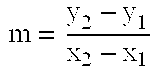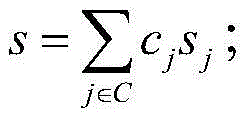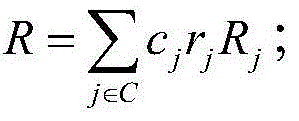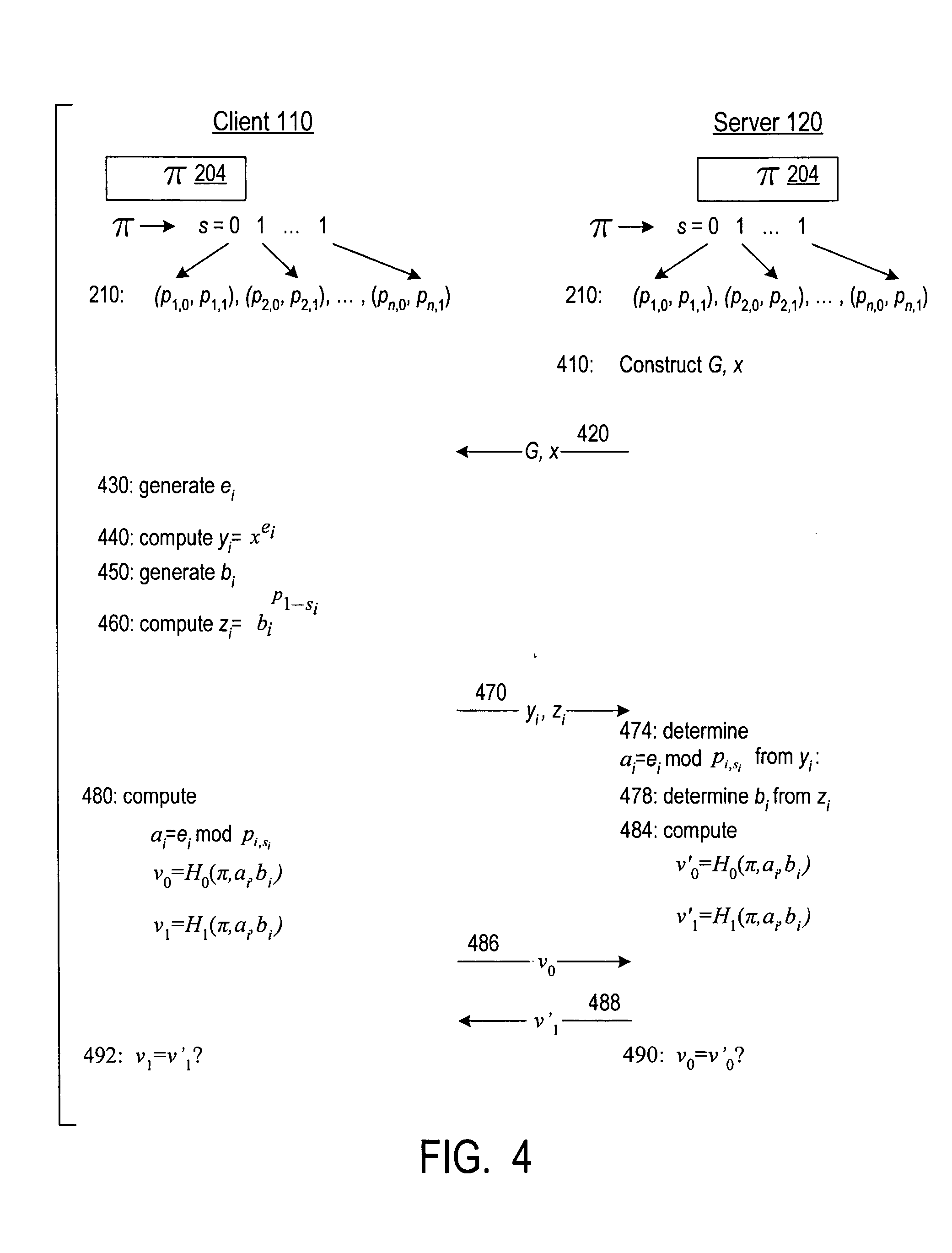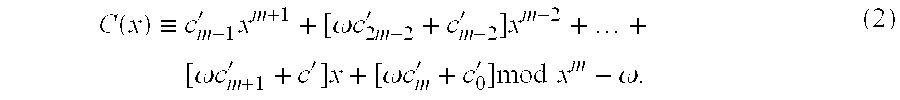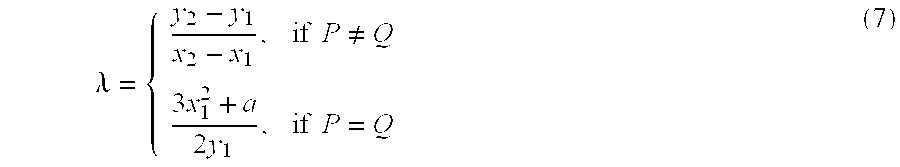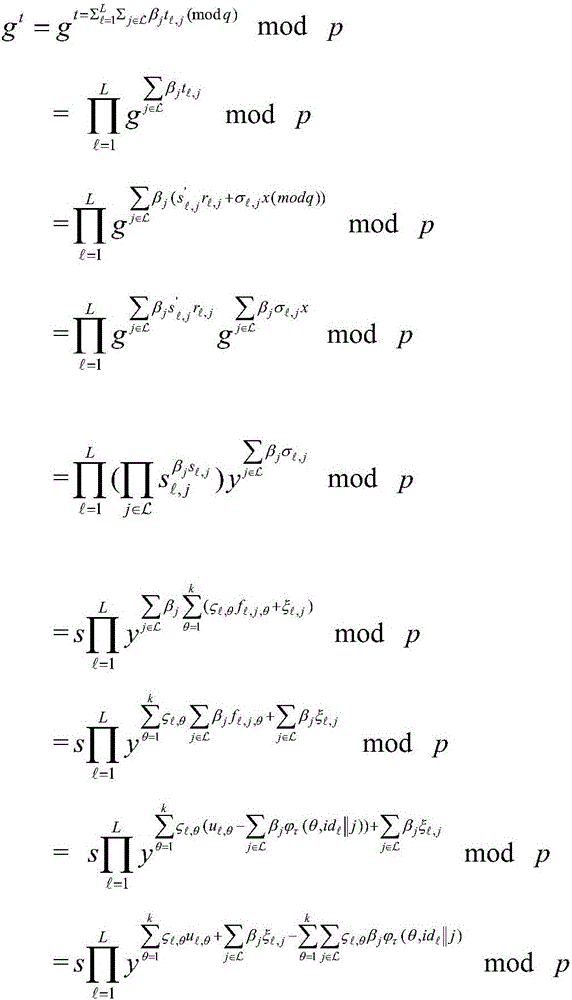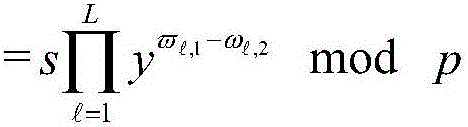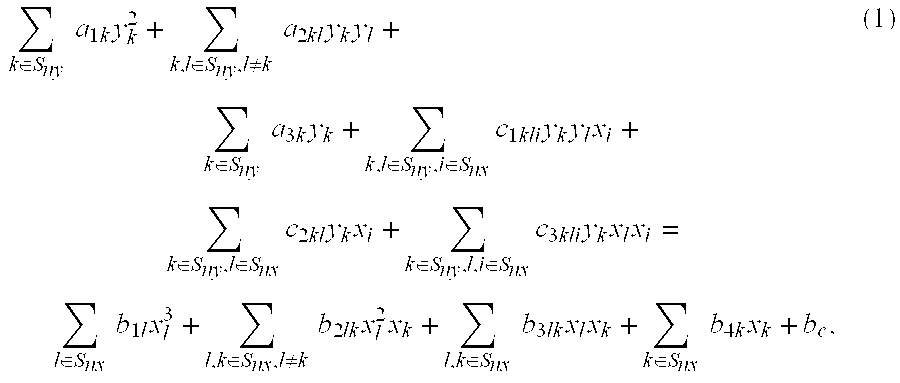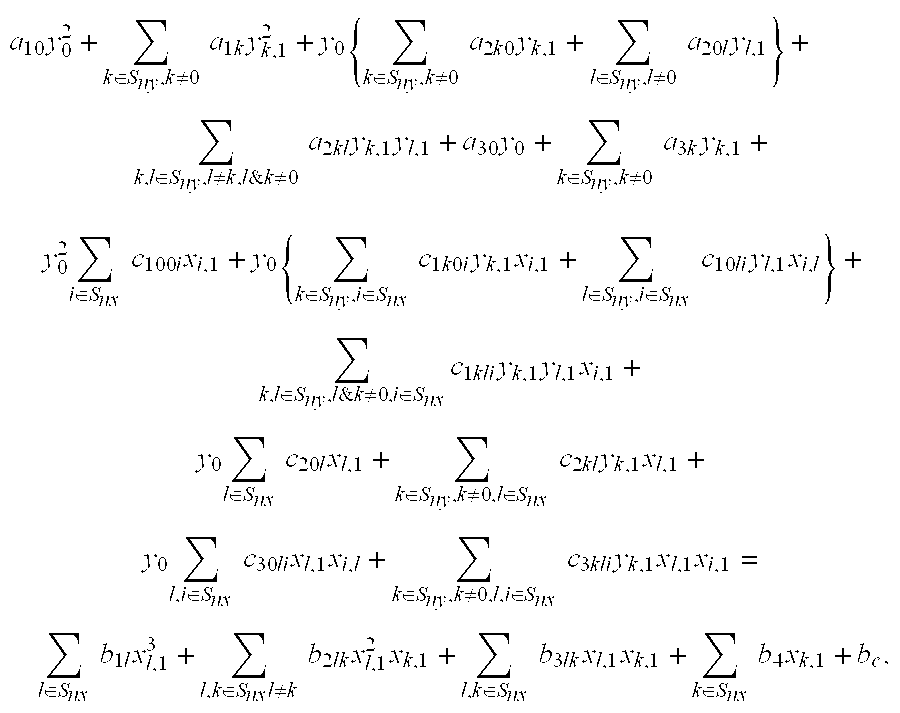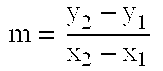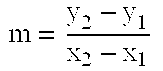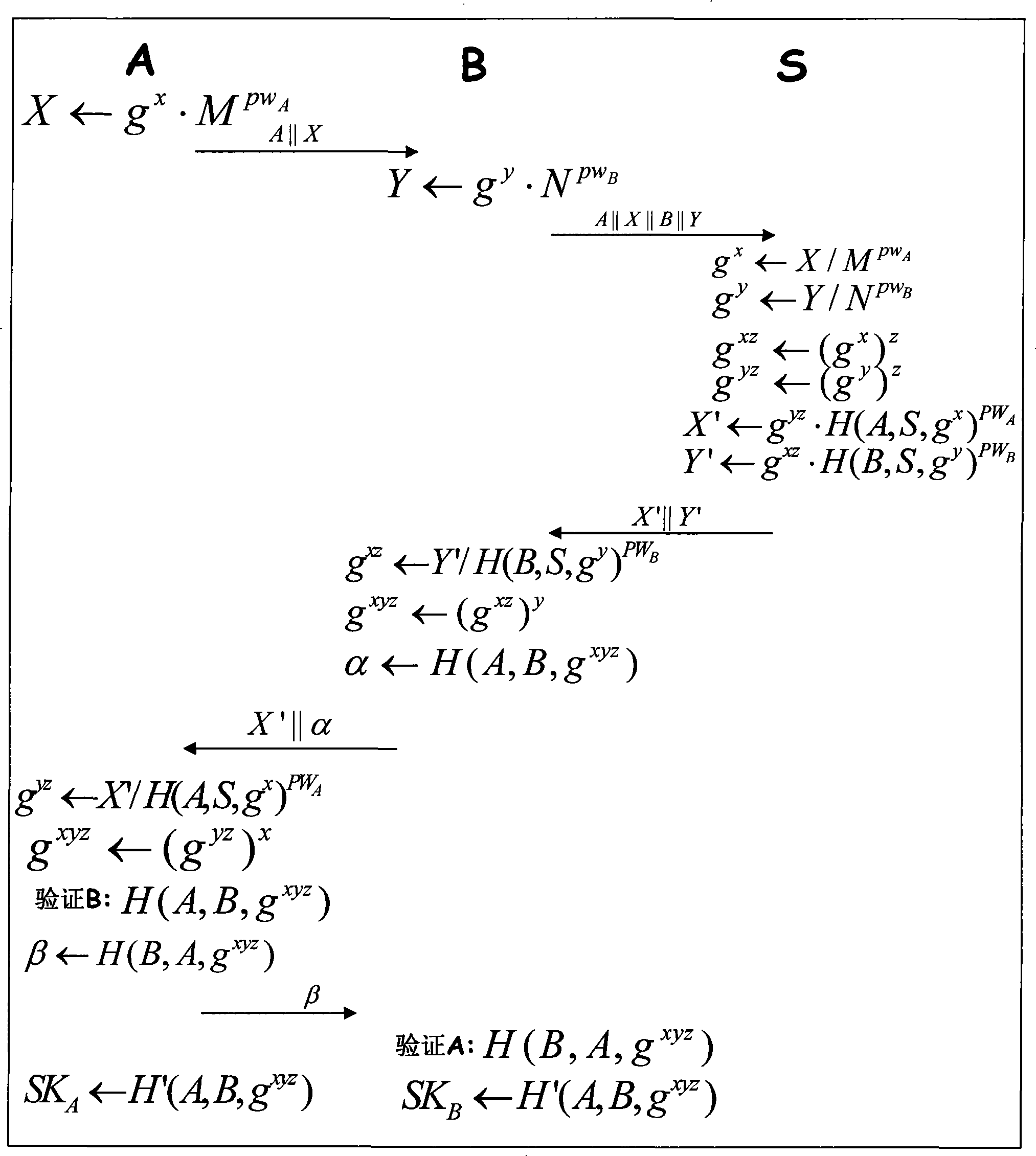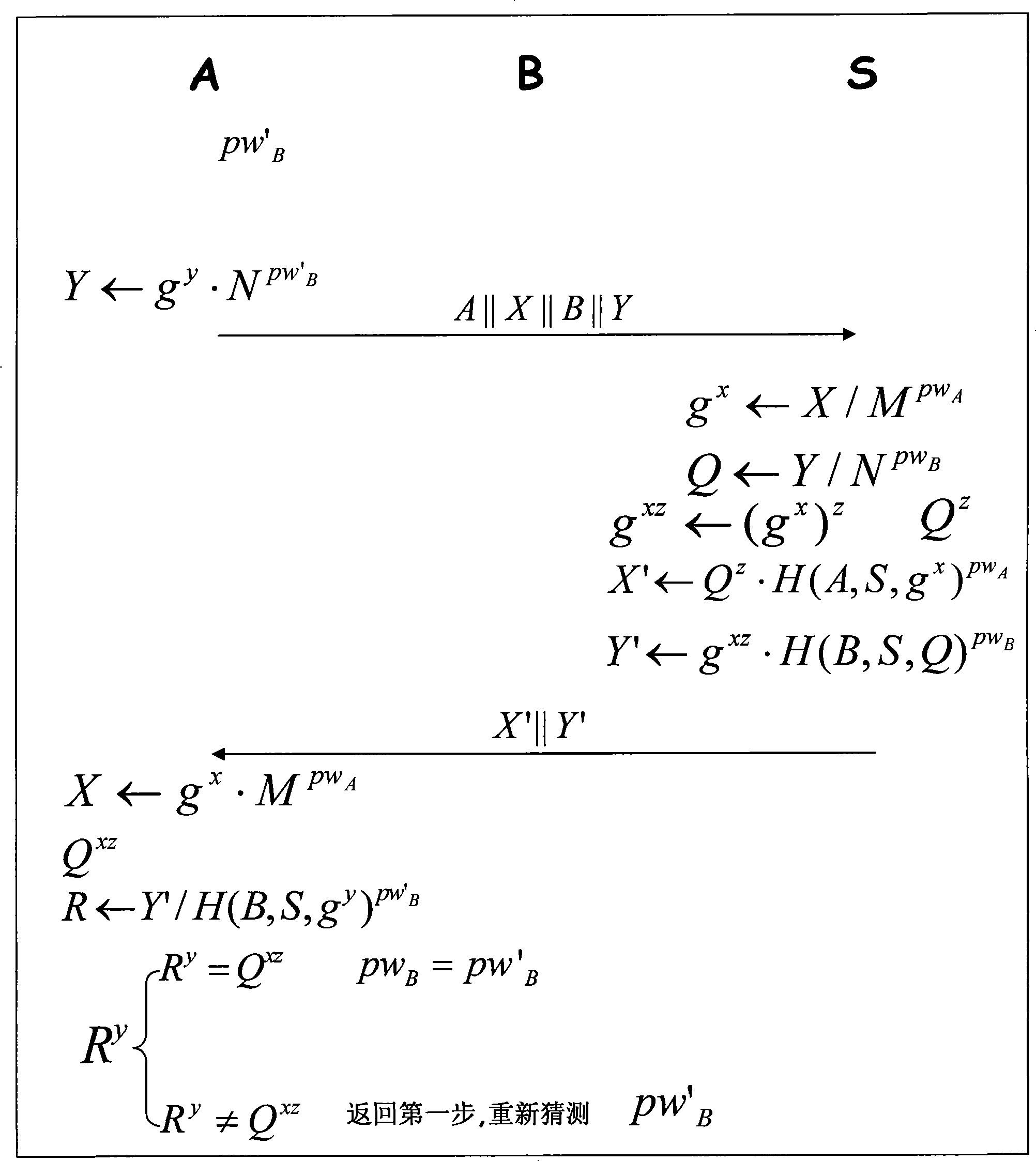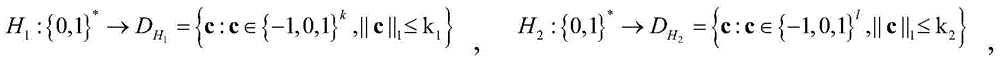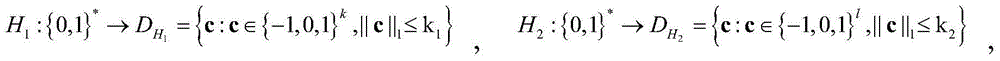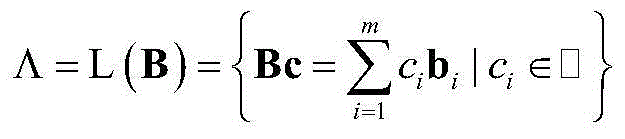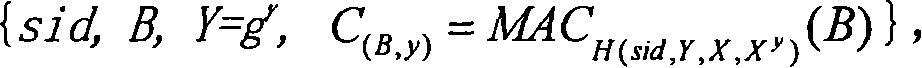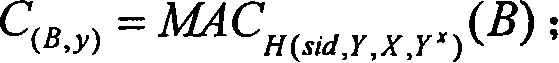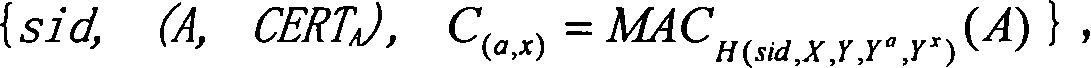Patents
Literature
123 results about "Discrete logarithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
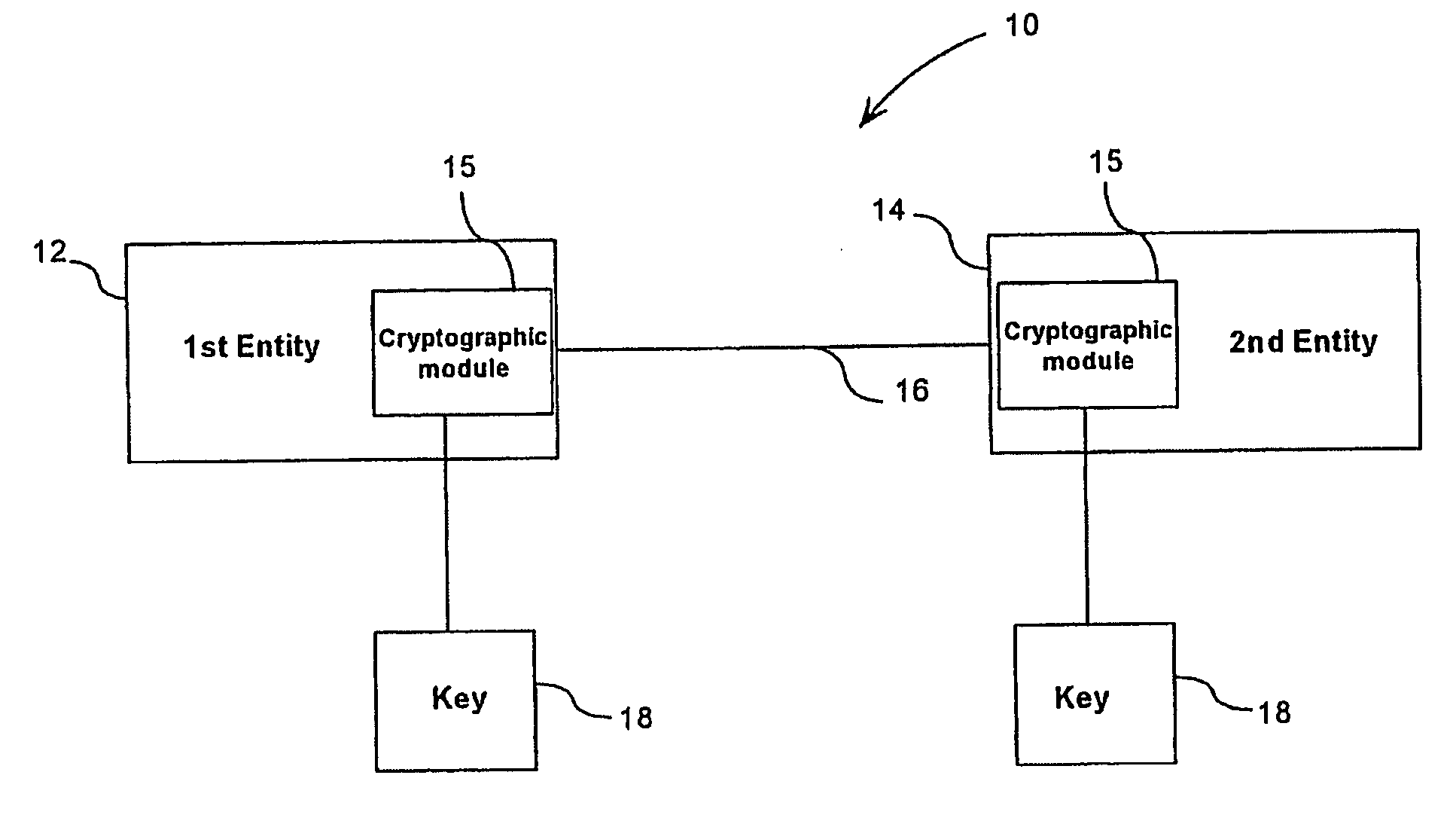
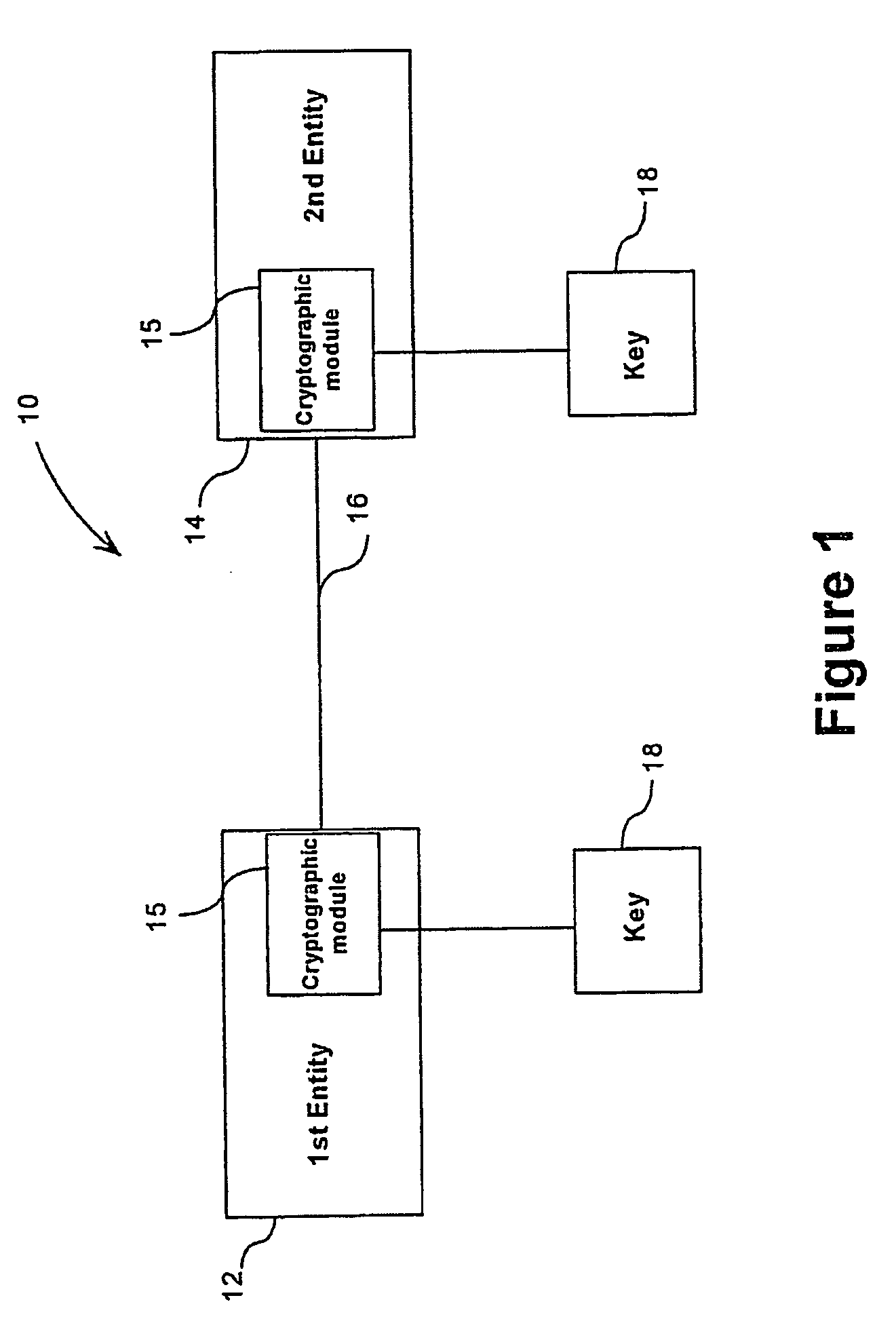
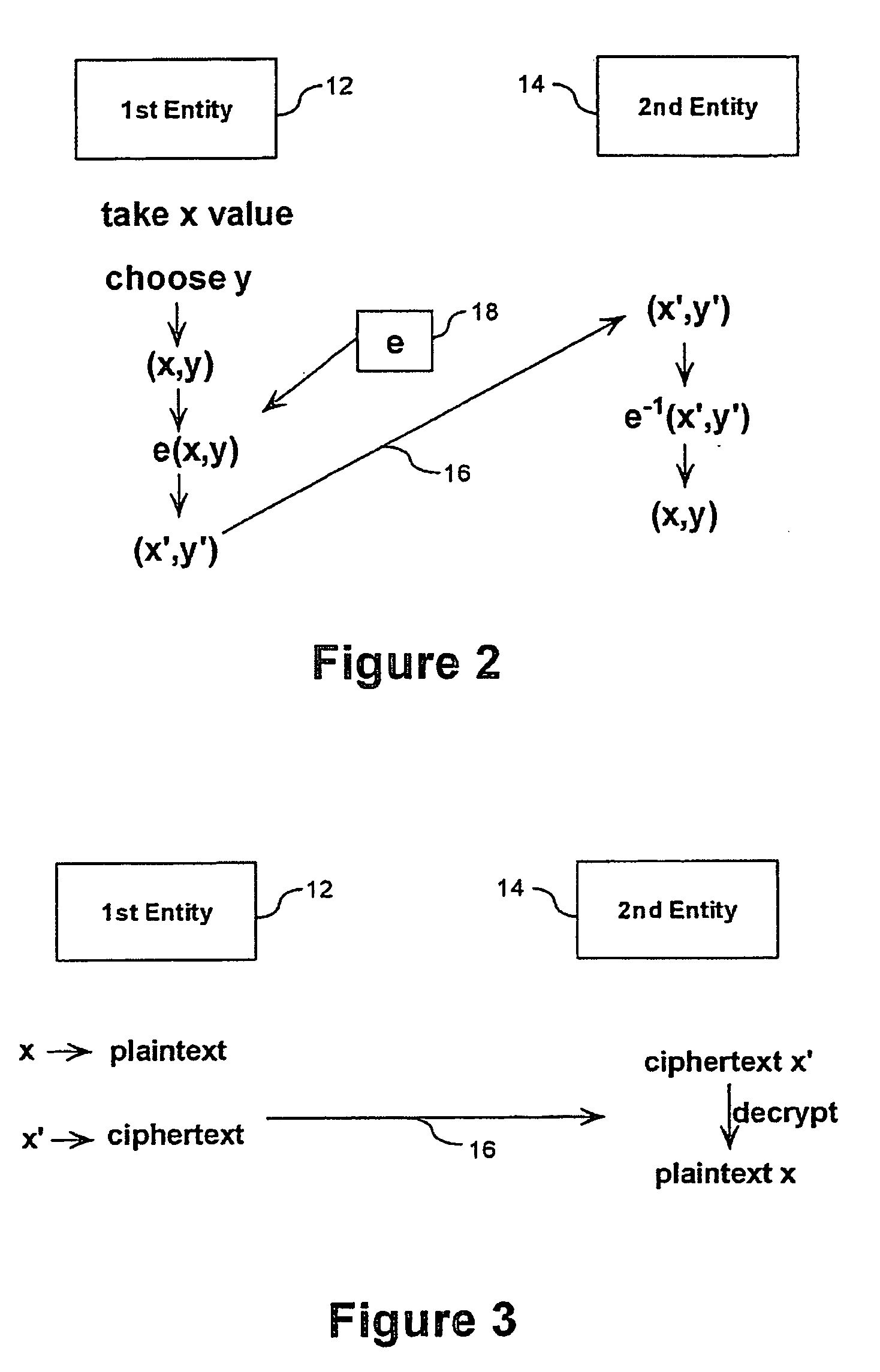
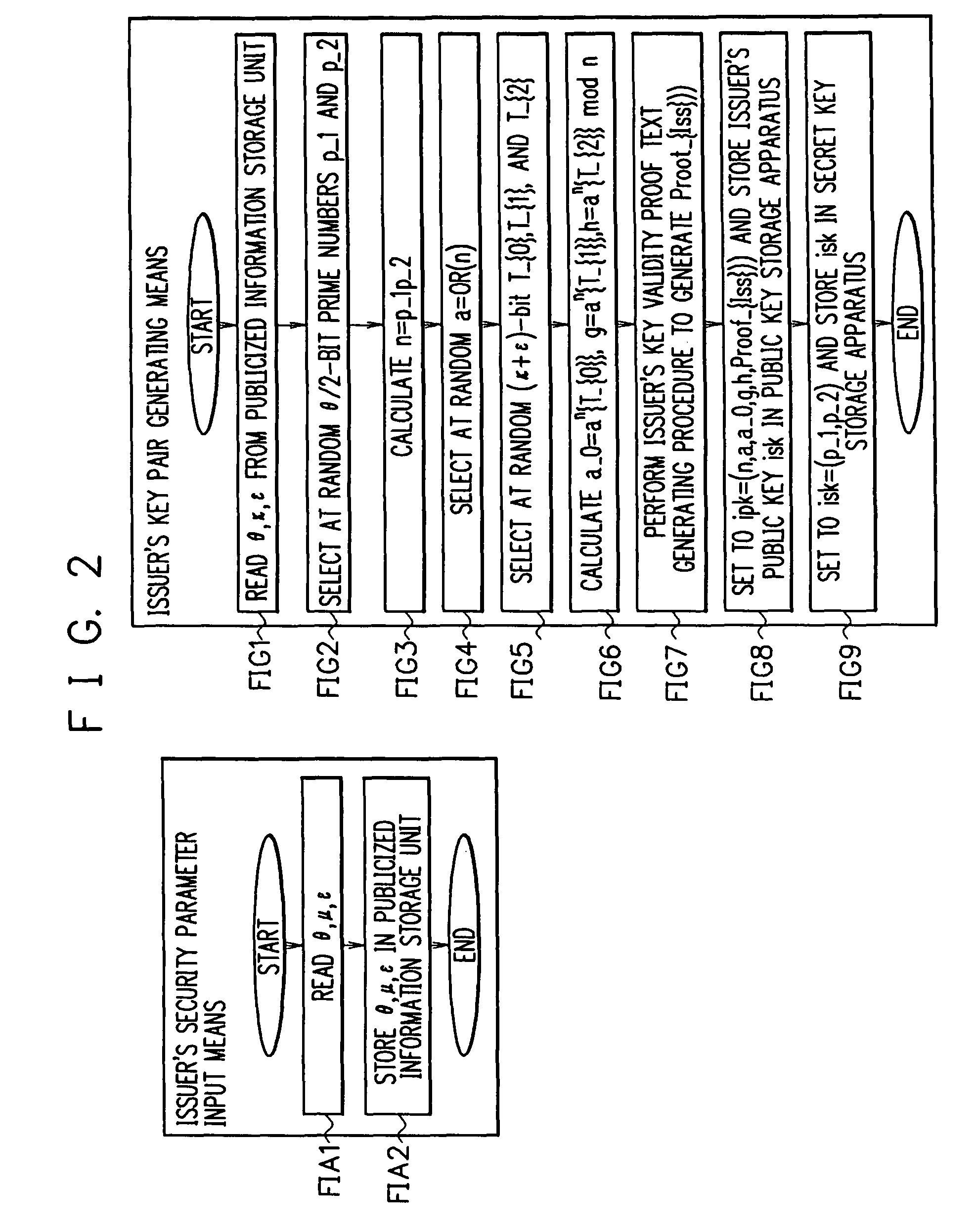
In the mathematics of the real numbers, the logarithm logb a is a number x such that b = a, for given numbers a and b. Analogously, in any group G, powers b can be defined for all integers k, and the discrete logarithm logb a is an integer k such that b = a. In number theory, the more commonly used term is index: we can write x = indᵣ a (mod m) (read the index of a to the base r modulo m) for r ≡ a (mod m) if r is a primitive root of m and gcd(a,m) = 1.
Low orbit satellite multi-sensor fault tolerance autonomous navigation method based on federal UKF algorithm
InactiveCN101216319AGuaranteed continuityGuaranteed stabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationEarth satelliteFault tolerance
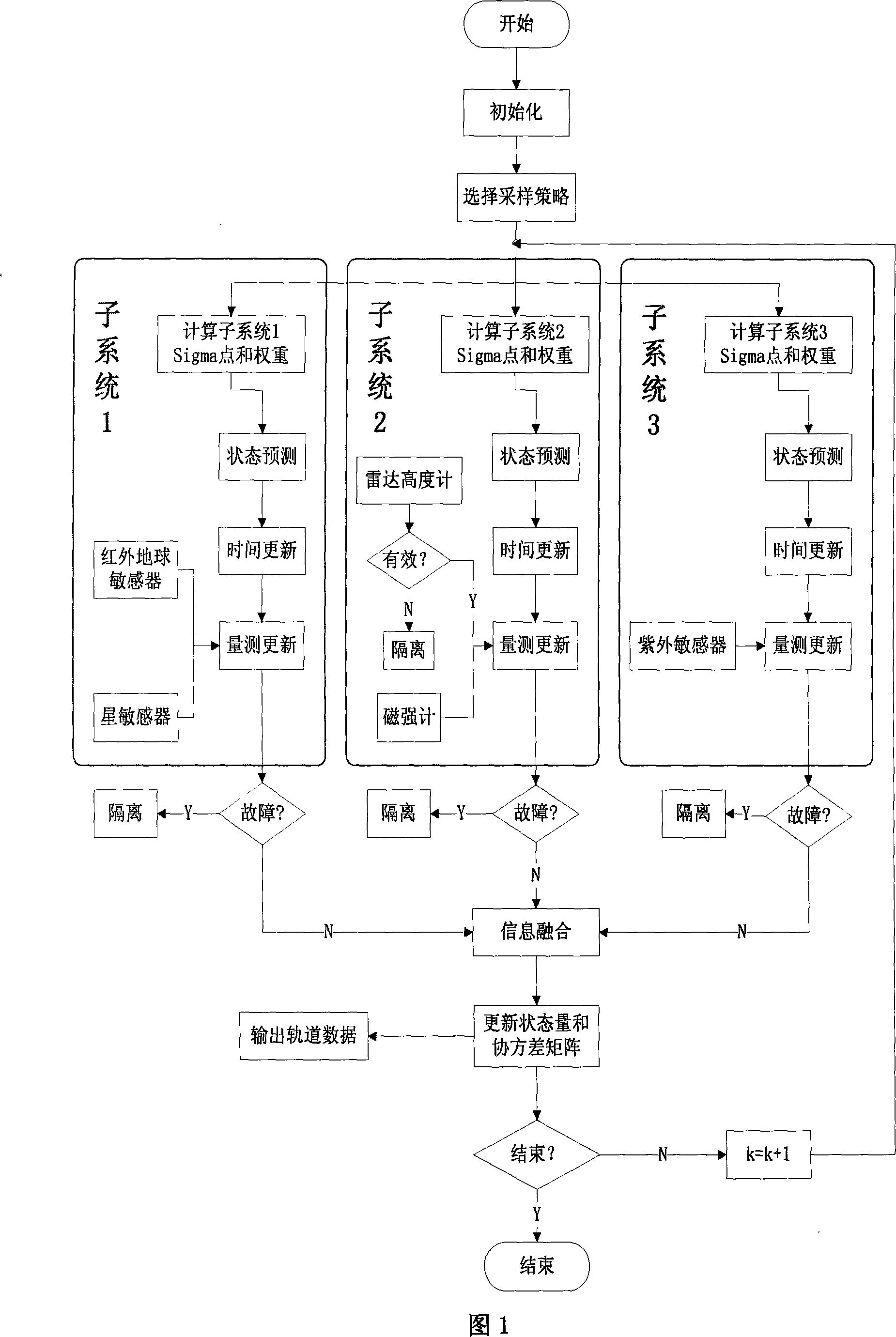
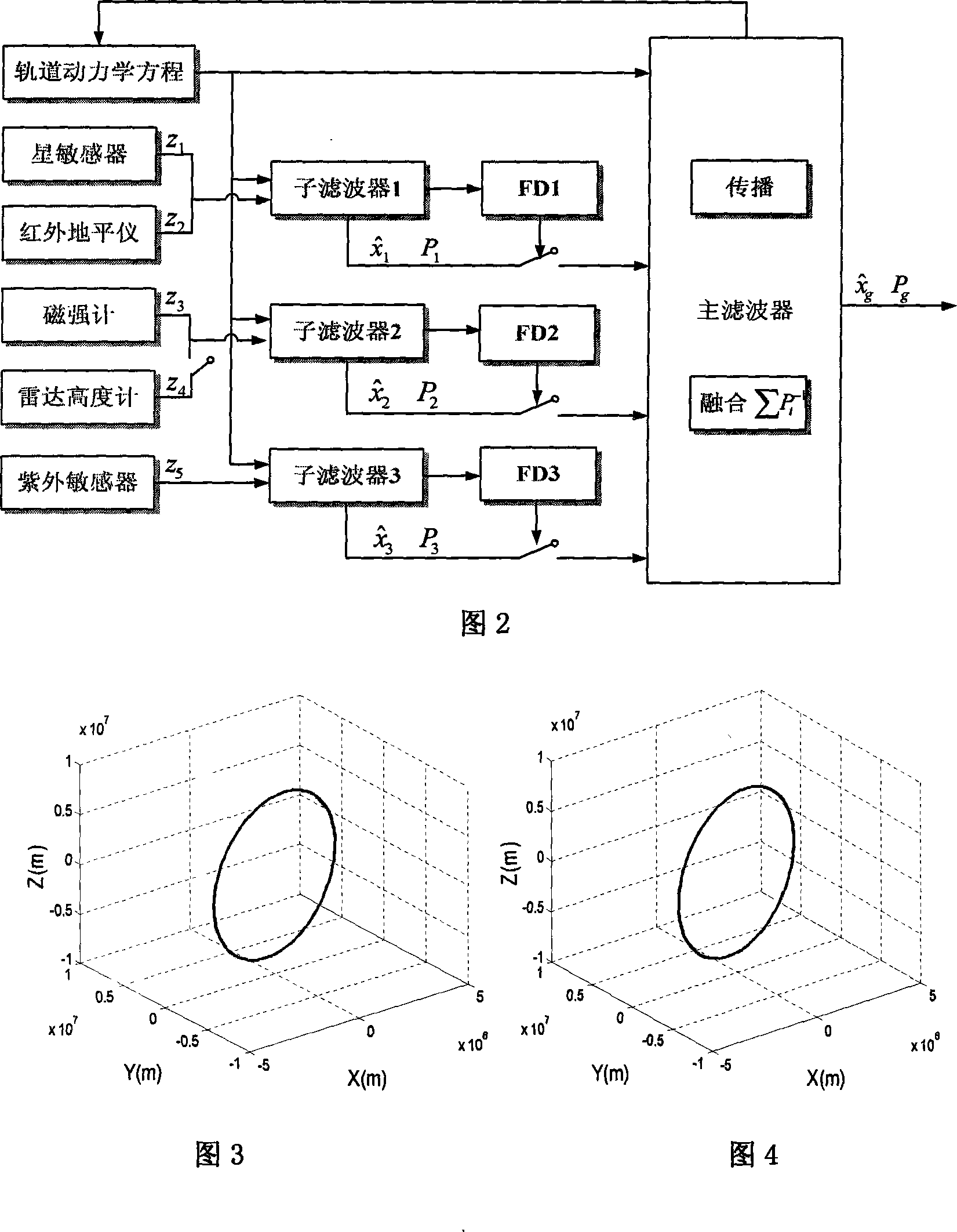
The invention relates to a multi-sensor autonomous navigation method for the low-orbiting satellite with fault-tolerance function and based on federated UKF algorithm, belonging to satellite autonomous navigation method. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing an orbital dynamics equation of earth satellite in a rectangular coordinate system; constructing a subsystem measurement equation with the output values of a star sensor and an infrared earth sensor as measurement quantities; constructing a subsystem measurement equation with the output values of magnetometer and a radar altimeter as measurement quantities; constructing a subsystem measurement equation with the output value of an ultraviolet sensor as measurement quantity; selecting a Sigma sampling point; constructing a predictive equation and an update equation of discrete UKF algorithm; respectively and independently performing Sigma sampling point calculation of each subsystem, and performing predictive update and measurement update; determining whether the output of each sub-filter is valid according to the predicted filter residual, isolating in case of malfunction, otherwise, inputting the filter result to a main filter for information fusion; constructing a non-reset federated UKF filter equation based on the UKF algorithm; and outputting earth satellite state estimated value X and variance matrix P thereof according to the steps.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method of performing cipher block chaining using elliptic polynomial cryptography
InactiveUS20110200188A1Finite divisionKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationTheoretical computer scienceDiscrete logarithm
The method of performing cipher block chaining using elliptic polynomial cryptography allows for the encryption of messages through elliptic polynomial cryptography and, particularly, with the utilization of cipher block chaining based upon both the elliptic polynomial and its twist, regardless of whether the elliptic polynomial and its twist are isomorphic with respect to one another. The method of performing cipher block chaining is based on the elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem. It is well known that an elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem is a computationally “difficult” or “hard” problem.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
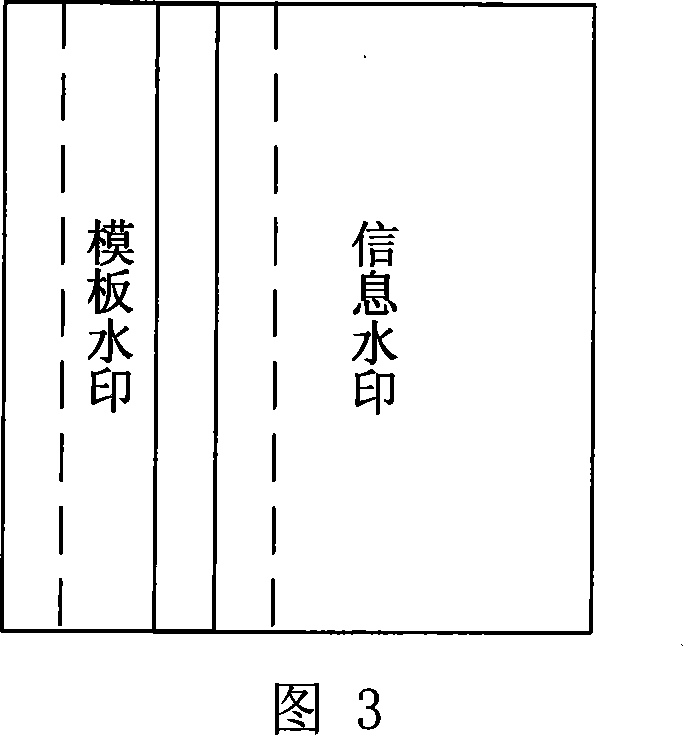
Multiple bit digital watermark method capable of resisting printing, scanning and geometric transformation
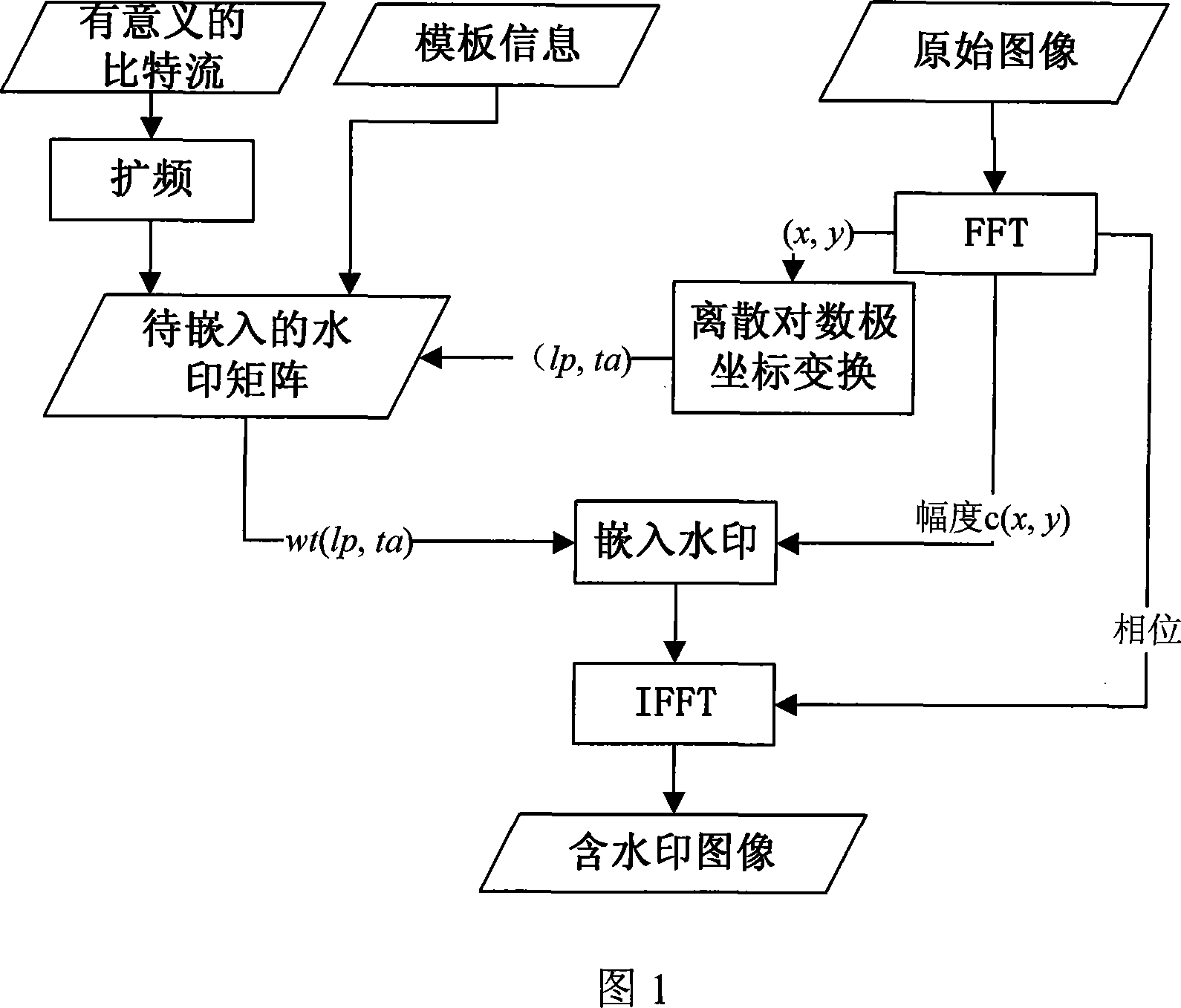
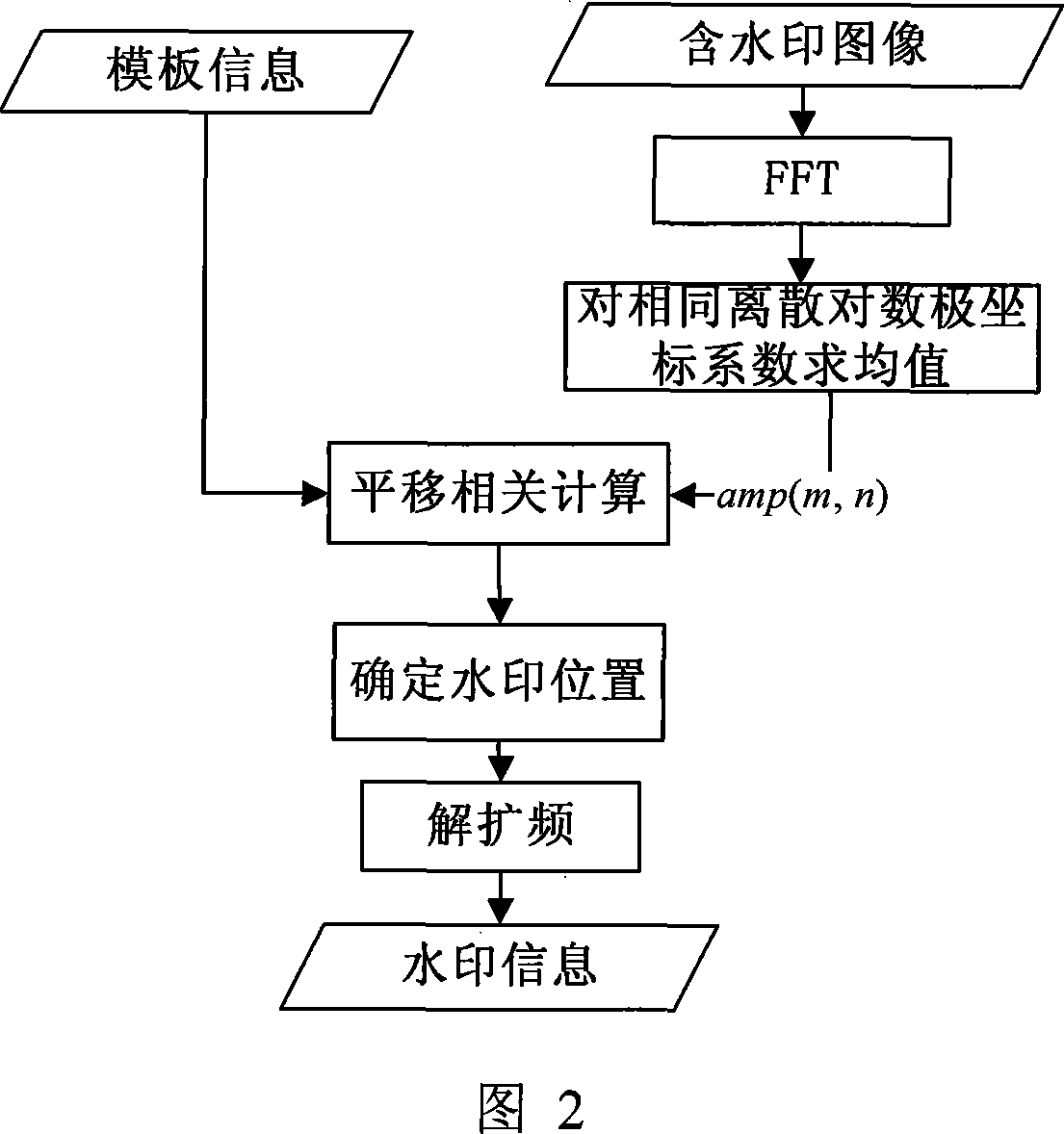
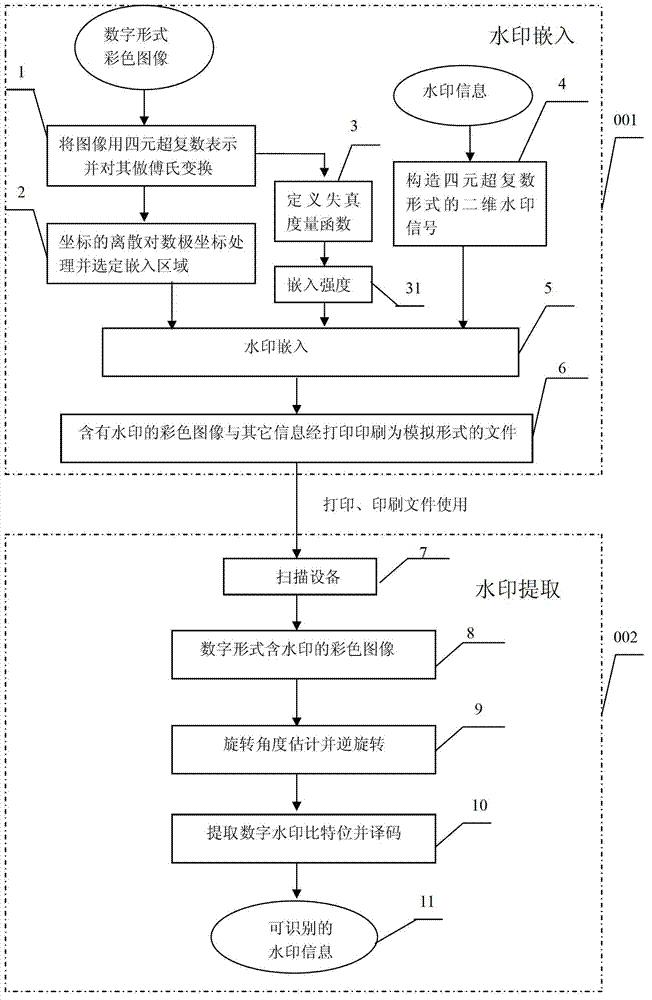
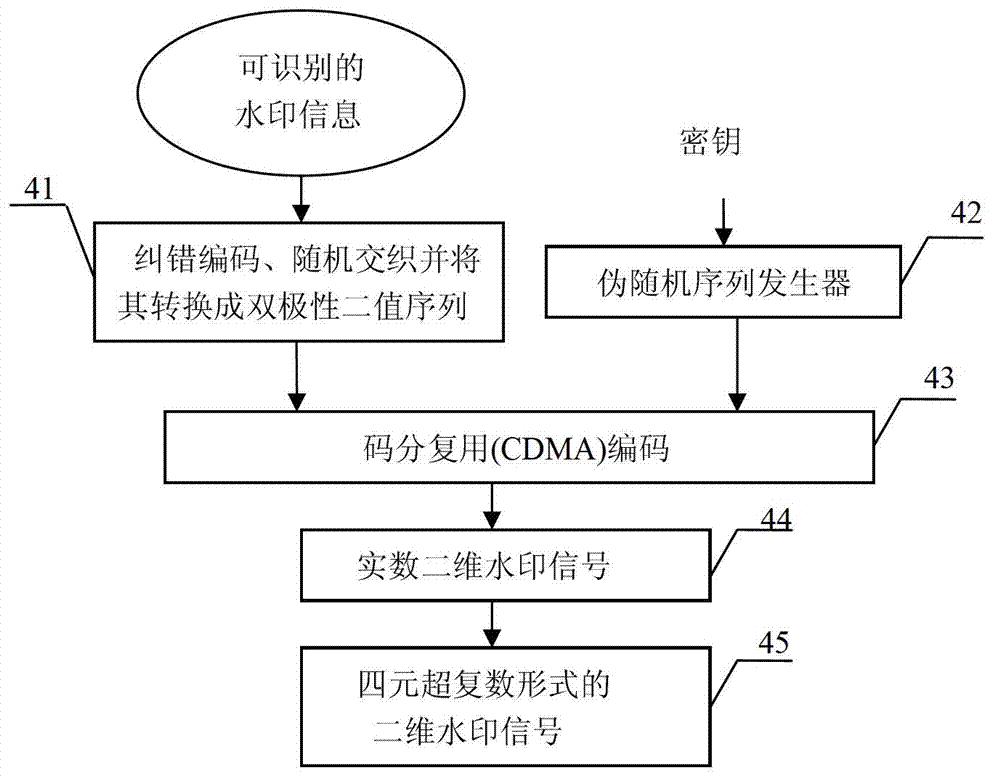
The invention discloses a multi-bit digital watermark method against the print scanning and the geometric transformation, which comprises the following steps: embedding the watermark in dispersion Fourier amplitude coefficient of the image; determining which Fourier amplitude coefficient every watermark bit embeds in according to the dispersion logarithmic polar coordinate of the Fourier amplitude coefficient; making the watermark detecting and extracting out-of-step when the image is carried out the geometric transformation of the pantographic rotating or the print scanning; synchronizing the information watermark according to the relation of the original mode and embedded mold when the watermark is detected and extracted because the pantograph and the rotating of the image corresponds with the translation of the Fourier logarithmic polar coordinate field at the radial and angel direction; extracting the meaning watermark information bit string; introducing the real interpolation and saving the time because the watermark embedding and detecting process doesn' t need the image interpolation arithmetic for the image and the Fourier amplitude coefficient; protecting the embedded mode. The invention can apply to the copyright protection of the digital image and video, false proof of the file and evidence, the monitoring of video broadcast.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method of generating a password protocol using elliptic polynomial cryptography
InactiveUS20110202773A1Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringPasswordTheoretical computer science
The method of generating password protocols based upon elliptic polynomial cryptography provides for the generation of password protocols based on the elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem. It is well known that an elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem is a computationally “difficult” or “hard” problem.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Cloud-storage data lightweight-level public auditing method with privacy protection
InactiveCN104023044AShort signature lengthSave storage spaceUser identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionOriginal dataPrivacy protection
The invention discloses a cloud-storage data lightweight-level public auditing method with privacy protection. The method comprises the steps of system initialization, signature, auditing certification, and auditing certification verification. The method uses a modified digital signature algorithm based on an elliptical curve, the security of the method depends on the discrete logarithm problem of a finite group of the elliptical curve, and the method is characterized by low signature length, small storage space and high computation speed, and is especially suitable for occasions with lightweight-level computation amount, limited storage space and high-efficiency realization. The method of the invention is simple and convenient to operate, solves the problems that cloud-storage data public auditing and present cloud-storage data are low in privacy and the completeness and accuracy of user data cannot be ensured, and ensures that original user data is not leaked out to a cloud server or a public auditor.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Cryptographic authentication and/or establishment of shared cryptographic keys, including, but not limited to, password authenticated key exchange (PAKE)
ActiveUS20060291661A1Improve efficiencySmall probabilityUser identity/authority verificationTransmission protocolAlgorithm
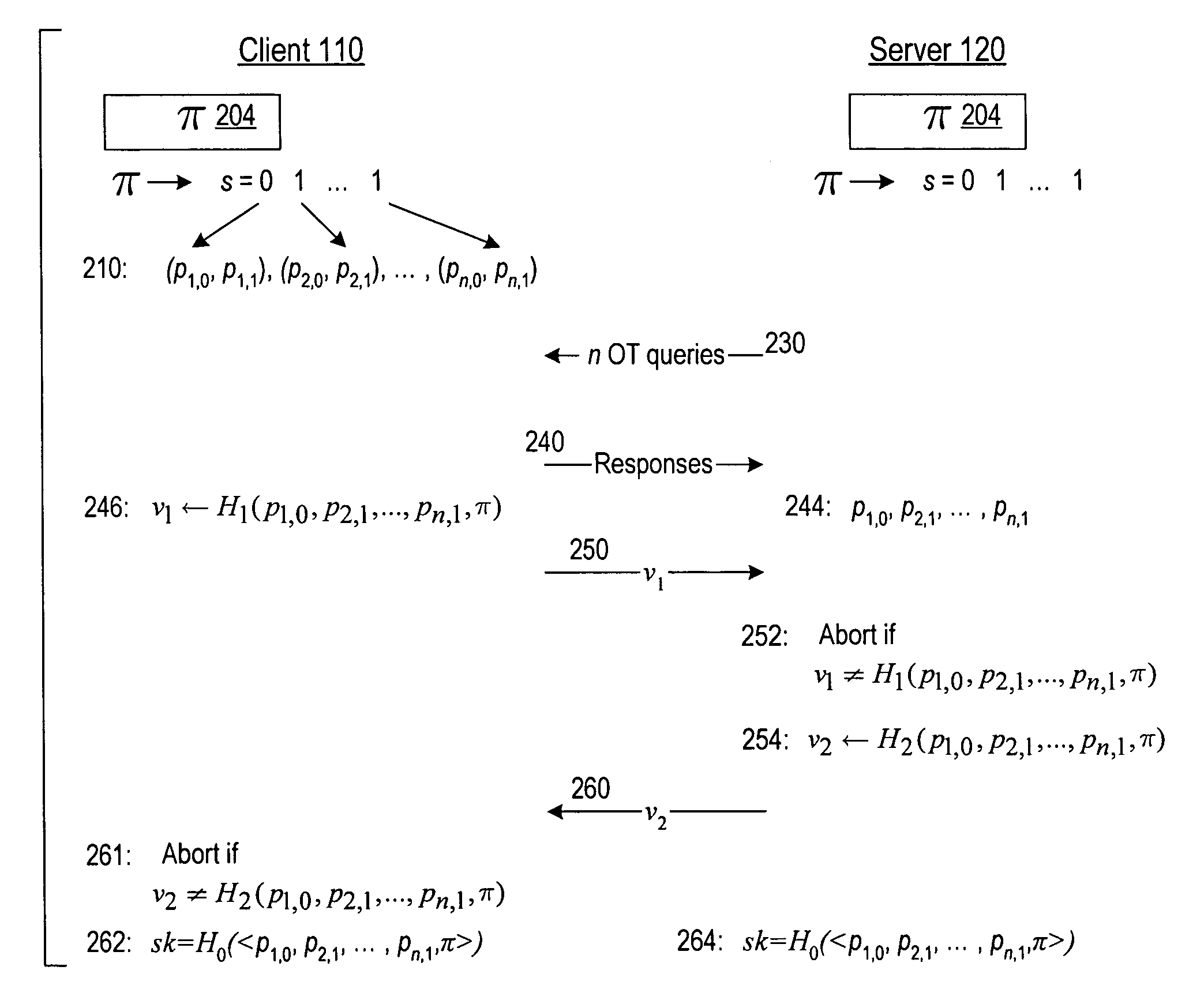
A server (120) uses a password (π) to construct a multiplicative group (ZN*) with a (hidden) smooth order subgroup (<x′>), where the group order (Pπ) depends on the password. The client (110) uses its knowledge of the password to generate a root extraction problem instance (z) in the group and to generate data (y) allowing the server to construct a discrete logarithm problem instance (y′) in the subgroup. The server uses its knowledge of the group order to solve the root extraction problem, and solves the discrete logarithm problem efficiently by leveraging the smoothness of the subgroup. A shared key (sk) can be computed as a function of the solutions to the discrete logarithm and root extraction problem instances. In some embodiments, in an oblivious transfer protocol, the server queries the client (at 230) for data whose position in a database (210) is defined by the password. The client provides (240) such data without knowing the data position associated with the server's query. The client obtains the data position independently from the password. The data positions and / or the respective data are used for authentication and shared secret key generation. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Steady audio-frequency water mark method based on Fourier discrete logarithmic coordinate transformation
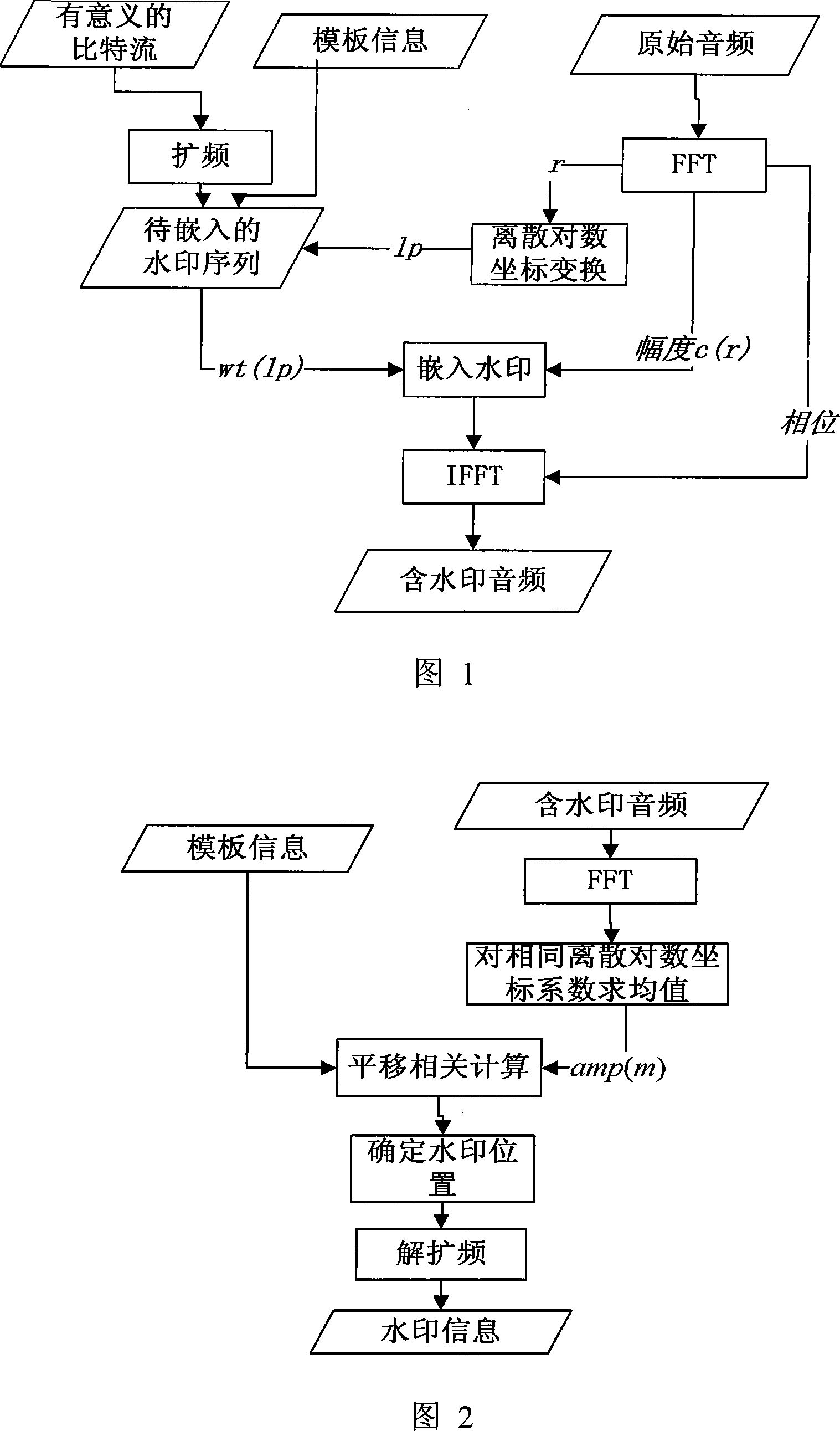
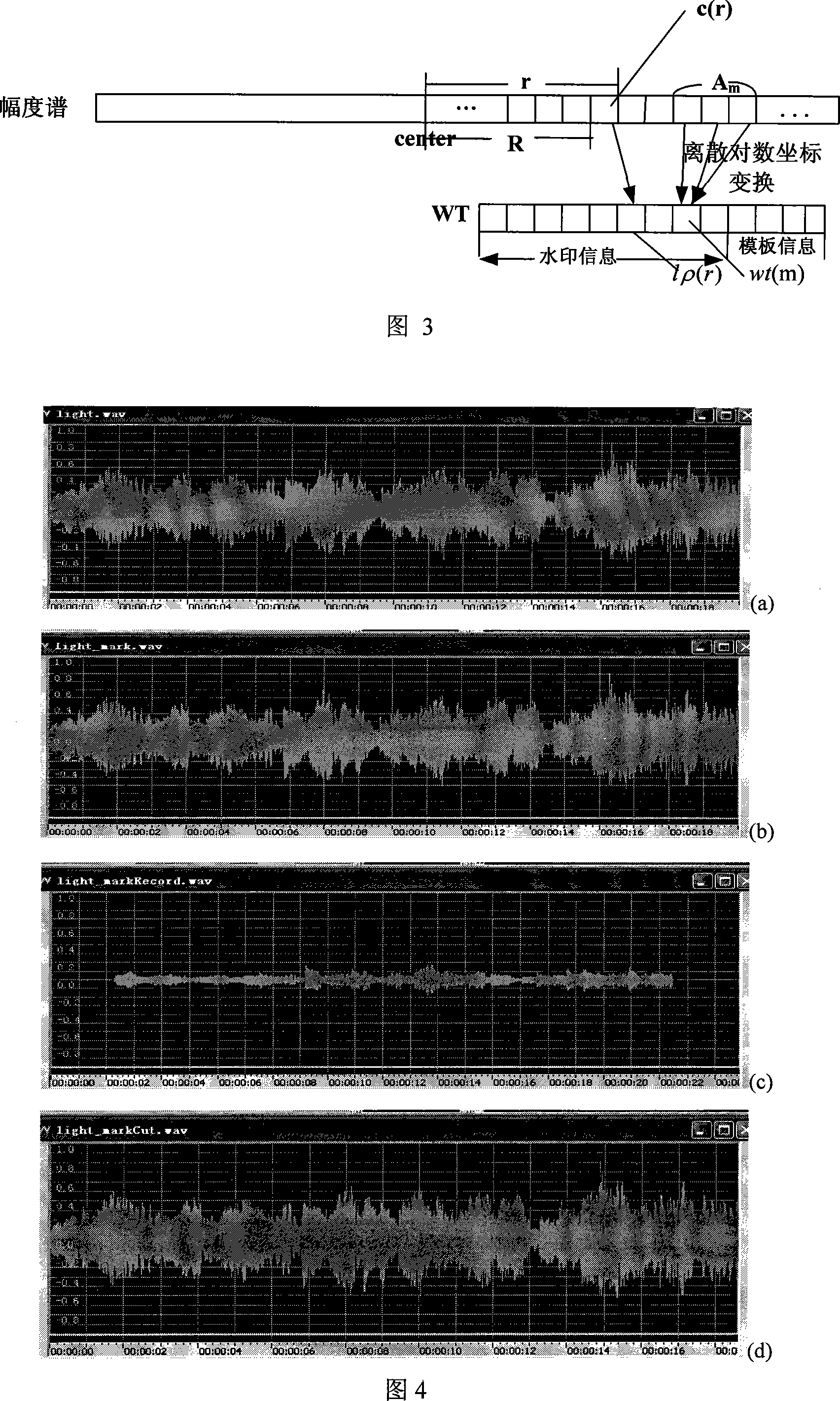
The inserted watermark includes the model board (MB) and the meaningful info (MI). This invention inserts the watermark into the audio scatter Fourier amplitude coefficient (FAC). Each watermark bit is inserted into which FACs according to the FAC scatter logarithm coordinate. When the audio info happens to be attacked, e.g. extended, cut or DA / AD converted, the amplitude coefficient (AC) and the watermark info are still strongly related in the Fourier scatter logarithm domain (FSLD). When the watermark is verified or drawn, the watermark info is re-synchronized according to the correlation between the FSLD ACs of the original MB and the inserting MB. Then the meaningful watermark info bit series is drawn. Due to audio inner-insert calculation on audio or its FAC is unnecessary during the watermark inserting and verifying process, the insert distortion is avoided and time is saved. As a novel audio watermark technique, this invention can be applied in areas of digital audio copyright protection, audio authentication and broadcast supervision, etc.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Trapdoor one-way functions on elliptic curves and their application to shorter signatures and asymmetric encryption
ActiveUS20060140400A1Reduced bandwidthPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEllipseShort signature
The present invention provides a new trapdoor one-way function. In a general sense, some quadratic algebraic integer z is used. One then finds a curve E and a rational map defining [z] on E. The rational map [z] is the trapdoor one-way function. A judicious selection of z will ensure that [z] can be efficiently computed, that it is difficult to invert, that determination of [z] from the rational functions defined by [z] is difficult, and knowledge of z allows one to invert [z] on a certain set of elliptic curve points. Every rational map is a composition of a translation and an endomorphism. The most secure part of the rational map is the endomorphism as the translation is easy to invert. If the problem of inverting the endomorphism and thus [z] is as hard as the discrete logarithm problem in E, then the size of the cryptographic group can be smaller than the group used for RSA trapdoor one-way functions.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method for efficient computation of odd characteristic extension fields
InactiveUS7069287B2Acceptable computational performanceLow costDigital computer detailsSecret communicationMicrocontrollerTheoretical computer science
A method for implementing an elliptic curve or discrete logarithm cryptosystem on inexpensive microprocessors is disclosed which provides for advantageous finite field computational performance on microprocessors having limited computational capabilities. The method can be employed with a variety of commercial and industrial imbedded microprocessor applications such as consumer smart cards, smart cards, wireless devices, personal digital assistants, and microprocessor controlled equipment. In one embodiment, a Galois Field (GF) implementation based on the finite field GF((28−17)17) is disclosed for an Intel 8051 microcontroller, a popular commercial smart card microprocessor. The method is particularly suited for low end 8-bit and 16-bit processors either with or without a coprocessor. The method provides for fast and efficient finite field multiplication on any microprocessor or coprocessor device having intrinsic computational characteristics such that a modular reduction has a greater computational cost than double precision, long number additions or accumulations. The disclosed method offers unique computational efficiencies in requiring only infrequent subfield modular reduction and in employing an adaptation of Itoh and Tsujii's inversion algorithm for the group operation. In one embodiment, a core operation for a signature generation, an elliptic curve scalar multiplication with a fixed point, is performed in a group of order approximately 2134 in less than 2 seconds. In contrast to conventional methods, the method does not utilize or require curves defined over a subfield such as Koblitz curves.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
Hash functions with elliptic polynomial hopping
InactiveUS20100177890A1Readily apparentPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareHash function
The hash functions with elliptic polynomial hopping are based upon an elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem. Security using hash functions is dependent upon the implementation of a computationally hard problem, and the elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem provides enough relative difficulty in computation to ensure that the produced hash functions, as applied to message bit strings, are optimally secure. The hash functions are produced as functions of both the elliptic polynomial as well as the twist of the elliptic polynomial, particularly using a method of polynomial hopping.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
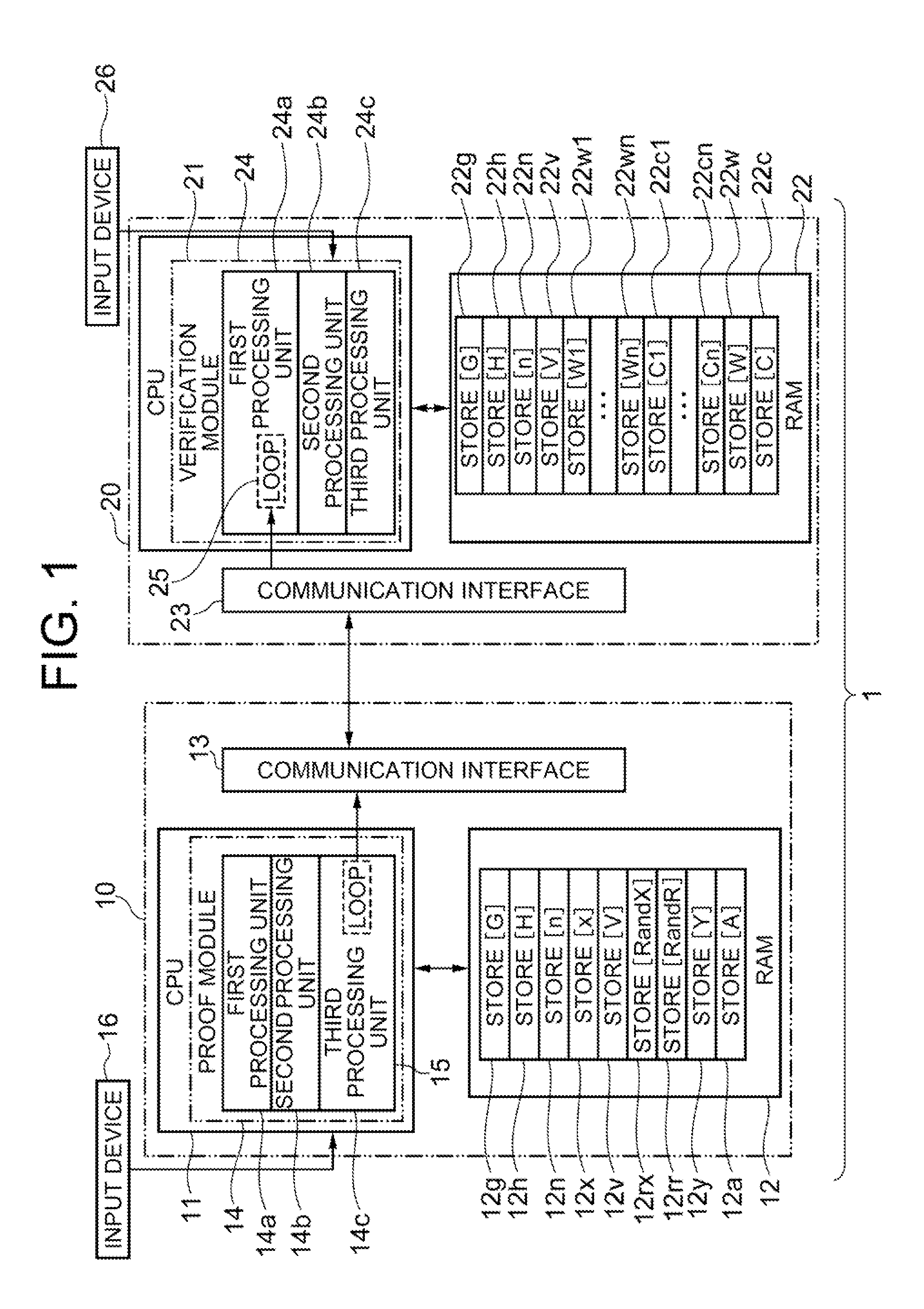
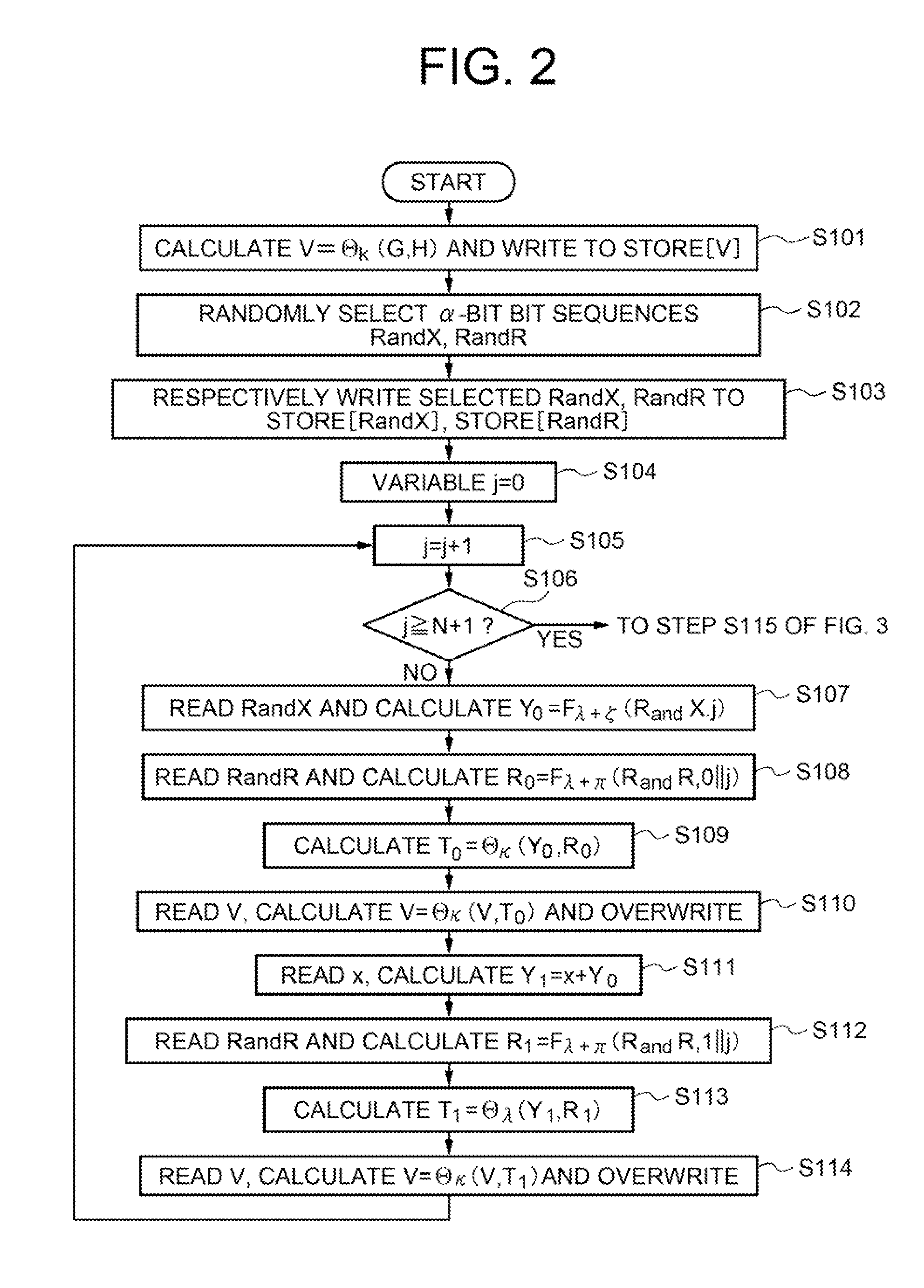
Zero-knowledge proof system, zero-knowledge proof device, zero-knowledge verification device, zero-knowledge proof method and program therefor
InactiveUS20110246779A1User identity/authority verificationSecurity arrangementTheoretical computer scienceDiscrete logarithm
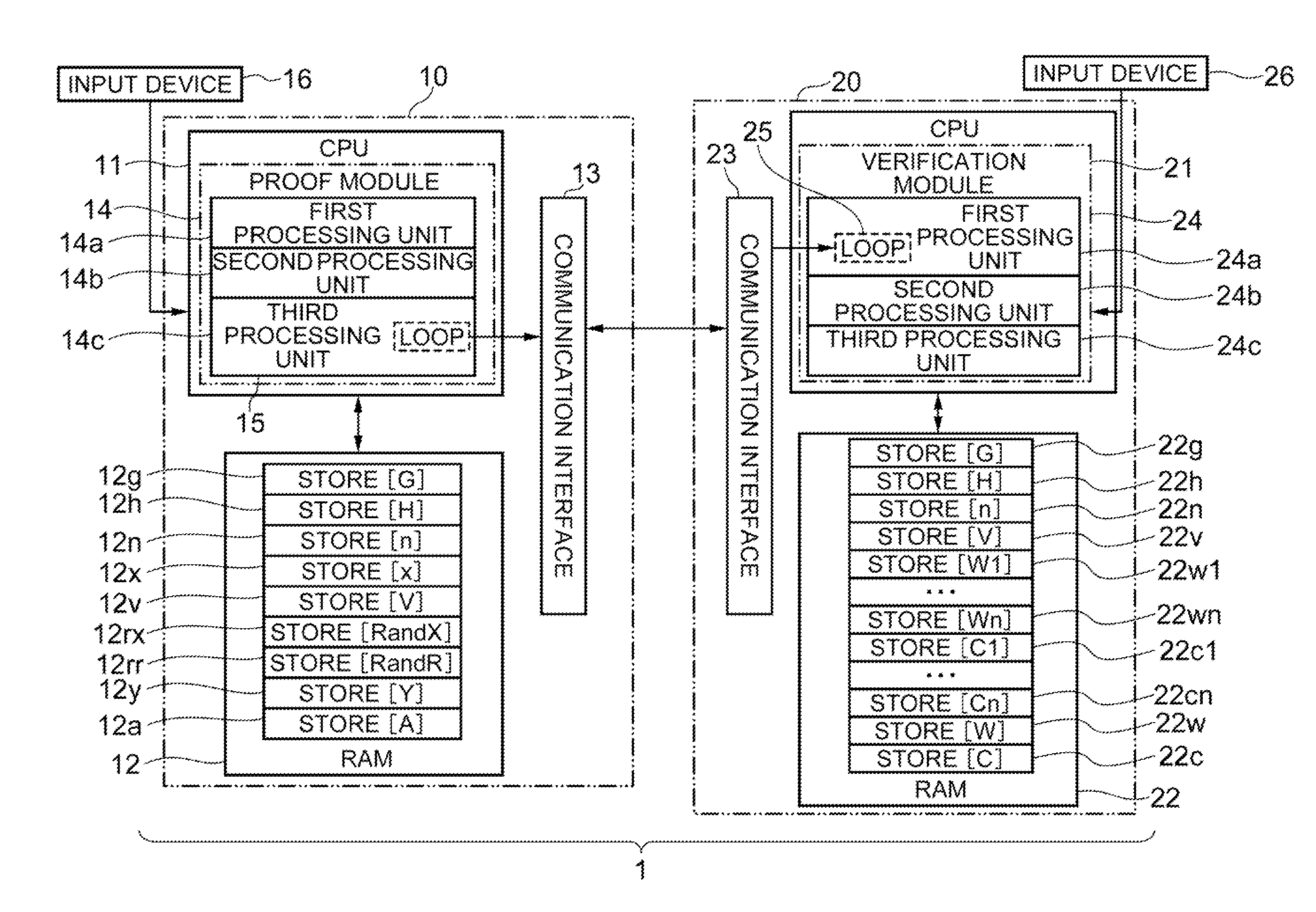
Provided is a zero-knowledge proof system that allows a discrete-logarithm zero-knowledge proof. The zero-knowledge proof device includes a temporary memory unit that stores pseudorandom numbers and previously determined hash values, a first processing unit that calculates multiple pseudorandom numbers and performs multiple iterations of processing to calculate hash values based on the calculated pseudorandom numbers and the information stored in the temporary memory unit, a second processing unit that determines some of the multiple pseudorandom numbers based on the hash values, and a third processing unit that re-calculates some of the pseudorandom numbers and sends the hash values obtained to a zero-knowledge verification device. The zero-knowledge verification device includes a temporary memory region, a data receiving module that sequentially receives new input data, and a processing module that overwrites hash values including variables and input data, as variables into the temporary memory region each time the input data are received.
Owner:NEC CORP
Cloud storage medical data batch self-auditing method based on wireless body area network
InactiveCN106789082AUser identity/authority verificationCommunication with homomorphic encryptionCloud userBody area network
The invention belongs to the technical field of information security, and particularly relates to a cloud storage medical data batch self-auditing method based on a wireless body area network. The security of a cryptographic algorithm designed by the method is based on discrete logarithm problems, and thus it is guaranteed that a malicious cloud server cannot produce a piece of forged auditing proof response information which cheats a cloud user and makes the user pass an auditing verification process. In the cloud storage medical data batch self-auditing method based on the wireless body area network, the cloud user makes use of a linear homomorphic aggregation signature algorithm to construct a homomorphic linear identifier, and can conduct batch auditing on the completeness of multiple medical data files simultaneously, and in the auditing process, the bilinear pairing operation with large expenses does not need to be conducted, and the cloud storage medical data batch self-auditing method is particularly applicable to an application scenario in which the lightweight class calculated amount is needed, the memory space is limited and the wireless body area network needs to be efficiently achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Cryptographic hash functions using elliptic polynomial cryptography
InactiveUS20100166175A1Readily apparentUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareCryptographic hash function
The cryptographic hash functions using of elliptic polynomial polynomials are based on the elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem, which is well known as a computationally hard problem. The hash functions are based on the elliptic polynomial equation in their generation, where different elliptic polynomials are used for different blocks of the same plain text. Particularly, the hash functions use an elliptic polynomial with more than one independent x-coordinate. More specifically, a set of elliptic polynomial points are used that satisfy an elliptic polynomial equation with more than one independent x-coordinate which is defined over a finite field F.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Method of performing xz-elliptic curve cryptography for use with network securtiy protocols
InactiveUS20140064491A1Avoid problemsEasy to upgradeKey distribution for secure communicationEllipseLogit
The method of performing XZ-elliptic curve cryptography for use with network security protocols provides a computerized method that allows for the encryption of messages through elliptic polynomial cryptography and, particularly, with the embedding of either a symmetric secret key or a public key in the message bit string. The method of performing XZ-elliptic polynomial cryptography is based on the elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem. It is well known that an elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem is a computationally “difficult” or “hard” problem.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Elliptic polynomial cryptography with secret key embedding
InactiveUS20110200187A1Finite divisionKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationDiscrete logarithmCryptography
Elliptic polynomial cryptography with secret key embedding is a method that allows for the encryption of messages through elliptic polynomial cryptography and, particularly, with the embedding of secret keys in the message bit string. The method of performing elliptic polynomial cryptography is based on the elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem. It is well known that an elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem is a computationally “difficult” or “hard” problem.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Elliptical polynomial-based message authentication code
InactiveUS20100166176A1Readily apparentEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareHash-based message authentication code
The elliptic-polynomial based Message Authentication Code (MAC) provides MAC generation methods based on the elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem. It is well known that an elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem is a computationally “difficult” or “hard” problem. The methods use both an elliptic polynomial polynomial and its twist, even if the polynomial and its twist are not isomorphic. Since both the polynomial and its twist are used, multiple x- and y-coordinates can be used to embed bit strings into a point that satisfies the elliptic polynomial, and the embedding process is non-iterative, so that the time required to embed the bit string is independent of the bit string content.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Zero-knowledge proving system and method
InactiveUS7003541B2User identity/authority verificationSecret communicationDiscrete logarithmComputer science
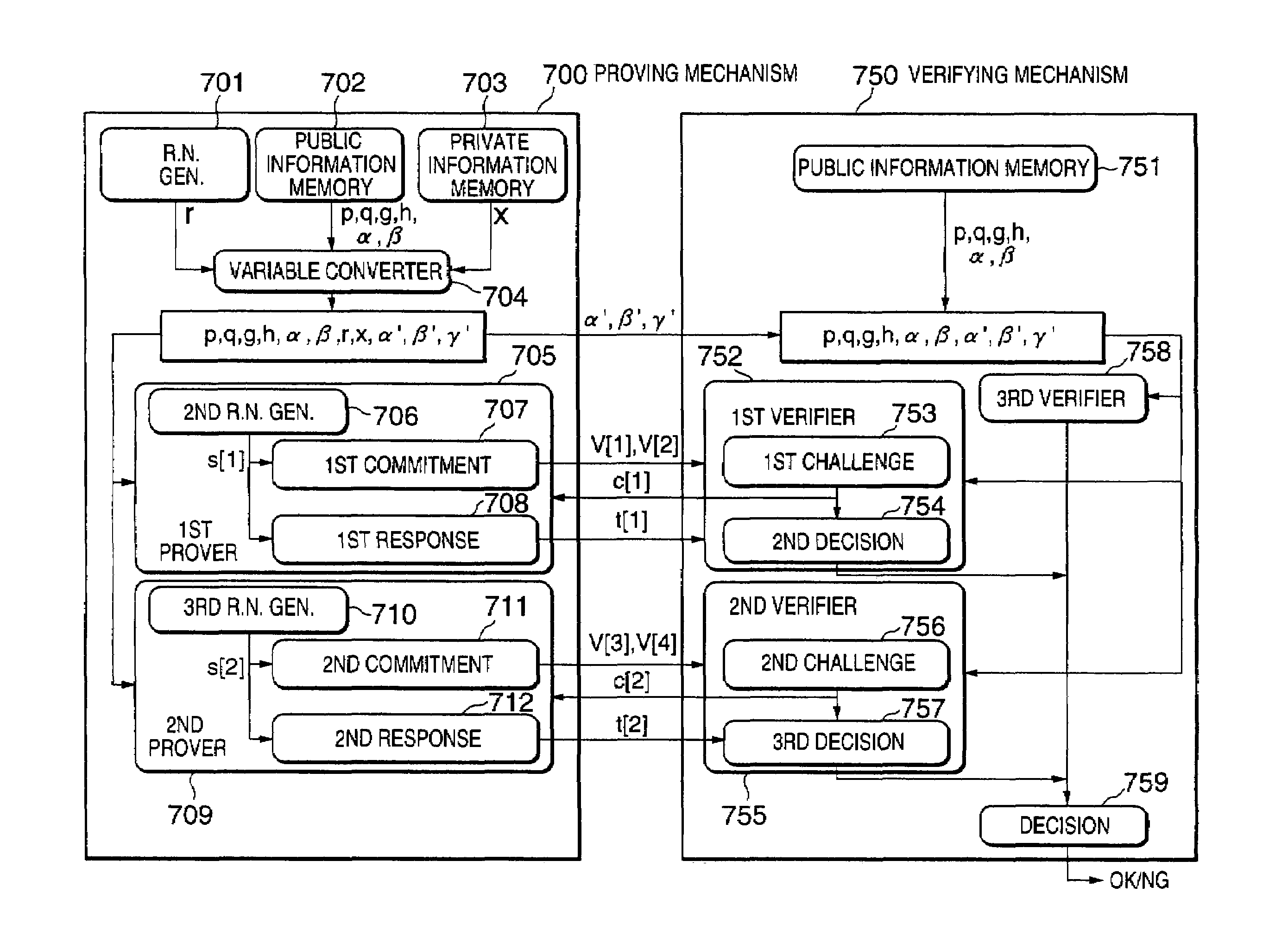
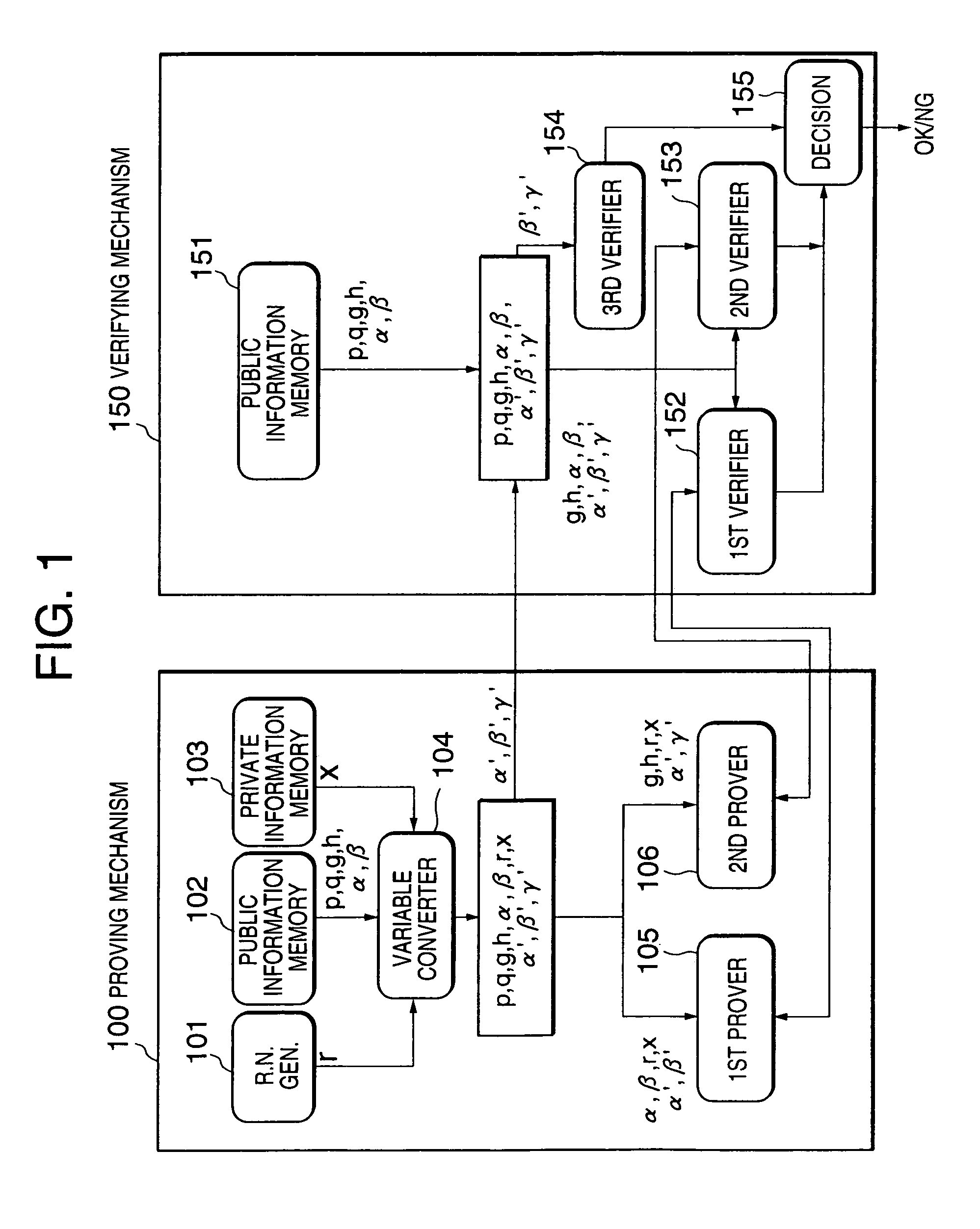
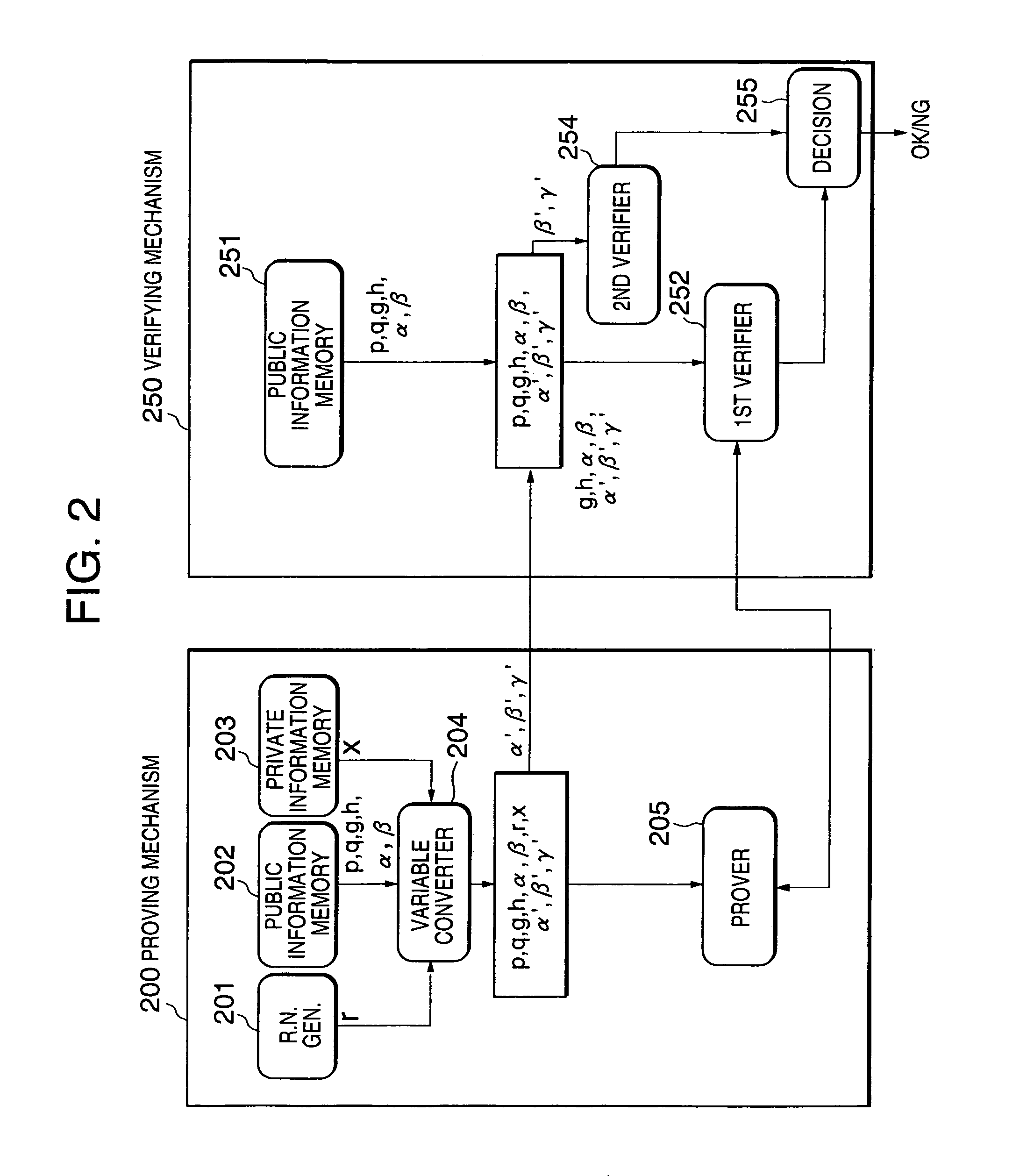
A zero-knowledge proving system includes a proving mechanism for proving equality or inequality of two discrete logarithms and a verifying mechanism for verifying said equality or inequality. The proving mechanism stores public information including a designated operation scheme, two input numbers α and β, and two predetermined bases g and h, private information x which is a discrete logarithm of α to the base g. After converting α, β and h to produce α′, β′ and γ′ as follows: α′=αr; β′=βr; and γ′=hxr, the equality of a logαα′ and logββ′ and the equality of loggα′ and loghγ′ are proved. The verifying mechanism verifies the equality of a logαα′ and logββ′ and the equality of loggα′ and loghγ′. Then, the received β′ and γ′ are checked to determine the equality or inequality thereof, and it is determined whether the proof is acceptable, depending on the verification and the check results.
Owner:NEC CORP
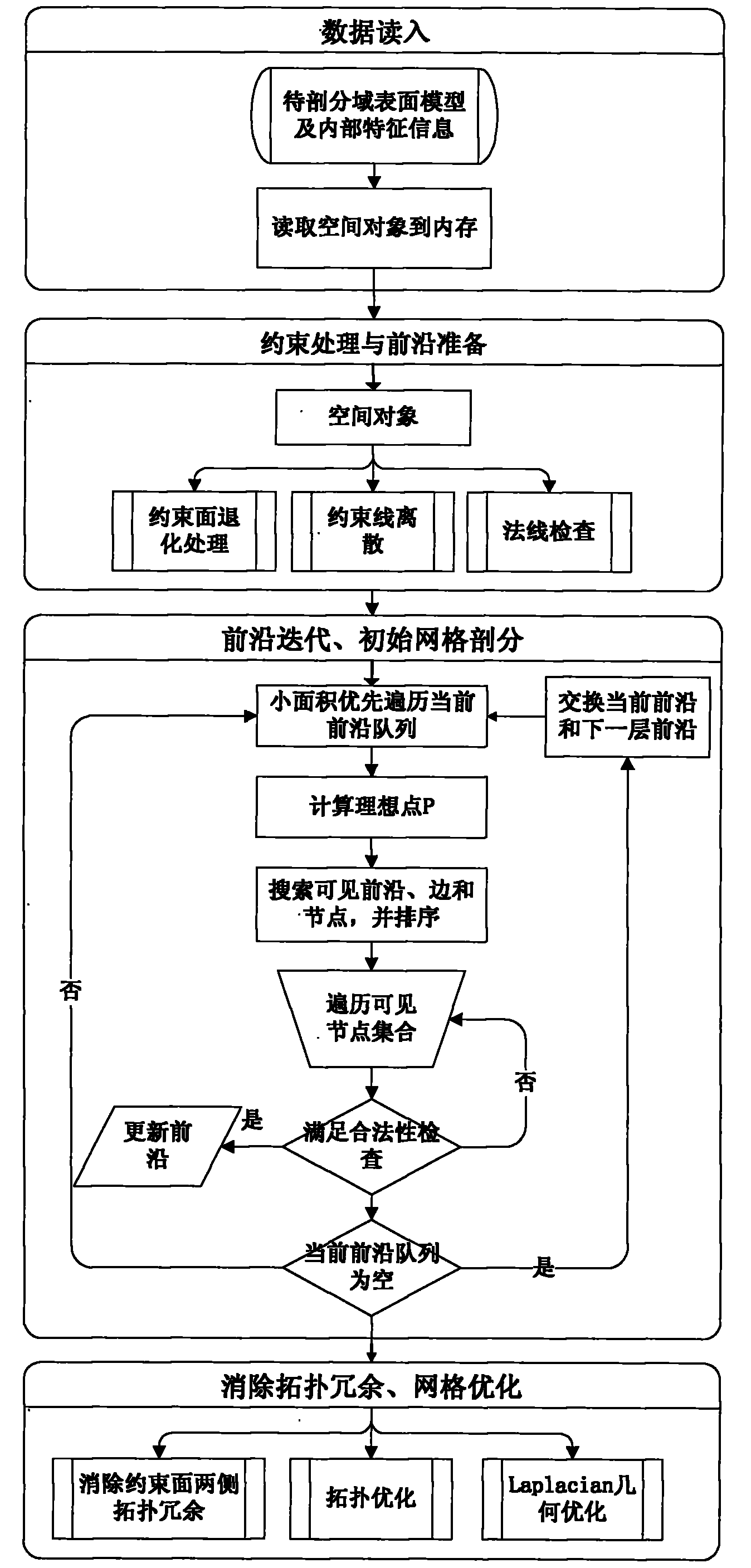
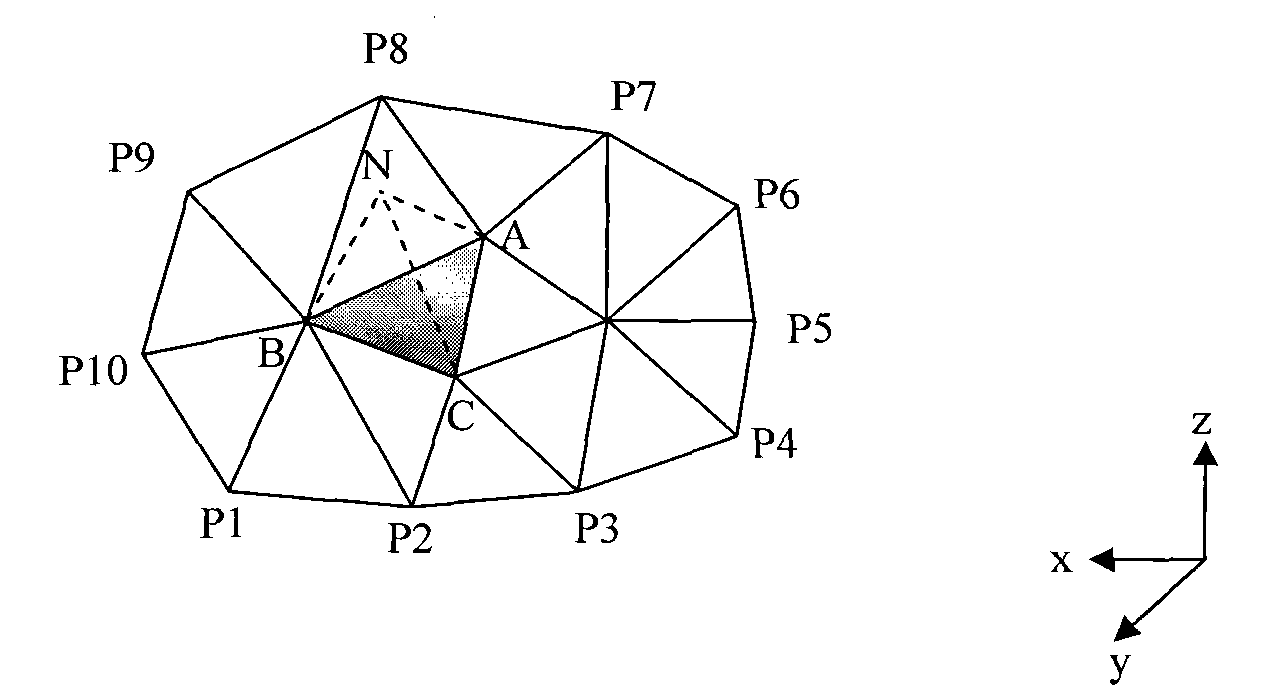
Discrete algorithm for tetrahedral mesh considering feature constraint
The invention relates to a discrete algorithm for a tetrahedral mesh considering feature constraint. The algorithm comprises the steps of: before dividing the mesh, performing feature constraint treatment firstly, considering the constrain face in the object as inner hole constraint with zero thickness, discretizing the constrain face by treatment method similar to hole constraint intotwo groups of triangular front edges overlapped in location but opposite in normal, and discretizing the constrain line to a plurality of sections according to the size control function, then generating the tetrahedronal unit by gradual propelling in the object based on the triangular front edges till the front edge arrays of the current and next layers are empty completely; dynamically maintaining the front edge arrays of the current and next layers when the front edges propel, and controlling the size of the tetrahedronal unit by using an area-independent method to generate the uniform mesh unit; adjusting the mesh topologies on both sides of the constrain face after discretizing the mesh, and finally carrying out topological optimization of mesh and Laplace geometry optimization.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
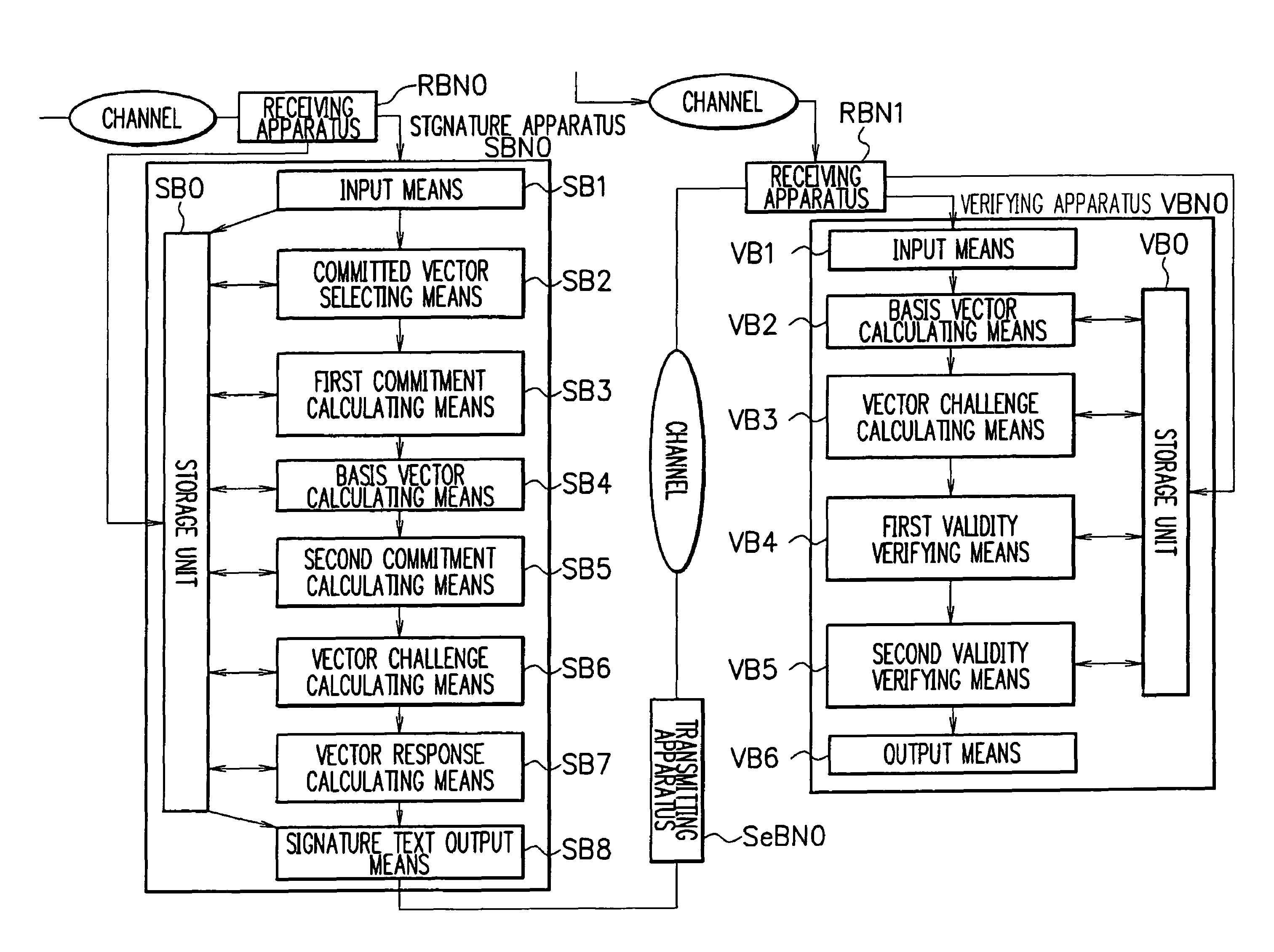
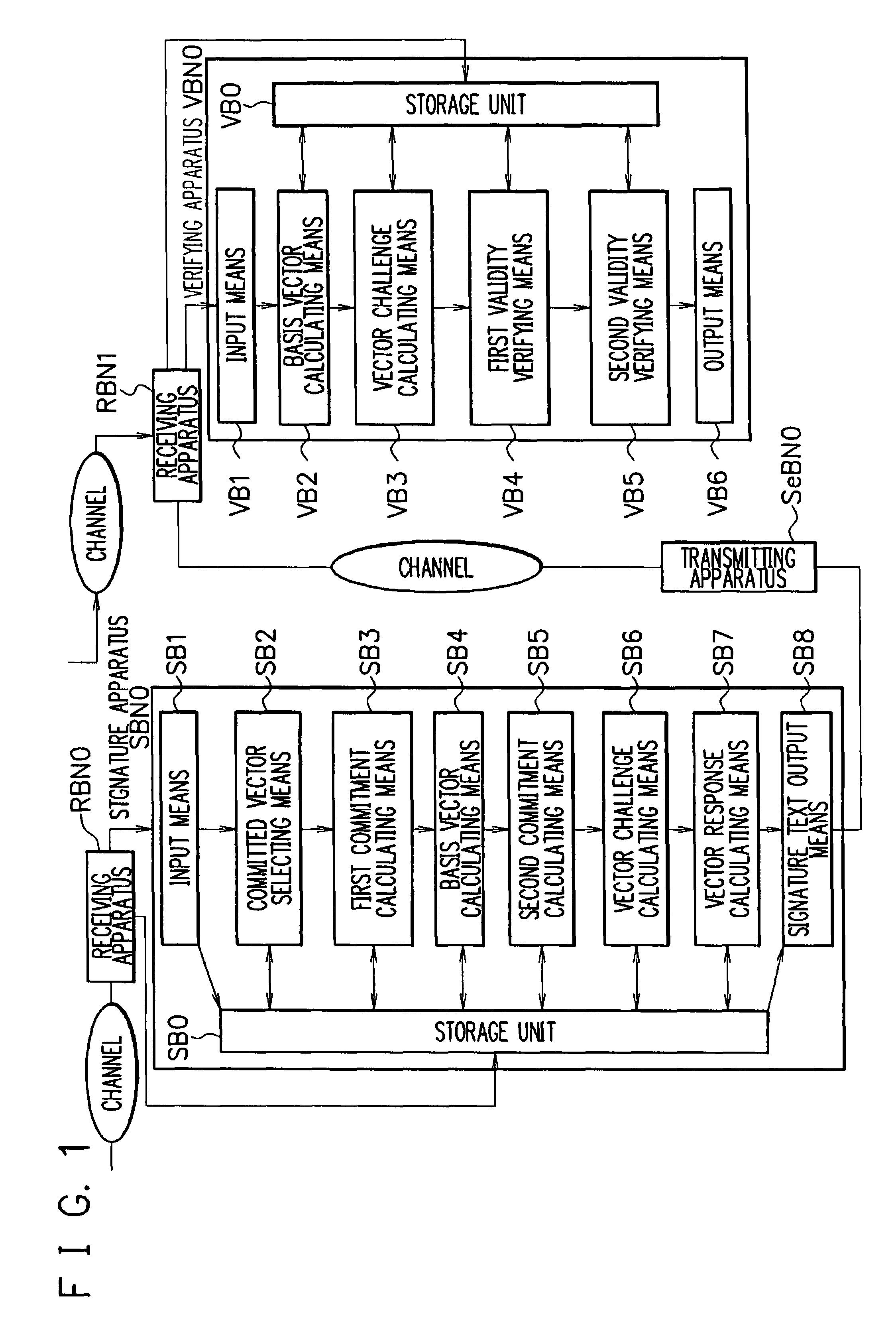
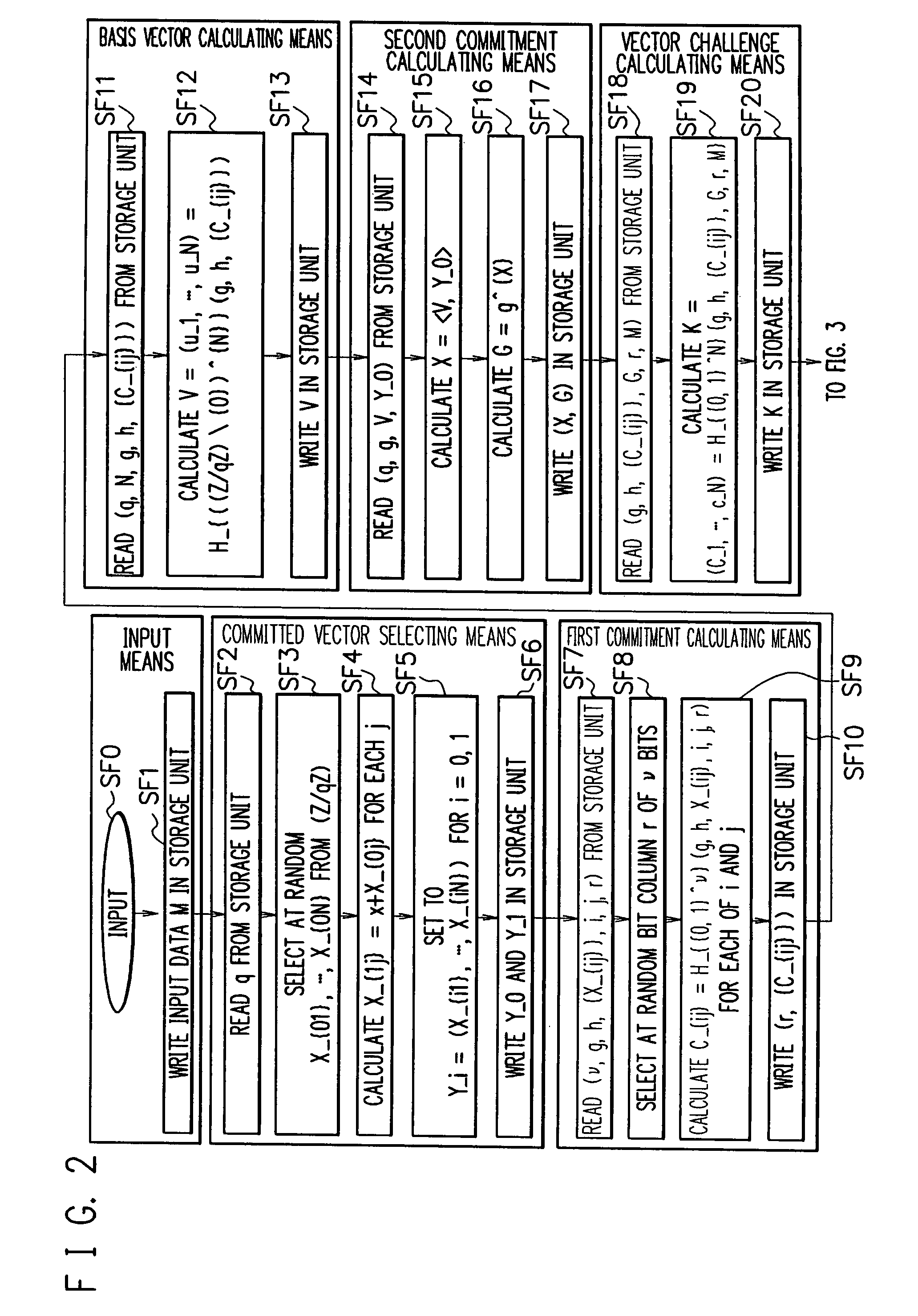
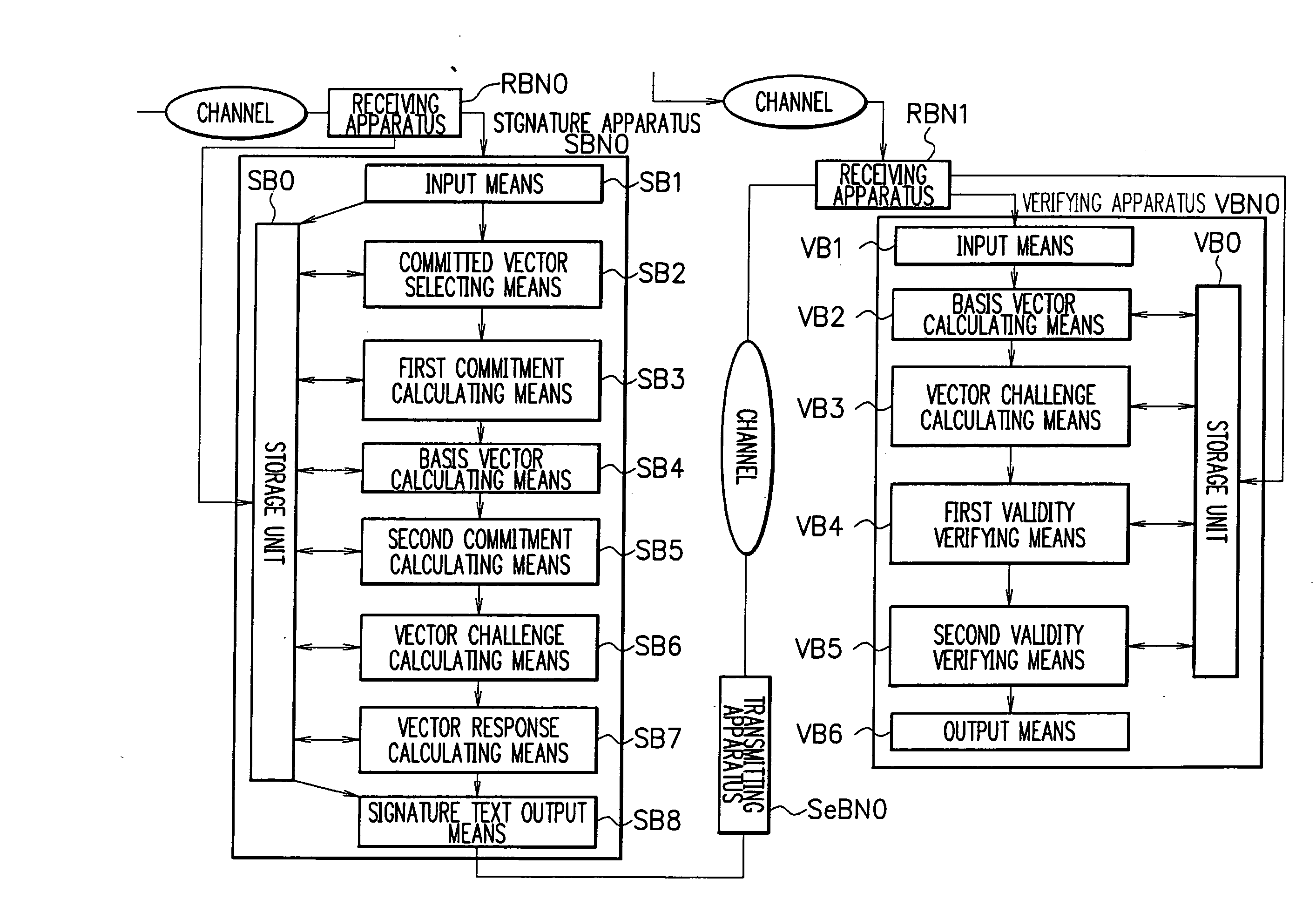
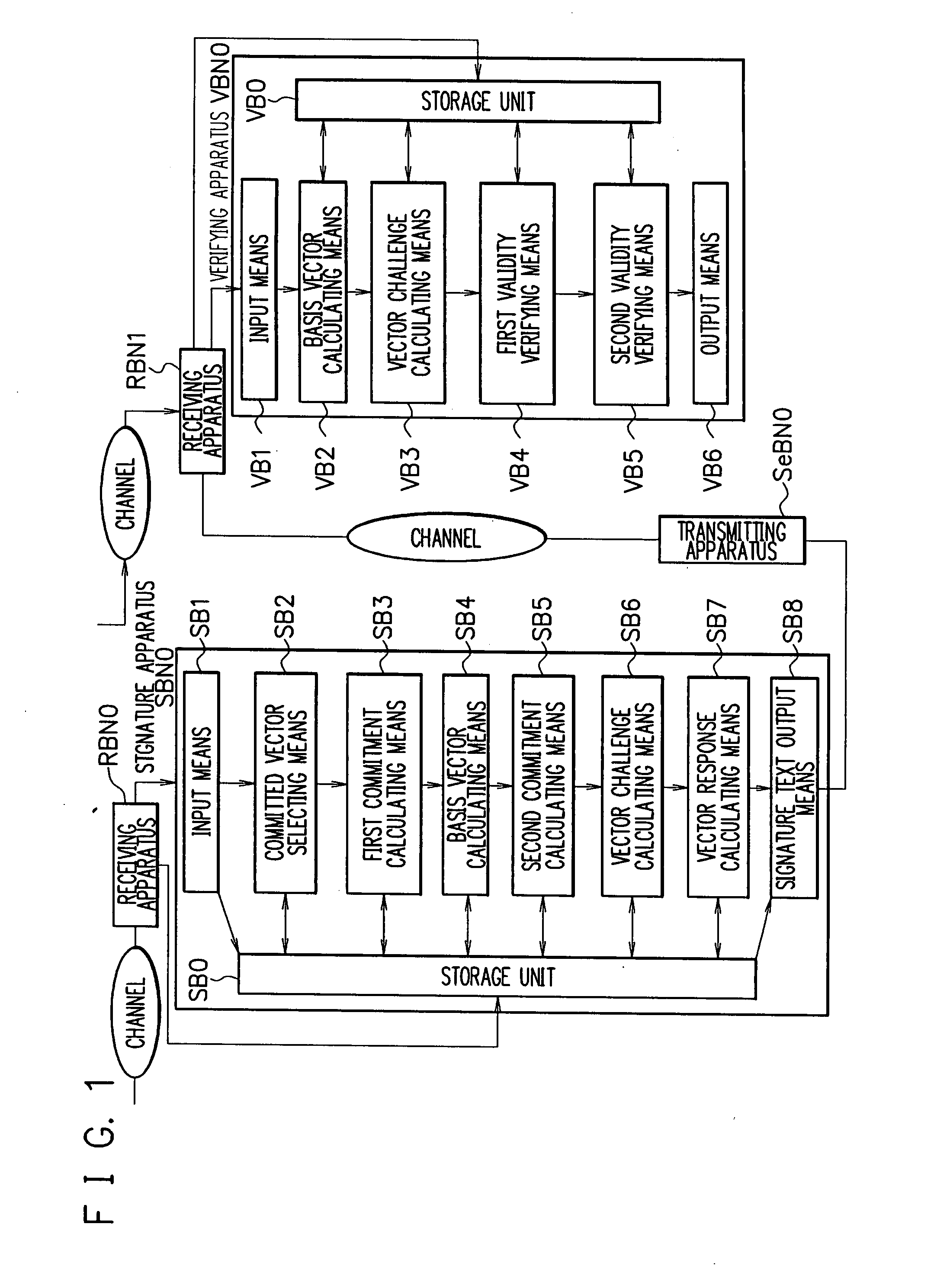
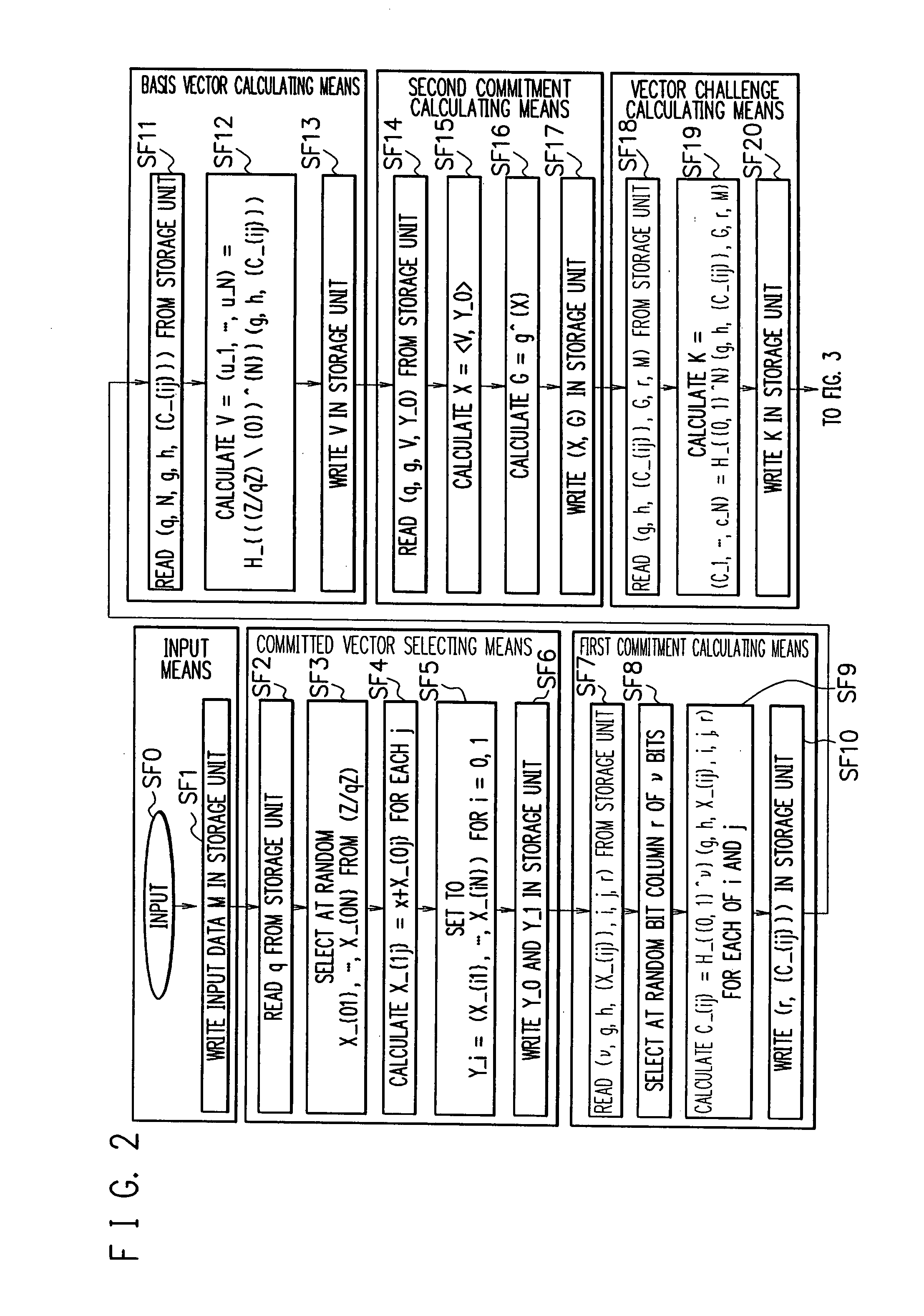
Signature apparatus, verifying apparatus, proving apparatus, encrypting apparatus, and decrypting apparatus
InactiveUS8028171B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationDiscrete logarithmSchnorr signature
Owner:NEC CORP
Signature Apparatus, Verifying Apparatus, Proving Apparatus, Encrypting Apparatus, and Decrypting Apparatus
ActiveUS20080301449A1Reduce the amount of calculationImprove securityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationDiscrete logarithmGGH signature scheme
Provided are a signature apparatus, a verifying apparatus, a proving apparatus, an encrypting apparatus, and a decrypting apparatus capable of efficiently reducing a signature text counterfeit problem to a discrete logarithm problem. The commitment is a hash value of a set of a value to be committed. Data including a pair of elements of a cyclic group associated with a discrete logarithm problem is used as a public key, and a discrete logarithm of an order of the pair is used as a secret key. Accordingly, it is possible to summarize secret information of an attacker from the commitment without rewinding the attacker and to ensure a higher safety than that of a Schnorr signature scheme. In addition, one-time power residue calculation is performed in each of the signature and verification calculations, so that it is possible to lower an amount of calculation in the signature and verification calculations.
Owner:NEC CORP
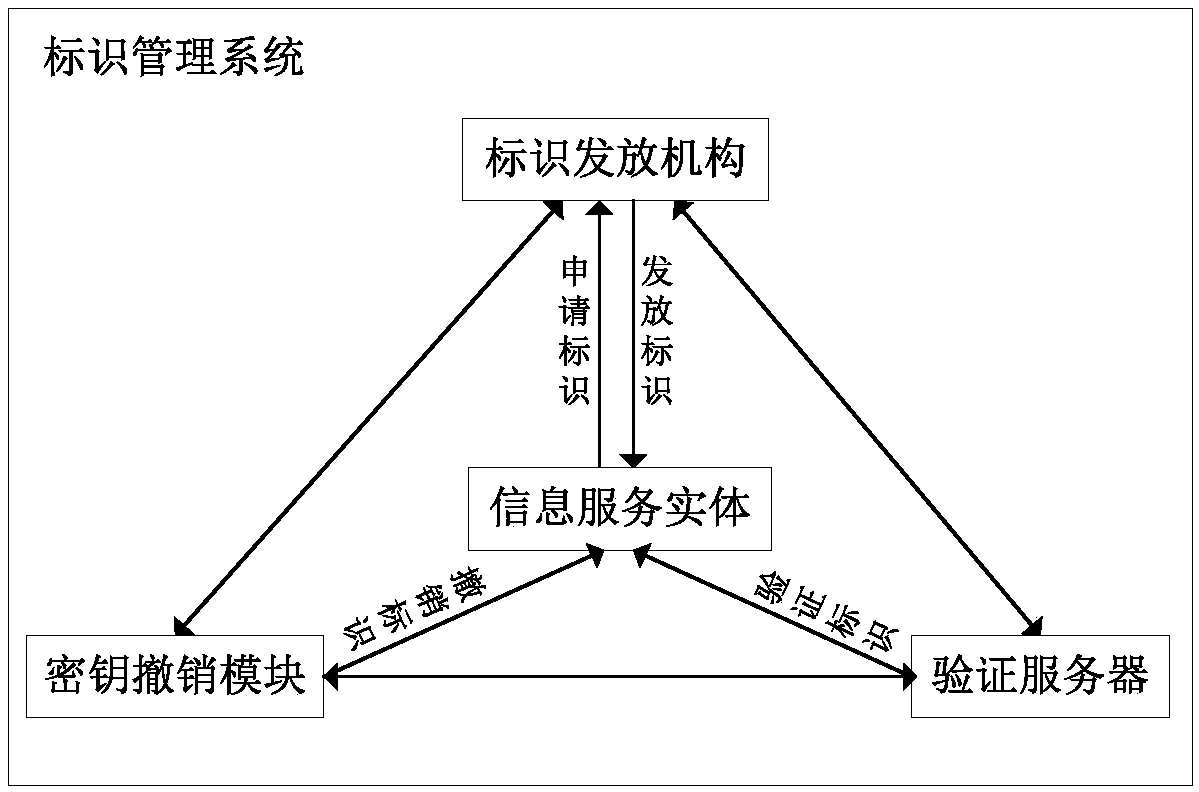
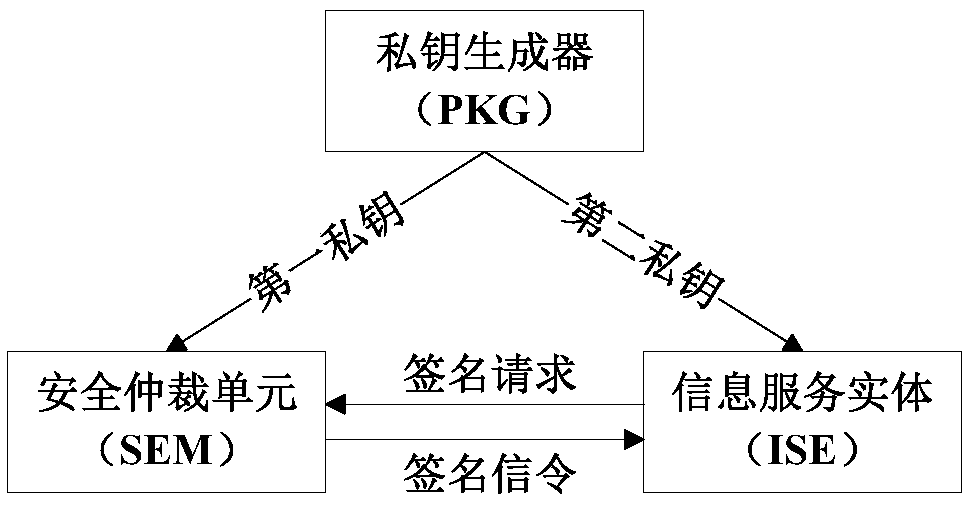
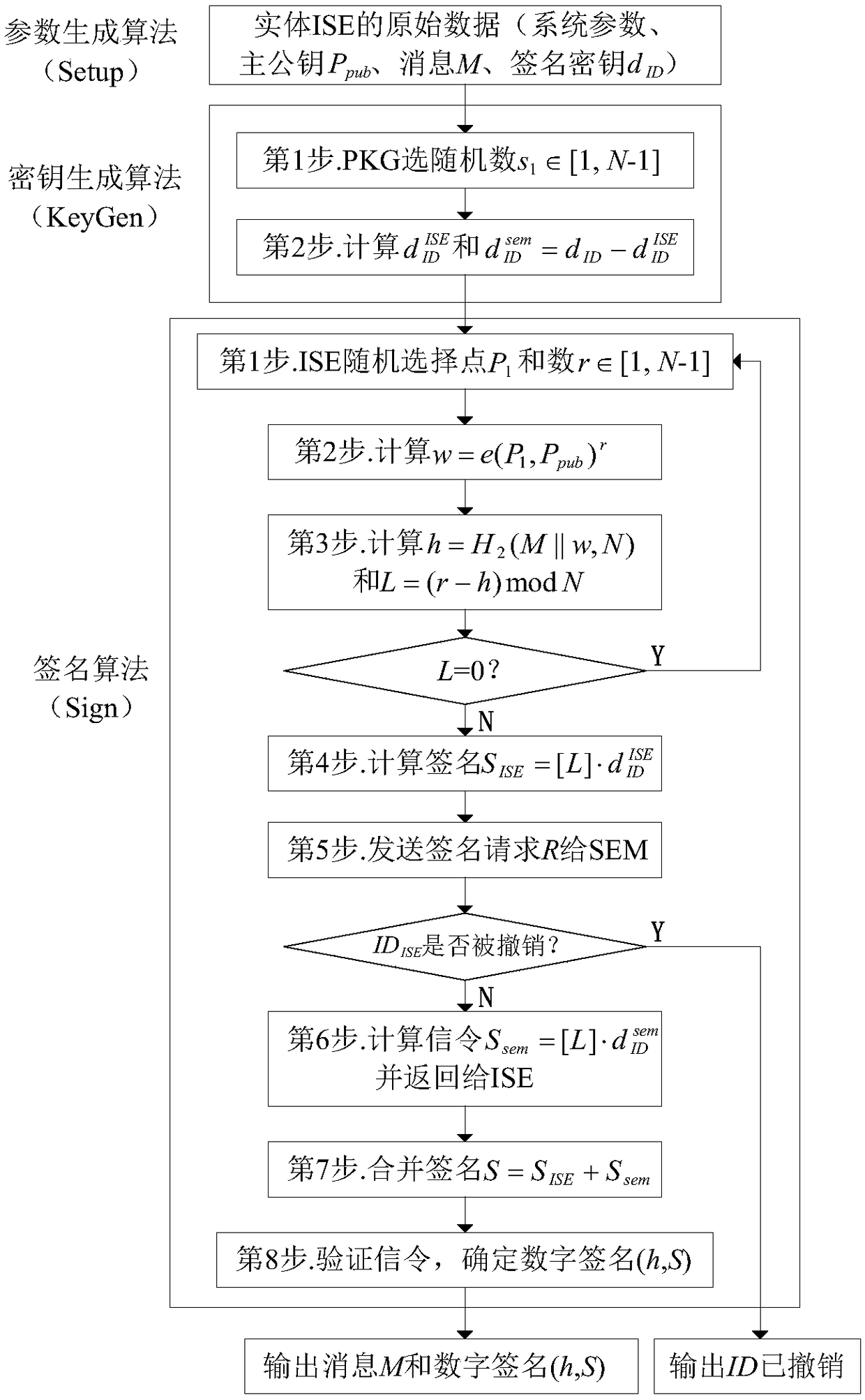
Information service entity identity management system and quick identity revocation method
ActiveCN108737391AImprove manageabilityImprove recognizabilityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputational securityDiscrete logarithm
The invention discloses an information service entity identity management system and a quick identity revocation method, which can solve the problem of instant revocation of an entity identity. A keyrevocation module is added in an identity management system, and the key revocation module includes a security arbitration unit, which can quickly revoke the identity of an information service entitywhen services of the information service entity are invalid or illegal. The implementation of the quick revocation method includes the following steps that: system initialization is performed, and keygeneration and segmentation of the information service entity is performed; and the information service entity and the security arbitration unit cooperate with part of private keys to implement the signature of a message, and a verification server verifies the signature of the message to achieve the unified management and authentication of a network space information service entity identity. According to the scheme of the invention, the invalid or illegal identity can be quickly revoked, the computational security is based on the difficulty of solving discrete logarithms on elliptic curves, the characteristic of quick revocation can be realized, high security can also be achieved, and the scheme is suitable for network environments with high security requirements.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
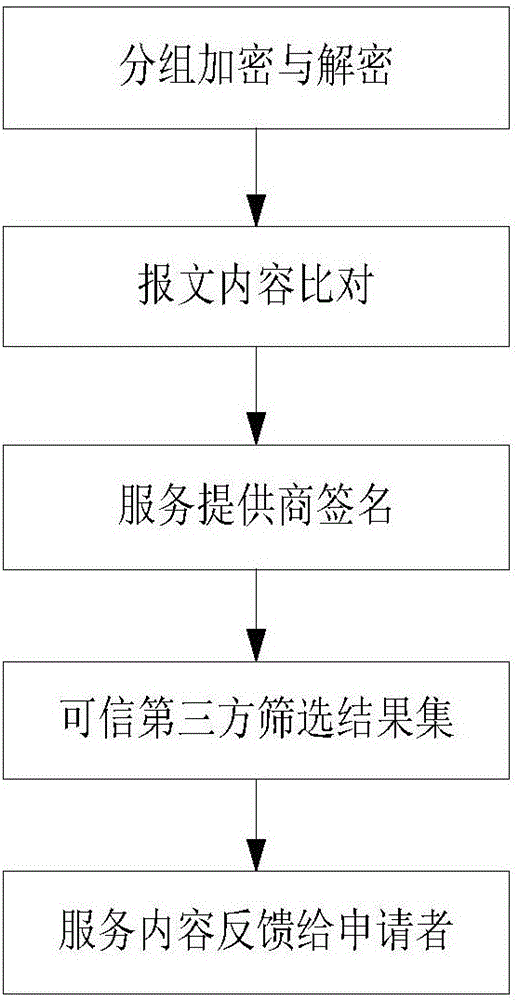
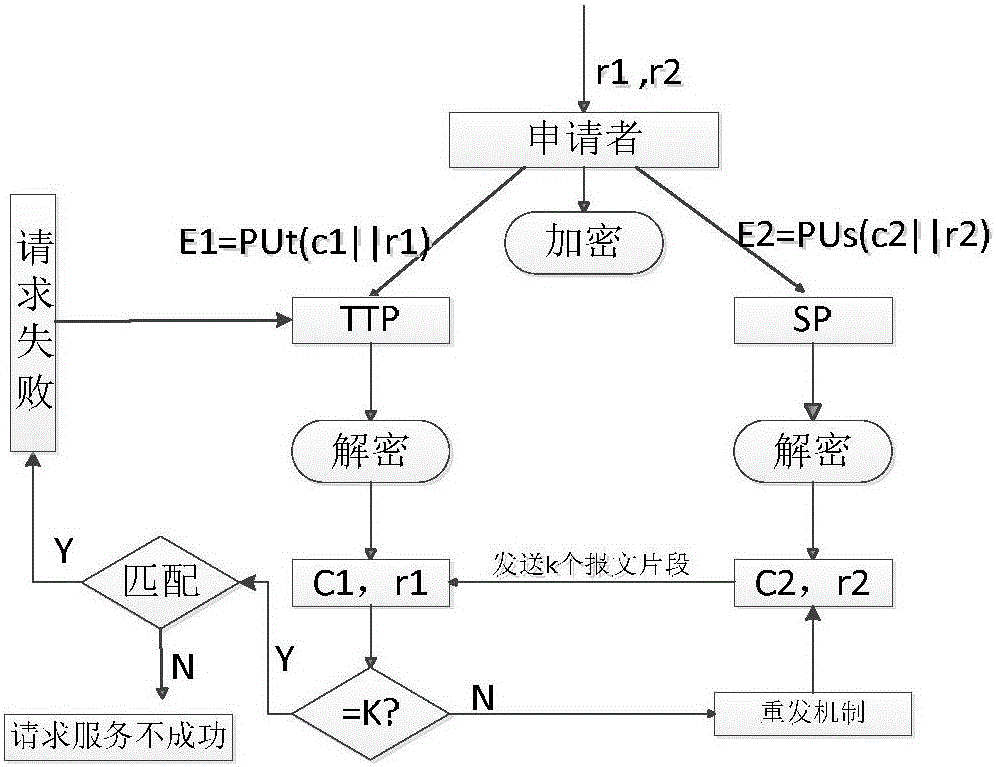
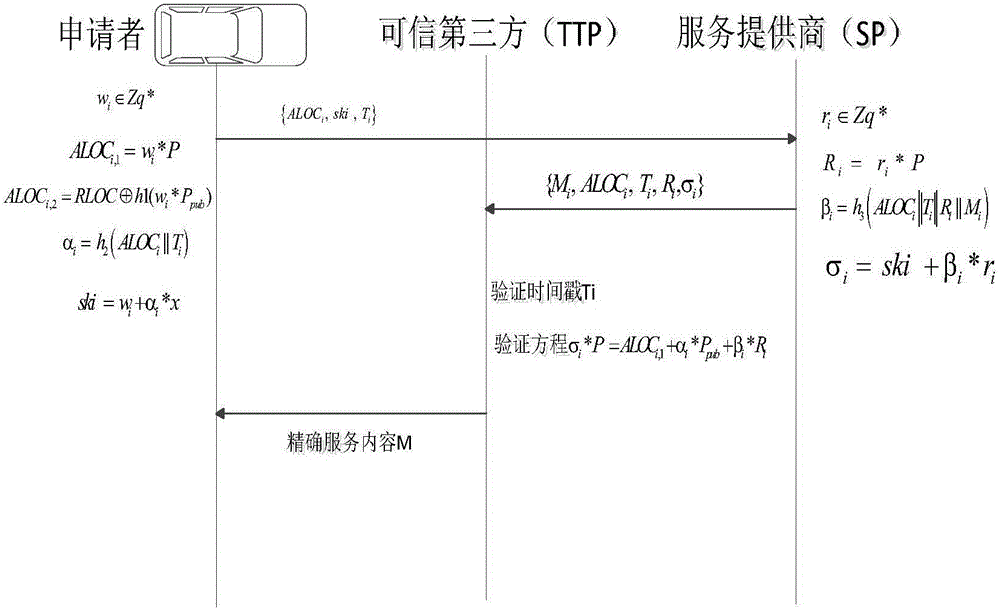
LBS-based anti-attack location privacy protection method for IoV
ActiveCN105812354ASatisfied location hidingService quality upgradeUser identity/authority verificationQuality of servicePrivacy protection
The invention discloses an LBS (Location Based Service) anti-attack location privacy protection method for IoV (Internet of Vehicles). The method specifically includes five steps of grouping encryption and decryption; message content comparison; service provider signing; result set screening by a trusted third party; feedback of service content to an applicant. According to the invention, the whole communication process is divided into two parts generally: a user requests service from a service provider; and the service provider returns the service content. Discrete logarithm and the Diffie-Hellman are adopted in the above model, bidirectional authentication is supported and save cost and computation cost are reduced substantially. Therefore, privacy protection and service quality are balanced effectively and different types of attacks can be resisted.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
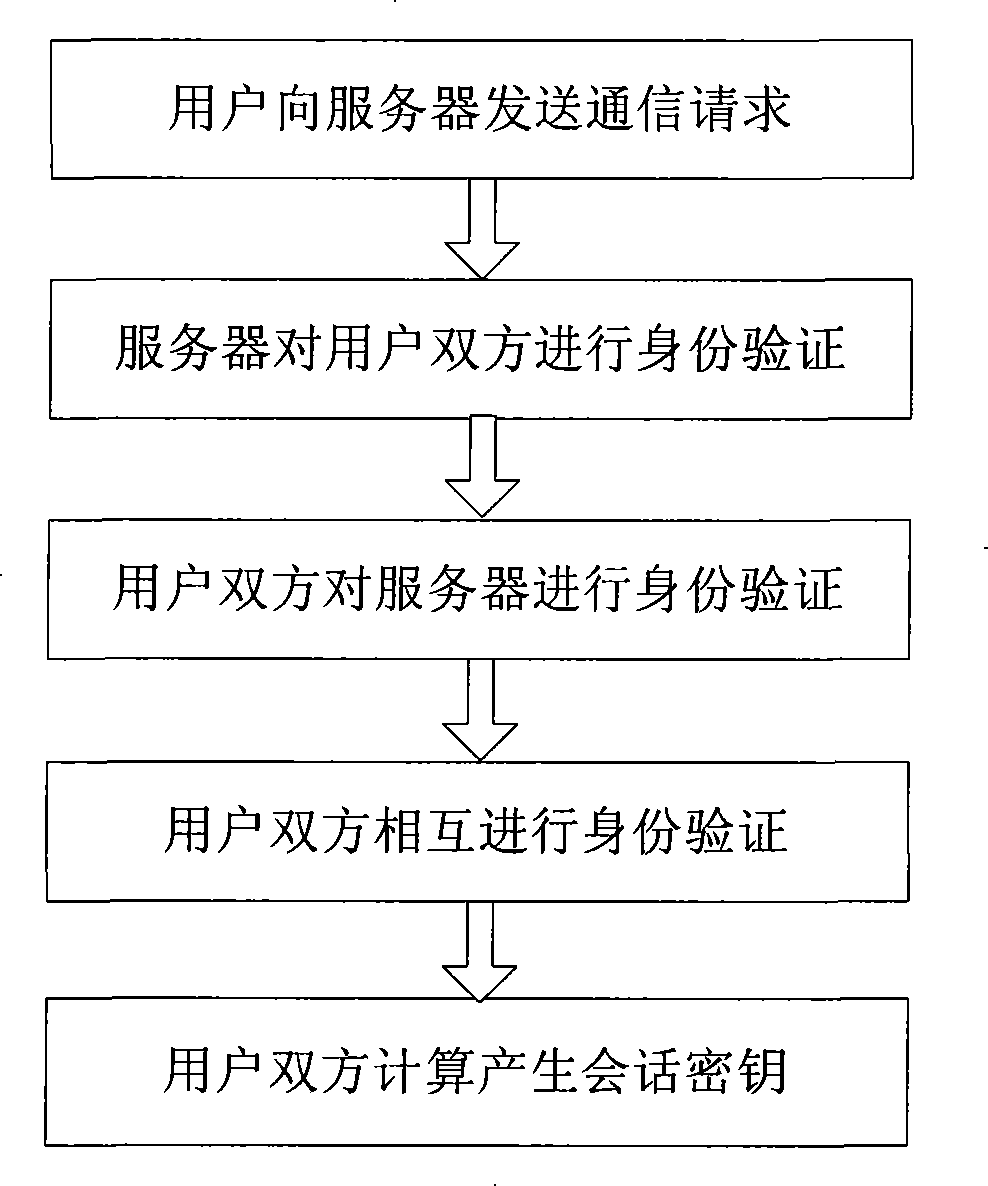
Method for generating three parts cipher key negotiation
InactiveCN101252577AKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey exchangeHash function
The invention belongs to the communication technical field, relating to the safety problem of network communication, in particular to the three party key exchange protocol, namely, 3PAKE protocol focusing on password authentication of a network structure. Basing on the CDH assumption and using the difficulty of discrete logarithm and the unilateralism of hash function, the invention includes three key steps that firstly, the certifications of the two users asking for communication are certified by the server; secondly, the certification of the server is verified by the two users asking for communication; thirdly, certifications of the two users asking for communication are mutually verified. The invention overcomes the vulnerabilities of masquerading attack for the starter, masquerading attack from the responder, the attack from the middleman and the on-line password guess attack all existed in the S-3PAKE protocol; has the capacities of resisting frequent attack, the attack from the middleman, the masquerading attack from the starter, the masquerading attack from the responder, the off-line guess attack and the replay attack; has forward security and known key security; and also has the characteristic of perfectly resisting on-line guess attack.
Owner:天津启云科技有限公司
Proxy signature method and system based on lattice
InactiveCN103986576ASmall sizeReduce computational complexityUser identity/authority verificationComputation complexityRound complexity
The invention provides a proxy signature method and system based on a lattice. The proxy signature method includes the steps of secret key generation, proxy signature secret key generation, proxy verification, proxy signature, verification and the like. The proxy signature method and system based on the lattice have the advantages that the proxy signature method based on a small integer problem on the lattice is disclosed, and the size of a proxy signature private key is reduced by reducing the dimension of the proxy signature private key. Besides, matrix multiplication is mainly used in the aspect of calculation. Compared with the methods of discrete logarithm and big integer problem factorization, modular exponentiation and match operation are not used, and accordingly computation complexity is lower.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Repudiation Internet key exchange protocol
InactiveCN101060530AKey distribution for secure communicationNetworks interconnectionKey exchangeTTEthernet
The disclosed repudiation internet key exchange protocol for message security and user privacy comprises: binding all of protocol message, user private key and DH key discrete logarithm proof with Harsh function H; taking output of H as message certification key to certify user ID, wherein user message refers no to other user's ID and public key. This invention provides safe, high efficient and repudiation key exchange service.
Owner:赵运磊
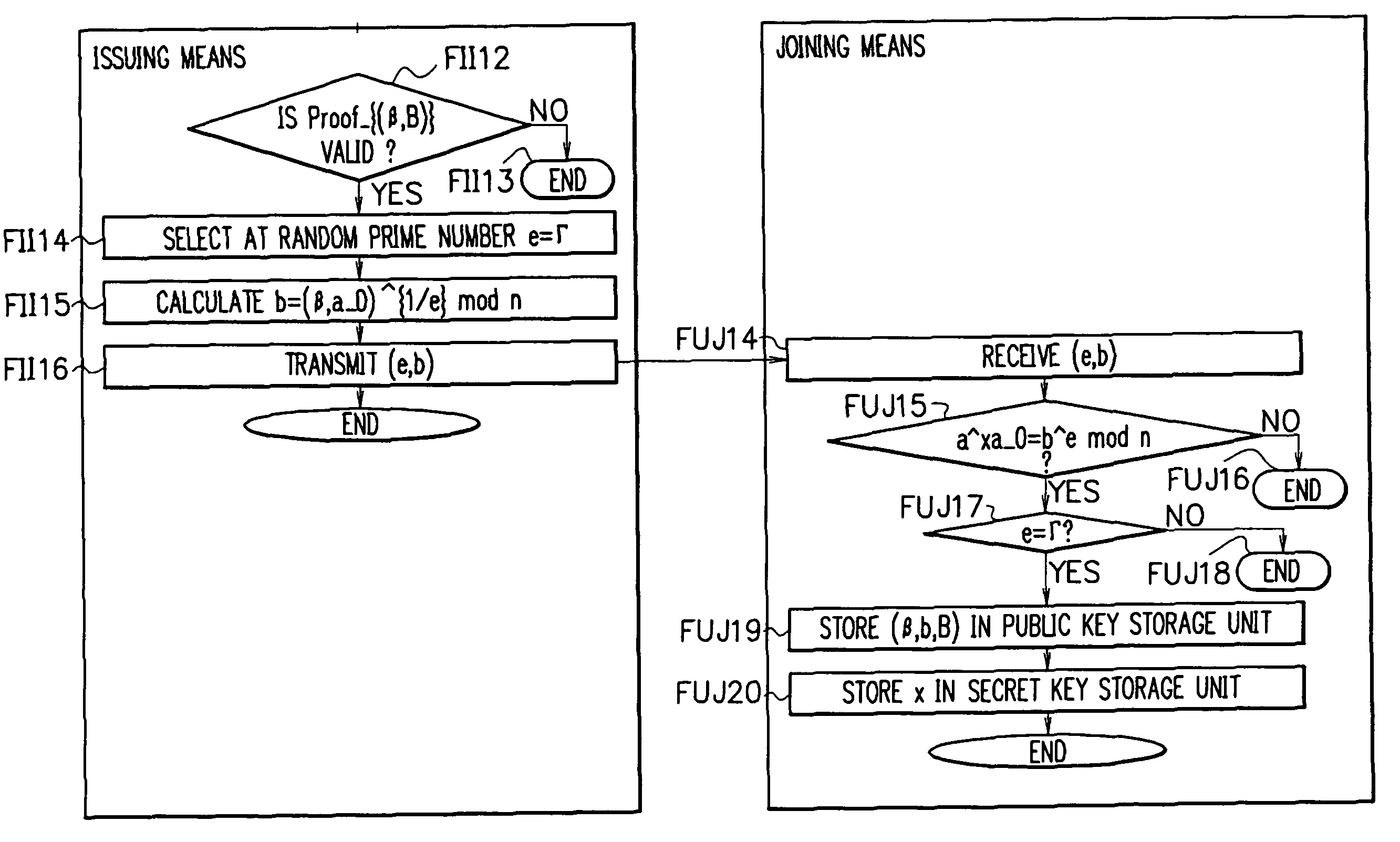
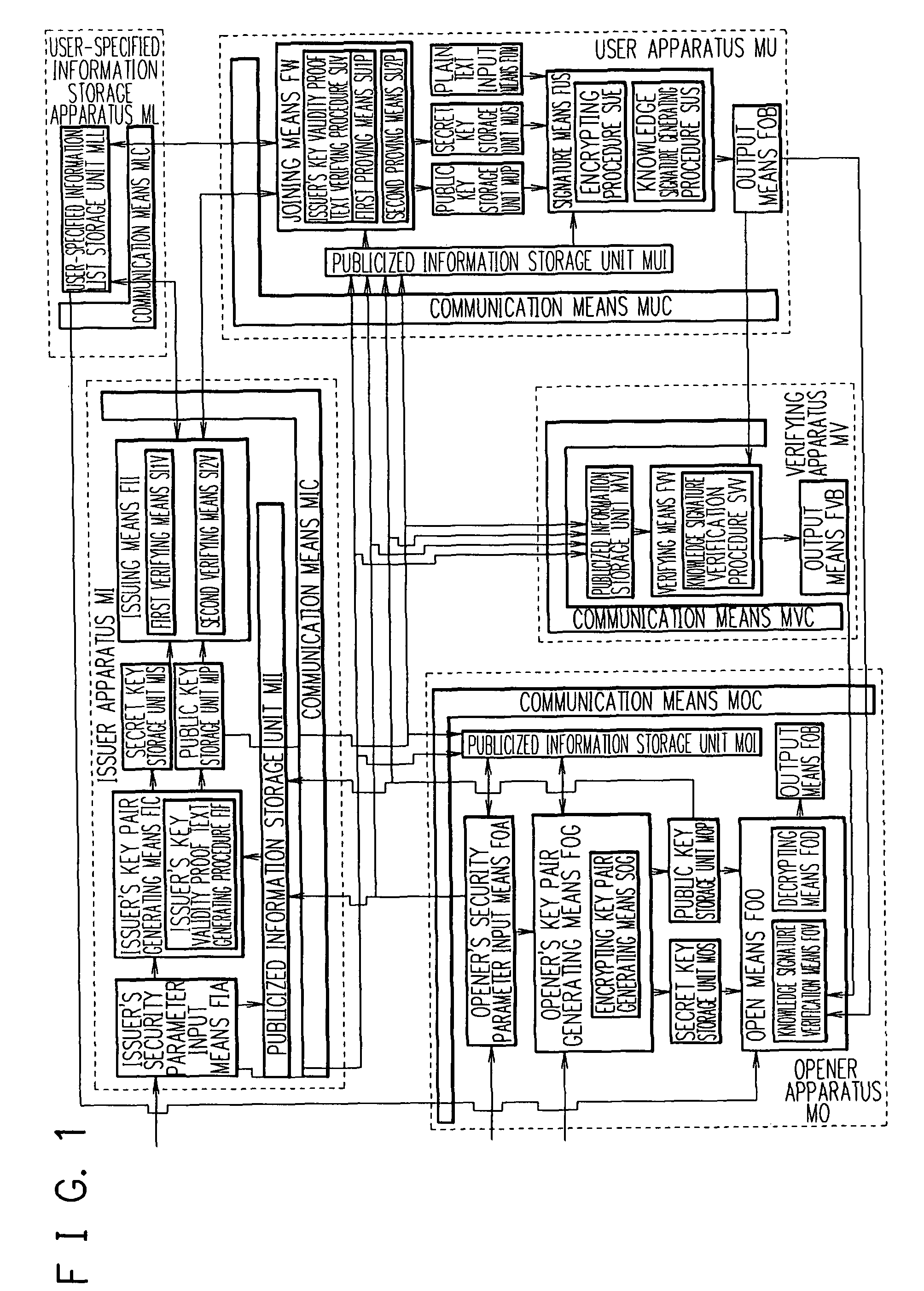
Group signature scheme
ActiveUS8127140B2Accurate operationReduce in quantityPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationRandom oracleDiscrete logarithm
An efficient and safe group signature scheme is provided. According to the present invention, an open unit is provided to not an issuer but an opener, and a data required for operating the open unit does not include a key pair of the issuer, so that it is possible to accurately operate the open unit even if the issuer generates the public key in an illegal manner. In addition, it is possible to prove that a key pair of a member cannot be counterfeited. It is possible to implement from a discrete logarithm assumption a feature that a cipher text, that is, a portion of a signature text can be decrypted only by the opener in a method which is the same as a method representing that an ElGamal crypto scheme is safe. In addition, it is possible to implement from a random oracle assumption a feature that a knowledge signature has an extractability in a method which is the same as a method proving that a Schnorr signature is safe.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method of producing a cryptographic unit for an asymmetric cryptography system using a discrete logarithm function
ActiveUS7330549B2Increases amortizationFast executionPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationDiscrete logarithmCryptographic nonce
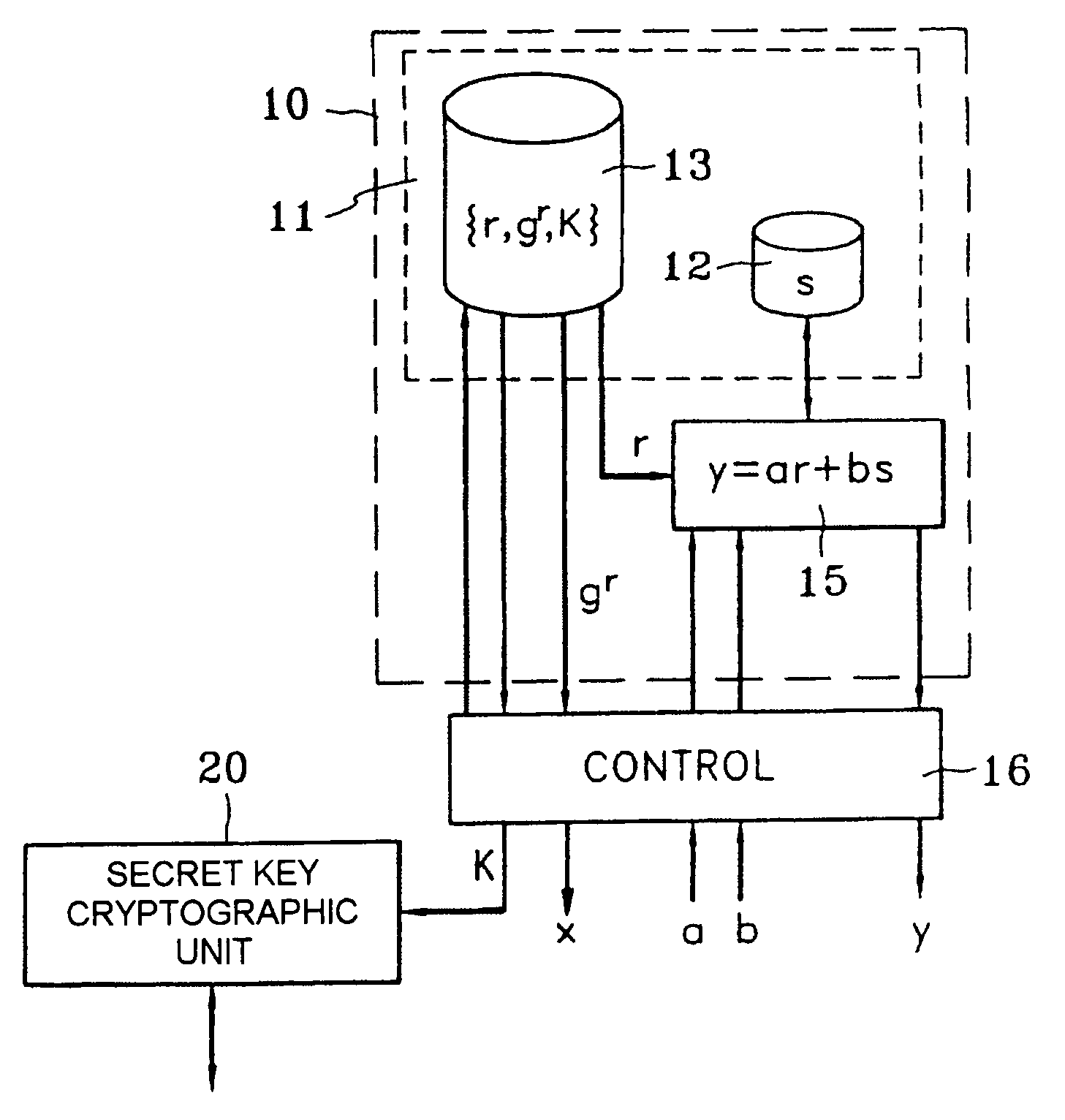
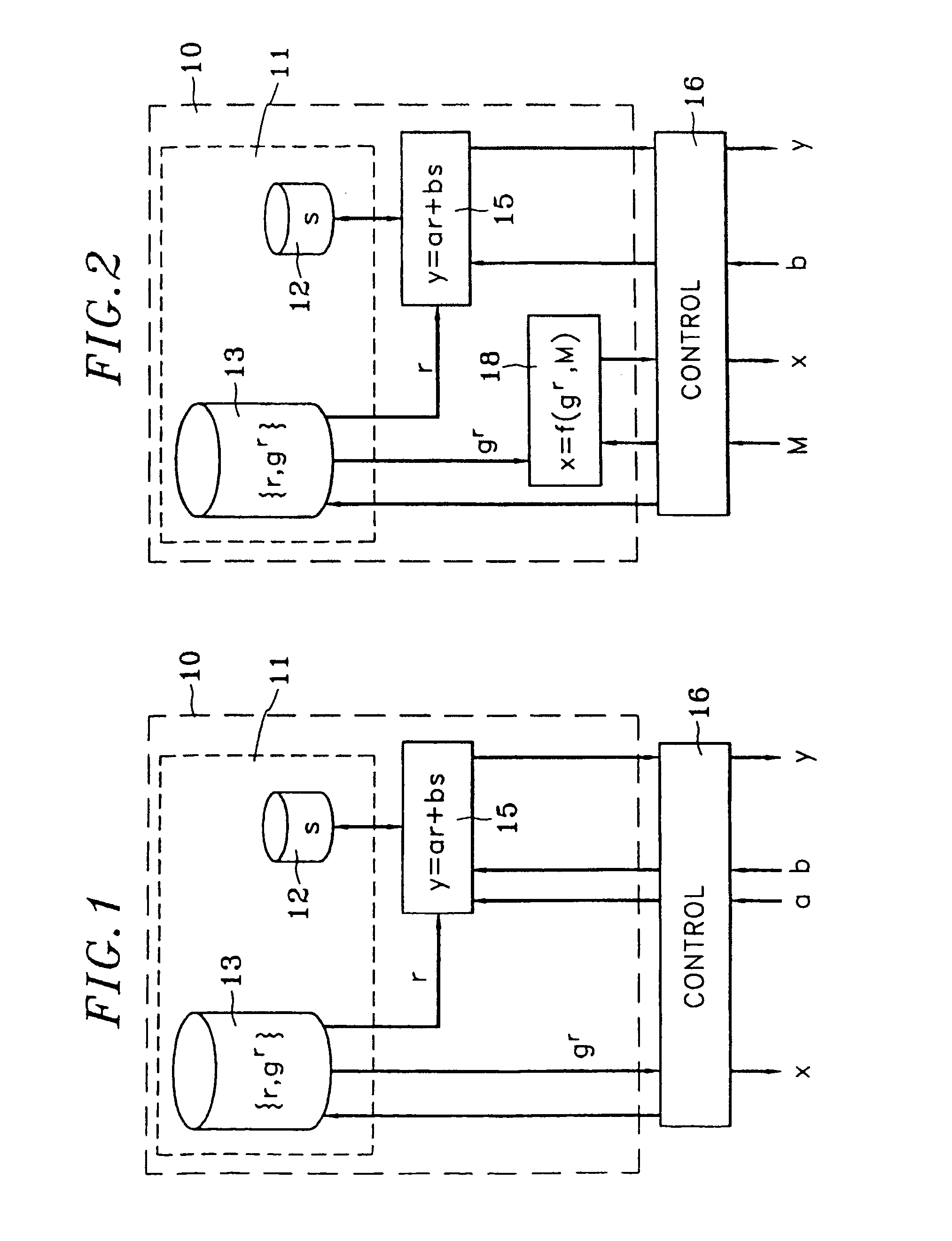
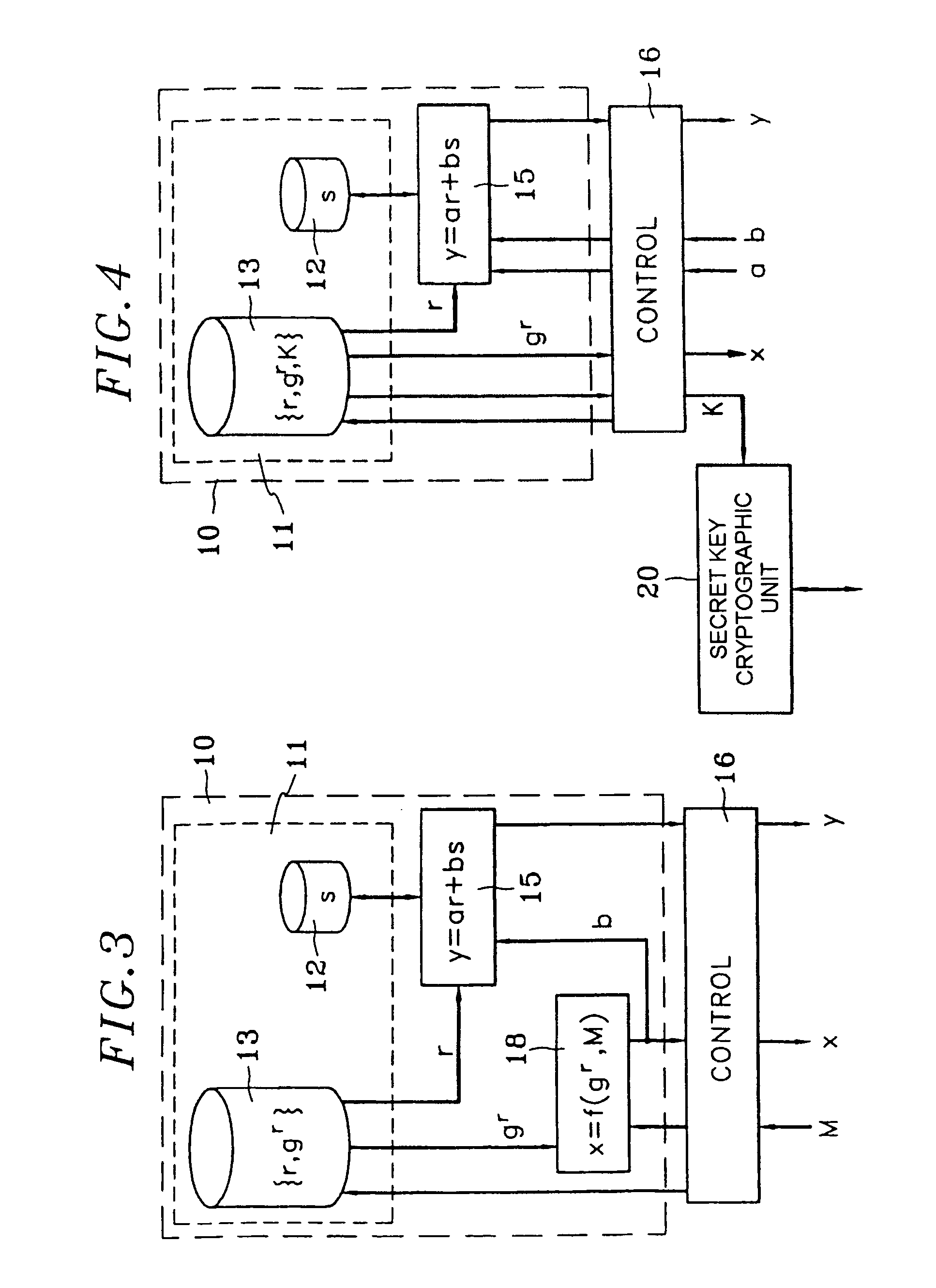
The invention relates to a group of public-key cryptography schemas that use the discrete logarithm problem with the purpose of reducing the cost of developing, producing and maintaining a cryptographic unit. One of the entities (10) performs a calculation comprising at most a small number of additions, subtractions and multiplications of integers, said calculation being common to all of the schemas of the group. The aforementioned calculation is preferably the main calculation to be performed by the entity in question while most of the other calculations can be performed in advance. In particular, said calculation is of the y=ar+bs type, wherein r is a random number and s is a secret key that is specific to the entity (10). The calculation is common to a group of schemas for entity authentication, message authentication, digital signatures and key exchange.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
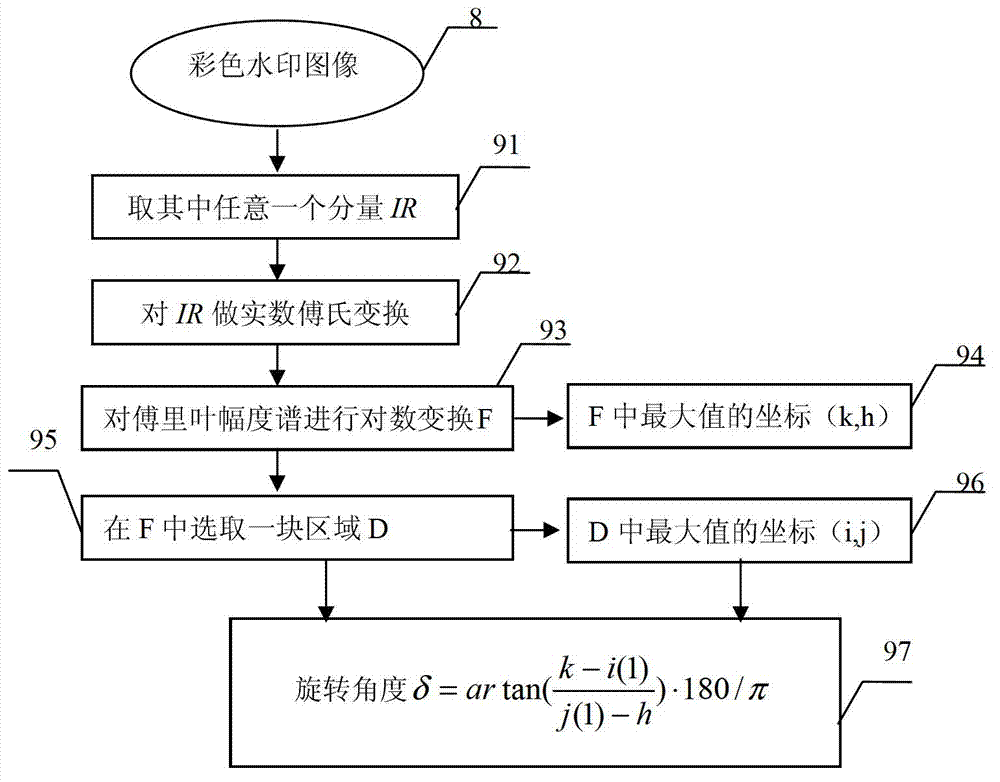
Color image digital watermark method capable of resisting stamping, printing and scanning processes
InactiveCN102880999AMovableFast estimate of rotation angleImage data processing detailsColor imageImaging quality
The invention relates to a color image digital watermark method capable of resisting stamping, printing and scanning processes and belongs to the technical fields of anti-counterfeit, authentication and information safety. The invention adopts the technical scheme that an L*a*b* color space of a color carrier image is represented by quaternary supercomplex number; readable watermark information is encoded and modulated to generate a two-dimensional watermark signal in a form of the quaternary supercomplex number; and the watermark embedding position is determined by a uniform discrete logarithmic polar coordinates method. The color image digital watermark method capable of resisting stamping, printing and scanning processes has the beneficial effects that the embedding capacity of watermarks is large; the robustness resisting synchronous distortion is strong; the gap of an image quality evaluation function of the color image is filled; self-adaption embedding of the watermarks with highest strength is realized; the robustness resisting rotation, compression, stamping, printing and scanning attacks is strong; and the method can be widely applied to anti-counterfeiting domain authentication of various certificates and printed products.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
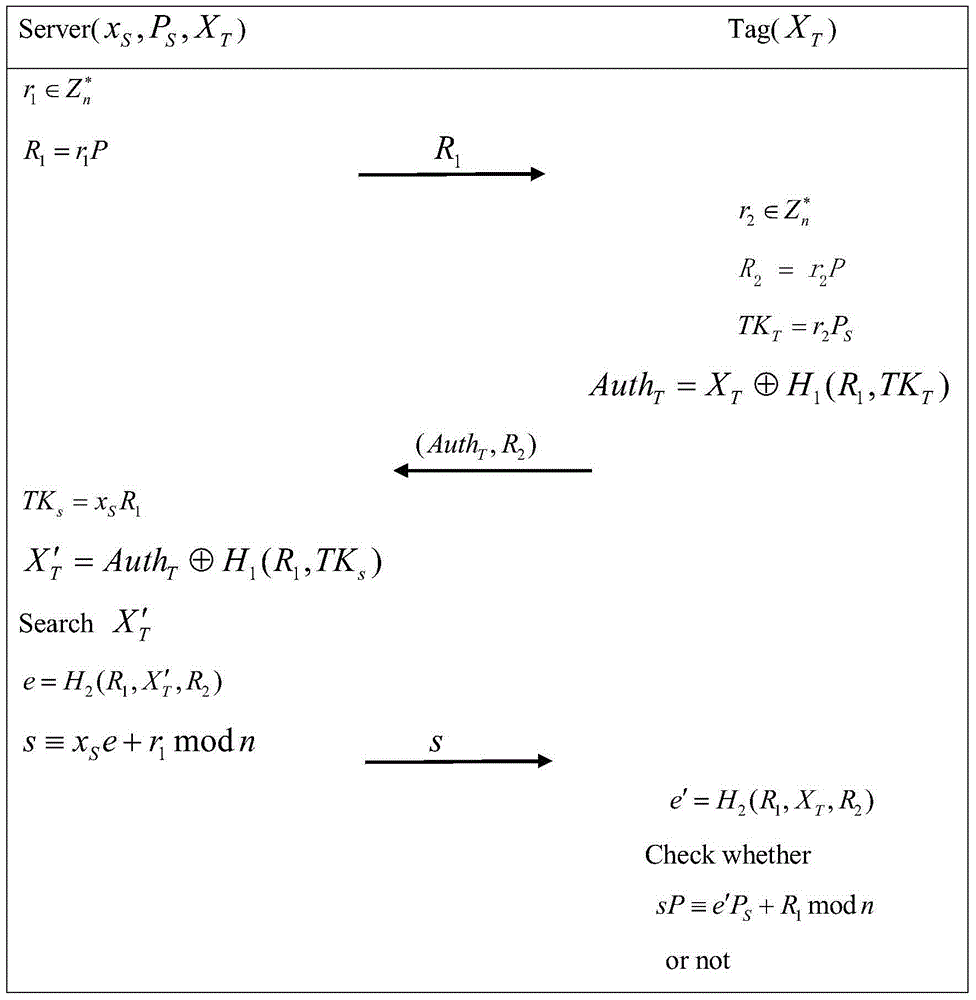
Mutual authentication method for lightweight-class RFID on elliptic curve
InactiveCN104363097AImprove identityAchieve mutual authenticationUser identity/authority verificationExclusive orDiscrete logarithm
The invention provides a mutual authentication method for a lightweight-class RFID on an elliptic curve. The mutual authentication method for the lightweight-class RFID on the elliptic curve aims to solve the problem that discrete logarithm on the elliptic curve is difficult. Under the same security strength condition, the algorithm of the mutual authentication method is smaller in key length, the operating speed is high, and storage space is small. Considering that the operating capability of a label is low, operation only relates to generation of a random number, Hash operation, point multiplication, addition and exclusive or in the authentication process. By the adoption of the mutual authentication method for the lightweight-class RFID on the elliptic curve, the identification information of the label is protected, mutual authentication between the label and a server is achieved, and a certain security and privacy requirement is met.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Identity authentication method based on public key certificate on ellipse curve
InactiveCN1444169AFast operationUser identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionElectronic businessDiscrete logarithm
The present invention discloses an identity identification method based on public key certification on the elliptic curve. It is an identify identification method by proceeding from discrete logarithm problem on the elliptic curve and utilizing anti-collision miscellaneous function and public key certificate to make identity identification. It has provable safety and rapid operation speed. It canbe extensively used in the fields of identity identification of network communication, electronic business, bill, certificate and identify identification, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com