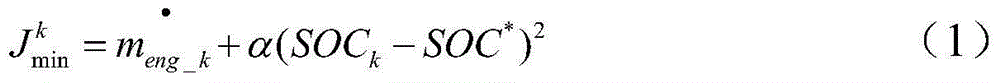Patents
Literature
1637 results about "Dynamic programming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dynamic programming is both a mathematical optimization method and a computer programming method. The method was developed by Richard Bellman in the 1950s and has found applications in numerous fields, from aerospace engineering to economics. In both contexts it refers to simplifying a complicated problem by breaking it down into simpler sub-problems in a recursive manner. While some decision problems cannot be taken apart this way, decisions that span several points in time do often break apart recursively. Likewise, in computer science, if a problem can be solved optimally by breaking it into sub-problems and then recursively finding the optimal solutions to the sub-problems, then it is said to have optimal substructure.
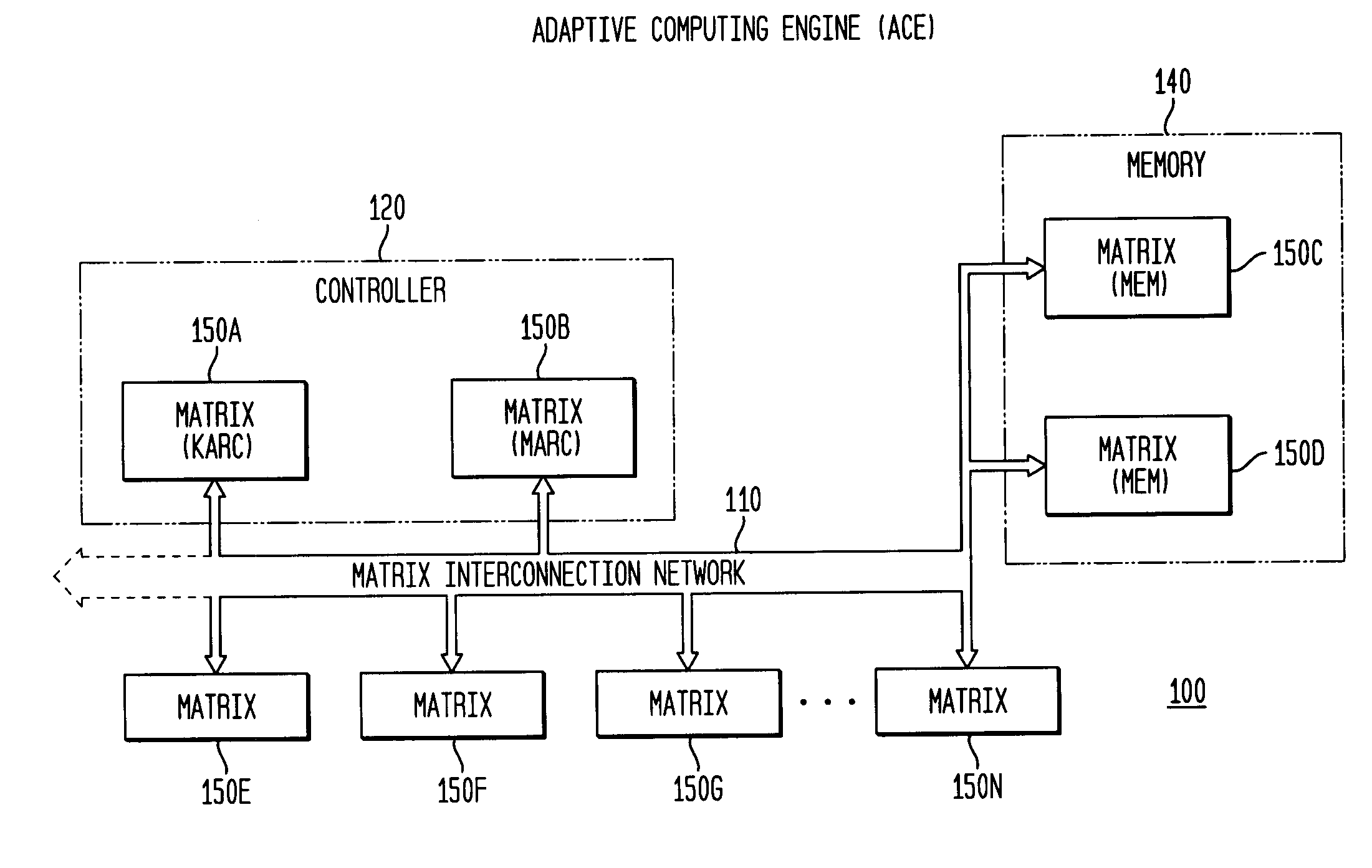
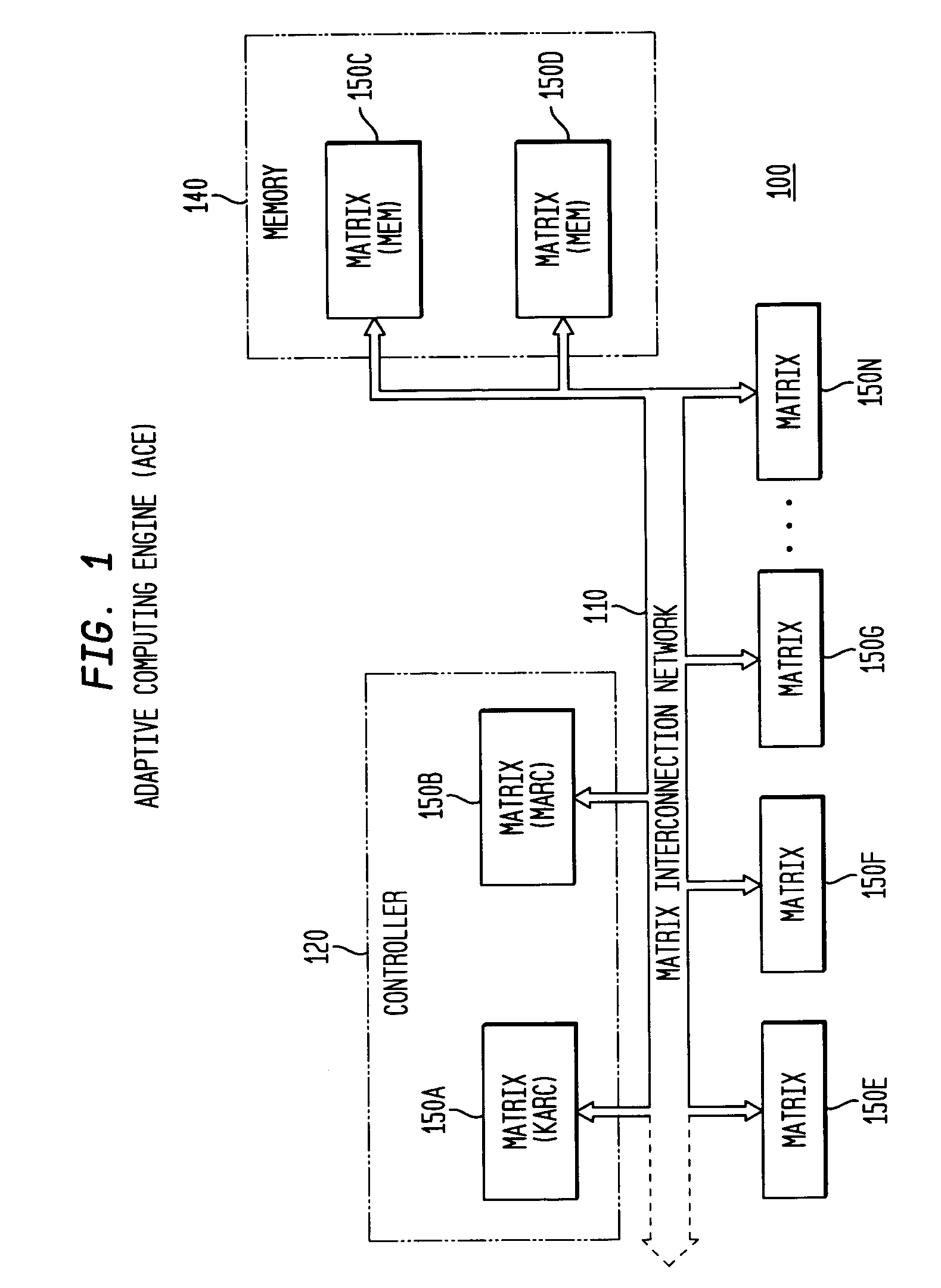
System, method and software for static and dynamic programming and configuration of an adaptive computing architecture
ActiveUS20050044344A1Architecture with single central processing unitSpecial data processing applicationsInterconnectionSystems approaches
The present invention provides a system, method and software for programming and configuring an adaptive computing architecture or device. The invention utilizes program constructs which correspond to and map directly to the adaptive hardware having a plurality of reconfigurable nodes coupled through a reconfigurable matrix interconnection network. A first program construct corresponds to a selected node. A second program construct corresponds to an executable task of the selected node and includes one or more firing conditions capable of determining the commencement of the executable task of the selected node. A third program construct corresponds to at least one input port coupling the selected node to the matrix interconnect network for input data to be consumed by the executable task. A fourth program construct corresponds to at least one output port coupling the selected node to the matrix interconnect network for output data to be produced by the executable task;
Owner:CORNAMI INC
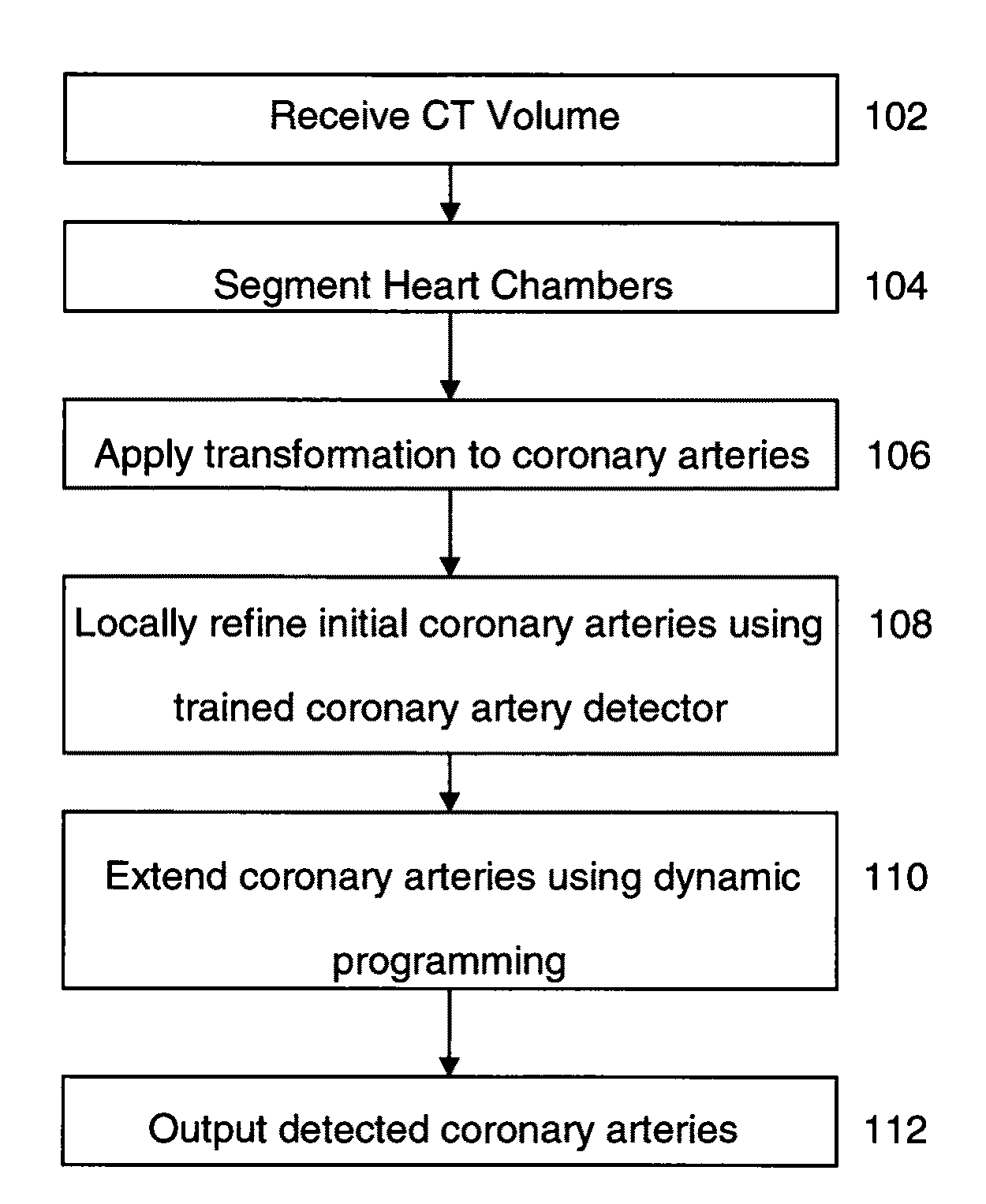
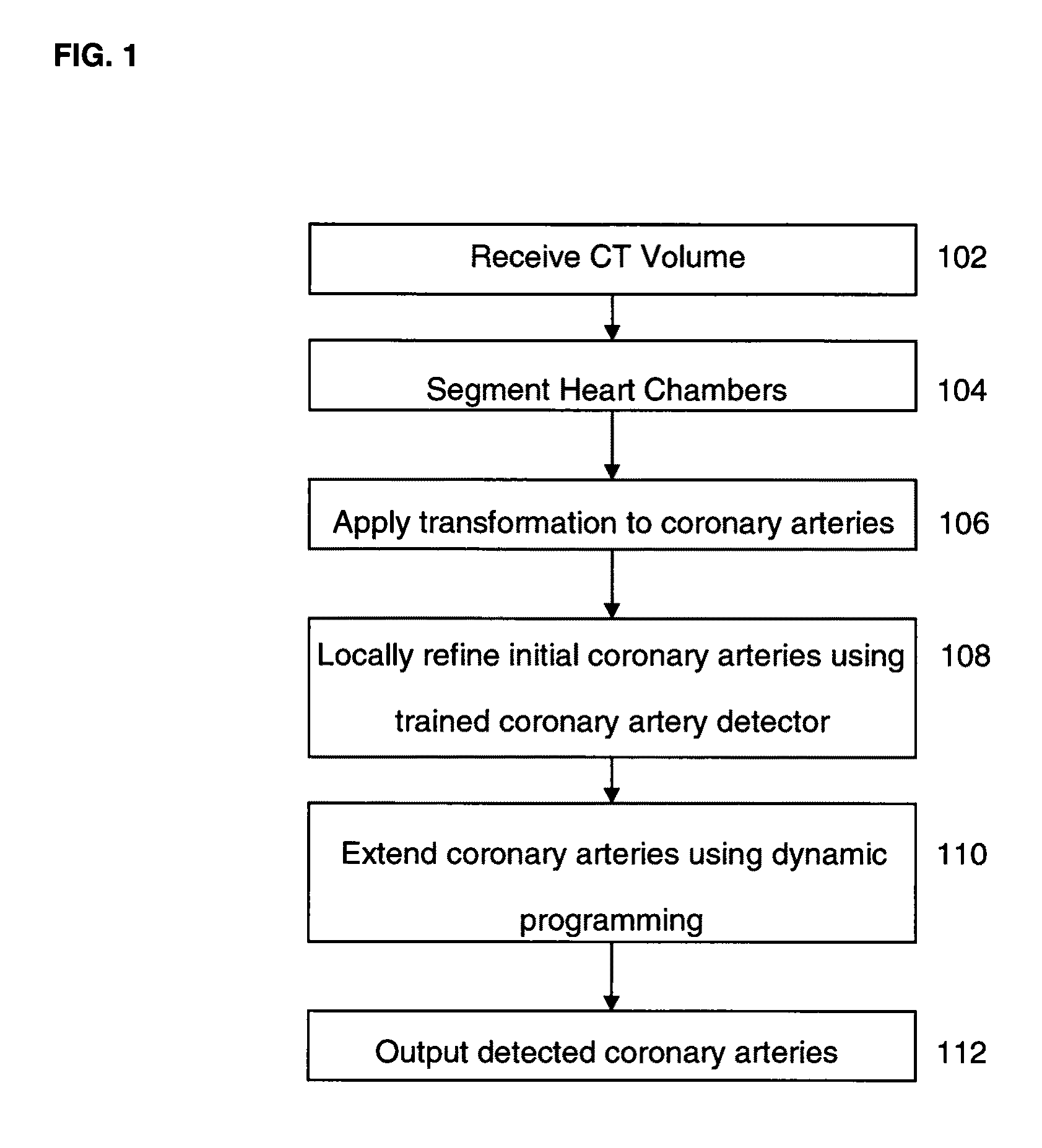
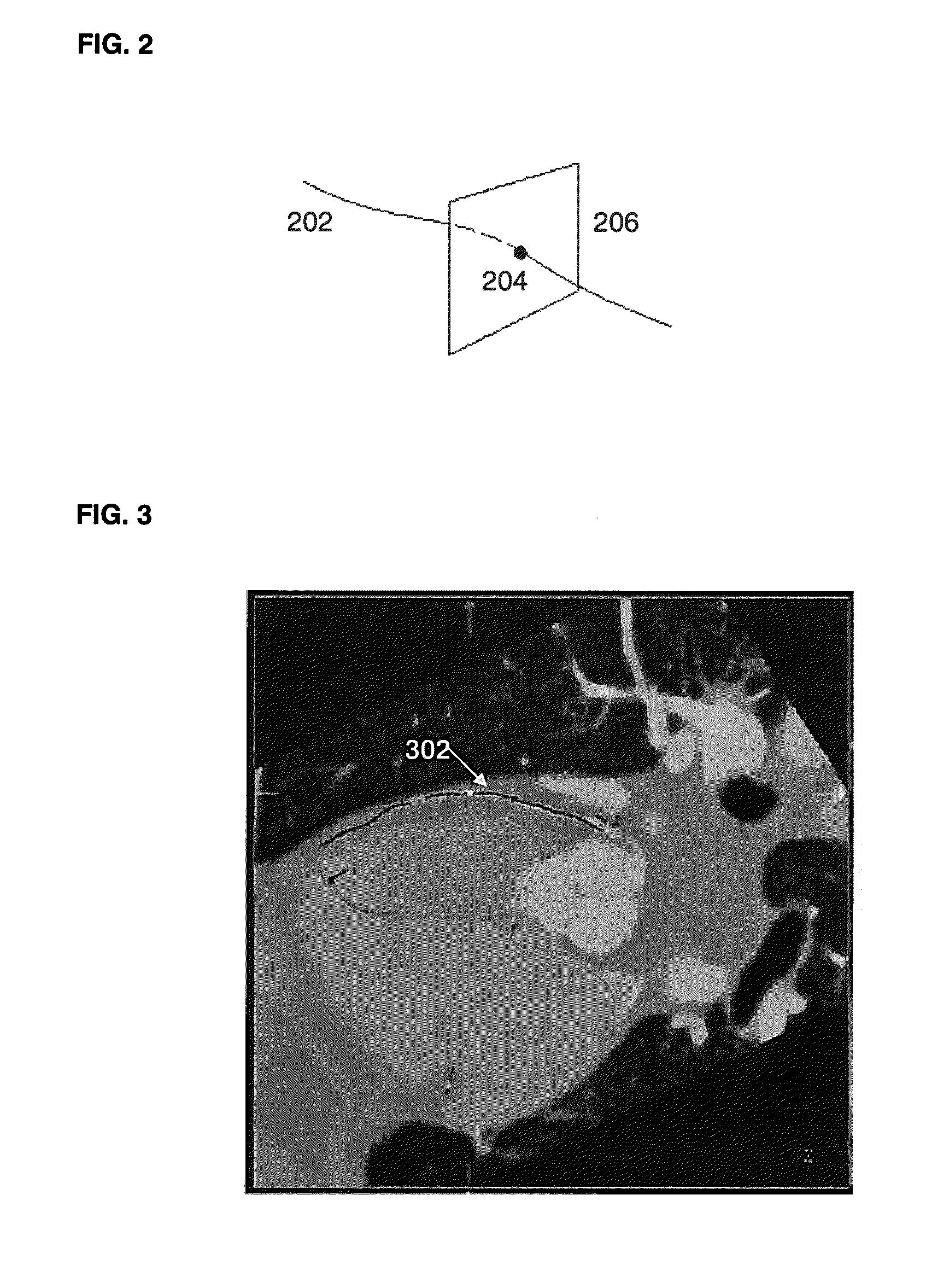
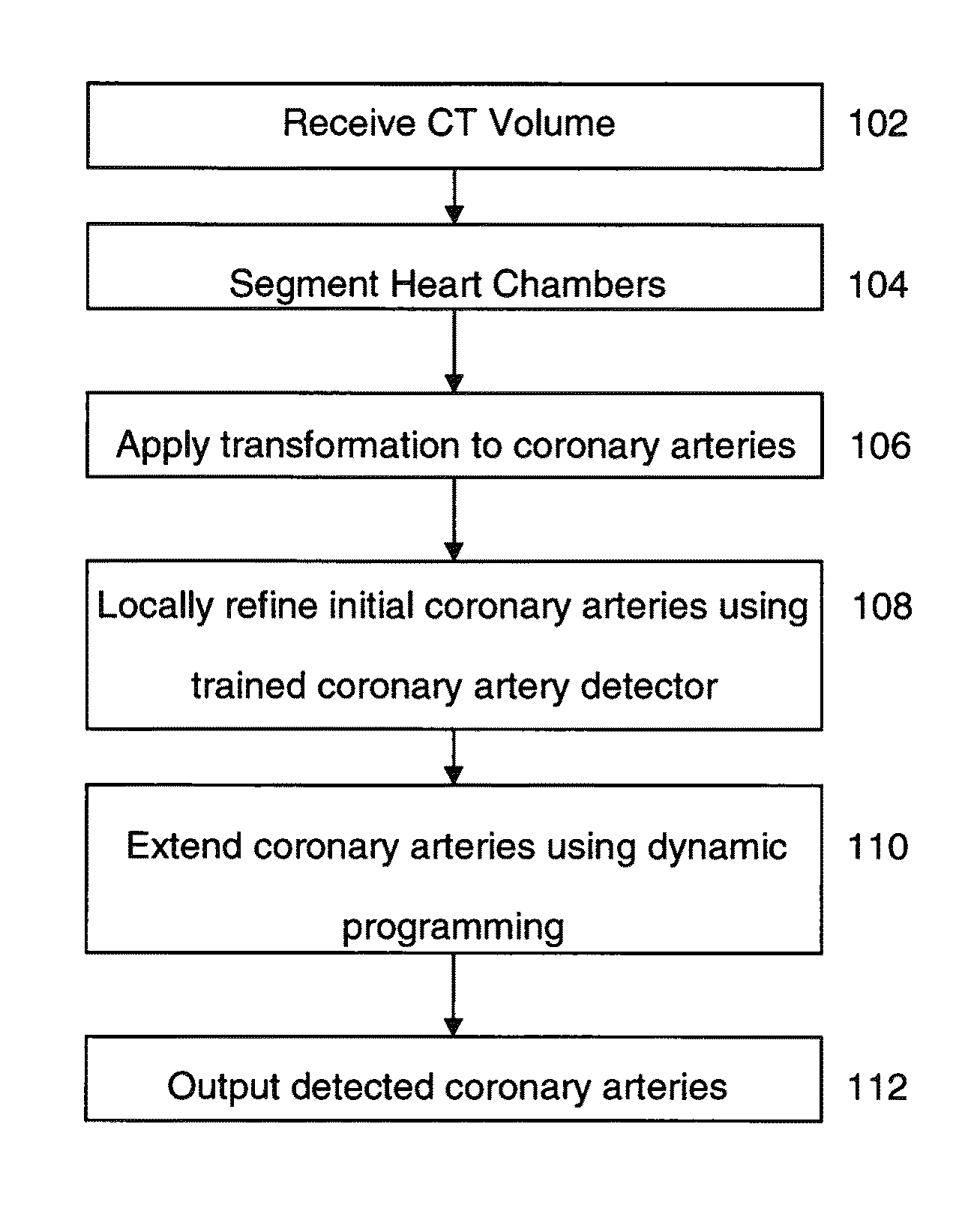
Method and System for Automatic Coronary Artery Detection
ActiveUS20100067760A1Efficiently and robustly detectImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesHeart chamber
A method and system for coronary artery detection in 3D cardiac volumes is disclosed. The heart chambers are segmented in the cardiac volume, and an initial estimation of a coronary artery is generated based on the segmented heart chambers. The initial estimation of the coronary artery is then refined based on local information in the cardiac volume in order to detect the coronary artery in the cardiac volume. The detected coronary artery can be extended using 3D dynamic programming.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
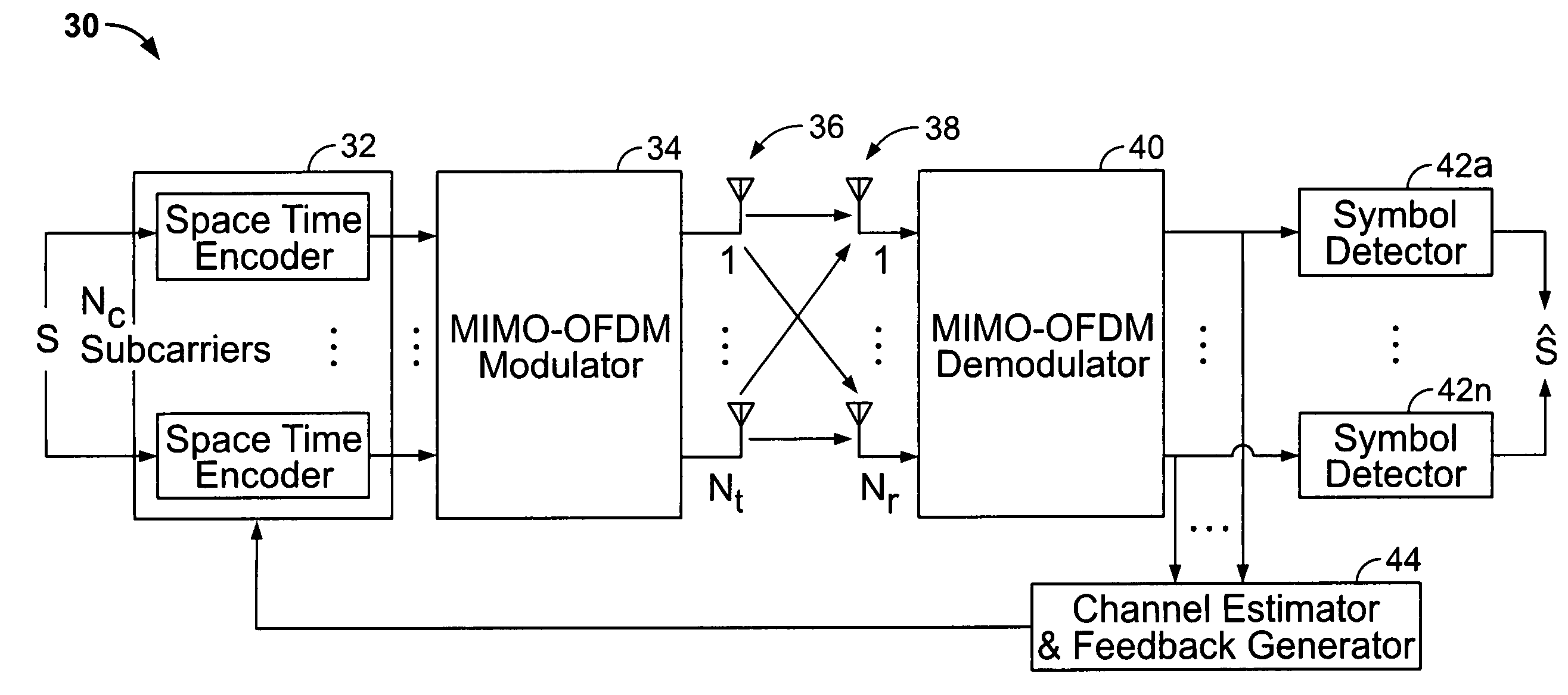
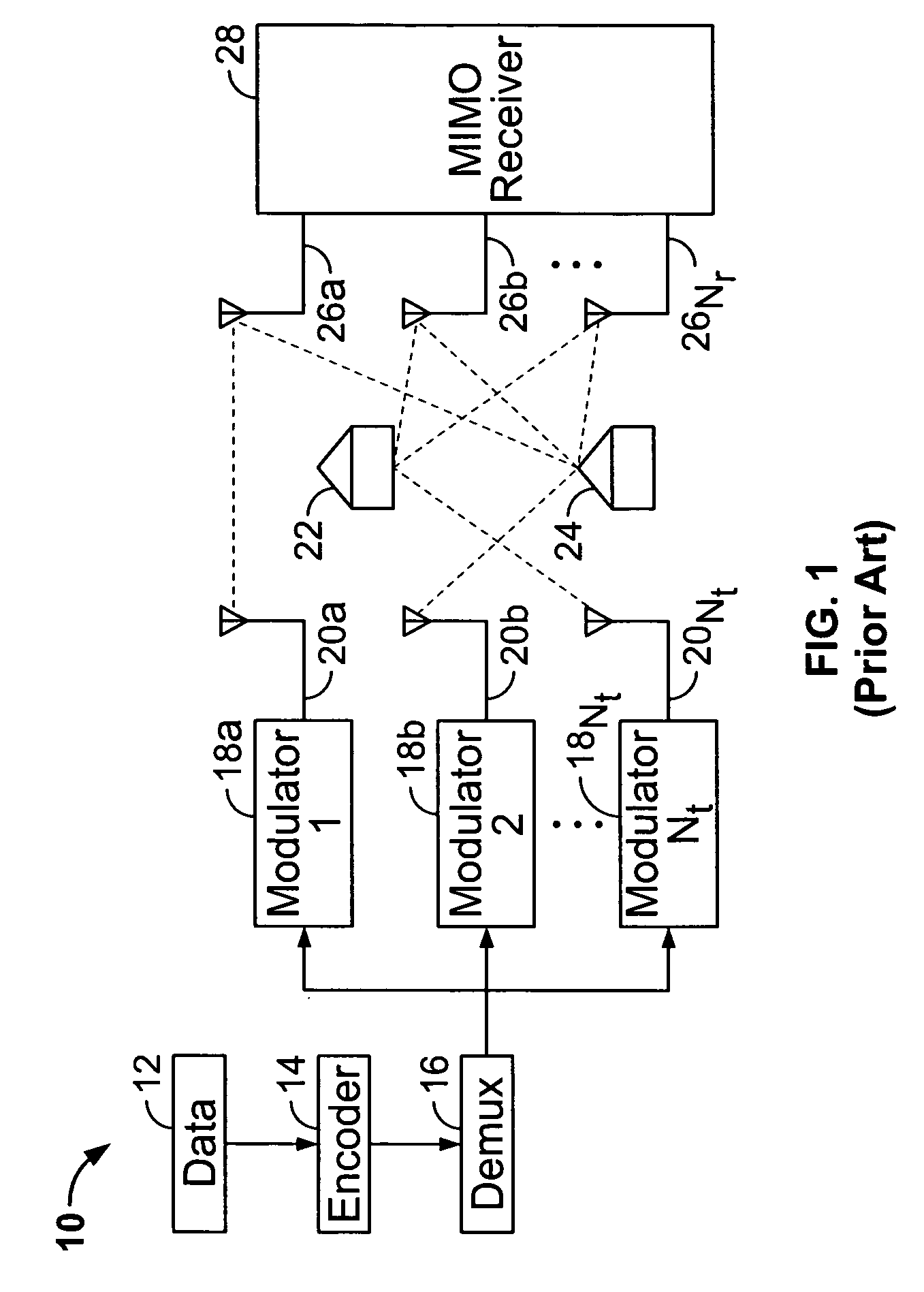
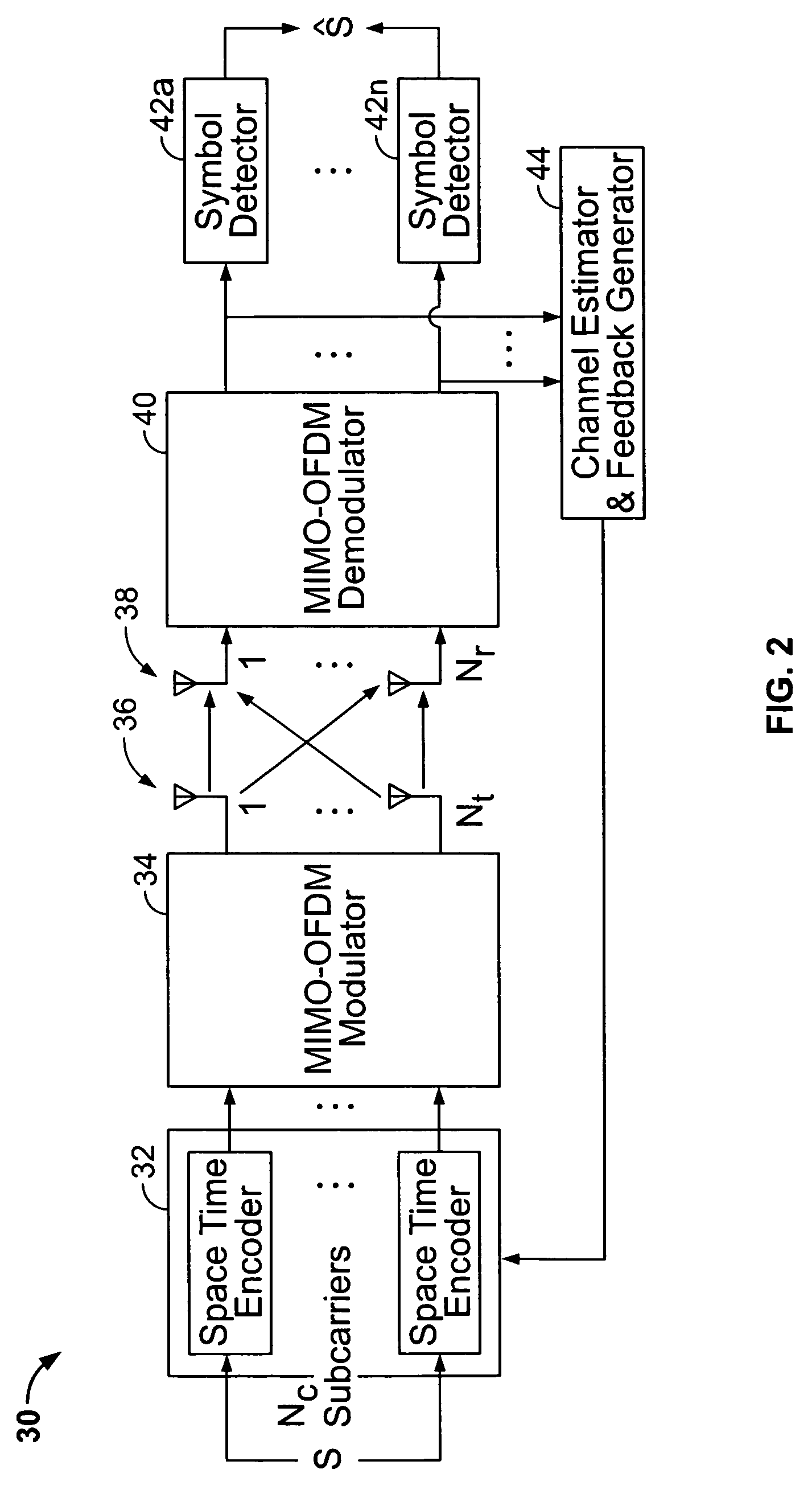
Recursive and trellis-based feedback reduction for MIMO-OFDM with rate-limited feedback
InactiveUS20070297529A1Reduce feedbackMaintain performanceModulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCarrier signalDynamic programming
Techniques are provided for reducing feedback while maintaining performance in a MIMO-OFDM system. The disclosed techniques employ finite-rate feedback methods that uses vector quantization compression. The disclosed methods / techniques generally involve: receiving a plurality of symbols from a plurality of sub-carriers at a receiver; selecting a plurality of indices of codewords corresponding to a codebook of pre-coding weighting matrices for the sub-carriers based on vector quantization compression of the codewords; and transmitting the selected indices over a wireless channel to a transmitter. Finite state vector quantization feedback makes use of a finite state vector quantizer (FSVQ), which is a recursive vector quantizer (VQ) with a finite number of states. In finite state vector quantization feedback, optimal precoding matrices (beamforming vectors) are selected sequentially across subcarriers. In a trellis-based feedback method, the optimal precoding matrices are selected at the same time for all subcarriers by searching for the optimum choice of matrices along a trellis using the Viterbi algorithm (dynamic programming).
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
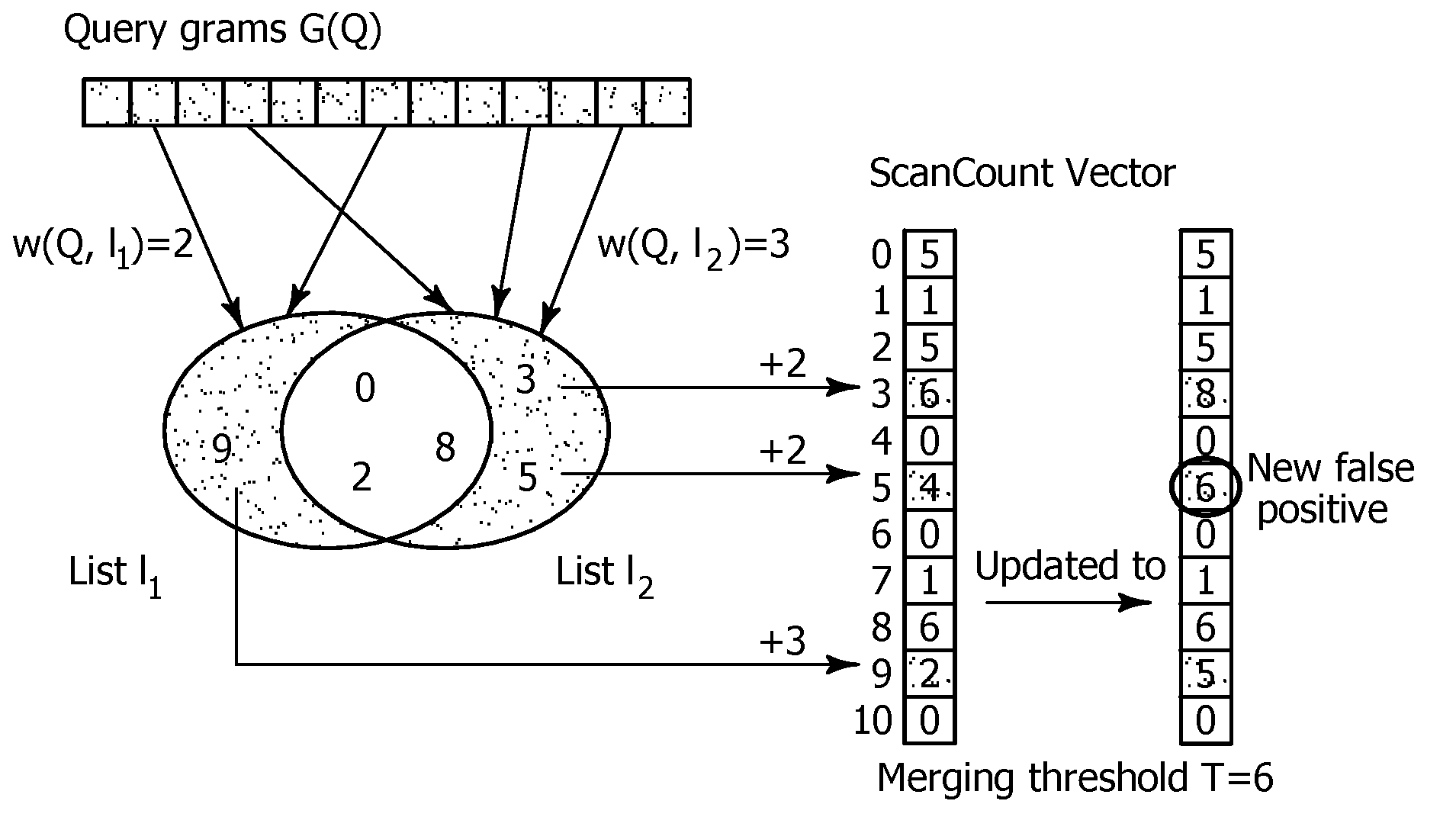
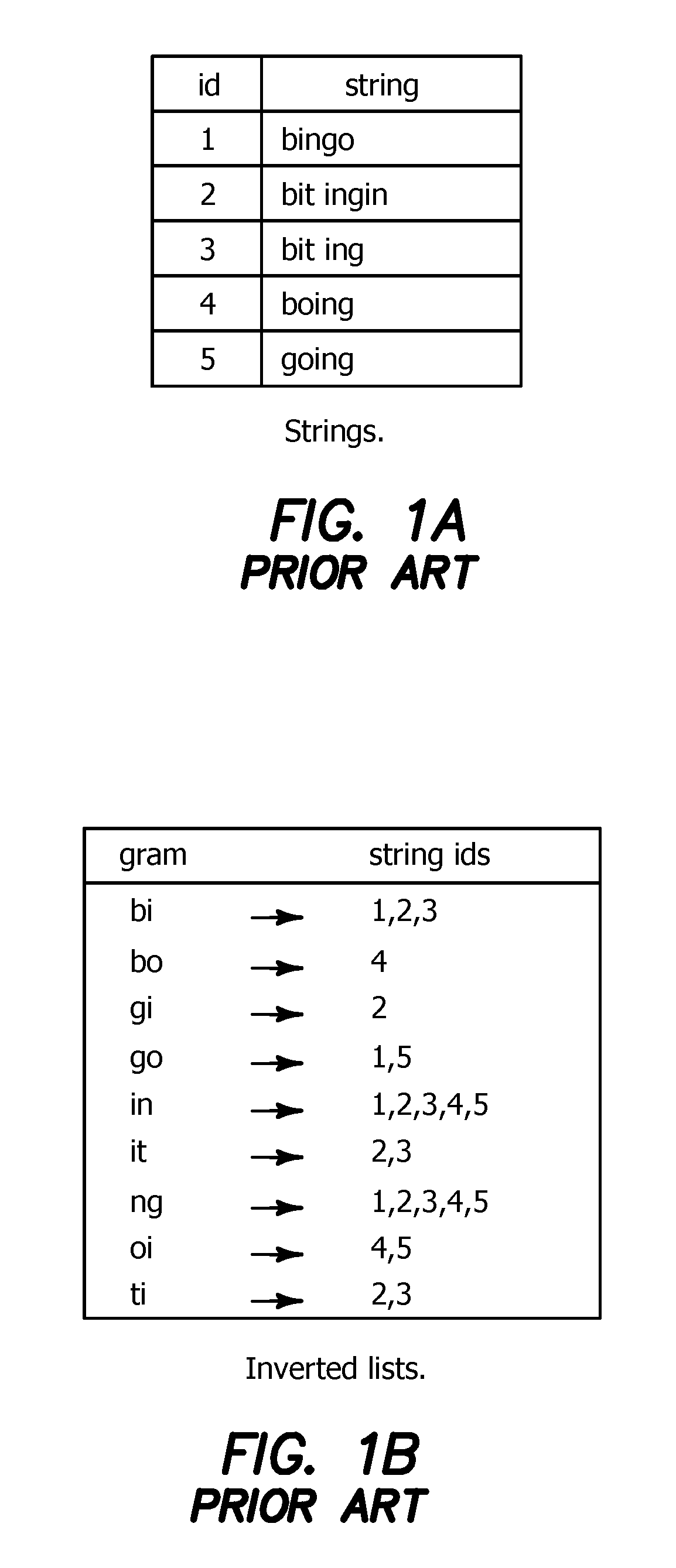
Method and Apparatus for Improving Performance of Approximate String Queries Using Variable Length High-Quality Grams
ActiveUS20100125594A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceWorkload
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
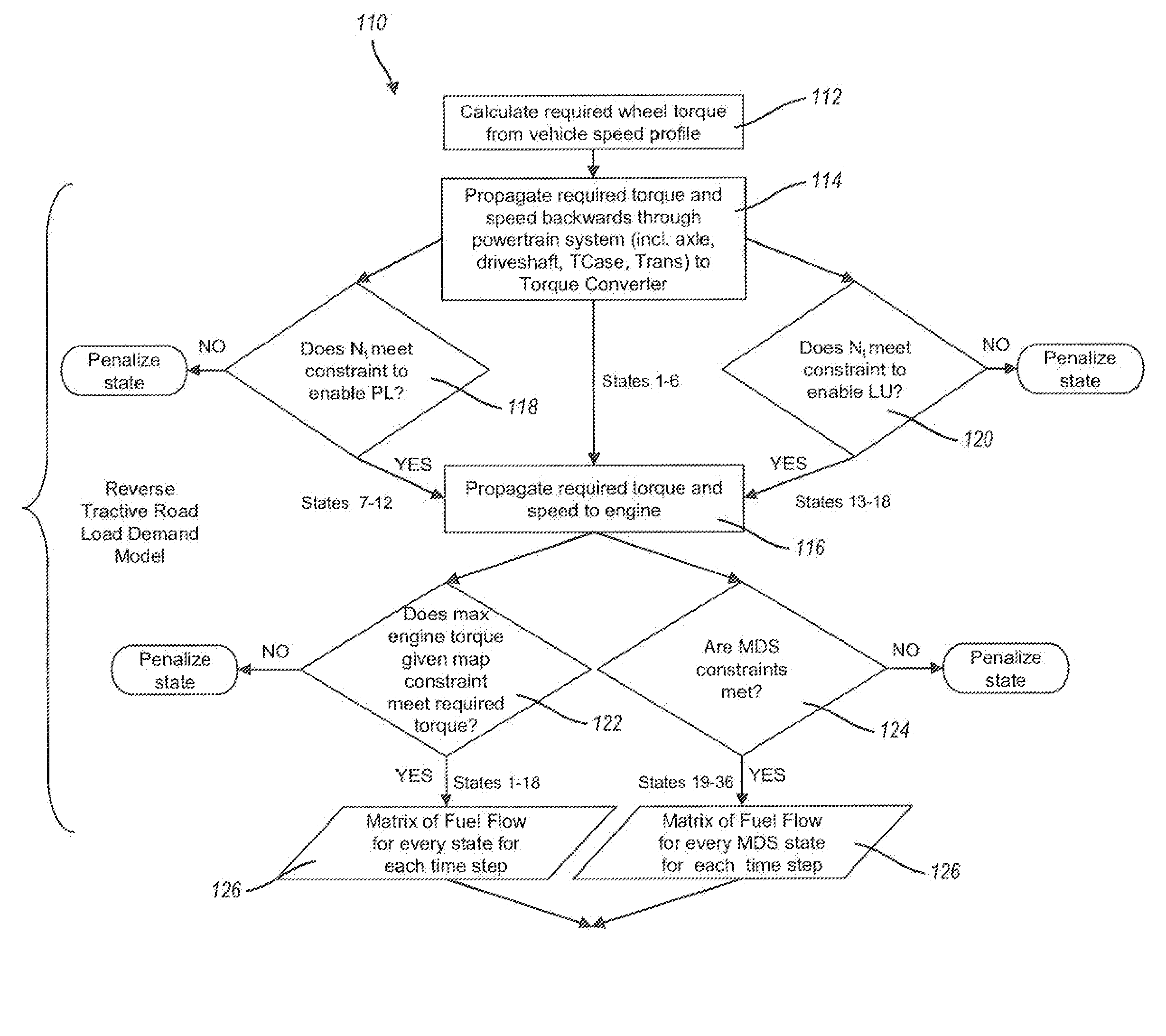
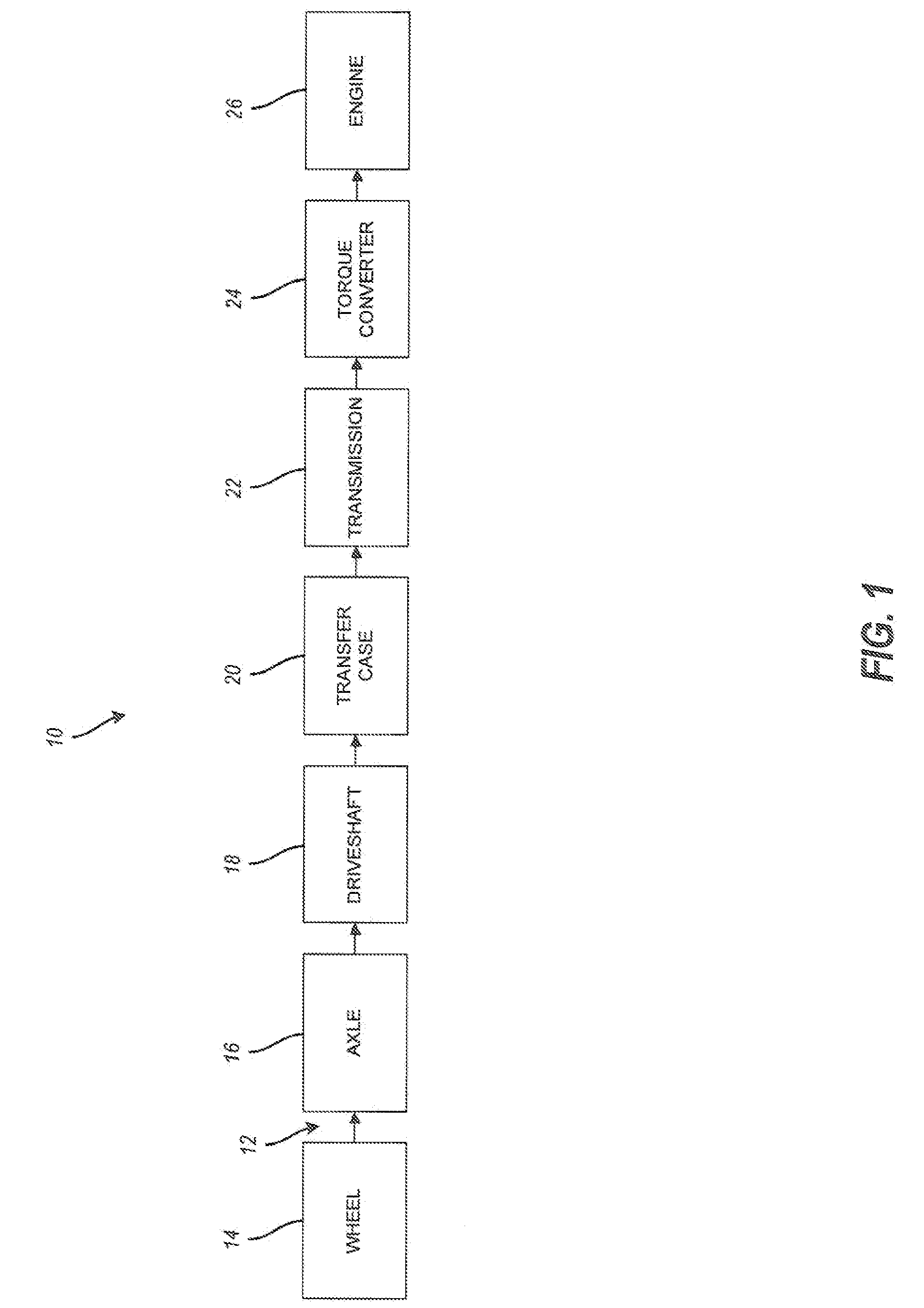
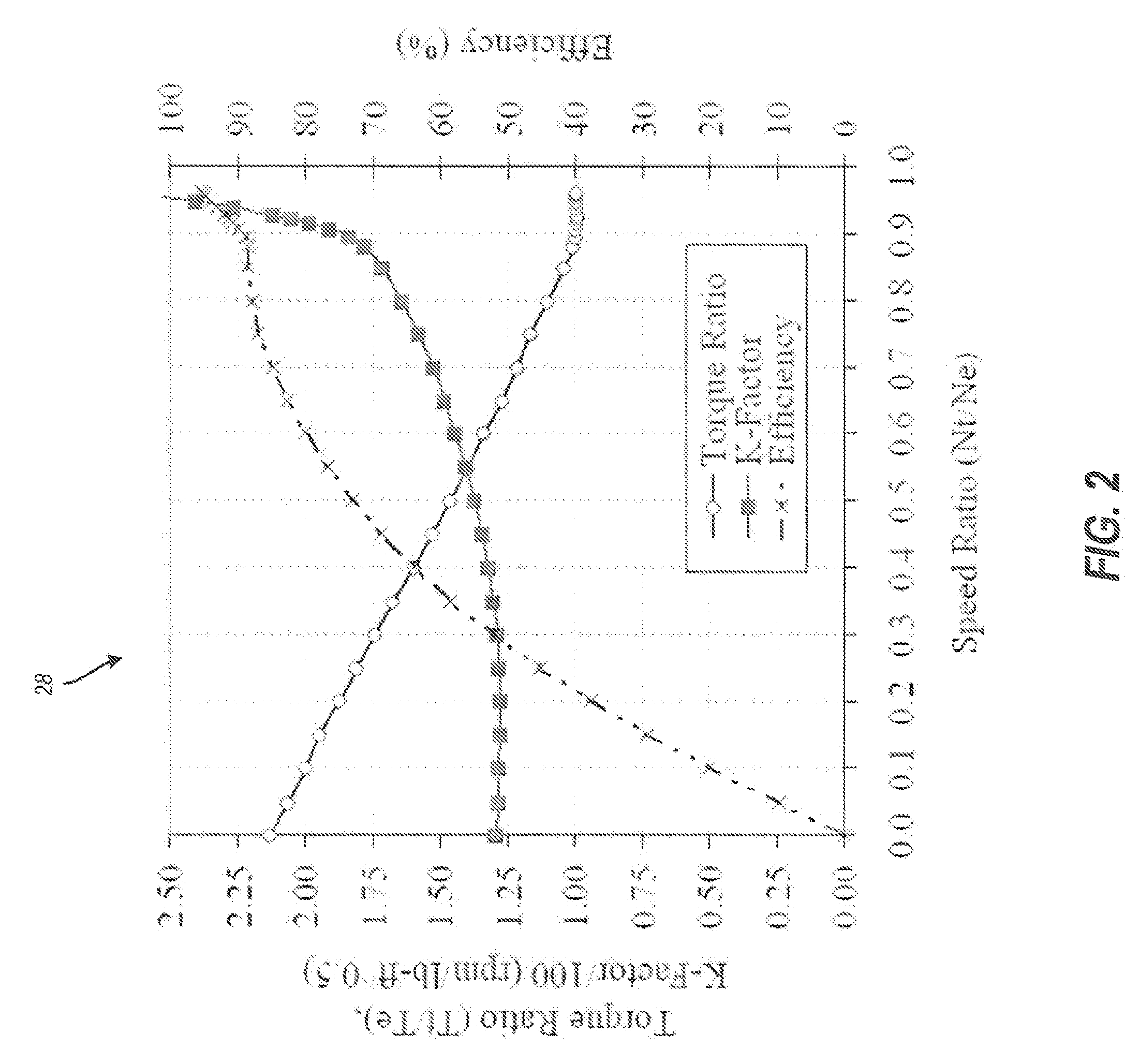
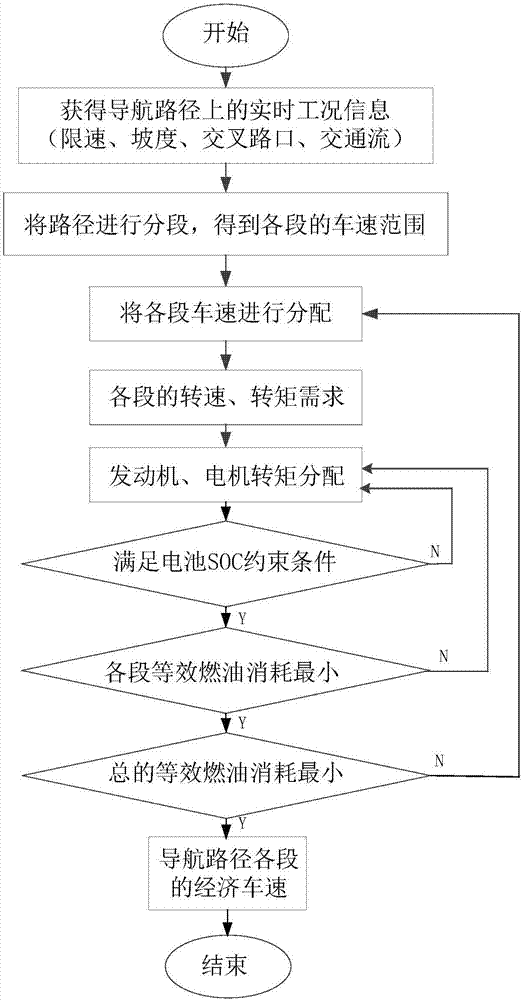
Methods and systems for powertrain optimization and improved fuel economy
InactiveUS20080262712A1Improve fuel economyMinimizes accumulated fuel flowAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlDynamical optimizationOptimal control
The technology described herein provides methods and systems for powertrain optimization and improved fuel economy including multiple displacement engine modeling and control optimization, automotive powertrain matching for fuel economy, cycle-based automotive shift and lock-up scheduling for fuel economy, and engine performance requirements based on vehicle attributes and drive cycle characteristics. Also provided is a reverse tractive road load demand simulation algorithm used to propagate a reverse tractive road load demand and a corresponding component torque and speed, derived from a vehicle speed trace, in a reverse direction through a powertrain system. Also provided is a dynamic optimization algorithm. The dynamic programming algorithm is applied to a matrix of fuel flow rates to find the optimal control path that maximizes the powertrain efficiency over a cycle.
Owner:FCA US
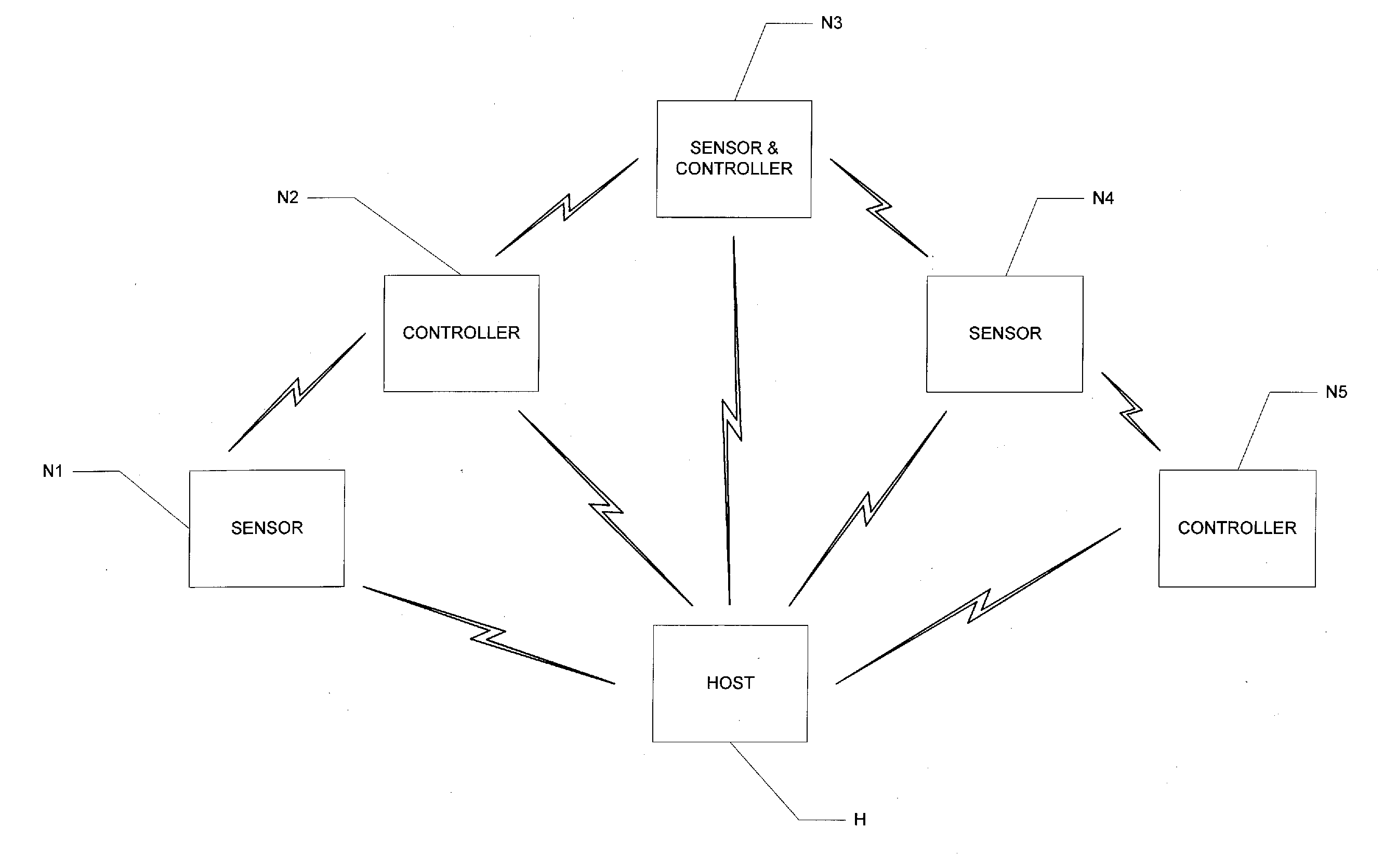
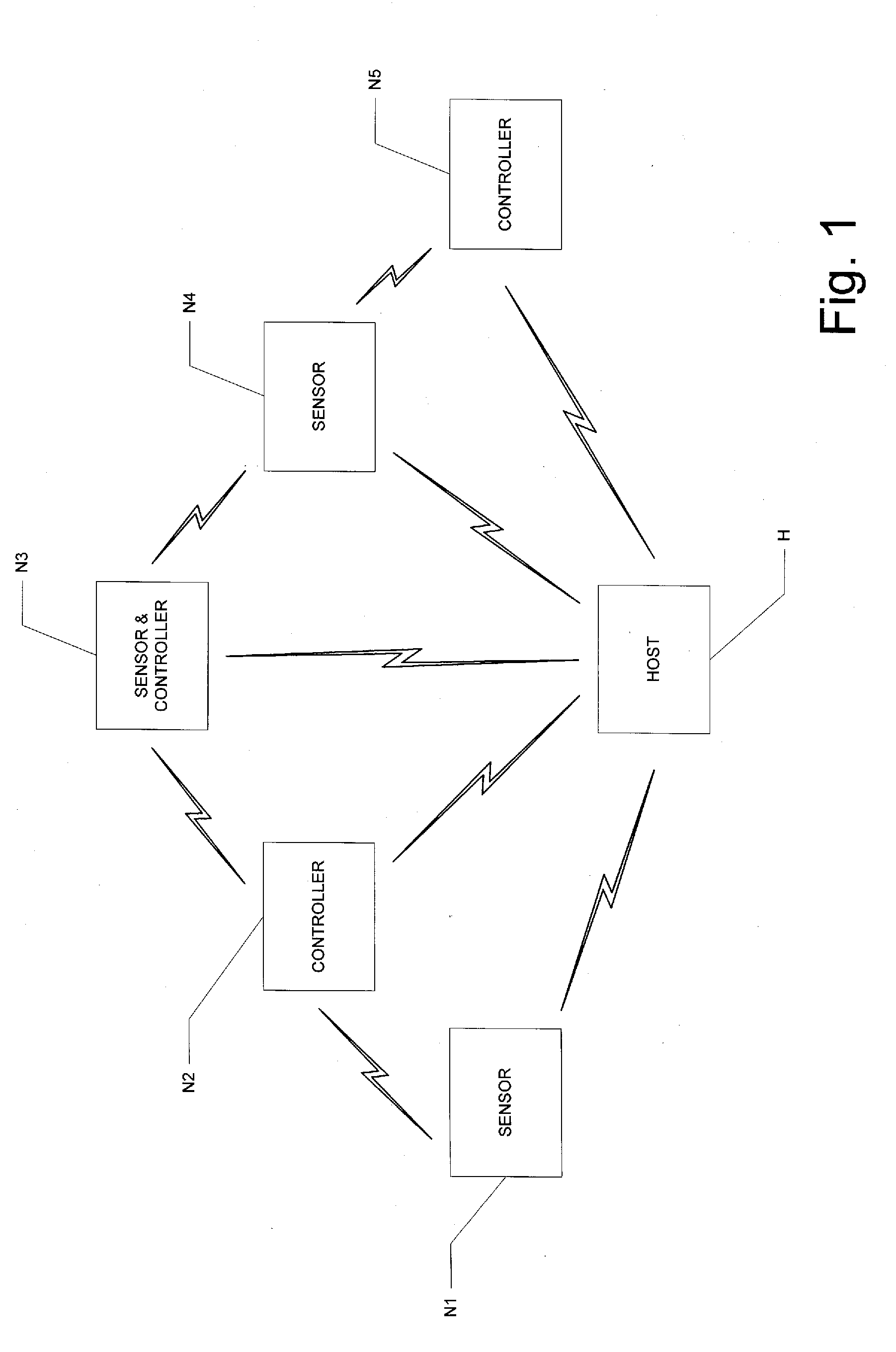
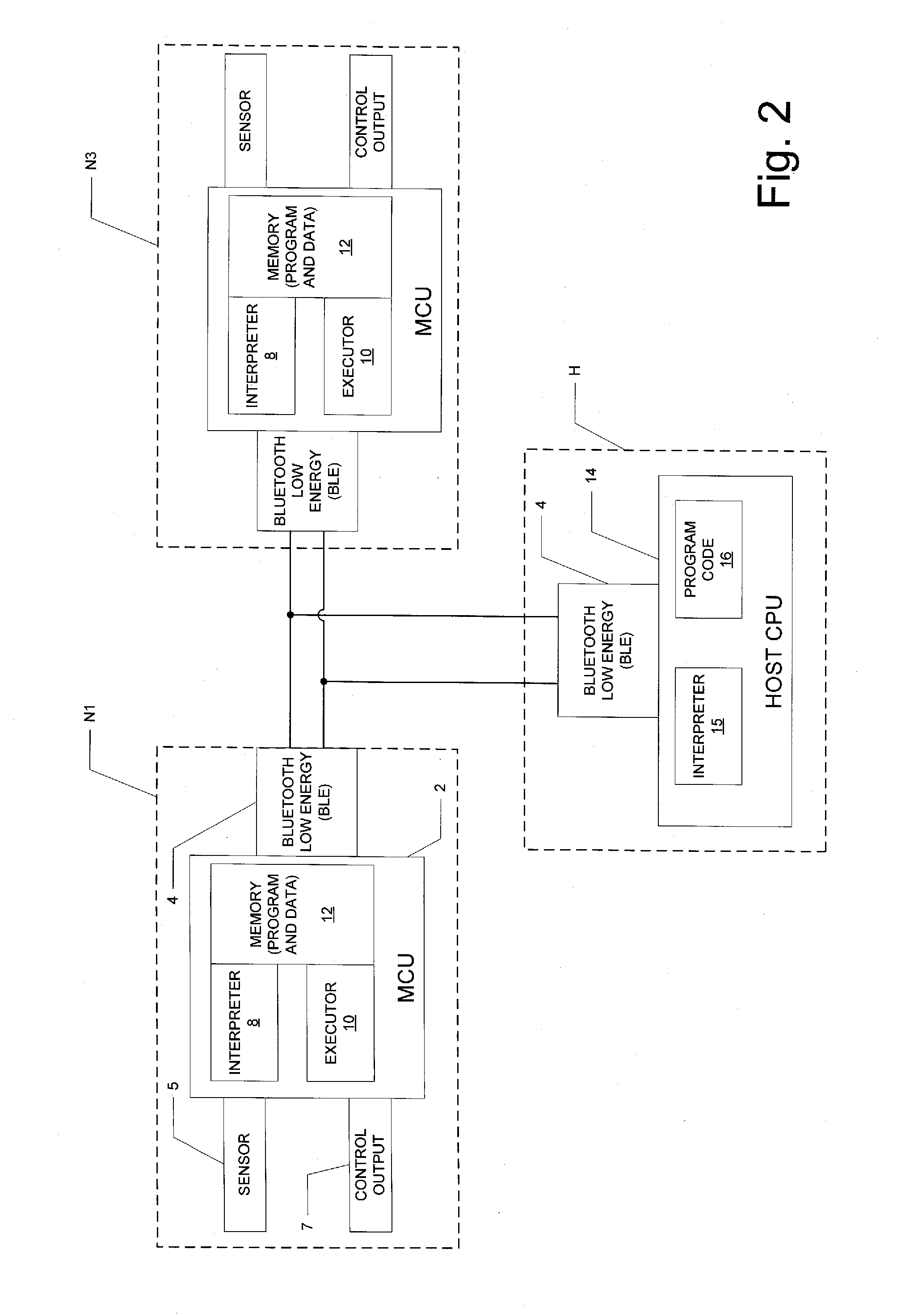
Dynamic Programming and Control of Networked Sensors and Microcontrollers
ActiveUS20150067119A1Adaptable to changeDigital computer detailsTransmissionMicrocontrollerProgram instruction
A network of sensor and controller nodes having the ability to be dynamically programmed and receive updated software from one another, and from a host system. Each network node includes multiple state machines, at least some of which are operable relative to physical pins at the network node; the physical pins correspond to inputs from sensor functions or outputs to control functions. The network nodes include microcontrollers that are operable in an operating mode to execute a state machine and respond to commands from other nodes or the host, and in a read mode to receive and store program instructions transmitted from other nodes or the host. A learn mode is also provided, by way of which a network node can store program code corresponding to instructions and actions at the node when under user control.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Language recognition using sequence frequency
InactiveUS6882970B1Image analysisData processing applicationsFrequency of occurrenceSimilarity measure
A system is provided for comparing an input query with a number of stored annotations to identify information to be retrieved from a database. The comparison technique divides the input query into a number of fixed-size fragments and identifies how many times each of the fragments occurs within each annotation using a dynamic programming matching technique. The frequencies of occurrence of the fragments in both the query and the annotation are then compared to provide a measure of the similarity between the query and the annotation. The information to be retrieved is then determined from the similarity measures obtained for all the annotations.
Owner:CANON KK
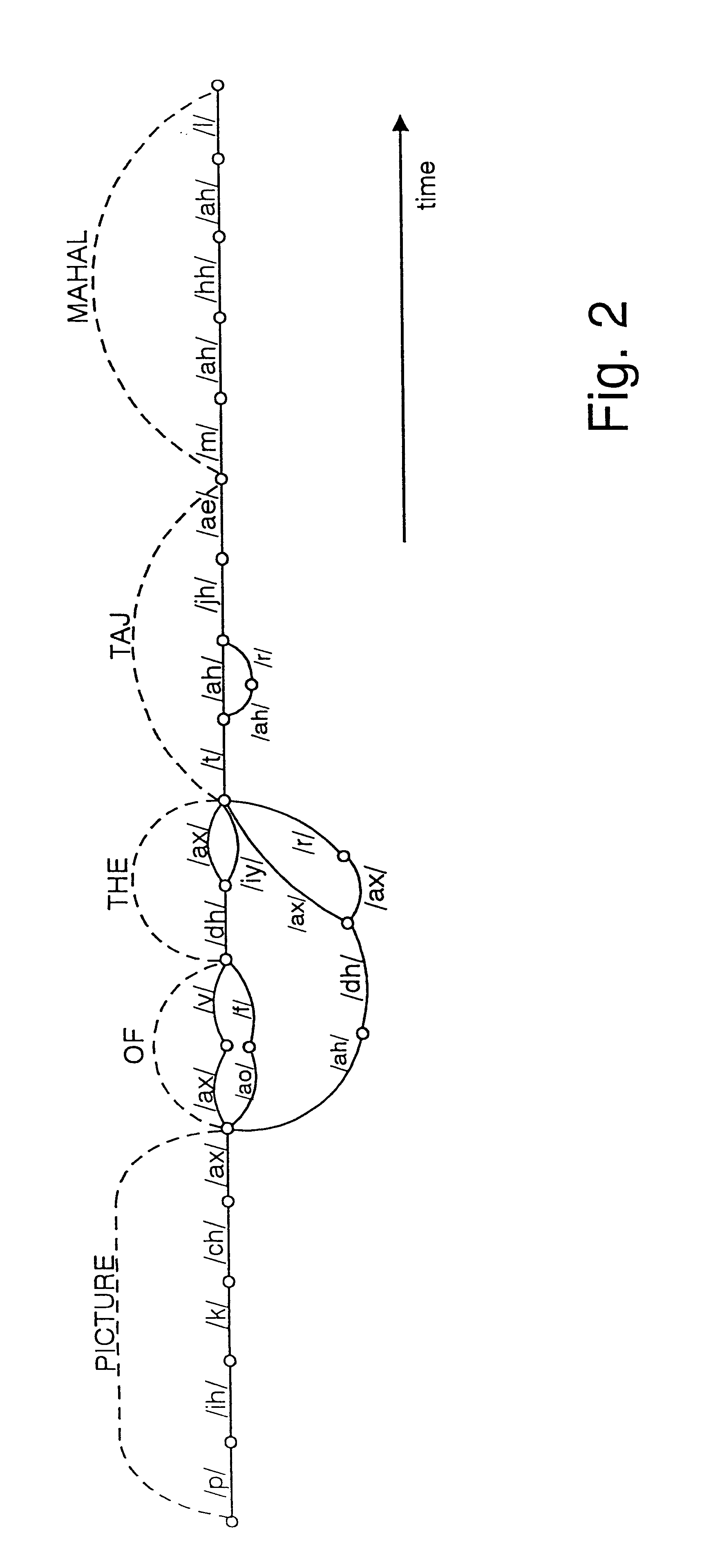
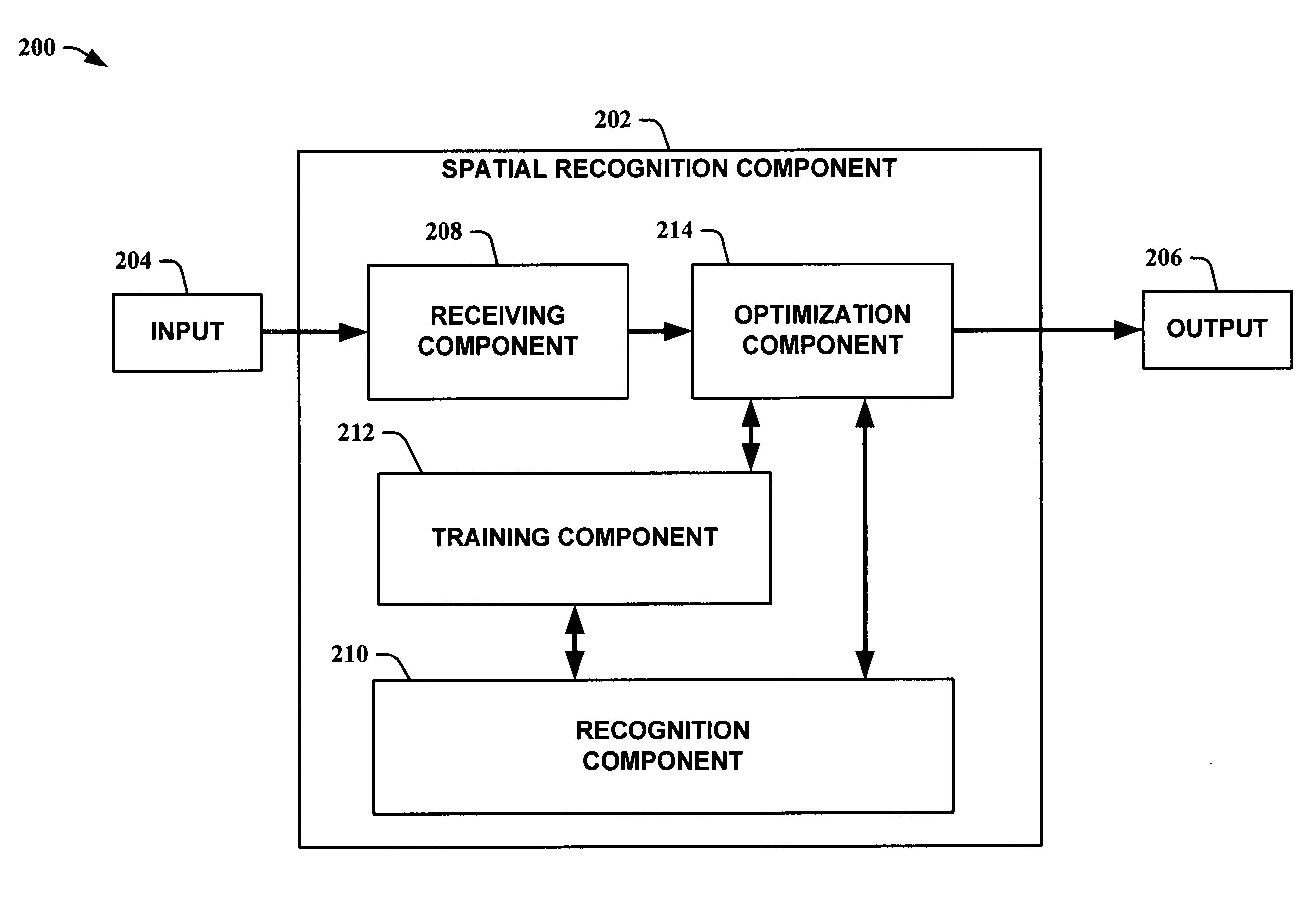
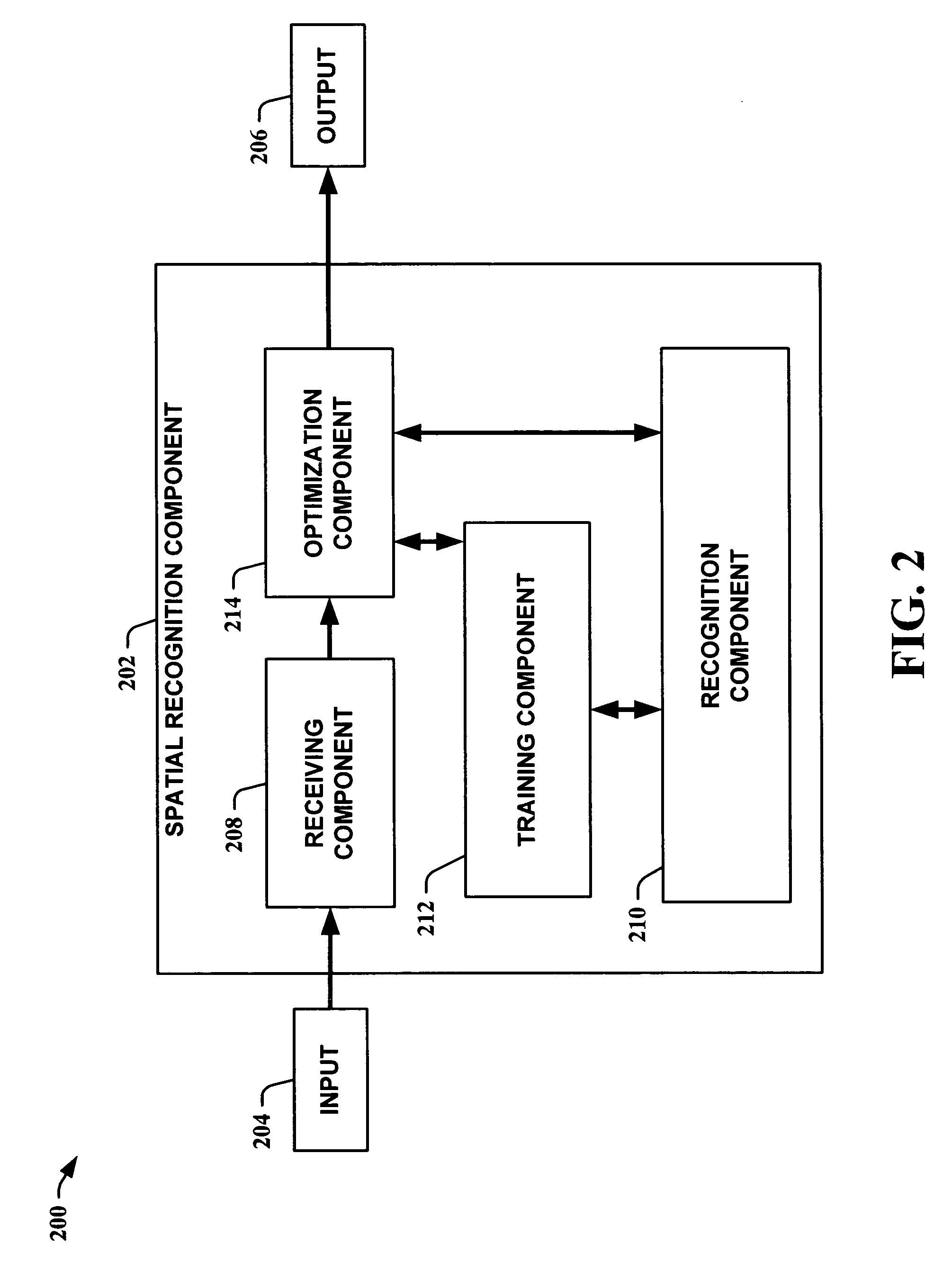
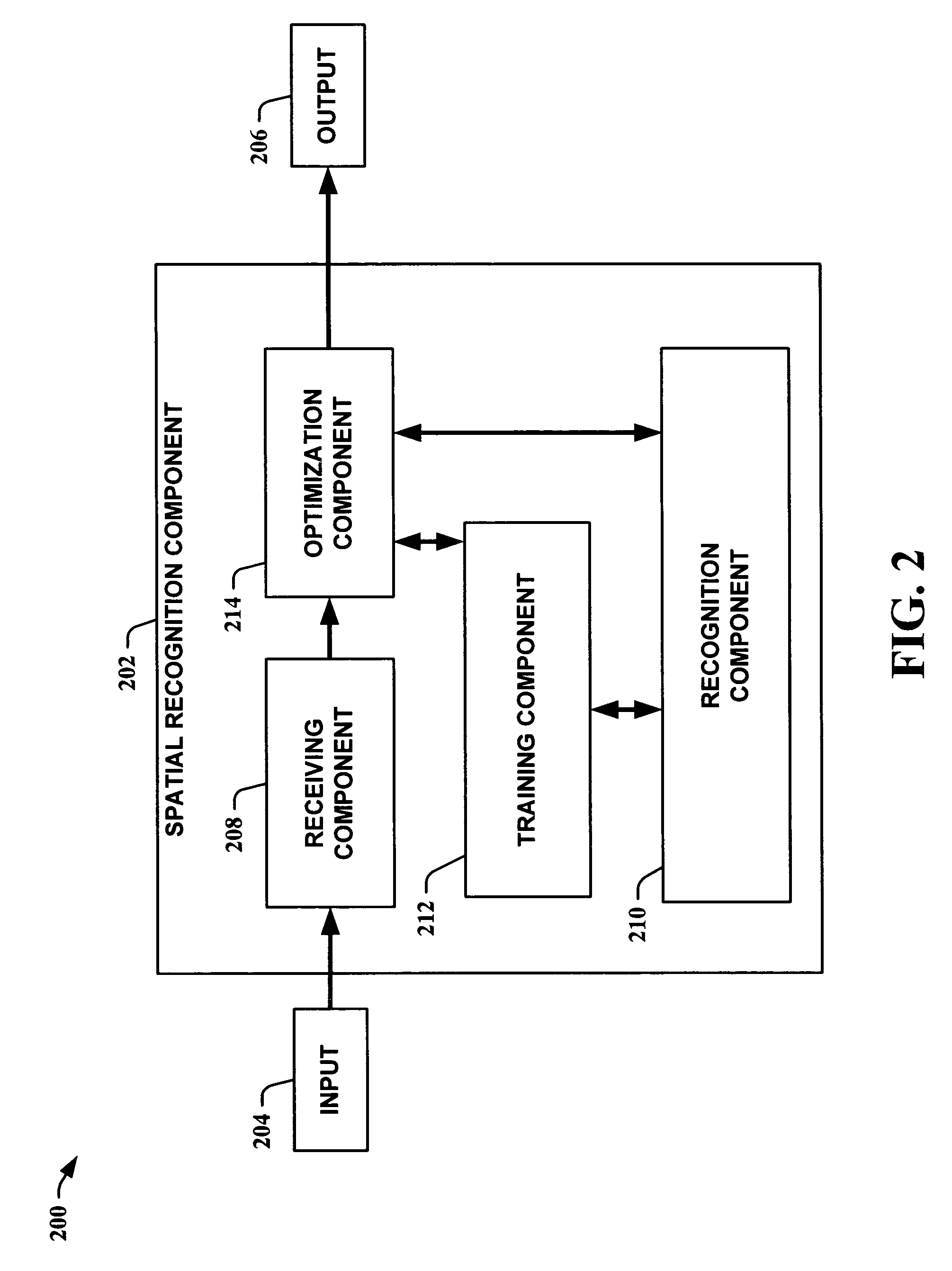
Spatial recognition and grouping of text and graphics
InactiveUS20060045337A1Facilitate in recognizing/classifyingImprove efficiencyDigital ink recognitionCharacter recognitionGraphicsAdaBoost
The present invention leverages spatial relationships to provide a systematic means to recognize text and / or graphics. This allows augmentation of a sketched shape with its symbolic meaning, enabling numerous features including smart editing, beautification, and interactive simulation of visual languages. The spatial recognition method obtains a search-based optimization over a large space of possible groupings from simultaneously grouped and recognized sketched shapes. The optimization utilizes a classifier that assigns a class label to a collection of strokes. The overall grouping optimization assumes the properties of the classifier so that if the classifier is scale and rotation invariant the optimization will be as well. Instances of the present invention employ a variant of AdaBoost to facilitate in recognizing / classifying symbols. Instances of the present invention employ dynamic programming and / or A-star search to perform optimization. The present invention applies to both hand-sketched shapes and printed handwritten text, and even heterogeneous mixtures of the two.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
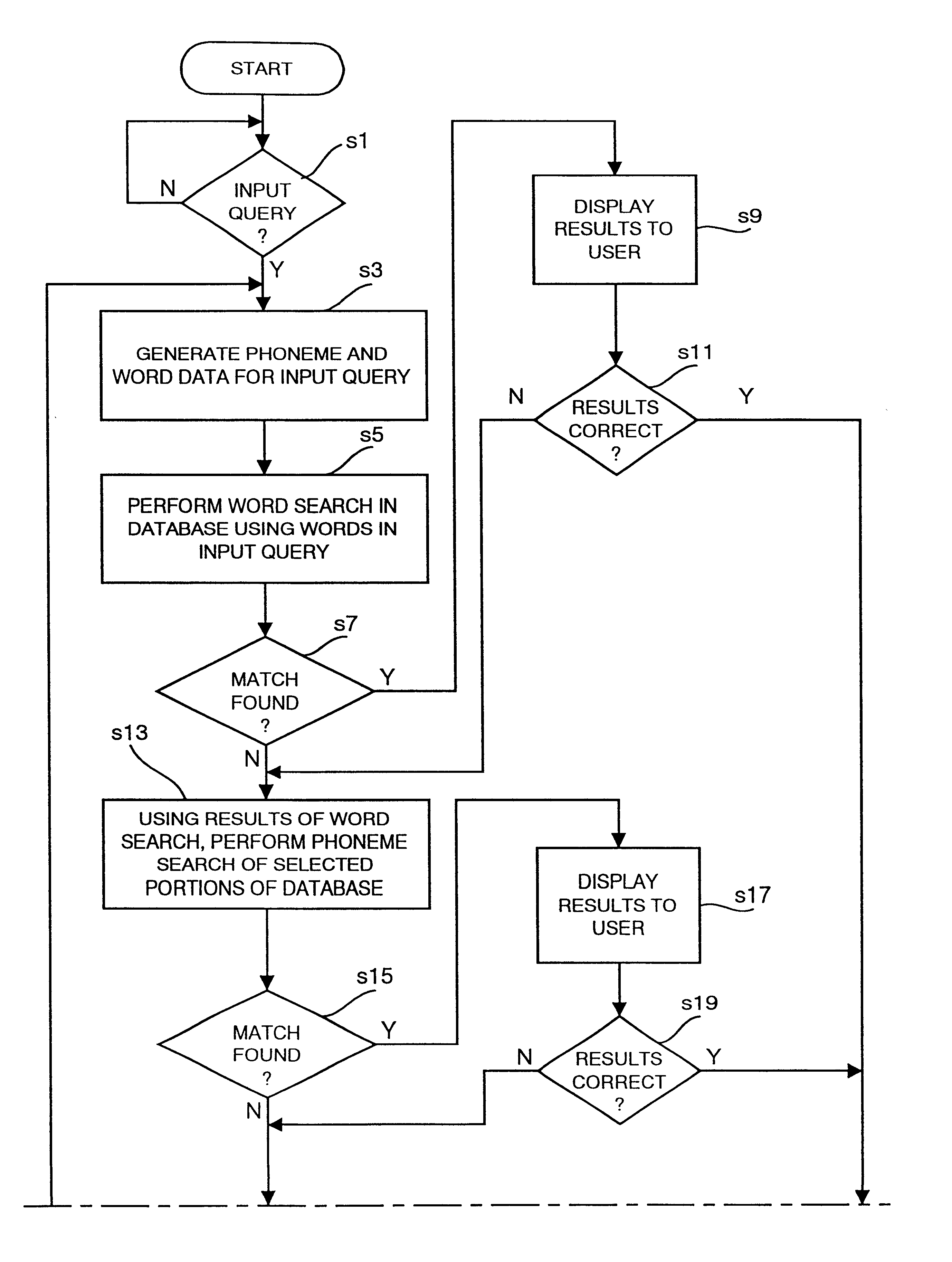
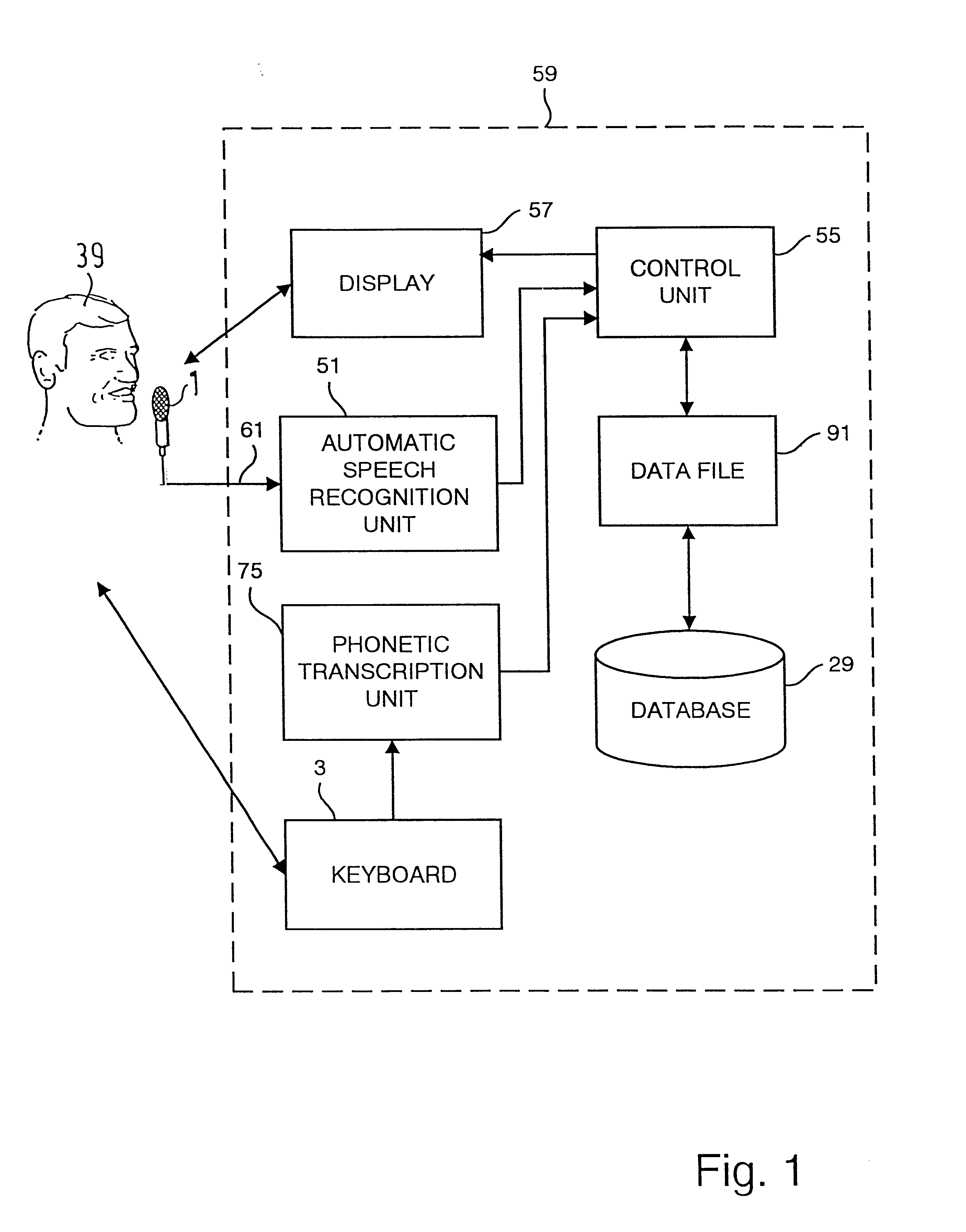
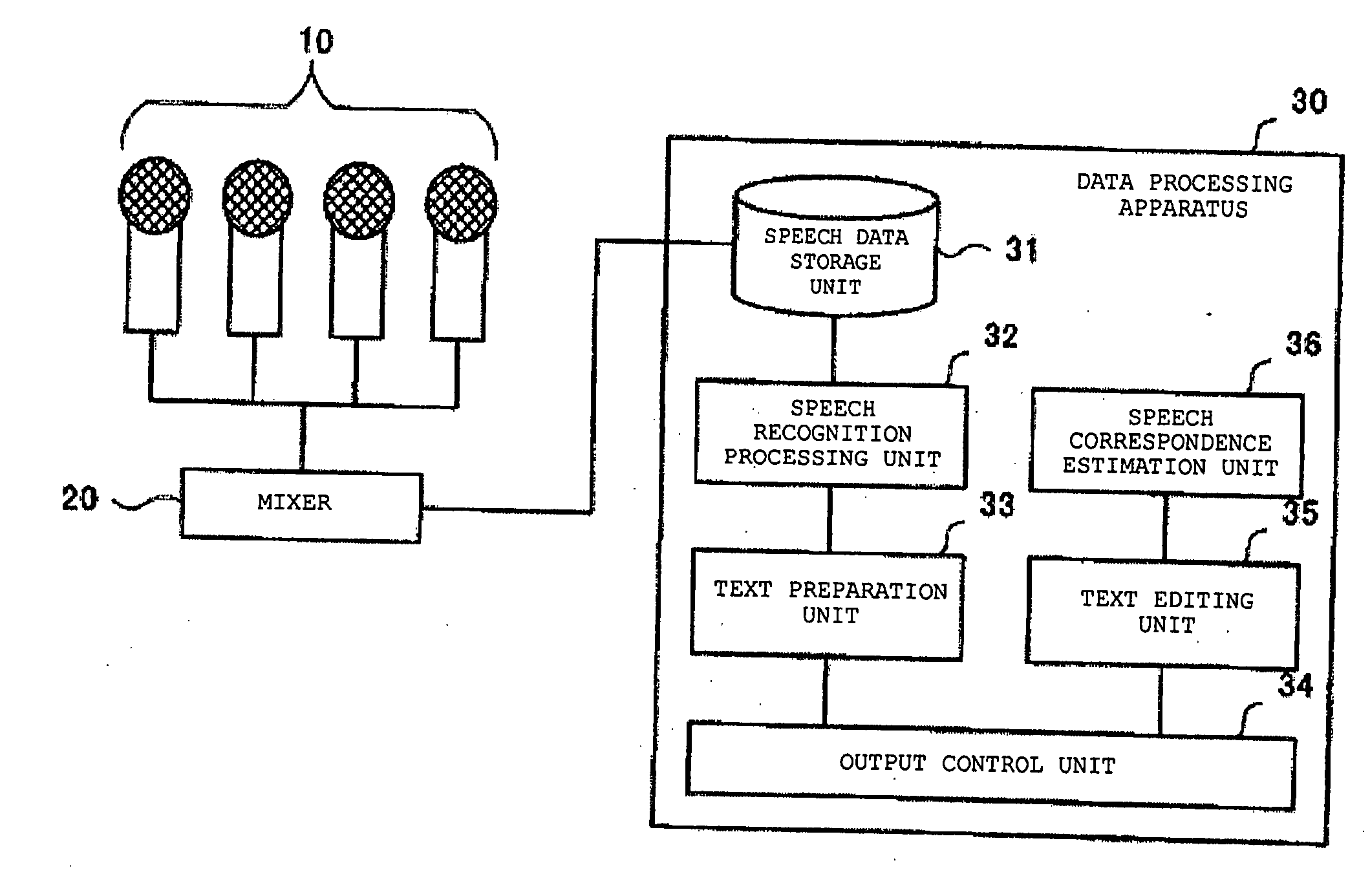
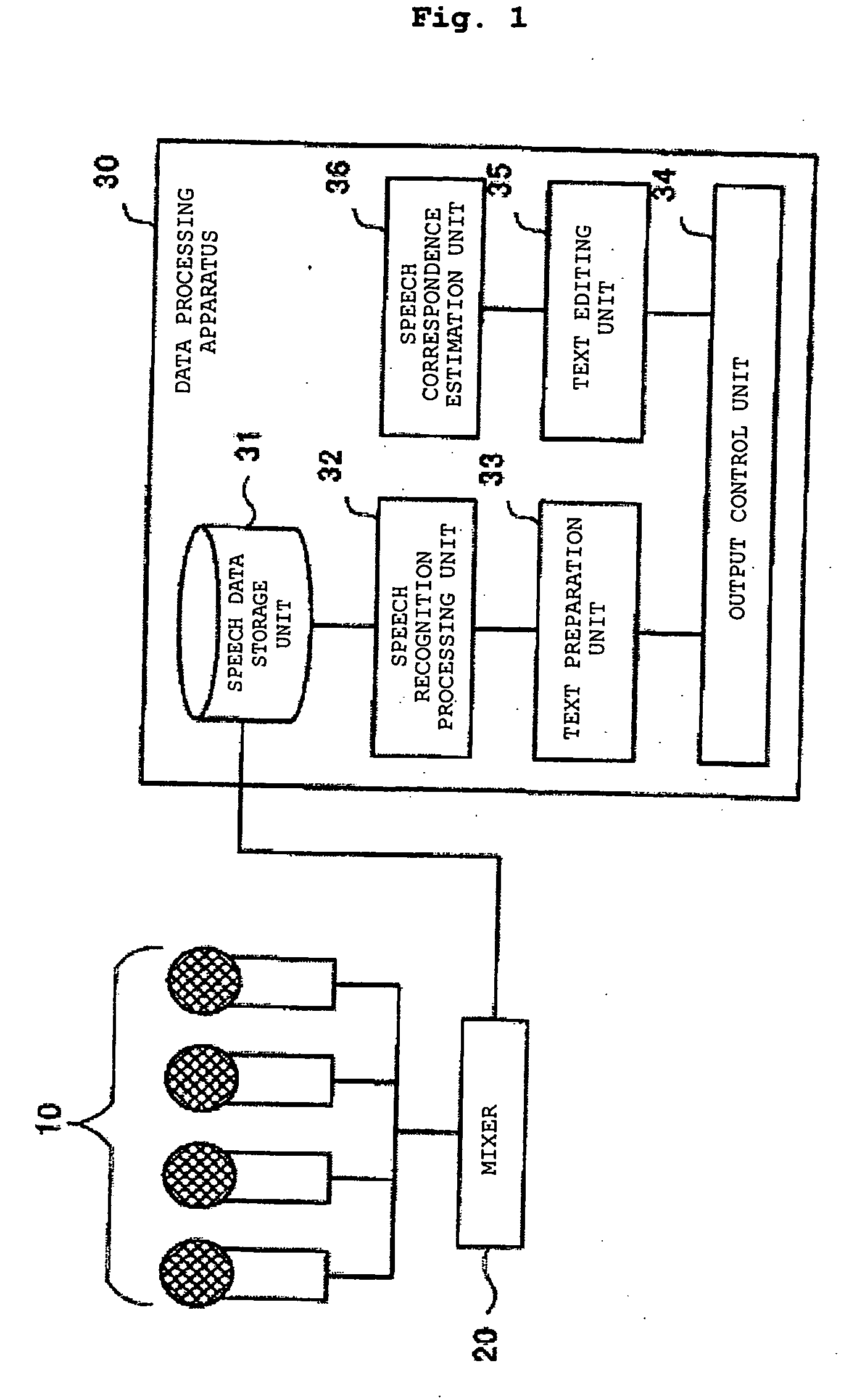
Recognizing speech, and processing data
An example embodiment of the invention includes a speech recognition processing unit for specifying speech segments for speech data, recognizing a speech in each of the speech segments, and associating a character string of obtained recognition data with the speech data for each speech segment, based on information on a time of the speech, and an output control unit for displaying / outputting the text prepared by sorting the recognition data in each speech segment. Sometimes, the system further includes a text editing unit for editing the prepared text, and a speech correspondence estimation unit for associating a character string in the edited text with the speech data by using a technique of dynamic programming.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
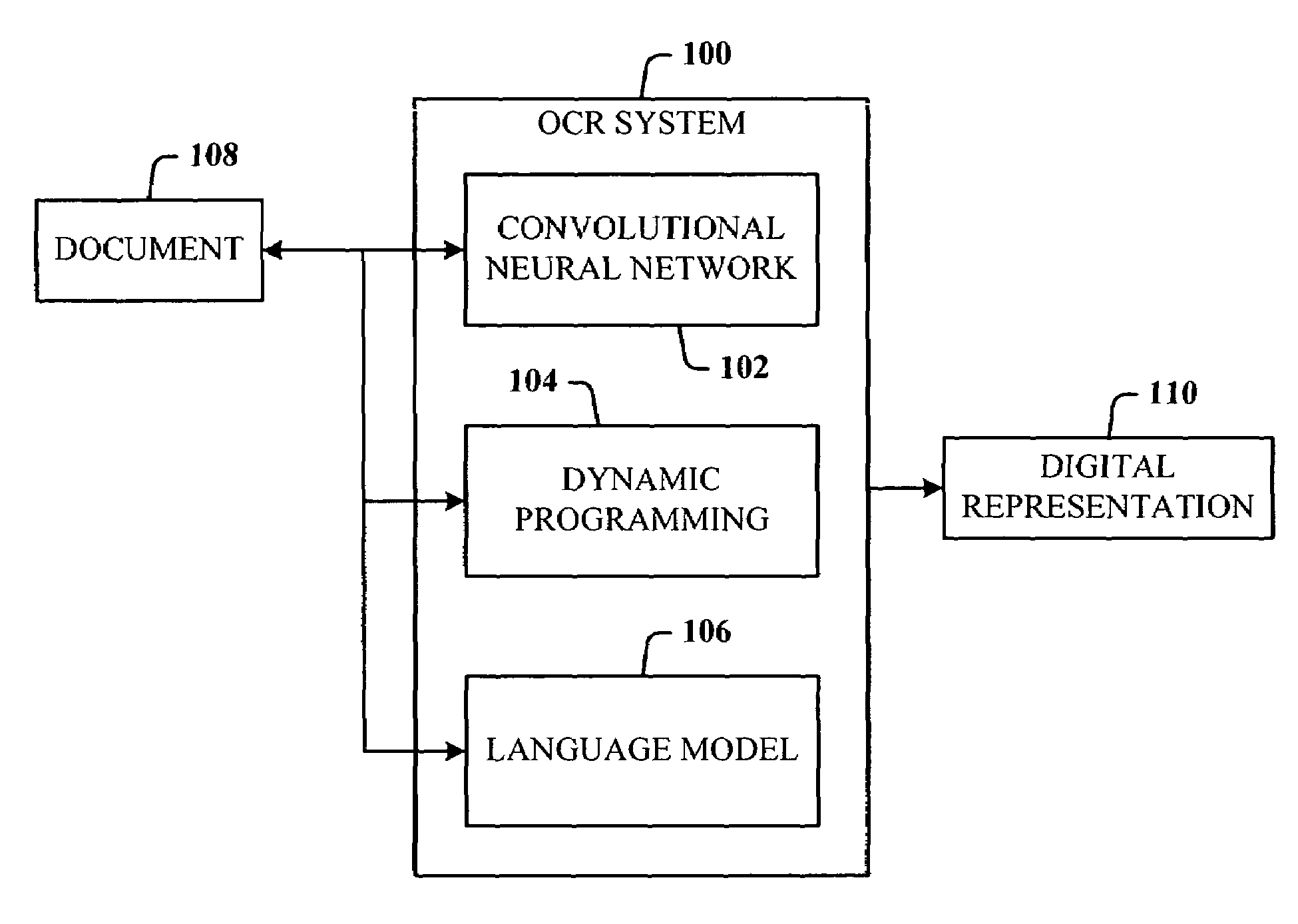
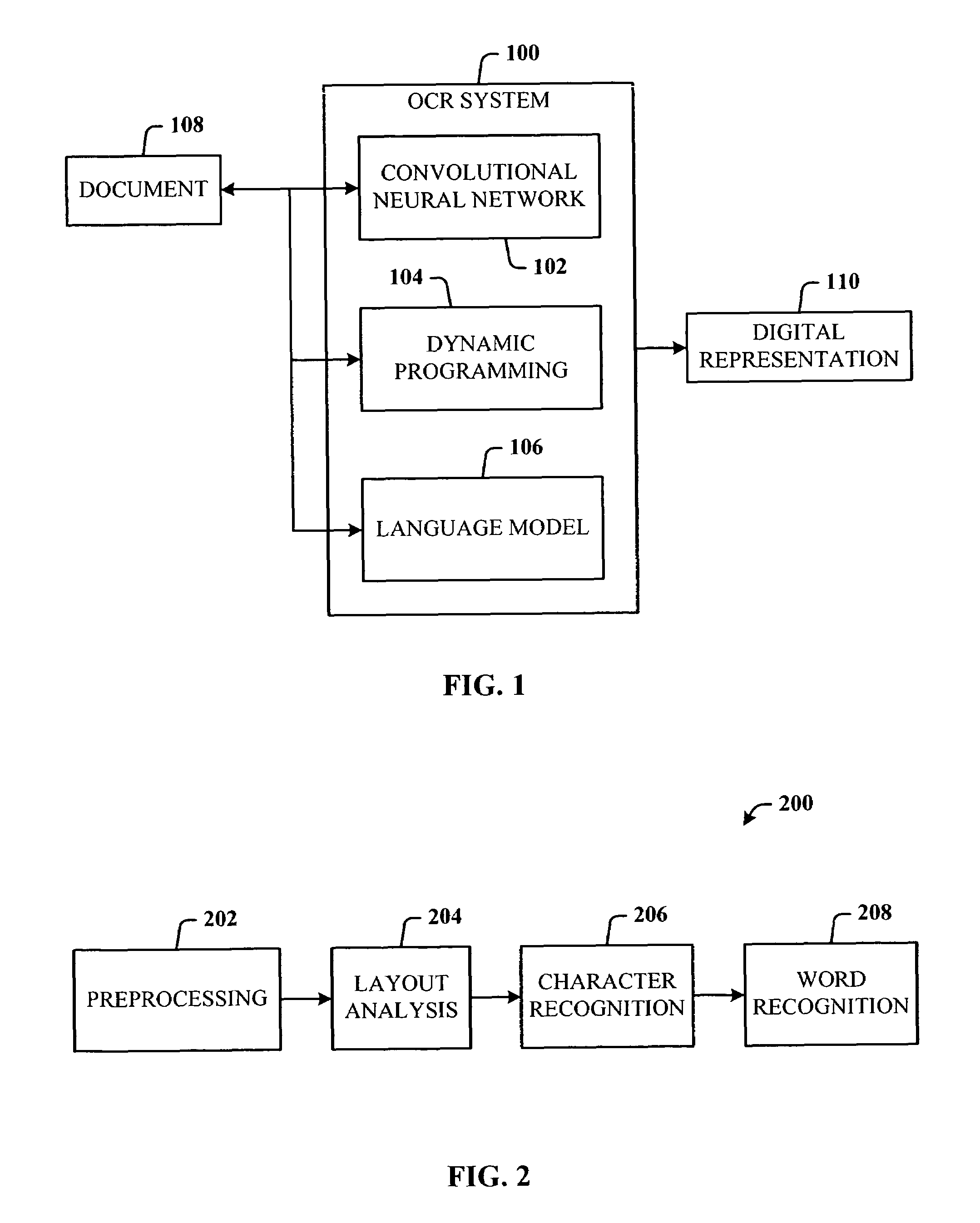
Low resolution OCR for camera acquired documents
ActiveUS7499588B2Low resolution OCRMaximum robustnessBiological modelsCharacter recognitionSingle processGrey level
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
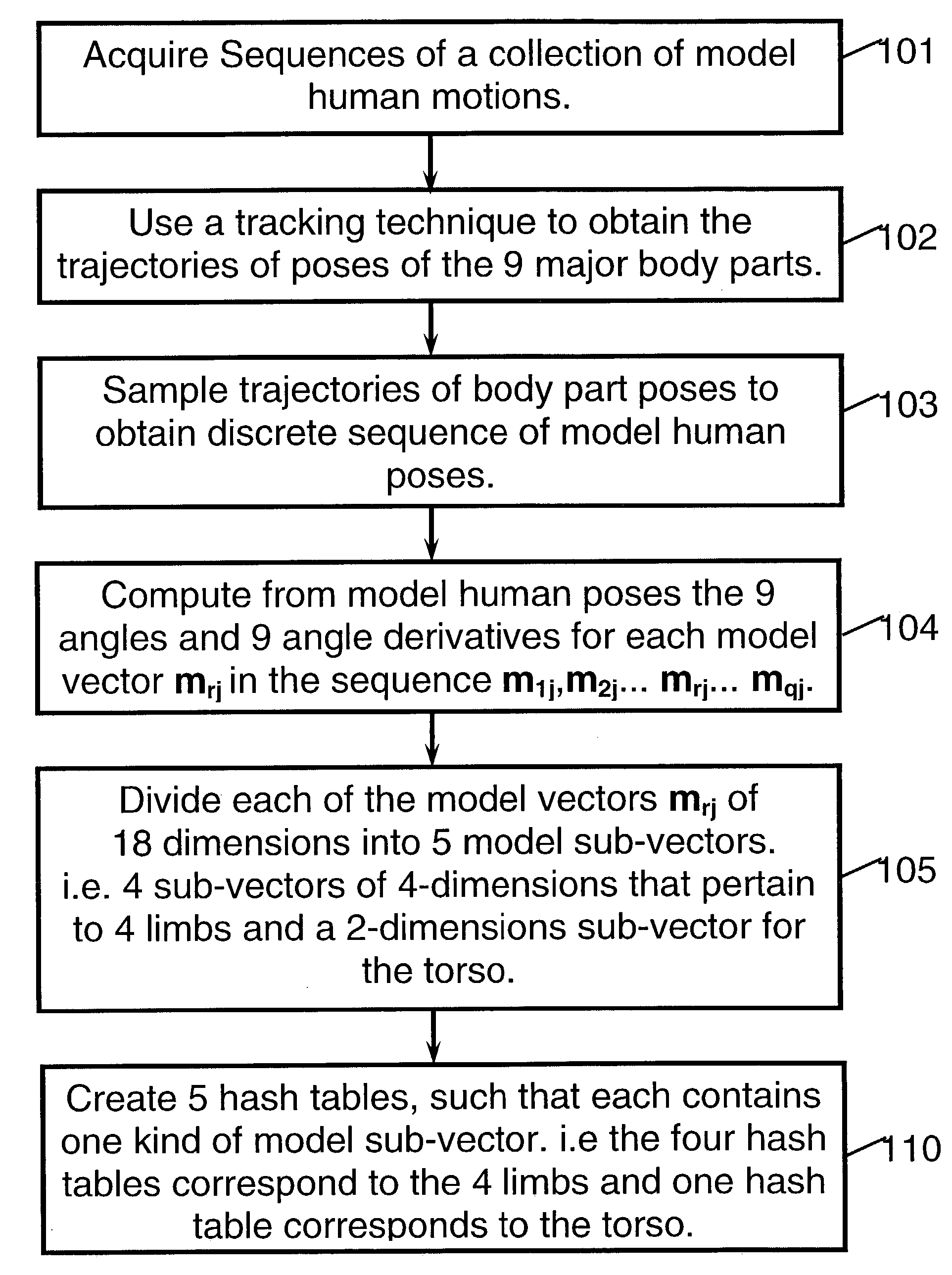
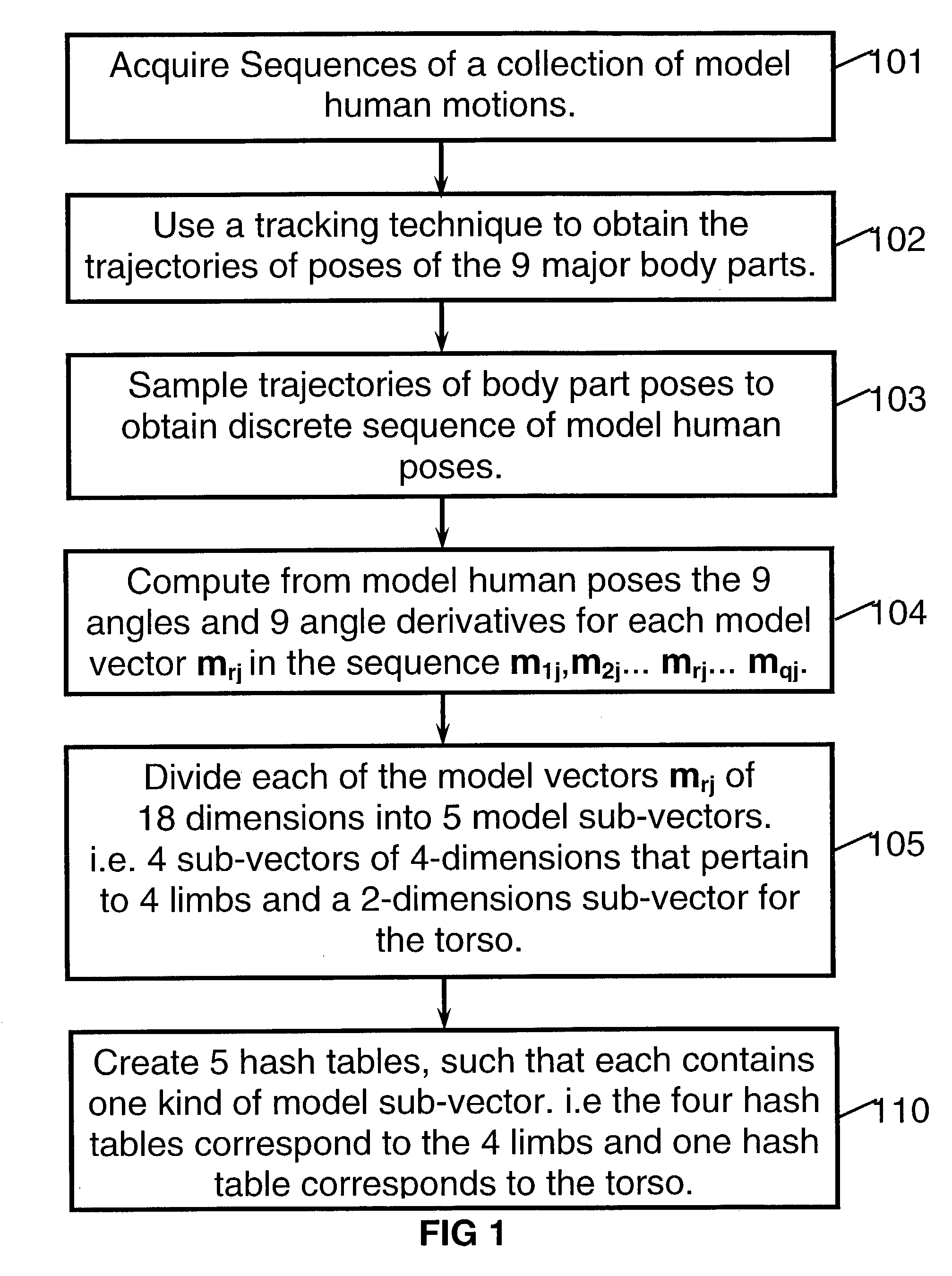
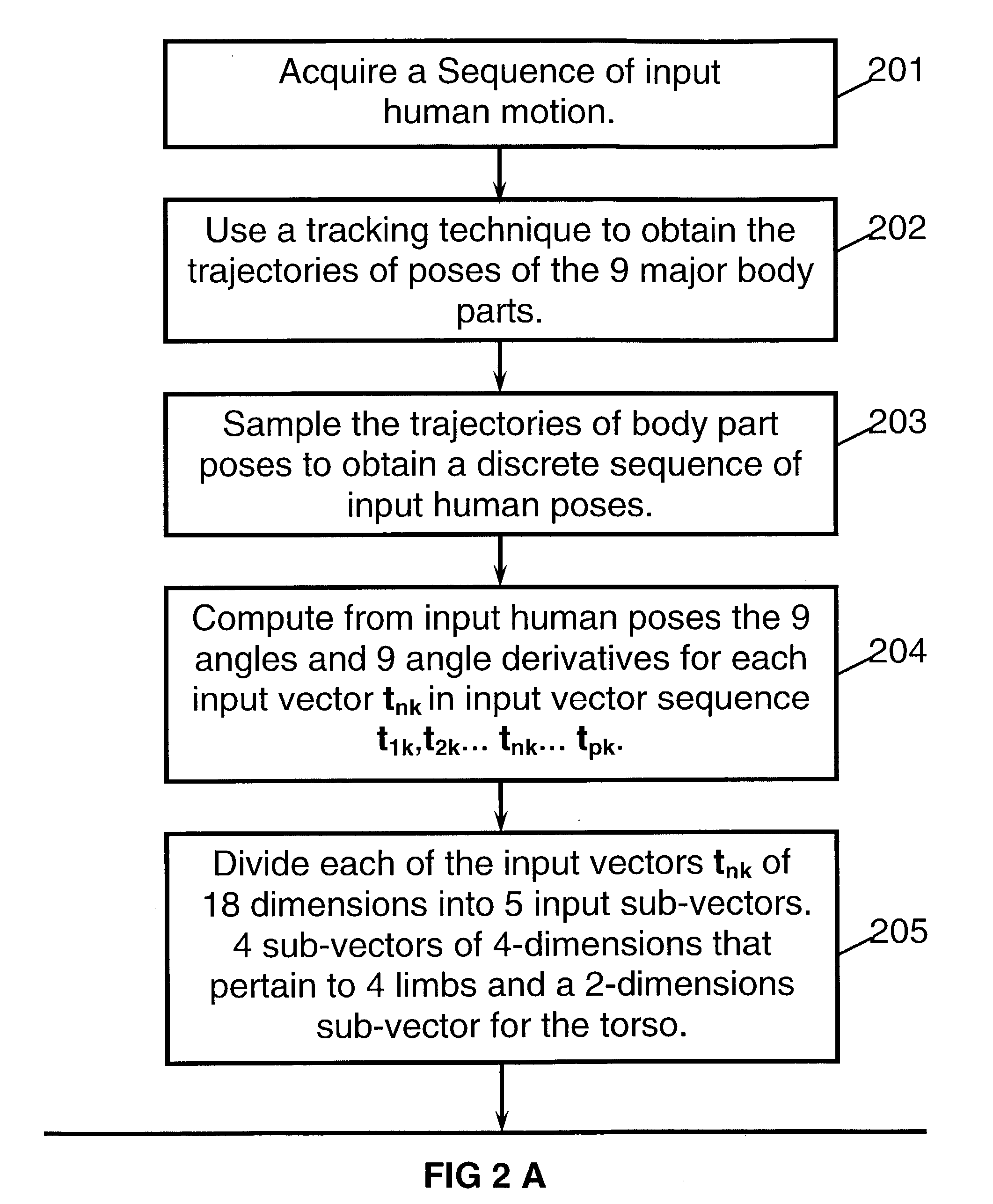
Method of recognition of human motion, vector sequences and speech
InactiveUS20030208289A1Robust recognitionReduce mistakesInput/output for user-computer interactionComputer controlPattern recognitionBody positions
A method for recognition of an input human motion as being the most similar to one model human motion out of a collection of stored model human motions. In the preferred method, both the input and the model human motions are represented by vector sequences that are derived from samples of angular poses of body parts. The input and model motions are sampled at substantially different rates. A special optimization algorithm that employs sequencing constraints and dynamic programming, is used for finding the optimal input-model matching scores. When only partial body pose information is available, candidate matching vector pairs for the optimization are found by indexing into a set of hash tables, where each table pertains to a sub-set of body parts. The invention also includes methods for recognition of vector sequences and for speech recognition.
Owner:BEN ARIE JEZEKIEL
Spatial recognition and grouping of text and graphics
InactiveUS7729538B2Facilitate in recognizing/classifyingImprove efficiencyDigital ink recognitionCharacter recognitionGraphicsAdaBoost
The present invention leverages spatial relationships to provide a systematic means to recognize text and / or graphics. This allows augmentation of a sketched shape with its symbolic meaning, enabling numerous features including smart editing, beautification, and interactive simulation of visual languages. The spatial recognition method obtains a search-based optimization over a large space of possible groupings from simultaneously grouped and recognized sketched shapes. The optimization utilizes a classifier that assigns a class label to a collection of strokes. The overall grouping optimization assumes the properties of the classifier so that if the classifier is scale and rotation invariant the optimization will be as well. Instances of the present invention employ a variant of AdaBoost to facilitate in recognizing / classifying symbols. Instances of the present invention employ dynamic programming and / or A-star search to perform optimization. The present invention applies to both hand-sketched shapes and printed handwritten text, and even heterogeneous mixtures of the two.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Speech recognition system and technique
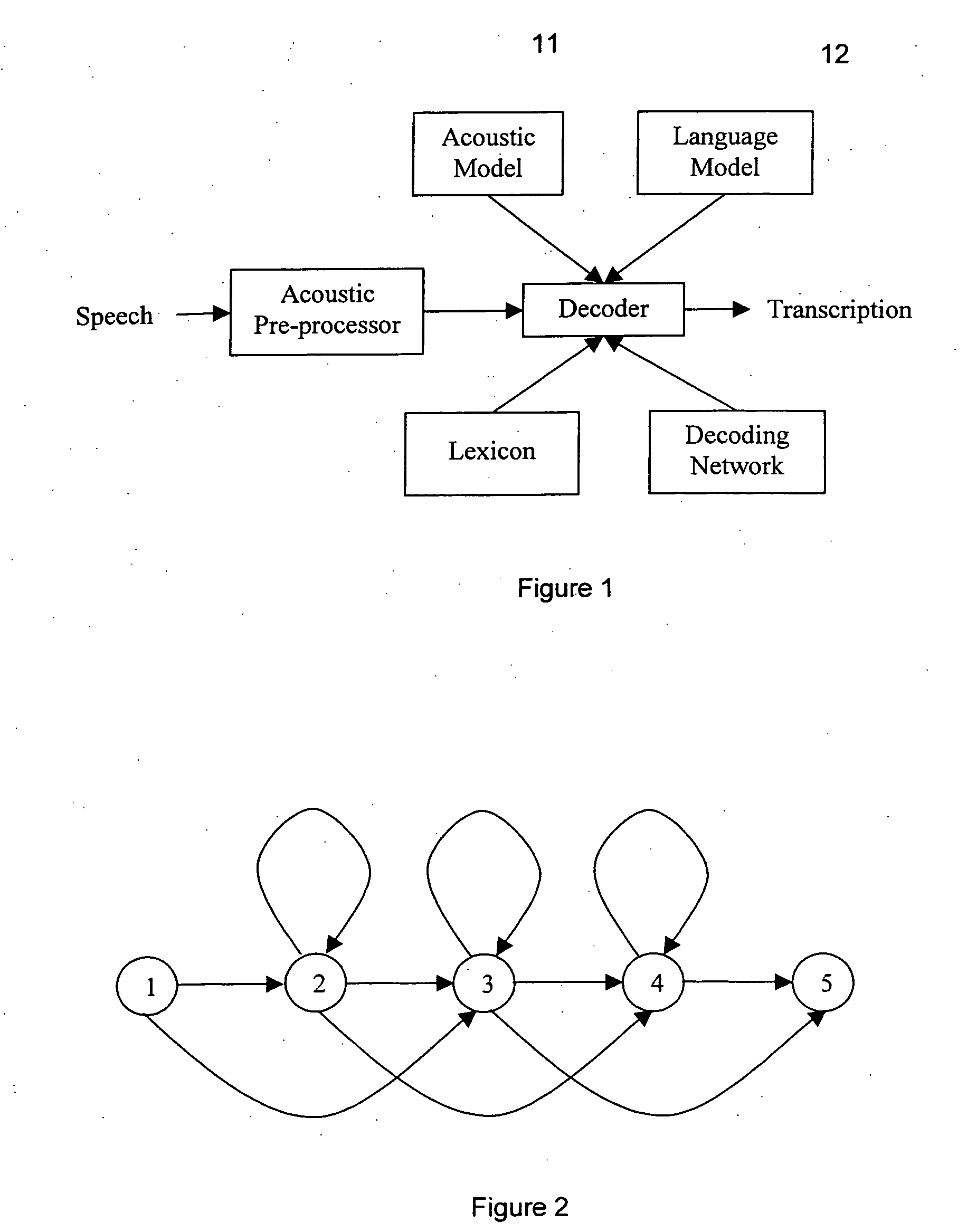
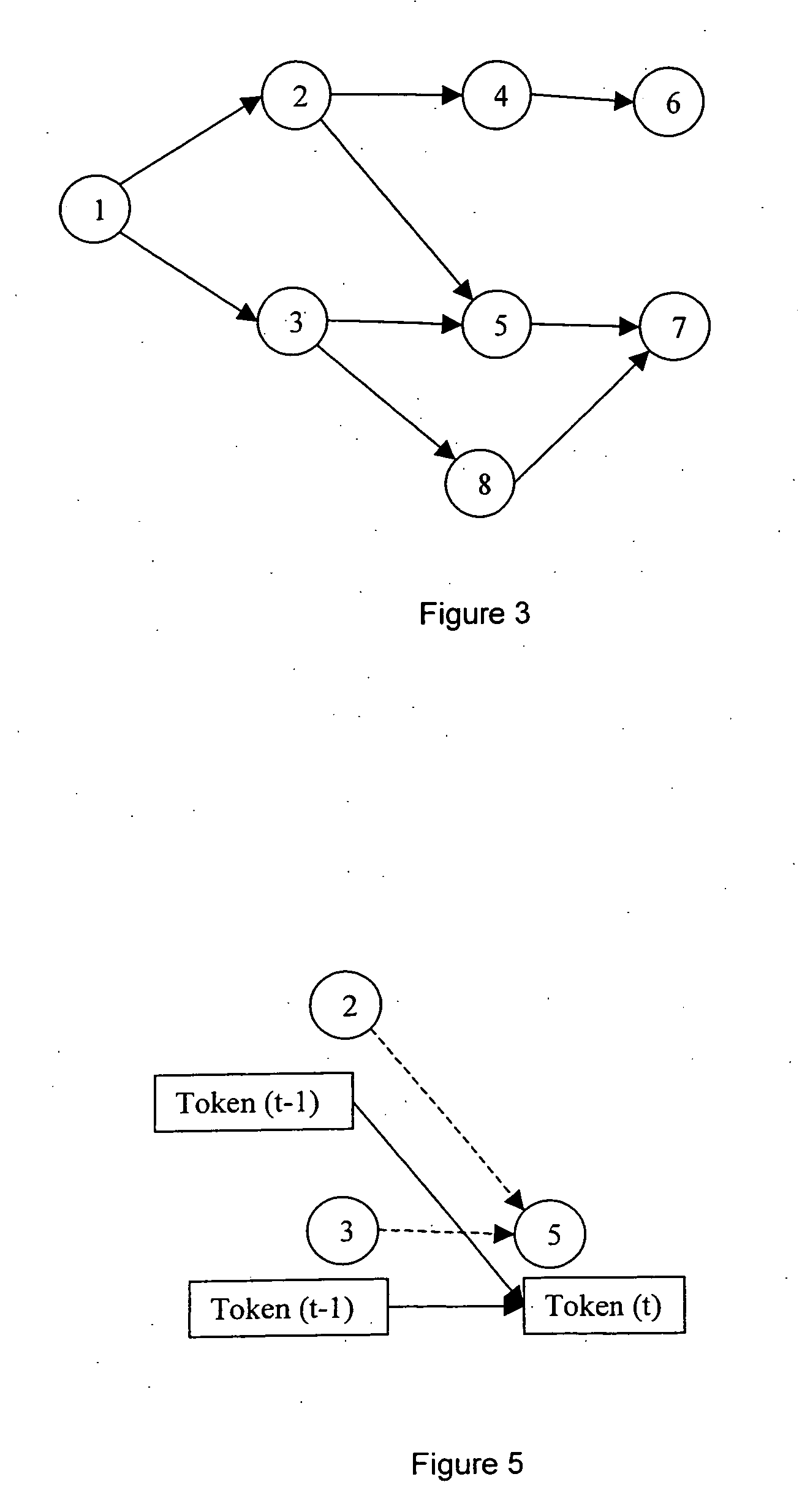
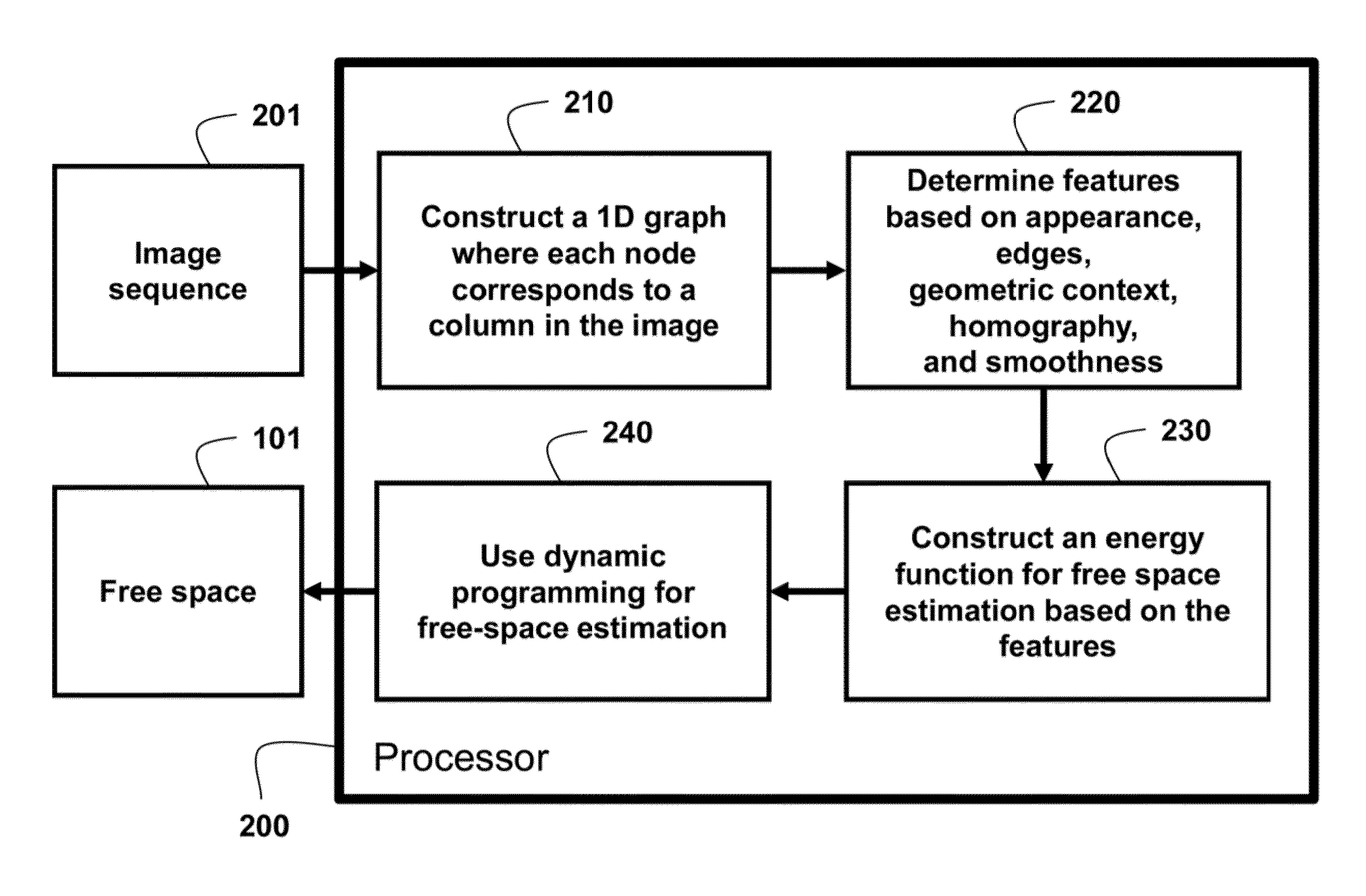
The present invention relates to speech recognition systems, particularly speech-to-text systems and software and decoders for the same. The present invention provides a decoder for an automatic speech recognition system for determining one or more candidate text unit concatenations according to a predetermined criterion and which correspond to a speech segment, the decoder comprising: means for receiving a sequence of feature vectors corresponding to the speech segment; means for mapping with different likelihood values the feature vectors to sequences of nodes in a decoding network, every sequence representing a concatenation of text units; means for determining one or more candidate node sequences in the decoding network corresponding to the candidate text unit concatenations by implementing a dynamic programming token passing algorithm in which each token corresponds to a node and is associated with a number of text unit concatenations and likelihood values for these concatenations, and wherein a token associated with a node in the decoding network is derived from the tokens associated with the previous nodes in the network; wherein tokens from different nodes that are to be passed to a common node are combined to generate a new token corresponding to the common node and associated with an identifier for text unit concatenations and likelihood values associated with the previous tokens of said different nodes. This is combined with means for merging a said token having a said identifier, the text unit concatenations of the said previous tokens being associated with said merged token dependent on their corresponding likelihood values.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
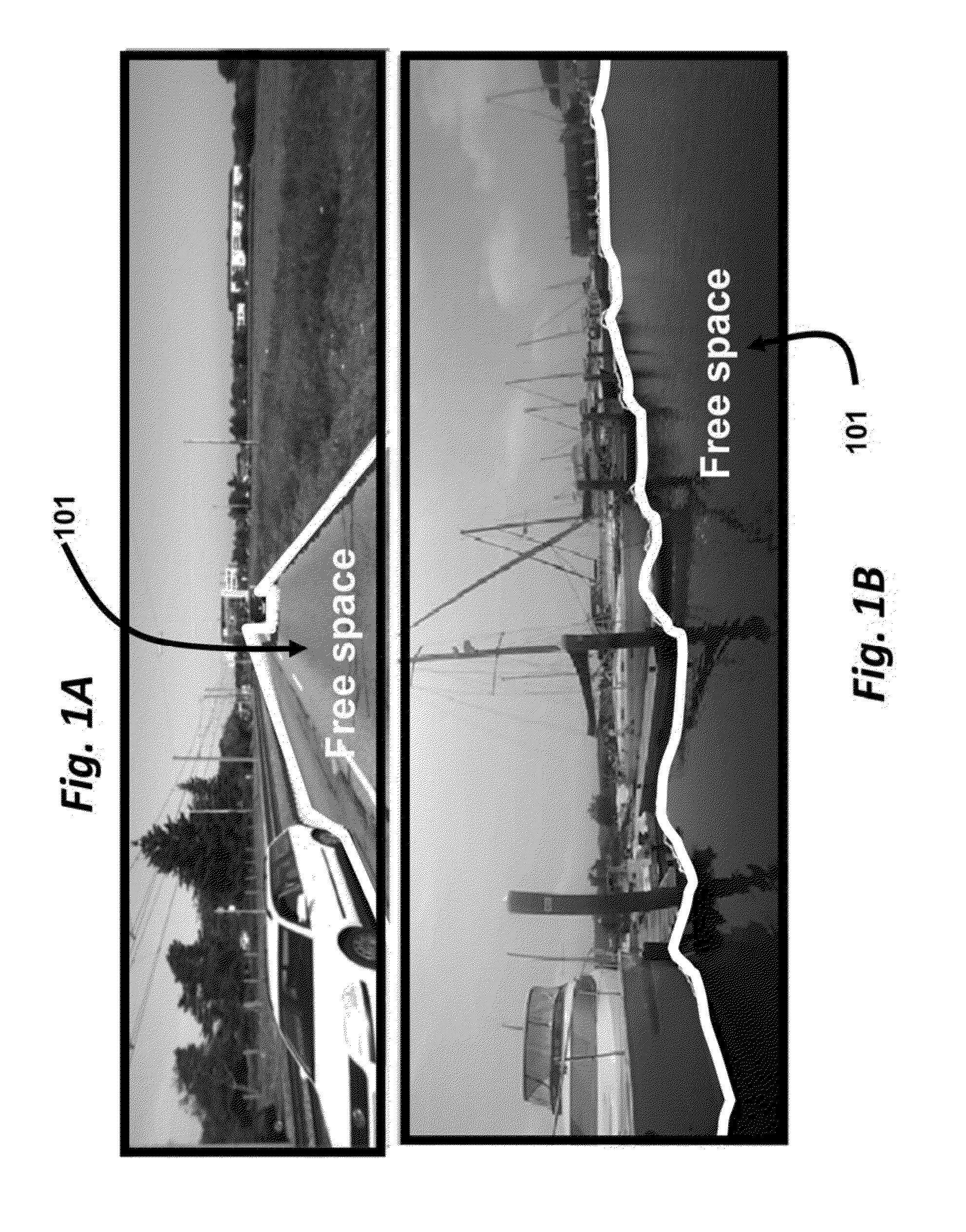
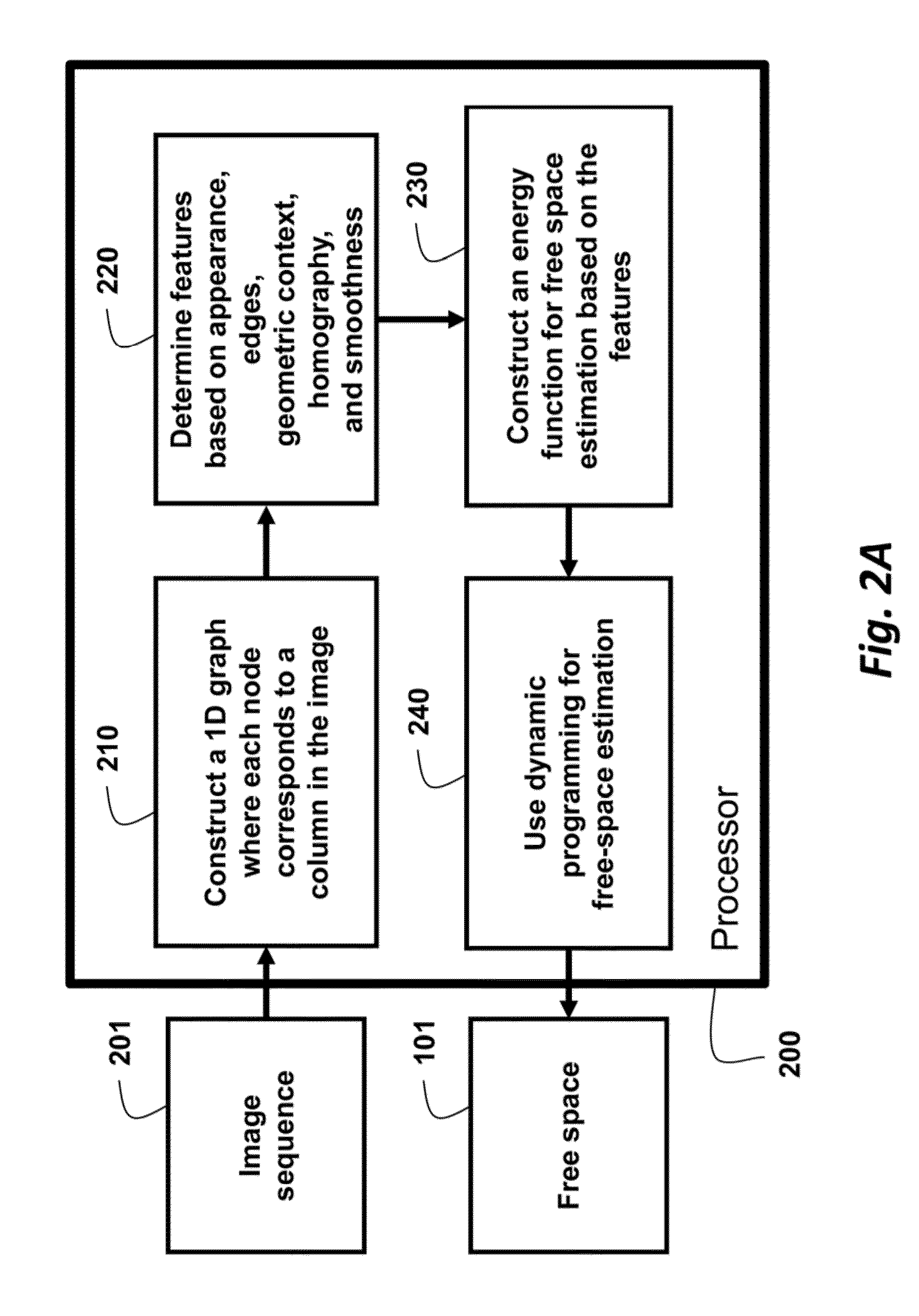
Method for estimating free space using a camera system
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Multi-robot path planning method based on time window
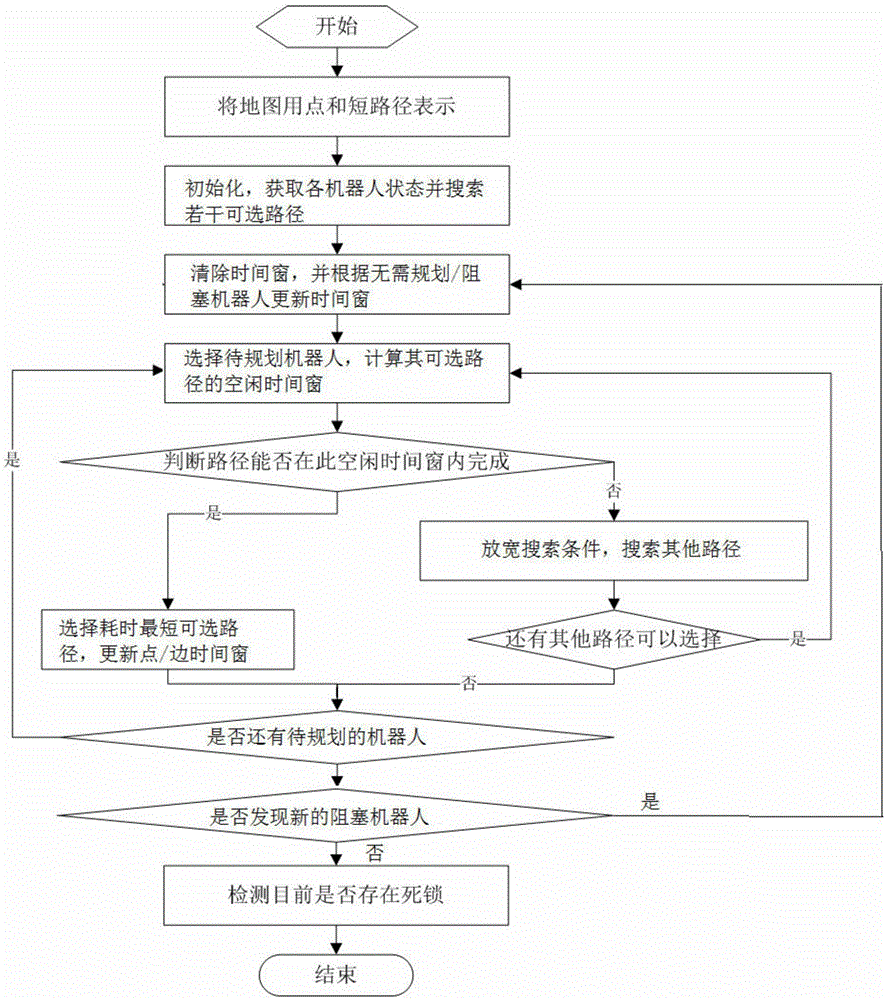
ActiveCN105652838ANo deadlockRelatively small amount of calculationTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlPlanning approachRobot path planning
The invention relates to a multi-robot path planning method based on a time window. According to the method provided by the invention, a feasible path of a new robot is planed through a point time window and an edge time window of a node occupied by an existing robot; and when the time window of the robot is disturbed, a path of each robot is dynamically re-planned, so that the conflict of a plurality of robots in a system can be avoided. According to the multi-robot path planning method provided by the invention, a plurality of times of iteration are not needed, and the possibility is only calculated on a limited path set; and the relative calculated quantity is relatively small so that the multi-robot path planning method is more suitable for being applied to a real dispatching scene.
Owner:江苏哈工智新科技股份有限公司
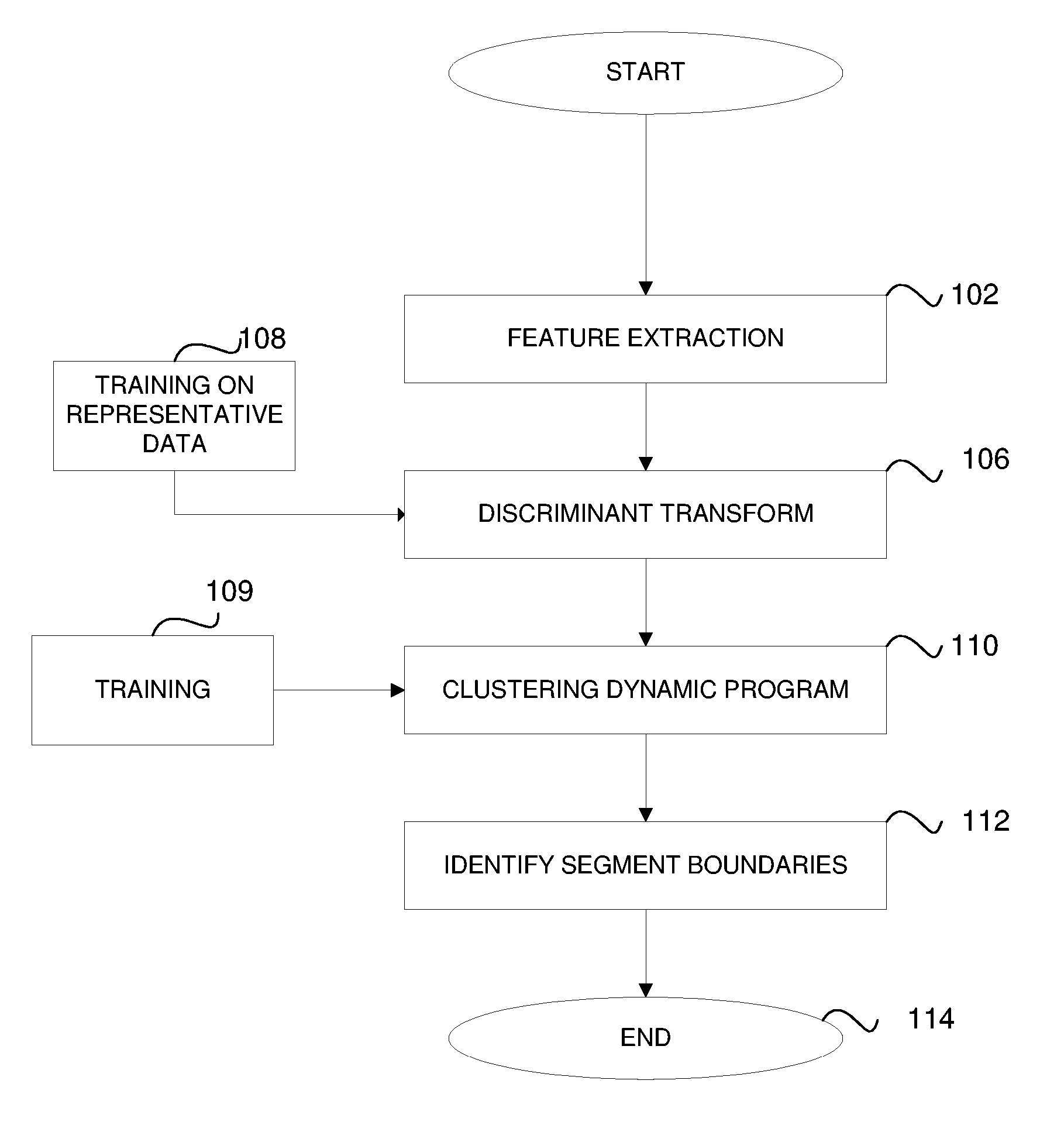
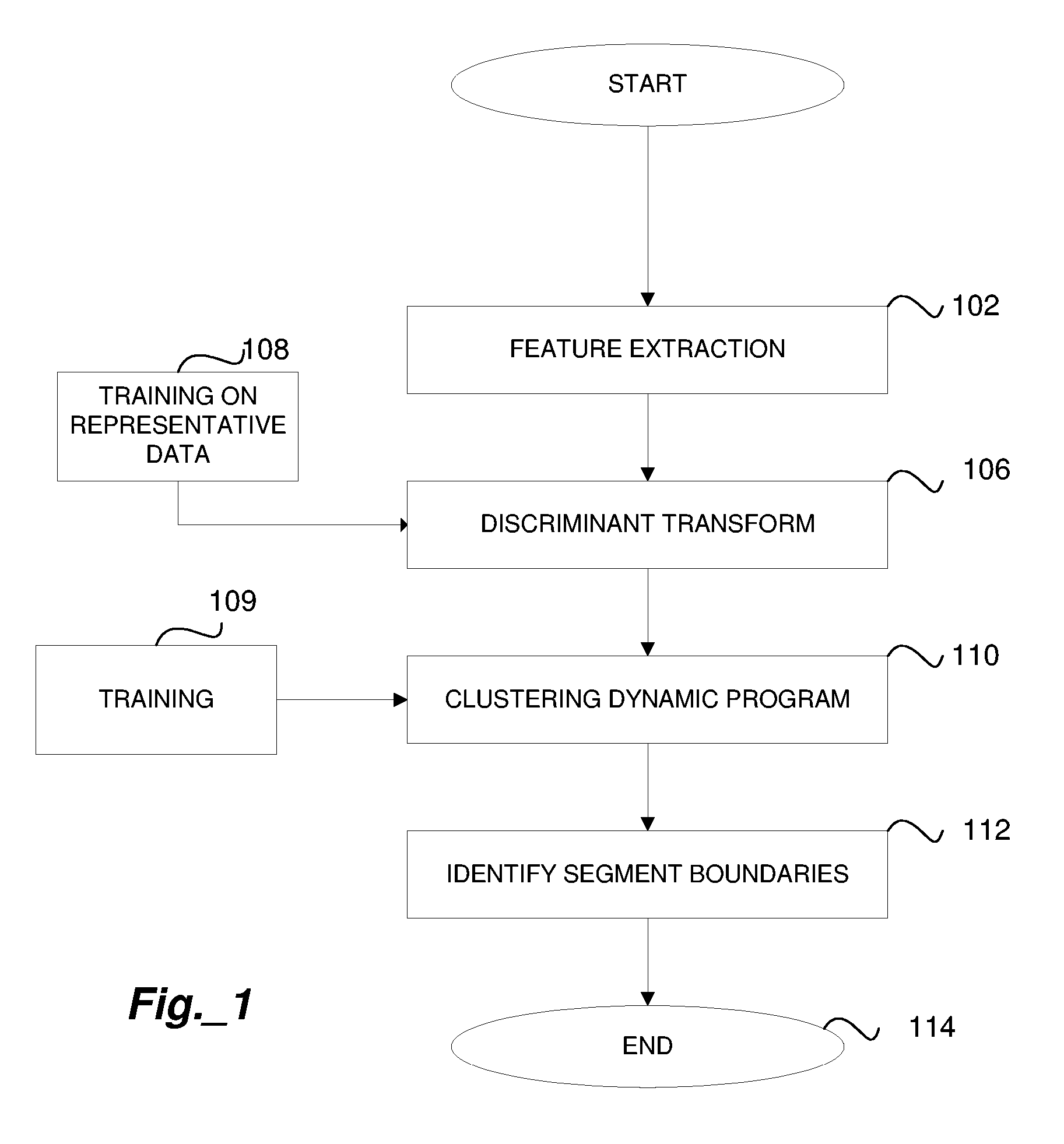
Method for Segmenting Audio Signals
ActiveUS20060085188A1Easy to separateGain controlDigital data processing detailsCharacteristic spaceDynamic programming
An input signal is converted to a feature-space representation. The feature-space representation is projected onto a discriminant subspace using a linear discriminant analysis transform to enhance the separation of feature clusters. Dynamic programming is used to find global changes to derive optimal cluster boundaries. The cluster boundaries are used to identify the segments of the audio signal.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
Adaptive network system with online learning and autonomous cross-layer optimization for delay-sensitive applications
InactiveUS20110019693A1Sub-optimal performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexReliable transmissionNetworked system
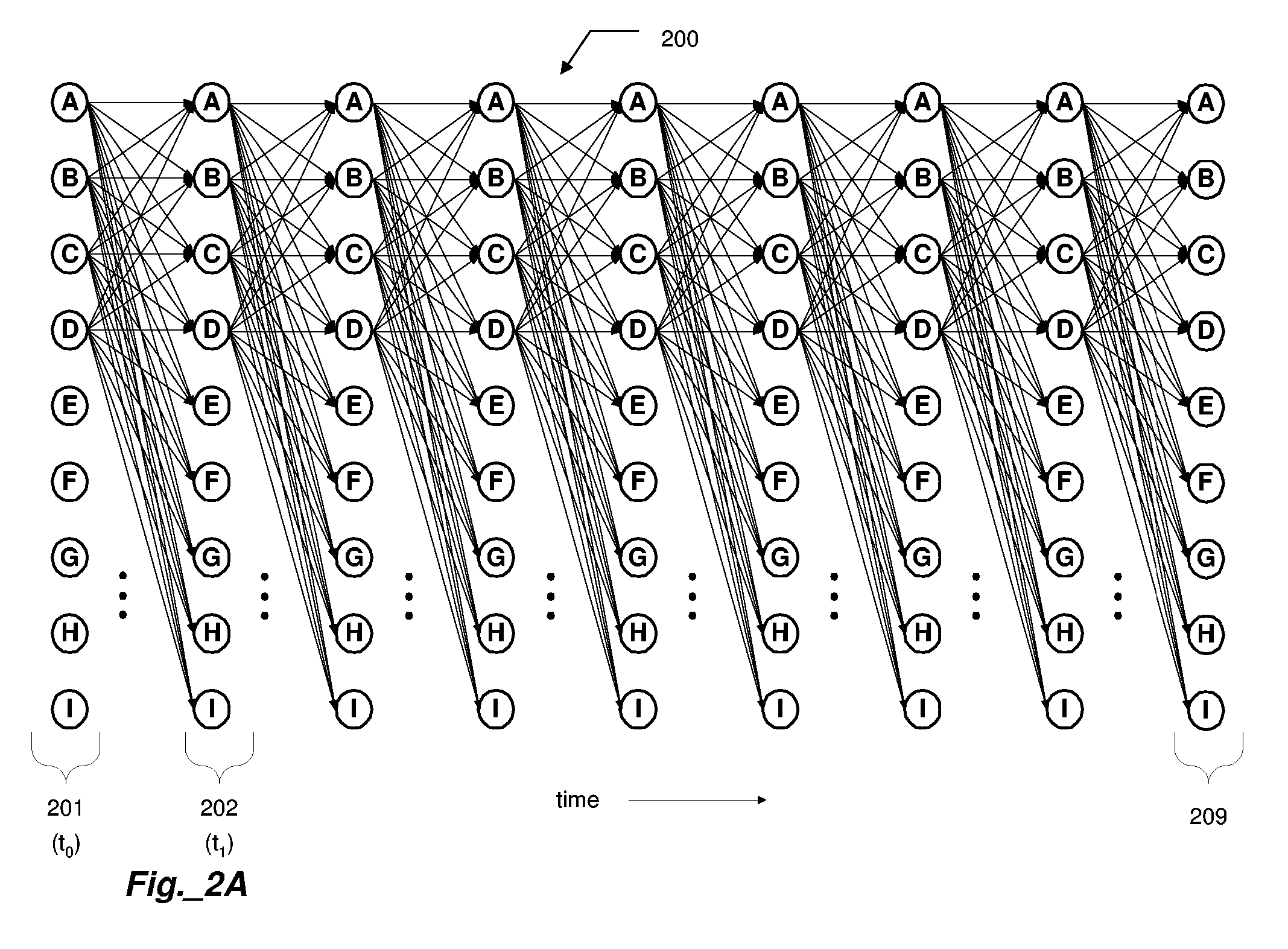
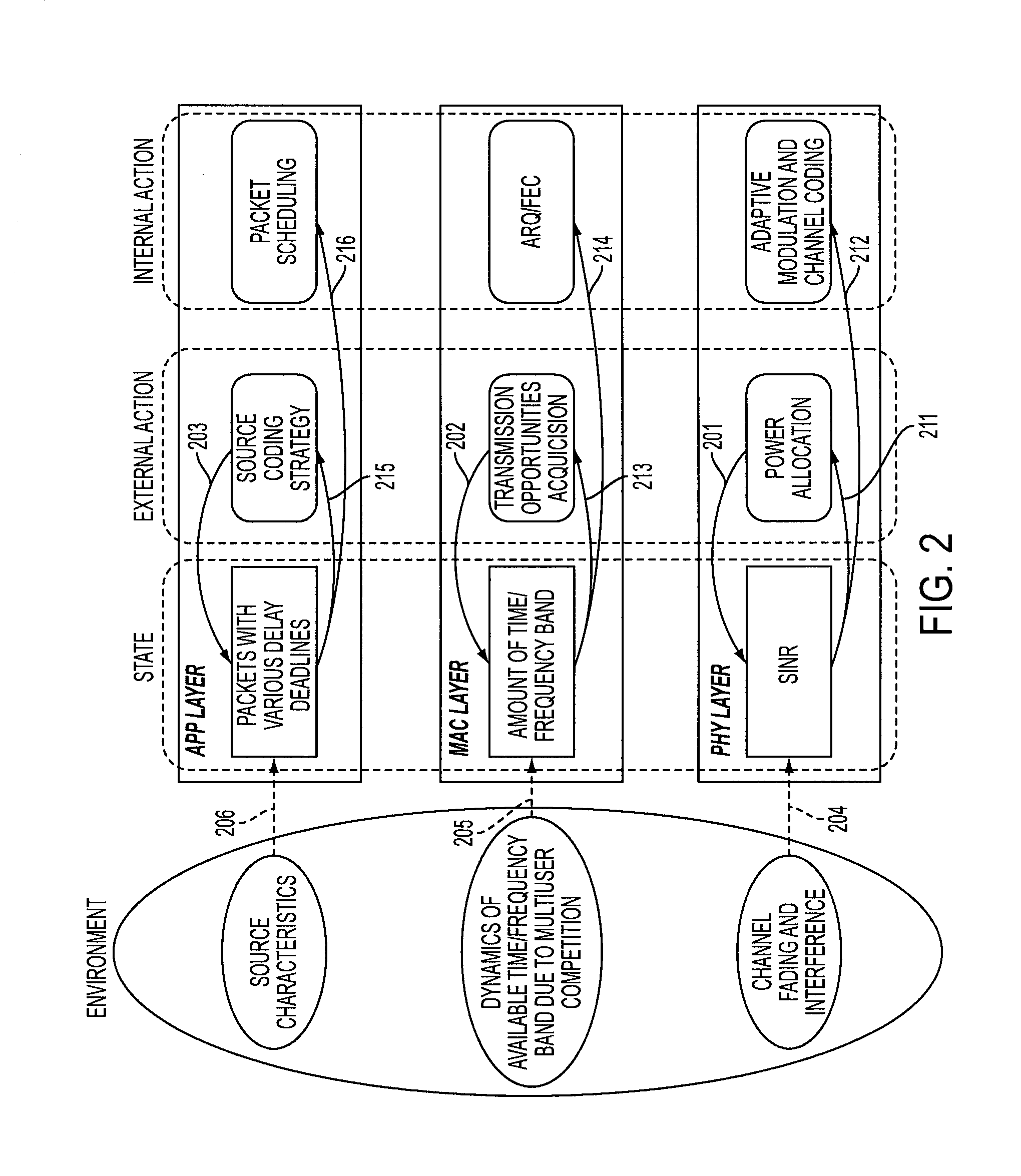
A network system providing highly reliable transmission quality for delay-sensitive applications with online learning and cross-layer optimization is disclosed. Each protocol layer is deployed to select its own optimization strategies, and cooperates with other layers to maximize the overall utility. This framework adheres to defined layered network architecture, allows layers to determine their own protocol parameters, and exchange only limited information with other layers. The network system considers heterogeneous and dynamically changing characteristics of delay-sensitive applications and the underlying time-varying network conditions, to perform cross-layer optimization. Data units (DUs), both independently decodable DUs and interdependent DUs, are considered. The optimization considers how the cross-layer strategies selected for one DU will impact its neighboring DUs and the DUs that depend on it. While attributes of future DU and network conditions may be unknown in real-time applications, the impact of current cross-layer actions on future DUs can be characterized by a state-value function in the Markov decision process (MDP) framework. Based on the dynamic programming solution to the MDP, the network system utilizes a low-complexity cross-layer optimization algorithm using online learning for each DU transmission.
Owner:SANYO NORTH AMERICA CORP +1
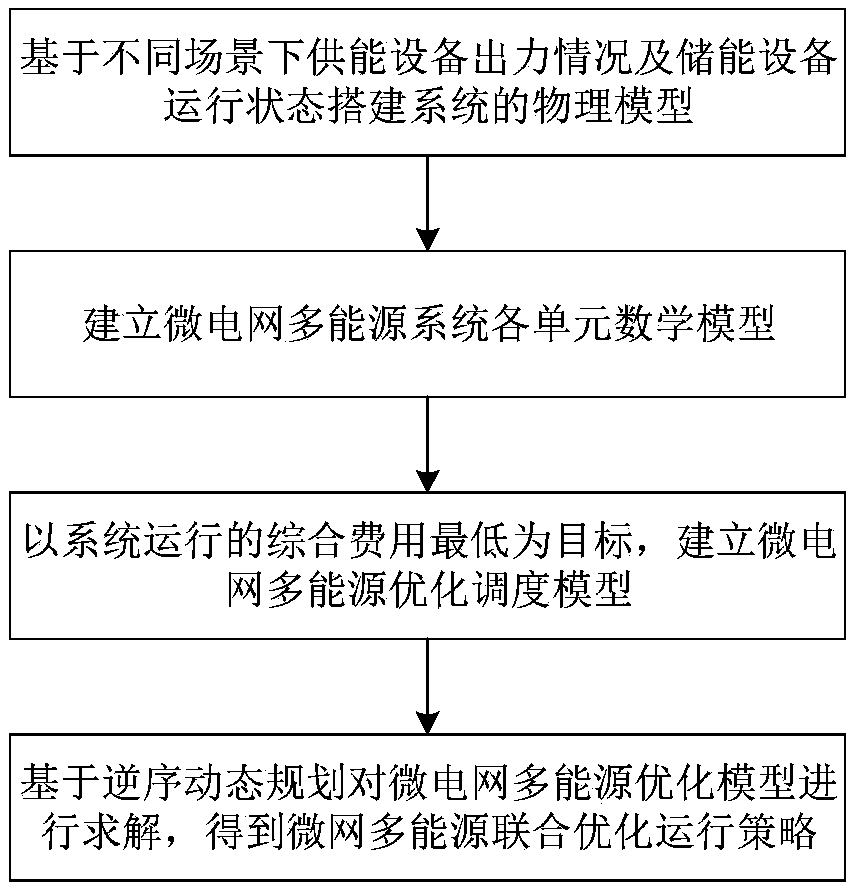
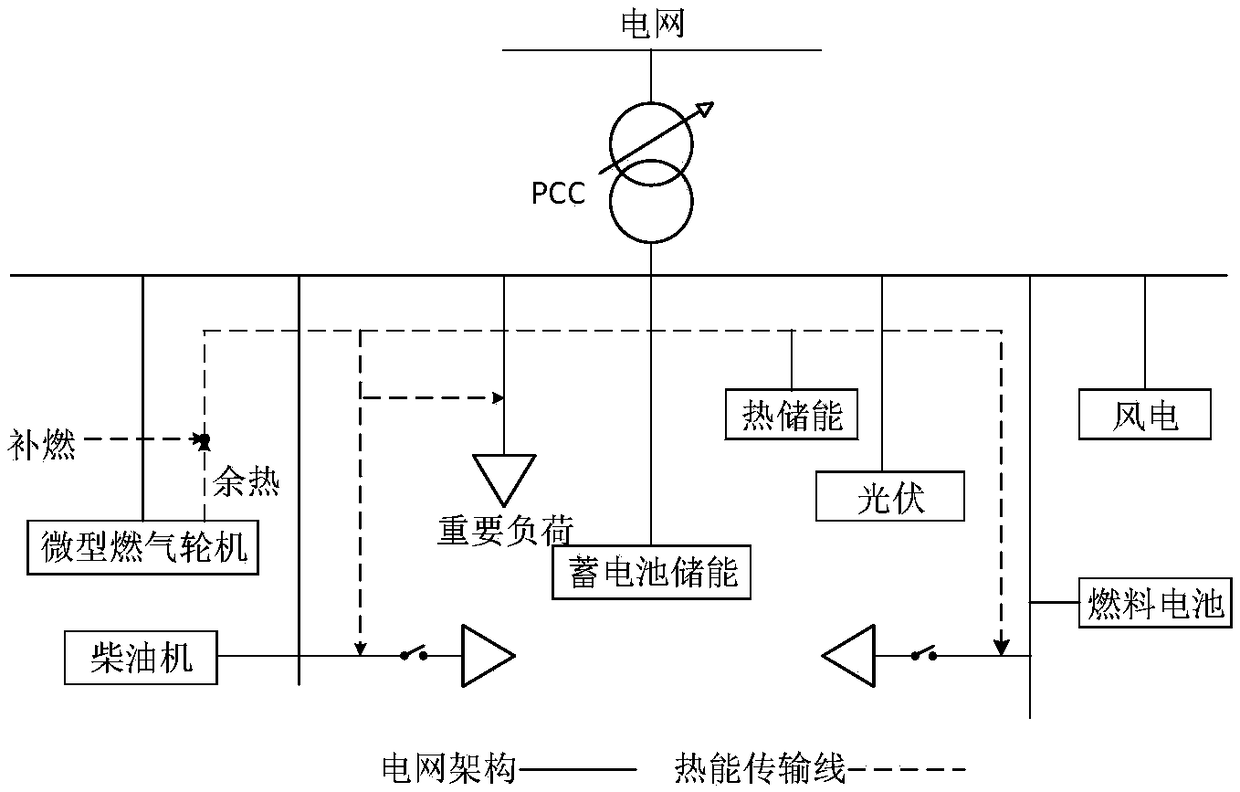
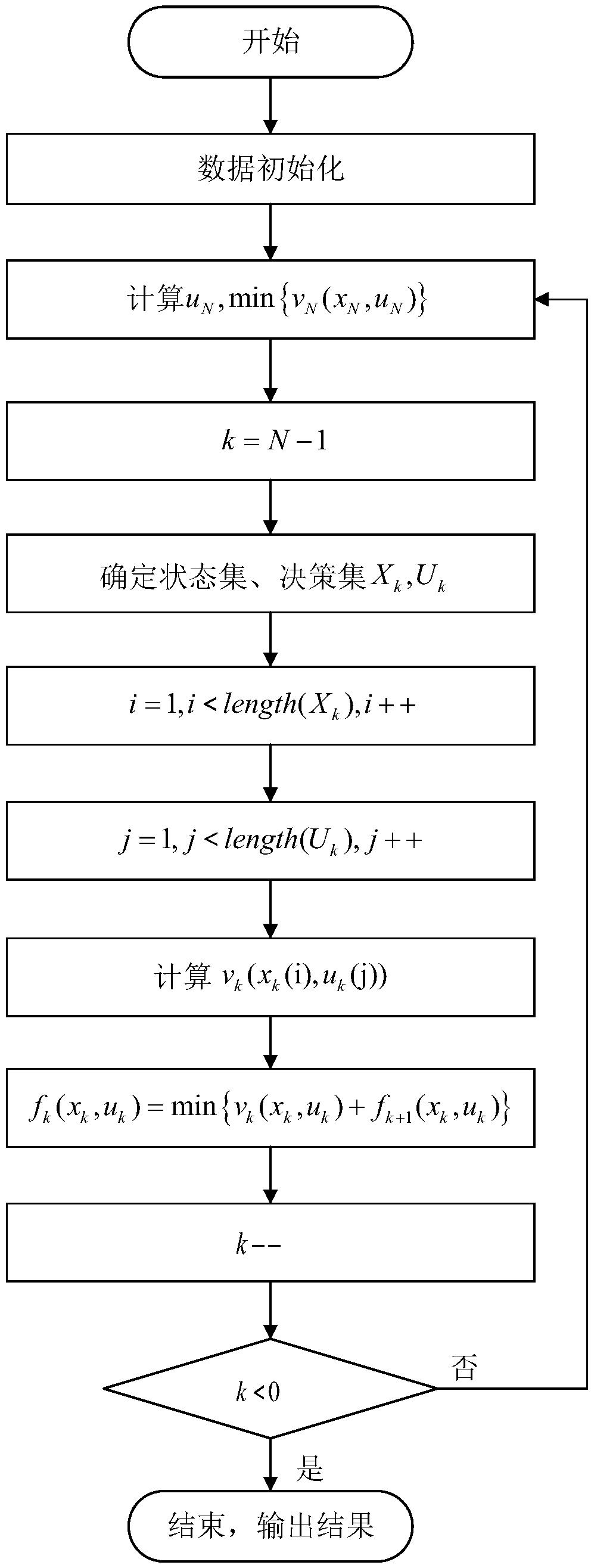
Microgrid multi-energy joint optimal scheduling method
ActiveCN109327042AEasy to guideGood motivationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationMicrogridDynamic planning
The invention relates to a microgrid multi-energy joint optimal scheduling method. The method includes: step 1, on the basis of force application conditions of energy supply equipment and operating states of energy storage equipment in different scenes, constructing a physical model of a multi-energy system; step 2, establishing unit mathematical models, including a wind power generator model, a photovoltaic power generation model, a micro-gas turbine model, a fuel cell model and an energy storage model, of the microgrid multi-energy system; step 3, in order to realize lowest comprehensive cost in system operation, constructing a microgrid multi-energy optimal scheduling model by taking DG operation constraints, system safety constraints and multi-energy coupling characteristics into comprehensive consideration; step 4, on the basis of reversed order dynamic planning, solving the microgrid multi-energy optimal scheduling model to obtain a microgrid multi-energy joint optimal operatingstrategy. By the microgrid multi-energy joint optimal scheduling method, operating demands in different scenes can be met, electricity-thermal coordinated optimal scheduling schemes are provided for operating of a comprehensive energy microgrid in different scenes, and high integral operating efficiency and high economic benefits are realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
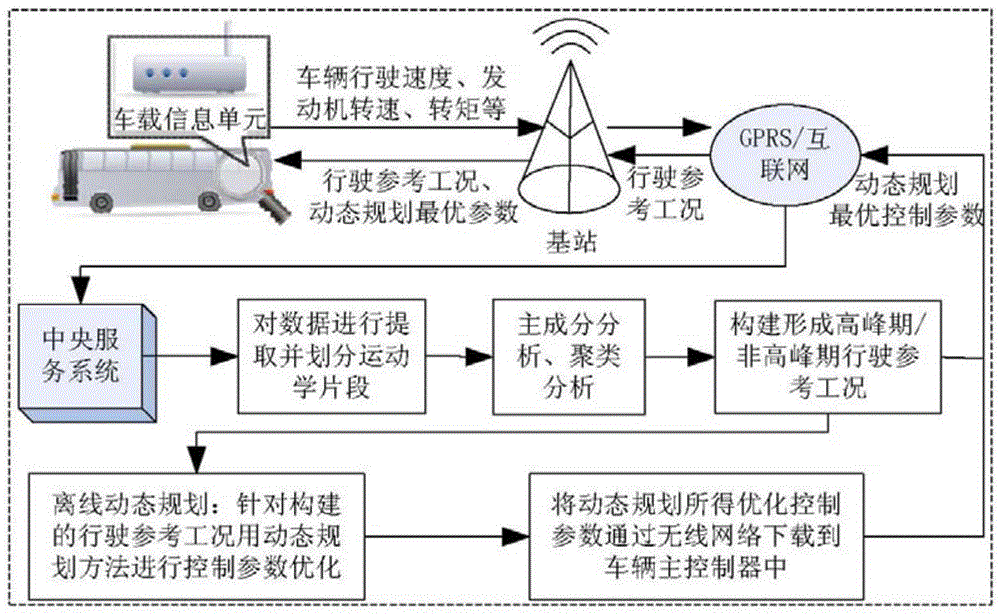
Method for controlling hybrid power urban buses
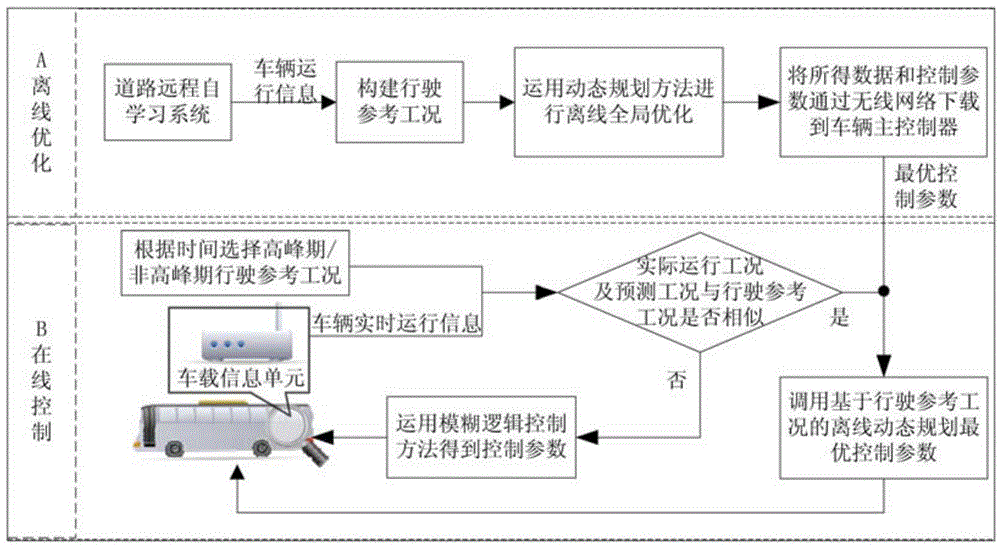
InactiveCN103606271AImprove fuel economyImprove emission effectRoad vehicles traffic controlElectric/fluid circuitDynamic planningOptimal control
The invention discloses a method for controlling hybrid power urban buses. The method comprises the steps of off-line optimizing and on-line controlling. The idea of control strategy switching is put forward, driving reference working conditions targeting regions and more conforming to actual bus driving routes are established, off-line overall optimizing is carried out based on the working conditions, the optimum control effect can be achieved, and the problem that the dynamic planning cannot be applied to on-line and real-time control because the calculated quantity of the dynamic planning is large is solved. When the hybrid buses are driven actually, whether the similarities between the actual driving working conditions and the established driving reference working conditions and between the road prediction working conditions and the established driving reference working conditions are judged on line, if yes, real-time torque distribution is carried out on the hybrid power urban buses by calling dynamic planning optimum control parameters stored in a bus main controller, or otherwise, control strategies are switched, on-line and real-time control is carried out on the buses by adopting the fuzzy logic rule control strategy which is high in self-adaptability and realizability, and accordingly the control strategy adaptation is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
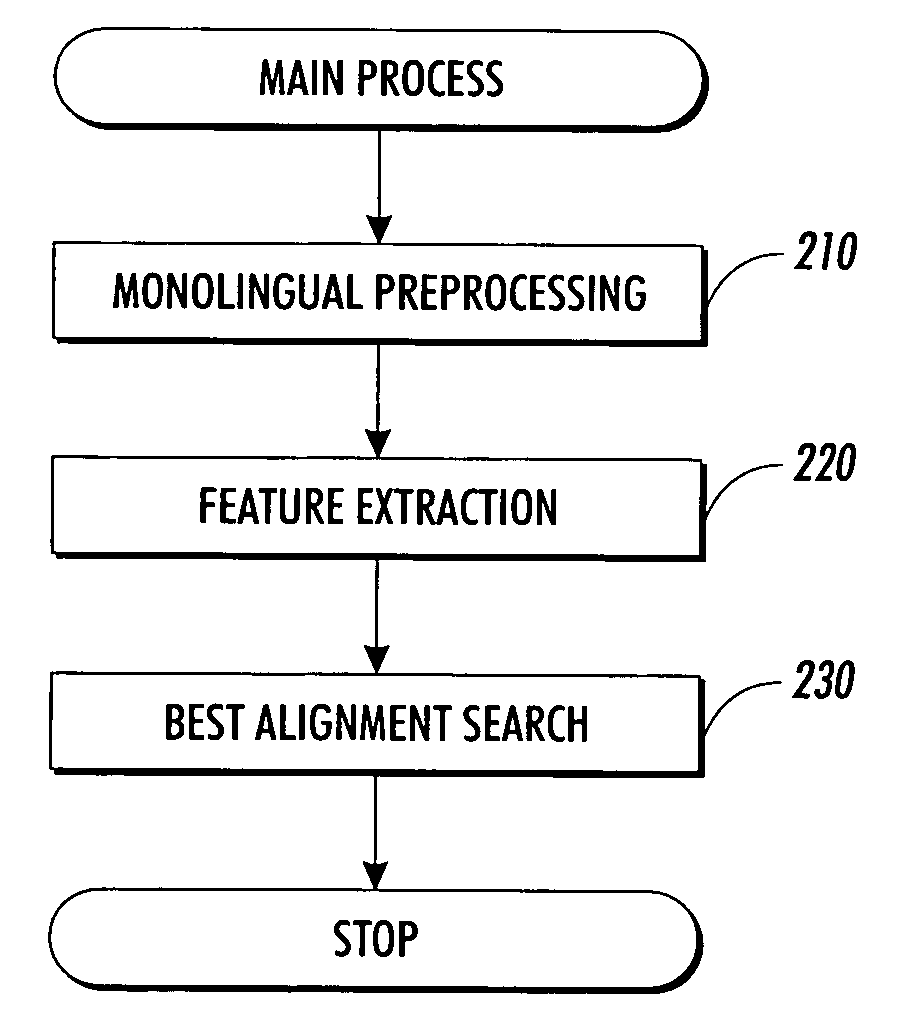
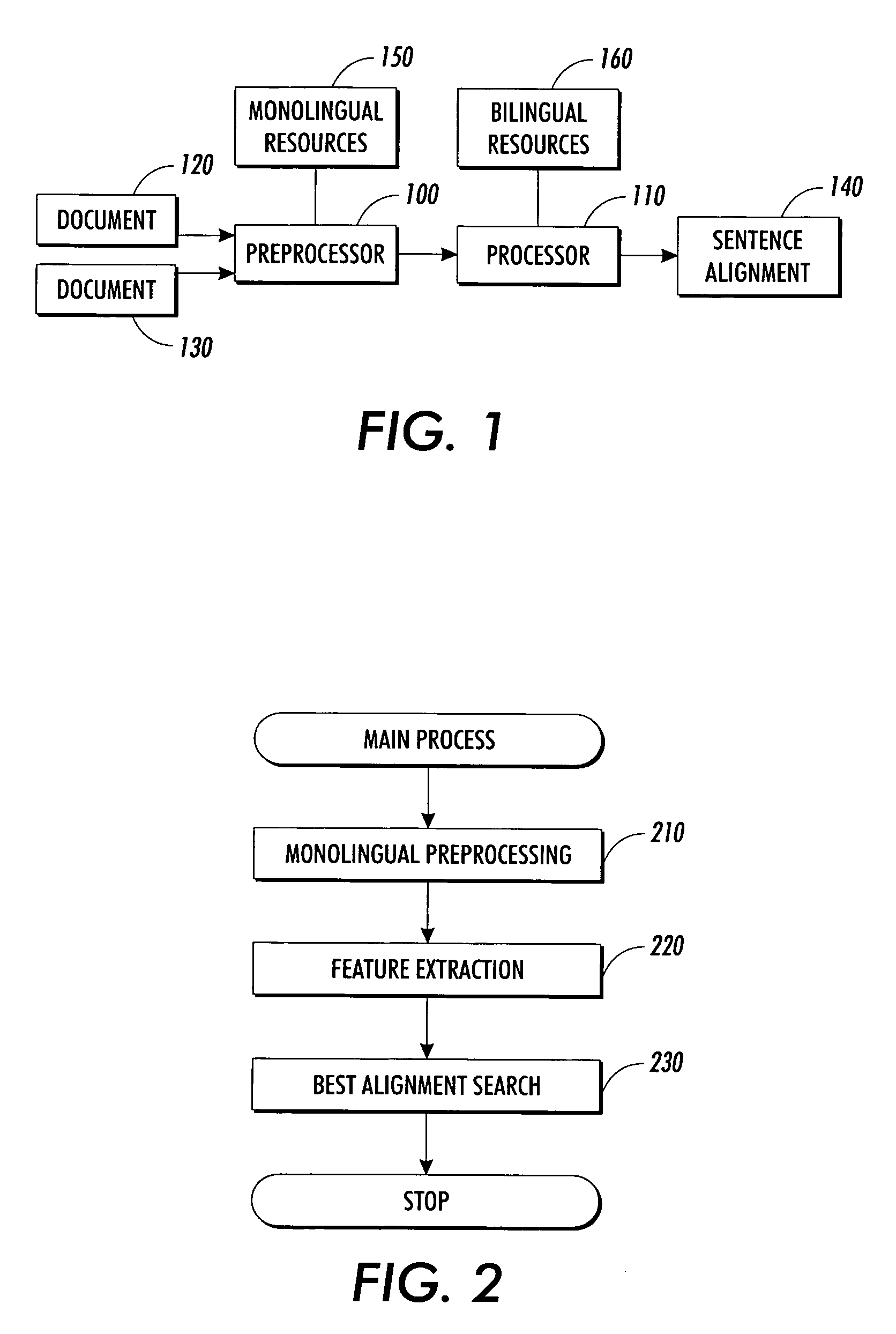
Extracting sentence translations from translated documents
InactiveUS7054803B2Efficient use ofReduce memory consumptionNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge sourcesMemory footprint
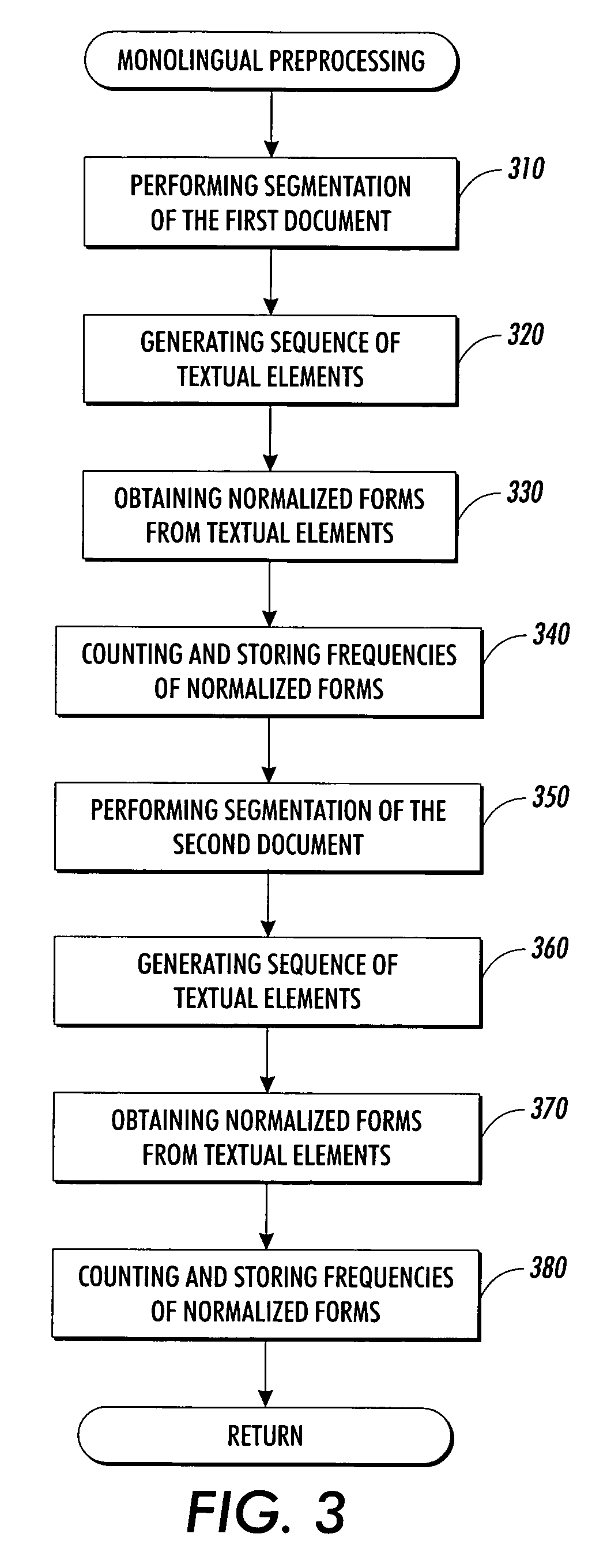
A system extracts translations from translated texts, such as sentence translations from translated versions of documents. A first and a second text are accessed and divided into a plurality of textual elements. From these textual elements, a sequence of pairs of text portions is formed, and a pair score is calculated for each pair, using weighted features. Then, an alignment score of the sequence is calculated using the pair scores, and the sequence is systematically varied to identify a sequence that optimizes the alignment score. The invention allows for fast, reliable and robust alignment of sentences within large translated documents. Further, it allows to exploit a broad variety of existing knowledge sources in a flexible way, without performance penalty. Further, a general implementation of dynamic programming search with online memory allocation and garbage collection allows for treating very long documents with limited memory footprint.
Owner:XEROX CORP
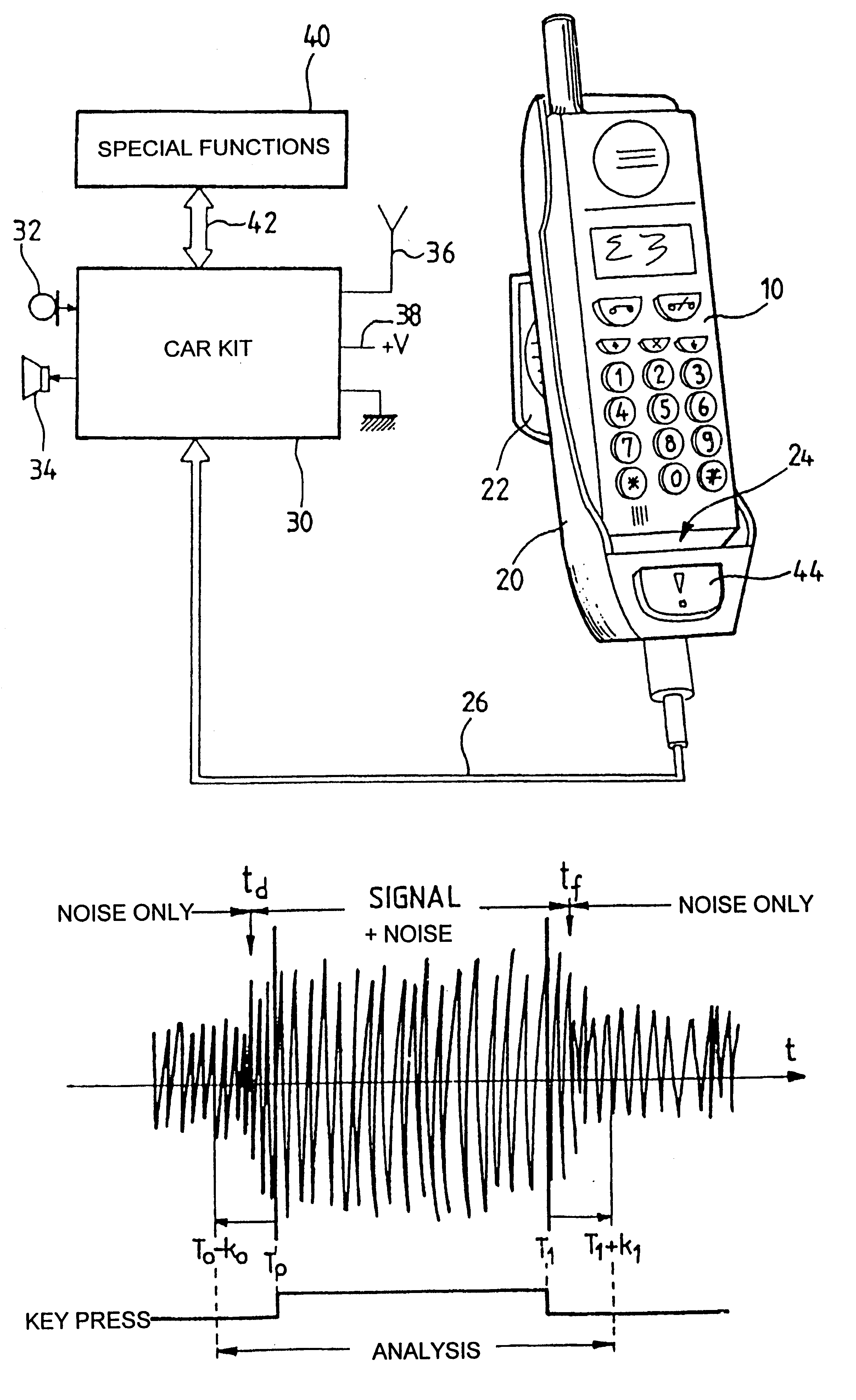
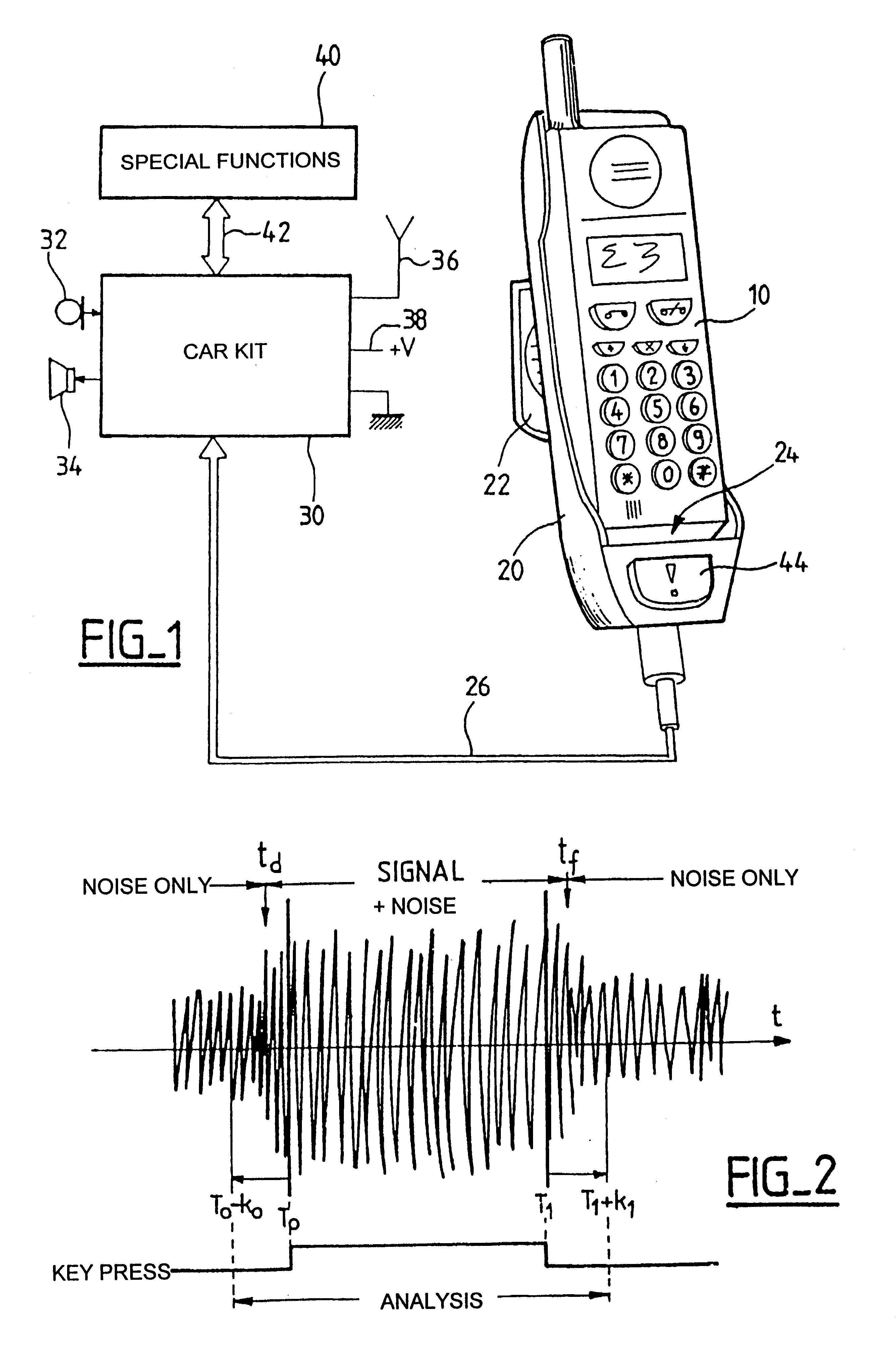
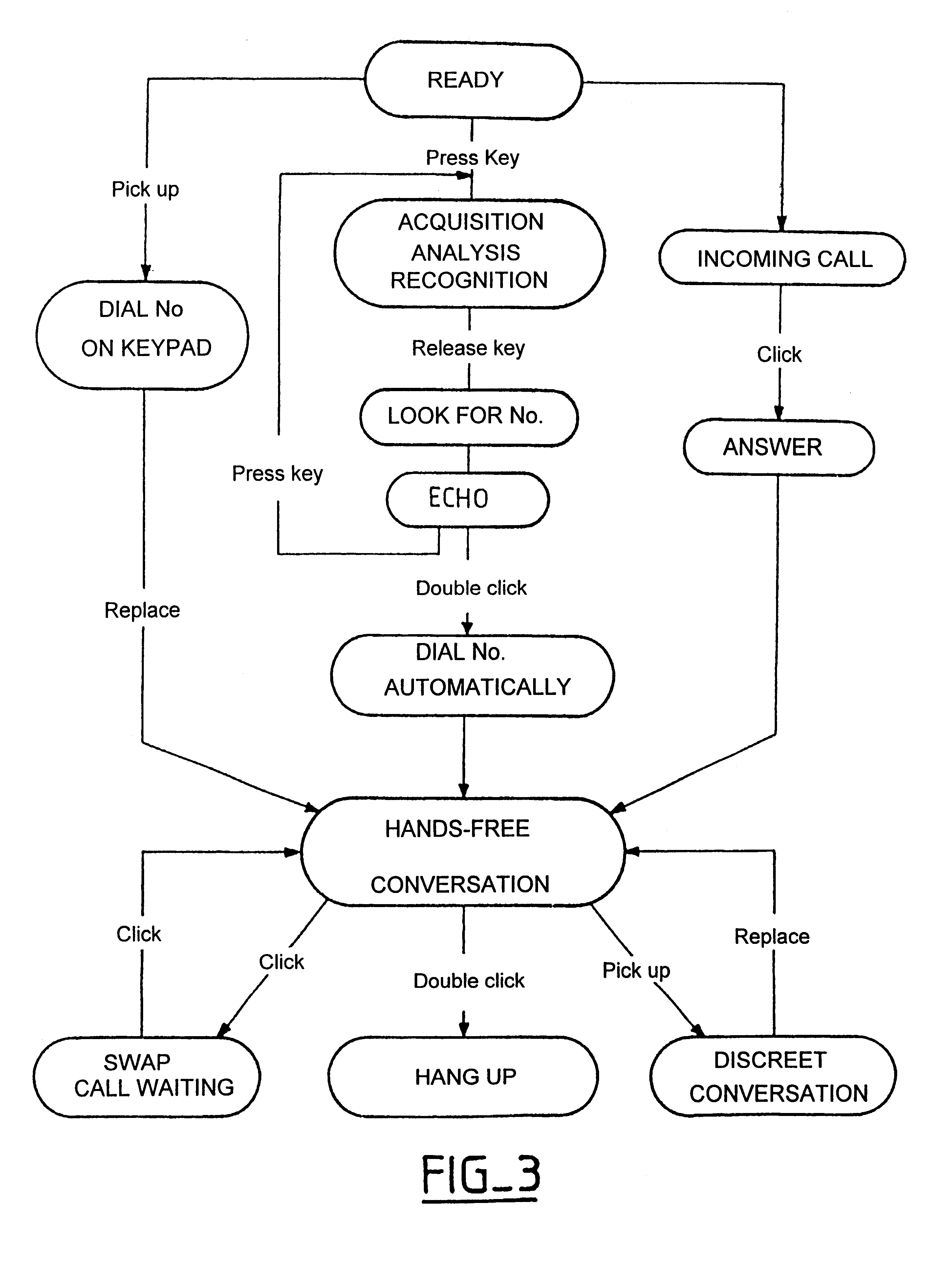
Radiotelephone voice control device, in particular for use in a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6263216B1Primary cell maintainance/servicingAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingMemory addressData memory
The apparatus comprises a data memory containing a series of correspondents' call numbers and, for each call number, at least one associated voice print; a sound transducer suitable for picking up the name of a desired corespondent as spoken by the user of the apparatus; voice recognition means suitable for analyzing the correspondent's name as picked up by the transducer and for transforming it into an associated voice print; selective memory addressing means including associative means suitable for finding a voice print in the memory corresponding to the print supplied by the voice recognition means, and in the event of a match, for addressing the corresponding memory position; and means co-operating with the associative means for applying the addressed call number to the radiotelephone circuits. The voice recognition means evaluate and store a current noise level as picked up by the transducer in the absence of a speech signal; when in the presence of a speech signal, they subtract the previously evaluated current noise level from the signal as picked up; and then they apply the resulting signal as obtained in this way to a DTW type voice recognition algorithm with pattern recognition by dynamic programming adapted to speech using dynamic parameter extraction functions, in particular a predictive dynamic algorithm with forward and / or backward and / or frequency masking.
Owner:PARROT AUTOMOTIVE
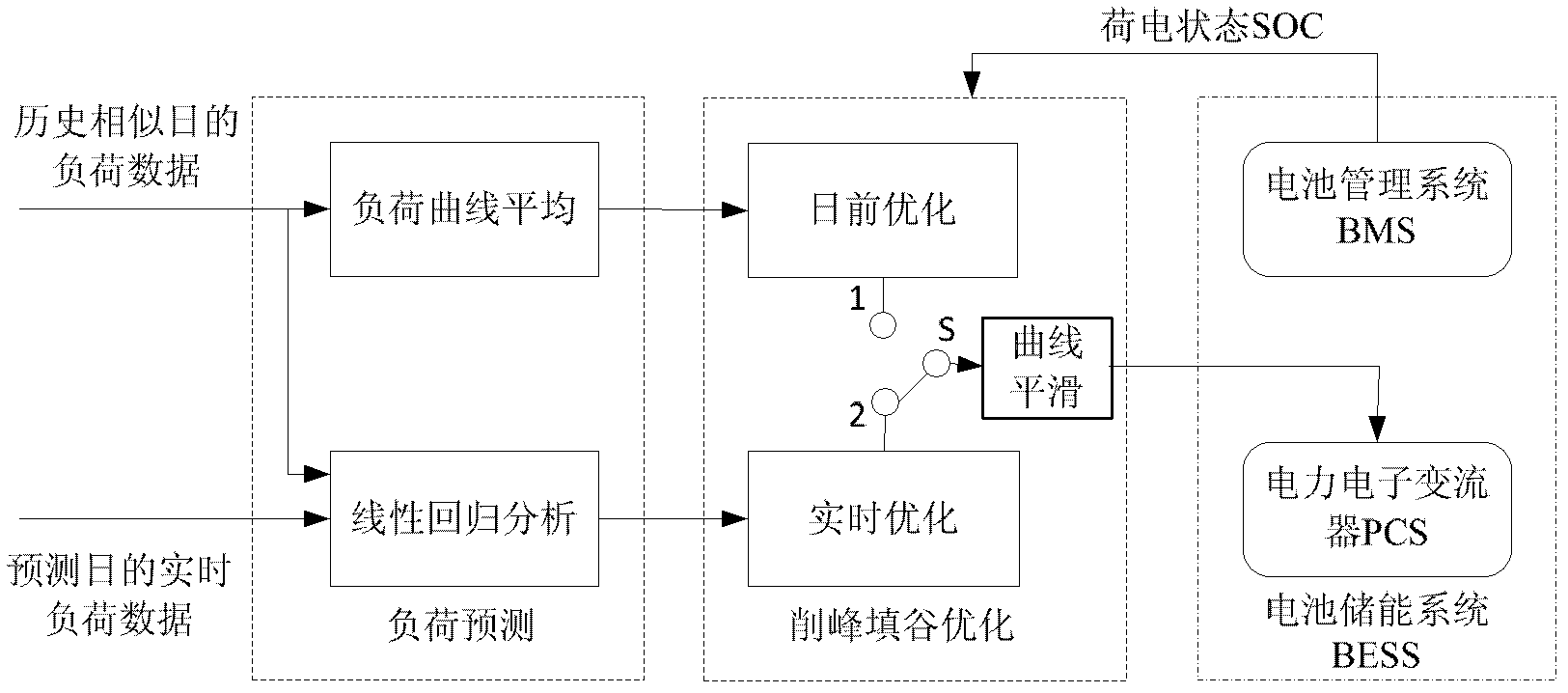
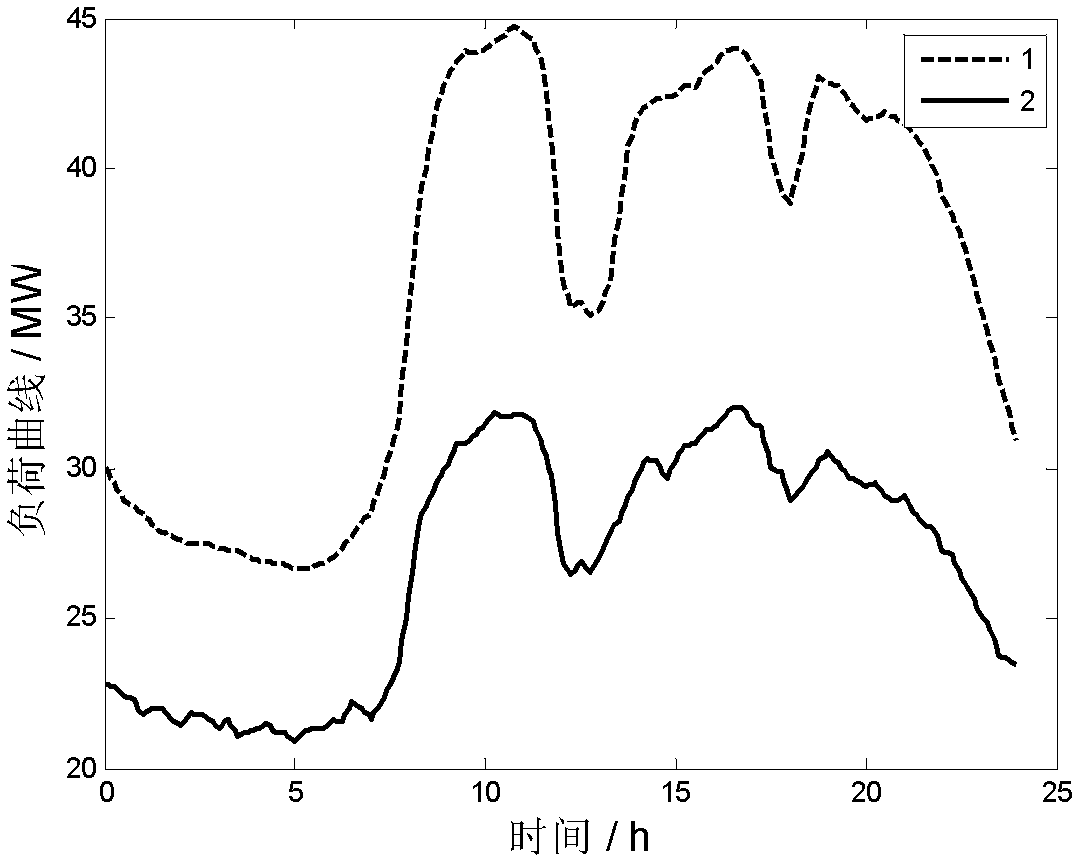
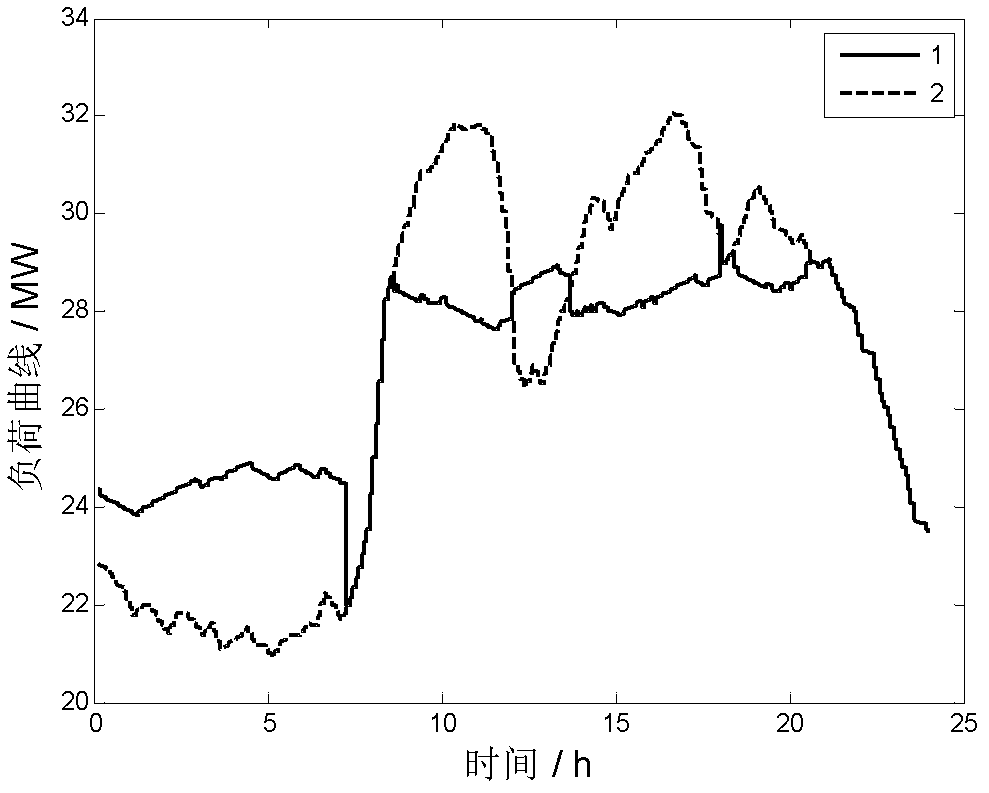
Battery energy storage system peak clipping and valley filling real-time control method based on load prediction
ActiveCN102624017AExtend your lifeReduce peak-to-valley differenceFlexible AC transmissionAc network load balancingAutomatic controlElectric power system
The invention relates to a battery energy storage system peak clipping and valley filling real-time control method based on load prediction and belongs to the field of power system automatic control. The control method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: firstly searching similar history daily load data, carrying out expanding short-term load prediction by adopting a linear regression analysis method, building a battery energy storage system peak clipping and valley filling real-time optimization model, solving the battery energy storage system peak clipping and valley filling real-time optimization model by adopting a dynamic programming algorithm, and obtaining the output power of a battery energy storage system at each moment. The control method provided by the invention comprises battery charging and discharging frequency constraint and discharge depth constraint in the real-time optimization model, is used for researching relation between battery life and the charging and discharging frequency and the relation between the battery life and the discharge depth and is beneficial to prolonging the battery life. Minimum load variance is taken as a target function, the peak-to-valley of a load curve can be reduced, the load curve is smoother while constraint conditions are met, and the peak clipping and valley filling application requirement can be met. Local part of the load curve can be smoother by adopting load smoothness constraint.
Owner:北京宝光智中能源科技有限公司
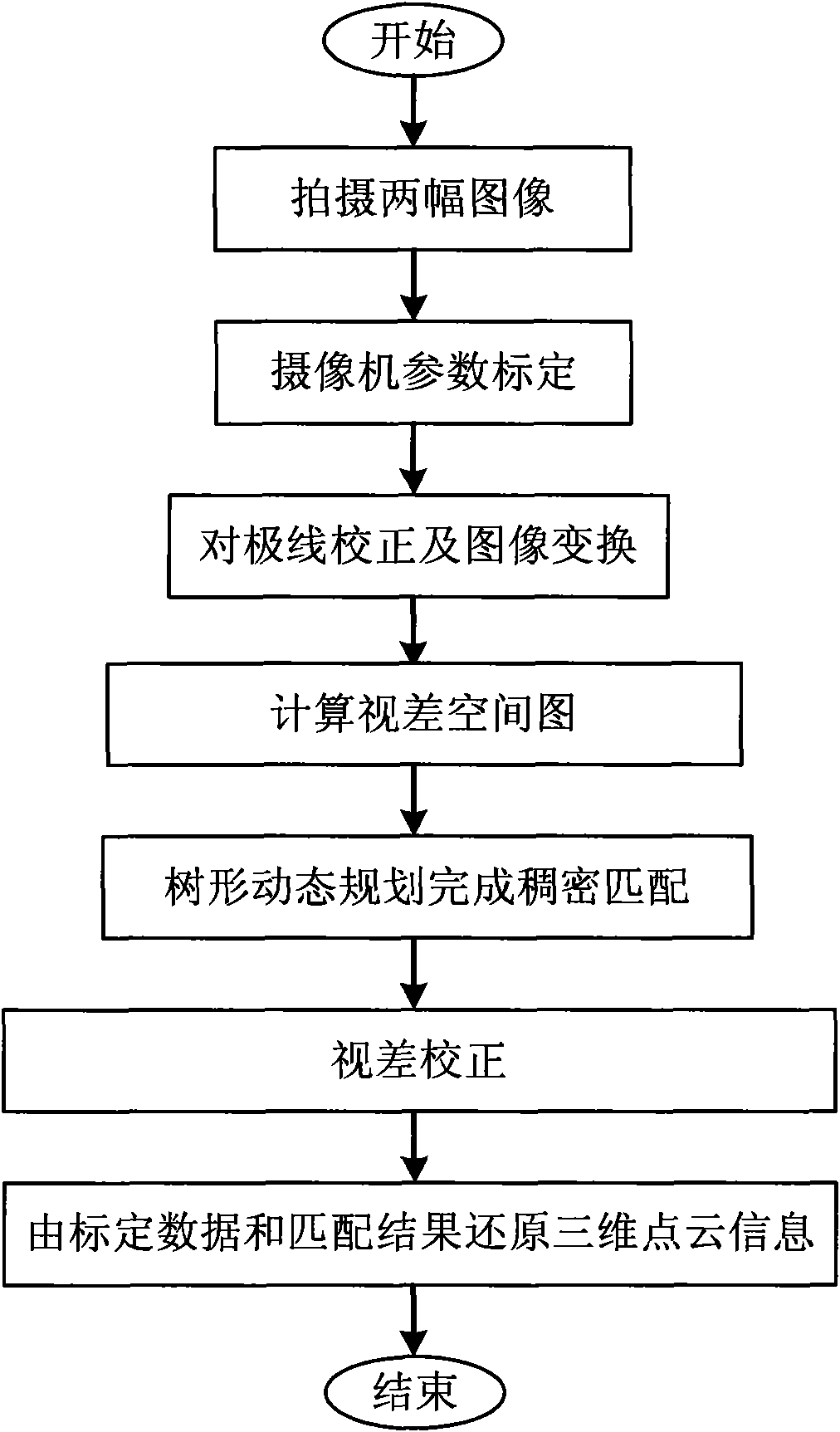
Stereoscopic vision-based real low-texture image reconstruction method
InactiveCN101887589AIncrease the differenceImprove recognitionImage analysis2D-image generationFiltrationObject point
The invention discloses a stereoscopic vision-based real low-texture image reconstruction method, which is implemented by the following steps: (1) shooting images by two cameras at two proper angles at the same time, respectively, wherein one image is used as a reference image and the other image is used as a registered image; (2) calibrating the inside and outside parameter matrixes of the two cameras respectively; (3) performing epipolar line correction, image transformation and Gauss filtration according to the calibrated data; (4) calculating a self-adaptive polygonal prop window of each point in the two calibrated images, and calculating the matching of pixel points to obtain a parallax space diagram; (5) completing dense matching by executing a tree dynamic programming algorithm pixel by pixel in the whole diagram; (6) extracting error matching points according to a left and right consistency principle, and performing parallax correction to obtain a final parallax diagram; and (7) calculating the three-dimensional coordinates of actual object points according to the calibrated data and a matching relationship to construct the three-dimensional point cloud of an object.
Owner:南通瑞银服饰有限公司 +1
Method for mining association rules in data
InactiveUS6185549B1Efficient use ofComputational complexity increaseDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsSales promotionData mining
An electronic data mining process for mining from an electronic data base using an electronic digital computer a listing of commercially useful information of the type known in the art as an association rule containing at least one uninstantiated condition. For example, the commercially useful information may be information useful for sales promotion, such as promotion of telephone usage. The computer retrieves from the database a plurality of stored parameters from which measures of the uninstatiated condition can be determined. The computer uses a dynamic programming algorithm and iterates over intervals or sub-ranges of the parameters to obtain what is called an at least partially optimized association rule, as optimized intervals or sub-ranges of at least some of the retrieved parameters, for example, time intervals of high usage of certain types of telephone connections. These optimized intervals are provided as the listed commercially useful information. The amount of needed iteration is reduced in some cases by using so-called bucketing and divide-and-conquer techniques. Extension of the process for a plurality of uninstantiated conditions is described.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
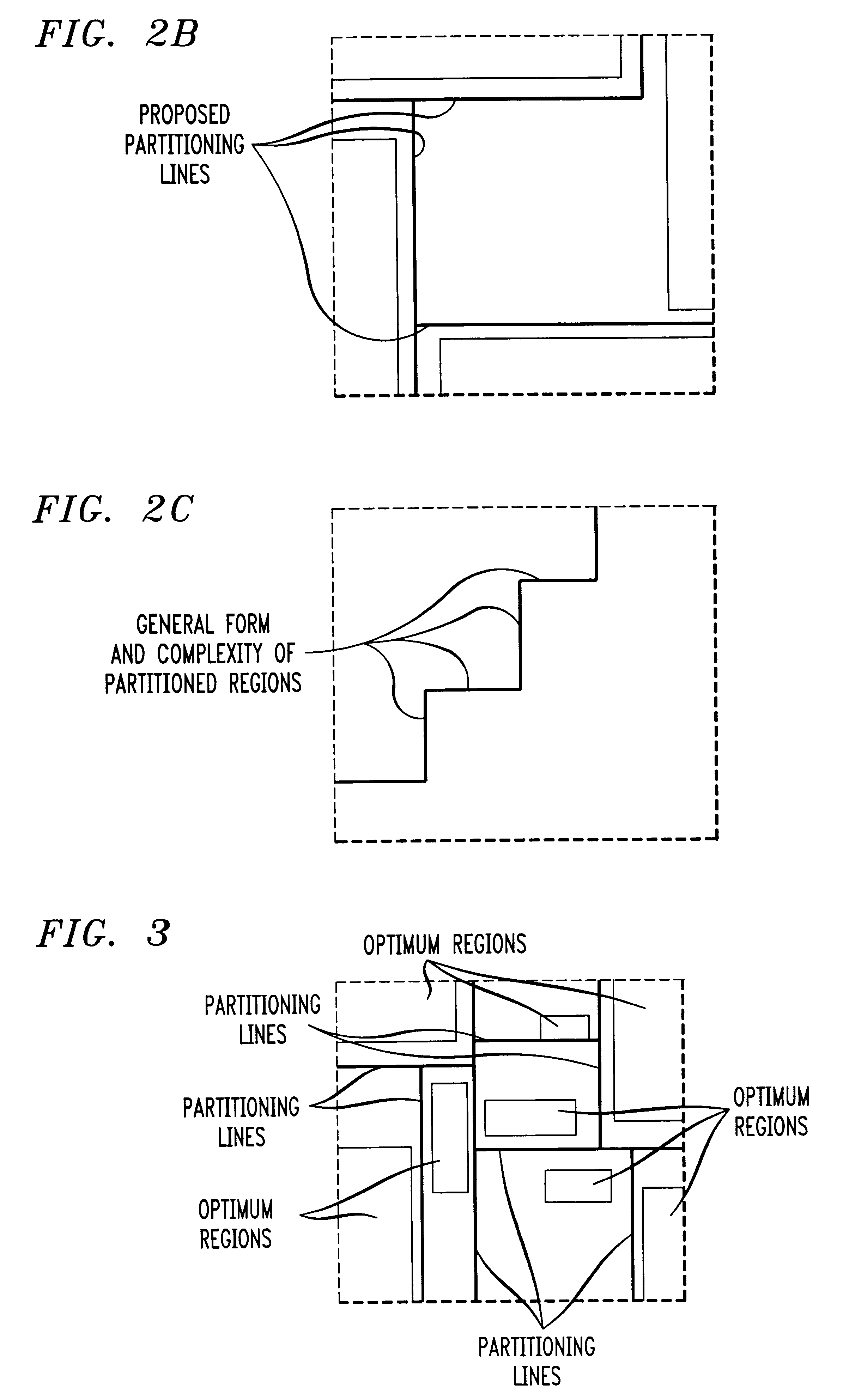
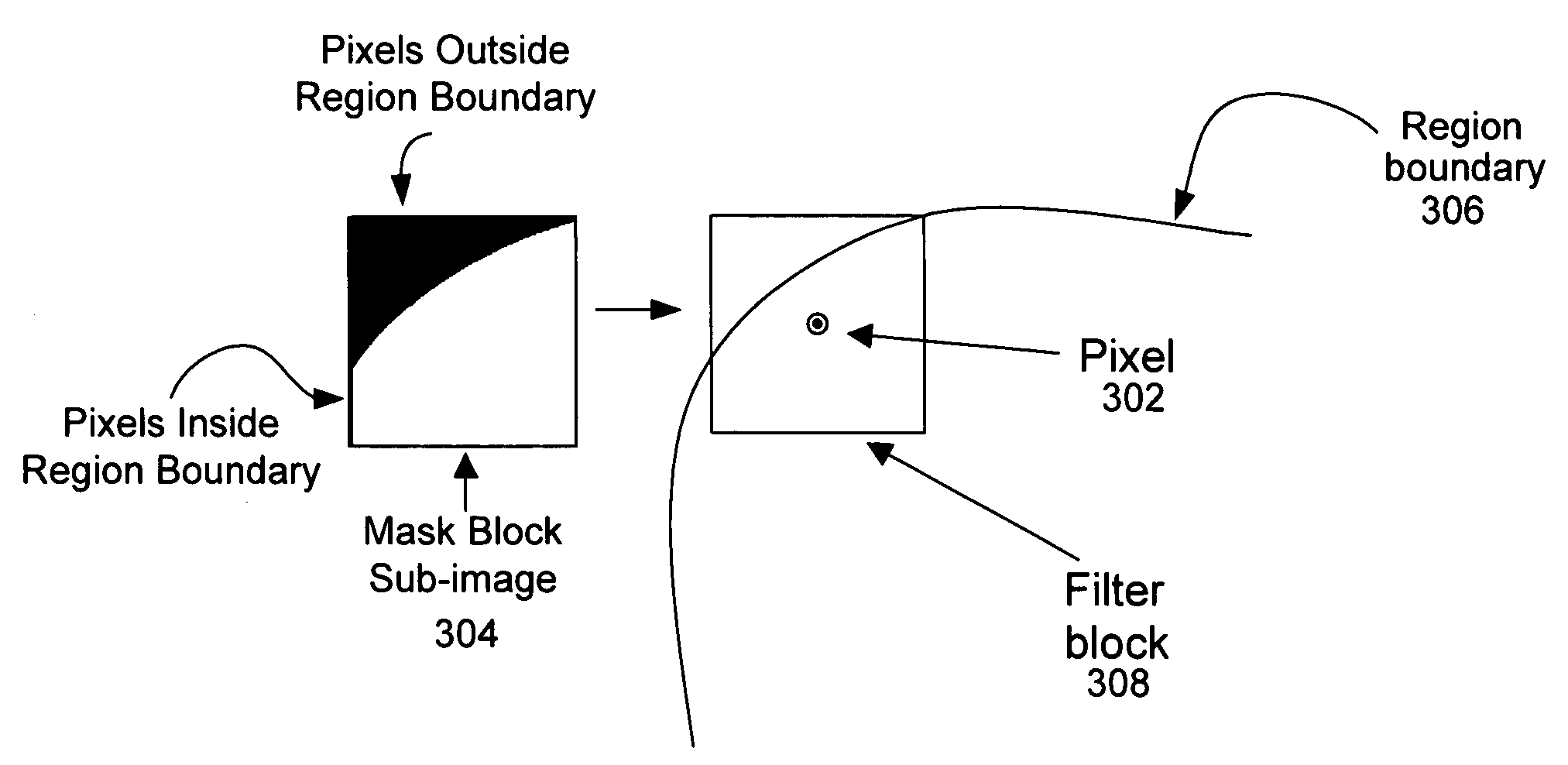
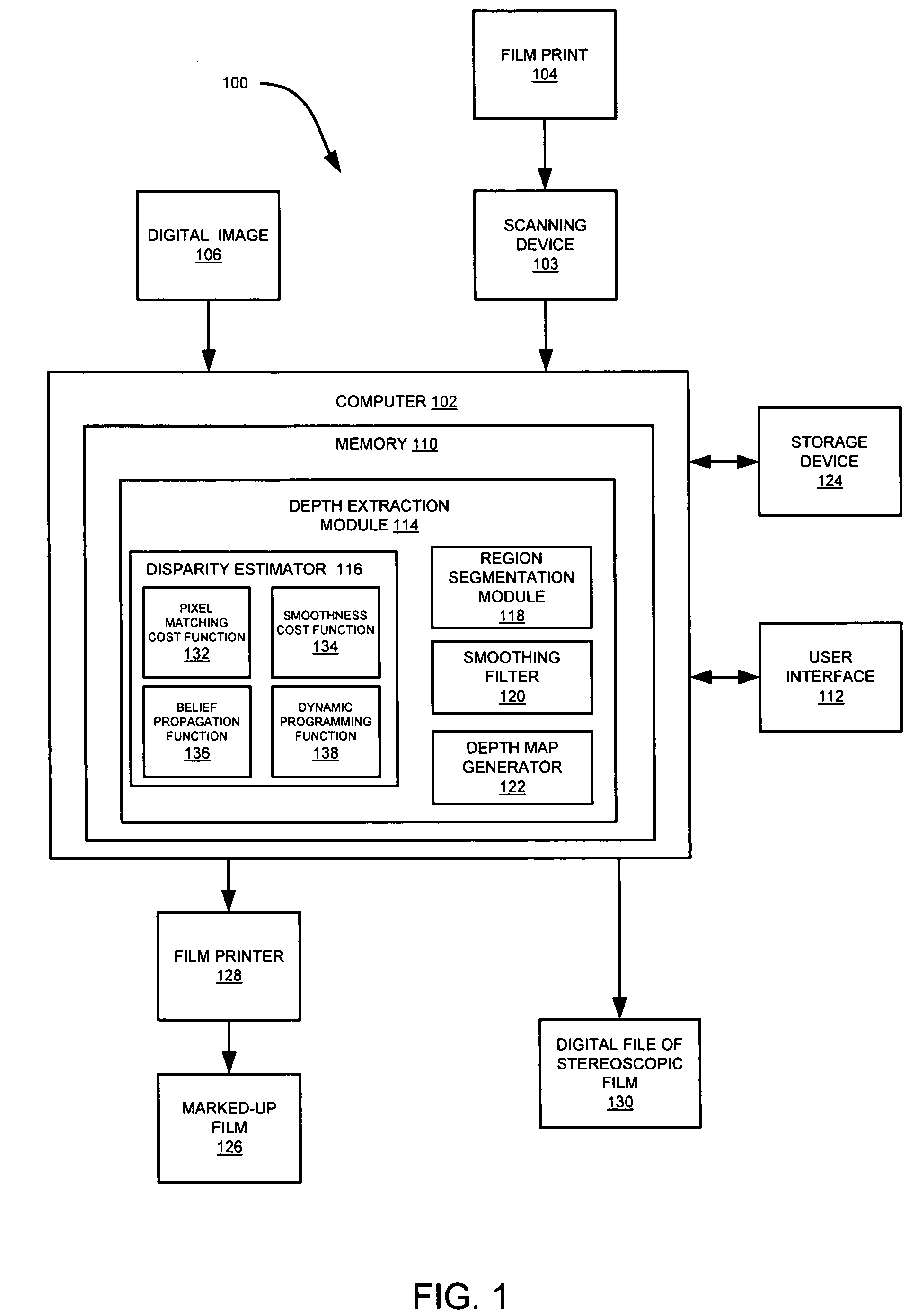
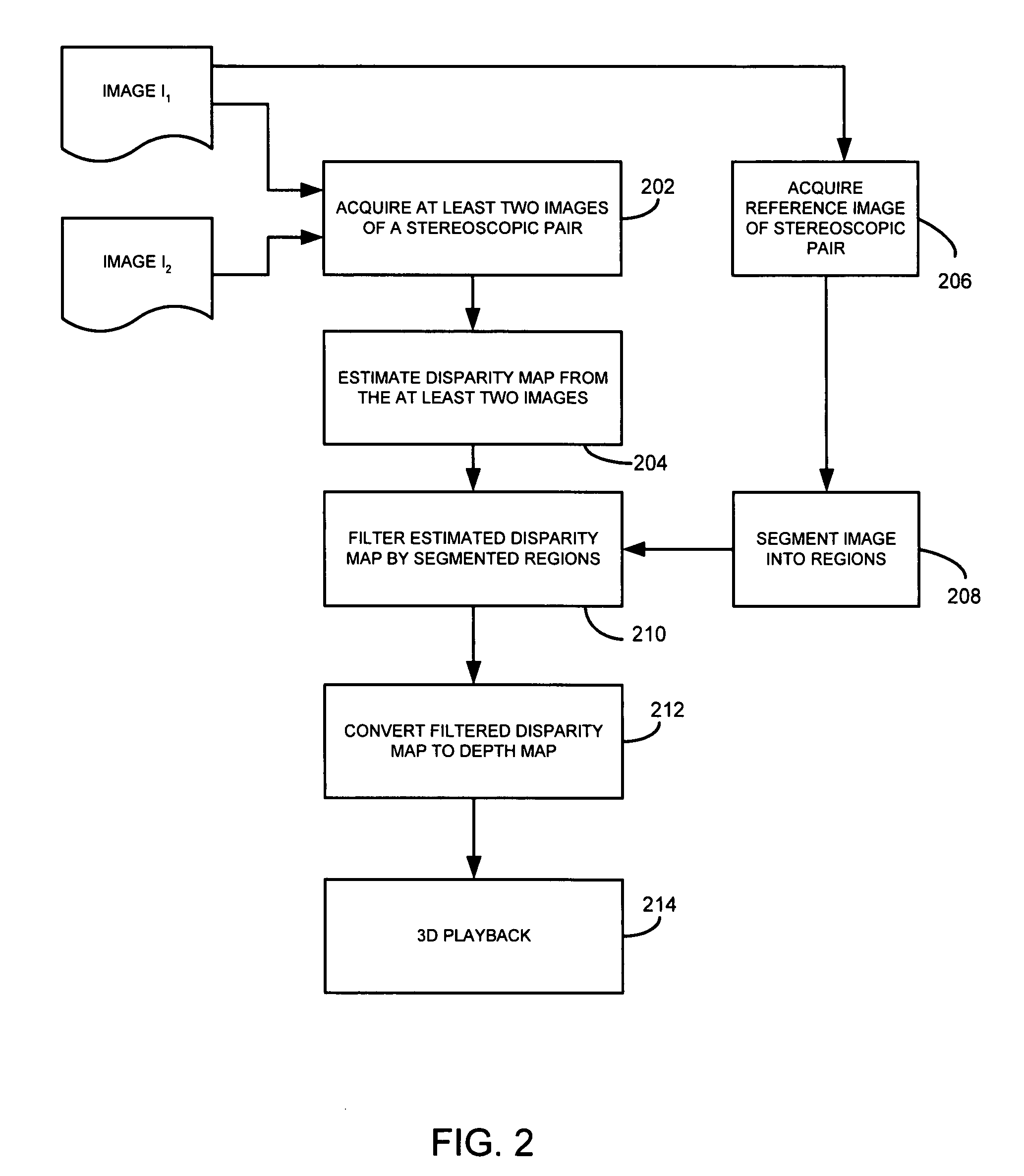
System and method for depth map extraction using region-based filtering
InactiveUS20110044531A1Reduce artifactsAdd depthImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxDynamic programming
A system and method for extracting depth information from at least two images employing region-based filtering for reducing artifacts are provided. The present disclosure provides a post-processing algorithm or function for reducing the artifacts generated by scanline Dynamic Programming (DP) or other similar methods. The system and method provides for acquiring a first image and a second image from a scene, estimating the disparity of at least one point in the first image with at least one corresponding point in the second image to generate a disparity map, segmenting at least one of the first or second images into at least one region, and filtering the disparity map based on the segmented regions. Furthermore, anisotropic filters are employed, which have a great smoothing effect along the vertical direction than that of the horizontal direction, and therefore, reduce stripe artifacts without significantly blurring the depth boundaries.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING INC
System for scheduling multiple time dependent events
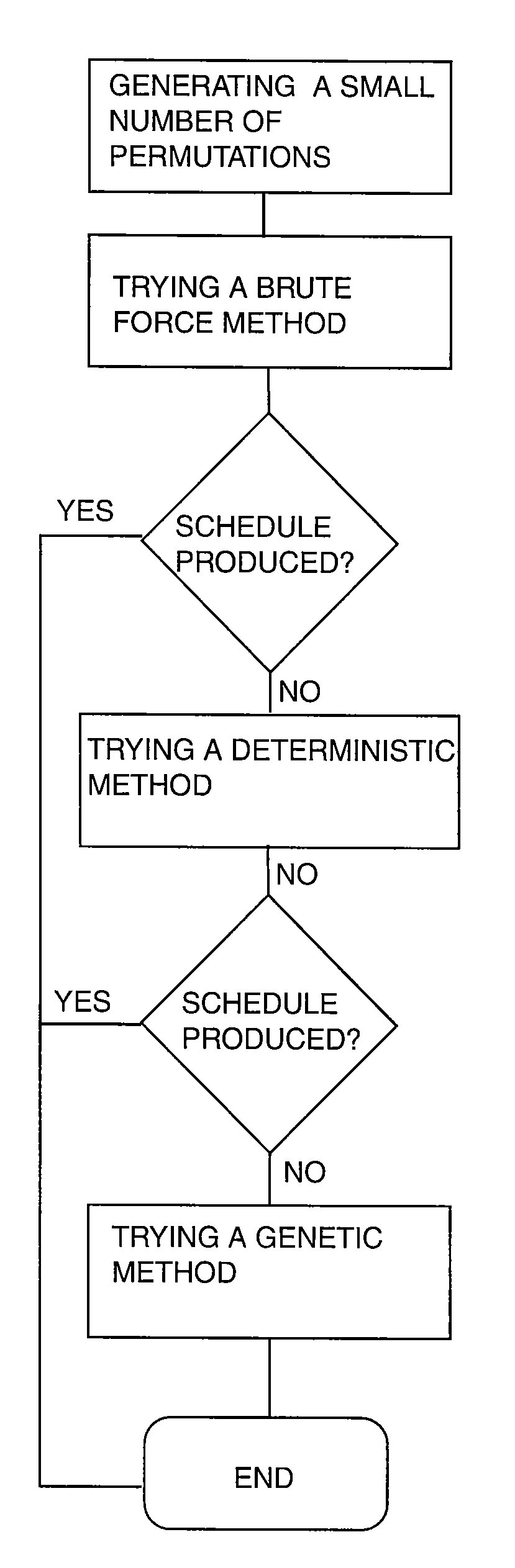
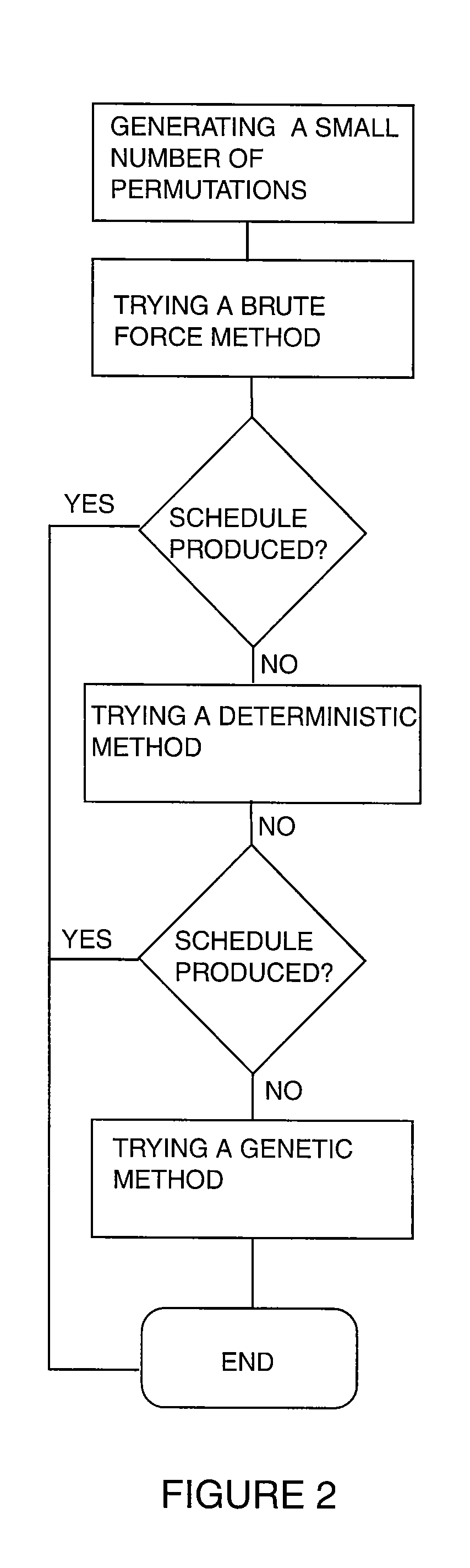
InactiveUS7246075B1Reduce the amount requiredSignificant memory savingResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsTime scheduleBrute force
A scheduling system for choosing the most appropriate heuristic for solving time-dependant scheduling problems. The invention includes a means for selecting the most appropriate heuristic method for generating a schedule from an enumerative (“brute force”) method, a dynamic programming method, and a genetic method. The invention further includes a hashing function that is capable of detecting duplicate solutions generated by the dynamic programming module and a height-balanced binary tree for providing search insertion and deletion operations.
Owner:MAGNOLIA CONSULTING INC
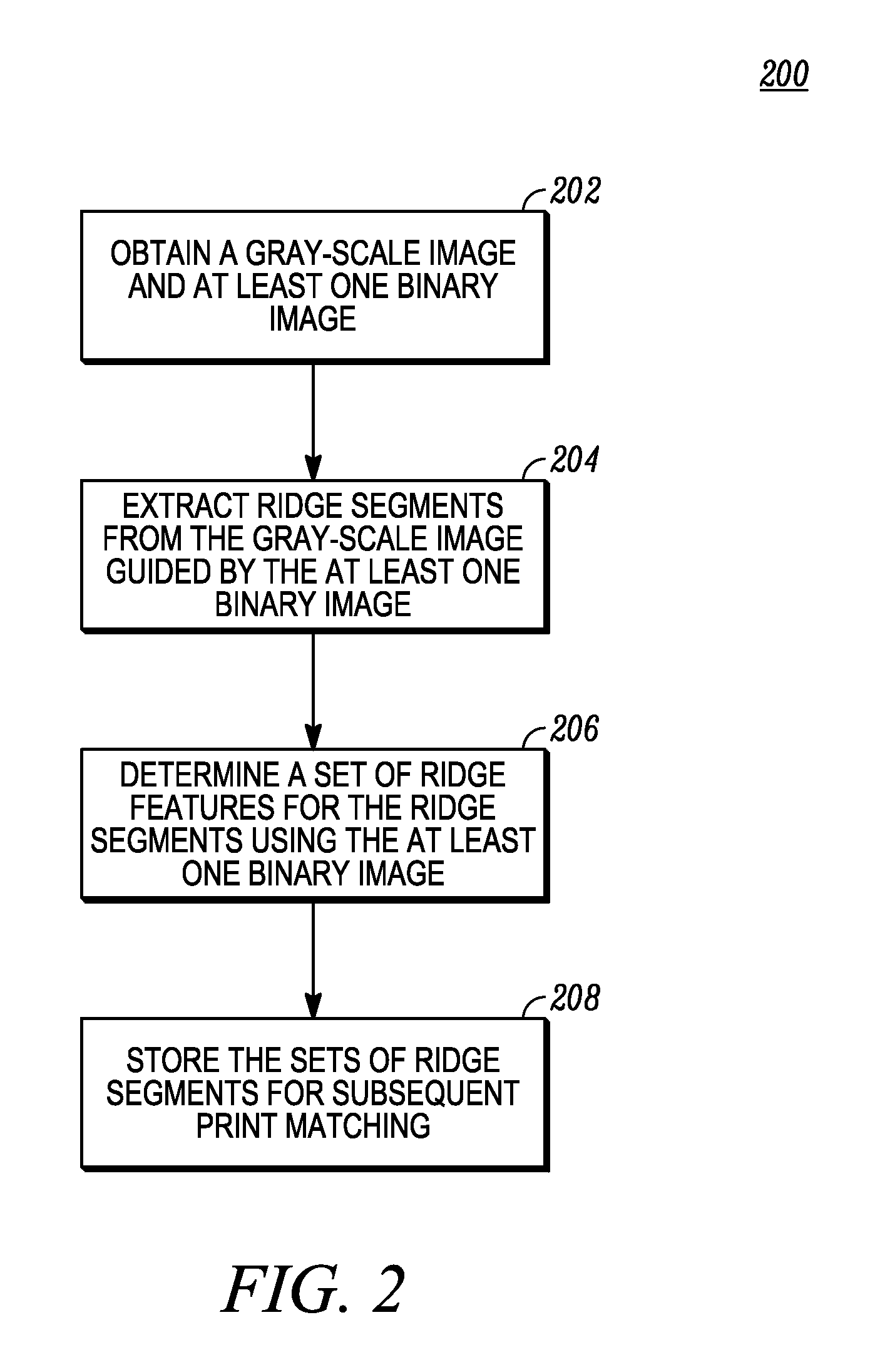
Methods for gray-level ridge feature extraction and associated print matching
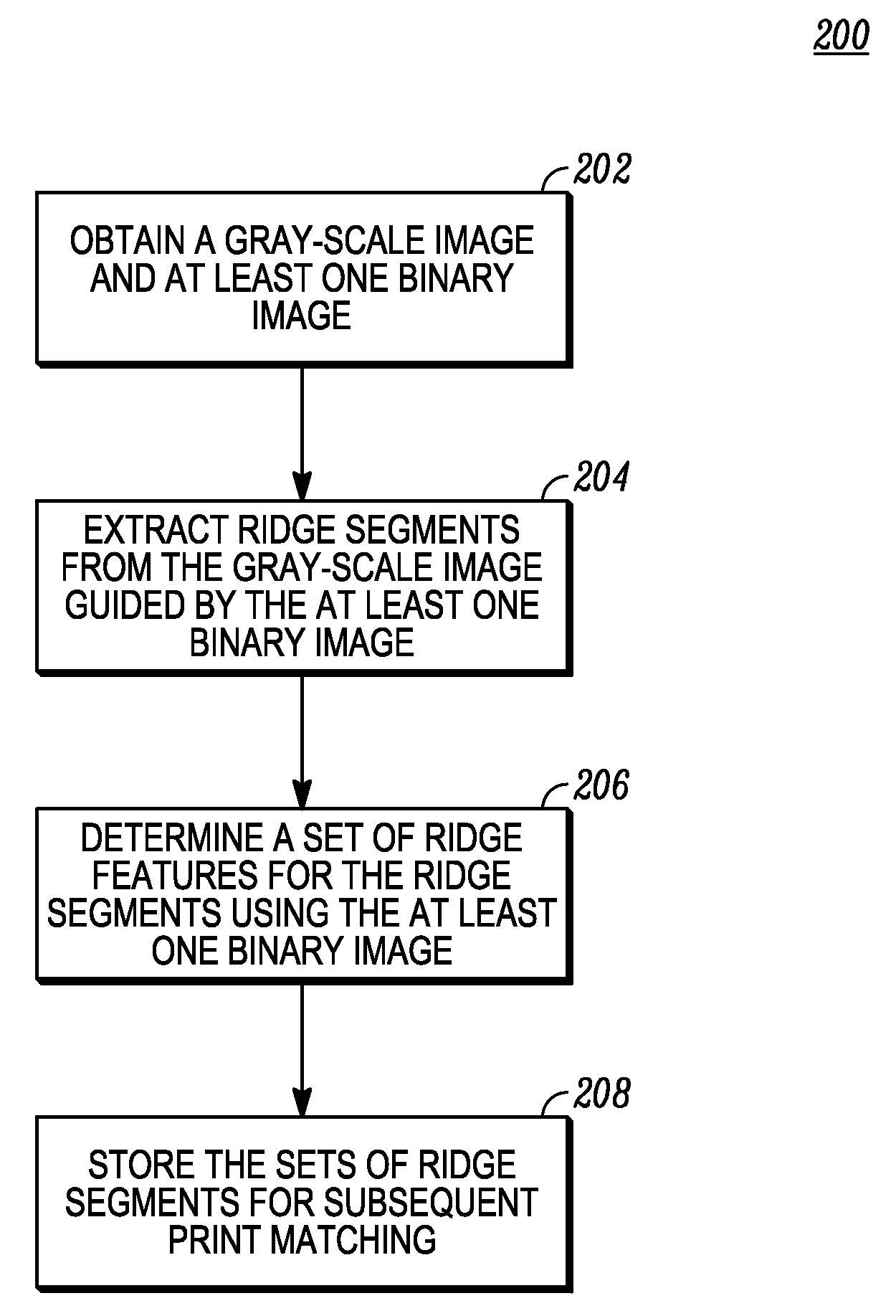
A method for level three feature extraction from a print image extracts features associated with a selected ridge segment using a gray-level image under the guidance of at least one binary image. The level three features are a sequence of vectors each corresponding to a different level three characteristic and each representing a sequence of values at selected points on a print image. The level three features are stored and used for level three matching of two prints. During the matching stage, ridge segments are correlated against each other by shifting or a dynamic programming method to determine a measure of similarity between the print images.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle energy optimization management method realizing real-time working condition adaption
ActiveCN107284441AHigh energy consumptionOptimized torque distributionHybrid vehiclesExternal condition input parametersDynamic planningSimulation
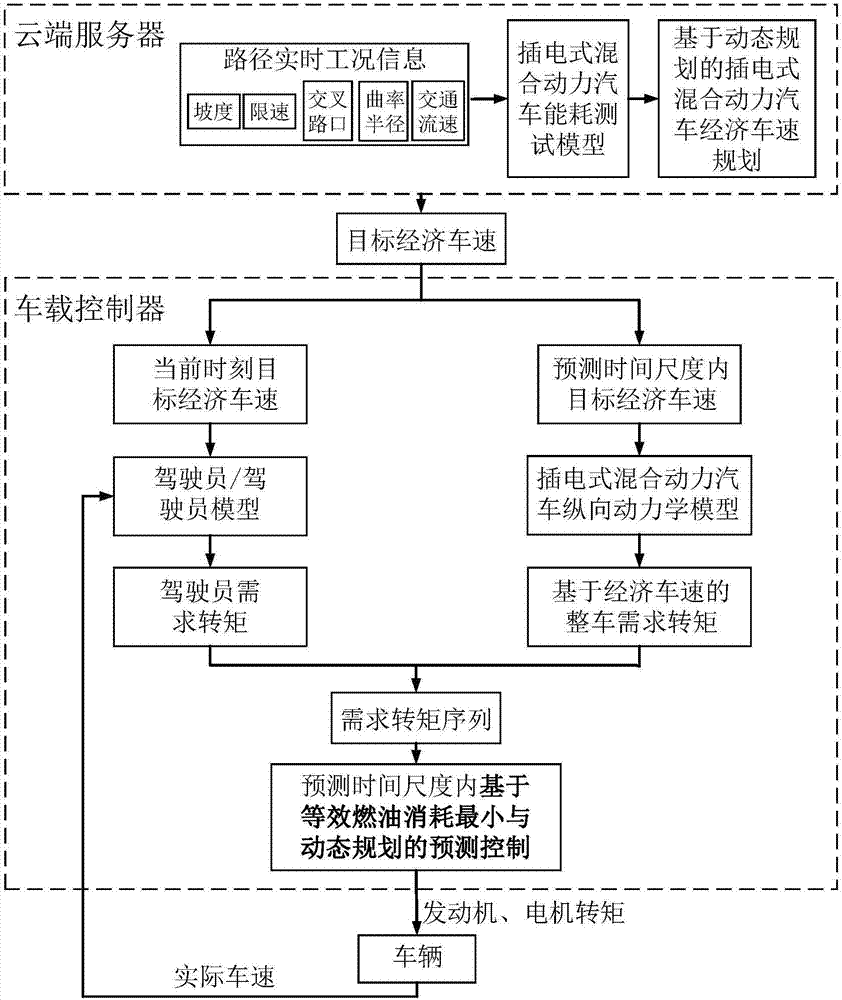
The invention relates to a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle energy optimization management method realizing real-time working condition adaption. The plug-in hybrid electric vehicle energy optimization management method includes the steps of (1), acquiring real-time working condition information of each section of each path; (2), setting the optimization target of minimizing accumulated equivalent fuel consumption of each section of each path, building the plug-in hybrid electric vehicle energy optimization management strategy based on the dynamic planning by taking the speed limit of each section of each path, the traffic flow velocity and the limit of power battery working current; (3), acquiring corresponding target economical speed of each section of each path and sending the same to a vehicular controller; (4), by the vehicular controller, acquiring demanded torque sequence of each moment within a predicted time scale; (5), taking the minimum accumulated equivalent fuel consumption within the predicted time scale as the target, and tracking the target economic speed in real time. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of combining the global optimum and the real-time optimum of the plug-in hybrid electric vehicle energy consumption according to the real-time working condition information, and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method and system for automatic coronary artery detection
ActiveUS8582854B2Efficiently and robustly detectImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesHeart chamber
A method and system for coronary artery detection in 3D cardiac volumes is disclosed. The heart chambers are segmented in the cardiac volume, and an initial estimation of a coronary artery is generated based on the segmented heart chambers. The initial estimation of the coronary artery is then refined based on local information in the cardiac volume in order to detect the coronary artery in the cardiac volume. The detected coronary artery can be extended using 3D dynamic programming.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Optimized smith-waterman search
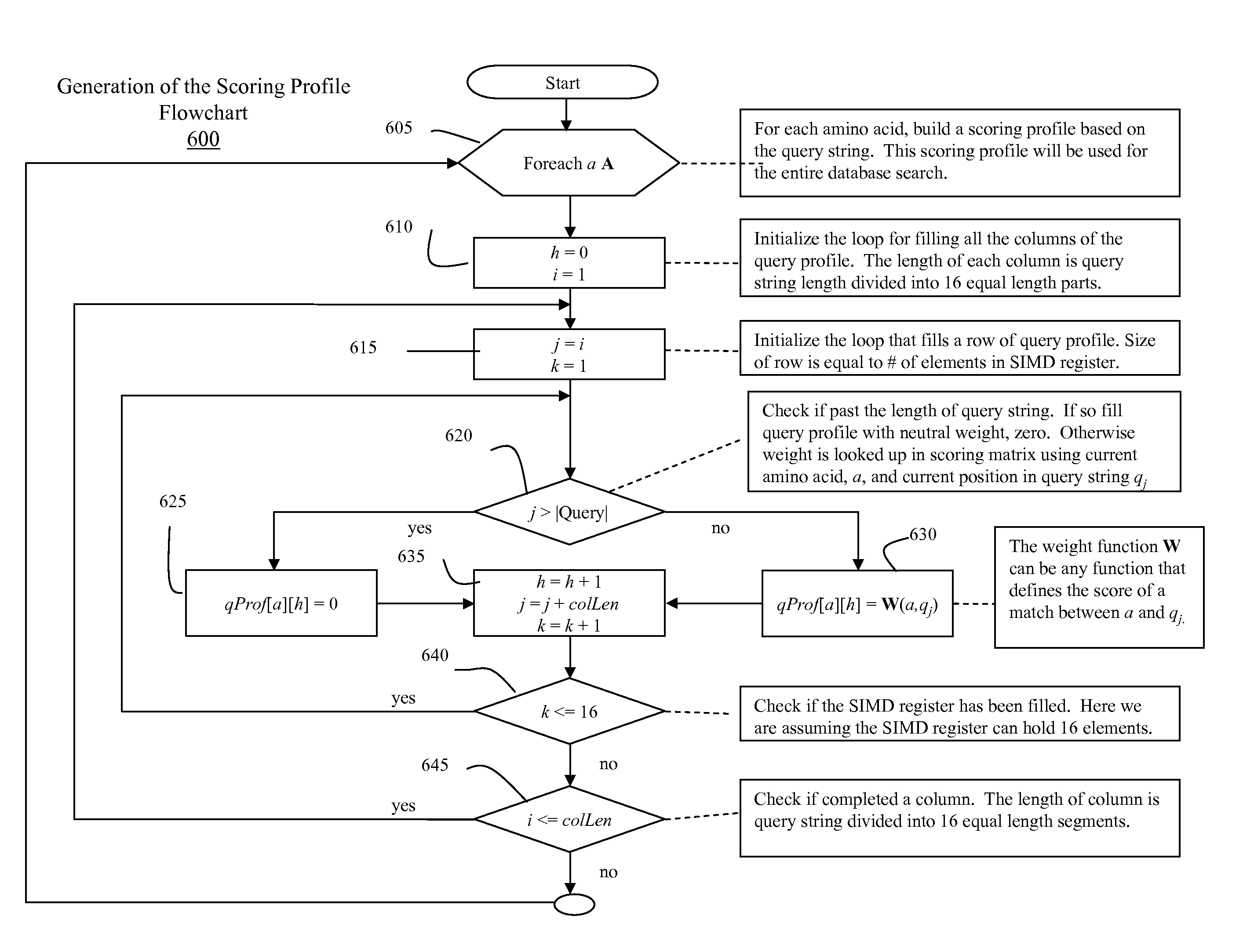
InactiveUS20080250016A1Sequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsData miningDynamic programming
An optimized database searching for a query sequence having a plurality of vectors arranged in a linear fashion, wherein the vectors are parallel to a query sequence, and a plurality of elements of the query sequence are reordered in a striped pattern, and wherein a set of dynamic programming scoring results are reported for further processing.
Owner:BIOSIMD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com