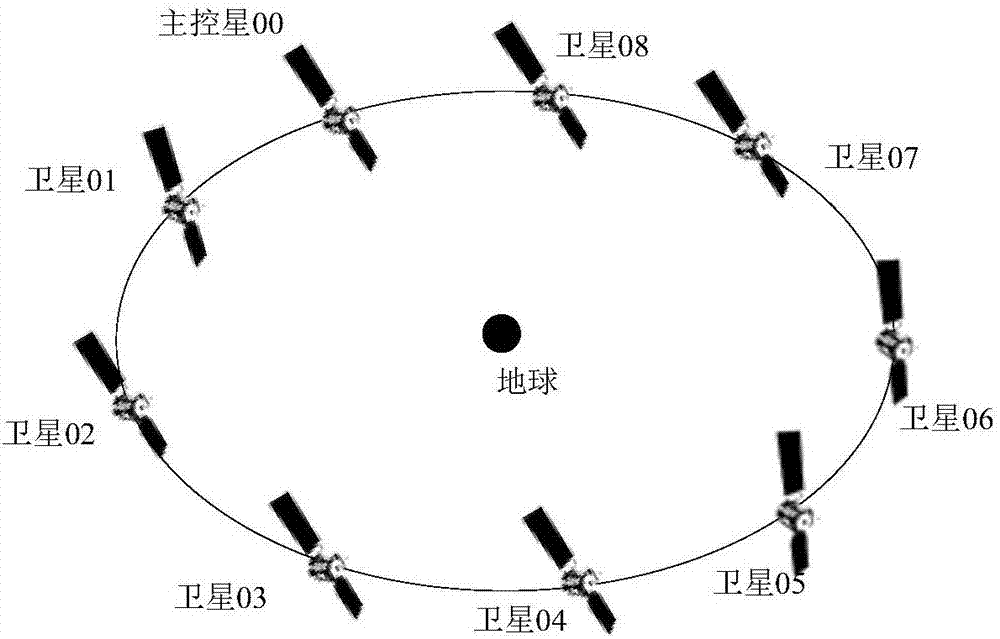
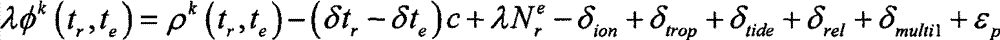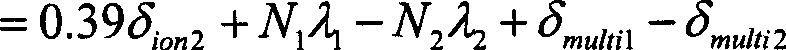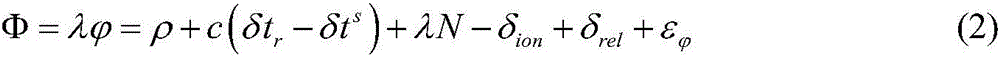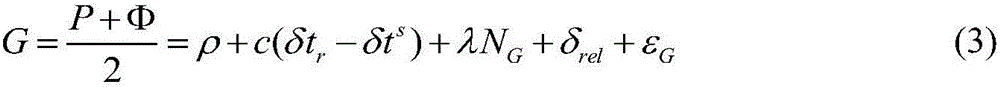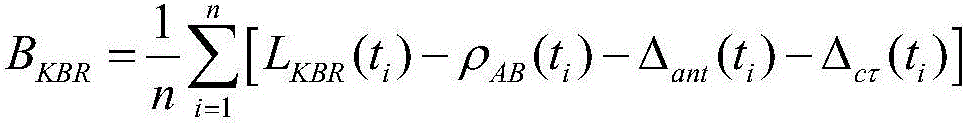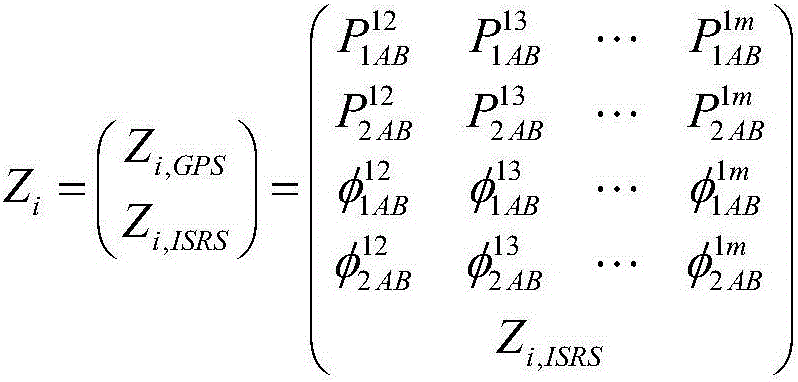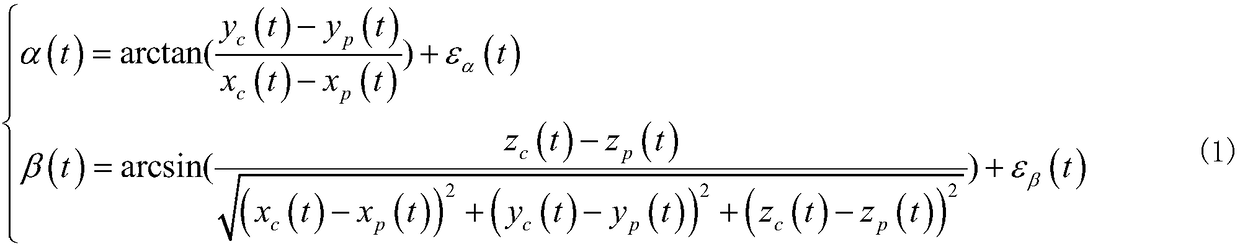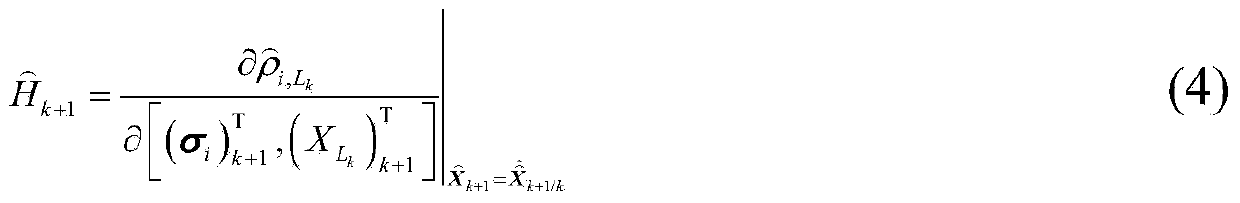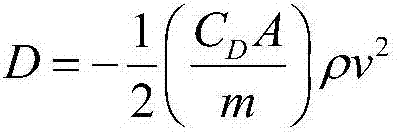Patents
Literature
355 results about "Orbit determination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
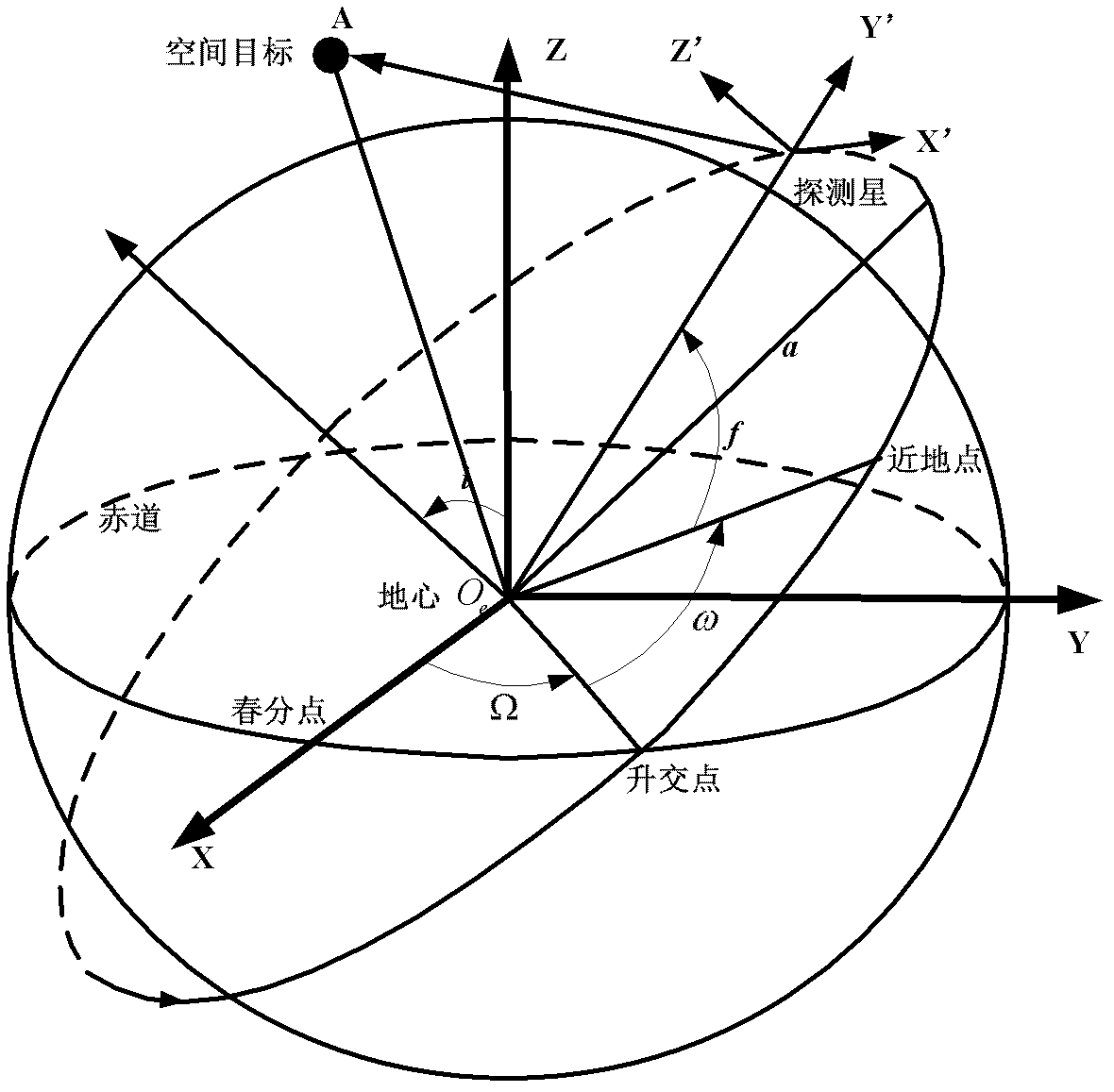
Orbit determination is the estimation of orbits of objects such as moons, planets, and spacecraft. One major application is to allow tracking newly observed asteroids and verify that they have not been previously discovered. The basic methods were discovered in the 17th century and have been continuously refined.
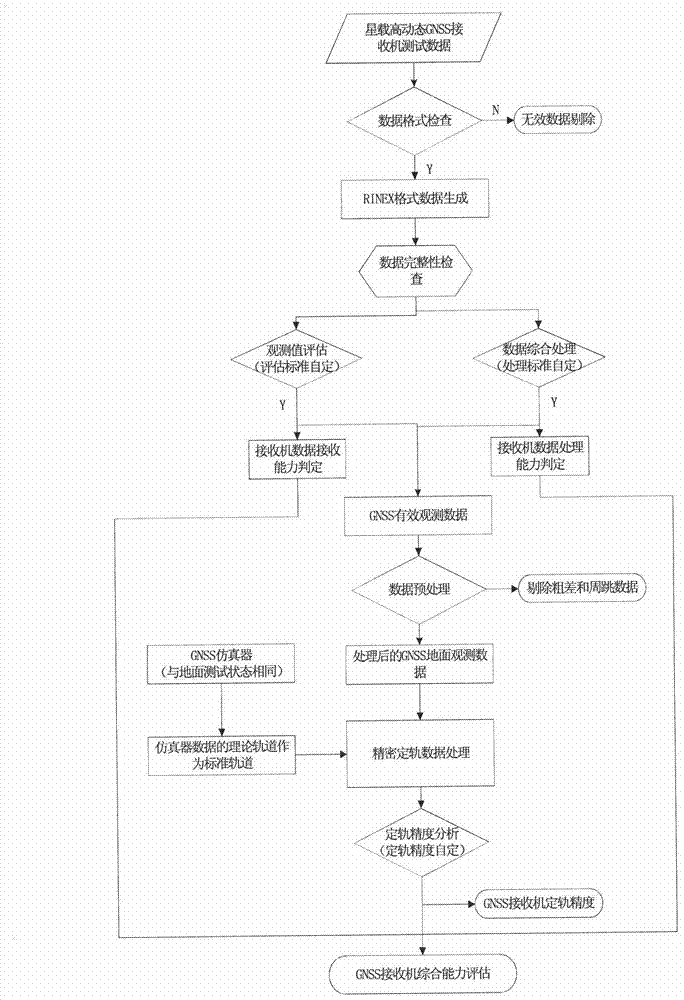
Method for performing ground check and performance evaluation on satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver
ActiveCN103076618AImprove the scope of performance assessmentImprove verification capabilitiesSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteSource Data Verification
The invention provides a method for performing ground check and performance evaluation on a satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly performing observation data verification on observation data generated by the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver; and after verification is finished, further performing orbit determination performance test on the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver by utilizing a geometrical orbit determination method. The process of performing data verification on the observation data mainly comprises four links, namely observation data standard format treatment, observation data type integrity checking, observation data quality evaluation based on calculation on observed value dual difference of different navigational satellites at a same frequency and observed value single difference of a same navigational satellite at different frequencies, and evaluation on pseudo range and carrier noise based on simulation data observation in a zero / short base line under the condition of no satellite; and during orbit determination performance test, by virtue of solving a linearized observation equation and comparing the linearized observation equation with a theoretical value, the orbit determination accuracy of the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver is obtained. The method provided by the invention can be used for directly and comprehensively evaluating the performance of the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
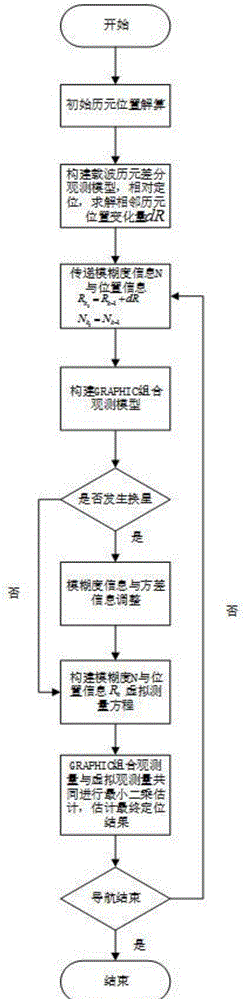
Single frequency high precision positioning method based on GNSS
ActiveCN106569241ASuppress result noiseSuppress noiseSatellite radio beaconingReal time navigationKinematics
The invention relates to a single frequency high precision positioning method based on GNSS. The method comprises steps that 1, preparation work is carried out; 2, initial epoch position solution is carried out; 3, a carrier wave phase epoch difference observation model is constructed, and a relative position variance is solved; 4, the fuzziness information and the position information are transmitted; 5, the fuzziness information and the variance information are adjusted; 6, a fuzziness and position information virtual observation equation is constructed; and 7, least square estimation for a GRAPHIC combined observation equation and a virtual observation equation is commonly carried out, and a final positioning result is solved. Through the method, a GRAPHIC combined kinetics positioning algorithm aided by carrier wave phase epoch difference is utilized, kinetics navigation positioning precision is improved, precise ephemeris energy is employed to carry out high precise orbit determination for LEO satellites, and broadcast ephemeris energy is employed to realize real-time navigation positioning. The method is advantaged in that the method is not influenced by satellite change in a navigation positioning process, high reliability, low cost and simple data processing are realized, and the method is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
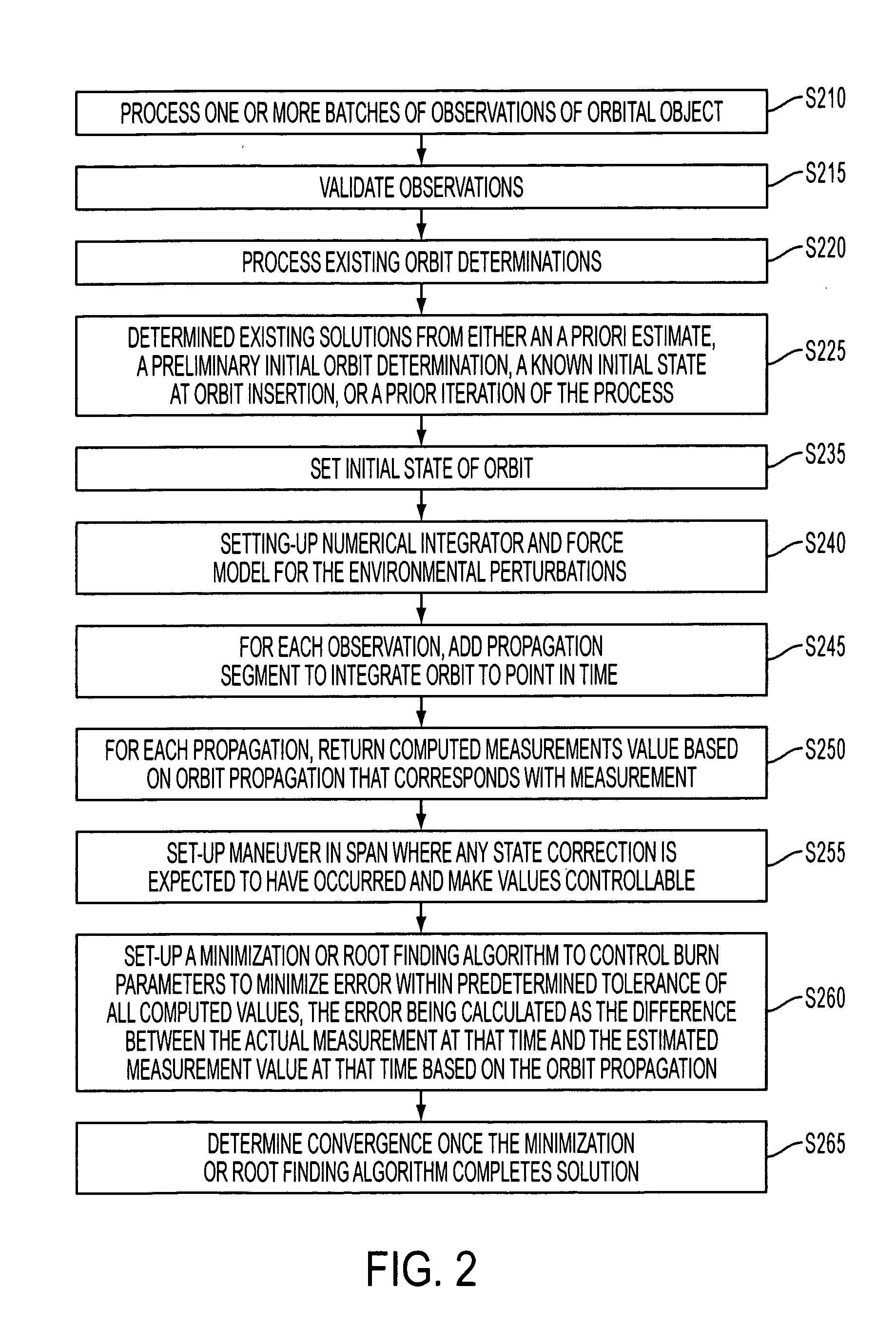
Method and apparatus for initial orbit determination using high-precision orbit propagation and maneuver modeling
ActiveUS20110196550A1Analogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationObservational errorObservation data
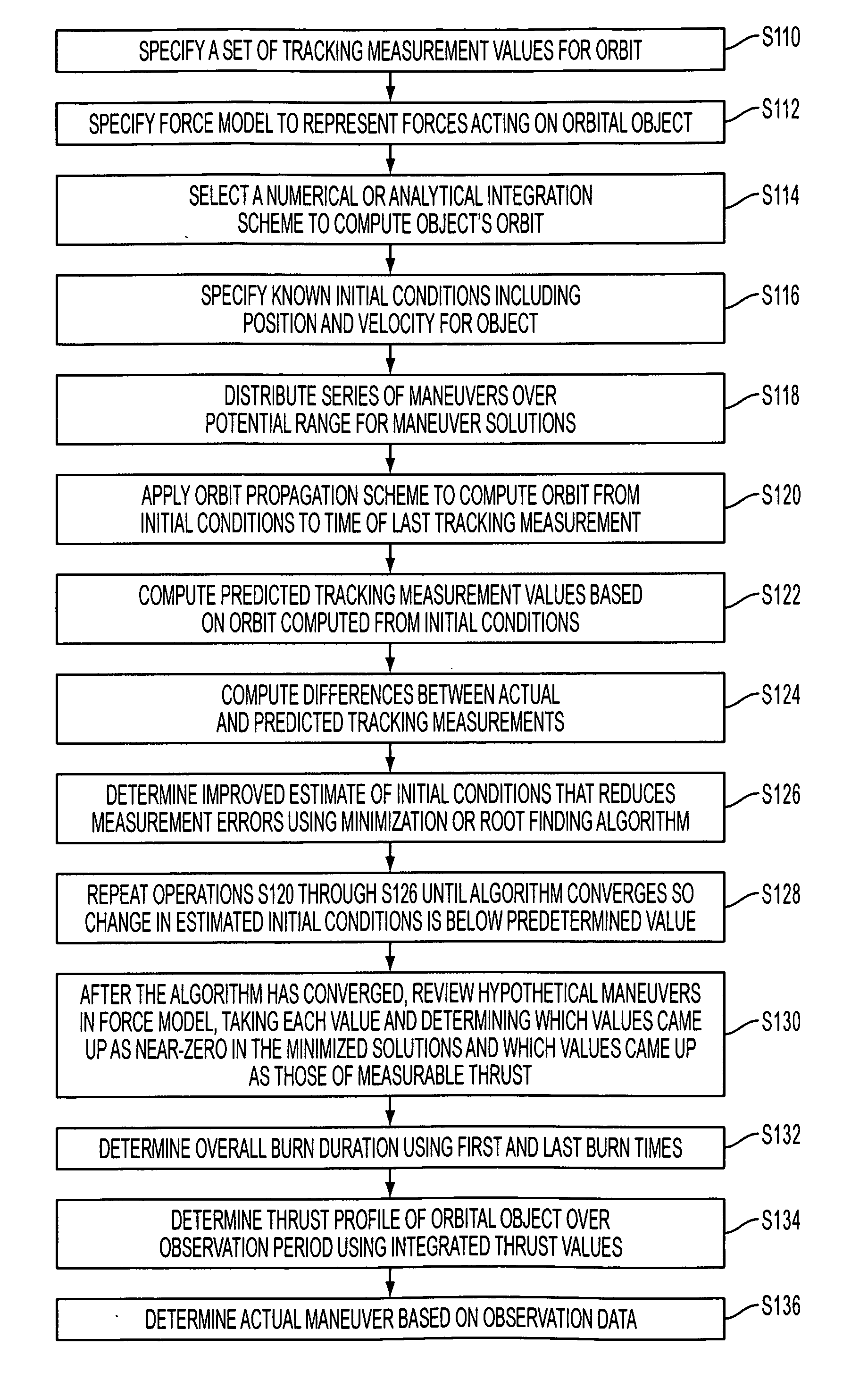
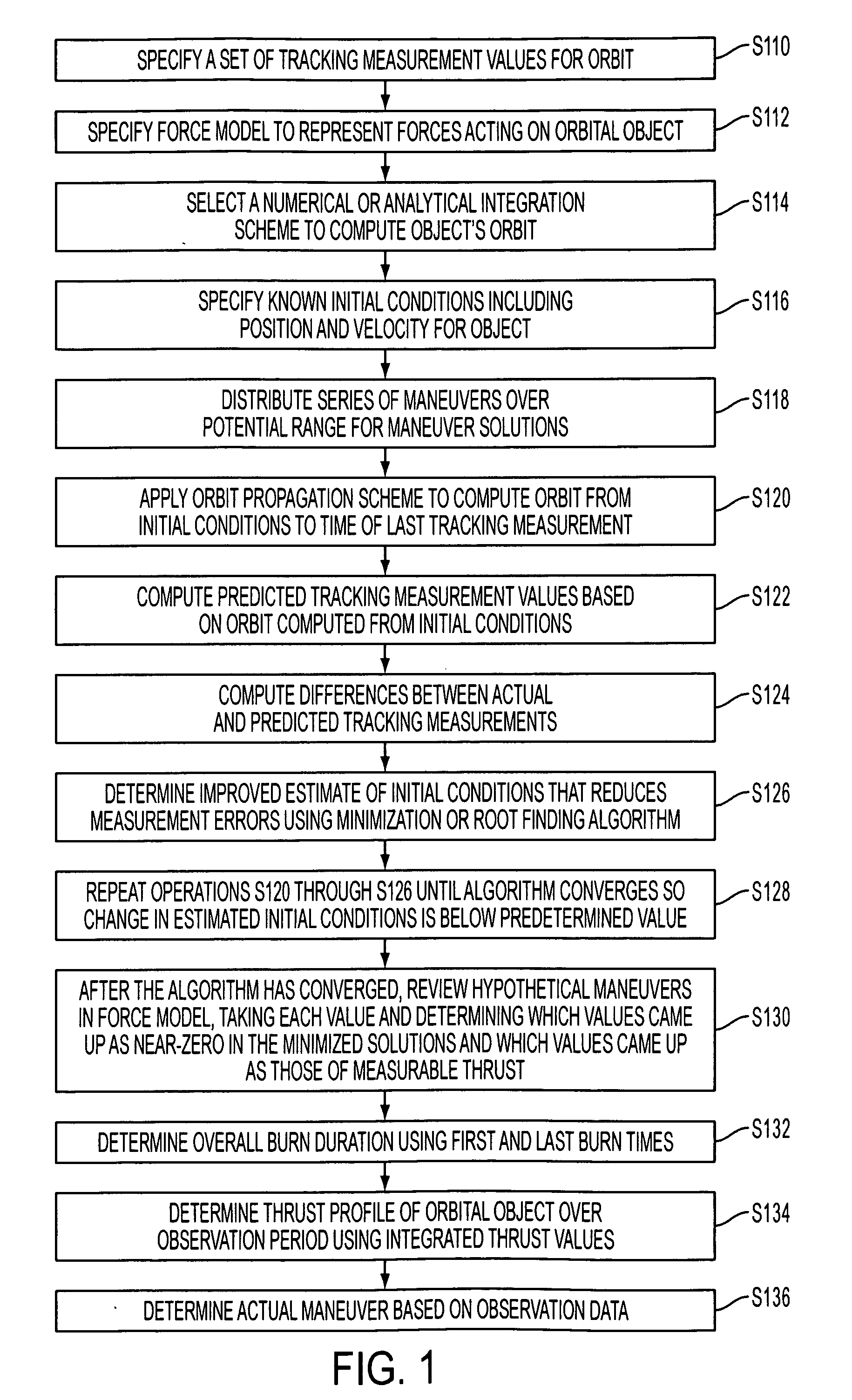
A method of determining an orbit of an orbital object includes computing predicted tracking measurement values based on the orbit computed from the initial conditions factoring in any modeled environmental forces and realistic maneuvers; computing the differences between the actual and predicted tracking measurements; determining an improved estimate of the initial conditions that reduces the measurement errors using a minimization or root finding algorithm; after the algorithm has converged, reviewing the hypothetical maneuvers in the force model, taking each value and determining which values came up as near-zero in the minimized solutions and which values came up as those of measurable thrust; determining overall burn duration using the first and last burn times; determining the thrust profile of the orbital object over the observation period using the integrated thrust values; and determining the actual maneuver based on the observation data.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
Combined scheduling method of satellite-ground measurement and control resources of low-mid-orbit satellite constellation based on orbit determination constraint satisfaction
InactiveCN103632053ASolve scheduling problemsGood geometrical conditionsInstruments for comonautical navigationSpecial data processing applicationsLink modelSatellite constellation
The invention discloses a combined scheduling method of satellite-ground measurement and control resources of a low-mid-orbit satellite constellation based on orbit determination constraint satisfaction, and belongs to the field of combined scheduling of the satellite-ground measurement and control resources. The method comprises the steps of (1) building a visible geometry model, (2) building a visible link model, (3) building the constraint condition of orbit determination, (4) carrying out preprocessing, (5) determining a resource distribution principle, (6) building a combined scheduling model of the satellite-ground measurement and control resources, and (7) carrying out algorithm solution. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the scheduling result is reasonable, the scheduling process is efficient, and the scheduling method is high in universality. The air-and-ground-based integrated scheduling of the measurement and control resources is achieved. The transition from ground-based measurement and control to air-and-ground-based combined measurement and control in China is achieved.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
Precise orbit determination method of navigation satellite for assisting clock error between stations
InactiveCN101702030AImprove errorImproved geometry factorSatellite radio beaconingArea networkCarrier signal
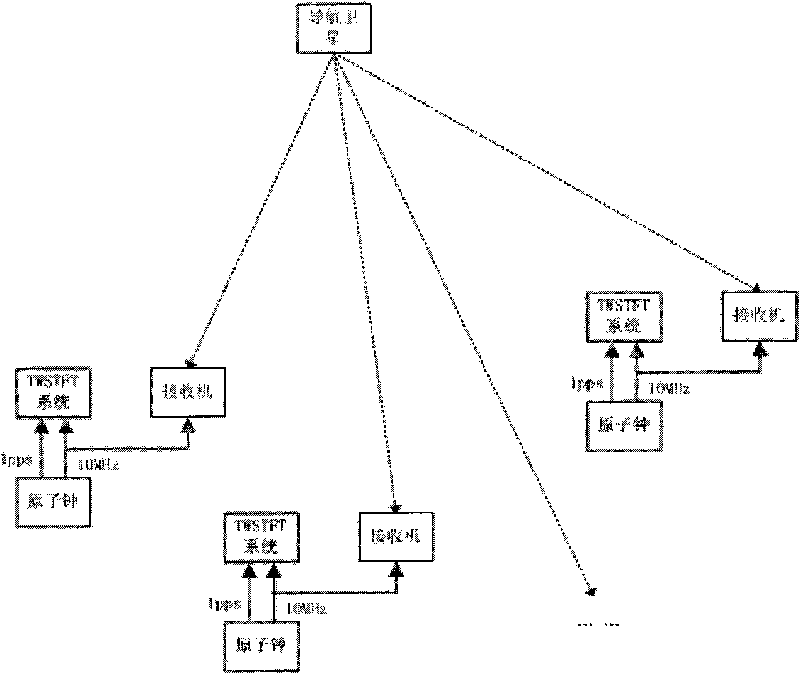
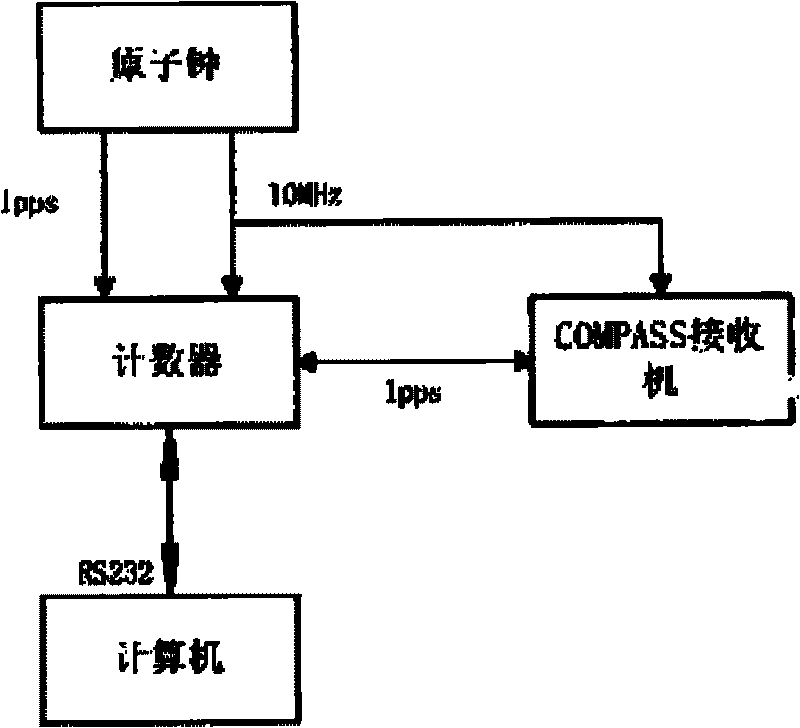
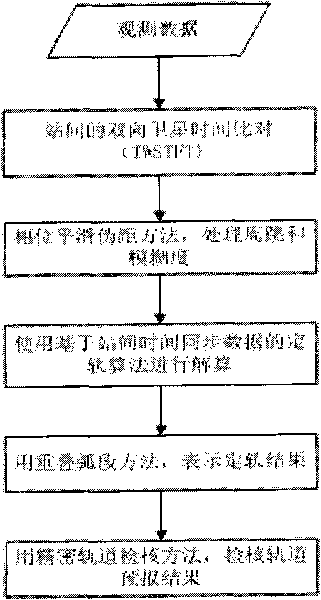
The invention relates to a precise orbit determination method of a navigation satellite for assisting a clock error between stations, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: configuring an atomic clock and a nanosecond stage time synchronization system at each station of an area network, receiving a distance measurement signal of a navigation satellite by each station of the area network to obtain the carrier phase data of each station, detecting the periodic trip generation moment of the carrier phase data by a Blewitt method and carrying out time synchronization between the stations by a two-way satellite time frequency transmission method TWSTFT to obtain a clock error between the stations; resolving a differential equation under an inertial coordinate system to obtain an orbit of the navigation satellite. Before orbit determination data are processed, the method firstly realizes the time synchronization between the stations with high accuracy (i.e.: obtaining the clock error between the stations). During the processing of the orbit determination data, an improved non-error method is adopted, only the orbit needs to be resolved, and the clock error between the stations does not need to be resolved, which not only can improve geometrical factors but also is beneficial to separating a system error (the clock error between the stations). Thus, the orbit determination accuracy can be enhanced.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Space-based phased-array radar space multi-target orbit determination method
InactiveCN102540180ASolve the near-far effectReduce estimation errorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTarget signalSatellite orbit
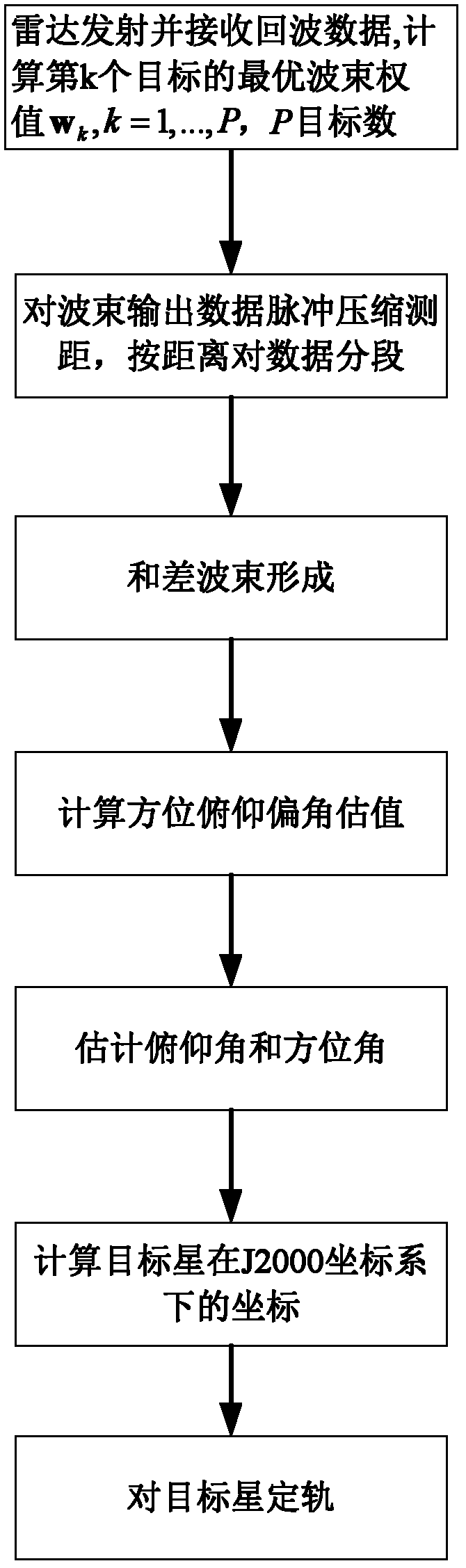
The invention discloses a space-based phased-array radar space multi-target orbit determination method, which mainly solves the problems that the space weak target cannot be evaluated effectively and the target orbit determination precision is low in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: processing target echo data by a zero-setting conformal algorithm, acquiring distance prior information by utilizing a distance pulse compression principle, and segmentally processing echo signals according to the distance prior information; segmenting the echo signals according to the number of the targets, wherein each segment of data is a target signal and an adjacent unit signal; performing multi-target two-dimensional angle evaluation on each segment of data by utilizing a sum-difference multi-beam angle-measuring principle; performing coordinate conversion based on a space target tracking result and detection satellite orbit information; and performing orbit determination on different space targets by a Laplace type iterative algorithm, and improving the orbit determination precision by a least square algorithm. According to the method, the influence of strong signals on weak targets can be reduced and the parameters of the weak targets can be evaluated accurately. The method can be applied in the actual application fields of space situation awareness, orbit resource management and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
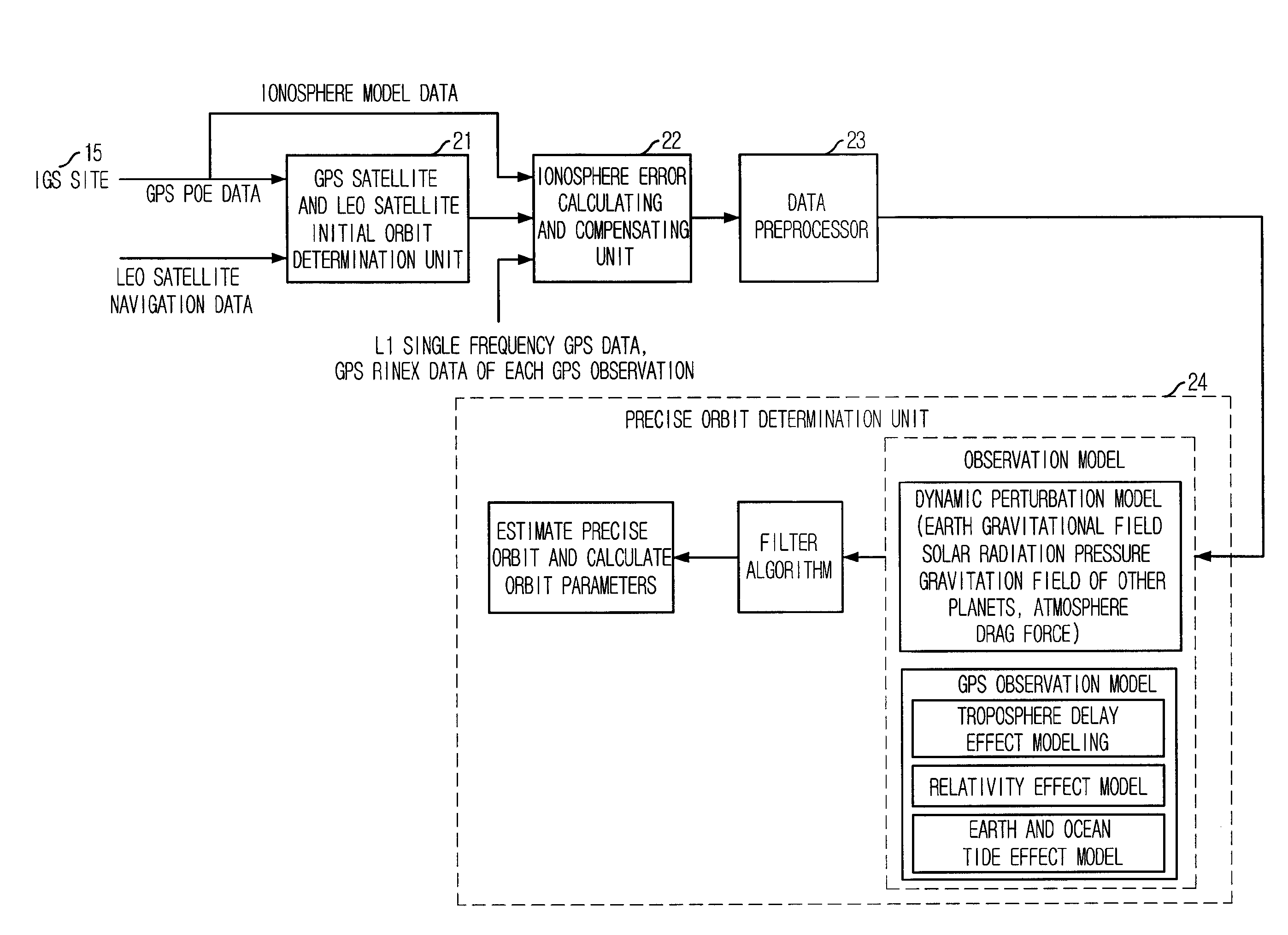
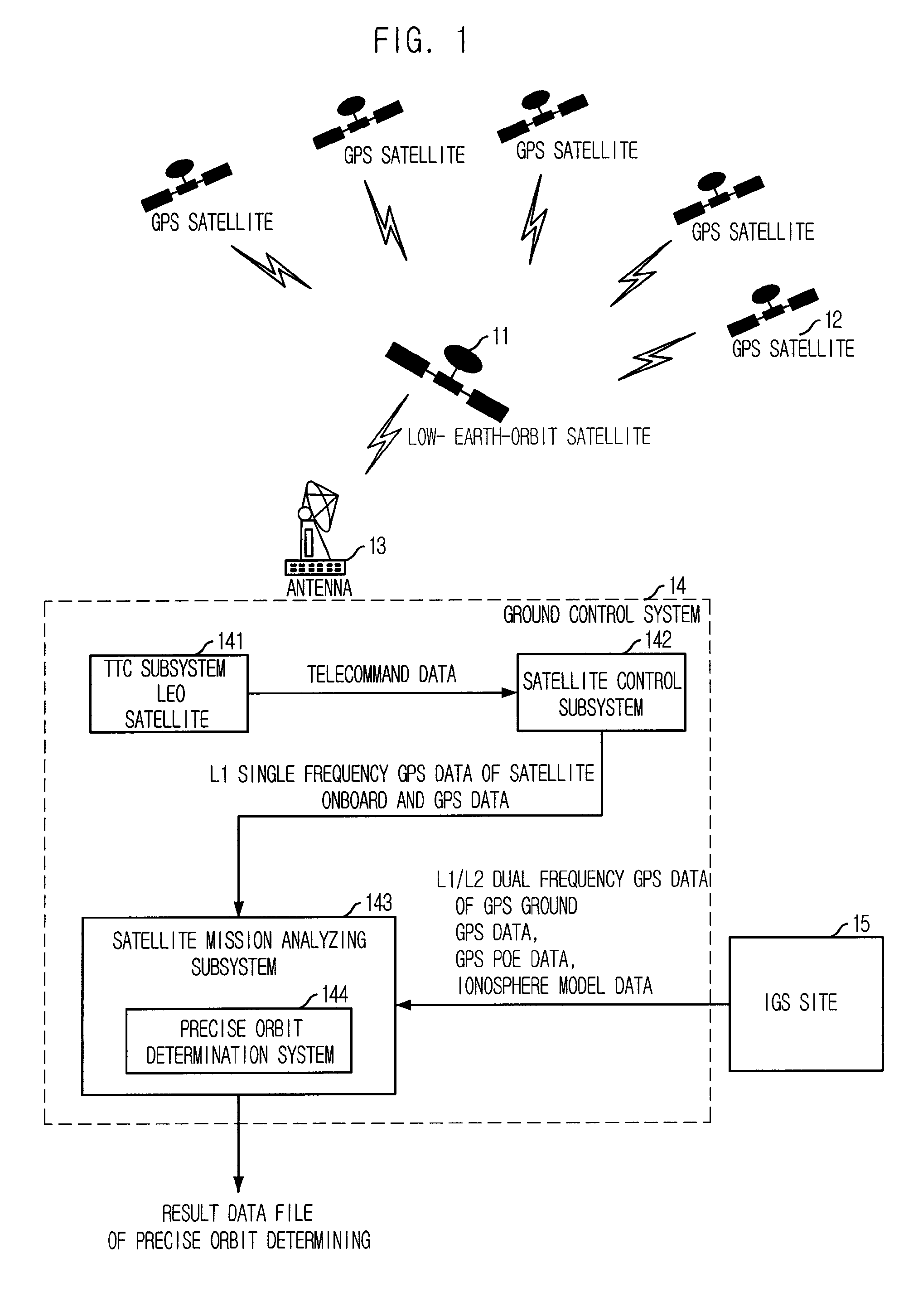
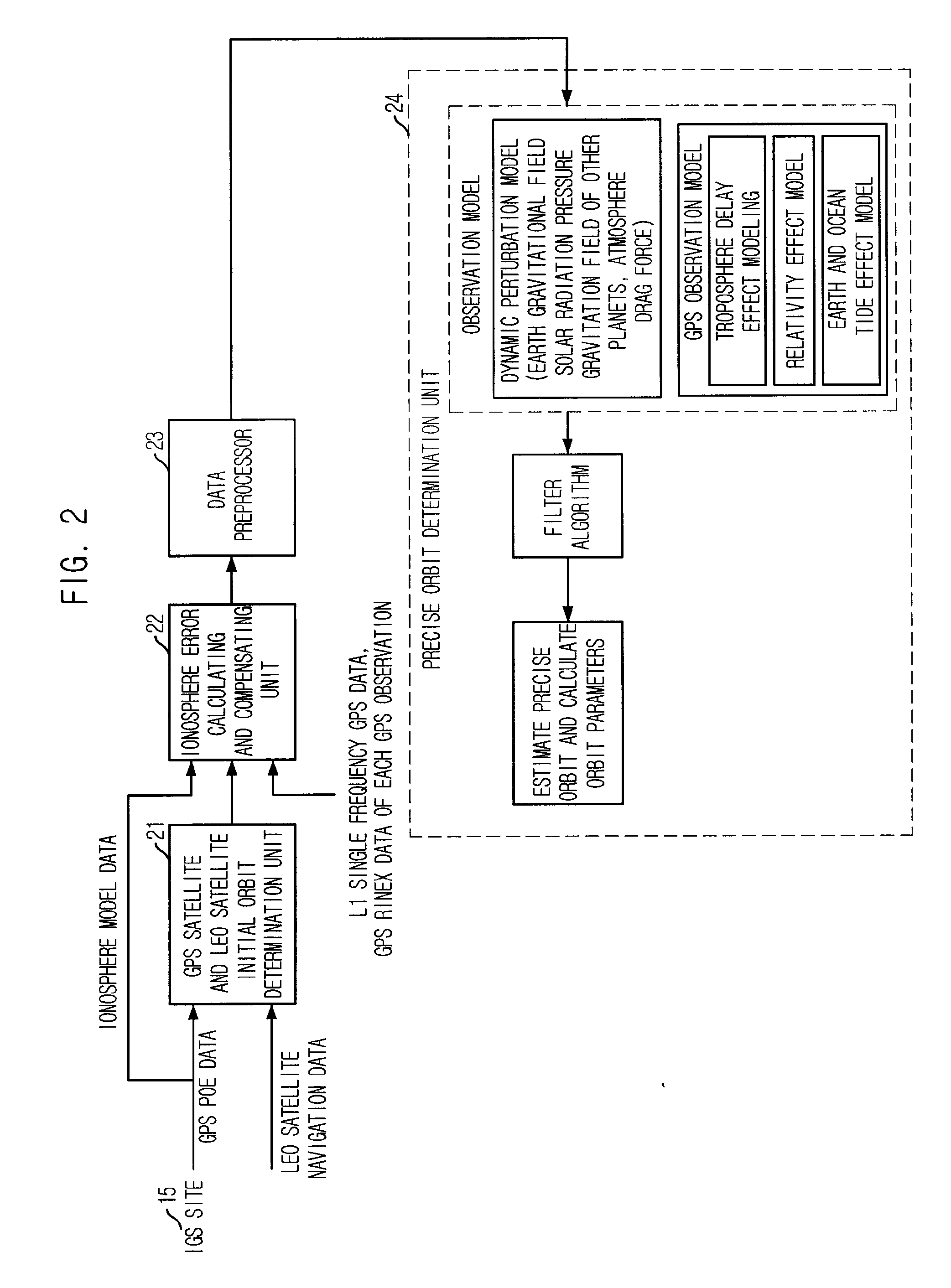
Method for correcting ionosphere error, and system and method for determining precision orbit using the same
InactiveUS20090091493A1Eliminate errorsAccurately determinePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingHigh elevationOne pass
Provided is a method of correcting an ionosphere error, a system of a precise orbit determination using the same and a method thereof. The method includes the steps of: a) determining a time of a highest elevation angle of a GPS satellite per one pass of each GPS satellite received at a LEO satellite or a receiver on a ground; b) determining a minimum total electron content found from an ionosphere model of the determined time per one pass of each GPS satellite; c) determining a total electron content directly calculated from the LEO satellite or a single frequency GPS data; d) determining an ionosphere error value of a single frequency GPS data by combining the minimum total electron content and the directly calculated total electron content; and e) correcting pseudorange data or carrier phase data based on the determined ionosphere error value.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
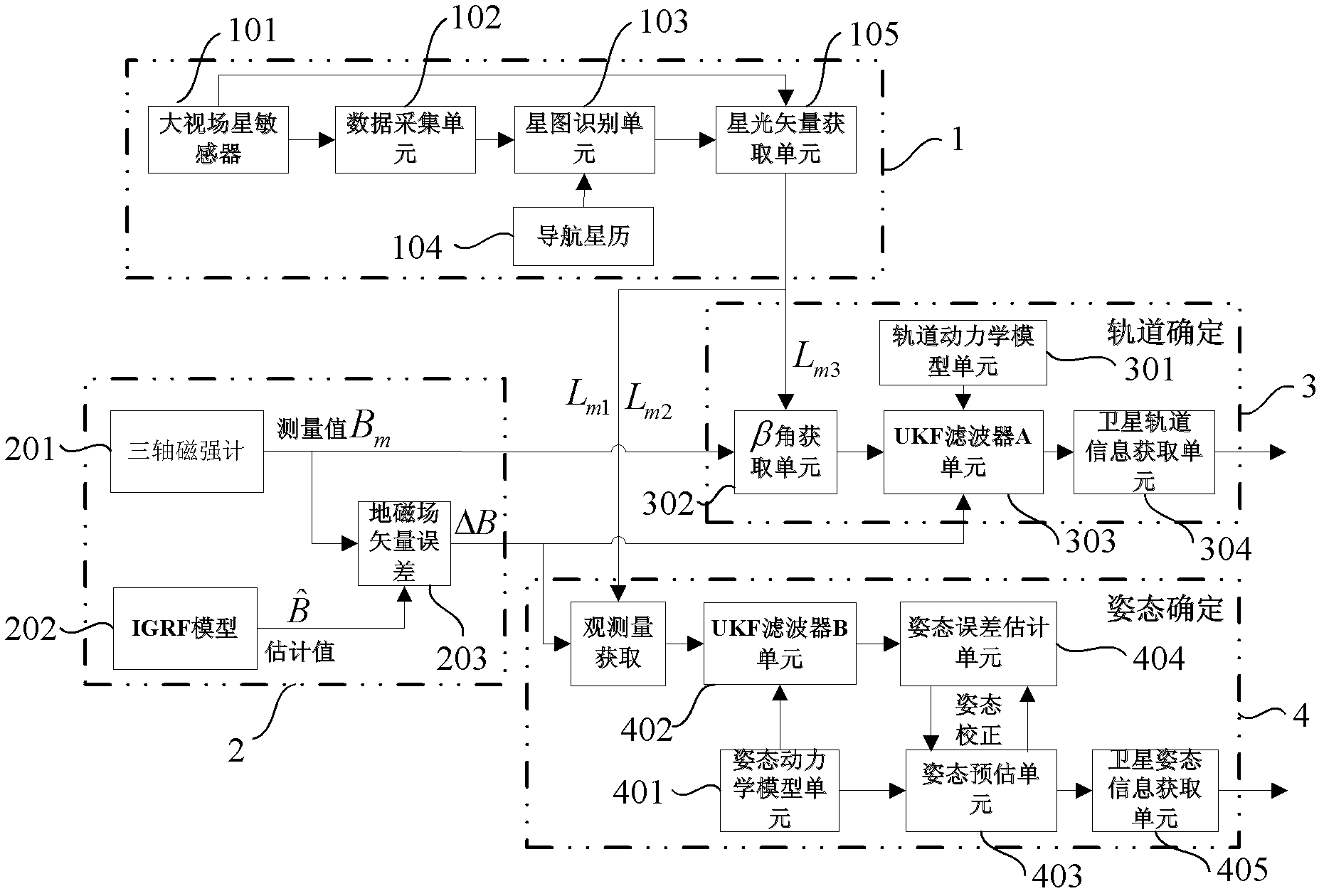
Small satellite autonomous navigation system based on starlight/ geomagnetism integrated information and navigation method thereof
InactiveCN102607564AImprove navigation accuracyImprove adaptabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingAutonomous Navigation SystemMarine navigation
The invention provides a small satellite autonomous navigation system based on starlight / geomagnetism integrated information and a navigation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of integrated navigation. The autonomous navigation system comprises a star sensor measuring system, an earth magnetic field measuring system, an orbit determination system and an attitude determination system. The navigation method comprises the following steps of: the establishment of a navigation system state equation, the measurement equation establishment of the navigation system and integrated navigation system information fusion based on UKF(unscented kalman filter). According to the method, a large view filed star sensor is utilized to simultaneously observe starlight vector information of multiple navigational stars, thereby making up the defect caused by overlarge measurement noise of a magnetometer and obtaining high navigation accuracy; based on track and attitude information contained in the measured values of a magnetometer and the star sensor and in comprehensive consideration of influences of various factors, a measurement equation of the system is established, the adaptability and the stability of a filter to measurement noise are improved; therefore, the method is suitable for navigation of a low earth rail small satellite adopting a cheap small autonomous navigation system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Software GNSS Receiver for High-Altitude Spacecraft Applications
ActiveUS20110254734A1Longer coherent integrationMinimization requirementsSatellite radio beaconingLow speedDelayed time
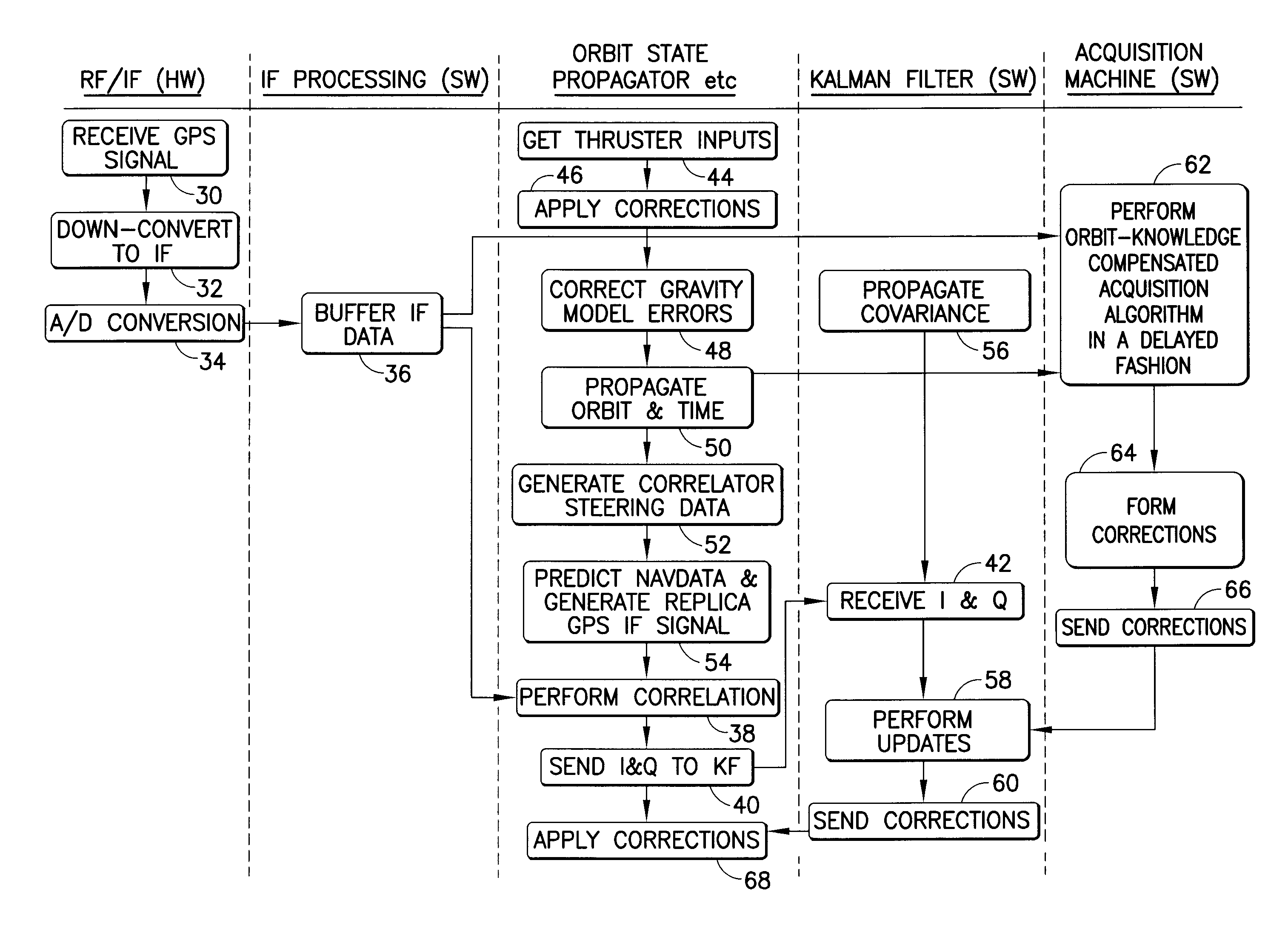
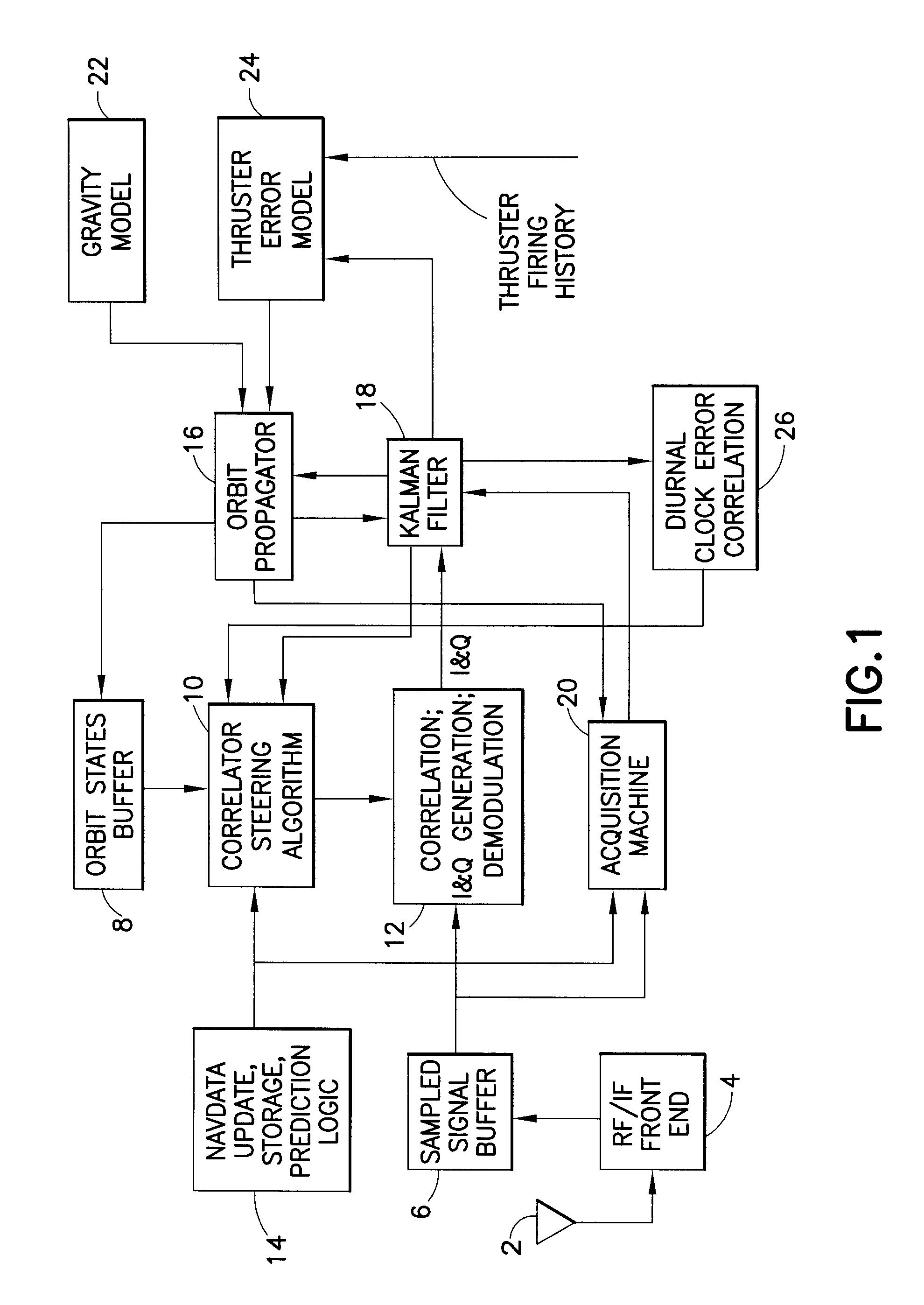
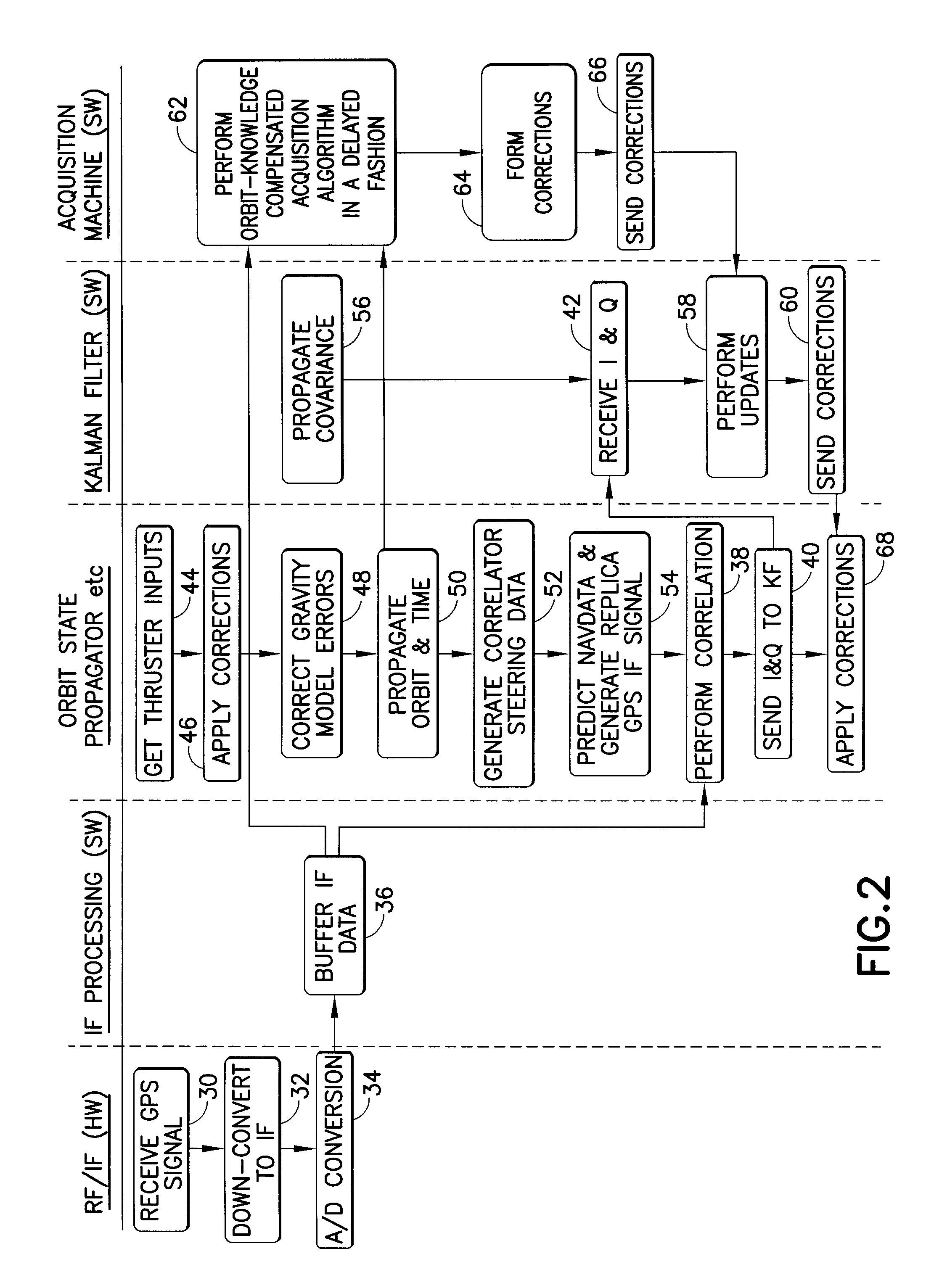
A system that provides GPS-based navigation / orbit determination capabilities for high-altitude spacecraft. The system uses an existing spacecraft processor and an easy-to-space-qualify minimum-hardware front end to minimize the need for new space-qualified hardware. The system also uses coherent integration to acquire and track the very weak GPS signals at high altitudes. The system also uses diurnal thermal modeling of a spacecraft clock and precision orbit propagation to enable longer coherent integration, a special Kalman filter to allow weak signal tracking by integrated operation of orbit determination and GPS signal tracking, and a segment-by-segment, post-processing, delayed-time approach to allow a low-speed spacecraft processor to provide the software GPS capability.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Geosynchronous orbit constellation orbit determination method based on ground station/satellite link/GNSS combined measurement
ActiveCN106338753AGuarantee the accuracy of orbit determinationSmall amount of calculationInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingGeosynchronous orbitGround station
The invention discloses a geosynchronous orbit constellation orbit determination method based on ground station / satellite link / GNSS combined measurement. The method comprises the steps of (1) establishing the state equation of a GSO constellation orbit determination system in a centralized structure, (2) establishing the measurement equation of the GSO constellation orbit determination system in a centralized structure, (3) carrying out combined optimization of a ground station for orbit determination and GNSS measurement combination, (4) determining the filtering method for realizing orbit parameter estimation according to the above established GSO constellation combined orbit determination system model based on ground station / satellite link / GNSS, and (5) carrying out the concrete realization of a GSO constellation orbit determination method based on ground station / satellite link / GNSS in the centralized structure. According to the method, the combined distribution optimization strategy of ground station and GNSS measurement is established based on a precision factor, and the calculation amount is reduced while the orbit determination precision is ensured.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Autonomous navigation signal enhancement method based on low-earth-orbit satellites
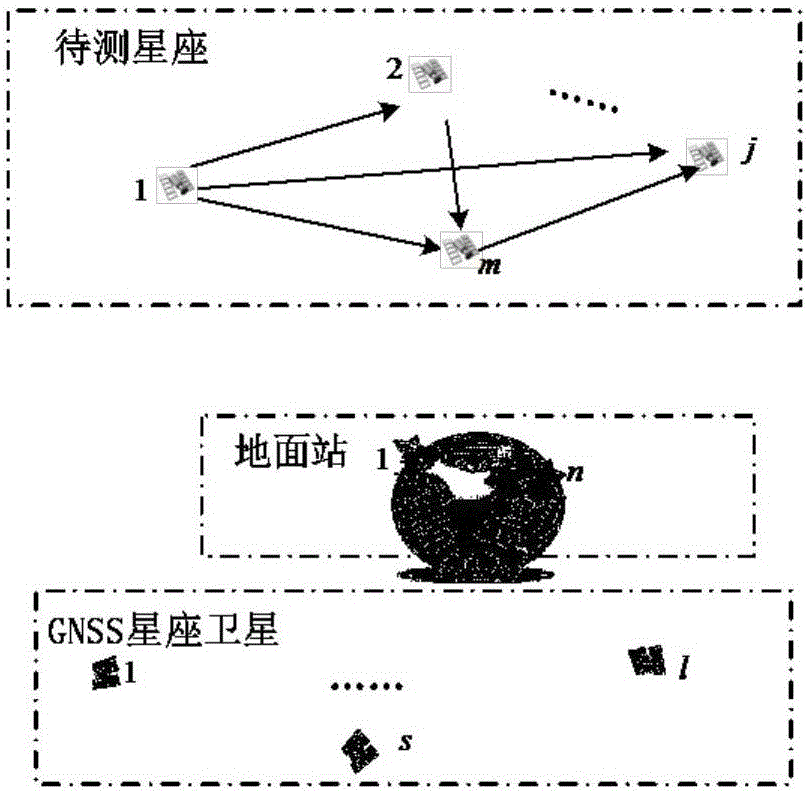
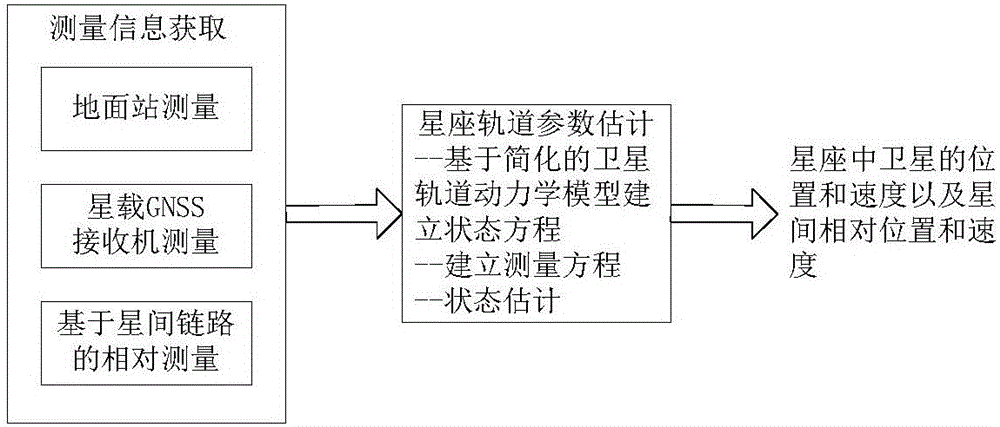
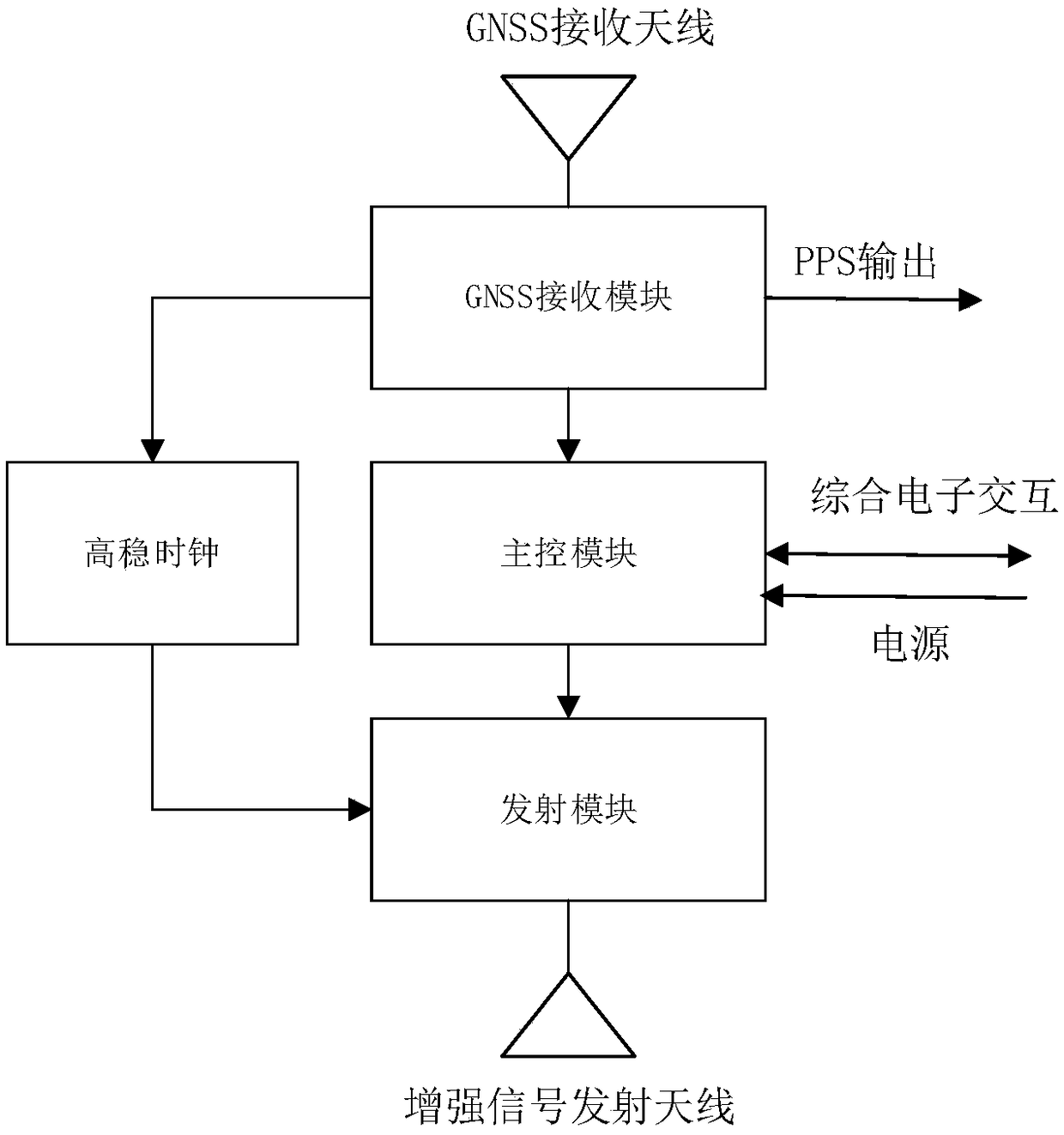
ActiveCN108919312AStrong invulnerabilityGood autonomous navigation abilitySatellite radio beaconingLow earth orbitGround station
The invention discloses an autonomous navigation signal enhancement method based on low-earth-orbit satellites. The method is implemented by use of a load carried on the low-earth-orbit satellites, wherein the load comprises a GNSS receiving module, a main control module, an emission module, a high-stability clock module, at least one set of GNSS signal receiving antennas and at least one set of enhancement information emission antennas; the GNSS receiving module is used for capturing and tracking navigation satellite signals and performing on-satellite autonomous orbit determination and autonomous time service; the main control module is used for interacting data with the GNSS receiving module and the emission module; the emission module is used for coding result data of on-satellite autonomous orbit determination and autonomous time service into telegraph texts and performing signal modulation and broadcasting; and the high-stability clock module is used for providing a time-frequency benchmark. According to the method, by uniting low-earth-orbit satellite navigation enhancement information and the navigation satellite signals to perform navigation positioning, the precision, availability and reliability of navigation positioning can be effectively improved. Besides, the method does not depend on a ground station, so that application is more flexible compared with a ground-based enhancement technology.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Satellite orbit maintenance and control method based on two lines of radicals
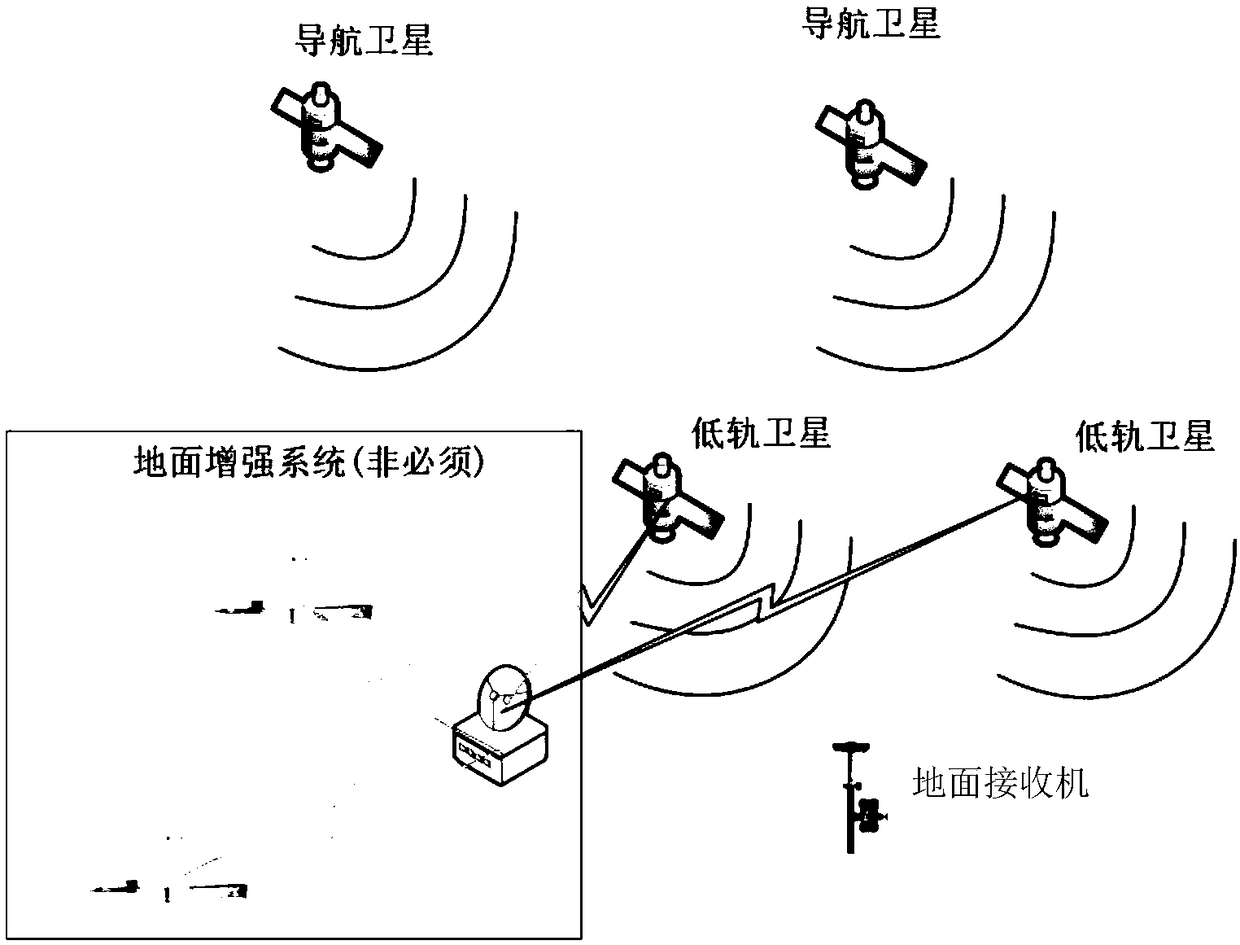
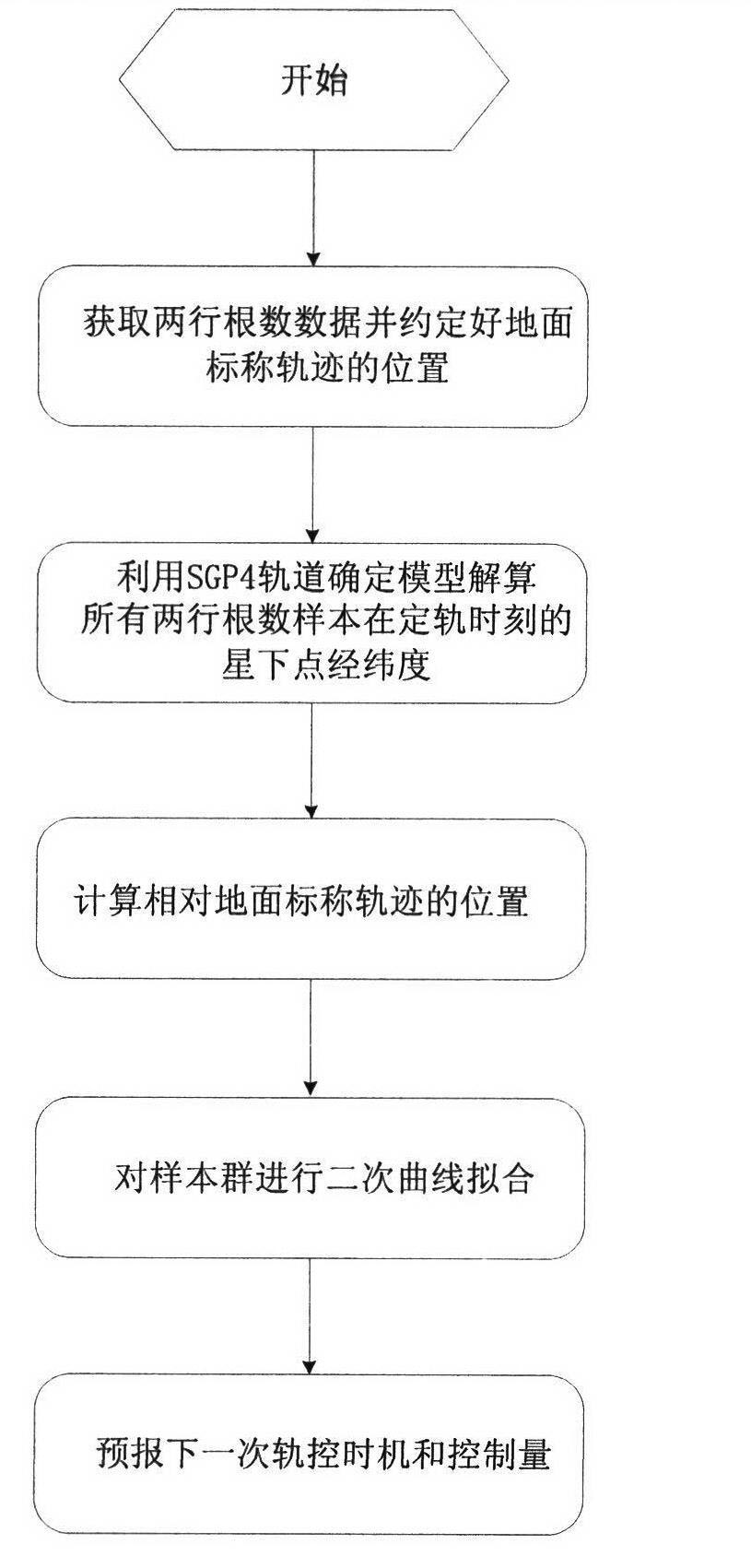
ActiveCN102591343AGood serviceFacilitate maintenance of control forecastsPosition/course control in two dimensionsUltrasound attenuationGeographical latitude
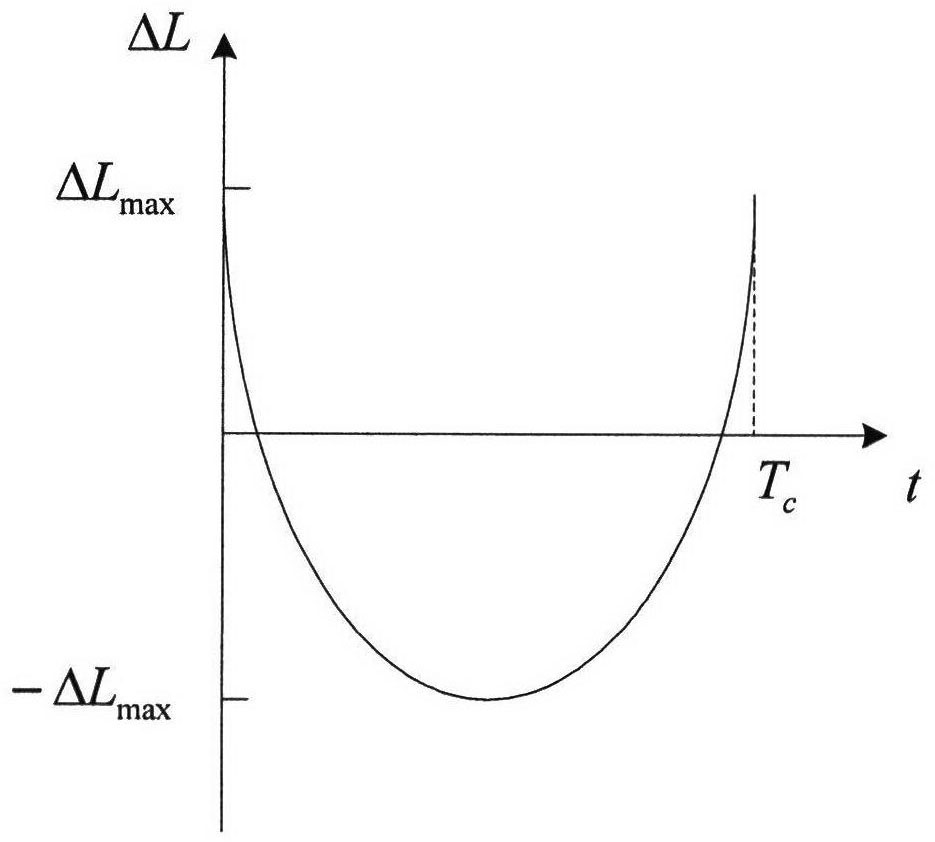
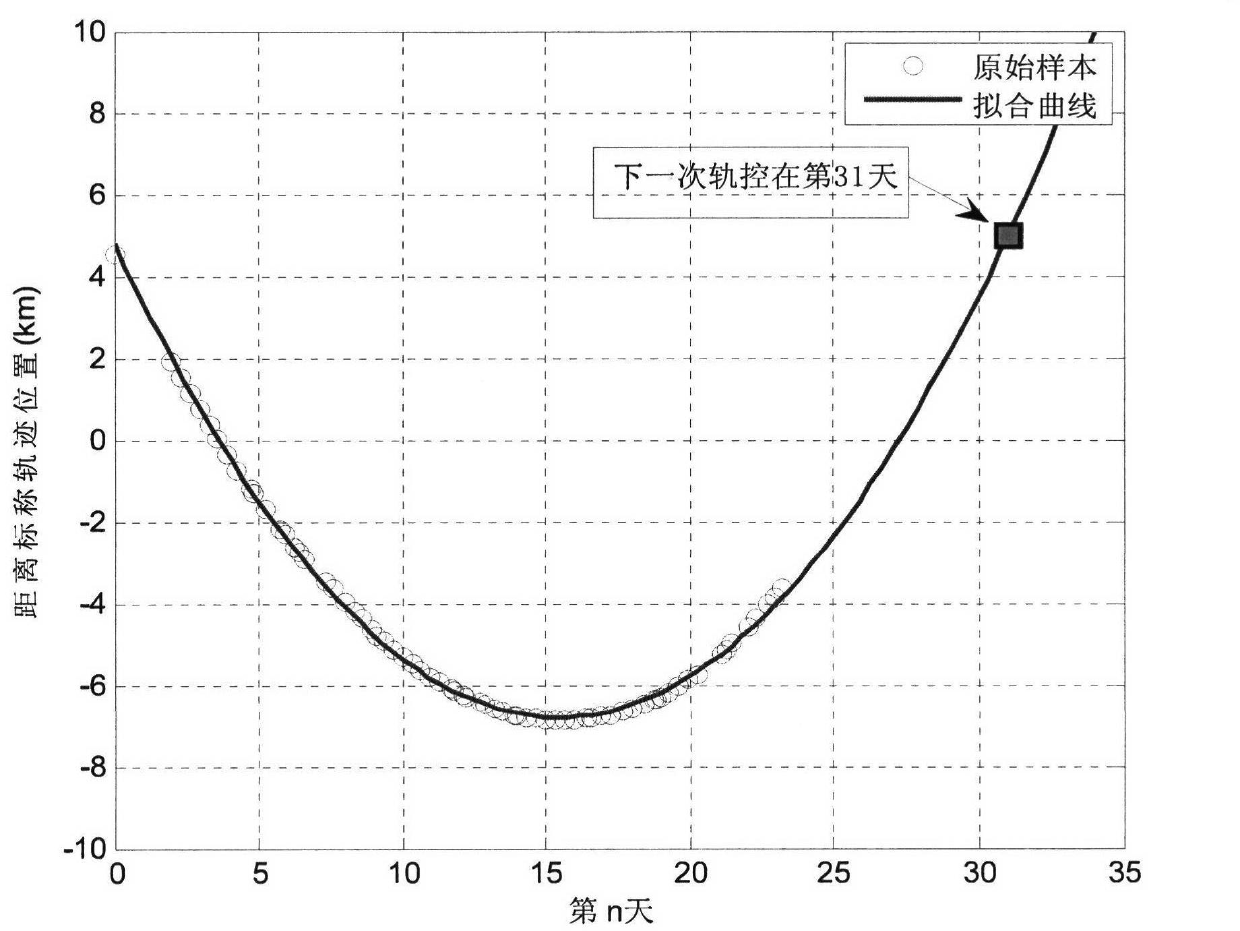
The invention relates to a satellite orbit maintenance and control method based on two lines of radicals, which comprises the following steps of: calculating two lines of radical data disclosed by a satellite by utilizing a SGP4 orbit determination model, calculating and obtaining a geographical latitude and a geographical longitude of a sub-satellite point of the satellite and comparing with an agreed ground nominal track. Through taking the duration of a first sample opposite to an orbit epoch moment as an independent variable and taking the ground track distance difference as a variable, all samples are subjected to quadratic curve fitting by using an average method; the difference delta at between an actual value of a satellite orbit semi-major axis and a nominal value by a latest sample moment as well as the average attenuation rate of the satellite orbit semi-major axis within the time interval of the sample are calculated and obtained through a fitting polynomial coefficient; and finally, the next orbit control time Tc as well as the control quantity delta af required to be used are predicted and obtained by utilizing a fitted secondary curve and an allowable drift range [-delta Lmax and delta Lmax] to ensure that the position of an actual ground track within the satellite next drift period opposite to a ground nominal track is within the allowrable drift range.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
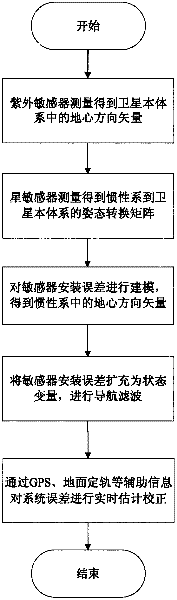
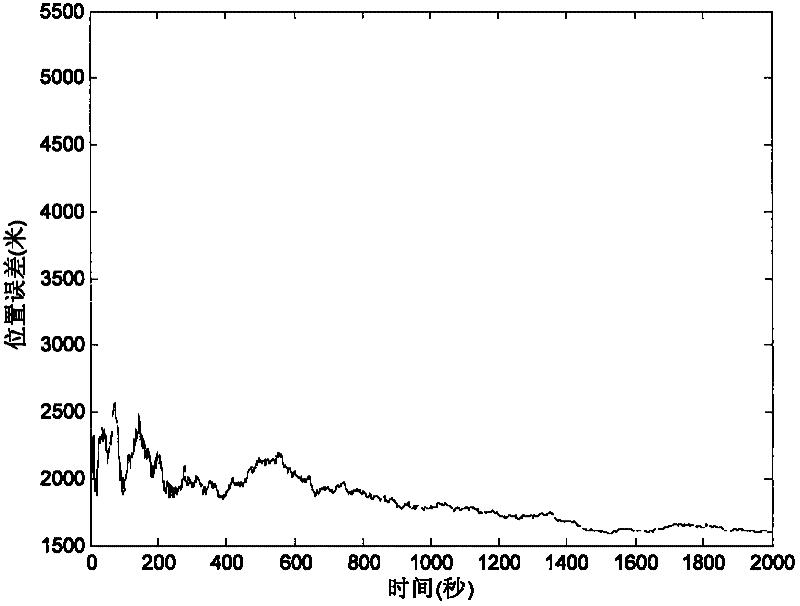
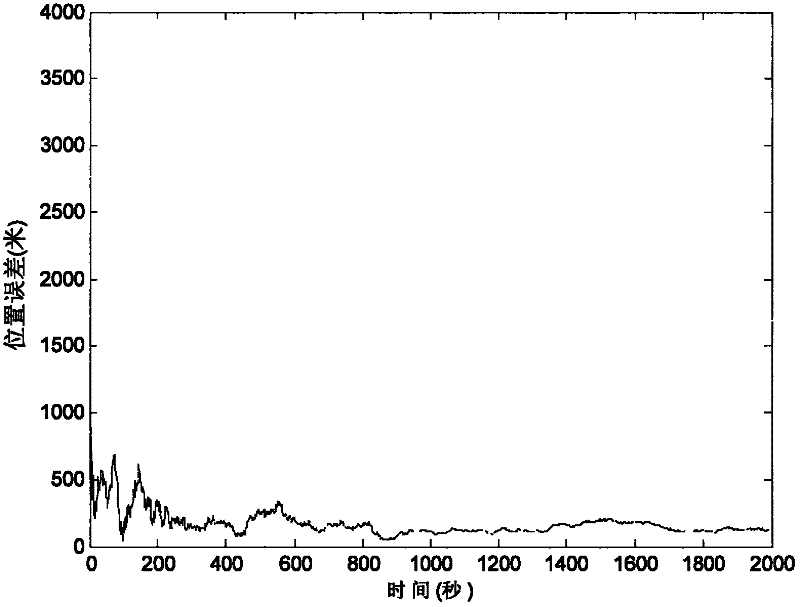
Error correction method of autonomous navigation system
ActiveCN102175260AImprove navigation accuracyMeasurement devicesAutonomous Navigation SystemState variable
The invention discloses an error correction method of an autonomous navigation system. In the autonomous navigation system based on an ultraviolet earth sensor and a star sensor, the ultraviolet earth sensor is used for measuring a geocentric vector in a satellite local system, and the star sensor is used for measuring an attitude transformation matrix of the satellite local system. Since the sensors inevitably have relative installation error, and a filter cannot eliminate the system error, the navigation accuracy becomes poor. In the method provided by the invention, the relative installation error of the ultraviolet earth sensor and the star sensor is modeled, and the installation error is expanded into a state variable so as to perform navigation filtering. Assuming that the satellite can obtain high-accuracy position measurement information by a GPS receiver or ground orbit determination within certain period of time, the system error can be estimated and corrected in time by filtering. The method provided by the invention has simple operation and can obviously improve the navigation accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
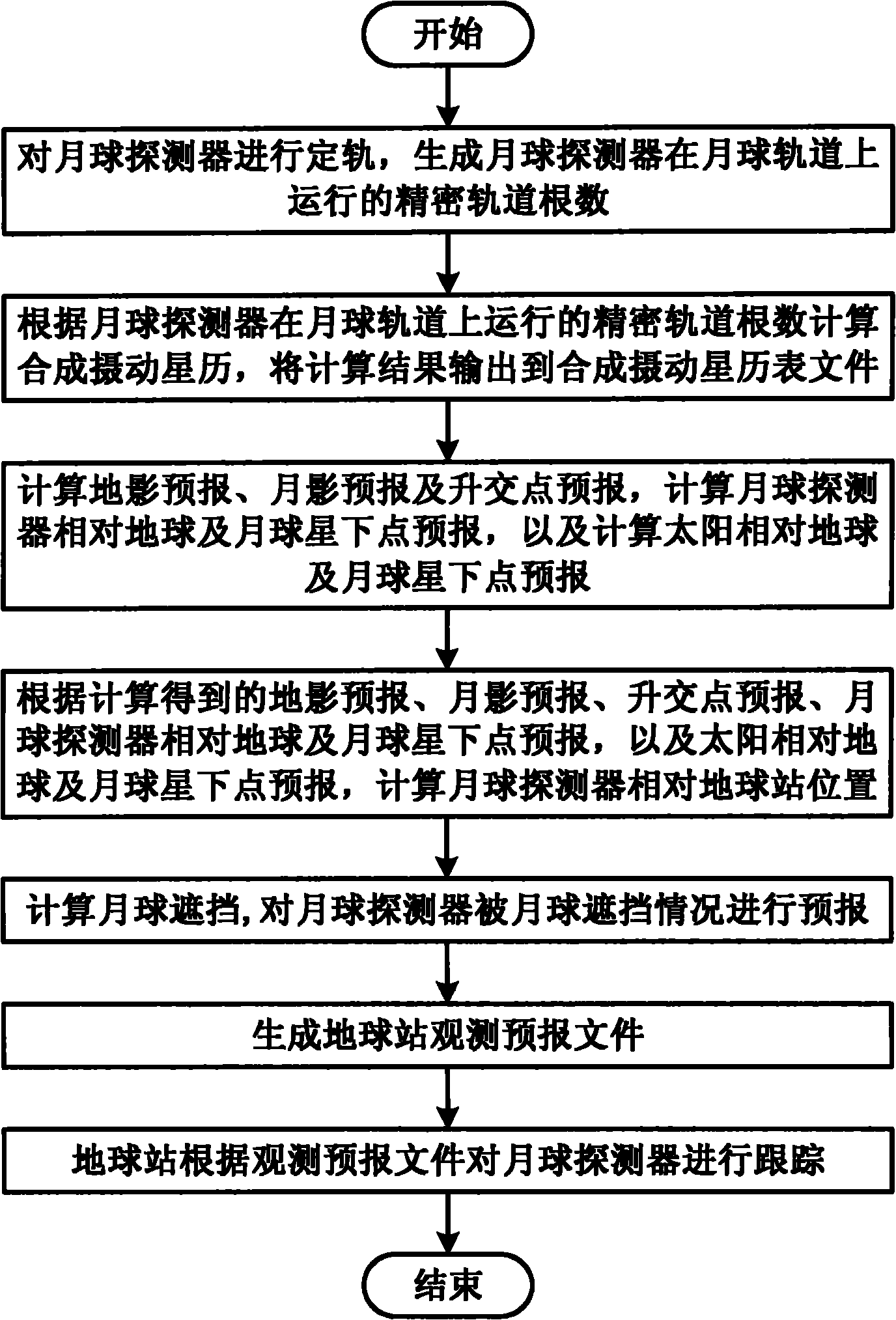
Method for tracking lunar probe by using earth station
ActiveCN101968542AImplement receipt trackingRealize precise orbit determinationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEphemerisLunar orbit
The invention discloses a method for tracking a lunar probe by using an earth station. The method comprises the following steps of: performing orbit determination on the lunar probe to generate a precise orbital element for the lunar probe to run on a lunar orbit; calculating a synthetic perturbation ephemeris according to the precise orbital element for the lunar probe to run on the lunar orbit and outputting a calculation result to a synthetic perturbation ephemeris file; calculating earth shadow forecast, moon shadow forecast and ascending node forecast, calculating substellar point forecast of the lunar probe relative to earth and moon and calculating the substellar point forecast of the sun relative to earth and moon; calculating the position of the lunar probe relative to the earth station; calculating shelter of the moon and forecasting the condition that the lunar probe is sheltered by the moon; generating an earth station observation forecast file; and tracking the lunar probe by the earth station according to the observation forecast file. By the method, the measurement and control of the lunar probe and the receiving of probe data are tracked by using the earth station.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pulse and pneumatic assistance combination-based low-orbit orbit plane transfer method
InactiveCN106383994AGreat changeabilityIncrease flexibilitySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsAviationDynamic equation
The invention discloses a pulse and pneumatic assistance combination-based low-orbit orbit plane transfer method, relates to a large-range orbit plane transfer method for an earth low-orbit spacecraft, and belongs to the field of aerospace. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing the number of orbits and a dynamic equation of a flight process in atmosphere; changing an orbit of the spacecraft to a highly elliptic orbit in a maneuvering manner by applying a pulse, and enabling the spacecraft to enter the atmosphere by applying an de-orbit pulse at an apogee; selecting an optimization target as a maximum change amount of an orbit plane, giving constraints and obtaining an optimal control rate and a terminal state variable meeting aerodynamic requirements, thereby finishing pneumatic assisted orbit plane transfer; and enabling the spacecraft to fly out of the atmosphere and run to a target orbit height along a transfer orbit, and enabling the spacecraft to enter a target orbit by applying an orbit determination pulse. According to the method, the orbit plane transfer of the low-orbit spacecraft can be finished with relatively low fuel consumption; and the method is good in robustness, high in repeatability, small in influence of spacecraft orbit orientation, high in flexibility of a pneumatic assistance process, and wide in application range for the target orbit.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Low-orbit navigation constellation enhanced network RTK (real-time kinematic) method
InactiveCN109946727ASolve the low positioning accuracyLow densitySatellite radio beaconingMathematical modelNetwork density
The invention belongs to the technical field of navigation and positioning and discloses a low-orbit navigation constellation enhanced network RTK (real-time kinematic) technology. The low-orbit navigation constellation enhanced network RTK technology comprises the following steps: design of a global navigation and positioning constellation and multiple low-orbit constellation schemes, a low-orbitsatellite collecting orbit determination and inter-satellite link autonomous orbit determination method, design of a low-orbit satellite broadcast ephemeris and a high, medium and low-orbit satellitefusion processing unified mathematical model. The problem in the prior art that the network RTK method is low in positioning precision is solved, the baseline distance can be increased, the network density can be reduced, the cost can be reduced, the precision and the ambiguity fixing rate are increased, and the convergence time can be shortened. The sub-satellite point track coverage range of the low-orbit constellation is wide and even covers polar regions, the three-dimensional orbit errors of 60 and 192-star constellation are 46 cm and 18 cm correspondingly, the forecast precision is increased by about 30 percent compared with that of a klobuchar model, and the final positioning precision is at horizontal millimeter and height centimeter level.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Navigation data processing method and system based on cloud computing
InactiveCN109001776ATime synchronizationReduce dependenceSatellite radio beaconingGround trackLow earth orbit
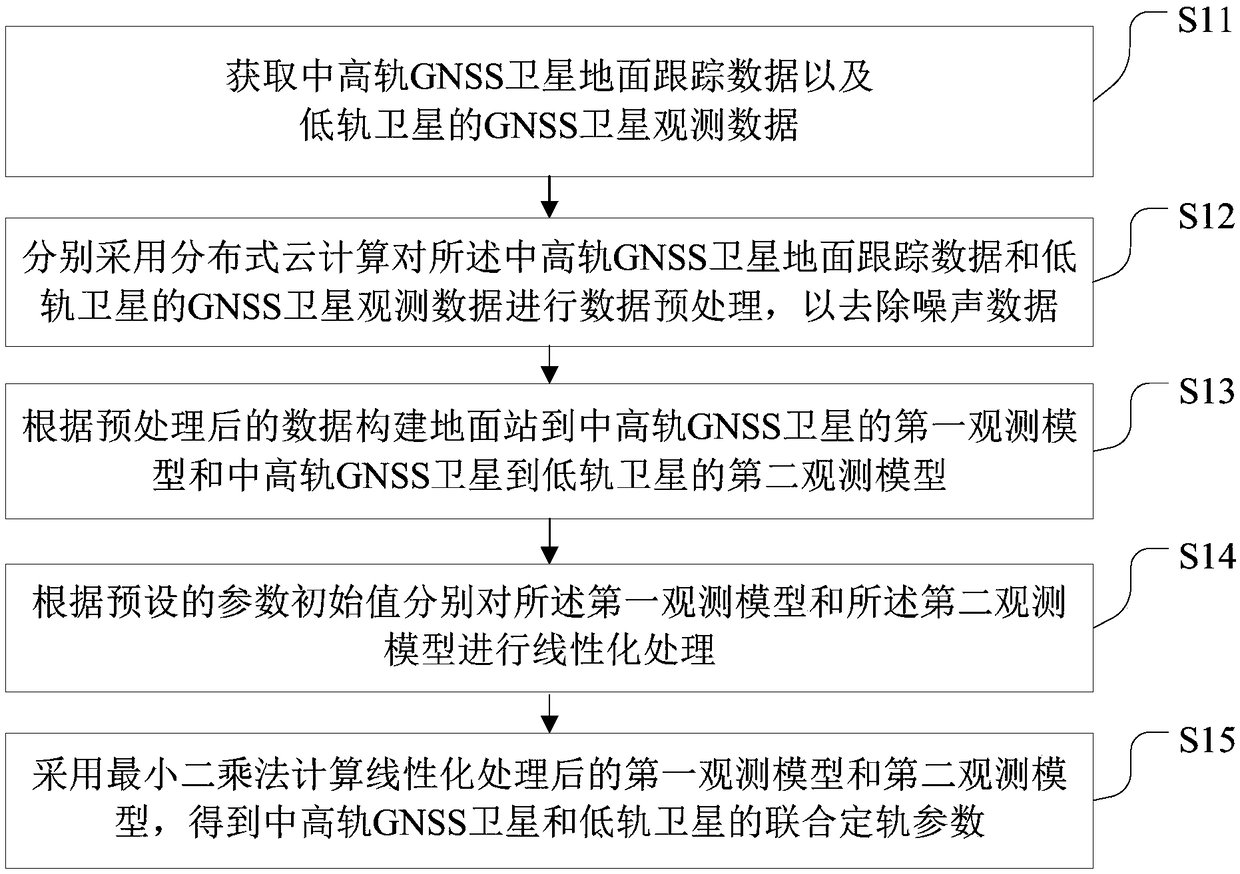
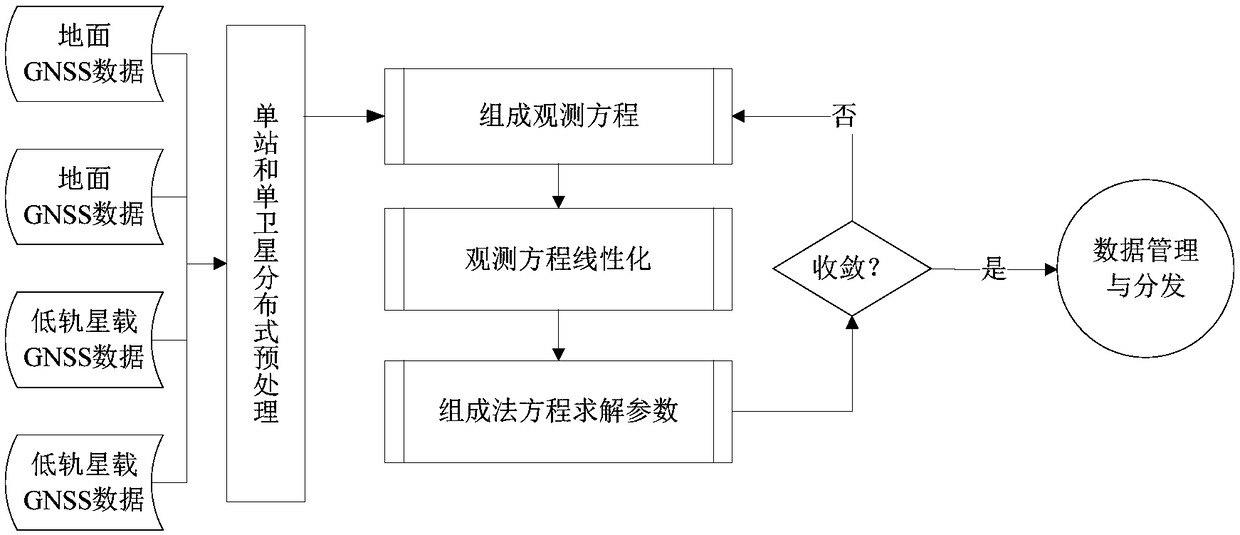
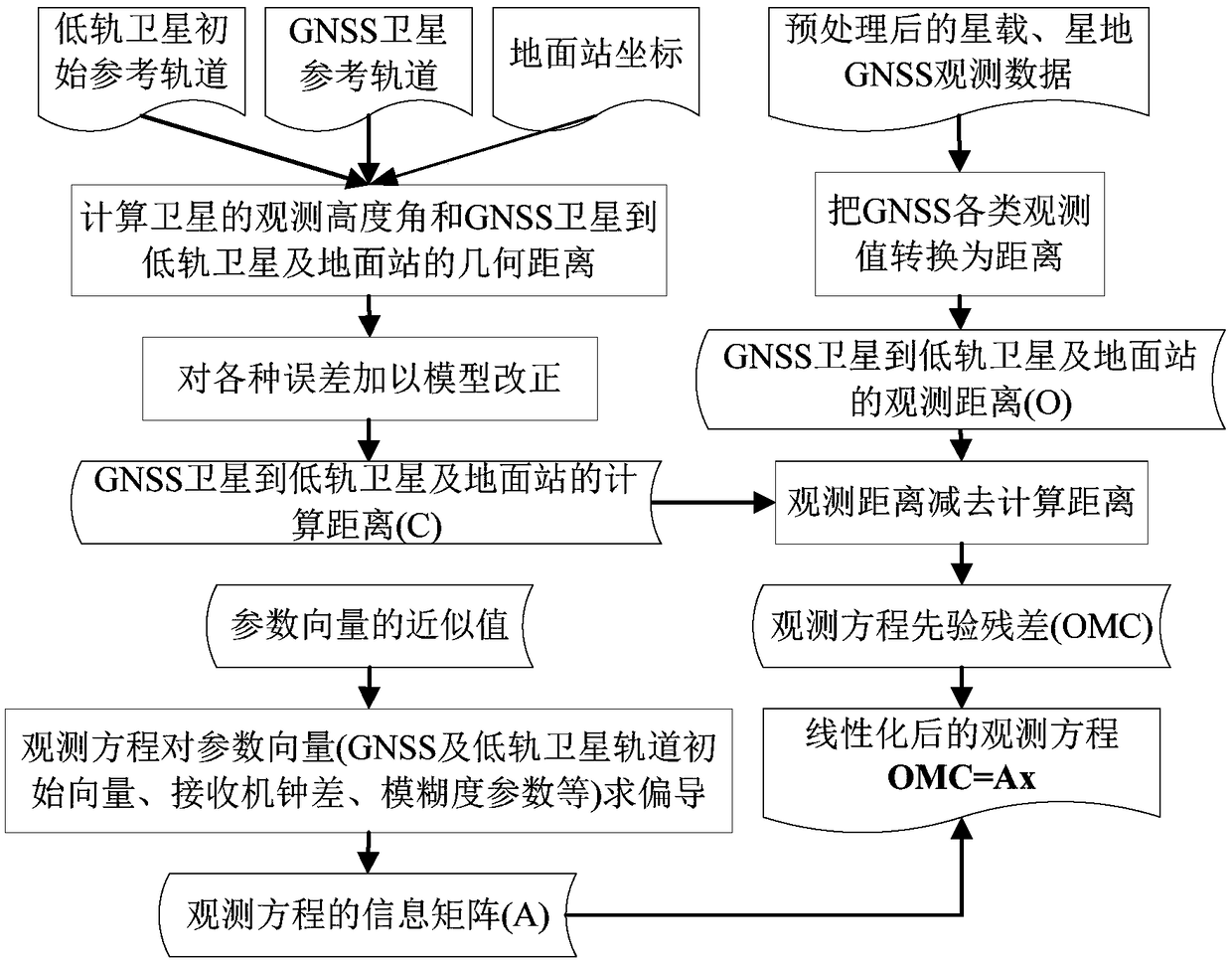
The invention provides a navigation data processing method and system based on cloud computing. The method comprises the steps that ground tracking data of a medium and high earth orbit GNSS satelliteand GNSS satellite observation data of a low earth orbit satellite are acquired; distributed cloud computing is adopted to preprocess the ground tracking data of the medium and high earth orbit GNSSsatellite and the GNSS satellite observation data of the low earth orbit satellite; a first observation model from a ground station to the medium and high earth orbit GNSS satellite and a second observation model from the medium and high earth orbit GNSS satellite to the low earth orbit satellite are constructed according to the preprocessed data; linearization processing is performed on the firstobservation model and the second observation model according to preset parameter initial values; and a least square method is adopted to calculate the first observation model and the second observation model after linearization, and joint orbit determination parameters of the medium and high earth orbit GNSS satellite and the low earth orbit satellite are obtained. Through the navigation data processing method and system, an orbit of the low earth orbit satellite can be determined with high precision, joint orbit determination and time synchronization of the navigation satellite and the low earth orbit satellite are realized, therefore, real-time high-precision service is provided for a user, and system service performance is improved.
Owner:BEIJING FUTURE NAVIGATION TECH CO LTD
Inter-satellite ranging enhancement-based satellite formation GPS (global positioning system) relative navigation system and method
InactiveCN106154298AEliminate the effects ofHigh-precision inter-satellite distance dataSatellite radio beaconingNavigation systemRadio frequency
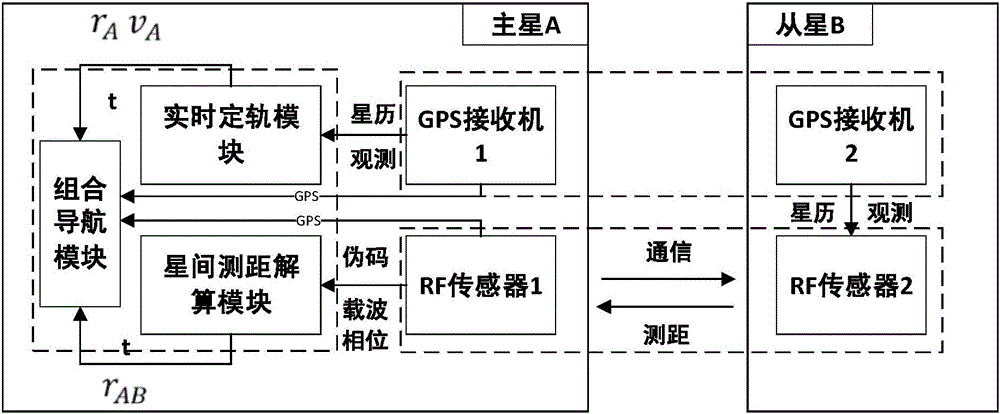
The invention discloses an inter-satellite ranging enhancement-based satellite formation GPS (global positioning system) relative navigation system and an inter-satellite ranging enhancement-based satellite formation GPS relative navigation system method, and relates to the technical field of satellite formation relative navigation. The system consists of a GPS receiver module, an inter-satellite ranging module and a relative navigation module, wherein the inter-satellite ranging module consists of two RF (radio frequency) sensors, and is used for acquiring an inter-satellite ranging pseudo code and a carrier phase observable by combining a composite pseudo code and a double-frequency two-way forwarding ranging system; the relative navigation module consists of an orbit determination module, an inter-satellite ranging calculation module and a combined navigation module, and is used for calculating inter-satellite relative distance and speed data by an extended Kalman filter method by virtue of observation data acquired by the GPS receiver module and the inter-satellite ranging module. The system and the method are applicable to inter-satellite formation at an inter-satellite distance of 0 to 30Km, and compared with a purely differential-GPS-based relative navigation system, have the advantage that the real-time relative navigation accuracy is higher than 1mm; required relative position and speed data can still be continuously output by the system in case of interruption of a GPS signal; the initialization time of the system is reduced from dozens of epochs of the differential-GPS-based relative navigation system to a single point.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +2
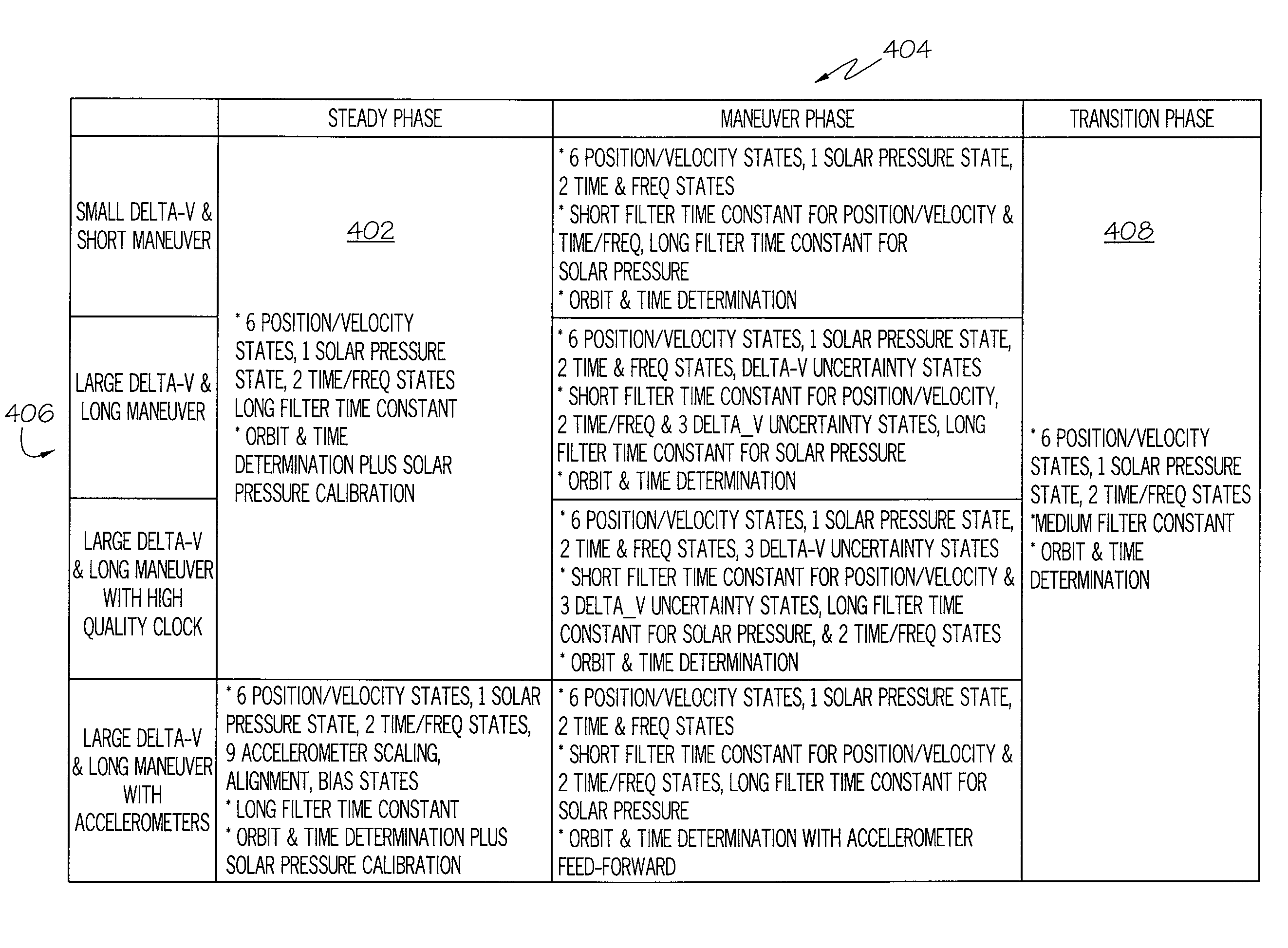
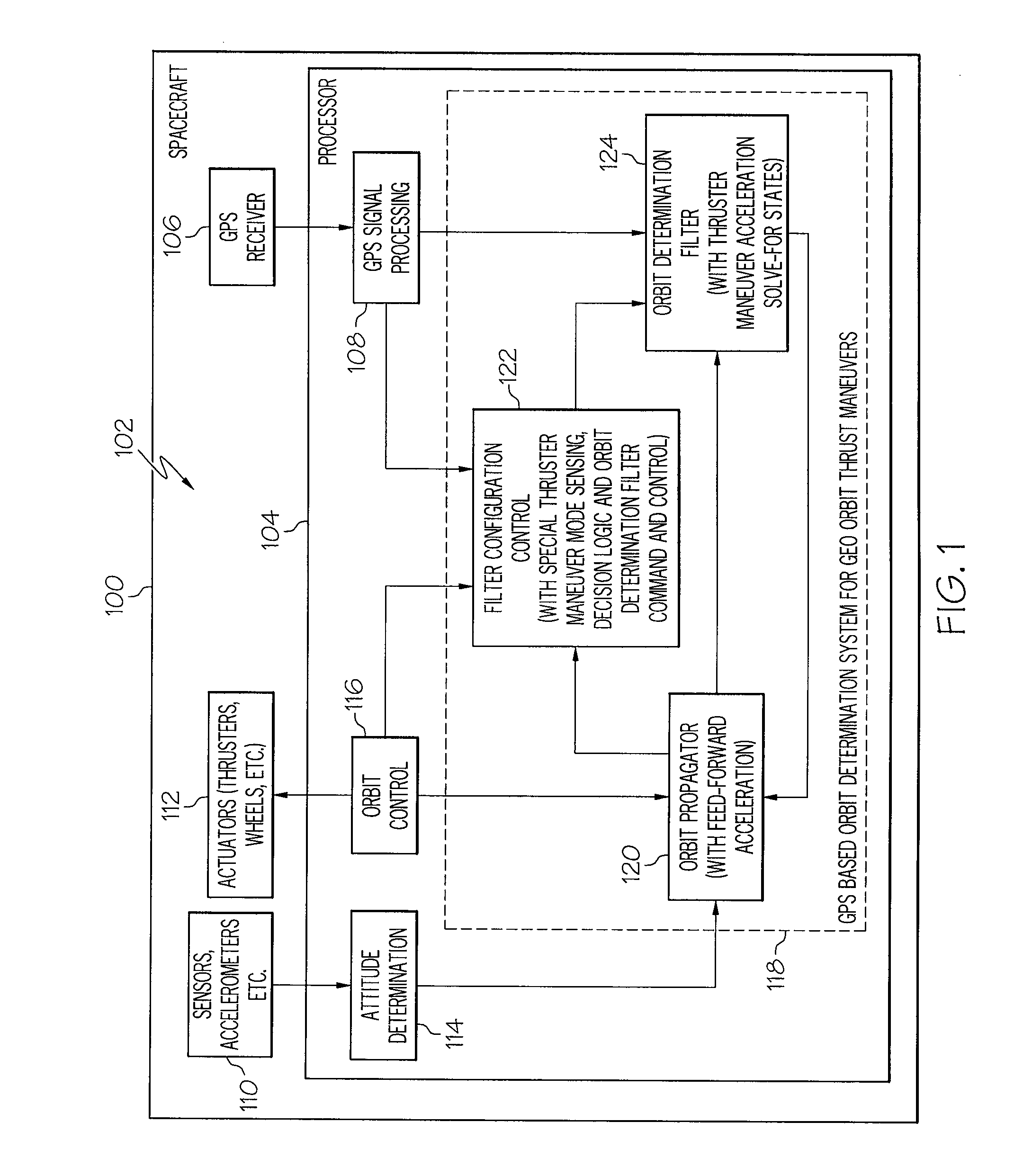
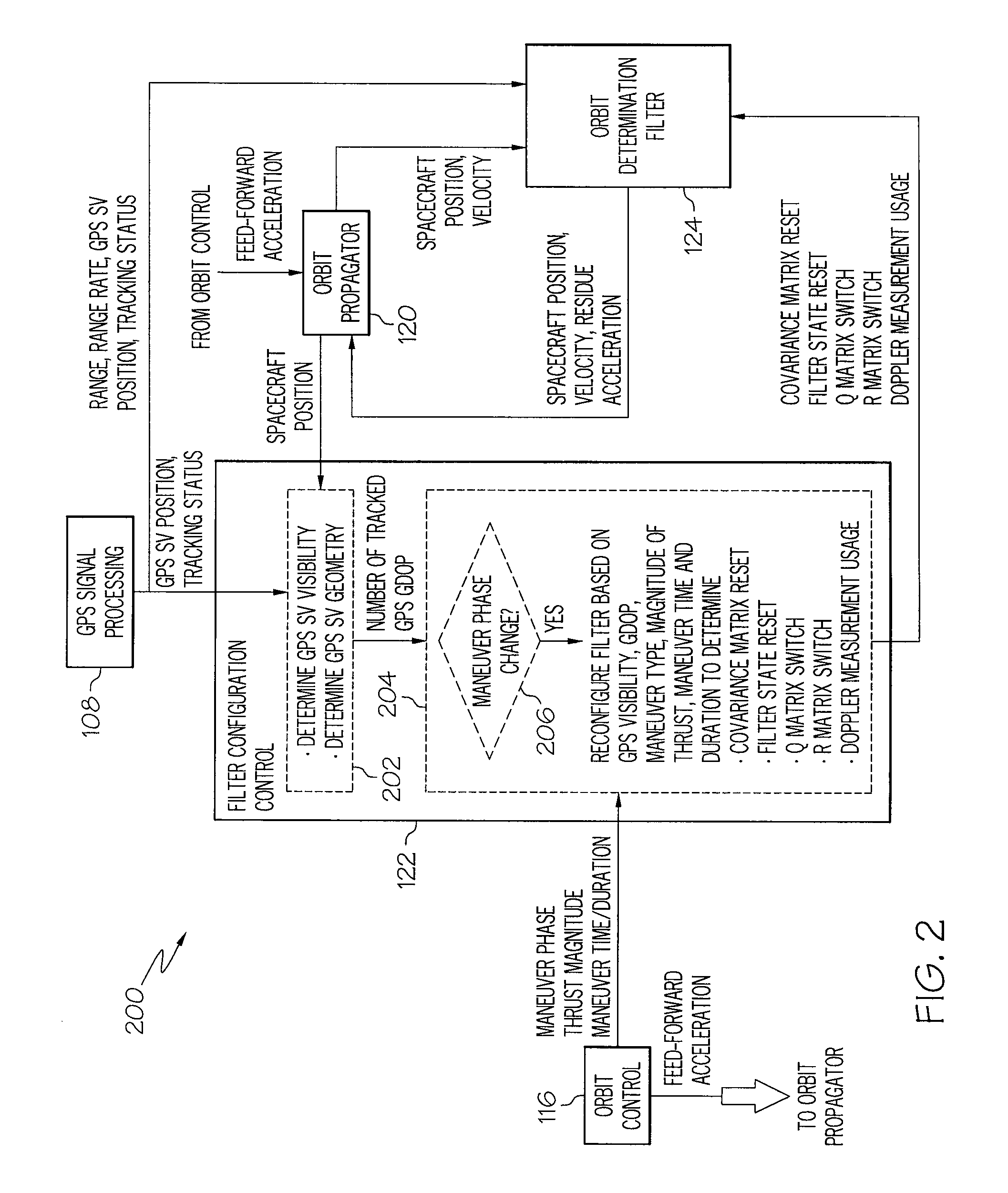
GPS based orbit determination of a spacecraft in the presence of thruster maneuvers
A system for determining and controlling an orbit of a spacecraft may include a GPS receiver mounted to the spacecraft to receive GPS information from a plurality of GPS satellites visible to the GPS receiver for determining a position of the spacecraft relative to a reference coordinate system. The system may also include a filter configuration control module to sense a thruster maneuver operation to adjust the orbit of the spacecraft. The system may also include an orbit determination filter to determine at least one of a spacecraft position, velocity, and residue acceleration based on the GPS information and information from the filter configuration control module related to the thruster maneuver operation.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
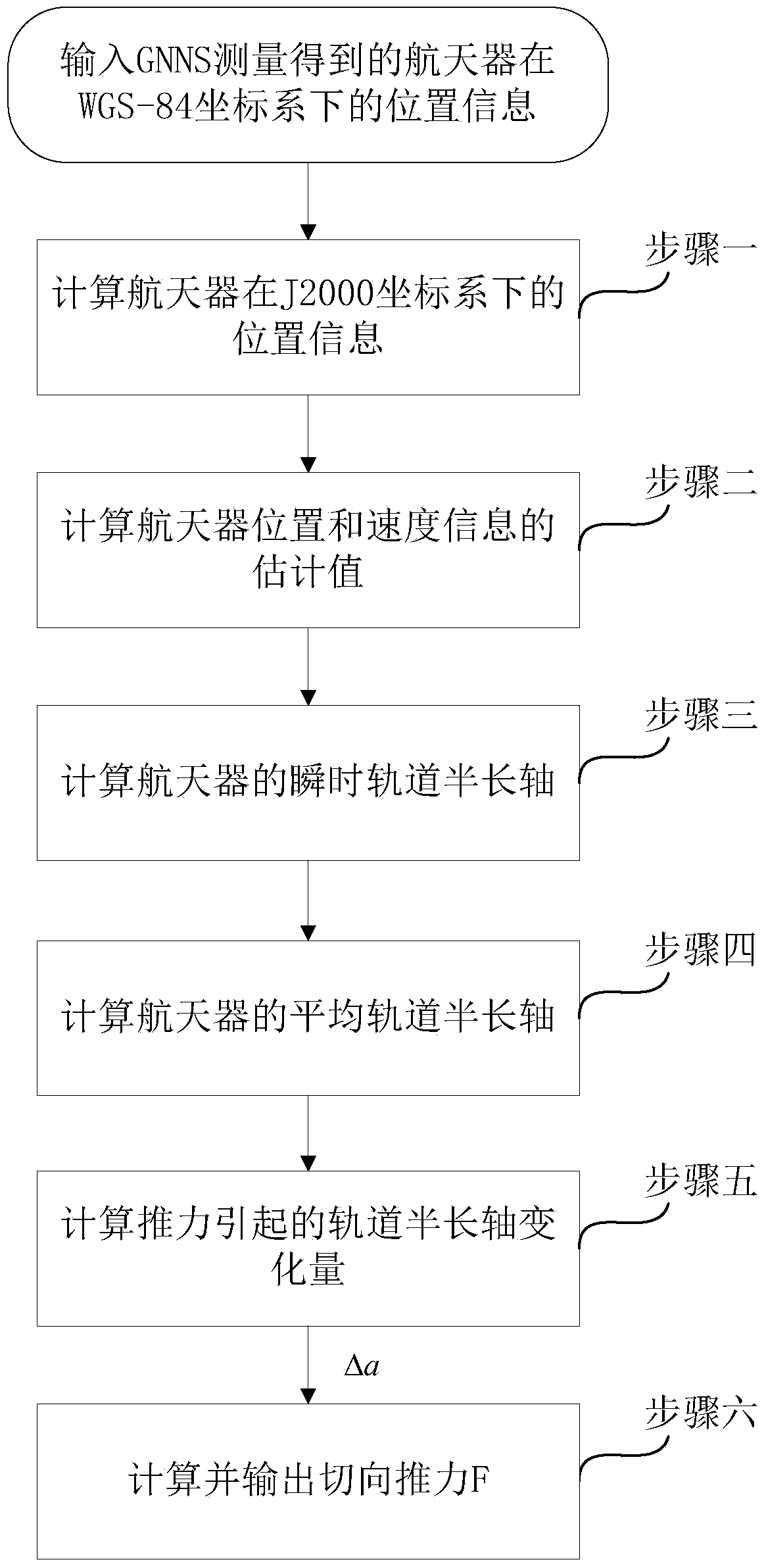
Tangential low-thrust in-orbit circular orbit calibration method based on (Global Navigation Satellite System) GNSS precise orbit determination
ActiveCN103940431AThe method calibration results are accurateMethod calibration results are reliableInstruments for comonautical navigationApparatus for force/torque/work measurementNODALIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
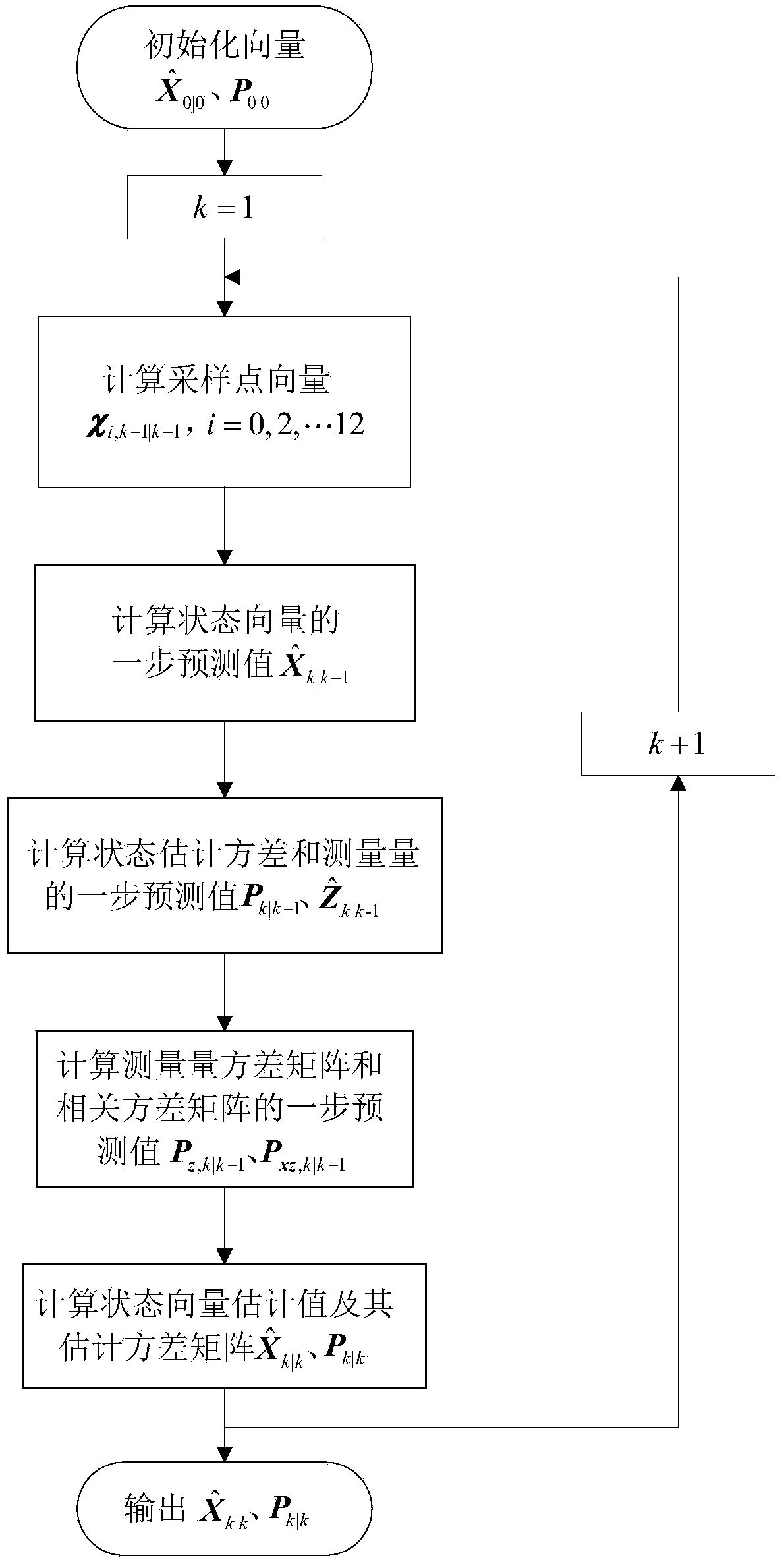
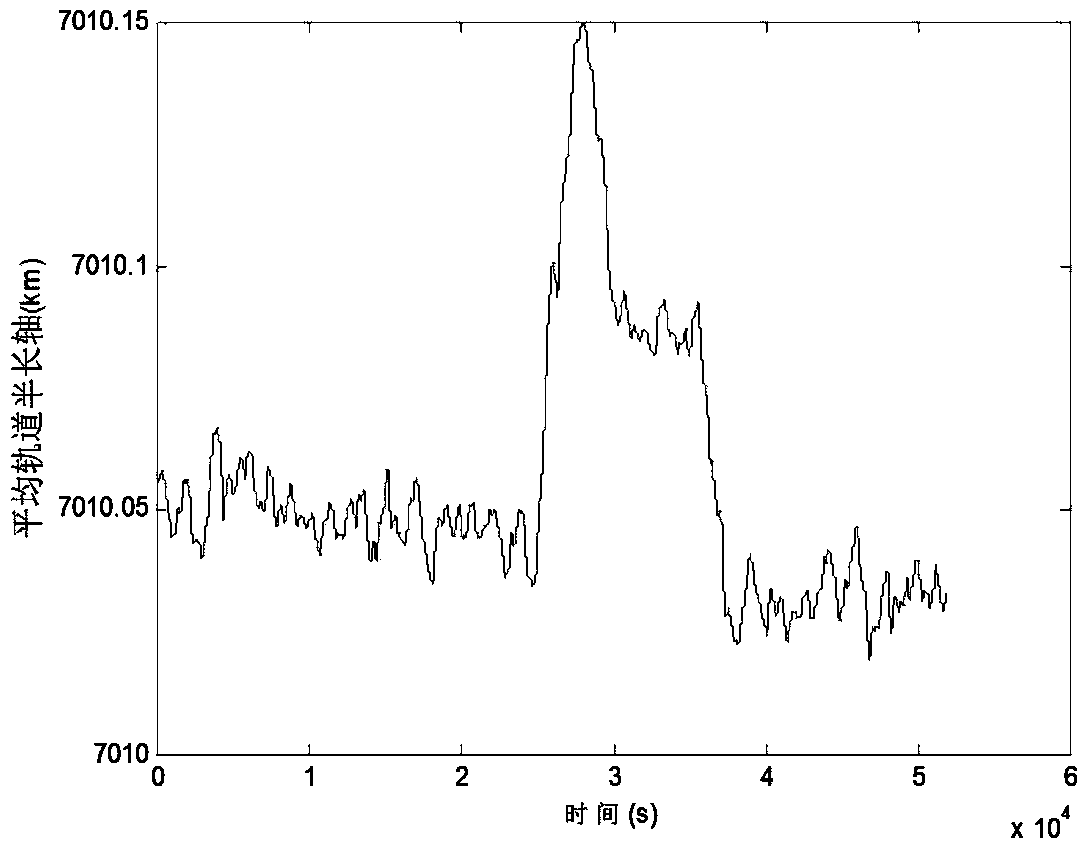
The invention provides a tangential low-thrust in-orbit circular orbit calibration method based on (Global Navigation Satellite System) GNSS precise orbit determination. The calibrated tangential thrust F is used for controlling a spacecraft orbit, and the tangential low-thrust in-orbit circular orbit calibration method is characterized by comprising the following steps: measuring by utilizing a GNSS to obtain the spacecraft position information, and performing a Unscented Kalman filtering method to obtain estimated values of spacecraft position and velocity information under a J2000 coordinate system; calculating an instantaneous orbit semi-major axis of a spacecraft according to the estimated values of the spacecraft position and the velocity information; averaging the instantaneous orbit semi-major axis in the orbital nodal period before each measurement moment to obtain the average orbit semi-major axis at the moment; and subtracting the average orbit semi-major axes before and after the action of the tangential thrust of a circular orbit to obtain orbit semi-major axis variation delta a, and calculating the tangential thrust calibration value of the circular orbit according to the delta a. In the calculation process, the GNSS is completely used to obtain the real-time orbital data without data support of a ground station, and the calibration method has accurate and reliable result and simplicity in calculation and is easy to realize.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Precise orbit determination system and method using GPS data and galileo data
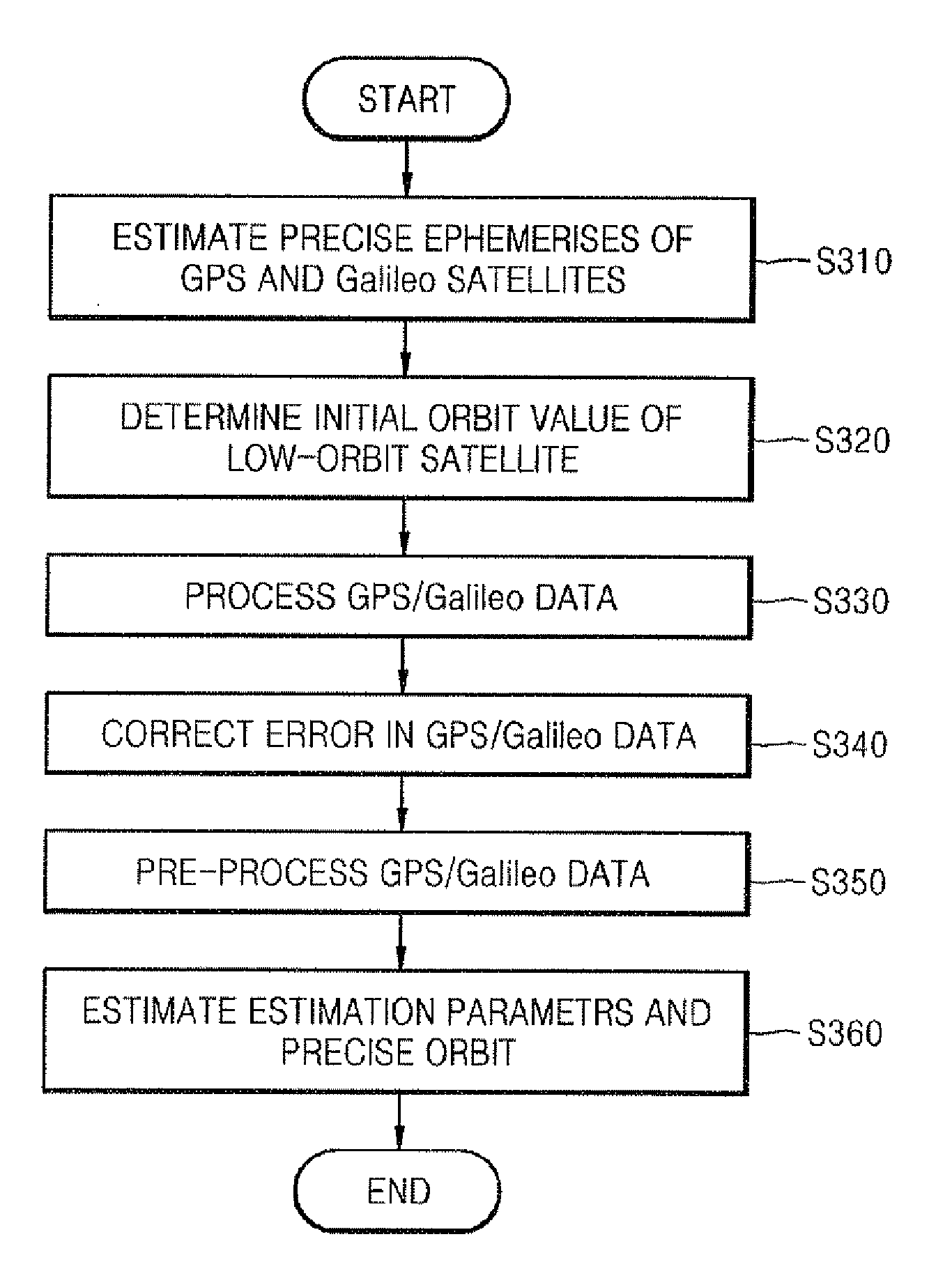
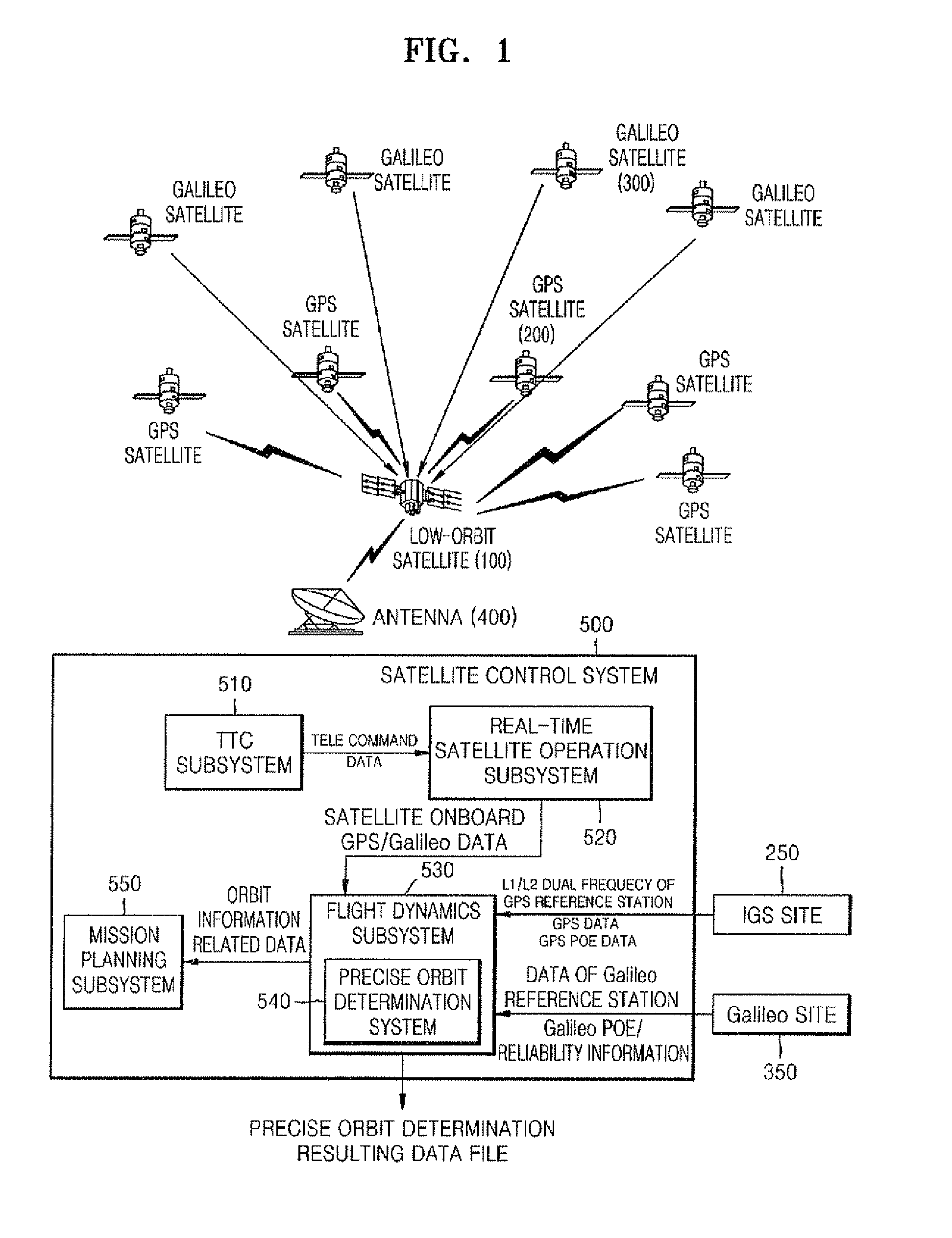
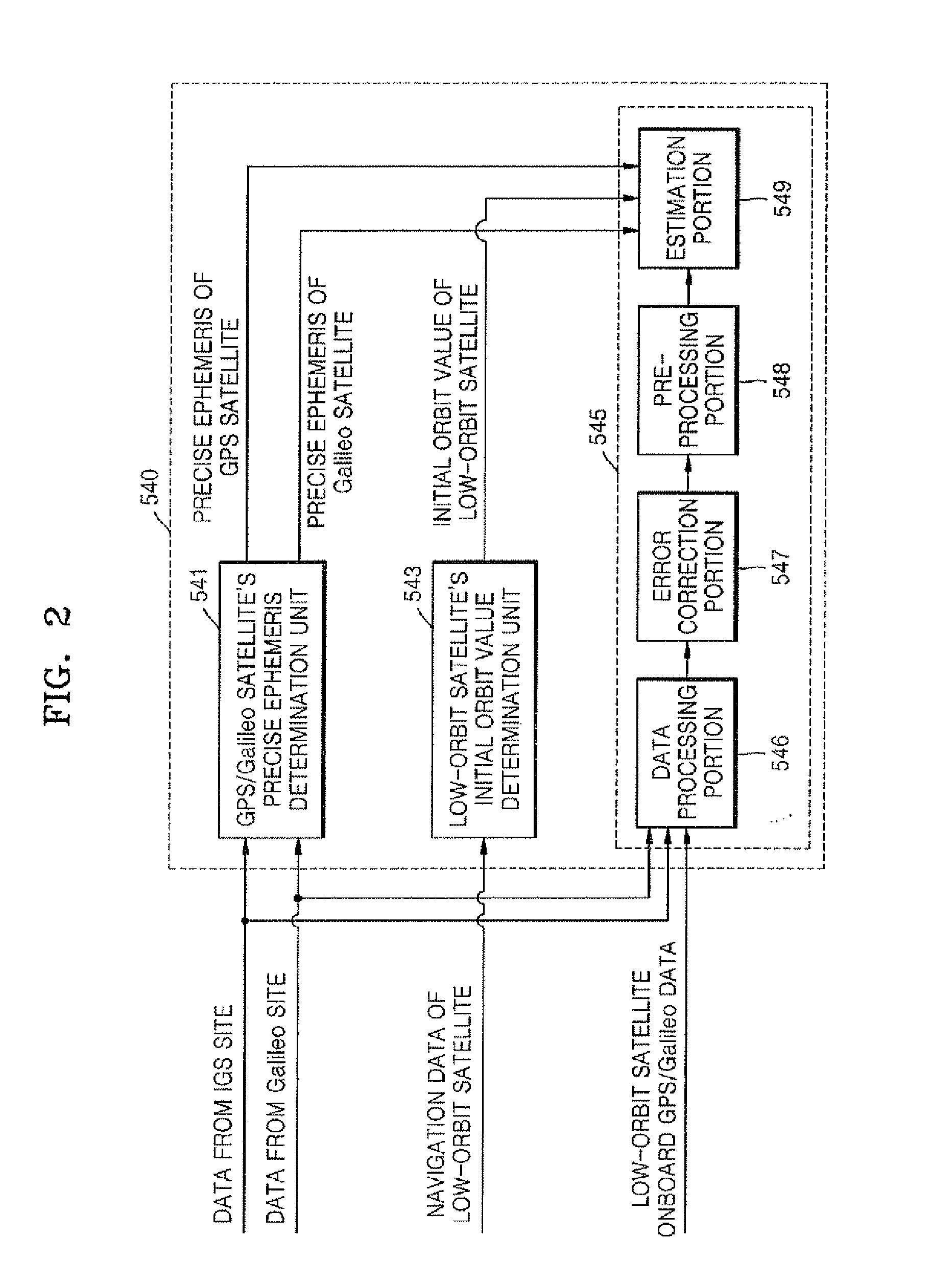
InactiveUS20100090889A1Improve convenienceAvoid disconnectionPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingOrbit perturbationDynamic models
Provided are a method and system for determining a precise orbit of a LEO satellite. The method includes: estimating a precise ephemeris of a global positioning system (GPS) satellite by fitting an orbit perturbation-based GPS dynamics model to observation data of the GPS satellite received from a GPS observatory and estimating a precise ephemeris of a Galileo satellite by fitting an orbit perturbation-based Galileo dynamics model to observation data of the Galileo satellite received from a Galileo observatory; determining an initial orbit value of a LEO satellite by fitting an orbit perturbation-based LEO satellite's basic dynamics model to navigation data received from the LEO satellite; and determining the precise orbit of the LEO satellite by calculating a difference between observation values, which are calculated based on a GPS and Galileo data received from the LEO satellite, the GPS observatory and the Galileo observatory, and calculated values, which are calculated based on an orbit perturbation-based LEO satellite's dynamics model that was calculated using the initial orbit value of the LEO satellite and the precise ephemeris of the GPS and Galileo satellites. Since both the GPS and Galileo data are received and used to determine the precise orbit of a LEO satellite, more precise orbit determination can be achieved.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
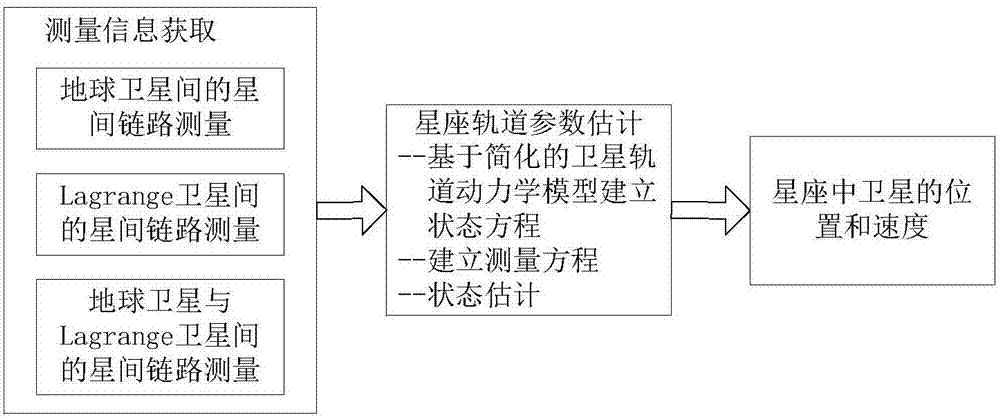
Earth-Lagrange combined constellation autonomous orbit determination method based on inter-satellite ranging
ActiveCN107421550AImproving the accuracy of long-term autonomous orbit determinationSolve the "deficit rank" problemInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by astronomical meansSatellite laser rangingNonlinear filter
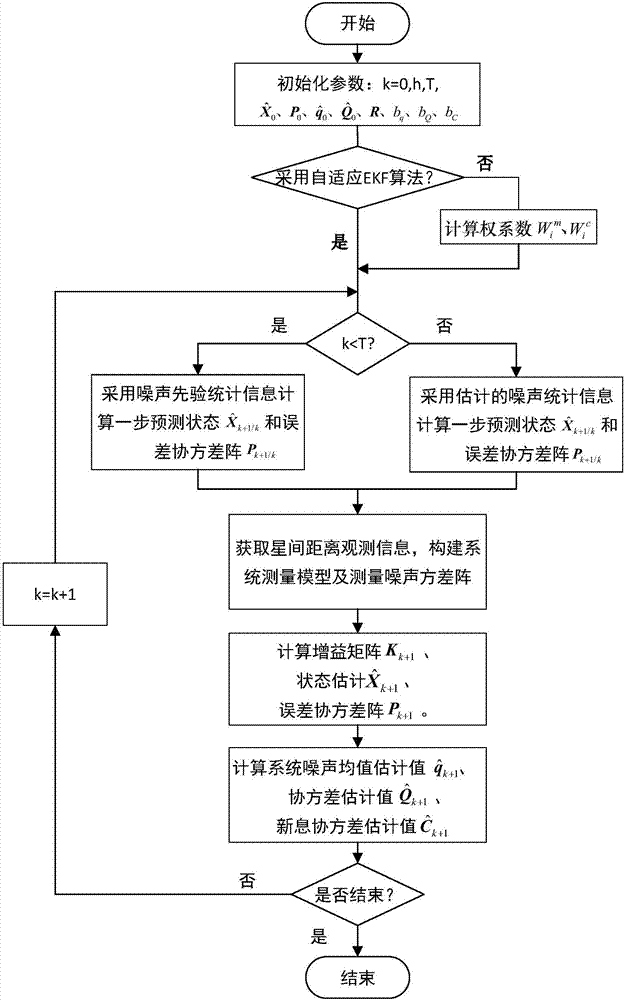
The invention discloses an earth-Lagrange combined constellation autonomous orbit determination method based on inter-satellite ranging. The method includes following steps: step 1, establishing a state equation of an earth-Lagrange combined constellation autonomous orbit determination system; step 2, establishing a measurement equation of the earth-Lagrange combined constellation autonomous orbit determination system; step 3, determining a filtering method for realizing orbit parameter estimation; step 4, specifically realizing the earth-Lagrange combined constellation autonomous orbit determination method based on a selected filtering algorithm. By introducing a Lagrange satellite, the problem of deficient range when only inter-satellite ranging information is utilized for autonomous orbit determination is solved effectively, and complexity of system equipment is lowered; statistical characteristics of system noise are estimated online in real time through a self-adaptive nonlinear filtering algorithm, so that requirements on noise prior information are low, stability of the autonomous orbit determination filtering algorithm is improved, and autonomous orbit determination accuracy is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Low earth orbit satellite autonomous orbit determination method utilizing space-based visible light camera
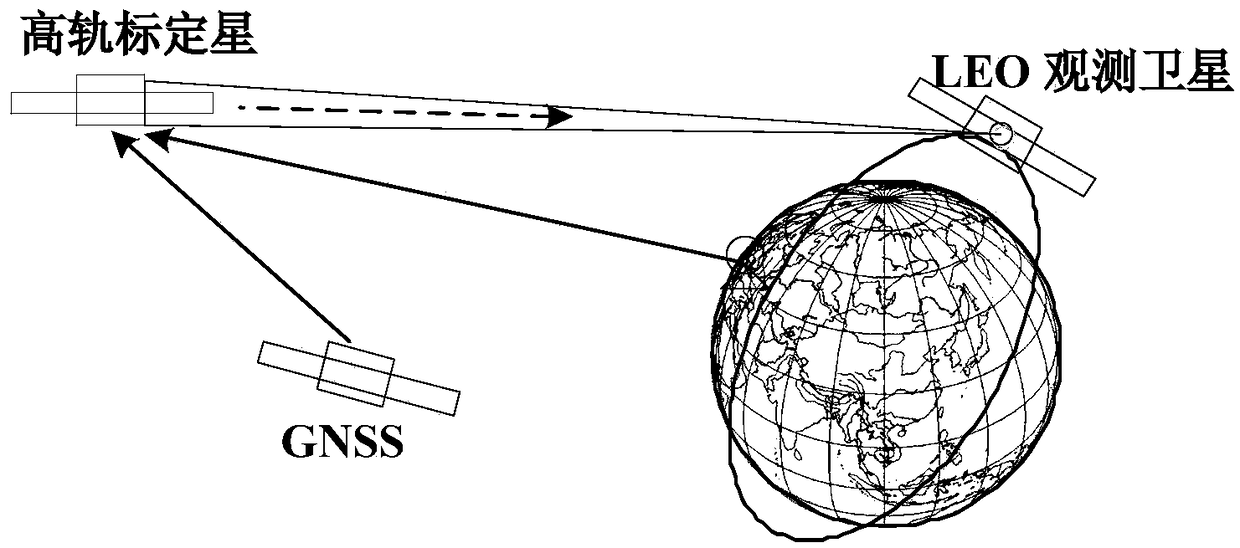
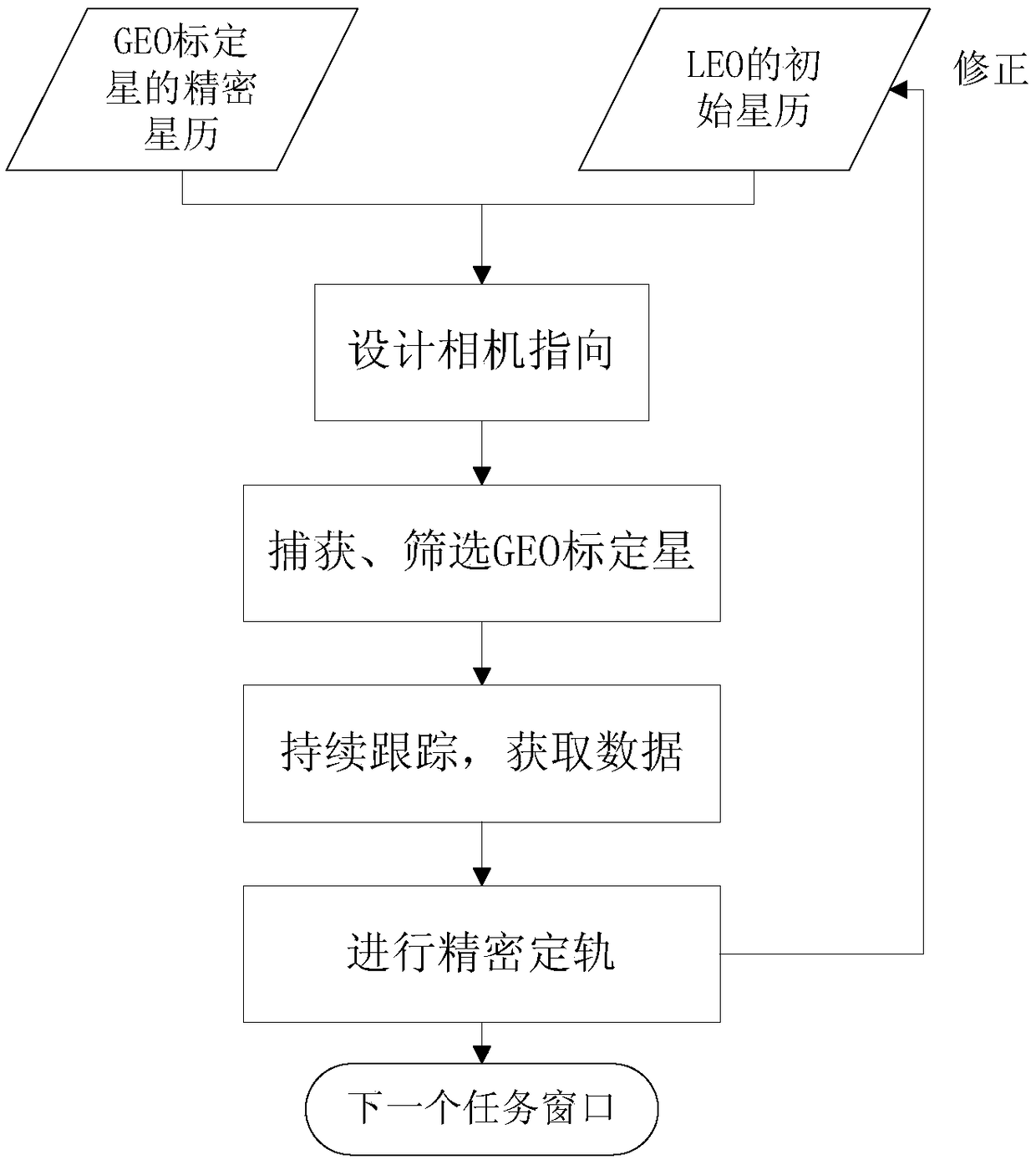
ActiveCN108871348AIncrease brightnessPromote improvementInstruments for comonautical navigationOn boardHigh Earth orbit
The invention relates to a low earth orbit satellite autonomous orbit determination method which comprises the following steps of selecting a plurality of high earth orbit objects (including large space debris) as calibrated satellites to acquire a precise ephemeris of the high earth orbit objects; when a low earth orbit satellite cannot acquire the precise ephemeris, utilizing a boarded space-based visible light camera to point to the high earth orbit calibrated satellites, performing tracking for a period of time to acquire an only angle measurement quantity; utilizing an on-board computer,combining rough ephemeris of the low earth orbit satellite, the precise ephemeris of the high earth orbit objects with the measurement quantity, performing reversed determination to obtain a precise orbit of the low earth orbit satellite. The invention provides a novel satellite autonomous orbit determination way; and when global positioning navigational satellite information cannot be utilized, the novel satellite autonomous orbit determination method can be used as an alternative method. The low earth orbit satellite autonomous orbit determination method provided by the invention is relatively simple in calculation model, fully utilizes space resources and meanwhile, is low in space-based visible light observation cost, small in energy consumption and strong in engineering applicability.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Precision orbit determination system and implementing method for satellites in middle and low orbits
InactiveCN1959430AConvenient researchEfficient use ofPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingLaser rangingSatellite laser ranging
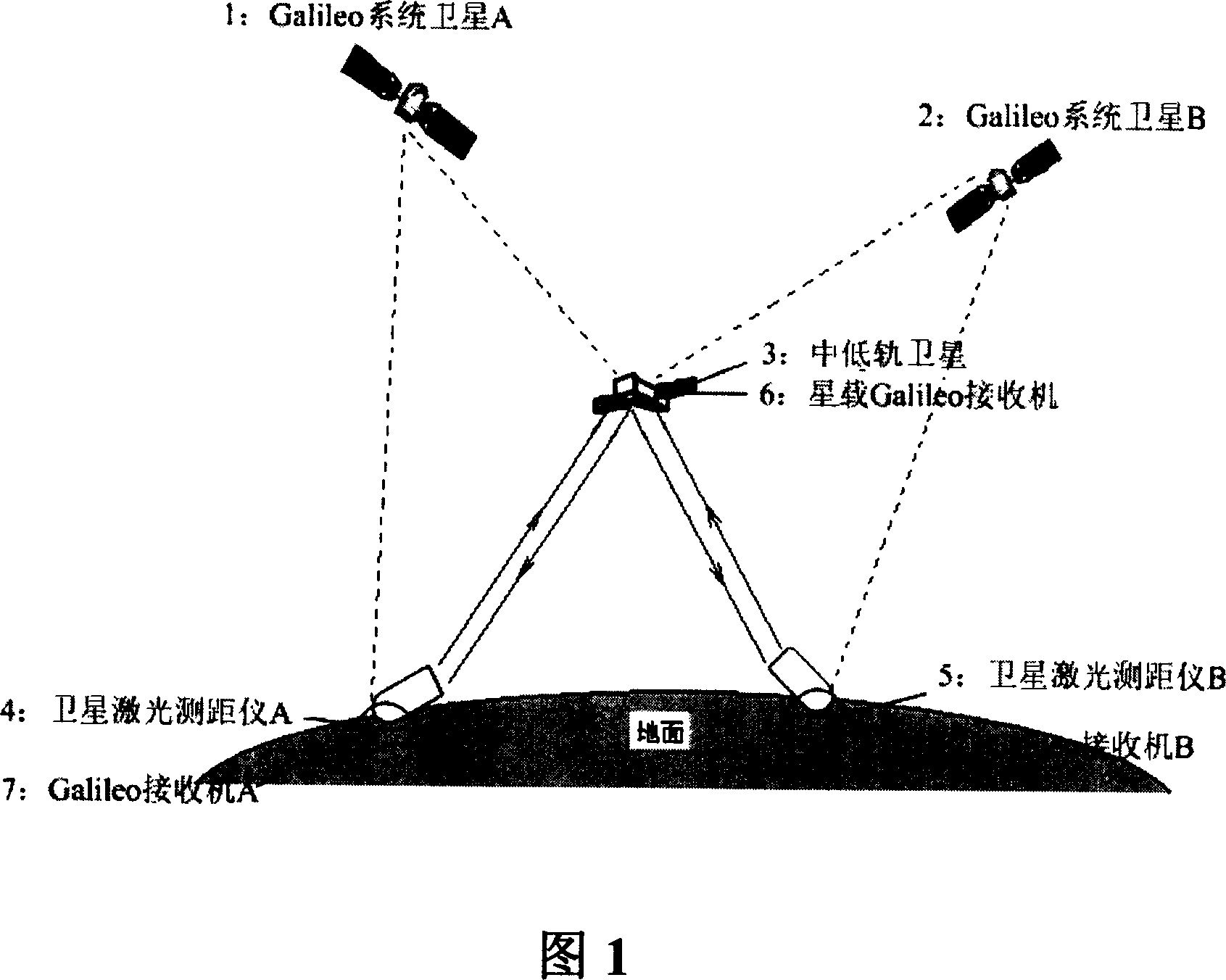
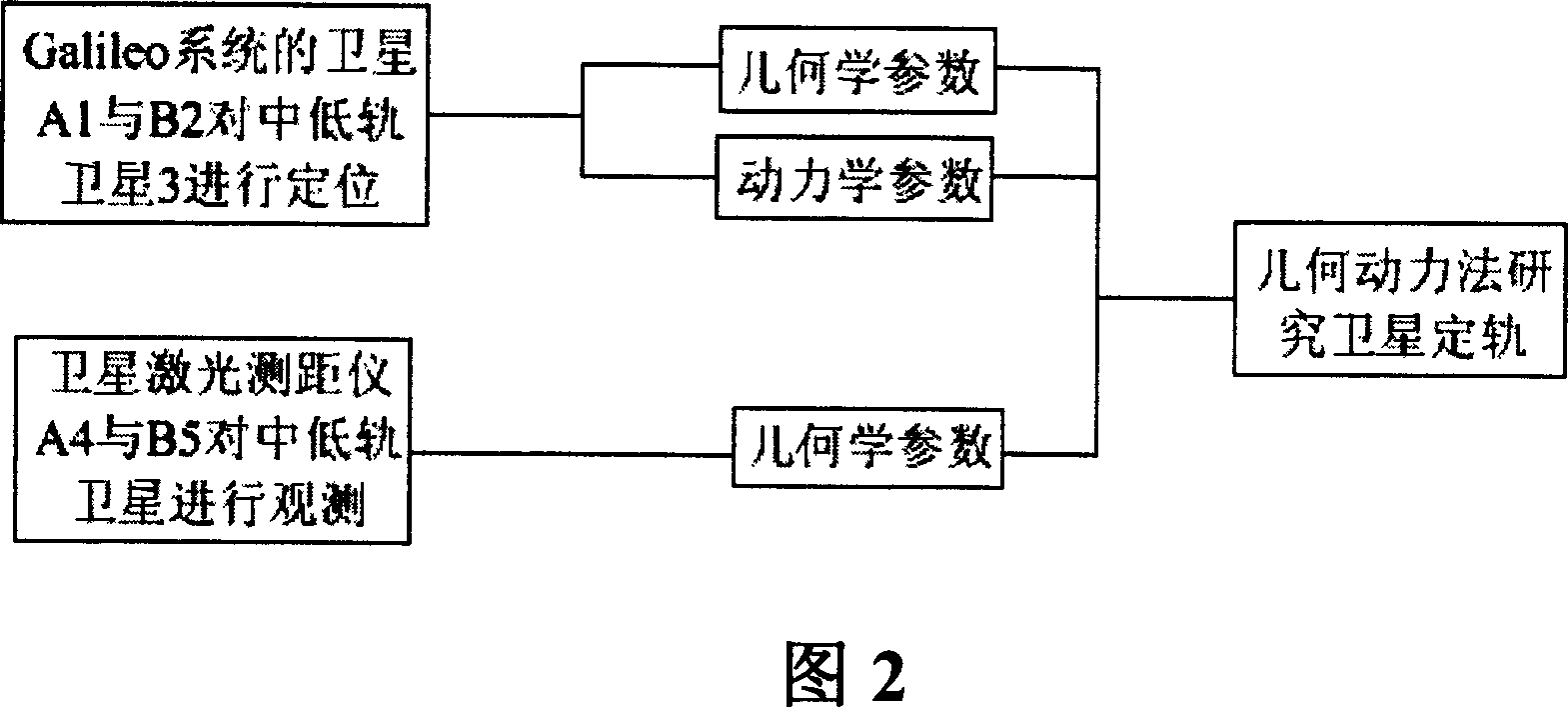
A method for realizing precise orbit determination of low-medium orbit satellite utilizes Galileo positioning system, satellite laser distance measurement technique and integrated precise orbit determination new means to optimize space-ground orbit determination system for realizing precise orbit determination of low-medium orbit satellite equipped with laser reflector.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Autonomous orbit determination method of navigation satellite constellation
InactiveCN104048664ASolve the rank deficit problemLong-term autonomous orbit determination with high precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite laser rangingObservation matrix
The invention belongs to the field of autonomous orbit determination of satellites and relates to an autonomous orbit determination method of a navigation satellite constellation. The autonomous orbit determination method of the navigation satellite constellation comprises the following steps: (1) starting autonomous orbit determination and initializing a system; (2) acquiring an inter-satellite ranging between satellites; (3) calculating an observation matrix of the inter-satellite ranging; (4) forecasting an orbit by using an orbit dynamical model; (5) updating measurement and estimating state by using a kalman filtering algorithm; and (6) judging whether the autonomous orbit determination is ended, operating the steps (2)-(6) again if the autonomous orbit determination is not ended, and conversely, ending and exiting an autonomous orbit determination program. Compared with the conventional autonomous orbit determination of navigation satellite constellation, the autonomous orbit determination method of the navigation satellite constellation has the advantages that the method is capable of avoiding the rank defect problem of autonomous orbit determination method of the navigation satellite constellation by using the inter-satellite ranging and is high in long-term autonomous orbit determination accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Autonomous orbit determination method for satellite based on synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN102323582AHigh precisionImproving the accuracy of autonomous orbit determination technologyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEarth satelliteSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses an autonomous orbit determination method for a satellite based on synthetic aperture radar, which belongs to the technical field of autonomous orbit determination of satellites and aims at achieving high-precision and real-time autonomous orbit determination of a low-orbiting satellite without being supported by a ground tracking telemetry and command station. The method comprises the following specific steps of: designing the shape and the material of a manual ground identification point; designing an arrangement mode of the ground identification point, arranging the ground identification point and measuring the position of the ground identification point in an earth-fixed coordinate system; storing information of the ground identification point in a space-borne computer; and after a space-borne synthetic aperture radar remotely senses the ground and identifies a ground identification, deriving the information of the ground identification point from a ground identification library on the satellite, applying an orbit determination equation to obtain the position and the speed of the satellite and further finish the real-time autonomous orbit determination of the satellite. The autonomous orbit determination technology for the satellite provides a novel autonomous orbit determination method for the satellite, which can be used for realizing high-precision real-time autonomous orbit determination of the low-orbiting satellite. The method disclosed by the invention is suitable for real-time autonomous orbit determination of a near earth satellite.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG PATENT TECH DEV
Satellite precise orbit determination method and device
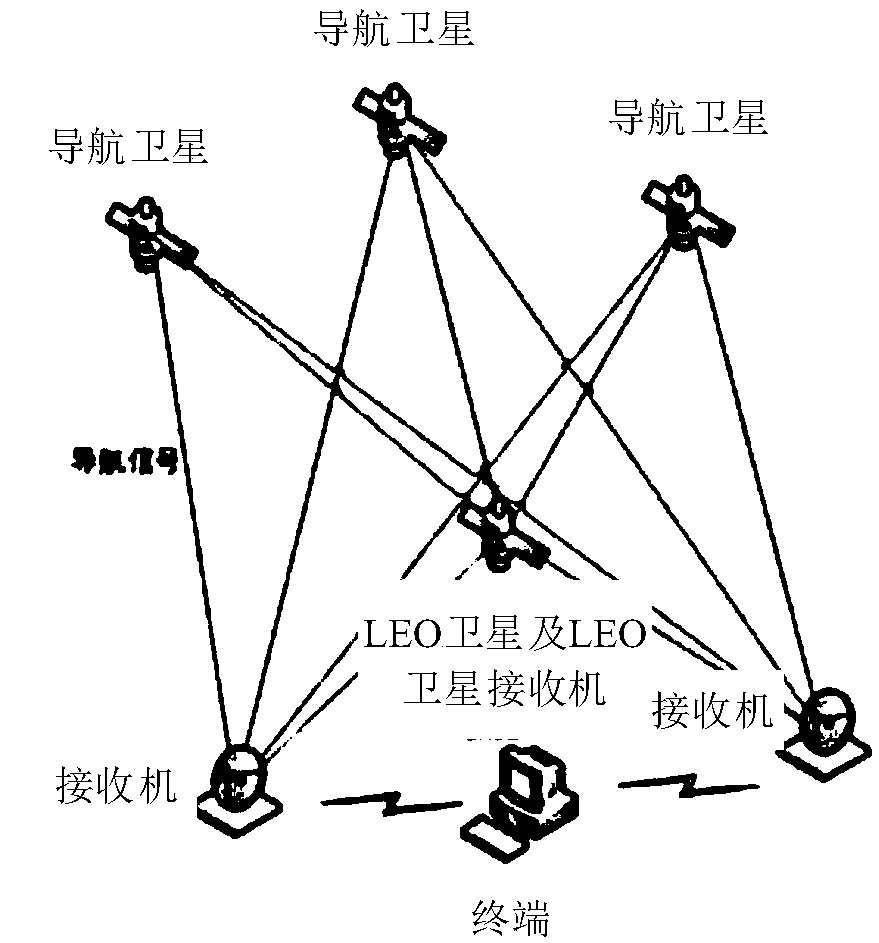
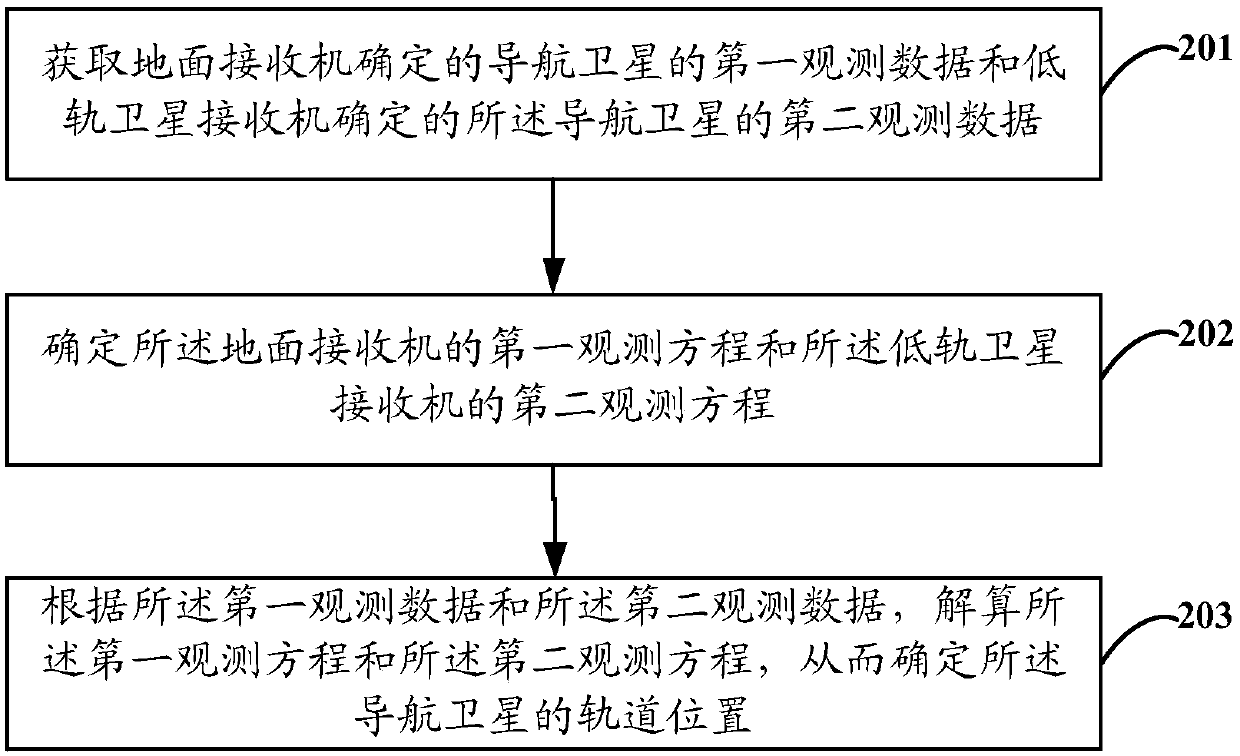
InactiveCN109520512AFast geometry changeSpeed up the convergence of ambiguity estimationInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingObservation dataOrbit determination
The embodiment of the invention discloses a satellite precise orbit determination method and device. The method comprises the steps that first observation data of a navigational satellite, determinedby a ground receiver and second observation data of the navigational satellite, determined by a low orbit satellite receiver are acquired; a first observation equation of the ground receiver and a second observation equation of the low orbit satellite receiver are determined; and the first observation equation and the second observation equation are solved according to the first observation data and the second observation data, and accordingly the orbital position of a navigational satellite is determined.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAIJI INFORMATION TECH
Coorbital satellite autonomous relative position keeping method based on laser loads
ActiveCN107298186ACosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
The invention relates to a coorbital satellite autonomous relative position keeping method based on laser loads. On-satellite autonomous orbit determination is achieved through a navigation constellation or orbit determination is measured through a ground station, the satellite position initial reference is obtained, determination of the relative positions between two space satellites and time unification of systems are achieved by combining inter-satellite laser ranging and communication integrated loads with rotary table pointing information, a target constellation is resolved through the current position of each star of the constellation, the existing position information and the target position information are compared, the relative position keeping requirement of each star is determined, the enveloping and pose deformation requirements of each star are resolved, the change rate of a satellite orbit is changed by solar wing position adjustment and deformation and adjustment of the perturbation influence, and accordingly relative position keeping of coorbital satellites is achieved, all the stars in the constellation can run in a relative good form after the orbit is affected by perturbation, and the orbit decay influence is reduced.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
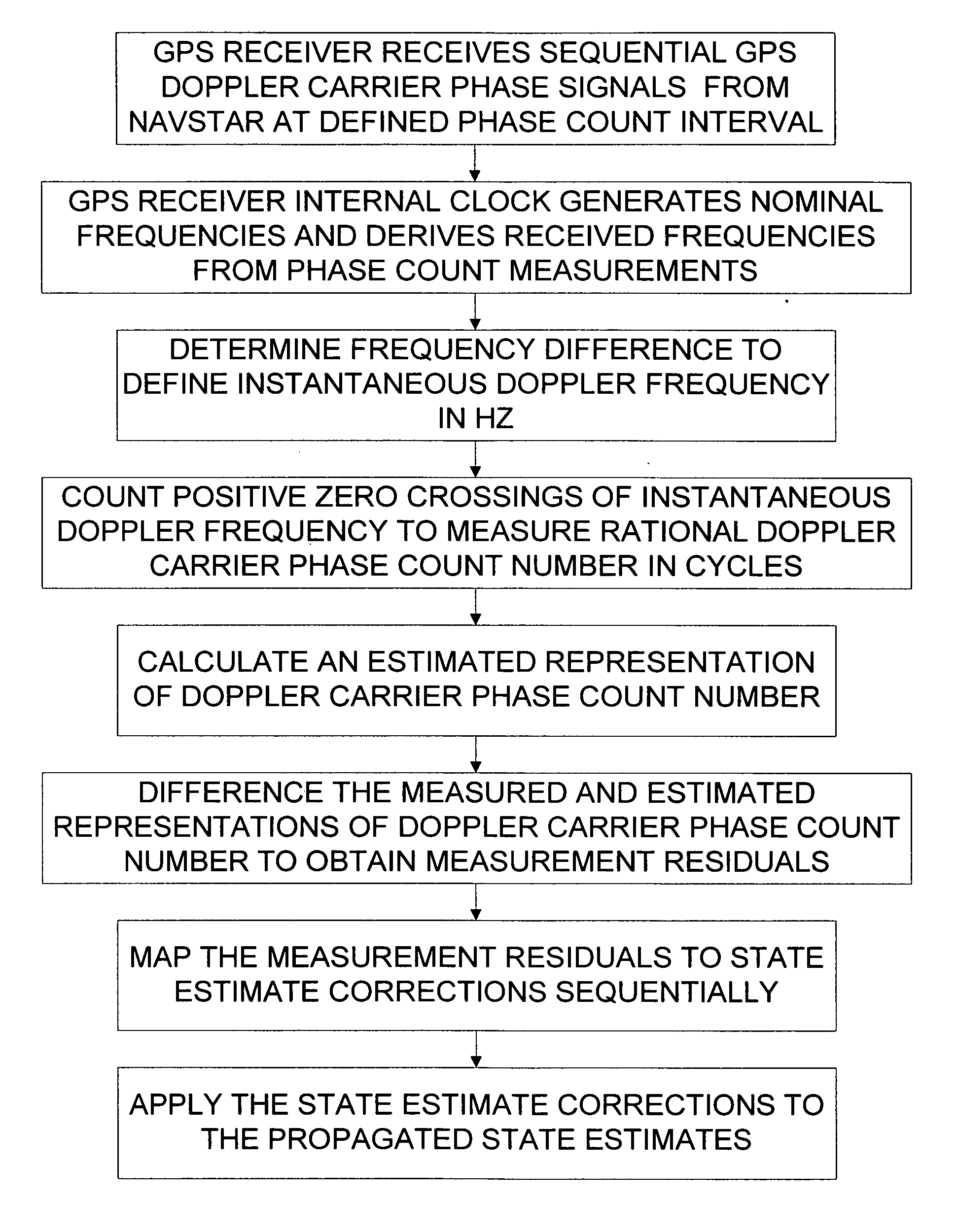
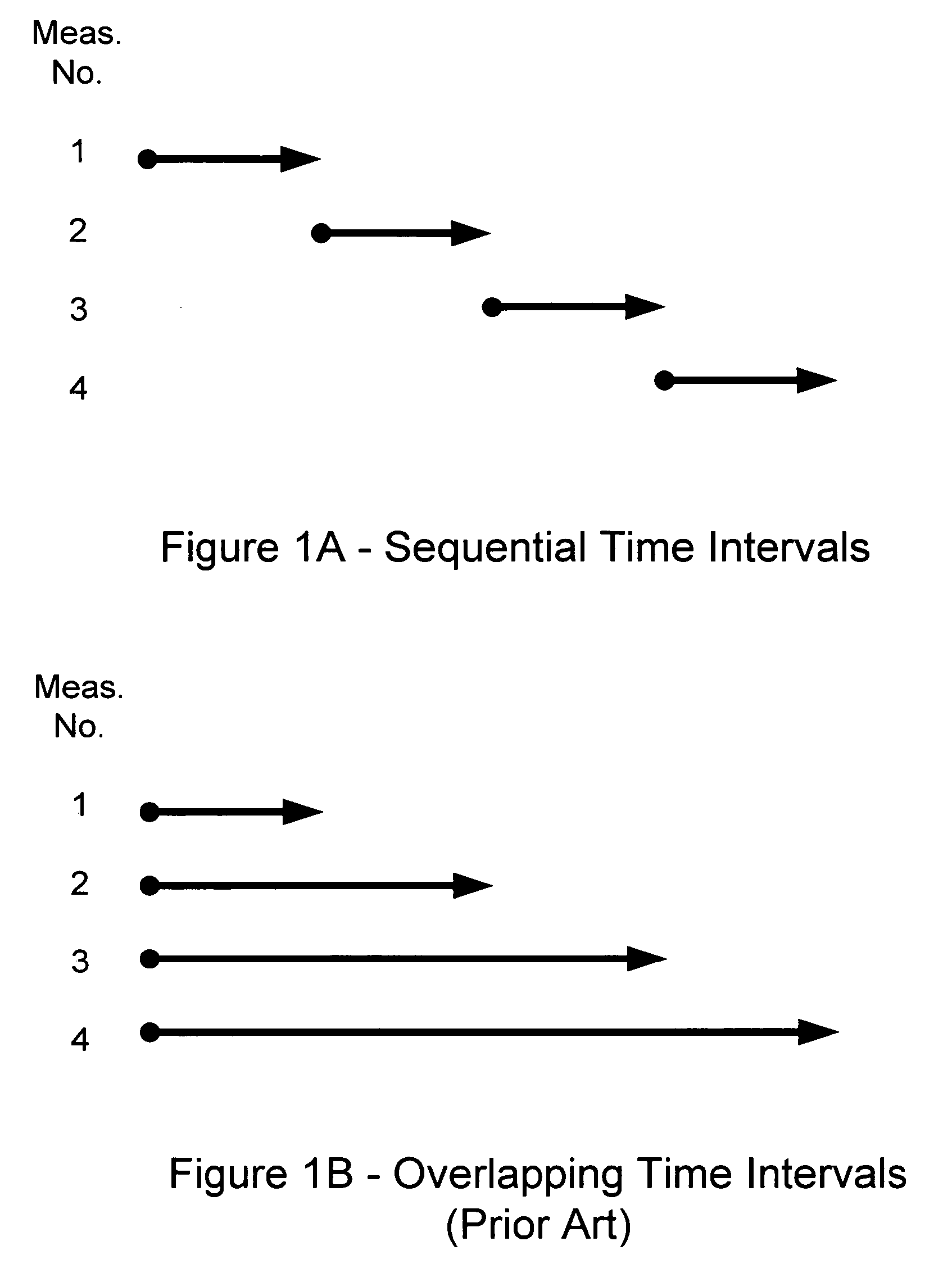
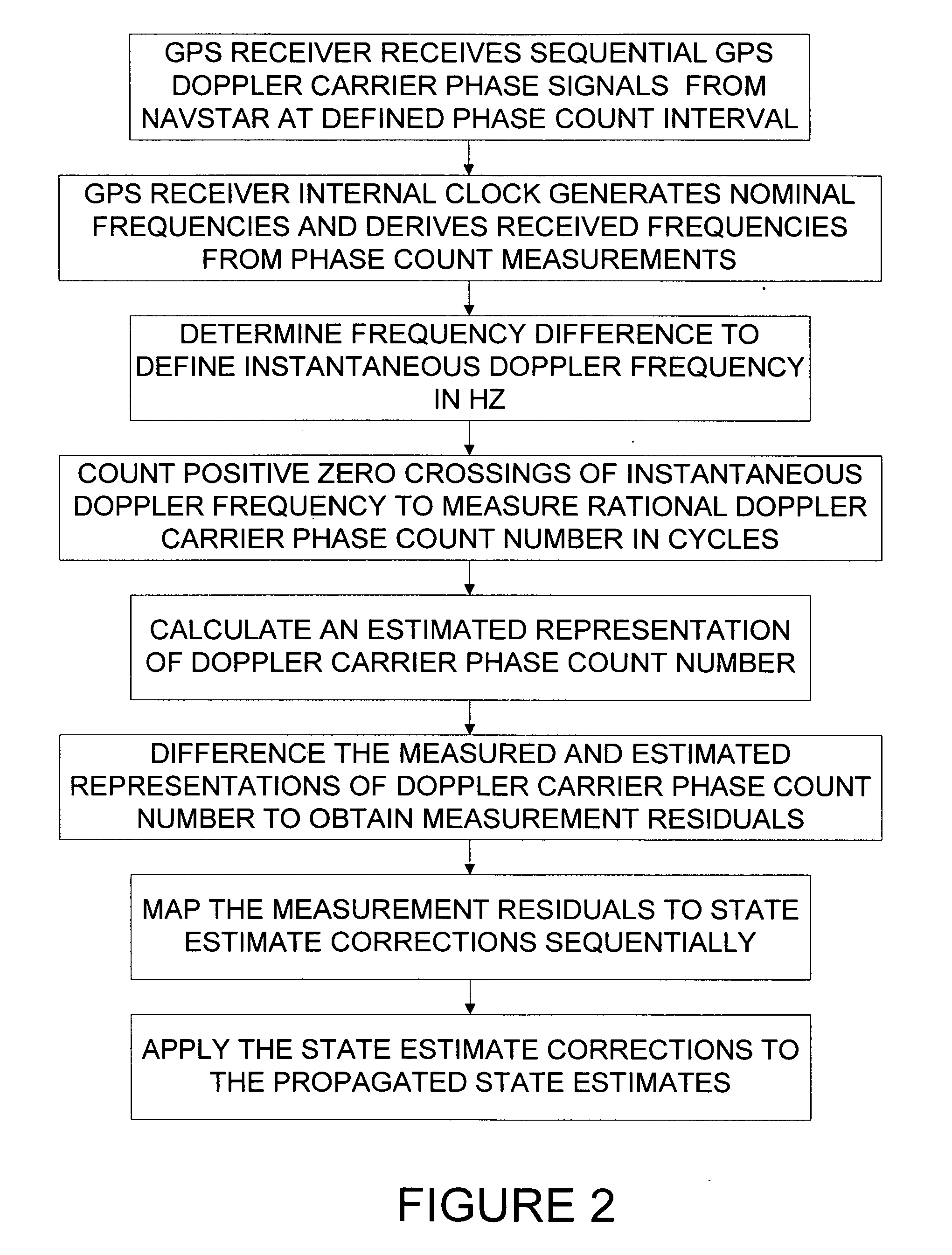
GPS carrier phase measurement representation and method of use
ActiveUS20070024496A1Optimal fixed-lag smootherReduce variationPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingPhase variationCW Doppler
Sequential GPS Doppler carrier phase count measurements are used for precision sequential determination of position and velocity of a GPS receiver, such as for orbit determination and geolocation, with minimum throughput time. Real-time orbit determination and geolocation performance is enabled with an optimal sequential filter, and near-real-time performance is enabled with an optimal fixed-lag smoother. Many problems associated with prior art orbit determination are eliminated by addressing the “cycle slip” problem, the unknown initial range problem with RANGECP measurement representations, the problem of serial correlation in the measurements due to reprocessing of overlapping thermal noise. Also, the present invention significantly attenuates the carrier signal phase variation due to rotation of receiver antenna relative to transmitter antenna because the sequential phase count time intervals are sufficiently short.
Owner:ANSYS GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES INC
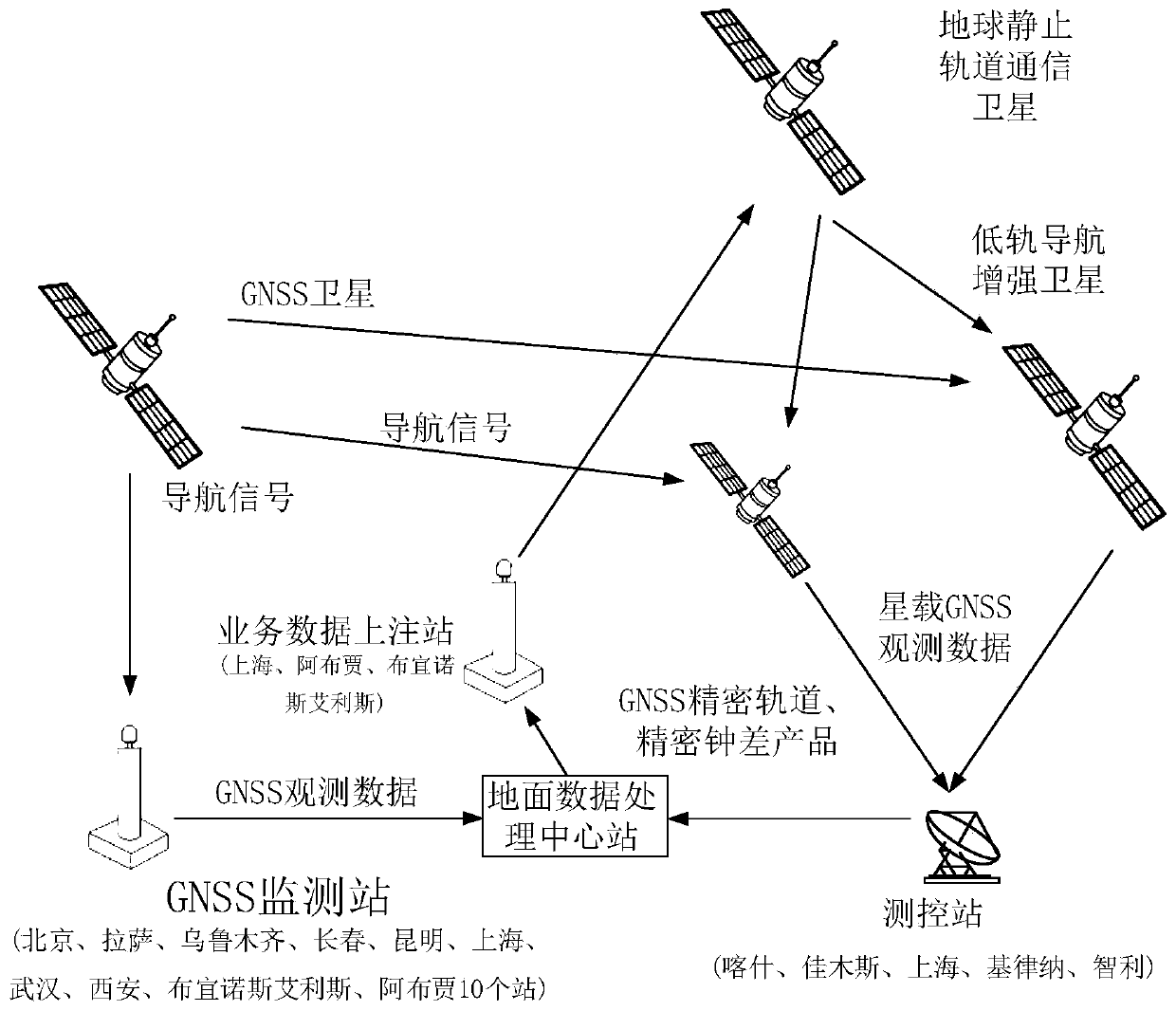
Low-orbit navigation enhancement precision correction data generation and uploading system and method
ActiveCN110187364AReduce in quantityReduce construction costsSatellite radio beaconingRadio transmissionGeostationary orbitDependability
The invention relates to a low-orbit navigation enhancement precision correction data generation and uploading system and method. A ground data processing central station combines monitoring data acquired by a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) monitoring station and low-orbit satellite monitoring data acquired by a satellite measurement and control station for processing to generate SSR (State Space Representation) data; the generated SSR data is evaluated and then transmitted to three service data uploading stations, the three service data uploading stations respectively transmit theSSR data to three geostationary orbit communication satellites as high elliptical orbit satellites through an uploading channel, a low-orbit navigation enhancement satellite receives the SSR data broadcasted by the geostationary orbit communication satellites, and processes the uploaded SSR data by adopting a navigation enhancement load t generate enhanced navigation signals so as to complete high-precision orbit determination and low-orbit navigation enhancement information generation. Compared to the prior art, the method for generating and uploading the SSR correction data of the navigationsystem required by the low-orbit navigation enhancement system is achieved without depending on low-orbit inter-satellite links, so that the complexity of the low-orbit system is reduced, the reliability of the low-orbit constellation system is improved, and the service life of the low-orbit constellation system is prolonged.
Owner:火眼位置数智科技服务有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com