Patents
Literature
447 results about "Avalanche diode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electronics, an avalanche diode is a diode (made from silicon or other semiconductor) that is designed to experience avalanche breakdown at a specified reverse bias voltage. The junction of an avalanche diode is designed to prevent current concentration and resulting hot spots, so that the diode is undamaged by the breakdown. The avalanche breakdown is due to minority carriers accelerated enough to create ionization in the crystal lattice, producing more carriers which in turn create more ionization. Because the avalanche breakdown is uniform across the whole junction, the breakdown voltage is nearly constant with changing current when compared to a non-avalanche diode.
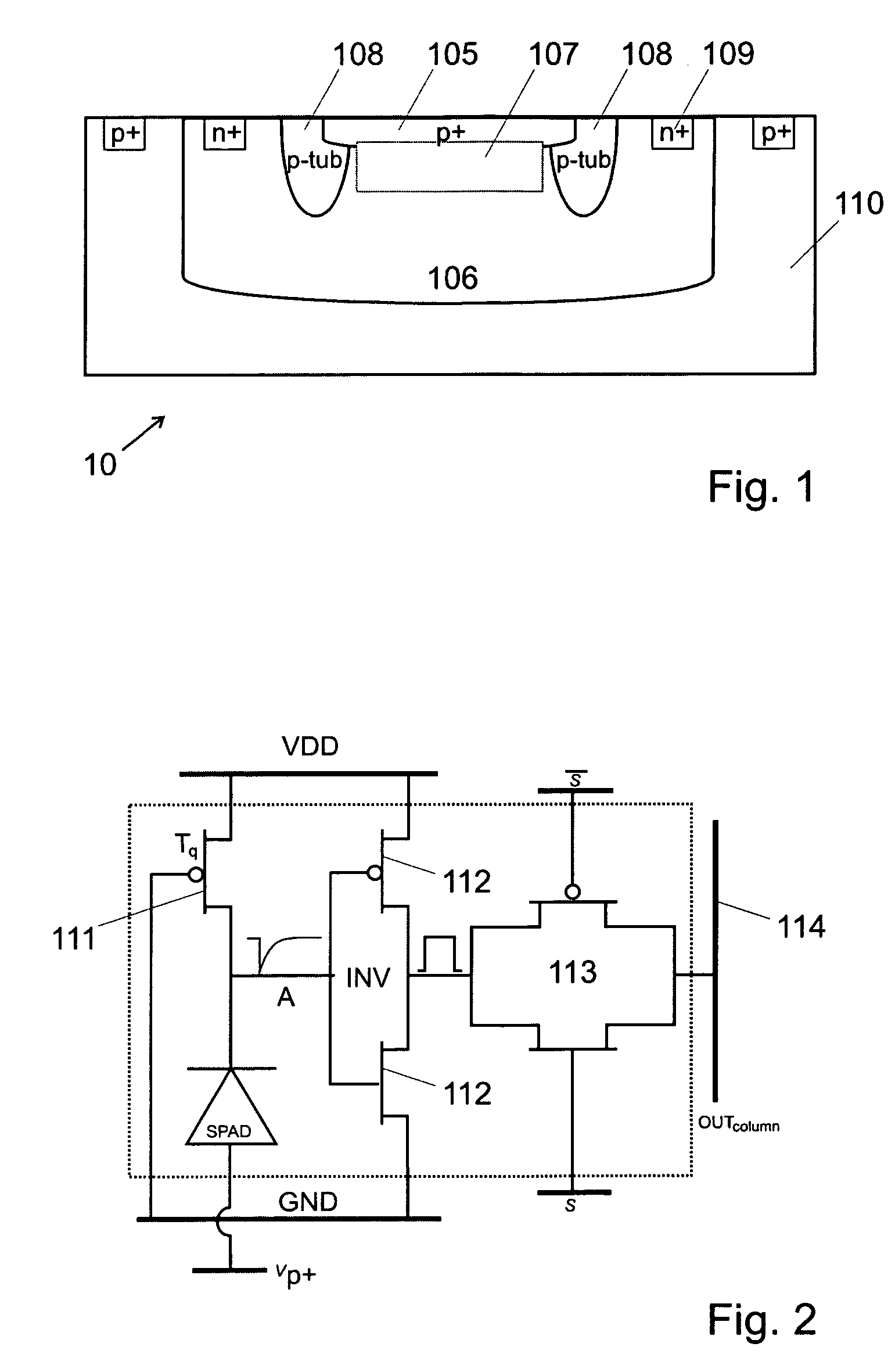
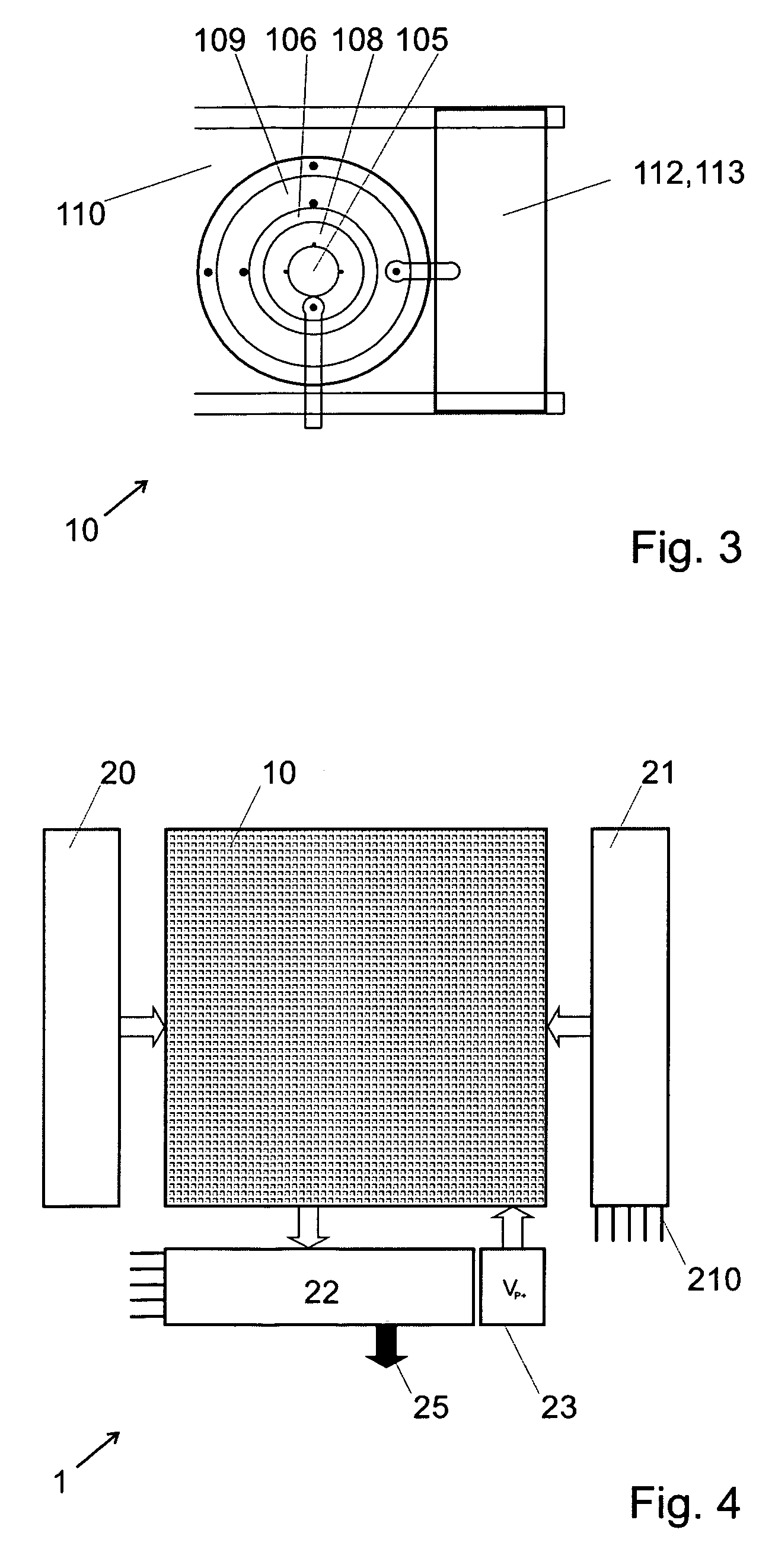
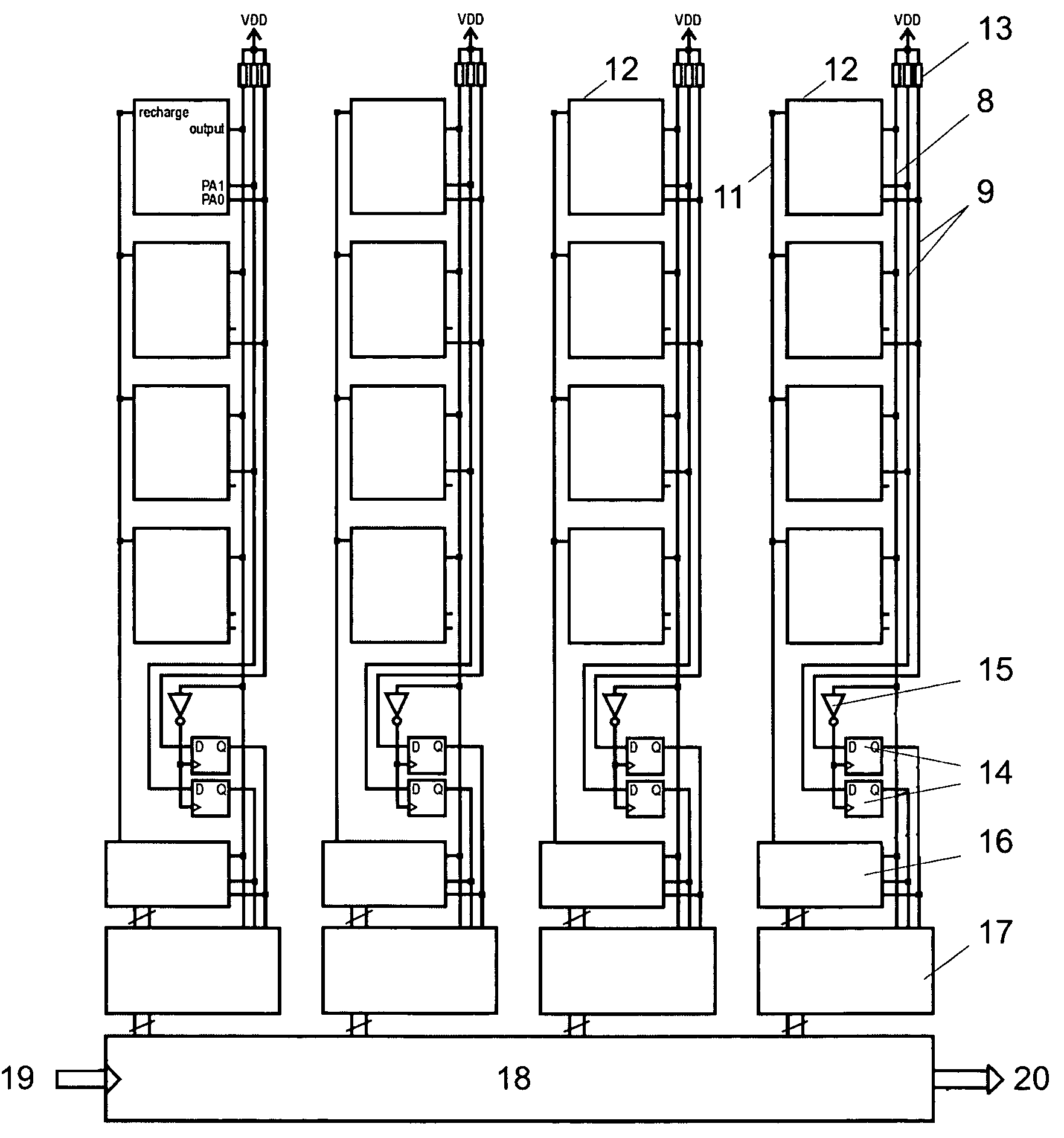
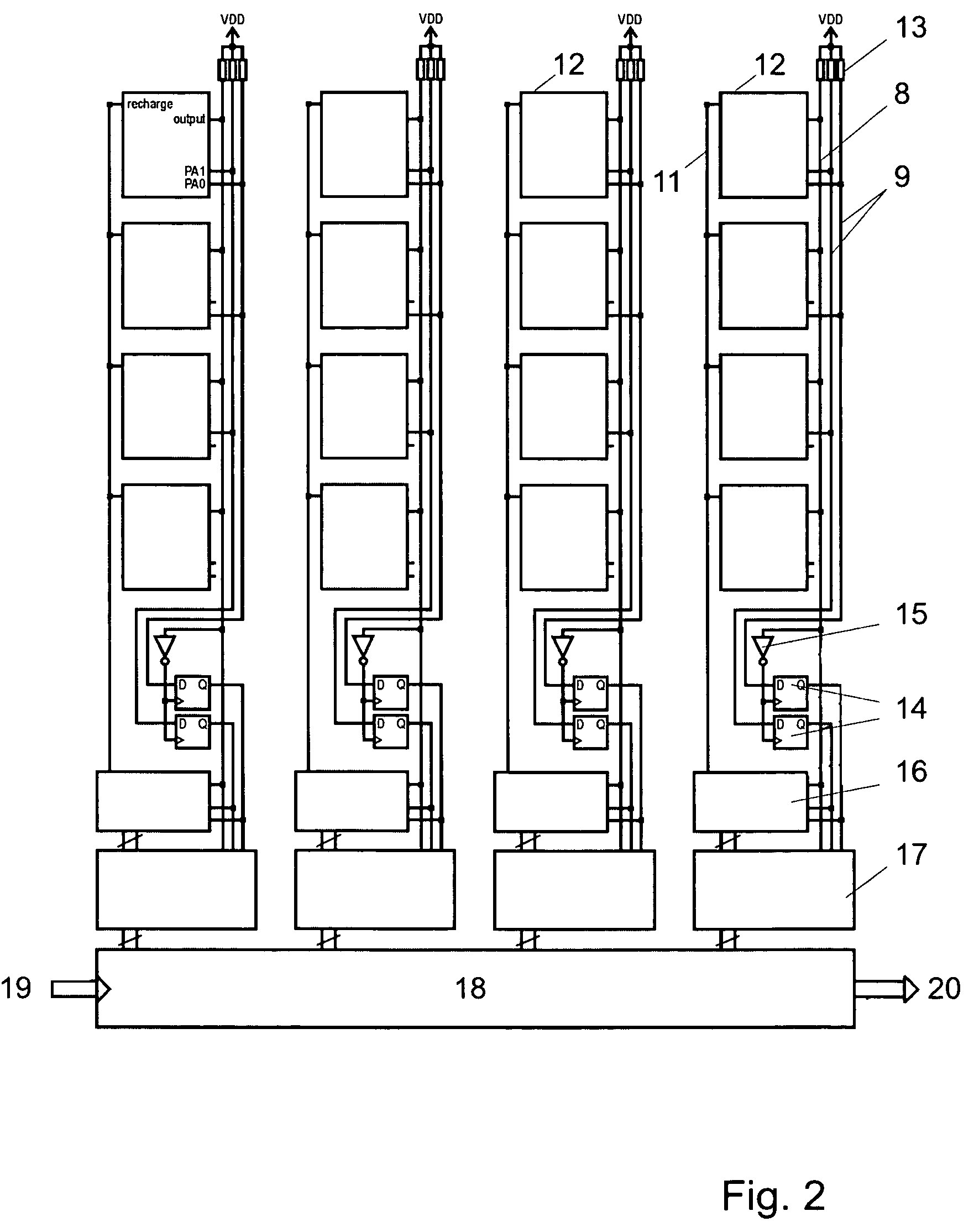
Integrated imager circuit comprising a monolithic array of single photon avalanche diodes
ActiveUS20060192086A1High sensitivityEliminate needOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesSingle-photon avalanche diodeAvalanche diode
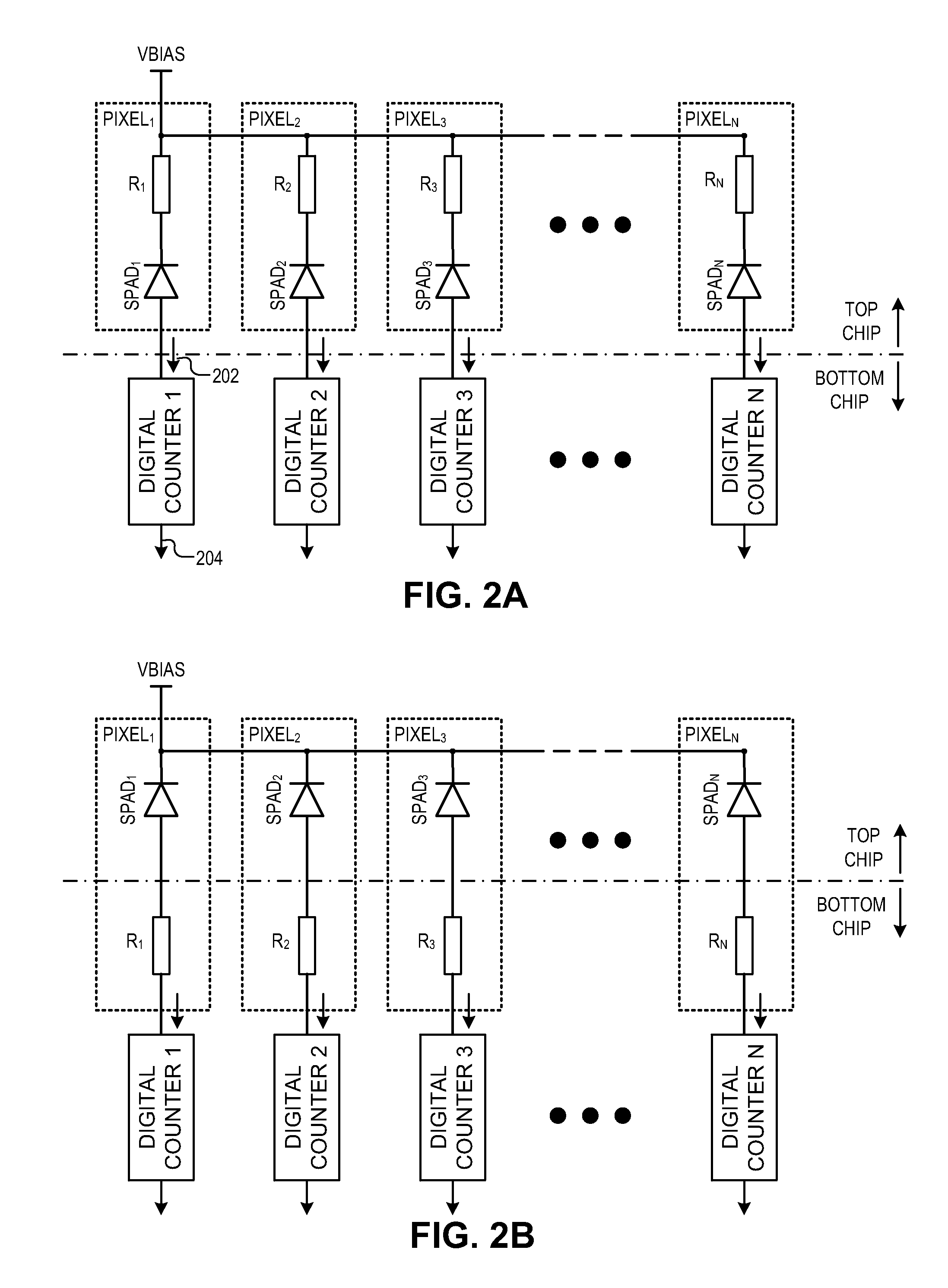
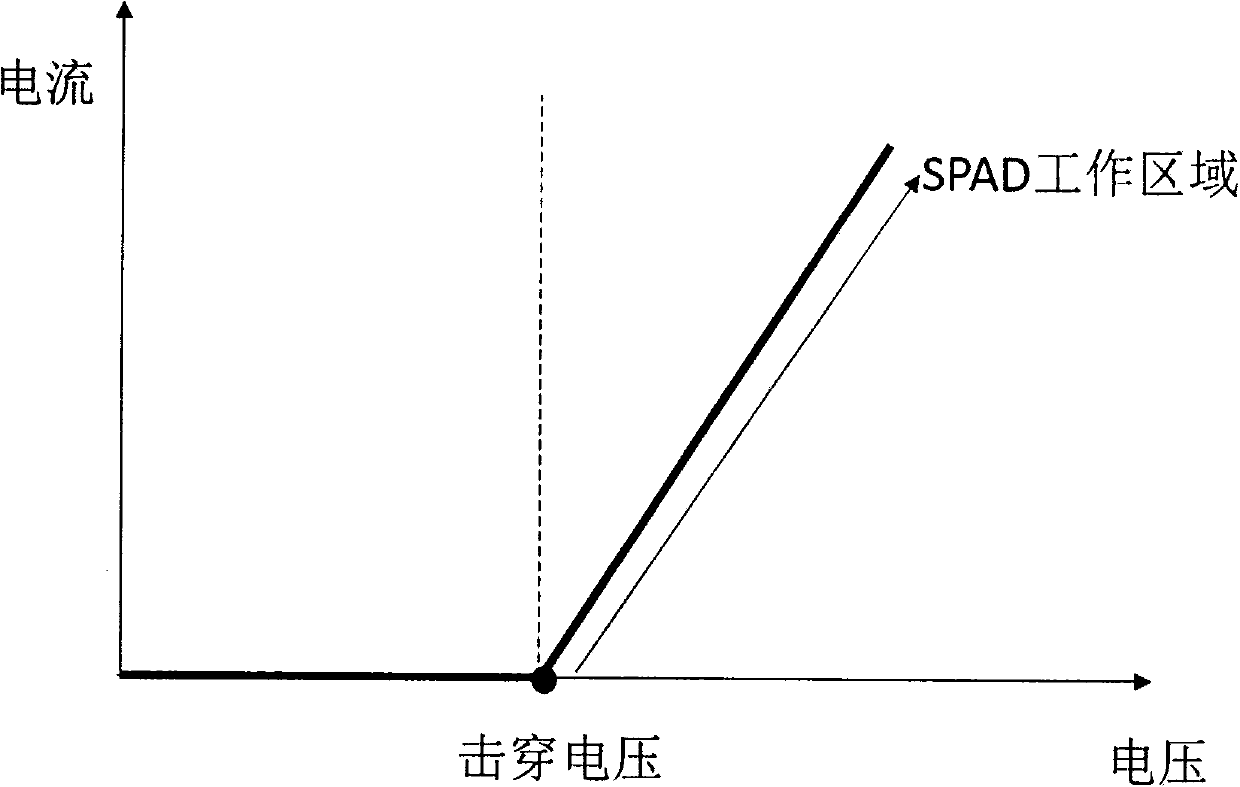
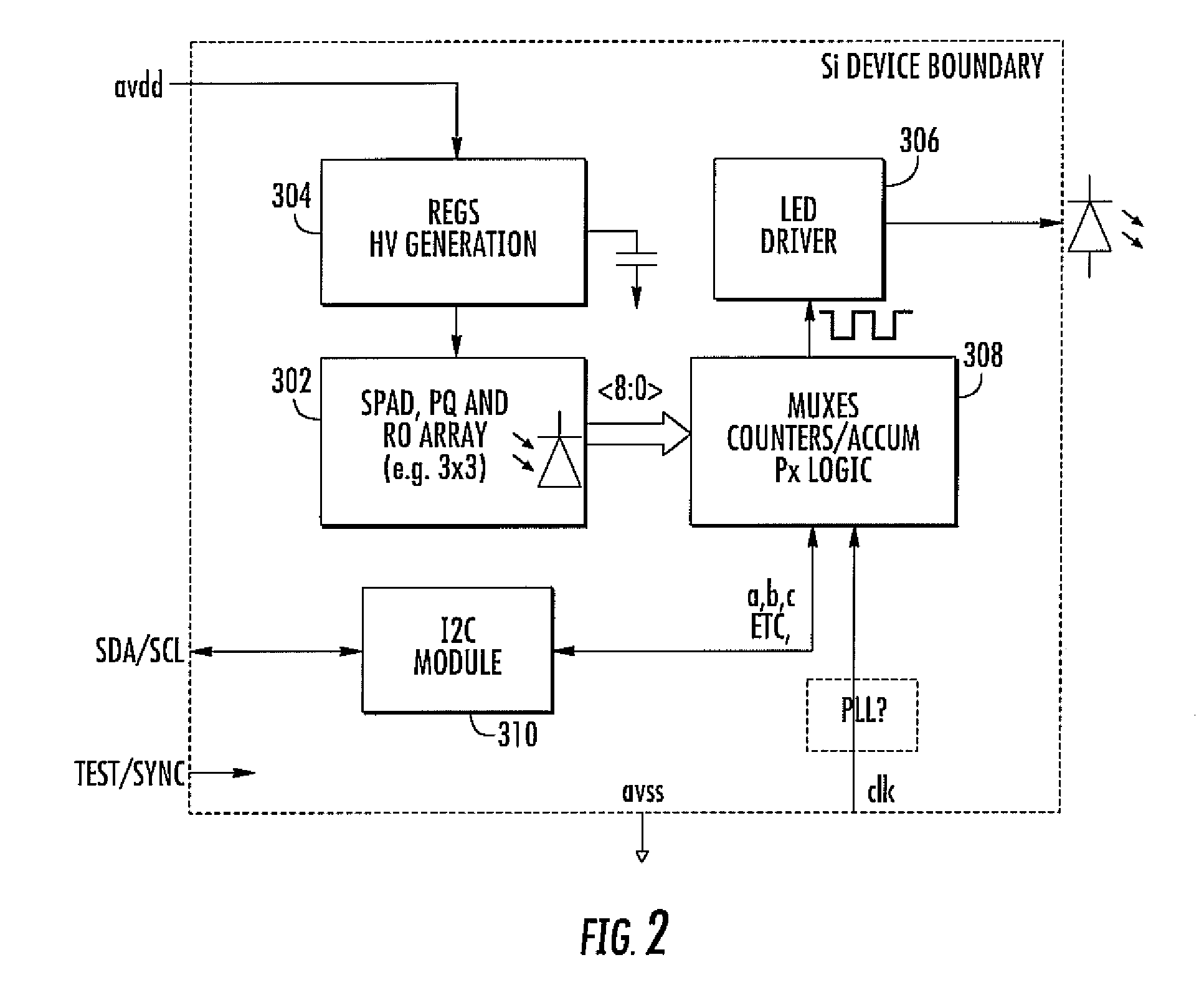
An integrated imager circuit comprising a monolithic array of single photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) for capturing an image of a scene when said scene is hit by an optical pulse, said array comprising: a plurality of SPADs connected to 2D readout circuits determines the intensity of the light reflected by said scene by counting the number of photons received by said SPADs during a period of time, a plurality of SPADs connected to 3D readout circuits determines the distance to said scene by determining the elapsed time between the emission of each pulse and reception of the corresponding reflected photons.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Integrated imager circuit comprising a monolithic array of single photon avalanche diodes
ActiveUS7262402B2Integrated inexpensivelyImprove good performanceOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesSingle-photon avalanche diodeAvalanche diode
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
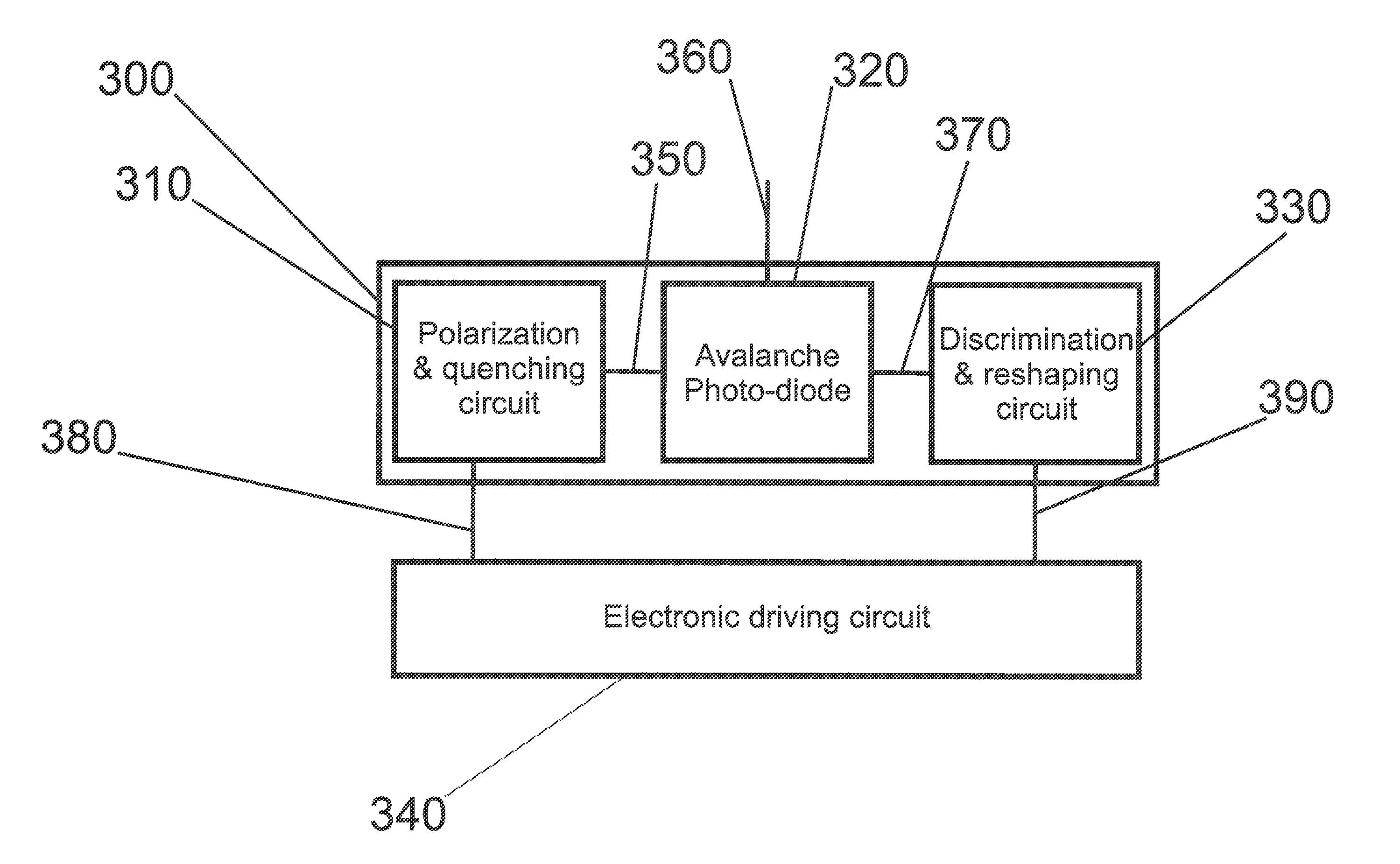
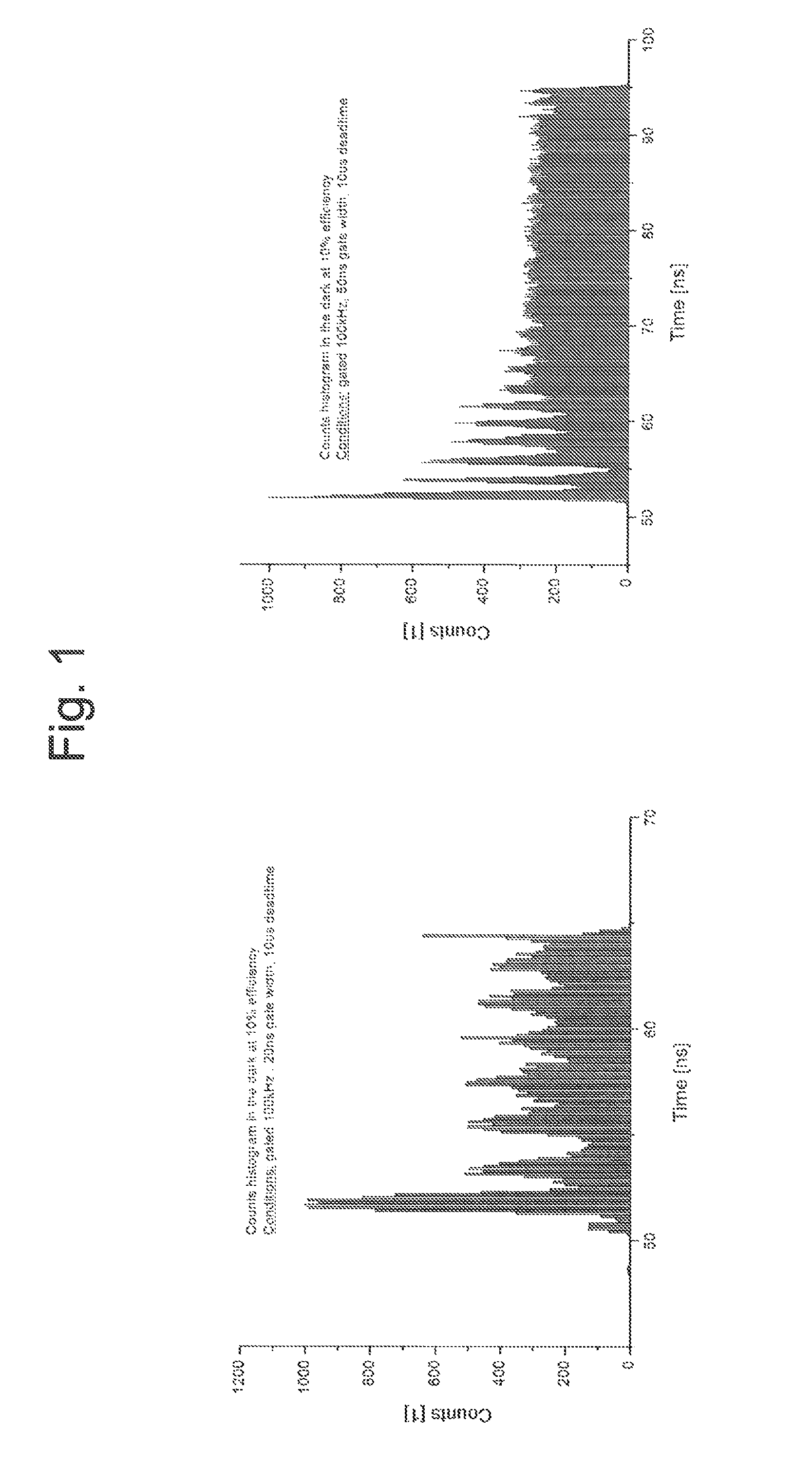
Apparatus and method for allowing avalanche photodiode based single-photon detectors to be driven by the same electrical circuit in gated and in free-running modes
An apparatus and method for allowing avalanche photodiode based single-photon detectors to be driven by the same electrical circuit in gated and in free-running modes is proposed. The high-performance working of all the running modes relies on the capability of tuning the rise-time value of the electrical pulse driver which activates the avalanche photodiode in Geiger mode.
Owner:ID QUANTIQUE SA
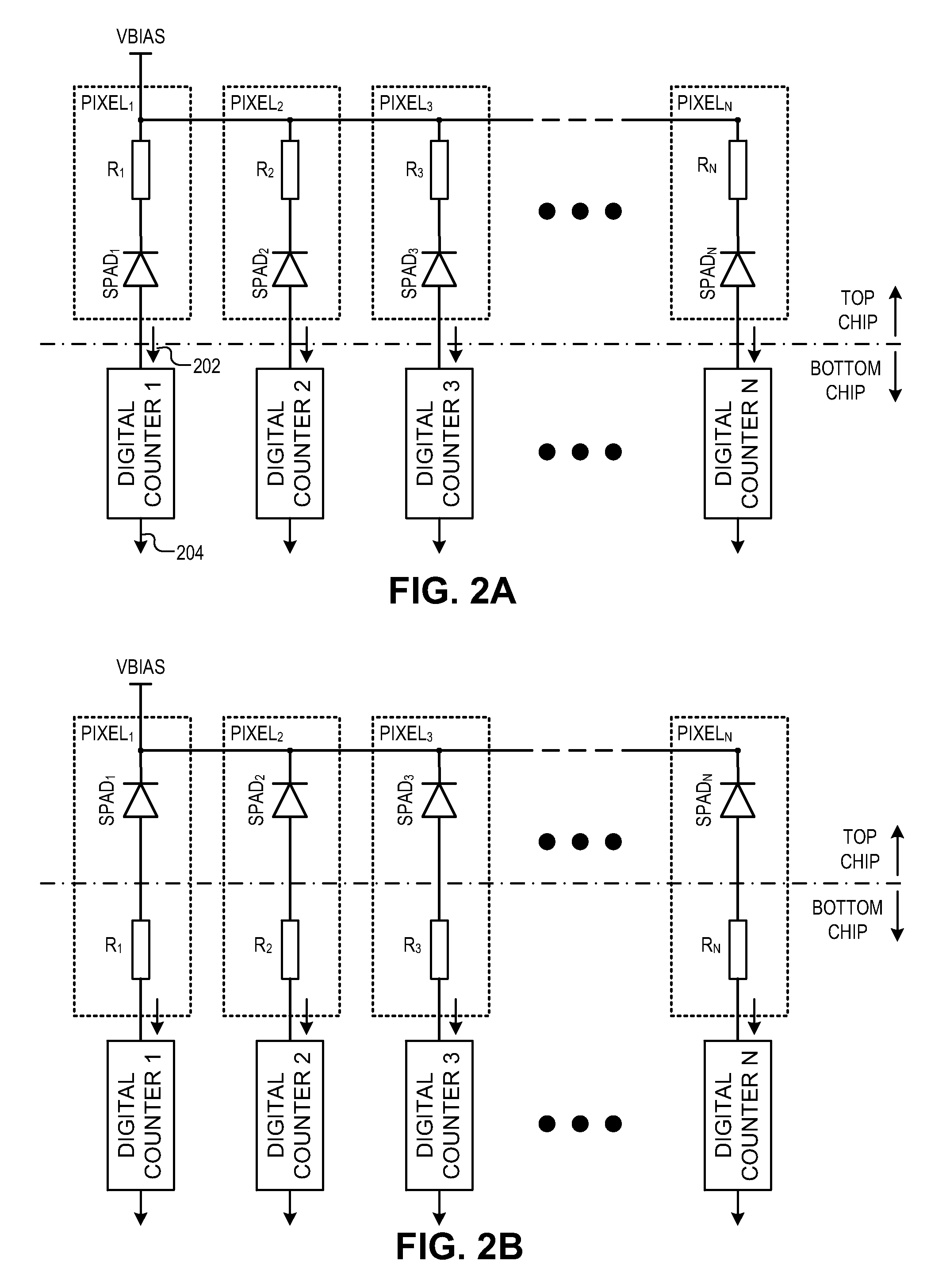
Stacked chip spad image sensor
ActiveUS20150115131A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSingle-photon avalanche diodeElectrical conductor
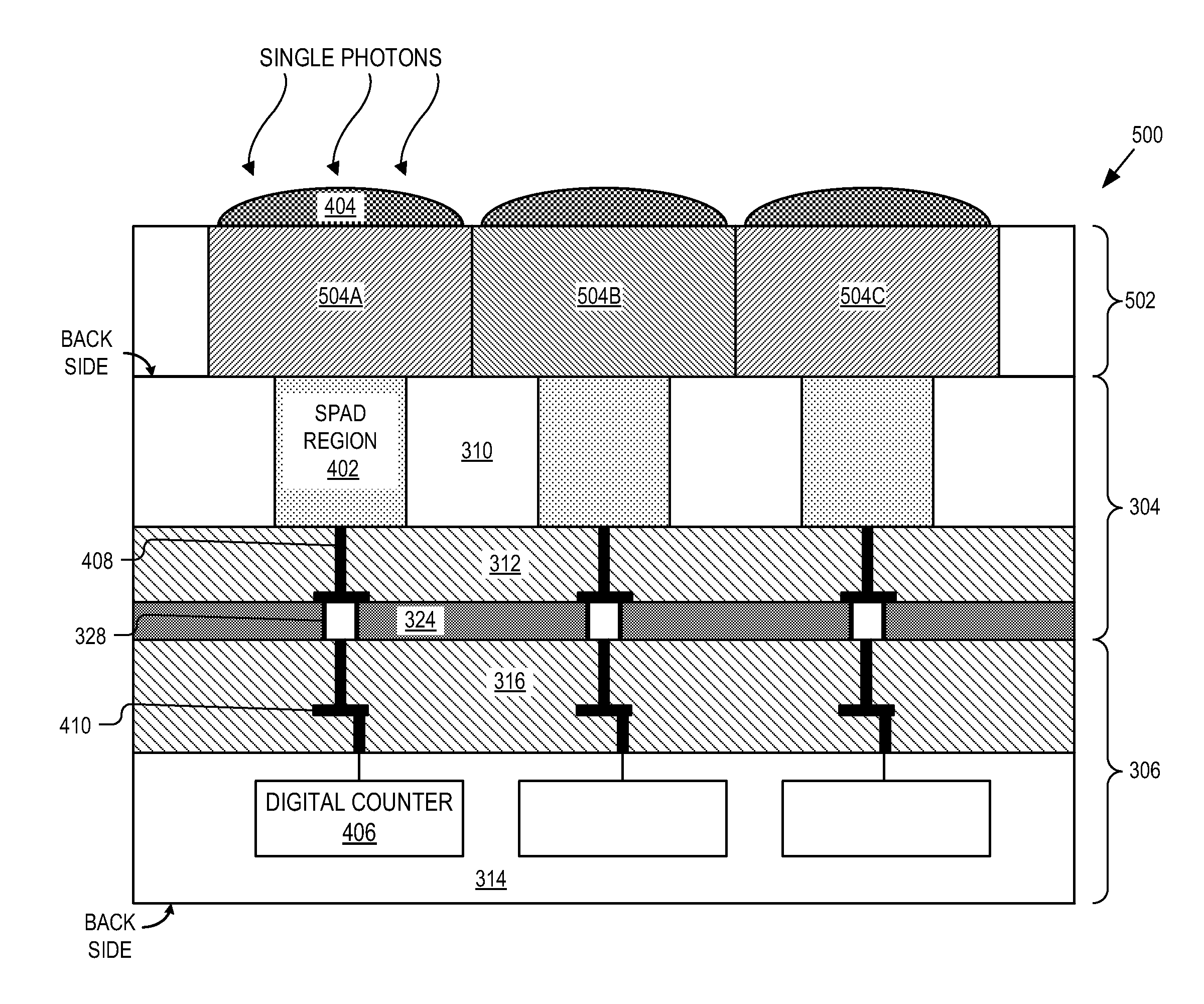
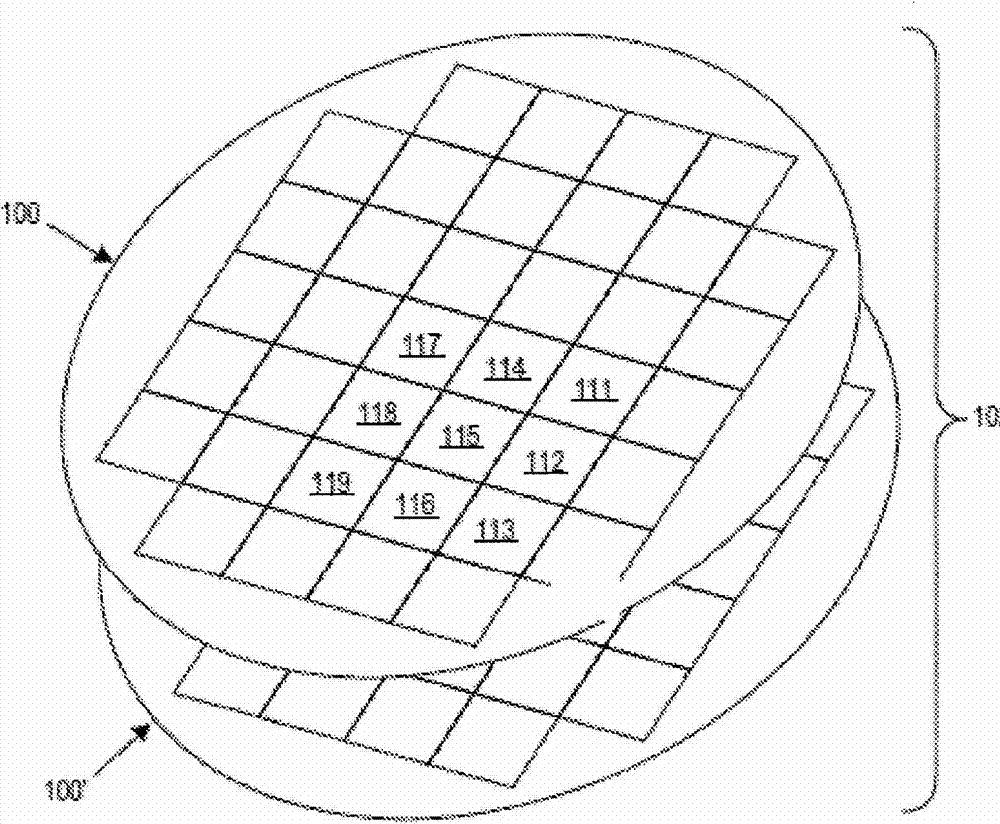
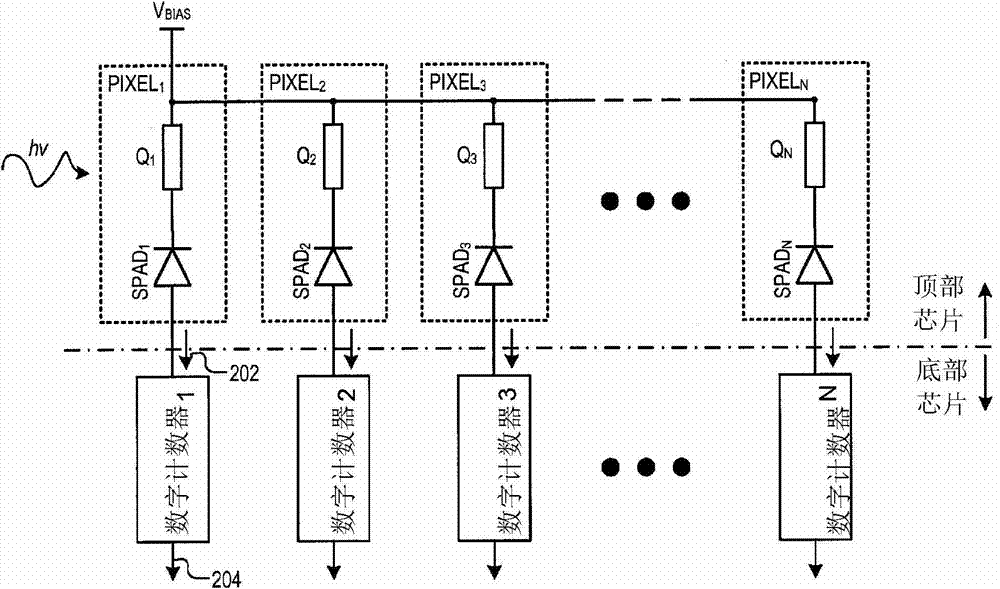
An example imaging sensor system includes a Single-Photon Avalanche Diode (SPAD) imaging array formed in a first semiconductor layer of a first wafer. The SPAD imaging array includes an N number of pixels, each including a SPAD region formed in a front side of the first semiconductor layer. The first wafer is bonded to a second wafer at a bonding interface between a first interconnect layer of the first wafer and the second interconnect layer of the second wafer. An N number of digital counters are formed in a second semiconductor layer of the second wafer. Each of the digital counters are configured to count output pulses generated by a respective SPAD region.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
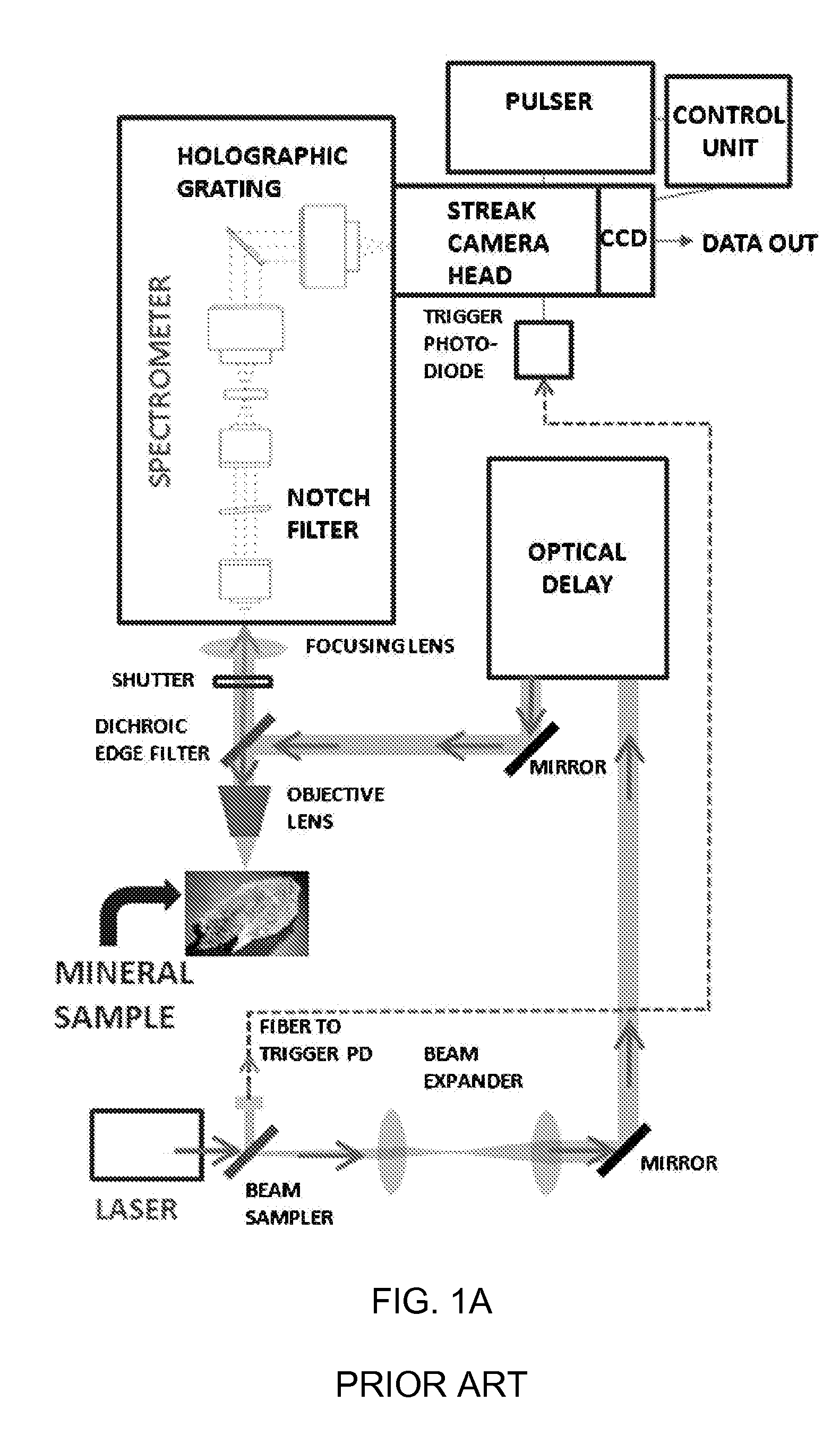
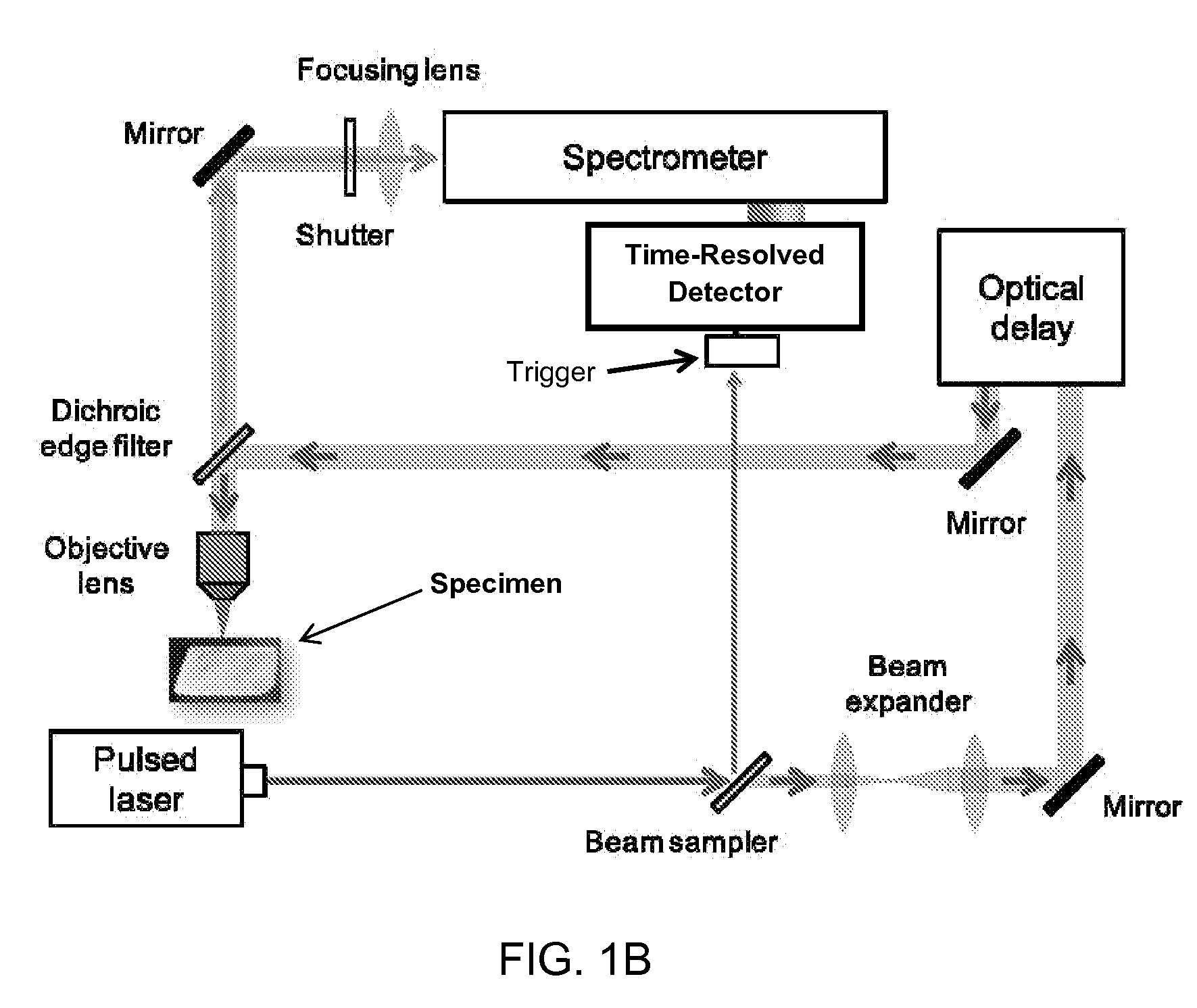
Time resolved laser raman spectroscopy using a single photon avalanche diode array
InactiveUS20130342835A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopySpectrometer
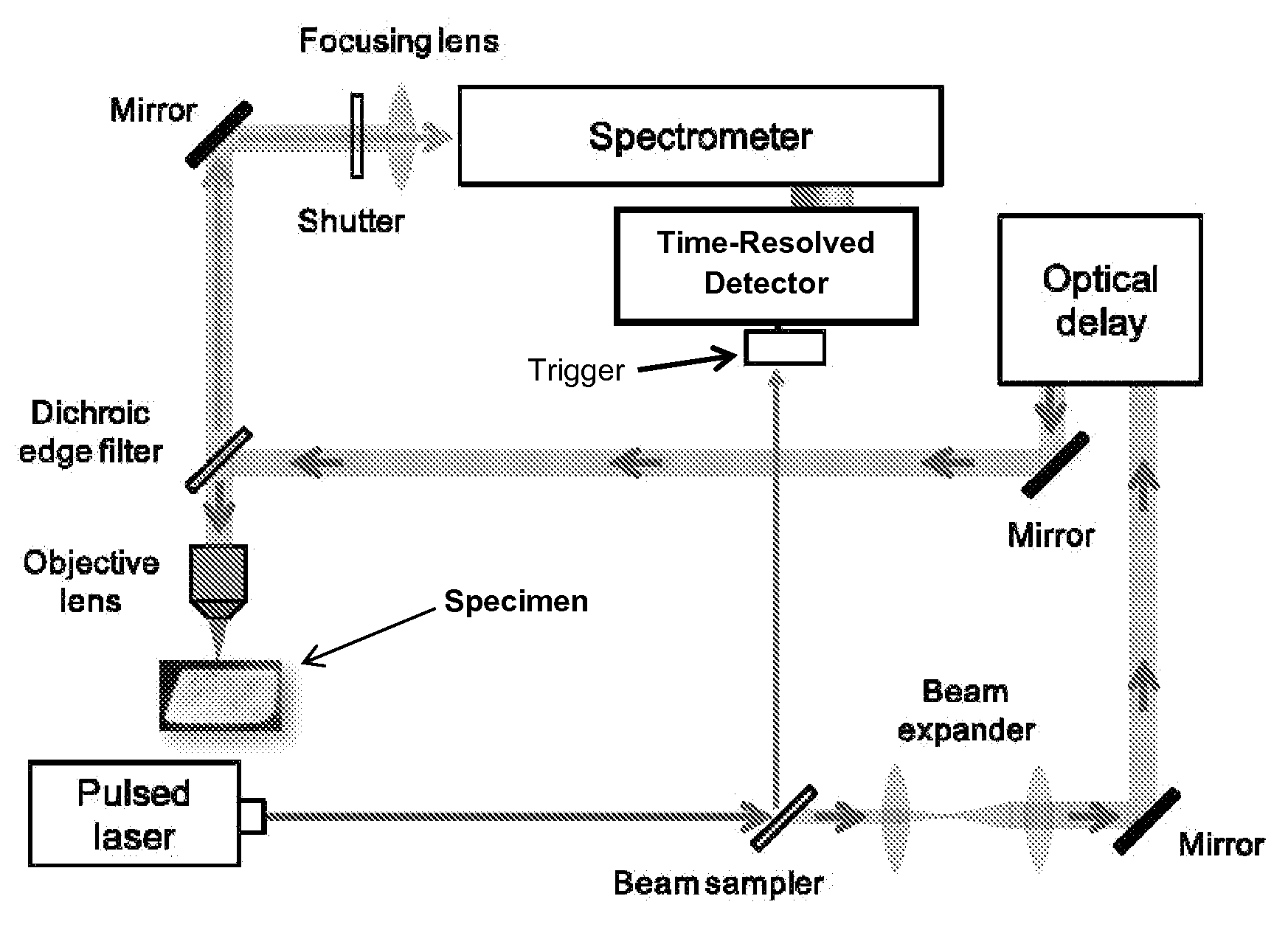
A Raman spectrometer that employs a time-gated single photon avalanche diode array as a sensor is described. The spectrometer can also perform fluorescence spectroscopy and laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). A laser is used to provide an excitation signal to excite a specimen of interest. A spectrometer is used to separate the various intensities over a range of wavelengths, which are then caused to impinge on the array to be recorded. The time-gated single photon avalanche diode array is triggered in synchrony with the excitation signal so as to allow time resolution of the response of the sample of interest to the excitation. The array can be time-gated to resolve signals that have shorter durations as a function of time while excluding signals that have a longer time duration. Raman and LIBS signals can be observed even from specimens that fluoresce strongly.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Integrated circuit comprising an array of single photon avalanche diodes
ActiveUS7547872B2Reduce in quantityImprove fill factorTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSingle-photon avalanche diodeTransformer
Owner:FASTREE 3D SA
Application using a single photon avalanche diode (SPAD)
ActiveUS9058081B2Function increaseImprove the level ofWave amplification devicesElectronic switchingSingle-photon avalanche diodeAvalanche diode
An electronic device may include a housing having a mousing surface, and a navigation device carried by the housing and comprising a proximity detector. The proximity detector may include a single photon avalanche diode (SPAD) configured to detect movement of an activator adjacent the mousing surface. For example, the proximity detector may detect movement along three axes.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (RES & DEV) LTD
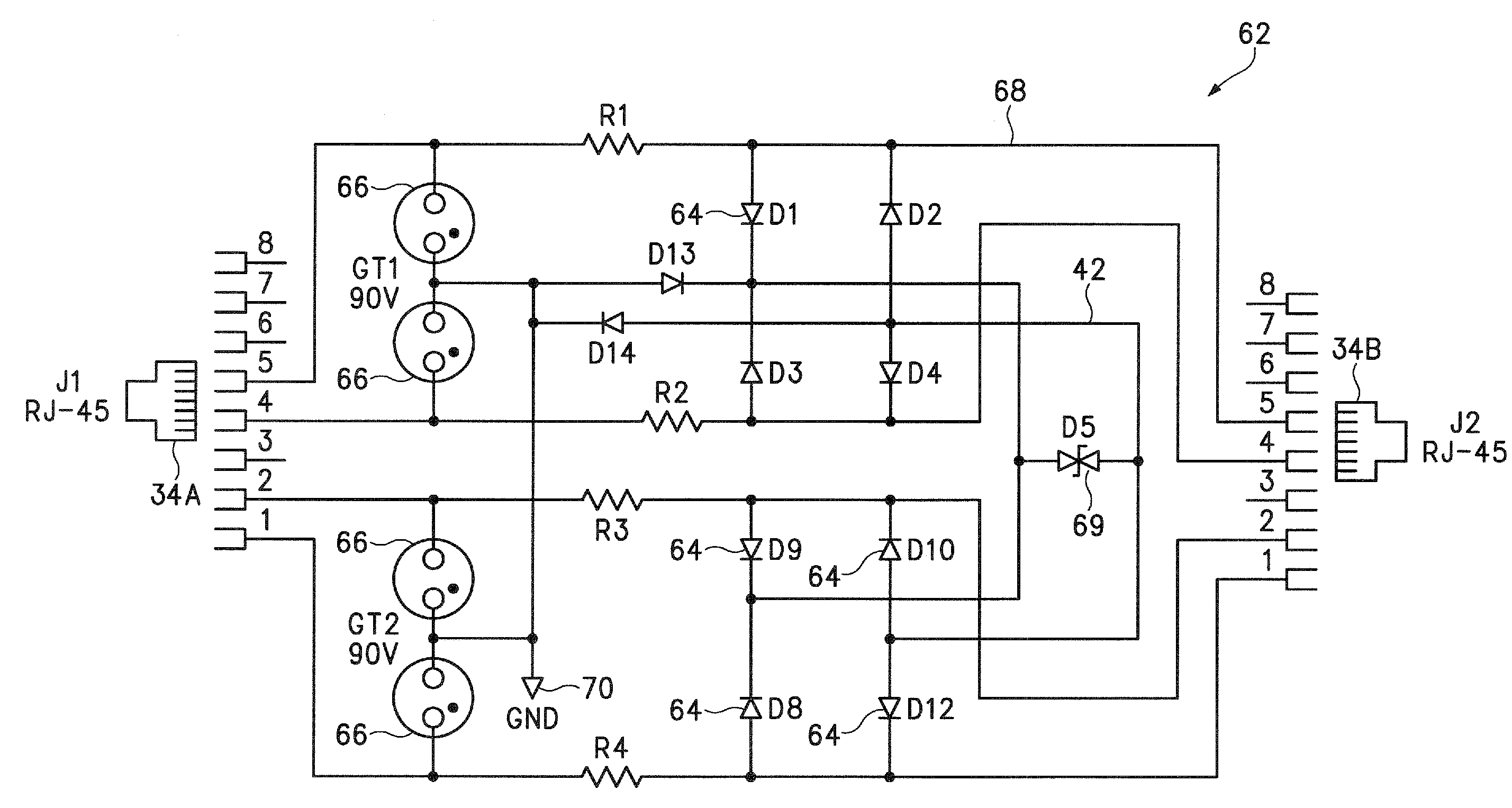
Transient voltage suppression device
InactiveUS6867436B1Lower clamping voltageOvercome disadvantagesThyristorSolid-state devicesRectifier diodesHigh resistivity
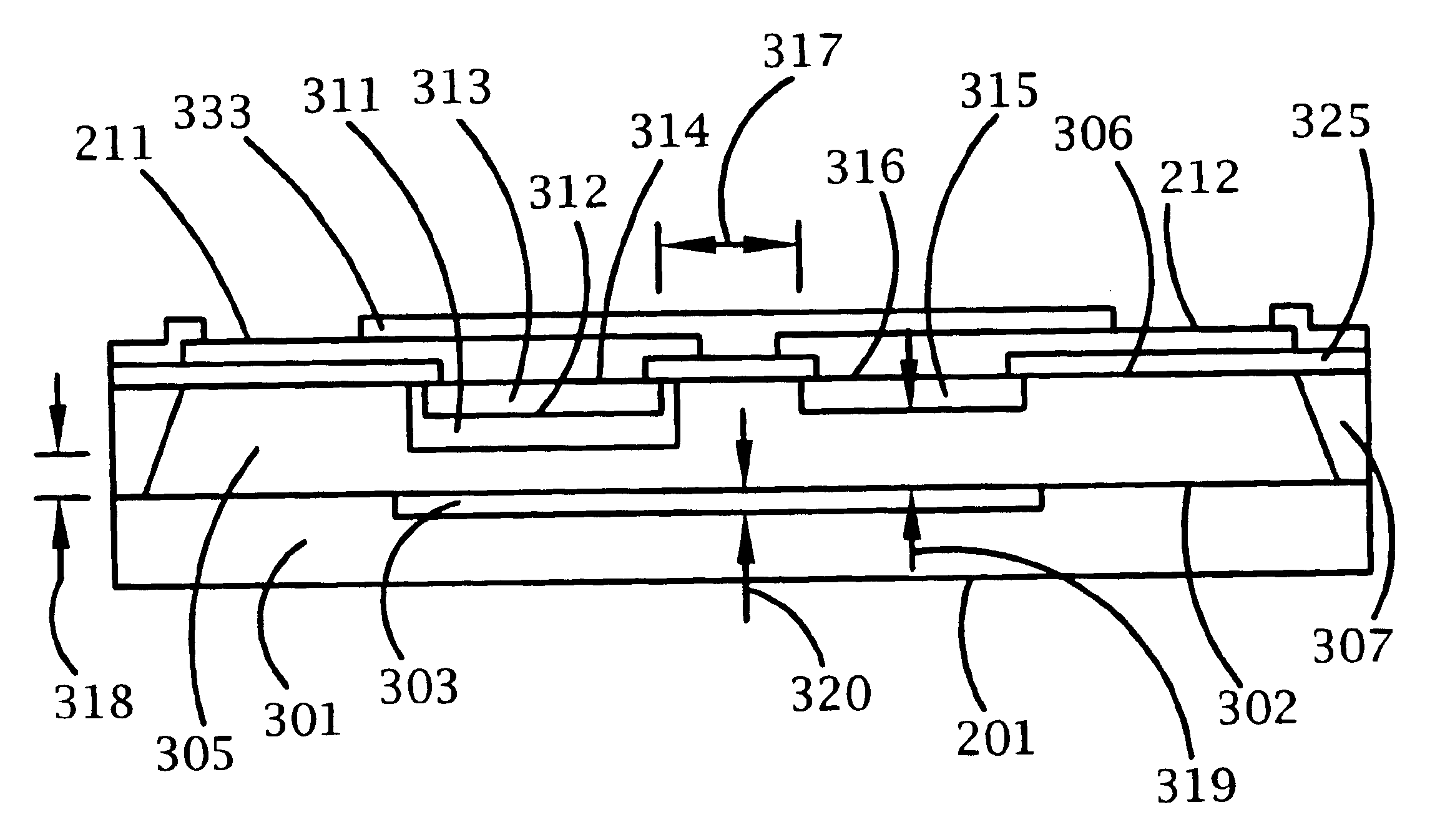
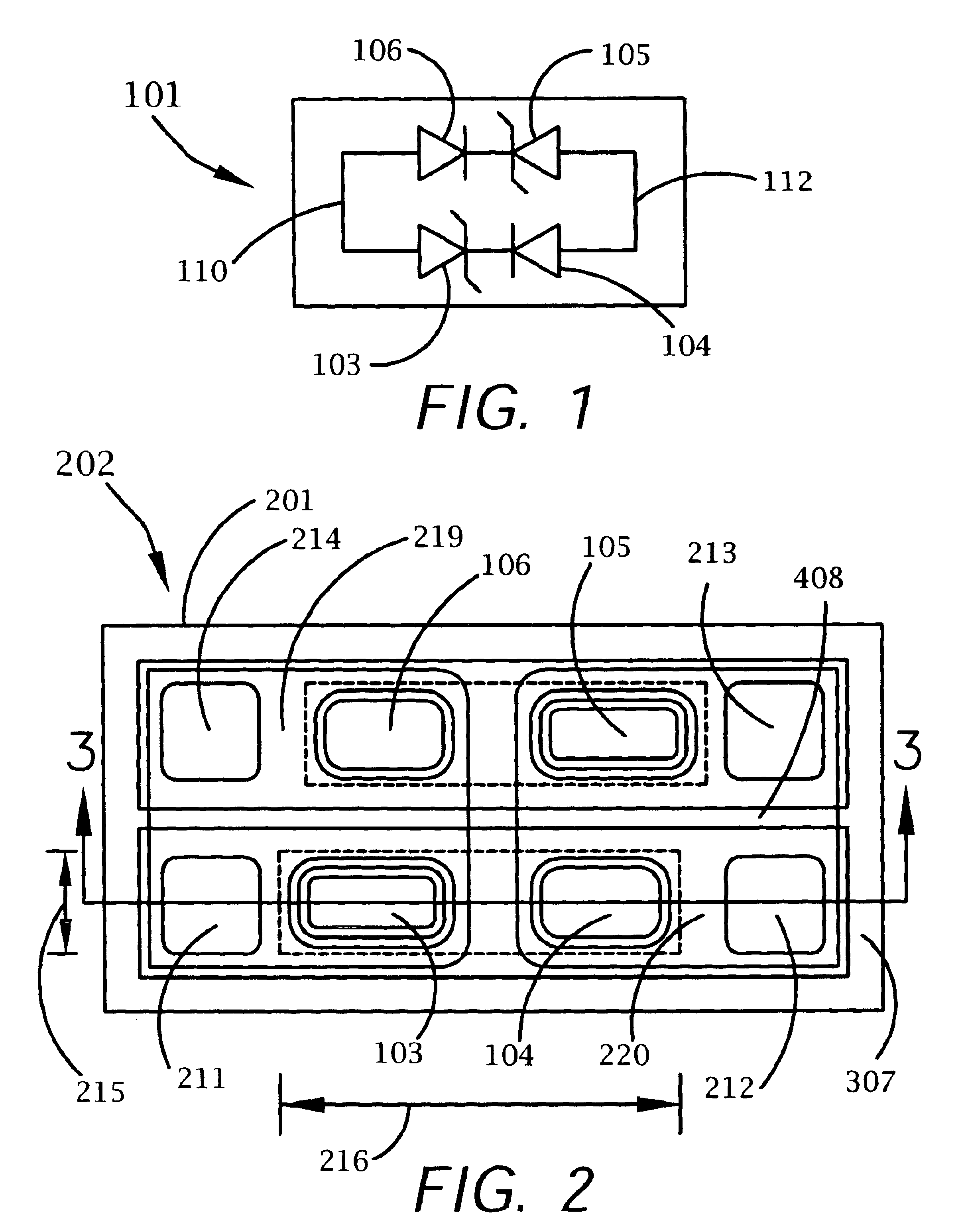
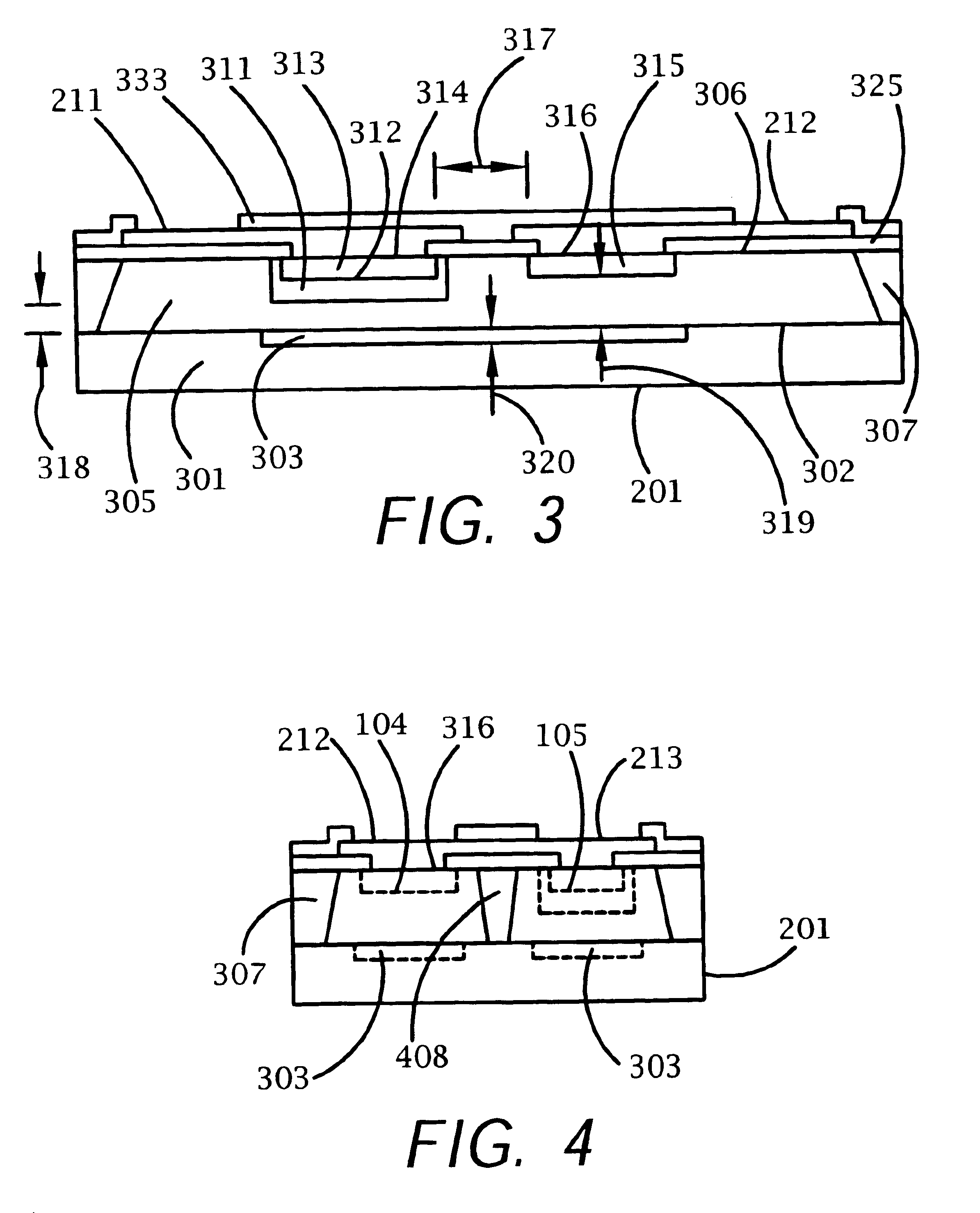
A bi-directional transient voltage suppression (“TVS”) device (101) includes a semiconductor die (201) that has a first avalanche diode (103) in series with a first rectifier diode (104) connected cathode to cathode, electrically coupled in an anti-parallel configuration with a second avalanche diode (105) in series with a second rectifier diode (106) also connected cathode to cathode. All the diodes of the TVS device are on a single semiconductor substrate (301). The die has a low resistivity buried diffused layer (303) having a first conductivity type disposed between a semiconductor substrate (301) having the opposite conductivity type and a high resistivity epitaxial layer (305) having the first conductivity type. The buried diffused layer shunts most of a transient current away from a portion of the epitaxial layer between the first avalanche diode and the first rectifier diode, thereby reducing the clamping voltage relative to the breakdown voltage. The TVS device is packaged as a flip chip (202) that has four solder bump pads (211-214). The abstract is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims pursuant to 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b).
Owner:PROTEK DEVICES
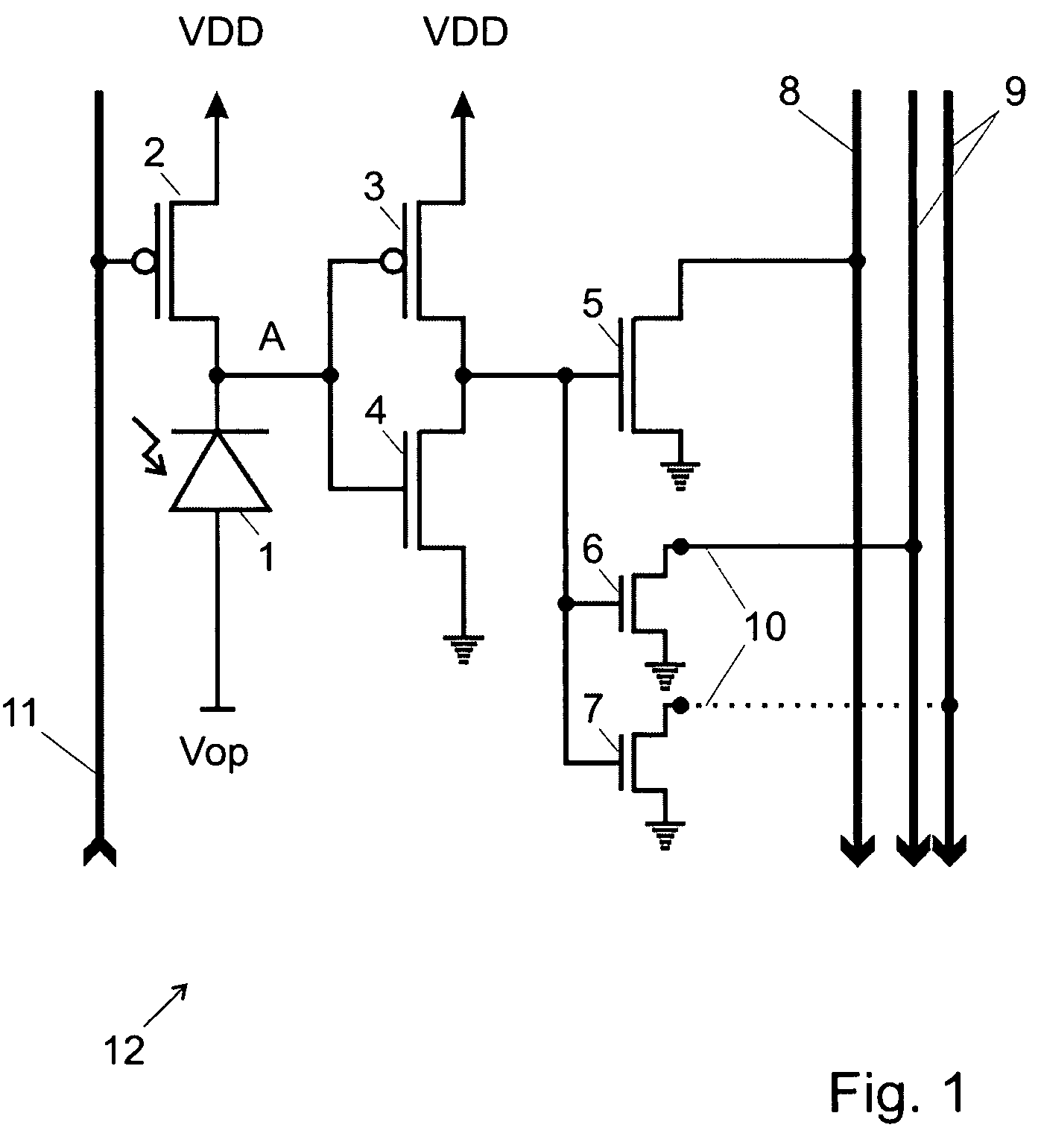
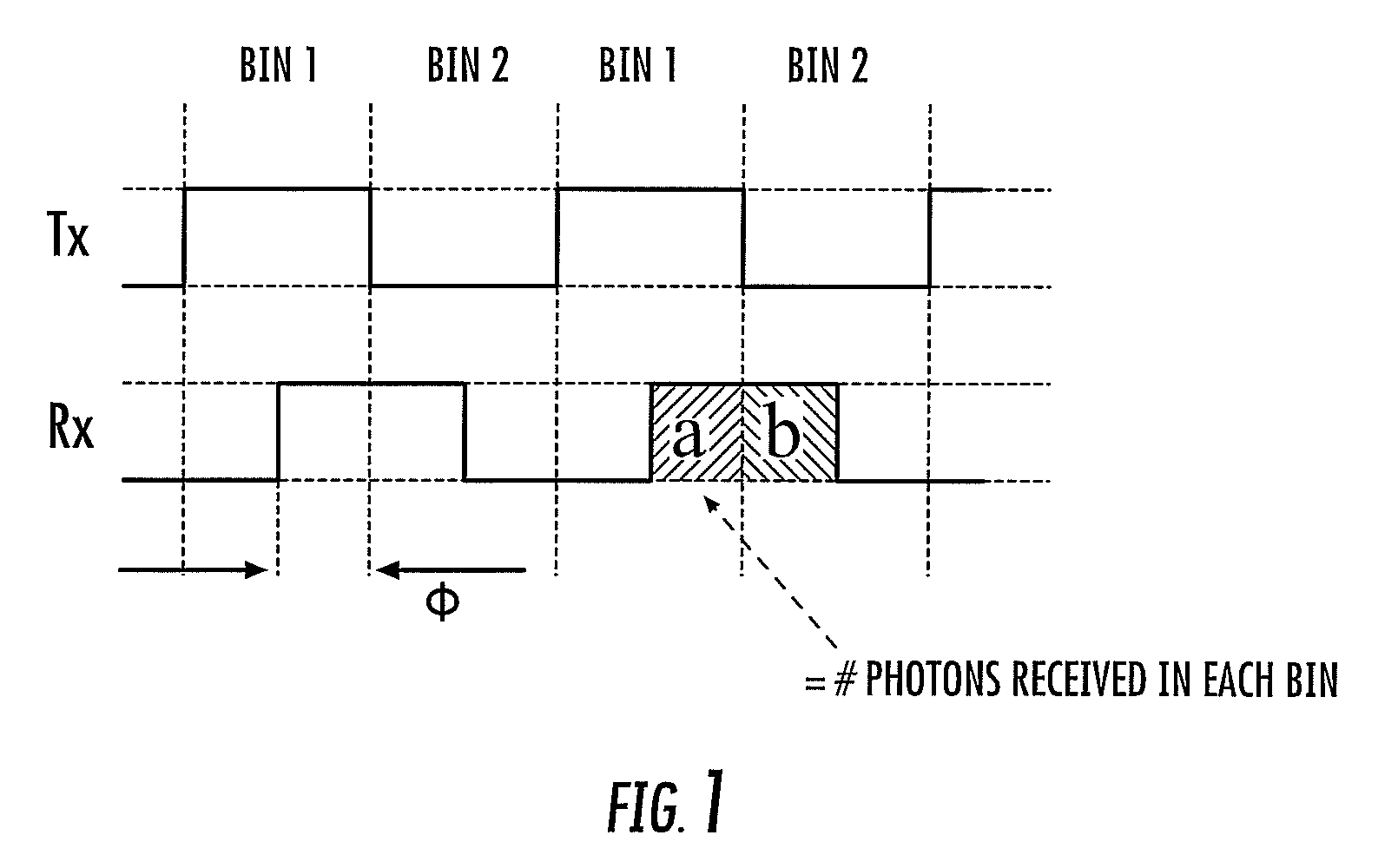
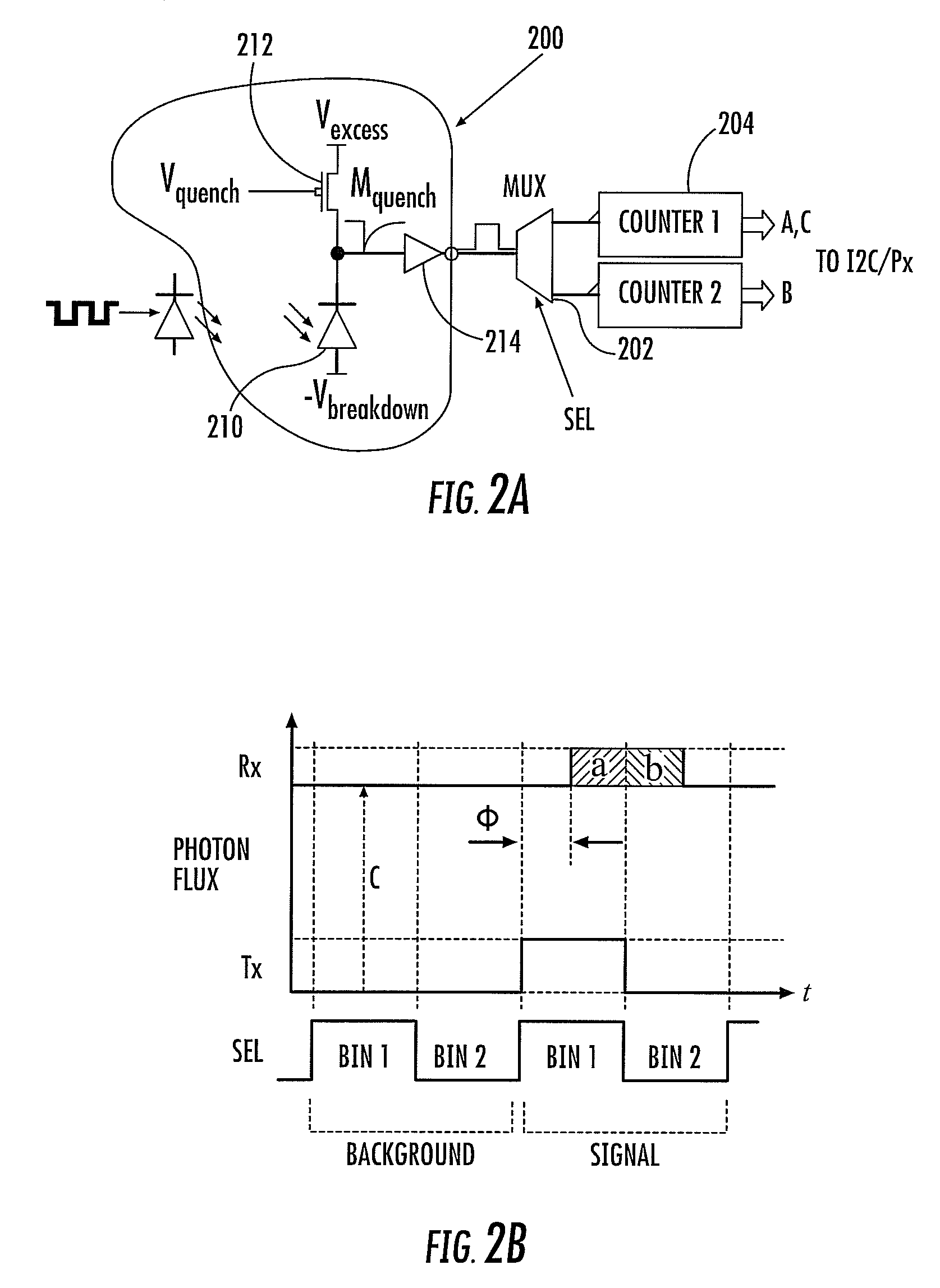
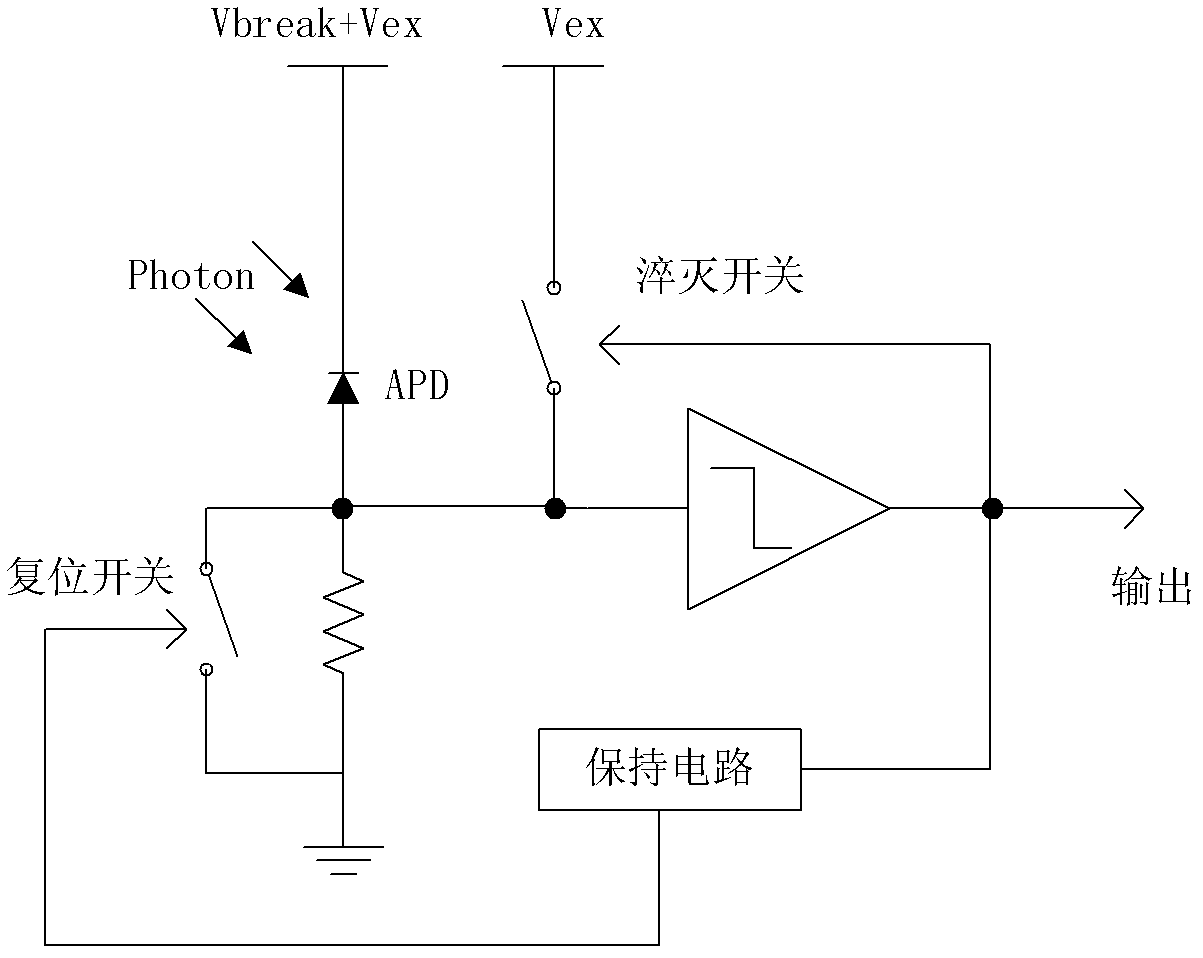
Quenching and reading circuit for single photon avalanche diode imaging device
ActiveCN102538988AHighly integratedSmall footprintTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSingle-photon avalanche diodeHemt circuits
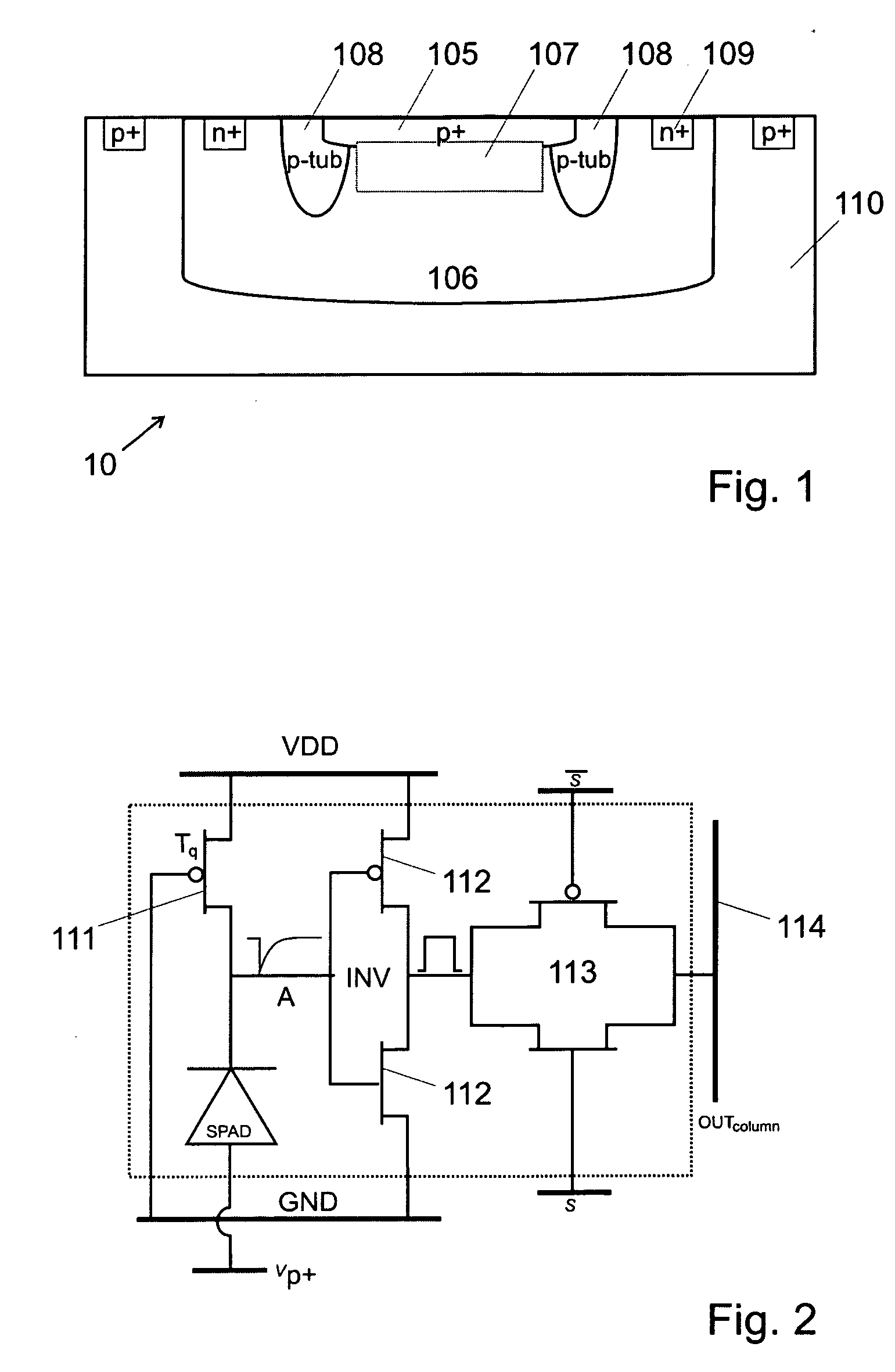
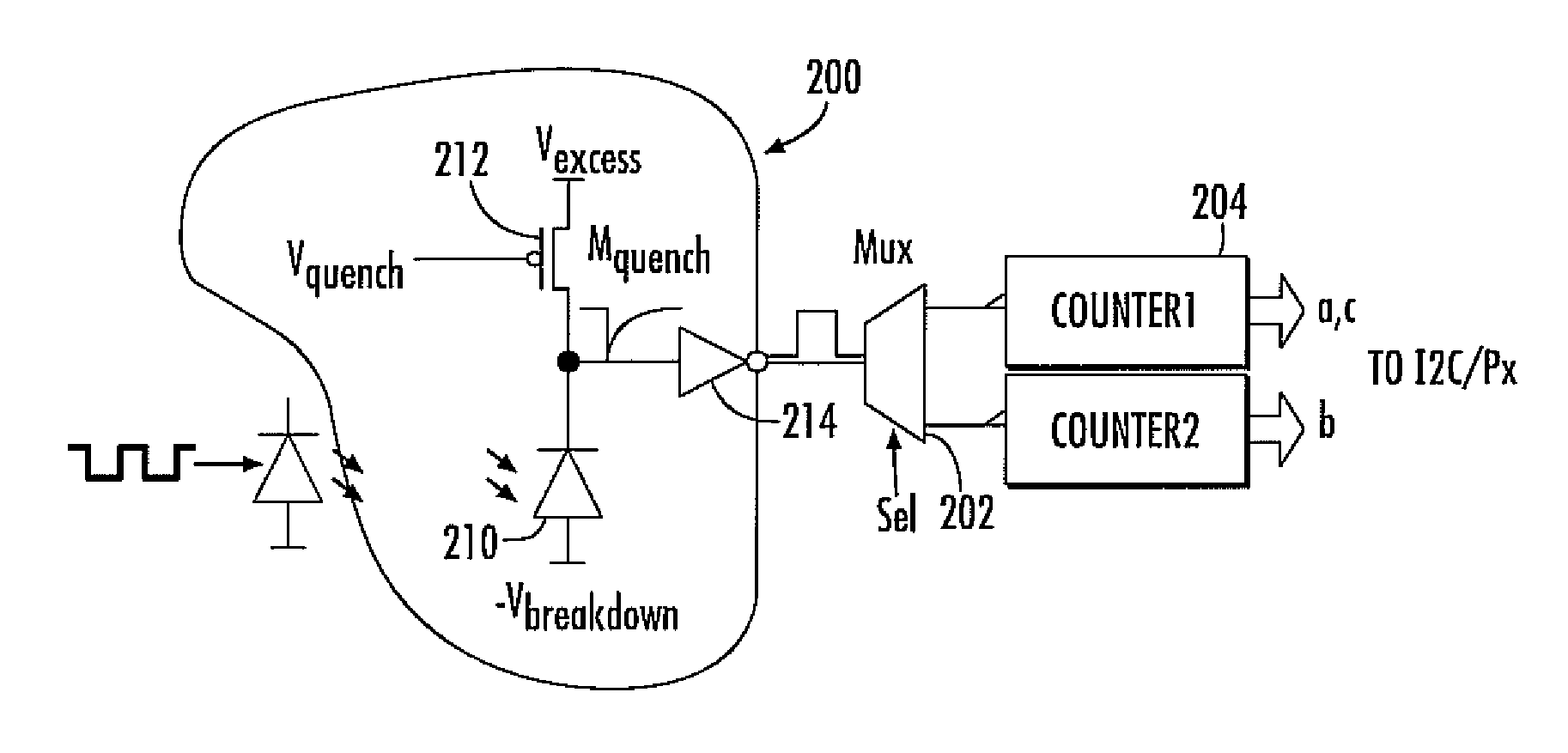
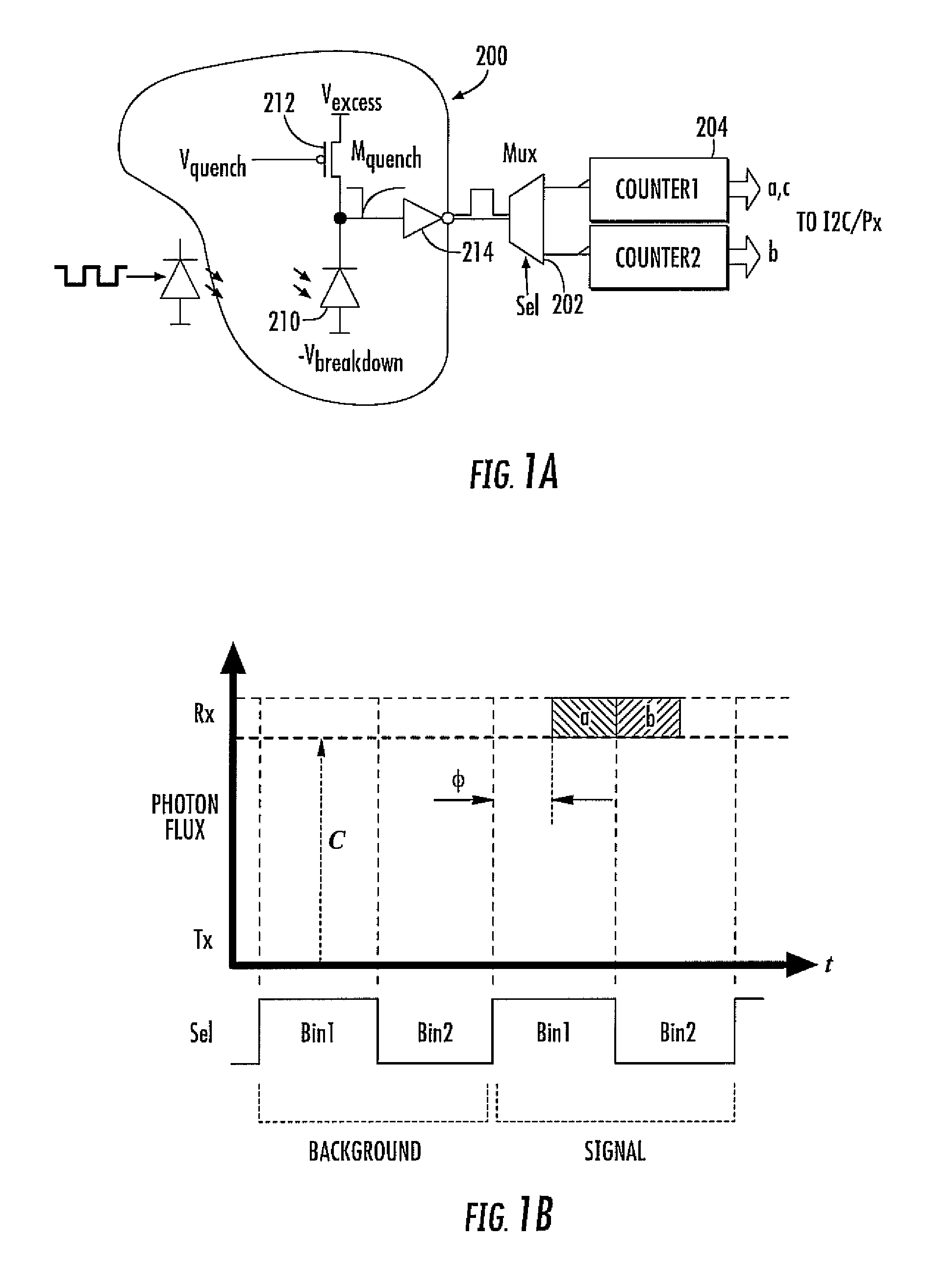
The invention aims at providing a quenching and reading circuit for a single photon avalanche diode imaging device, which is composed of three modules including a quenching circuit, a holding circuit and a reading circuit, wherein the quenching circuit is used for generating a pulse signal having the same frequency with an incident photon signal, the holding circuit is used for generating a reset signal, the phase of the reset signal is different from the phase of quenching output, the frequency of the reset signal is the same with the frequency of the quenching output, and the reading circuit is used for performing count processing on the quenching output pulse signal and outputting the signal in a linear and logarithmic mode. Quenching processing is performed on an avalanche diode after photon incidence by utilizing the quenching circuit, pulse signal output with the same frequency as incident photons is generated and directly sent into the reading circuit, the reading circuit selects to output a final result in a linear or a logarithmic mode according to the control of a plus signal, and simultaneously the quenching output pulse is delayed to keep the frequency unchanged and the phase changed to serve as the reset signal for controlling the staring or stopping of quenching.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM INST AT NANJING CO LTD
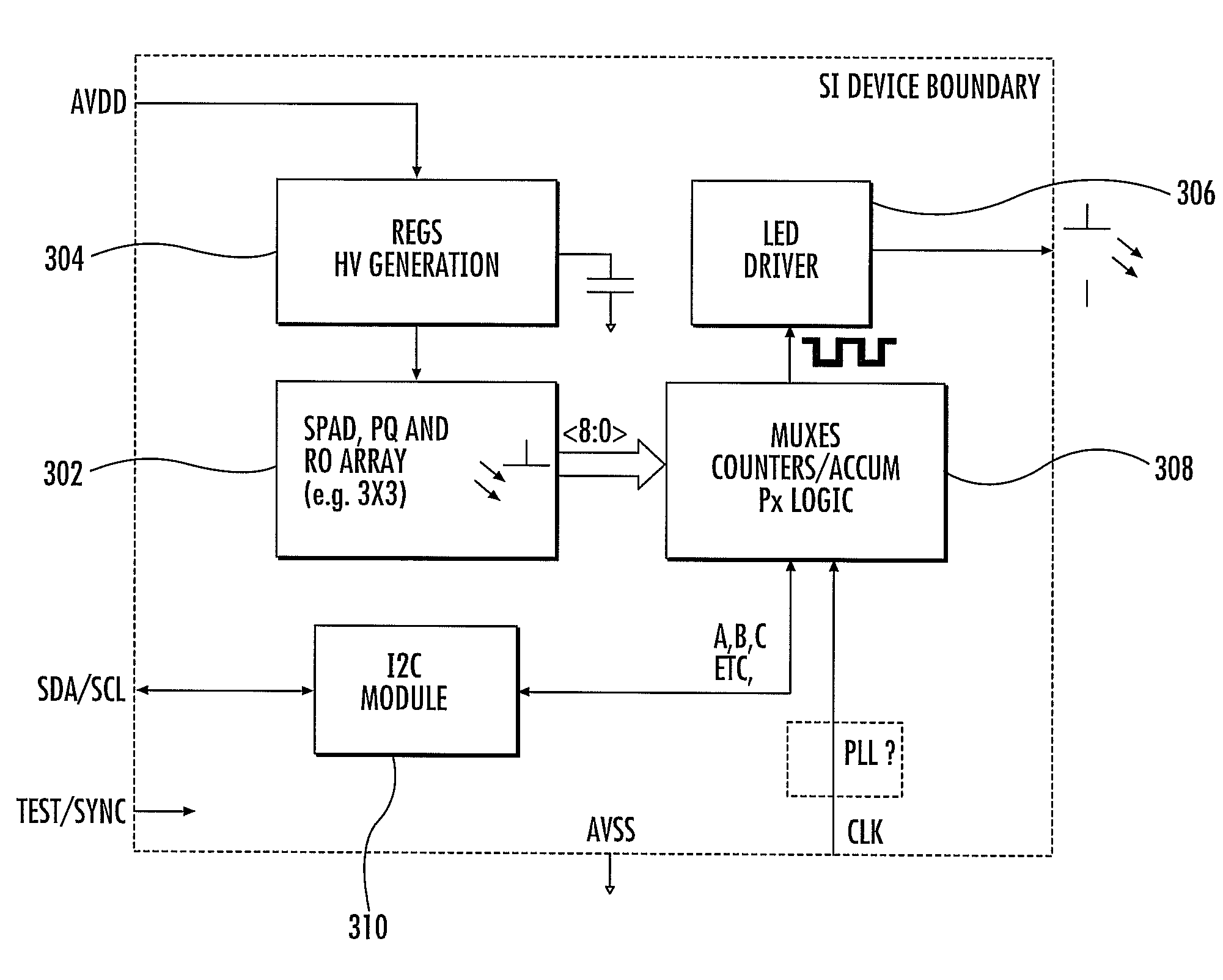
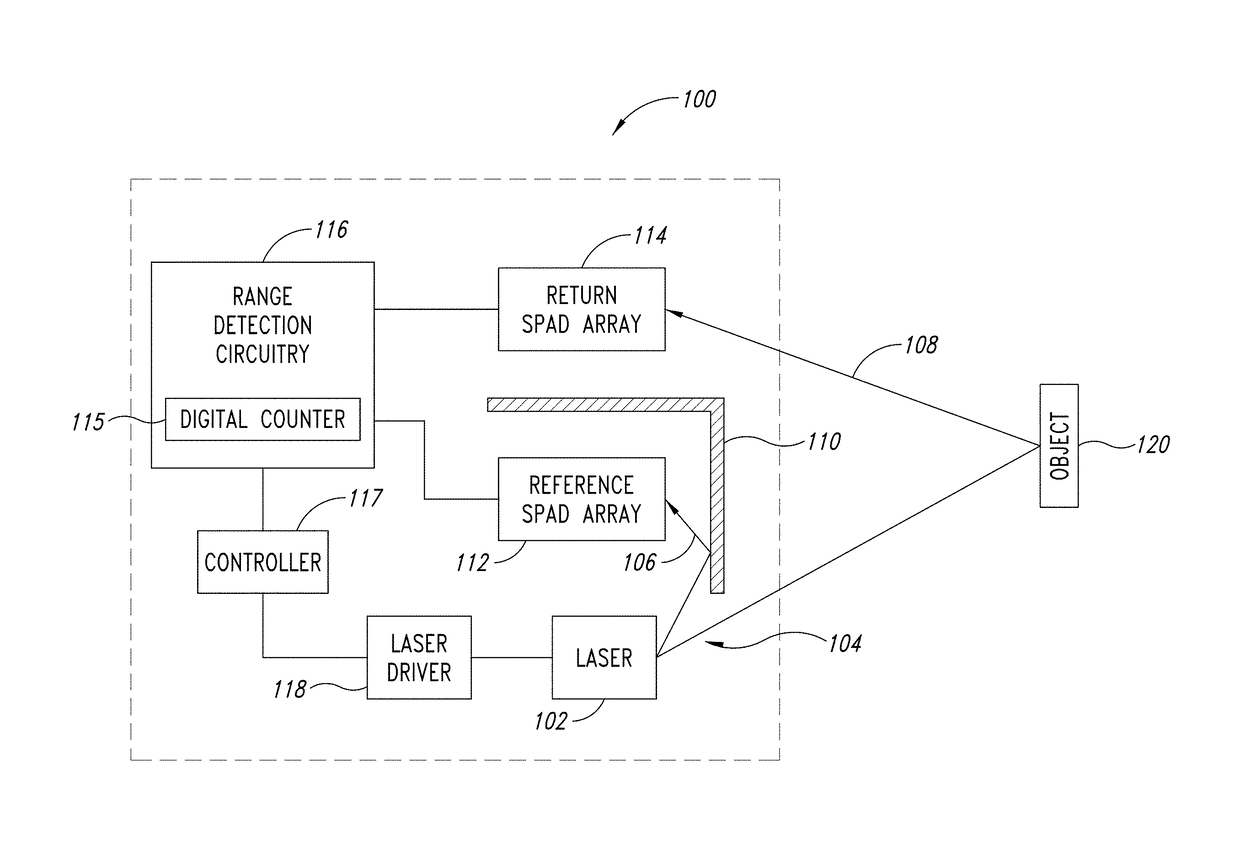
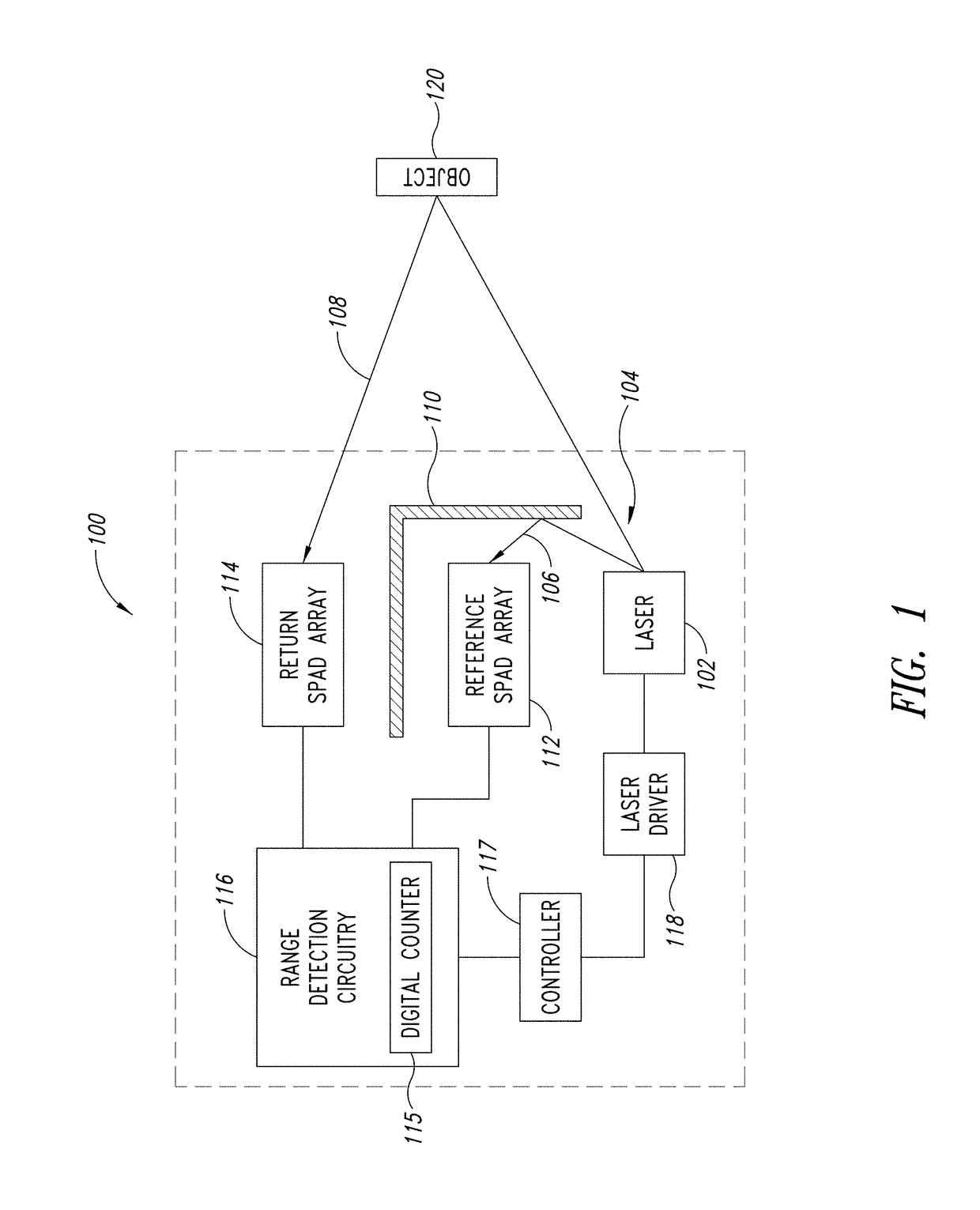
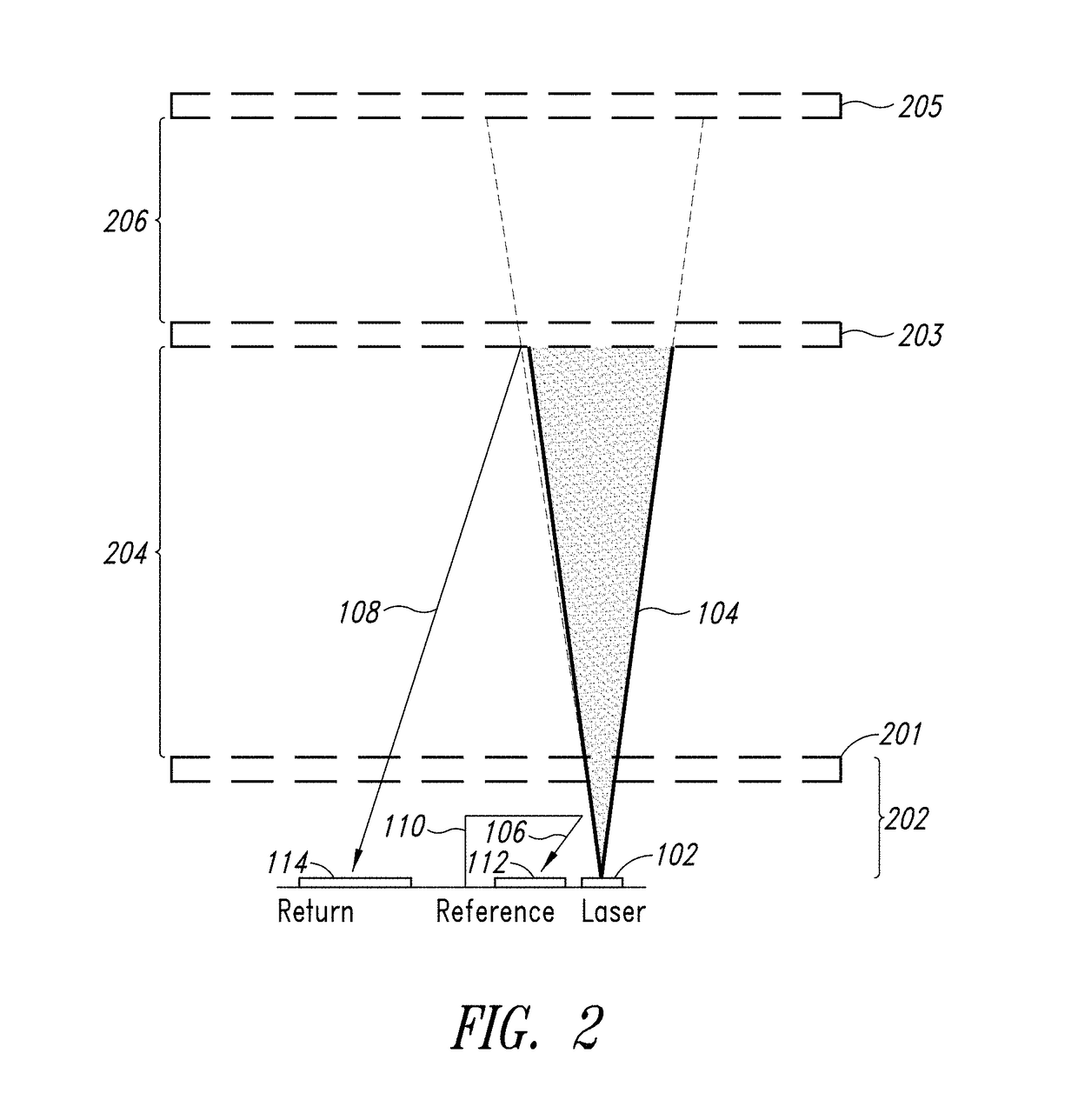
Adaptive laser power and ranging limit for time of flight sensor
ActiveUS20170356981A1Increase rangeImprove accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationDriver circuitSingle-photon avalanche diode
A time of flight range detection device includes a laser configured to transmit an optical pulse into an image scene, a return single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) array, a reference SPAD array, a range detection circuit coupled to the return SPAD array and the reference SPAD array, and a laser driver circuit. The range detection circuit in operation determines a distance to an object based on signals from the return SPAD array and the reference SPAD array. The laser driver circuit in operation varies an output power level of the laser in response to the determined distance to the object.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
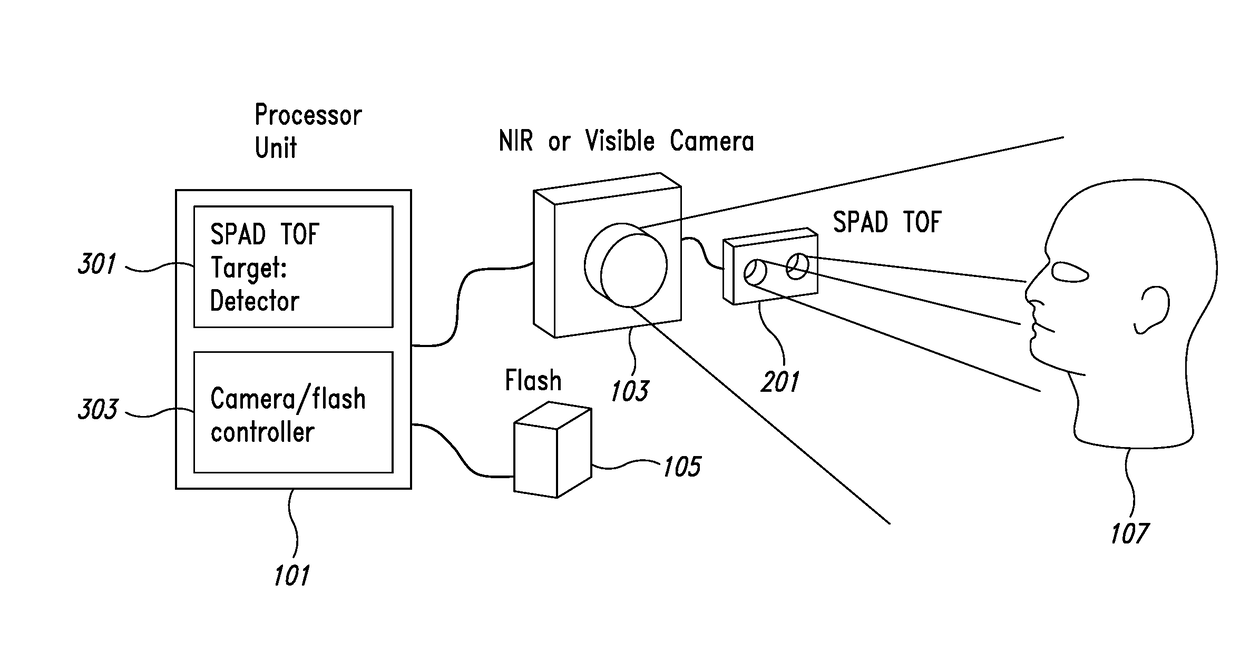
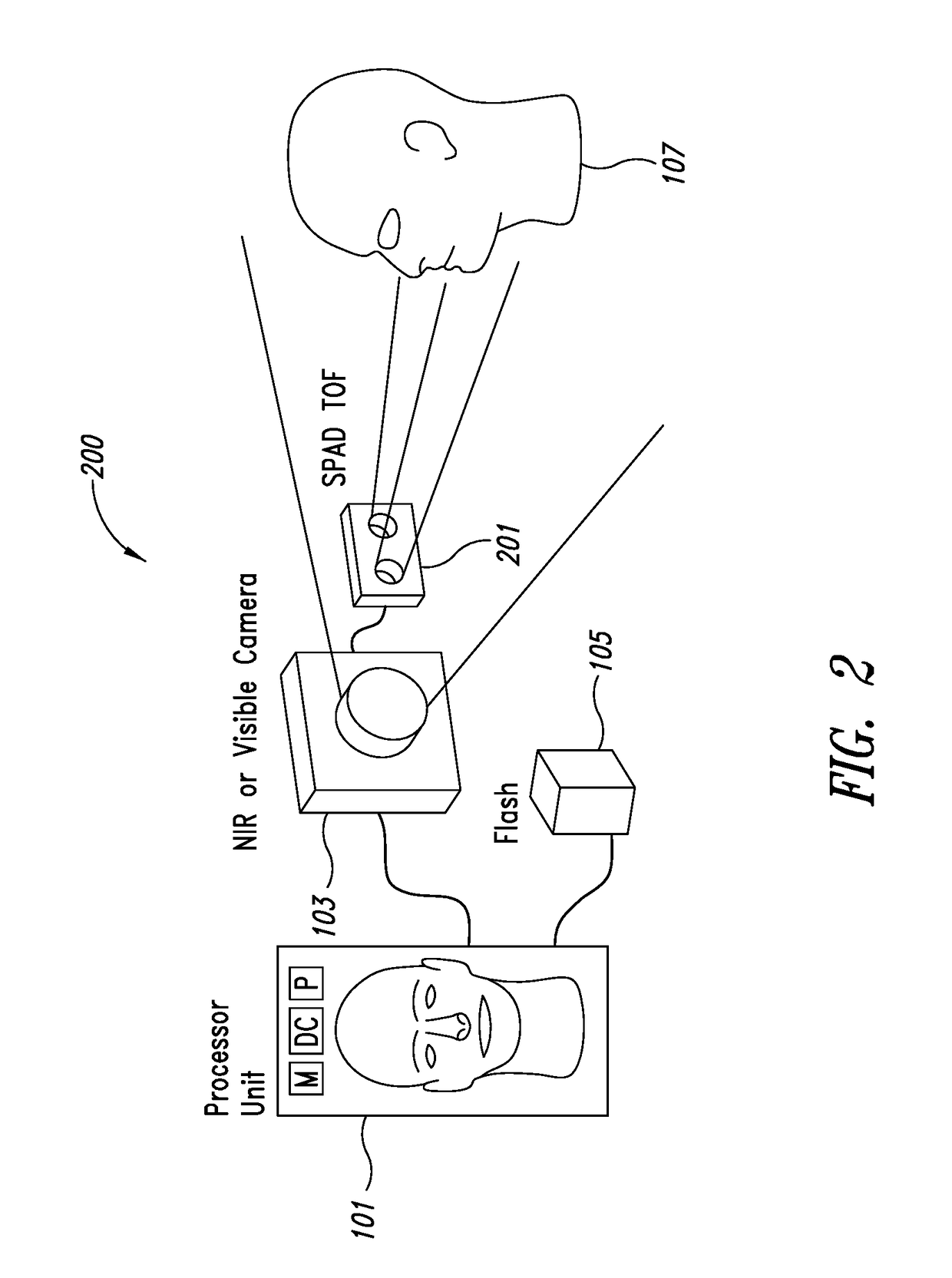
Image capturing apparatus, system and method
ActiveUS20180089848A1Image enhancementTelevision system detailsSingle-photon avalanche diodeAvalanche diode
An apparatus includes time of flight single-photon avalanche diode (ToF SPAD) circuitry. The ToF SPAD circuitry generates indications of distance between the apparatus and an object within a field of view. A processor receives the indications of distance and controls at least one image sensor, such as a camera, to capture at least one image based on at least one indication of distance. The processor determines whether an image is a true representation of an expected object by comparing multiple indications of distance associated with the object to an expected object distance profile and comparing the image to at least one expected object image.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (RES & DEV) LTD +1
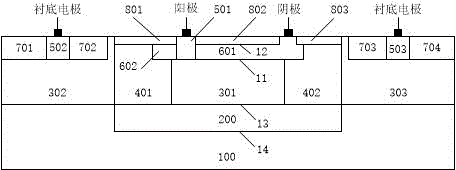
Single-photon-level resolution ratio sensor unit structure based on standard CMOS technology
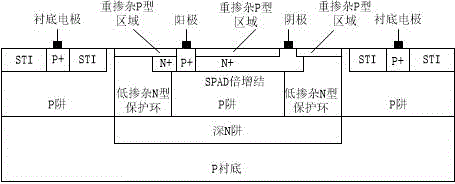
InactiveCN103779437ASimple structureReduce dark noiseSemiconductor devicesConcentration gradientEngineering
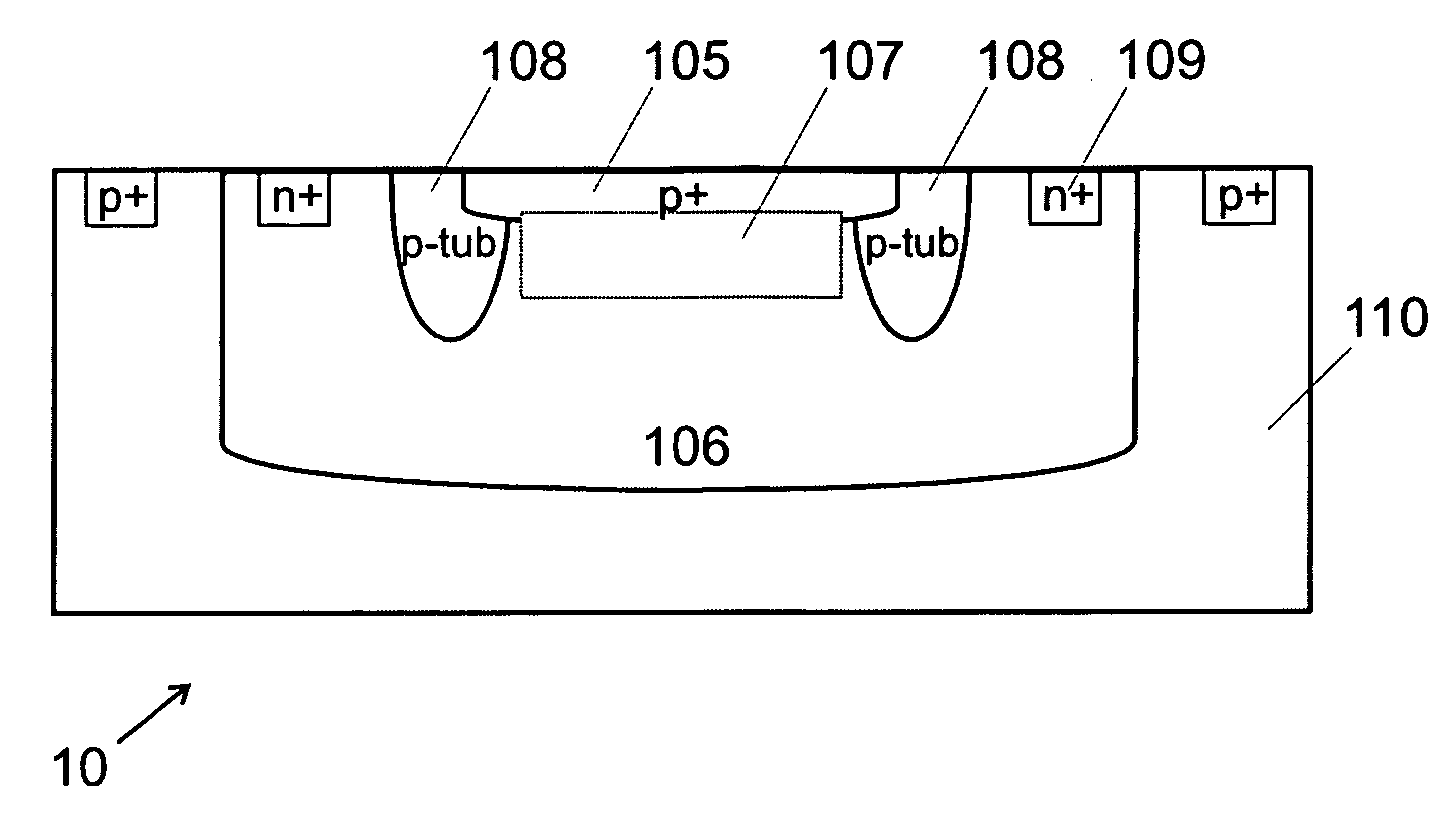
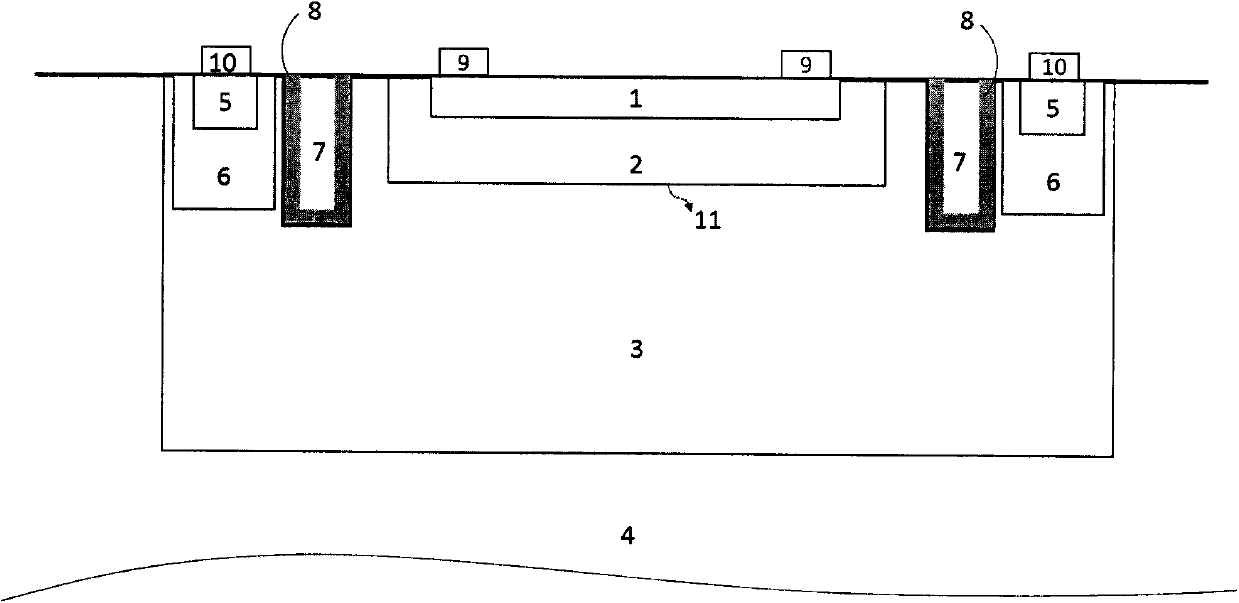
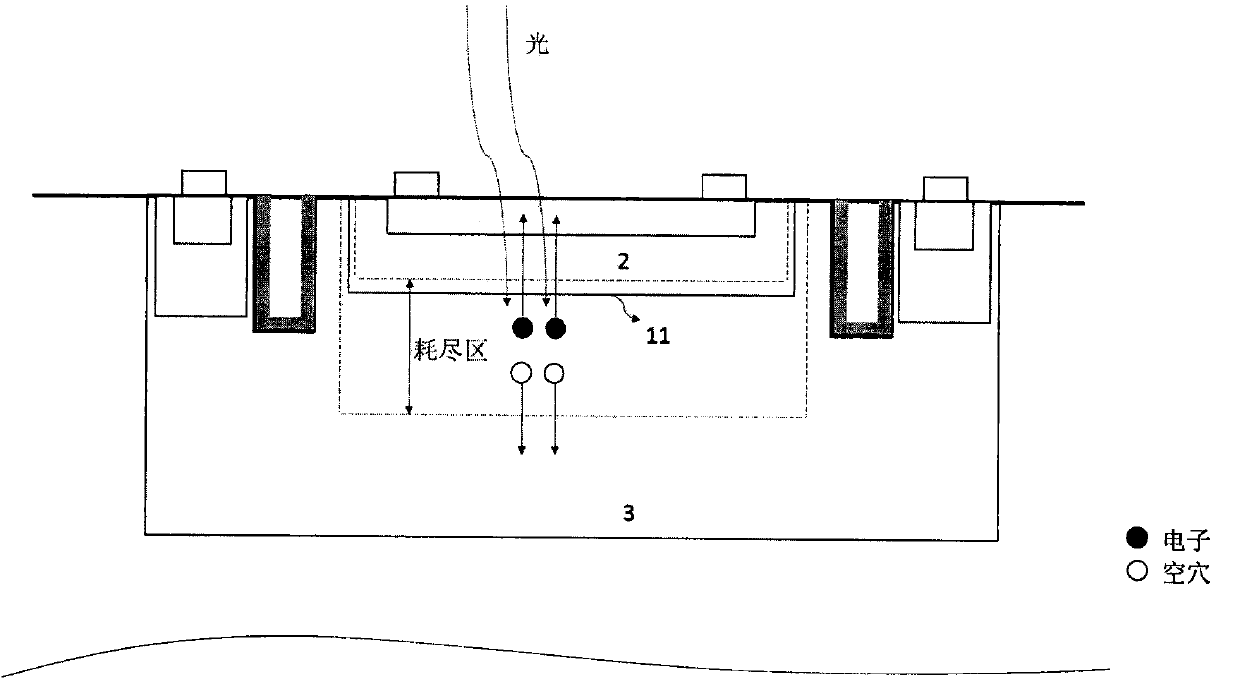
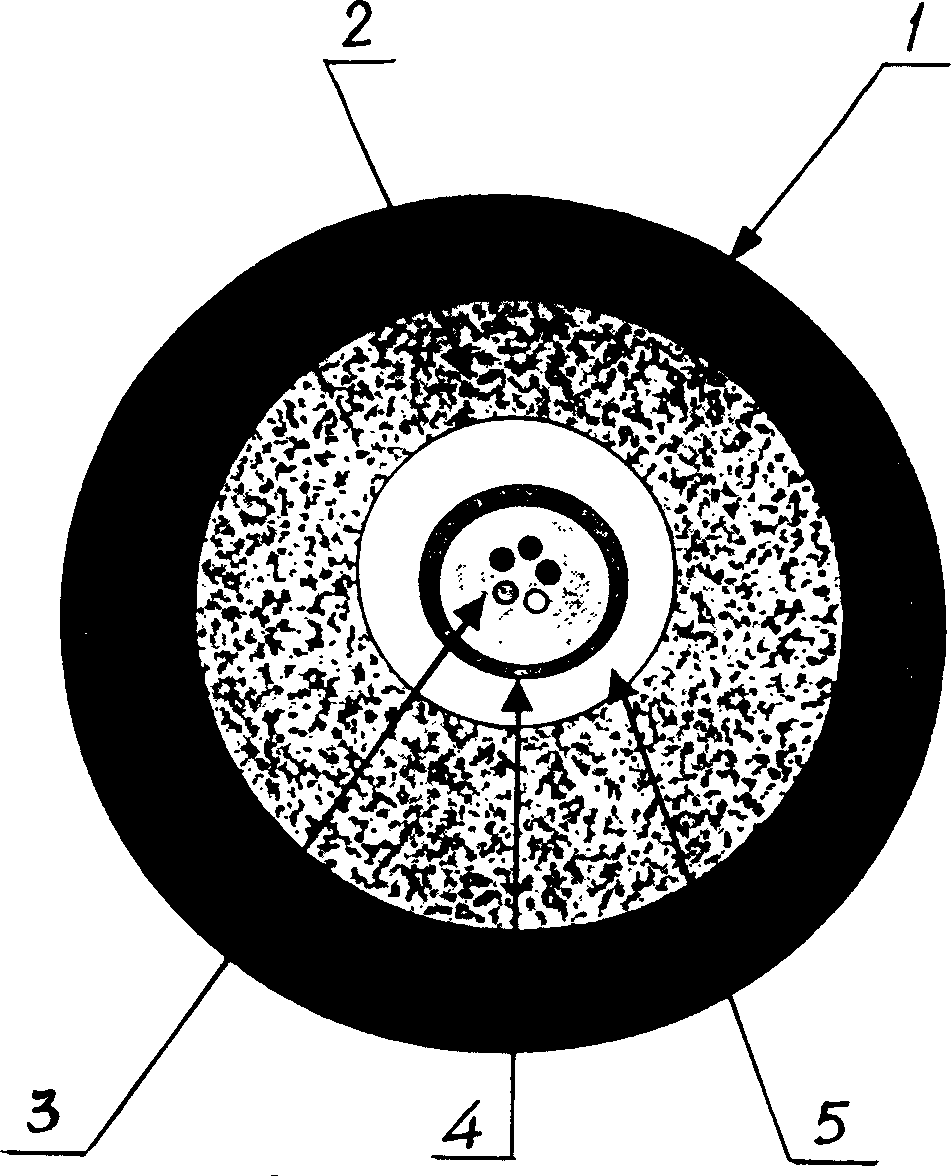
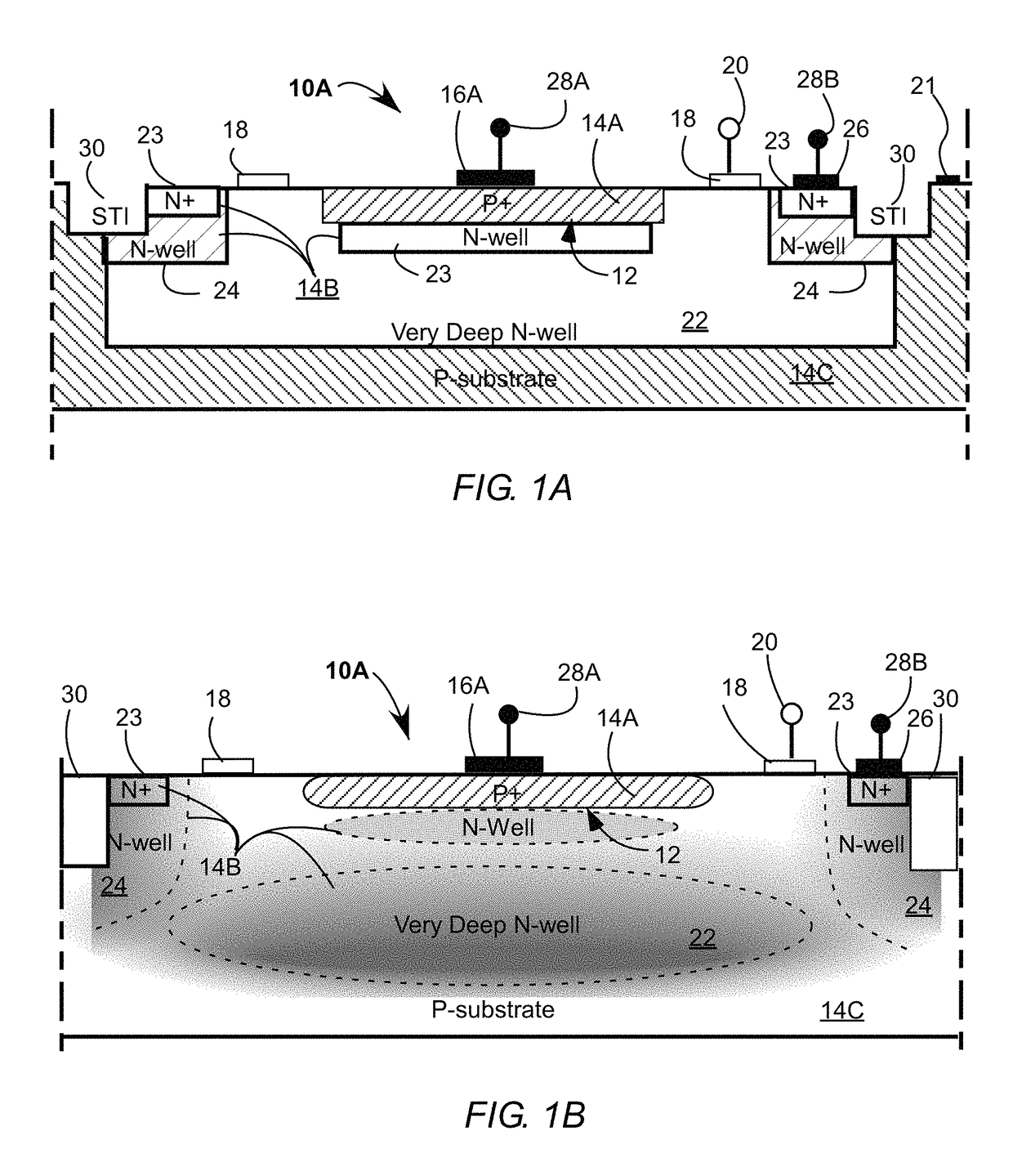
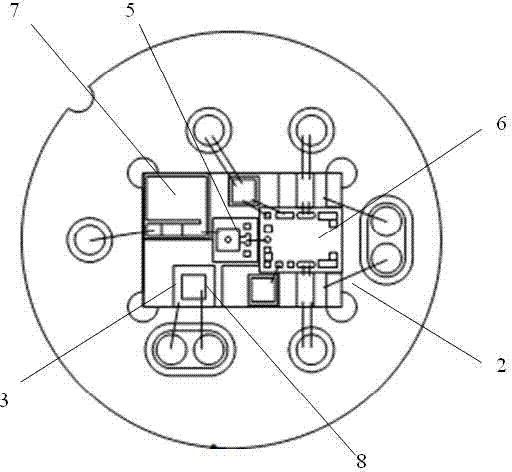
Disclosed is a single-photon-level resolution ratio sensor unit structure based on the standard CMOS technology. The single-photon-level resolution ratio sensor unit structure uses an SPAD. According to the single-photon-level resolution ratio sensor unit structure, basically, a deep N-well (3) is arranged above a P-type silicon substrate (4), a P-well area (2) is formed above the deep N-well (3) and wrapped by the deep N-well (3), an anode contact (9) is connected to the P-well area (2) through a heavy-doping P-well area (1), a cathode contact (10) is connected to an N-well area (6) and the deep N-well (3) through a heavy-doping N-well area (5), a shallow trench isolation area (7) is located between the P-well area (2) and the N-well area (6) to isolate a P-well from an N-well, a P-type doped protection ring (8) surrounds the shallow trench isolation area (7) so as to restrain dark noise caused by defects in shallow trench isolation, and a PN junction (11) is arranged between the bottom of the P-well area (2) and the deep N-well (3); the PN junction generates a high-voltage area when proper bias voltage is applied between the cathode and the anode, and an SPAD multiplication area is formed so as to explore photons; the breakdown voltage of the edge of the PN junction is higher than that of the SPAD plane multiplication area by controlling the concentration gradient of the deep N-well (3).
Owner:苏州超锐微电子有限公司
Distributed optical fiber temperature sensing and monitoring device and method for positioning dam leakage
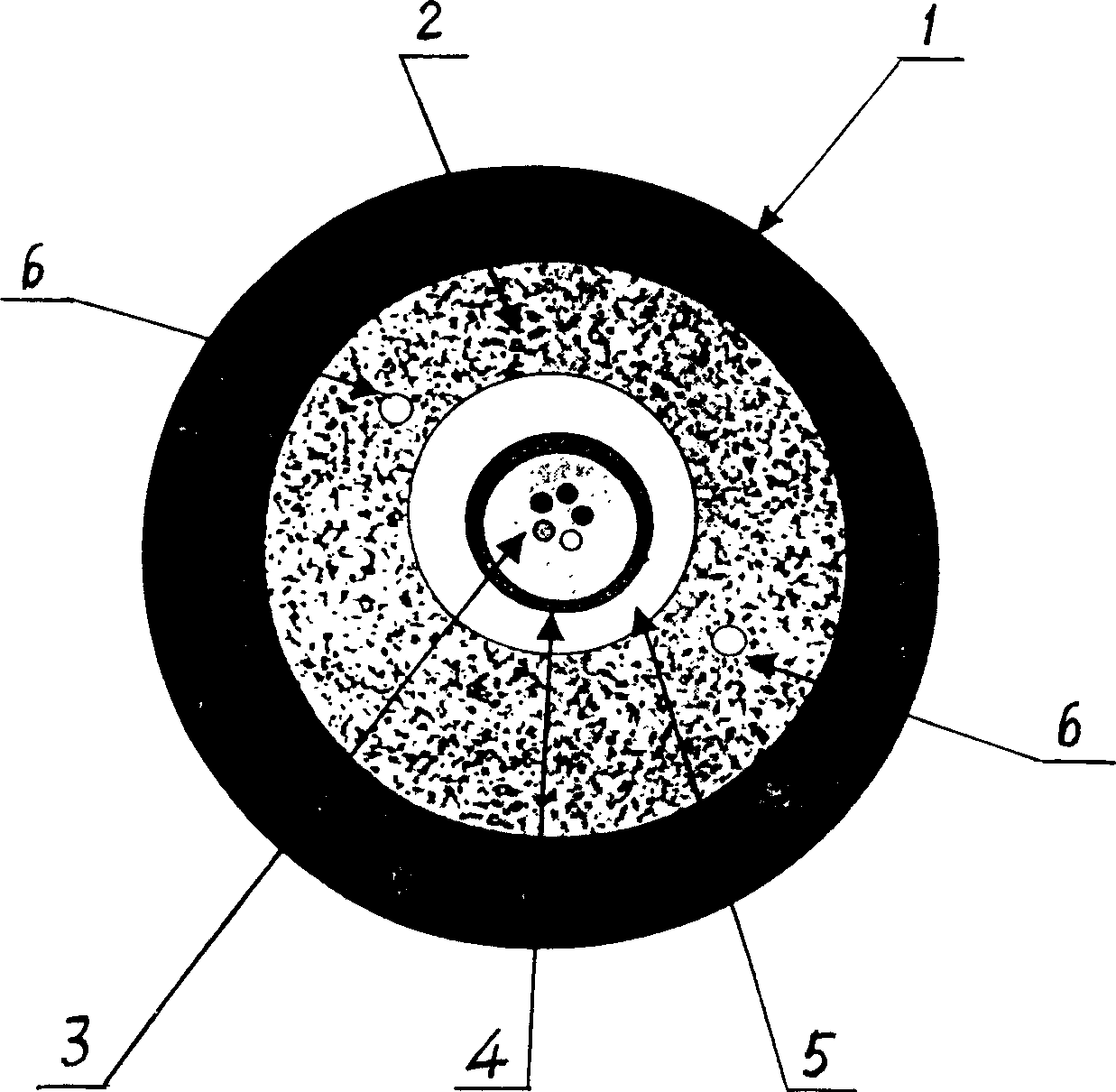
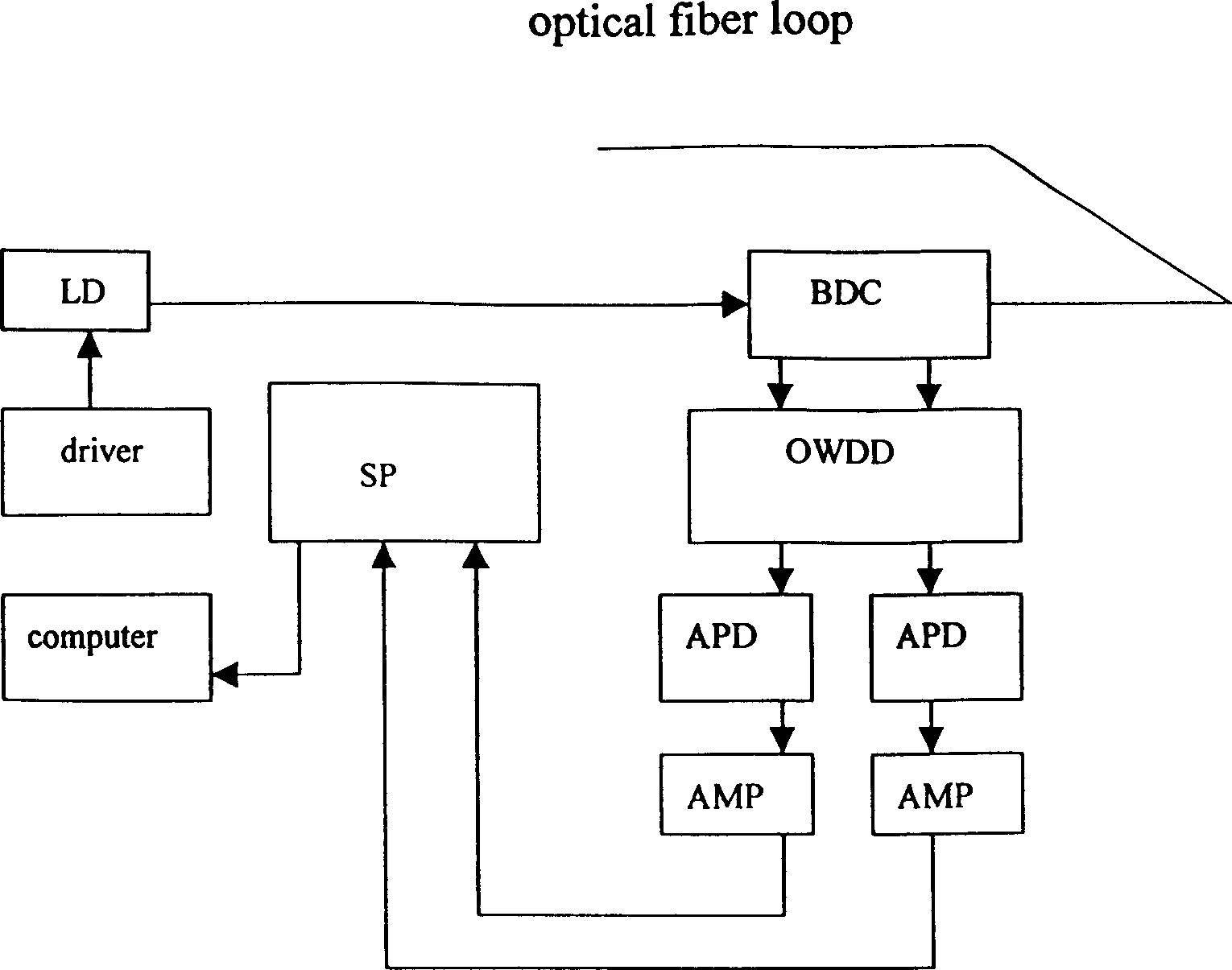
This invention relates to water works engineering safety protection equipments field and a dam leak position distribution light fiber temperature sensor monitoring apparatus and its method. The apparatus is formed by connecting the double-coupler, wavelength-division multiplex, snow-slide diode, main amplifier, sampling even device and sum device, computer, driver, laser diode and sensor cable. The sensor cable has two structures: one is the sensor light cable core of fiber, and the outer layer of the fiber is metal center protective cover, water-tight isolation layer, aramid fiber, outer protective layer; the other is heating sensor cable with isolation heating conductor in one of its structures. íí
Owner:秦一涛 +2
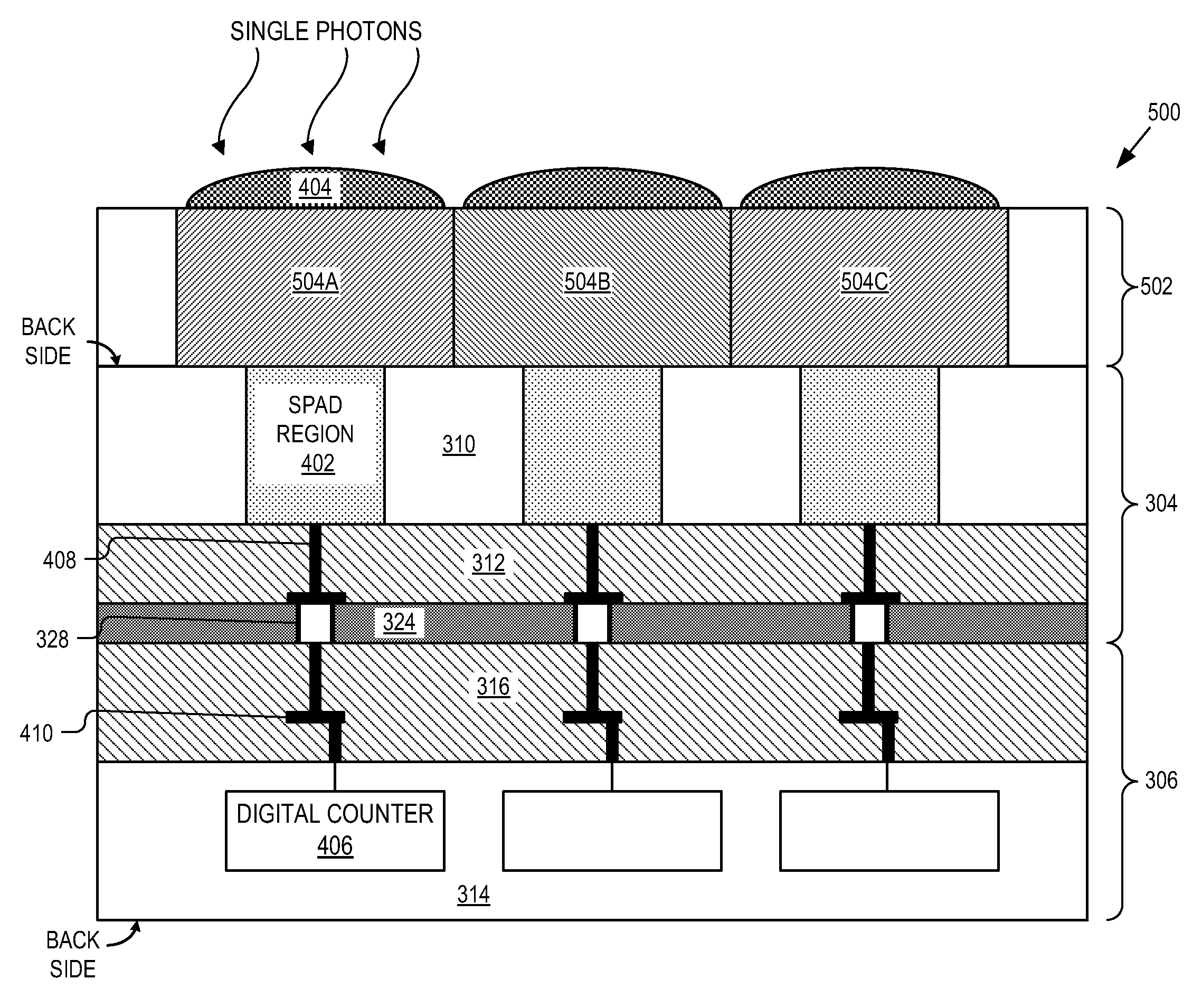
Stacked chip SPAD image sensor
An example imaging sensor system includes a Single-Photon Avalanche Diode (SPAD) imaging array formed in a first semiconductor layer of a first wafer. The SPAD imaging array includes an N number of pixels, each including a SPAD region formed in a front side of the first semiconductor layer. The first wafer is bonded to a second wafer at a bonding interface between a first interconnect layer of the first wafer and the second interconnect layer of the second wafer. An N number of digital counters are formed in a second semiconductor layer of the second wafer. Each of the digital counters are configured to count output pulses generated by a respective SPAD region.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
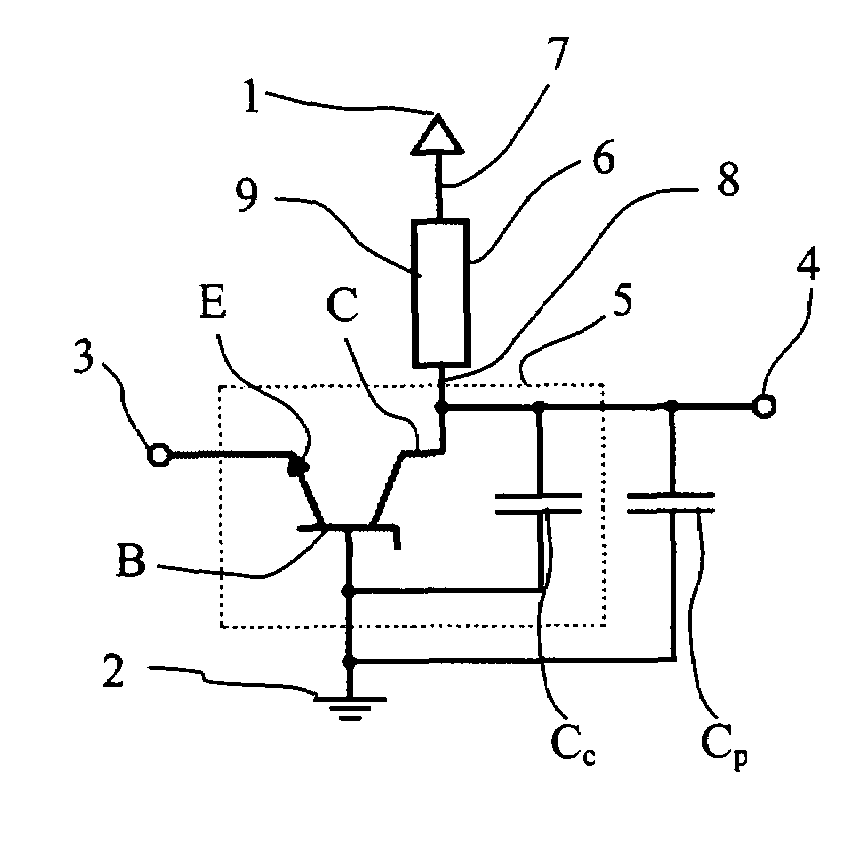
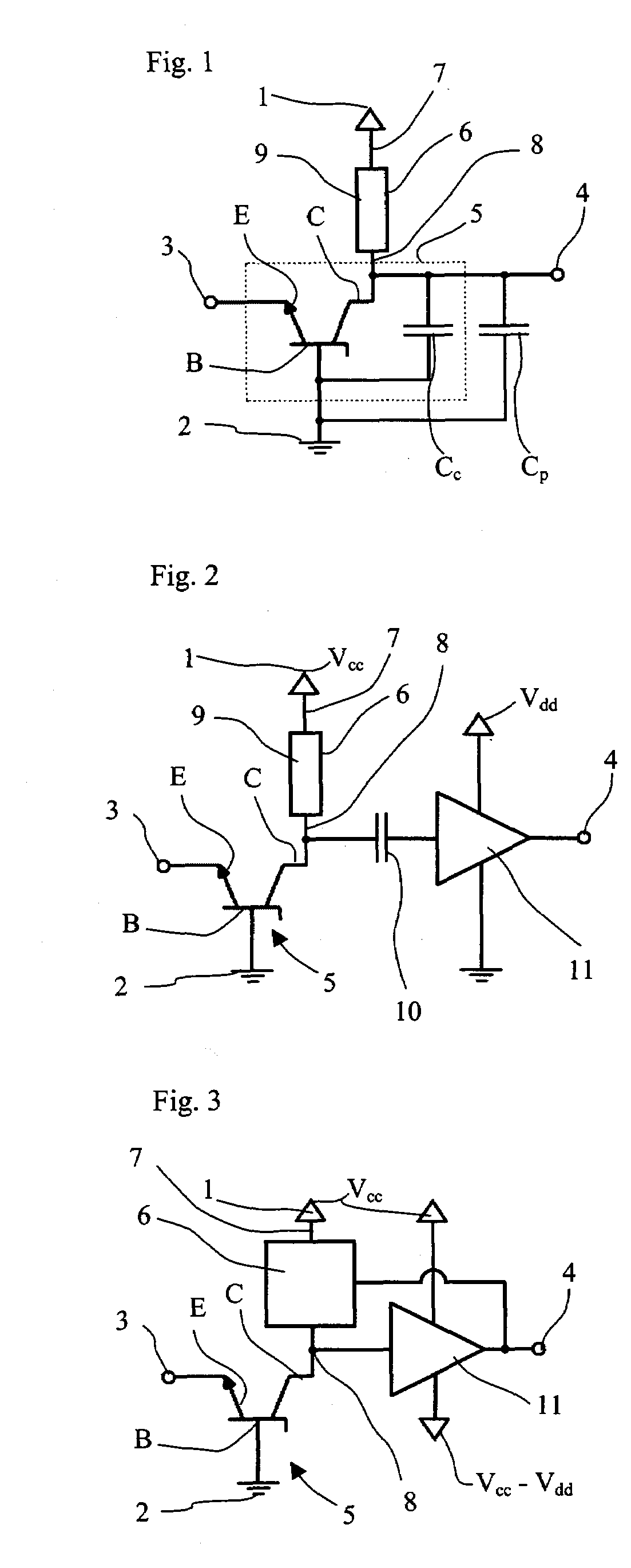
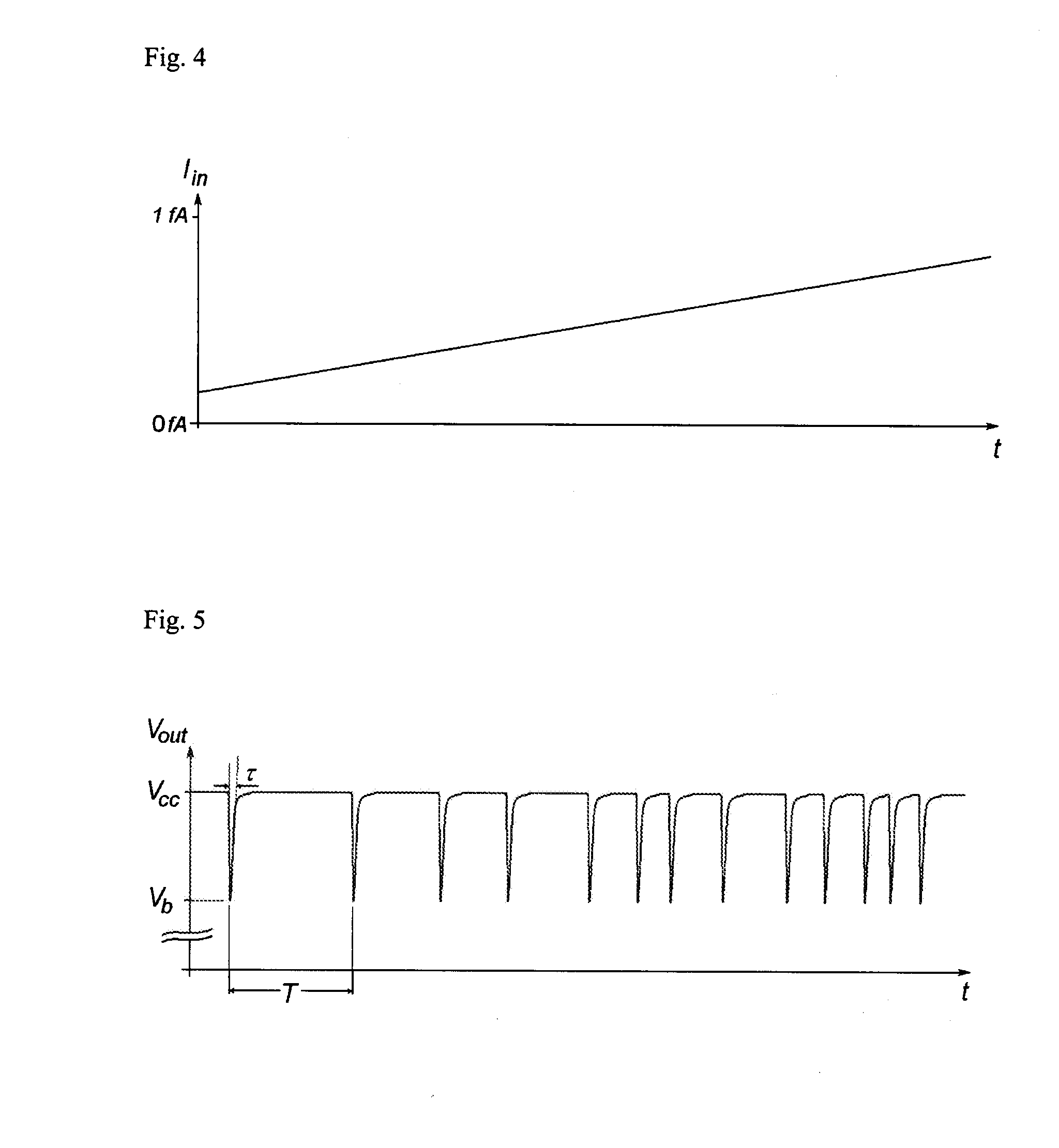
Semiconductor Device For Measuring Ultra Small Electrical Currents And Small Voltages
InactiveUS20100013458A1Reduce bias voltageIncrease kinetic energyElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingSingle electronLow voltage
A semiconductor device for measuring ultra low currents down to the level of single electrons or low voltages comprises a first and a second voltage supply terminal, an input terminal for receiving an electrical current or being supplied with a voltage to be measured, a bipolar transistor having a base, an emitter and a collector, wherein a first PN junction is formed between the base and the collector and a second PN junction is formed between the base and the emitter, wherein the emitter is coupled to the input terminal and the base is coupled to the second voltage supply terminal, and wherein the first PN junction is designed for reverse biased operation as an avalanche diode, and a quenching and recharging circuit having a first terminal coupled to the first voltage supply terminal and a second terminal coupled to the collector of the bipolar transistors, the quenching and recharging circuit permitting operation of the first PN junction reverse biased above the breakdown voltage of the first PN junction.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
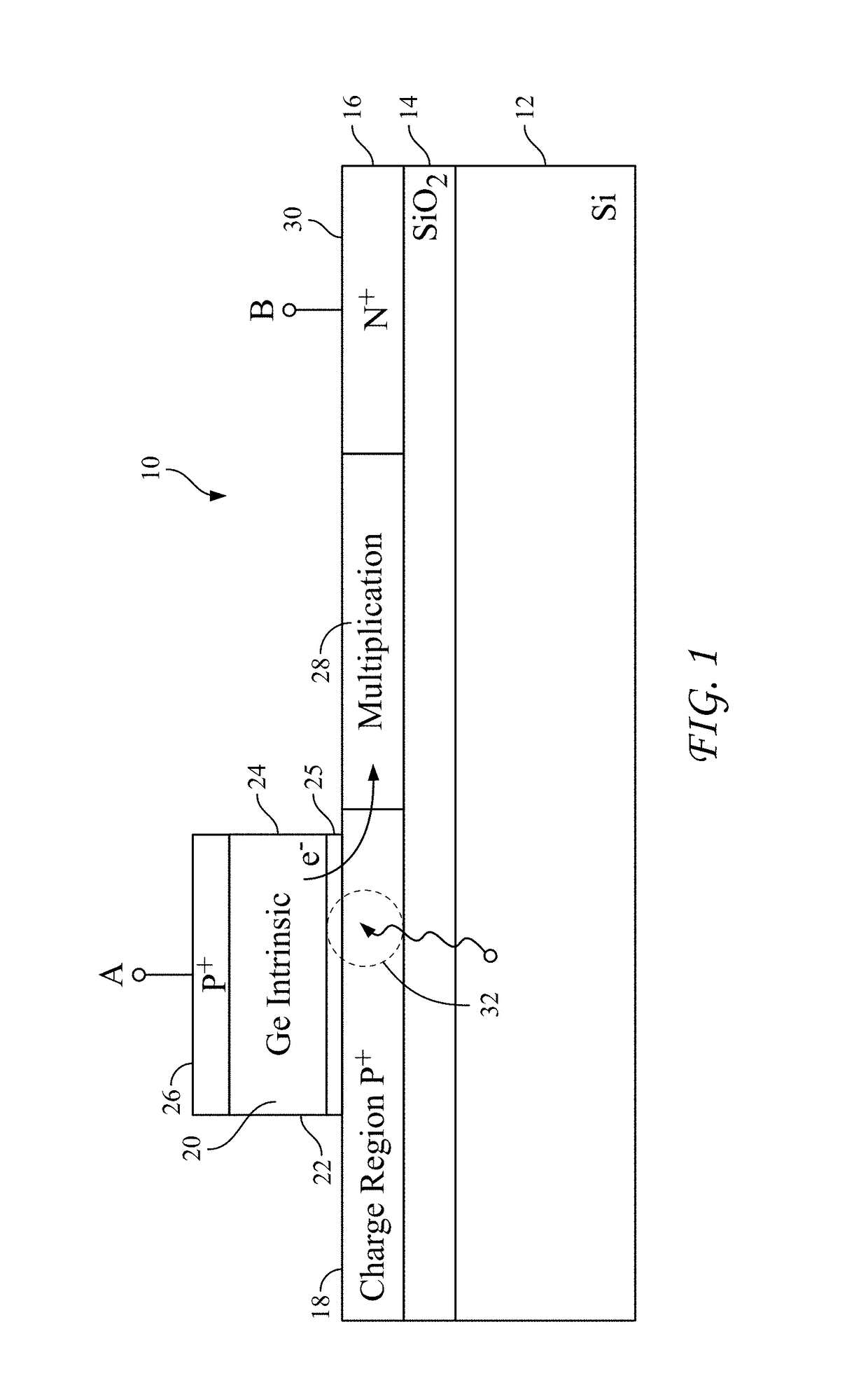
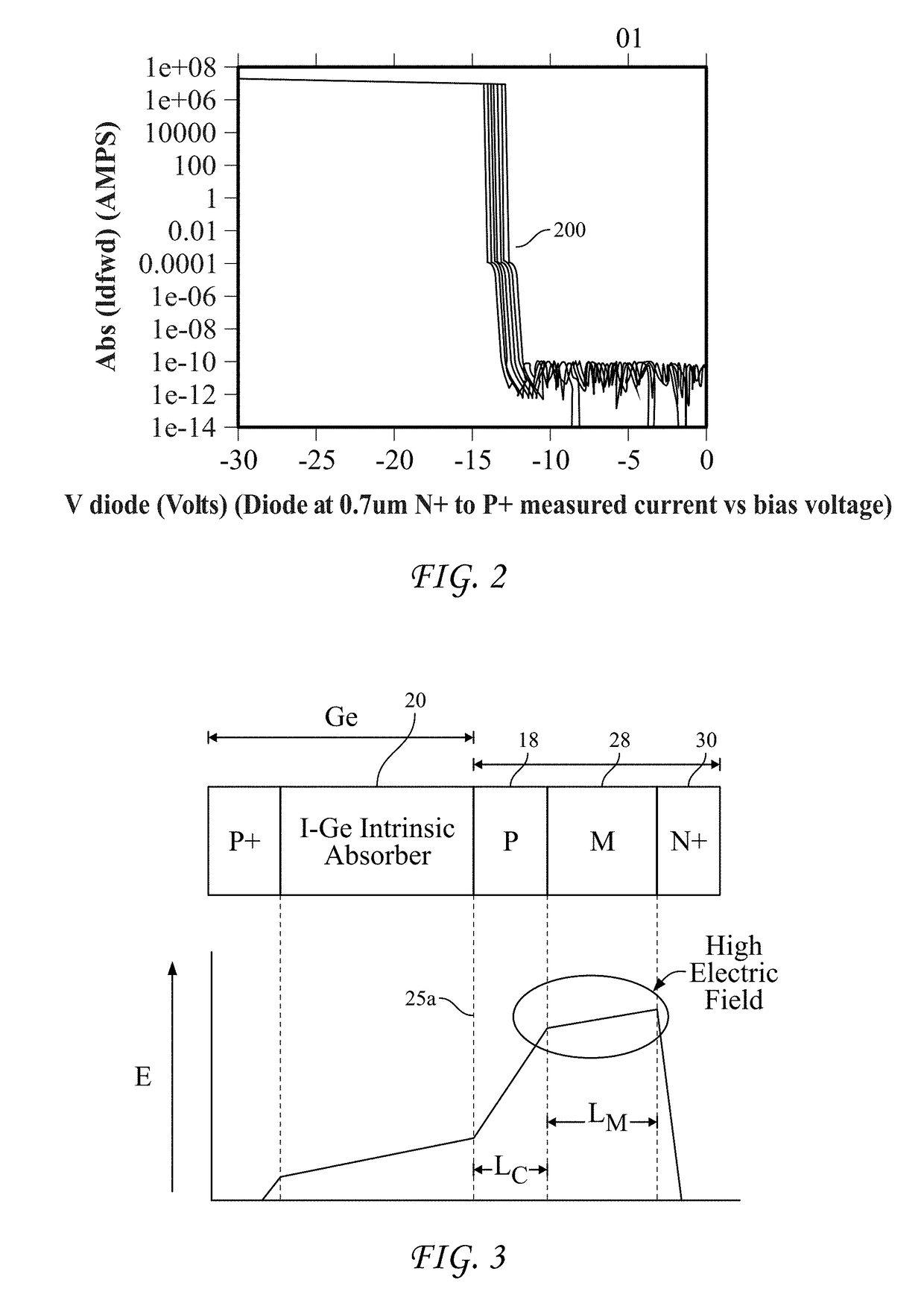
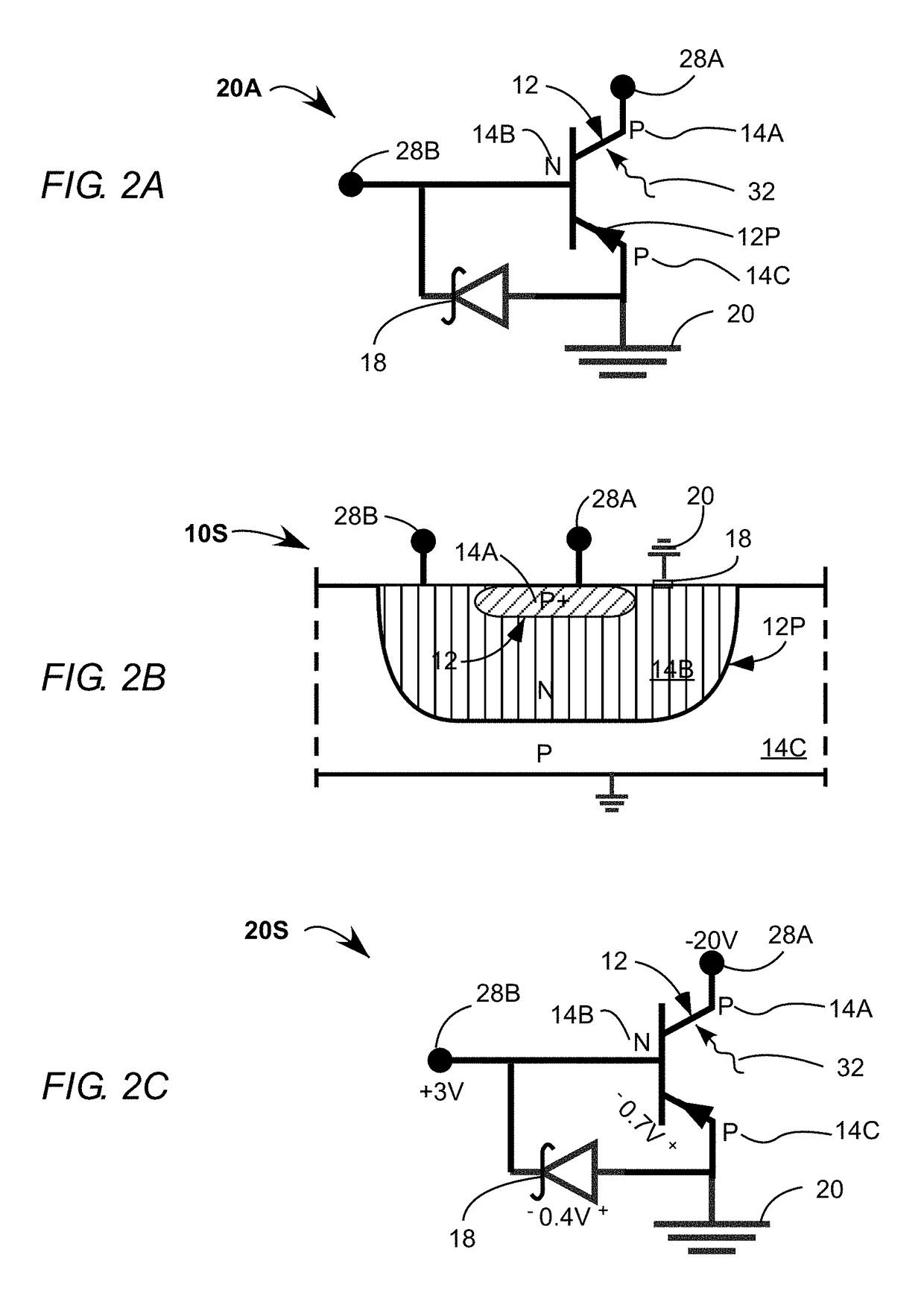
Avalanche diode having reduced dark current and method for its manufacture
An avalanche diode includes an absorption region in a germanium body epitaxially grown on a silicon body including a multiplication region. Aspect-ratio trapping is used to suppress dislocation growth in the vicinity of the absorption region.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Solid state photomultiplier using buried P-N junction
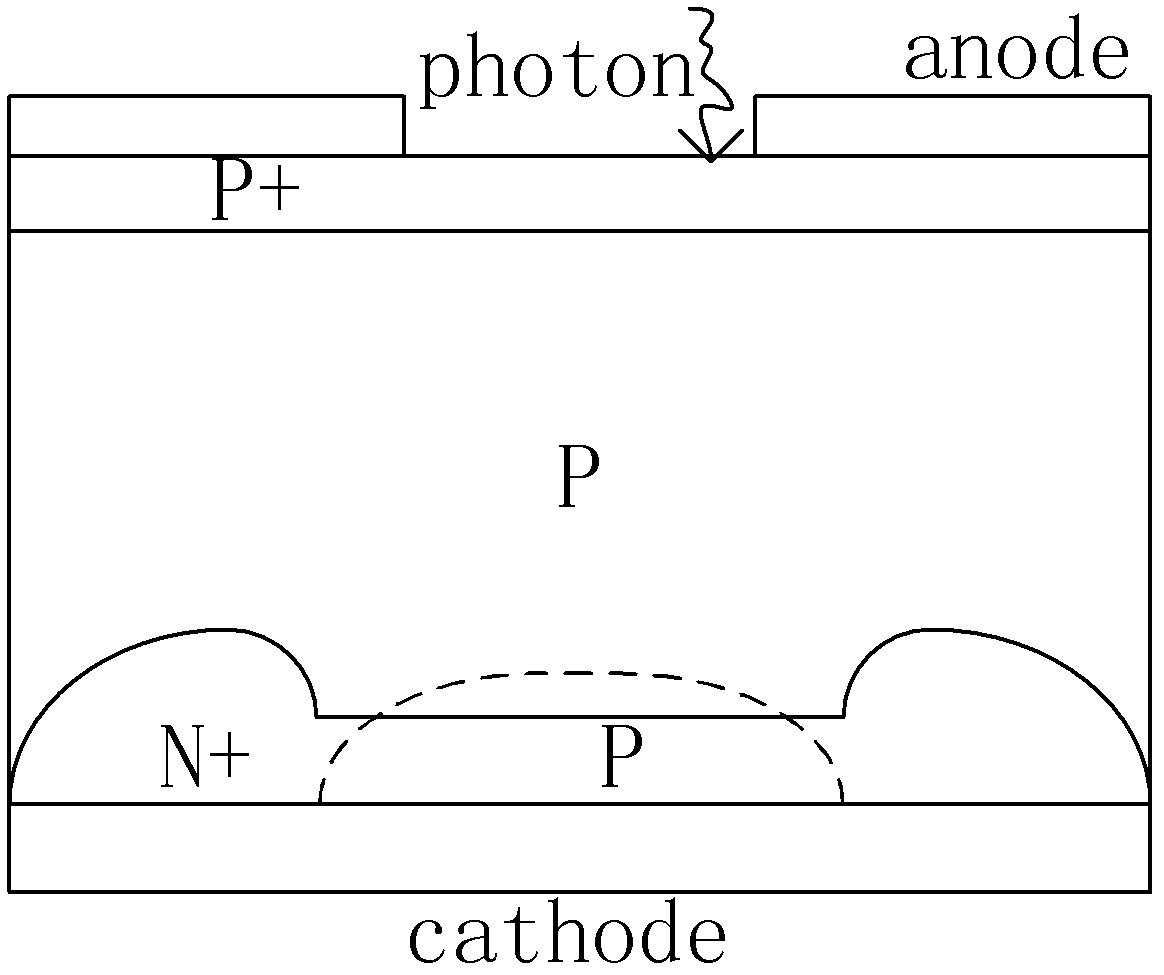
A device that detects single optical and radiation events and that provides improved blue detection efficiency and lower dark currents than prior silicon SSPM devices. The sensing element of the devices is a photodiode that may be used to provide single photon detection through the process of generating a self-sustained avalanche. The type of diode is called a Geiger photodiode or signal photon-counting avalanche diode. A CMOS photodiode can be fabricated using a “buried” doping layer for the P-N junction, where the high doping concentration and P-N junction is deep beneath the surface, and the doping concentration at the surface of the diode may be low. The use of a buried layer with a high doping concentration compared to the near surface layer of the primary P-N junction allows for the electric field of the depletion region to extend up near the surface of the diode. With a low doping concentration through the bulk of the diode, the induced bulk defects are limited, which may reduce the dark current. The resulting structure provides a diode with improved quantum efficiency and dark current.
Owner:RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES
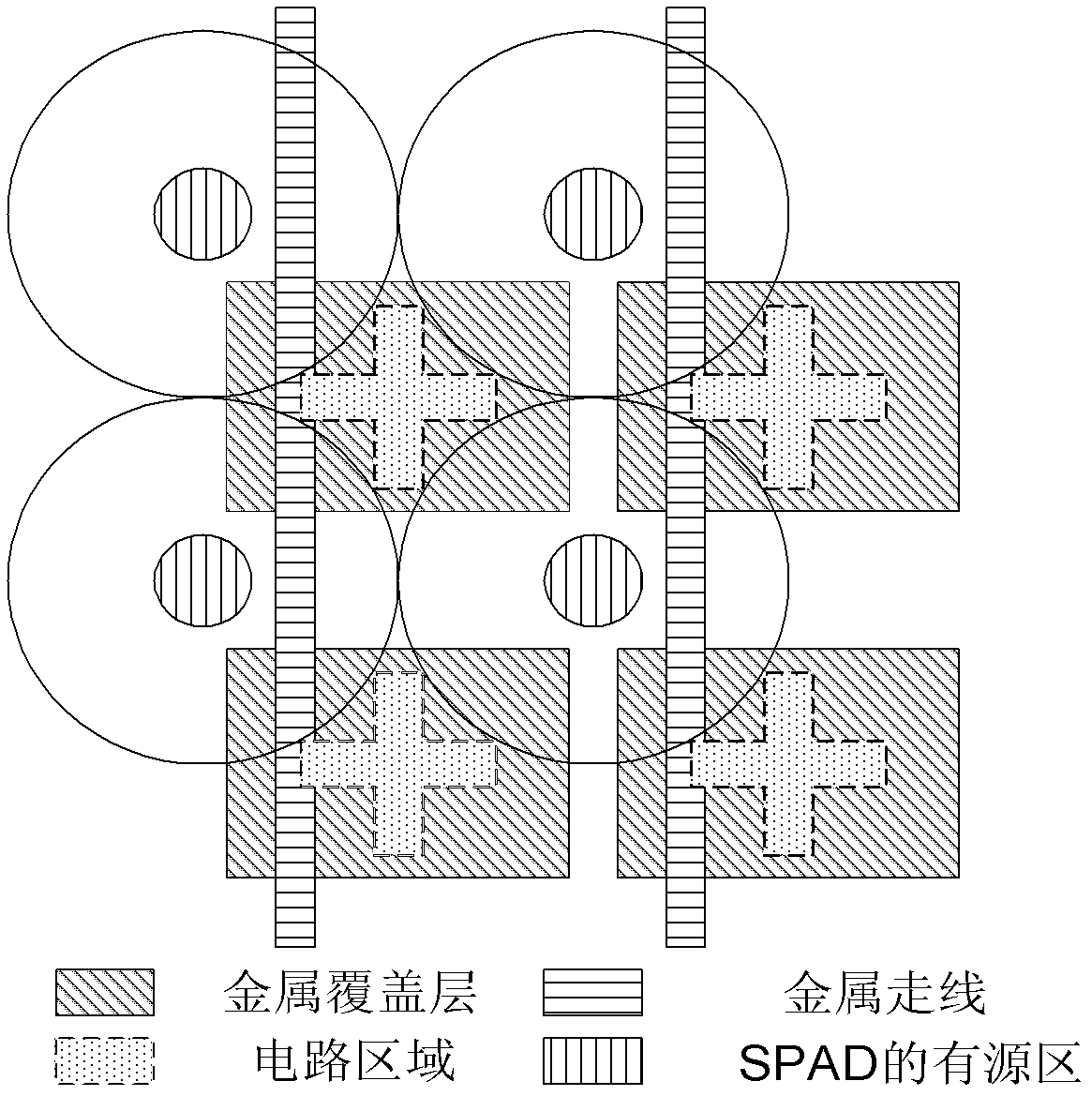
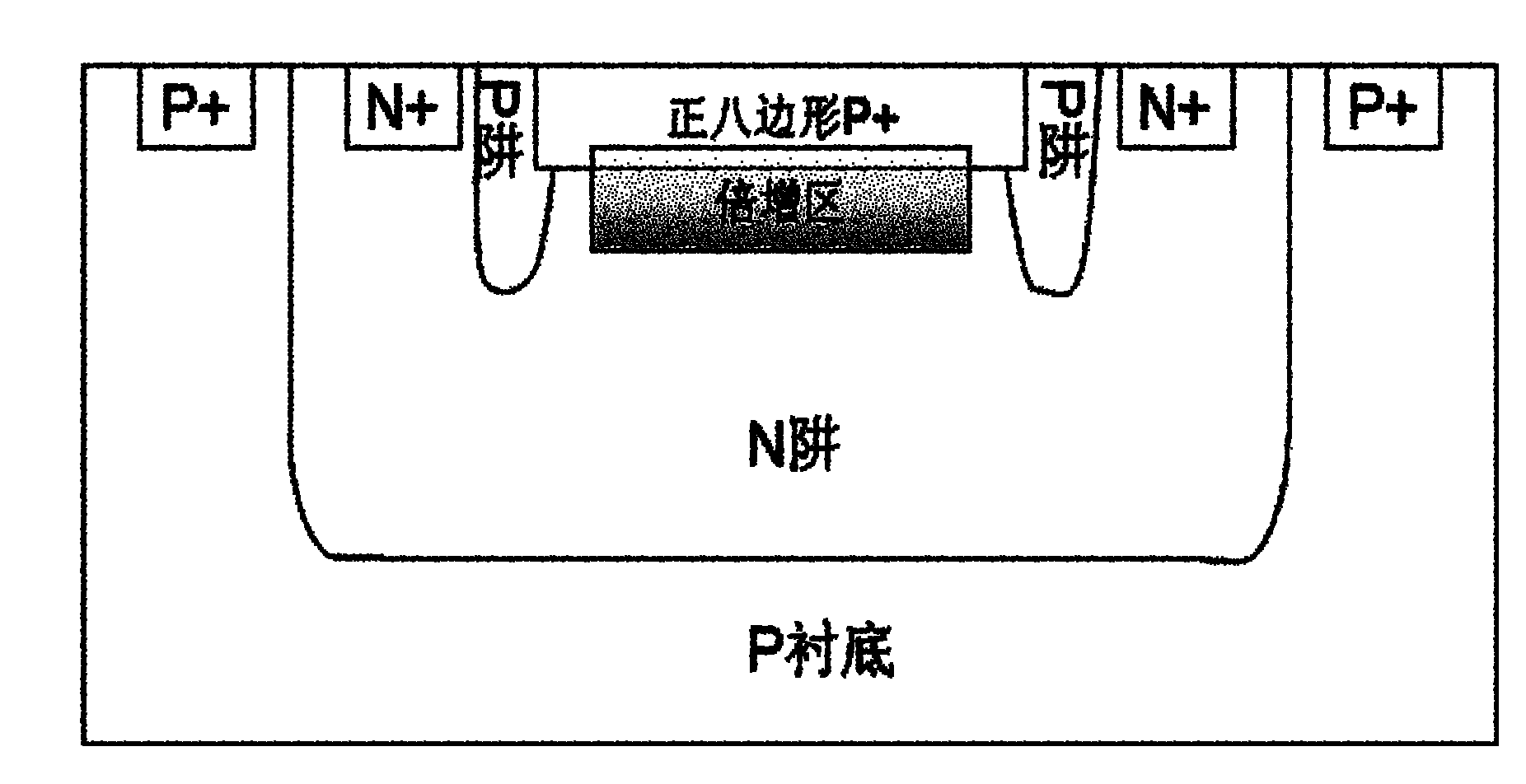
Single-photon avalanche diode and three-dimensional CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) image sensor based on same
InactiveCN101931021AImprove uniformityFully magnifiedTelevision system detailsFinal product manufactureHorizontal and verticalElectron
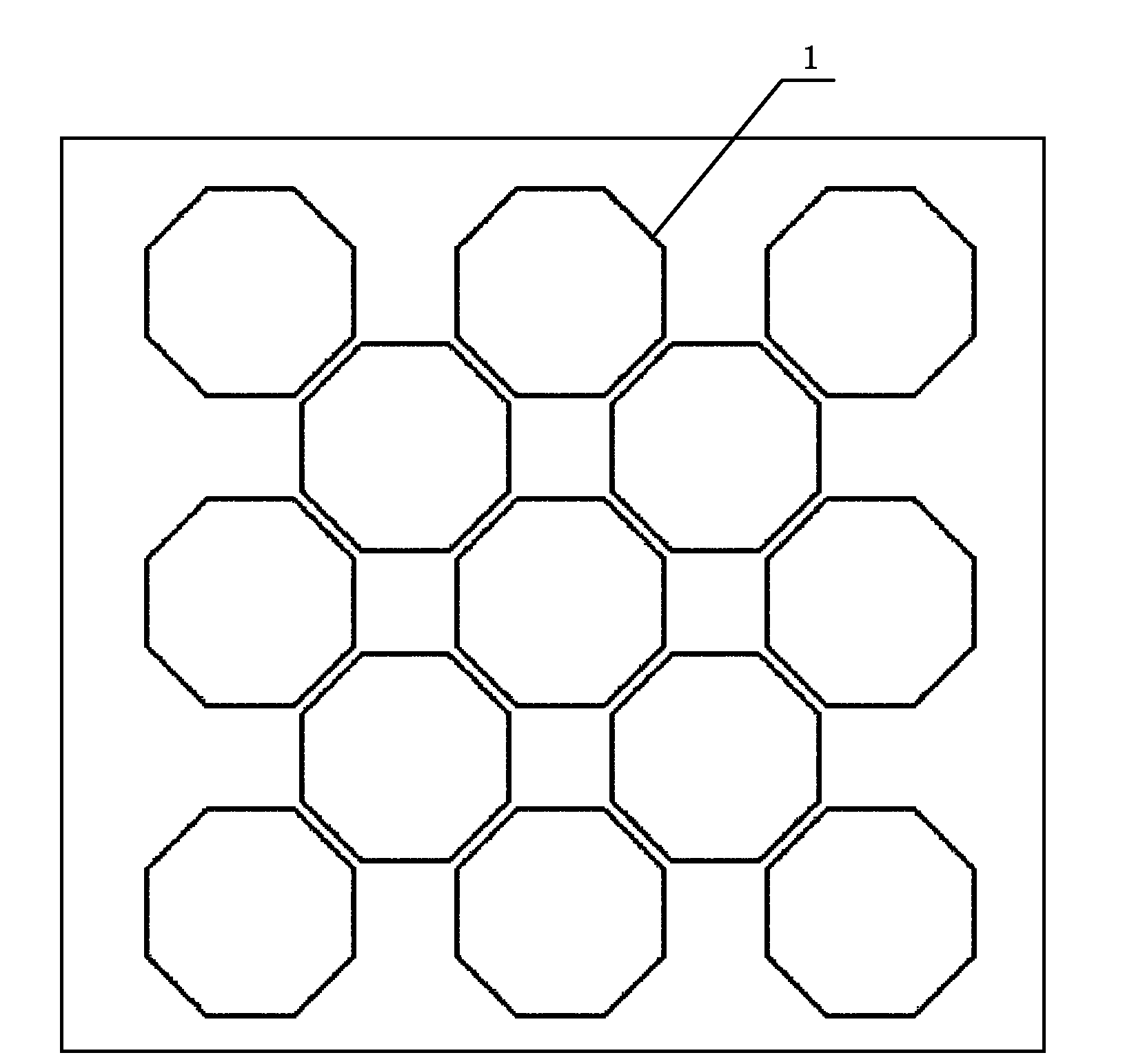
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronic technologies and photoelectronic imaging technologies, in particular relates to a single-photon avalanche diode and a three-dimensional CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) image sensor based on the diode. The single-photon avalanche diode of the invention improves the traditional rectangular photosensitive PN junction into a regular octagon and can conveniently and simply weaken edge breakdown and improve gain uniformity. A two-dimensional pixel array of the three-dimensional CMOS image sensor based on the diode comprises unit pixels of the regular octagon-shaped single-photon avalanche diode and is arrayed in a honeycomb-shape, thereby being convenient for interpolation and improving resolution in horizontal and vertical direction.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Single photo avalanche diode imaging sensor for complementary metal oxide semiconductor stacked chip applications
ActiveCN104779259ATelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSingle-photon avalanche diode
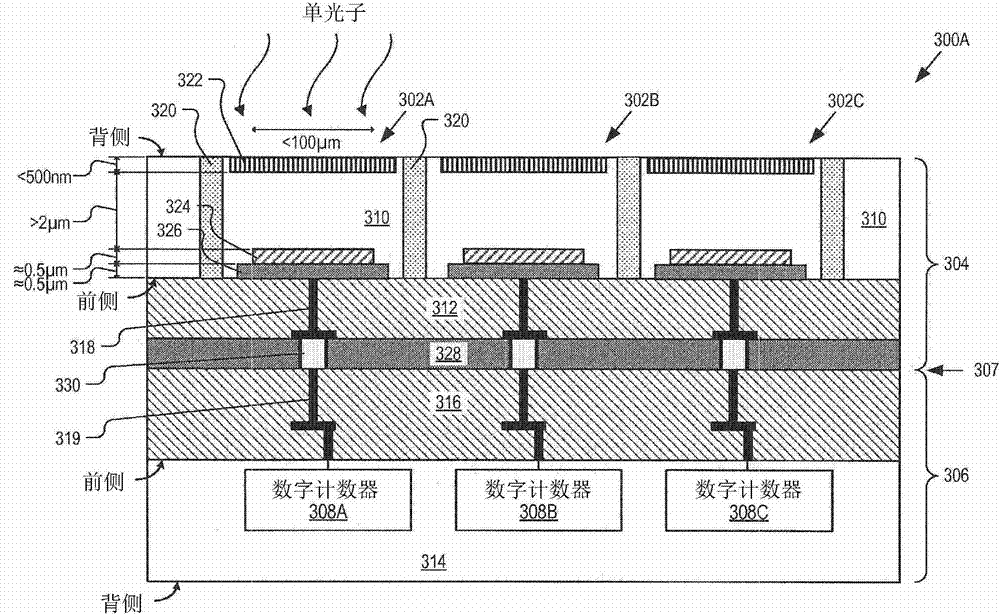
An imaging sensor system includes a single photon avalanche diode (SPAD) imaging array including N pixels formed in a first semiconductor layer of a first wafer. Substantially an entire thickness of the first semiconductor layer of each pixel is fully depleted such that a multiplication region included in each pixel near a front side is configured to be illuminated with photons through a back side and through the substantially entire thickness of the fully depleted first semiconductor layer. Deep n type isolation regions are disposed in the first semiconductor layer between the pixels to isolate the pixels. N digital counters are formed in a second semiconductor layer of a second wafer that is bonded to the first wafer. Each of the N digital counters is coupled to the SPAD imaging array and coupled to count output pulses generated by a respective one of the pixels.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Surge suppression system for power over network cables
InactiveUS20080037188A1Improve voltage clampingGood power deliveryData switching current supplyEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentEngineeringPower over
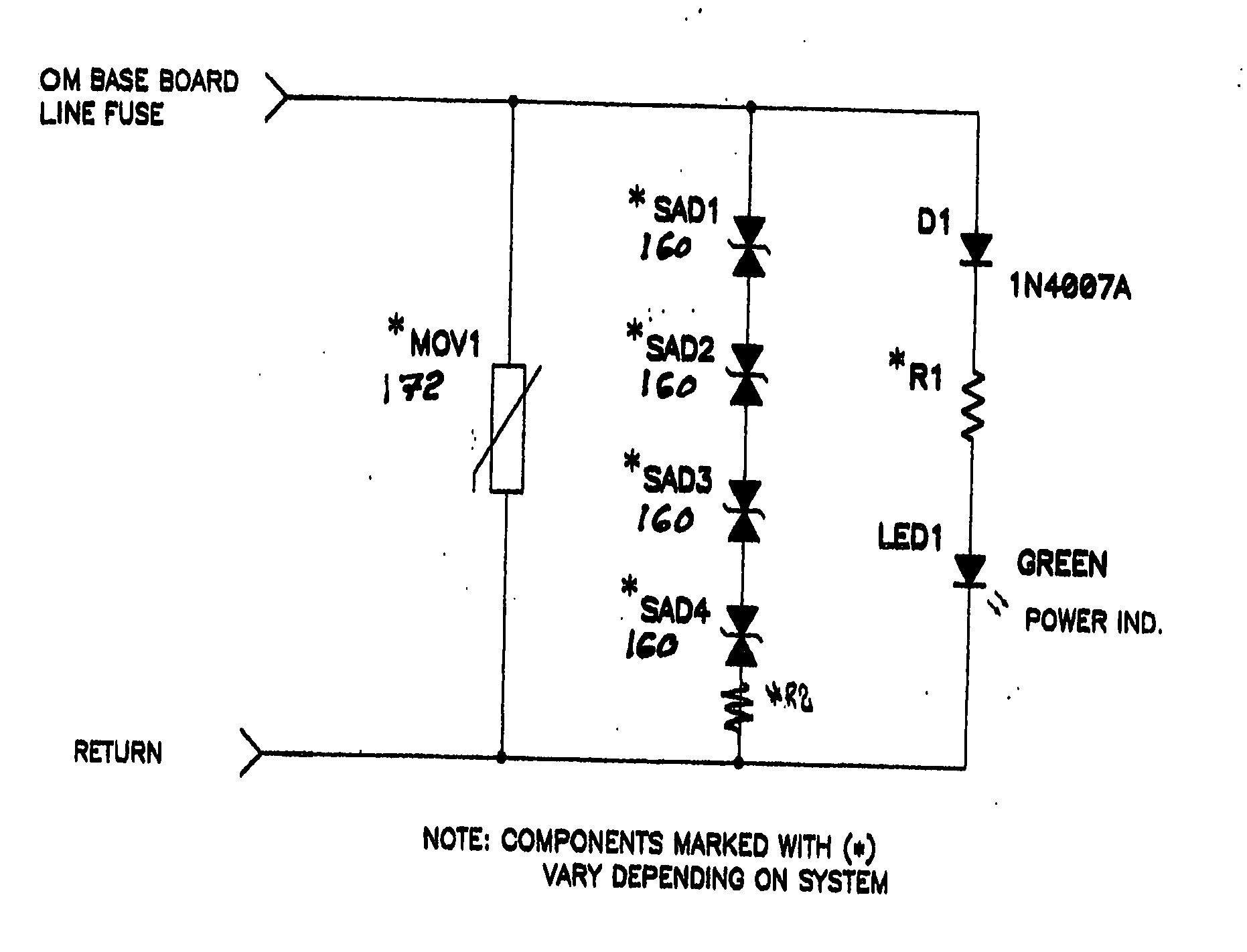
A surge suppression unit comprises connection circuitry for coupling the surge suppression unit in a communication cable. Surge suppression circuitry uses Silicon Avalanche Diodes (SADs) that couple power surges on the communication cable to ground. In one embodiment, the surge suppression unit includes multiple surge suppression modules configured for inserting into different slots in a same enclosure. The surge suppression modules can be quickly and easily inserted and then removed for connection with different communication cables
Owner:A C DATA SYST INC
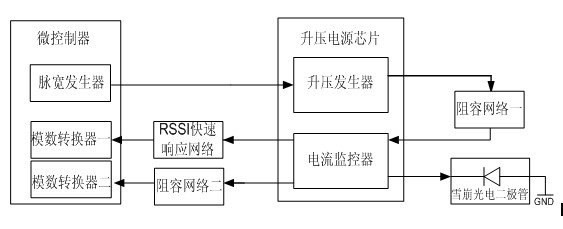
Protector and protection method of avalanche photodiode (APD)
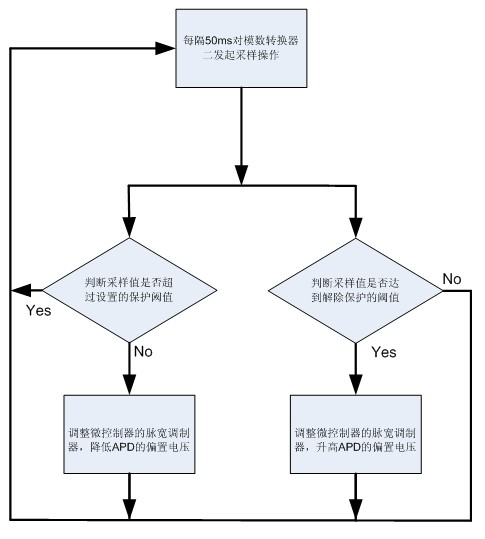
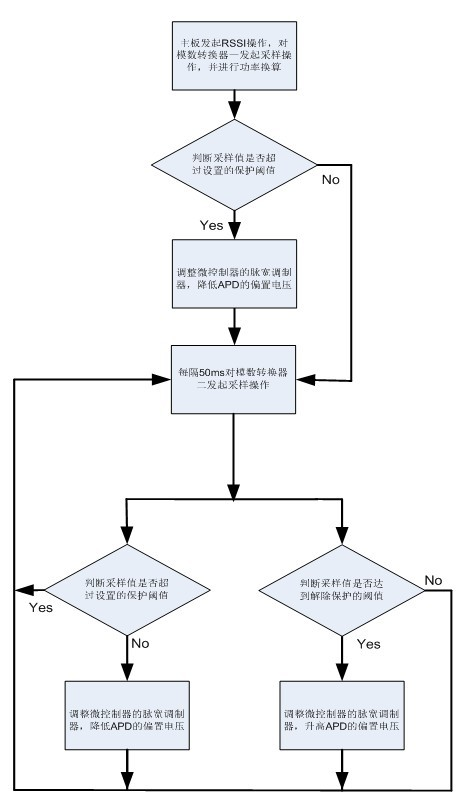
InactiveCN102013676ASo as not to damageEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentMicrocontrollerAutomatic control
The invention discloses a protector and protection method of an avalanche photodiode (APD) in a passive optical network (PON) burst mode. A chip with a two-path current monitoring and boosting function is used to provide a bias voltage and current for the APD. A microcontroller capable of pulse width modulation (PWM) and analog-to-digital conversion is used for modulating the voltage and sampling of the APD. A received signal strength indication (RSSI) fast response system is utilized to finish light current sampling and holding in the presence of an ultrashort optical signal. In the invention, based on a principle of automatic control, when the luminous power of the APD is excessively input, a pulser configured by software is used for reducing the output voltage of a power supply chip, so as to reduce the gain current and response current of the power supply chip, thereby preventing the overcurrent damage of the APD.
Owner:CHENGDU SUPERXON COMM TECH CO LTD
CMOS image sensor technology-based NP type single-photon avalanche diode
InactiveCN105810775AImplement detectionSimple structureSemiconductor devicesCMOSSingle-photon avalanche diode
The inventioN discloses a CMOS image sensor technology-based NP type single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD). The basic structure of the SPAD comprises a deep N-well arranged above a P-type silicon substrate; a P-well formed above the deep N-well; a lightly-doped guard ring surrounding the P-well; a N+ region formed above the P-well and overlapped with the guard ring; a PN-junction formed between the N+ region and the P-well; a cathode electrode and an anode electrode respectively led out of the N+ and P+; a heavily-doped P-type region formed above the N+ region and the guard ring; a P-well surrounding the guard ring and a substrate electrode led out of the P+. According to the technical scheme of the invention, through forming the heavily-doped P-type region on the surface of the N+ region, the dark counting caused by defects on the interface of an NP-type SPAD device can be reduced. Based on the effective layout technique, the dark counting caused by defects in the STI is reduced. Based on the effective guard ring technique, the edge breakdown of the SPAD device is prevented. Through applying an appropriate bias voltage between the electrodes, the response within the blue band is enhanced.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Proximity sensor and associated method, computer readable medium and firmware
ActiveUS20120153120A1Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansProximity sensorSingle-photon avalanche diode
A proximity detector may include an array of single photon avalanche diodes (SPADs) and an illumination source. Illumination from the illumination source may be reflected by a target to the array of single photon avalanche diodes. The SPADs may be operable to detect events. A number of events detected may be dependent on a level of illumination incident on the SPADs. The proximity detector may then determine a quality metric and calculate an output when the quality metric is at a predetermined level. A related method may include regulating the quality of the data on which such a proximity detector apparatus calculates its output.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (RES & DEV) LTD
Aerosol particle double channel laser detector and detecting method thereof
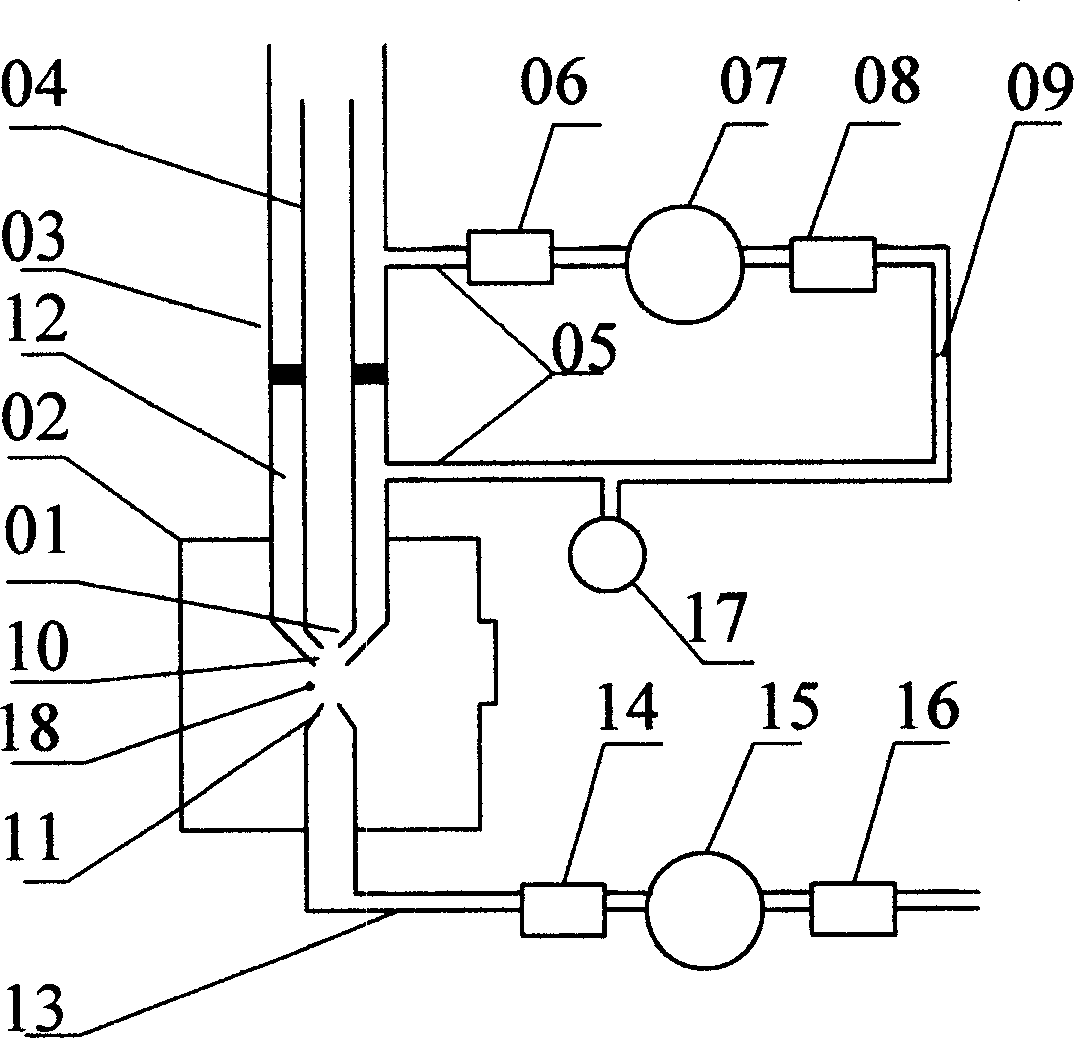
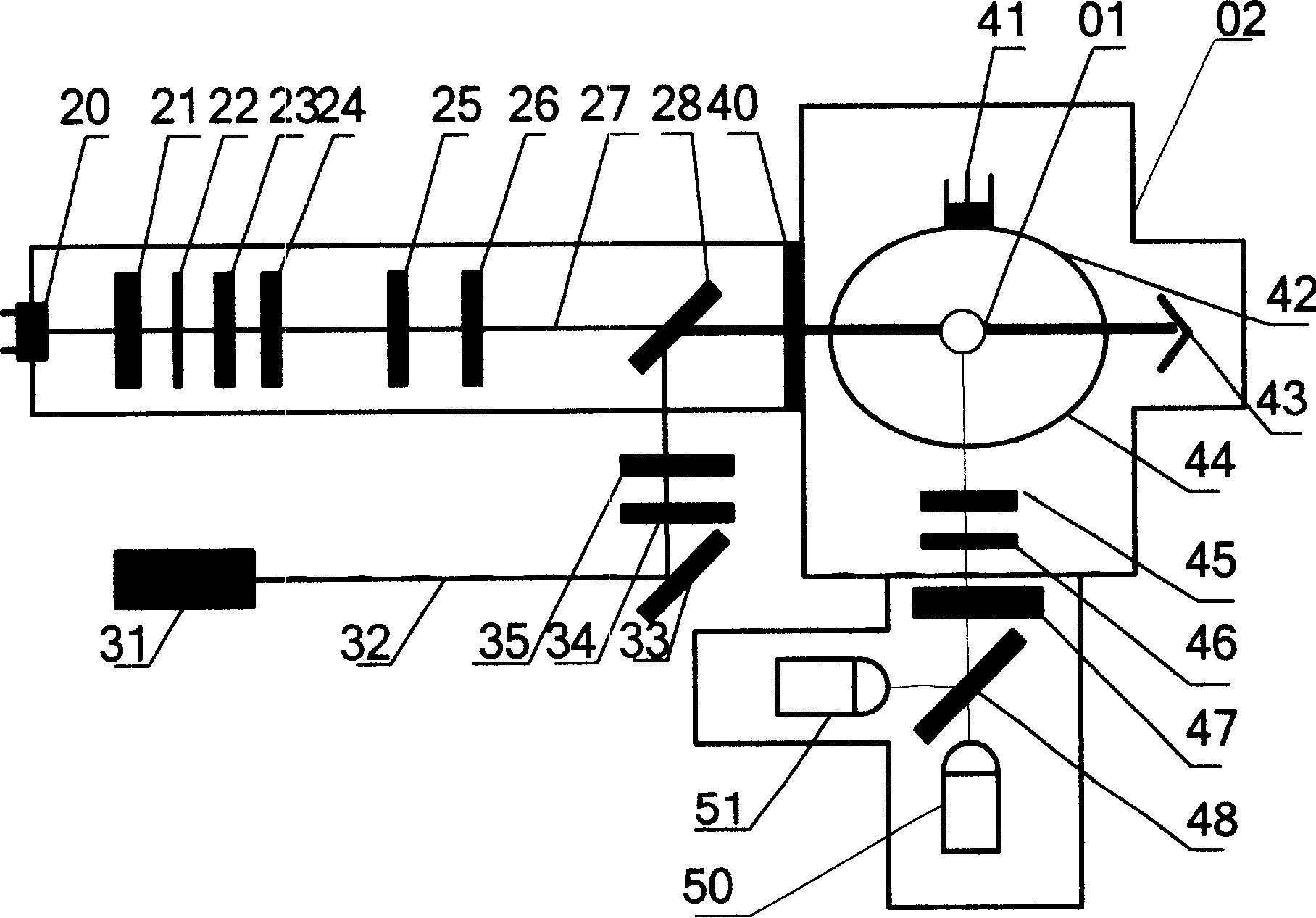
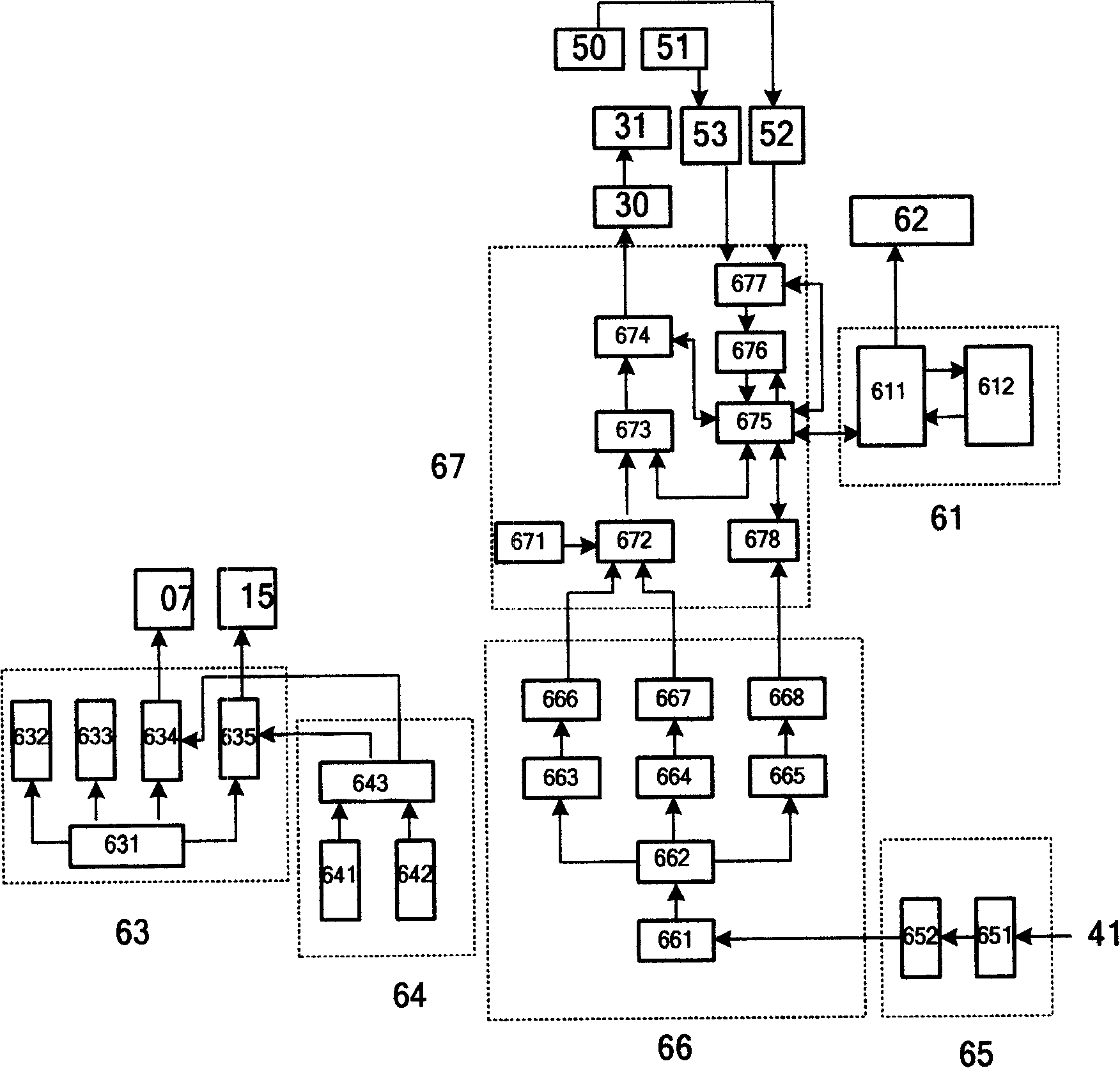
InactiveCN101173886AStable flow rateHigh precisionScattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisFluorescenceDisplay device
The invention discloses a dual-channel laser detector of aerosol particles and a detection method. The detector is composed of a particles sample injection part and an optical sampling part which are connected, and a controlling and processing part composed of a power supply module (63), a gas control module (64), a detection module (65), a simulating module (66), a data module (67), an industrial control computer module (61) and a display (62) which is respectively electrically connected with a gas pressure sensor (17, 18), an airflow pump (07, 15), a laser (20), an ultraviolet laser (31), an avalanche diode (41) and a photoelectricity multiplication tube (50, 51). The method is that setting the working pressure ratio of the airflow pump, and according to the time difference and intensity of the signals twice output by the avalanche diode, acquiring the particle sizes of the aerosol particles, the distribution information of the particle spectrum and the information of biological active substance and riboflavin to generate corresponding images, then storing and transporting to the display to display. The invention can be used for real-time on-line detection of the aerosol particles in atmosphere.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
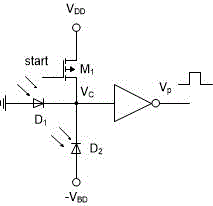
Clamped avalanche photodiode
An avalanche photodiode device operated in Geiger-mode, the device comprising a P-N junction formed on a substrate with a first semiconductor region and a second semiconductor region with an anode and cathode. The device further comprising a third semiconductor region, the third semiconductor region in physical contact with the second region, not in physical contact with the first region, and being the same semiconductor-type as the first semiconductor region. Additionally comprising a diode on the second semiconductor region and having a turn-on voltage than the P-N junction.
Owner:LADARSYST INC
SPAD photodiode covered with a network
ActiveUS9741879B2Solid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesSemiconductor materialsRefractive index
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
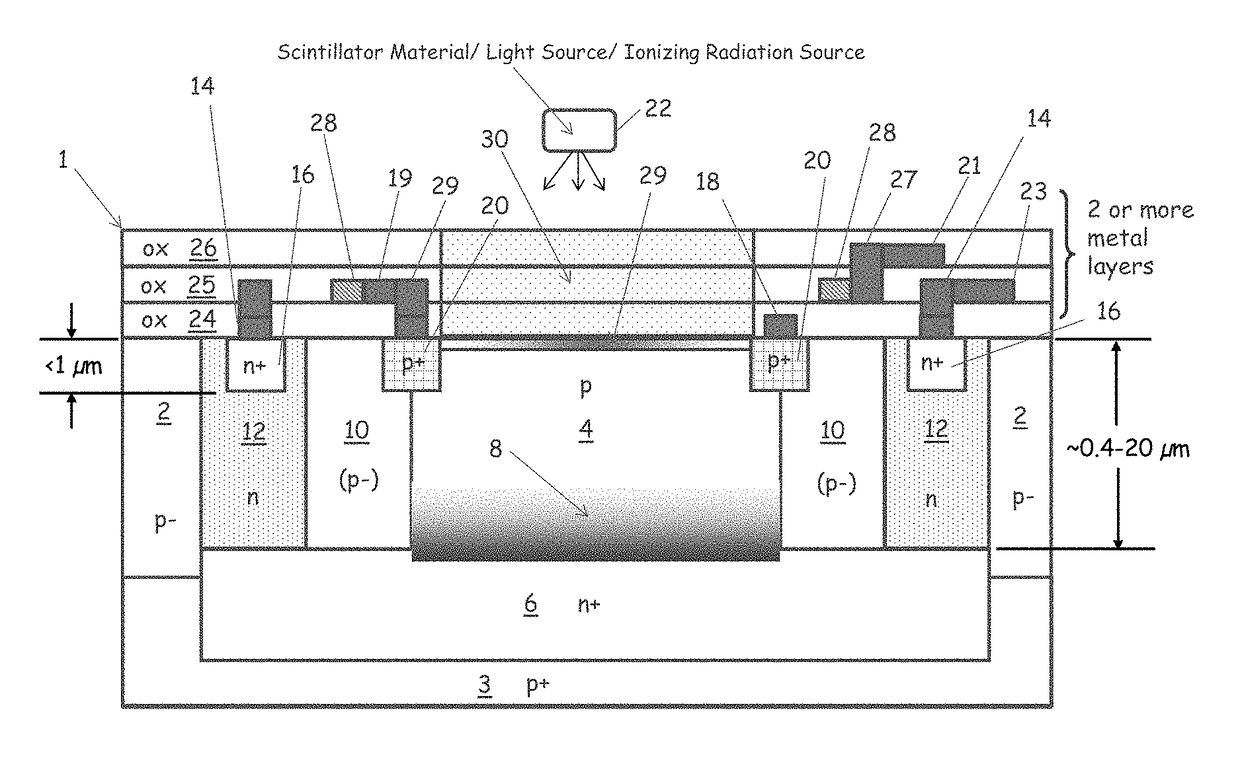
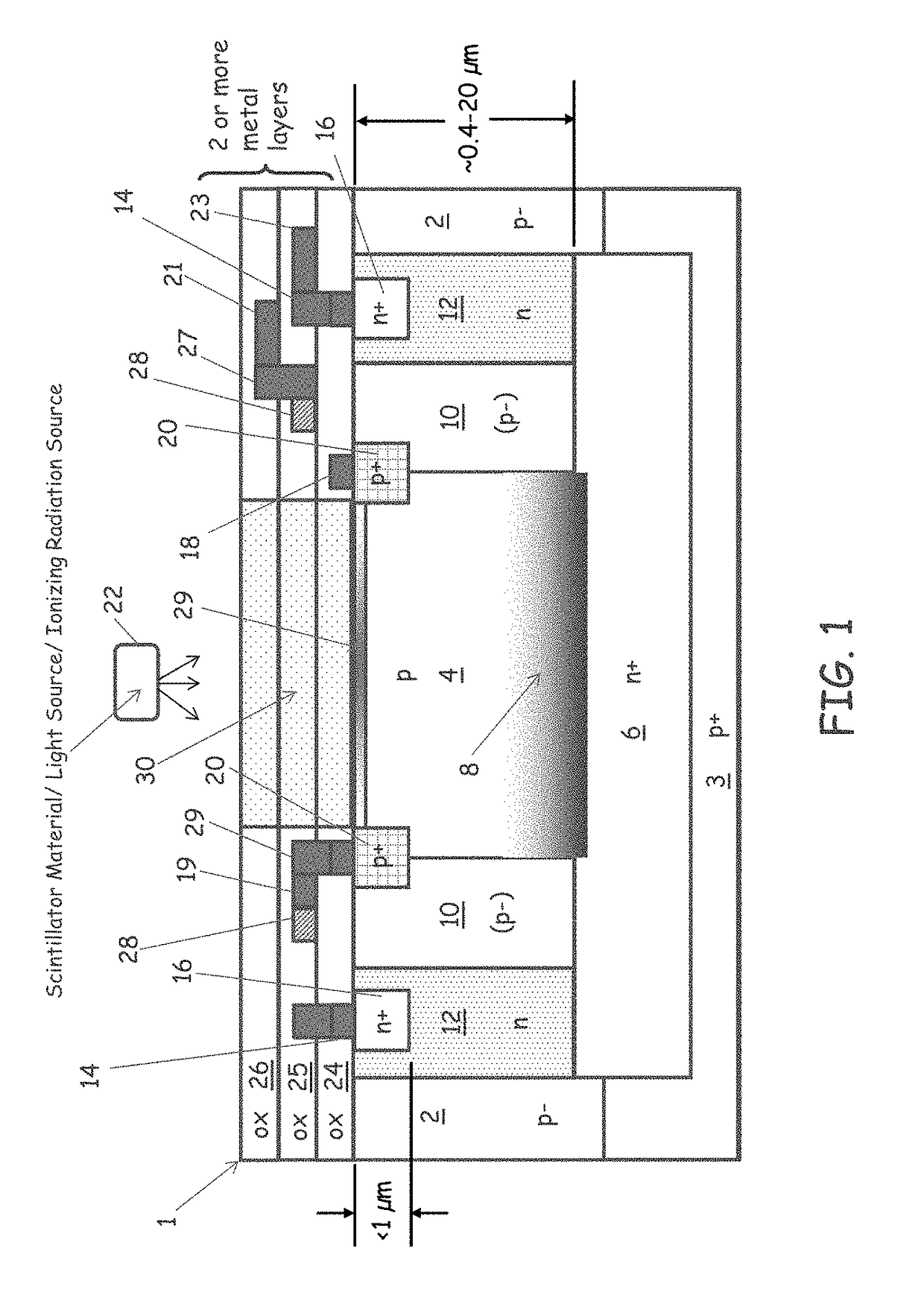
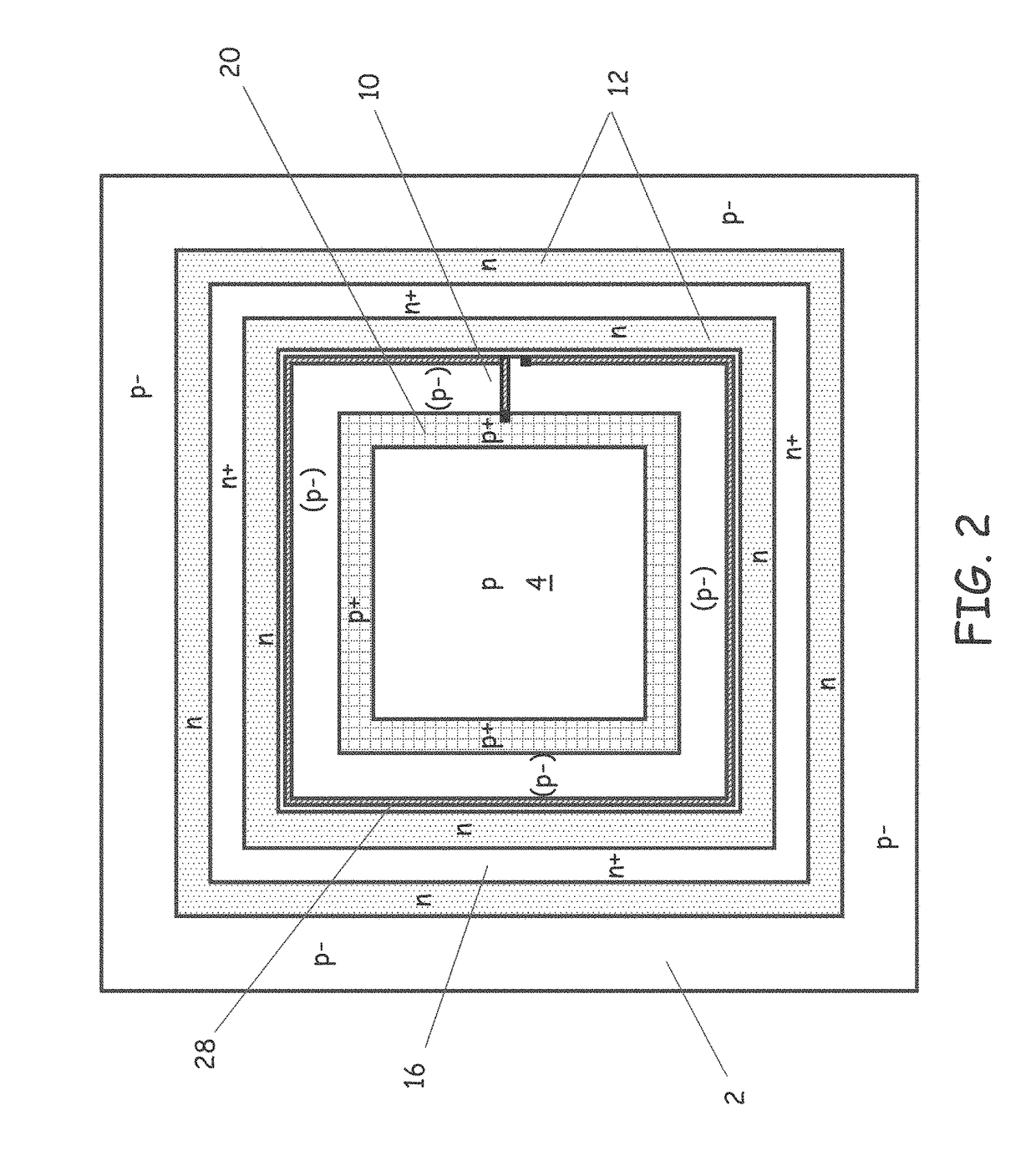
Scintillator and detector assembly
ActiveUS20100314531A1Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSemiconductor materialsPhotovoltaic detectors
A detector comprising a photodetector including a single photon avalanche diode (SPAD), wherein the SPAD comprises a wide band-gap semiconductor material, and a quenching circuit electrically coupled to the photodetector comprising a first device, wherein the first device comprises a wide band-gap semiconductor material having a band-gap of at least about 1.7 eV at about 26° C.
Owner:LUXIUM SOLUTIONS LLC
Transient voltage surge suppression systems
InactiveUS20060120005A1Intensifying skin-effect conditionIncrease surface areaCross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted circuit aspectsElectrical conductorEngineering
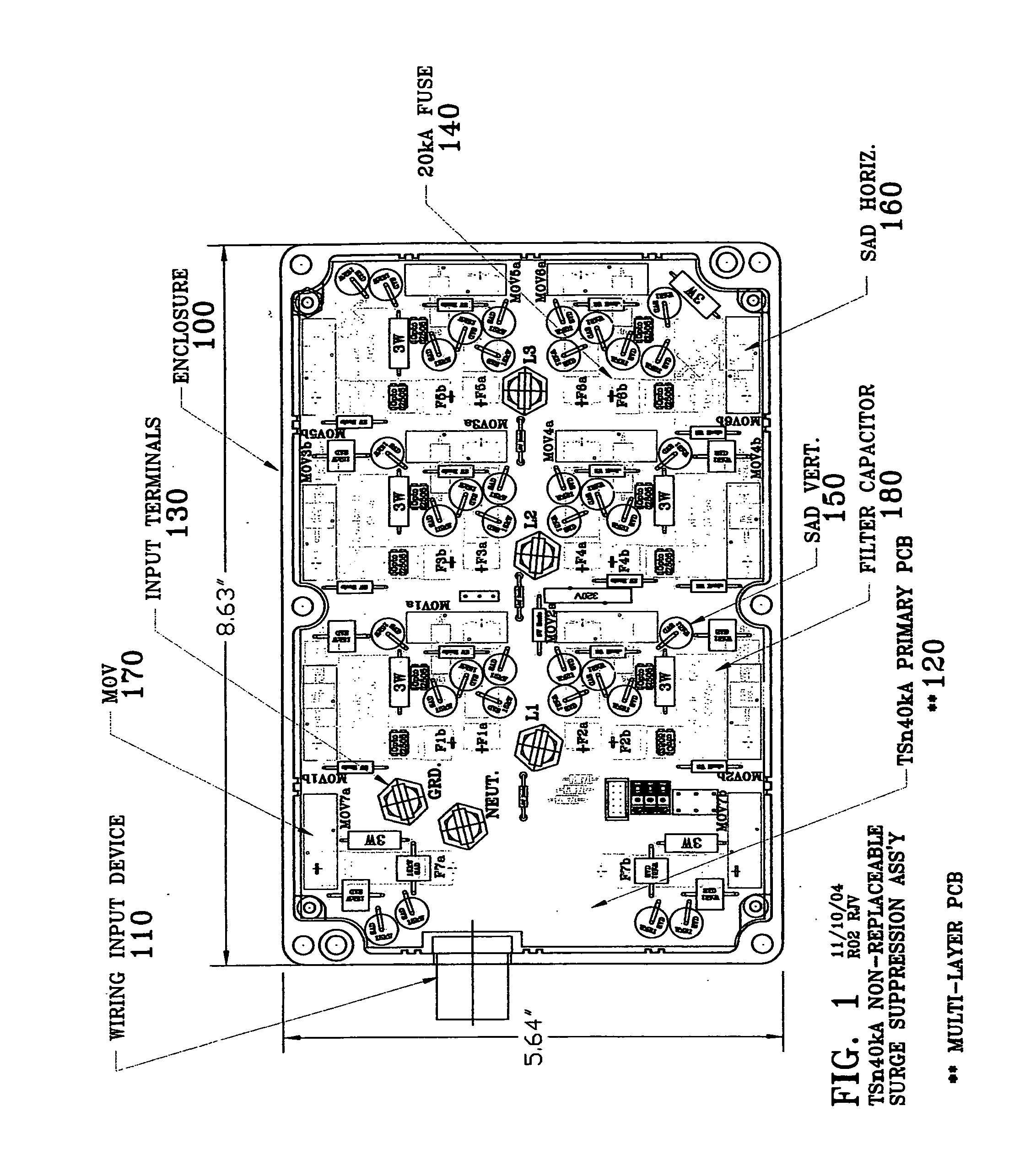
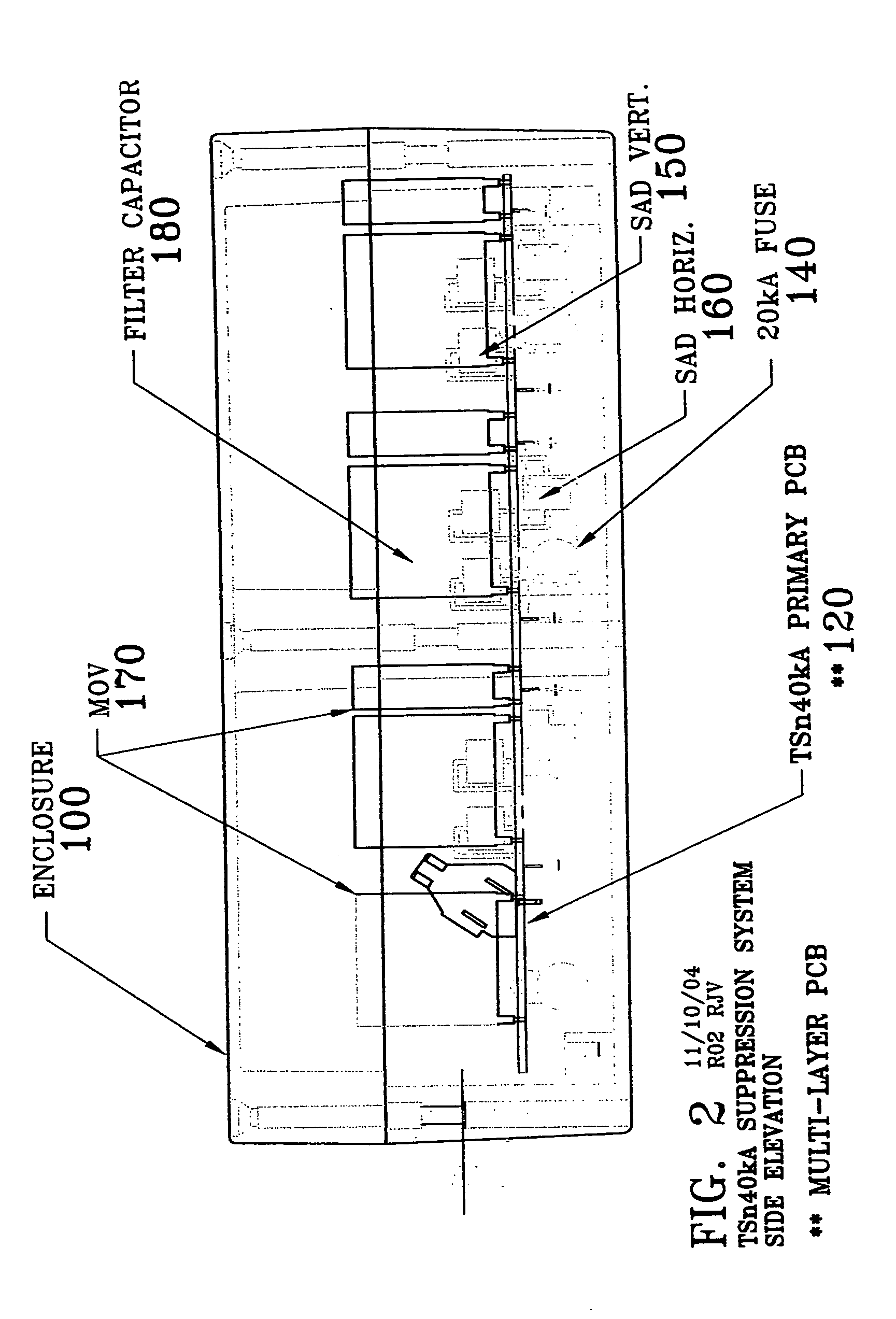
A surge-suppression system utilizing a hybrid design comprised of metal oxide varistors, silicon avalanche diodes, a fuse element, filter capacitor and multiple surge planes and surge paths to dissipate and divert transient over-voltages away from sensitive electronic equipment. These multiple surge conduction paths provide redundant parallel planes which optimize the skin-effect phenomena, which is the flow of electrical current at the conductor surface. This design provides a very low impedance which produces a high performance surge-suppression system.
Owner:VAN SICKLE ROBERT JACKSON
APD-TIA (Avalanche Photodiode-Transfer-Impedance Amplifier) coaxial photoelectric module with temperature control function and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN102412240APrecise and controllable temperatureStable temperatureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceTemperature control
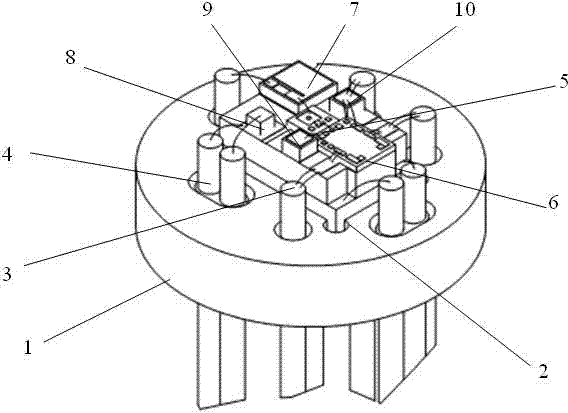
The invention discloses an Avalanche Photodiode-Transfer-Impedance Amplifier (APD-TIA) coaxial photoelectric module with a temperature control function and a fabrication method thereof. The APD-TIA coaxial photoelectric module mainly comprises a TO56 base with eight pins plus one pin, a thermoelectric cooler (TEC), an AIN (aluminium nitride) ceramic circuit substrate, an APD, a TIA, a RC (resistor-capacitor) filter module, a thermistor, a first filter capacitor and a second filter capacitor, wherein the TEC as a first layer is attached on the upper surface of the coaxial TO56 base, the AIN ceramic circuit substrate as a second layer is attached on the upper surface of the TEC, and the ADP, the TIA, the thermistor, the RC filter module, the first filter capacitor and the second filter capacitor are arranged on the surface of the AIN ceramic circuit substrate to form a third layer. The coaxial photoelectric module has the advantages of small size, good temperature characteristic, stable photoelectric properties and high reliability.
Owner:WUHAN HUAGONG GENUINE OPTICS TECH
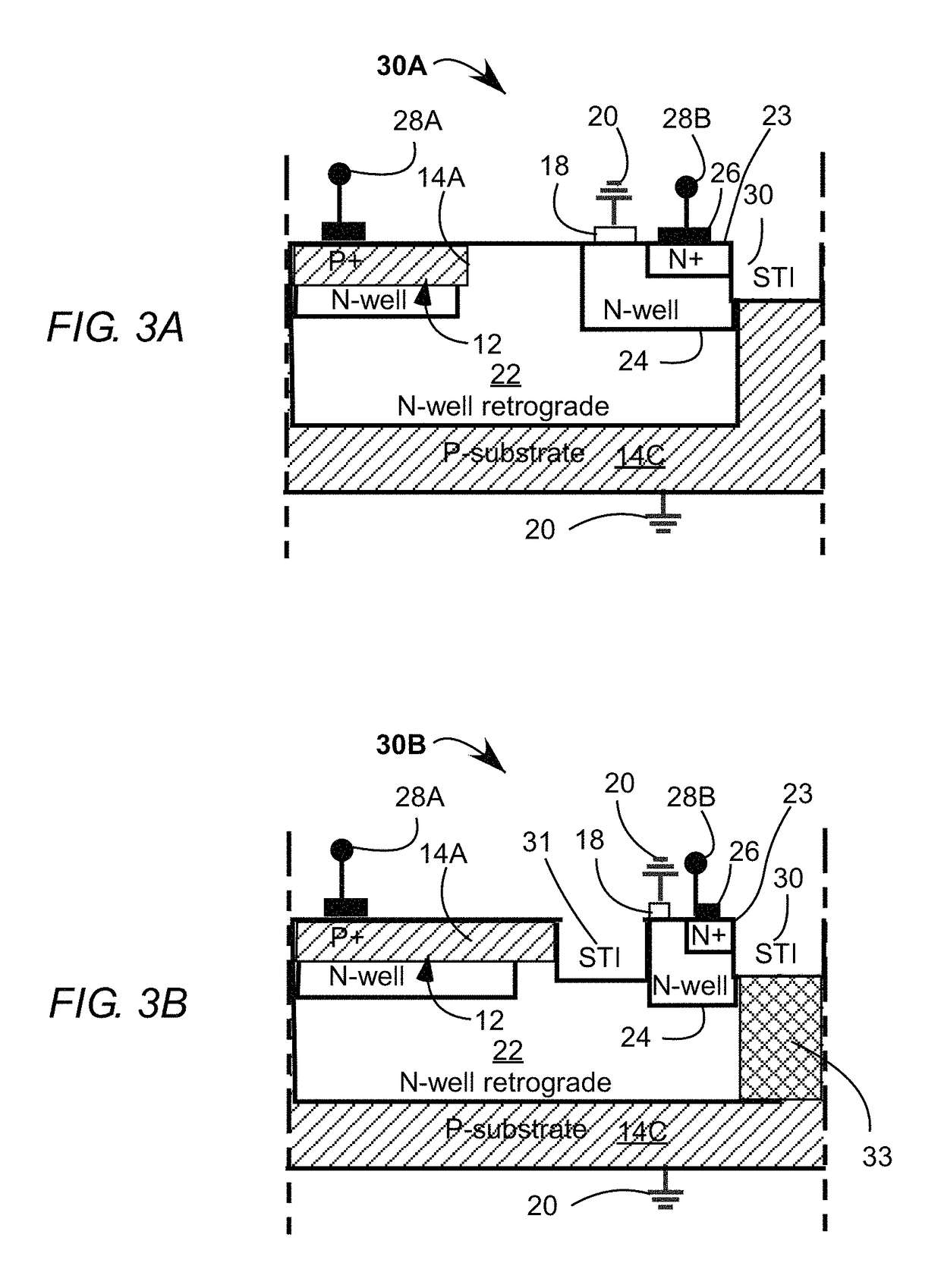
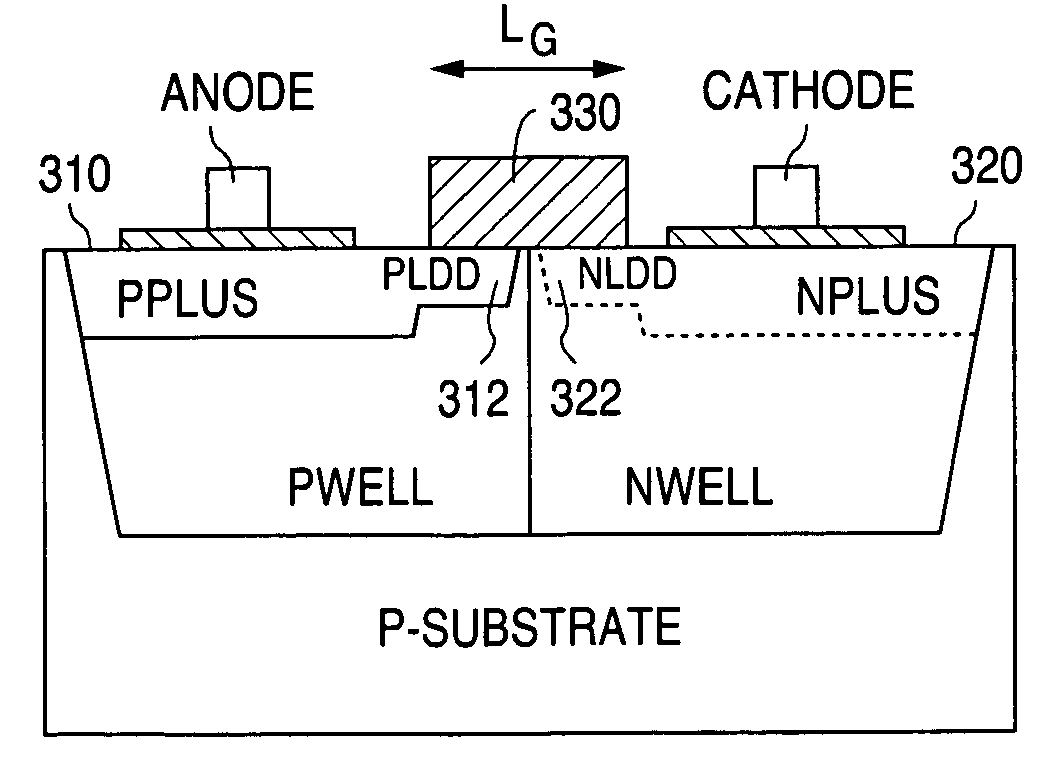
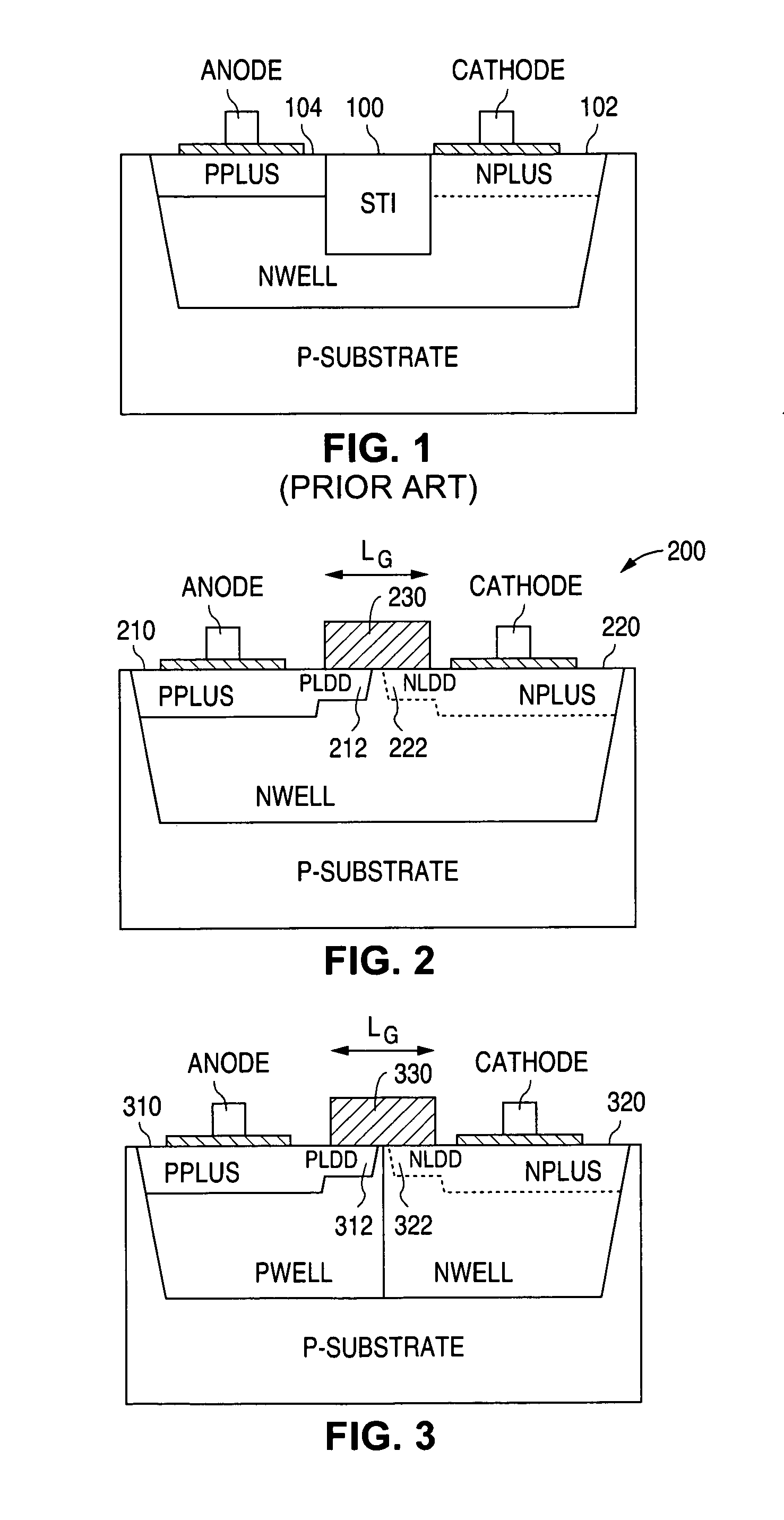
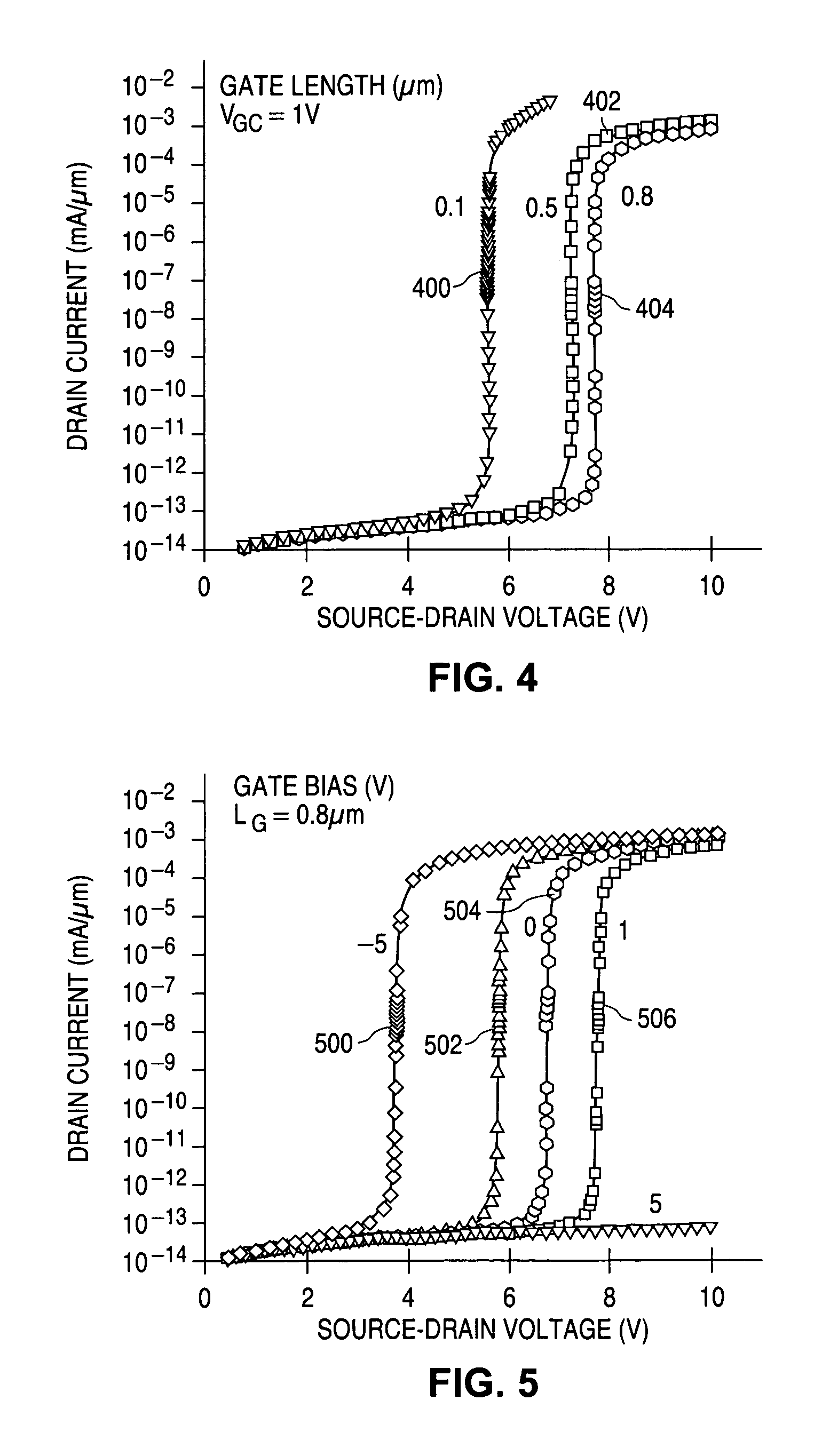
Avalanche diode with breakdown voltage controlled by gate length
InactiveUS7056761B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringAvalanche diode
In an avalanche structure, different breakdown voltages are achieved by making use of a polygate and forming a highly doped p-n junction beneath the polygate, and adjusting the gate length and optionally the bias voltage of the gate.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com