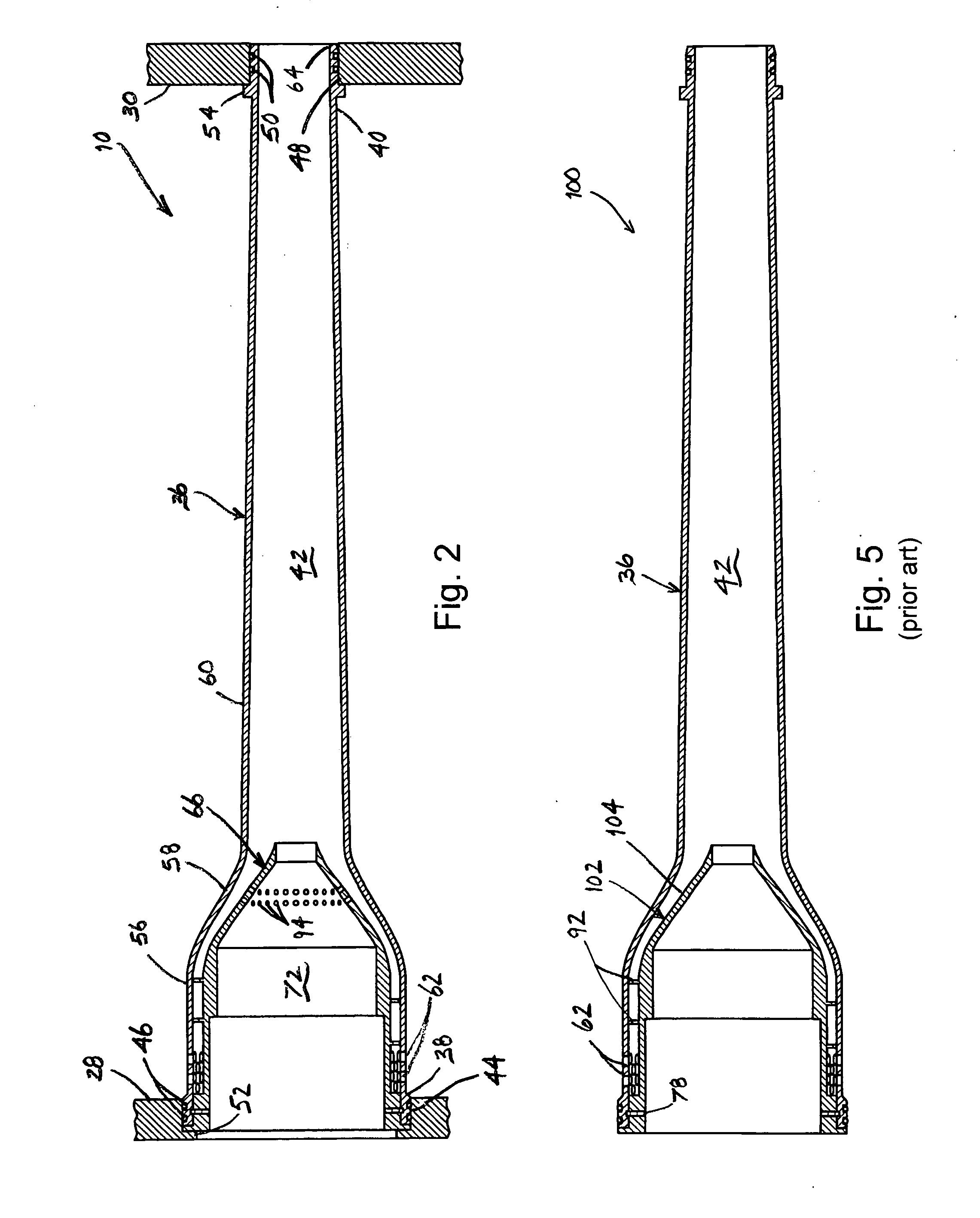
A clamp on apparatus 10,110 is provided that measures the speed of sound or acoustic disturbances propagating in a fluid or mixture having entrained gas / air to determine the gas volume fraction of the flow 12 propagating through a pipe 14. The apparatus includes an array of pressure sensors clamped onto the exterior of the pipe and disposed axially along the length of the pipe. The apparatus measures the speed of sound propagating through the fluid to determine the gas volume fraction of the mixture using adaptive array processing techniques to define an acoustic ridge in the k-ω plane. The slope of the acoustic ridge 61 defines the speed of sound propagating through the fluid in the pipe.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
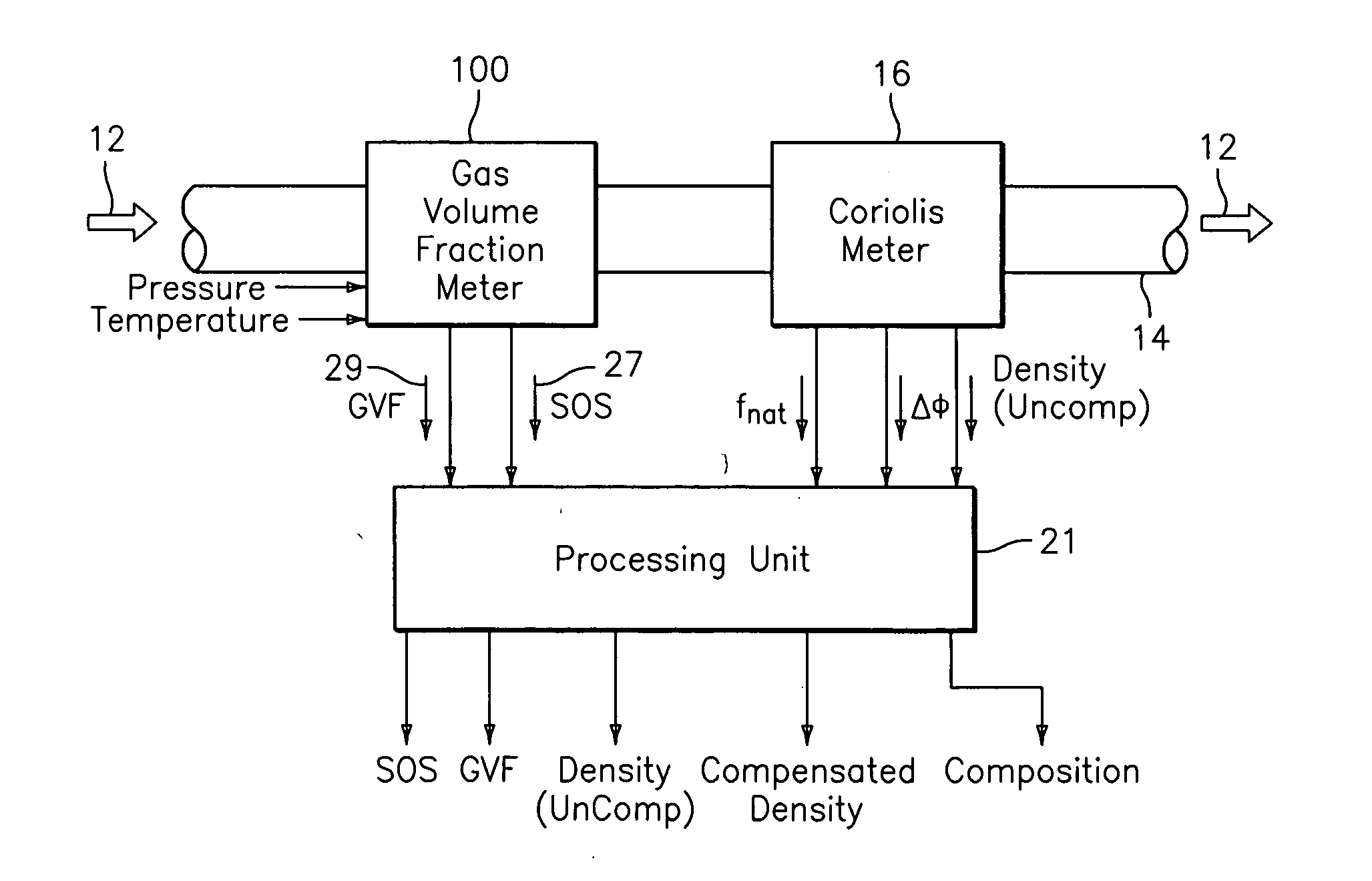
Apparatus and method for augmenting a Coriolis meter
ActiveUS7299705B2High densityAdd additional massMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume meteringDischarge measurementsUsage analysis
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Apparatus and method of measuring gas volume fraction of a fluid flowing within a pipe
ActiveUS7062976B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow propertiesEngineeringGas volume fraction
An apparatus 10,110 is provided that measures the speed of sound or acoustic disturbances propagating in a fluid or mixture having entrained gas / air to determine the gas volume fraction of the flow 12 propagating through a pipe 14. The apparatus includes an array of pressure sensors disposed axially along the length of the pipe. The apparatus measures the speed of sound propagating through the fluid to determine the gas volume fraction of the mixture using adaptive array processing techniques to define an acoustic ridge in the k-ω plane. The slope of the acoustic ridge 61 defines the speed of sound propagating through the fluid in the pipe.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
System for measuring a parameter of an aerated multi-phase mixture flowing in a pipe
ActiveUS20060096388A1Volume variation compensation/correction apparatusIndirect mass flowmetersVolumetric Mass DensityMulti phase
A method and apparatus for measuring at least one characteristic of an aerated fluid flowing within a pipe is provided, wherein the method includes generating a measured sound speed, a measured density, a pressure and a gas volume fraction for the aerated fluid. The method also includes correcting the measured density responsive to the measured sound speed, the pressure and the gas volume fraction to generate a corrected density. The method further includes calculating a liquid phase density, determining whether the gas volume fraction is above a predetermined threshold value and generating a mass flow rate responsive to whether the gas volume fraction is above the predetermined threshold value.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Apparatus and method for augmenting a Coriolis meter
ActiveUS20060169058A1High densityAdd additional massMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume meteringDischarge measurementsUsage analysis
A flow measuring system is provided that provides at least one of a compensated mass flow rate measurement and a compensated density measurement. The flow measuring system includes a gas volume fraction meter in combination with a coriolis meter. The GVF meter measures acoustic pressures propagating through the fluids to measure the speed of sound αmix propagating through the fluid to calculate at least gas volume fraction of the fluid and / or the reduced natural frequency. For determining an improved density for the coriolis meter, the calculated gas volume fraction and / or reduced frequency is provided to a processing unit. The improved density is determined using analytically derived or empirically derived density calibration models (or formulas derived therefore), which is a function of the measured natural frequency and at least one of the determined GVF, reduced frequency and speed of sound, or any combination thereof. The gas volume fraction (GVF) meter may include a sensing device having a plurality of strain-based or pressure sensors spaced axially along the pipe for measuring the acoustic pressures propagating through the flow.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
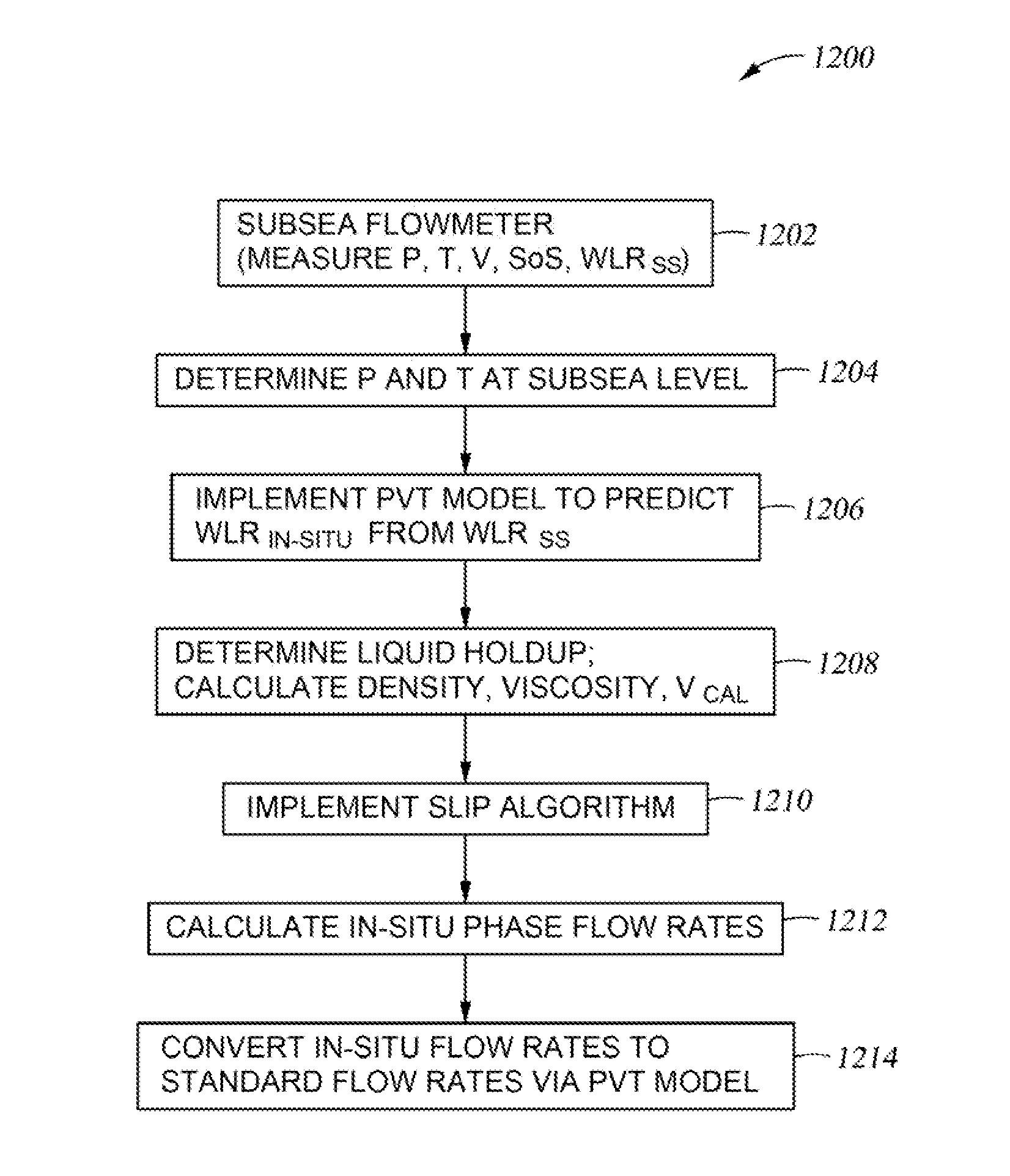
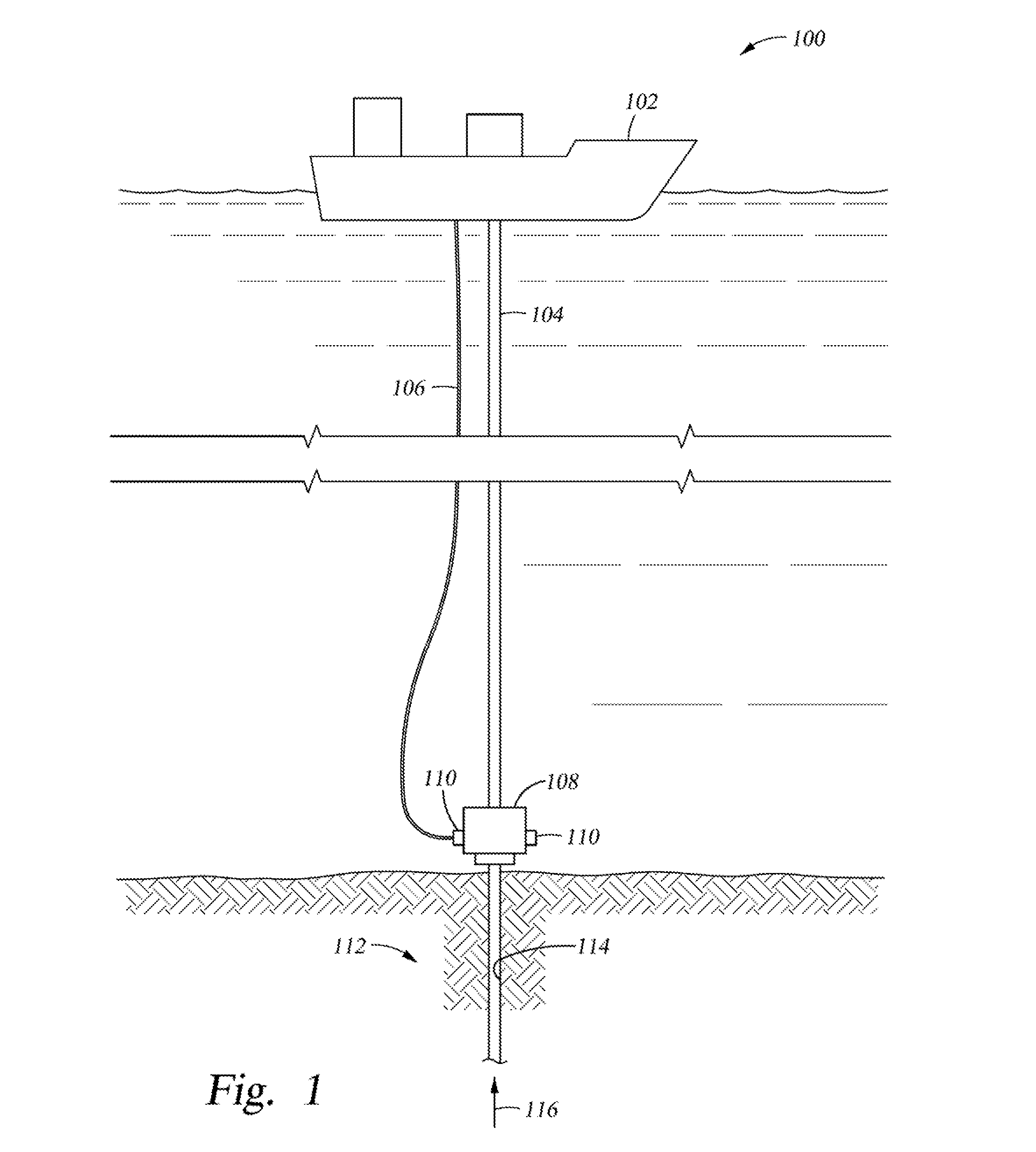
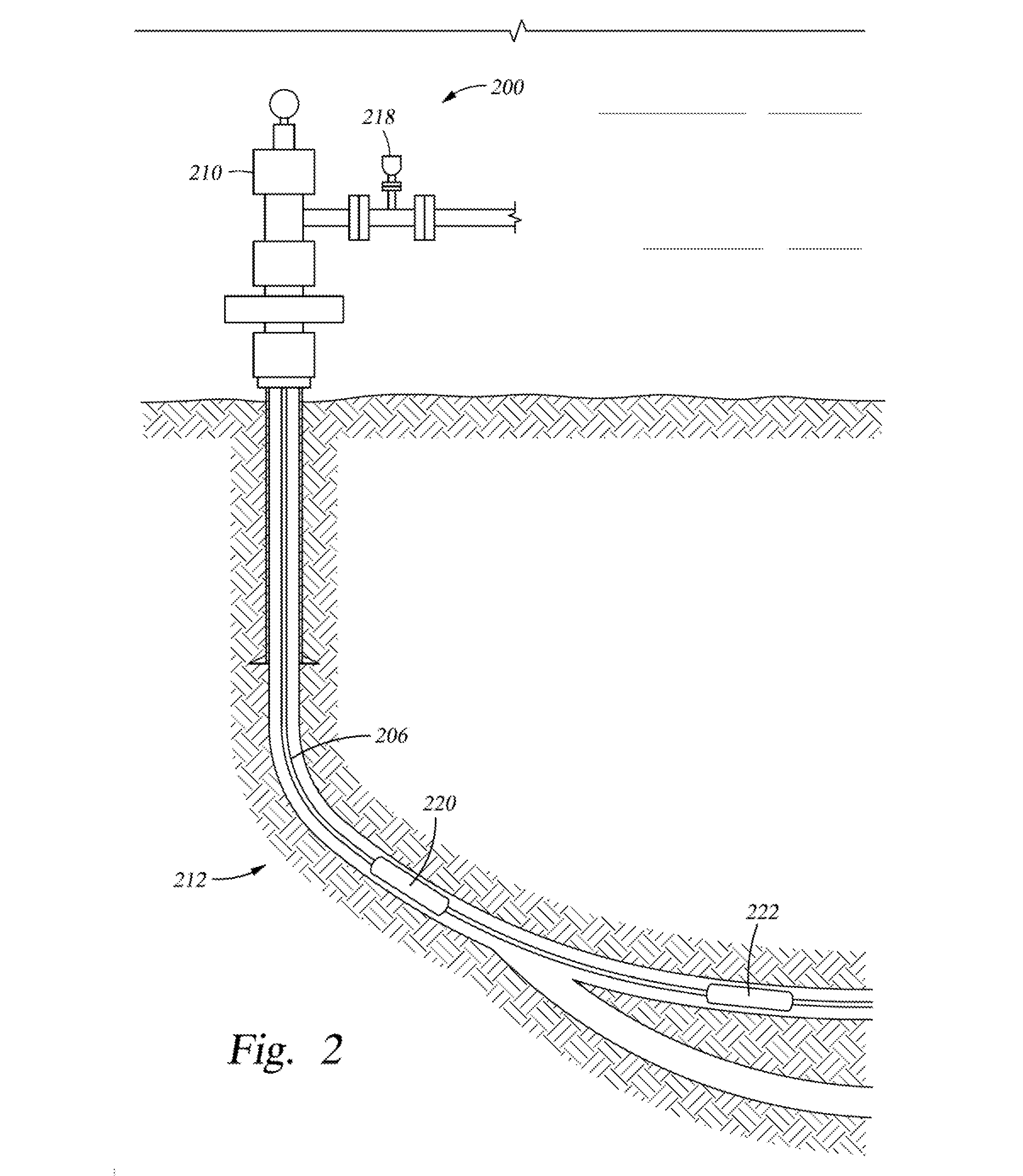
Multiphase flowmeter for subsea applications
Multiphase flow measurement in extreme environments such as subsea or in-well is a difficult task for many reasons including reliability, survivability, and longevity issues; accessibility to the equipment; and complexity of the varying flow field as a function of position and time. Embodiments of the present invention provide techniques and apparatus for performing subsea multiphase flow measurement by combining two technologies. One is based on infrared water-cut measurement technology which is capable of measuring water and oil concentrations in multiphase flow with up to 99.5% gas volume fractions. The second technology is based on in-well fiber-optic flow measurement capable of resolving gas and total liquid flow through the measurements of flow velocity, fluid mixture speed of sound, and absolute pressure and temperature at meter location. This hybrid system represents an approach to subsea multiphase metering that may offer advantages compared to traditional systems for some applications.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
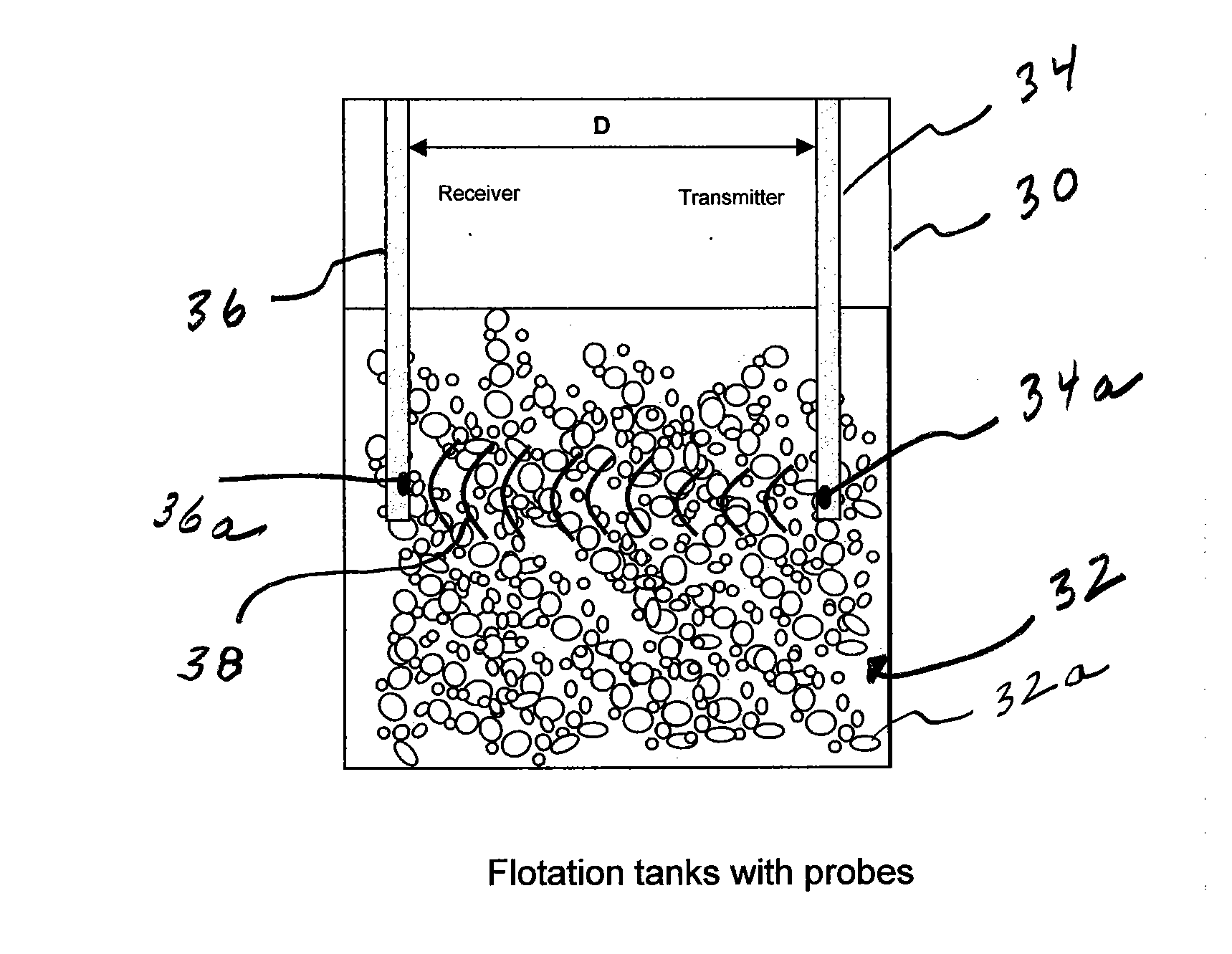
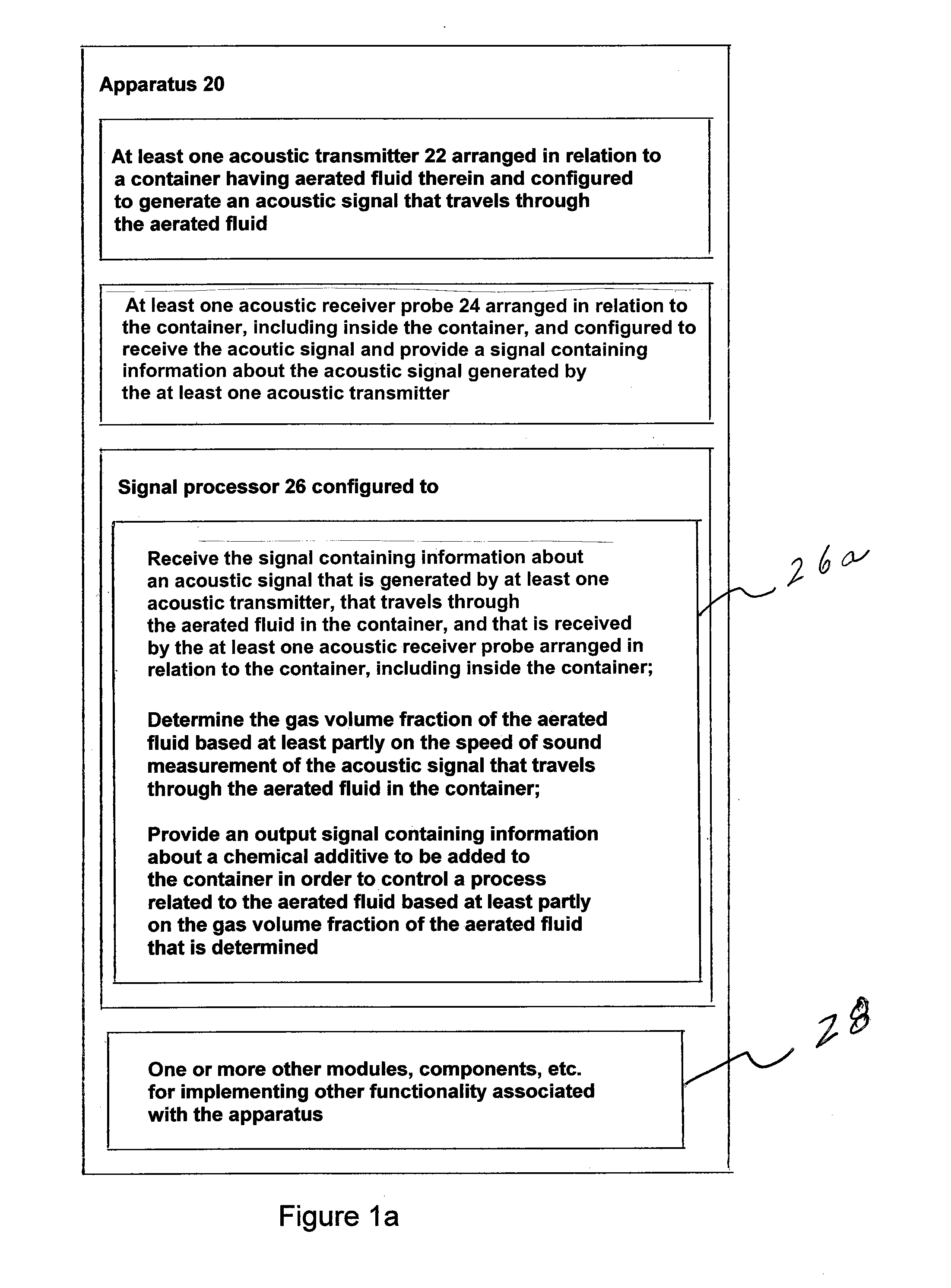
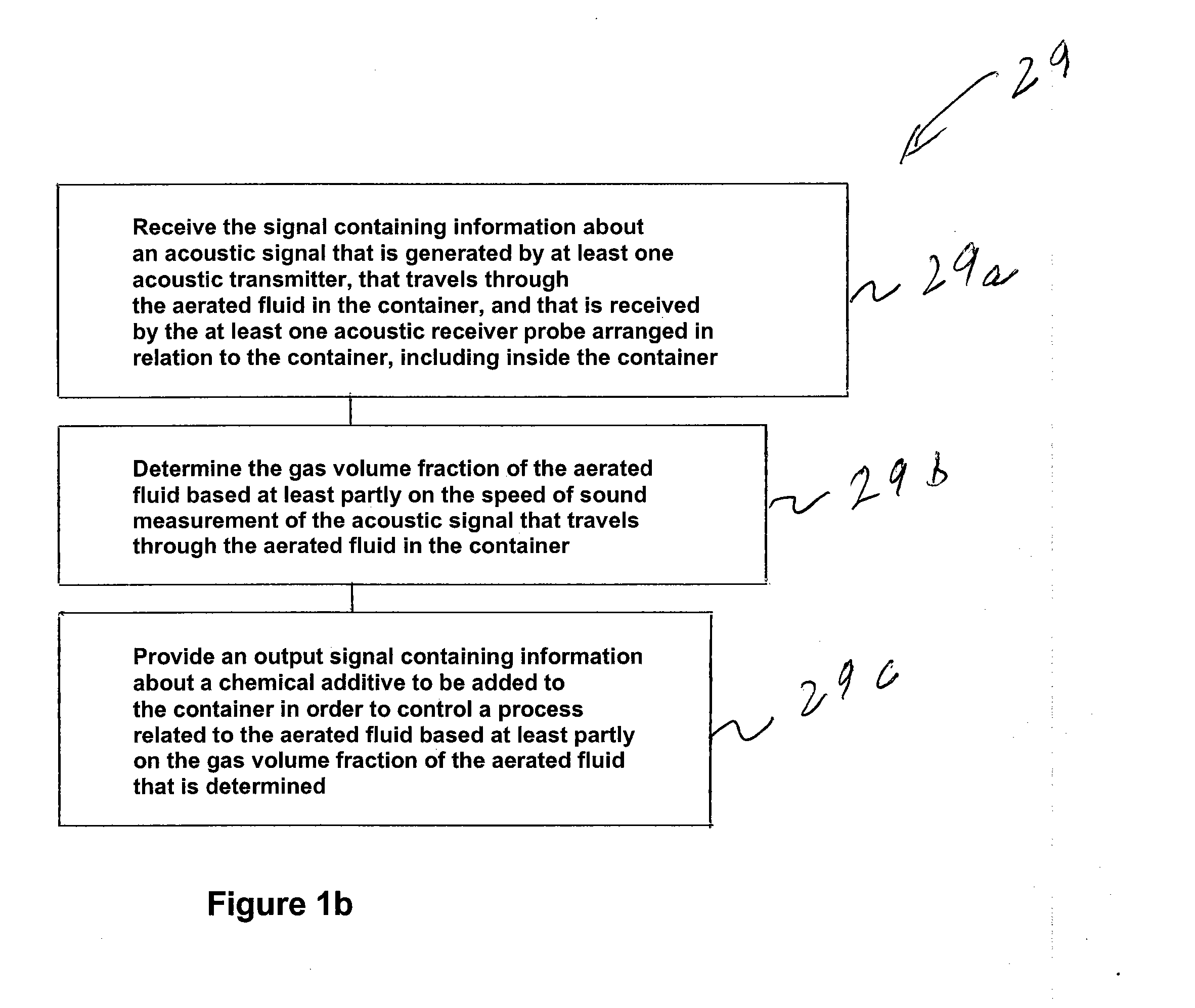
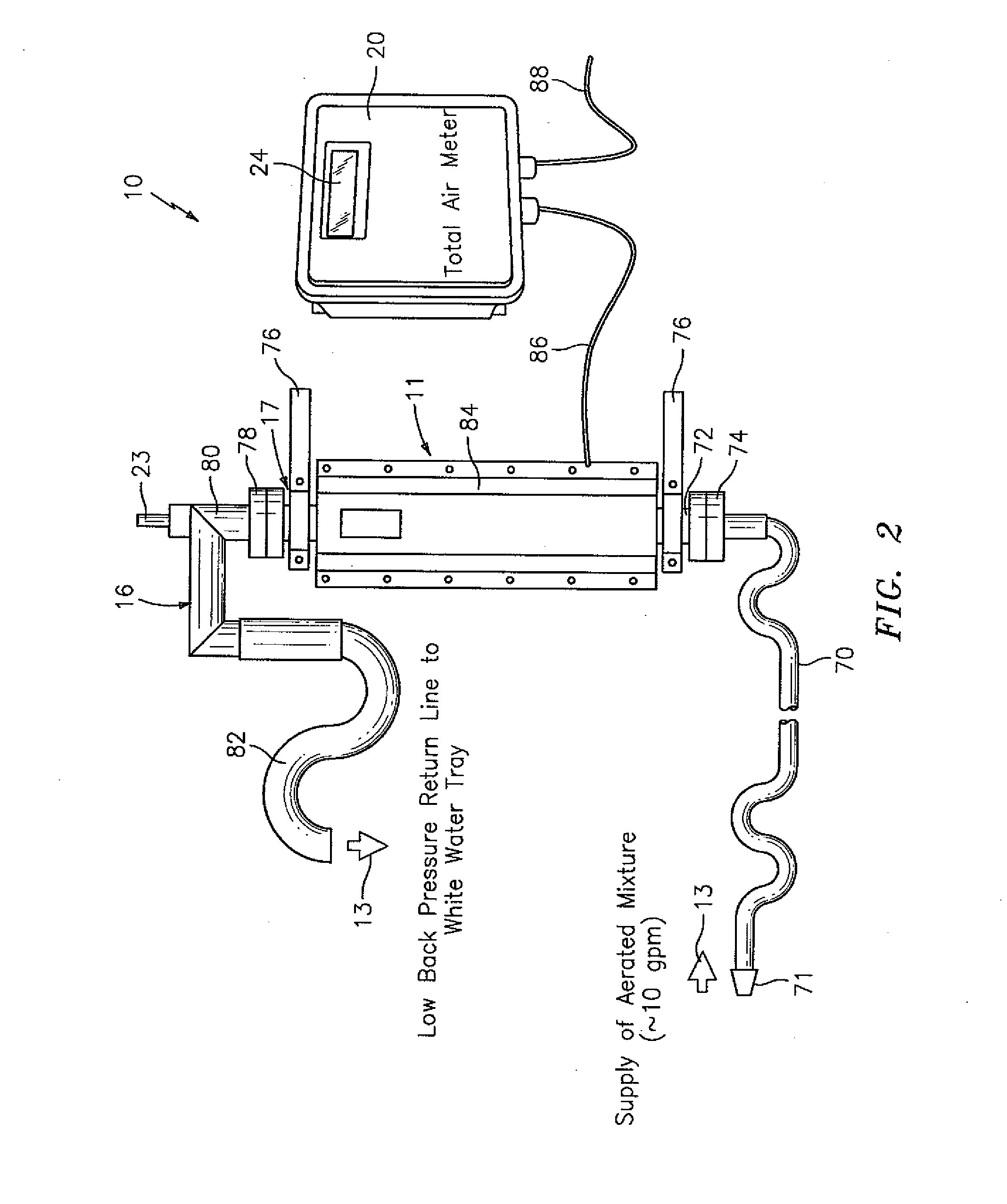
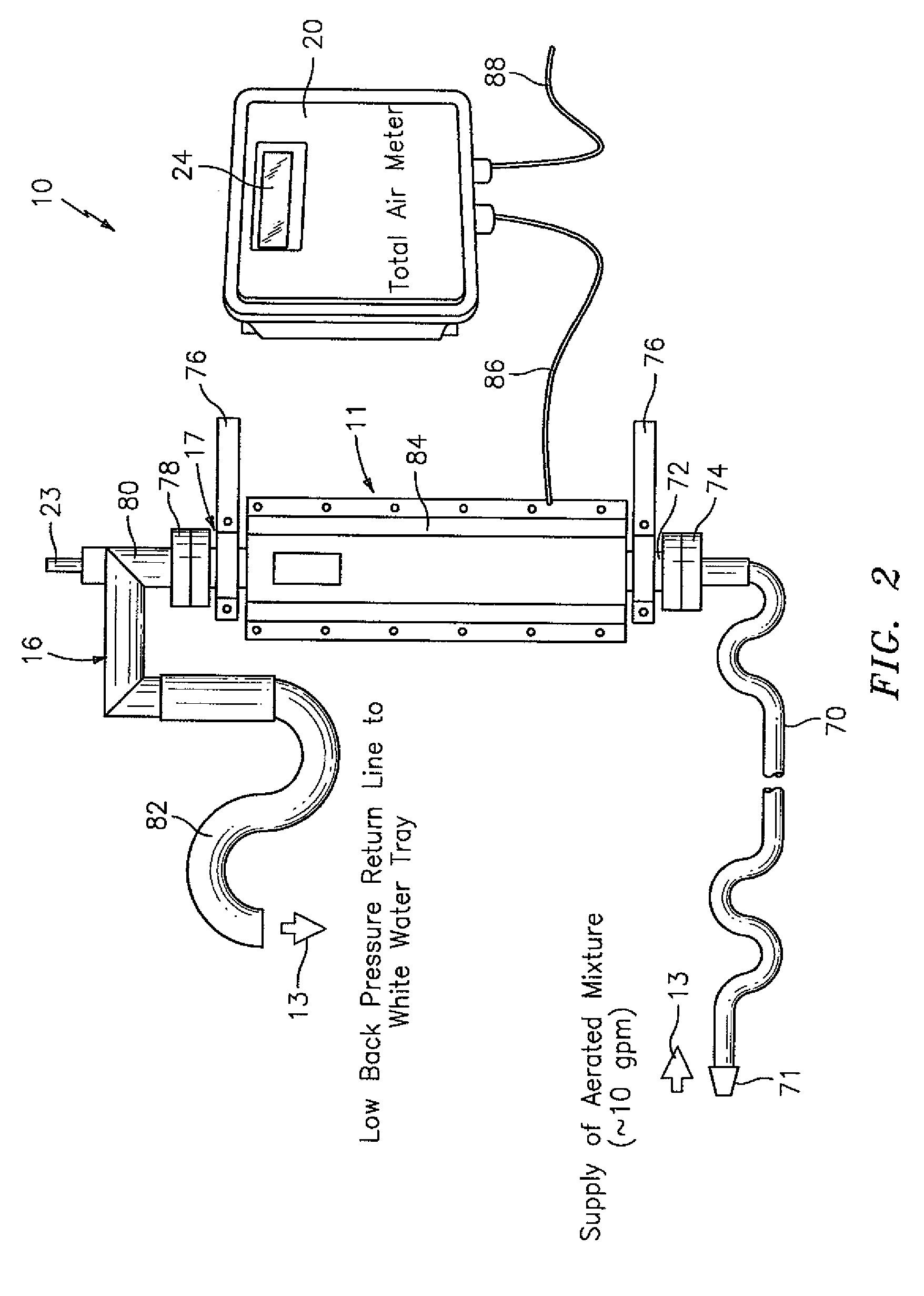
Method and apparatus for determining gvf (gas volume fraction) for aerated fluids and liquids in flotation tanks, columns, drums, tubes, vats
InactiveUS20130192351A1Effective controlImprove breathabilityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesRotating receptacle mixersEngineeringGas volume fraction
The invention provides a signal processor that receives a signal containing information about an acoustic signal that is generated by at least one acoustic transmitter, that travels through an aerated fluid in a container, and that is received by at least one acoustic receiver arranged in relation to the container, including inside the container; and determines the gas volume fraction of the aerated fluid based at least partly on the speed of sound measurement of the acoustic signal that travels through the aerated fluid in the container. The signal processor also sends an output signal containing information about the gas volume fraction of the aerated fluid. The signal processor may be configured together with at least one acoustic transmitter, the at least one acoustic receiver, or both.
Owner:CIDRA CONCRETE SYST INC
Reflective insulating architectural paint for exterior wall and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a reflective insulating architectural paint for an exterior wall, and belongs to the technical field of an exterior wall paint of a building. The reflective insulating architectural paint for the exterior wall comprises the following materials in parts by weight: a proper amount of water, 0.2-0.3 parts of cellulose, 0.15-0.2 parts of pH regulator, 0.5-0.7 parts of dispersing agent, 0.15-0.4 parts of wetting agent, 0.15-0.3 parts of defoamer 1, 18-25 parts of titanium dioxide, 8-12 parts of padding, 2-3 parts of far-infrared ceramic powder (1250 meshes), 0-4 parts of hollow glass microsphere (65 microns), 0-8 parts of hollow glass microsphere (50 microns), 0-6 parts of hollow glass microsphere (40 microns), 20-28 parts of elastic acrylate copolymer emulsion, 0.15-0.3 parts of defoamer 2, 1.0-2.5 parts of anti-freezing agent, 1.0-1.5 parts of coalescing agent, 0.2-0.4 parts of antiseptic and anti-mildew agent, and 1.0-1.5 parts of thickening agent. The reflective insulating architectural paint for the exterior wall disclosed by the invention can be compounded by hollow glass microspheres with different sizes according to a certain ratio. Therefore, the reflective insulating architectural paint can ensure smooth coating surface, high solar reflectivity and good fouling resistance, and also can ensure increase of volume fraction of gas in the coating, so as to greatly improve the thermal insulation performance of the coating.
Owner:SKSHU PAINT
Apparatus and method for providing a fluid cut measurement of a multi-liquid mixture compensated for entrained gas
ActiveUS20060053869A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTesting/calibration apparatusEngineeringPermittivity
An apparatus for determining a fluid cut measurement of a multi-liquid mixture includes a first device configured to sense at least one parameter of the mixture to determine a fluid cut of a liquid in the mixture. A second device is configured to determine a concentration of gas in the mixture in response to a speed of sound in the mixture; and a signal processor is configured to adjust the fluid cut of the liquid using the concentration of the gas to determine a compensated fluid cut of the liquid. The parameter of the mixture sensed by the first device may include a density of the mixture (e.g., by way of a Coriolis meter), a permittivity of the mixture (e.g., by way of a resonant microwave oscillator), or an amount of microwave energy absorbed by the mixture (e.g., by way of a microwave absorption watercut meter). The signal processor may employ different correction factors depending on the type of fluid cut device used. The second device may include a gas volume fraction meter.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Method and apparatus for determining the gas flow rate of a gas-liquid mixture
ActiveUS7240568B2Improves mixing)Avoid layeringVolume/mass flow by differential pressureIndirect mass flowmetersDifferential pressureGas volume fraction
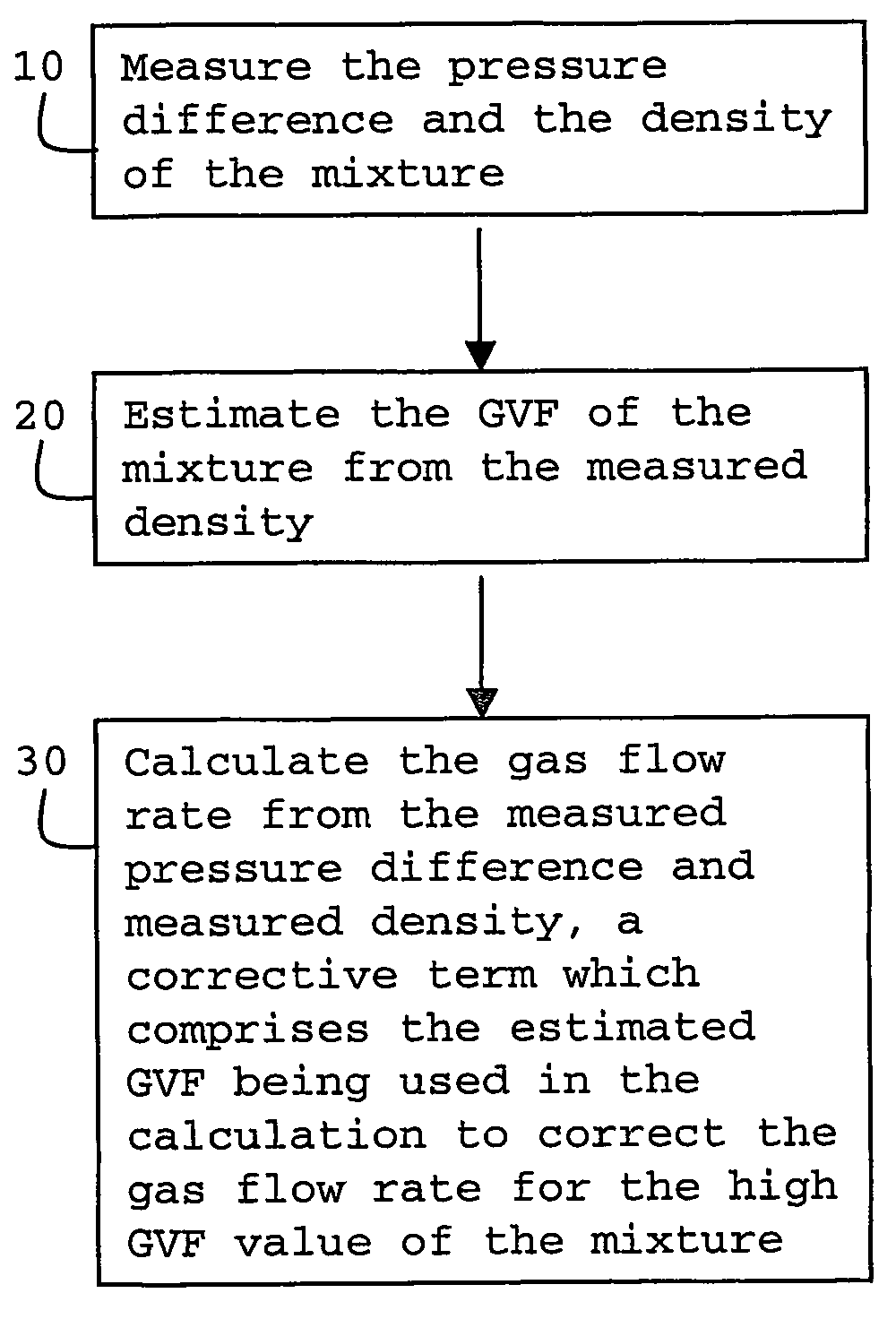
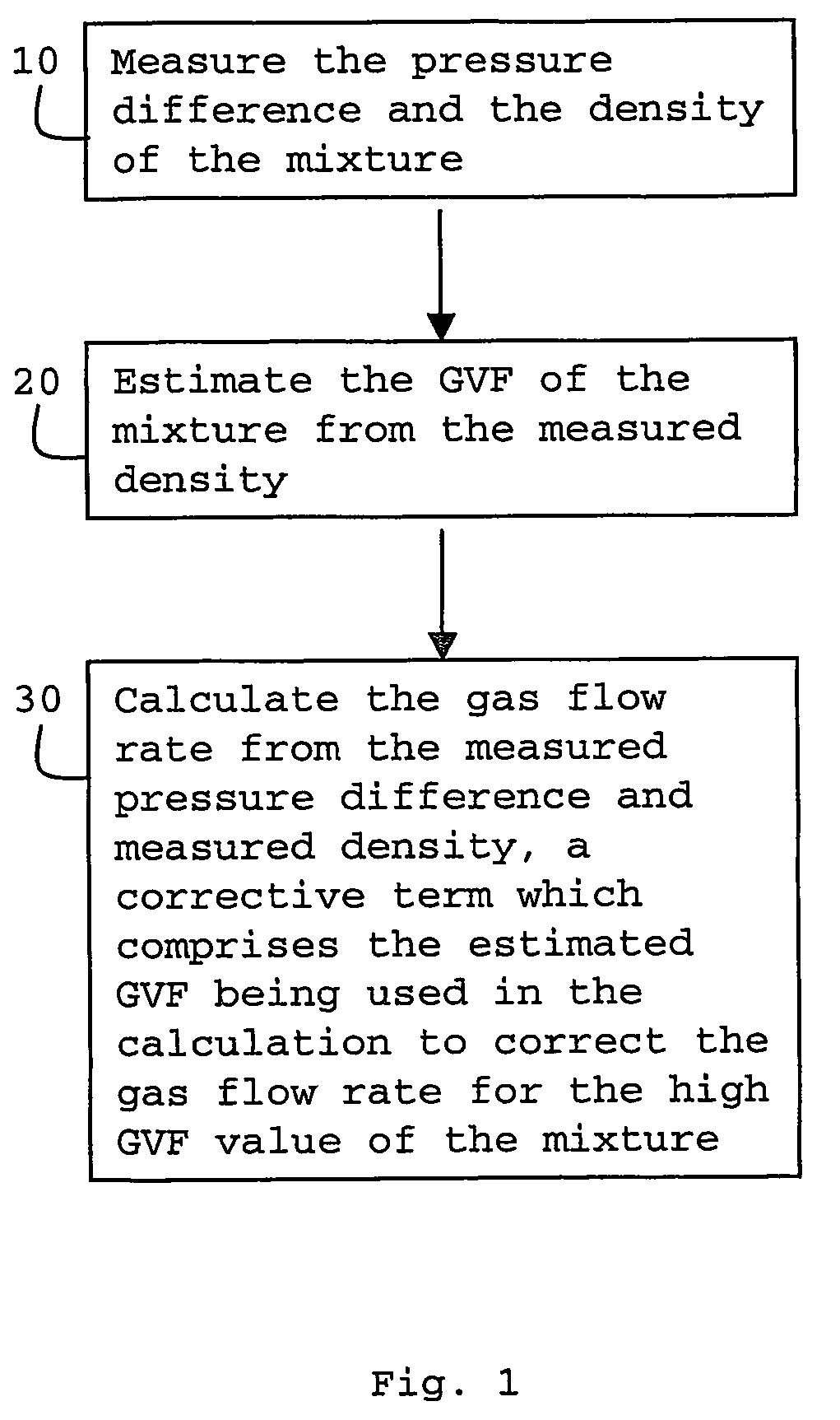
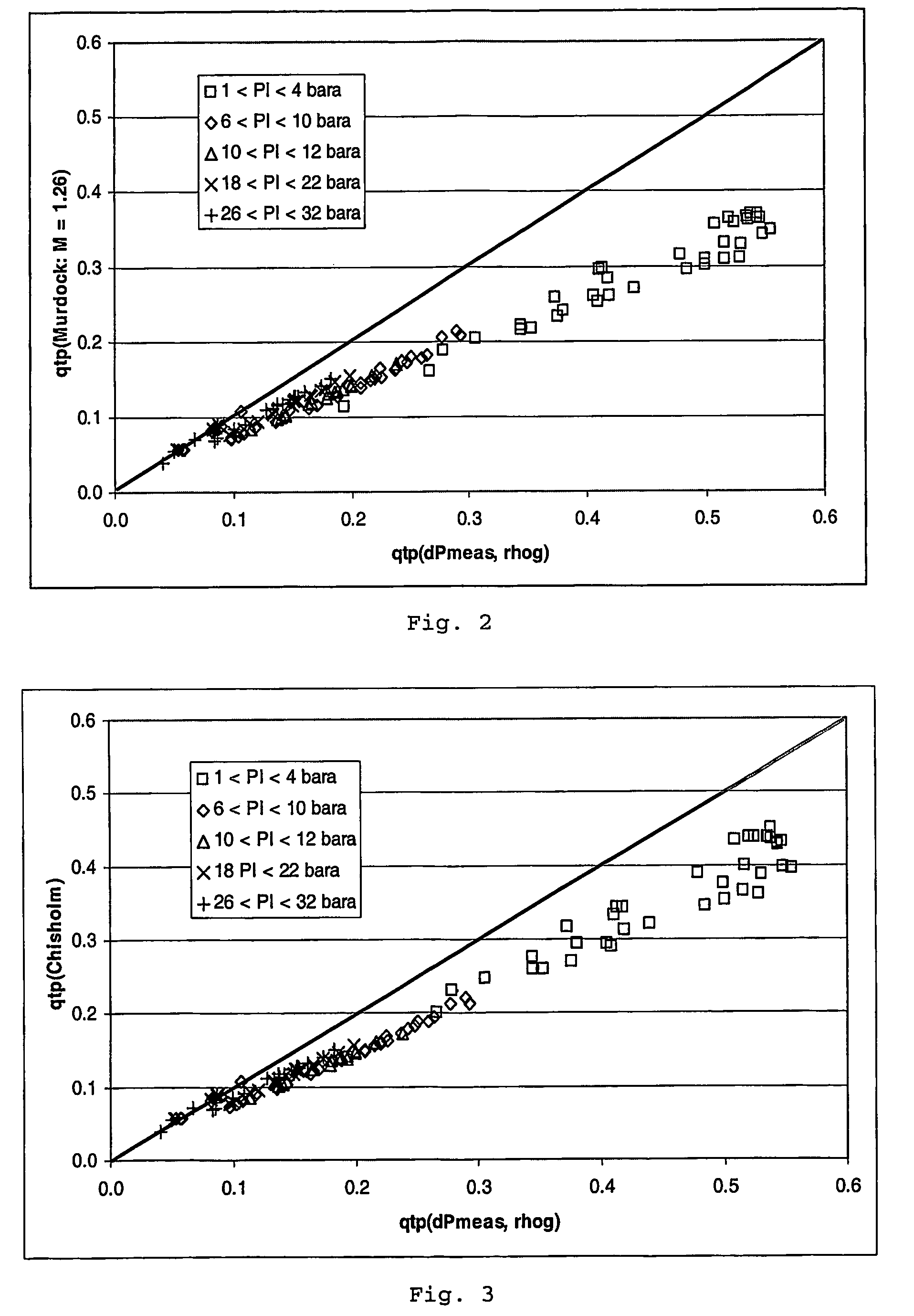
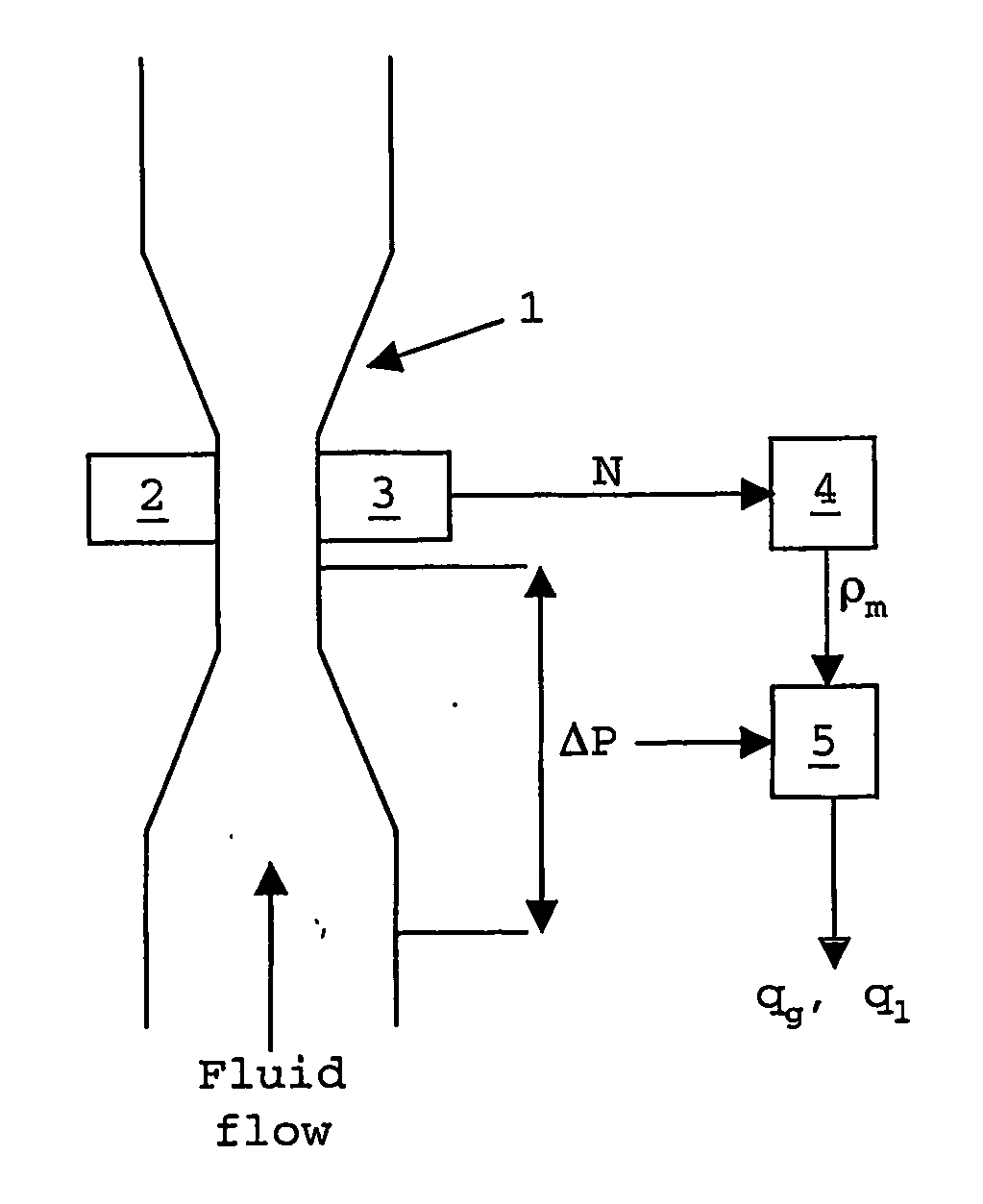
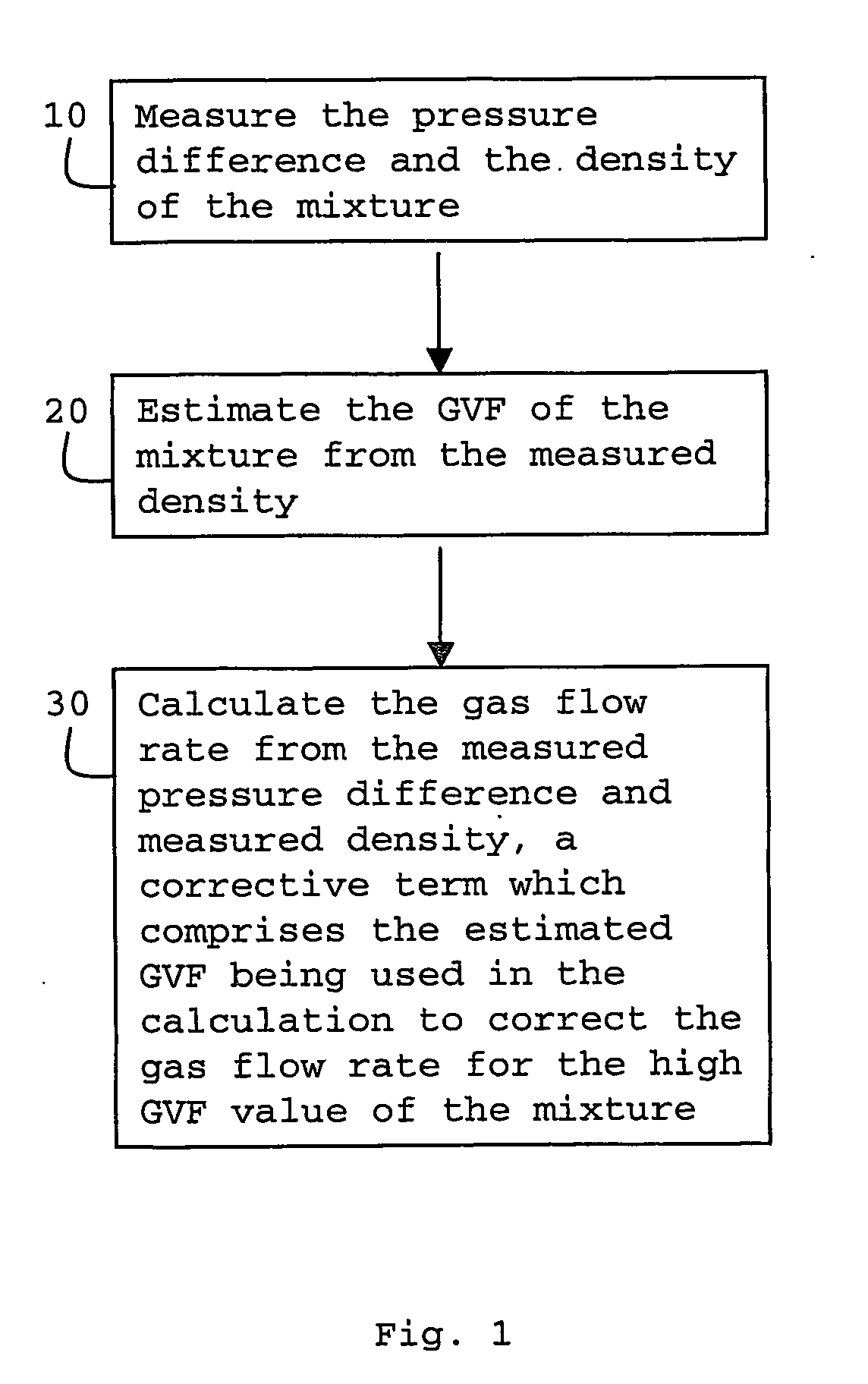
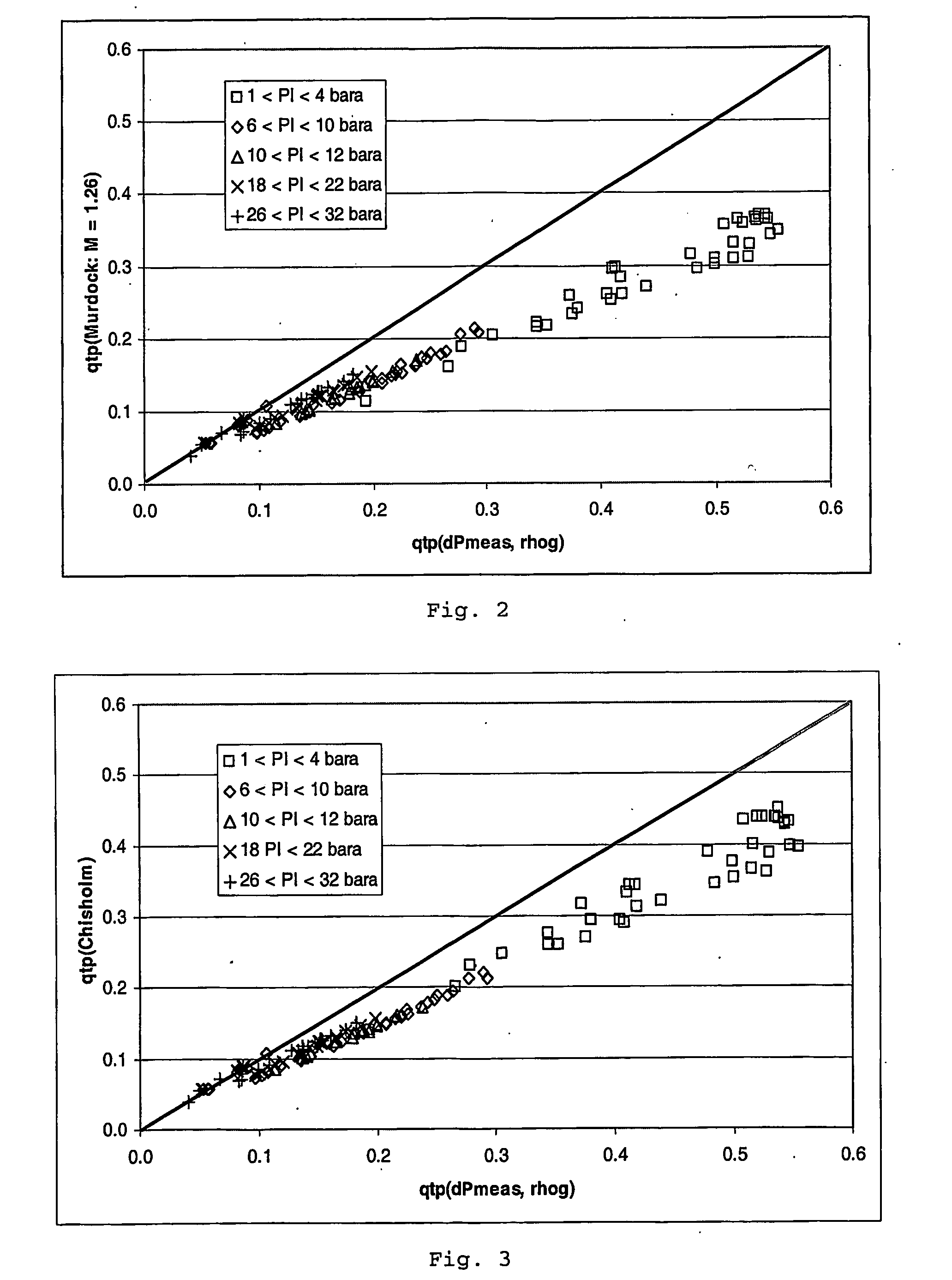
A method and apparatus are provided for determining the gas flow rate of a gas-liquid mixture which has a gas volume fraction (GVF) of at least 85% and which is conveyed along a conduit. The conduit is fitted with a differential pressure flow meter and a fluid densitometer. The method comprises: measuring the pressure difference across the differential pressure flow meter and measuring the density of the mixture using the densitometer; estimating the GVF of the mixture from the measured density; and calculating the gas flow rate from the measured pressure difference and measured density. A corrective term which comprises the estimated GVF is used in the calculation to correct the gas flow rate for the high GVF value of the mixture.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for determing the gas flow rate of a gas-liquid mixture
ActiveUS20060236779A1Improves mixing)Avoid layeringVolume variation compensation/correction apparatusVolume/mass flow by differential pressureDifferential pressureStream flow
A method and apparatus are provided for determining the gas flow rate of a gas-liquid mixture which has a gas volume fraction (GVF) of at least 85% and which is conveyed along a conduit. The conduit is fitted with a differential pressure flow meter and a fluid densitometer. The method comprises: measuring the pressure difference across the differential pressure flow meter and measuring the density of the mixture using the densitometer; estimating the GVF of the mixture from the measured density; and calculating the gas flow rate from the measured pressure difference and measured is used in the calculation to correct the gas flow rate for the high GVF value of the mixture.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Immersion probe using ultraviolet and infrared radiation for multi-phase flow analysis
ActiveUS20130016336A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingRadiation pyrometryInfraredUltraviolet
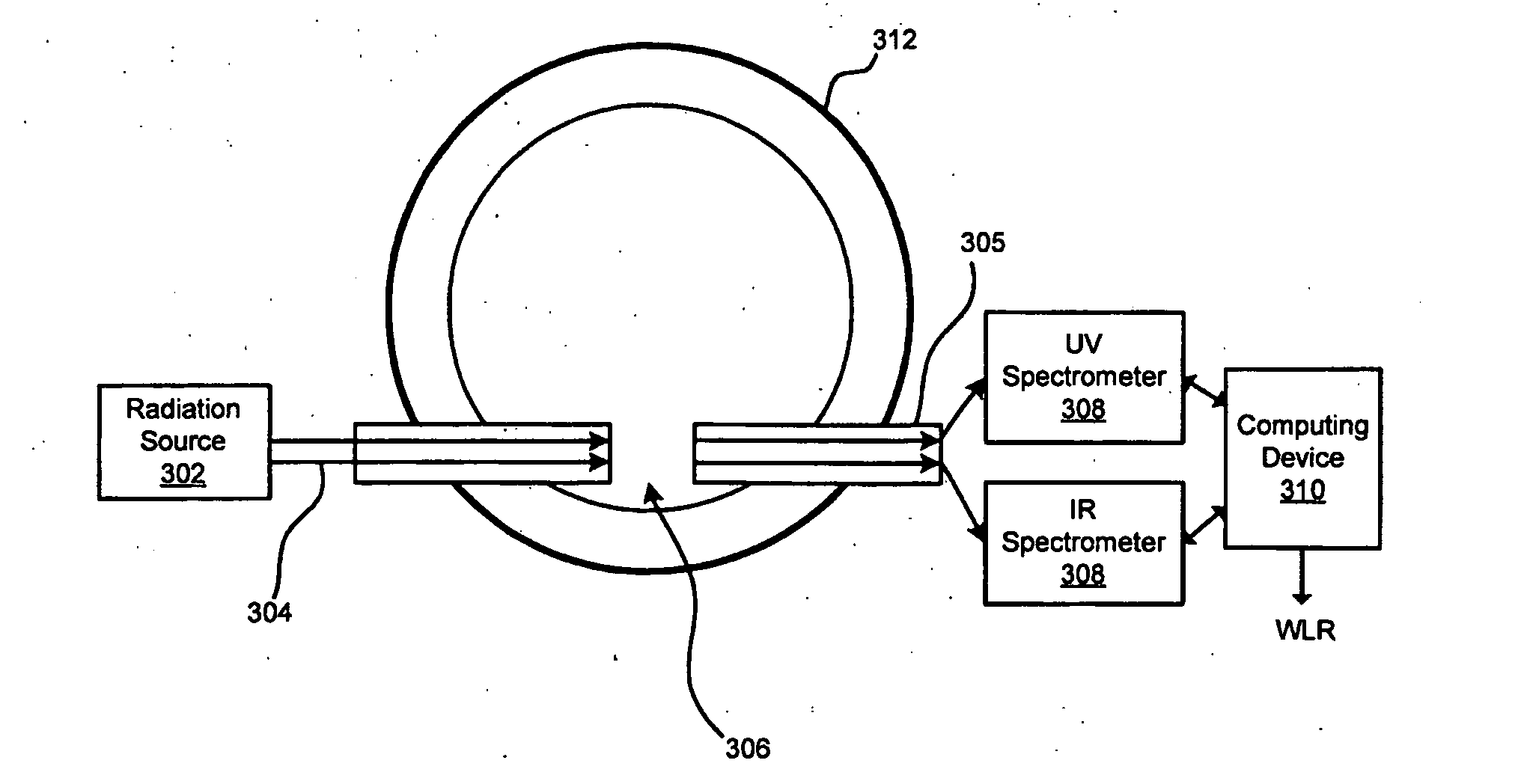
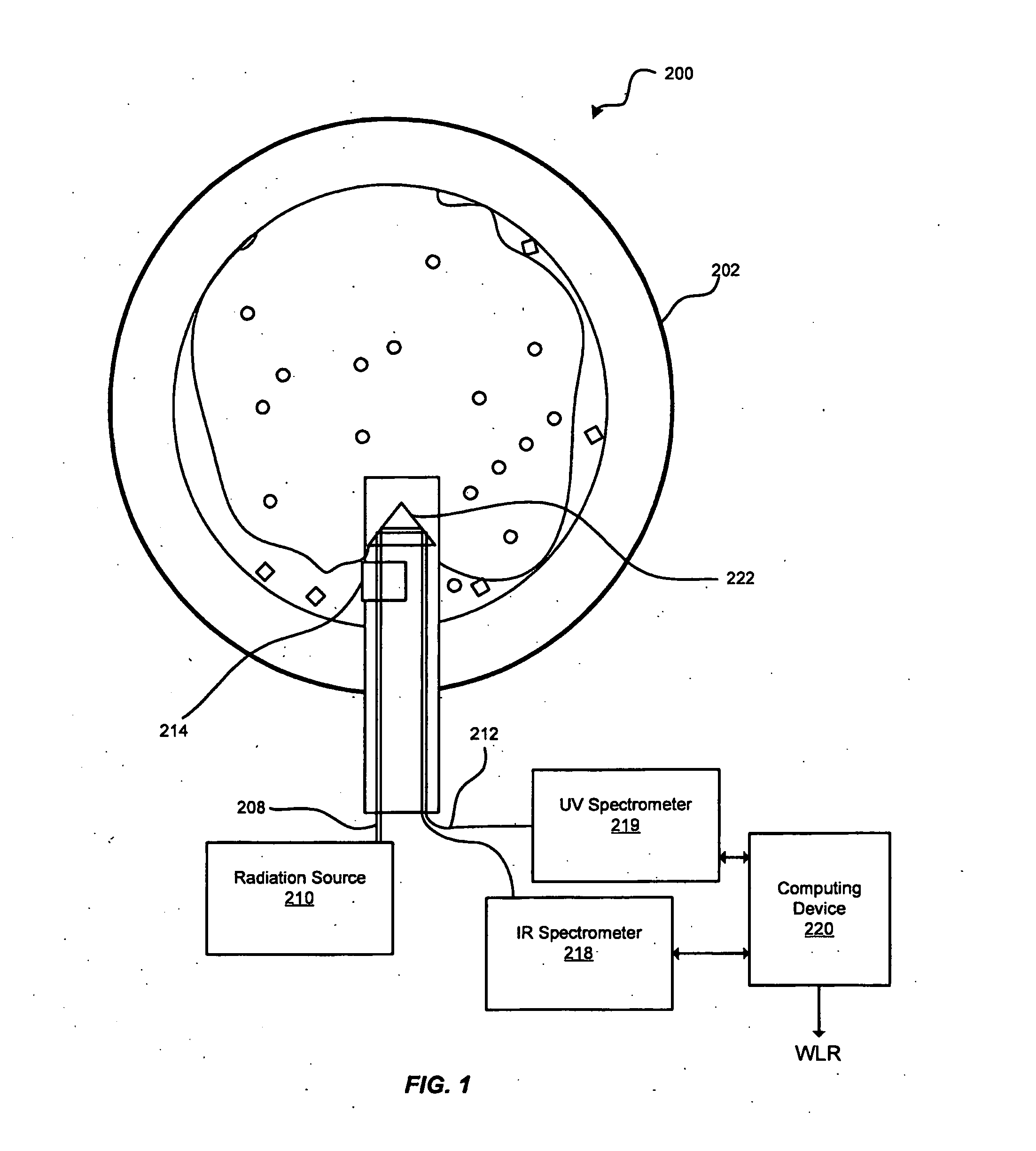
A system and method for determining characteristics of a multiphase flow in a well / pipe are disclosed. The disclosed system and method use an optical immersion probe including a flow gap across which two or more types of radiation are transmitted in order to measure absorptions of two or more substances within the multiphase flow. Primarily, broadband ultraviolet (UV) and / or near infrared radiations (NIR) are utilized with the probe to gather absorption data at and / or around at least one of the water peaks and at and / or around one or more oil or oil-condensate peaks. This data may be utilized to calculate the water-cut of the multiphase flow over a wider range of gas volume fractions. Additionally, pressure ports having pressure sensors being located on the optical immersion probe for determining the impact pressures and flow rates of different phases of the multiphase flow may also be used.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Multiphase fluid characterization system
ActiveUS8820147B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTesting/calibration for volume flowUltrasound attenuationResonance
A measurement system and method for permitting multiple independent measurements of several physical parameters of multiphase fluids flowing through pipes are described. Multiple acoustic transducers are placed in acoustic communication with or attached to the outside surface of a section of existing spool (metal pipe), typically less than 3 feet in length, for noninvasive measurements. Sound speed, sound attenuation, fluid density, fluid flow, container wall resonance characteristics, and Doppler measurements for gas volume fraction may be measured simultaneously by the system. Temperature measurements are made using a temperature sensor for oil-cut correction.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Multiphase flowmeter for subsea applications
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Apparatus and method of measuring gas volume fraction of a fluid flowing within a pipe
ActiveUS20070044571A1Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesEngineeringGas volume fraction
A clamp on apparatus10,110 is provided that measures the speed of sound or acoustic disturbances propagating in a fluid or mixture having entrained gas / air to determine the gas volume fraction of the flow 12 propagating through a pipe 14. The apparatus includes an array of pressure sensors clamped onto the exterior of the pipe and disposed axially along the length of the pipe. The apparatus measures the speed of sound propagating through the fluid to determine the gas volume fraction of the mixture using adaptive array processing techniques to define an acoustic ridge in the k-ω plane. The slope of the acoustic ridge 61 defines the speed of sound propagating through the fluid in the pipe.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Tracer-gas-volume-fraction-based integral measurement and calculation method for air leakage of working face behind support
InactiveCN106568553AImprove accuracySimple methodDetection of fluid at leakage pointComponent separationUltrasound attenuationAir volume
The invention discloses a tracer-gas-volume-fraction-based integral measurement and calculation method for an air leakage of a working face behind a support. At a lower corner angle of a working face, tracer gas is released to a place with the certain depth in a goaf region near the lower corner angle of the working face at a constant amount; gas is extracted from gaps between supports by using gas measuring pipes at certain intervals along the working face length direction; a tracer gas volume fraction at a measuring point is analyzed; a tracer gas volume fraction distribution curve after supports is drawn, wherein a horizontal coordinate region included under the curve is a goaf facing working face tunnel air-leak region. With the integral method, the area encircled by the tracer gas volume fraction curve is solved and a tracer gas volume fraction of goaf air-leak attenuation is obtained; the attenuation tracer gas volume is divided by the tracer gas volume fraction to obtain a total air leak value of leaking in the goaf of the U-shaped ventilating working face. A ratio value of all segments of tracer gas volume fractions to volume fractions after integration is multiplied by the total air leak value of the goaf to obtain all air leak values of the working face.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Total gas meter using speed of sound and velocity measurements
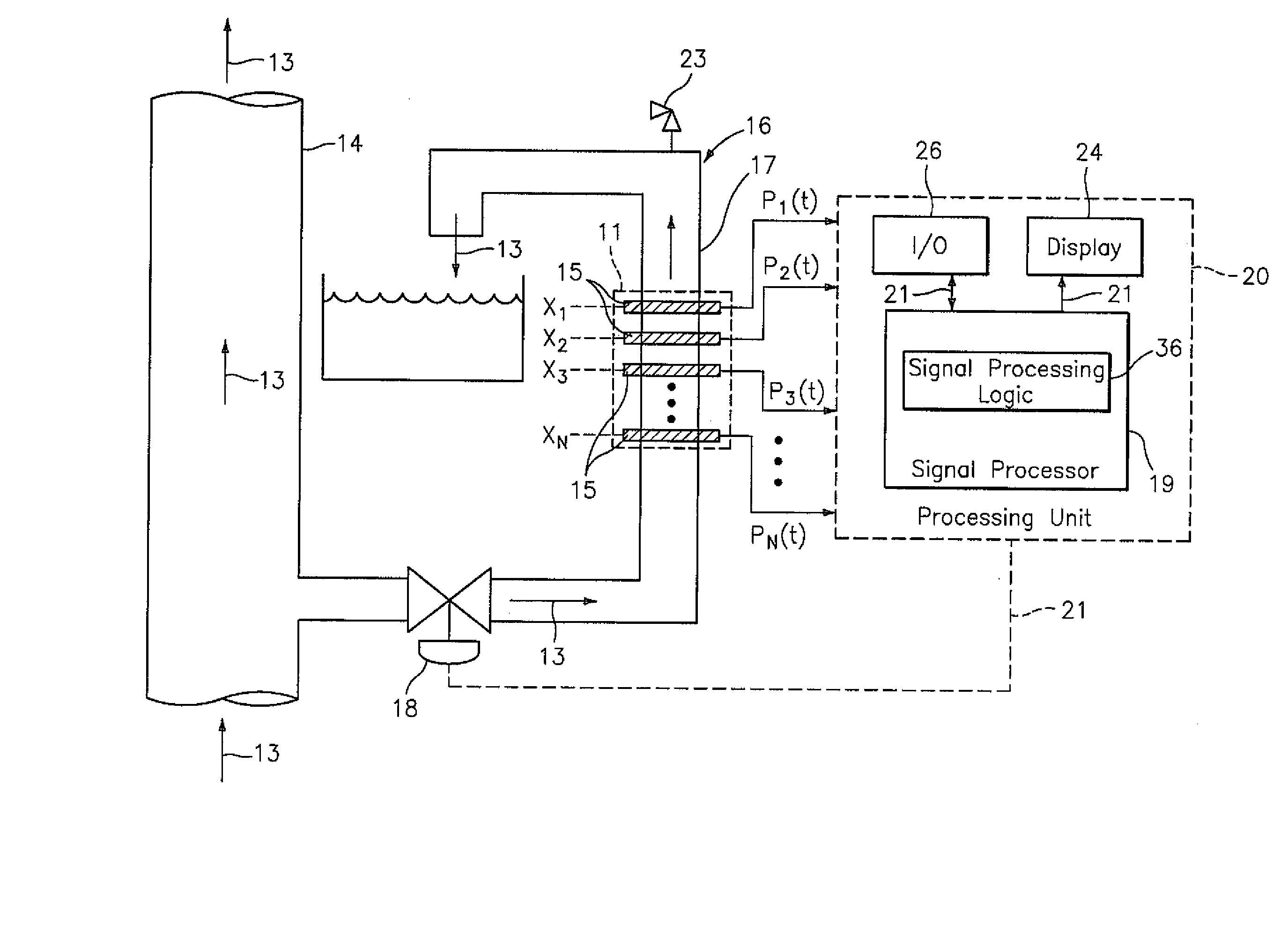
ActiveUS20070234780A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume/mass flow measurementLine tubingMeasurement point
An apparatus is provided for measuring total gas content of a fluid flowing through a process line. The apparatus comprises a bleed line in fluid communication with the process line for bleeding a portion of the fluid from the process line at a bleed line pressure that is lower than the process line pressure. A speed of sound propagating through the fluid in the bleed line is determined and is, in turn, used to determine a gas volume fraction of the fluid in the bleed line. In one aspect, the total gas content of the fluid flowing through the process line is calculated as a function of the gas volume fraction of the fluid in the bleed line and a velocity of the fluid in the bleed line. In another aspect, the velocity of the fluid in the bleed line is adjusted to be approximately equal to a predetermined velocity. In yet another aspect, dissolved gas in the process fluid 13 is released before the gas content measurement point by applying a high intensity ultrasonic field to the fluid 13.
Owner:CIDRA CORP SERVICES
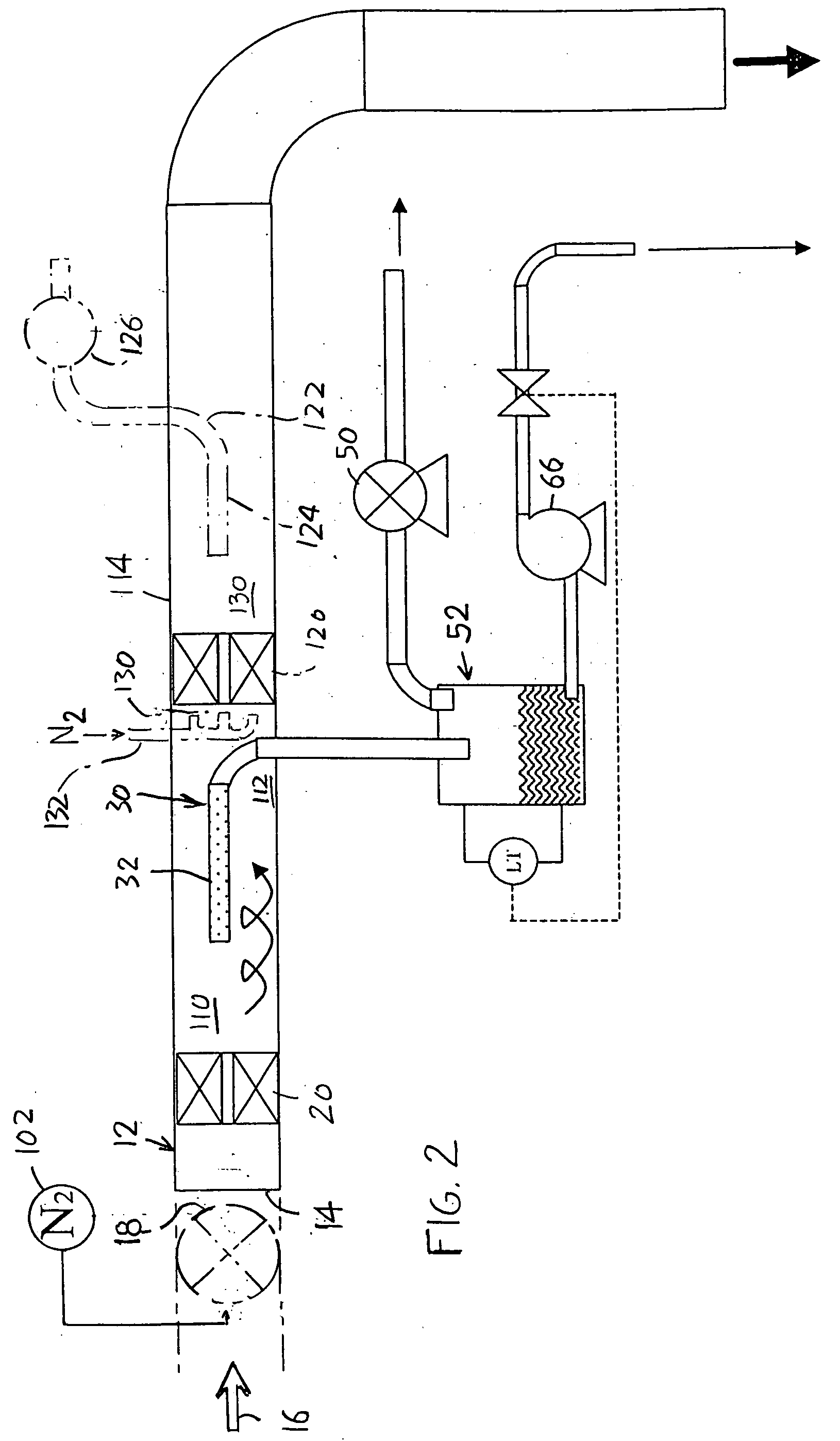
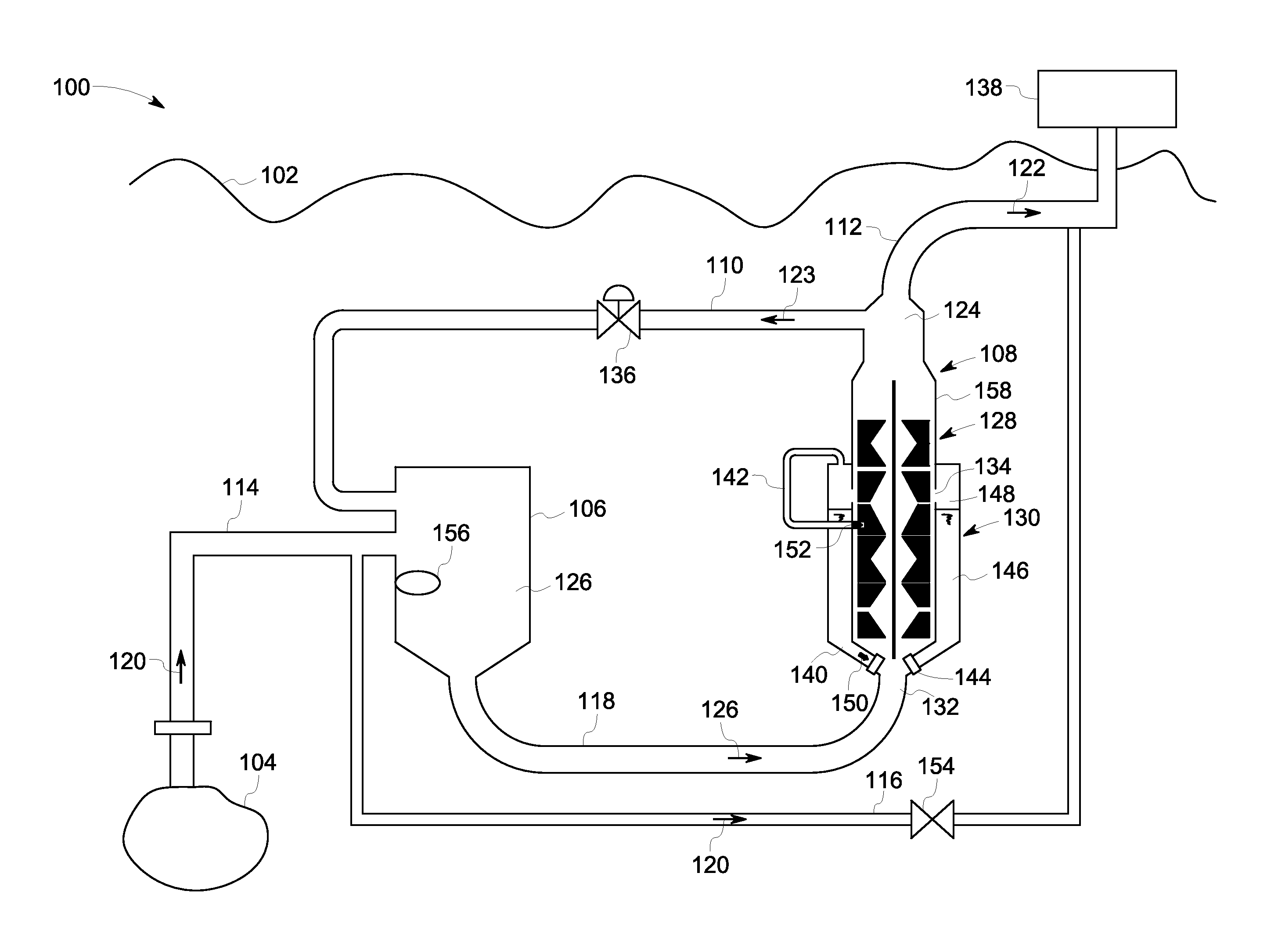
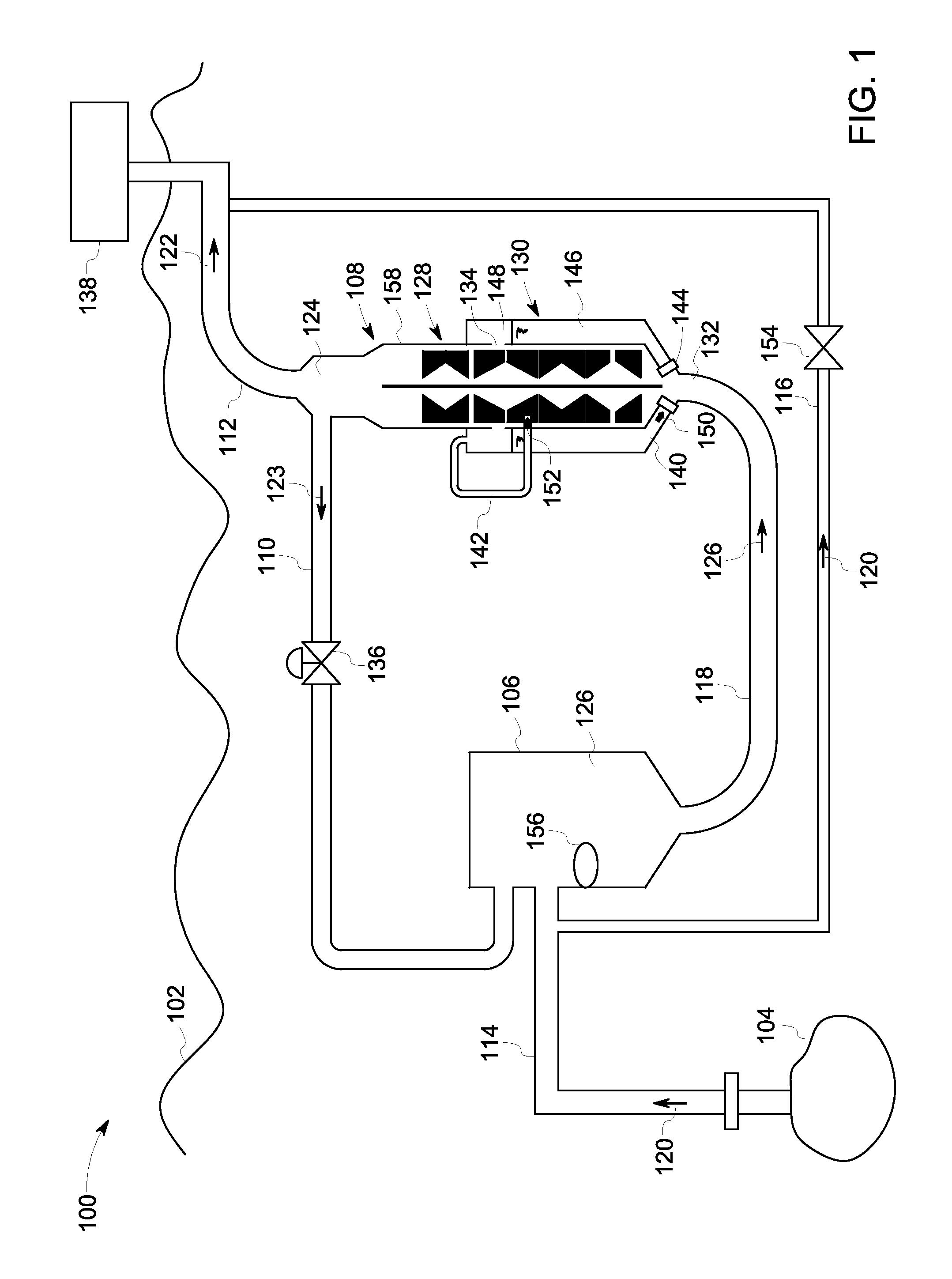
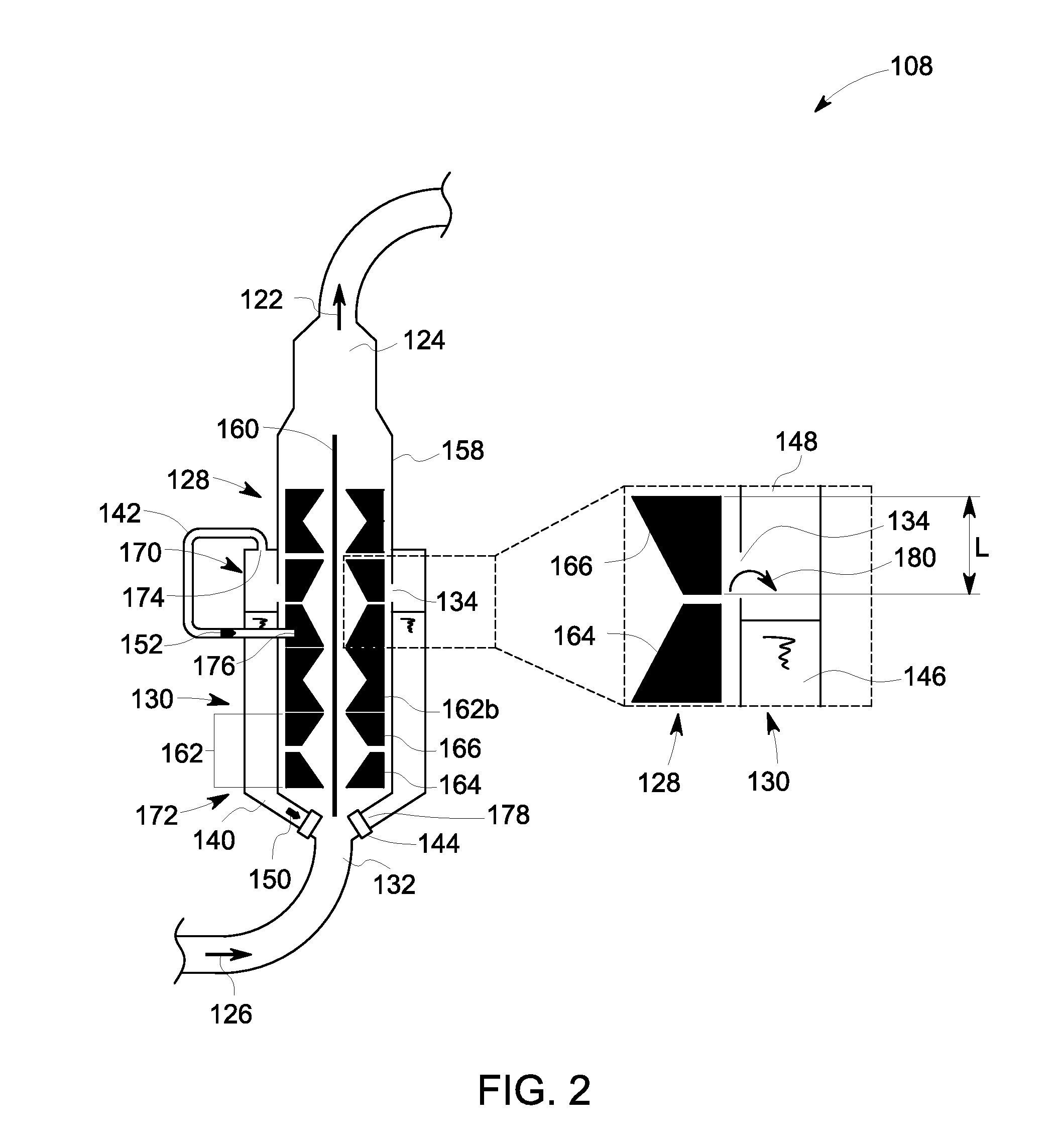
Gas/liquid separation in water injection into hydrocarbon reservoir
InactiveUS20050120879A1Reduce oxygenLow oxygenLiquid degasificationWater/sewage treatment by degassingDissolutionOxygen
A stream of primarily water is treated to remove oxygen before injecting the water into an underground hydrocarbon reservoir. The pressure of water moving through a conduit (12) is reduced to a low level to maximize the dissolution of oxygen and other gases that are dissolved in the water. The resulting two phase mixture is separated by centrifugal action caused by rotating the water inside the conduit. The rotation is induced by flowing the water past fixed spin blades (20). The oxygen and any other gases are removed from the center of the conduit through a gas pipe (30) and eventually pass out of the system to the atmosphere via a vacuum pump (50). As an enhancement, nitrogen may be introduced upstream of the centrifuge. The nitrogen injection saturates the water-gas solution to improve the dissolution of oxygen from the low pressure water, and also improves the efficiency of the gas-liquid separation by adjusting the gas volume fraction downstream of the fixed spin blades (20) to an optimal proportion of the total flow.
Owner:SINGLE BUOY MOORINGS NC
Subsea fluid processing system with intermediate re-circulation
InactiveUS20160138595A1Easy to handleIncrease gas volumeFluid removalPump controlOcean bottomEngineering
A fluid processing system is provided containing a pump and a fluid reservoir. The pump includes a casing, one or more pump stages, a pump inlet, and a pump outlet. The casing includes one or more slots, with at least one slot configured to extract at least a portion of a multiphase fluid flowing within the pump. The fluid reservoir encompasses at least a portion of the casing and is configured to receive and separate the portion of the multiphase fluid into an extracted liquid phase and an extracted gaseous phase. The fluid reservoir includes a re-circulation conduit disposed proximate to the pump inlet and a discharge device coupled to the re-circulation conduit. The discharge device regulates re-circulation of at least a portion of the extracted liquid phase to the pump via the pump inlet for reducing a gas volume fraction of the multiphase fluid being fed to the pump.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cyclone separator for high gas volume fraction fluids
ActiveUS20120227585A1High heavy fraction/medium fraction separation efficienciesIncrease in sizeLiquid degasificationReversed direction vortexCycloneEngineering
A cyclone separator for separating a heavy fraction from a multiphase fluid comprising a mixture of the heavy fraction, a medium fraction and a light fraction includes an elongated cyclone tube which comprises a fluid inlet, a heavy fraction outlet and a flow bore that extends between the fluid inlet and the heavy fraction outlet. A mandrel is positioned concentrically within the cyclone tube and comprises a light fraction outlet that extends generally axially therethrough and an outer diameter surface that together with the cyclone tube defines an annular flow path for the multiphase fluid which extends between the fluid inlet and the flow bore. The outer diameter surface comprises a generally cylindrical section which extends from proximate the fluid inlet to a convergence section which extends toward an outlet port that connects the light fraction outlet with the flow bore, and the mandrel further comprises a plurality of outlet holes which extend through the convergence section between the flow path and the light fraction outlet.
Owner:FMC SEPARATION SYST BV
Total gas meter using speed of sound and velocity measurements
ActiveUS7617716B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume/mass flow measurementLine tubingMeasurement point
An apparatus is provided for measuring total gas content of a fluid flowing through a process line. The apparatus comprises a bleed line in fluid communication with the process line for bleeding a portion of the fluid from the process line at a bleed line pressure that is lower than the process line pressure. A speed of sound propagating through the fluid in the bleed line is determined and is, in turn, used to determine a gas volume fraction of the fluid in the bleed line. In one aspect, the total gas content of the fluid flowing through the process line is calculated as a function of the gas volume fraction of the fluid in the bleed line and a velocity of the fluid in the bleed line. In another aspect, the velocity of the fluid in the bleed line is adjusted to be approximately equal to a predetermined velocity. In yet another aspect, dissolved gas in the process fluid 13 is released before the gas content measurement point by applying a high intensity ultrasonic field to the fluid 13.
Owner:CIDRA CORP SERVICES
Chemical-looping combustion system of parallel fluidized bed
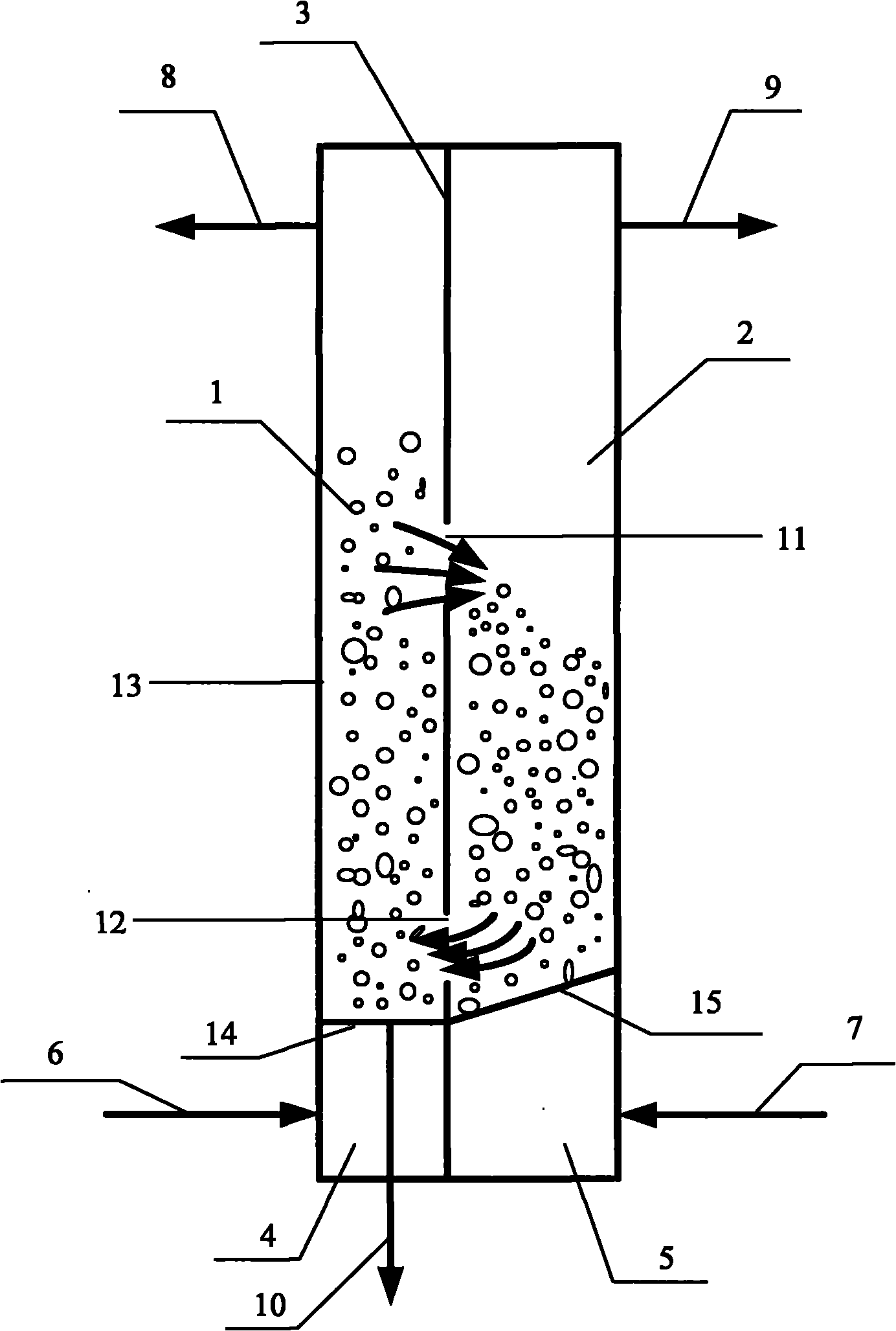
InactiveCN101865458ASolve the oxygen carrying capacitySolve problems such as insufficient heatFluidized bed combustionIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationCombustion systemEngineering
The invention belongs to a chemical-looping combustion system of a parallel fluidized bed in the technical field of clean combustion and efficient use of fuel. A cylinder of the parallel fluidized bed is divided into two cavities by a partition plate, one cavity is of a fuel reactor, and the other cavity is of an air reactor; and a hole a and a hole b are arranged on the partition plate, and materials pass through the hole a and the hole b on the partition plate to carry out the exchange of matter and energy. The system breaks the design idea of the interconnected fluidized bed of the more traditional chemical-looping combustion device, and adopts the concept of the parallel fluidized bed; the partition plate is used for partitioning the air reactor from the fuel reactor, and oxygen carriers are transferred between the two reactors only by the partition plate; the transfer distance and the transfer resistance are reduced, so that the transfer amount of the oxygen carriers can be ensured; and the volume fraction of gas flowing into the air reactor from the fuel reactor is within 5 to 10%, and the conversion rate of the fuel is 95%. The chemical-looping combustion reactor of the parallel fluidized bed is easy to enlarge the scale.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com