Patents
Literature
3222 results about "Optimal control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optimal control theory is a branch of applied mathematics that deals with finding a control law for a dynamical system over a period of time such that an objective function is optimized. It has numerous applications in both science and engineering. For example, the dynamical system might be a spacecraft with controls corresponding to rocket thrusters, and the objective might be to reach the moon with minimum fuel expenditure. Or the dynamical system could be a nation's economy, with the objective to minimize unemployment; the controls in this case could be fiscal and monetary policy.
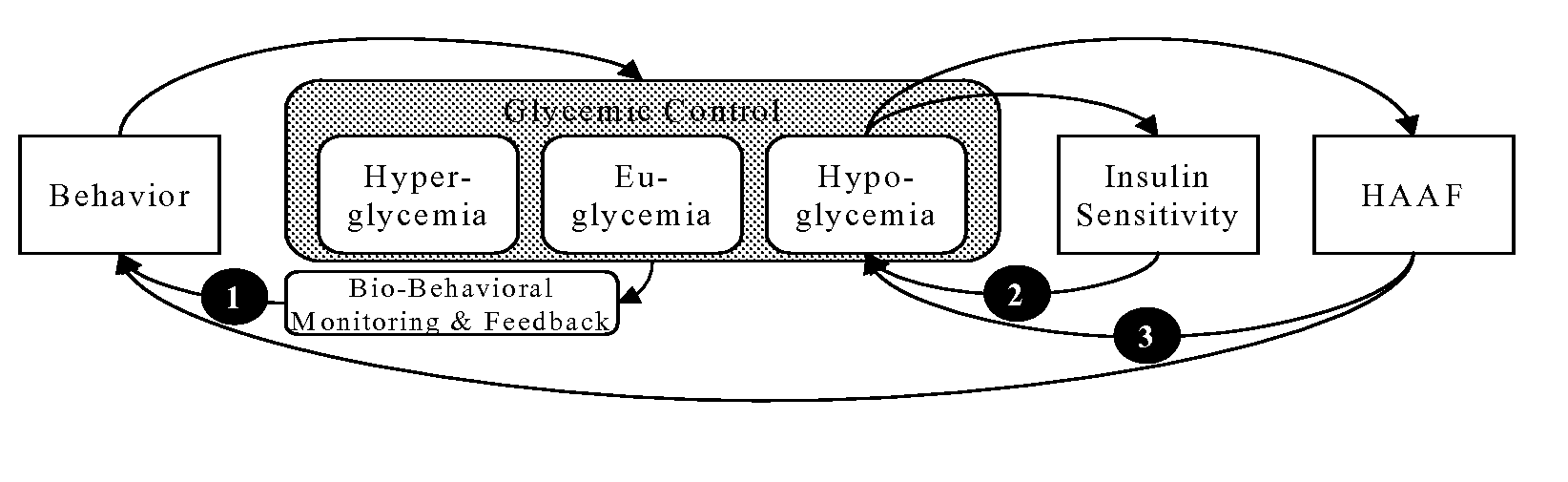
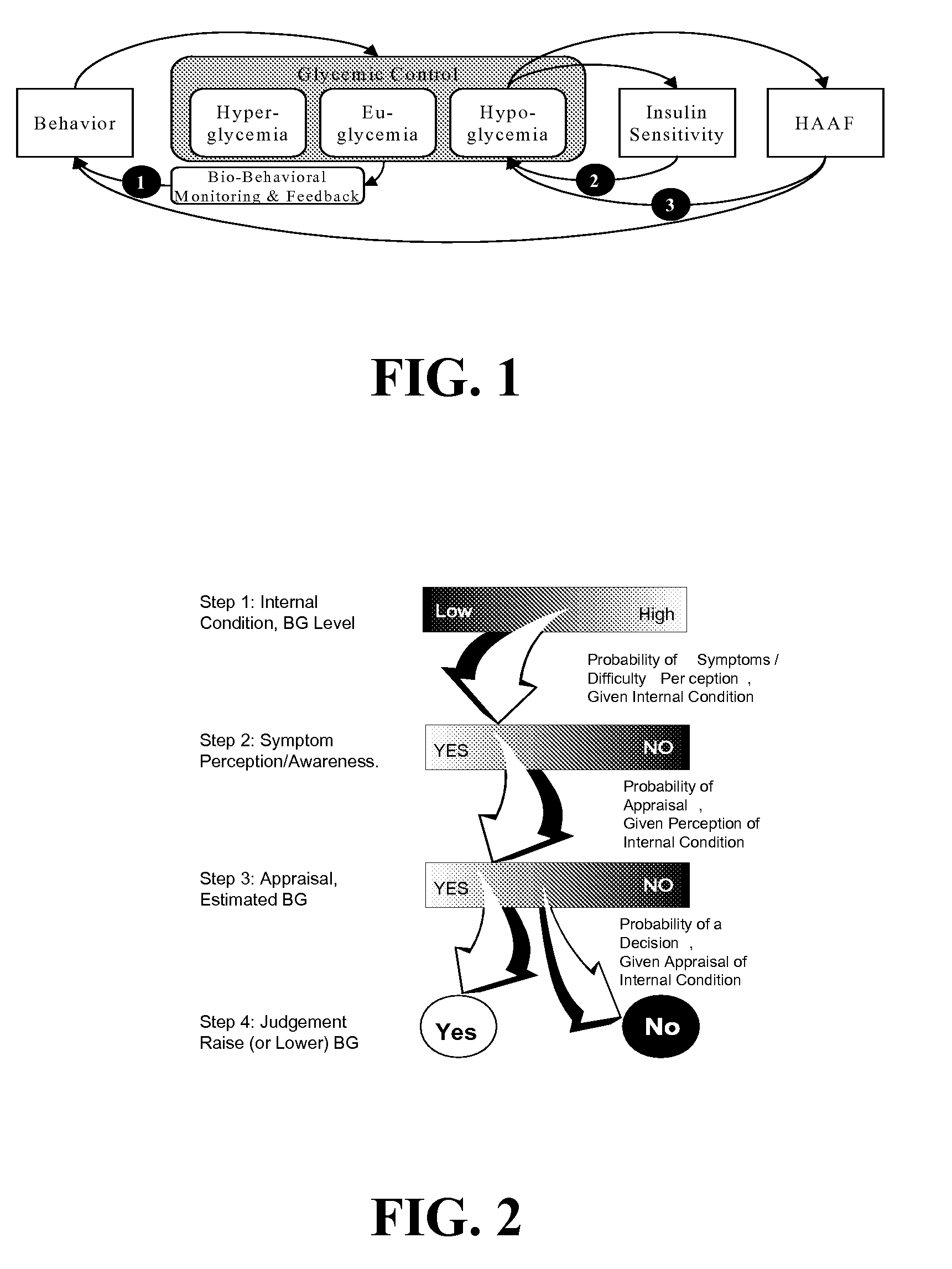
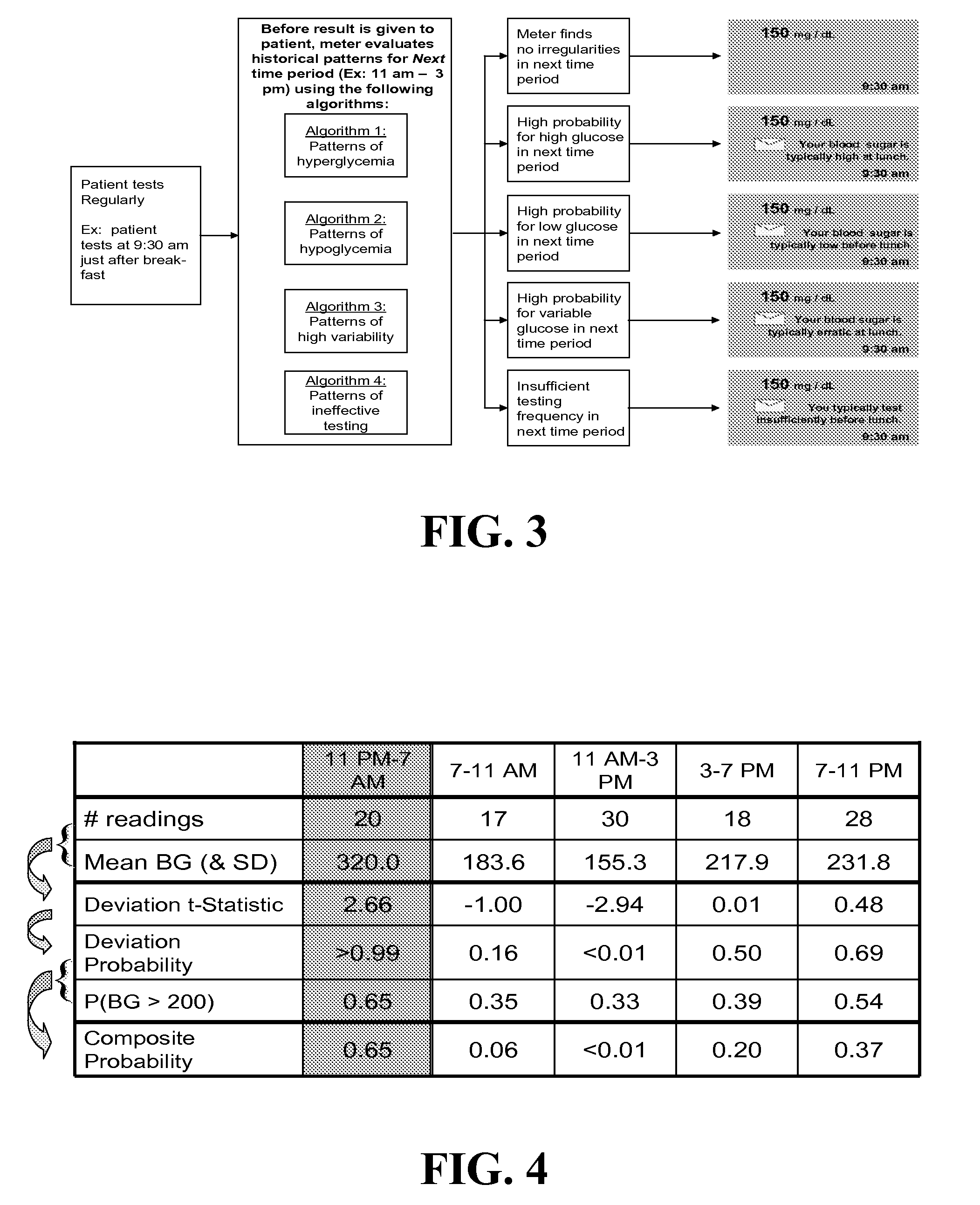
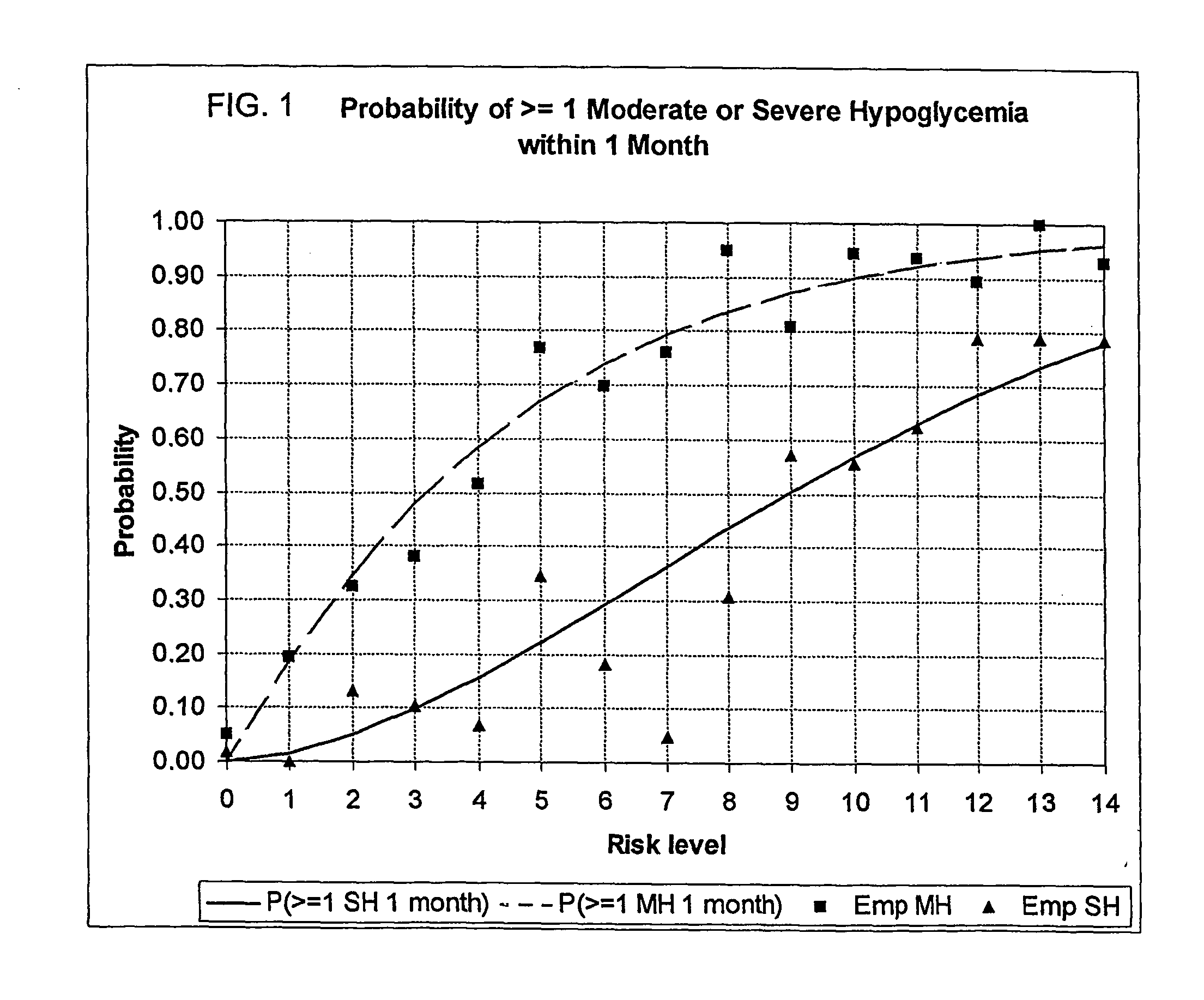
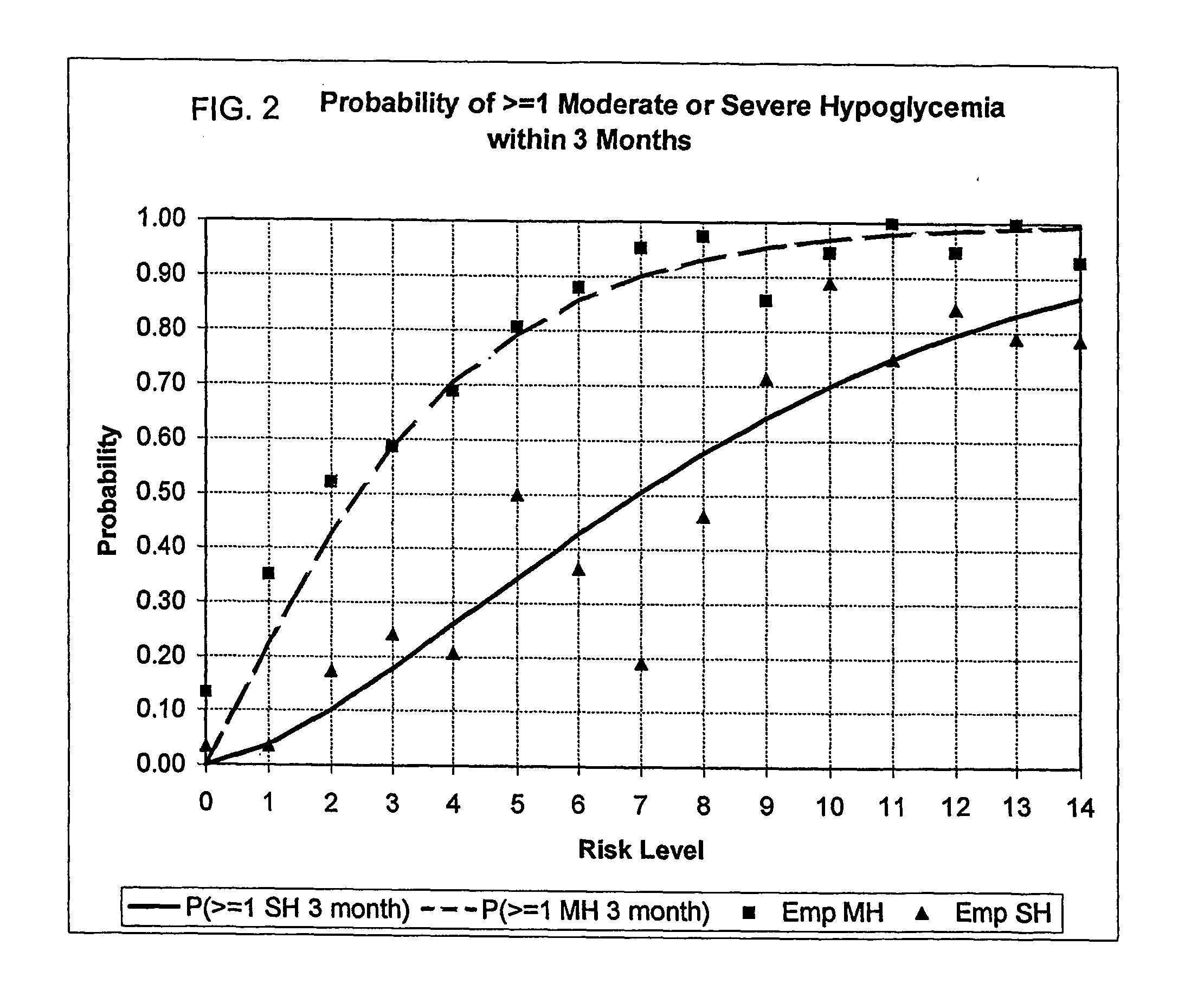
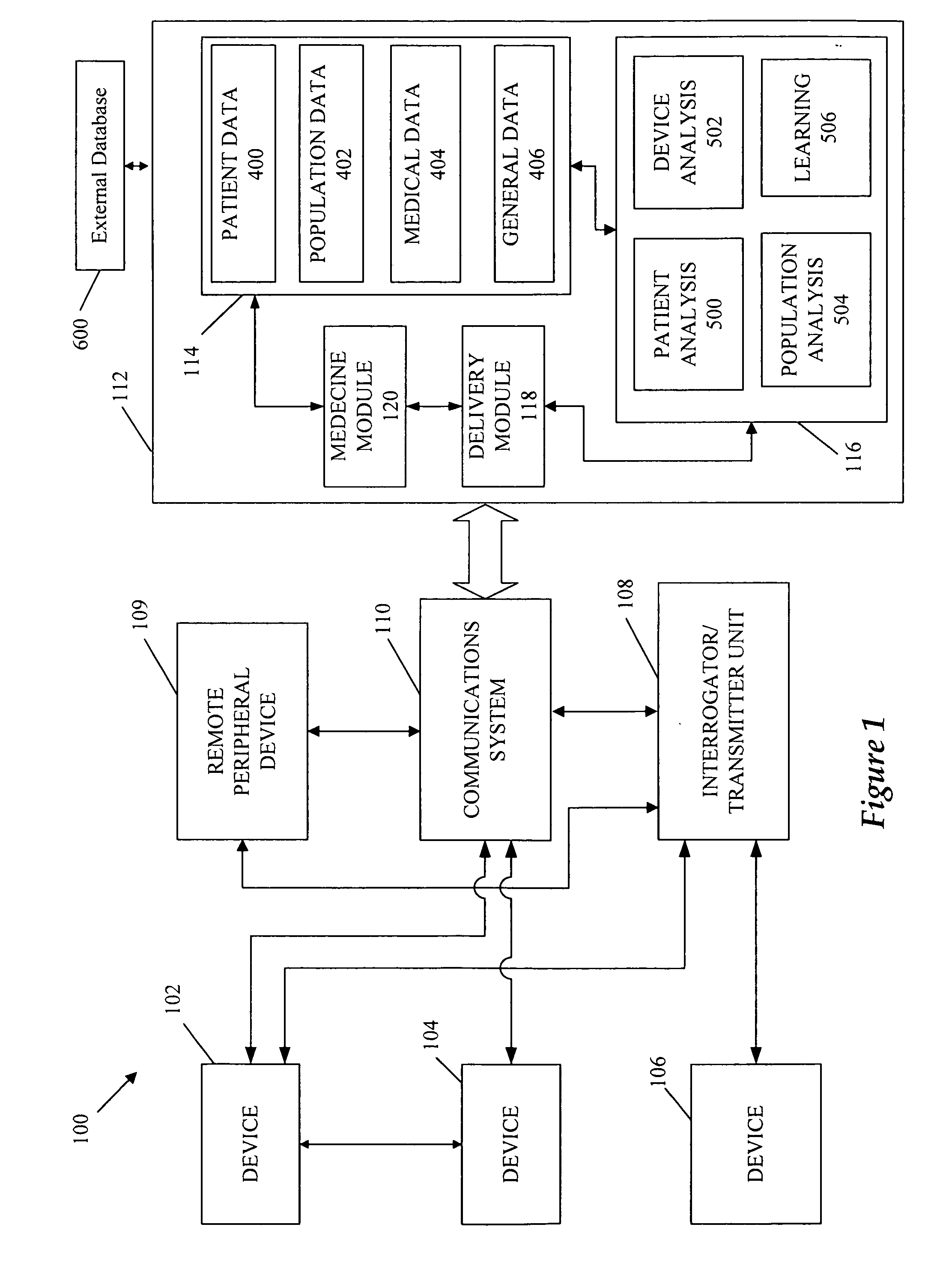
Systems, Methods and Computer Program Codes for Recognition of Patterns of Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia, Increased Glucose Variability, and Ineffective Self-Monitoring in Diabetes
InactiveUS20080154513A1Evaluate effectivenessEnhance existing SMBG devicesDrug and medicationsDigital computer detailsAcute hyperglycaemiaOptimal control
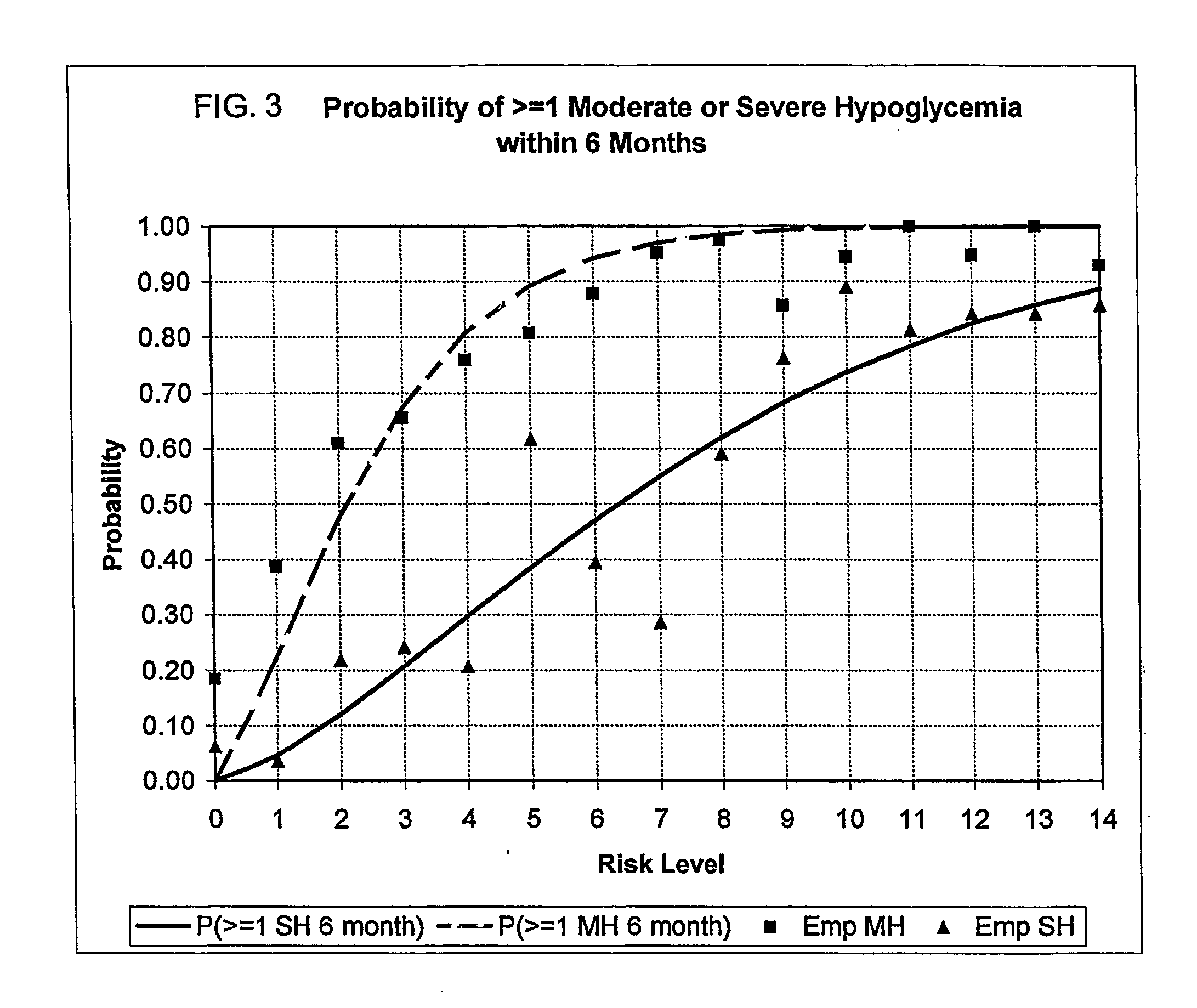
A method, system, and computer program product related to the maintenance of optimal control of diabetes, and is directed to predicting patterns of hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, increased glucose variability, and insufficient or excessive testing for the upcoming period of time, based on blood glucose readings collected by a self-monitoring blood glucose device. The method, system, and computer program product pertain directly to the enhancement of existing home blood glucose monitoring devices, by introducing an intelligent data interpretation component capable of predicting and alerting the user to periods of increased risk for hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, increased glucose variability, and ineffective testing, and to the enhancement of emerging self-monitoring blood glucose devices by the same features. With these predictions the diabetic can take steps to prevent the adverse consequences associated with hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and increased glucose variability.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +1
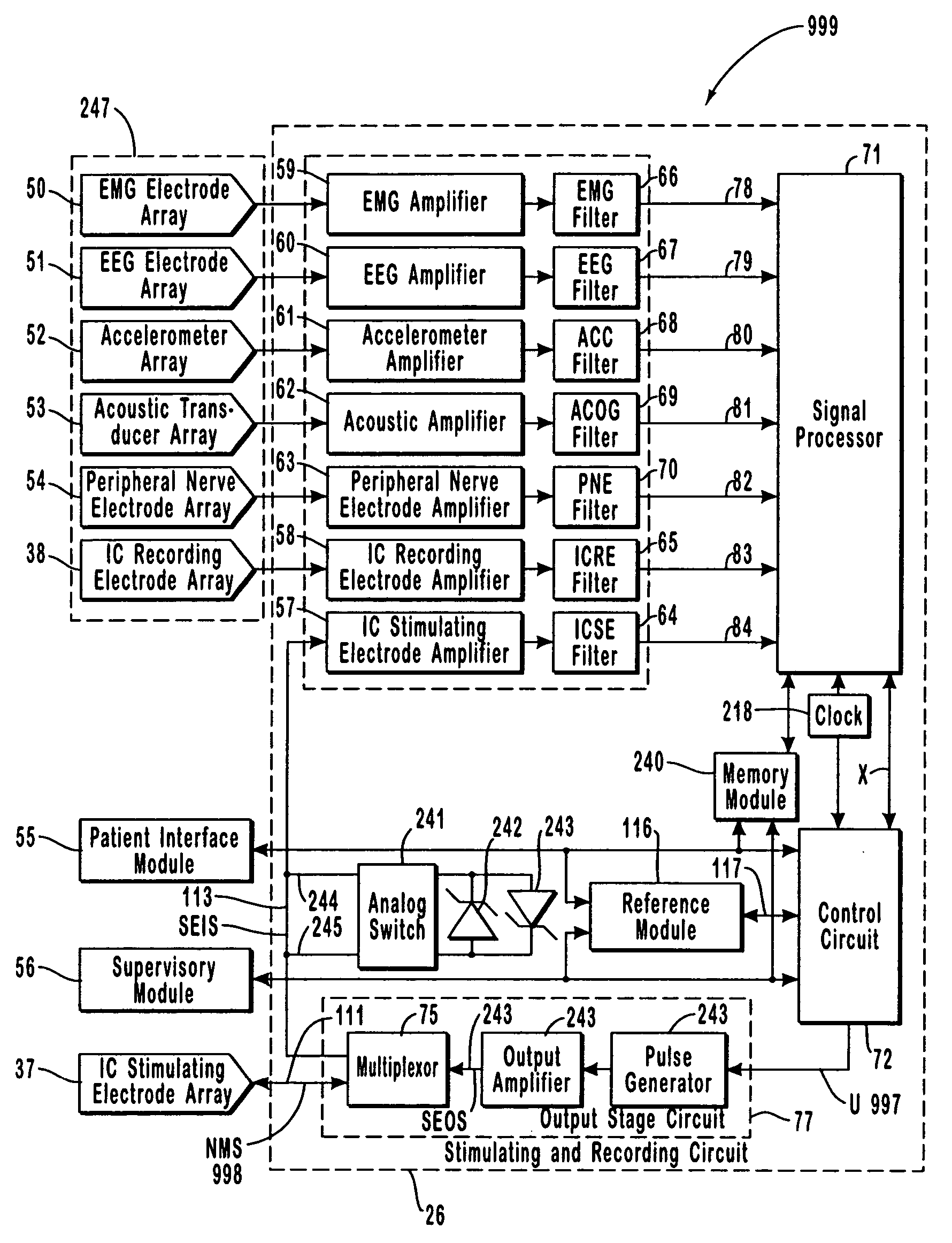
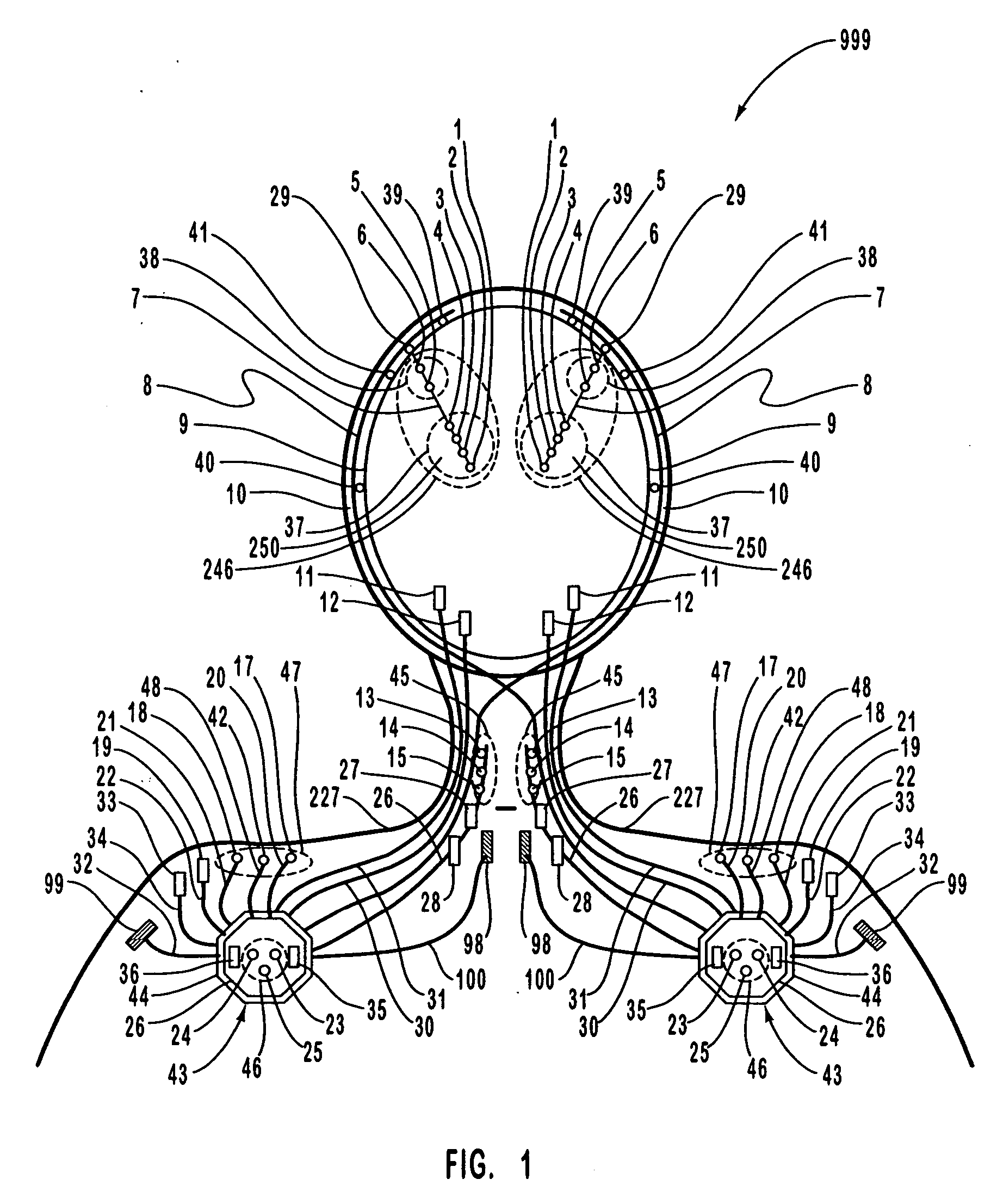
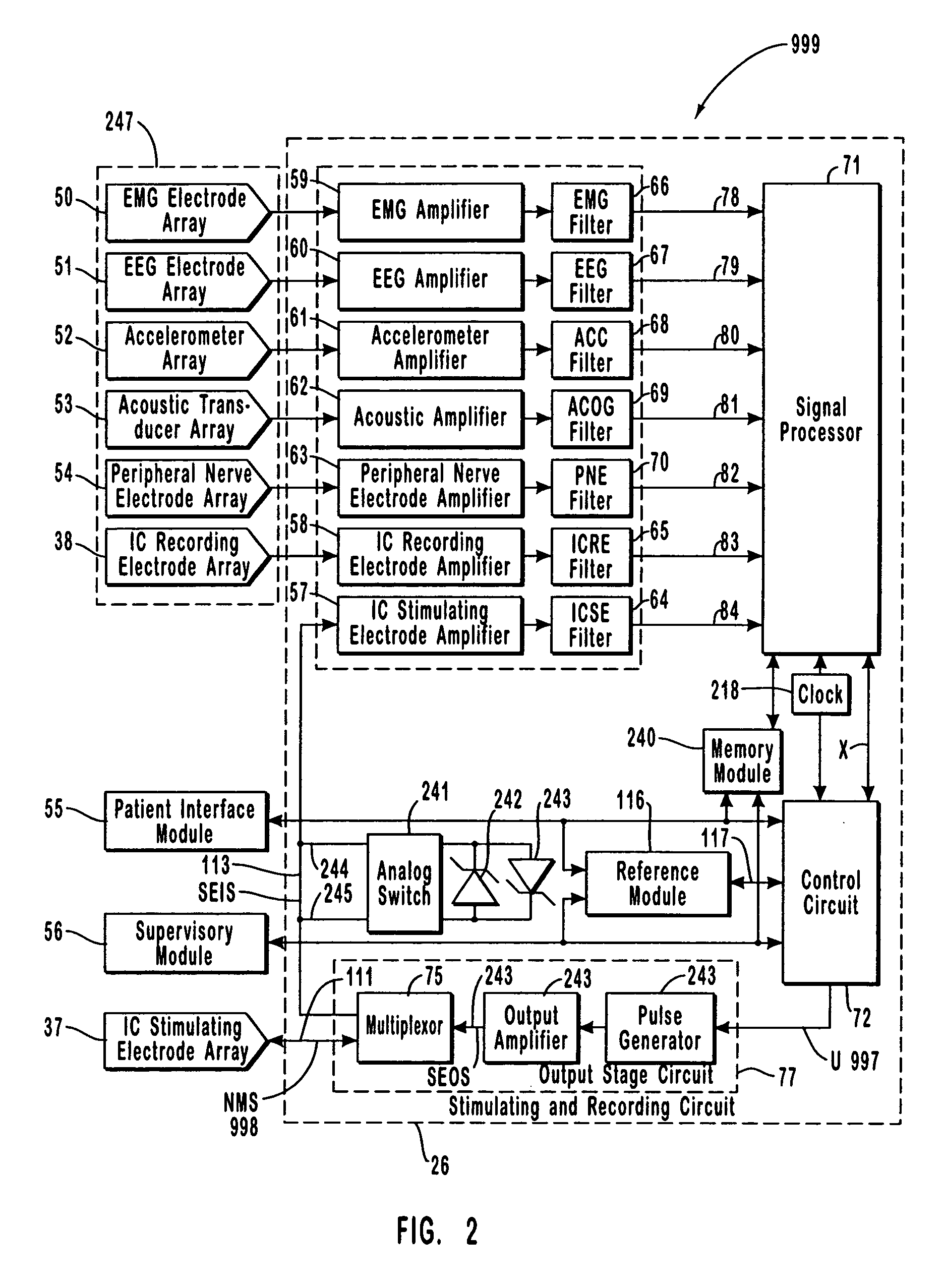
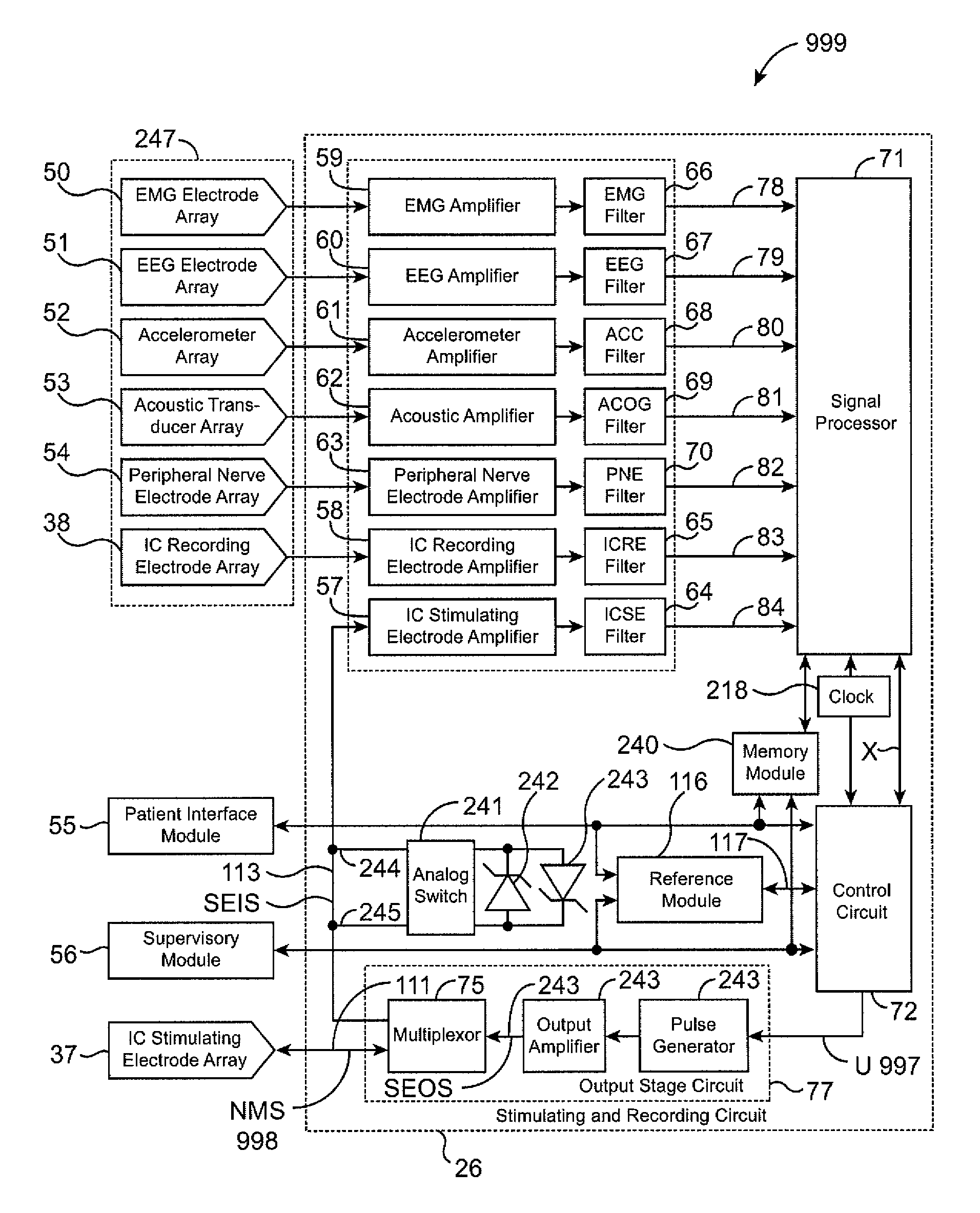
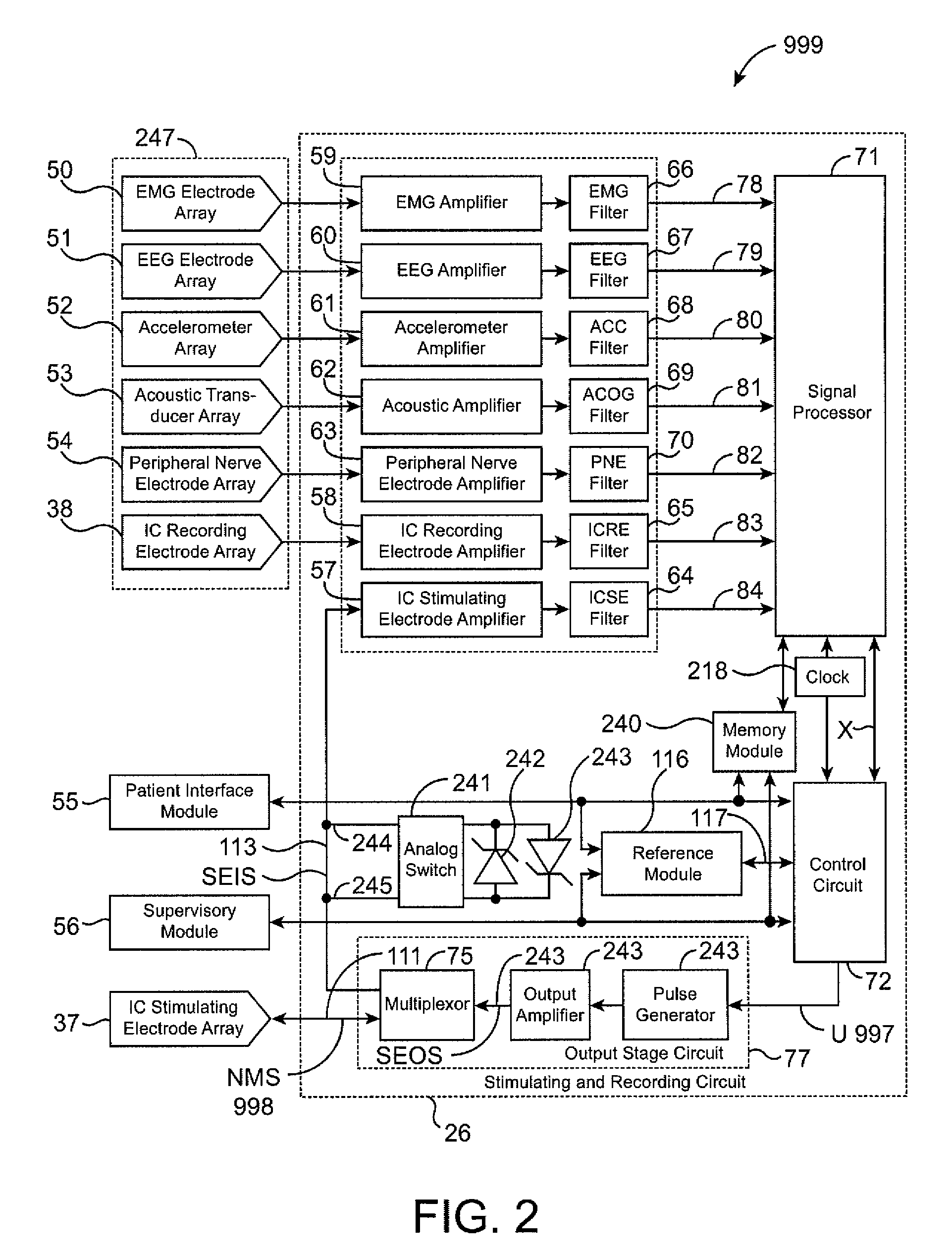
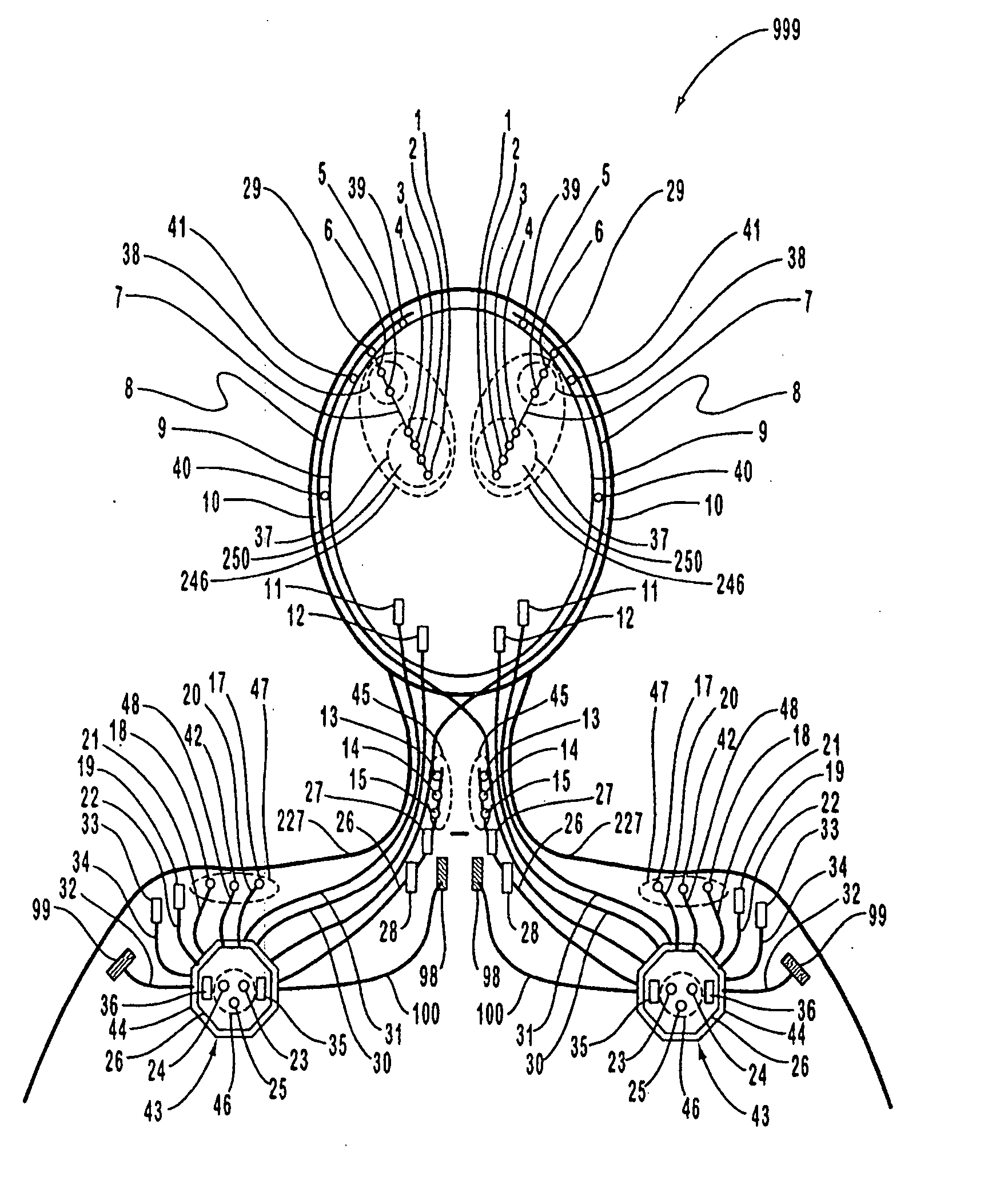
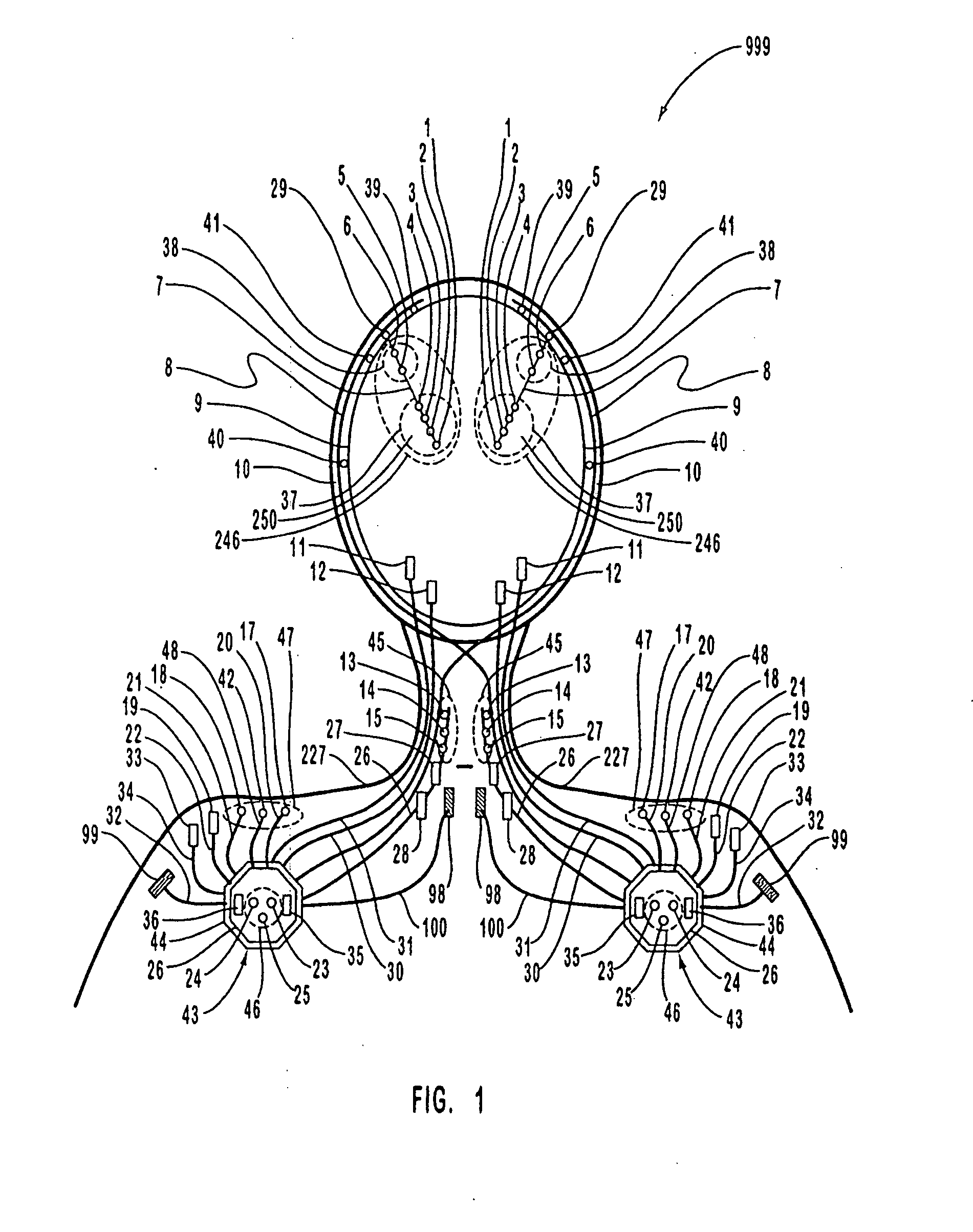
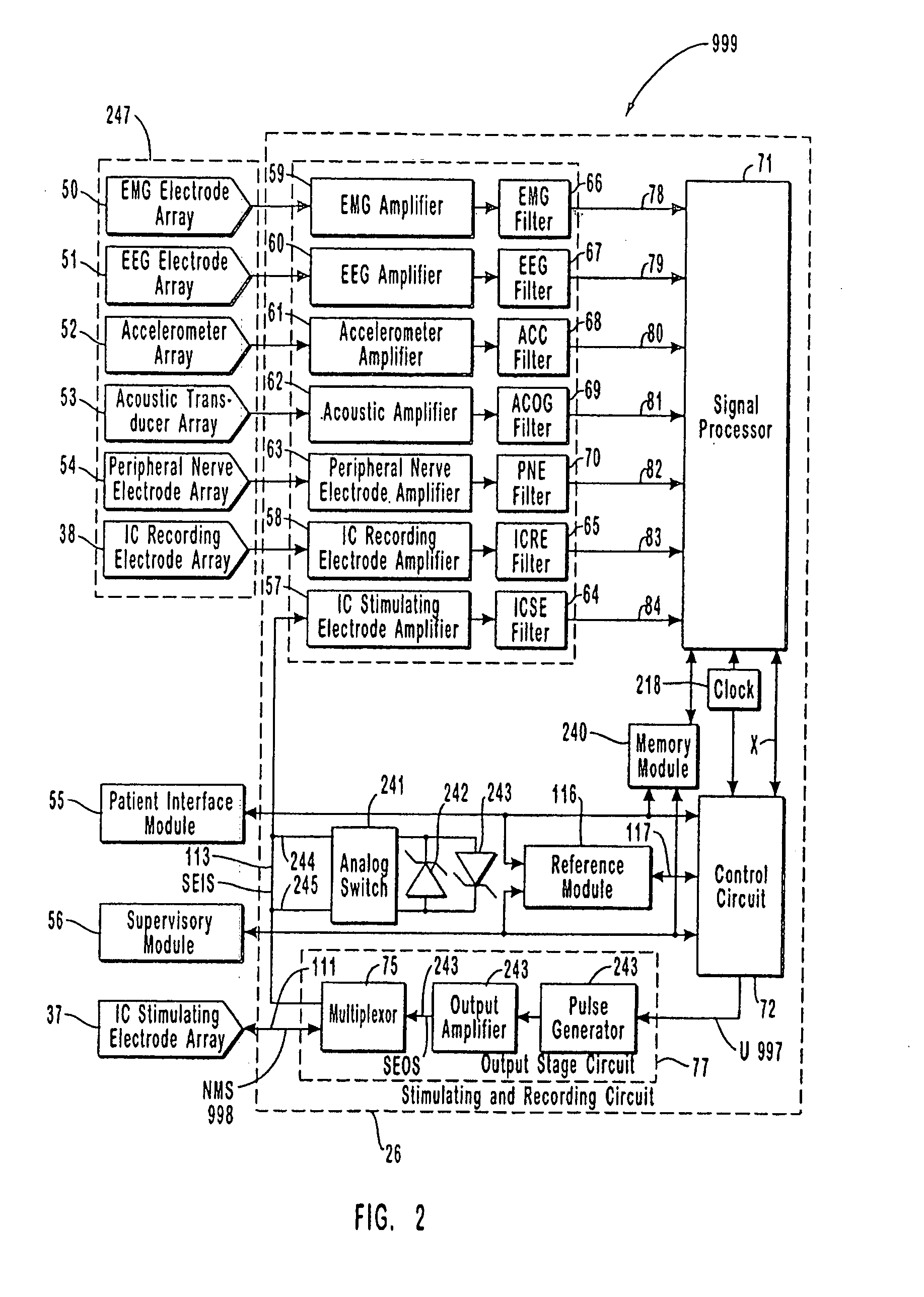
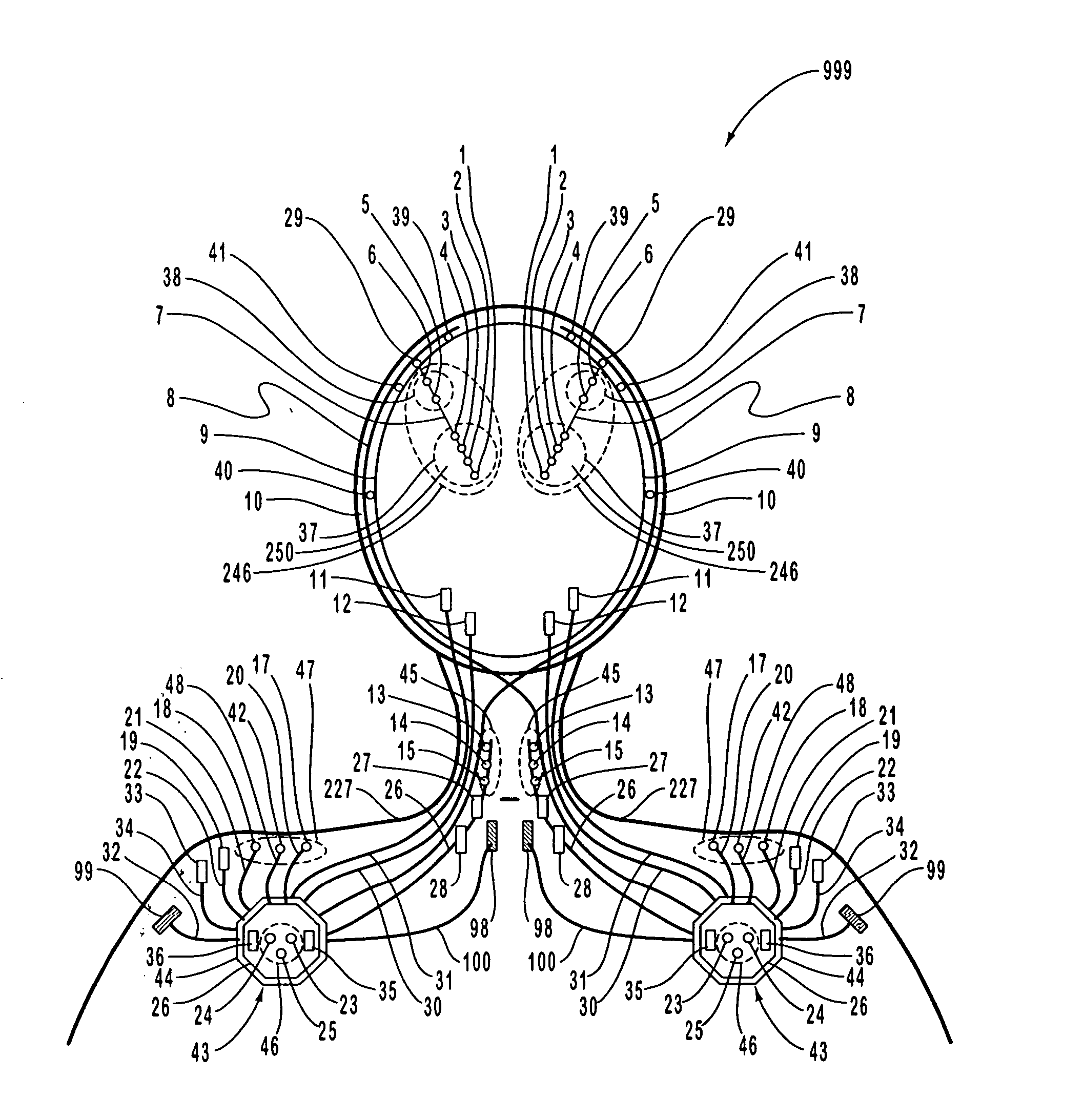
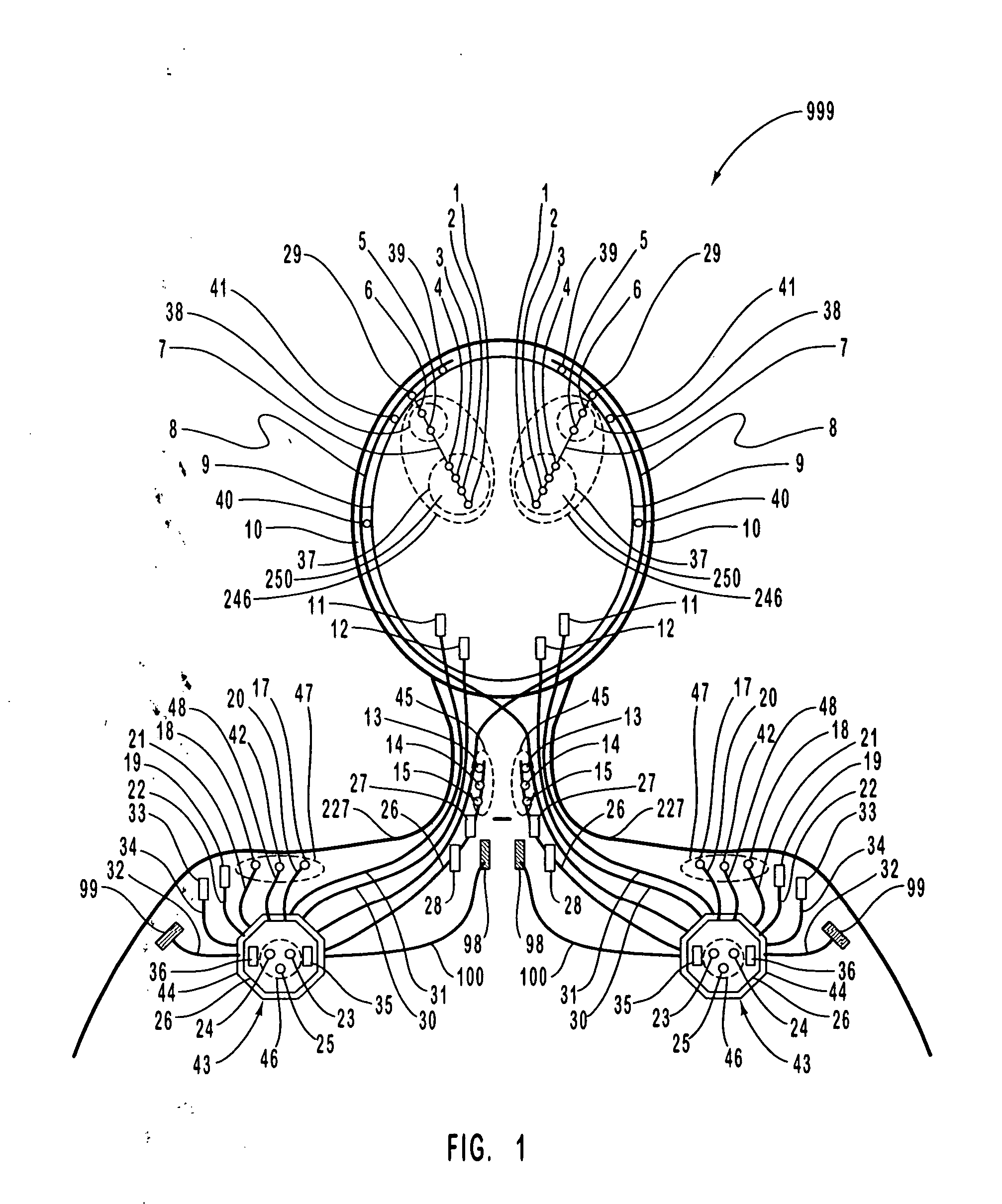
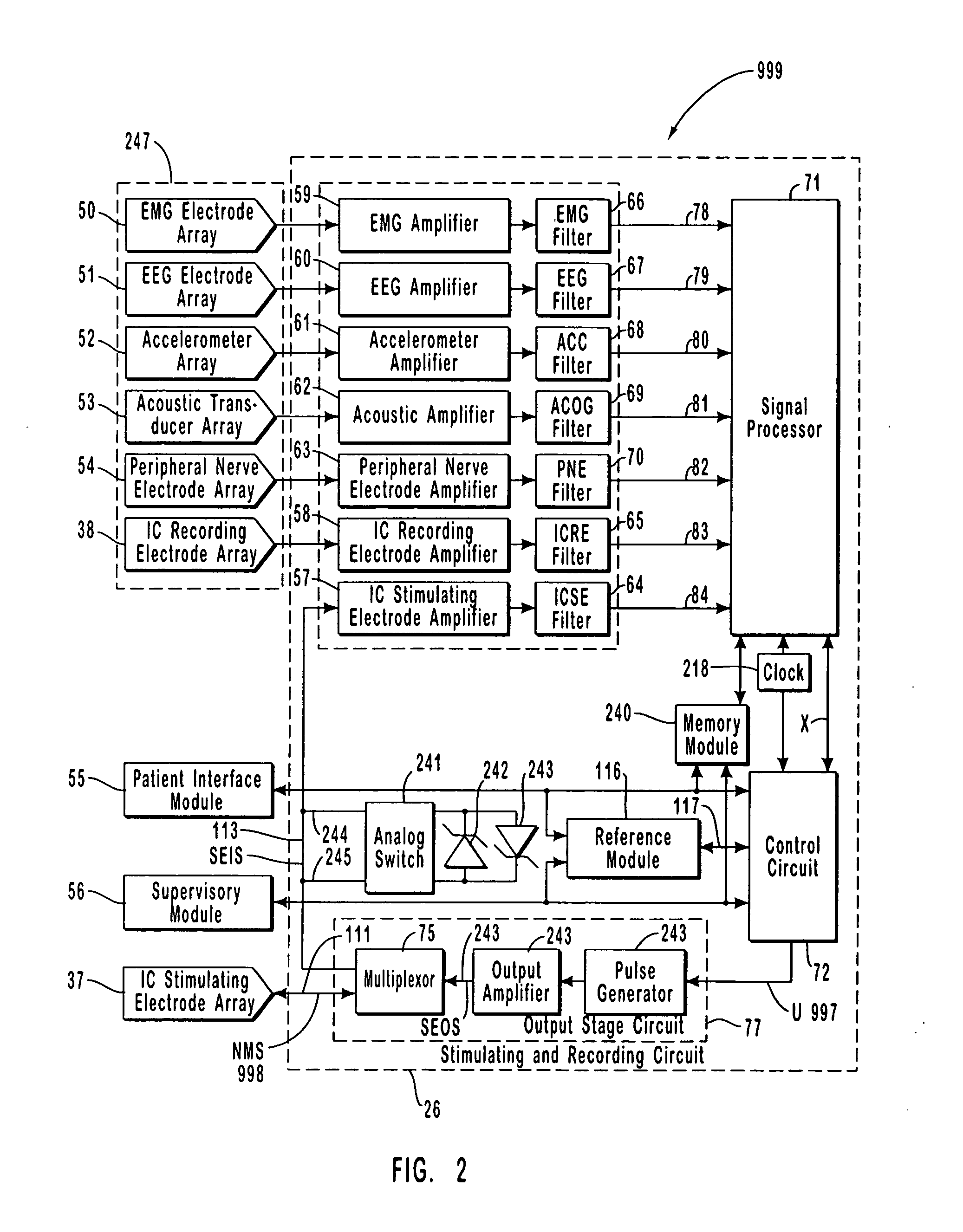
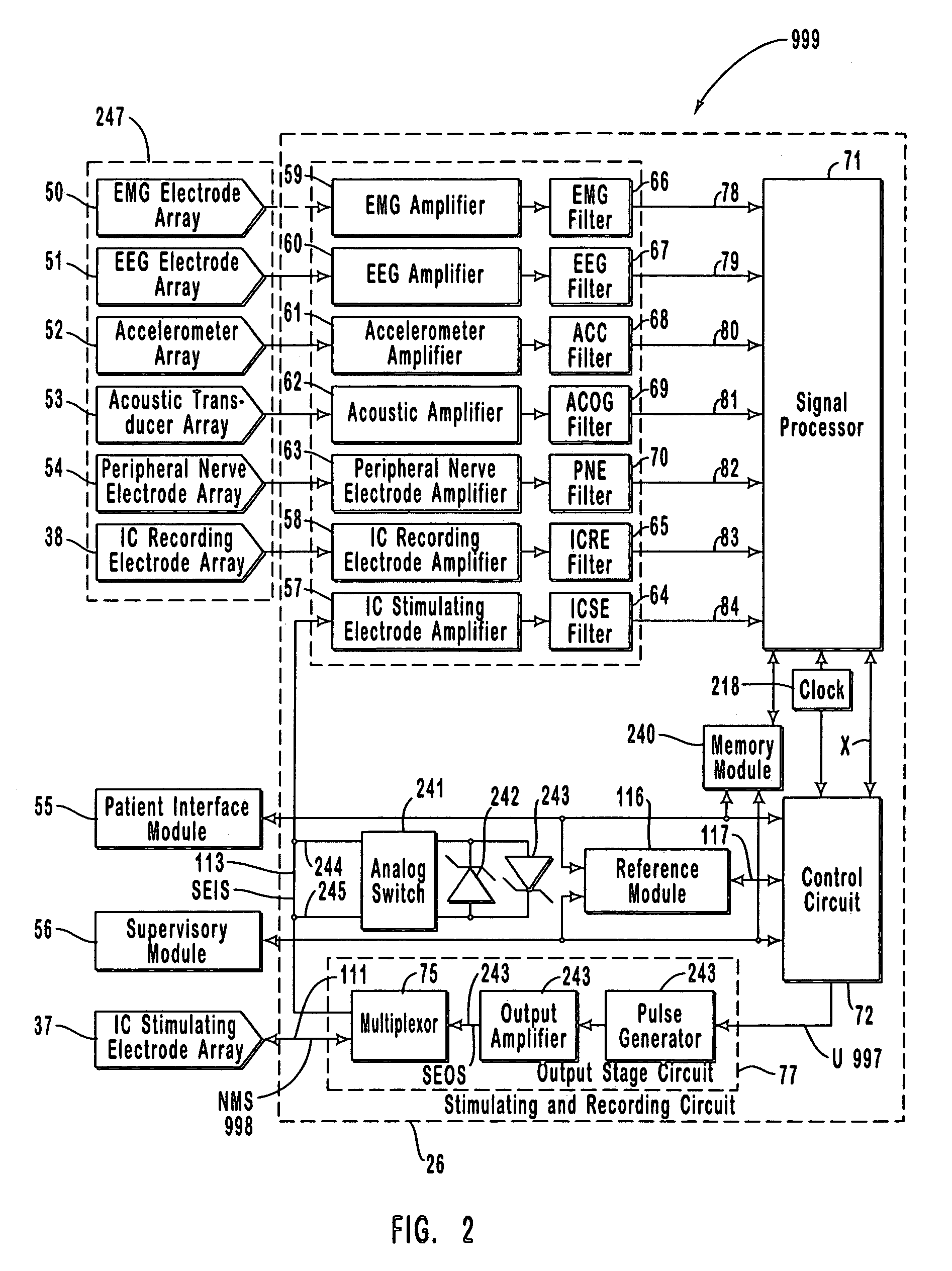
Apparatus and method for closed-loop intracranial stimulation for optimal control of neurological disease
InactiveUS20050021104A1Reducing time and number of interactionSatisfactory treatmentHead electrodesExternal electrodesDiseaseNervous system
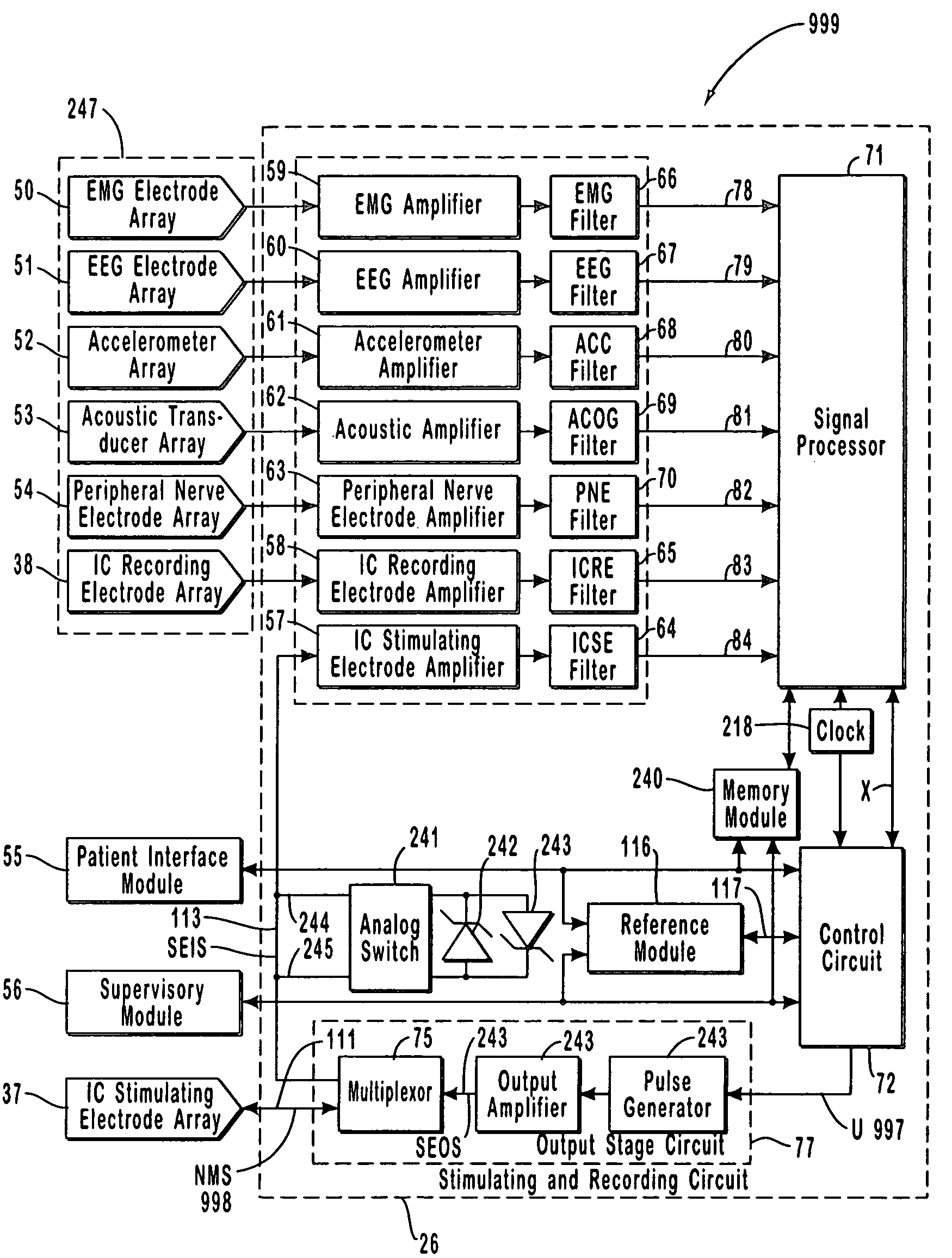
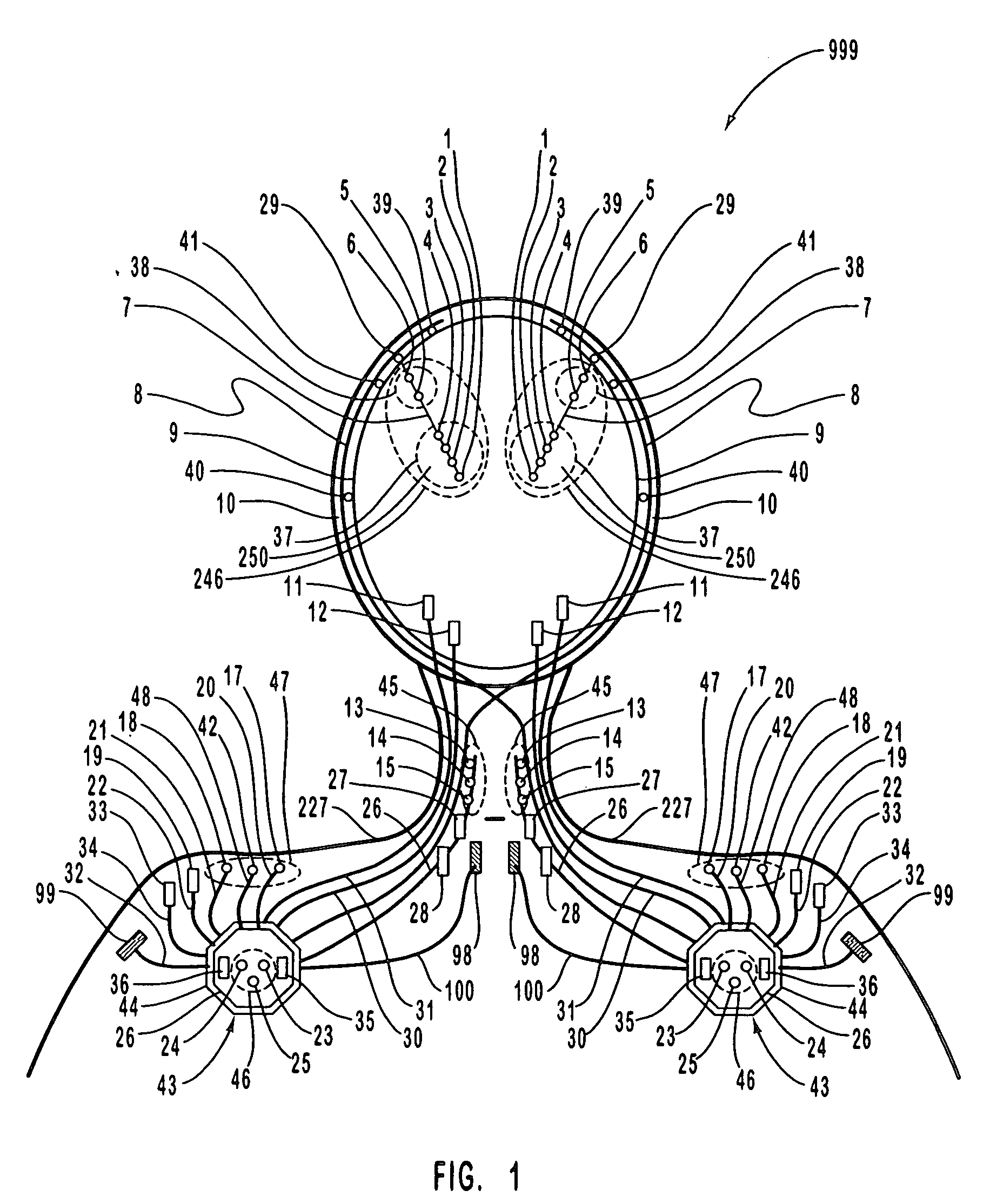
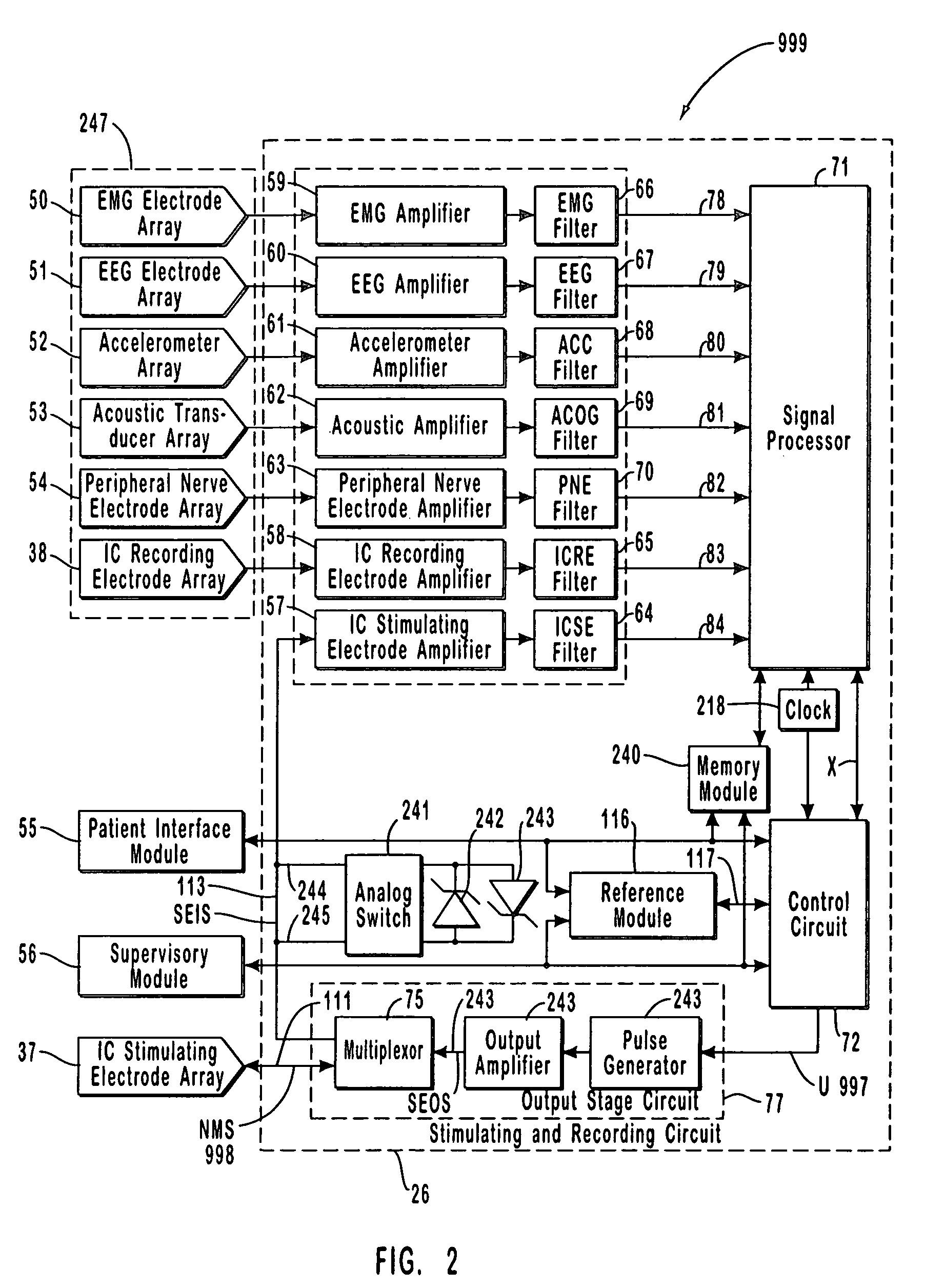
A neurological control system for modulating activity of any component or structure comprising the entirety or portion of the nervous system, or any structure interfaced thereto, generally referred to herein as a “nervous system component.” The neurological control system generates neural modulation signals delivered to a nervous system component through one or more intracranial (IC) stimulating electrodes in accordance with treatment parameters. Such treatment parameters may be derived from a neural response to previously delivered neural modulation signals sensed by one or more sensors, each configured to sense a particular characteristic indicative of a neurological or psychiatric condition.
Owner:CYBERONICS INC
Method, system, and computer program product for the processing of self-monitoring blood glucose(smbg)data to enhance diabetic self-management
ActiveUS20050214892A1Easy to monitorContinuous informationMedical simulationMicrobiological testing/measurementAcute hyperglycaemiaOptimal control
A method, system, and computer program product related to the maintenance of optimal control of diabetes, and is directed to predicting the long-term exposure to hyperglycemia, and the long-term and short-term risks of severe or moderate hypoglycemia in diabetics, based on blood blucose readings collected by a self-monitoring blood glucose device. The method, system, and computer program product pertain directly to the enhancement of existing home blood glucose monitoring devices, by introducing an intelligent data interpretation component capable of predicting both HbA1c and periods of increased risk of hypoglycemia, and to the enhancement of emerging continuous monitoring devices by the same features. With these predictions the diabetic can take steps to prevent the adverse consequences associated with hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Apparatus and method for closed-loop intracranial stimulation for optimal control of neurological disease
InactiveUS20050021103A1Shorten the timeReduce the numberHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsNervous systemIntracranial stimulation
A neurological control system for modulating activity of any component or structure comprising the entirety or portion of the nervous system, or any structure interfaced thereto, generally referred to herein as a “nervous system component.” The neurological control system generates neural modulation signals delivered to a nervous system component through one or more intracranial (IC) stimulating electrodes in accordance with treatment parameters. Such treatment parameters may be derived from a neural response to previously delivered neural modulation signals sensed by one or more sensors, each configured to sense a particular characteristic indicative of a neurological or psychiatric condition.
Owner:CYBERONICS INC
Apparatus and method for closed-loop intracranial stimulation for optimal control of neurological disease
InactiveUS7242984B2Reducing time and number of interactionSatisfactory treatmentHead electrodesExternal electrodesDiseaseIntracranial stimulation
A neurological control system for modulating activity of any component or structure comprising the entirety or portion of the nervous system, or any structure interfaced thereto, generally referred to herein as a “nervous system component.” The neurological control system generates neural modulation signals delivered to a nervous system component through one or more intracranial (IC) stimulating electrodes in accordance with treatment parameters. Such treatment parameters may be derived from a neural response to previously delivered neural modulation signals sensed by one or more sensors, each configured to sense a particular characteristic indicative of a neurological or psychiatric condition.
Owner:CYBERONICS INC
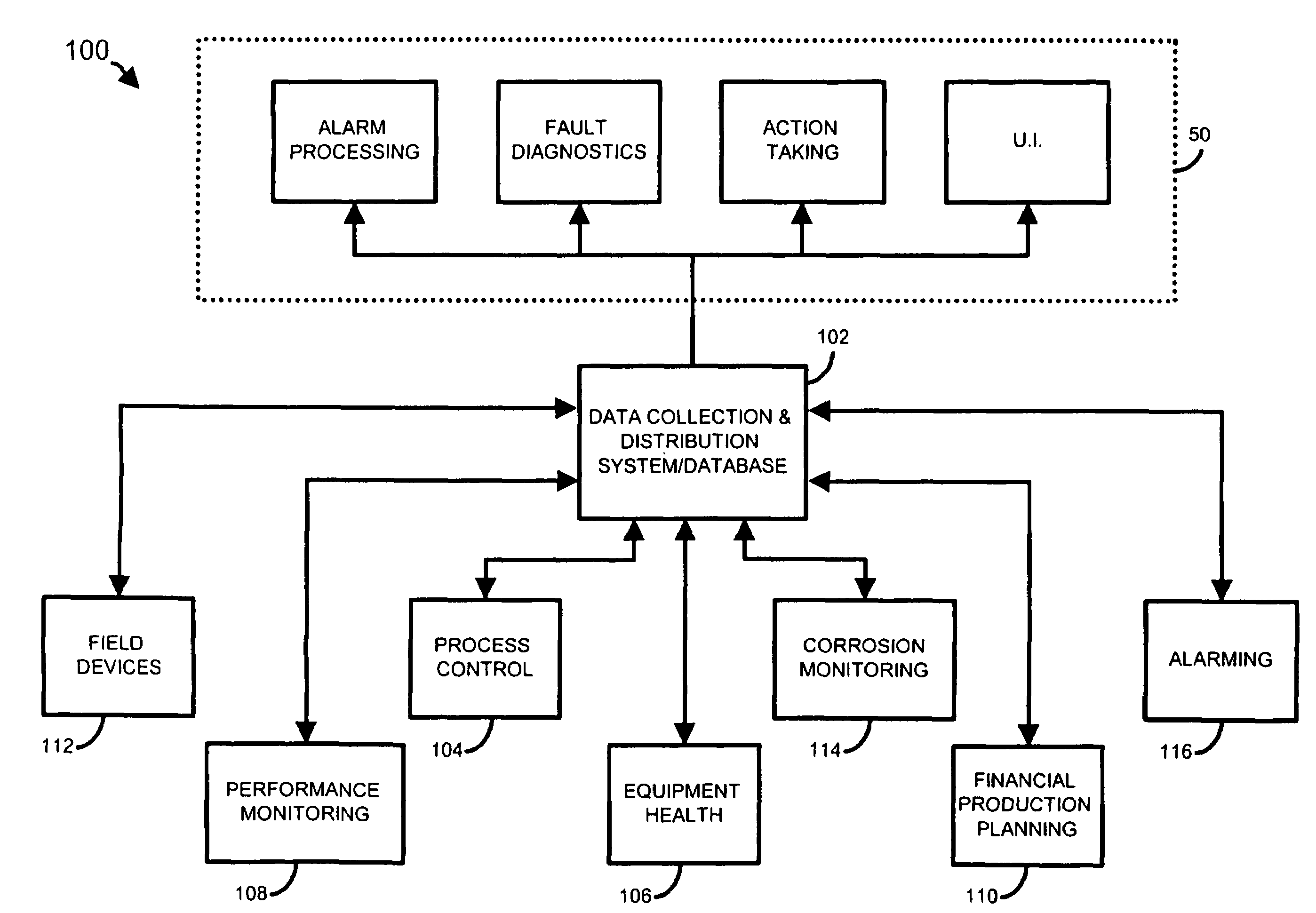
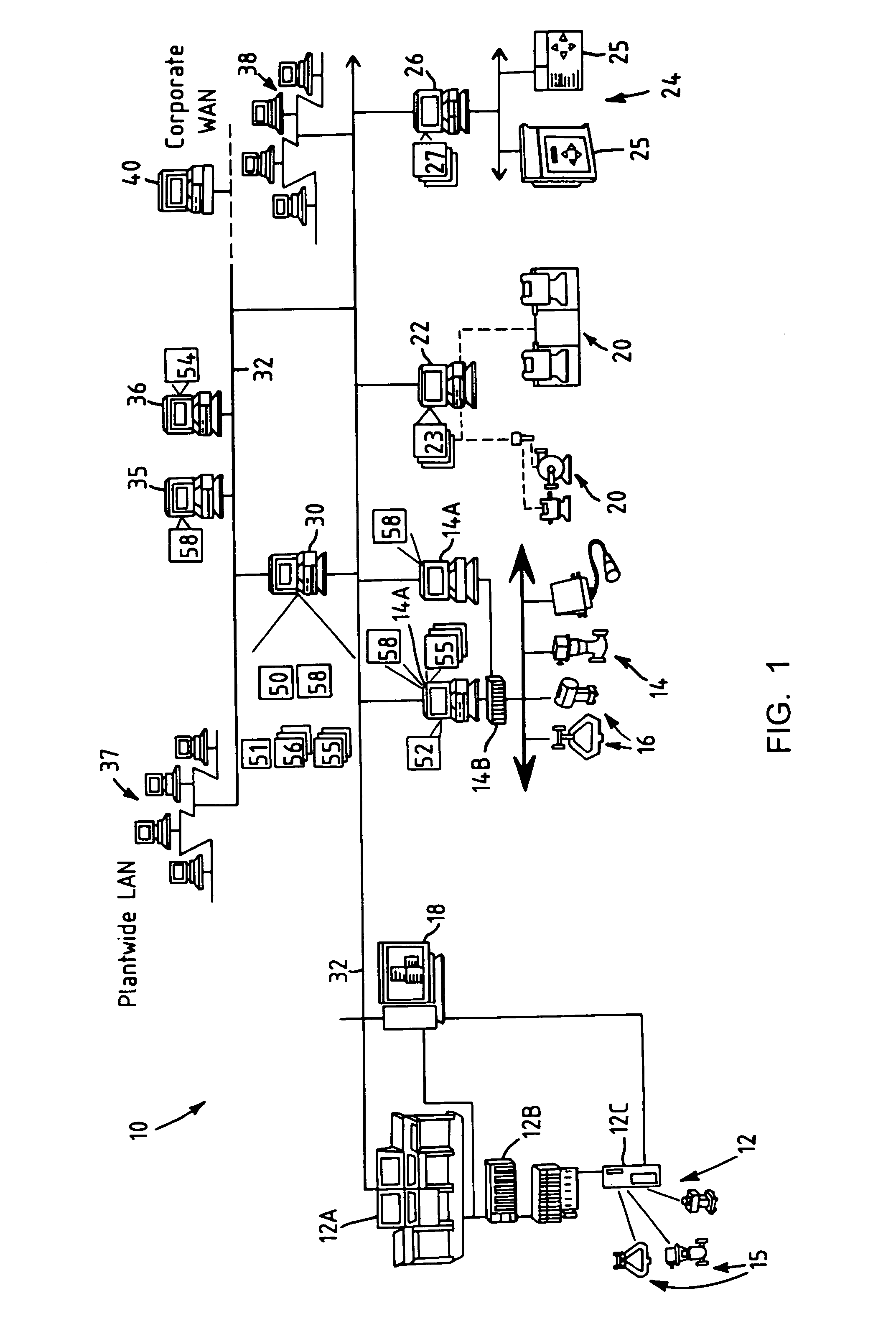
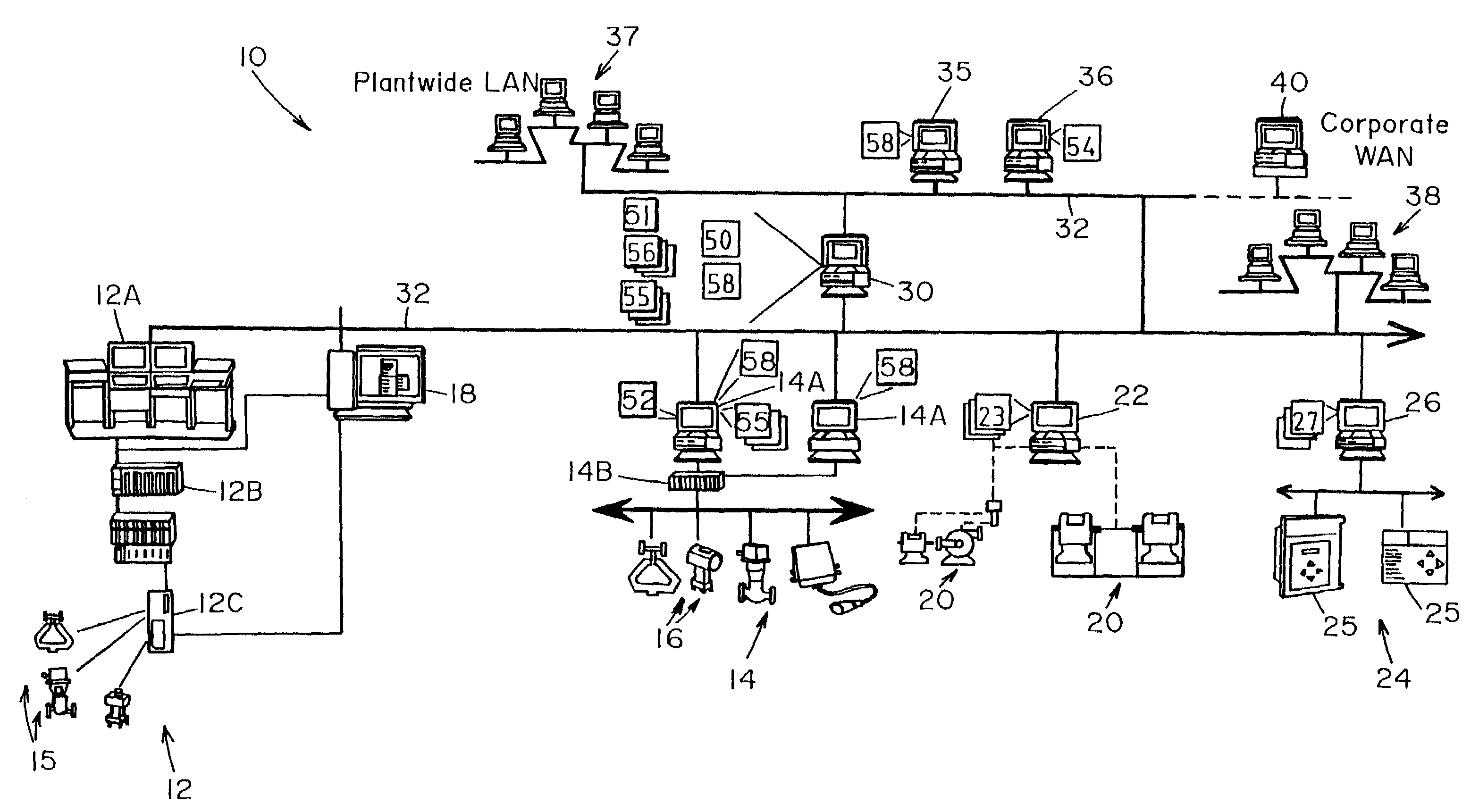
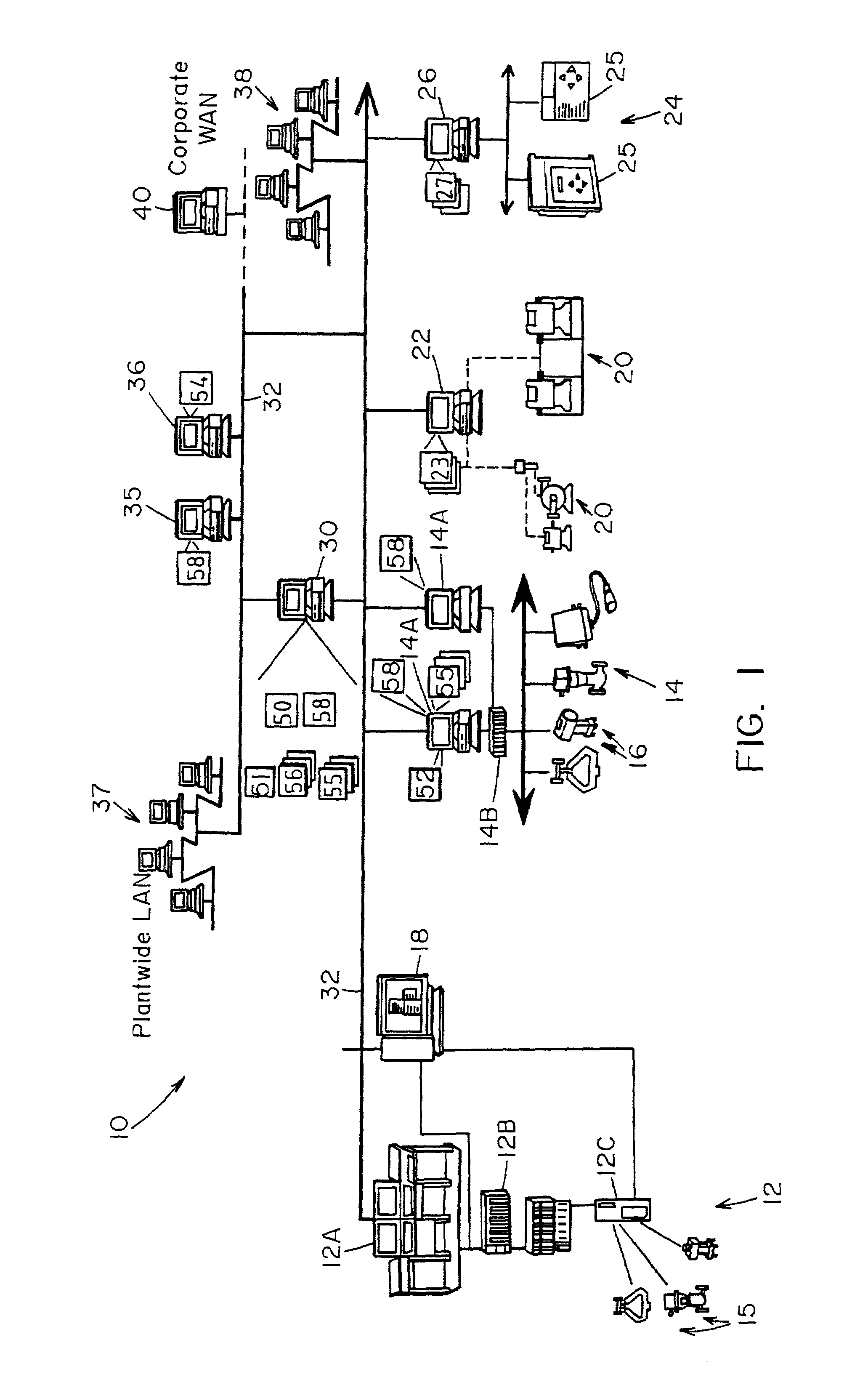
Method and apparatus for performing a function in a plant using process performance monitoring with process equipment monitoring and control
InactiveUS7206646B2Easy to operateBetter stateSafety arrangmentsCatalytic crackingProcess equipmentOptimal control
A process control system uses a data collection and distribution system and an asset utilization suite to collect data or information pertaining to the assets of a process plant from various sources or functional areas of the plant including, for example, the process control functional areas, the maintenance functional areas and the process performance monitoring functional areas. This data and information is manipulated in a coordinated manner by the data collection and distribution system and is redistributed to other applications where this it is used to perform overall better or more optimal control, maintenance and business activities. Information or data may be collected by maintenance functions pertaining to the health, variability, performance or utilization of a device, loop, unit, area, etc. and this information may then be sent to and displayed to a process operator or maintenance person to inform that person of a current or future problem. A user interface is provided that enables users to access and manipulate the expert engine to optimize plant operation or cause optimization of plant operation, to get information about the operation of the plant, etc. Furthermore, applications, such as work order generation applications may automatically generate work orders, parts or supplies orders, etc. based on events occurring within the plant.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
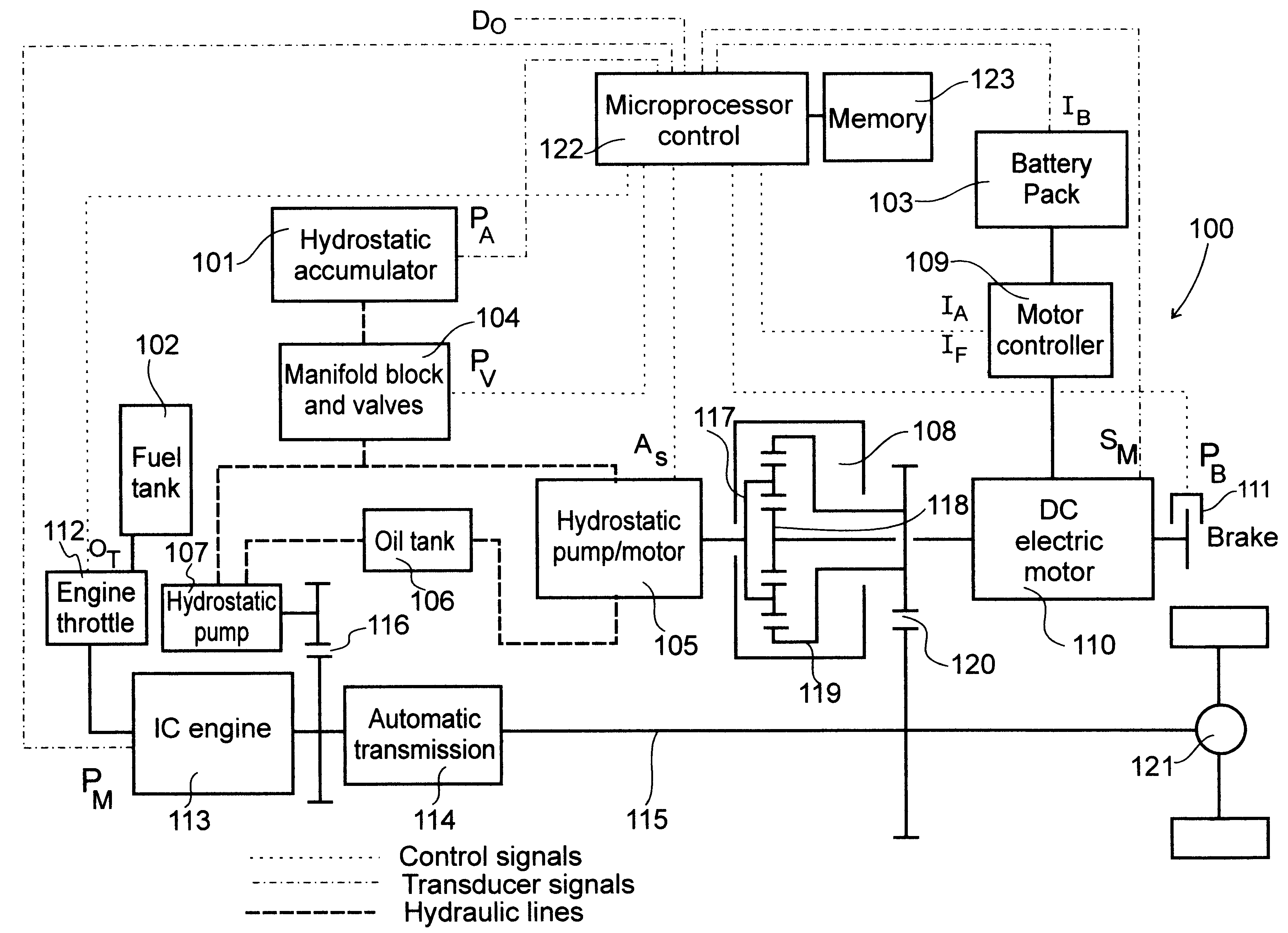
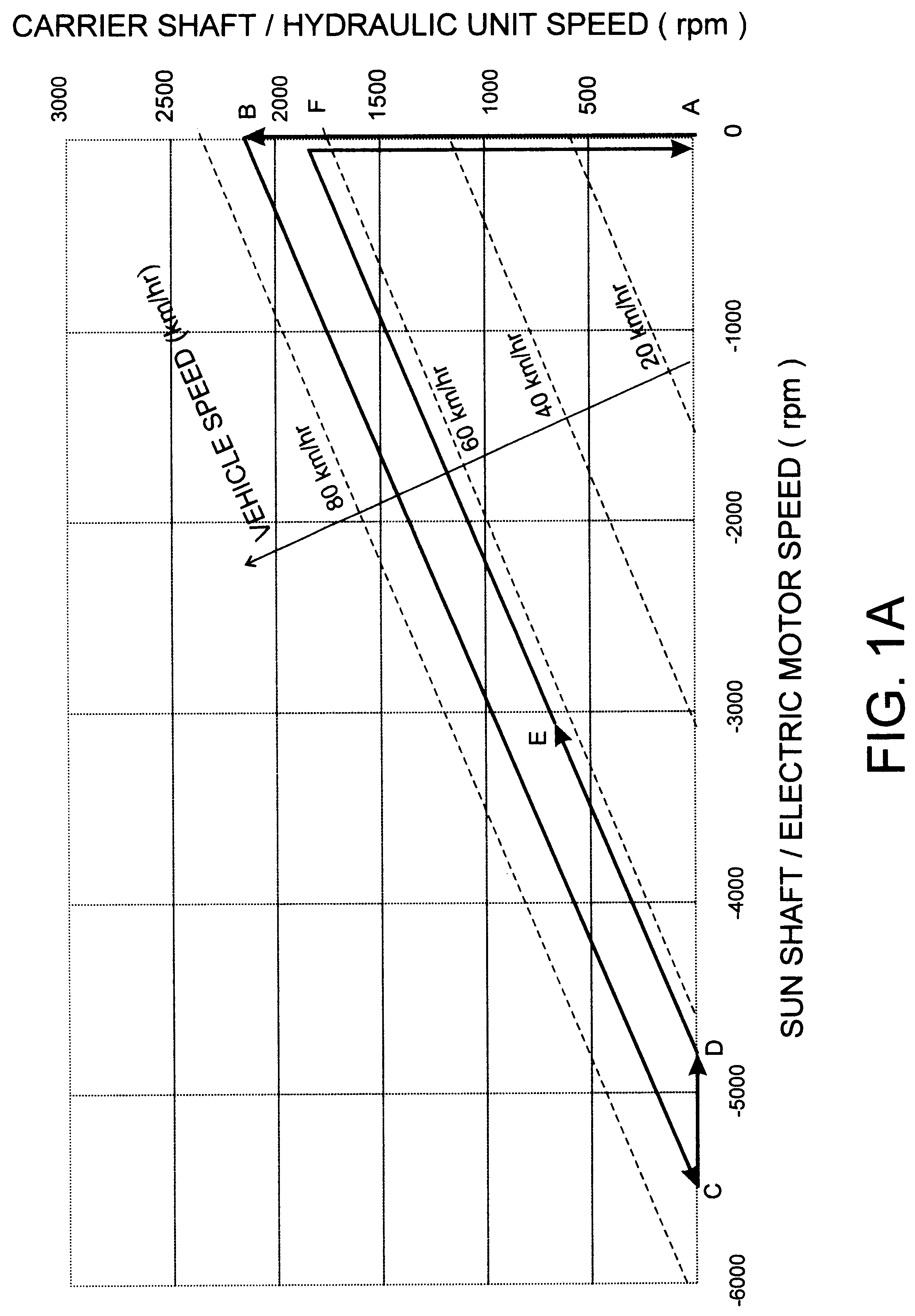
Hybrid propulsion system for road vehicles
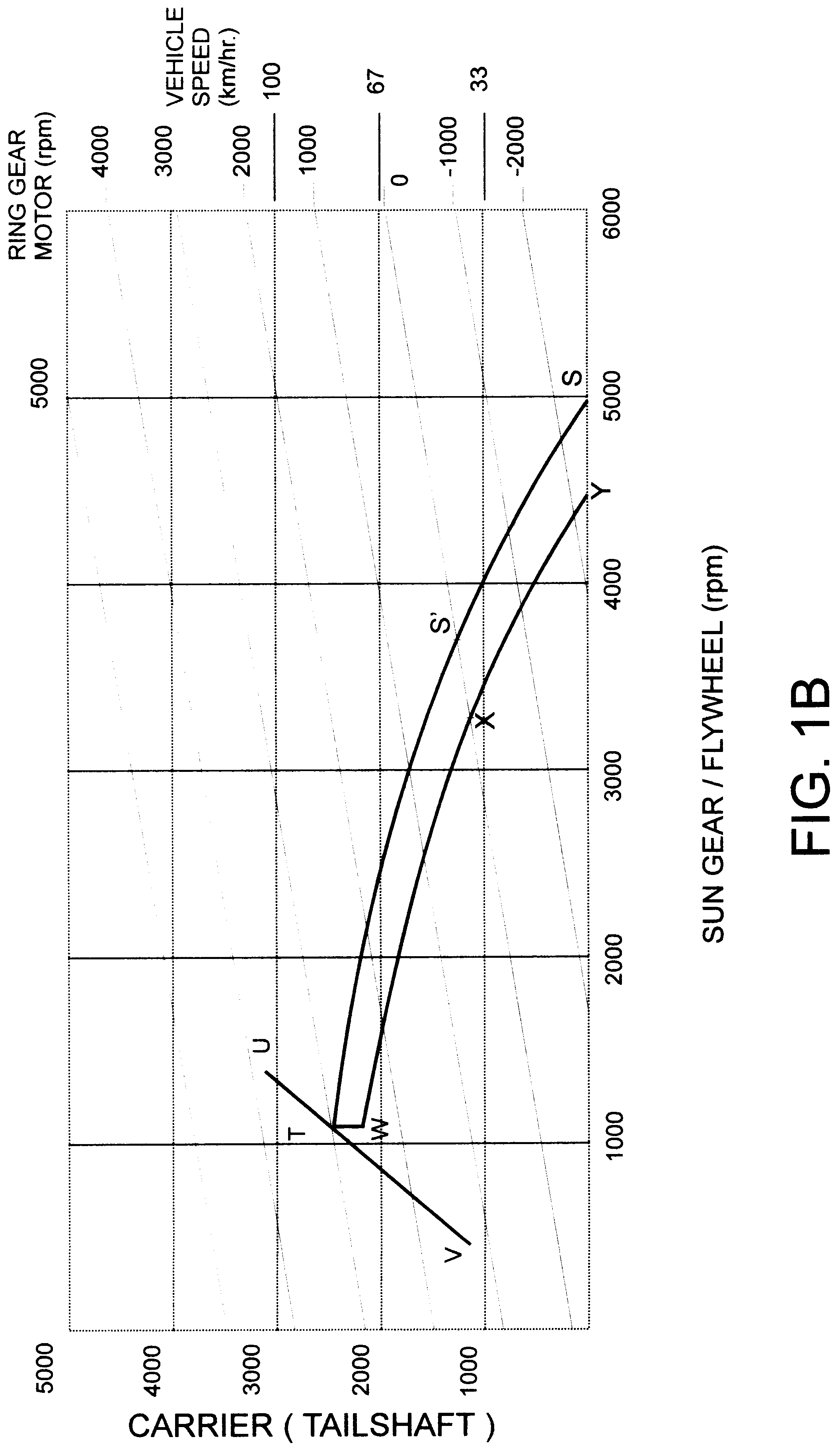
A hybrid propulsion system (100) for use in road vehicle operations, which propulsion system includes a power splitting mechanical transmission (108), suitably a three shaft epicyclic gearbox (117, 118, 119), for coupling to a tailshaft (115) of the vehicle; a first drive unit (105) arranged for regenerative operation and coupled to the power splitting mechanical transmission (108); a second drive unit (110) arranged for regenerative operation and coupled, independently of said first drive unit, to the power splitting mechanical transmission (108); a non-regenerative third drive unit (113) for coupling, in parallel to said power splitting mechanical transmission, to the tailshaft; and a propulsion control system (122) for coordinating operation of the drive units in accordance with a plurality of predetermined modes corresponding to a drive cycle of the vehicle. Two forms of the invention are disclosed, being suited to non-transit and transit operations, respectively. Methods for the optimal control of the hybrid propulsion system of each form of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:TRANSPORT ENERGY SYST
Apparatus and method for closed-loop intracranial stimulation for optimal control of neurological disease
InactiveUS20070073355A1Reducing time and number of interactionSatisfactory treatmentHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsIntracranial stimulationNervous system
A neurological control system for modulating activity of any component or structure comprising the entirety or portion of the nervous system, or any structure interfaced thereto, generally referred to herein as a “nervous system component.” The neurological control system generates neural modulation signals delivered to a nervous system component through one or more intracranial (IC) stimulating electrodes in accordance with treatment parameters. Such treatment parameters may be derived from a neural response to previously delivered neural modulation signals sensed by one or more sensors, each configured to sense a particular characteristic indicative of a neurological or psychiatric condition.
Owner:CYBERONICS INC
Apparatus and method for closed-loop intracranial stimulation for optimal control of neurological disease
InactiveUS20050119703A1Shorten the timeSatisfactory treatmentHead electrodesExternal electrodesNervous systemIntracranial stimulation
A neurological control system for modulating activity of any component or structure comprising the entirety or portion of the nervous system, or any structure interfaced thereto, generally referred to herein as a “nervous system component.” The neurological control system generates neural modulation signals delivered to a nervous system component through one or more intracranial (IC) stimulating electrodes in accordance with treatment parameters. Such treatment parameters may be derived from a neural response to previously delivered neural modulation signals sensed by one or more sensors, each configured to sense a particular characteristic indicative of a neurological or psychiatric condition.
Owner:CYBERONICS INC
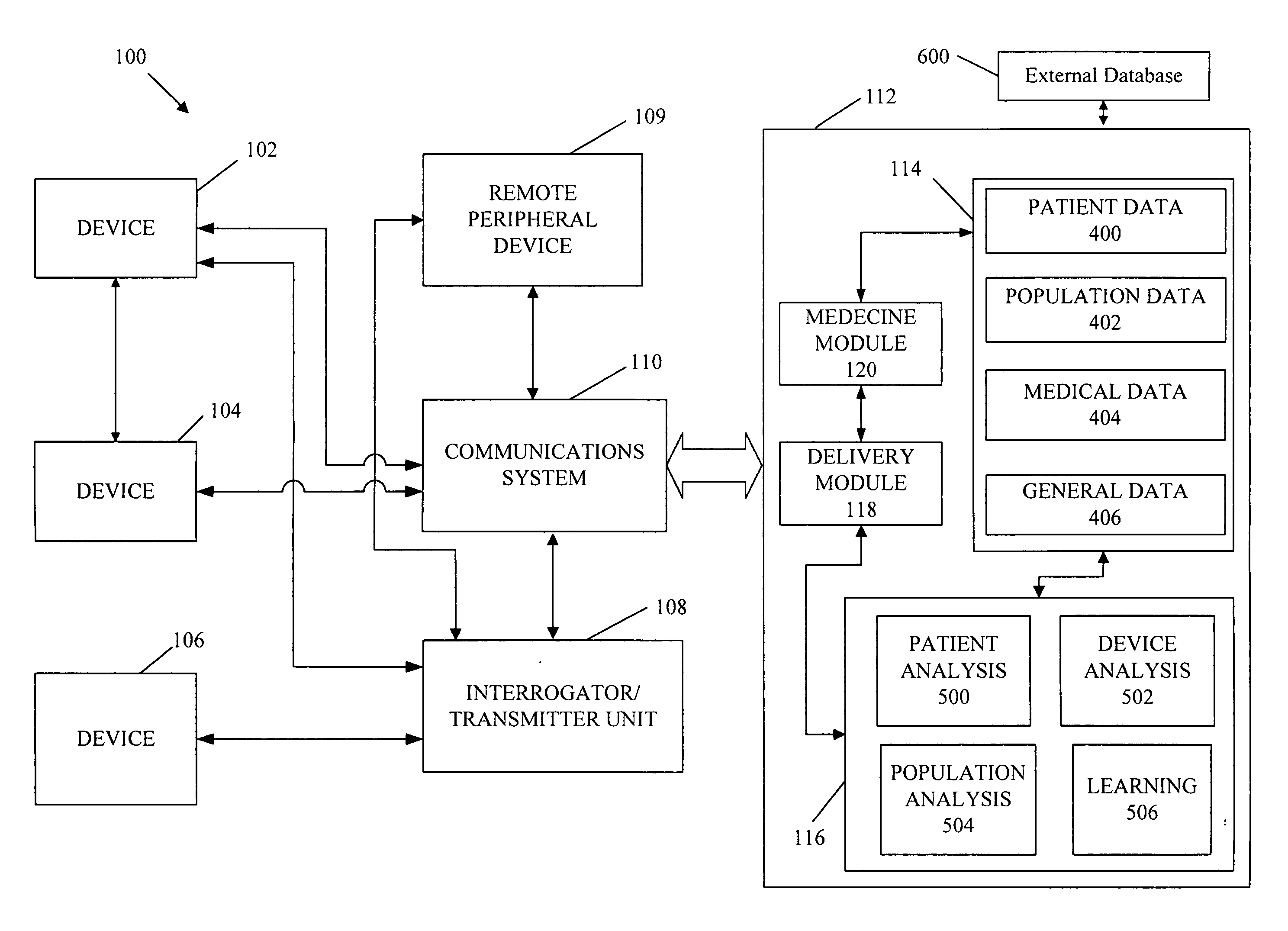
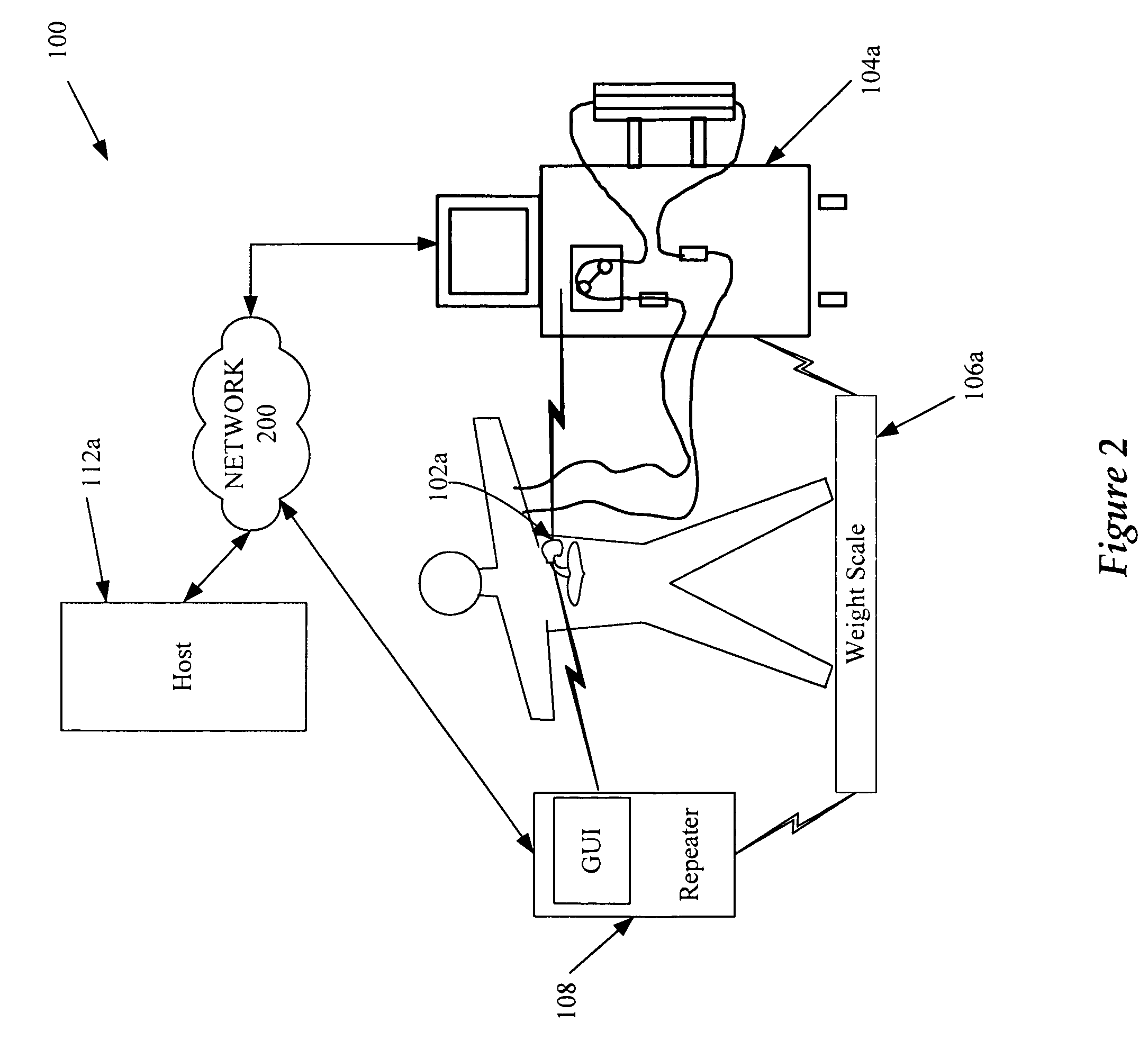
Cardiac rhythm management device and sensor-suite for the optimal control of ultrafiltration and renal replacement therapies
ActiveUS20070175827A1ElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesUltrafiltrationOptimal control
A cardiorenal patient monitoring system comprising, either implanted or non-implanted device(s), remote peripheral device(s), computer network(s), host, and communication means between the device(s), computer network(s), and host. The preferred embodiment shows an advanced patient monitoring system for using an implanted cardiac device and a dialysis machine in renal therapy. In addition, the method of advanced patient monitoring is in conjunction with the advanced patient monitoring system is disclosed.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
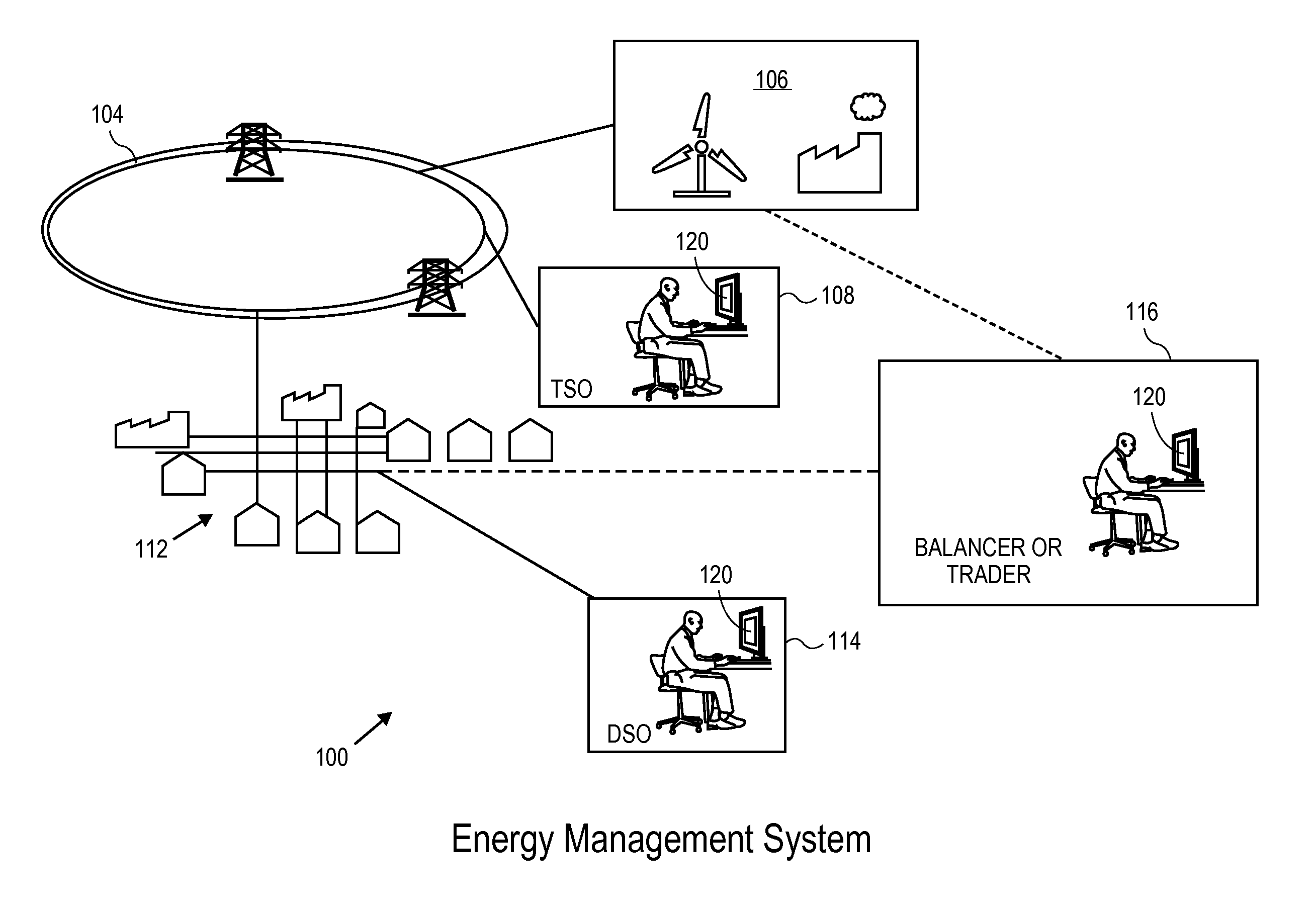
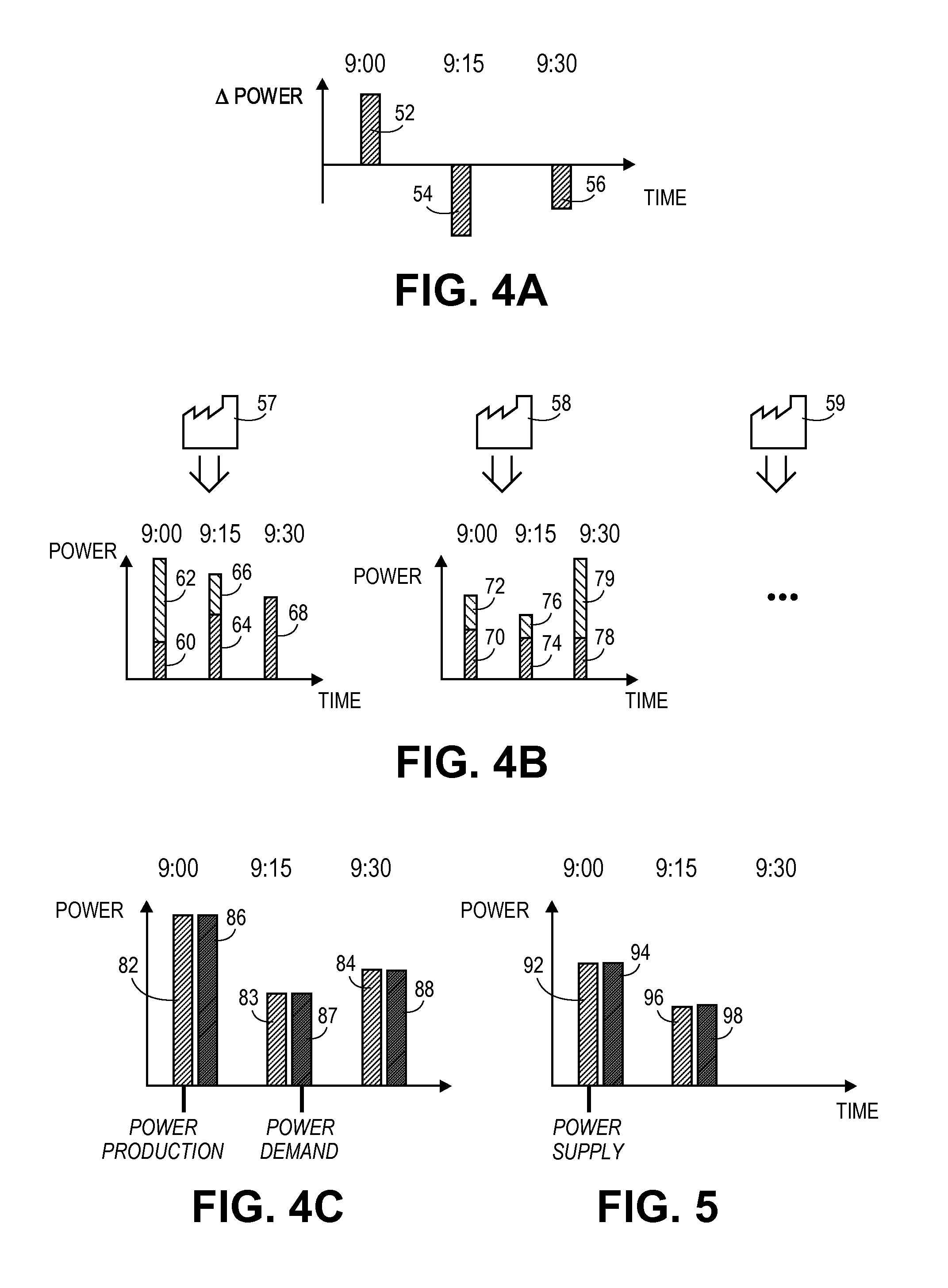
Automated demand response energy management system
The power flexibility of energy loads is maximized using a value function for each load and outputting optimal control parameters. Loads are aggregated into a virtual load by maximizing a global value function. The solution yields a dispatch function providing: a percentage of energy for each individual load, a time-varying power level for each load, and control parameters and values. An economic term represents the value of the power flexibility to different players. A user interface includes for each time interval upper and lower bounds representing respectively the maximum power that may be reduced to the virtual load and the maximum power that may be consumed. A trader modifies an energy level in a time interval relative to the reference curve for the virtual load. Automatically, energy compensation for other intervals and recalculation of upper and lower boundaries occurs. The energy schedule for the virtual load is distributed to the actual loads.
Owner:RESTORE
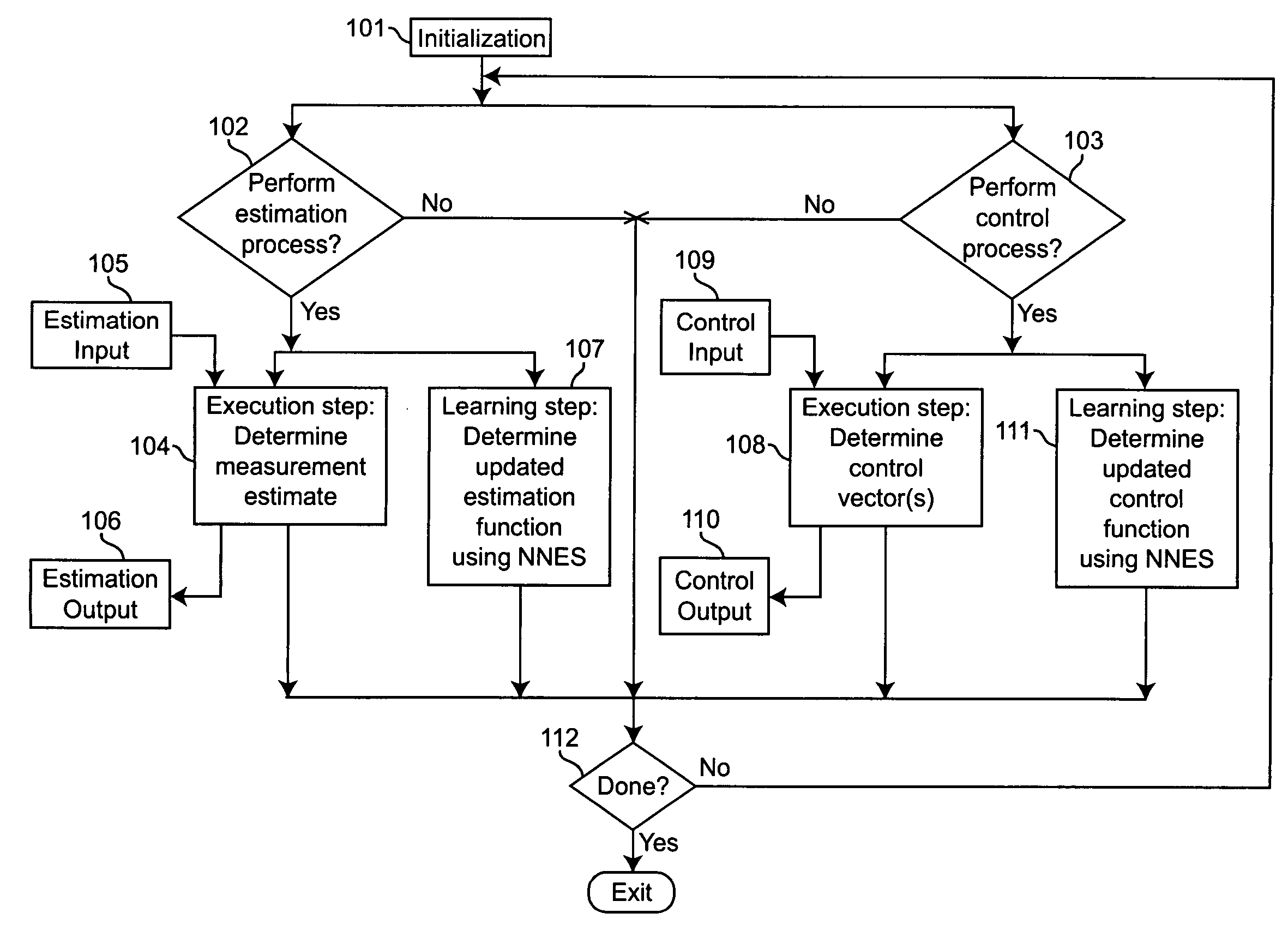
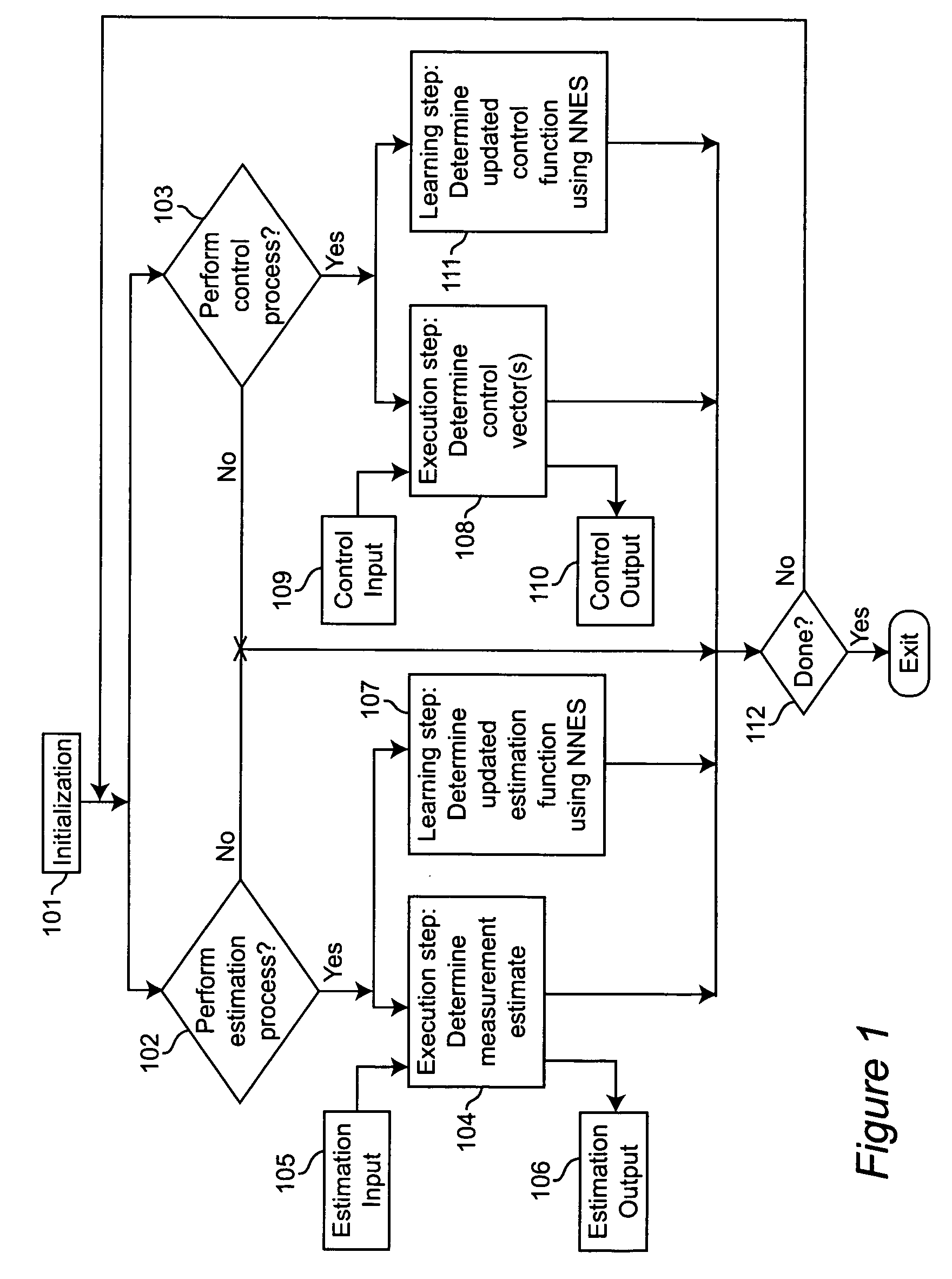
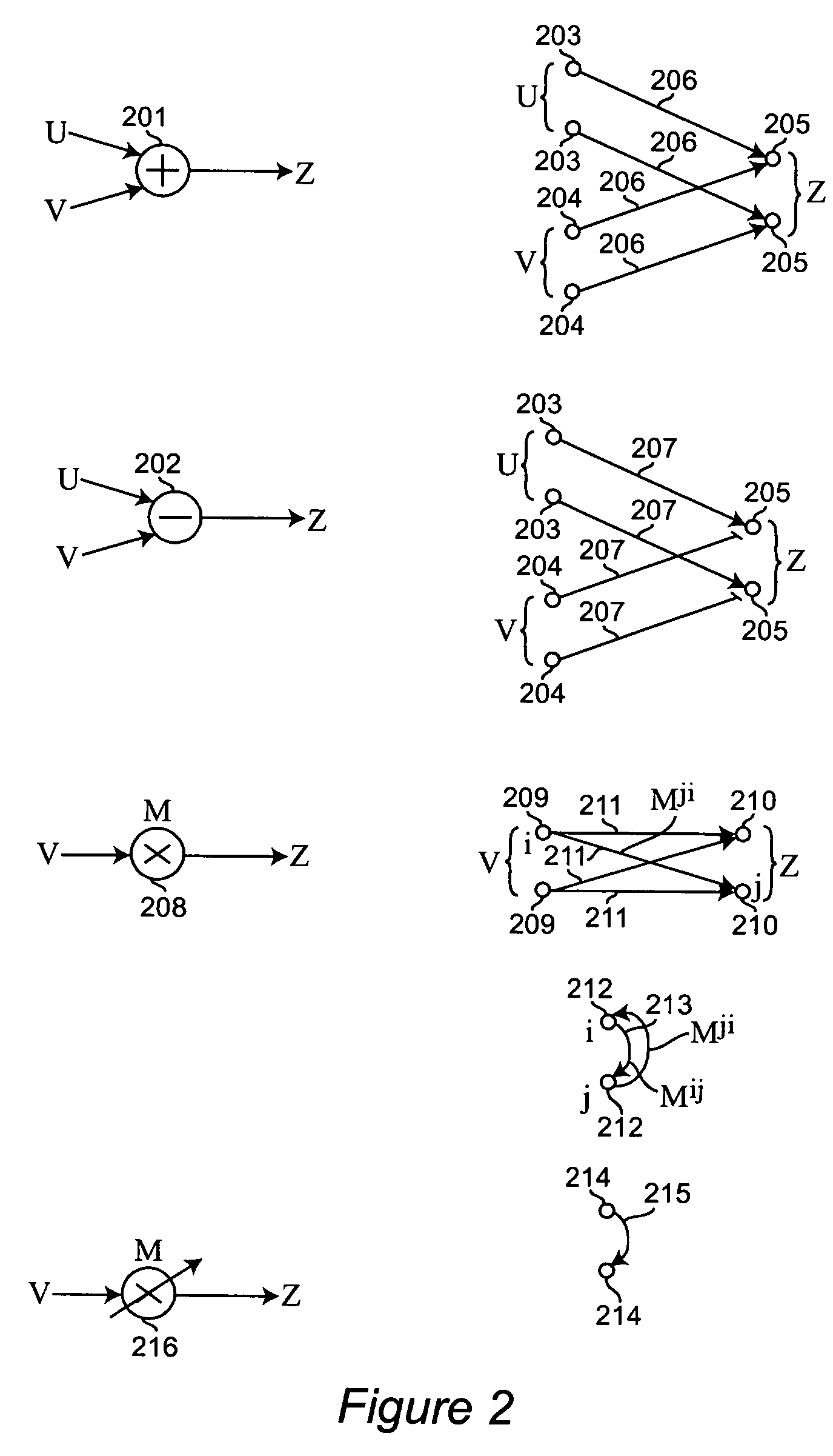
Neural networks for prediction and control
Neural networks for optimal estimation (including prediction) and / or control involve an execution step and a learning step, and are characterized by the learning step being performed by neural computations. The set of learning rules cause the circuit's connection strengths to learn to approximate the optimal estimation and / or control function that minimizes estimation error and / or a measure of control cost. The classical Kalman filter and the classical Kalman optimal controller are important examples of such an optimal estimation and / or control function. The circuit uses only a stream of noisy measurements to infer relevant properties of the external dynamical system, learn the optimal estimation and / or control function, and apply its learning of this optimal function to input data streams in an online manner. In this way, the circuit simultaneously learns and generates estimates and / or control output signals that are optimal, given the network's current state of learning.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
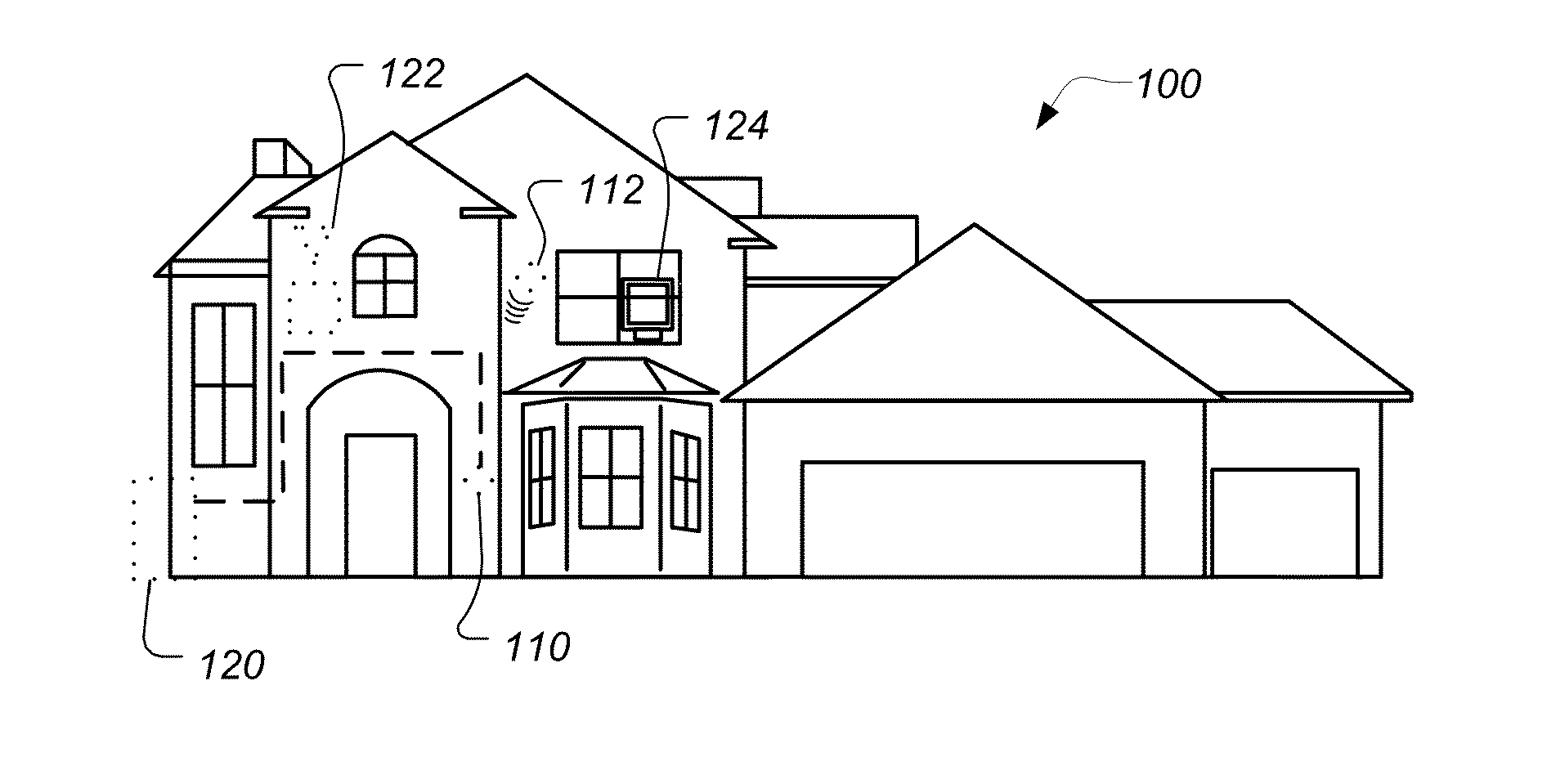
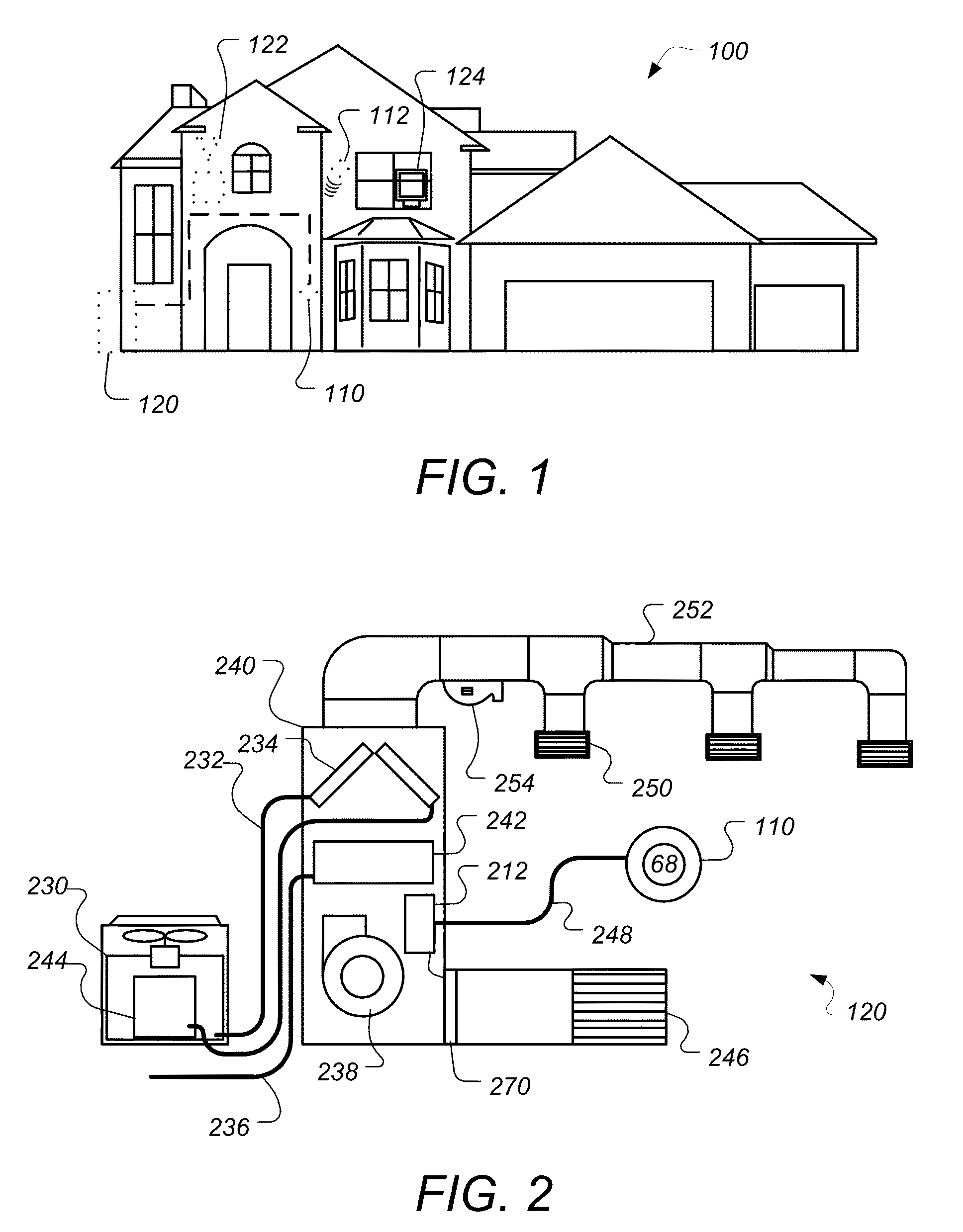
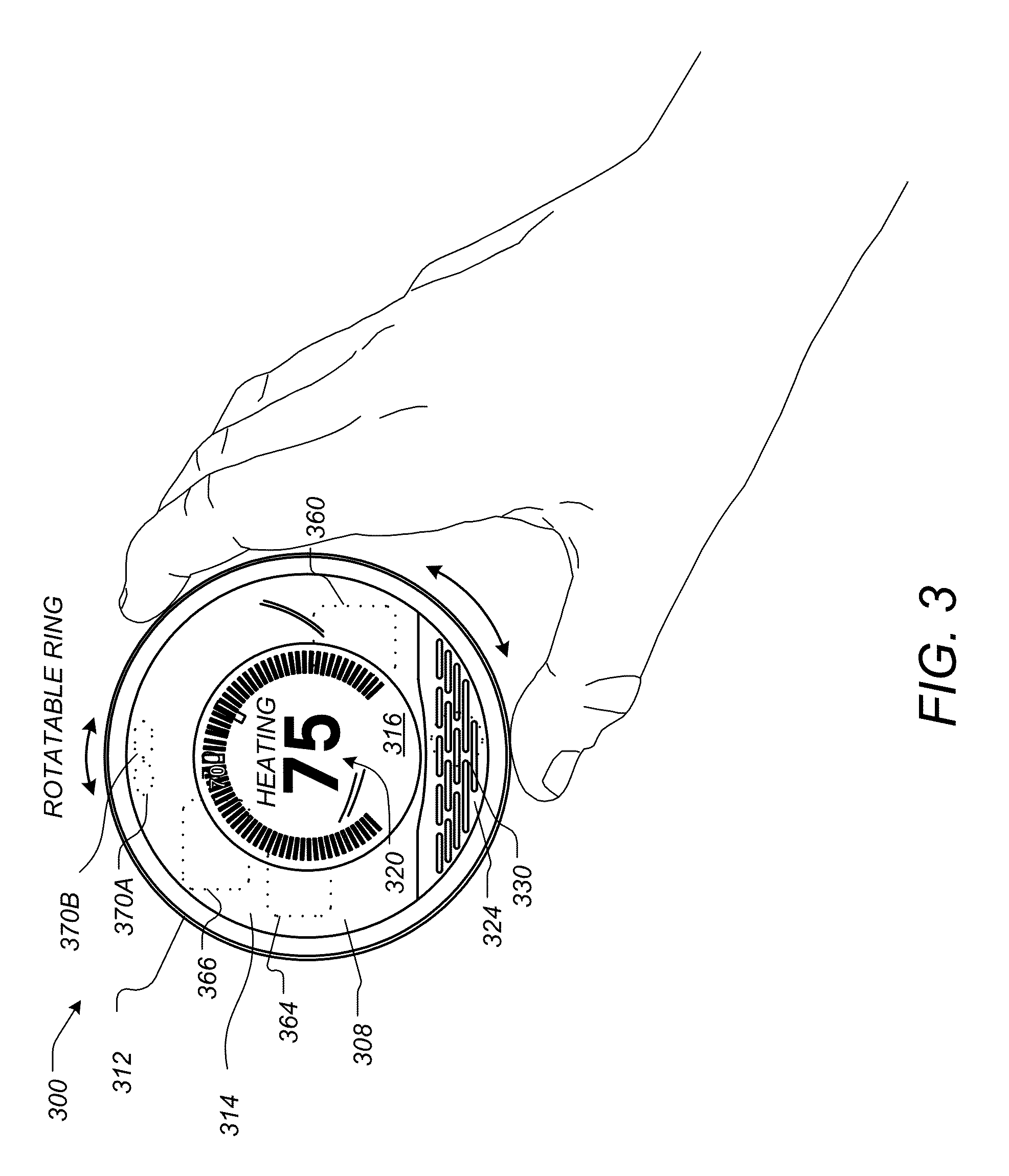
Radiant heating controls and methods for an environmental control system
ActiveUS8600561B1Function increaseIncrease valueMechanical apparatusStatic/dynamic balance measurementPrediction algorithmsOptimal control
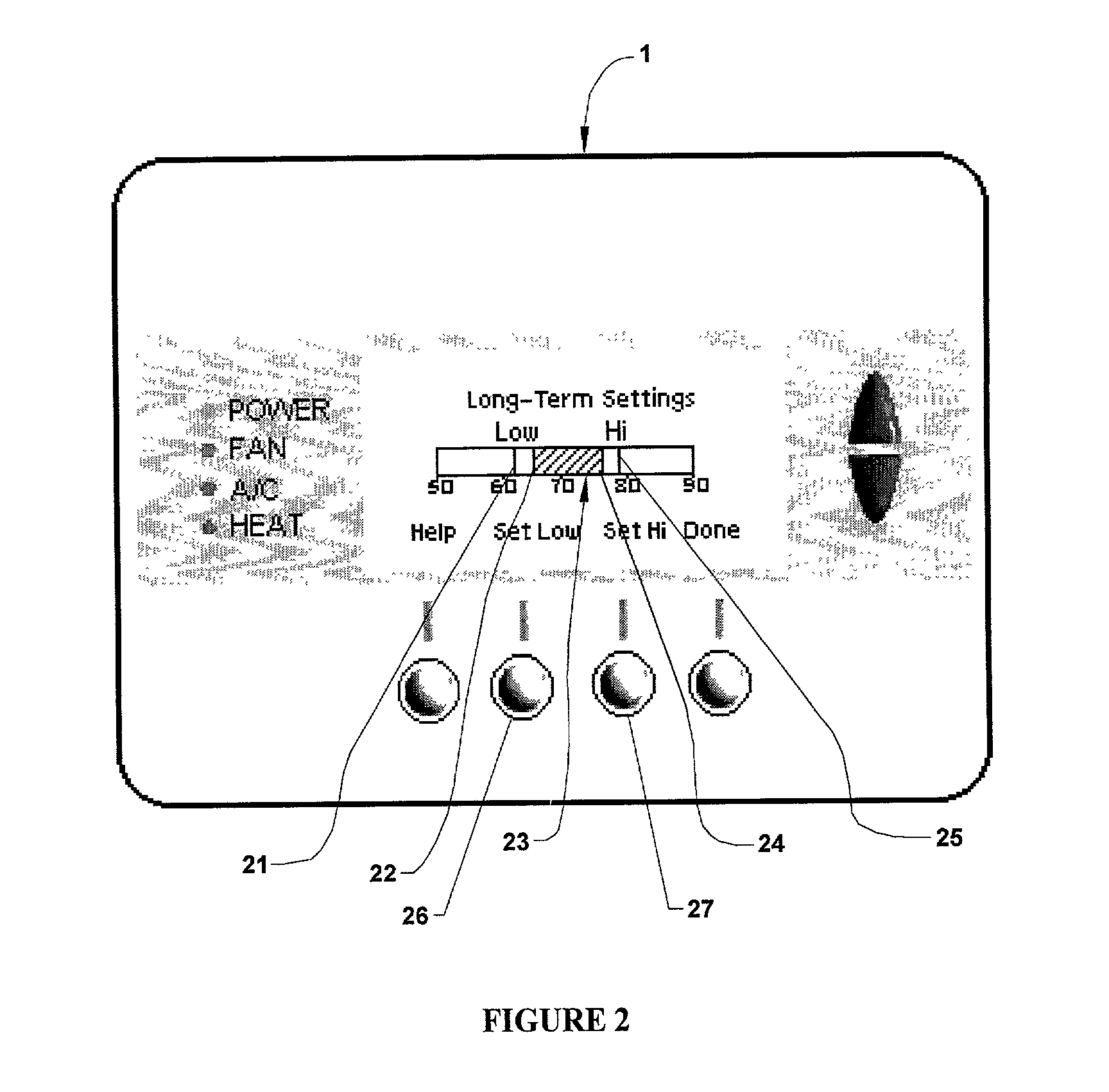
Embodiments of the invention describe thermostats that use model predictive controls and related methods. A method of controlling a thermostat using a model predictive control may involve determining a parameterized model. The parameterized model may be used to predicted ambient temperature values for an enclosure. A set of radiant heating system control strategies may be selected for evaluation to determine an optimal control strategy from the set of control strategies. To determine the optimal control strategy, a predictive algorithm may be executed, in which each control strategy is applied to the parameterized model to predict an ambient temperature trajectory and each ambient temperature trajectory is processed in view of a predetermined assessment function. Processing the ambient temperature trajectory in this manner may involve minimizing a cost value associated with the ambient temperature trajectory. The radiant heating system may subsequently be controlled according to the selected optimal control strategy.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
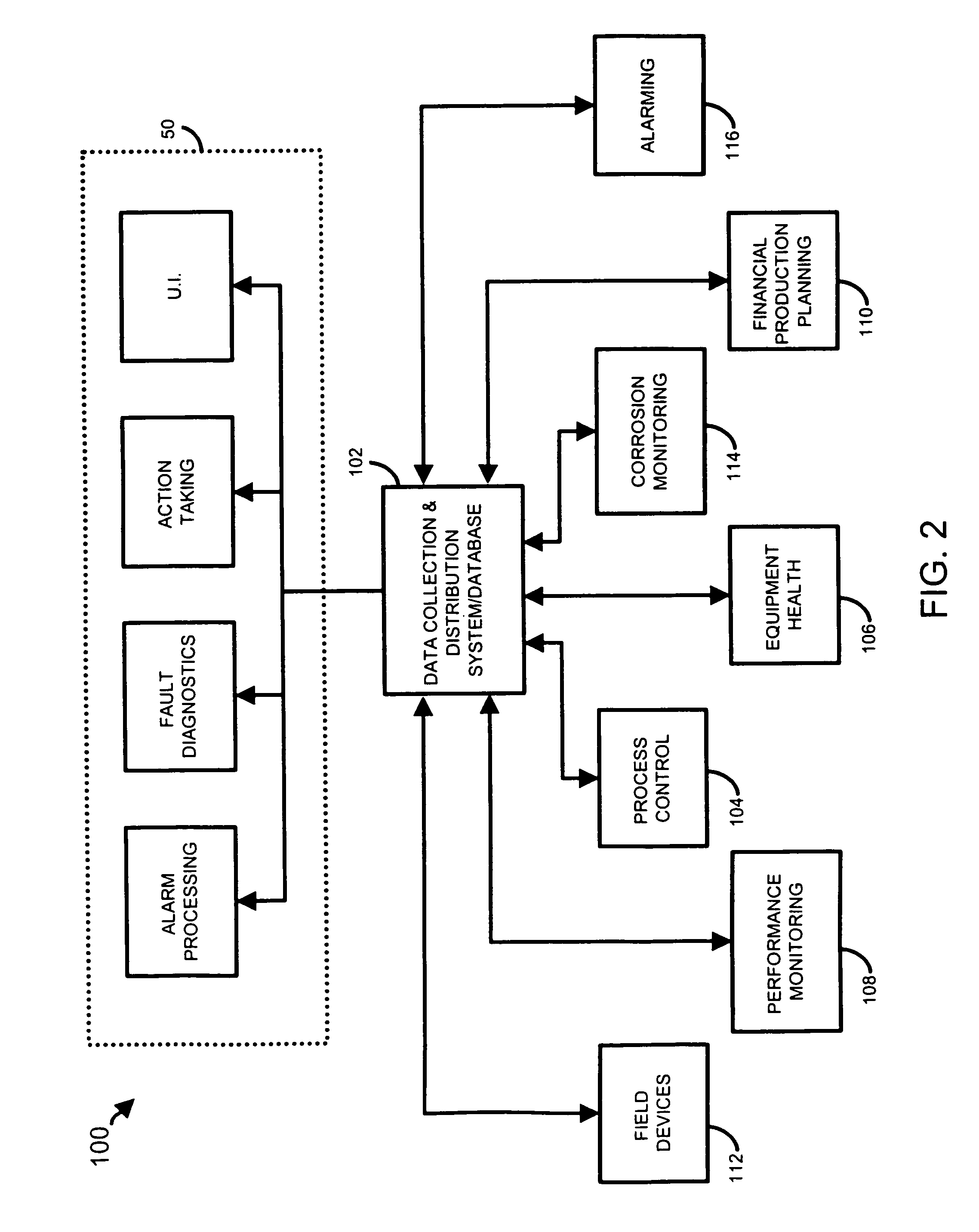
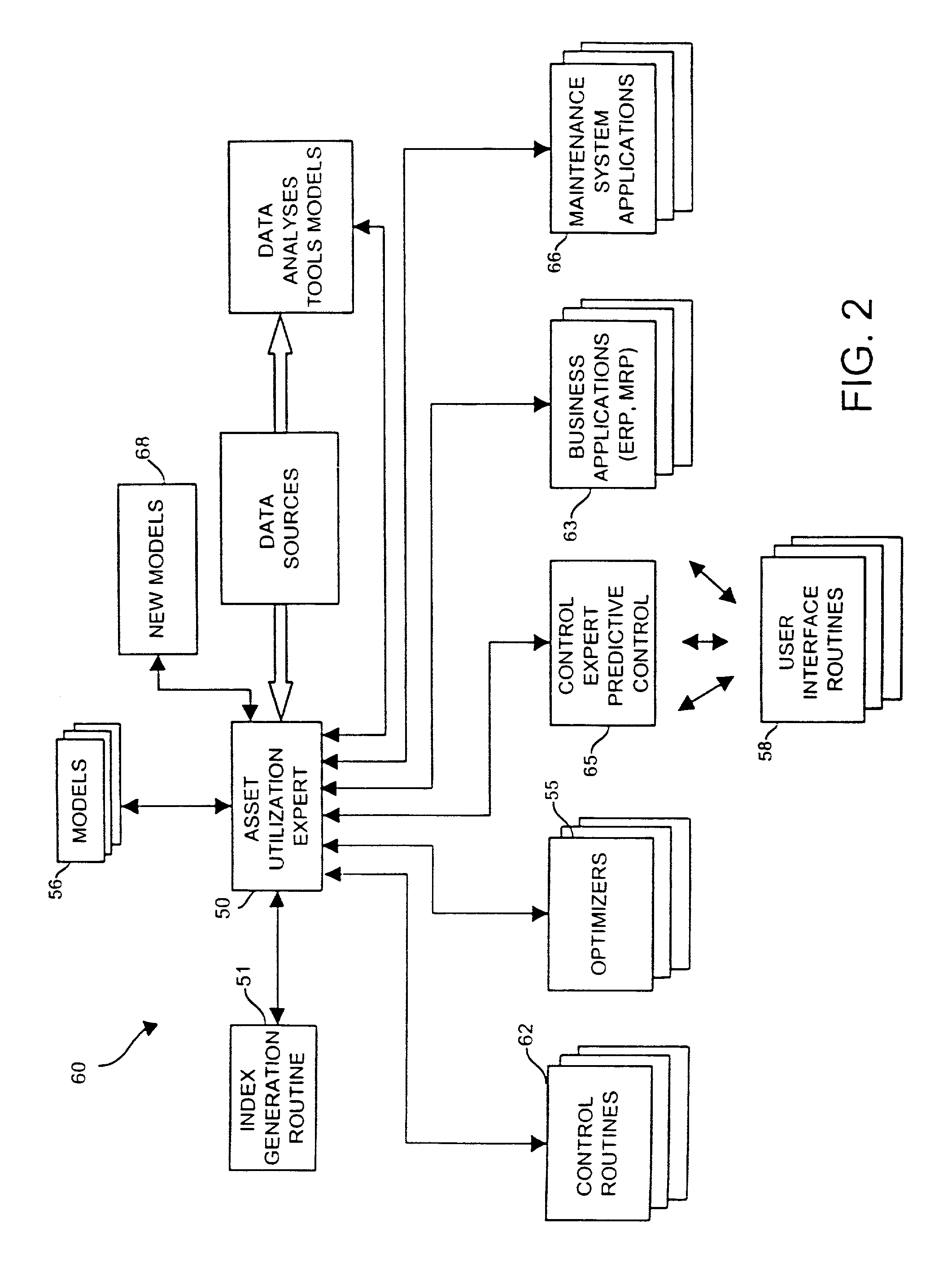
Data sharing in a process plant
InactiveUS7346404B2Sampled-variable control systemsComputer controlOptimal controlBusiness activities
A process plant uses an asset utilization expert to collect data or information pertaining to the assets of the process plant from various sources or functional areas of the plant including, for example, the process control functional areas, the maintenance functional areas and the business systems functional areas. This data and information is stored in a database and is sent to and manipulated in a coordinated manner by tools, such as optimization and modeling tools. This data is also redistributed to other areas or tools where it is used to perform overall better or more optimal control, maintenance and business activities. Information or data may be collected by maintenance functions pertaining to the health, variability, performance or utilization of a device, loop, unit, etc. and this information may then be sent to and displayed to a process operator or maintenance person to inform that person of a current or future problem.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
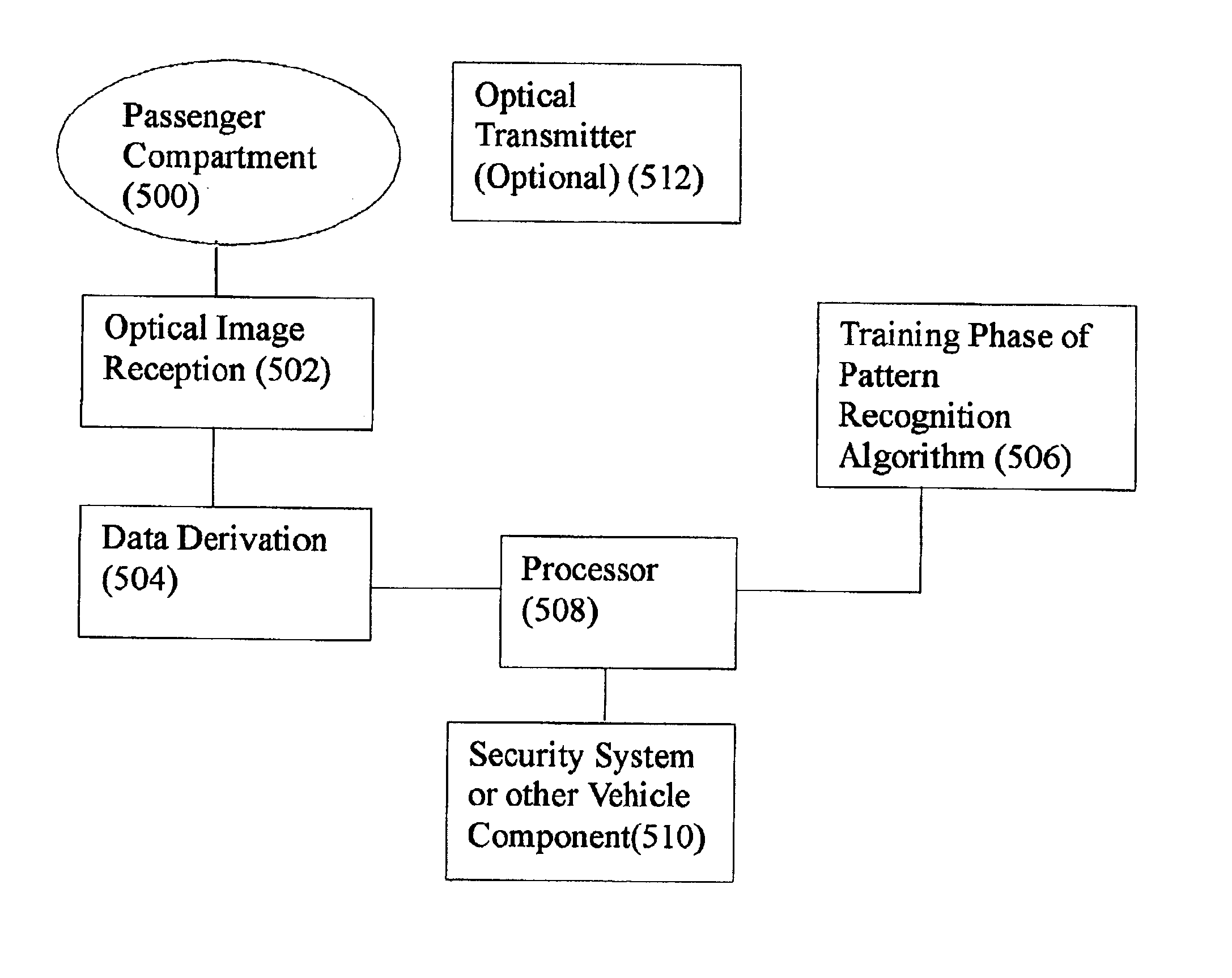
Vehicular monitoring systems using image processing
InactiveUS6856873B2Accurate identificationReduce glareVehicle seatsDigital data processing detailsImaging processingMonitoring system
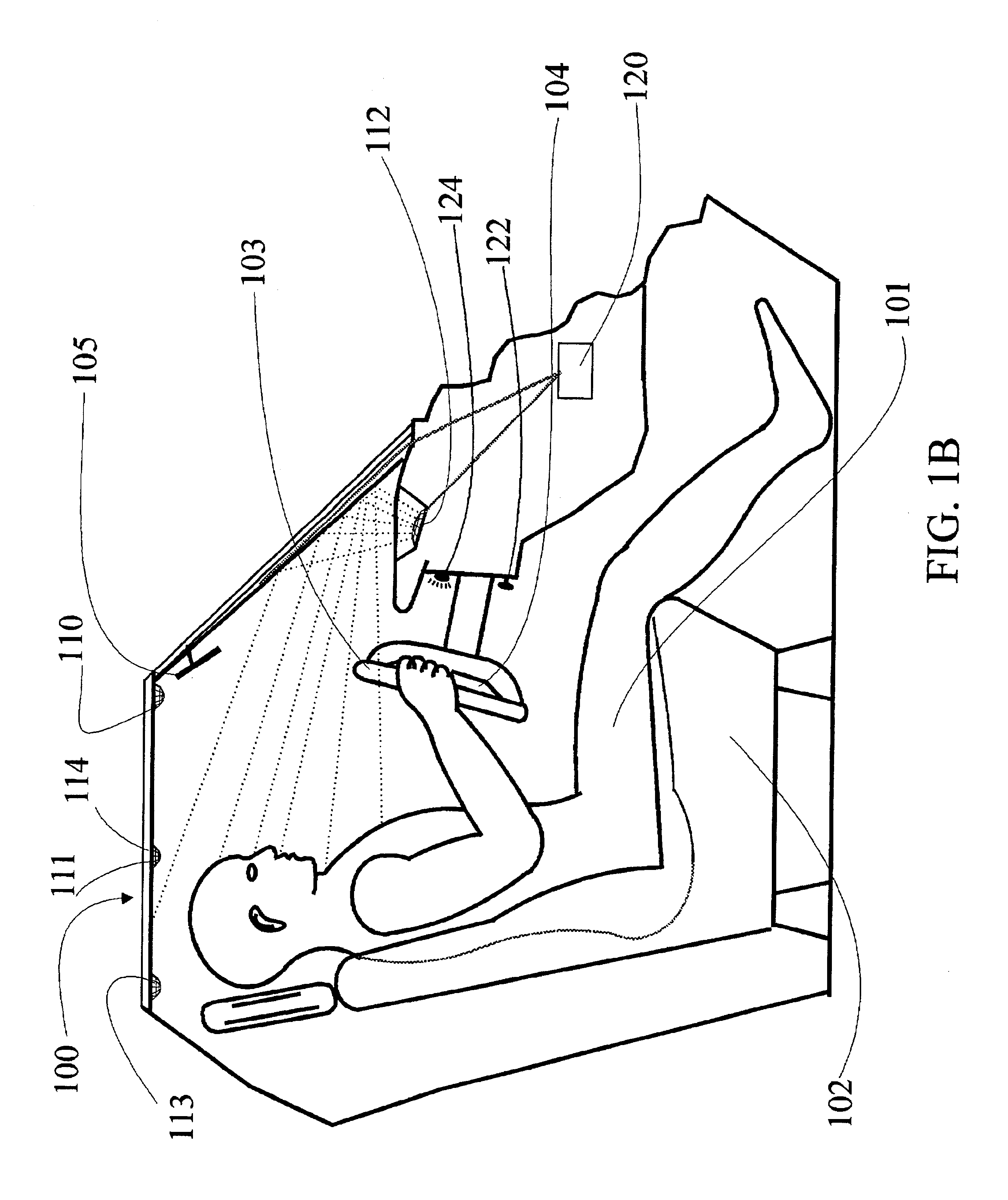
Vehicular monitoring arrangement for monitoring an environment of the vehicle including at least one active pixel camera for obtaining images of the environment of the vehicle and a processor coupled to the active pixel camera(s) for determining at least one characteristic of an object in the environment based on the images obtained by the active pixel camera(s). The active pixel camera can be arranged in a headliner, roof or ceiling of the vehicle to obtain images of an interior environment of the vehicle, in an A-pillar or B-pillar of the vehicle to obtain images of an interior environment of the vehicle, or in a roof, ceiling, B-pillar or C-pillar of the vehicle to obtain images of an interior environment of the vehicle behind a front seat of the vehicle. The determined characteristic can be used to enable optimal control of a reactive component, system or subsystem coupled to the processor. When the reactive component is an airbag assembly including at least one airbag, the processor can be designed to control at least one deployment parameter of the airbag(s).
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
Methods and systems for powertrain optimization and improved fuel economy
InactiveUS20080262712A1Improve fuel economyMinimizes accumulated fuel flowAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlDynamical optimizationOptimal control
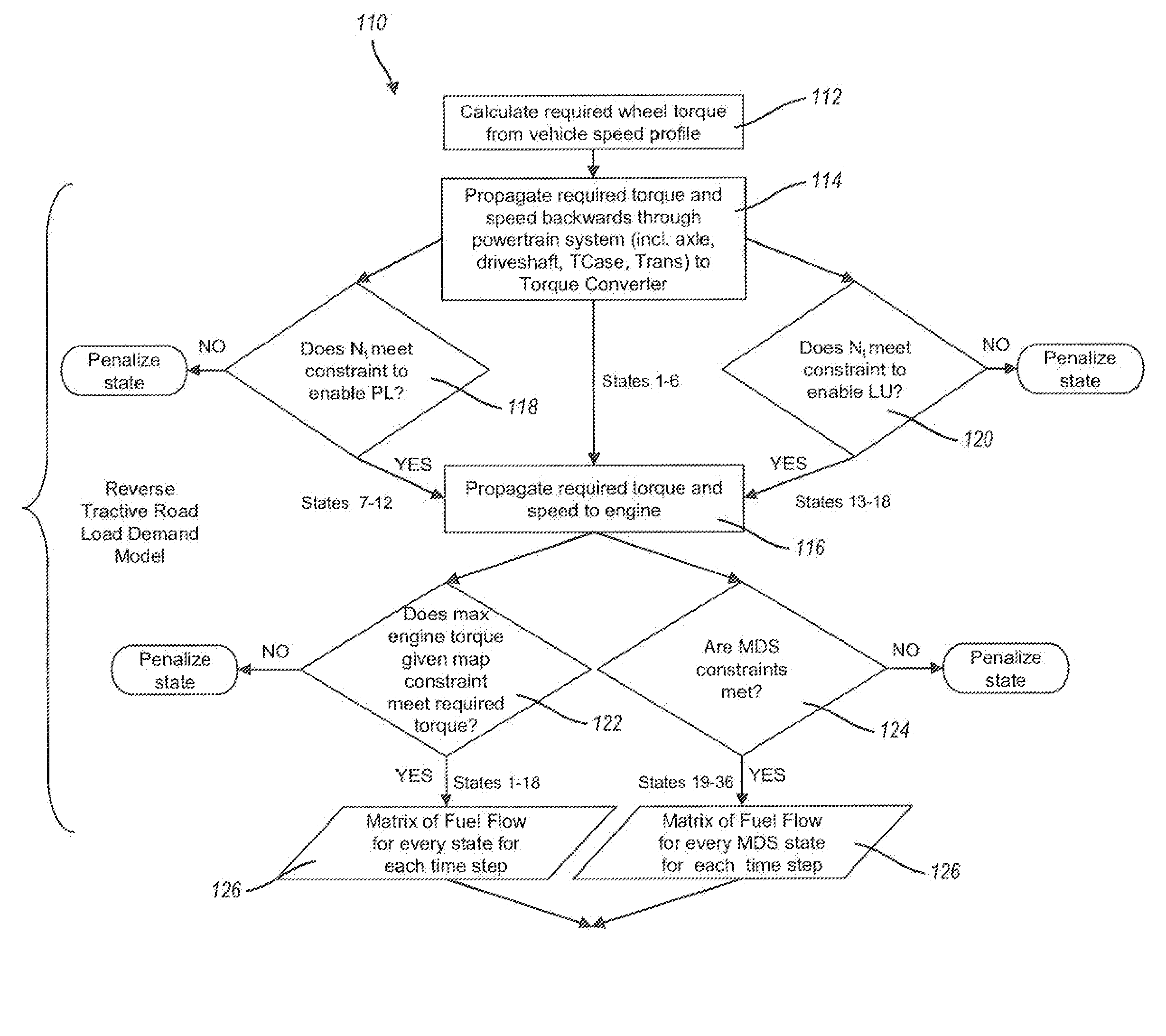
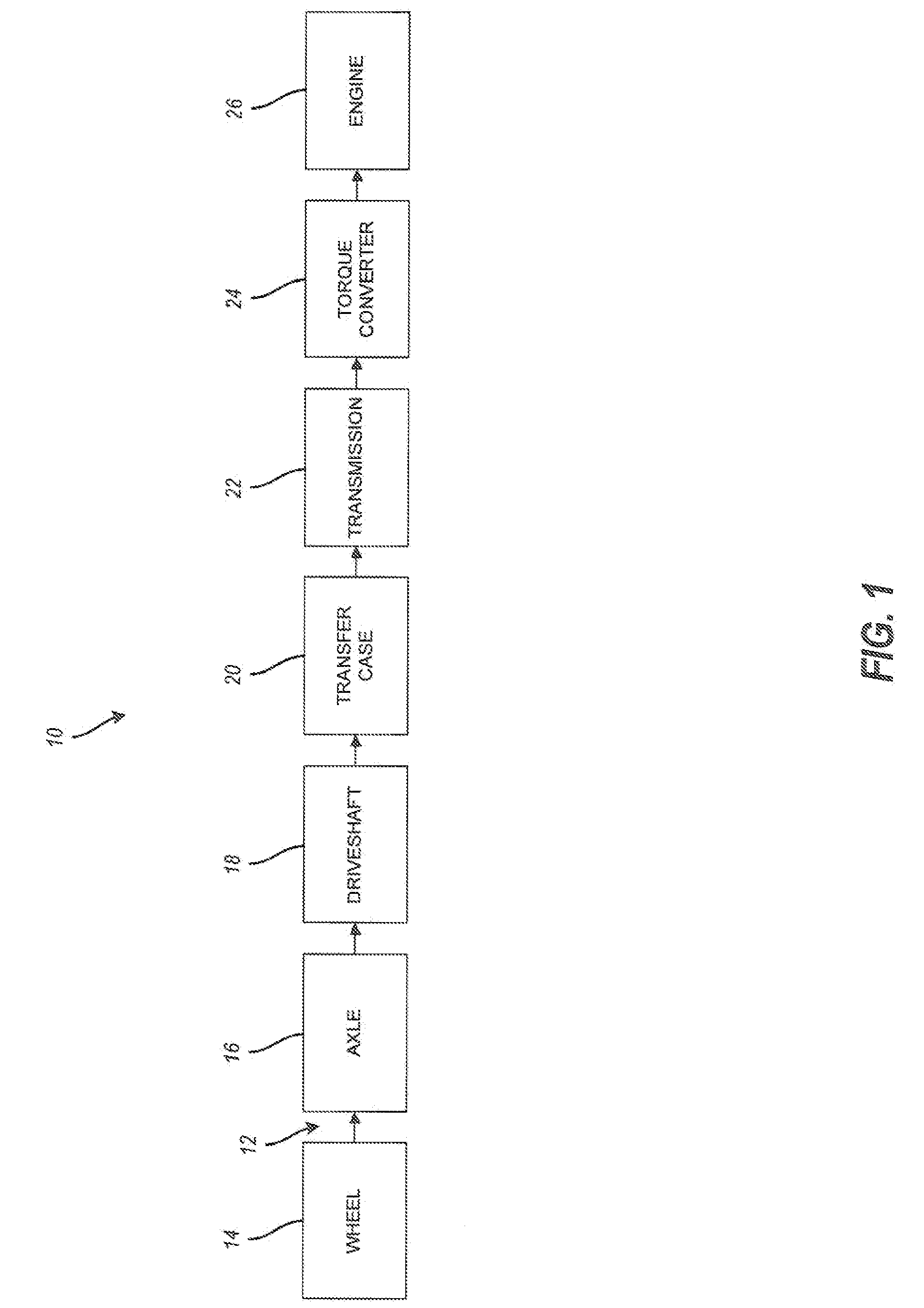
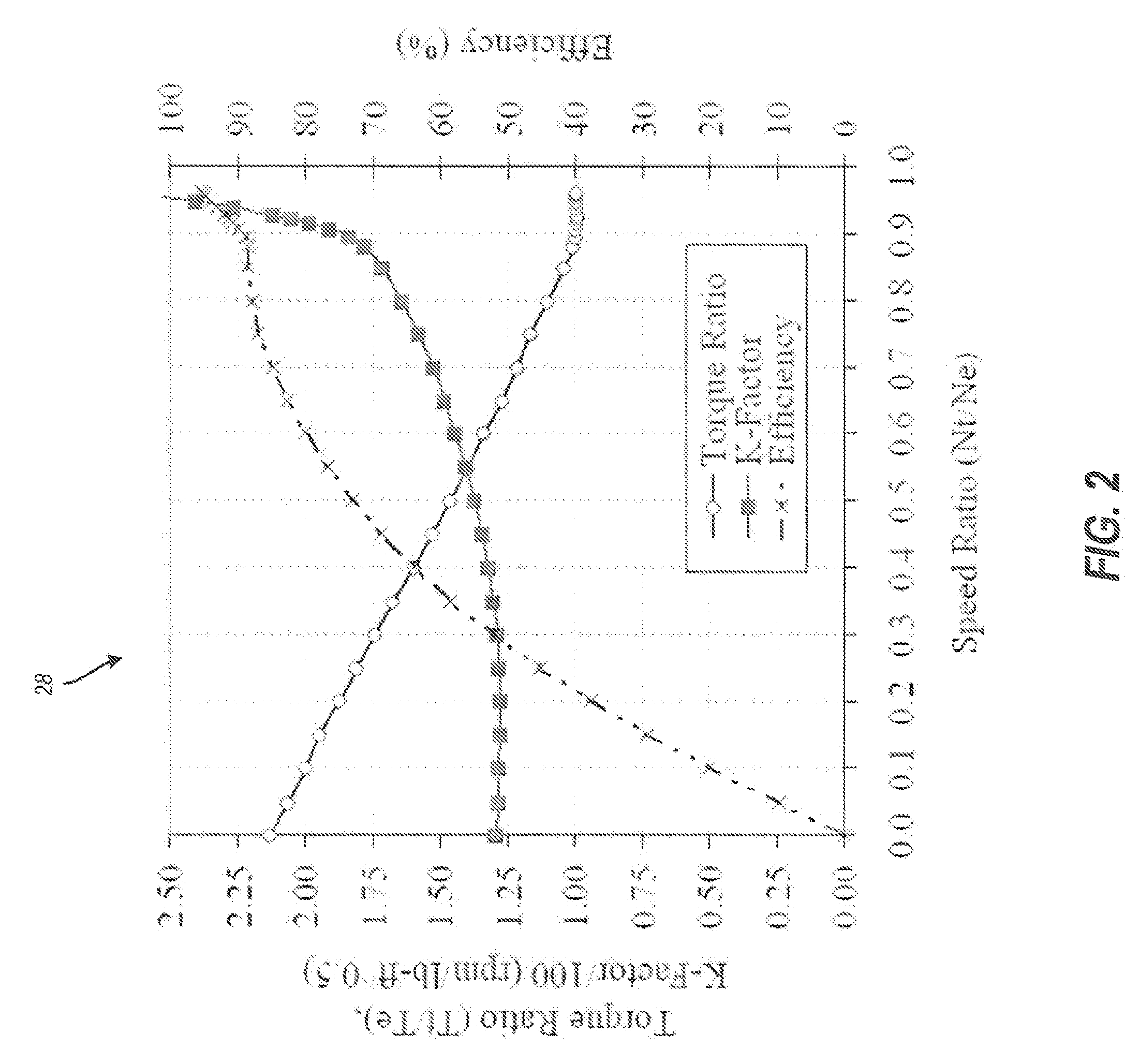
The technology described herein provides methods and systems for powertrain optimization and improved fuel economy including multiple displacement engine modeling and control optimization, automotive powertrain matching for fuel economy, cycle-based automotive shift and lock-up scheduling for fuel economy, and engine performance requirements based on vehicle attributes and drive cycle characteristics. Also provided is a reverse tractive road load demand simulation algorithm used to propagate a reverse tractive road load demand and a corresponding component torque and speed, derived from a vehicle speed trace, in a reverse direction through a powertrain system. Also provided is a dynamic optimization algorithm. The dynamic programming algorithm is applied to a matrix of fuel flow rates to find the optimal control path that maximizes the powertrain efficiency over a cycle.
Owner:FCA US
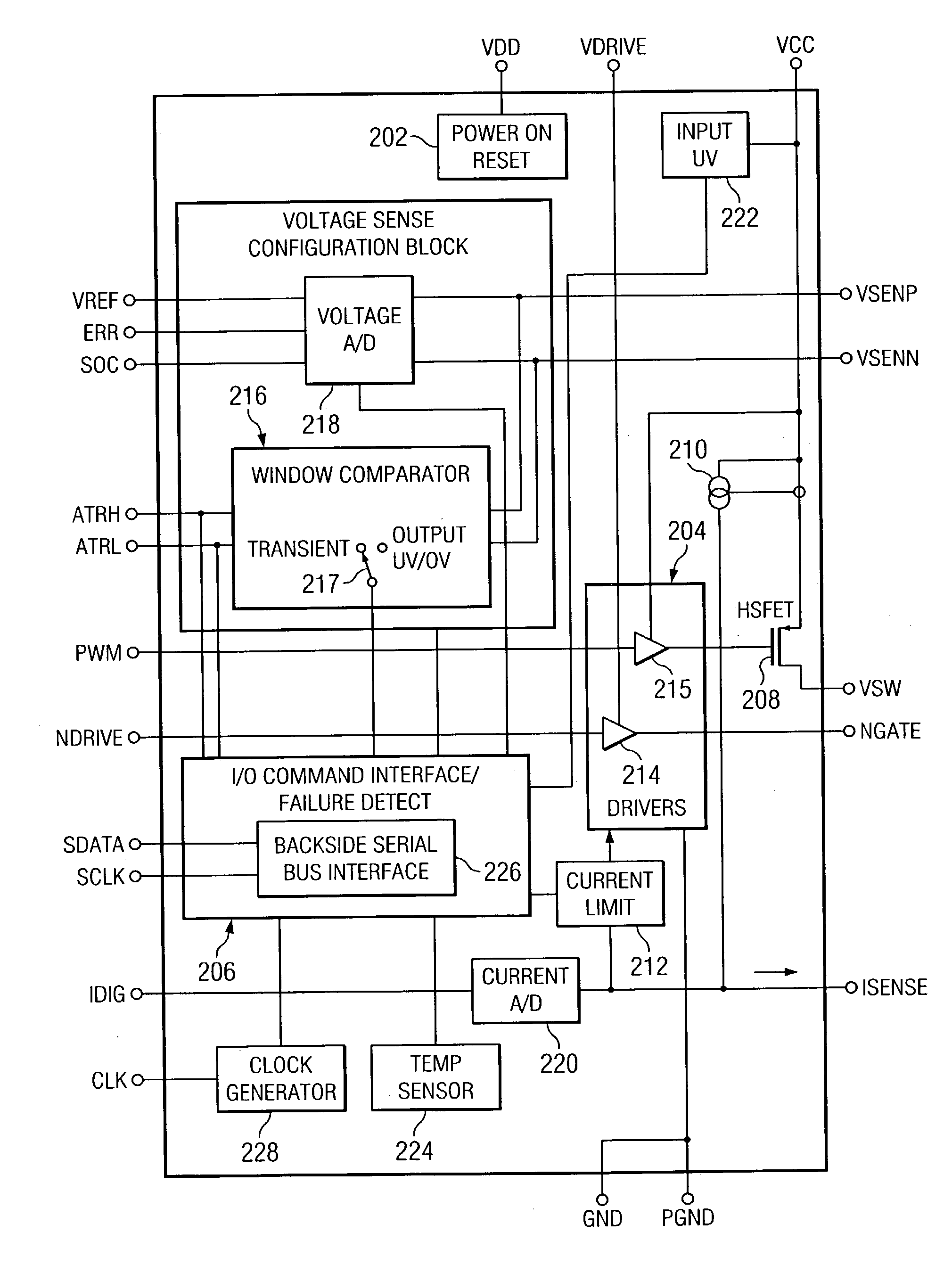
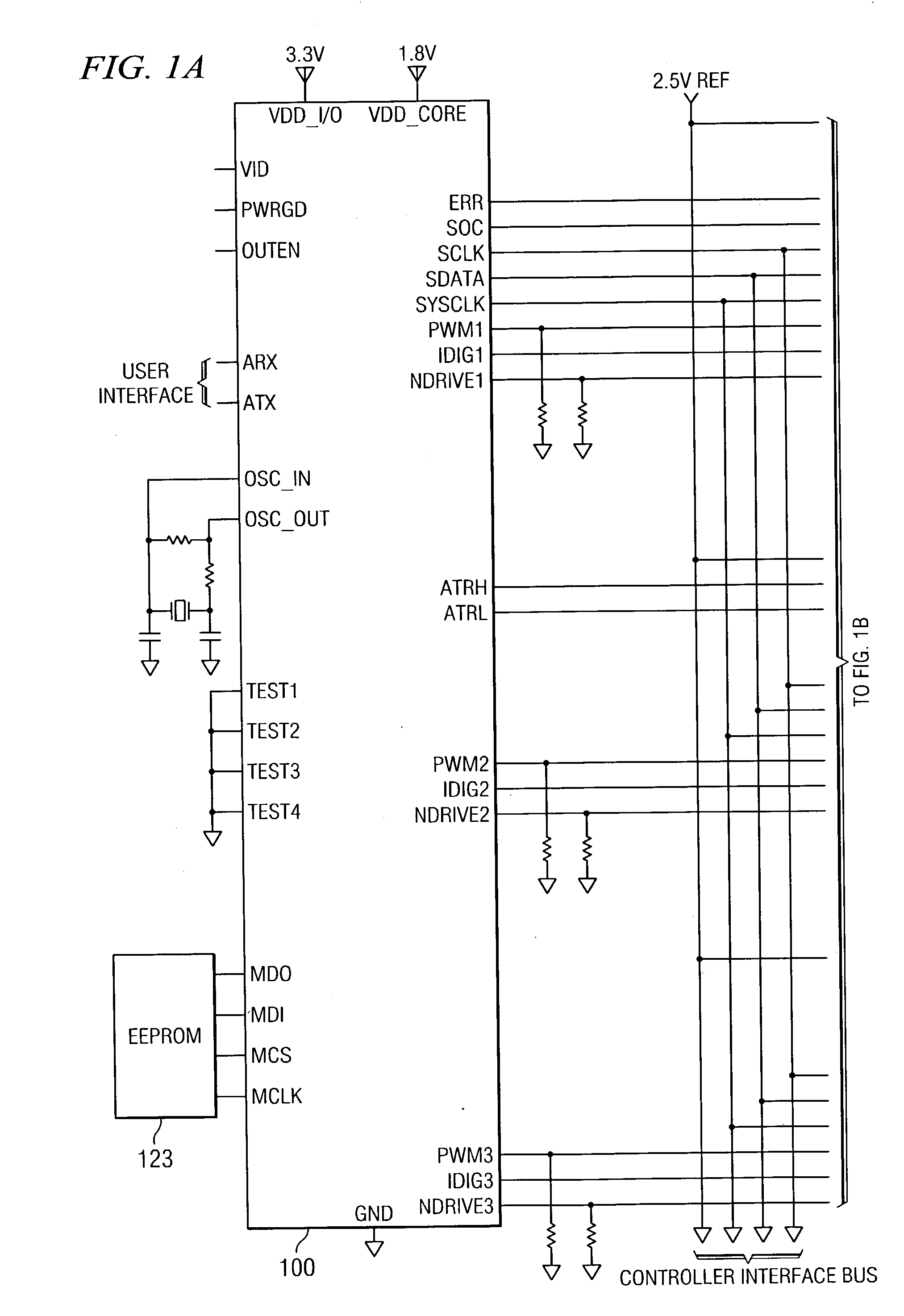
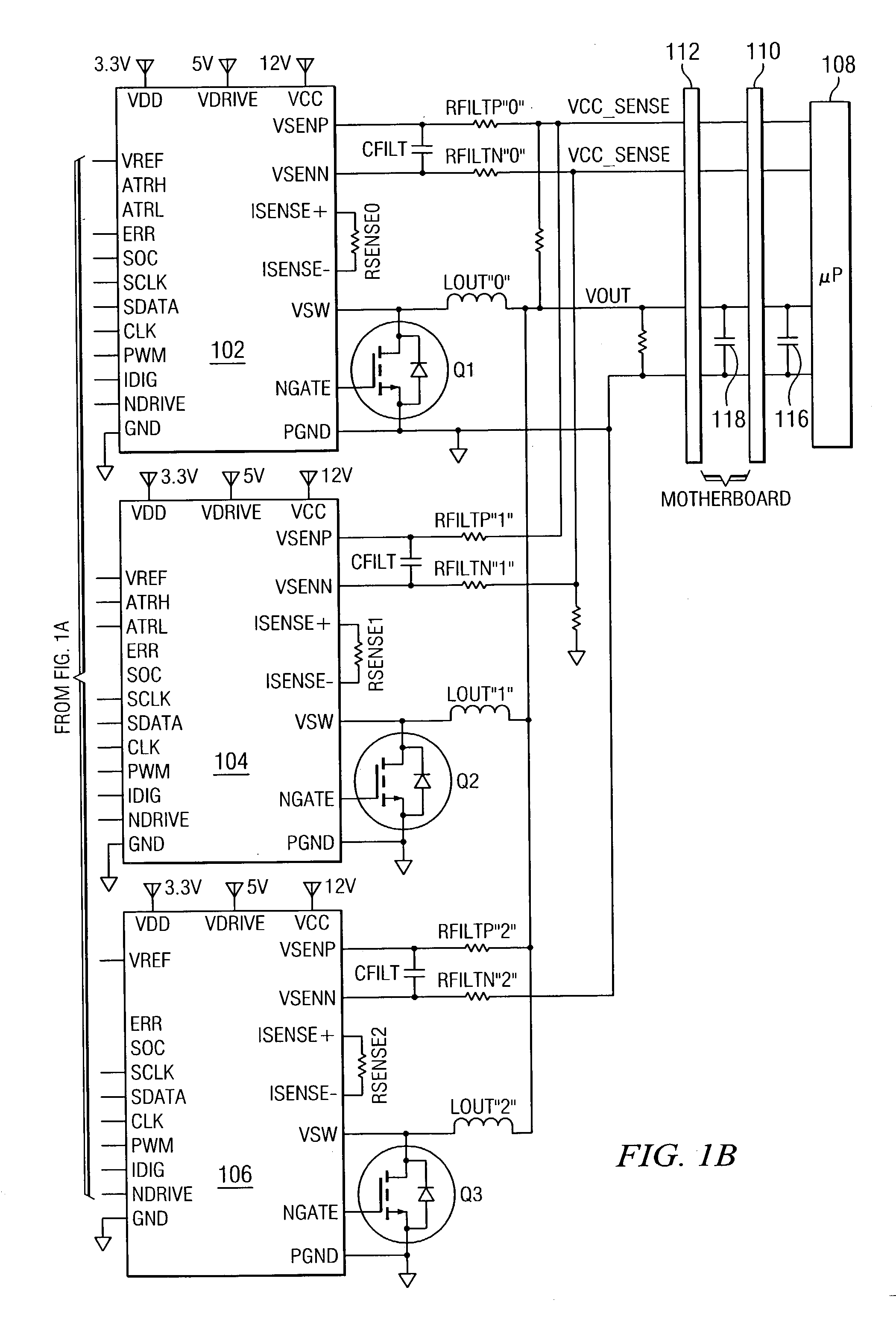
Digitally controlled voltage regulator
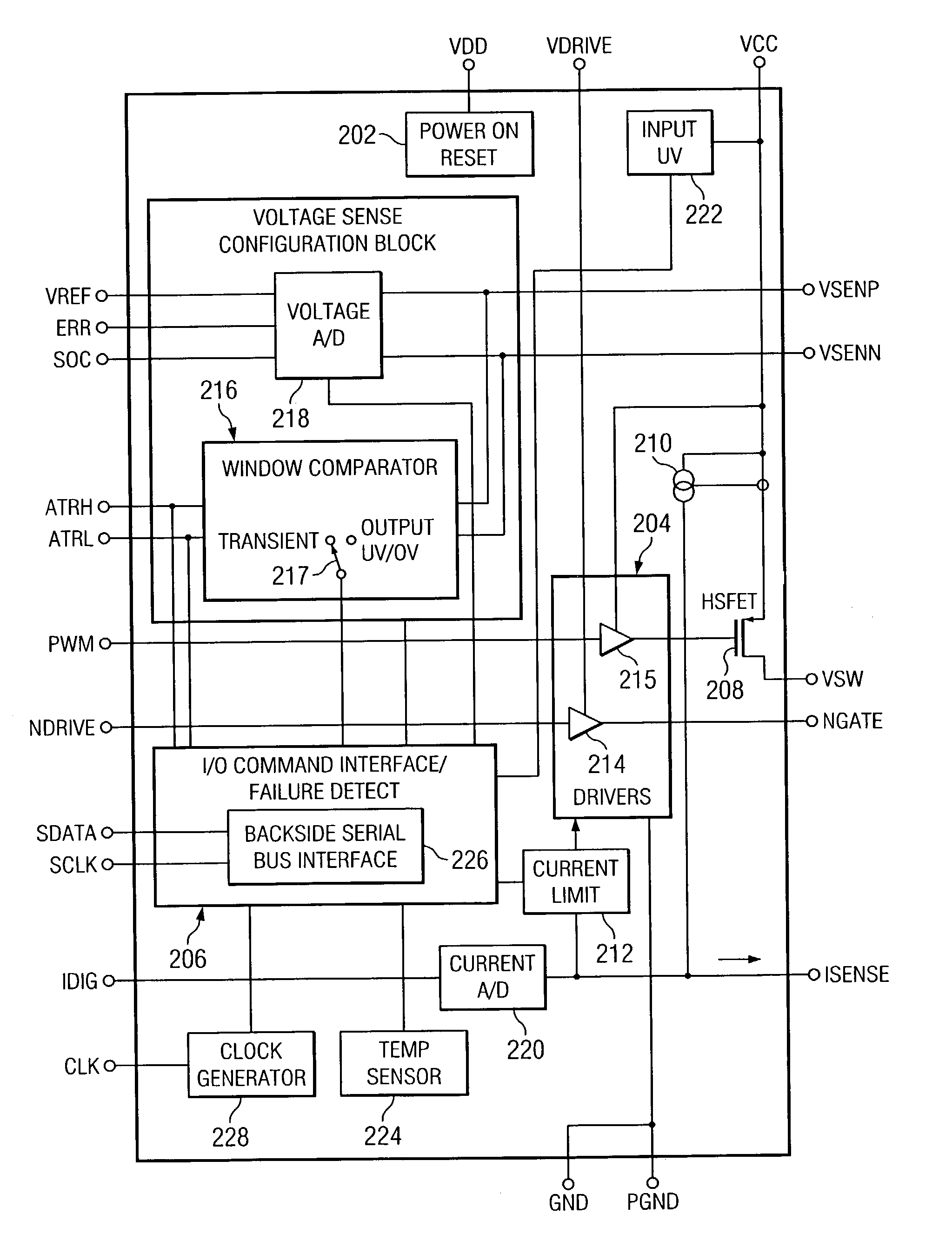
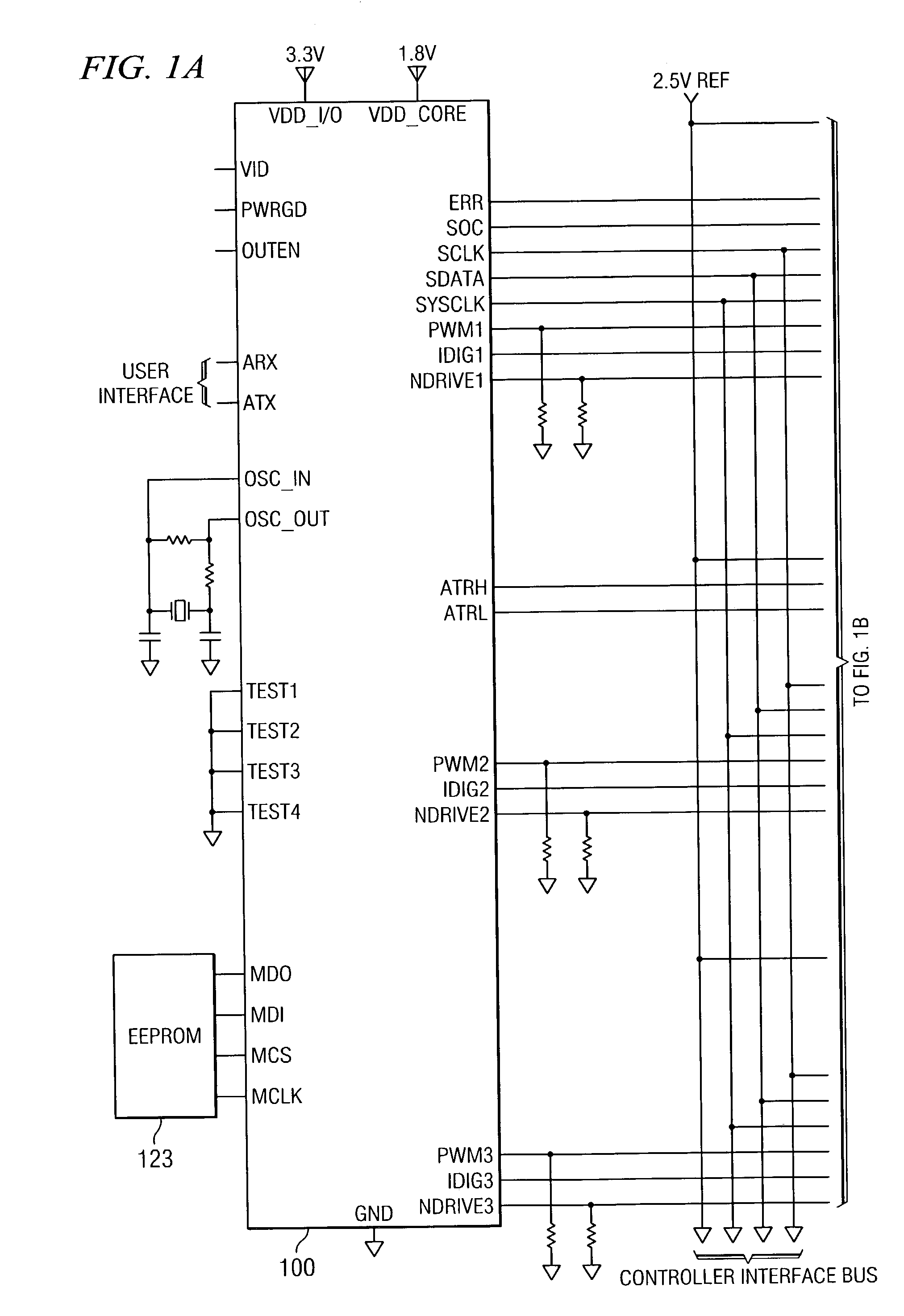
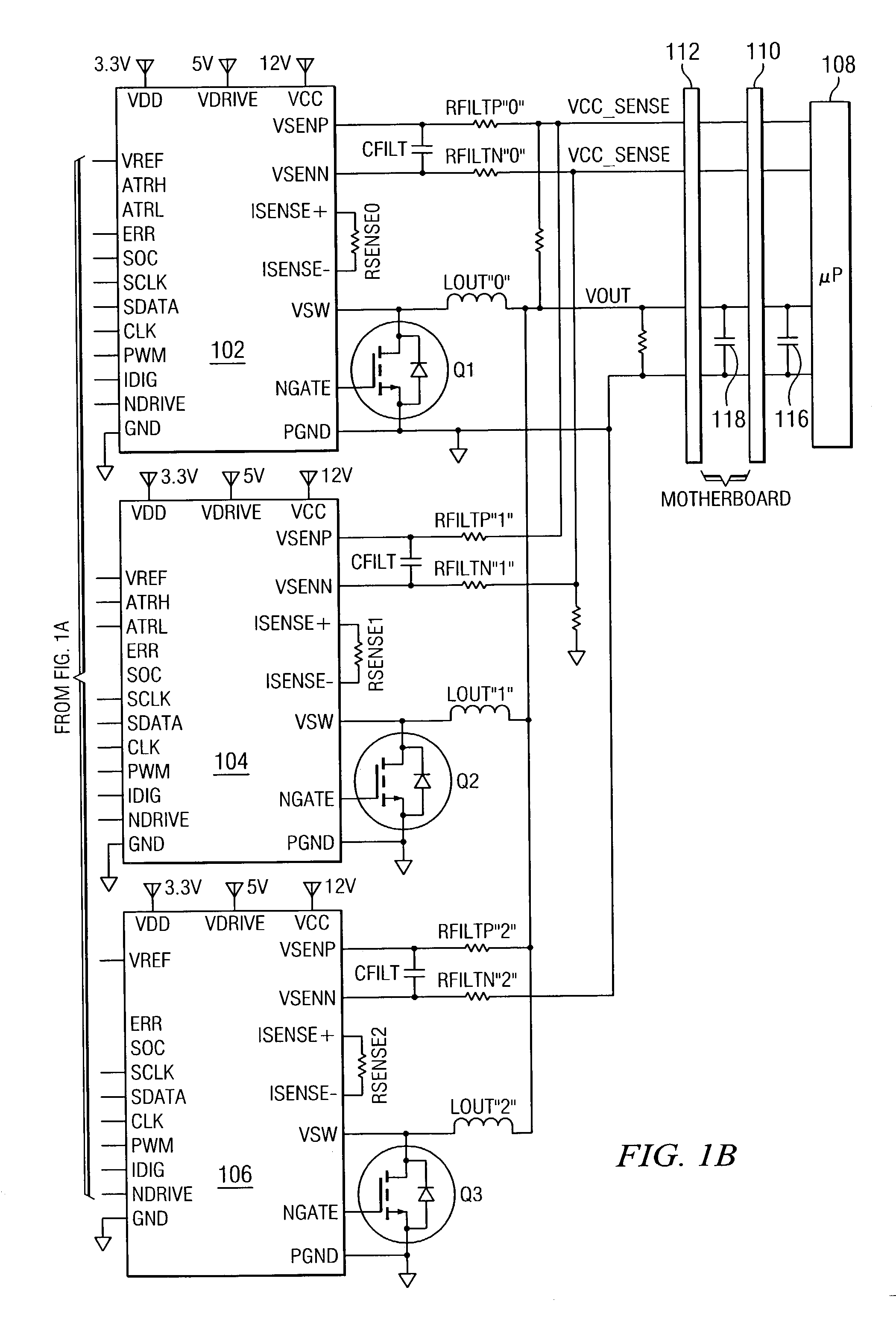
ActiveUS7023672B2Easy to customizePrecise power controlEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalOptimal control
Disclosed is a digitally controlled multi-phase voltage regulator system providing regulated power to electronic components that have variable power requirements. Power is supplied by one or more power integrated circuits (IC) each having a high side power switch controlled by pulse width modulated signals and a low side power switch. The power IC senses voltage at the load and has an on-chip current mirror for generating a current that is a ratio of current delivered to the load. The power IC also has current limiting and on-chip temperature sensing components. The voltage and current information is digitized and provided to a control integrated circuit (IC). The control IC receives this digitized information as well as user provided parameters and, in the regulation mode of operation, provides digitized pulse width modulated control signals to the power IC. In an active transient response mode of operation, the control IC provides signals to turn either the high side switches or low side switches ON. Fault detection circuitry identifies over voltage, under voltage, and excessive temperatures. All communications between the control IC and the power IC are digital providing high bandwidth, optimal control frequency response, noise immunity and efficient active transient response.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
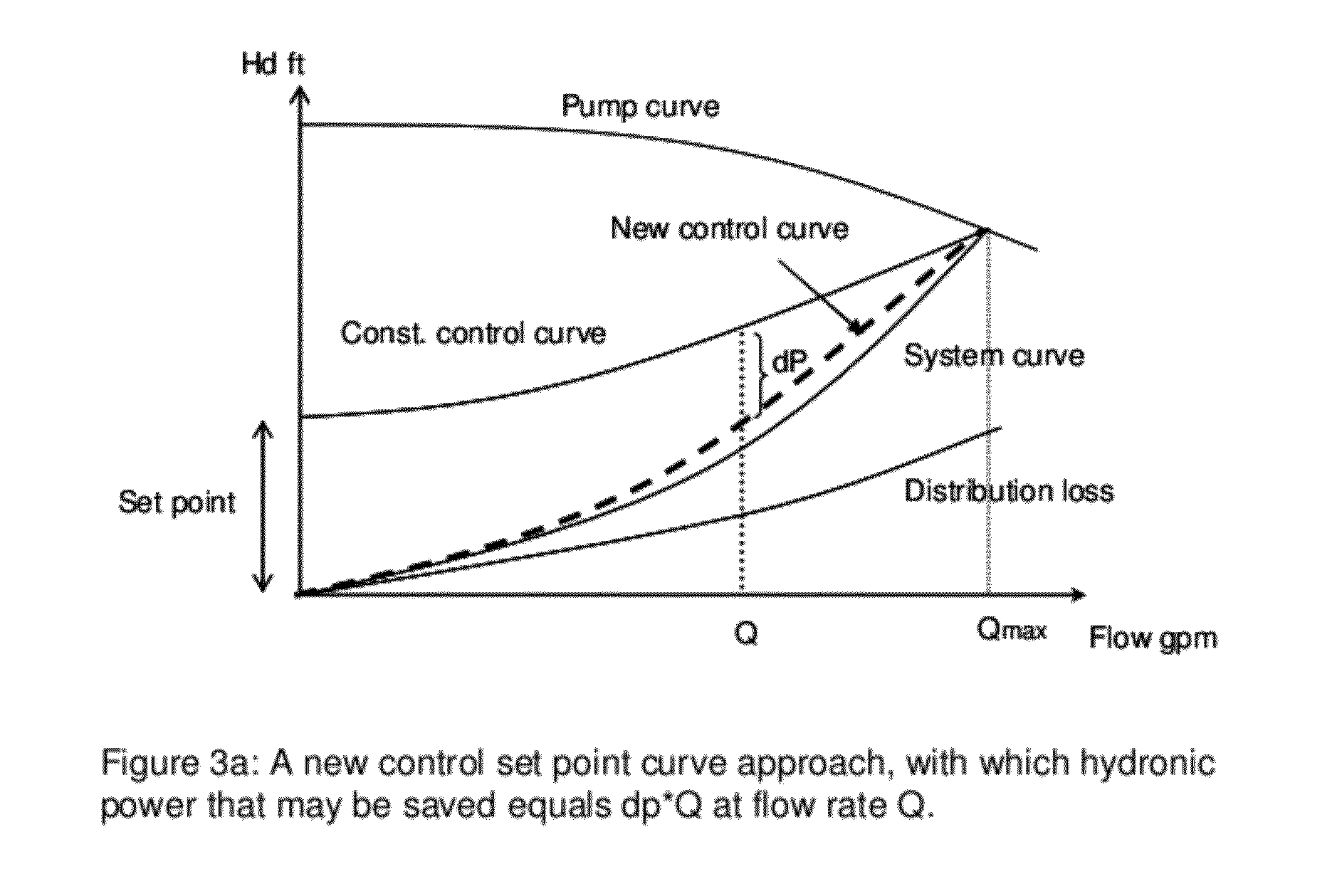
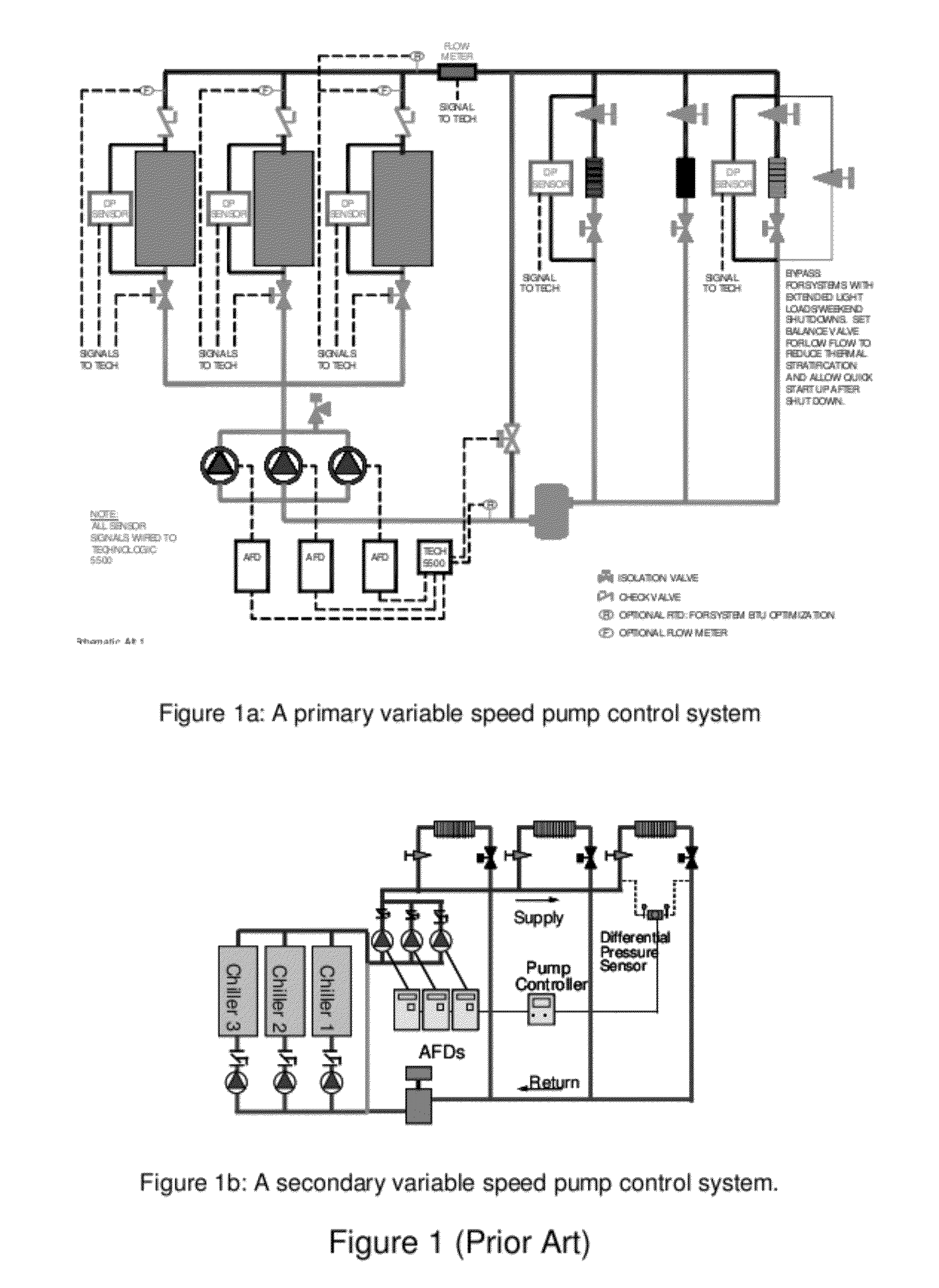
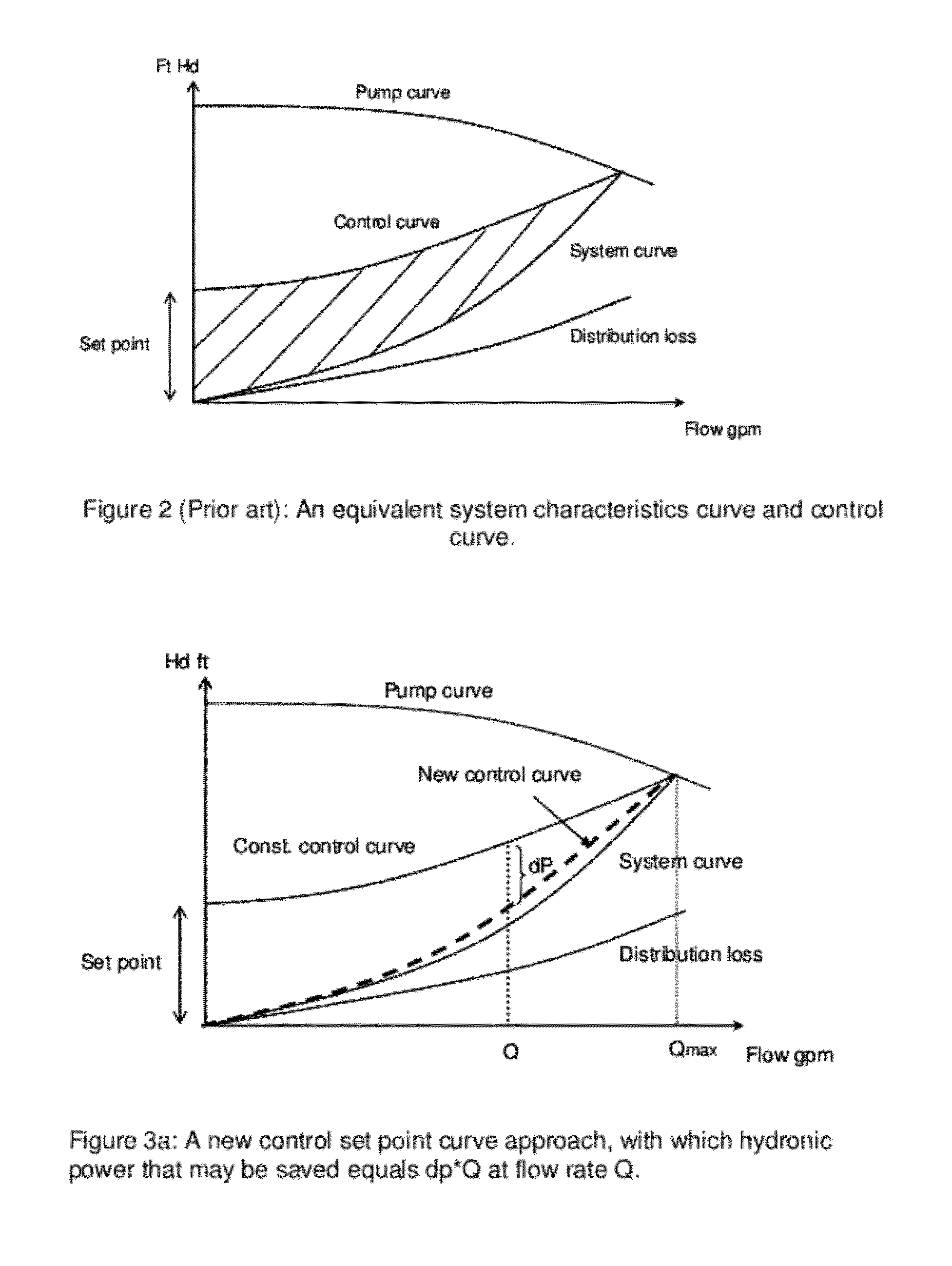
Method and Apparatus for Pump Control Using Varying Equivalent System Characteristic Curve, AKA an Adaptive Control Curve
ActiveUS20120173027A1Reduce energy consumptionReduce operating costsFlow control using electric meansFluid pressure control using electric meansMoving averageAverage filter
The present invention provides, e.g., apparatus comprising at least one processor; at least one memory including computer program code; the at least one memory and computer program code being configured, with at least one processor, to cause the apparatus at least to: respond to signaling containing information about an instant pressure and a flow rate of fluid being pumped in a pumping system, and obtain an adaptive control curve based at least partly on the instant pressure and flow rate using an adaptive moving average filter. The adaptive moving average filter may be based at least partly on a system flow equation: SAMAt=AMAF(Qt / √{square root over (ΔPt)}), where the function AMAF is an adaptive moving average filter (AMAF), and the parameters Q and ΔP are a system flow rate and differential pressure respectively. The at least one memory and computer program code may be configured to, with the at least one processor, to cause the apparatus at least to obtain an optimal control pressure set point from the adaptive control curve with respect to an instant flow rate or a moving average flow rate as SPt=MA(Qt) / SAMAt, where the function MA is a moving average filter (MA), to obtain a desired pump speed through a PID control.
Owner:FLUID HANDLING
Controlling an HVAC system in association with a demand-response event
ActiveUS20140277761A1Minimize cost functionSampled-variable control systemsMechanical apparatusNetwork connectionOptimal control
Apparatus, systems, methods, and related computer program products for carrying out a demand response (DR) event via an intelligent, network-connected thermostat associated with a structure. The systems disclosed include an energy management system in operation with an intelligent, network-connected thermostat located at a structure. The thermostat is operable to control an HVAC system. Control during a DR event period may be performed based on an optimal control trajectory of the HVAC system, where the control trajectory is optimal in that it minimizes a cost function comprising a combination of a first factor representative of a total energy consumption during the DR event period, a second factor representative of a metric of occupant discomfort, and a third factor representative of deviations of a rate of energy consumption over the DR event period.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
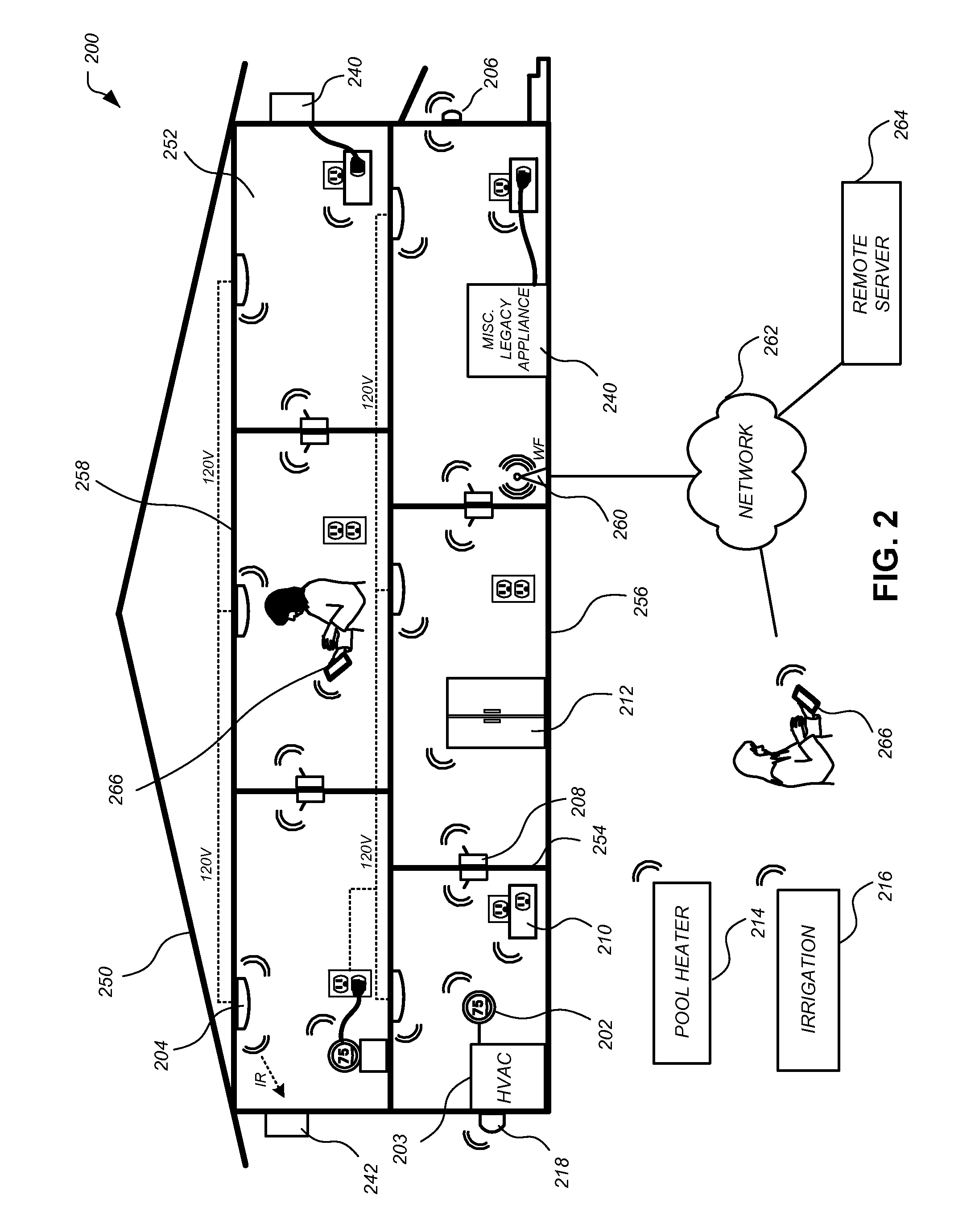
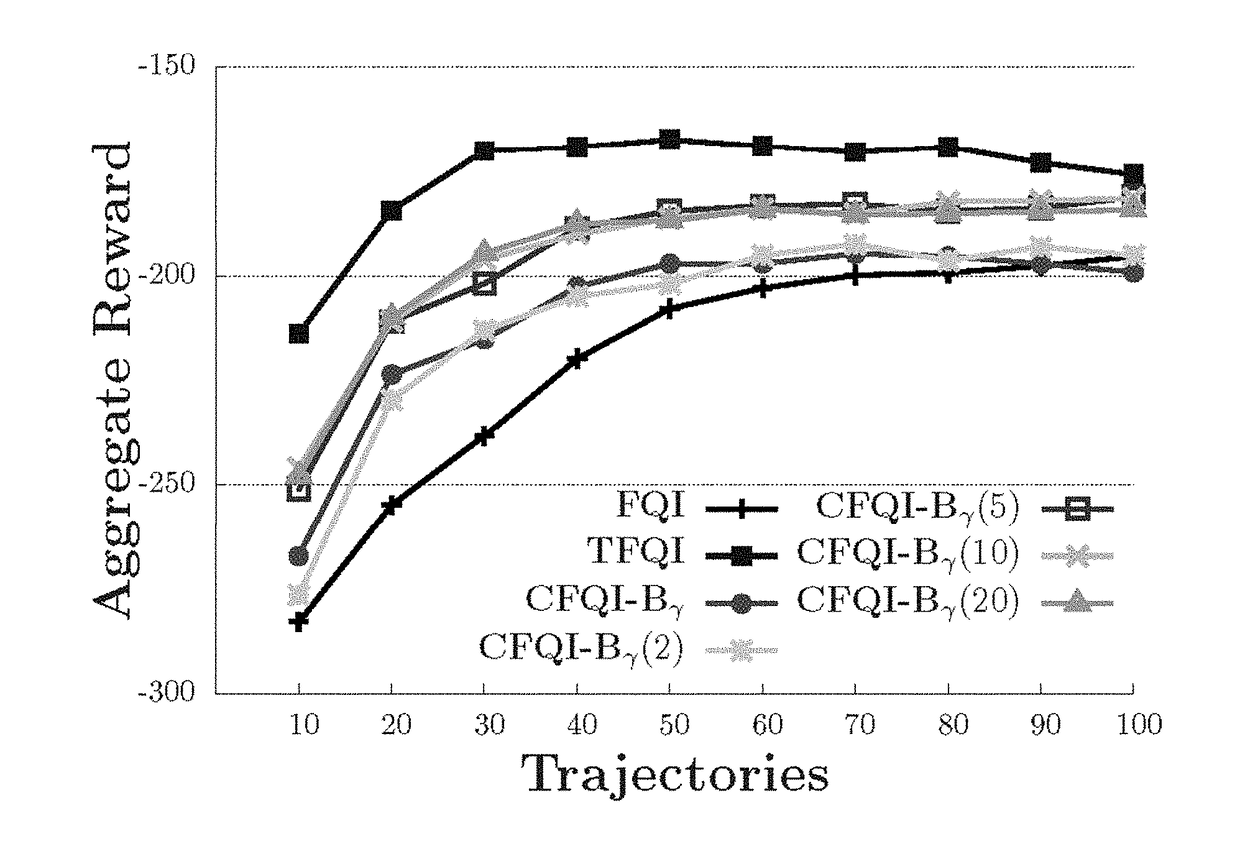
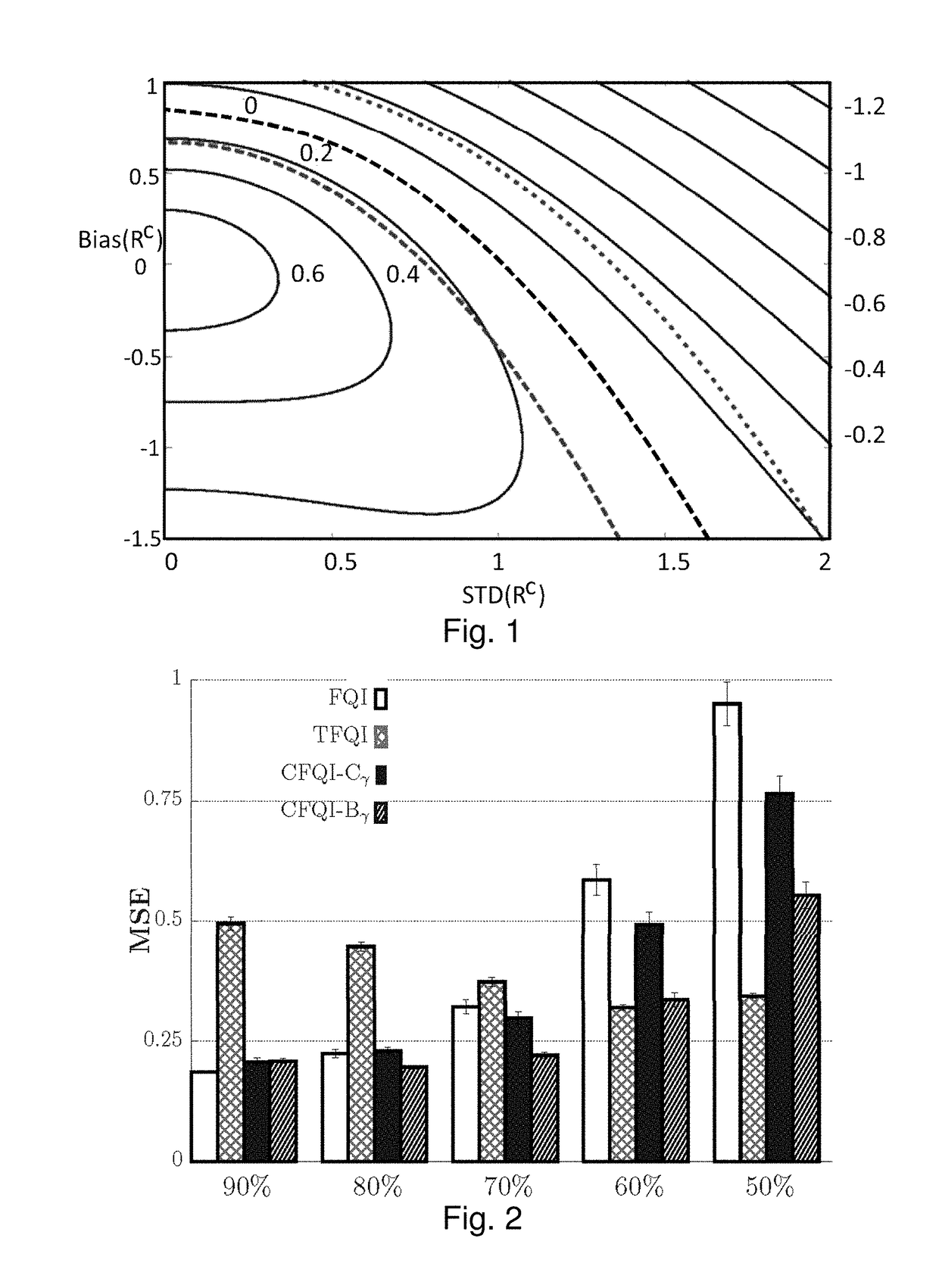
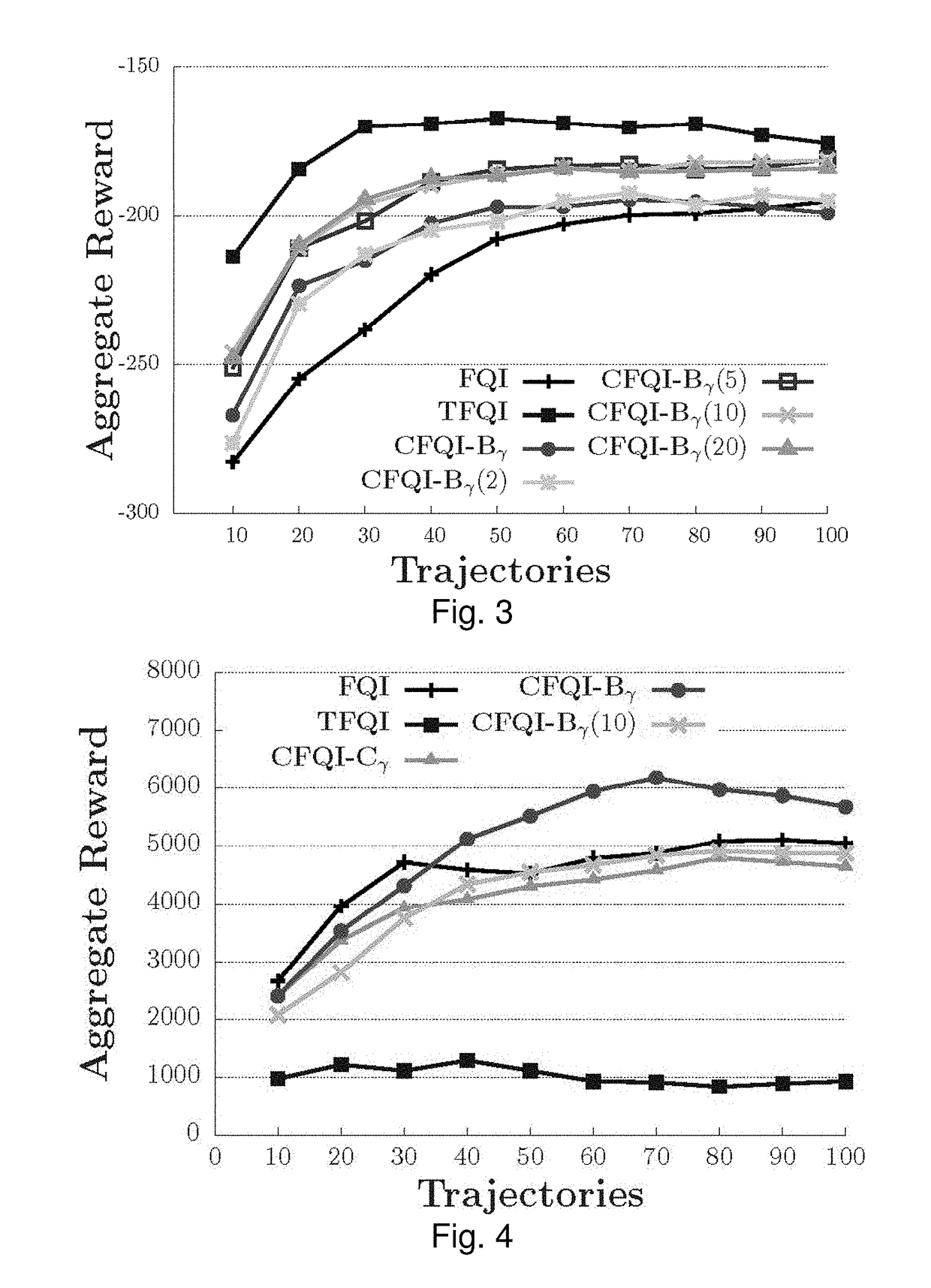
Approximate value iteration with complex returns by bounding
ActiveUS20180012137A1Reduce varianceBetter estimatorComputer controlProbabilistic networksData setControl system
A control system and method for controlling a system, which employs a data set representing a plurality of states and associated trajectories of an environment of the system; and which iteratively determines an estimate of an optimal control policy for the system. The iterative process performs the substeps, until convergence, of estimating a long term value for operation at a respective state of the environment over a series of predicted future environmental states; using a complex return of the data set to determine a bound to improve the estimated long term value; and producing an updated estimate of an optimal control policy dependent on the improved estimate of the long term value. The control system may produce an output signal to control the system directly, or output the optimized control policy. The system preferably is a reinforcement learning system which continually improves.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Integrated ventilation cooling system
InactiveUS20020124992A1Reduce energy useEasy temperature controlDucting arrangementsMechanical apparatusIndoor air qualityAir handler
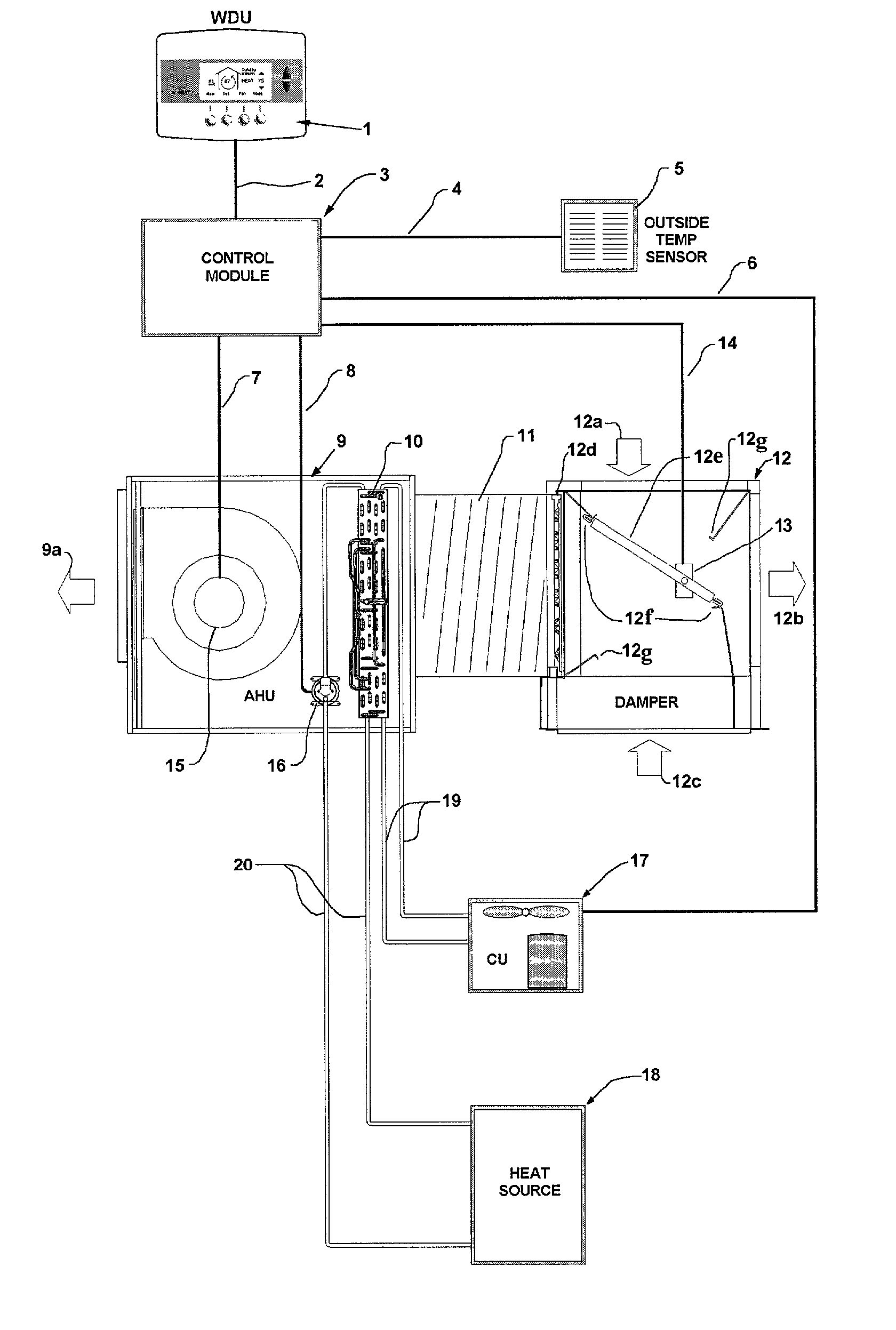
A system and method for cooling and heating of buildings consisting of an integrated assembly of devices, including a variable speed air handler, hot water heating coil, outside air damper, controller, and optional compressor-based air conditioner. During summer the system utilizes nighttime outside air for cooling and uses air temperature predictions to provide information about optimal control settings and to maintain comfort. During winter the system varies airflow with heating demand and ventilates with outside air to maintain indoor air quality.
Owner:NIGHTBREEZE
Autonomously identifying and capturing method of non-cooperative target of space robot
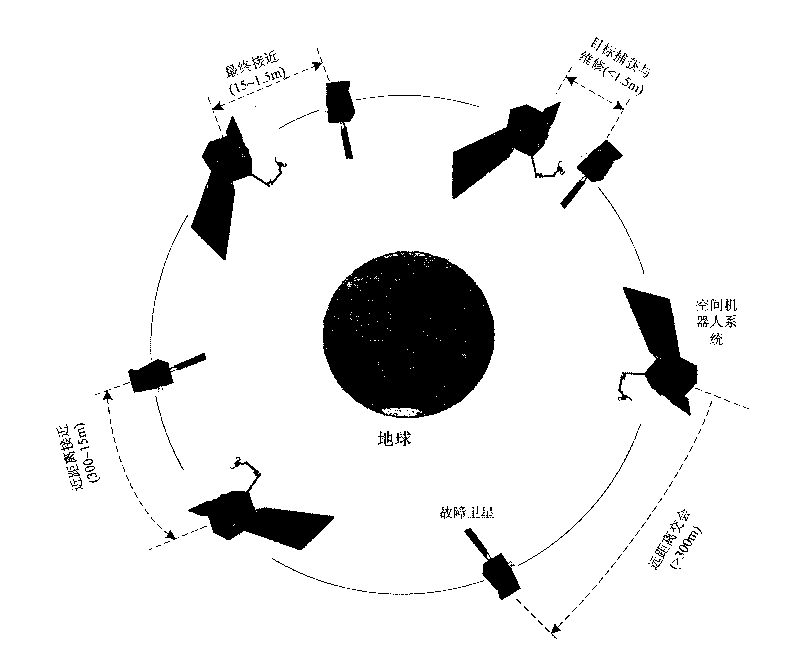
InactiveCN101733746AReal-time prediction of motion statusPredict interference in real timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorToolsKinematicsTarget capture
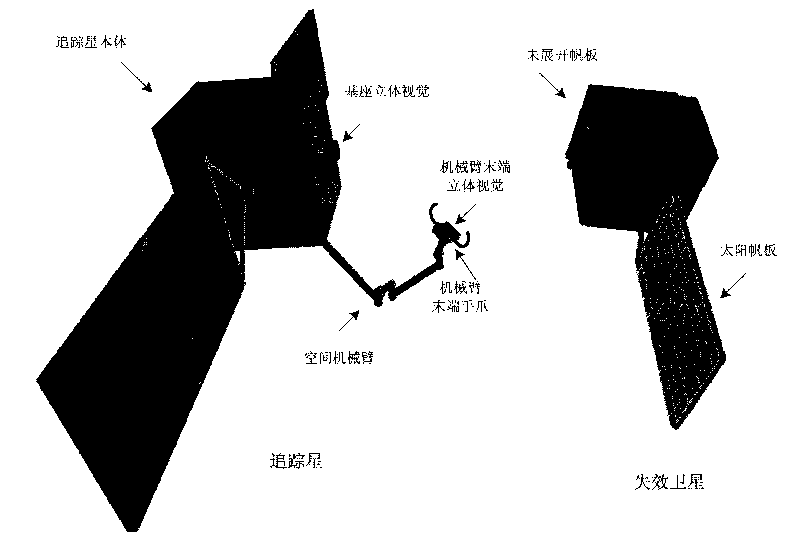
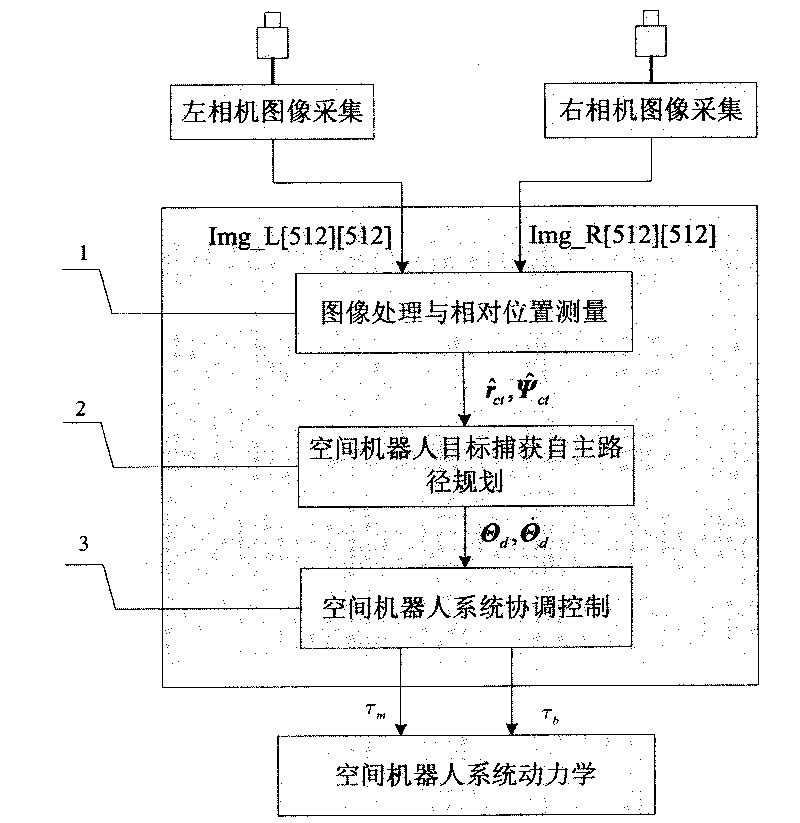
The invention relates to an autonomously identifying and capturing method of a non-cooperative target of a space robot, comprising the main steps of (1) pose measurement based on stereoscopic vision, (2) autonomous path planning of the target capture of the space robot and (3) coordinative control of a space robot system, and the like. The pose measurement based on the stereoscopic vision is realized by processing images of a left camera and a right camera in real time, and computing the pose of a non-cooperative target star relative to a base and a tail end, wherein the processing comprises smoothing filtering, edge detection, linear extraction, and the like. The autonomous path planning of the target capture of the space robot comprises is realized by planning the motion tracks of joints in real time according to the pose measurement results. The coordinative control of the space robot system is realized by coordinately controlling mechanical arms and the base to realize the optimal control property of the whole system. In the autonomously identifying and capturing method, a self part of a spacecraft is directly used as an identifying and capturing object without installing a marker or a comer reflector on the target star or knowing the geometric dimension of the object, and the planned path can effectively avoid the singular point of dynamics and kinematics.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Closed-loop autonomic neuromodulation for optimal control of neurological and metabolic disease
InactiveUS7974696B1Shorten the timeSatisfactory treatmentElectroencephalographyHead electrodesDiseaseNervous system
A neurological control system for modulating activity of any component or structure of some or all of the nervous system, or any structure interfaced thereto, generally referred to herein as a “nervous system component.” This system generates neural modulation signals delivered to a nervous system component through one or more neuromodulators to control neurological state or autonomic state and prevent neurological or metabolic signs and symptoms. Such treatment parameters may be derived from a neural response to previously delivered neural modulation signals, with sensors configured to sense a particular characteristic indicative of a neurological, psychiatric, or metabolic condition.
Owner:DILORENZO BIOMEDICAL
System and method for the longitudinal analysis of education outcomes using cohort life cycles, cluster analytics-based cohort analysis, and probabilistic data schemas
InactiveUS7930262B2Digital computer detailsKnowledge representationData processing systemOptimal control
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
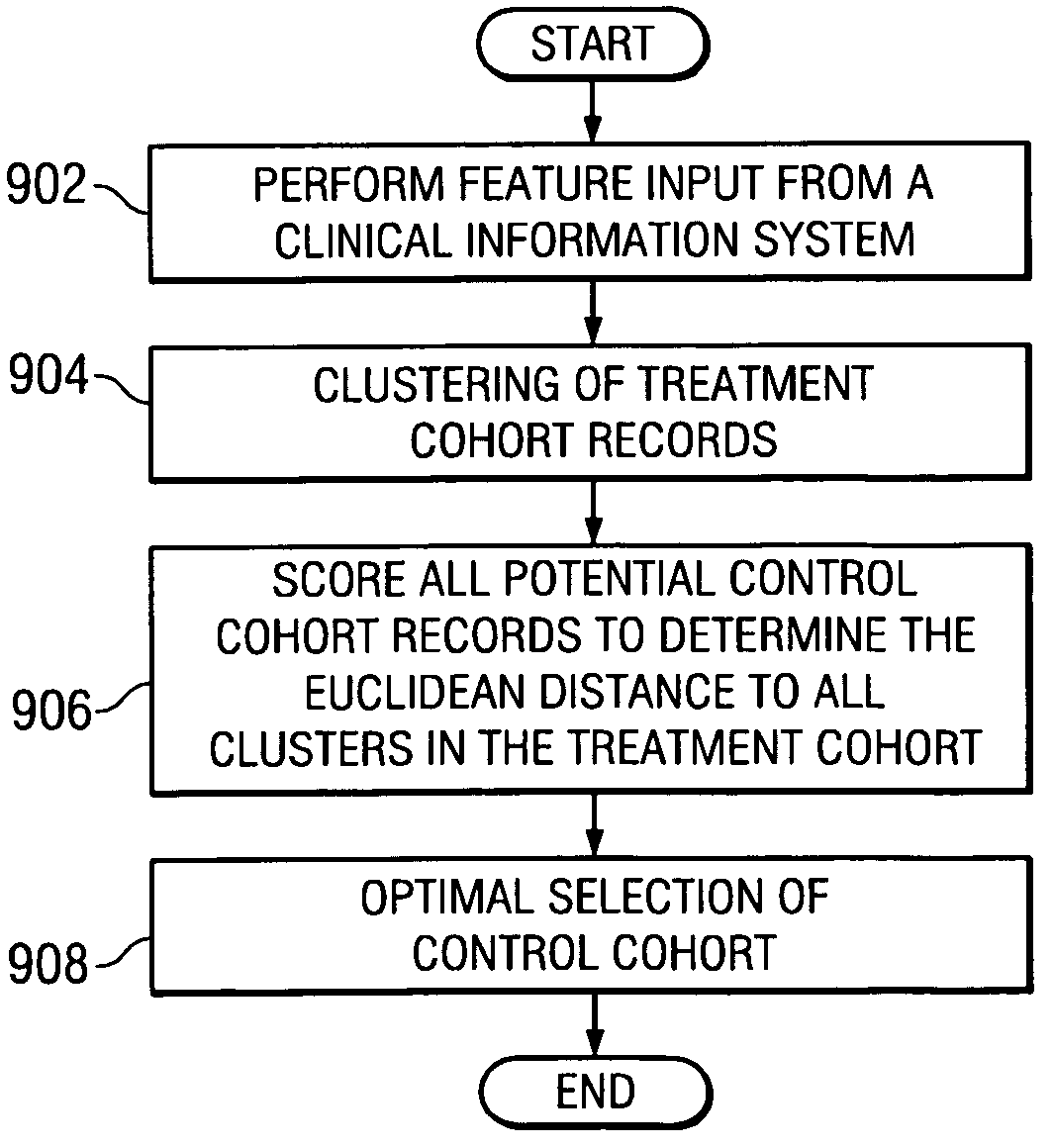
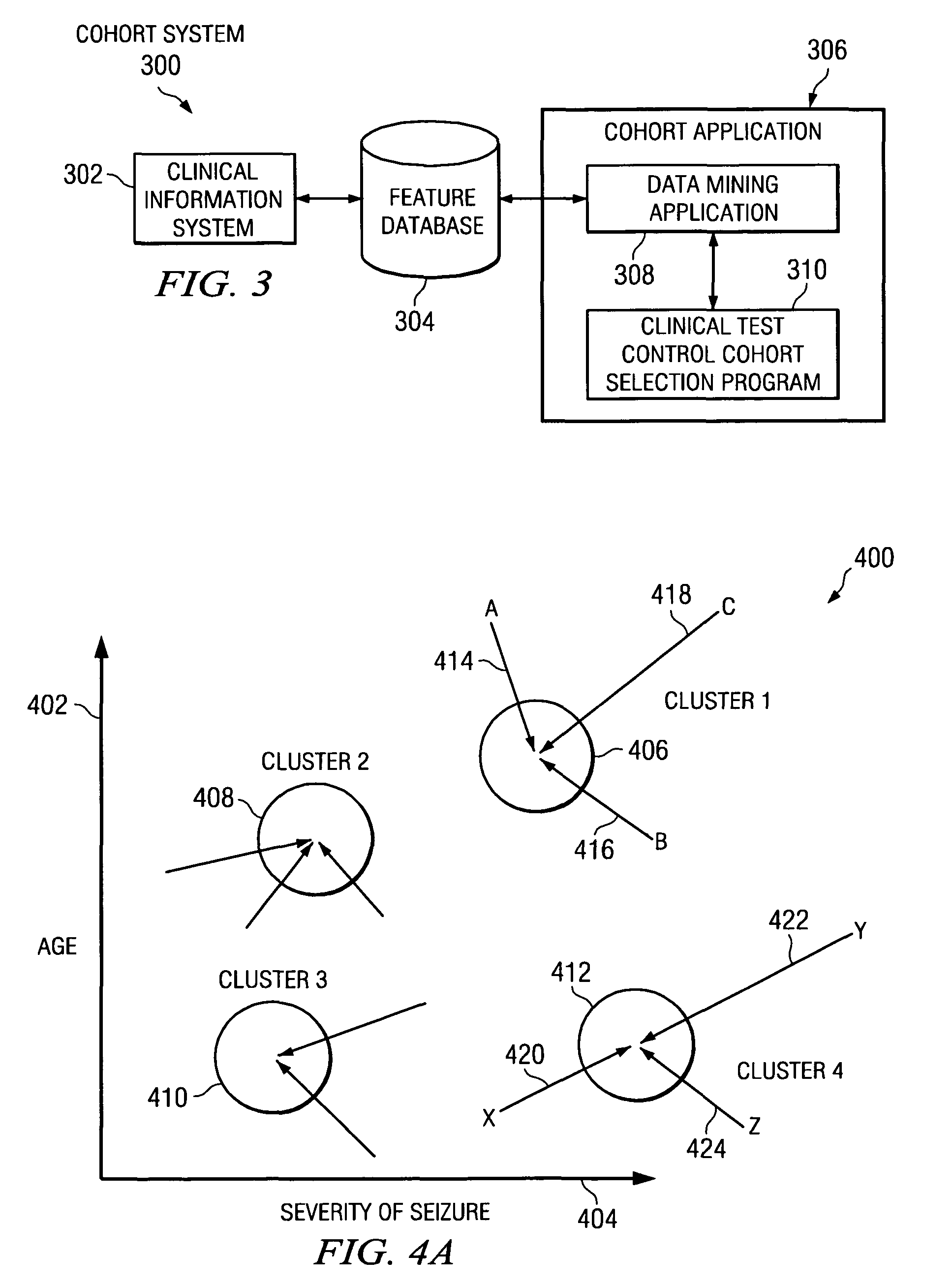
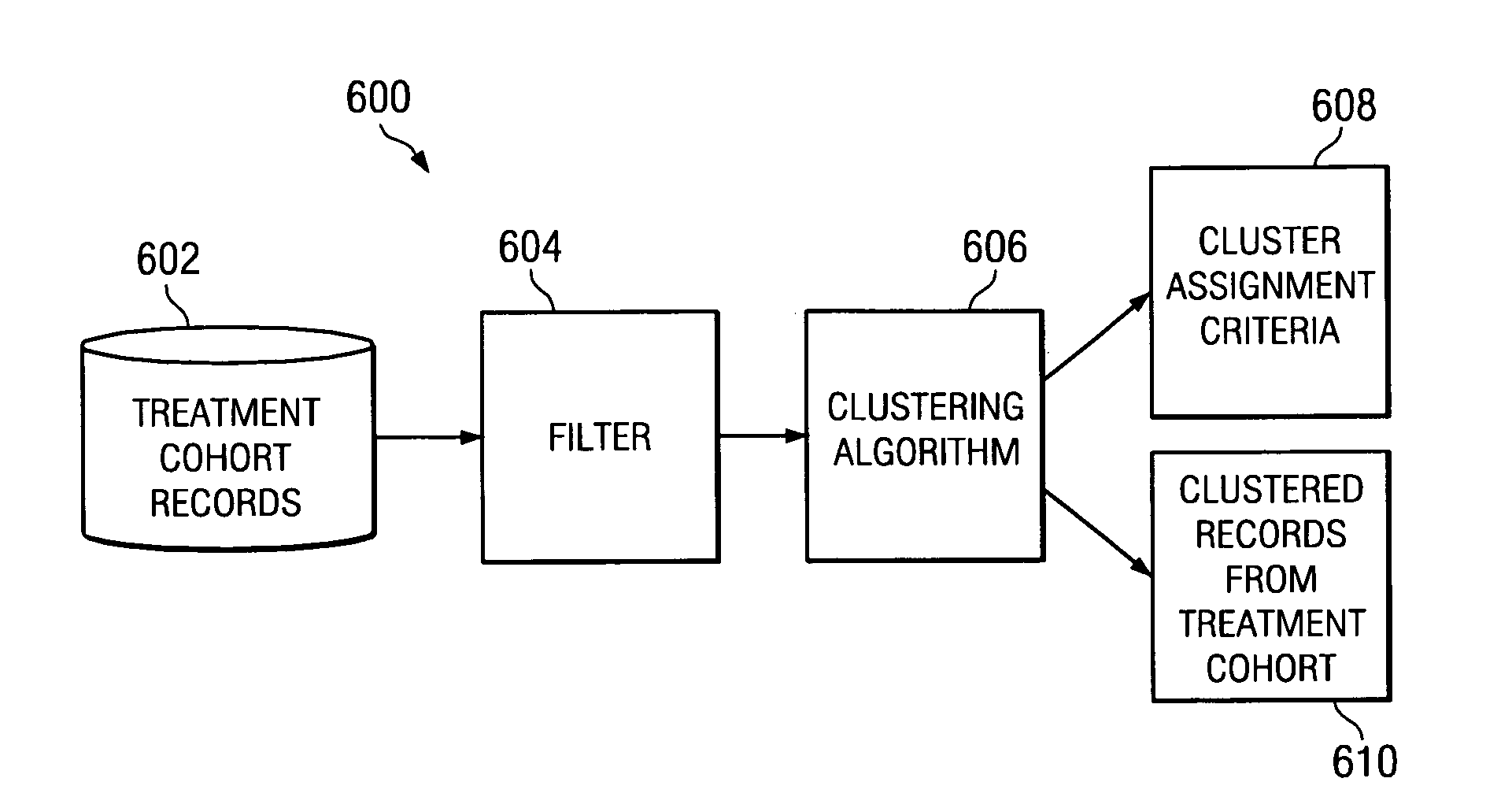
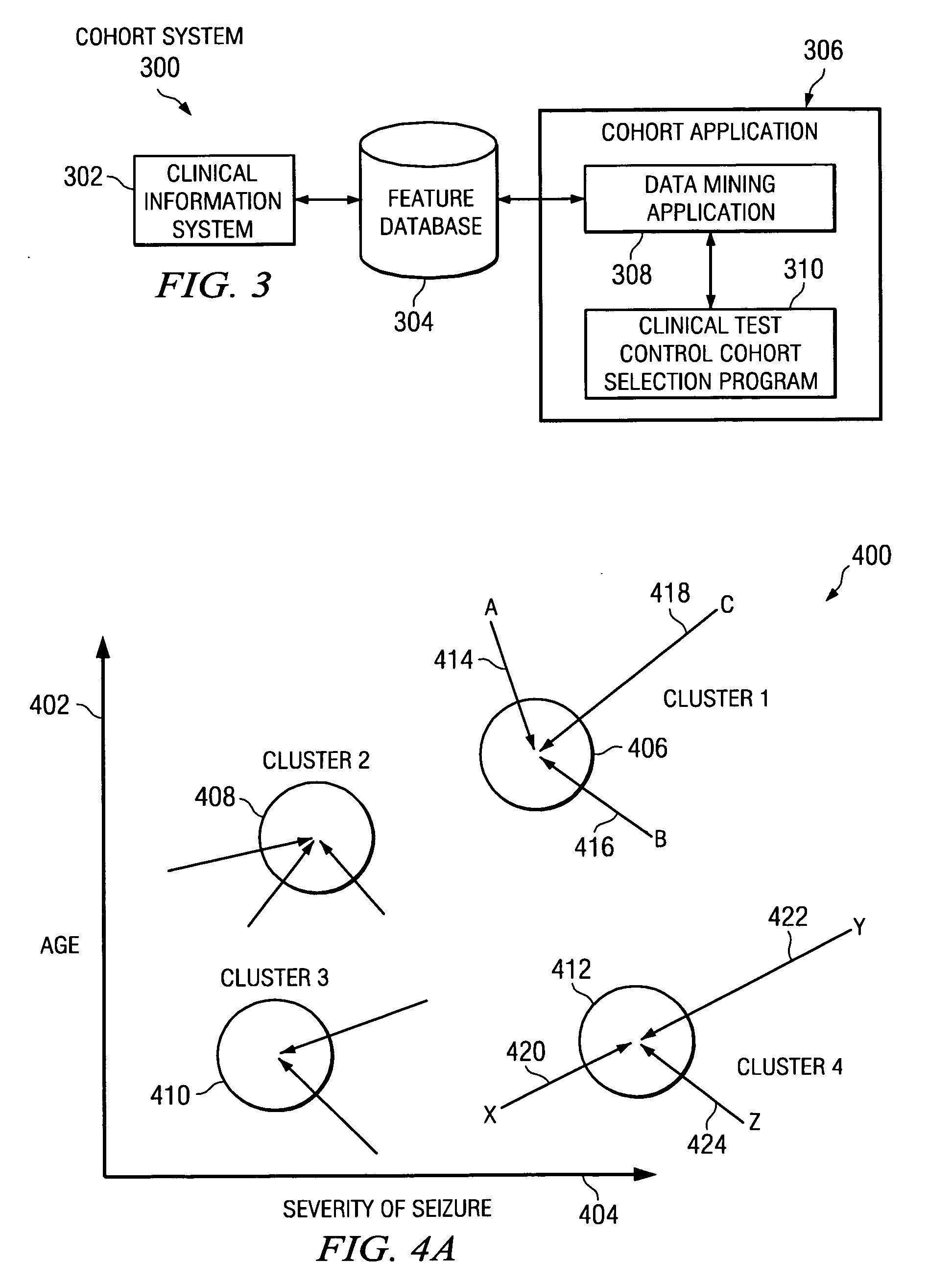
System and method to optimize control cohorts using clustering algorithms
InactiveUS7809660B2Minimize the differenceTherapiesHospital data managementCluster algorithmOptimal control
A computer implemented method, apparatus, and computer usable program code for automatically selecting an optimal control cohort. Attributes are selected based on patient data. Treatment cohort records are clustered to form clustered treatment cohorts. Control cohort records are scored to form potential control cohort members. The optimal control cohort is selected by minimizing differences between the potential control cohort members and the clustered treatment cohorts.
Owner:LINKEDIN
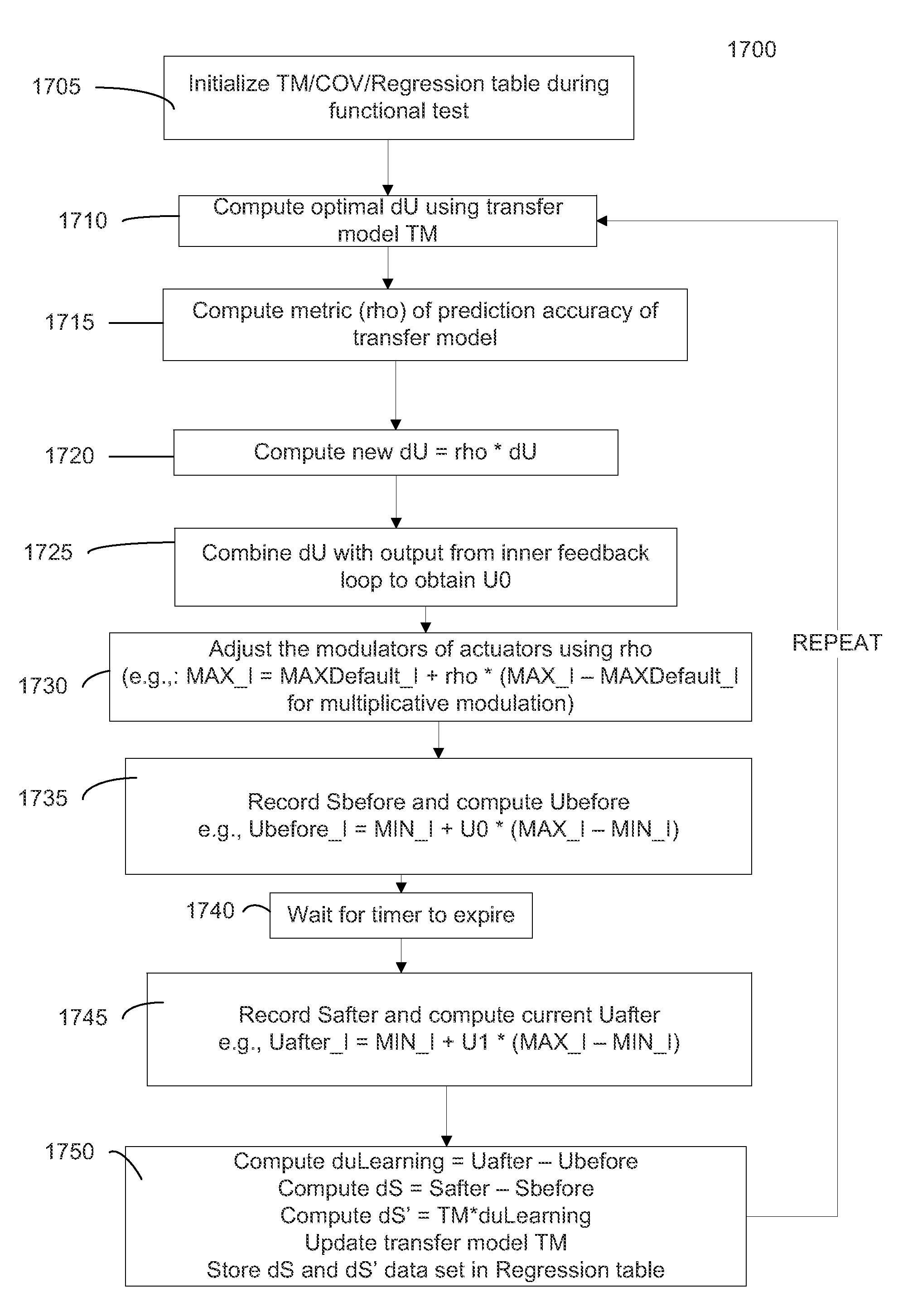
Energy-Optimal Control Decisions for Systems
ActiveUS20120101648A1Minimal energyImprove accuracyMechanical apparatusLevel controlTransfer modelOptimal control
Methods, systems, and apparatuses are provided for controlling an environmental maintenance system that includes a plurality of sensors and a plurality of actuators. The operation levels of the actuators can be determined by optimizing a penalty function. As part of the penalty function, the sensor values can be compared to reference values. The optimized values of the operation levels can account for energy use of actuators at various operation levels and predicted differences of the sensor values relative to the reference values at various operation levels. The predicted difference can be determined using a transfer model. An accuracy of the transfer model can be determined by comparing predicted values to measured values. This accuracy can be used in determining new operational levels from an output of the transfer model (e.g., attenuating the output of the transfer model based on the accuracy).
Owner:VIGILENT CORP
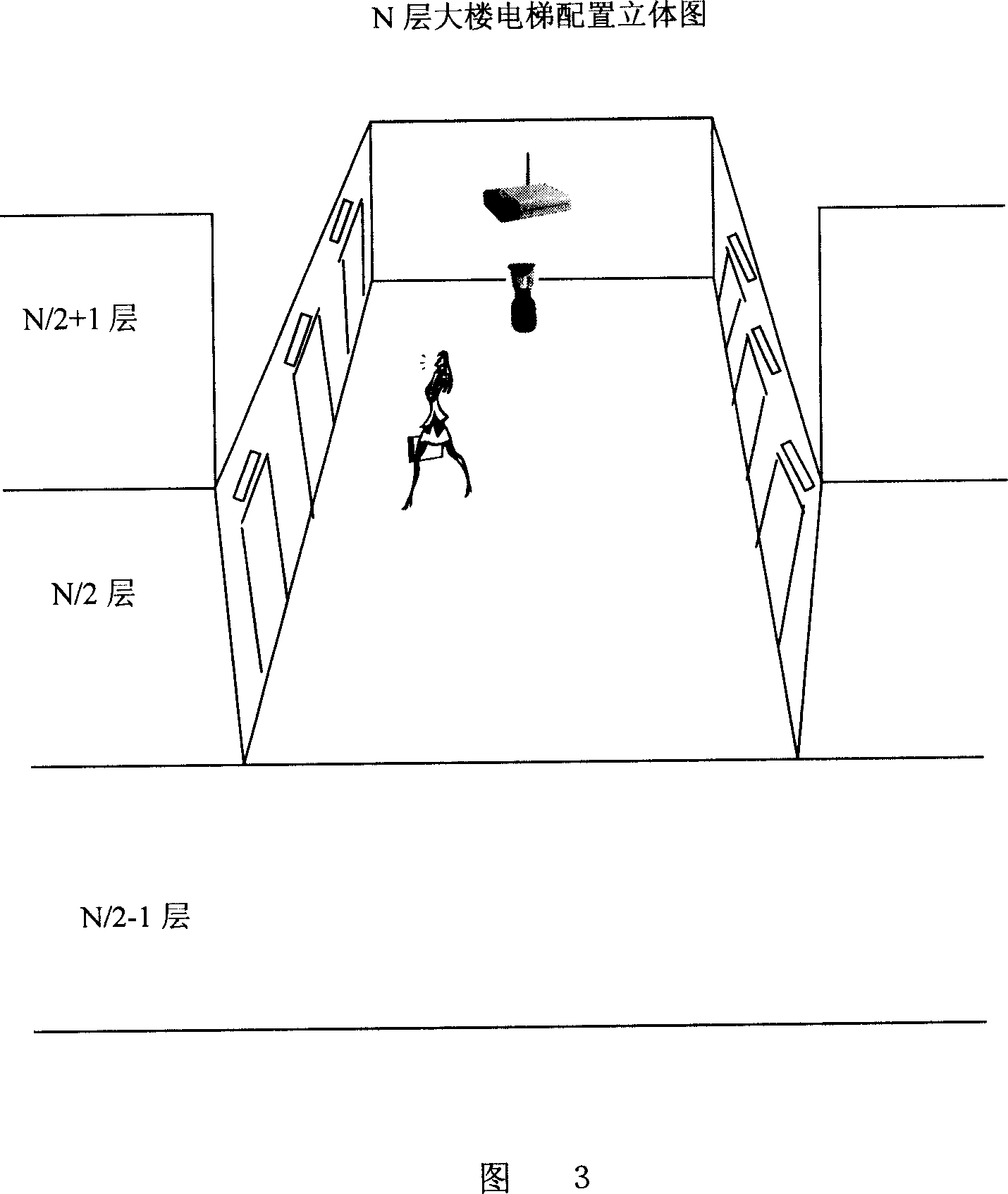
Intelligent dispatcher for group controlled lifts based on image recognizing technology
The intelligent dispatcher for group controlled lifts based on image recognizing technology includes one central dispatching computer for group controlled lifts and with one dispatching control strategy module for the optimized control of the lifts in the building, visual car sensors for acquiring the passenger flow information, and omnibearing visual sensors for acquiring the waiting passenger information, with the visual car sensors and the omnibearing visual sensors being connected to the central dispatching computer. The central computer includes also a lift passenger flow calculating module, and a running mode recognizing module to divide different lift group running modes, except its dispatching control strategy module for selecting dispatching control strategy fitting different running modes. The present invention can detect real-time passenger flow information and has precise group control dispatching.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) servo system control method based on fuzzy and active disturbance rejection control
InactiveCN103401501AWide speed rangeImprove robustnessElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlDifferential coefficientFriction torque
The invention relates to a PMSM servo system control method based on fuzzy and active disturbance rejection control. A position signal is given by a differential tracker to arrange a transition process so that the contradiction between rapidness and overshoot of a system is solved, and uncertainty, friction torques and external disturbance due to modeling errors of the system are observed via an expansion state observer; according to the error between the differentials generated by the differential tracker and state variation generated by the expansion state observer, a fuzzy inference rule is obtained with application of experimental experience of technical staff, so that a fuzzy rule control table of an error proportion coefficient, a differential coefficient and an integration coefficient is established; accurate control amount is obtained after de-fuzzification, so that parameter self-adaptive adjustment of a nonlinear error feedback control law is realized; and compensation amounts of the nonlinear error feedback control law and the expansion state observer to the total disturbance forms the control amount, thereby realizing optimal control for an controlled object. The method of the invention improves both tracking precision and disturbance rejection capability of the system.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
System and method to optimize control cohorts using clustering algorithms
InactiveUS20080082356A1Minimize the differenceTherapiesHospital data managementCluster algorithmOptimal control
A computer implemented method, apparatus, and computer usable program code for automatically selecting an optimal control cohort. Attributes are selected based on patient data. Treatment cohort records are clustered to form clustered treatment cohorts. Control cohort records are scored to form potential control cohort members. The optimal control cohort is selected by minimizing differences between the potential control cohort members and the clustered treatment cohorts.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Digitally controlled voltage regulator
ActiveUS20040150928A1Easy to customizePrecise power controlEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalOptimal control
Disclosed is a digitally controlled multi-phase voltage regulator system providing regulated power to electronic components that have variable power requirements. Power is supplied by one or more power integrated circuits (IC) each having a high side power switch controlled by pulse width modulated signals and a low side power switch. The power IC senses voltage at the load and has an on-chip current mirror for generating a current that is a ratio of current delivered to the load. The power IC also has current limiting and on-chip temperature sensing components. The voltage and current information is digitized and provided to a control integrated circuit (IC). The control IC receives this digitized information as well as user provided parameters and, in the regulation mode of operation, provides digitized pulse width modulated control signals to the power IC. In an active transient response mode of operation, the control IC provides signals to turn either the high side switches or low side switches ON. Fault detection circuitry identifies over voltage, under voltage, and excessive temperatures. All communications between the control IC and the power IC are digital providing high bandwidth, optimal control frequency response, noise immunity and efficient active transient response.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com