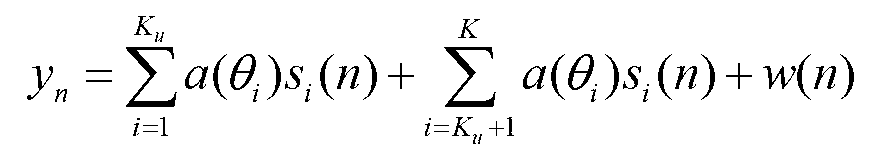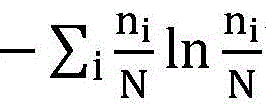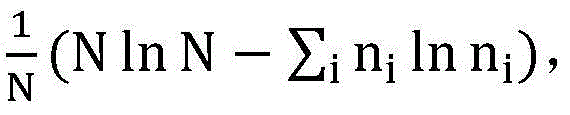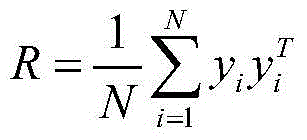Patents
Literature
39 results about "Minimum description length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The minimum description length (MDL) principle is a formalization of Occam's razor in which the best hypothesis (a model and its parameters) for a given set of data is the one that leads to the best compression of the data. MDL was introduced by Jorma Rissanen in 1978. It is an important concept in information theory and computational learning theory.
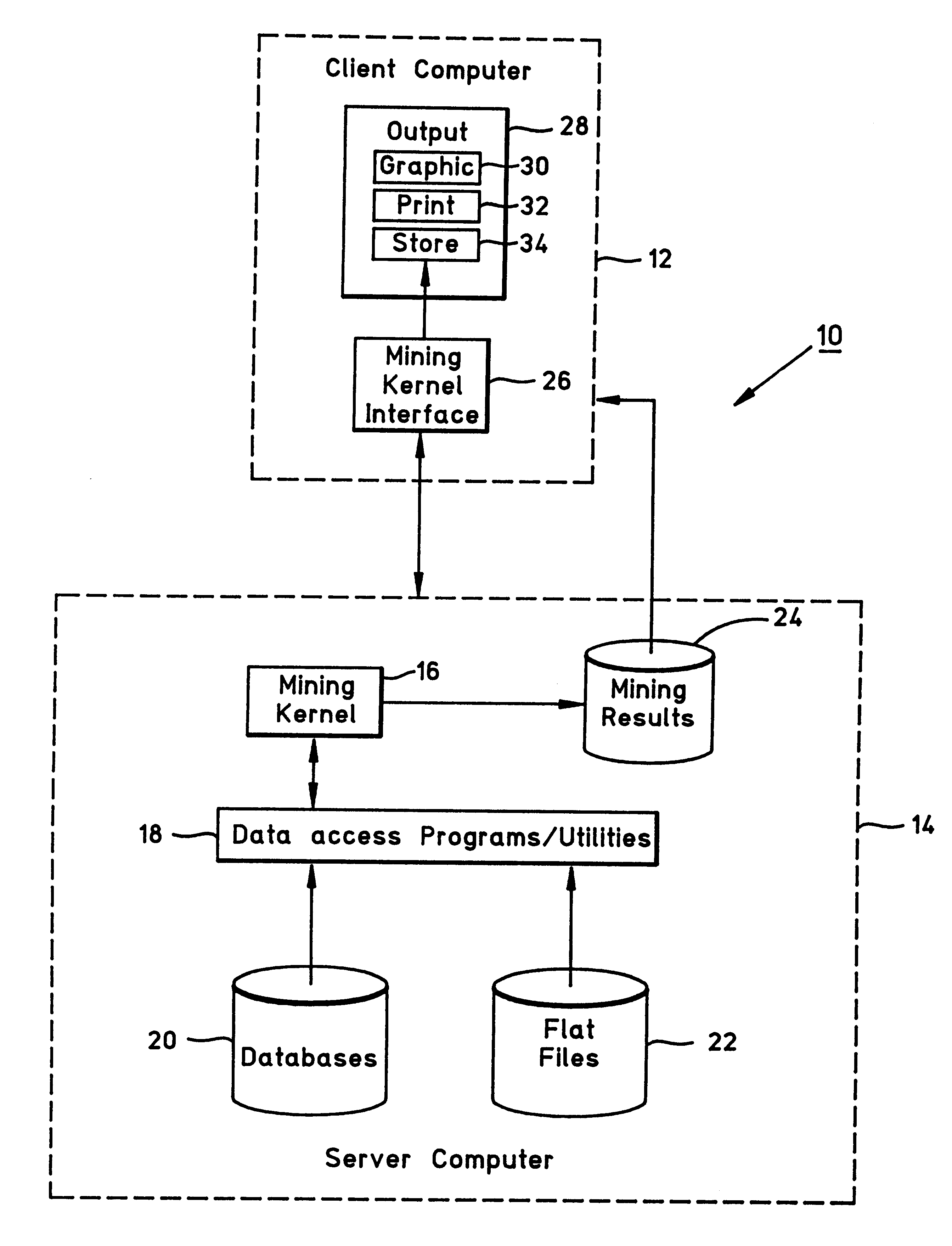
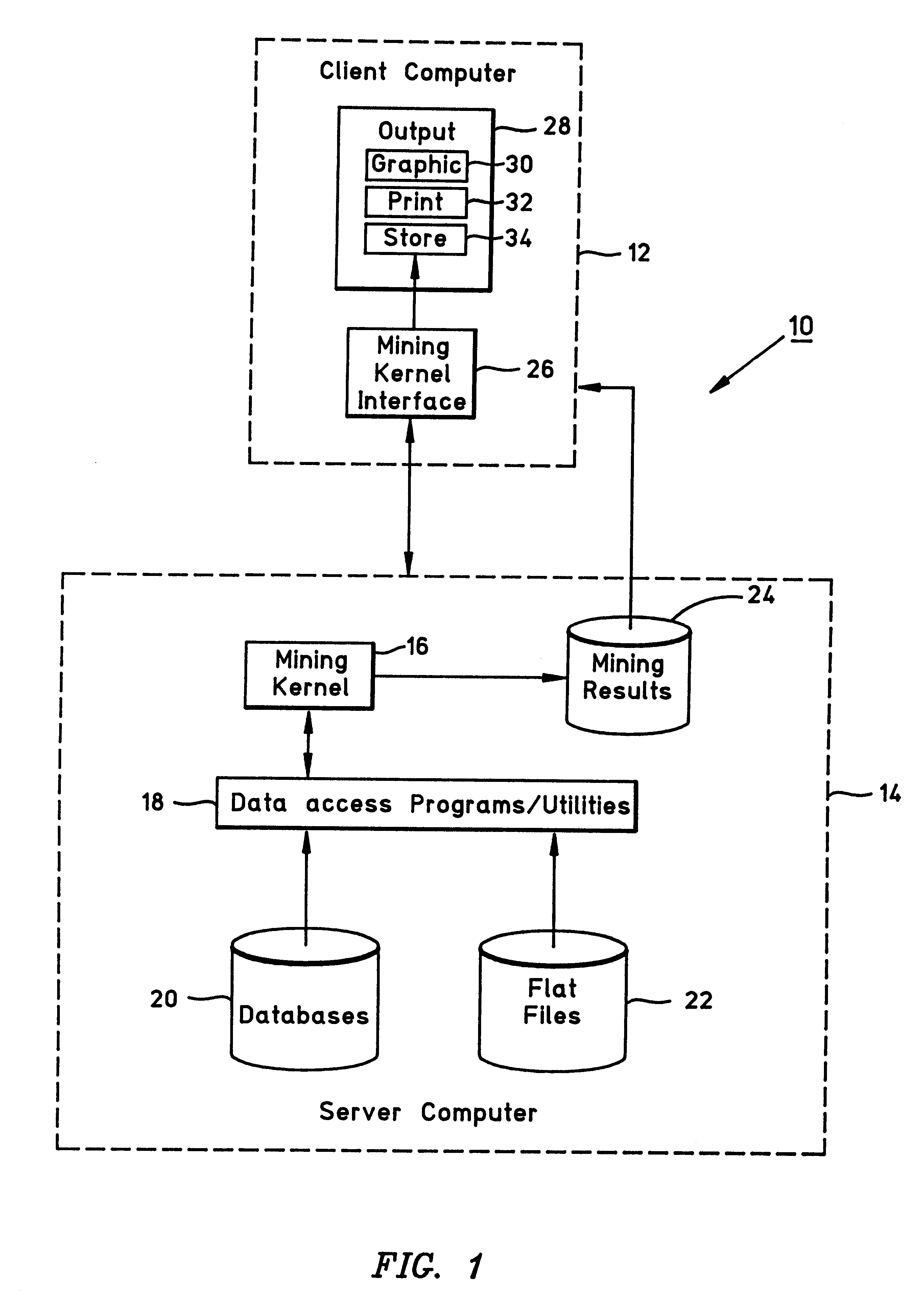
System and method for mining surprising temporal patterns
InactiveUS6189005B1Improve system accuracyAccurate representationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalMinimum description lengthMachine learning
A system and method for data mining is provided in which temporal patterns of itemsets in transactions having unexpected support values are identified. A surprising temporal pattern is an itemset whose support changes over time. The method may use a minimum description length formulation to discover these surprising temporal patterns.
Owner:IBM CORP
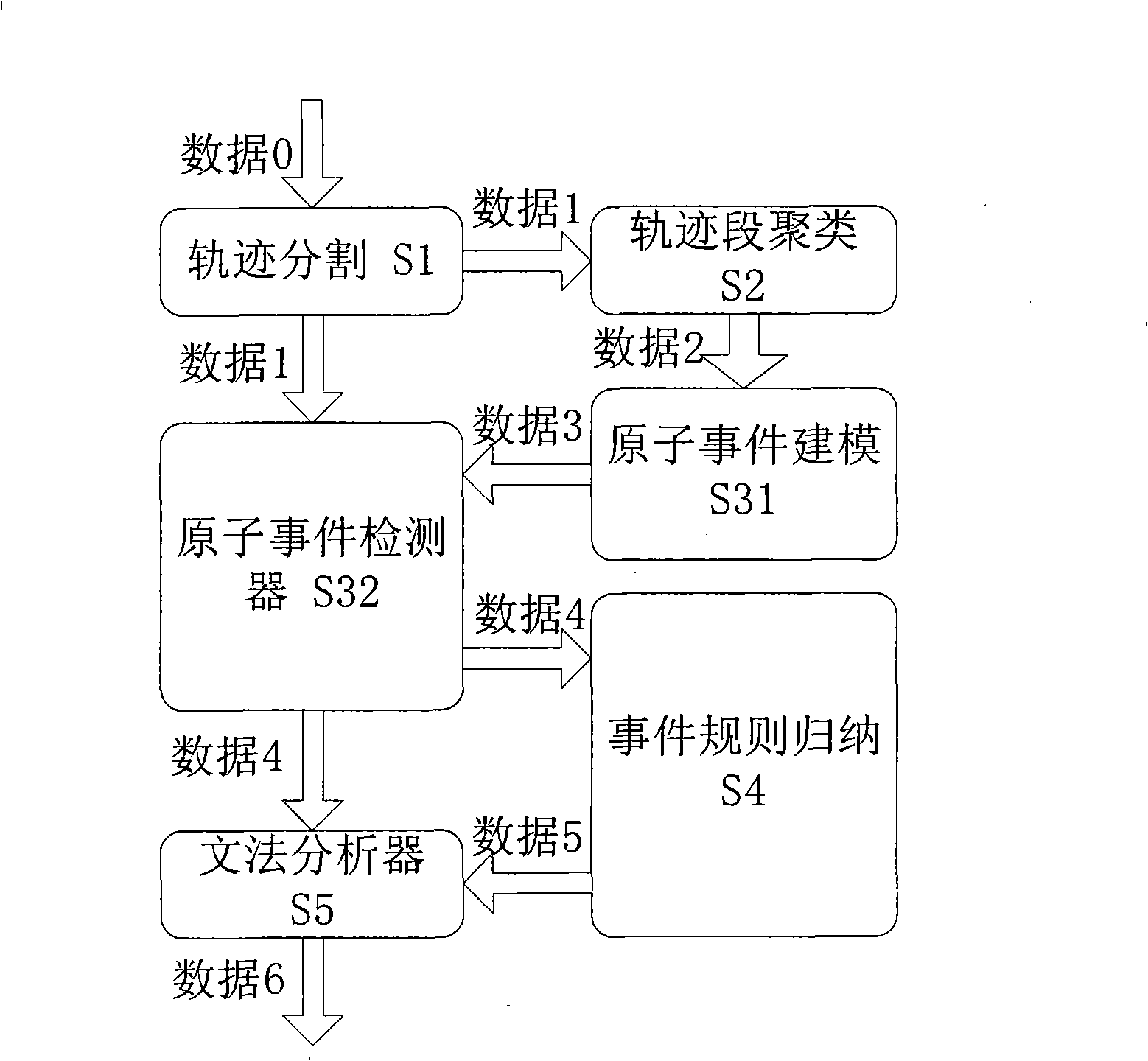
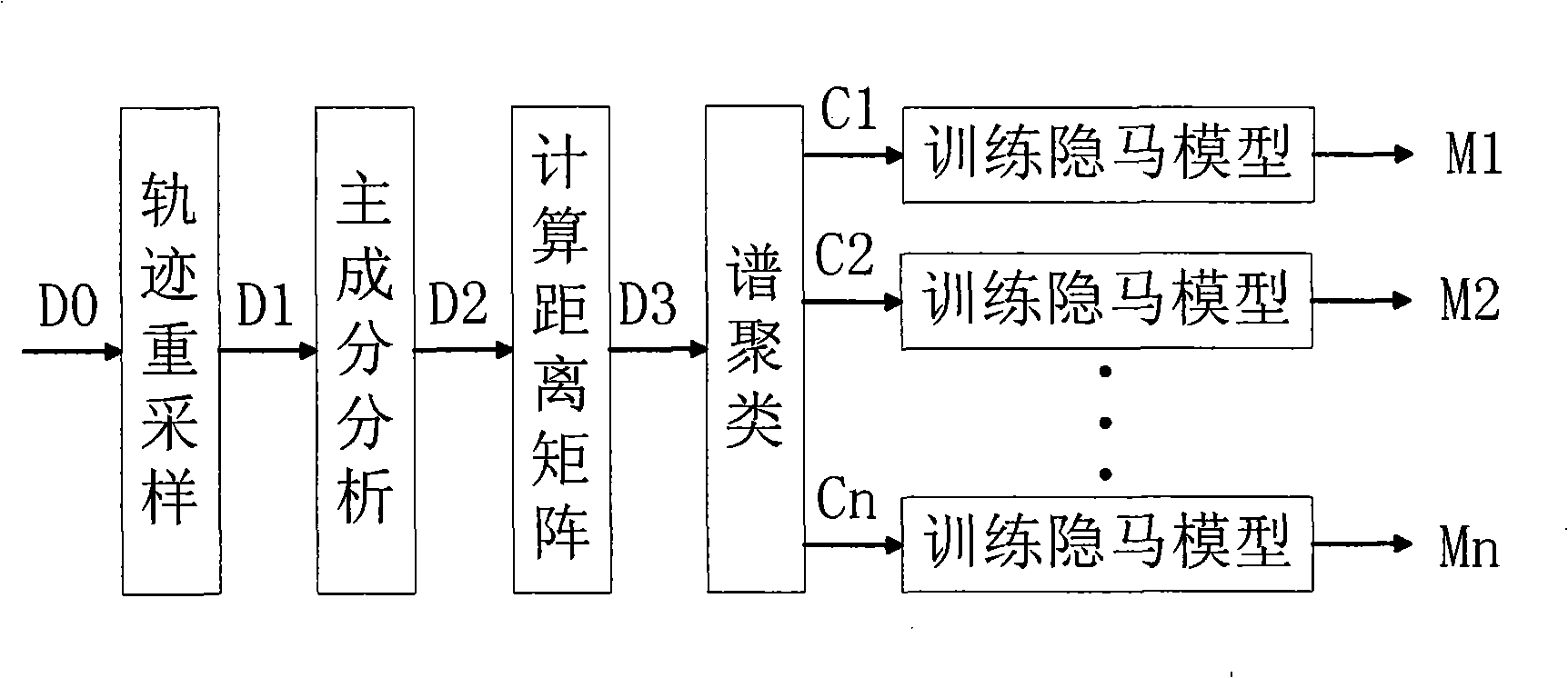
Video frequency behaviors recognition method based on track sequence analysis and rule induction
InactiveCN101334845AReduce manpower consumptionCharacter and pattern recognitionVideo monitoringSequence analysis
The invention discloses a method for identifying the video action based on trajectory sequence analysis and rule induction, which solves the problems of large labor intensity. The method of the invention divides a complete trajectory in a scene into a plurality of trajectory section with basic meaning, and obtains a plurality of basic movement modes as atomic events through the trajectory clustering; meanwhile, a hidden Markov model is utilized for establishing a model to obtain the event rule contained in the trajectory sequence by inducting the algorithm based on the minimum description length and based on the event rule, an expanded grammar analyzer is used for identifying an interested event. The invention provides a complete video action identification frame and also a multi-layer rule induction strategy by taking the space-time attribute, which significantly improves the effectiveness of the rule learning and promotes the application of the pattern recognition in the identification of the video action. The method of the invention can be applied to the intelligent video surveillance and automatic analysis of movements of automobiles or pedestrians under the current monitored scene so as to lead a computer to assist people or substitute people to complete monitor tasks.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
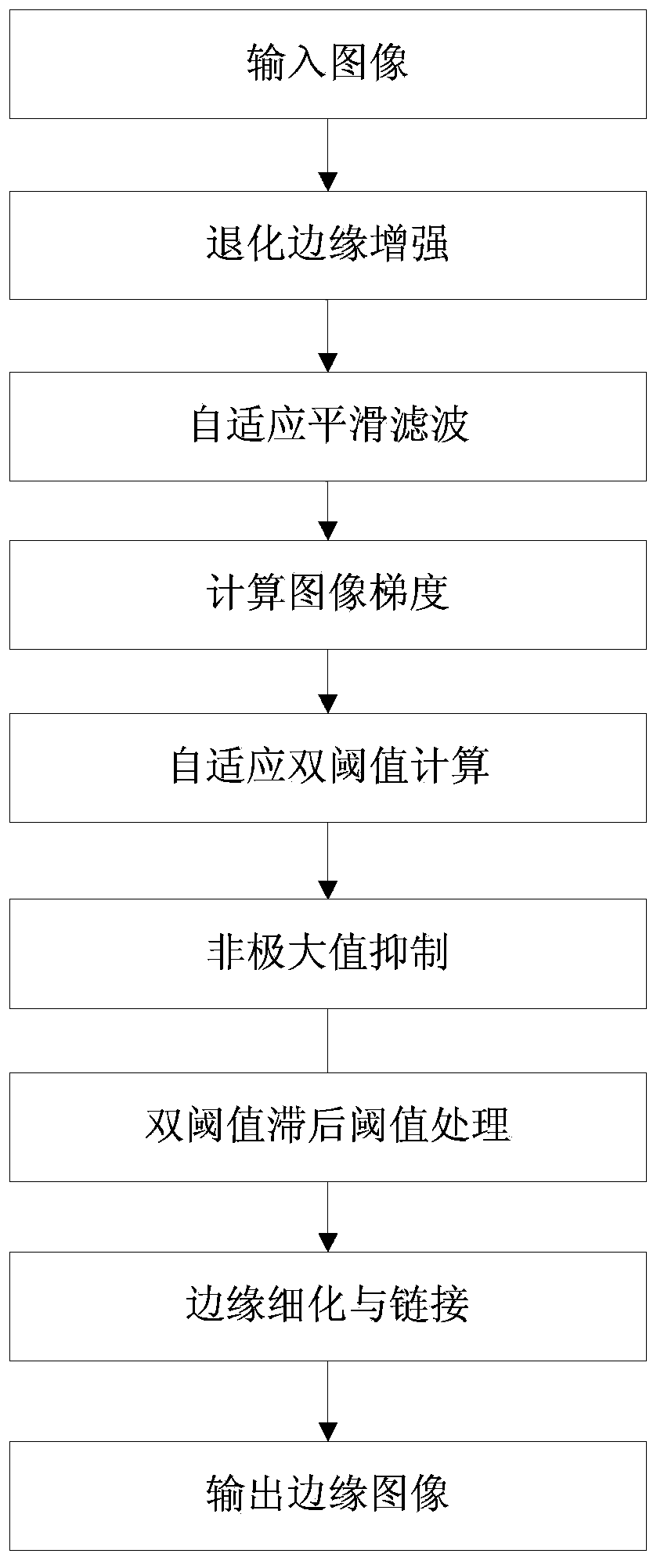
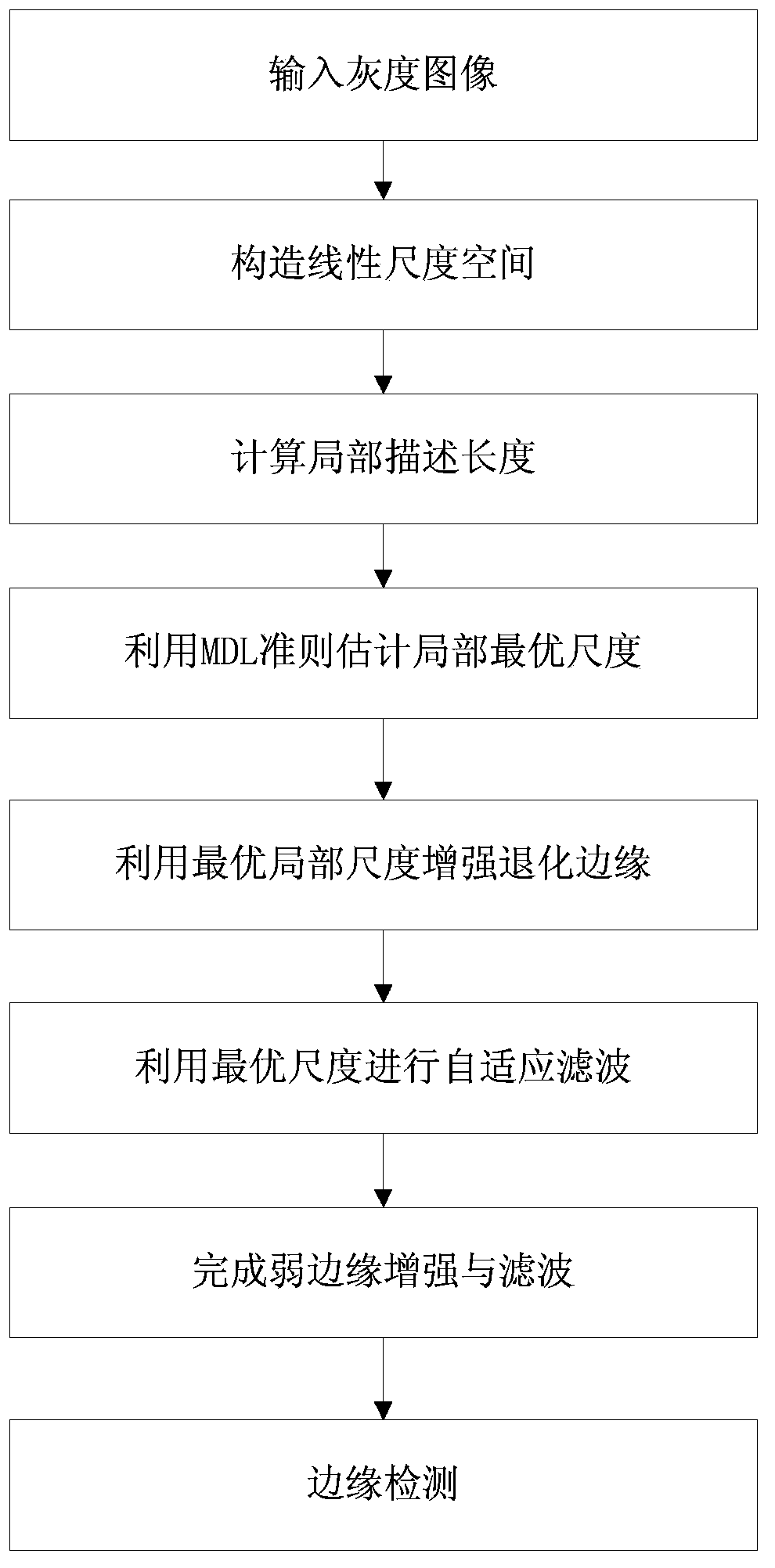
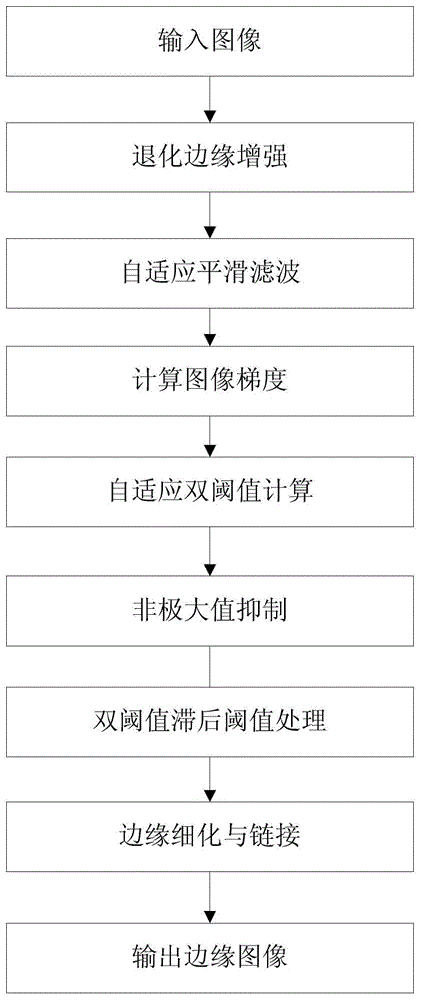
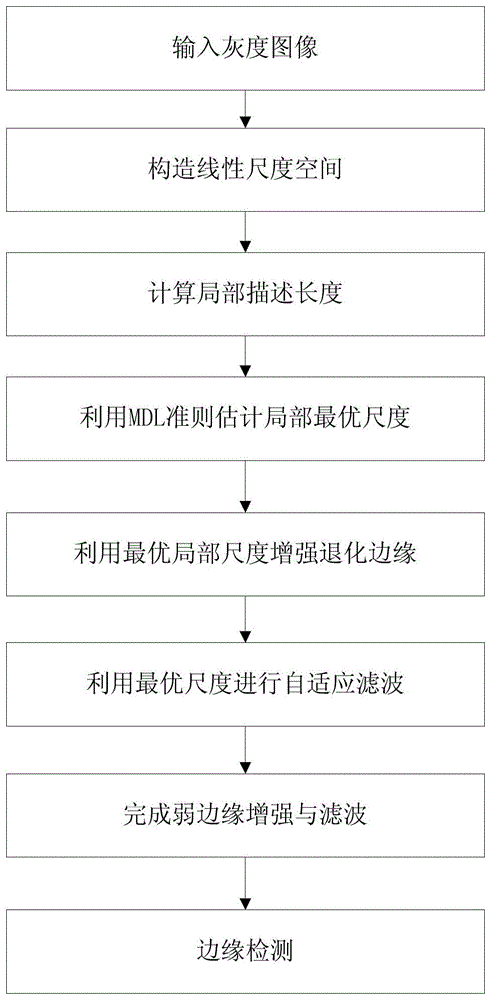
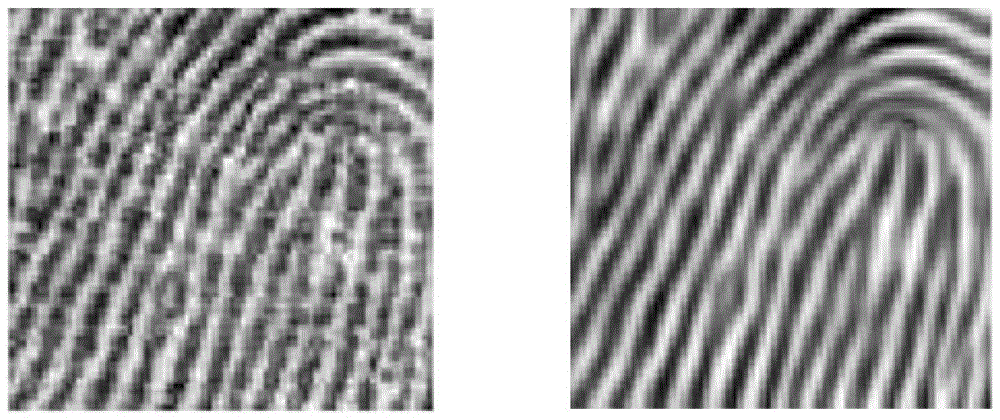
Multi-scale image weak edge detection method based on minimum description length
ActiveCN103440644AImprove stabilityGood filter smoothing effectImage enhancementImage analysisScale spaceSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a self-adaptive multi-scale image weak edge detection method based on the minimum description length (MDL) principle. The self-adaptive multi-scale image weak edge detection method based on the minimum description length principle comprises the steps that firstly, a linear scale space is constructed by means of multi-scale Gaussian smoothing, then the local description length of an image is calculated and the optimum local smoothness scale is determined by means of the minimum description length principle, and finally edge detection is carried out on the image treated with local smoothing to obtain all edges of the weak edge image. The self-adaptive multi-scale image weak edge detection method based on the minimum description length principle has the advantages that common noise can be filtered effectively, a real weak edge can be extracted, and the phenomena of edge fracture, edge deviation, false edge responses and the like can be avoided; in addition, the algorithm used in the method is a non-iterative filter method, the computing speed is greatly improved, and the stability of the algorithm is greatly improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Fast movable object orbit clustering method based on sampling
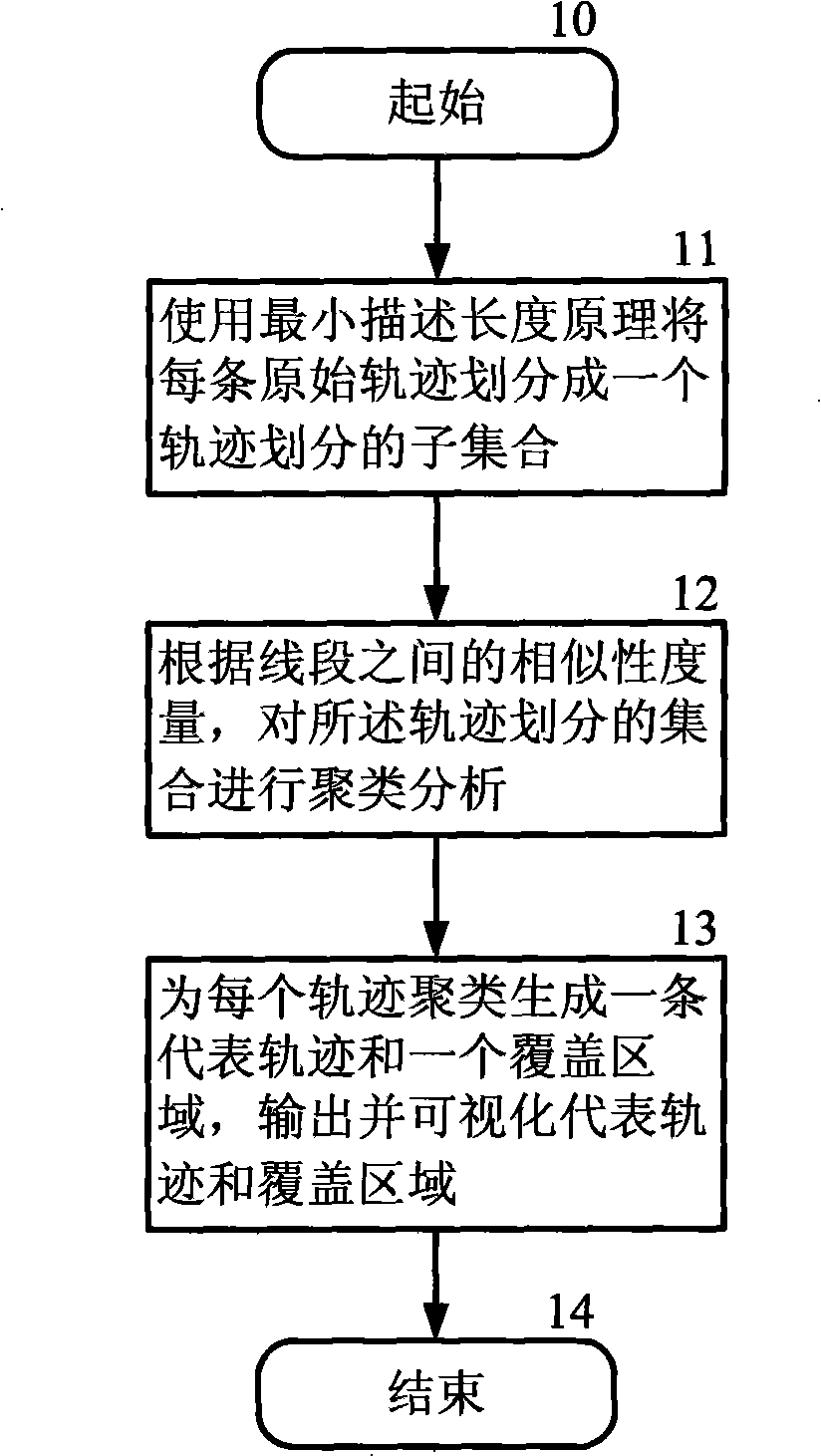
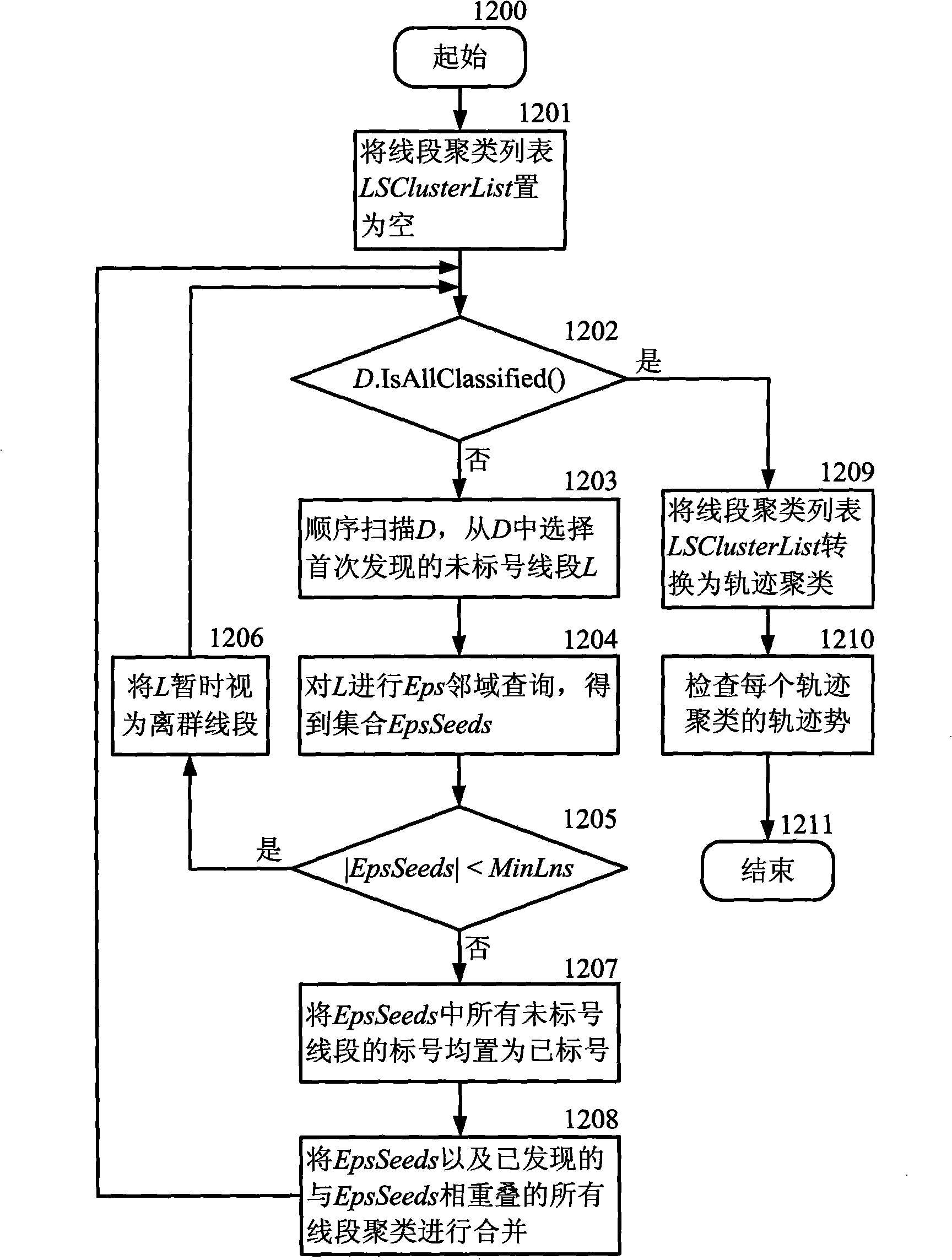
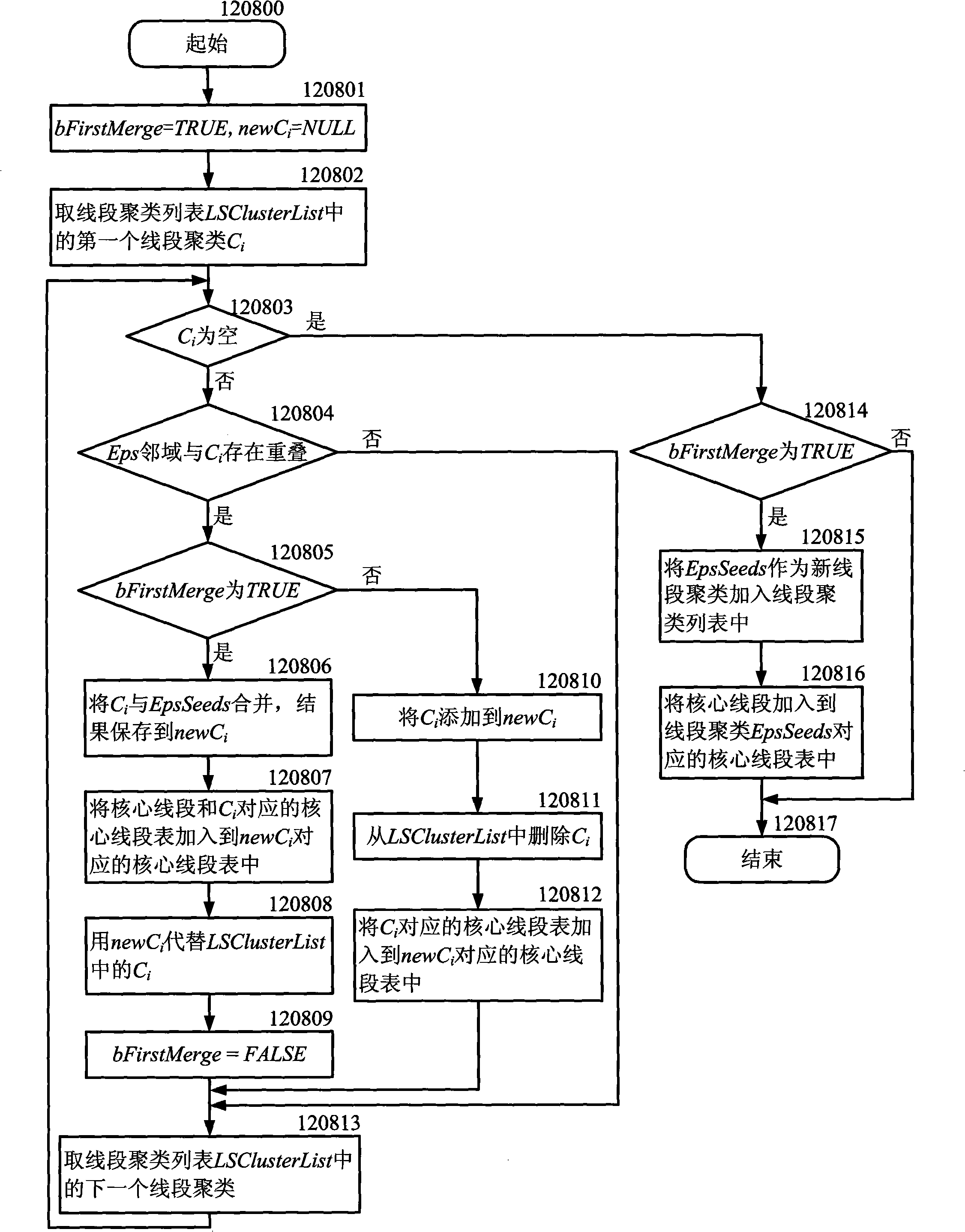
InactiveCN101527000APreserve clustering qualityImprove time and efficiencyWeather condition predictionCharacter and pattern recognitionTrajectory clusteringMinimum description length
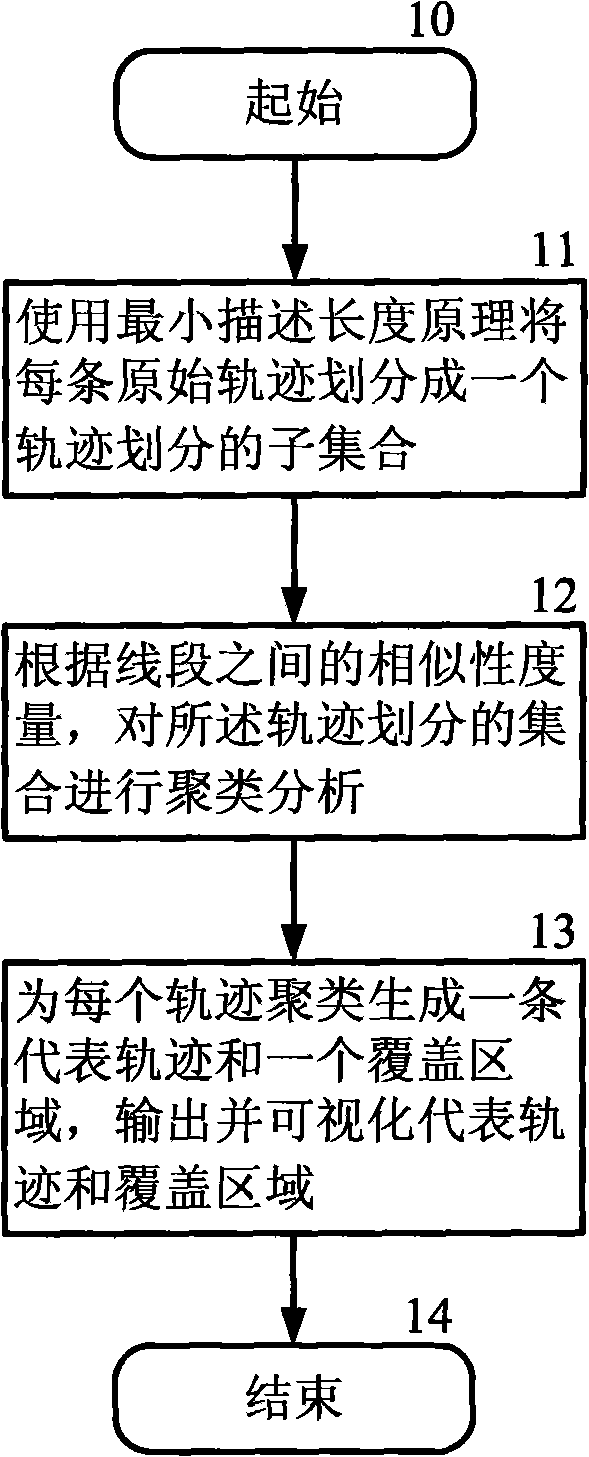
The invention discloses a fast movable object orbit clustering method based on sampling, belonging to the field of orbit data clustering. The method comprises the following steps: dividing each original orbit into an orbit dividing subset by utilizing a minimum length describing principle after a user sets an input parameter and sends a clustering analysis request; carrying out clustering analysis for the orbit dividing subset according to the similarity measurement among line sections to obtain an orbit clustering set; finally generating a representing orbit and a coverage area in a clustering way by each orbit, outputting and visualizing the representing orbit and the coverage area and returning a result to the user. The invention has the advantages that the method is used for the clustering analysis of data of a large-scale low-particlesize movable object orbit and can still keep the orbit clustering effect and also effectively discover the orbit clustering under the condition of very low particlesize of orbit data to be analyzed, thereby enhancing the system efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for estimating weak signal separation on basis of positioning for external radiation sources
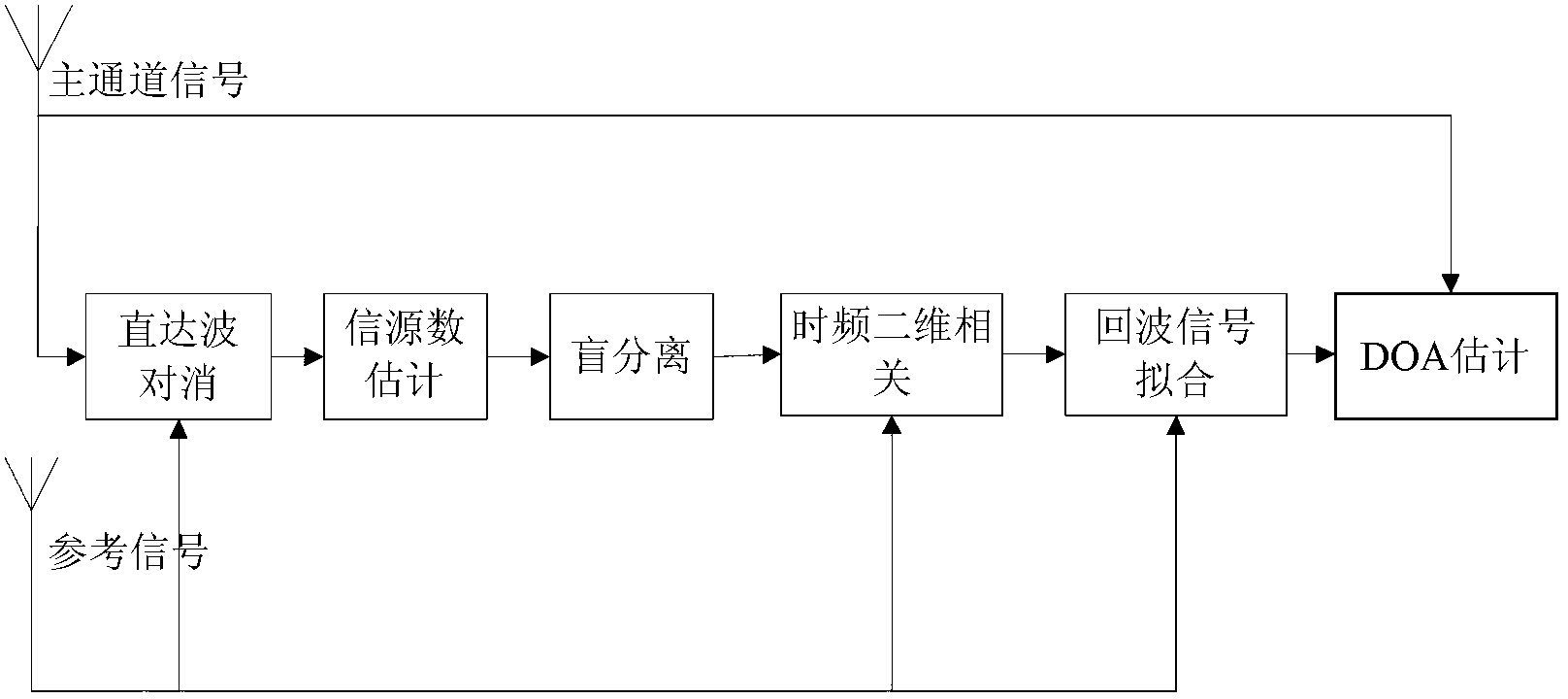
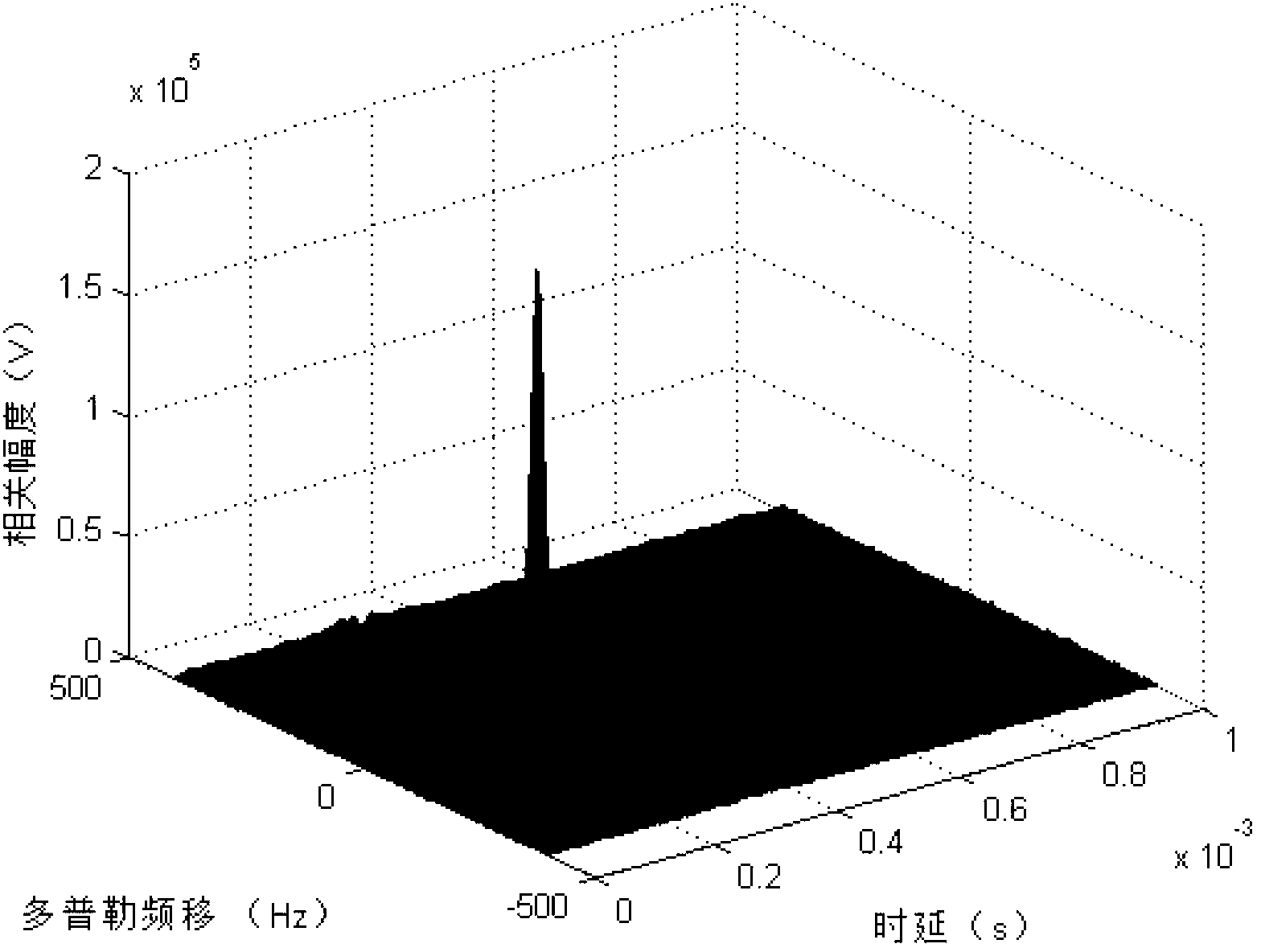
InactiveCN103235294AHelp delayDoppler shiftWave based measurement systemsMain channelSample sequence
The invention provides a method for estimating weak signal separation on the basis of positioning for external radiation sources. The method includes steps of performing direct-wave and multi-path cancellation for a sample sequence x (t) of a main channel by means of NLMS (normalized least mean square) to obtain output signals y<NLMS>(t); estimating the number of source signals of the output signals y<NLMS>(t) by an AIC (Akaike information criterion) or an MDL (minimum description length) criterion, preliminarily whitening the output signals y<NLMS>(t) to obtain whitened signals z(t), and updating a separation matrix W by an ICA (independent component analysis) algorithm to obtain M channels of estimated signals y(t); respectively performing time-frequency two-dimensional correlation for the M channels of estimated signals y<1>(t), ..., y<M>(t) and reference signals s<ref>(t); and searching a peak point in absolute correlation values phi(tau, f) corresponding to the M channels of estimated signals, and determining time delay and Doppler frequency shift which correspond to the peak point as time delay and Doppler frequency shift of a target when a signal-to-noise ratio of a certain channel of signals is larger than or equal to a threshold value.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
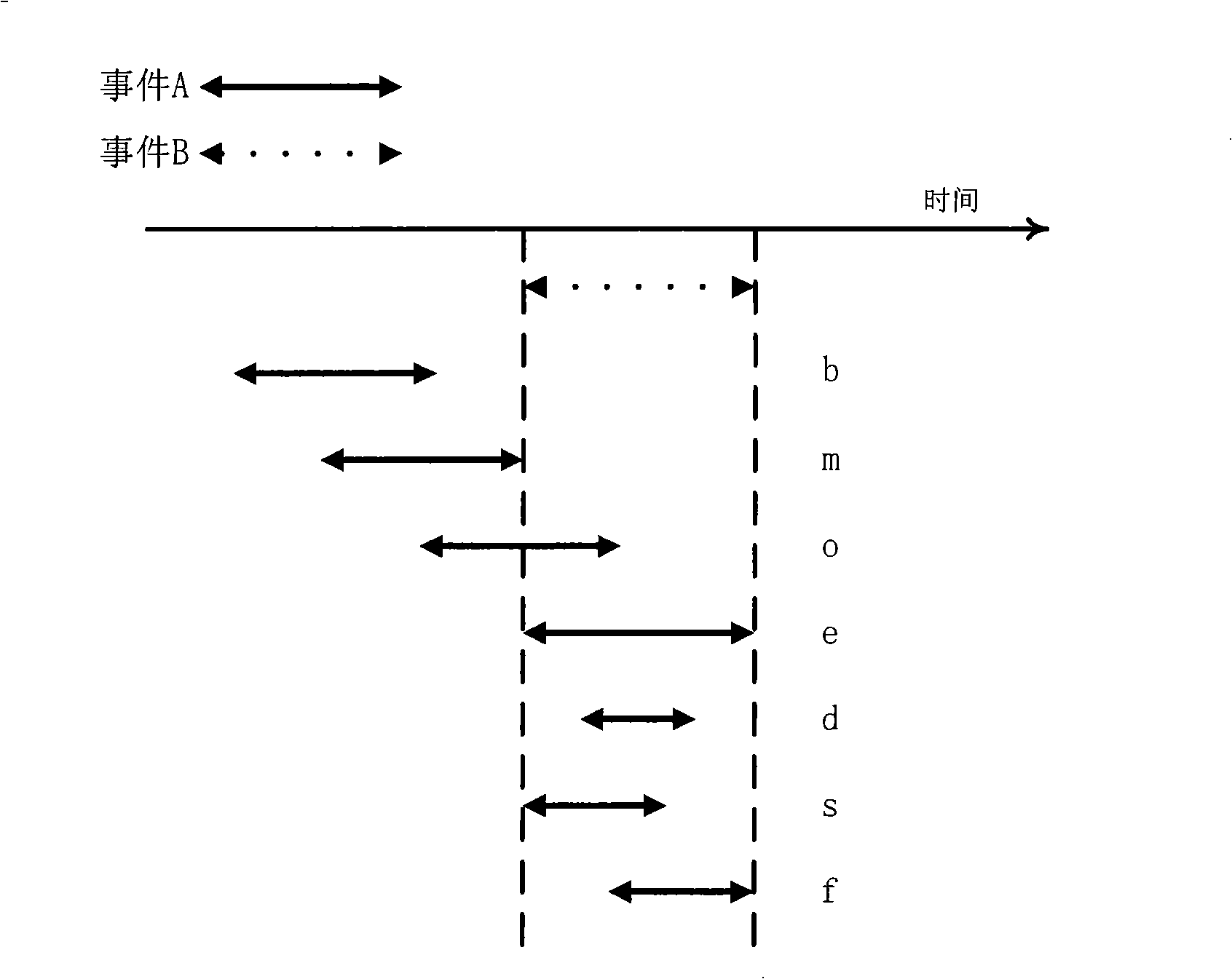
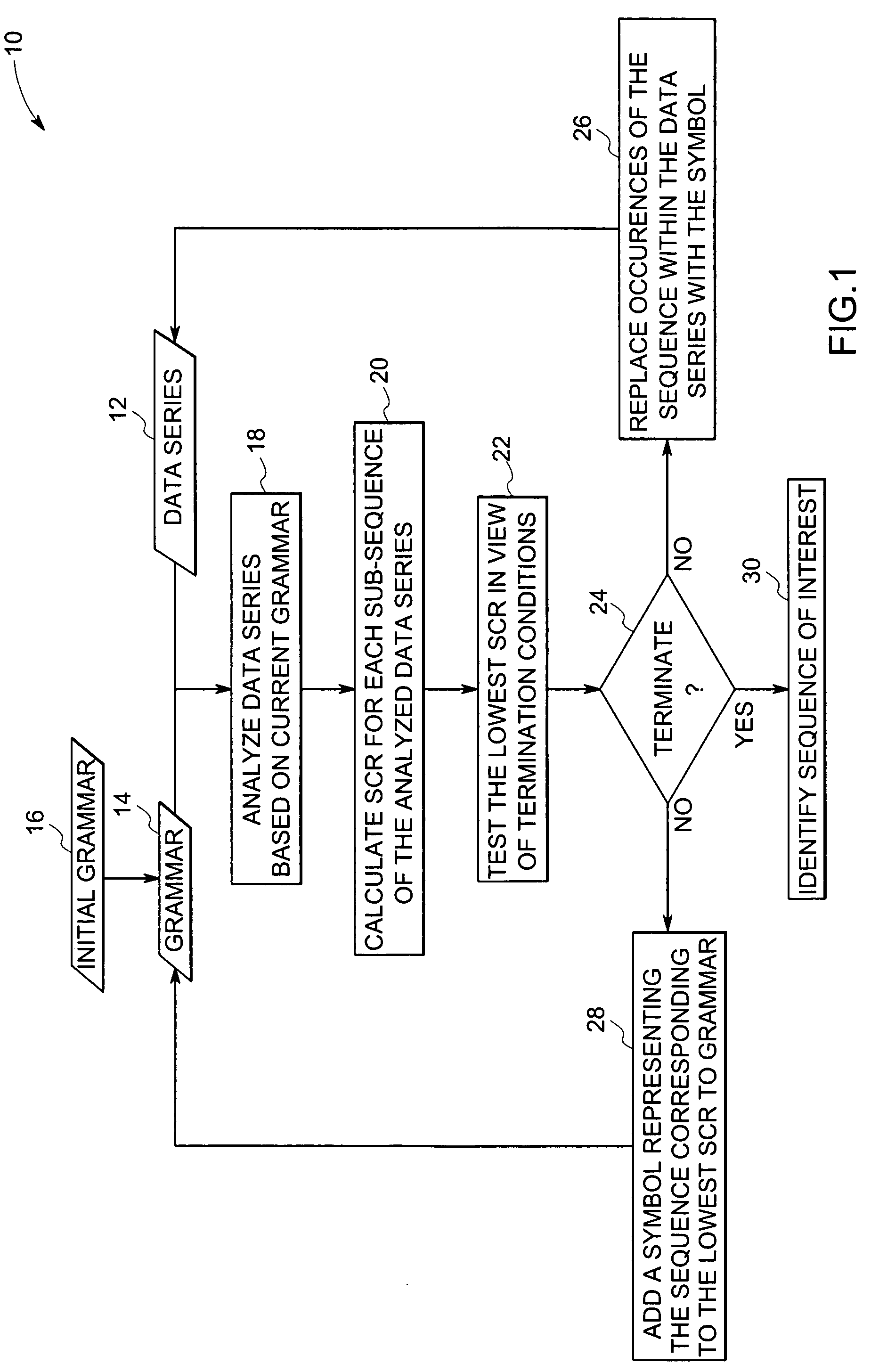
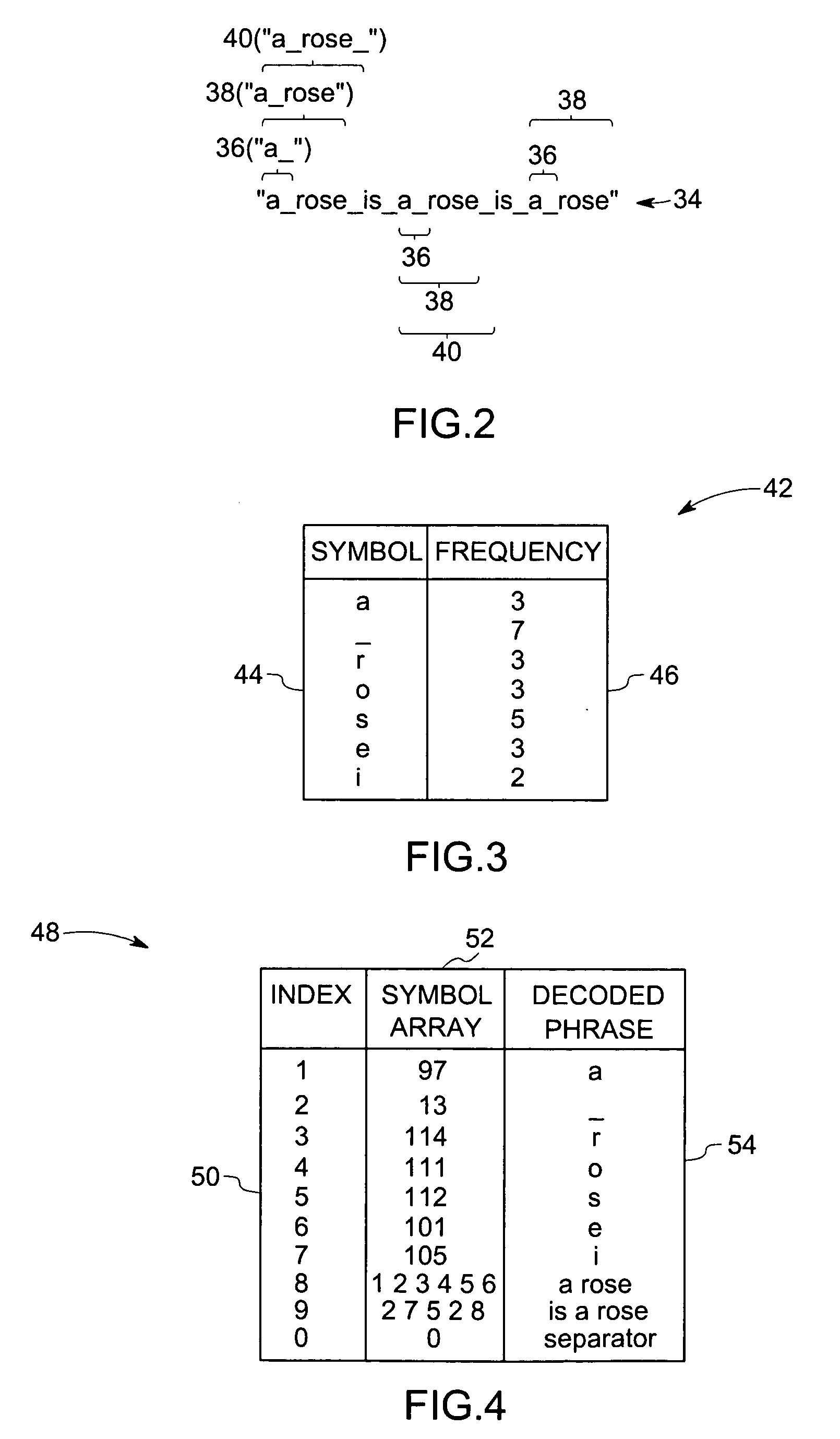
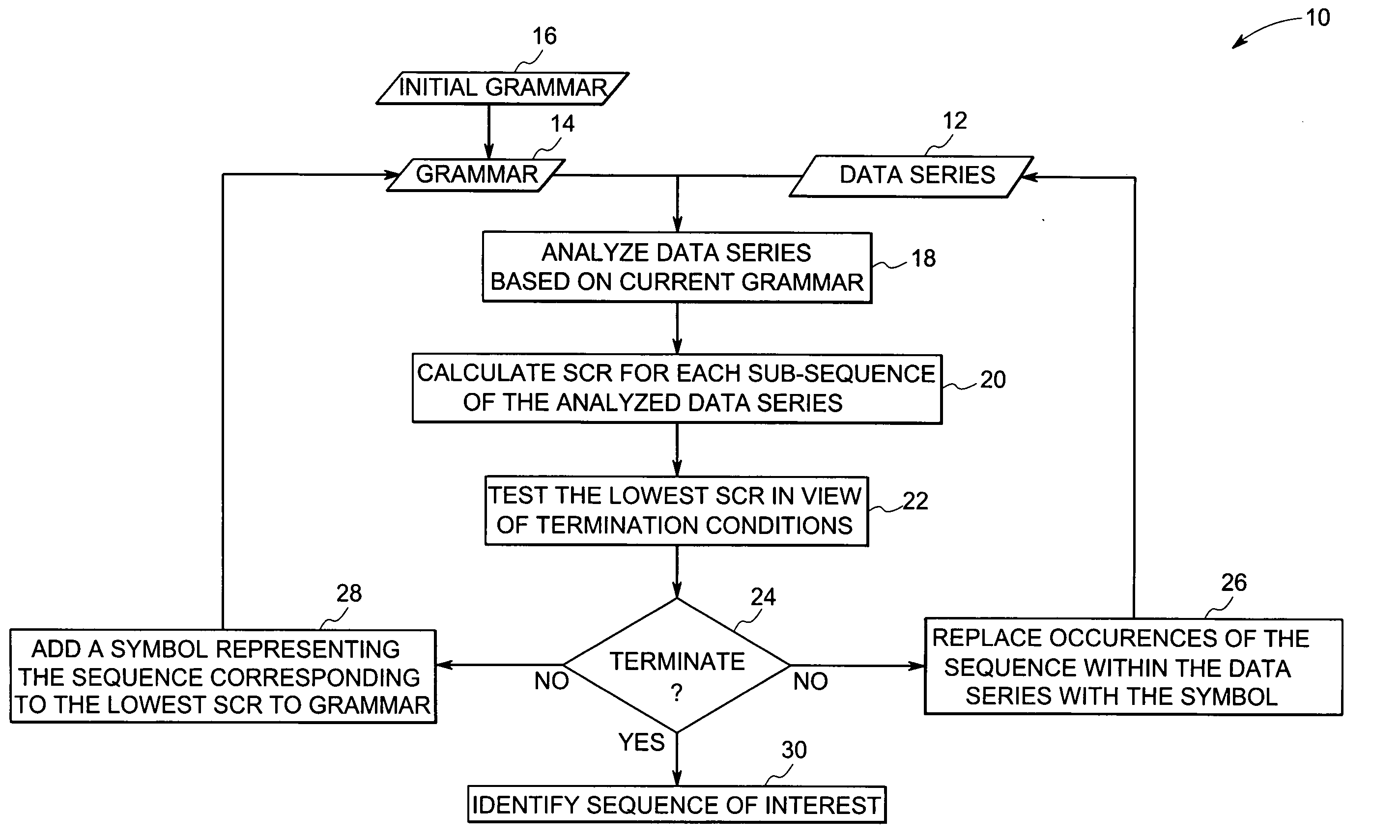
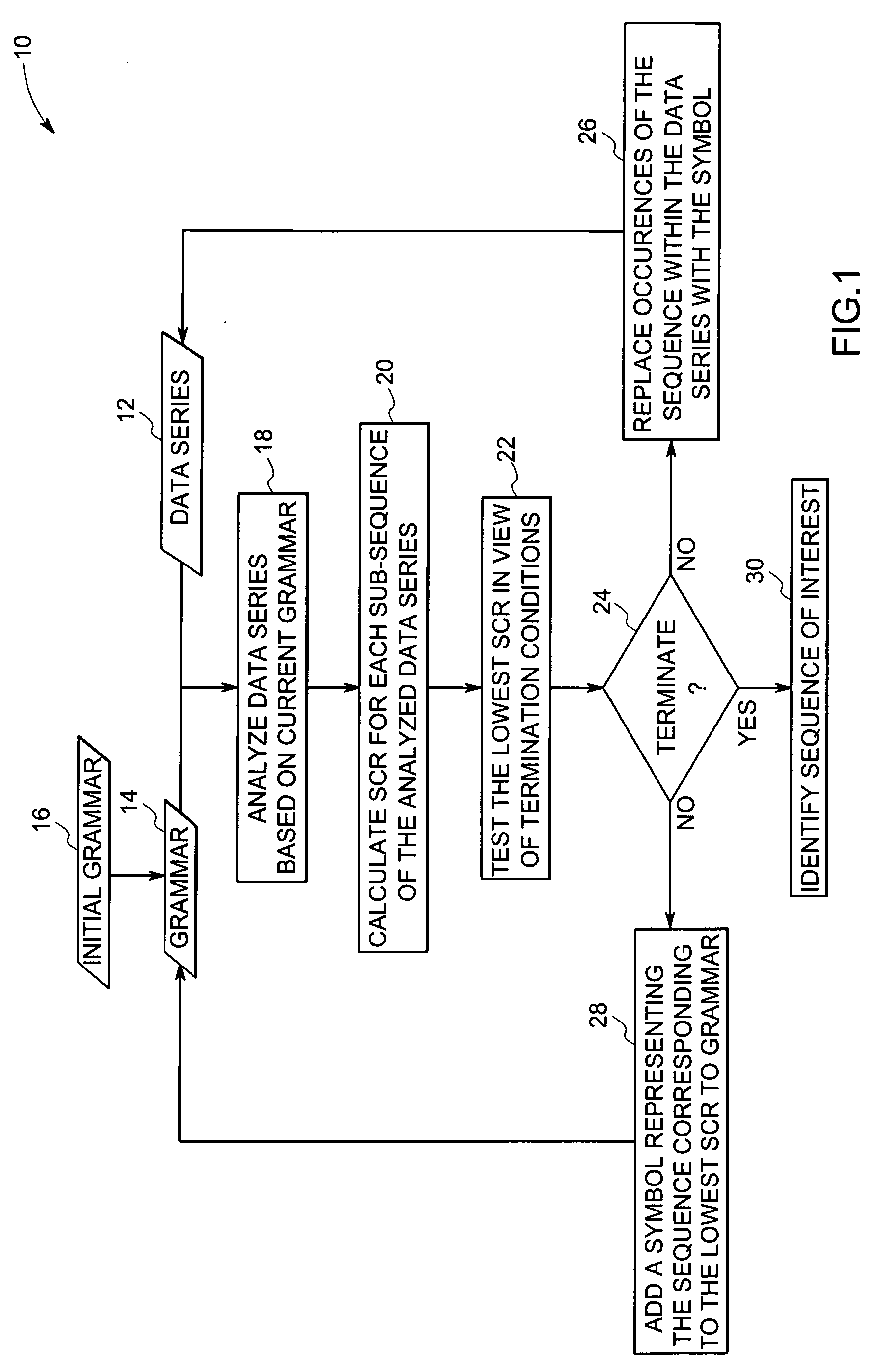
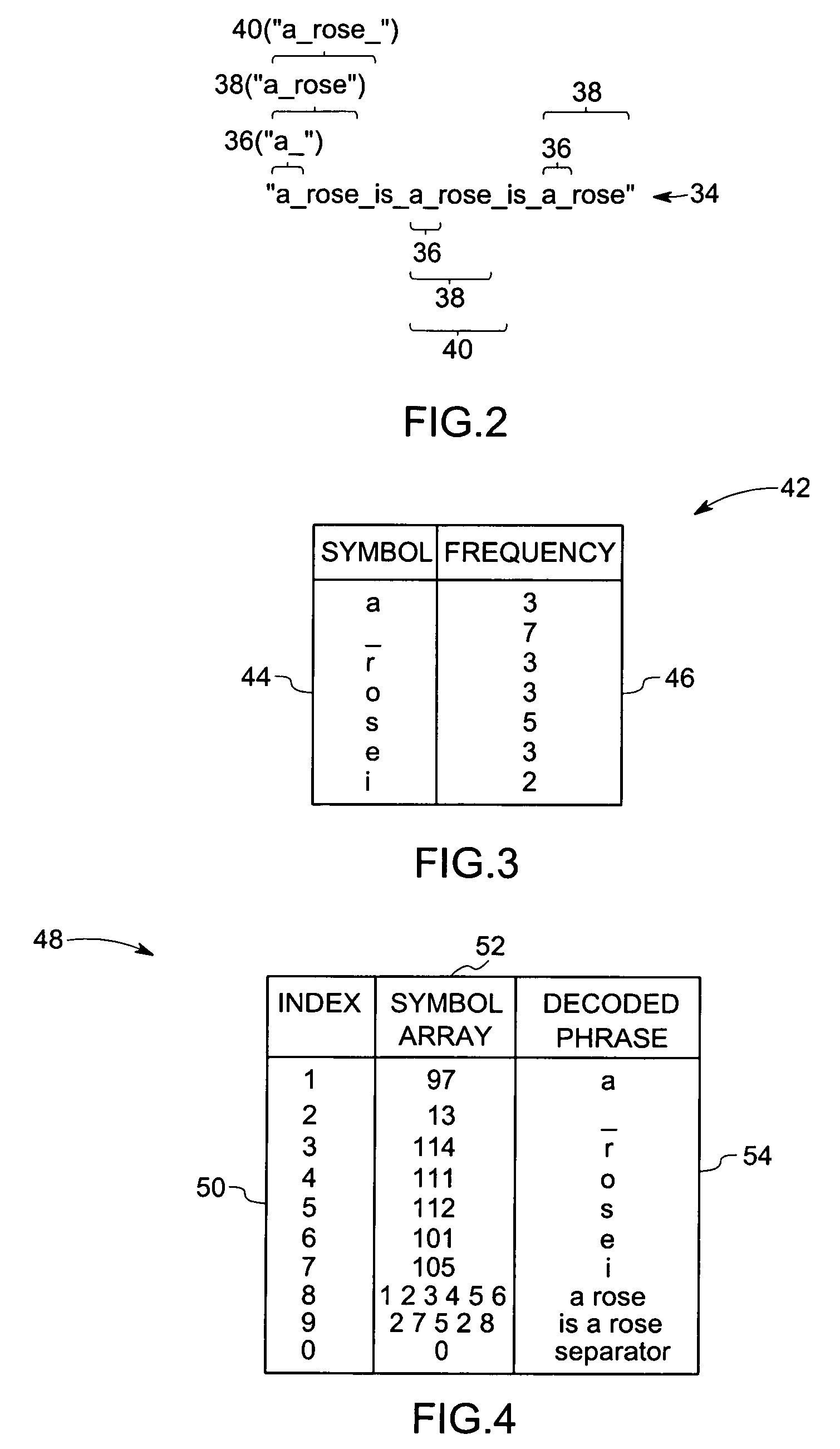
Method for identifying sub-sequences of interest in a sequence
The present technique provides for the analysis of a data series to identify sequences of interest within the series. The analysis may be used to iteratively update a grammar used to analyze the data series or updated versions of the data series. Furthermore, the technique provides for the calculation of a minimum description length heuristic, such as a symbol compression ratio, for each sub-sequence of the analyzed data sequence. The technique may then compare a selected heuristic value against one or more reference conditions to determine if additional iteration is to be performed. The grammar and the data sequence may be updated between iterations to include a symbol representing a string corresponding to the selected heuristic value based upon a non-termination result of the comparison. Alternatively, the string corresponding to the selected heuristic value may be identified as a sequence of interest based upon a termination result of the comparison.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
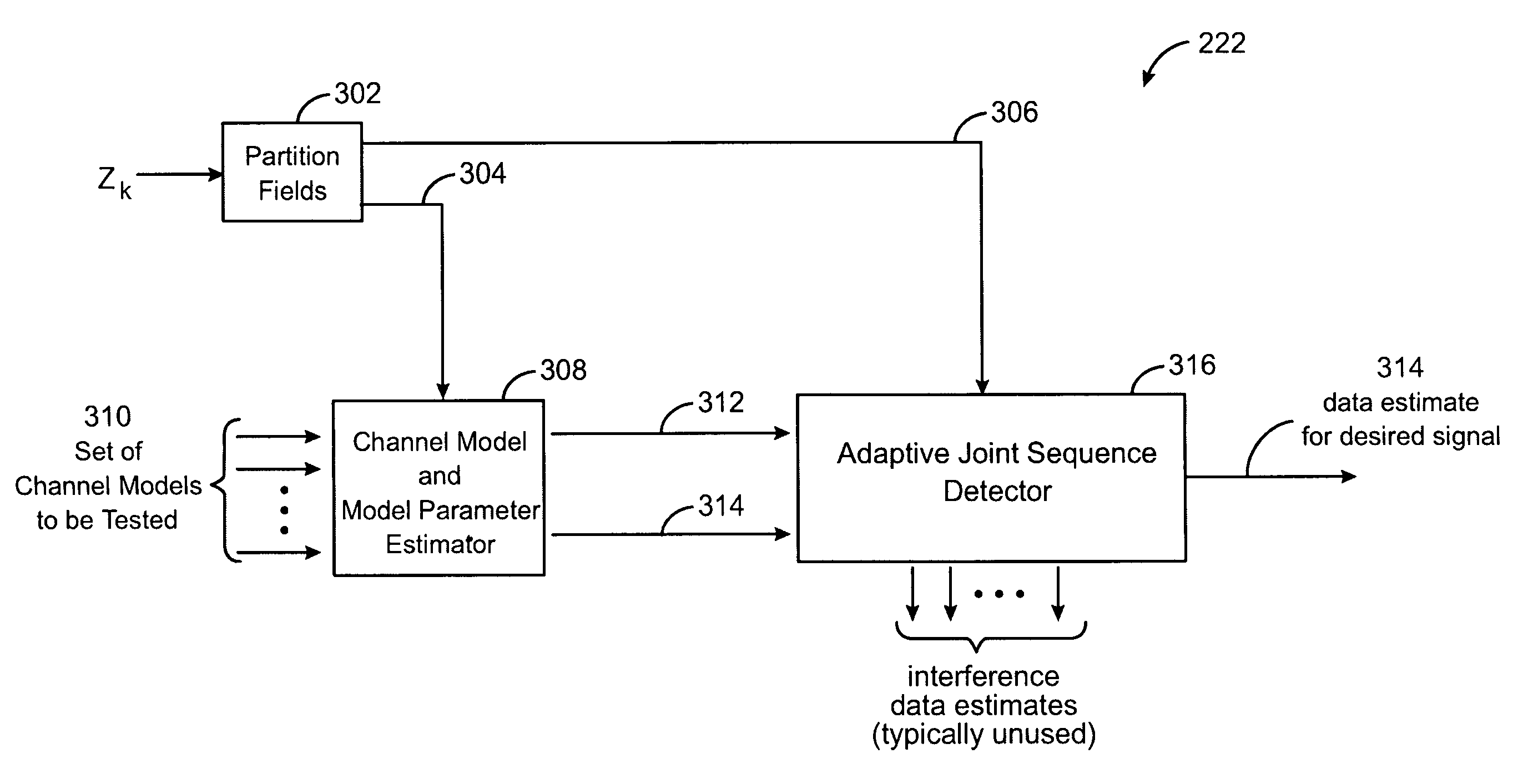
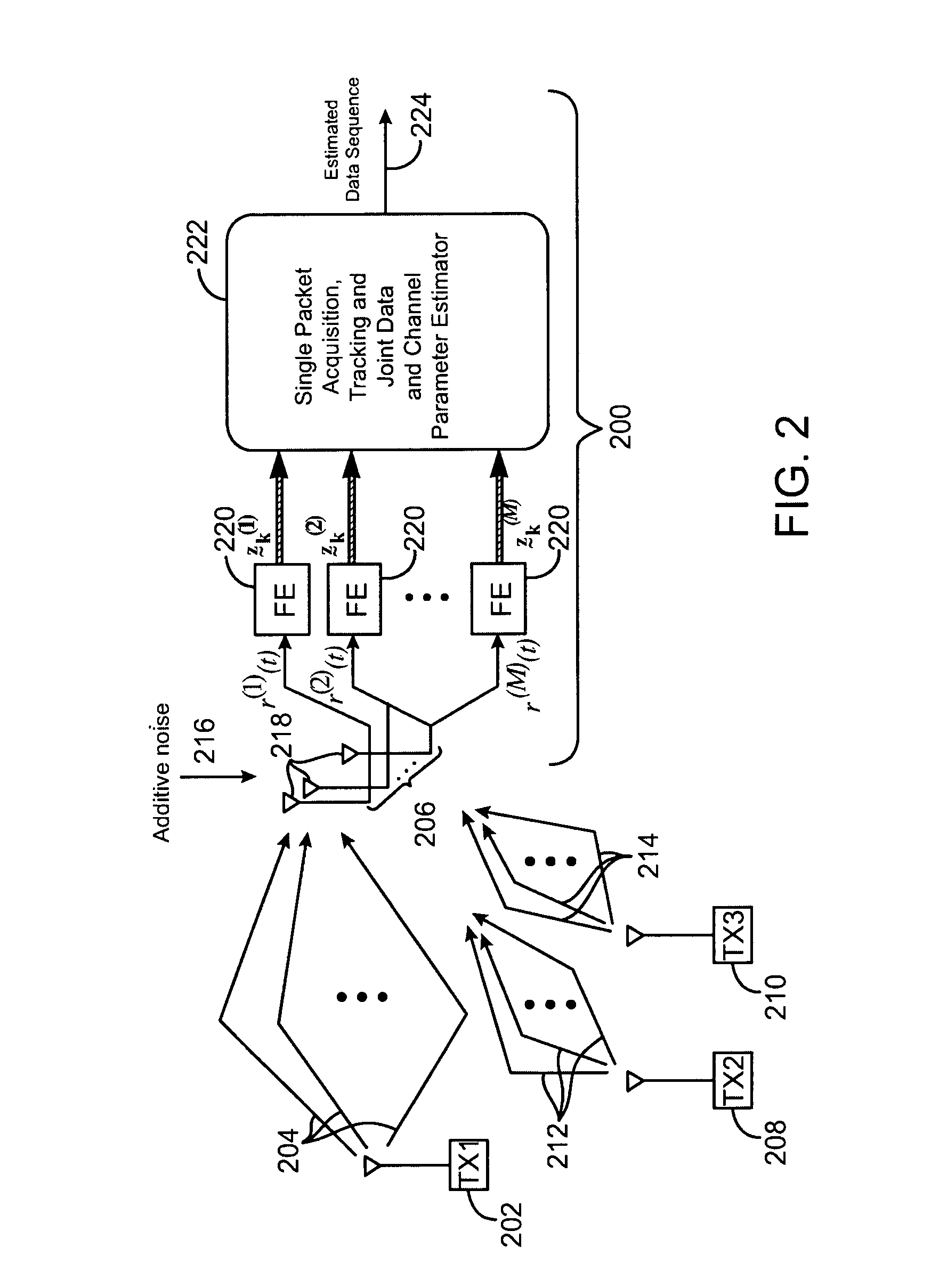
Method for co-channel interference identification and mitigation
ActiveUS7010069B2Error preventionPolarisation/directional diversityTime division multiple accessSignal of interest
A method for co-channel interference identification and mitigation employs adaptive sequence detection in connection with a model composed of a signal of interest and a combination of other signals which constitute interference in a channel of interest, wherein the signal of interest is distinguished from the interference by adaptive tracking of signal parameters of all identifiable signals. In a particular embodiment, the process involves estimating the number and time spans of co-channel interference channels based on maximum likelihood estimation and minimum description length from training information derived from a single time division multiple access packet; and then applying the estimate to mitigation of co-channel interference at a receiver. Per-survivor-processing is one technique for adaptive sequence detection.
Owner:TRELLIS WARE TECH
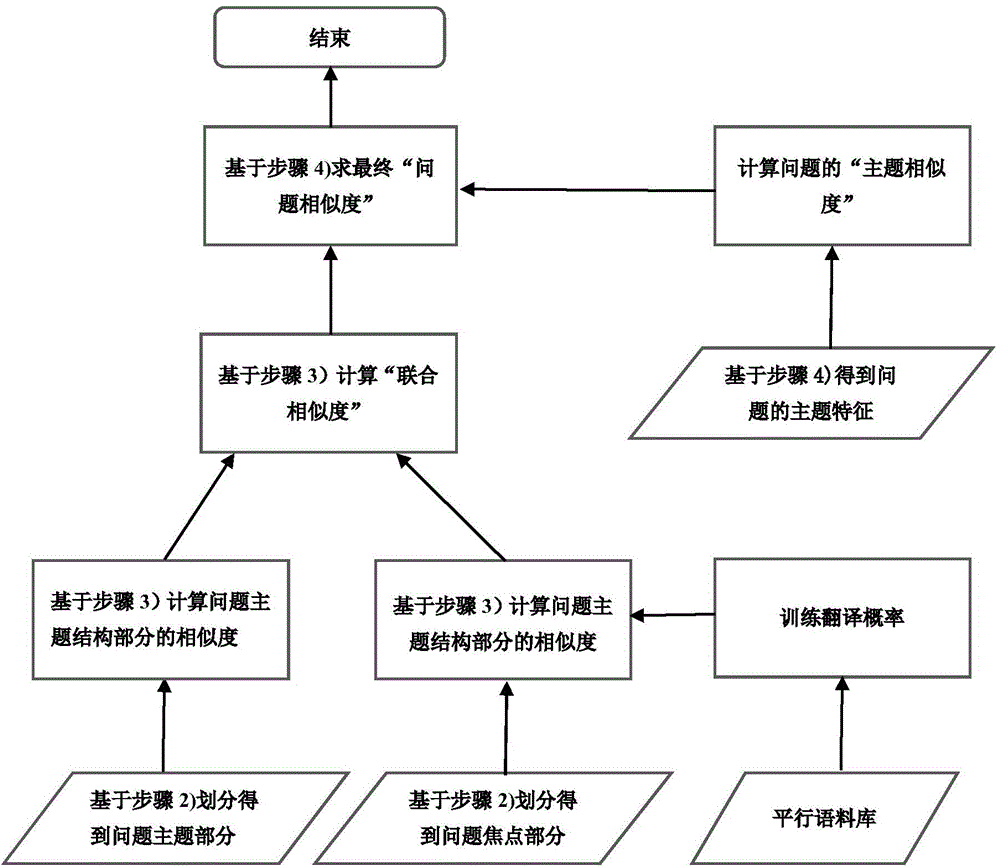
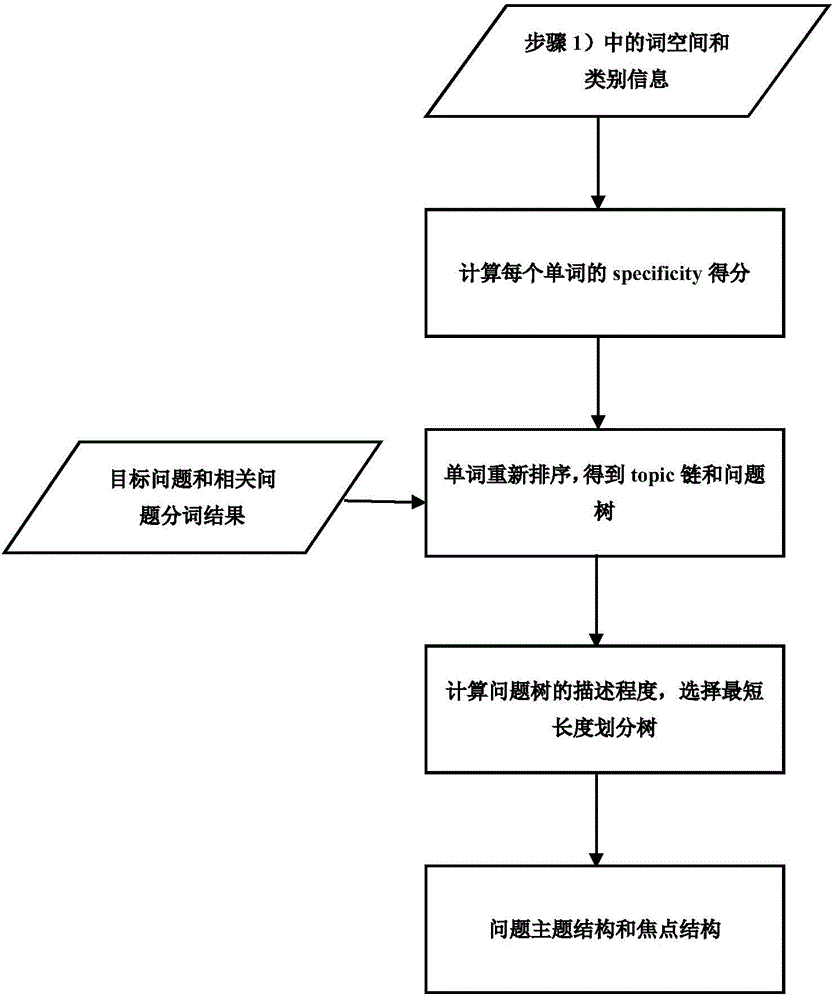
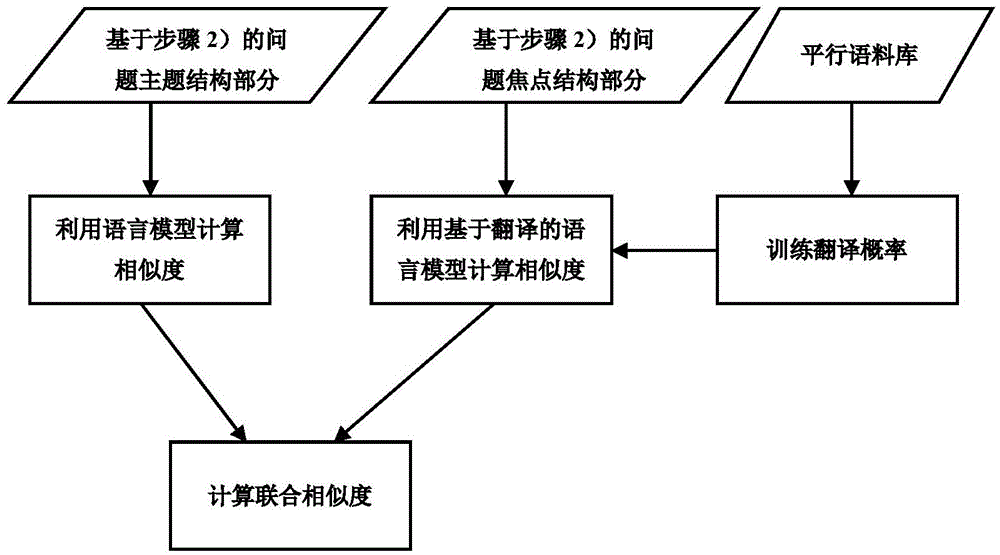
Problem similarity calculation method based on subjects and focuses of problems
InactiveCN104899188ATake advantage ofThe calculation result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum description lengthCalculation methods
The present invention discloses a problem similarity calculation method based on subjects and focuses of problems Basic preprocessing, such as word segmentation and the like, is carried out on problem data by using a tokenizer, and based on the basic preprocessing, a tree tailor model based on the minimum description length divides each problem into a problem subject and a problem focus; with respect to subject structures and focus structures of two problems, a language model and a language model based on translation are respectively used to calculate a similarity score, and a joint similarity is obtained by means of weighted summation; and a subject similarity between the two problems is calculated by using a method based on a BTM subject model, and two similarities are finally subjected to weighted summation to obtain the final problem similarity. According to the present invention, architectural features and subject information of the problems are introduced into the problem similarity calculation, the information of the problems is more sufficiently used, and by introducing the subject information of the problems besides word statistics information into the problem similarity calculation, accuracy of the problem similarity calculation is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
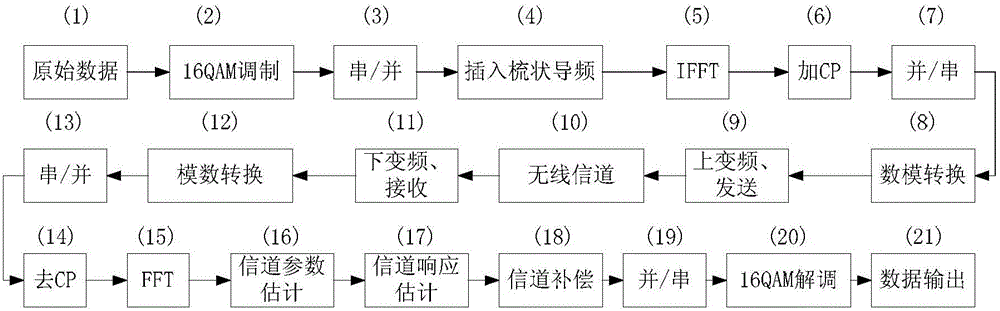
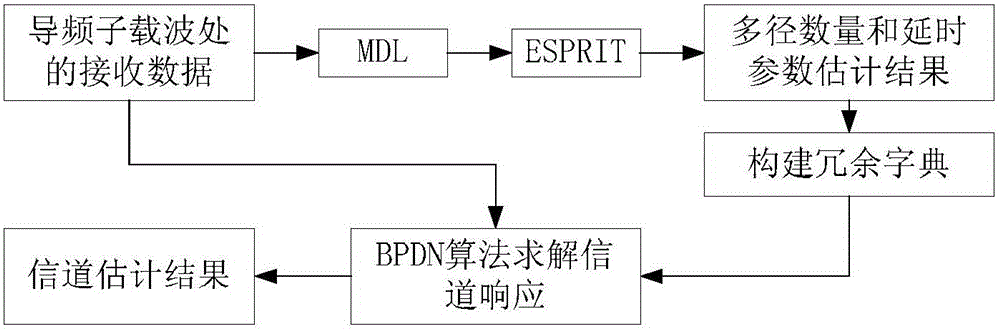
OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) system parametric channel estimation and equalization method based on compressed sensing technology
ActiveCN105915473AImprove performanceThe result error is smallChannel estimationMulti-frequency code systemsEstimation methodsEqualization
The invention discloses an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) system parametric channel estimation and equalization method based on compressed sensing technology. The channel estimation method comprises the following steps: 1) an OFDM frequency domain at a pilot subcarrier receives data, and parameter estimation is carried out on the channel based on a channel parametric model: firstly, according to a MDL (Minimum Description Length) criterion, a multipath number estimation value L<^> of the channel is obtained; then, the ESPRIT (estimation of signal parameters by rotational invariance techniques) technology is used for estimating delay parameters for each path, and multipath delay estimation values tau<^>=[tau<^>1, tau<^>2,..., tau<^> < L<^>>] are obtained; and 2) a parameter estimation result is used for building a redundant dictionary matrix, and a channel response estimation value is solved through a BPDN algorithm. Based on parametric channel modeling, the signal parameter estimation technology is combined with a compressed sensing frame, the channel estimation precision and the communication efficiency are improved, and the communication bit error rate is reduced. Compared with the traditional channel estimation method, the method of the invention has obvious performance advantages.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
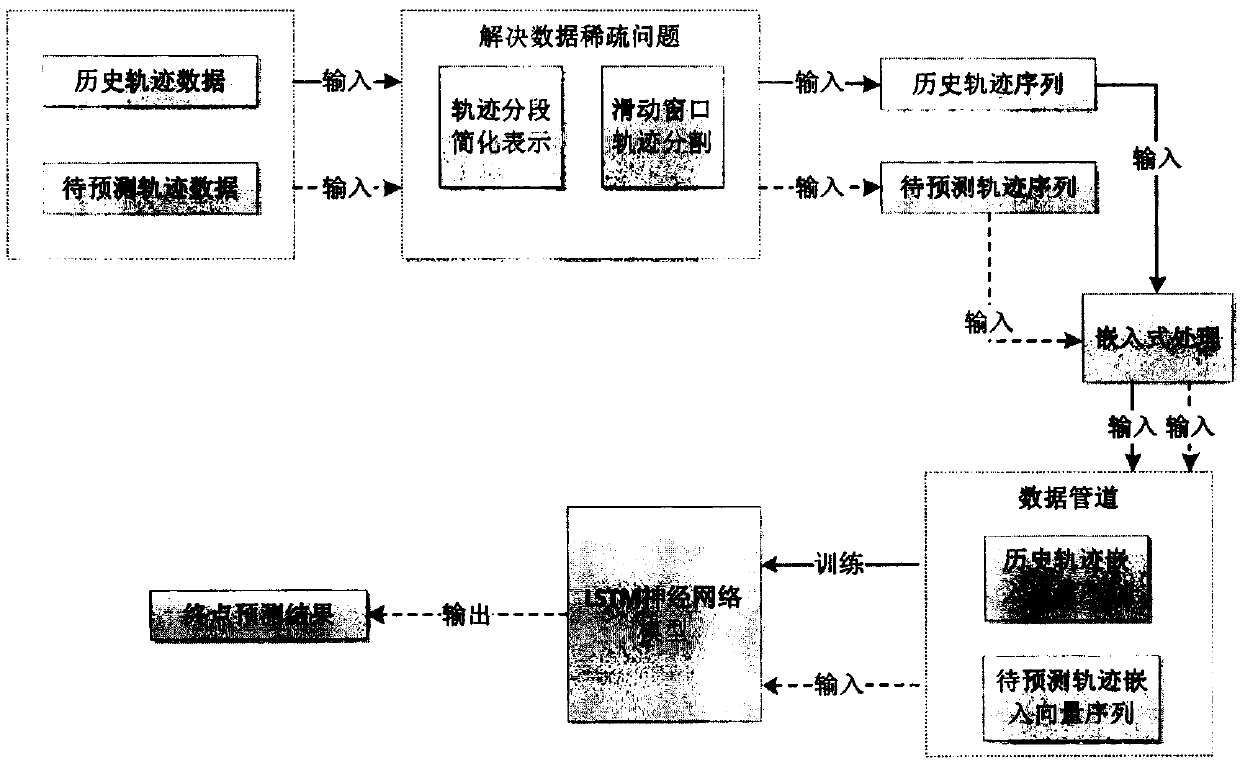
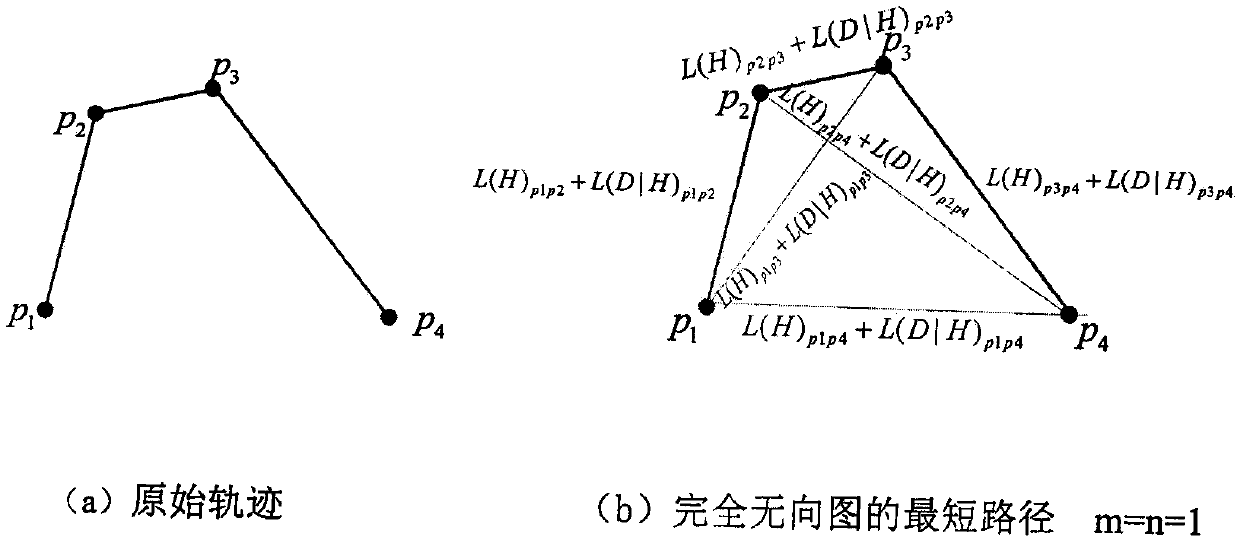
Novel moving object destination prediction algorithm
PendingCN110738370ASolve data sparsityAchieve dimensionality reductionForecastingGeographical information databasesPathPingPrediction algorithms
The invention discloses a moving object destination prediction algorithm. The method comprises the steps that firstly, an improved track segmentation method with the minimum description length (IMDL)is provided, weight parameters are introduced, meanwhile, a Dijkstra algorithm is used for converting the track segmentation problem into the shortest path problem of an undirected graph, the optimalsegmentation of a track is obtained, and therefore the track is simplified; then, a deep learning prediction model EP-LSTM based on embedded processing and long-short-term memory fusion is provided, and a high-dimensional input vector is converted into an embedded vector to serve as input of the model. The method has the advantages that the problems of data sparseness and long-term dependence in moving object destination prediction are effectively solved, and an excellent prediction effect is achieved by performing a large number of experimental verifications on a real data set.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
A convolutional neural network-based moving object destination prediction method
ActiveCN109739926AReduce varianceHigh similarityVisual data miningStructured data browsingEffective solutionFeature extraction
The invention discloses a convolutional neural network-based moving object destination prediction method, which comprises the following steps of: introducing a parameterized minimum description length(PMDL) strategy to carry out optimal segmented representation on an original trajectory, weakening the difference degree between similar trajectories, and enhancing respective important characteristics of the different trajectories; proposing a trajectory pixelated representation method (PRT), and converting the one-dimensional trajectory sequence into a two-dimensional pixel image; and intercepting important feature parts from the track image and inputting the important feature parts into a convolutional neural network (CNN) model, and performing feature extraction and destination prediction. The method has the advantages that a one-dimensional track sequence is converted into a two-dimensional pixel image, and destination coordinates are determined by mining spatial features of the track image; the invention provides an effective solution for the data sparsity problem which is common in destination prediction but cannot be solved in many traditional methods, and high-accuracy destination prediction is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
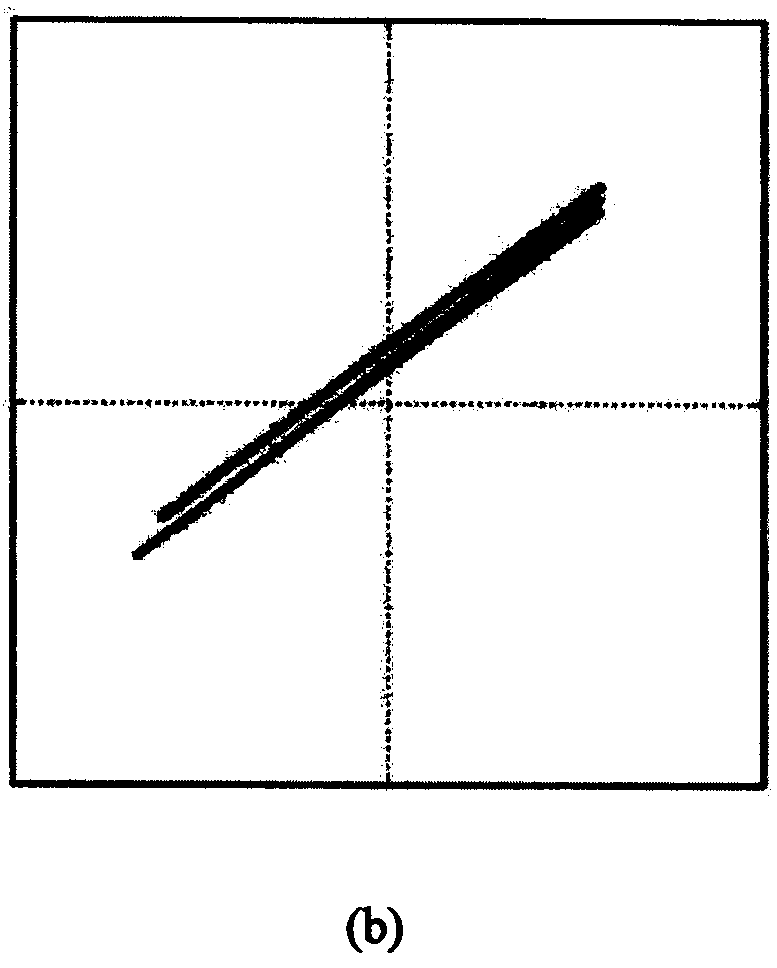
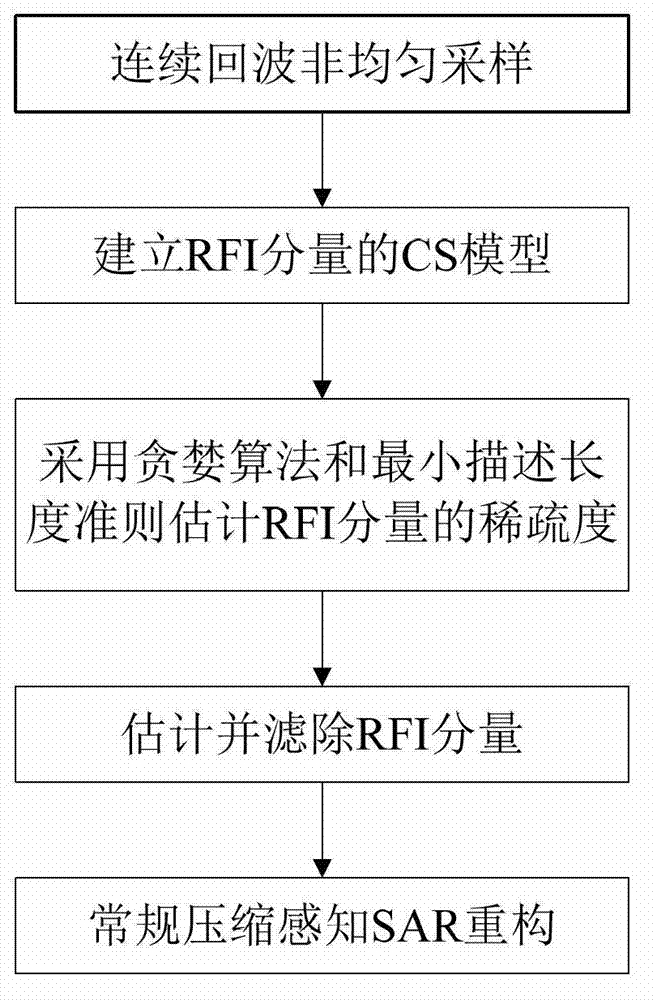
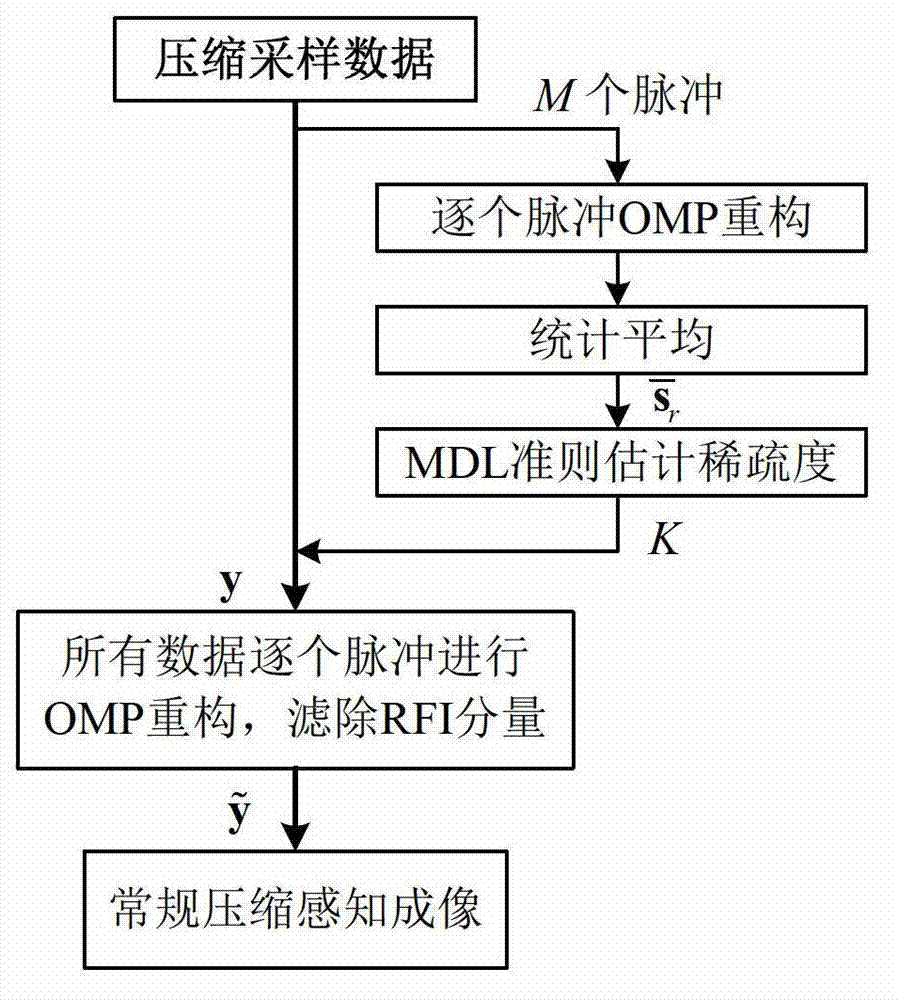
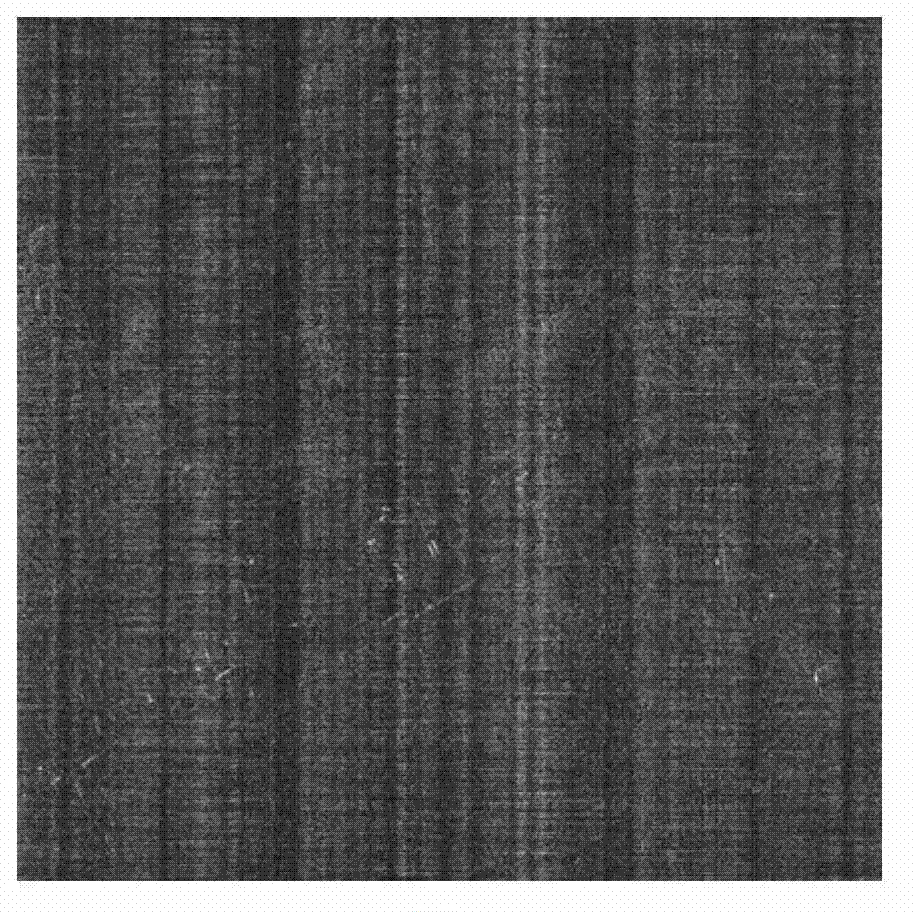
Compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar radio frequency interference suppression handling method
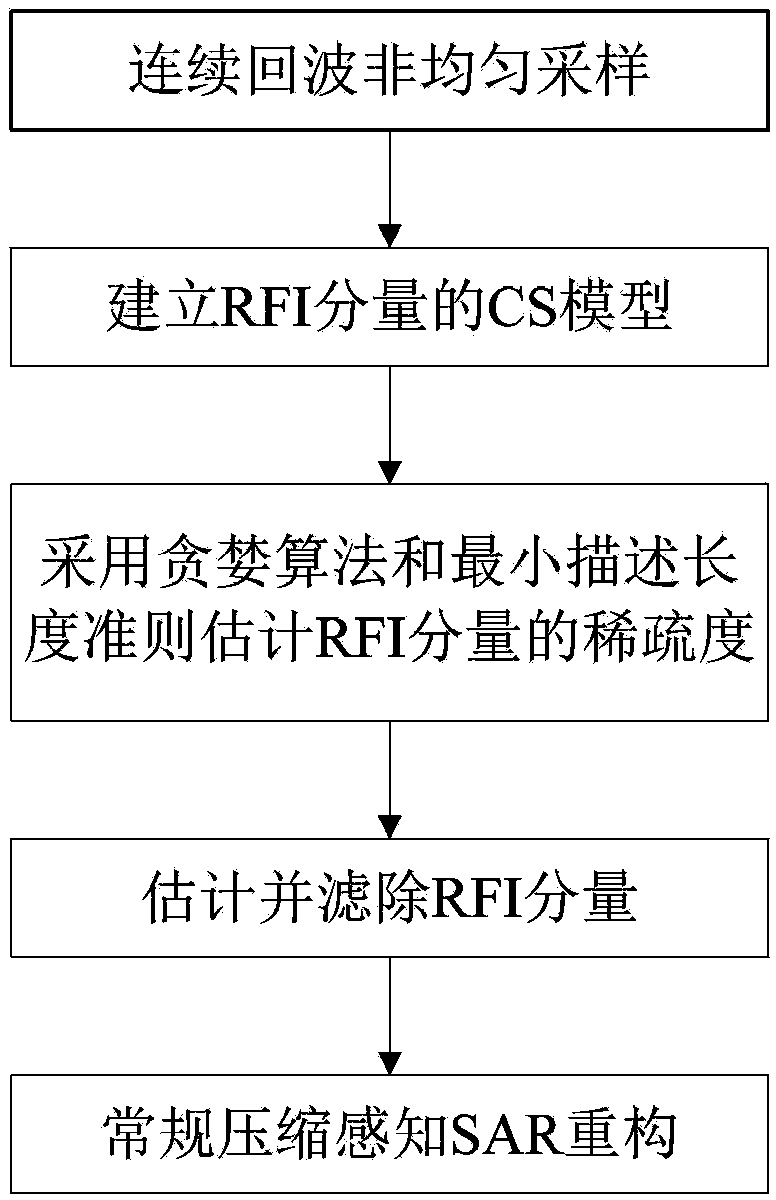
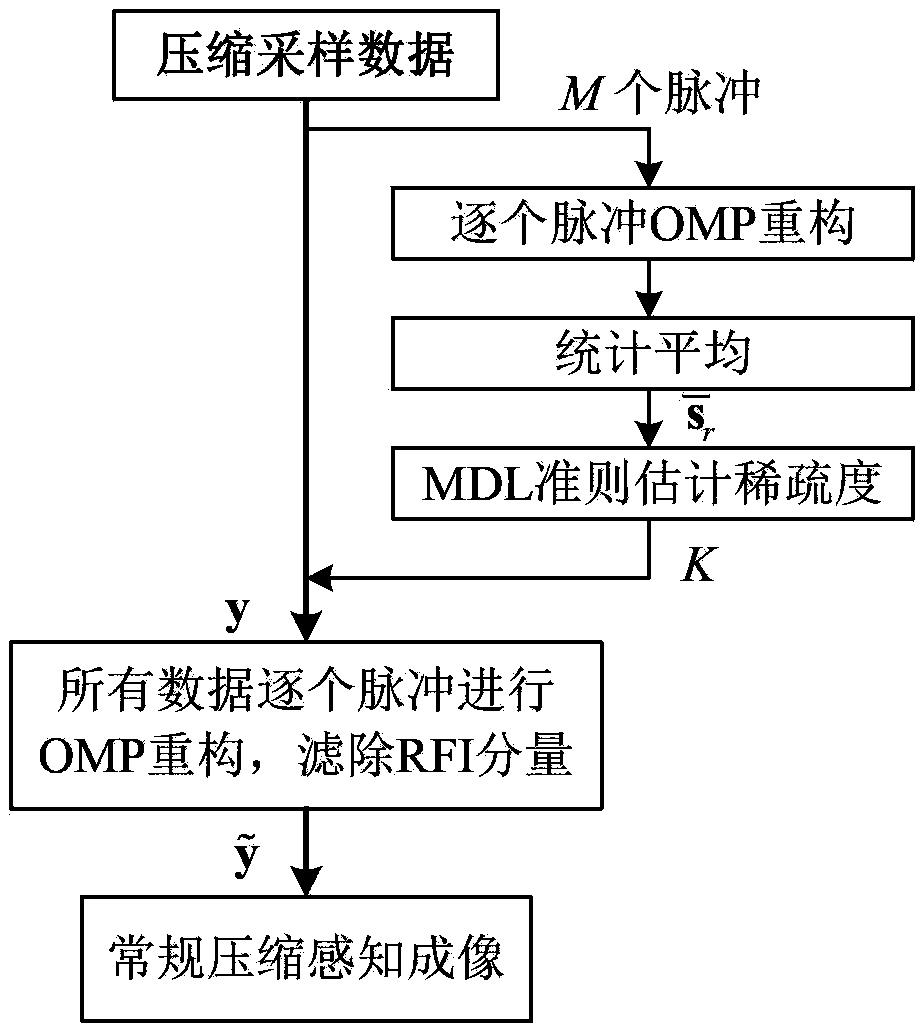
InactiveCN103091665AApparent sparsenessEstimated sparsityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarMinimum description length
The invention provides a compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar radio frequency interference suppression handling method. The method includes the following steps: (1) building a compressed sensing model of a radio frequency interference (RFI) signal based on an obvious sparse feature of a RFI component in frequency domain, (2) estimating sparseness of the RFI component by using a greedy algorithm to combine with minimum description length, (3) estimating a RFI signal component and filtering directly in time domain to an echo signal of each pulse, and (4) achieving imaging process by using an conventional compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar (SAR) reconstructing algorithm. The compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar radio frequency interference suppression handling method is based on the sparse feature of the RFI component in the frequency domain and builds a RFI sparse model based on a compressed sensing theory, restrains narrow-band and broadband RFI signals effectively by using the iterative greedy algorithm to estimate and filter the RFI component in the echo signal.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
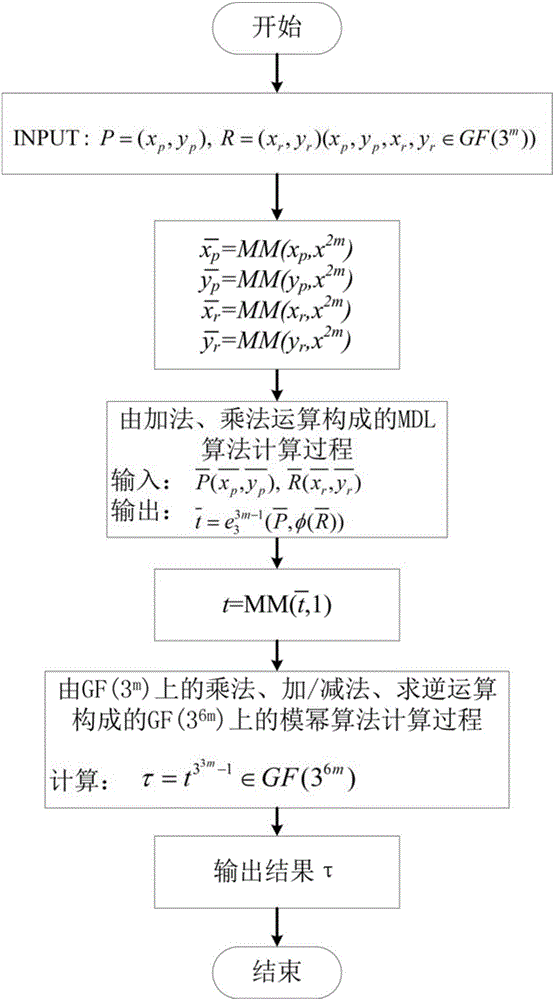
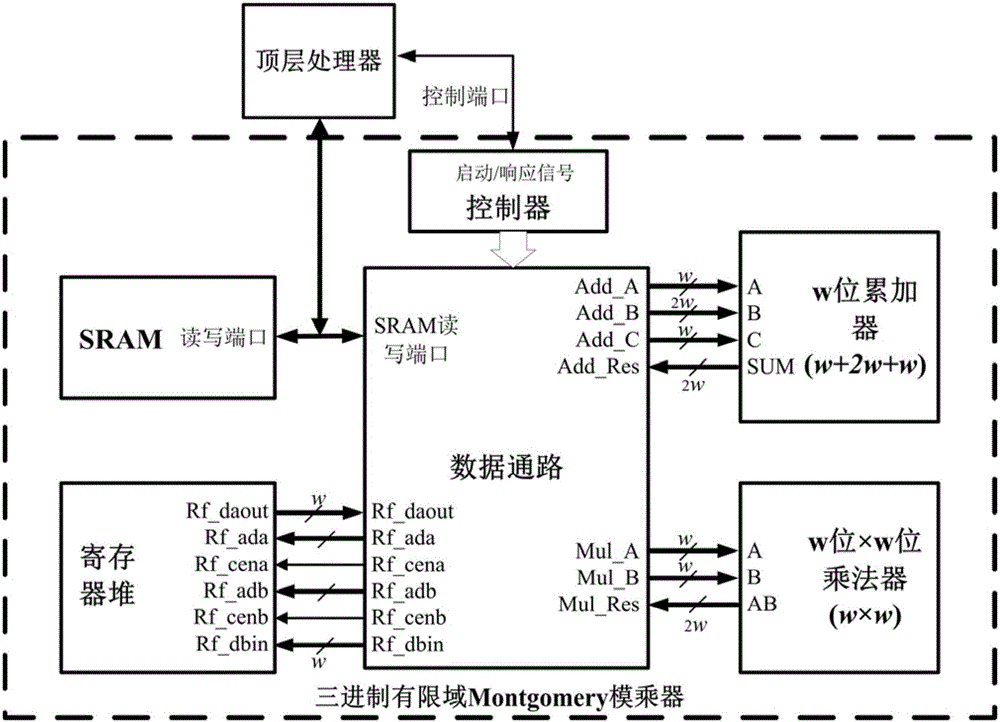
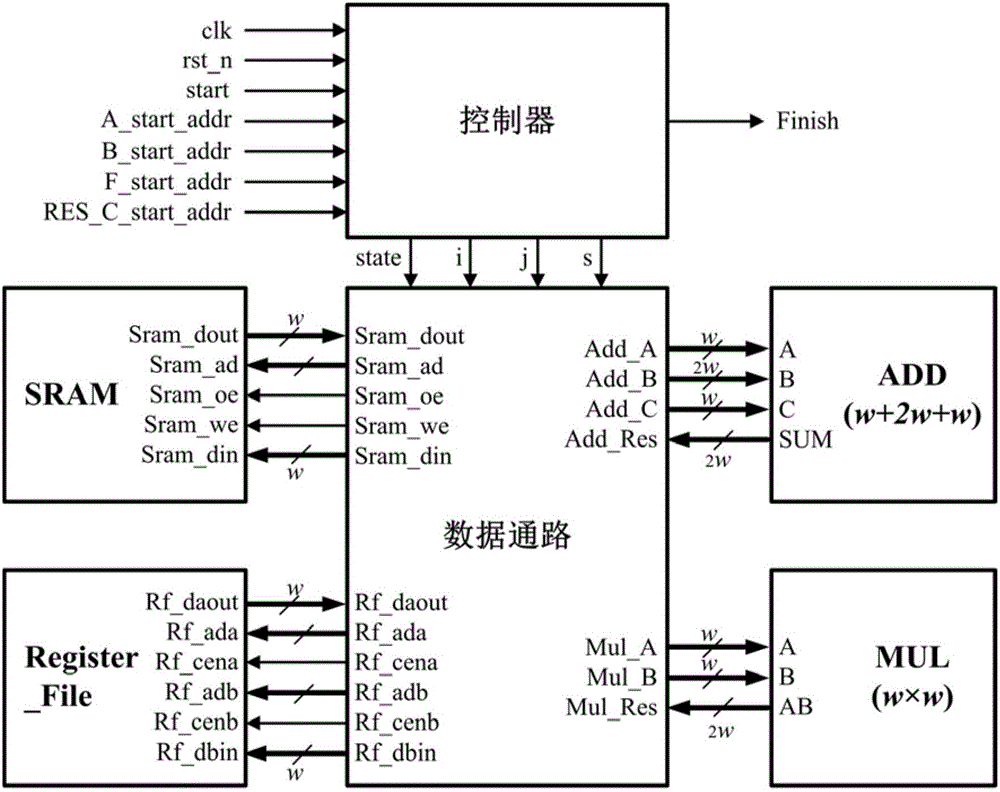
Montgomery modular multiplication based Tate pairing algorithm and hardware structure therefor
ActiveCN105068784AReduce hardware overheadReduce power overheadDigital data processing detailsHardware structureStatic random-access memory
The invention belongs to the technical field of realization of cryptographic algorithms of embedded systems and particularly relates to a ternary finite field Montgomery modular multiplication based Tate pairing algorithm and a hardware structure for realizing the algorithm. The algorithm comprises: converting X coordinates and Y coordinates of two input points P and R on an elliptic curve to a Montgomery domain from a defined GF(3m) domain; according to an MDL (minimum description length) algorithm procedure taking multiplication, addition / subtraction and cubic operation on GF(3m) as basic operations, performing operation in the Montgomery domain; and converting a calculation result to the GF(3m) domain from the Montgomery domain, and performing 33m-1-power modular exponentiation on the calculation result. The hardware structure comprises a top-level processor, a controller, a ternary accumulator, a ternary multiplier, a register file and an SRAM (static random access memory), wherein the controller is used for controlling input of the ternary accumulator and the ternary multiplier and read-write operation of the SRAM and the register file so as to control data transmission of the whole circuit.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Pseudo-code sequence blind estimation of synchronous DS-CDMA (Direct Sequence-Code Division Multiple Access) signal containing residual frequency offsets
The invention claims to protect a pseudo-code sequence blind estimation method of a synchronous DS-CDMA (Direct Sequence-Code Division Multiple Access) signal containing residual frequency offsets based on the combination of eigen decomposition and a DPLL (Digital Phase Lock Loop), and belongs to the technical field of signal processing. The pseudo-code sequence blind estimation method comprises the following steps: on the premise of knowing a pseudo-code sequence period and a chip width, segmenting a received signal according to a single-fold pseudo-code period in order to construct a signal covariance matrix and performing eigenvalue decomposition; estimating the user number of the DS-CDMA signal according to an MDL (Minimum Description Length) principle in order to further extract a feature vector corresponding to a maximum eigenvalue which is equal to the user number, and realize rough extraction of each user pseudo-code sequence; lastly, inputting the pseudo-code sequence undergoing the rough estimation into the DPLL to eliminate the residual frequency offsets, wherein an I-path signal output by the DPLL is taken as a pseudo-code sequence undergoing final blind estimation. By adopting the method, aliasing residual frequency offsets in the pseudo-code sequence are eliminated through the DPLL, and the estimation problem of the pseudo-code sequence of the DS-CDMA signal containing the residual frequency offsets under a low signal-to-noise ratio is solved effectively; moreover, an algorithm is easy to operate and is not limited by a spreading code type, and the method has important engineering practical significance.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Incremental parallel structure exception detection method for dynamic graph
InactiveCN106919650AScalableReduce running timeOther databases queryingSpecial data processing applicationsData setAnomaly detection
The invention relates to an incremental parallel structure exception detection method for a dynamic graph. The method comprises the steps of firstly, dividing the graph by using a time sliding window, and selecting N sub-graphs in an initialization stage to detect normal modes and exceptional sub-structures in parallel; and secondly, iteratively determining normal modes and exceptional sub-structures in the residual sub-graphs in parallel. A minimum description length principle is used in the normal mode detection, so that an original graph can be subjected to compression and exception detection in multiple levels. A proposed algorithm is verified in a plurality of large-scale graph data sets, and an experimental result shows that the proposed method can effectively and incrementally detect exceptions in large-scale graph flow data.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Bayesian network structure learning method and system and reliability model construction method
InactiveCN105184373AAvoid repeated climbingImprove search efficiencyMathematical modelsGuidelineStructure learning
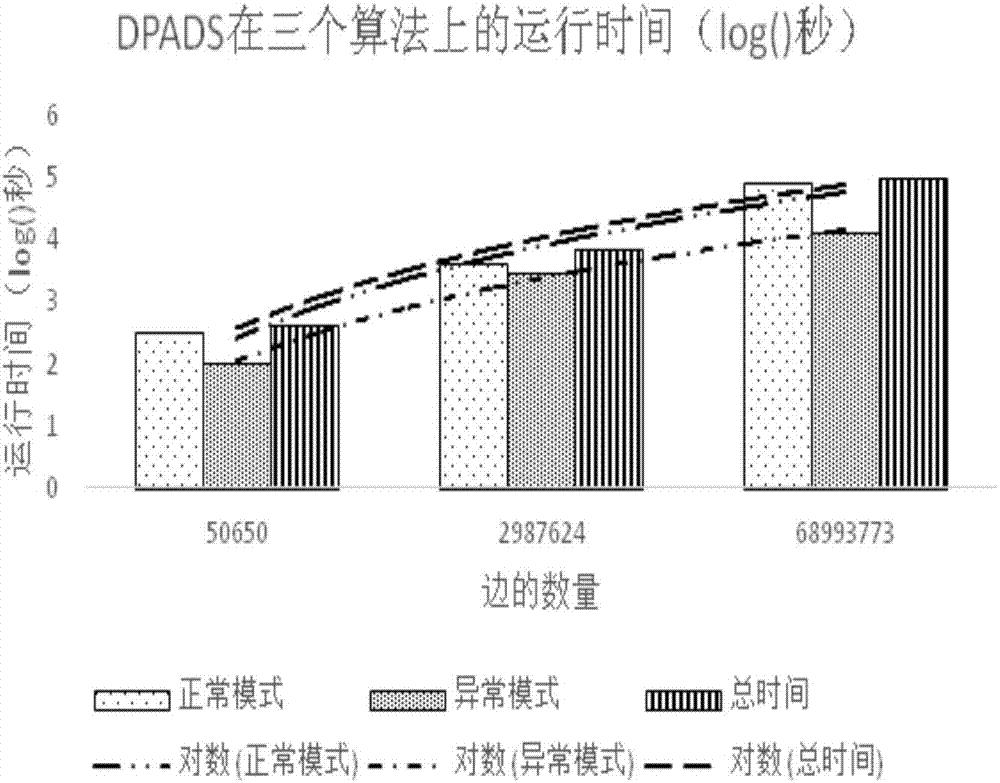
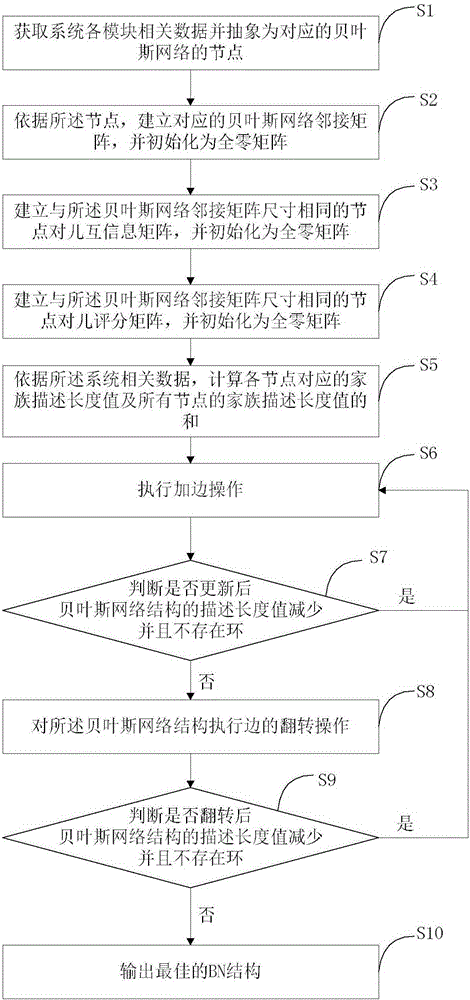
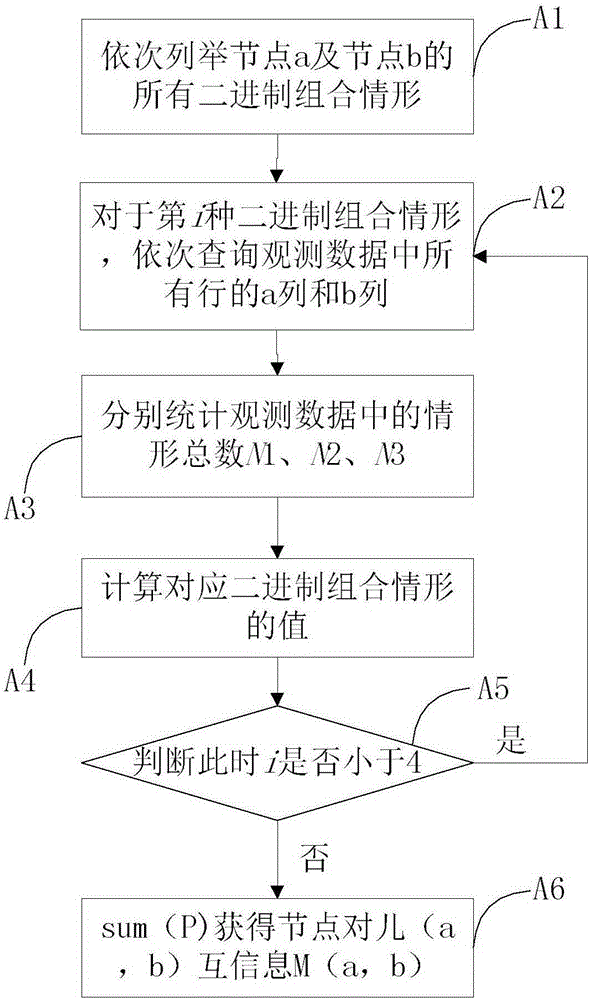
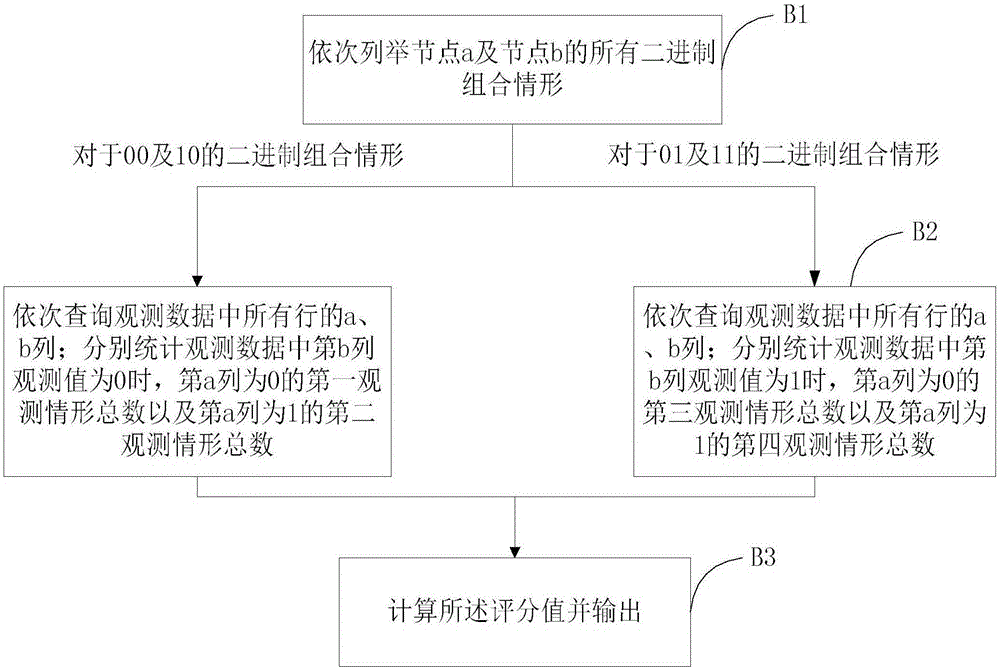
The invention provides a Bayesian network structure learning method and system and reliability model construction method. The learning method comprises the steps that relevant data of each module of a system are acquired and are abstracted into corresponding Bayesian network nodes; according to the relevant data of the system, a node mutual information matrix and a node to BIC scoring matrix are calculated and established; a corresponding adjacency matrix is established; and according to relevant data of the system, a family description length value corresponding to each node and the sum of the family description length values of all nodes are calculated. Bordered operation is carried out. Whether a BN structure continues to be updated is judged through a minimum description length principle. Side flipping is carried out. Whether the BN structure continues to be updated is judged through the minimum description length principle. In bordered operation, an MDL standard and a BIC evaluation standard are combined to avoid repeated climbing. The learning method still belongs to a greedy search algorithm. Due to combined specific scoring standards, the search efficiency and the accuracy rate are greatly improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
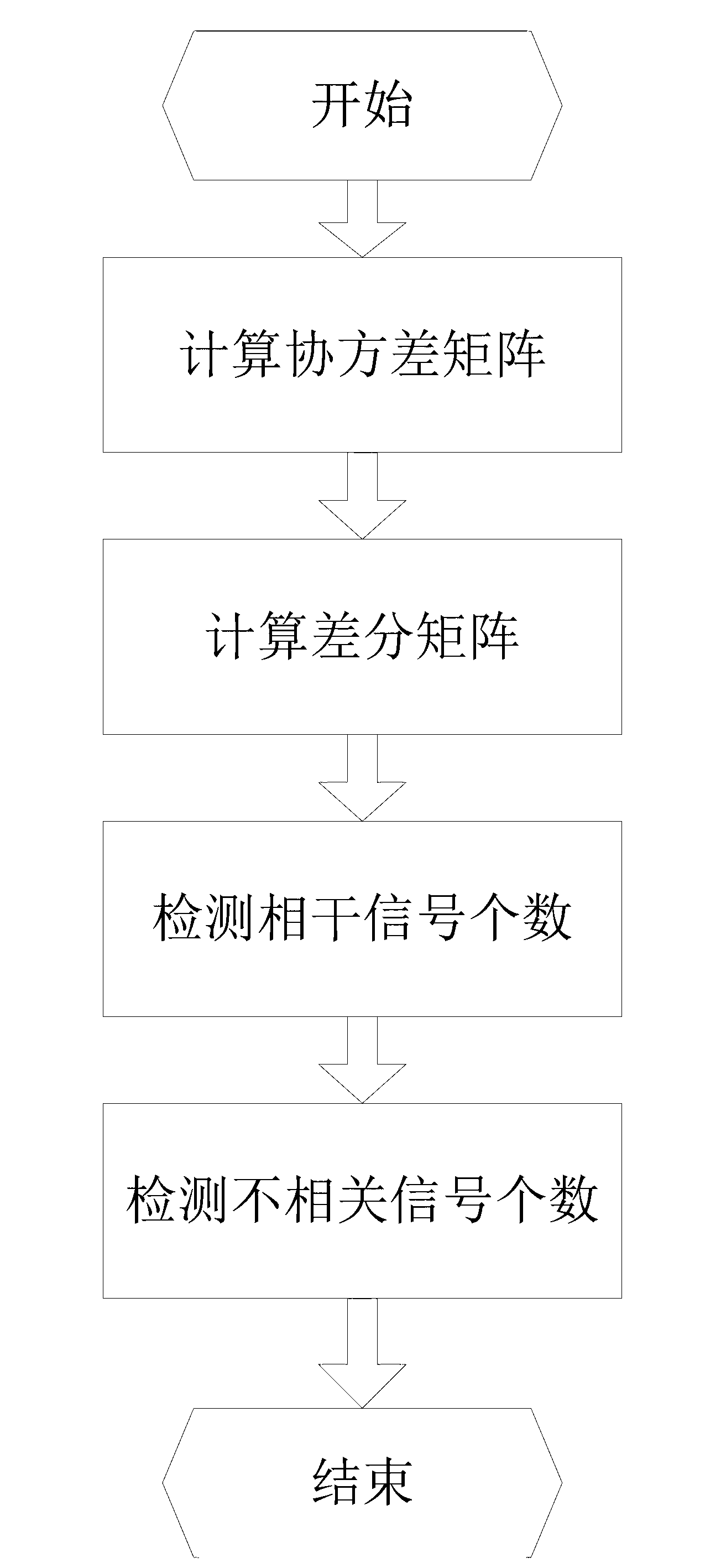
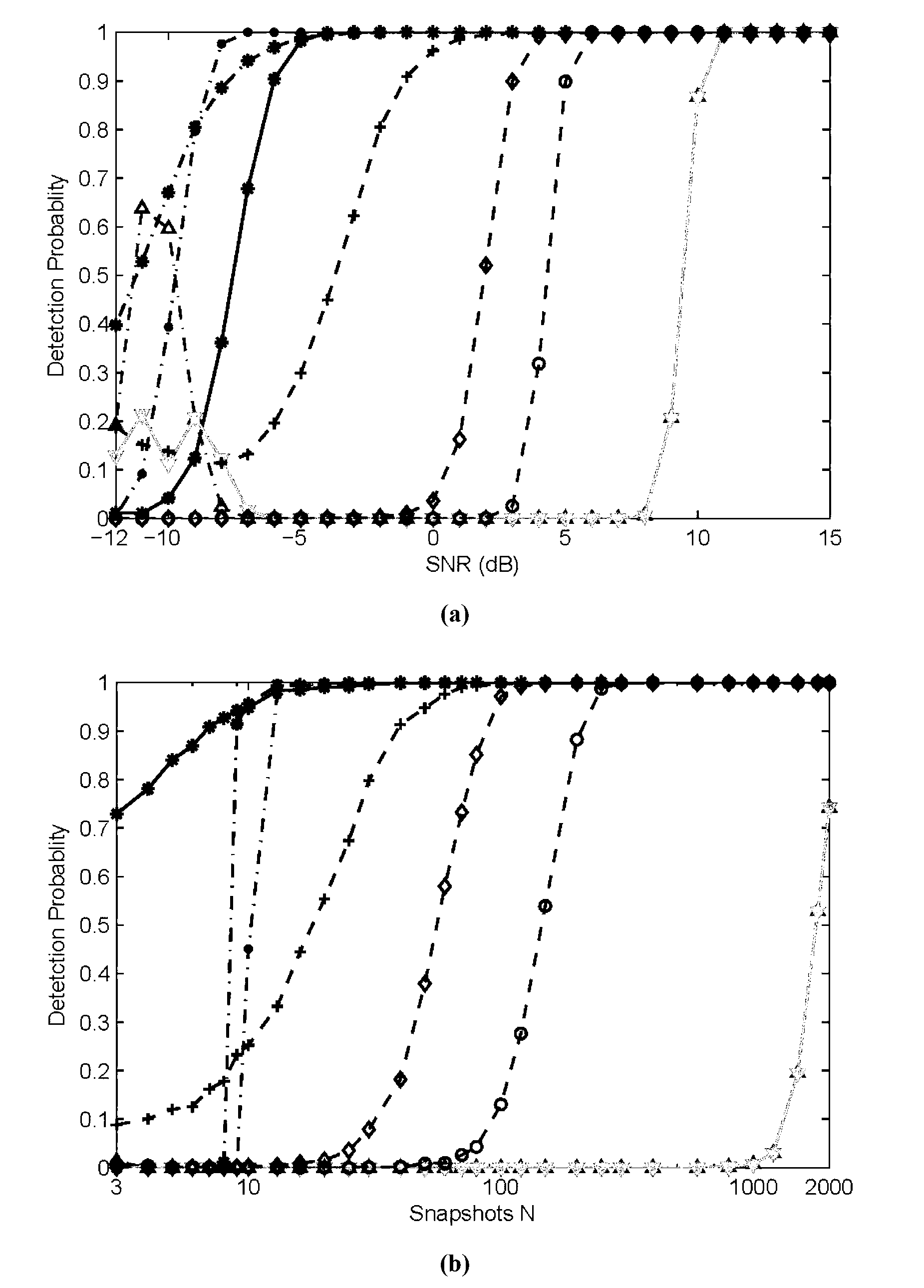
Method for detecting number of signals under condition of mixing of uncorrelated and correlated signals in uniform linear array
The invention discloses a method for detecting the number of signals under the condition of mixing of uncorrelated and correlated signals in a uniform linear array. The method for detecting the number of the signals is characterized by including steps of constructing a difference matrix, dividing the difference matrix into superimposition submatrixes, constructing a connecting matrix, and acquiring the number of the correlated signals in incident signals by solving a rank of the connecting matrix; and acquiring a rank of an array covariance of the incident signals by a ratio criterion based on singular value decomposition, and acquiring the estimated number of the uncorrelated signals. Large quantities of simulation experiments prove that the method for detecting the number of the signals is superior to an MDL (minimum description length) method / an AIC (akaike information criterion) method, an MENSE method and an SRP (smoothing rank profile) method which are pre-processed by an FBSS (forward-backward spatial smoothing) under the conditions of fewer snapshots and low signal noise ratio.
Owner:RES INST OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV & SUZHOU
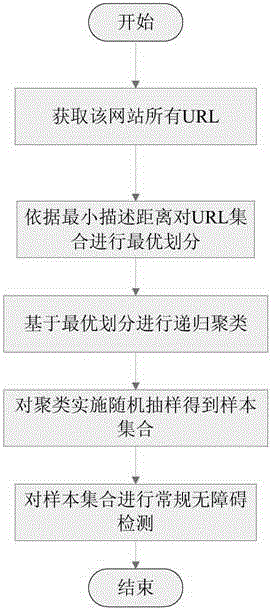
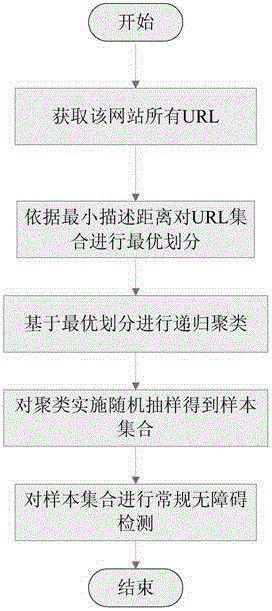
Webpage sampling method oriented at barrier-free webpage content detection
ActiveCN103823753AReduce time complexityImprove algorithm performanceSoftware testing/debuggingGreedy algorithmUniform resource locator
The invention discloses a webpage sampling method oriented at barrier-free webpage content detection. The webpage sampling method includes capturing URLs (uniform resource locators) of all related webpages of a website according to a to-be-detected URL, creating an MDL (minimum description length) model for URL sets of the website, clustering all the URLs by an MDL-based greedy algorithm, performing random sampling on each cluster according to a sampling proportion lambada to acquire samples, and performing conventional barrier-free compliance detection on sample sets.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Greedy algorithm-based self-adapting compression perception signal restoring method
InactiveCN104485965ASave communication resourcesSmall amount of calculationCode conversionAdaptive compressionEstimation methods
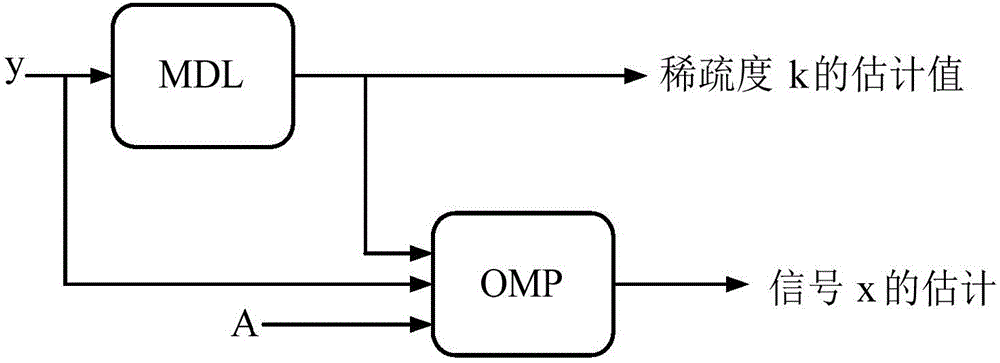
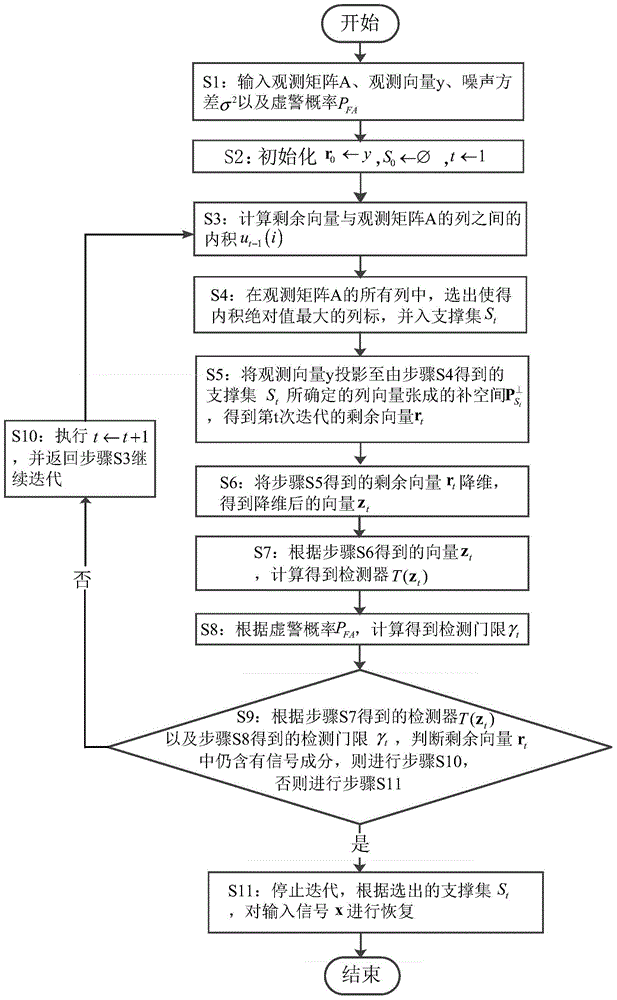
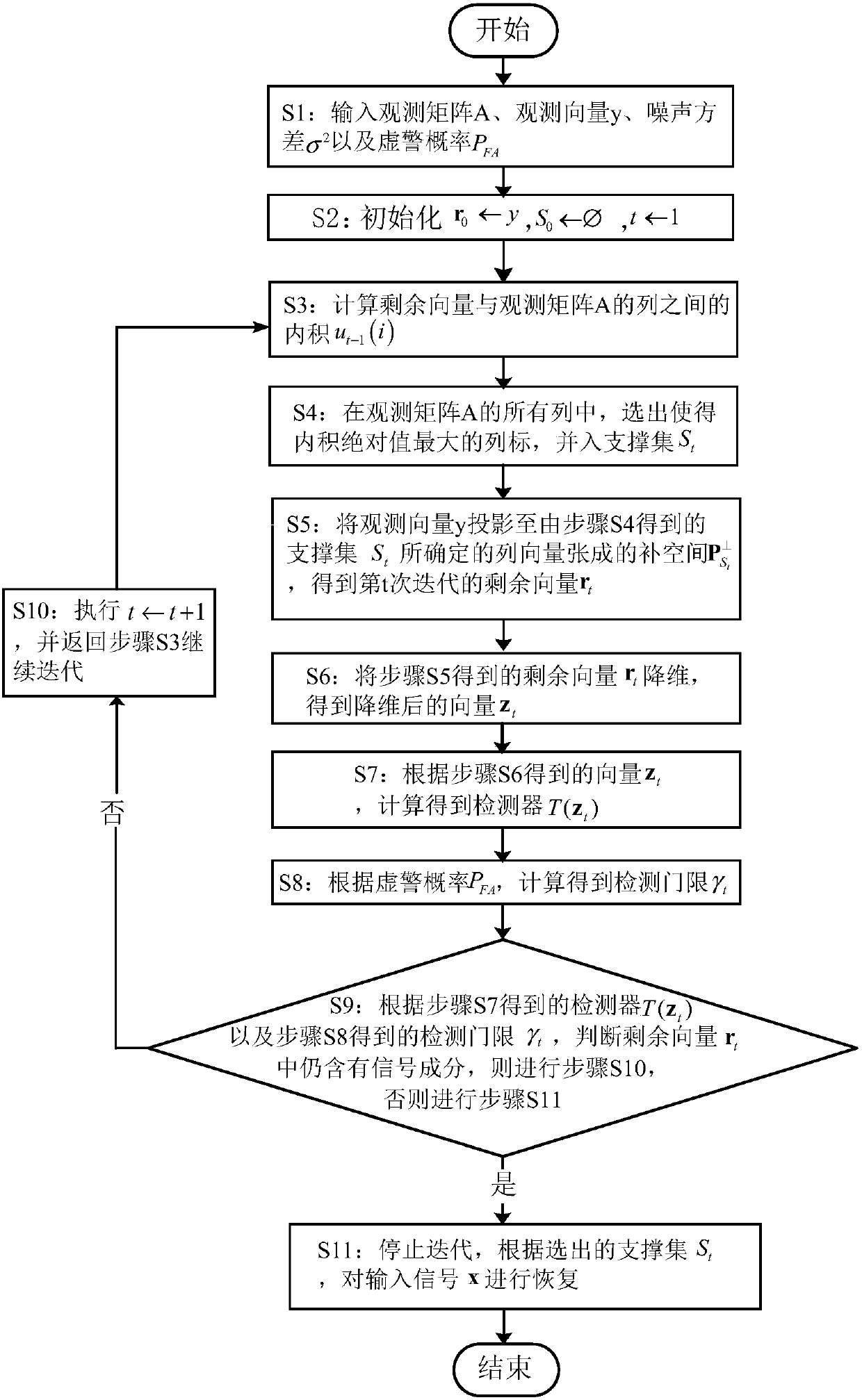
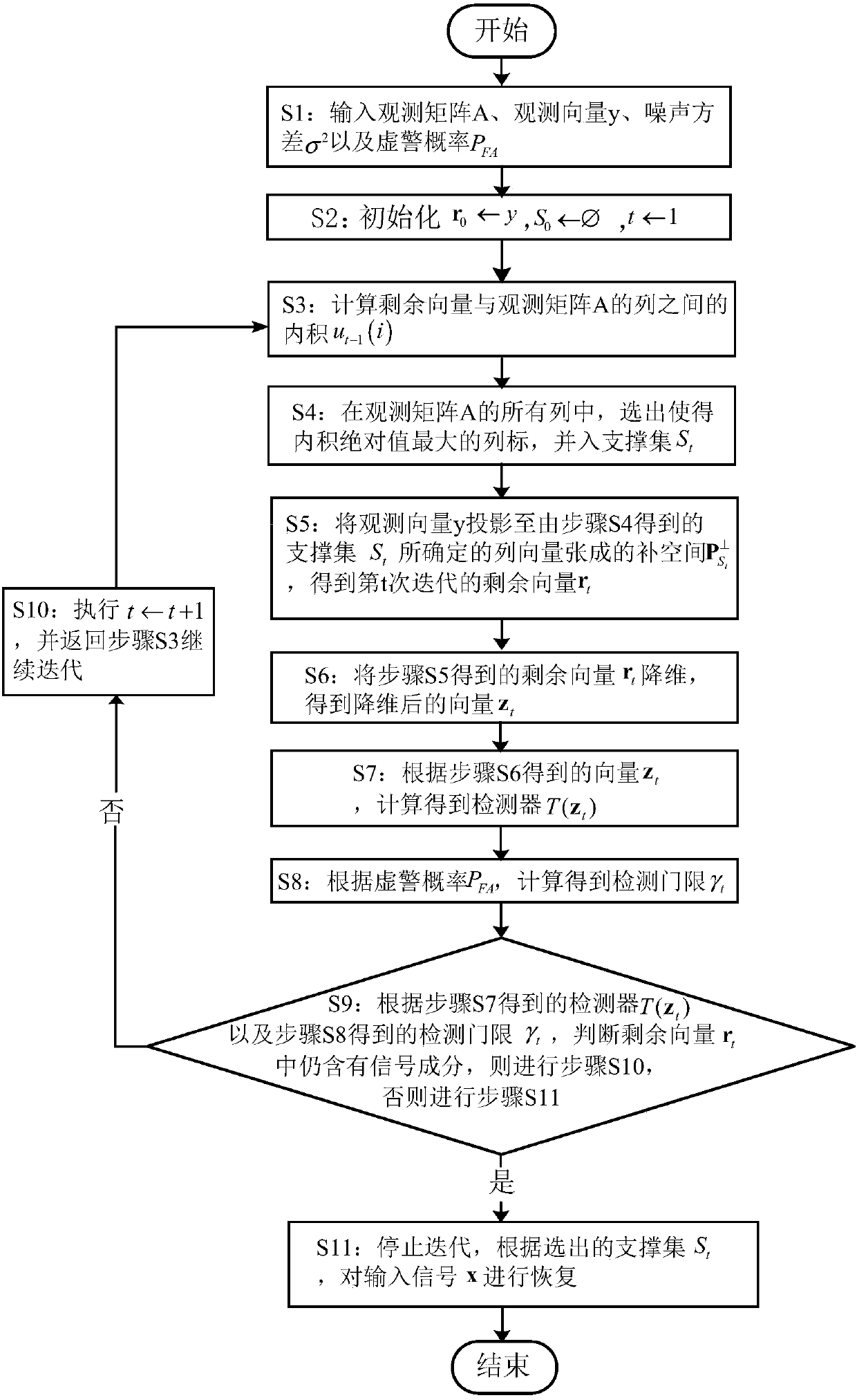
The invention discloses a greedy algorithm-based self-adapting compression perception signal restoring method. On the basis of an OMP (Orthogonal Matching Pursuit) algorithm, a detector used for judging whether a signal component exists in residual vector or not is designed, the detector is obtained through a hypothesis test model in the signal detection theory, the threshold of the detector is given through preset false alarm probability, when the threshold of the detector is smaller than the given threshold, the state that the signal component does not exist in residual vector can be judged, at the moment, iteration is stopped in the algorithm and restoring value of the signal is obtained, otherwise, iteration is continued. According to the method, the greedy algorithm serves as a channel estimation method without depending on the multipath number of a channel; compared with the MDL (Minimum Description Length), the method has the advantage that communication resources are saved due to the fact that observation for multiple times is not required; the method has the advantage of smaller calculation amount of the greedy algorithm, the problem that the requirement of the greedy algorithm on the real-time capability of sparse signal restoration is relatively high is solved, and the method can be applied to the condition that the signal sparsity is unknown.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Vehicle trajectory clustering method based on bag-of-word model and metric learning
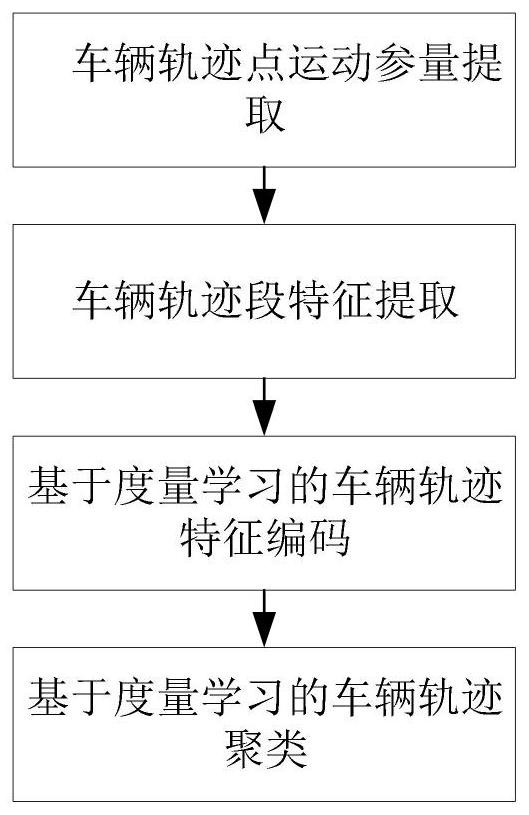
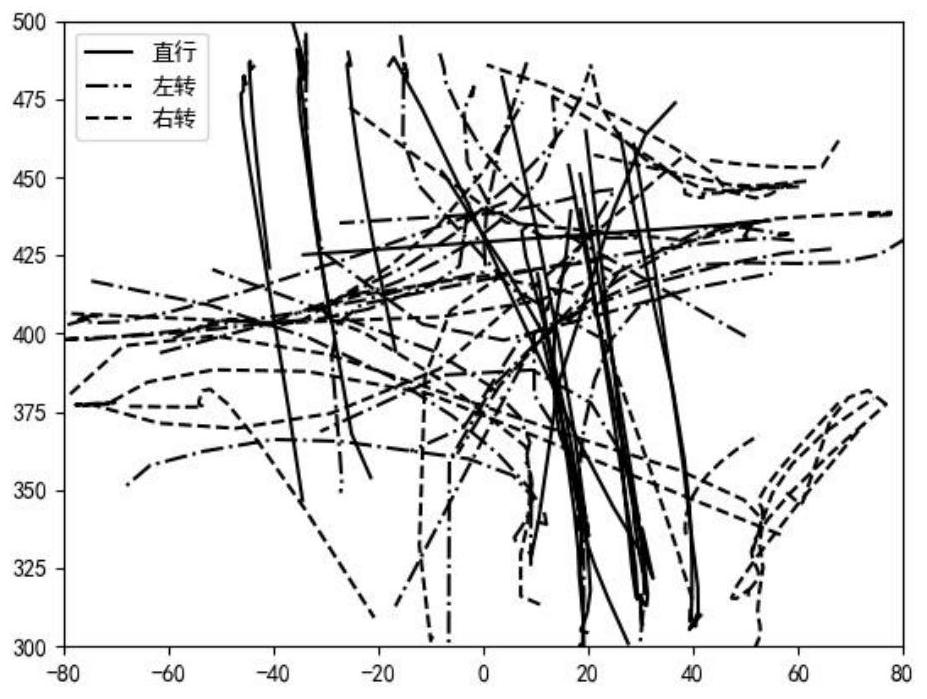
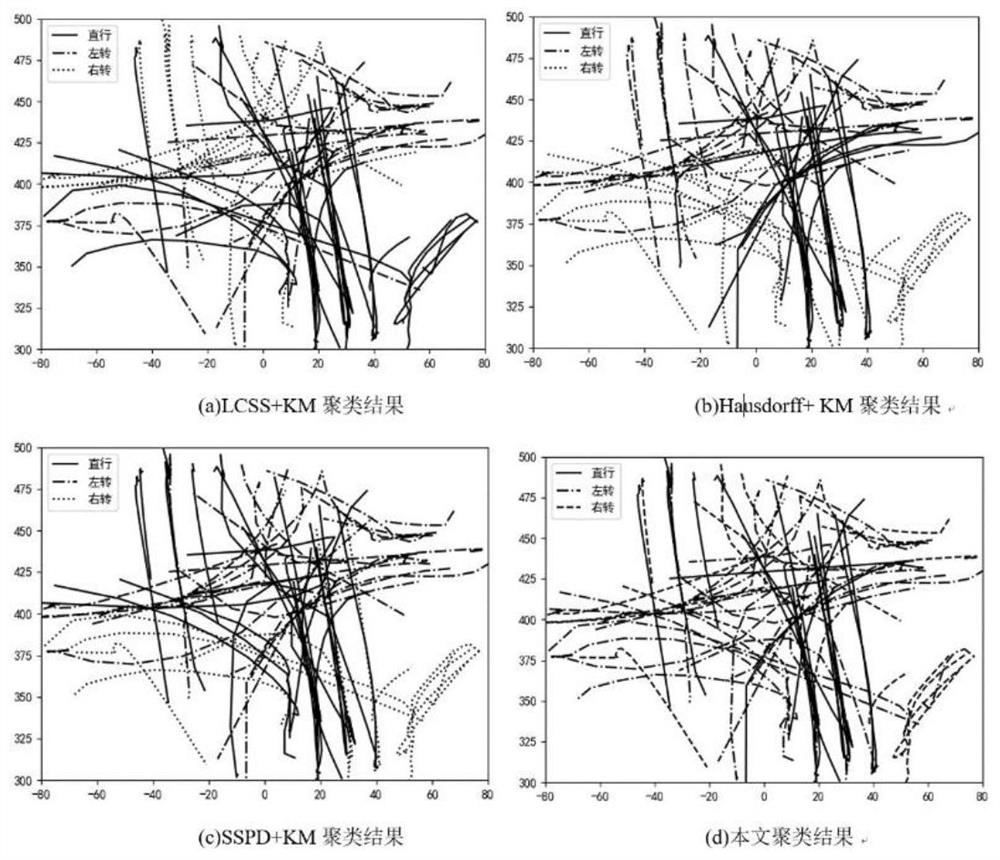
PendingCN113128569AImproving Similarity Metric PerformanceCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningFeature setSteering angle
The invention discloses a vehicle trajectory clustering method based on a bag-of-word model and metric learning. The method comprises the following steps: extracting vehicle trajectory point motion parameters; dividing the vehicle track into a plurality of optimal homogeneous vehicle track segments based on a minimum description length principle, and obtaining statistical features of each segment to obtain a vehicle track segment feature set; coding each optimal homogeneous vehicle track segment into a fixed-length vector based on a bag-of-word model and a non-convex low-rank constraint metric learning method so as to obtain a feature descriptor of the optimal homogeneous vehicle track segment; and gathering the feature descriptors through a K-means algorithm and the non-convex low-rank constraint metric learning method to realize vehicle trajectory clustering. According to the method, speed, acceleration and steering angle information is introduced, feature coding is carried out on vehicle tracks, and then the vehicle tracks in different time periods and areas are gathered; in addition, a non-convex low-rank constraint-based metric learning method is provided to improve the similarity measurement performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for Identifying Sub-Sequences of Interest in a Sequence
The present technique provides for the analysis of a data series to identify sequences of interest within the series. The analysis may be used to iteratively update a grammar used to analyze the data series or updated versions of the data series. Furthermore, the technique provides for the calculation of a minimum description length heuristic, such as a symbol compression ratio, for each sub-sequence of the analyzed data sequence. The technique may then compare a selected heuristic value against one or more reference conditions to determine if additional iteration is to be performed. The grammar and the data sequence may be updated between iterations to include a symbol representing a string corresponding to the selected heuristic value based upon a non-termination result of the comparison. Alternatively, the string corresponding to the selected heuristic value may be identified as a sequence of interest based upon a termination result of the comparison.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Fast movable object orbit clustering method based on sampling
InactiveCN101527000BPreserve clustering qualityImprove time and efficiencyWeather condition predictionCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum description lengthOrbit
The invention discloses a fast movable object orbit clustering method based on sampling, belonging to the field of orbit data clustering. The method comprises the following steps: dividing each original orbit into an orbit dividing subset by utilizing a minimum length describing principle after a user sets an input parameter and sends a clustering analysis request; carrying out clustering analysis for the orbit dividing subset according to the similarity measurement among line sections to obtain an orbit clustering set; finally generating a representing orbit and a coverage area in a clustering way by each orbit, outputting and visualizing the representing orbit and the coverage area and returning a result to the user. The invention has the advantages that the method is used for the clustering analysis of data of a large-scale low-particlesize movable object orbit and can still keep the orbit clustering effect and also effectively discover the orbit clustering under the condition of very low particlesize of orbit data to be analyzed, thereby enhancing the system efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar radio frequency interference suppression handling method
InactiveCN103091665BApparent sparsenessEstimated sparsityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar radio frequency interference suppression handling method. The method includes the following steps: (1) building a compressed sensing model of a radio frequency interference (RFI) signal based on an obvious sparse feature of a RFI component in frequency domain, (2) estimating sparseness of the RFI component by using a greedy algorithm to combine with minimum description length, (3) estimating a RFI signal component and filtering directly in time domain to an echo signal of each pulse, and (4) achieving imaging process by using an conventional compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar (SAR) reconstructing algorithm. The compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar radio frequency interference suppression handling method is based on the sparse feature of the RFI component in the frequency domain and builds a RFI sparse model based on a compressed sensing theory, restrains narrow-band and broadband RFI signals effectively by using the iterative greedy algorithm to estimate and filter the RFI component in the echo signal.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
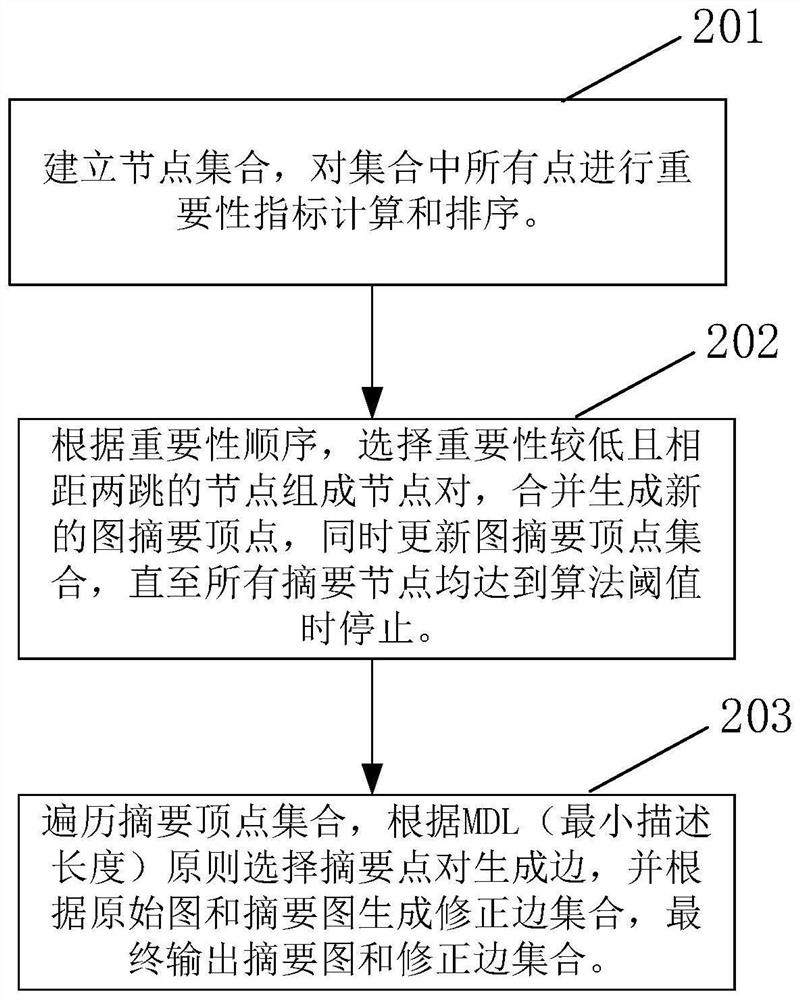
Graph digest algorithm based on node importance
PendingCN114491166AAvoid the pitfalls of early mergingValid reservationOther databases indexingOther databases browsing/visualisationGraph generationTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a graph digest algorithm based on node importance, which comprises the following steps of: establishing a node set, and carrying out importance index calculation and sorting on all points in the set; according to the importance sequence, nodes which are low in importance and are spaced by two hops are selected to form node pairs, new graph abstract vertexes are generated through combination, and meanwhile, a graph abstract vertex set is updated until all abstract nodes reach an algorithm threshold value; and traversing the summary vertex set, selecting summary point pairs to generate edges according to an MDL (minimum description length) principle, generating a correction edge set according to the original graph and the summary graph, and finally outputting the summary graph and the correction edge set. According to the method, abstracting can be carried out according to the importance of the nodes in the large graph, the defect that important nodes are merged in advance in a traditional graph abstracting algorithm is overcome, and the method has wide practical value and application prospects in the field of graph processing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A Webpage Sampling Method Oriented to Webpage Content Accessibility Detection
ActiveCN103823753BReduce time complexityImprove algorithm performanceSoftware testing/debuggingGreedy algorithmUniform resource locator
The invention discloses a webpage sampling method oriented at barrier-free webpage content detection. The webpage sampling method includes capturing URLs (uniform resource locators) of all related webpages of a website according to a to-be-detected URL, creating an MDL (minimum description length) model for URL sets of the website, clustering all the URLs by an MDL-based greedy algorithm, performing random sampling on each cluster according to a sampling proportion lambada to acquire samples, and performing conventional barrier-free compliance detection on sample sets.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Model optimization method, device and equipment and readable storage medium
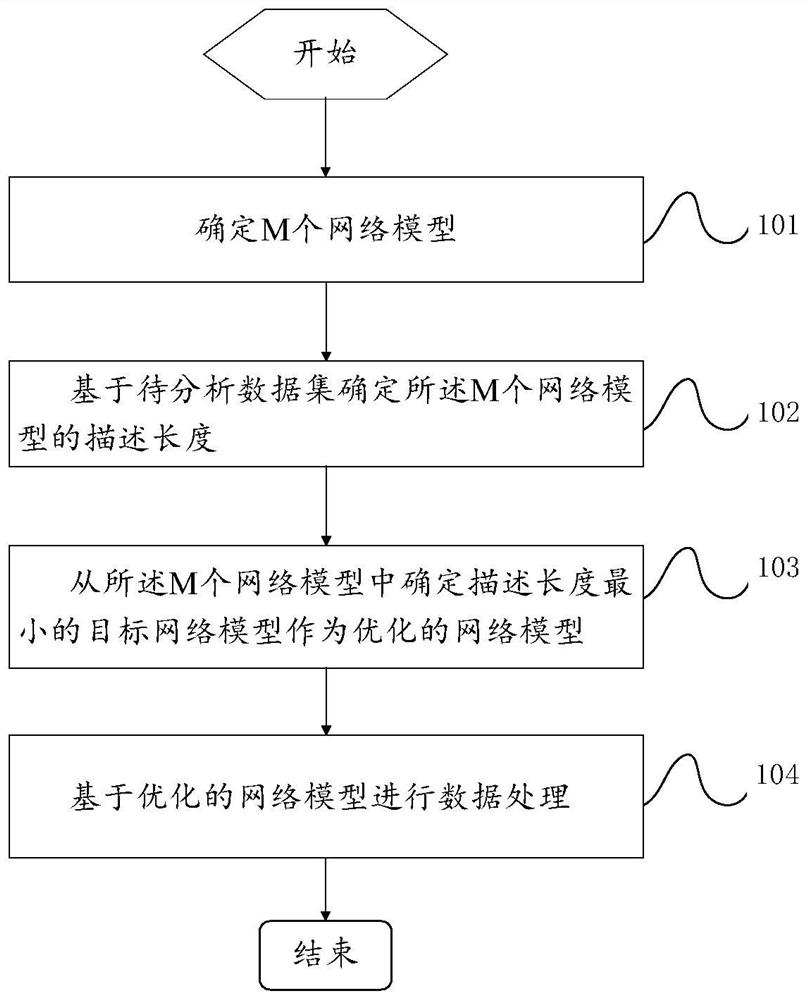
PendingCN114169490ABalance accuracyBalance complexityNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsData setTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a model optimization method, device and equipment and a readable storage medium, and relates to the technical field of deep learning, and the model optimization method comprises the steps: determining M network models; determining description lengths of the M network models based on a to-be-analyzed data set; and determining a target network model with the minimum description length from the M network models as an optimized network model, and carrying out data processing based on the optimized network model. In this way, the problems that the optimization degree of an existing deep learning network model is weak, and the complexity of the deep learning network model cannot be effectively reduced are solved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM LTD RES INST +1
An Adaptive Compressed Sensing Signal Restoration Method Based on Greedy Algorithm
InactiveCN104485965BSave communication resourcesSmall amount of calculationCode conversionAdaptive compressionGreedy algorithm
The invention discloses an adaptive compressed sensing signal recovery method based on a greedy algorithm. On the basis of the OMP algorithm, a detector is designed to judge whether there is still a signal component in the remaining vector, and through the hypothesis testing model in the signal detection theory, Calculate the detector, and then give the threshold of the detector through the preset false alarm probability. When the detector is smaller than the given threshold, it can be judged that there is no signal component in the remaining vector. At this time, the algorithm can stop iterating, and Get the restored value of the signal, otherwise continue to iterate. The present invention uses the greedy algorithm as channel estimation, does not depend on the multipath number of the channel; Compared with MDL, the method of the present invention does not need multiple observations, thereby saving communication resources; The method of the present invention has less computing power of the greedy algorithm The advantage is that the greedy algorithm solves the problem of high real-time requirements for sparse signal recovery, and its application in the problem of unknown signal sparsity.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
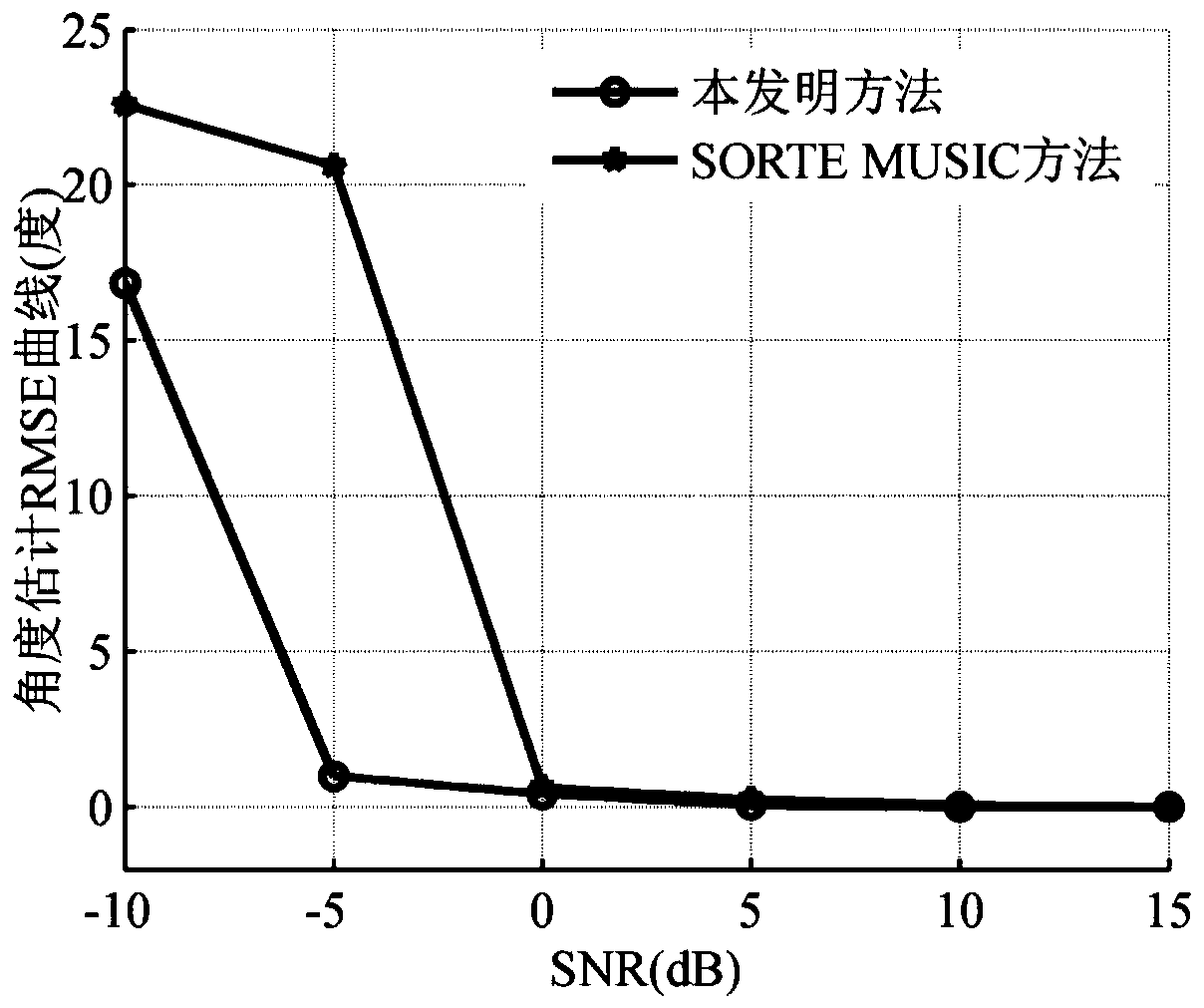
Target number and target angle estimation method based on MDL criterion
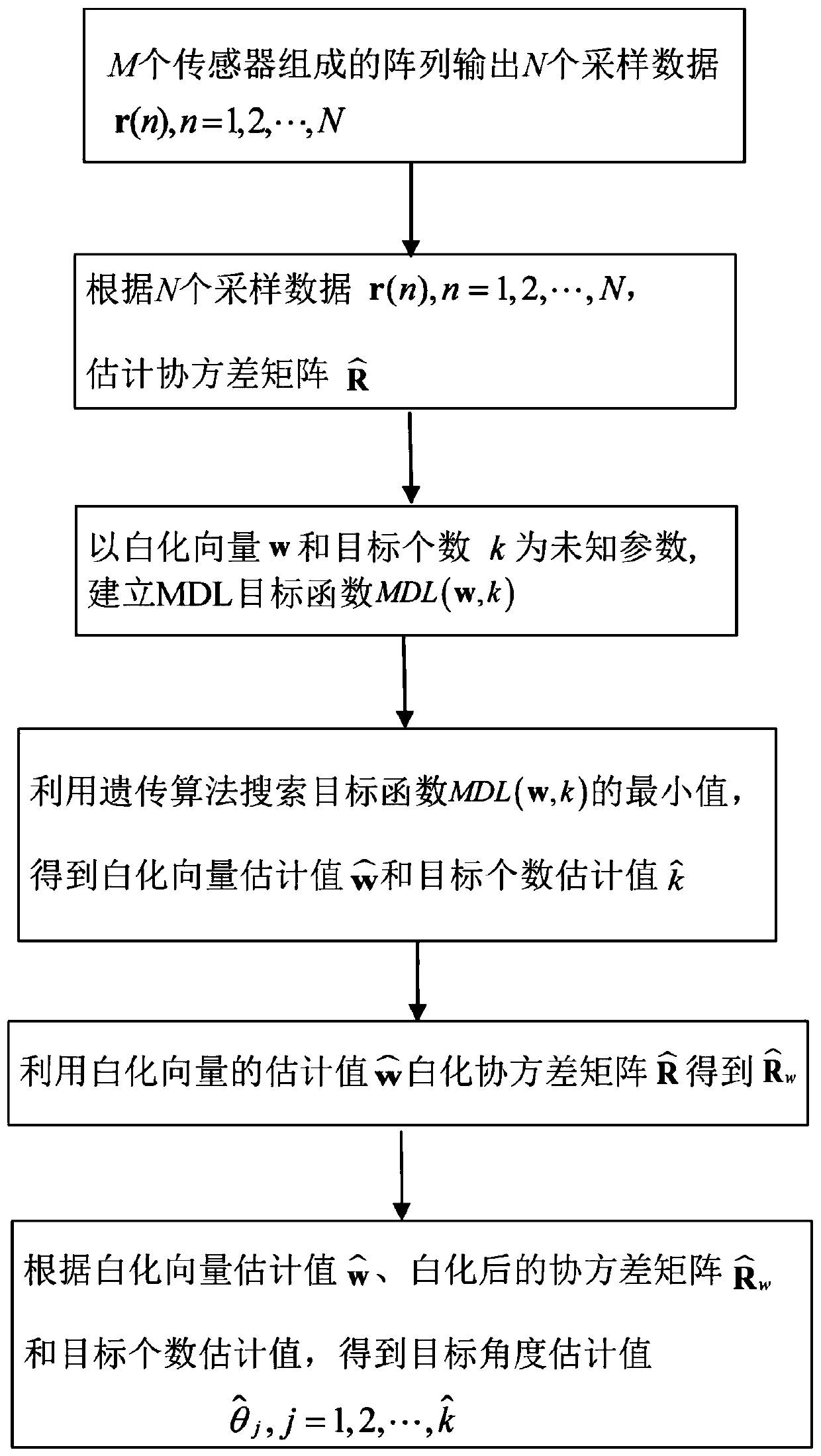
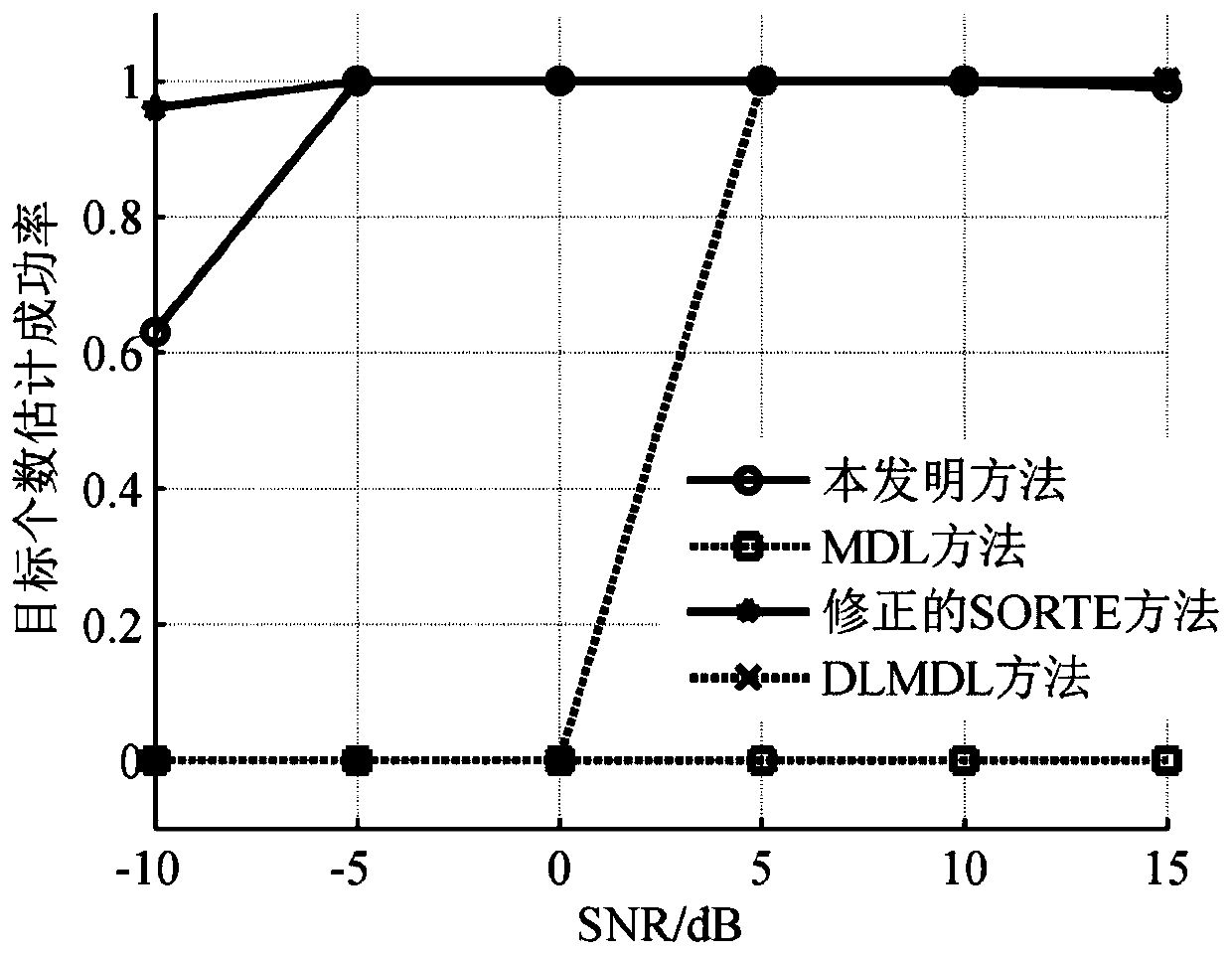
ActiveCN111323744AAccurate estimateImprove estimation performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsEstimation methodsGenetics algorithms
The invention provides a target number and target angle estimation method based on an MDL criterion, and belongs to the field of array signal processing. The method has an advantage that under the condition of a non-uniform noise, correct estimation of a target number and a target angle can be realized. The method mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, taking the target number and a whitening vector as unknown parameters, and establishing a target function taking a minimum description length (MDL) as the criterion; solving a minimum value of the MDL target function by using a genetic algorithm so as to obtain an estimated value of the target number and an estimated value of a whitening vector; whitening a received signal covariance matrix by using the estimated value of the whitening vector; and finally, according to the whitened covariance matrix, the estimated value of the whitening vector and the estimated value of the target number, realizing accurate estimation of the target angle.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
A Weak Edge Detection Method for Multi-Scale Images Based on Minimum Description Length
ActiveCN103440644BImprove stabilityGood filter smoothing effectImage enhancementImage analysisScale spaceMinimum description length
The invention discloses a self-adaptive multi-scale image weak edge detection method based on the minimum description length (MDL) principle. The self-adaptive multi-scale image weak edge detection method based on the minimum description length principle comprises the steps that firstly, a linear scale space is constructed by means of multi-scale Gaussian smoothing, then the local description length of an image is calculated and the optimum local smoothness scale is determined by means of the minimum description length principle, and finally edge detection is carried out on the image treated with local smoothing to obtain all edges of the weak edge image. The self-adaptive multi-scale image weak edge detection method based on the minimum description length principle has the advantages that common noise can be filtered effectively, a real weak edge can be extracted, and the phenomena of edge fracture, edge deviation, false edge responses and the like can be avoided; in addition, the algorithm used in the method is a non-iterative filter method, the computing speed is greatly improved, and the stability of the algorithm is greatly improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Methods and systems for optimized visual summarization for sequences of temporal event data
PendingCN110945559AEasy to exploreReduce visual clutterDrawing from basic elementsVisual data miningGraphicsData mining
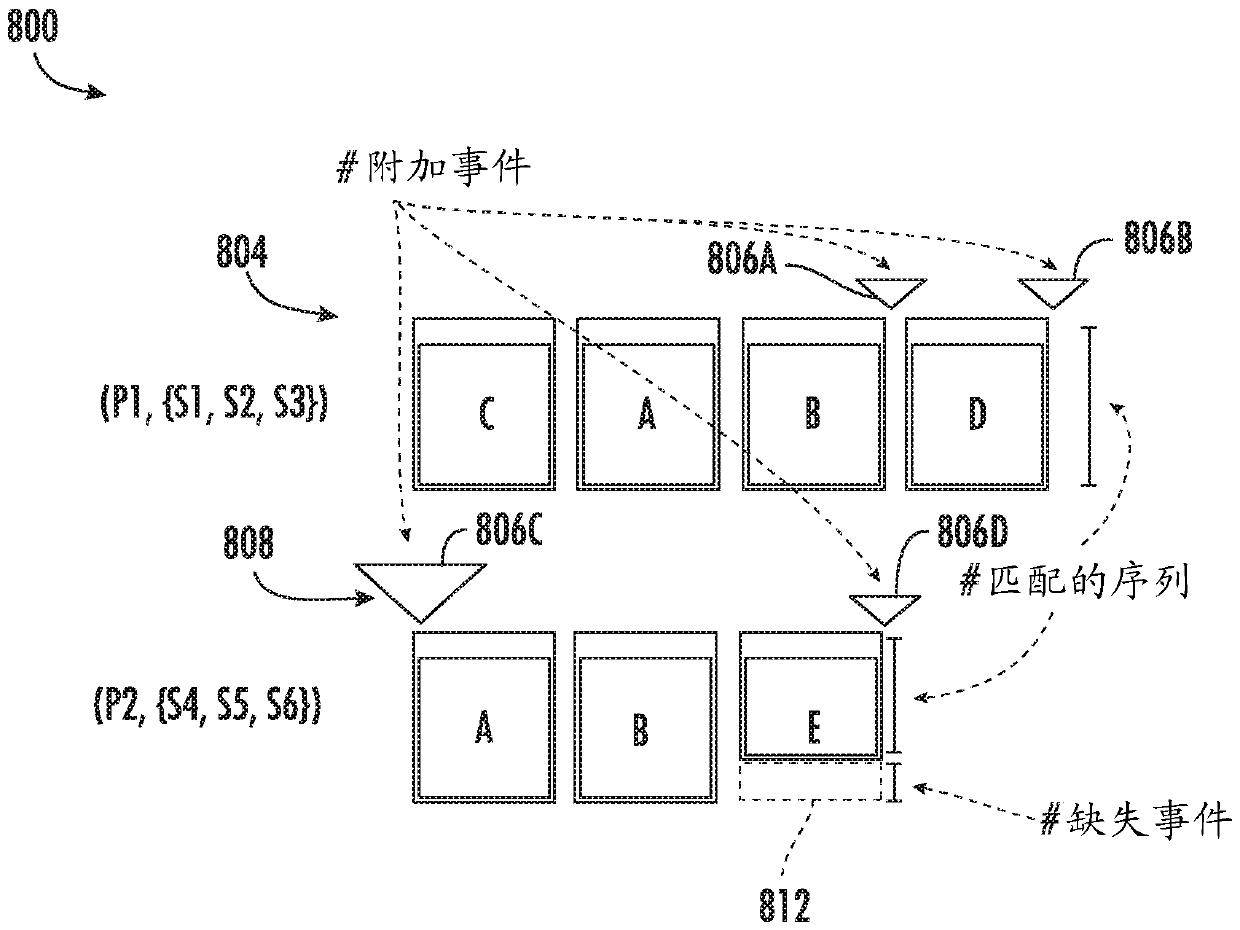
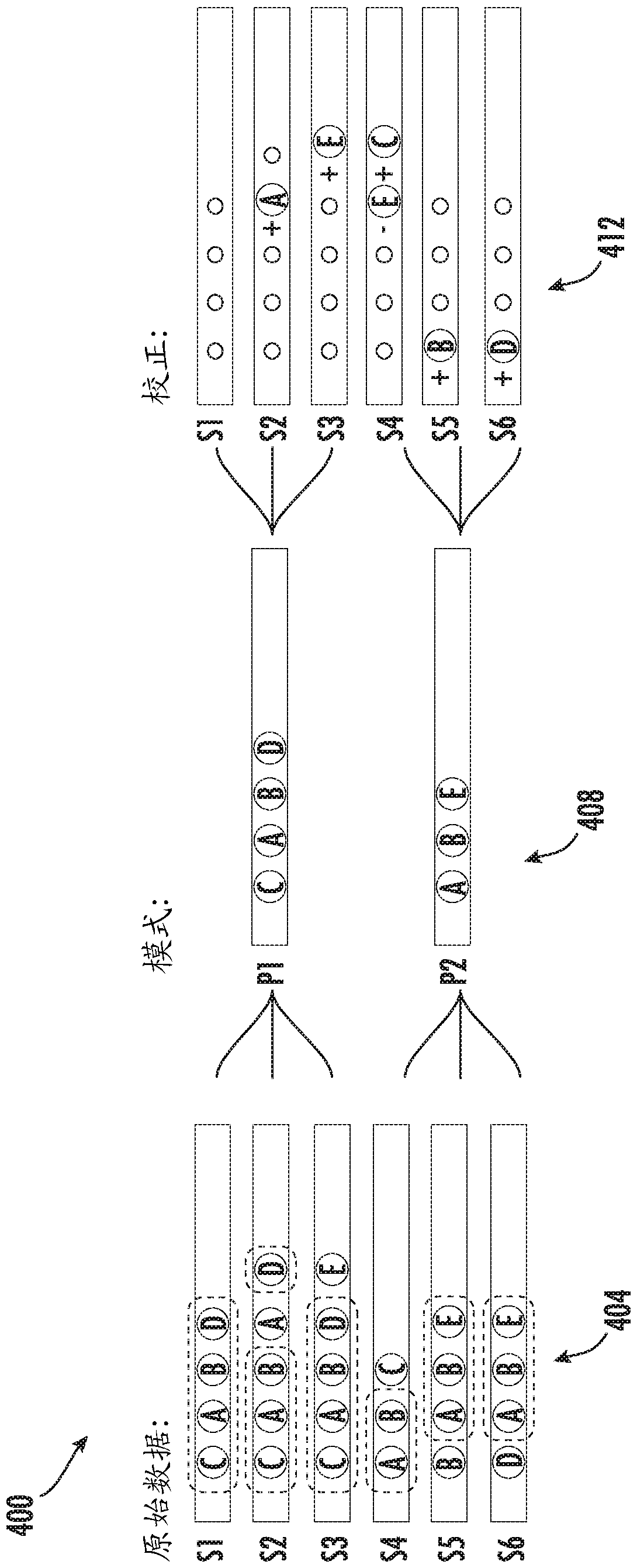
A method for generating a graphical depiction of summarized event sequences includes receiving a plurality of event sequences, each event sequence in the plurality of event sequences including a plurality of events, and generating a plurality of clusters using a minimum description length (MDL) optimization process. Each cluster in the plurality of clusters including a set of at least two event sequences in the plurality of event sequences that maps to a pattern in each cluster. The pattern in each cluster further includes a plurality of events included in at least one event sequence in the set of at least two event sequences in the cluster. The method includes generating a graphical depiction of a first cluster in the plurality of clusters, the graphical depiction including a graphical depiction of a first plurality of events in the pattern of the first cluster.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com