Patents
Literature
2011 results about "Distributed control system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
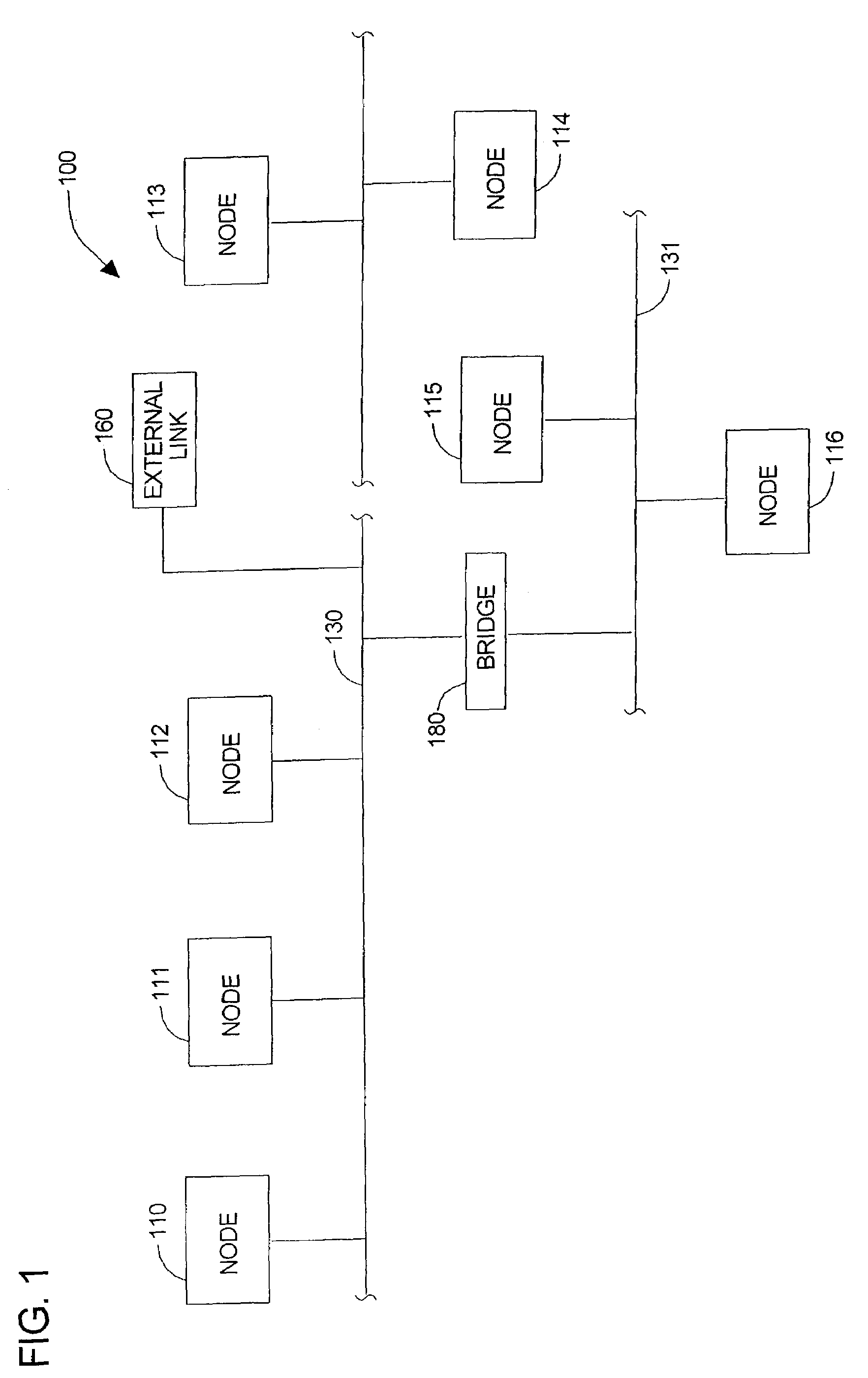
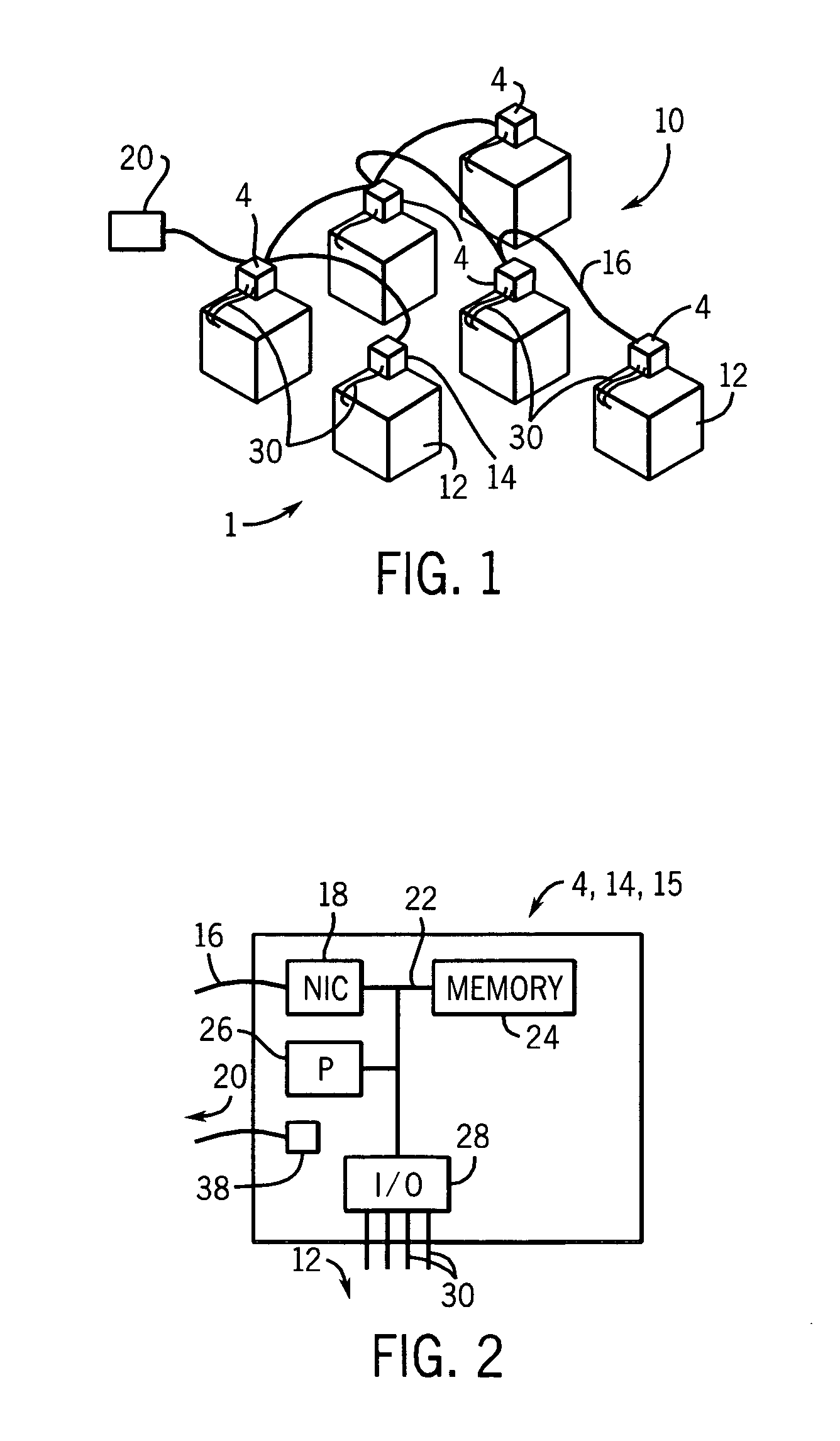
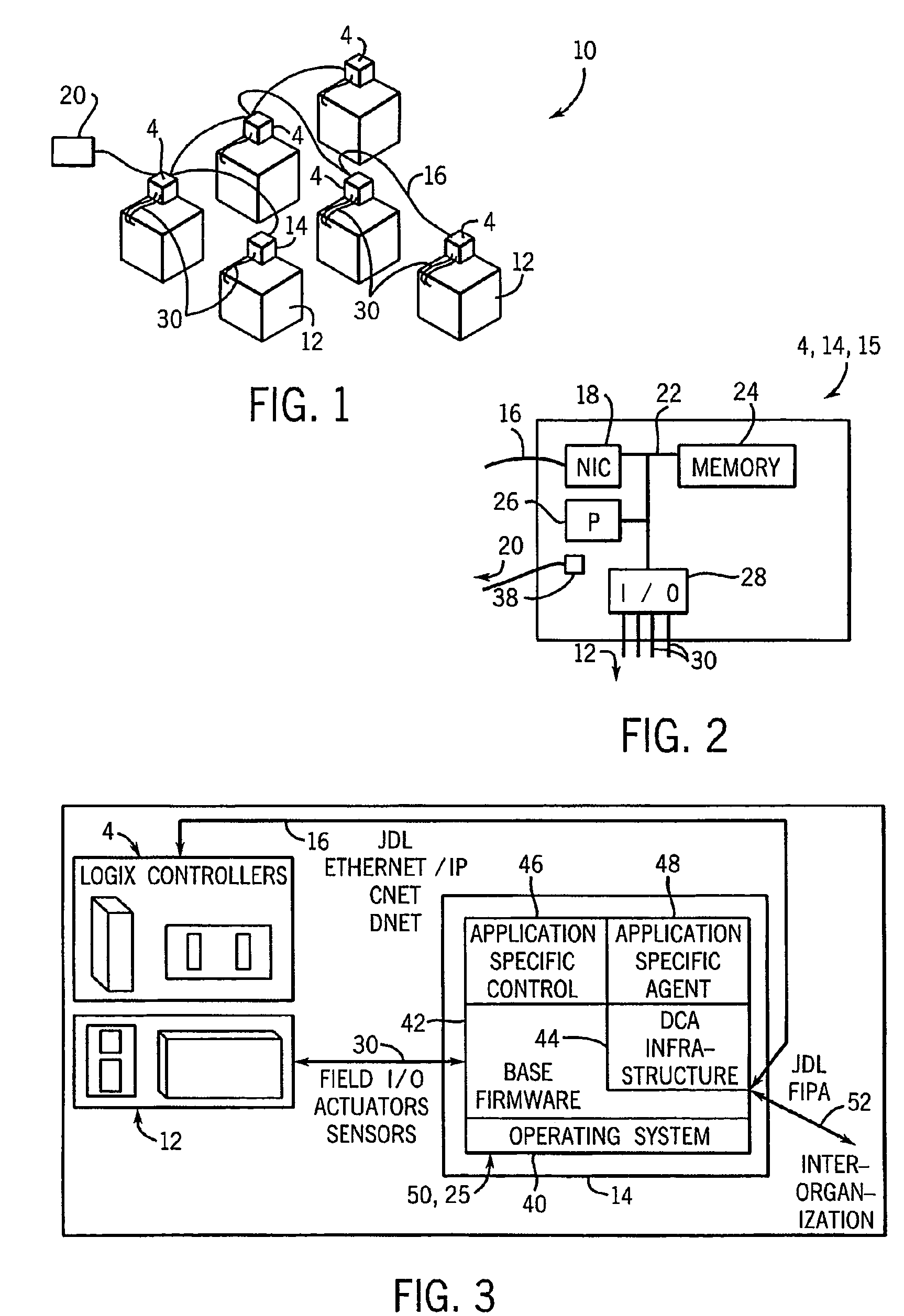
A distributed control system (DCS) is a computerised control system for a process or plant usually with many control loops, in which autonomous controllers are distributed throughout the system, but there is no central operator supervisory control. This is in contrast to systems that use centralized controllers; either discrete controllers located at a central control room or within a central computer. The DCS concept increases reliability and reduces installation costs by localising control functions near the process plant, with remote monitoring and supervision.
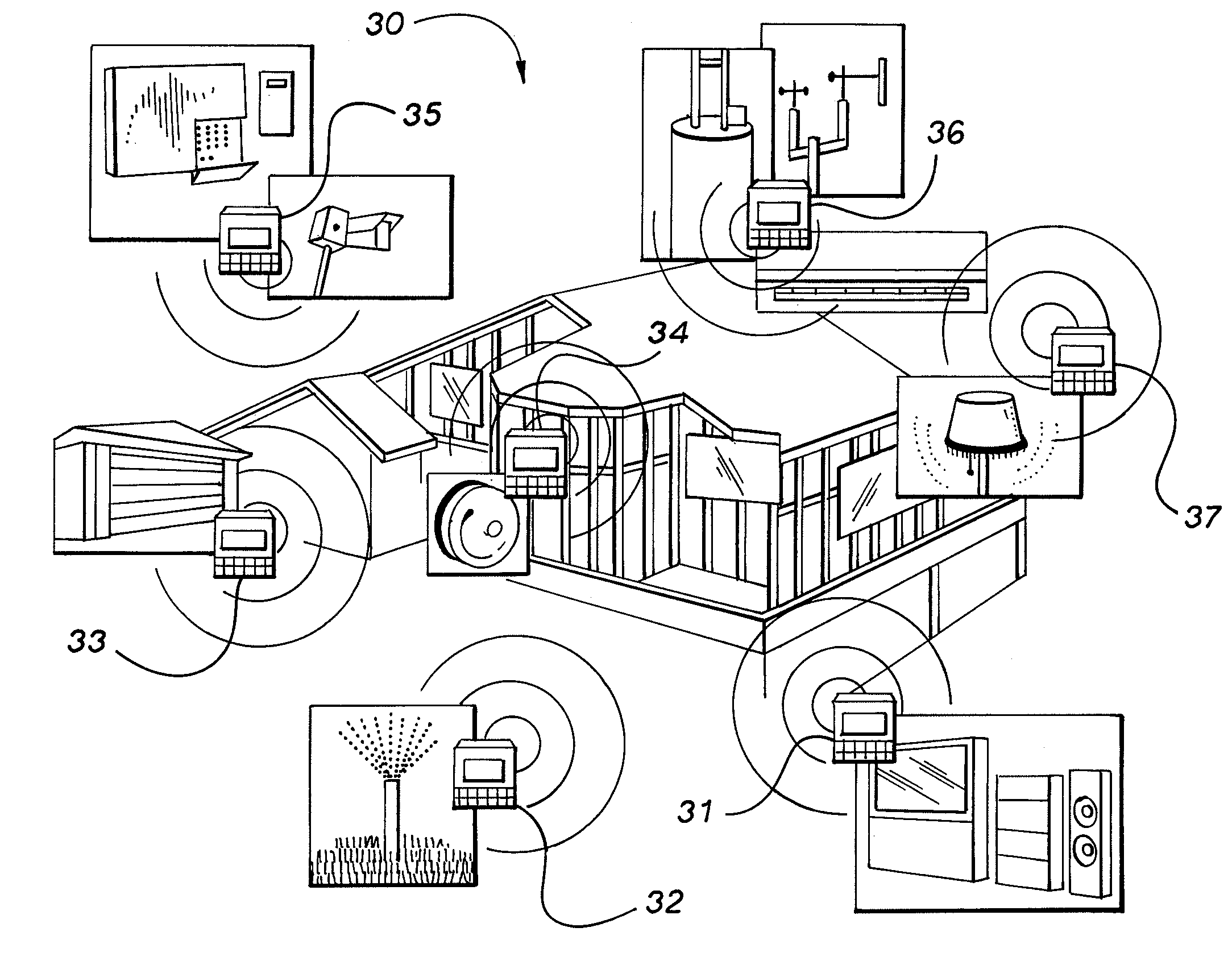
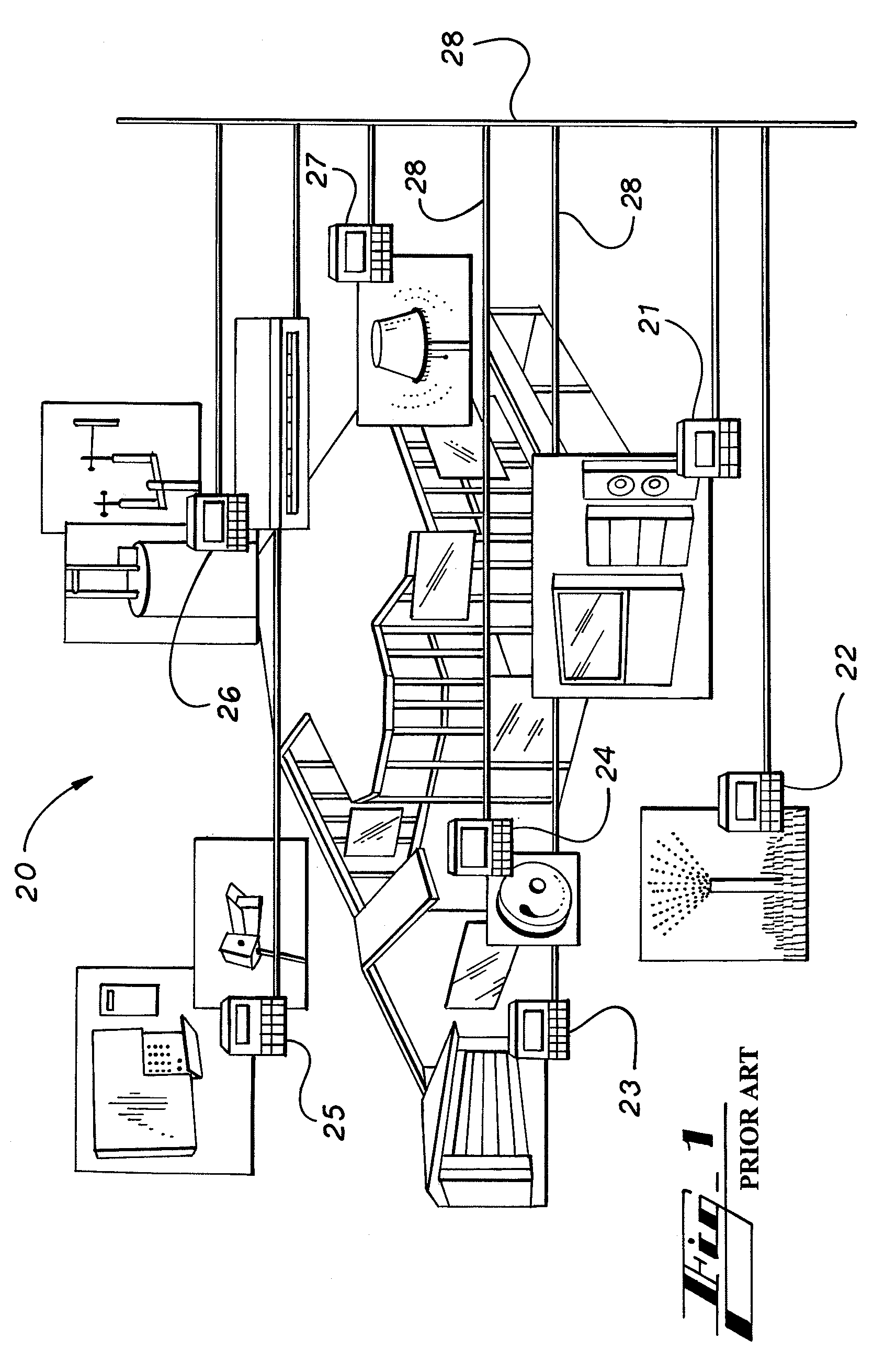
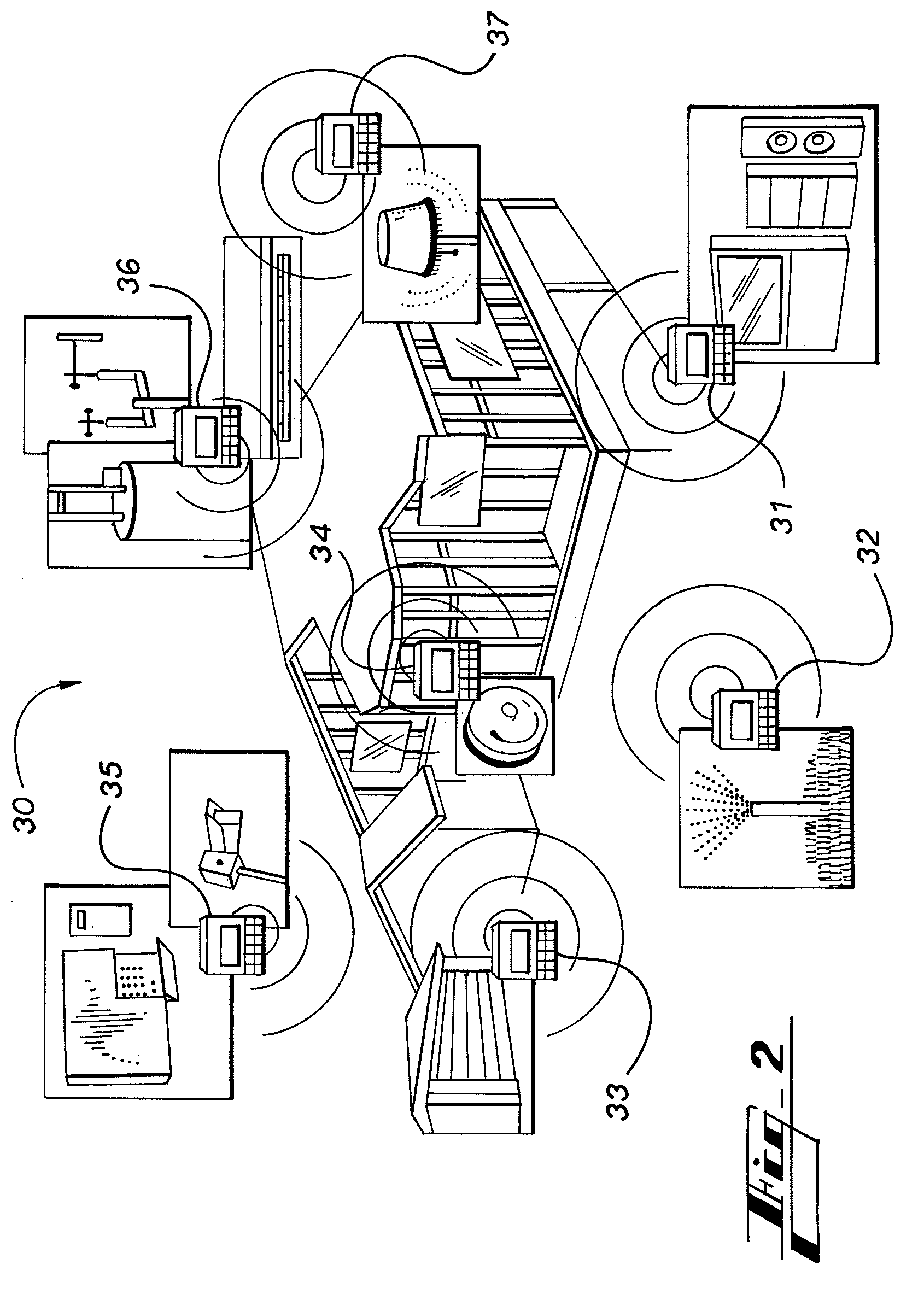
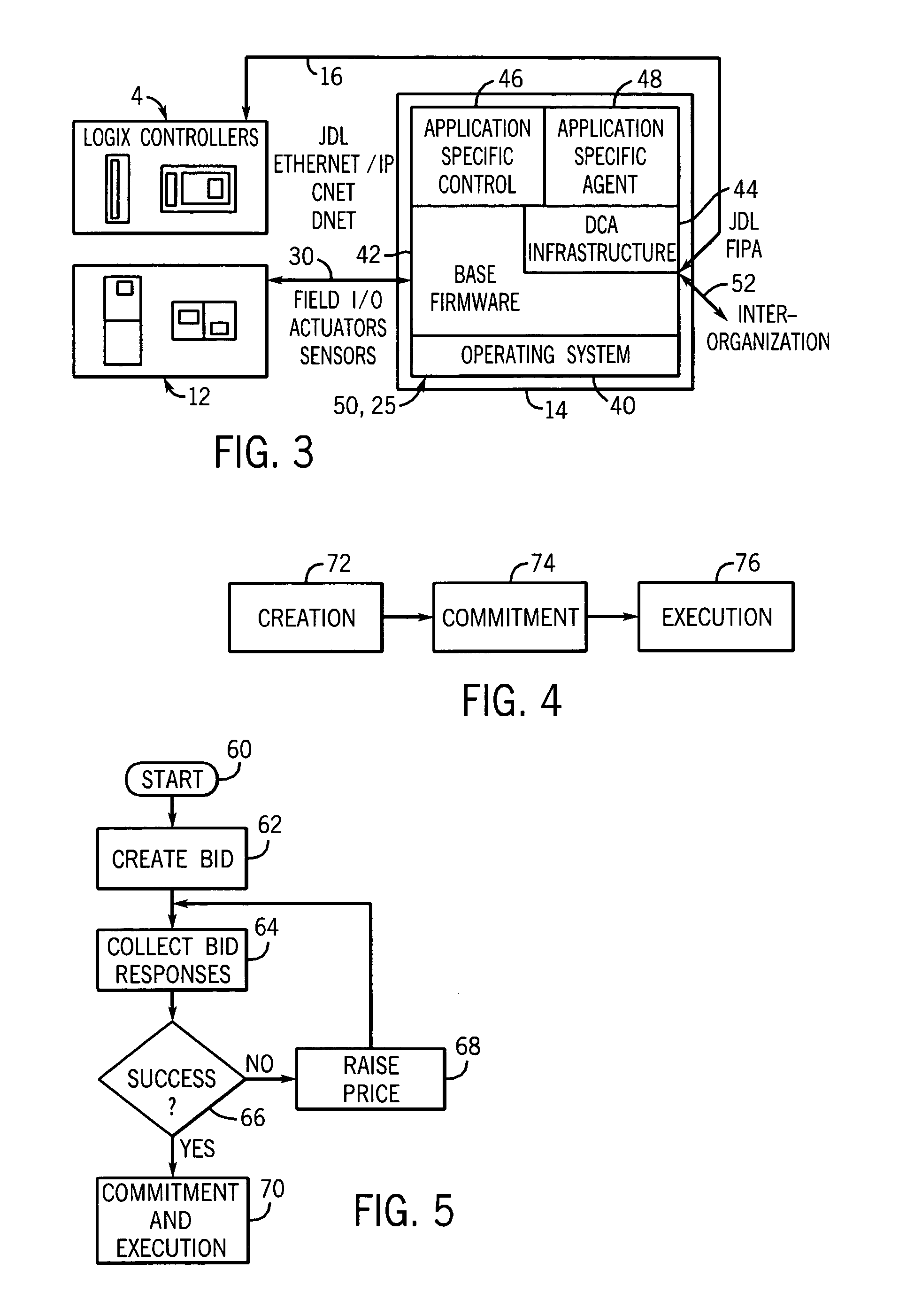
System and method for implementing logic control in programmable controllers in distributed control systems
ActiveUS7225037B2Easy to installEasy to modifyTemperatue controlStatic/dynamic balance measurementProgrammable logic controllerDistributed control system
The present invention provides a system and method for implementing logic control in programmable controllers in distributed control systems using a wired or wireless network. A software application is used to define the configuration of the network. Based on the network configuration, a compiler engine automatically assigns each statement of the control program to at least one programmable logic controller in the network. Each statement is then transmitted over a data transmission medium to the programmable logic controller assigned to the statement.
Owner:UNITRONICS 1989 RG
System and method for implementing logic control in programmable controllers in distributed control systems
ActiveUS20050085928A1EliminateAchieve modularityTemperatue controlStatic/dynamic balance measurementProgrammable logic controllerDistributed control system
Owner:UNITRONICS 1989 RG
Field device and method for transferring the field device's signals
ActiveUS20060092039A1Simplify the linkMinimal costProgramme controlPower managementWireless transmissionDistributed control system
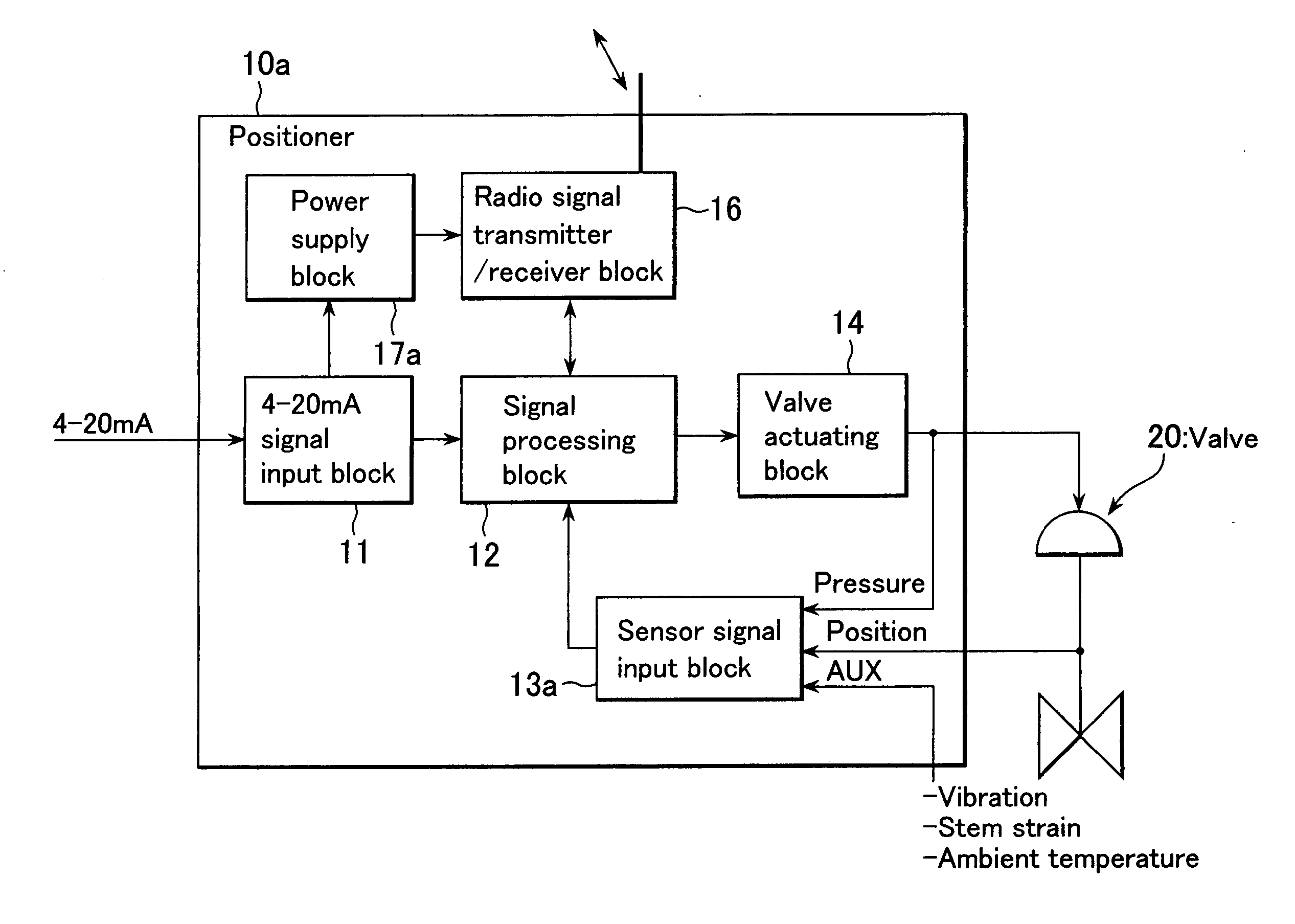
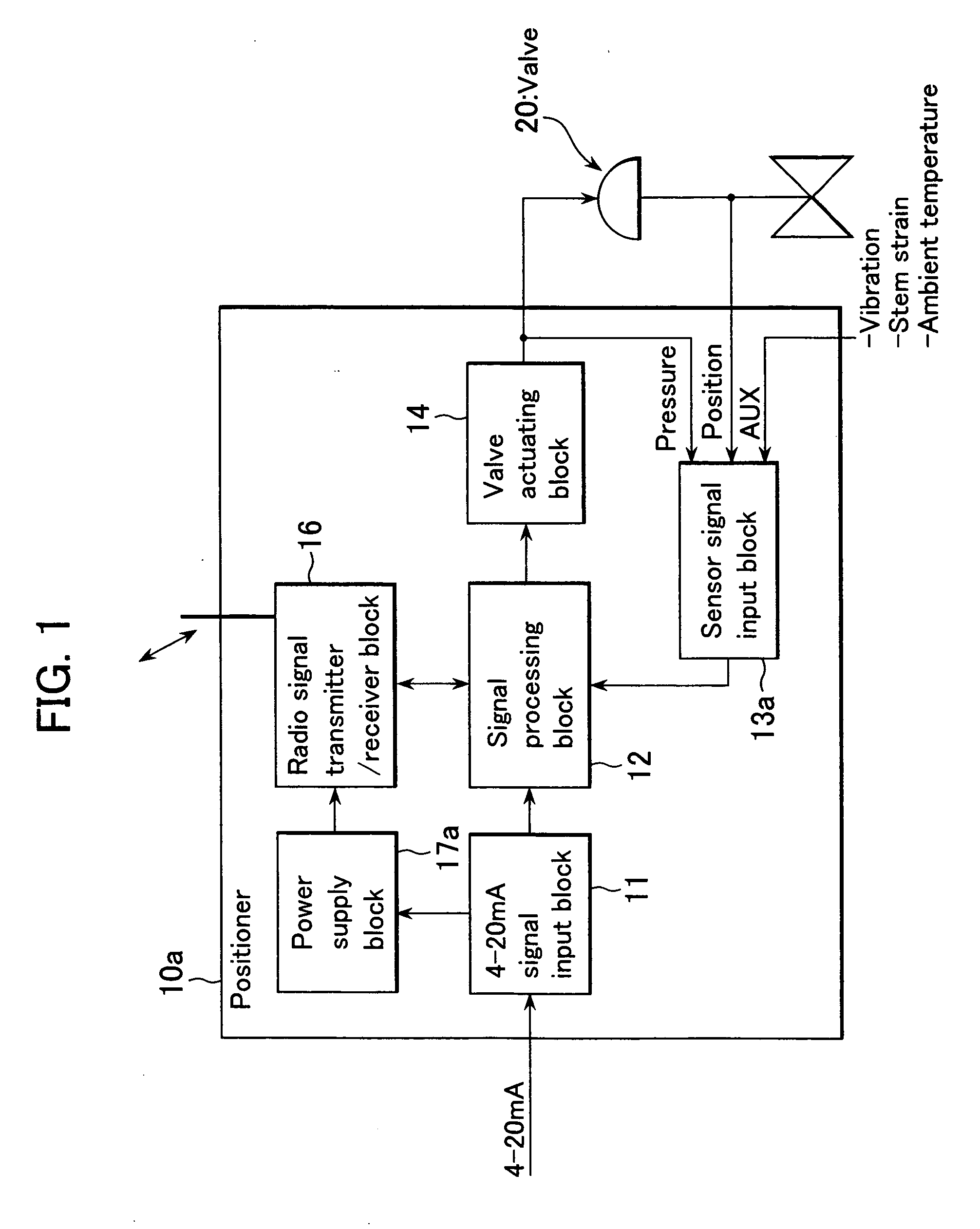
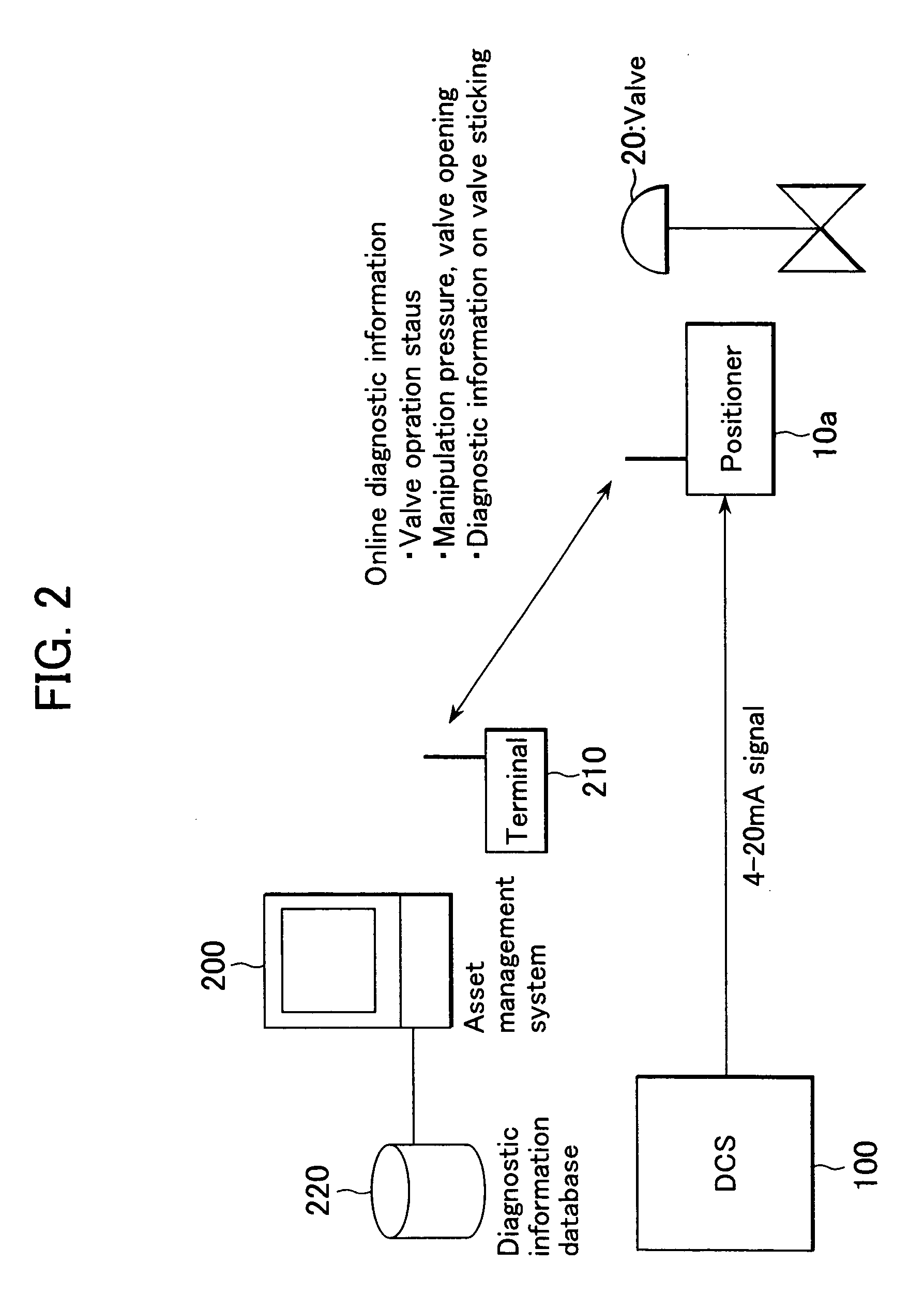
The present invention provides a field device whereby the device's additional information can be transmitted wirelessly without the need for battery replacement or external wiring. The present invention also provides a field device whereby the firmware of a wireless module in the field device can be developed at minimum cost and whereby it can be made easy to link the firmware to applications, such as an asset management system, on the host system side. The field device in accordance with the present invention is installed in a plant, factory, or the like, connected to a higher-order distributed control system through a signal line, configured to input or output 4-20 mA signals, and comprised of: an RF unit for transmitting or receiving radio signals; and a power supply block for accumulating extra electric currents when the block is neither transmitting nor receiving radio signals; wherein electric currents accumulated in the power supply block are supplied to the RF unit so as to be used as electric power for transmitting or receiving radio signals.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Distributed control system
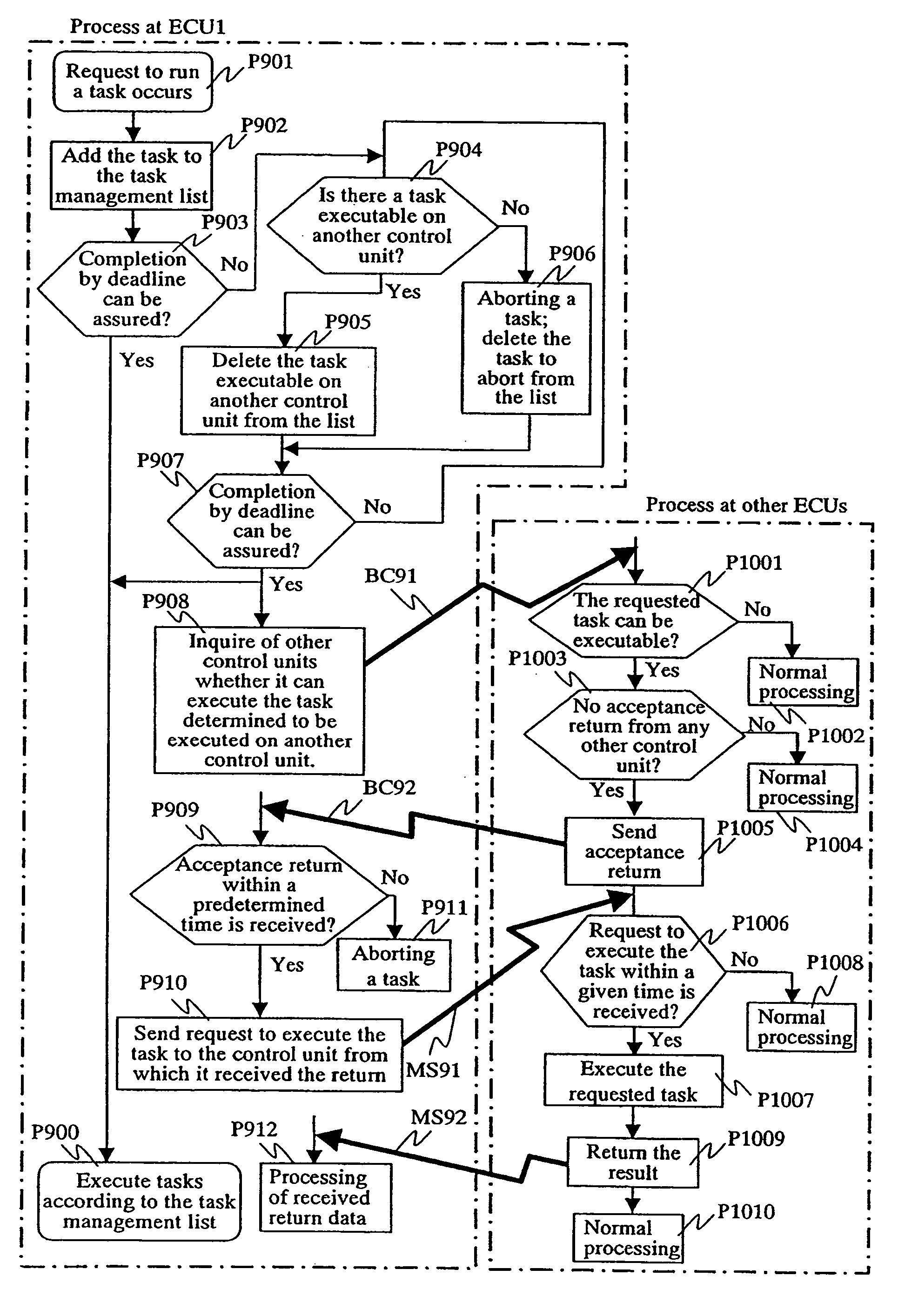
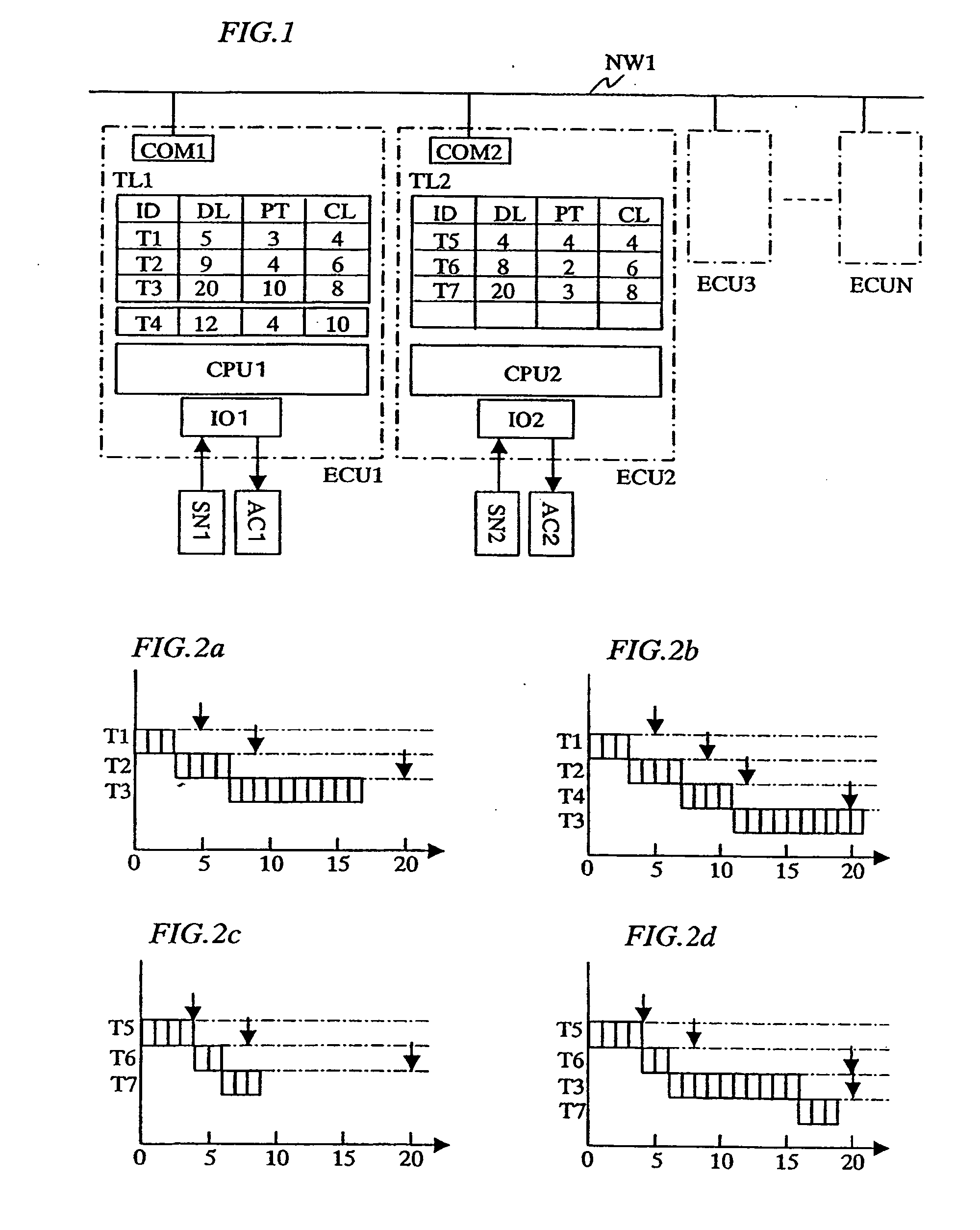
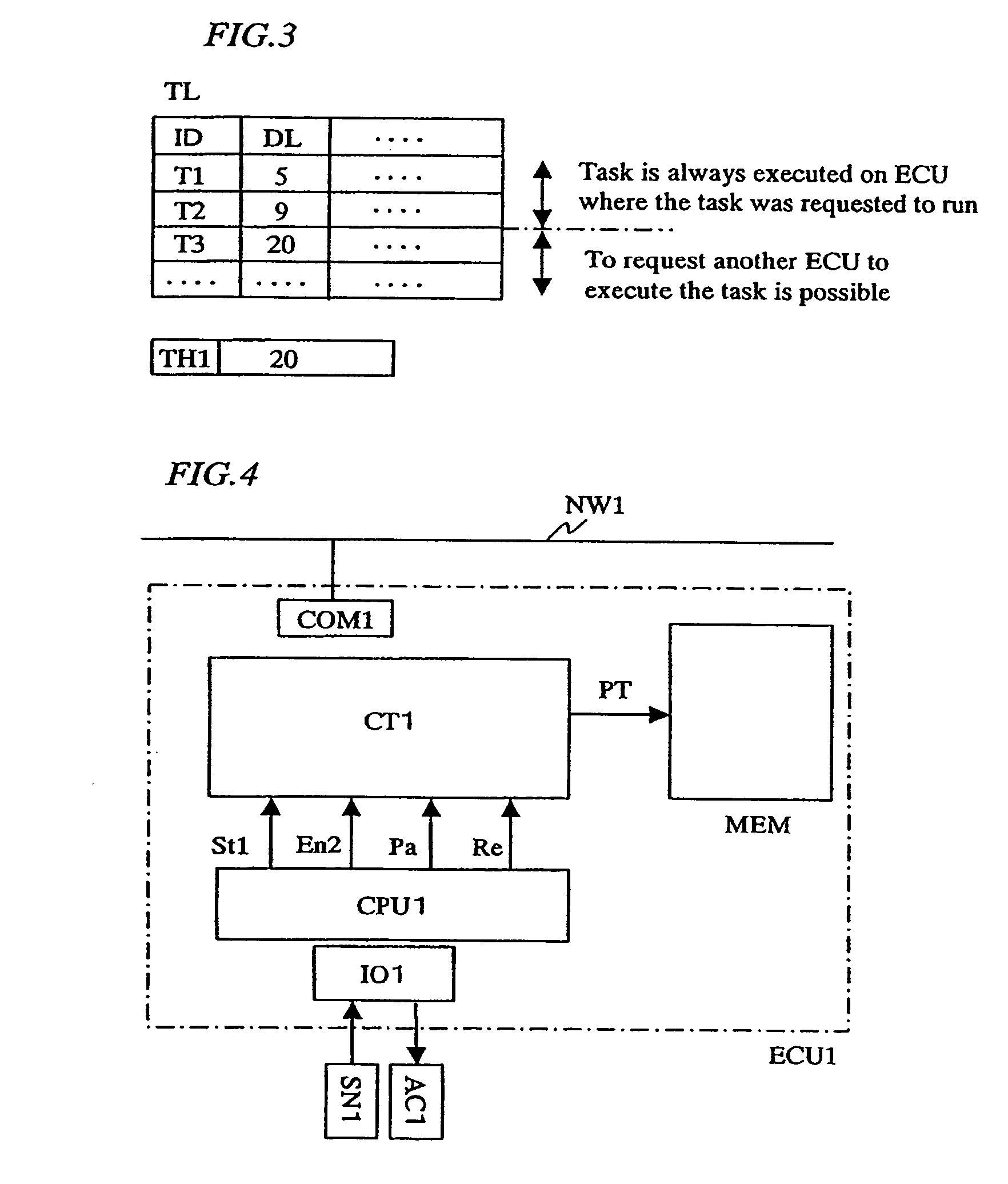
InactiveUS20060101465A1Easy to operateEnsure performanceProgramme controlMultiprogramming arrangementsFault toleranceTask completion
In a distributed control system where a plurality of control units are connected via a network, the invention allows for efficient operation of each control unit, while ensuring real-time processing. To provide a distributed control system in which ensured real-time processing and enhanced fault tolerance are achieved, information of a deadline or task run cycle period as time required until task completion is given for each task and a control unit on which a task will be executed is selected according to the deadline or task cycle period. A first control circuit and related sensors and actuators are connected by a dedicated path on which fast response time is easy to ensure and another control circuit and related sensors and actuators are connected via a network. When the first control circuit operates normally with sufficient throughput, the first control circuit is used for control; in case the first control circuit fails or if its throughput is insufficient, another control circuit is used.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Distributed network control apparatus and method
ActiveUS20130058225A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed control systemNetwork control
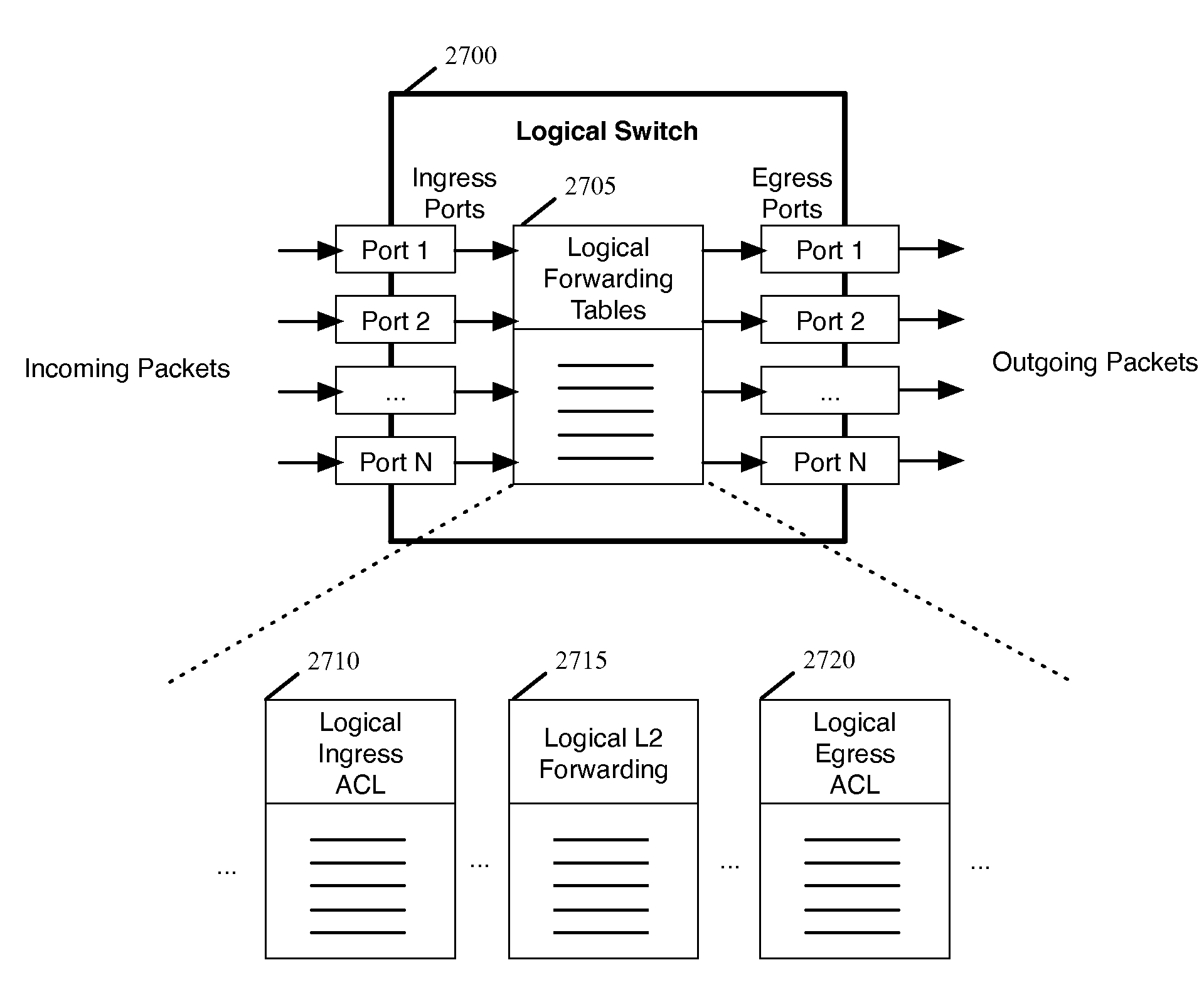
Some embodiments provide a distributed control system for controlling managed switching elements of a network. The distributed control system comprises a first controller for converting a first set of input logical control plane data to a first set of output logical forwarding plane data. It also includes a second controller for converting a second set of input logical control plane data to a second set of output logical forwarding plane data. The logical forwarding plane data is translated into physical forwarding behaviors that direct the forwarding of data by the managed switching elements.
Owner:NICIRA
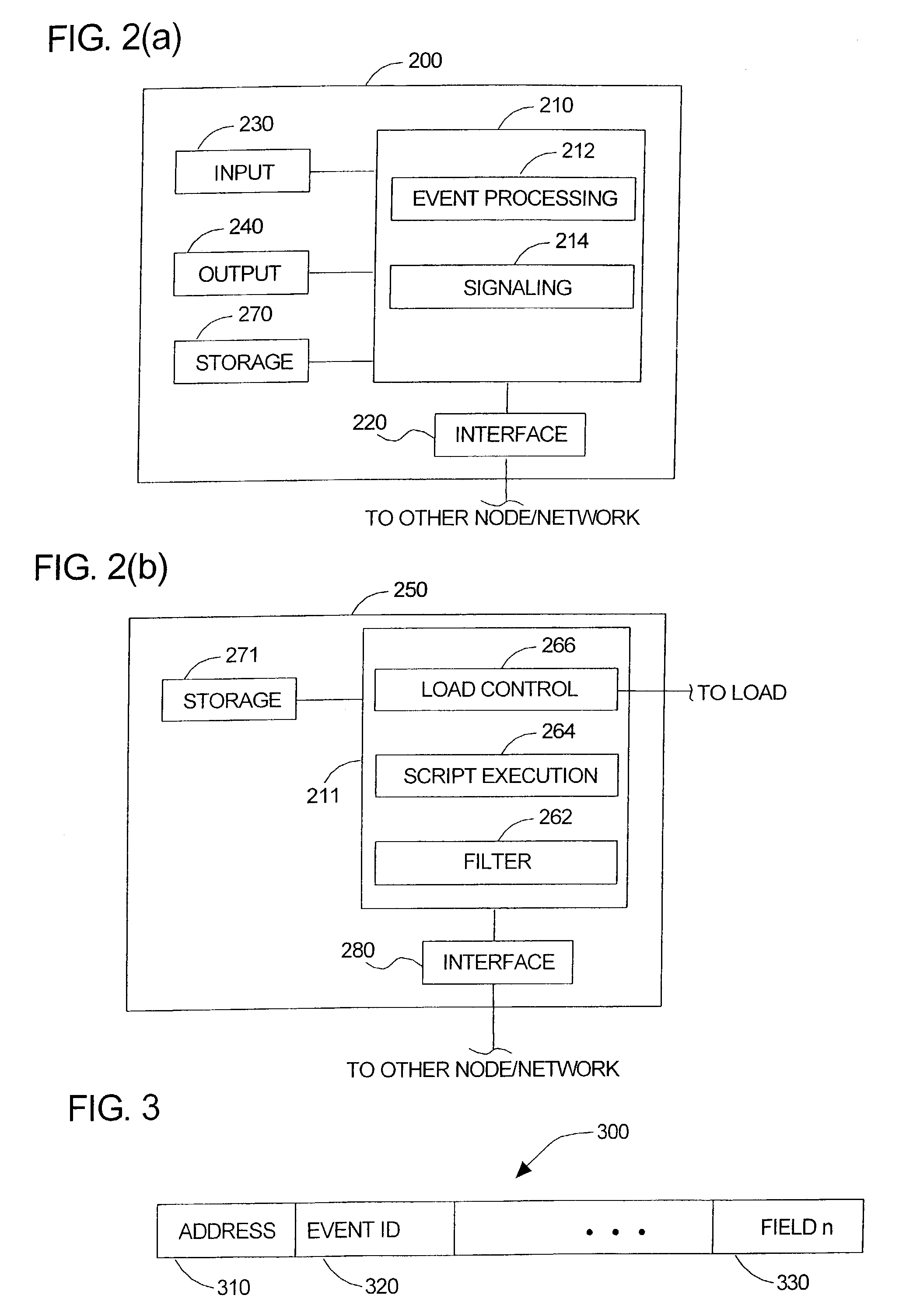
Distributed control systems and methods
ActiveUS7089066B2Level controlHeating and refrigeration combinationsDistributed control systemComputer science
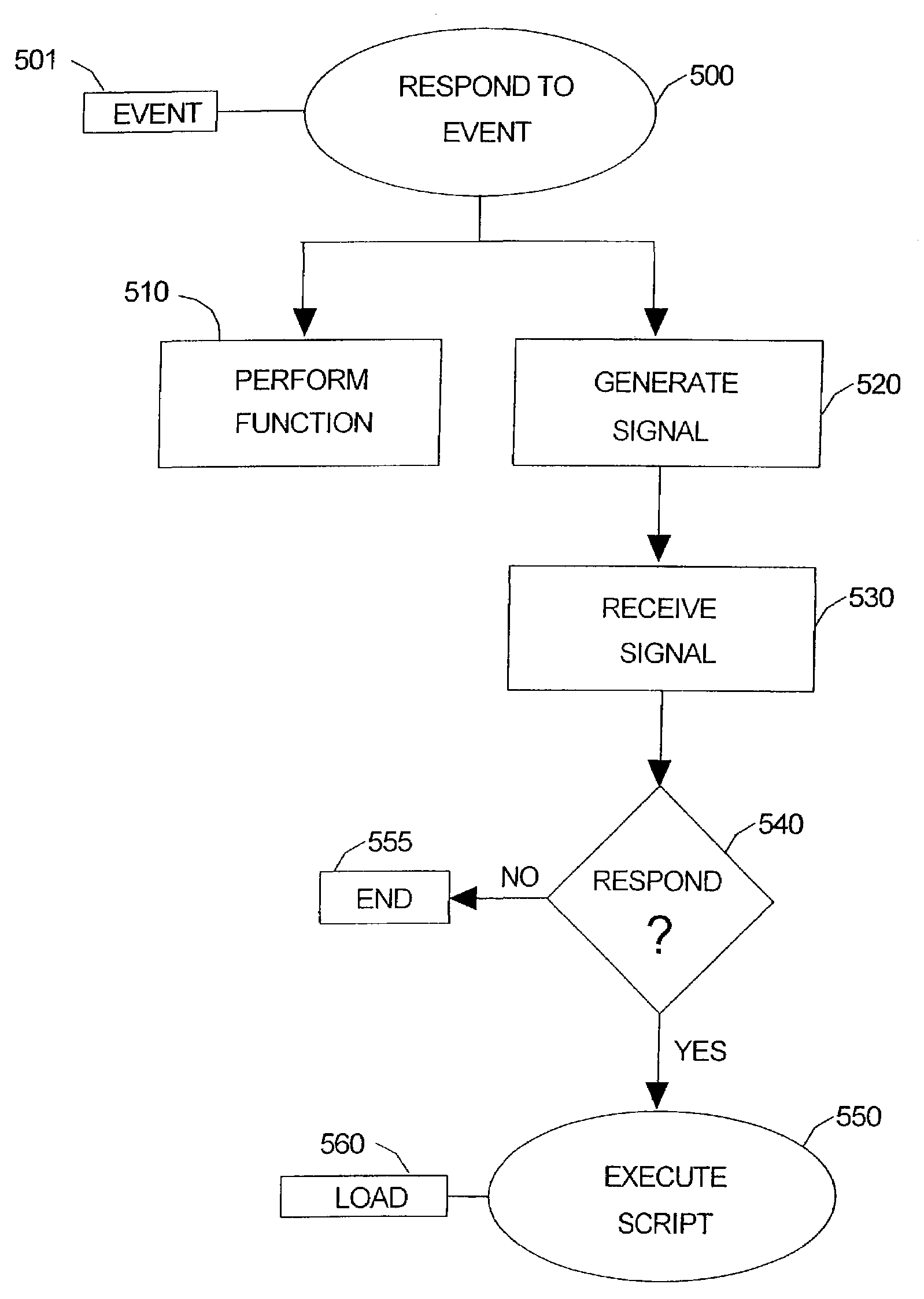
Distributed control systems and methods. An embodiment of distributed control system may comprise at least first and second nodes operatively associated with one another, the first node issuing a signal to at least the second node in response to an event. A load controlled by the second node, and a distributed controller provided at the second node. The distributed controller executing at least one script corresponding to the signal to control the load.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Distributed control system
Owner:LIQUID SKY STUDIOS
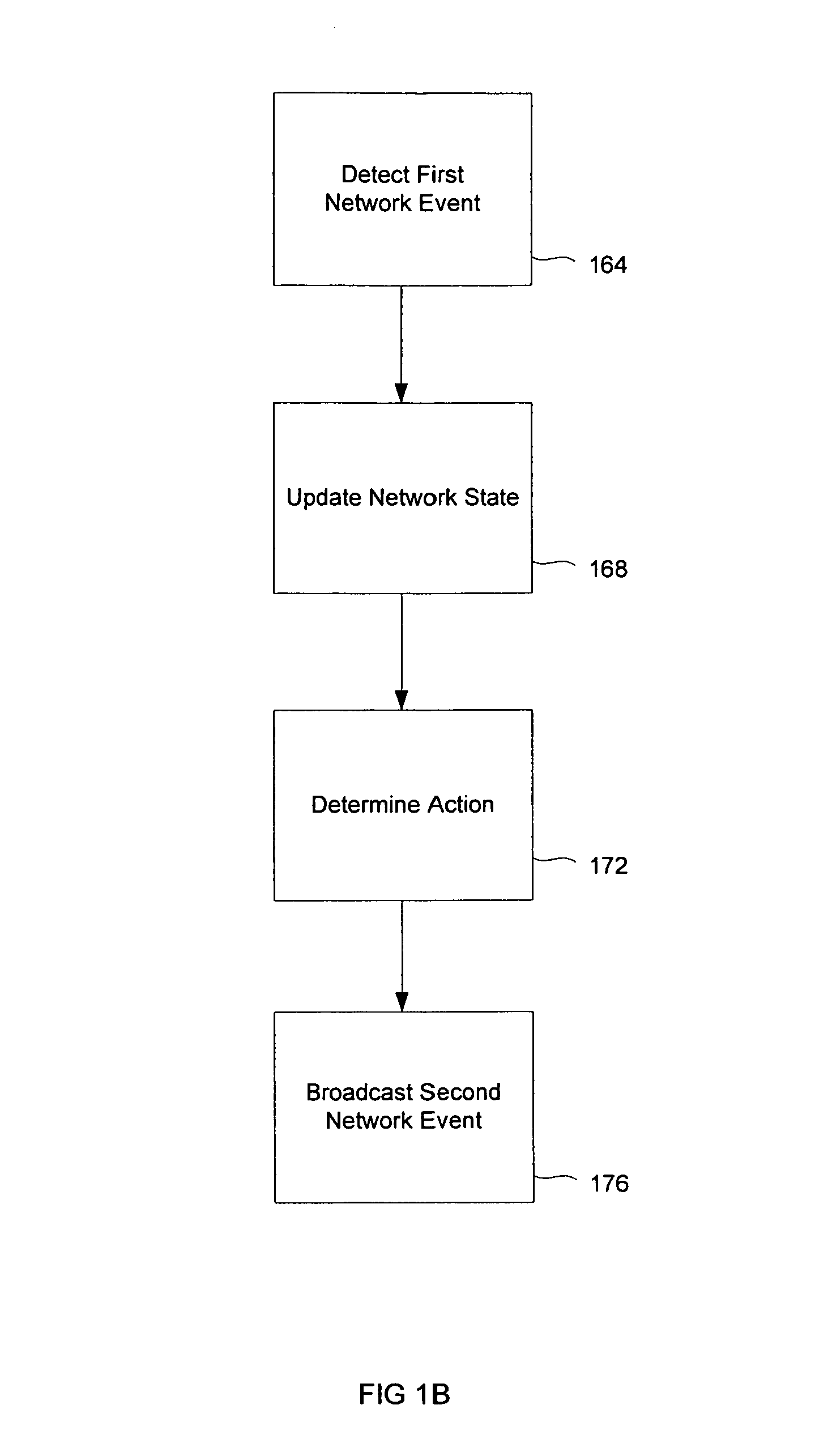
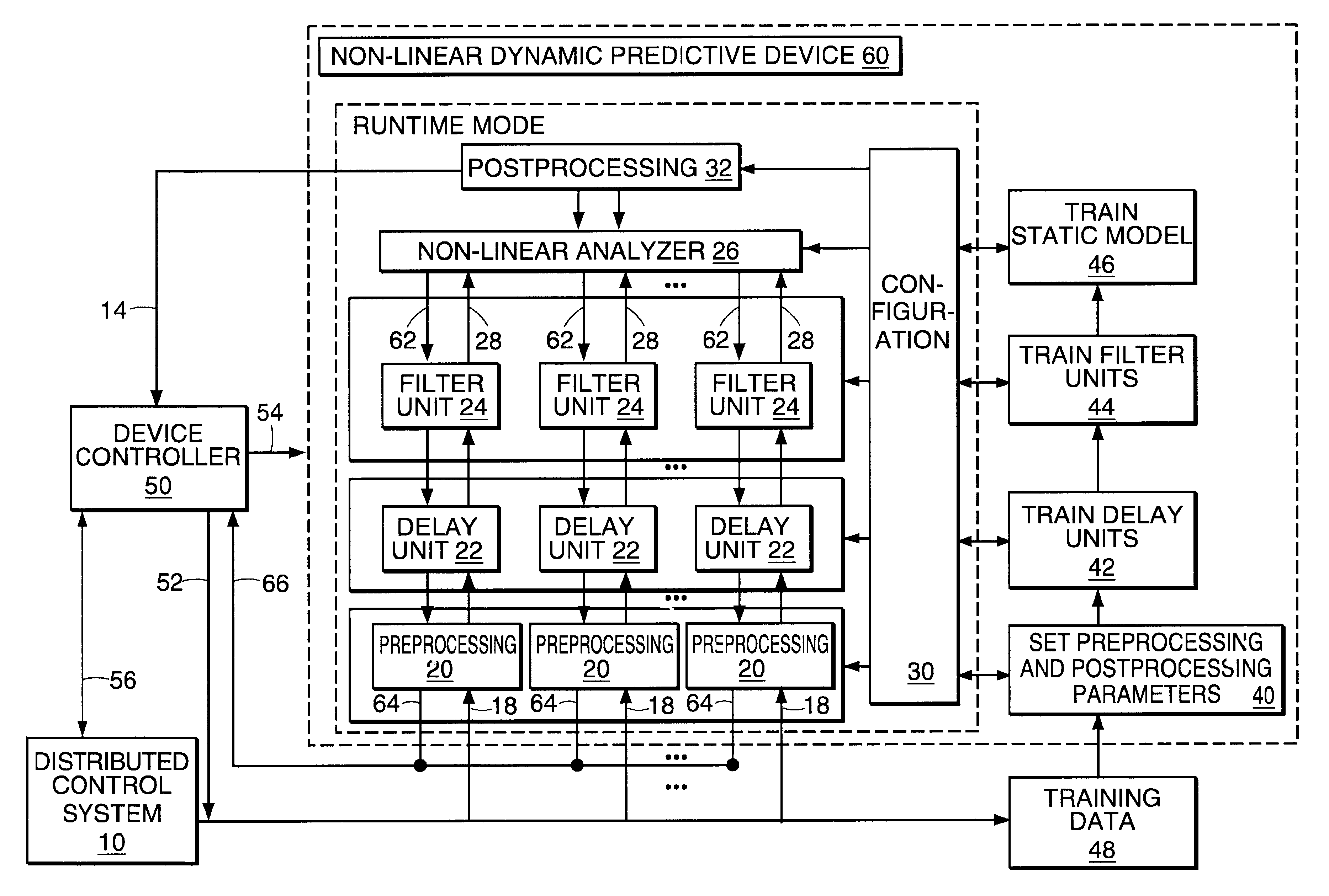
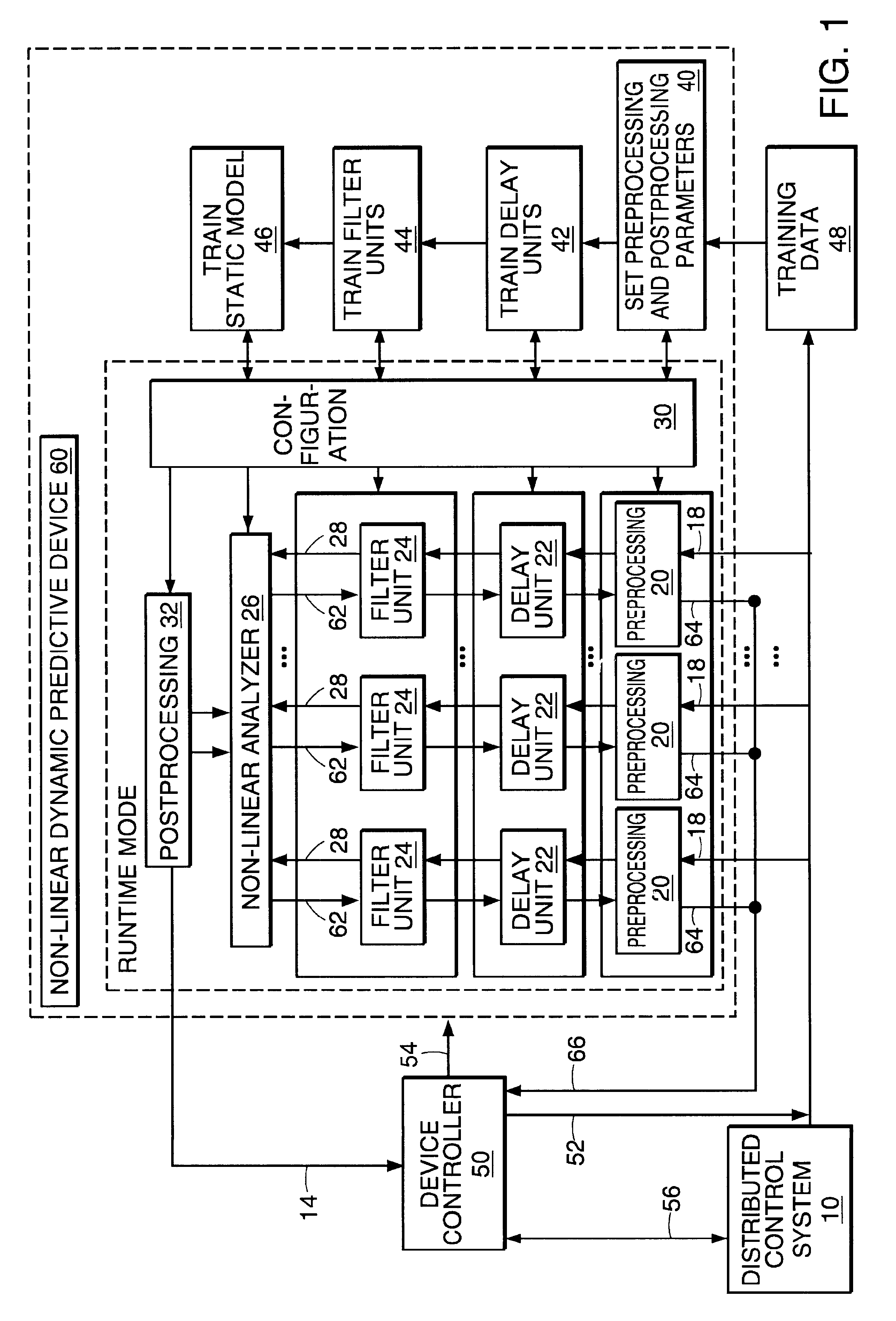
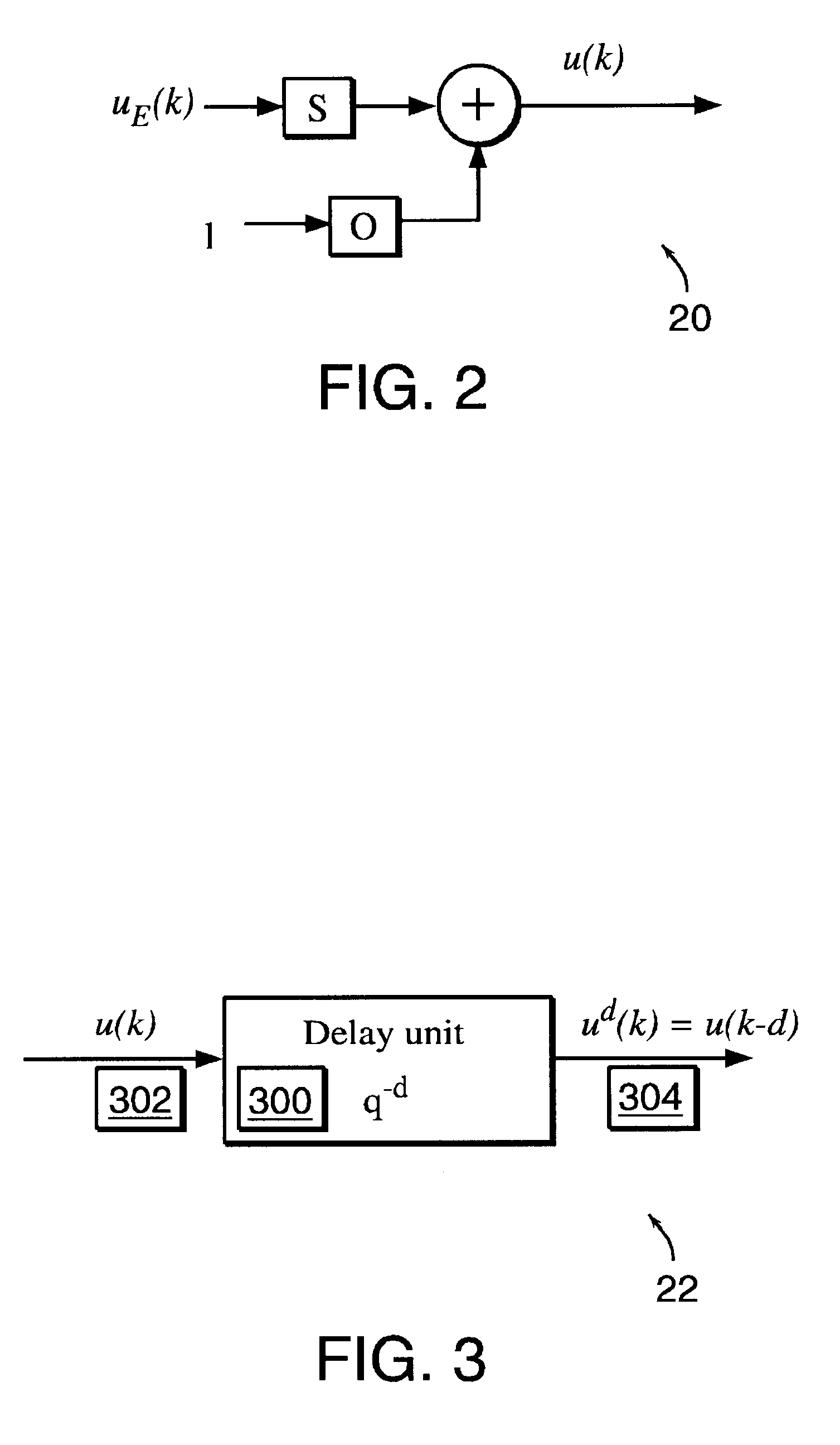
Non-linear dynamic predictive device
InactiveUS6453308B1Improve accuracyFast computerSimulator controlElectric testing/monitoringHorizonDead time
A non-linear dynamic predictive device (60) is disclosed which operates either in a configuration mode or in one of three runtime modes: prediction mode, horizon mode, or reverse horizon mode. An external device controller (50) sets the mode and determines the data source and the frequency of data. In prediction mode, the input data are such as might be received from a distributed control system (DCS) (10) as found in a manufacturing process; the device controller ensures that a contiguous stream of data from the DCS is provided to the predictive device at a synchronous discrete base sample time. In prediction mode, the device controller operates the predictive device once per base sample time and receives the output from the predictive device through path (14). In horizon mode and reverse horizon mode, the device controller operates the predictive device additionally many times during base sample time interval. In horizon mode, additional data is provided through path (52). In reverse horizon mode data is passed in a reverse direction through the device, utilizing information stored during horizon mode, and returned to the device controller through path (66). In the forward modes, the data are passed to a series of preprocessing units (20) which convert each input variable (18) from engineering units to normalized units. Each preprocessing unit feeds a delay unit (22) that time-aligns the input to take into account dead time effects such as pipeline transport delay. The output of each delay unit is passed to a dynamic filter unit (24). Each dynamic filter unit internally utilizes one or more feedback paths that are essential for representing the dynamic information in the process. The filter units themselves are configured into loosely coupled subfilters which are automatically set up during the configuration mode and allow the capability of practical operator override of the automatic configuration settings. The outputs (28) of the dynamic filter units are passed to a non-linear analyzer (26) which outputs a value in normalized units. The output of the analyzer is passed to a post-processing unit (32) that converts the output to engineering units. This output represents a prediction of the output of the modeled process. In reverse horizon mode, a value of 1 is presented at the output of the predictive device and data is passed through the device in a reverse flow to produce a set of outputs (64) at the input of the predictive device. These are returned to the device controller through path (66). The purpose of the reverse horizon mode is to provide essential information for process control and optimization. The precise operation of the predictive device is configured by a set of parameters. that are determined during the configuration mode and stored in a storage device (30). The configuration mode makes use of one or more files of training data (48) collected from the DCS during standard operation of the process, or through structured plant testing. The predictive device is trained in four phases (40, 42, 44, and 46) correspo
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
Tether energy supply system
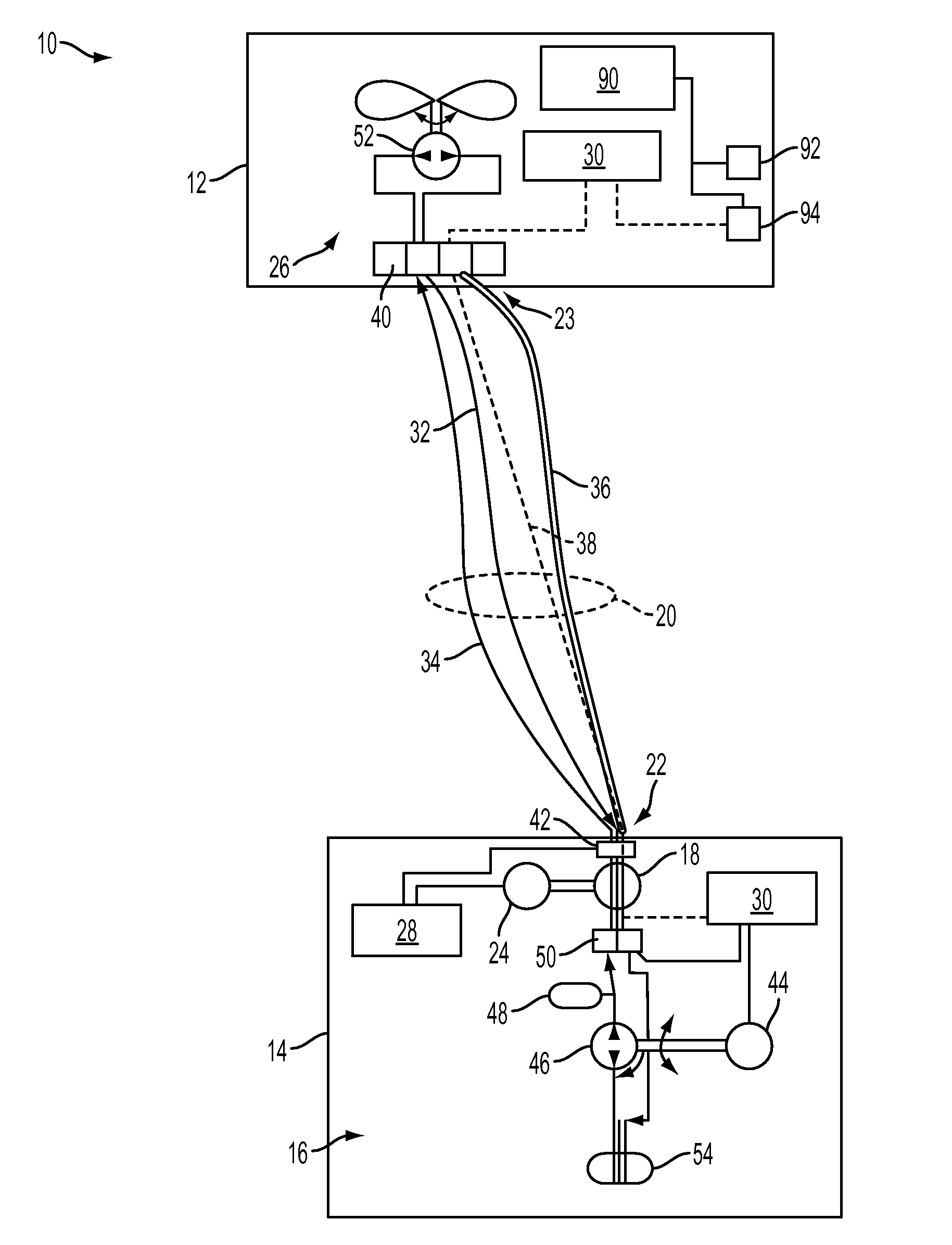
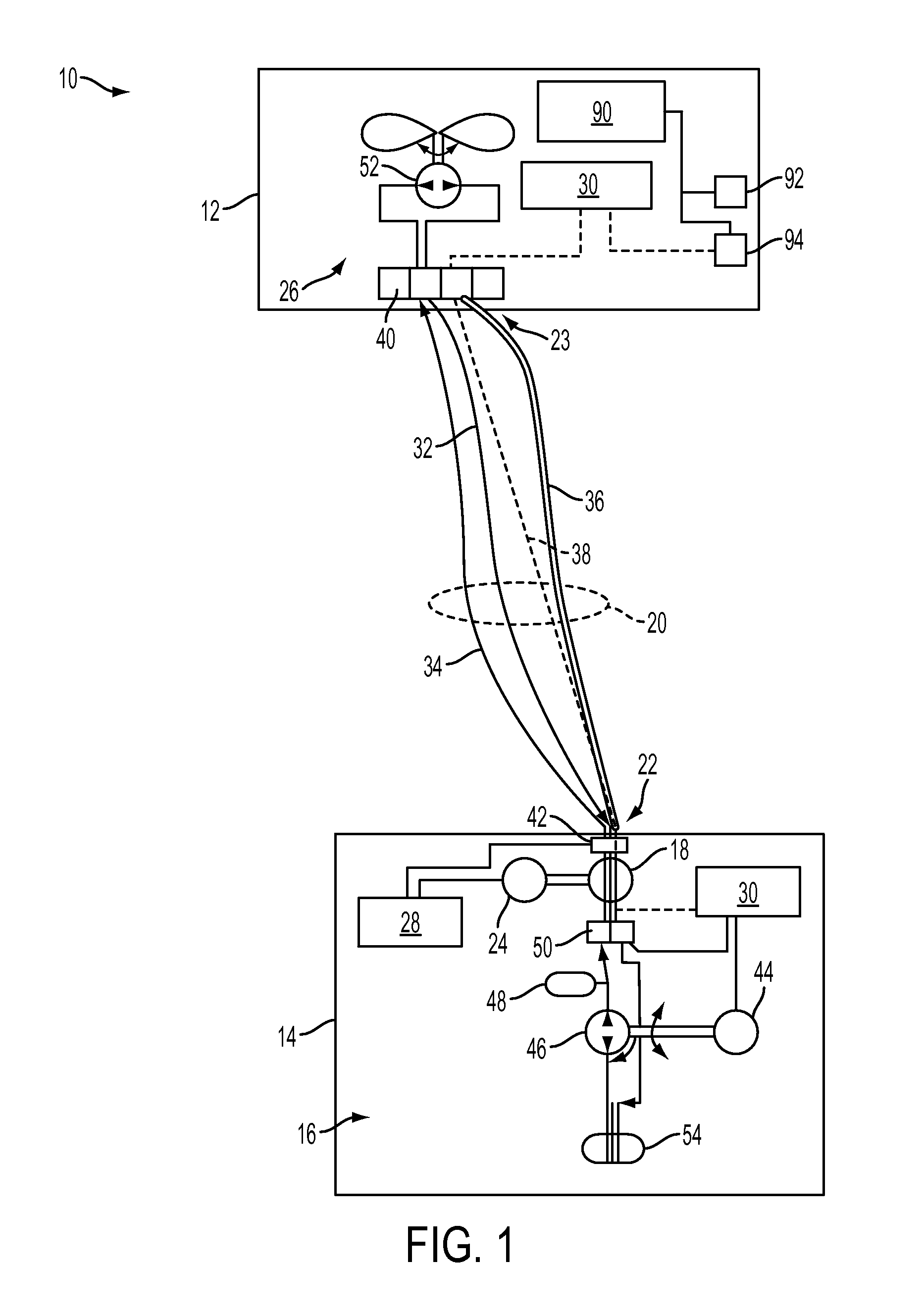
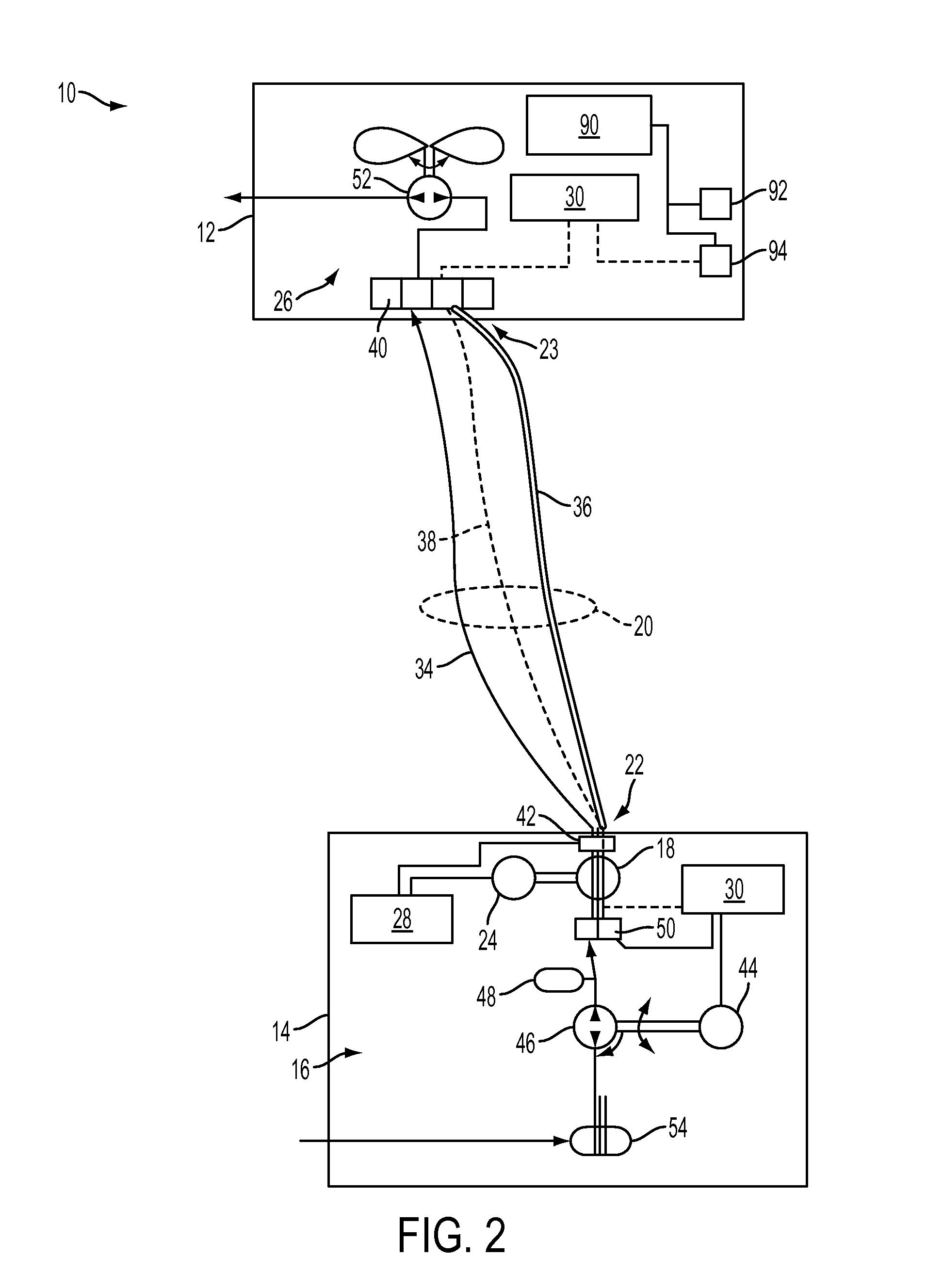
InactiveUS20110180667A1Eliminate weightEliminate riskTethered aircraftPower plant fuel tanksDistributed control systemElectric machinery
A tether continuous energy supply system for an unmanned aerial vehicle comprising: a ground station, a ground station energy system, a spool coupled to the ground station energy system at a rotating joint, a tether that is wound about the spool, wherein a first end of the tether is coupled to the rotating joint, a tension control motor coupled to both the spool and the ground station energy system, an unmanned aerial vehicle coupled to a second end of the tether, a UAV energy system, a fluid that moves throughout the tether continuous energy supply system, a tension control system that receives and transmits signals from a plurality of sensors contained within the tether continuous energy supply system, and a distributed controls system that receives and transmits signals from the plurality of sensors contained within the tether continuous energy supply system.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
System and method for interfacing multi-agent system
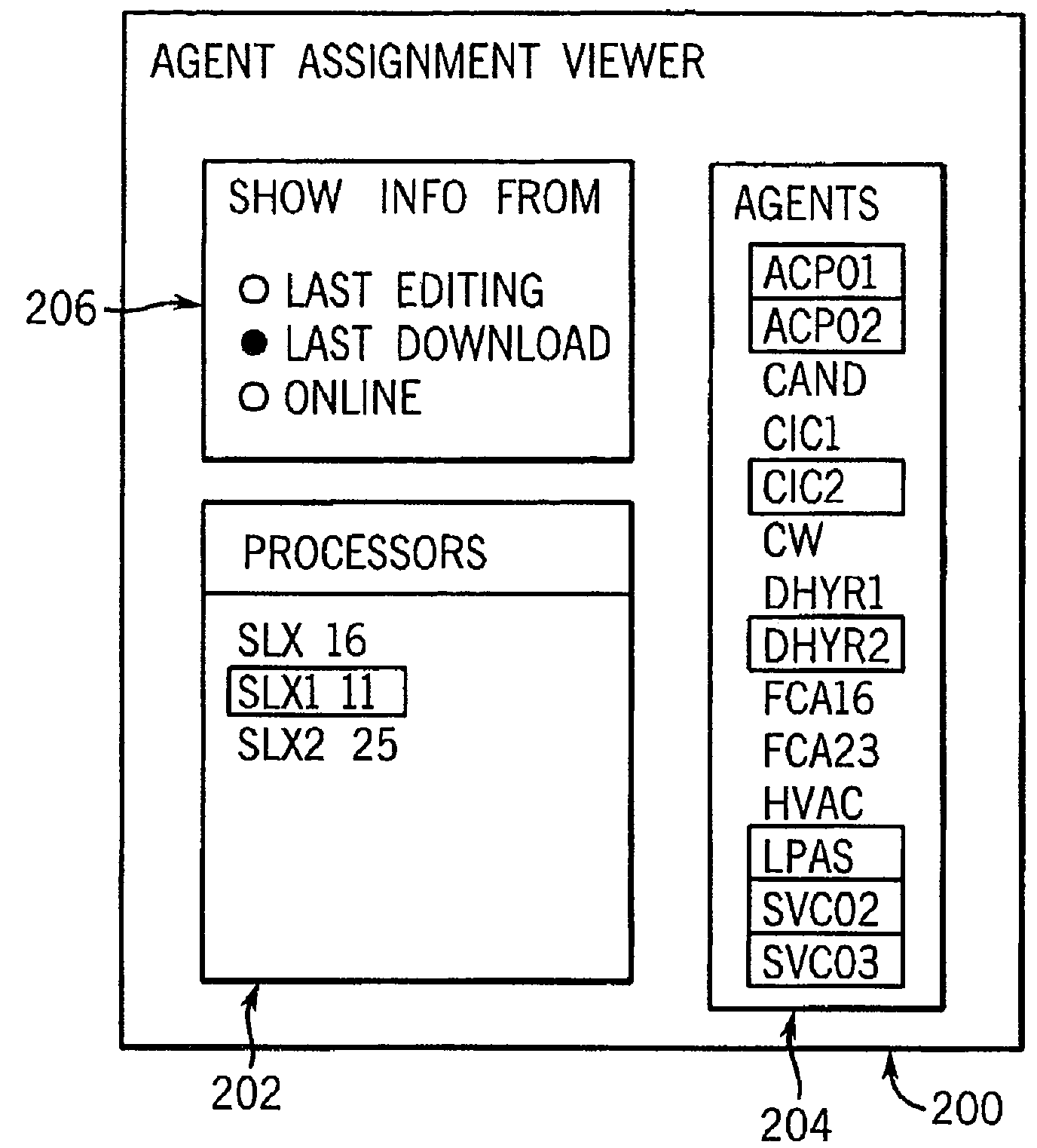
InactiveUS7228187B2Digital dataKnowledge representationRelevant informationDistributed control system
A system and method of interacting with a multi-agent distributed control system employing a plurality of controllers on which are programmed a plurality of agents in which the controllers are coupled by a network are disclosed. The method includes providing a computer program capable of operating a user interface, where the computer program is in communication with the agents via the network. The method further includes displaying agent-related information on the user interface by way of a plurality of windows, where within a first of the windows is further displayed a workflow among at least some of the agents, and within a second of the windows is further displayed at least one of a plurality of messages communicated among at least some of the agents, a work unit requested by at least one of the agents, and message content associated with at least one of the messages.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
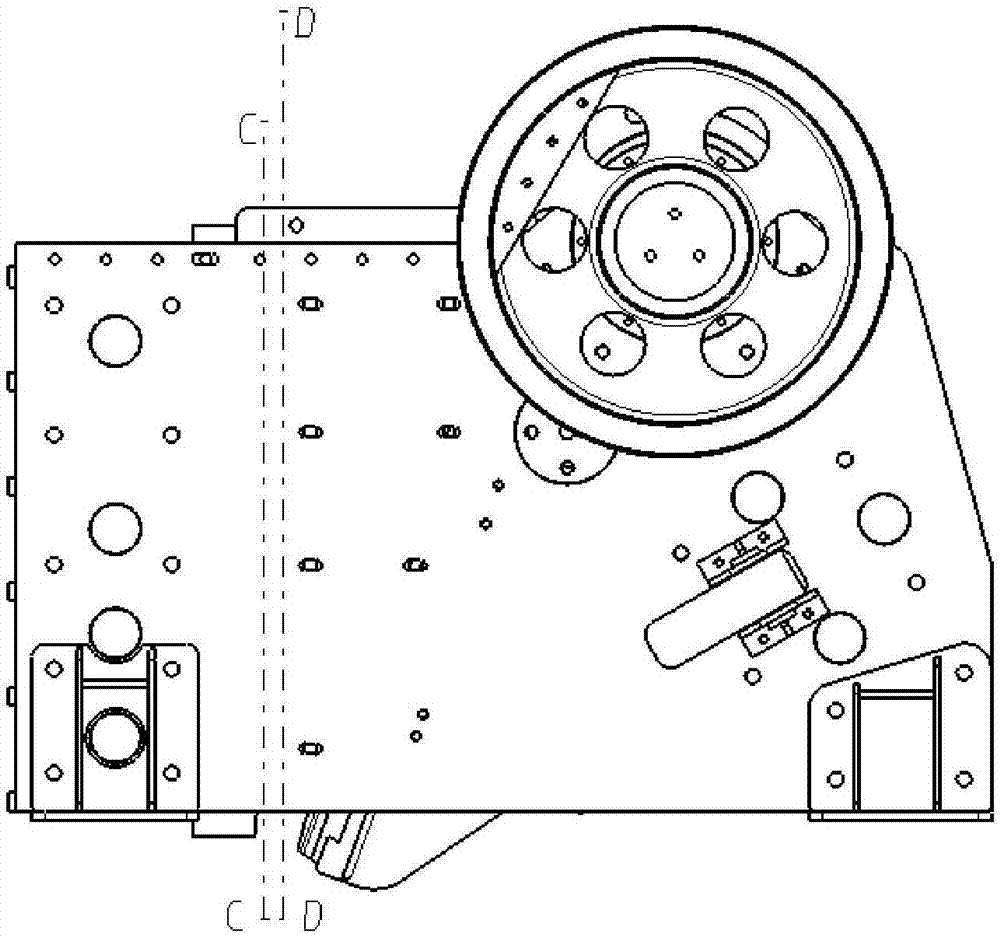
Multiple-degree-of-freedom anti-explosion mechanical arm
InactiveCN101797748AAvoid damageSo as not to damageProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsJoint componentDistributed control system
A multiple-degree-of-freedom anti-explosion mechanical arm relates to an anti-explosion mechanical arm. The anti-explosion mechanical arm comprises a six-degree-of-freedom joint component, a double-camera system, a distributed control system and an expansion system, wherein a front paw can be operated flexibly and diversely through the cooperative control of six joints; the double-camera system is used to provide front vision for rear operating staff so that the mechanical arm can be conveniently controlled to complete special tasks, the double-camera system comprises a main camera fixed on a front arm and a front-end camera fixed on a paw joint; the main camera has broad vision, the focus of the front-end camera is fine; the distributed control system is used to control the synergy movement of the six-degree-of-freedom component and various movements of the six-degree-of-freedom component, the distributed control system comprises a distributed control module, a magnetic absolute position sensing system and the like; and the expansion system is used to add different functions to meet different demands and increase the application range of the mechanical arm.
Owner:武汉若比特机器人有限公司
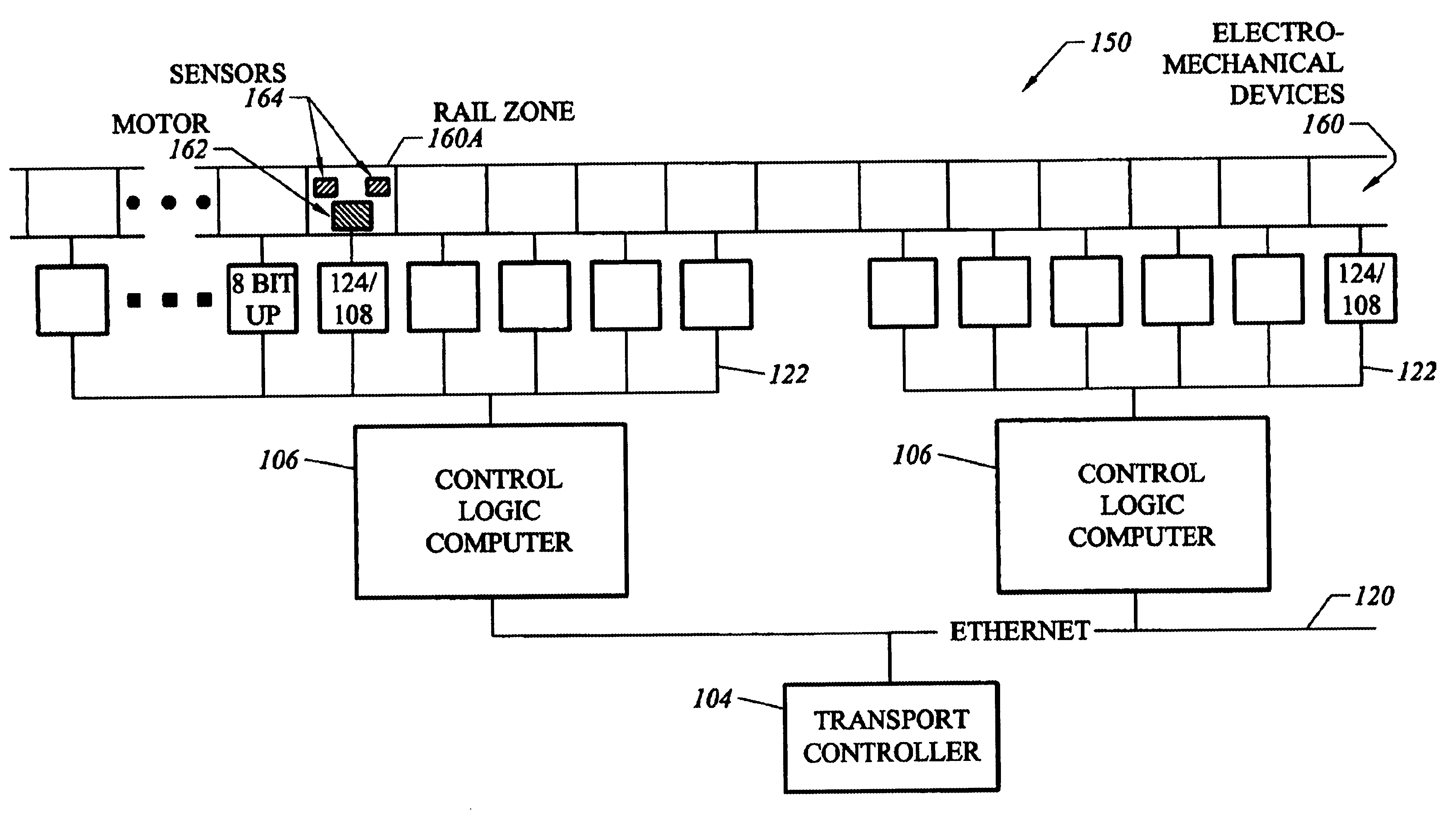
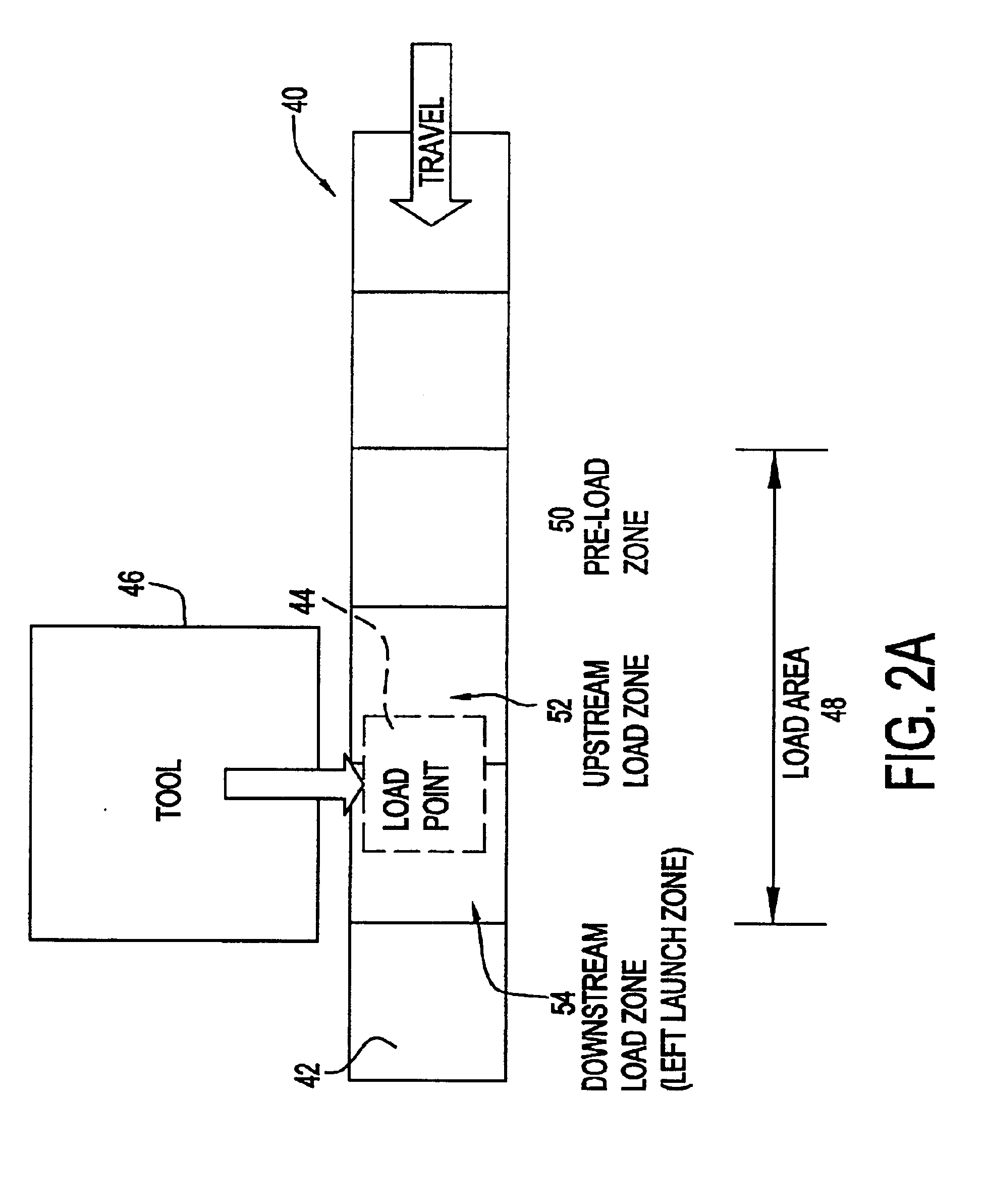
Distributed control system architecture and method for a material transport system
InactiveUS6853876B2Computer controlDigital data processing detailsTransport systemDistributed control system
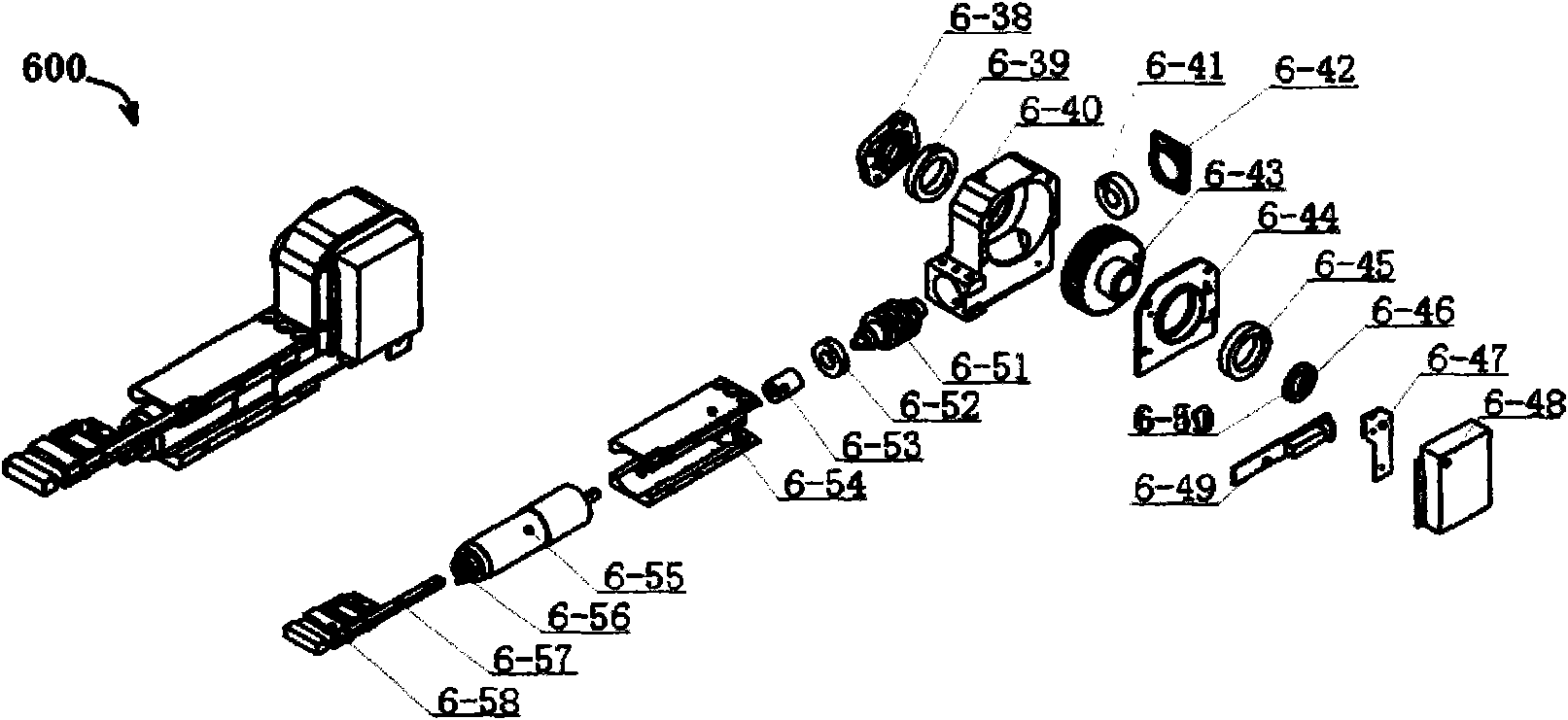
An automated transport system for use in a material handling system. The automated transport system employs a distributed control system including a top level controller (transport controller), a plurality of second-level controllers (control logic computers) and a plurality of third-level controllers (intelligent drivers). The transport controller (TC) receives material commands from a conventional material control system (MCS). The TC breaks the command into sub-commands directing selected control logic computers (CLCs) to acquire, move to a destination or otherwise interact with a particular container designated by the MCS command. The transport controller selects the CLCs based on the transport system topology, the content of the MCS command and knowledge of which regions of the transport system are controlled by respective CLCs. Each CLC implements the sub-commands by issuing to the intelligent drivers low level control commands to accelerate, elevate, rotate, load or unload the container. Each intelligent driver directly controls one of the electromechanical devices that compose the transport system hardware in accordance with these low level commands. The electromechanical devices can include rail sections (zones), directors, elevators, load port transfer devices and tag readers.
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD
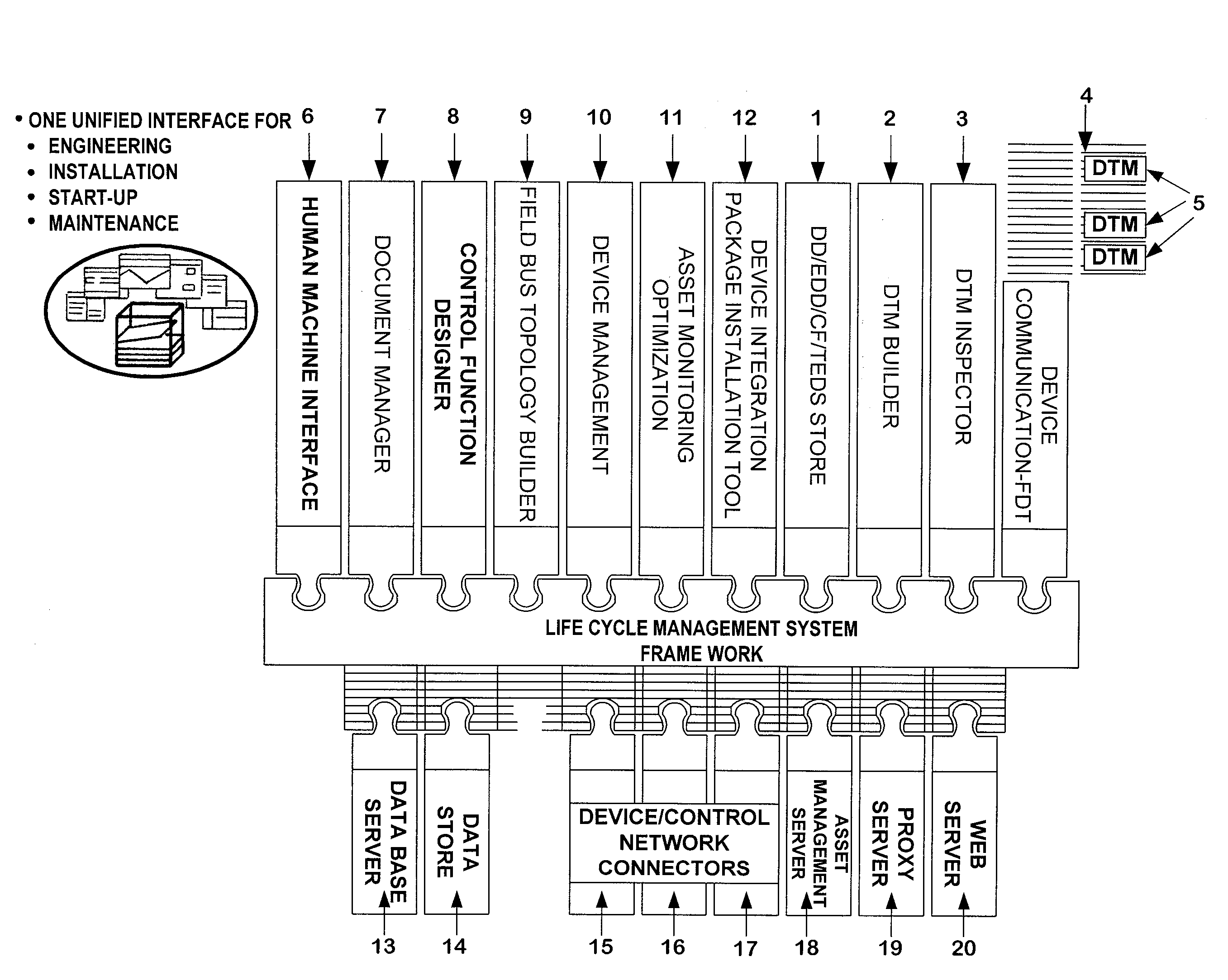
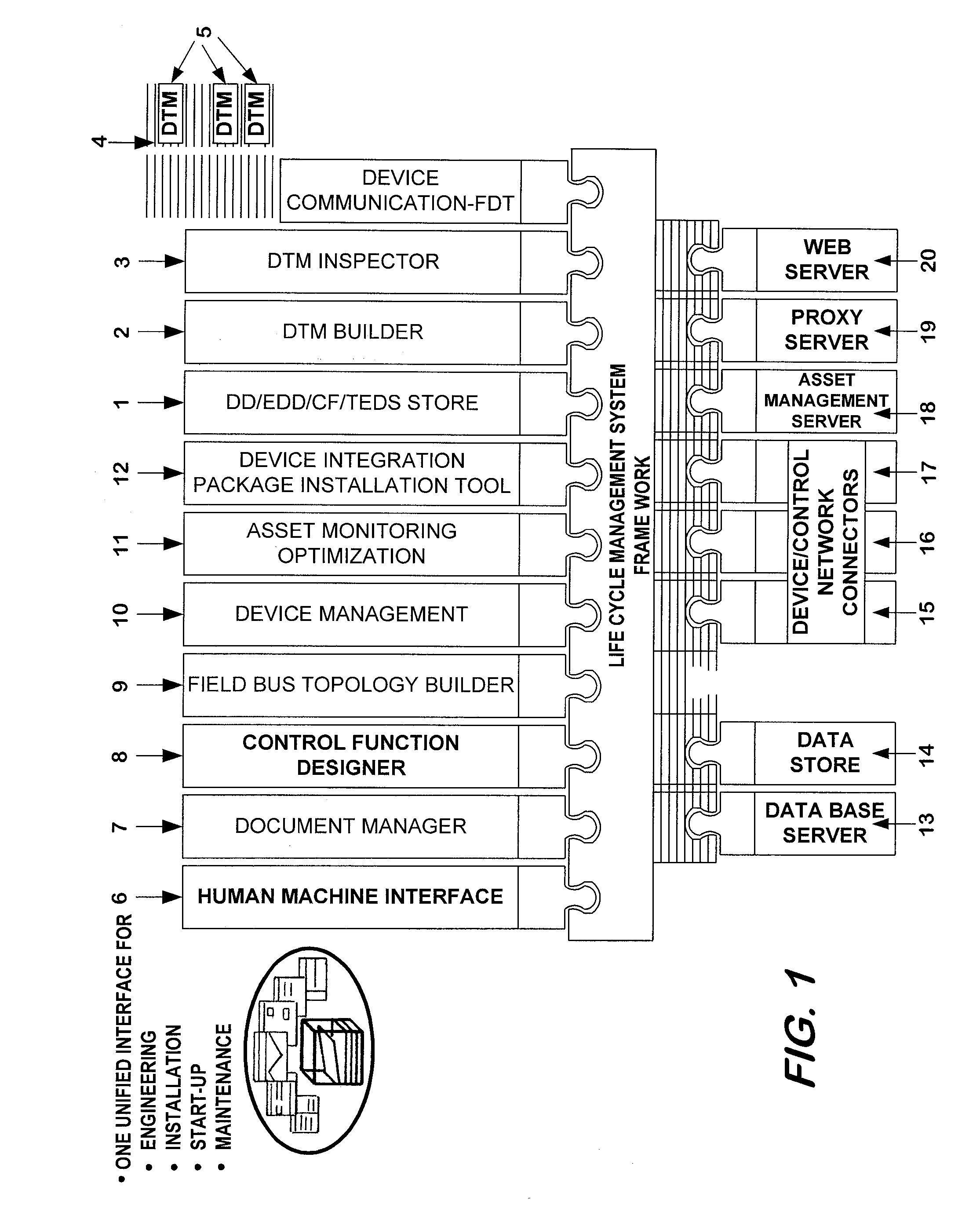
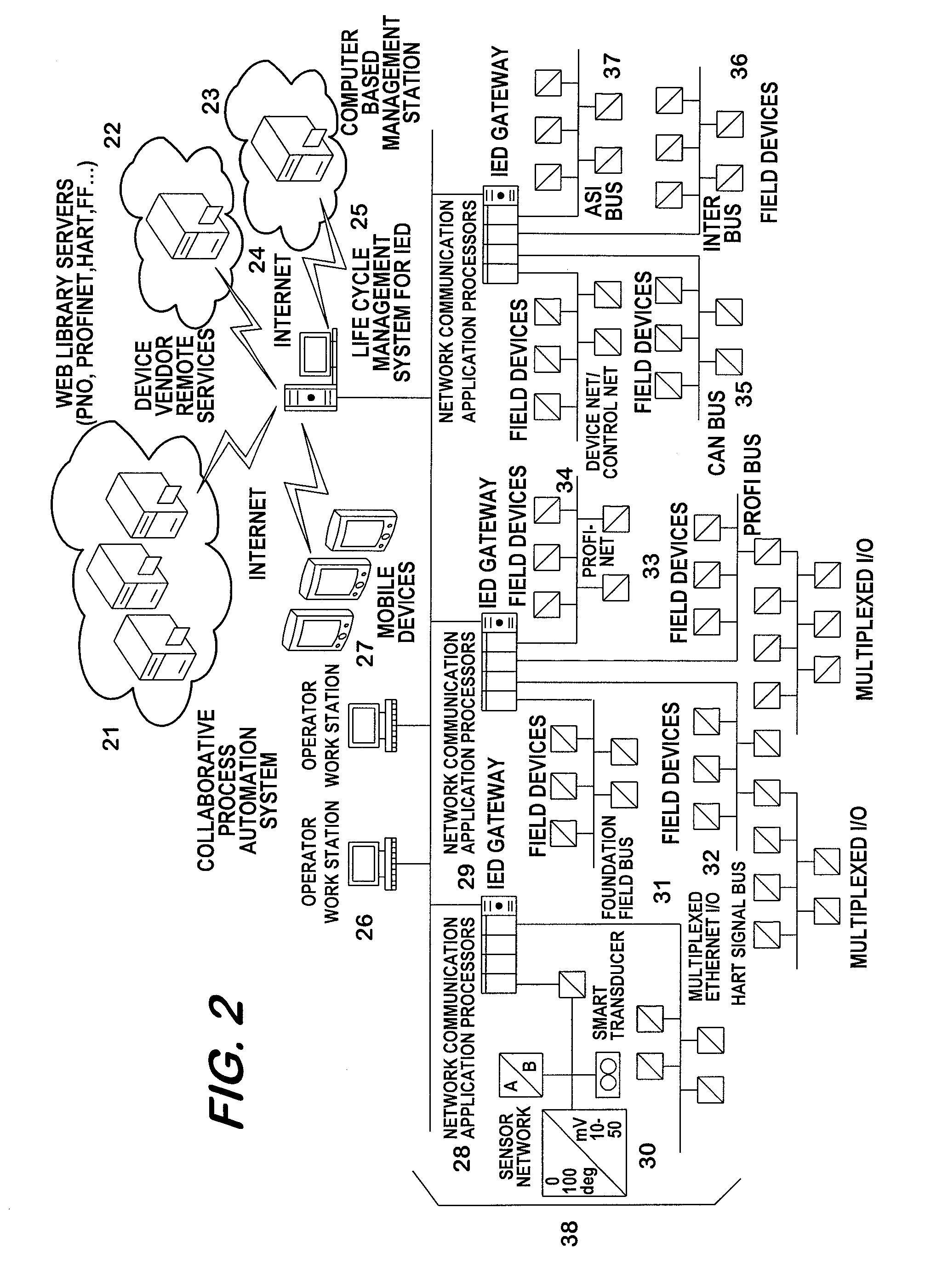
Life Cycle Management System for Intelligent Electronic Devices
ActiveUS20090204458A1Solve complexityHighly control environmentDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringDesign phaseMaintainability
This invention relates to the Life Cycle Management System for distributed Intelligent Electronic Devices (IED) starting from the design phase to the end of service phase. Hence, it caters to the needs from installation via engineering, installation / commissioning phases, until asset management and remote service support of the devices during the operational phase The increasing decentralization of the involved components via networks, especially via the Internet, is a key criterion and needs to be addressed by the life cycle management. The added value for the customer grows disproportionately with the degree of integration of multiple independent software components into a complex and often highly distributed control system. The architecture of today's control systems must be sufficiently flexible to allow customers to regard their plant components from various locations. Additionally, the stability, security and maintainability of such a system is strongly dependent on the homogeneity and interoperability of all involved components.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
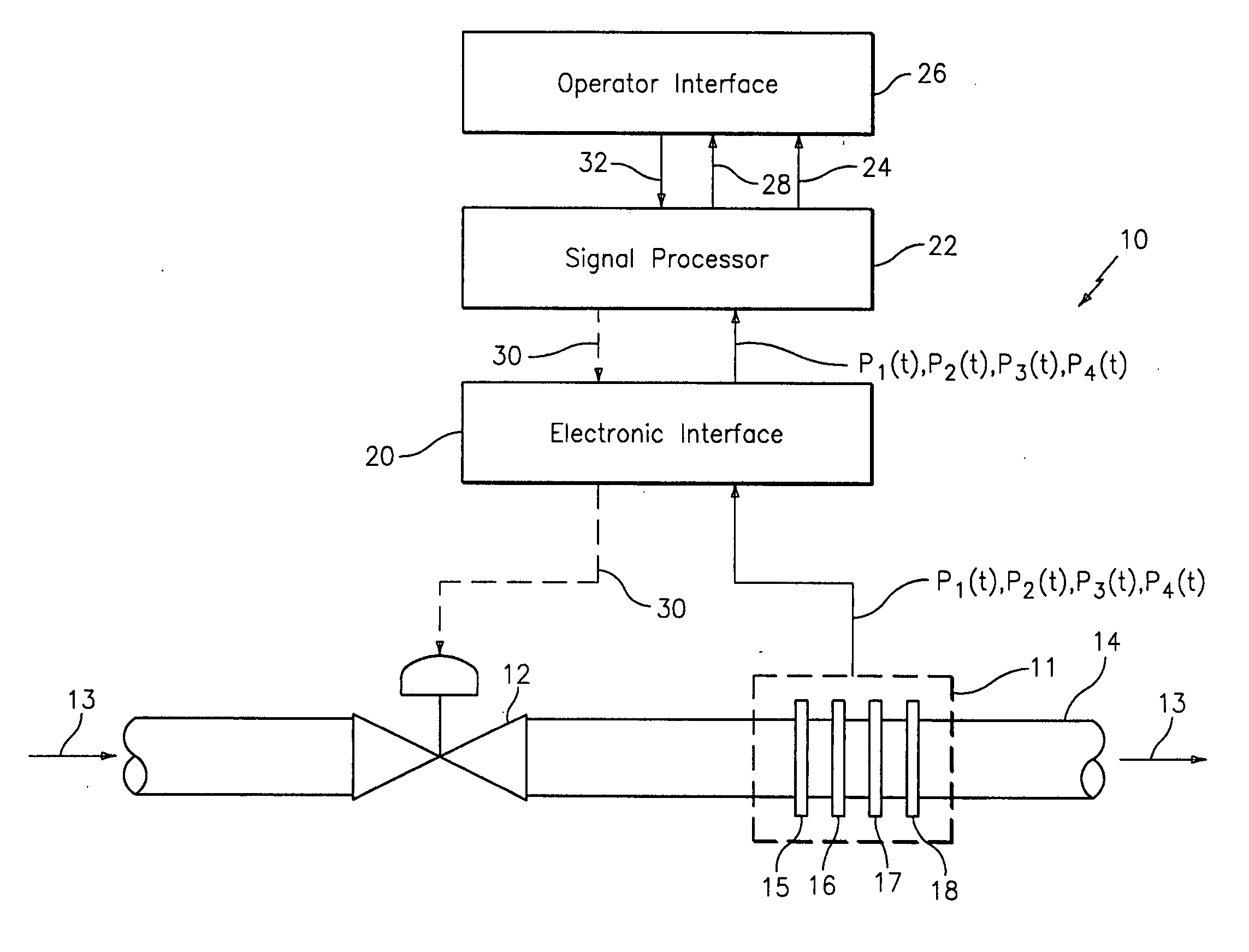
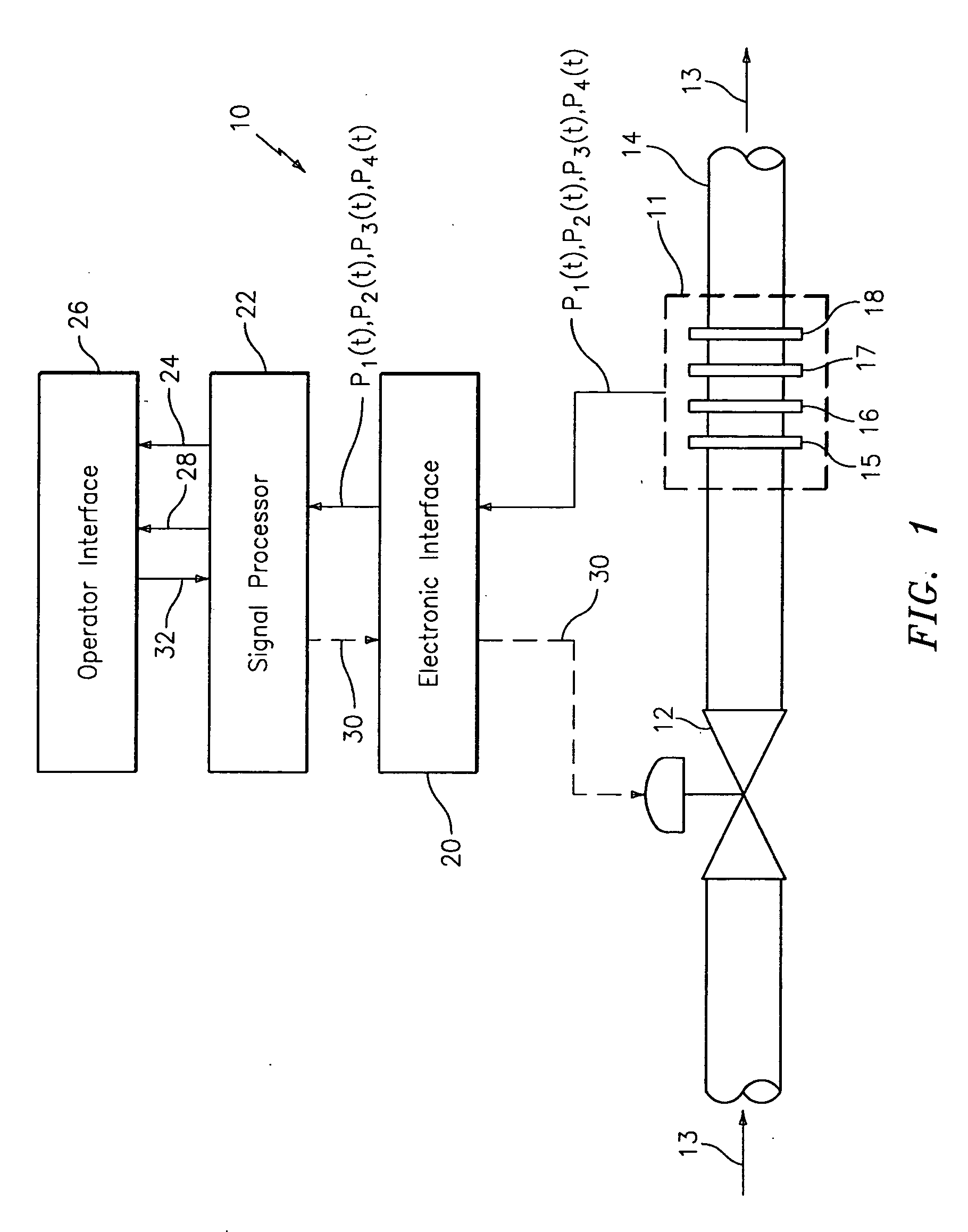
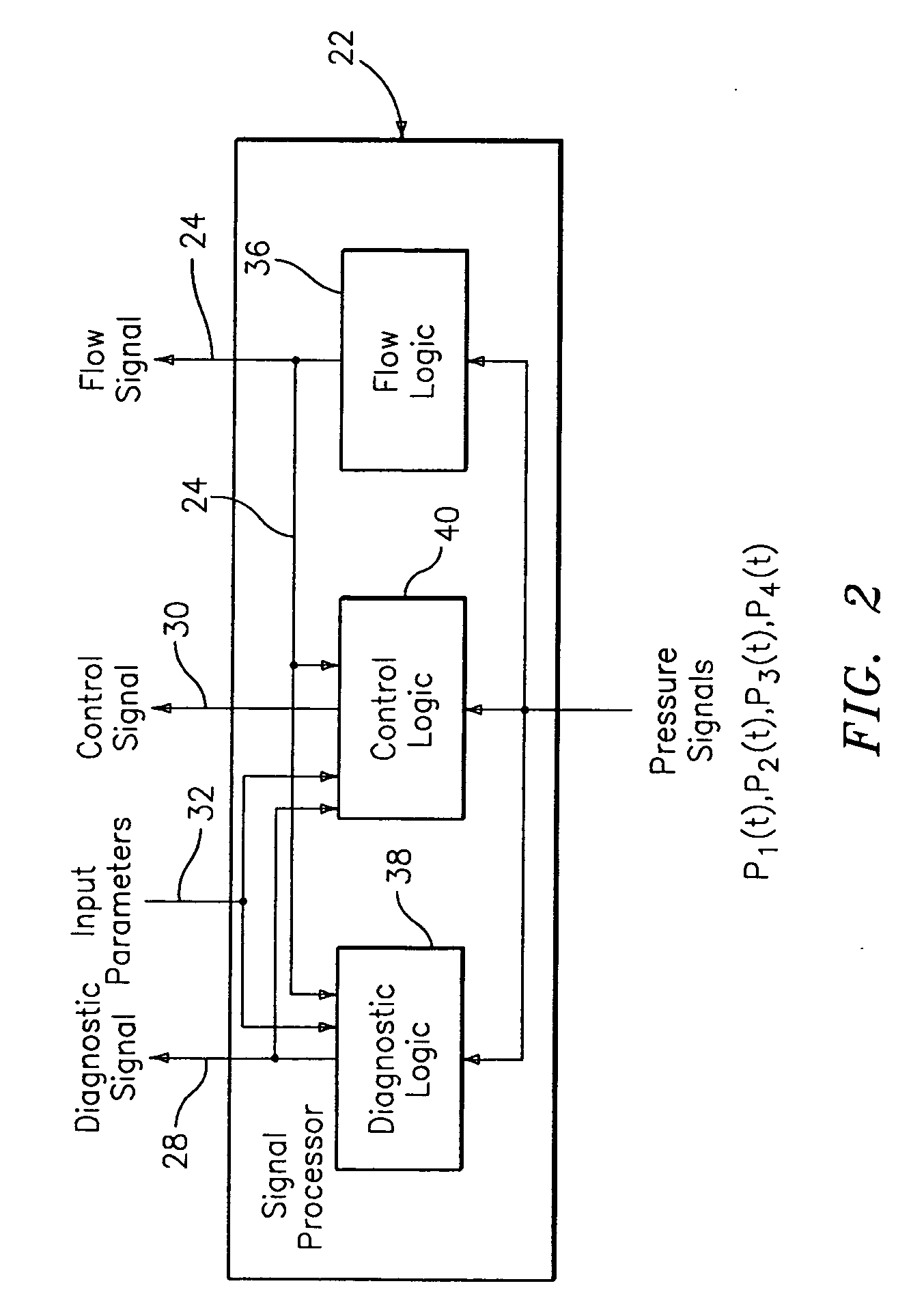
System and method for operating a flow process
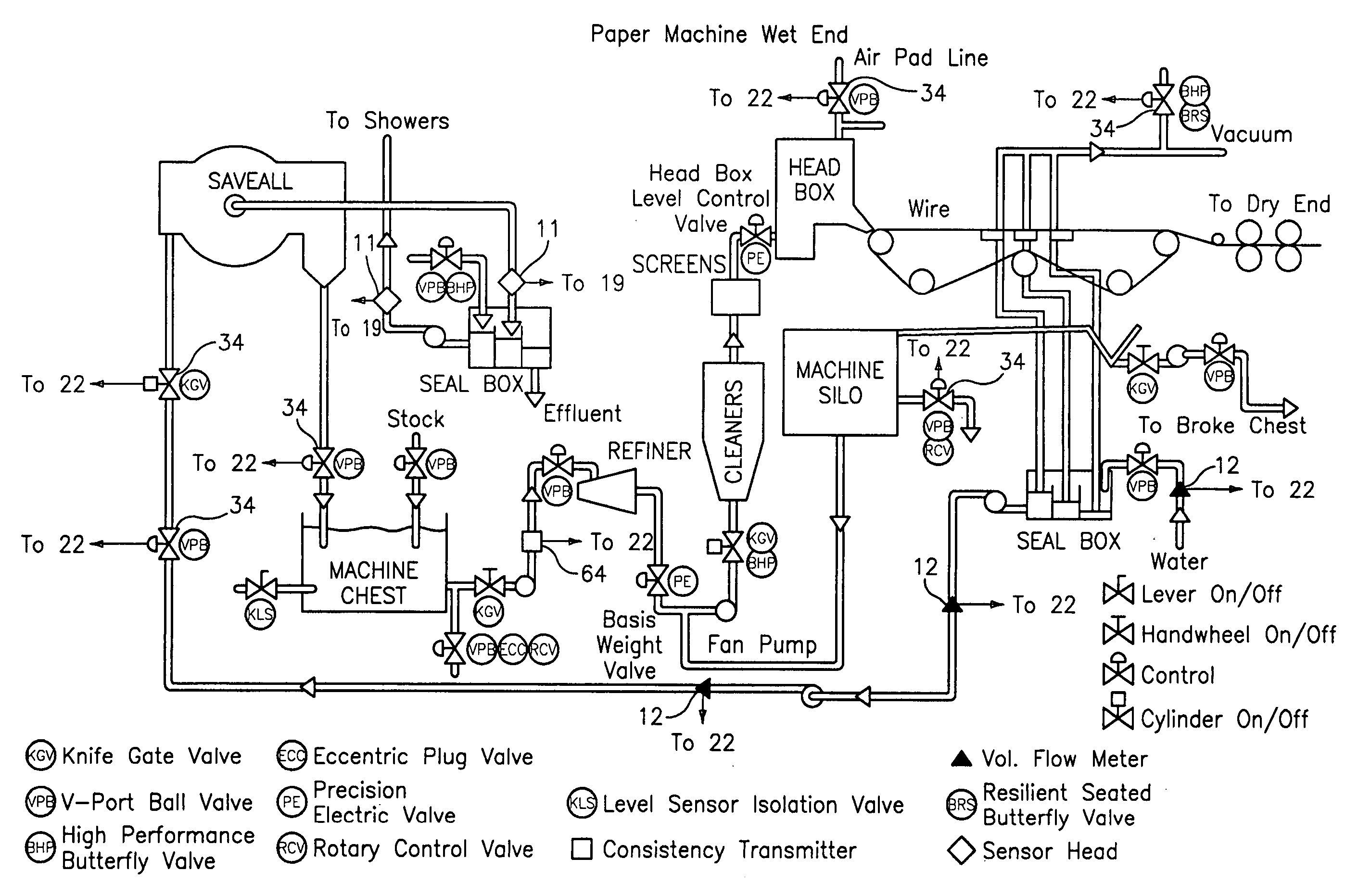
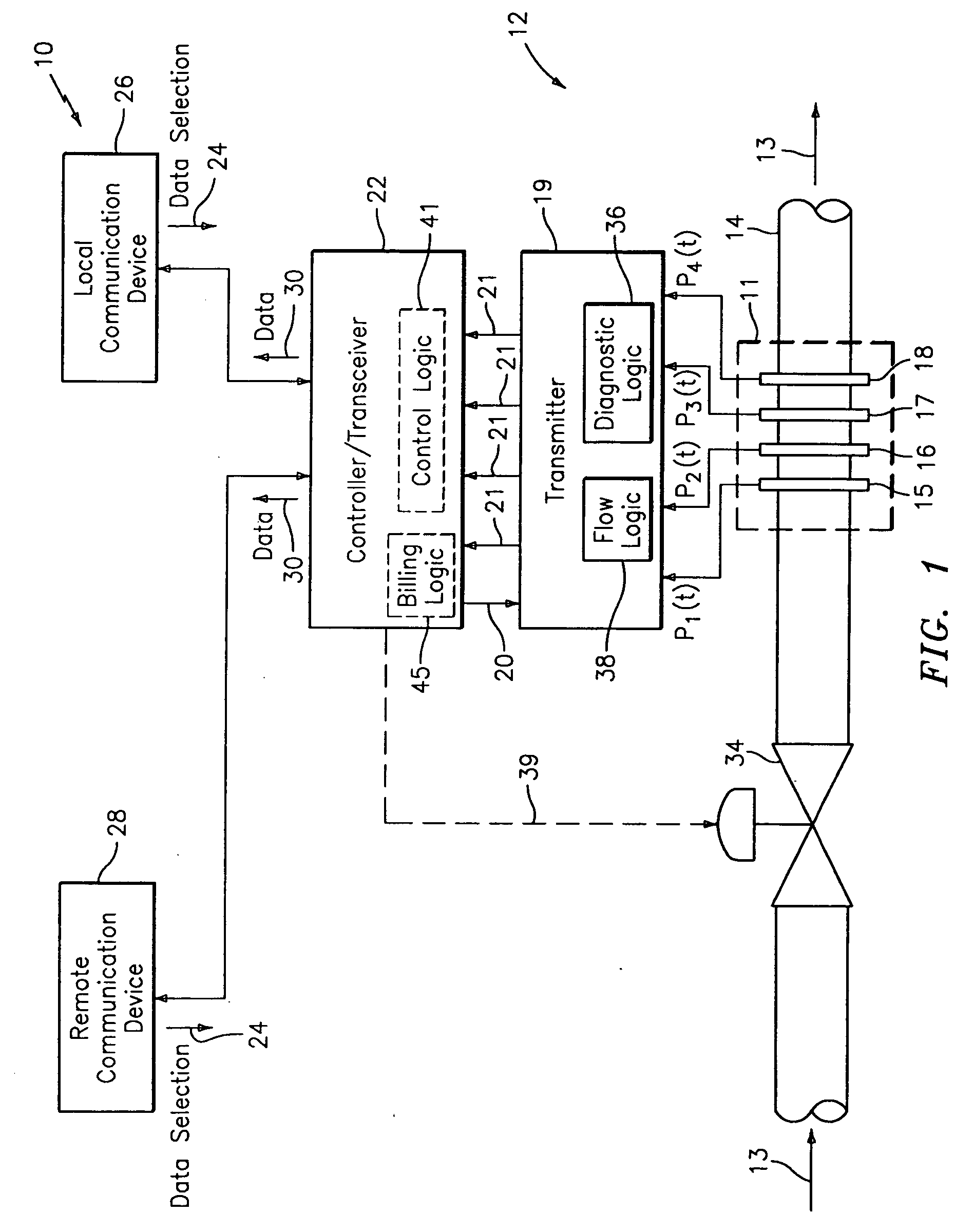
ActiveUS20050005711A1Effective regulationTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsTesting/calibration apparatusControl signalDistributed control system
A system for monitoring, diagnosing, and / or controlling a flow process uses one or more flow meters based on an array of pressure sensors. A signal processor outputs at least one of a flow signal, a diagnostic signal, and a control signal in response to the pressure signals from the pressure sensors. The flow signal indicates the at least one parameter of the fluid, the diagnostic signal indicates a diagnostic condition of a device in the flow process, and the control signal is effective in adjusting an operating parameter of at least one device in the flow process. The system may be arranged as a distributed control system (DCS) architecture for monitoring a plurality of flow meters based on array-processing installed at various locations throughout a flow process.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
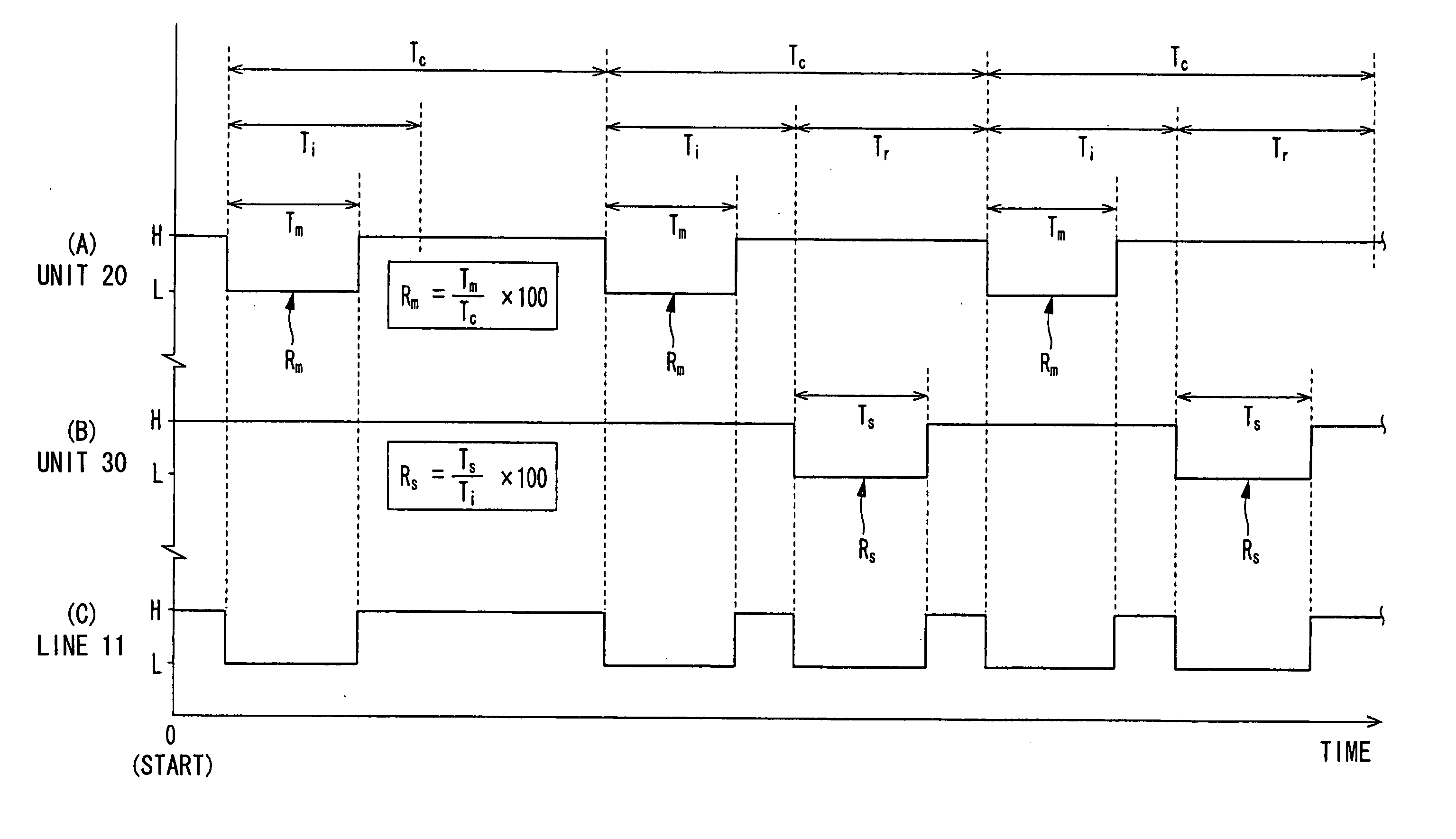
Communication system and method, and distributed control system and method
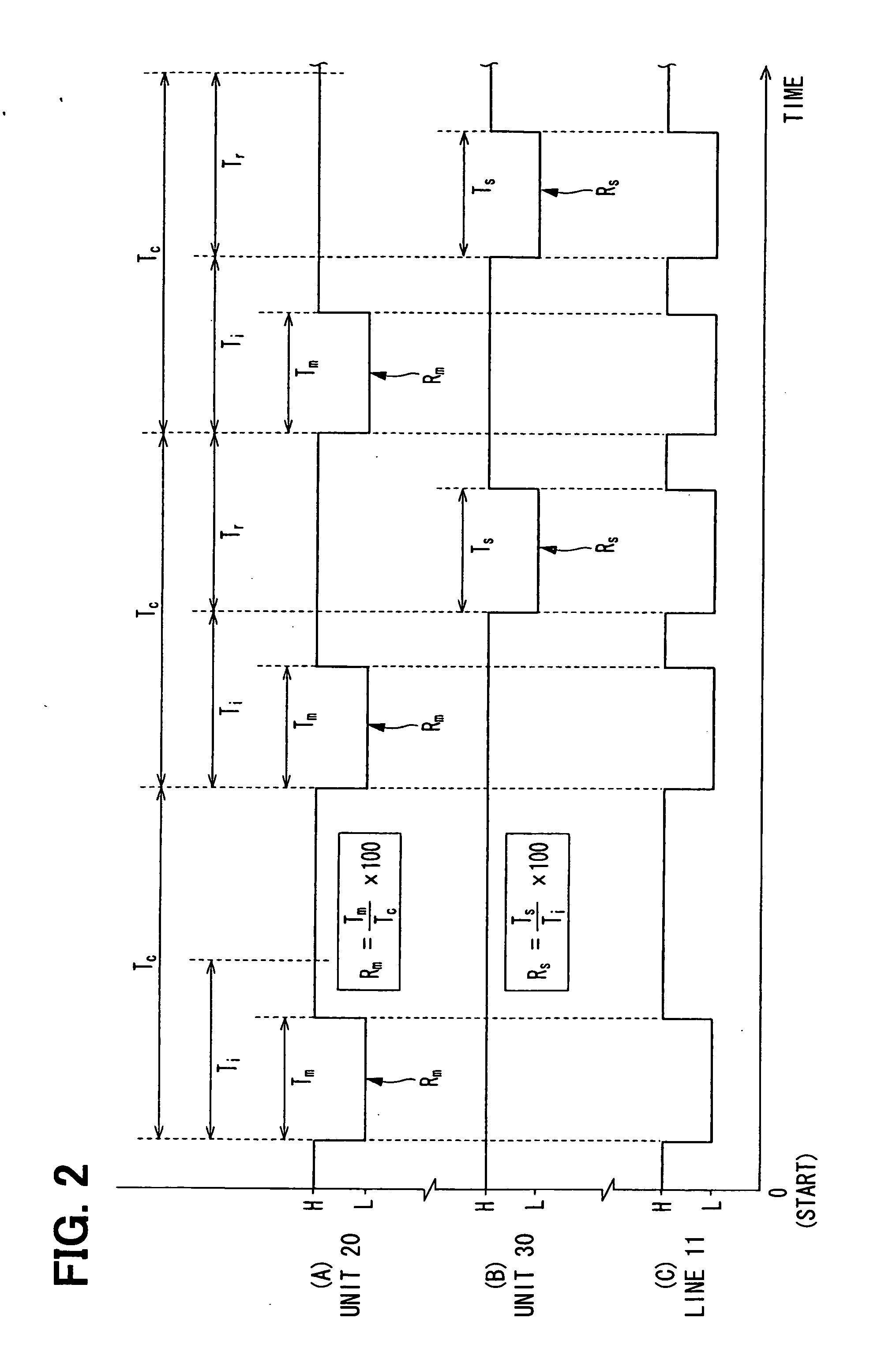
InactiveUS20070088883A1Low costAccurate communicationSuspensionsElectrical controlCommunications systemTime segment
A communication system performs bidirectional communication through a same communication path every communication cycle period between a master station and a slave station. From the start of the communication cycle period until an interval period shorter than the communication cycle period elapses, the master station transmits master data represented at a first ratio of first pulse width to the communication cycle period to the slave station. In a remaining period after the interval period in the communication cycle period, the slave station transmits slave data represented at a second ratio of second pulse width to the interval period to the master station.
Owner:DENSO CORP
System of distributed configurable flowmeters
Owner:CIDRA CORP SERVICES
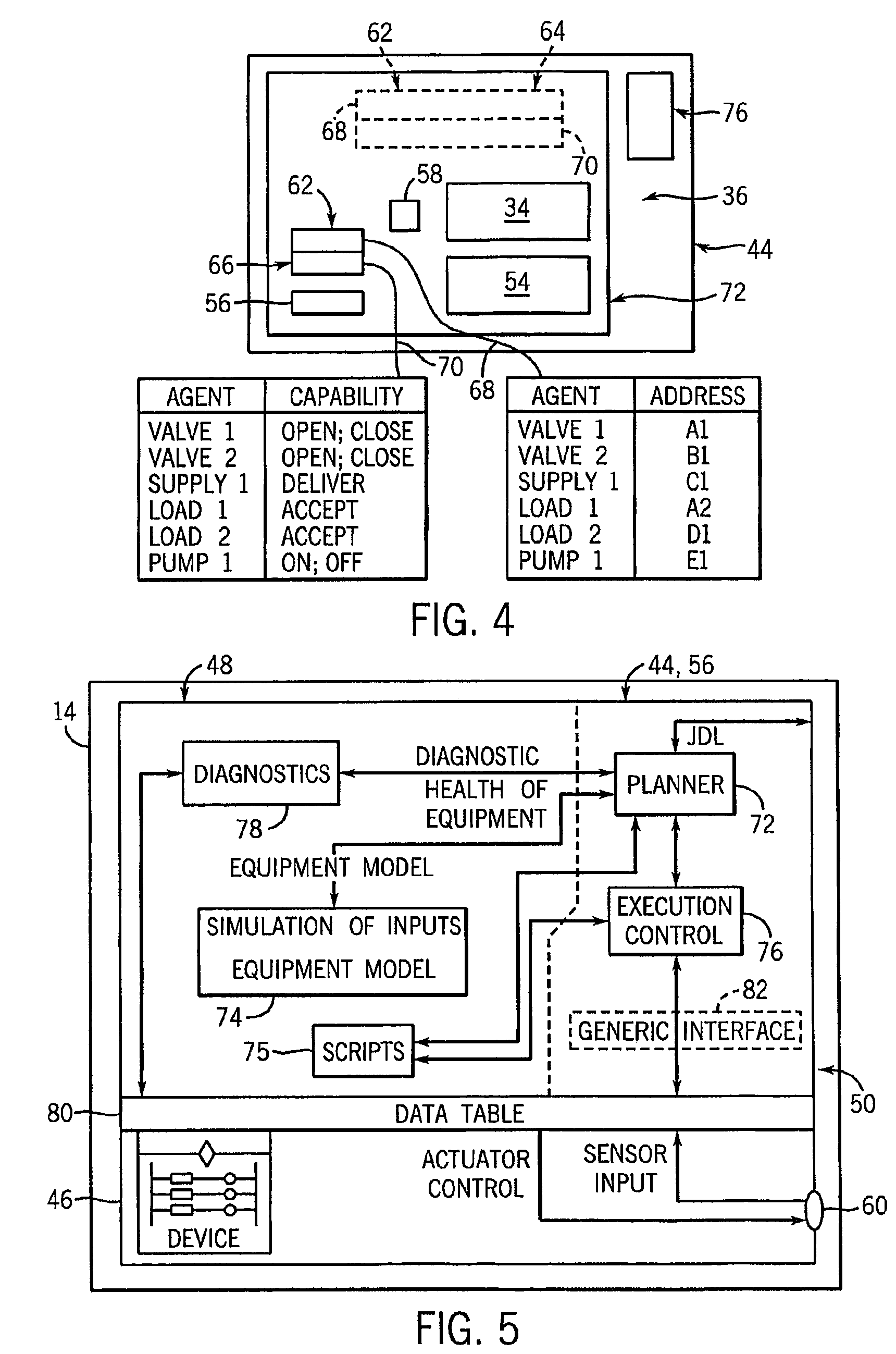
Agent-equipped controller having data table interface between agent-type programming and non-agent-type programming
InactiveUS7640291B2Minimal customizationImprove developmentComputer controlSimulator controlDistributed control systemOperating system
A controller capable of being employed in a distributed control system, where the distributed control system controls operations of a plurality of devices that operate together to perform a process, and a method of communicating information between a first program portion and a second program portion of such a controller, are disclosed. The controller includes at least one processing component configured to perform a first plurality of program portions that operate in relation with one another as a first agent. The plurality of program portions includes a first program portion that controls agent-type behavior of the controller, and a second program portion that at least one of controls and monitors at least one of the devices. The controller further includes at least one memory component that stores a data table that is accessed by each of the first and second program portions to allow communication between those program portions.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
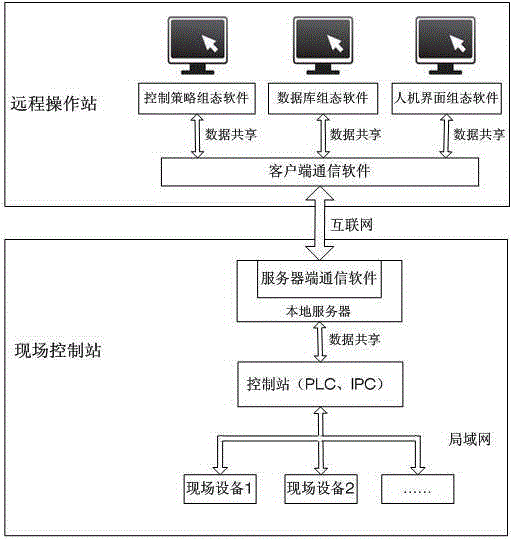
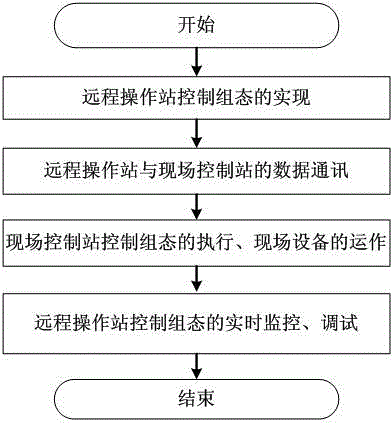
Remote distributed control system and distributed control method based on Internet
InactiveCN103605342AImprove production management efficiencyWill not affect the running statusTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlHuman–machine interfaceReal-time data
The invention relates to a remote distributed control system and a distributed control method based on the Internet. The system comprises a remote operation station, a field control station and the Internet, wherein the remote operation station comprises a control strategy configuration software module, a database configuration software module, a man-machine interface configuration software module and a client end communication software module, the field control station comprises a local server, a server end communication software module, a control station and field equipment, and a client end and the server end communication software module are connected through the Internet. The method comprises the steps that: 1, control configuration is accomplished in the configuration software of the remote operation station; 2, data communication is established between the remote operation station and the field control station; 3, corresponding control logic configuration is carried out by the field control station, the field equipment is driven to operate, and real-time data is acquired and updated; and 4, real-time monitoring and debugging on control configuration are accomplished through the configuration software of the remote operation station. The control system and the control method have advantages of good control effects, high real-time performance and wide application scope.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
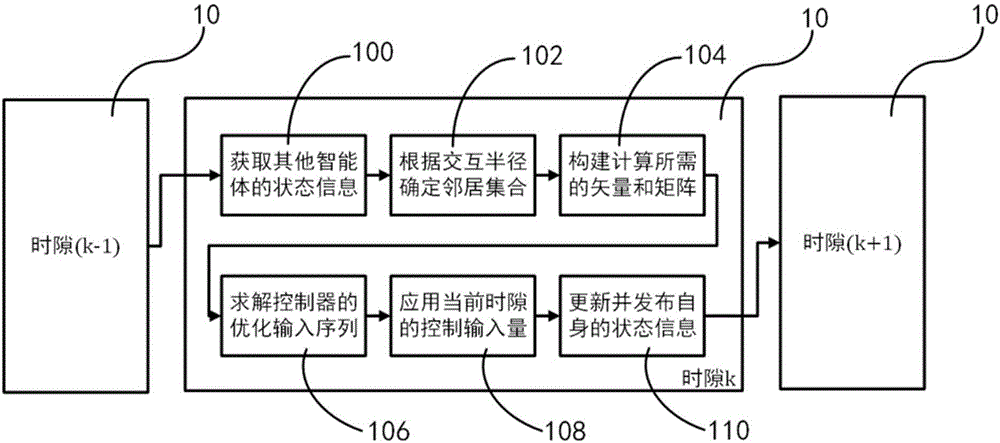
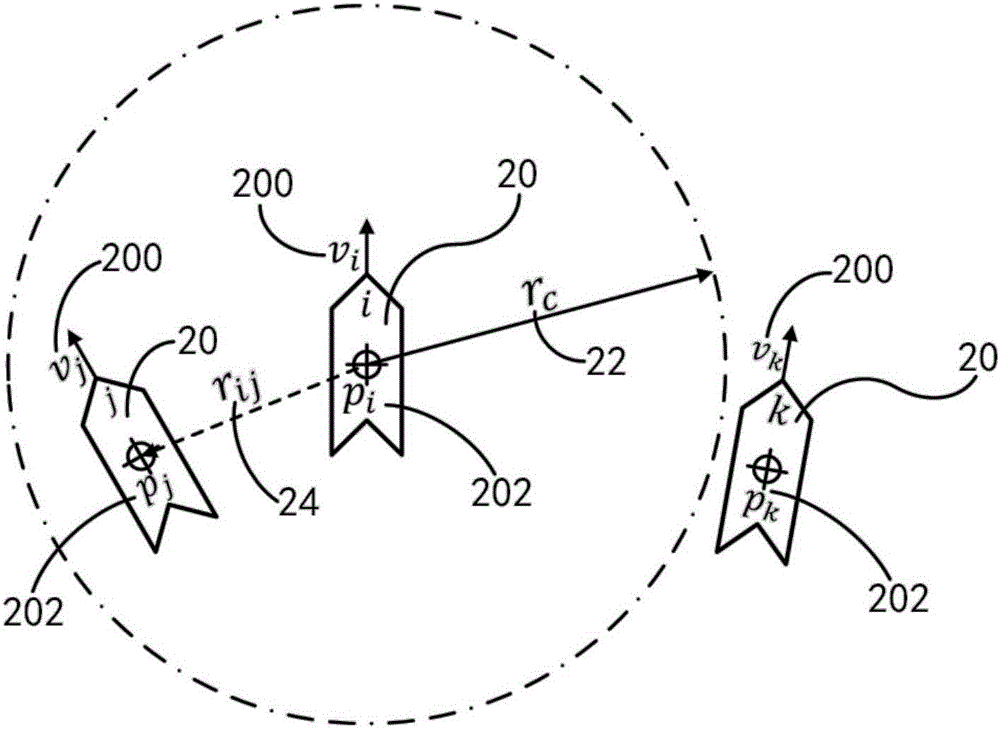
Multi-agent cluster coordination method and multi-UAV cluster coordination system
InactiveCN107179777APredictiveImprove efficiencyPosition/course control in three dimensionsDistributed control systemAerial photography
The invention belongs to the technical field of a distributed control system and relates, specifically, to a multi-agent cluster coordination method and a multi-UAV cluster coordination system. The multi-agent cluster coordination method of the invention allows agents to exchange information with neighbors within their respective interaction ranges and to form a cluster in a self-organized manner by solving for the control input through distributed mode predictive control. The method further allows the presence of a leader agent in the system to lead the overall motion trajectory of the agent cluster. The multi-UAV cluster coordination system provided by the invention enables multiple UAVs to autonomously achieve cluster flight through data exchange thereamong, enhances the efficiency of executing the tasks that need the coverage of a large area, such as aerial photography, monitoring, search and rescue, and the like, and has high adaptivity and redundancy.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Task-based robot control system for multi-tasking
InactiveUS20070168082A1Improve productivityLow costProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsControl signal
The present invention relates to a PC-based robot control system, which is a new type of a robot control machine. The present invention has aimed at a task-based control machine configuration not a centralized control configuration so that a multi-tasking function is possible through a distributed control system. An embodiment of the present invention provides a task-based robot control system, including robot system interface means that receives a control command for controlling a robot; system kernel means that controls the creation and distinction of one or more software-based virtual robot control machines of virtual robot controller means, which will be described later, in a software way and controls the synchronization between the virtual robot control machines, based on the control command received from the robot system interface means; the virtual robot controller means having one or more software-based virtual robot control machines whose creation and distinction are controlled under the control of the system kernel means, wherein a generated virtual robot control machine processes a robot control execution sentence input through the robot system interface means; and hardware means that actually drives the robot according to a control signal generated by the processing of the execution sentence by the virtual robot control machine.
Owner:ROBOSTAR
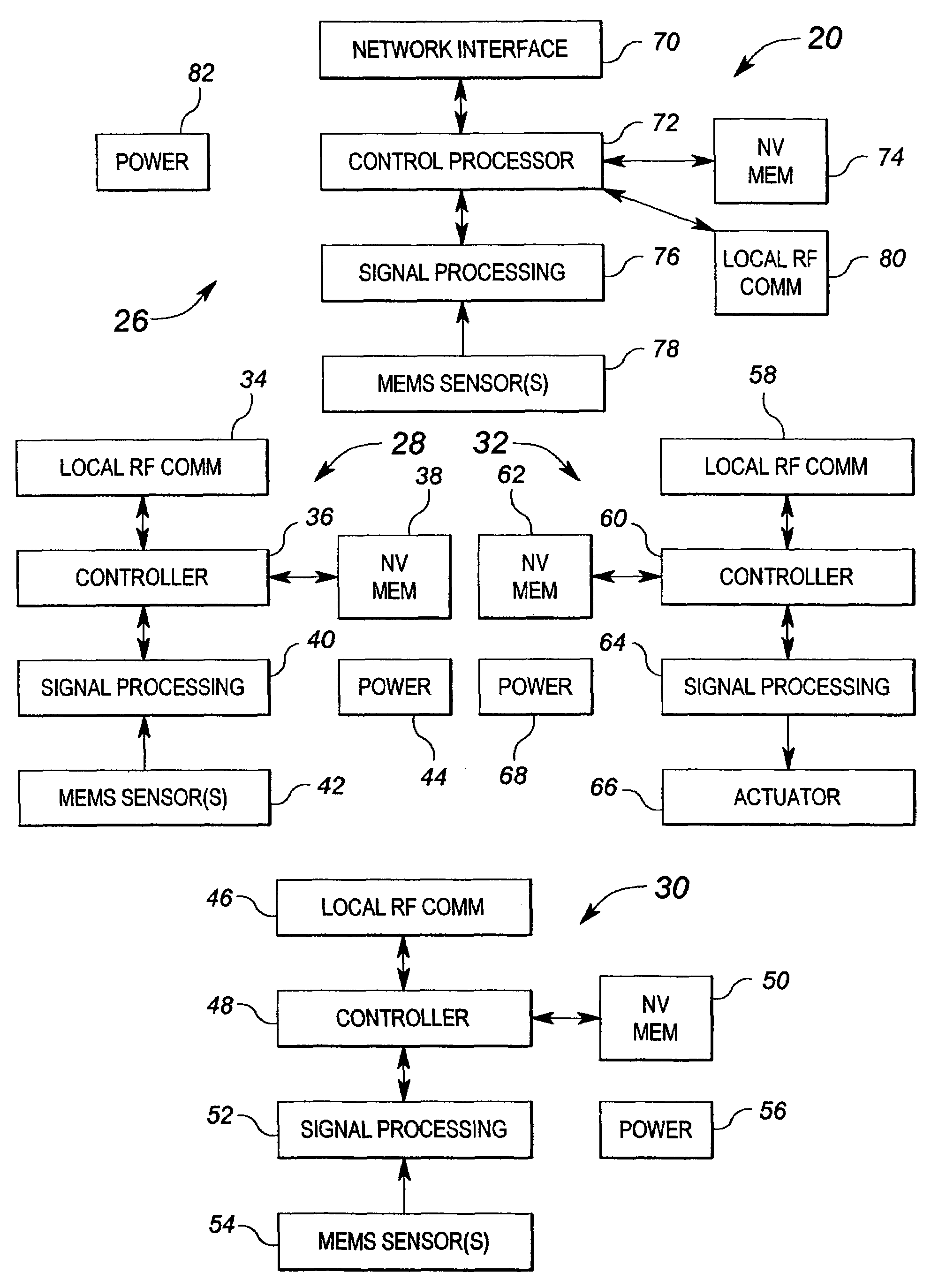
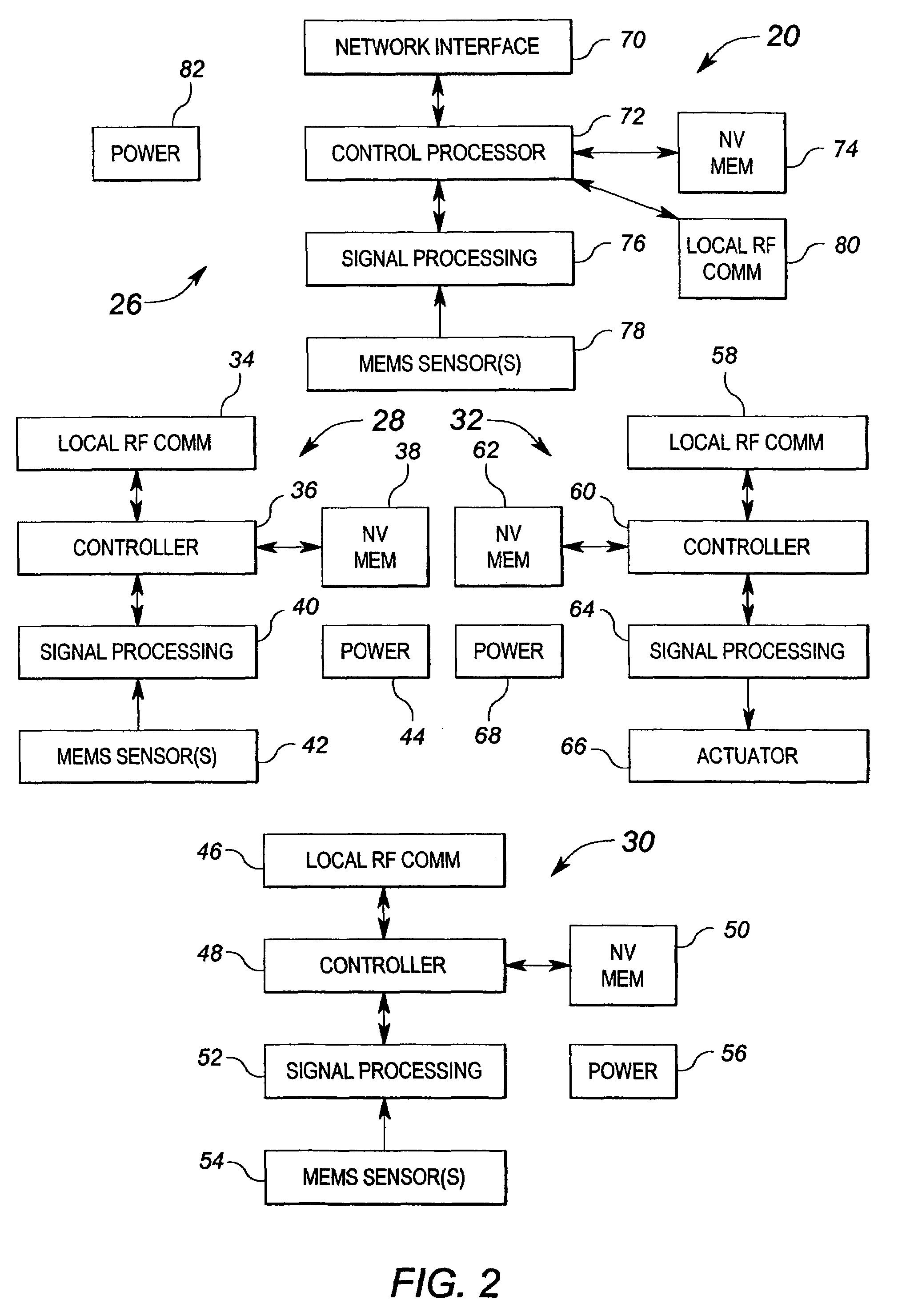
Method and apparatus for an integrated distributed MEMS based control system
ActiveUS7665670B2Space heating and ventilationTemperatue controlDistributed control systemComputer module
An integrated distributed control system incorporates a plurality of micro electromechanical system (MEMS) modules formed into a functional network which is in turn integrated into a management network. The functional network is configured to sense a condition such as an operating characteristic of a machine or the temperature within an area and to provide control functions to effect changes in the condition.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
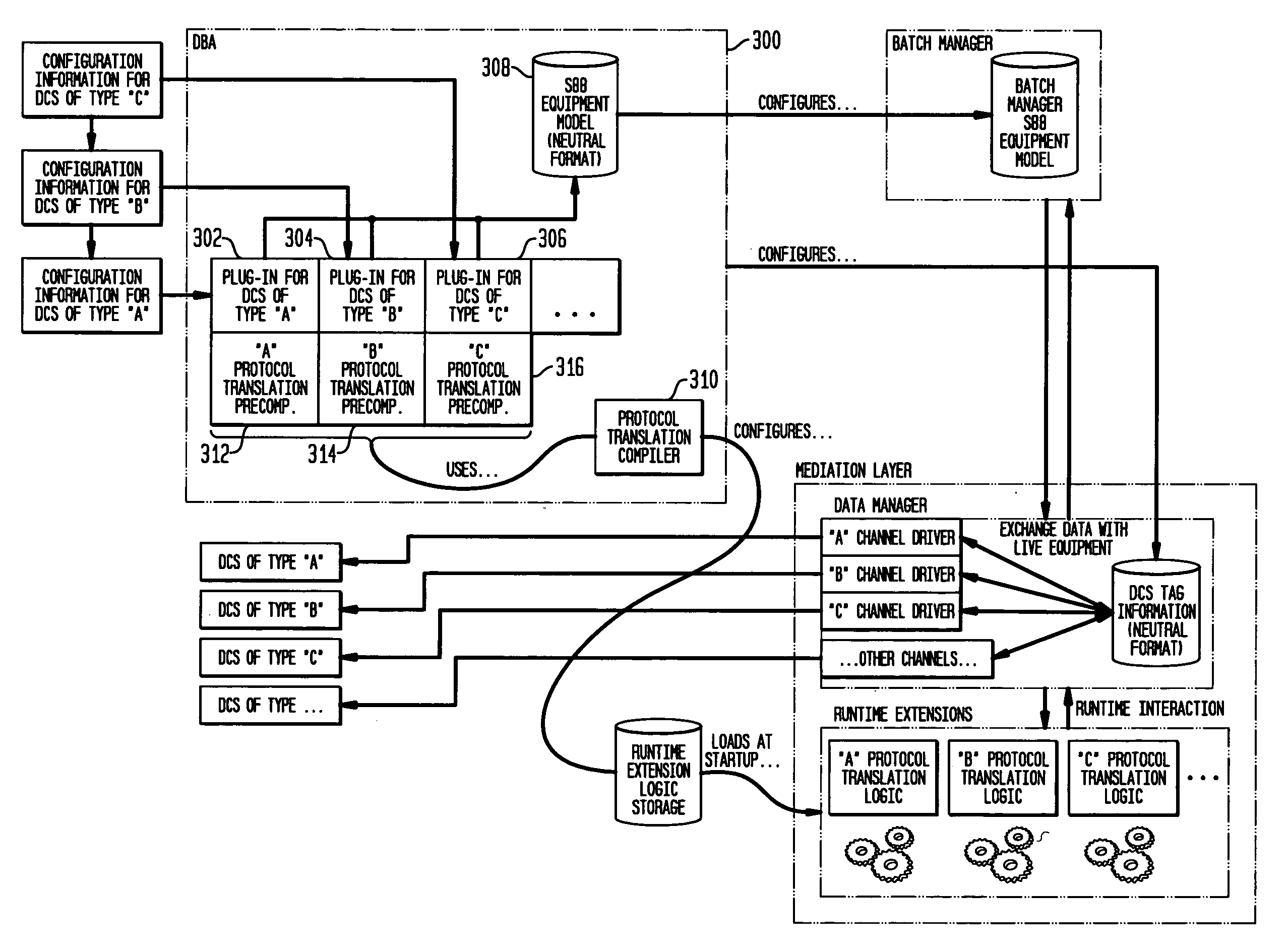
System and method for batch process control with diverse distributed control system protocols
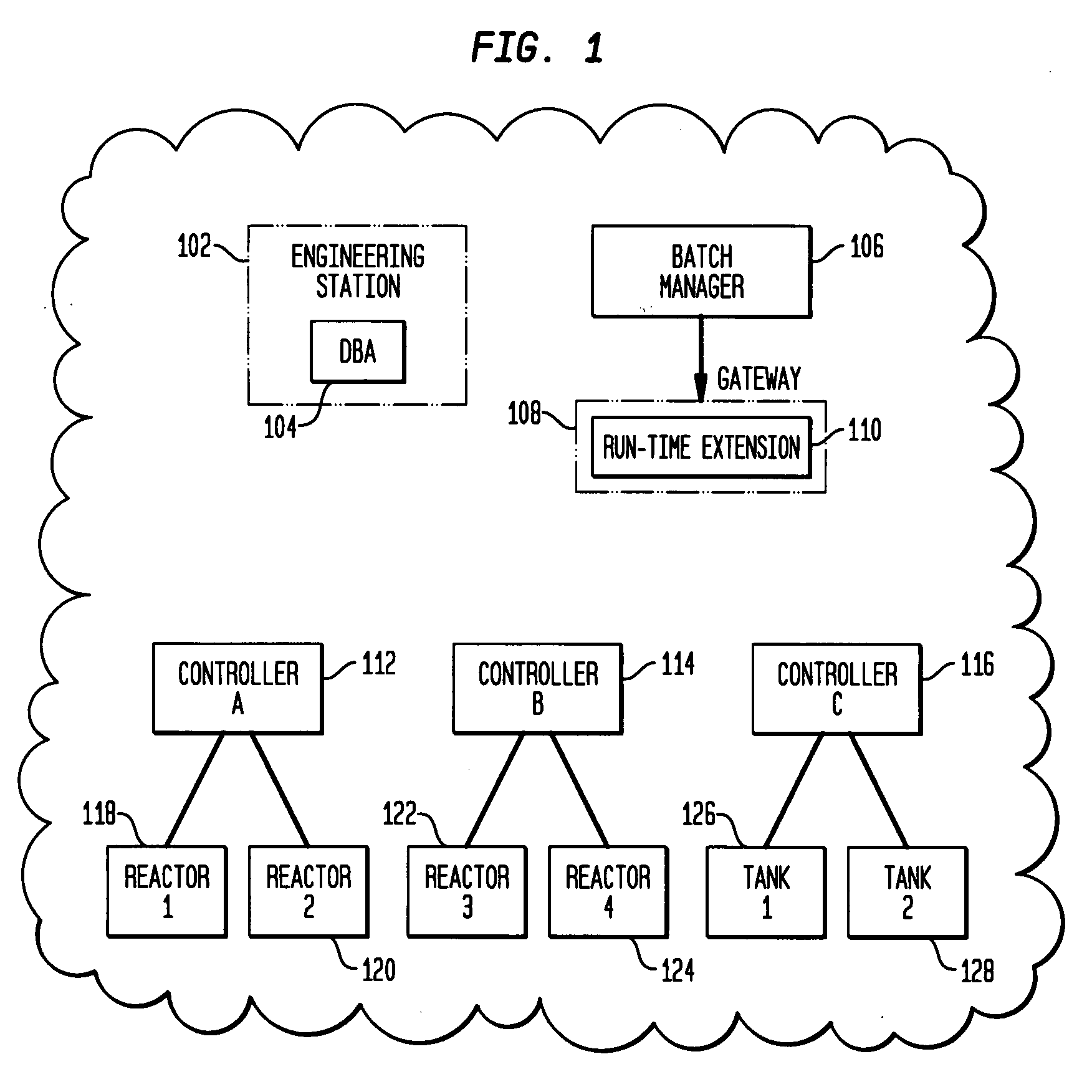
InactiveUS20070283030A1Enhanced interactionProgramme controlMultiple digital computer combinationsDistributed control systemRunning time
A system and method for batch process control with diverse distributed control system (DCS) protocols is disclosed. A run-time extension acts as an adaptation layer that allows a single batch manager to supervise controllers utilizing diverse DCS protocols. The run-time extension receives commands transmitted from the batch supervisor in a first DCS protocol, translates the commands to a second DCS protocol utilized by a controller, and transmits the translated command to the controller to control various equipment associated with the controller. A database automation object (DBA) inputs configuration information from controllers utilizing diverse DCS protocols, extracts equipment information from the configuration information, generates protocol translation logic based on the configuration information, and translates recipe and formula information included in the configuration information into a common format.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Intelligent gravel aggregate production line
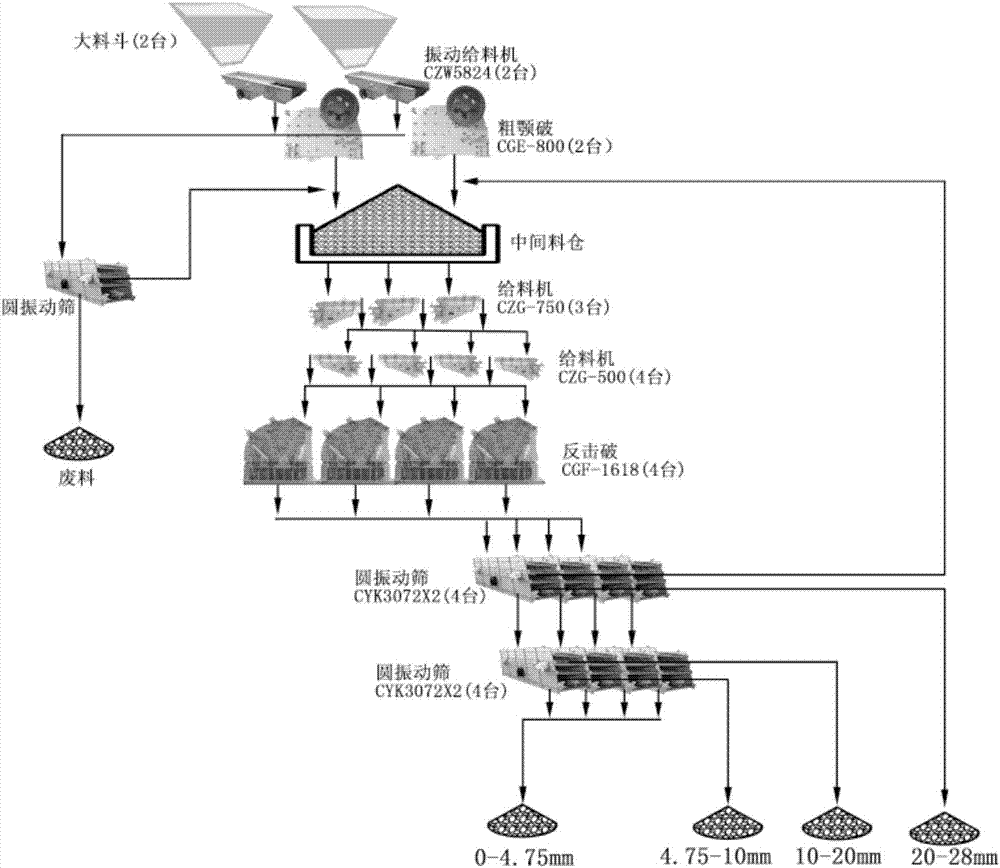
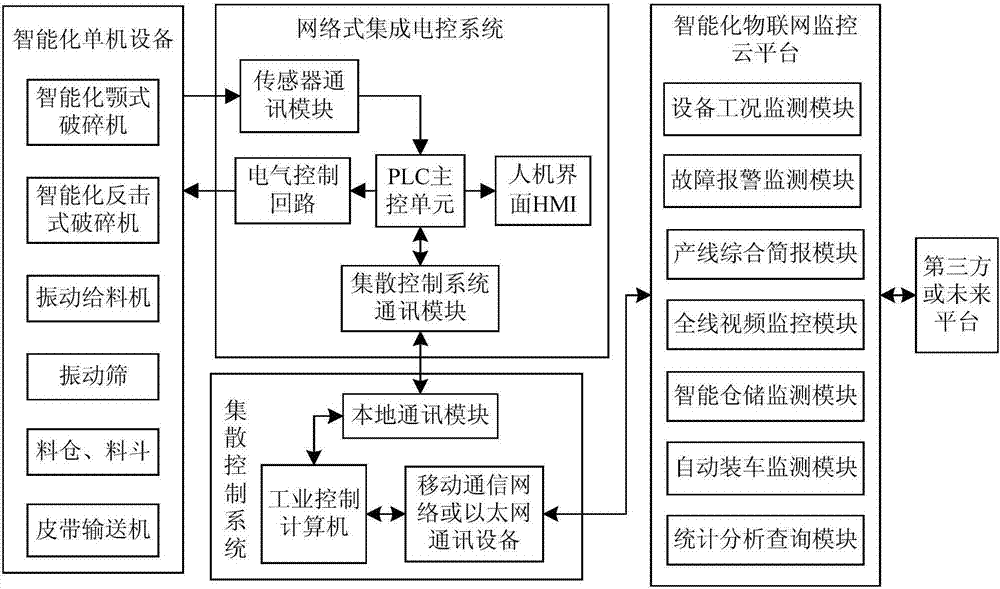
ActiveCN107153410AIncrease the level of automationReduce work intensityTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlProduction lineDowntime
The invention provides an intelligent gravel aggregate production line, and relates to the technical field of gravel aggregate production. The intelligent gravel aggregate production line comprises an intelligent jaw type crusher, an intelligent impact type crusher, a vibrating screen, a vibrating feeder, a material bin, a hopper, a belt conveyor, a control-related network type integrated electric control system, a distributed control system and an intelligent internet of things monitoring cloud platform, wherein various sensors are additionally arranged on the basis of an original crushing screening production line; sensor information is transmitted to the distributed control system through the network type integrated electric control system, so that automatic regulation and control on the production process is realized, and therefore, the sensor information is transmitted to the intelligent internet of things monitoring cloud platform; and production data storage and safety are managed in a unified mode on the basis of classifying and combing through cloud computation. The intelligent gravel aggregate production line has a fault early-warning function and a real-time alarm function, and quickly increases response speed; internet of things intelligent control and remote monitoring are introduced, the production process is automatically regulated and control, operation is performed with optimal load, the yield is increased, and downtime maintenance is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITRUSTON INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
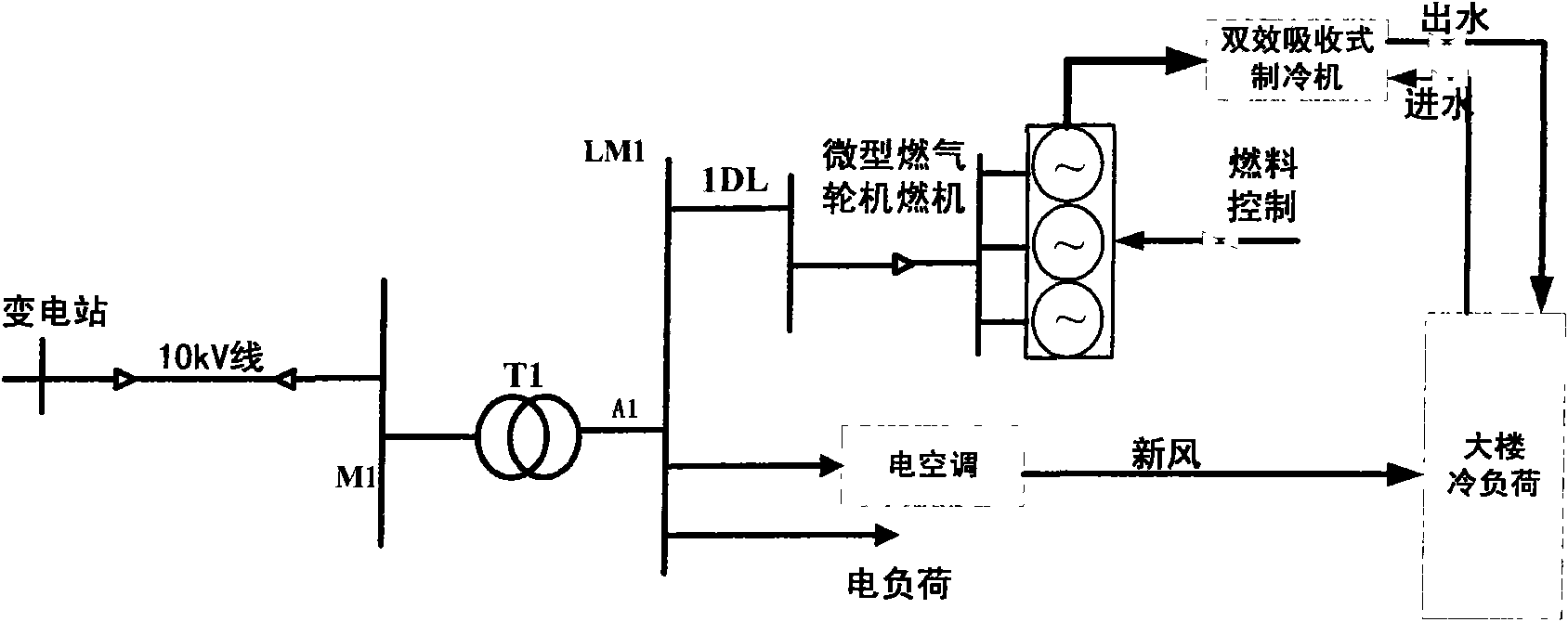
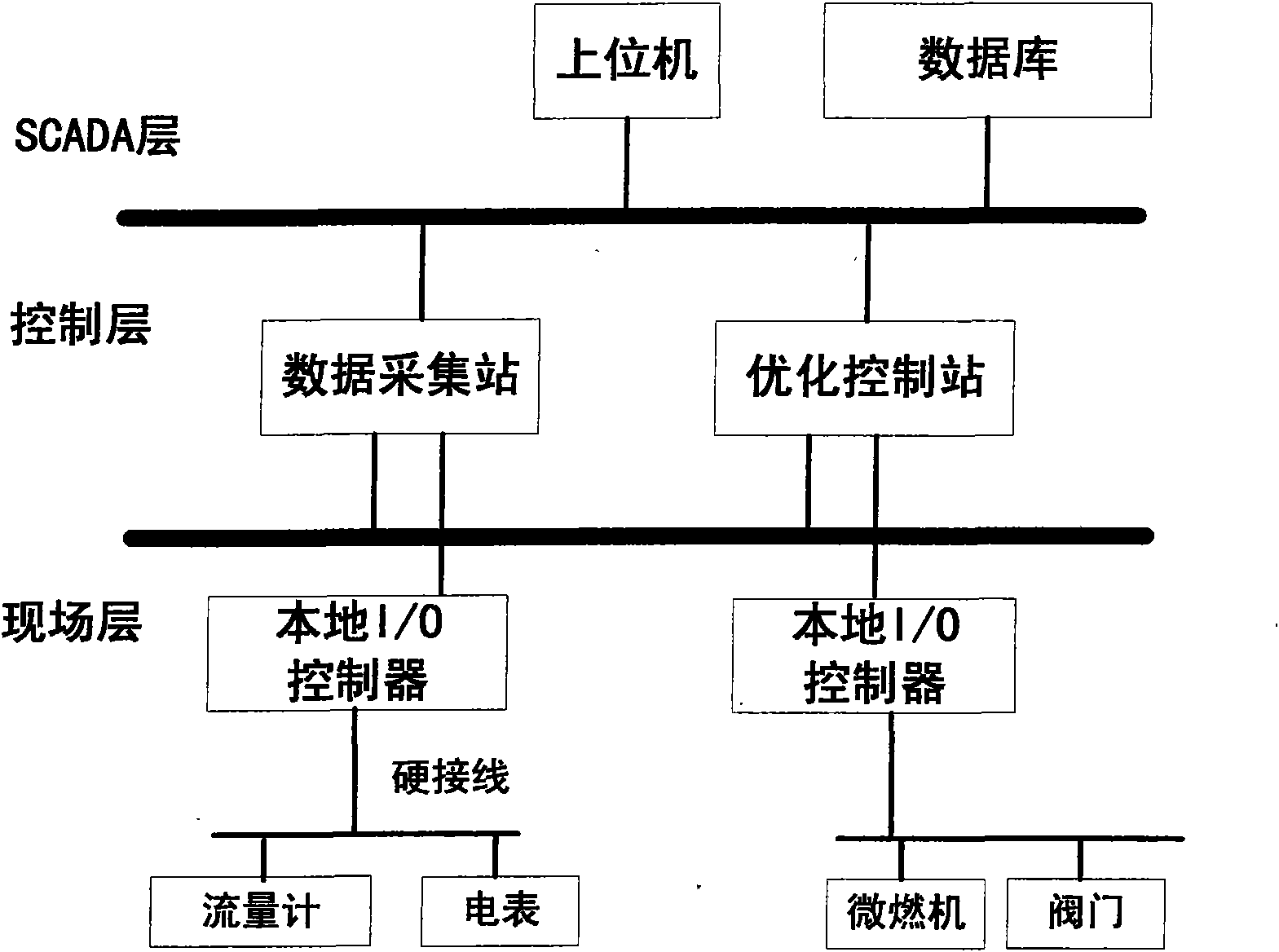
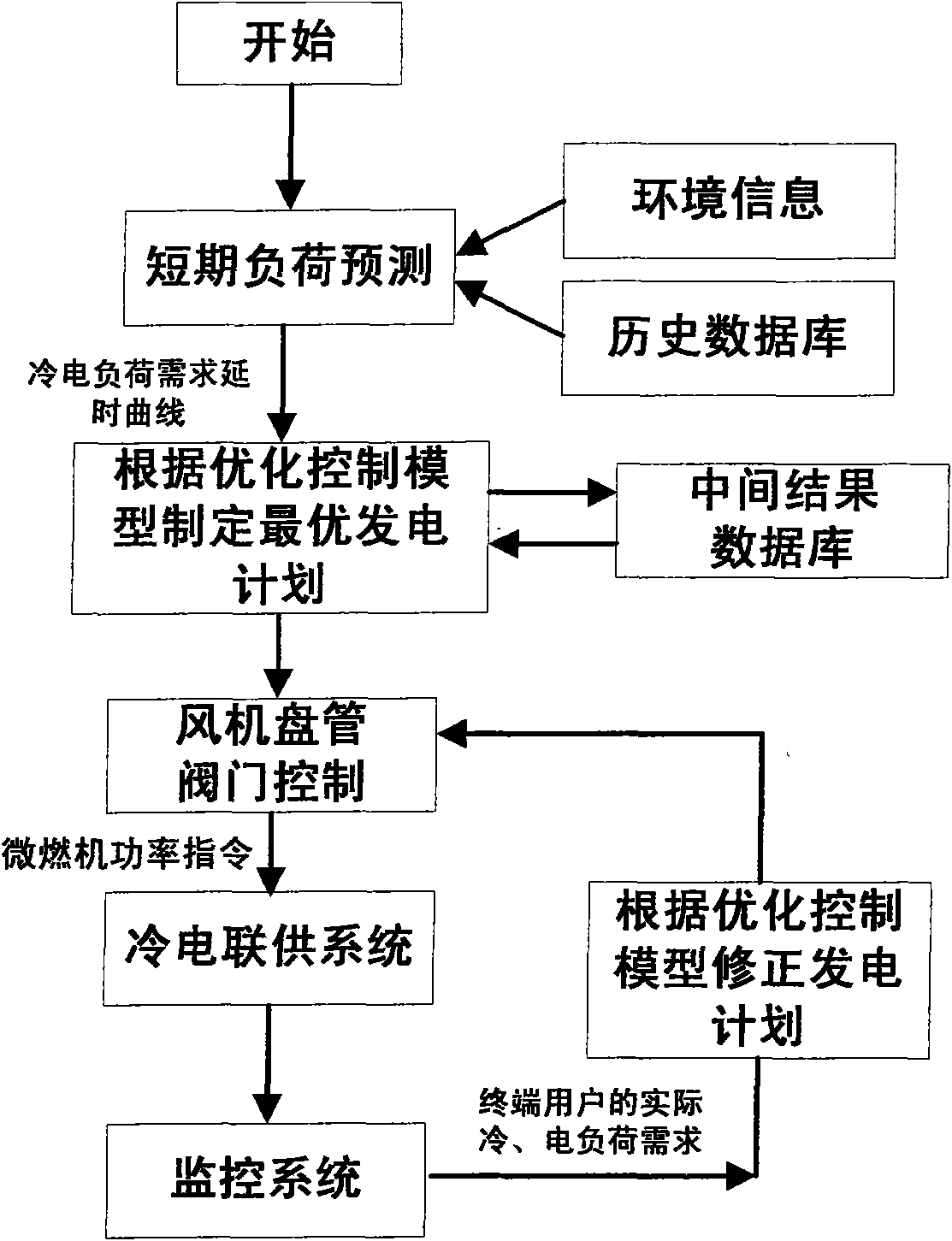
Control method of optimized running of combined cooling and power distributed energy supply system of micro gas turbine
ActiveCN101667013AIncrease economic benefitsHigh Utilization MetricsClimate change adaptationGas turbine plantsMathematical modelMicro gas turbine
The invention belongs to the technical field of energy management of distributed generation energy supply systems of electric power systems. The control method comprises the following steps: before running a combined system on every workday, extracting history cooling load data and power load data of a terminal user from a historical data base and obtaining the delay variation curve of the coolingload and the power load of the terminal user during the whole workday by lone-term load predicting; according to load predicting results, working out the optimal generated output plan of the combinedsystem by adopting optimization control mathematical model; during the running of the combined system, carrying out optimization control calculation again by utilizing the terminal user real-time cooling and power load need obtained from the distributed control system, and modifying the generating capacity and the refrigerating capacity of the combined system. The invention utilizes a distributedmonitoring system to monitor the actual cooling and power load need of the terminal user and can modify the load forecasting result in real time and adjusting the respective controlled variable of the combined system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +2
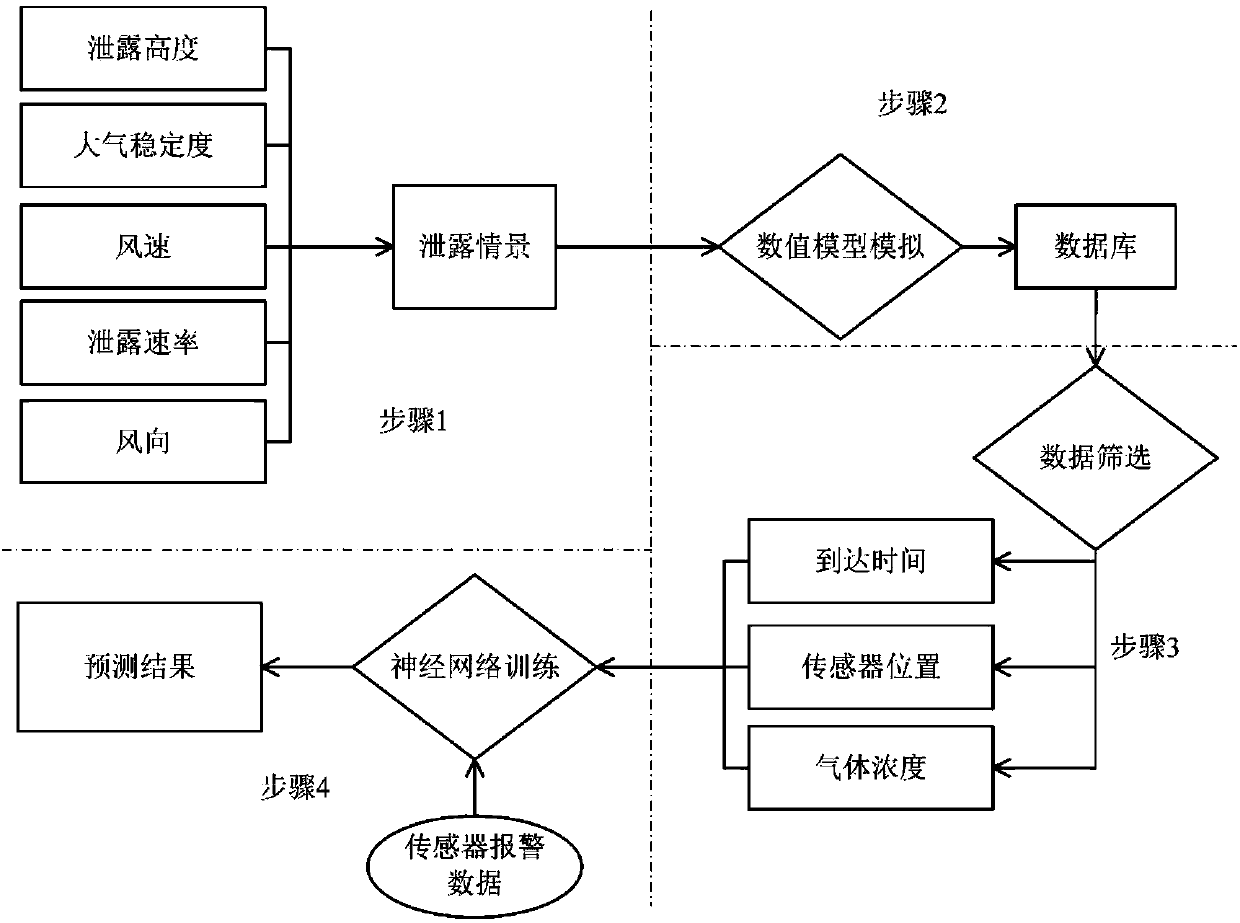
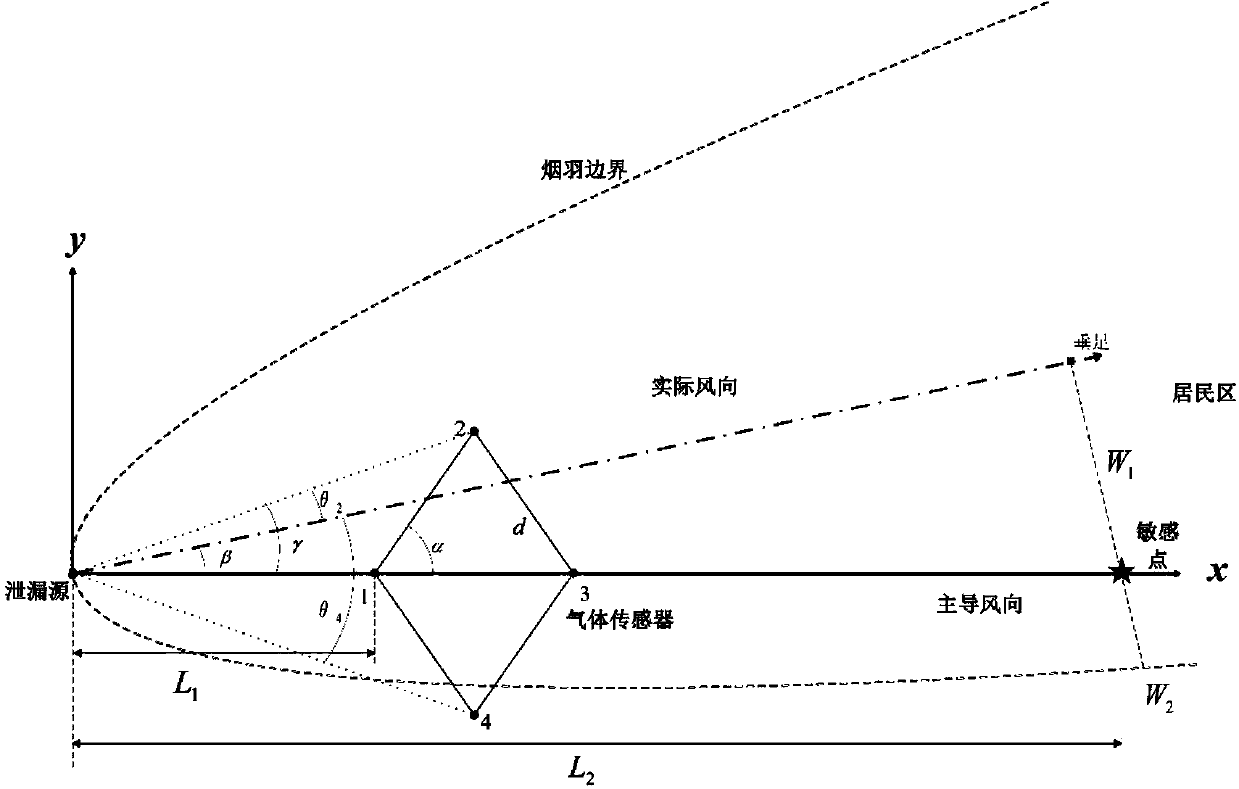
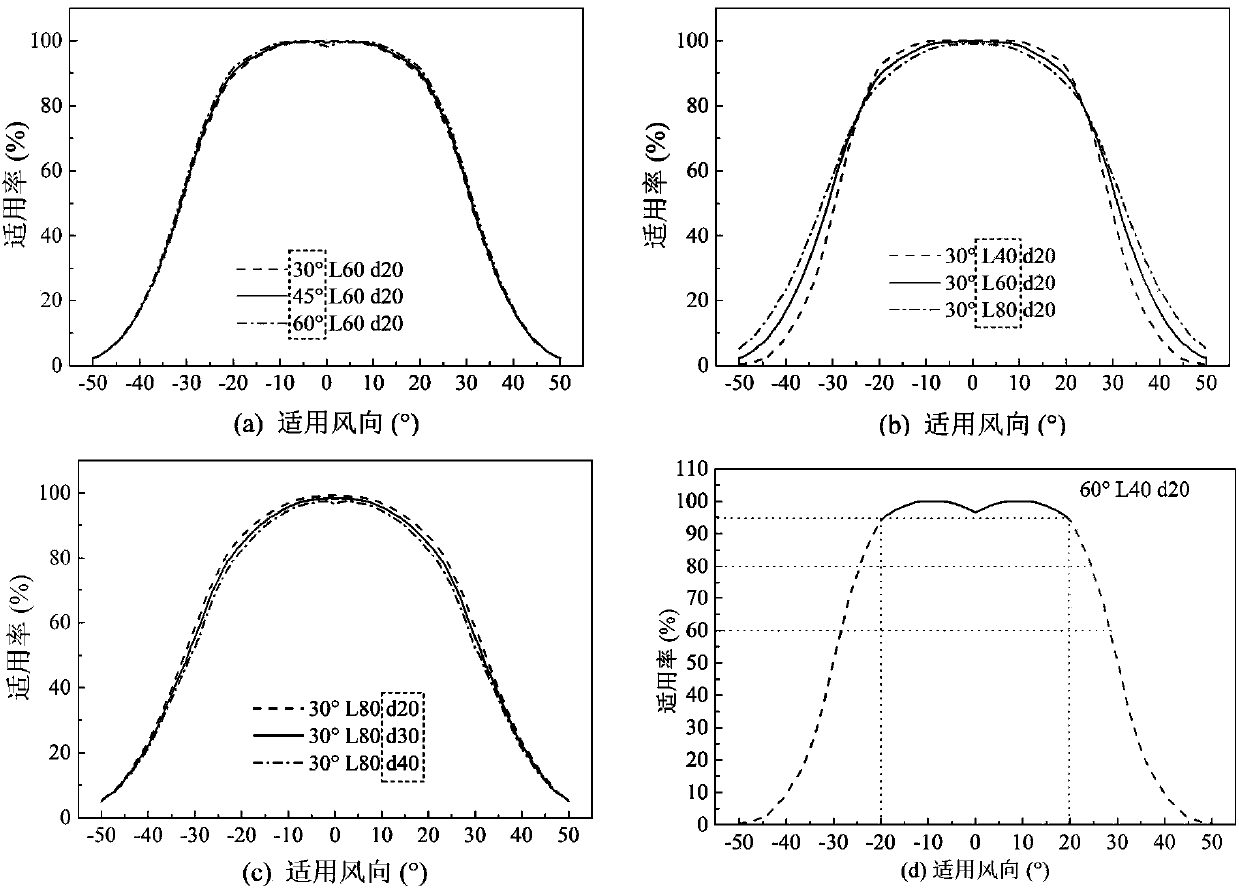
Quick chemical leakage predicating and warning emergency response decision-making method
ActiveCN103914622AAppropriate layoutSimple optimization of concentration distributionSpecial data processing applicationsDistributed control systemModel parameters
The invention relates to a quick chemical leakage predicating and warning emergency response decision-making method which combines diffusion model simulation with a neural network and a gas sensor system and is applied to quick warning and aid decision making of leakage of harmful gas in an industrial park. The method includes park risk factor identification, numerical simulation, data screening, neural network training and sensor system and neural network model integration, wherein the park risk factor identification is used for identifying various possible leakage accidents, the numerical simulation includes simulating all the possible accidents to obtain a range of influences of the harmful gas, the data screening includes extracting and reconstructing an effective part in a numerical simulation result according to actual sensor layout, the neural network training includes training specific neural network models by the aid of screened data so as to acquire model parameters aiming for the specific industrial park and surrounding conditions and using redundant data for parameter validation, and sensor system and neural network model integration includes combining the models with a sensor DCS (distributed control system).
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
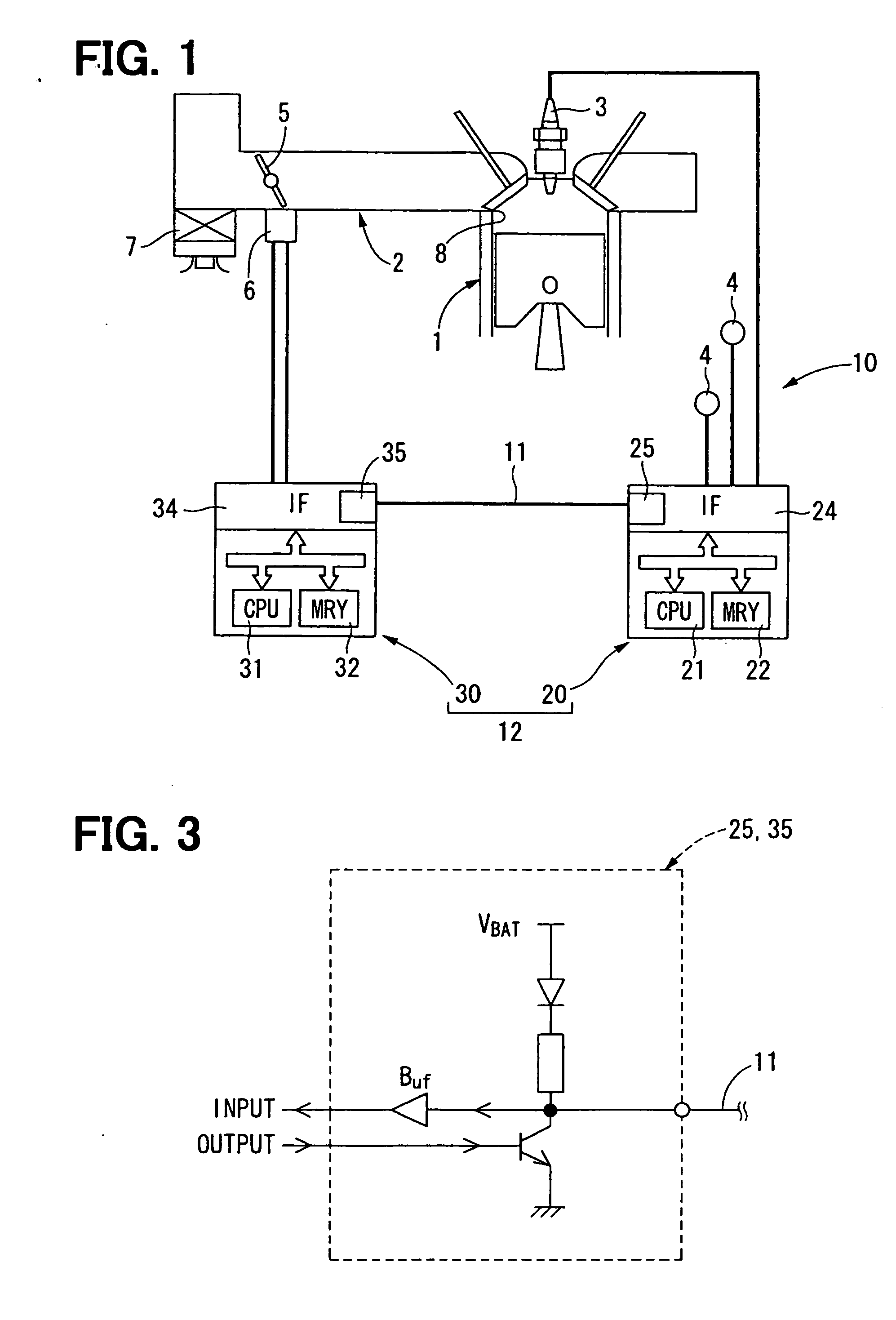
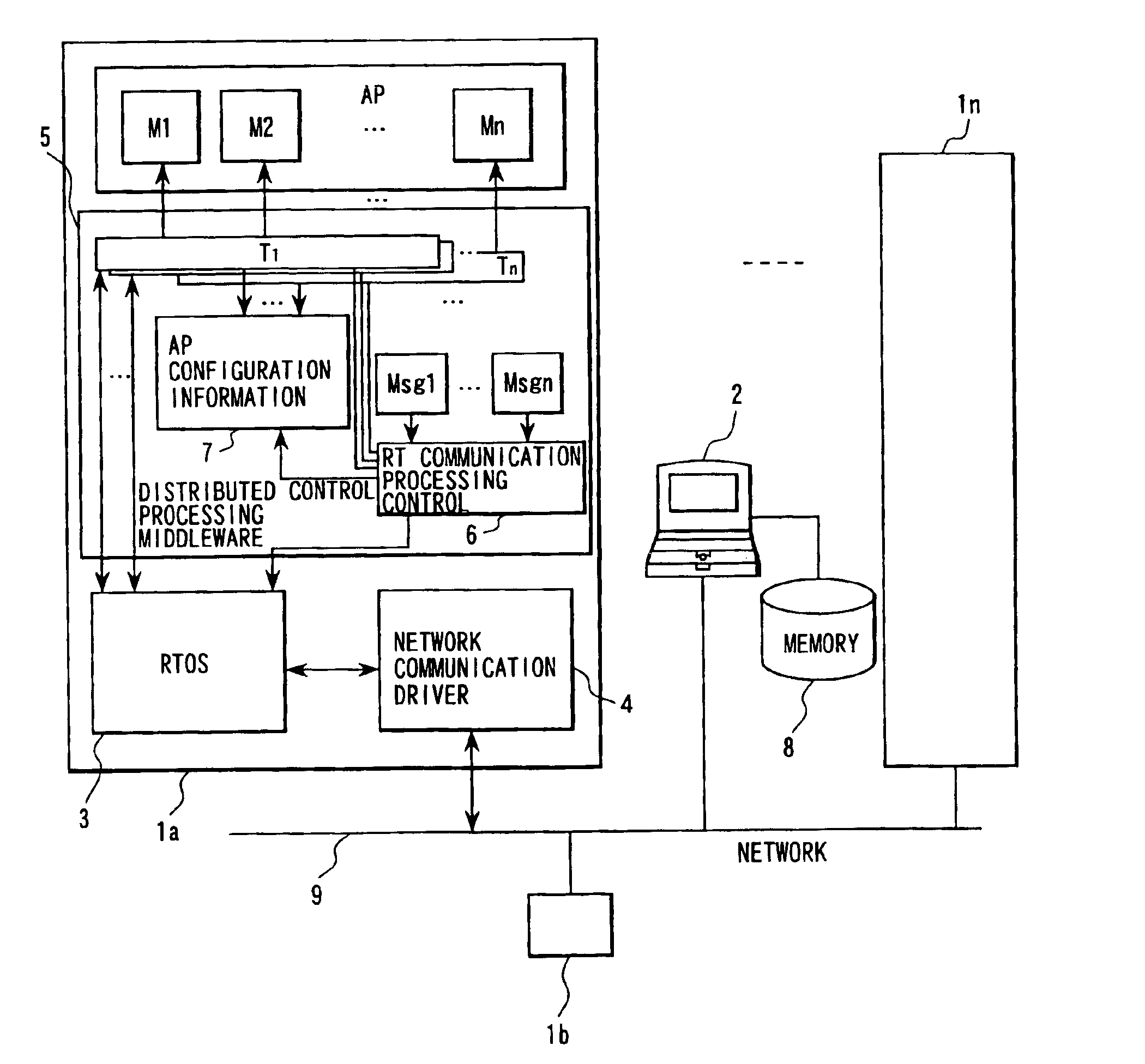
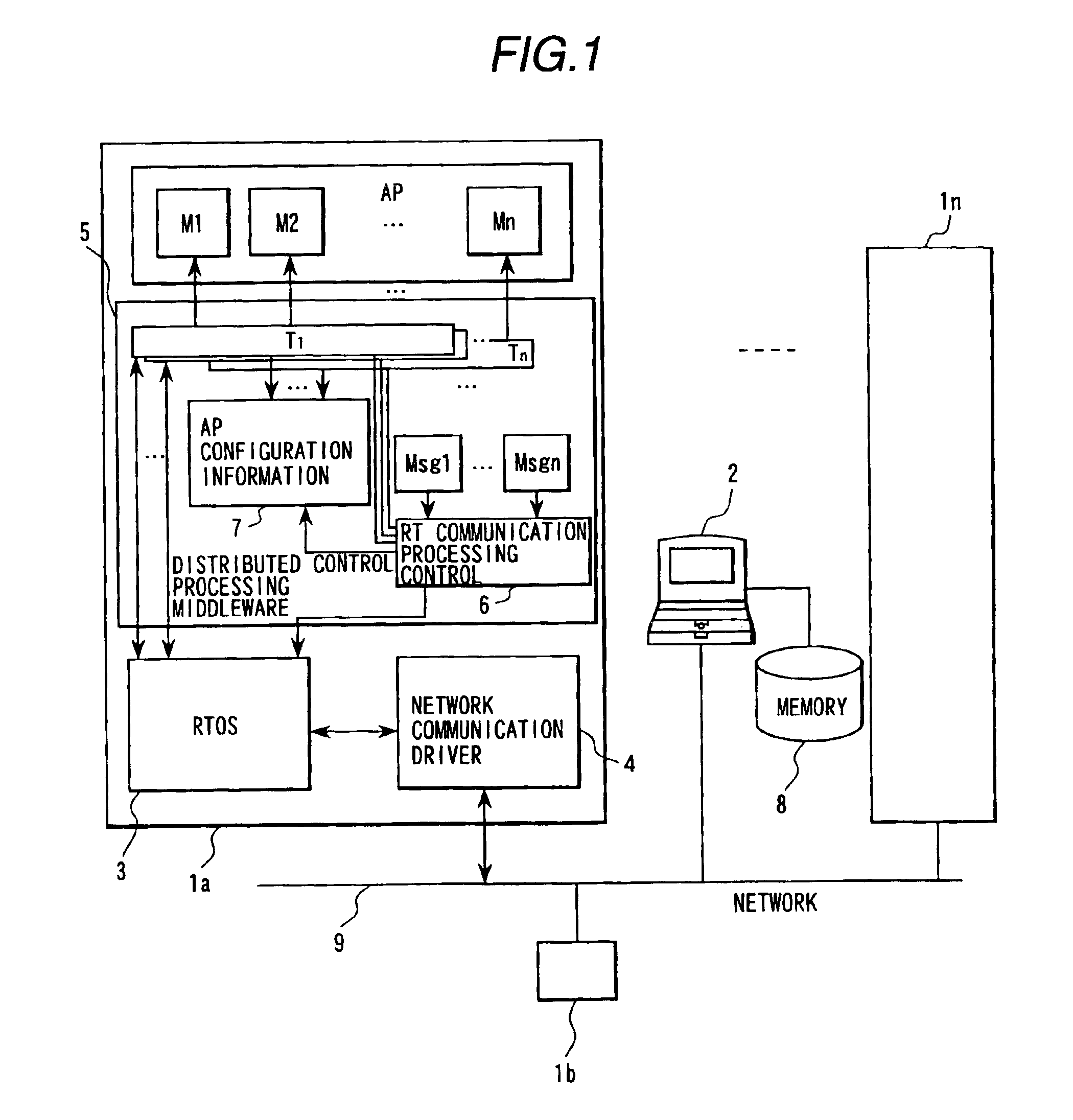
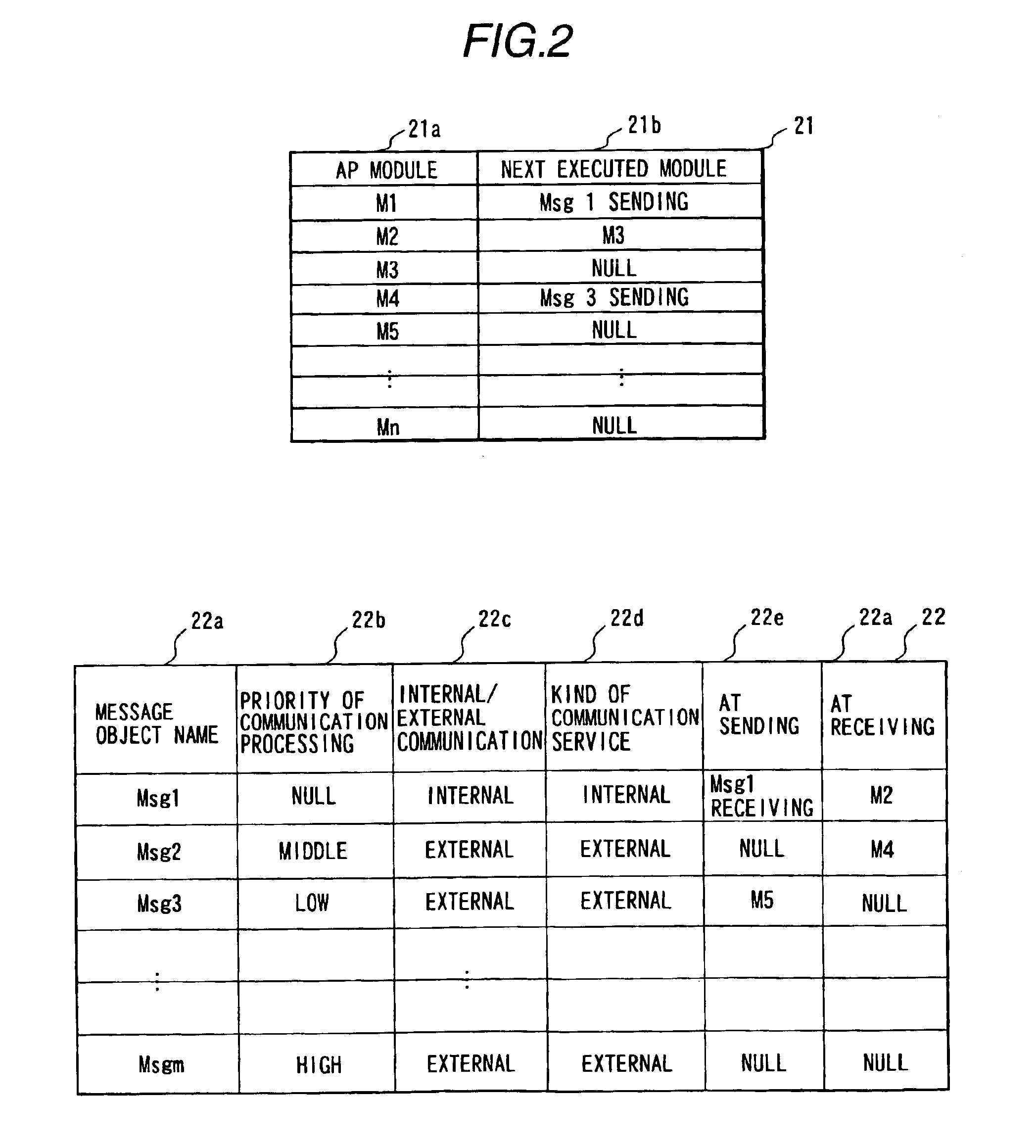
Distributed control system and information processing system
InactiveUS7103646B1Easy networkingEasy to produceDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsNetwork communicationApplication module
In a real-time distributed control system in which a plurality of network controllers are connected, a middleware module in each control unit executes starting of application modules and calling RT communication processing according to starting order information in application configuration information. RT communication service sends and receives messages between the application modules corresponding to the calling. The application configuration information and the messages are generated by an information processor based on user defined information, and transmitted to each of the units. A network driver executes network communication using a network controller which stores sending and receiving messages. A network driver priority manager determines priority of processing of the network driver corresponding to priorities of sent and received messages, and a scheduler executes processing of the network driver according to the priority of the processing of the network driver.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
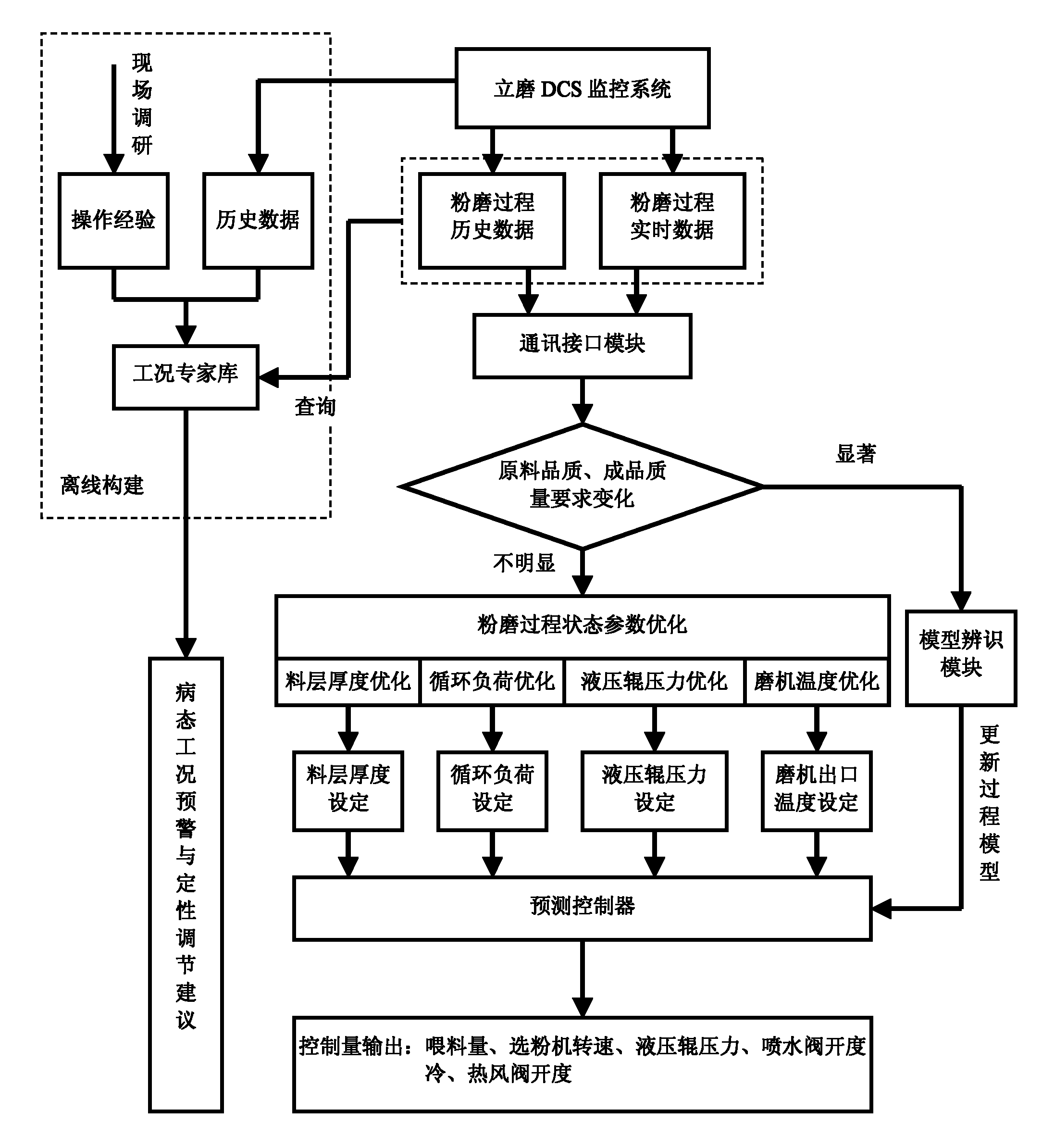
Advanced control method and system for vertical mill based on model identification and predictive control
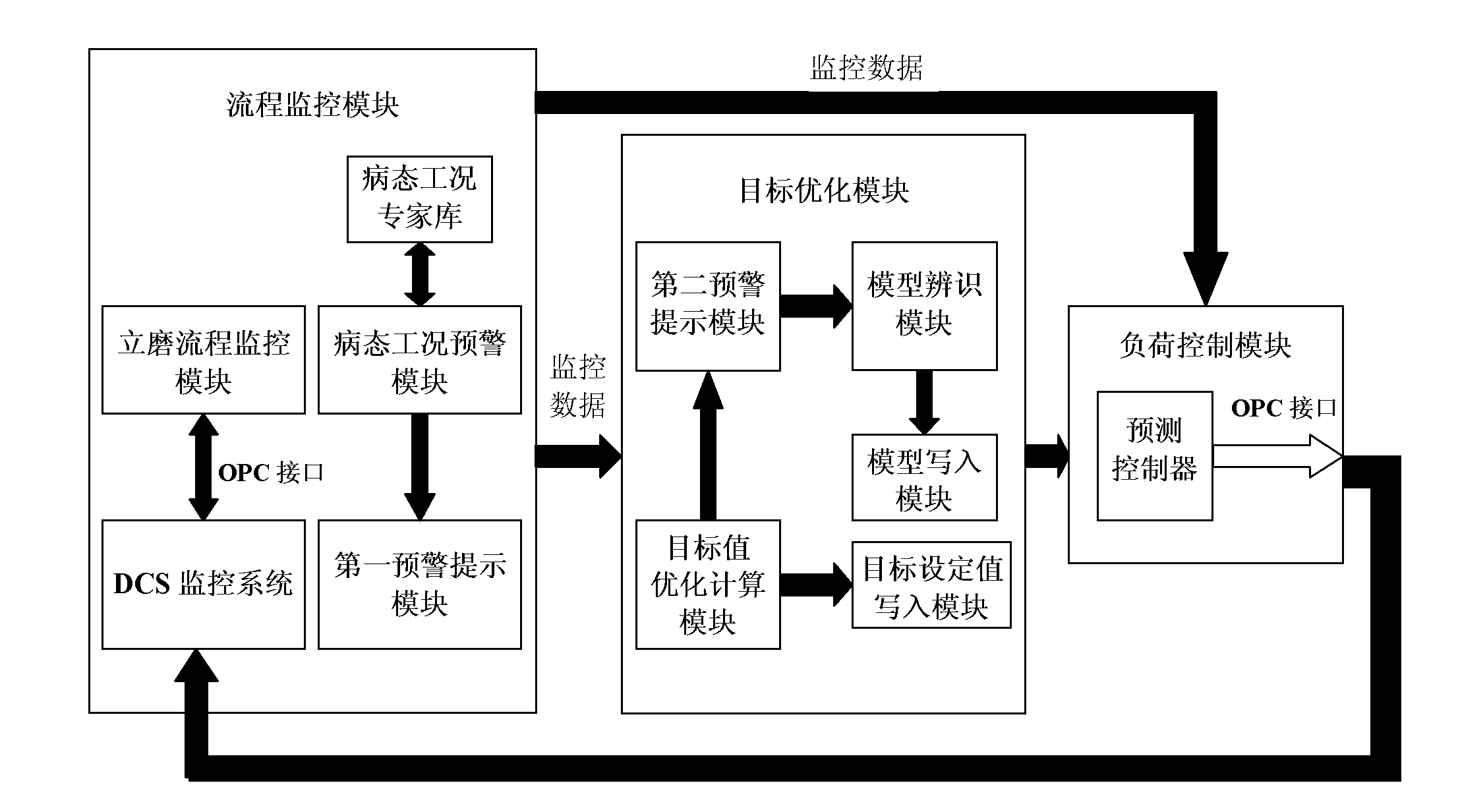
InactiveCN102151605AIncrease the level of automationQuality improvementCement grindingCement productionMathematical modelOptimal control
The invention relates to raw material grinding in the field of cement process industries, and aims to provide an advanced control method and system for a vertical mill based on model identification and predictive control. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring real-time data from a distributed control system (DCS) monitoring system; analyzing a variation trend of the operation and technology parameters, and then invoking a pathological working condition expert database for performing trend matching; if a pathological working condition appears, issuing early warning display and giving qualitative adjustment suggestion remind; giving an optimal target set value according to the basic operation condition of the vertical mill and the variation situation of the product quality requirement, and writing into a predictive controller; setting an optimal controlled quantity output according to the optimal target set value, and outputting to the DCS monitoring system to control a field actuator to take action. By adopting the invention, the qualitative adjustment suggestion can be precisely given; a mathematical model of the grinding process of the vertical mill is established and updated in real time; the steady-state error of the control system is reduced; and the grinding process of the vertical mill is instructed, so that the mill can operate stably for long term at a maximum efficiency point, and stable margin is maintained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
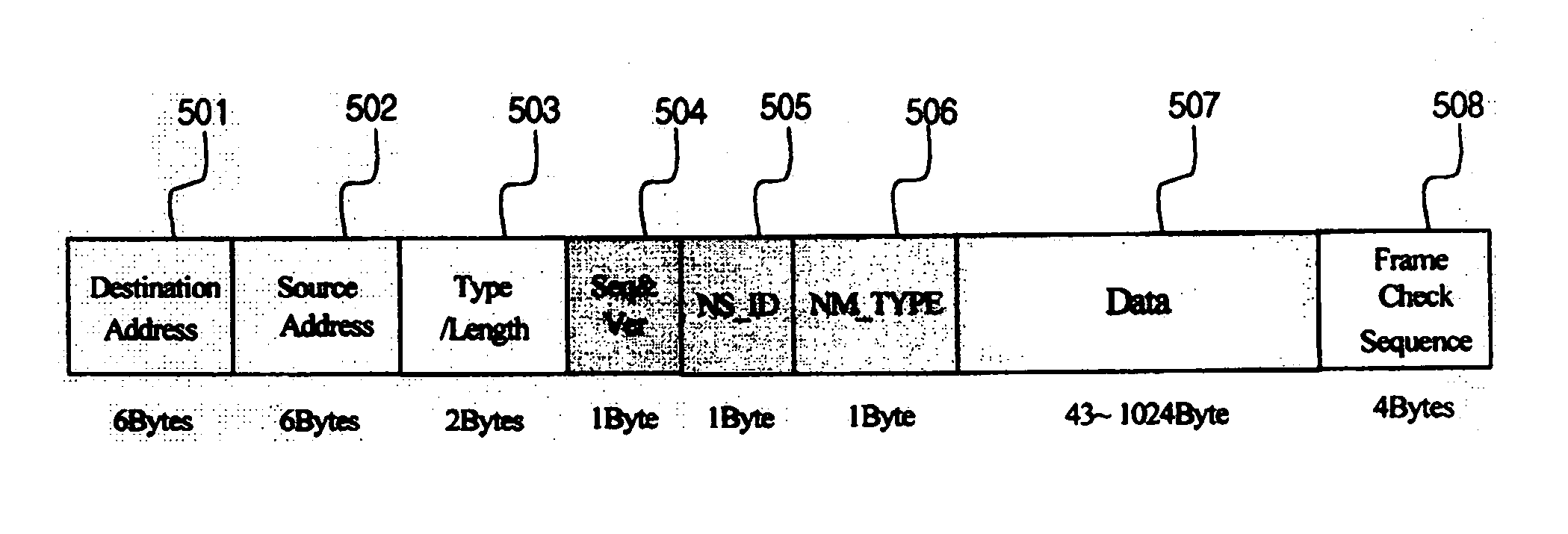
Transmission frame structure for control communication network of distributed control system for nuclear power plant
InactiveUS20060007927A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl communicationsData field
A transmission frame structure for use in a control communication network allows all process control stations contained in the control communication network to share monitoring / control information received from a field communication network or an information communication network, and properly copes with faulty operations of channels (i.e., ring-shaped lines) or process control stations for use in the control communication network. The transmission frame structure of a control communication network for use in a nuclear-power-plant distributed control system which broadcasts data received from a node having transmission authority to all nodes via a bypass line, and allows a ring accelerator to detour the data and to isolate an erroneous station from normal stations, includes a transmission frame. The transmission frame includes: a destination address for performing the broadcasting operation; a source address for recording a source node address (ID) therein; a type / length field for classifying frames into a control data frame and a network management event frame; a network management (NM_TYPE) field which is valid only when it is designated by type / length field, and performs different roles according to network management event frame types; a Seq&Ver field for including the number of transmissions of a data frame and frame upgrade version information; a NS_ID field for recording number information of a node equal to the next token reception node, and being used when one station transmits a token to the next station; a data field having a predetermined maximum size of 1 kbyte, for including not only general control information according to a value of the type / length field, but also 7 event frames such as a token frame; and a CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Code) field for inspecting the presence or absence of a CRC error, whereby the transmission frame operates the communication network, solves a malfunction or error of the communication network, and recovers the communication network.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRIC POWER CORP
Method and system for modular interoperable distributed control
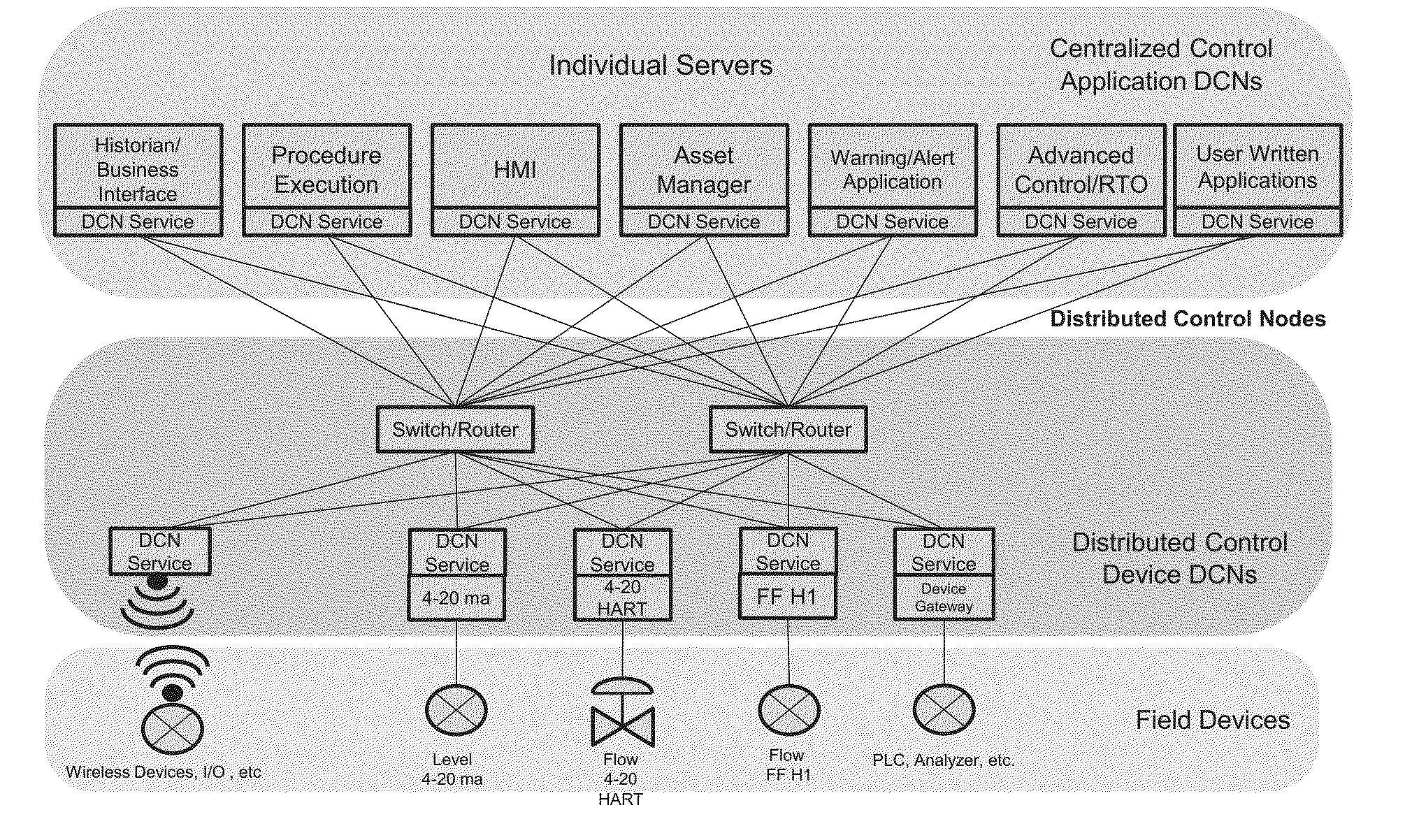
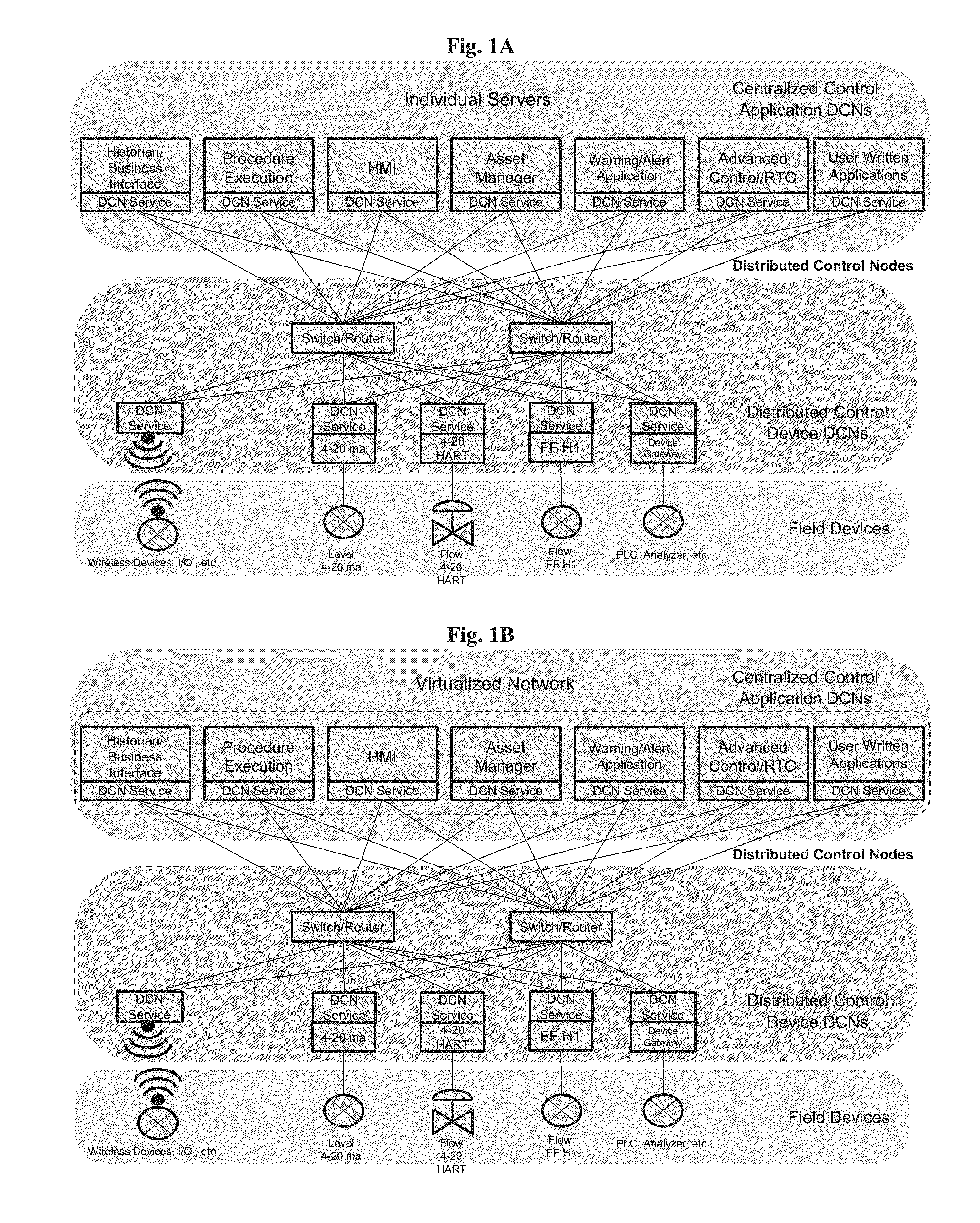
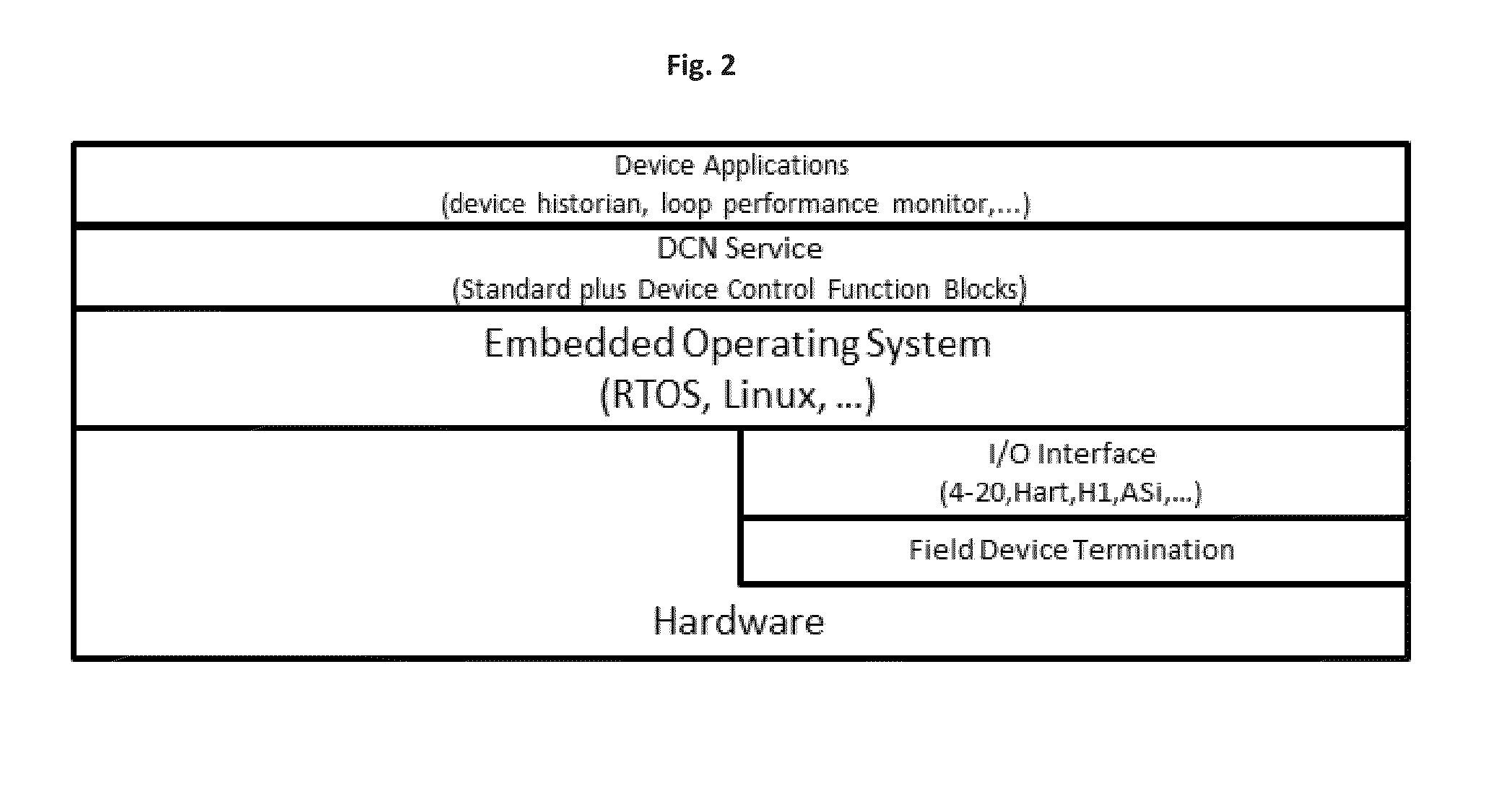
A distributed control system (DCS) for controlling an industrial process using a plurality of distributed control nodes (DCNs) can include a plurality of Device DCNs, each Device DCN including an I / O interface coupled with a field device for single channel input or output, a plurality of Application DCNs, and one or more Ethernet switches. The plurality of Device DCNs and the plurality of Application DCNs can be adapted to host a software runtime and communicatively coupled via the one or more Ethernet switches. The DCS architecture can include of two types of DCNs; Application DCNs and Device DCNs. The software runtime can be configured to selectively provide control application level communication and function block execution services.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
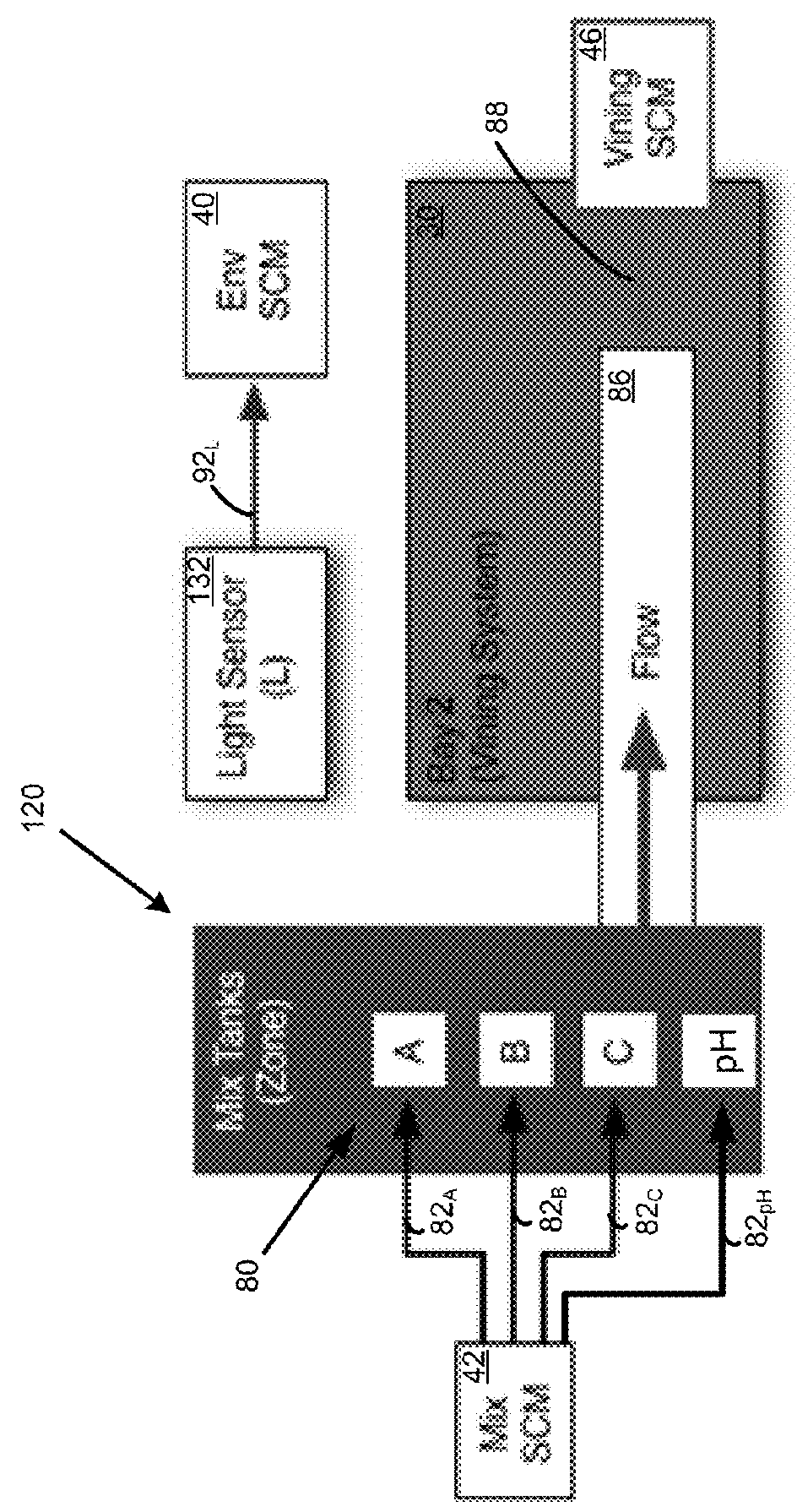
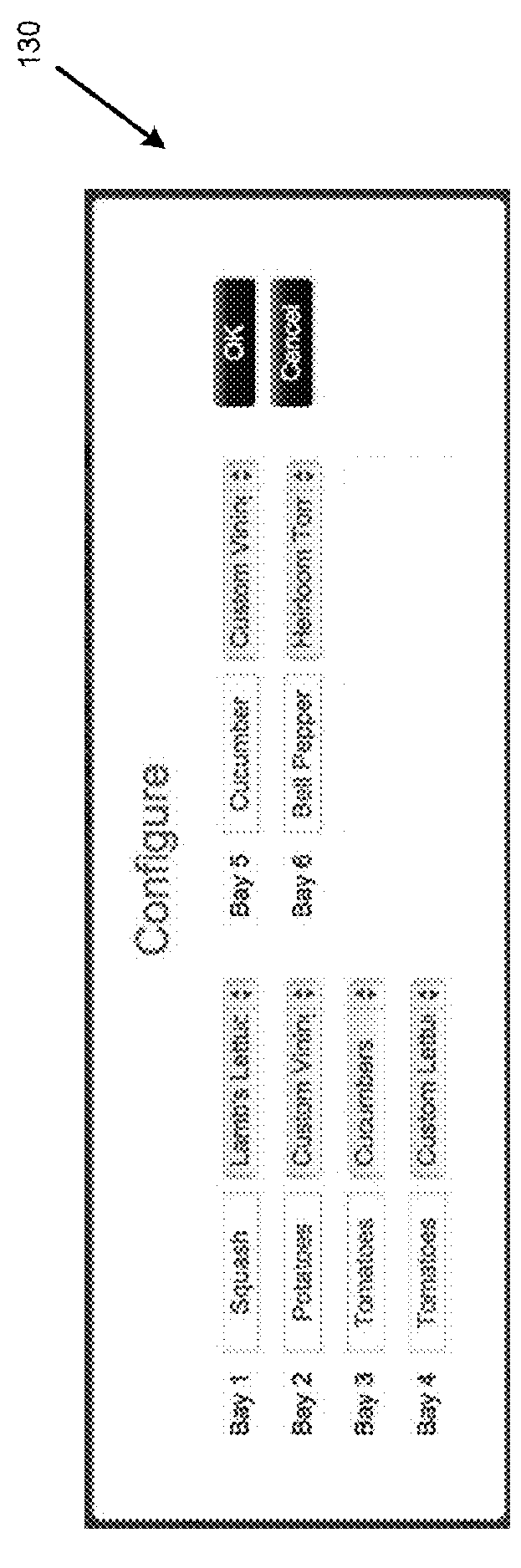
Control system for a hydroponic greenhouse growing environment
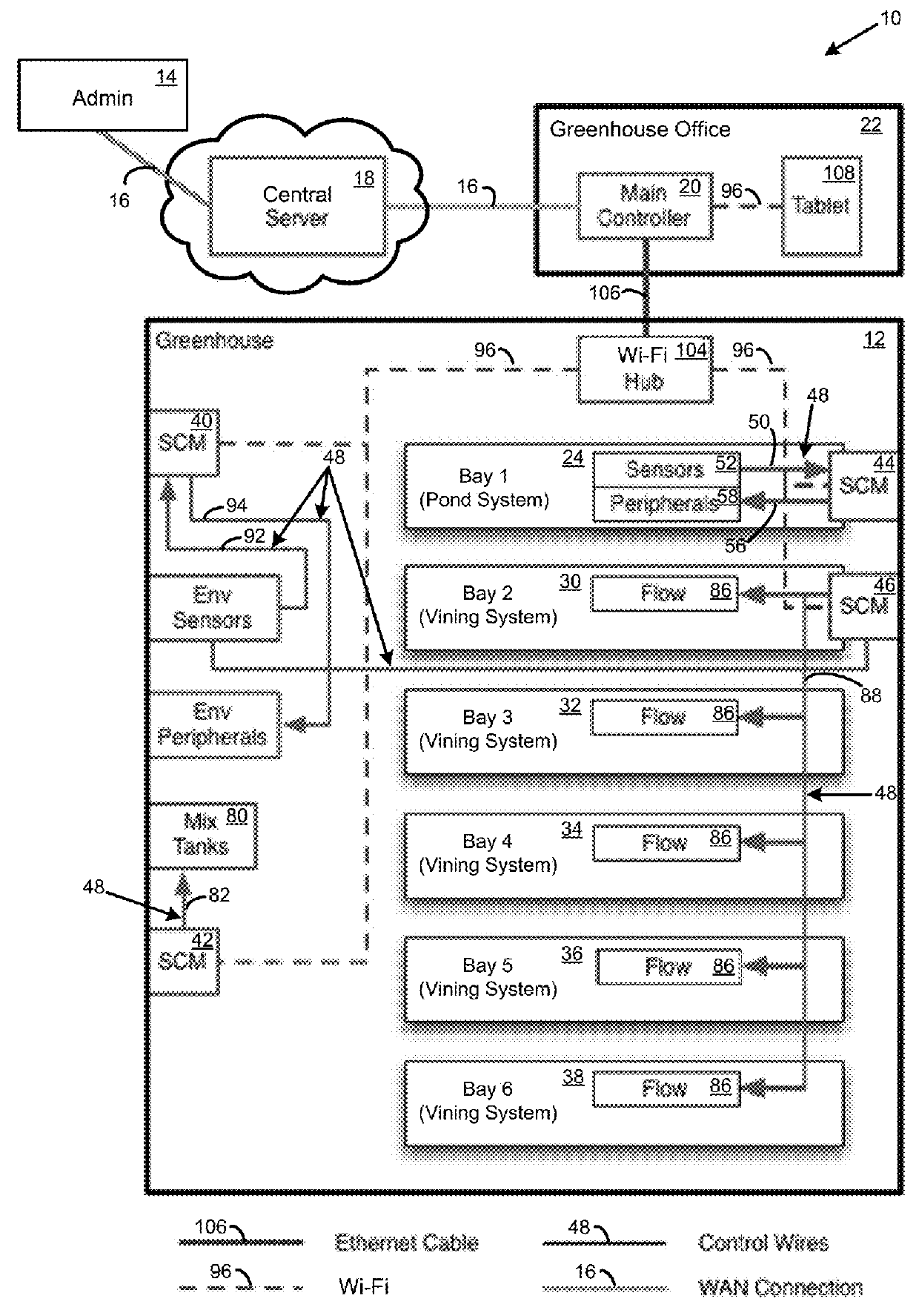
InactiveUS20160050862A1Reduces temperature control expendituresProvides thermal stabilityGreenhouse cultivationCultivating equipmentsGrowth plantGreenhouse
A greenhouse growing environment has a distributed control system for selecting, monitoring, and administering hydroponic nutrient solution mixtures that are tailored to crop varieties of the greenhouse. The crop varieties are preselected based on location characteristics of the greenhouse and analysis results of source water. The analysis results indicate a nutrient composition of the source water. A predefined nutrient formulation is then automatically combined with the source water by a nutrient dispensing subsystem, to achieve a desired nutrient solution mixture that is applied to a hydroponic bay. A computational system automatically monitors the state of a hydroponic environment and directs input modules as programmed, in order to increase plant growth, plant quality, and volume of plant yield.
Owner:GOT PROD FRANCHISING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com