Patents
Literature
339 results about "Array processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
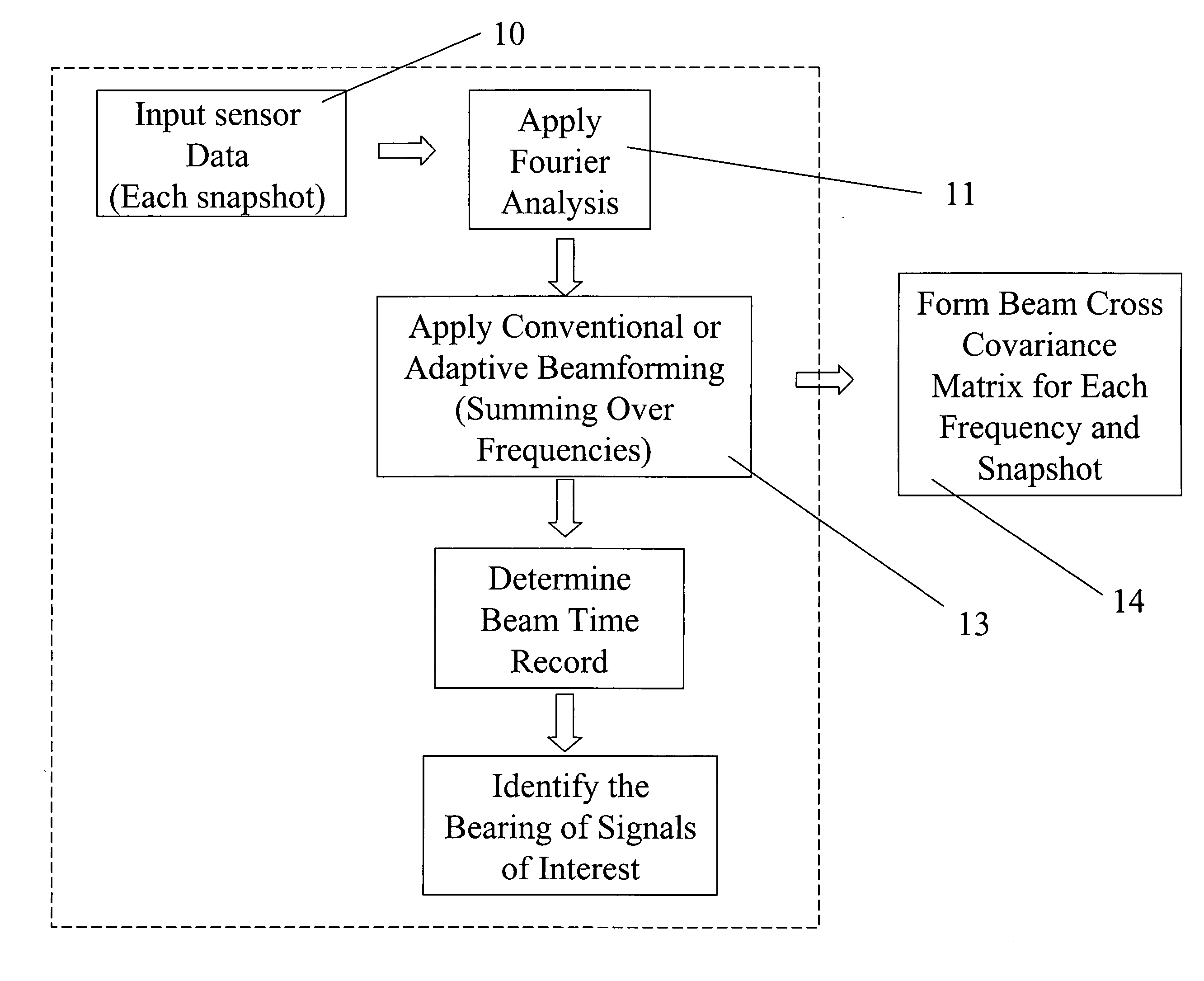
Array processing is a wide area of research in the field of signal processing that extends from the simplest form of 1 dimensional line arrays to 2 and 3 dimensional array geometries. Array structure can be defined as a set of sensors that are spatially separated, e.g. radio antenna and seimic arrays. The sensors used for a specific problem may vary widely, for example microphones, accelerometers and telescopes. However, many similarities exist, the most fundamental of which may be an assumption of wave propagation. Wave propagation means there is a systemic relationship between the signal received on spatially separated sensors. By creating a physical model of the wave propagation, or in machine learning applications a training data set, the relationships between the signals received on spatially separated sensors can be leveraged for many applications.
Multicarrier Sub-Layer for Direct Sequence Channel and Multiple-Access Coding
InactiveUS20070211786A1Low costImprove system performanceSecret communicationMultiplex code generationUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
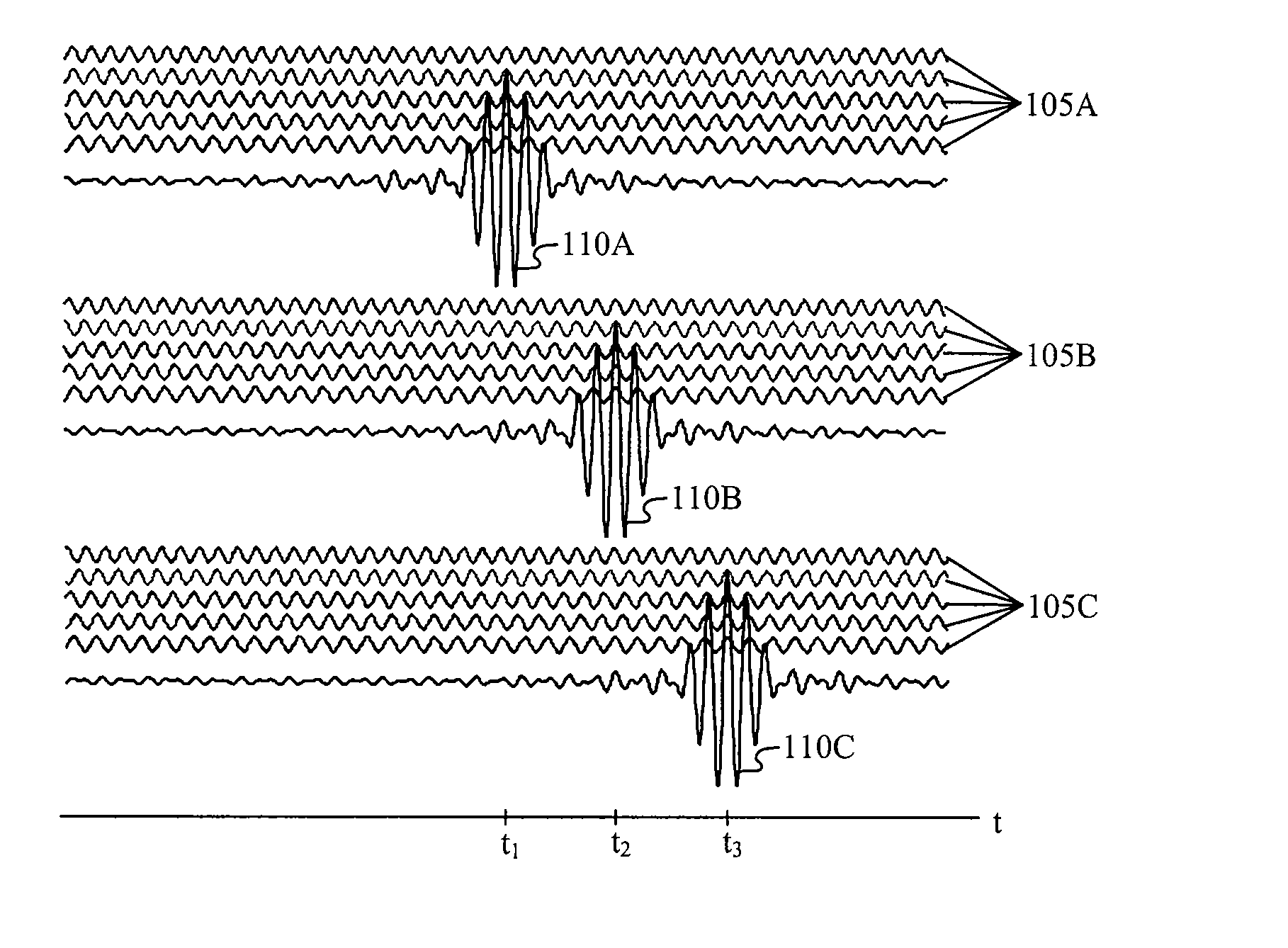
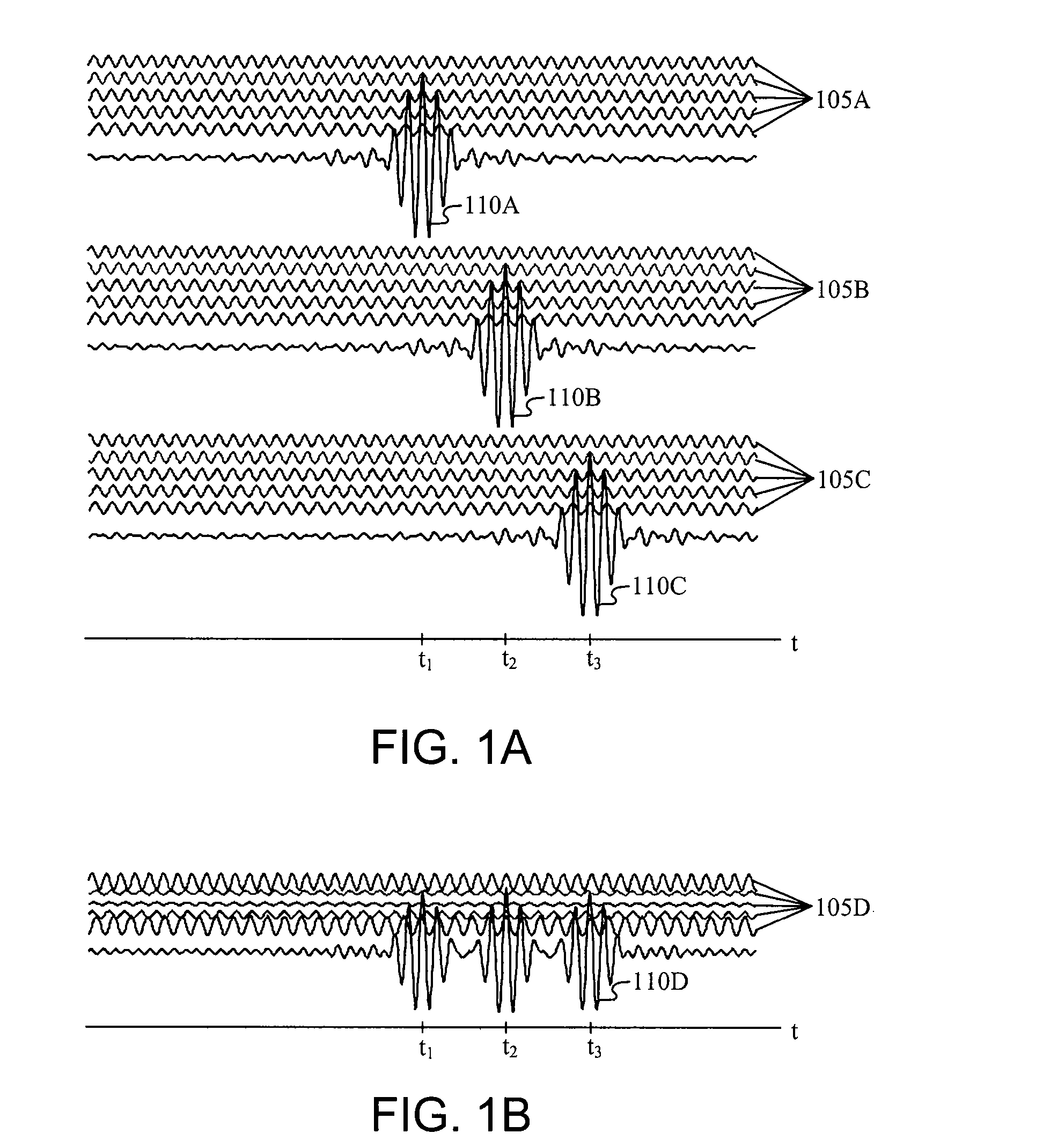
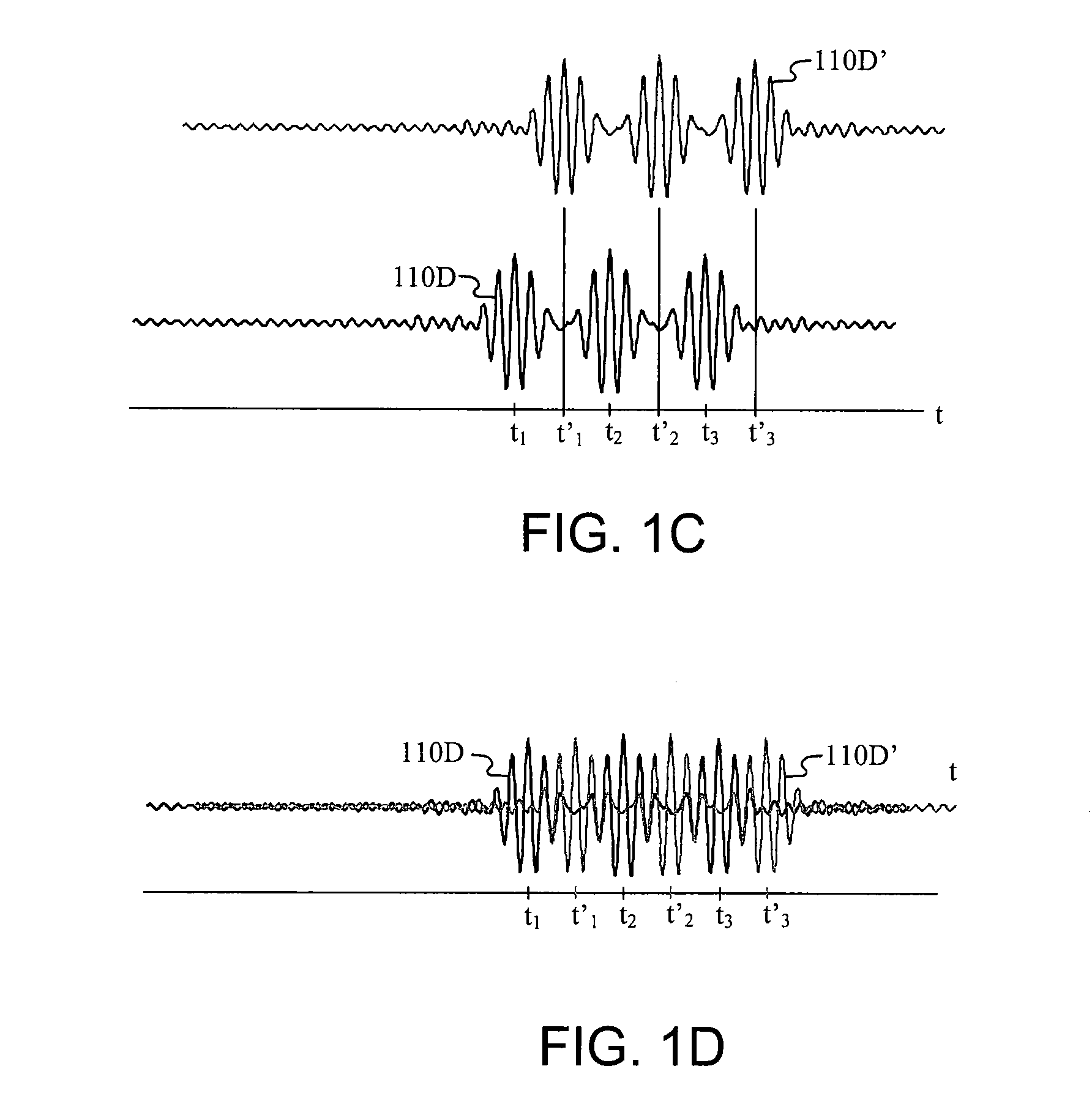
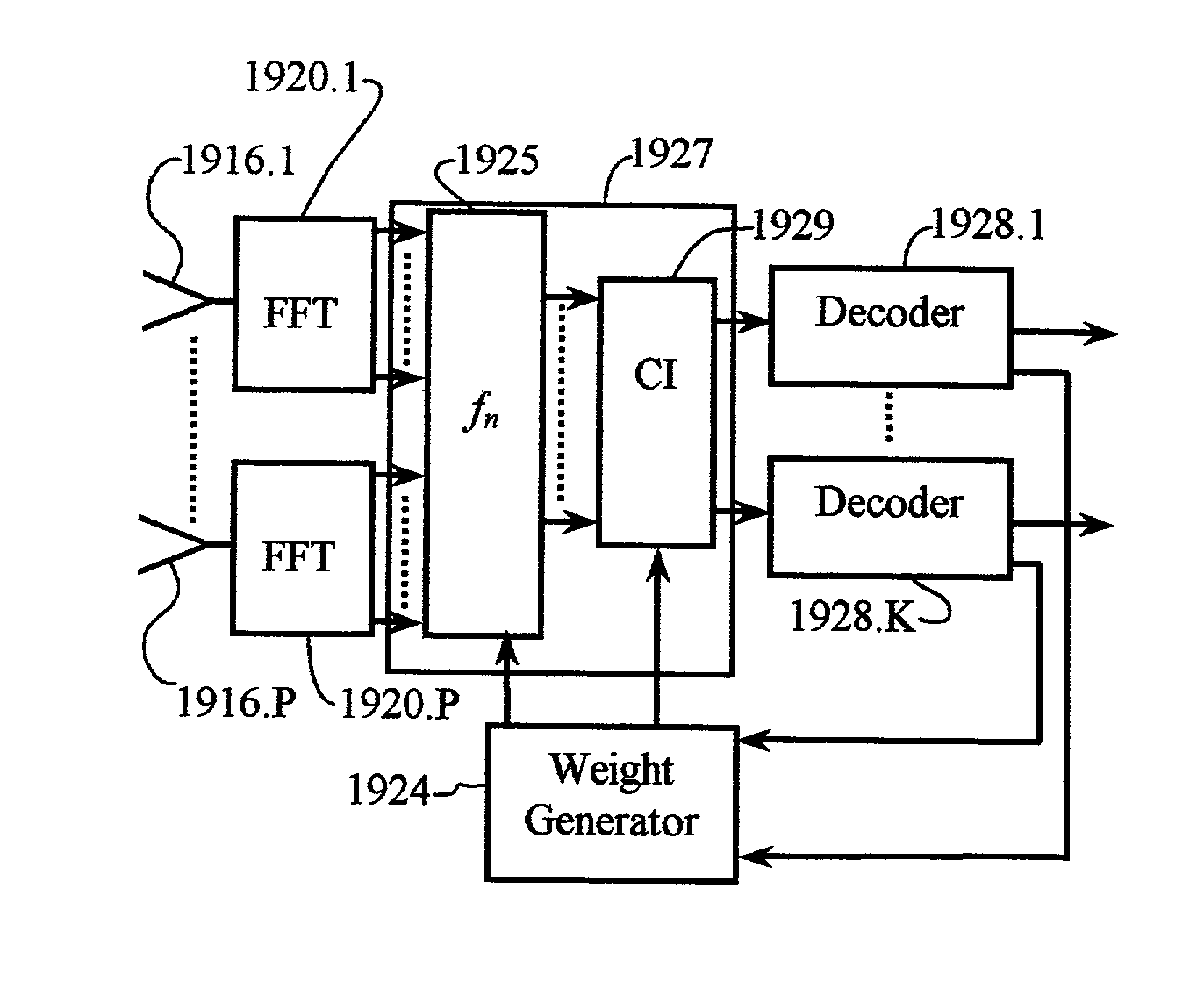
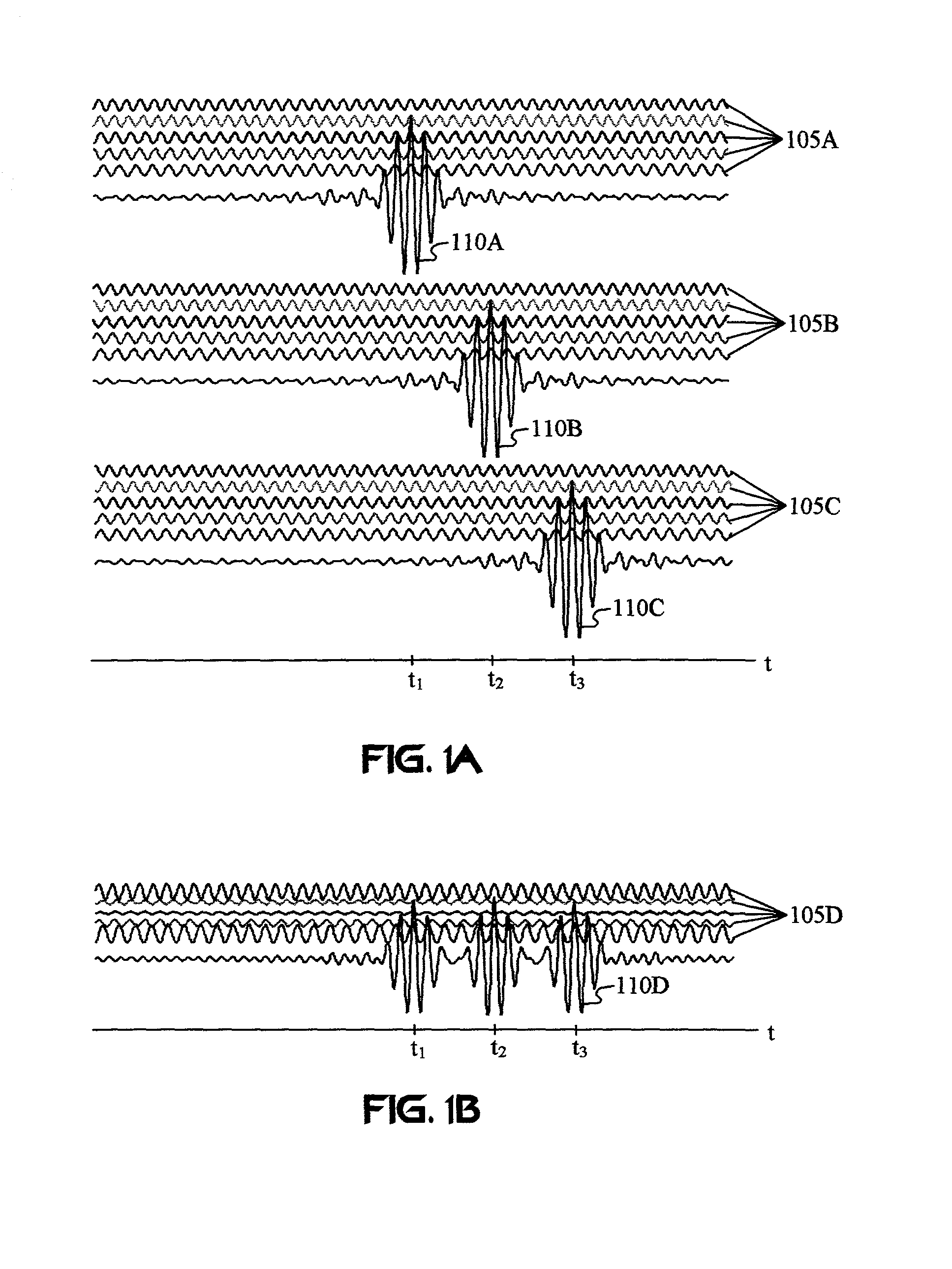
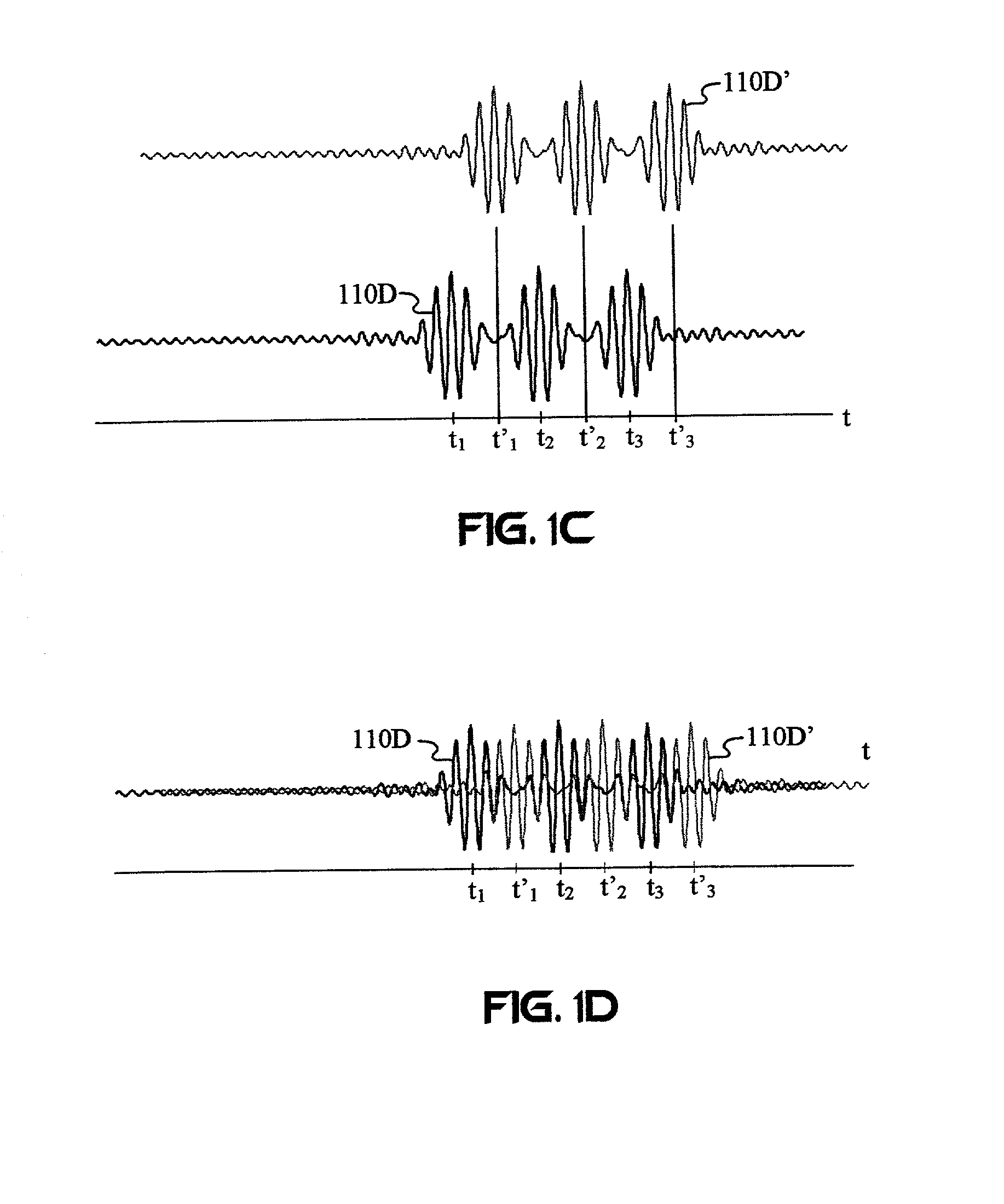
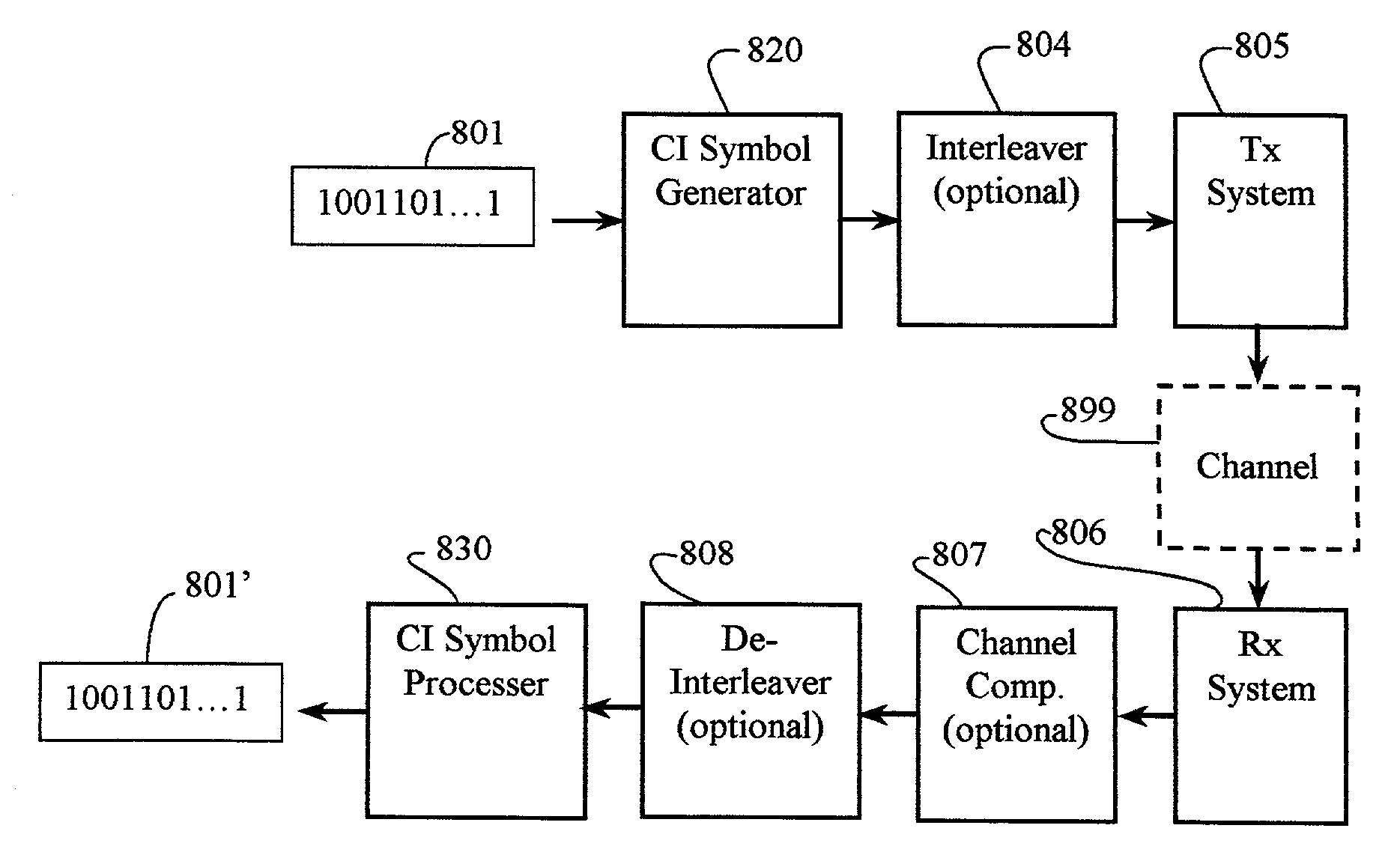
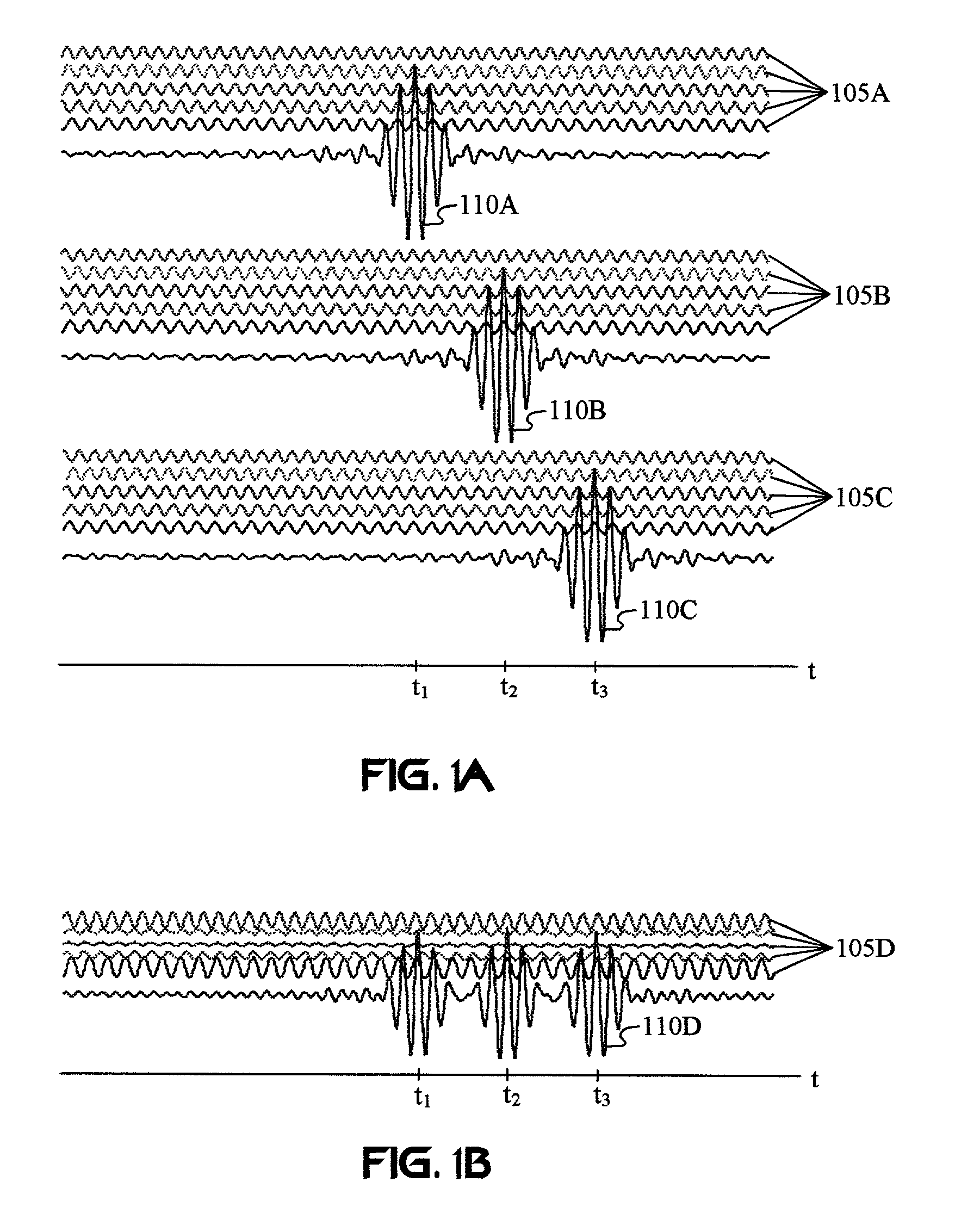
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Multicarrier sub-layer for direct sequence channel and multiple-access coding
InactiveUS7430257B1Low costPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Carrier interferometry networks
ActiveUS20080095121A1Improve throughputImprove bit error rateEnergy efficient ICTModulated-carrier systemsWireless mesh networkTelecommunications link
Applications of CI processing to ad-hoc and peer-to-peer networking significantly improve throughput, network capacity, range, power efficiency, and spectral efficiency. CI-based subscriber units perform network-control functions to optimize network performance relative to channel conditions, network loads, and subscriber services. CI codes are used to identify and address network transmissions. Channel characteristics of communication links are employed to encode, address, and authenticate network transmissions. CI transceivers used as relays and routers employ unique characteristics of transmission paths to code and decode network transmissions. A central processor is adapted to perform array processing with signals received from, and transmitted by, a plurality of subscriber units in a wireless network.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
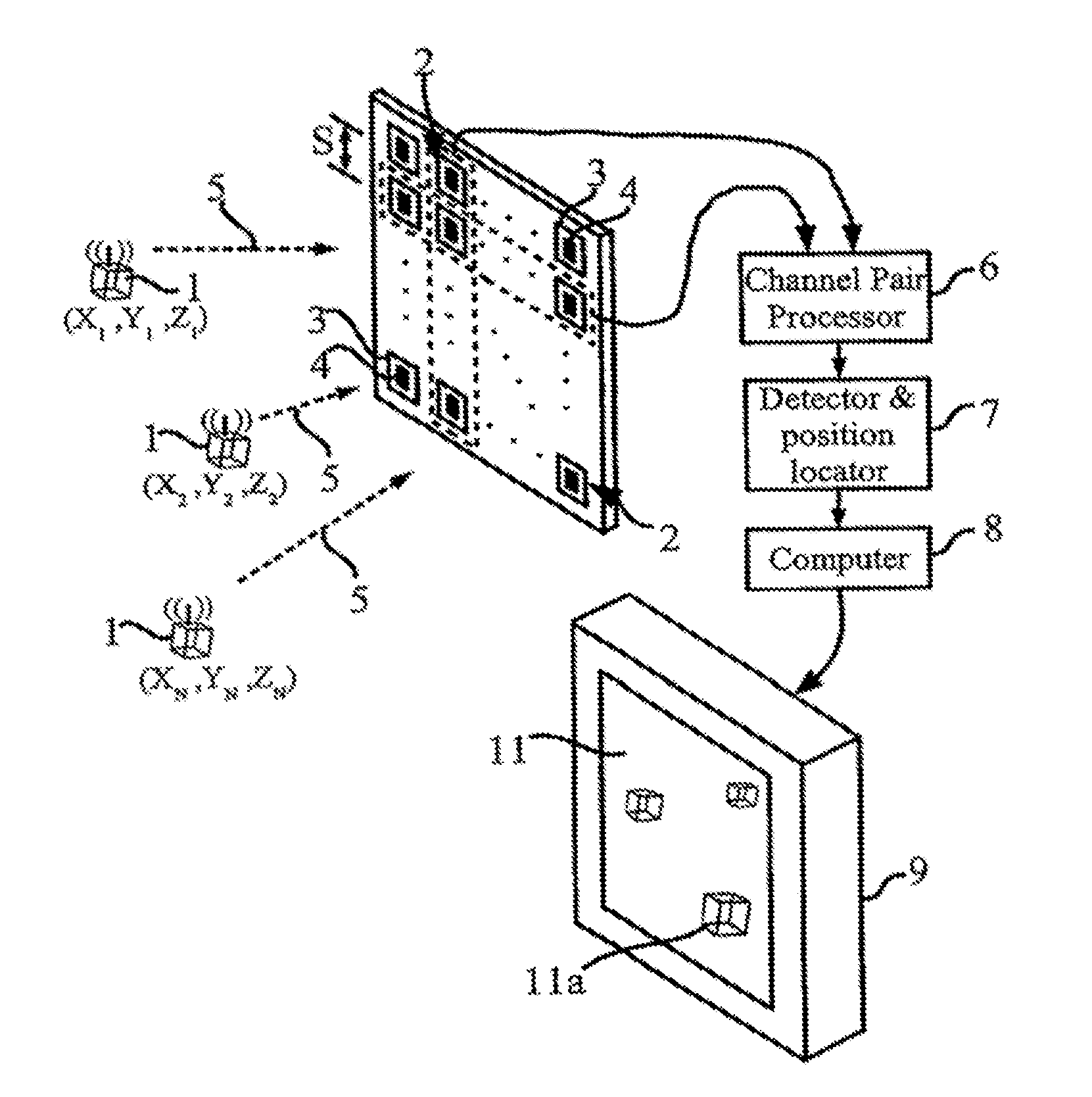
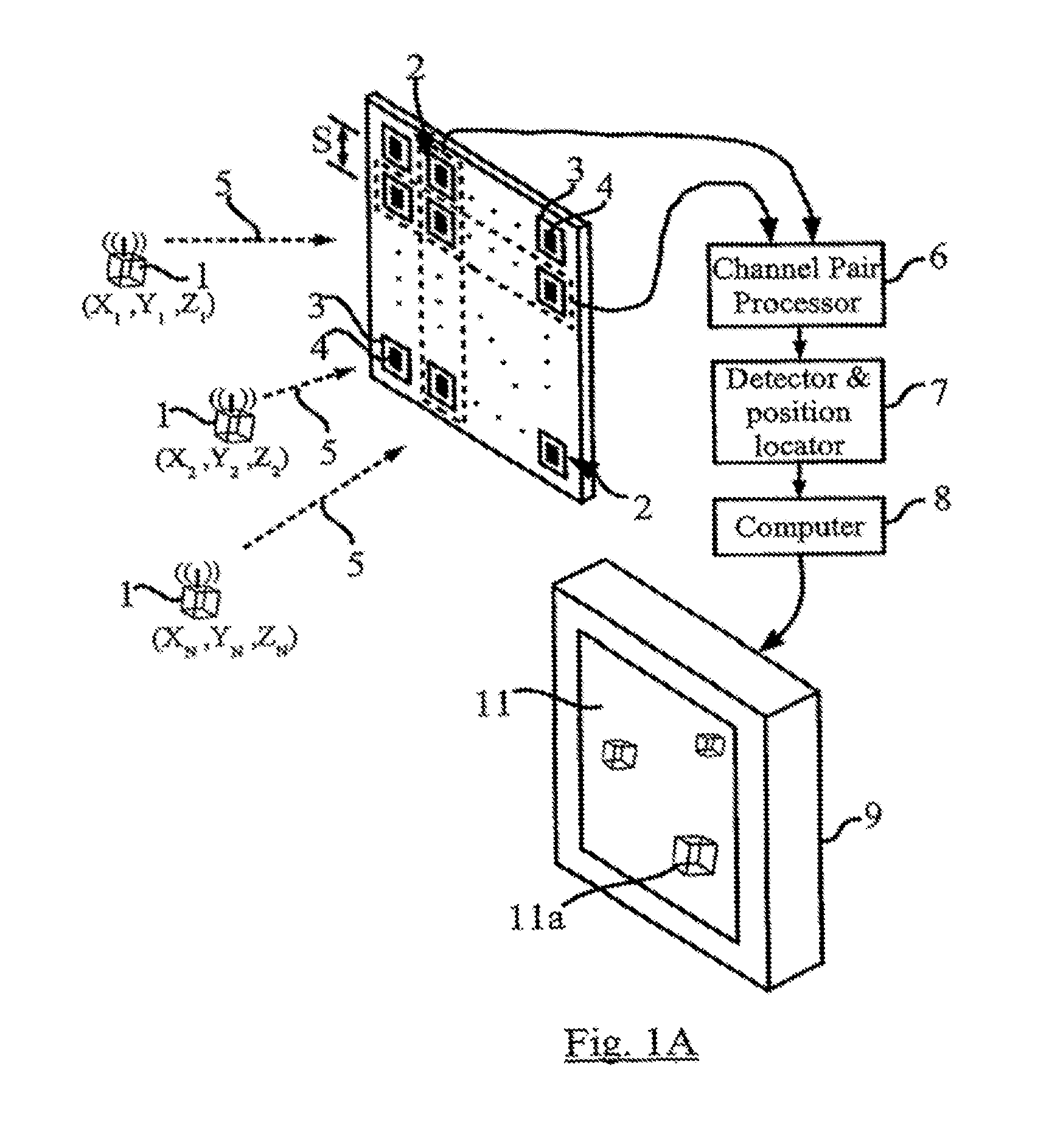
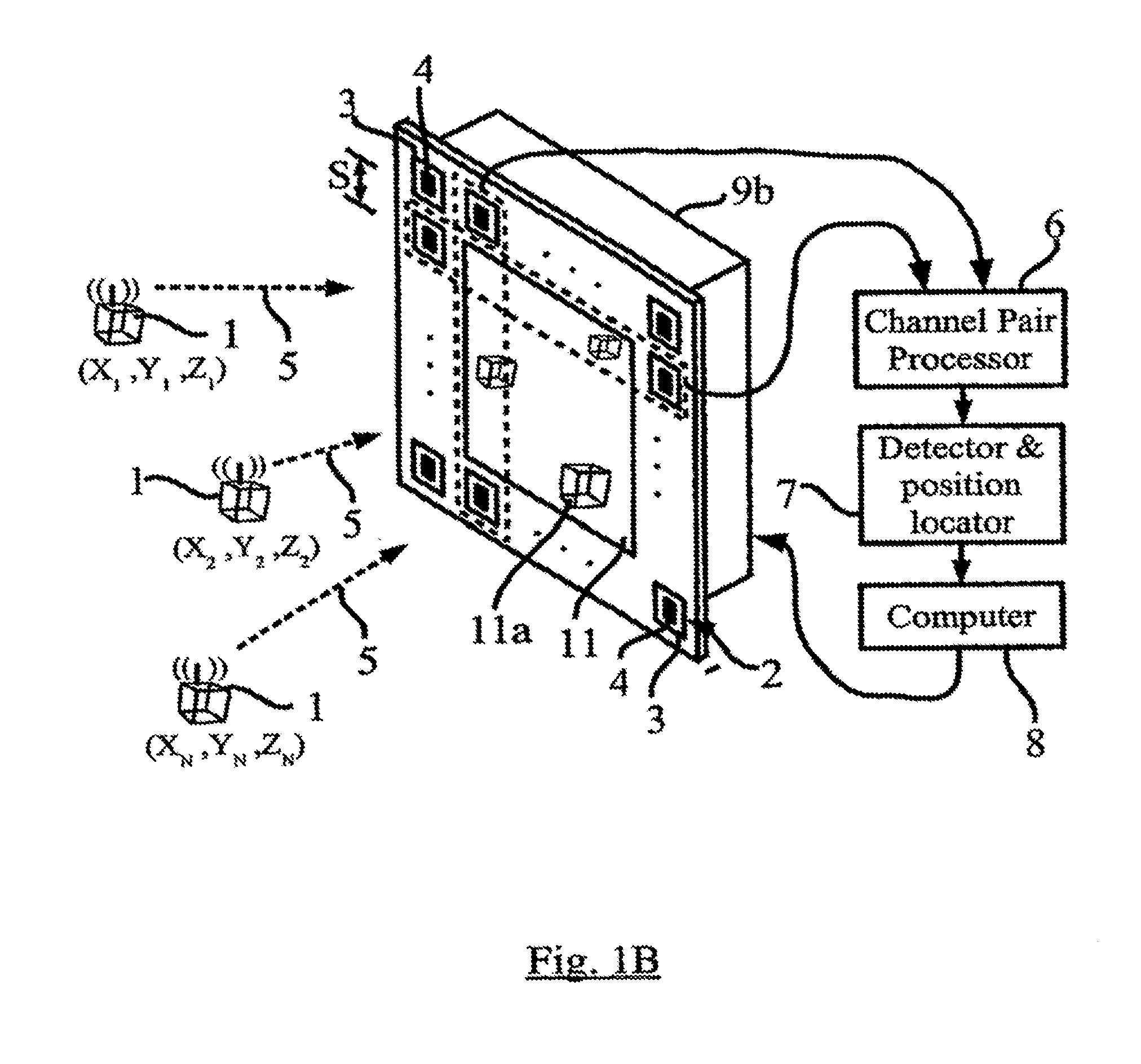
Method and apparatus for position sensing
InactiveUS20060166681A1Direction finders using radio wavesTransmission control/equalisingData signalCombined use
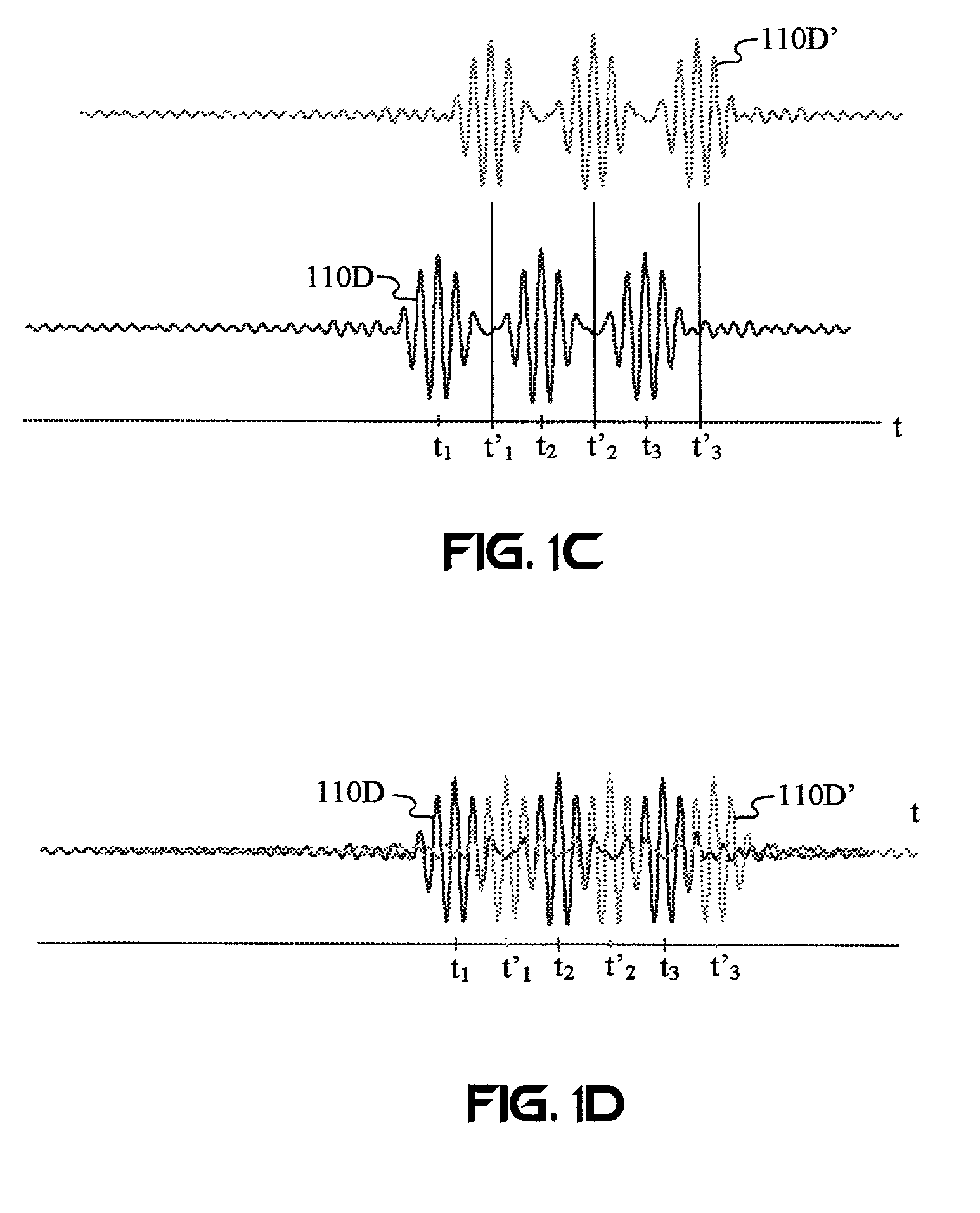
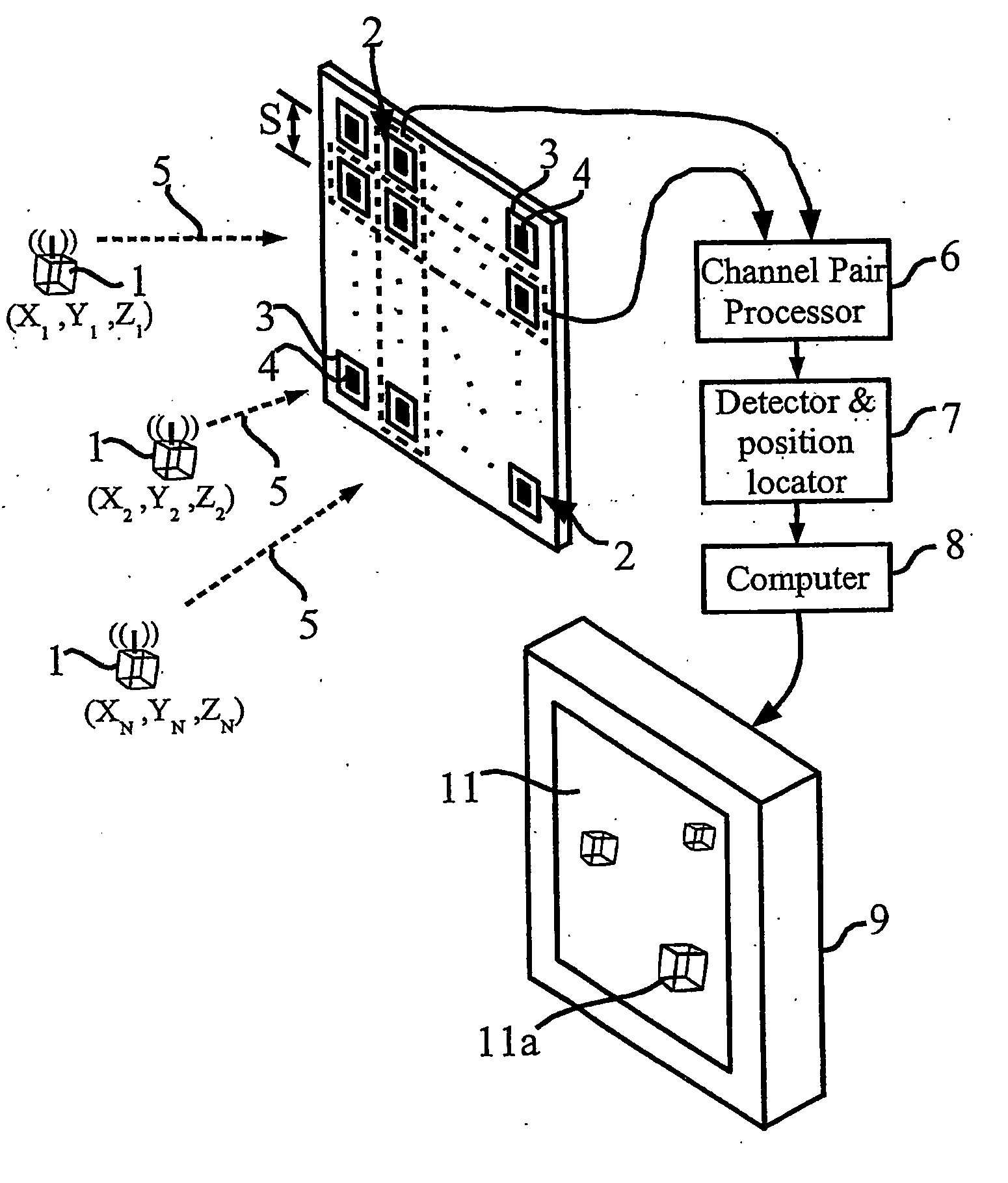
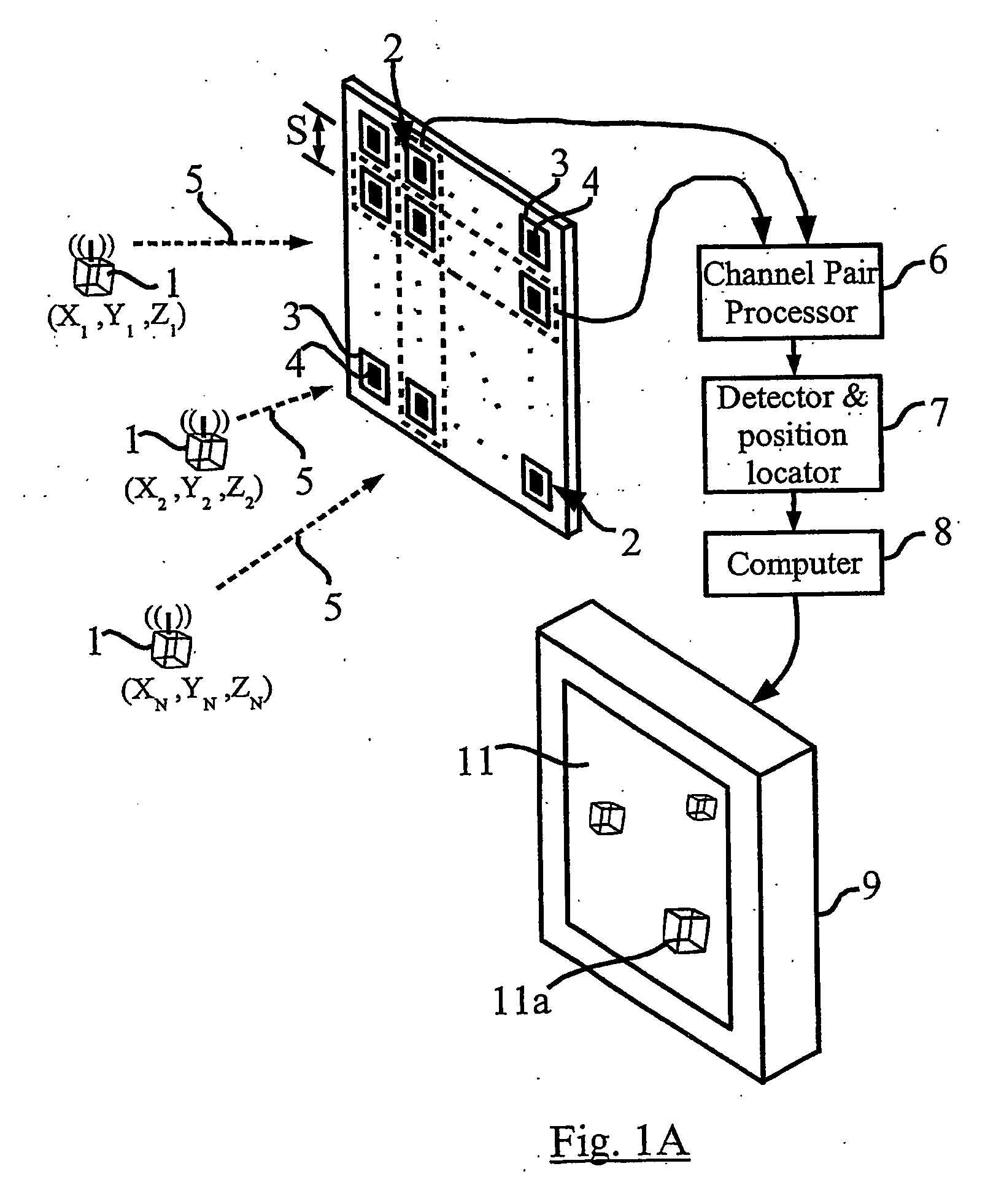
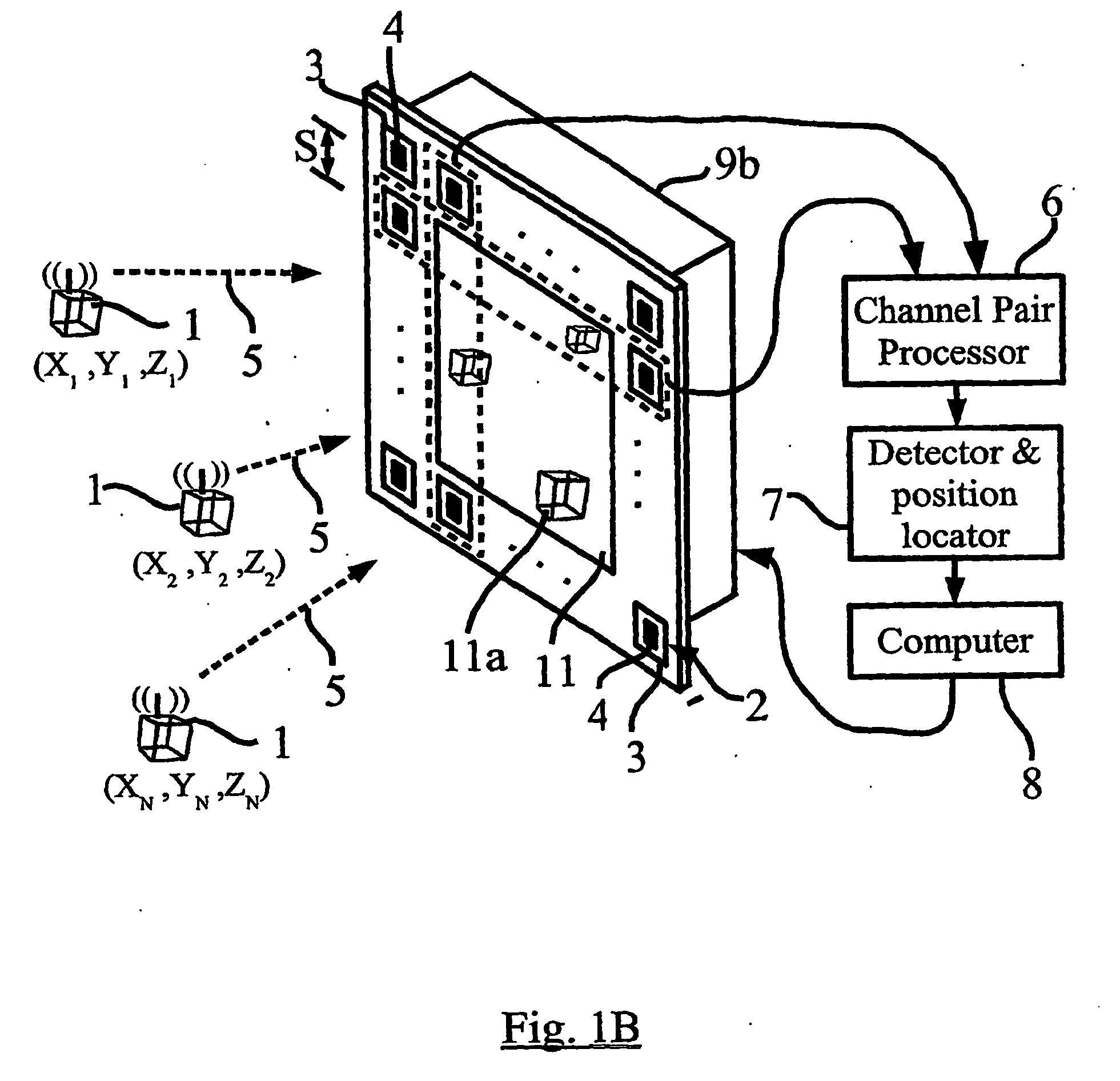
Embodiments of the present invention include one or more wireless transmitting devices and an array of receiver units for receiving wireless communications from the transmitting devices. The transmitter devices and receiver units can be arranged in one, two or three dimensional configurations. Signals are transmitted from the devices for identification and accurate location determination. Spread spectrum techniques can be used, such as DSSS, FHSS, THSS, and pseudo-noise (PN) coding schemes, or combinations thereof. The transmitting devices can generate one or a plurality of data signals that are orthogonal-code modulated, to be decoded by the receiver units and a processor associated therewith. A plurality of transmitter signals can be received, identified, located, and data demodulated substantially simultaneously using embodiments of the invention. The combined use of array processing methods and diversity schemes can be used to reduce the effects of signal multi-path and occlusion.
Owner:XYZ INTERACTIVE TECH
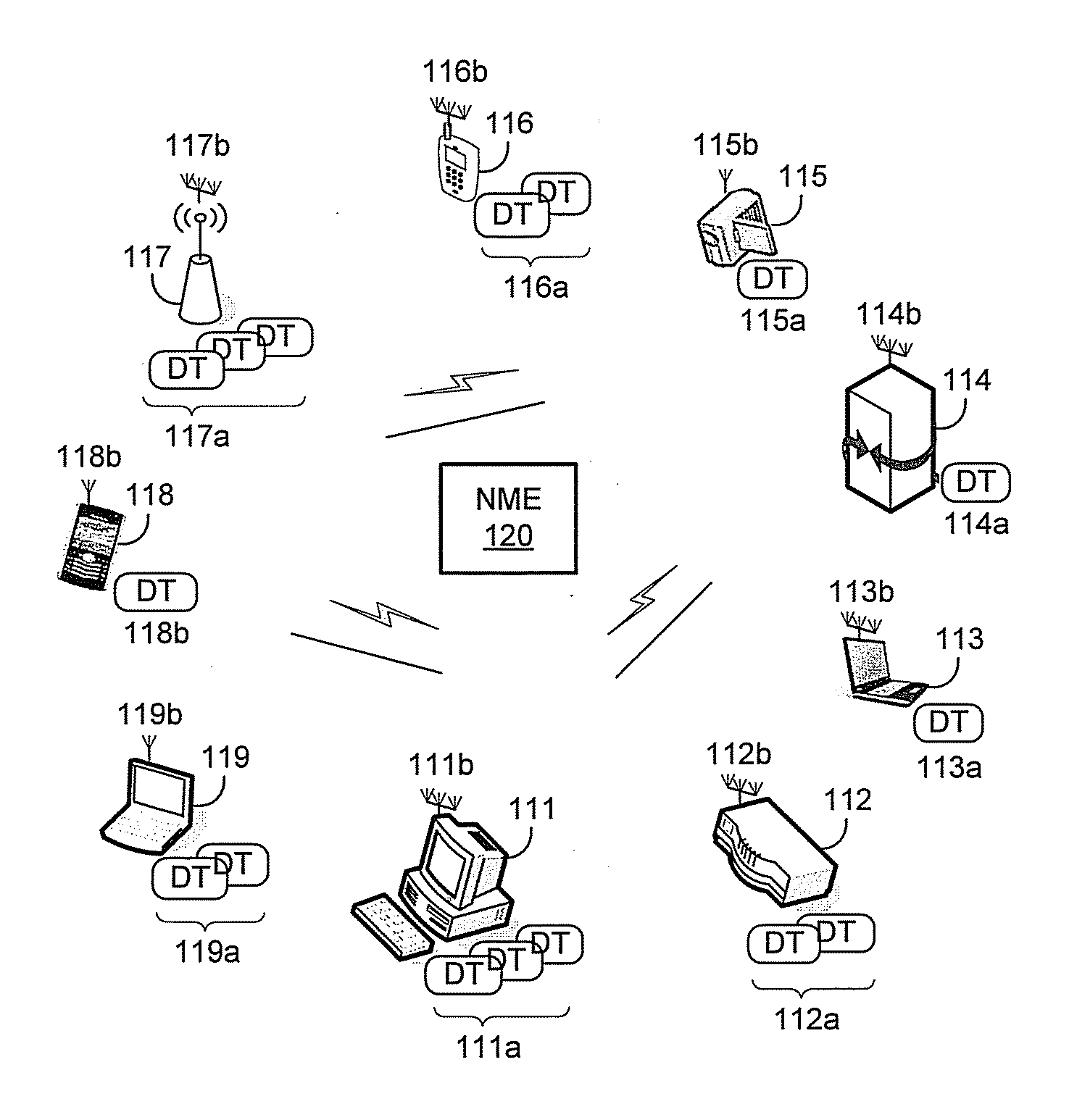
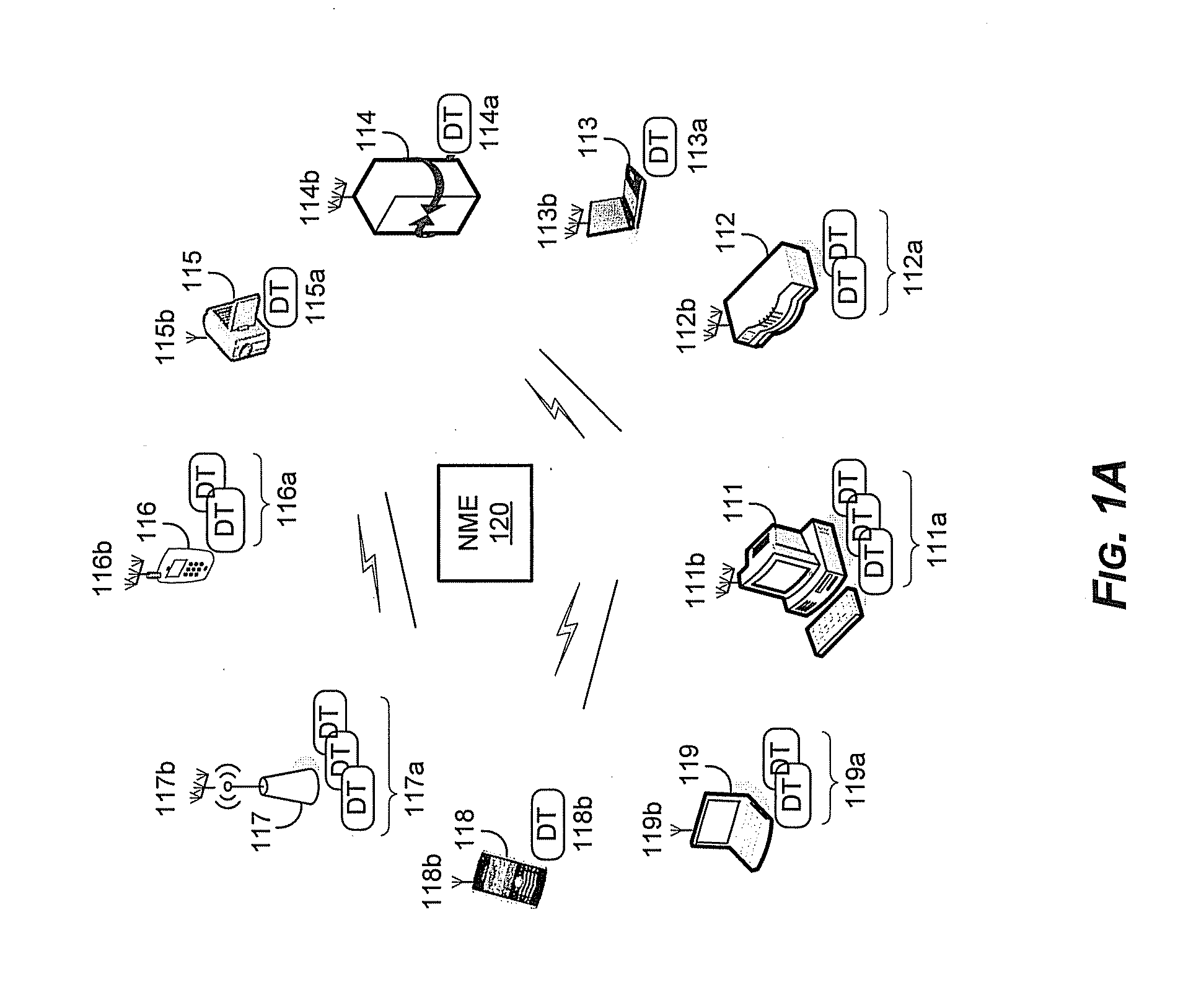
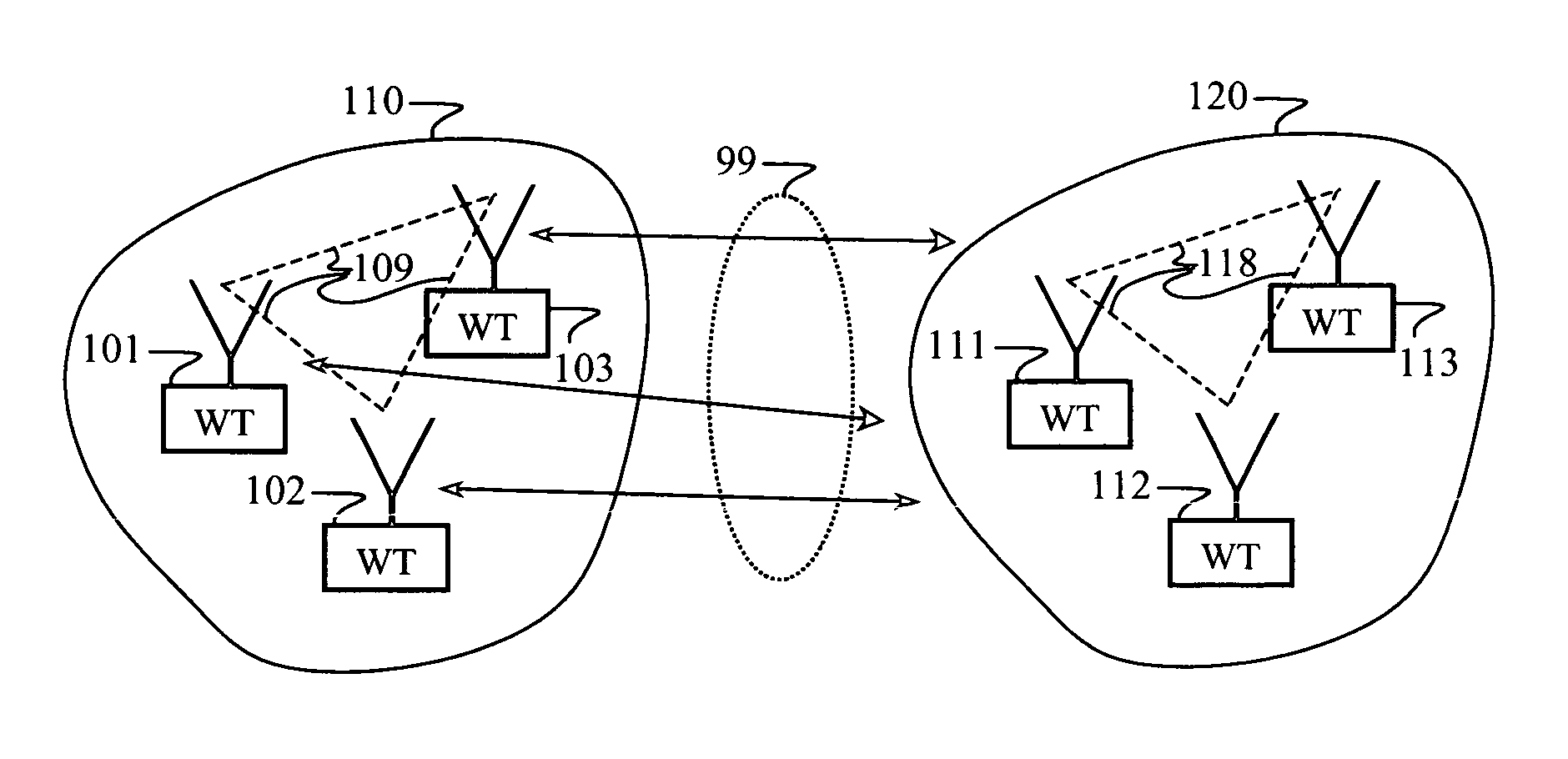
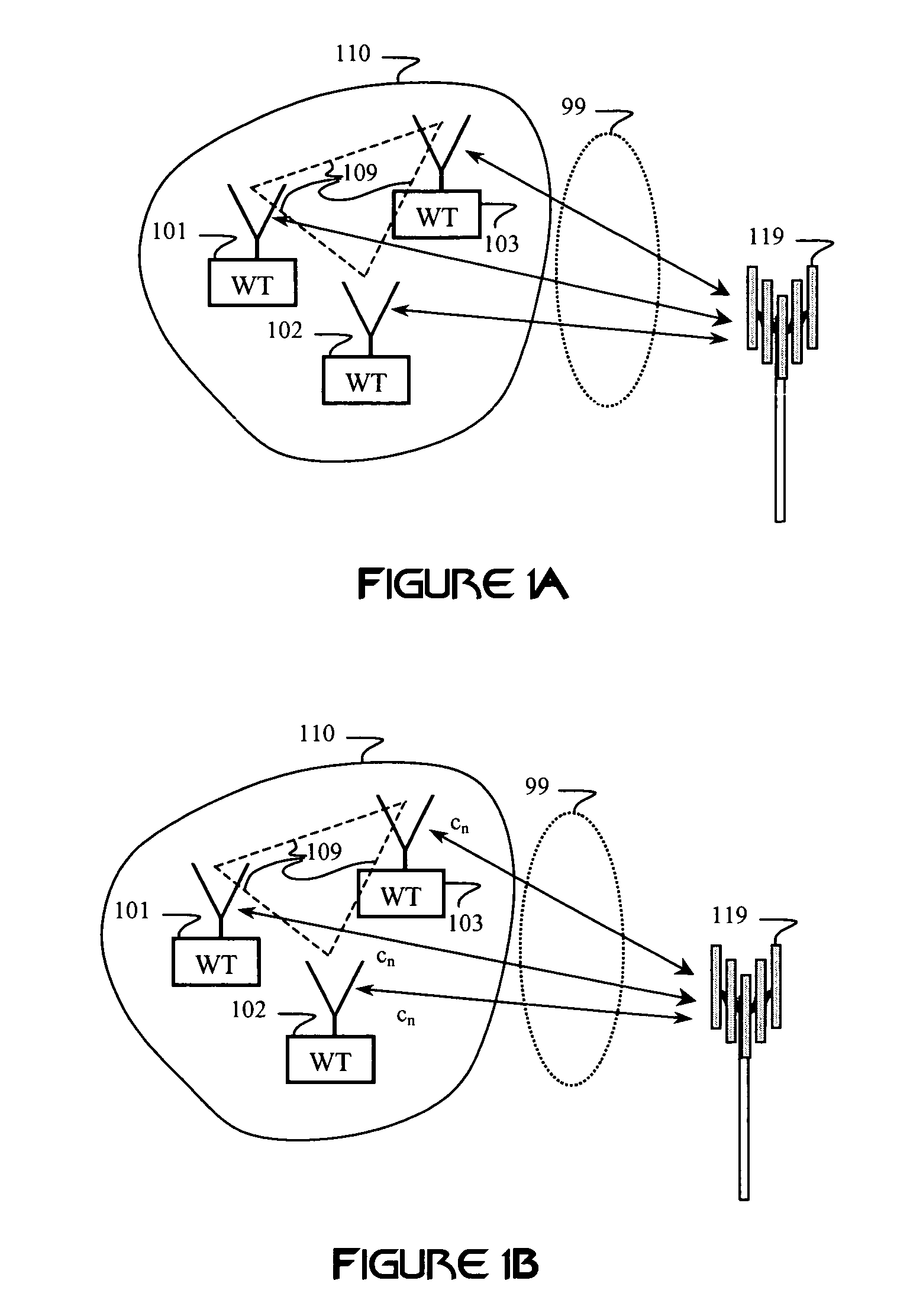
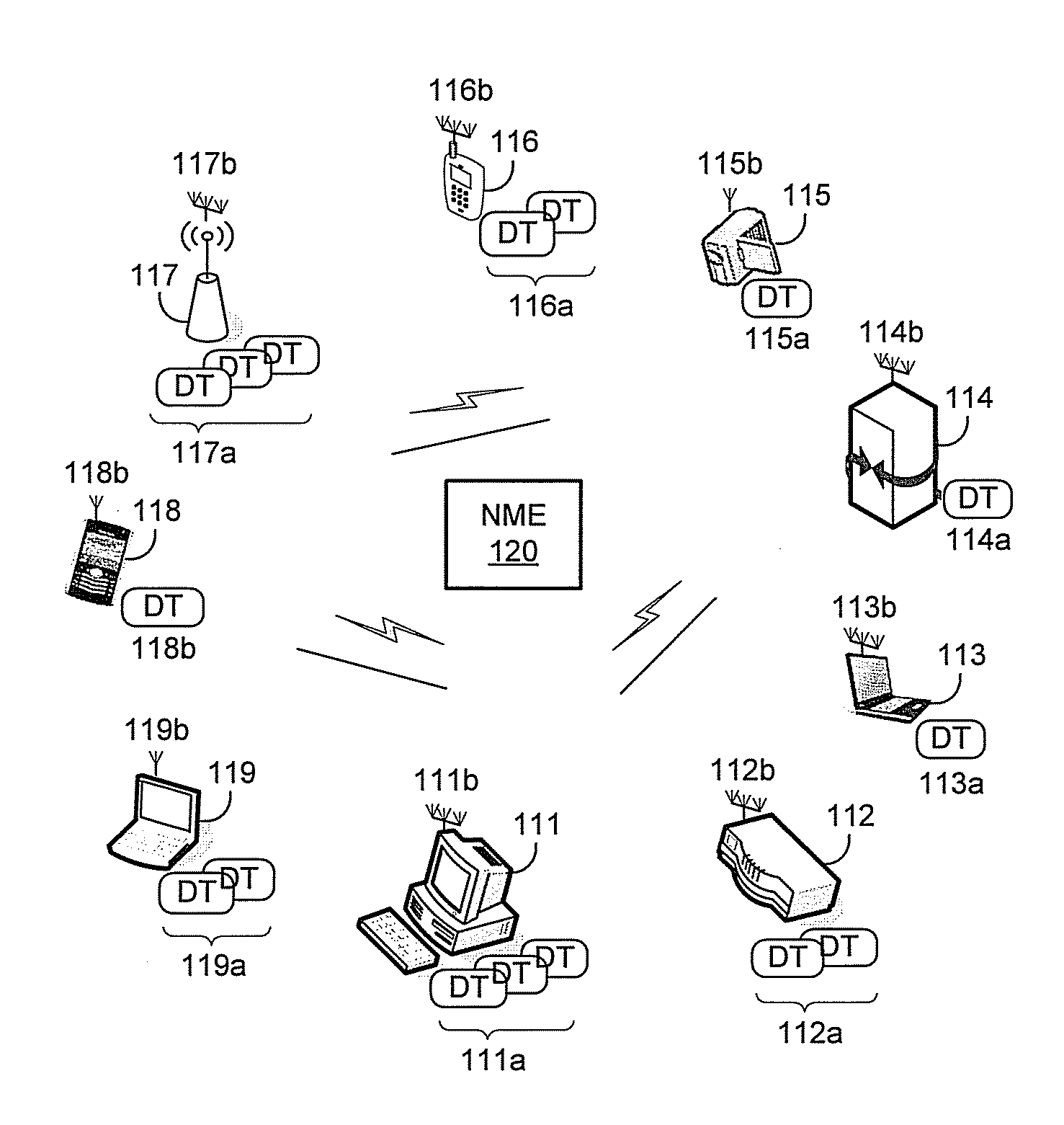
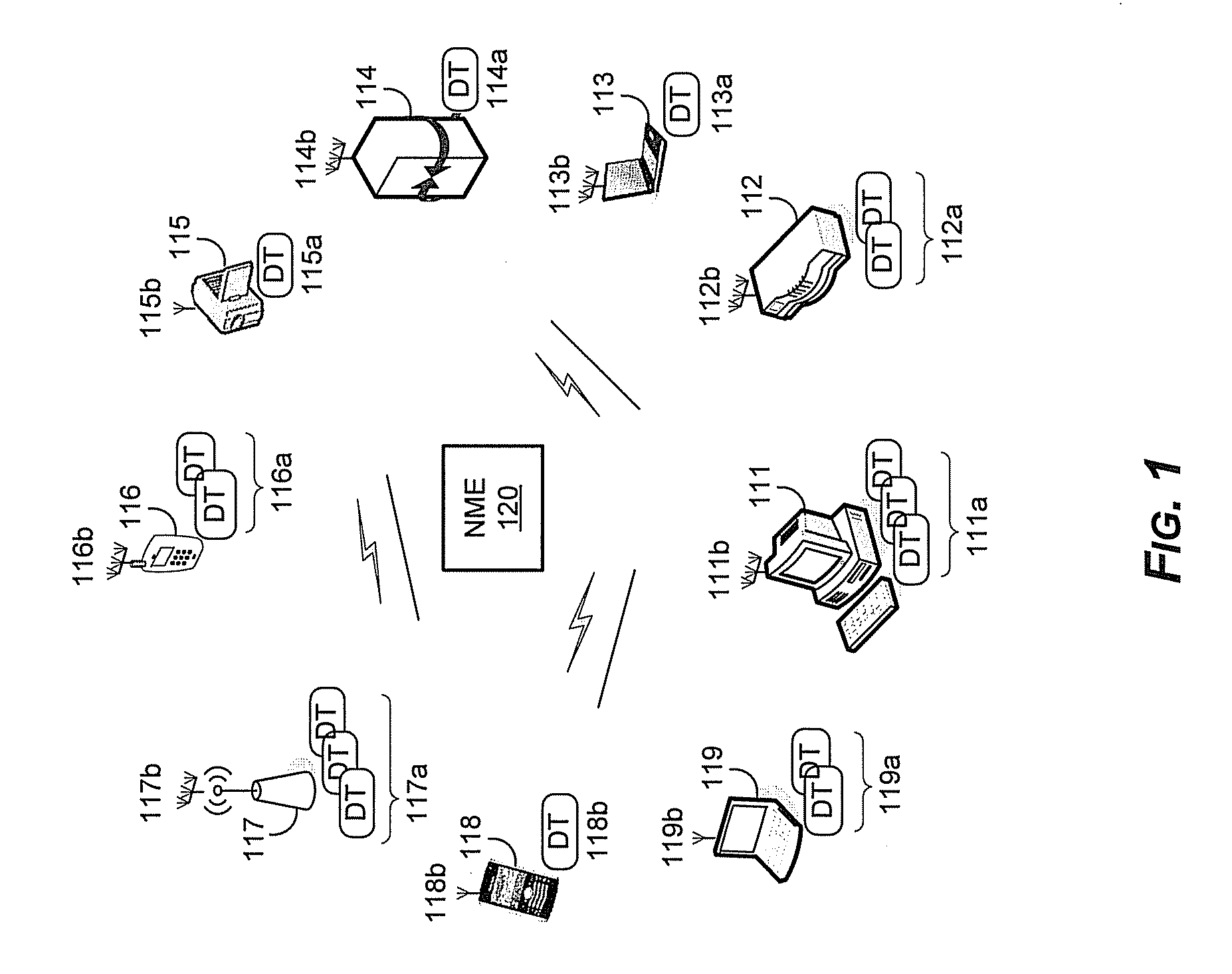
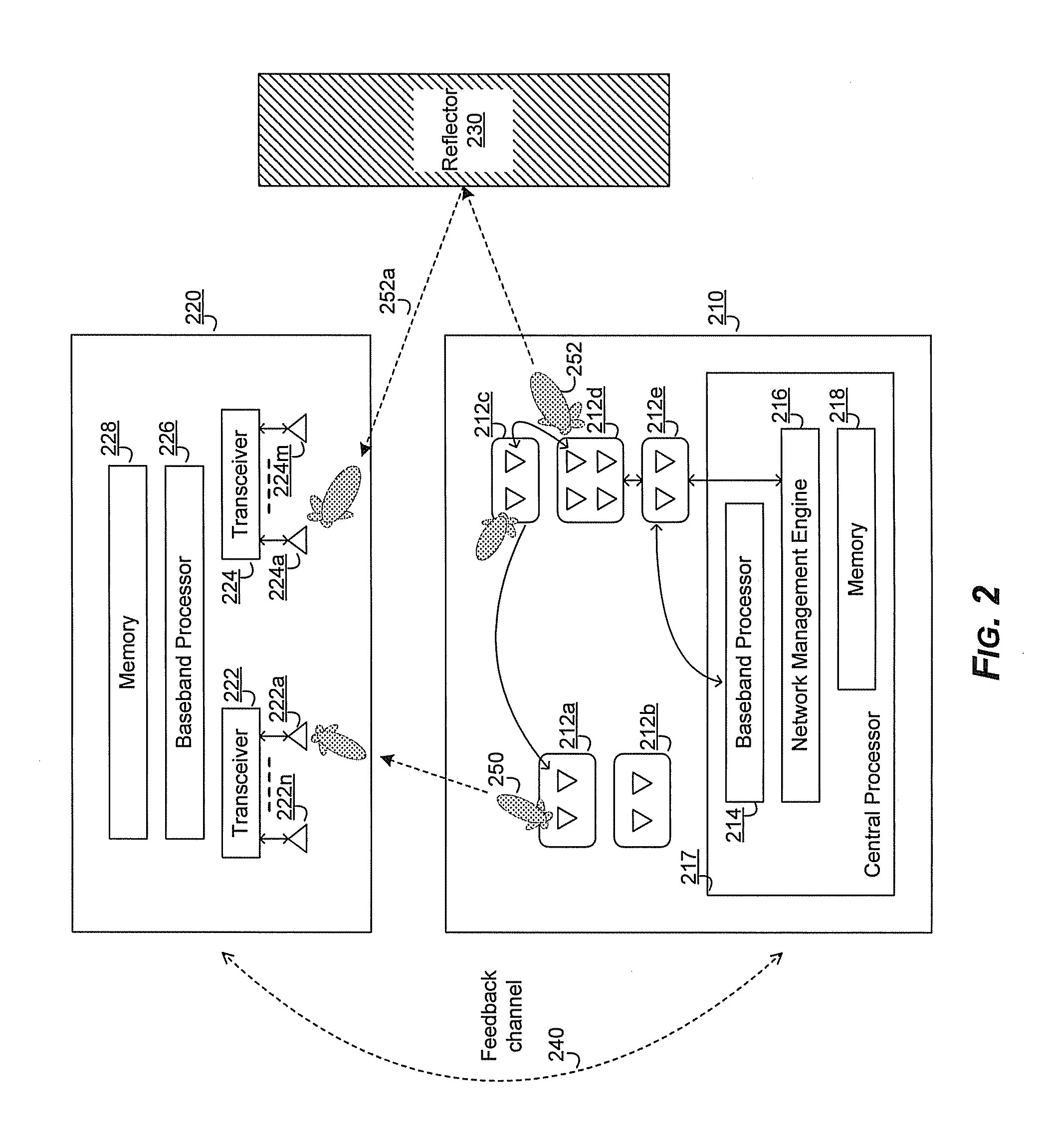
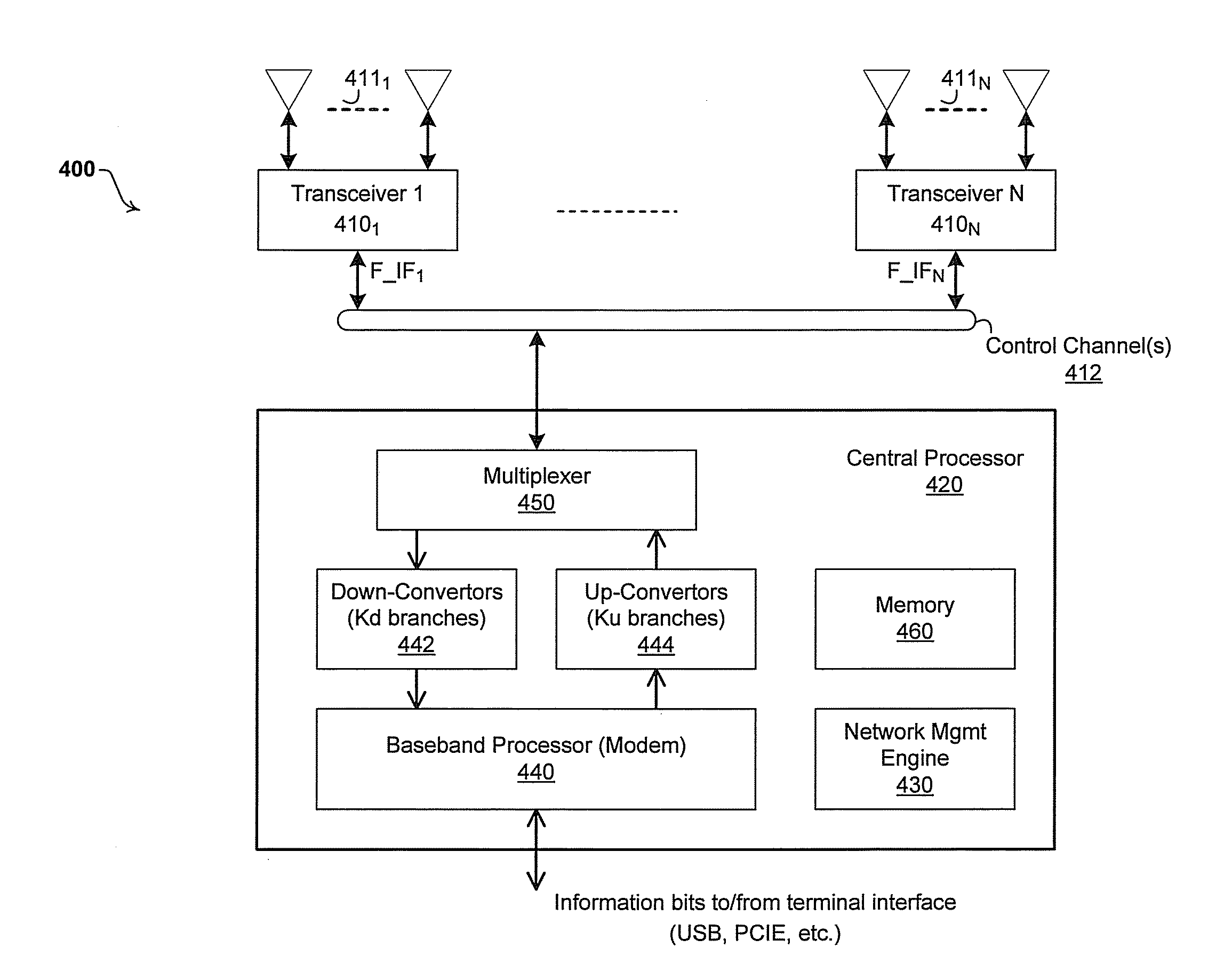
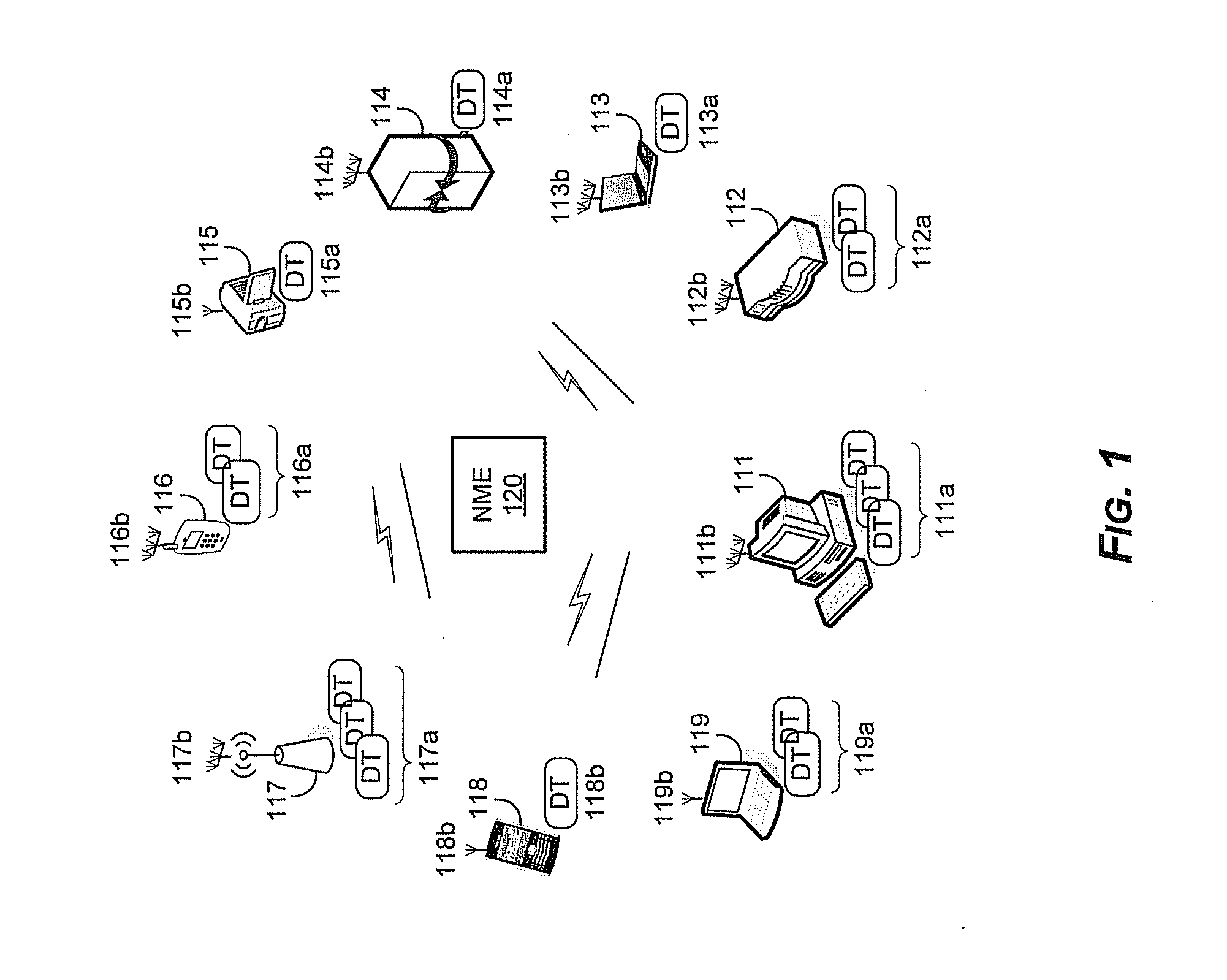
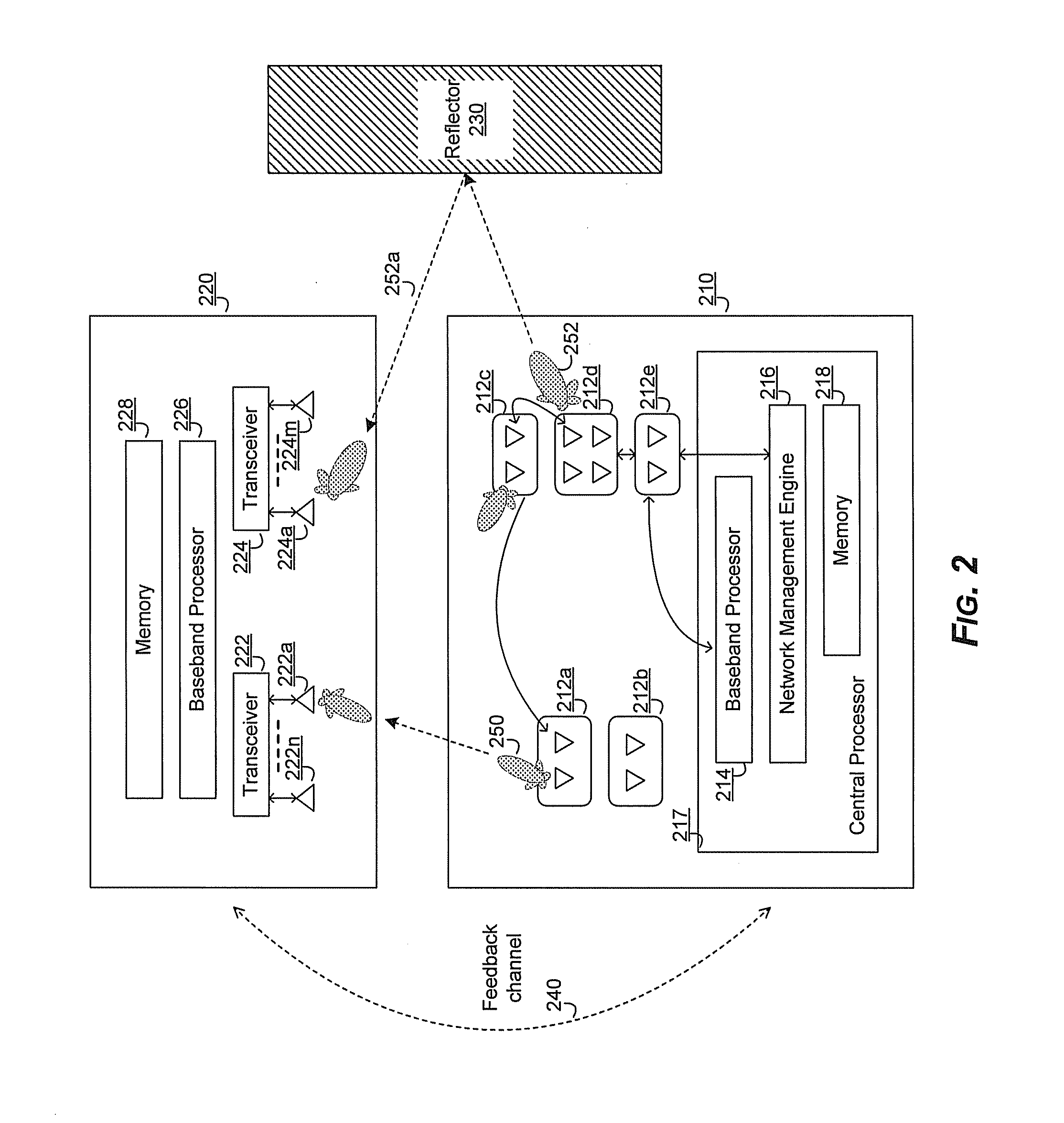
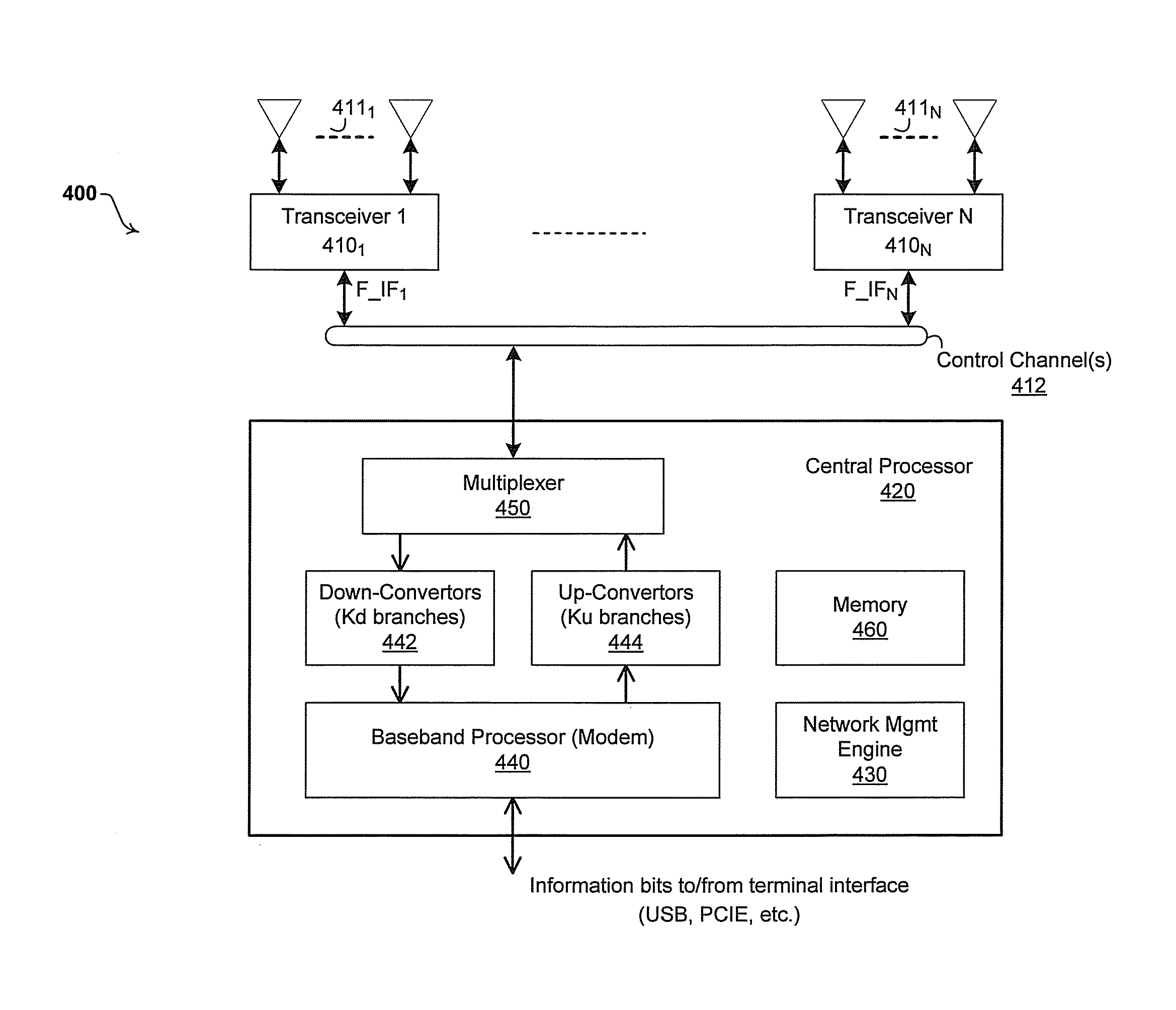
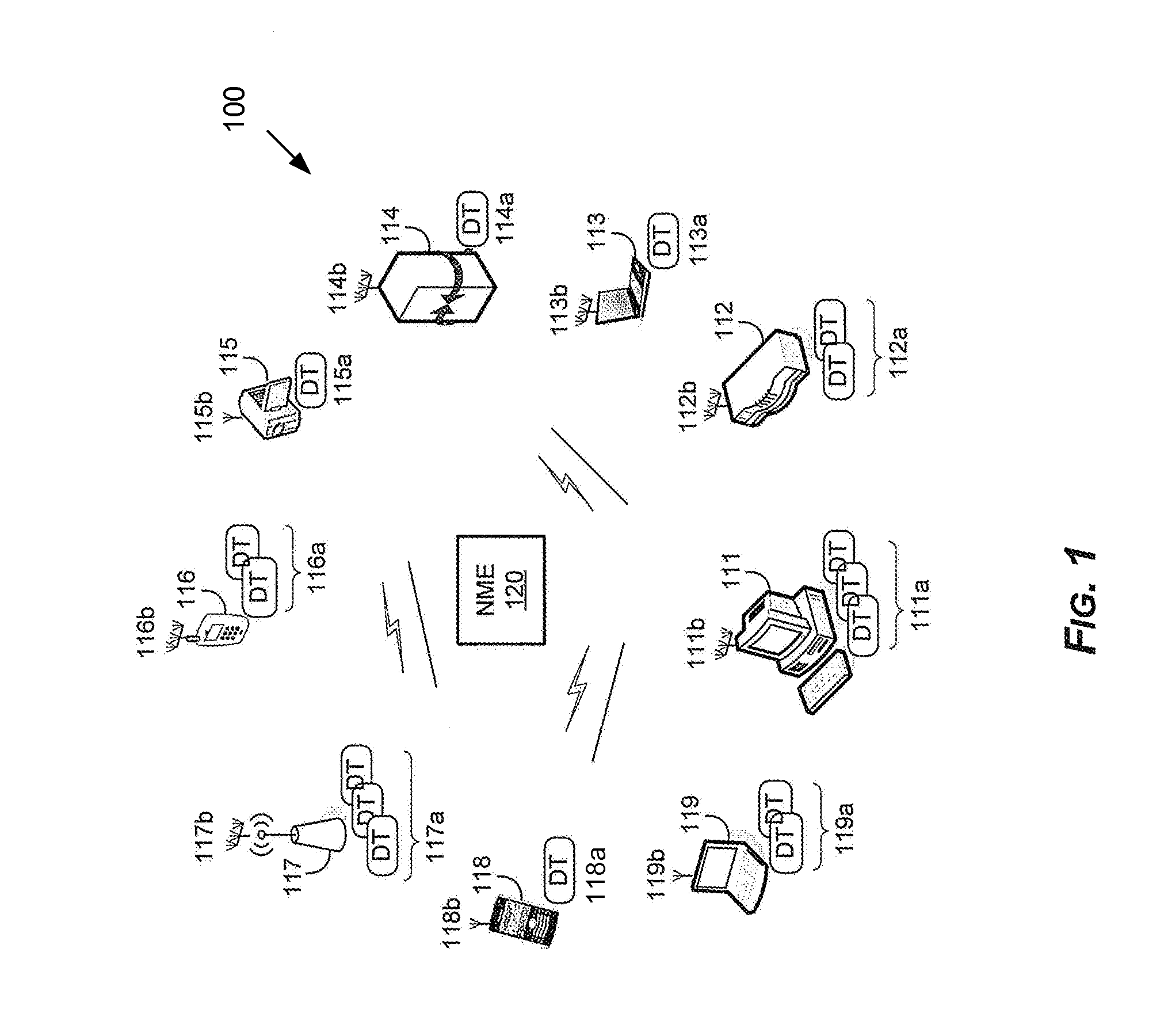
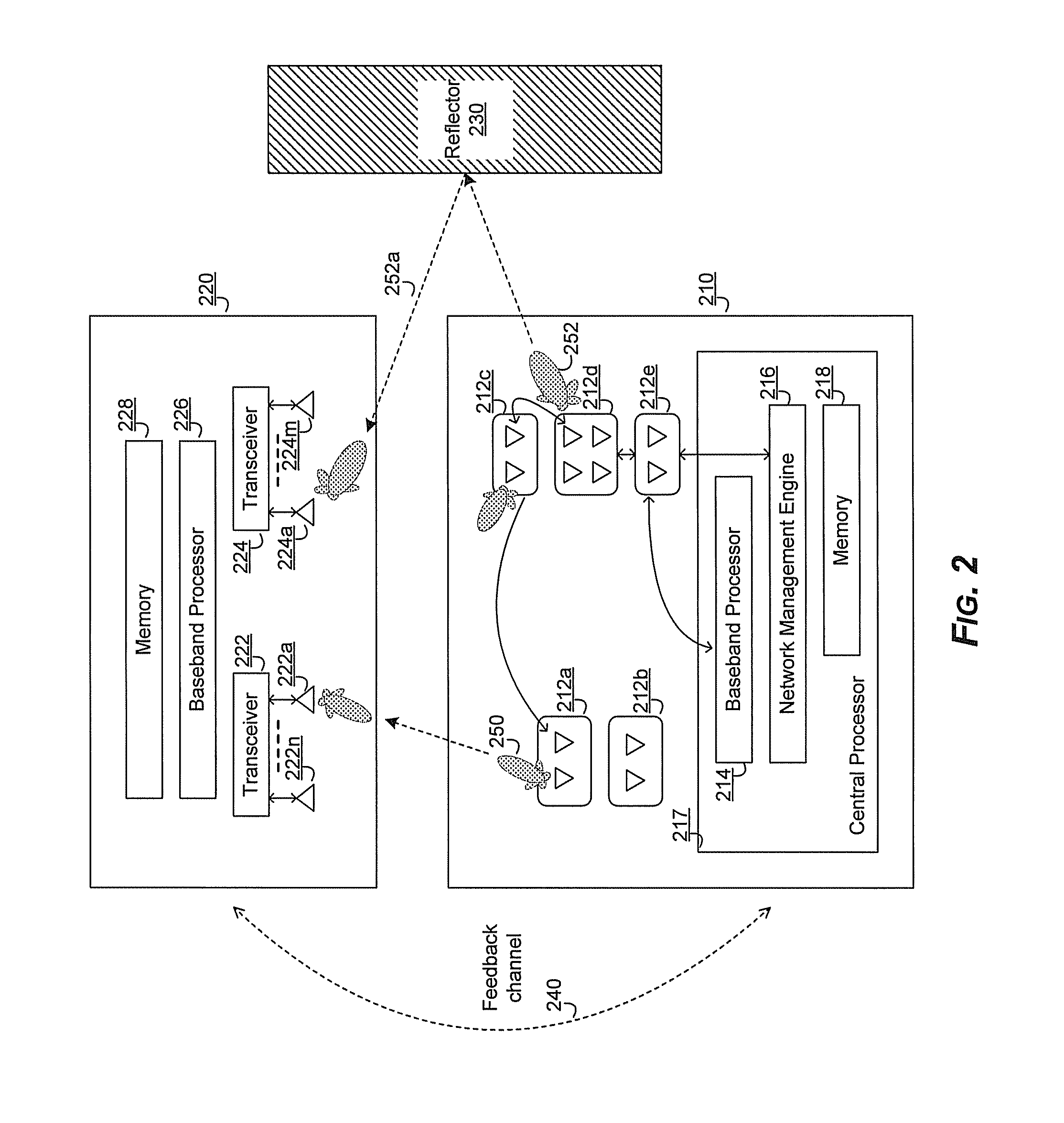
Method and system for a repeater network that utilizes distributed transceivers with array processing
A device that comprises a plurality of distributed transceivers, a central processor and a network management engine may be configured to function as relay device, relaying an input data stream from a source device to at least one other device. The relaying may include configuring one or more of the plurality of distributed transceivers to particular mode of relay operation and receiving the input data stream from the source device via at least one of the configured one or more of the plurality of distributed transceivers. The relaying may also include transmitting at least one relay data stream corresponding to the input data stream to the at least one other device, via at least one of the configured one or more of the plurality of distributed transceivers.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
Fluid parameter measurement in pipes using acoustic pressures
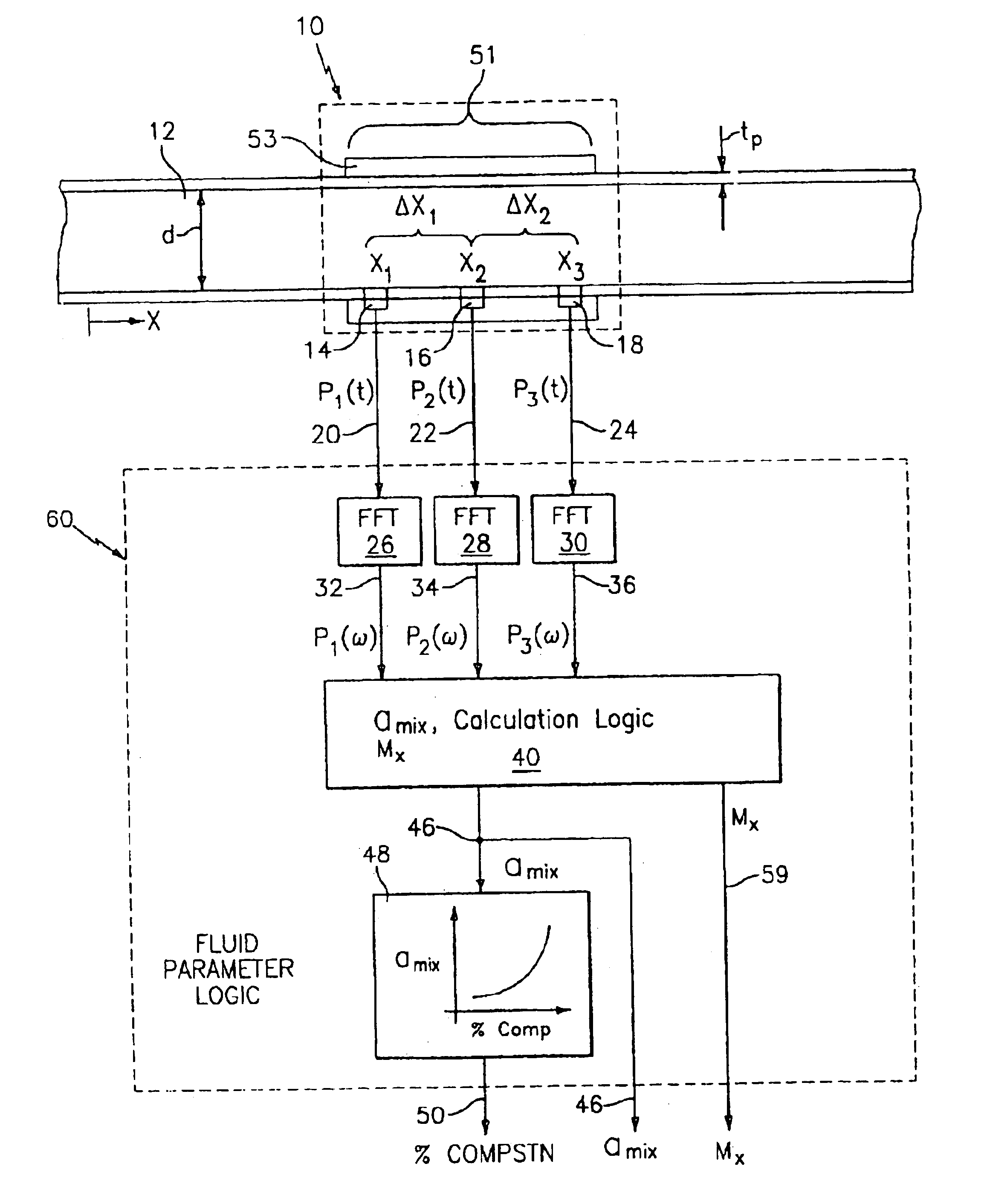
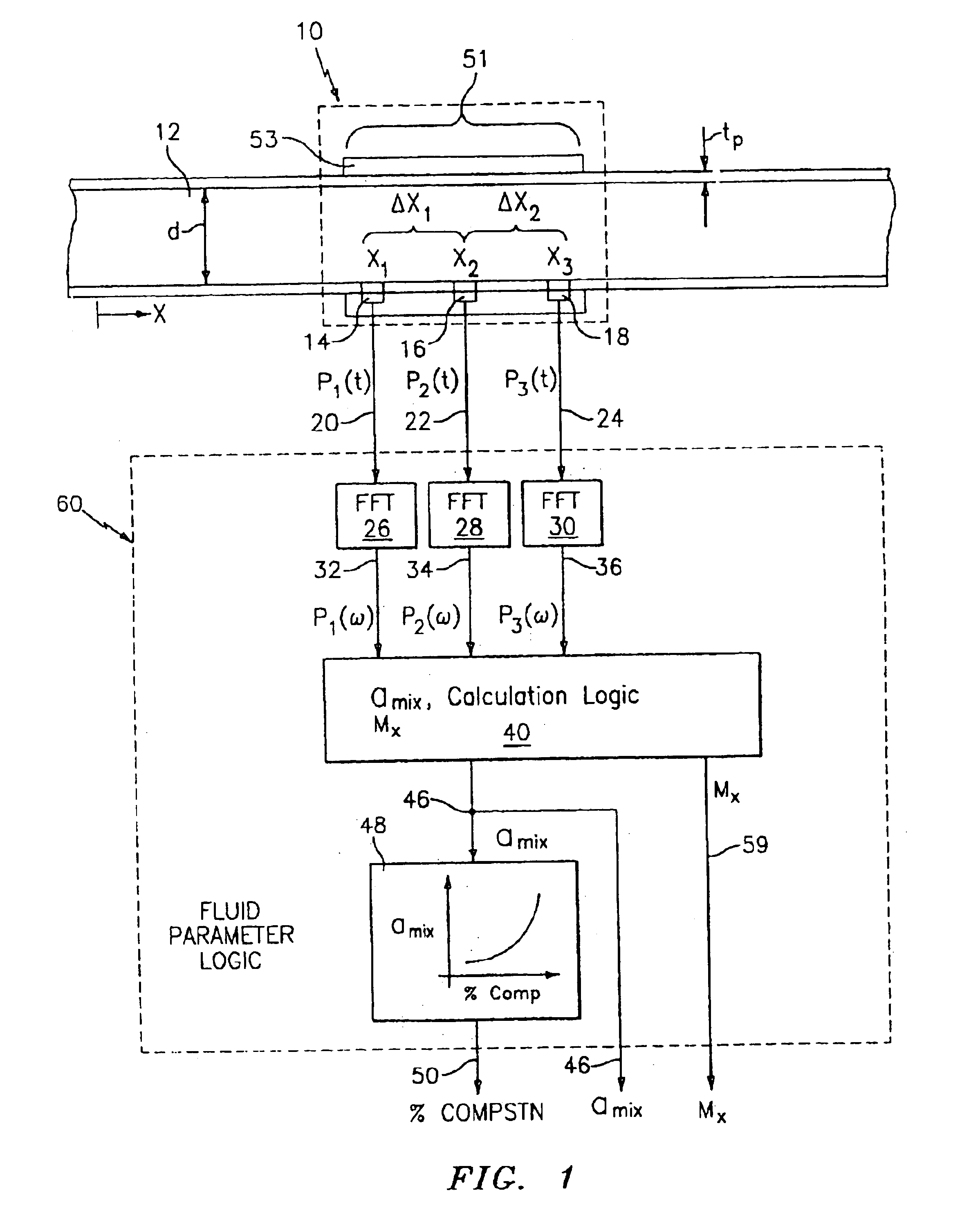
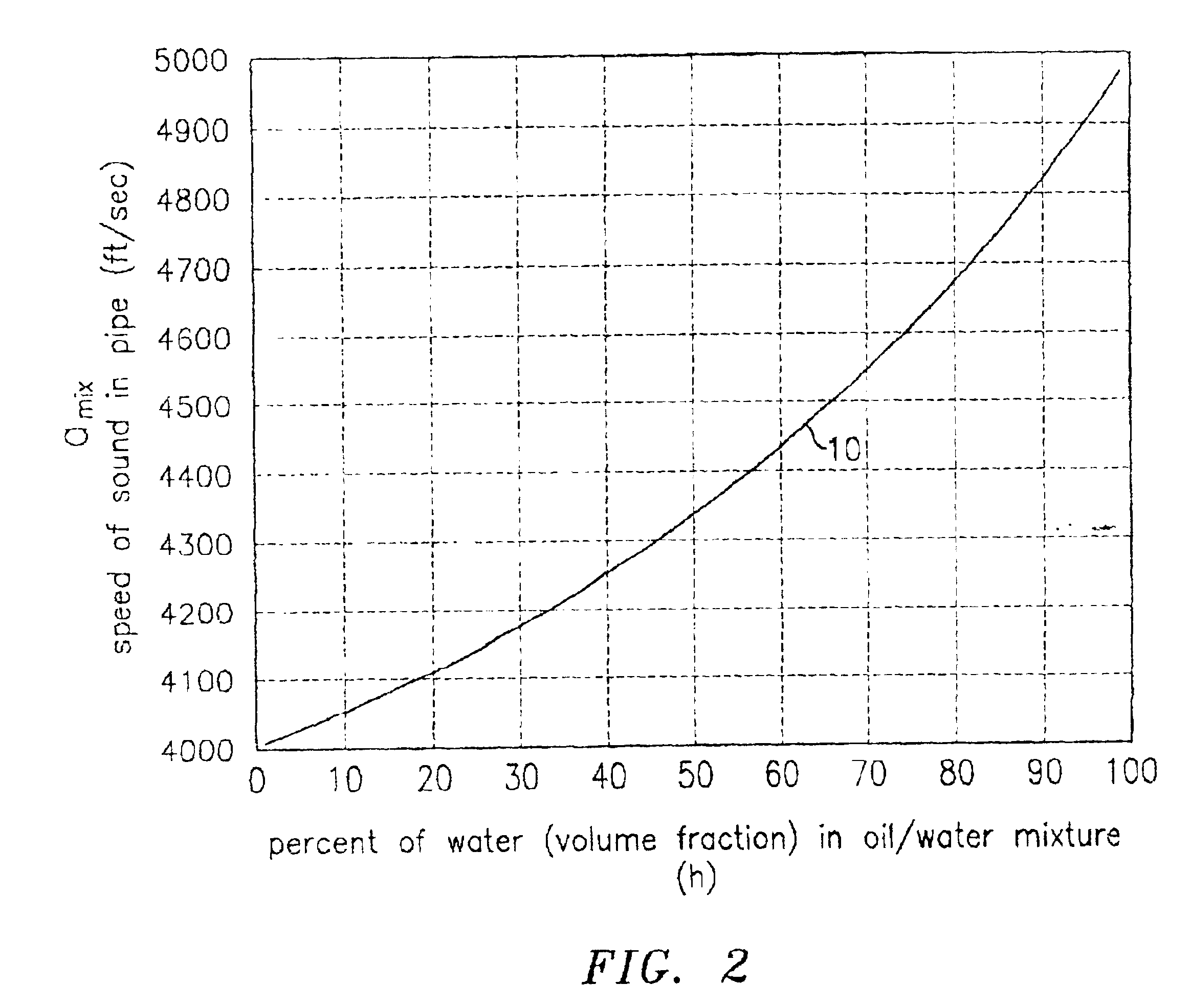
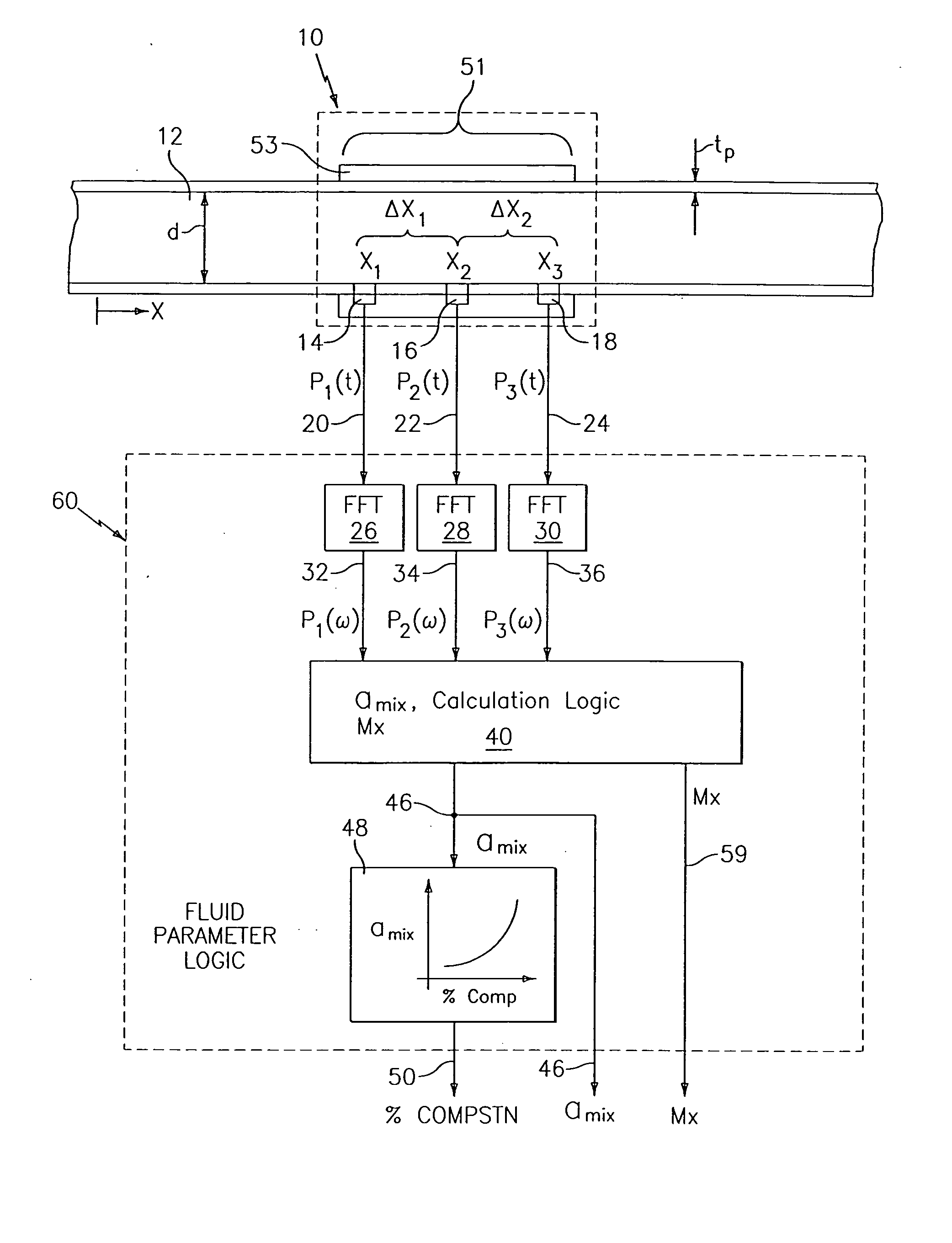
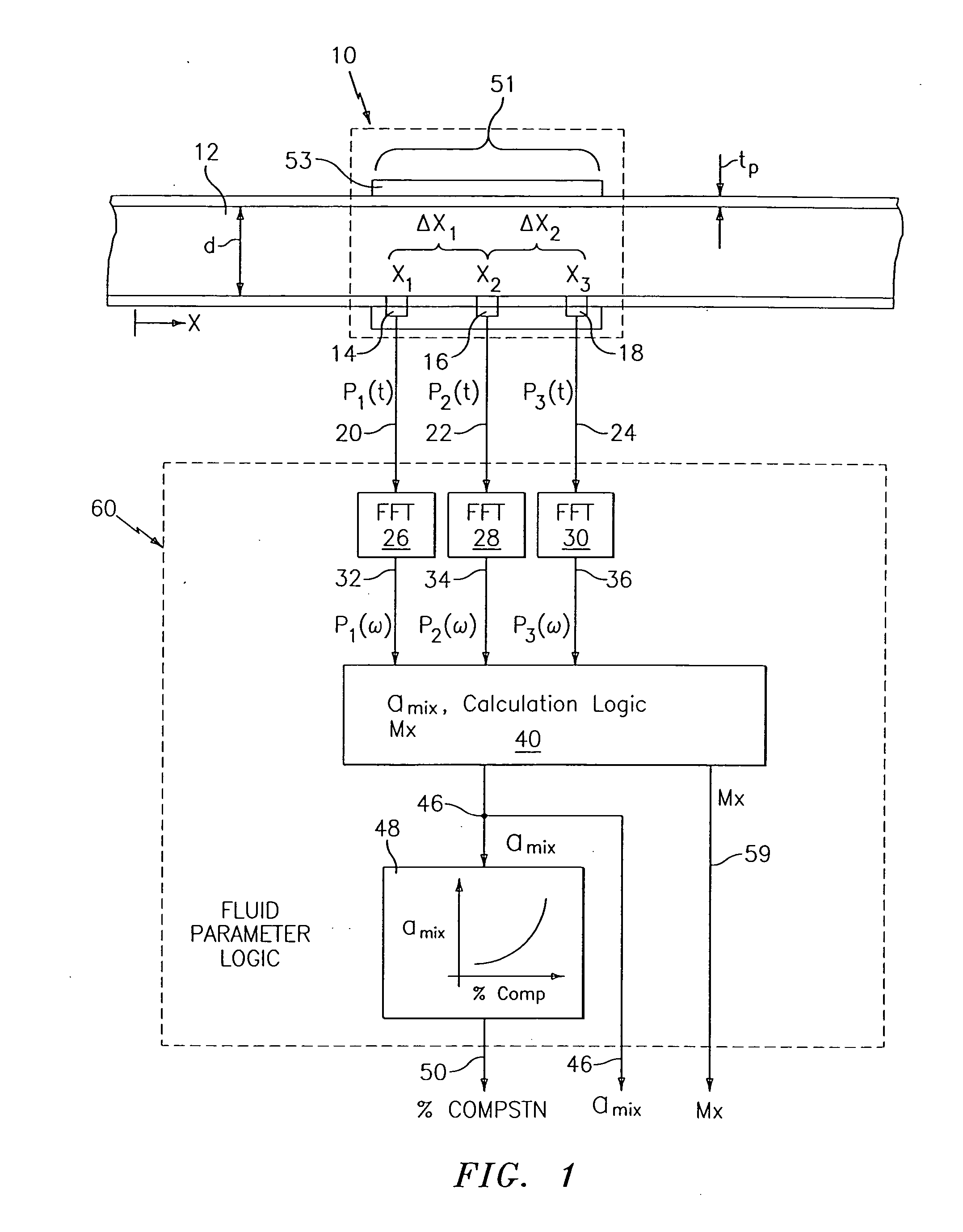
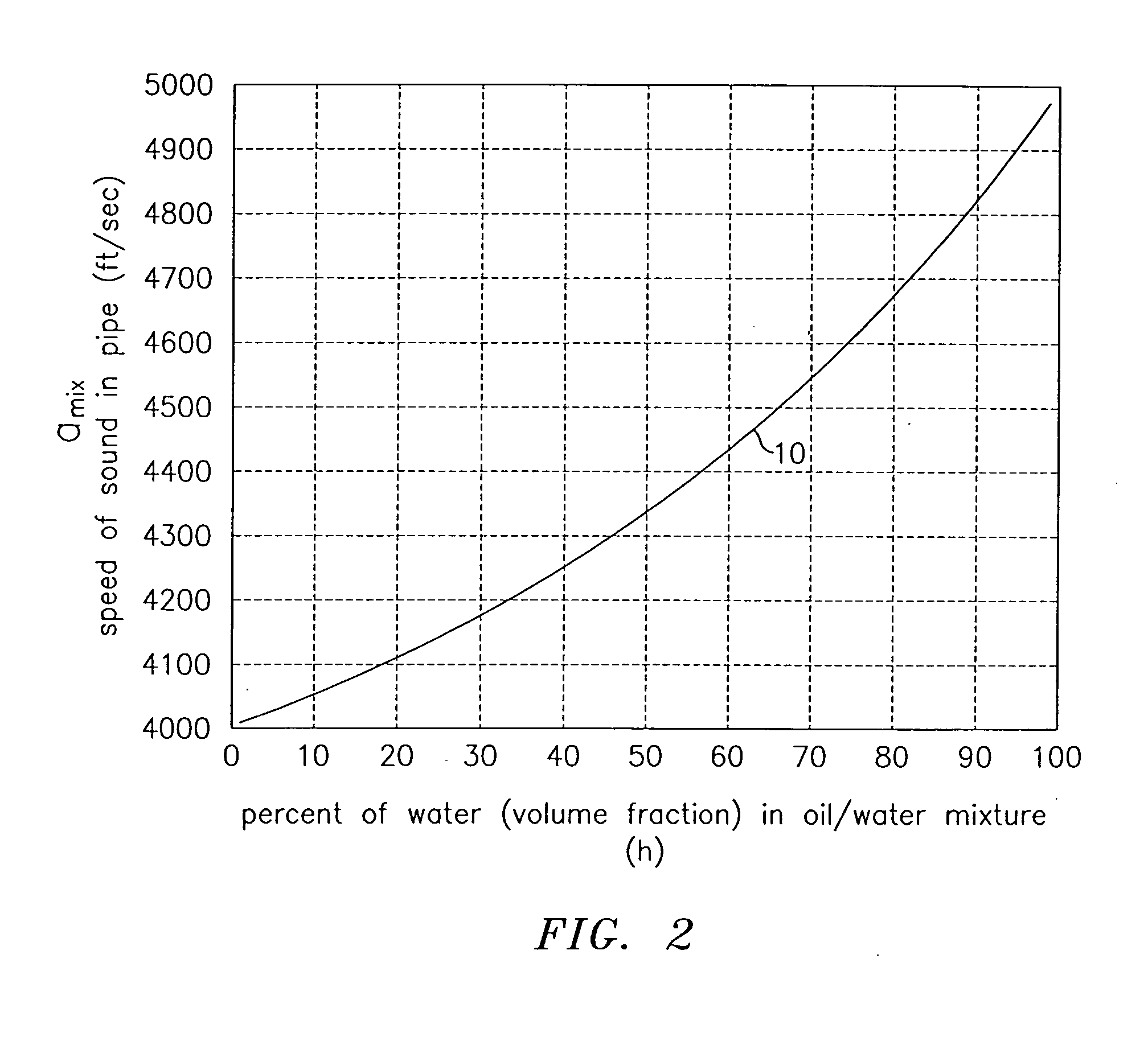
InactiveUS6862920B2Less sensitive to static shifts (or errors) in sensingImprove measurement reliabilityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringWater fraction
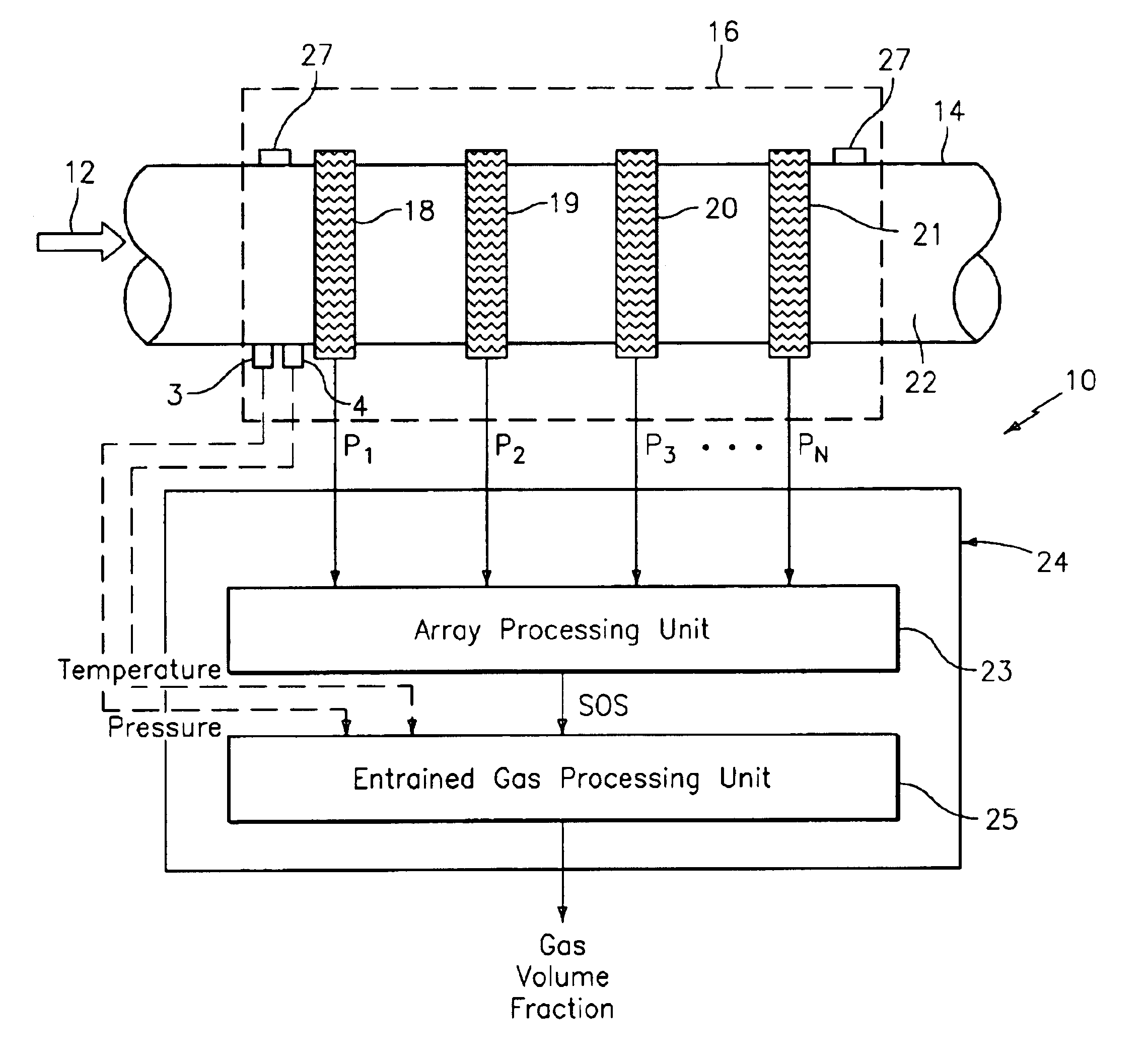
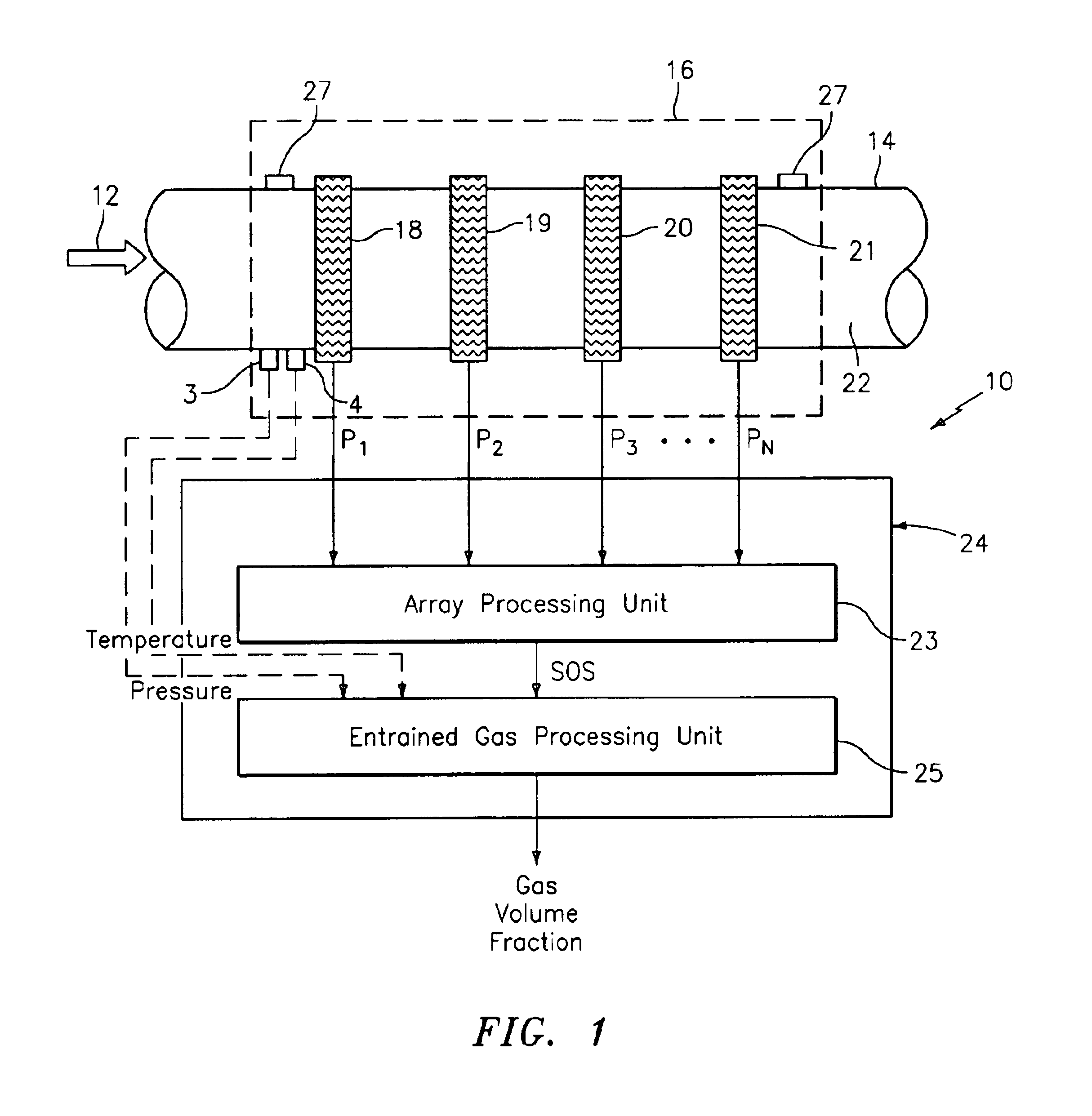
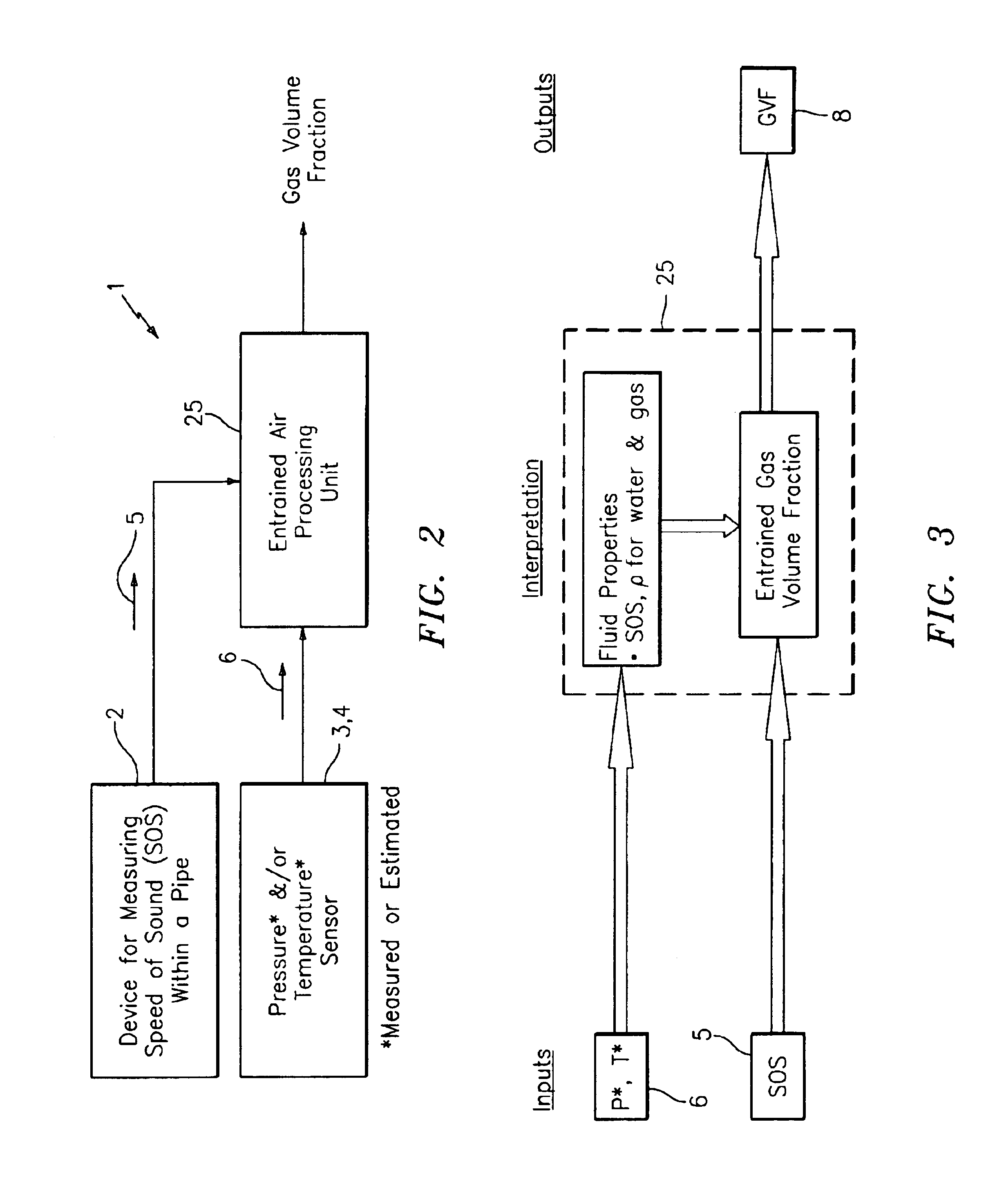
At least one parameter of at least one fluid in a pipe is measured using a spatial array of acoustic pressure sensors placed at predetermined axial locations along the pipe 12. The pressure sensors provide acoustic pressure signals, which are provided to a signal processing system that determines the speed of sound amix of the fluid (or mixture) in the pipe 12 using acoustic spatial array signal processing techniques. Numerous spatial array processing techniques may be employed to determine the speed of sound amix. The speed of sound amix is provided to another logic system that calculates the percent composition of the mixture, e.g., water fraction, or any other parameter of the mixture or fluid which is related to the sound speed amix. The signal processing system may also determine the Mach number Mx of the fluid. The acoustic pressure signals measured are lower frequency (and longer wavelength) signals than those used for ultrasonic flow meters, and thus are more tolerant to inhomogeneities in the flow. No external source is required and thus may operate using passive listening. The invention will work with arbitrary sensor spacing and with as few as two sensors if certain information is known about the acoustic properties of the system.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
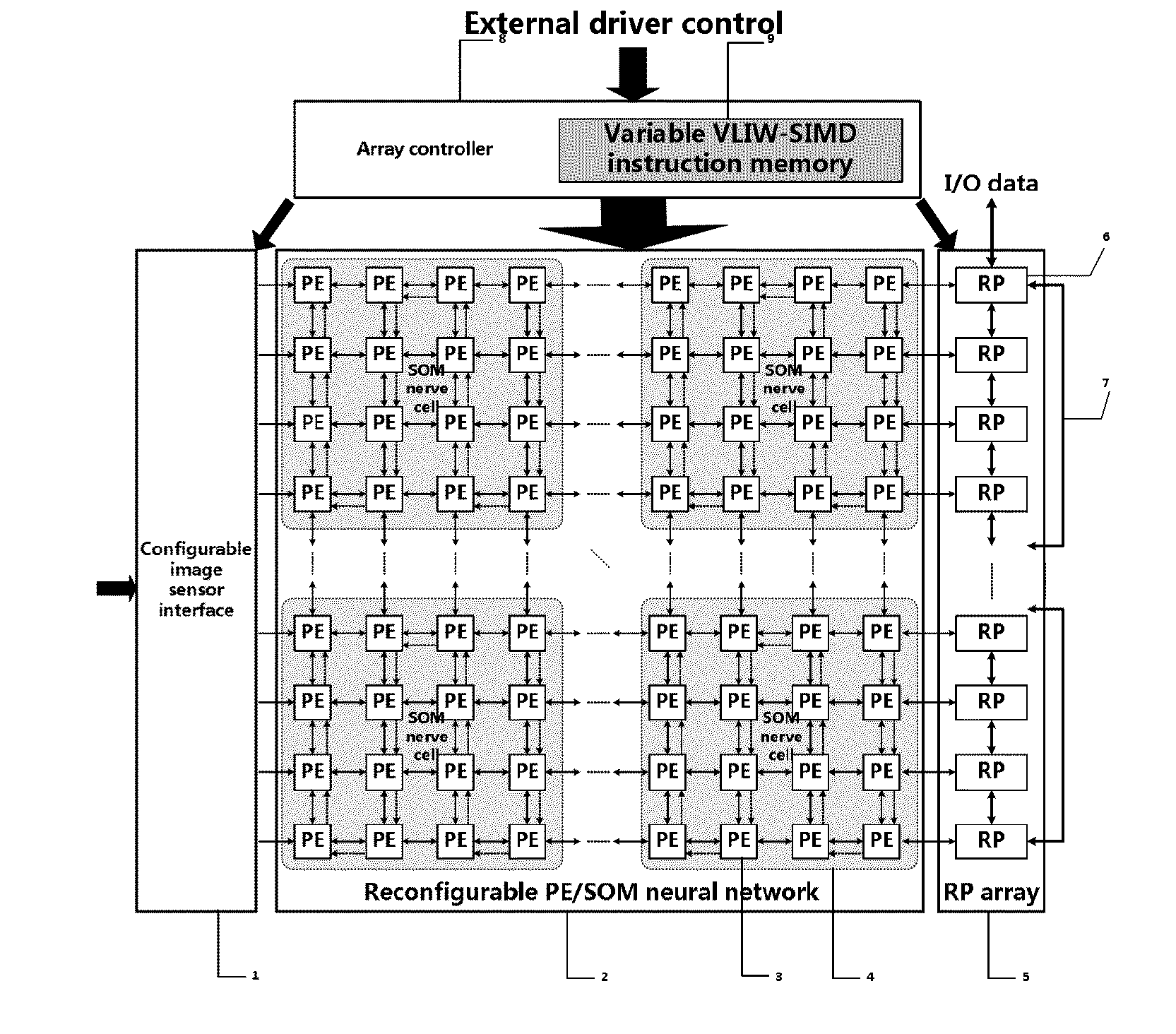
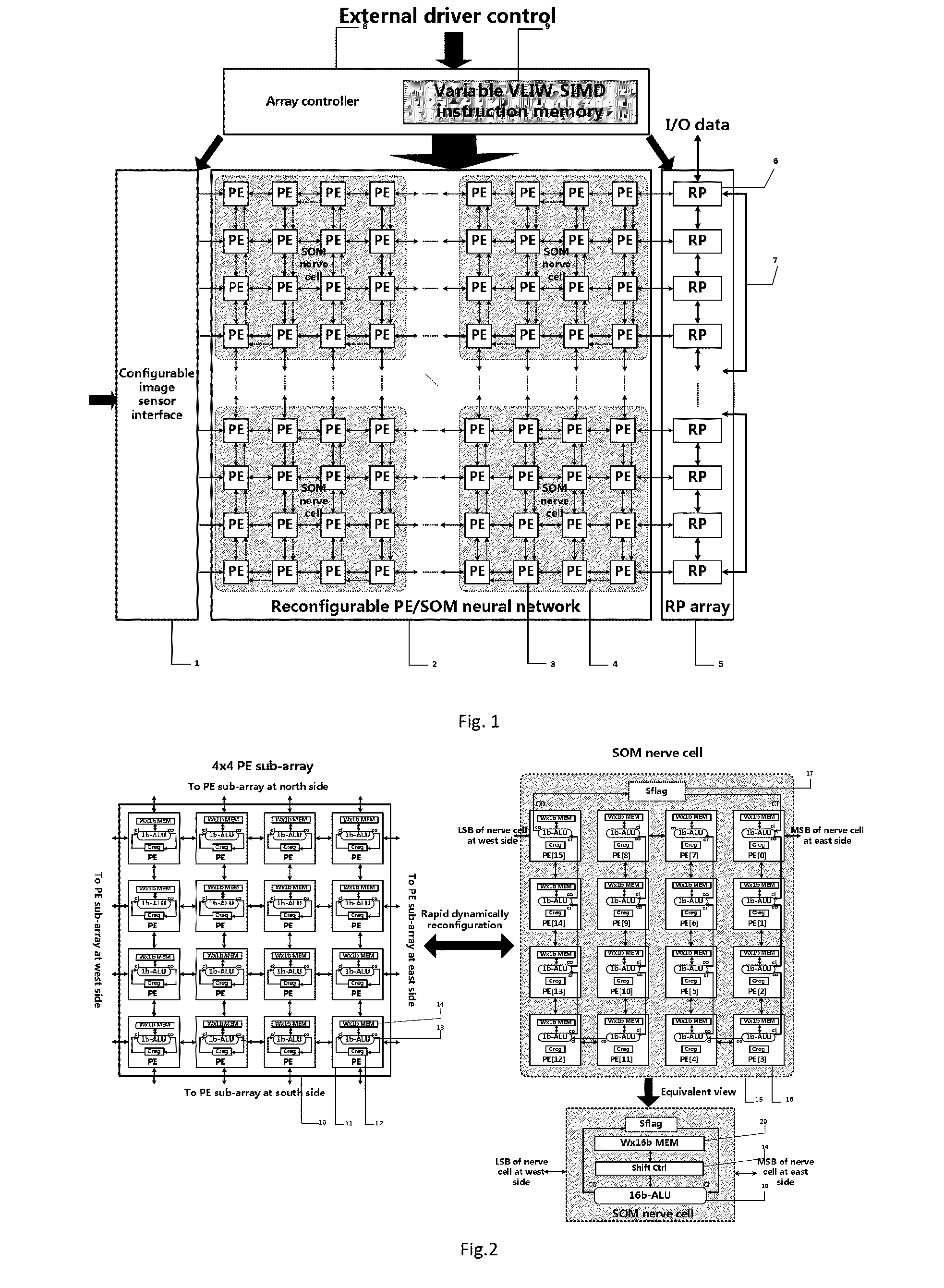
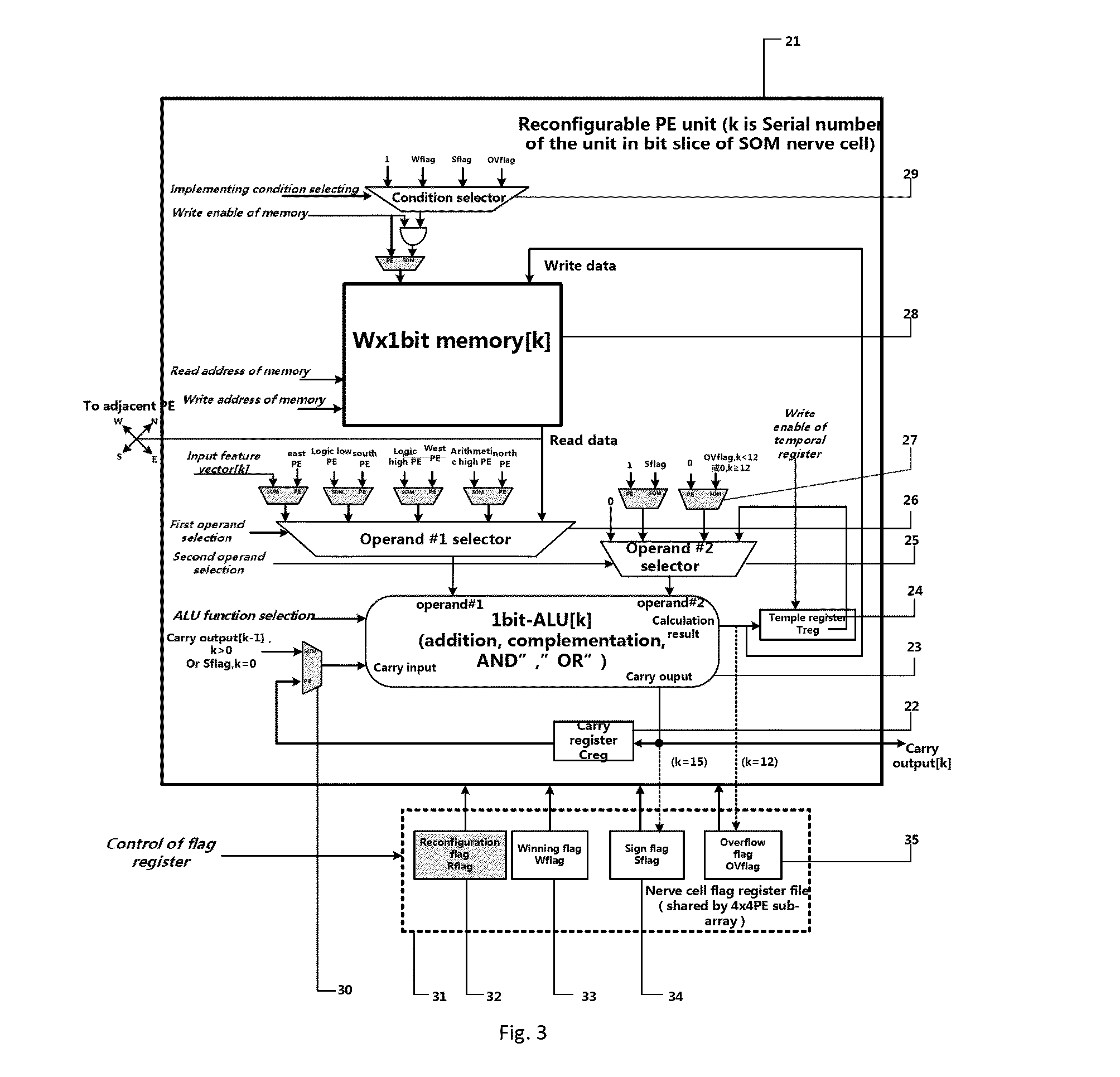
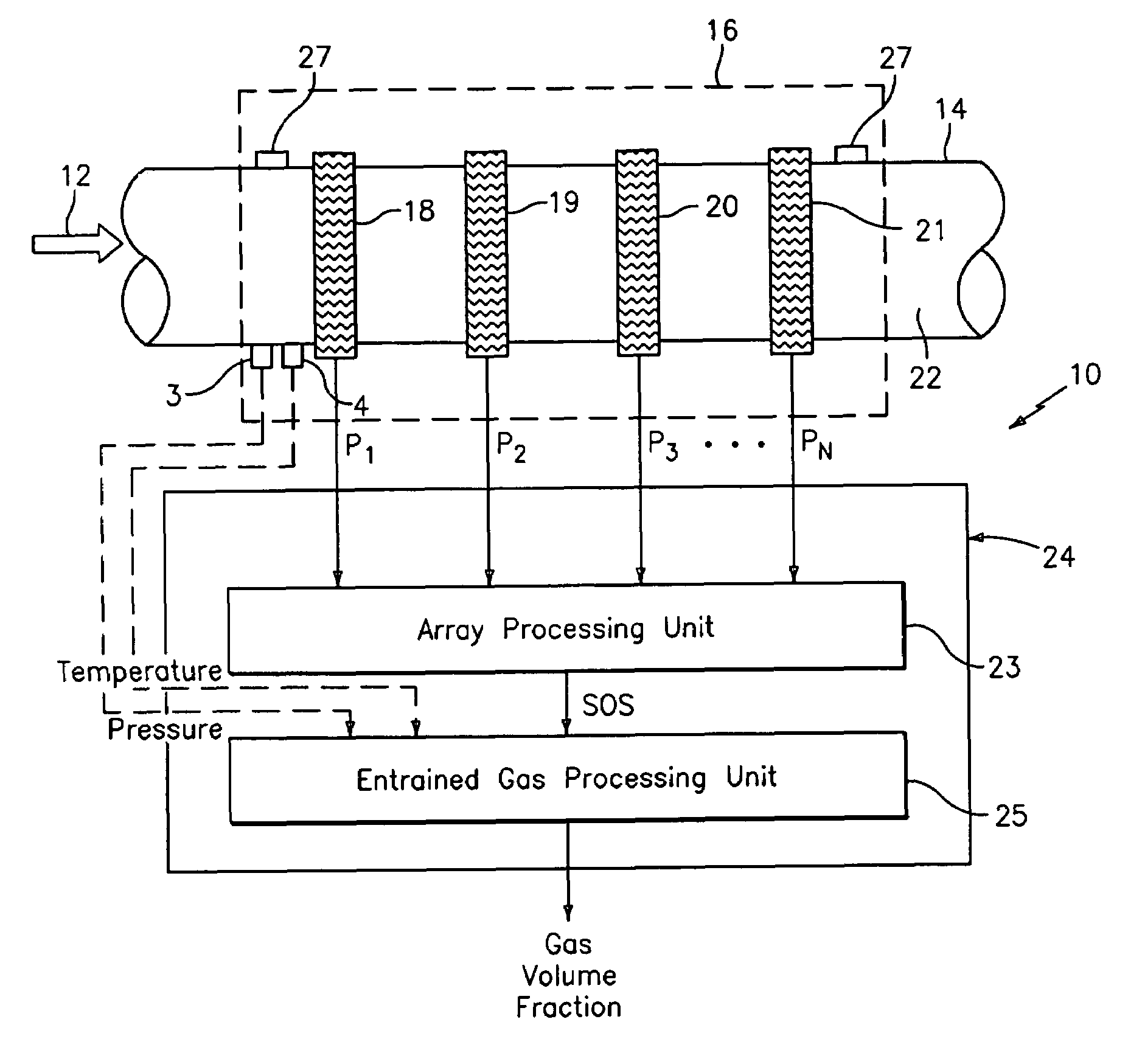
Dynamically reconfigurable multi-stage parallel single instruction multiple data array processing system
ActiveCN103019656AFunctionalImplement image feature extractionConcurrent instruction executionImaging processingReconfigurable computing
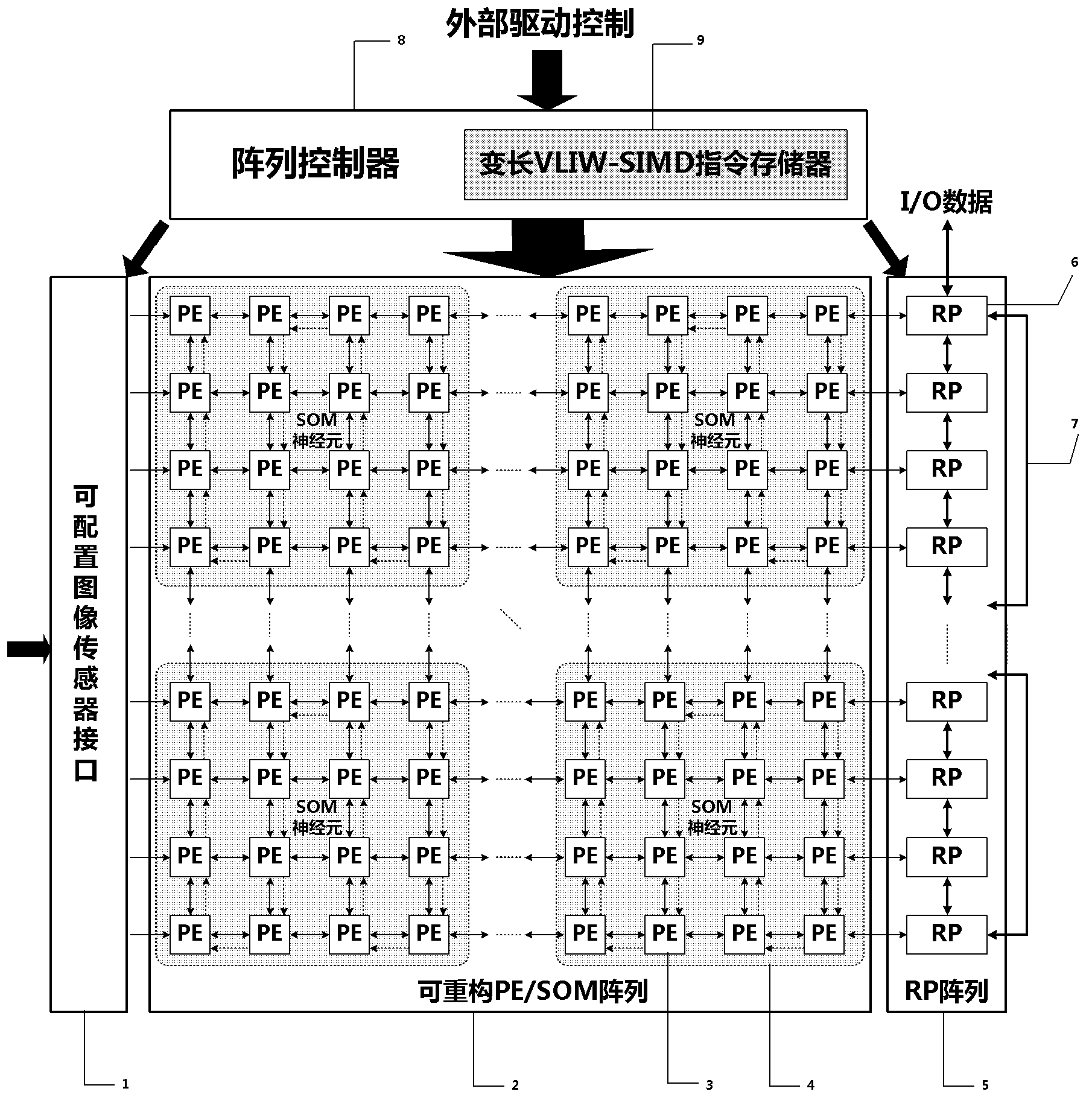
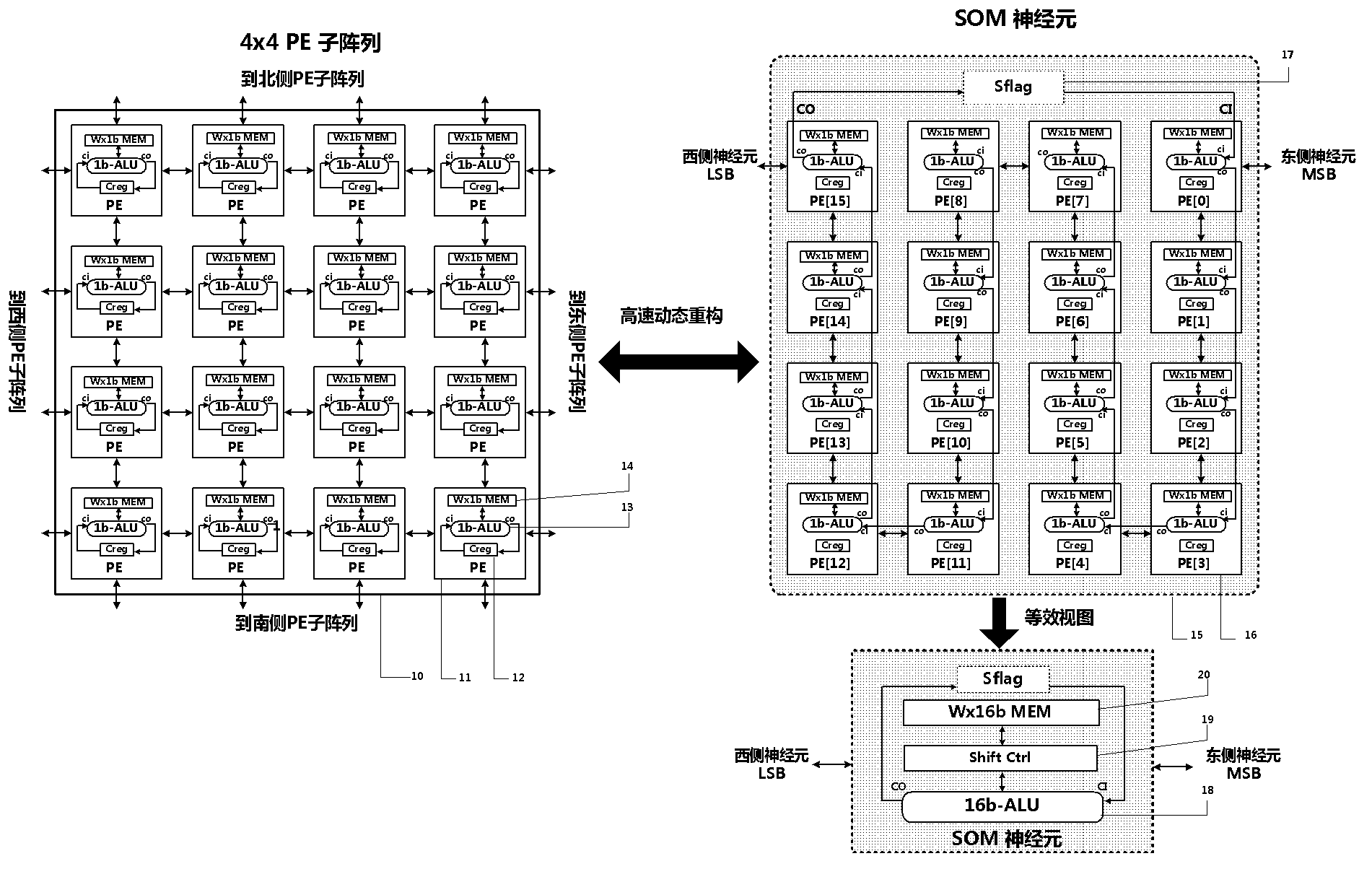
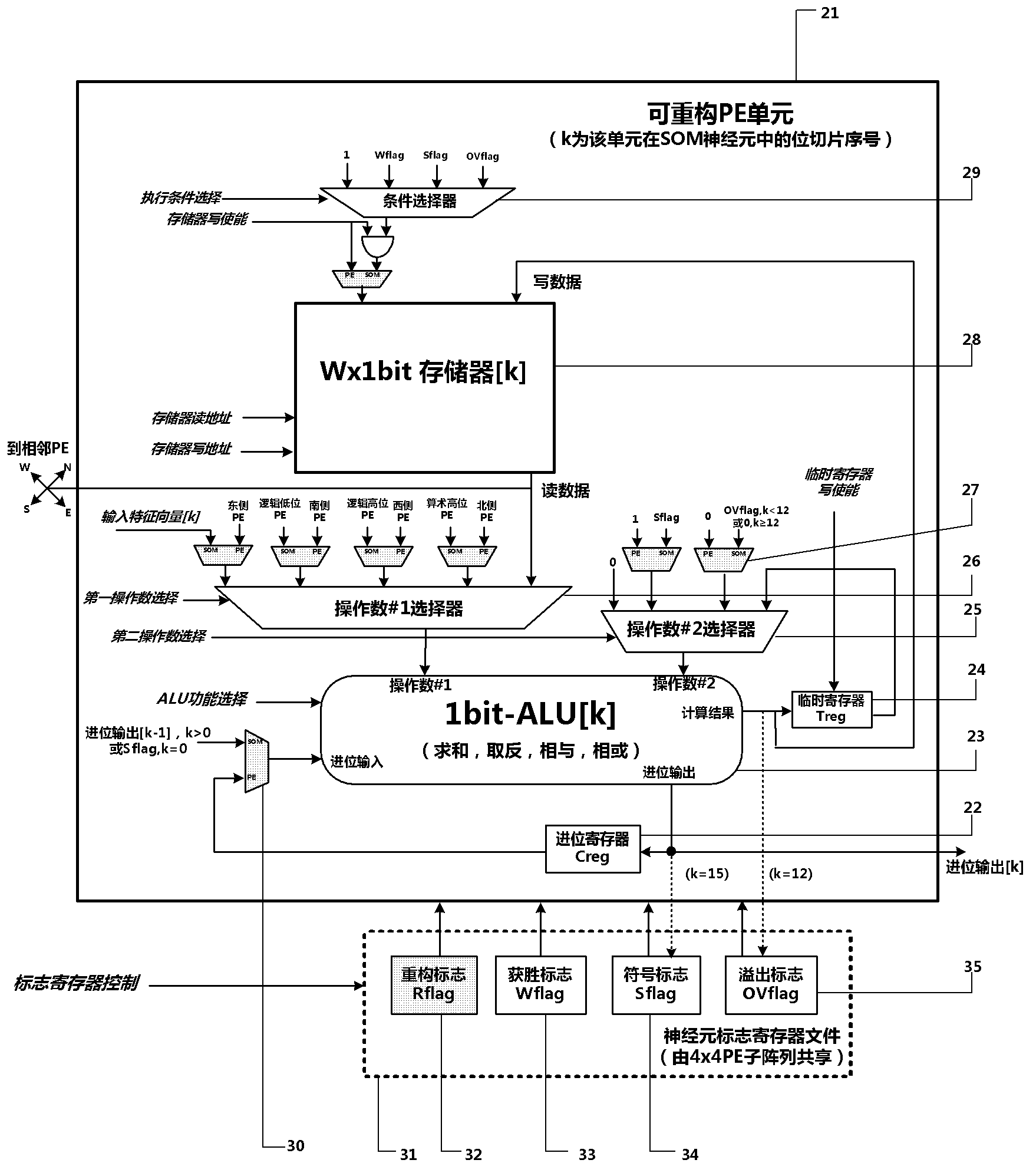
The invention discloses a dynamically reconfigurable multi-stage parallel single instruction multiple data array processing system, which comprises a pixel level parallel processing element (PE) array and a row parallel row processor (RP) array, wherein the PE array is mainly used for finishing a linear operation part suitable for the parallel execution of all pixels in low-level and intermediate-level image processing; the RP array is used for operation suitable to be finished in a row parallel way or complex nonlinear operation in the low-level and intermediate-level processing; and particularly, the PE array can also be dynamically reconfigured into a two-dimensional self-organizing map (SOM) neural network with extremely low performance and area overhead, and the neural network can realize advanced image processing functions of high-speed parallel online training, feature recognition and the like with the coordination of RPs. The shortcoming that advanced image processing cannot be used for pixel level parallel RP arrays in the conventional programmable vision chip and the conventional parallel vision processor is completely overcome, and the implementation of a fully-functional, low-cost, low-power consumption, intelligent and portable high-speed real-time visual image system on chip is facilitated.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radio apparatus, method for receiving its signal, method for measuring its filter coefficient, and program for measuring its filter coefficient
InactiveUS7110795B2Accurately determineError minimizationSpatial transmit diversityDigital technique networkRadio equipmentEngineering
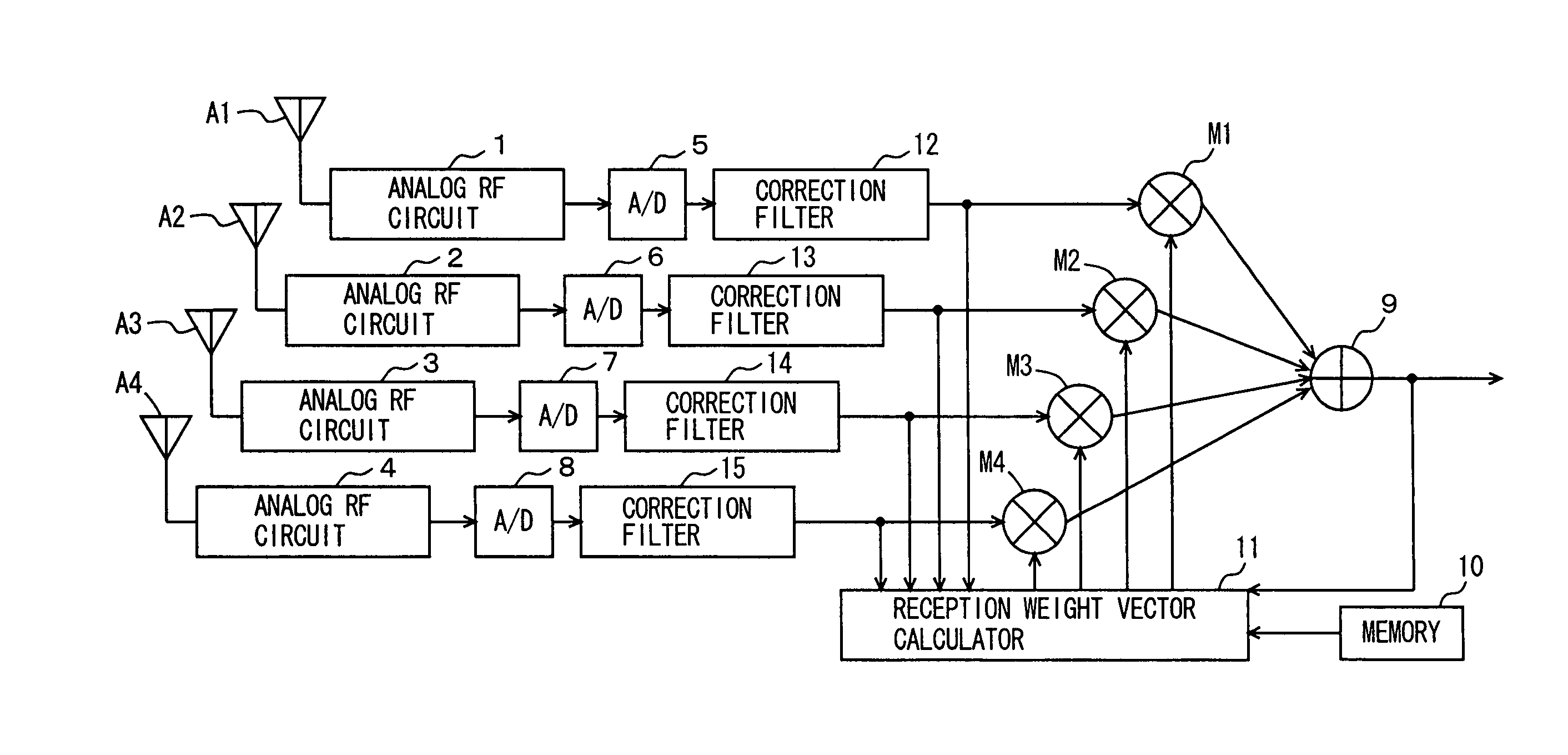
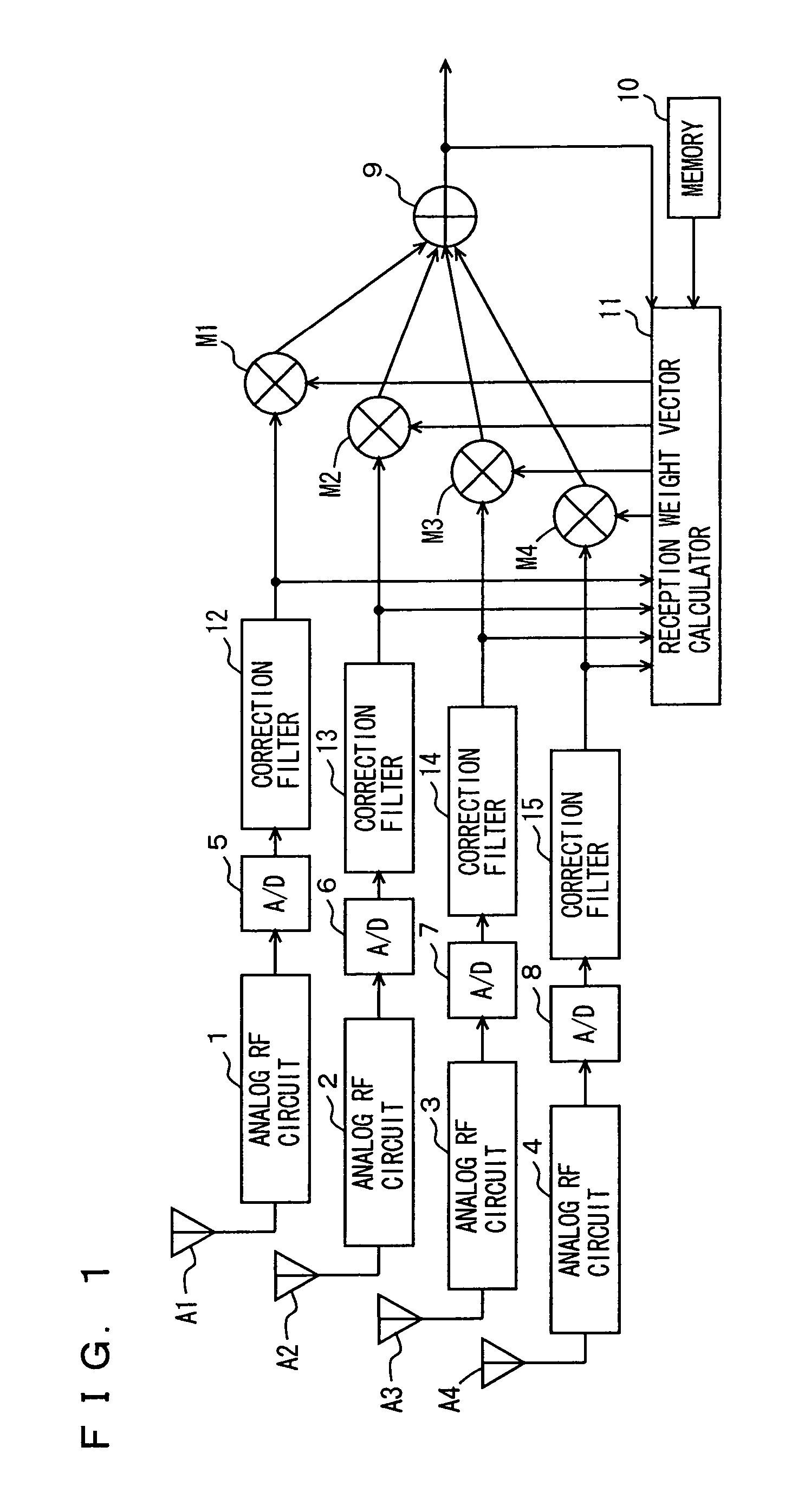
Corresponding to antennas analog RF circuits are provided and their outputs are converted by A / D converters to digital signals. Subsequent thereto and preceding an adaptive array processing, correction filters are arranged. Each correction filter has a filter coefficient for compensating for a difference between a characteristic of an analog RF circuit corresponding thereto and an ideal circuit characteristic. Thus an error of a characteristic between the analog RF circuits can be compensated for. The series of operations are implemented by software.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Cooperative beam-forming in wireless networks
ActiveUS8670390B2Site diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency reuseWireless mesh network
A beam-forming system comprises a cooperative array of wireless terminals coupled to at least one wireless wide area network (WWAN) and communicatively coupled to a wireless local area network (WLAN) configured to provide information exchanges between the wireless terminals. A cooperative beam-forming system employing the WLAN provides antenna-array processing benefits (such as frequency reuse, interference rejection, array-processing gain, antenna-switching diversity) to the individual wireless terminals. A network access operator facilitates network control functionality between the WWAN and the cooperative array of wireless terminals.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Method and system for providing diversity in a network that utilizes distributed transceivers and array processing
ActiveUS20130095874A1Improved range/throughputEnergy efficient ICTSite diversityTransceiverPolarization diversity
A communication device that comprises a plurality of distributed transceivers, a central processor and a network management engine may be configured based on one or more diversity modes of operations. The diversity modes of operations may comprise a spatial diversity mode, a frequency diversity mode, and / or a polarization diversity mode. Diversity mode configuration may comprise forming, based on selected diversity mode, a plurality of communication modules from the plurality of distributed transceivers, wherein each of the plurality of communication modules may comprise one or more antennas and / or antenna array elements, and one or more of said plurality of distributed transceivers associated with said one or more antennas and / or antenna array elements. The plurality of communication modules may be utilized to concurrently communicate multiple data streams. The multiple data streams may comprise the same data.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
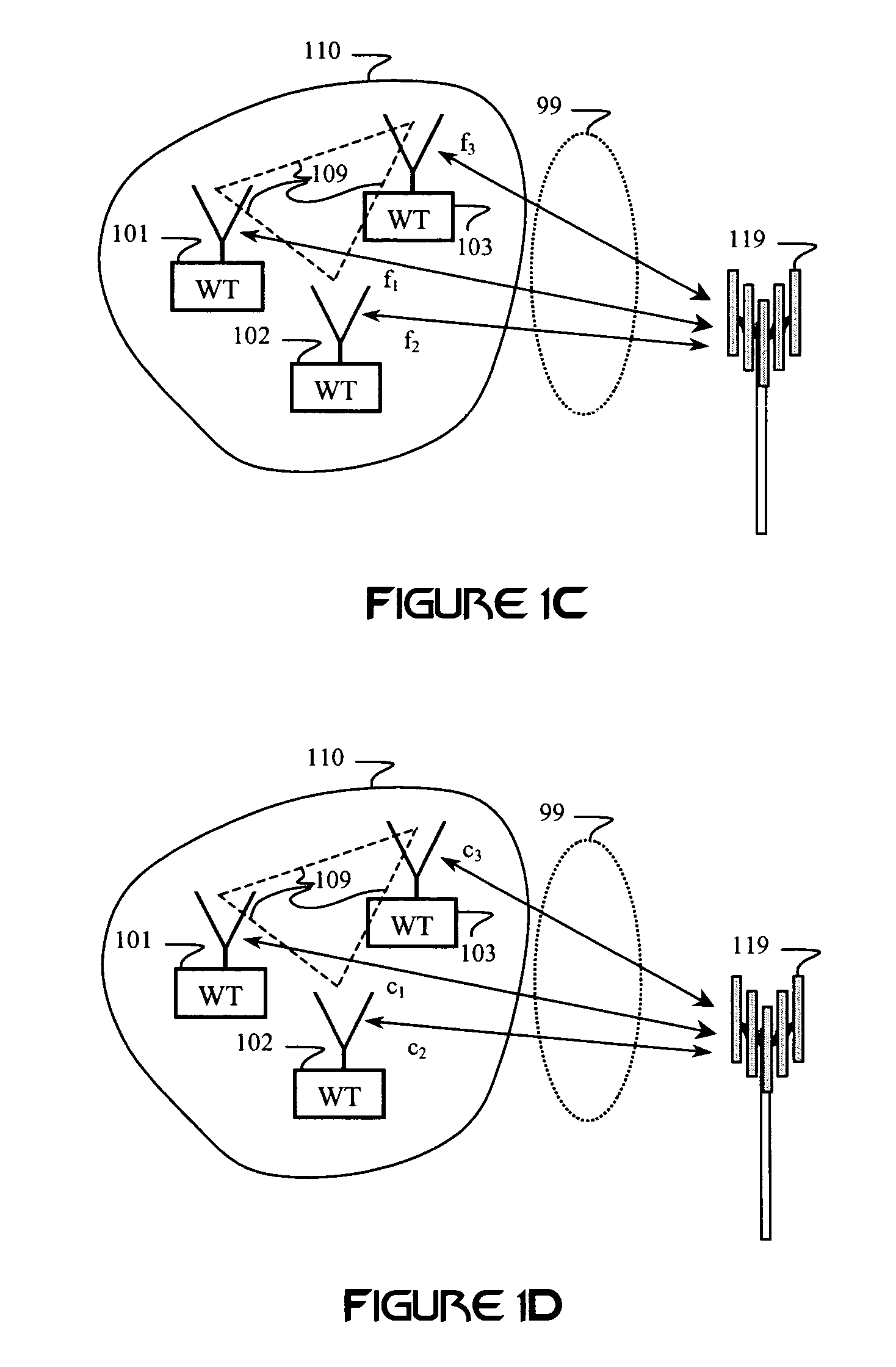
Method and system for utilizing multiplexing to increase throughput in a network of distributed transceivers with array processing
A communication device that comprises a plurality of distributed transceivers, a central processor and a network management engine, may be configured for a multiplexing mode of operation. Configuring of the multiplexing mode of operation may include configuring one or more communication modules for multiplexing a plurality of data streams. Each of the communication modules may comprise one or more antennas and / or antenna array elements and one or more of said plurality of distributed transceivers associated with said one or more antennas and / or antenna array elements. The communication modules may be configured to be spatially distinct and / or to use different frequency channels. The data streams may be communicated to a single target device or to a plurality of target devices.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
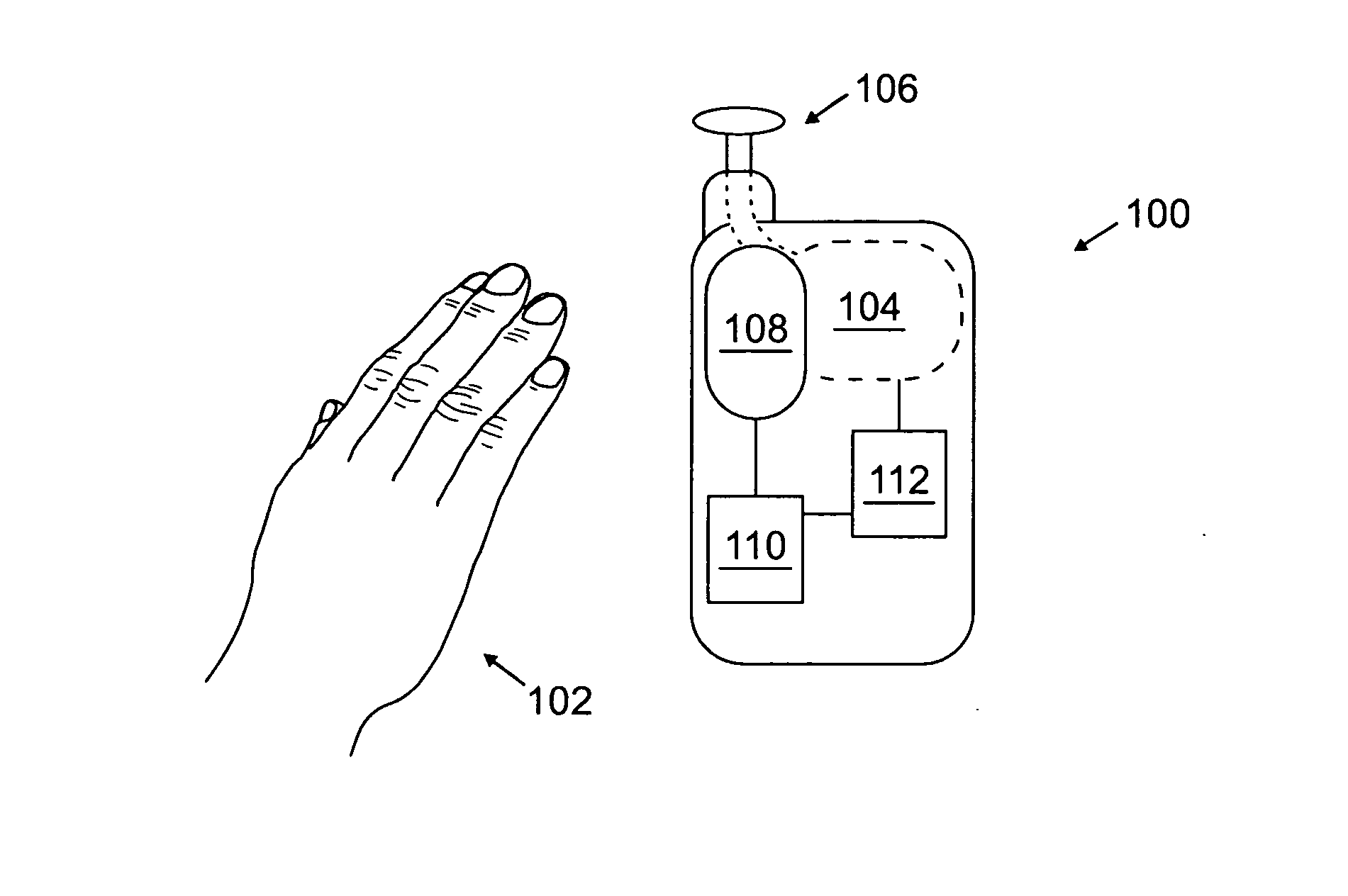
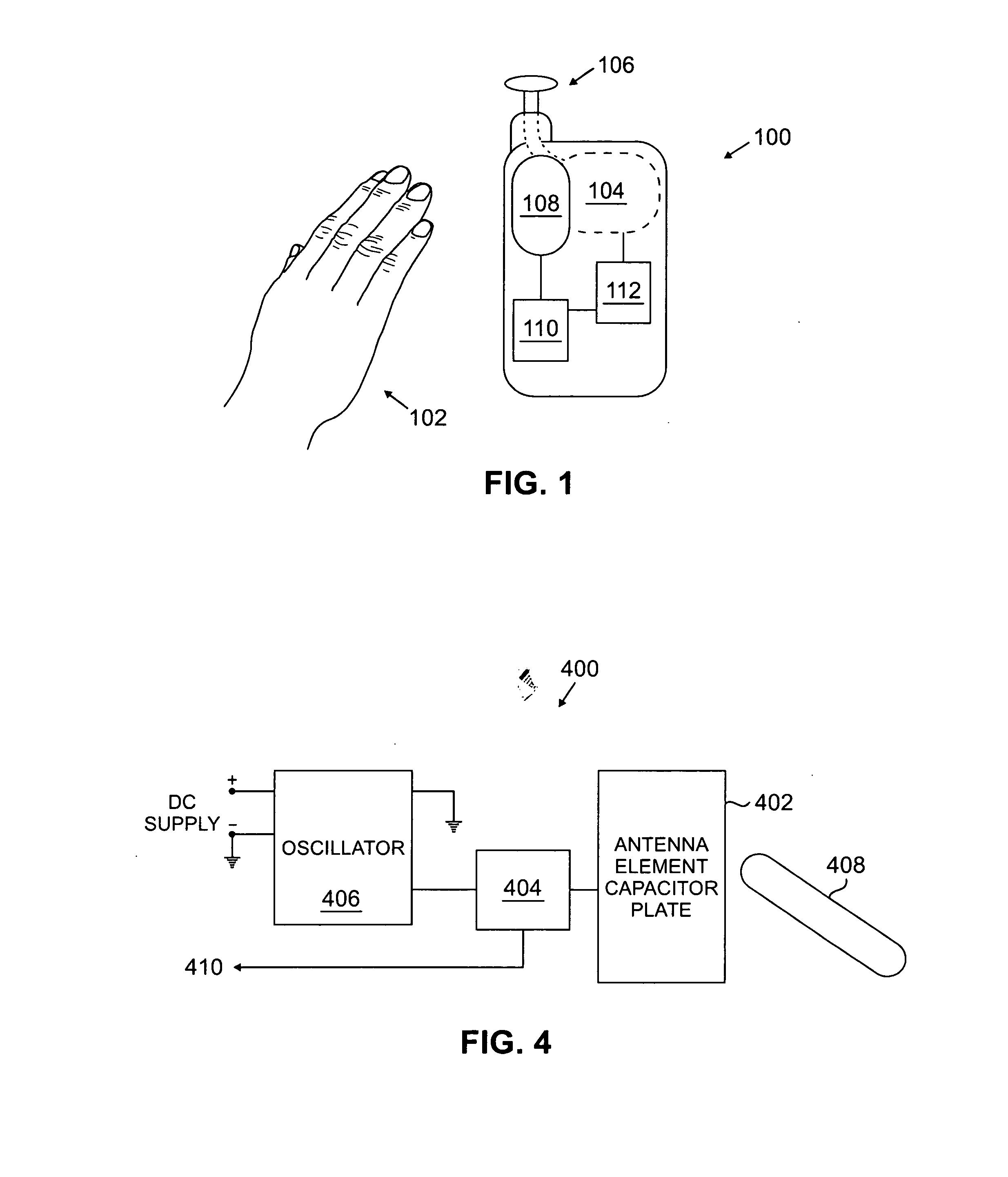
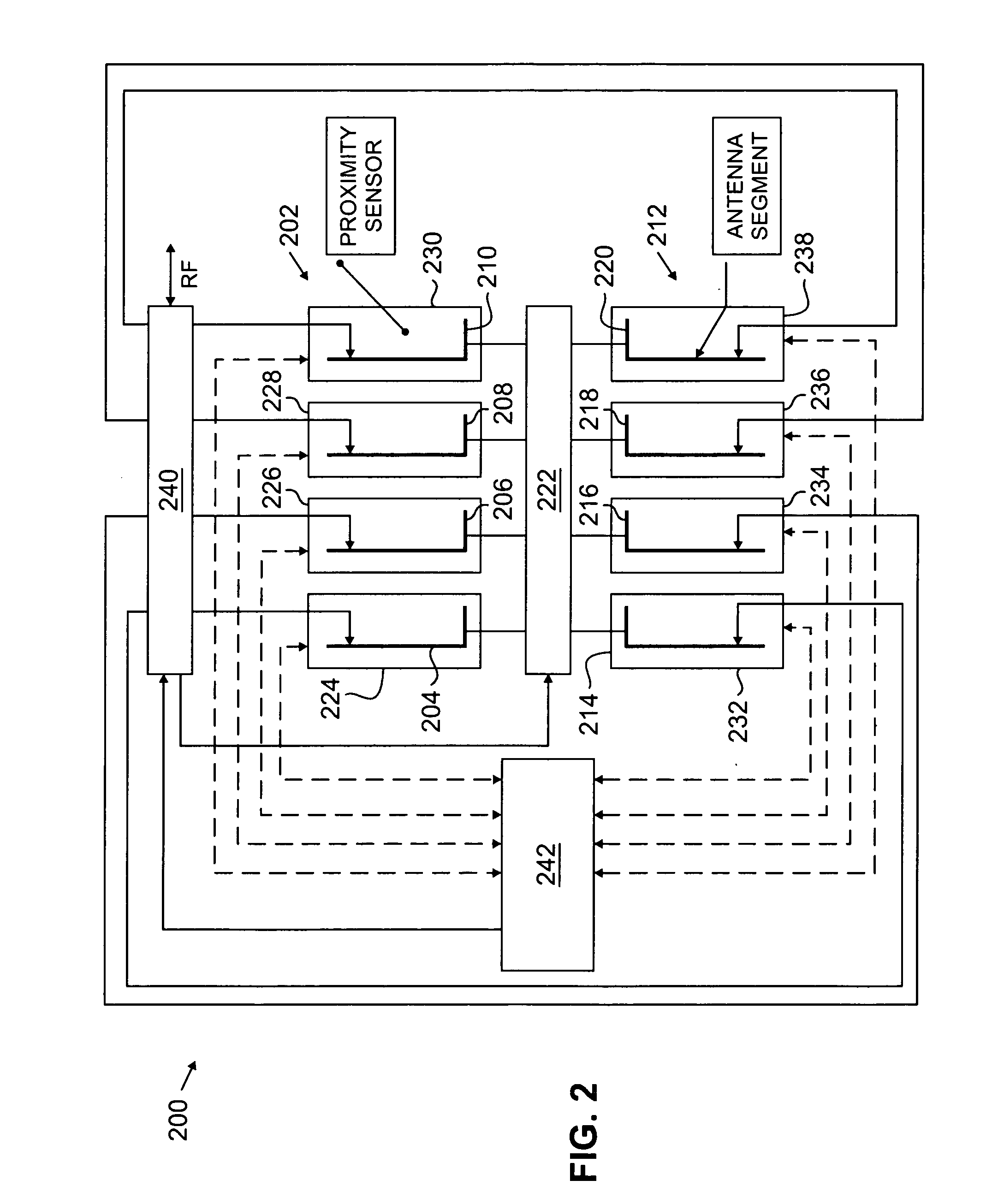
Versatile system for adaptive mobile station antenna
InactiveUS20070238496A1Minimize obviate impactMinimize obviate of and reliabilitySubstation equipmentRadio transmissionForeign objectEngineering
A system for providing an adaptive antenna system in a mobile communications device is disclosed. An array of antenna elements is provided. A sensing component is disposed along a surface of the mobile communications device, proximal to the array of antenna elements. A processor component is communicatively coupled to the sensing component. An implementation element is communicatively coupled to the processor component, and to the array of antenna elements. The sensor component generates data characterizing the proximity of a foreign object to the array of antenna elements; which the processing component uses to determine a configuration for the array of antenna elements. The implementation element modifies the array of antenna elements, responsive to the configuration determined by the processor component.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
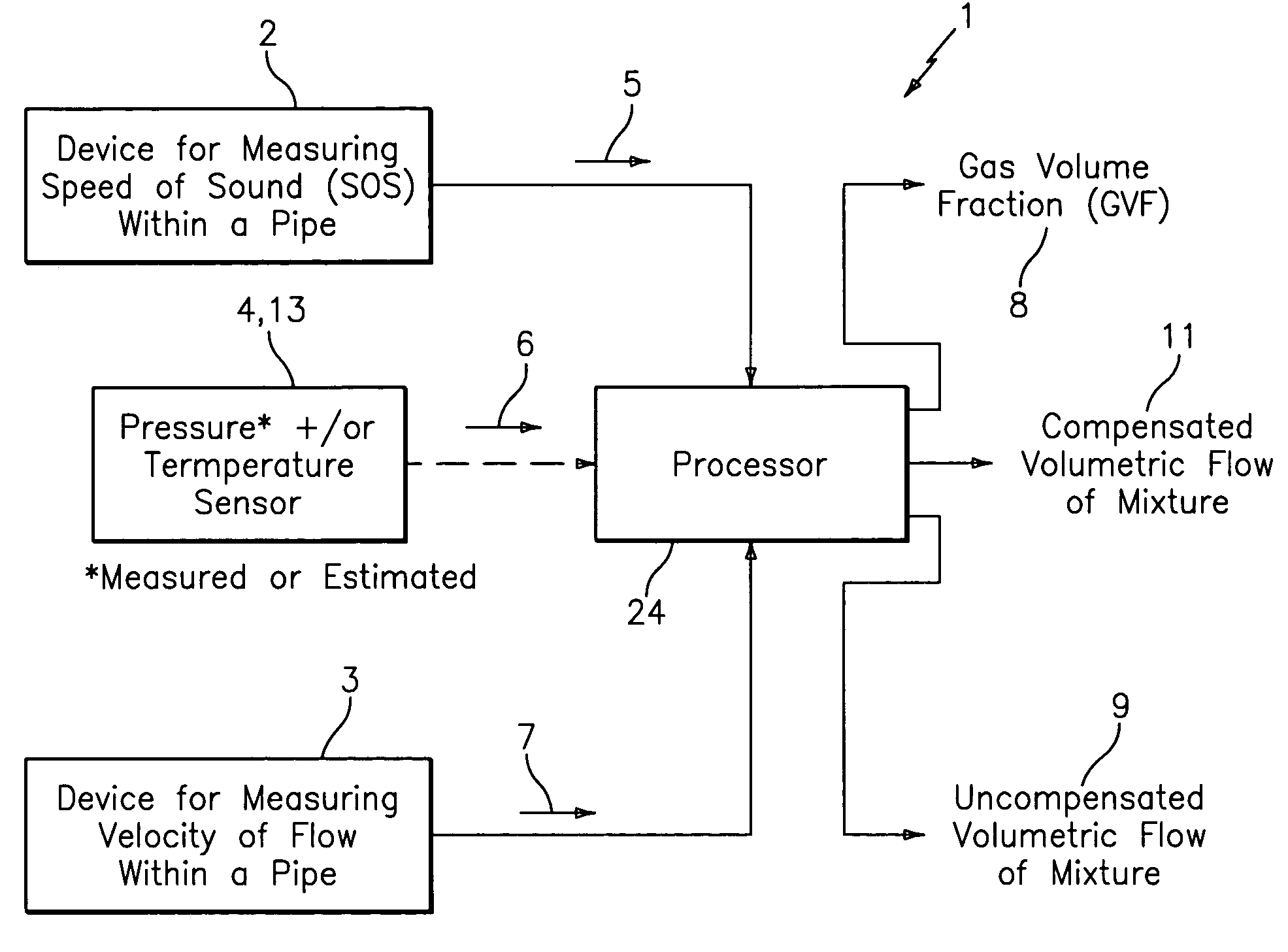
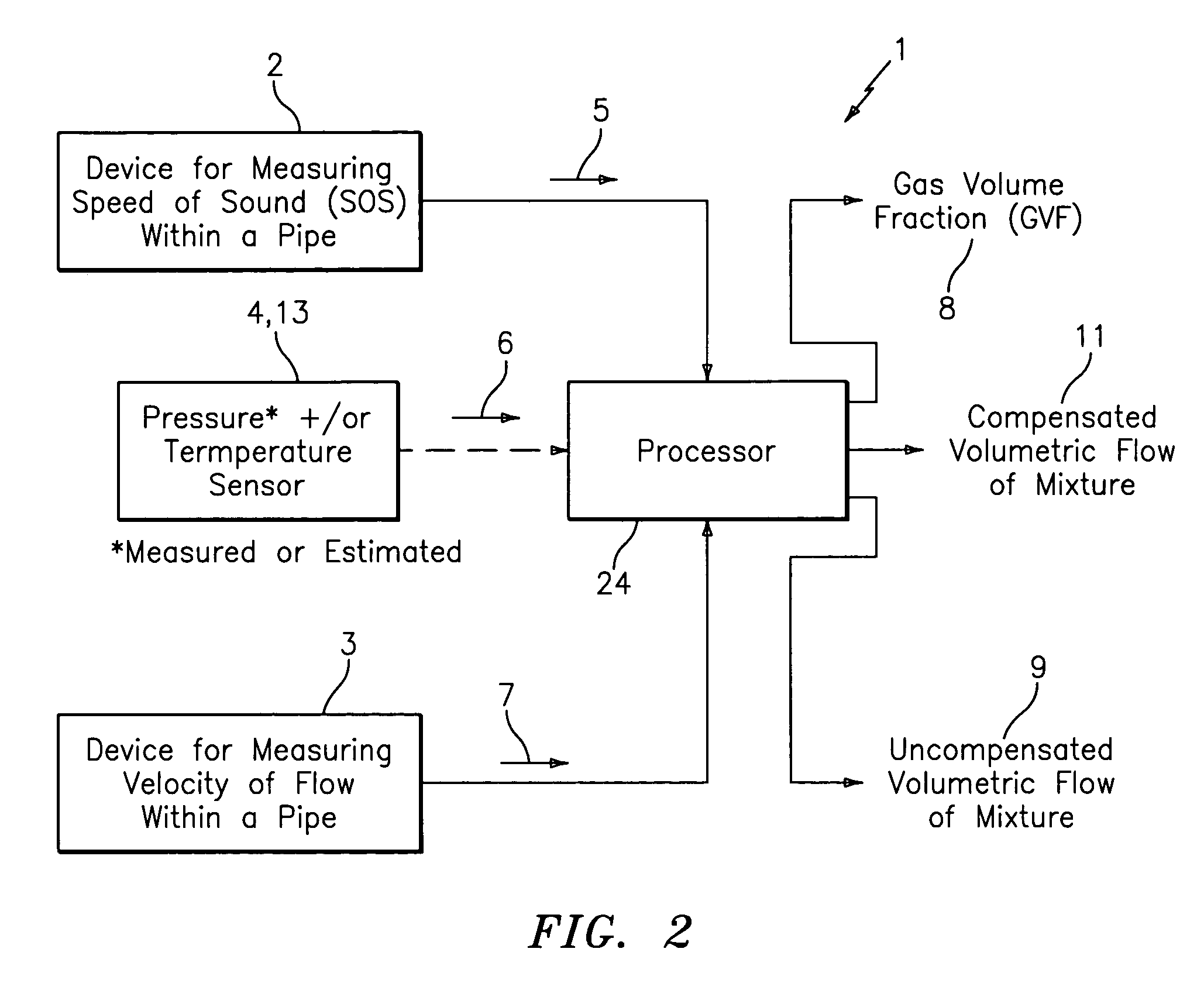
Apparatus and method for providing a flow measurement compensated for entrained gas
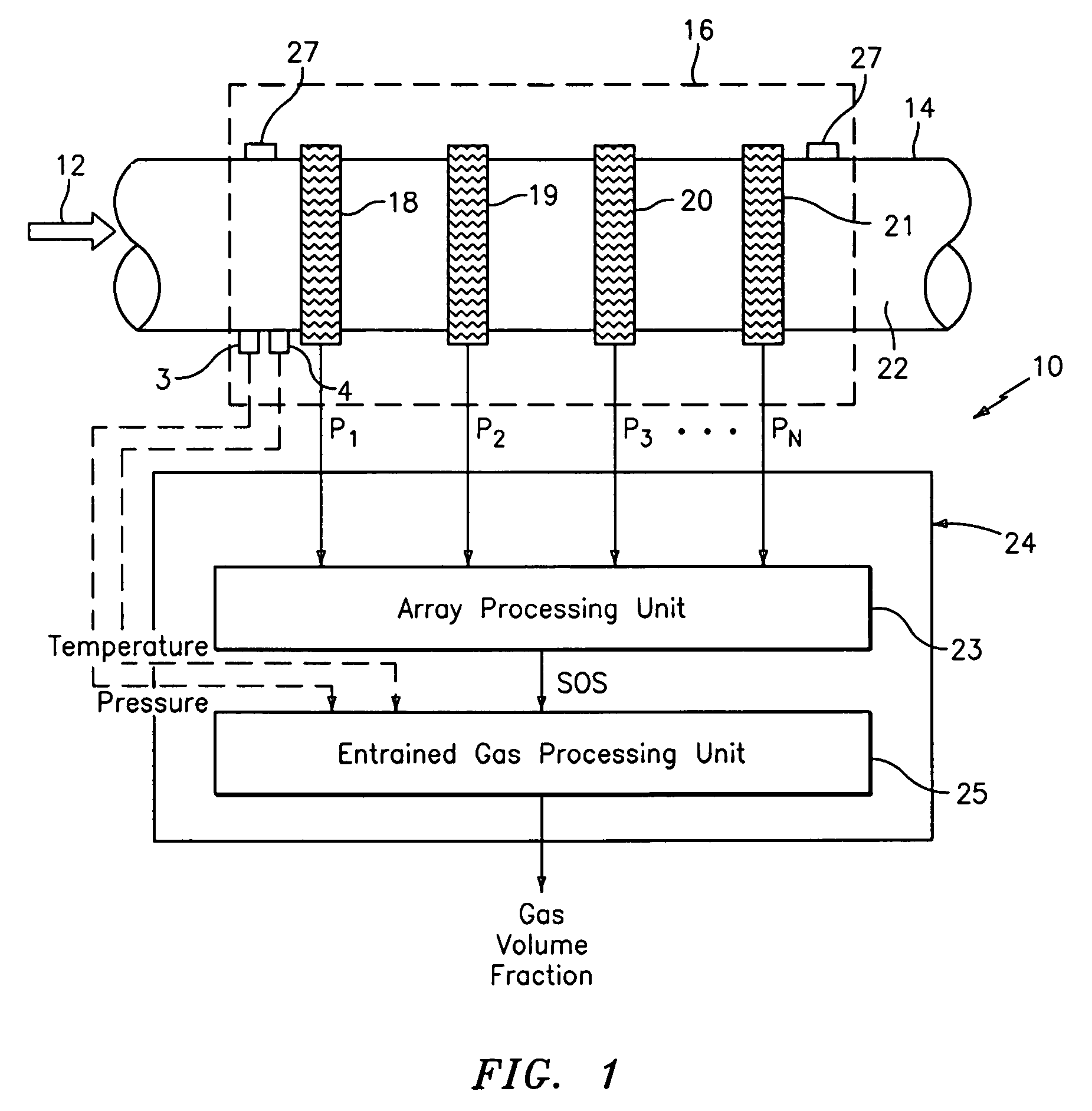
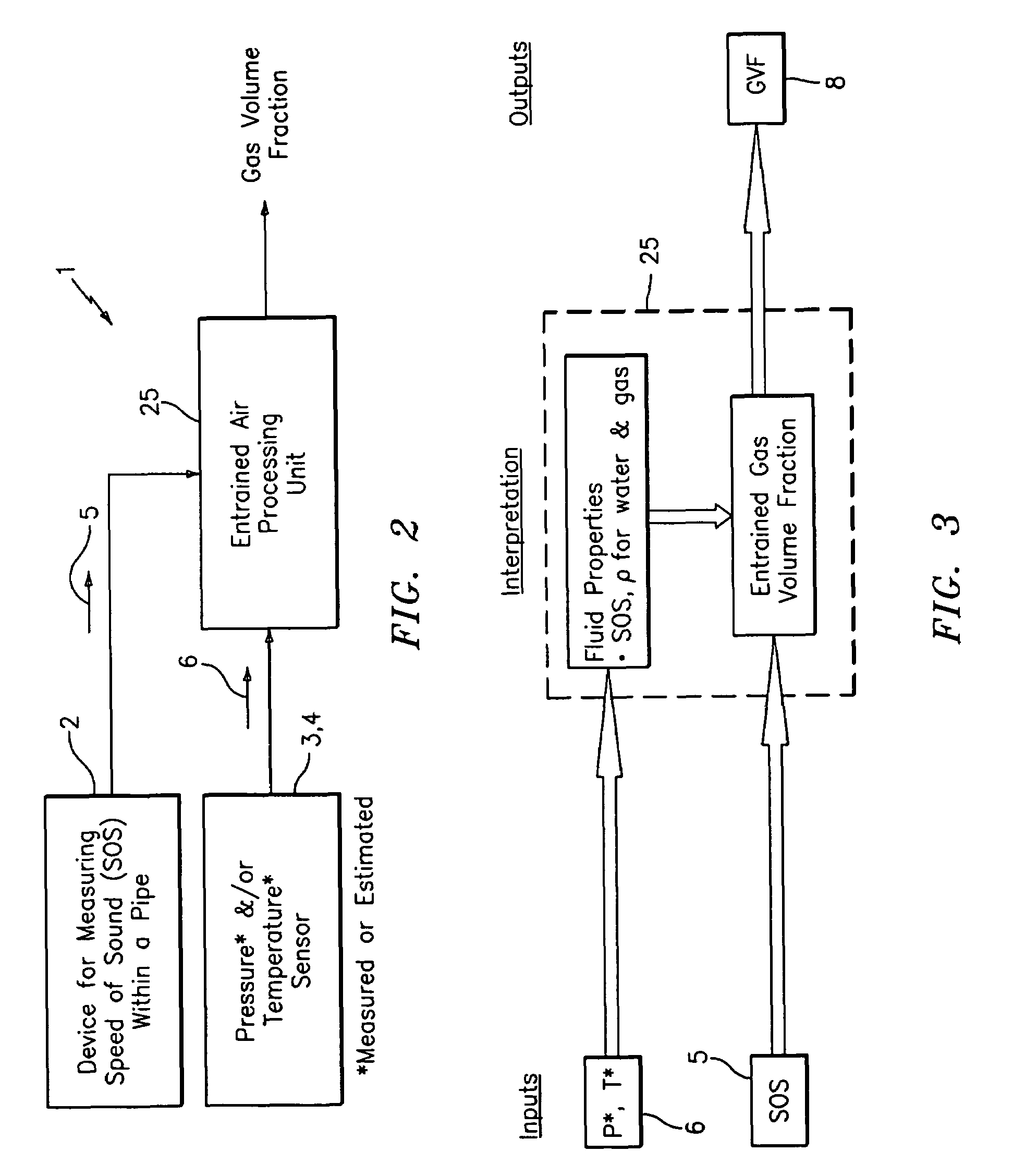
ActiveUS7165464B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using microwave meansSensor arrayAir entrainment
A apparatus 10,110 is provided that measures the speed of sound and / or vortical disturbances propagating in a fluid or mixture having entrained gas / air to determine the gas volume fraction of the flow 12 propagating through a pipes and compensating or correcting the volumetric flow measurement for entrained air. The GVF meter includes and array of sensor disposed axially along the length of the pipe. The GVF measures the speed of sound propagating through the pipe and fluid to determine the gas volume fraction of the mixture using array processing. The GVF meter can be used with an electromagnetic meter and a consistency meter to compensate for volumetric flow rate and consistency measurement respective, to correct for errors due to entrained gas / air.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
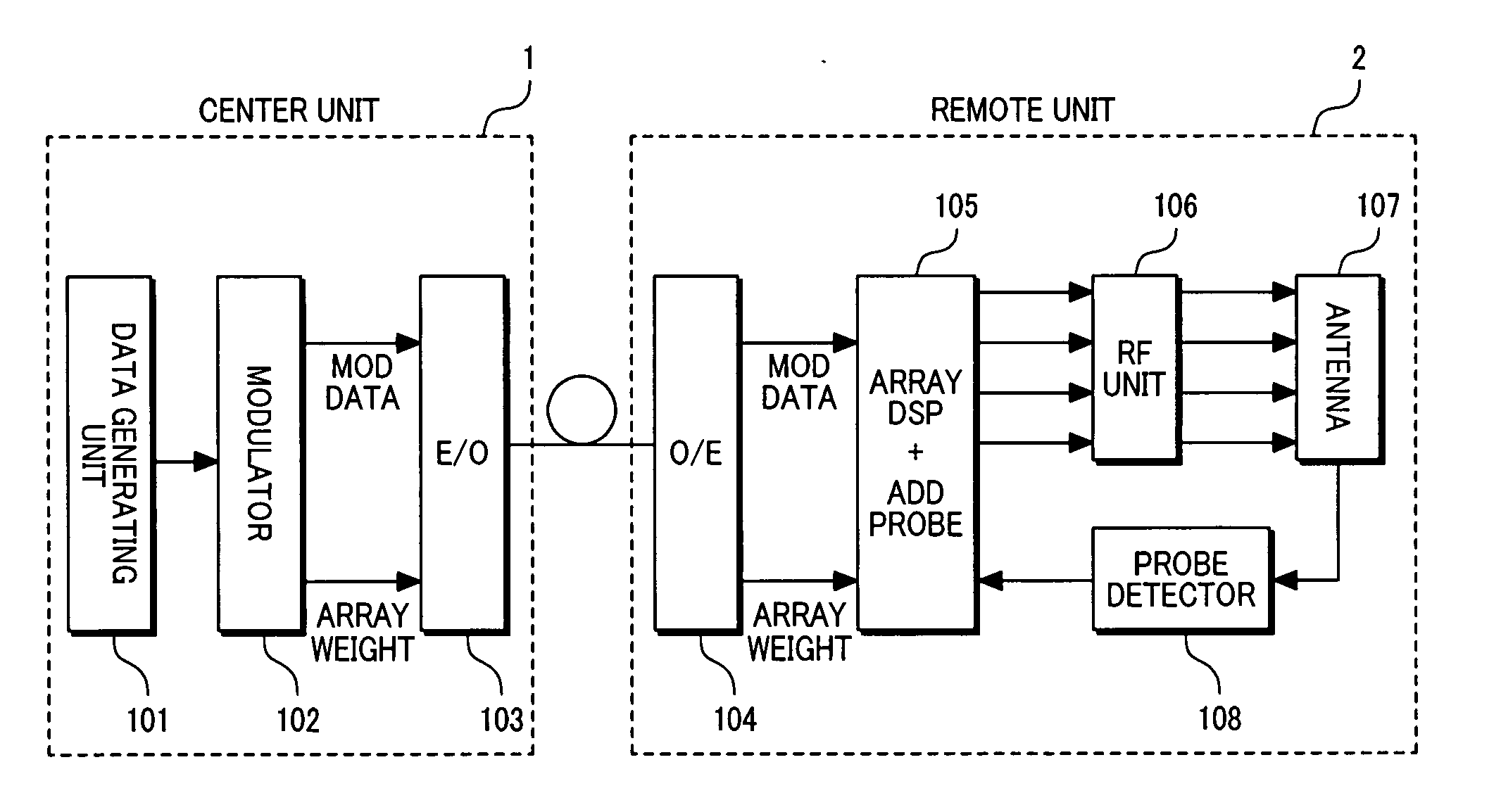
Wireless base station and communication method therefor
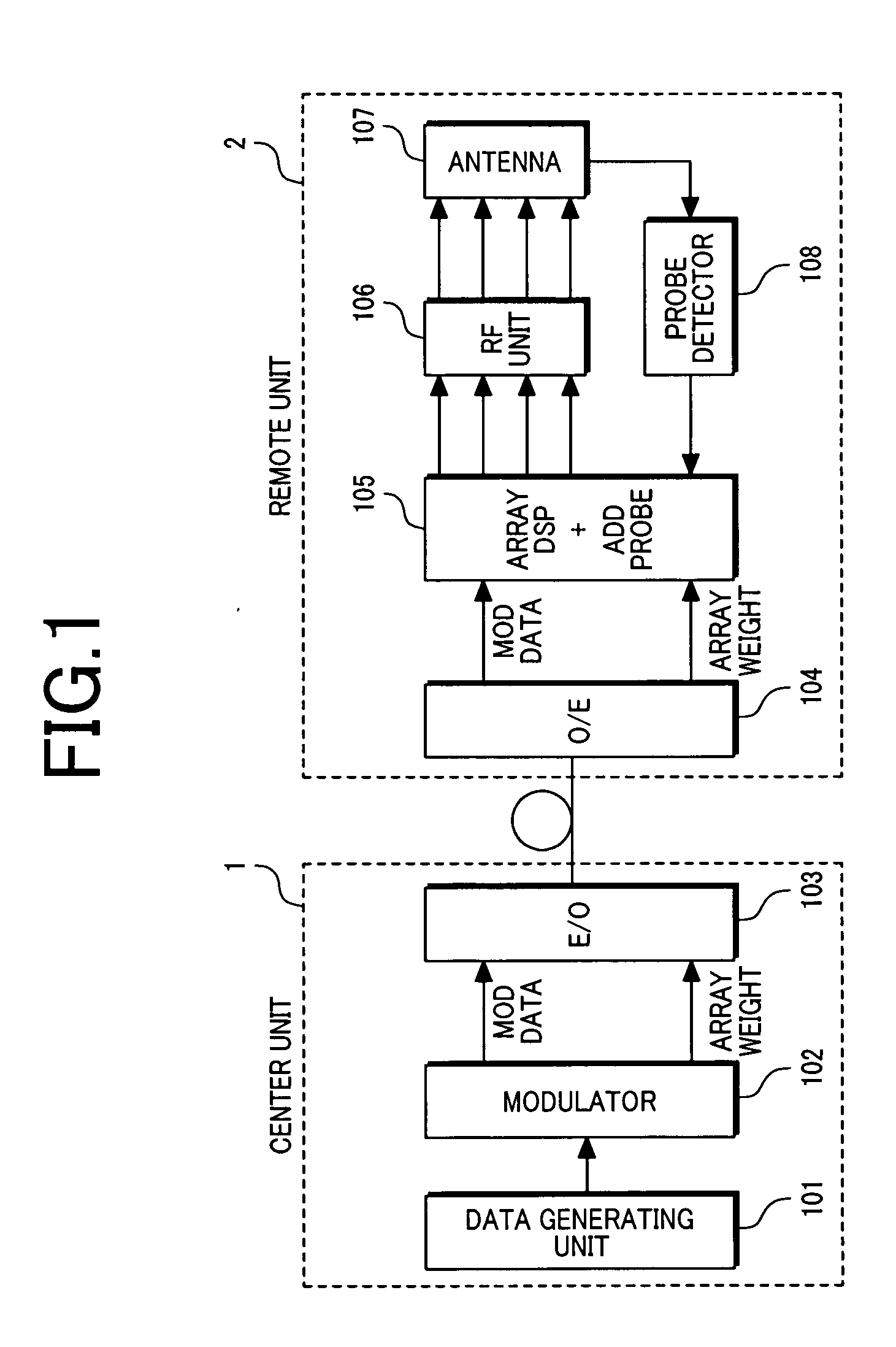
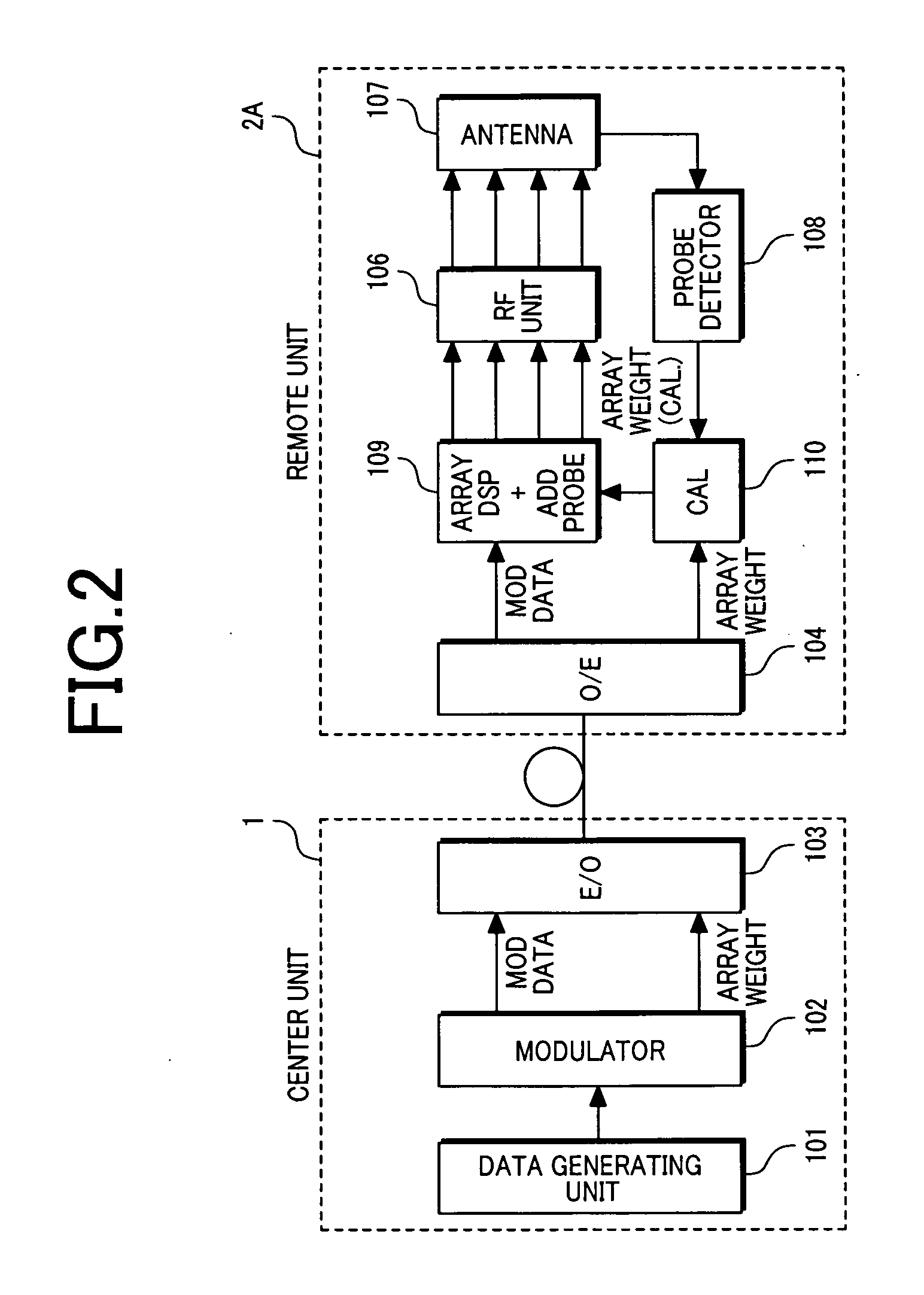
InactiveUS20070072646A1Attenuation bandwidthRunning cost can be reducedSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityAntenna elementBaseband
In a wireless base station comprising a center unit, and a remote unit provided with an array antenna and connected to the center unit through an optical fiber, the center unit outputs to the optical fiber a transmission signal in a base band state prior to array processing, the remote unit performs the array processing of transmission signals in accordance with array weights and converts the transmission signals into RF signals, thereby to localize the compensation for transmission signal deviations occurring among the antenna elements on the remote unit side.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
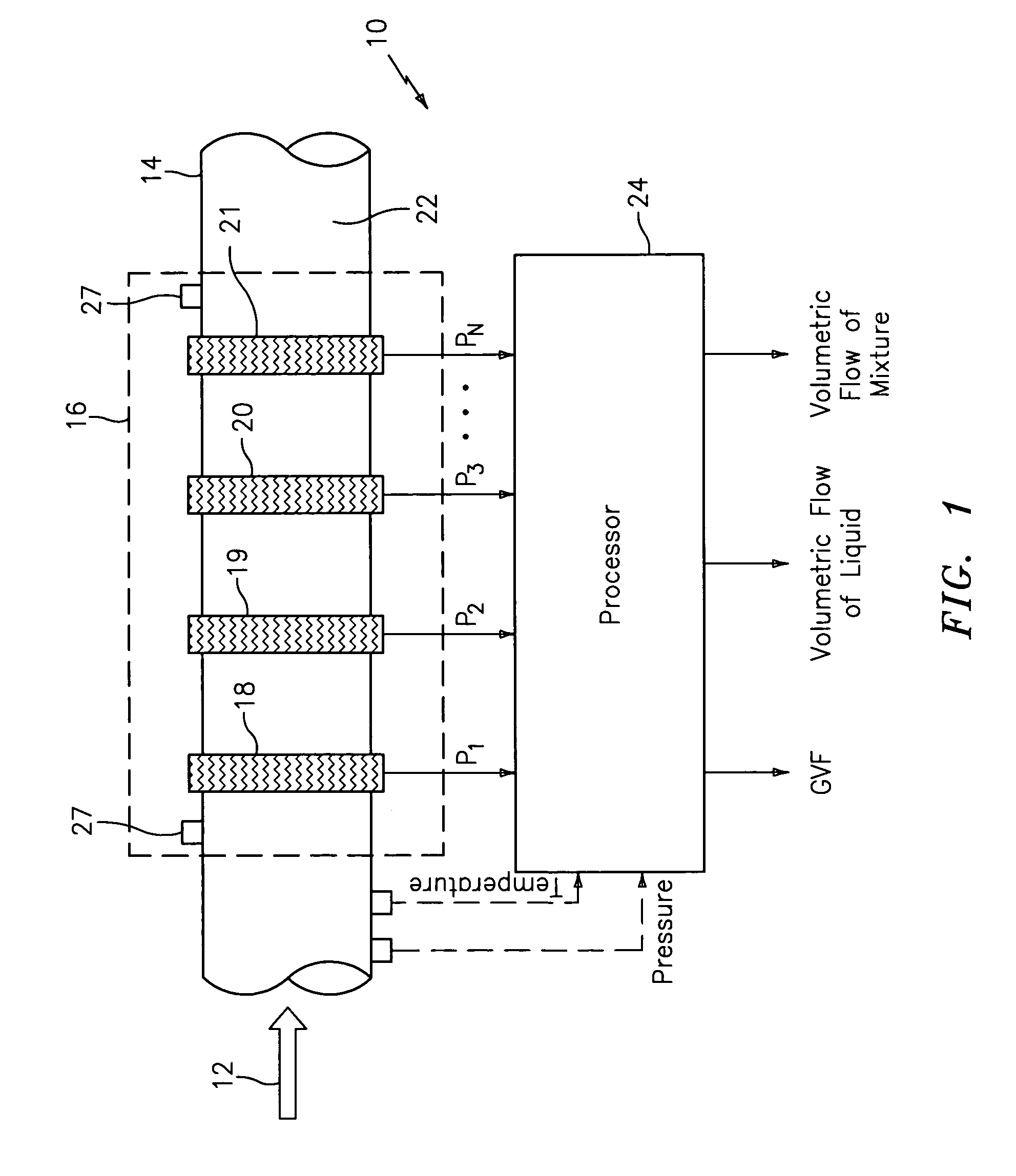
Fluid parameter measurement for industrial sensing applications using acoustic pressures
InactiveUS20050000289A1Less sensitiveImprove measurement reliabilityVibration measurement in solidsVibration measurement in fluidEngineeringOpto electronic
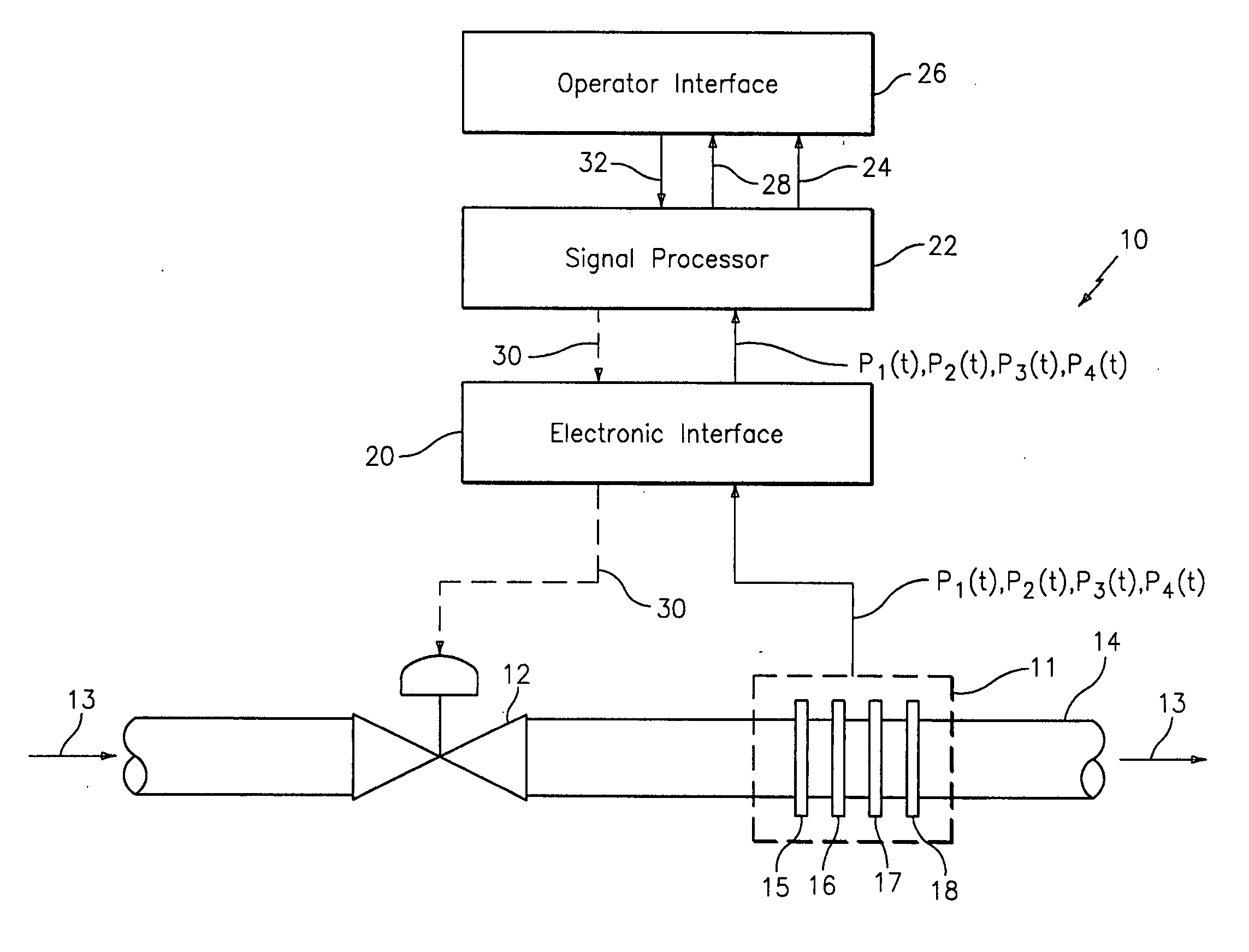
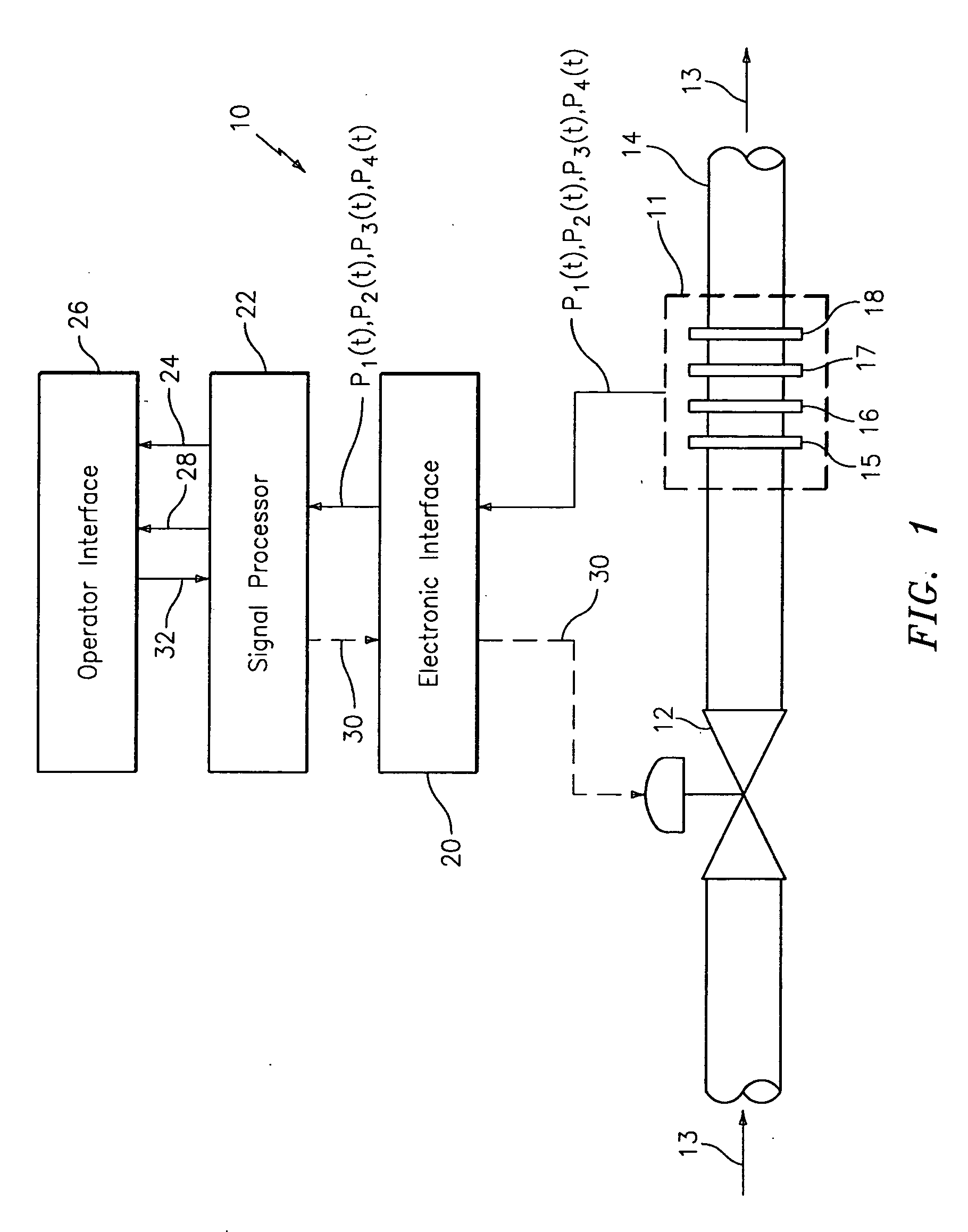
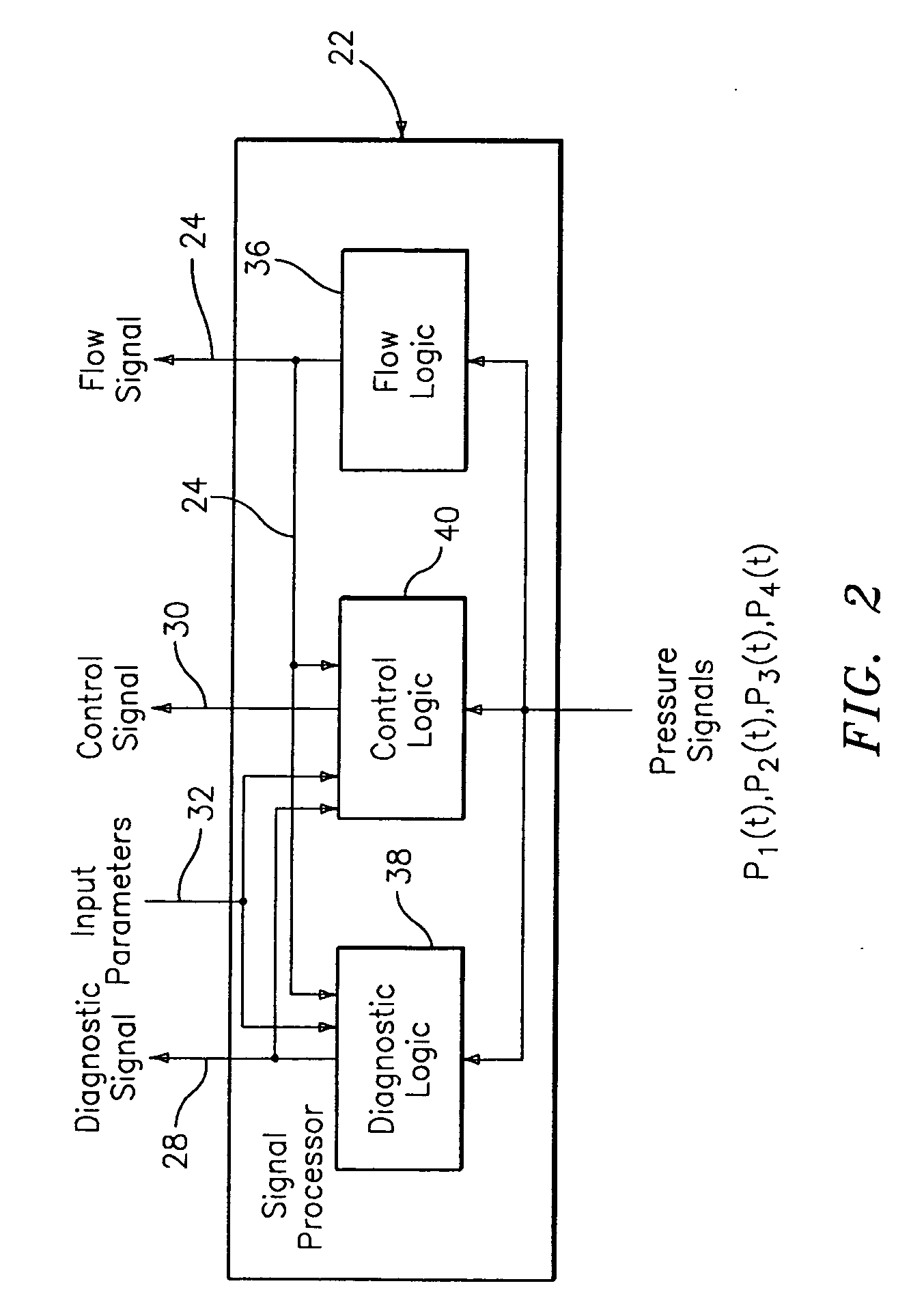
In industrial sensing applications at least one parameter of at least one fluid in a pipe 12 is measured using a spatial array of acoustic pressure sensors 14,16,18 placed at predetermined axial locations x1, x2, x3 along the pipe 12. The pressure sensors 14,16,18 provide acoustic pressure signals P1(t), P2(t), P3(t) on lines 20,22,24 which are provided to signal processing logic 60 which determines the speed of sound amix of the fluid (or mixture) in the pipe 12 using acoustic spatial array signal processing techniques with the direction of propagation of the acoustic signals along the longitudinal axis of the pipe 12. Numerous spatial array-processing techniques may be employed to determine the speed of sound amix. The speed of sound amix is provided to logic 48, which calculates the percent composition of the mixture, e.g., water fraction, or any other parameter of the mixture, or fluid, which is related to the sound speed amix. The logic 60 may also determine the Mach number Mx of the fluid. The acoustic pressure signals P1(t), P2(t), P3(t) measured are lower frequency (and longer wavelength) signals than those used for ultrasonic flow meters, and thus is more tolerant to inhomogeneities in the flow. No external source is required and thus may operate using passive listening. The invention will work with arbitrary sensor spacing and with as few as two sensors if certain information is known about the acoustic properties of the system. The sensor may also be combined with an instrument, an opto-electronic converter and a controller in an industrial process control system.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
High throughput resequencing and variation detection using high density microarrays
InactiveUS20030124539A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh throughput genotypingHigh-Density Microarray
In one embodiment of the invention, methods and systems are provided for high thoughput genotyping. The system includes an automated sample preparation system, a sample tracking system, automated array processing and system for data analysis.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC +1
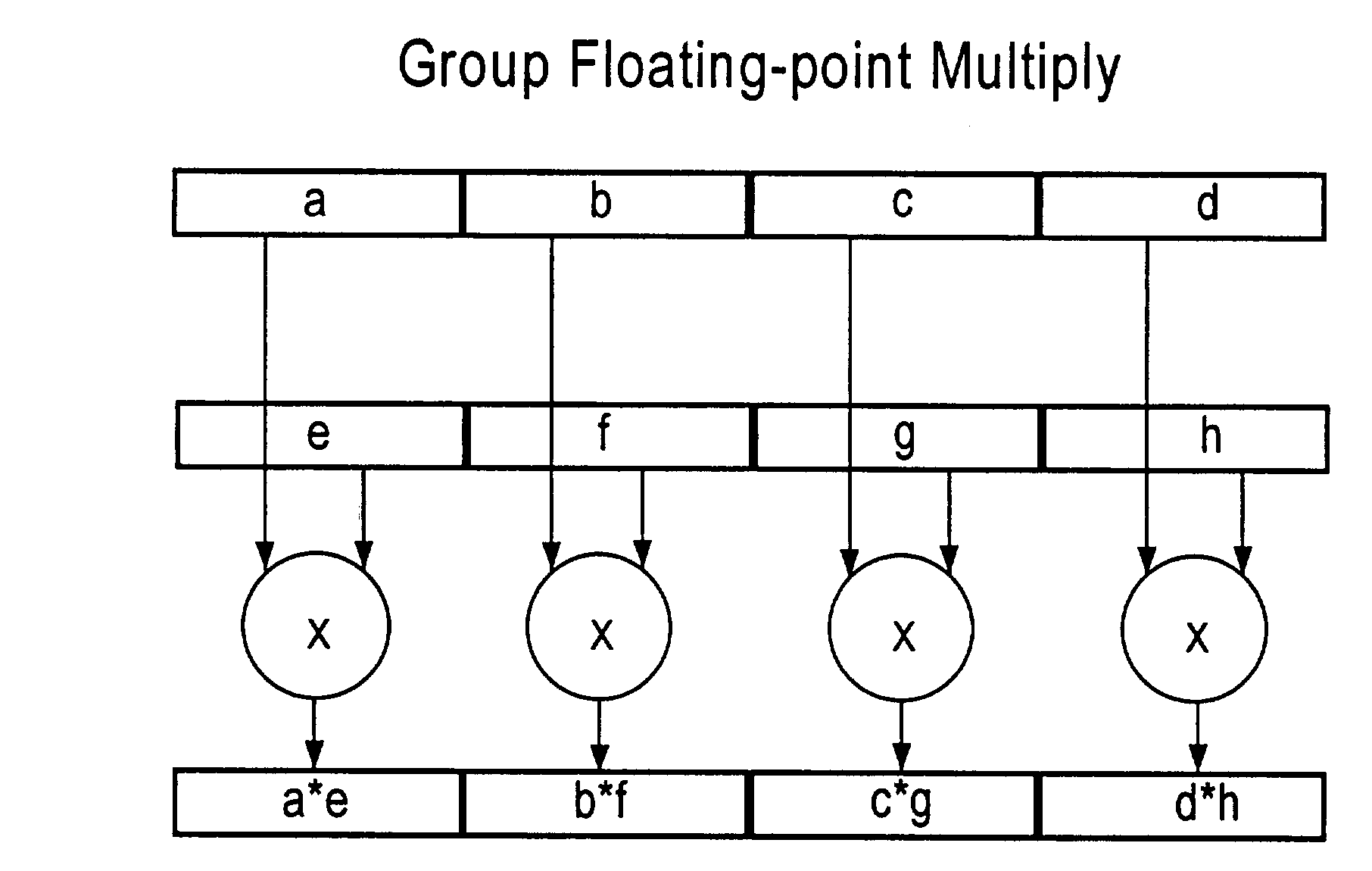
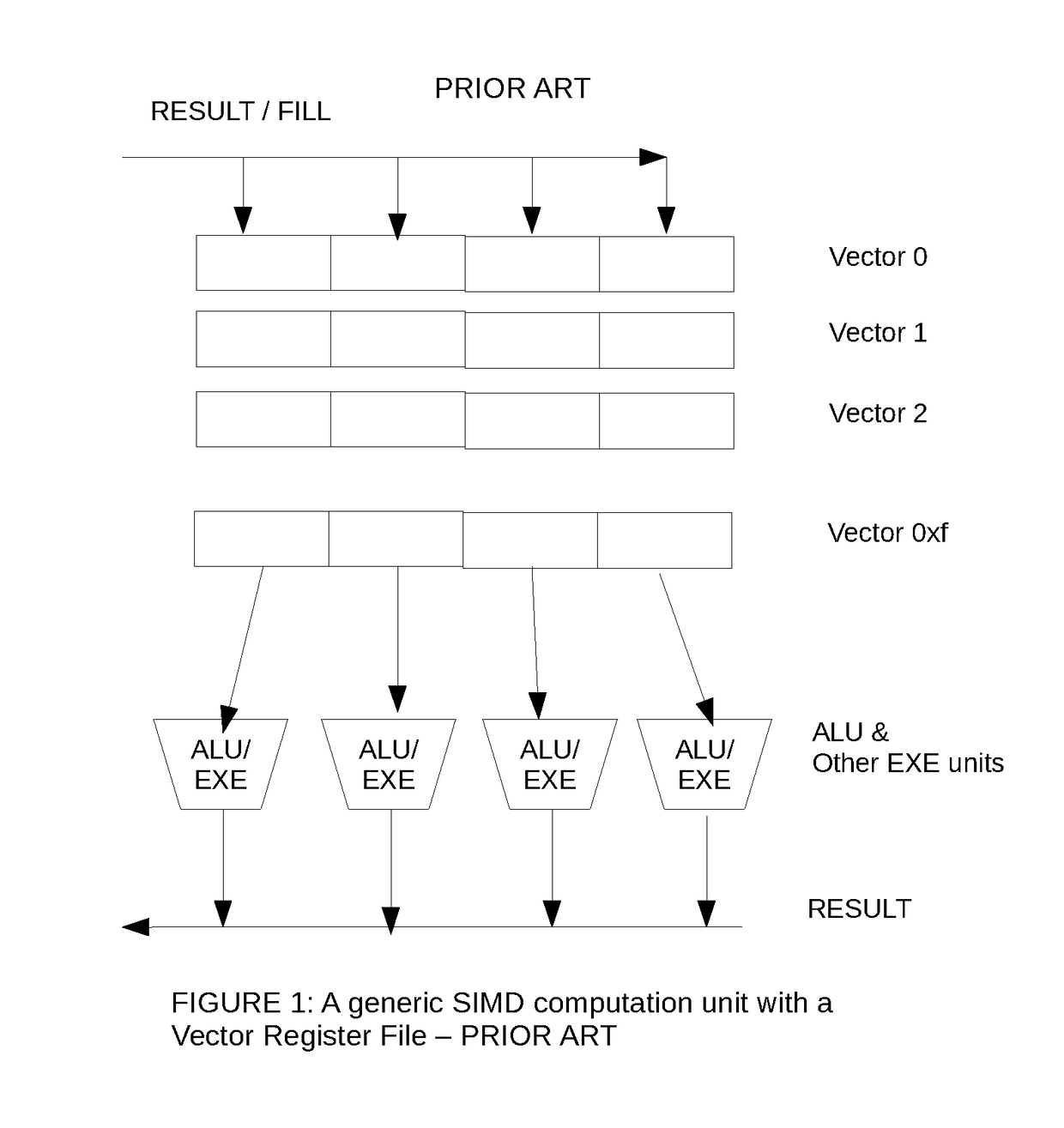
Multiplier array processing system with enhanced utilization at lower precision
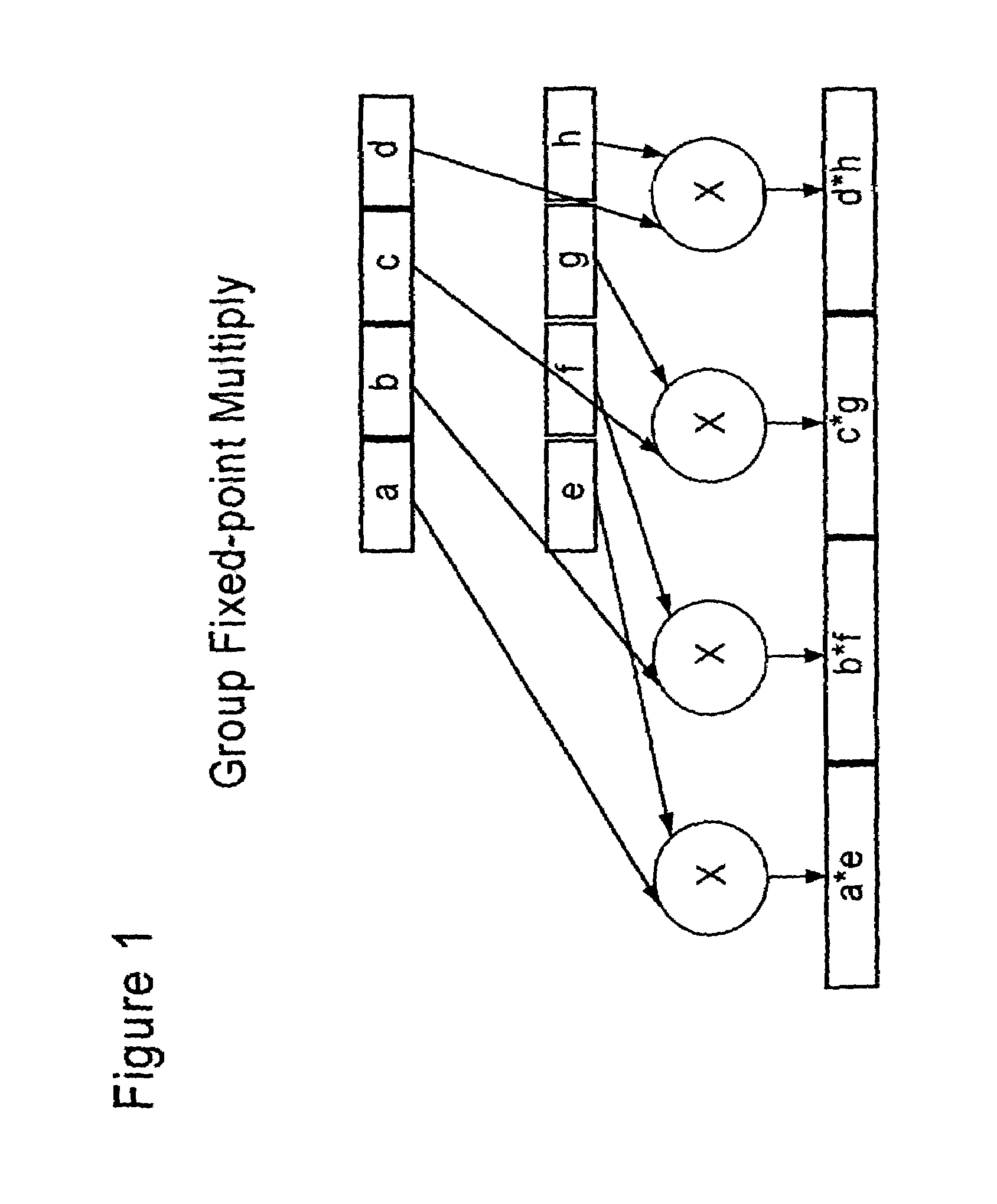
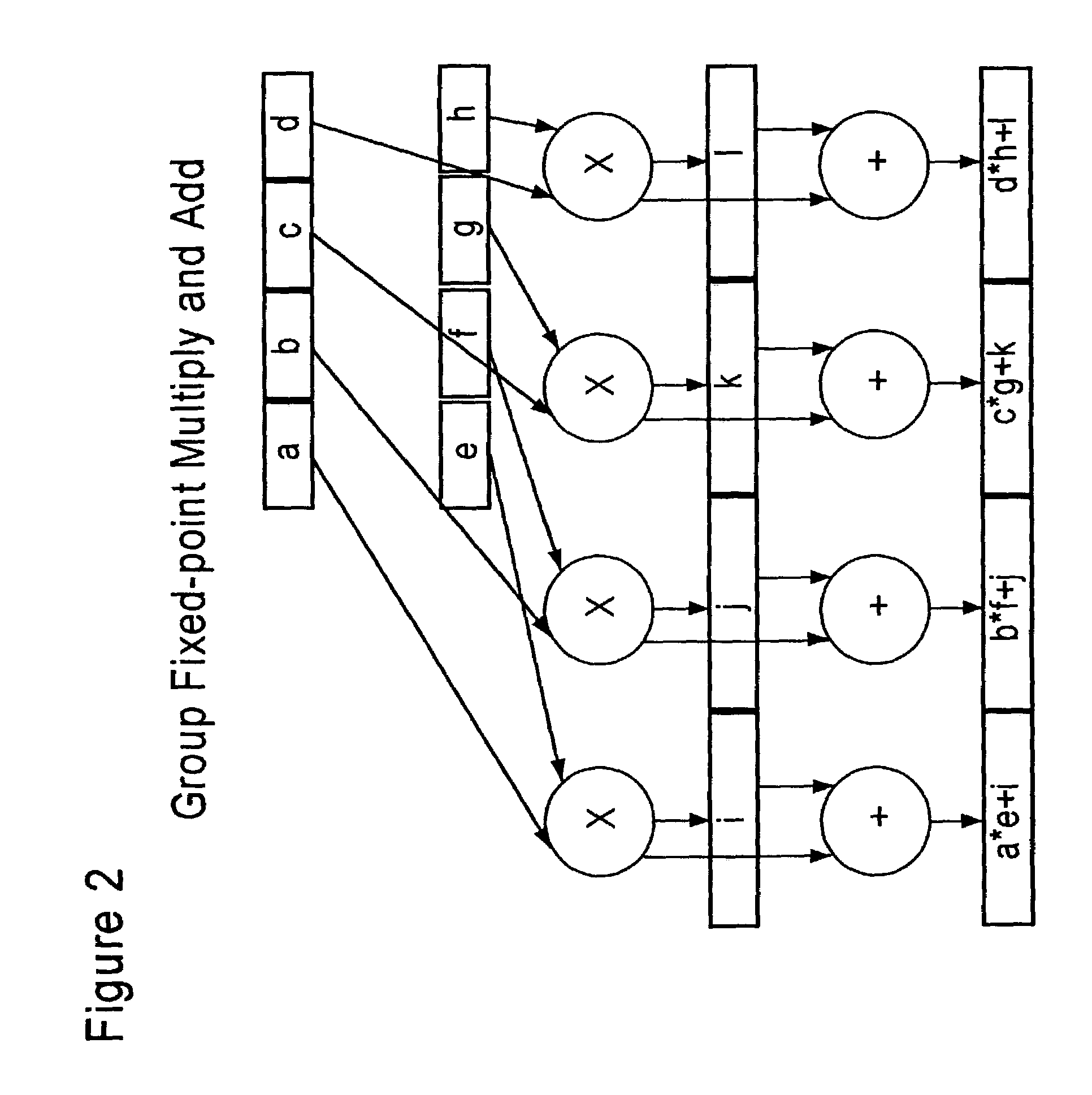
InactiveUS7509366B2Increase profitSolve high precisionEnergy efficient ICTInstruction analysisBinary multiplierOperand
A multiplier array processing system which improves the utilization of the multiplier and adder array for lower-precision arithmetic is described. New instructions are defined which provide for the deployment of additional multiply and add operations as a result of a single instruction, and for the deployment of greater multiply and add operands as the symbol size is decreased.
Owner:MICROUNITY
System and method for operating a flow process
ActiveUS20050005711A1Effective regulationTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsTesting/calibration apparatusControl signalDistributed control system
A system for monitoring, diagnosing, and / or controlling a flow process uses one or more flow meters based on an array of pressure sensors. A signal processor outputs at least one of a flow signal, a diagnostic signal, and a control signal in response to the pressure signals from the pressure sensors. The flow signal indicates the at least one parameter of the fluid, the diagnostic signal indicates a diagnostic condition of a device in the flow process, and the control signal is effective in adjusting an operating parameter of at least one device in the flow process. The system may be arranged as a distributed control system (DCS) architecture for monitoring a plurality of flow meters based on array-processing installed at various locations throughout a flow process.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Method and apparatus for high rate data communication utilizing an adaptive antenna array
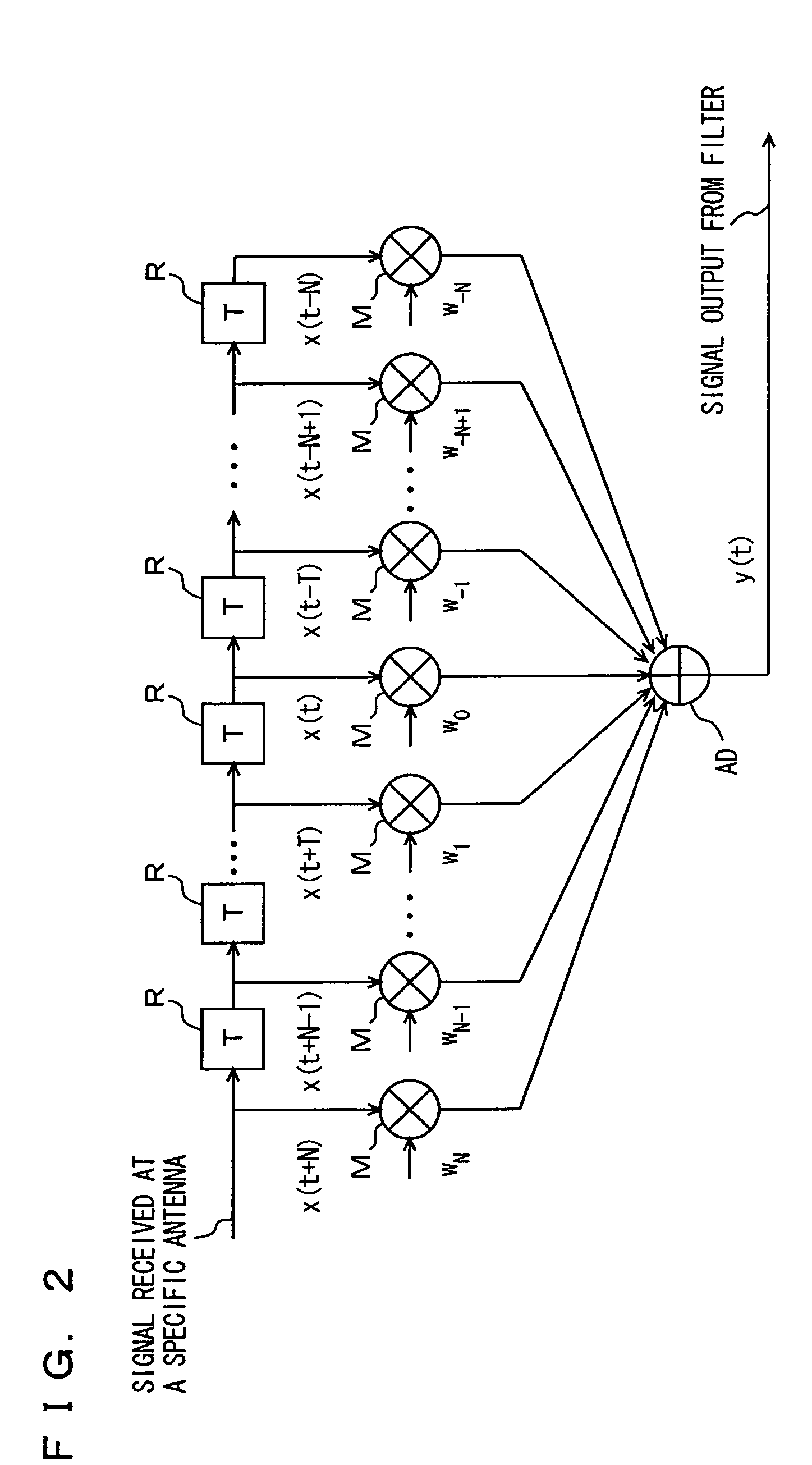
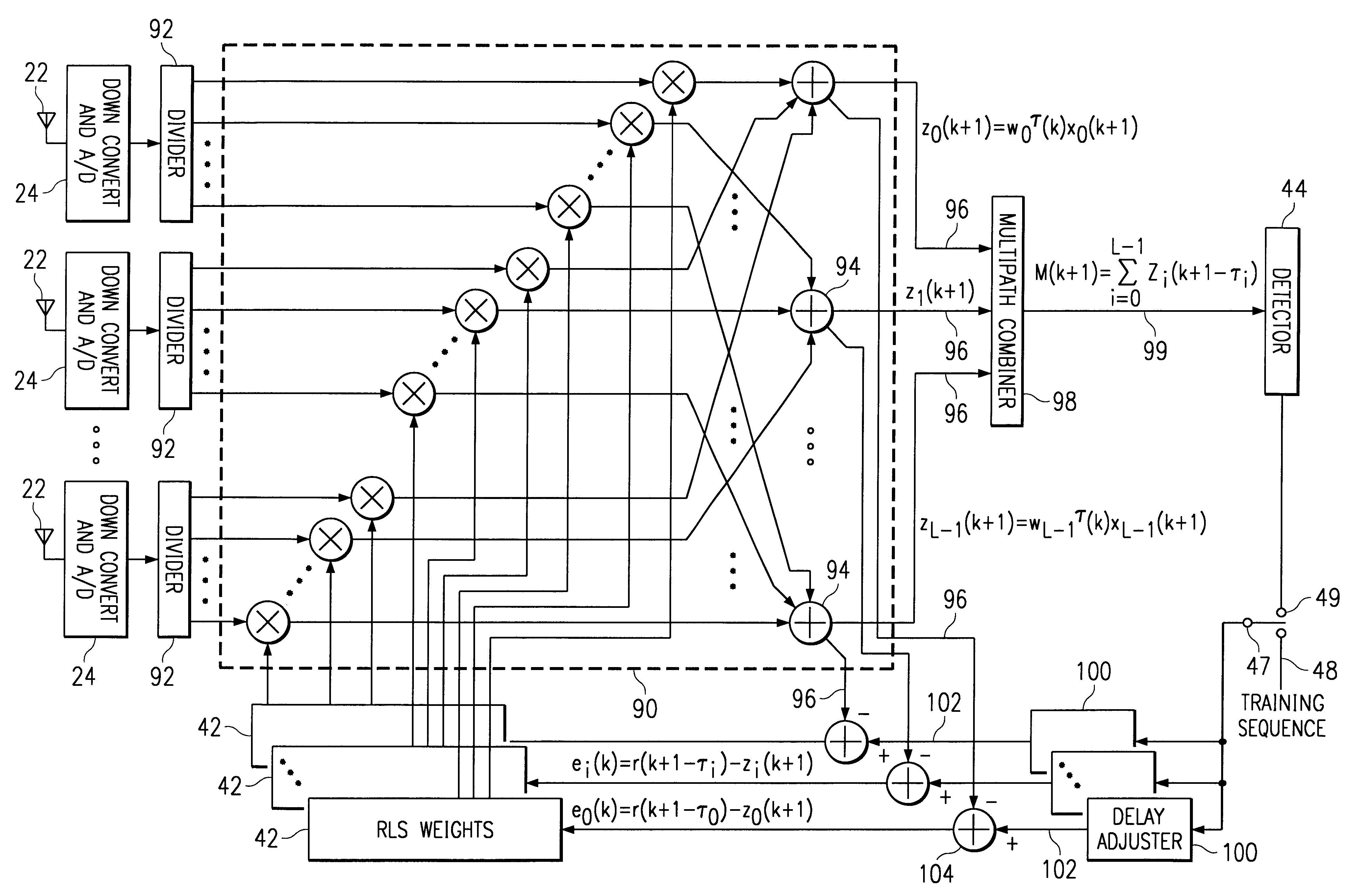
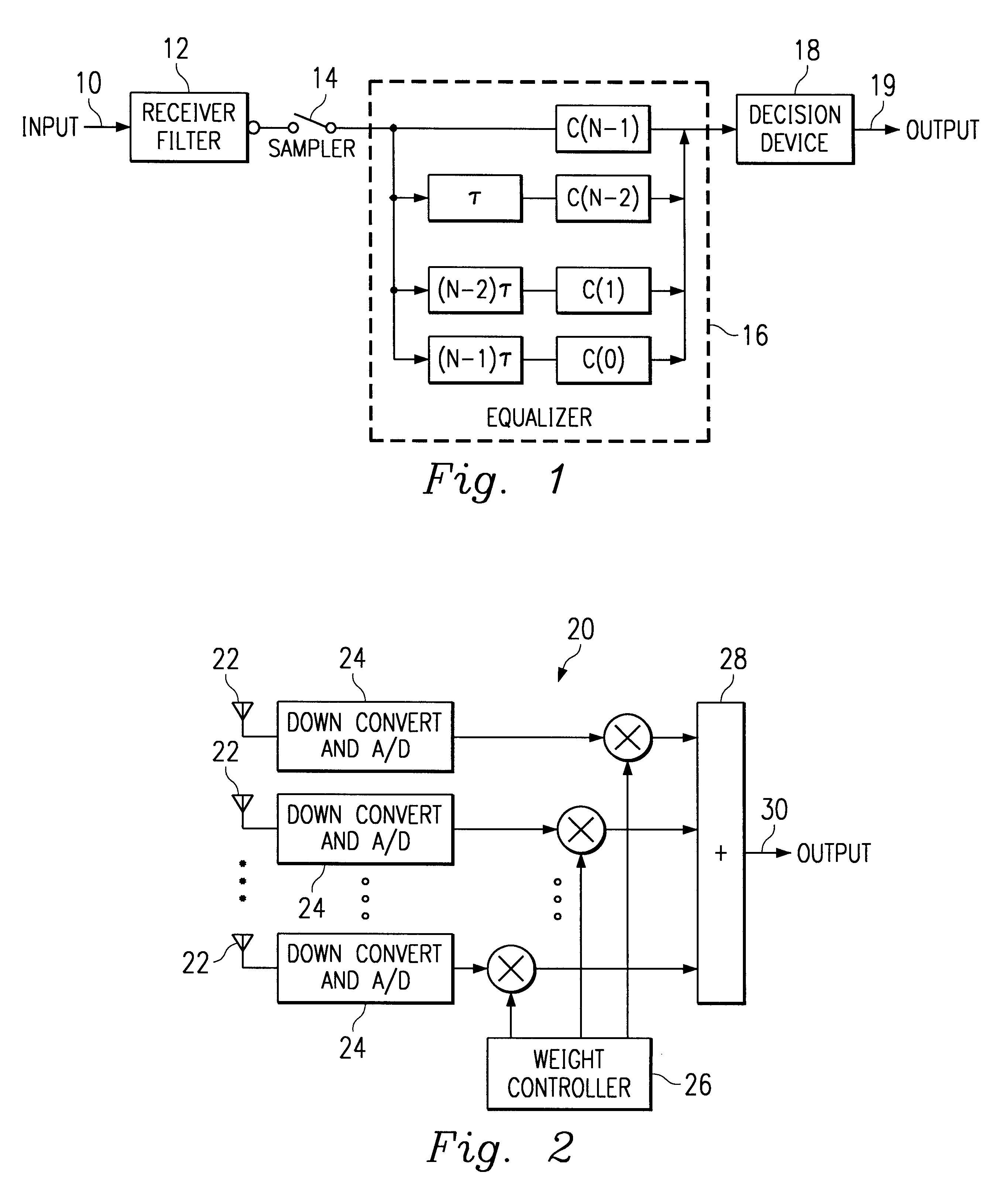
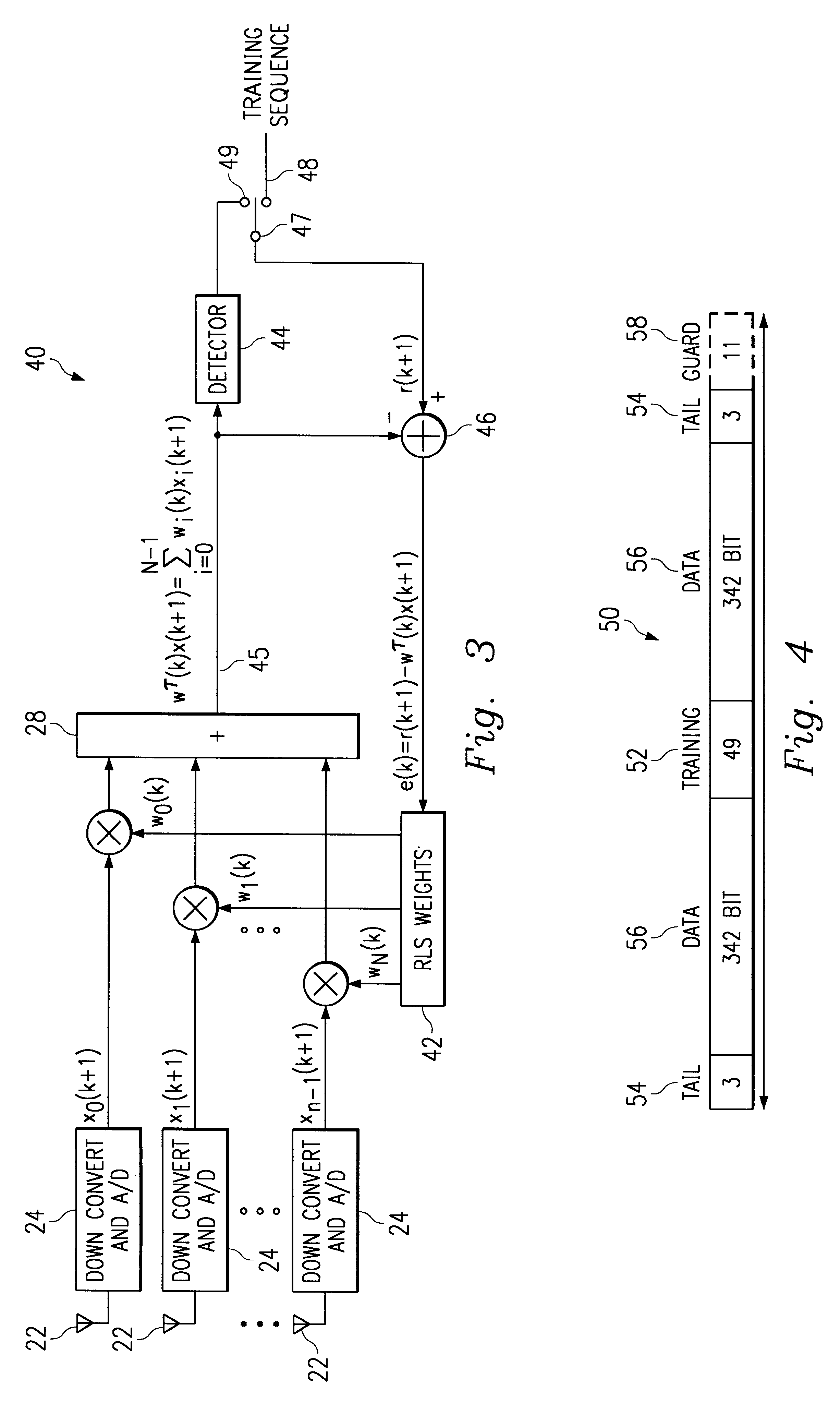
In a wideband Personal Communication Services system, a method and system are proposed for suppressing co-channel interference and reducing inter-symbol interference generated during the transfer of a data packet through a selected radio frequency channel. The system includes a weight controller utilizing recursive least squares algorithm to generate a plurality of appropriate weights to be integrated into received signals in order to maximize signal-to-noise ratio. A detected signal or a training sequence is intelligently switched in as a reference sequence in order to generate a plurality of appropriate weights. To further enhance the adaptive array system and take advantage of the multi-path radio frequency communication environment, two multi-path diversity schemes are included. One embodiment includes an adaptive array system with parallel array processors and another embodiment includes a system with tapped delay line processors.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for utilizing multiplexing to increase throughput in a network of distributed transceivers with array processing
A communication device that comprises a plurality of distributed transceivers, a central processor and a network management engine, may be configured for a multiplexing mode of operation. Configuring of the multiplexing mode of operation may include configuring one or more communication modules for multiplexing a plurality of data streams. Each of the communication modules may comprise one or more antennas and / or antenna array elements and one or more of said plurality of distributed transceivers associated with said one or more antennas and / or antenna array elements. The communication modules may be configured to be spatially distinct and / or to use different frequency channels. The data streams may be communicated to a single target device or to a plurality of target devices.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
Dynamically reconstructable multistage parallel single instruction multiple data array processing system
ActiveUS20150310311A1Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsCharacter and pattern recognitionHandling systemLinearity
The present invention proposes a dynamically reconfigurable multistage parallel single instruction multiple data array processing system which has a pixel level parallel image processing element array and a row processor array parallel. The PE array mainly implements a linear operation which is adapted to be executed in parallel in the low and middle levels of image processing and the RP array implements an operation which is adapted to be executed in row-parallel in the low and middle levels of image processing or more complex nonlinear operations. In particularly, such a system may dynamically reconfigure a SOM neural network in a low cost of performance and area, and the neural network supports high level of image processing such as a high speed online neural network training and image feature recognition, and completely overcomes a defect in which a high level of image processing can't be done by pixel-level parallel processing array in the existing programmable vision chip and parallel vision processor, and facilitate an intelligent and portable real time on-chip vision image system with a complete function at low device cost and low power consumption.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus and method of measuring gas volume fraction of a fluid flowing within a pipe
ActiveUS7343818B2Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesEngineeringProduct gas
A clamp on apparatus 10,110 is provided that measures the speed of sound or acoustic disturbances propagating in a fluid or mixture having entrained gas / air to determine the gas volume fraction of the flow 12 propagating through a pipe 14. The apparatus includes an array of pressure sensors clamped onto the exterior of the pipe and disposed axially along the length of the pipe. The apparatus measures the speed of sound propagating through the fluid to determine the gas volume fraction of the mixture using adaptive array processing techniques to define an acoustic ridge in the k-ω plane. The slope of the acoustic ridge 61 defines the speed of sound propagating through the fluid in the pipe.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Method and Apparatus for Position Sensing
Embodiments of the present invention include one or more wireless transmitting devices and an array of receiver units for receiving wireless communications from the transmitting devices. The transmitter devices and receiver units can be arranged in one, two or three dimensional configurations. Signals are transmitted from the devices for identification and accurate location determination. Spread spectrum techniques can be used, such as DSSS, FHSS, THSS, and pseudo-noise (PN) coding schemes, or combinations thereof. The transmitting devices can generate one or a plurality of data signals that are orthogonal-code modulated, to be decoded by the receiver units and a processor associated therewith. A plurality of transmitter signals can be received, identified, located, and data demodulated substantially simultaneously using embodiments of the invention. The combined use of array processing methods and diversity schemes can be used to reduce the effects of signal multi-path and occlusion.
Owner:XYZ INTERACTIVE TECH
Apparatus and method of measuring gas volume fraction of a fluid flowing within a pipe
ActiveUS7062976B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow propertiesEngineeringGas volume fraction
An apparatus 10,110 is provided that measures the speed of sound or acoustic disturbances propagating in a fluid or mixture having entrained gas / air to determine the gas volume fraction of the flow 12 propagating through a pipe 14. The apparatus includes an array of pressure sensors disposed axially along the length of the pipe. The apparatus measures the speed of sound propagating through the fluid to determine the gas volume fraction of the mixture using adaptive array processing techniques to define an acoustic ridge in the k-ω plane. The slope of the acoustic ridge 61 defines the speed of sound propagating through the fluid in the pipe.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
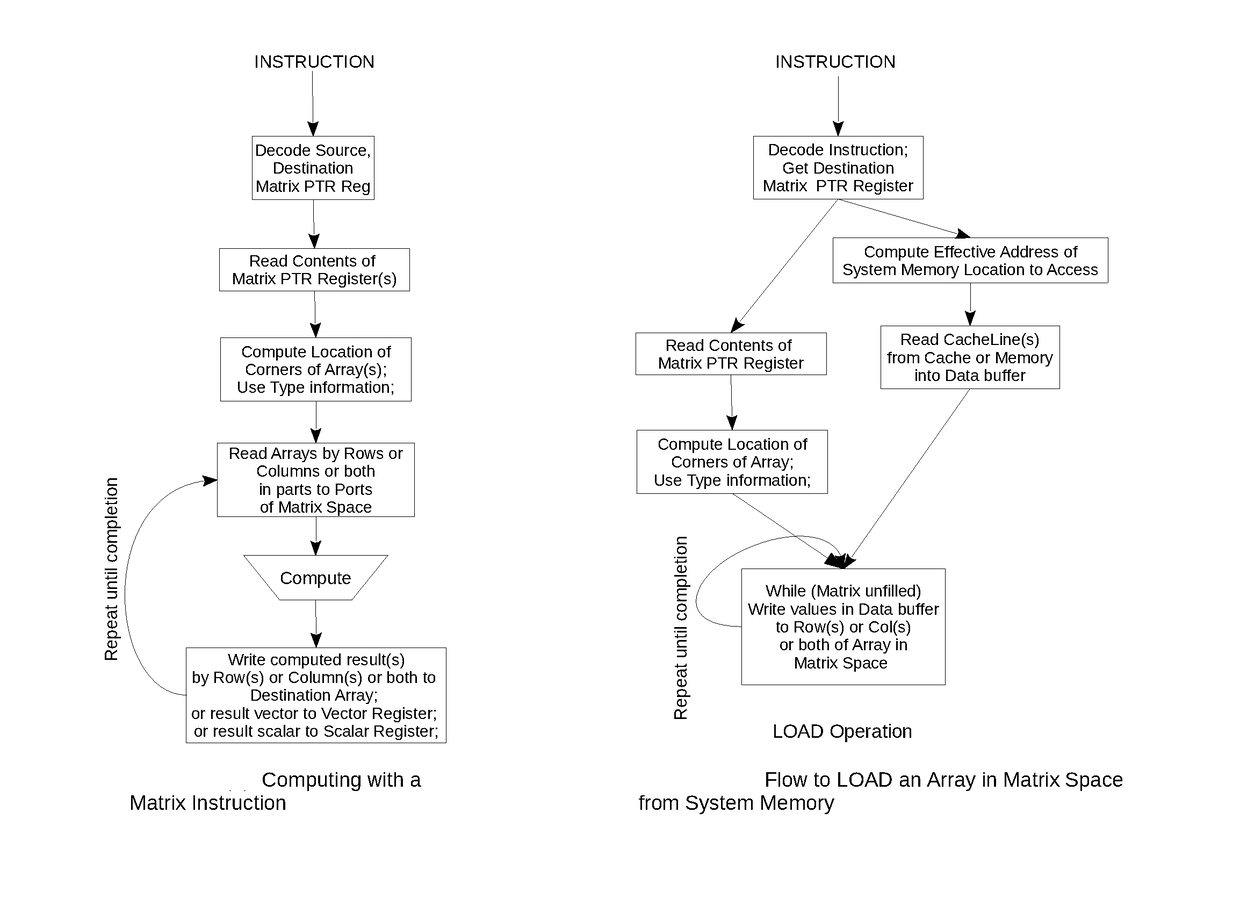
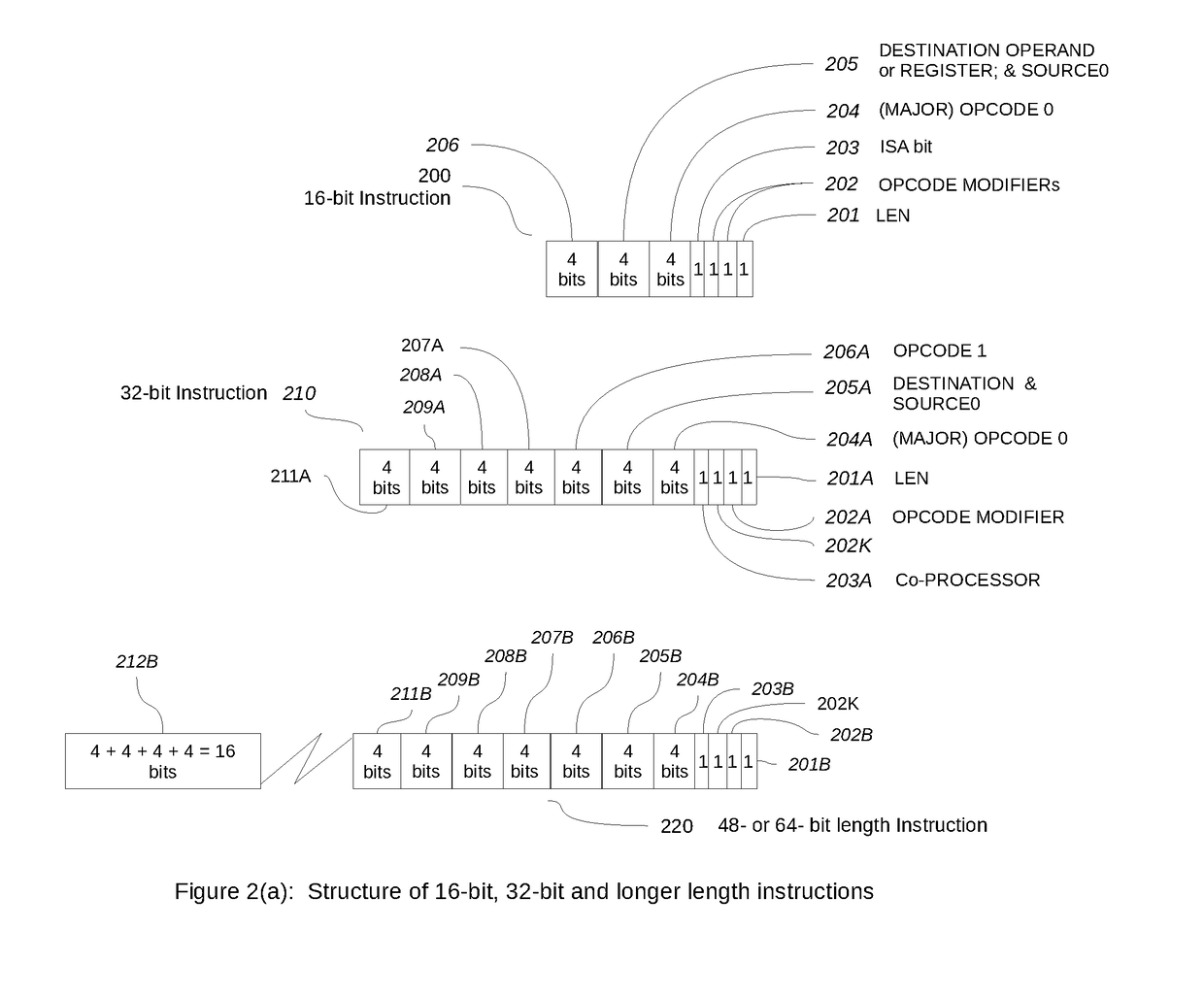
Computing machine architecture for matrix and array processing
InactiveUS20170337156A1Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsProgram synchronisationOperational systemOperand
This invention discloses a novel paradigm, method and apparatus for Matrix Computing which include a novel machine architecture with an embedded storage space for holding matrices and arrays for computing which can be accessed by its columns or by its rows or both concurrently. A large capacity multi length instruction set with instructions and methods to load, store and compute with these matrices and arrays are also disclosed; a method and apparatus to secure, share, lock and unlock this embedded space for matrices under the control of an Operating System or a Virtual Machine Monitor by a plurality of threads and processes are also disclosed. A novel method and apparatus to handle immediate operands used by Immediate Instructions are also disclosed. The structure of the instructions with some key fields and a method for determining instruction length easily are also disclosed.
Owner:ONNIVATION LLC
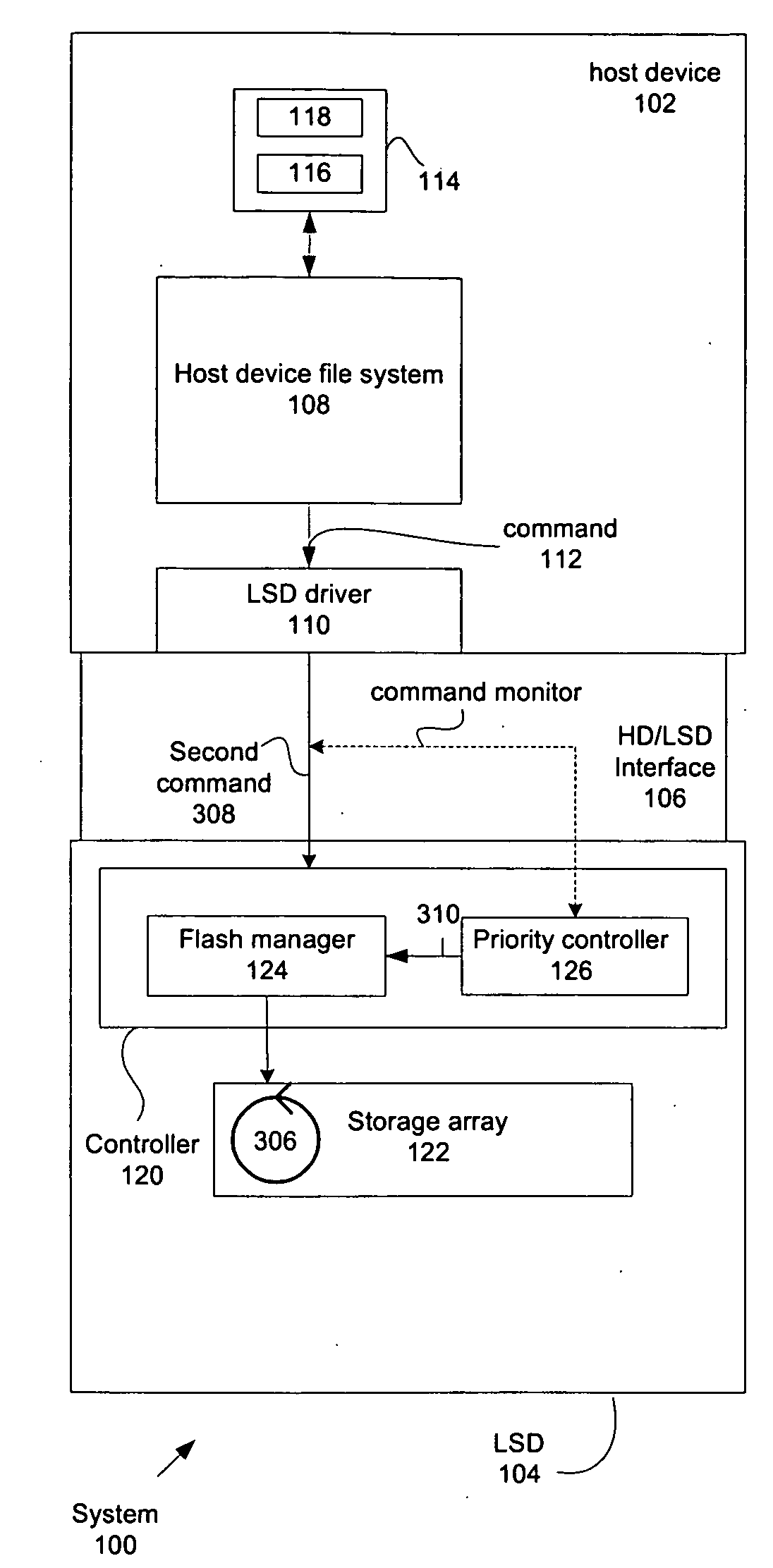
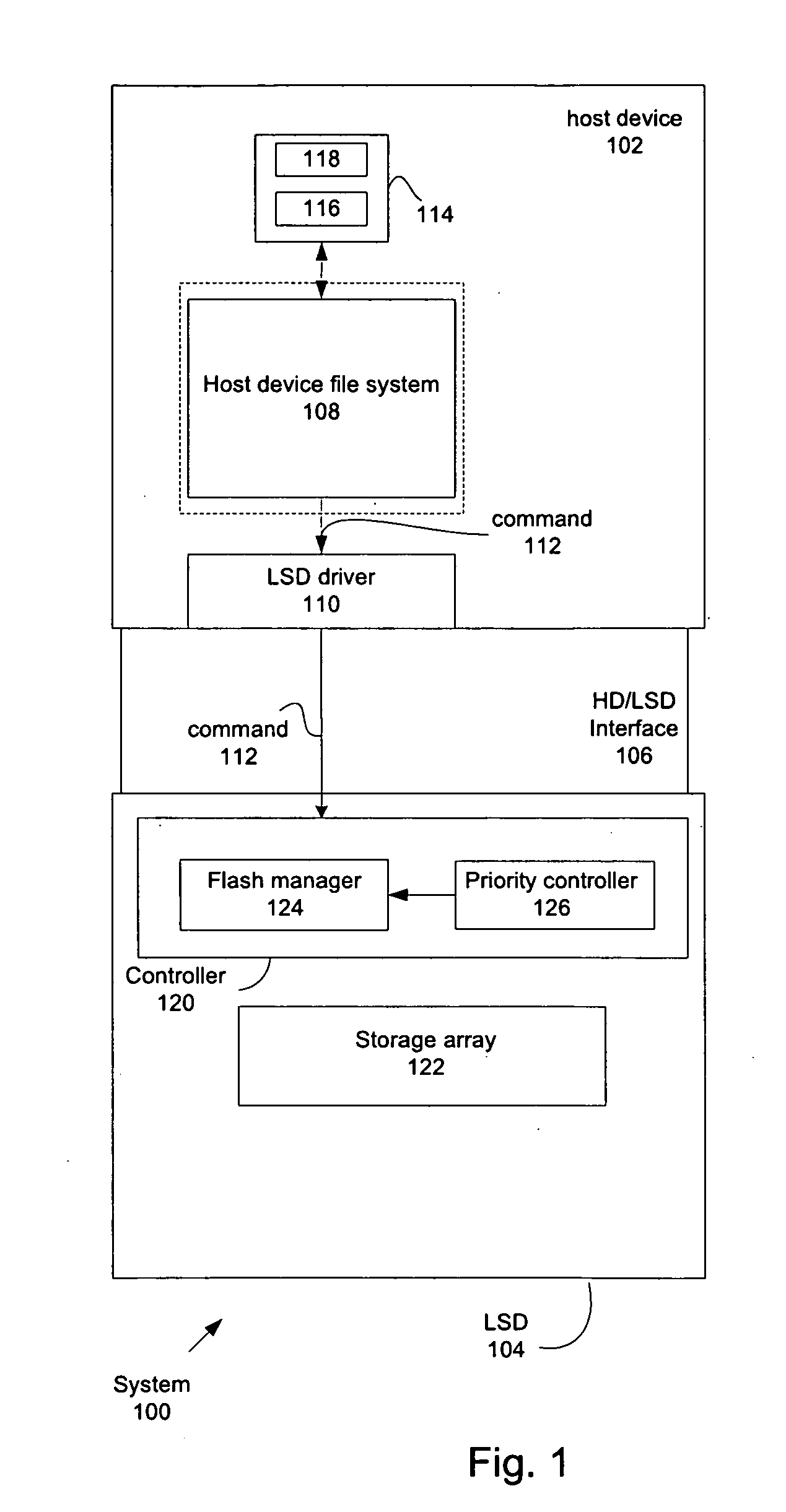
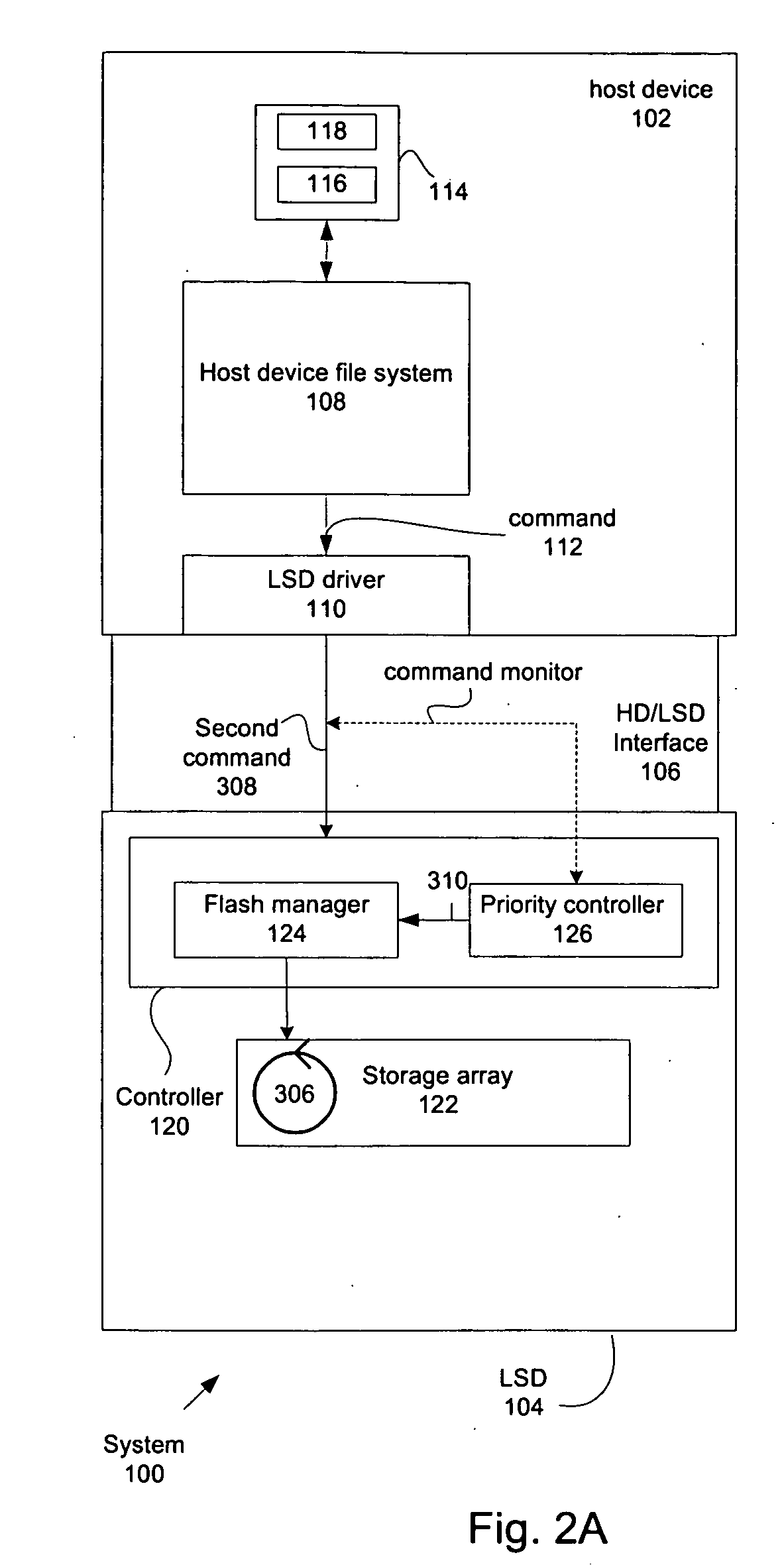
Managing multiple concurrent operations with various priority levels in a local storage device
ActiveUS20100049913A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingProcess supportOperating system
Techniques for rendering the management of processes supported by a storage device are described. In particular, the efficient allocation of storage array processing resources when managing concurrent processes on a storage array is described.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
Method for array processing of surface acoustic wave devices
InactiveUS6928718B2Sufficient clearancePrevent bridgingPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface acoustic wave sensorEngineering
An assembly and method for array processing of hermetically sealed Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Devices employs a non-conductive material having an array of spaced cavities extending into the material for receiving a SAW die face down, in a flip-chip arrangement. Each cavity has a peripheral recess dimensioned to receive a lid for hermetically sealing the die within the cavity. Conductive paths are provided from the interior of the cavity to the surface of the array for providing an electrical contact with the SAW die. Individual SAW devices are then provided by cutting along separation lines between adjacent cavities after a plurality of die have been hermetically sealed within its cavity.
Owner:TRIQUINT
Calibration method of array antenna receiving system of navigation satellite
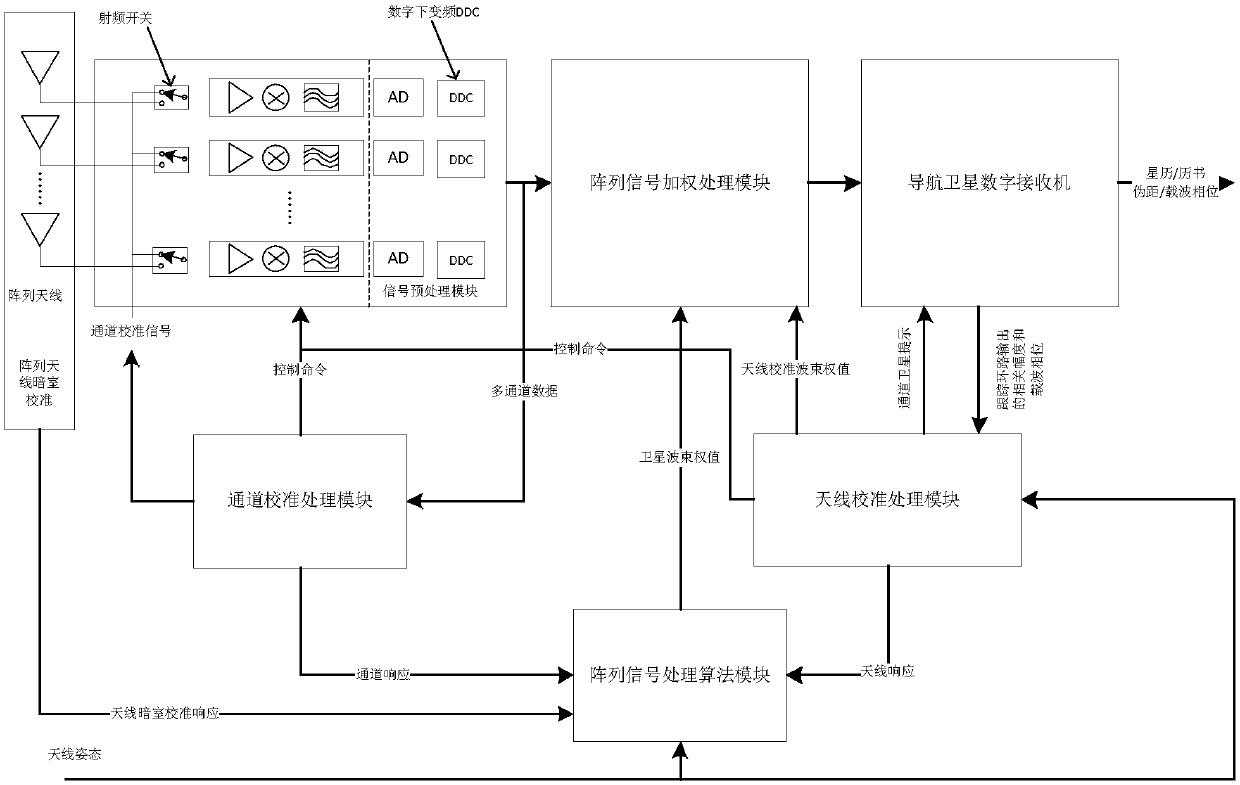
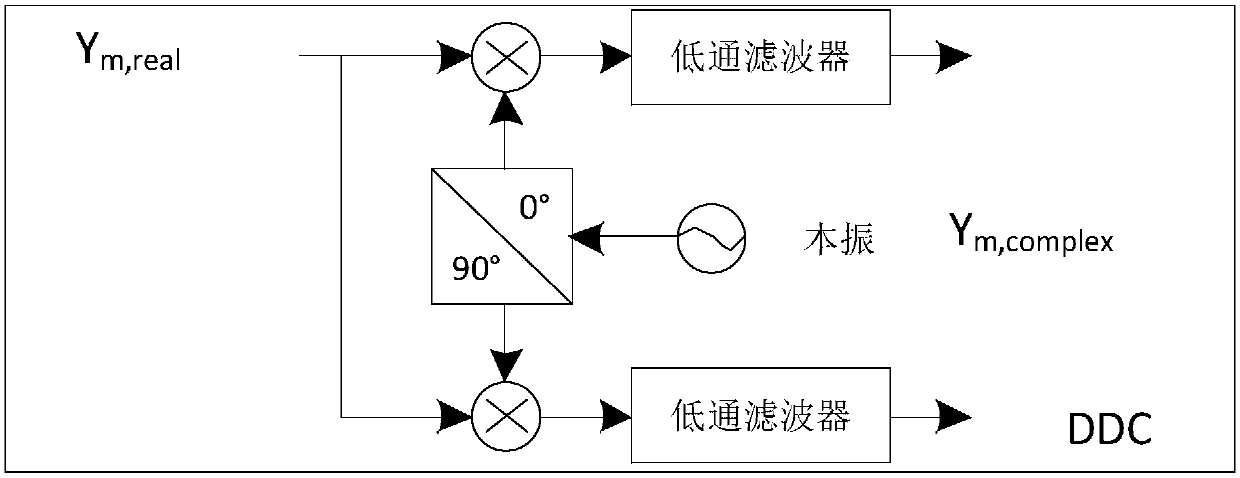
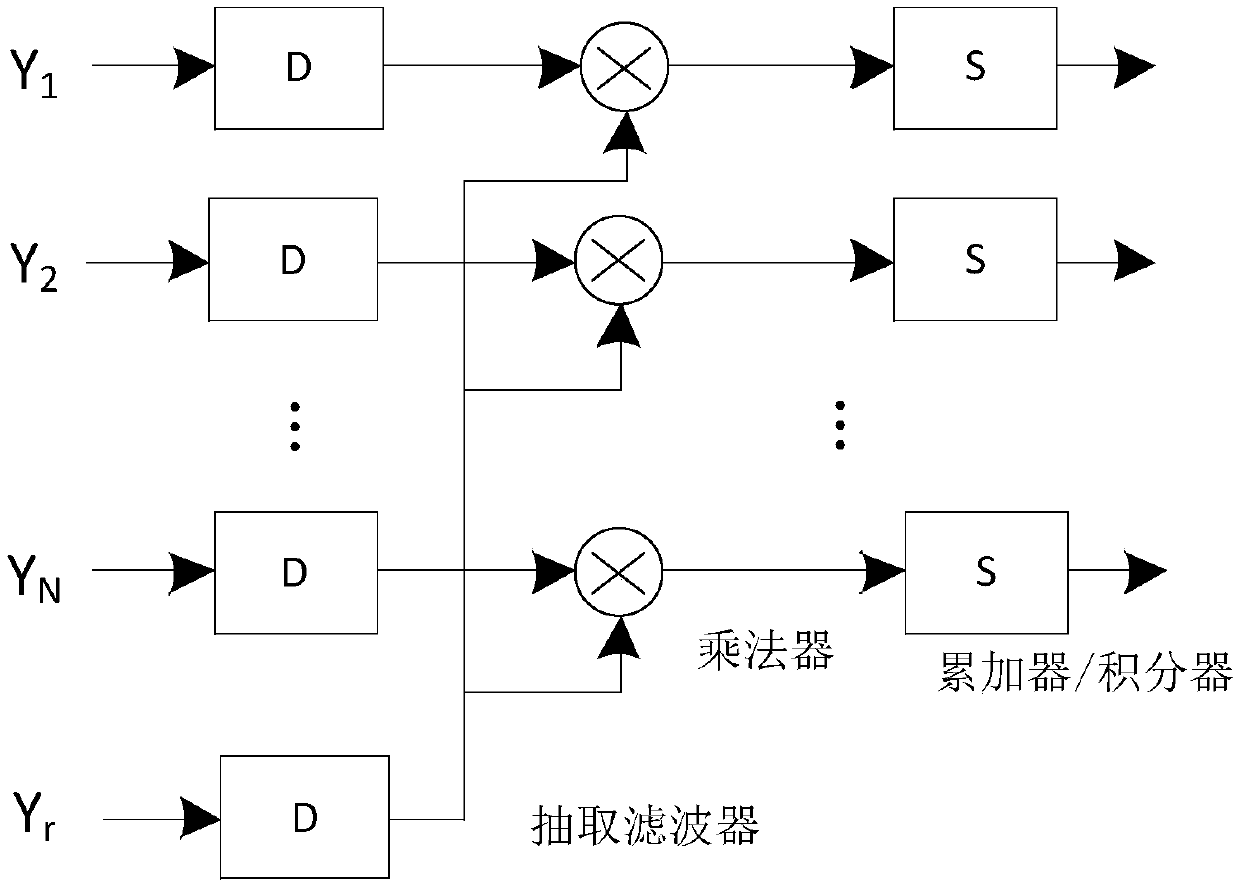
ActiveCN107315183ASave resourcesControl relative phase relationshipSatellite radio beaconingTime changesEngineering
The invention provides a calibration method of an array antenna receiving system of a navigation satellite. The objective of the invention is to provide the calibration method which is capable of restraining interference and improving estimation accuracy of guidance vectors of the antenna array. The calibration method comprises steps of during channel calibration, sending multi-channel data output by multiple paths of analog-digital converters into a channel calibration processing module for channel calibration signal processing, measuring inconsistency between channels, successively selecting at least two channels from the channels, keeping the other channels to be normally operated, updating channel consistency response along with the time change, calculating to obtain channel responses used by an array processing algorithm module, and finishing the channel calibration; and during antenna calibration, by taking satellite signals as measurement signals, multiple paths of antenna calibration signals are synthesized through an array signal weighting processing module DBF and then sent to a navigation satellite digital receiver, outputting the antenna calibration signals to an antenna calibration processing module, calculating antenna responses of the array in the incidence direction of the satellite signals and finishing the antenna calibration.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Method and apparatus for acoustic source tracking using a horizontal line array
InactiveUS20060133211A1Improve abilitiesEasy to solveSignal processingMicrophones signal combinationSound sourcesEnvironmental acoustics
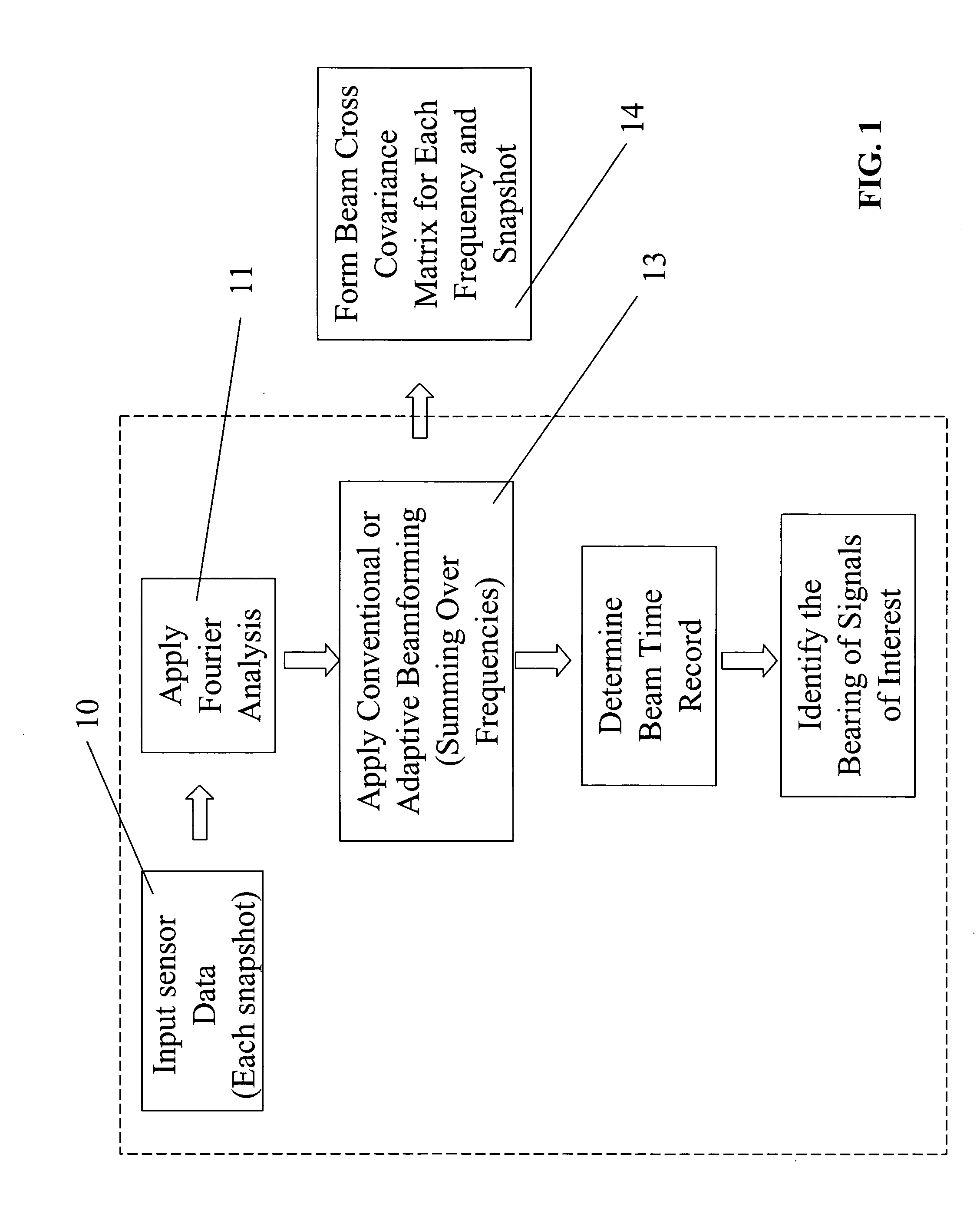
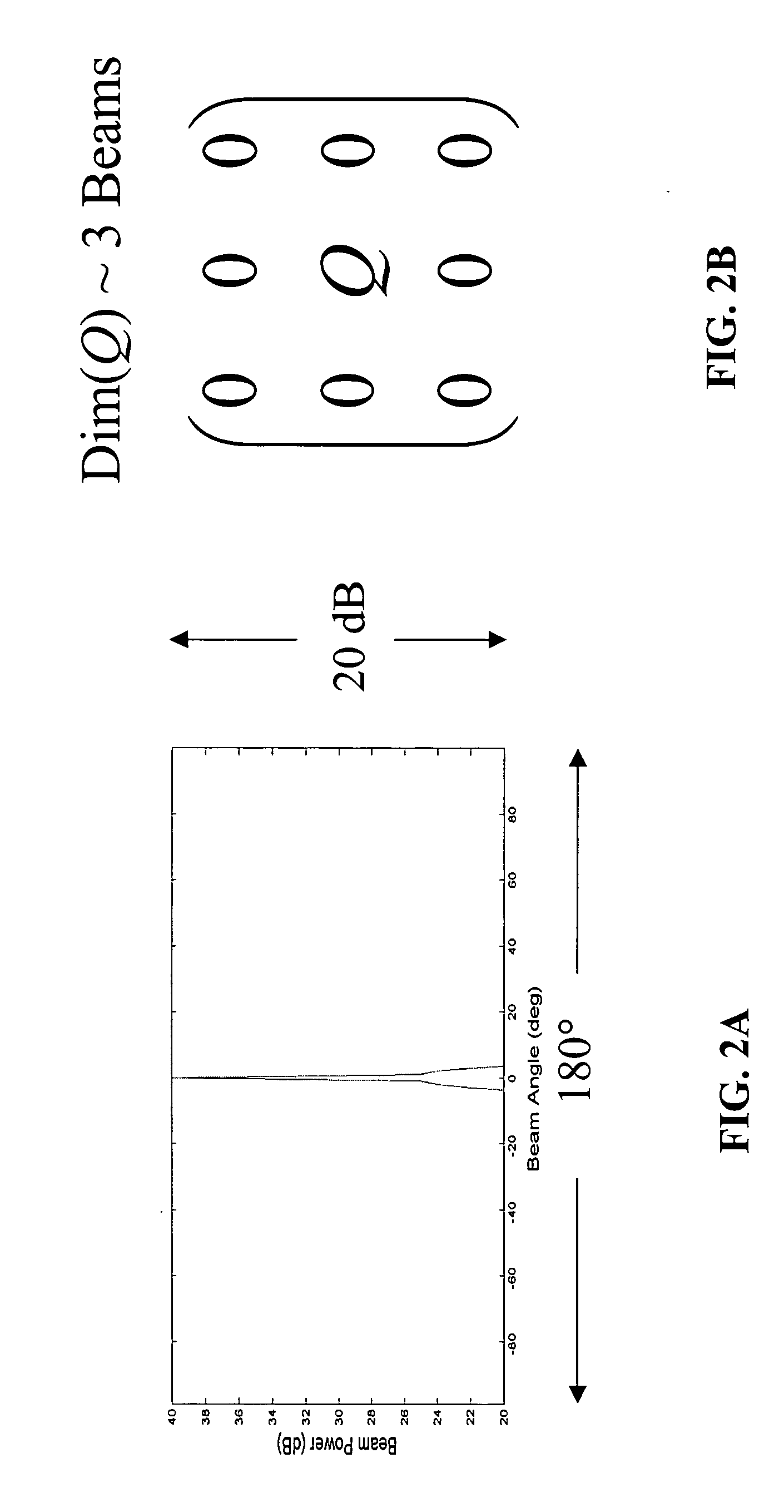
An apparatus for processing passive acoustic signals received on a horizontal line array that were either emitted from an underwater object or echo returned from an object, is proposed to track the motion (bearing change and range change) of an object (target) relative to the receiver horizontal line array. Adaptive array processing for a moving object is biased for a moving source when the number of data samples is limited by the stationariness condition. Motion compensation can be carried out in the beam domain by beam shifting for a bearing changing object and frequency shifting for a range changing object. The method includes receiving acoustic signals from the target, determining the beam covariance matrices, determining the target bearing rate and range rate, processing the beam covariance matrices by compensating for the target motion, and producing a beam power plot versus time. Interference signal is suppressed when the interference source does not have the same motion (bearing and range rate) as the target. The method does not need detailed environmental acoustic information of the sound channel normally required to model the sound propagation.
Owner:USA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY THE
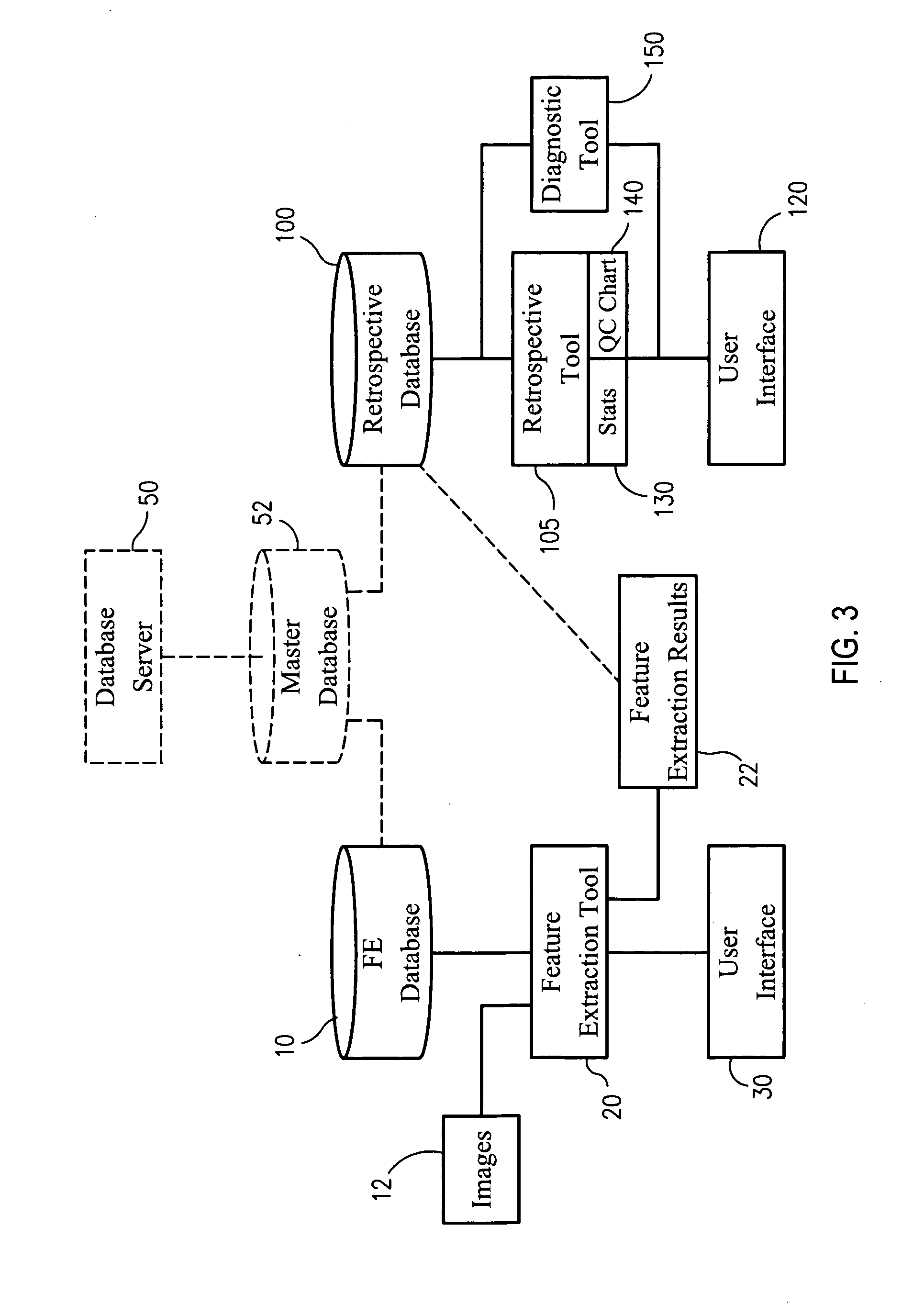
Methods and systems for facilitating analysis of feature extraction outputs
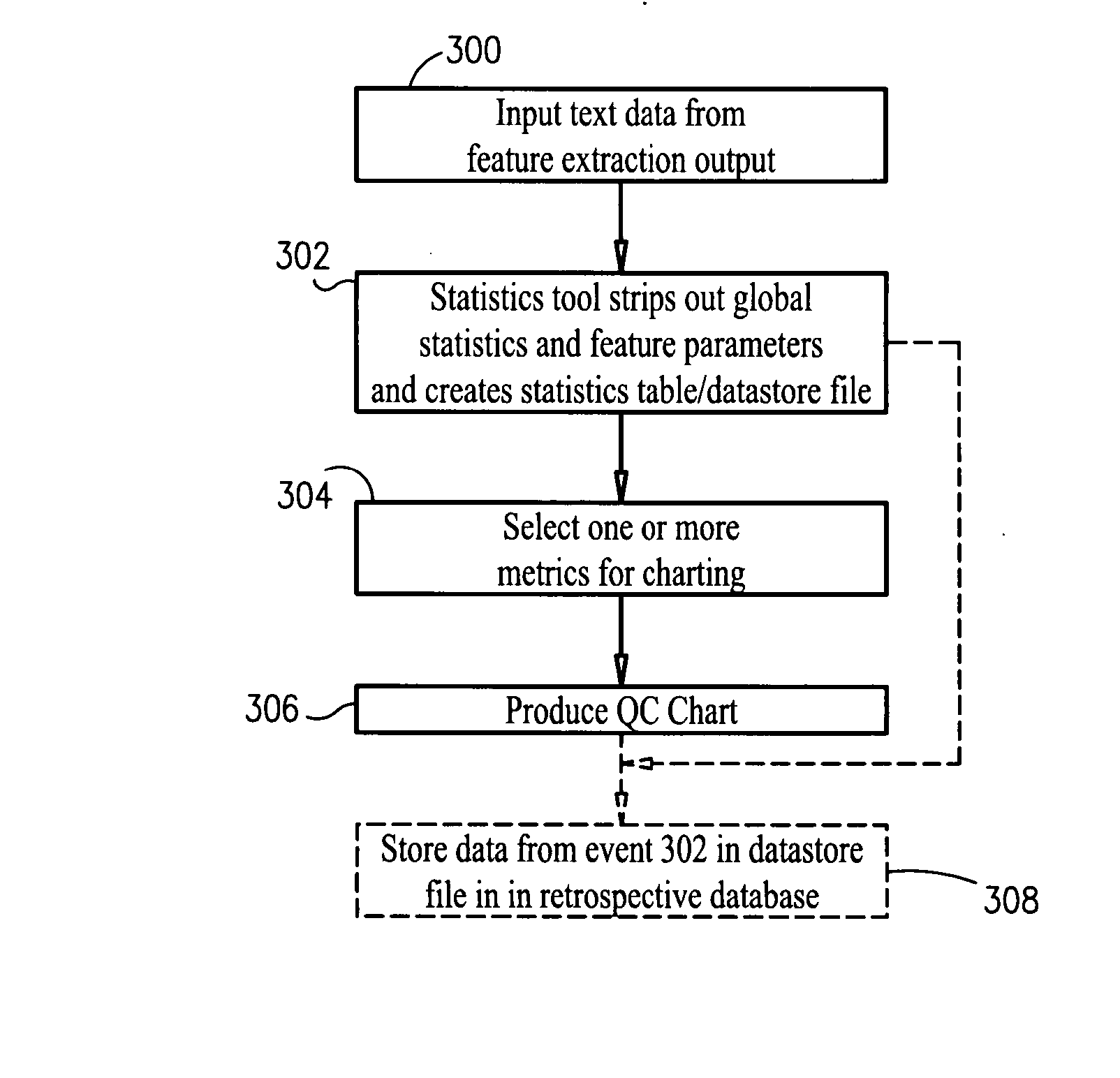
InactiveUS20070255512A1Readily cross-comparedEasy to analyzeAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsFeature extractionValue set
Methods, systems and computer readable media for facilitating analysis of feature extraction outputs across multiple extractions. A feature extraction output of an extraction resulting from feature extraction of an array is inputted, and global statistics and array processing parameters are extracted from the feature extraction output. A table / file is populated with the extracted global statistics and array processing parameters of the extraction. The inputting, extracting and populating steps are repeated for at least one additional feature extraction output of another extraction, so that the table / file includes global statistics that can be readily cross-compared over multiple extractions with reference to a single table or file. Methods, systems and computer readable media are provided for setting threshold values for metrics that global statistics are provided for. An evaluation metric may be set by a user, based upon the threshold values set for the metrics. A metric set including the metrics and optionally one or more thresholds and optionally an evaluation metric may be stored and / or applied to additional global statistics for those metrics to evaluate the quality of one or more extractions. A set of reports are provided for facilitating analysis of feature extraction outputs across multiple extractions. A diagnostic tool is provided for identifying and diagnosing potential problems in feature extraction outputs.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com