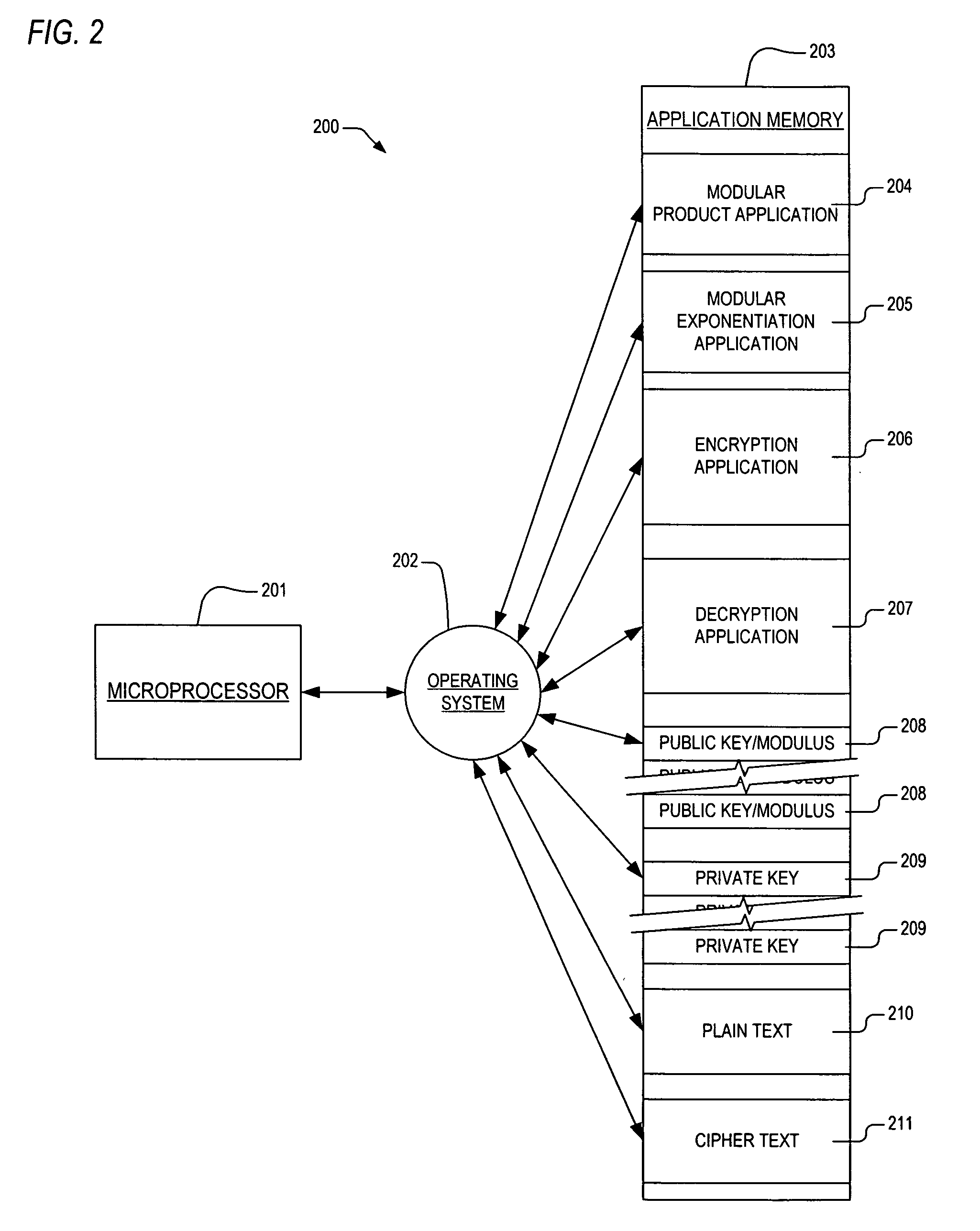
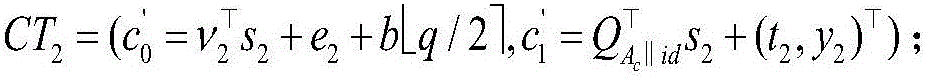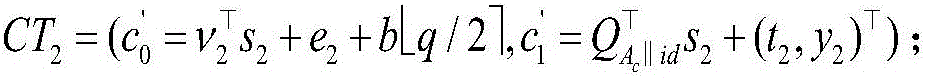Patents
Literature
221 results about "Modular exponentiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
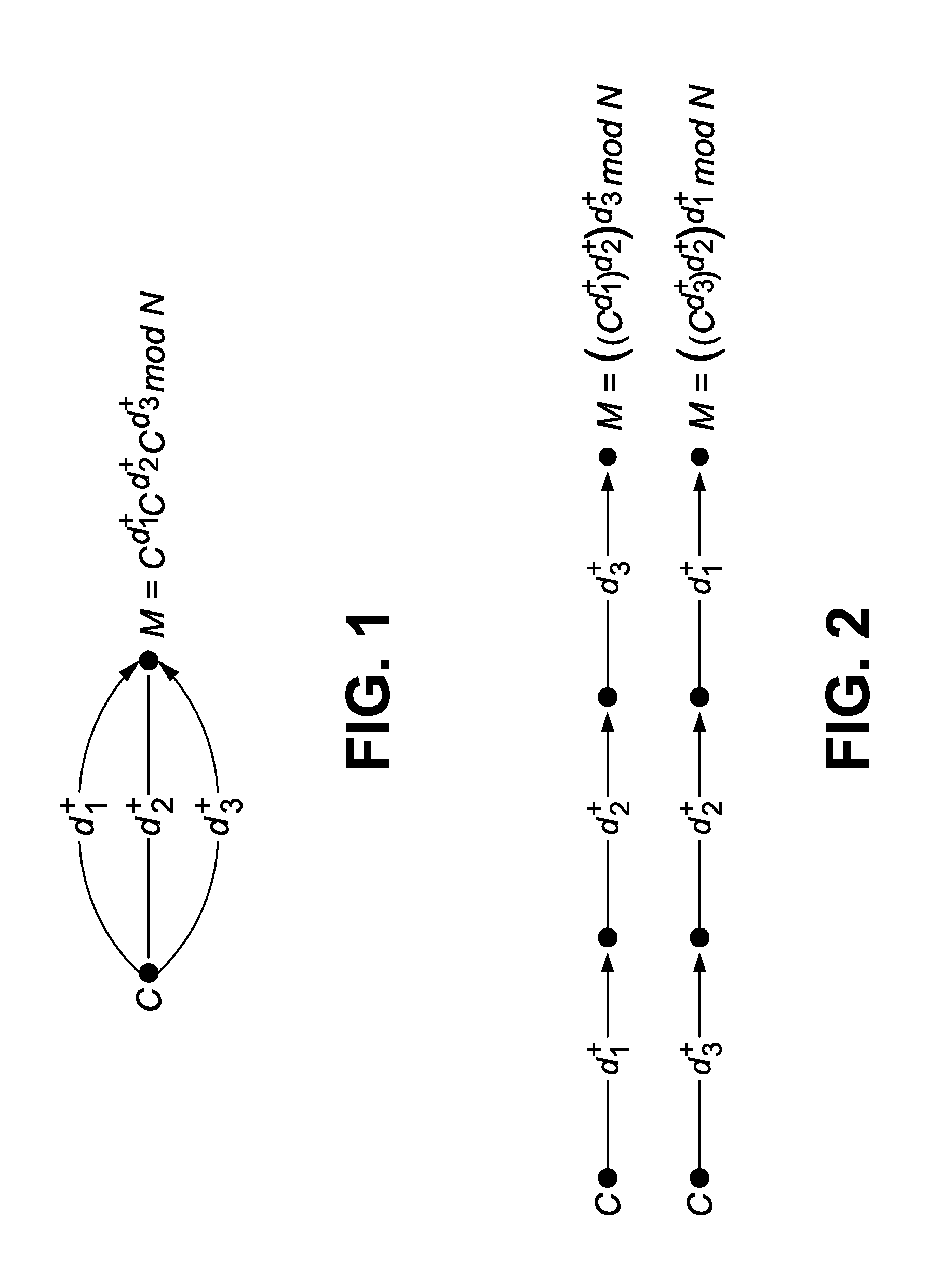
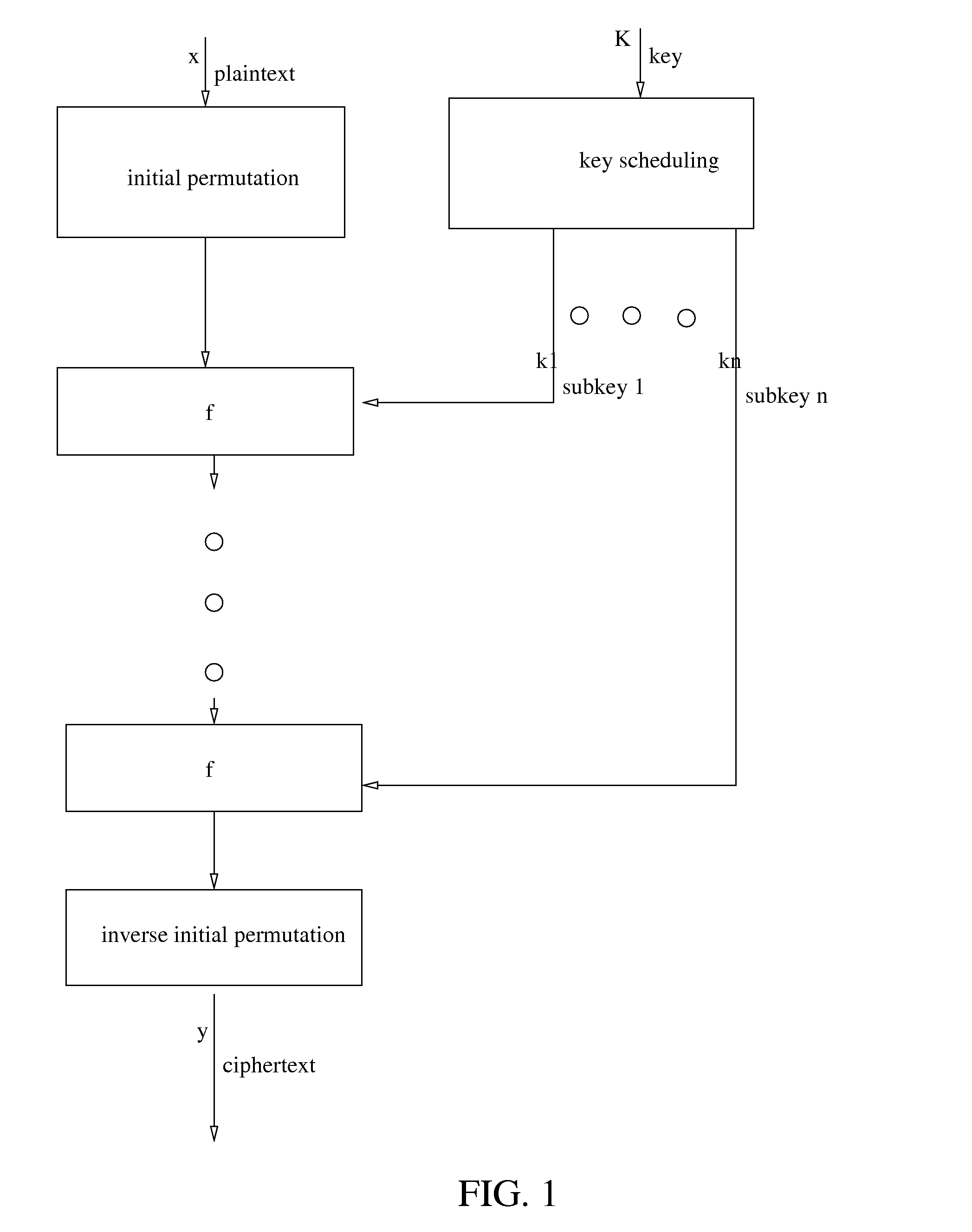
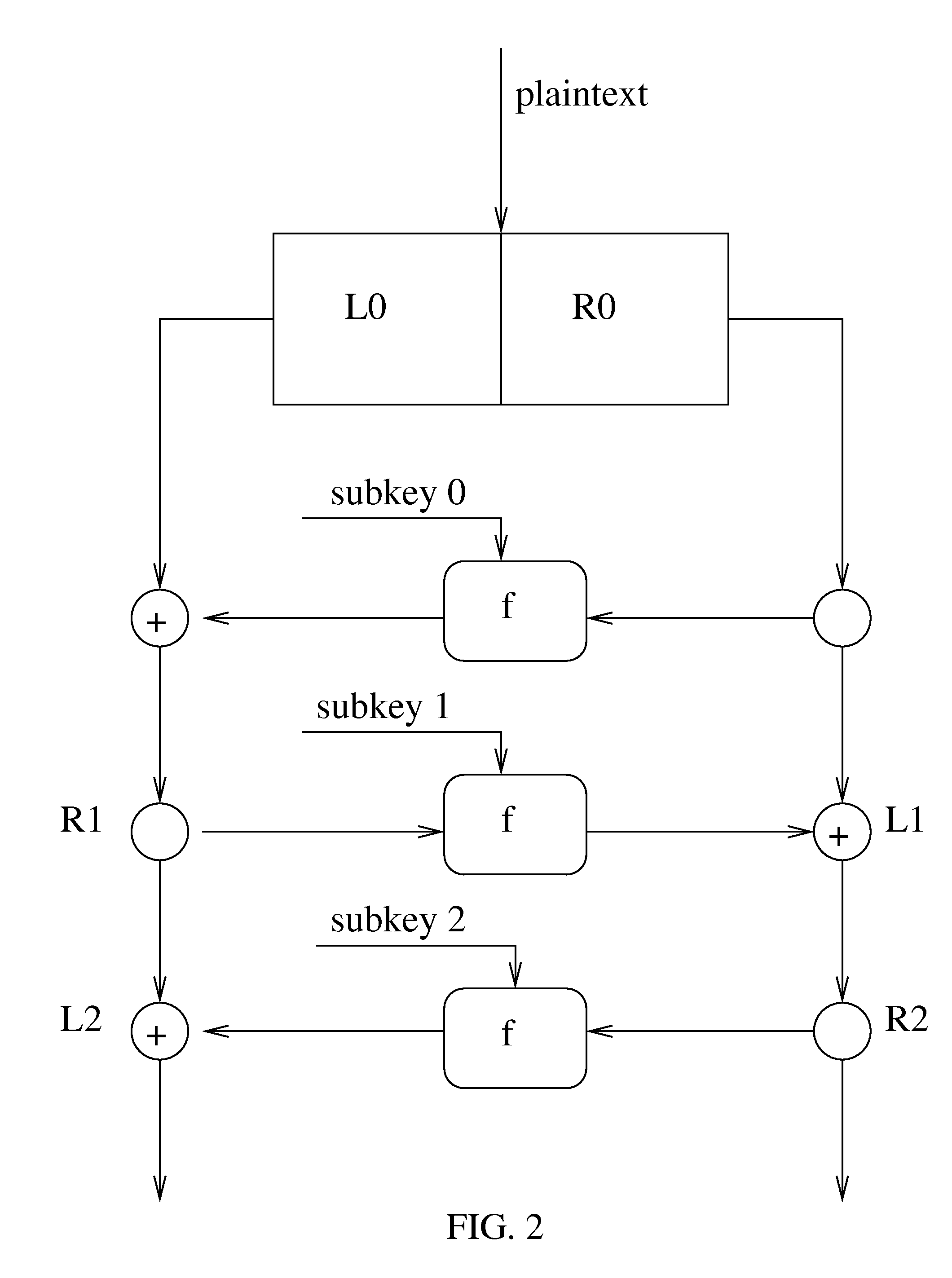
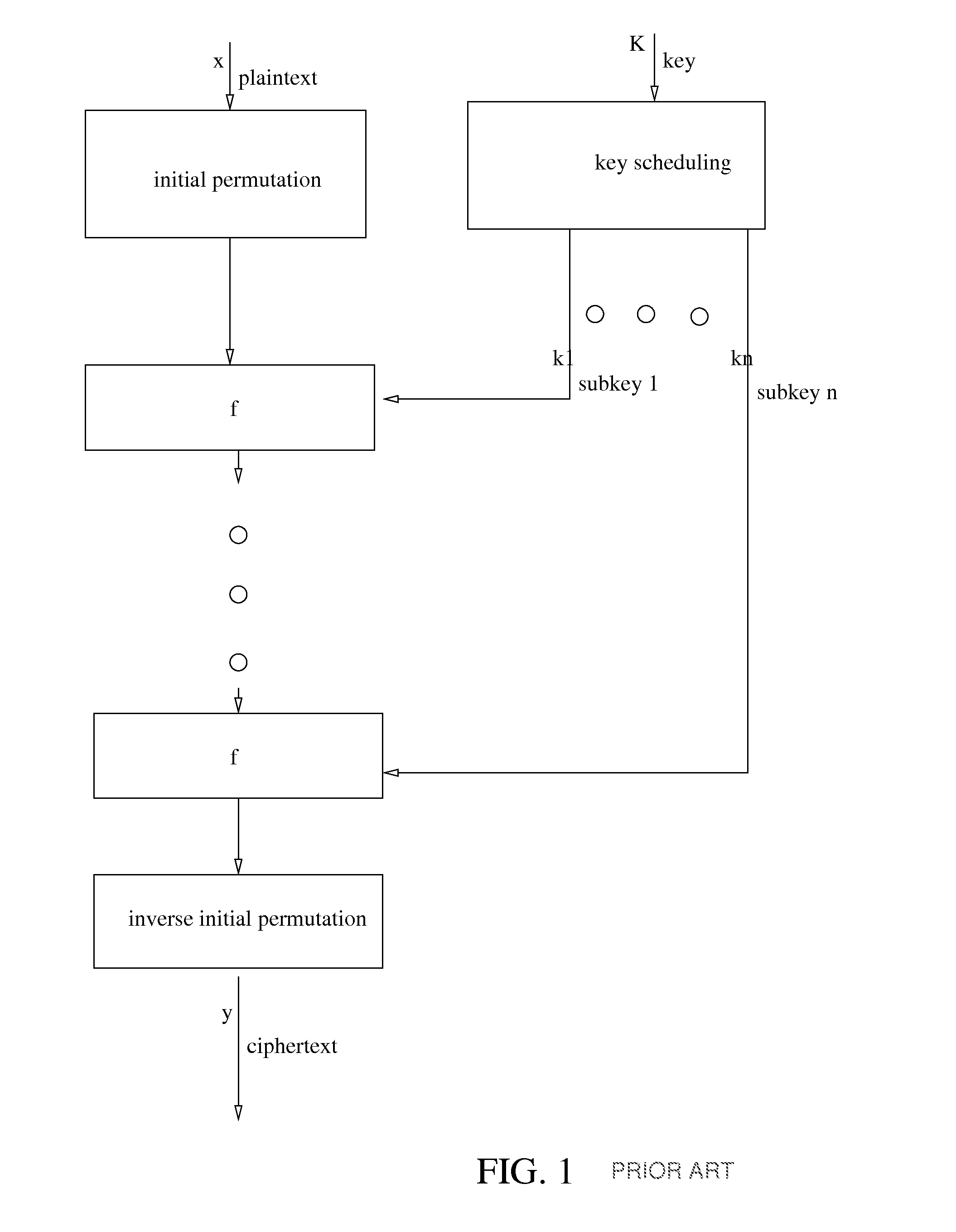
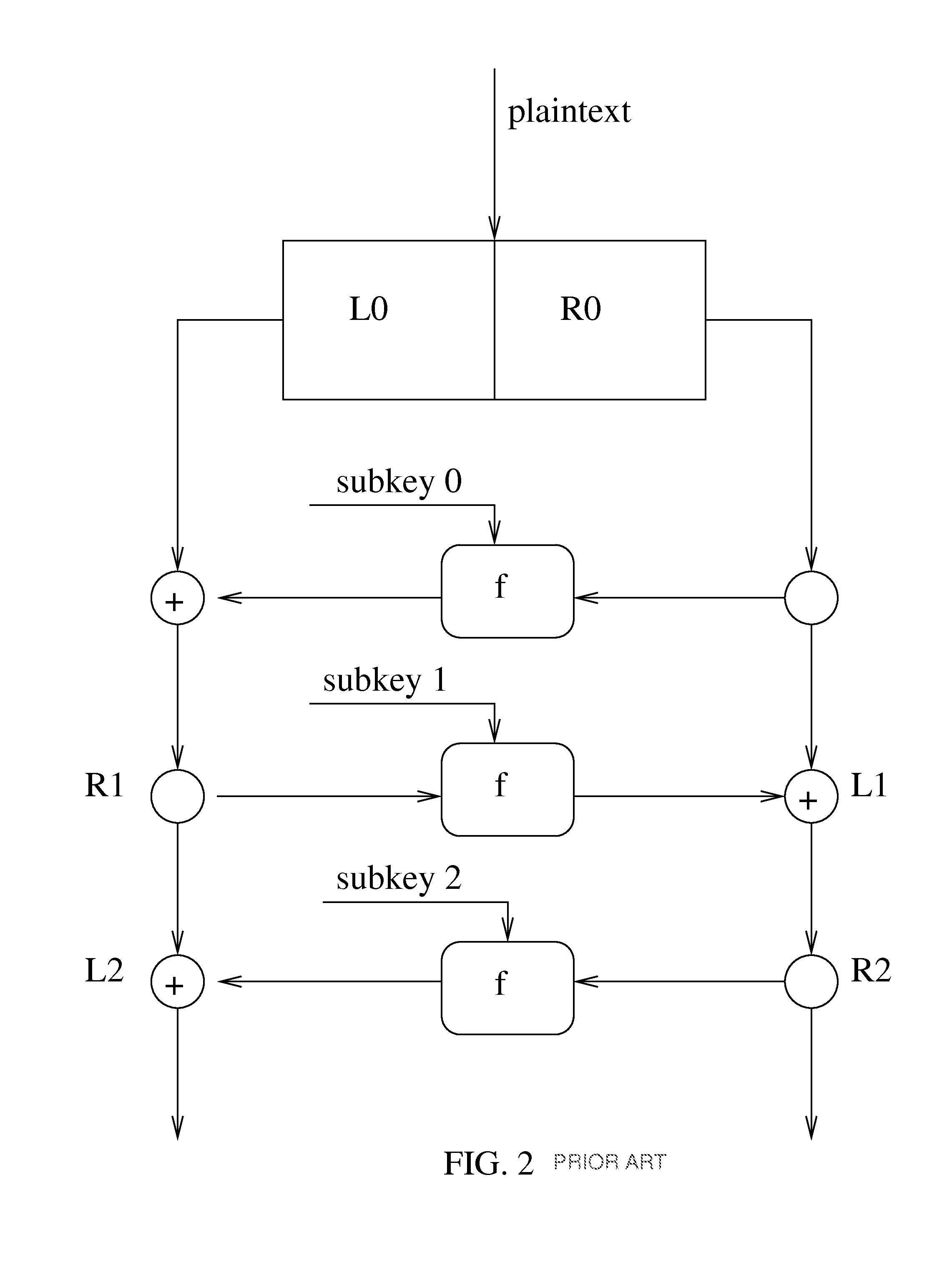
Modular exponentiation is a type of exponentiation performed over a modulus. It is useful in computer science, especially in the field of public-key cryptography. The operation of modular exponentiation calculates the remainder when an integer b (the base) raised to the eth power (the exponent), b, is divided by a positive integer m (the modulus). In symbols, given base b, exponent e, and modulus m, the modular exponentiation c is: c = b mod m. From the definition of c, it follows that 0 ≤ c < m.
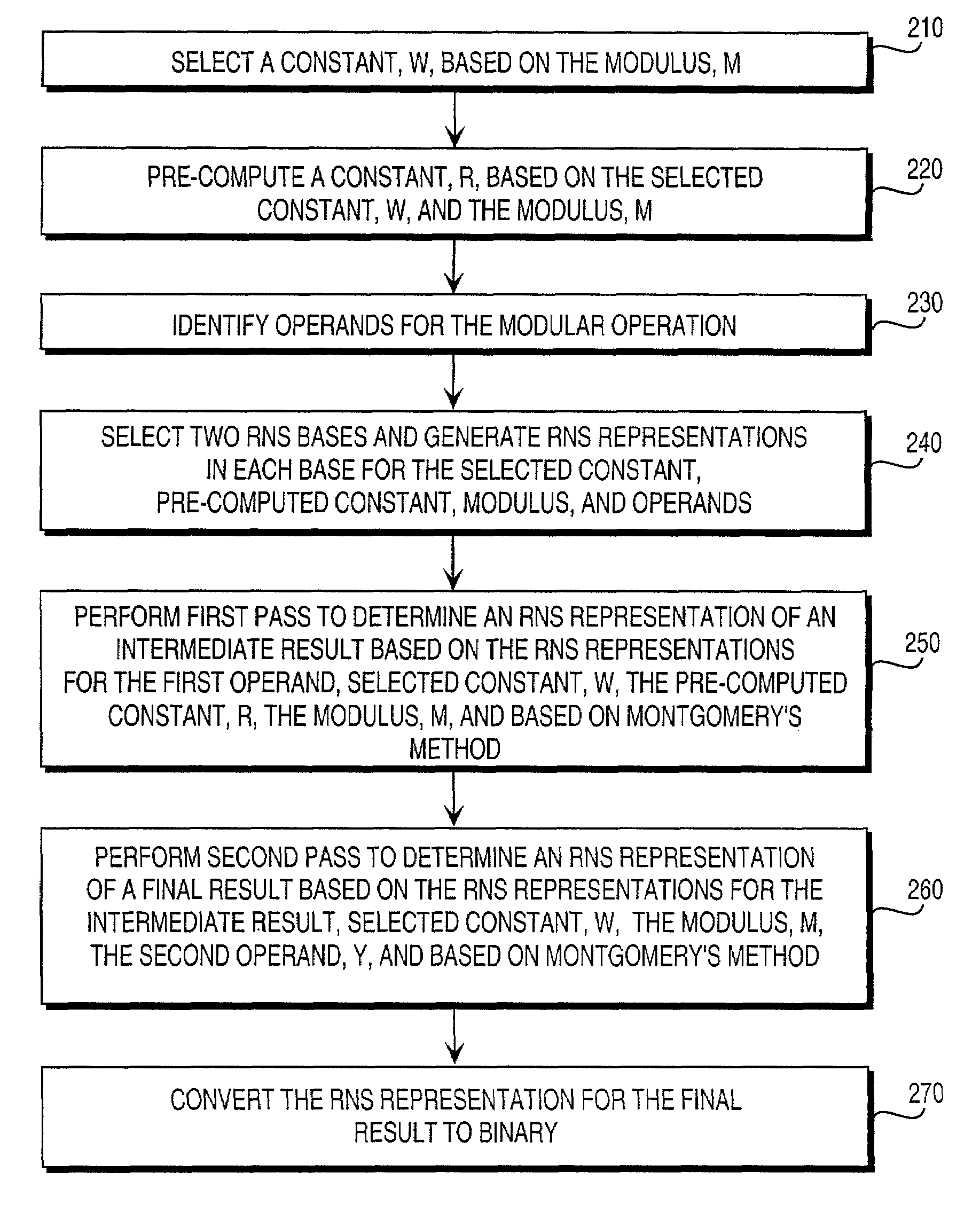
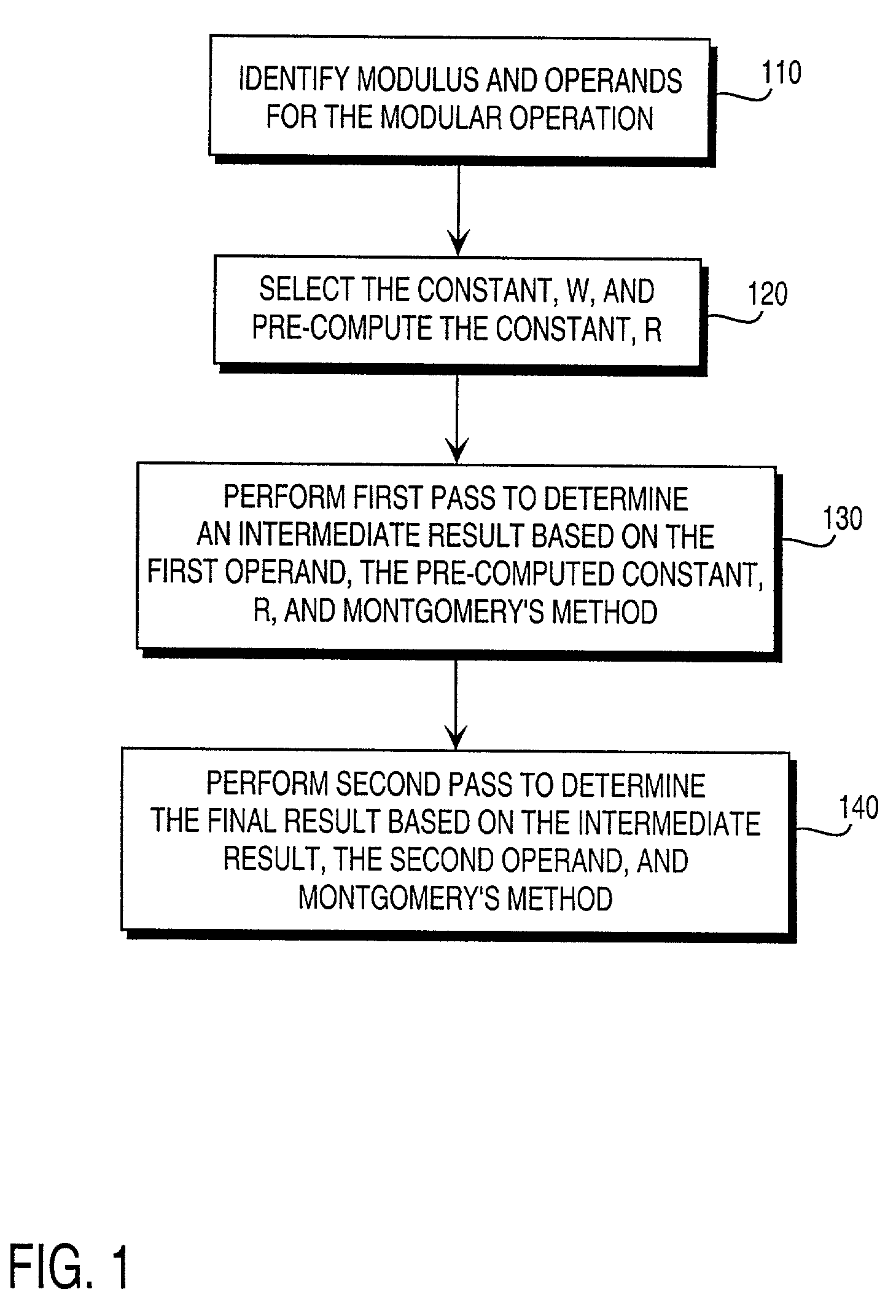
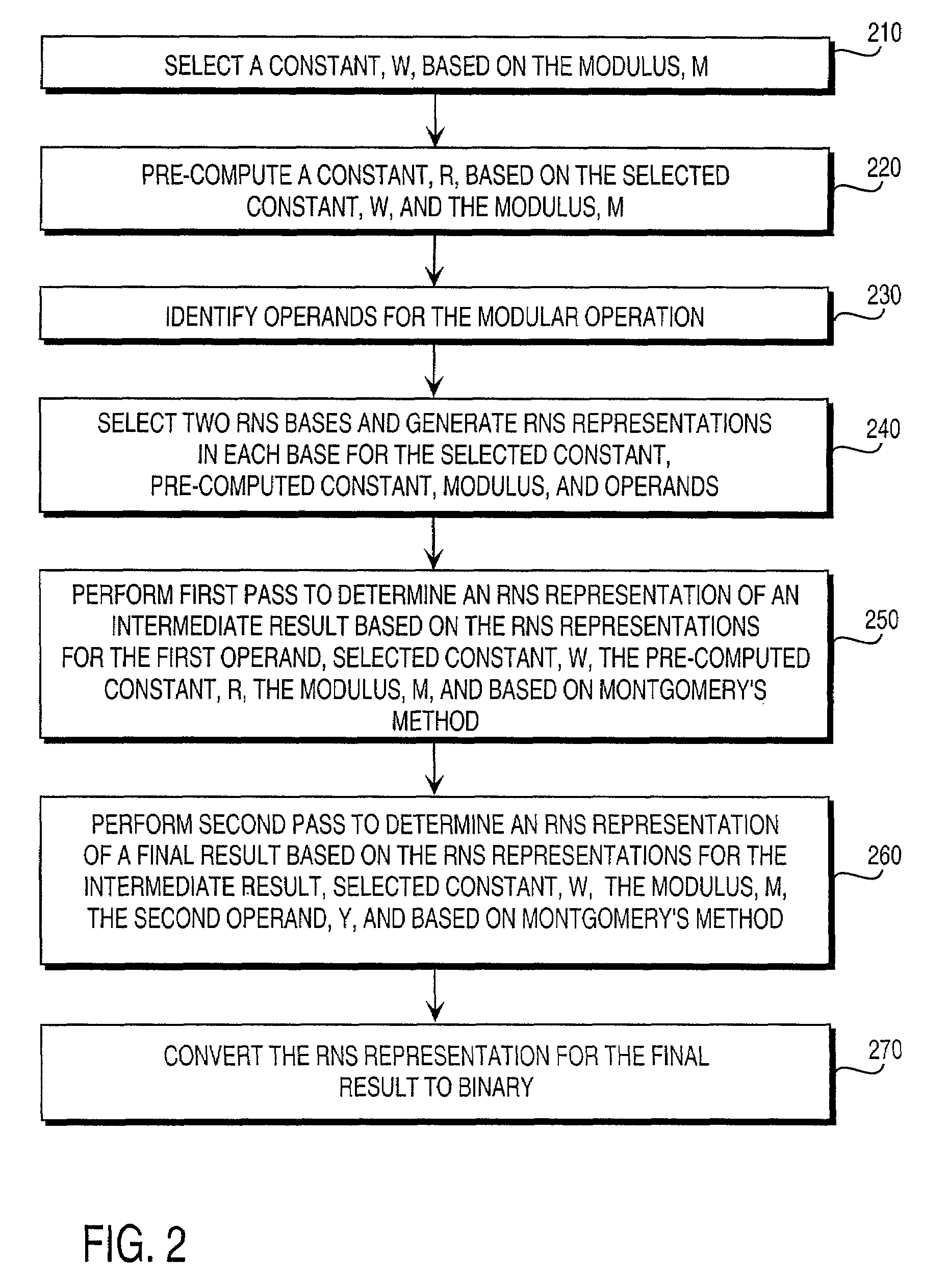
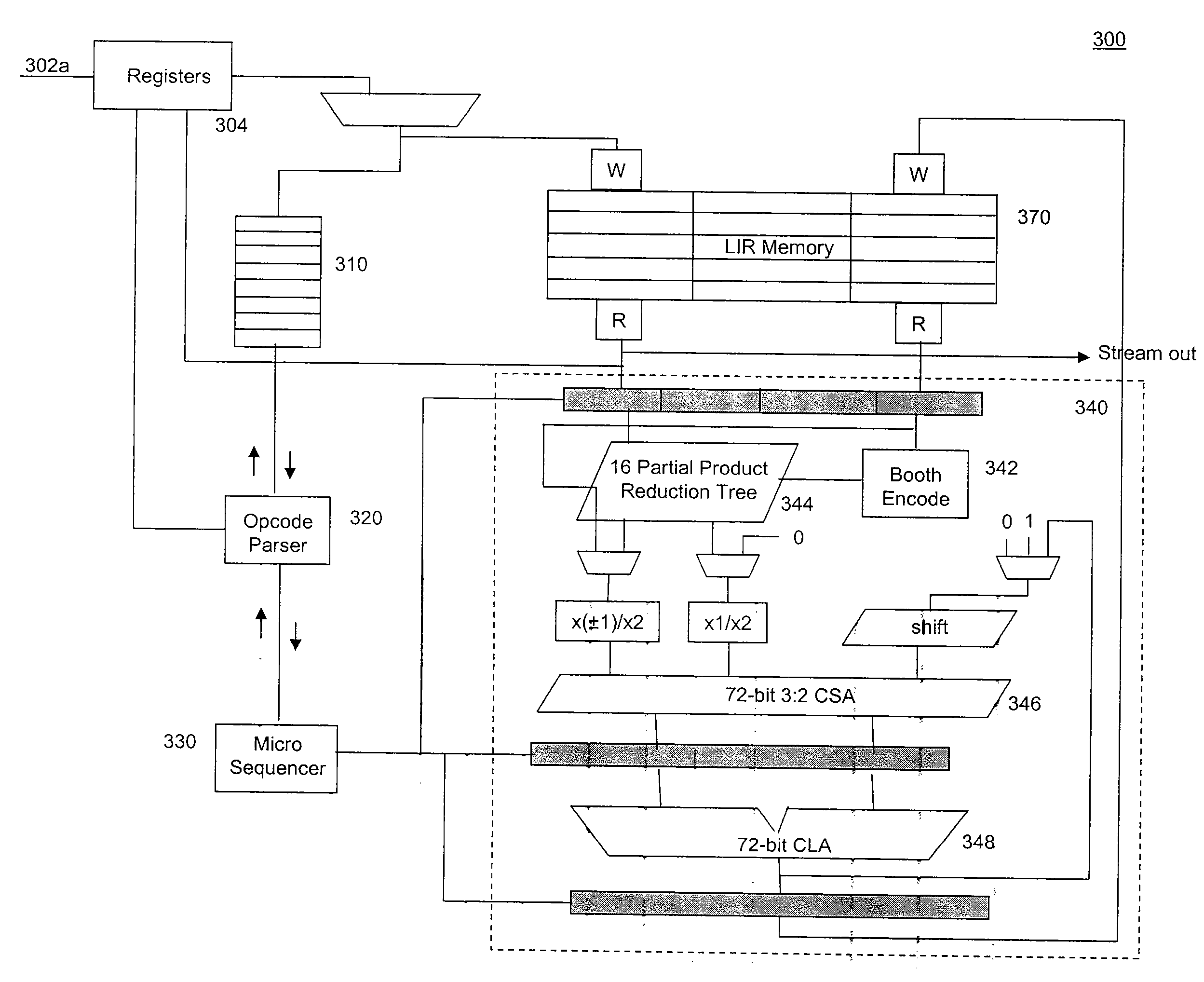
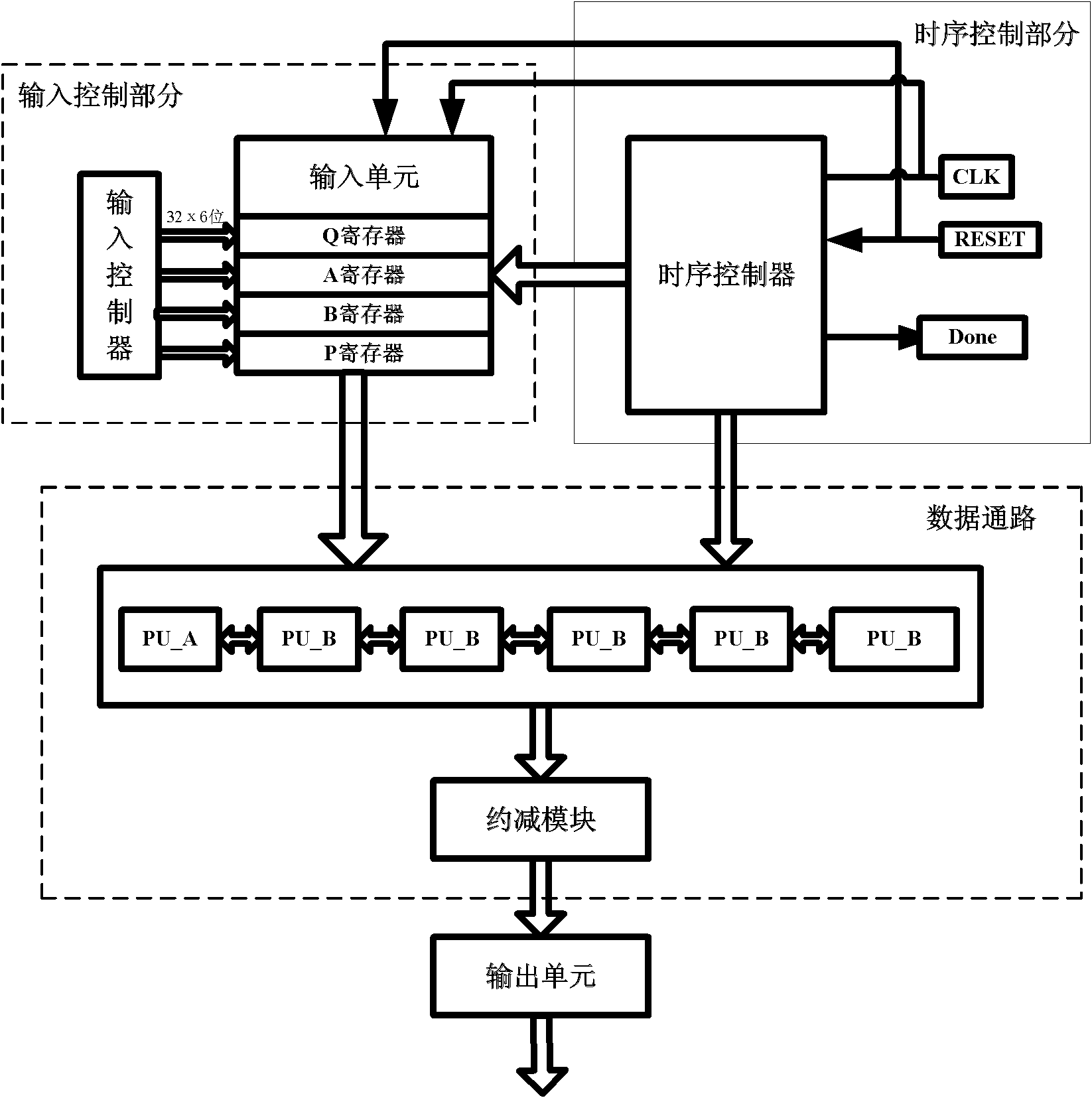
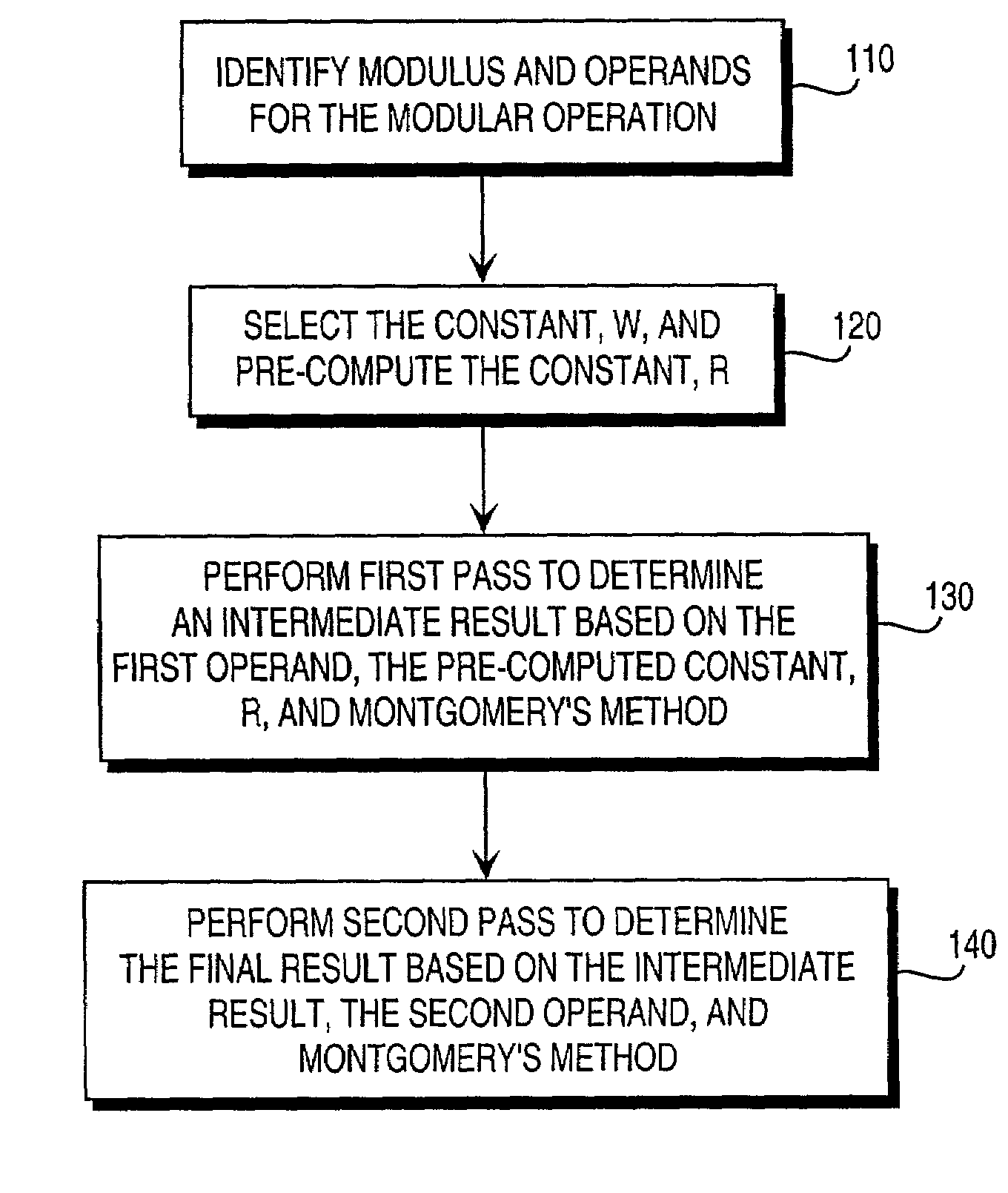
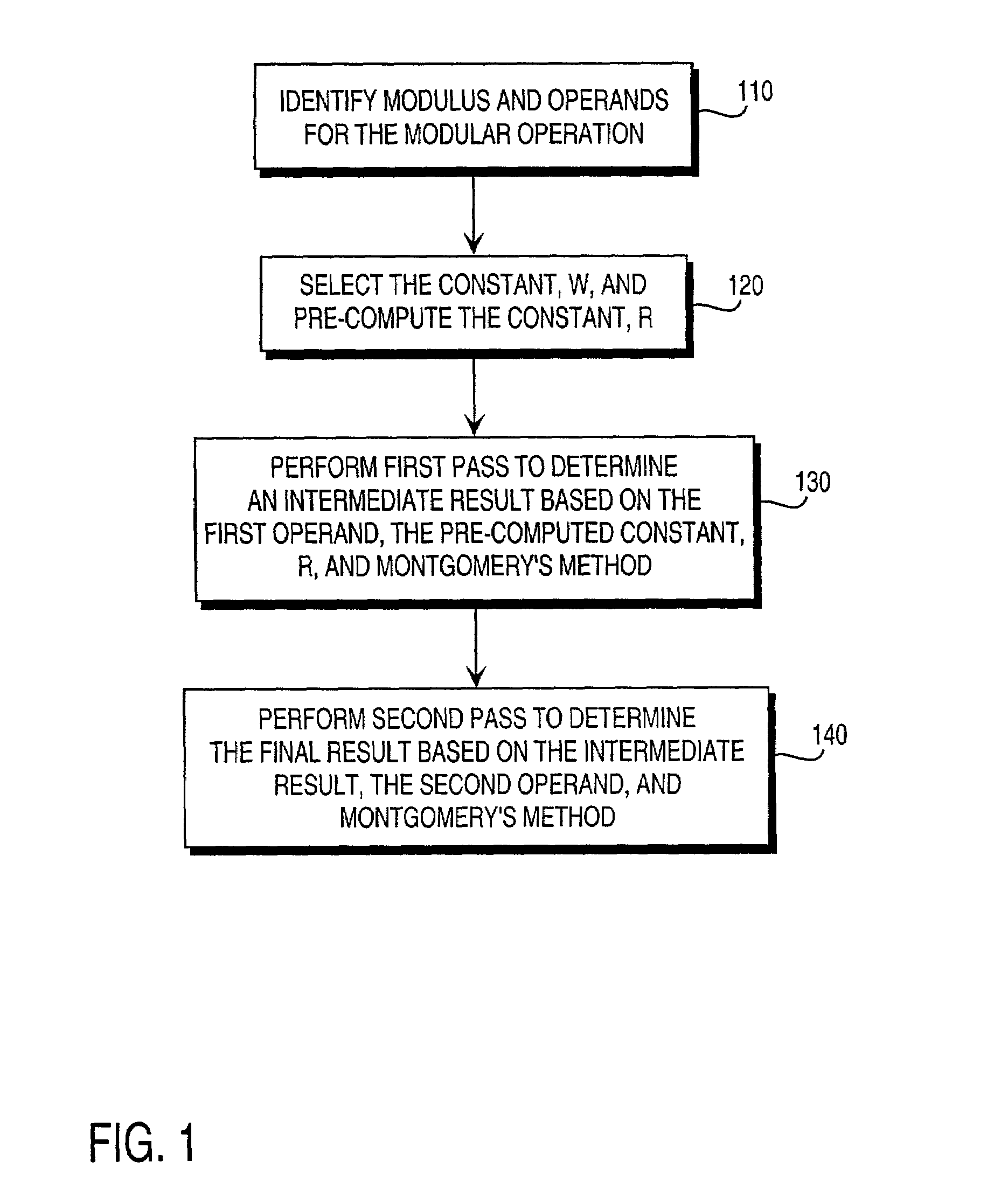
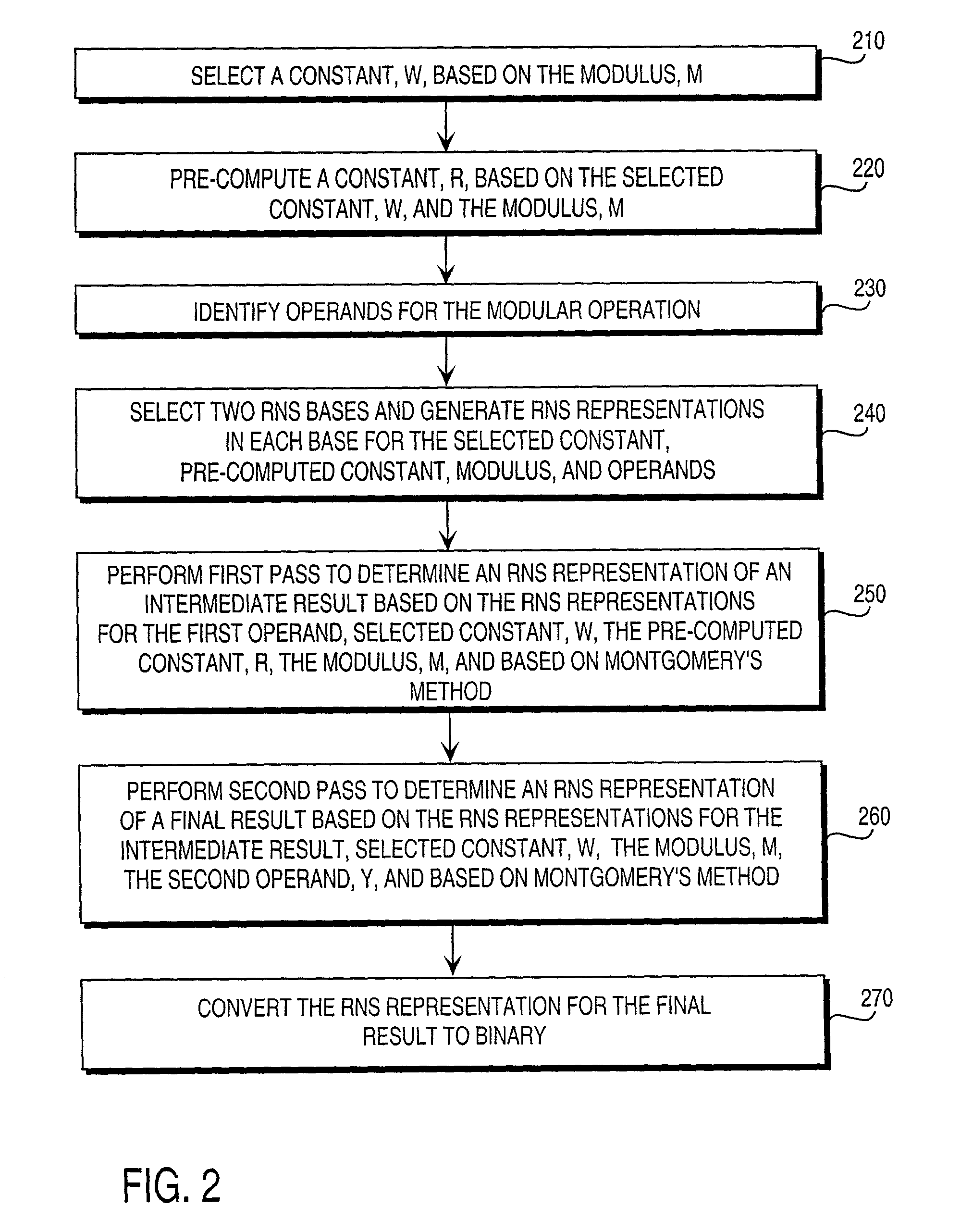
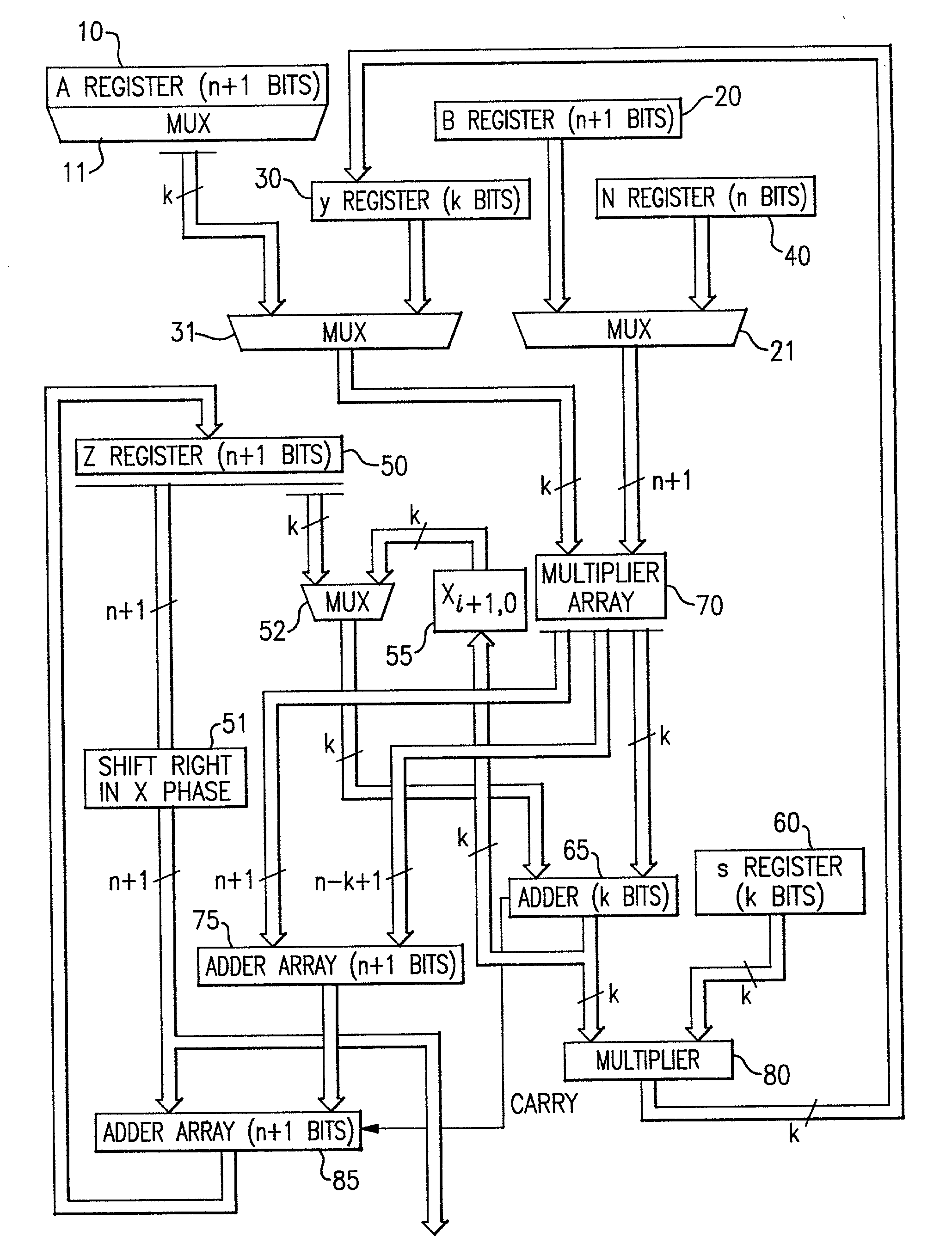
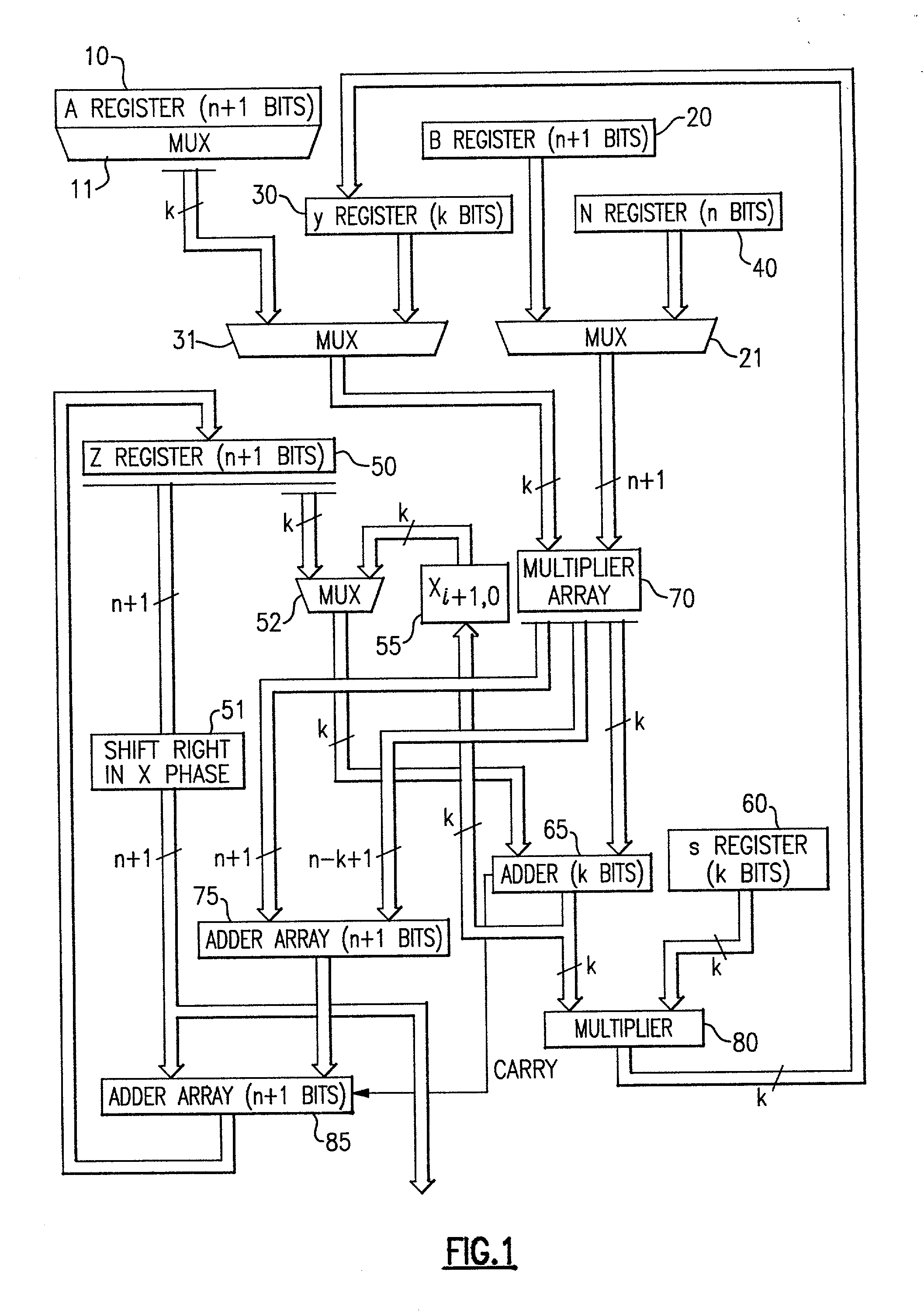
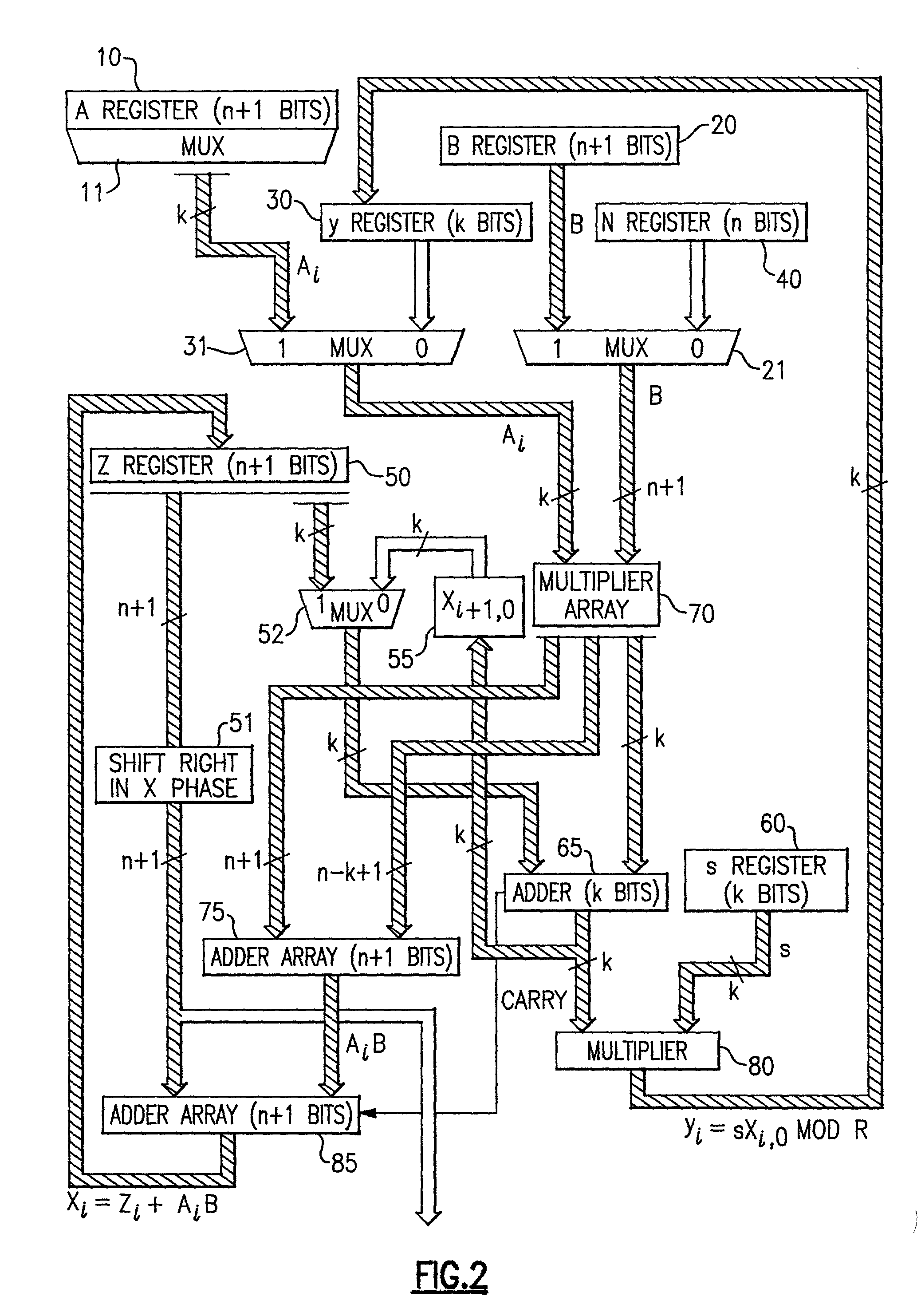
Residue number system based pre-computation and dual-pass arithmetic modular operation approach to implement encryption protocols efficiently in electronic integrated circuits
InactiveUS7027598B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerModularity
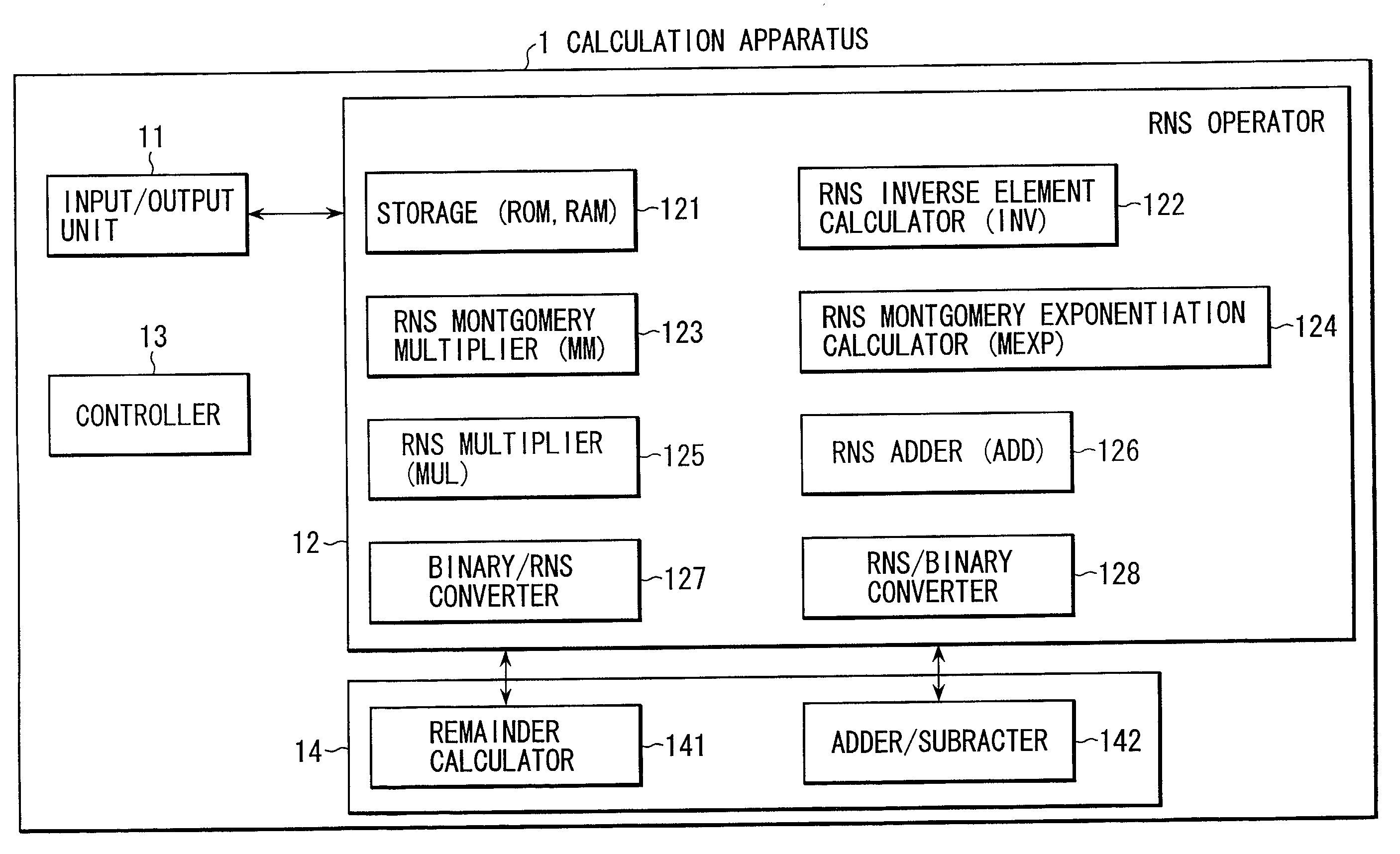
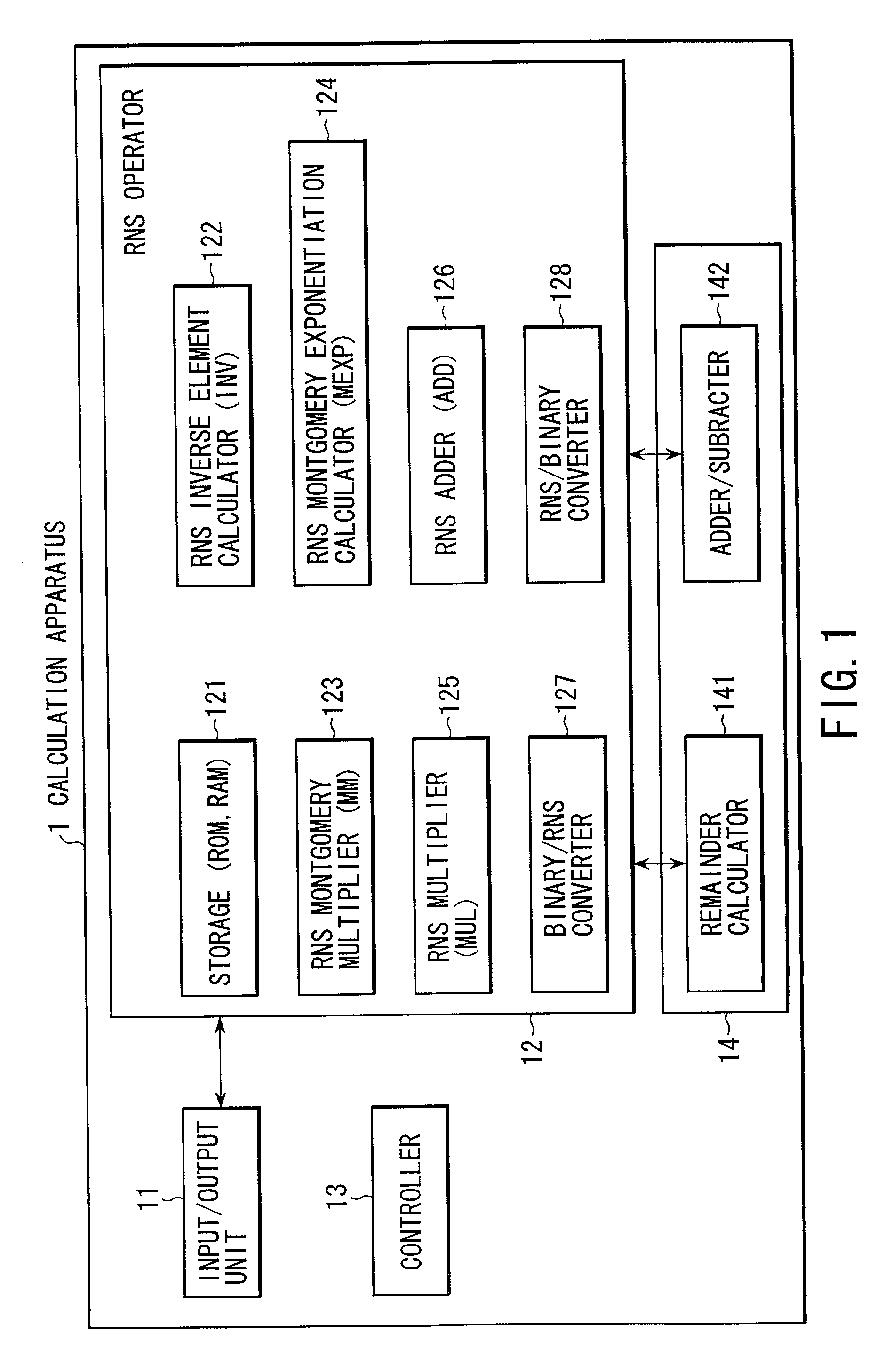
A pre-computation and dual-pass modular operation approach to implement encryption protocols efficiently in electronic integrated circuits is disclosed. An encrypted electronic message is received and another electronic message generated based on the encryption protocol. Two passes of Montgomery's method are used for a modular operation that is associated with the encryption protocol along with pre-computation of a constant based on a modulus. The modular operation may be a modular multiplication or a modular exponentiation. Modular arithmetic may be performed using the residue number system (RNS) and two RNS bases with conversions between the two RNS bases. A minimal number of register files are used for the computations along with an array of multiplier circuits and an array of modular reduction circuits. The approach described allows for high throughput for large encryption keys with a relatively small number of logical gates.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
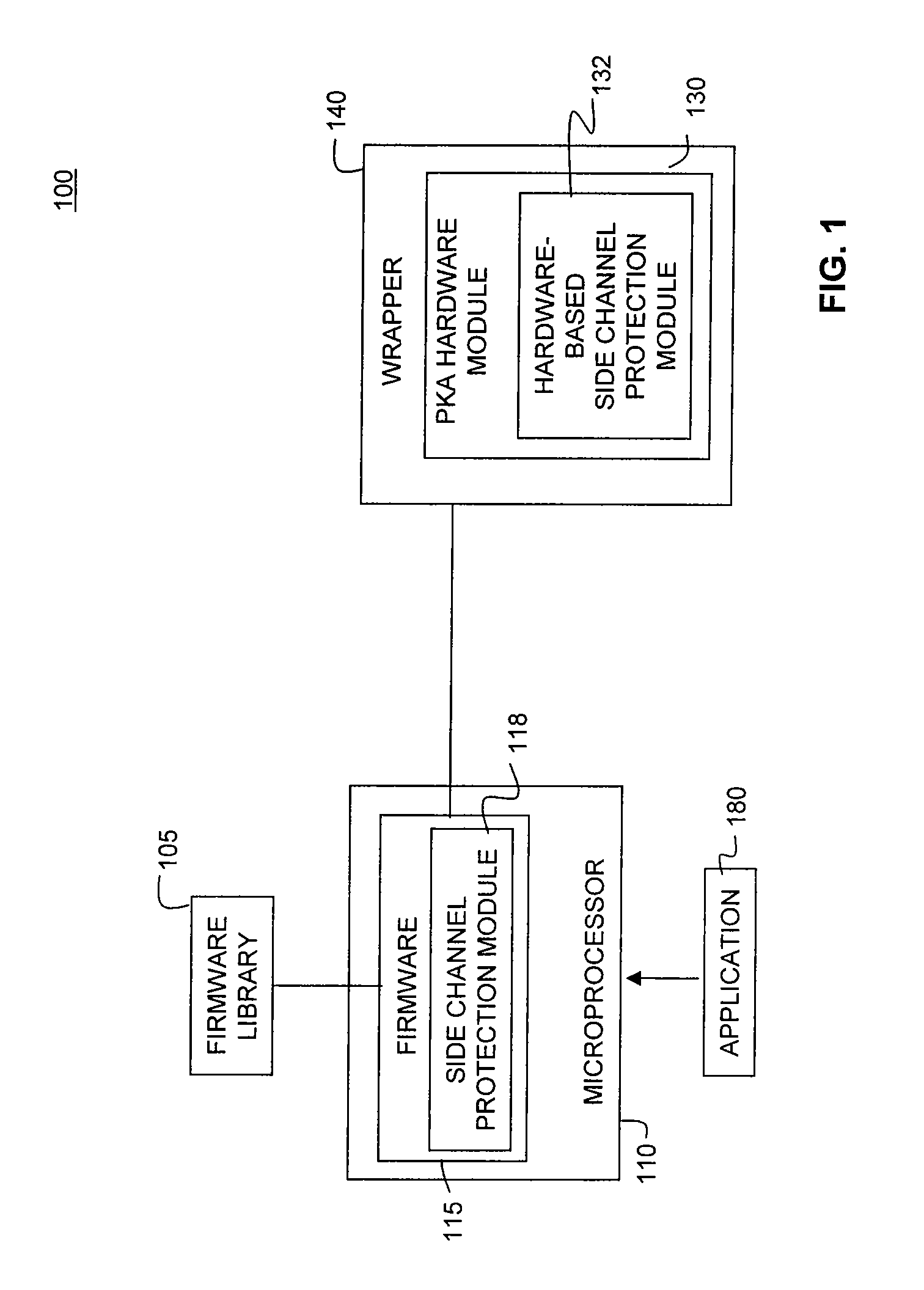
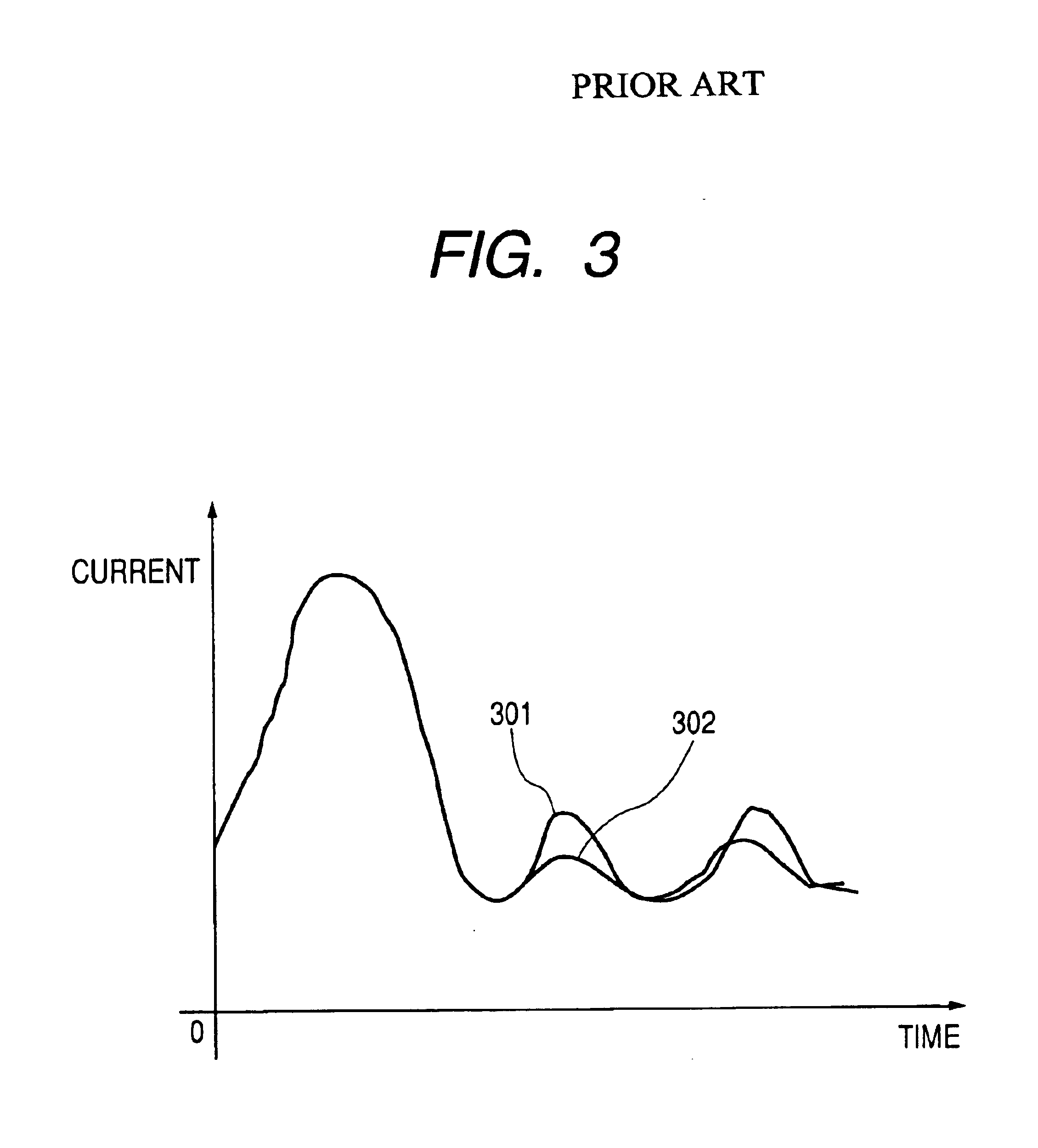
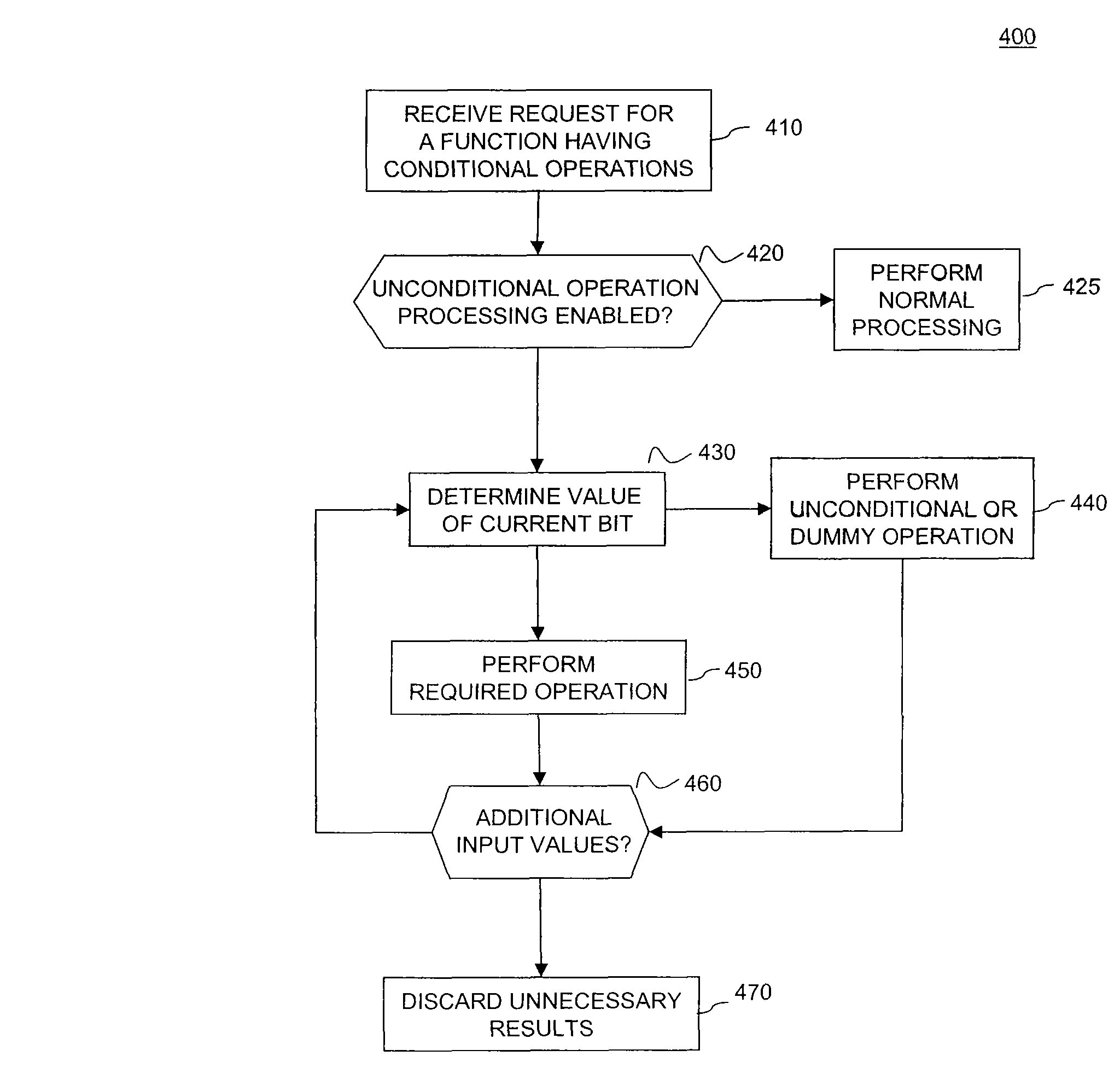
System and Methods for Side-Channel Attack Prevention
InactiveUS20090010424A1Internal/peripheral component protectionSecret communicationProcessor registerCryptosystem
A side channel attack utilizes information gained from the physical implementation of a cryptosystem. Software and hardware-based systems and methods for preventing side channel attacks are presented. Cryptographic hardware may introduce dummy operations to compensate for conditional math operations in certain functions such as modular exponentiation. Cryptographic hardware may also introduce random stalls of the data path to introduce alterations in the power profile for the operation. A cryptographic function may be mapped to a micro code sequence having a plurality of instructions. Firmware in the cryptosystem may alter the micro code sequence by altering the order of instructions, add dummy operations in the micro code sequence, break the micro code sequence into multiple sub micro code sequences and / or change the register location for source and destination operands used in the sequence. These alterations are designed to randomly change the timing and power profile of the requested function.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and device for executing a decrypting mechanism through calculating a standardized modular exponentiation for thwarting timing attacks
InactiveUS6366673B1Allow useSufficient freedomKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationModular exponentiationComputer science
An encrypting exponentiation modulo M is effected by a modular multiplication X*YmodM, where M is a temporally steady but instance-wise non-uniform modulus. The method involves an iterative series of steps. Each step executes one or two first multiplications to produce a first result, and a trim-down reduction of the size of the first result by one or more second multiplications to produce a second result. The method furthermore takes a distinctive measure for keeping the final result of each step below a predetermined multiplicity of the modulus. In particular, the method postpones substantially any subtraction of the modulus as pertaining to the measure to a terminal phase of the modular exponentiation. This is possible through choosing in an appropriate manner one or more parameters figuring in the method. This further maintains overall temporal performance.
Owner:IPG ELECTRONICS 503
Cryptographic system and method for encrypting input data
ActiveUS20080044010A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageDigital data processing detailsModular exponentiationScalar multiplication
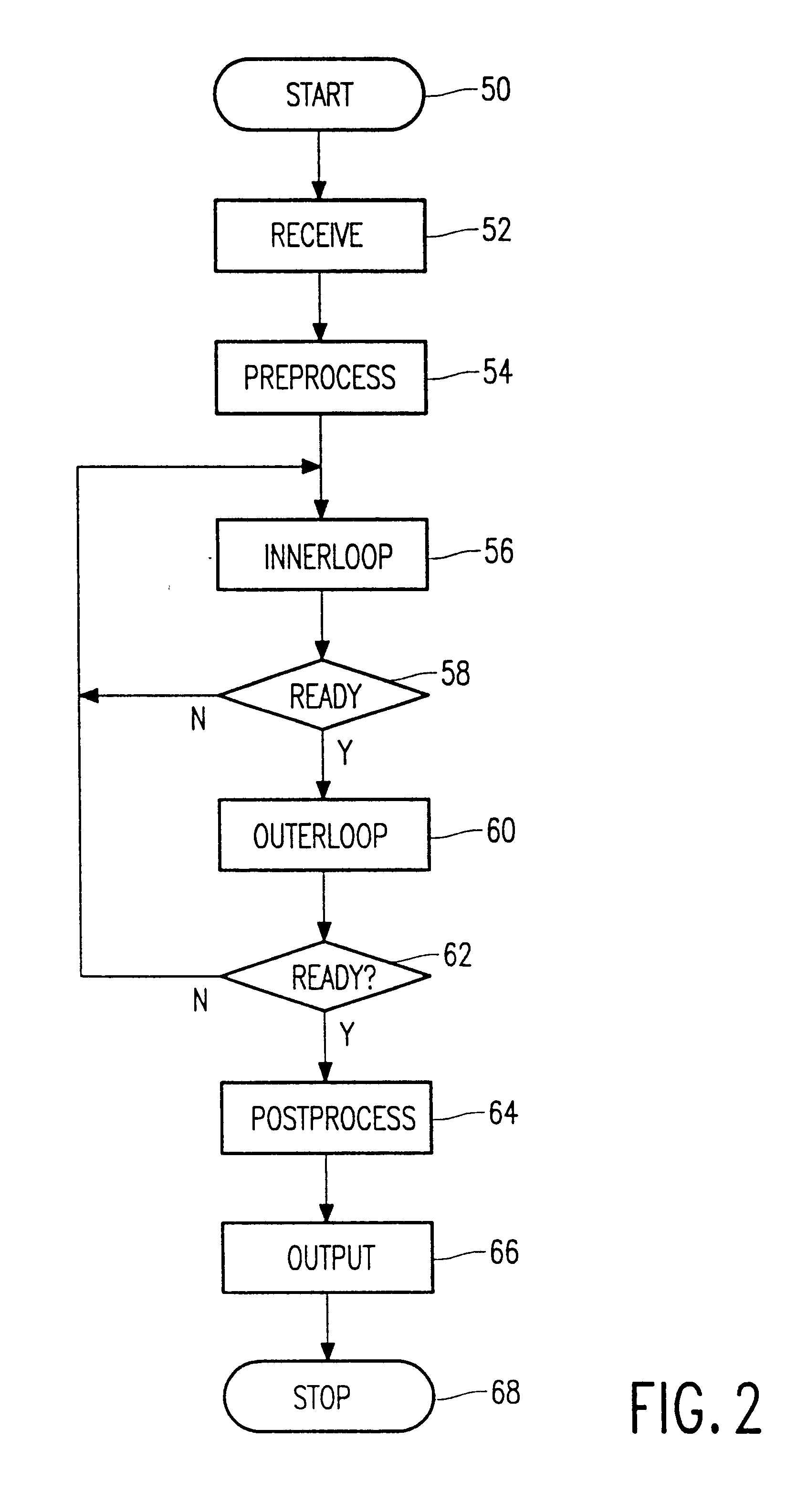
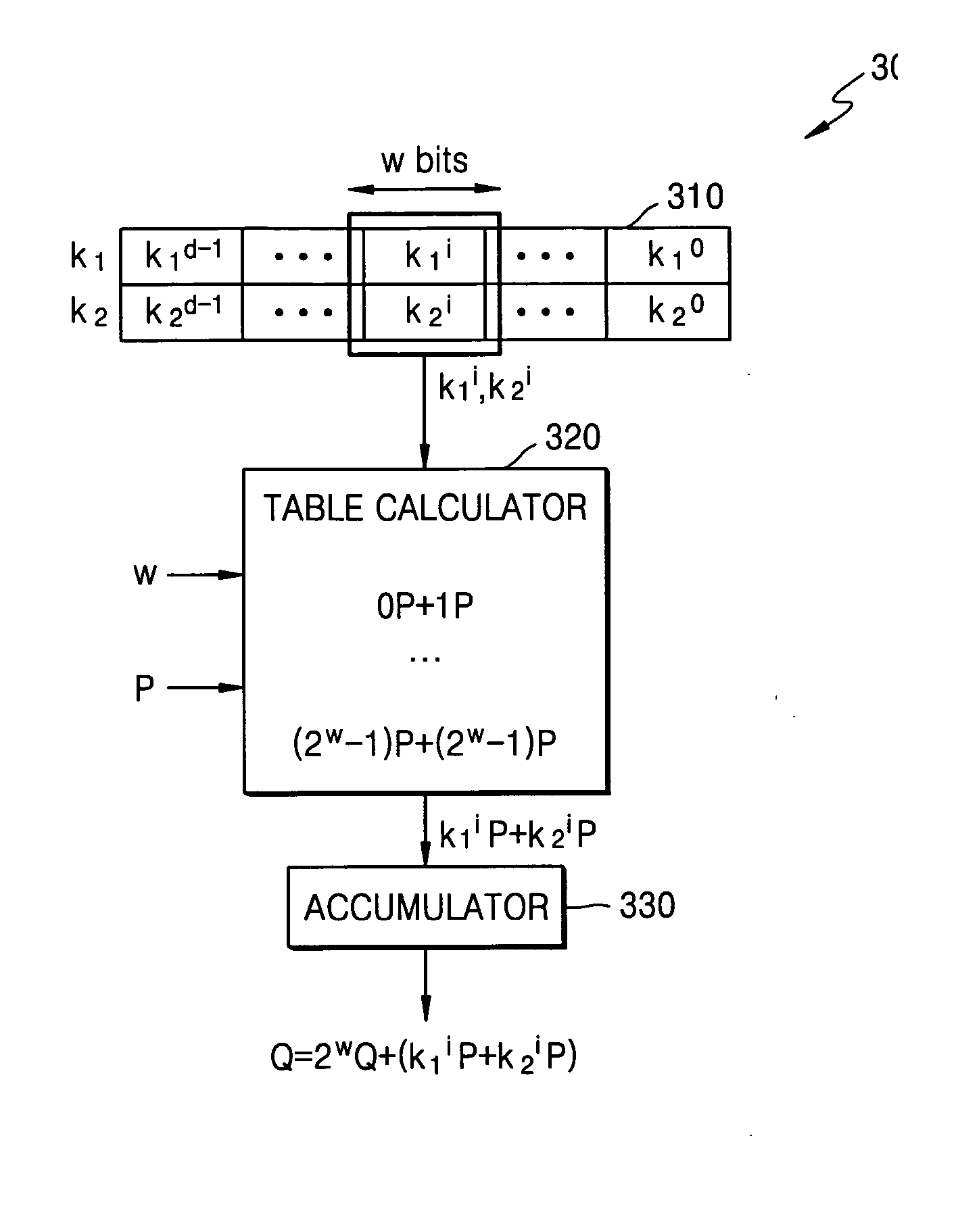
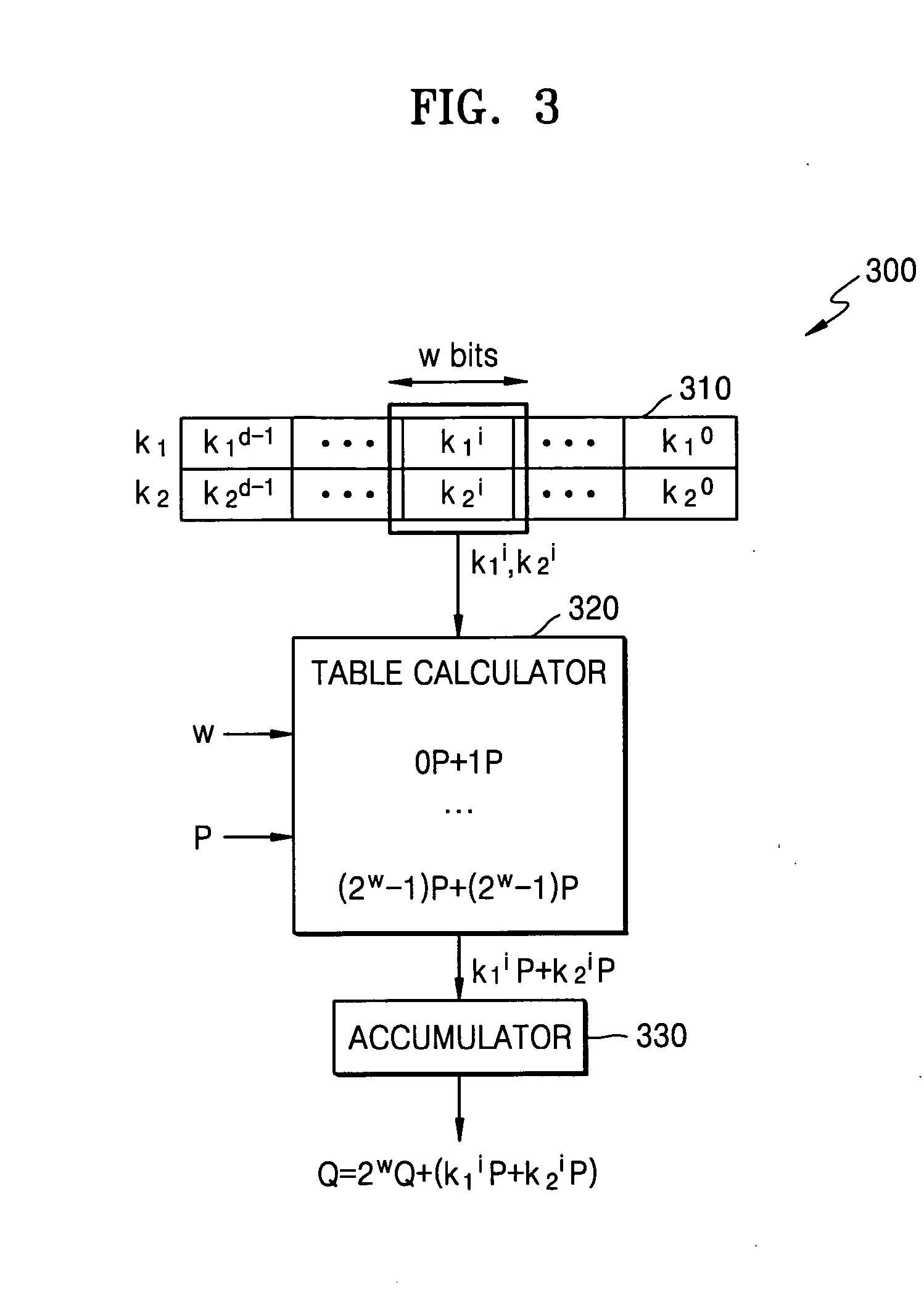
A cryptographic system and method for encrypting input data, in which an example system includes a table calculator configured to calculate table values composed of one of scalar multiplication values by Elliptic Curve (EC) operation, or exponentiation values by modular exponentiation operation, based on input data and the number of a portion of bits of each of secret keys. The table calculator may output one of scalar multiplication values or exponentiation values corresponding to a window that includes given bits of each of the secret keys from among the calculated table values. A logic circuit may be configured to output encrypted data by accumulating the output scalar multiplication values or by performing involution on the output exponentiation values.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for processing RSA password based on residue number system and coprocessor
ActiveCN102231102AImprove decryption performanceImprove parallelismComputations using residue arithmeticCoprocessorPassword
The invention relates to information technology security and microprocessor design. Aiming at increasing RSA (Ron Rivest, Adi Shamirh and LenAdleman) modular multiplication operation speed and improving RSA encryption and decryption performances, the invention provides the technical scheme as follows: a method for processing an RSA password based on a residue number system comprises the followingsteps of performs encryption and decryption operations by using an RSA algorithm and performing large-number modular exponentiation of the RSA algorithm by using an L-R (Left-Right) binary scanning modular power algorithm; an improved Montgomery algorithm is specifically as follows: 1024-bit large numbers with are expressed as numbers under the residue number system, namely two sets of 33 32-bit decimal numbers and one 32-bit number expressed under a redundancy base; an expression process is a mould solving process; the decomposed 32-bit decimal numbers respectively participate in 32-bit modular multiplication, modular multiplication accumulation and modular addition operation independently; furthermore, 32-bit data performs parallel execution operation without dependence; and the method disclosed by the invention is mainly applicable for the information technology security and microprocessor design.
Owner:PHYTIUM TECH CO LTD
Data encryption and decryption processing method and device based on Montgomery modular multiplication operation
InactiveCN102207847AReduce clock cyclesImprove efficiencyComputations using residue arithmeticComputer hardwareMontgomery reduction
The invention discloses a data encryption and decryption processing method and device based on Montgomery modular multiplication operation. During the data encryption or decryption processing, the modular exponentiation operation is transformed to the Montgomery modular multiplication operation which is divided into an external circulation part and an internal circulation part. The internal circulation part mainly performs the multiplication operation, while the external circulation part mainly conducts the reduction operation. After the external circulation operation and the internal circulation operation are completed, the operation result is reduced to a range smaller than a modulus P if the operation result is determined to be larger than the modulus P, and otherwise, the operation result is outputted directly. For the hardware implementation, the internal circulation and the external circulation are designed to a parallel processing pipeline architecture, which can reduce the clock period consumed by one modular multiplication operation and can improve the overall modular multiplication efficiency, thereby improving the efficiency and the speed for data encryption and decryption.
Owner:GCI SCI & TECH
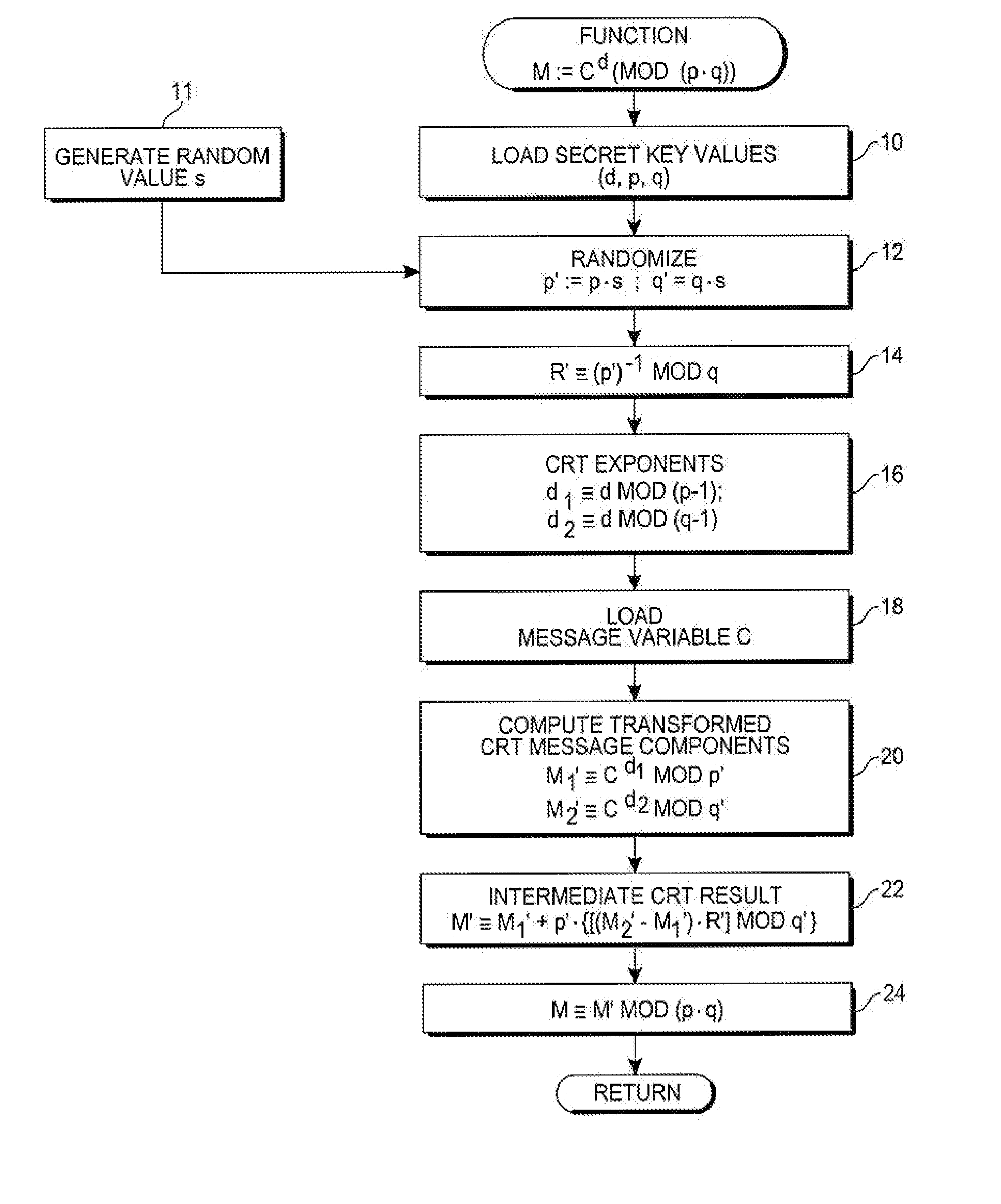
Chinese remainder theorem - based computation method for cryptosystems
ActiveUS20080226064A1Less computational intenseSecure against cryptanalysisRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationChinese remainder theoremCryptosystem
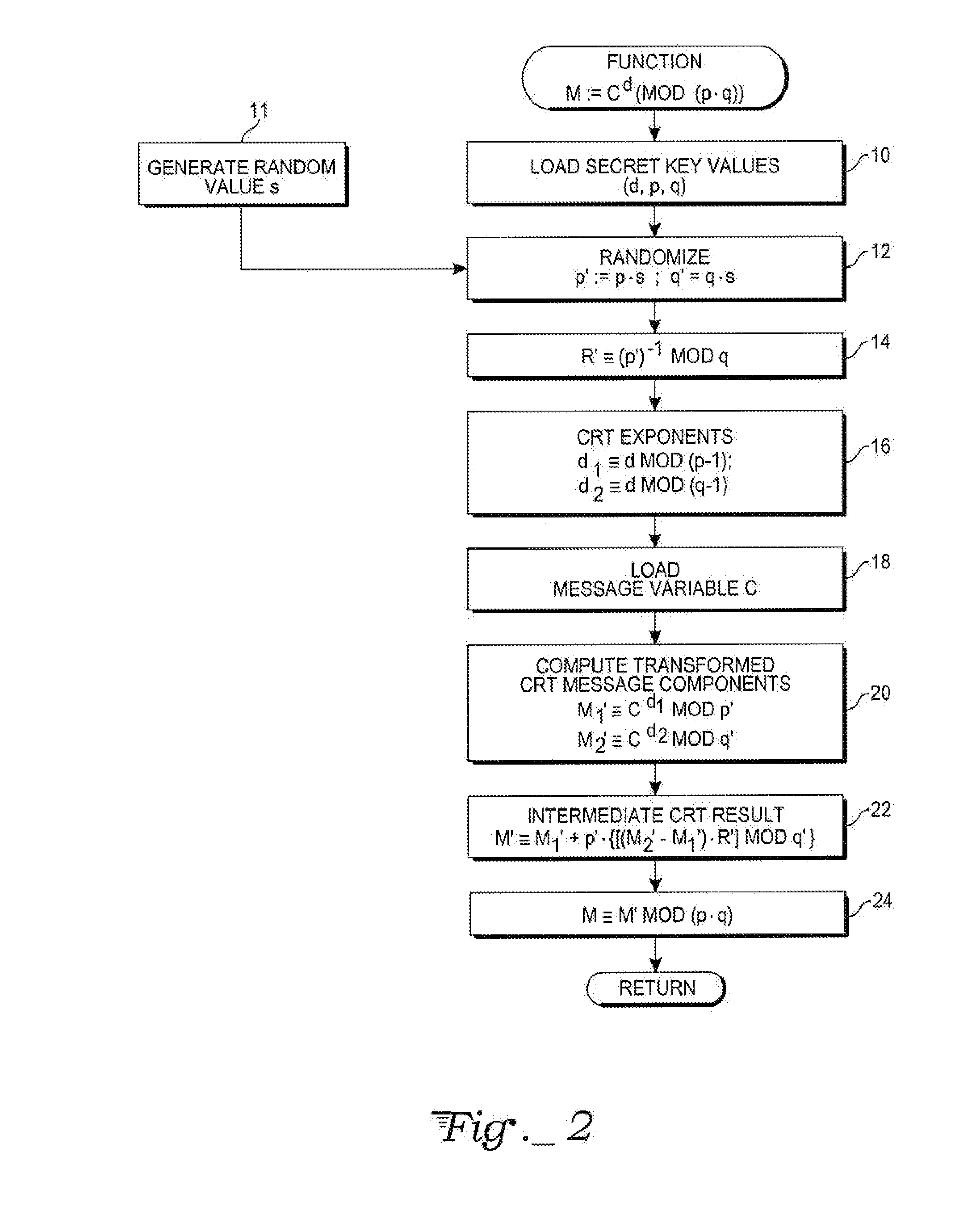
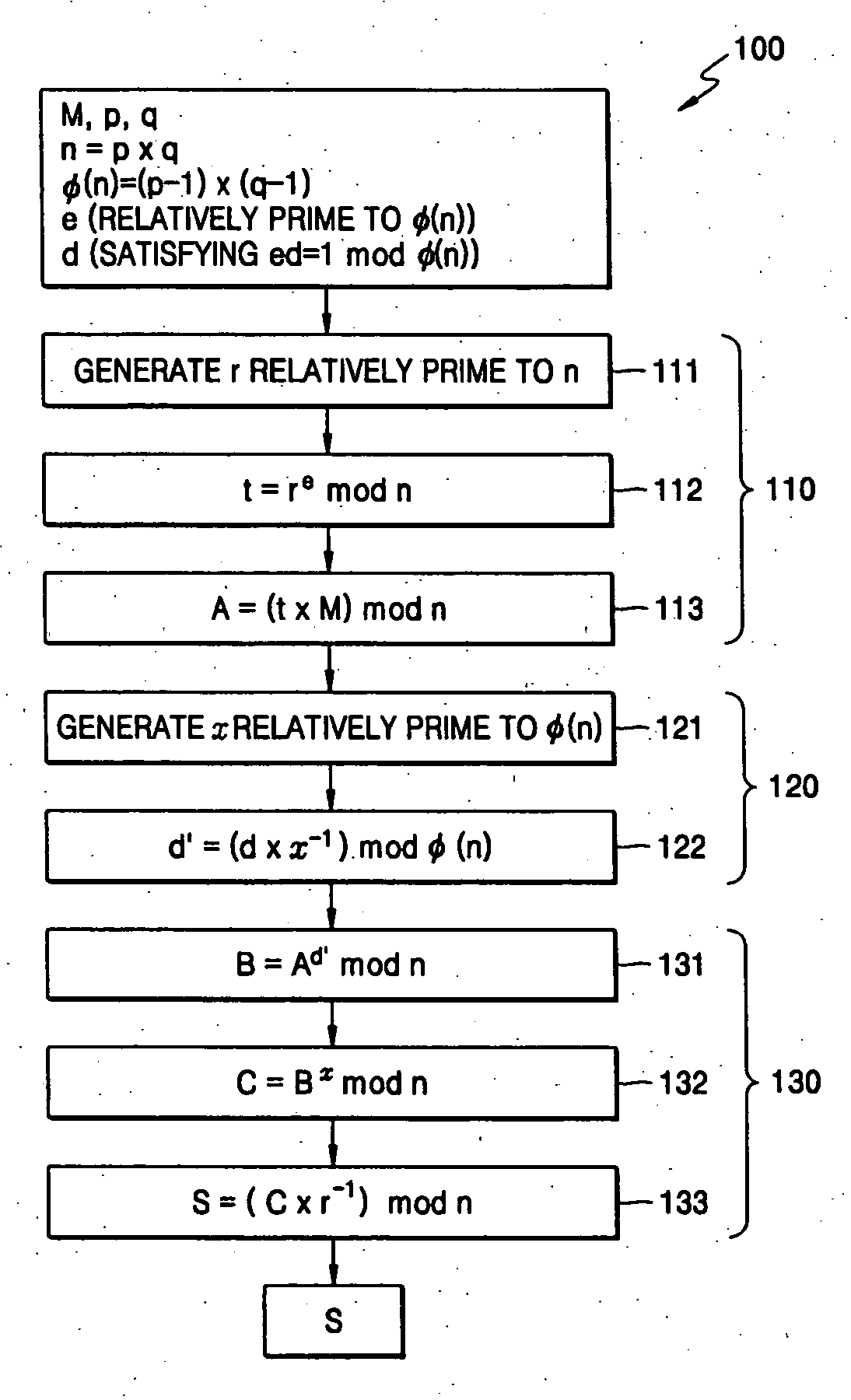
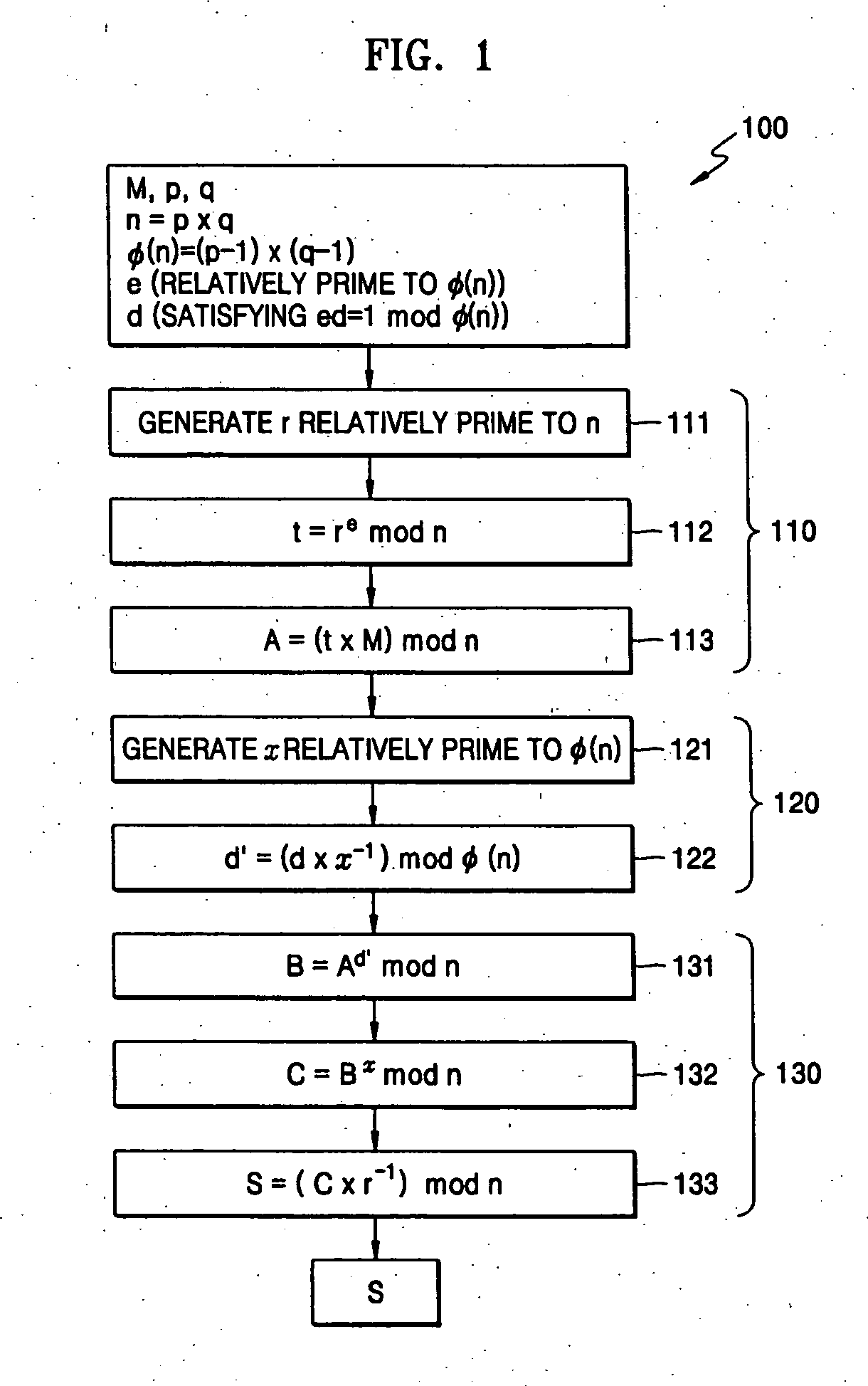
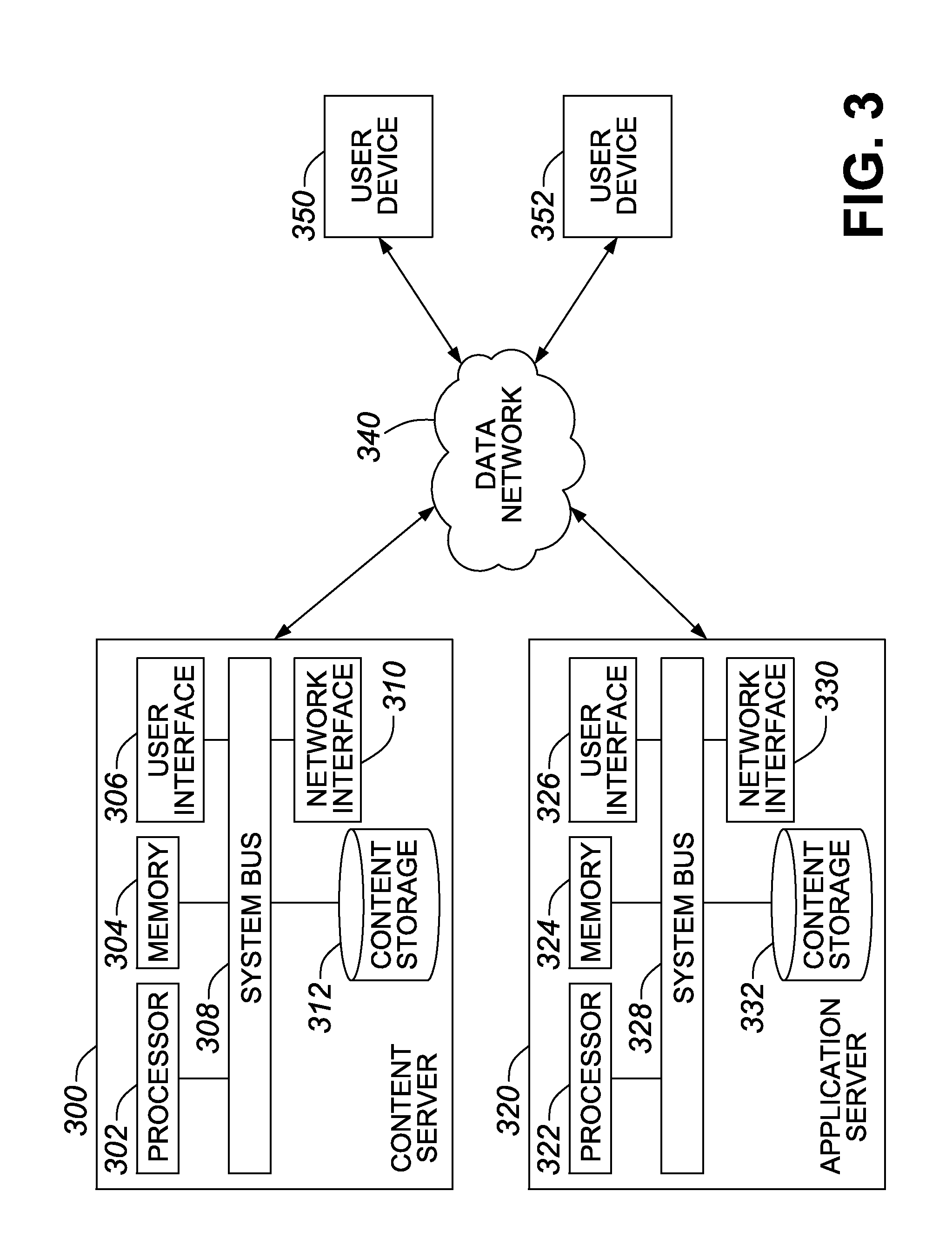
A computer hardware implemented cryptography method computes a modular exponentiation, M:=Cd (mod p·q) upon a message data value C using a Chinese Remainder Theorem (CRT) based technique. To secure against cryptanalysis,, the private key moduli p and q are transformed by multiplication with a generated random value s, so that p′:=p·s and q′:=q·s. The CRT steps of the modular exponentiation are applied using the transformed moduli p′ and q′ to obtain a random intermediate message data value M′. A final reduction of M′ modulo p·q yields the final message data value M. Values needed for the computation are loaded into data storage and accessed as needed by electronic processing hardware.
Owner:CRYPTOGRAPHY RESEARCH
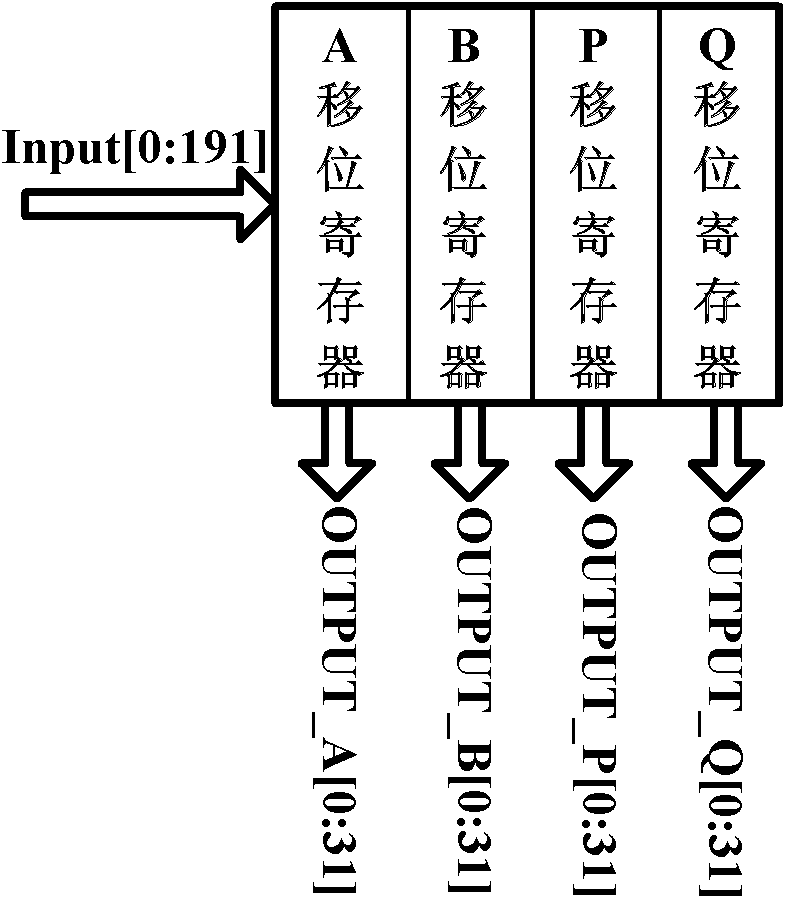
Modular exponentiation calculation apparatus and modular exponentiation calculation method
InactiveUS20020126838A1Efficient executionSecret communicationComputations using residue arithmeticSoftware engineeringModular exponentiation
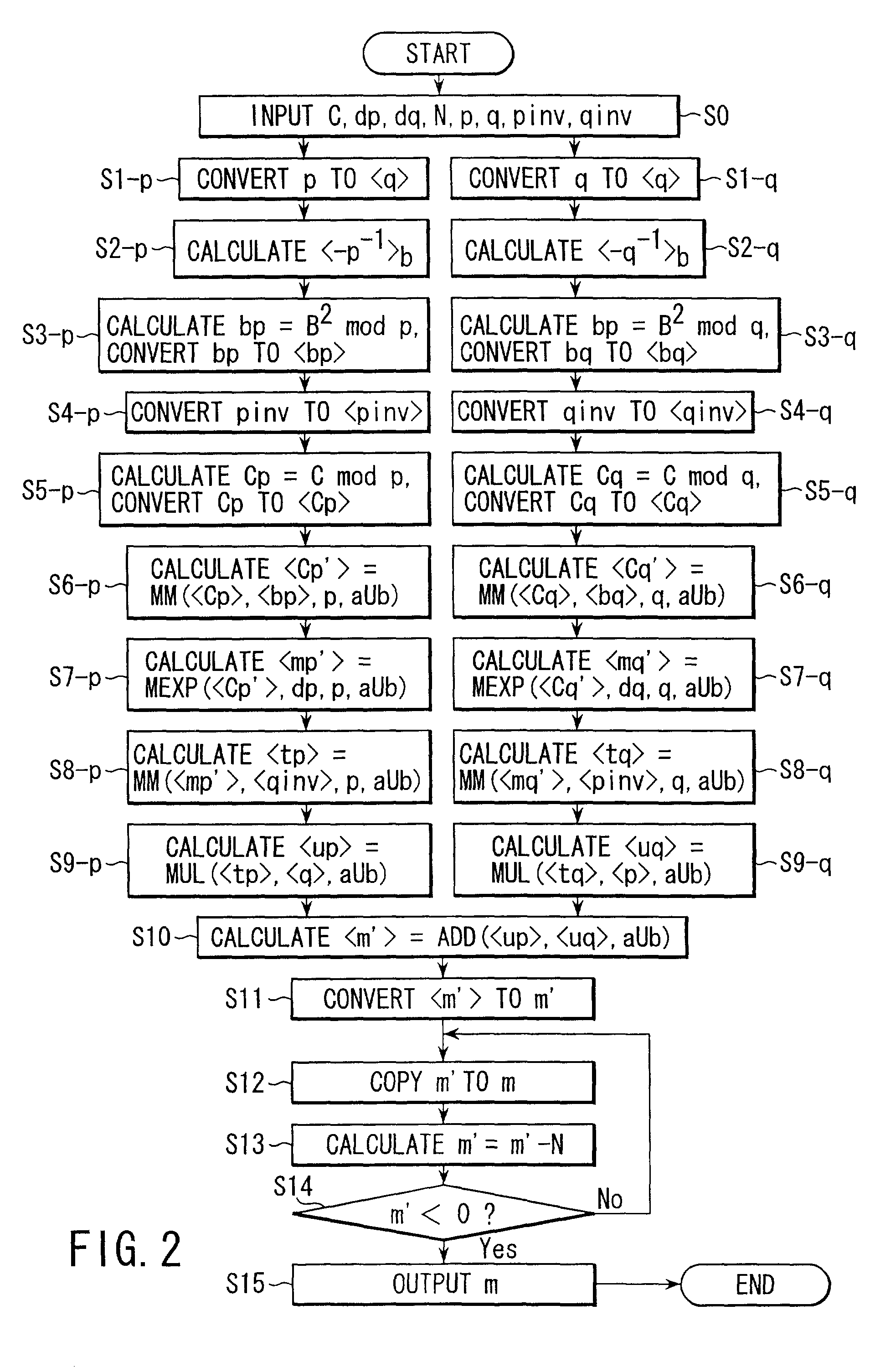
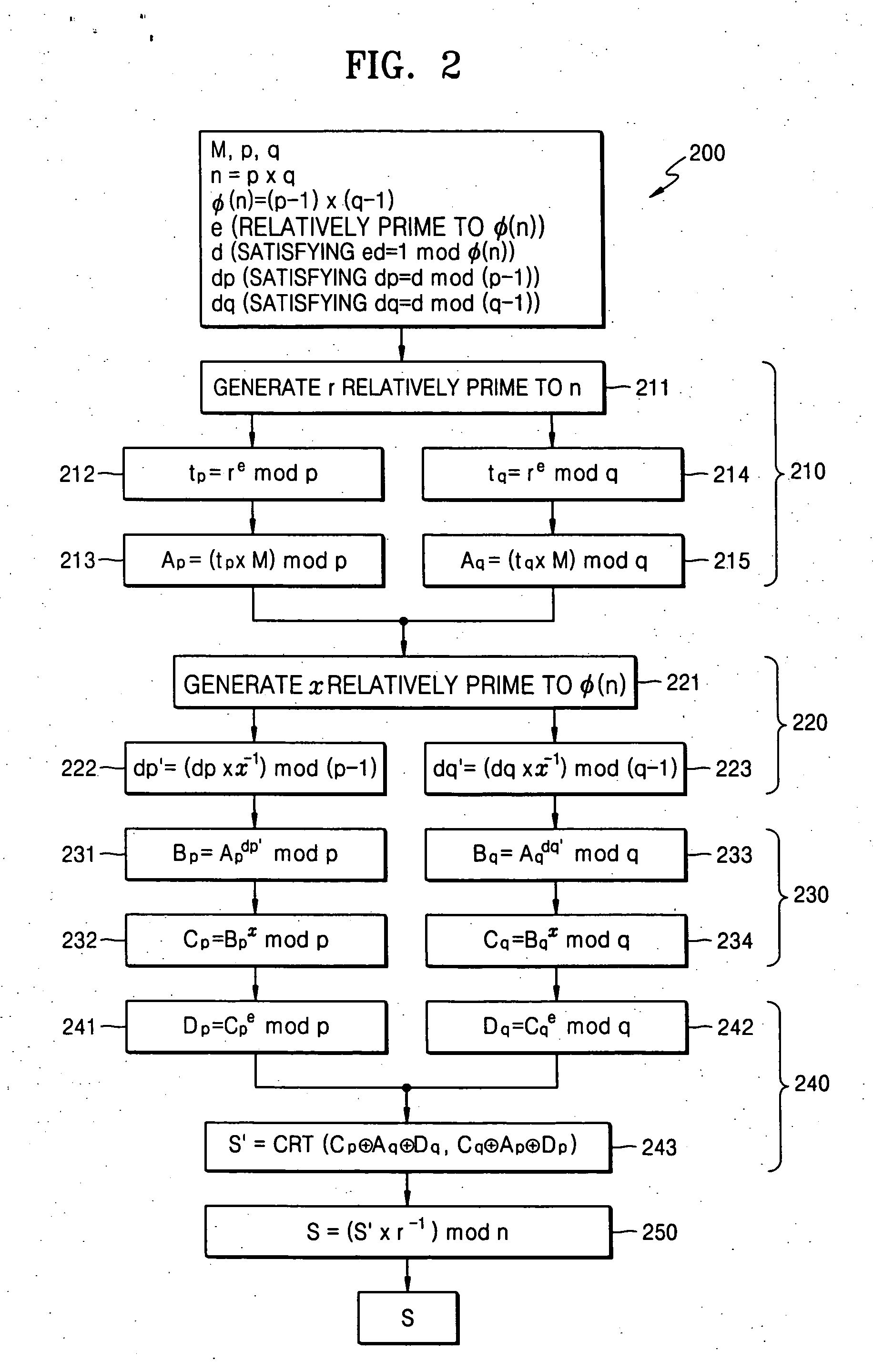
A modular exponentiation calculation apparatus obtains a first RNS representation of a value Cp.sup.dp.times.B mod p based on an RNS representation of a remainder value Cp=C mod p and a remainder value dp=d mod (p-1), obtains a second RNS representation of a value Cq.sup.dq.times.B mod q based on an RNS representation of a remainder value Cq=C mod q and a remainder value dq=d mod (p-1), obtains a third RNS representation of an integer m' congruent with C.sup.d mod (p.times.q) based on both the first and second RNS representations, and obtains m=C.sup.d mod (p.times.q) based on a value of the integer m' obtained by converting the third RNS representation into a binary representation.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Pre-computation and dual-pass modular arithmetic operation approach to implement encryption protocols efficiently in electronic integrated circuits
InactiveUS7027597B1Effective encryptionEfficient implementationComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerModularity
A pre-computation and dual-pass modular operation approach to implement encryption protocols efficiently in electronic integrated circuits is disclosed. An encrypted electronic message is received and another electronic message generated based on the encryption protocol. Two passes of Montgomery's method are used for a modular operation that is associated with the encryption protocol along with pre-computation of a constant based on a modulus. The modular operation may be a modular multiplication or a modular exponentiation. Modular arithmetic may be performed using the residue number system (RNS) and two RNS bases with conversions between the two RNS bases. A minimal number of register files are used for the computations along with an array of multiplier circuits and an array of modular reduction circuits. The approach described allows for high throughput for large encryption keys with a relatively small number of logical gates.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
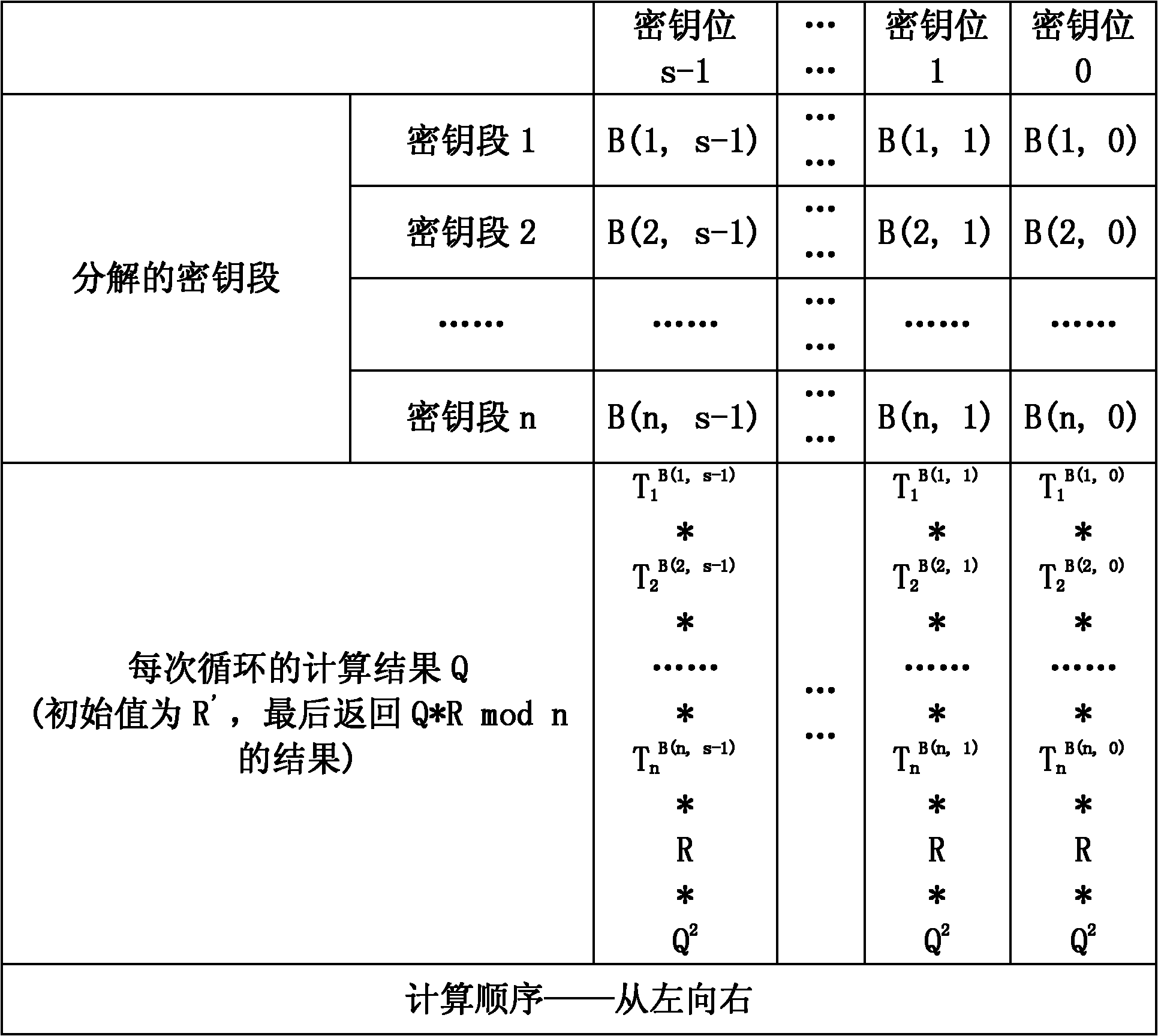
Method suitable for RSA modular exponentiation calculation
InactiveCN102468956ACalculation is fast and safeReduce the number of cyclesPublic key for secure communicationModular exponentiationTime cost
The invention discloses a method suitable for RSA modular exponentiation calculation. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring a random number R'; 2, calculating a modular inverse value R of R' to an RSA modulus n, namely R=R'-1mod n; 3, averagely dividing an index into r segments, and ensuring that the length of each segment is s-bit; 4, calculating T1=M (RSA modular exponentiation base number) and Ti+1=2s.Ti, wherein i=1,2,..., n; and 5, performing RSA modular exponentiation calculation. By the quick and safe method suitable for the RSA modular exponentiation calculation, the RSA modular exponentiation calculation can be completed by taking measures of combining average segmentation of the index and base number mask, so that the cycle index in the modular exponentiation calculation is reduced, time cost required by the modular exponentiation calculation is reduced, calculation flows in various conditional branches are balanced, and random elements are added in an input part of modular exponentiation; and therefore, the modular exponentiation calculation can be carried out more quickly and safely.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
System and recording medium for securing data and methods thereof
InactiveUS20060029224A1Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationModular exponentiationHuman–computer interaction
A system and recording medium for securing data and methods thereof including a modular exponentiation. One embodiment includes first masking a message, second masking an exponent, and executing a modular exponentiation based at least one of the first and second maskings. Another embodiment includes first masking a message, second masking at least one exponent, executing a modular exponentiation based at least one of the first and second maskings, detecting an error, executing a modular multiplication operation based on the detection and diffusing the detected error to generate an electronic signature. Yet another embodiment includes first masking a message, second masking at least one exponent, executing a modular exponentiation based at least one of the first and second maskings, detecting an error, and generating an electronic signature based on the detected error.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Rsa decryption using multiplicative secret sharing
InactiveUS20170012948A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareCiphertext
An embodiment features an RSA process in which the private key is separated into shares. Decryption (and authentication and other RSA objectives) may be accomplished by successive modular exponentiation of, for example, a ciphertext or a signature.
Owner:NXP BV
RSA (Rivest-Shamirh-Adleman) algorithm and IP core
InactiveCN101834723AEasy to operateImprove performancePublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationHardware structureModular exponentiation
The invention discloses an RSA (Rivest-Shamirh-Adleman) algorithm and an IP core, relating to the technical field of electronic information encryption and aiming to solve the technical problems of overlarge IP core area and lower computing speed of the RAS algorithm. The IP core for operating the RAS algorithm comprises an interface module, a control module, a memory module, a modular exponentiation module and a modular reduction module, wherein the control module is respectively connected with the modular reduction module, the memory module, the modular exponentiation module and the interface module; the modular reduction module is respectively connected with the modular exponentiation module and the memory module; and the memory module is respectively connected with the modular exponentiation module and the interface module. The invention has the characteristics of emphasis on small area, high performance, lowend-oriented RAS IP core, adoption of advanced encryption algorithms and proper hardware structures and demand on less addition and storage space.
Owner:SHANGHAI AISINOCHIP ELECTRONICS TECH
Lattice-based cloud storage data safety auditing method supporting data proxy uploading
InactiveCN107124272AAvoid complex managementResist attackKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCommunications securityOriginal data
The invention belongs to the technical field of information safety, and in particular relates to a lattice-based cloud storage data safety auditing method supporting data proxy uploading. The auditing method provided by the invention helps a data owner authorize a proxy signature generating data to a proxy signer and upload the proxy signature to a cloud server, and also helps a credible auditor to audit completeness of the cloud storage data. The auditing method provided by the invention achieves construction of a random mask code based on an original image sampling algorithm on the lattice, so that the credible auditor can be effectively prevented from recovering original data block information of an original signer from a data file. The credible auditor only needs to compute a linear combination with limited a computation amount instead of computing bilinear pairings with higher cost and modular exponentiation during a cloud storage data completeness verification process, so that the auditing method is very beneficial to the credible auditor in the aspect of computing efficiency. Meanwhile the method provided by the invention can effectively resist attacks of a quantum computer, and thus have very important application value in cloud computing environment of post-quantum communication security.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
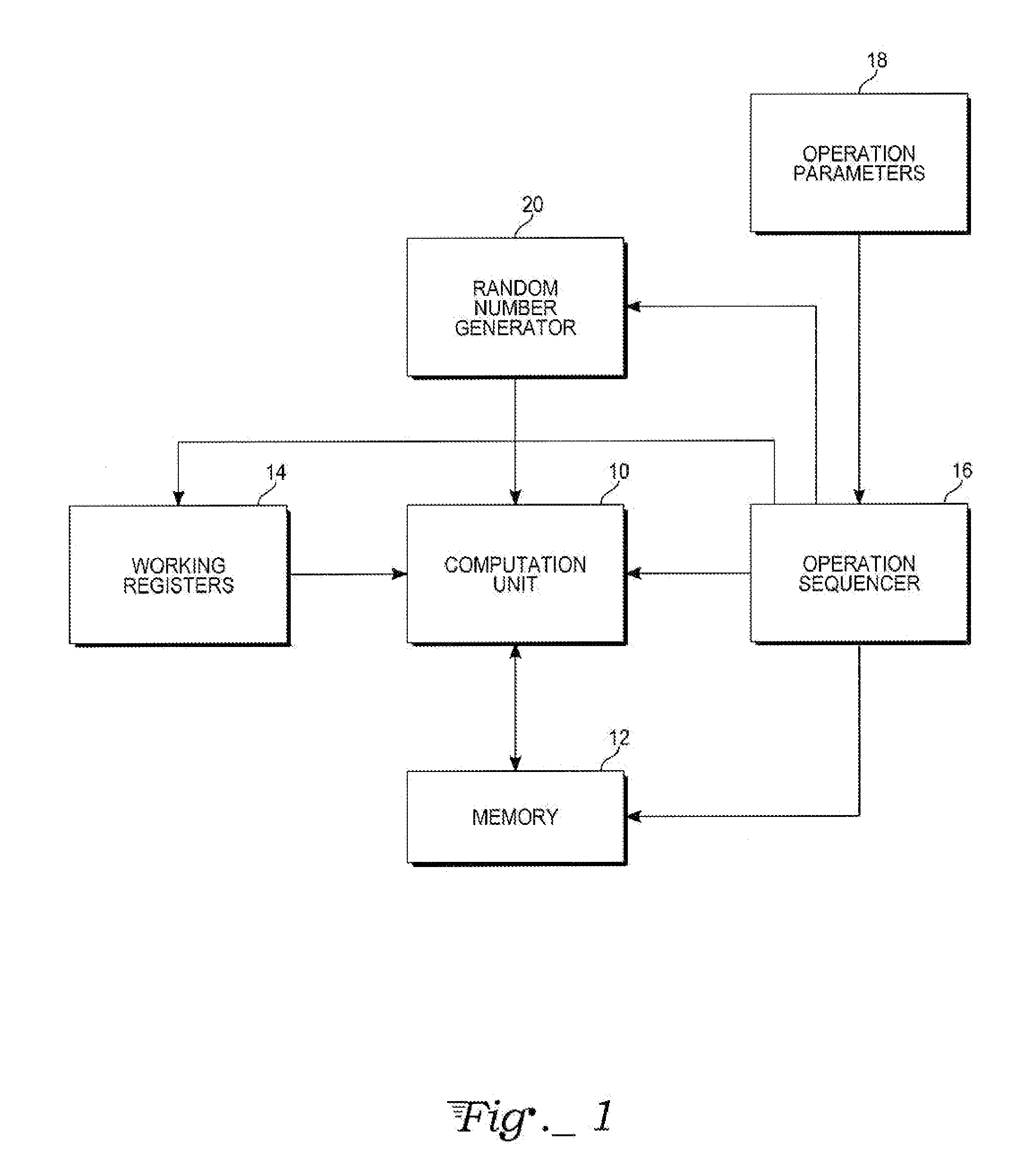
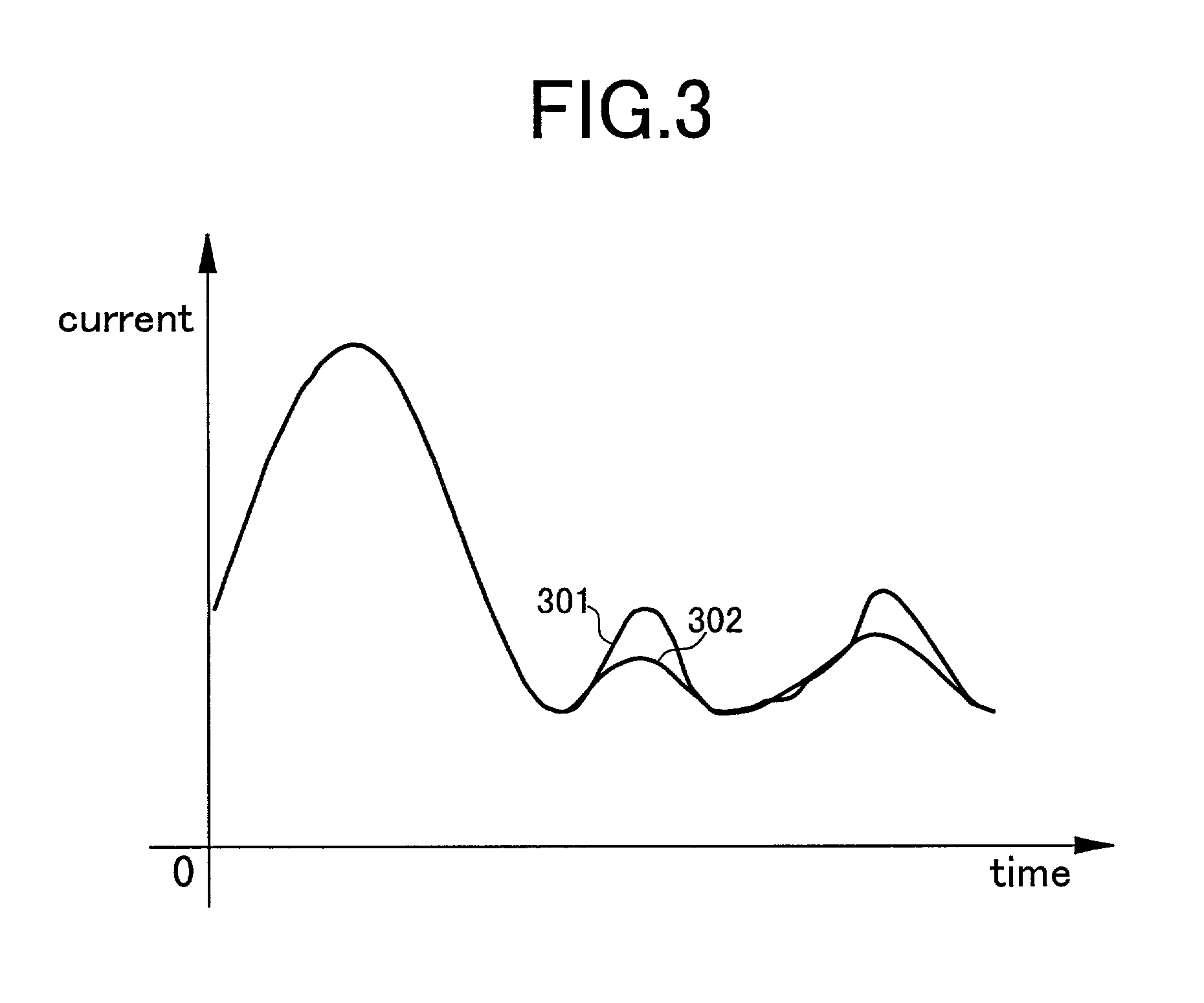
Tamper-resistant modular multiplication method
InactiveUS6968354B2Good effectDigital computer detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionInformation processingModularity
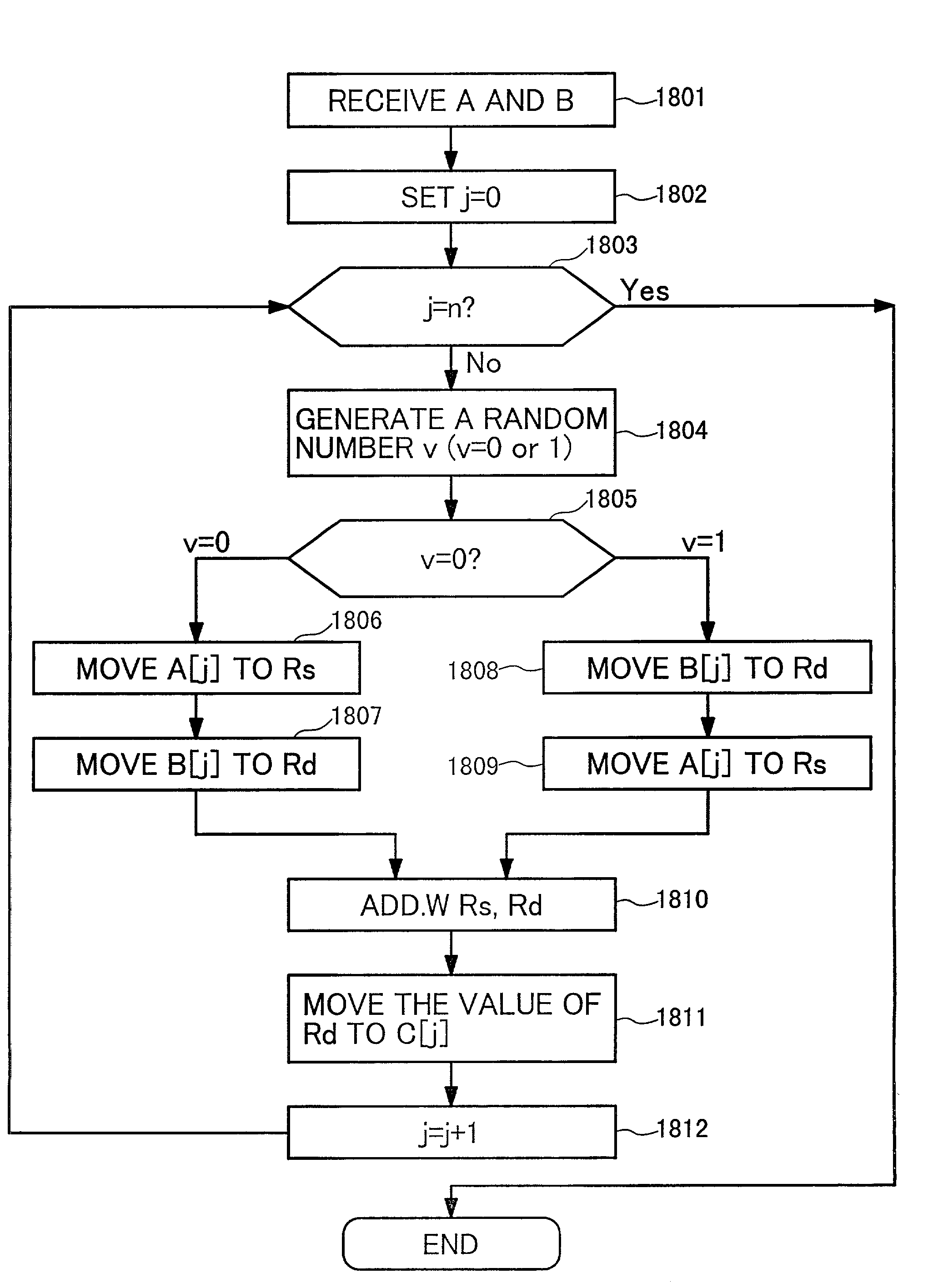
The disclosed technology of the present invention relates to an information processing device such as an IC card, and specifically to the overflow processing which occurs in a modular multiplication operation during crypto-processing. Such overflow processing exhibits a particular pattern of consumption current. It is the subject of the present invention to decrease the relationship between the data processing and the pattern of the consumption current. In the processing procedures for performing a modular exponentiation operation according to the 2 bit addition chain method, the modular multiplication operation to be executed is selected at random, the selected modular multiplication operation is executed for each 2 bits, the correction of the result is performed, and the result of the calculation (i.e, a corrected value or uncorrected value) is outputted.
Owner:HIGH CONNECTION DENSITY INC +1
System and methods for side-channel attack prevention
InactiveUS8781111B2Digital data processing detailsInternal/peripheral component protectionProcessor registerCryptosystem
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Circuits for calculating modular multiplicative inverse
InactiveUS20050185791A1Small sizeObvious advantagesPublic key for secure communicationComputation using non-contact making devicesHardware structureChinese remainder theorem
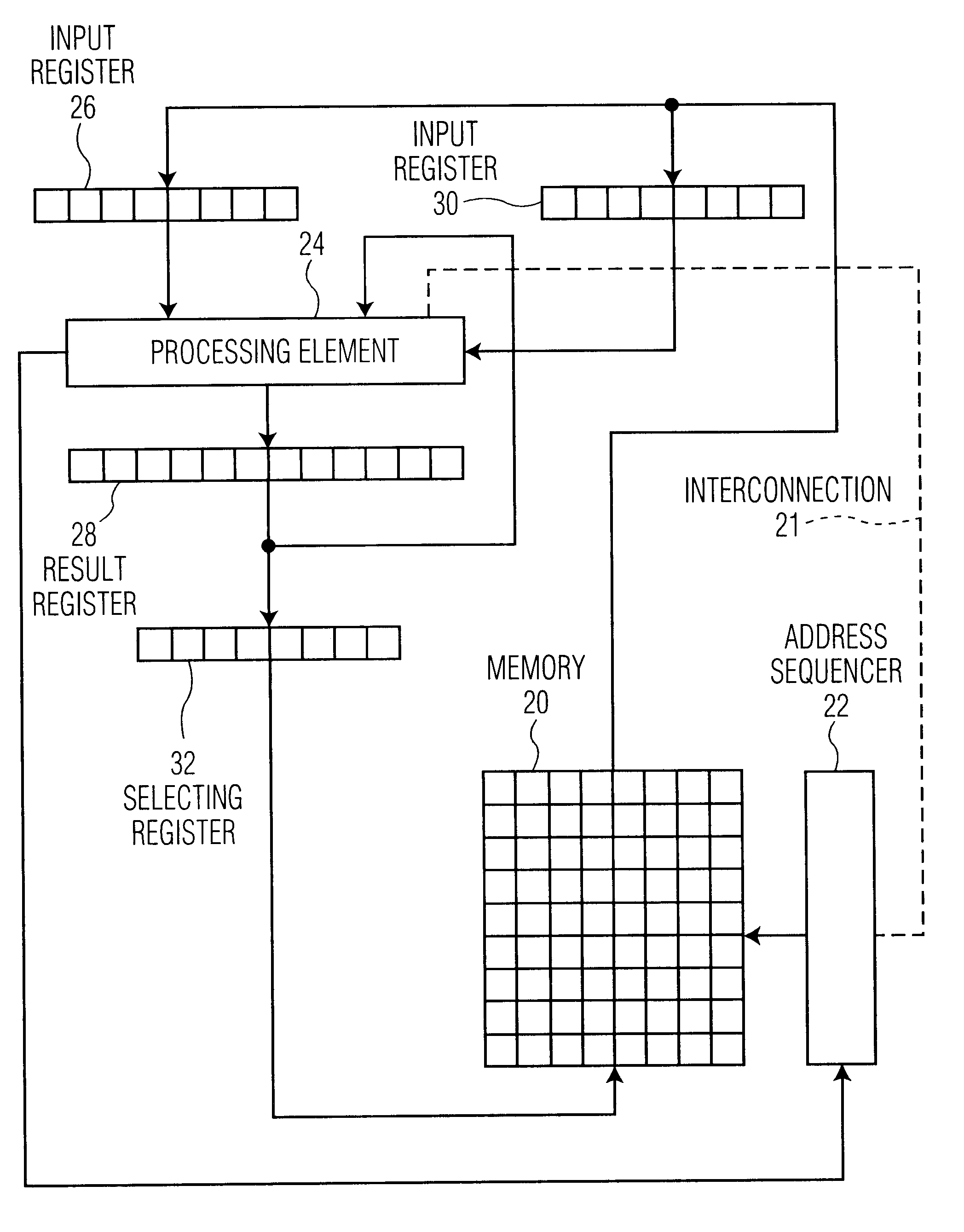
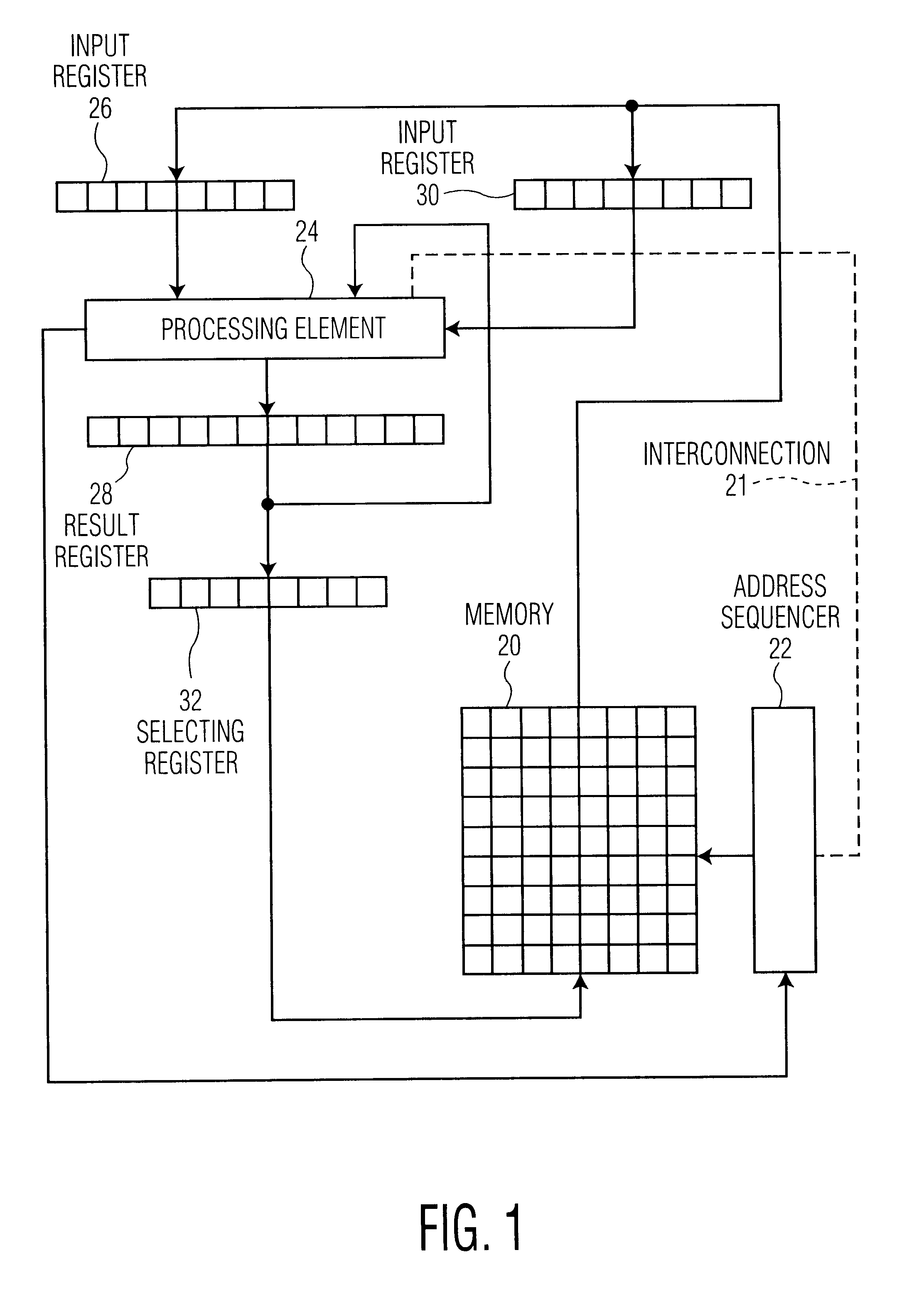
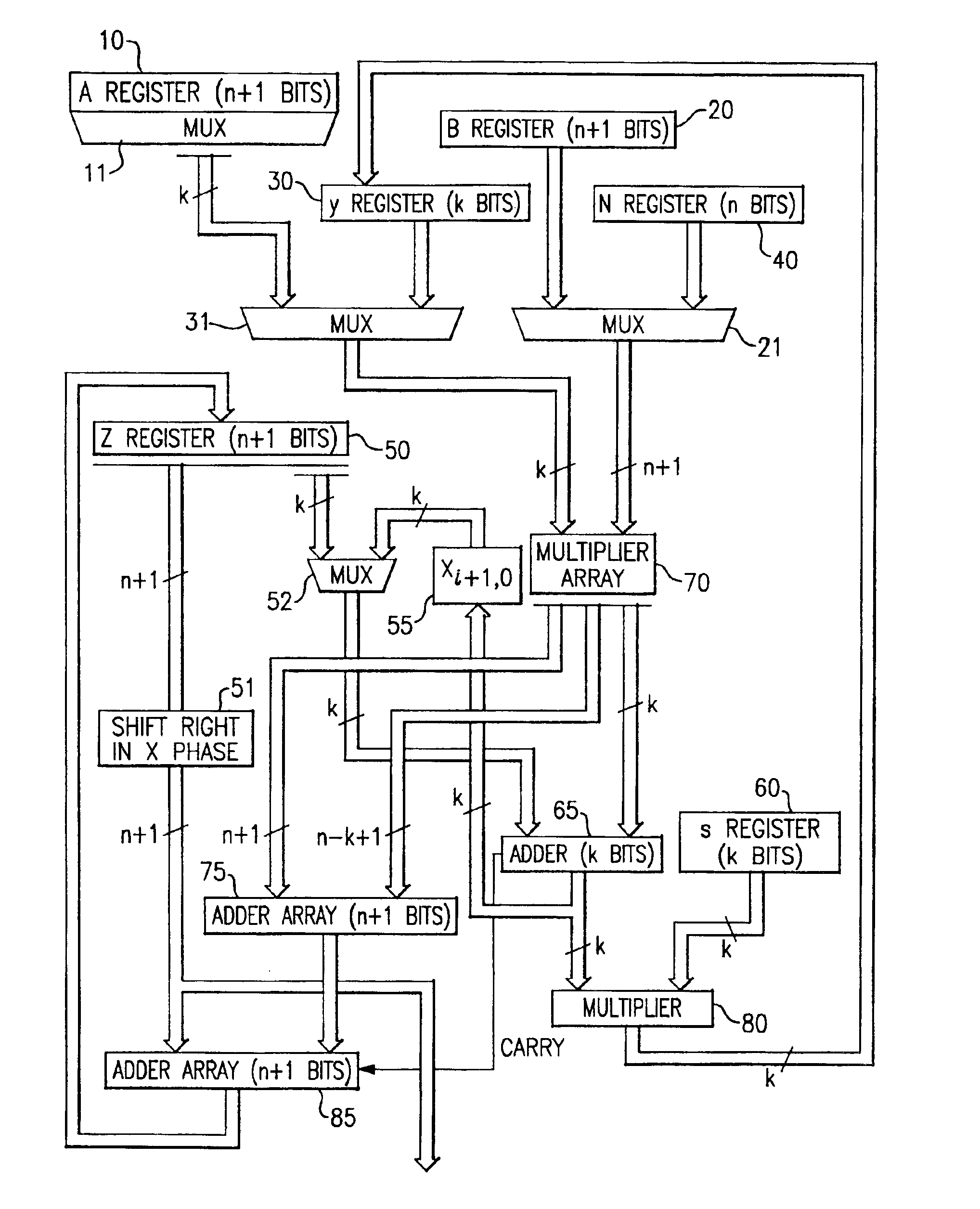
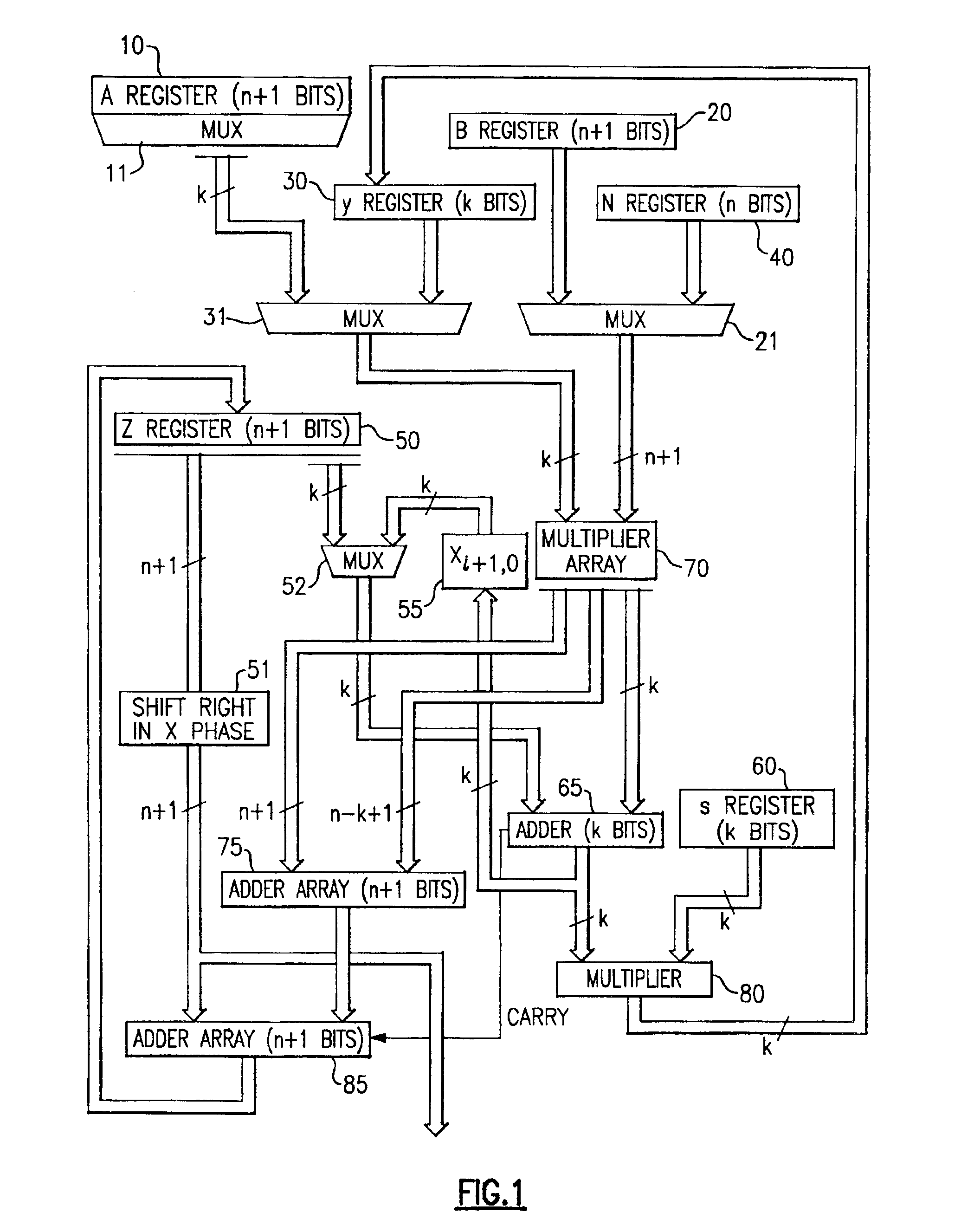
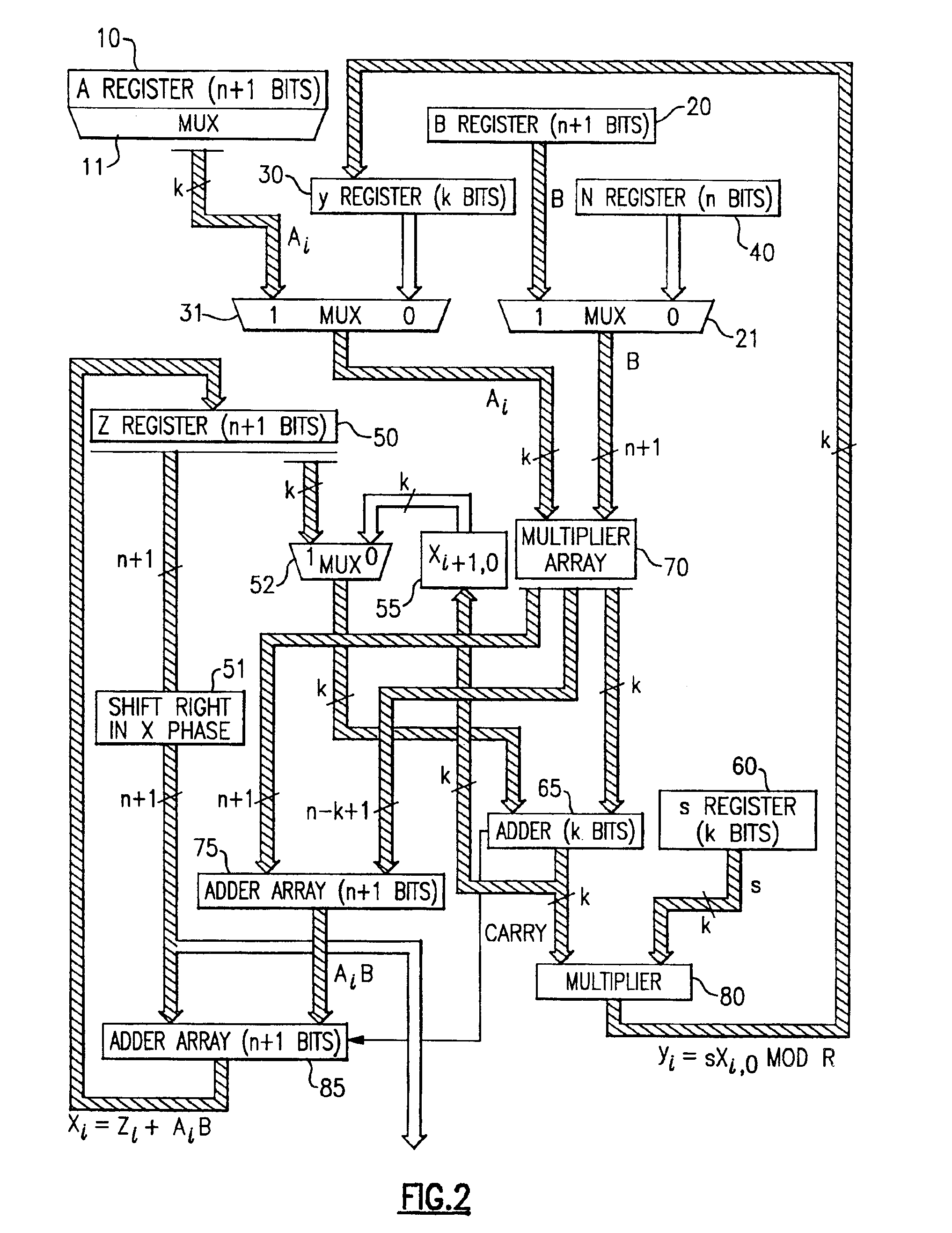
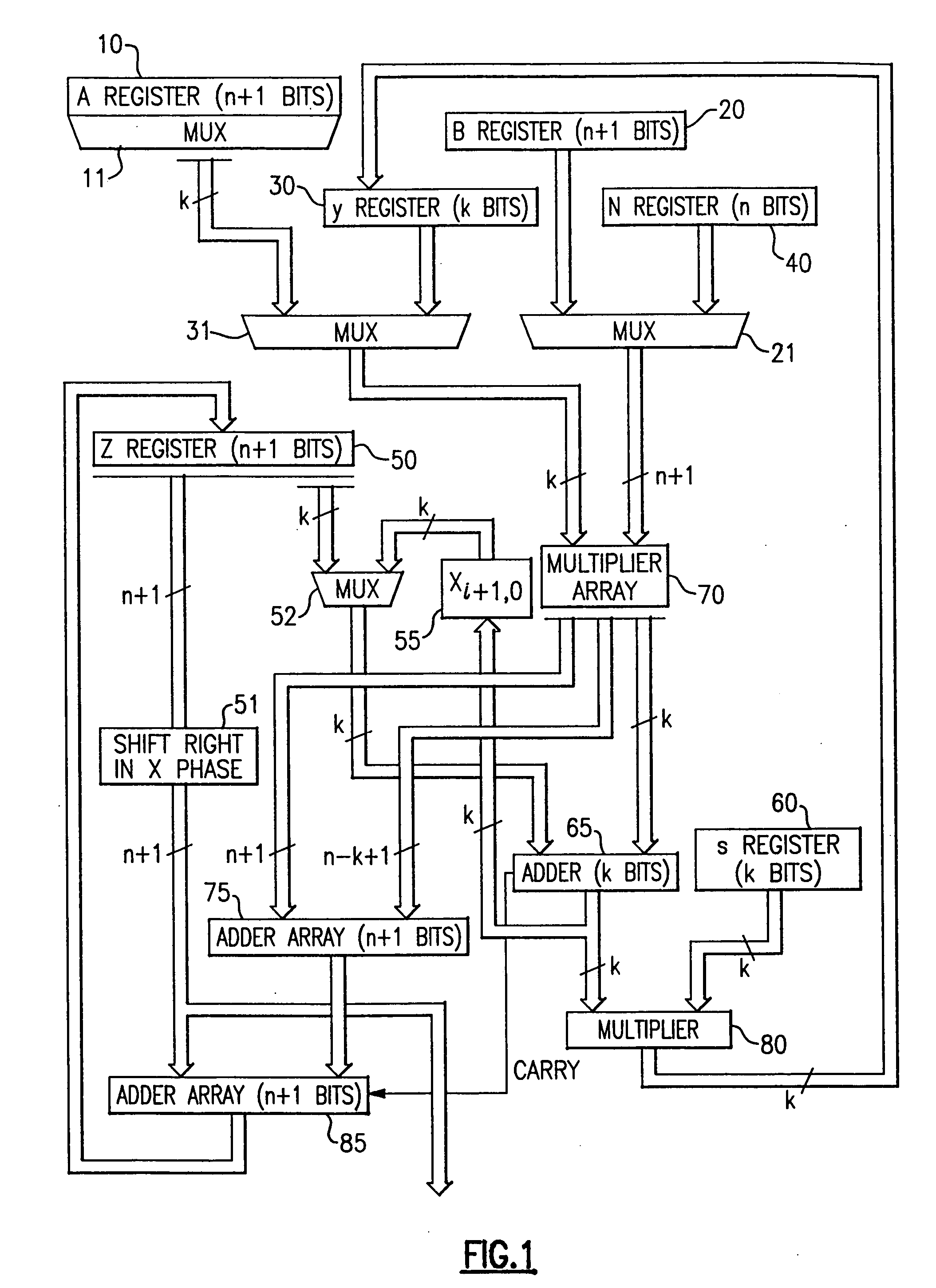
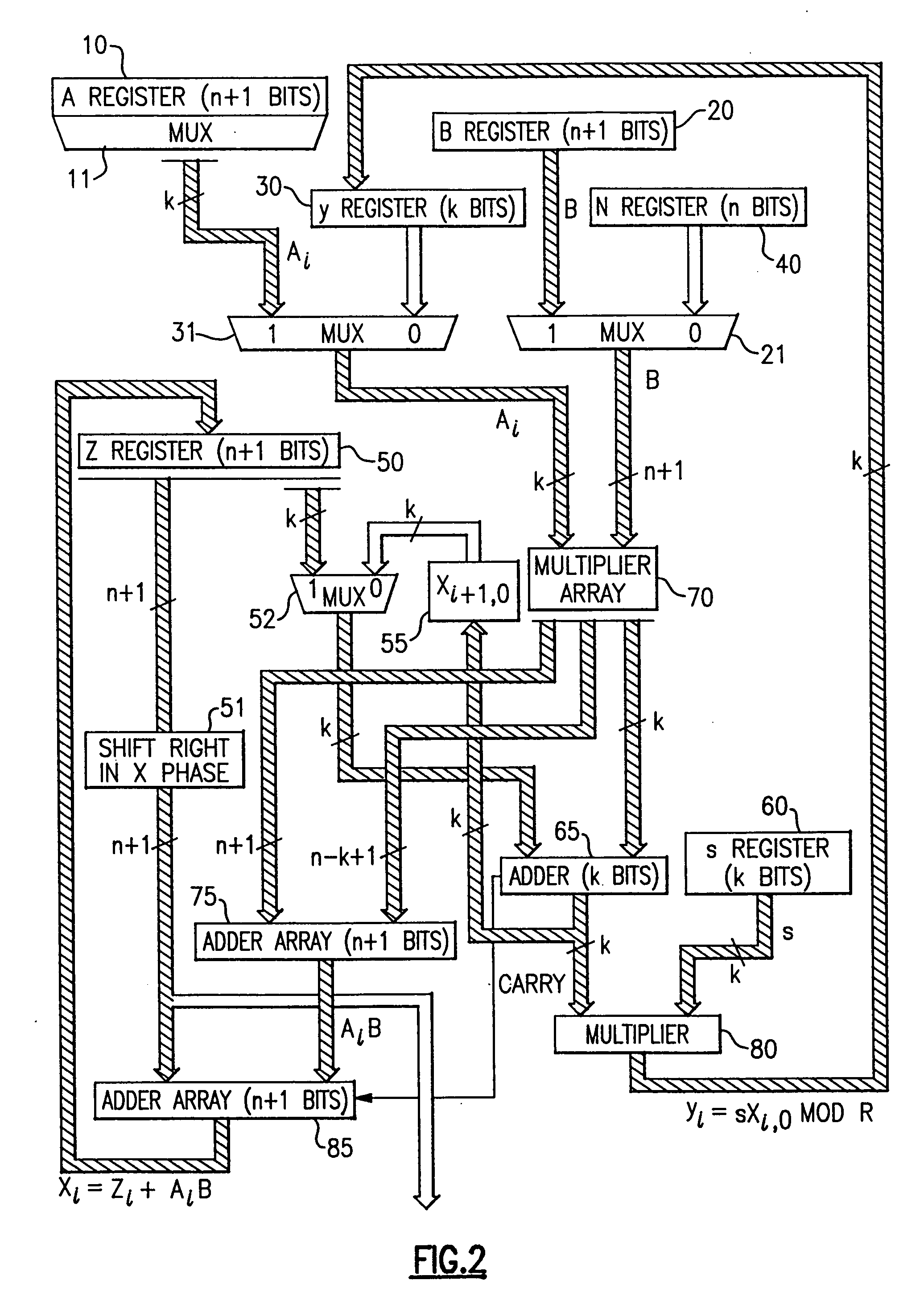
The modular exponentiation function used in public key encryption and decryption systems is implemented in a standalone engine having at its core modular multiplication circuits which operate in two phases which share overlapping hardware structures. The partitioning of large arrays in the hardware structure, for multiplication and addition, into smaller structures results in a multiplier design comprising a series of nearly identical processing elements linked together in a chained fashion. As a result of the two-phase operation and the chaining together of partitioned processing elements, the overall structure is operable in a pipelined fashion to improve throughput and speed. The chained processing elements are constructed so as to provide a partitionable chain with separate parts for processing factors of the modulus. In this mode, the system is particularly useful for exploiting characteristics of the Chinese Remainder Theorem to perform rapid exponentiation operations. A checksum mechanism is also provided to insure accurate operation without impacting speed and without significantly increasing complexity. While the present disclosure is directed to a complex system which includes a number of features, the present application is particularly directed to the incorporation and integration of circuits used for calculating a modular multiplicative inverse used as an input parameter to the process.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY INC
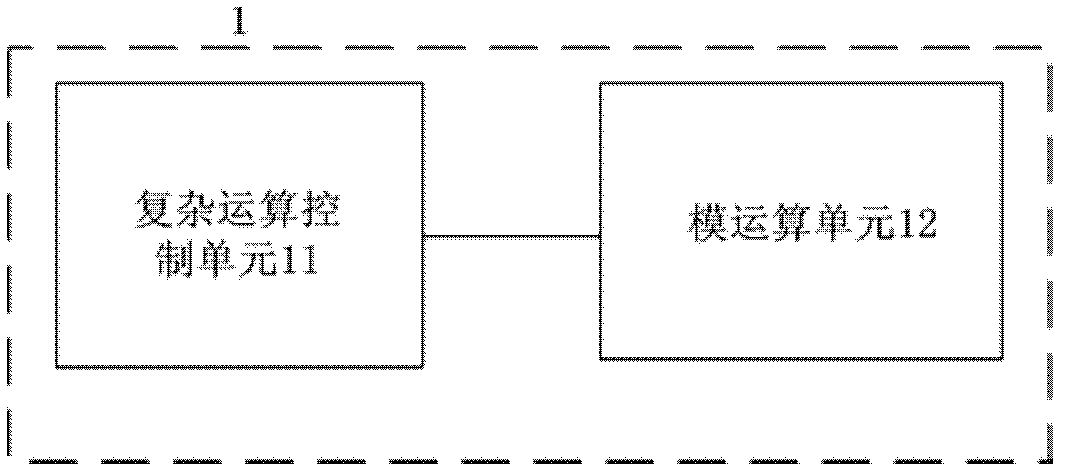
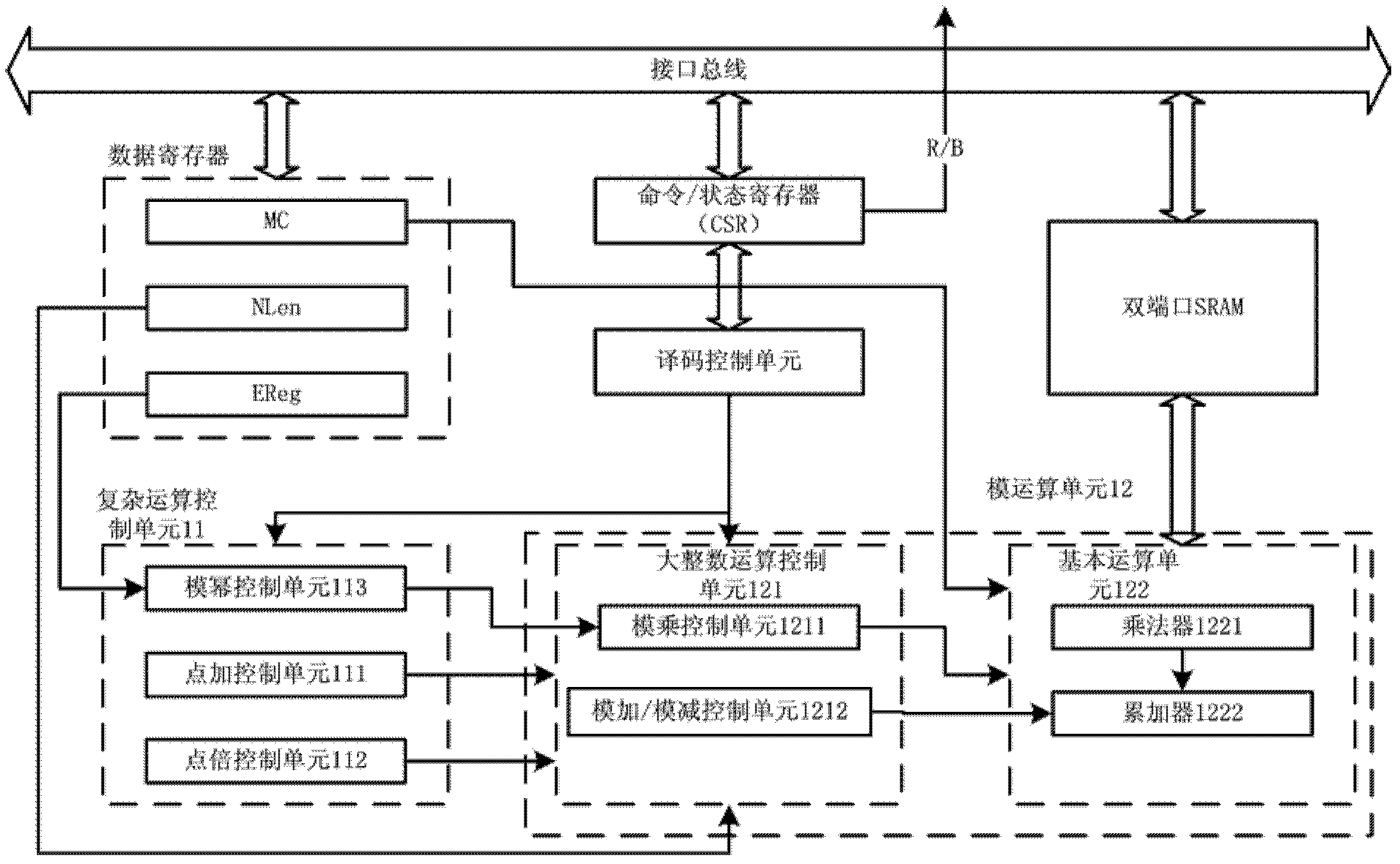
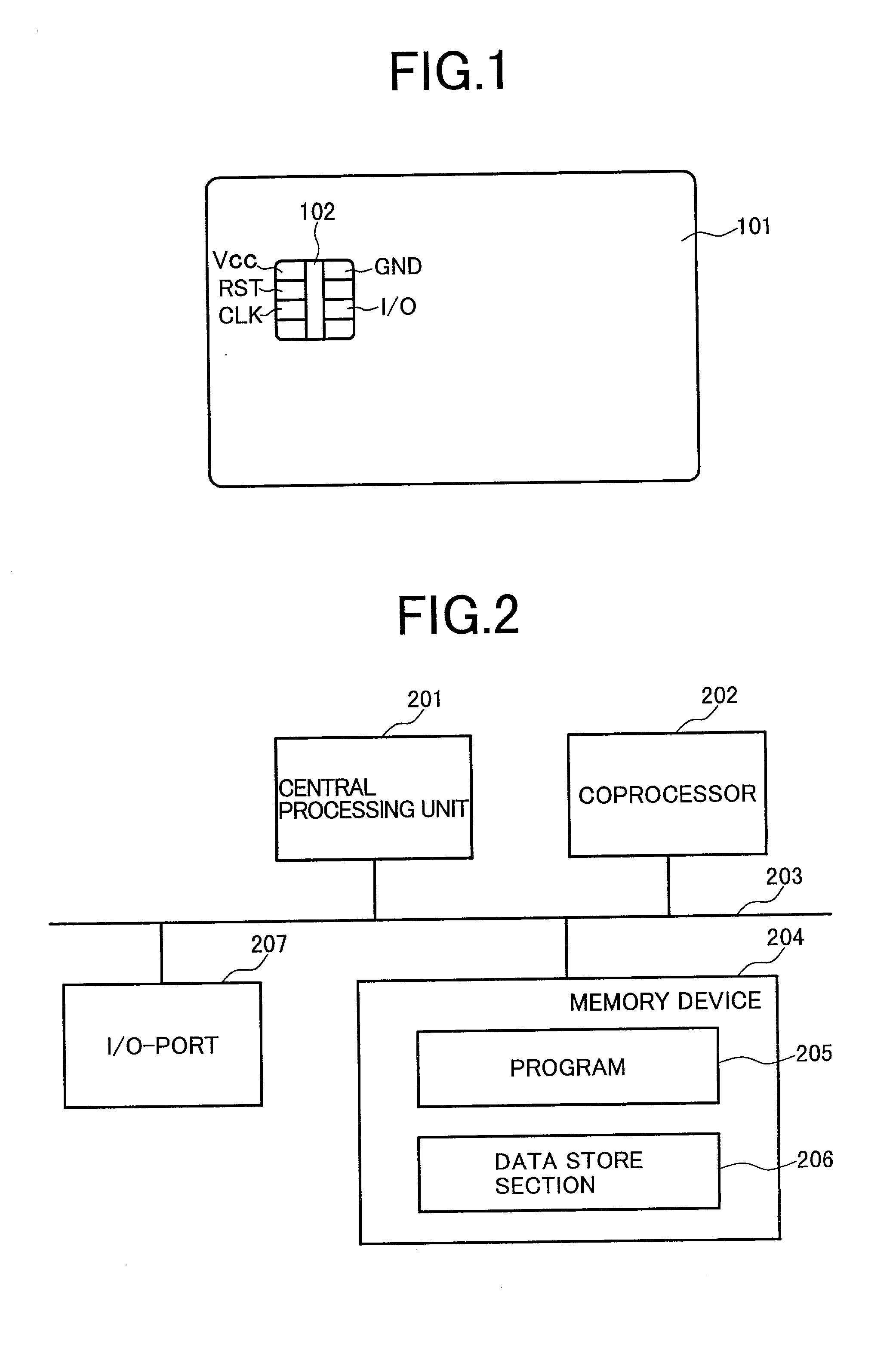
ecc coprocessor
The invention provides an ECC coprocessor, which includes a command / status register, a decoding control unit, a data register, a dual-port SRAM, a dot addition control unit, a dot multiplication control unit, a modular power control unit, a modular multiplication control unit, Modular addition / modulus subtraction control unit, basic arithmetic unit. The ECC coprocessor of the present invention realizes and provides externally the functions of large integer modular multiplication, modular addition / modulus subtraction, modular exponentiation and elliptic curve point addition / point multiplication, and the coordinates of elliptic curve points in the external interface of point addition and point multiplication operations The use of Jacobian coordinates can support external controllers to flexibly implement multiple point multiplication operations.
Owner:BEIJING HUADA INFOSEC TECH
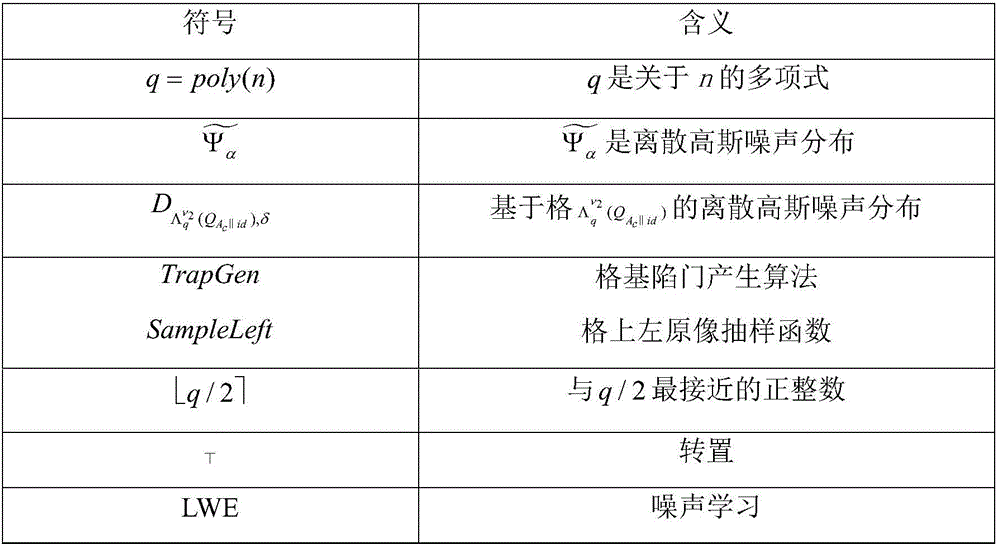
PEKS (public-key encryption with keyword search) method for lattice-based cloud stored cyphertext data under standard model
ActiveCN106789044AReaction securityResist attackKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTechnical standardModular exponentiation
The invention belongs to the technical field of cyberspace security and particularly relates to a PEKS (public-key encryption with keyword search) method for lattice-based cloud stored cyphertext data under standard model. The method of the invention has no need for a random oracle so that the security of the designed PEKS method can more truly reflected; a designed cryptographic algorithm is based on assumption of LWE (learning with errors) hard problems, quantum computer attacks can be resisted effectively. The method of the invention has a need for specifying a unique cloud server to perform testing and return corresponding search results, so that no malicious servers are able to execute search test operation, and malicious server attacks are partly avoided accordingly. In addition, the algorithm can ensure that cyphertext is undistinguishable. Furthermore, in keyword cyphertext generation phase, the method of the invention needs no computing of high-overhead modular exponentiation and bilinear pairing operation, but the computing of finite linear algebraic operation, and accordingly is highly worthy of practical application in post-quantum communication environments.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
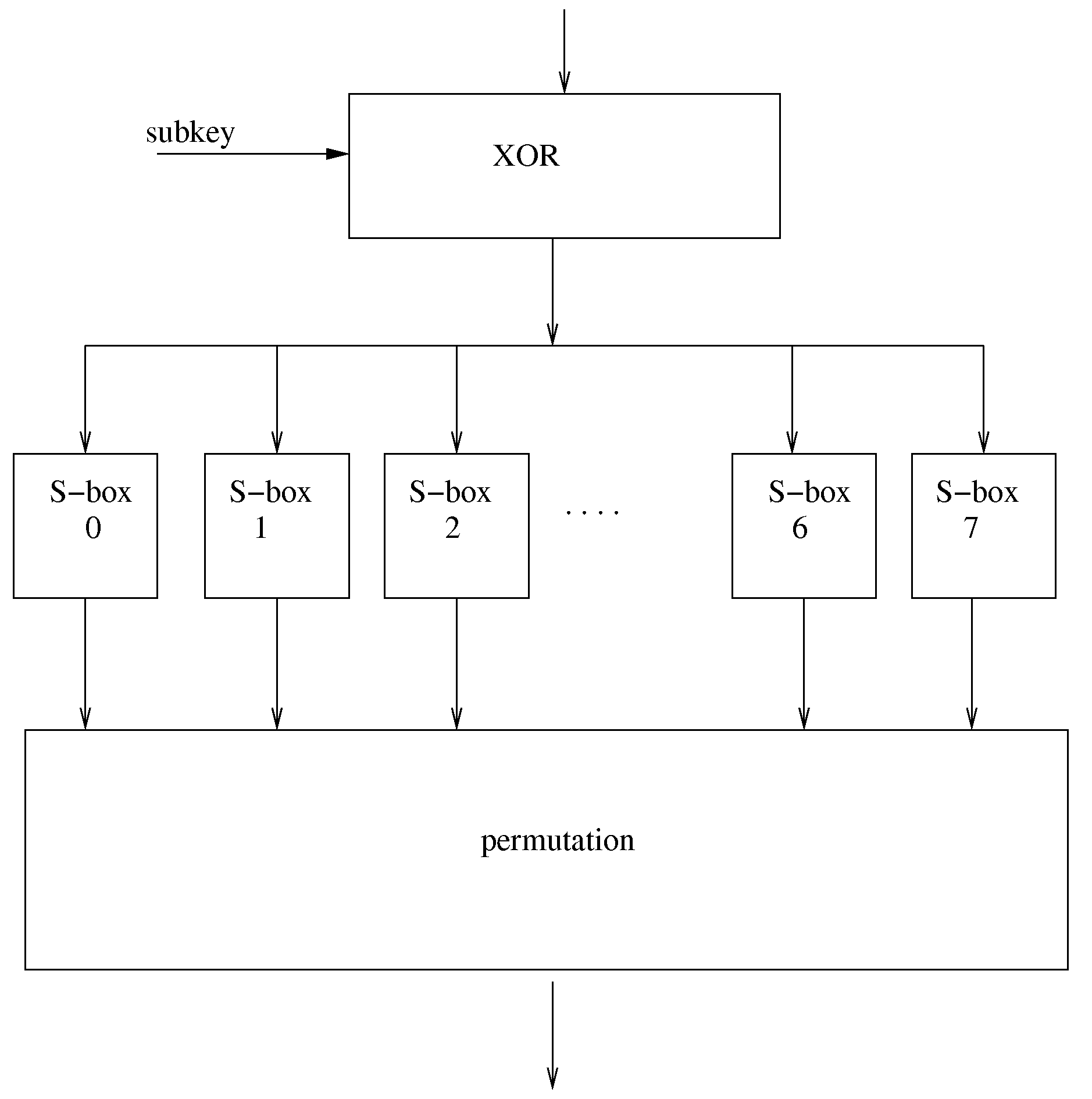
Iterative symmetric key ciphers with keyed s-boxes using modular exponentiation
InactiveUS20080232597A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareS-box
Disclosed is the design and development of a new cipher called the Dragonfire Cipher. The Dragon cipher includes message authentication code and keyed random number generator. Dragonfire cipher takes this transparent method of generating S-boxes and uses them to create a cipher with keyed S-boxes. This defeats most precomputations for cryptanalysis as the S-boxes are now different between sessions.
Owner:DE MARE MICHAEL
Tamper-resistant processing method
InactiveUS7254718B2Decrease relationDifficult to estimatePublic key for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionInformation processingCountermeasure
Owner:HITACHI LTD
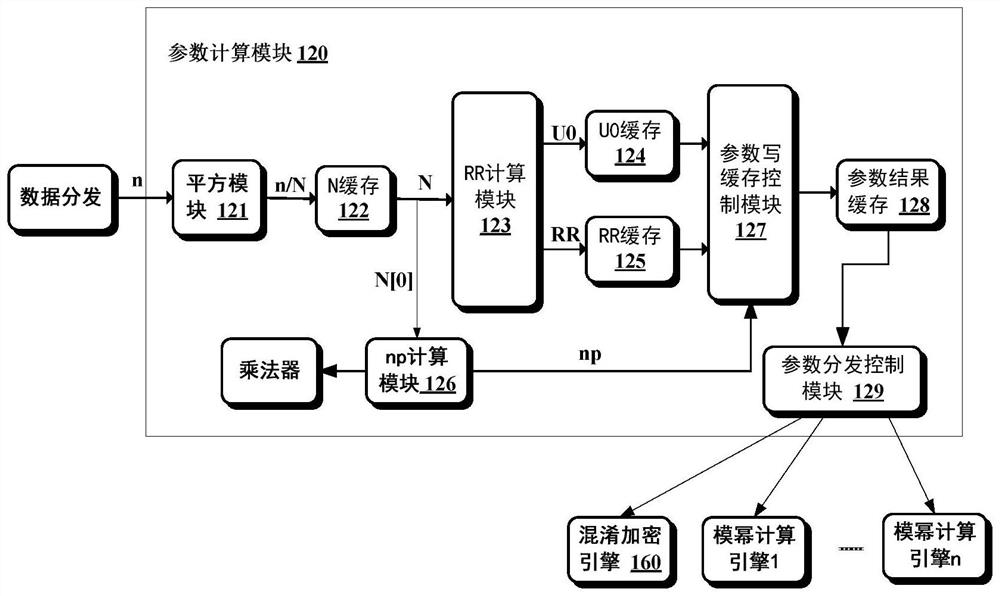
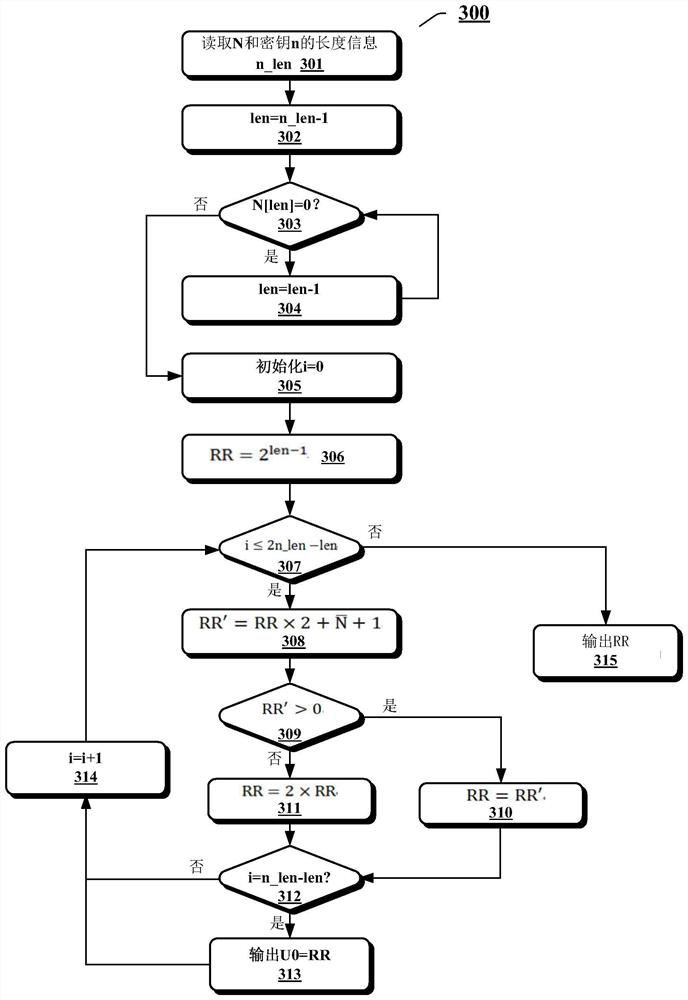
Method for realizing Paillier encryption based on FPGA chip and used for federated learning
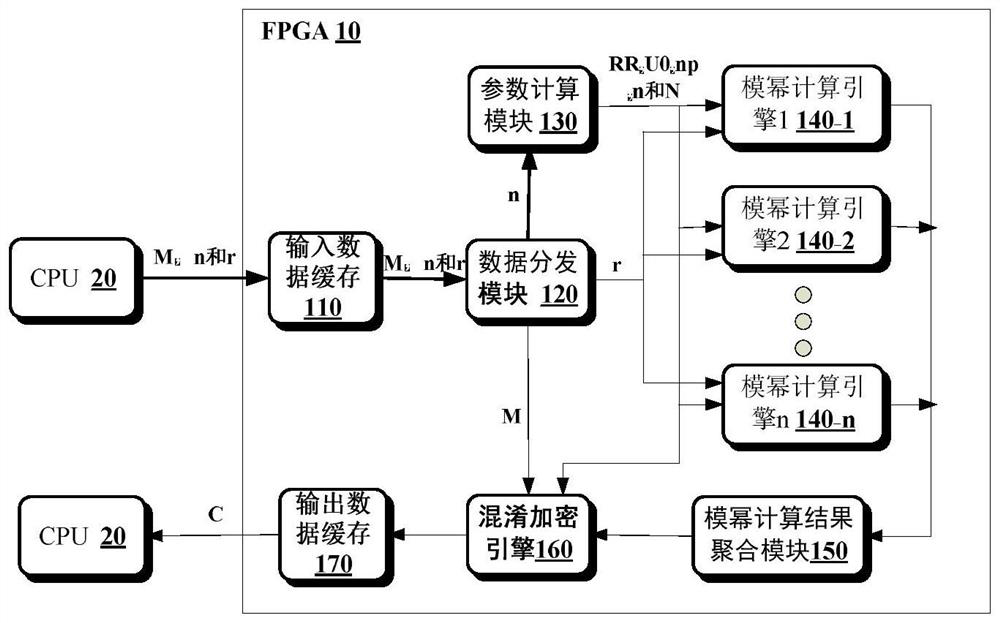
ActiveCN111832050ADigital data protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionData setConcurrent computation
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for realizing Paillier encryption based on an FPGA chip. In the method, a data distribution module respectively distributes a plaintext data set M, akey n and a random number set r to a confusion encryption engine, a parameter calculation module and a plurality of modular exponentiation calculation engines. And the parameter calculation module determines parameters N, RR, U0 and np required by Paillier encryption according to the key n, and distributes the key n and the parameters N, RR, U0 and np to a plurality of modular exponentiation calculation engines and confusion encryption engines. And the modular exponentiation calculation engines perform parallel modular exponentiation calculation by using the random number set r, the key n andthe parameters N, RR, U0 and np. And the obtained modular exponentiation calculation result is provided to a confusion encryption engine after aggregation processing. And the confusion encryption engine performs confusion encryption by using the aggregation processing result, the key n, the parameters N, RR, U0 and np and the plaintext data set to obtain a ciphertext data set. By utilizing the method, the calculation efficiency of the Paillier encryption algorithm can be improved by utilizing the high parallel calculation characteristic of the FPGA.
Owner:CLUSTAR TECH LO LTD
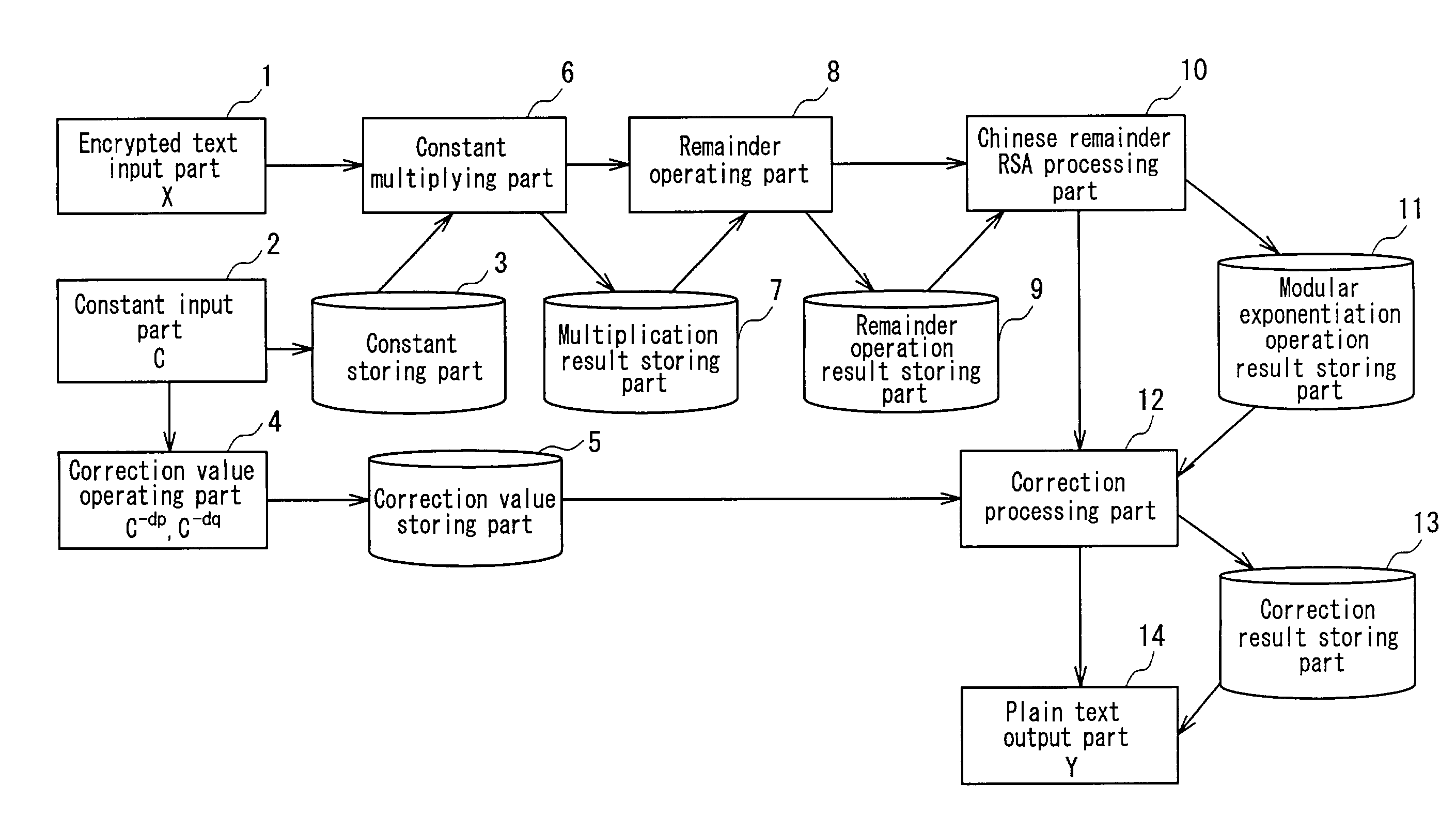
Encryption operating apparatus and method having side-channel attack resistance
ActiveUS7065788B2Increase speedSafe to attackMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareChinese remainder theorem
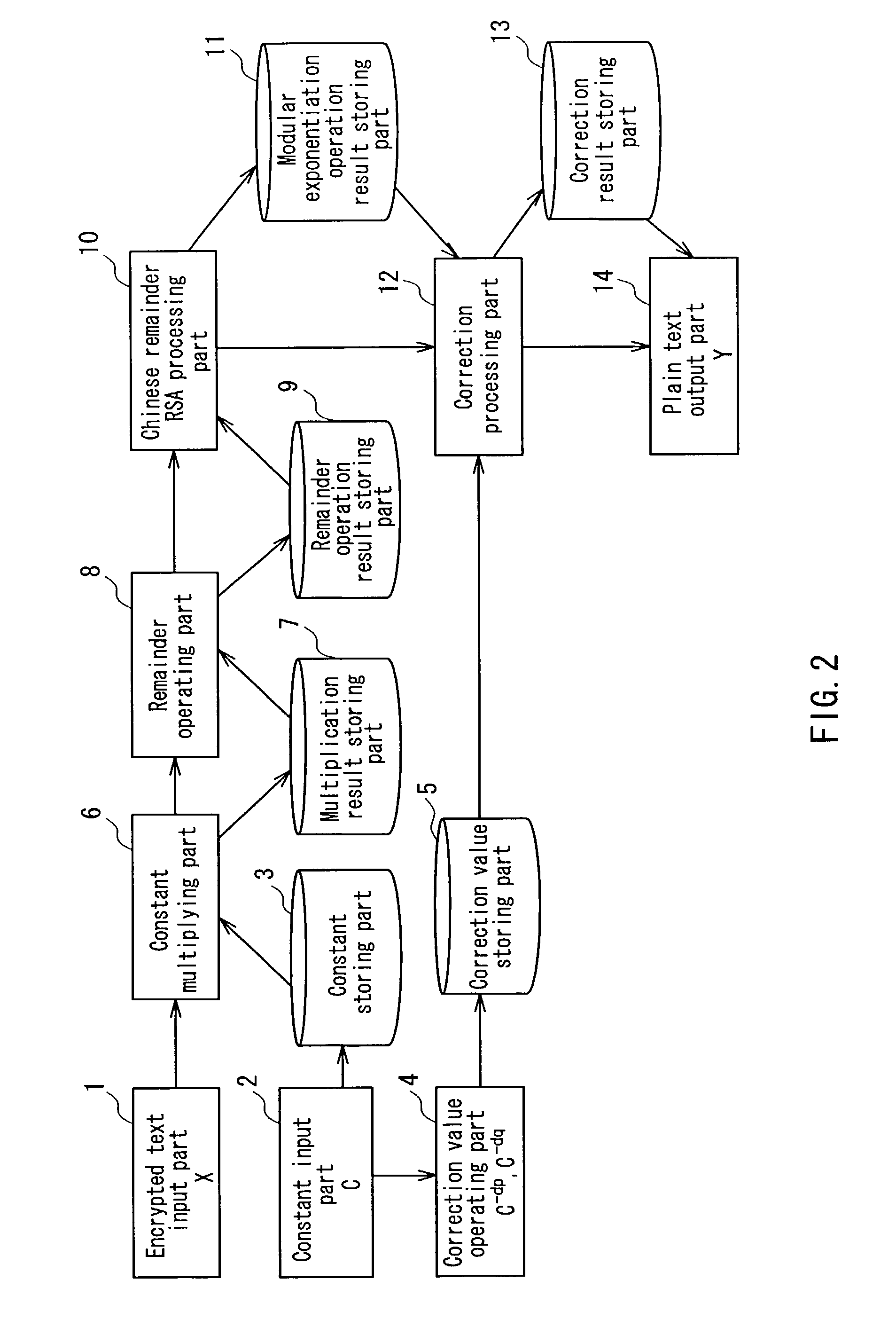
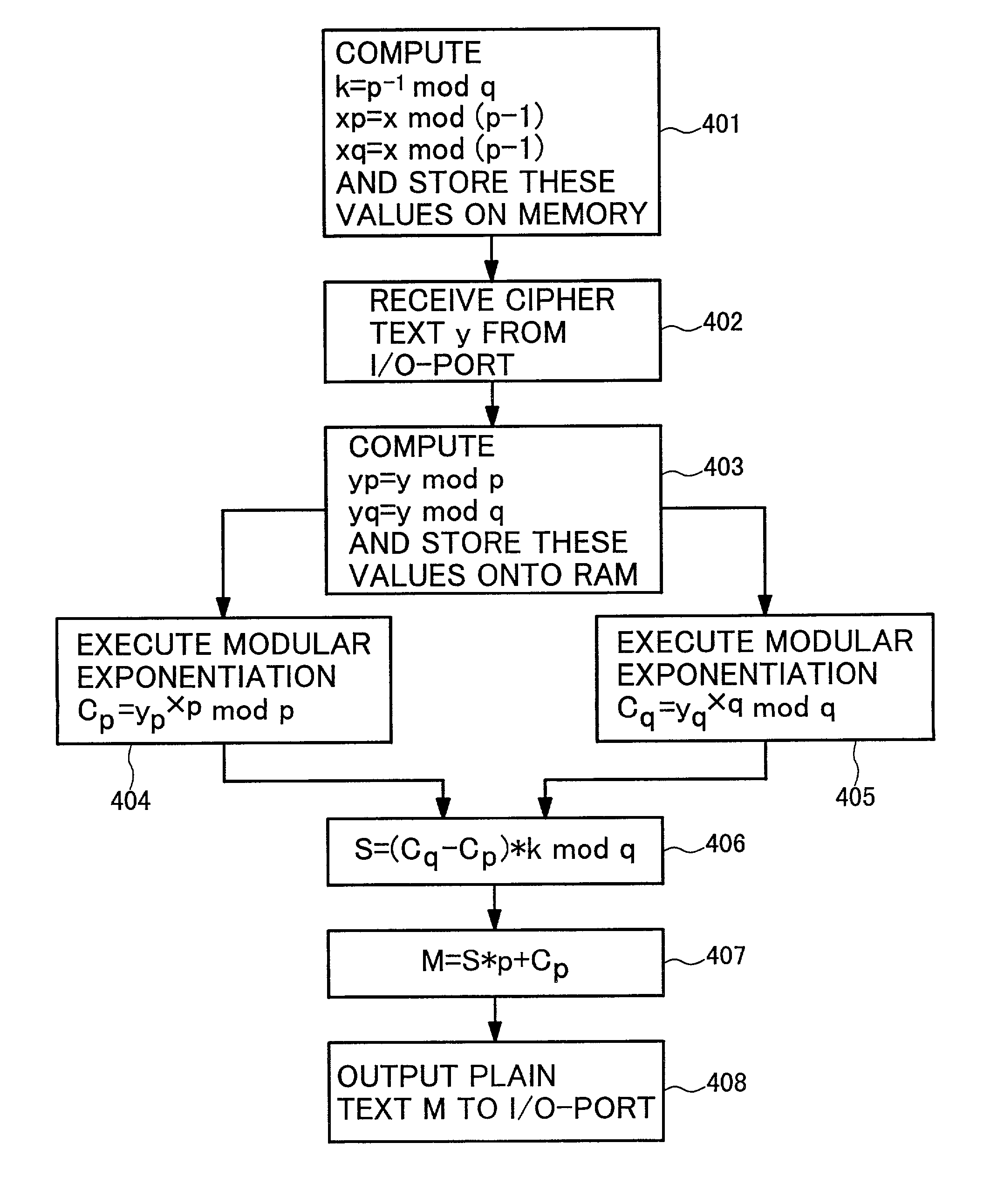
Ciphertext X and a constant C having relationships C>p and C>q with respect to secret keys p and q are input, and correction values C−dp and C−dq (dp=d mod (p−1), dq=d mod (q−1)) are obtained. Then, the ciphertext X is multiplied by the constant C. A remainder operation using the secret key p or q as a remainder value is conducted with respect to the multiplication result. A modular exponentiation operation based on a Chinese remainder theorem is conducted with respect to the remainder operation result, and a correction operation using a correction value C−dp or C−dq is conducted. Thereafter, plaintext Y before being encrypted is calculated.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for checking modular multiplication
InactiveUS6914983B2Improve performanceSmall sizeError detection/correctionSecret communicationHardware structureChinese remainder theorem
The modular exponentiation function used in public key encryption and decryption systems is implemented in a standalone engine having at its core modular multiplication circuits which operate in two phases which share overlapping hardware structures. The partitioning of large arrays in the hardware structure, for multiplication and addition, into smaller structures results in a multiplier design comprising a series of nearly identical processing elements linked together in a chained fashion. As a result of the two-phase operation and the chaining together of partitioned processing elements, the overall structure is operable in a pipelined fashion to improve throughput and speed. The chained processing elements are constructed so as to provide a partitionable chain with separate parts for processing factors of the modulus. In this mode, the system is particularly useful for exploiting characteristics of the Chinese Remainder Theorem to perform rapid exponentiation operations. A checksum mechanism is also provided to insure accurate operation without impacting speed and without significantly increasing complexity. While the present disclosure is directed to a complex system which includes a number of features, the present application is particularly directed a system and method for performing modular checksum operations.
Owner:IBM CORP
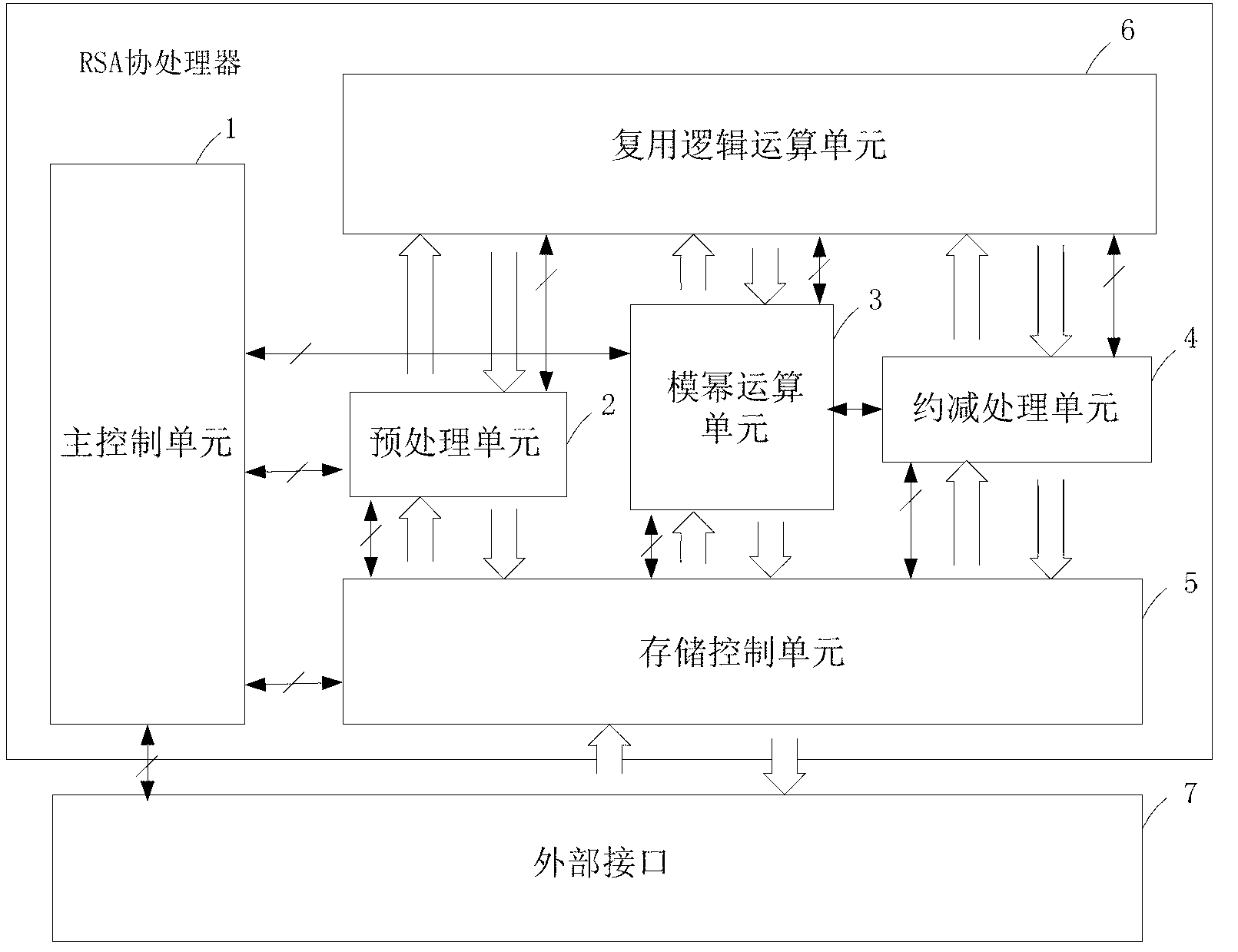
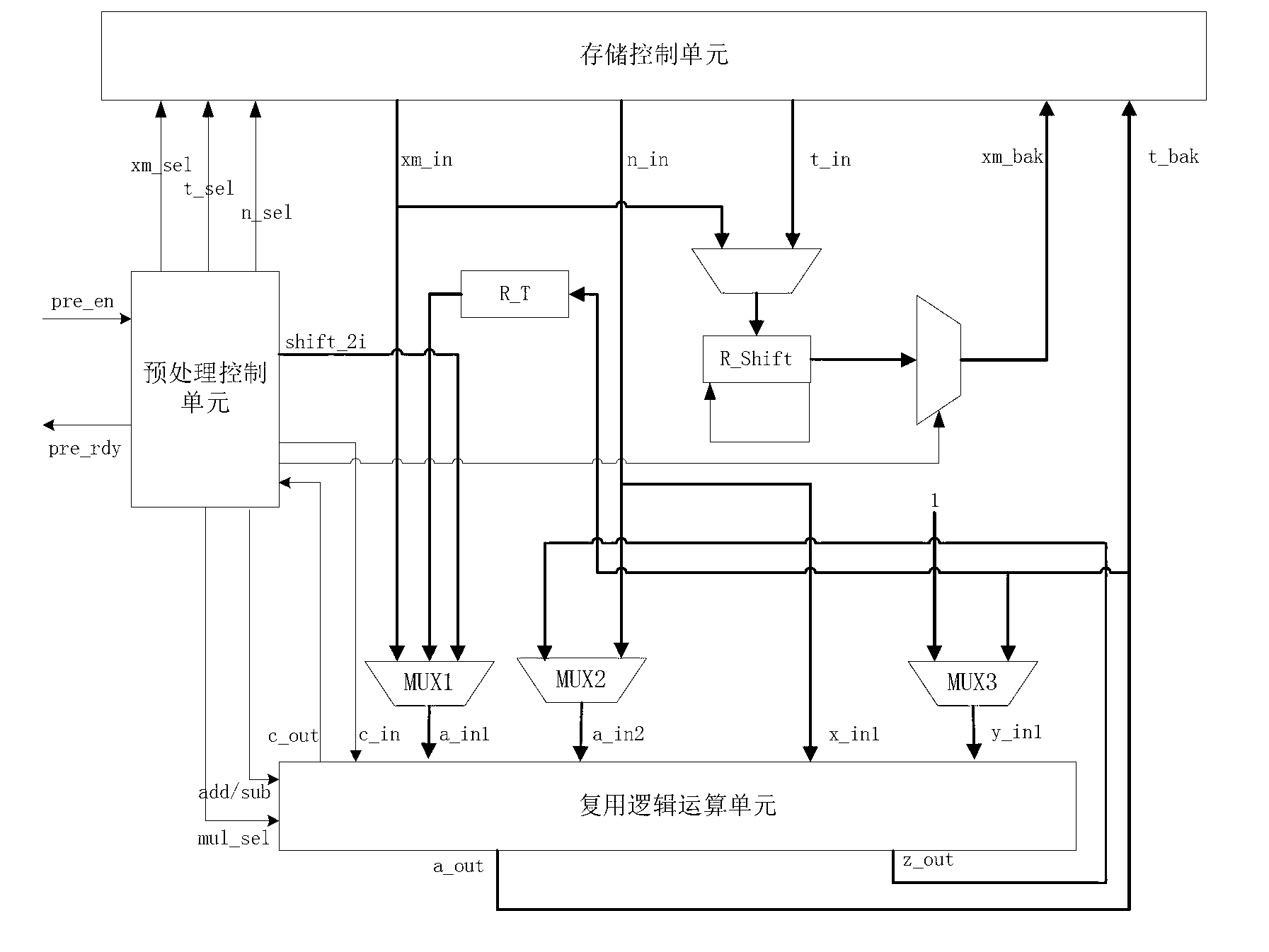
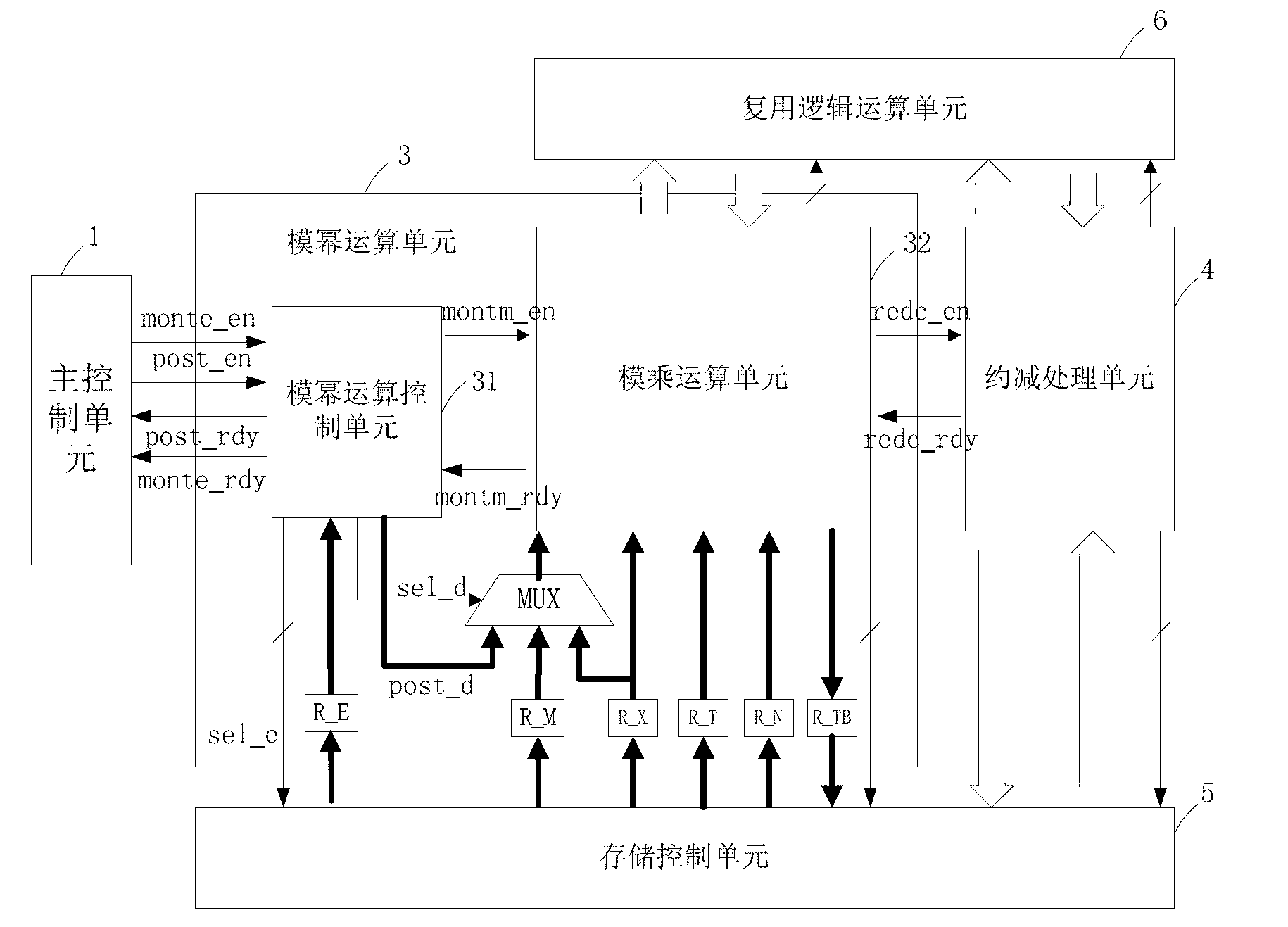
RSA coprocessor for RFID (radio frequency identification device) intelligent card chip
ActiveCN102707924AImprove data processing efficiencyStrong scalabilityComputation using non-denominational number representationRecord carriers used with machinesCoprocessorControl line
The invention discloses an RSA coprocessor for an RFID (radio frequency identification device) intelligent card chip. The RSA coprocessor comprises a main control unit for controlling the whole RSA encryption and decryption process, wherein the main control unit is connected with a storing control unit, a preprocessing unit and a modular exponentiation unit respectively through control lines; the modular exponentiation unit is connected with a subtracting processing unit through the control line; the preprocessing unit, the modular exponentiation unit and the subtracting processing unit are connected with a multiplexing logical operation unit; a storing control unit is connected with the preprocessing unit, the modular exponentiation unit and the subtracting processing unit, and connected to an intelligent card CPU (Central Processing Unit) through an external interface. The RSA coprocessor disclosed by the invention greatly improves the data processing efficiency, releases the data processing pressure of the intelligent card CPU, and meets the requirements on the efficiency and the stability of the encryption and decryption algorithm of the intelligent card chip RSA.
Owner:广州南菱汽车股份有限公司
Iterative symmetric key ciphers with keyed S-boxes using modular exponentiation
InactiveUS8130946B2Key distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareS-box
Disclosed is the design and development of a new cipher called the Dragonfire Cipher. The Dragon cipher includes message authentication code and keyed random number generator. Dragonfire cipher takes this transparent method of generating S-boxes and uses them to create a cipher with keyed S-boxes. This defeats most precomputations for cryptanalysis as the S-boxes are now different between sessions.
Owner:DE MARE MICHAEL
Temper-resistant processing method
InactiveUS20020166057A1Cancel noiseEfficient processPublic key for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionInformation processingCountermeasure
The subject of the disclosed technology is, when a crypto-processing is performed utilizing an information processing device buried in an IC card, etc., to decrease the relationship between the waveform of the consumption current and the contents of the crypto-processing as a countermeasure against a tamper which observes the waveform of a consumption current. A solution means is shown in the following. When a decryption processing of an RSA cryptogram is performed according to CRT, in step 608, for every unit bit block of XP a modular exponentiation calculation is performed, and the partial result of CP up to the calculated bit block is stored in a memory. In step 609, for every unit bit block of XQ a modular exponentiation calculation is performed and the partial result of CQ up to the calculated bit block is stored in a memory. In step 606, a random number is generated, and in step 607, it is decided that step 608 is to be executed or step 609 is to be executed corresponding to the value of the random number.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
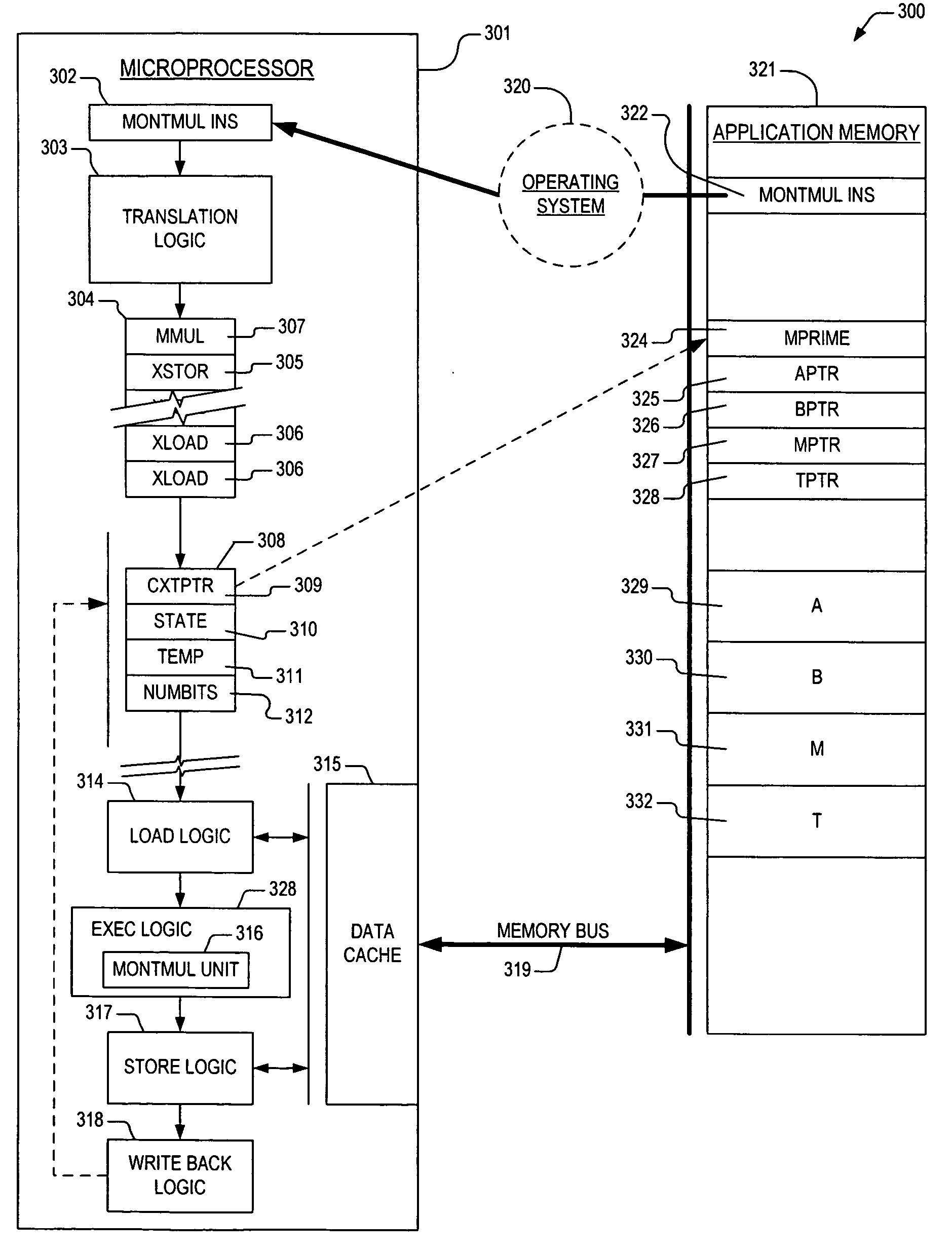
Microprocessor apparatus and method for modular exponentiation
ActiveUS20050256920A1Runtime instruction translationMemory systemsModular exponentiationOperating system
A technique is provided for performing modular multiplication. In one embodiment, an apparatus in a microprocessor is provided for accomplishing modular multiplication operations. The apparatus includes translation logic and execution logic. The translation logic receives a Montgomery multiplication instruction from a source therefrom, where the Montgomery multiplication instruction prescribes generation of a Montgomery product. The translation logic translates the Montgomery multiplication instruction into a sequence of micro instructions specifying sub-operations required to accomplish generation of the Montgomery product. The execution logic is operatively coupled to the translation logic. The execution logic receives the sequence of micro instructions, and performs the sub-operations to generate the Montgomery product.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Circuits and methods for modular exponentiation
InactiveUS20050188209A1Improve performanceSmall sizeComputer security arrangementsSecret communicationHardware structureChinese remainder theorem
The modular exponentiation function used in public key encryption and decryption systems is implemented in a standalone engine having at its core modular multiplication circuits which operate in two phases which share overlapping hardware structures. The partitioning of large arrays in the hardware structure, for multiplication and addition, into smaller structures results in a multiplier design comprising a series of nearly identical processing elements linked together in a chained fashion. As a result of the two-phase operation and the chaining together of partitioned processing elements, the overall structure is operable in a pipelined fashion to improve throughput and speed. The chained processing elements are constructed so as to provide a partitionable chain with separate parts for processing factors of the modulus. In this mode, the system is particularly useful for exploiting characteristics of the Chinese Remainder Theorem to perform rapid exponentiation operations. A checksum mechanism is also provided to insure accurate operation without impacting speed and without significantly increasing complexity. While the present disclosure is directed to a complex system which includes a number of features, the present application is particularly directed to circuits and methods for carrying out modular exponentiation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Protecting modular exponentiation in cryptographic operations
InactiveUS20130279692A1Addressing slow performanceKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsModular exponentiationConcatenation
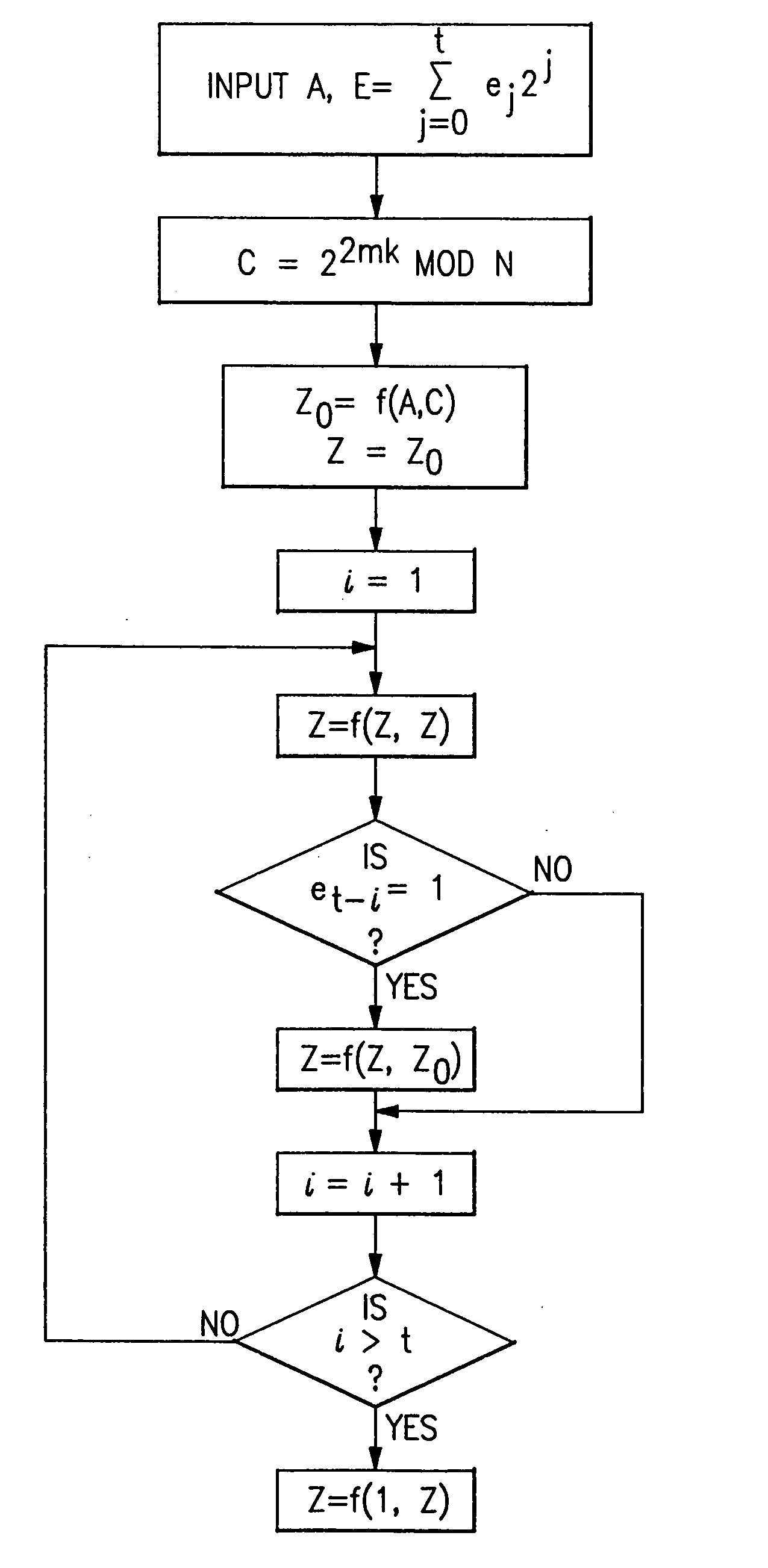
The present invention proposes a method for executing a blinded modular exponentiation, based on a window method with a window size of k bits so using 2k pre-calculated variables (Yi=Xi mod N for i=0 to 2k−1), on input data X of n bits to obtain output data S of n bits, S=Xd mod N, where d is the exponent of size m bits and N is the modulus of n bits, comprising the steps of: •blinding the pre-calculated variables by a blinding value Bi being a pseudo-random variable of the size of the modulus (n bits) and lower than the modulus (Yj=Yi×B1 mod N for i=0 to 2k−1) •executing the modular exponentiation with the blinded pre-calculated variables, to obtain an intermediate result (A), •unblinding the intermediate result by a unblinding value C1=(B1g)−1 mod N where g equals the concatenation of m / k times the value “1” coded on k bits, to obtain the output data S.
Owner:NAGRAVISION SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com