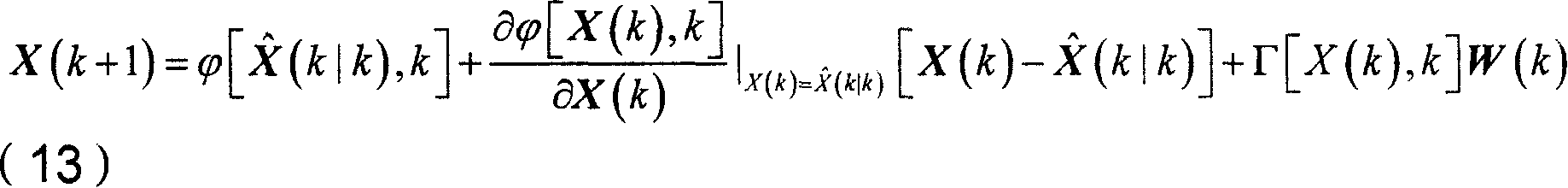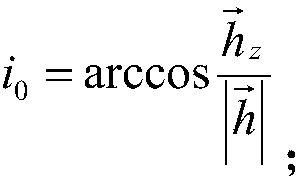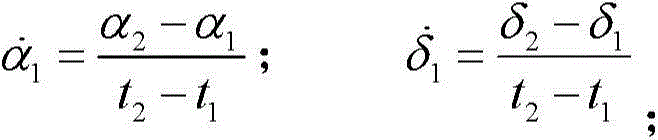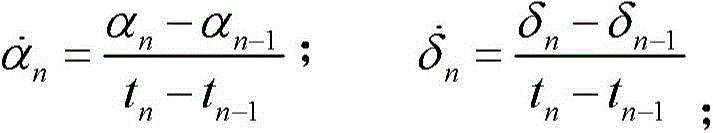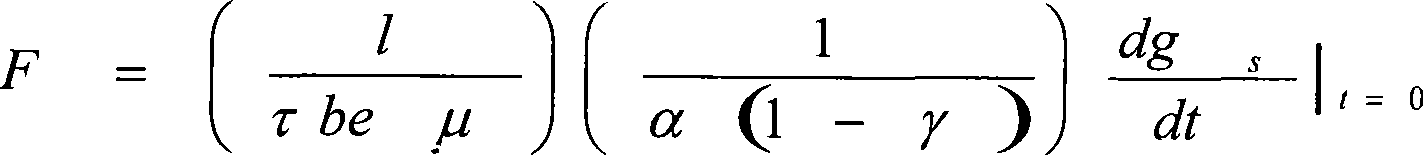Patents
Literature
78 results about "Earth satellite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
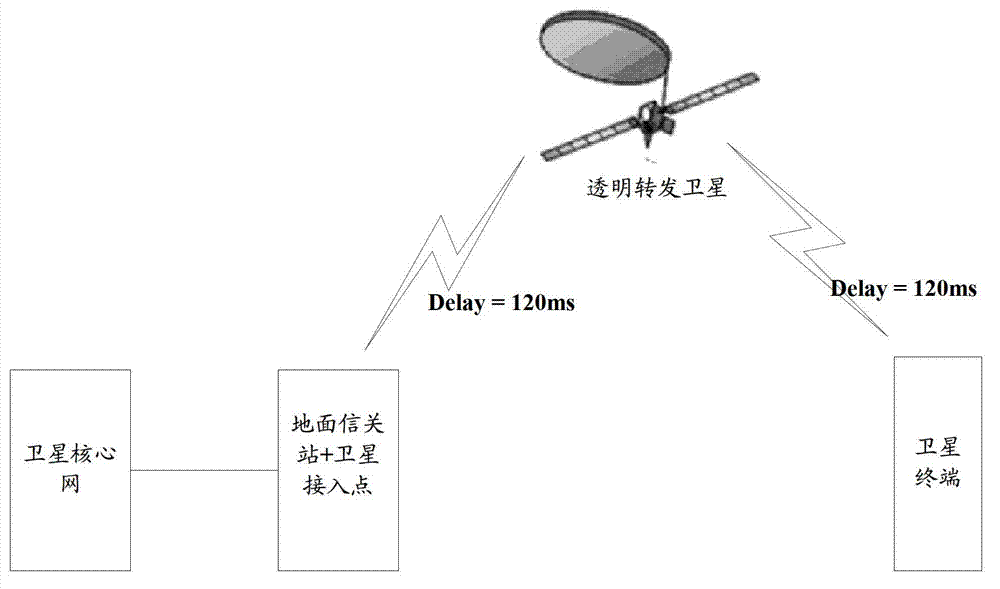
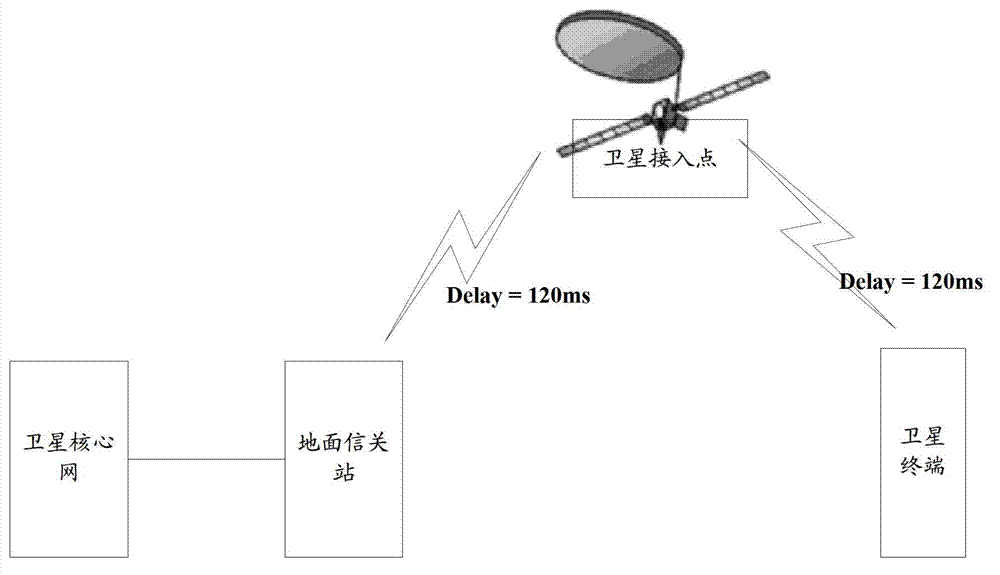
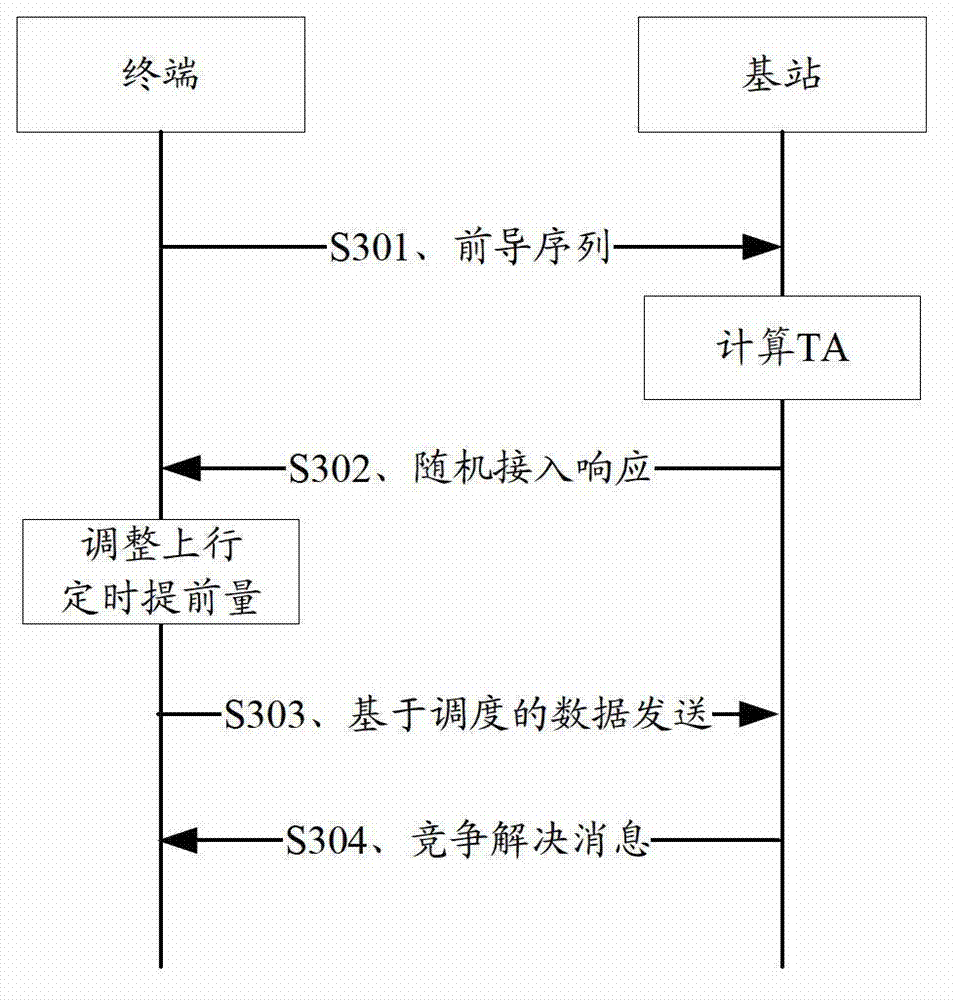
Cell switching method and device
ActiveCN103945471AAvoid long interruptionsReduce downtimeSynchronisation arrangementRadio transmissionEarth satelliteTerminal equipment
The embodiment of the invention discloses a cell switching method and device. According to the technical scheme provided by applying the cell switching method and device, in the process of conducting data transmission at a terminal device and a service access point, if the service access point of the terminal device determines that cell switching needs to be carried out on the terminal device, the service access point indicates the terminal device to build presynchronization with the uplink of an alternate target cell, and the terminal device is made to obtain a timing advance value of the corresponding alternate target cell; then, cell switching is carried out on the terminal device according to the obtained timing advance value, so that long-time data interruption caused when the terminal device conducts synchronization with the uplink of the target cell after receiving a switching instruction for switching to the target cell is avoided, and the user plane data interruption time spent when cell switching is carried out on the terminal device, particularly large-span switching between cells such as earth satellites or satellites is shortened.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
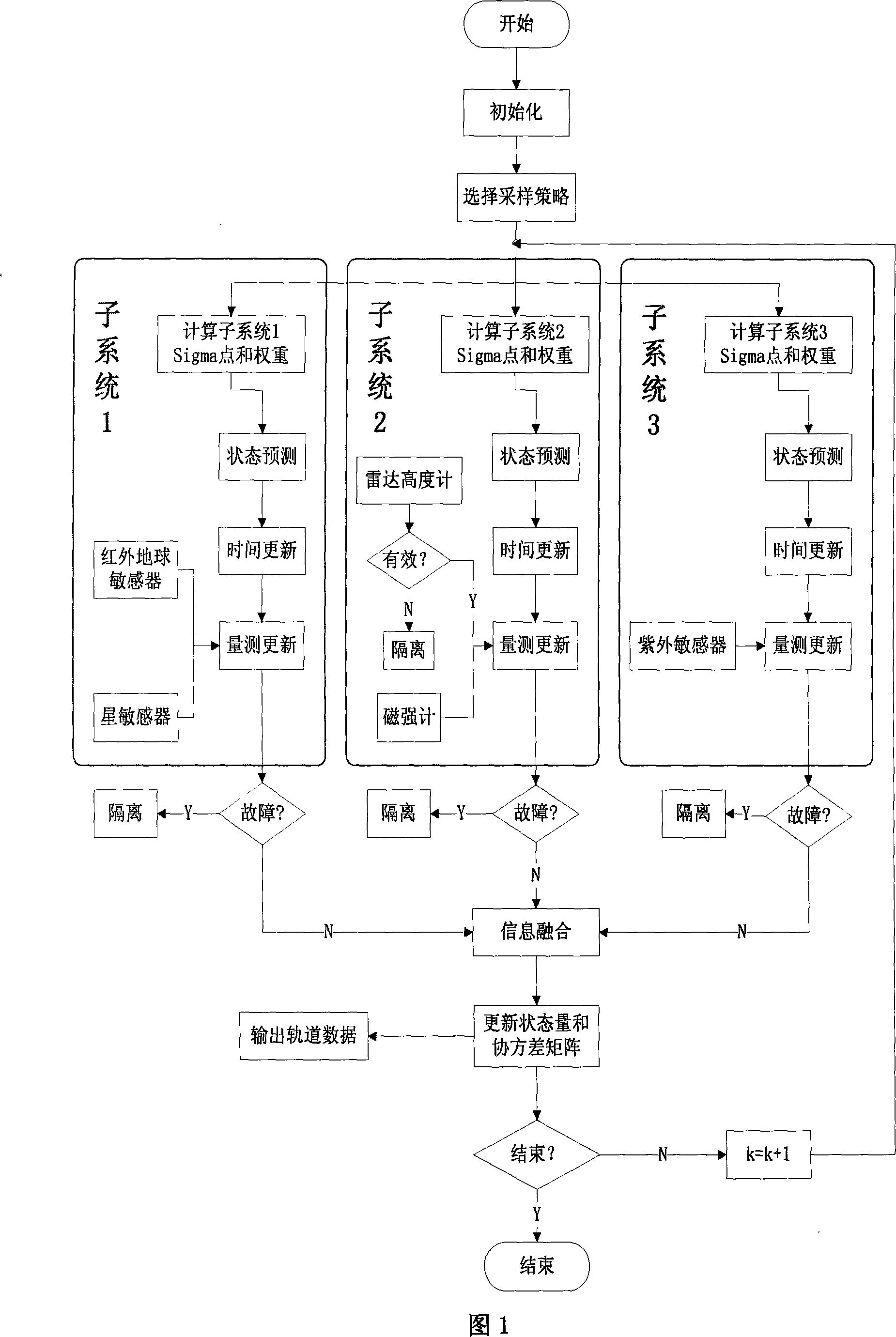
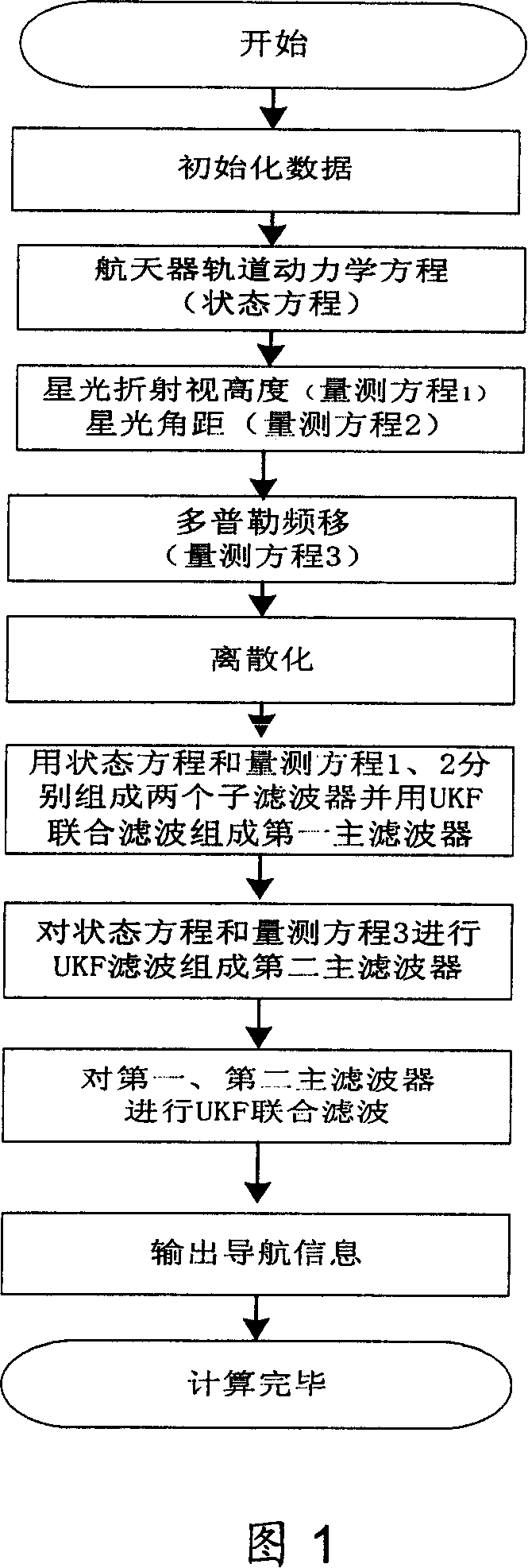
Low orbit satellite multi-sensor fault tolerance autonomous navigation method based on federal UKF algorithm
InactiveCN101216319AGuaranteed continuityGuaranteed stabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationEarth satelliteFault tolerance
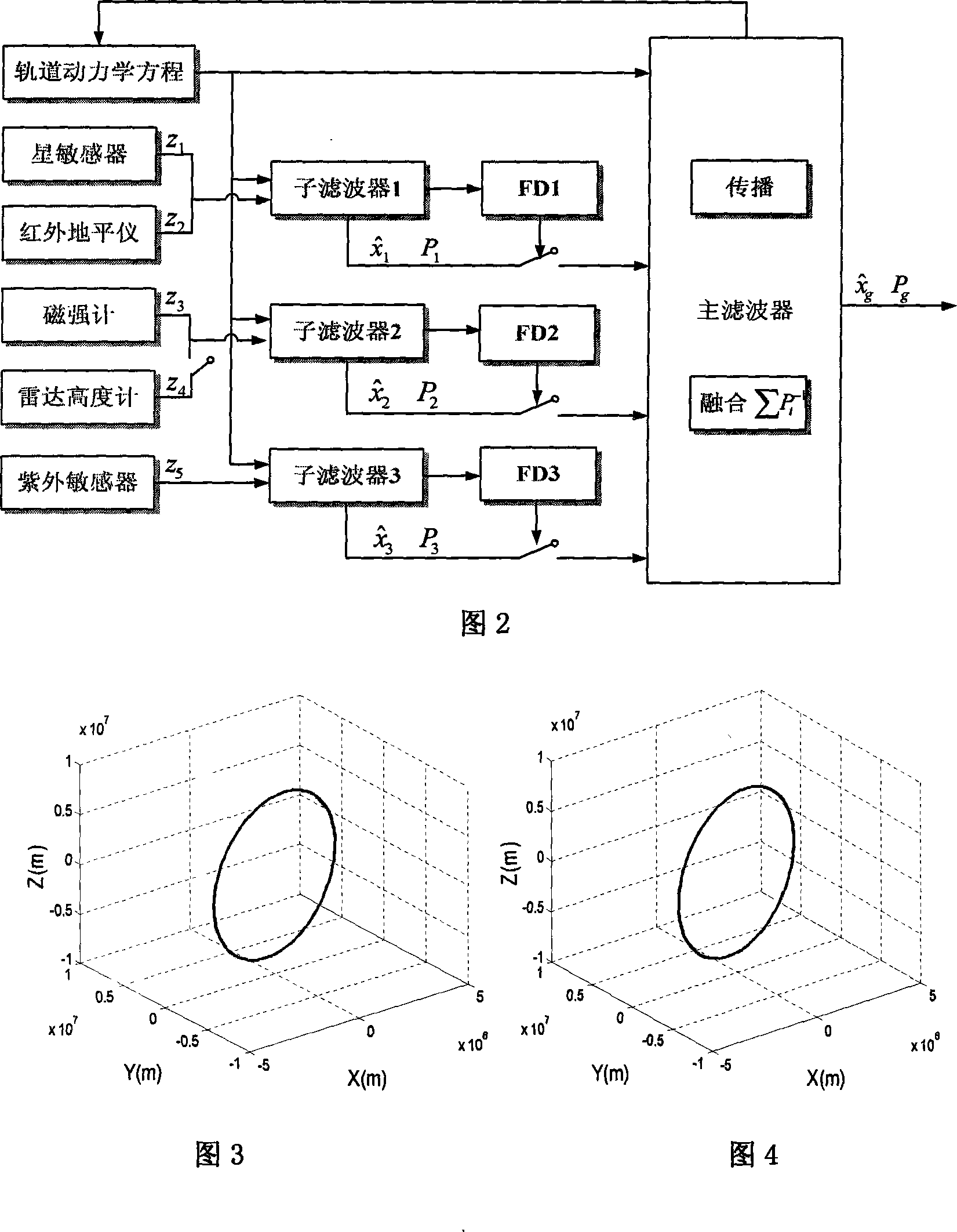
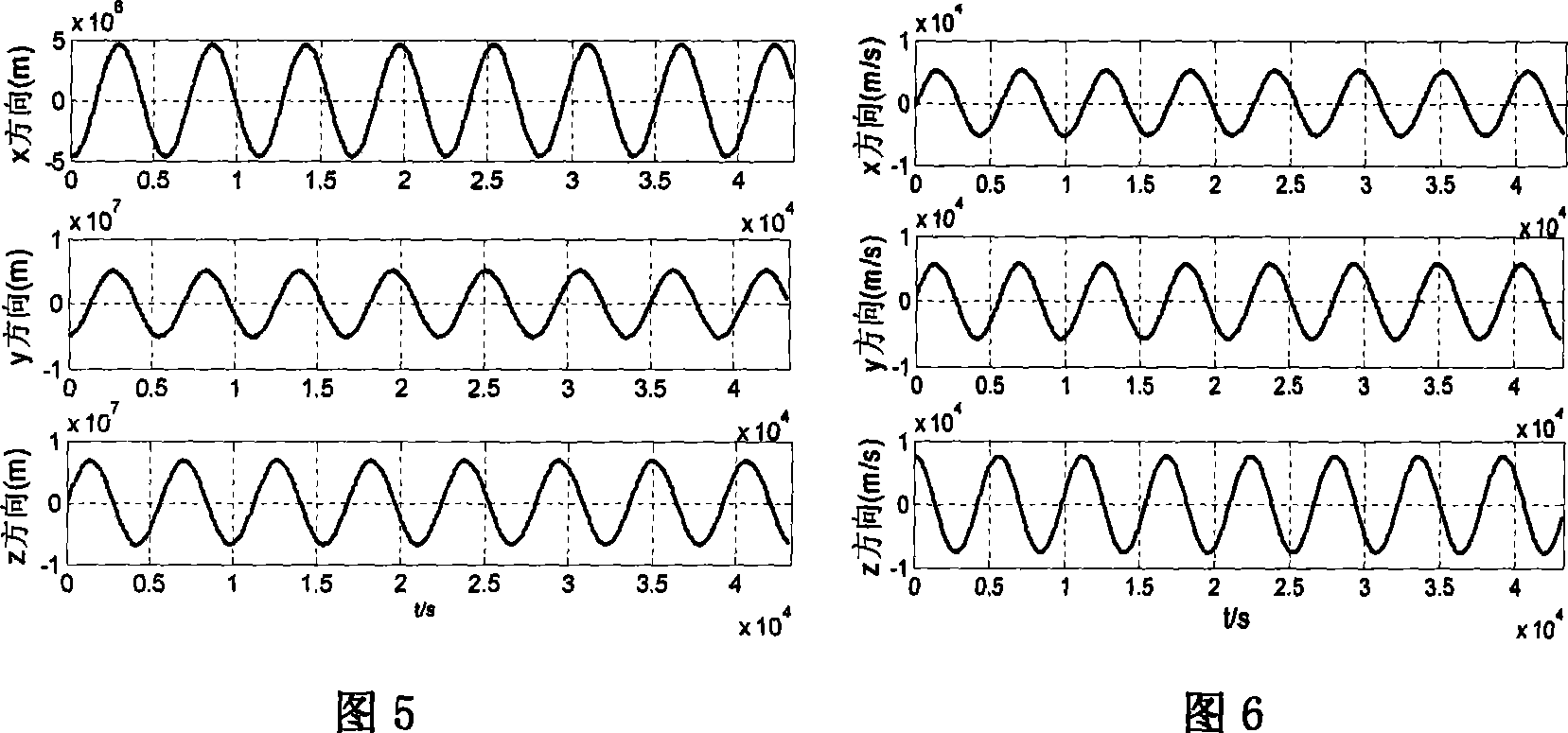
The invention relates to a multi-sensor autonomous navigation method for the low-orbiting satellite with fault-tolerance function and based on federated UKF algorithm, belonging to satellite autonomous navigation method. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing an orbital dynamics equation of earth satellite in a rectangular coordinate system; constructing a subsystem measurement equation with the output values of a star sensor and an infrared earth sensor as measurement quantities; constructing a subsystem measurement equation with the output values of magnetometer and a radar altimeter as measurement quantities; constructing a subsystem measurement equation with the output value of an ultraviolet sensor as measurement quantity; selecting a Sigma sampling point; constructing a predictive equation and an update equation of discrete UKF algorithm; respectively and independently performing Sigma sampling point calculation of each subsystem, and performing predictive update and measurement update; determining whether the output of each sub-filter is valid according to the predicted filter residual, isolating in case of malfunction, otherwise, inputting the filter result to a main filter for information fusion; constructing a non-reset federated UKF filter equation based on the UKF algorithm; and outputting earth satellite state estimated value X and variance matrix P thereof according to the steps.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Separable micro and nano-satellite configuration
InactiveCN103612774AStable attitude maneuverStable postureCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusArtificial satellitesEarth satelliteEngineering
The invention discloses separable micro and nano-satellite configuration which comprises a satellite body, a plurality of separate release sub-satellites, mechanical net claws, a flexible solar cell array and a variable-structure mechanical arm. The separable micro and nano-satellite configuration has the advantages that the integral separable micro and nano-satellite configuration is in such a configuration form that a primary satellite carries the multiple sub-satellites, and functions of separately releasing and hovering the micro and nano-satellites can be realized; the efficiency of the solar cell array can be improved owing to combined configuration comprising flexible solar wings and the variable-structure mechanical arm; mechanical net claw mechanisms are carried on the micro and nano-satellites, so that a function of capturing space targets can be realized; the separable micro and nano-satellite configuration is provided with a plurality of stereoscopic vision imaging cameras, so that a stereoscopic monitoring function can be realized; attitude maneuver and attitude stabilization of the micro and nano-satellites can be implemented by the aid of a solid miniature propulsion technology, so that the sub-satellite separate release control ability can be improved; the separable micro and nano-satellite configuration is applicable to fifty-kilogram-level micro-miniature artificial earth satellites on near-earth orbits and is also applicable to micro-satellite networking, scientific detection aircrafts and relevant micro and nano-satellite space demonstration and experiments.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
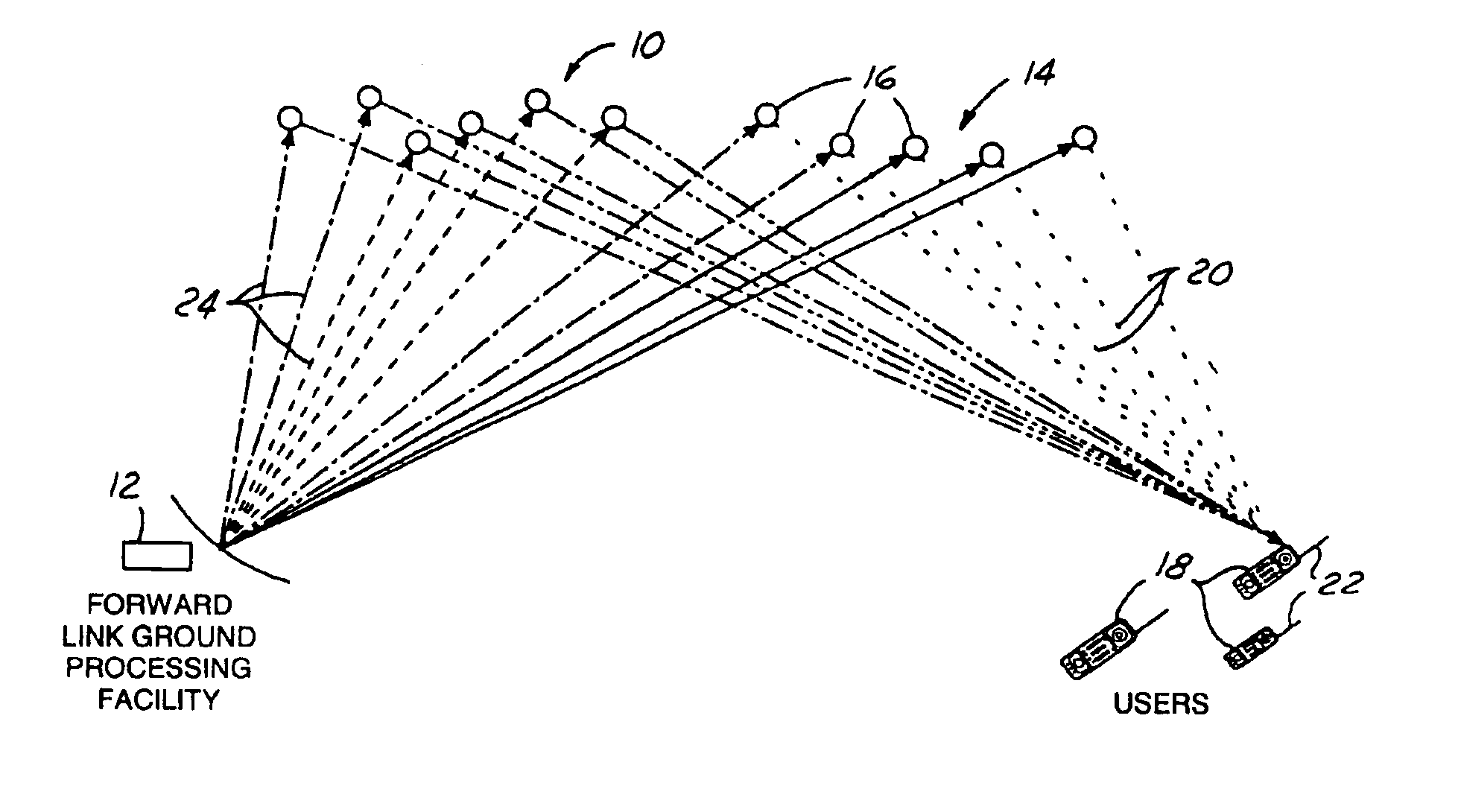
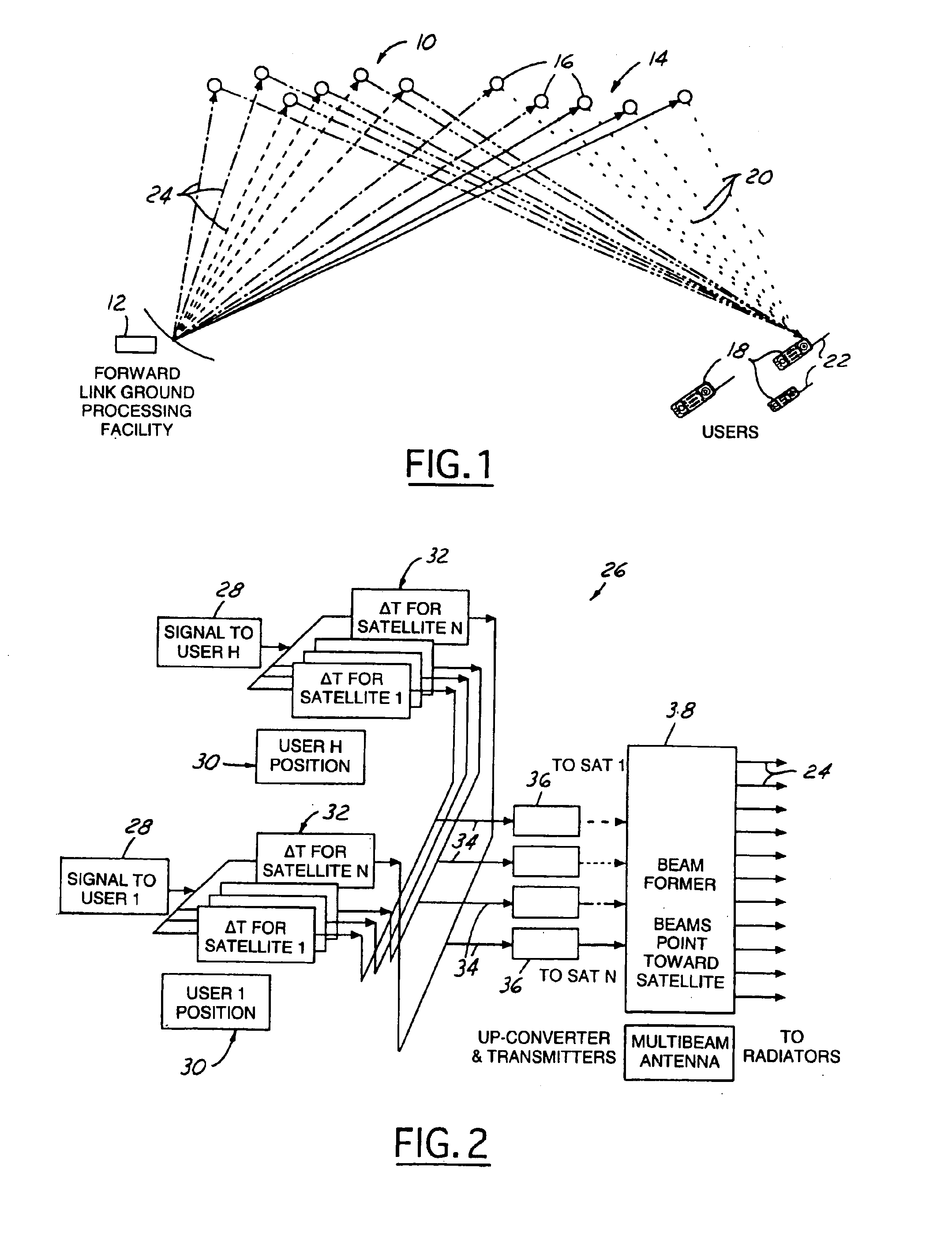
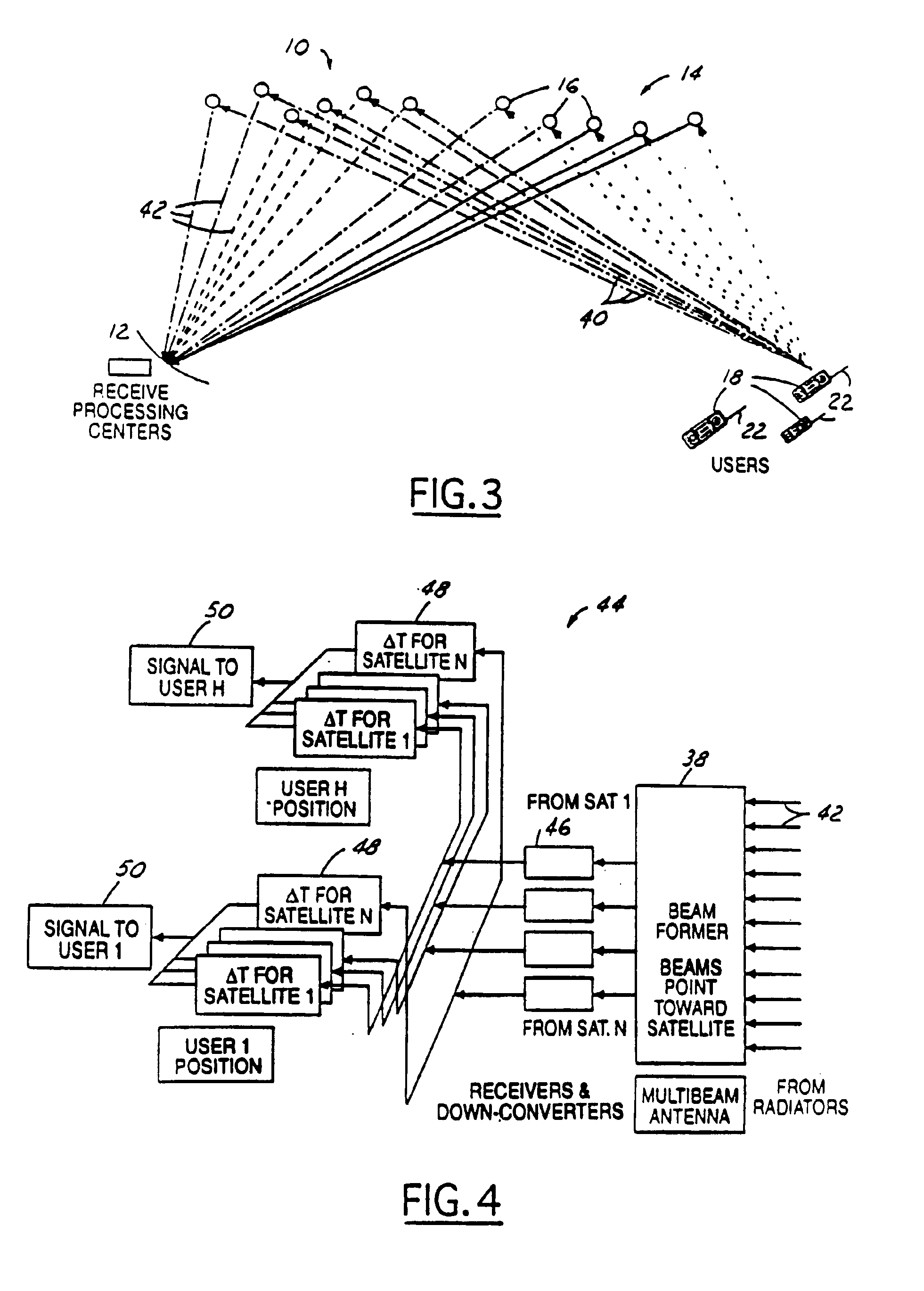
Multi-node point-to-point satellite communication system employing multiple geo satellites
InactiveUS6990314B1Reduce restrictionsReduce complexityActive radio relay systemsWireless commuication servicesEarth satelliteCommunications system
A wireless communication system includes a satellite constellation consisting of a plurality of satellites. Each of the plurality of satellites is in an orbit whose eccentricity and inclination are perturbed relative to the same geosynchronous orbit. Each of the satellites in the constellation is capable of relaying signals in either direction between a central ground hub and a plurality of mobile user terminals. The plurality of satellites are configured such that the period of their geosynchronous orbit remains substantially constant at one sidereal day.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Quick retrieval method for satellite attitude
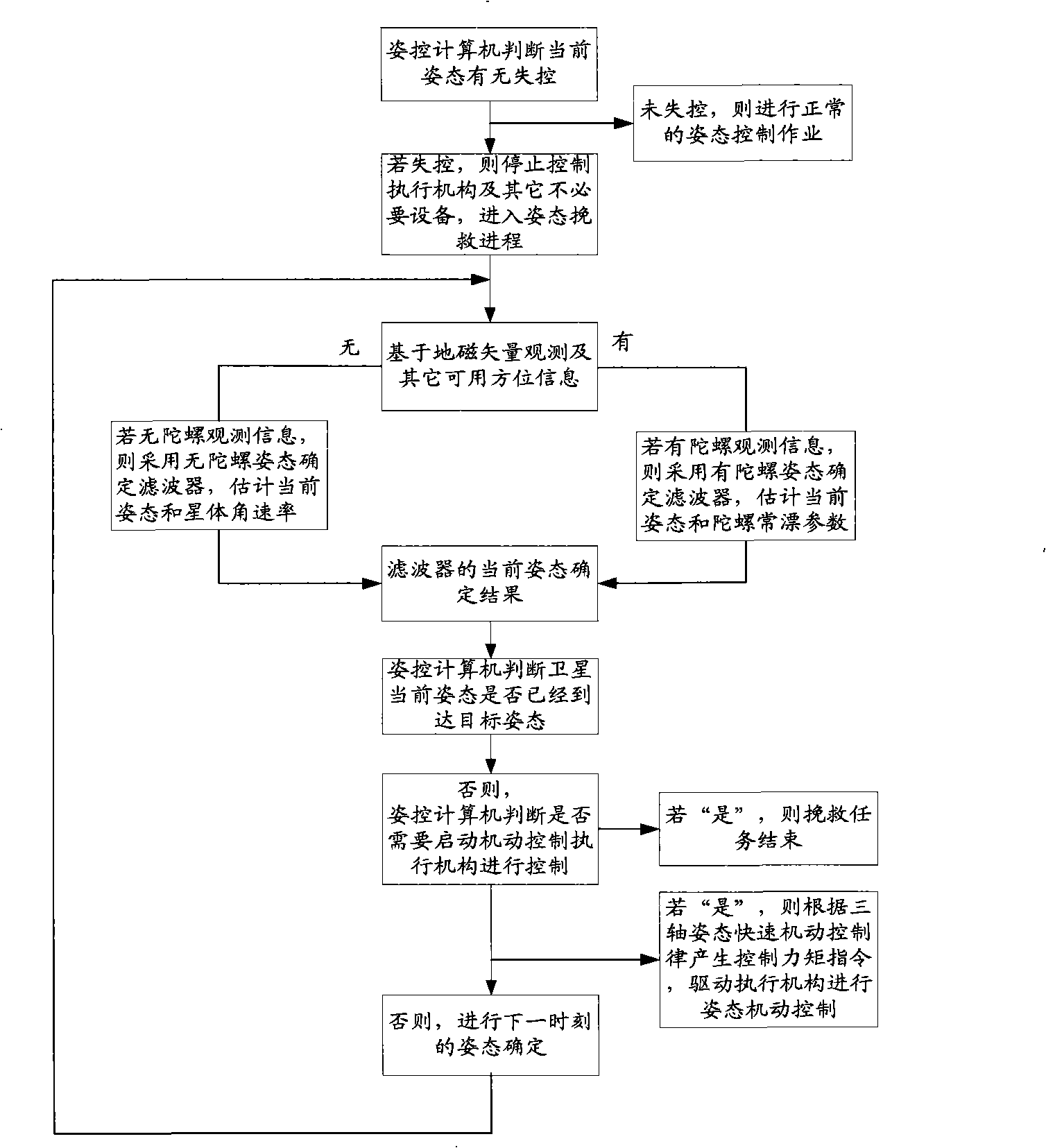
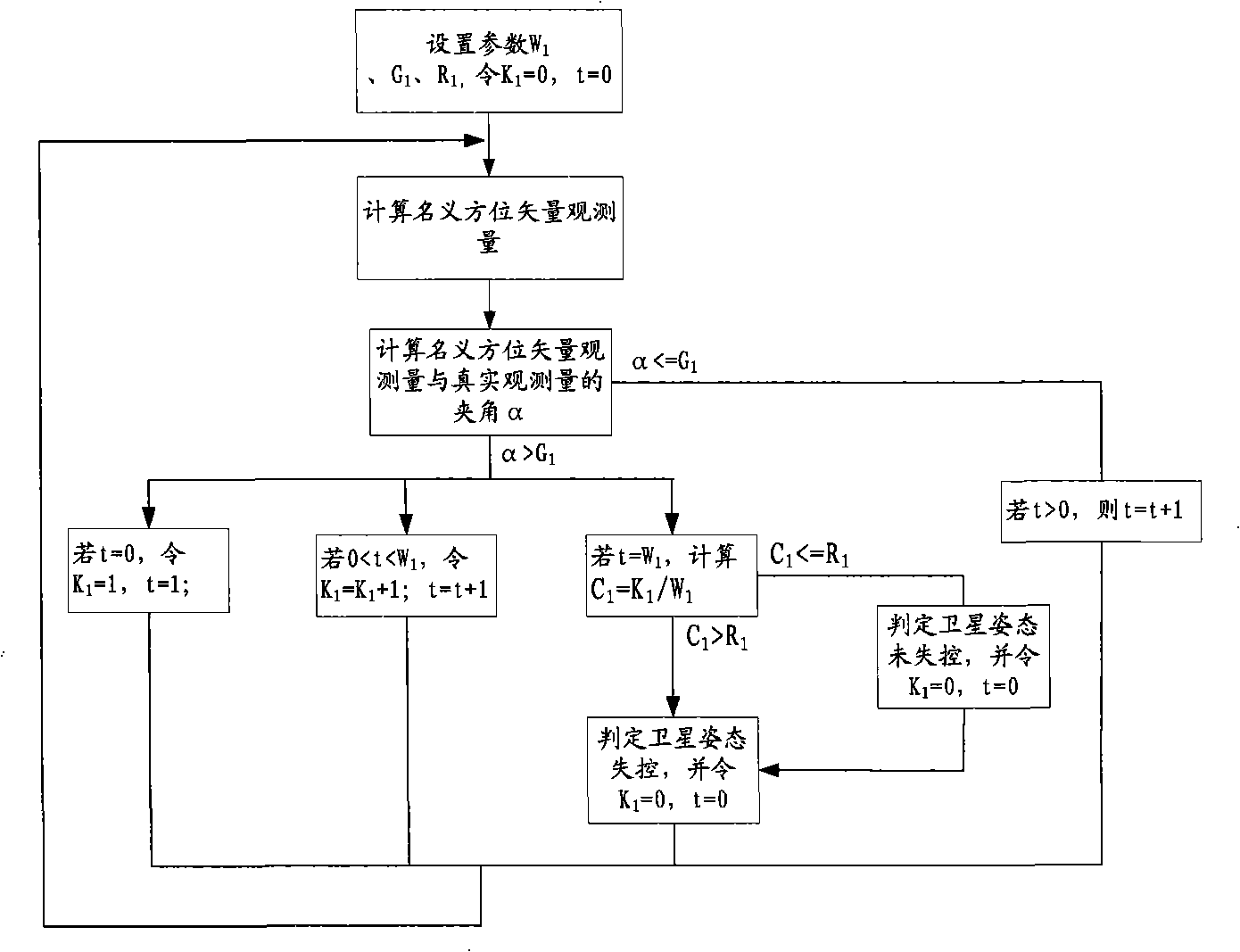
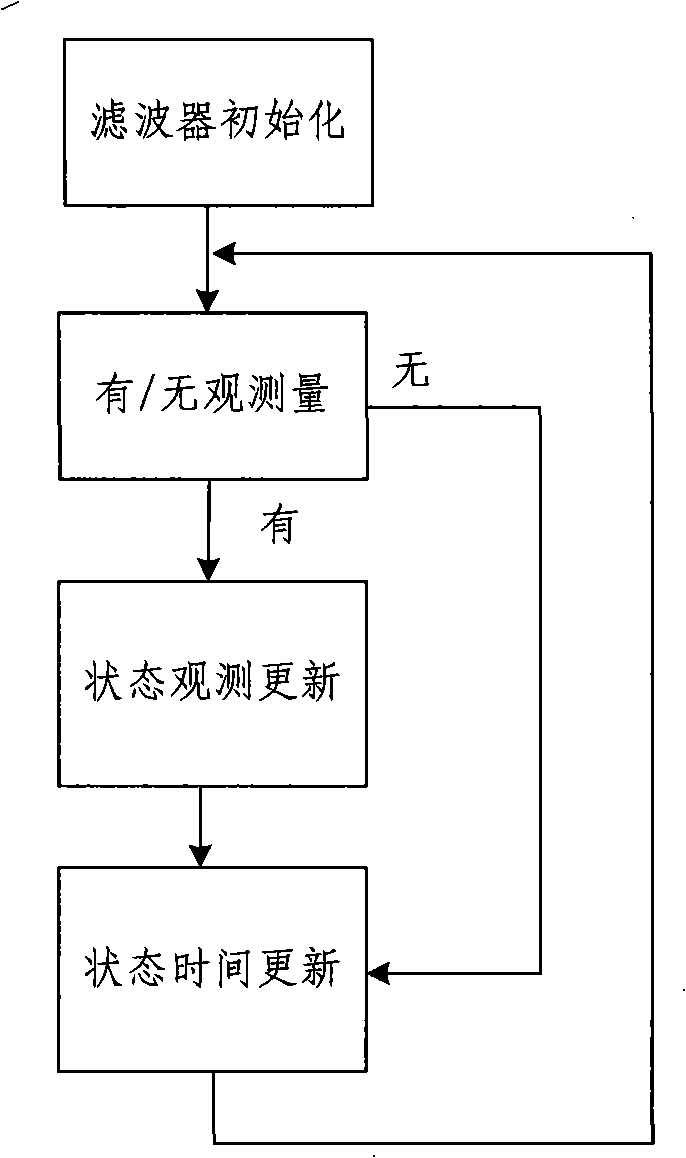
ActiveCN101402398AReduce lossReduce ineffective control energy consumptionCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusEarth satelliteAttitude control
The invention relates to a satellite attitude quick rescue method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, judgment is made whether the current attitude is out of control or not, and normal attitude control is performed if the current attitude is not out of control, otherwise the current actuator stops controlling satellite attitude; secondly, a filter is determined according to existence of gyroscopic observation information, and the current satellite attitude and the angular rate are observed and updated and time update is forecasted; and thirdly, judgment is made whether the target attitude is reached according to the current satellite attitude, judgment is made that the current moment needs controlling the actuator or not if the target attitude is not reached, and attitude maneuver control is performed by utilization of the current attitude determination information and the target attitude command if the current moment needs controlling the actuator, or the procedures are repeated if the current moment does not need controlling the actuator. The satellite attitude quick rescue method can quickly rescue the attitude of an out-of-control near earth satellite, eliminates the dependency of the satellite on earth stations and the work load of the earth stations on one hand and is the backup of each other with the prior spaceborne self-rescue method on the other hand, improves the quick spaceborne self-rescue ability, and guarantees the normal operating life of the satellite.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
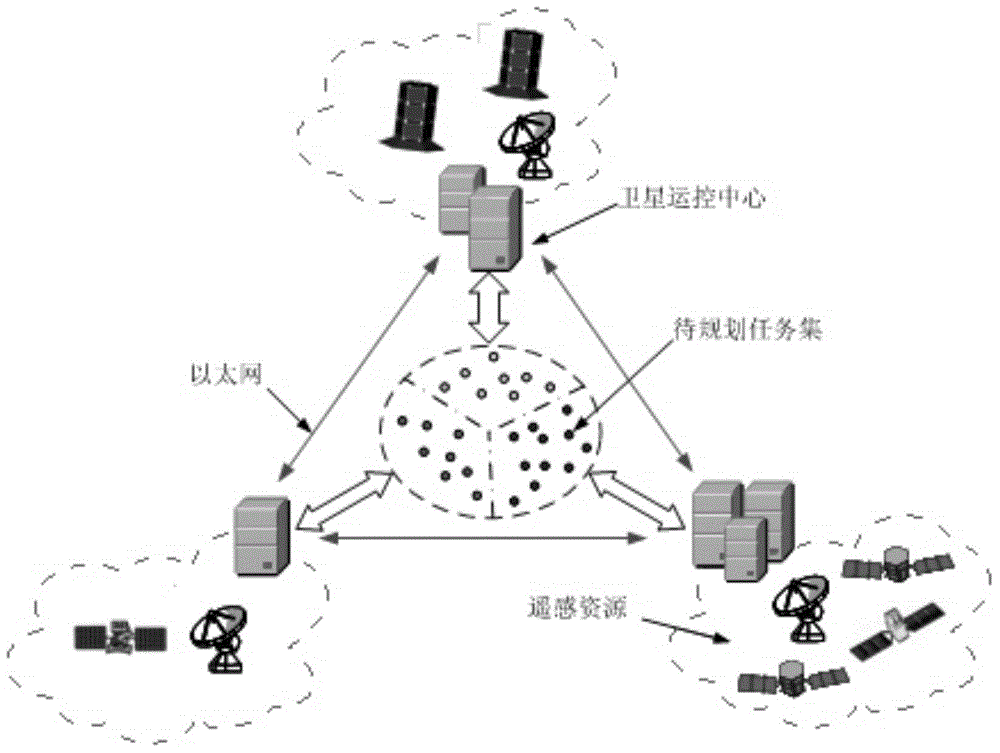
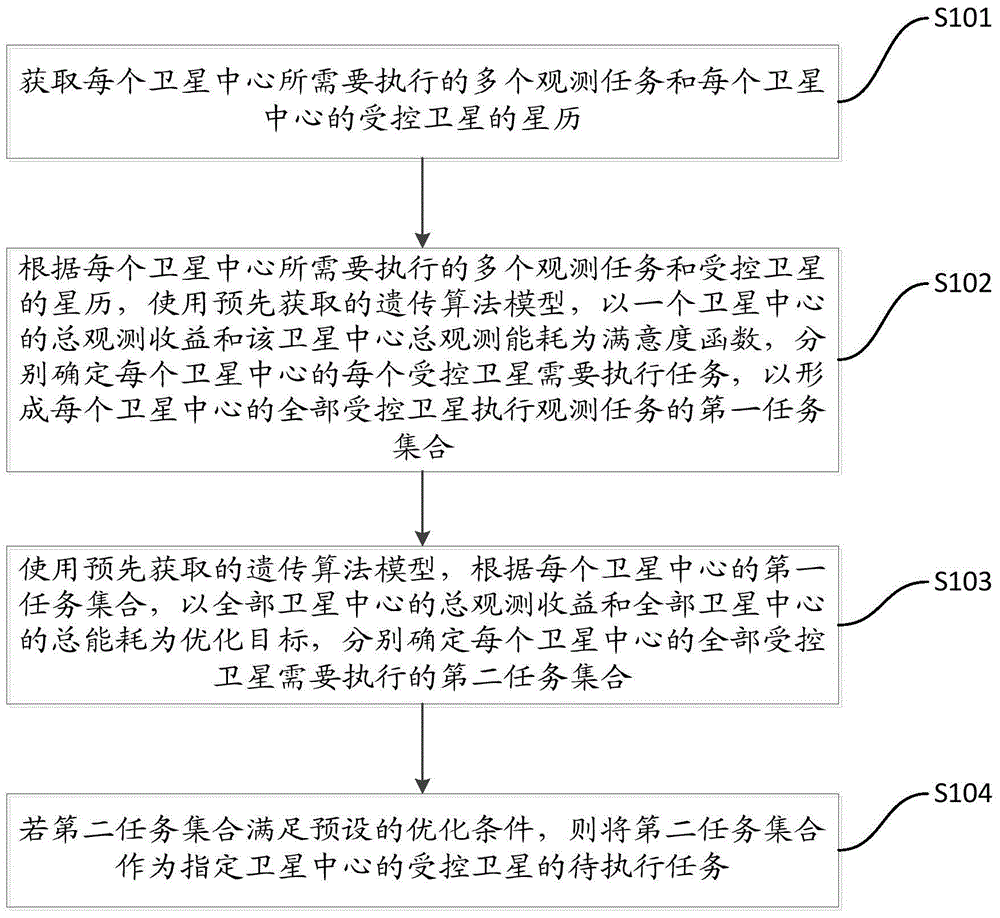
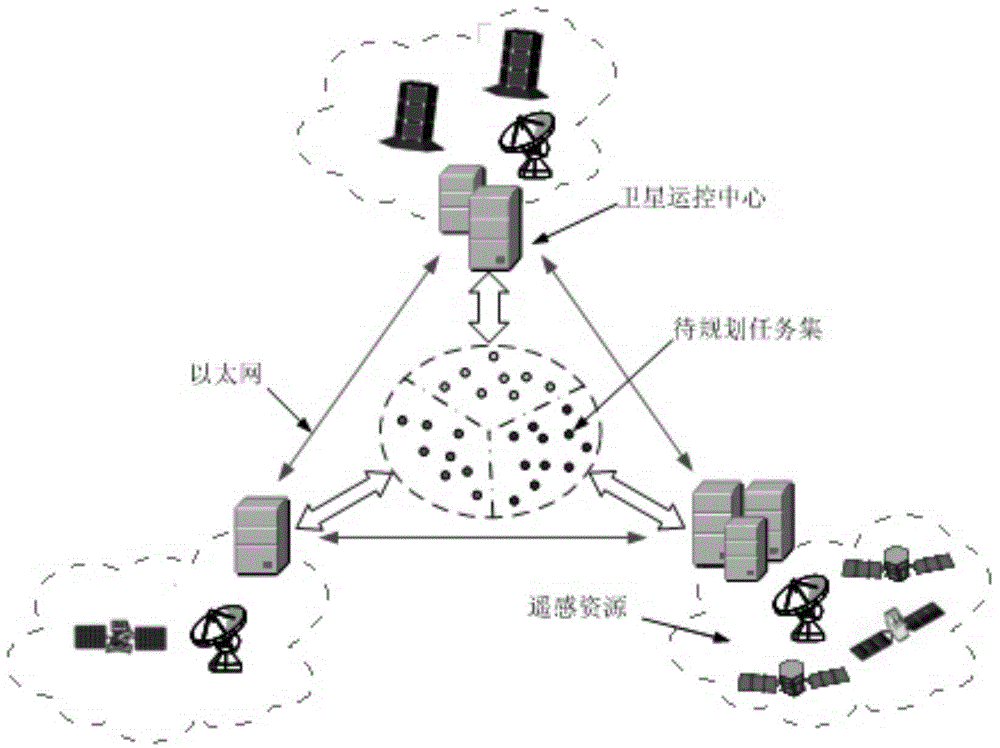
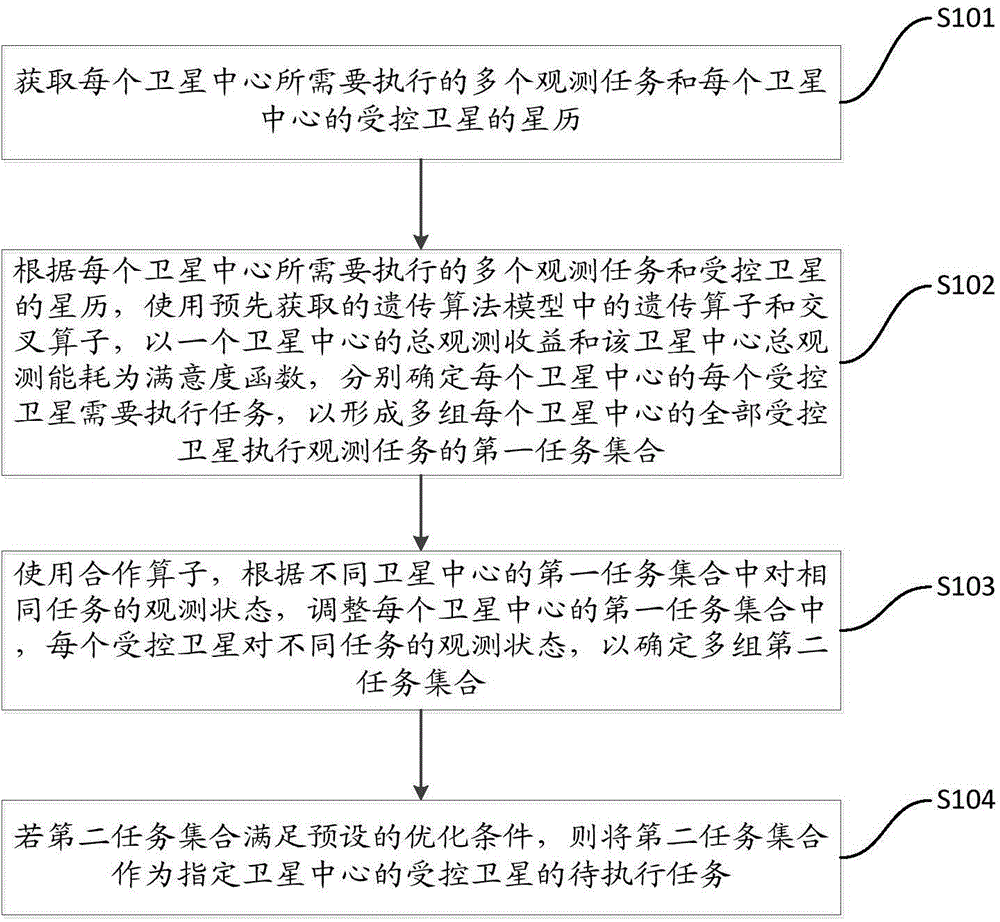
To-be-observed task determination method and device of multi-satellite earth synergetic observation
The invention provides a to-be-observed task determination method and device of multi-satellite earth synergetic observation, and relates to the earth satellite observation field. The to-be-observed task determination method of the multi-satellite earth synergetic observation comprises the following steps: enabling each satellite center to acquire a corresponding observation task and an ephemeris of each controlled satellite, computing a first task set of observation tasks executed by all the controlled satellites in each satellite center aiming the observation task of each satellite center and the ephemerides of the controlled satellites by using a genetic algorithm, and computing an optimal solution with maximum total observation benefit and lowest total energy consumption in all the satellites by using the genetic algorithm after the first task set of each satellite center is determined, namely, a second task set; if the second task set meets a preset optimal condition, executing the task by the appointed satellite center by using the second task set as the reference, so that the globally optimal solution search is finished by using the genetic algorithm.
Owner:INST OF RADAR & ELECTRONICS CONFRONTATION ARMY AIR FORCE EQUIP RES INST OF PLA
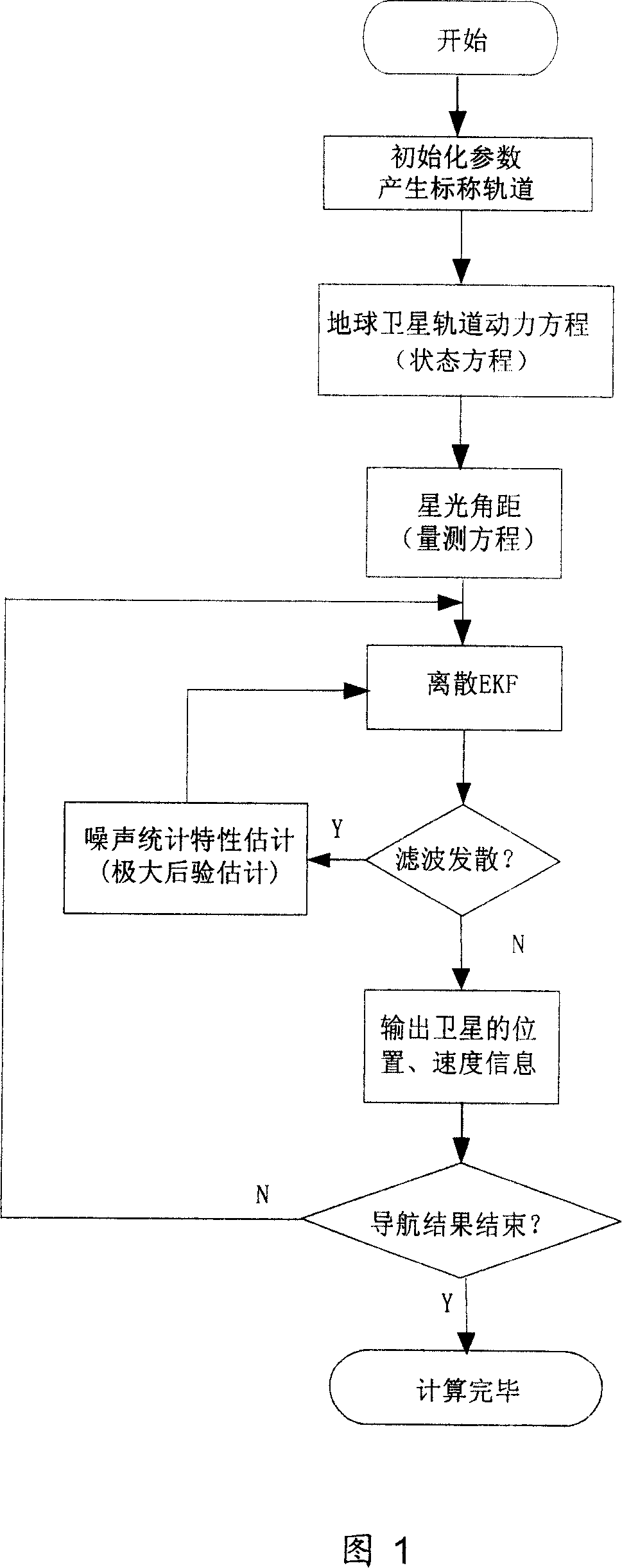
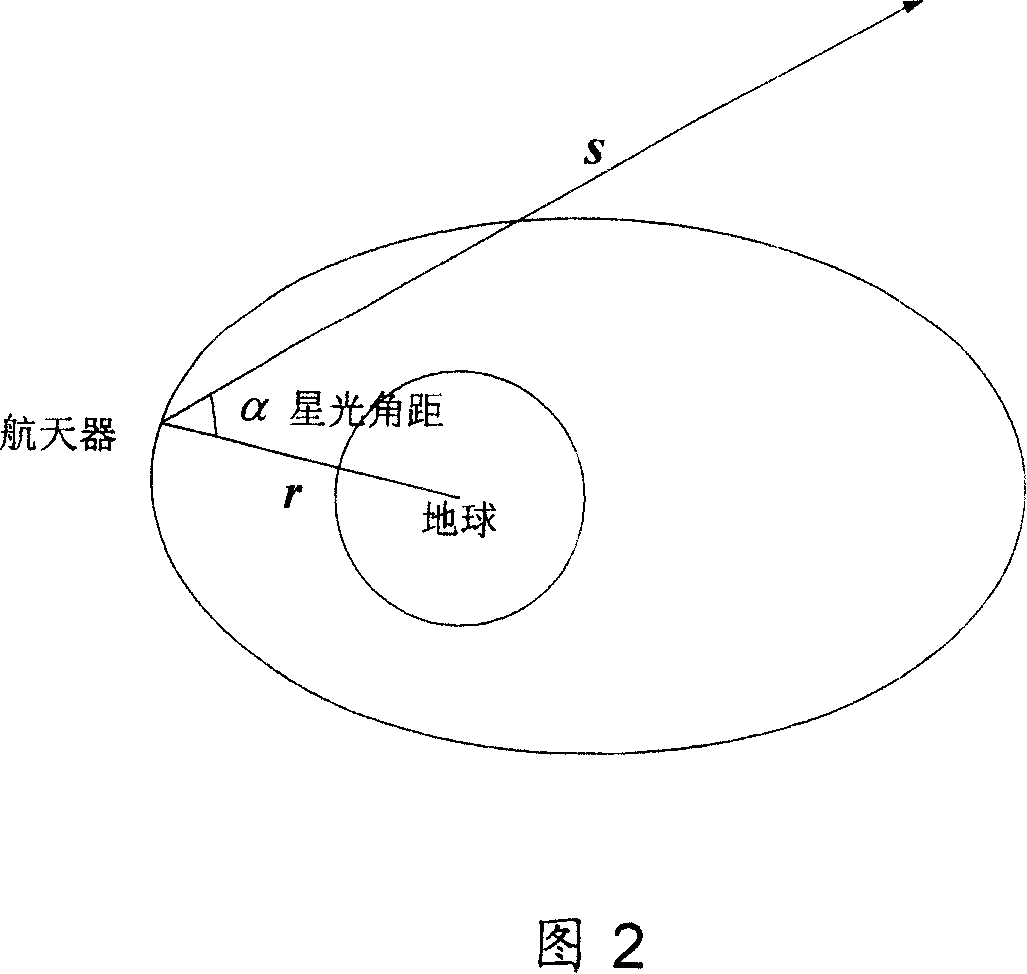
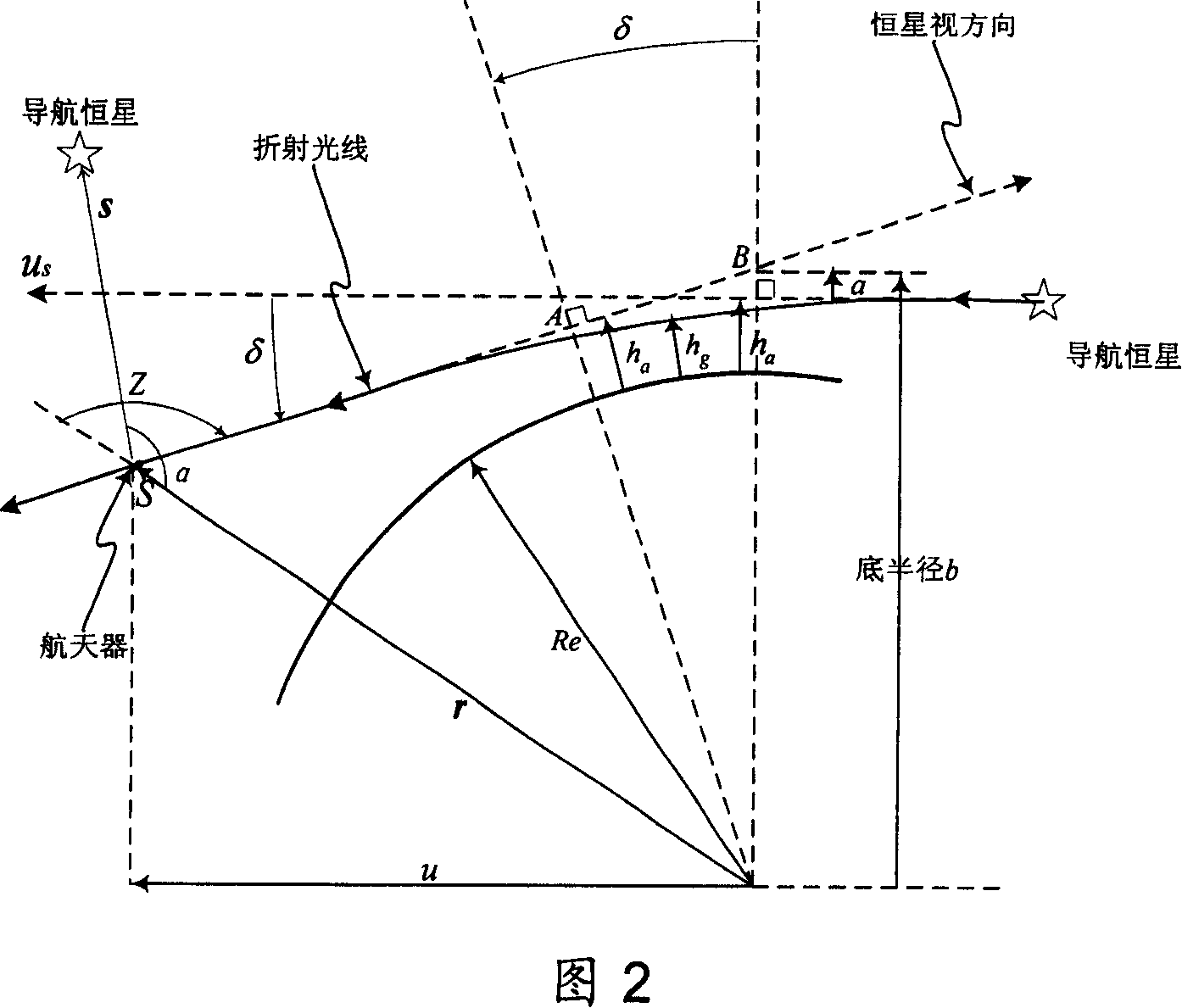
Earth satellite self astronomical navigation method based on self adaptive expansion kalman filtering
InactiveCN1987355AImprove navigation accuracyOvercome the problem of divergenceNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationEarth satelliteKinematics equations
The method includes steps: building up kinematical equation of earth satellite orbit based on rectangular coordinate system; building up measurement equation based on angular distance of starlight as measuring quantity; building up discrete type extended Kalman filtering equation to determine whether extended Kalman filtering is divergent; using prognostic filtering residual to determine whether extended Kalman filter is divergent; if yes, then the method carries out estimating statistic characteristics of noise; otherwise, carrying out calculation according to standard extended Kalman filtering program. The invention solves issue that divergence of noise filter caused by inaccurate determination of statistic characteristics of noise influences on navigation accuracy. Advantages are: independent, flexible and simple, and high precision. The invention is especially suitable to earth application satellite needed high navigation accuracy in resource, weather areas etc.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multiple coupled resonant loop antenna
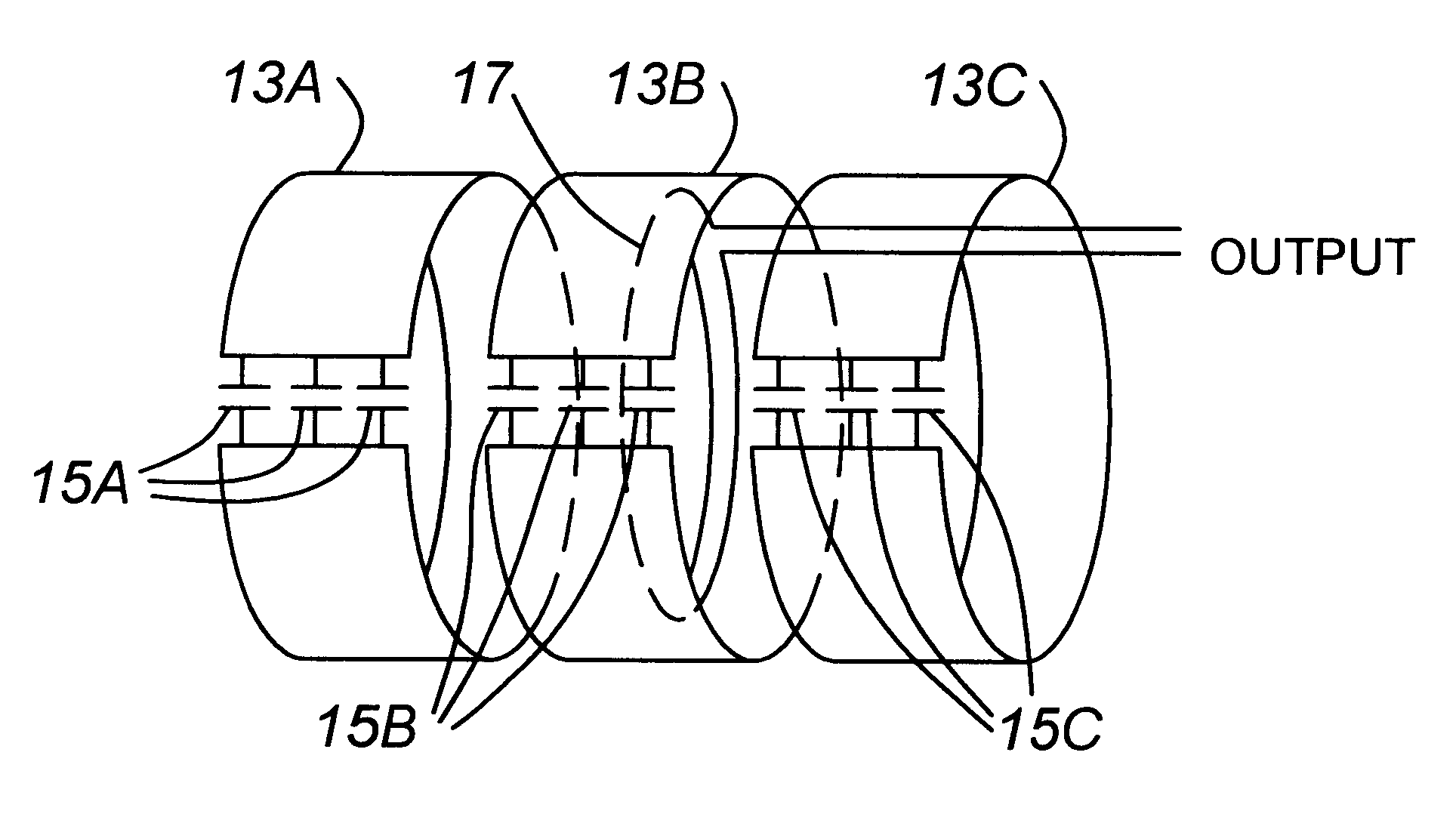
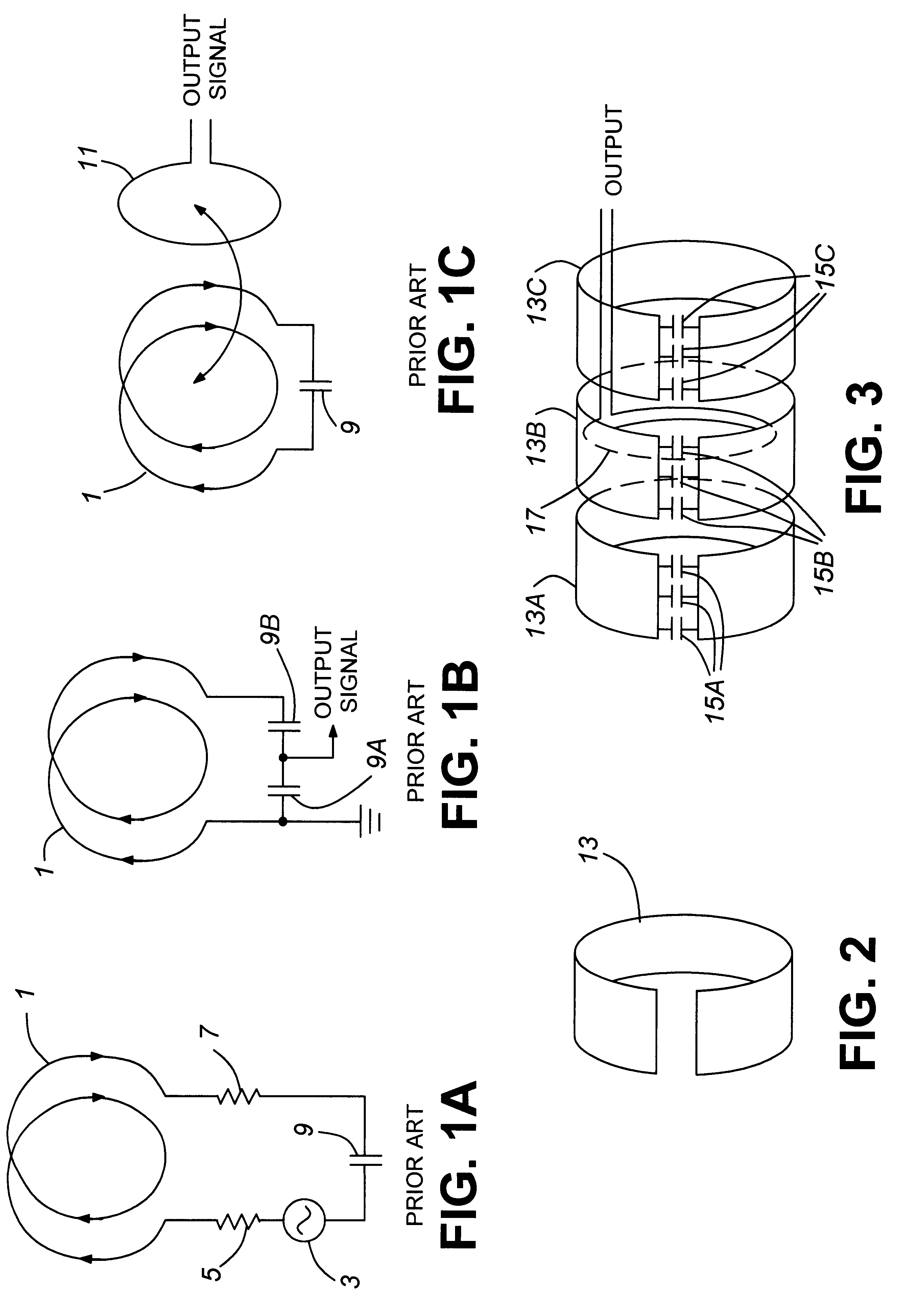
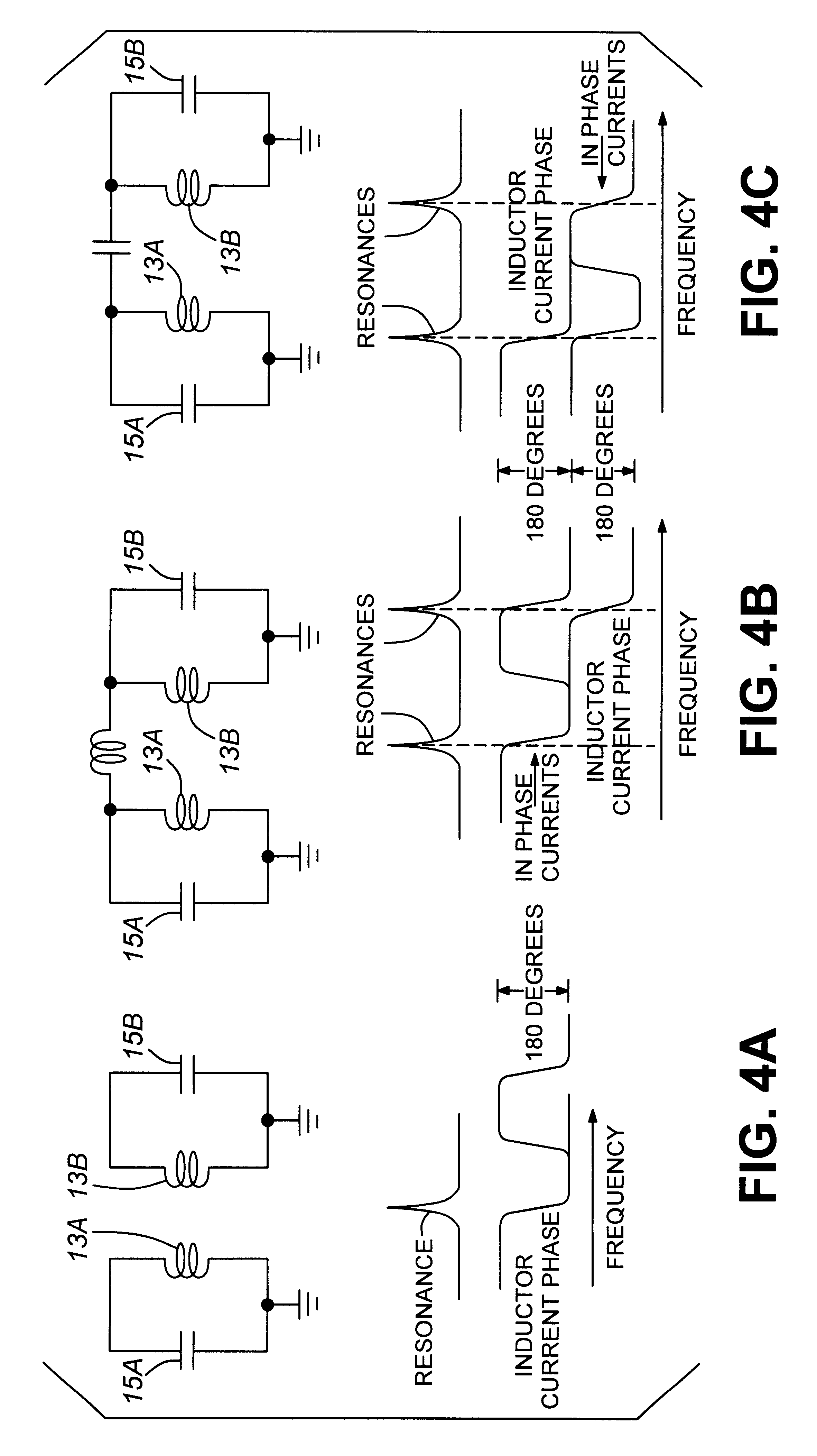
InactiveUS6304230B1Resonant long antennasAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesEarth satelliteLength wave
A loop antenna which is electrically small relative to a wavelength of a signal which it is designed to receive. The antenna is an electrically small, low profile, band switchable antenna which can be mounted on a metallic surface such as a truck or railway car rooftop and can be used to communicate with earth satellites. The antenna is polarized such that the plane containing the electric field is horizontal. Alternatively, the antenna can receive circularly polarized signals.
Owner:MOBILE KNOWLEDGE
Algorith for deducing possibilities of all possible scenarios of satellite members in low earth satellite constellation
InactiveUS20080251645A1Accurate calculationProbability is accurateCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesEarth satelliteLow earth orbit
An algorithm for deducing all possible scenarios of satellite members and possibilities thereof in a low earth orbiting (LEO) satellite constellation is described, which is achieved mainly by relying on the spherical geometry analysis and probabilities and statistics technologies, in an attempt to rapidly and precisely obtain the concerned scenarios and possibilities thereof observed on the earth ground. With any user-defined orbital parameters and a position of an observation station for the scenarios on the earth ground inputted, all the possible scenarios and possibilities thereof can be obtained with the algorithm.
Owner:NATIONAL DEFENSE UNIVERSITY
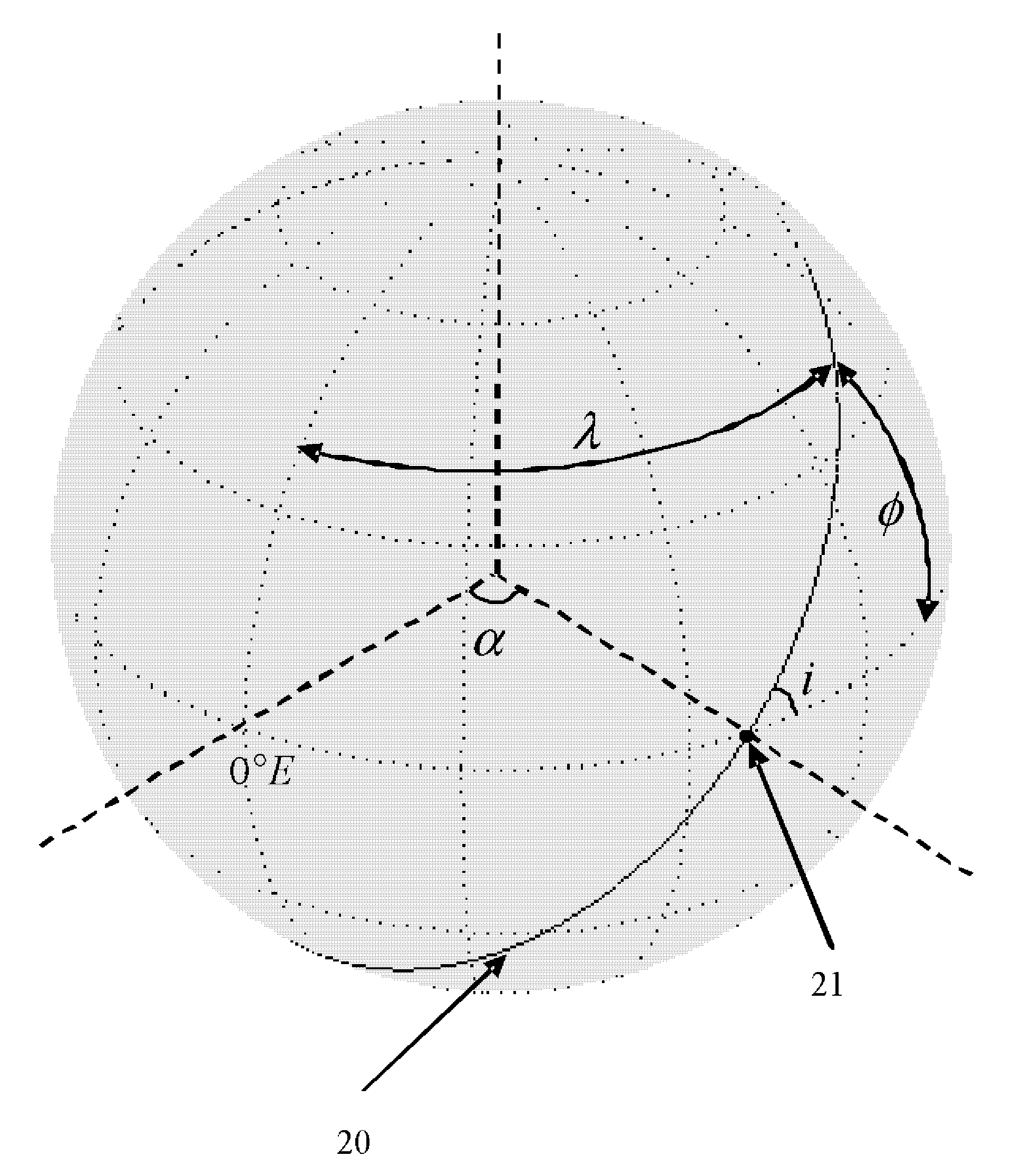
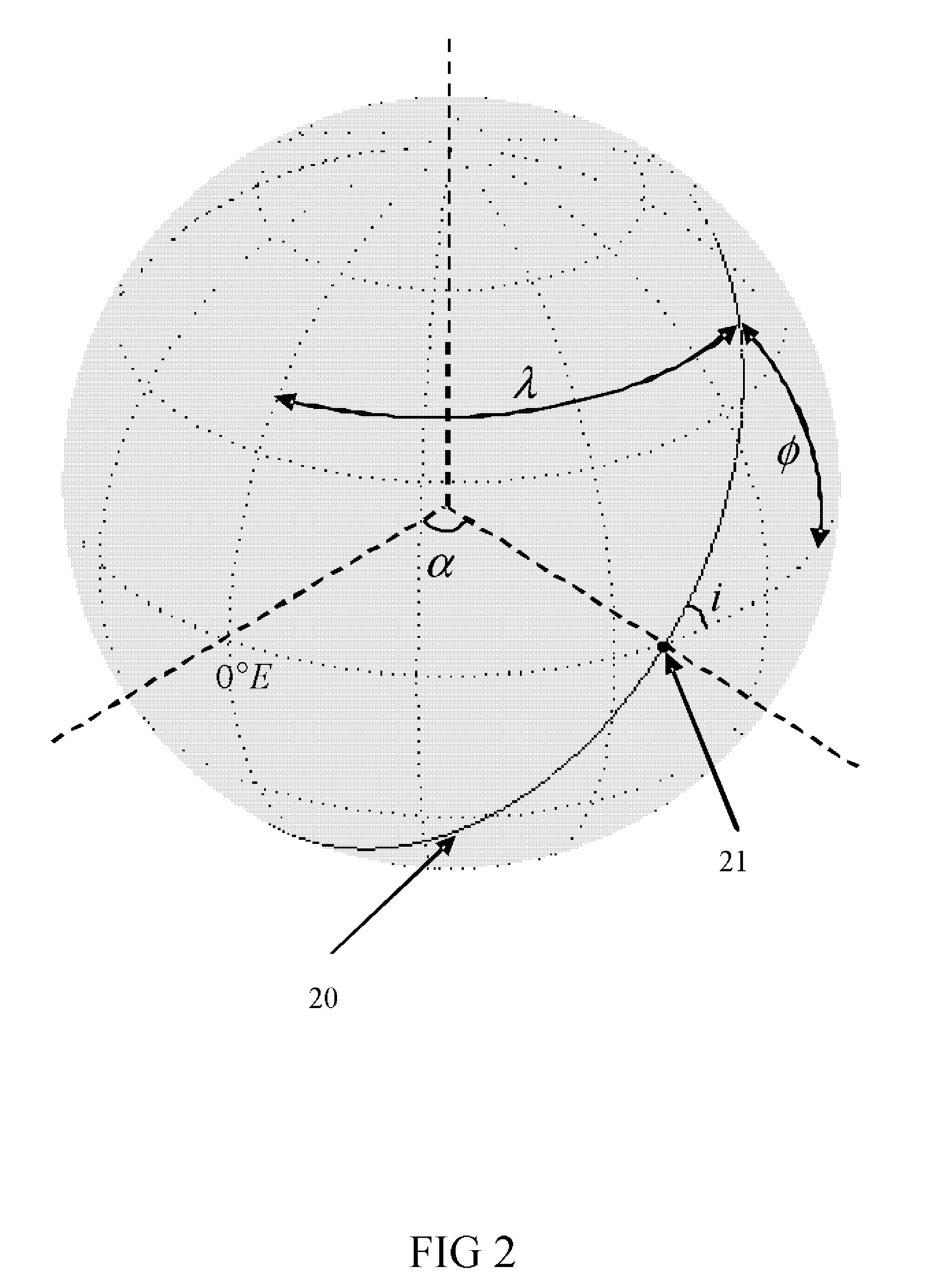
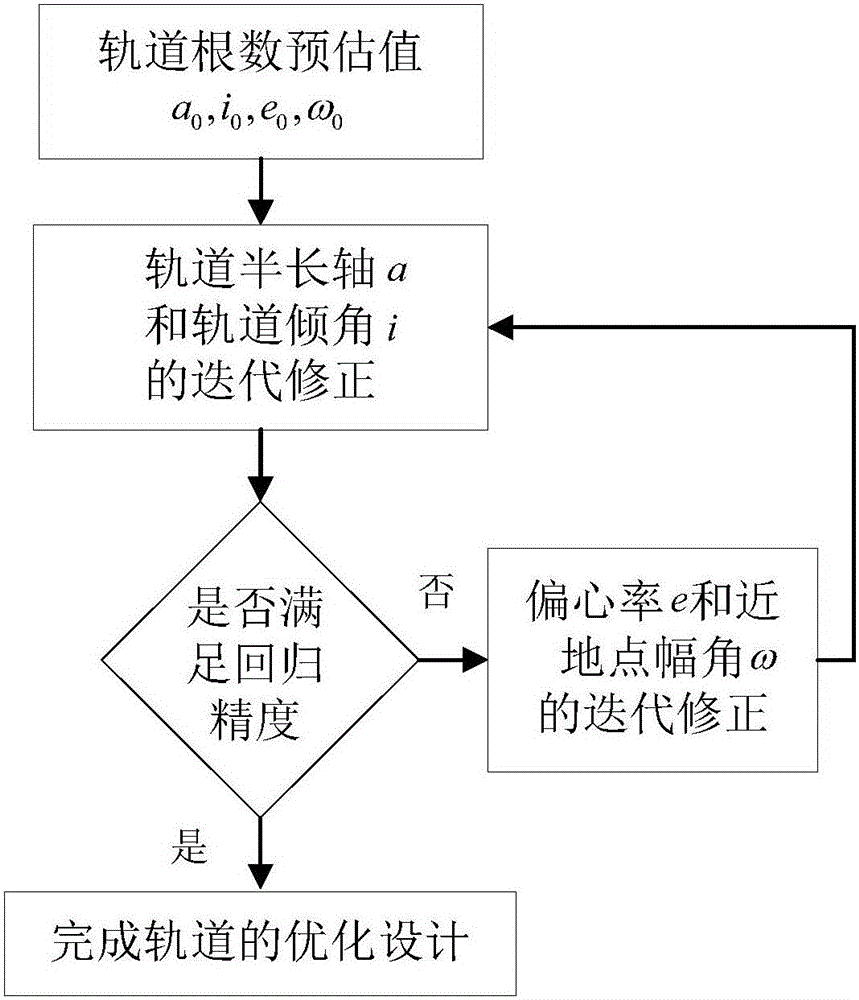
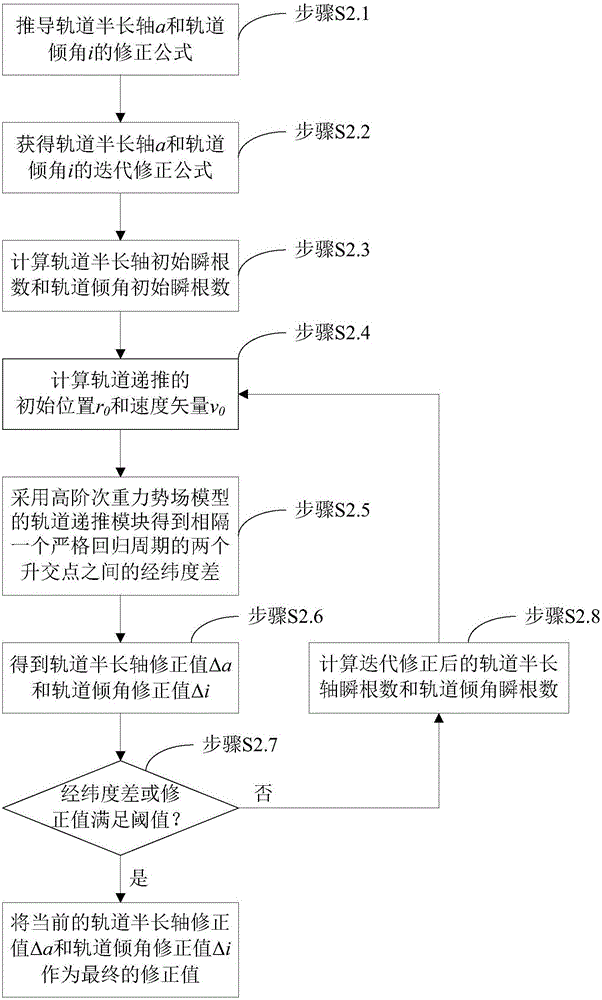
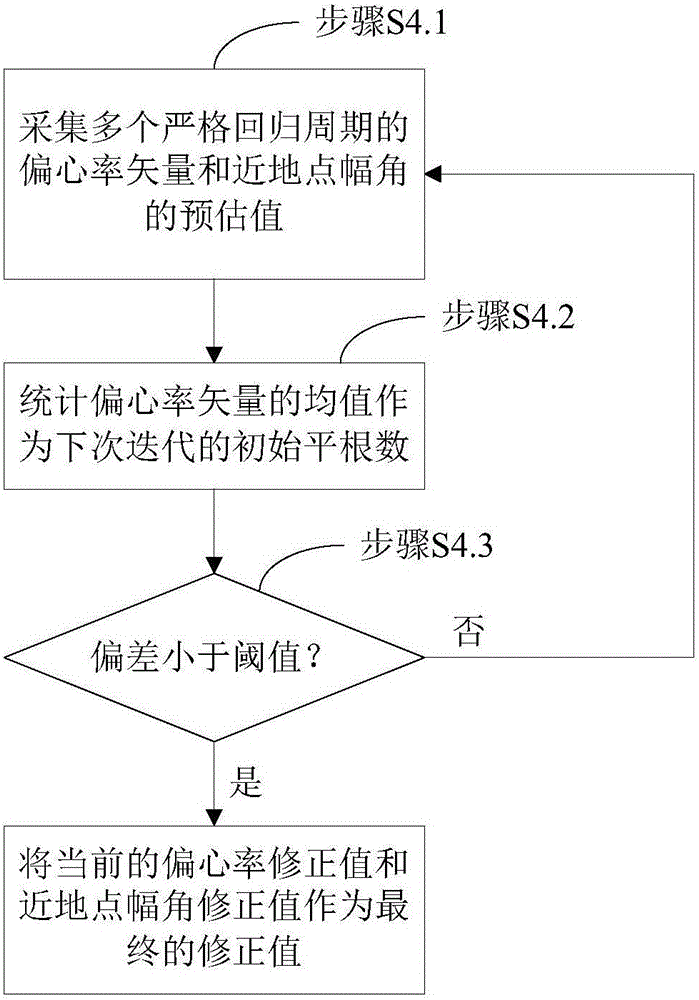
Method for determining strictly-regressive orbit of near-earth satellite
InactiveCN106092105AHigh precisionInstruments for comonautical navigationEarth satellitePotential field
A method for determining strictly-regressive orbit of a near-earth satellite is disclosed. The method comprises: on the basis that an orbit element prediction value of a regressive orbit in a low-order gravity potential field, combining an orbit semi-major axis a and an orbit inclination angle i, performing repeated iteration correction on the orbit semi-major axis a and the orbit inclination angle i according to the relationship of the orbit semi-major axis a and the orbit inclination angle i with the longitude and latitude of a sub-satellite point and based on an orbit recursion module of a high-order gravity potential filed module, combining an eccentricity ratio e and a perigee argument omega, and performing repeated irritation correction on the eccentricity ratio e and the perigee argument omega by employing an average process according to the characteristics of a vector limit cycle of the eccentricity ratio until the regression precision of an ascending node satisfies a preset value. The method determines the strictly-regressive orbit of the near-earth satellite based on high-precision orbit dynamics, the determined orbit possesses relatively high regression precision for a space target point, and compared with a conventional method based on a low-order gravity potential field, the high-precision orbit dynamics is relatively close to reality and possesses relatively high application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Method and Associated Apparatus for Capturing, Servicing, and De-Orbiting Earth Satellites Using Robotics
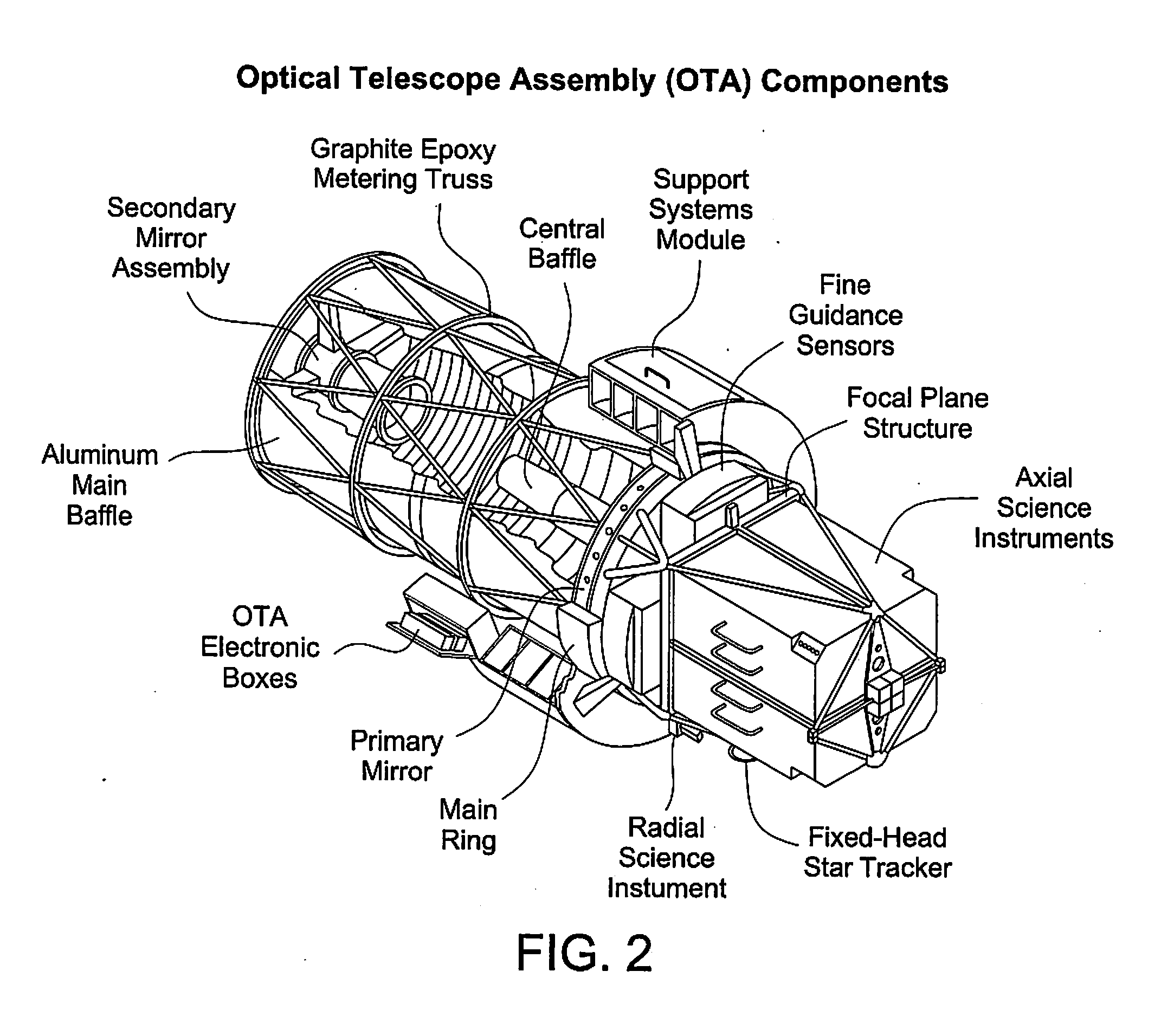
InactiveUS20070138344A1High altitudeUpgrading the scientific capabilities of the spacecraftLaunch systemsToolsEarth satelliteRadar
Owner:NASA
Autonomous orbit determination method for satellite based on synthetic aperture radar
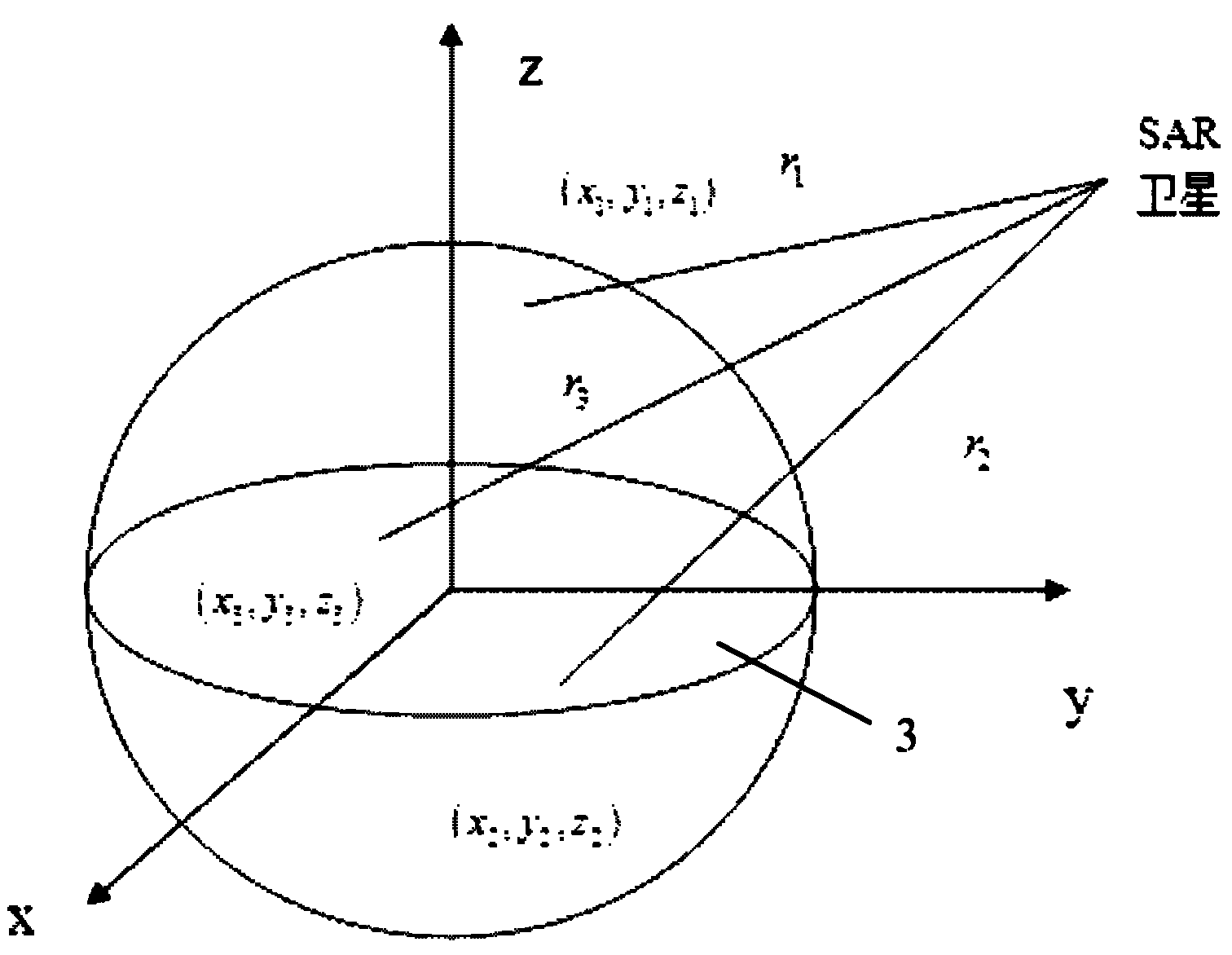
InactiveCN102323582AHigh precisionImproving the accuracy of autonomous orbit determination technologyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEarth satelliteSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses an autonomous orbit determination method for a satellite based on synthetic aperture radar, which belongs to the technical field of autonomous orbit determination of satellites and aims at achieving high-precision and real-time autonomous orbit determination of a low-orbiting satellite without being supported by a ground tracking telemetry and command station. The method comprises the following specific steps of: designing the shape and the material of a manual ground identification point; designing an arrangement mode of the ground identification point, arranging the ground identification point and measuring the position of the ground identification point in an earth-fixed coordinate system; storing information of the ground identification point in a space-borne computer; and after a space-borne synthetic aperture radar remotely senses the ground and identifies a ground identification, deriving the information of the ground identification point from a ground identification library on the satellite, applying an orbit determination equation to obtain the position and the speed of the satellite and further finish the real-time autonomous orbit determination of the satellite. The autonomous orbit determination technology for the satellite provides a novel autonomous orbit determination method for the satellite, which can be used for realizing high-precision real-time autonomous orbit determination of the low-orbiting satellite. The method disclosed by the invention is suitable for real-time autonomous orbit determination of a near earth satellite.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG PATENT TECH DEV
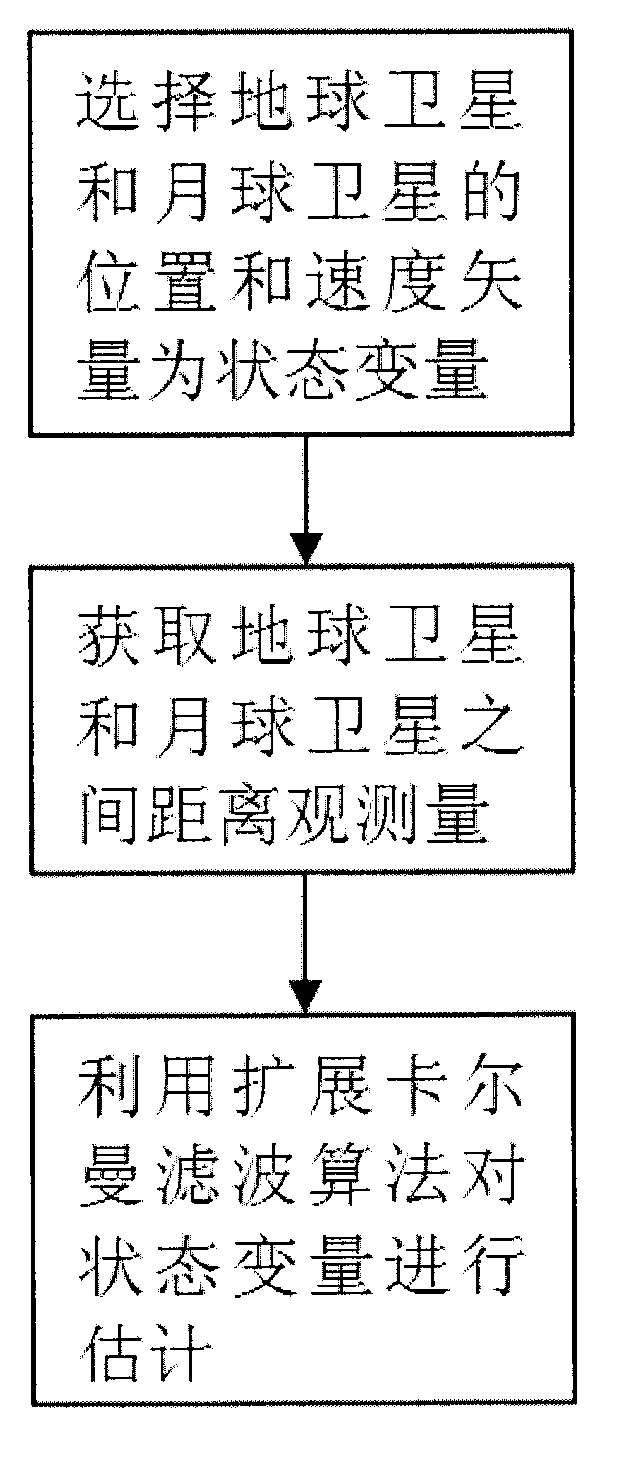
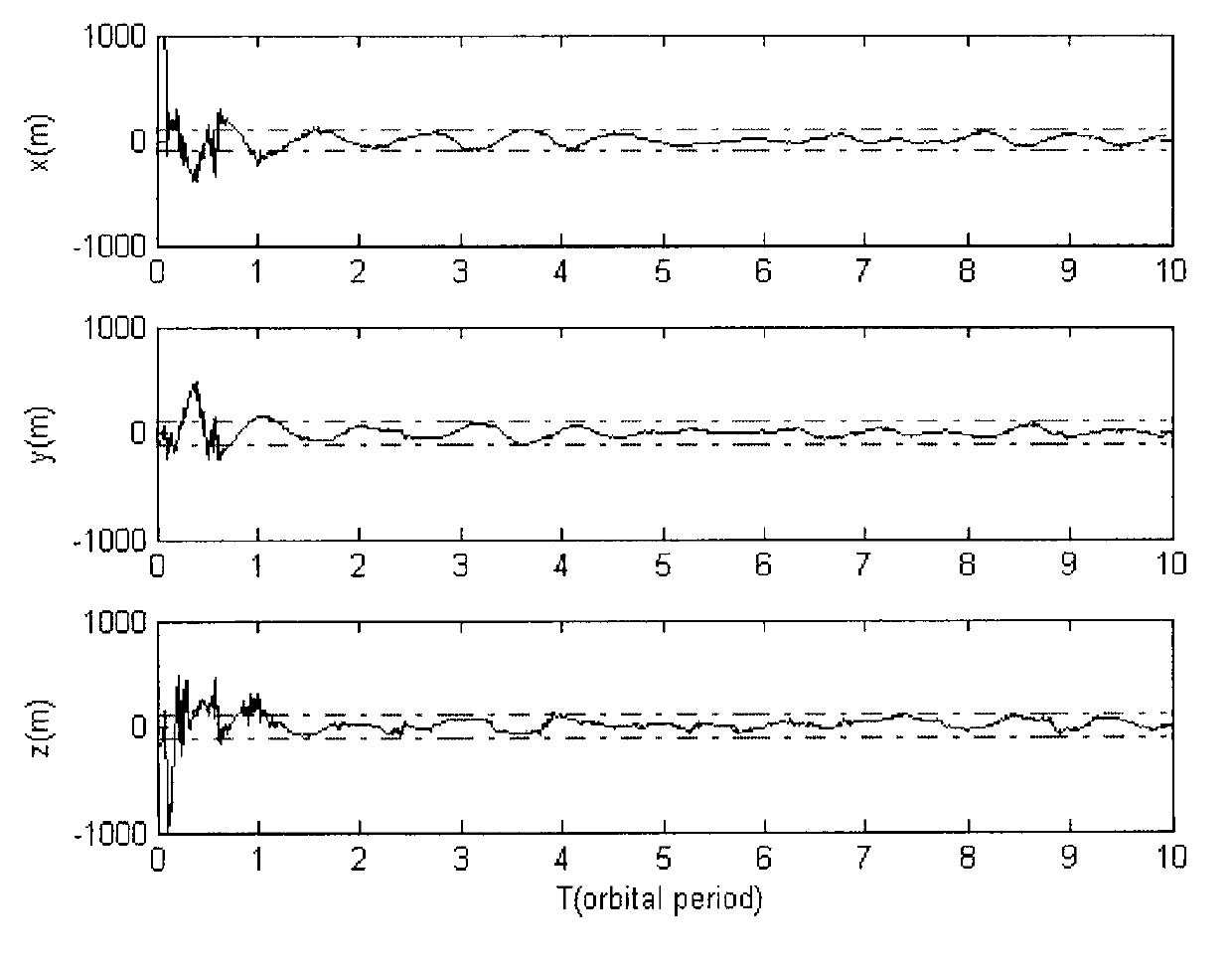
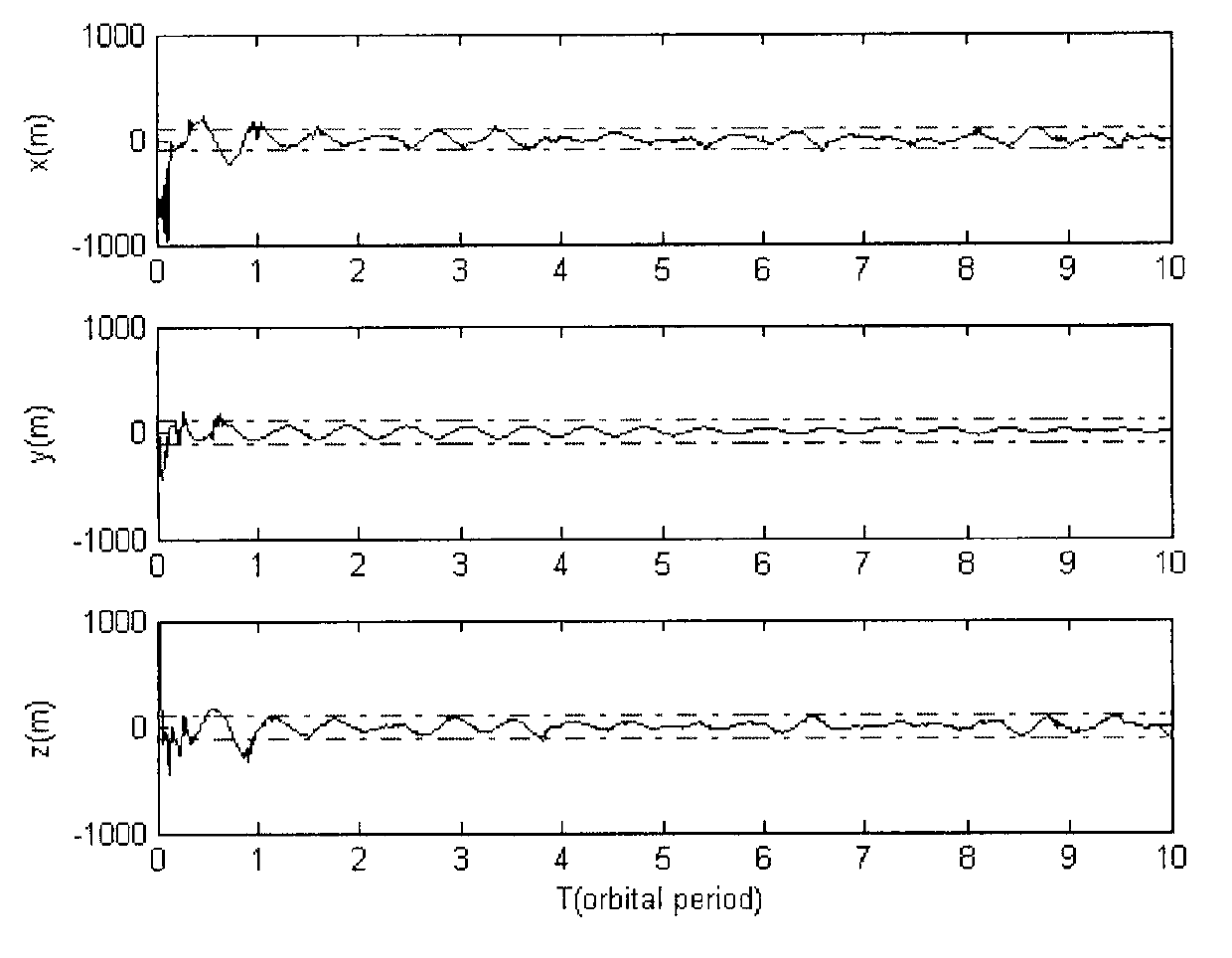
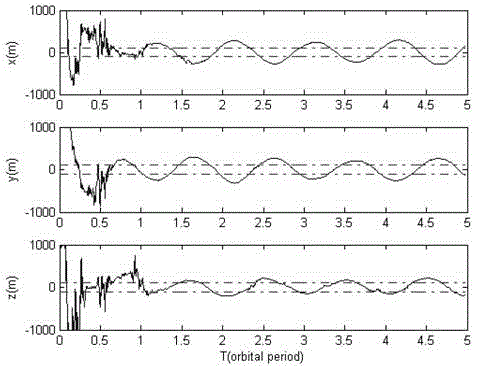
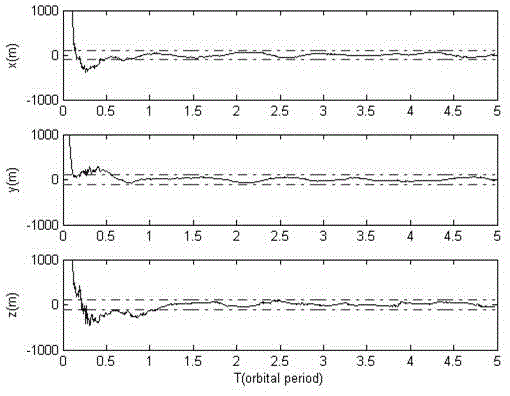
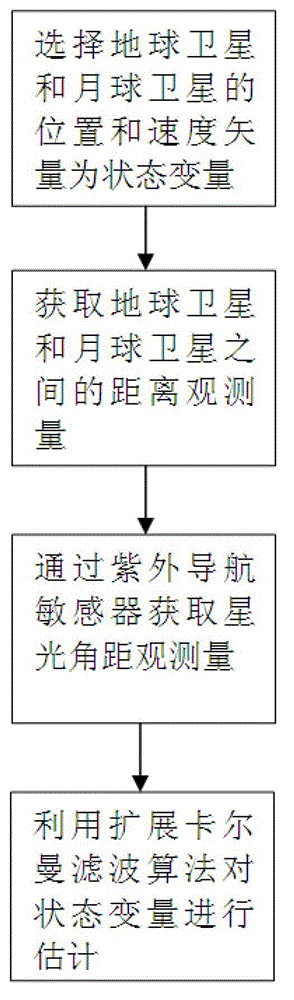
Autonomous navigation method based on earth satellite and lunar satellite combined ranging
Provided is an autonomous navigation method based on earth satellite and lunar satellite combined ranging. A basic method is that an inter-satellite link is built between an earth satellite and a lunar satellite and used for conducting inter-satellite distance measuring; and on the basis of the distance information between the earth satellite and the lunar satellite and a three-body track kinetic equation and by means of an extend kalman filter algorithm, and simultaneously by estimating an absolute position of the earth satellite and the lunar satellite, high-precision autonomous navigation only depending on the inter-satellite distance measuring information is achieved. The method can be used for achieving satellite autonomous navigation tasks with high precision requirements, is favorable for reducing depending degree of satellites on ground observation and control, and improves independent survival ability of a satellite system under an emergency condition.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Combined navigation method based on earth-moon satellite united distance measurement and ultraviolet sensor
ActiveCN103148849AHigh precisionAccurate prior location informationNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by astronomical meansEarth satelliteSurvivability
The invention discloses a combined navigation method based on earth-moon satellite united distance measurement and an ultraviolet sensor. The combined navigation method comprises the following steps of: obtaining earth-moon satellite united distance measurement information through a satellite link between an earth satellite and a lunar satellite, and obtaining satellite-light angular distance metrical information through the ultraviolet sensor; adopting an extension kalman filter algorithm, and obtaining an estimated value of navigational earth satellite and the position and speed of the satellite through processing an observed quantity order by recurrence calculation. The method provided by the invention can be used for a satellite autonomous navigation task with higher precision requirement, the dependence severity of the satellite to ground measurement and control is reduced, and the autonomous viability of a satellite system is strengthened in emergency.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
To-be-observed task determination method for multi-satellite synergistic earth observation
The invention provides a to-be-observed task determination method for multi-satellite synergistic earth observation and relates to the field of earth satellite observation. According to the to-be-observed task determination method for multi-satellite synergistic earth observation provided by the embodiment of the invention, each satellite center obtains corresponding observation tasks and an ephemeris of each controlled satellite, and a first task set of observation tasks executed by all controlled satellites of the satellite center is calculated for the observation tasks of the satellite center and the ephemerides of the controlled satellites through a genetic algorithm, wherein the first task set carries different observation states of the satellite to the tasks; after the first task set of the satellite center is confirmed, an optimal solution with maximized total observation benefit and lowest total energy consumption in all the satellites is calculated through the genetic algorithm, and a second task set can serve as a reference for task execution by an appointed satellite center, so that a scheme for searching a global optimal solution is finished by the genetic algorithm.
Owner:INST OF RADAR & ELECTRONICS CONFRONTATION ARMY AIR FORCE EQUIP RES INST OF PLA
Analytical calculation method of airway shortcut from measurement and control station to sub-satellite point
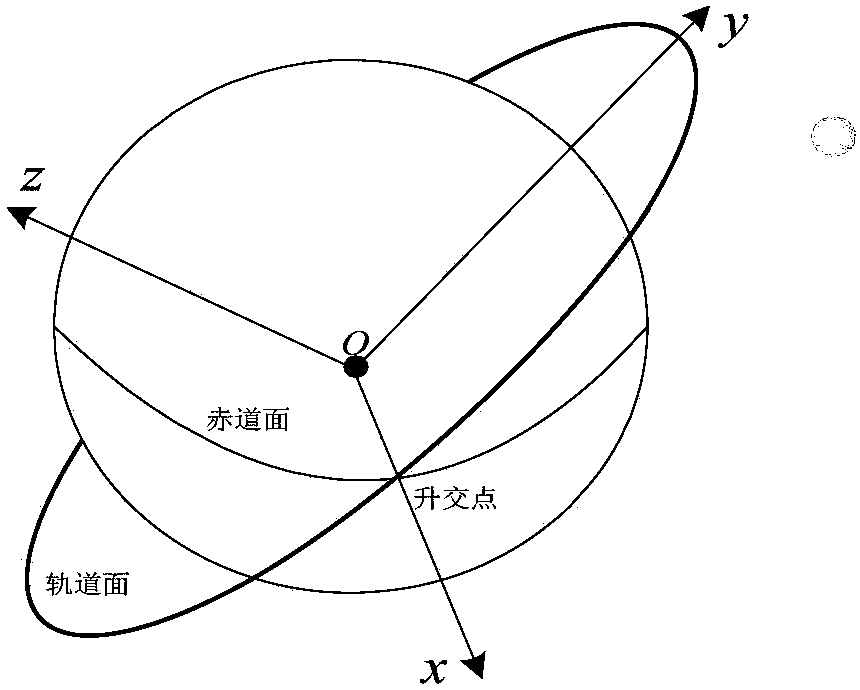
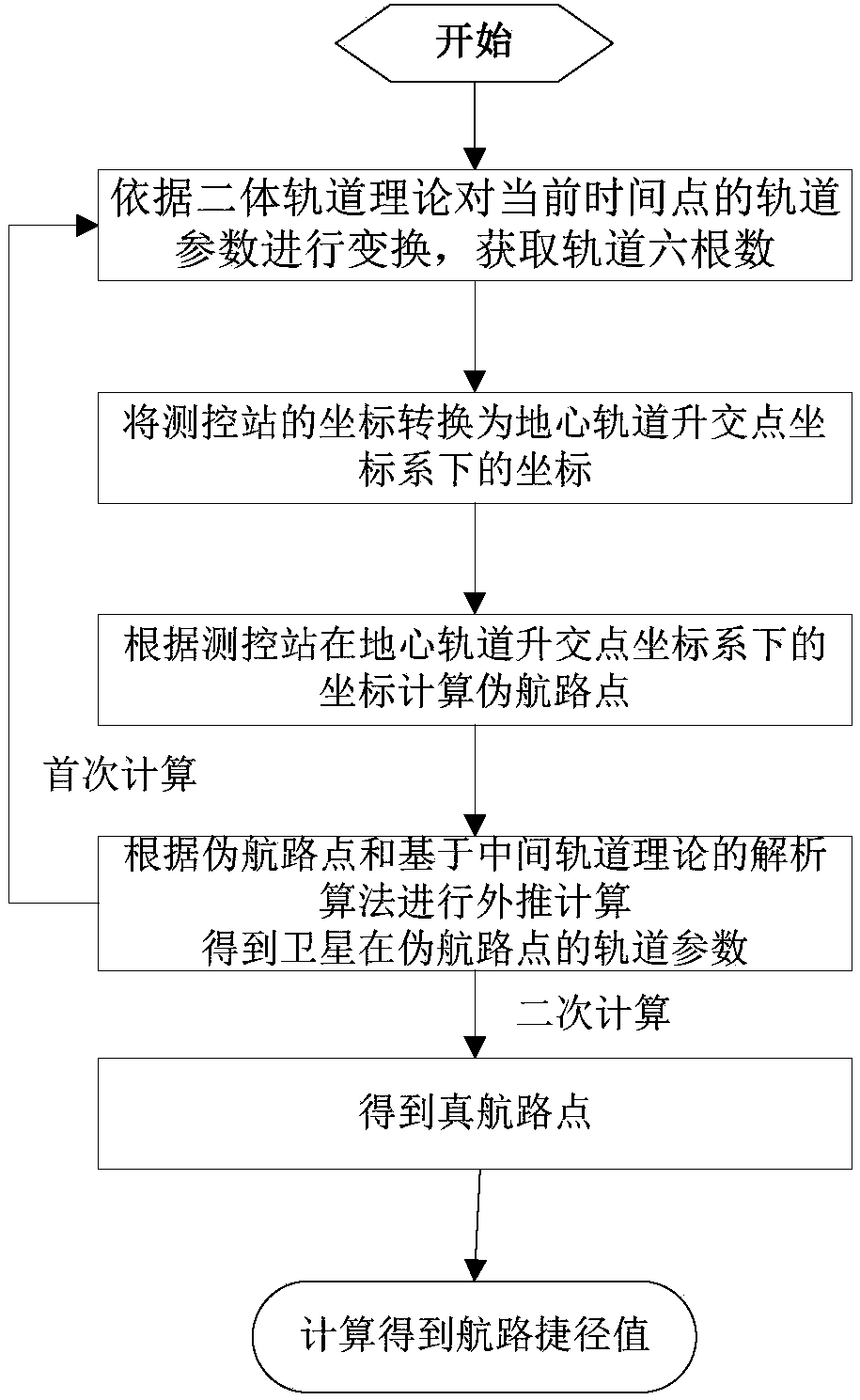
ActiveCN108279426AAccurate calculationOvercome the disadvantage of long calculation timeSatellite radio beaconingEarth satelliteIntegration algorithm
The invention discloses an analytical calculation method of an airway shortcut from a measurement and control station to a sub-satellite point. The method includes the steps: transforming orbit parameters of a current time point according to an earth-satellite orbit theory, and acquiring six orbit elements; transforming a coordinate of the measurement and control station into a coordinate under ageocentric orbit ascending node coordinate system; calculating a false waypoint according to the coordinate of the measurement and control station under the geocentric orbit ascending node coordinatesystem; performing extrapolation calculation according to the false waypoint and an analytical algorithm based on an intermediary orbit theory to obtain an orbit parameter of a satellite in the falsewaypoint; returning the orbit parameter of the satellite in the false waypoint to the first step to perform iteration calculation once to obtain a true waypoint; calculating an airway shortcut value through the true waypoint. According to the calculation method, compared with the prior art, the shortcoming of long calculation time of an existing integration algorithm can be overcome on the premiseof ensuring accuracy, and the airway shortcut can be rapidly and accurately calculated.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ELECTRONICS SYST ENG
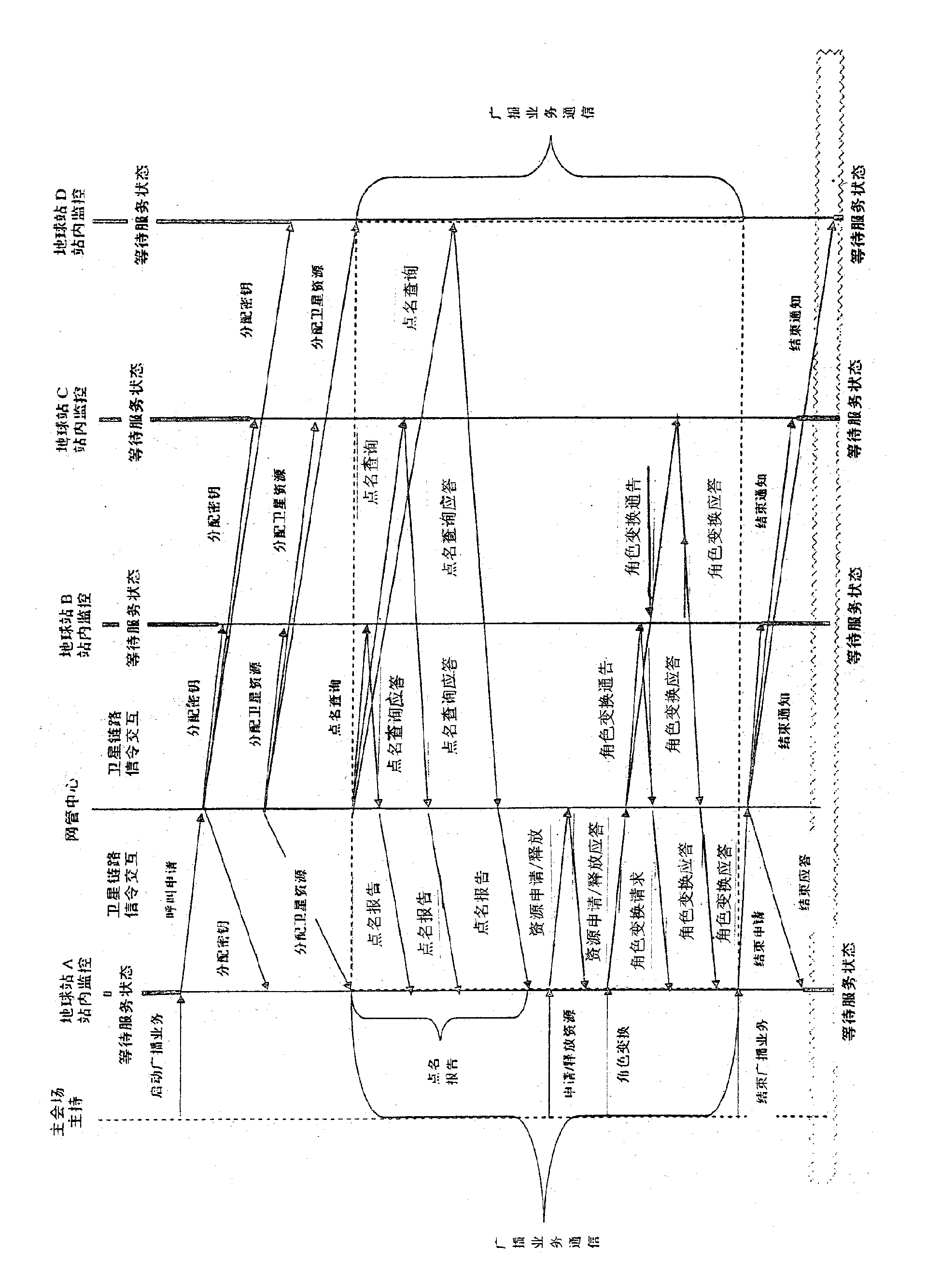
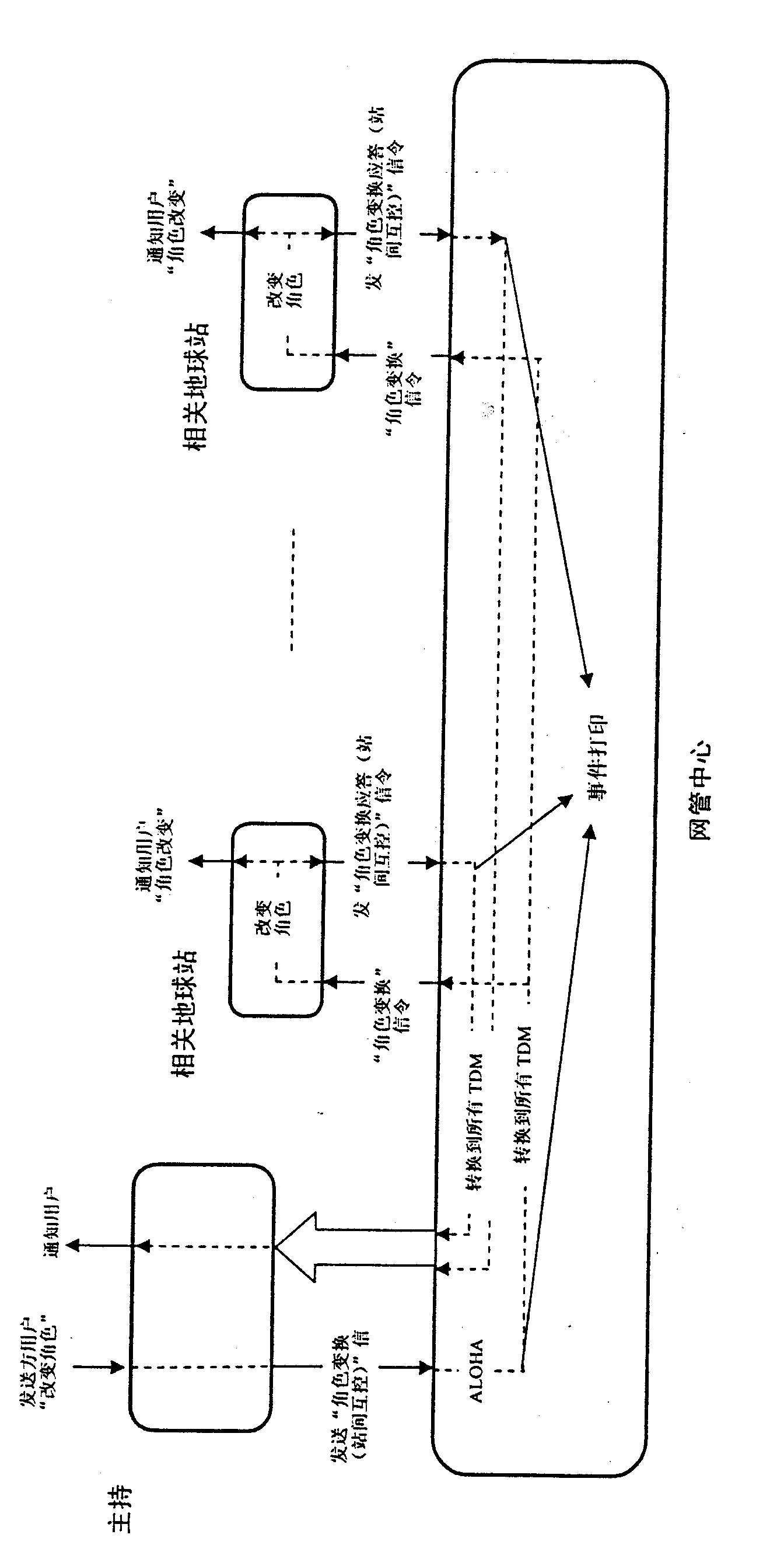
Method for realizing fully automatic configuration of broadband video conference broadcasting service based on earth satellite station
InactiveCN101674529AFunction increaseImprove intelligenceTelevision conference systemsNetwork topologiesEarth satelliteTelevision system
The invention discloses a method for realizing fully automatic configuration of a broadband video conference broadcasting service based on an earth satellite station, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, an operator of the earth satellite station of a main meeting place starts an application for broadcasting service from an in-station monitor interface to a network management center according to the actual needs; secondly, after receiving the application from the earth satellite station of the main meeting place, the network management center sends down a secretekey and satellite resources which are needed by communication to relative earth satellite stations which participate in a conference; thirdly, the network management center starts roll call to a communication state of the relative earth satellite stations which participate in the conference; and fourthly, during the broadcasting service, the operator of the earth satellite station of the main meeting place can dynamically apply for or release multiple sets of satellite resources to the network management center according to the needs, and the network management center carries out corresponding processing of dynamic distribution or recovering the satellite resources. The invention can be used as an independent video conference system with complete functions, is convenient to use and has wide application prospect in occasions of important communication guarantee, emergency rescue, disaster relief, sudden events and the like.
Owner:PANDA ELECTRONICS GROUP +2
Data source generating method for passive direction finding location
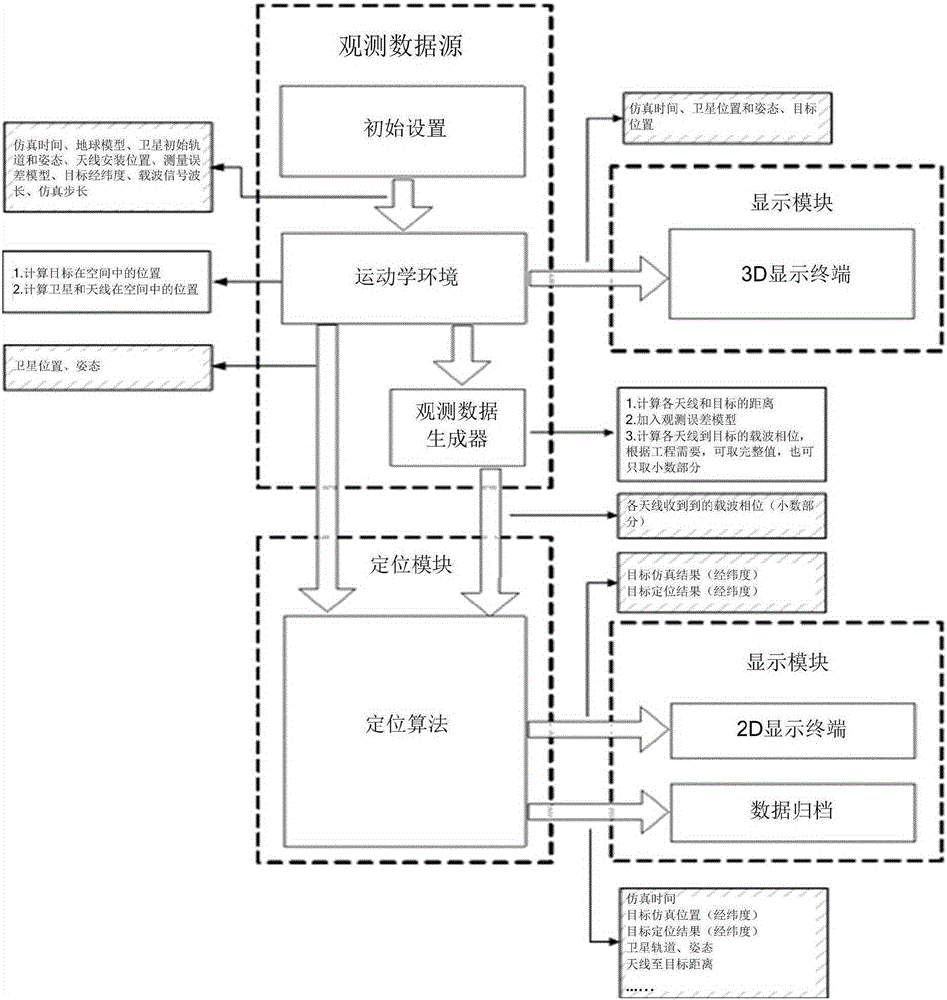
ActiveCN105158777AFlexible parameter settingCalculation speedSatellite radio beaconingEarth satelliteKinematics
The invention provides a data source generating method for passive direction finding location. The method aims at high cost of satellite passive direction finding location, is based on the theory of passive direction finding location, and includes initial setup, earth satellite kinematics environment recursion, observation data generation and other links. The invention has the characteristics of flexible parameter setting, high computing speed, and high accuracy of output observed quantity. Practical engineering problems in the process of on-satellite location algorithm design, namely, difficult calibration and low calibration efficiency, are solved. A large number of reliable data sources can be provided for location algorithm verification. A location result obtained by the method can be used as the basis for checking the accuracy of a direction finding location algorithm.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
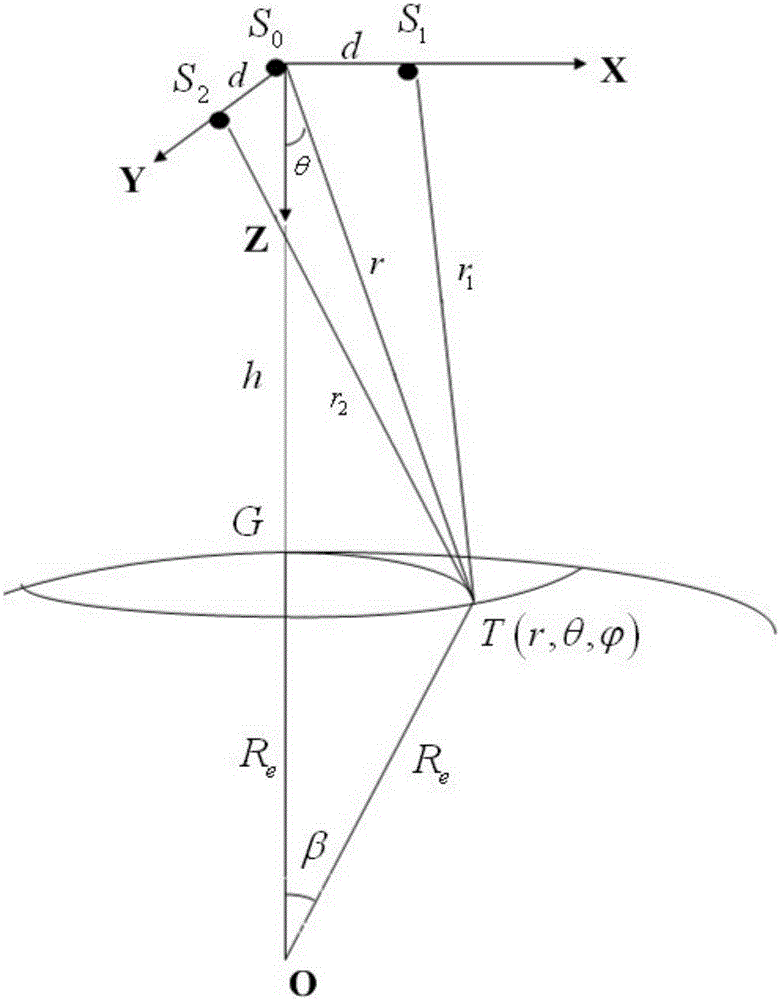
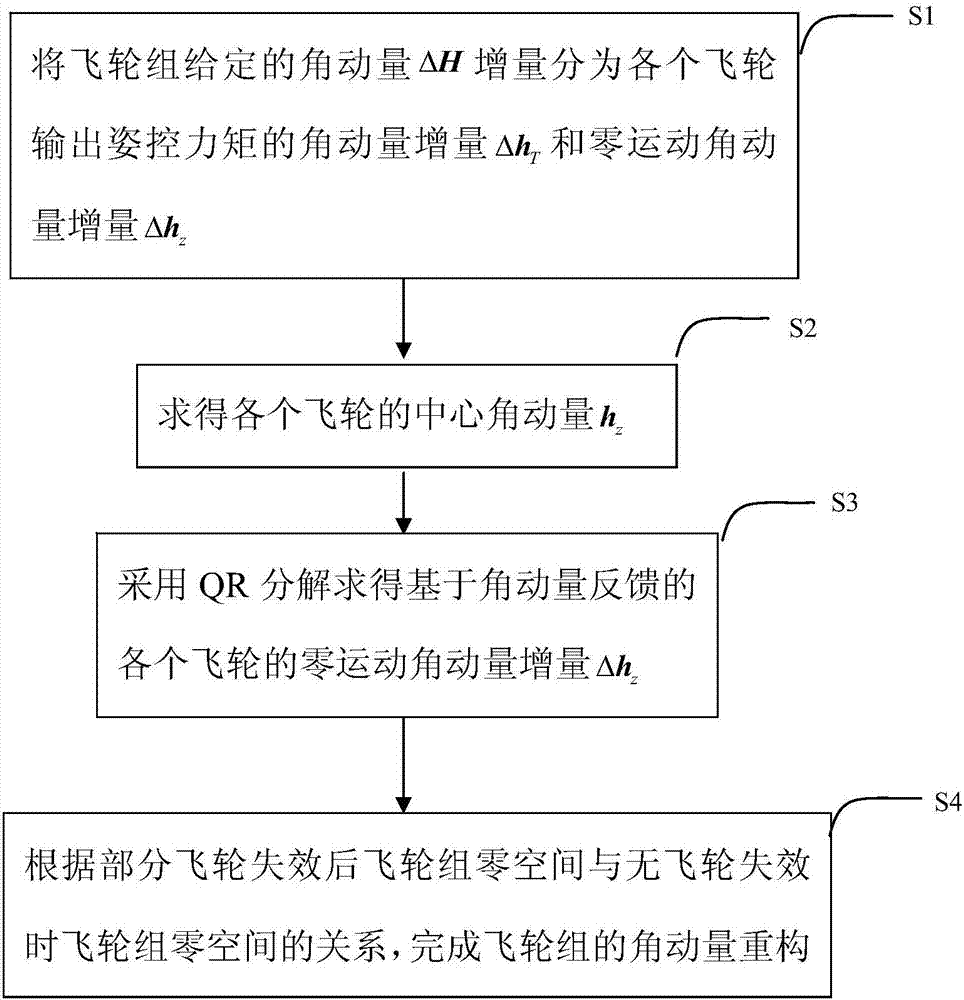
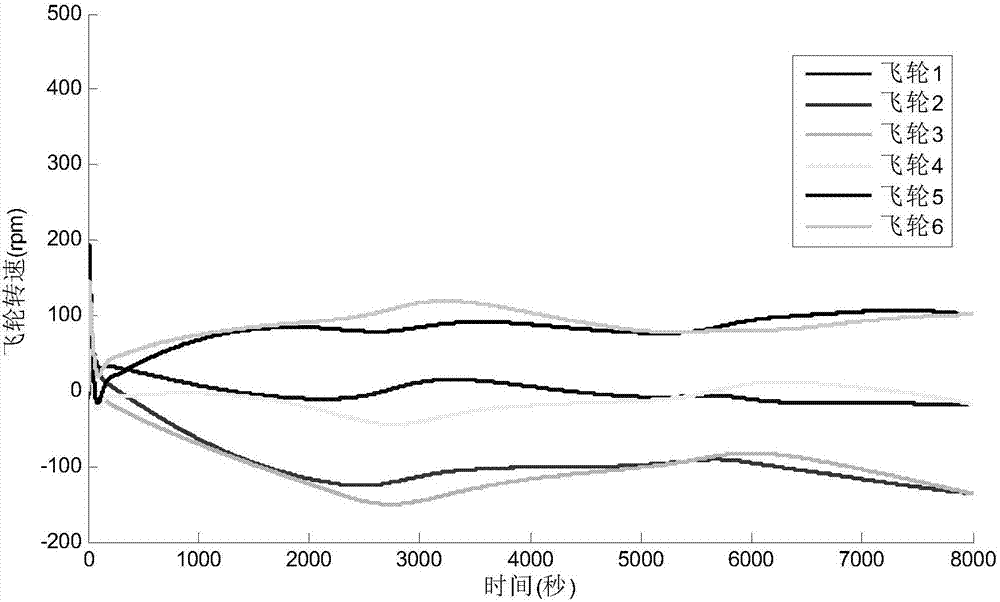
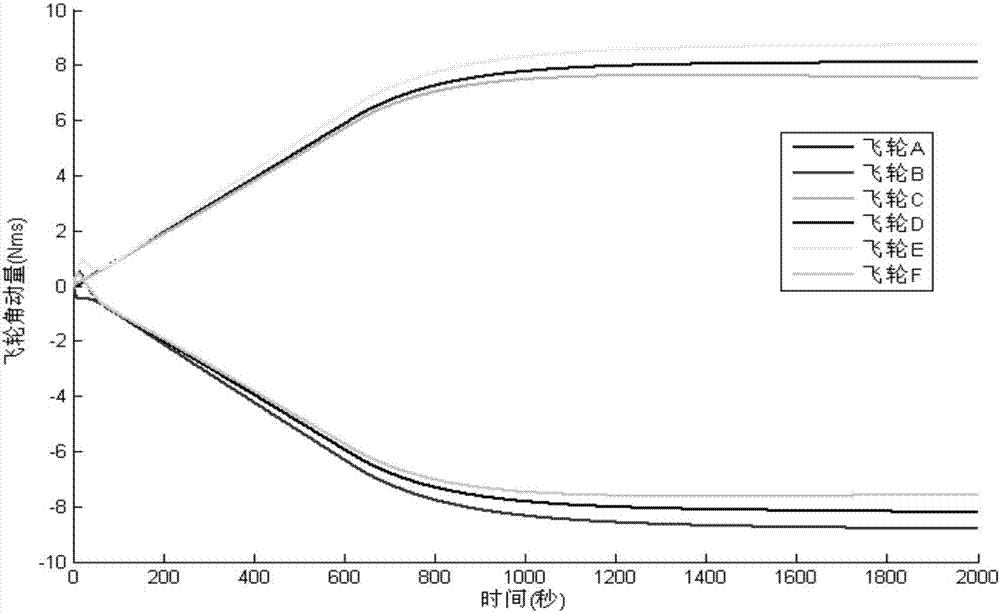
Near-earth satellite redundant flywheel angular momentum autonomous management method
ActiveCN107239036AAvoid speed zero crossingAvoider satietyAdaptive controlEarth satelliteQR decomposition
The invention discloses a near-earth satellite redundant flywheel angular momentum autonomous management method, including the steps of S1. dividing given angular momentum increments of a flywheel group into an angular momentum increment of attitude control output by each flywheel in the flywheel group and an angular momentum increment of zero motion; S2. obtaining the central angular momentum of the flywheels; S3. converting a problem of solving flywheel group zero movement into a constrained quadratic form optimization problem, adopting QR decomposition to convert the constrained quadratic form optimization problem into an unconstrained optimization problem, and obtaining a zero movement angular momentum increment of each flywheel, so that the angular momentum of each flywheel approaches the central angular momentum; and S4. according to a relation between flywheel group null space after part of flywheels fail and flywheel group null space when no flywheel fails, completing angular momentum reconstruction of the flywheel group. The advantages of the method are that while the flywheel group generates given moment of force, the rotating speed of each flywheel can approach preset desired rotating speed, thereby preventing frequent zero passage or saturation of the rotating speed of flywheels and realizing on-line reconstruction of a whole system when part of the flywheels fail.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Astronomical/doppler combined navigation method for spacecraft
InactiveCN1987356AImprove observation accuracyAchieve precise positioningNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationEarth satelliteHorizon
The invention combines independent astronavigation with Doppler method. Method combines direct sensing horizon with indirect sensing horizon is adopted in astronavigation. One-way Doppler is adopted in Doppler method. Using method of Unscented Kalman filtering carries out united filtering, estimating position of spacecraft and speed guidance message. The invention can be in use for determining navigation parameters of earth satellite, manned spacecraft accurately in applications of observation over the ground, communication, and positioning navigation etc.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
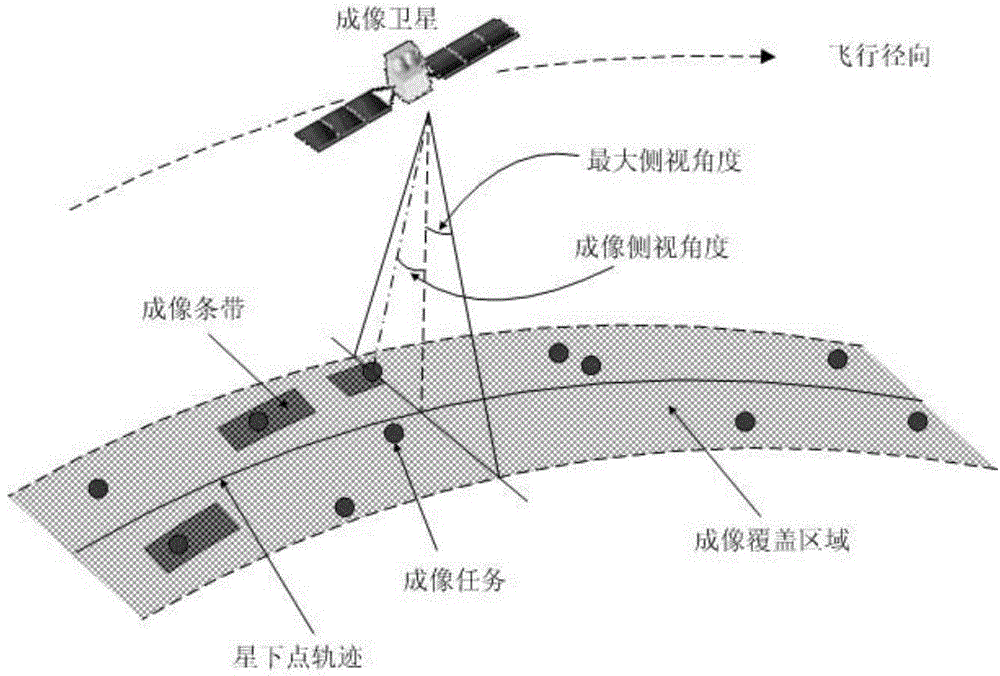
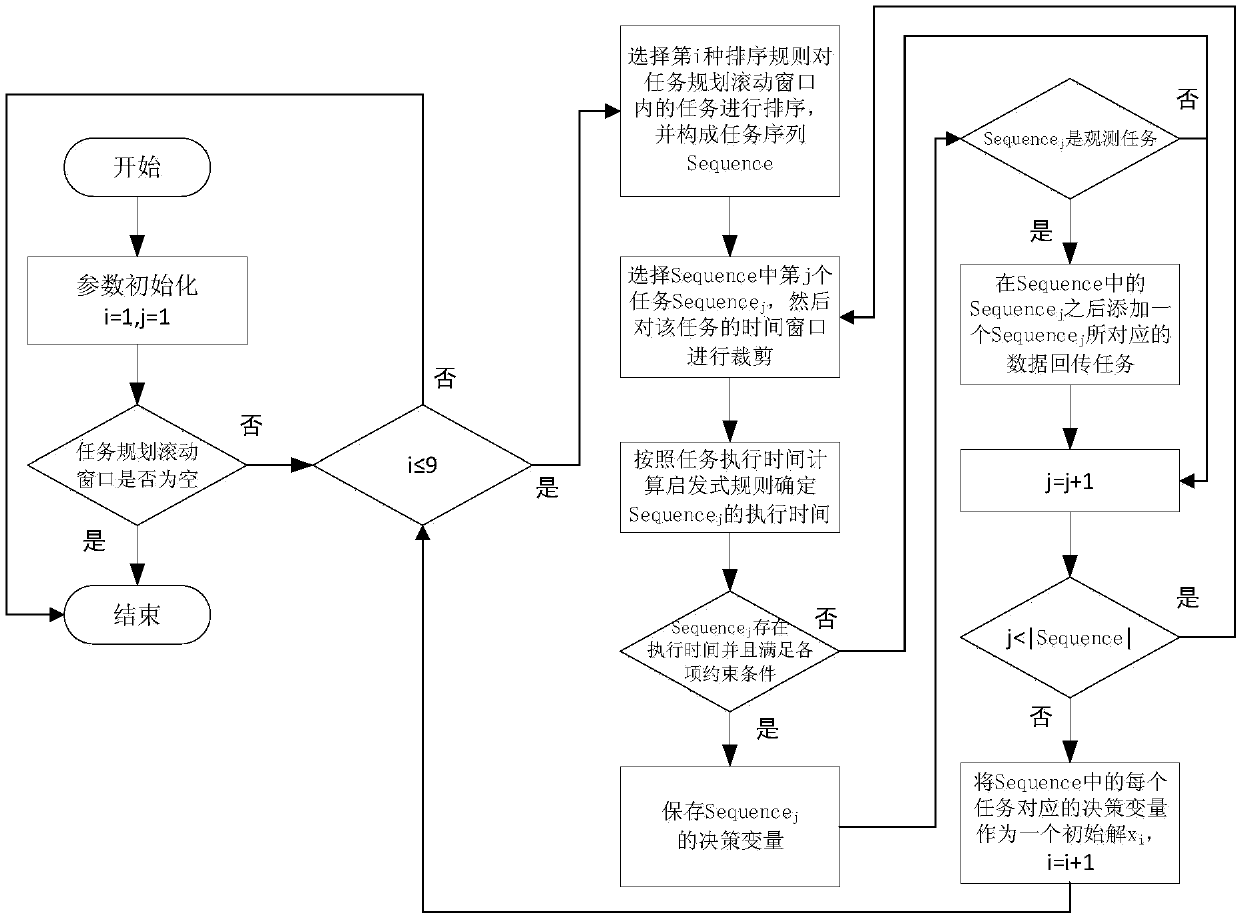
Task planning method for agile earth satellite
The invention discloses a task planning method for an agile earth satellite. The method comprises the following steps of 1, selecting a target function; 2, according to the target function in the step1, generating an initial solution x, and taking x as a starting point of local search; 3, performing parameter initialization, wherein parameters include a neighborhood number kmax, an iterative search frequency lmin used for judging whether a process of falling into local optimum exists or not, a maximum iterative search frequency lmax used for judging whether an algorithm is stopped or not, iterative counters m and n, and a neighborhood counter k, and k, m and n are set to be 1, 0 and 0 respectively; 4, randomly determining a feasible solution y in a kth neighborhood structure of the solution x, and enabling n to be equal to n+1; 5, if y is superior to x, enabling x to be equal to y and m to be equal to 0, or otherwise, enabling m to be equal to m+1; 6, if n==lmax, going to the step 9;7, if m==lmin, indicating that the process of falling into the local optimum already exists and k=k+1, or otherwise, going to the step 4; 8, if k<=kmax, enabling m to be equal to 0, and going to the step 4; and 9, ending the algorithm, and outputting x. According to the method, resources and time can be allocated for observation tasks or data return tasks; and on the premise of meeting task constraints and resource constraints, the observation benefits are maximized.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) group mounted polarization array attitude measurement and target detection method
ActiveCN108196290ASolve the accuracy problemSolve the frequency drift problemNavigation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingEarth satelliteEigenvalue algorithm
The invention relates to a UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) group mounted polarization array attitude measurement and target detection method, and the invention reveals the change rule between the attitude position of a multi-loss electromagnetic vector sensor and the receiving of signals, and achieves the attitude measurement of a platform according to the signals of a plurality of earth satellite navigation systems which achieves the cooperative navigation or the spectrum of a UAV base station signal and maximization. A feature value algorithm is employed for calculating a general electromagnetic wave generalized spatial spectrum, and the polarization signal of a blind signal, the position of a plane, and the frequency shift information are obtained. The installation attitude and position information of a sensor in a plane body is maintained, and the method achieves the multi-target DOA under the conditions that the position of a UAV is not accurate and there is the frequency shift problem.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Asteroid orbit identifying method based on observation angle data
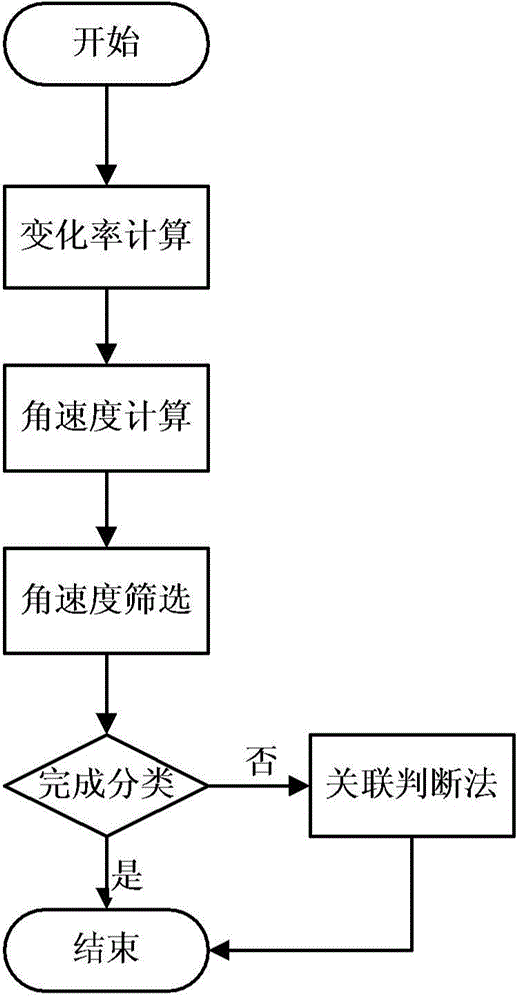
ActiveCN104792299AEliminate distractionsSimple methodAngle measurementLinear/angular speed measurementEarth satelliteNatural satellite
The invention discloses an asteroid orbit identifying method based on observation angle data. The method comprises steps as follows: calculation of the change rate, that is, calculation of the observation angle data along with the time change rate; calculation of the angular velocity; screening of the angular velocity: the angular velocity of a current observation arc section is compared with a given threshold, and whether data of the section belong to an asteroid or a man-made earth satellite or are undetermined is judged preliminarily; correlation judgment: observation forecast is performed by using orbit elements of the catalogued man-made earth satellite, theoretically calculated values and measured values of all observation epochs are compared, if the error is small enough, the arc section is judged to belong to the man-made earth satellite, and otherwise, the arc section belongs to the asteroid. The method is convenient and easy to implement, can be applied to multiple research fields related to astronomical observation as well as quick recognition of near-earth asteroids, and wins precious early warning and emergency time for follow-up work.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coordinated control strategy of agile earth satellite
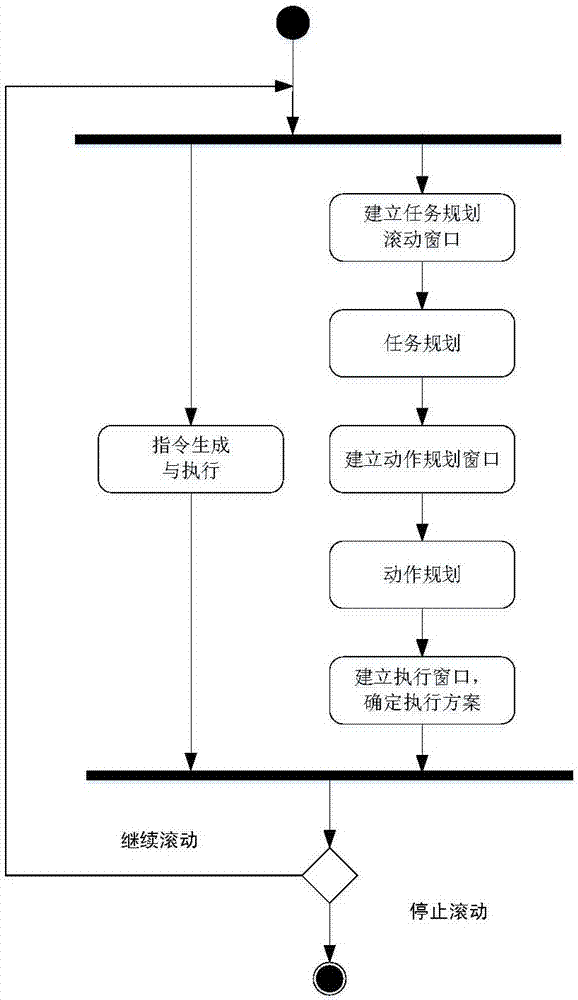
InactiveCN107957895AShorten the planning cycleNarrow down the planning scopeExecution paradigmsResourcesEarth satelliteDistributed computing
The invention discloses a coordinated control strategy of an agile earth satellite. In the coordinated control strategy of the agile earth satellite, each complete scheduling process and a satellite implementation and execution scheme are conducted simultaneously in terms of time, a part of satellite motions in the motion scheduling scheme are selected after motion scheduling ends to establish anexecution window, and a satellite motion sequence in the execution window serves as the final scheduling result of scheduling, namely the execution scheme. Each complete scheduling process of the coordinated control strategy includes the following steps of establishing a task scheduling rolling window, scheduling a task, establishing a motion scheduling window, scheduling motions and establishingthe execution window.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
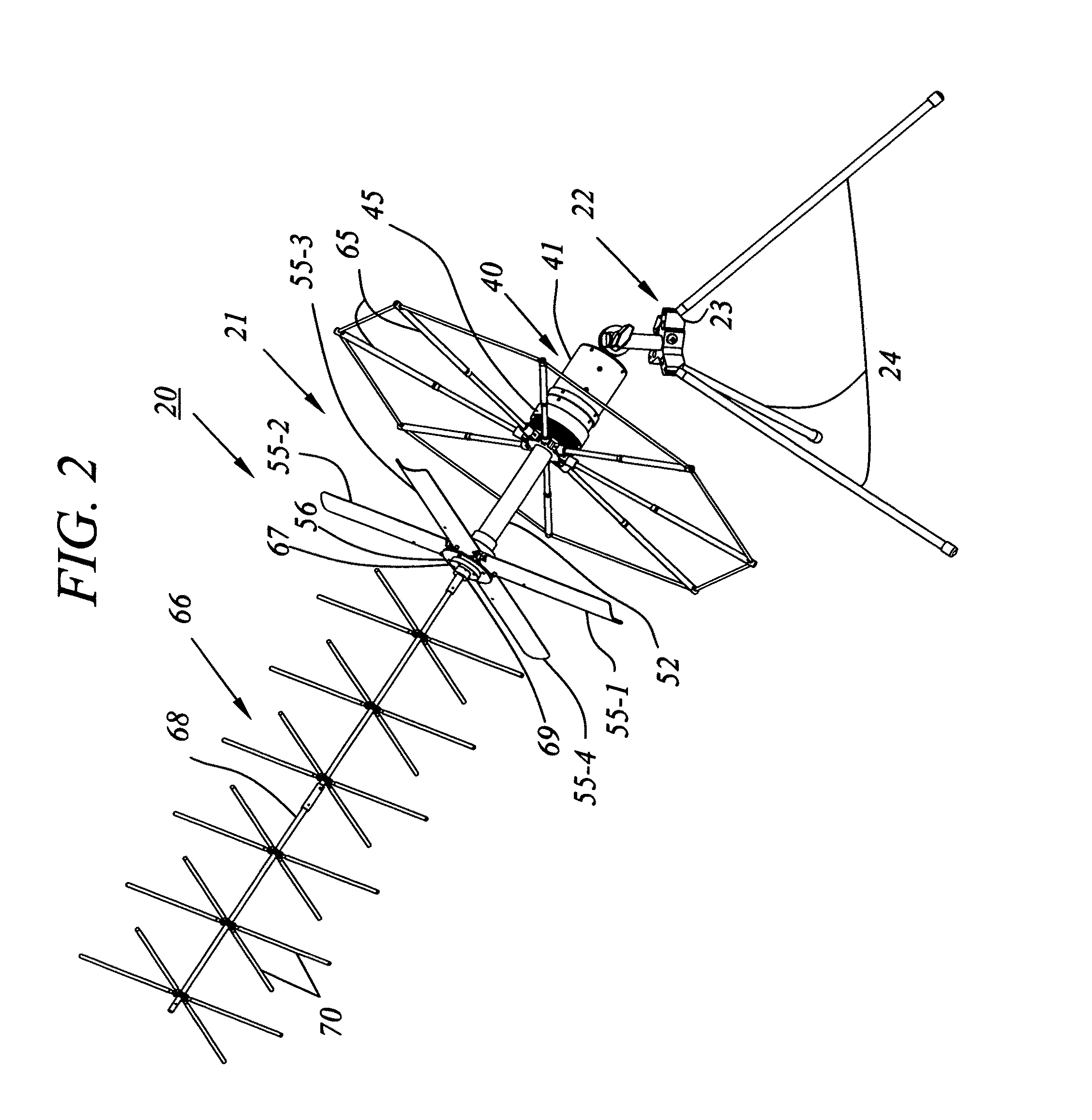
Multi-band portable SATCOM antenna with integral diplexer
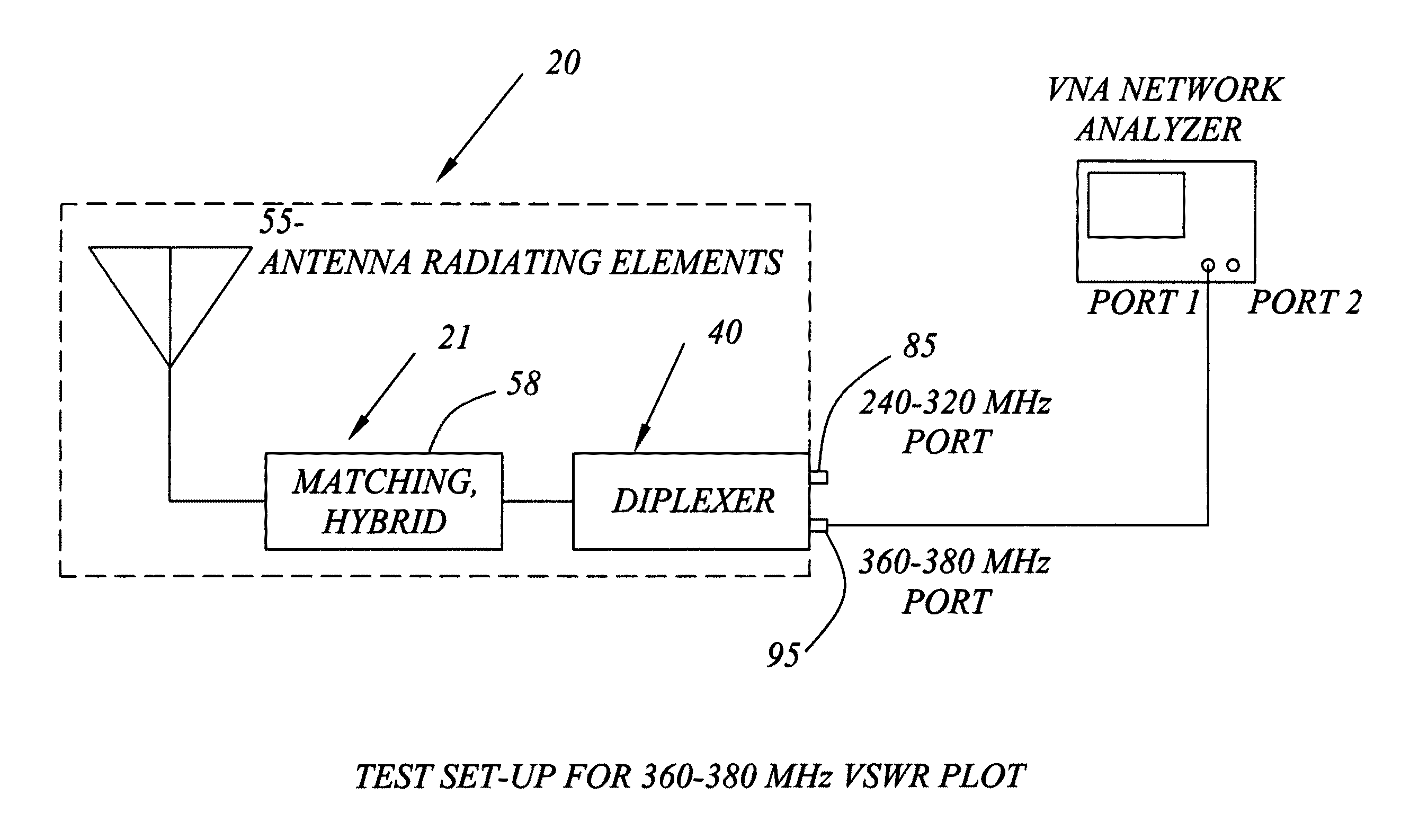
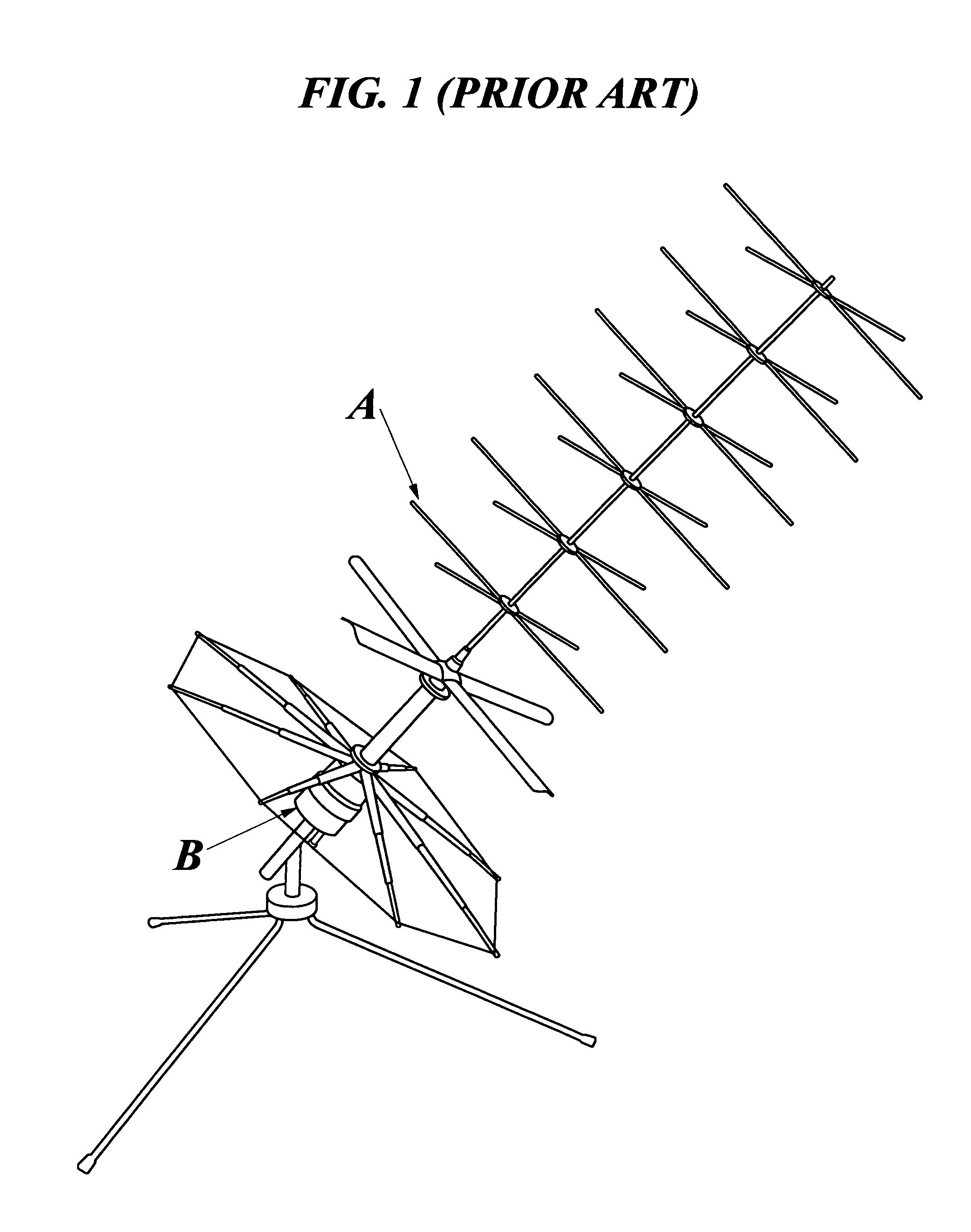
InactiveUS8055209B1Easy to operateMaintain size and weight and form factorSimultaneous aerial operationsSubstation equipmentEarth satelliteMulti band
A man-pack portable, multi-band ultra-high frequency turnstile-type SATCOM radio antenna for transmitting and receiving radio signals between terrestrial locations and an orbiting earth satellite includes a cylindrically shaped antenna superstructure base which has an elongated mast extending forward from a front transverse end wall of the base, and circumferentially spaced apart pairs of radiating elements which extend radially outwards from the mast, each opposed pair comprising in combination an electric dipole antenna which is electrically connected via coaxial cables disposed longitudinally through the mast to zero and ninety degree ports of a hybrid antenna matching network located in the base and having an input port electrically connected to a coaxial antenna base connector located in a rear transverse end wall of the base. A diplexer which includes a cylindrical housing longitudinally alignable with the base contains a low-frequency band-pass filter and a high-frequency band-pass filter having low and high center frequencies, respectively, the filters having a common output node electrically connected to coaxial diplexer output connector located on a front transverse end wall of the diplexer housing and longitudinally engageable with the antenna base connector. The diplexer has on a rear transverse end wall thereof two coaxial transceiver connectors connected to separate nodes of the high and low frequency filters, the transceiver connectors being connectable via coaxial cables to one or more radio transceivers, which are thus enabled to operate simultaneously in different frequency bands, without requiring any external diplexer.
Owner:KAMIS ISA PRESIDENT
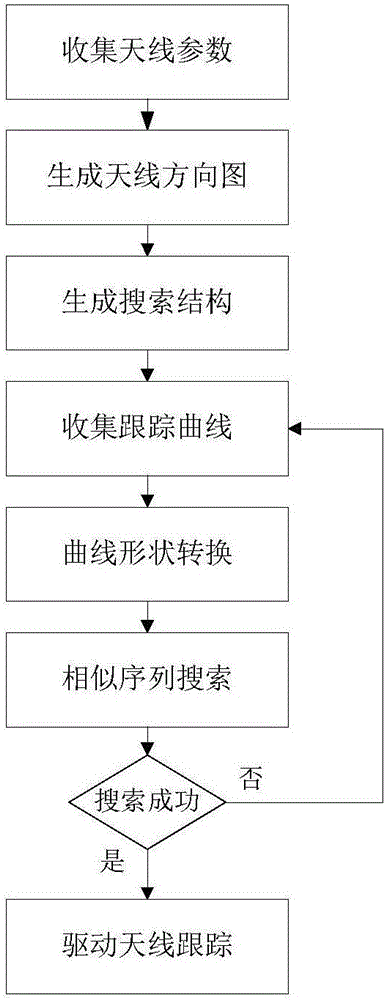
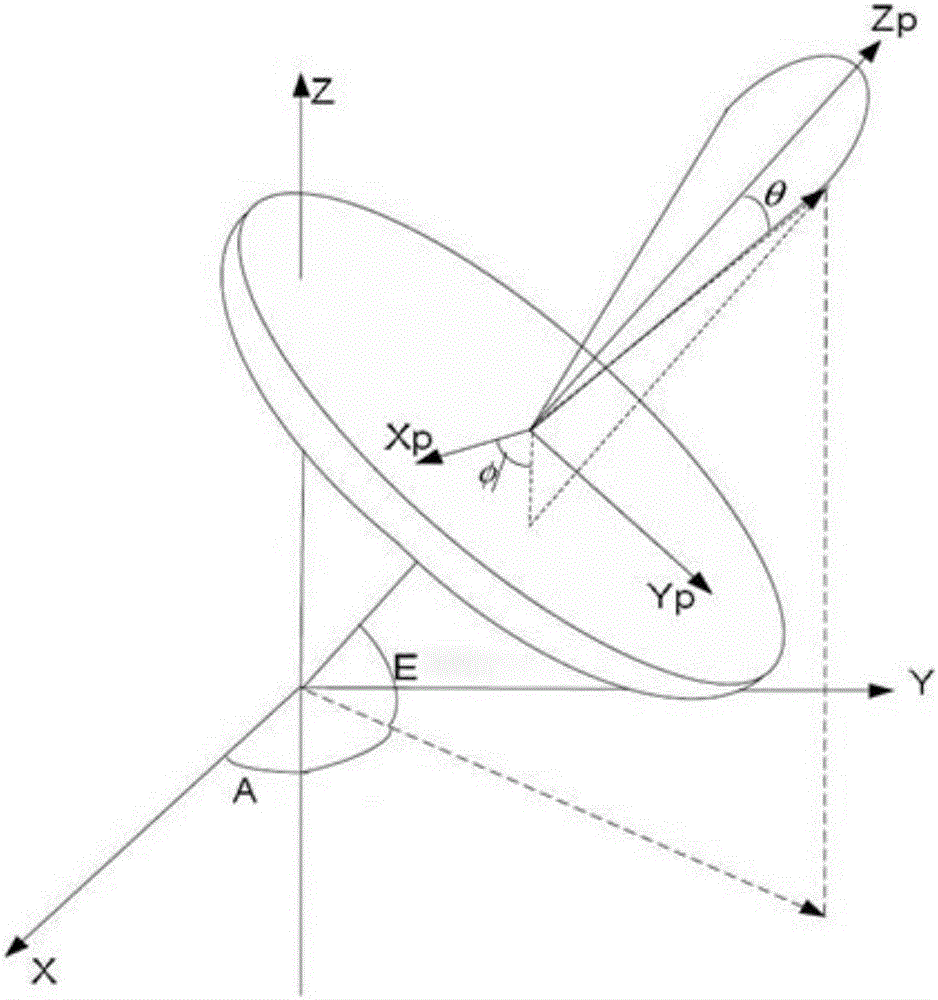
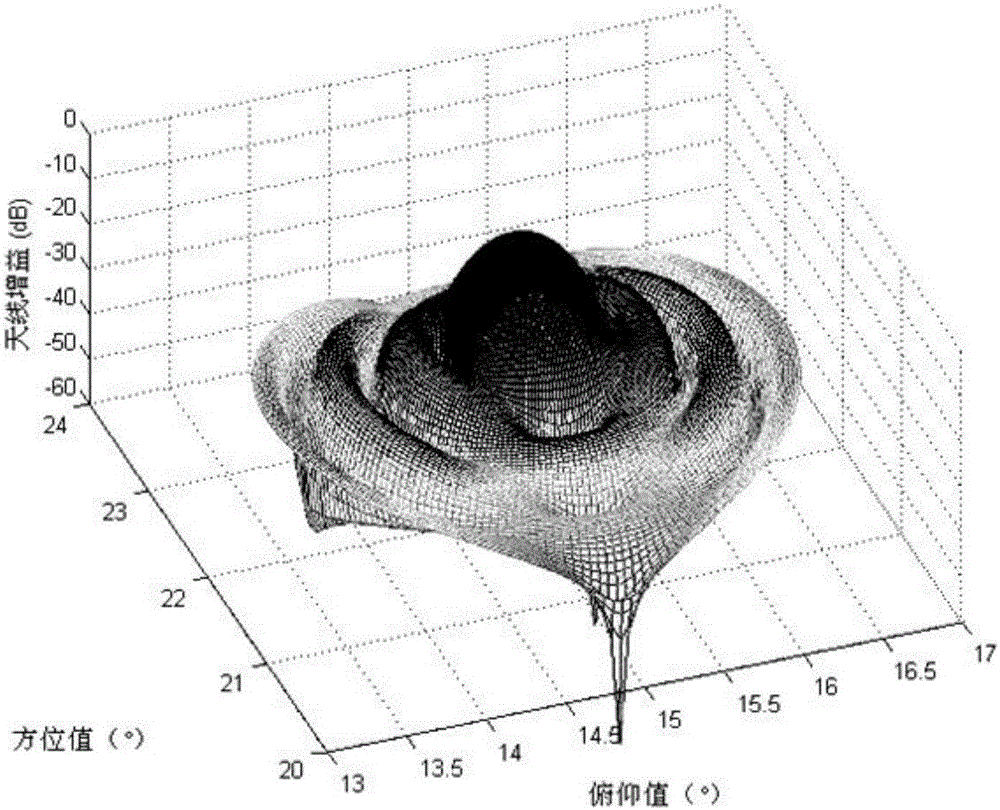
Automatic acquisition algorithm for near-earth satellite target based on shape feature search
ActiveCN106772466AExpand your searchIncrease the success rate of automationSatellite radio beaconingEarth satelliteAcquisition time
The invention provides an automatic acquisition algorithm for a near-earth satellite target based on shape feature search. The automatic acquisition algorithm is characterized in that a directional diagram model of an antenna is built, then a change rate curve of voltage formed by relative movements of a target and the antenna is enabled to act as a curve to be detected, a starting point and an ending point which most conform features of the curve are searched in the directional diagram model of the antenna, and finally relative positions of the target and an electrical shaft of the antenna are determined by using the ending point, so that the antenna is controlled to complete acquisition and tracking for the target. It is proved by a practical verification result that the method can automatically complete acquisition and tracking for the target when the target moves in a sidelobe range, and manual scanning intervention is not required. Meanwhile, the method can also be applied to mainlobe and sidelobe discrimination. The method can effectively improves the search range of the antenna, shorten the acquisition time and improve the automatic success rate.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
Repeatedly-usable atomic oxygen probe and detection system
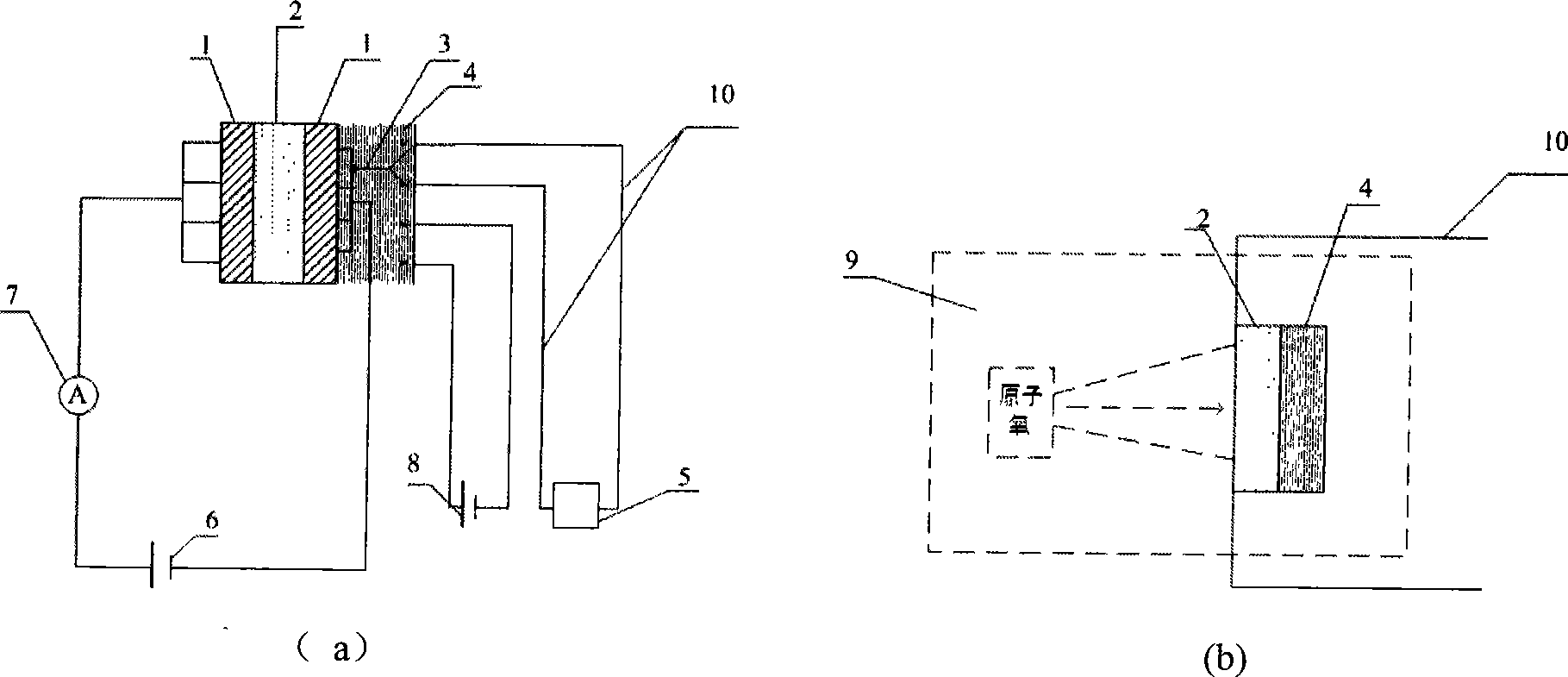
ActiveCN101470090AHigh measurement accuracyLow costMaterial resistanceMaterial electrochemical variablesEarth satelliteMetal electrodes
The invention discloses an atomic oxygen probe and a detection system which can be repeatedly used, belonging to gas detection field. The invention adopts a zinc oxide semiconductor film prepared on a sapphire substrate as a probe plated with metal electrodes and connected with a direct current power supply and a current meter via wire. The probe is mounted on a semiconductor heater, whose side surface is mounted with a thermocouple for measuring and controlling probe temperature. When atomic oxygen is acted with the probe, the resistance change of the zinc oxide film resistor can be measured to obtain the flux change of atomic oxygen beam, thereby realizing detection. The atomic oxygen absorbed on the surface of the semiconductor film can be desorbed via the heating of the heater, to return the resistance value to initial value, thereby realizing repeated application. The invention atomic oxygen probe and detection system have good response characteristic to atomic oxygen, and via heating, the probe has stable repeated application characteristic. The invention can be used to detect the atomic oxygen on ground and the orbit of low earth satellite.
Owner:NO 510 INST THE FIFTH RES INST OFCHINA AEROSPAE SCI & TECH
Retrieval method and device for mass transportation remote sensing data
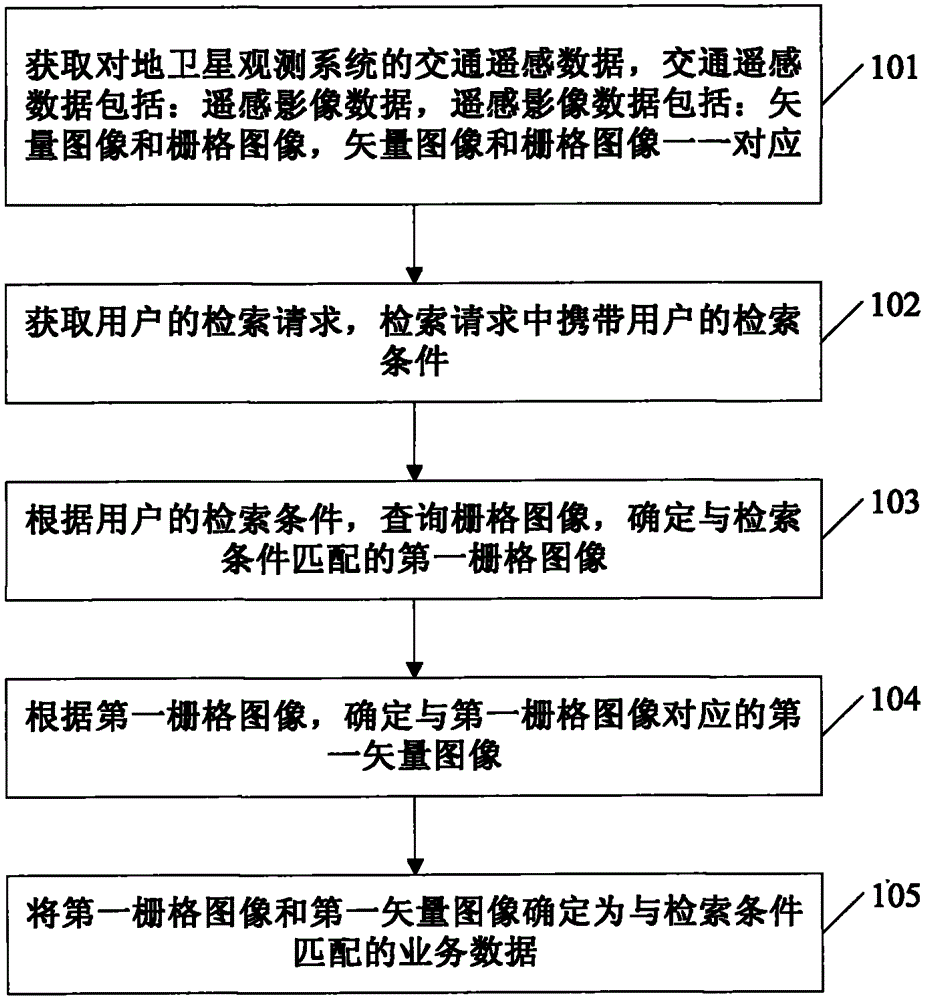
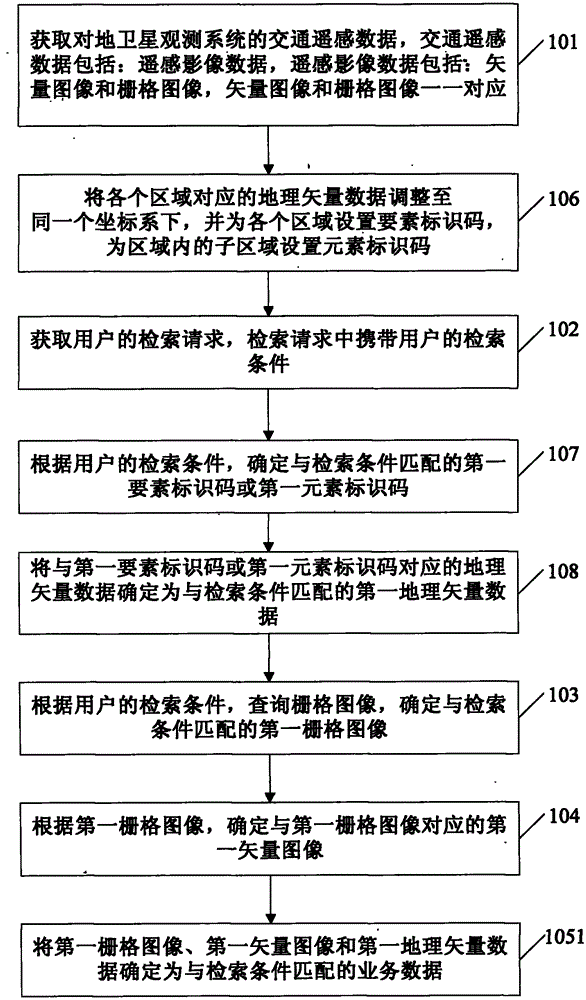
InactiveCN104063421AMeet the needs of quickly obtaining business dataImprove retrieval efficiencyVectoral format still image dataSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataEarth satellite
The invention relates to a retrieval method and device for mass transportation remote sensing data. The retrieval method comprises the following steps: acquiring transportation remote sensing data of an earth satellite observation system, wherein the transportation remote sensing data comprises remote sensing image data, the remote sensing image data comprises vector images and raster images, the vector images are in one-to-one correspondence with the raster images; acquiring the retrieval request of a user, wherein the retrieval request carries the search conditions of the user; inquiring the raster data first according to the retrieval request of the user; acquiring a first raster image matched with the retrieval request; acquiring a corresponding first vector image according to the first grid image; determining the first raster image and the first vector image as the business data matched with the request conditions, so that only requiring to search raster data according to the retrieval request, but not searching and matching all the images in the raster data and the vector data in sequence. Therefore, the data retrieval efficiency is improved and the user's requirement for quickly acquiring business data can be met.
Owner:中交宇科(北京)空间信息技术有限公司 +1
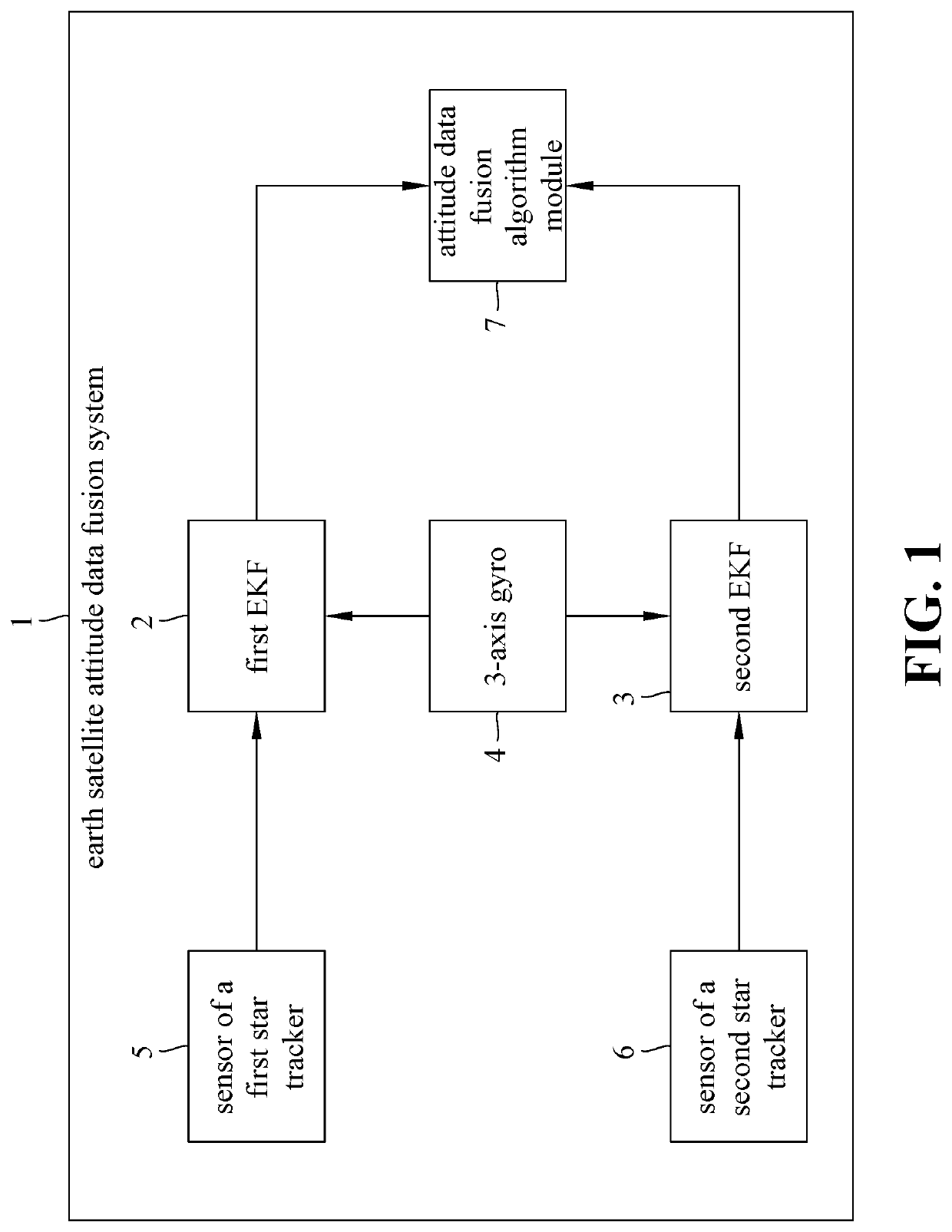
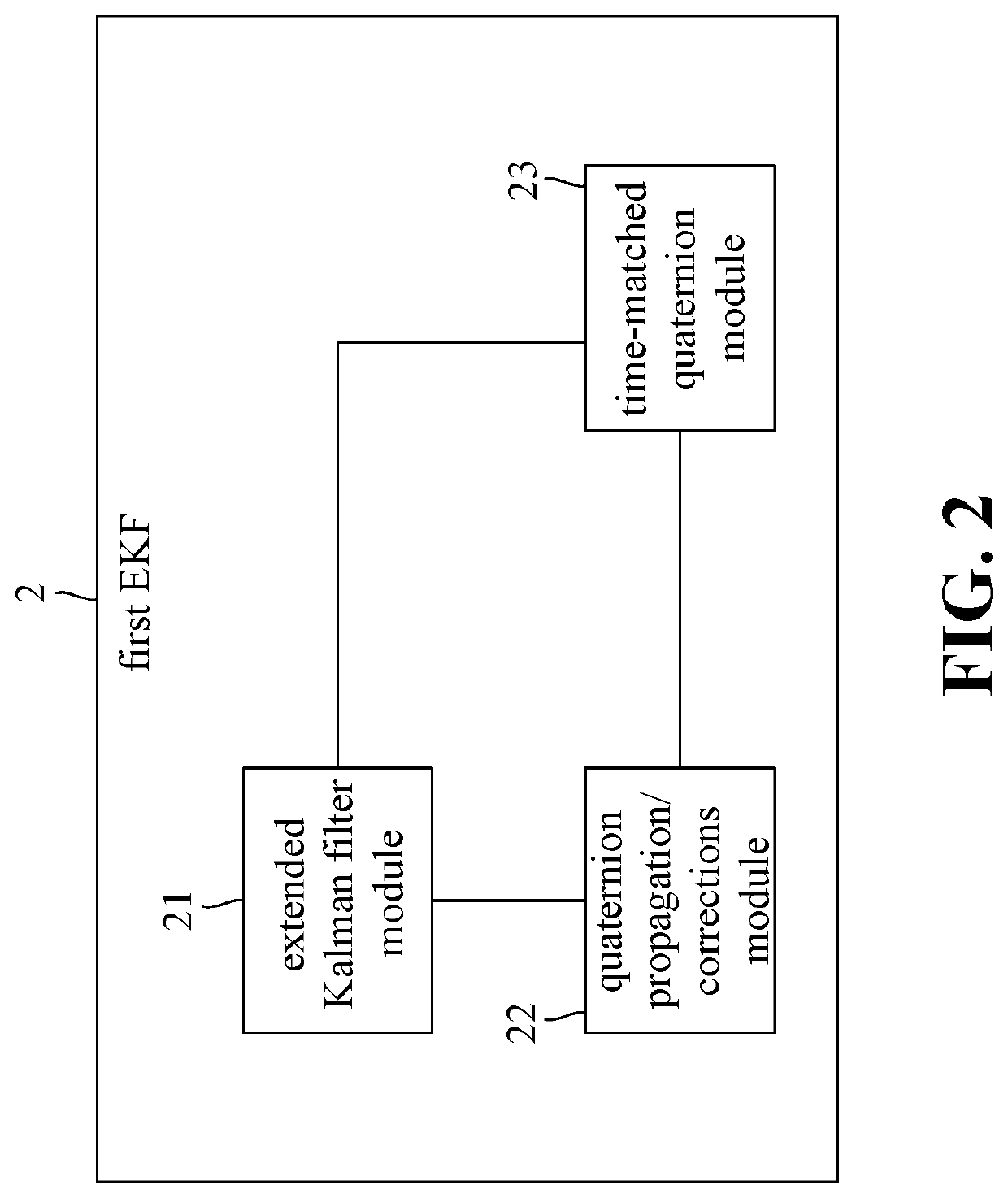
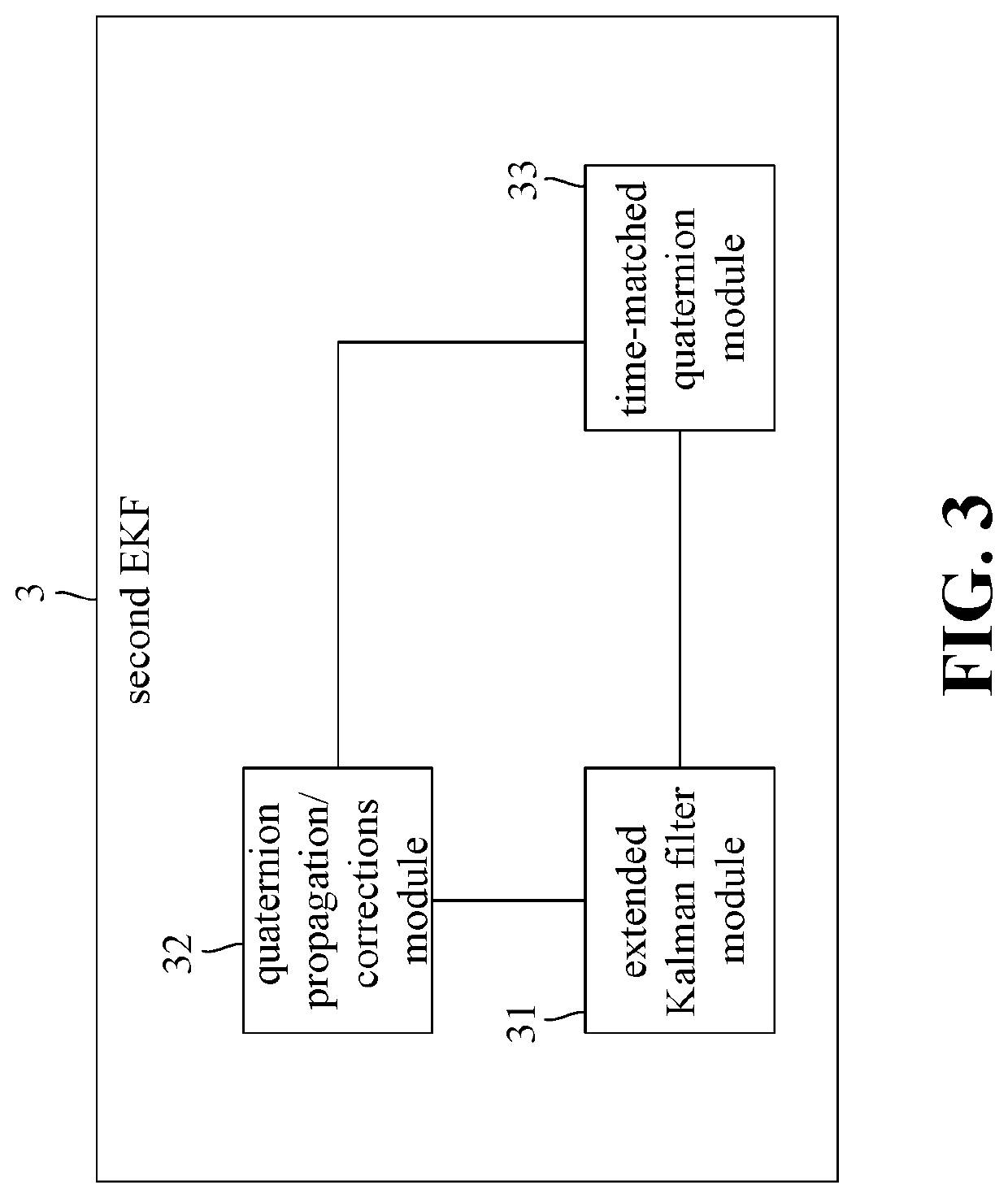
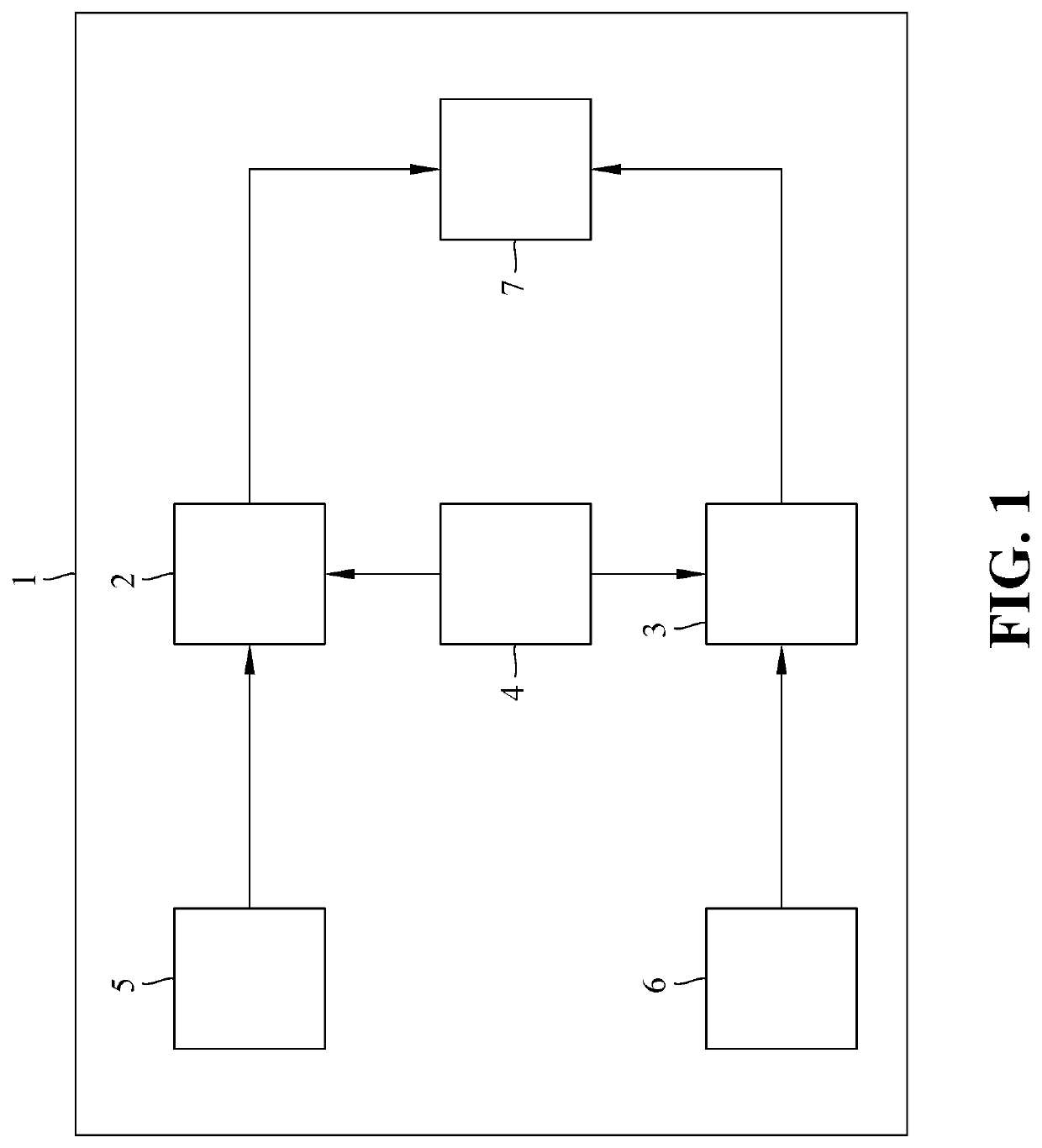
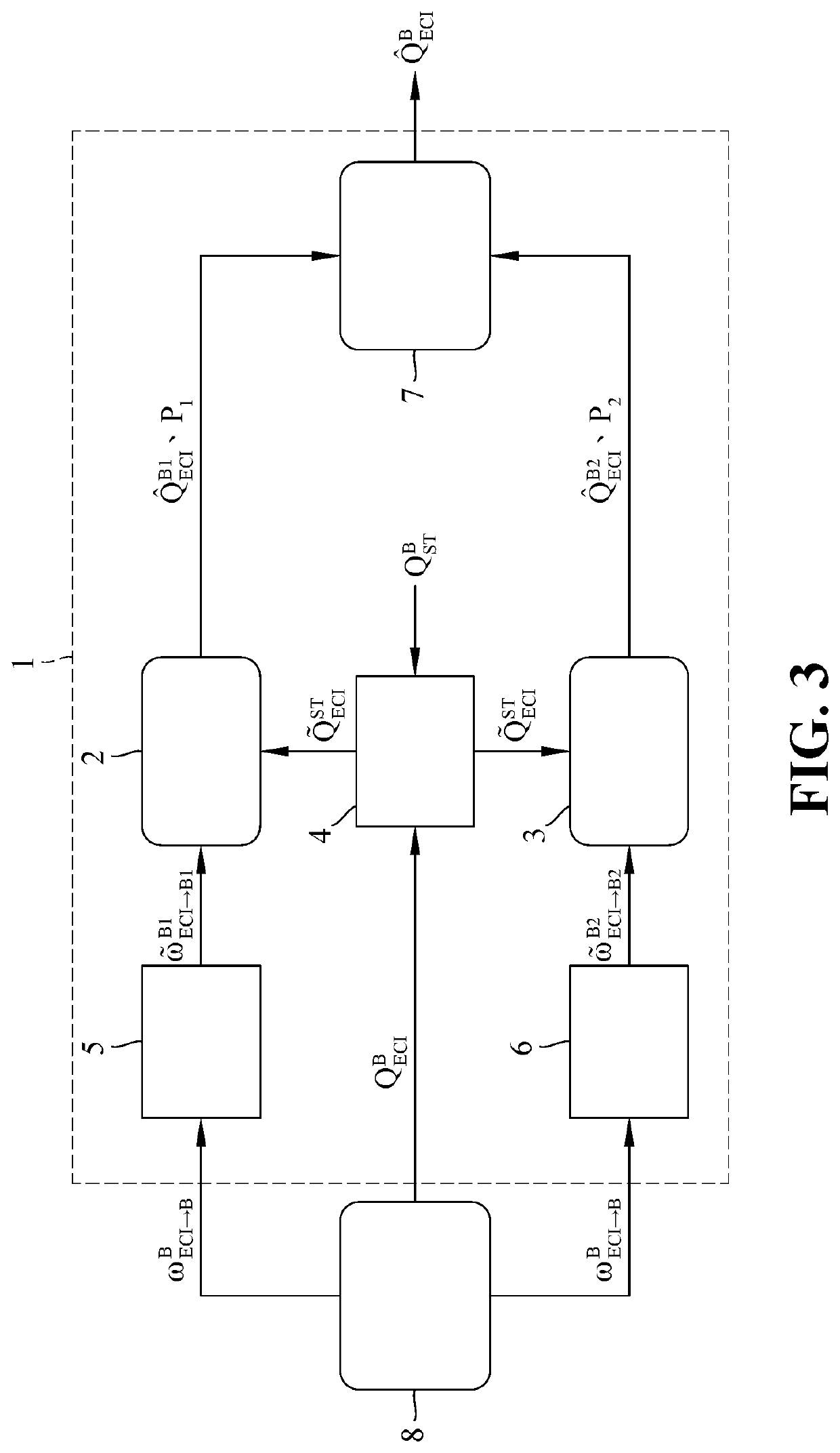
Earth satellite attitude data fusion system and method thereof
ActiveUS20200346789A1Optimize dataGood estimateAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDigital technique networkEarth satelliteSpace environment
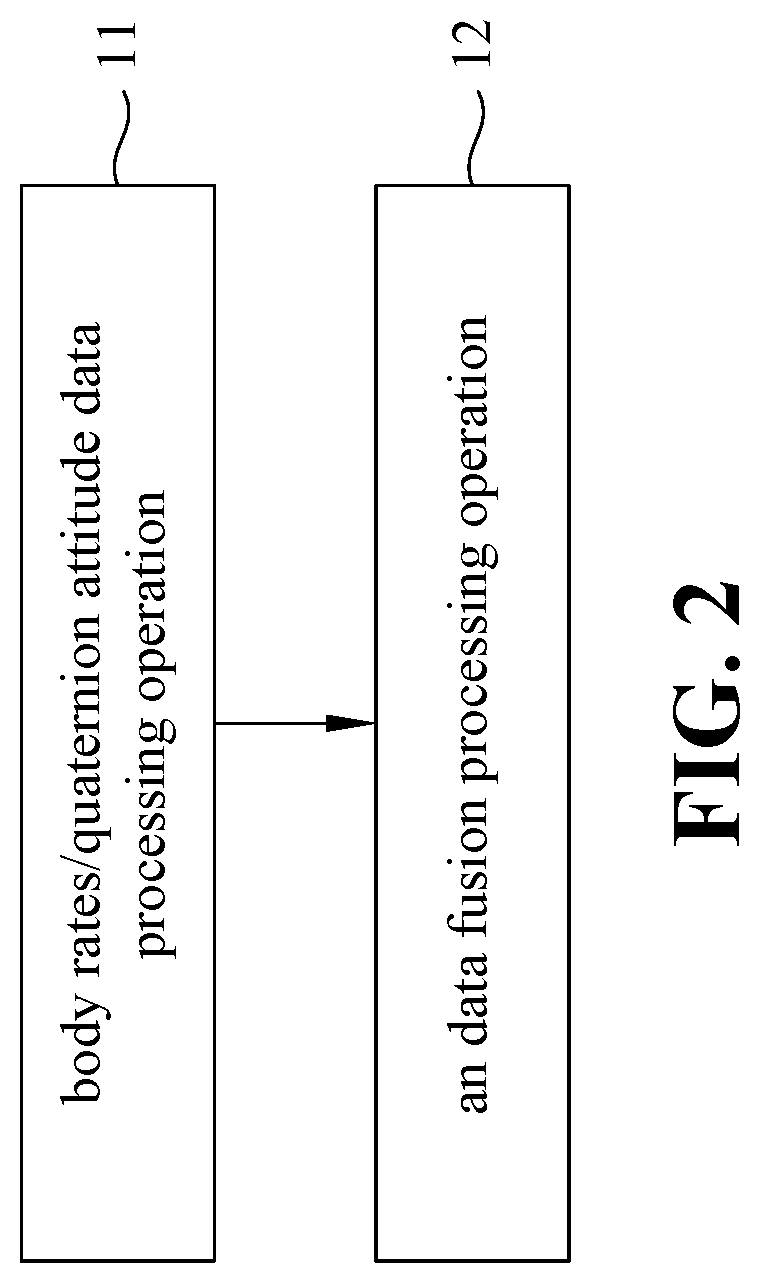
Provided are an earth satellite attitude data fusion system and method, applicable to an earth satellite space environment to estimate attitude data of a satellite. When the earth satellite attitude data fusion system of the present invention is used to perform the earth satellite attitude data fusion method, the first step is to perform a body rates / quaternion attitude data processing operation. Then, the next step is to perform an attitude / rates data fusion processing operation, wherein an attitude data fusion algorithm module receives a first IAE result data from a first EKF, and a second IAE result data from a second EKF, and performs an attitude / rates data fusion algorithm in a subsystem level to evaluate an attitude estimation IAE performance based on the first IAE result data, and the second IAE result data.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
Satellite attitude data fusion system and method thereof
ActiveUS20200122863A1Optimize dataGood estimateArtificial satellitesNavigation by astronomical meansEarth satelliteQuaternion
A satellite attitude data fusion system and method is disclosed, applicable to the earth satellite environment to estimate attitude data of the satellite. When the satellite attitude data fusion system of the present invention is used to perform the satellite attitude data fusion method, the first step is to perform a body rates quaternion attitude data processing operation. Then, the next step is to perform an attitude / rates data fusion processing operation, wherein an attitude data fusion algorithm module receives the first IAE result data from the first EKF, and the second JAE result data from the second EKF, and performs an attitude / rates data fusion algorithm in a subsystem level to evaluate an attitude estimation JAE performance.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com