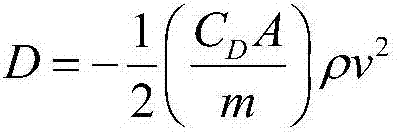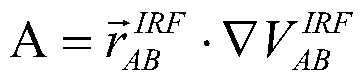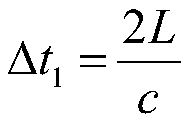Patents
Literature
38 results about "Satellite laser ranging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In satellite laser ranging (SLR) a global network of observation stations that measures the round trip time of flight of ultrashort pulses of light to satellites equipped with retroreflectors. This provides instantaneous range measurements of millimeter level precision which can be accumulated to provide accurate measurement of orbits and a host of important scientific data.
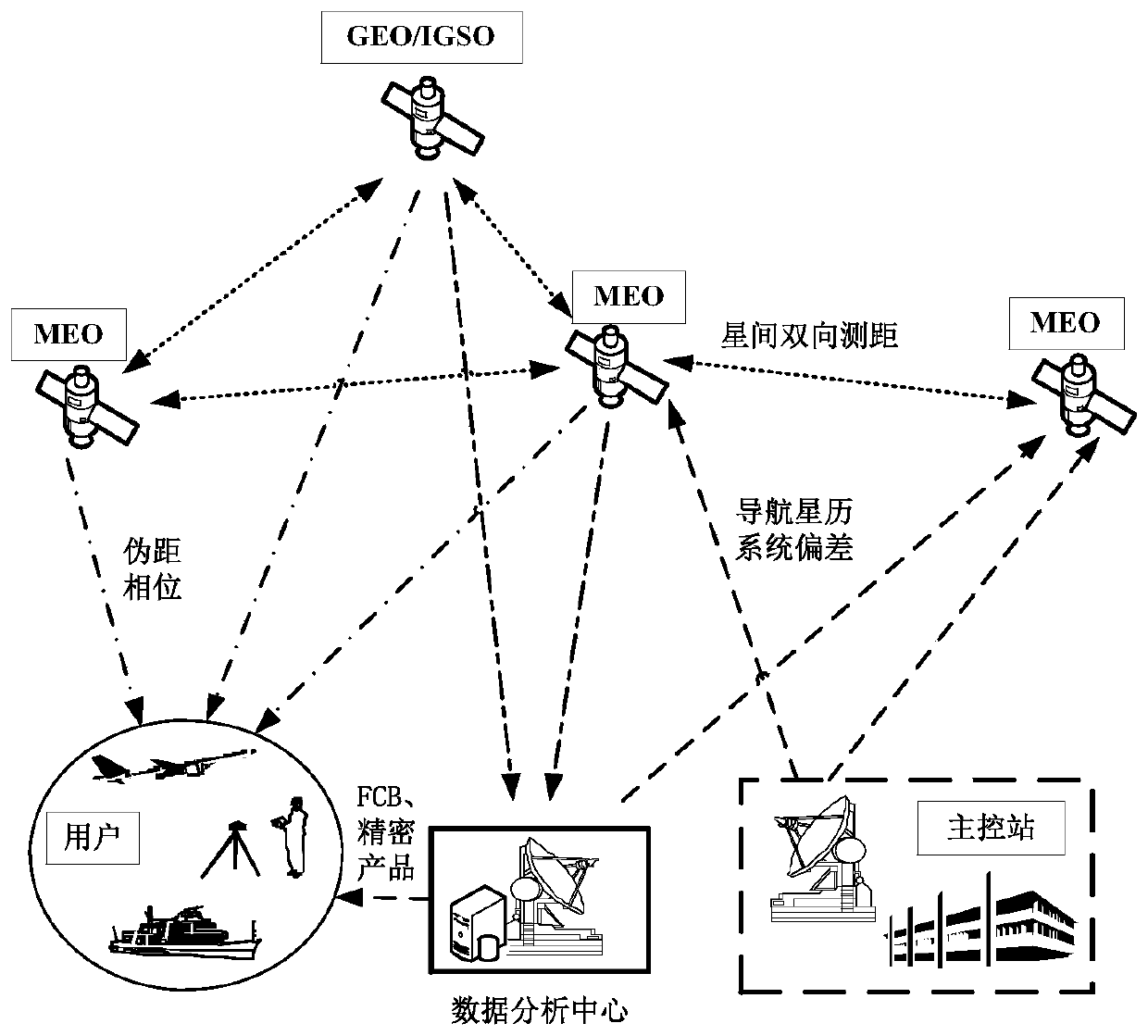
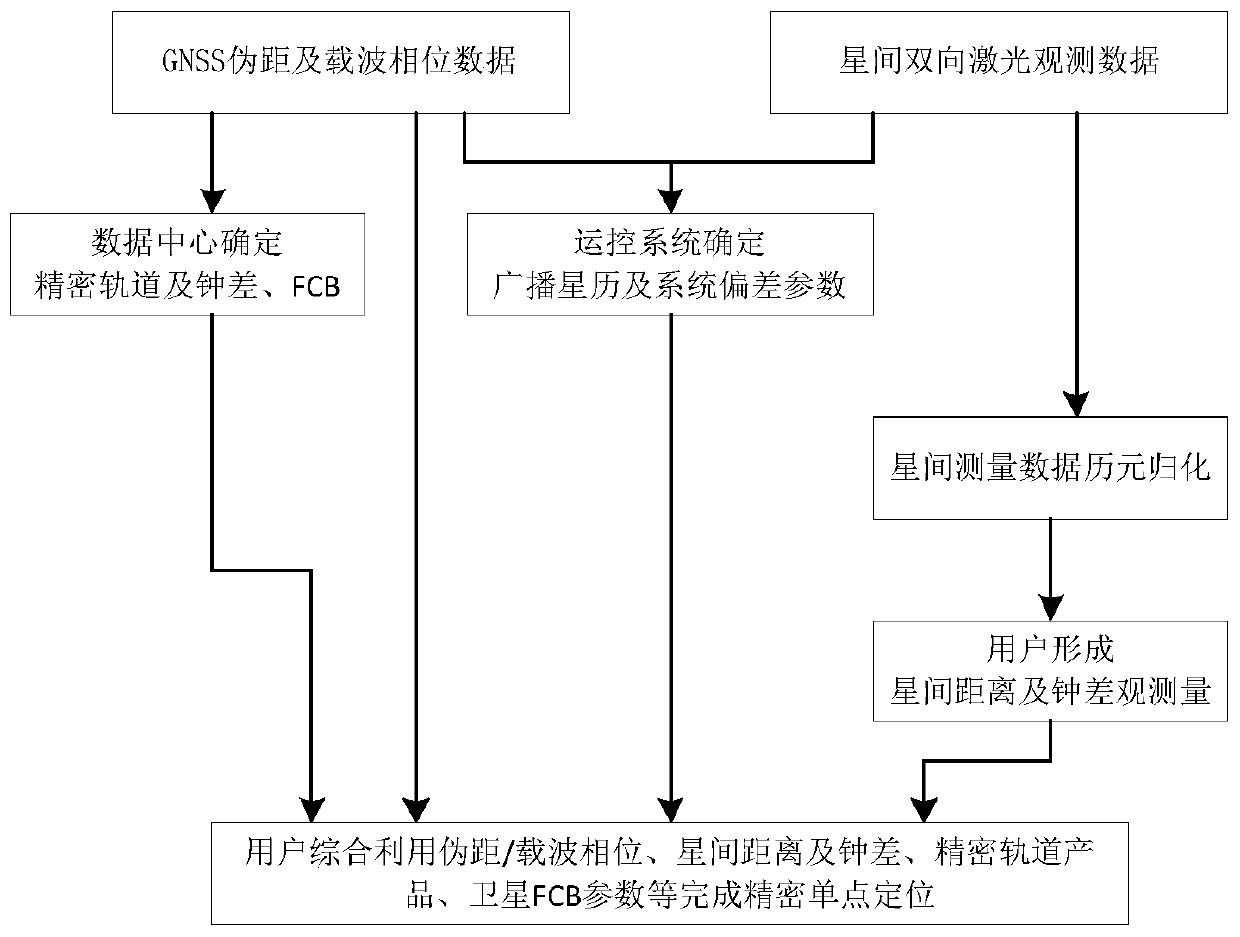
High-precision inter-satellite laser ranging assistant precise point positioning method
ActiveCN110031881AReduced update frequency requirementsImprove positioning efficiencySatellite radio beaconingElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
The invention provides a high-precision inter-satellite laser ranging assistant precise point positioning method. According to the method, a navigation satellite carries a high-precision inter-satellite laser ranging load; a ground operation control system determines a system deviation parameter between a signal receiving and transmitting starting point of satellite laser ranging equipment and a phase center of an L-waveband satellite load antenna and uploads the system deviation parameter to the satellite; the satellite arranges inter-satellite ranging information and system deviation information into a transmitting sign; a ground point positioning user receives the inter-satellite laser ranging information and the system deviation information while receiving an L-waveband navigation signal; and an inter-satellite laser ranging observed quantity, an L-waveband pseudo-range, a carrier phase observed quantity, a navigation message, a precise orbit product and other data are utilized ina combined mode to complete precise point positioning, so that the precise position of the user is determined. Through the method, positioning initialization time can be shortened, the requirement onprecise clock correction and orbit product update frequency is lowered, and kinematic precise point positioning efficiency is improved.
Owner:中国人民解放军61540部队
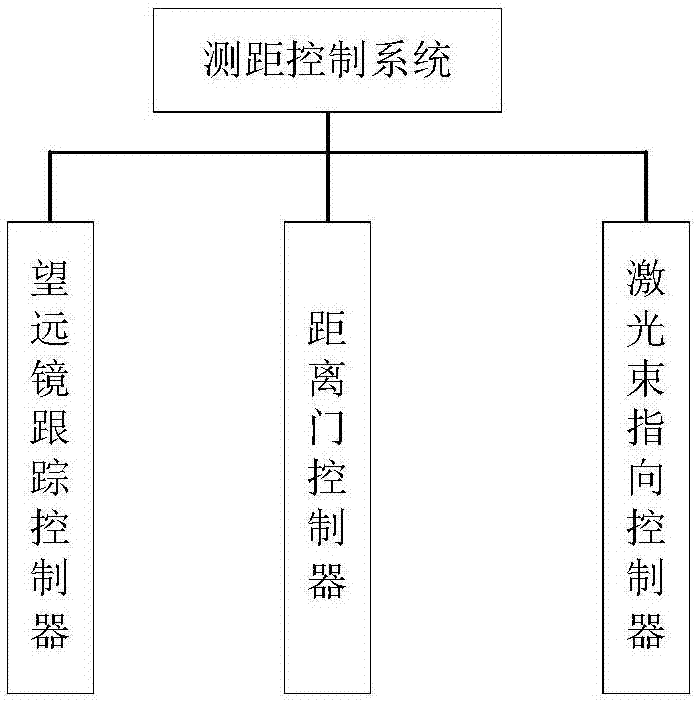
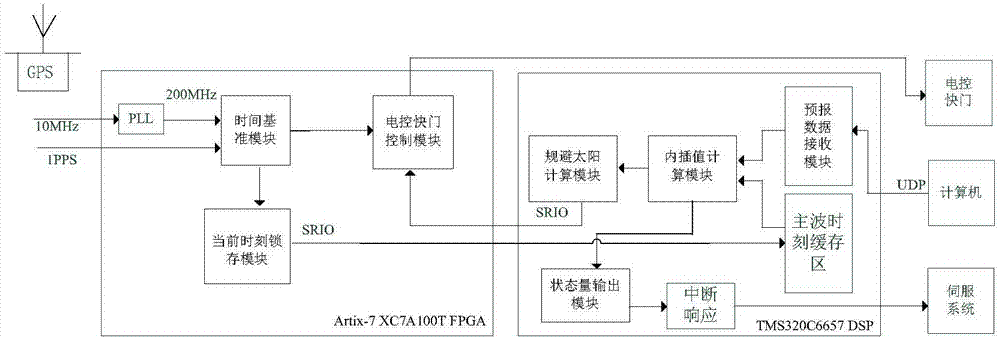
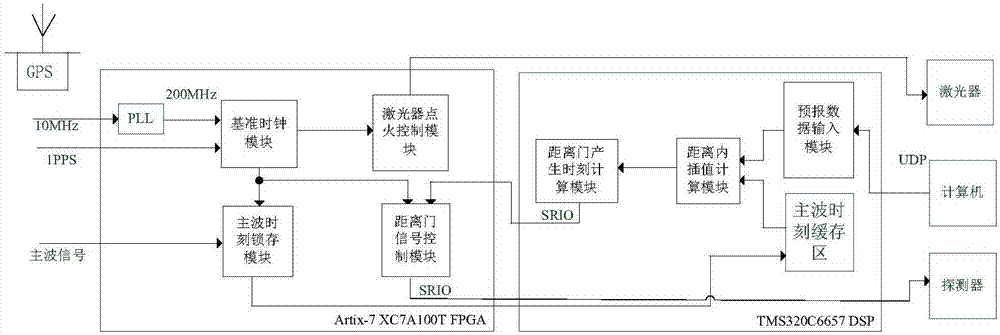
Embedded satellite laser ranging control system
ActiveCN107015234AIncrease flexibilityEasy to handleElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite laser rangingOrbit prediction
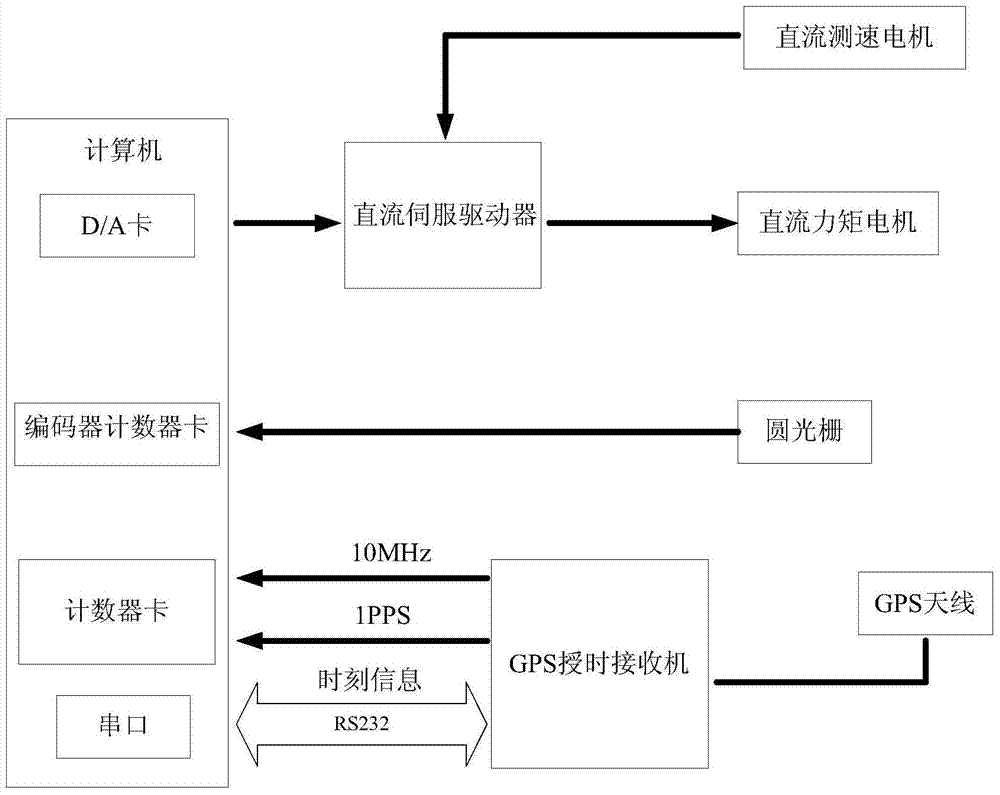
The invention relates to an embedded satellite laser ranging control system, and solves problems that the satellite laser ranging control technology implemented through a main control computer is complex in ranging method, is low response speed and causes the data loss. A telescope tracking controller reads a current observation moment, calculates the azimuth and height position at the current moment through orbit prediction interpolating of an observation station, and outputs the azimuth and height position to a servo system of a motor. A distance gate controller outputs an igniting signal of a laser according to a distance measuring frequency, locks a main wave signal, and calculates the moment when a distance gate signal corresponding to a main wave is generated. A gate control signal is outputted through the distance gate controller. A laser beam direction controller recognizes a light beam image, obtains a light peak position, calculates the deviation between the light peak point and the center of a receiving visual field, and corrects the direction deviation of a laser beam through a control algorithm. The system can meet the demands of higher-repetition-frequency laser ranging through employing an FPGA+DSP heterogeneous processor configuration, and facilitates the upgrading of the whole ranging system.
Owner:中国科学院国家天文台长春人造卫星观测站
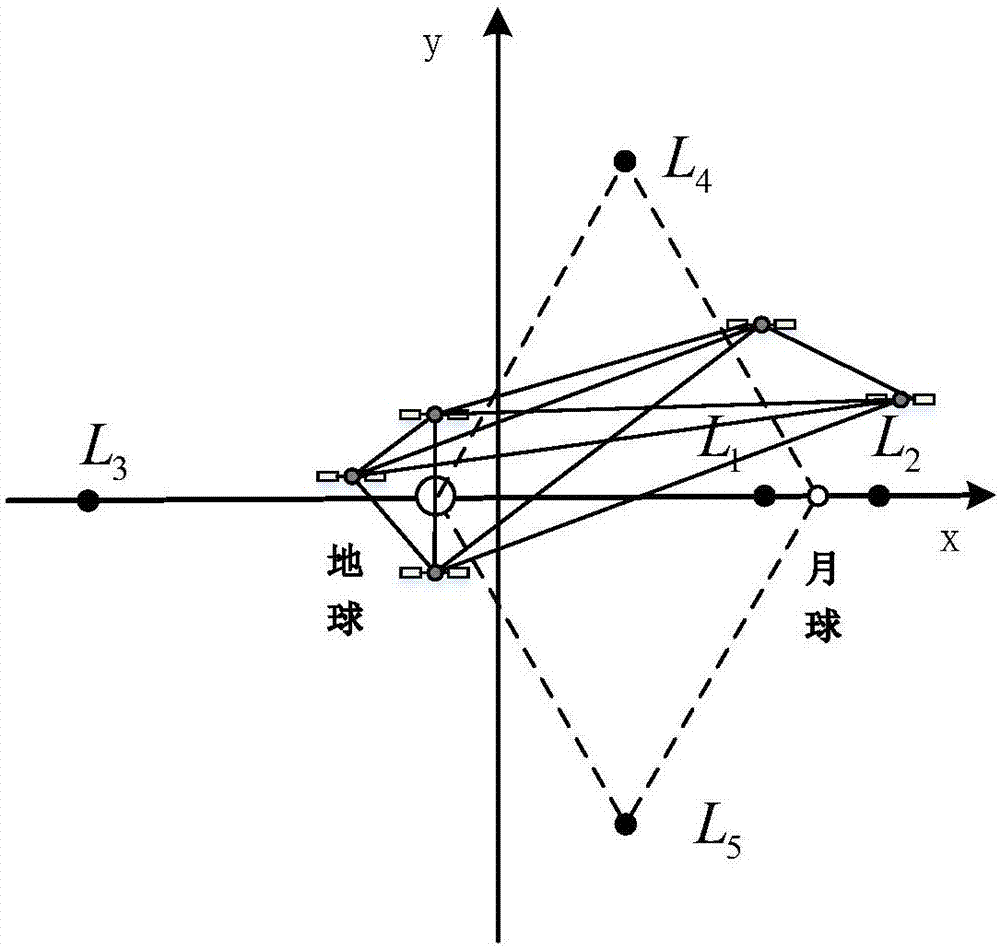
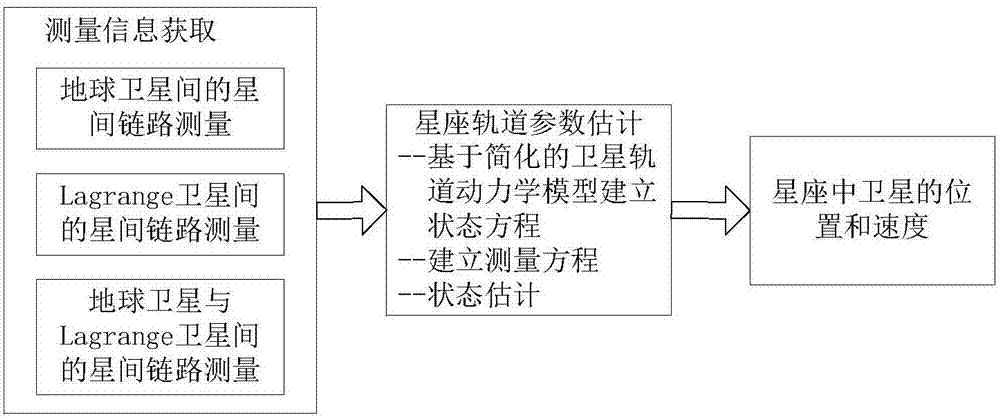
Earth-Lagrange combined constellation autonomous orbit determination method based on inter-satellite ranging
ActiveCN107421550AImproving the accuracy of long-term autonomous orbit determinationSolve the "deficit rank" problemInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by astronomical meansSatellite laser rangingNonlinear filter
The invention discloses an earth-Lagrange combined constellation autonomous orbit determination method based on inter-satellite ranging. The method includes following steps: step 1, establishing a state equation of an earth-Lagrange combined constellation autonomous orbit determination system; step 2, establishing a measurement equation of the earth-Lagrange combined constellation autonomous orbit determination system; step 3, determining a filtering method for realizing orbit parameter estimation; step 4, specifically realizing the earth-Lagrange combined constellation autonomous orbit determination method based on a selected filtering algorithm. By introducing a Lagrange satellite, the problem of deficient range when only inter-satellite ranging information is utilized for autonomous orbit determination is solved effectively, and complexity of system equipment is lowered; statistical characteristics of system noise are estimated online in real time through a self-adaptive nonlinear filtering algorithm, so that requirements on noise prior information are low, stability of the autonomous orbit determination filtering algorithm is improved, and autonomous orbit determination accuracy is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Precision orbit determination system and implementing method for satellites in middle and low orbits
InactiveCN1959430AConvenient researchEfficient use ofPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingLaser rangingSatellite laser ranging
A method for realizing precise orbit determination of low-medium orbit satellite utilizes Galileo positioning system, satellite laser distance measurement technique and integrated precise orbit determination new means to optimize space-ground orbit determination system for realizing precise orbit determination of low-medium orbit satellite equipped with laser reflector.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Autonomous orbit determination method of navigation satellite constellation
InactiveCN104048664ASolve the rank deficit problemLong-term autonomous orbit determination with high precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite laser rangingObservation matrix
The invention belongs to the field of autonomous orbit determination of satellites and relates to an autonomous orbit determination method of a navigation satellite constellation. The autonomous orbit determination method of the navigation satellite constellation comprises the following steps: (1) starting autonomous orbit determination and initializing a system; (2) acquiring an inter-satellite ranging between satellites; (3) calculating an observation matrix of the inter-satellite ranging; (4) forecasting an orbit by using an orbit dynamical model; (5) updating measurement and estimating state by using a kalman filtering algorithm; and (6) judging whether the autonomous orbit determination is ended, operating the steps (2)-(6) again if the autonomous orbit determination is not ended, and conversely, ending and exiting an autonomous orbit determination program. Compared with the conventional autonomous orbit determination of navigation satellite constellation, the autonomous orbit determination method of the navigation satellite constellation has the advantages that the method is capable of avoiding the rank defect problem of autonomous orbit determination method of the navigation satellite constellation by using the inter-satellite ranging and is high in long-term autonomous orbit determination accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
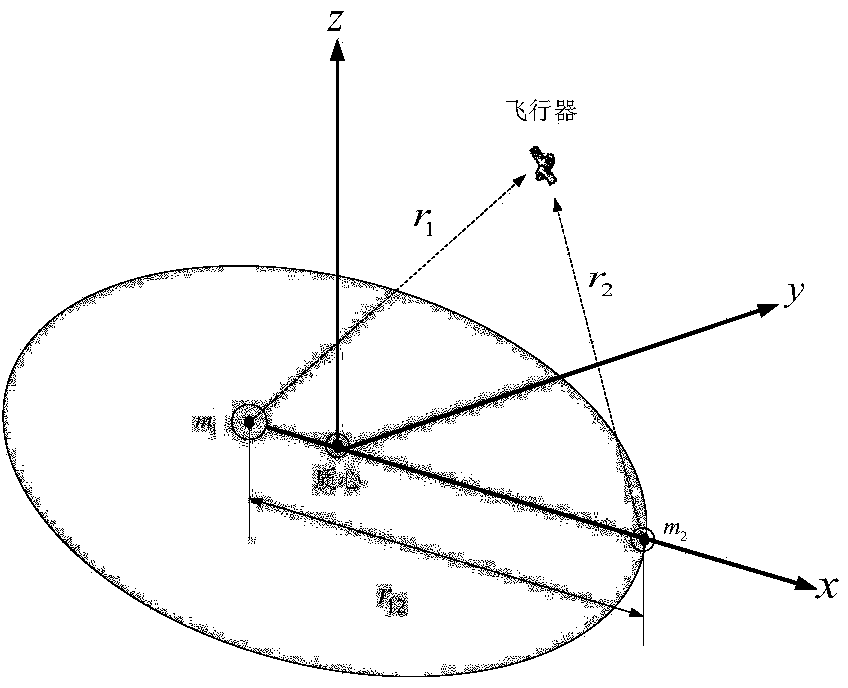
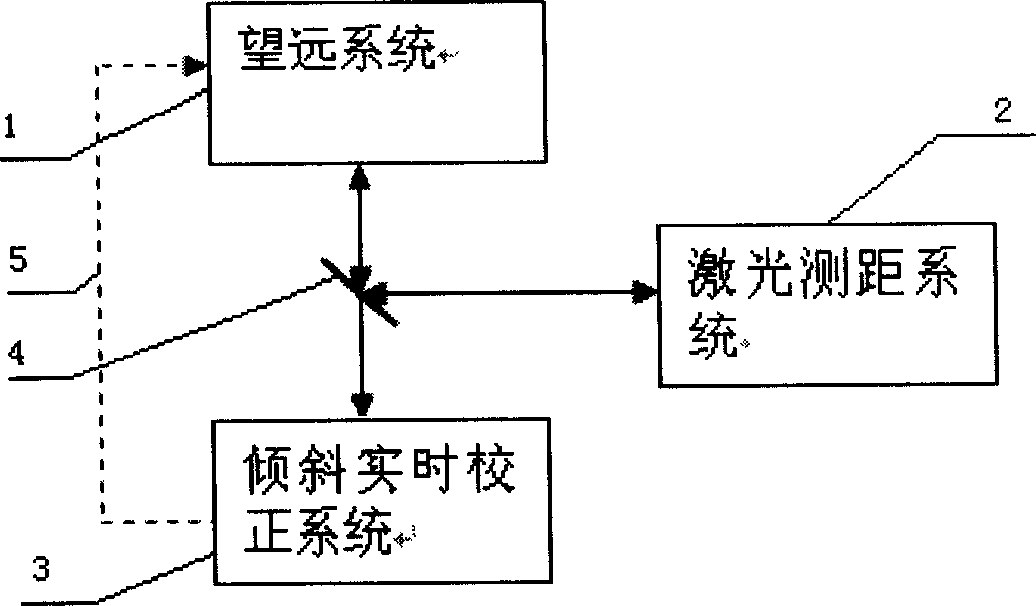
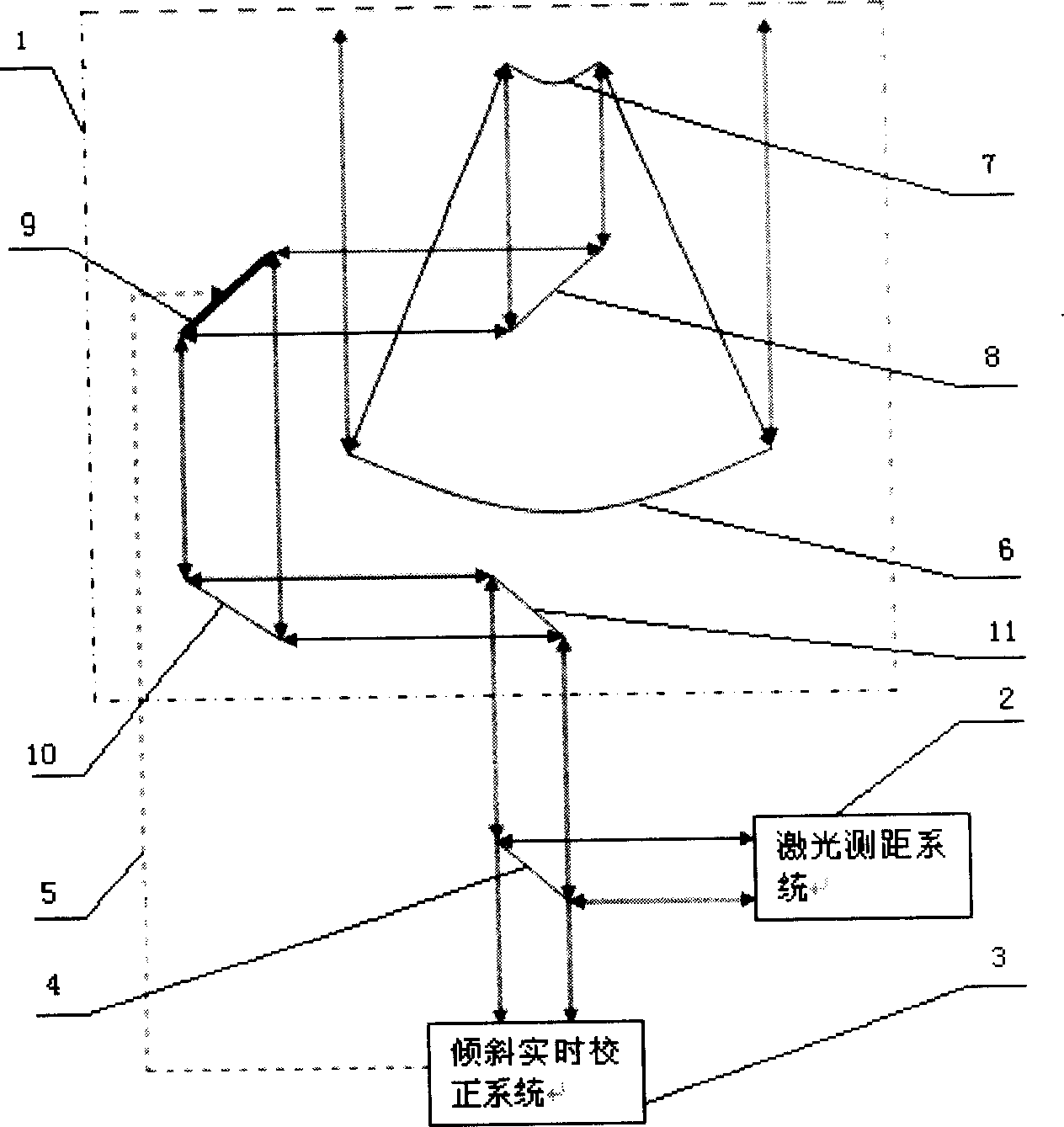
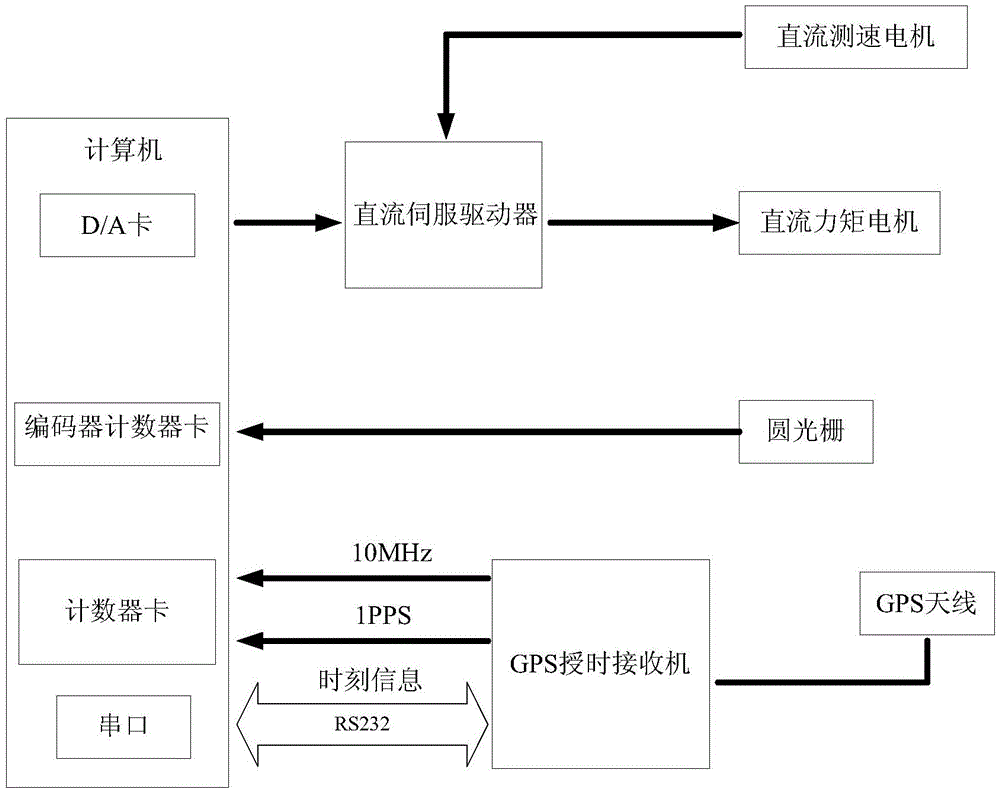
Satellite laser range-measurement system based on tilt correction
InactiveCN1831559AHigh precisionAchieve real-time closed-loop correctionElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite laser rangingControl signal
A satellite laser distance measurement system based on tilt calibration is featured as setting high speed tilt reflector in telescoping unit, using tilt tracking transducer to carry out wave front detection on light wave received by receiving telescope, outputting calibration control signal to high speed tilt mirror in telescope by high speed processor after error signal is restored, starting up satellite laser distance measurement system in telescoping unit to send out laser with specific wavelength for carrying out satellite laser distance measurement after tilt closed loop real time calibration is finished.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
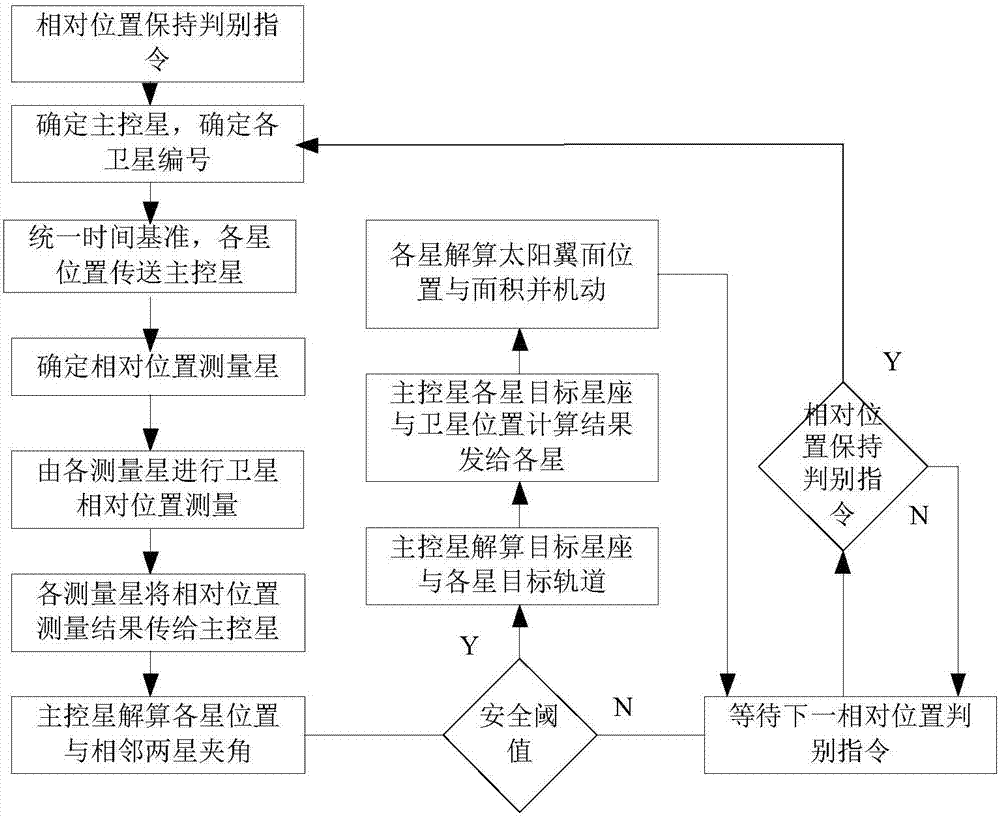
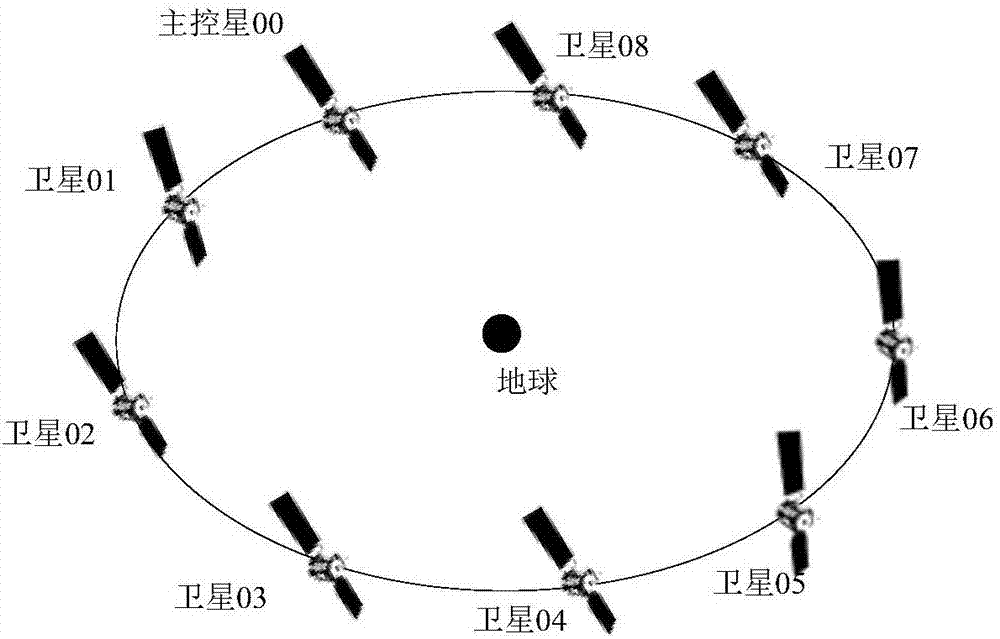
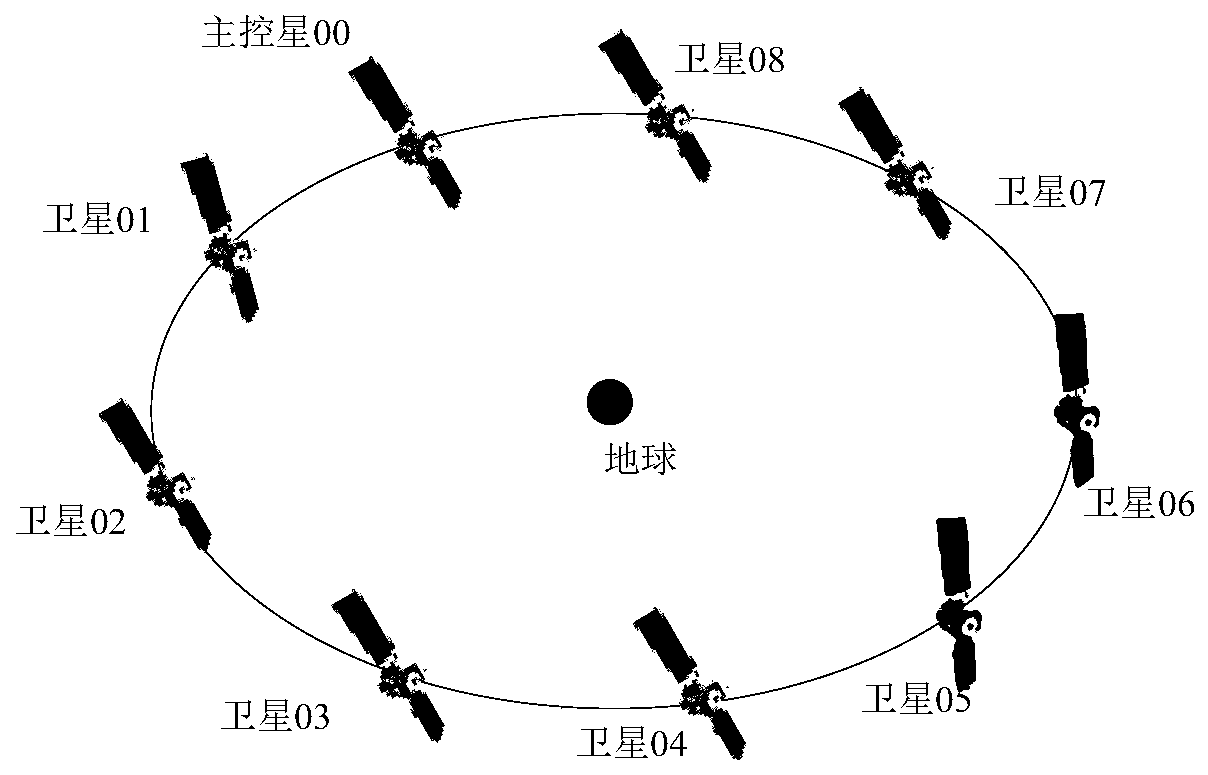
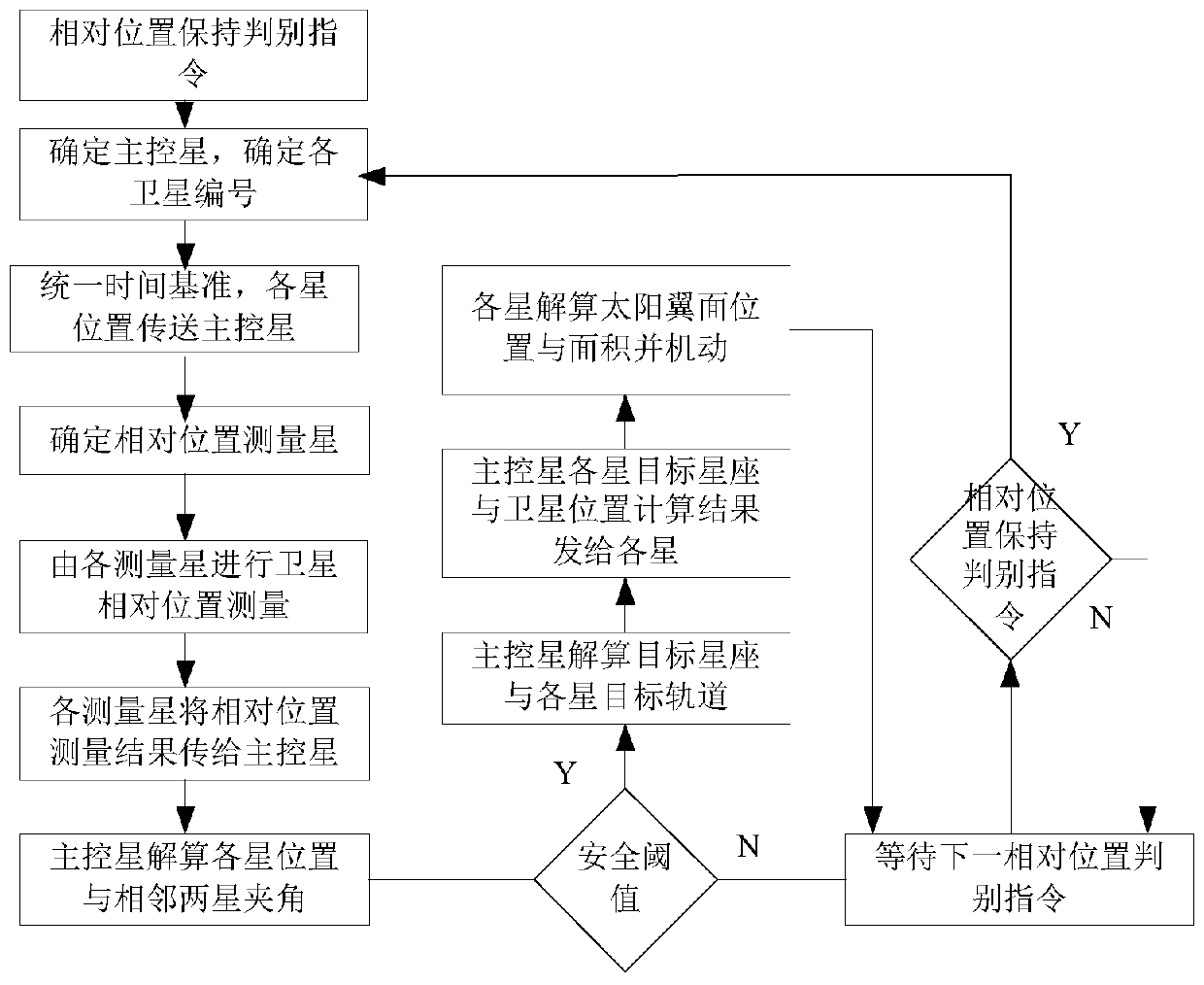
Coorbital satellite autonomous relative position keeping method based on laser loads
ActiveCN107298186ACosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
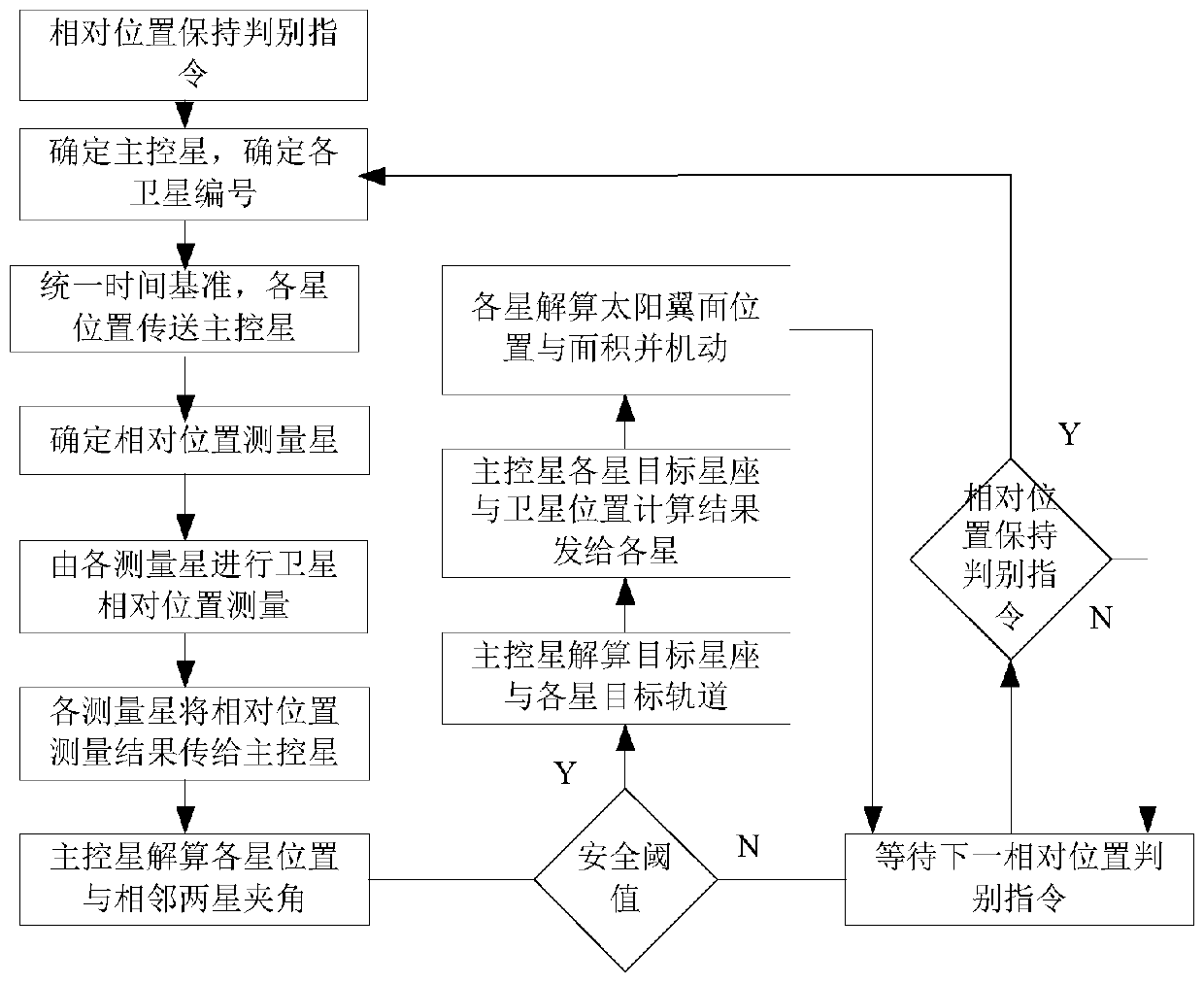
The invention relates to a coorbital satellite autonomous relative position keeping method based on laser loads. On-satellite autonomous orbit determination is achieved through a navigation constellation or orbit determination is measured through a ground station, the satellite position initial reference is obtained, determination of the relative positions between two space satellites and time unification of systems are achieved by combining inter-satellite laser ranging and communication integrated loads with rotary table pointing information, a target constellation is resolved through the current position of each star of the constellation, the existing position information and the target position information are compared, the relative position keeping requirement of each star is determined, the enveloping and pose deformation requirements of each star are resolved, the change rate of a satellite orbit is changed by solar wing position adjustment and deformation and adjustment of the perturbation influence, and accordingly relative position keeping of coorbital satellites is achieved, all the stars in the constellation can run in a relative good form after the orbit is affected by perturbation, and the orbit decay influence is reduced.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
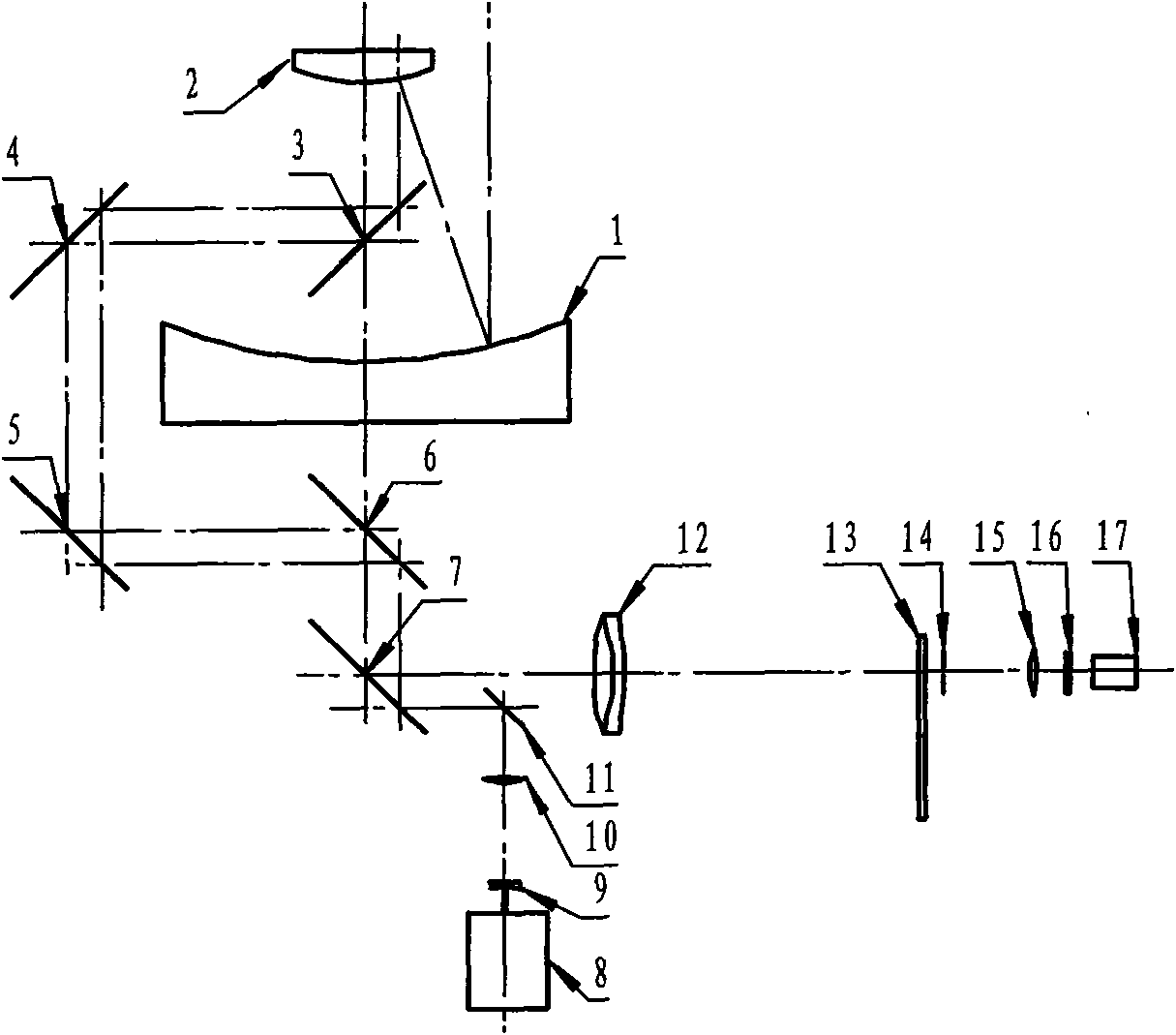
Kilohertz common light path satellite laser ranging (SLR) optical device
InactiveCN101650438AEliminate bulkinessImprove ranging accuracyOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
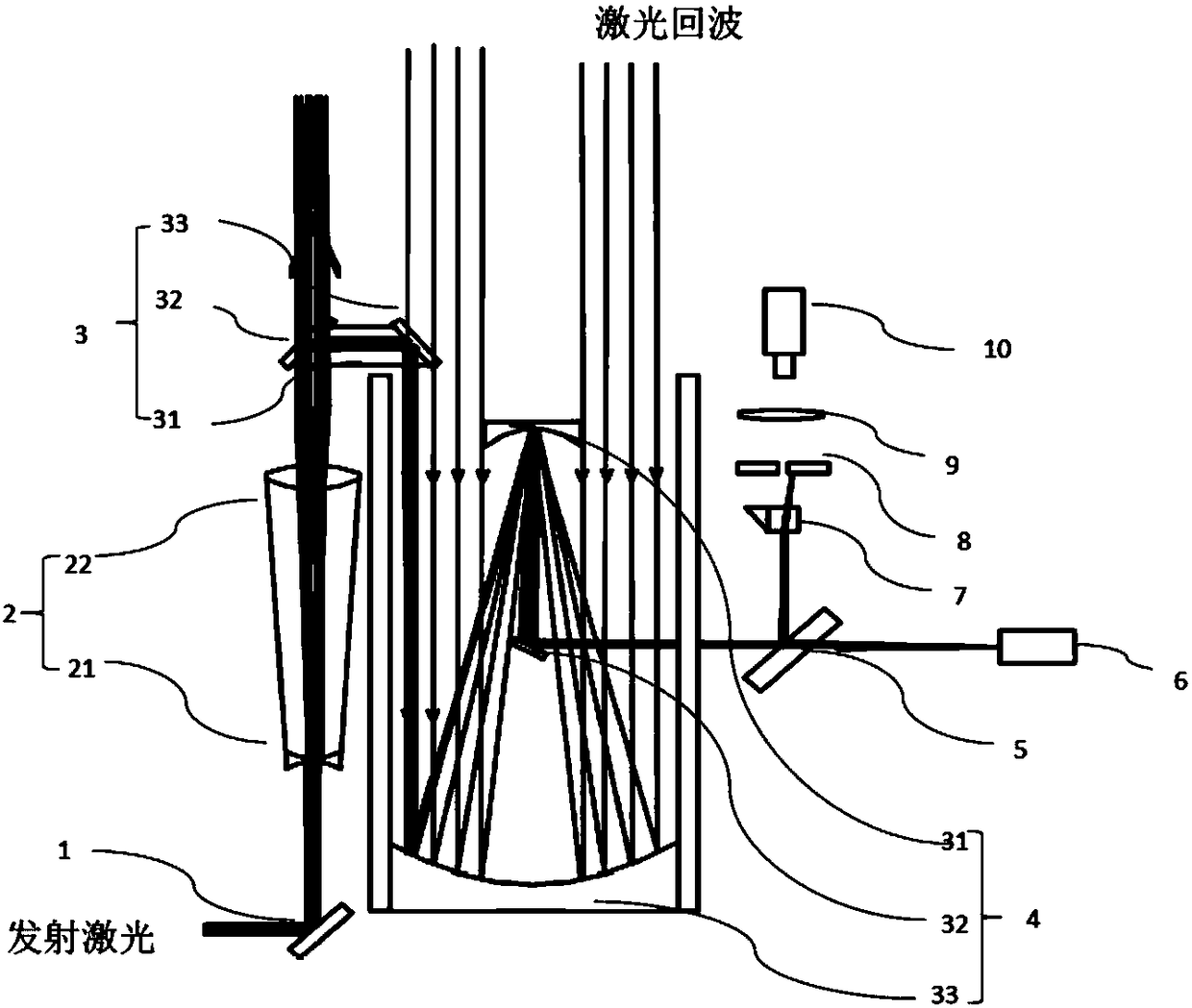
The invention relates to a kilohertz common light path satellite laser ranging (SLR) optical device, belonging to laser ranging systems and comprising a reflective ranging telescope, a laser emissionlight path and an echo-receiving light path. The ranging telescope comprises a paraboloidal primary mirror, a paraboloidal secondary mirror and an elbow reflector; the laser emission light path comprises a kilohertz laser, a negative lens, a positive lens and a docking mirror; wherein the negative lens and the positive lens are formed a laser-expanding structure capable of adjusting a divergence angle; a coupling lens and a collimating lens in the echo-receiving light path are confocal to be formed an afocal system; the diameter of a compressed echo ray behind the collimating lens is matched with the pupil-entrance diameter of a single-photon detector; a rotary shutter is arranged in front of a focus of the echo coupling lens; an iris diaphragm is arranged on the focus of the echo couplinglens; and an optical filter is arranged in front of the single-photon detector. The kilohertz common light path SLR optical device selects a ranging frequency within 1-4 KHz, has high ranging accuracy and great echo amount and improves the ranging capability and the ranging level of the system.
Owner:YUNNAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
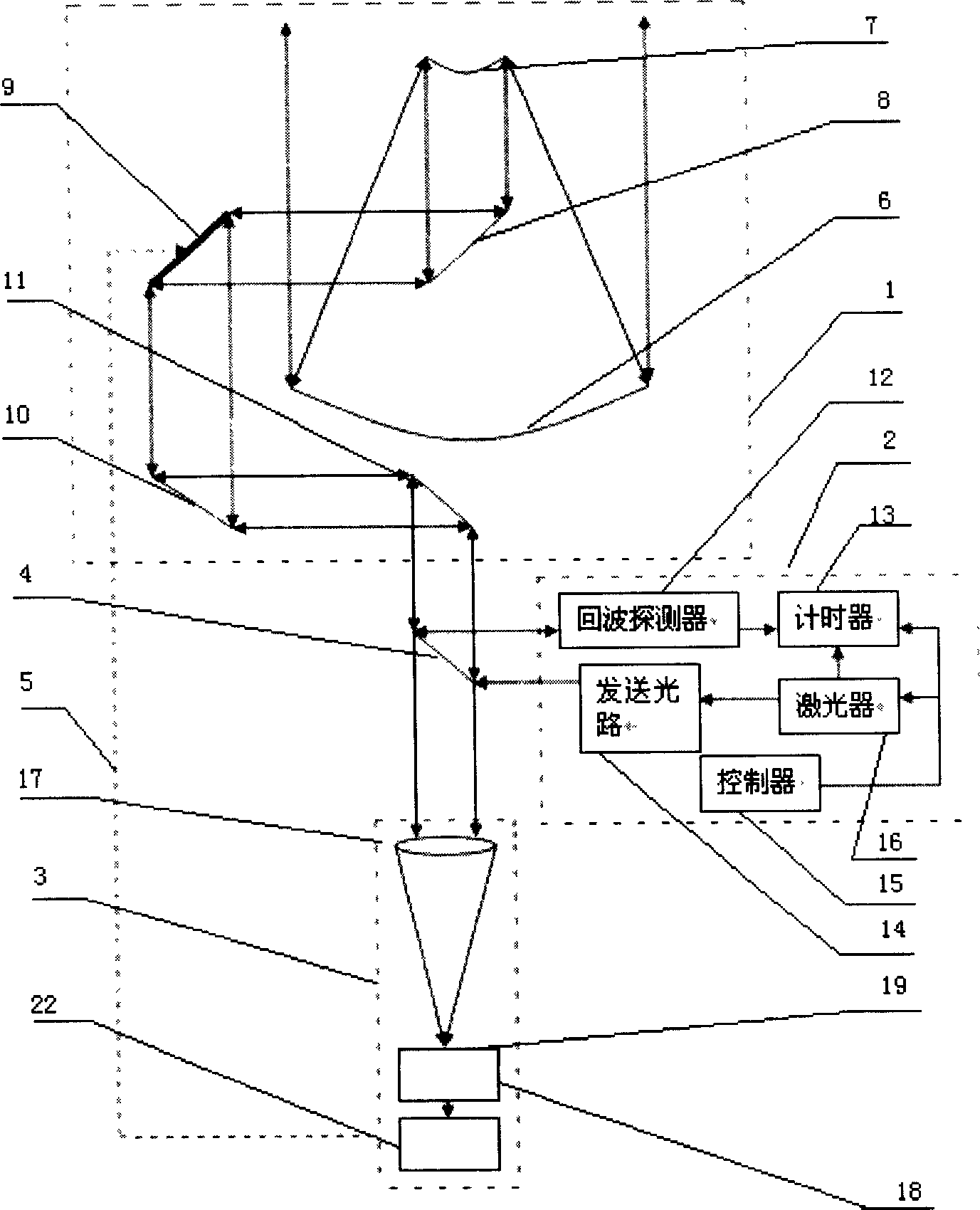
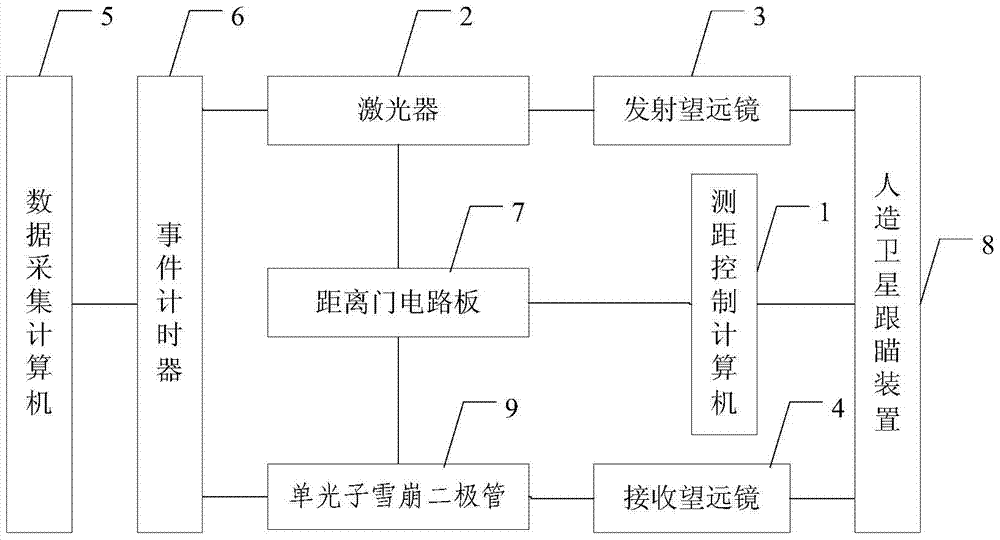
Artificial satellite laser ranging system
InactiveCN104535992AImprove signal-to-noise ratioIncrease the amount of effective echo dataElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSatellite laser rangingData acquisition
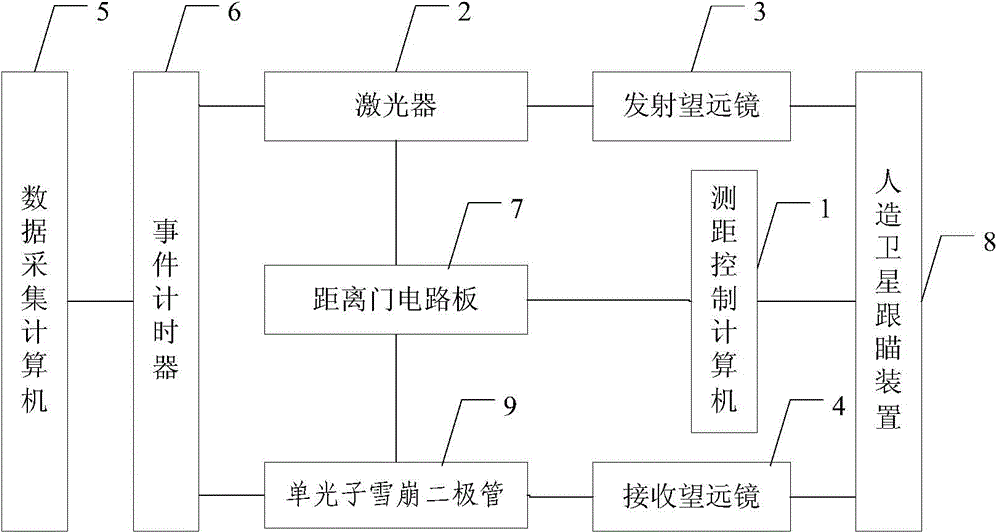
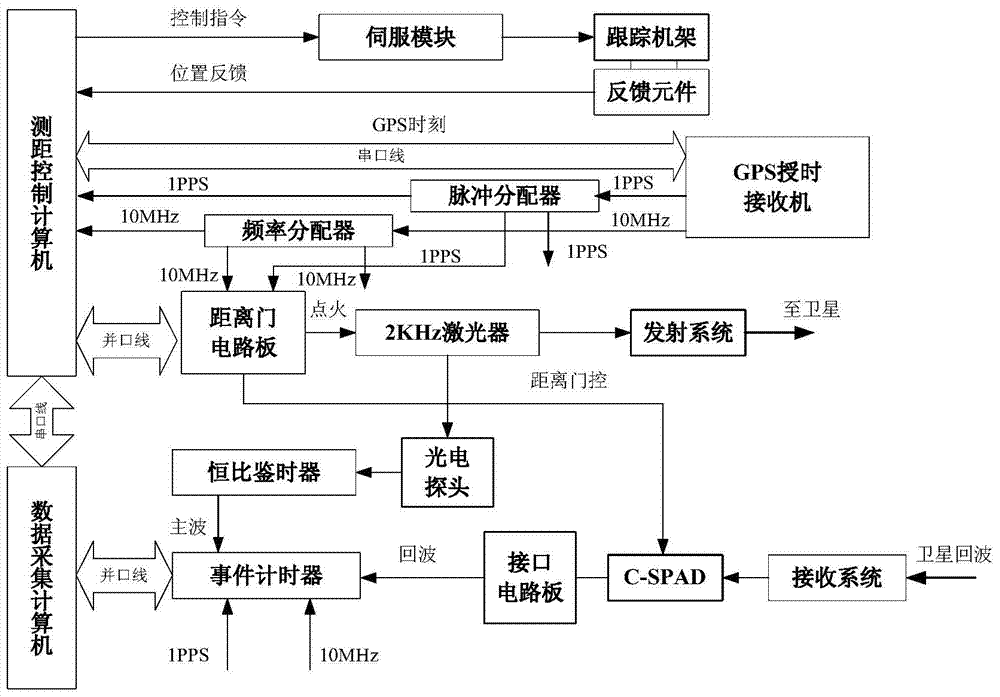
The invention provides an artificial satellite laser ranging system. The artificial satellite laser ranging system is characterized by comprising a ranging control computer, a laser, a transmitter-telescope, a receiving telescope, a data collection computer, an event timer, a range gate circuit board, an artificial satellite tracking and pointing device and a single-photon avalanche diode. By means of the artificial satellite laser ranging system, the event timer records the dominant wave moment and the return wave moment, the signal to noise ratio of the system is greatly improved by application of a high-resolution-ratio and high-precision range door, then the effective return wave data size is improved, and the ranging precision and ranging capacity of the system are improved remarkably.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
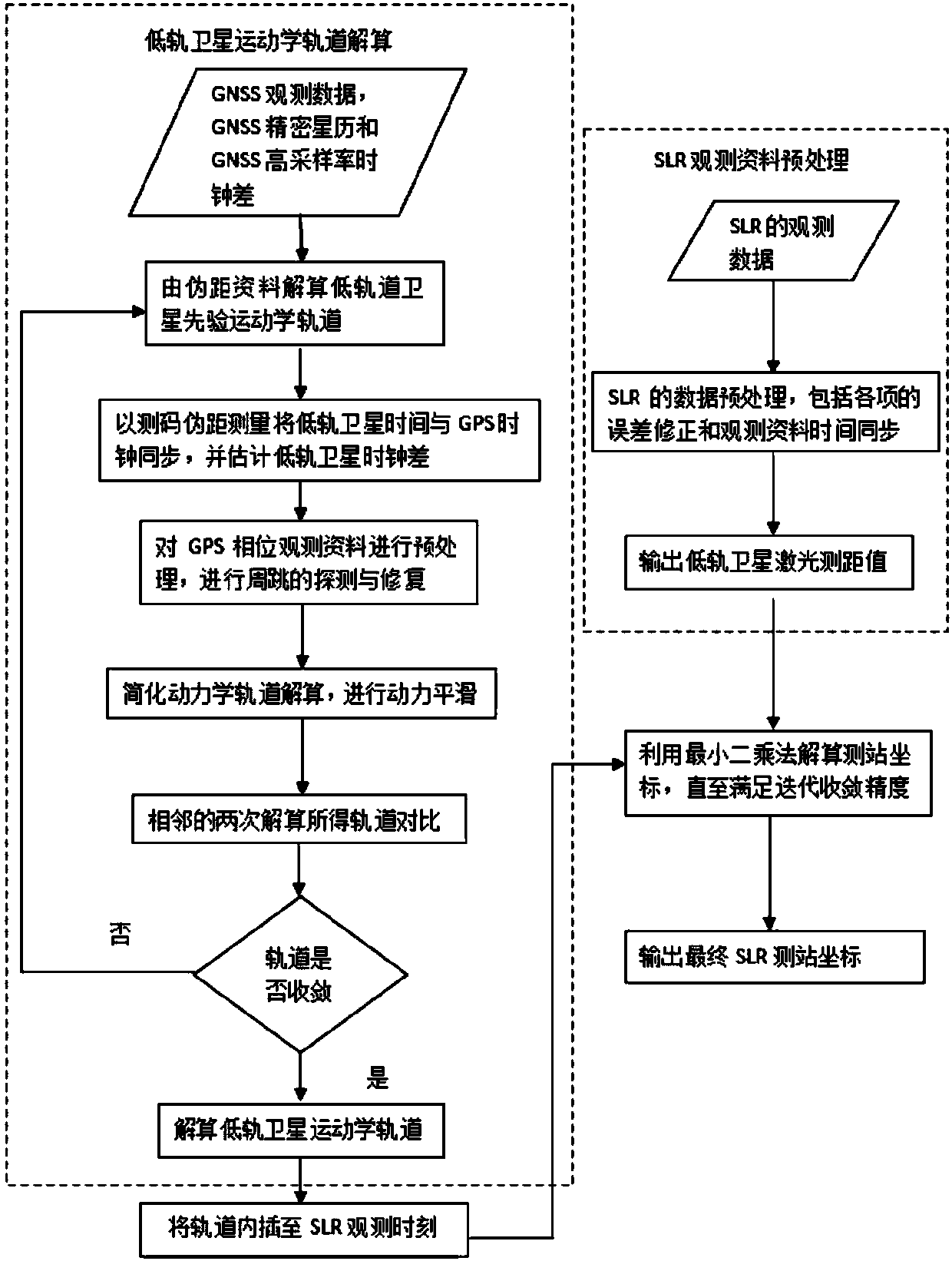
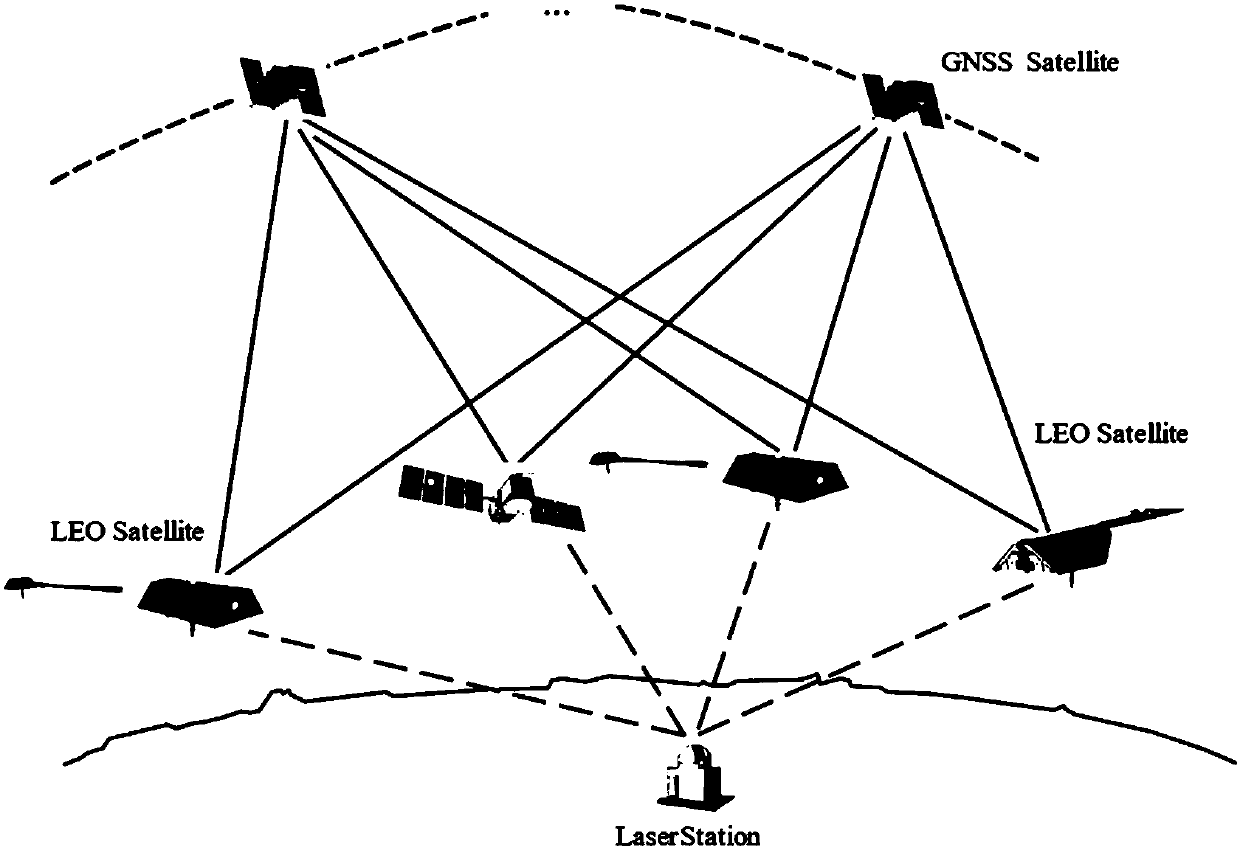
SLR station three-dimensional coordinate geometric solution method based on low-orbit satellite satellite-borne GNSS technology
ActiveCN108061908AAvoid complex processSimple methodOptical rangefindersSatellite radio beaconingSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
The invention discloses an SLR station three-dimensional coordinate geometric solution method based on low-orbit satellite satellite-borne GNSS technology. According to the geometric solution method,a GNSS receiver mounted on a low-orbit satellite is used to perform continuous tracking observation, and an undifferenced method is used to perform a precise kinematic orbit determination for the low-orbit satellite; then a satellite laser ranging rangle reflection prism carried in the low-orbit satellite is used to obtain an SLR laser ranging value, the system error correction is carried out on an SLR observation material, the material is converted into a distance between a high precision SLR station and a centroid of the low-orbit satellite, and combined with a precise geometric orbit of a multi-epoh single or multiple low-orbit satellites, according to the distance intersection positioning principle, the three-dimensional geometric coordinates of the ground SLR observation station are calculated by a least-squares method. The satellite-borne GNSS data and SLR tracking observation data of low-orbit satellites are used, a geometric method is used to realize high-precision geometric coordinates solution of the ground SLR observation station, and the solution has the advantage that a complex dynamics model is avoided compared with a classical dynamics solution.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Signal echo rate real-time controllable satellite laser ranging system, method and device
PendingCN110082772AShorten the timeReduce drift errorElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
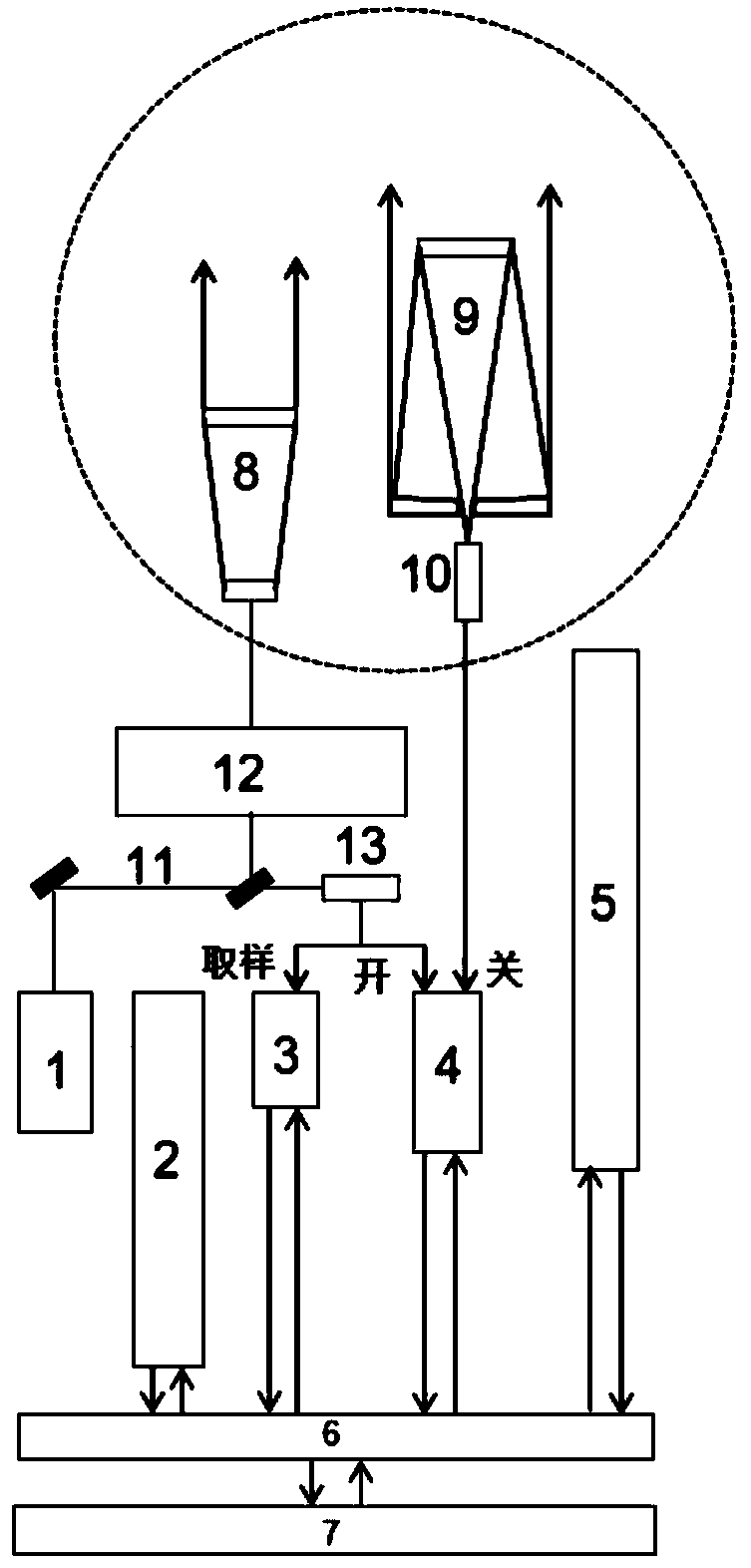
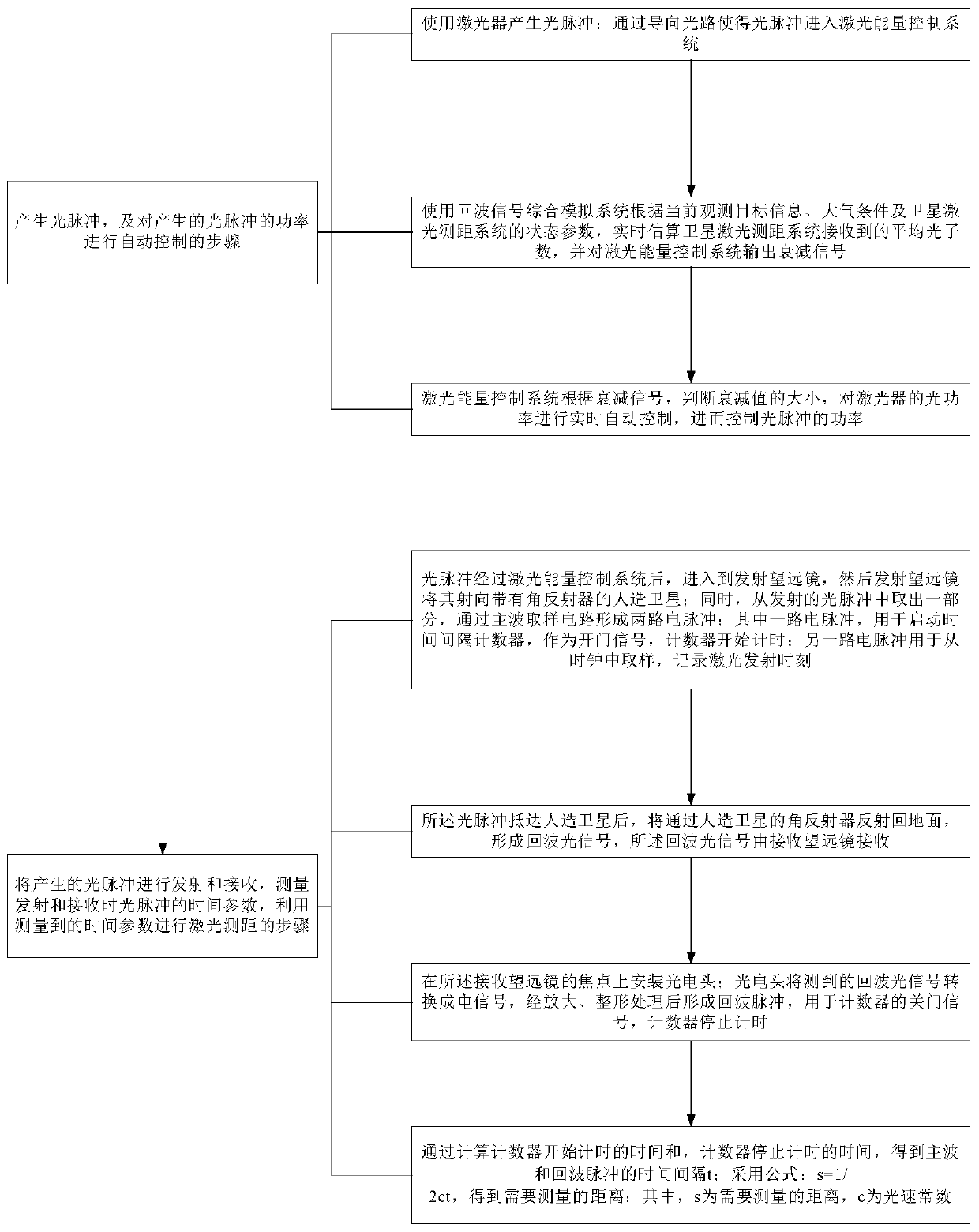
The invention belongs to the technical field of the laser ranging, and specifically relates to signal echo rate real-time controllable satellite laser ranging system, method and device. The system further comprises a laser device, a laser energy control system, an echo signal comprehensive simulation system, an transmitter-telescope, a dominant wave sampling circuit, a counter, a receiving telescope, a dominant wave sampling circuit and the counter; the laser device is used for producing light pulse and connected with the laser energy control system; the produced light pulse enters the laserenergy control system; the laser energy control system is connected with each of the echo signal comprehensive simulation system, the transmitter telescope and the dominant wave sampling circuit; thedominant sampling circuit is connected with the counter; and the counter is connected with the receiver telescope. The system precision is improved, and the system stability and effectiveness are improved.
Owner:中国科学院国家天文台长春人造卫星观测站
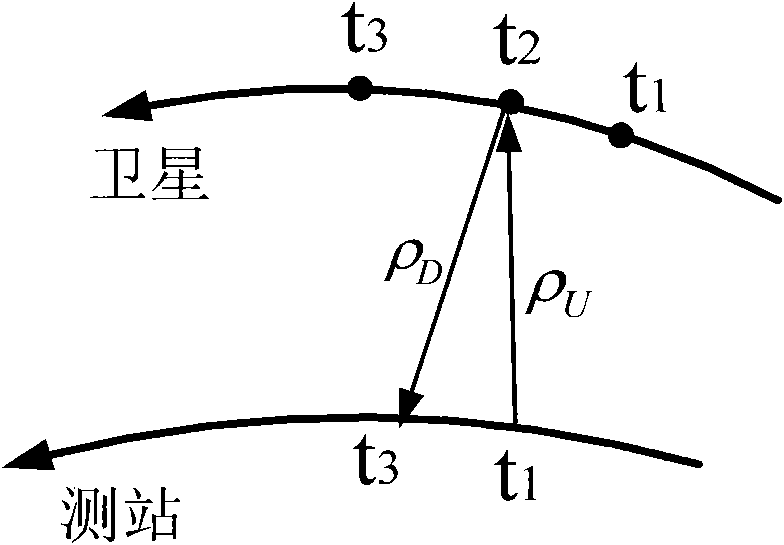
Method for confirming one-way distance in satellite laser ranging (SLR)
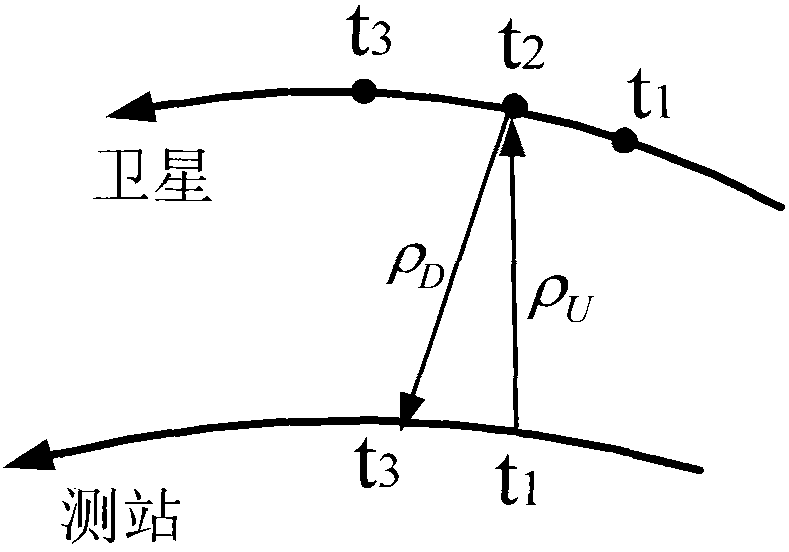
The invention relates to a method for confirming one-way distance in satellite laser ranging (SLR), which comprises the following steps of: acquiring SLR data by utilizing an SLR telescope; and calculating relatively accurate uplink or downlink distance in laser ranging by utilizing a measurement value. Particularly, when a track is confirmed by using single-station ranging and angle measurement, a complete vector having accurate length (ranging value) and accurate direction value in space is needed, and the calculating method of the invention is quite applicable. In short, the method for calculating the one-way distance is more explicit in physical significance and clearer in space geometry.
Owner:YUNNAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser far field divergence angle measurement method and device in satellite laser ranging
ActiveCN105928689AAvoid Tilt ErrorsEliminate Uncertainty ErrorsWave based measurement systemsTesting optical propertiesSatellite laser rangingMeasurement device
Owner:YUNNAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Satellite laser ranging (SLR) super short distance target calibration method
InactiveCN101876708ASimple installation and debuggingEasy to aimElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingSatellite laser ranging
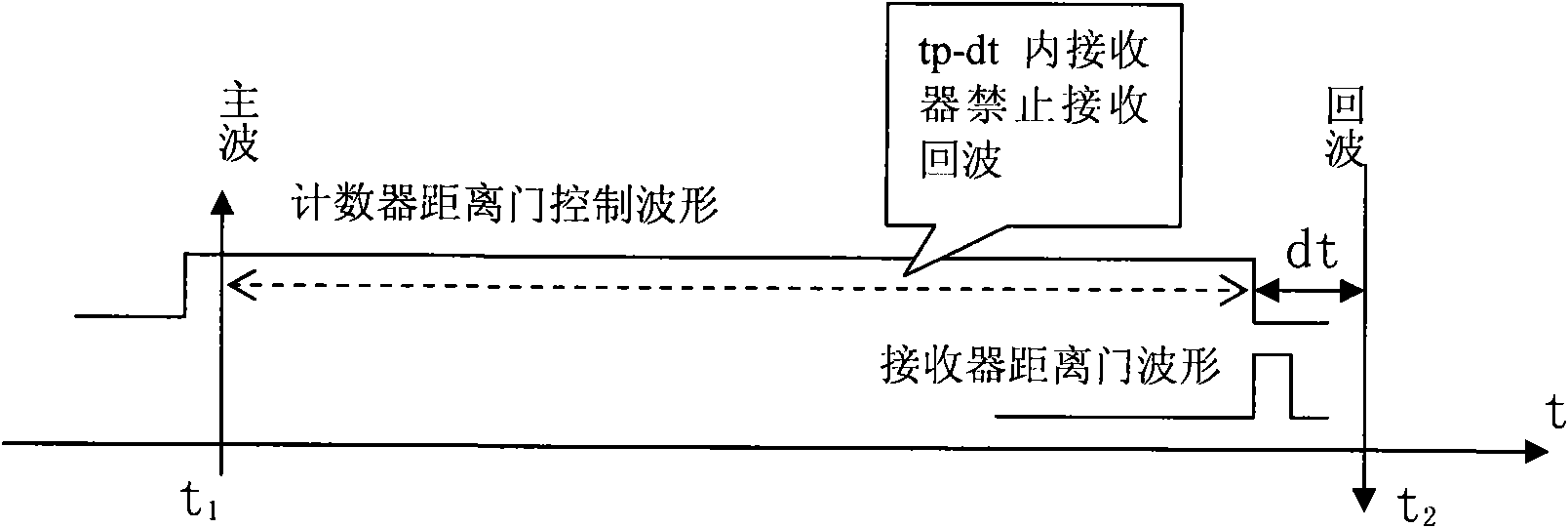
The invention relates to a super short-distance (less than 1m) target distance measuring technology in satellite laser ranging (SLR), and is composed of a distance gate control mode, and an optical and mechanical structure for calibrating a target. A near-earth target is arranged between a transmitting column and a receiving column of a telescope and can rotate along with the telescope to calibrate time delay of various light paths and circuits in a satellite laser ranging system.
Owner:INST OF EARTHQUAKE CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTRATION
Time interval digitally quantized event counter
InactiveCN101727068AElectric unknown time interval measurementSatellite laser rangingDigital interface
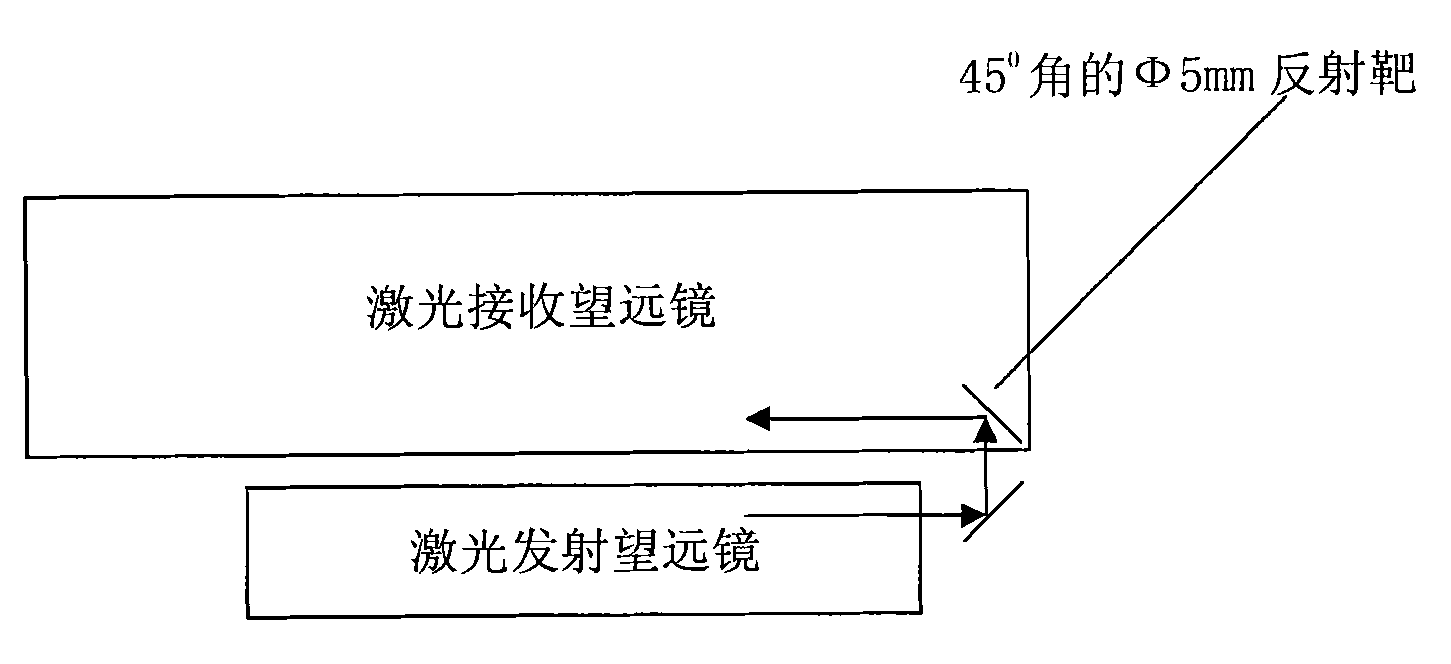
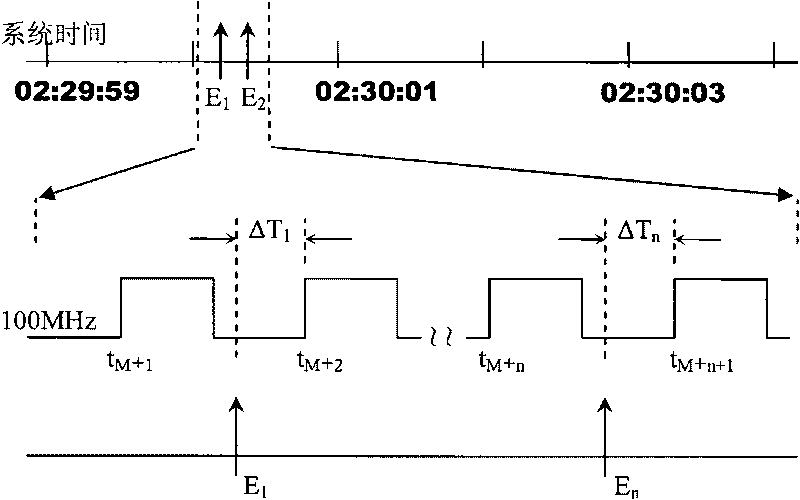
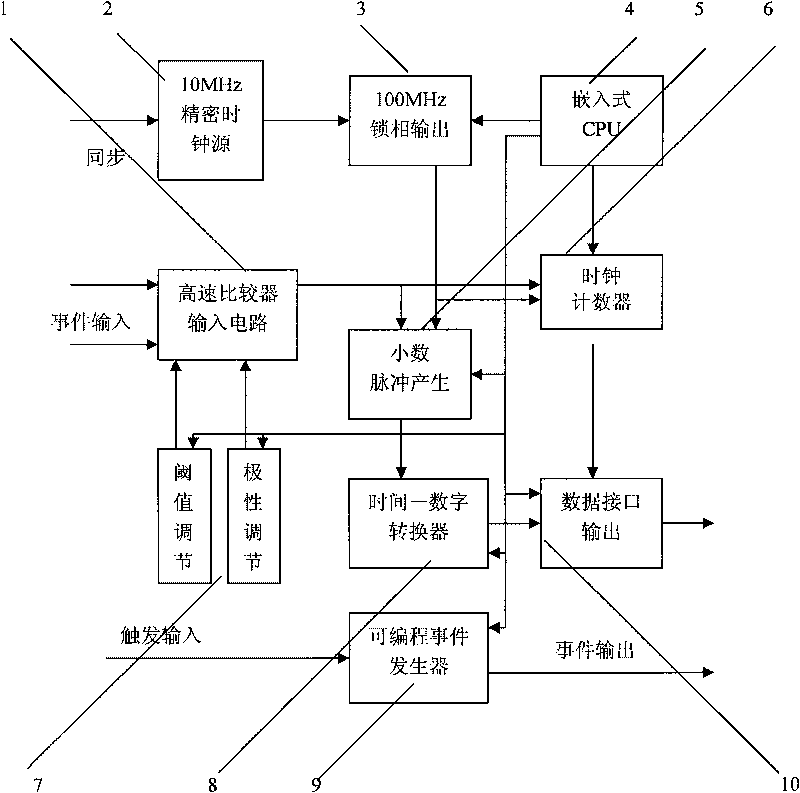
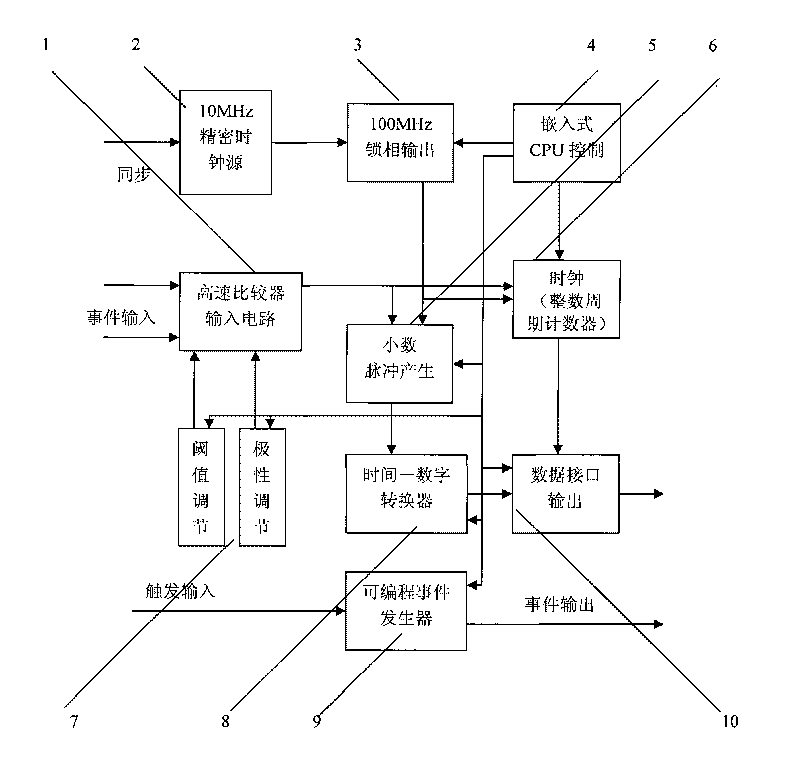
The invention relates to a time interval digitally quantized event counter applied to high repetition frequency satellite laser ranging. The time interval digitally quantized event counter belongs to equipment which is capable of measuring a moment when an event occurs, and is established by using a digitized time interval measuring chip, a high-speed comparator input circuit, a high-speed digital counter circuit, a high-speed digital interface circuit and an accurate pulse generator circuit. The event counter can be widely applied in fields of satellite laser ranging, space debris determination, accurate time event, time interval measurement and the like.
Owner:INST OF EARTHQUAKE CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTRATION
Real time resolving method for satellite laser distance measuring multiple pulse fuzzy degree
ActiveCN1821807ARecover energy instability problemSolve the problem of odd waveform changesElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite laser rangingTruth value
This invention discloses a real time calculation method for multi-pulse fuzziness in the distance test of satellite laser, which utilizes the global information got in real time and the extrapolate satellite theory orbit to compare it with the actual test result to determine the true value from multiple fuzzy values, 1, getting observation data of part of SLR observation stations of the globe and instant star calendar from the network, 2, utilizing relative software and instant observation data to compute the satellite theory distance value of the latter period of time, 3, applying the precise orbit extrapolation method to select a correct value from the multiple values.
Owner:INST OF EARTHQUAKE CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTRATION
Full-waveform satellite laser ranging system and method
ActiveCN111751835ASimple designIncrease the number of echo pointsSatellite radio beaconingElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite laser rangingEngineering
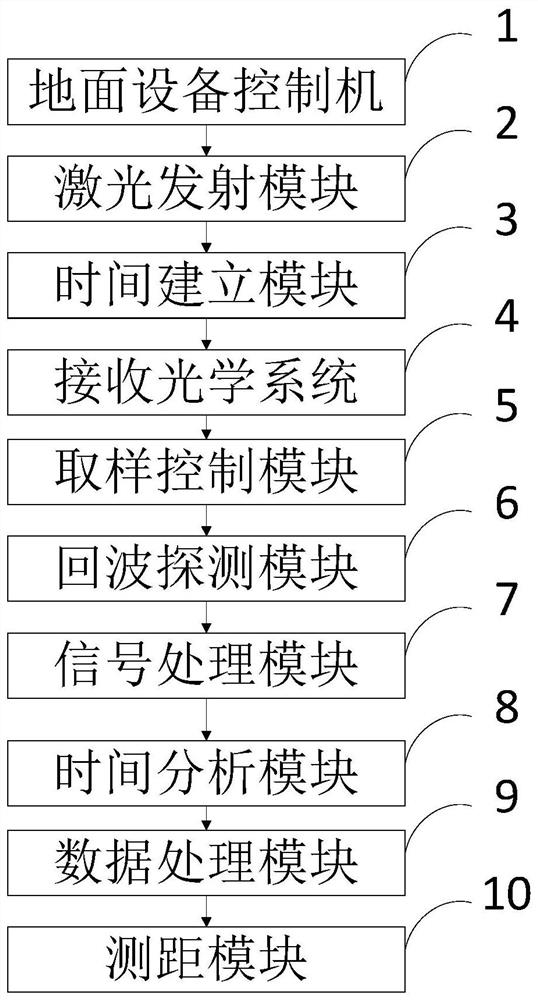
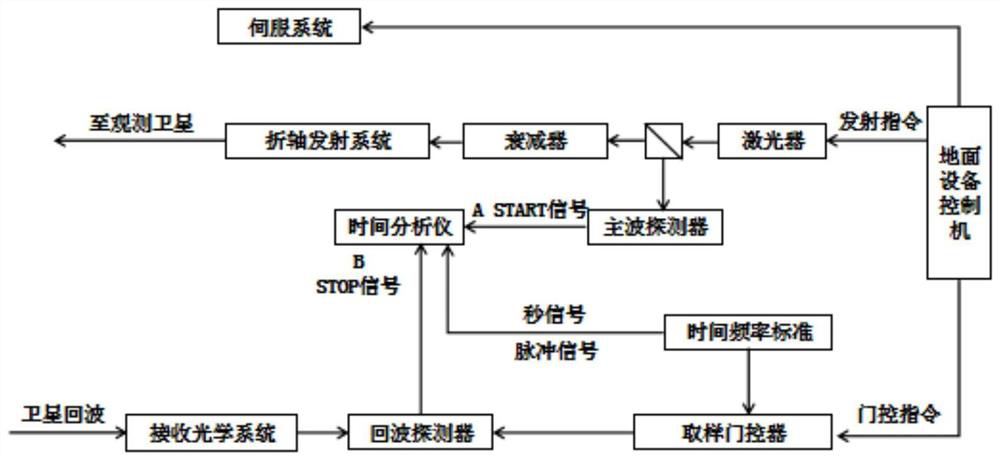
The invention belongs to the technical field of laser ranging, and discloses a full-waveform satellite laser ranging system and method. The system comprises: a ground equipment controller which is used for transmitting an instruction; a laser emission module, which is used for emitting laser pulse; a receiving optical system, which is used for receiving echo signals returned by a satellite; a sampling control module, which is used for starting a sampling door controller; an echo detection module, which is used for conducting sampling for multiple times; a signal processing module, which is used for acquiring SLR full-waveform echo data in a time grid arc section; an time analysis module, which is used for performing converting to obtain echo photon flight time for counting and accumulating; a data processing module, which is used for decomposing the acquired multi-peak echo data into a plurality of sub-waveforms; and a ranging module, which is used for acquiring the distance S betweenthe satellite and the ground. The system has direct application value for optimization design of a high-precision SLR system and design of a target recognition algorithm, and further has very important scientific value for perfection of a laser ranging theoretical system.
Owner:中国科学院国家天文台长春人造卫星观测站
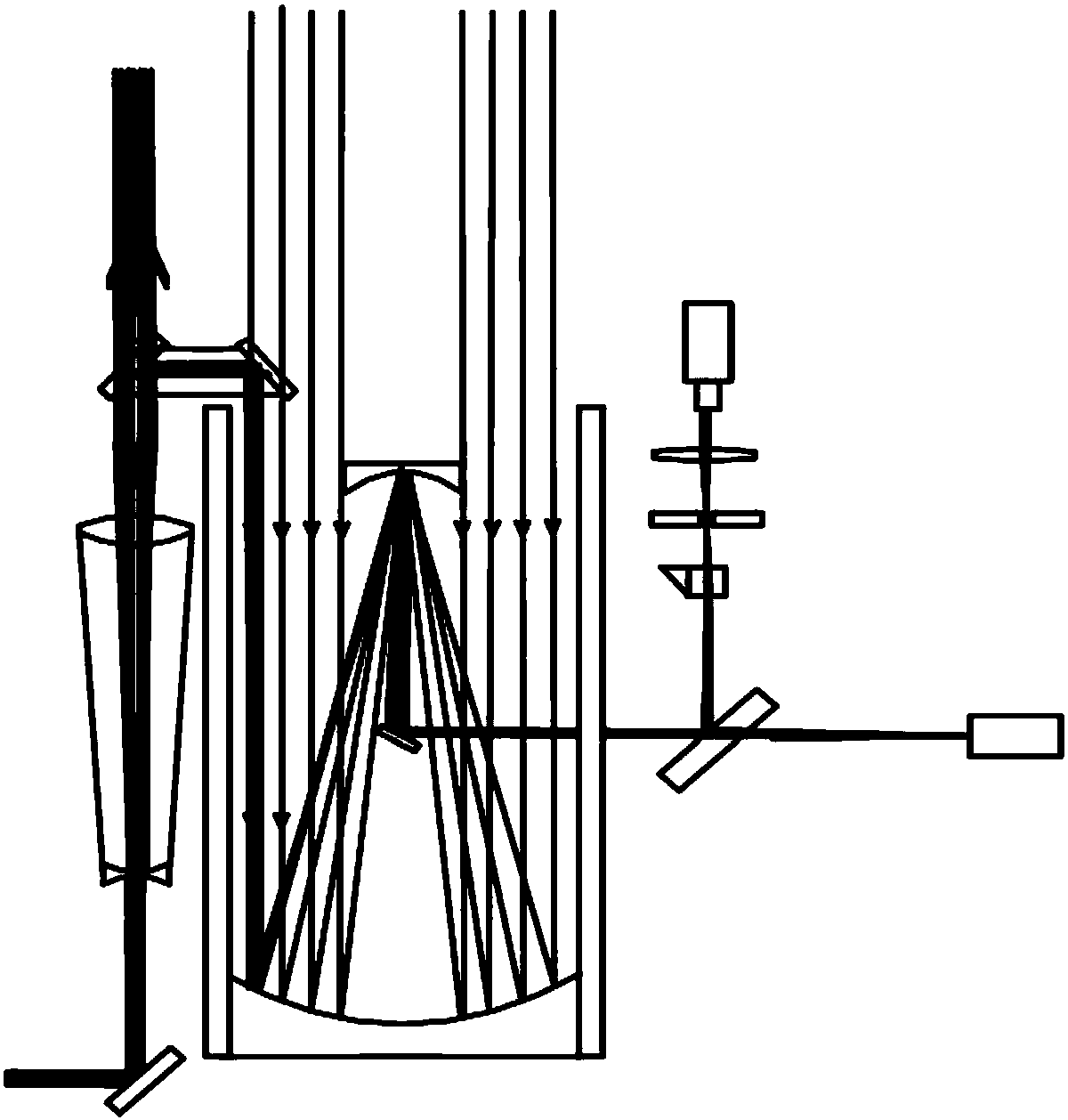
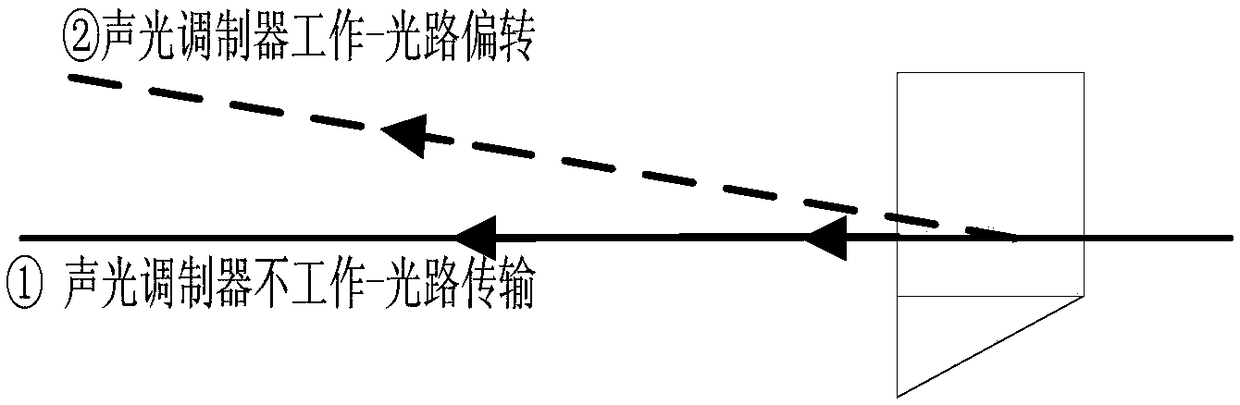
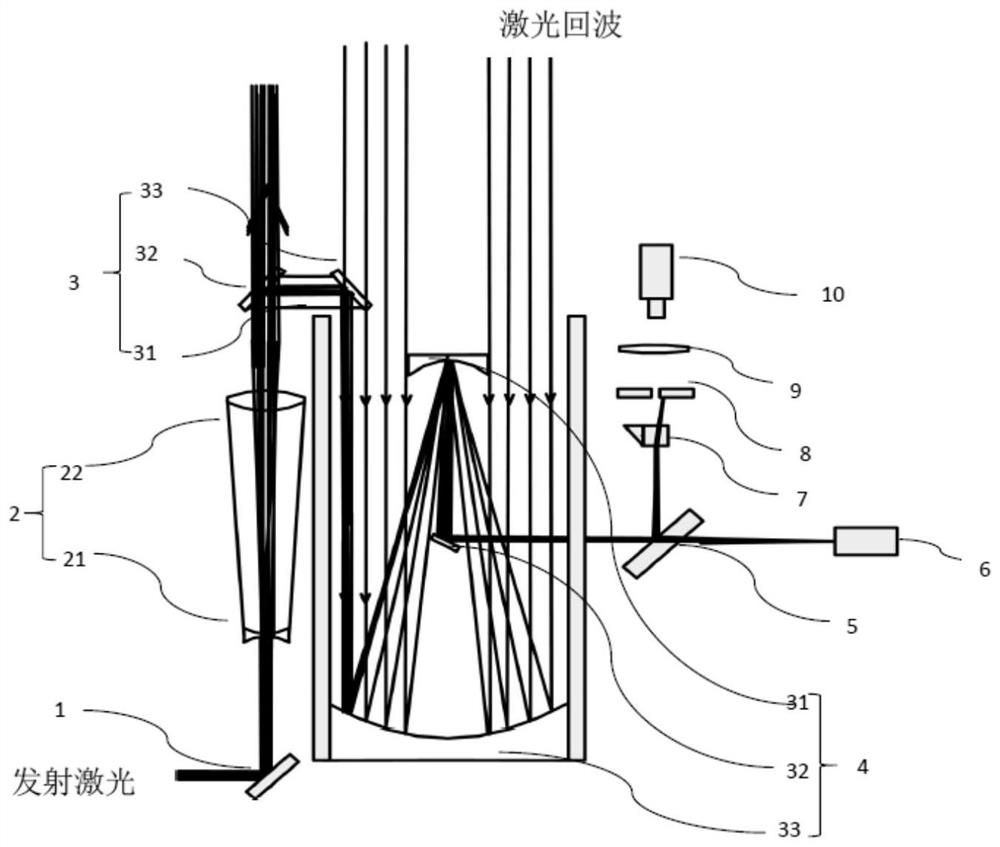
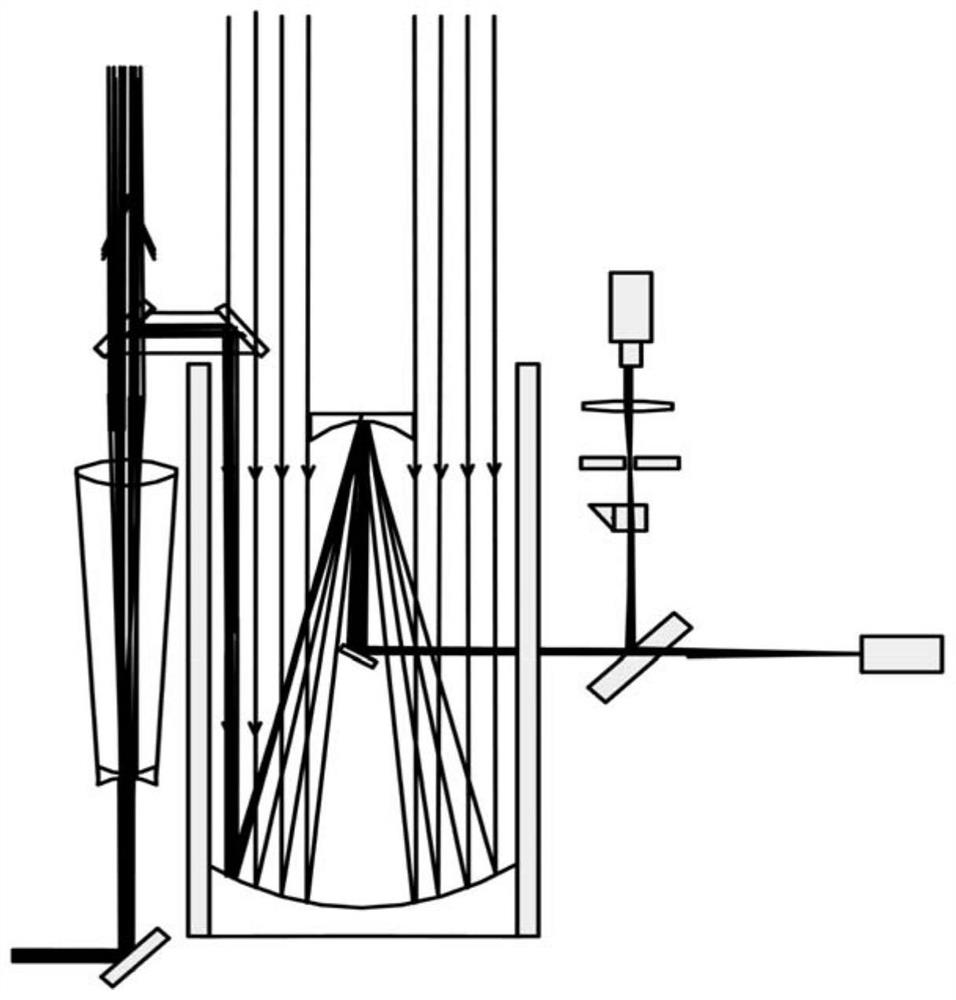
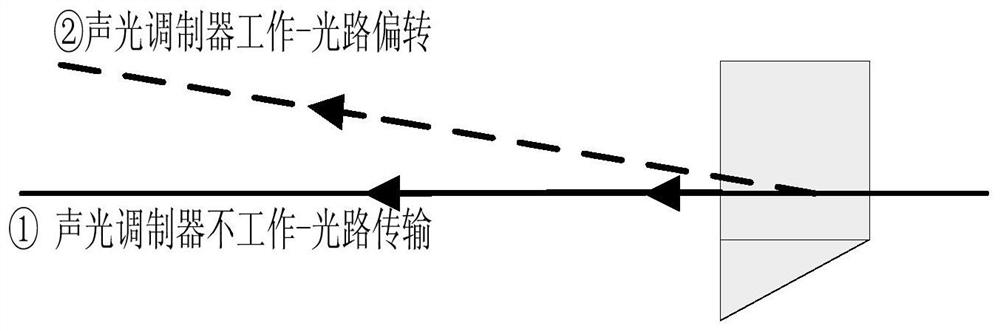
Device for real-time and high-precision monitoring of direction of laser-range finding light beam
ActiveCN108519591AImprove aimingAccurate monitoringWave based measurement systemsLaser rangingSatellite laser ranging
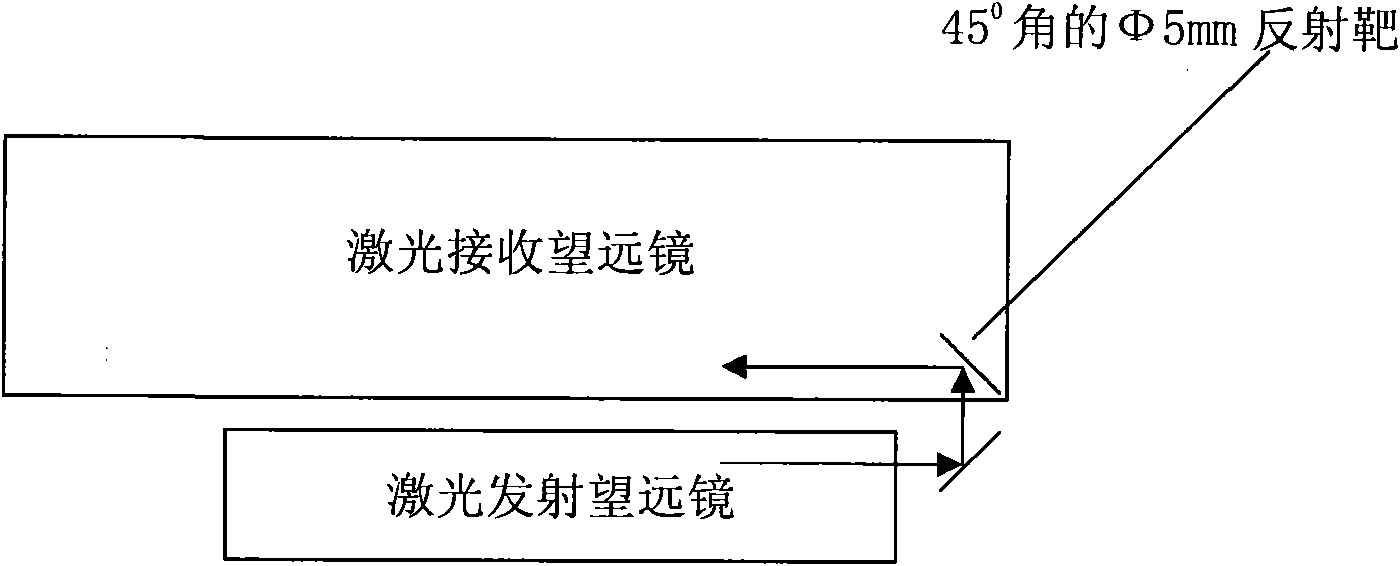
The invention relates to a device for the real-time and high-precision monitoring of the direction of a laser-range finding light beam, and the device comprises a 45-degree reflector, a transmitting telescope, a right-angle combined reflector, a receiving telescope, a beam splitter, a monitoring CCD, an acousto-optic modulator, a controllable small aperture diaphragm, a collimating mirror, and a detector. Transmitted laser is transmitted by the transmitting telescope, wherein most of the laser passes through the right-angle combined reflector on a transmitting light path, and a part of laser is reflected by the right-angle combined reflector, and is transmitted in an opposite direction in a manner of being parallel to the transmitting light path to the receiving telescope to reach the beamsplitter. A small part of laser passes through the beam splitter to be detected by the monitoring CCD, and other parts of laser are reflected. When the acousto-optic modulator works, a reflecting light beam deflects to the edge of the controllable small aperture diaphragm, thereby avoiding the damages caused by light to the detector. When the acousto-optic modulator is not in a working state, a laser echo is enabled to pass through the controllable small aperture diaphragm and the collimating mirror to reach the detector. The real-time monitoring of the direction of the light beam facilitatesthe real-time collimation of a detection target in the laser range finding, and promotes the development of the laser range finding, especially the satellite laser range finding.
Owner:SHANGHAI ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
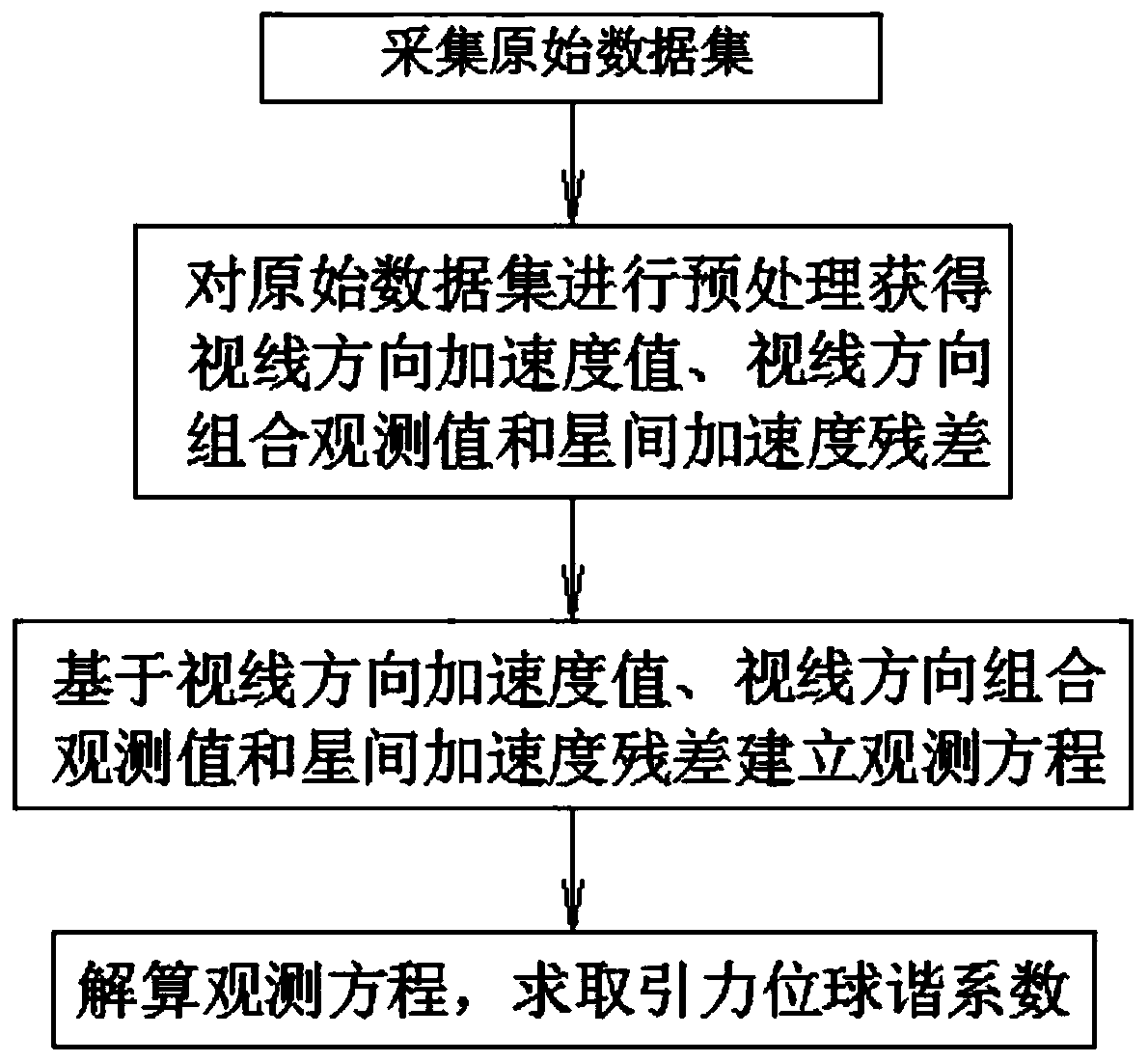
Method for determining gravitational field model based on gravity satellite inter-satellite laser ranging system
ActiveCN111366984AHigh solution accuracyHigh measurement accuracyGravitational wave measurementSatellite laser rangingSatellite technology
The invention relates to a method for determining a gravitational field model based on a gravity satellite inter-satellite laser ranging system, and belongs to the technical field of satellite gravitydetection. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an original data set; preprocessing the original data set to obtain a sight line direction acceleration value, a sight line direction combined observation value and an inter-satellite acceleration residual error; establishing an observation equation based on the line-of-sight direction acceleration value, the line-of-sight direction combined observation value and the inter-satellite acceleration residual error; and solving an observation equation, and solving a gravitation potential spherical harmonic coefficient. According to themethod, the inter-satellite distance, the change rate of the inter-satellite distance and the inter-satellite acceleration are obtained on the basis of a gravity satellite inter-satellite laser ranging system, an observation equation is established according to the Newton's second law of motion, and finally the gravitation potential spherical harmonic coefficient is estimated through least squares. Compared with a classic high-low satellite tracking satellite technology inversion method, the method does not need numerical value micro-decomposition calculation, and can effectively avoid high-frequency error amplification, thereby improving the gravitational field model calculation precision.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Kilohertz common light path satellite laser ranging (SLR) optical device
InactiveCN101650438BEliminate bulkinessImprove ranging accuracyOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
The invention relates to a kilohertz common light path satellite laser ranging (SLR) optical device, belonging to laser ranging systems and comprising a reflective ranging telescope, a laser emission light path and an echo-receiving light path. The ranging telescope comprises a paraboloidal primary mirror, a paraboloidal secondary mirror and an elbow reflector; the laser emission light path comprises a kilohertz laser, a negative lens, a positive lens and a docking mirror; wherein the negative lens and the positive lens are formed a laser-expanding structure capable of adjusting a divergence angle; a coupling lens and a collimating lens in the echo-receiving light path are confocal to be formed an afocal system; the diameter of a compressed echo ray behind the collimating lens is matched with the pupil-entrance diameter of a single-photon detector; a rotary shutter is arranged in front of a focus of the echo coupling lens; an iris diaphragm is arranged on the focus of the echo coupling lens; and an optical filter is arranged in front of the single-photon detector. The kilohertz common light path SLR optical device selects a ranging frequency within 1-4 KHz, has high ranging accuracy and great echo amount and improves the ranging capability and the ranging level of the system.
Owner:YUNNAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Comprehensive low-noise constant-temperature laser receiving system
ActiveCN1936617BHigh temperature regulation accuracyNo human intervention requiredElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical elementsLow noiseSatellite laser ranging
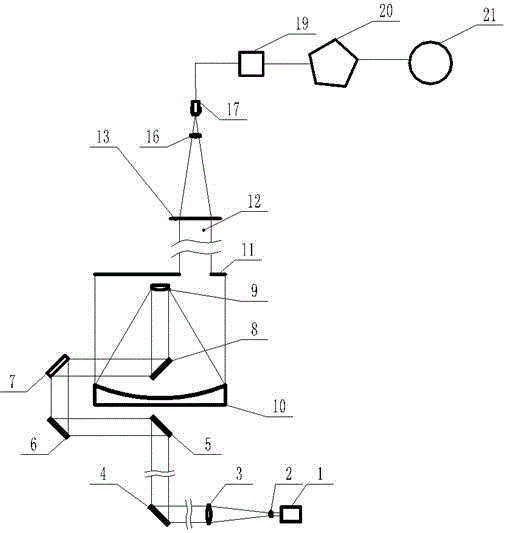
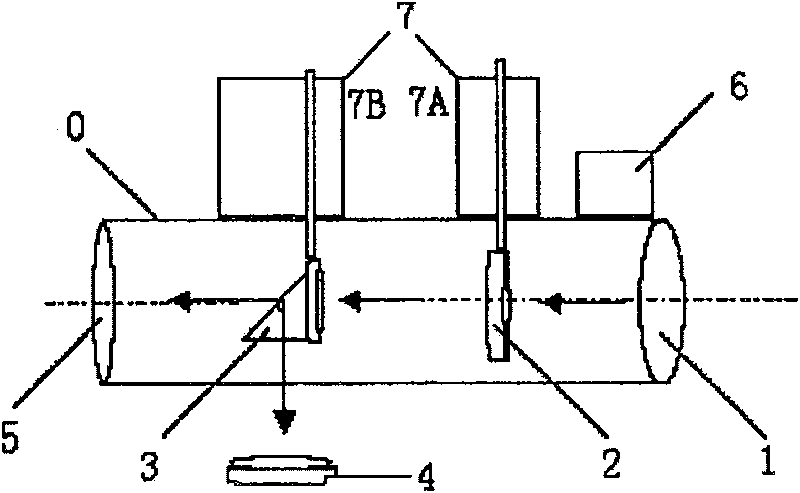
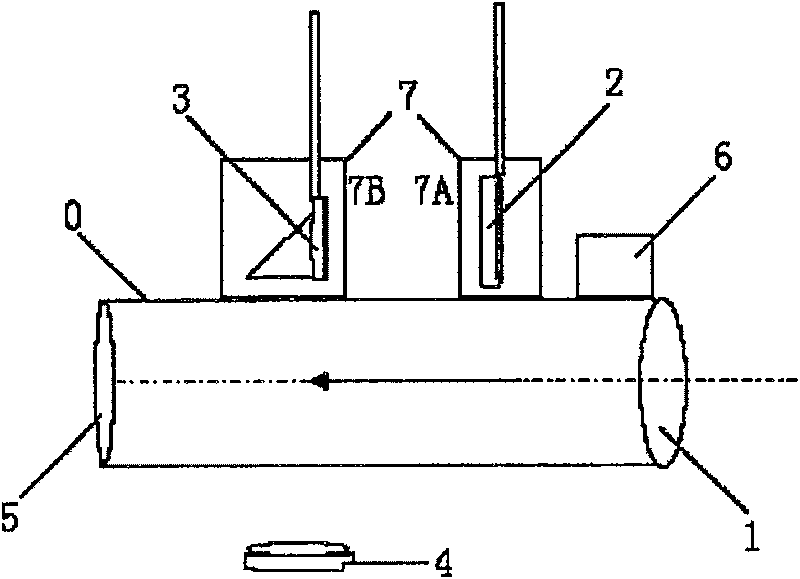
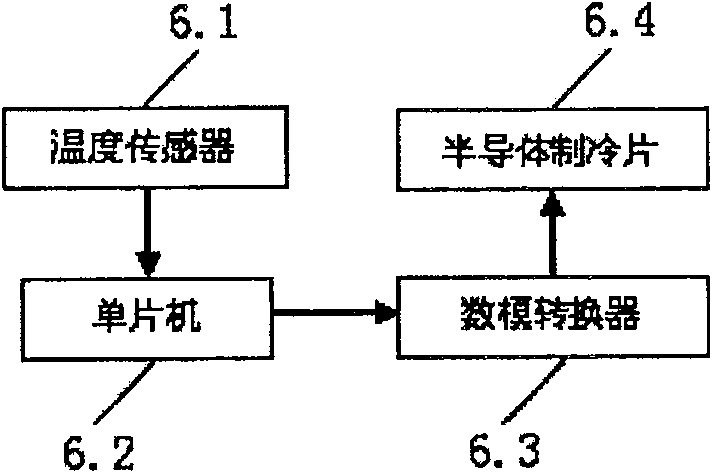
The invention discloses a laser receiver system of low yawp and constant temperature. The collimating lens (1), the light filter (2), the angle reflector (3), the photoelectric receiver (5) are set inthe cylinder (0) from the right to the left. The CCD (4), the temperature adjustment system (6) and the transmission gear (7) are set on the top of the cylinder; the transmission gear (7) includes thefirst transmission gear (7A) and the second transmission gear (7B); the light filter (2) is connected to the first transmission gear and the reflector (3) is connected to the second transmission gear (7B); the position of the CCD is correspond to the angle reflector (3). The invention has the function of constant temperature, light filter and light tine adjustment. So it can be used for the lidar , the satellite laser ranging, the spacecraft tracking, the stellar tracking observation and the space fragment dynamic tracking.
Owner:INST OF EARTHQUAKE CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTRATION
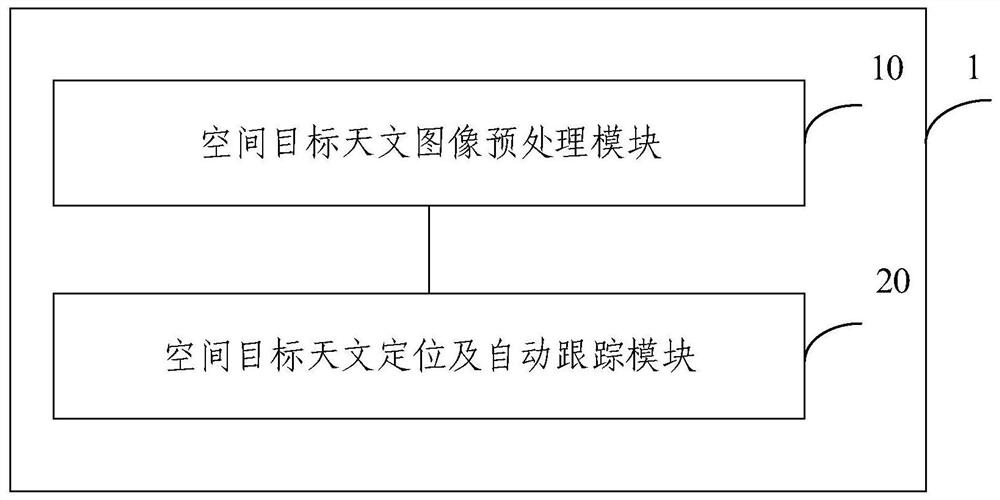
Astronomical positioning and automatic tracking method and system for space target and electronic equipment
PendingCN113552648AImprove the degree of automation of observationOvercoming the problem of low automationOptical detectionPicture interpretationSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
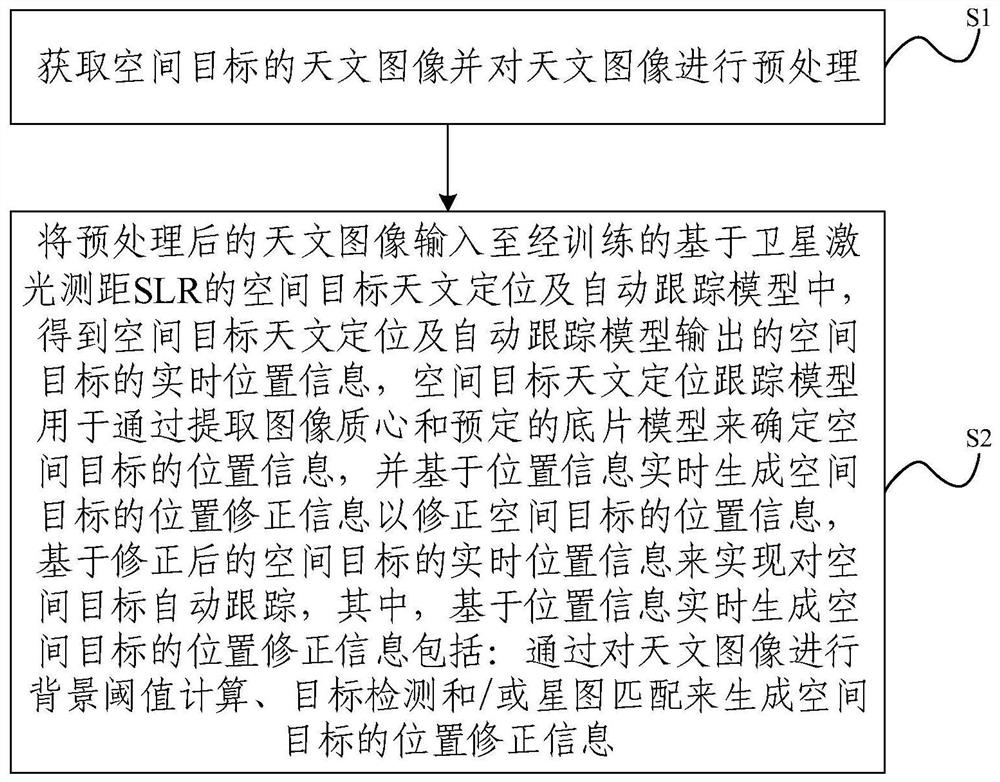
The invention provides an astronomical positioning and automatic tracking method and system for a space target and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an astronomical image of a space target and preprocessing the astronomical image; inputting the preprocessed astronomical image into a trained space target astronomical positioning and automatic tracking model based on satellite laser ranging (SLR) to obtain real-time position information of the space target output by the space target astronomical positioning and automatic tracking model, wherein the space target astronomical positioning and tracking model is used for determining position information of the space target by extracting an image centroid and a predetermined negative film model, and generating position correction information of the space target in real time based on the position information so as to correct the position information of the space target; and realizing automatic tracking of the space target based on the corrected real-time position information of the space target, and generating position correction information of the space target by performing background threshold calculation, target detection and / or star map matching on the astronomical image.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
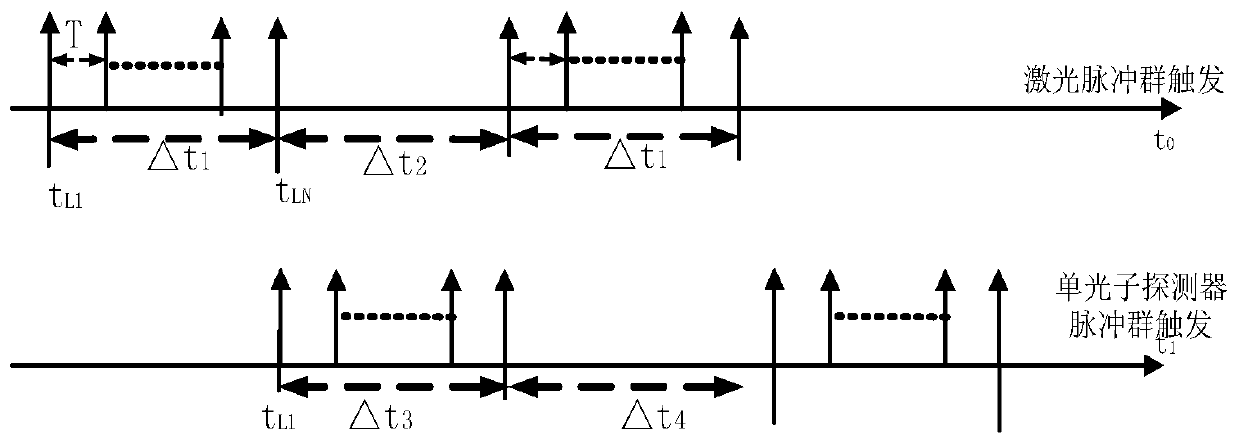
Pulse train type repetition frequency-adjustable laser ranging method
ActiveCN111505658AControl frequencyAvoid distractionsElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
The invention discloses a pulse train type repetition frequency-adjustable laser ranging method. A computer terminal, a distance gate controller, an event timer, a laser, a photoelectric detector, a reflector group, a transmitting telescope, a receiving telescope and a single-photon detector are adopted. The computer terminal outputs a satellite distance forecast value to the distance gate controller; an ignition pulse train triggers the laser to output a laser pulse train; hundreds of pulses exist in the laser pulse train; part of the light is detected by the photoelectric detector, and the other light is transmitted to a satellite through the reflector group and the transmitting telescope; laser pulse train echoes returned by the satellite are received by the receiving telescope, and atthis moment, the distance gate controller outputs gate control pulse train signals to trigger the single-photon detector to receive the laser echoes; the event timer records the moment; and satellitedistance measurement is achieved through the processing of the computer terminal. By controlling the number of the pulses in the pulse train and the frequency period of the pulse train, adjustable ultrahigh repetition frequency satellite laser ranging can be achieved, and the development and application of laser ranging are promoted.
Owner:SHANGHAI ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
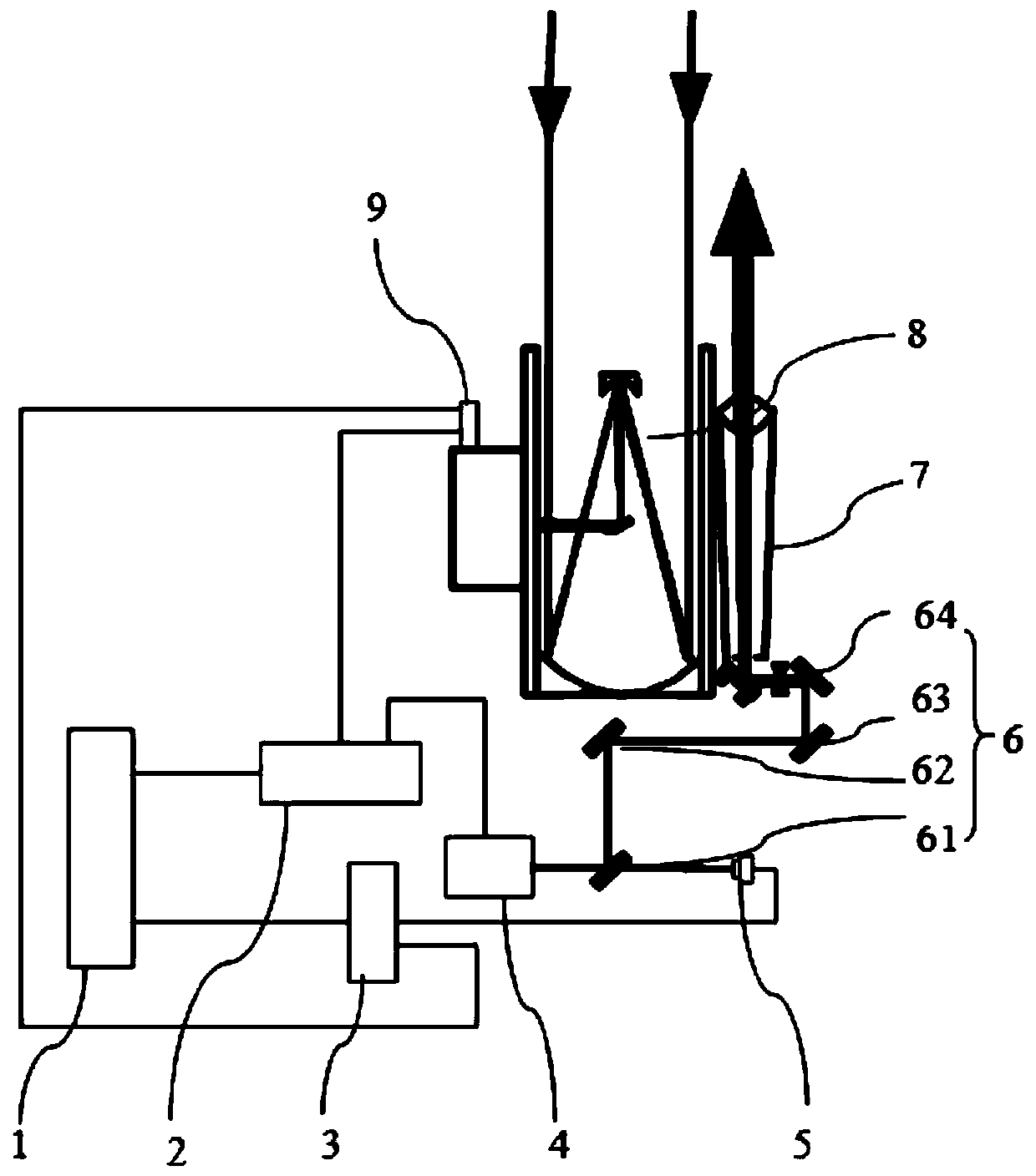
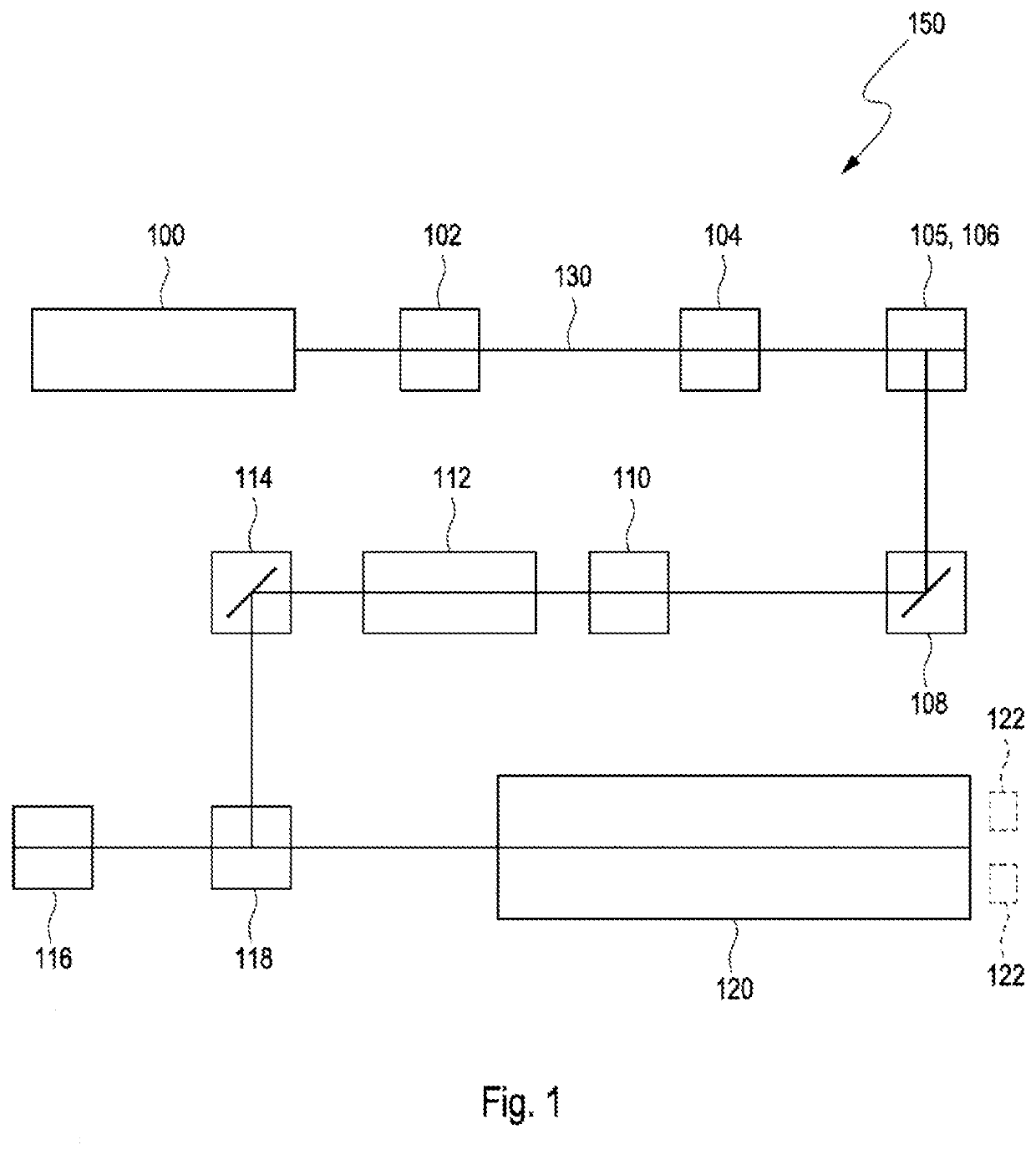
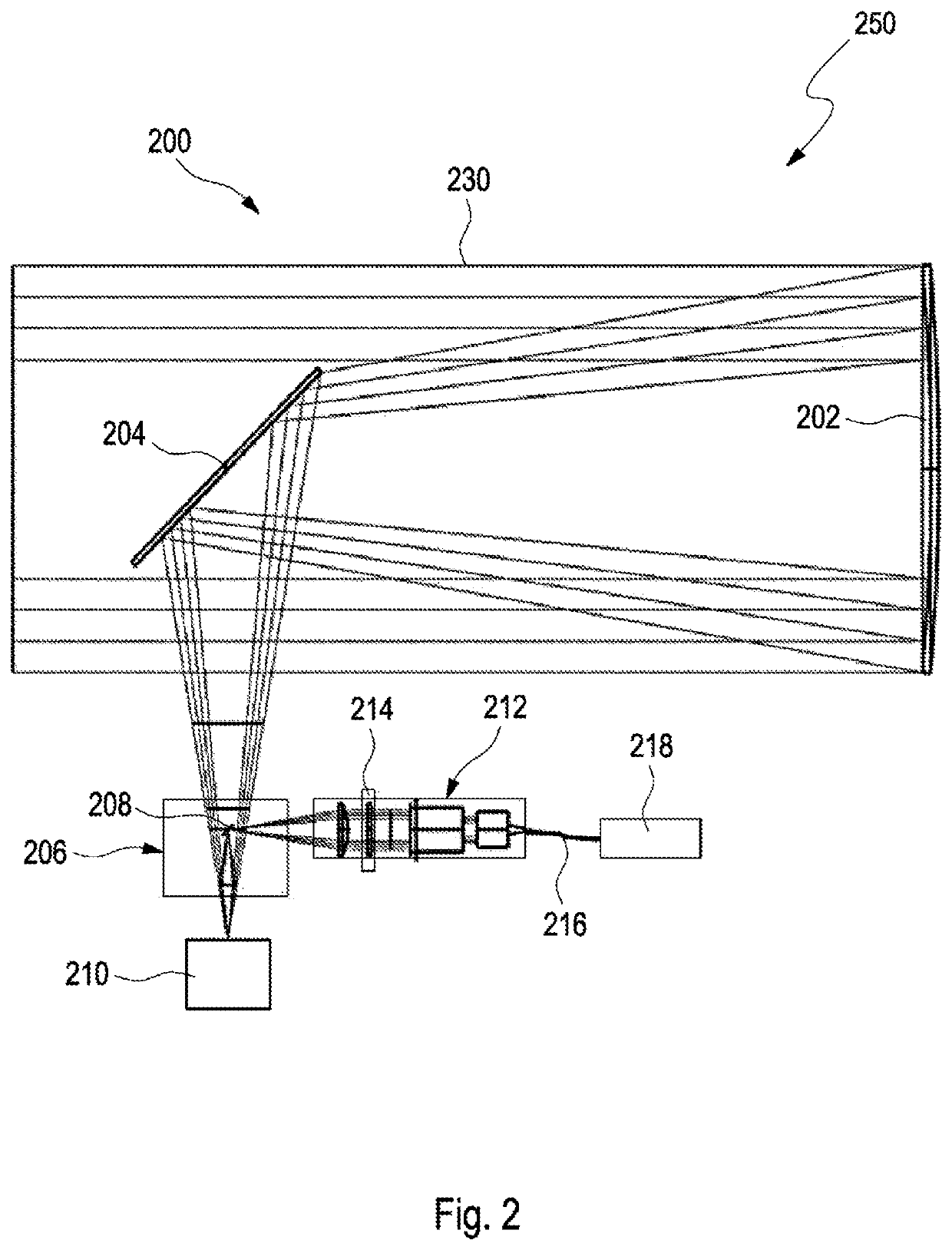
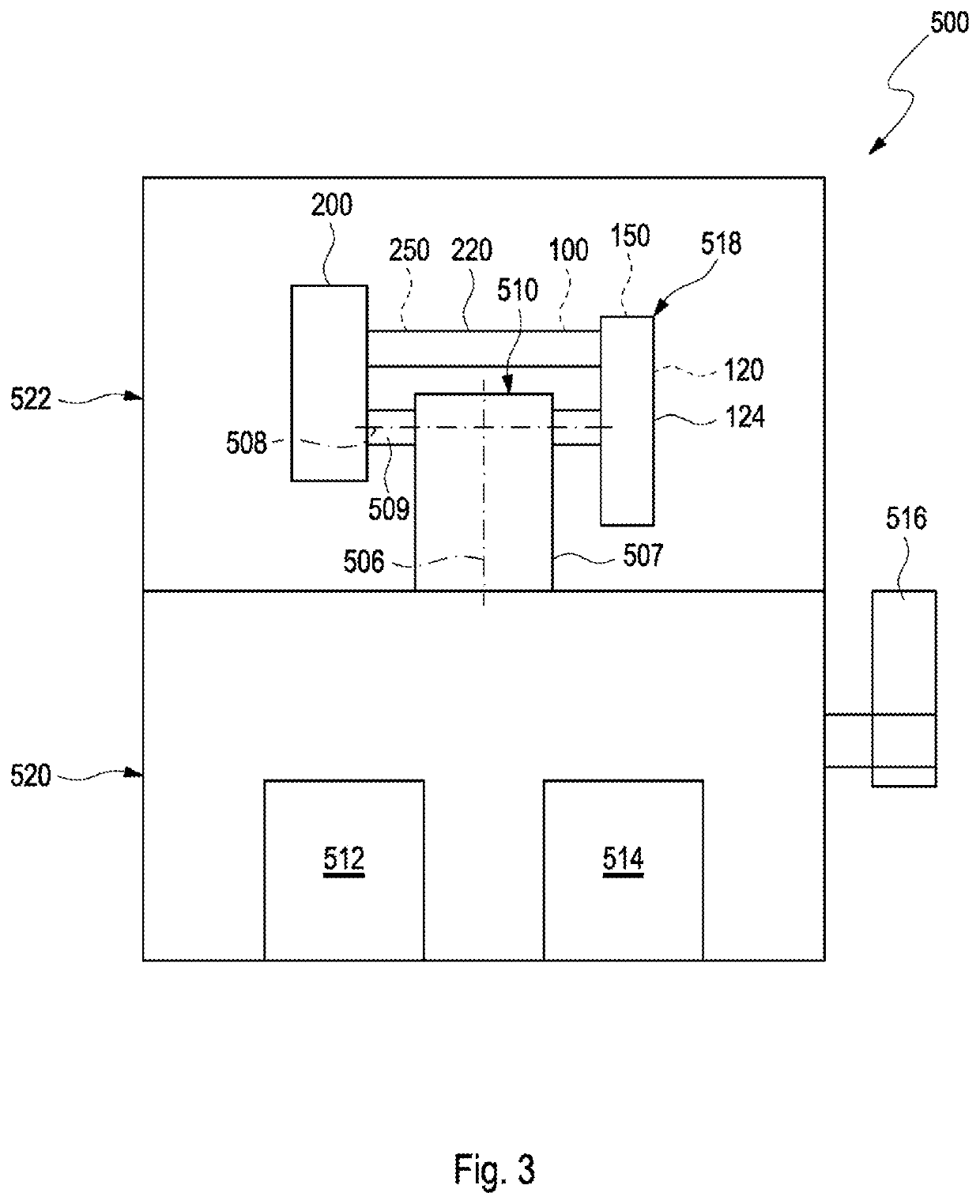
Device for a satellite laser distance measurement, and method for a satellite laser distance measurement
PendingUS20220342043A1Reduce designSmall sizeCosmonautic vehicle trackingElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
A device for a satellite distance measurement includes a base segment and an optical segment which is supported by the base segment and has a telescope mounting with an azimuth axis and an elevation axis, wherein a transmitter telescope, a receiving telescope, and a laser coupled to the transmitter telescope are arranged on the telescope mounting. A method for operating such a device is also provided.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
A device for real-time high-precision monitoring of laser ranging beam pointing
ActiveCN108519591BImprove aimingAccurate monitoringWave based measurement systemsSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
Owner:SHANGHAI ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for confirming one-way distance in satellite laser ranging (SLR)
ActiveCN101915926BOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingSatellite laser ranging
The invention relates to a method for confirming one-way distance in satellite laser ranging (SLR), which comprises the following steps of: acquiring SLR data by utilizing an SLR telescope; and calculating relatively accurate uplink or downlink distance in laser ranging by utilizing a measurement value. Particularly, when a track is confirmed by using single-station ranging and angle measurement,a complete vector having accurate length (ranging value) and accurate direction value in space is needed, and the calculating method of the invention is quite applicable. In short, the method for calculating the one-way distance is more explicit in physical significance and clearer in space geometry.
Owner:YUNNAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
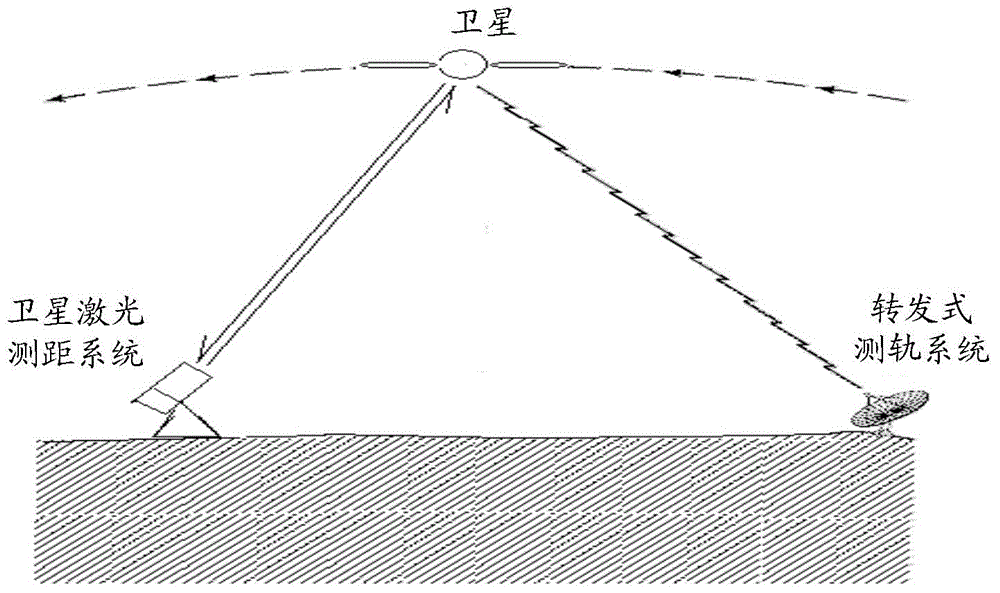
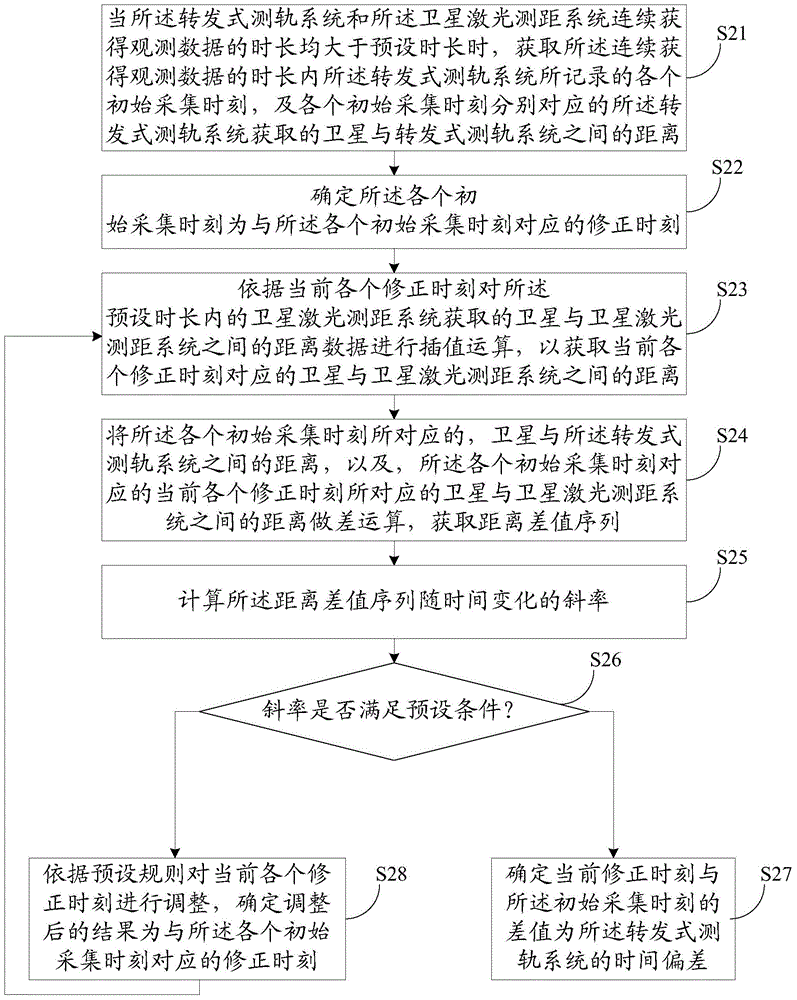
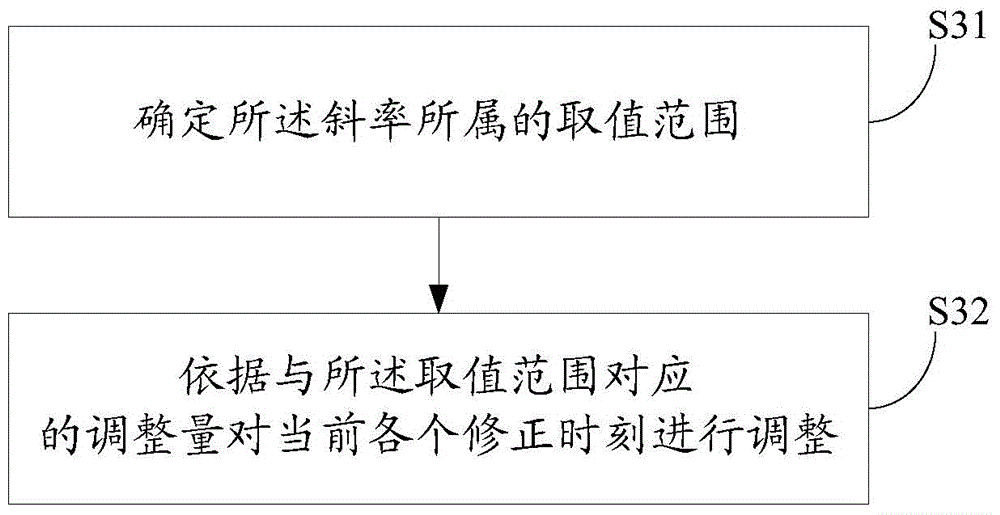
Method and device for measuring time deviation of forwarding orbit measurement system
ActiveCN103763052BImprove accuracyRadio transmissionRelay systems monitoringTime deviationSatellite laser ranging
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and system for measuring time deviation of a forwarding type track measuring system. A synchronous observing method of a satellite laser range measurement system and the forwarding type track measuring system is adopted to achieve real-time measurement of the time deviation of the forwarding type track measuring system, and therefore accuracy of star station range measurement of the forwarding type track measuring system is improved. In addition, the method and system are easy to achieve and low in achieving cost.
Owner:中国科学院国家天文台长春人造卫星观测站
Satellite Laser Ranging System
InactiveCN104535992BImprove signal-to-noise ratioIncrease the amount of effective echo dataElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSatellite laser rangingData acquisition
The invention provides an artificial satellite laser ranging system. The artificial satellite laser ranging system is characterized by comprising a ranging control computer, a laser, a transmitter-telescope, a receiving telescope, a data collection computer, an event timer, a range gate circuit board, an artificial satellite tracking and pointing device and a single-photon avalanche diode. By means of the artificial satellite laser ranging system, the event timer records the dominant wave moment and the return wave moment, the signal to noise ratio of the system is greatly improved by application of a high-resolution-ratio and high-precision range door, then the effective return wave data size is improved, and the ranging precision and ranging capacity of the system are improved remarkably.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
Real time resolving method for satellite laser distance measuring multiple pulse fuzzy degree
ActiveCN100474001CRecover energy instability problemSolve the problem of odd waveform changesElectromagnetic wave reradiationSatellite laser rangingTruth value
This invention discloses a real time calculation method for multi-pulse fuzziness in the distance test of satellite laser, which utilizes the global information got in real time and the extrapolate satellite theory orbit to compare it with the actual test result to determine the true value from multiple fuzzy values, 1, getting observation data of part of SLR observation stations of the globe and instant star calendar from the network, 2, utilizing relative software and instant observation data to compute the satellite theory distance value of the latter period of time, 3, applying the precise orbit extrapolation method to select a correct value from the multiple values.
Owner:INST OF EARTHQUAKE CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTRATION
A method for maintaining autonomous relative position of co-orbital satellites based on laser payload
ActiveCN107298186BCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusSatellite laser rangingLaser ranging
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com