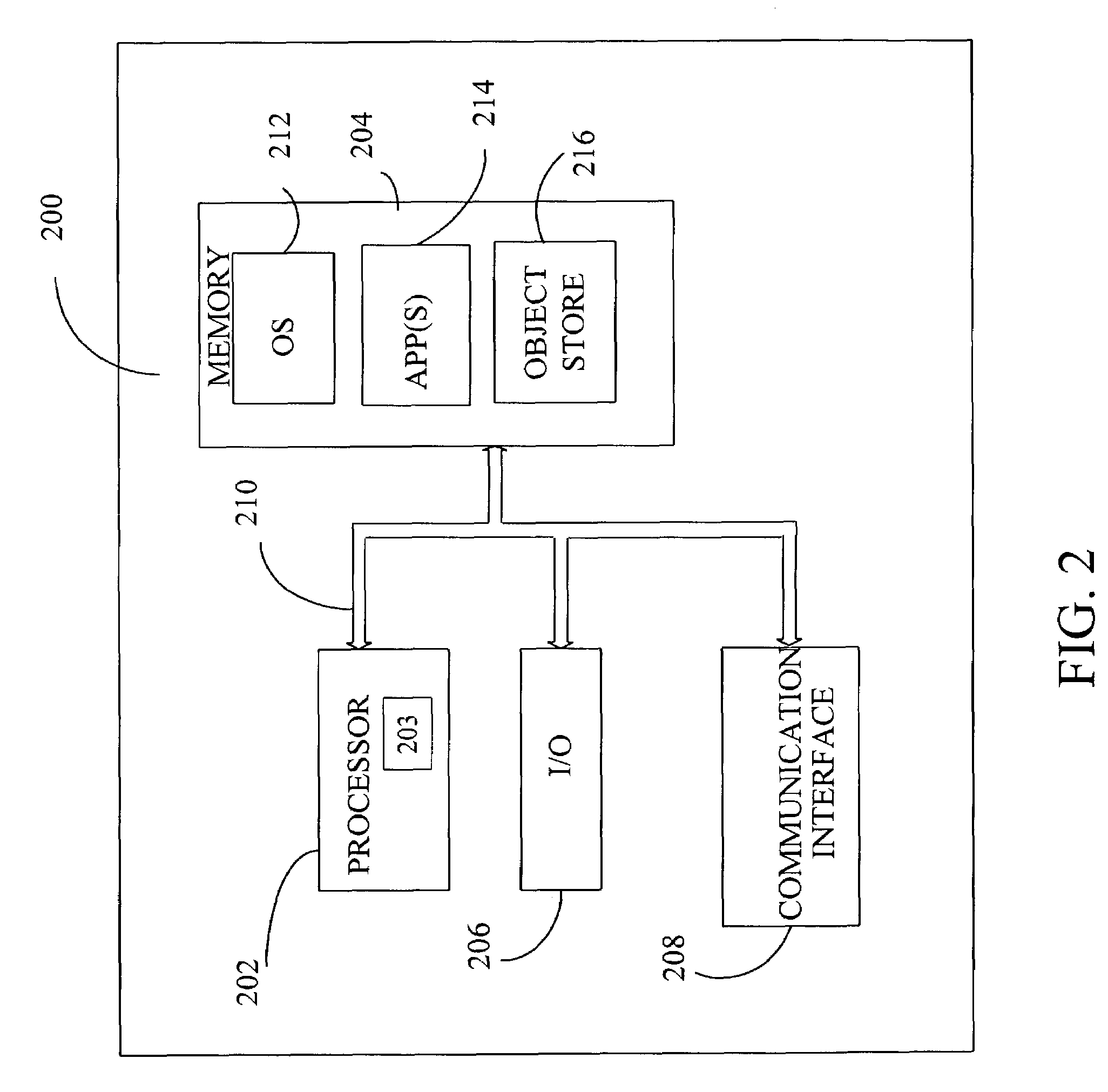
Patents
Literature
1465 results about "Hide markov model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
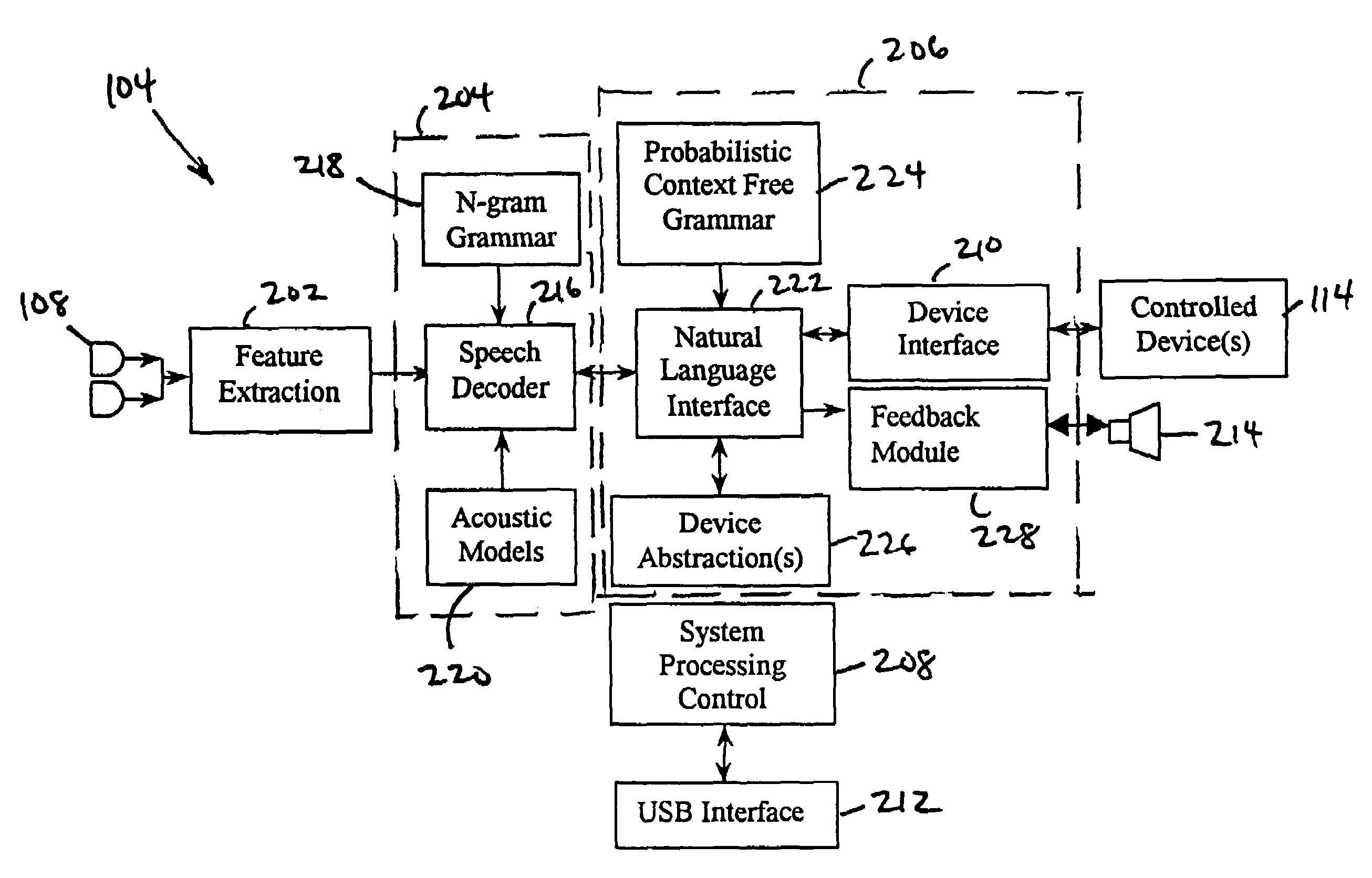
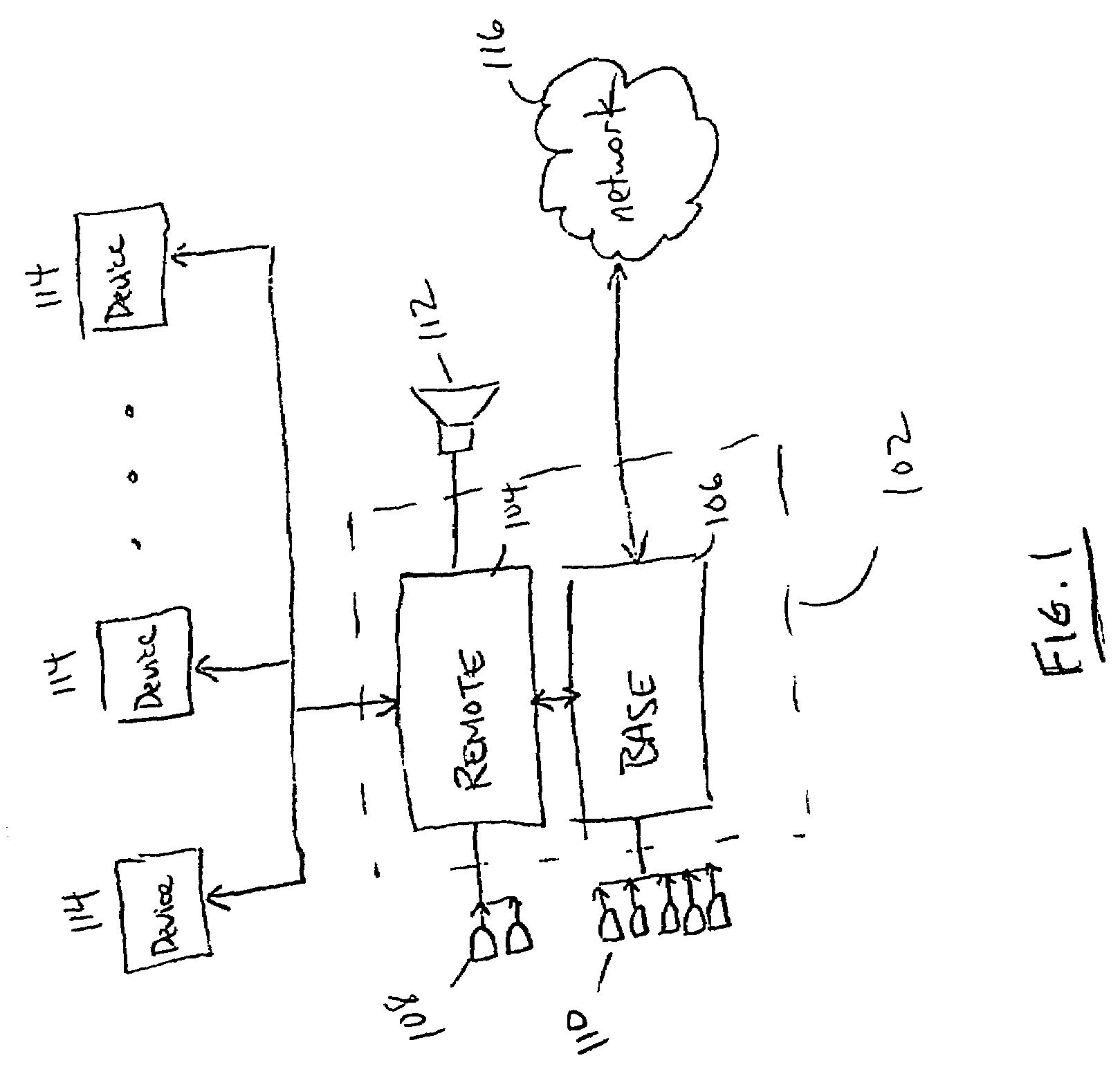
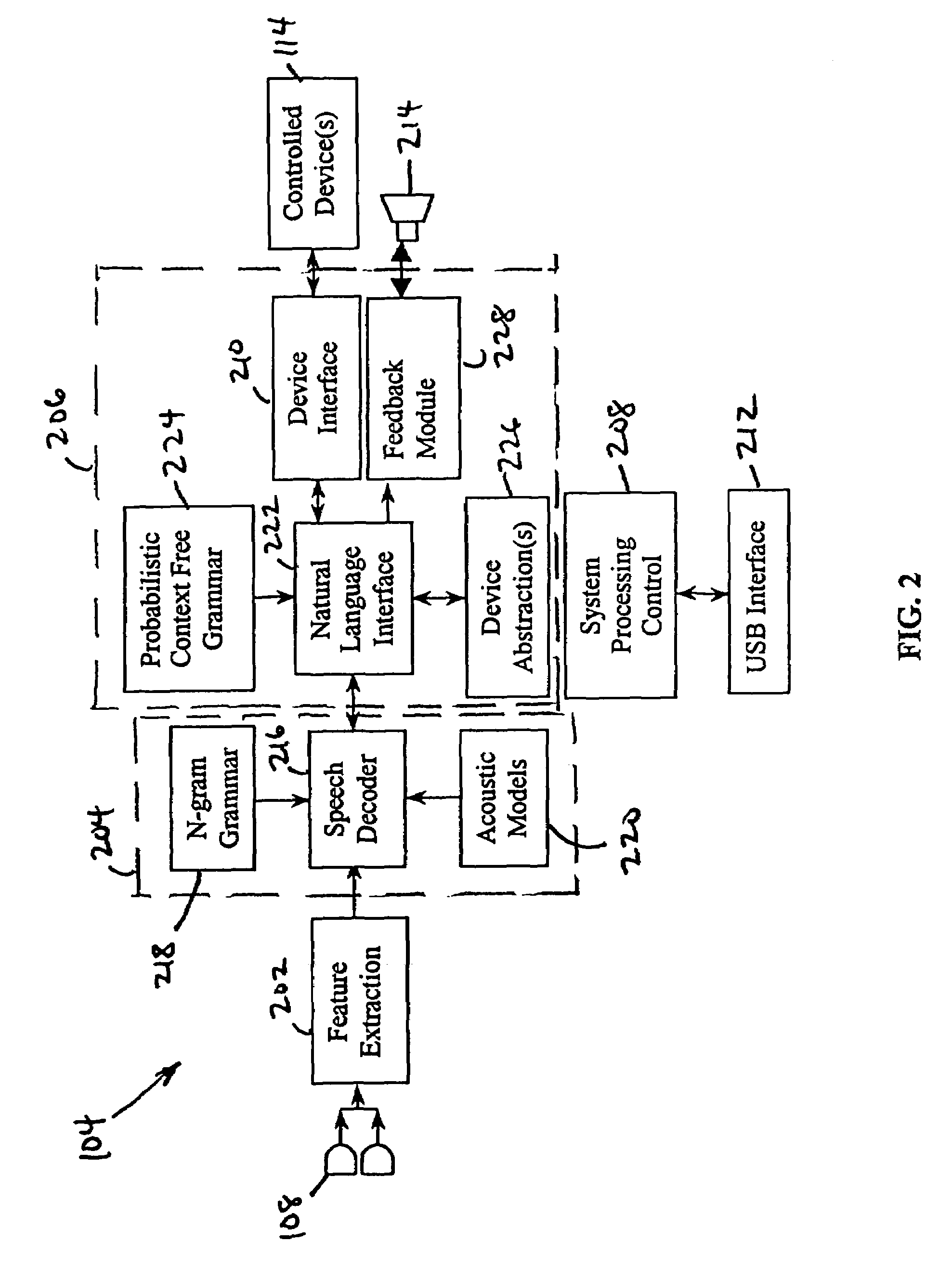
Natural language interface control system
InactiveUS7447635B1Speech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsFeature extractionHide markov model
A natural language interface control system for operating a plurality of devices consists of a first microphone array, a feature extraction module coupled to the first microphone array, and a speech recognition module coupled to the feature extraction module, wherein the speech recognition module utilizes hidden Markov models. The system also comprises a natural language interface module coupled to the speech recognition module and a device interface coupled to the natural language interface module, wherein the natural language interface module is for operating a plurality of devices coupled to the device interface based upon non-prompted, open-ended natural language requests from a user.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
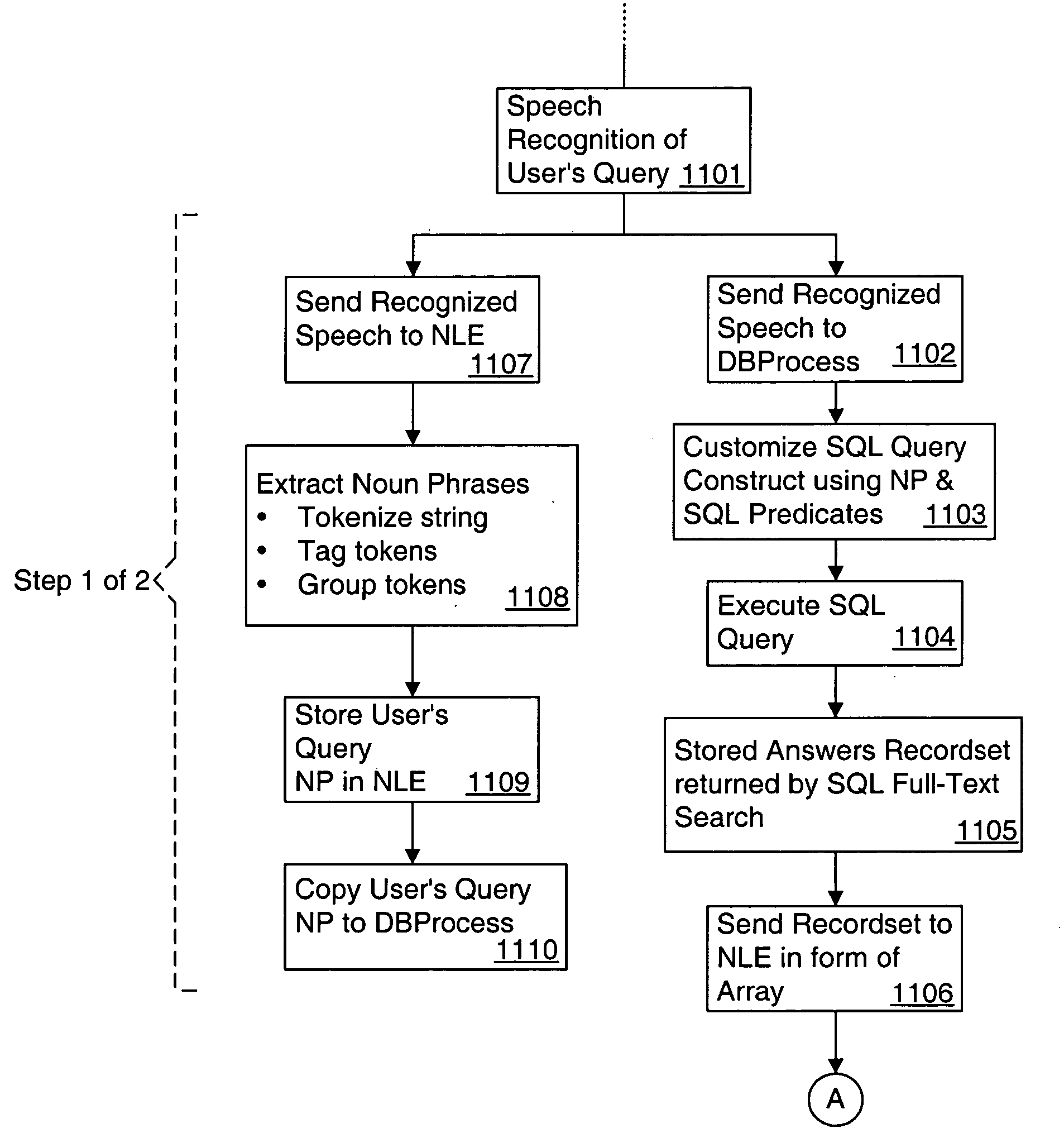
Distributed real time speech recognition system
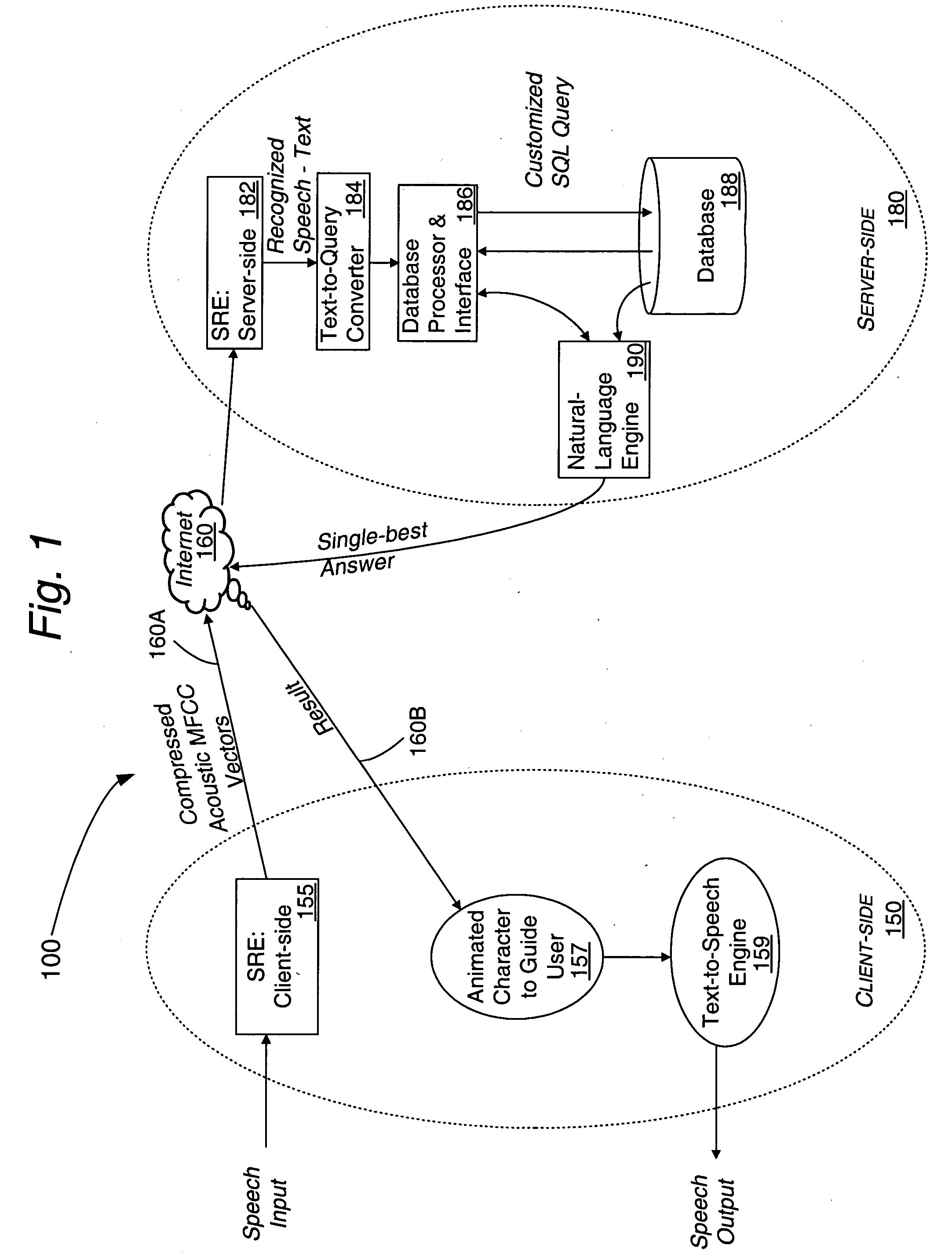
InactiveUS20050080625A1Facilitates query recognitionAccurate best responseNatural language translationData processing applicationsFull text searchTime system
A real-time system incorporating speech recognition and linguistic processing for recognizing a spoken query by a user and distributed between client and server, is disclosed. The system accepts user's queries in the form of speech at the client where minimal processing extracts a sufficient number of acoustic speech vectors representing the utterance. These vectors are sent via a communications channel to the server where additional acoustic vectors are derived. Using Hidden Markov Models (HMMs), and appropriate grammars and dictionaries conditioned by the selections made by the user, the speech representing the user's query is fully decoded into text (or some other suitable form) at the server. This text corresponding to the user's query is then simultaneously sent to a natural language engine and a database processor where optimized SQL statements are constructed for a full-text search from a database for a recordset of several stored questions that best matches the user's query. Further processing in the natural language engine narrows the search to a single stored question. The answer corresponding to this single stored question is next retrieved from the file path and sent to the client in compressed form. At the client, the answer to the user's query is articulated to the user using a text-to-speech engine in his or her native natural language. The system requires no training and can operate in several natural languages.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Block synchronous decoding
InactiveUS7529671B2Improved pattern recognition speedImprove cache localityKitchenware cleanersGlovesHide markov modelCache locality
A pattern recognition system and method are provided. Aspects of the invention are particularly useful in combination with multi-state Hidden Markov Models. Pattern recognition is effected by processing Hidden Markov Model Blocks. This block-processing allows the processor to perform more operations upon data while such data is in cache memory. By so increasing cache locality, aspects of the invention provide significantly improved pattern recognition speed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
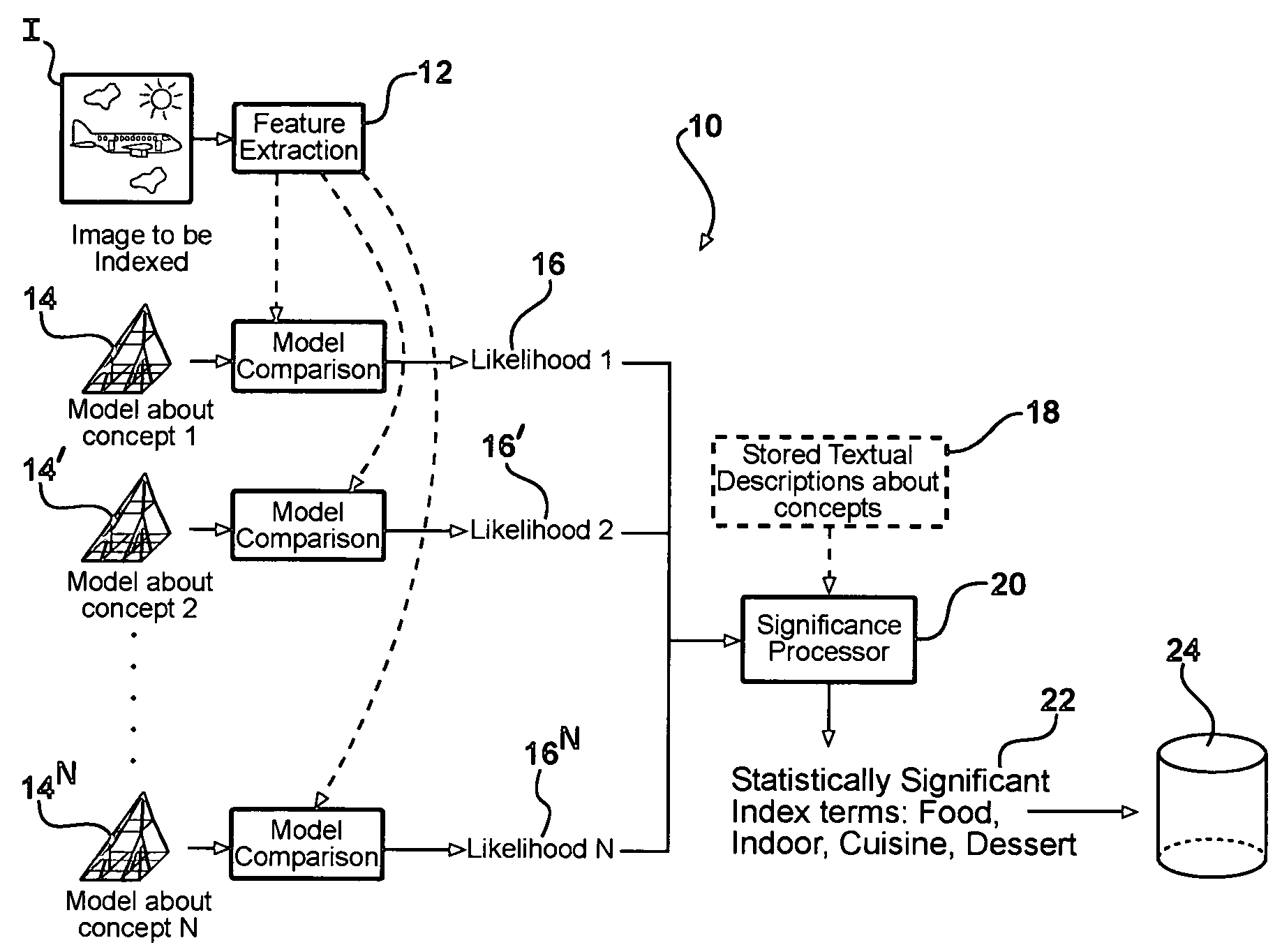
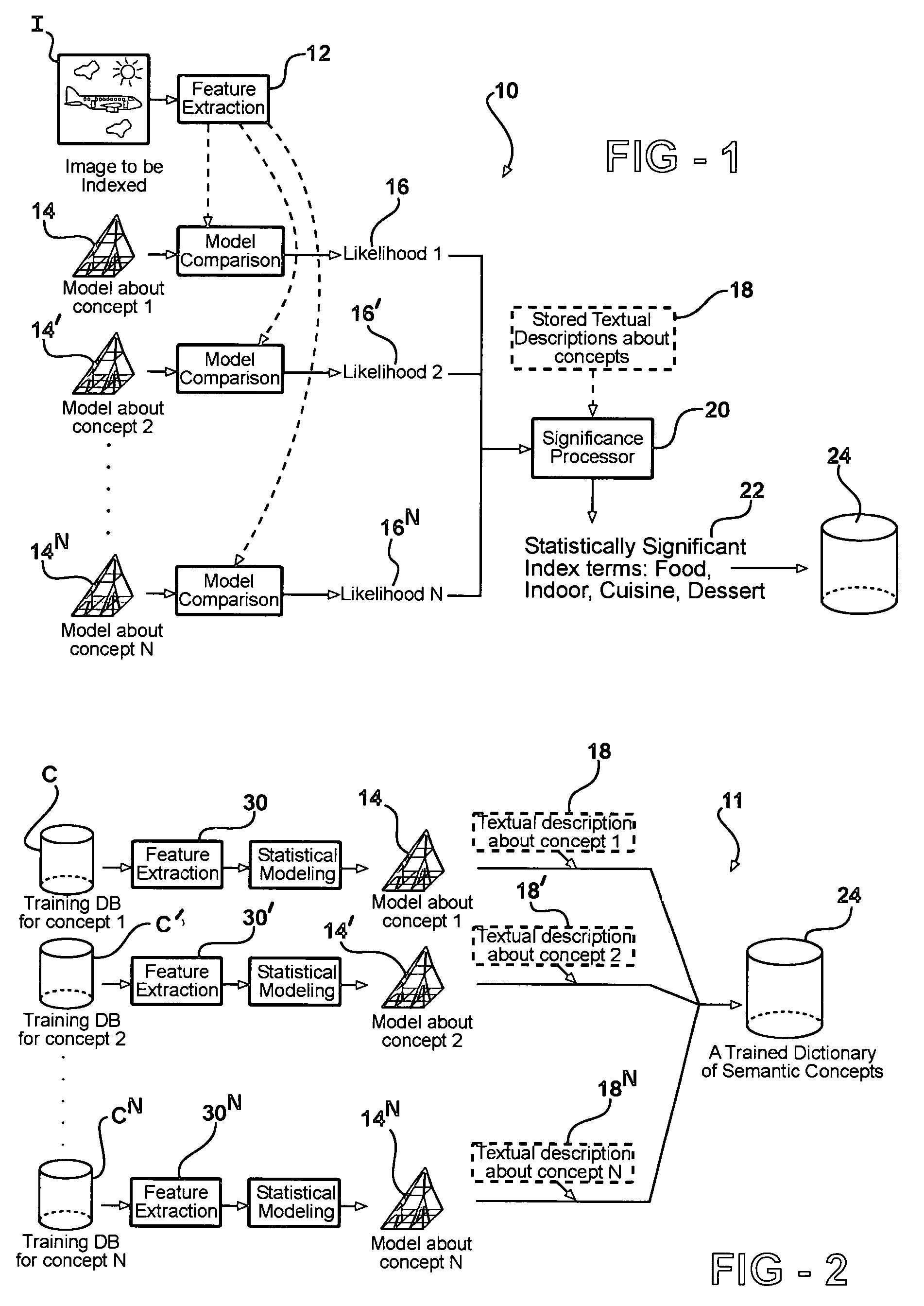
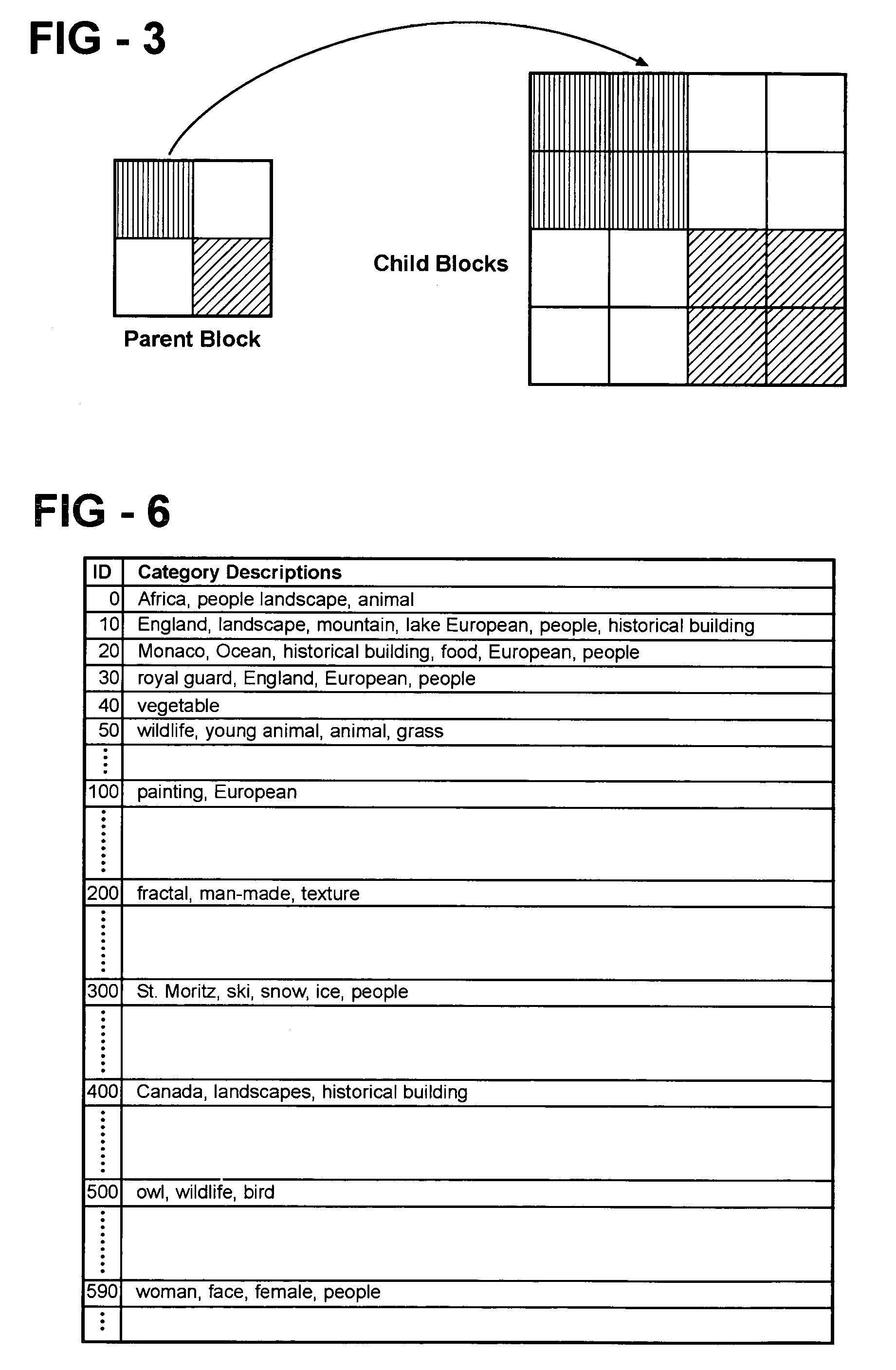
System and method for automatic linguistic indexing of images by a statistical modeling approach
ActiveUS7394947B2Increase the number ofData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionHide markov modelMulti resolution
The present invention provides a statistical modeling approach to automatic linguistic indexing of photographic images. The invention uses categorized images to train a dictionary of hundreds of statistical models each representing a concept. Images of any given concept are regarded as instances of a stochastic process that characterizes the concept. To measure the extent of association between an image and a textual description associated with a predefined concept, the likelihood of the occurrence of the image based on the characterizing stochastic process is computed. A high likelihood indicates a strong association between the textual description and the image. The invention utilizes two-dimensional multi-resolution hidden Markov models that demonstrate accuracy and high potential in linguistic indexing of photographic images.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Systems and methods for spell correction of non-roman characters and words
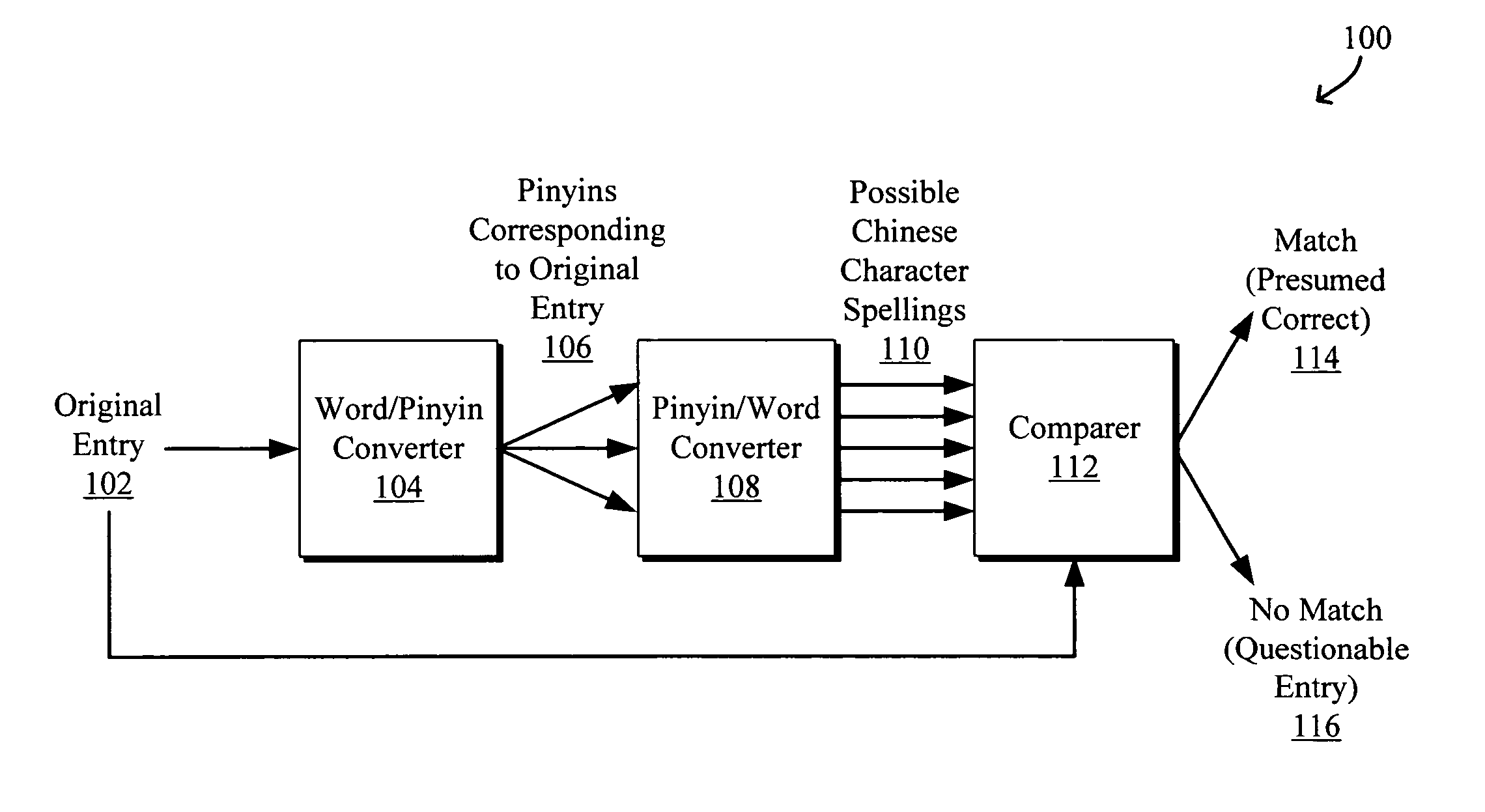
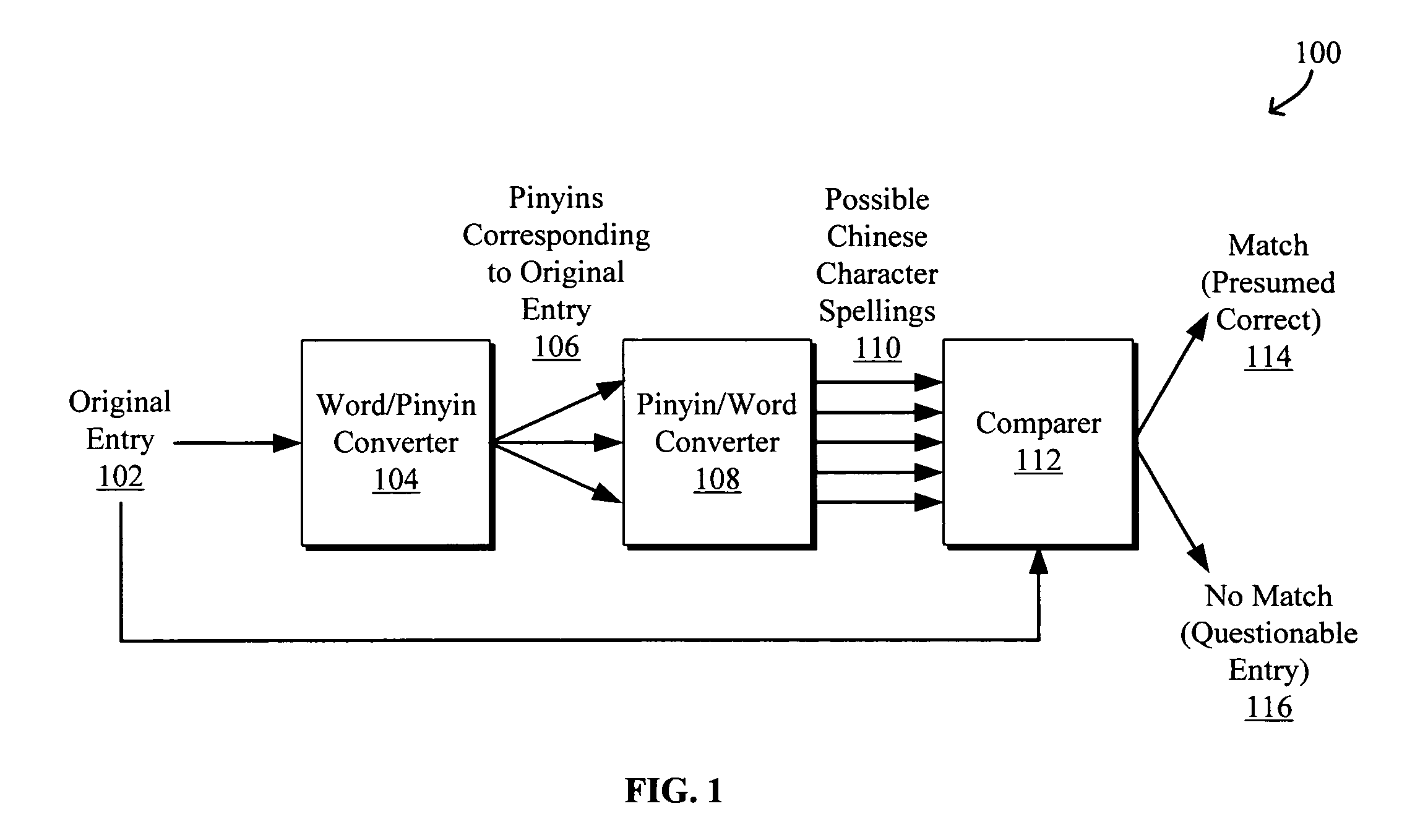
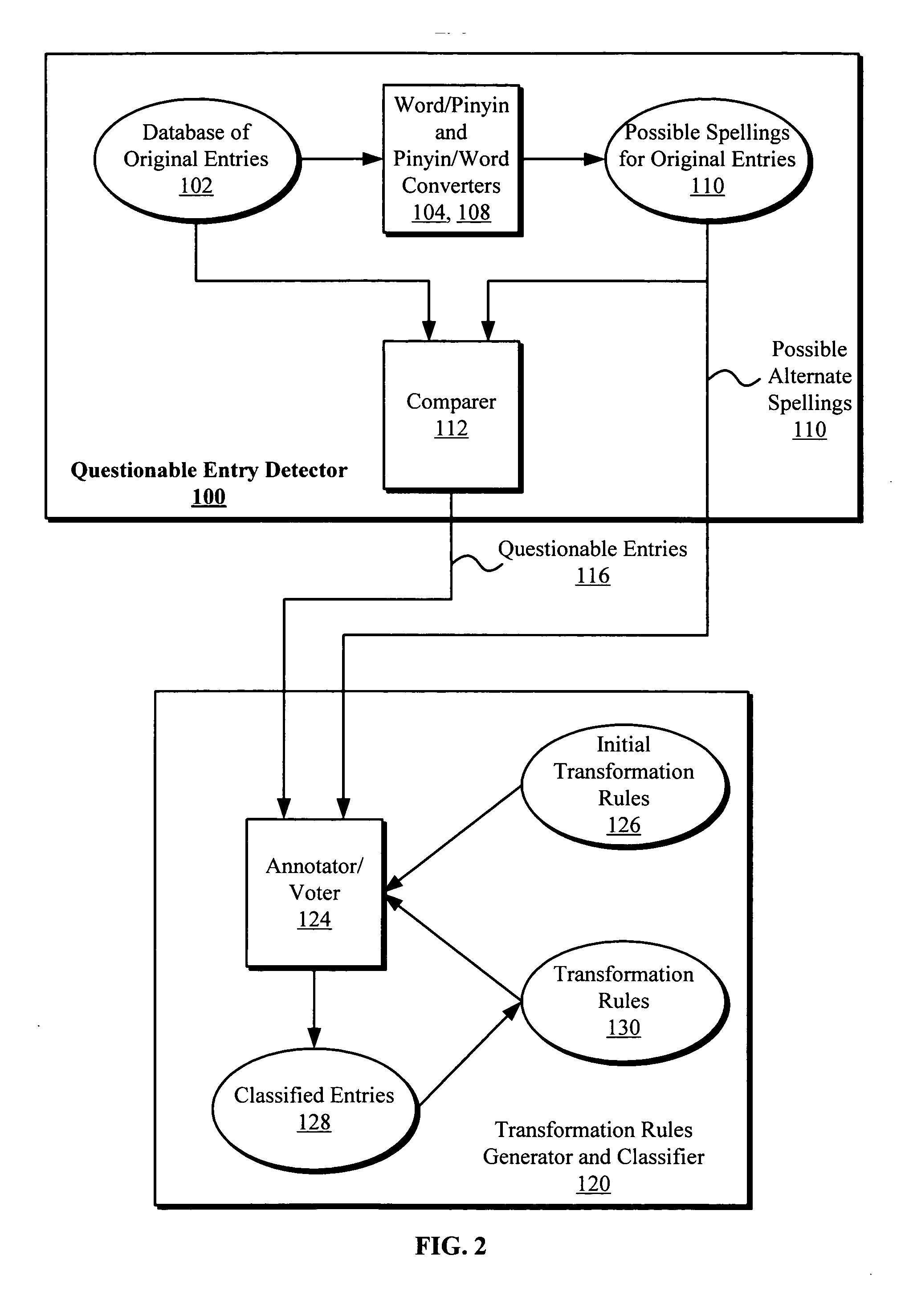
InactiveUS20050289463A1Digital computer detailsNatural language data processingNatural language processingHide markov model
Systems and methods to process and correct spelling errors for non-Roman based words such as in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean languages using a rule-based classifier and a hidden Markov model are disclosed. The method generally includes converting an input entry in a first language such as Chinese to at least one intermediate entry in an intermediate representation, such as pinyin, different from the first language, converting the intermediate entry to at least one possible alternative spelling or form of the input in the first language, and determining that the input entry is either a correct or questionable input entry when a match between the input entry and all possible alternative spellings to the input entry is or is not located, respectively. The questionable input entry may be classified using, for example, a transformation rule based classifier based on transformation rules generated by a transformation rules generator.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
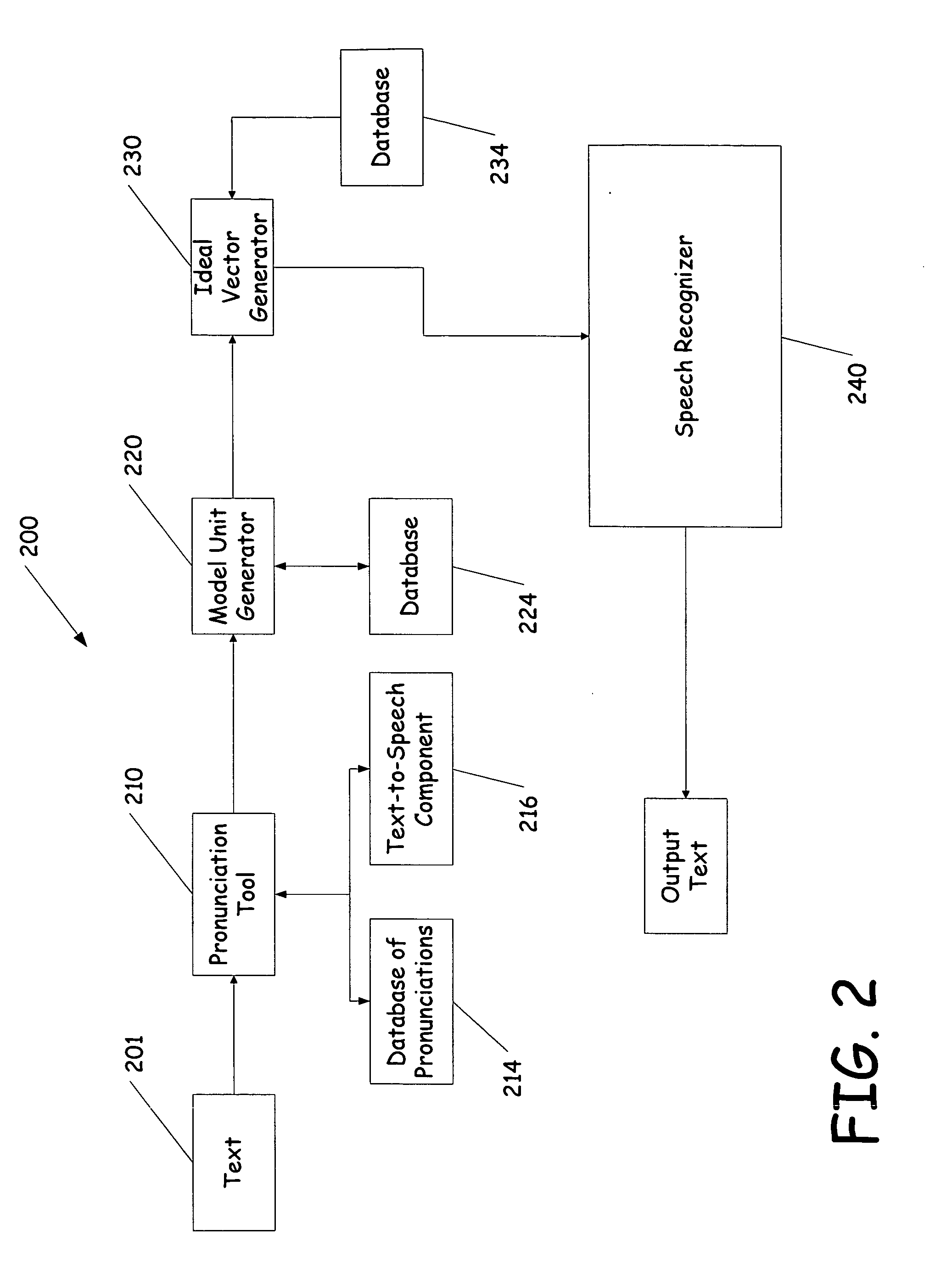
Testing and tuning of automatic speech recognition systems using synthetic inputs generated from its acoustic models
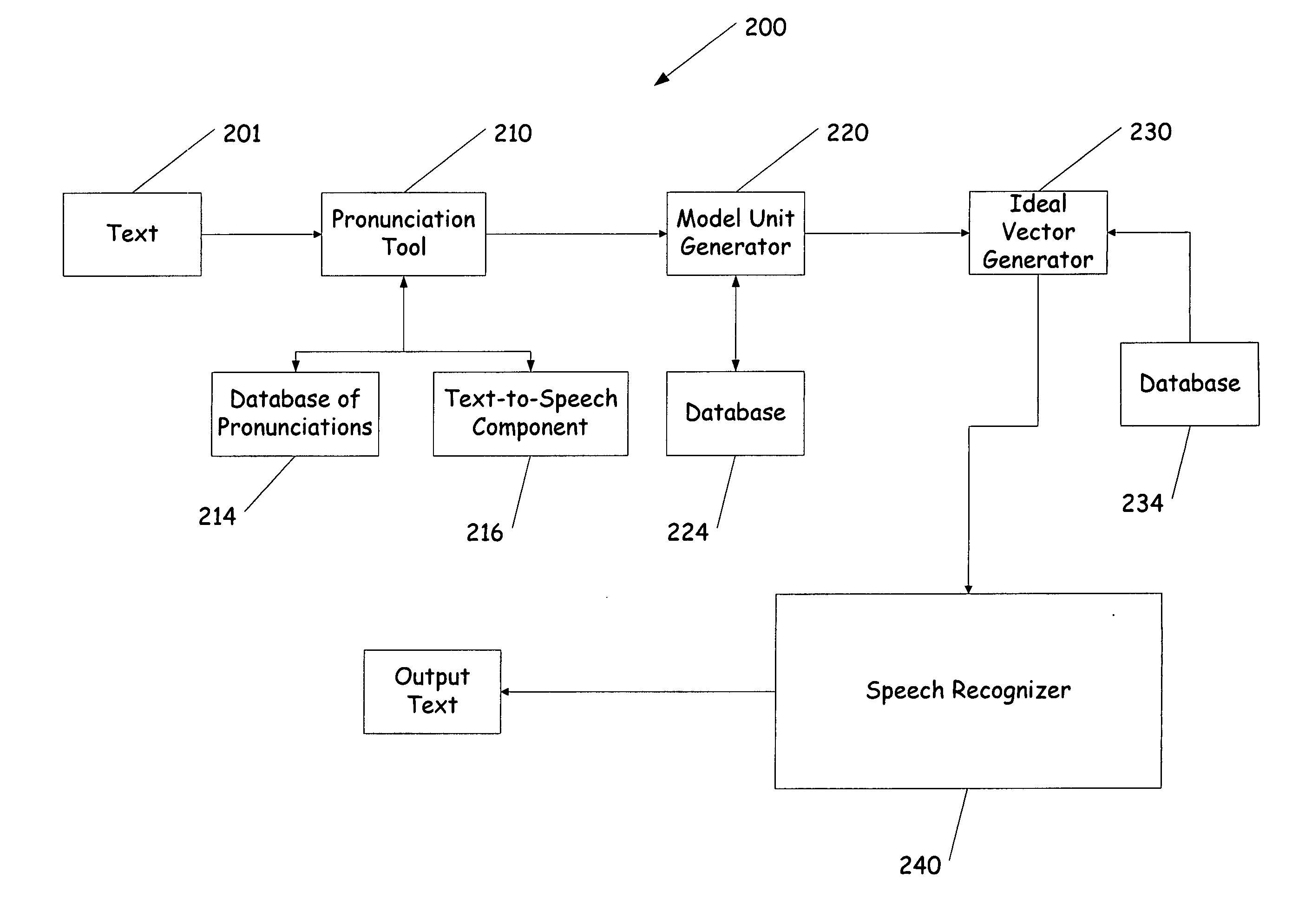
InactiveUS20060085187A1Errors in predictingAvoids acoustic mismatchesSpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisFeature vectorModel selection
A system and method of testing and tuning a speech recognition system by providing pronunciations to the speech recognizer. First a text document is provided to the system and converted into a sequence of phonemes representative of the words in the text. The phonemes are then converted to model units, such as Hidden Markov Models. From the models a probability is obtained for each model or state, and feature vectors are determined. The feature vector matching the most probable vector for each state is selected for each model. These ideal feature vectors are provided to the speech recognizer, and processed. The end result is compared with the original text, and modifications to the system can be made based on the output text.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
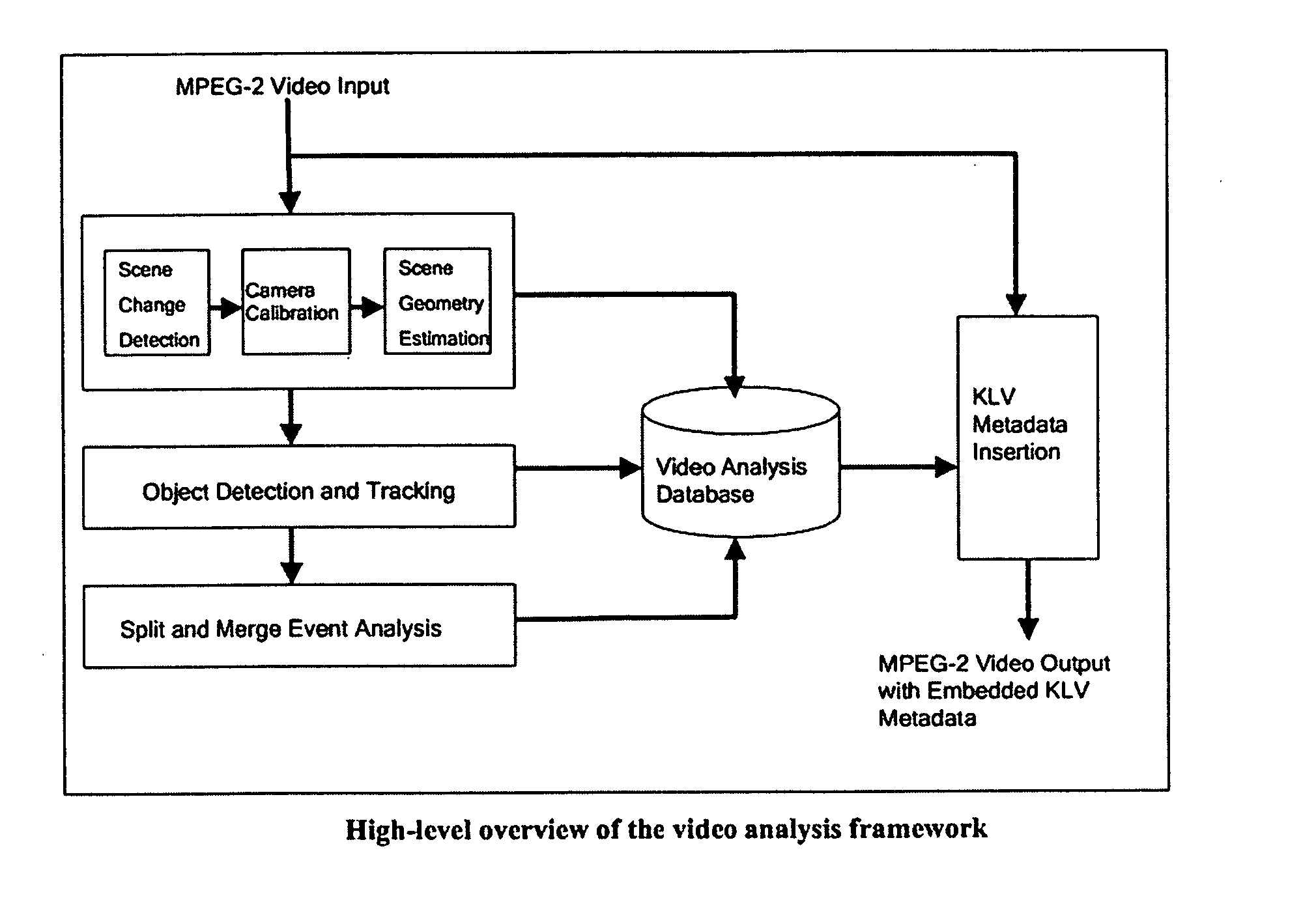
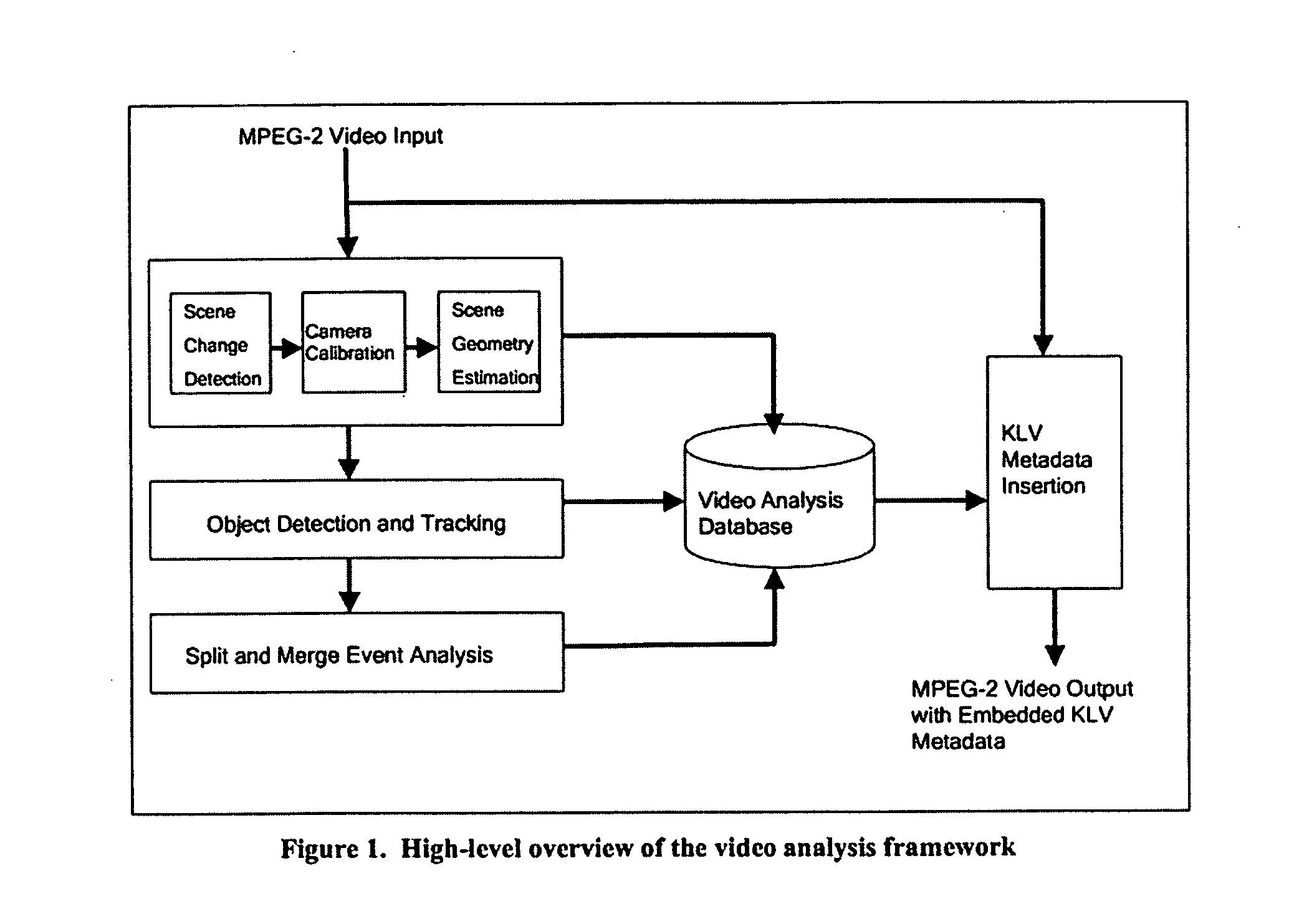
Split and merge behavior analysis and understanding using Hidden Markov Models
InactiveUS20040113933A1Shorten the timeImprove accuracy and productivityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionProcess supportHide markov model
A process for video content analysis to enable productive surveillance, intelligence extraction, and timely investigations using large volumes of video data. The process for video analysis includes: automatic detection of key split and merge events from video streams typical of those found in area security and surveillance environments; and the efficient coding and insertion of necessary analysis metadata into the video streams. The process supports the analysis of both live and archived video from multiple streams for detecting and tracking the objects in a way to extract key split and merge behaviors to detect events. Information about the camera, scene, objects and events whether measured or inferred, are embedded in the video stream as metadata so the information will stay intact when the original video is edited, cut, and repurposed.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
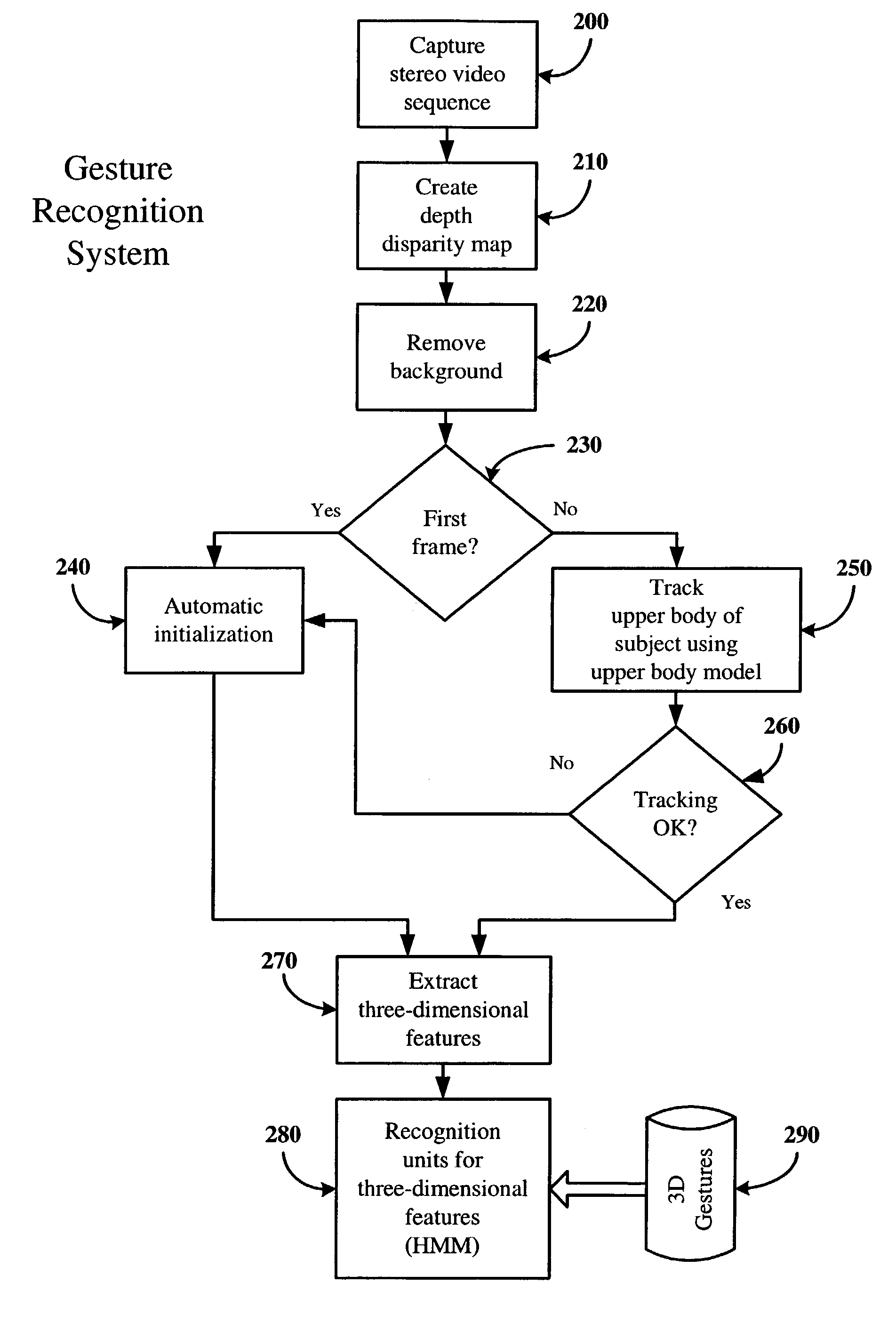
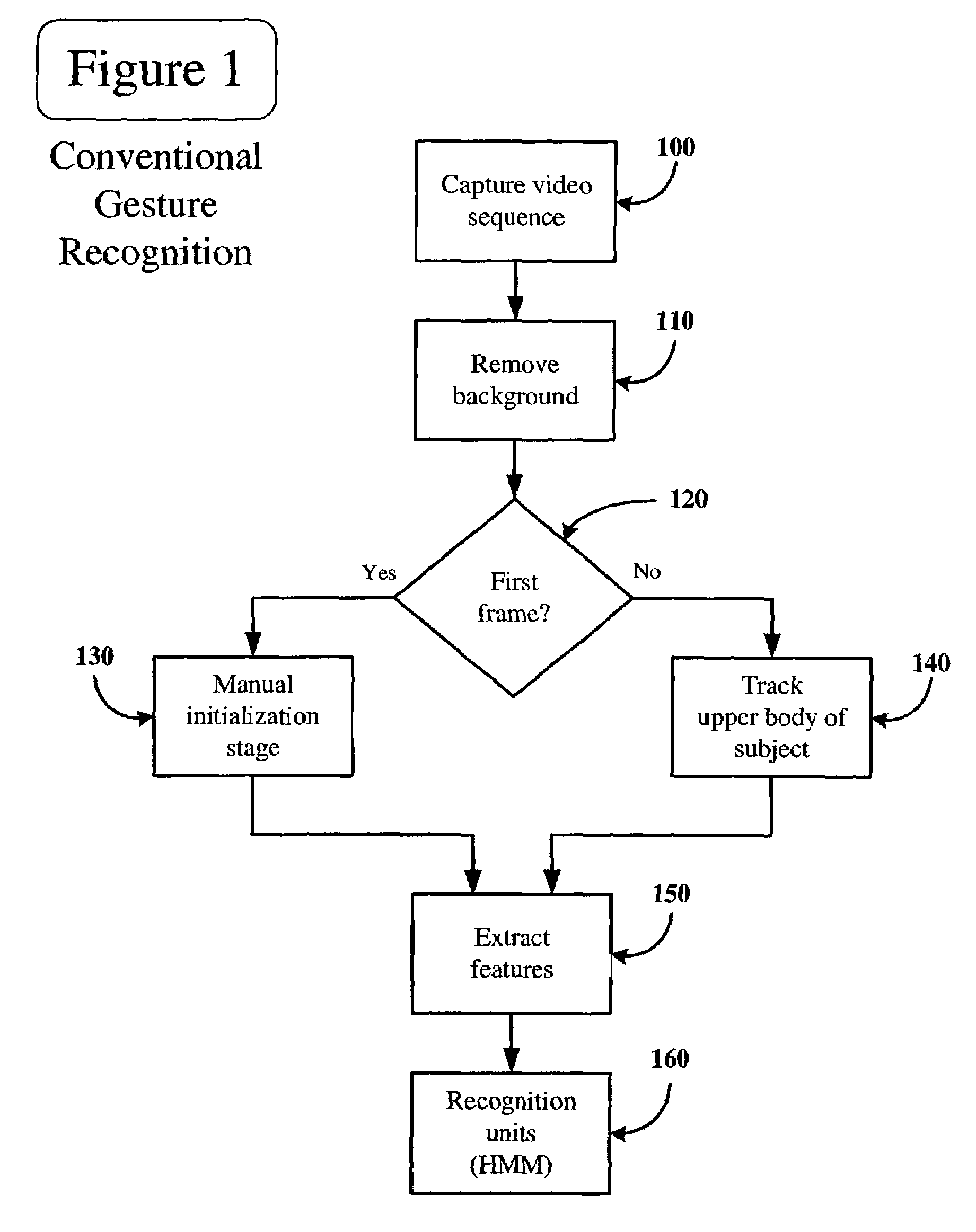
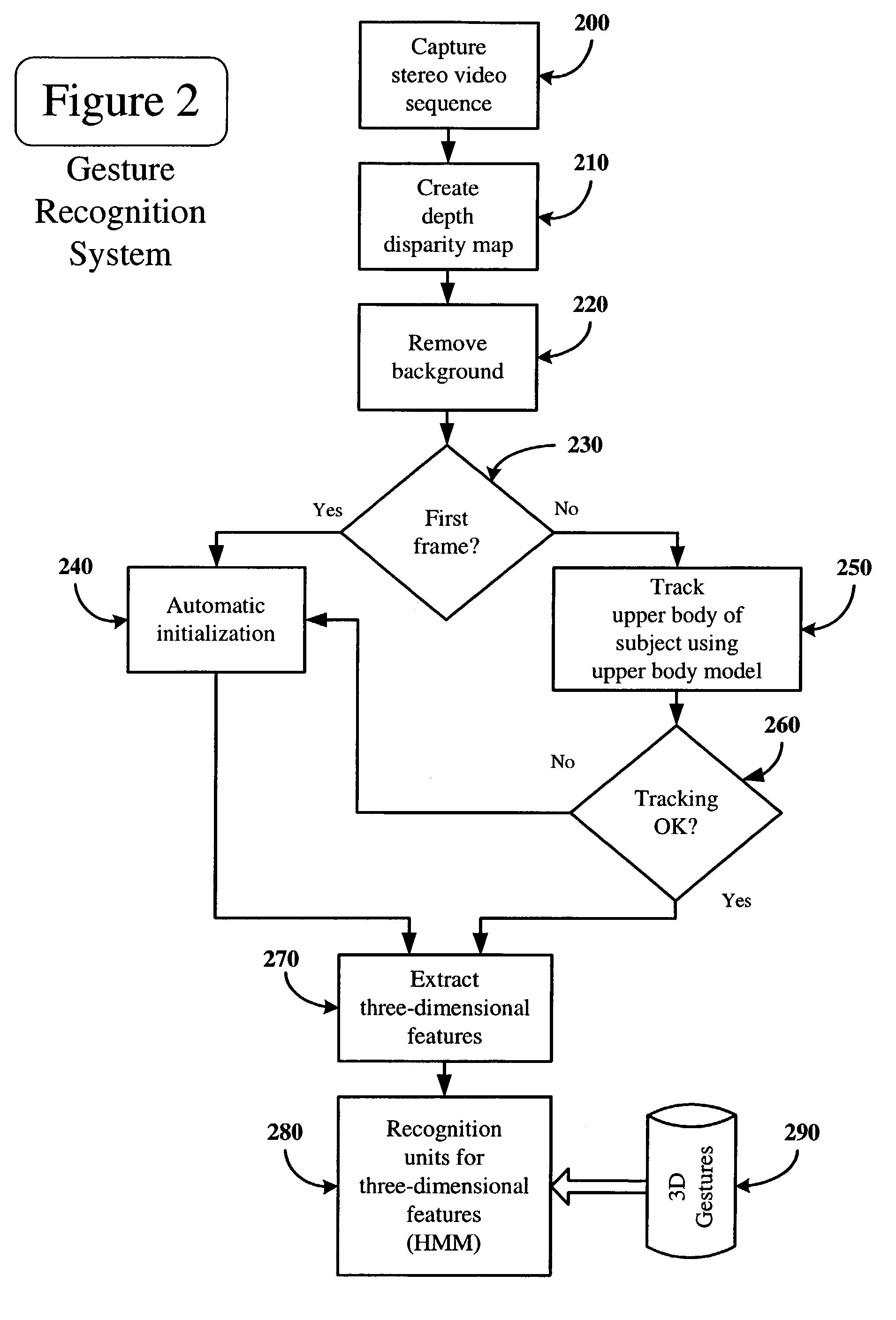
Dynamic gesture recognition from stereo sequences
InactiveUS7274800B2Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionHide markov modelComputer vision
According to an embodiment, an apparatus and method are disclosed for dynamic gesture recognition from stereo sequences. In an embodiment, a stereo sequence of images of a subject is obtained and a depth disparity map is generated from the stereo sequence. The system is initiated automatically based upon a statistical model of the upper body of the subject. The upper body of the subject is modeled as three planes, representing the torso and arms of the subject, and three Gaussian components, representing the head and hands of the subject. The system tracks the upper body of the subject using the statistical upper body model and extracts three-dimensional features of the gestures performed. The system recognizes the gestures using recognition units, which, under a particular embodiment, utilizes hidden Markov models for the three-dimensional gestures.
Owner:INTEL CORP
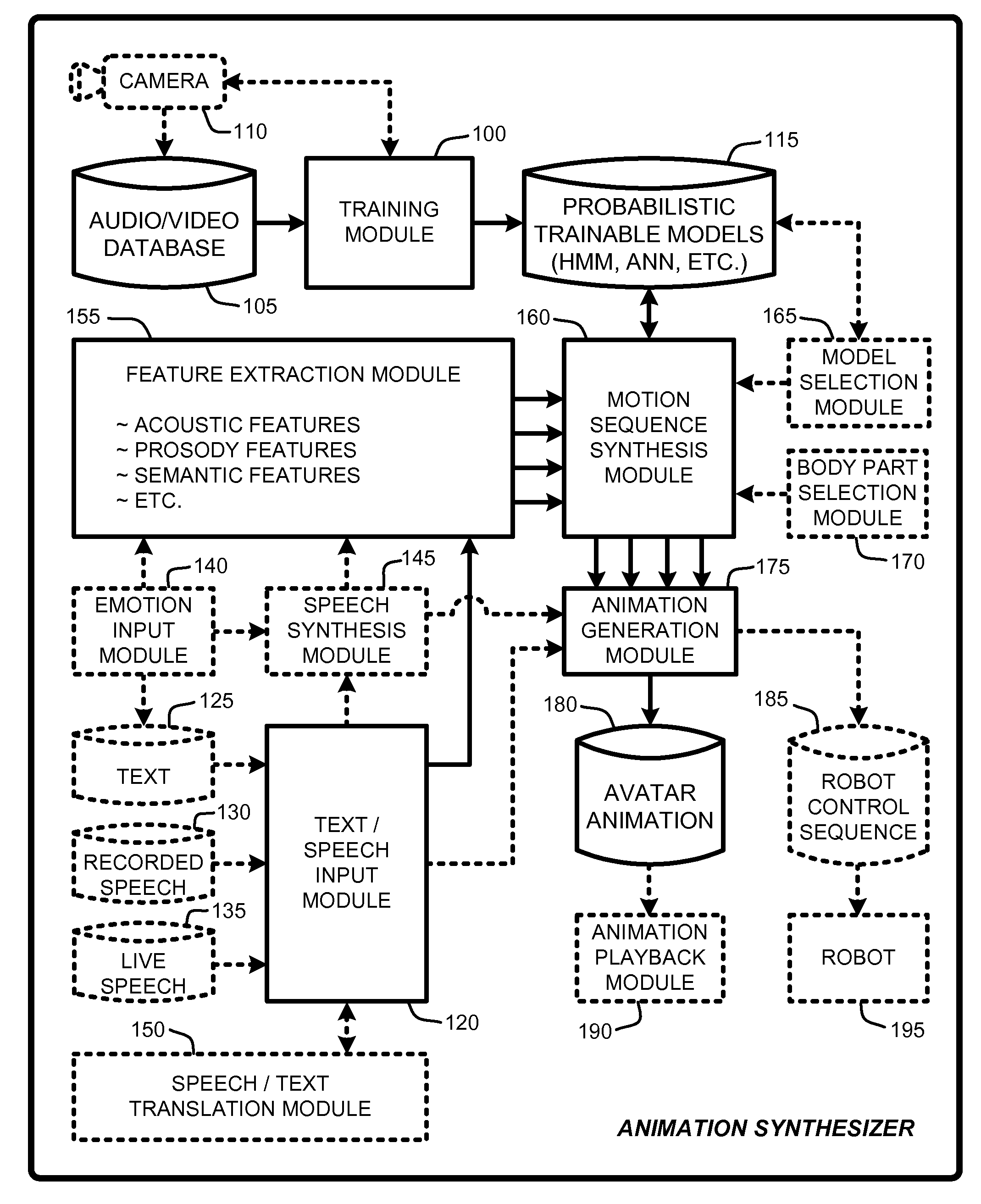
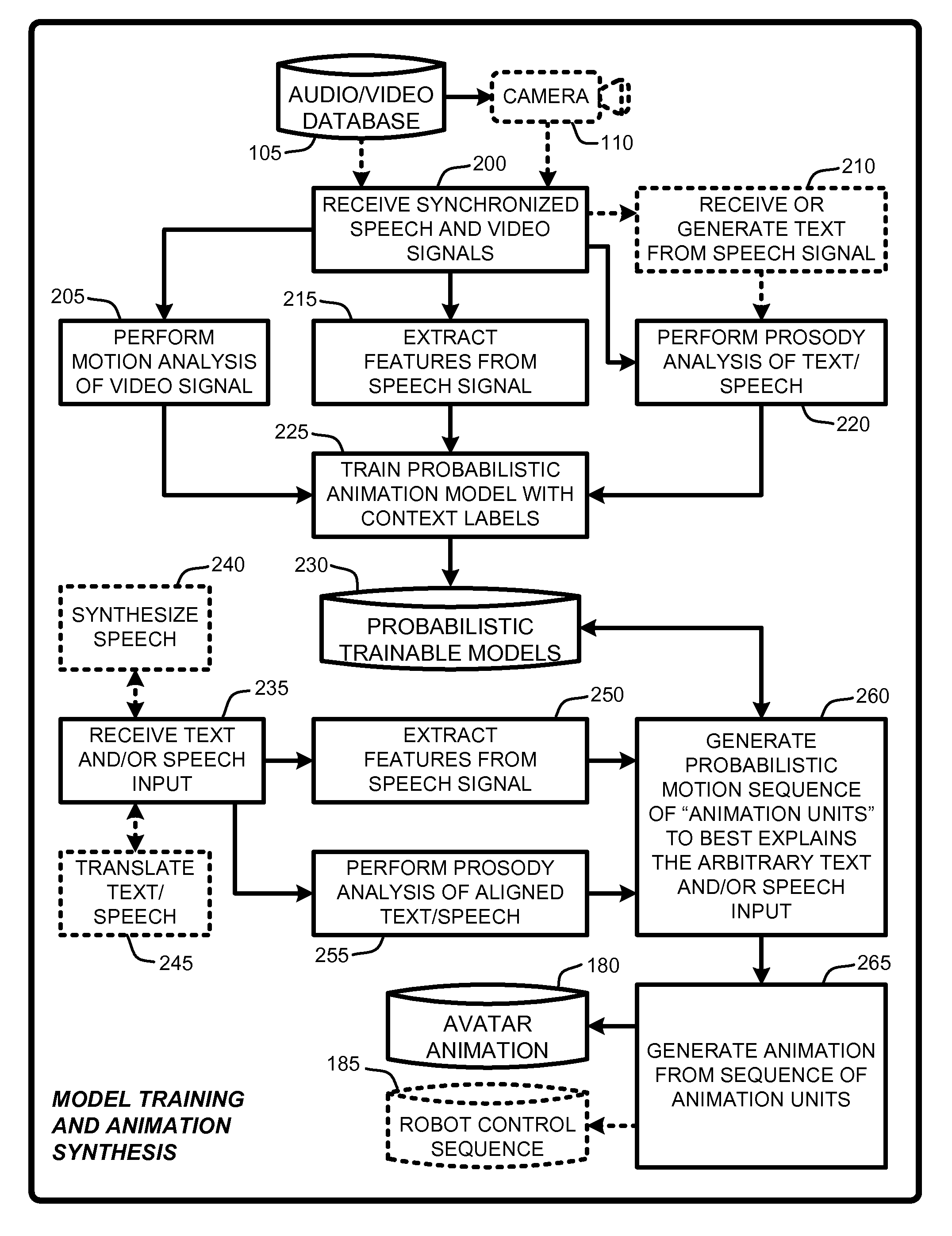
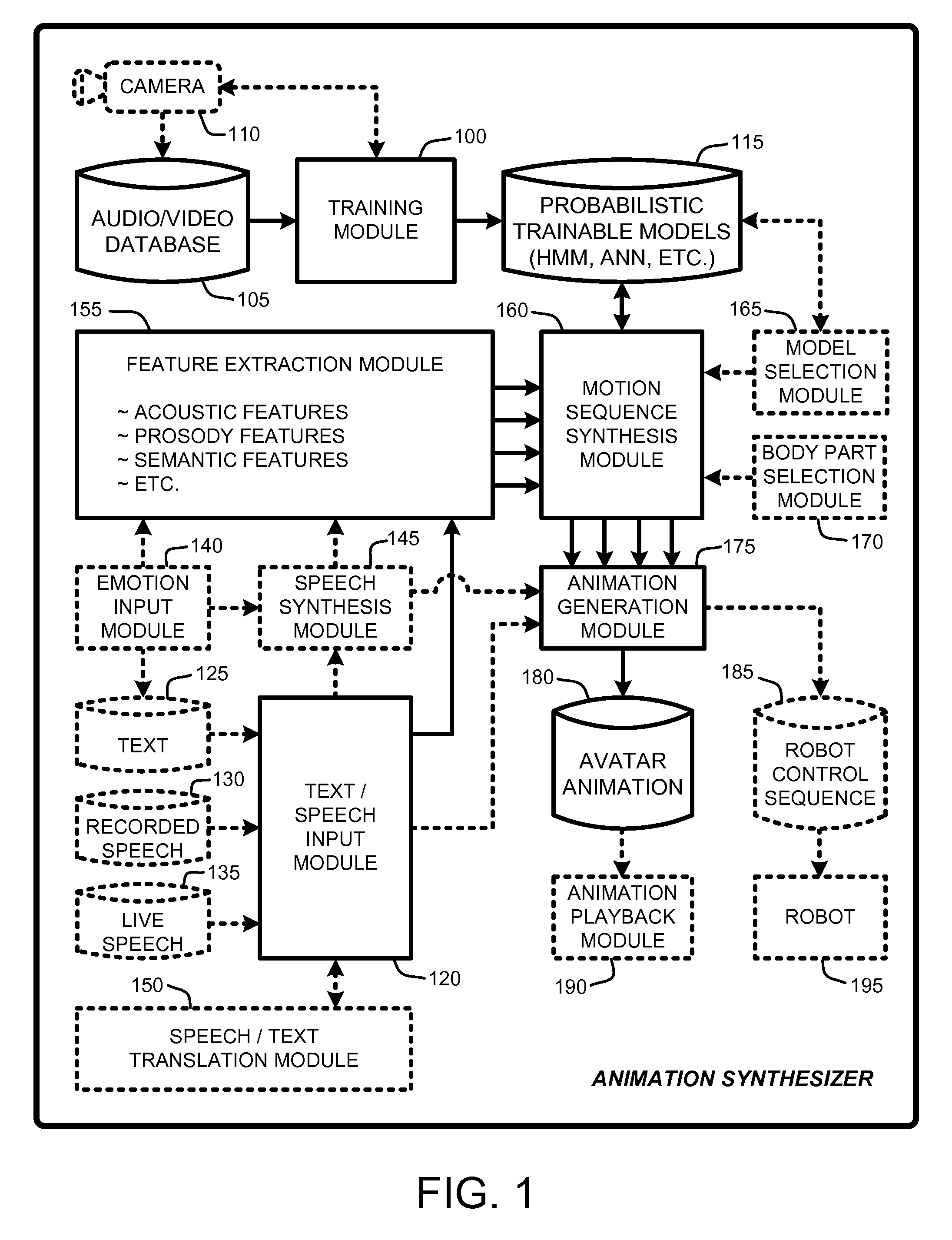
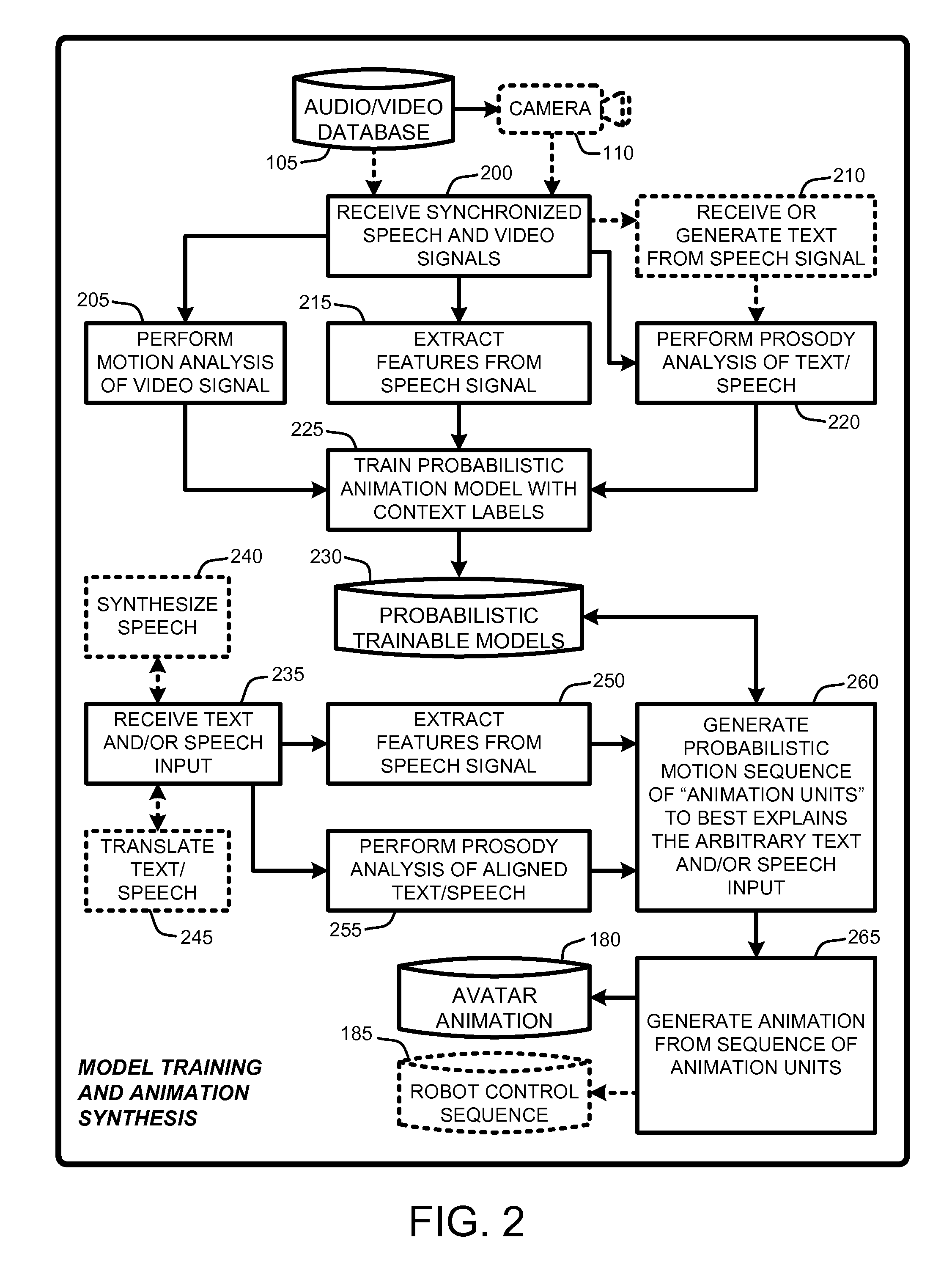
Speech and text driven hmm-based body animation synthesis
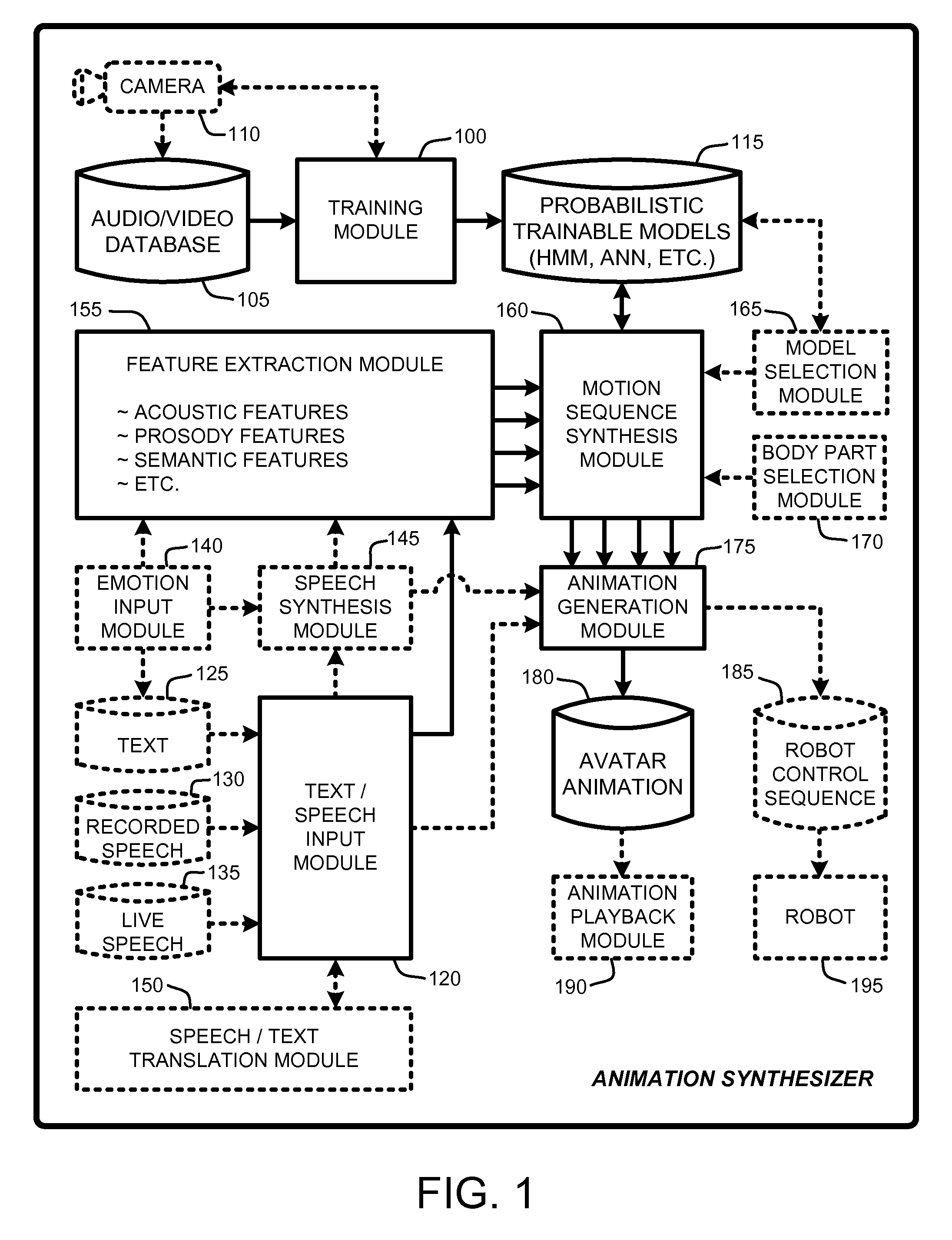
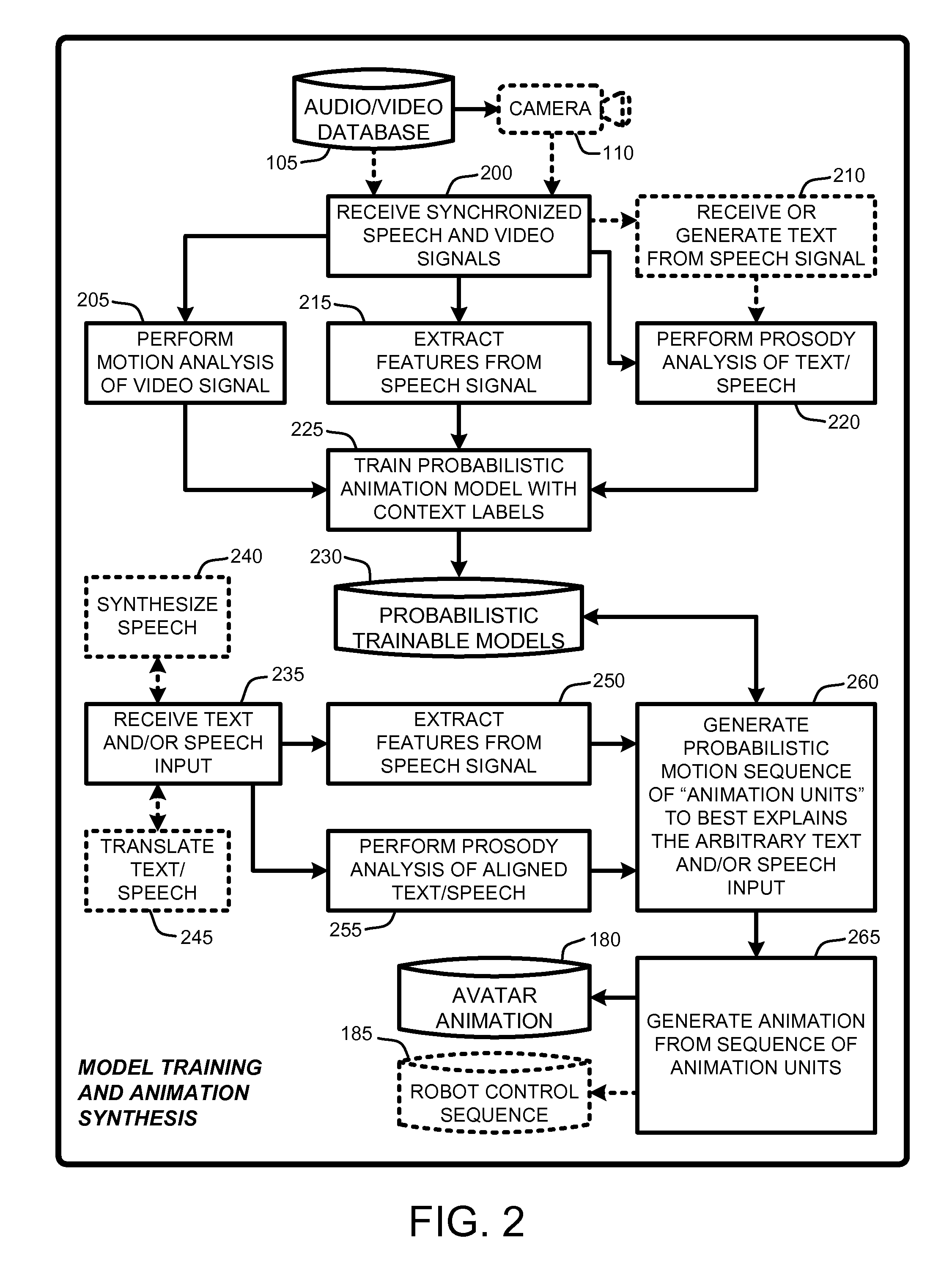
An “Animation Synthesizer” uses trainable probabilistic models, such as Hidden Markov Models (HMM), Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), etc., to provide speech and text driven body animation synthesis. Probabilistic models are trained using synchronized motion and speech inputs (e.g., live or recorded audio / video feeds) at various speech levels, such as sentences, phrases, words, phonemes, sub-phonemes, etc., depending upon the available data, and the motion type or body part being modeled. The Animation Synthesizer then uses the trainable probabilistic model for selecting animation trajectories for one or more different body parts (e.g., face, head, hands, arms, etc.) based on an arbitrary text and / or speech input. These animation trajectories are then used to synthesize a sequence of animations for digital avatars, cartoon characters, computer generated anthropomorphic persons or creatures, actual motions for physical robots, etc., that are synchronized with a speech output corresponding to the text and / or speech input.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
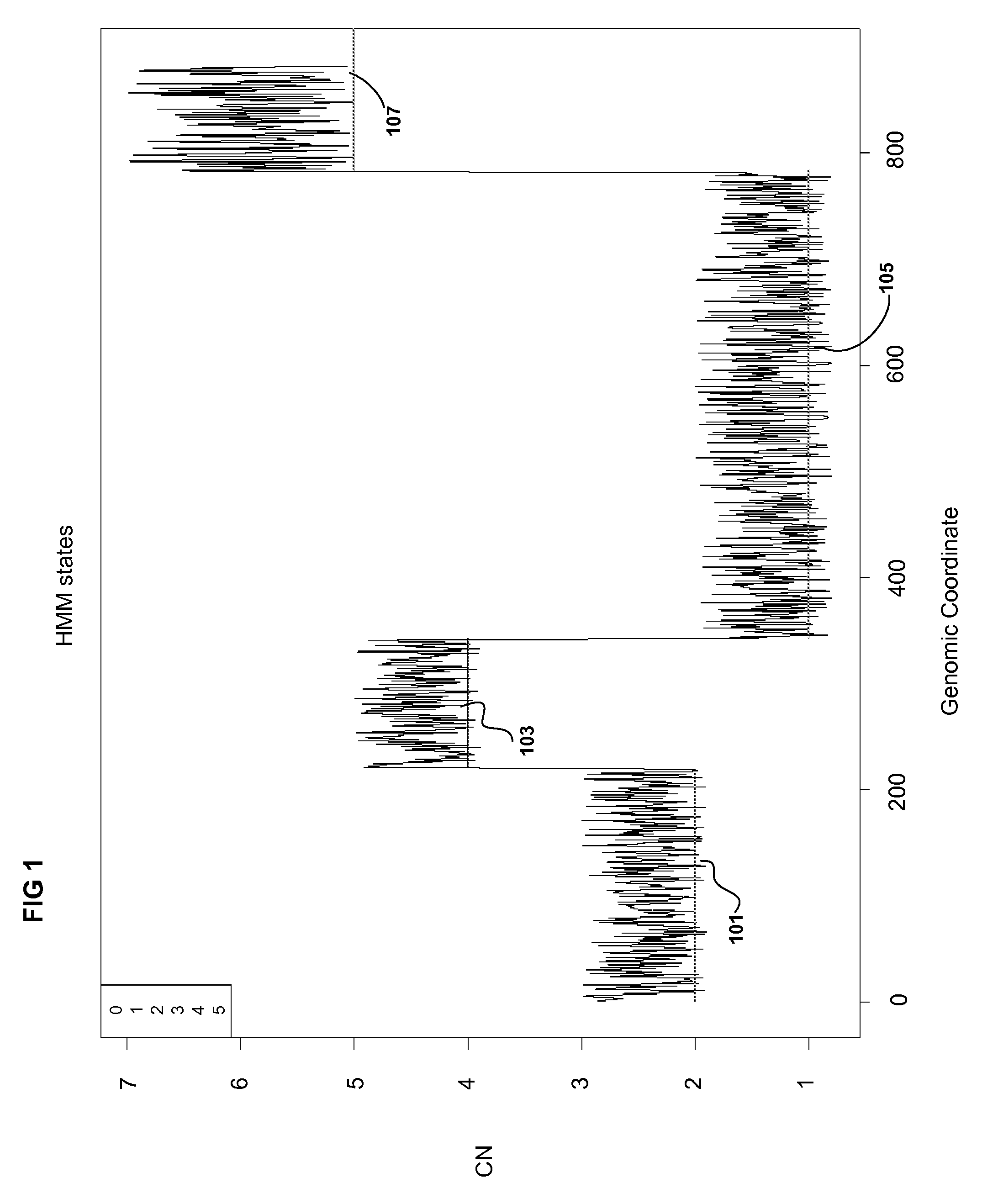
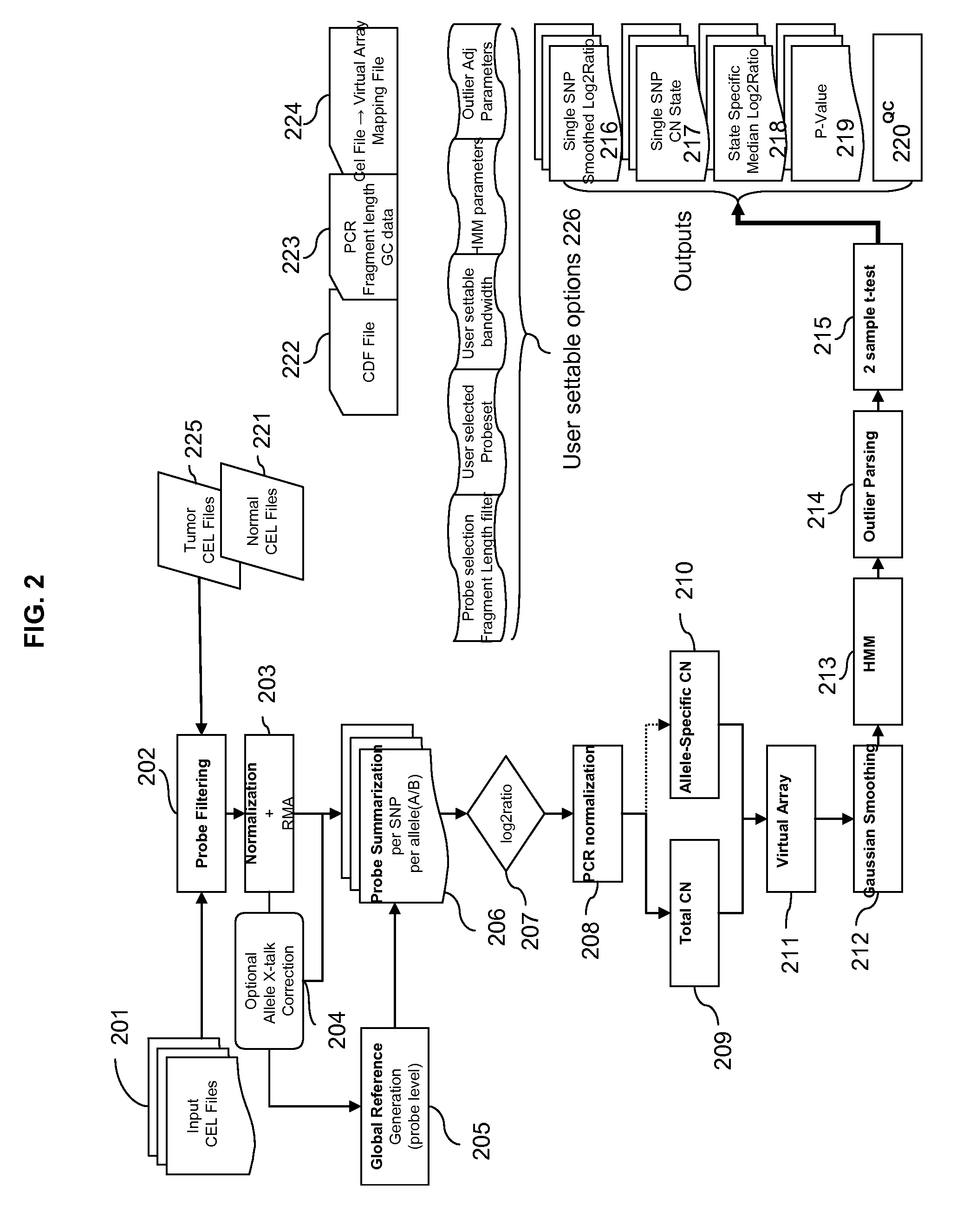
Methods for Identifying DNA Copy Number Changes Using Hidden Markov Model Based Estimations
Methods for estimating genomic copy number and loss of heterozygosity using Hidden Markov Model based estimation are disclosed.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
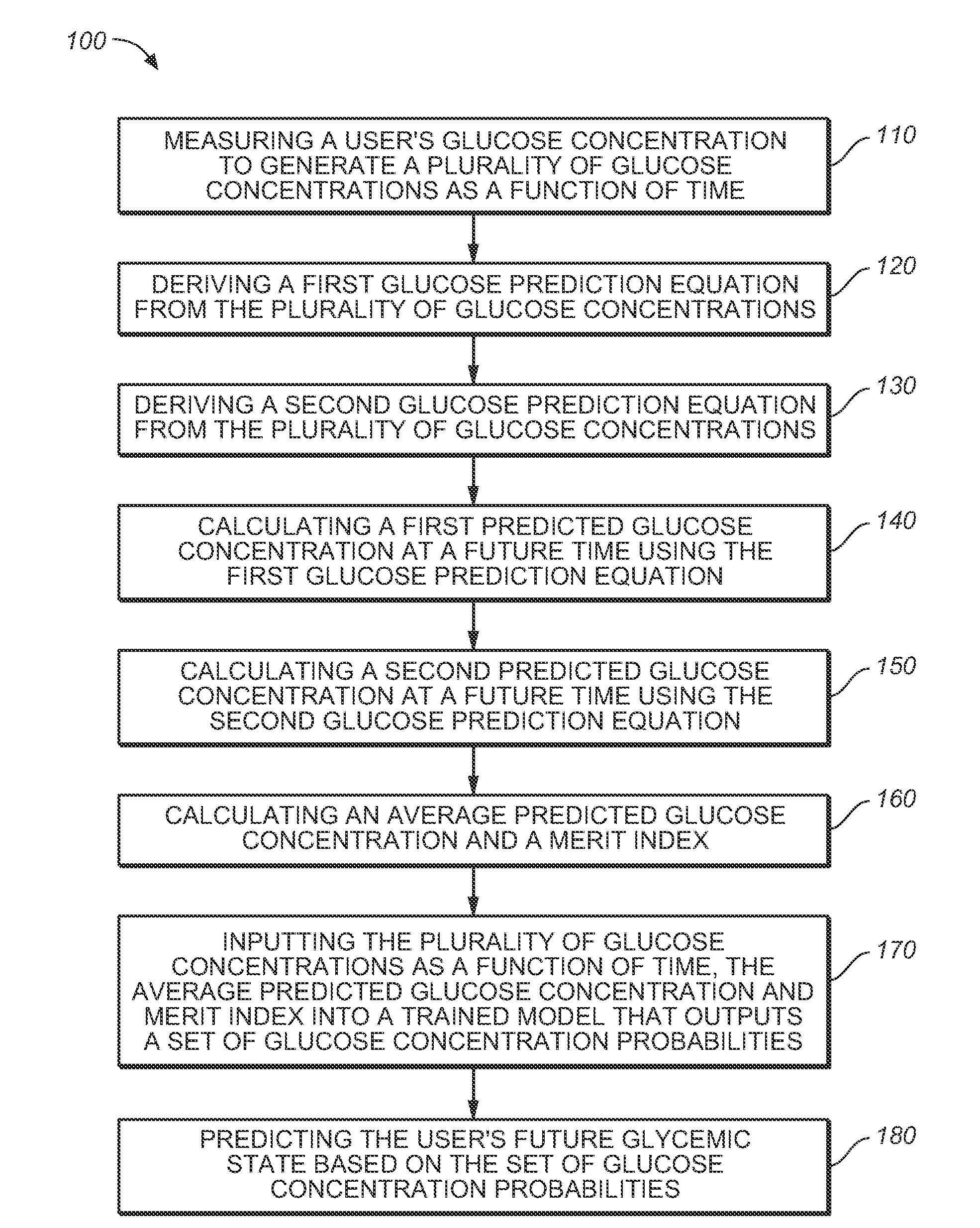
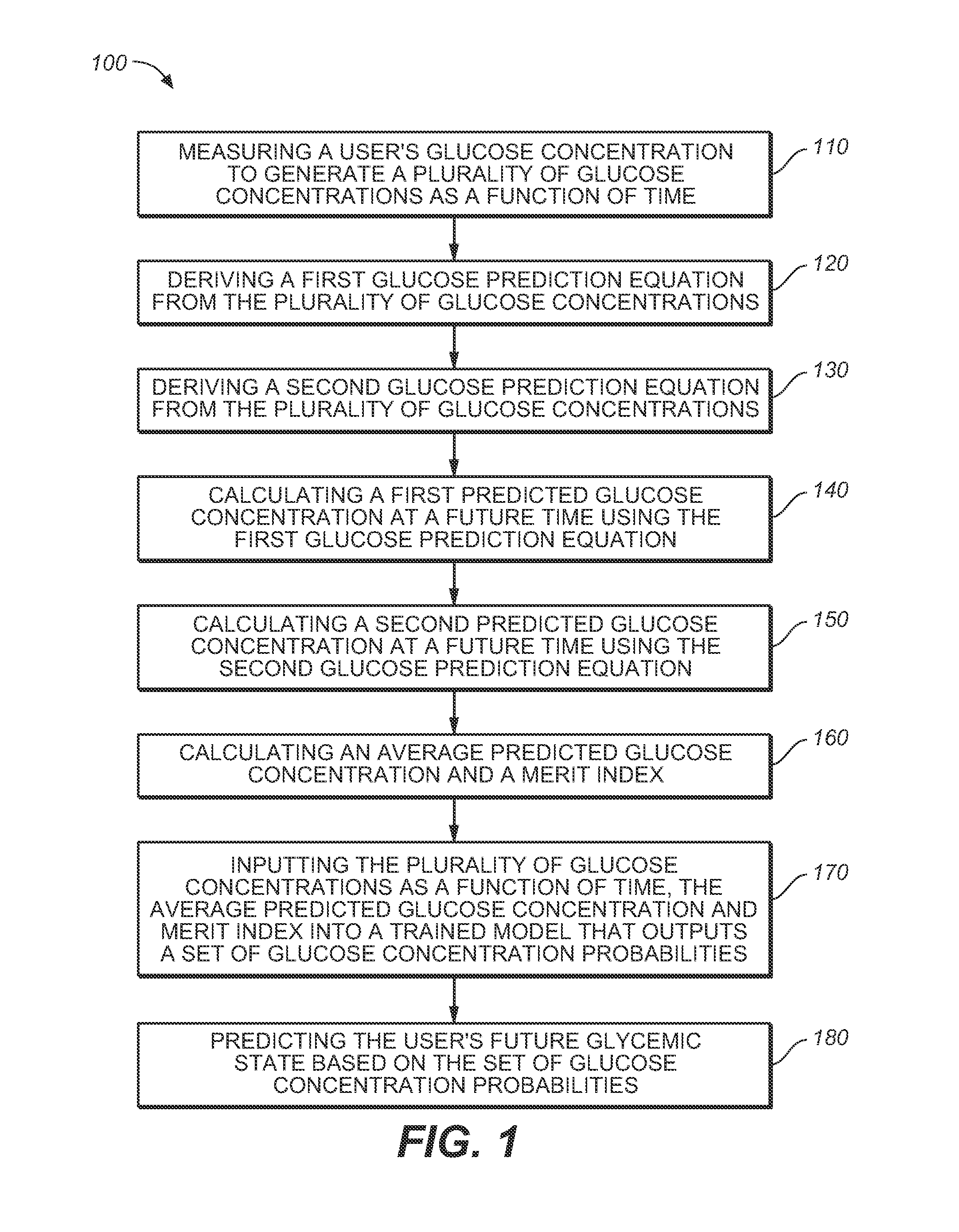
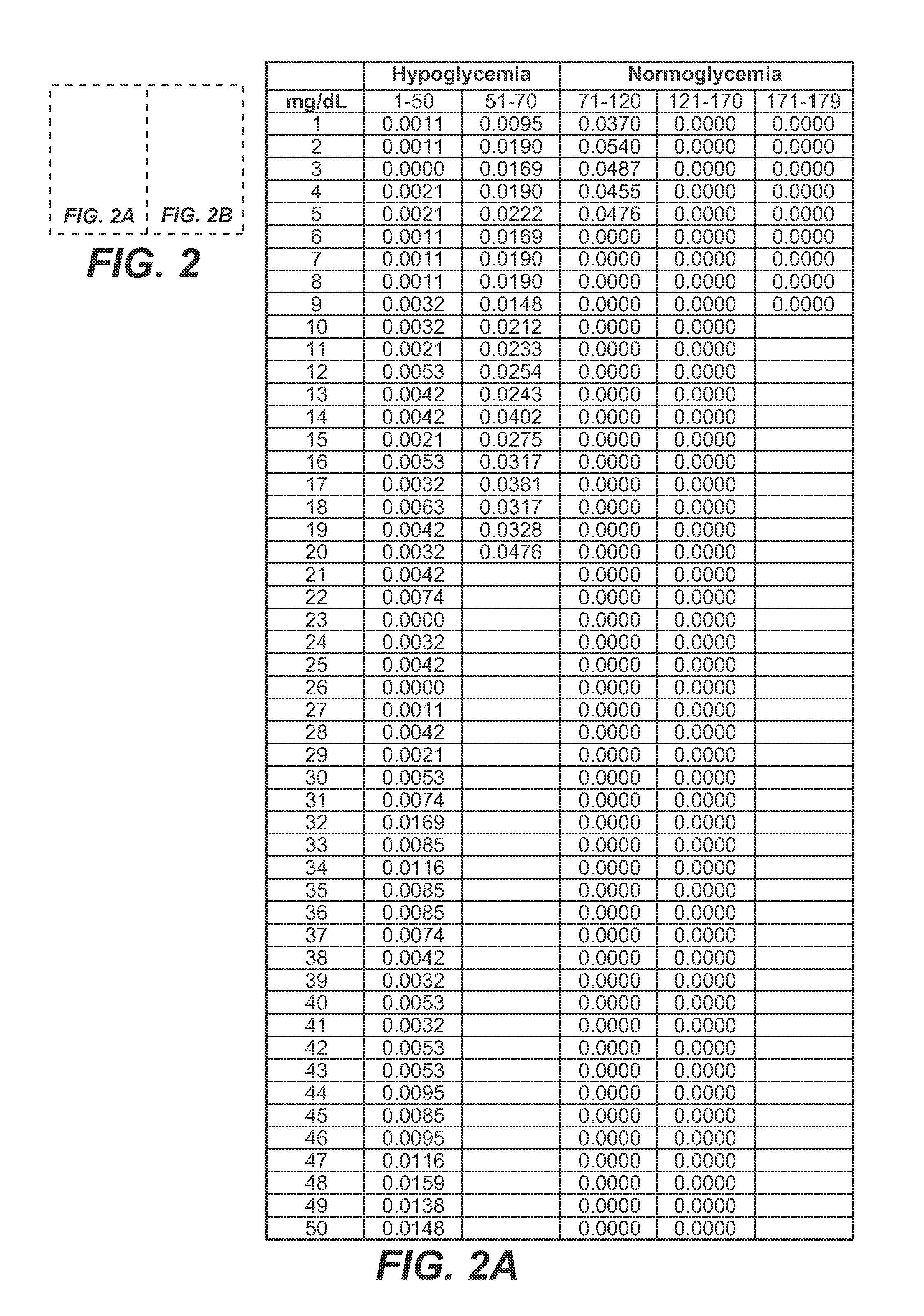
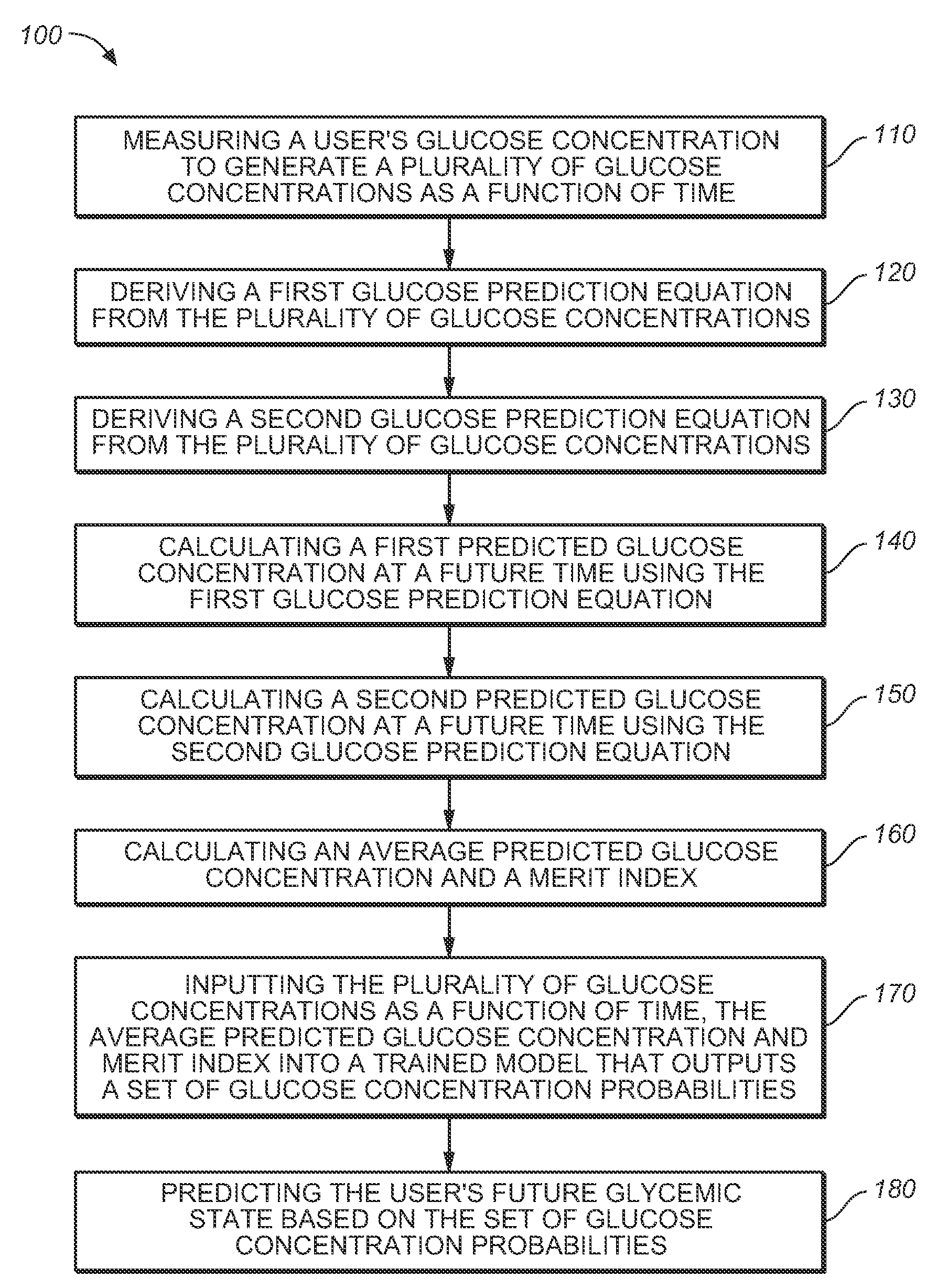
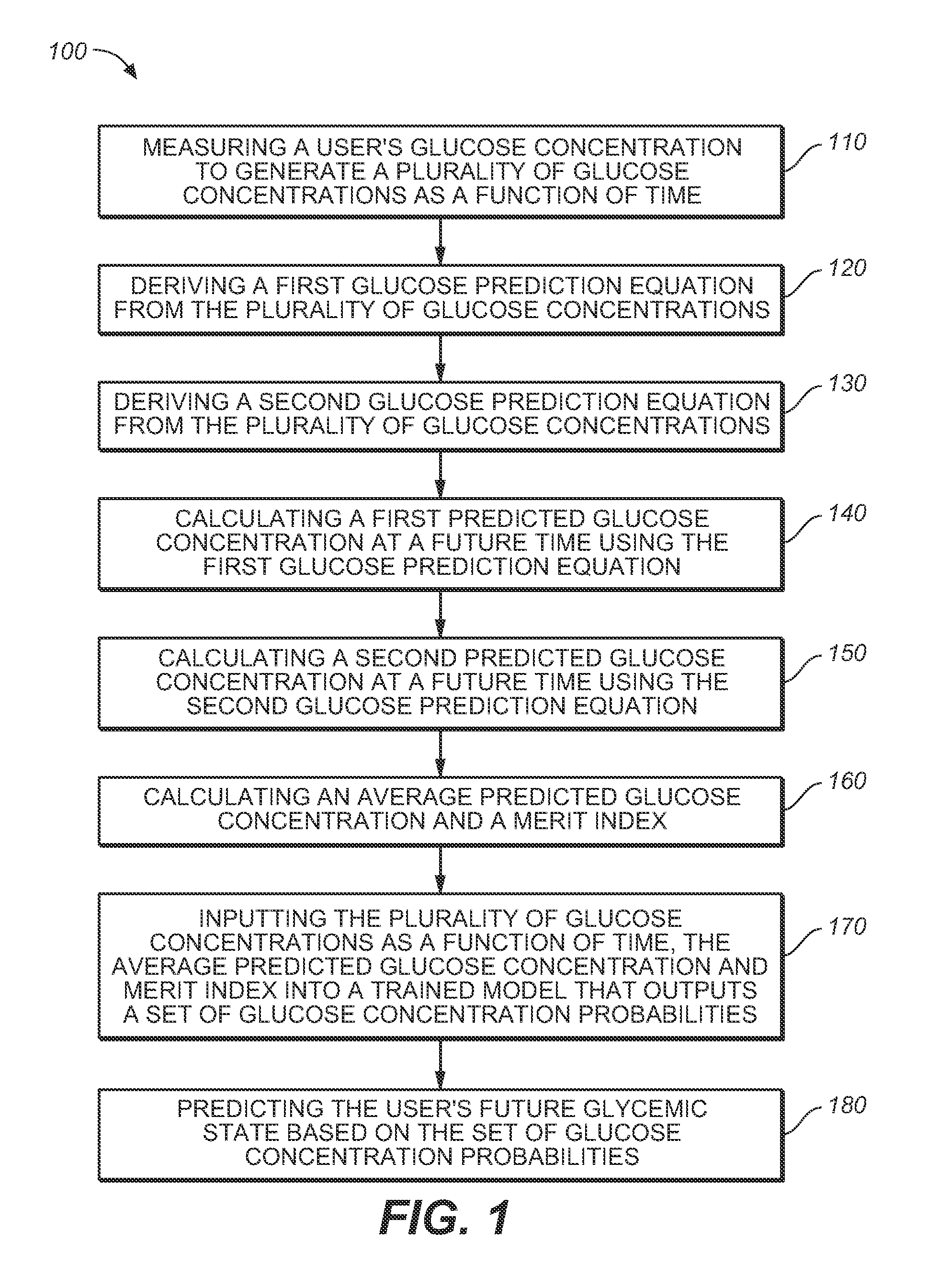
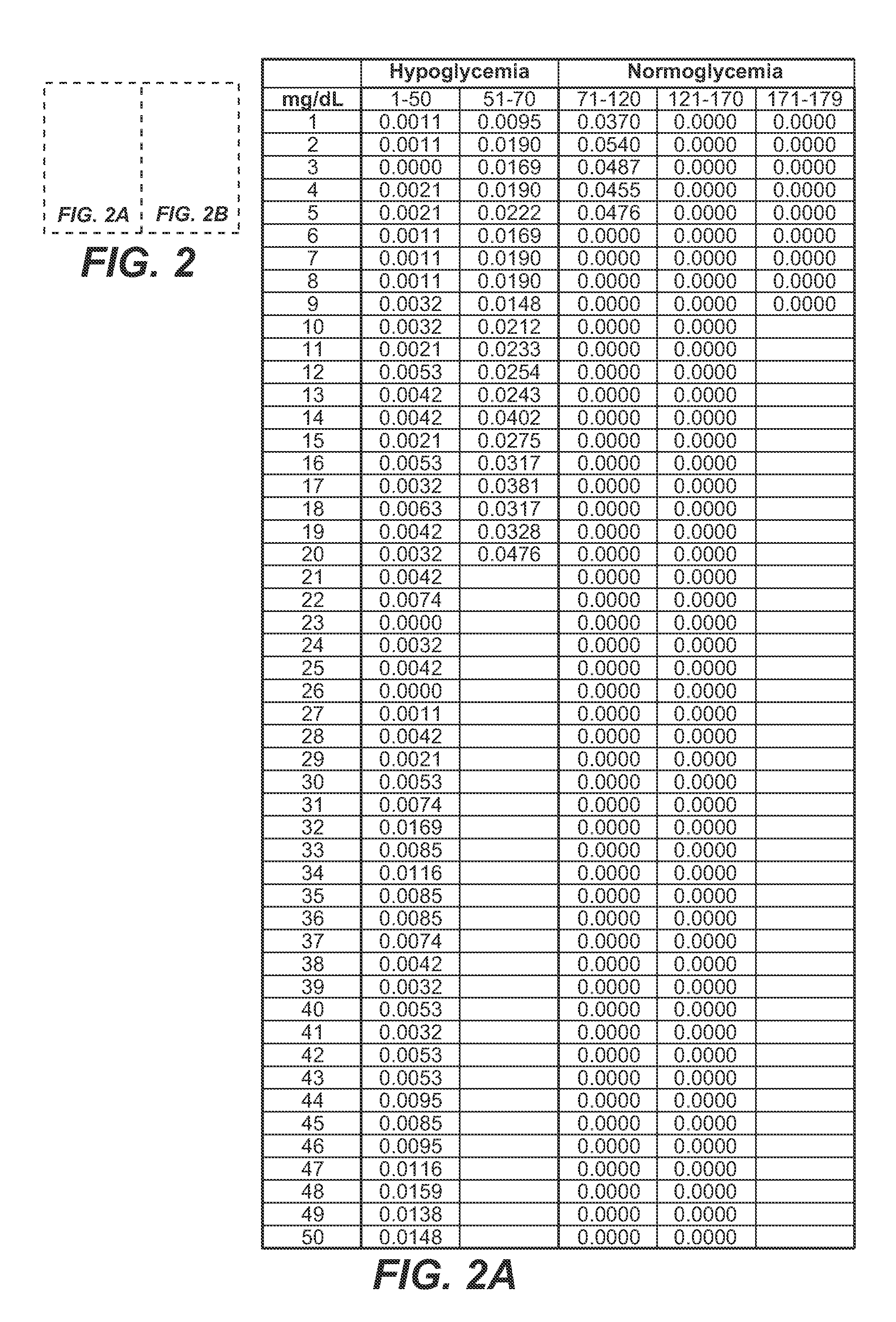
Medical device for predicting a user's future glycemic state
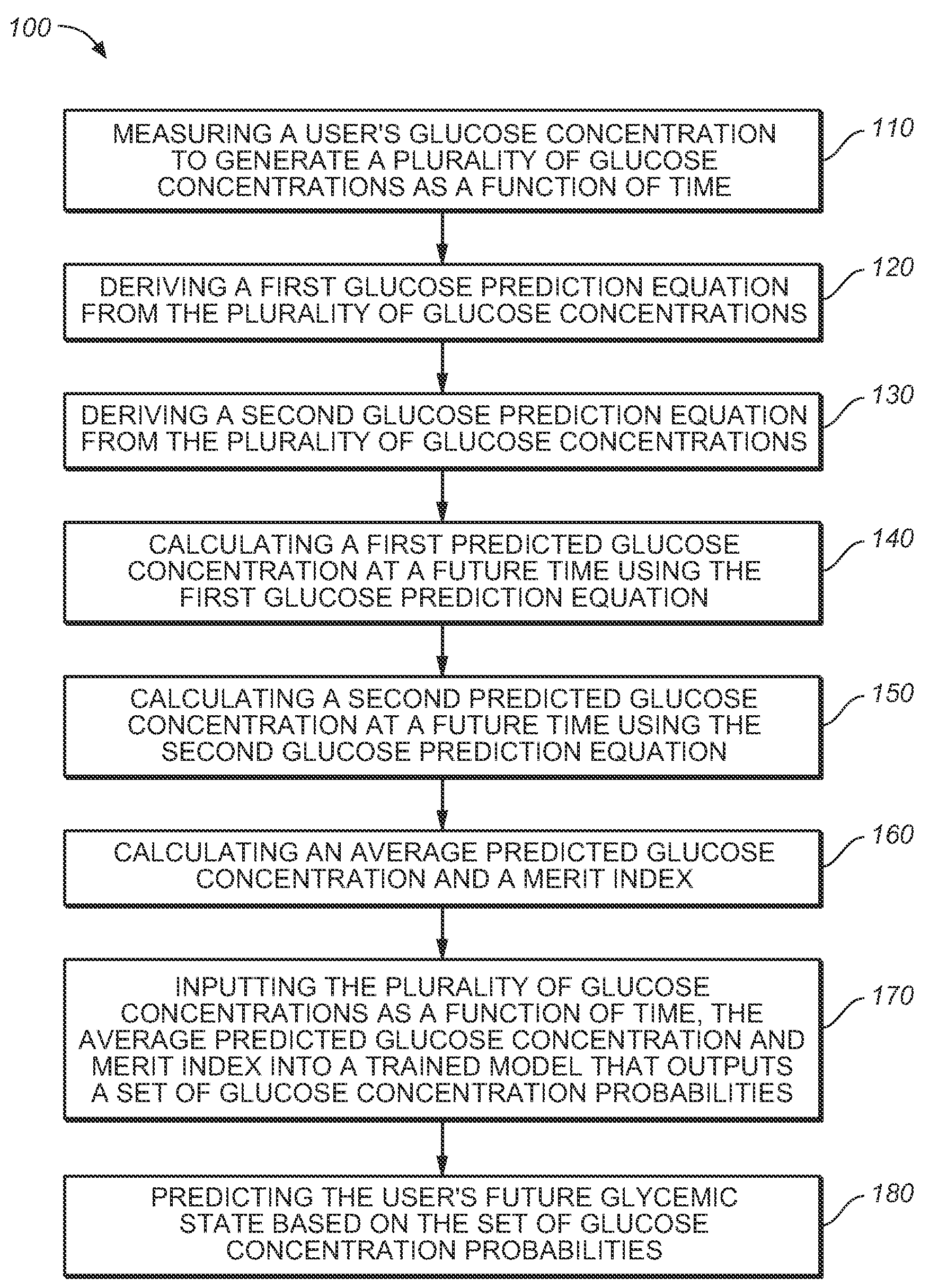
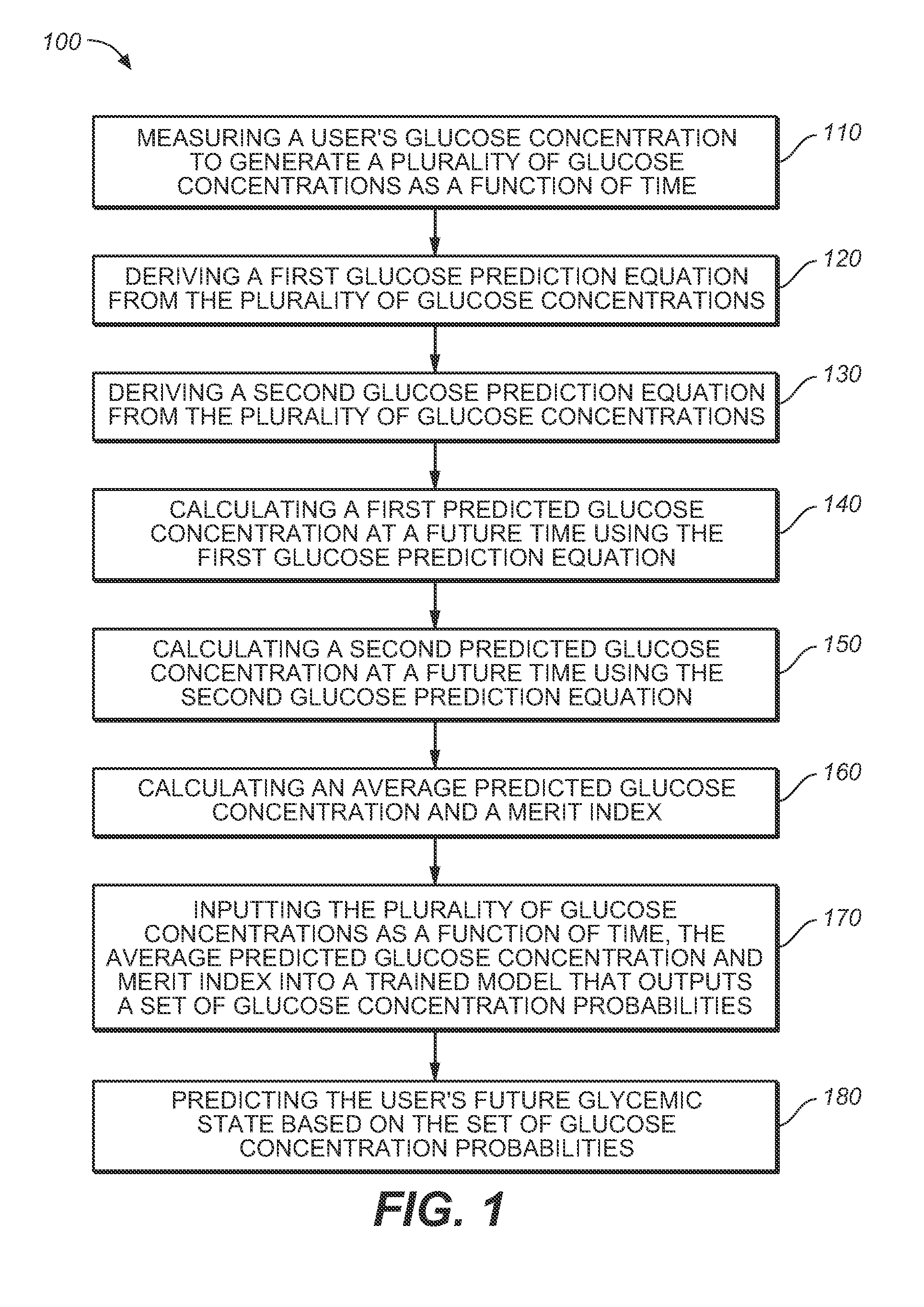
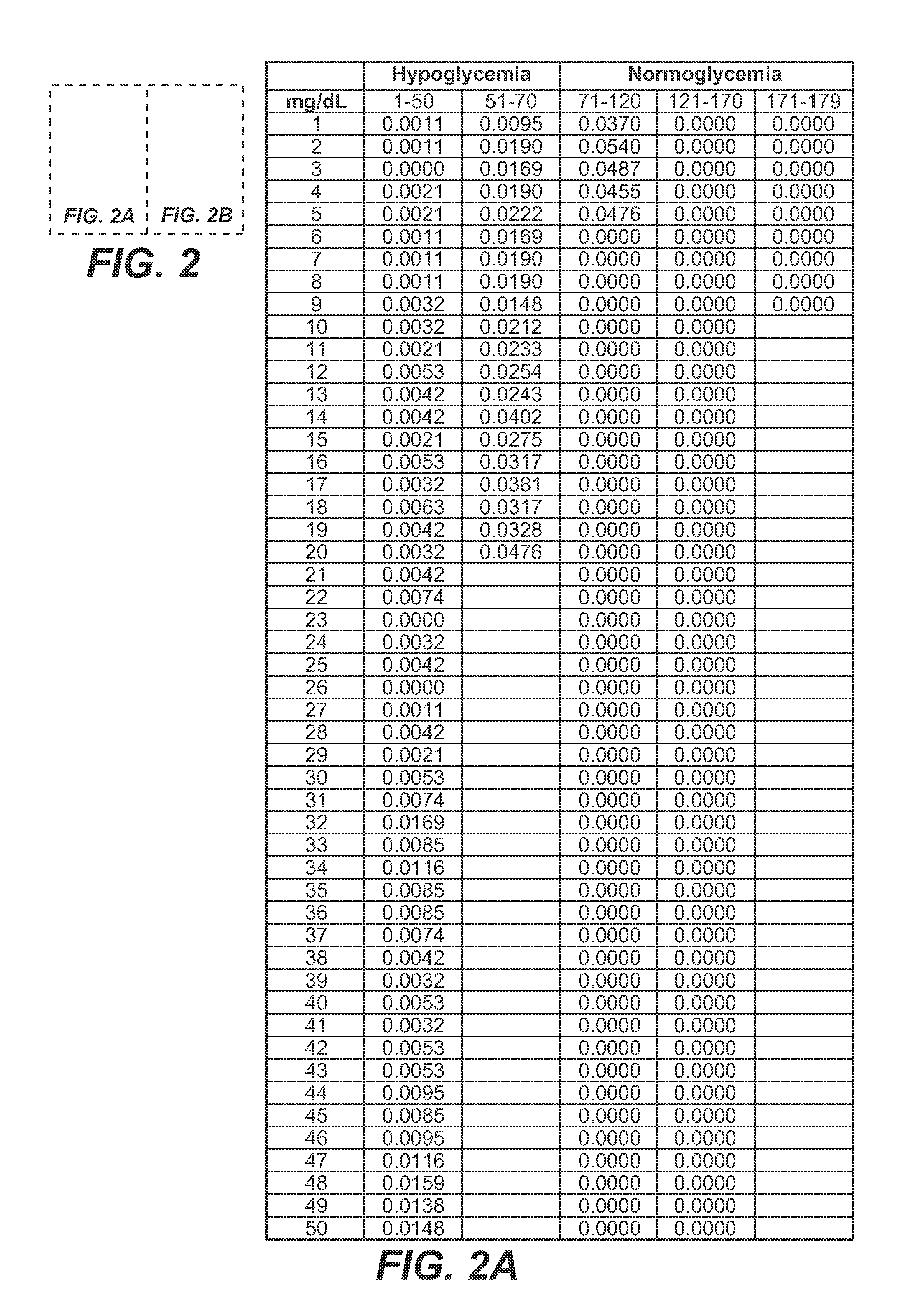
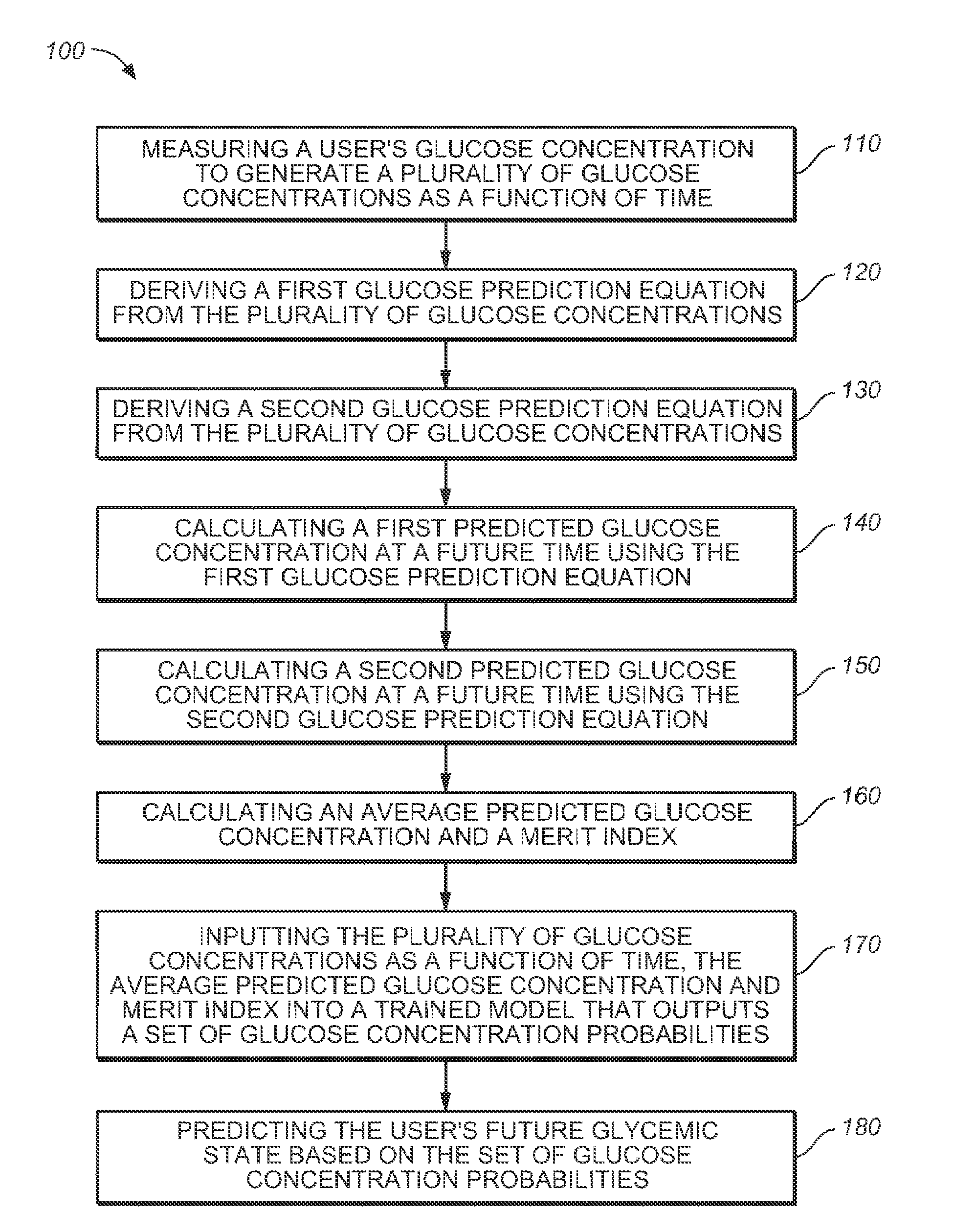
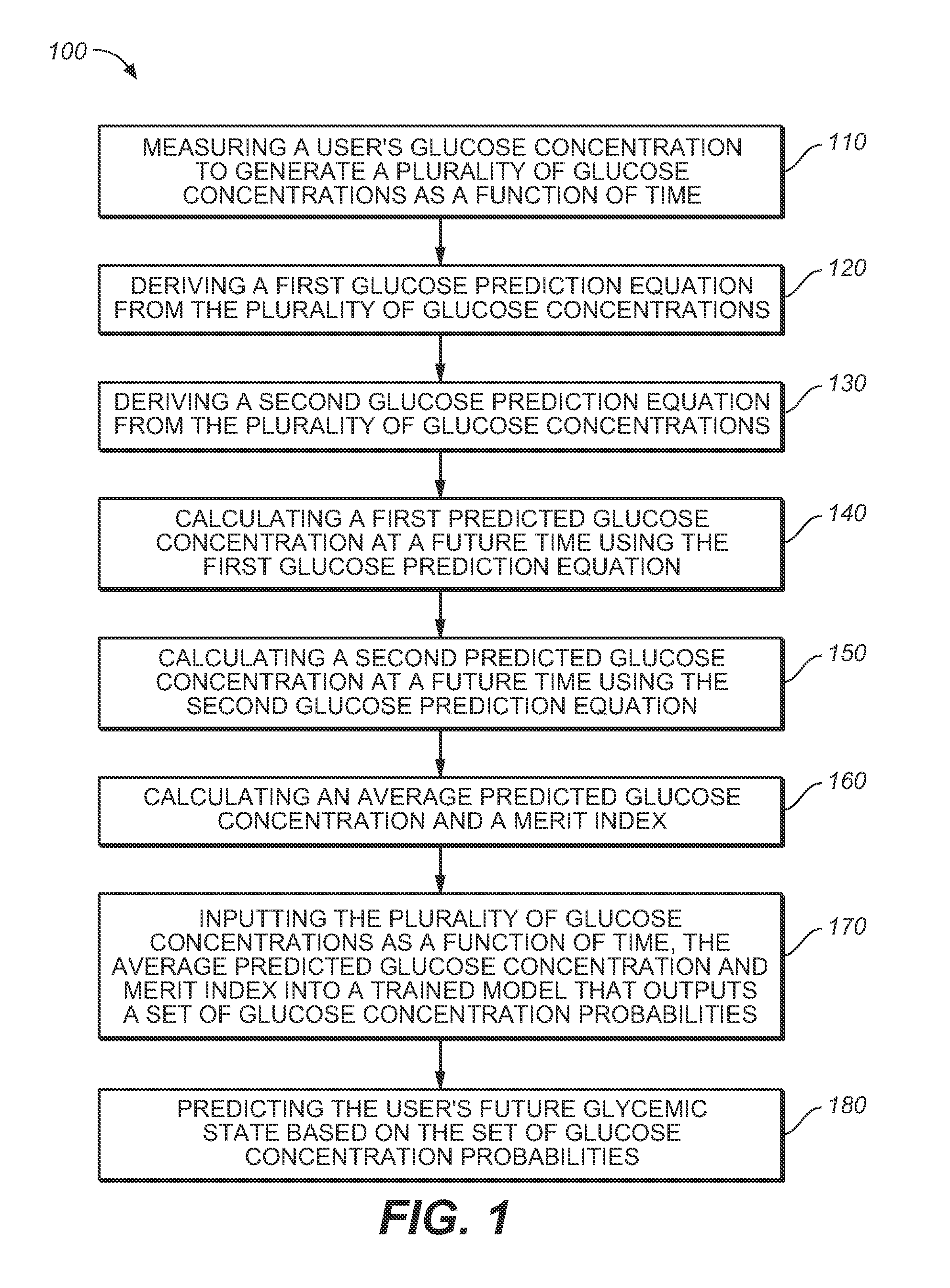
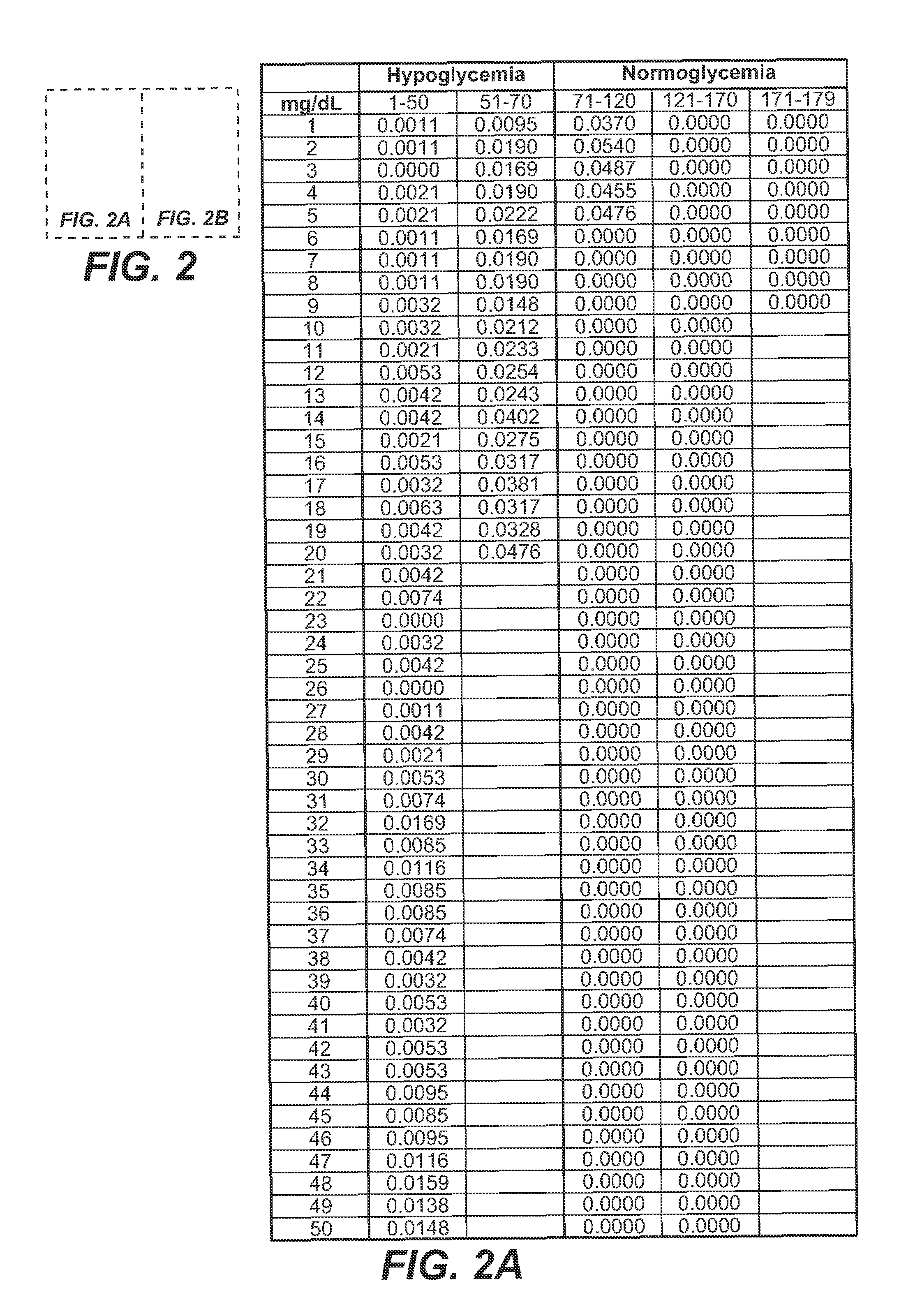
A medical device for predicting a user's future glycemic state includes a memory module, a processor module and a user alert module. The memory module is configured to receive and store a plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time that were generated by a user's use of a continuous glucose monitor. The processor module is configured to derive first and second glucose prediction equations that are fits to the plurality of glucose concentrations stored in the memory module with the fits being based on first and second mathematical models, respectively. The processor module is also configured to calculate first and second predicted glucose concentrations at a future time using the first and second glucose prediction equations, respectively, and to also calculate an average predicted glucose concentration and a merit index based on the first and second predicted glucose calculations. The processor module is further configured to input the plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time, the average predicted glucose concentration and the merit index into a trained model (e.g., a Hidden Markov Model) that outputs a set of glucose concentration probabilities for the future time and to then predict the user's future glycemic state based on the set of glucose concentration probabilities. The user alert module is configured to alert the user in a manner dependent on the predicted user's future glycemic state.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
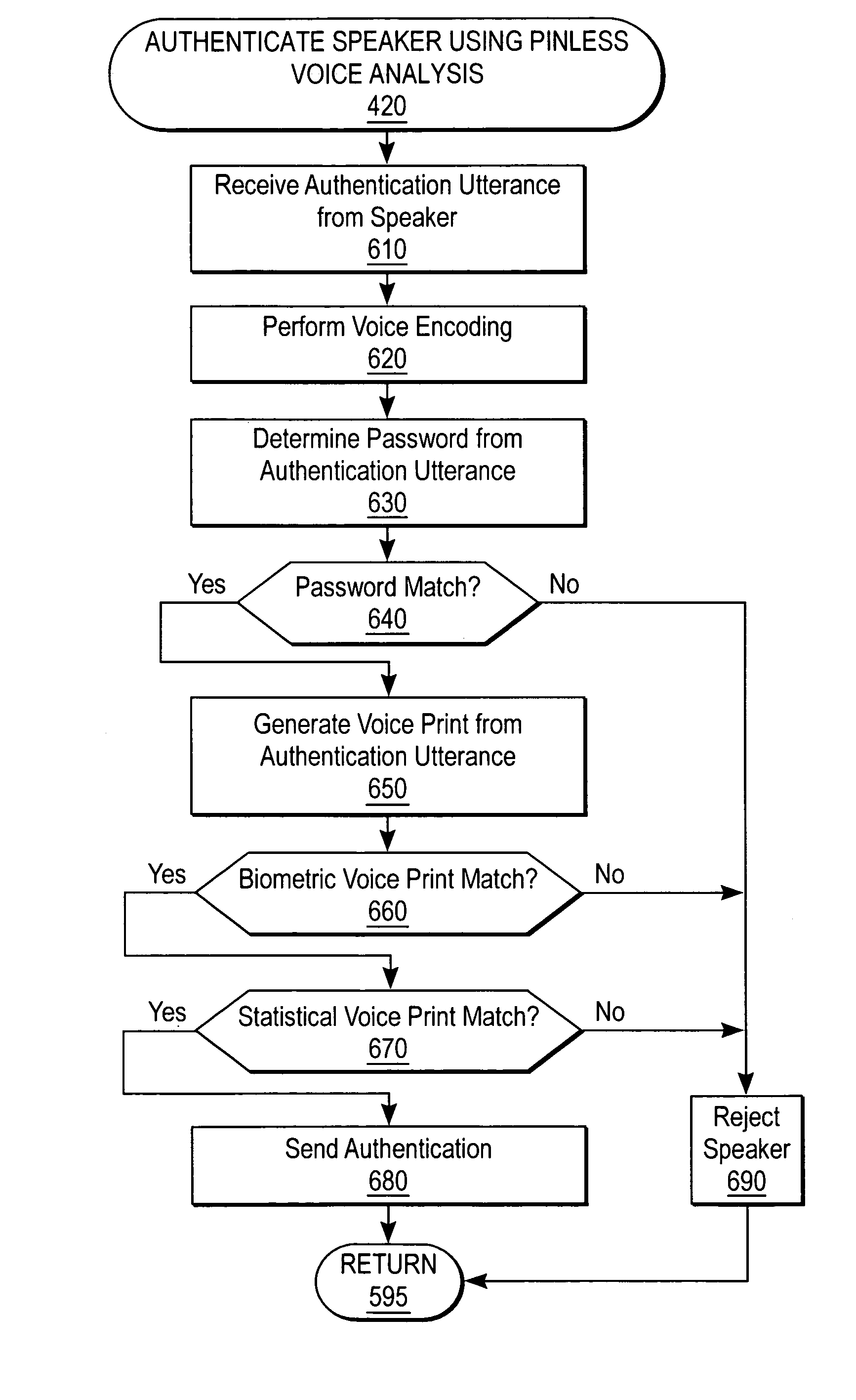
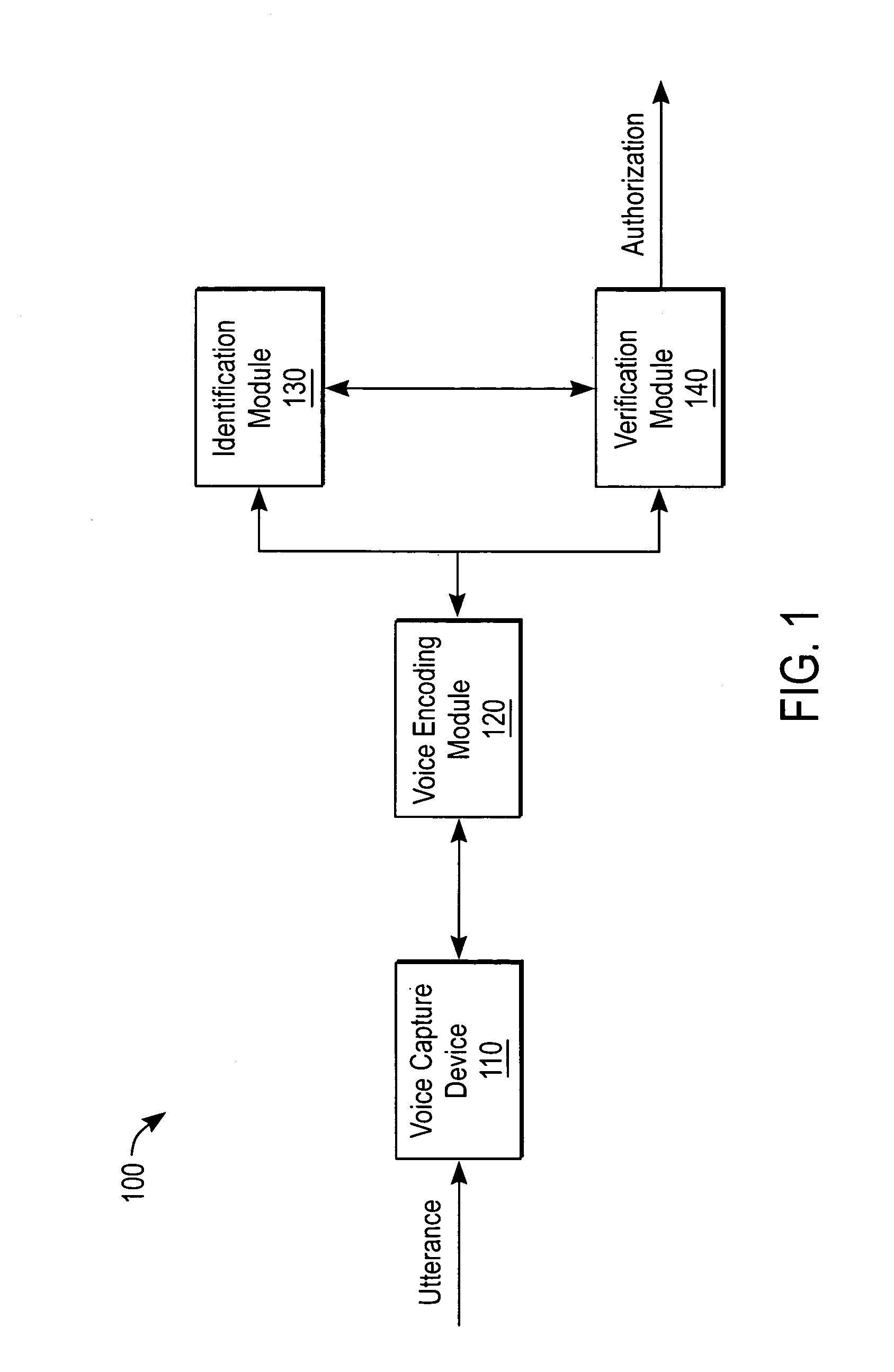
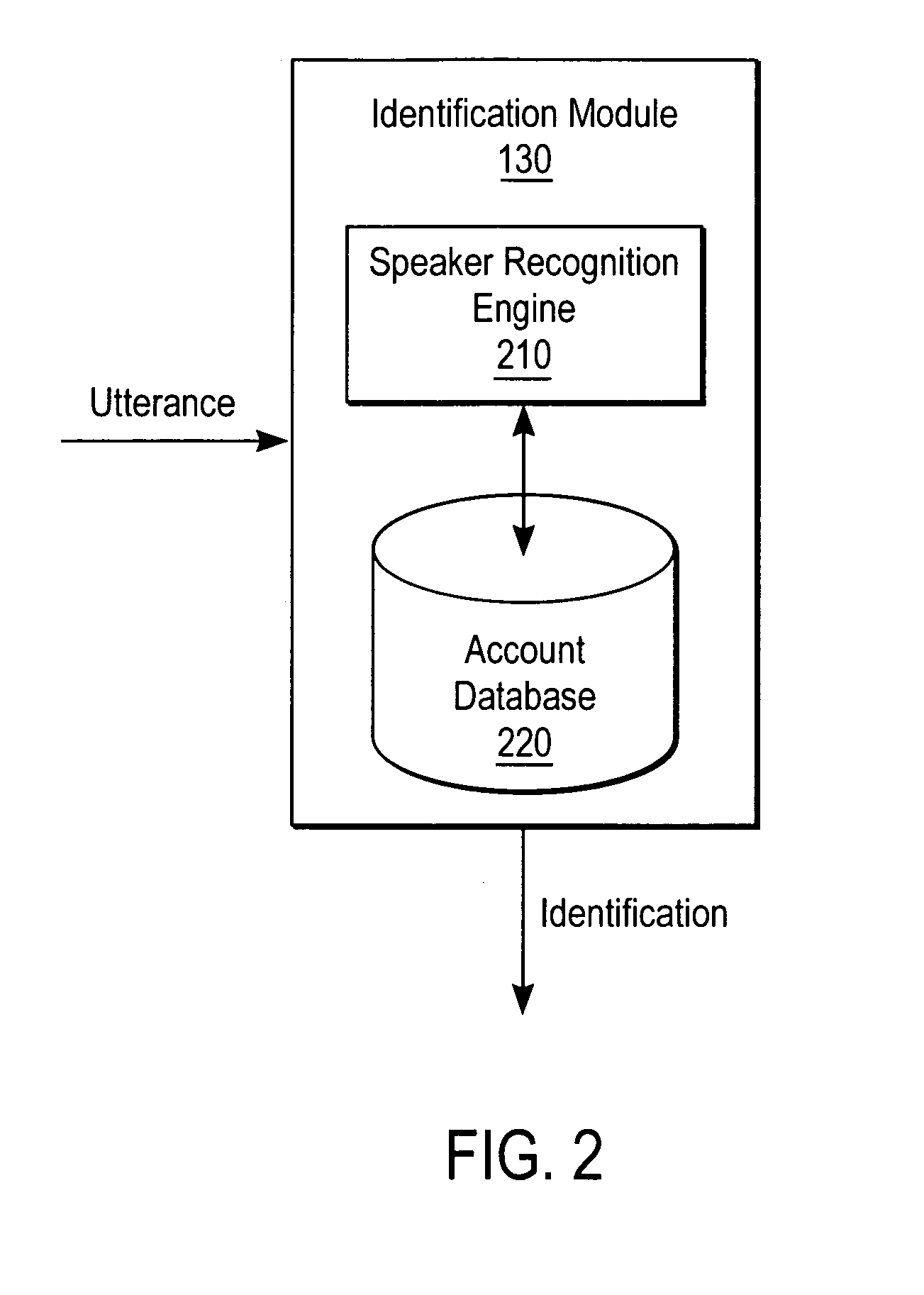
Biometric voice authentication
ActiveUS7386448B1Reducing user complexityReduce complexityAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingAutomatic exchangesBiometric dataPersonal identification number
A system and method enrolls a speaker with an enrollment utterance and authenticates a user with a biometric analysis of an authentication utterance, without the need for a PIN (Personal Identification Number). During authentication, the system uses the same authentication utterance to identify who a speaker claims to be with speaker recognition, and verify whether is the speaker is actually the claimed person. Thus, it is not necessary for the speaker to identify biometric data using a PIN. The biometric analysis includes a neural tree network to determine unique aspects of the authentication utterances for comparison to the enrollment authentication. The biometric analysis leverages a statistical analysis using Hidden Markov Models to before authorizing the speaker.
Owner:SECURUS TECH LLC
Medical device for predicting a user's future glycemic state
ActiveUS20090105573A1Medical simulationHealth-index calculationHide markov modelConcentrations glucose
A medical device for predicting a user's future glycemic state includes a memory module, a processor module and a user alert module. The memory module is configured to receive and store a plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time that were generated by a user's use of a continuous glucose monitor. The processor module is configured to derive first and second glucose prediction equations that are fits to the plurality of glucose concentrations stored in the memory module with the fits being based on first and second mathematical models, respectively. The processor module is also configured to calculate first and second predicted glucose concentrations at a future time using the first and second glucose prediction equations, respectively, and to also calculate an average predicted glucose concentration and a merit index based on the first and second predicted glucose calculations. The processor module is further configured to input the plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time, the average predicted glucose concentration and the merit index into a trained model (e.g., a Hidden Markov Model) that outputs a set of glucose concentration probabilities for the future time and to then predict the user's future glycemic state based on the set of glucose concentration probabilities. The user alert module is configured to alert the user in a manner dependent on the predicted user's future glycemic state.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Personalized Monitoring and Healthcare Information Management Using Physiological Basis Functions
InactiveUS20110004110A1Accurate trackingAccurate classificationMedical data miningMedical automated diagnosisPersonalizationSide effect
Analysis of individual's serial changes, also referred to as the physiological, pathophysiological, medical or health dynamics, is the backbone of medical diagnosis, monitoring and patient healthcare management. However, such an analysis is complicated by enormous intra-individual and inter-individual variability. To address this problem, a novel serial-analysis method and system based on the concept of personalized basis functions (PBFs) is disclosed. Due to more accurate reference information provided by the PBFs, individual's changes associated with specific physiological activity or a sequence, transition or combination of activities (for example, a transition from sleep to wakefulness and transition from rest to exercise) can be monitored more accurately. Hence, subtle but clinically important changes can be detected earlier than using other methods. A library of individual's PBFs and their transition probabilities (which can be described by Hidden Markov Models) can completely describe individual's physiological dynamics. The system can be adapted for healthcare information management, diagnosis, medical decision support, treatment and side-effect control. It can also be adapted for guiding health, fitness and wellness training, subject identification and more efficient management of clinical trials.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
System and method for observing the swimming activity of a person
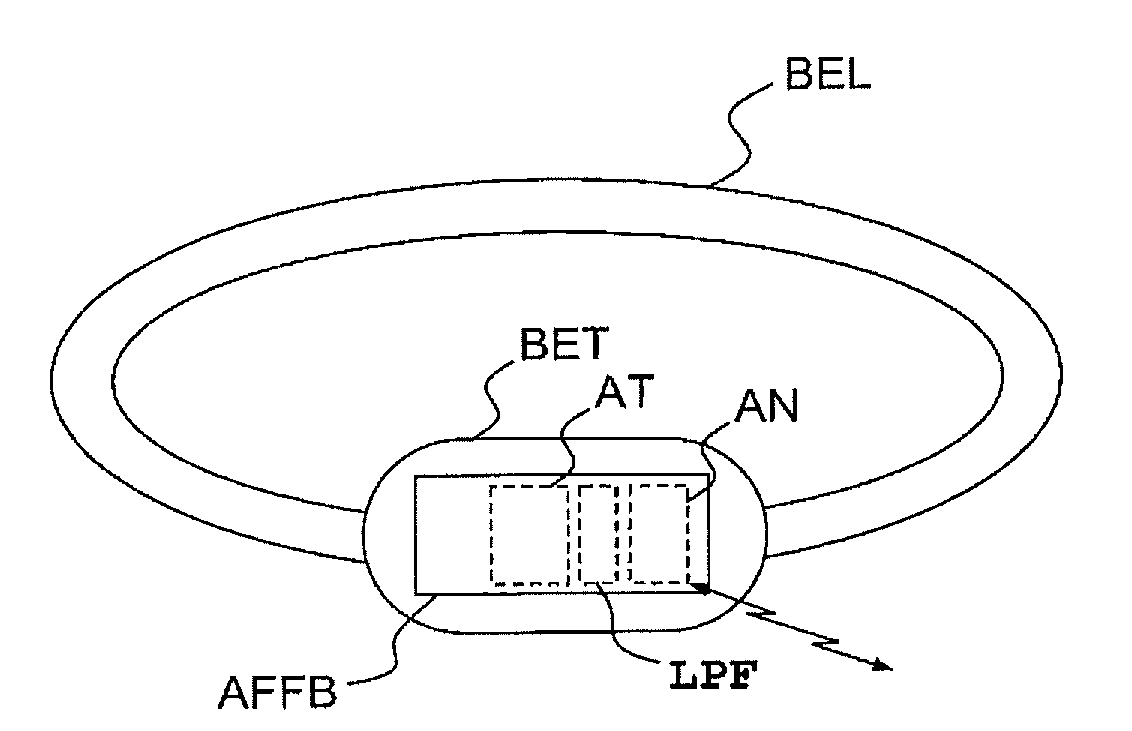
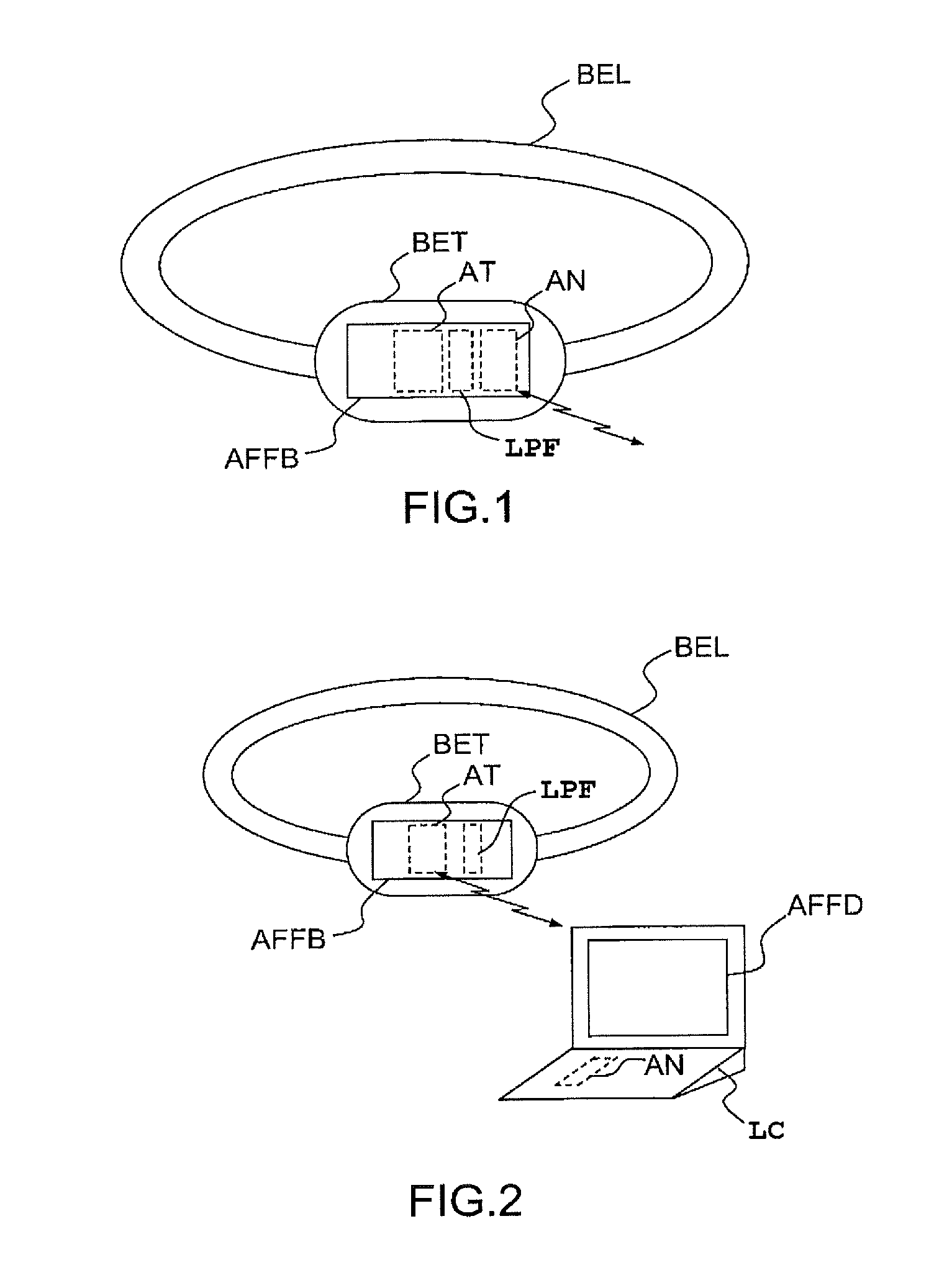
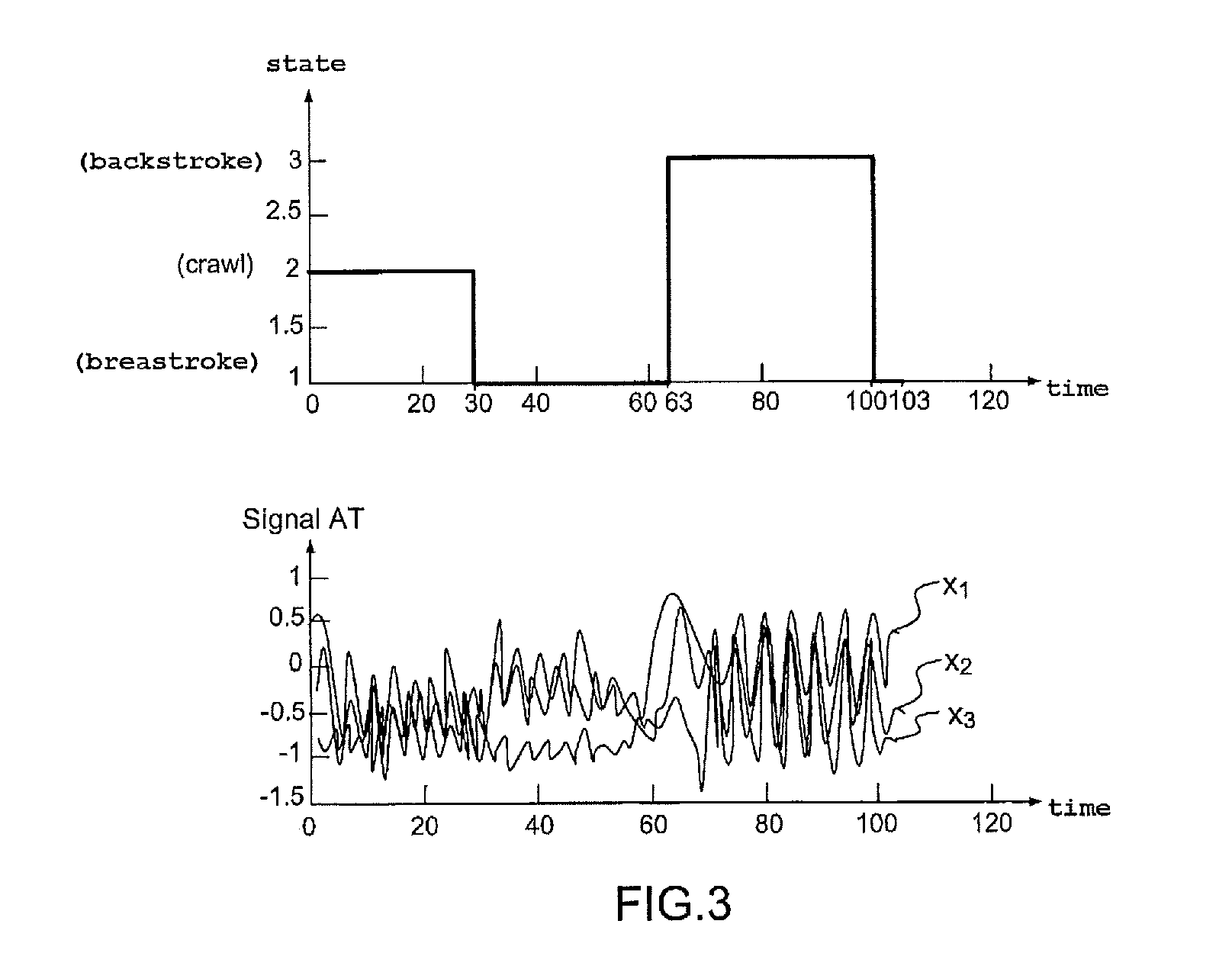
ActiveUS20120072165A1Easy to fixSuppress noiseAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSwimming detailsHide markov modelEngineering
A system for observing a swimming activity of a person includes a waterproof housing (BET) having a motion sensor (MS), and is furnished with fixing means (BEL) for securely fastening the housing (BET) to a part of the body of a user. The system has analysis means (AN) for analyzing the signals transmitted by the motion sensor (MS) to at least one measurement axis and which are adapted for determining the type of swimming of the user as a function of time by using a hidden Markov model with N states corresponding respectively to N types of swimming.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Method for predicting a user's future glycemic state
ActiveUS7731659B2Medical simulationDiagnostic recording/measuringMathematical modelConcentrations glucose
A method for predicting a user's future glycemic state includes measuring a user's glucose concentration at intervals over a time duration, thereby generating a plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time. First and second glucose prediction equations that are fits to the plurality of glucose concentrations based on first and second non-identical mathematical models, respectively, are then derived. The method also includes calculating first and second predicted glucose concentrations at a future time using the first and second glucose prediction equations, respectively. Thereafter, an average predicted glucose concentration and a merit index are calculated based on the first and second predicted glucose calculations. The plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time, the merit index and average predicted glucose concentration are input into a trained model (for example, a Hidden Markov Model) that outputs a set of glucose concentration probabilities. The user's future glycemic state is then predicted based on the set of glucose concentration probabilities.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Multi-resolution hidden markov model using class specific features
A method for classifying data includes selecting an elemental size and features for the data that are representative of possible subclasses. Resolution widths are selected in conjunction with these features. Models associated with symbols are developed from these resolution widths and features. Data is compared with these models to give a likelihood that the model applies. The best model is determined and a signal is provided related to the symbol associated with the best model.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
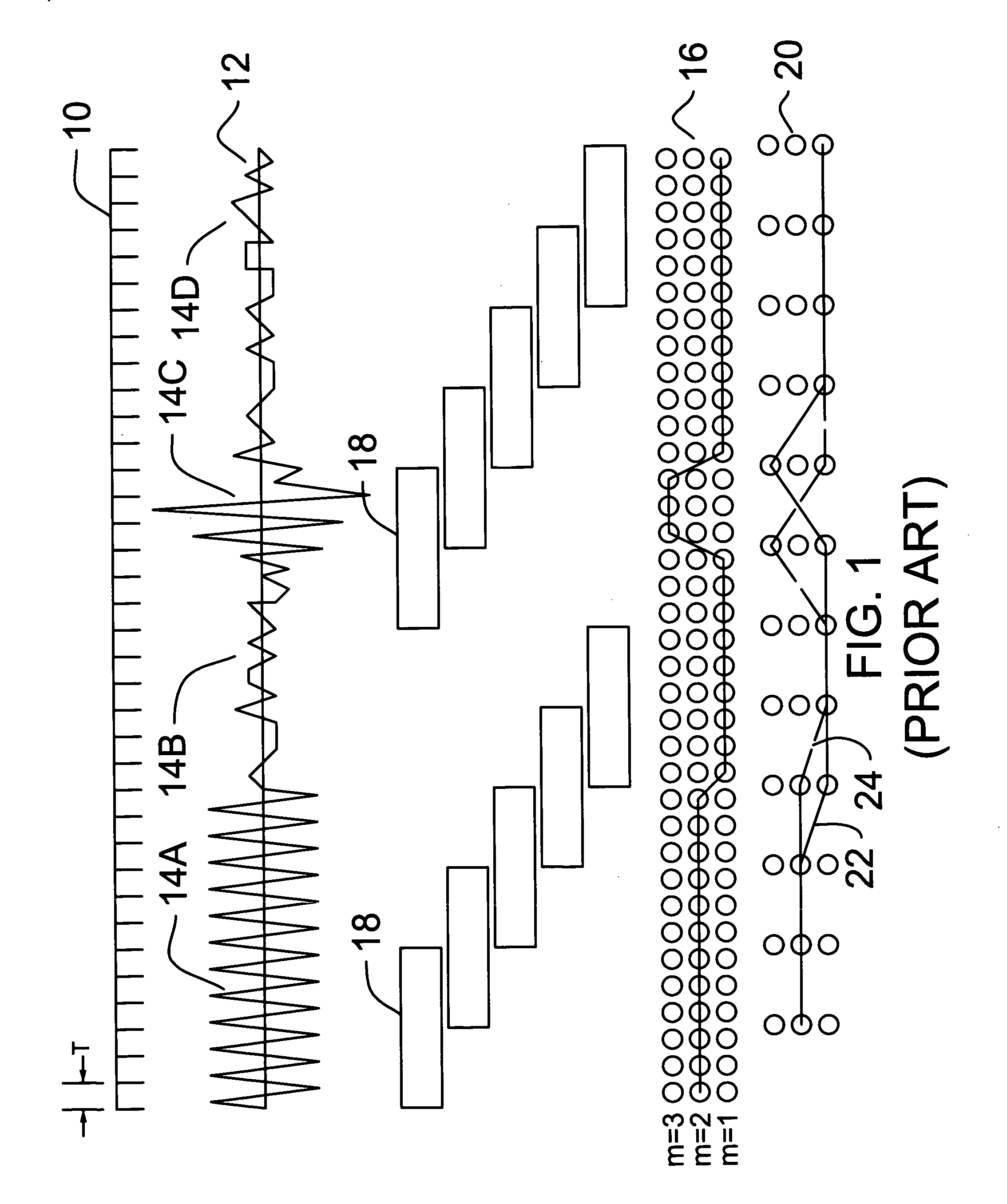
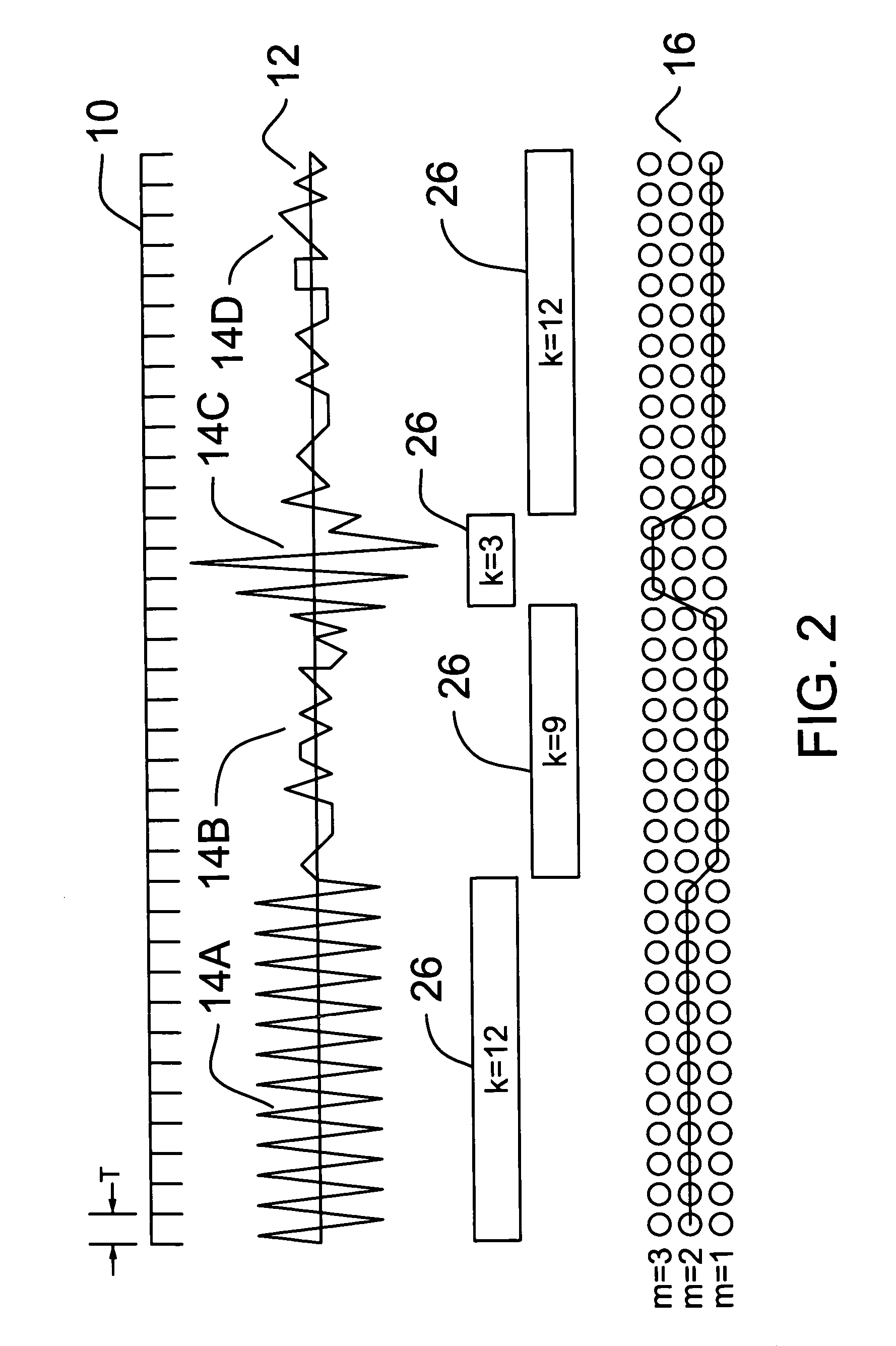
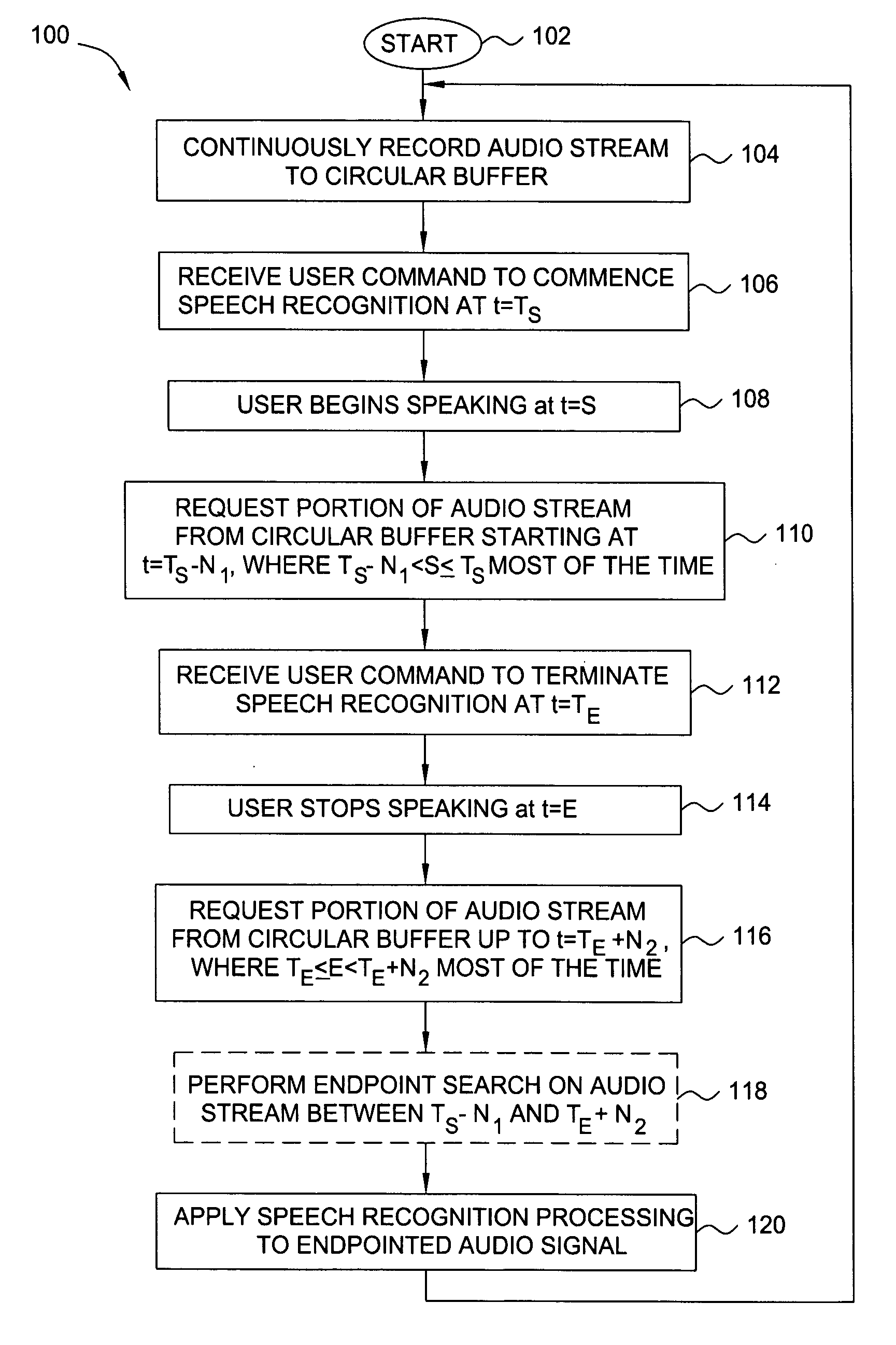
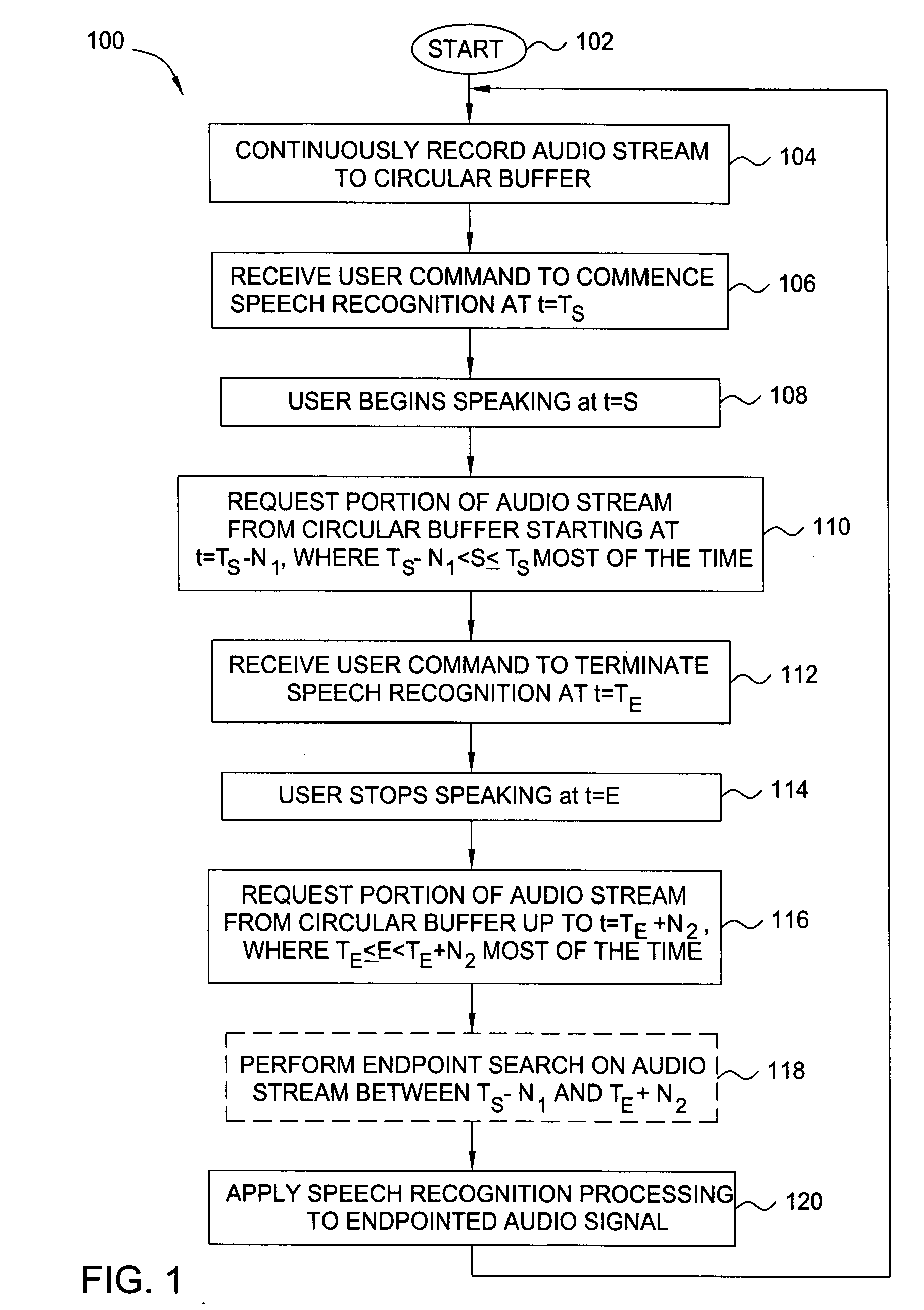
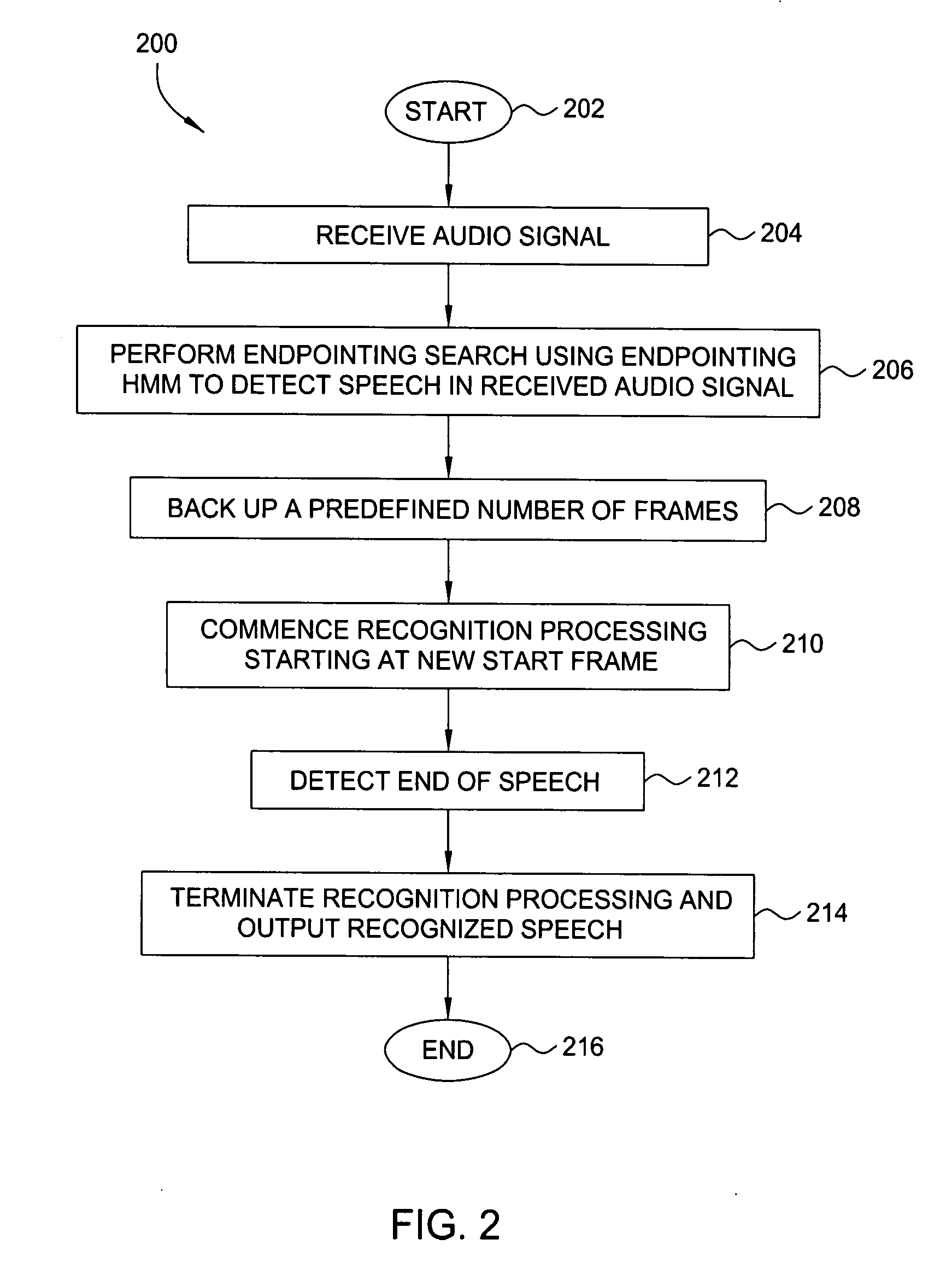
Method and apparatus for obtaining complete speech signals for speech recognition applications
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for obtaining complete speech signals for speech recognition applications. In one embodiment, the method continuously records an audio stream comprising a sequence of frames to a circular buffer. When a user command to commence or terminate speech recognition is received, the method obtains a number of frames of the audio stream occurring before or after the user command in order to identify an augmented audio signal for speech recognition processing. In further embodiments, the method analyzes the augmented audio signal in order to locate starting and ending speech endpoints that bound at least a portion of speech to be processed for recognition. At least one of the speech endpoints is located using a Hidden Markov Model.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Method for predicting a user's future glycemic state
A method for predicting a user's future glycemic state includes measuring a user's glucose concentration at intervals over a time duration, thereby generating a plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time. First and second glucose prediction equations that are fits to the plurality of glucose concentrations based on first and second non-identical mathematical models, respectively, are then derived. The method also includes calculating first and second predicted glucose concentrations at a future time using the first and second glucose prediction equations, respectively. Thereafter, an average predicted glucose concentration and a merit index are calculated based on the first and second predicted glucose calculations. The plurality of glucose concentrations as a function of time, the merit index and average predicted glucose concentration are input into a trained model (for example, a Hidden Markov Model) that outputs a set of glucose concentration probabilities. The user's future glycemic state is then predicted based on the set of glucose concentration probabilities.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Probabilistic Map Matching From A Plurality Of Observational And Contextual Factors
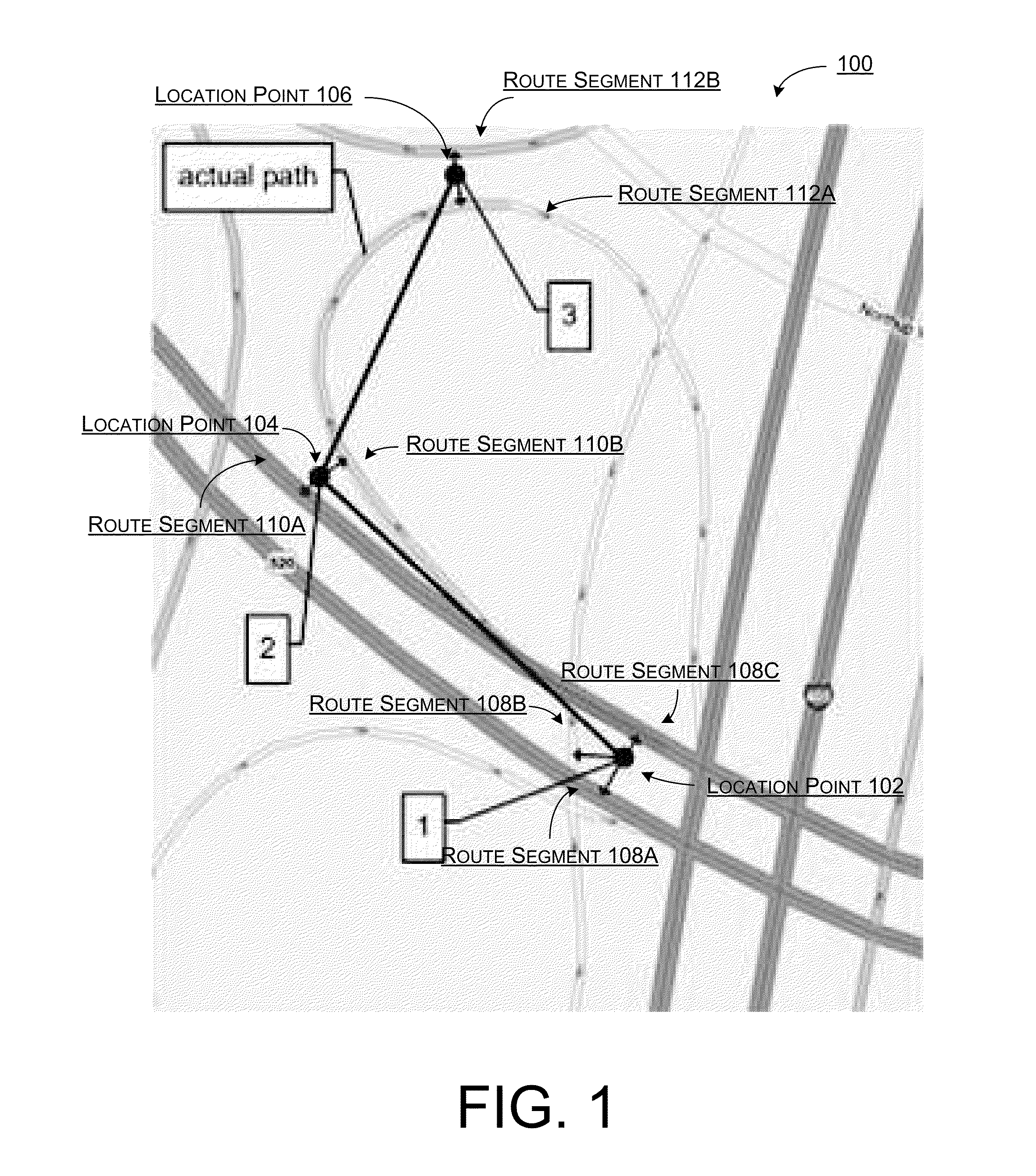
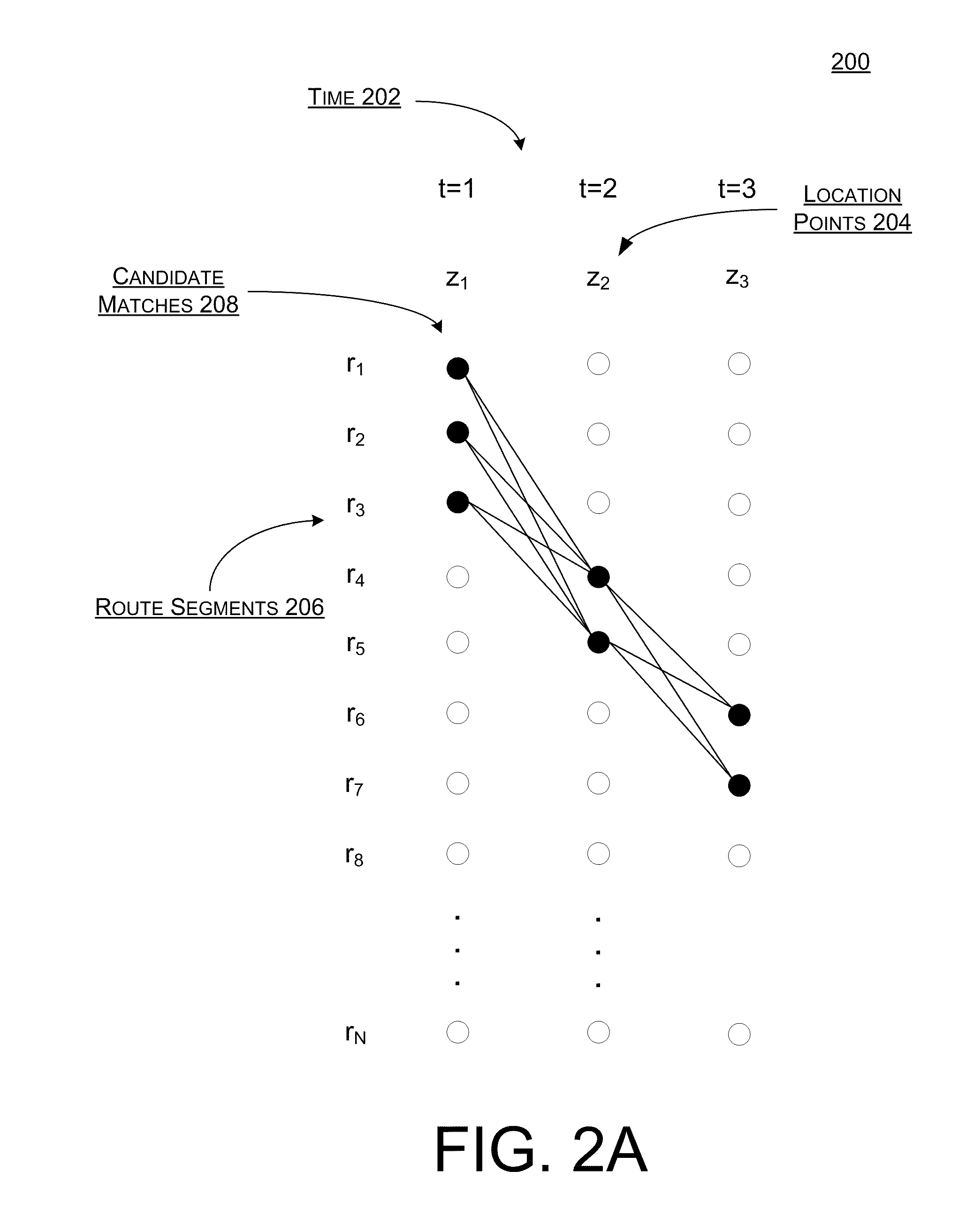
ActiveUS20110313648A1Well formedInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlProbit modelHide markov model
Systems, methods, and devices are described for implementing map matching techniques relating to measured location data. Probabilistic models, including temporal Bayesian network models and Hidden Markov Models, may be used for combining multiple classes of evidence relating to potential locations of points traversed on routes over time. Multiple route segments and overall routes may be maintained under relative uncertainty as candidates. The candidate route segments and overall routes may then be reduced into a smaller number of candidates or a single most likely route as a trip progresses. As the trip progresses, route segments in proximity to each location point are identified and candidate matches are determined. A probability of an entity traversing a candidate match at a given time and a probability of an entity traversing between a first candidate match at a first time and a second candidate match at a second time are determined based on a plurality of factors. Different modalities may be used to measure and transmit the location data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
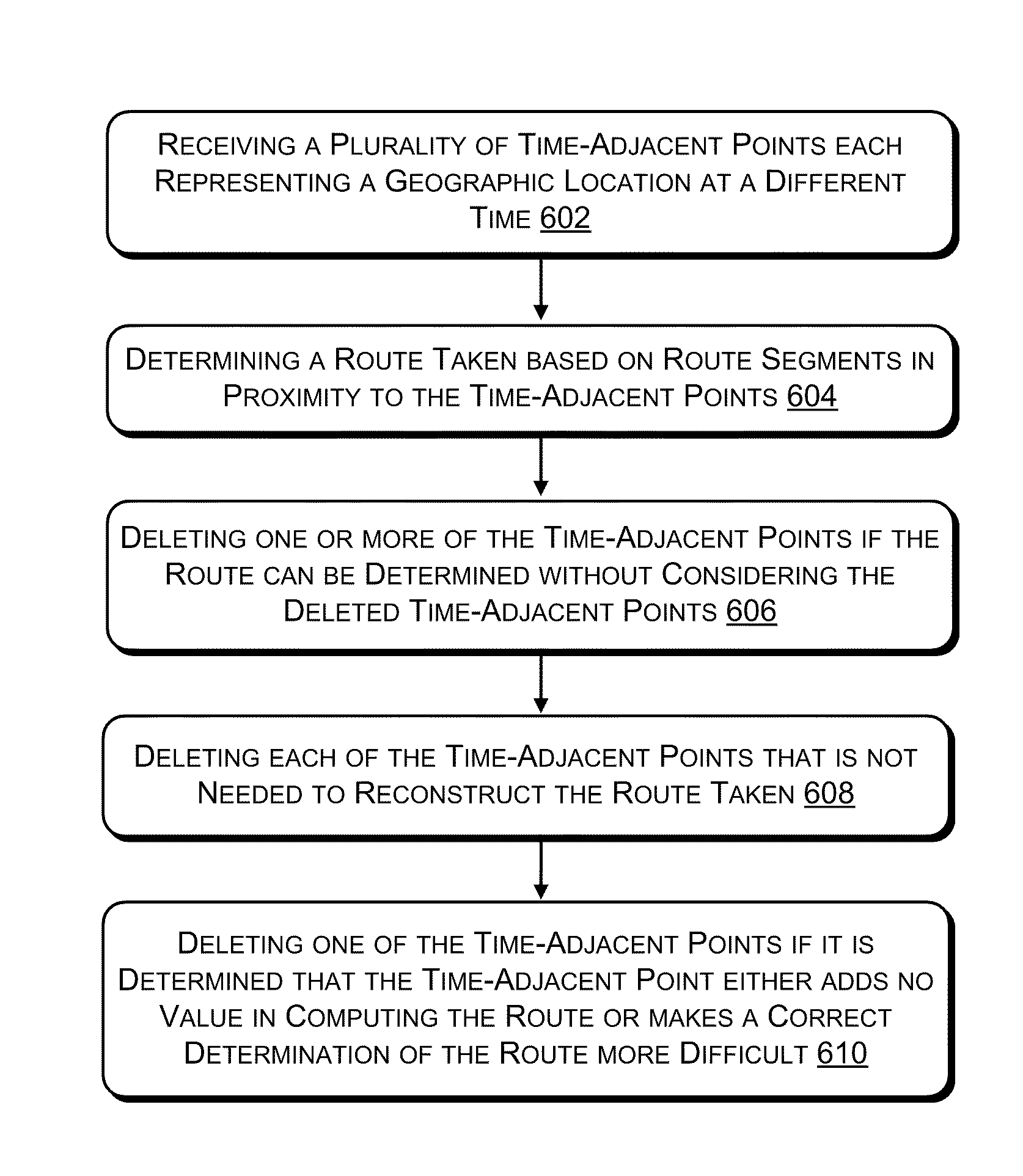
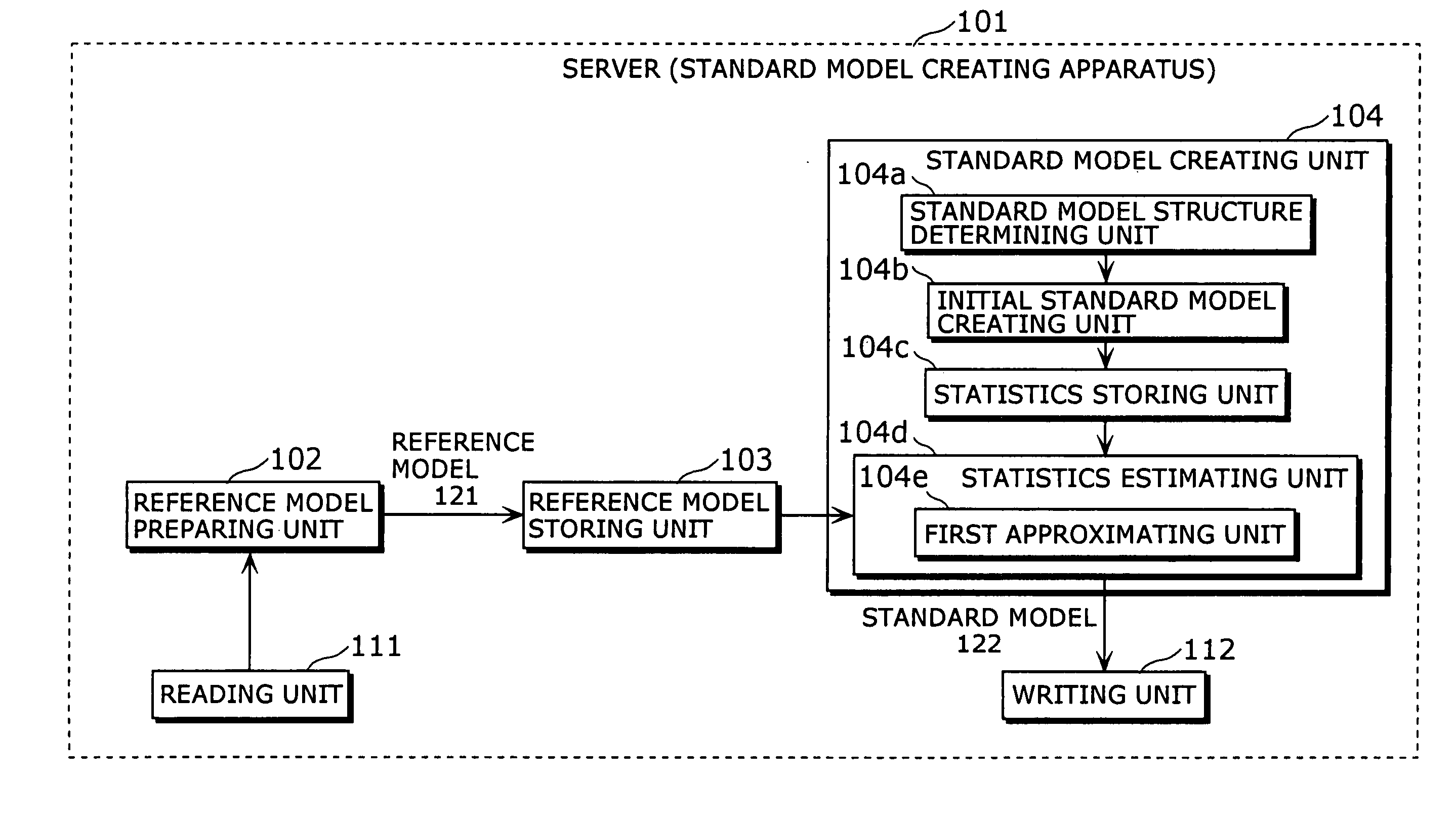
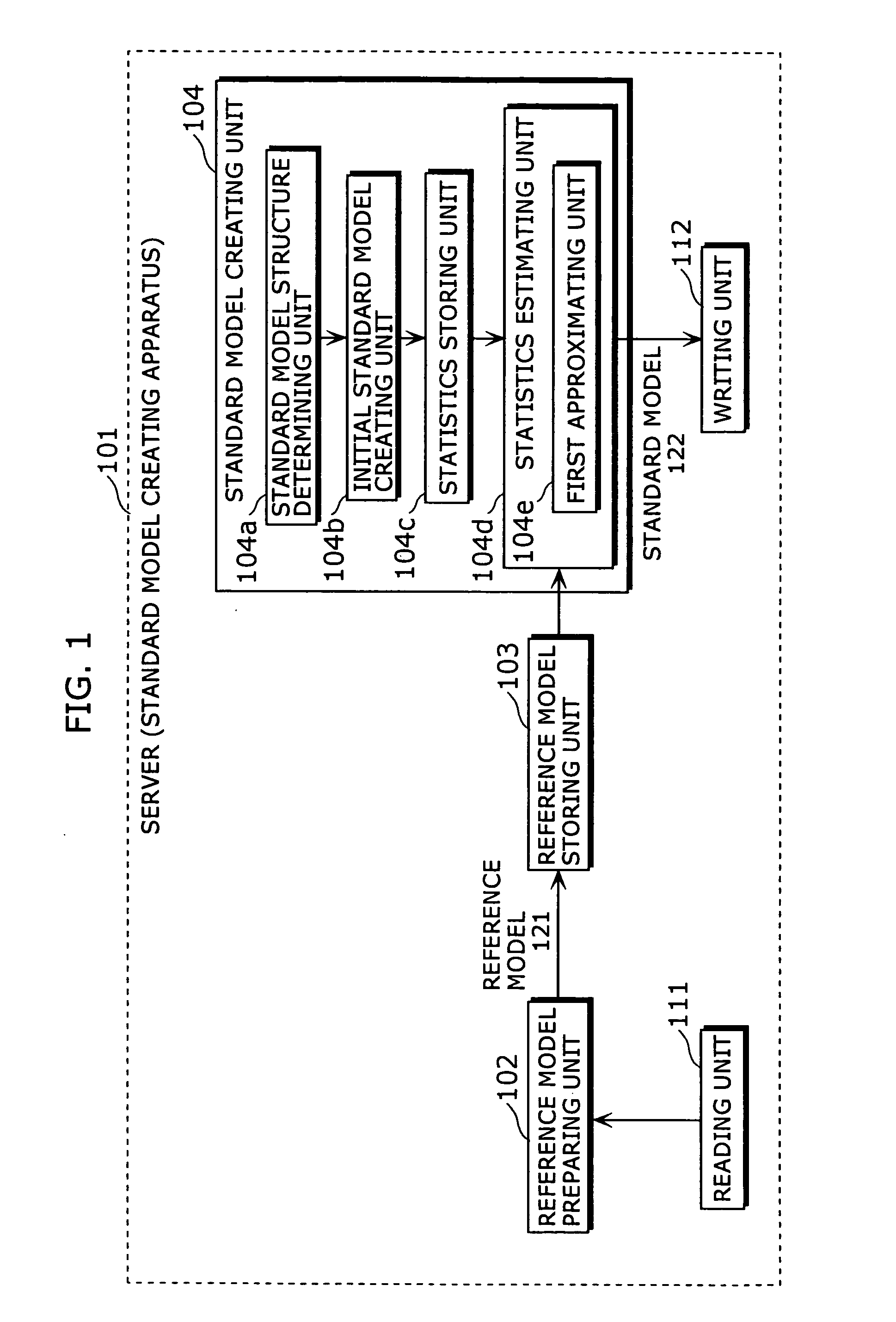
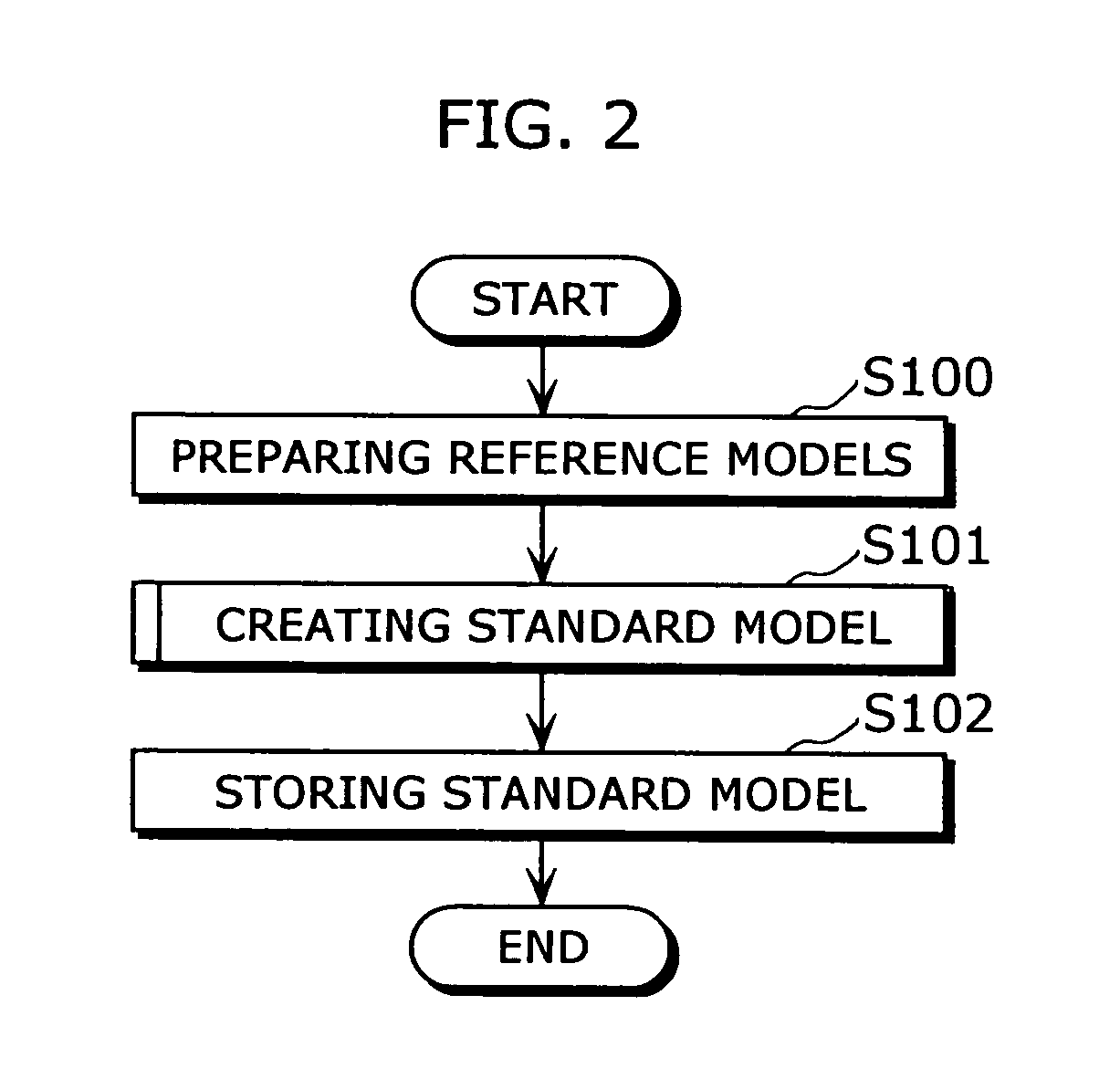
Standard model creating device and standard model creating method
ActiveUS20060053014A1Easy to createHigh practical valueSpeech recognitionReference modelHide markov model
The standard model creating apparatus which provides a high-precision standard model used for: pattern recognition such as speech recognition, character recognition, or image recognition using a probability model based on a hidden Markov model, Bayesian theory, or linear discrimination analysis; intention interpretation using a probability model such as a Bayesian net; data-mining performed using a probability model; and so forth, the apparatus comprising: a reference model preparing unit (102) operable to prepare at least one reference model; a reference model storing unit (103) operable to store the reference model (121) prepared by the reference model preparing unit (102); and a standard model creating unit (104) operable to create a standard model (122) by calculating statistics of the standard model so as to maximize or locally maximize the probability or likelihood with respect to the at least one reference model stored in the reference model storing unit (103).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Speech and text driven HMM-based body animation synthesis
An “Animation Synthesizer” uses trainable probabilistic models, such as Hidden Markov Models (HMM), Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), etc., to provide speech and text driven body animation synthesis. Probabilistic models are trained using synchronized motion and speech inputs (e.g., live or recorded audio / video feeds) at various speech levels, such as sentences, phrases, words, phonemes, sub-phonemes, etc., depending upon the available data, and the motion type or body part being modeled. The Animation Synthesizer then uses the trainable probabilistic model for selecting animation trajectories for one or more different body parts (e.g., face, head, hands, arms, etc.) based on an arbitrary text and / or speech input. These animation trajectories are then used to synthesize a sequence of animations for digital avatars, cartoon characters, computer generated anthropomorphic persons or creatures, actual motions for physical robots, etc., that are synchronized with a speech output corresponding to the text and / or speech input.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
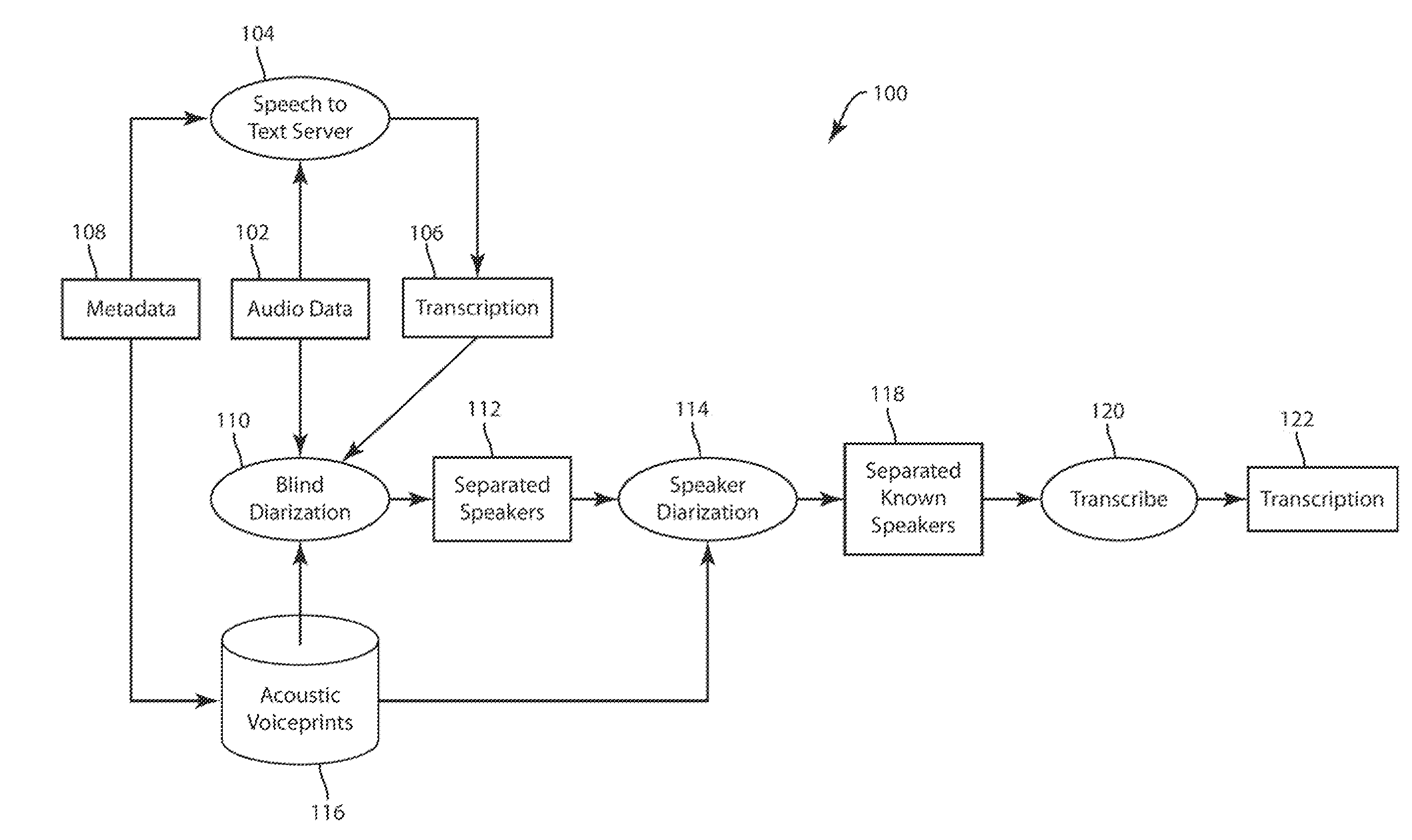
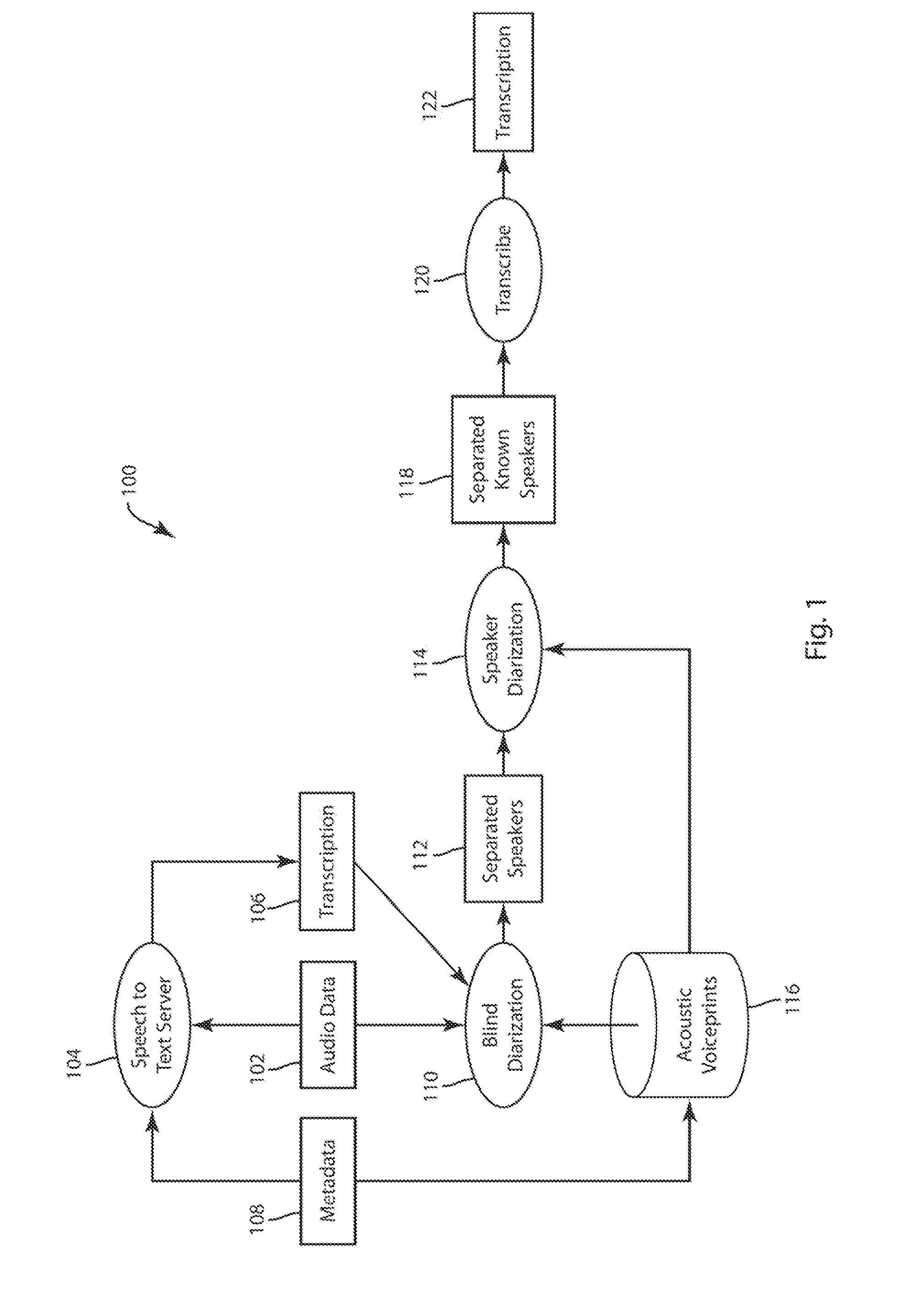
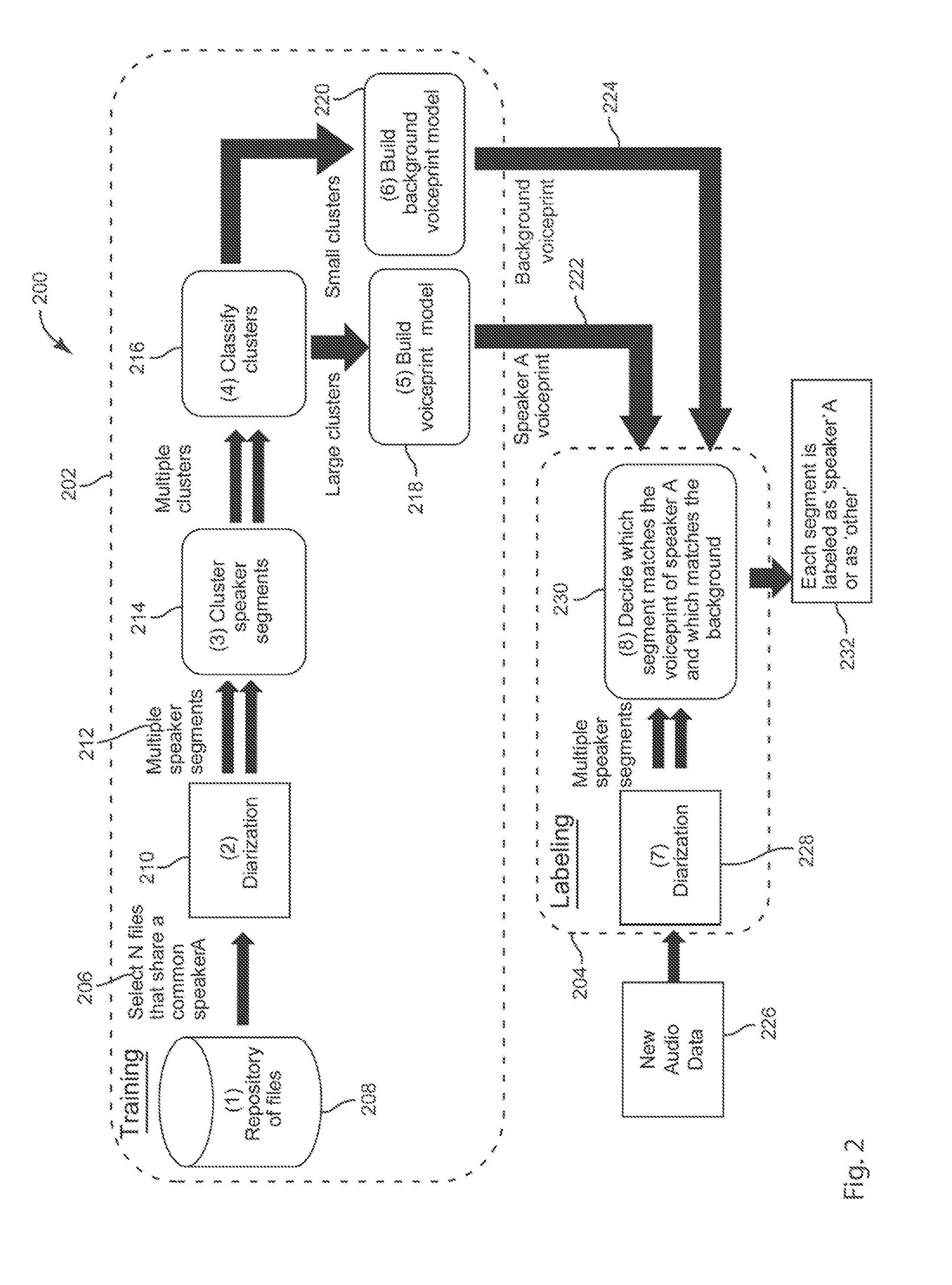
Blind Diarization of Recorded Calls with Arbitrary Number of Speakers
In a method of diarization of audio data, audio data is segmented into a plurality of utterances. Each utterance is represented as an utterance model representative of a plurality of feature vectors. The utterance models are clustered. A plurality of speaker models are constructed from the clustered utterance models. A hidden Markov model is constructed of the plurality of speaker models. A sequence of identified speaker models is decoded.
Owner:VERINT SYST INC
Hidden markov model based object tracking and similarity metrics
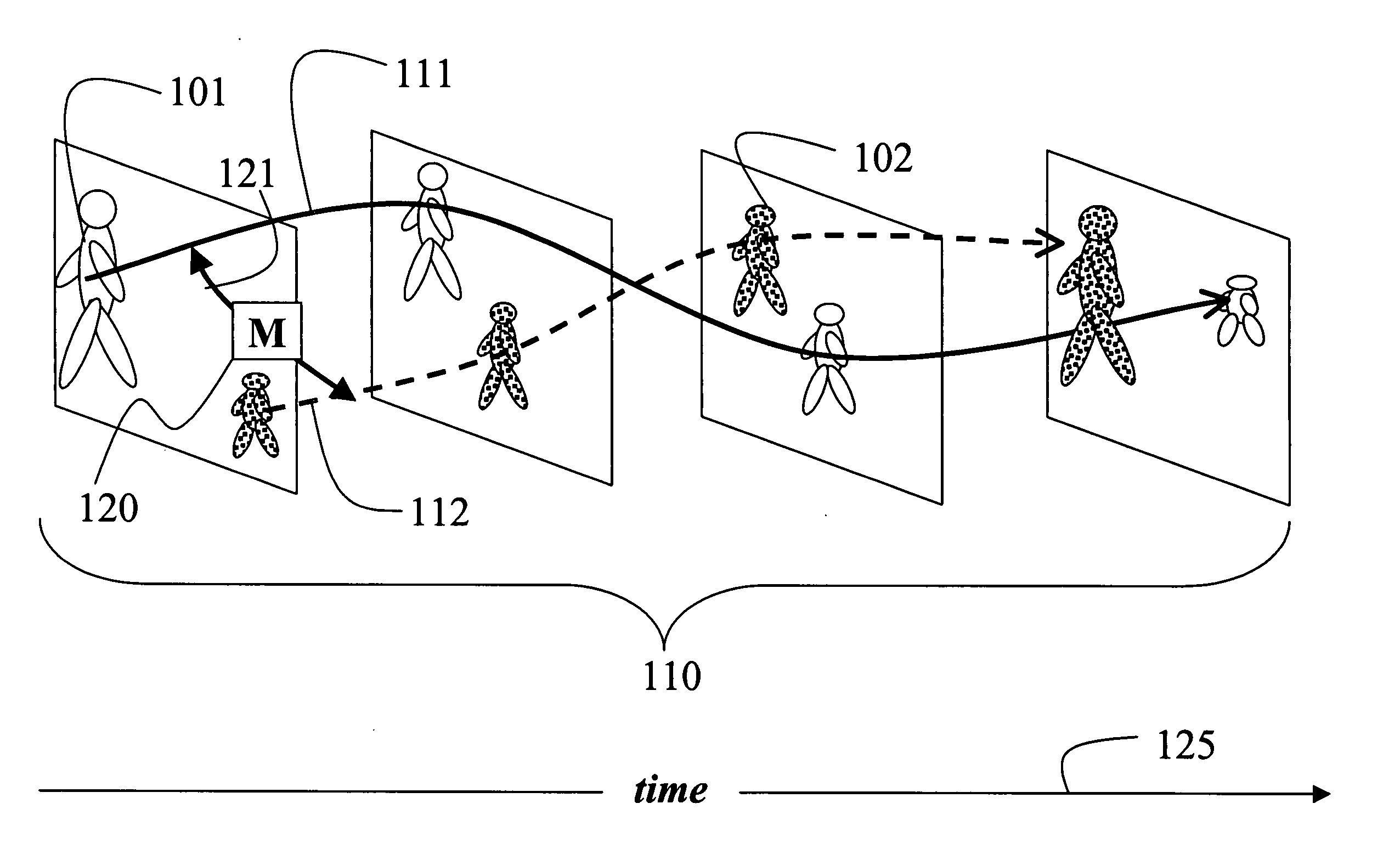
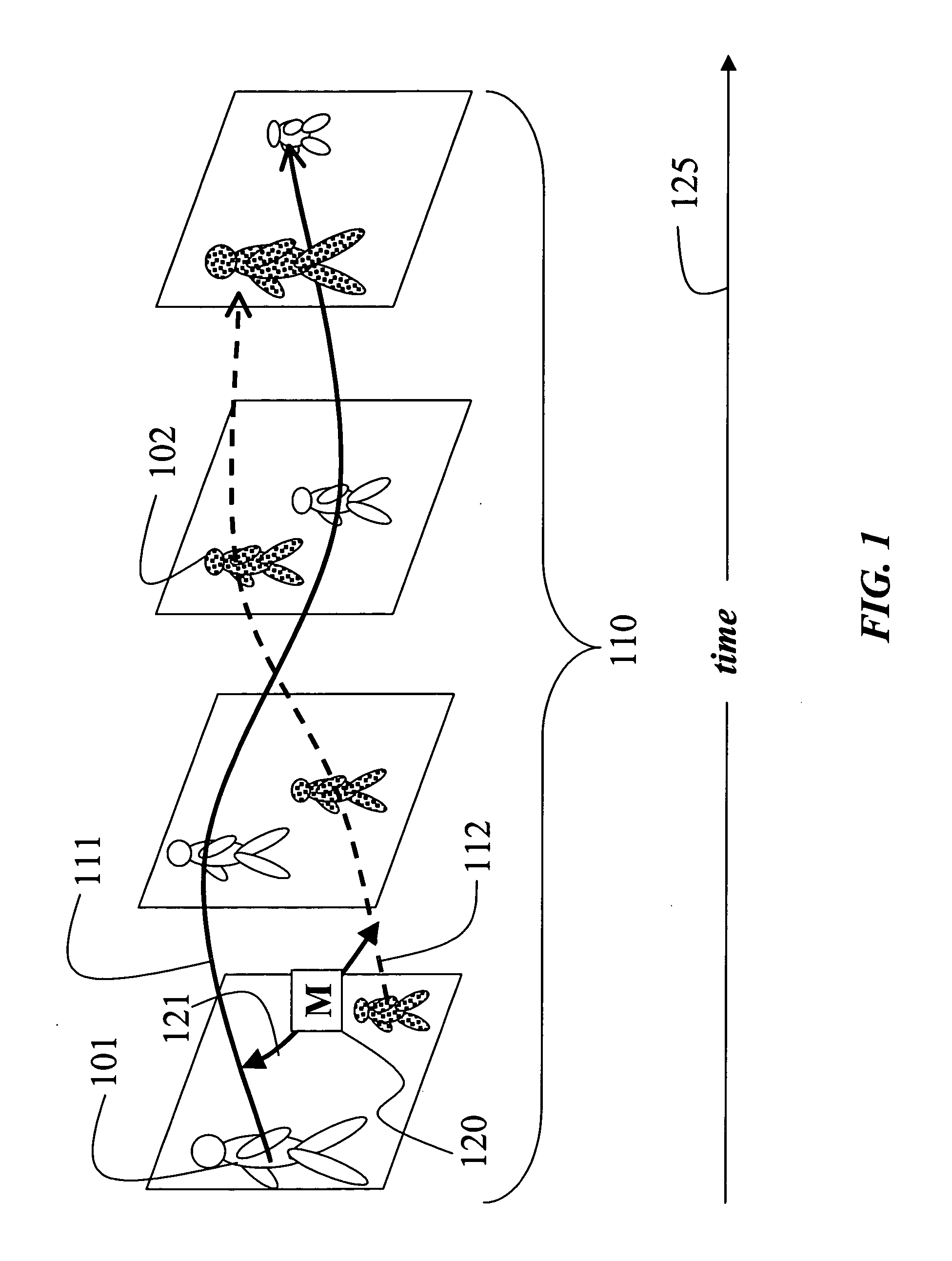
A method models a set of trajectories of a set of objects; there is one trajectory for each object. A sequence of positions of each object is obtained over a duration of time to define a trajectory of the object. The sequence of positions is then projected to a hidden Markov model to model the trajectory of each object.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
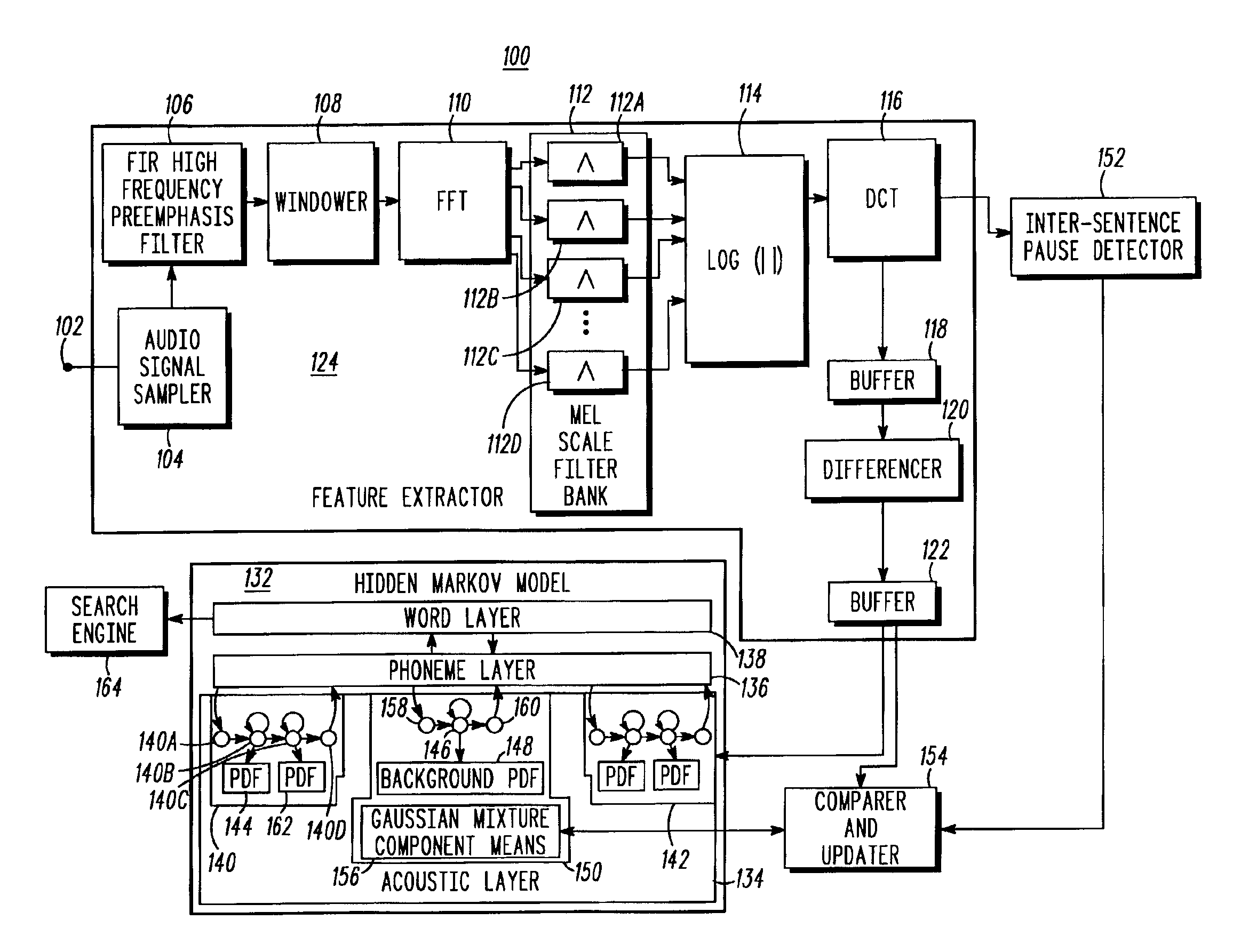
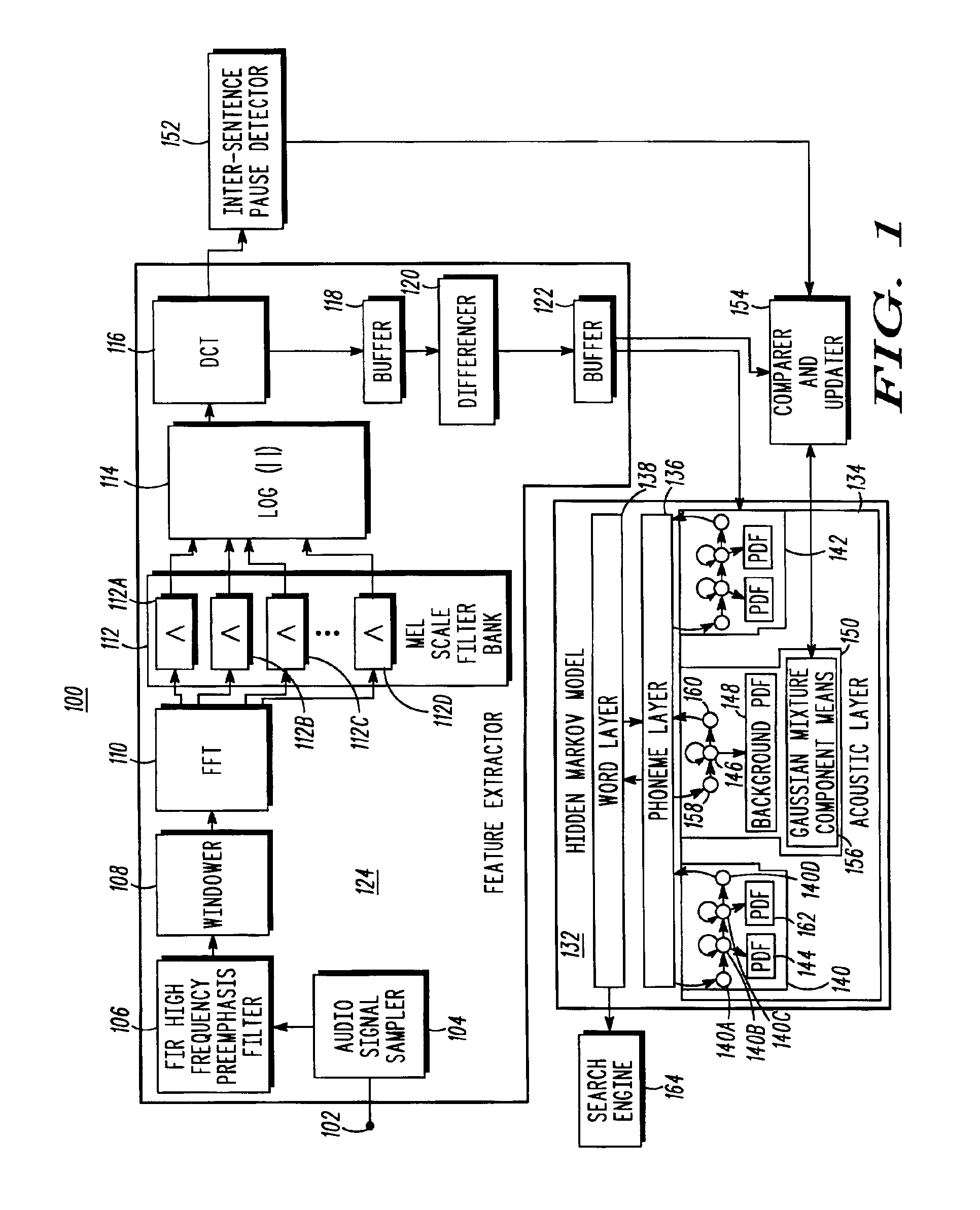
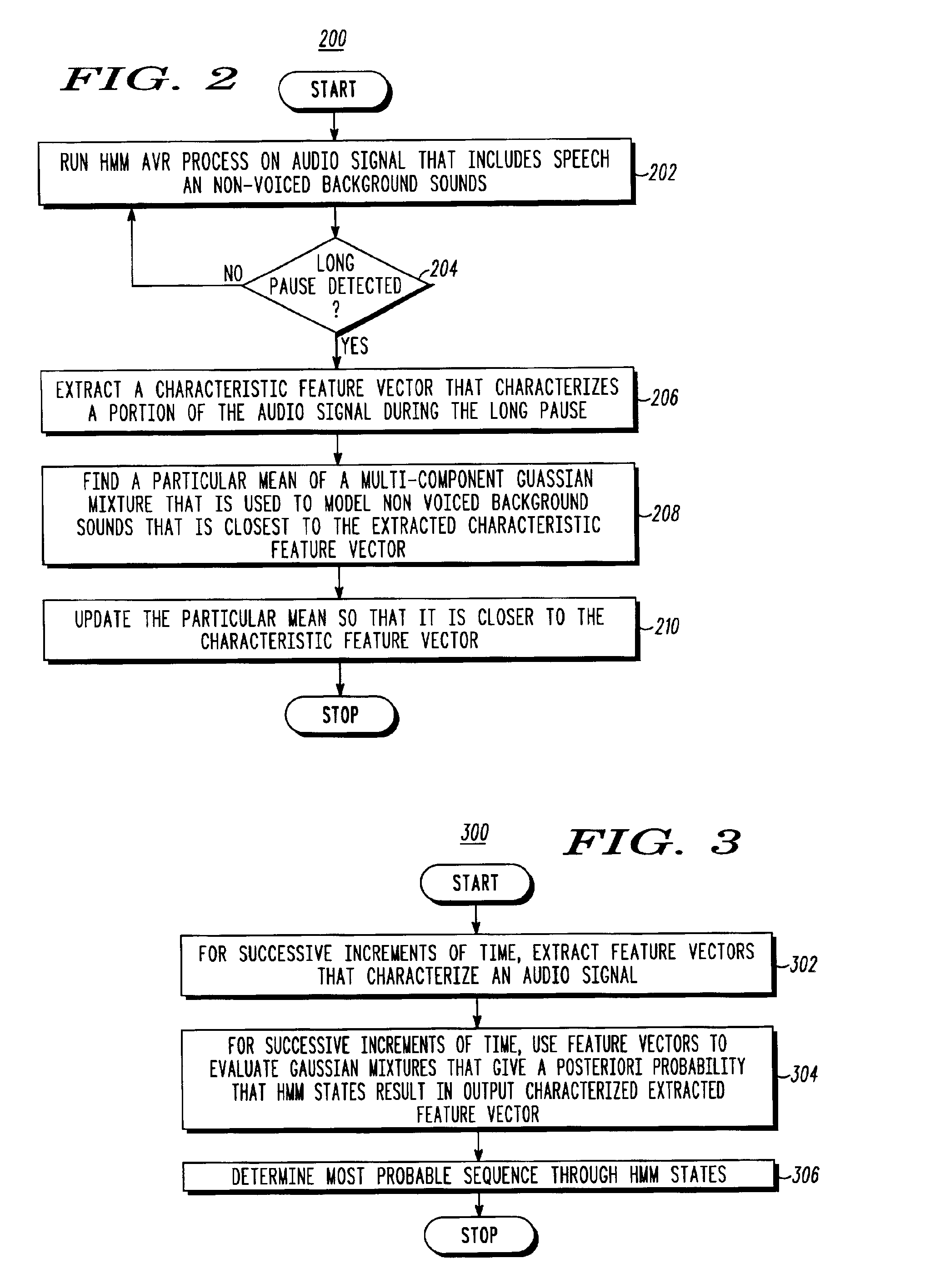
Speech recognition by dynamical noise model adaptation
The invention provides a Hidden Markov Model (132) based automated speech recognition system (100) that dynamically adapts to changing background noise by detecting long pauses in speech, and for each pause processing background noise during the pause to extract a feature vector that characterizes the background noise, identifying a Gaussian mixture component of noise states that most closely matches the extracted feature vector, and updating the mean of the identified Gaussian mixture component so that it more closely matches the extracted feature vector, and consequently more closely matches the current noise environment. Alternatively, the process is also applied to refine the Gaussian mixtures associated with other emitting states of the Hidden Markov Model.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Clickstream Purchase Prediction Using Hidden Markov Models
Technology for predicting online user shopping behavior, such as whether a user will purchase a product, is described. An example method includes receiving current session data describing a current session for a current user, extracting a current clickstream from the current session data classifying the current clickstream as a purchase clickstream or a non-purchase clickstream by processing the current clickstream using one or more sets of Hidden Markov Model parameters produced by one or more Hidden Markov Models, and computing, using the one or more computing devices, a purchase probability that the current user will purchase a product during the current session based on the classifying.
Owner:STAPLES INC
Sequence-based positioning technique
ActiveUS20050136944A1Reduce uncertaintyReducing locationTelephonic communicationPosition fixationProbit modelHide markov model
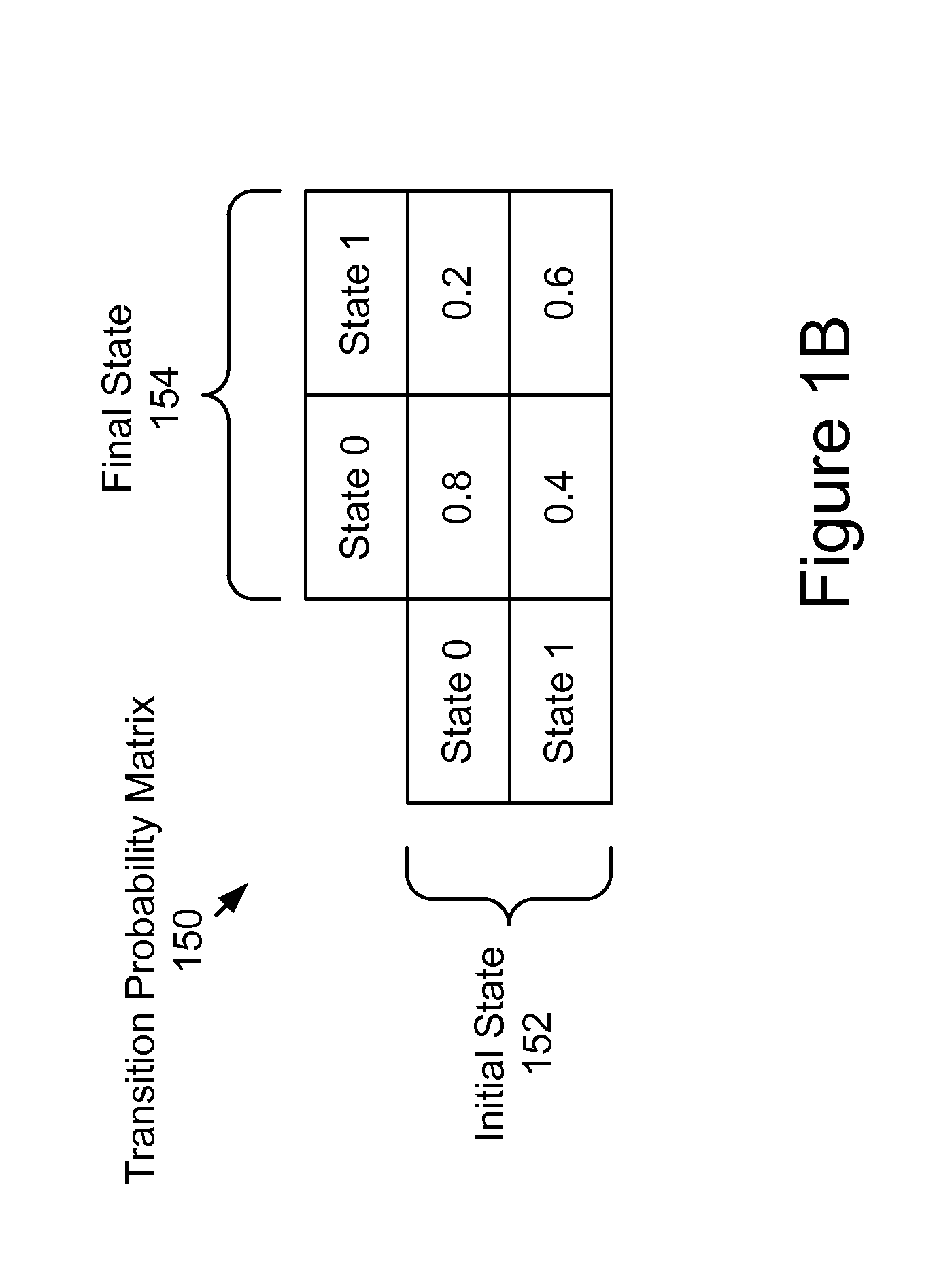
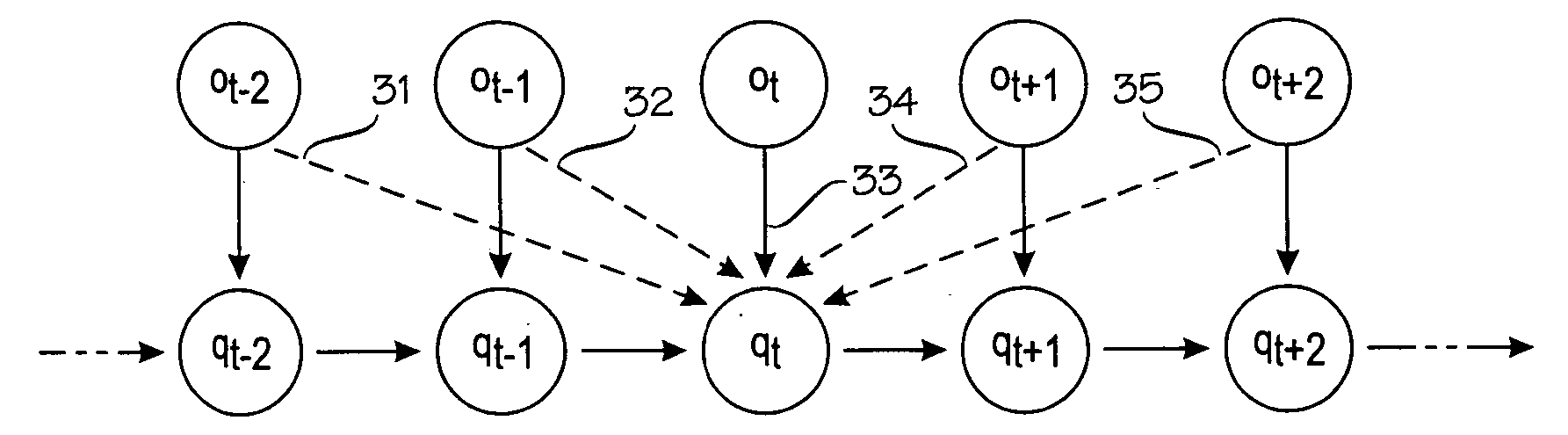
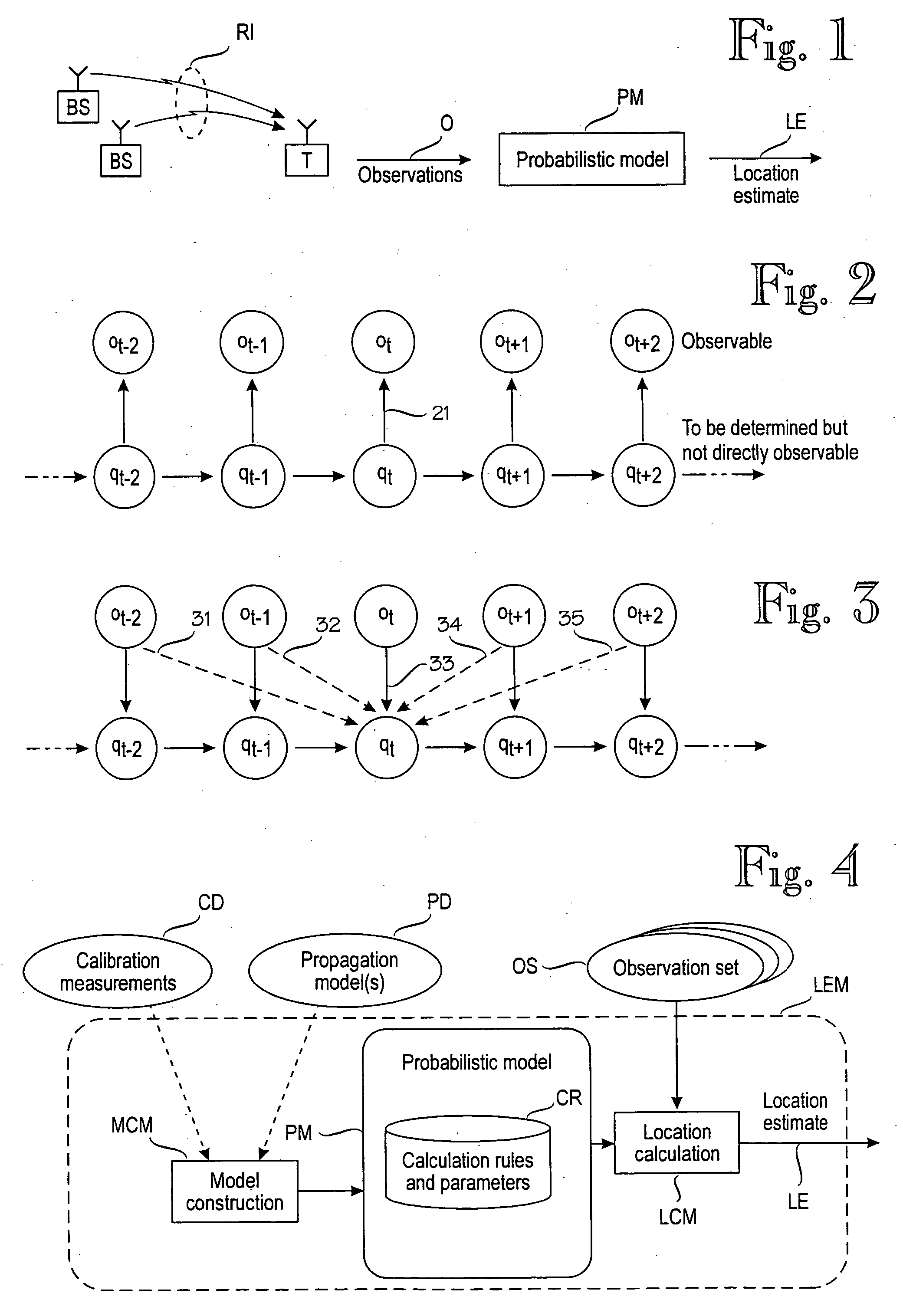
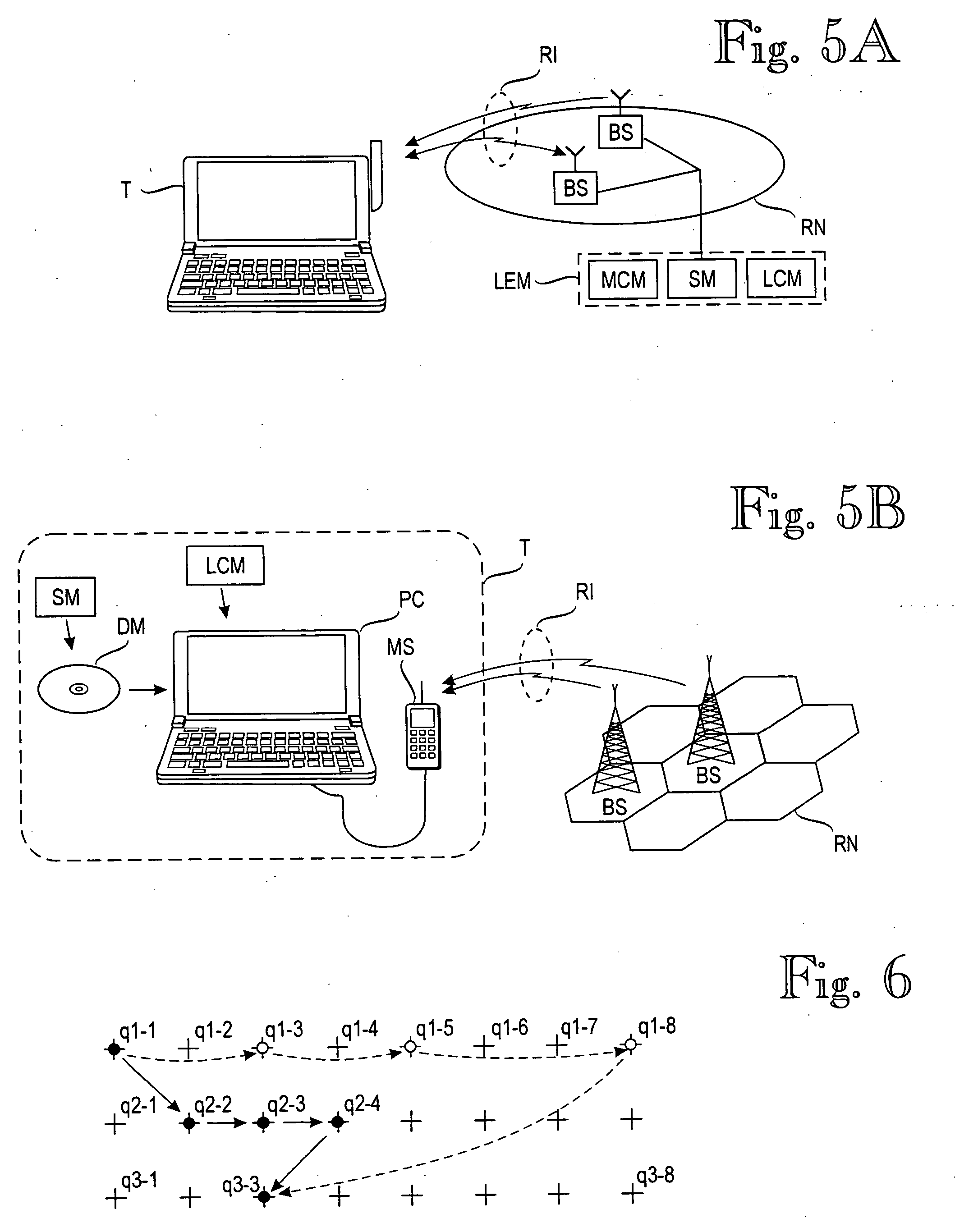
A target device's location is estimated by a location estimation module (LEM) that comprises a probabilistic model (PM) for a plurality of sample points, each of which comprises a sample location and an expected distribution of signal values at that sample point. The location estimation module (LEM) makes a sequence (OS) of observations on, n=1, 2, 3 . . . , of signal values. Each observation corresponds to a respective location qn along the target device's path. The sequence of observations and the respective location constitute a hidden Markov model. The module estimates the target device's location qn based on the probabilistic model (PM) and the sequence of observations, wherein the sequence of observations comprises one or more future observations on+m for which m is a positive integer. In other words, the target device's location is estimated, at least partially, based on knowledge of its future.
Owner:AIRISTA FLOW INC +1
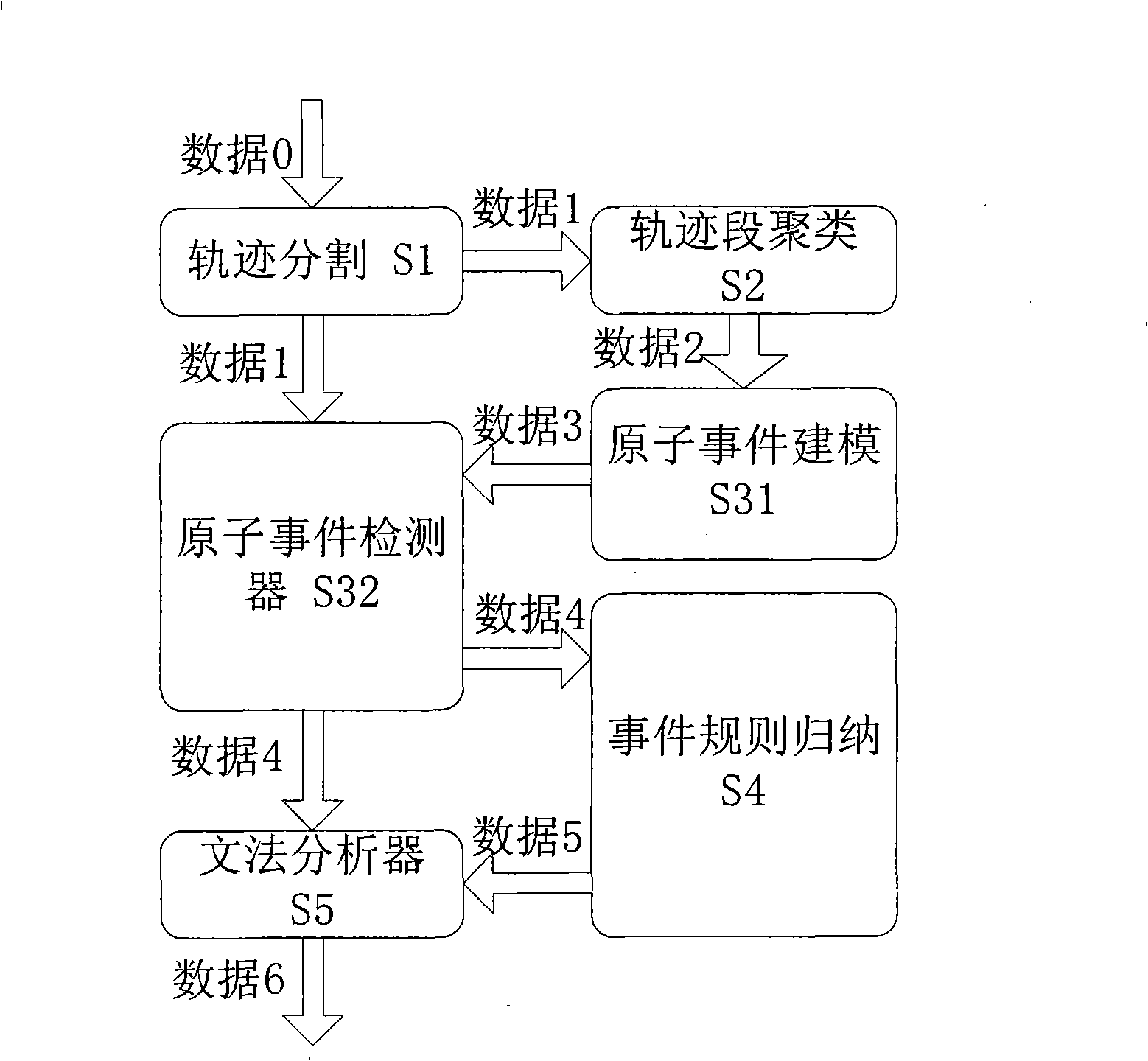
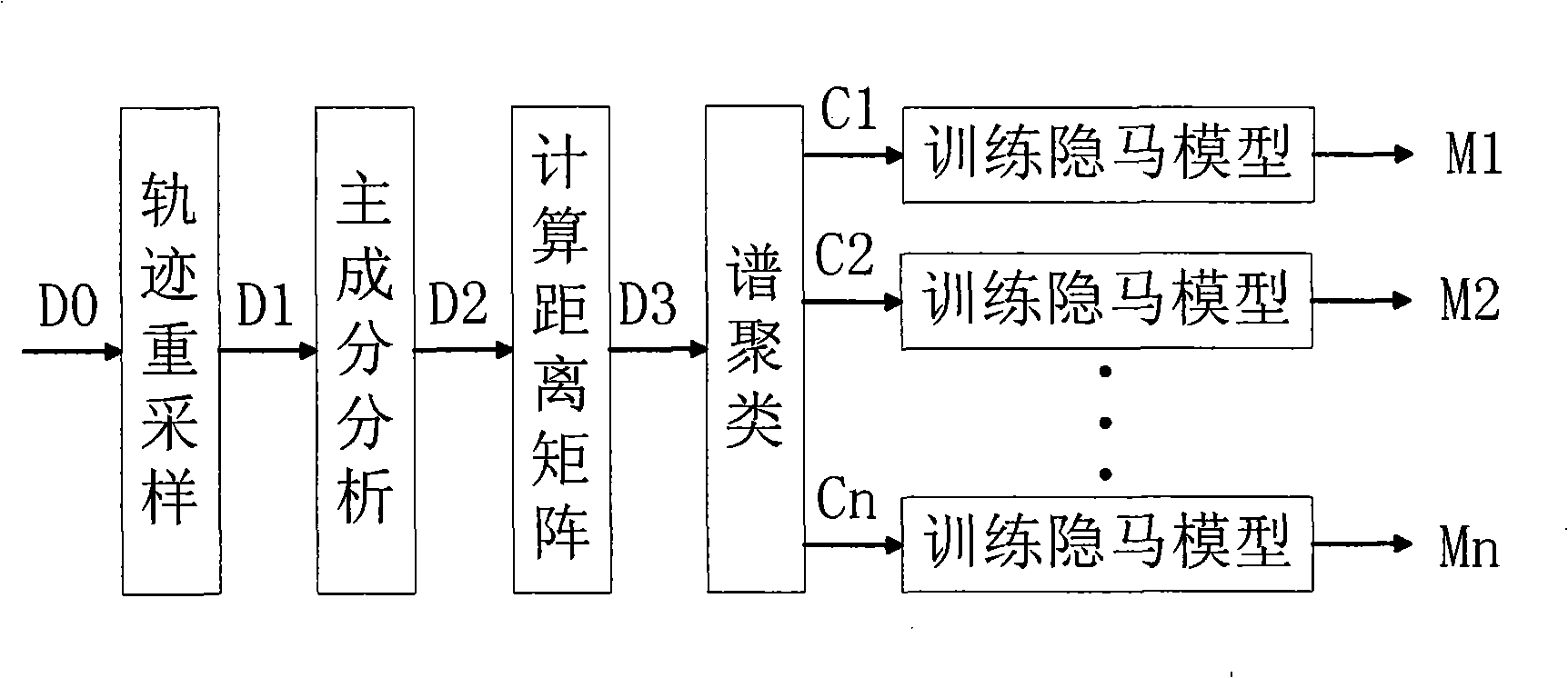
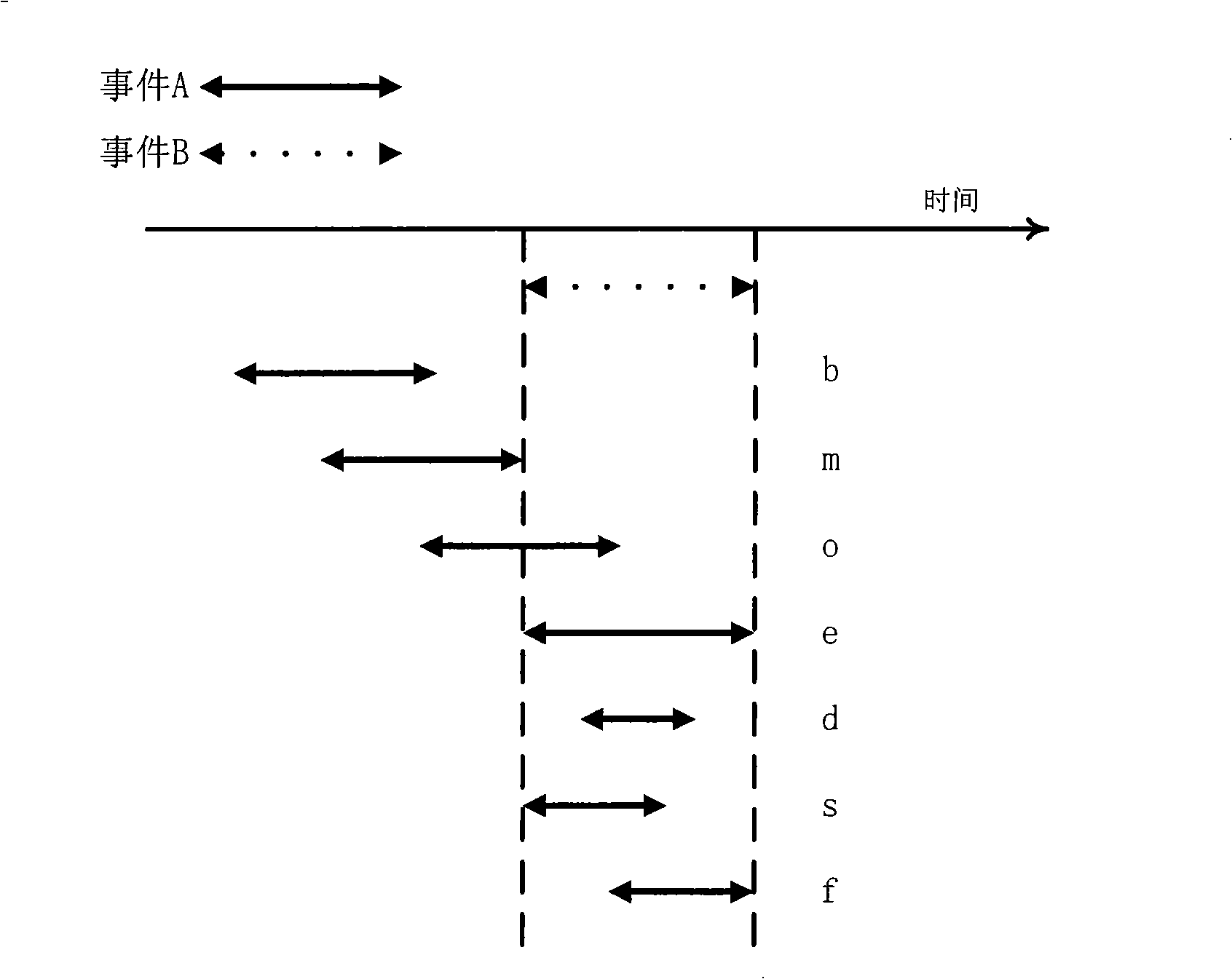
Video frequency behaviors recognition method based on track sequence analysis and rule induction
InactiveCN101334845AReduce manpower consumptionCharacter and pattern recognitionVideo monitoringSequence analysis
The invention discloses a method for identifying the video action based on trajectory sequence analysis and rule induction, which solves the problems of large labor intensity. The method of the invention divides a complete trajectory in a scene into a plurality of trajectory section with basic meaning, and obtains a plurality of basic movement modes as atomic events through the trajectory clustering; meanwhile, a hidden Markov model is utilized for establishing a model to obtain the event rule contained in the trajectory sequence by inducting the algorithm based on the minimum description length and based on the event rule, an expanded grammar analyzer is used for identifying an interested event. The invention provides a complete video action identification frame and also a multi-layer rule induction strategy by taking the space-time attribute, which significantly improves the effectiveness of the rule learning and promotes the application of the pattern recognition in the identification of the video action. The method of the invention can be applied to the intelligent video surveillance and automatic analysis of movements of automobiles or pedestrians under the current monitored scene so as to lead a computer to assist people or substitute people to complete monitor tasks.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
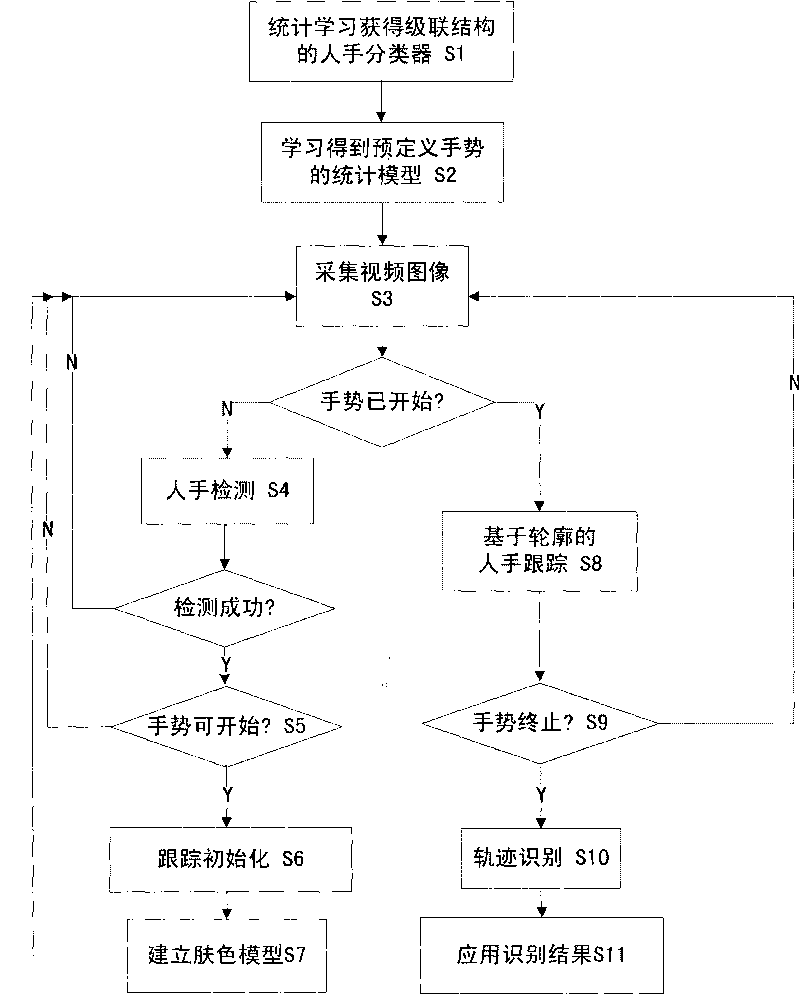
Real-time gesture interaction method based on computer vision
InactiveCN101763515AVisual technology is matureComprehensive effectCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer usersCombined method
The invention discloses a real-time gesture interaction method based on computer vision, which comprises the following steps: acquiring a digital image from an image input device; detecting hands by a statistical learning method; initializing a hand contour tracker according to the detecting result, and calculating a skin color model of a specific hand; tracking the hand contour by a combined method of a conditional probability density transmission algorithm and a heuristic search technology; analyzing the moving track of the hands by a Hidden Markov Model to obtain the gesture identifying result; and applying the gesture analyzing result to the interaction of various application programs. The real-time gesture interaction method of the invention expands the interactive mode of the traditional mouse and keyboard, realizes automatic hand detection, tracking and gesture identification by the computer vision and image processing techniques, has real-time performance, robustness and easy realization and operation, and can enable computer users to interact with the computer more naturally, visually and intelligently by hand gestures.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
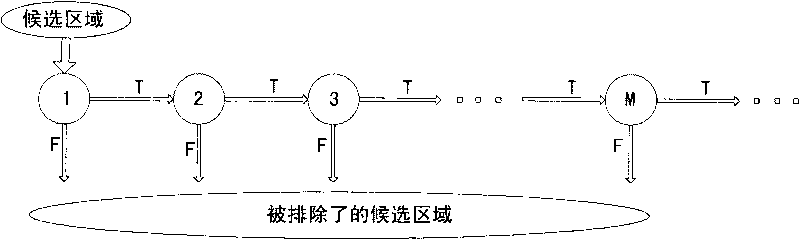
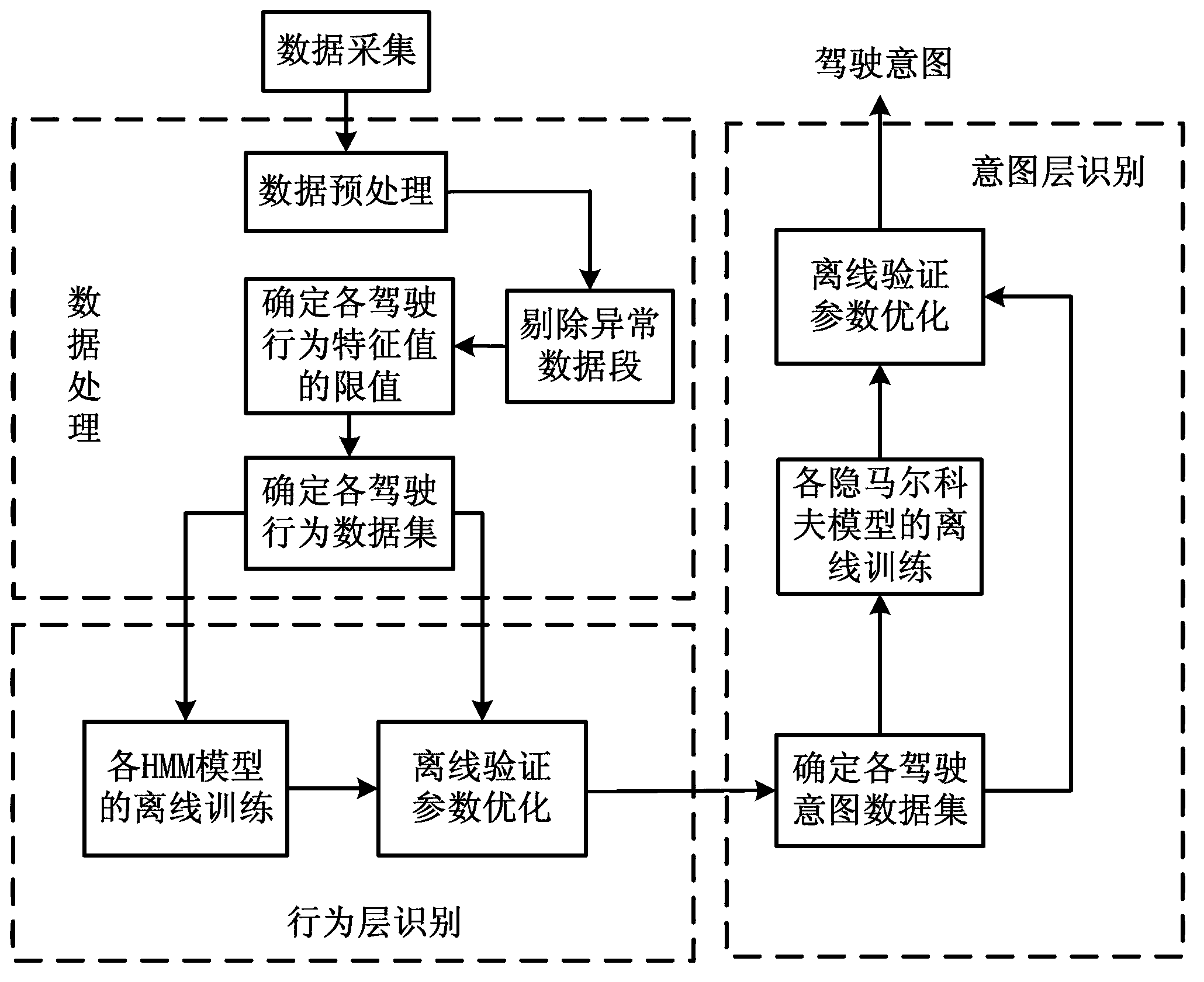
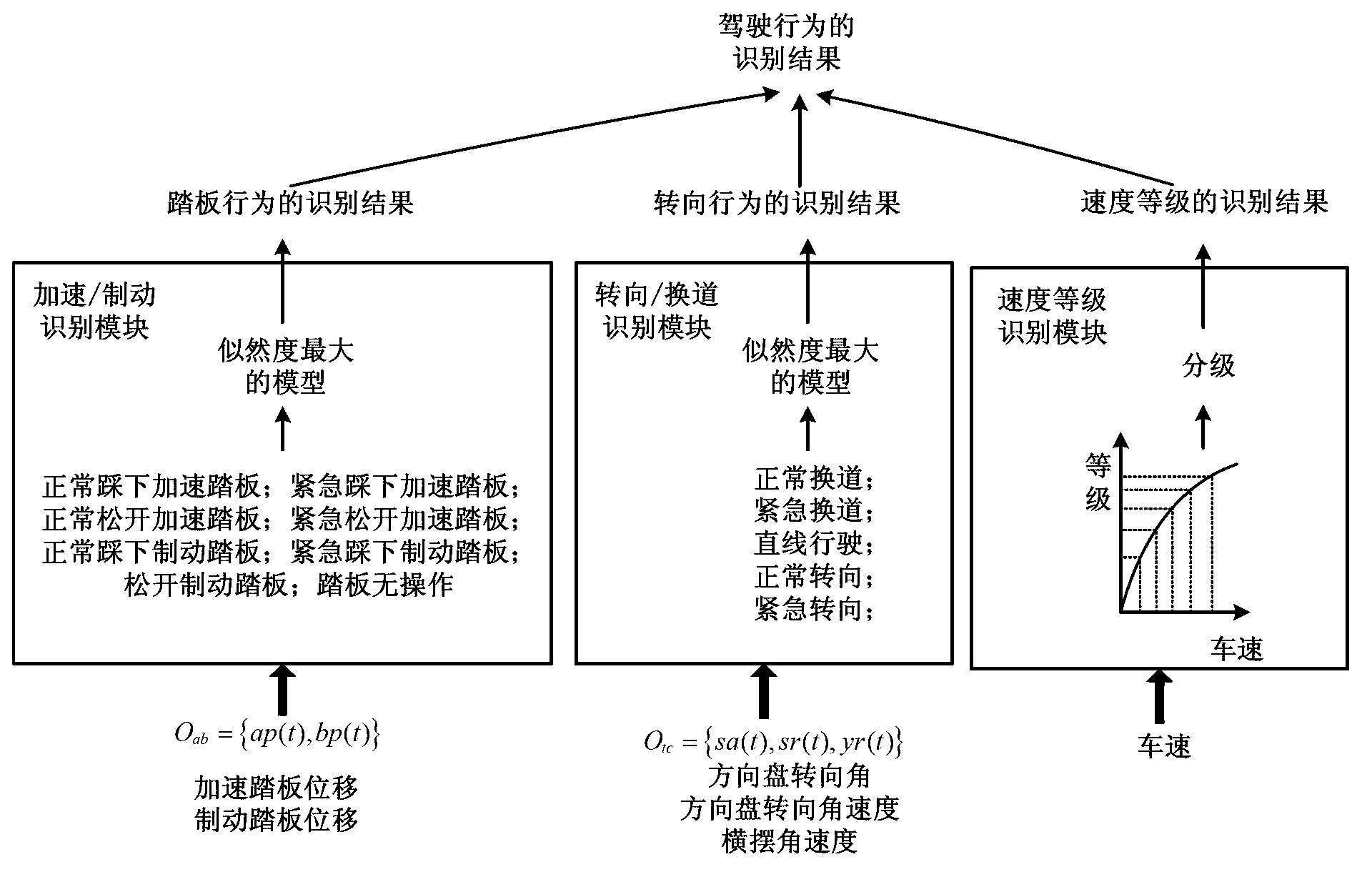
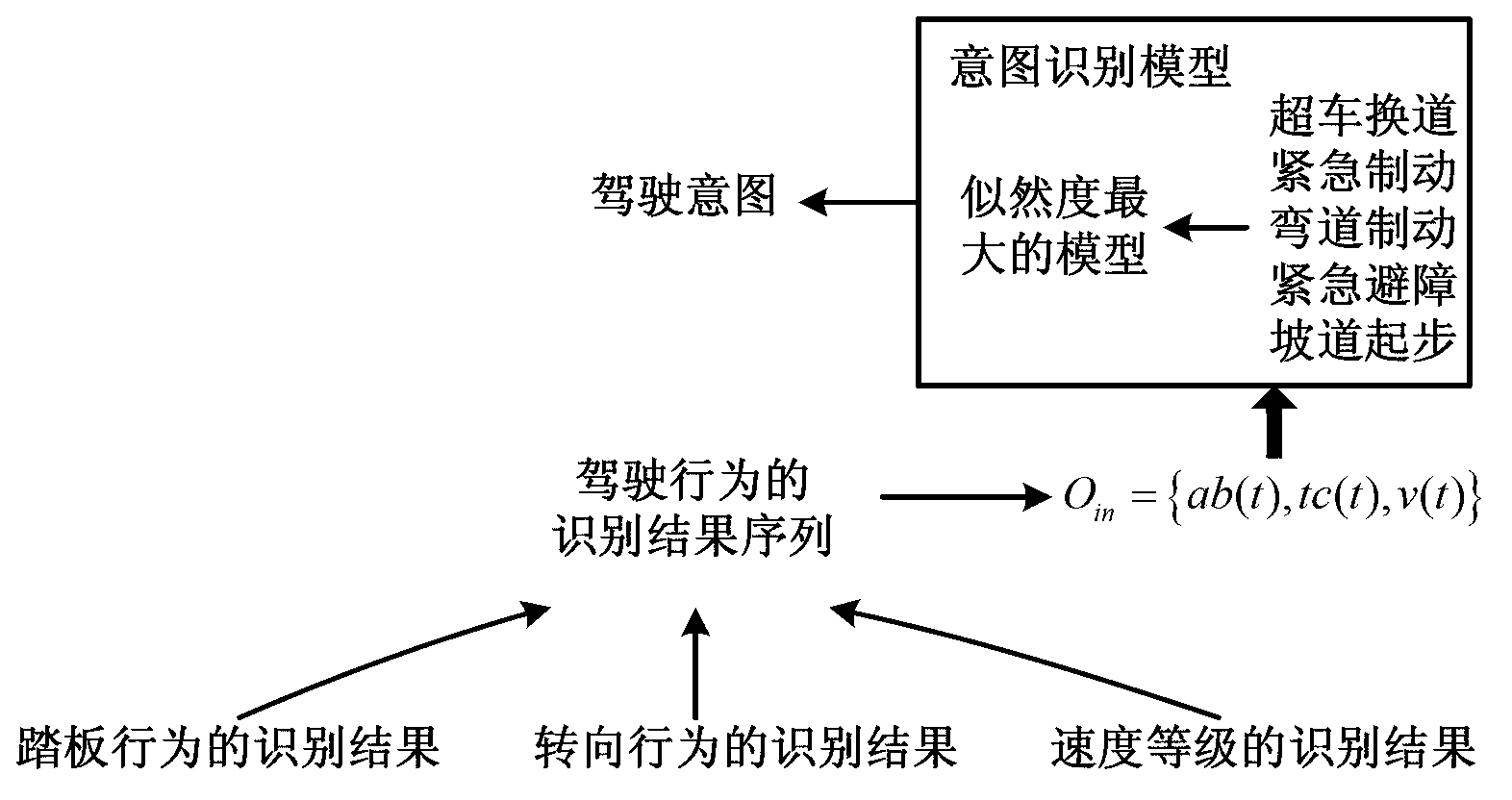
Driver intention recognition method
InactiveCN103318181AAccurately judge the operation intentionImprove accuracyHide markov modelDependability
The invention provides a driver intention recognition method. A double-layer recognition structure is proposed based on a multi-dimensional discrete hidden Markov model, behaviors and intentions of a driver are respectively recognized, the behaviors of the driver serve as input for recognizing the intentions of the driver, and recognition accuracy and reliability are enhanced. According to vehicle operating information and vehicle speed, the current operating intention of the driver can be accurately judged, so that conditions are created for improving a vehicular safety auxiliary system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com