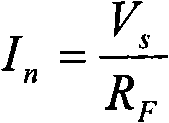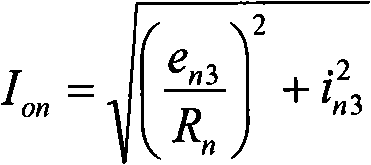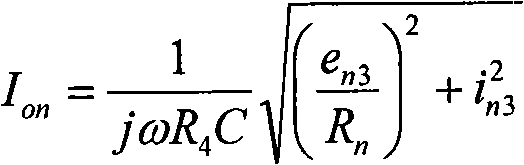Patents
Literature
350 results about "Current noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Noise current. noise current: 1. Interfering and unwanted electrical currents in a device or system. 2. In optical communications, the rms component of the optical detector output electrical current with no incoming signal present.
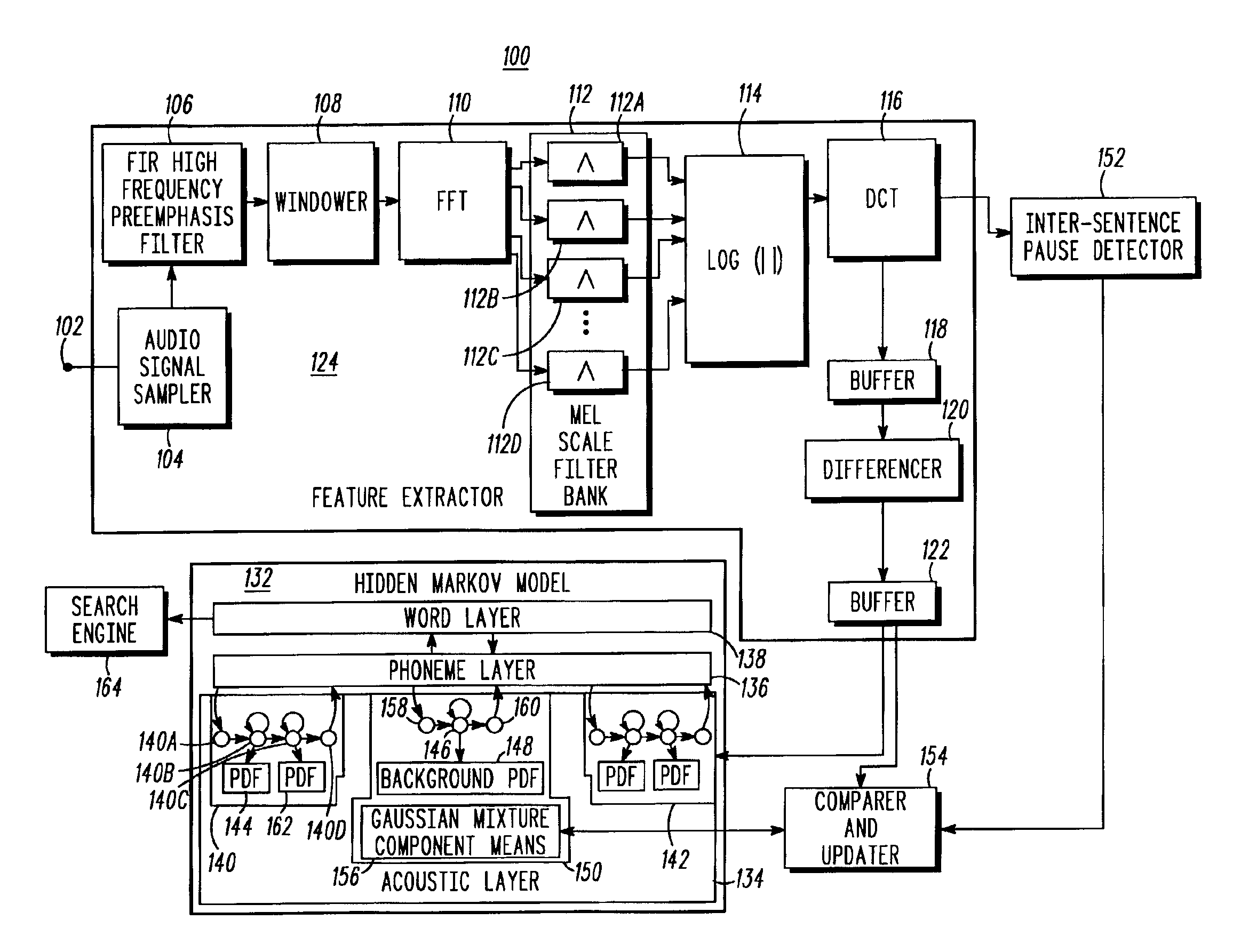
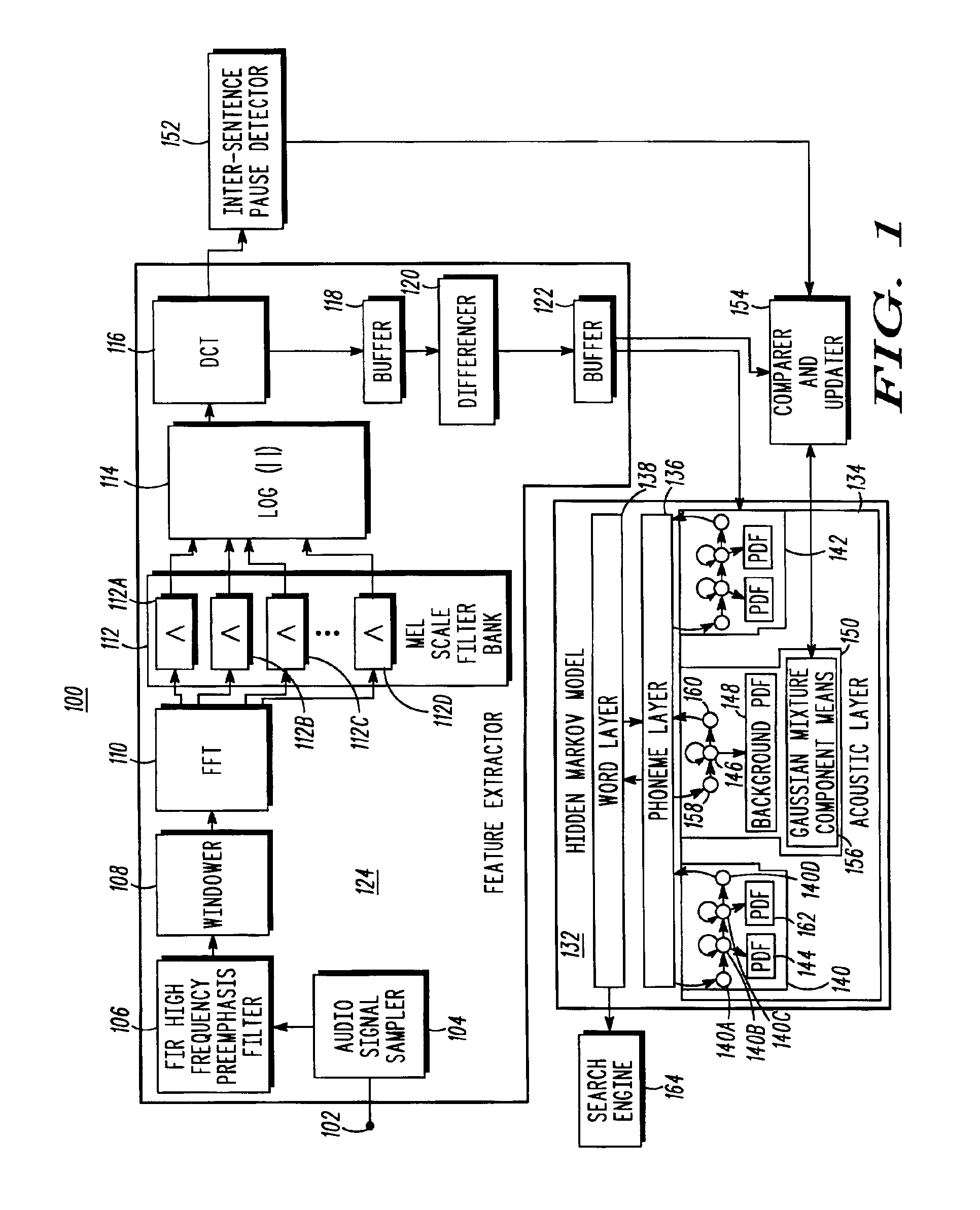
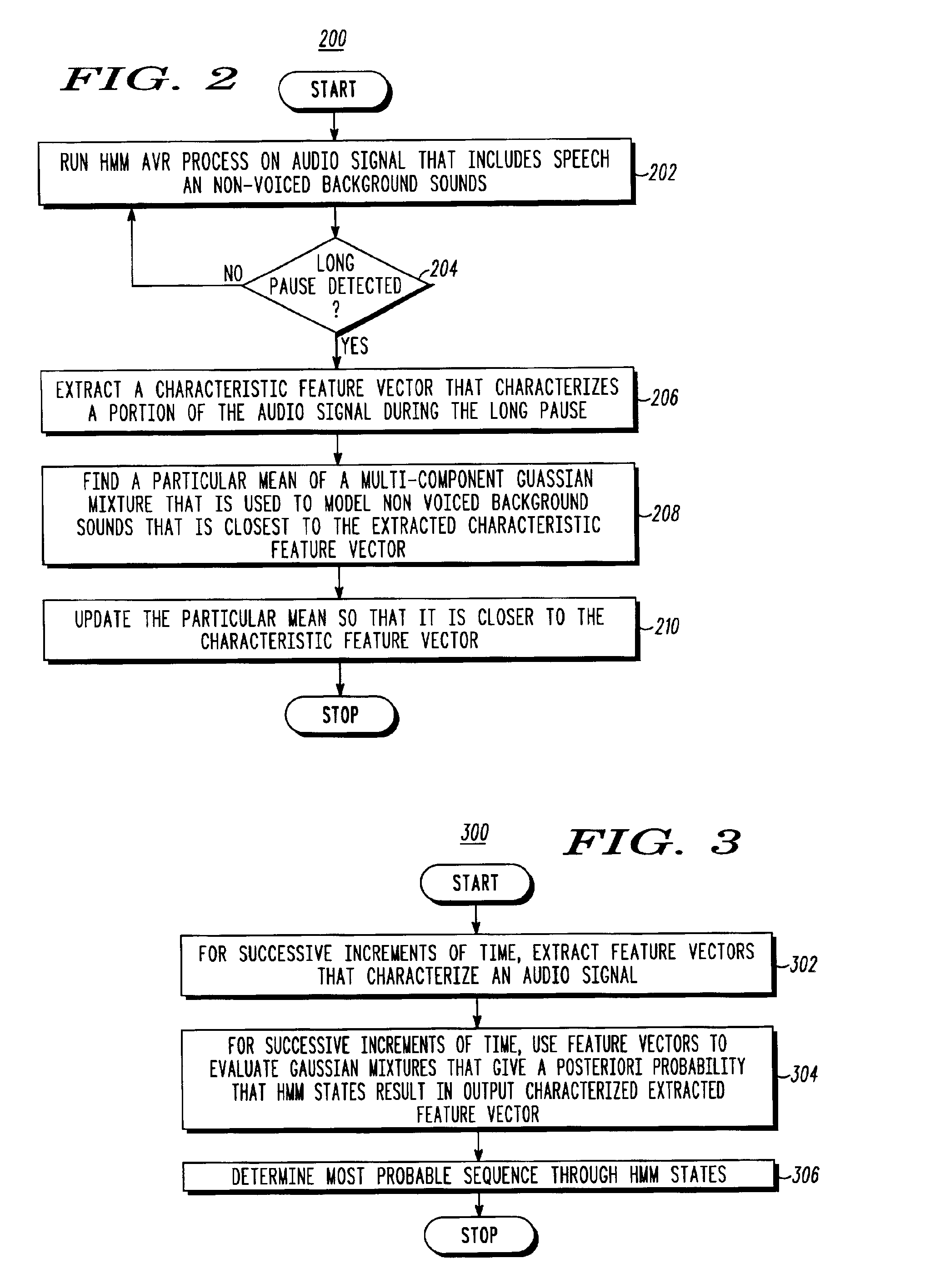
Speech recognition by dynamical noise model adaptation
The invention provides a Hidden Markov Model (132) based automated speech recognition system (100) that dynamically adapts to changing background noise by detecting long pauses in speech, and for each pause processing background noise during the pause to extract a feature vector that characterizes the background noise, identifying a Gaussian mixture component of noise states that most closely matches the extracted feature vector, and updating the mean of the identified Gaussian mixture component so that it more closely matches the extracted feature vector, and consequently more closely matches the current noise environment. Alternatively, the process is also applied to refine the Gaussian mixtures associated with other emitting states of the Hidden Markov Model.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
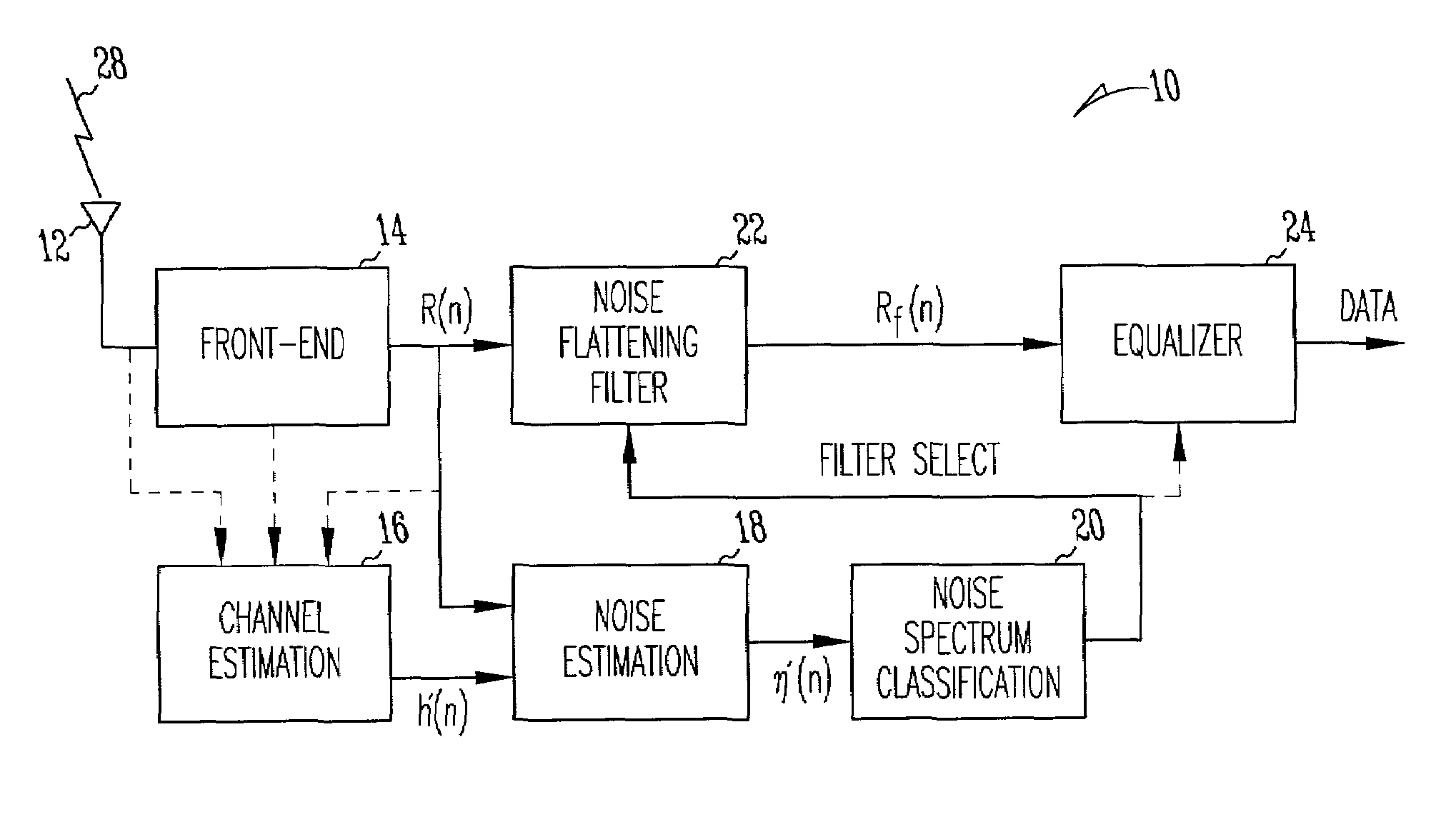
Noise dependent filter
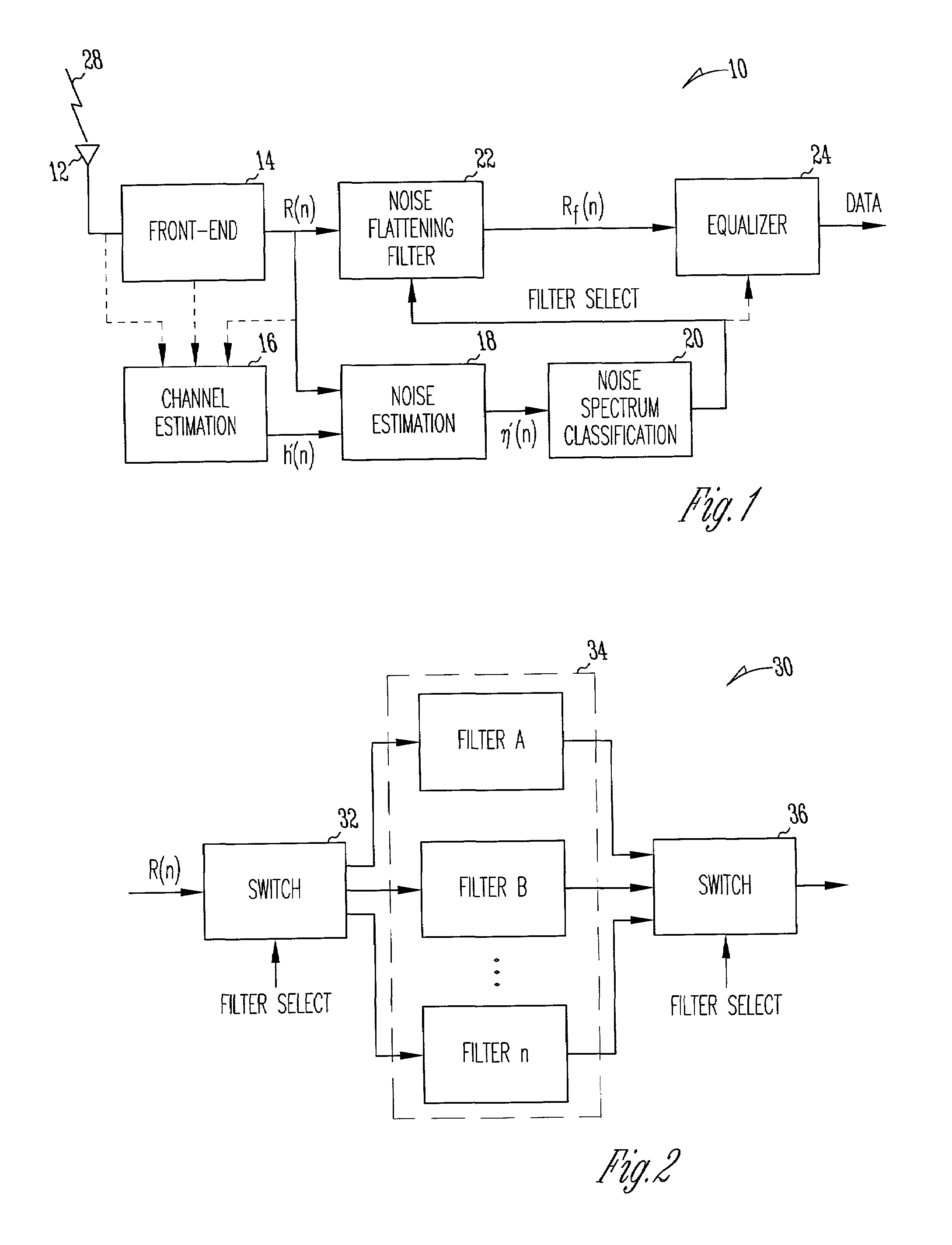
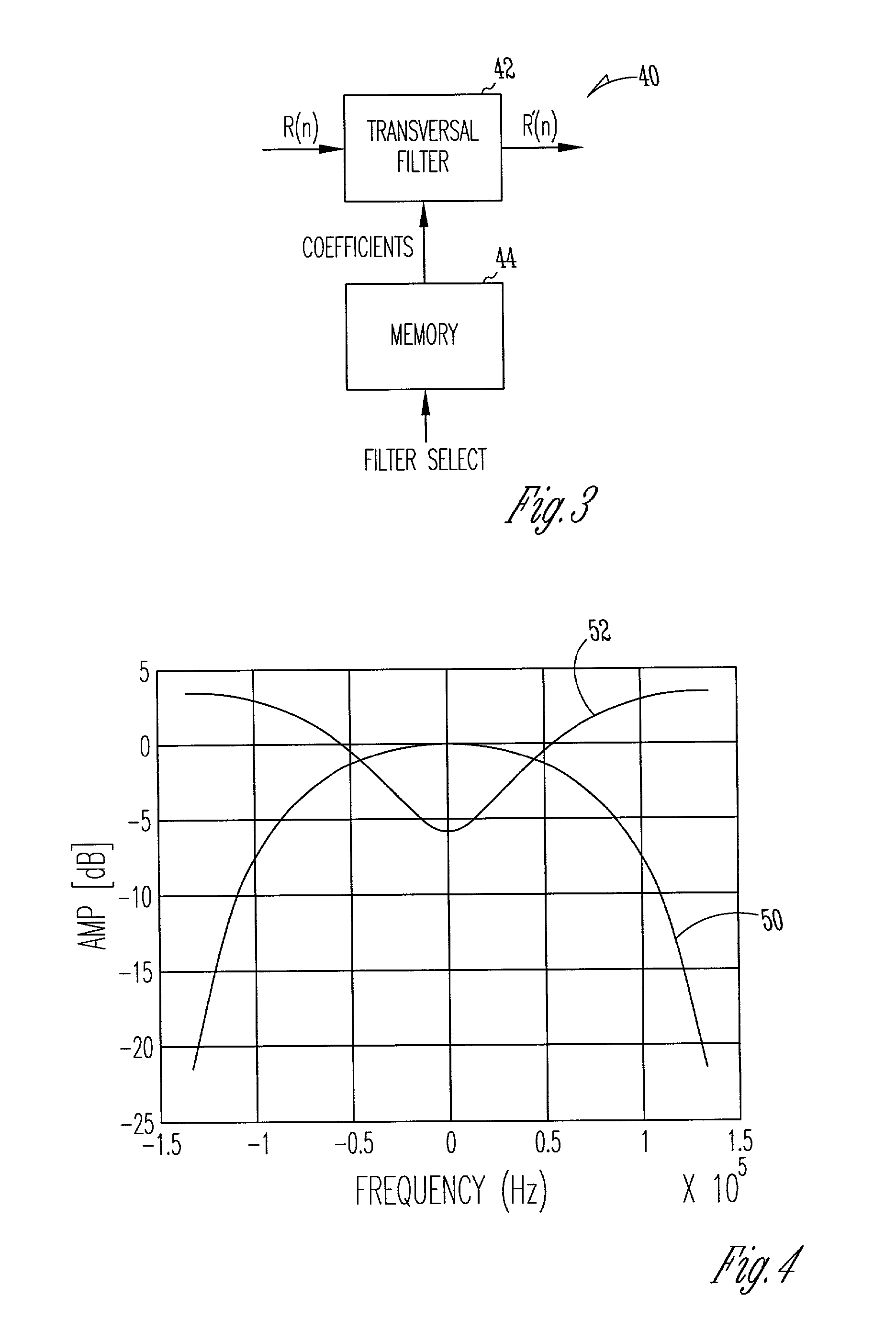
A communication device includes a noise flattening filter having a filter response that dynamically adjusts based on the current noise spectrum in a wireless channel. The noise spectrum of the wireless channel is estimated and used to determine a noise classification for the channel. A noise flattening filter response is then selected based upon the noise classification for use in filtering signals received from the channel. The filtered signals are then delivered to an equalizer for further processing.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for reducing noise in speech and audio signals
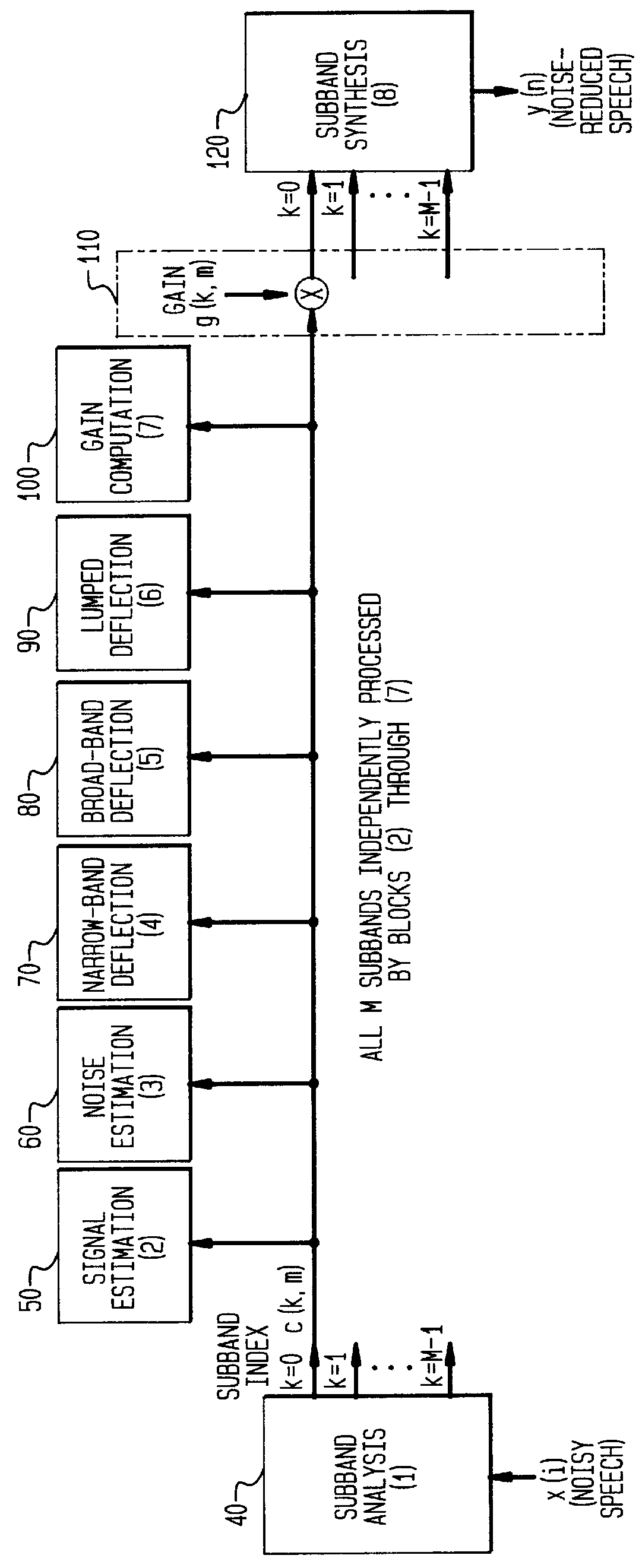
A method and apparatus are disclosed for enhancing, within a signal bandwidth, a corrupted audio-frequency signal. The signal which is to be enhanced is analyzed into plural sub-band signals, each occupying a frequency sub-band smaller than the signal bandwidth. A respective signal gain function is applied to each sub-band signal, and the respective sub-band signals are then synthesized into an enhanced signal of the signal bandwidth. The signal gain function is derived, in part, by measuring speech energy and noise energy, and from these determining a relative amount of speech energy, within the corresponding sub-band. In certain embodiments of the invention, the signal gain function is also derived, in part, by determining a relative amount of speech energy within a frequency range greater than, but centered on, the corresponding sub-band. In other embodiments of the invention, the sub-band noise energy is determined from a noise estimate that is updated at periodic intervals, but is not updated if the newest sample of the signal to be enhanced exceeds the current noise estimate by a multiplicative threshold (i.e., a threshold expressible in decibels). In still other embodiments of the invention, the value of the noise estimate is limited by an upper bound that is matched to the dynamic range of the signal to be enhanced.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for adaptive transmission of comfort noise parameters during discontinuous speech transmission
ActiveUS20060293885A1Solve the real problemImprove efficiencySpeech analysisSubstation equipmentCurrent noiseComfort noise
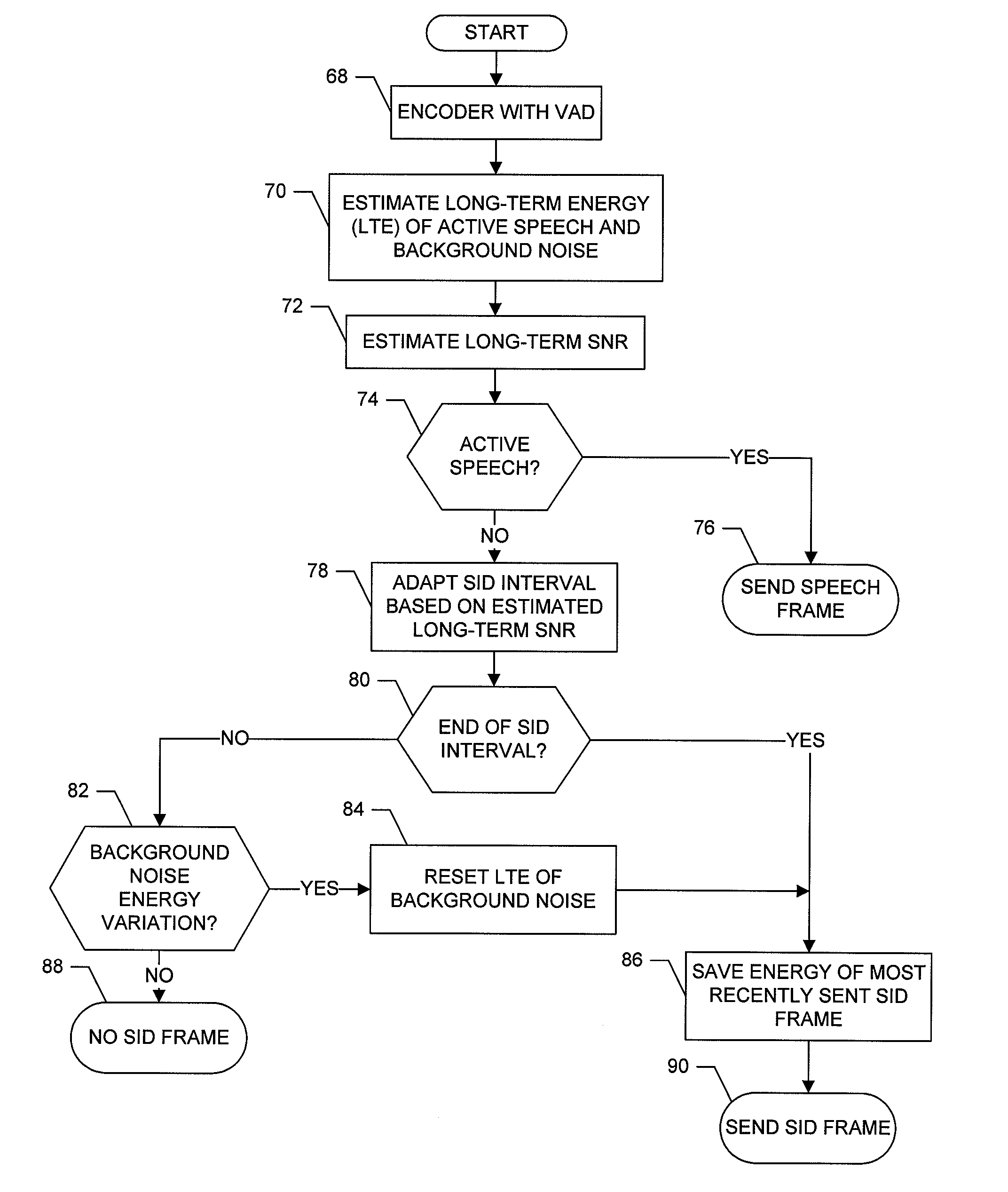
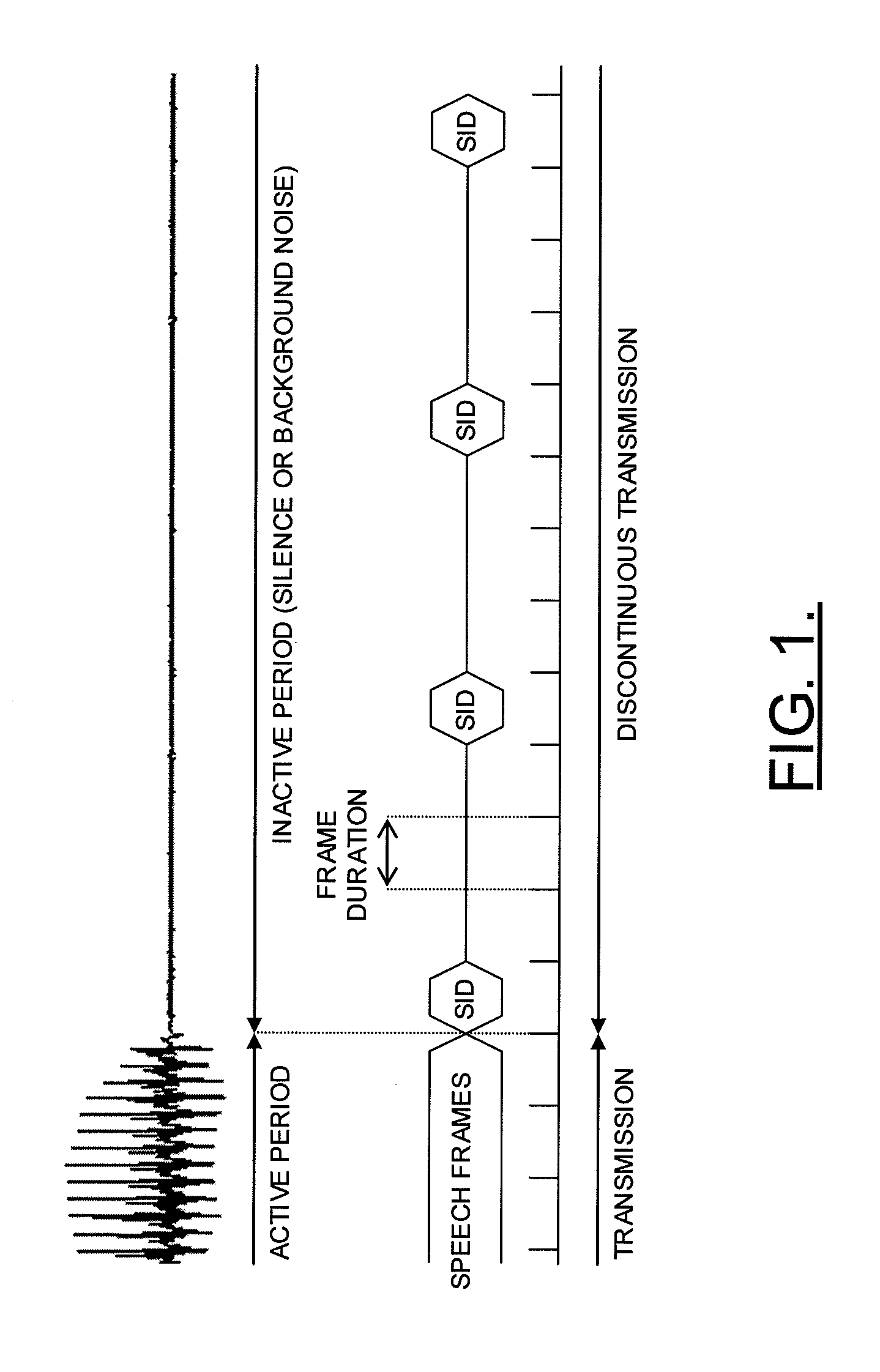
Apparatus is provided that includes at least one entity for transmitting speech signals in a discontinuous transmission mode including transmitting speech frames interspersed with frames including comfort noise parameters during periods of speech pauses. The entit(ies) include a first entity for estimating a current noise value. In addition, the apparatus includes a second entity for selectively controlling a rate at which the frames including comfort noise parameters are transmitted during the periods of speech pauses based upon the estimated current noise value.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
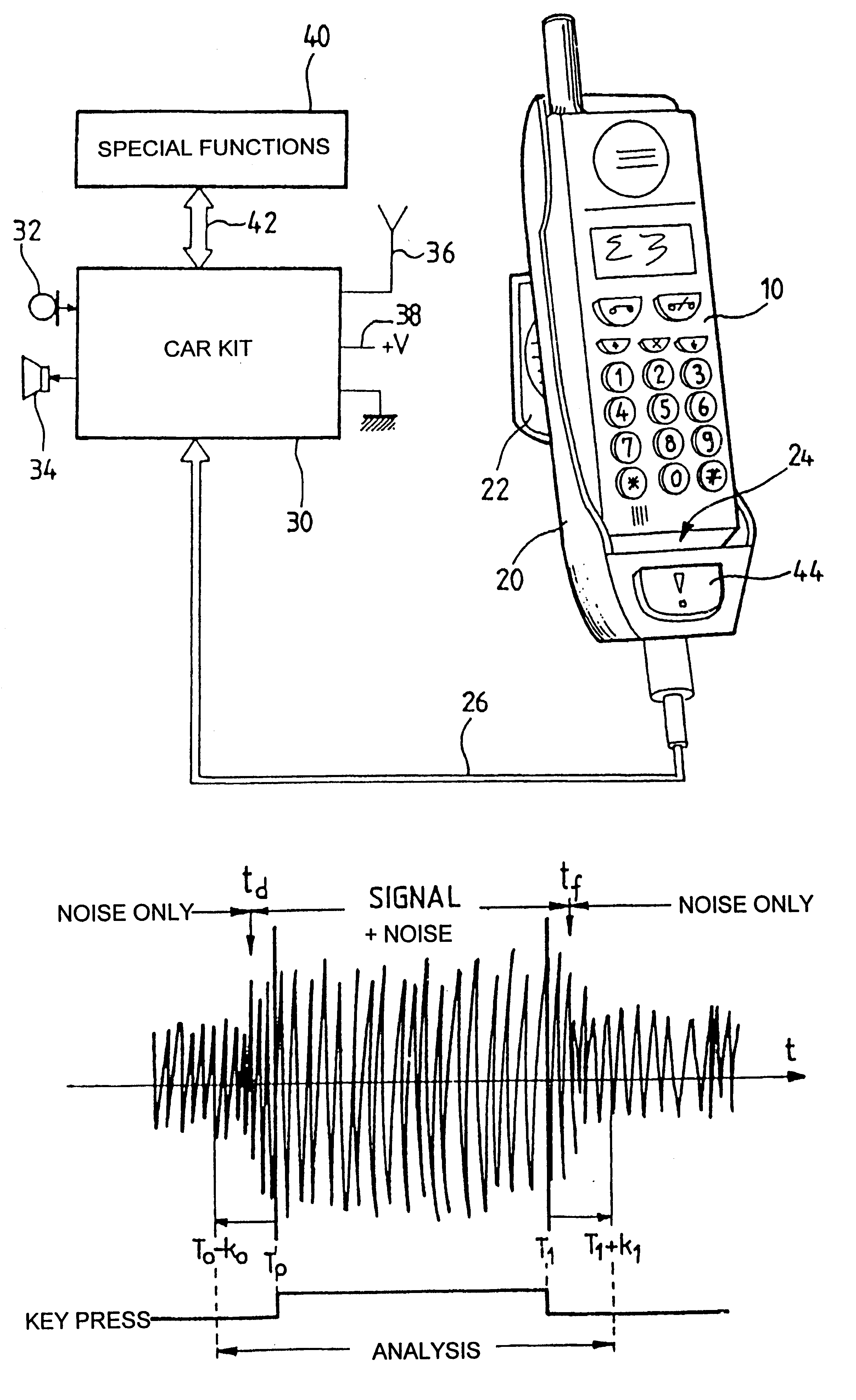
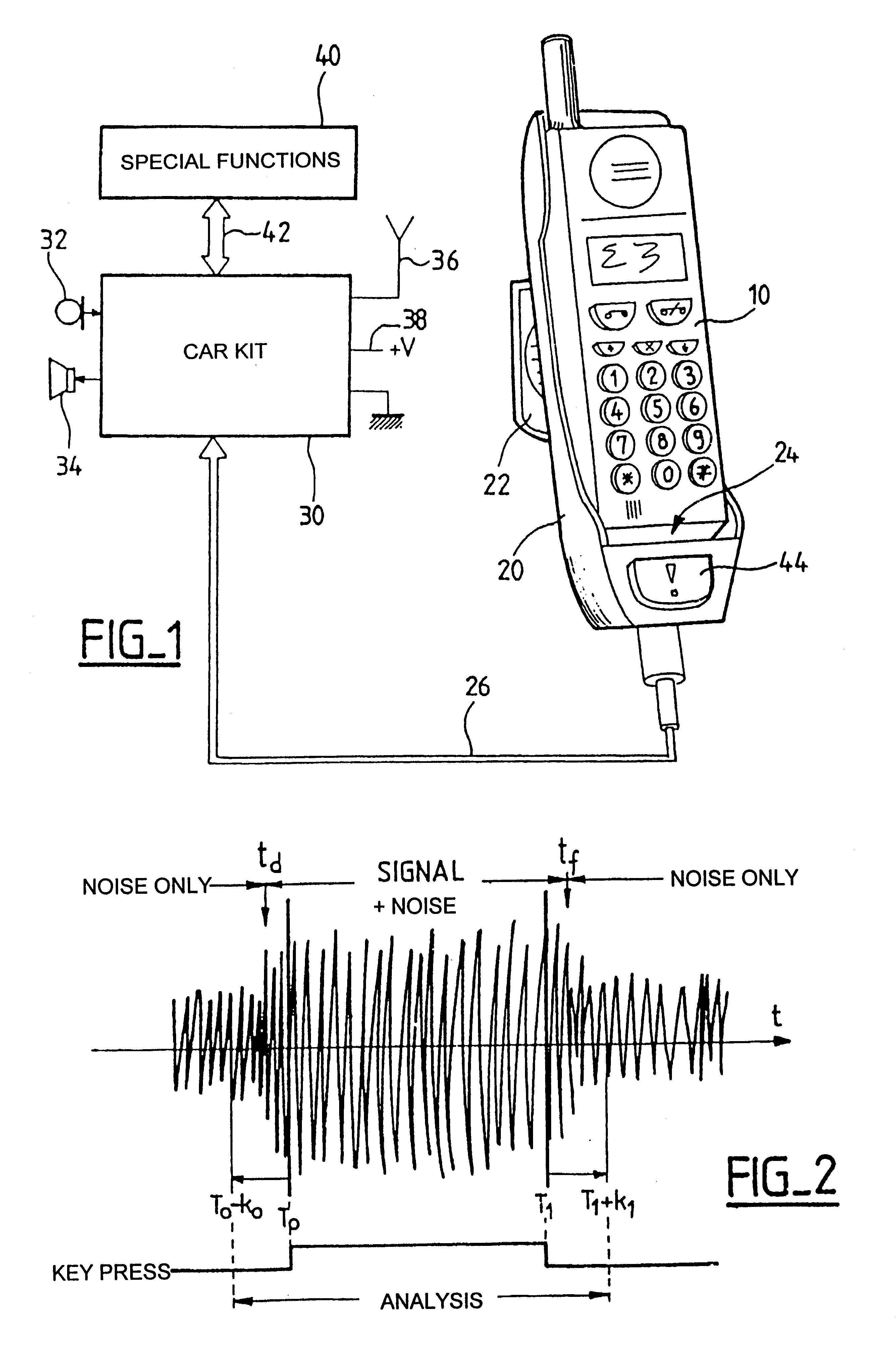
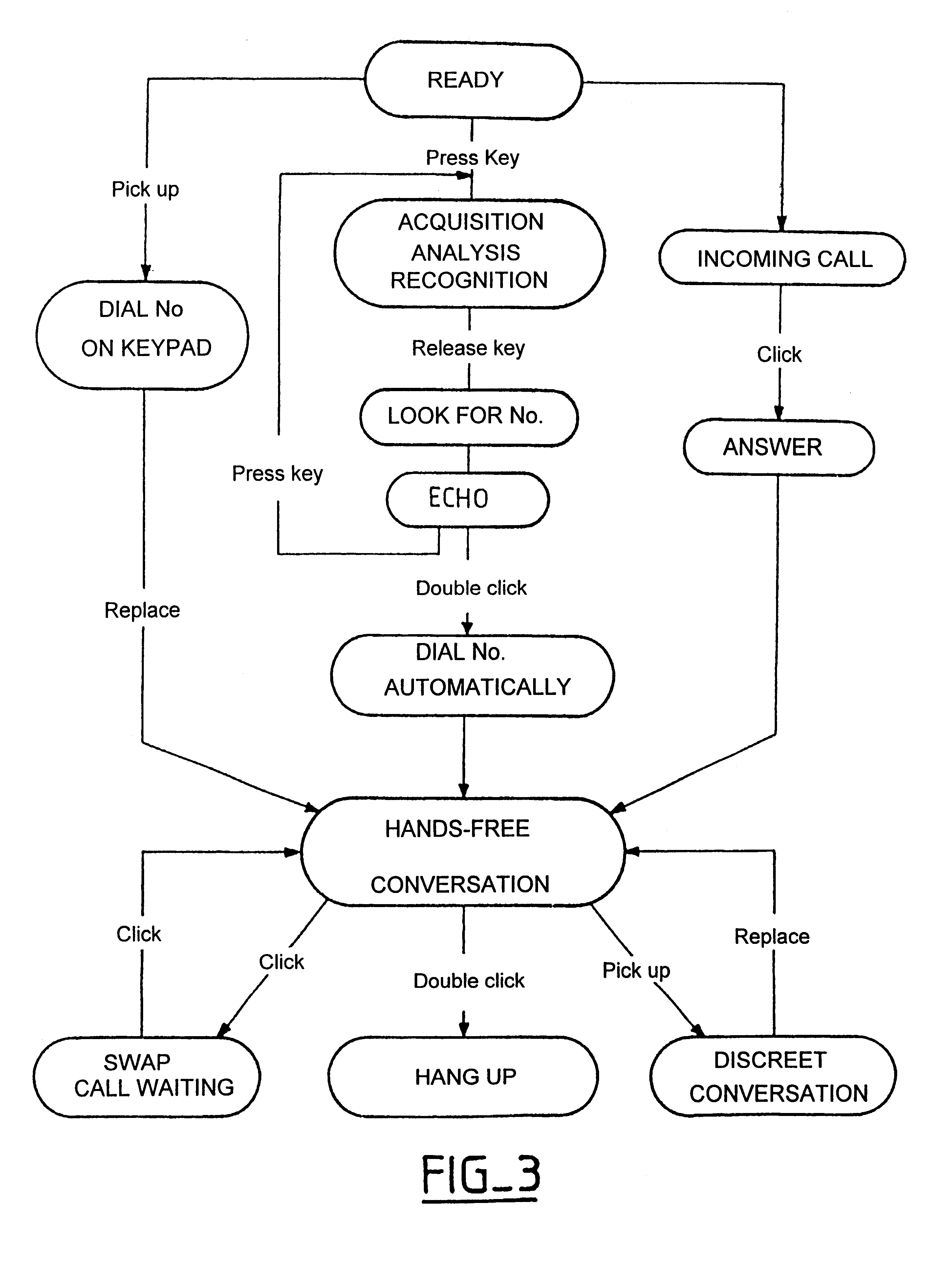
Radiotelephone voice control device, in particular for use in a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6263216B1Primary cell maintainance/servicingAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingMemory addressData memory
The apparatus comprises a data memory containing a series of correspondents' call numbers and, for each call number, at least one associated voice print; a sound transducer suitable for picking up the name of a desired corespondent as spoken by the user of the apparatus; voice recognition means suitable for analyzing the correspondent's name as picked up by the transducer and for transforming it into an associated voice print; selective memory addressing means including associative means suitable for finding a voice print in the memory corresponding to the print supplied by the voice recognition means, and in the event of a match, for addressing the corresponding memory position; and means co-operating with the associative means for applying the addressed call number to the radiotelephone circuits. The voice recognition means evaluate and store a current noise level as picked up by the transducer in the absence of a speech signal; when in the presence of a speech signal, they subtract the previously evaluated current noise level from the signal as picked up; and then they apply the resulting signal as obtained in this way to a DTW type voice recognition algorithm with pattern recognition by dynamic programming adapted to speech using dynamic parameter extraction functions, in particular a predictive dynamic algorithm with forward and / or backward and / or frequency masking.
Owner:PARROT AUTOMOTIVE
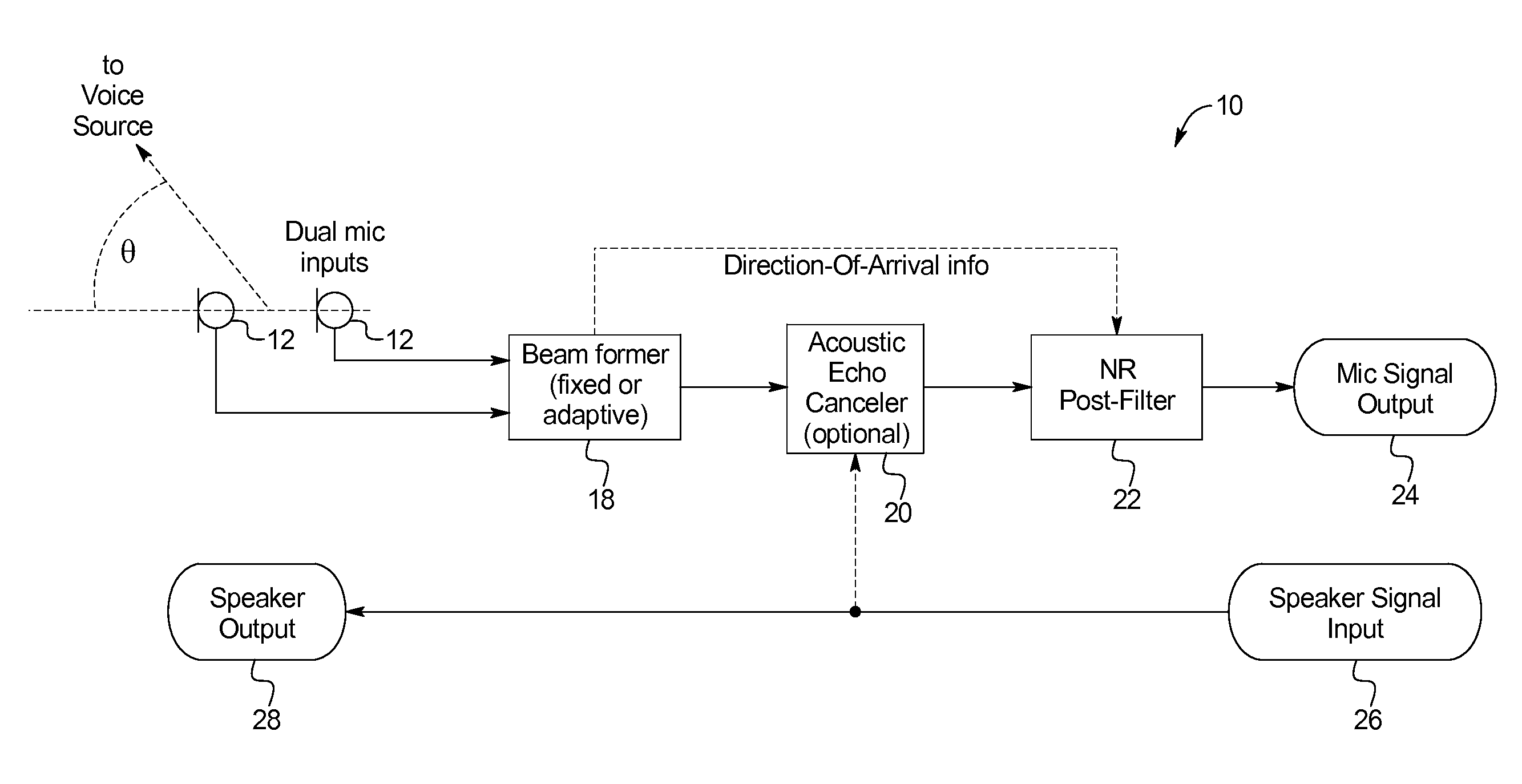
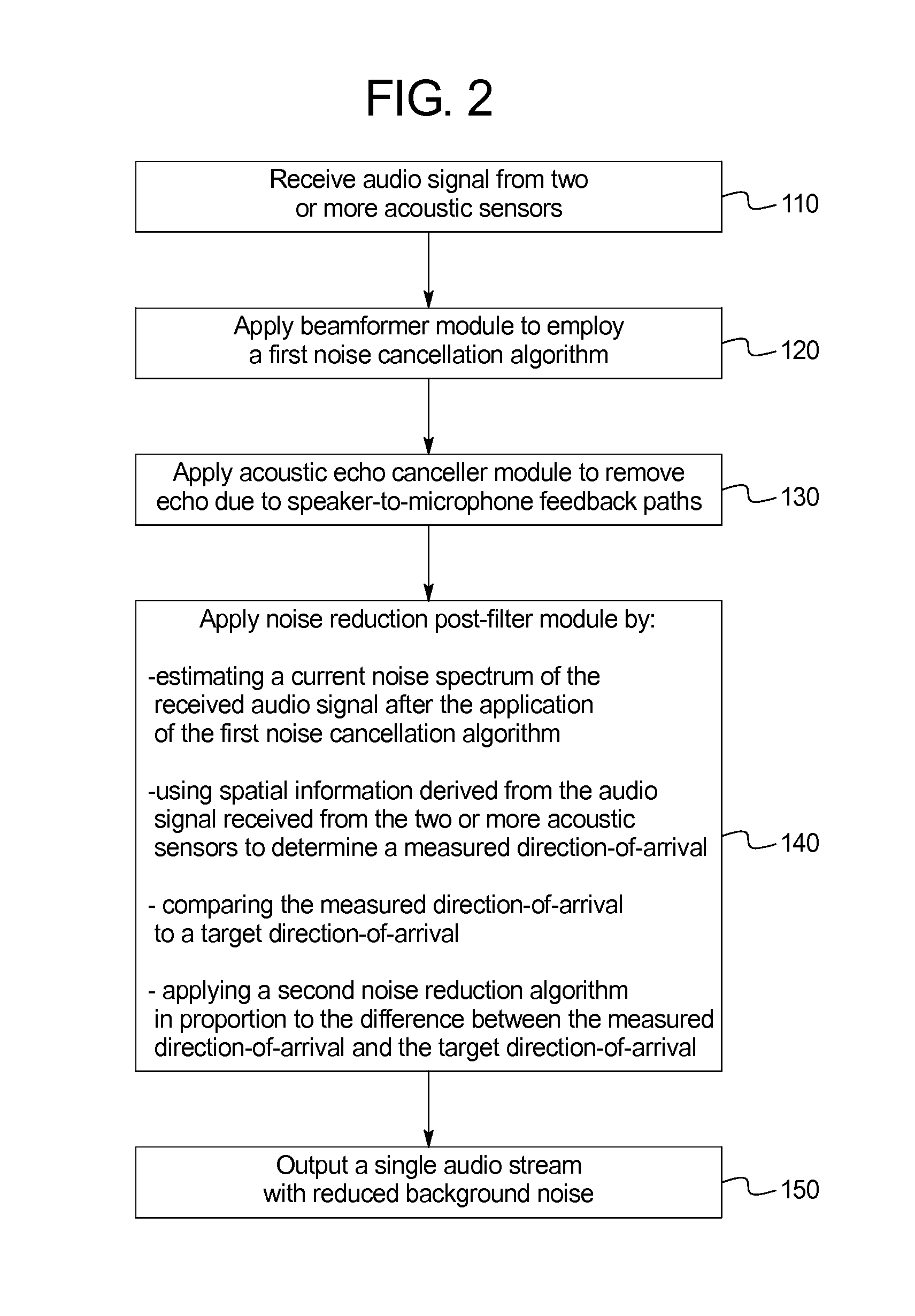
Noise reduction using direction-of-arrival information
ActiveUS20140023199A1Improve noise reductionReduce background noiseEar treatmentSpeech analysisCurrent noiseFrequency spectrum
Systems and methods of improved noise reduction using direction of arrival information include: receiving an audio signal from two or more acoustic sensors; applying a beamformer module to employ a first noise cancellation algorithm to the audio signal; applying a noise reduction post-filter module to the audio signal, the application of which includes: estimating a current noise spectrum of the received audio signal after the application of the first noise cancellation algorithm; using spatial information derived from the audio signal received from the two or more acoustic sensors to determine a measured direction-of-arrival by estimating the current time-delay between the acoustic sensor inputs; comparing the measured direction-of-arrival to a target direction-of-arrival; applying a second noise reduction algorithm to the audio signal in proportion to the difference between the measured direction-of-arrival and the target direction-of-arrival; and outputting a single audio stream with reduced background noise.
Owner:QSOUND LABS
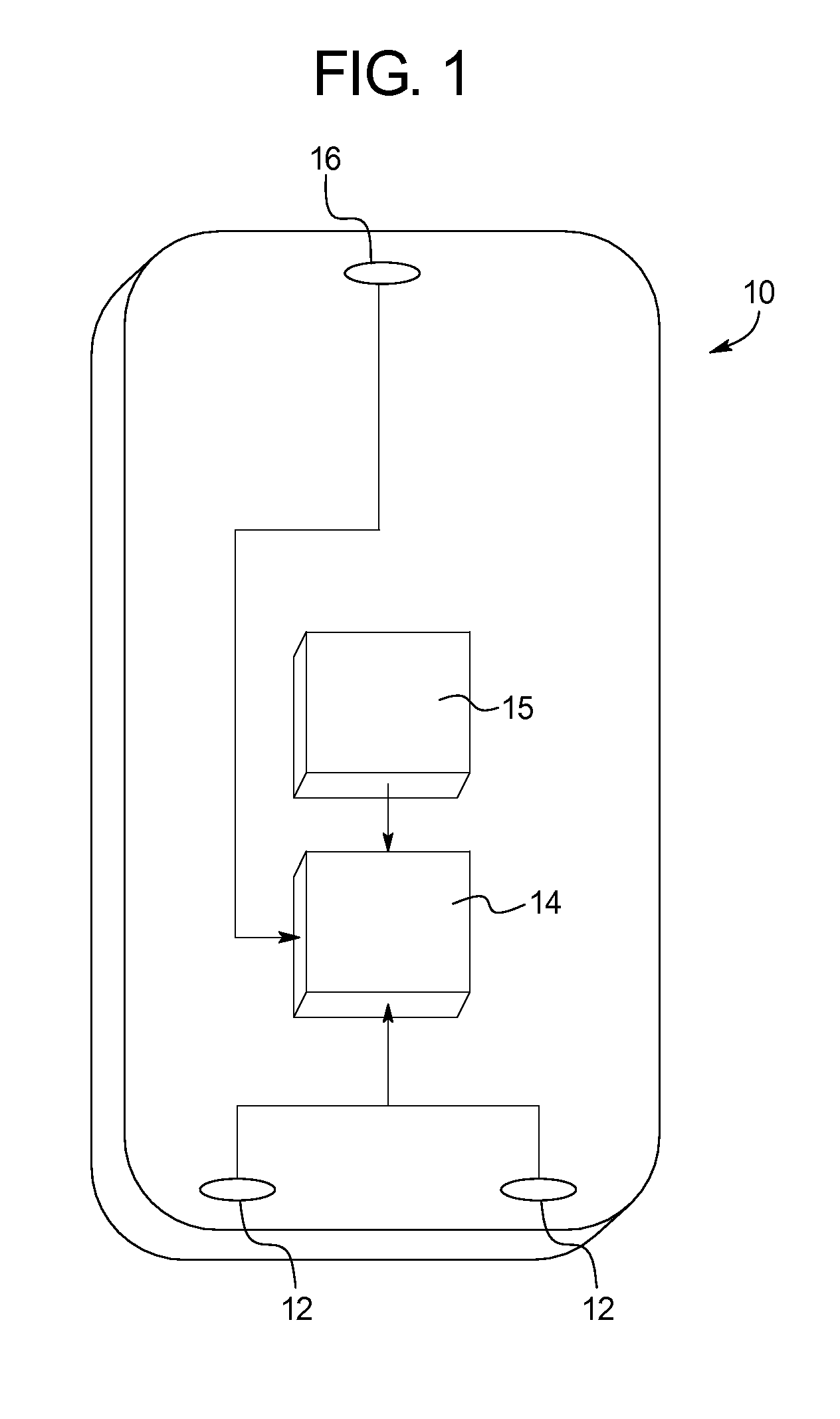
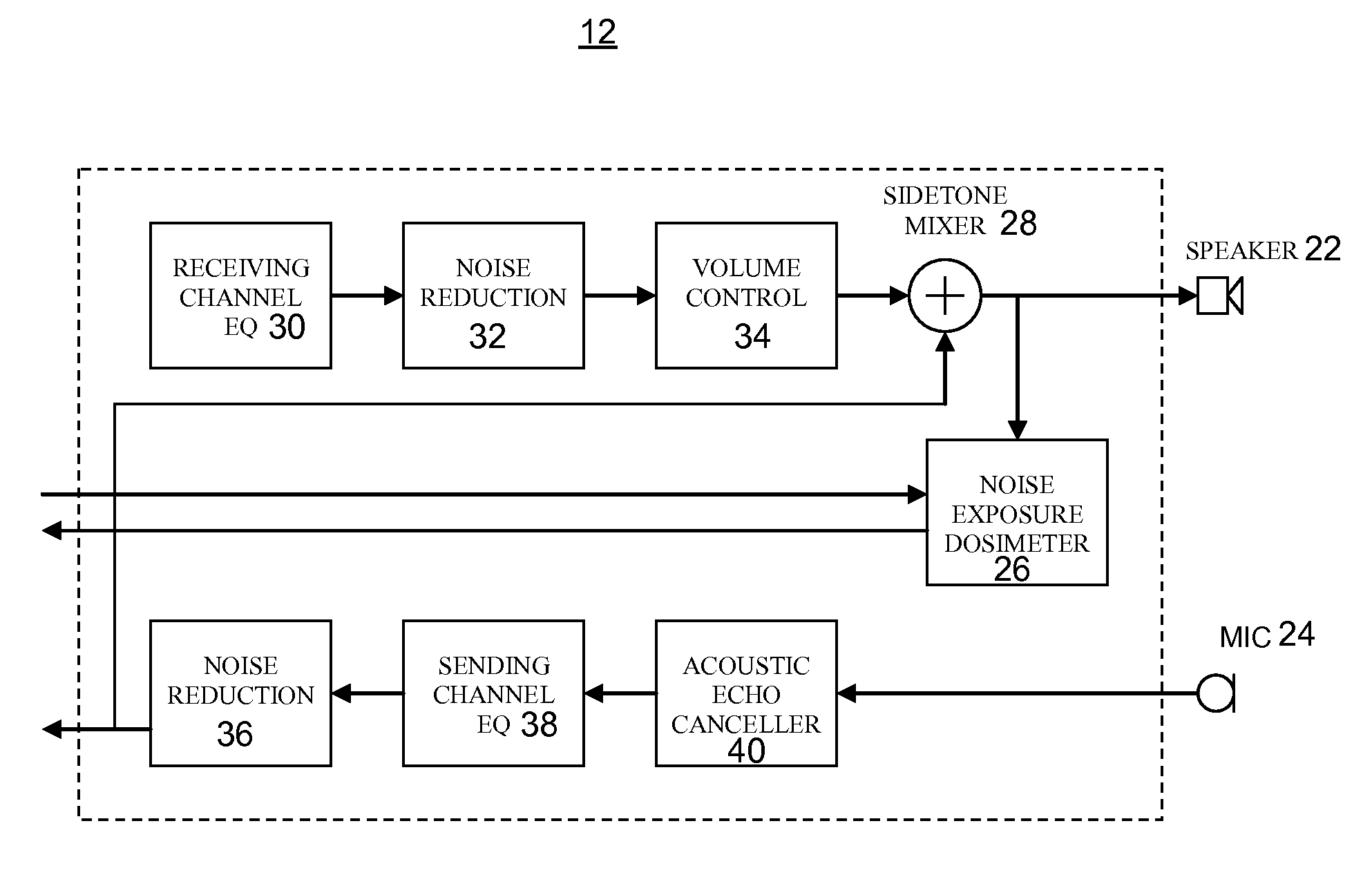
Wireless Headset Noise Exposure Dosimeter
Systems and methods for measuring noise exposure associated with use of a wireless headset are presented. In one example, a transition from a wireless headset standby mode operation to a wireless headset active mode operation is identified. A stored noise dose measurement at the wireless headset is recalled, and a current noise dose measurement is calculated at the wireless headset for a duration of the active mode operation. A transition from the wireless headset active mode operation to the wireless headset standby mode operation is identified, and an updated noise dose measurement is recorded at the wireless headset.
Owner:PLANTRONICS
Loop antenna input circuit for am and am radio receiver using the same
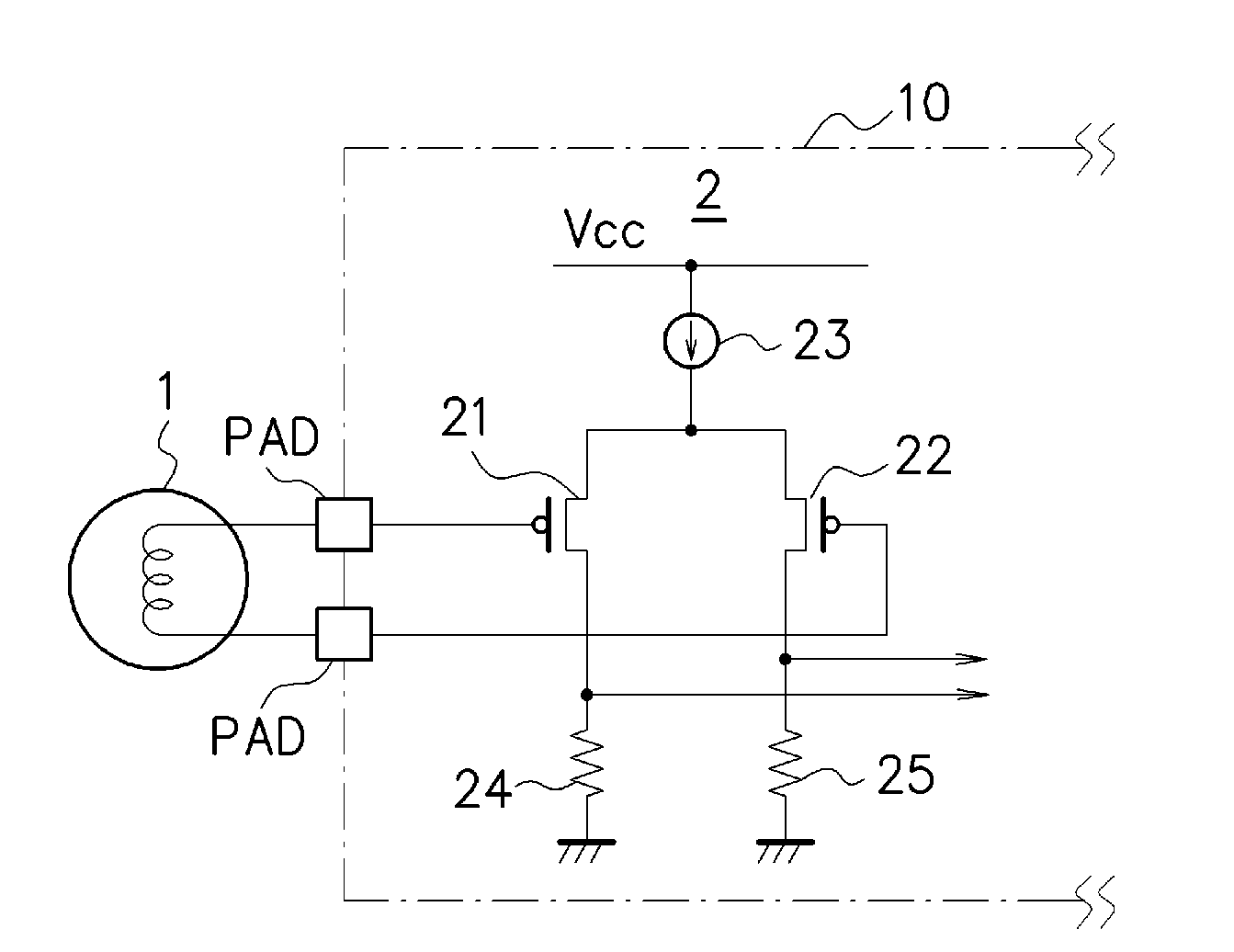
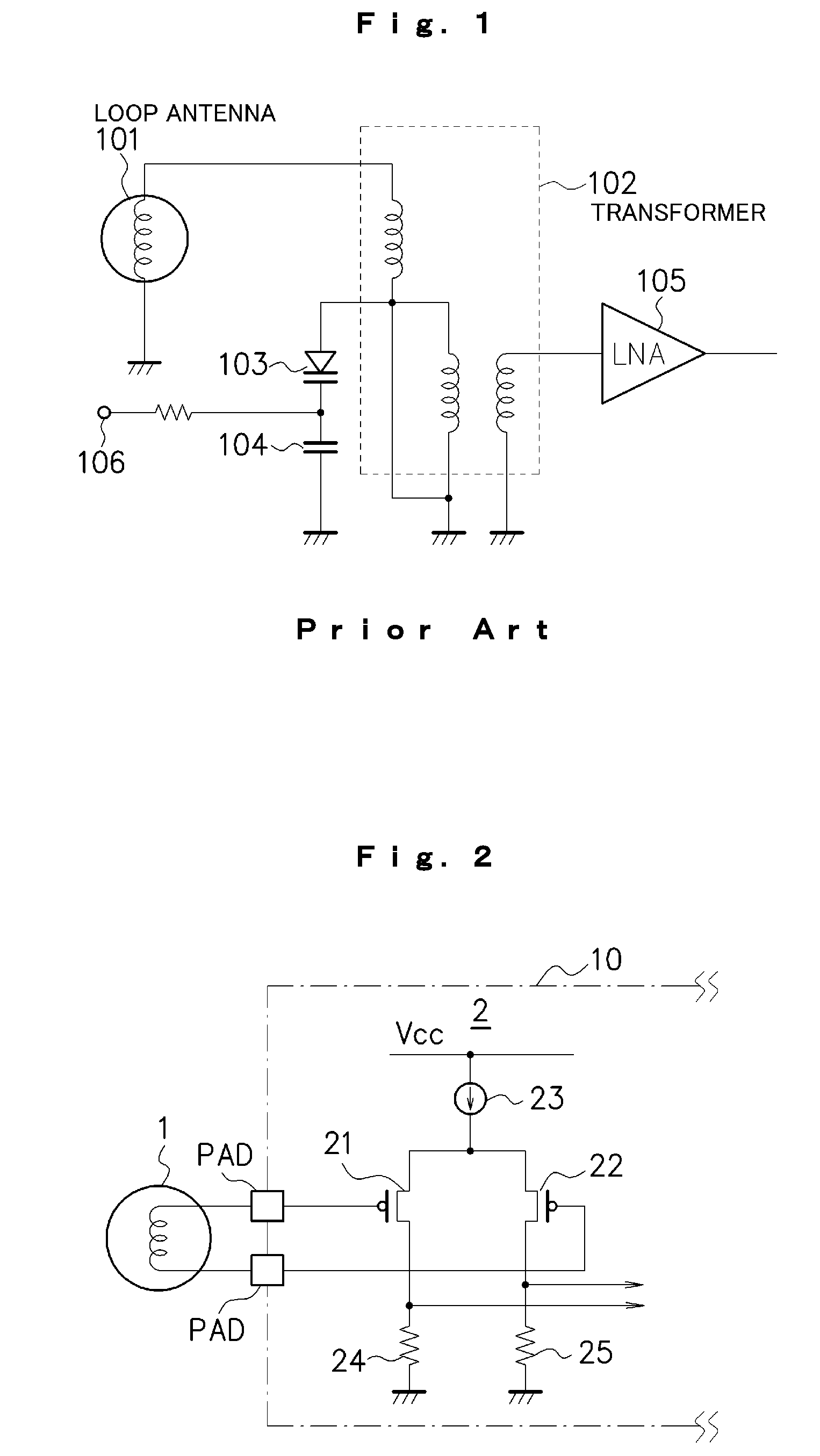
InactiveUS20100003942A1Reduce necessityImprove noiseHigh frequency amplifiersRadio transmissionMOSFETCurrent noise
p-MOSFETs (21) and (22) are used as amplifying elements for amplifying a signal input from a loop antenna (1) and are directly connected to the loop antenna (1). Thus, the signal input from the loop antenna (1) can be received in a high impedance through the p-MOSFETs (21) and (22). Consequently, a transformer for carrying out a conversion into a high impedance or the like is not required, and furthermore, the impedance of the loop antenna 1 itself does not need to be increased, thereby suppressing the occurrence of a current noise.
Owner:NSC CO LTD +1
Method and system for setting volume of mobile terminal and mobile terminal
InactiveCN103078997AChanging the preset volume settingImprove experienceSubstation speech amplifiersCurrent noiseEarcon
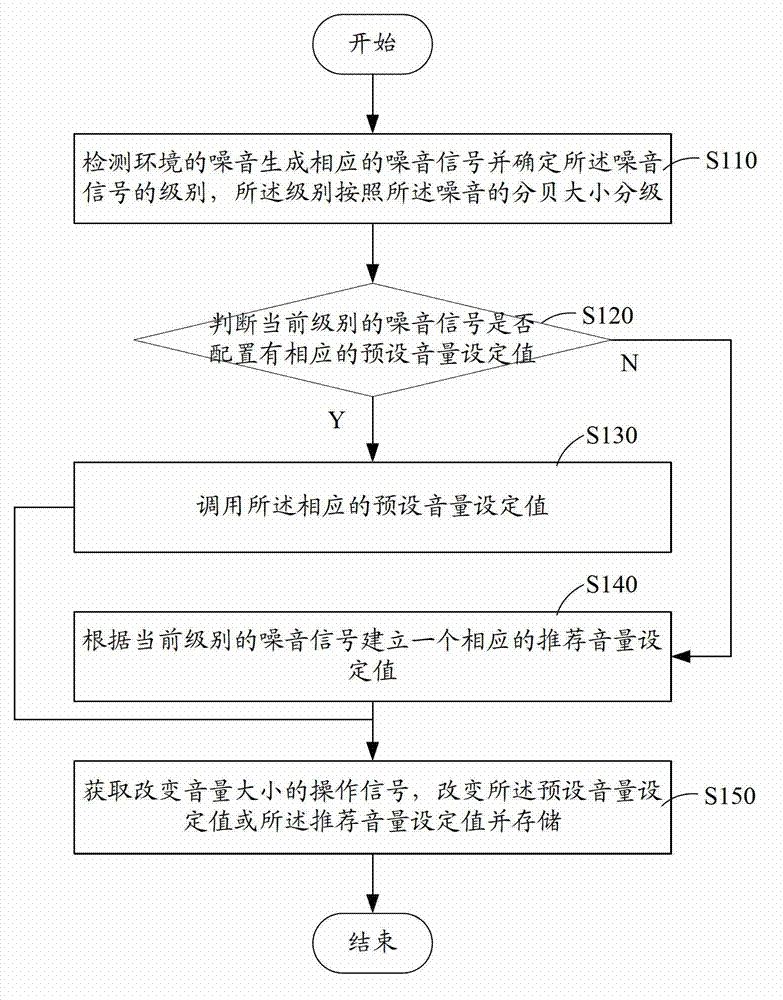
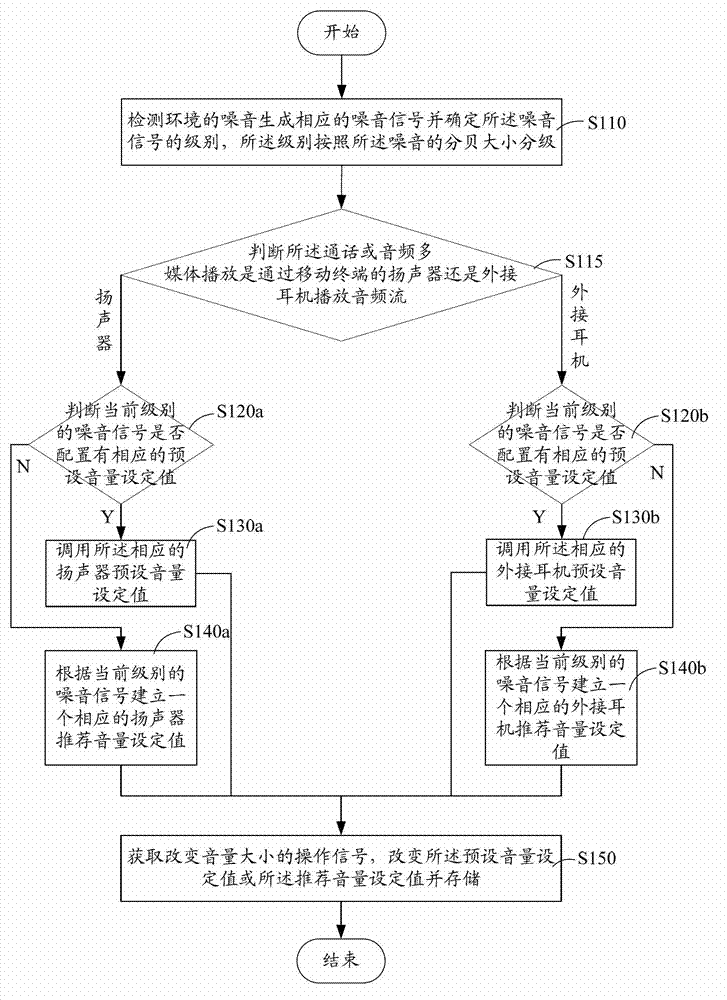
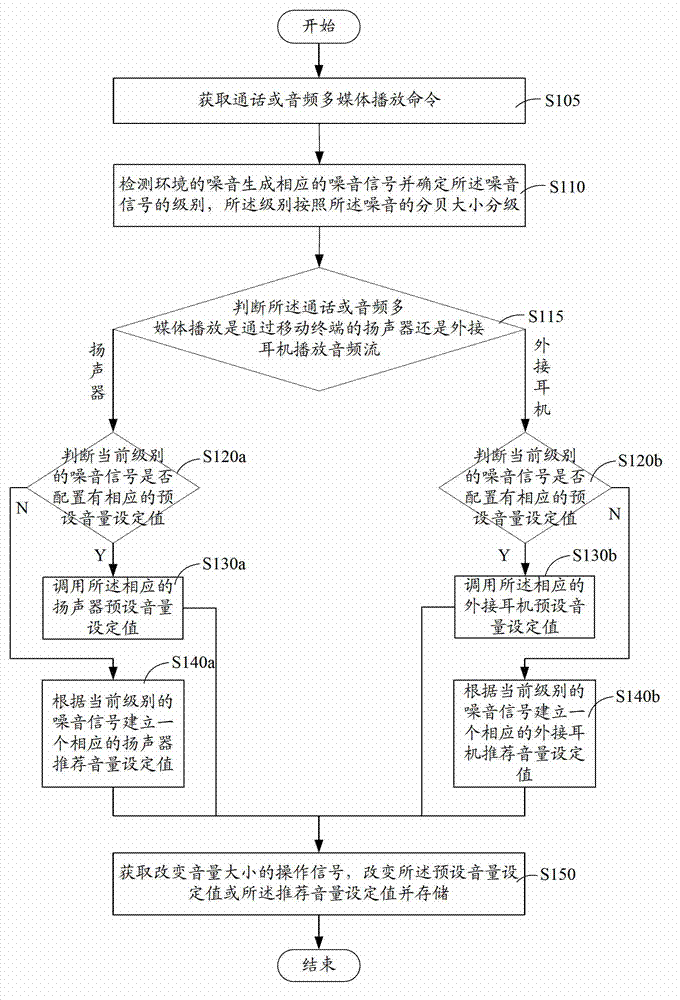
The invention is suitable for the technical field of communications, and provides a method for setting volume of a mobile terminal. The method comprises the following steps of detecting noise of an environment to generate a corresponding noise signal, and determining the level of the noise signal, wherein the level is classified according to the decibel size of the noise; calling a corresponding preset volume setting, or according to the current level of noise signal, establishing a corresponding recommended volume setting; and obtaining an operation signal for changing the volume size, changing the preset volume setting or the recommended volume setting, and storing. The noise of the current environment is detected and classified, and then the volume setting of a loudspeaker or an external earphone corresponding to the current noise level is called or recommended for the user, so by calling or recommending the playing volume of an audio stream for the user habit, the user can obtain a good experience when the mobile terminal is used for conversation or a multimedia is played.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Photovoltaic system direct-current arc fault detection method, device, processor and system
ActiveCN104092440AImprove detection accuracyPhotovoltaic monitoringNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCurrent noiseEngineering
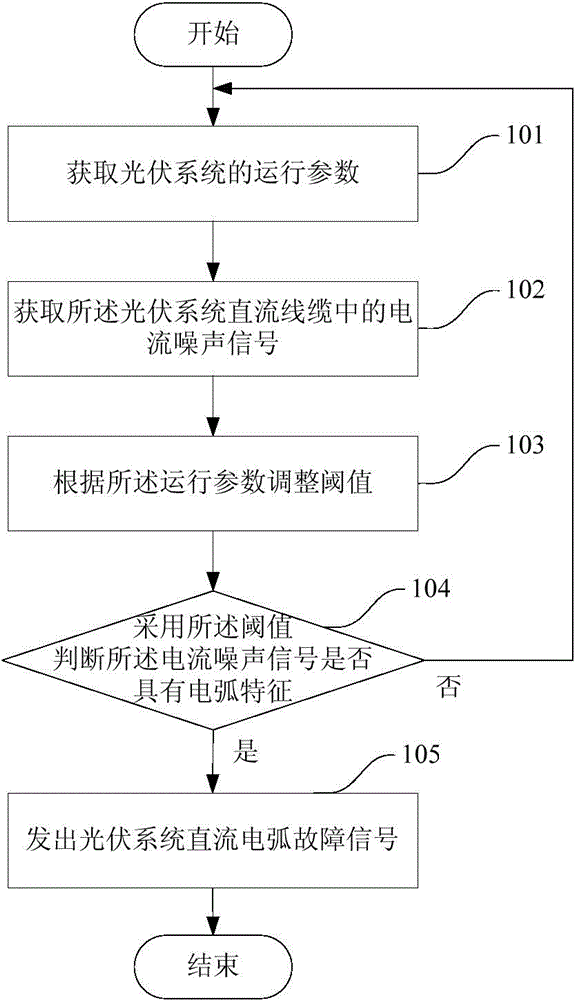
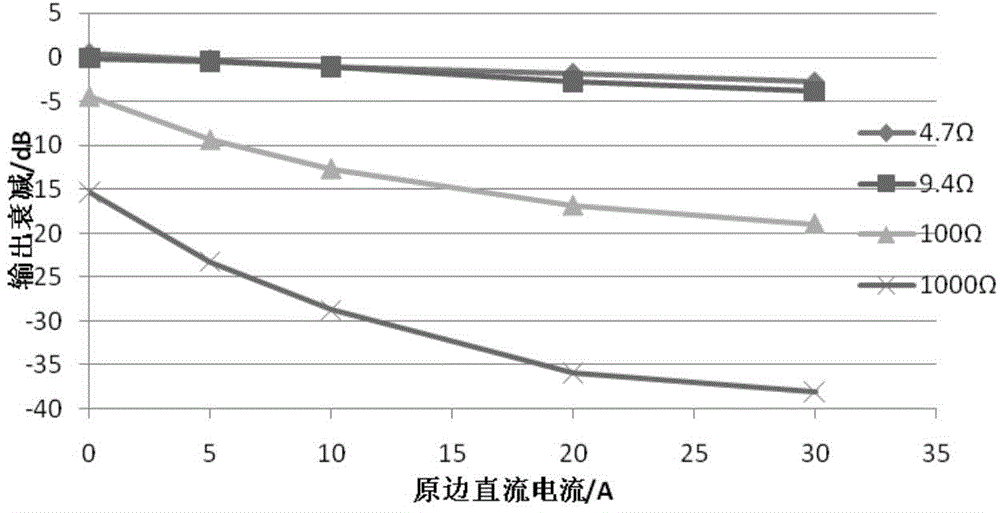
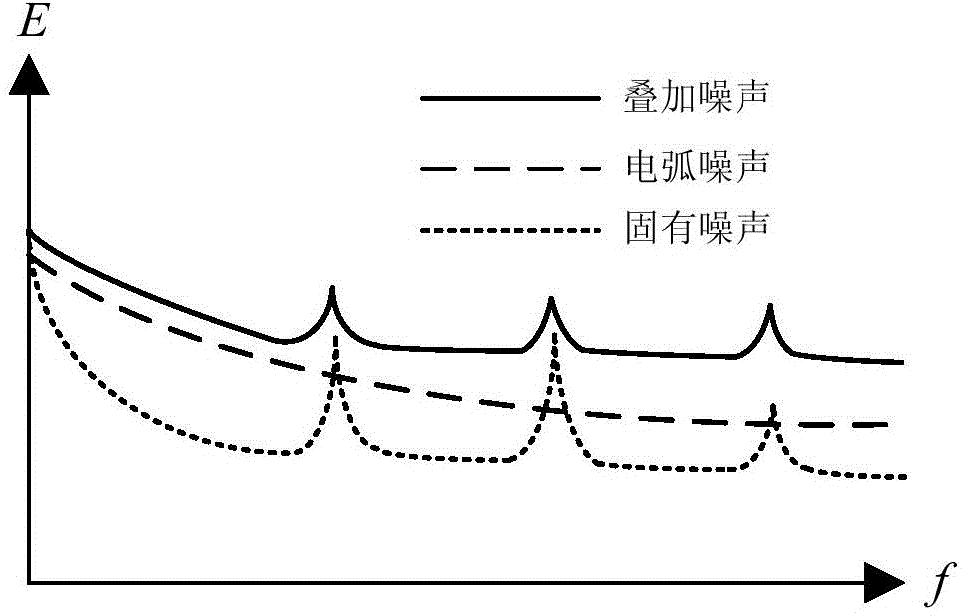
The invention discloses a photovoltaic system direct-current arc fault detection method. The method includes the steps of obtaining operation parameters of a photovoltaic system and current noise signals in photovoltaic system direct-current cables respectively, adjusting a threshold according to the operation parameters, and sending out photovoltaic system direct-current arc fault signals when it is judged that the current noise signal has an arc feature through the threshold, wherein the threshold is used for judging whether the current noise signal has the arc feature. Accordingly, photovoltaic system direct-current arc fault detection precision is improved. Besides, the invention further discloses a photovoltaic system direct-current arc fault detector, a processor and a photovoltaic system direct-current arc fault detection system.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
Multi-microphone noise reduction using enhanced reference noise signal
InactiveUS20140037100A1Improve performanceMinimal suppressionMicrophonesSignal processingFrequency spectrumNoise reduction algorithm
Systems and methods of improved noise reduction include the steps of: receiving an audio signal from two or more acoustic sensors; applying a beamformer to employ a first noise cancellation algorithm; applying a noise reduction post-filter module to the audio signal including: estimating a current noise spectrum of the received audio signal after the application of the first noise cancellation algorithm, wherein the current noise spectrum is estimated using the audio signal received by the second acoustic sensor; determining a punished noise spectrum using the time-average level difference between the audio signal received by the first acoustic sensor and the current noise spectrum; determining a final noise estimate by subtracting the punished noise spectrum from the current noise spectrum; and applying a second noise reduction algorithm to the audio signal received by the first acoustic sensor using the final noise estimate; and outputting an audio stream with reduced background noise.
Owner:QSOUND LABS
Method and device for determining earphone noise reduction parameters and computer readable medium
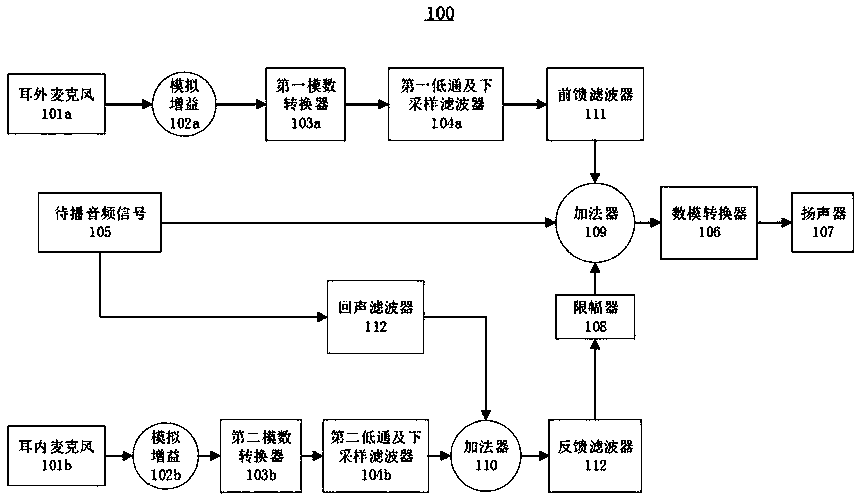
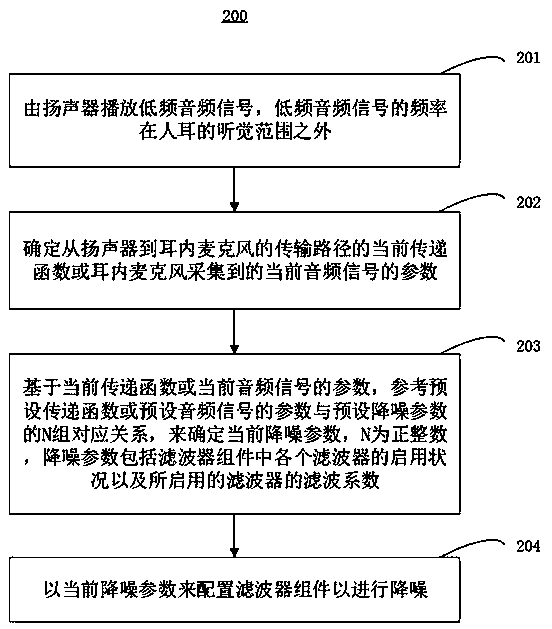
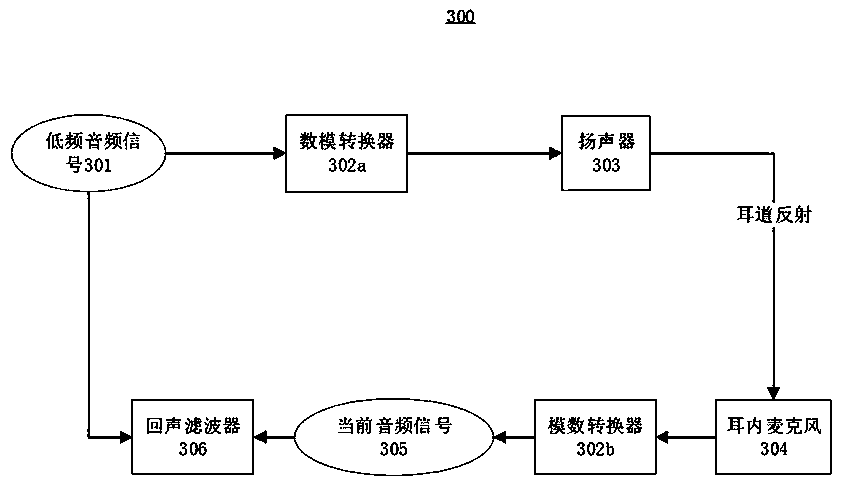
ActiveCN110996215ARealize dynamic adjustmentEnhance listening experienceMicrophonesLoudspeakersCurrent noiseHuman ear
The invention relates to a method and device for determining earphone noise reduction parameters and a computer readable medium. The earphone comprises a loudspeaker, an in-ear microphone and a filterassembly. The method comprises the following steps of: playing a low-frequency audio signal of which the frequency is out of the auditory range of human ears by a loudspeaker, determining a current transfer function of a transmission path from the loudspeaker to the in-ear microphone or a parameter of a current audio signal acquired by the in-ear microphone, determining a current noise reductionparameter based on the current transfer function or the parameter of the current audio signal by referring to N groups of corresponding relationships between a preset transfer function or a parameterof a preset audio signal and a preset noise reduction parameter, the noise reduction parameter comprising a filter coefficient of a filter enabled in the filter assembly, and configuring the filter assembly with the current noise reduction parameter to perform noise reduction. By playing the low-frequency audio signals beyond the auditory range of the human ears for many times, the dynamic adjustment of the noise reduction parameters of the earphone can be realized, the noise reduction effect in different use scenes is ensured, and meanwhile, the listening experience of a user is improved.
Owner:恒玄科技(北京)有限公司
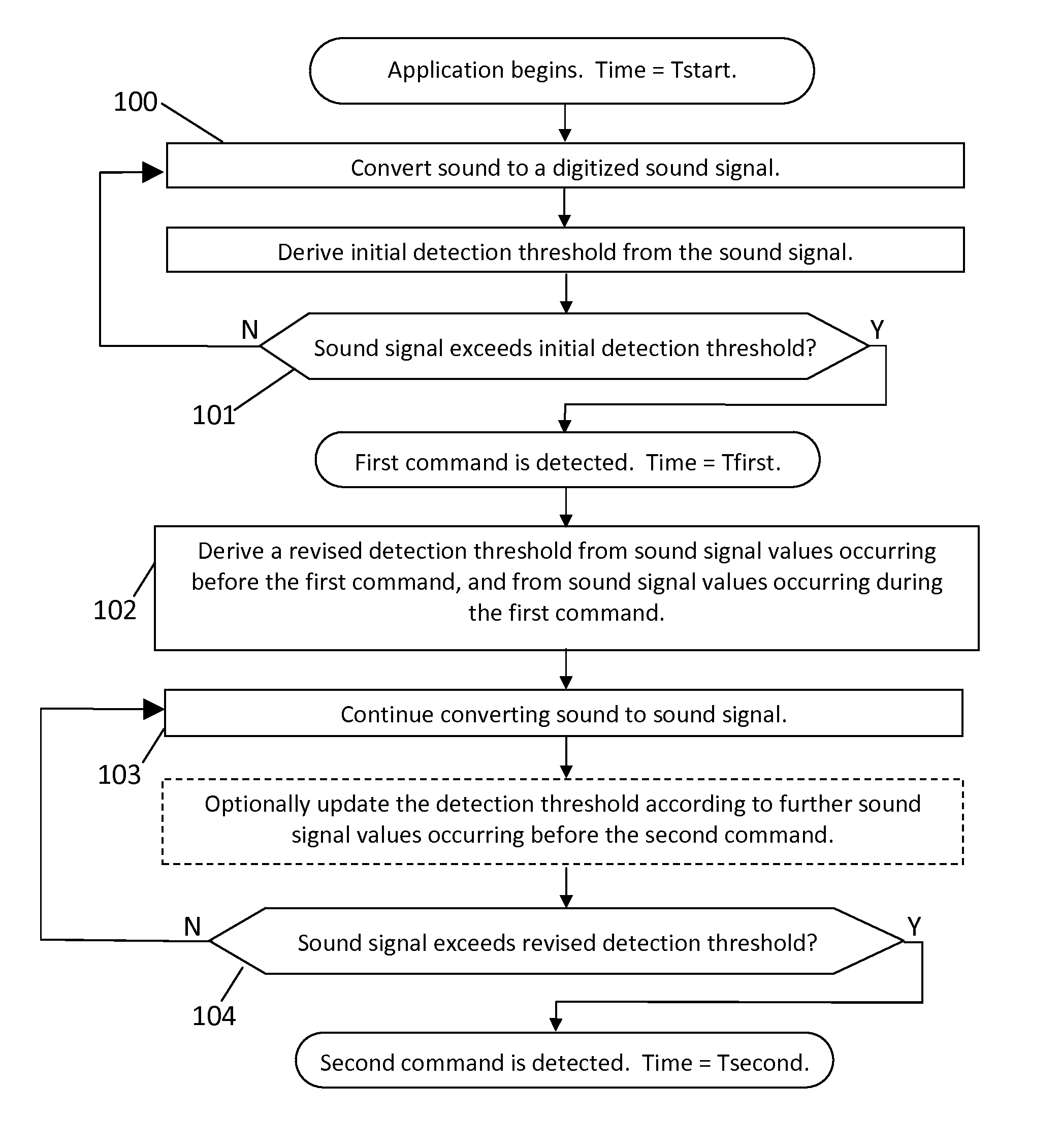
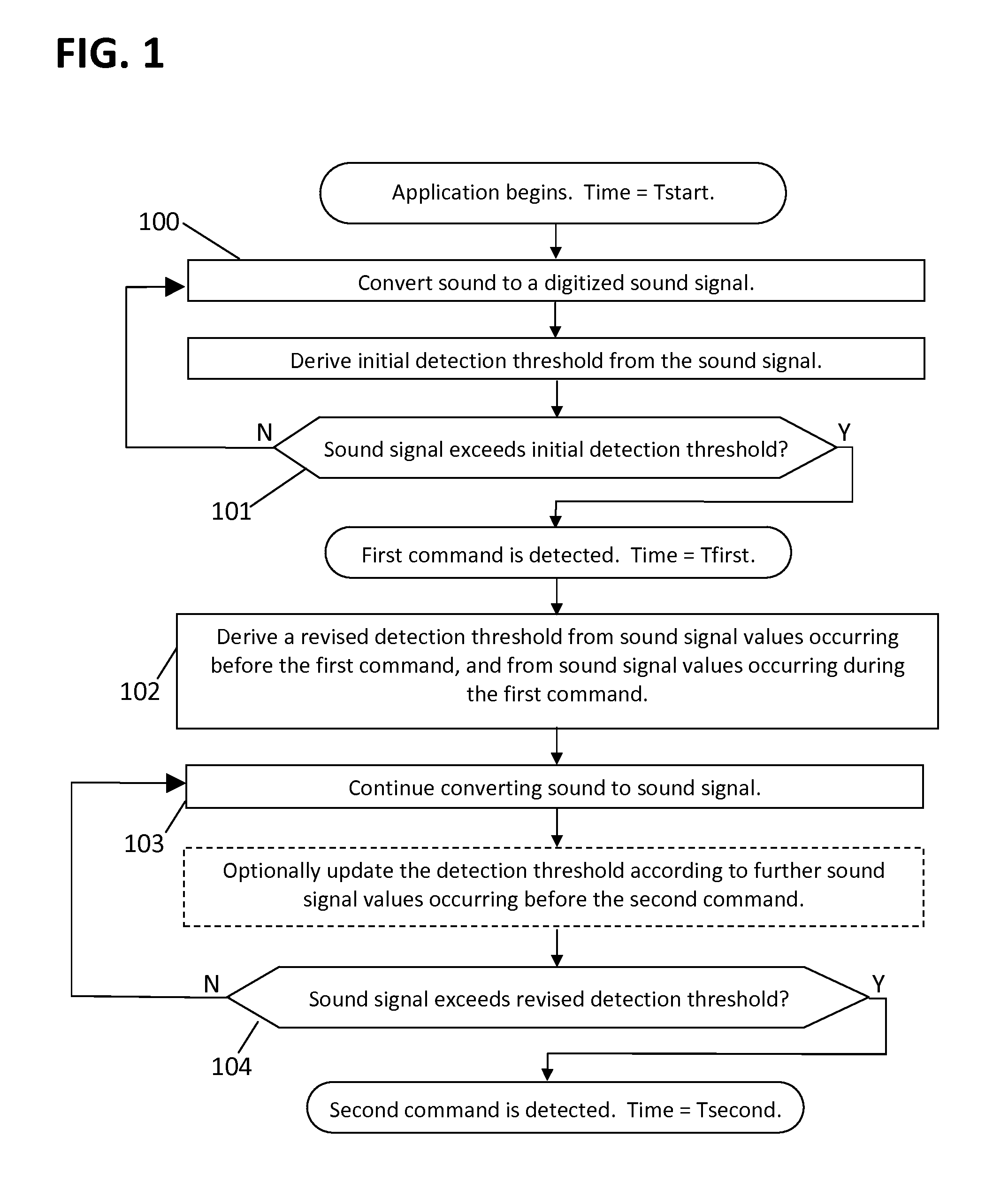
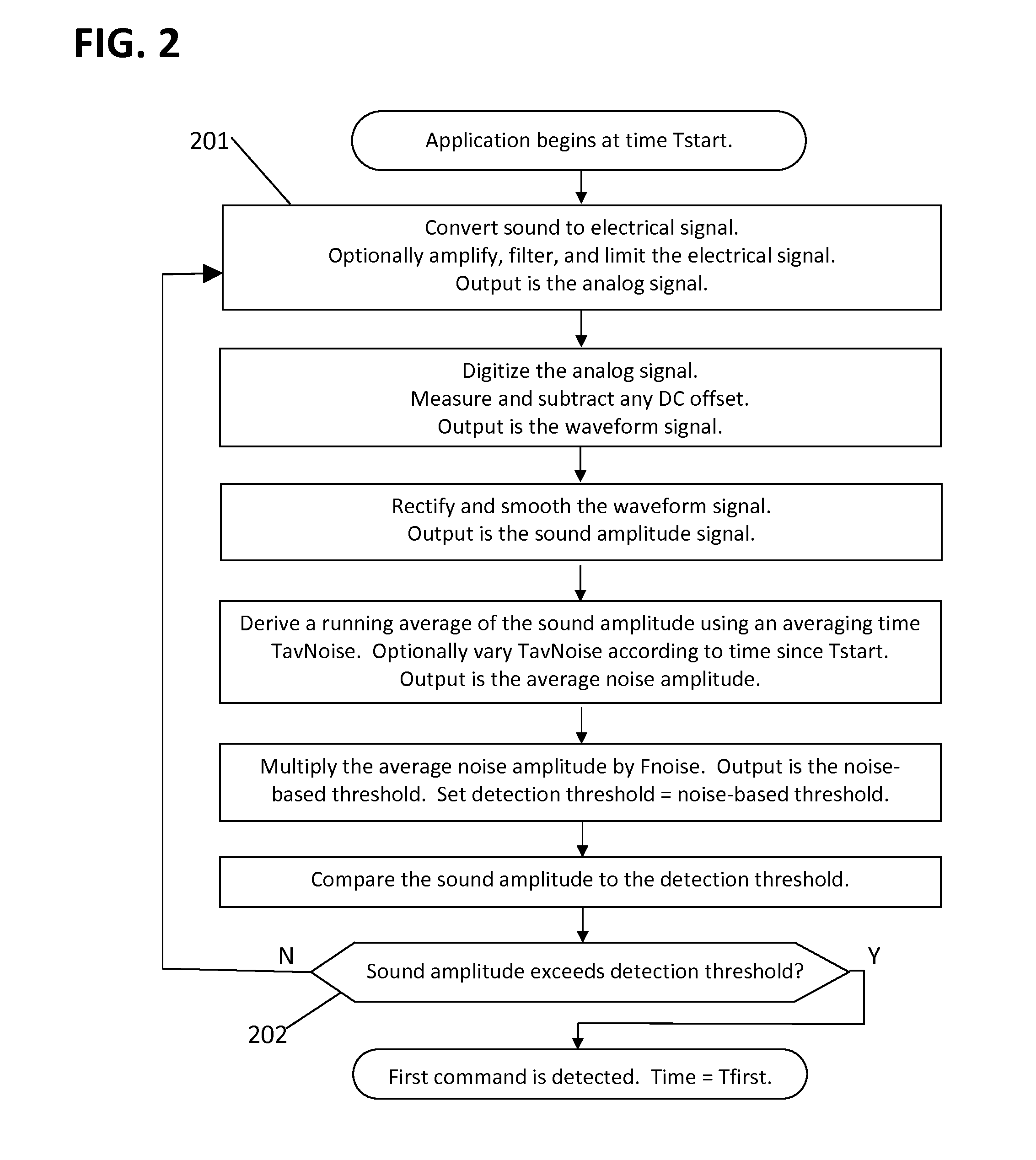
Automatic calibration of command-detection thresholds
When a voice-activated device or application is first started, the signal levels corresponding to spoken commands are initially unknown, making it difficult to set detection thresholds. The inventive method provides an initial command-detection threshold based on the noise level alone. The first command is detected using this initial threshold. Then the threshold is revised according to the first command sound, and a second command is detected using the revised threshold. After detecting each command, the detection threshold is further refined according to the current noise and command sounds. Methods are also disclosed for optimizing the thresholds, adjusting parameters according to sound, and detecting voiced and unvoiced sounds separately. These capabilities enable many emerging voice-activated products and applications.
Owner:ZANAVOX
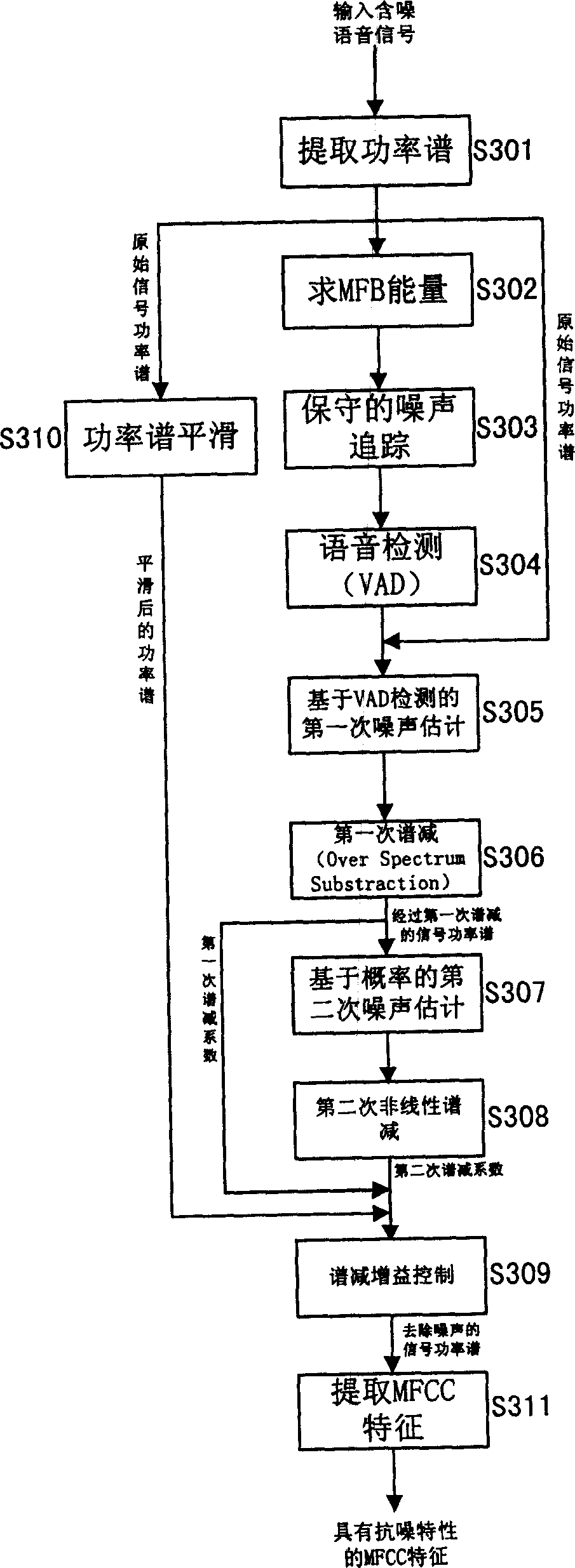
Method and apparatus for resisting noise based on adaptive nonlinear spectral subtraction
ActiveCN1841500AImprove recognition rateImprove signal-to-noise ratioSpeech recognitionCurrent noisePattern recognition
The disclosed speech recognition anti-noise method based on adaptive nonlinear spectrum reduction comprises: detecting speech, if average SNR over set threshold, recognizing as speech information, or else as noise information; updating current noise estimation according to noise frame in last step for the first spectrum reduction calculation to obtain the speech with high SNR; then, taking the second calculation to further eliminate noise.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
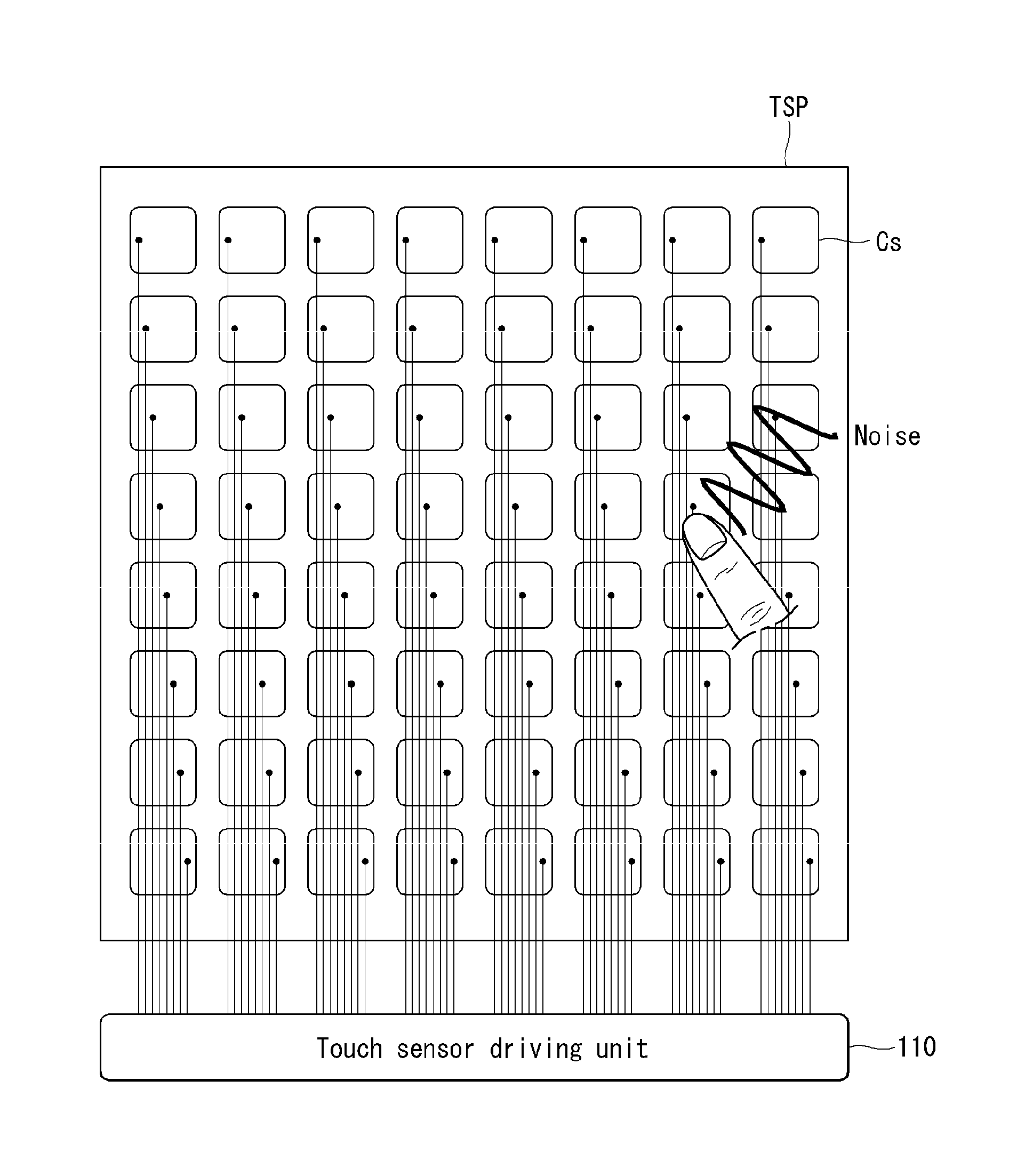
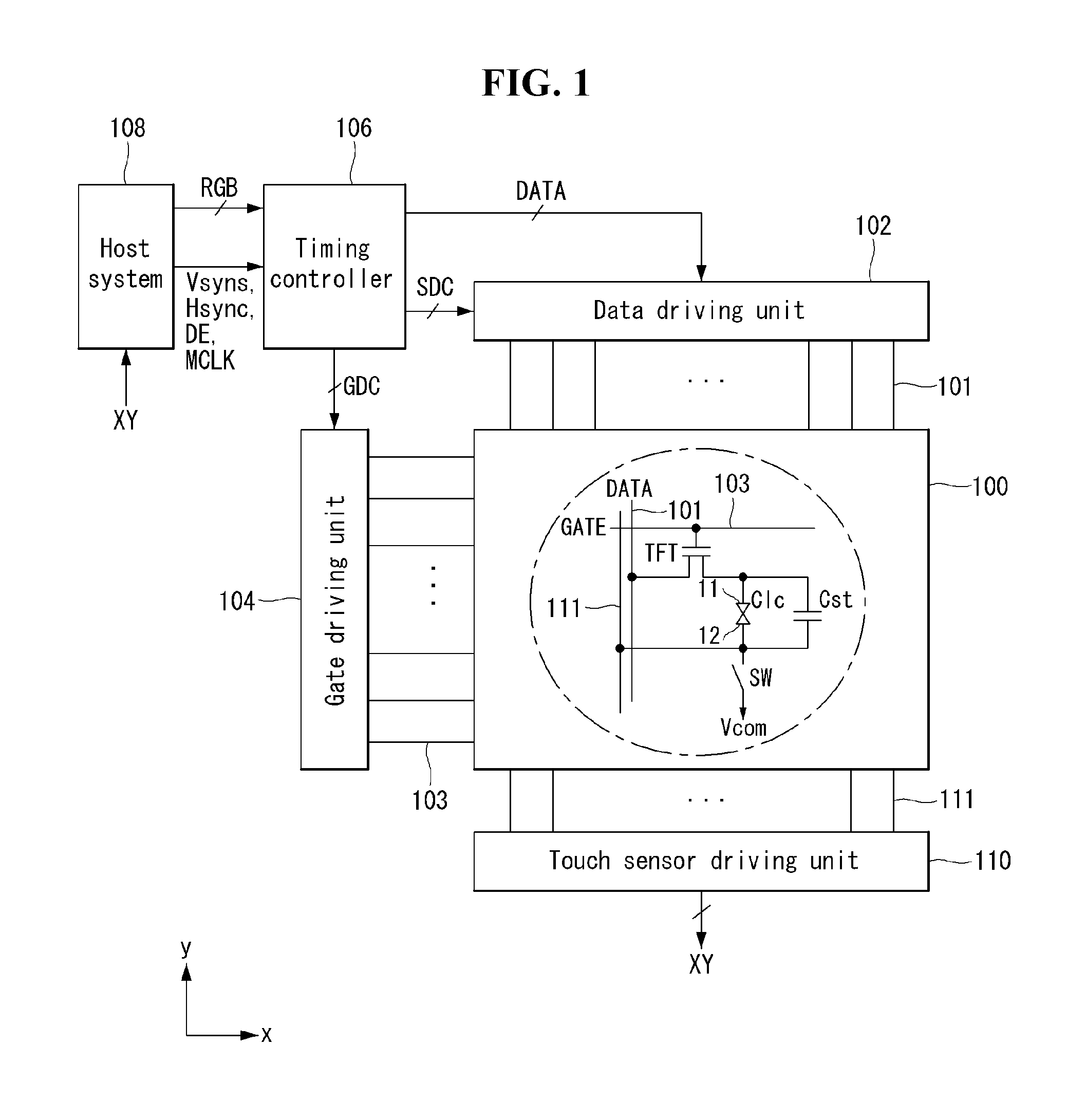
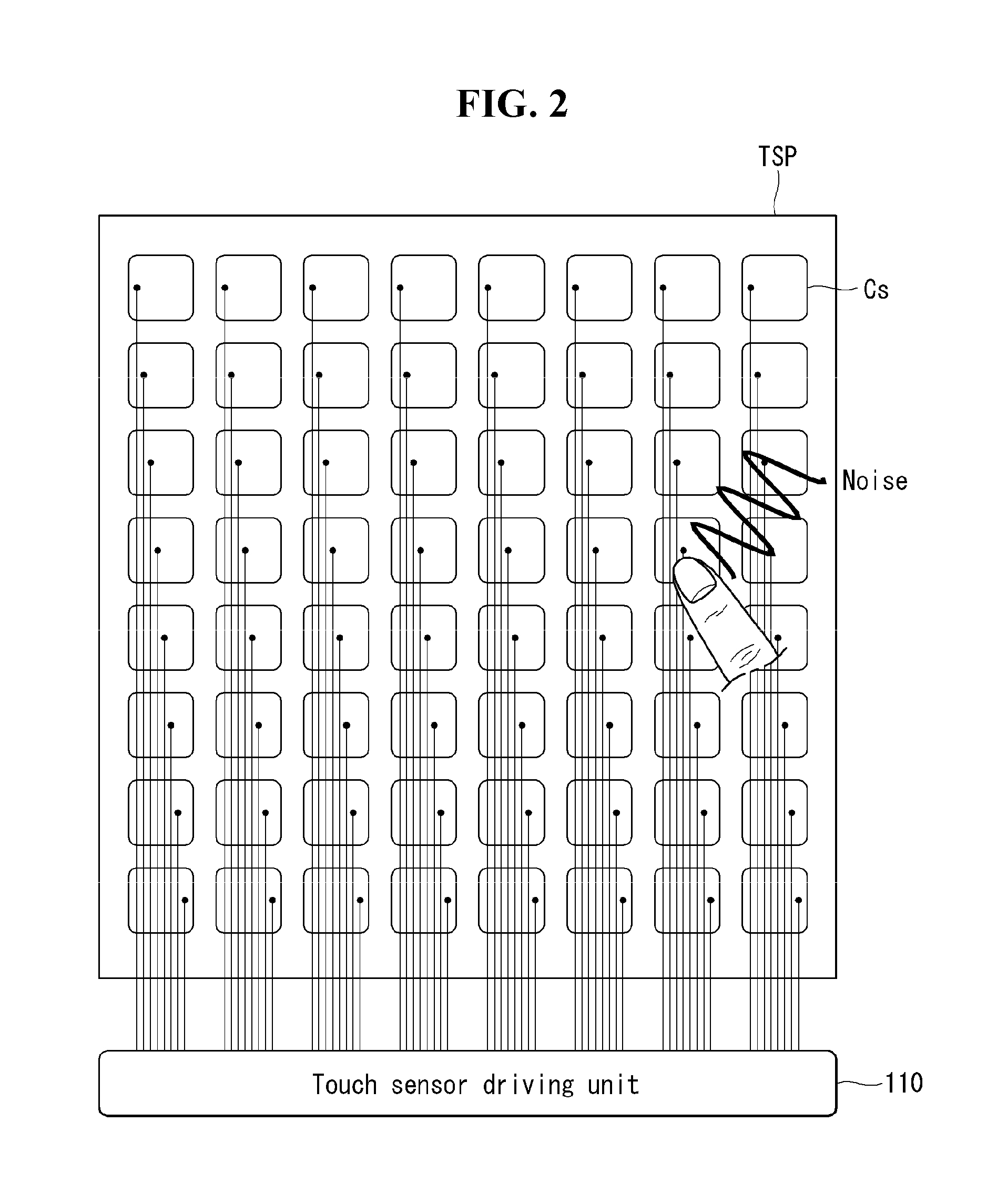
Method and circuit for driving touch sensors to reduce noise measurement time and display device using the same
Disclosed herein are a method and circuit for driving touch sensors and a display device using the same. A method of driving touch sensors includes supplying a touch sensor driving signal to the touch sensors or an amplifier and sensing a touch input during a touch input sensing portion and measuring current noise received through the touch sensors without the touch sensor driving signal during a noise measurement portion.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Wideband radar detecting method for correcting correlation matrix based on high resolution target distance image
InactiveCN101509972AImprove object detection performanceRealize accumulationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLinear contractionCurrent noise
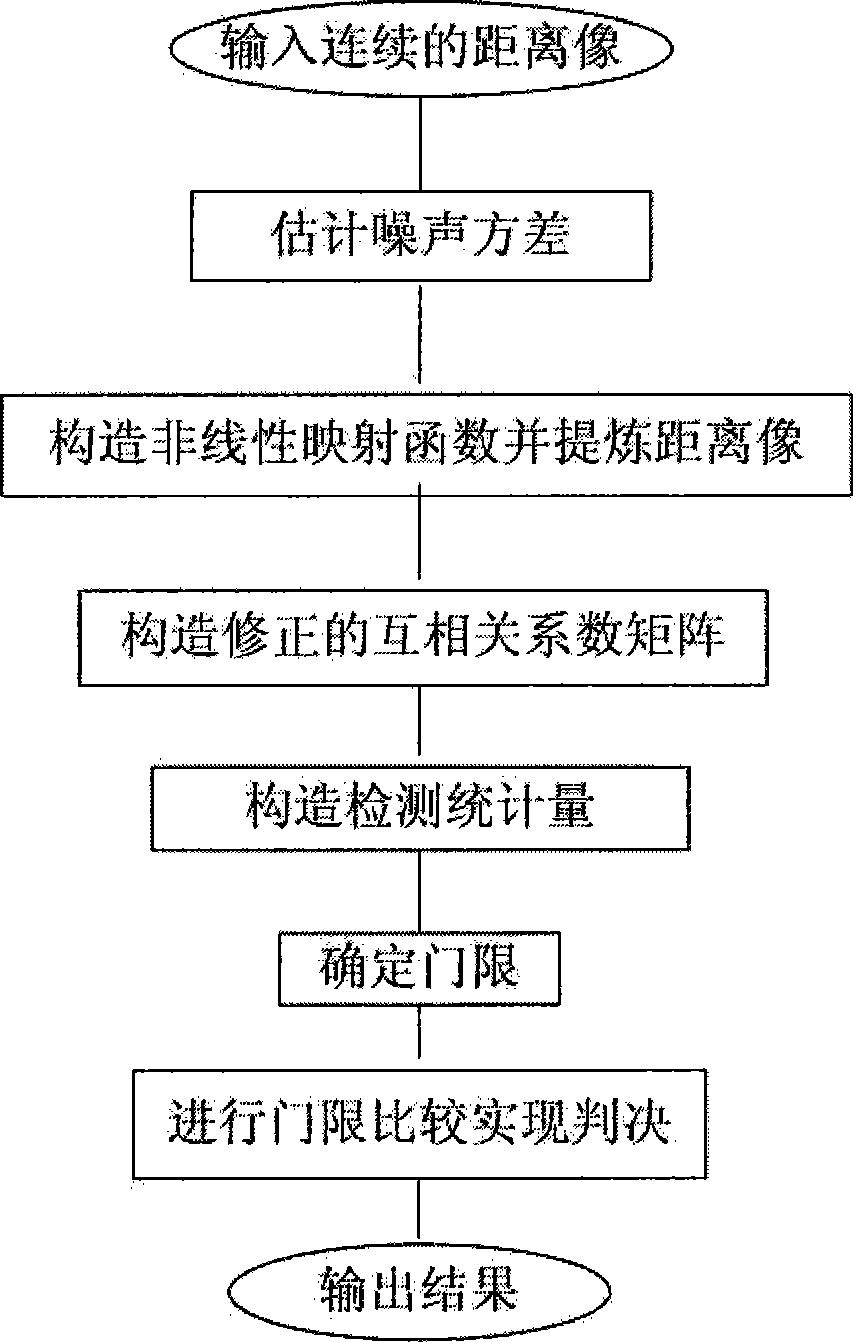
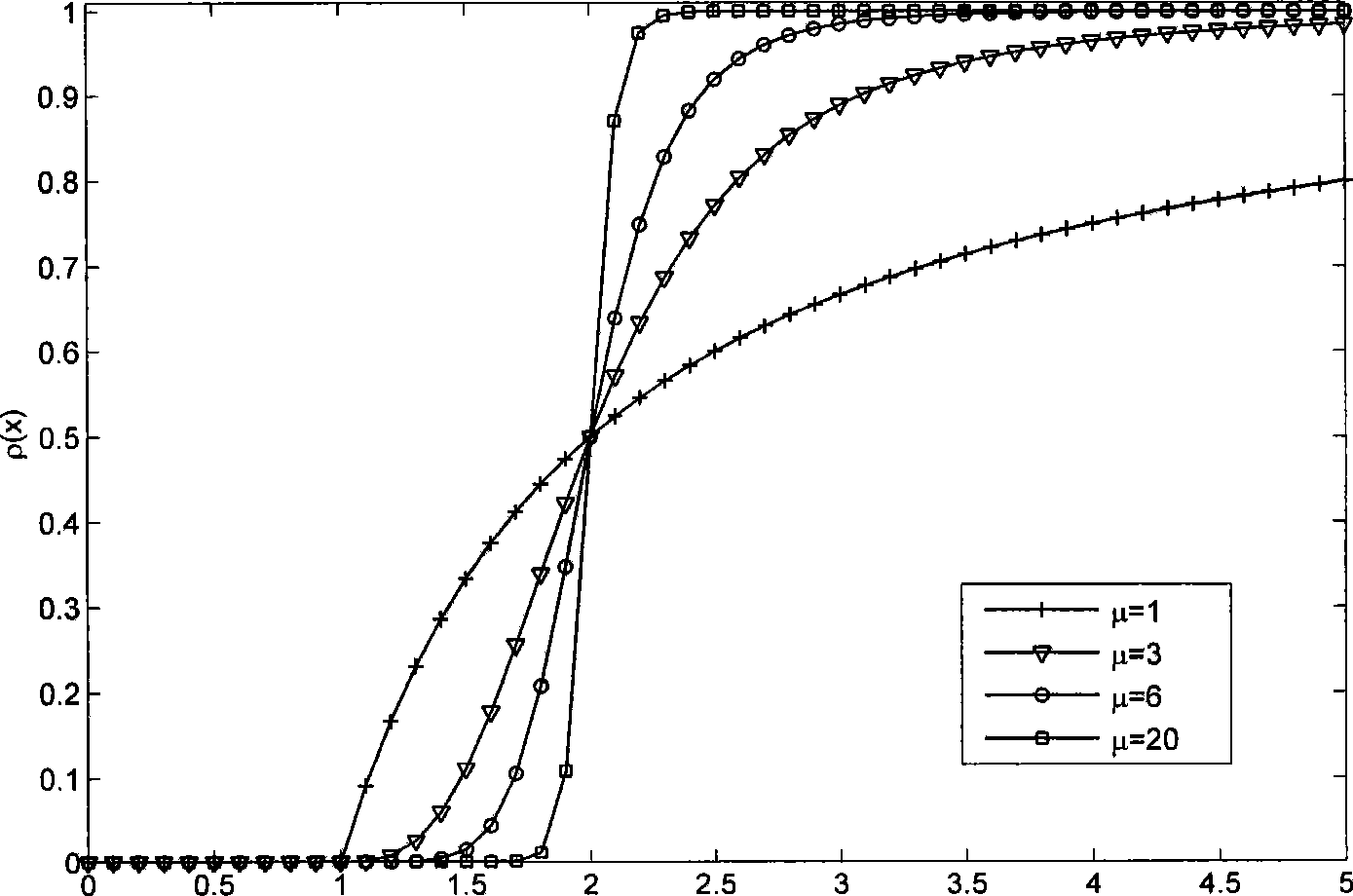
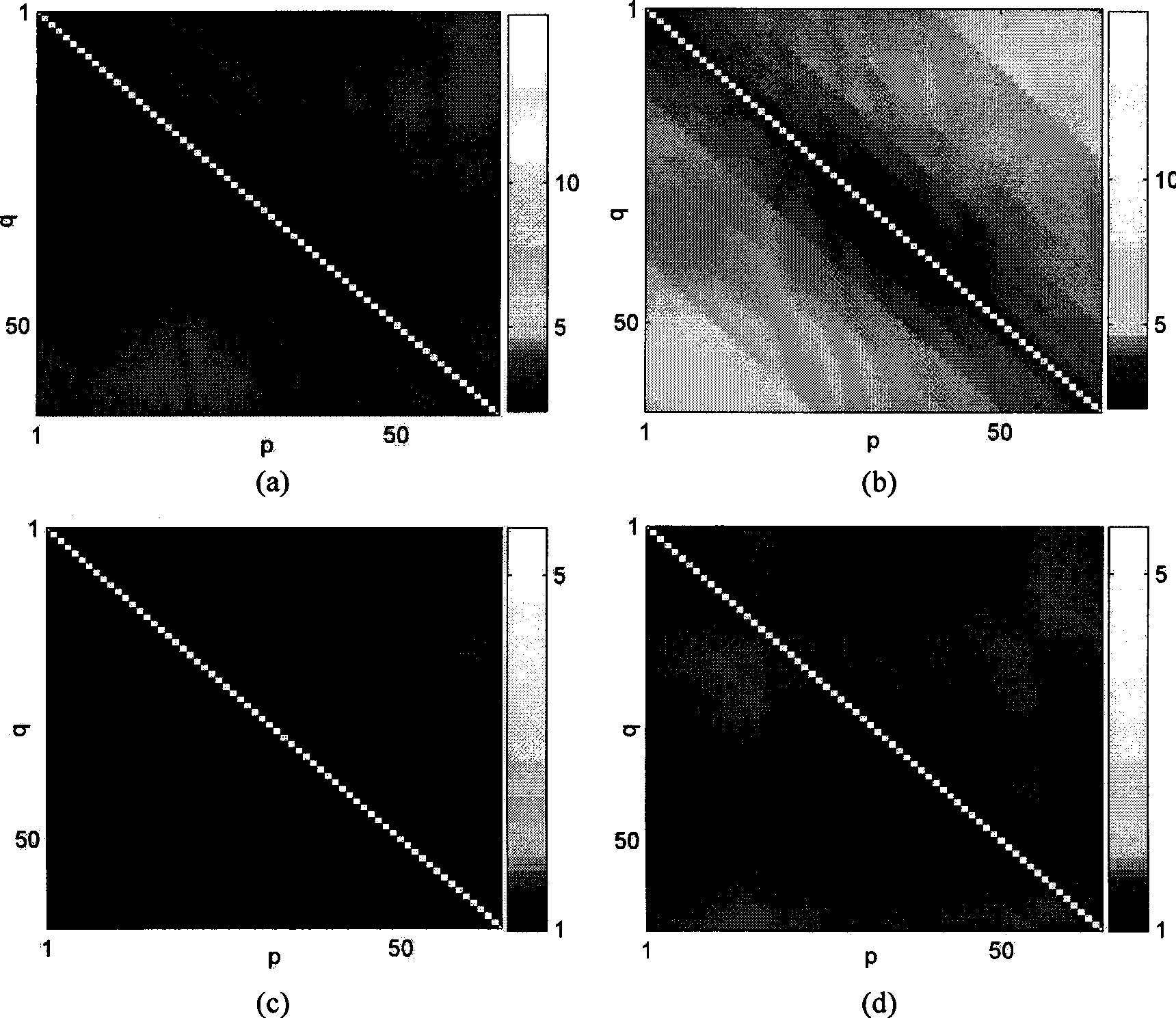
The invention provides a method for detecting a broadband radar on the basis of continuous high-resolution target distance image-correction correlation matrix, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) standard deviation estimation is carried out to the noise of distance images that contain noise; (2) based on the standard deviation, a set of non-linear contraction mapping is established, and then the distance images that contain noise are refined according to the contraction mapping, thus obtaining refined multi-pulse distance images; (3) based on the multi-pulse distance images, cross correlation coefficient between every two refined distance images is calculated, thus obtaining a corrected cross correlation coefficient matrix; (4) the cross correlation coefficient matrixes are accumulated to establish the detecting statistic value, and the detecting threshold of current noise variance is set; (5) the detecting statistic value and the detecting threshold are compared to judge whether the target exists. The method has the advantages of cross distance unit detection and multi-pulse accumulation and is used for detecting a non-cooperative target under unknown prior information condition.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Line identification module, driving method for line identification module, and display apparatus
ActiveCN106897696AImprove signal-to-noise ratioAvoid Leakage Current NoiseStatic indicating devicesPrint image acquisitionCurrent noiseSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a line identification module, a driving method for the line identification module, and a display apparatus. A synchronous scanning part is added to an induction surface of a photosensitive device array and can be divided into a first light shading region and a first light transmitting region which are dynamically changed when photosensitive devices perform line identification, wherein the first light transmitting region is at least formed above the photosensitive devices that are performing line identification scanning, so that the photosensitive devices that are performing the line identification scanning can smoothly receive reflected light of a finger through the first light transmitting region. The first light shading region can shade the photosensitive devices that do not need to perform the line identification scanning, so that no light is irradiated to the photosensitive devices and the photosensitive devices can be prevented from generating leak current noises and transmitting the leak current noises to connected data lines. With the scanning of the photosensitive devices, the first light shading region and the first light transmitting region in the synchronous scanning part are synchronously changed, so that a signal-to-noise ratio of signals read out from the data lines can be increased.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
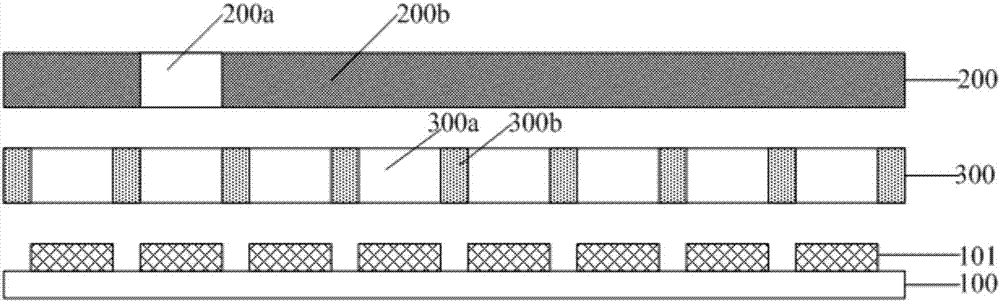
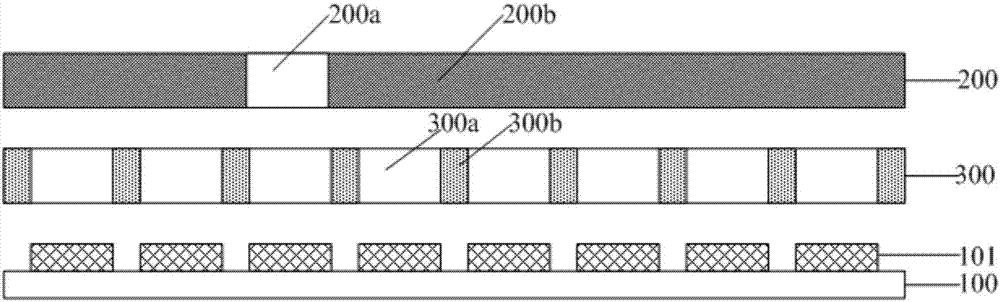
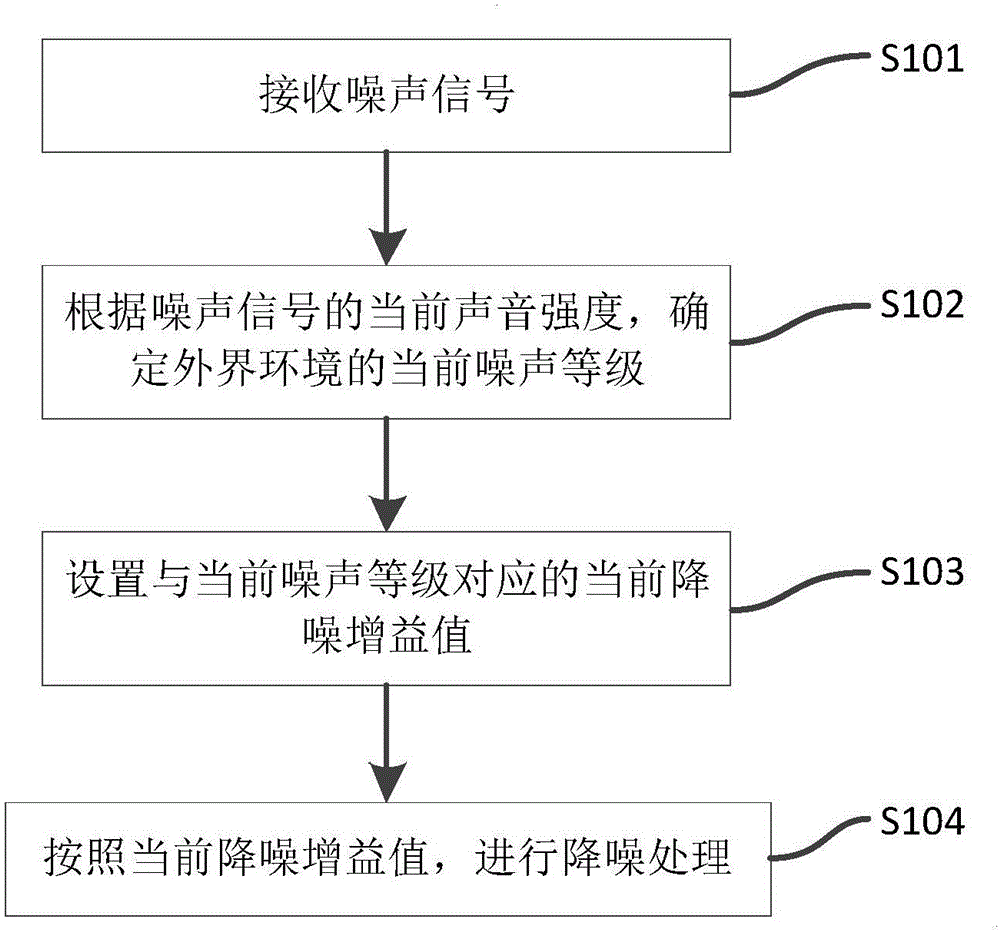
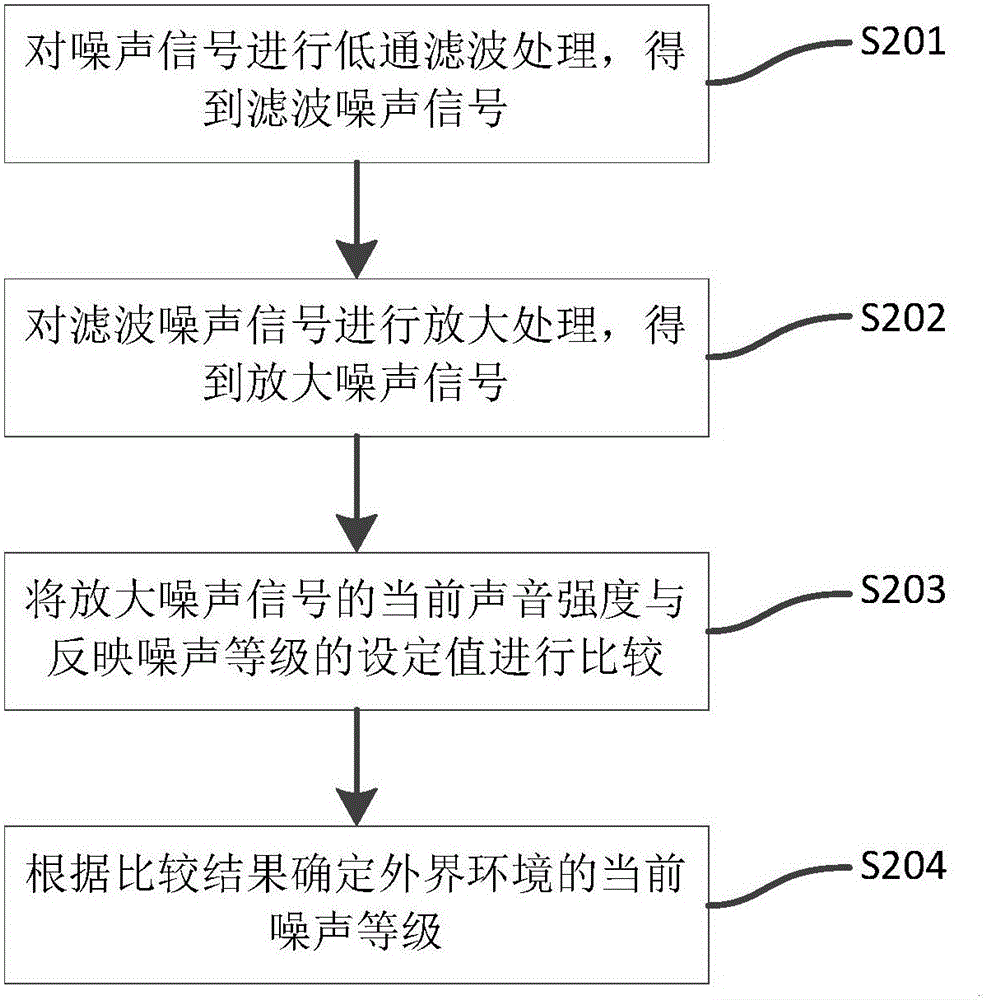
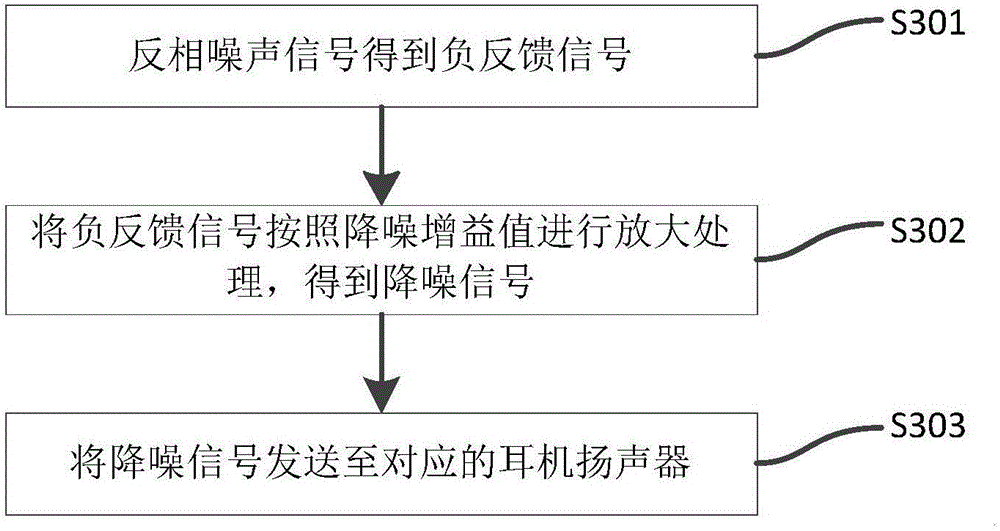
Noise reduction method capable of realizing self-adaptive adjustment of noise reduction gain, device thereof, and noise reduction earphone
ActiveCN105979415AImprove experienceHearing device active noise cancellationMicrophones signal combinationCurrent noiseEngineering
The invention discloses a noise reduction method capable of realizing self-adaptive adjustment of noise reduction gain, a device thereof, and a noise reduction earphone. The noise reduction method is characterized in that a voice signal acquired by a microphone disposed on an earphone receiver is received, and is used as a noise signal; a current noise level of external environment is determined according to the current voice intensity of the noise signal; current noise reduction gain value corresponding to the current noise level is set; according to the current noise reduction gain value, the noise reduction treatment of the noise signal is carried out. According to the current noise level of the external environment, the noise reduction gain value corresponding to the current noise level is set, and therefore the noise reduction earphone is capable of realizing the self-adaptive adjustment of the noise reduction gain, and user experience is effectively improved.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
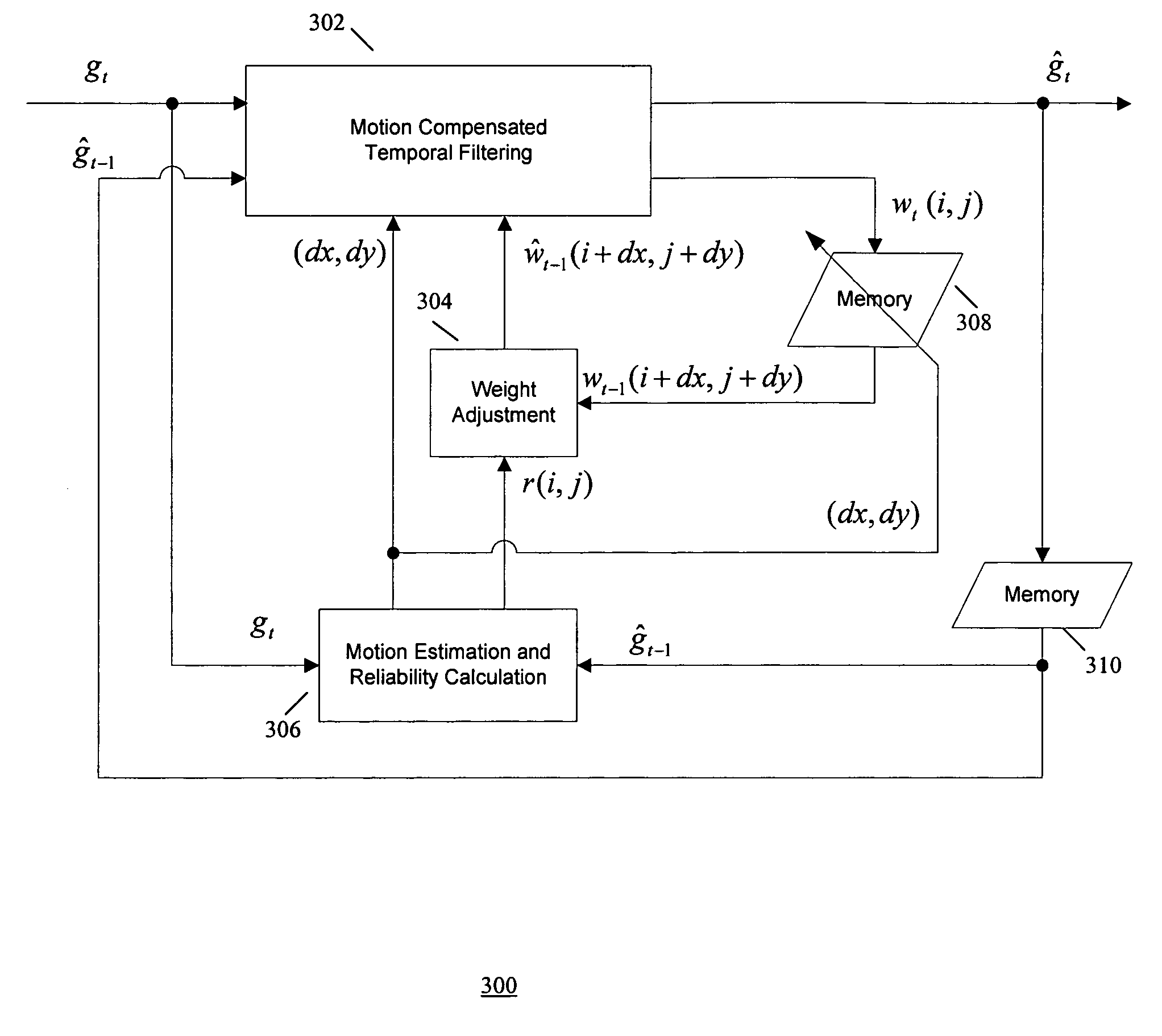
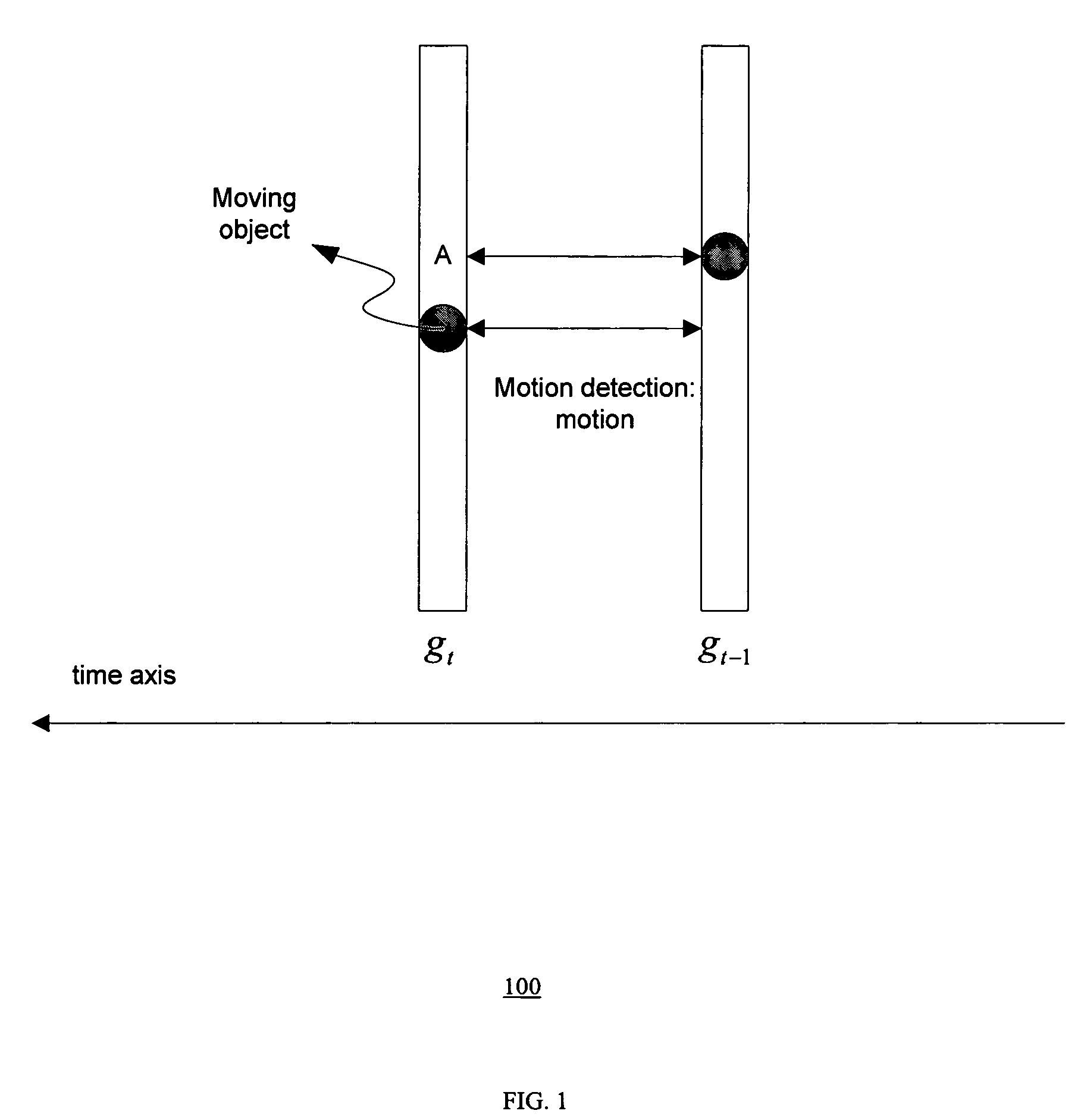
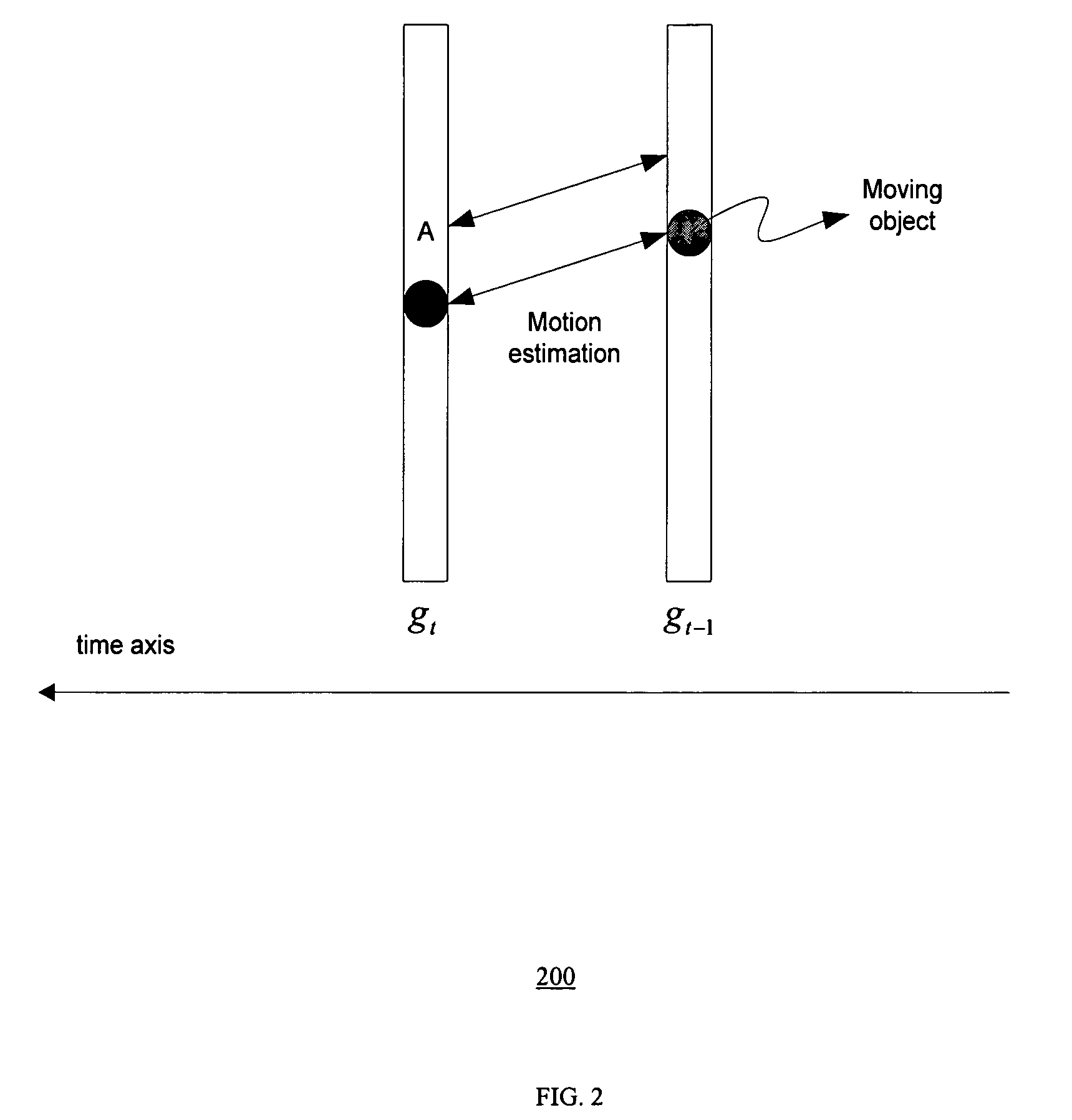
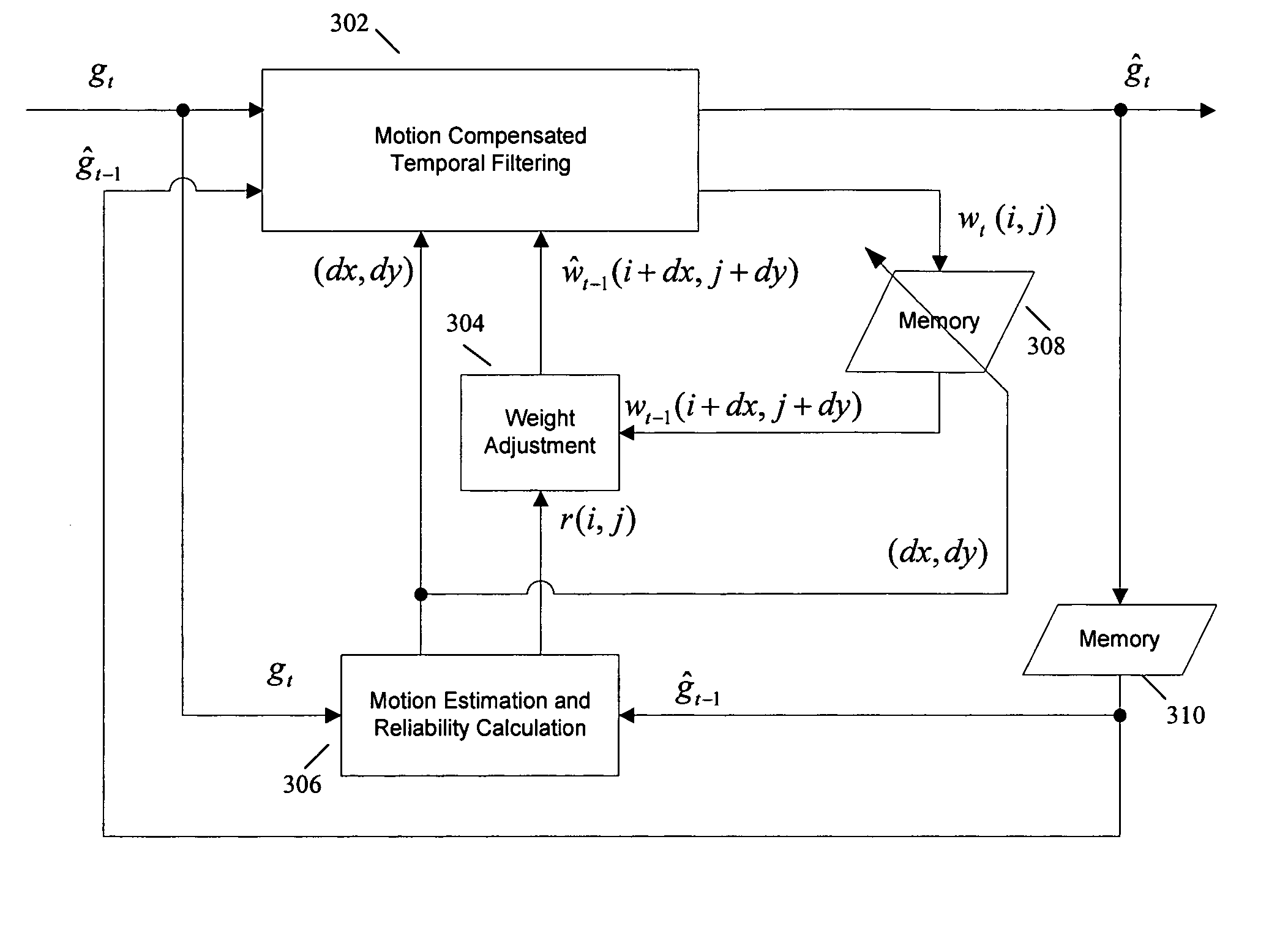
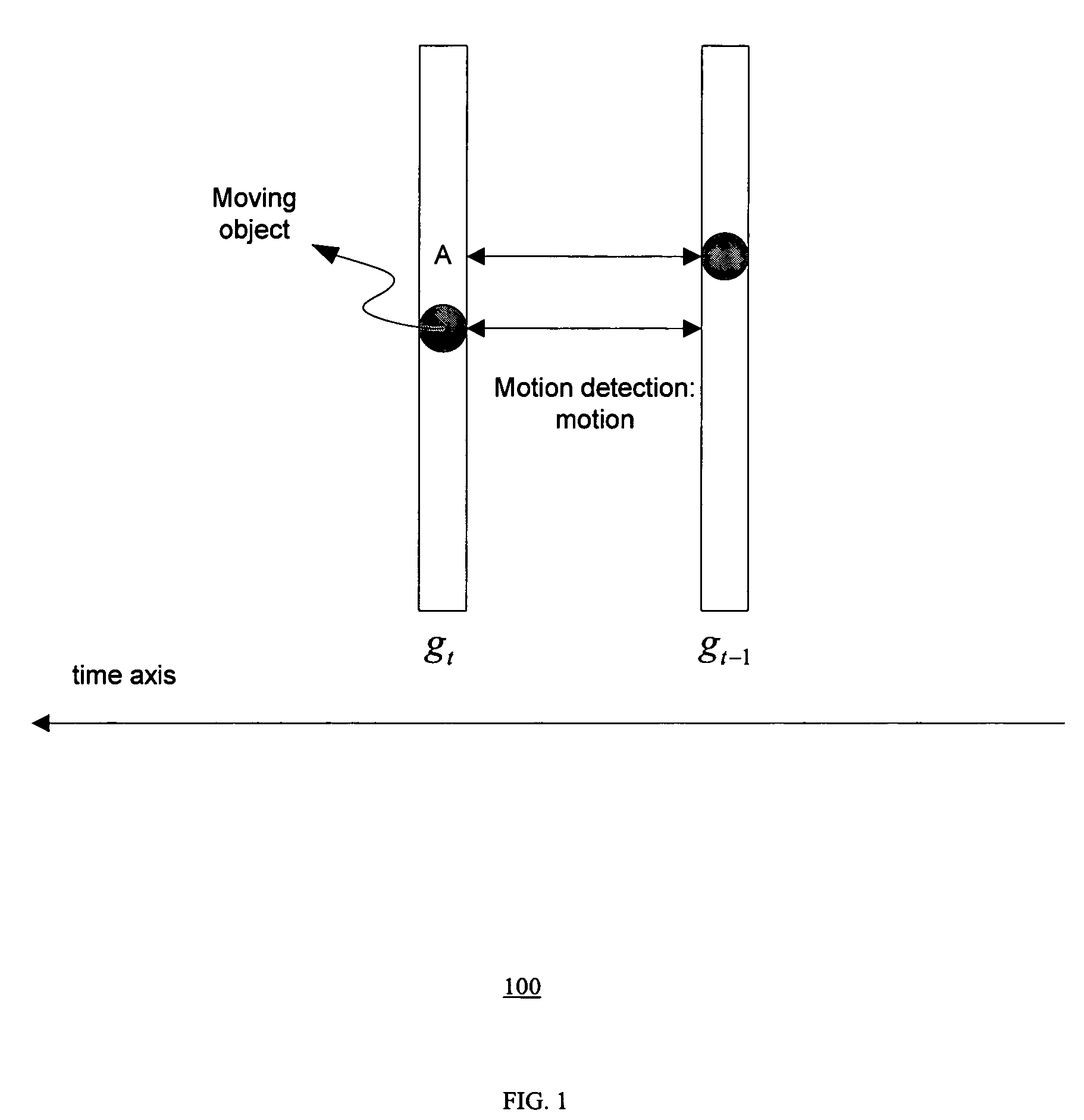
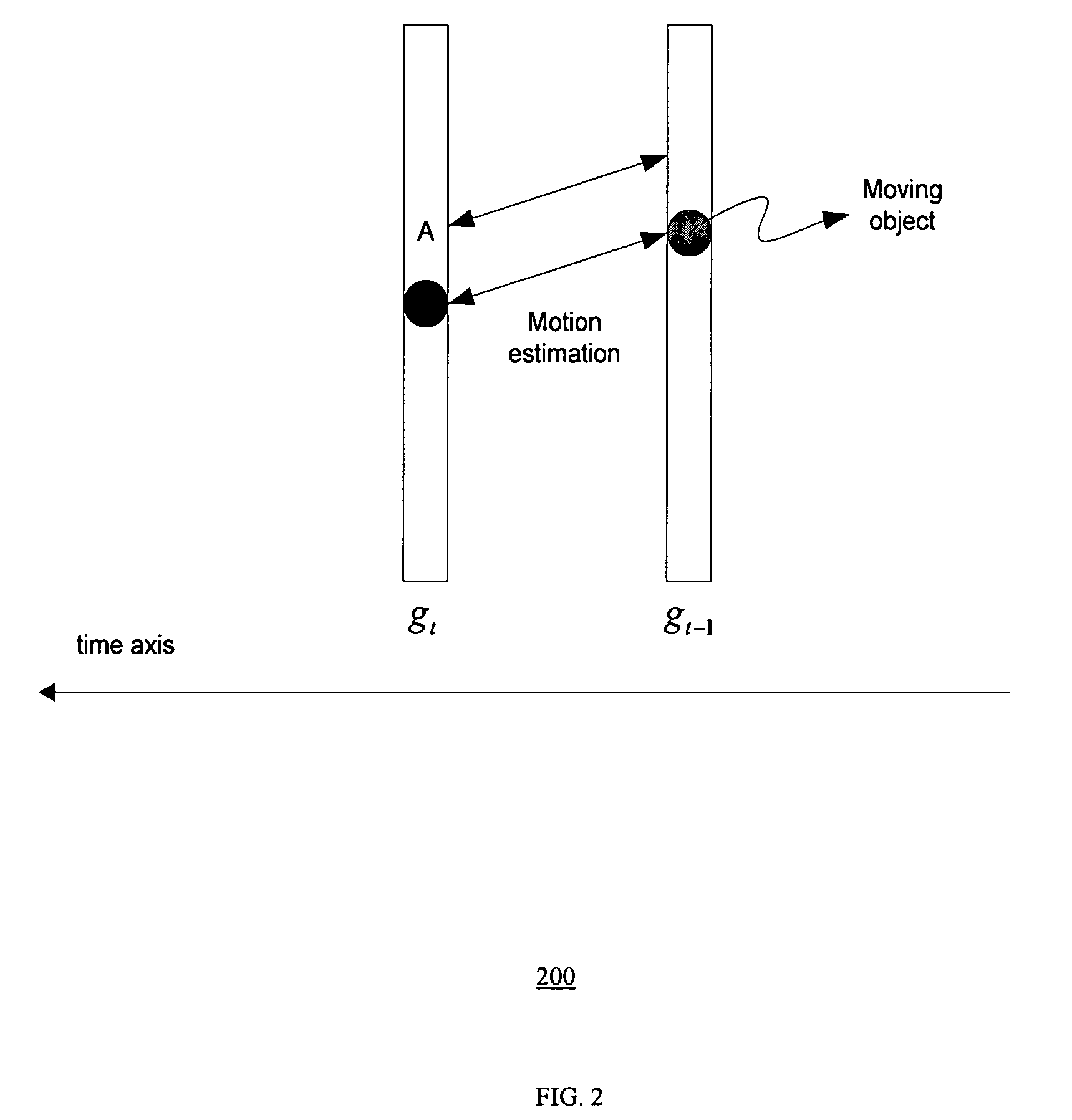
Method of motion compensated temporal noise reduction
InactiveUS20060232712A1Reduce noiseReduce temporal noiseTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionDigital video
A method of reducing noise in a sequence of digital video frames is performed by motion estimation between a current noisy frame and a previous noise-reduced frame, to generate motion vectors indicating relative motion between the pixels in the current noisy frame and the corresponding pixels in the previous noise-reduced frame; and removing noise from the current noisy frame by computing the weighted average of pixels in the current noise frame and the corresponding pixels in the previous noise-reduced frame based on the motion vectors, to generate a noise-reduced output frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
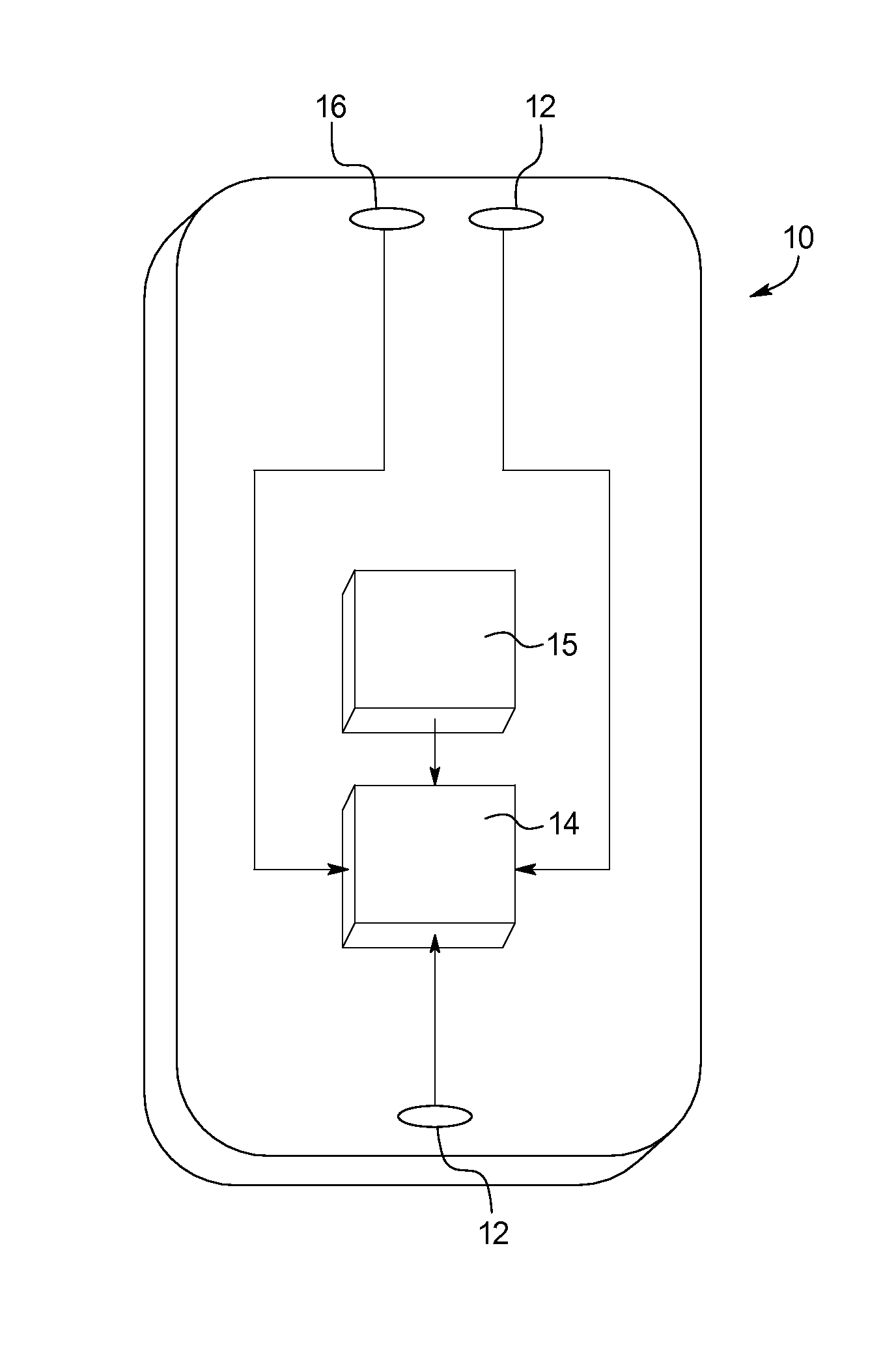
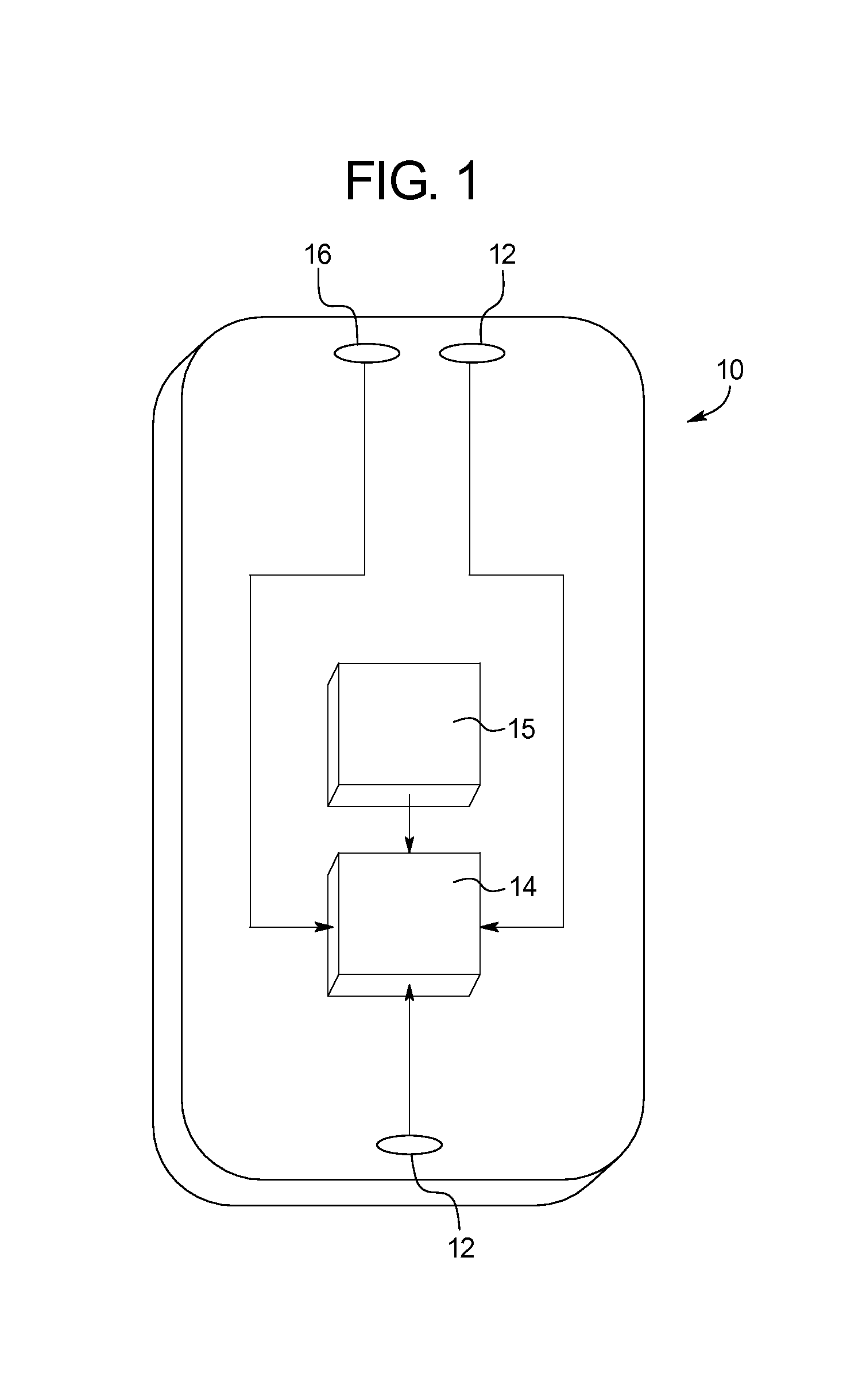
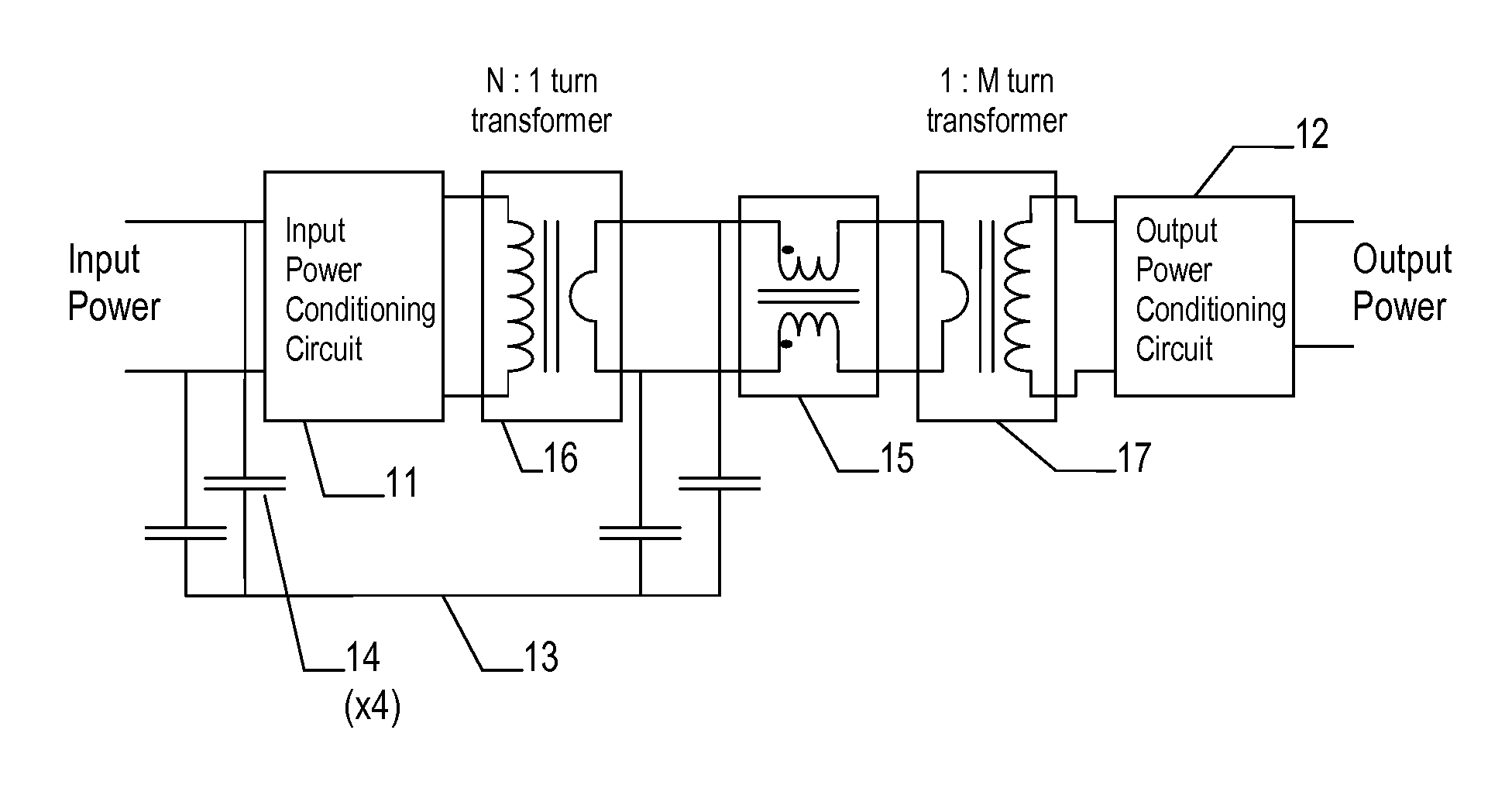
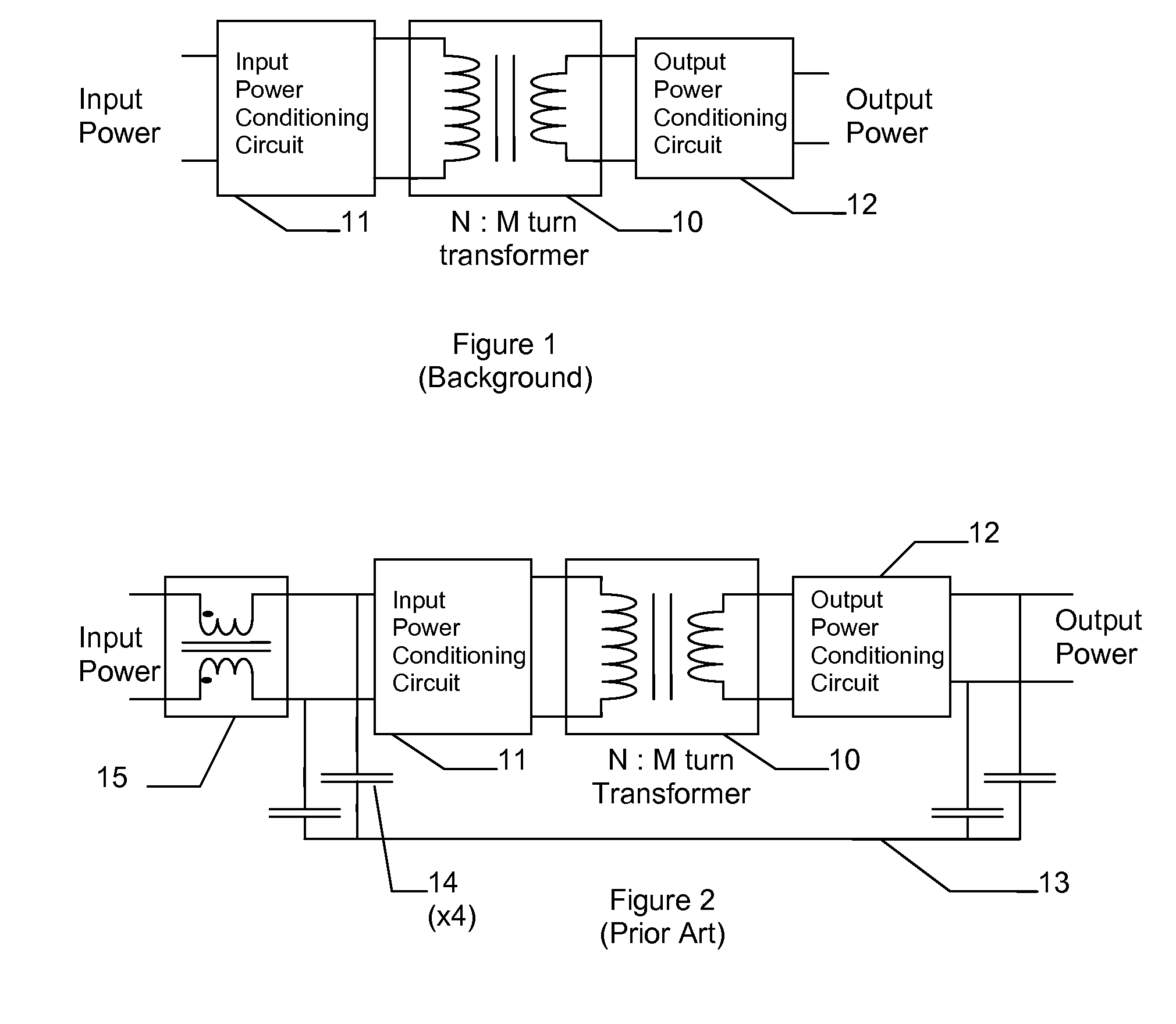
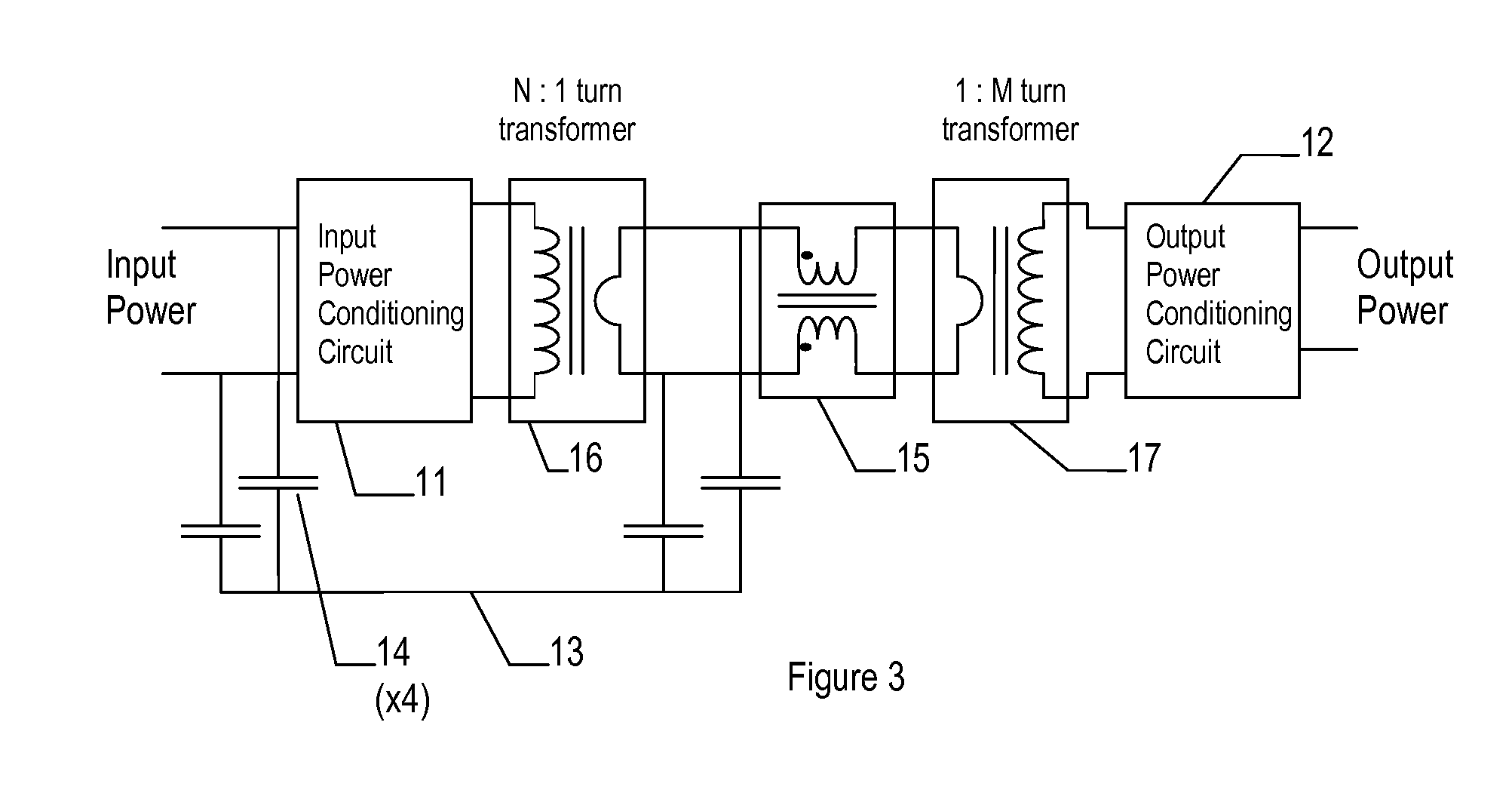
Method of Reducing Common Mode Current Noise in Power Conversion Applications
InactiveUS20090195303A1Reduced isolationOscillations generatorsElectrical apparatus interference reductionCurrent noiseCapacitive coupling
A transformer and filter circuit for reducing common mode noise current in isolated power conversion circuits, comprising a series connection of: a first transformer having an N:1 turns ratio, a common mode current filter, and a second transformer having a 1:M turns ratio. The overall effect being a transformer with N:M turns ratio and with low capacitive coupling from the primary N turns to the secondary M turns thus providing a high impedance to common mode currents crossing the isolation. The series connection of two transformers allows one to be bridged with additional common mode filter components without significant reduction in isolation impedance.
Owner:TERADYNE
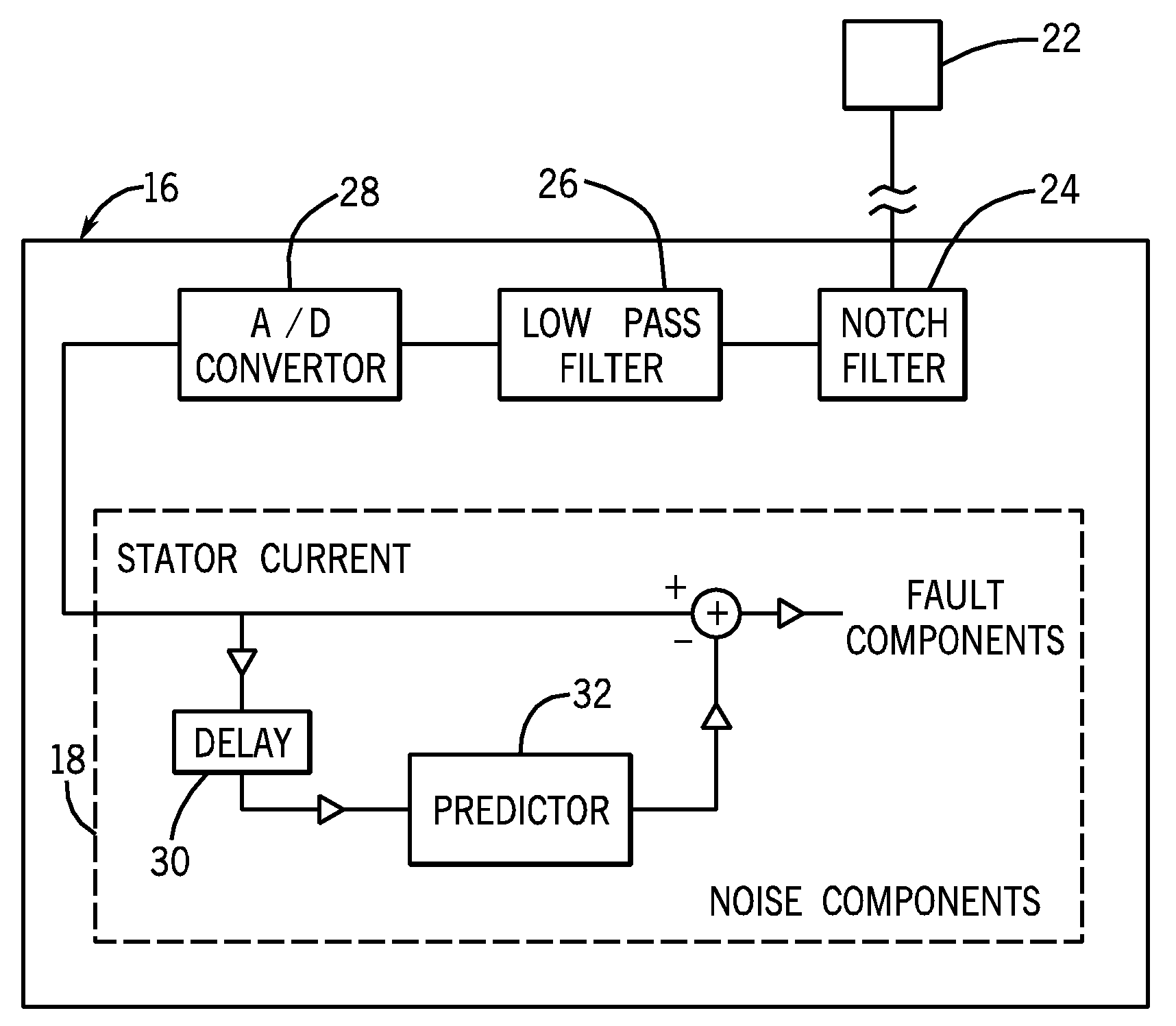
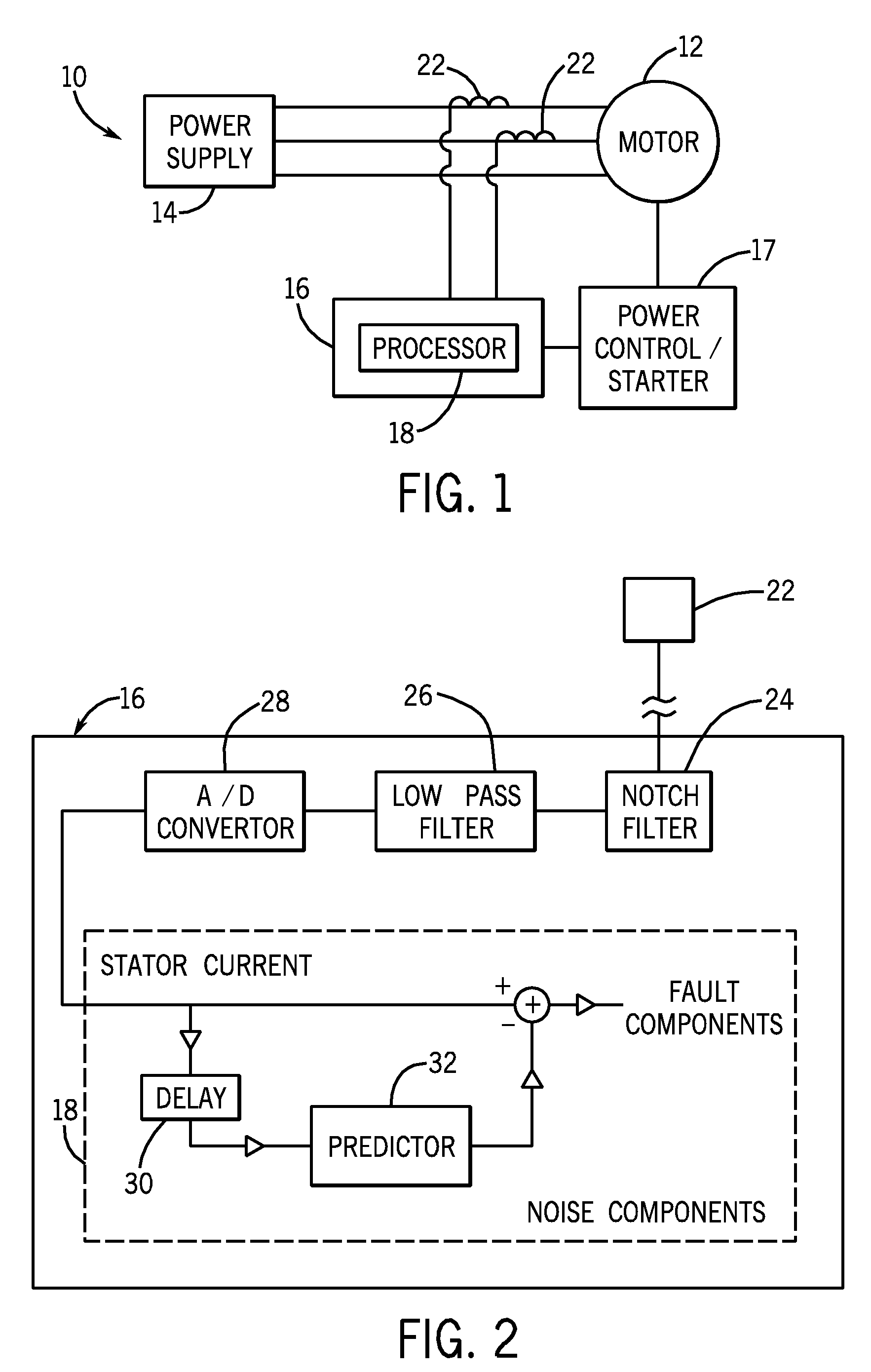
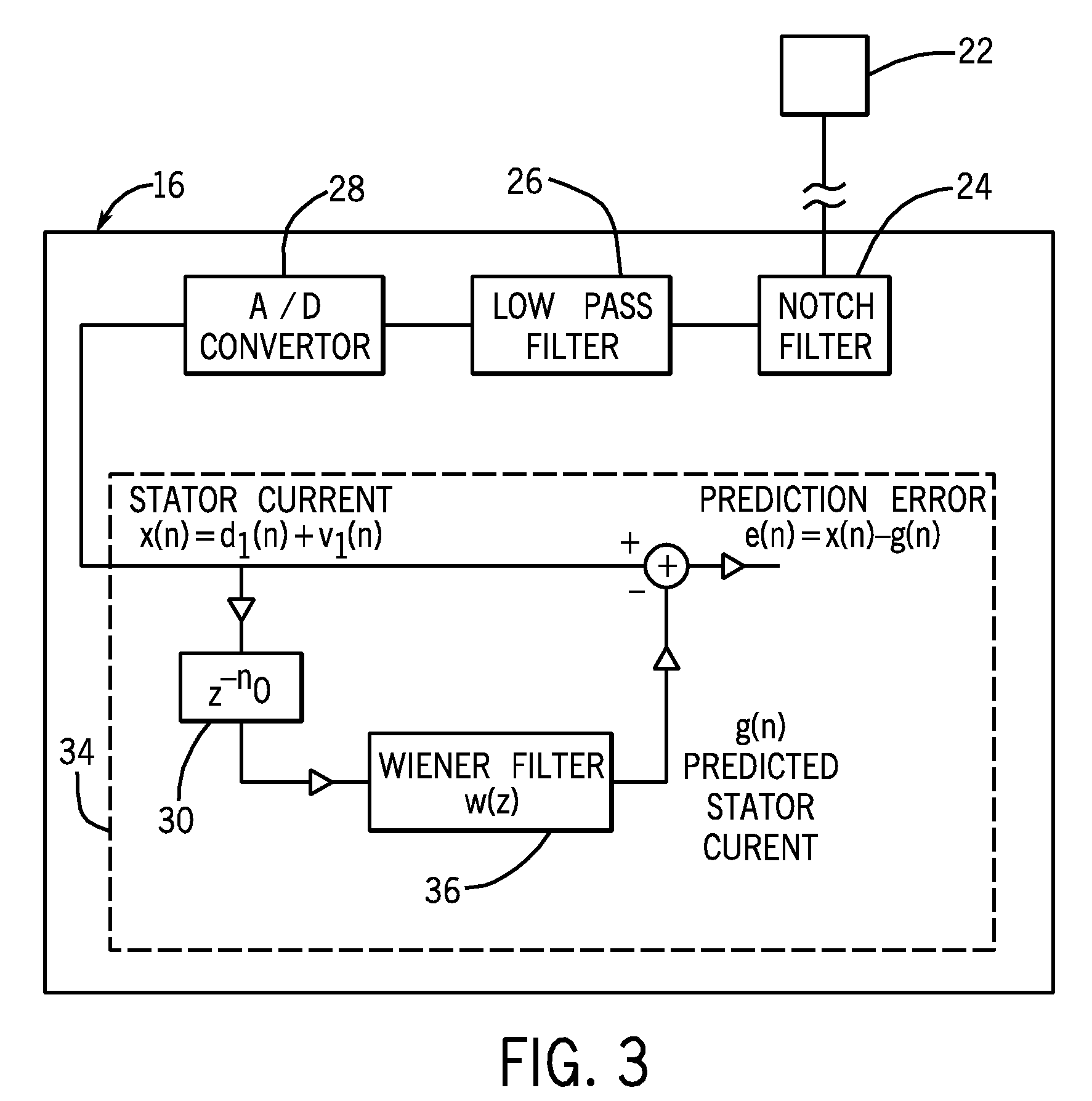
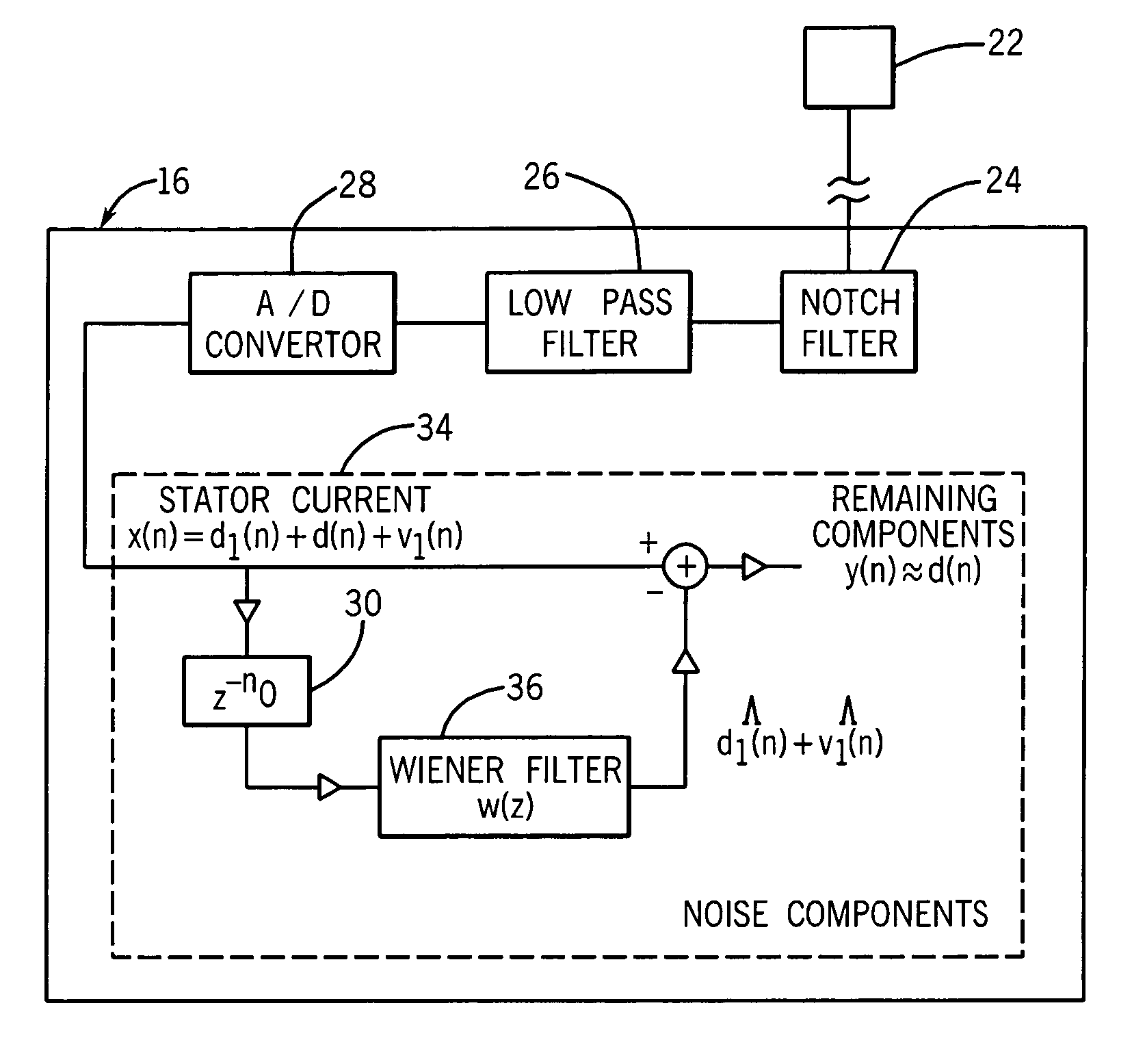
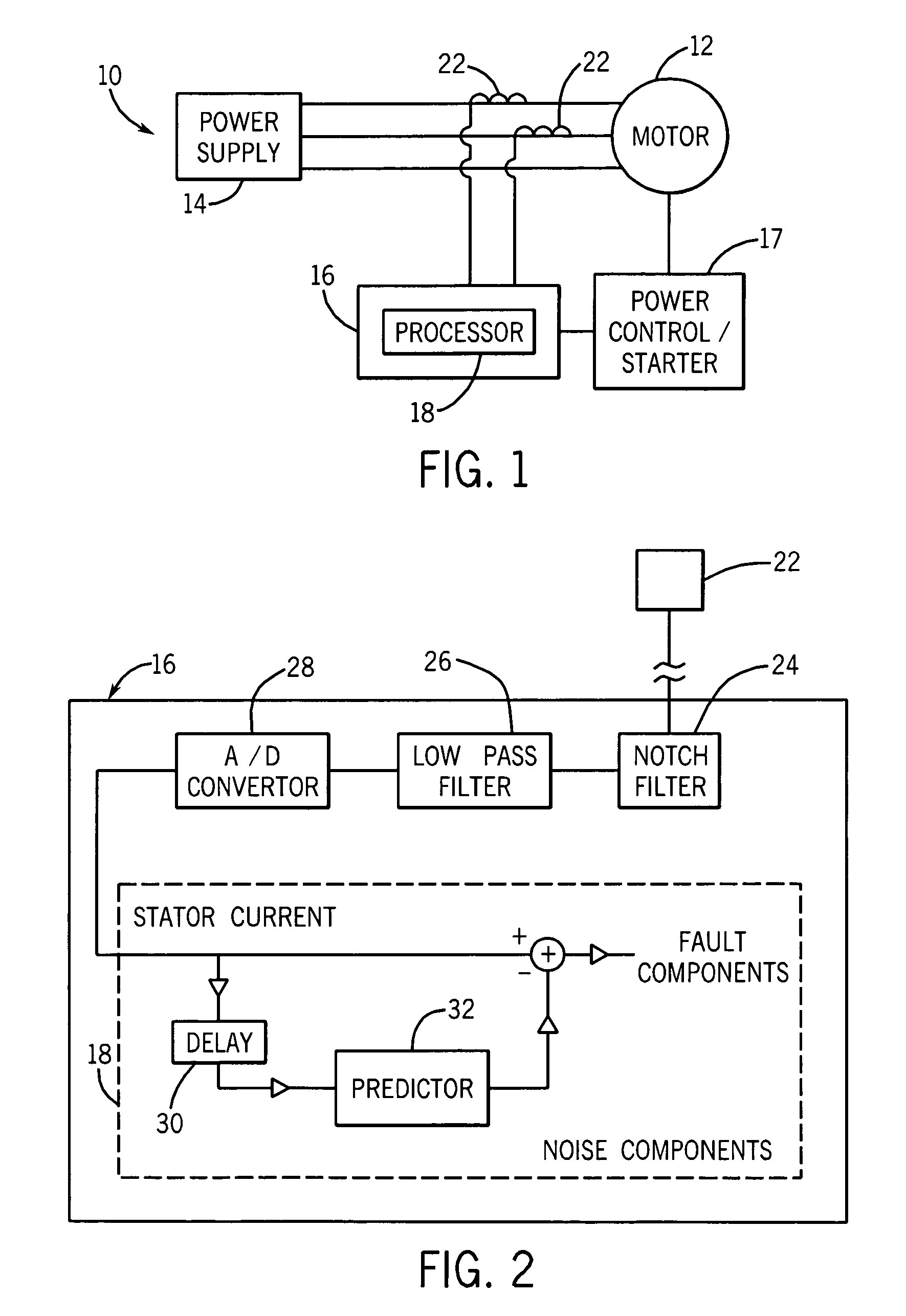
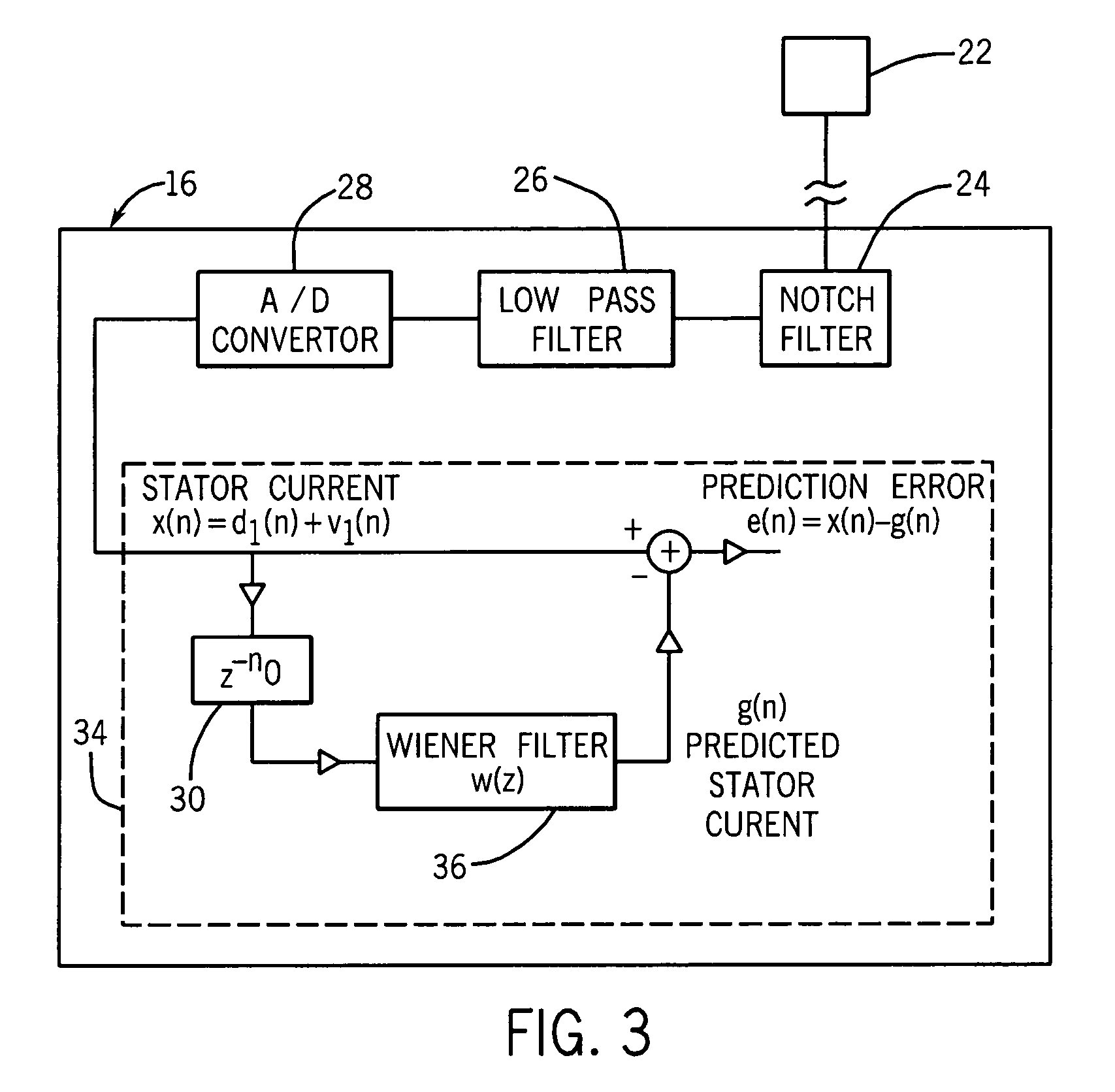
System and method for motor fault detection using stator current noise cancellation
ActiveUS20090146599A1Overcomes drawbackEarly detectionMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlCurrent noiseControl theory
A system and method for detecting incipient mechanical motor faults by way of current noise cancellation is disclosed. The system includes a controller configured to detect indicia of incipient mechanical motor faults. The controller further includes a processor programmed to receive a baseline set of current data from an operating motor and define a noise component in the baseline set of current data. The processor is also programmed to acquire at least on additional set of real-time operating current data from the motor during operation, redefine the noise component present in each additional set of real-time operating current data, and remove the noise component from the operating current data in real-time to isolate any fault components present in the operating current data. The processor is then programmed to generate a fault index for the operating current data based on any isolated fault components.
Owner:EATON CORP
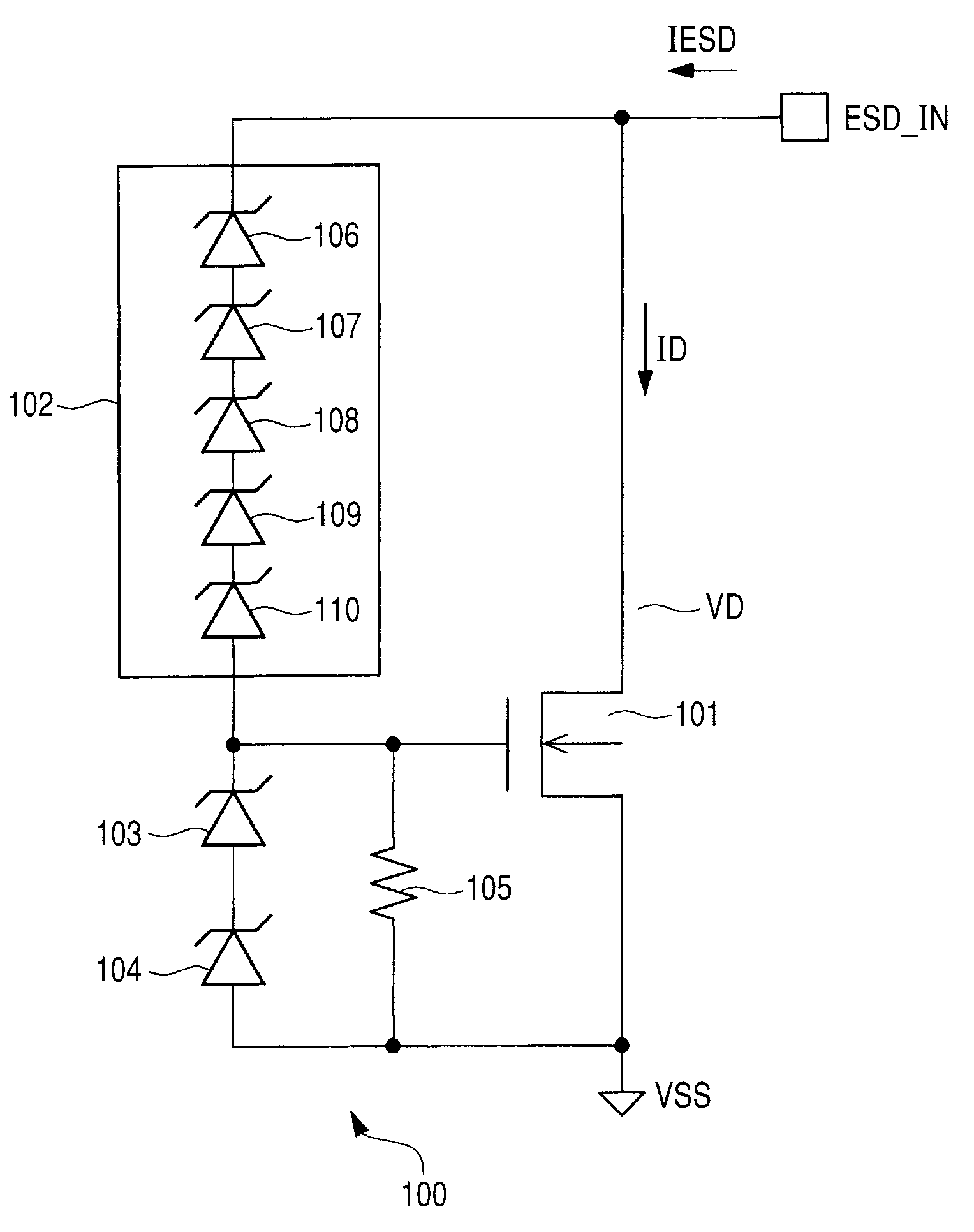
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
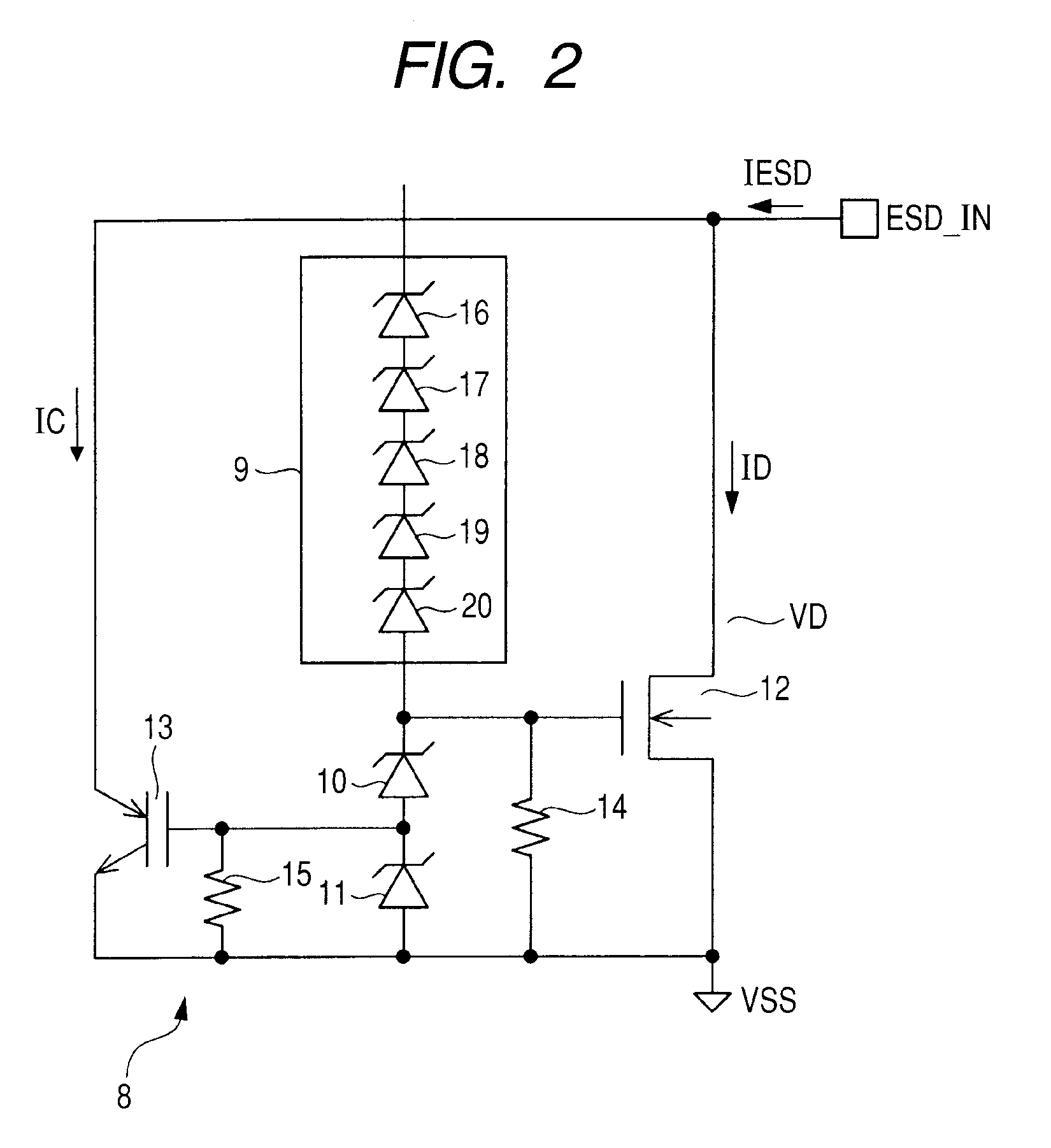
InactiveUS20100302693A1Promote absorptionDegrade ESD protectionSolid-state devicesEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCurrent noiseZener diode
The present invention provides a technique capable of realizing an ESD protection performance having a high ESD withstand voltage in a small layout area. An ESD protection circuit includes a clamping circuit, Zener diodes, a transistor comprised of a DMOS, a transistor comprised of an IGBT, and resistors. The ESD protection circuit effectively protects the protected circuit such that the transistor comprised of the DMOS is caused to absorb the current noise at the time of operating the protected circuit to prevent malfunction due to latchup and the IGBT (the transistor comprised of IGBT) whose current absorption capacity is increased by the thyristor effect is operated in parallel for a large current at the time of ESD.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
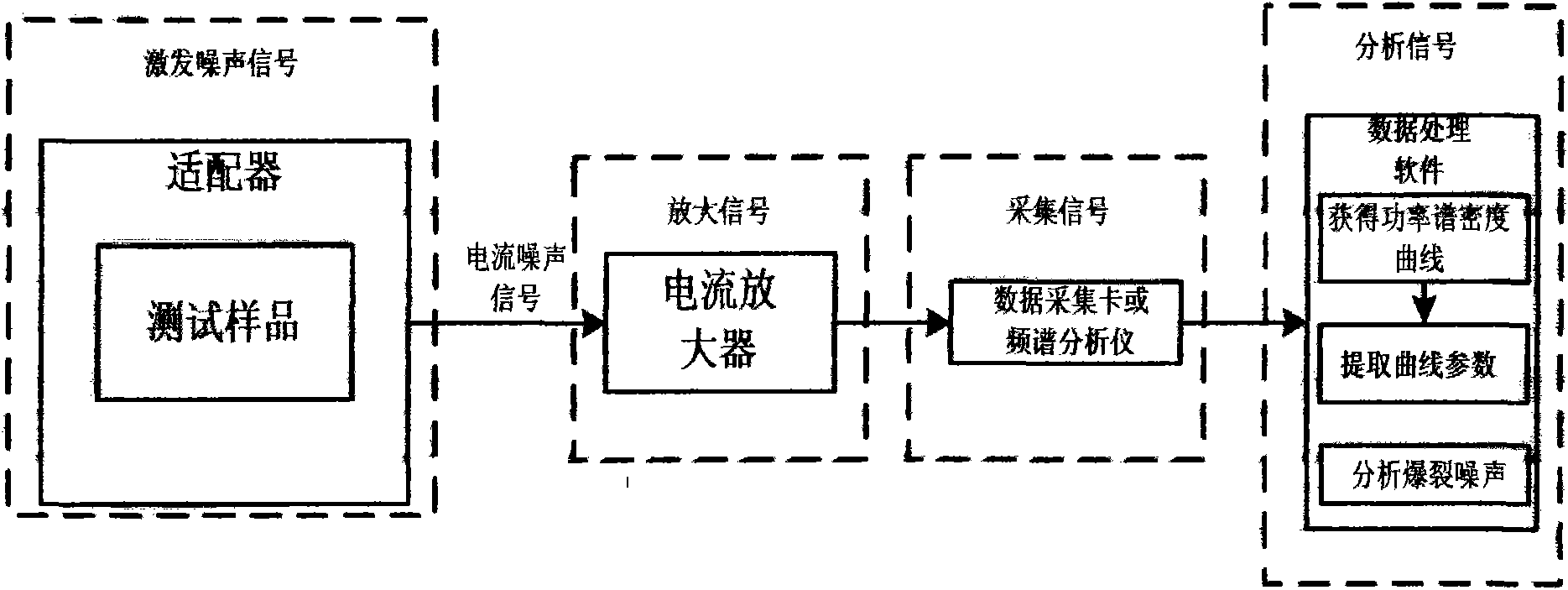
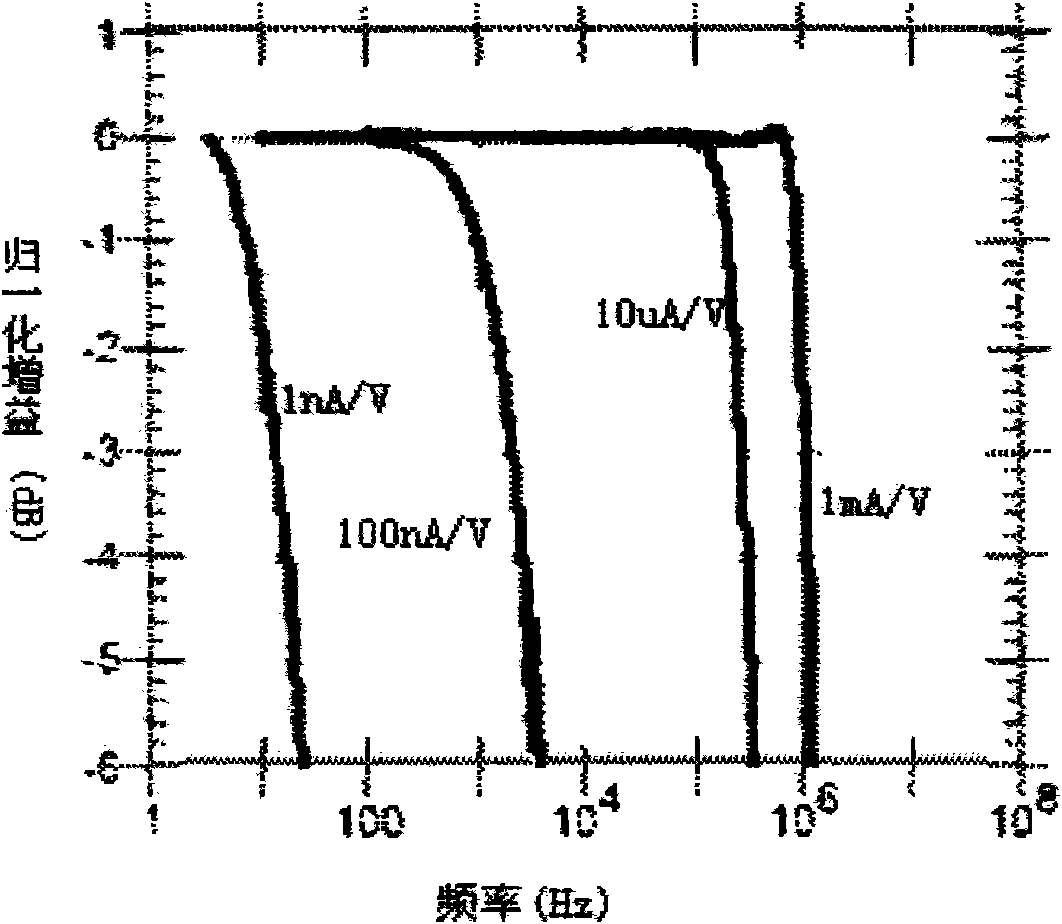
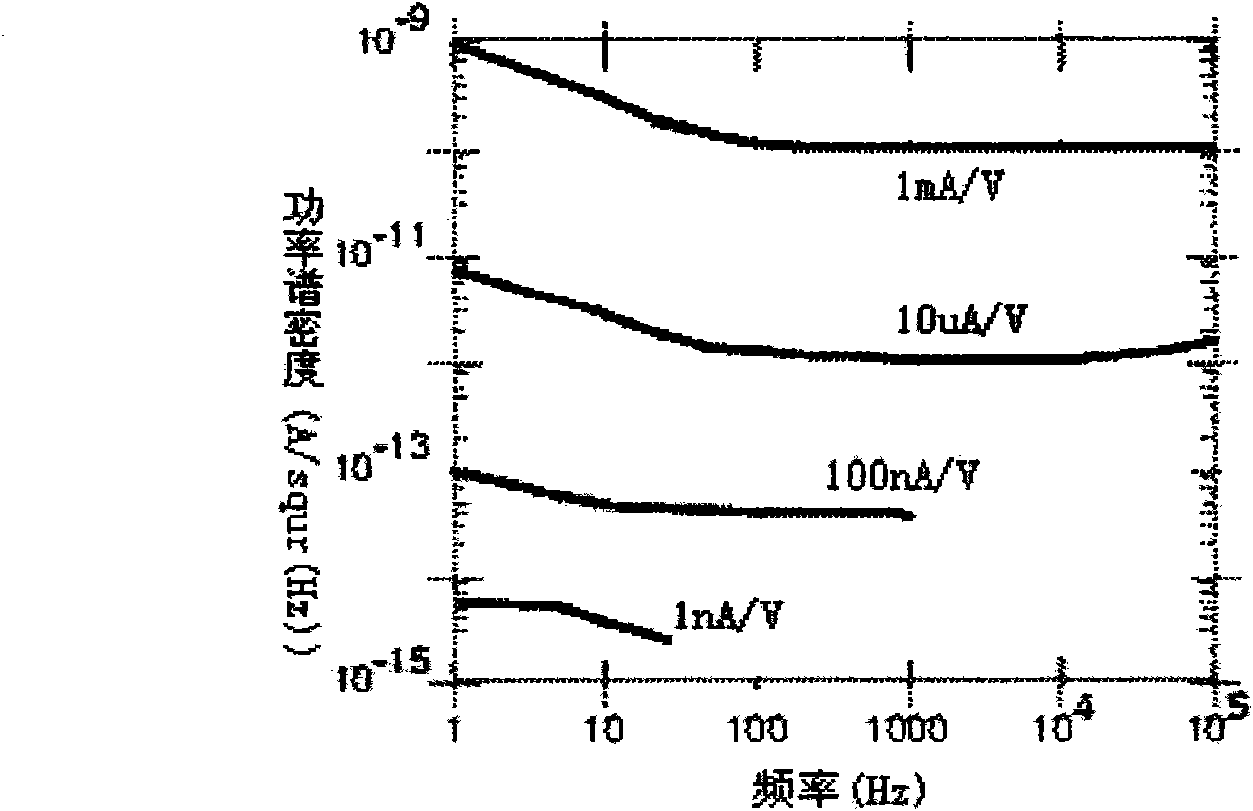
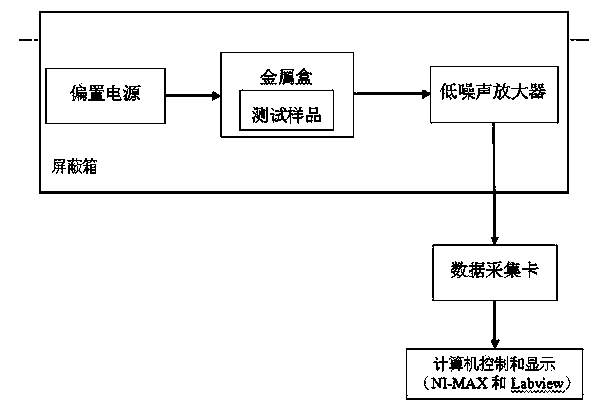
Test method for current noise of high-resistance device and medium material
InactiveCN102095917AWide signal bandwidthSimple structureSpectral/fourier analysisCurrent/voltage measurementHigh resistanceLow noise
The invention discloses a test method for current noise of a high-resistance device and a medium material, comprising the following test steps: firstly, arousing the low-frequency current noise of a high-resistance sample by utilizing a sample adapter; then amplifying the sample low-frequency noise by utilizing a low-noise current amplifier; collecting amplified noise signals by utilizing a data acquisition card; calculating the power spectrum density S0(f) of the collected current noise signals of which the high-frequency parts are attenuated by the amplifier; obtaining the amplitude-frequency characteristic curve of the current amplifier by utilizing a locking amplifier, and calculating a normalized curve Q(f) according to the amplitude-frequency characteristic curve; reducing the attenuated power spectrum density S0(f) by utilizing the Q(f), thus obtaining a power spectrum density curve S(f) of a reduced band spread; and finally, carrying out data analysis on the S(f) to screen devices or research sample reliability. By utilizing the test method, the problems of narrow times-number transmission band and insufficient test data in the existing test method for high-resistance sample noise are solved; and the test method provided by the invention has the advantages of high efficiency, automated operation and high precision of reduced data.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Automatic gain control system applied to an audio signal as a function of ambient noise
ActiveUS20090304191A1Good estimateCancel noiseEar treatmentGain controlEnvironmental noiseAutomatic control
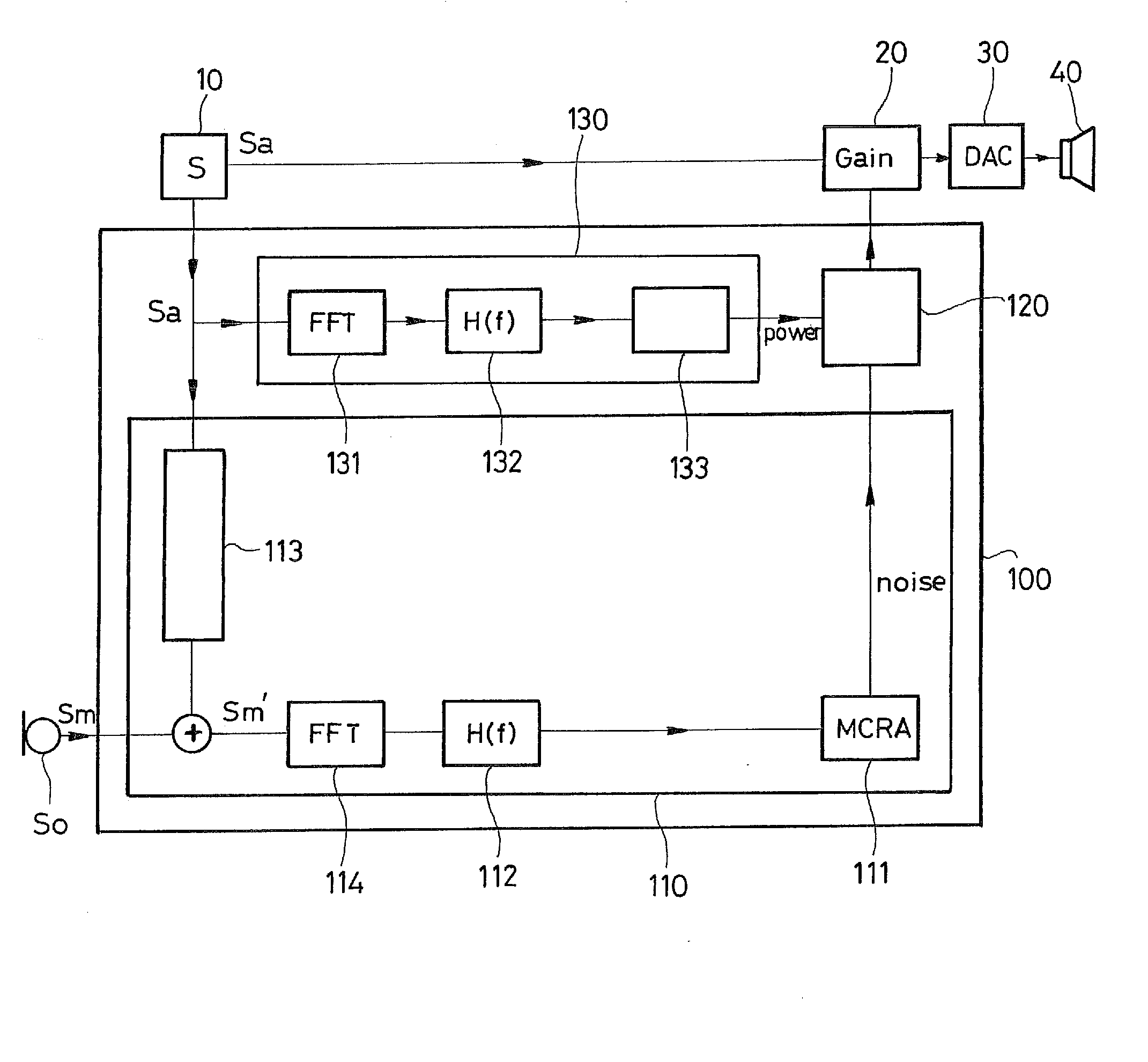
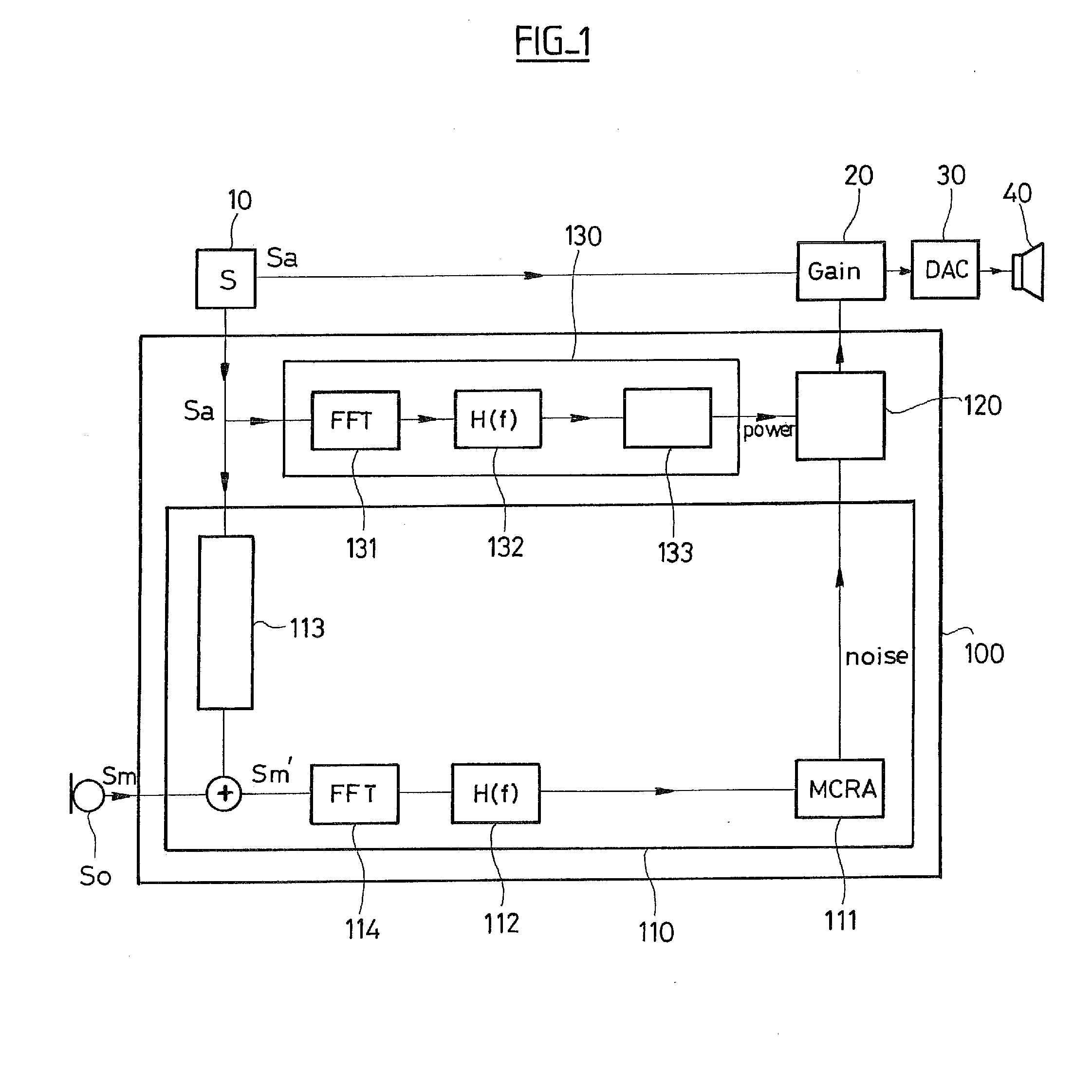
An automatic gain control system applied to a audio signal as a function of the ambient noise, the system comprising: an ambient noise estimator module suitable for establishing a current noise value estimated at least from a signal provided by a microphone; and an automatic gain control module suitable for applying to the audio signal gain of a value that is determined as a function of the current noise value received from the ambient noise estimator module. According to the invention, the ambient noise estimator module comprises an MCRA estimator suitable for establishing the current noise value from a signal provided by the microphone picking up the real noise, the echo of the music, and where appropriate speech. The system also includes a module for estimating the power of the audio signal and suitable for providing the automatic gain control module with a current power value for the audio signal.
Owner:PARROT AUTOMOTIVE
DC small current constant-current source and calibration method thereof
ActiveCN101295188AGood constant current characteristicsCancel noiseElectric variable regulationConstant current sourceSampling circuits
The invention provides a DC small current constant-current source and a method for adjusting the constant-current source and aims at solving the problem of the noise of the output current caused by the noise of an amplifier in a feedback circuit of the existing DC small current source. The DC small current constant-current source comprises a voltage source, a differential amplification circuit, a V / I conversion circuit, a current output terminal and a feedback circuit; the voltage source is connected in series with the differential amplification circuit and outputs voltage to the differential amplification circuit; the differential amplification circuit is connected in series with the V / I conversion circuit; the V / I conversion circuit generates the current and outputs the current by the current output terminal; the feedback circuit comprises a sampling circuit and a filter circuit which are connected in series; after sampling at the output current terminal of the V / I conversion circuit, the sampling circuit outputs the voltage signal which is fed back and filtrated by the filter circuit to the input terminal of the differential amplification circuit. Meanwhile, the output voltage of a feedback branch is taken as the following output voltage of the current output terminal. The invention can provide the DC small current with high precision.
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG MEASUREMENT & TEST INST
System and method for bearing fault detection using stator current noise cancellation
A system and method for detecting incipient mechanical motor faults by way of current noise cancellation is disclosed. The system includes a controller configured to detect indicia of incipient mechanical motor faults. The controller further includes a processor programmed to receive a baseline set of current data from an operating motor and define a noise component in the baseline set of current data. The processor is also programmed to repeatedly receive real-time operating current data from the operating motor and remove the noise component from the operating current data in real-time to isolate any fault components present in the operating current data. The processor is then programmed to generate a fault index for the operating current data based on any isolated fault components.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Method of motion compensated temporal noise reduction
InactiveUS7535517B2Reduce noiseNoise-reducedTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsCurrent noisePattern recognition
A method of reducing noise in a sequence of digital video frames is performed by motion estimation between a current noisy frame and a previous noise-reduced frame, to generate motion vectors indicating relative motion between the pixels in the current noisy frame and the corresponding pixels in the previous noise-reduced frame; and removing noise from the current noisy frame by computing the weighted average of pixels in the current noise frame and the corresponding pixels in the previous noise-reduced frame based on the motion vectors, to generate a noise-reduced output frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
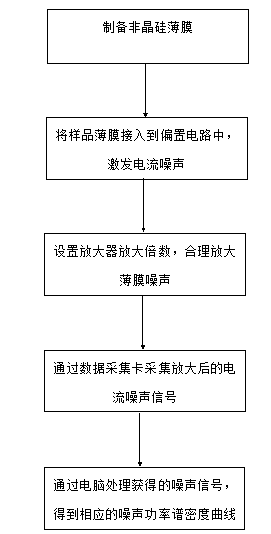
Method for testing low-frequency noise of amorphous silicon membrane
InactiveCN104020365AReduce the impact of noiseGuaranteed temperature stabilityNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCurrent noiseAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a method for testing low-frequency noise of an amorphous silicon membrane, and specifically relates to a testing technology of low-frequency current noise of the amorphous silicon membrane. A testing system adopted by the testing technology comprises a biasing circuit, an electromagnetic shielding device, a noise amplifying system and a data acquisition and processing system. Firstly, the low-frequency current noise of the amorphous silicon membrane is motivated through the biasing circuit, sample low-frequency noise is amplified through a low-frequency noise current amplifier, amplified noise signals are acquired through a data acquisition card, corresponding current noise signal power spectral density is calculated, finally data are analyzed and processed through a computer, and a power spectral density curve of the low-frequency noise of the amorphous silicon membrane is obtained. The method for testing the low-frequency noise of the amorphous silicon membrane can be used for testing the low-frequency noise of the amorphous silicon membrane repeatedly and accurately, and is fast and convenient.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
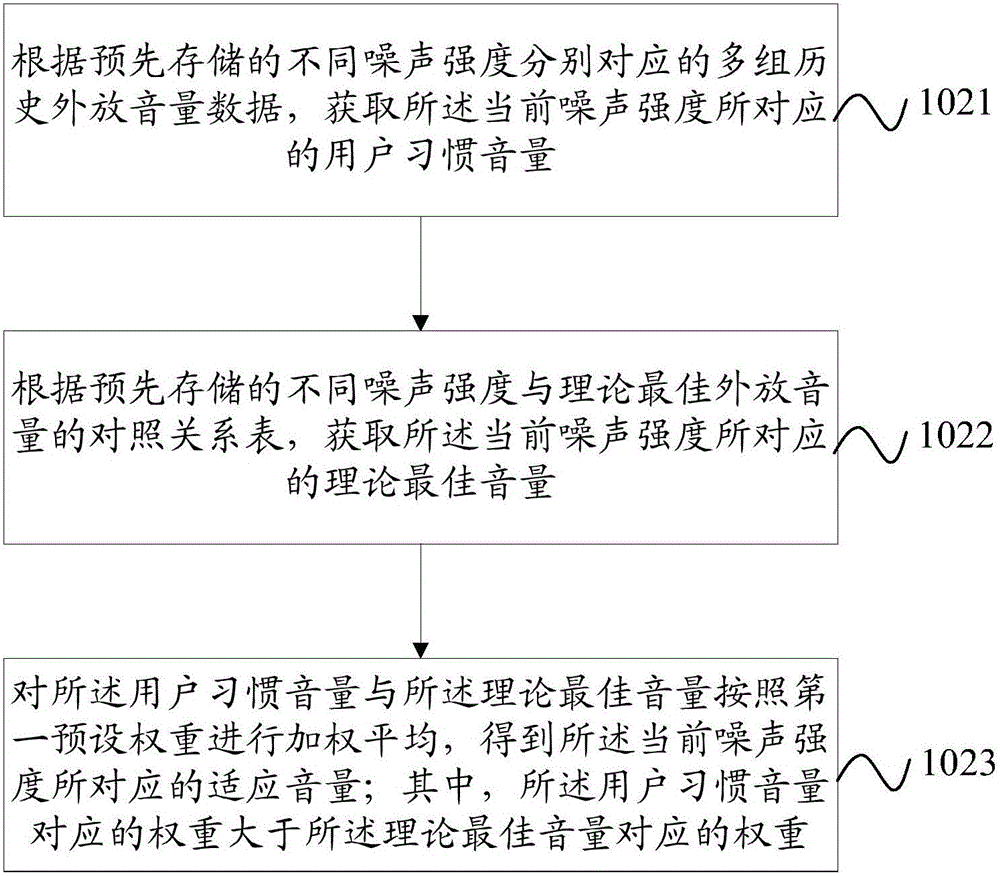
Method for controlling terminal loudspeaker volume output and mobile terminal
ActiveCN105827853AImprove experienceSolve the problem of poor experienceSubstation equipmentSound input/outputCurrent noiseComputer terminal
The invention provides a method for controlling volume output of a terminal loudspeaker and a mobile terminal, and relates to the field of electronic technology. The method aims at addressing the problem of poor user experience due to the fact that a user often has to manually adjust the volume of a loudspeaker when the volume is not appropriate each time the terminal turns on the loudspeaker. The method is applied to terminals. The method comprises the following steps: when the terminal turns on the loudspeaker and operates volume output, detecting the current noise intensity of ambient environment whereby the terminal is; based on the prestored appropriate volume data corresponding to different noise intensity, acquiring an appropriate volume corresponding to the current noise intensity; the appropriate volume data including a contrasting relationship table between a plurality of groups of historic loudspeaker volume data and / or different noise intensity corresponding to different noise intensity and a theoretical best loudspeaker volume; based on the appropriate volume, determining the volume of the terminal loudspeaker and outputting the volume. According to the invention, the method realizes that once the terminal is turned on, the loudspeaker voice can achieve the ideal sound effect which is adapt to noisy level of the ambient environment, which increases user experience and increases practicality and convenience.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
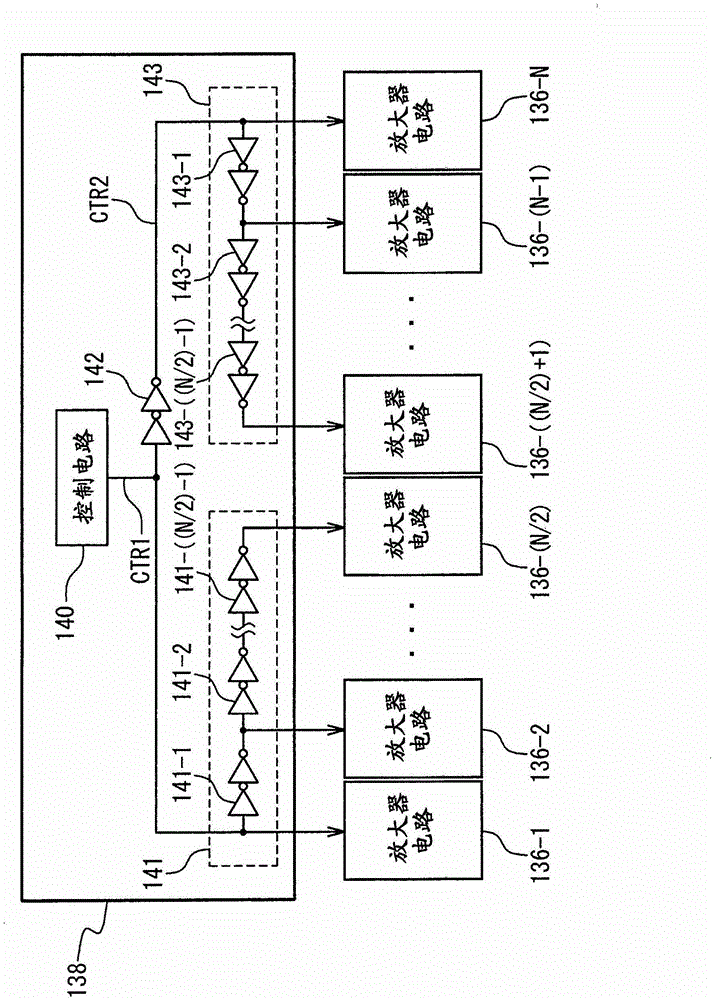
Data driver, display panel driving device, and display device
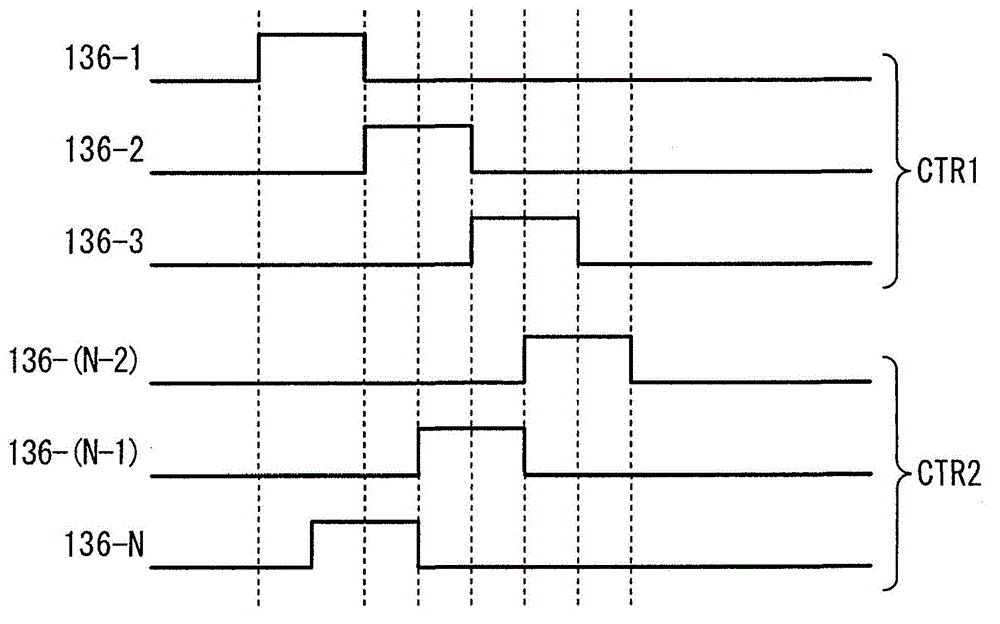
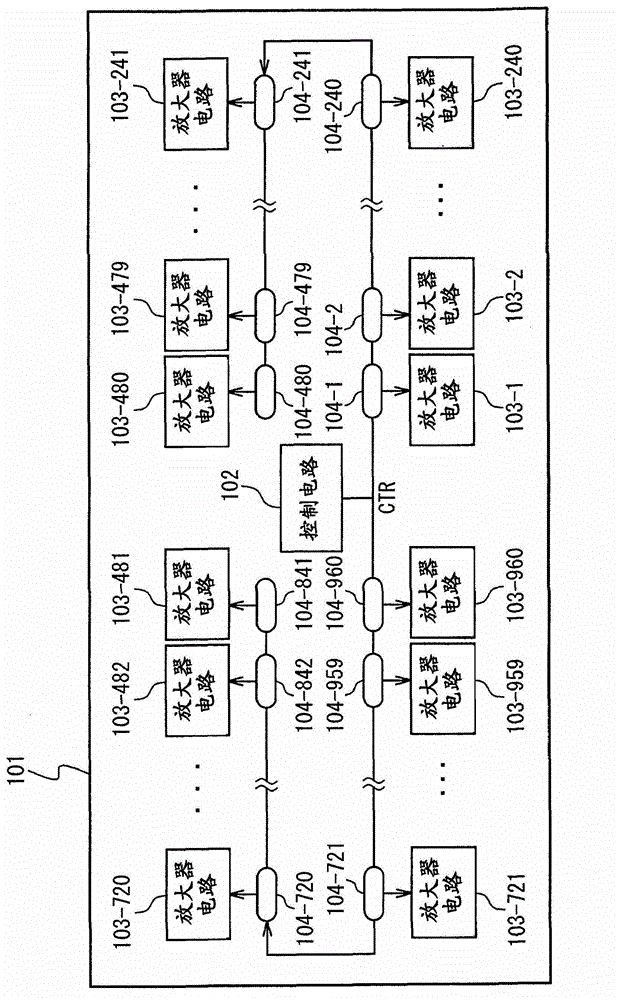
InactiveCN103151003AReduce current noiseImprove EMI characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCurrent noisePower flow
The present disclosure provides a data driver, a display panel driving device, and a display device. To reduce current noise by reducing the current peak value and the current rise slope, a data driver includes a delay unit and a plurality of output circuits. The delay unit sequentially delays a control signal and outputs delay control signals. The output circuits start outputting in response to the delay control signals. The delay unit generates the delay control signals to be output to the output circuits.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com