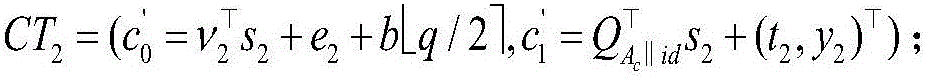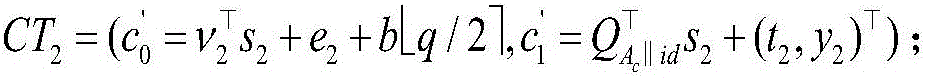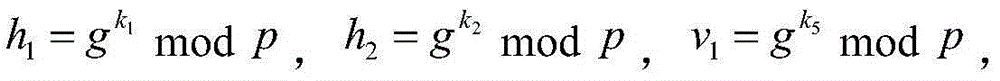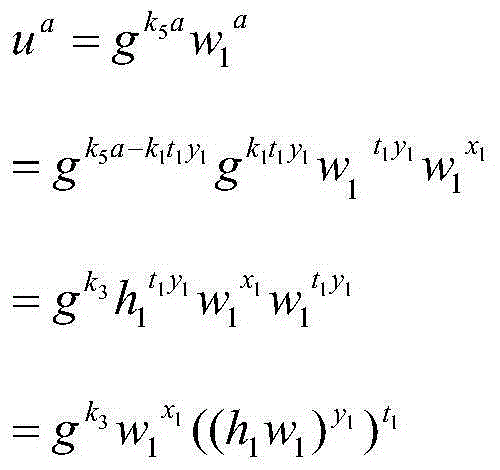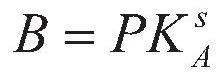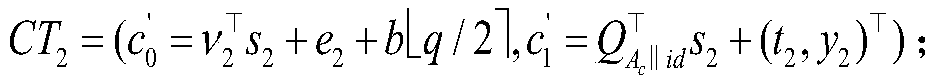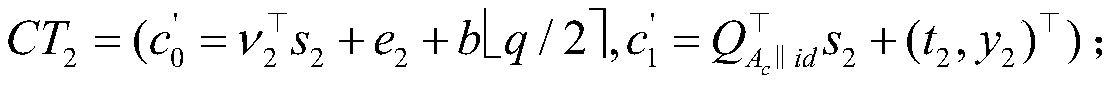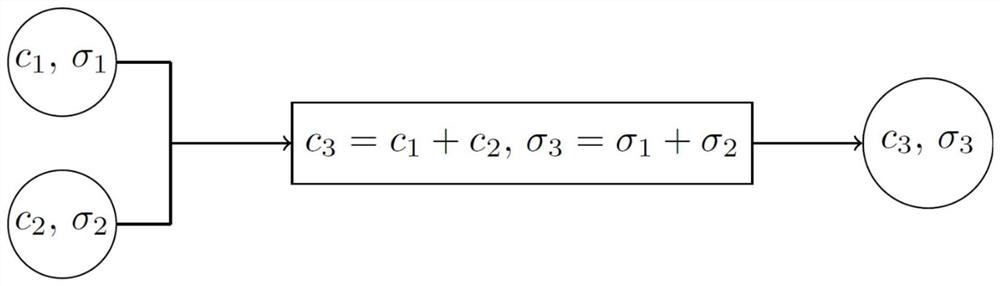Patents
Literature
40 results about "Random oracle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cryptography, a random oracle is an oracle (a theoretical black box) that responds to every unique query with a (truly) random response chosen uniformly from its output domain. If a query is repeated it responds the same way every time that query is submitted.
Cognitive training using formant frequency sweeps
InactiveUS20070134635A1Increase awarenessImprove abilitiesElectrical appliancesTeaching apparatusRandom oracleRandom order
A method on a computing device for enhancing the memory and cognitive ability of a participant by requiring the participant to differentiate between rapidly presented aural stimuli. The method trains the time order judgment of the participant by iteratively presenting sequences of upward and downward formant frequency sweeps, in random order, separated by an inter-stimulus interval (ISI). The upward and downward formant frequency sweeps utilize frequencies common in formants, i.e., the characteristic frequency components common in human speech. Icons are associated with the upward and downward formant frequency sweeps to allow the participant to indicate an order in which the sweeps are presented (i.e., UP-UP, UP-DOWN, DOWN-UP, and DOWN-DOWN). Correct / incorrect selection of an order causes the ISI and / or the duration of the frequency sweeps to be adaptively shortened / lengthened. A maximum likelihood procedure may be used to dynamically modify the stimulus presentation, and / or, to assess the participant's performance in the exercise.
Owner:POSIT SCI CORP
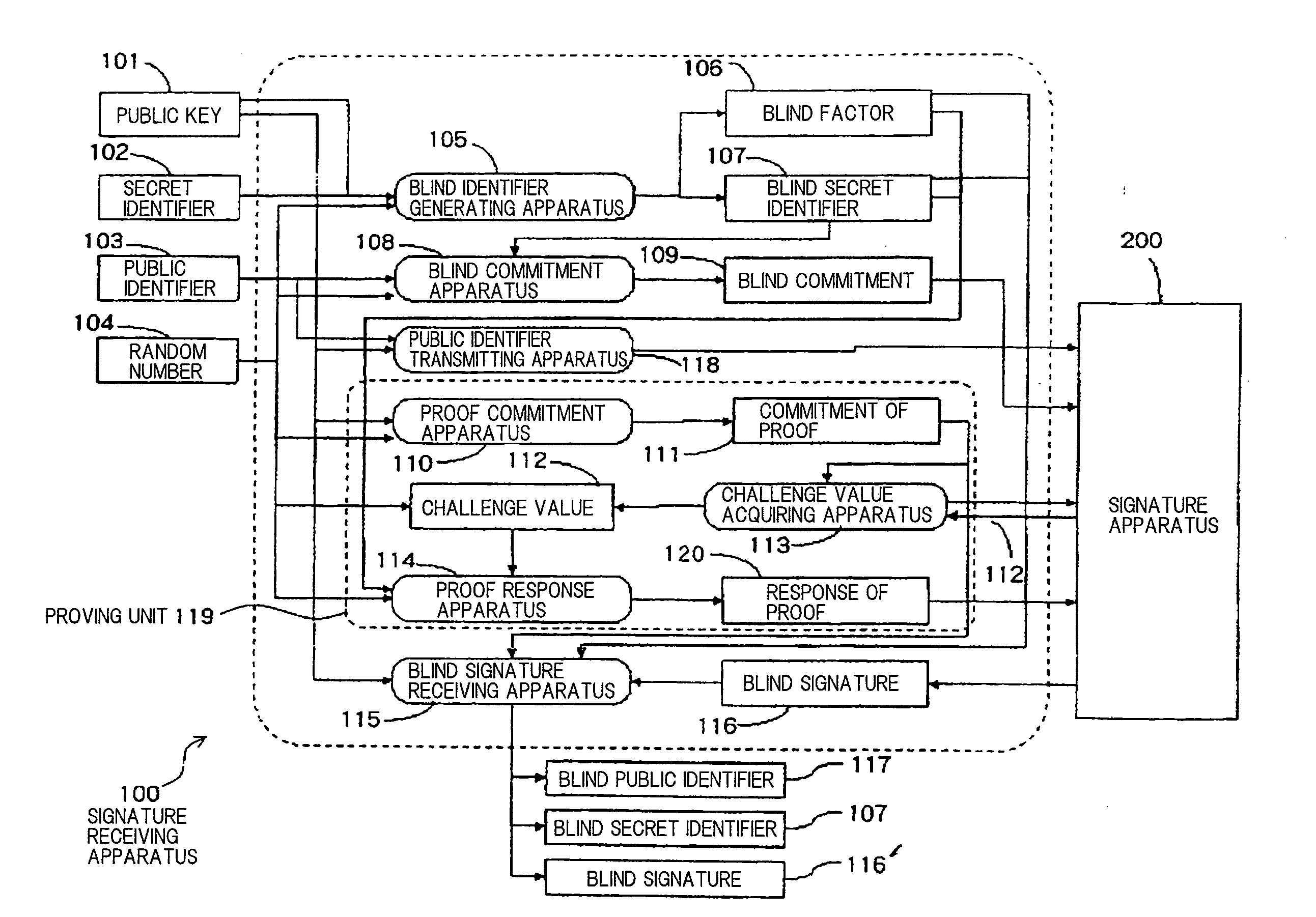
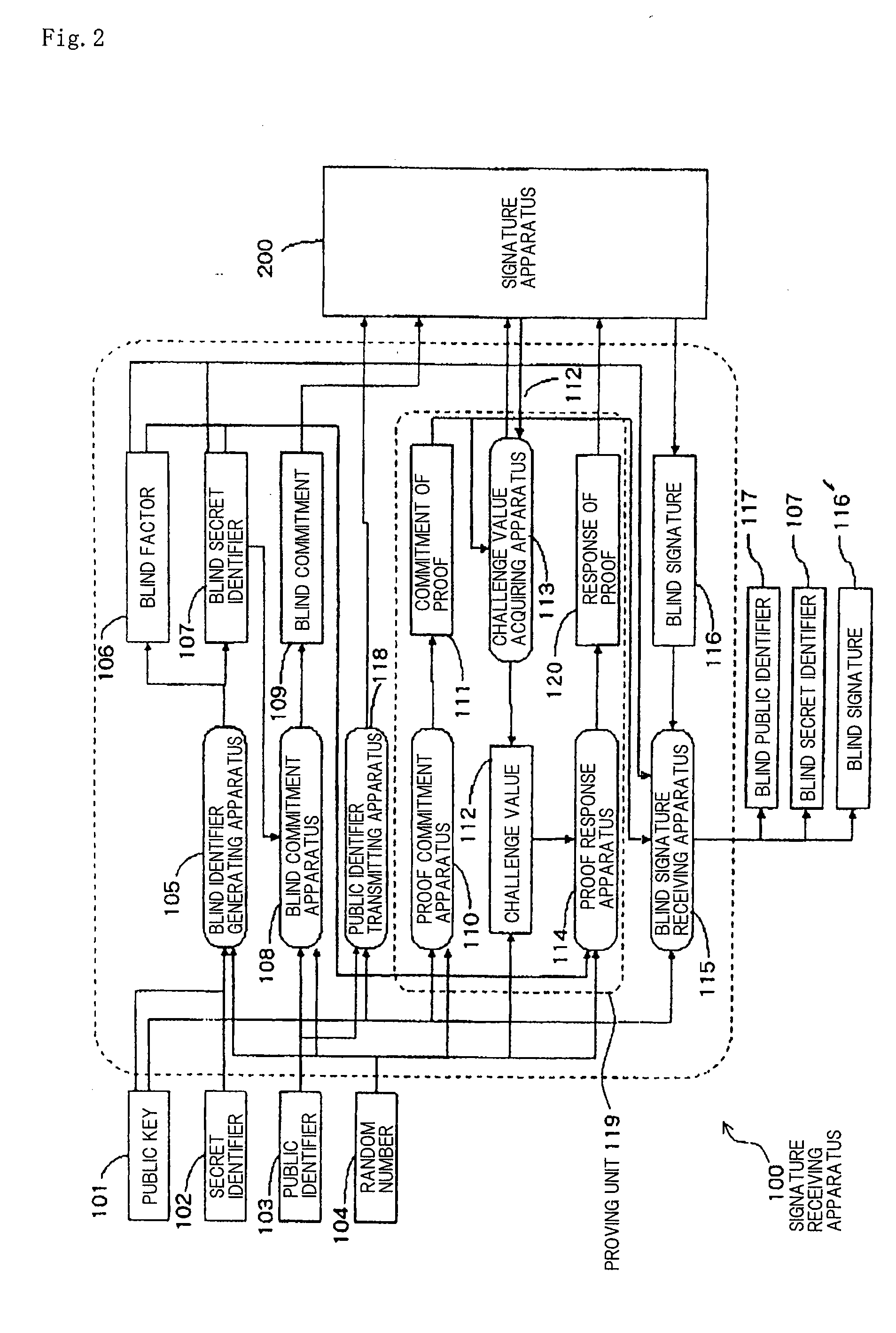
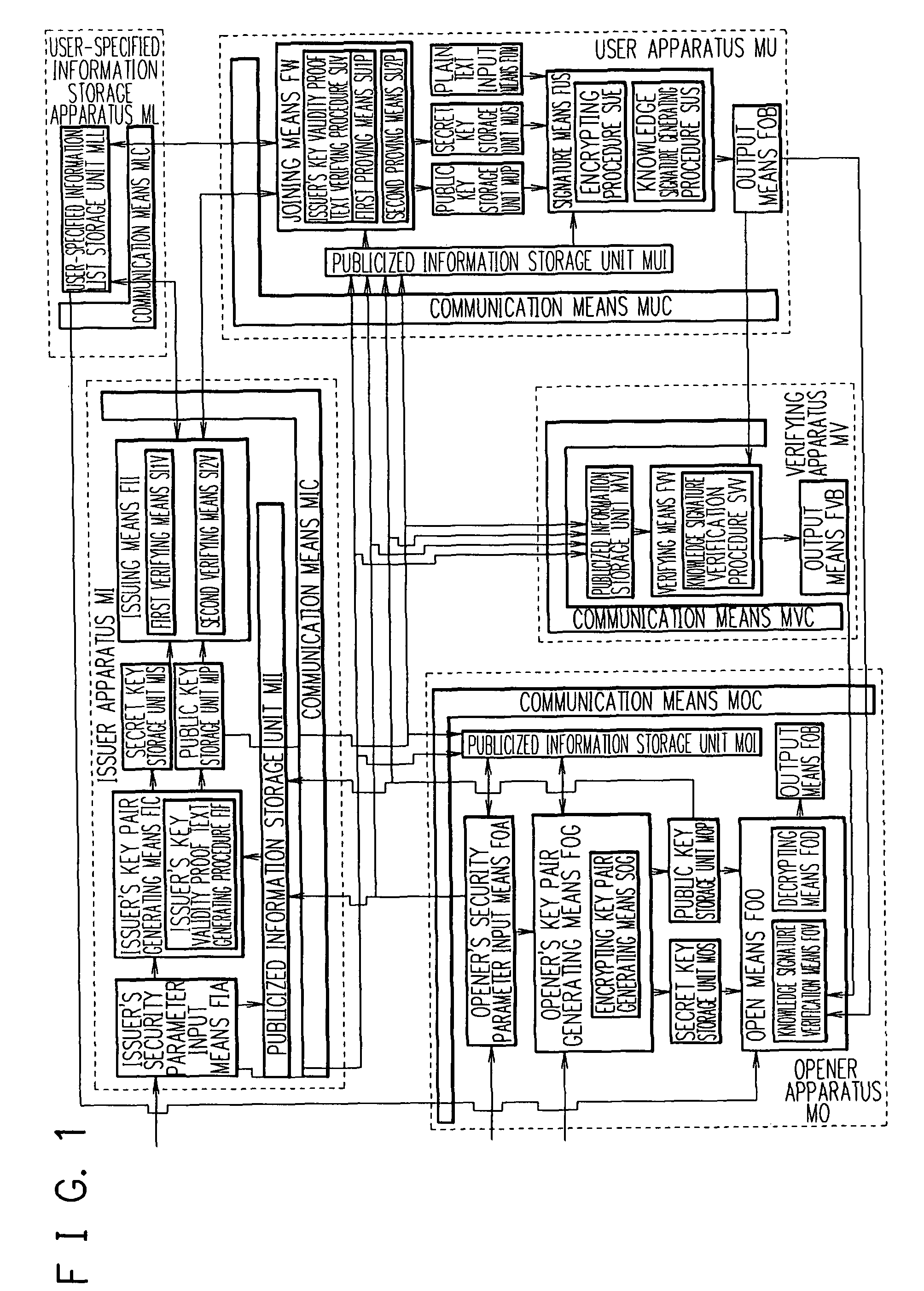
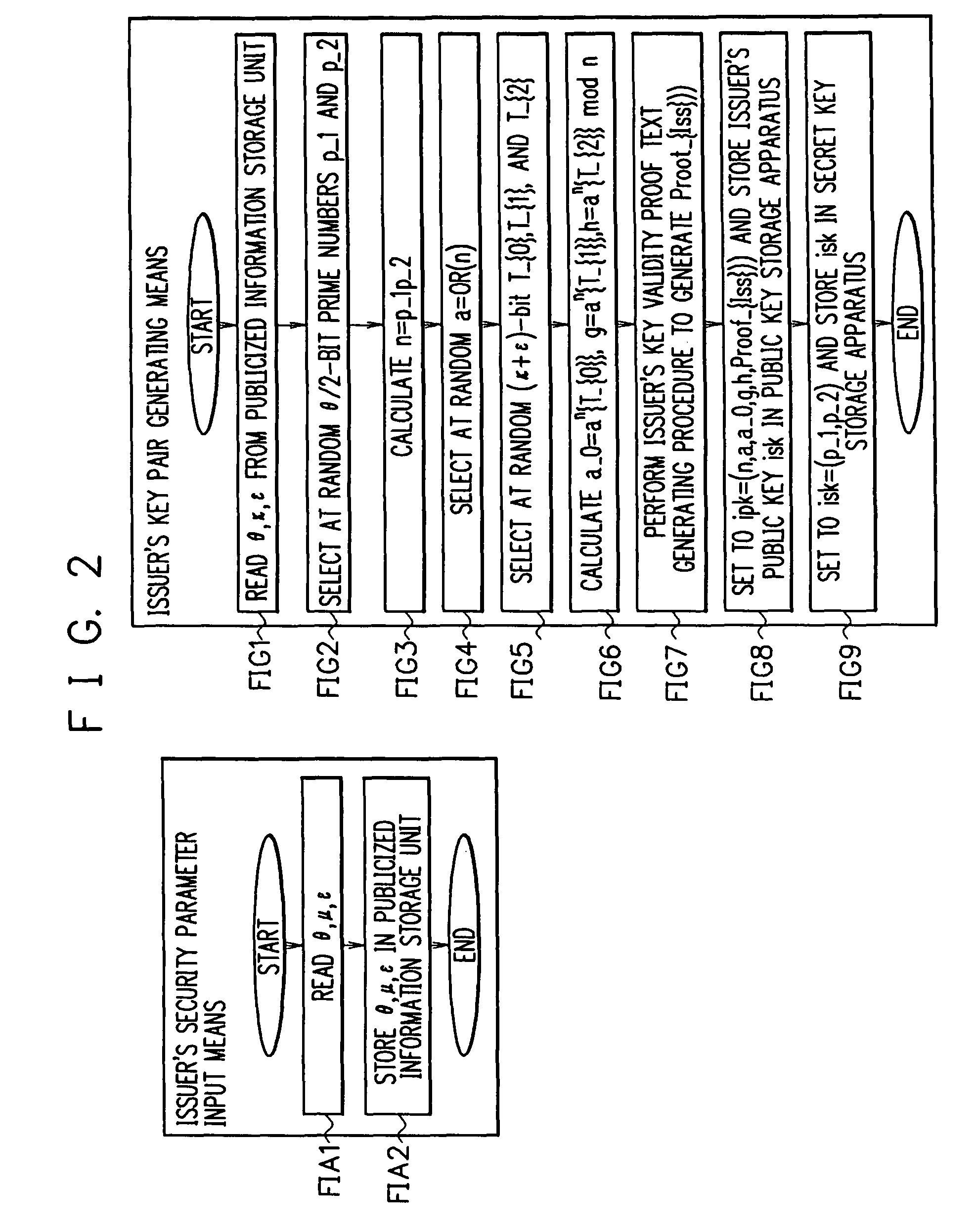
Limited Blind Signature System
InactiveUS20080141035A1Reduce the possibilityUser identity/authority verificationRandom oracleBlind signature
The present invention is aimed at the proposal of a limited blind signature system which is highly safe such that its safety can be proven without the assumption of a random oracle model. A signature presenting apparatus is supplied with a public key, a blind secret identifier, a blind public identifier, a blind signature, and a random number. A signature verifying apparatus outputs “valid” if the signature presenting apparatus is supplied with the data and otherwise outputs “invalid”.
Owner:NEC CORP
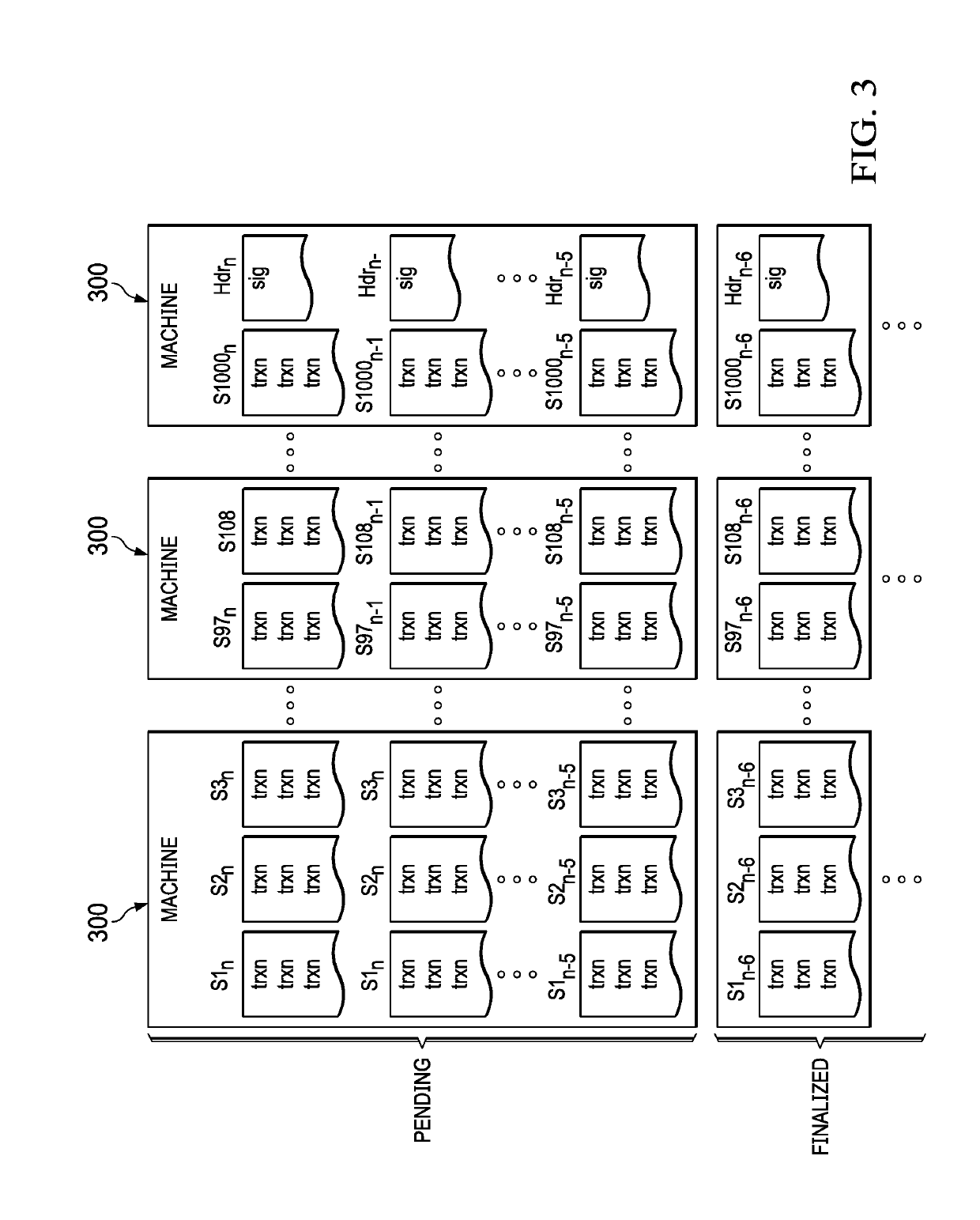
High performance distributed system of record with distributed random oracle
PendingUS20190220324A1Improve performanceLittle synchronizationKey distribution for secure communicationResource allocationRandom oracleLatency (engineering)
A high-performance distributed ledger and transaction computing network fabric over which large numbers of transactions (involving the transformation, conversion or transfer of information or value) are processed concurrently in a scalable, reliable, secure and efficient manner. In one embodiment, the computing network fabric or “core” is configured to support a distributed blockchain network that organizes data in a manner that allows communication, processing and storage of blocks of the chain to be performed concurrently, with little synchronization, at very high performance and low latency, even when the transactions themselves originate from distant sources. This data organization relies on segmenting a transaction space within autonomous but cooperating computing nodes that are configured as a processing mesh. Each computing node typically is functionally-equivalent to all other nodes in the core. The nodes operate on blocks independently from one another while still maintaining a consistent and logically-complete view of the blockchain as a whole. According to another feature, secure transaction processing is facilitated by storing cryptographic key materials in secure and trusted computing environments associated with the computing nodes to facilitate construction mining proofs during the validation of a block.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
PEKS (public-key encryption with keyword search) method for lattice-based cloud stored cyphertext data under standard model
ActiveCN106789044AReaction securityResist attackKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTechnical standardModular exponentiation
The invention belongs to the technical field of cyberspace security and particularly relates to a PEKS (public-key encryption with keyword search) method for lattice-based cloud stored cyphertext data under standard model. The method of the invention has no need for a random oracle so that the security of the designed PEKS method can more truly reflected; a designed cryptographic algorithm is based on assumption of LWE (learning with errors) hard problems, quantum computer attacks can be resisted effectively. The method of the invention has a need for specifying a unique cloud server to perform testing and return corresponding search results, so that no malicious servers are able to execute search test operation, and malicious server attacks are partly avoided accordingly. In addition, the algorithm can ensure that cyphertext is undistinguishable. Furthermore, in keyword cyphertext generation phase, the method of the invention needs no computing of high-overhead modular exponentiation and bilinear pairing operation, but the computing of finite linear algebraic operation, and accordingly is highly worthy of practical application in post-quantum communication environments.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
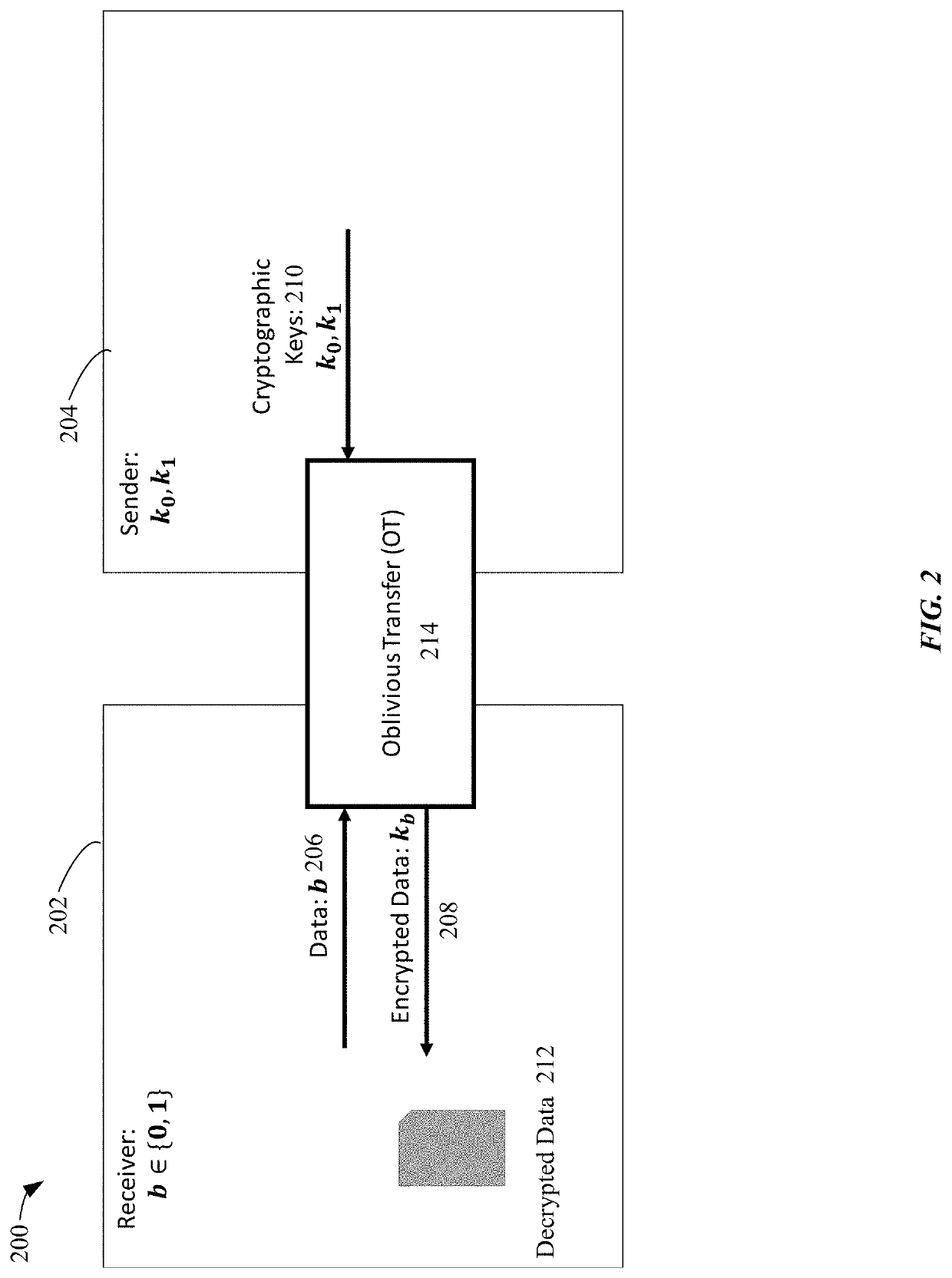
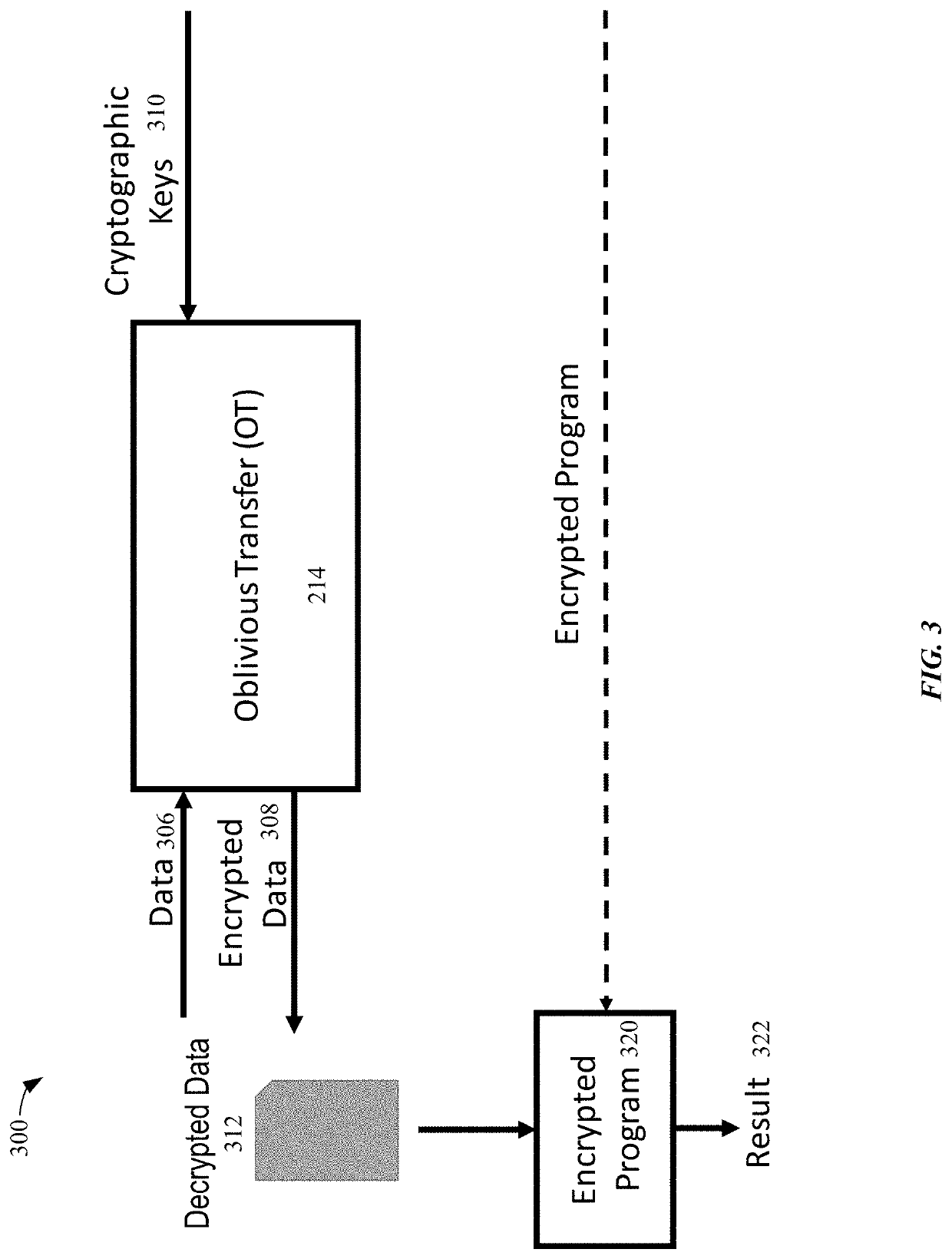
Fast oblivious transfers
ActiveUS20200259800A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageRandom oracleKey exchange
Systems, methods, and computing device readable media for implementing fast oblivious transfer between two computing devices may improve data security and computational efficiency. The various aspects may use random oracles with or without key agreements to improve the security of oblivious transfer key exchanges. Some techniques may include public / private key strategies for oblivious transfer, while other techniques may use key agreements to achieve simultaneous and efficient cryptographic key exchange.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
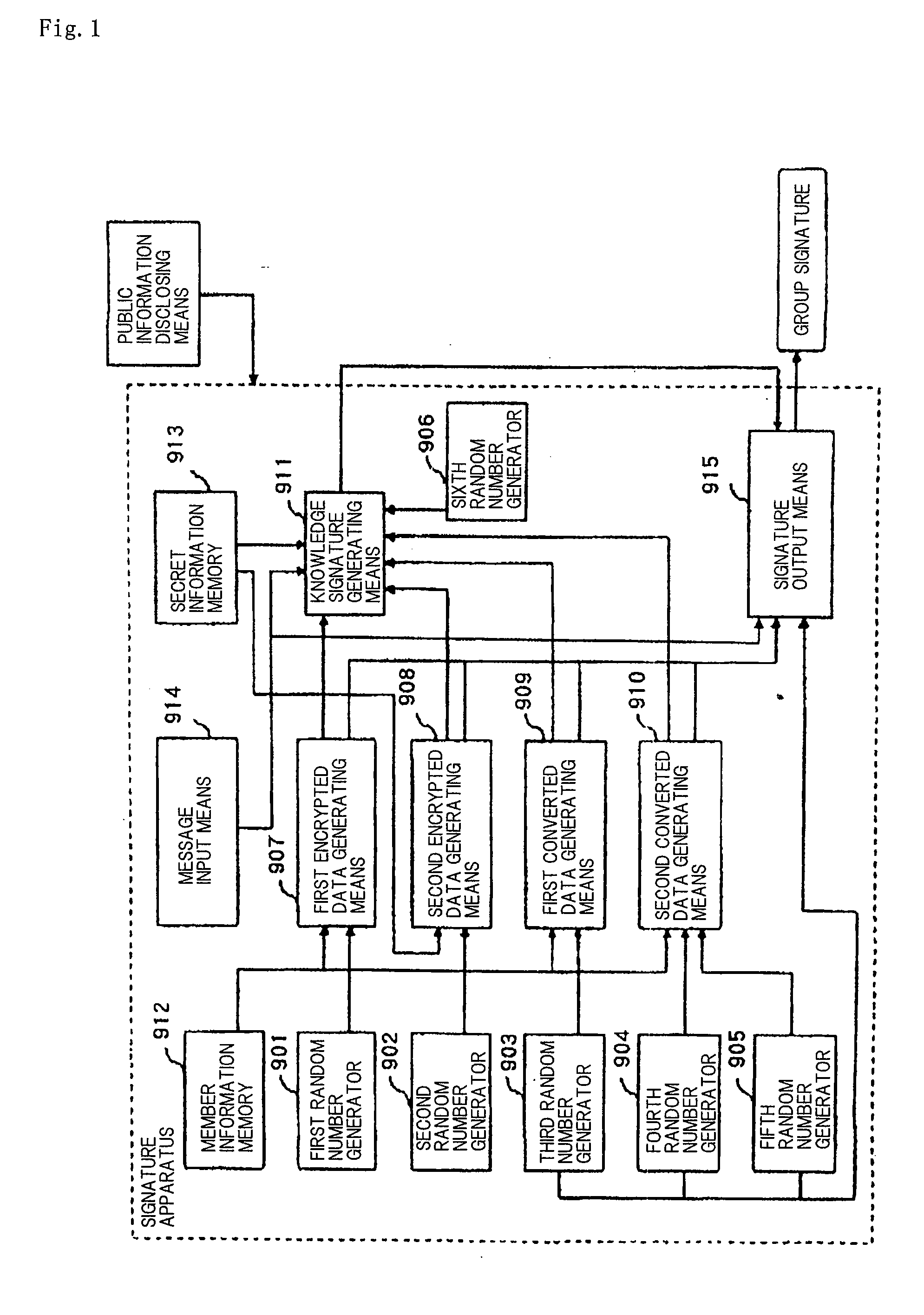
Group signature scheme
ActiveUS8127140B2Accurate operationReduce in quantityPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationRandom oracleDiscrete logarithm
An efficient and safe group signature scheme is provided. According to the present invention, an open unit is provided to not an issuer but an opener, and a data required for operating the open unit does not include a key pair of the issuer, so that it is possible to accurately operate the open unit even if the issuer generates the public key in an illegal manner. In addition, it is possible to prove that a key pair of a member cannot be counterfeited. It is possible to implement from a discrete logarithm assumption a feature that a cipher text, that is, a portion of a signature text can be decrypted only by the opener in a method which is the same as a method representing that an ElGamal crypto scheme is safe. In addition, it is possible to implement from a random oracle assumption a feature that a knowledge signature has an extractability in a method which is the same as a method proving that a Schnorr signature is safe.
Owner:NEC CORP
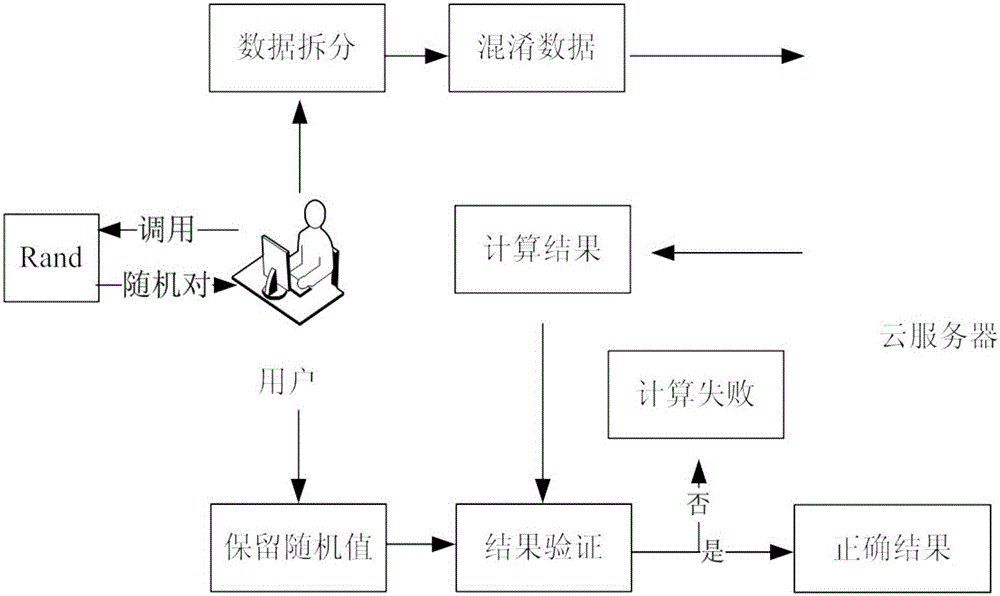
Safe mode index outsourcing method and system under single malicious cloud server
The invention discloses a safe mode index outsourcing method and a safe mode index outsourcing system under a single malicious cloud server. The method comprises the steps as follows: step1, a user T calls a sub-program Rand for six times to obtain six random pairs; step 2, the user T splits a mode index which needs to calculate according to the random pairs returned by the sub-program Rand, and simultaneously, the user T selects a random value r and multiplies the index of the mode index by r to obtain a new mode index, and splits the new mode index; step 3, the user T requests a server U to separately calculate the values which needs to calculate after splitting; step 4, the user T multiplies a random value which is related to ua and which is remained by the T by a result which is related to the ua and which is returned by the server U, and multiplies the results for r times to obtain a verification result 1; and the user T multiplies a random value which is related to ura and which is remained by the T by a result which is related to the ura and which is returned by the server U to obtain a verification result 2; comparing the result 1 and the result 2, and judging that the server could accurately perform calculation if the result 1 and the result 2 are equal to each other.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Practical reusable fuzzy extractor based on the learning-with-error assumption and random oracle
ActiveUS20190020472A1Simple and efficient operationGuaranteed normal processingKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareRandom oracle
Described is a system for biometric authentication. The system converts biometric data into a cryptographic key r′ using a reusable fuzzy extractor process having an underlying hash function modeling a random oracle model. The system allows access to secured services when a comparison of r′ to a previously computed cryptographic key r shows a match.
Owner:HRL LAB
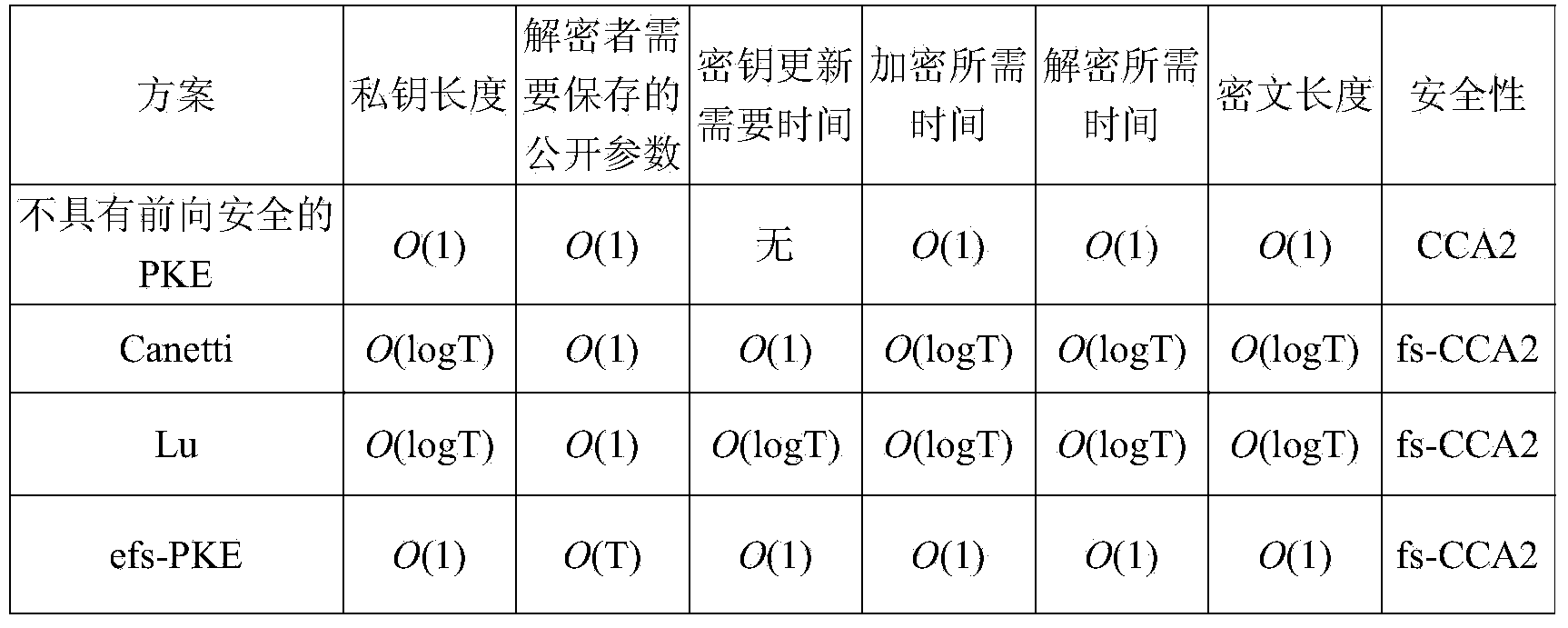
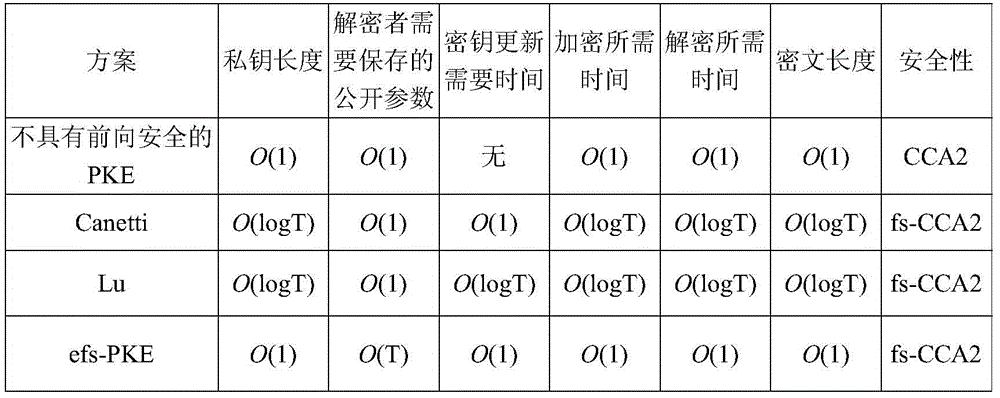
Method for efficient public key encryption with forward security
ActiveCN103684764AStrong security goalsConstant lengthPublic key for secure communicationPlaintextRandom oracle
The invention discloses a method for efficient public key encryption with forward security. The method comprises the following steps that step 1, system initialization is conducted and a PK and an initial SK1 of a user are calculated; step 2, the secret keys are updated; step 3, a plaintext m is encrypted through the PK so that a CT of the plaintext m at the current period i can be obtained; step 4, the CT is decrypted through an SK i at the current time period i so that the plaintext m can be obtained. The method has the advantages that an encryptor only needs to own one cluster element so that a public key of each time period can be obtained through public information. In addition, the public keys can be identity information. On the basis, an encryption scheme based on the identity can be converted into a public encryption scheme with forward security and an efficient public key encryption scheme with forward security which achieves adaptive selection ciphertext security under a random prediction machine model is obtained.
Owner:NO 30 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP
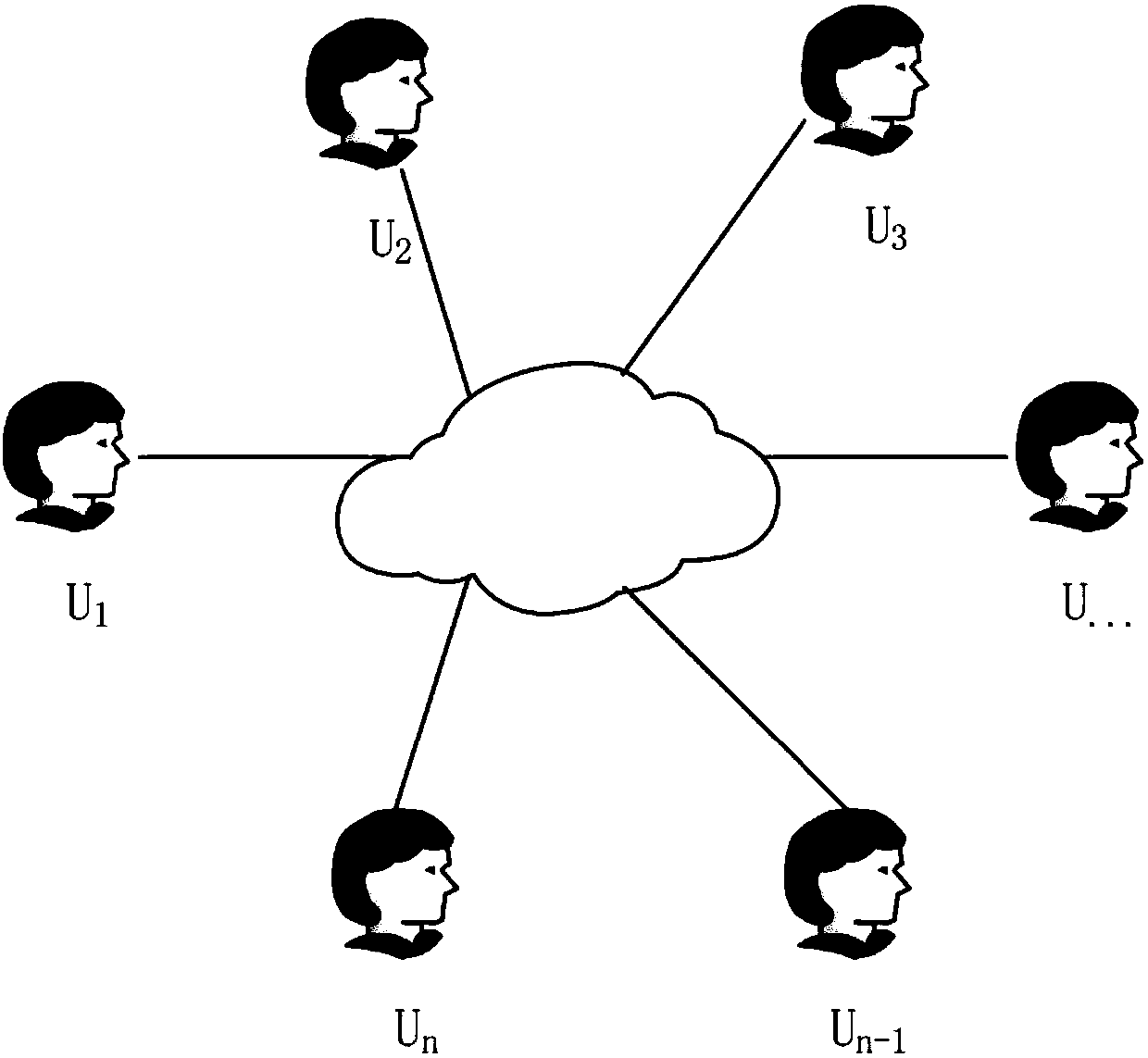
Anti-leakage group key negotiation system and method in group communication
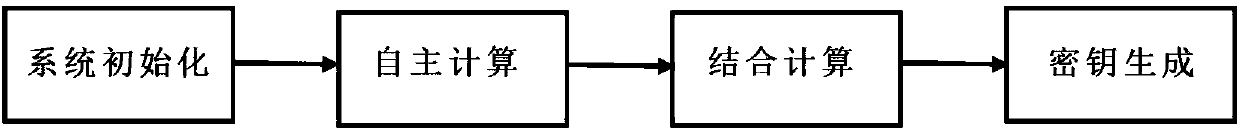
ActiveCN108259185AMeet group communicationSafe and stable operationKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationRandom oraclePassword
The invention discloses an anti-leakage group key negotiation system and method in group communication. The system comprises n users. All users share the same password pw. The system has a continuouspost-event leakage prevention security model. The system specifically comprises protocol participants, an opponent and a random oracle. The protocol participants are online devices participating in aprotocol. The opponent is a probability polynomial time algorithm through which various attacks possibly occur in a network are simulated. The random oracle communicates with the opponent to simulateinformation possibly obtained by the opponent in the network. According to the system and the method, the system is initialized; each protocol participant carries out automatic computing; each protocol participant carries out combined computing; and each protocol participant generates a common session key. According to the system and the method, under the condition that leakage attacks are resisted, a group key is negotiated, so the system and the method have relatively high practicability; and a high quality key negotiation protocol based on password authentication is provided, so the efficiency of the scheme is improved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
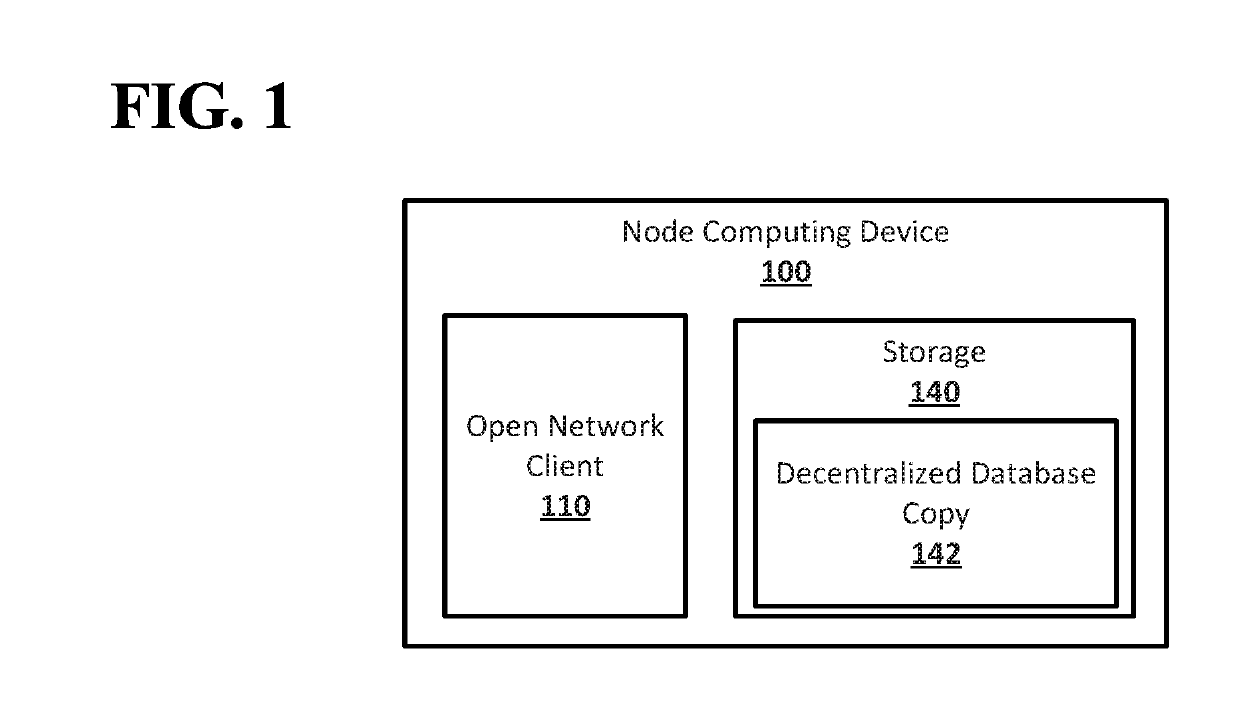
Random oracles in open networks
ActiveUS20190253242A1Key distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesRandom oracleAlphanumeric
Systems and techniques are provided for random oracles in open networks. A node computing device of an open network may choose a random secret. The random secret may be a numeric or alphanumeric value. The node computing device may distribute shares of the random secret to node computing devices that are members of essential subsets for the node computing device. The node computing device may receive a share of a random secret from a second node computing device. The node computing device may be a member of an essential subset of the second node computing device. The node computing device may sign a deterministic seed message using the share of the random secret received from the second node computing device to generate a signature share. The node computing device may reveal the signature share and may receive a random value in response.
Owner:RIPPLE LABS INC
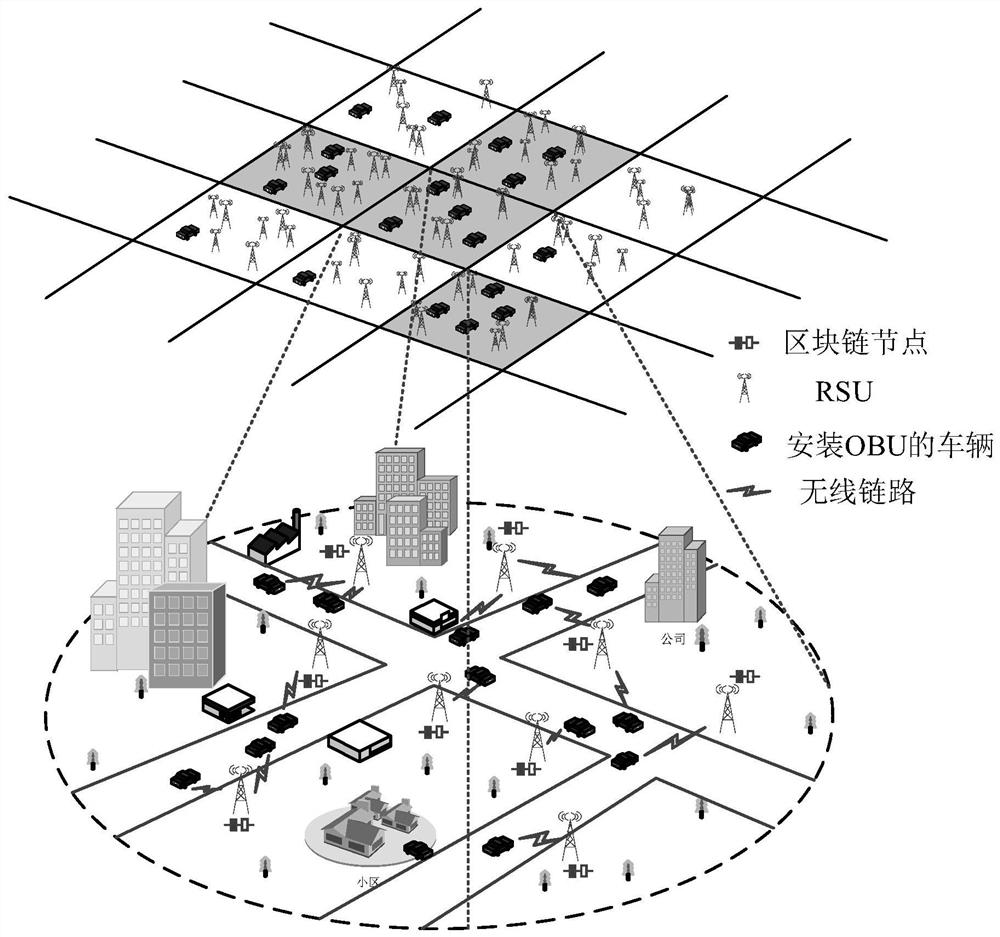
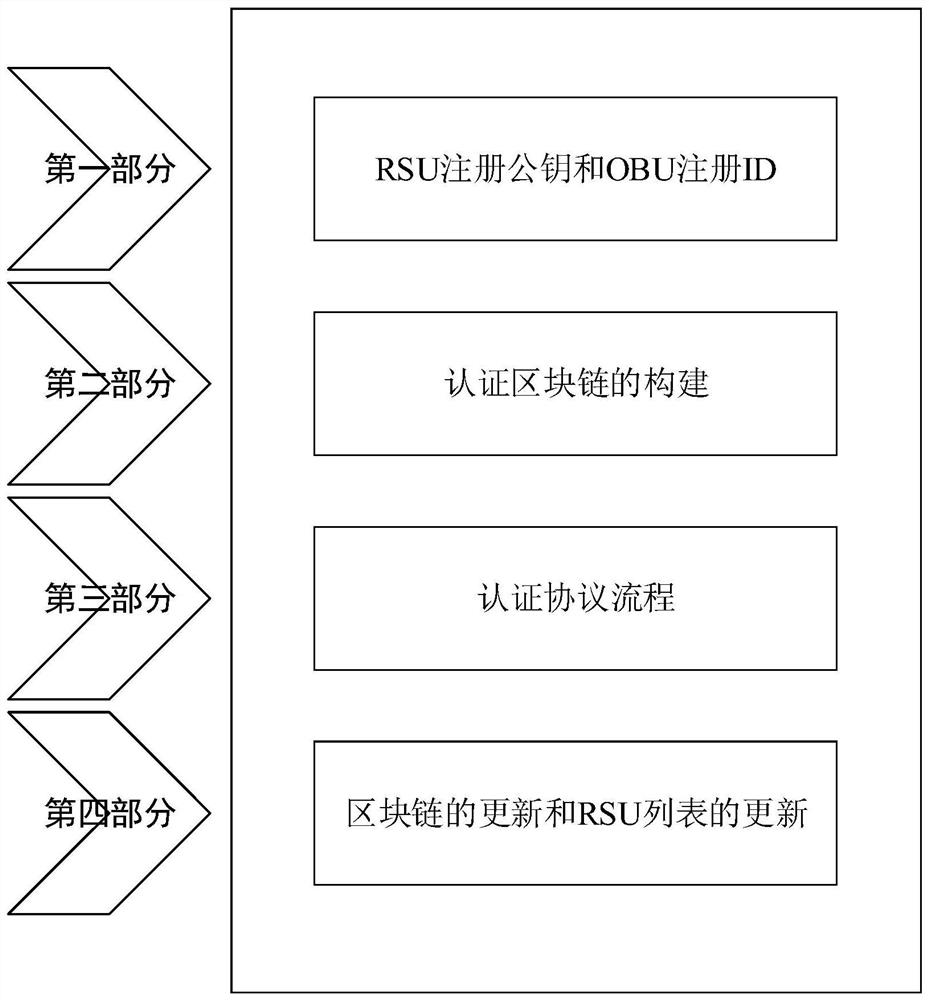
Distributed authentication method of Internet of Vehicles based on blockchain technology
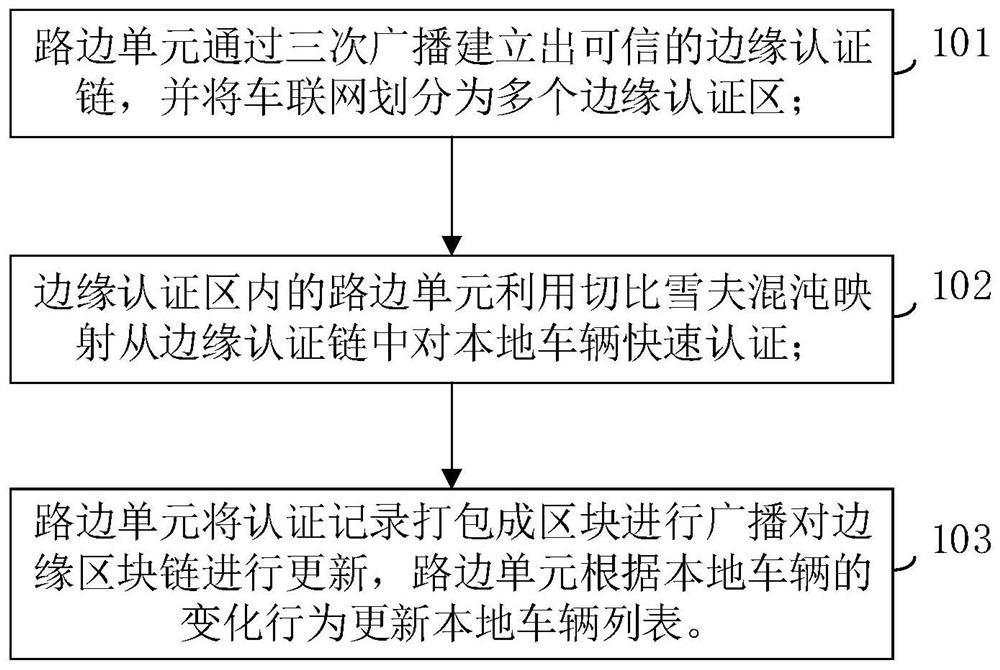
ActiveCN113453170AMeet the needs of real-time authenticationReduce dependenceParticular environment based servicesBroadcast service distributionRandom oracleVehicle behavior
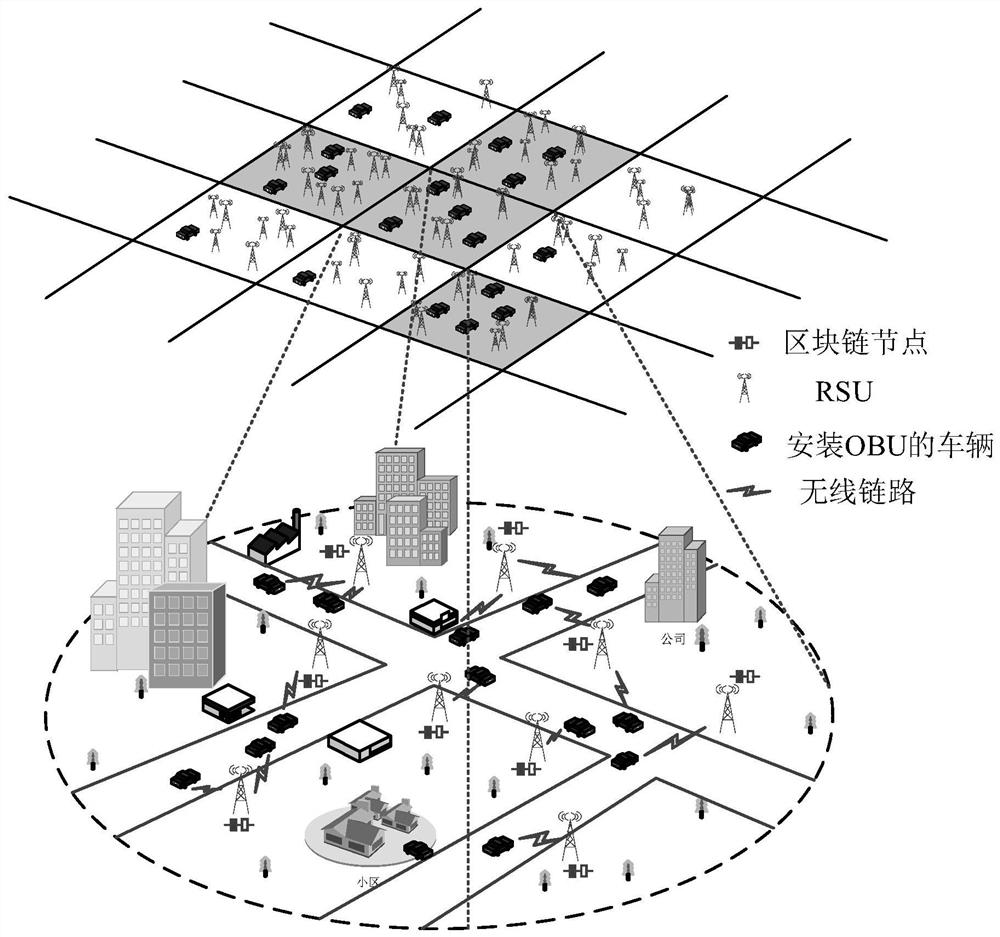
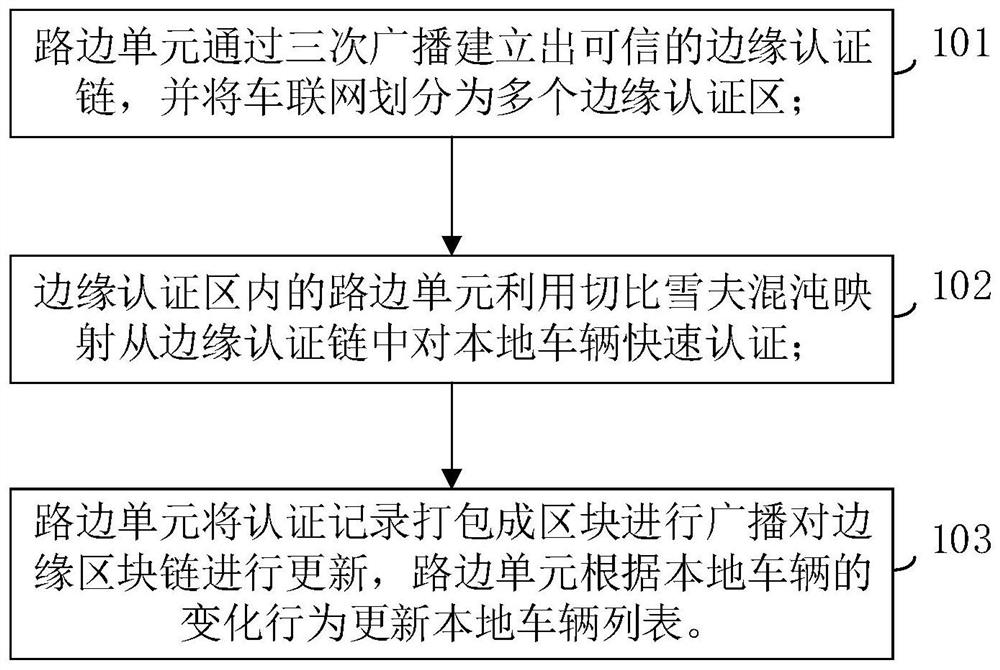
The invention relates to the field of access authentication in the Internet of Vehicles, in particular to a distributed authentication method for the Internet of Vehicles based on the blockchain technology. The method comprises the steps that when access authentication is carried out on a vehicle identity in an Internet of Vehicles distributed authentication system, by taking high reliability and high efficiency of authentication as a principle on the premise of considering an edge node trust problem, an RSU spontaneously establishes an edge authentication chain through three-stage broadcast, so that the Internet of Vehicles is divided into a plurality of edge authentication areas; the RSU in the area realizes the rapid authentication of local vehicles through half-group characteristics of Chebyshev mapping; the RSU serving as a blockchain node stores the authentication record of the vehicle, and when the behavior of the vehicle changes, the local vehicle list is updated in time; and finally, the security of the proposed authentication scheme is proved by using a random oracle model. According to the invention, high-efficiency and high-reliability distributed access authentication can be realized on the premise of considering the RSU trust problem.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
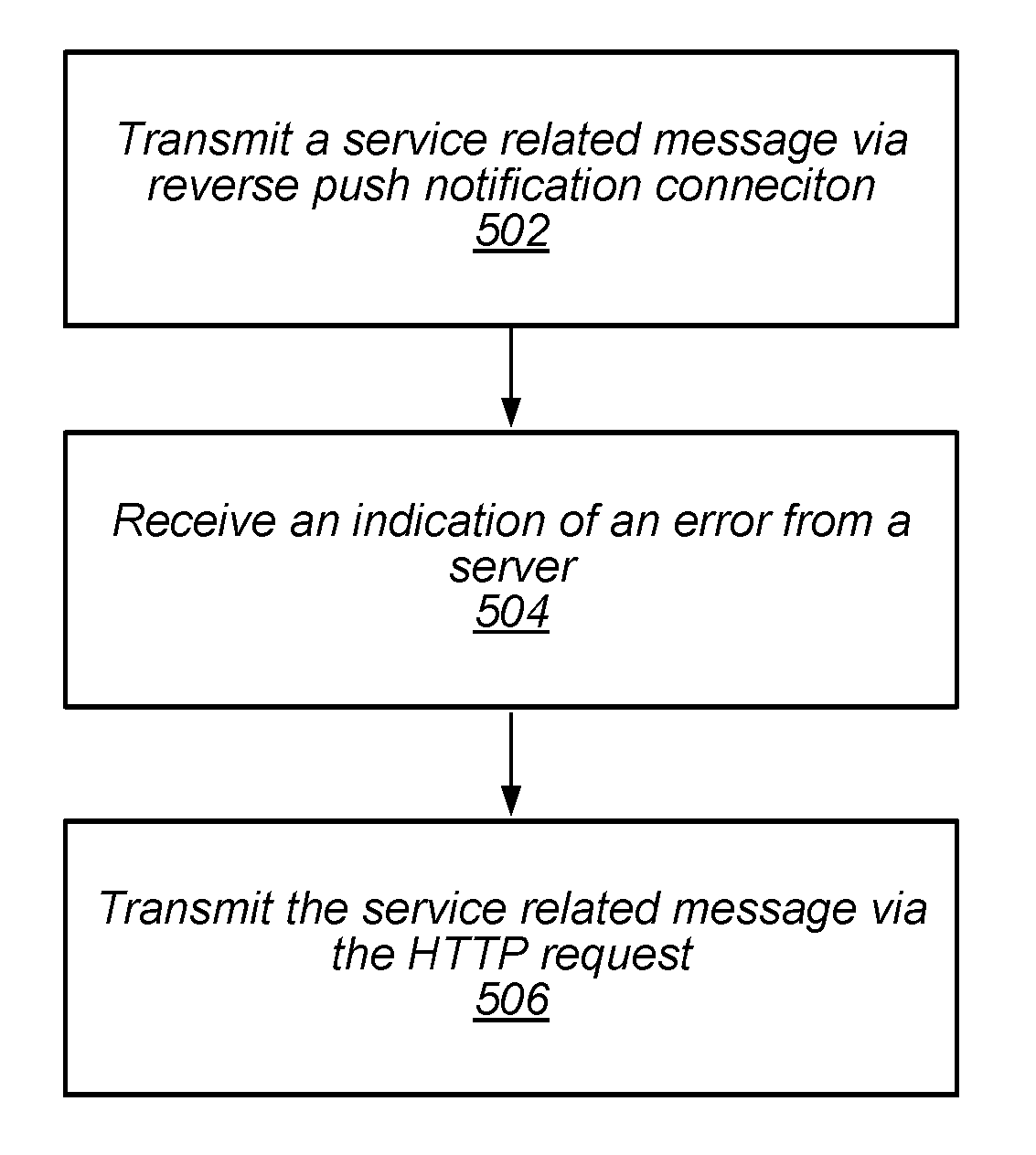
Dual Channel Delivery
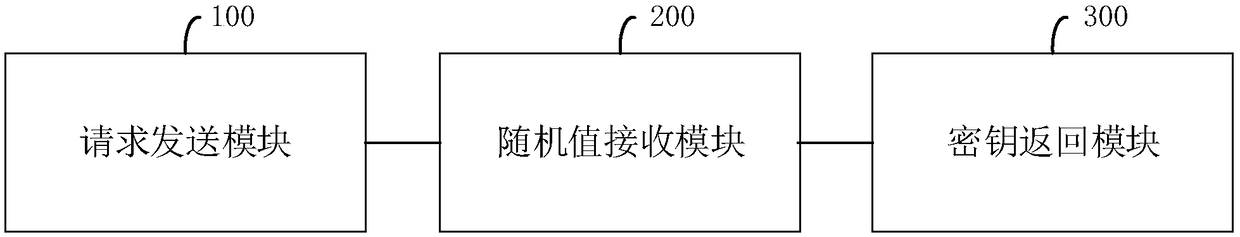
Embodiments described herein relate to systems and methods for transmitting service related messages, e.g., via a reverse push connection. In some embodiments, a UE may be configured to receive a random value from a server, the random value based at least in part on a capacity of the server and / or network. The UE may be configured to compare the random value to a generated value, and determine, based at least in part on the comparison, to transmit a service related message over a reverse push connection rather than via a hypertext transport protocol (HTTP) request. In some embodiments, the service related message may be any message that relates to a service available between devices, such as an identity (ID) query request, a service (de-) registration request, and / or a device listing request, among other types of messages.
Owner:APPLE INC
Controlling a device
ActiveUS20170277882A1Industrial applicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationRandom oracleProcessing core
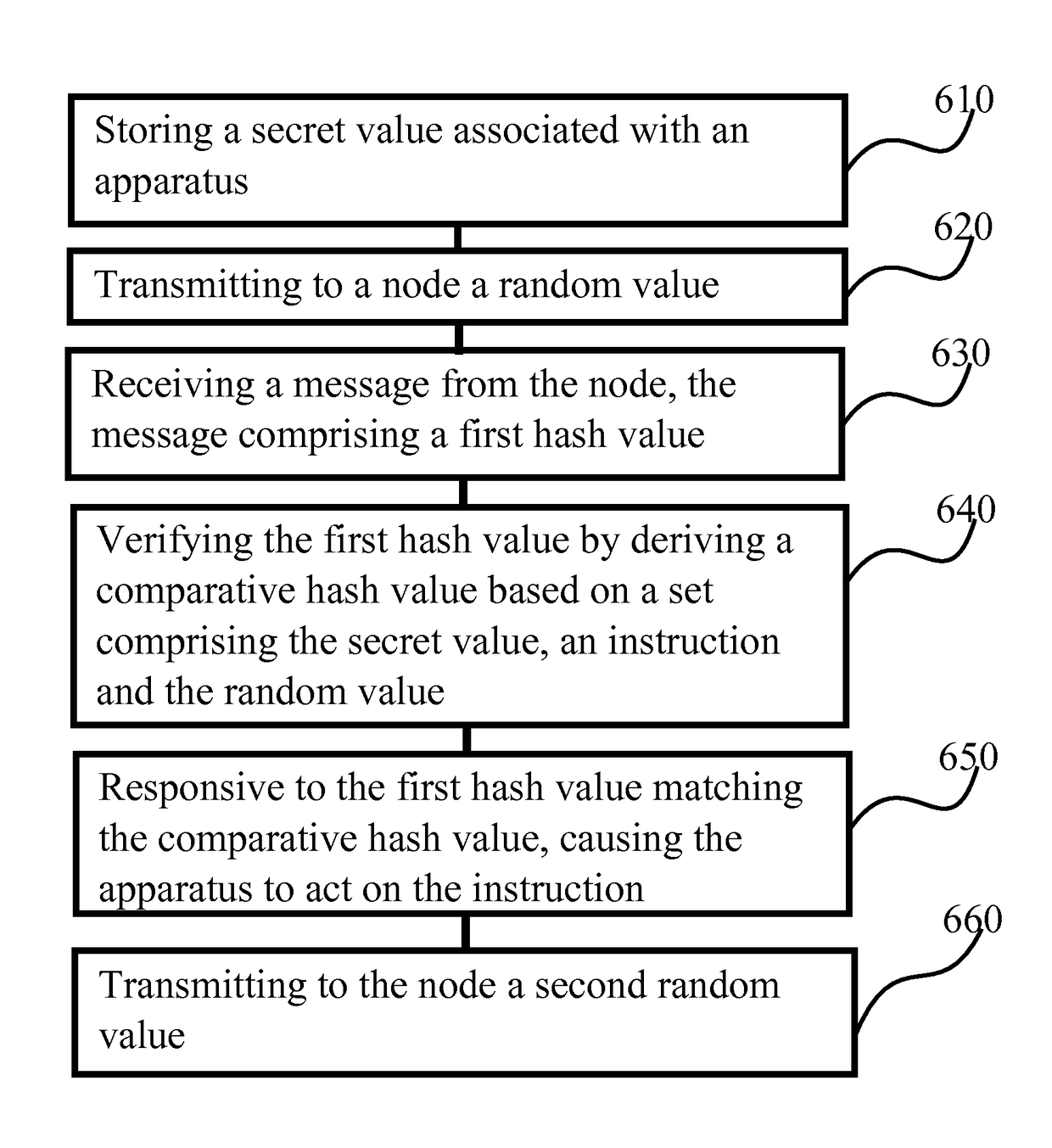
In accordance with an example aspect of the present invention, there is provided an apparatus comprising at least one receiver configured to receive, via a first channel, a secret value and an identifier of a local node and, via a second channel, a random value, and at least one processing core configured to cause transmission to the local node of a first message comprising a hash value, the hash value being derived based on a set comprising the secret value, the random value, and an instruction.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
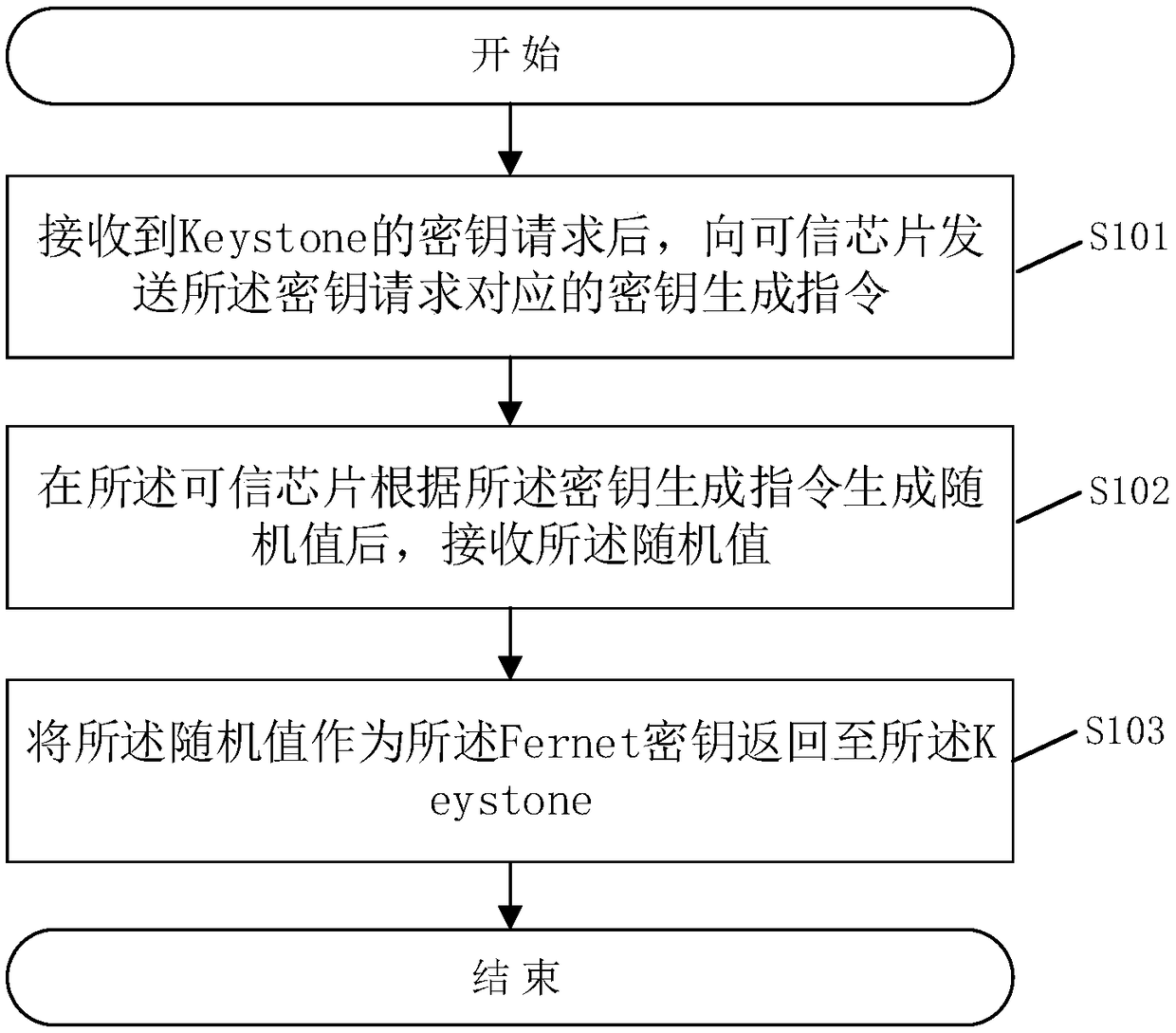
Generation method of Fernet key in Keystone and related device
InactiveCN109462474ASolve randomnessSolve efficiency problemsKey distribution for secure communicationRandom oracleWork performance
The application provides a generation method of a Fernet key in Keystone. The method comprises the following steps: sending a key generation instruction corresponding to a key request to a credible chip after receiving the key request of keystone; receiving a random value after the credible chip generates a random value according to a key generation instruction; returning the random value to the Keystone as the Fernet key. The credible chip is used as a random source of the Fernet key, the disadvantage of the existing system random source on the aspects of randomness and efficiency of generating a random value is solved, the randomness of the random value is improved, and the security and the working performance of the Fernet key are improved. The application further provides a generationsystem of the Fernet key in the Keystone, a computer readable storage medium and a server with above advantages.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
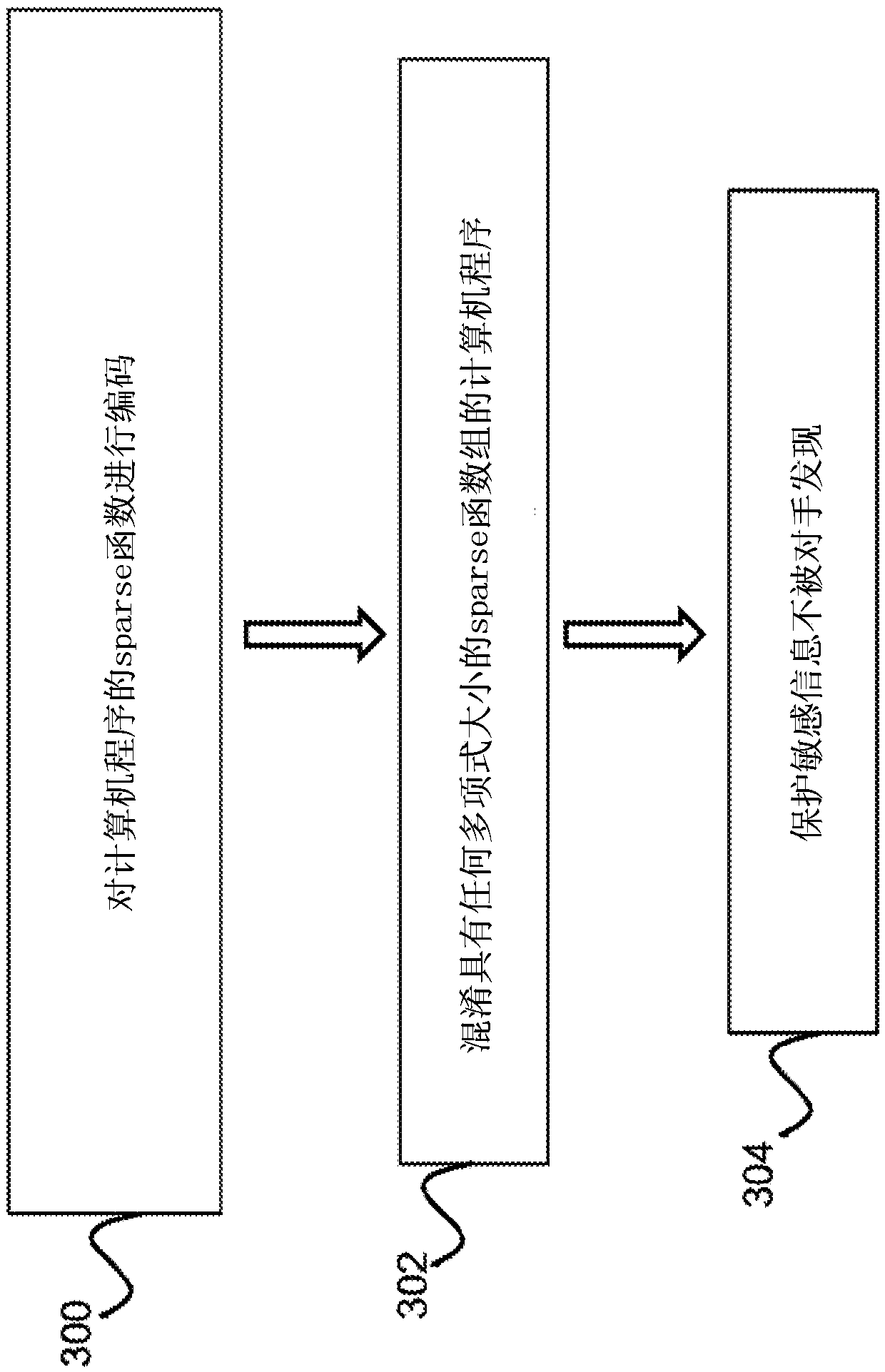
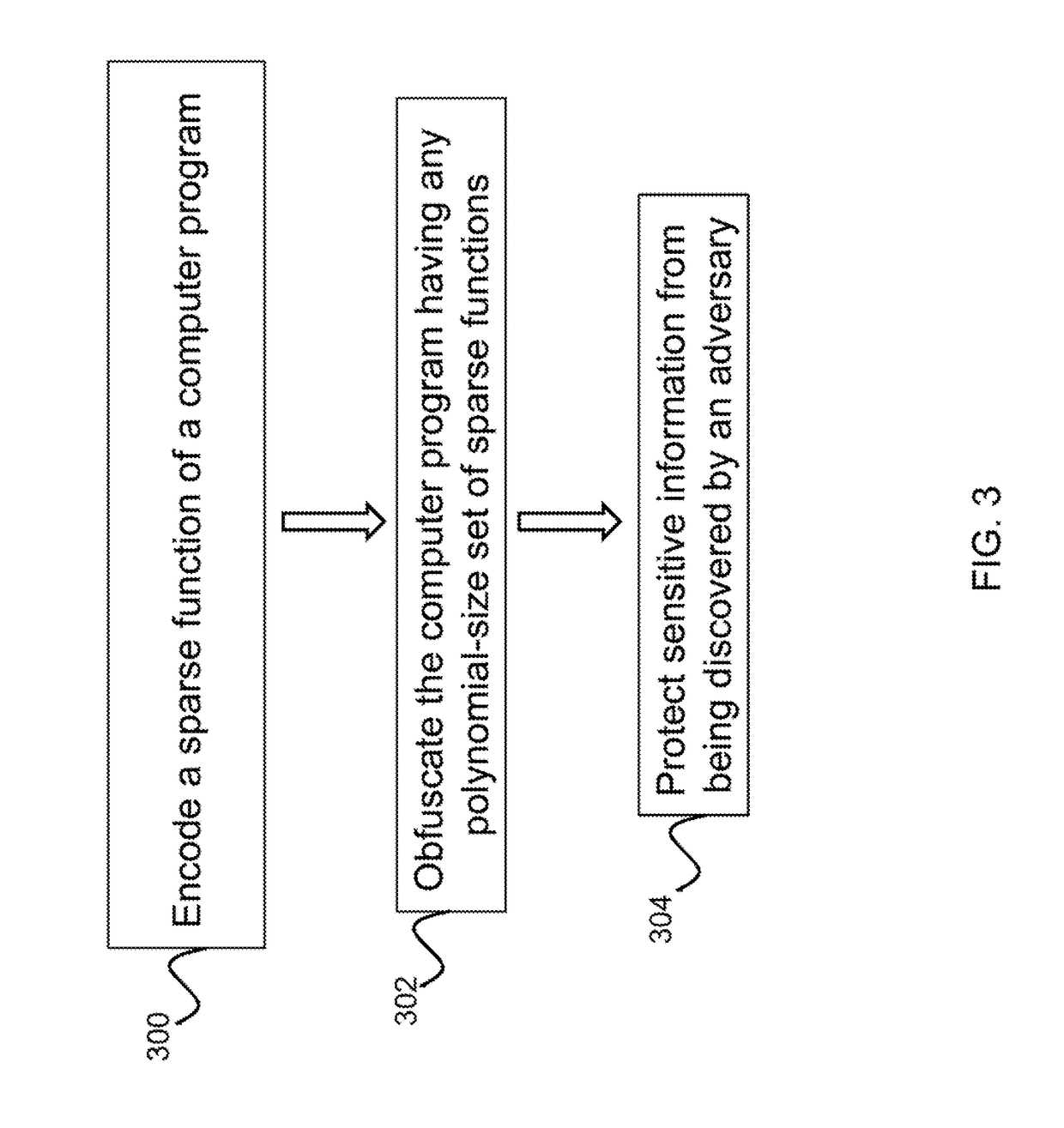
Non-malleable obfuscator for sparse functions
ActiveUS20170316214A1Digital data protectionCryptographic attack countermeasuresRandom oracleTheoretical computer science
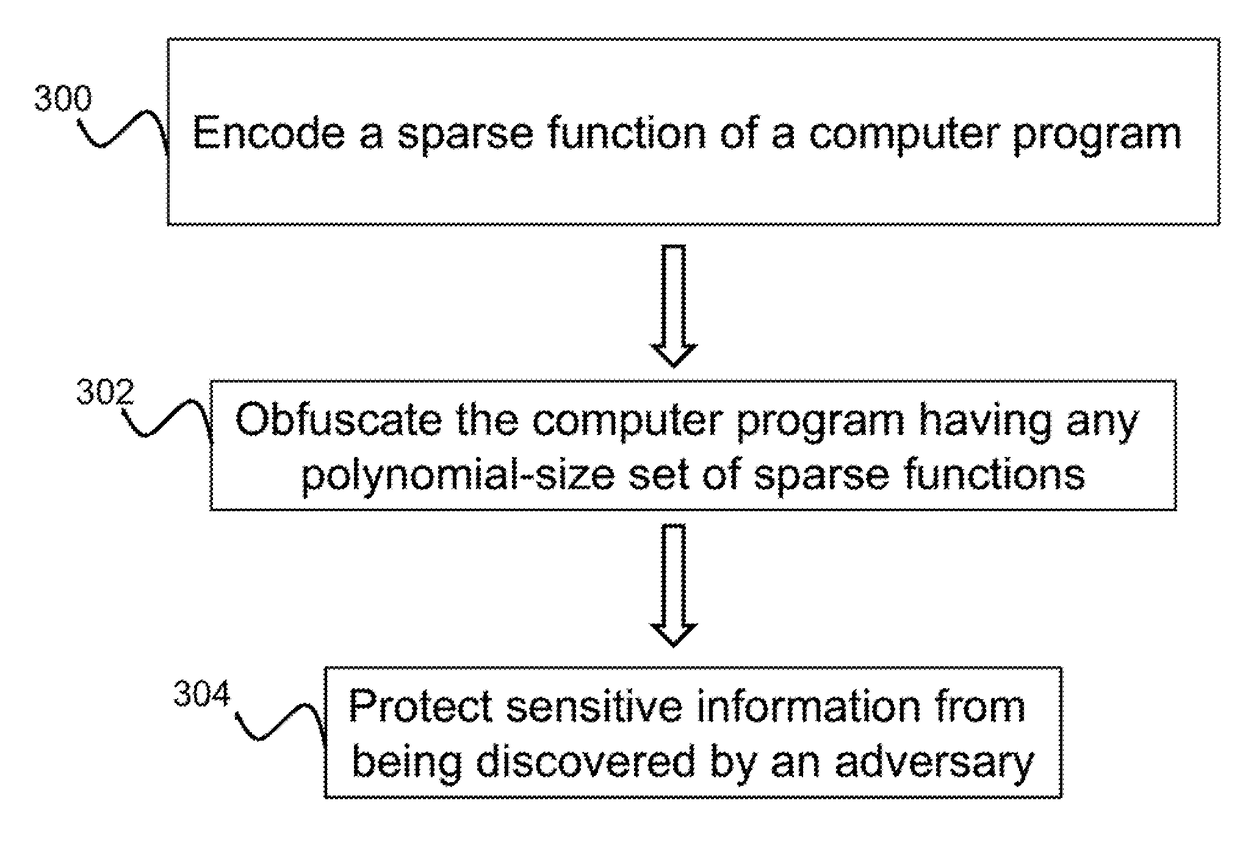
Described is a system for obfuscating a computer program. Sensitive data of an unprotected computer program is received as input. A random oracle is used to algebraically hide a set of polynomial-size point functions representing the sensitive data. The system outputs a set of obfuscated instructions internally hiding the sensitive data. The set of obfuscated instructions are used to transform the unprotected computer program into a protected, obfuscated computer program that is accepting of the set of polynomial-size point functions. The obfuscated computer program is written to a non-volatile computer-readable medium.
Owner:HRL LAB
Controlling a device
ActiveCN106797315AUser identity/authority verificationNetwork topologiesRandom oracleProcessing core
In accordance with an example aspect of the present invention, there is provided an apparatus comprising at least one receiver configured to receive, via a first channel, a secret value and an identifier of a local node and, via a second channel, a random value, and at least one processing core configured to cause transmission to the local node of a first message comprising a hash value, the hash value being derived based on a set comprising the secret value, the random value, and an instruction.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
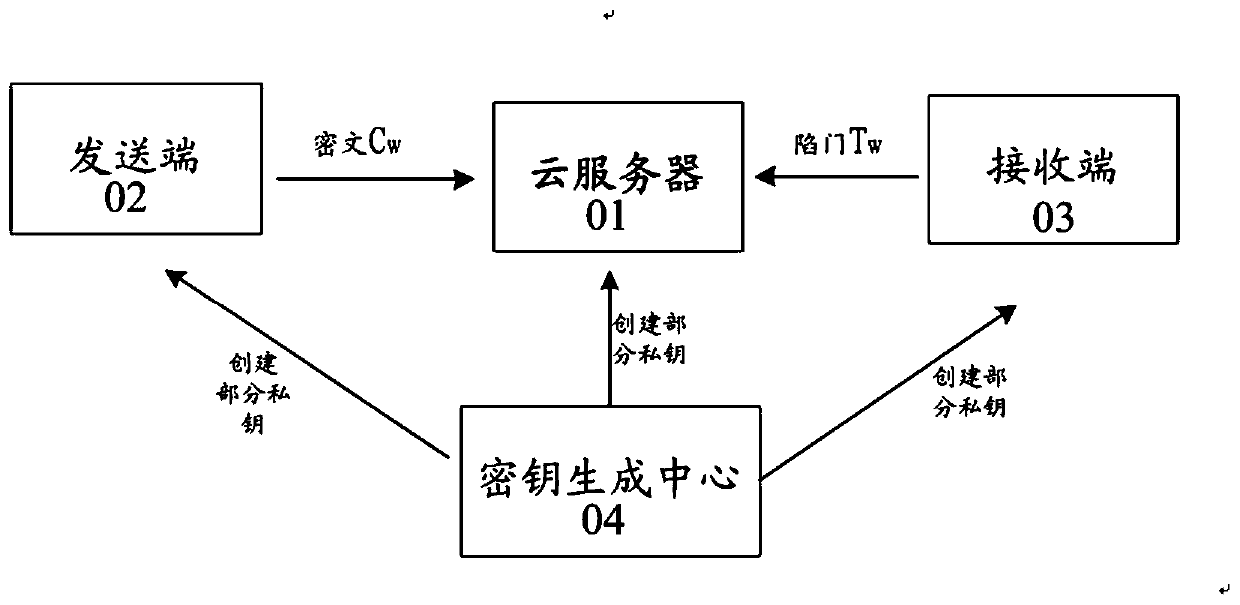
Certificateless public key searchable encryption method and certificateless public key searchable encryption system
ActiveCN111464292AImplement the search functionGuaranteed indistinguishabilityKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesRandom oracleCiphertext
The invention discloses a certificateless public key searchable encryption method and a certificateless public key searchable encryption system. The certificateless public key searchable encryption method does not need to be based on a random oracle machine model; the system comprises a secret key generation center, a data sending end, a data receiving end and a cloud server, and the secret key generation center is responsible for generating part of private keys for the data sending end, the data receiving end and the cloud server; the data sending end is responsible for encrypting the data; the data receiving end is responsible for generating a trap door of a keyword to be retrieved; and the cloud server is responsible for storing and retrieving ciphertext data. Public and private key pairs are added to the data sending end and the cloud server, trap door transmission can be conducted through a public channel, attacks of keyword guessing can be resisted, the ciphertext data retrievalfunction is achieved, and meanwhile the indistinguishability of ciphertext data and the indistinguishability of a trap door are guaranteed.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
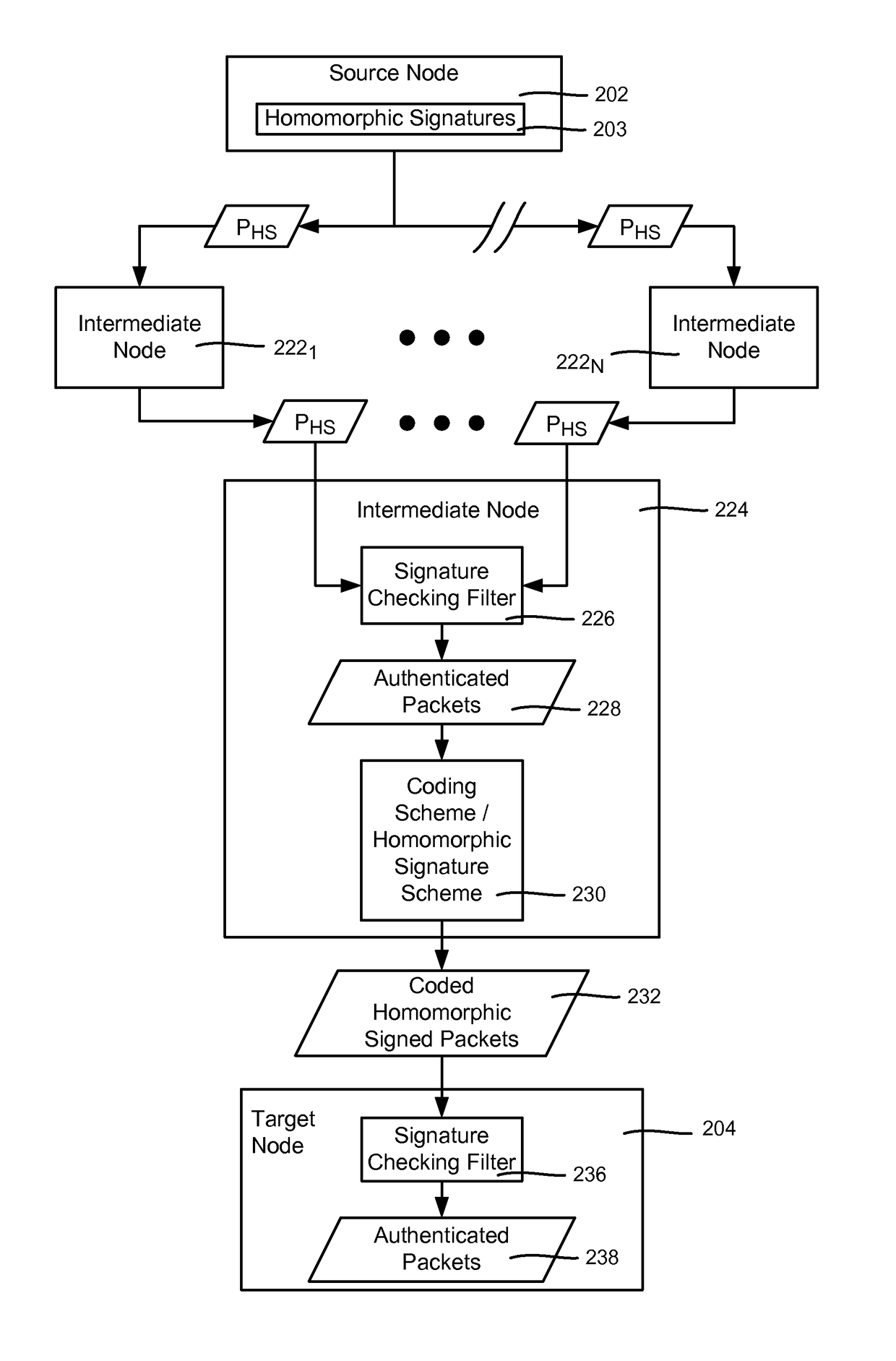
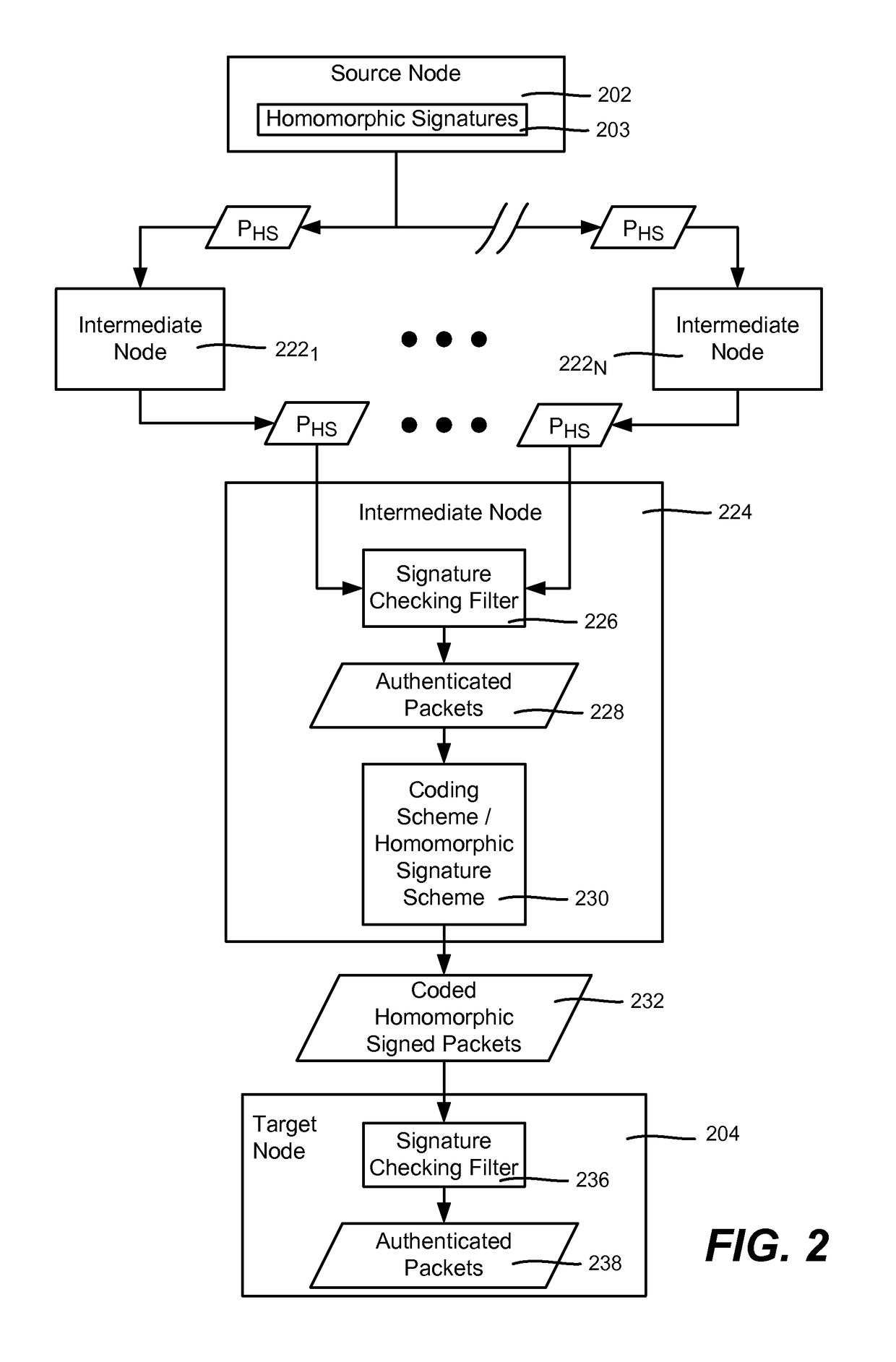
Homomorphic signatures and network coding signatures
ActiveUS9722776B2Well formedSecure distributionPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationRandom oracleData set
The subject disclosure is directed towards a technology by which data is securely distributed using a homomorphic signature scheme and homomorphic network coding signature schemes. A homomorphic signature scheme for signing the data is based upon binary pairing with standard prime order groups. Sets of data are signed based upon dividing a larger block of data into smaller blocks, and separately signing each smaller block. The smaller blocks may be distributed to nodes of a network topology that are configured for network coding. In one alternative, the homomorphic signature scheme protects against changes to the block identifier. Proof data may be provided independent of a random oracle, may be provided by providing parameters for verification in a Groth-Sahai proof system, or may be provided by providing parameters for verification independent of a Groth-Sahai proof system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of generating cryptographic key pairs
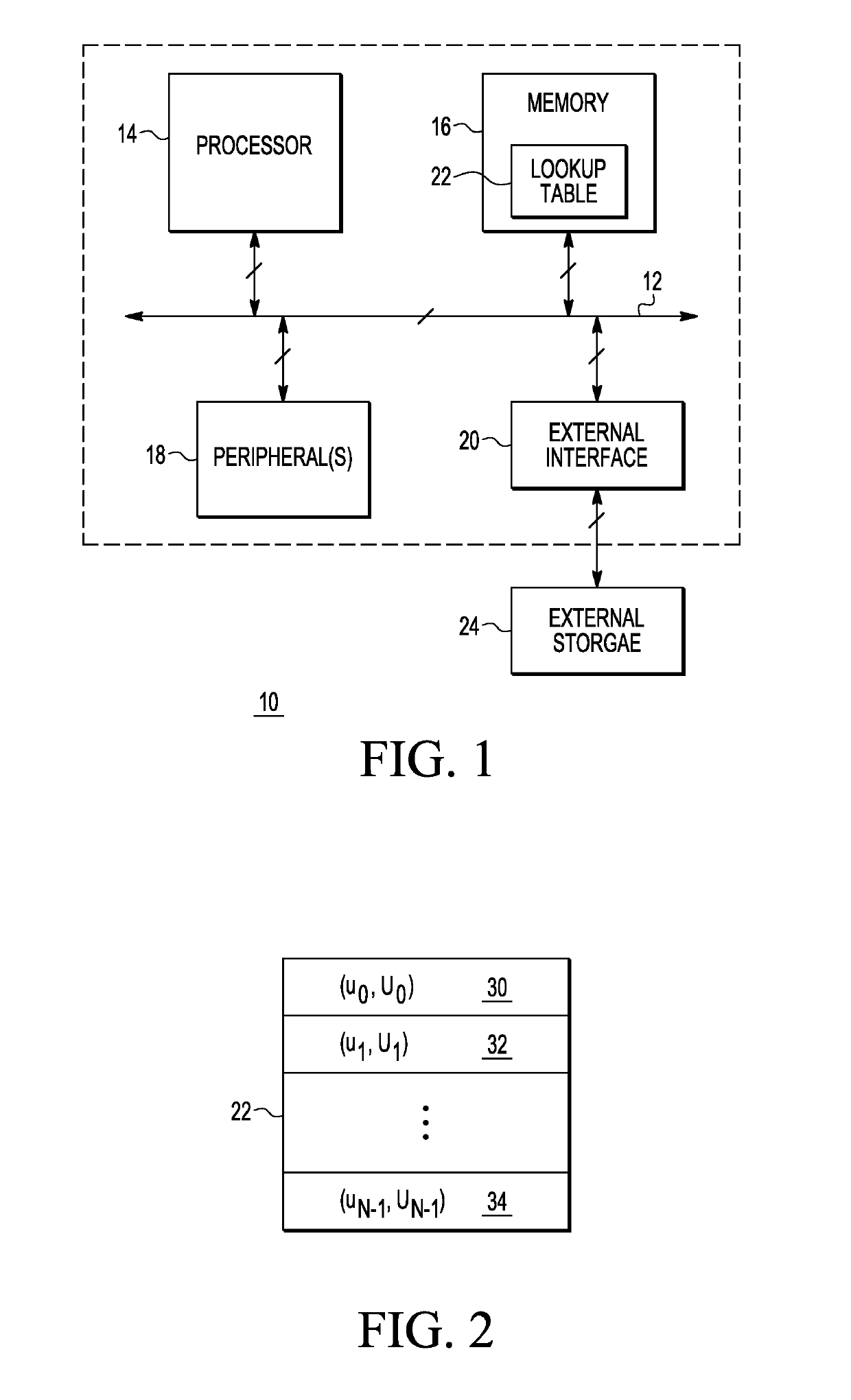
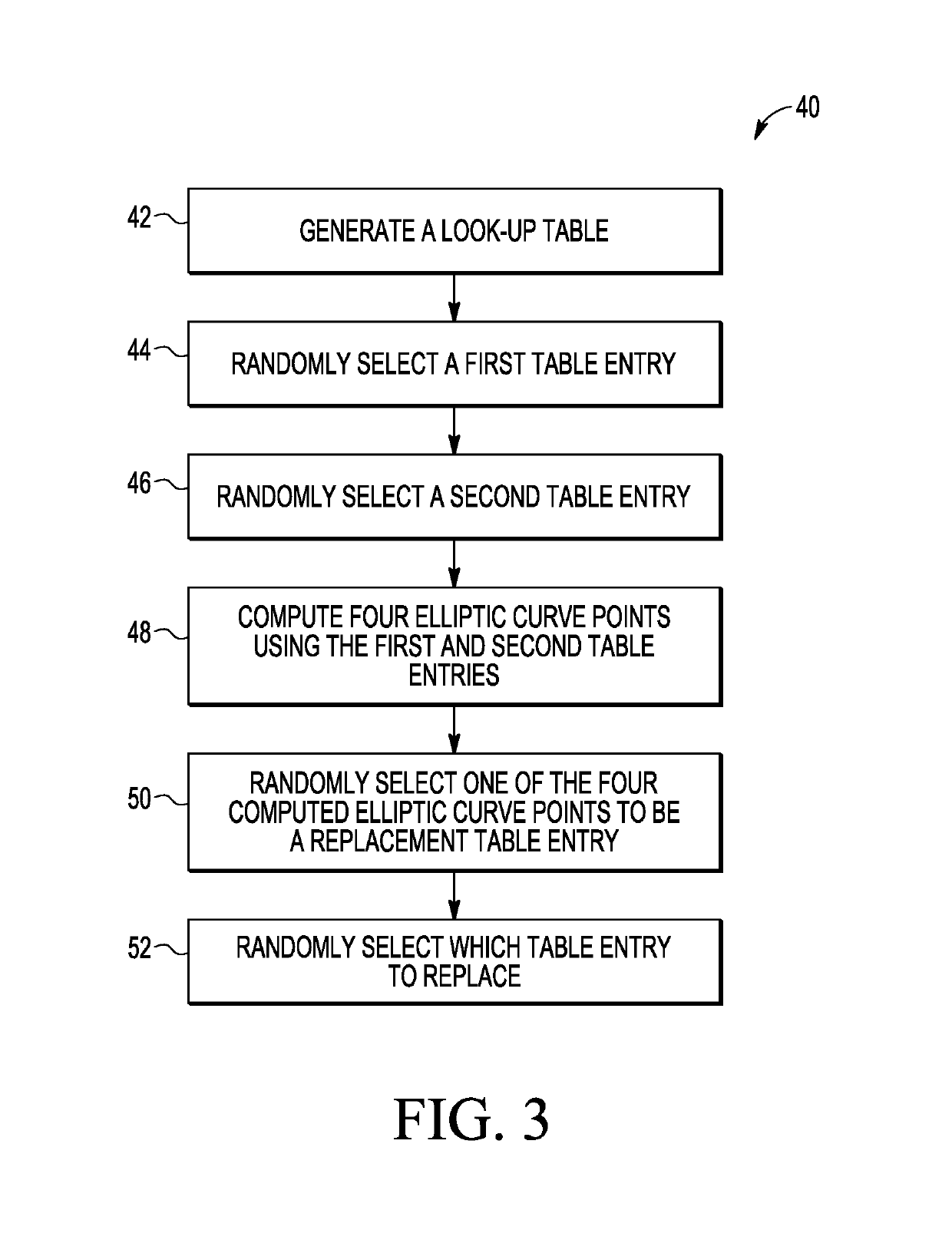
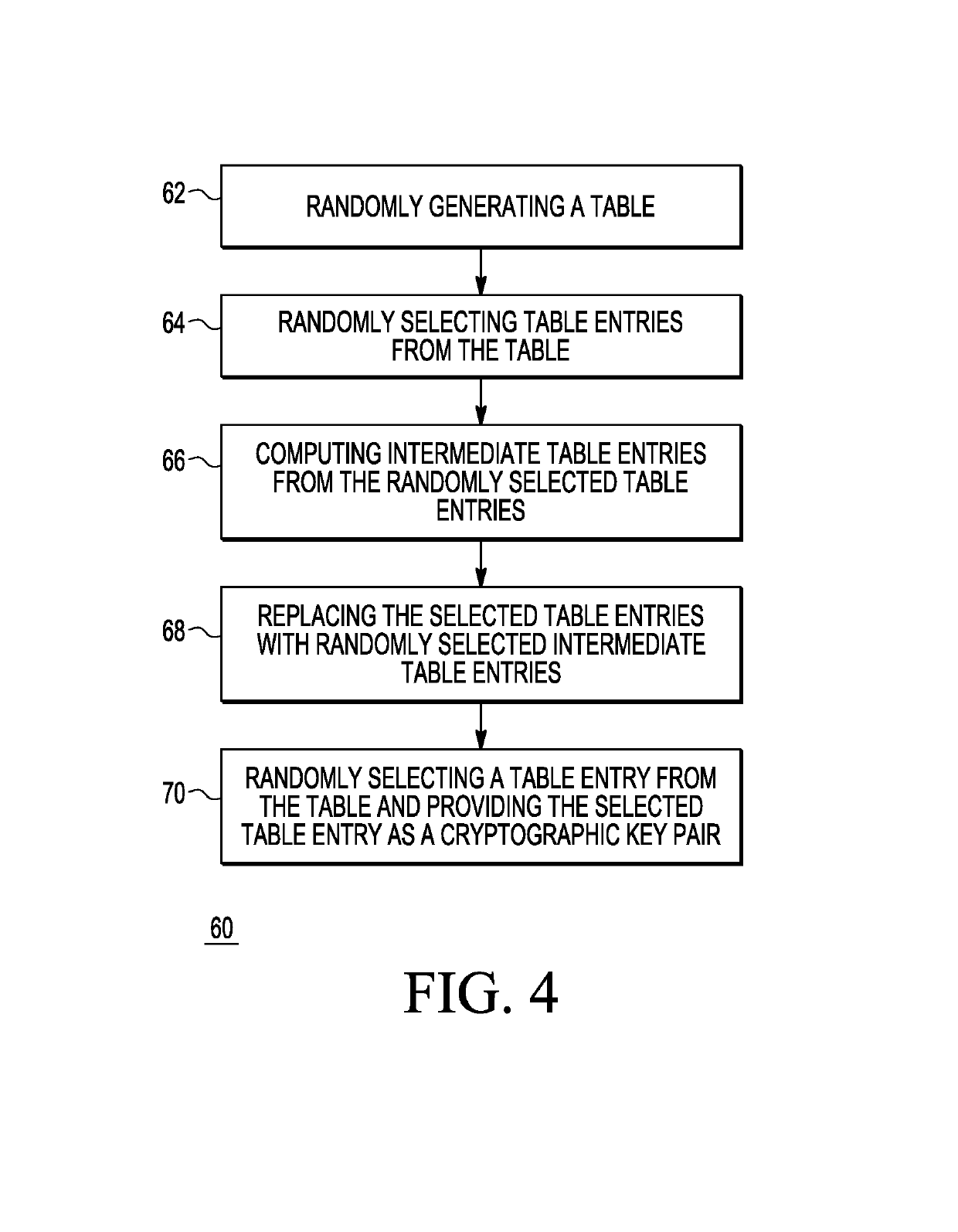
ActiveUS10341098B2Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageRandom oracleScalar Value
A method is provided for performing elliptic curve cryptography that reduces the number of required computations to produce, for example, a key pair. The number of computations is reduced by changing how a random nonce used in the computations is selected. In an embodiment, a look-up table is generated having pre-computed scalar values and elliptic curve points. Every time a new pseudo-random value is created for use in the ECDSA, a combination of the look-up table values is used to create multiple intermediate values. One of the multiple intermediate values is randomly chosen as a replacement value for one of the existing table entries. Each time the look-up table is used, multiple entries in the look-up table are updated to new look-up table values as described. In this manner, new randomness is provided in every step to generate the next pseudo-random nonce as a combination of multiple internally stored temporary look-up table values. Alternately, another mathematical group may be used.
Owner:NXP BV
Non-malleable obfuscator for sparse functions
ActiveCN107667368ADigital data protectionCryptographic attack countermeasuresRandom oracleSoftware engineering
Described is a system for obfuscating a computer program. Sensitive data of an unprotected computer program is received as input. A random oracle is used to algebraically hide a set of polynomial-sizepoint functions representing the sensitive data. The system outputs a set of obfuscated instructions internally hiding the sensitive data. The set of obfuscated instructions are used to transform theunprotected computer program into a protected, obfuscated computer program that is accepting of the set of polynomial-size point functions. The obfuscated computer program is written to a non-volatile computer-readable medium.
Owner:HRL LAB
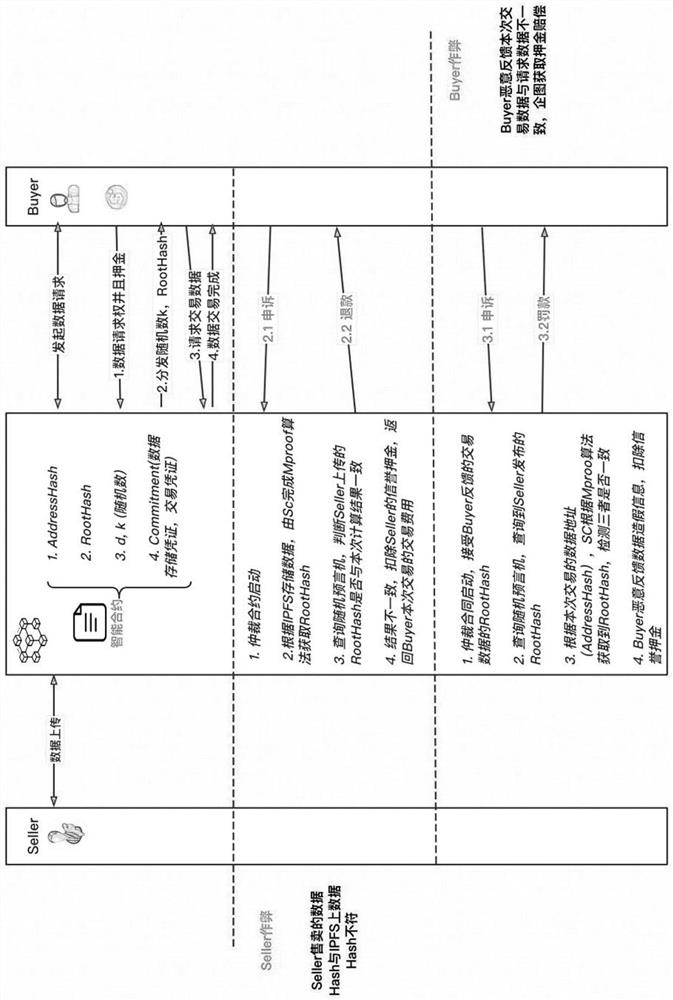
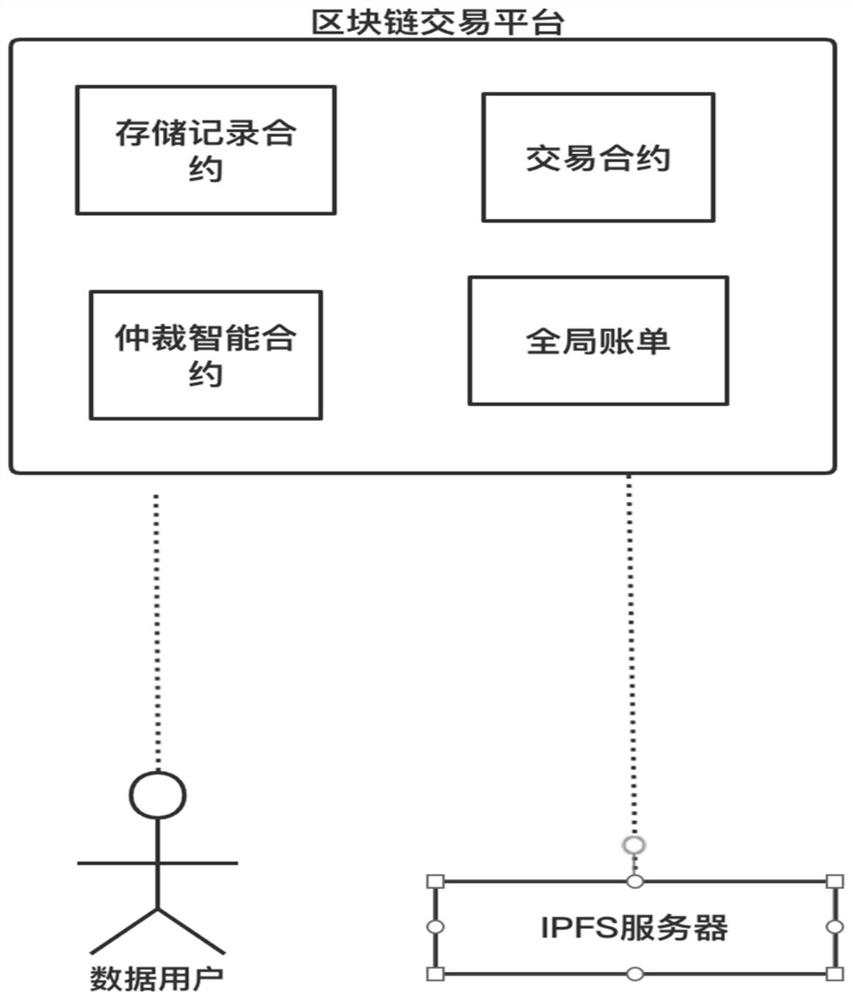
Data transaction verification and data ownership tracing method and system based on block chain
PendingCN114529310ASolve the problem of forgeryAddressing Loss of Data OwnershipFinanceCommerceRandom oracleFinancial transaction
The invention discloses a block chain-based data transaction verification and data ownership tracing method and system, and the method comprises the steps: enabling a data user to upload data to an IPFS server through a block chain transaction platform, and returning a data address; generating a data label by using a file anti-counterfeiting mechanism, and generating a data commitment by using a random oracle machine; uploading the data label of the current data when an arbitration request is initiated for the authenticity of the data; a random oracle machine is used for inquiring to obtain a data label released by the data user, a data label stored in the IPFS server is obtained according to the data address, consistency comparison is carried out on the data label uploaded by the data buyer and the data label released by the data user, and whether data counterfeiting exists in the data user and the data buyer or not is judged. Through the technical scheme of the invention, data transaction verification and data ownership traceability can be completed, and the problems of data falsification and data ownership loss of two data transaction parties are solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
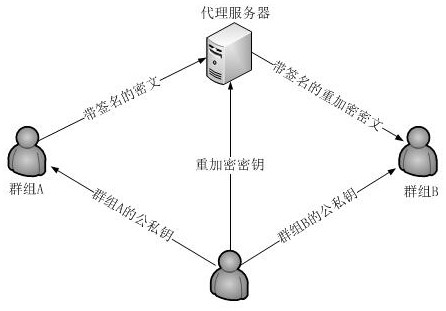
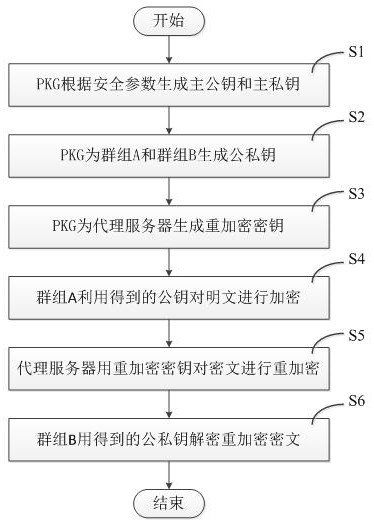
An Intergroup Proxy Re-encryption Method Resistant to Selected Ciphertext Attacks
ActiveCN106713349BReduce computational complexityReduce complexityTransmissionRandom oracleComputation complexity
The present invention discloses an inter-group proxy re-encryption method capable of resisting selected ciphertext attack. A ciphertext is re-encrypted through proxy, a decryption capability is designated based on the group, and any member in the group can decrypt the ciphertext independently, so that the method is more flexible than an individual-based proxy re-encryption method. A reliable, convenient data sharing manner is provided for cloud storage. The calculation complexity of a licensor and a licensee is relatively low, and encryption and decryption can be performed conveniently. Particularly, compared with existing inter-group proxy re-encryption methods, the method has the advantage that the calculation complexity in the key generation phase is lower. A primary strong unforgeable signature is added when the ciphertext is generated, so that the ciphertext and the re-encrypted ciphertext cannot be tampered. Finally, if a dual linear Diffie_Hellman assumption is valid, the selected ciphertext attack is resisted in a random oracle model.
Owner:郑州埃文计算机科技有限公司
Non-malleable obfuscator for sparse functions
ActiveUS10198584B2Digital data protectionCryptographic attack countermeasuresRandom oracleTheoretical computer science
Described is a system for obfuscating a computer program. Sensitive data of an unprotected computer program is received as input. A random oracle is used to algebraically hide a set of polynomial-size point functions representing the sensitive data. The system outputs a set of obfuscated instructions internally hiding the sensitive data. The set of obfuscated instructions are used to transform the unprotected computer program into a protected, obfuscated computer program that is accepting of the set of polynomial-size point functions. The obfuscated computer program is written to a non-volatile computer-readable medium.
Owner:HRL LAB
Fast oblivious transfers
ActiveUS11190496B2Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageRandom oracleKey exchange
Systems, methods, and computing device readable media for implementing fast oblivious transfer between two computing devices may improve data security and computational efficiency. The various aspects may use random oracles with or without key agreements to improve the security of oblivious transfer key exchanges. Some techniques may include public / private key strategies for oblivious transfer, while other techniques may use key agreements to achieve simultaneous and efficient cryptographic key exchange.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
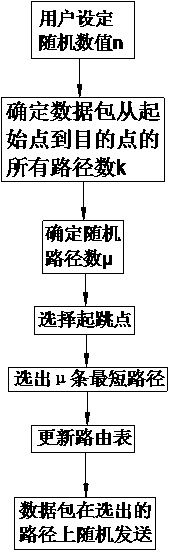
Random Shortest Path Routing Method
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless network communication, in particular to a random shortest path routing method. The method comprises the steps that 1, a random value n is set by a user, and the n represents the number of transmission paths of a data packet; 2, the number k of all usable paths of the data packet from an initial point to a destination point is determined; 3, mu random paths are determined, n is compared with k, if n is larger than k, mu is equal to k, otherwise, mu is equal to n; 4, a routing table is updated; 5, the data packet is sent on the mu random paths determined in the third step in a random mode. According to the random shortest path routing method, randomness is introduced, transmission of the data packet is unpredictable, the transmission paths of the data packet is jointly determined by the n set by the user and a network topological structure, the paths passed by the data packet are unpredictable, data passing through each path is only one part of the data packet, and a network intruder cannot obtain a complete data packet.
Owner:GUANGDONG ELINK INFORMATION TECH
A distributed authentication method for Internet of Vehicles based on block chain technology
ActiveCN113453170BImprove reliabilityMeet the needs of real-time authenticationParticular environment based servicesBroadcast service distributionRandom oracleVehicle behavior
The present invention relates to the field of access authentication in the Internet of Vehicles, in particular to a distributed authentication method for the Internet of Vehicles based on block chain technology. Based on the principle of high reliability and high efficiency, under the premise of considering the trust of edge nodes, RSU spontaneously establishes an edge authentication chain through three-stage broadcasting, thereby dividing the Internet of Vehicles into multiple edge authentication areas; RSUs in the area pass Chebyshev The semi-group characteristics of the mapping realize the rapid authentication of local vehicles; the RSU as a blockchain node stores the authentication records of the vehicles, and when the vehicle behavior changes, the local vehicle list is updated in time; finally, the random oracle model is used to verify the proposed authentication scheme. The security of the invention is proved; the invention can realize distributed access authentication with high efficiency and high reliability under the premise of considering the RSU trust problem.
Owner:南京清科链谷科技服务有限公司
Cloud storage ciphertext data public key searchable encryption method under the standard model
ActiveCN106789044BReaction securityResist attackKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationRandom oracleLearning with errors
The invention belongs to the technical field of cyberspace security and particularly relates to a PEKS (public-key encryption with keyword search) method for lattice-based cloud stored cyphertext data under standard model. The method of the invention has no need for a random oracle so that the security of the designed PEKS method can more truly reflected; a designed cryptographic algorithm is based on assumption of LWE (learning with errors) hard problems, quantum computer attacks can be resisted effectively. The method of the invention has a need for specifying a unique cloud server to perform testing and return corresponding search results, so that no malicious servers are able to execute search test operation, and malicious server attacks are partly avoided accordingly. In addition, the algorithm can ensure that cyphertext is undistinguishable. Furthermore, in keyword cyphertext generation phase, the method of the invention needs no computing of high-overhead modular exponentiation and bilinear pairing operation, but the computing of finite linear algebraic operation, and accordingly is highly worthy of practical application in post-quantum communication environments.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
An Efficient Public Key Encryption Method with Forward Security
ActiveCN103684764BConstant lengthConstant encryption and decryption overheadPublic key for secure communicationRandom oraclePlaintext
The invention discloses an efficient public key encryption method with forward security, comprising the following steps: step 1, system initialization, calculating the user's public key PK and initial private key SK1; step 2, updating the key; step 3 1. Use the public key PK to encrypt the plaintext m, and obtain the ciphertext CT of the plaintext m in the current time period i; step 4, use the private key SKi of the current time period i to decrypt the ciphertext CT, and obtain the plaintext m. The positive effect of the invention is: the encryptor only needs to hold one group element, and can obtain public keys of various time periods through public information. In addition, the public key can be identity information. On this basis, the identity-based encryption scheme can be converted into a forward-secure public-key encryption scheme, and the forward-secure security of adaptively selected ciphertexts can be obtained under the random oracle model. Efficient public-key encryption scheme.
Owner:NO 30 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP
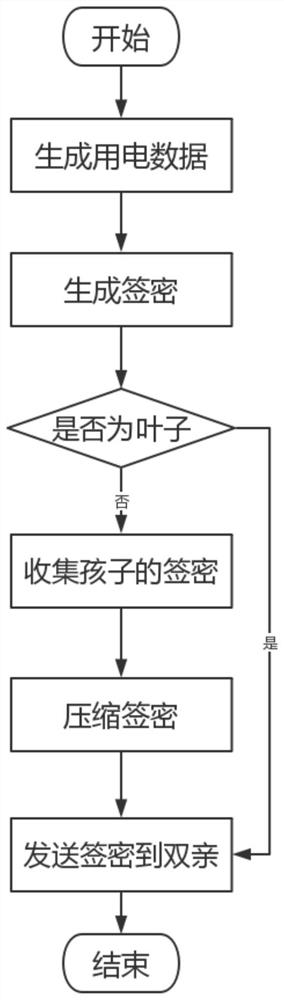
A smart grid system based on batch signcryption and its construction method
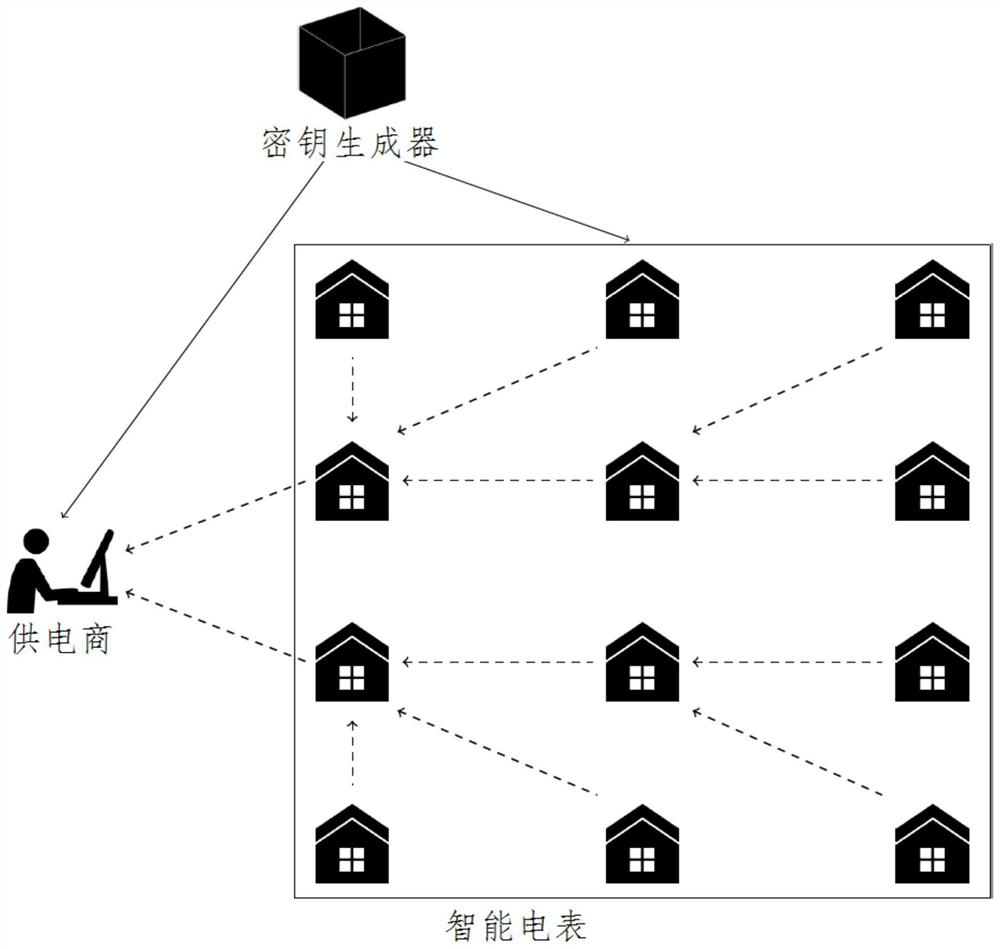
ActiveCN110445255BSolve protection problemsIntegrity guaranteedPower network operation systems integrationCircuit arrangementsCommunications securityRandom oracle
The invention discloses a smart grid system based on batch sign encryption and its construction method. The user report is protected by a key. As long as the key is not disclosed, the user's electricity consumption data will not be tampered with or leaked during the transmission process. , the integrity and validity of electricity consumption reports are guaranteed, which can solve the problems of communication security and privacy protection in smart grids. In addition, in the technical solution provided by the present invention, a tree topology is used to collect power consumption data, and the computing cost of the power supplier is distributed to each smart meter. In addition, the technical solution provided by the present invention constructs a signcryption scheme without a random oracle, and each smart meter uses a constant level of calculation to verify multiple signcryptions. Moreover, the smart meter generates a new signature and ciphertext by simply adding the signature and the key, and no longer needs re-encryption and re-signature with a large amount of calculation, thereby reducing the calculation time of the system.
Owner:CENTRAL UNIVERSITY OF FINANCE AND ECONOMICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com