Patents
Literature
1091 results about "Received signal strength indication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunications, received signal strength indicator (RSSI) is a measurement of the power present in a received radio signal. RSSI is usually invisible to a user of a receiving device. However, because signal strength can vary greatly and affect functionality in wireless networking, IEEE 802.11 devices often make the measurement available to users.
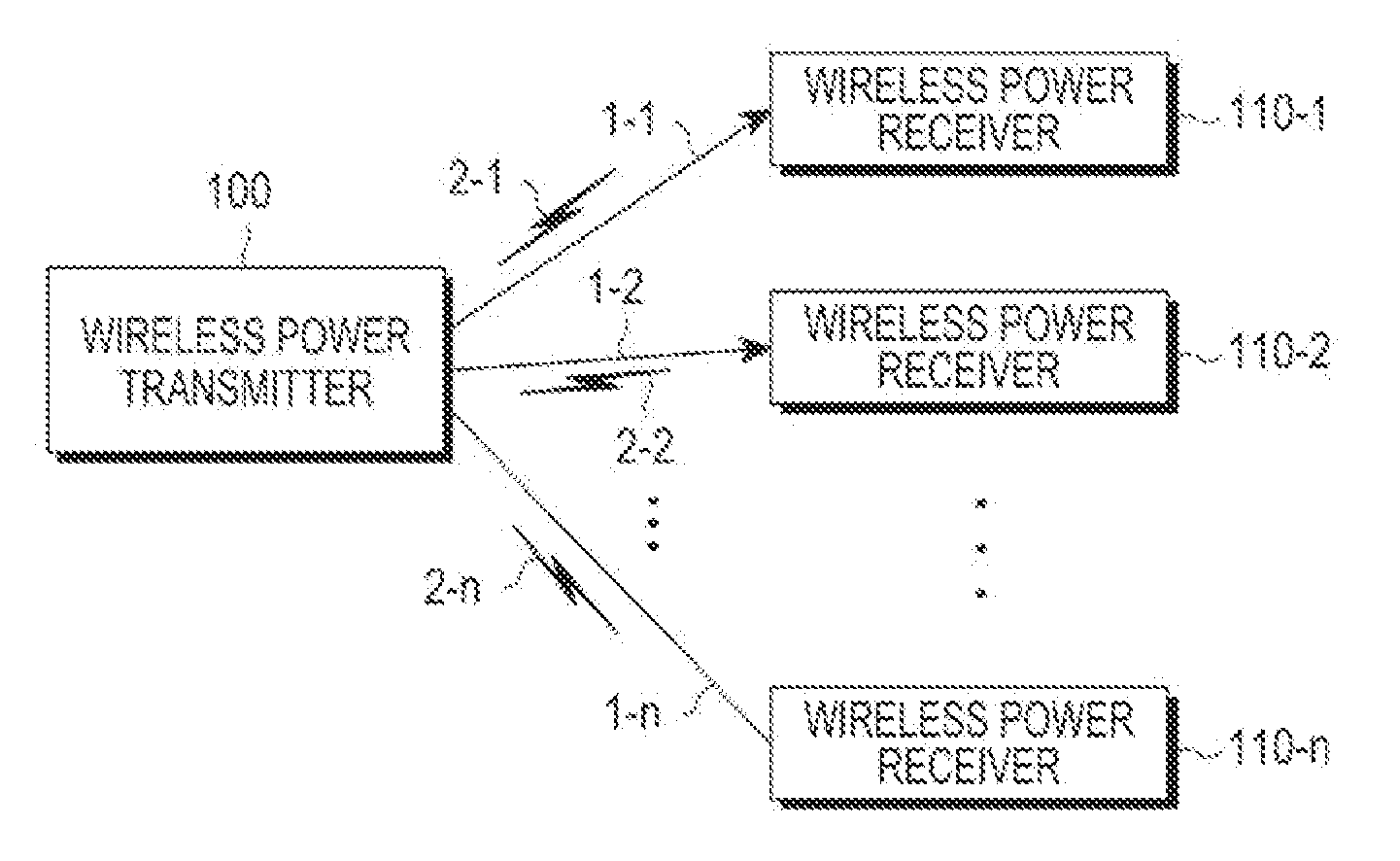
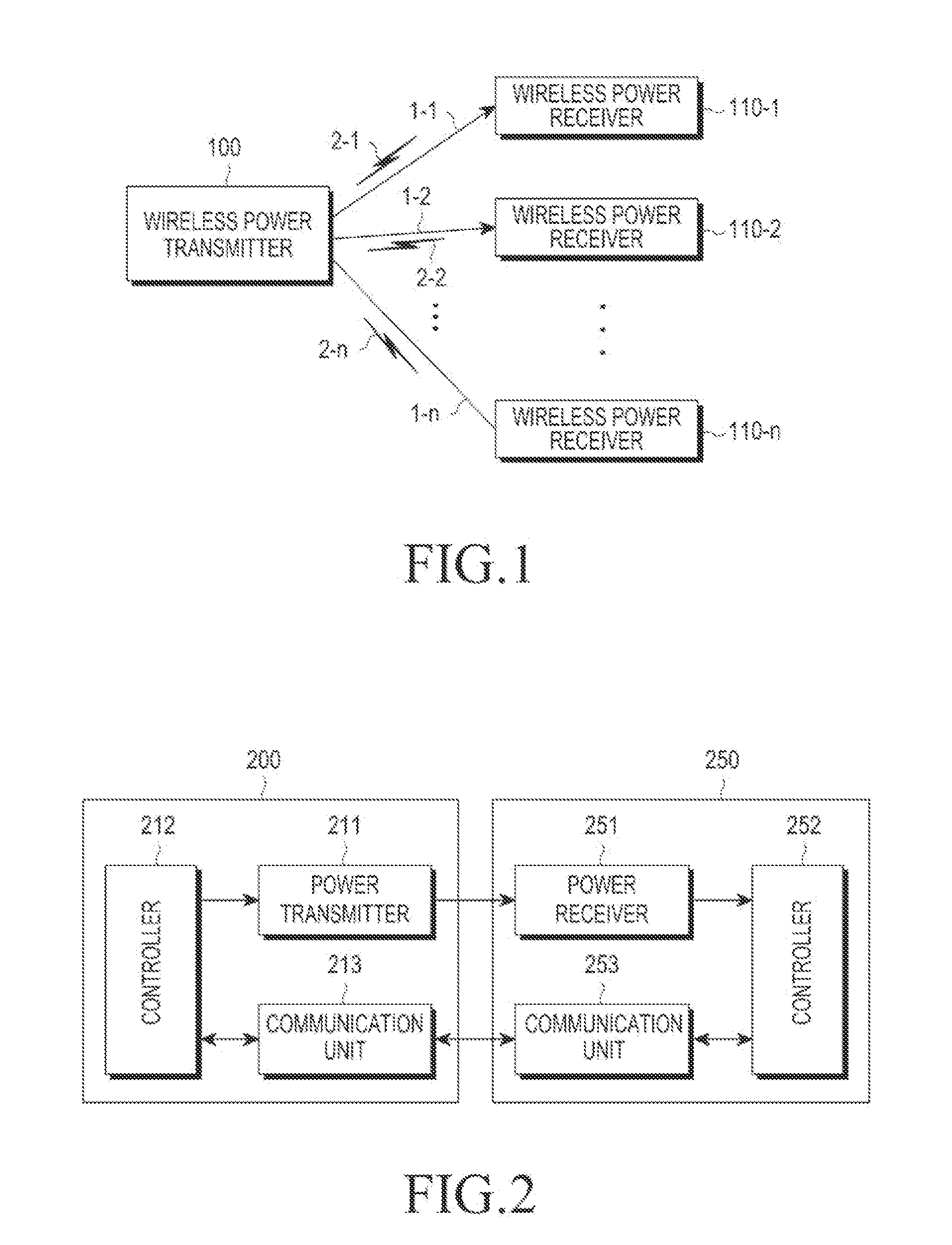
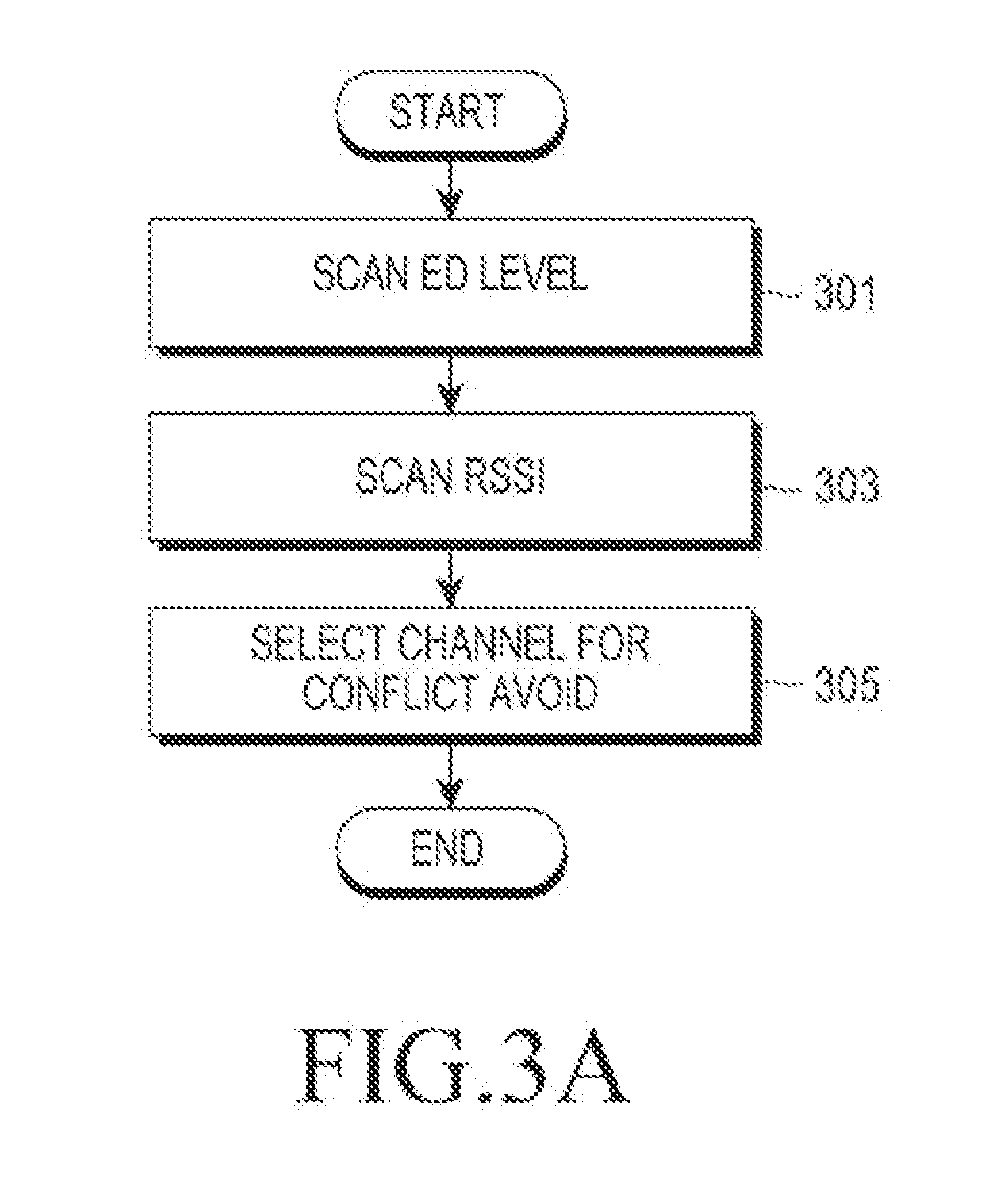
Apparatus and method for transmitting wireless power
ActiveUS20130154387A1Minimizing conflictElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersReceived signal strength indicationEngineering
A method and a wireless power transmitter are provided for transmitting wireless power to at least one wireless power receiver. The method includes setting, by the wireless power transmitter, a search channel to be used for communication with the at least one wireless power receiver; detecting at least one of an energy level and a Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI) value of a signal received on the search channel; and determining whether to designate the search channel as a communication channel based on the detection results.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
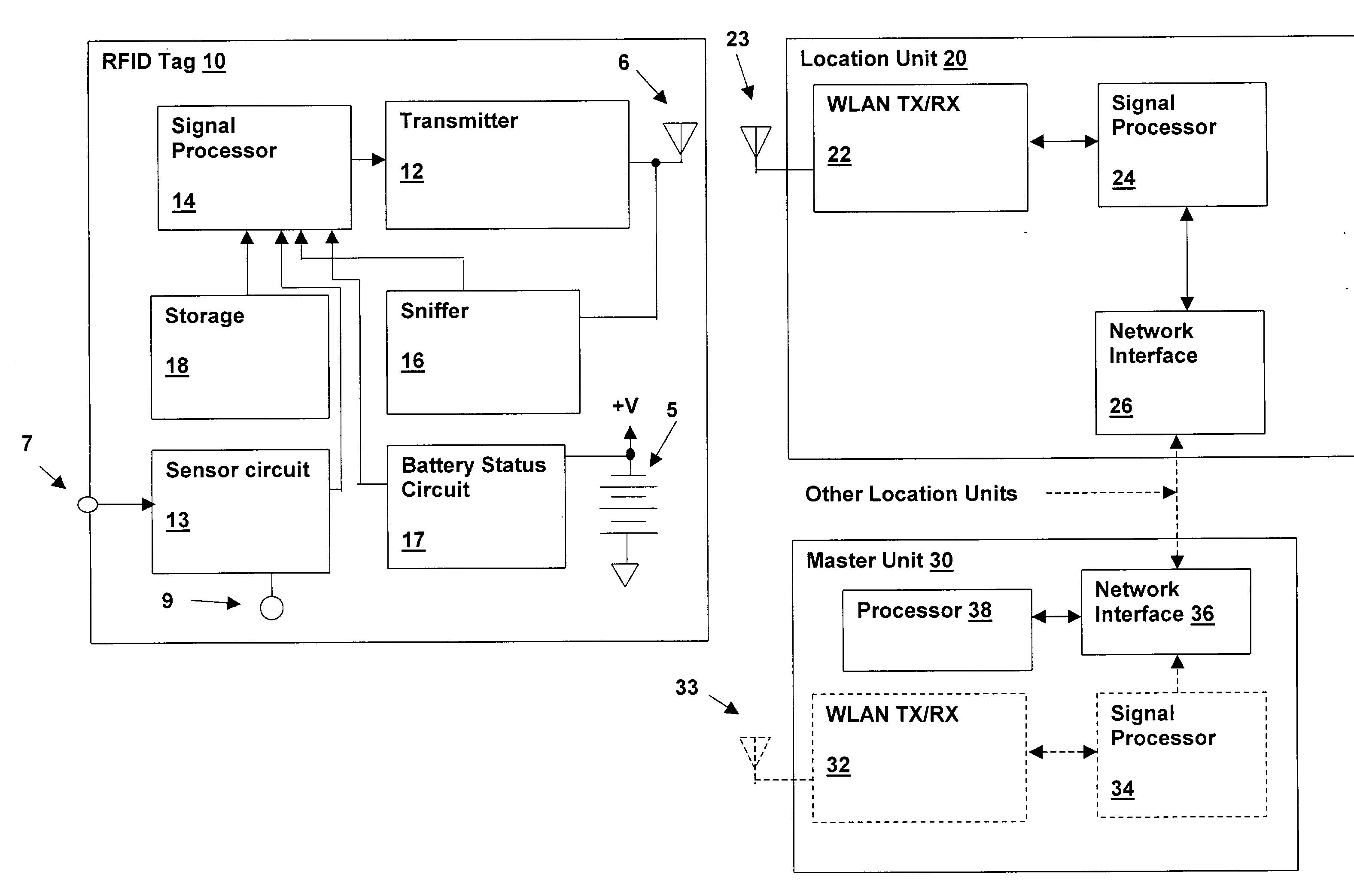
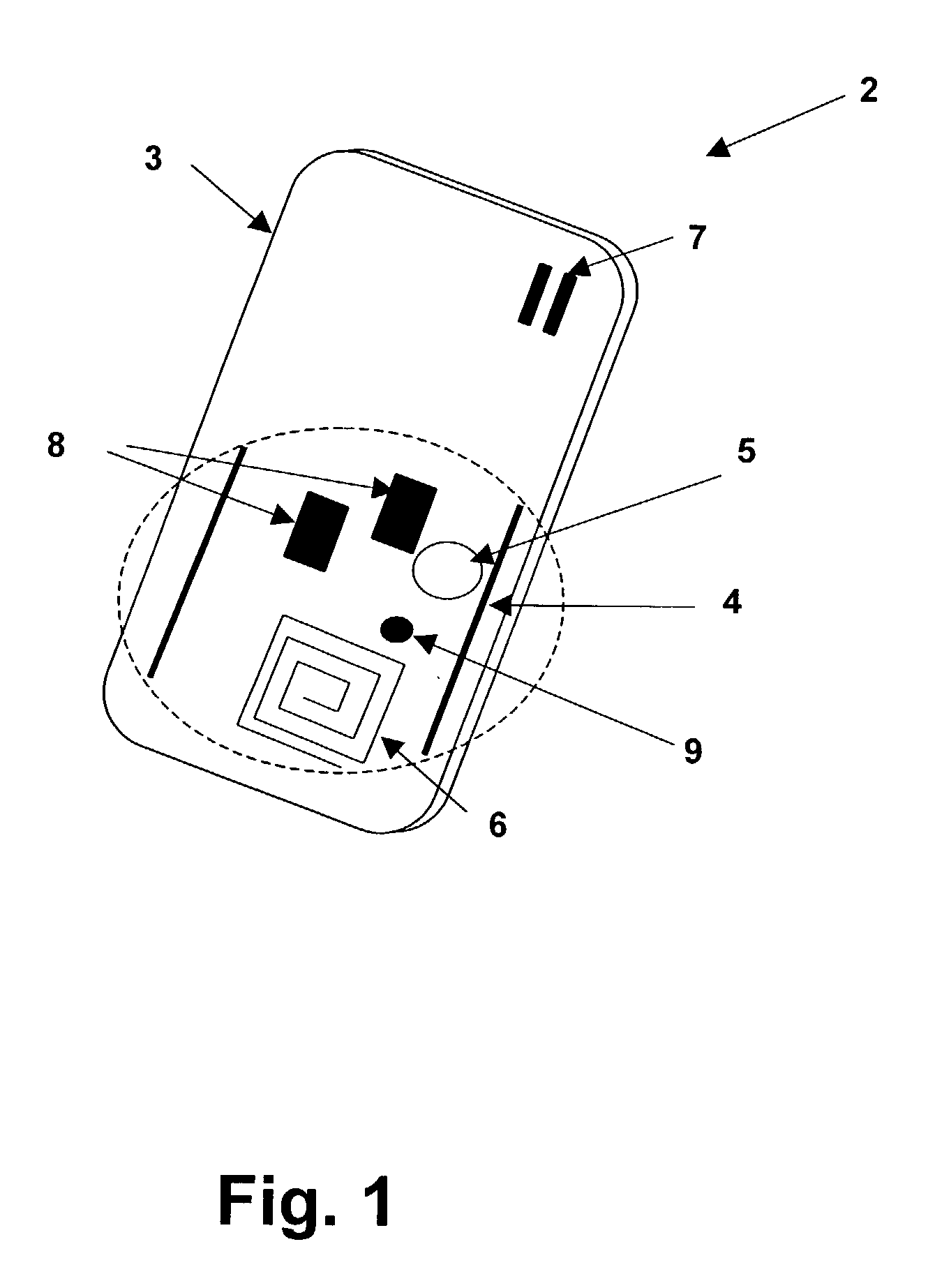
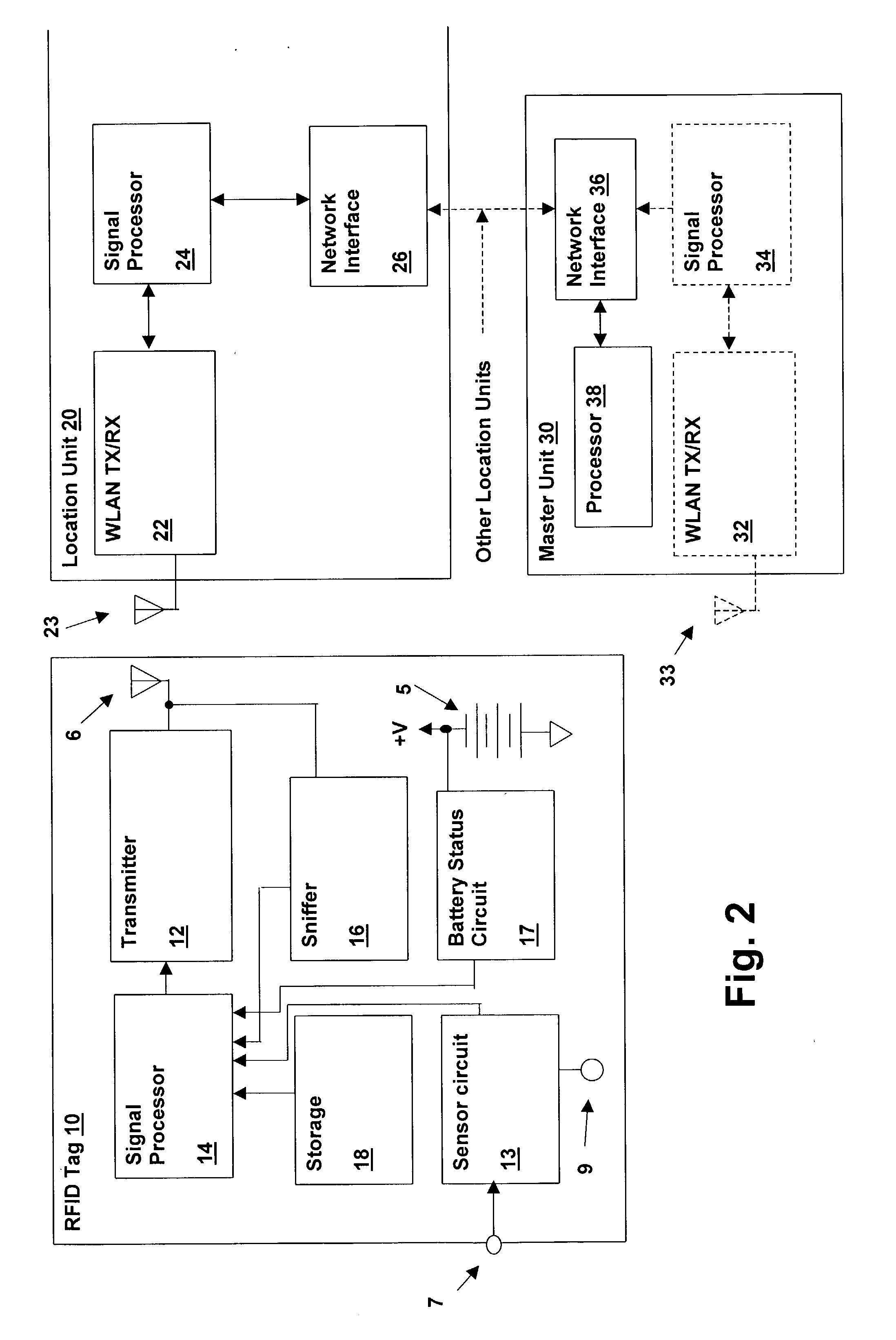
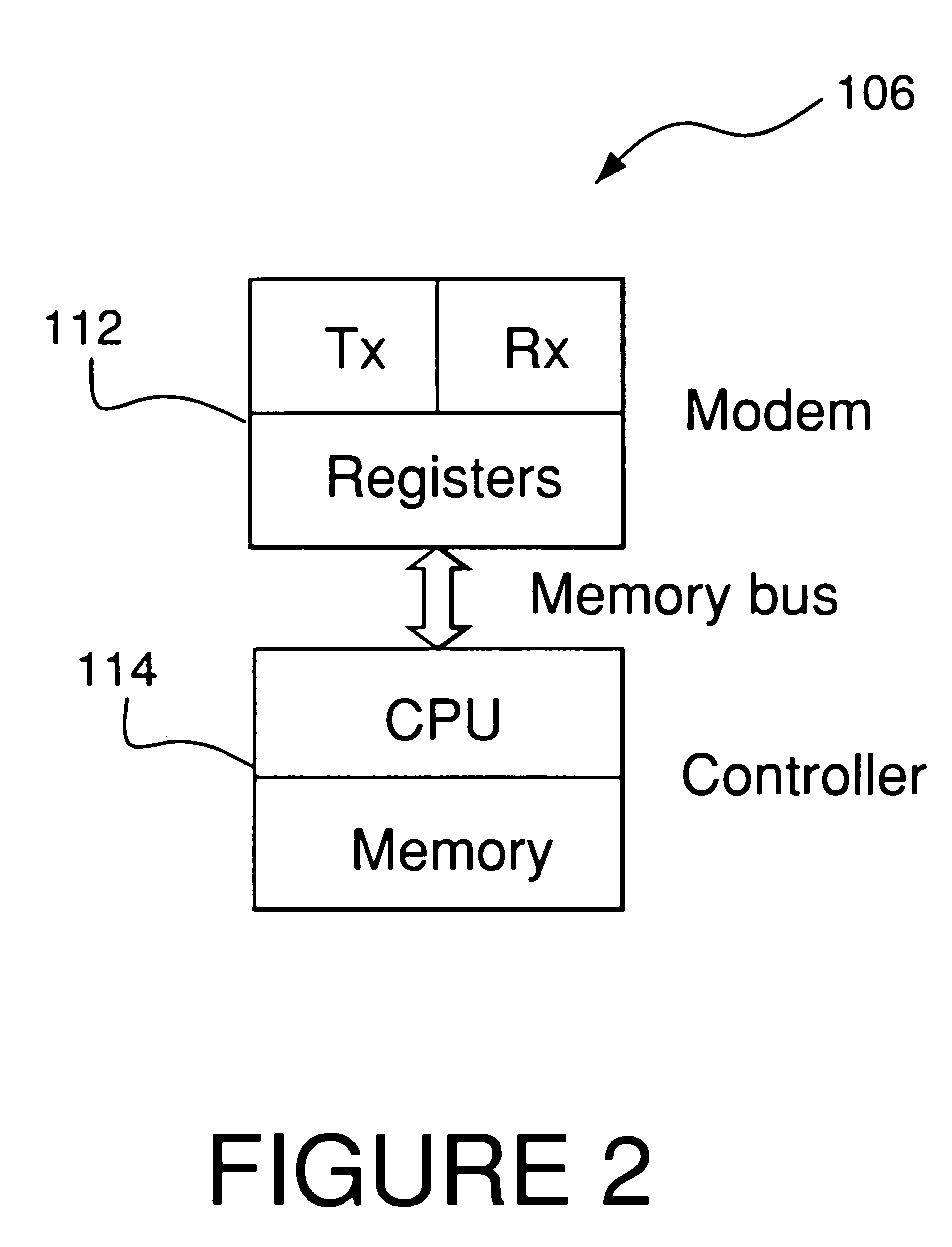
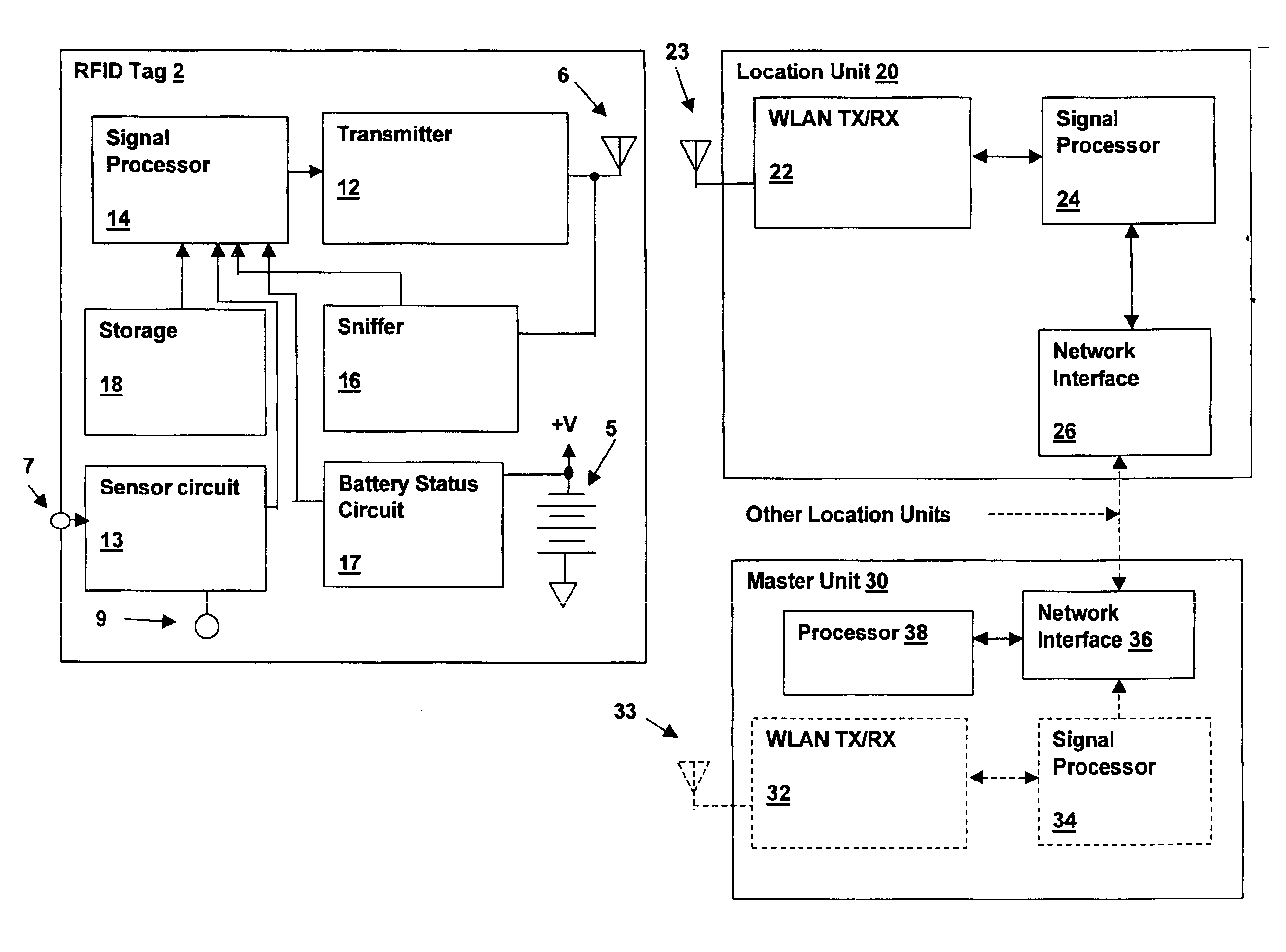
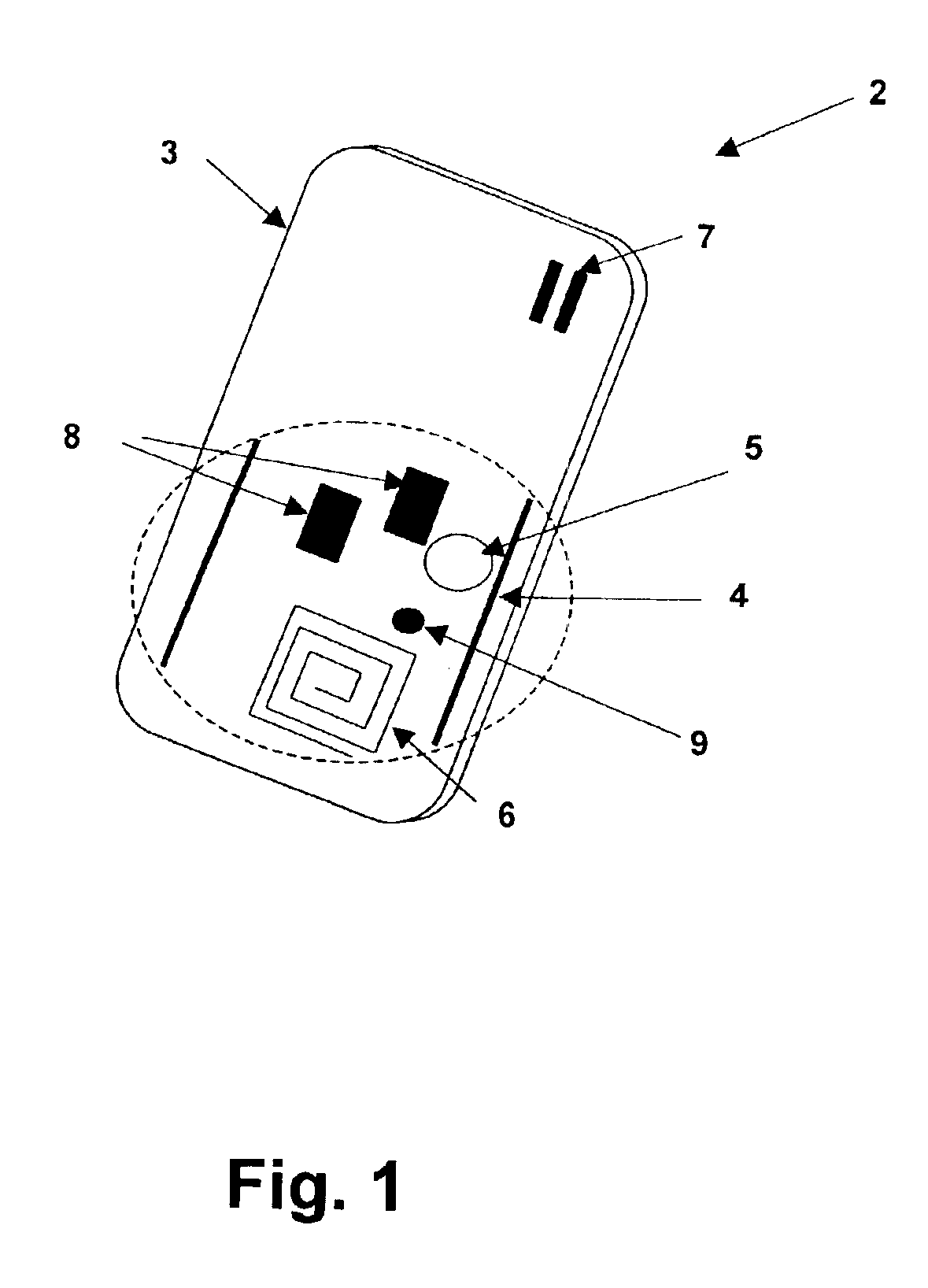
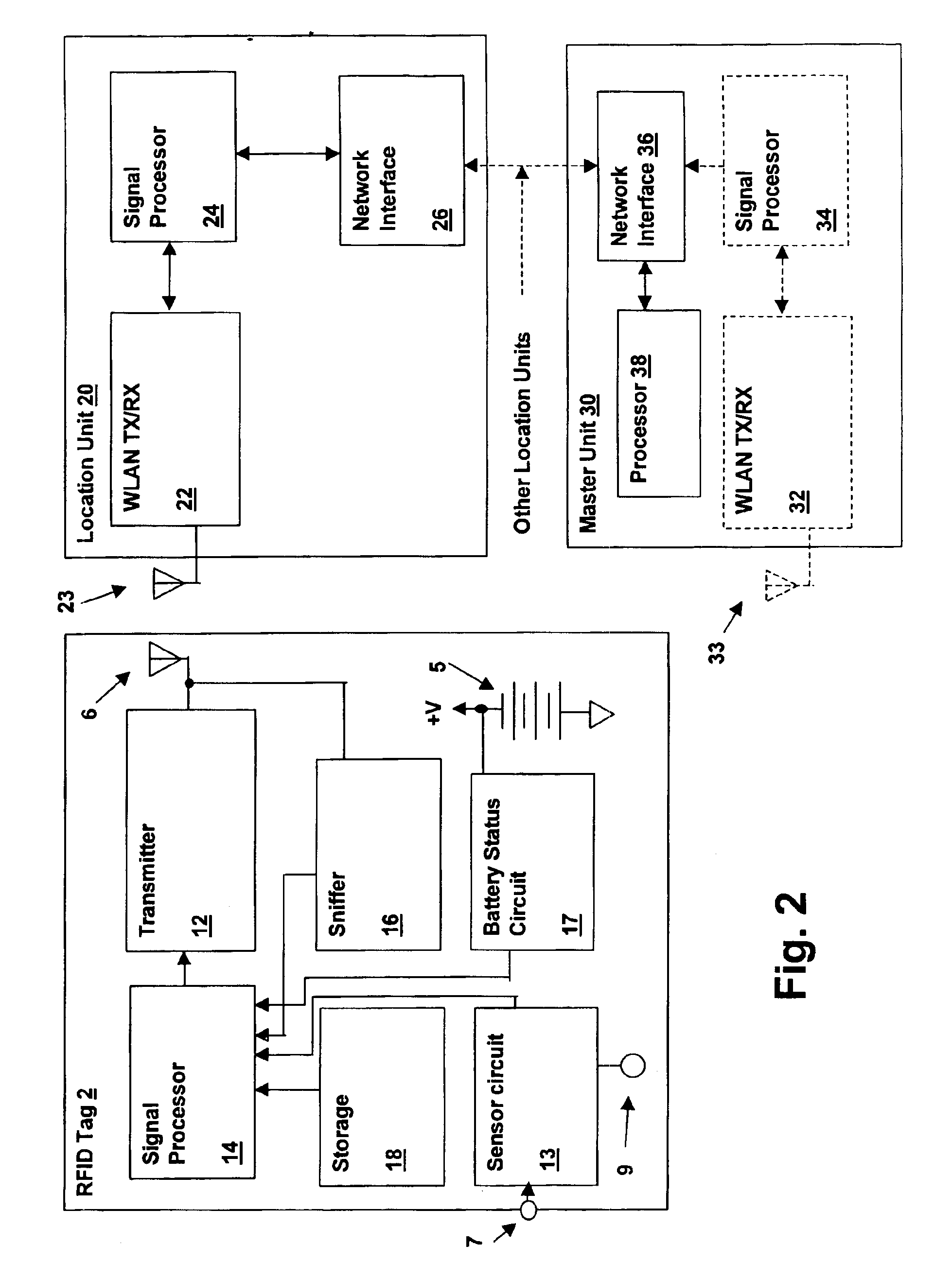
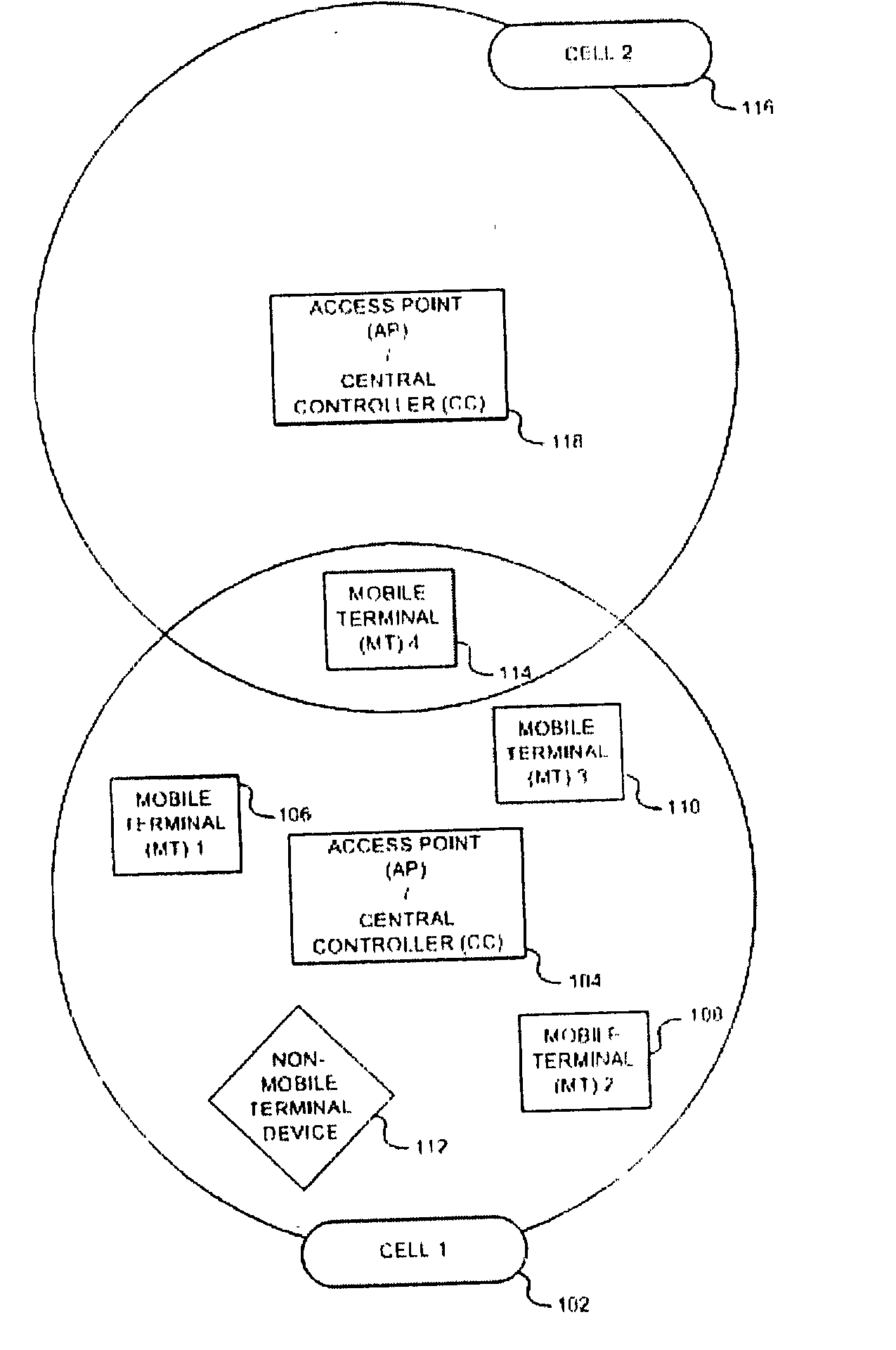
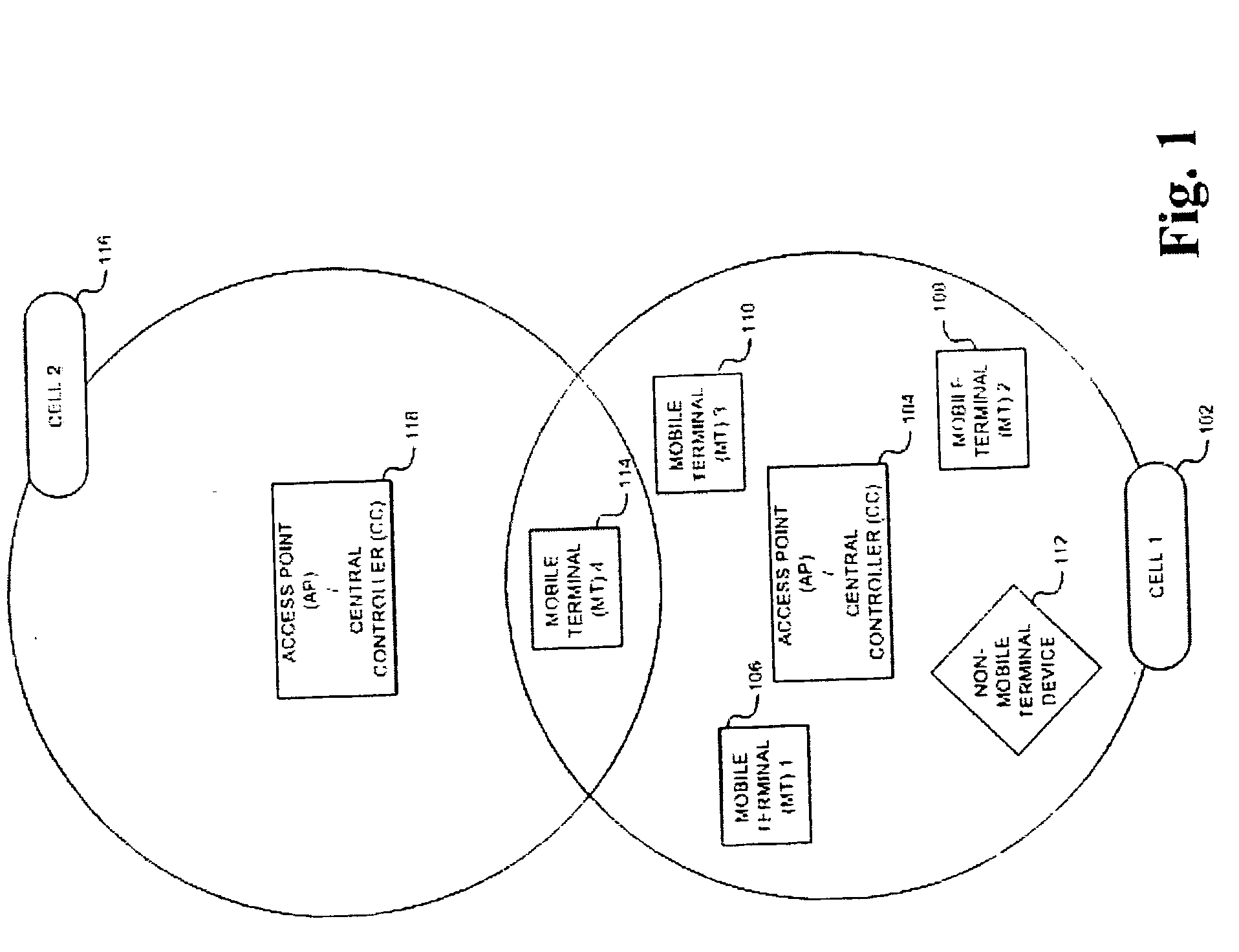
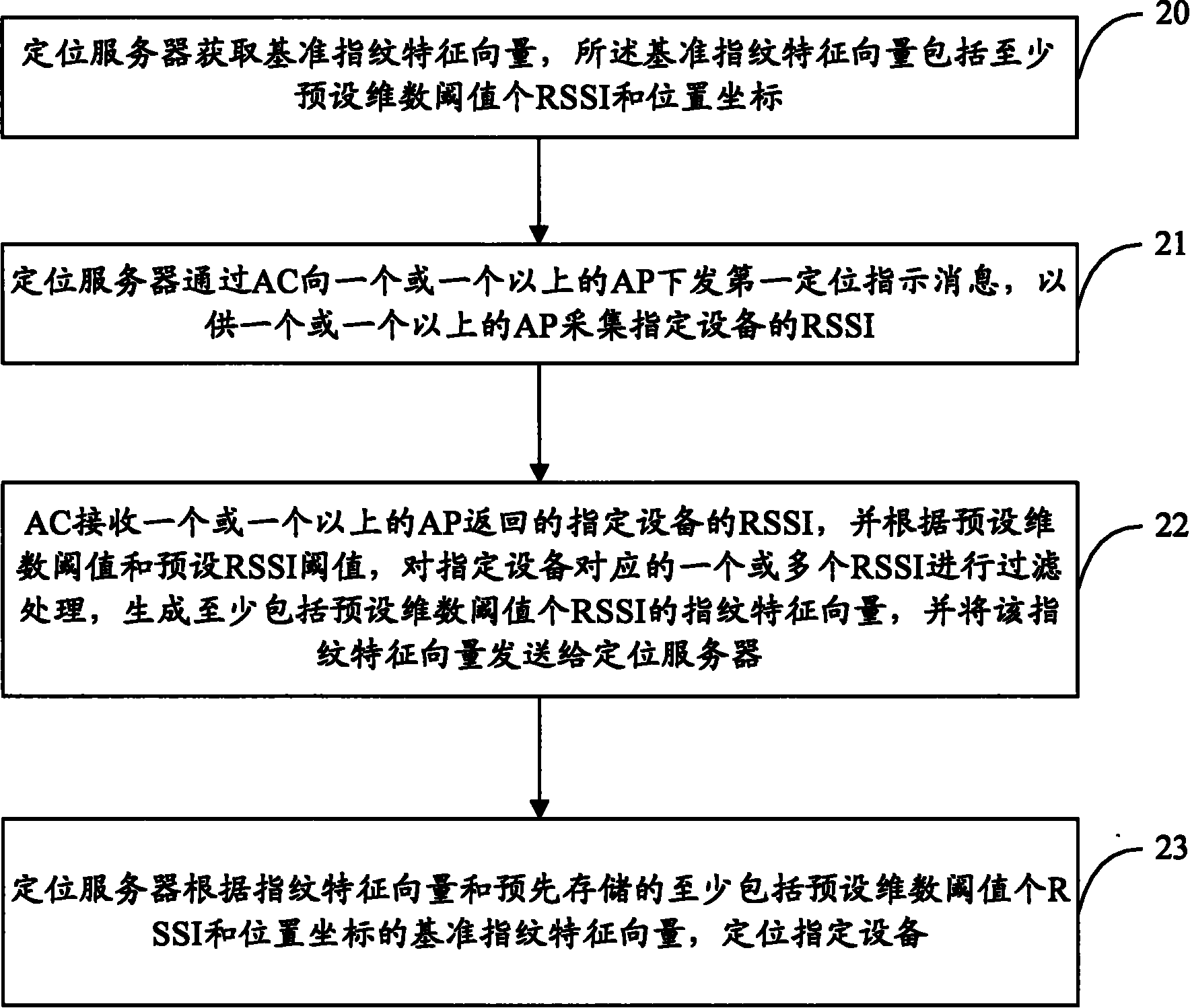
Wireless local area network (WLAN) channel radio-frequency identification (RFID) tag system and method therefor
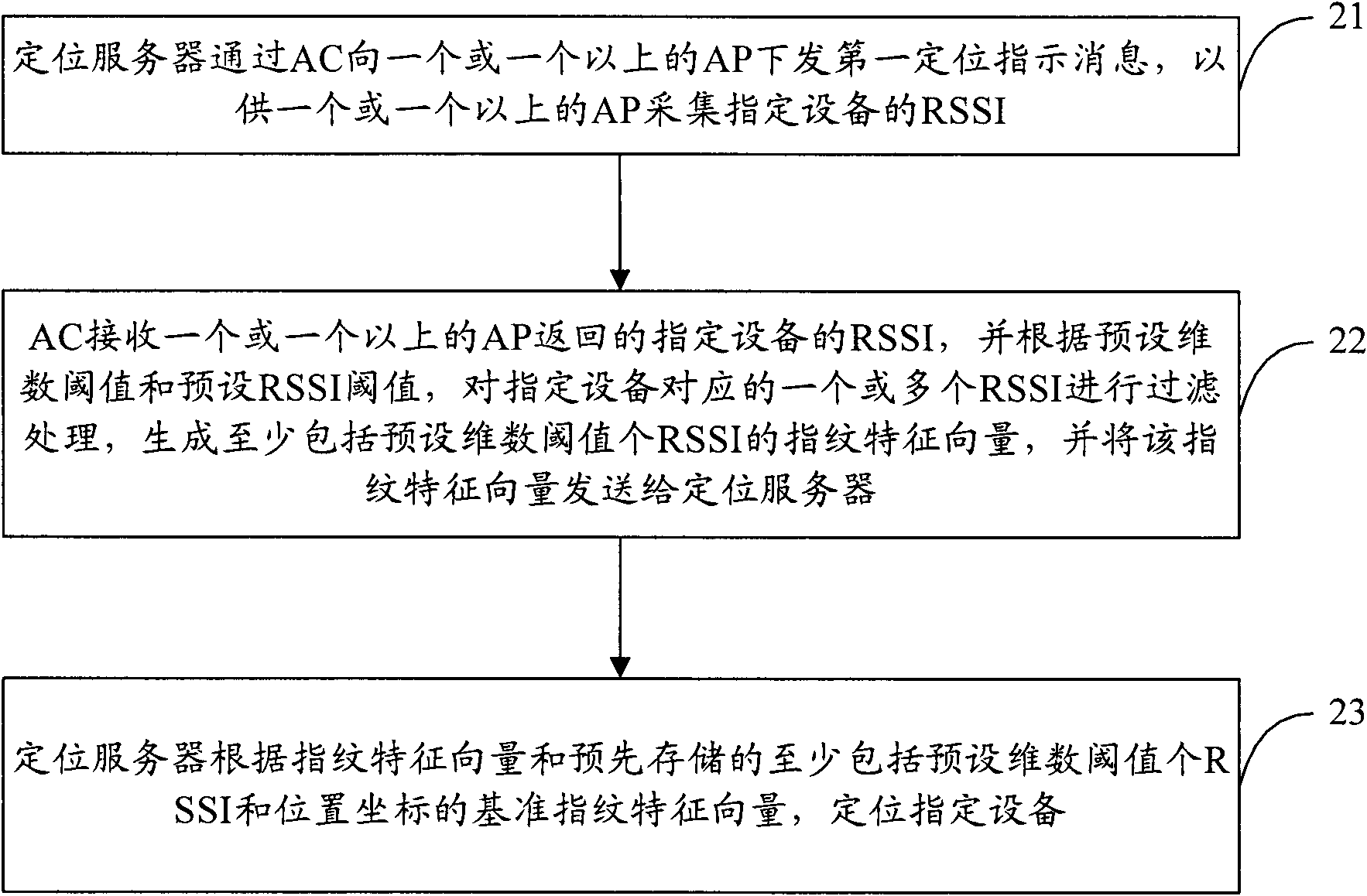
InactiveUS20040078151A1Network topologiesPosition fixationNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet ProtocolTelecommunications
A wireless local area network (WLAN) radio-frequency identification (RFID) tag system provides location finding in a wireless local area network (WLAN), using a WLAN channel. Interference with the WLAN is prevented by either using a sniffer circuit to determine that no network transmission is in progress, using a modified coding sequence or preamble to cause standard WLAN receivers to ignore the RFID tag transmissions, or transmitting a message using a standard WLAN signal addressed to an address not corresponding to a unit within the WLAN. Location units (LUs) and a master unit (MU) within the WLAN receive the RFID tag transmissions and can determine the location of a tag by triangulation based on differences between the signals received at the location units from the tag. The master unit receives the signal information from the location units and computes the location of the tag. Time-difference-of-Arrival (TDOA), received signal strength indication (RSSI) or other triangulation techniques may be used.
Owner:AEROSCOUT
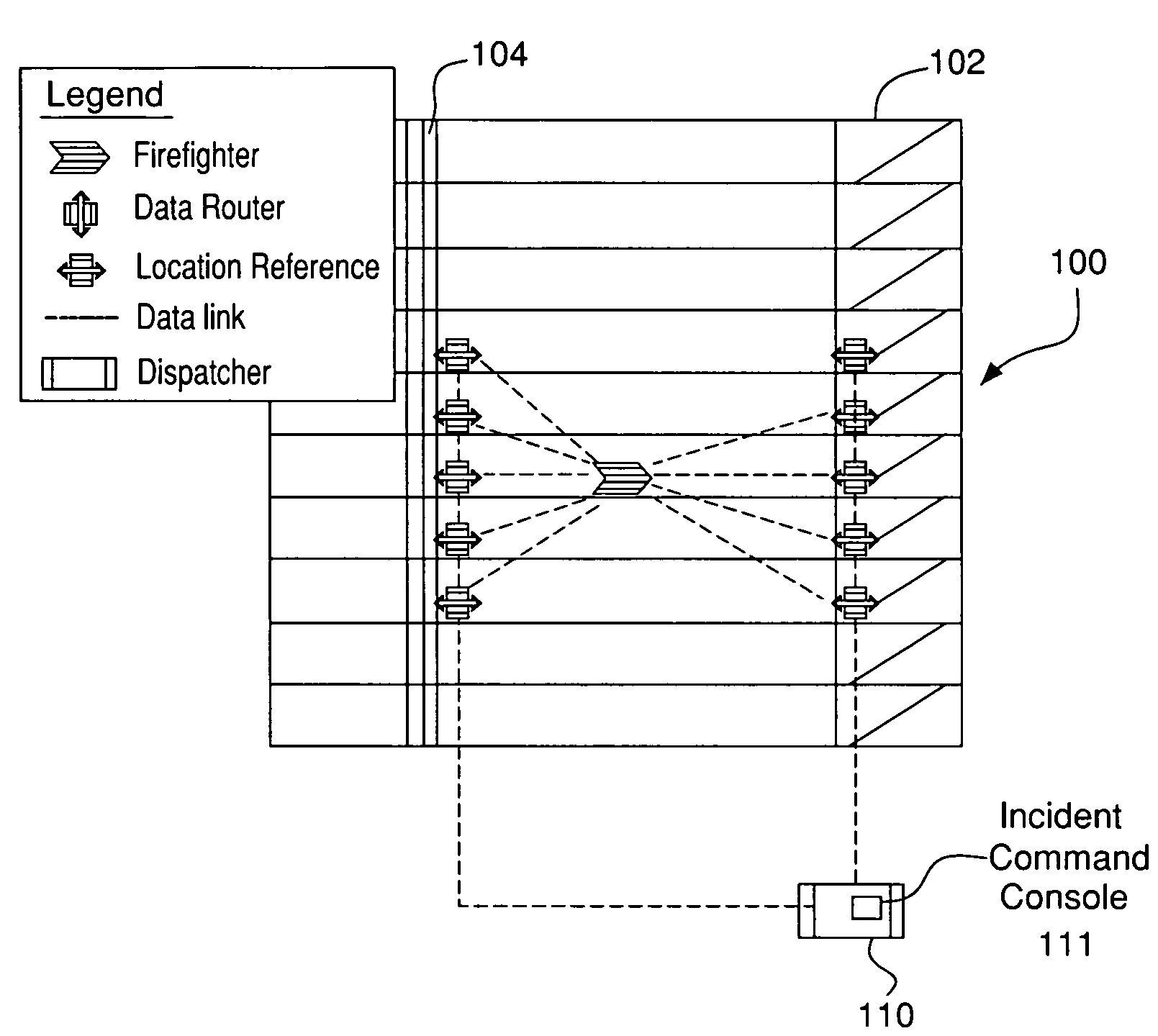
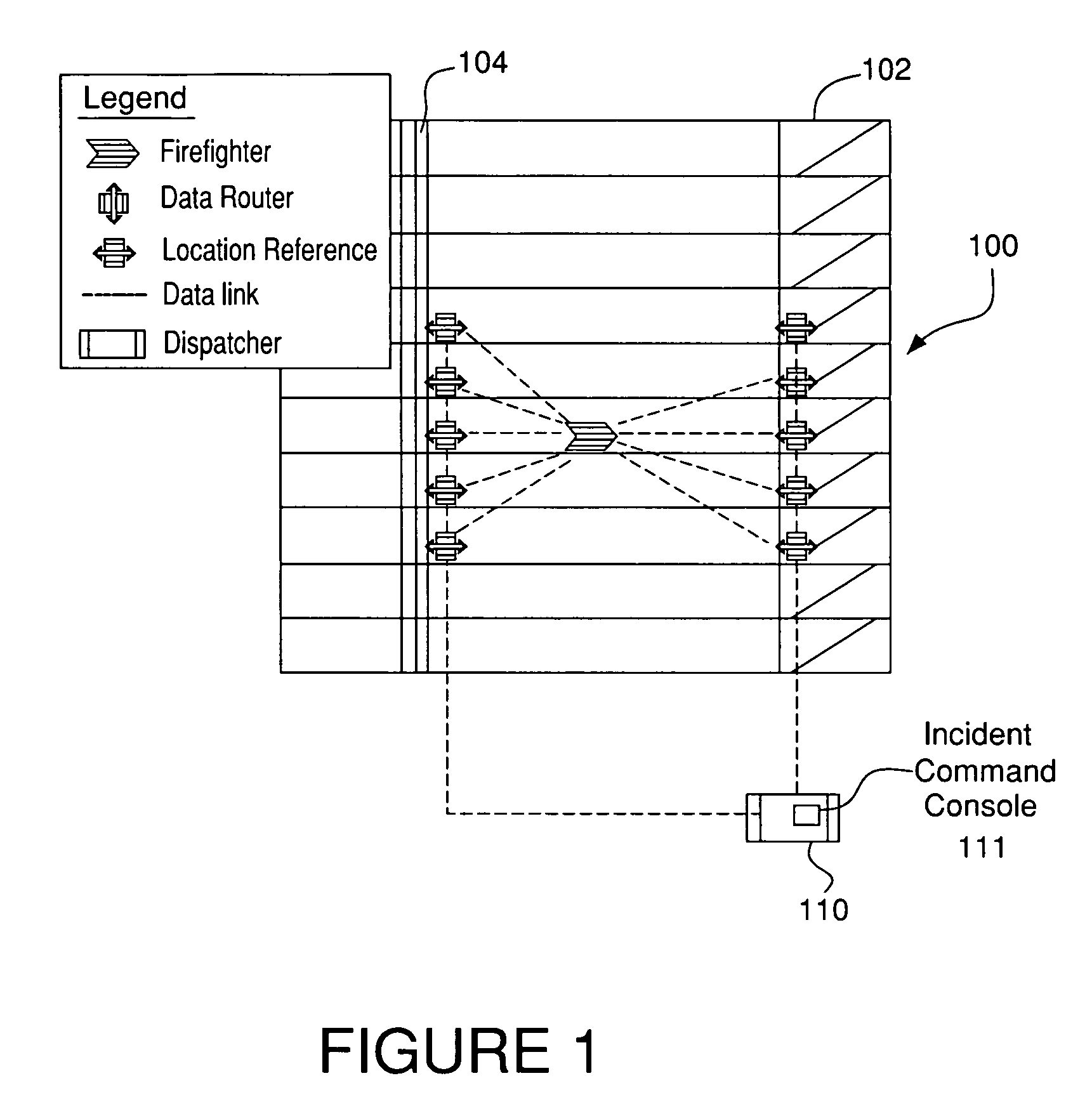
System and method for identifying the floor number where a firefighter in need of help is located using received signal strength indicator and signal propagation time
ActiveUS7126951B2Quickly and accurately identifyPower managementTransmission control/equalisingWireless routerPropagation time
A system and method for deploying a network of wireless devices, including mobile terminals, wireless routers and a least one control console, within a three dimensional deployment area such as a building, so that communication, identification and position calculations of personnel, such as firefighters, using the mobile terminals can be achieved regardless of building structure. The wireless routers are deployed in a substantial vertical manner in staircases and elevator shafts of a building of interest, either in advance as part of a safety program or immediately upon arrival of firefighters or other team at the building during an emergency. The system and method according to the embodiment of the present invention described herein uses both TOF and RSSI between the mobile terminals and wireless routers to identify the floor numbers where firefighters are located and to track firefighter movements.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Wireless local area network (WLAN) channel radio-frequency identification (RFID) tag system and method therefor
InactiveUS6963289B2Reduce stepsNetwork topologiesPosition fixationTelecommunicationsNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol
A wireless local area network (WLAN) radio-frequency identification (RFID) tag system provides location finding in a wireless local area network (WLAN), using a WLAN channel. Interference with the WLAN is prevented by either using a sniffer circuit to determine that no network transmission is in progress, using a modified coding sequence or preamble to cause standard WLAN receivers to ignore the RFID tag transmissions, or transmitting a message using a standard WLAN signal addressed to an address not corresponding to a unit within the WLAN. Location units (LUs) and a master unit (MU) within the WLAN receive the RFID tag transmissions and can determine the location of a tag by triangulation based on differences between the signals received at the location units from the tag. The master unit receives the signal information from the location units and computes the location of the tag. Time-difference-of-Arrival (TDOA), received signal strength indication (RSSI) or other triangulation techniques may be used.
Owner:AEROSCOUT
System and method of improving sampling of WLAN packet information to improve estimates of Doppler frequency of a WLAN positioning device
ActiveUS7768963B2Enhanced informationIncrease frequencyDirection finders using radio wavesNetwork topologiesReceived signal strength indicationComputer module
Systems and methods of improving sampling of WLAN packet information to improve estimates of Doppler frequency of a WLAN positioning device. A device estimates the position of itself. The device includes a WLAN radio module for receiving WLAN signals transmitted by WLAN APs in range of said device, extraction logic for extracting information from said received WLAN signals to identify the WLAN APs, and logic to cooperate with a WLAN-based positioning system to estimate the position of the device based at least in part on the extracted information identifying the WLAN APs in the range of said device. The WLAN radio module includes logic for measuring multiple received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values for sufficiently long WLAN packets to increase the sampled rate of RSSI of WLAN packets from WLAN APs and to thereby improve an estimate of the Doppler frequency of said device.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
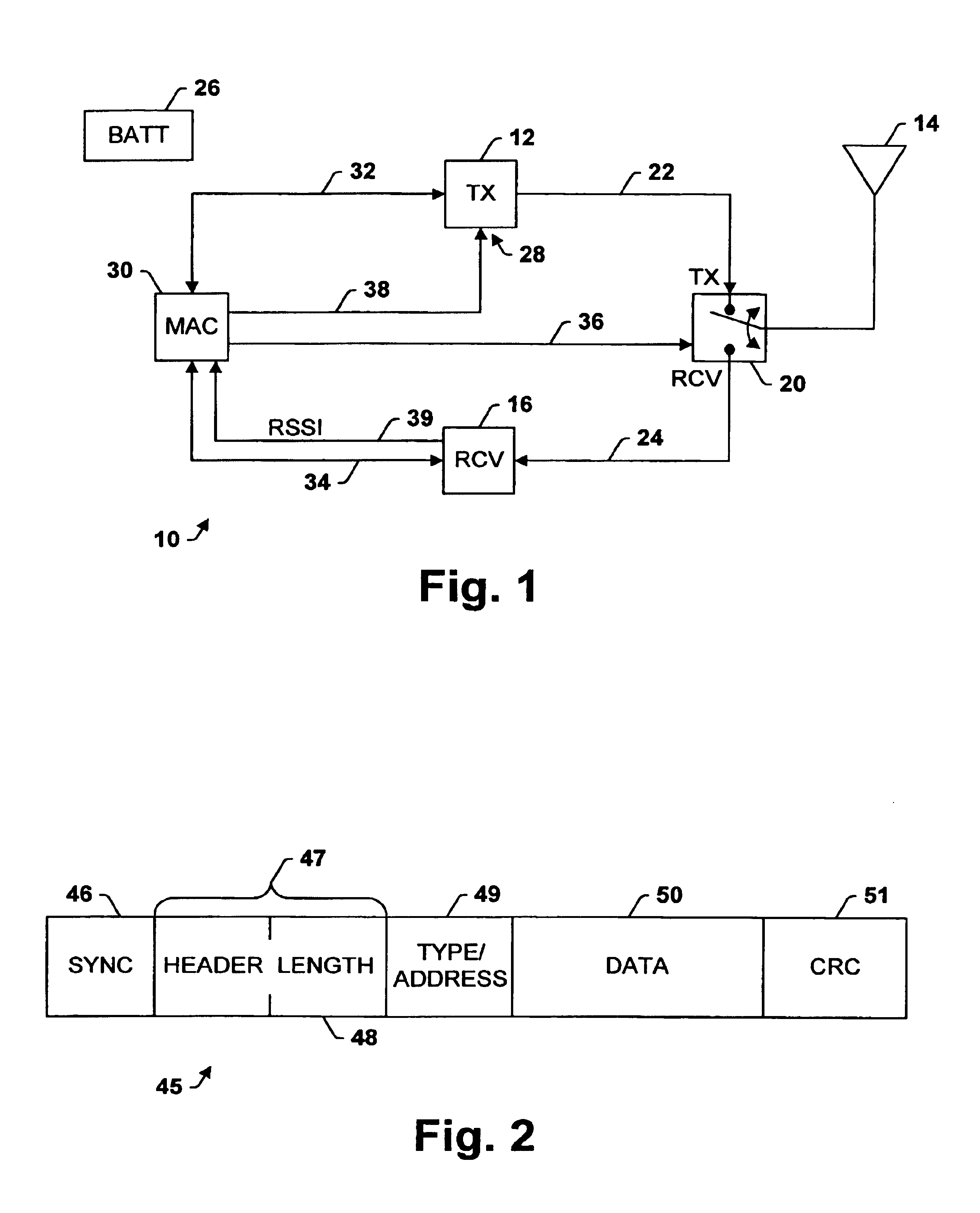
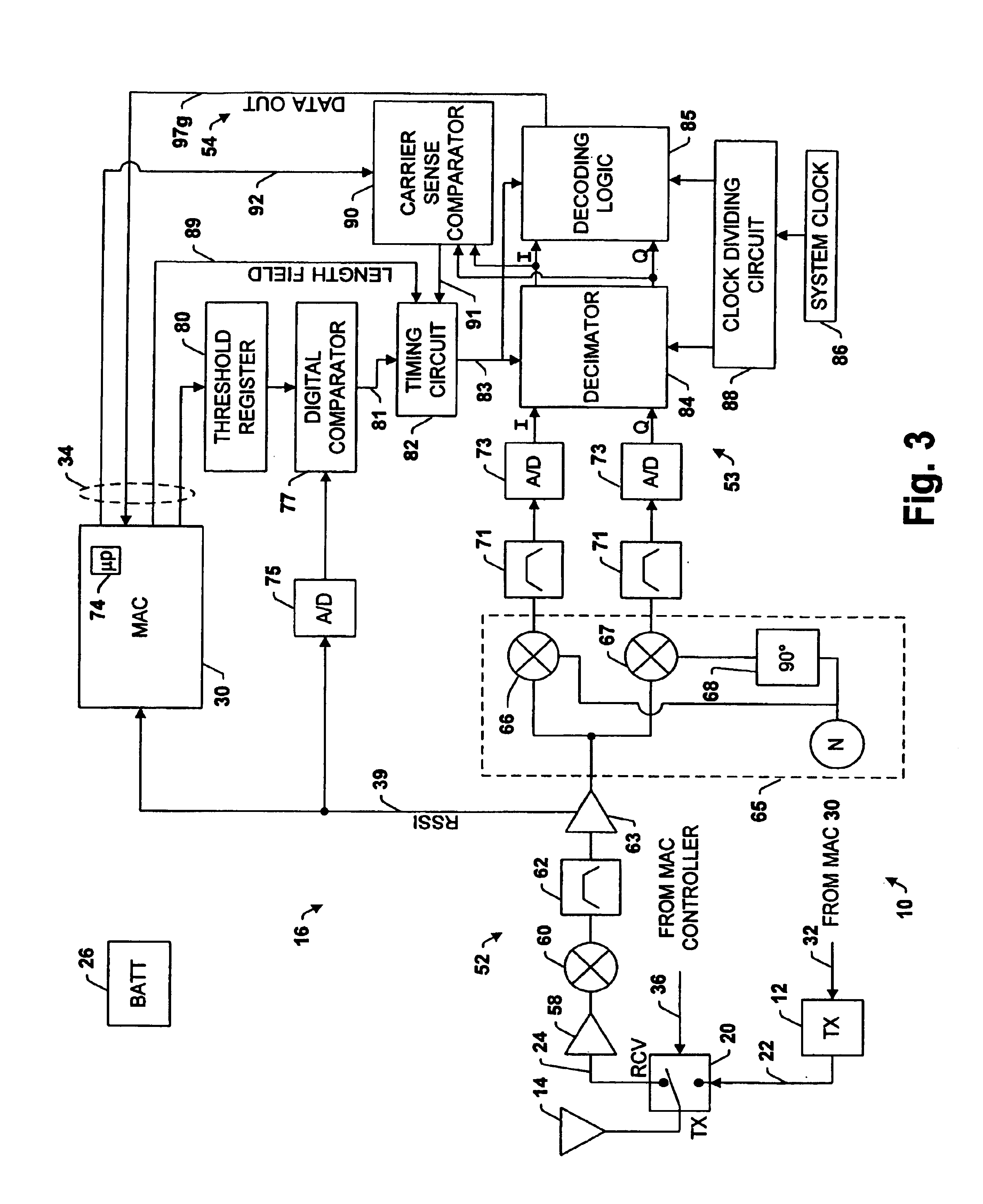
Transceiver control with sleep mode operation
InactiveUS6978149B1No delay exchangeHigh strengthEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTransceiverControl signal
A transceiver which keeps circuitry associated with a receiver in a powered down state during periods when a Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) indicates that a signal being received is below a pre-determined threshold level, and which begins to power up the transmitter as soon as it is determined that a packet being received requires a response. The RSSI signal represents the strength of any signal current being received, and if the RSSI signal falls below a given threshold level, digital circuitry associated with the back-end circuitry of the receiver system is disabled. If the RSSI signal rises above the threshold level, the digital circuitry of the receiver is enabled. A control circuit within the transceiver processes the packet as it is received to determine whether the packet requires a response. If it is determined that a response is necessary, the control circuit provides a control signal to the transmitter to power up the transmitter from a sleep mode even before the entire packet has been received and processed. The control circuit then continues to process the remainder of the packet as it is received while the transmitter powers up from the sleep mode. In this manner, the transmitter will become stabilized much earlier. Accordingly, the transceiver is able to respond more quickly than conventional devices and is thus able to increase response times and overall data exchange rates. Moreover, battery power of the transceiver is utilized more efficiently compared to devices which must continuously maintain the receiver and transmitter in fully powered modes.
Owner:TELXON INC
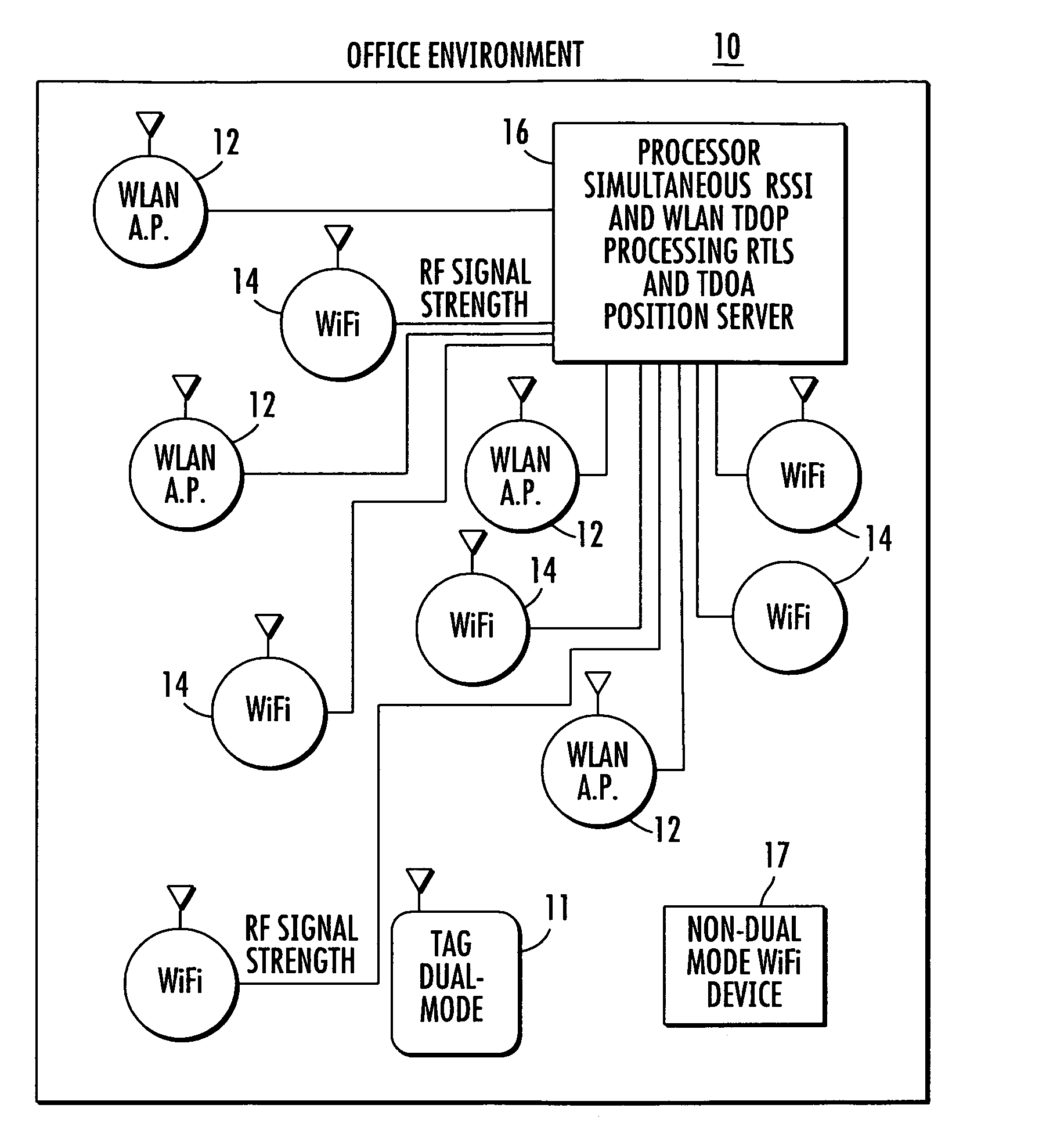
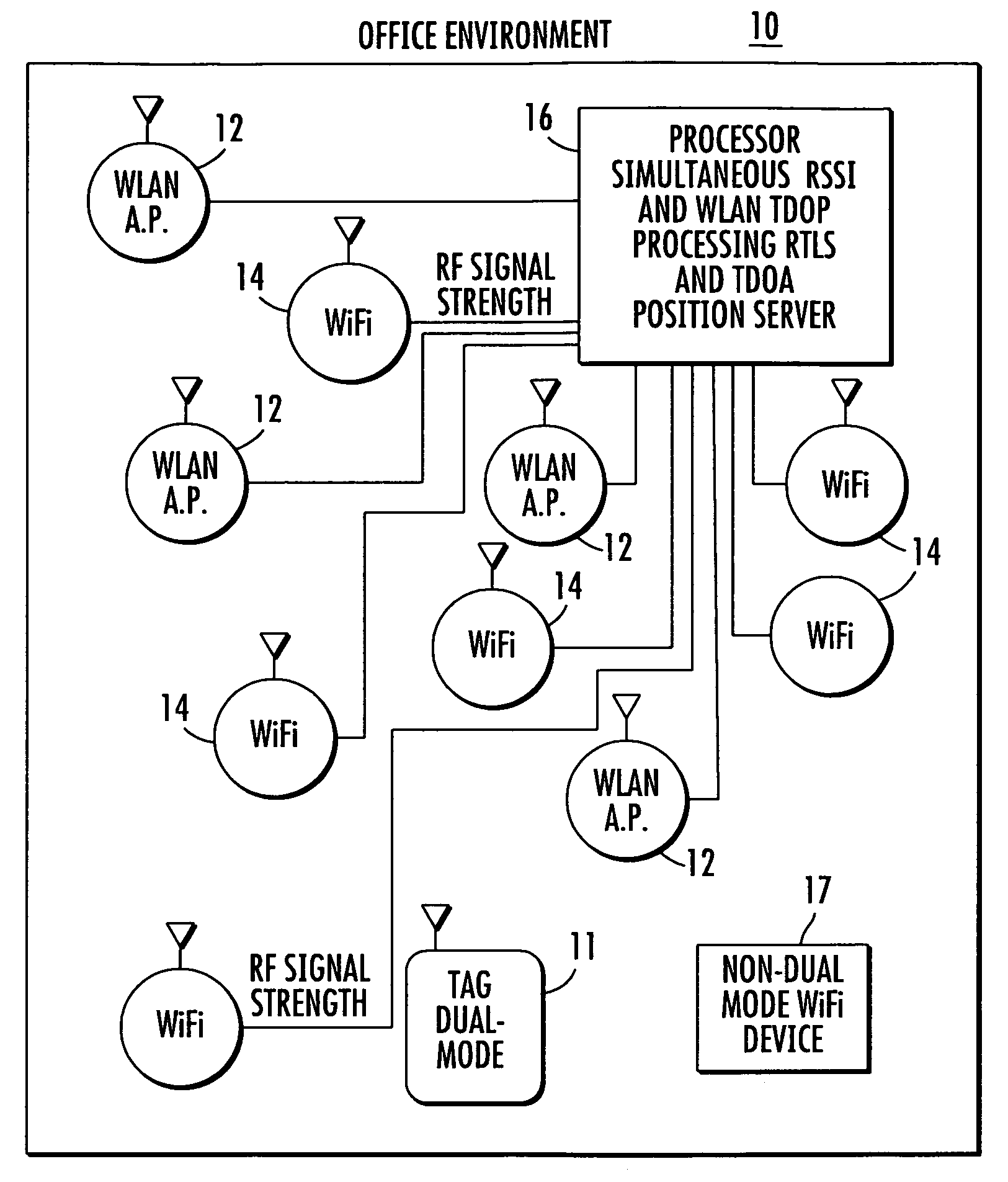
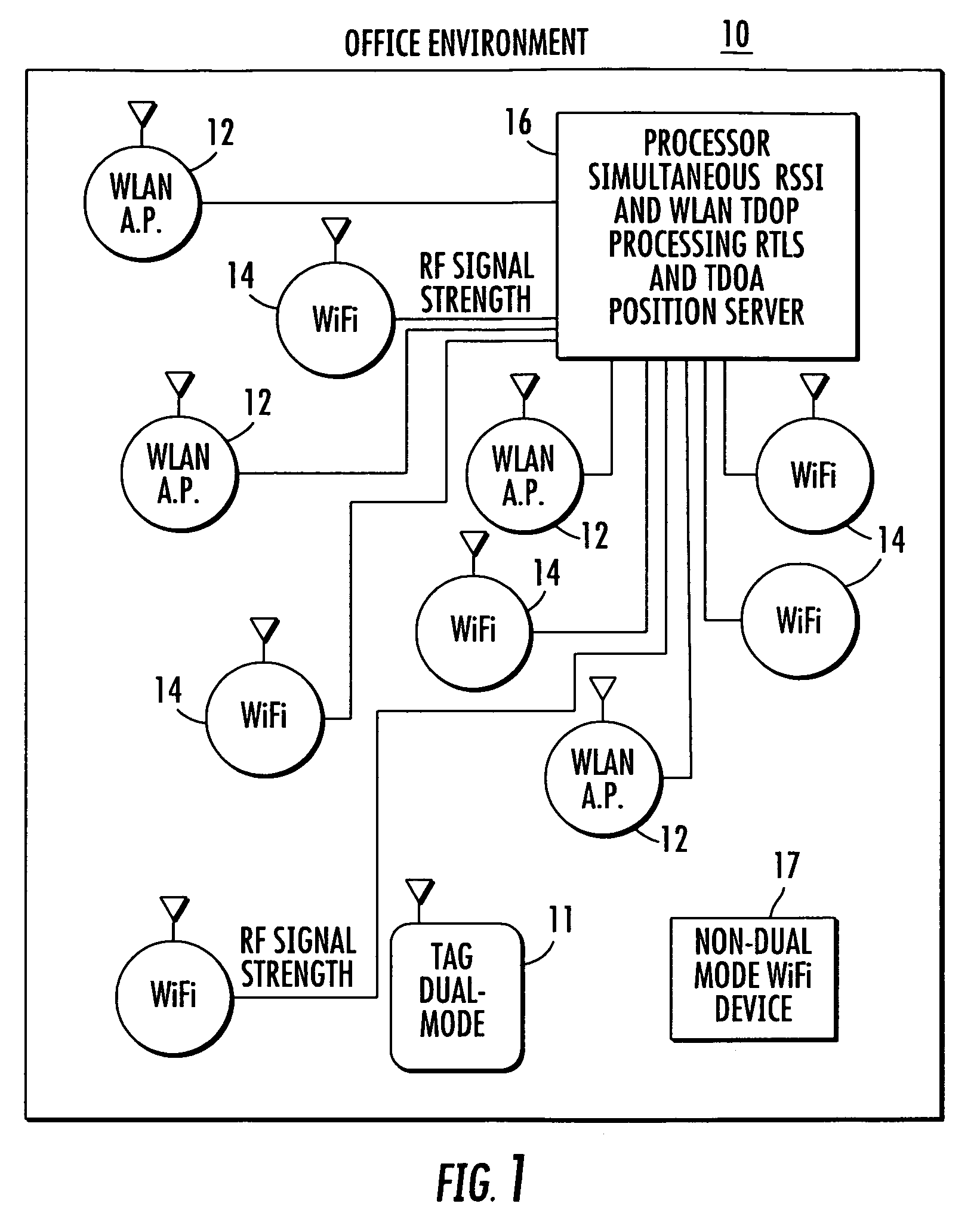
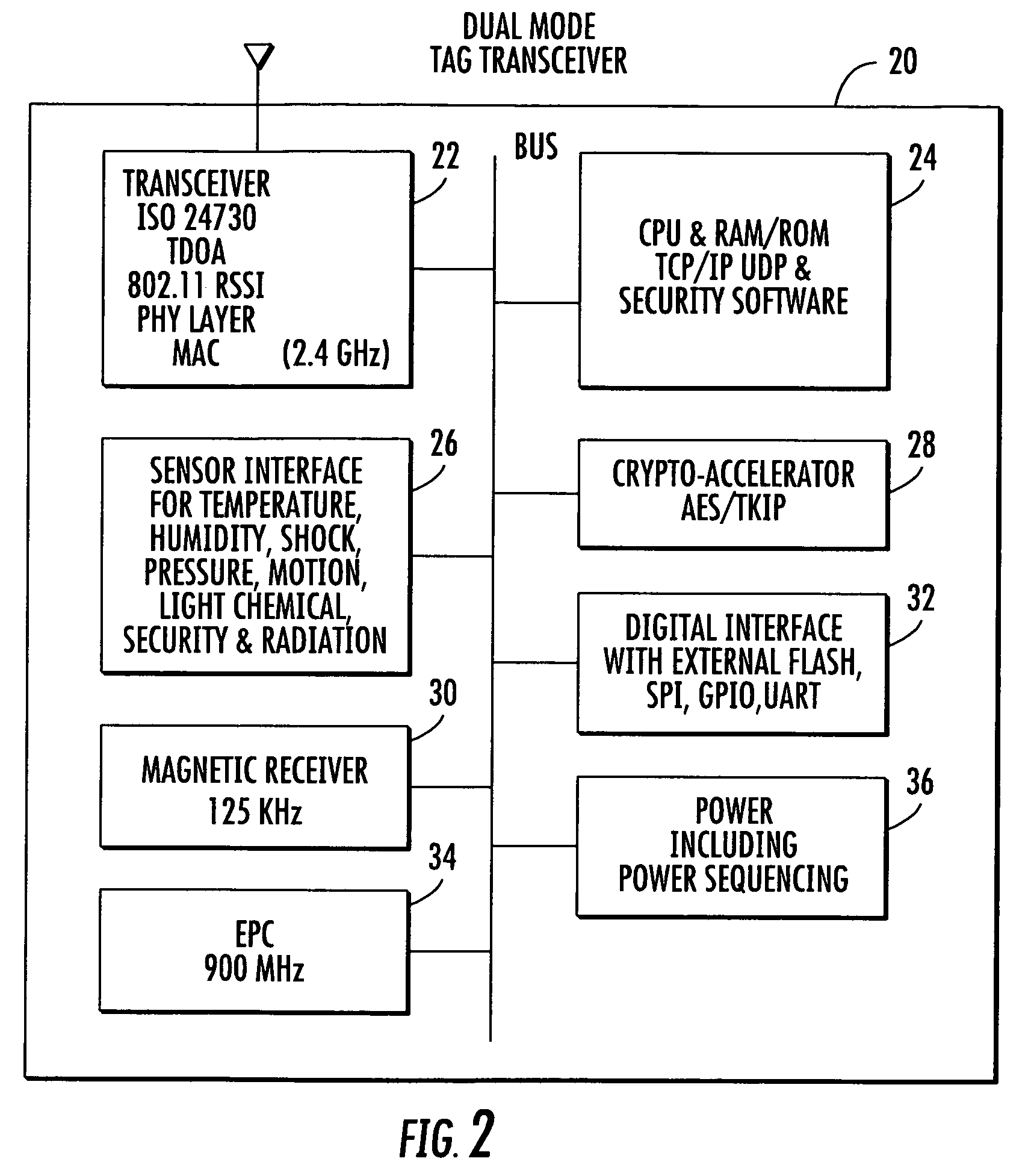
Location system for wireless local area network (WLAN) using RSSI and time difference of arrival (TDOA) processing
ActiveUS20080130604A1Direction finders using radio wavesNetwork topologiesDual modeReceived signal strength indication
A wireless local area network includes a plurality of access point stations that receive and transmit communications signals within the wireless local area network. A first set of access point stations are WiFi compliant and measure signal strength and determine the received signal strength indication (RSSI). A second set of access point stations are operable in accordance with the time of arrival (TOA) real time location standard (RTLS). A dual mode mobile station is operative for multimode communication with both the WiFi and RTLS compliant access point stations. A location processor is operatively connected with each of the access point stations and processes the RSSI and creates a RSSI locate map and processes communication signals from the second set of access point stations and determines which signals are first-to-arrive signals to locate the mobile station and update the RSSI locate map and locate any non-dual mode WiFi devices.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Method and system for providing physical security in an area of interest
InactiveUS20050055568A1Keep trackDigital data processing detailsHardware monitoringWi-FiPhysical security
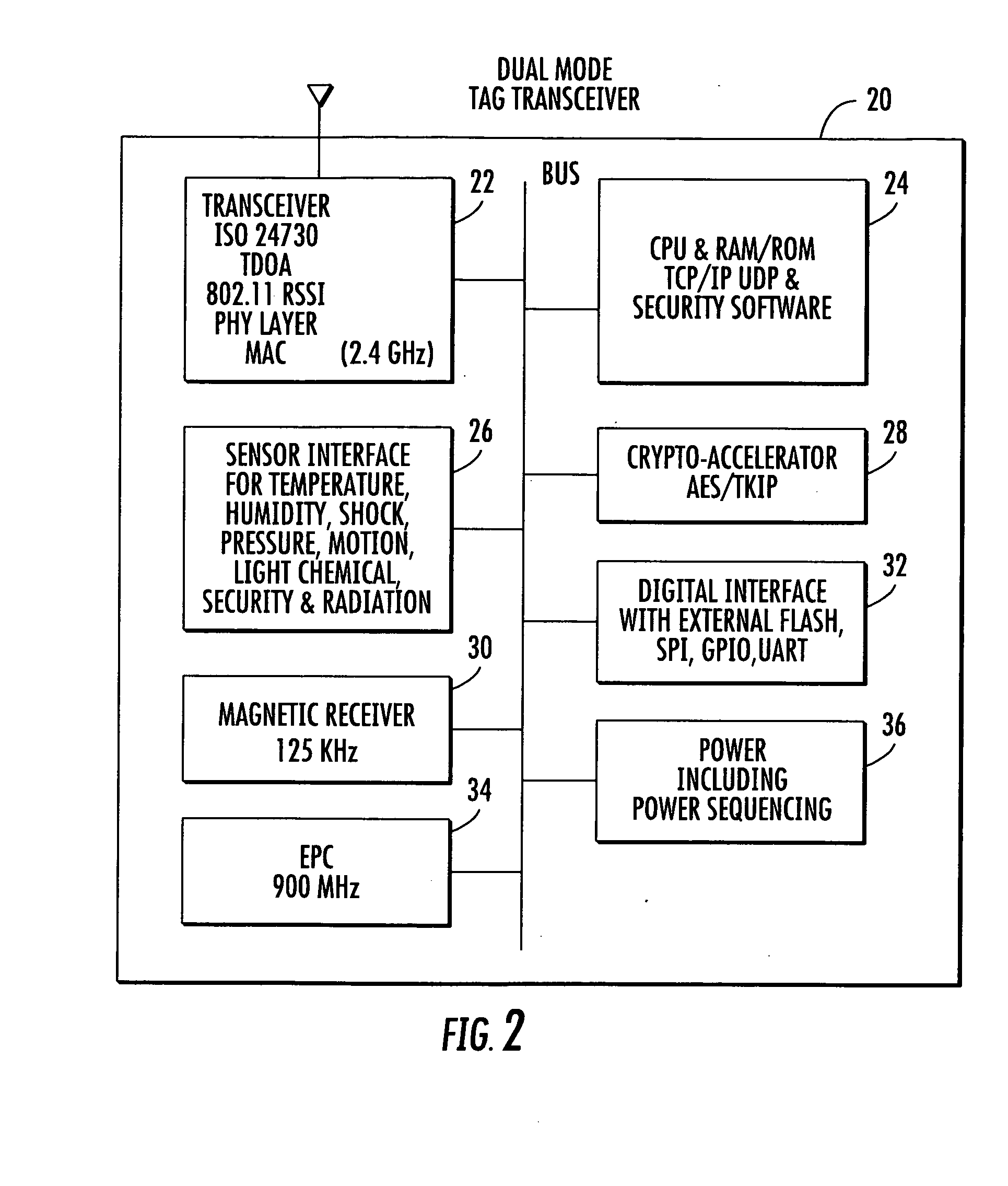
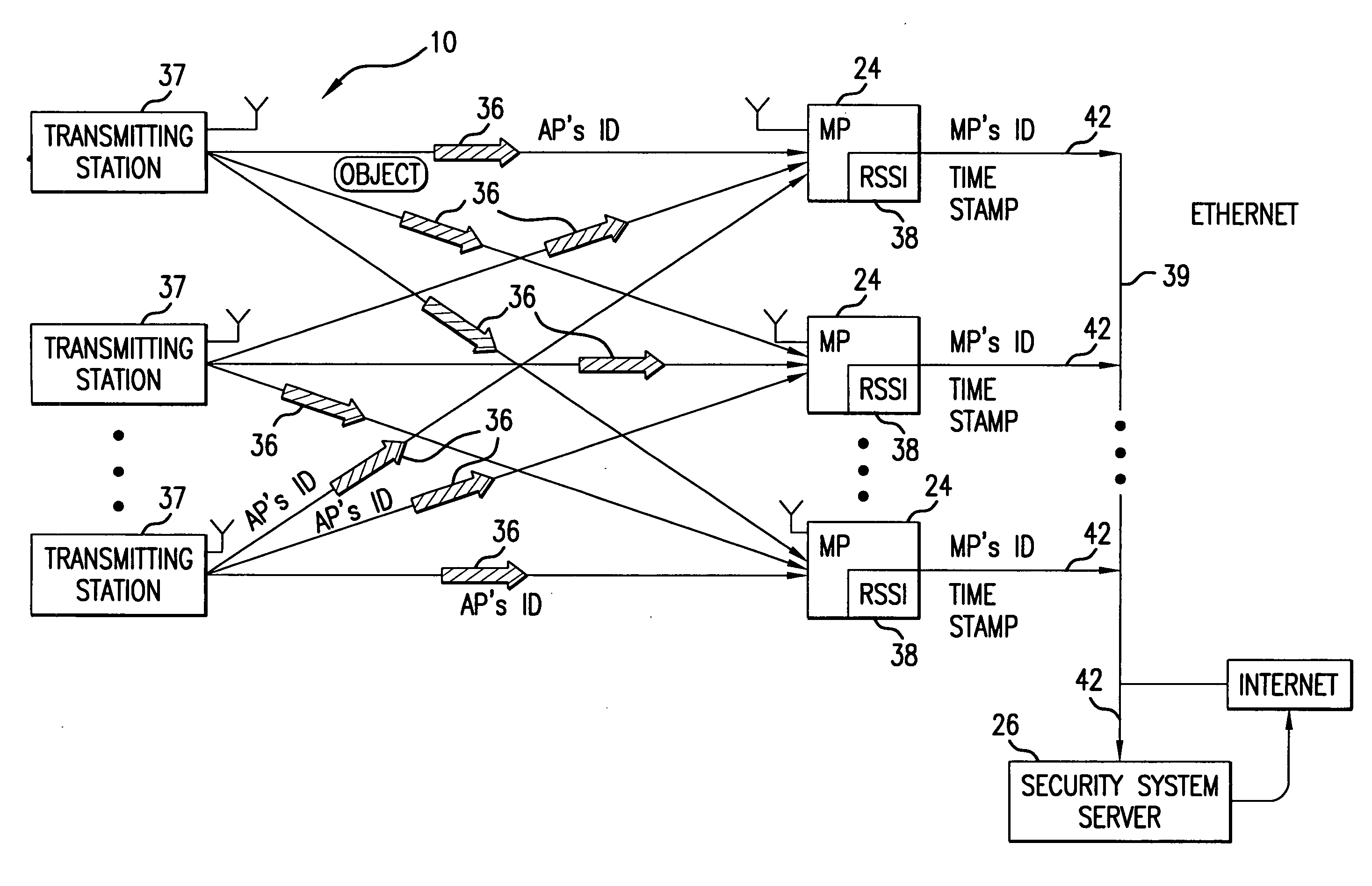
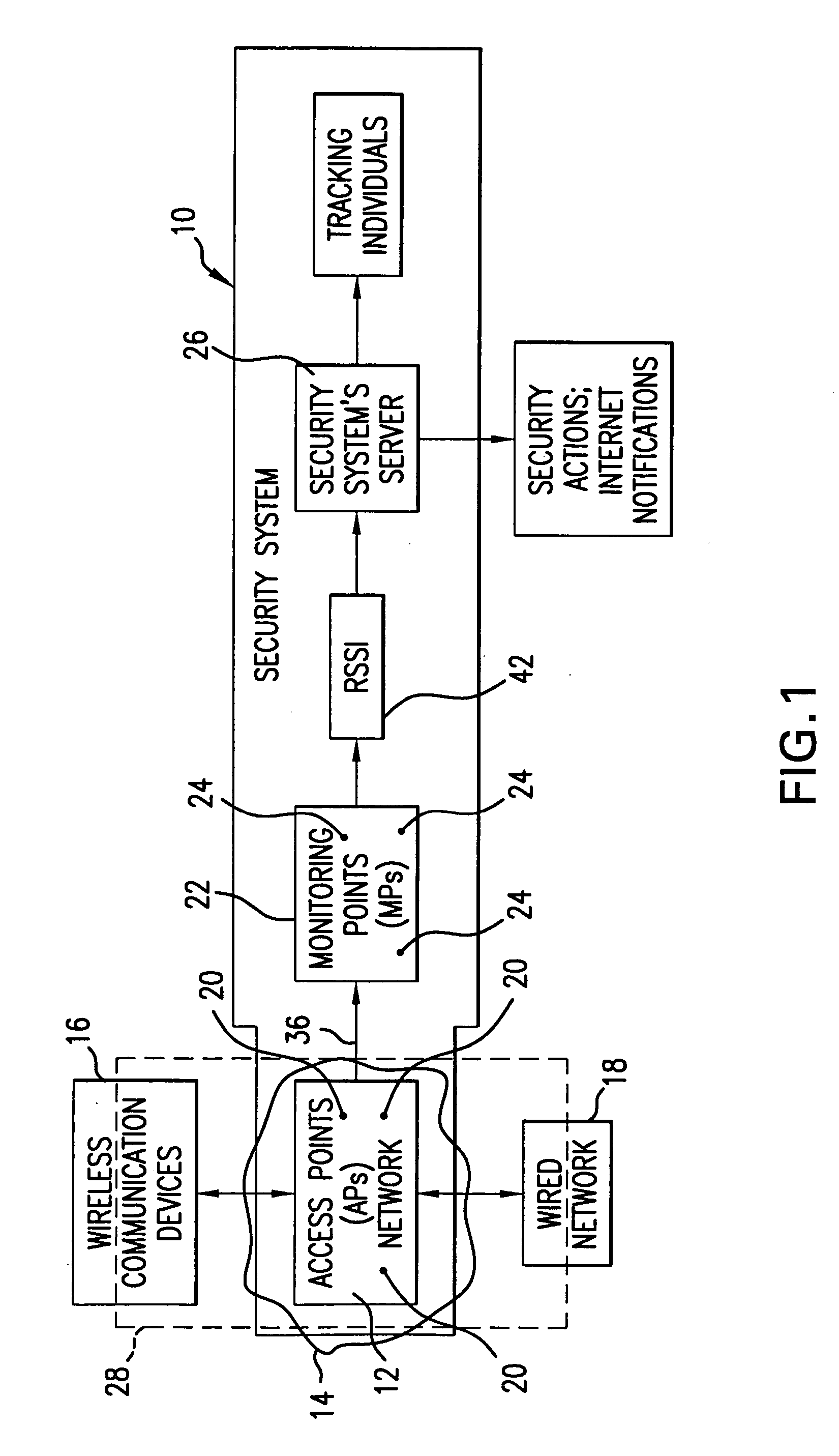
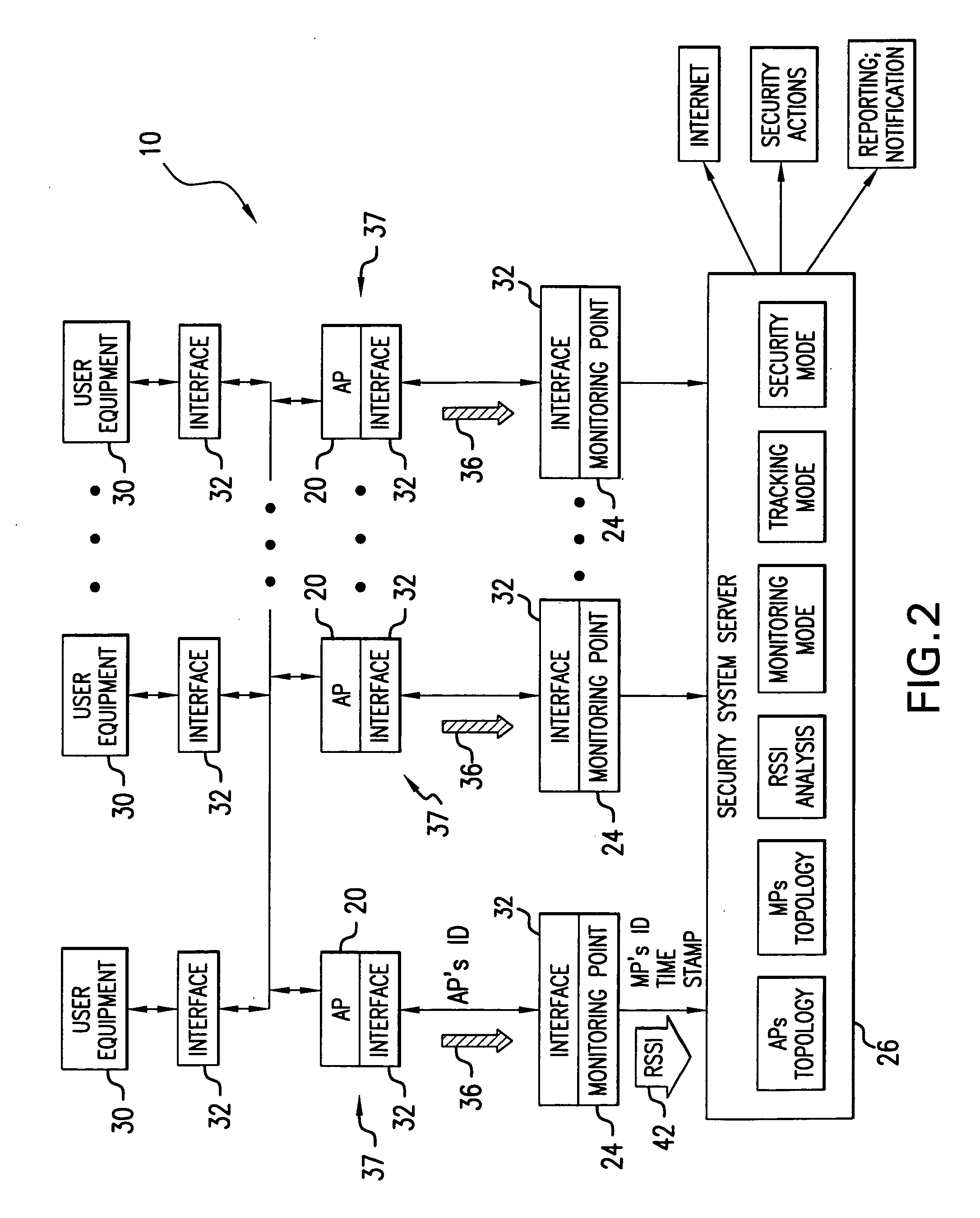
A system for detecting the presence of an intruder in a protected area utilizes a received signal strength indicator (RSSI) value of signals broadcast from transmitting stations deployed in the protected area. The system includes monitoring points for receiving broadcast signals, measuring the RSSI values of the received signals, and transmitting the measured RSSI values to a security system server. The security system server analyzes the RSSI values, and initiates security measures when the physical security of the protected area is violated which is detected when the measured RSSI values deviate from a predetermined strength of the broadcast signals. The security system also has the ability to track objects in the protected area and keep track of their movement in real time and report such movement. The system may be based on a Wi-Fi infrastructure in the protected area.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
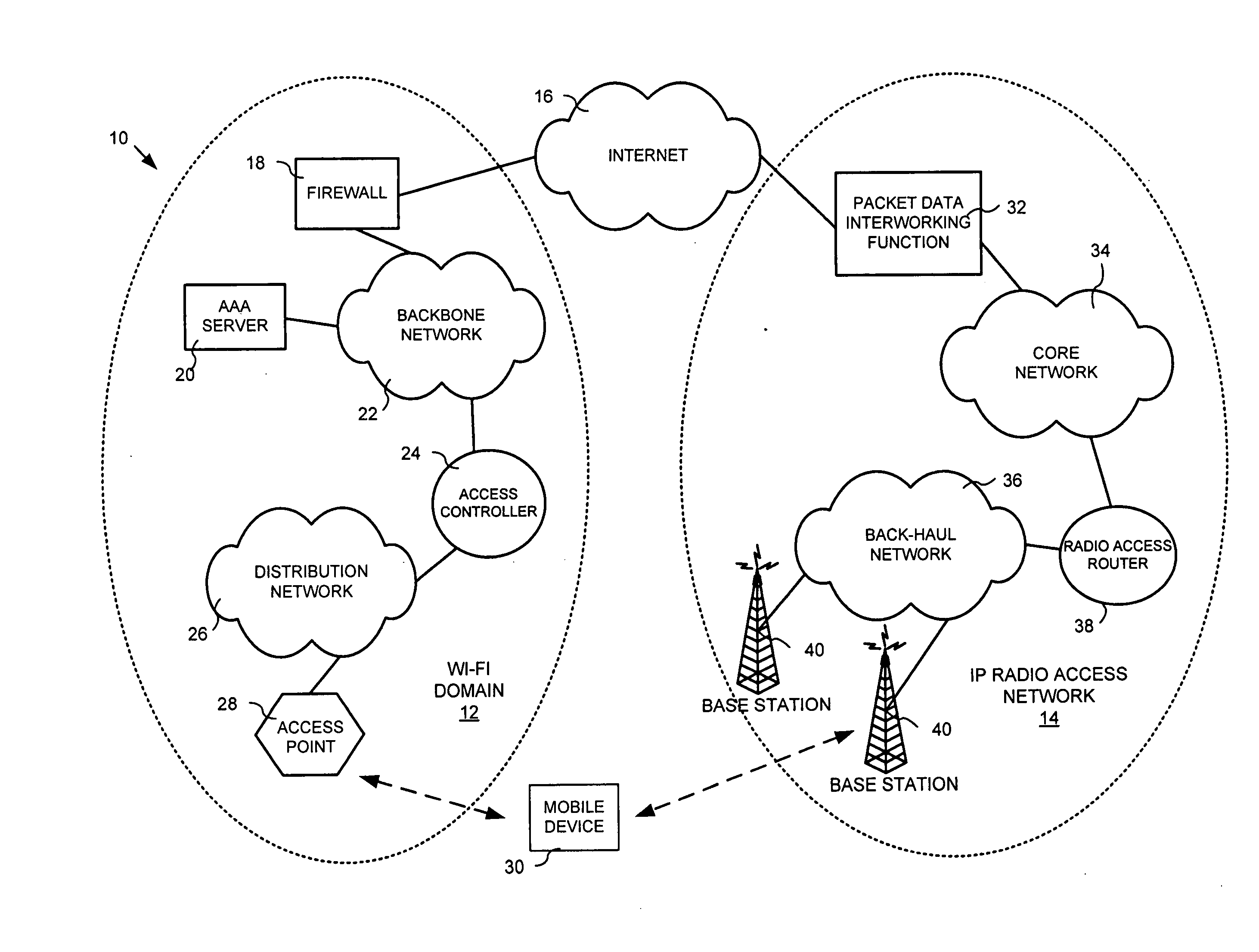
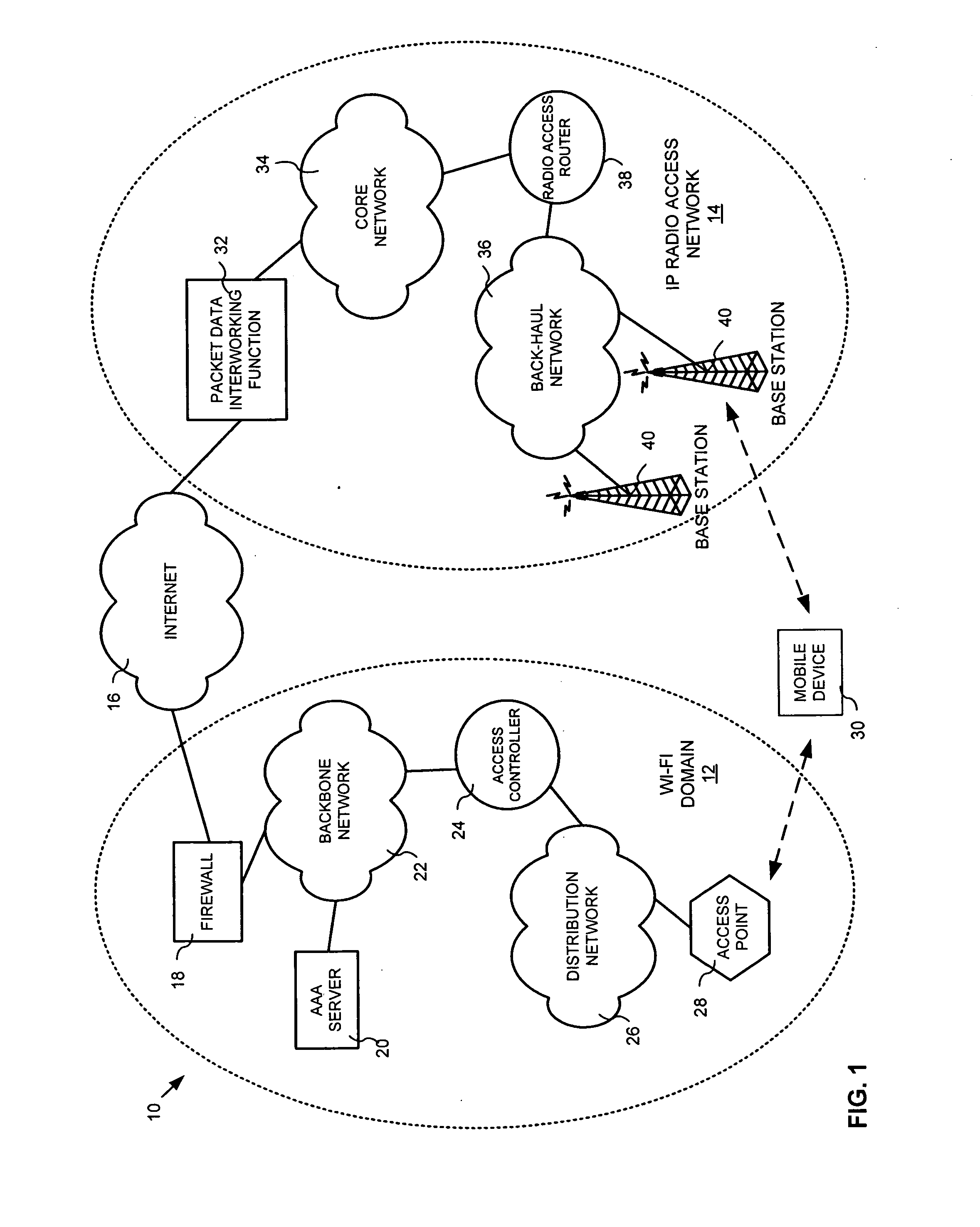
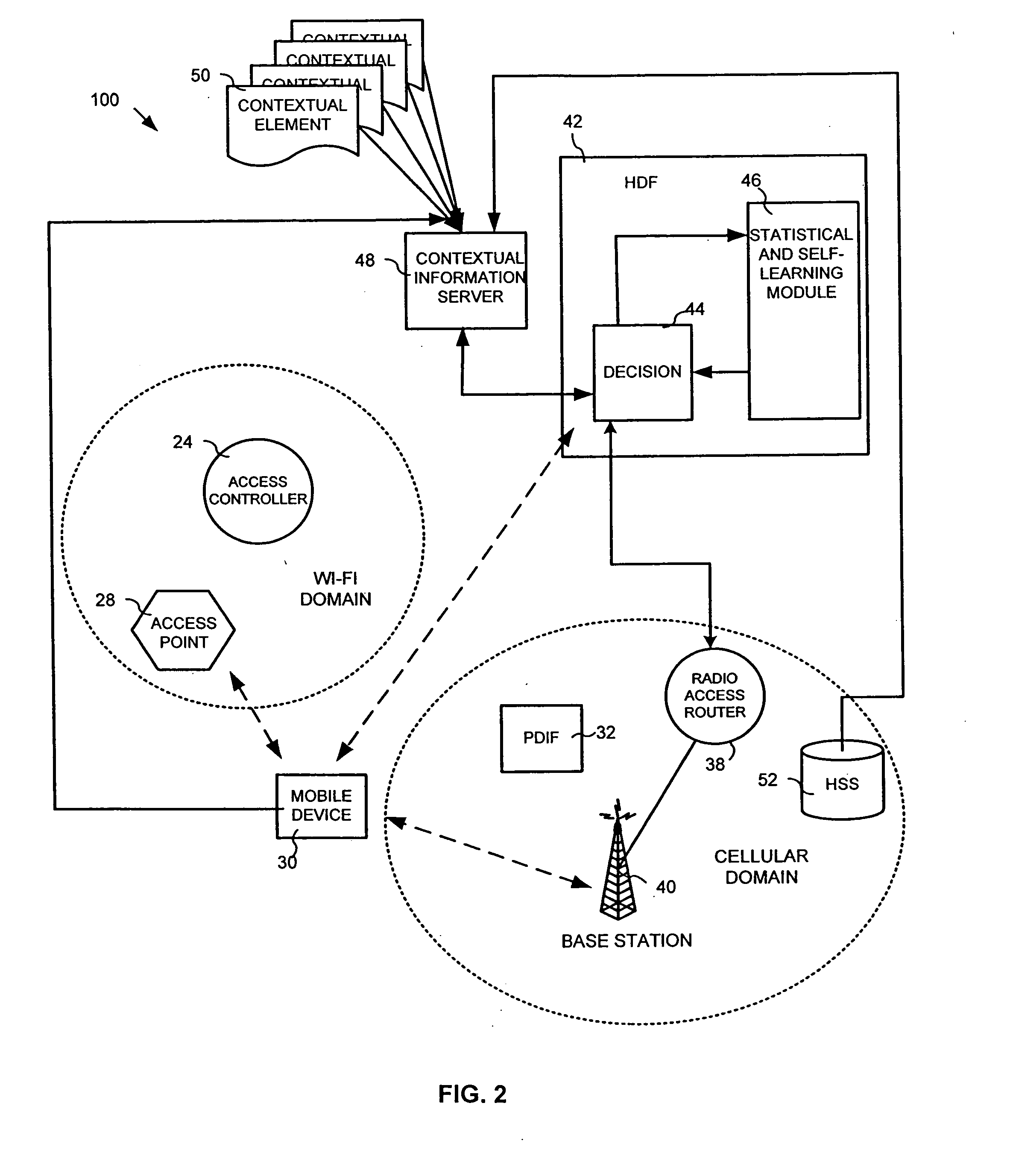
System and method for ensuring handoffs across heterogeneous networks
InactiveUS20080096560A1Convenient handoverRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork data managementReceived signal strength indicationHeterogeneous network
This invention provides a system, method and apparatus for facilitating handoffs from a first communication network to a second communication network, the first communication network and second communication network being heterogeneous with respect to each other. The system, method and apparatus may further include a contextual information server, which stores contextual elements corresponding to a user device and the operating environment of the user device, and a handoff decision function module that evaluates at least one of the contextual elements to determine whether to handoff user device communications from the first communication network to the second communication network. The method and apparatus may further include obtaining at least one contextual element corresponding to a user device and the operating environment of the user device, evaluating the at least one contextual element with a handoff decision function module to establish a handoff decision, establishing a handoff decision, and notifying the user device of the handoff decision. The method for facilitating handoffs from a first communication network to a second communication network may further include receiving a received signal strength indication, receiving a link quality determination, receiving a characteristic of the user device, and determining the location of the user device.
Owner:APPLE INC
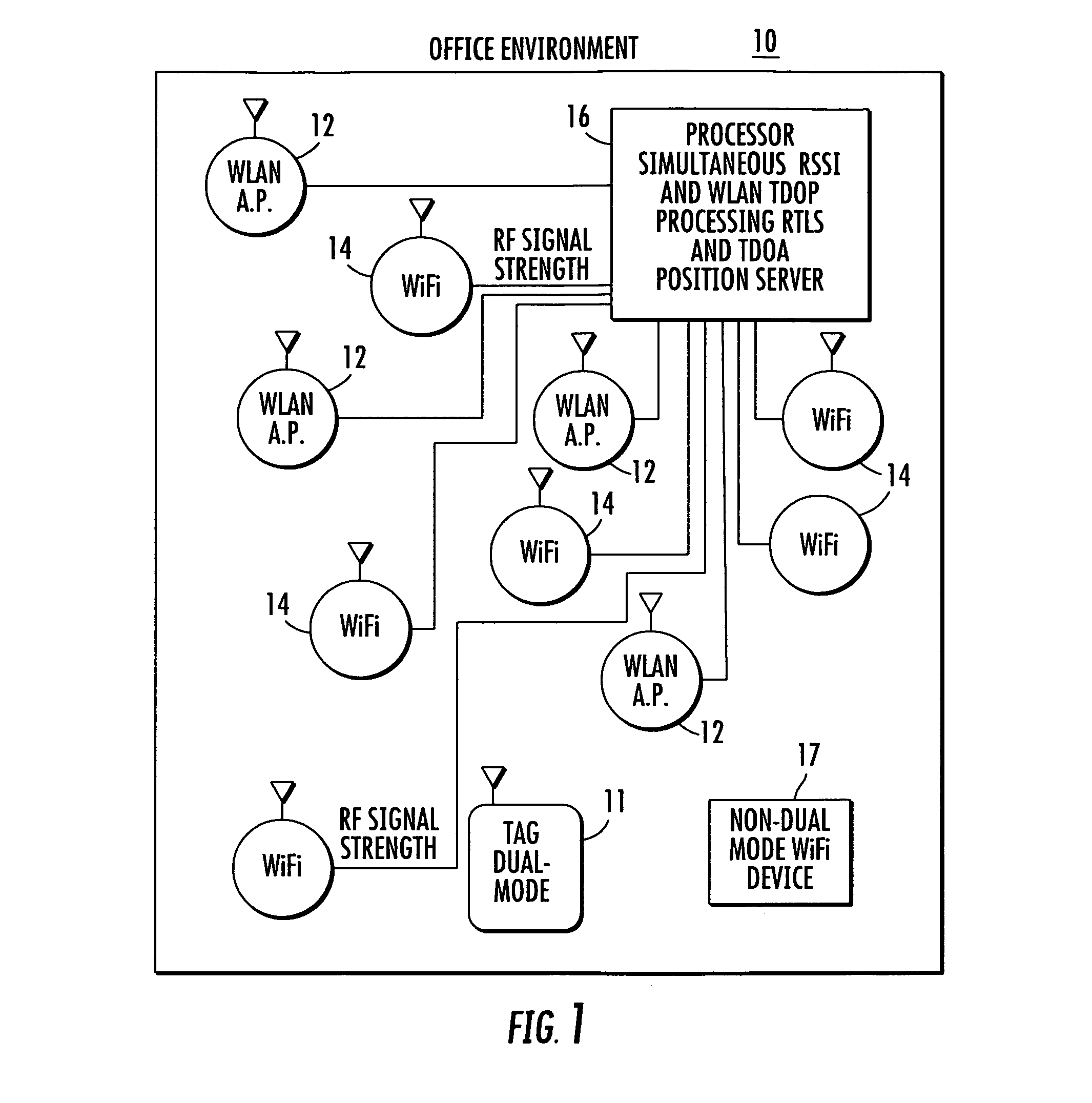
Location system for wireless local area network (WLAN) using RSSI and time difference of arrival (TDOA) processing
A wireless local area network includes a plurality of access point stations that receive and transmit communications signals within the wireless local area network. A first set of access point stations are WiFi compliant and measure signal strength and determine the received signal strength indication (RSSI). A second set of access point stations are operable in accordance with the time of arrival (TOA) real time location standard (RTLS). A dual mode mobile station is operative for multimode communication with both the WiFi and RTLS compliant access point stations. A location processor is operatively connected with each of the access point stations and processes the RSSI and creates a RSSI locate map and processes communication signals from the second set of access point stations and determines which signals are first-to-arrive signals to locate the mobile station and update the RSSI locate map and locate any non-dual mode WiFi devices.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
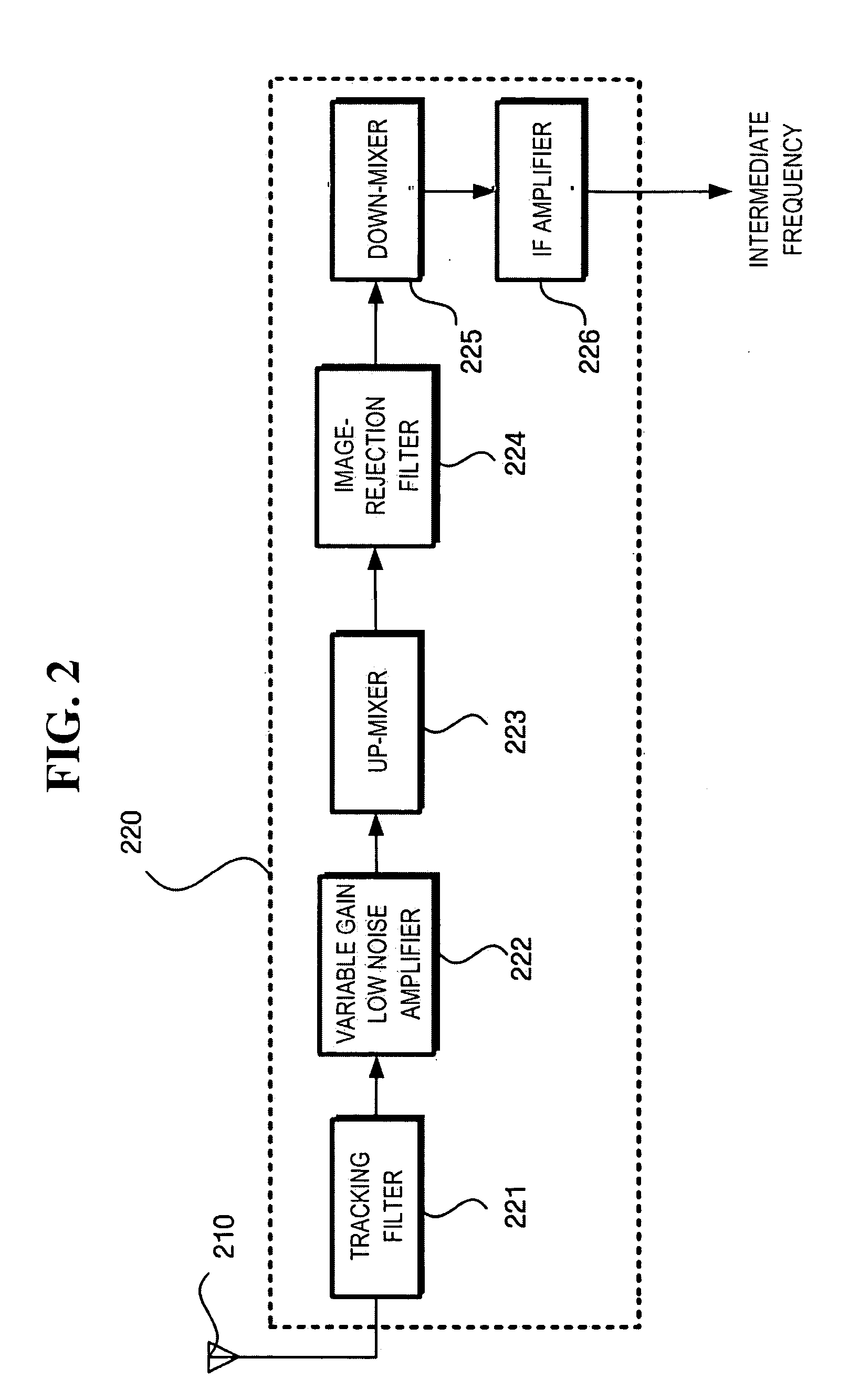
Tuner and broadcasting signal receiver including the same
InactiveUS20070042734A1Improve featuresImprove performanceTelevision system detailsContinuous tuning detailsReceived signal strength indicationEngineering
A tuner and a broadcasting signal receiver including the tuner. The tuner includes a band selection module that selects an RF broadcasting signal within the frequency band corresponding to a selected channel, and a low noise amplifier module that amplifies the signal with a specific received signal strength indicator (RSSI) to produce an RF broadcasting signal with a specific gain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
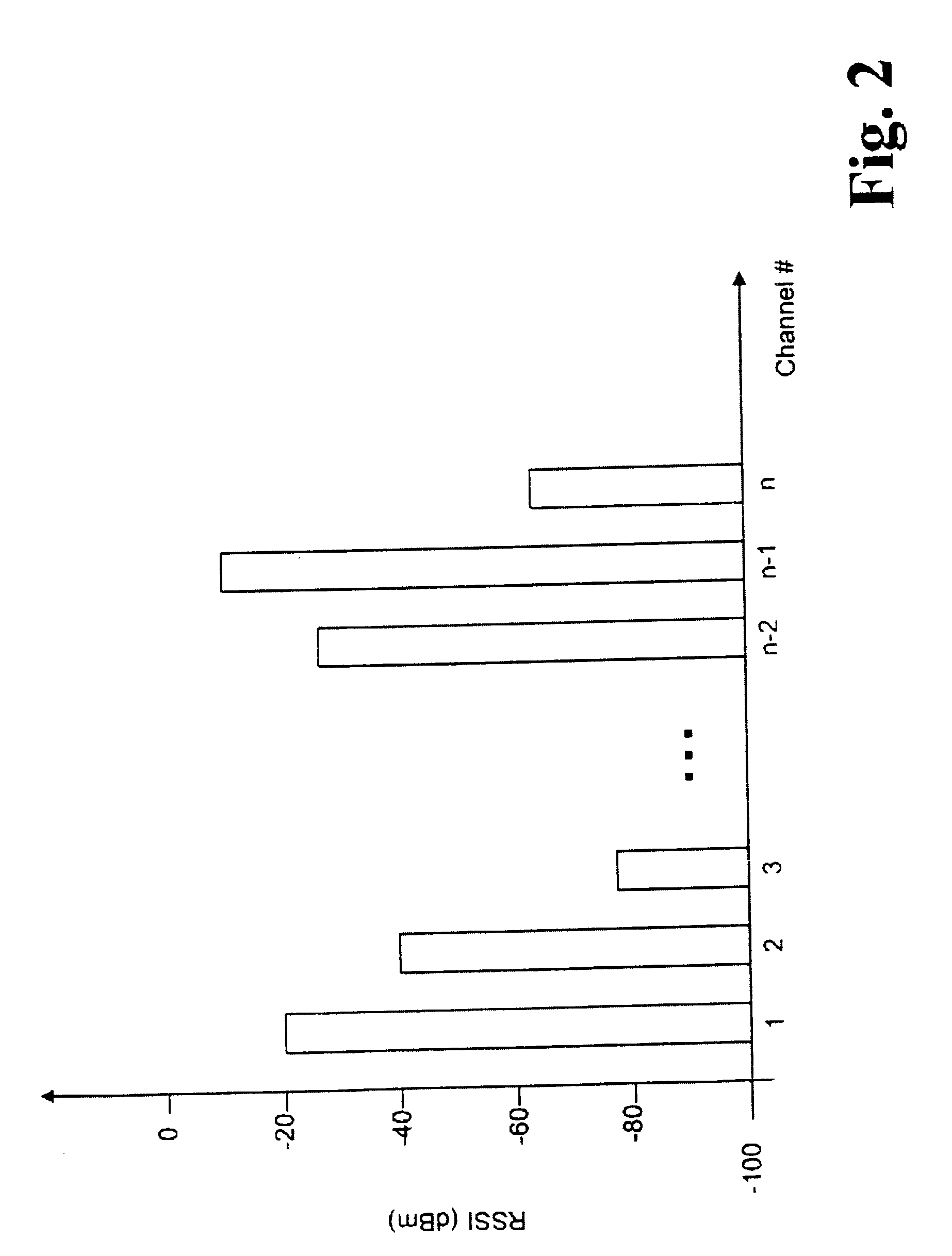
Frequency hopping in 5GHz WLAN via dynamic frequency selection
ActiveUS20040037247A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsReceived signal strength indication
Disclosed is a method and system for dynamically selecting a communication channel between an access point (AP) and a plurality of mobile terminals (MTs) in a wireless local area network (WLAN), the method having the steps of: (a) measuring a channel quality of a plurality of frequency channels; (b) reporting to said AP from said plurality of MTs of said candidate channels including a received signal strength indication (RSSI) of all channels measured; and, (c) selecting one of said channels based on said channel quality report for use in communication between said AP and said plurality of MTs.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
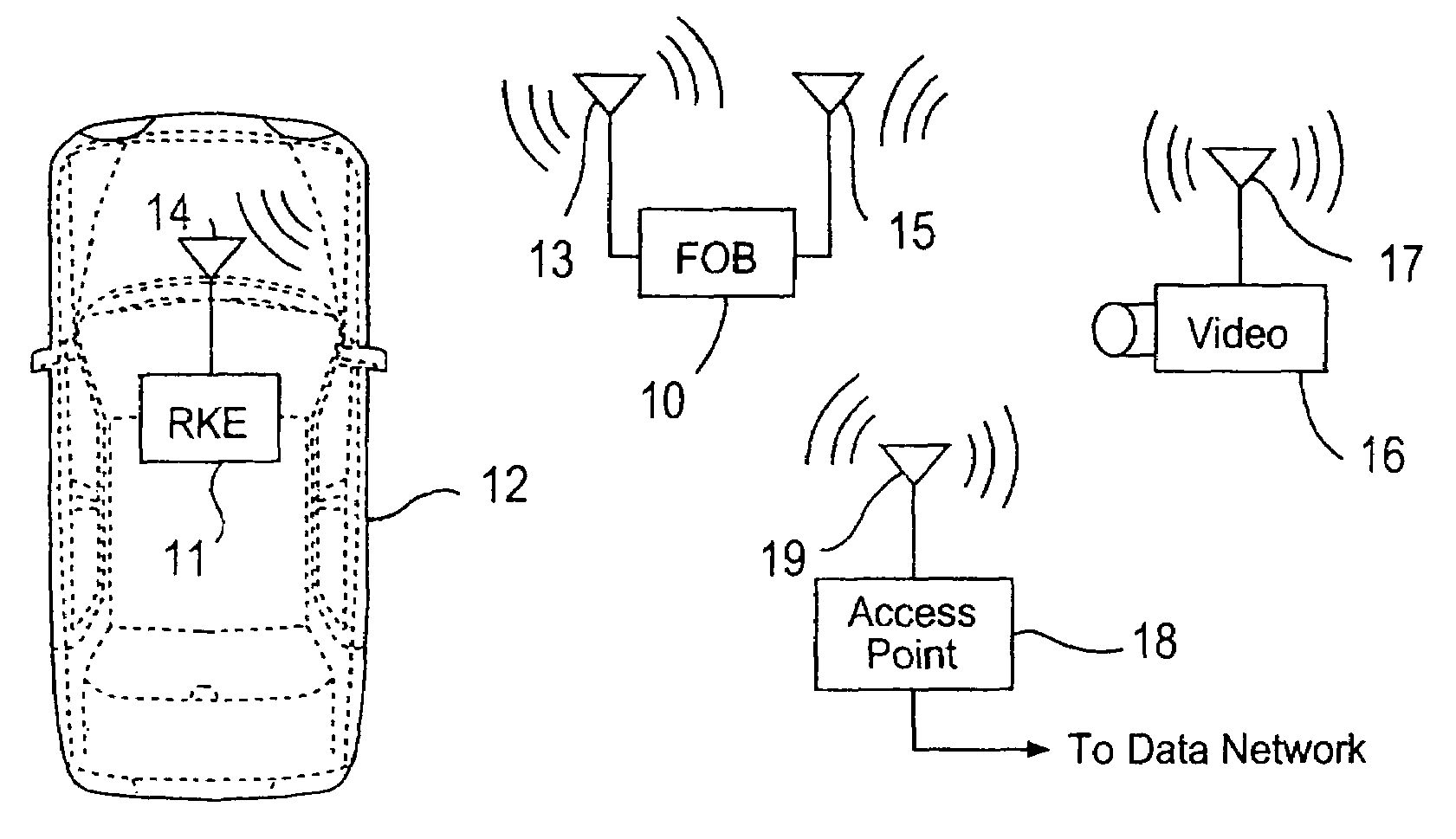
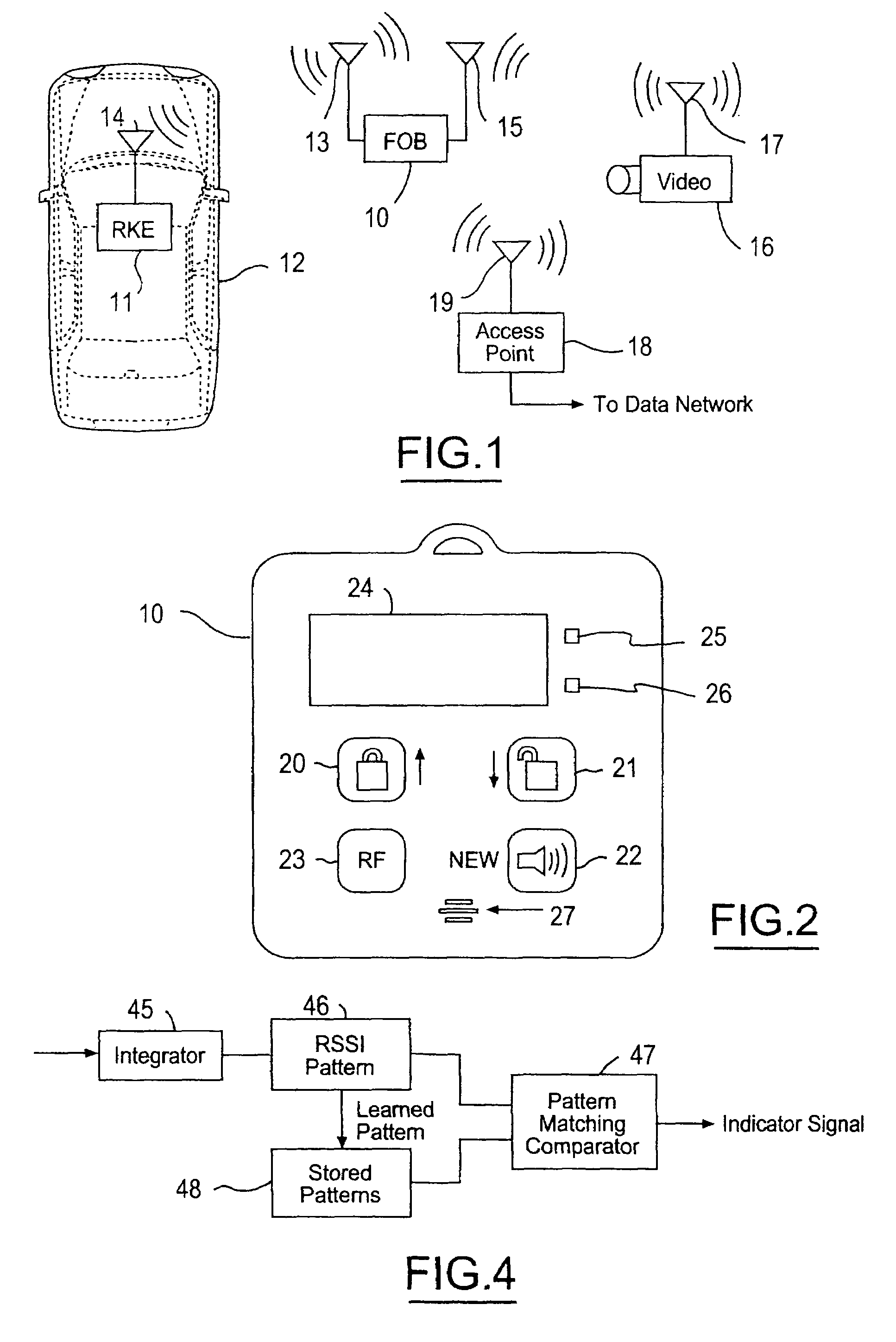
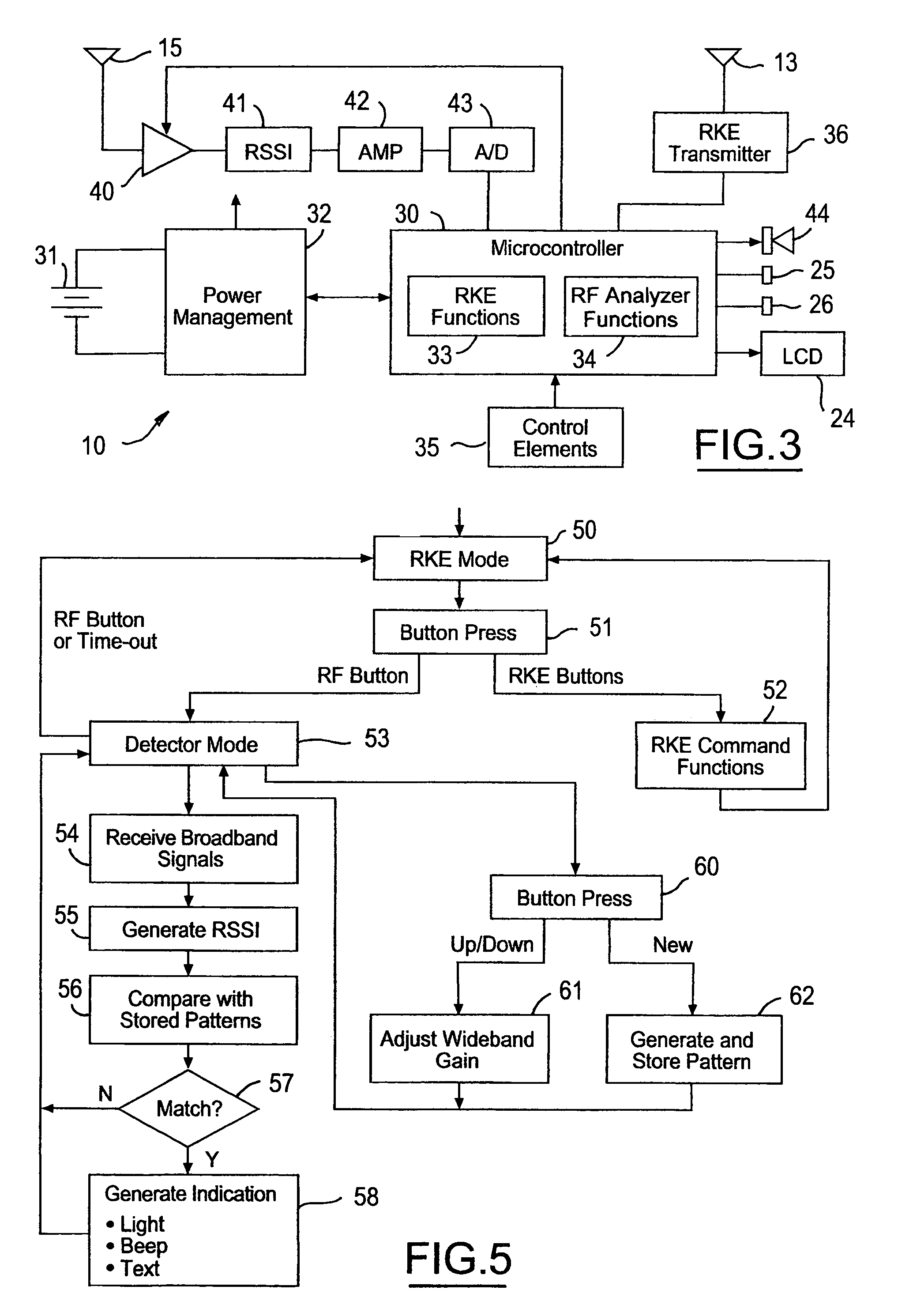
Remote keyless entry transmitter fob with RF analyzer
InactiveUS7042342B2Efficient and cost-effectiveMinimize power consumptionProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsReceived signal strength indicationDisplay device
Owner:LEAR CORP
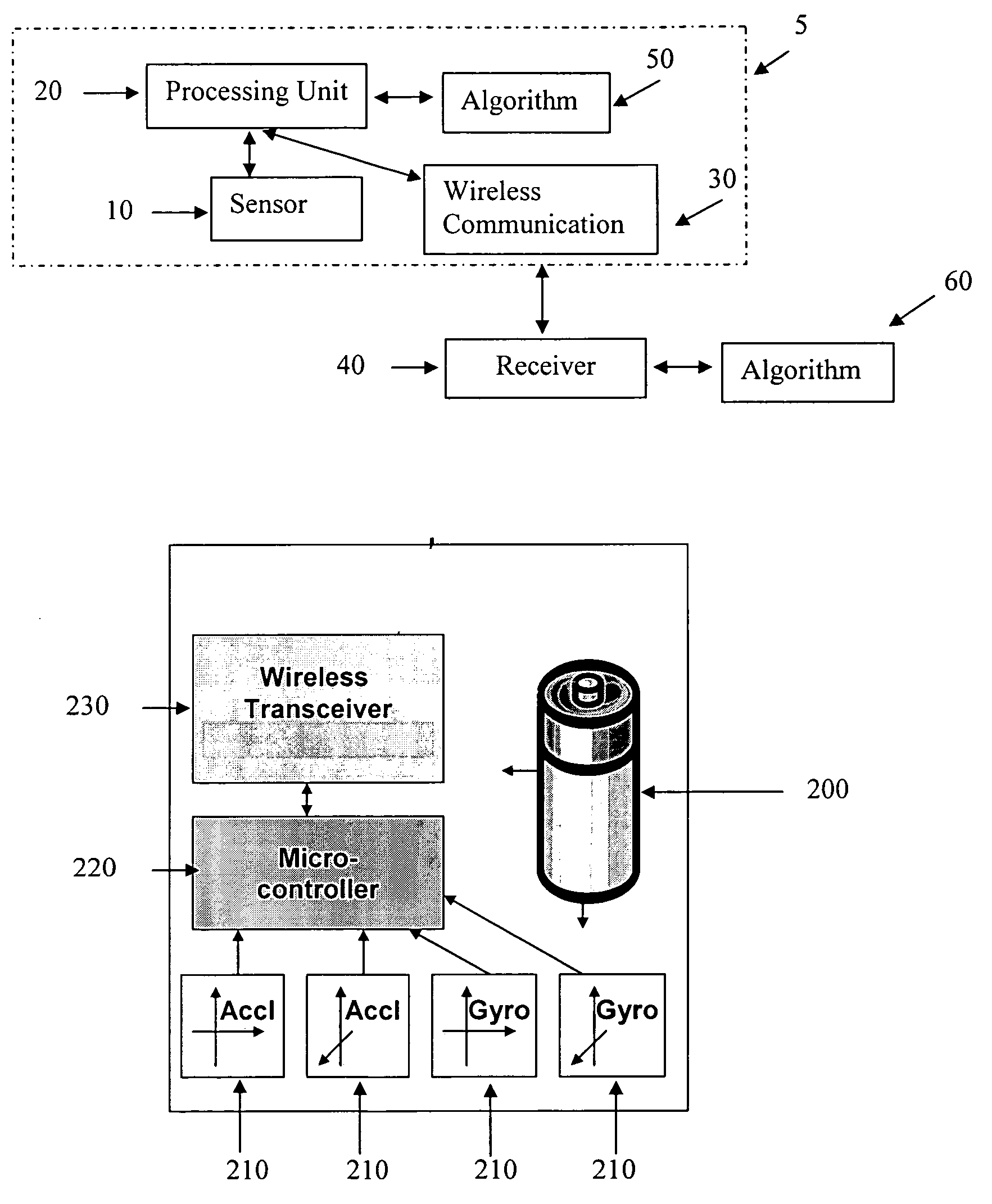
Location and tracking system, method and device using wireless technology
InactiveUS20070168127A1Easily and quickly incorporatedEnable mobilityBeacon systems using radio wavesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsReceived signal strength indicationProcessing element
A system, method, and device for locating one or more objects, in which the system includes one or more objects having an unknown location, each object comprising at least one mobility sensor for providing sensory data about the object, a wireless communications package for providing received signal strength indication and a processing unit for transmitting data about the object. The data includes the sensory data and the received signal strength indication. The system also includes at least one receiver for receiving the data about each object and at least one algorithm for processing the data about each object and identifying a location estimate about each object, thereby locating one or more objects having an unknown location.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
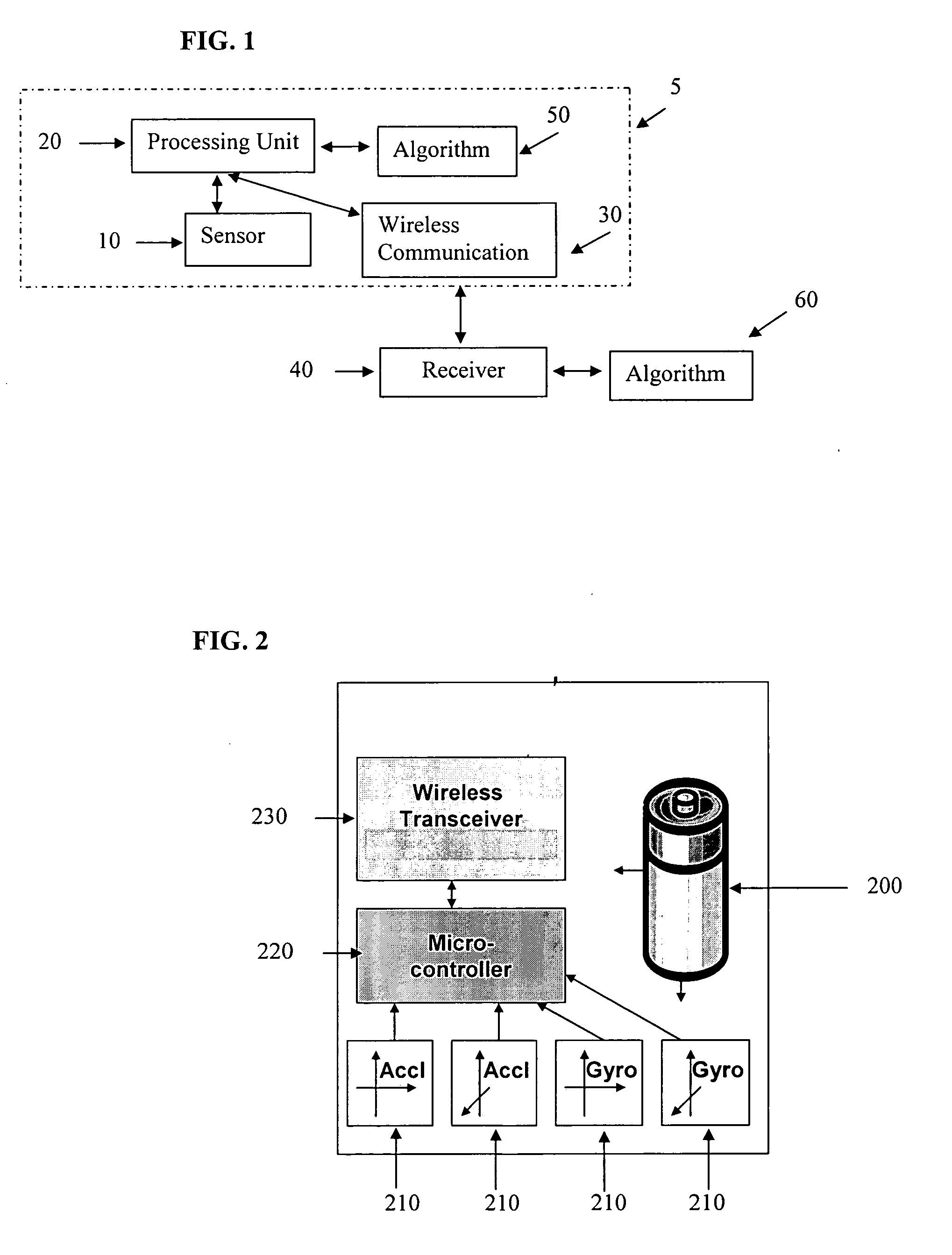
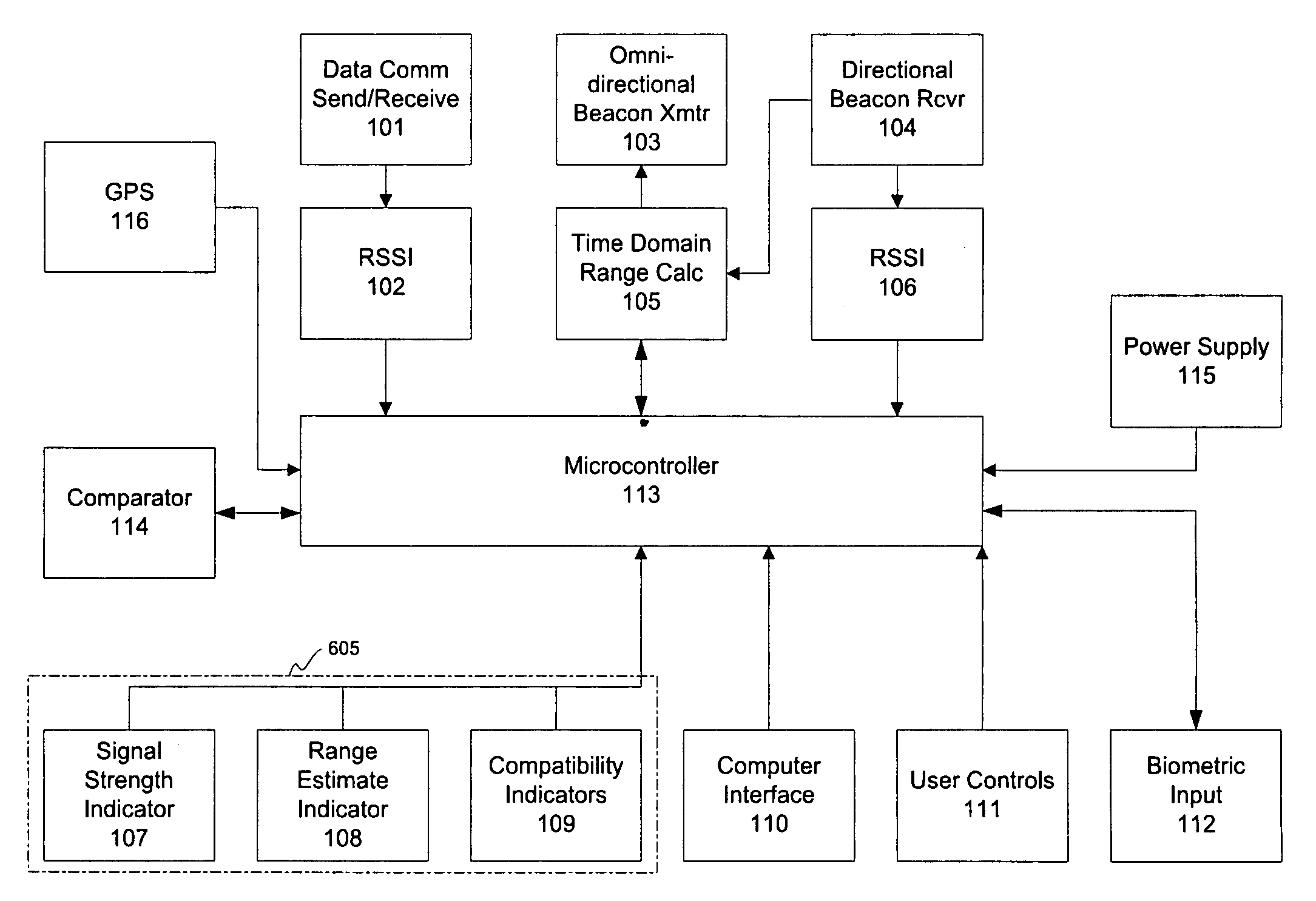
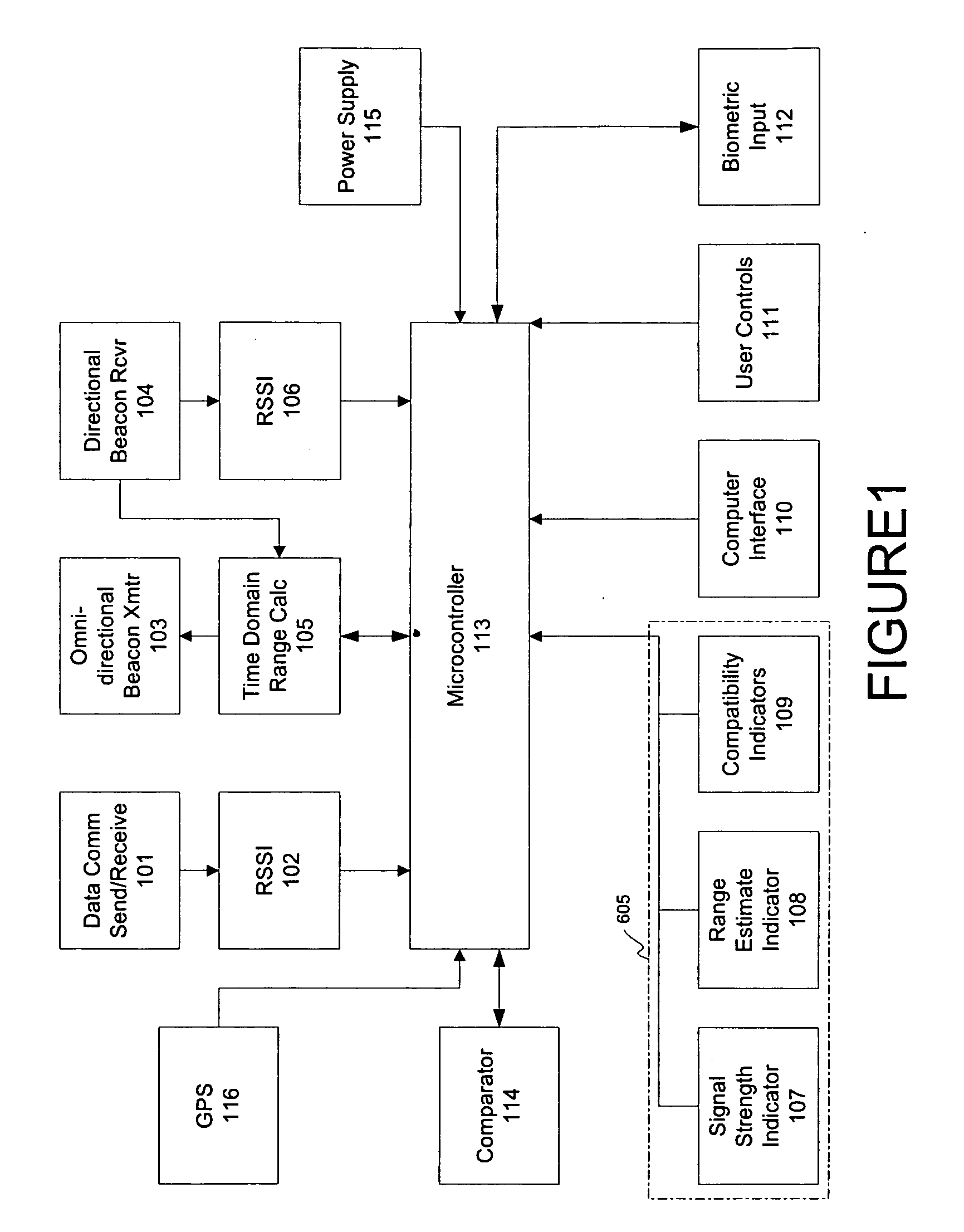
Portable wireless compatibility detection, location and communication device
A portable (e.g., watch-sized) wireless electronic device configurable to reflect the identity, preferences or characteristics of the user, and adapted to determine the nearby presence and location of a compatibly configured device includes a microcontroller, data communications subsystem configured to enable two way digital radio communication; a received signal strength indicator subsystem operably coupled to the data communications subsystem and configured to provides a micro-controller subsystem with information about the strength of received signals; a range estimate indicator subsystem operably coupled to the microcontroller and configured to display an estimate of the range to a target unit based on signal strength observed during a scan for the direction of maximum signal strength; a compatibility indicator subsystem operably coupled to the microcontroller and configured to provide an indication of a possible degree of compatibility of a user assigned to a opposing unit; a computer interface subsystem adapted to communicate with a user's computer; and a user control subsystem configured to enable user input.
Owner:CARSON DALE
System and method of improving sampling of WLAN packet information to improve estimates of doppler frequency of a WLAN positioning device
ActiveUS20080008120A1Enhanced informationIncrease frequencyNetwork topologiesPosition fixationReceived signal strength indicationComputer module
Systems and methods of improving sampling of WLAN packet information to improve estimates of Doppler frequency of a WLAN positioning device. A device estimates the position of itself. The device includes a WLAN radio module for receiving WLAN signals transmitted by WLAN APs in range of said device, extraction logic for extracting information from said received WLAN signals to identify the WLAN APs, and logic to cooperate with a WLAN-based positioning system to estimate the position of the device based at least in part on the extracted information identifying the WLAN APs in the range of said device. The WLAN radio module includes logic for measuring multiple received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values for sufficiently long WLAN packets to increase the sampled rate of RSSI of WLAN packets from WLAN APs and to thereby improve an estimate of the Doppler frequency of said device.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
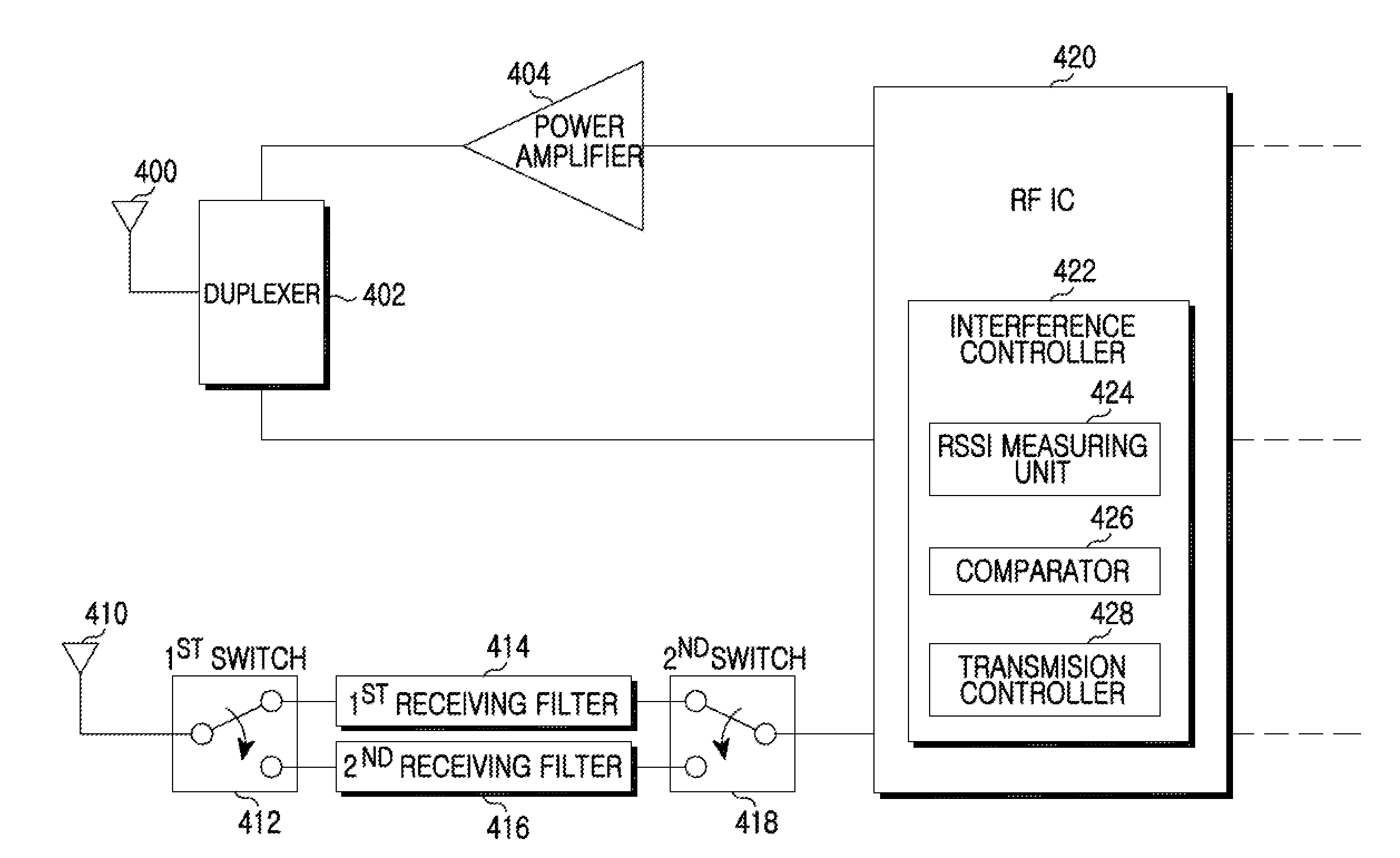
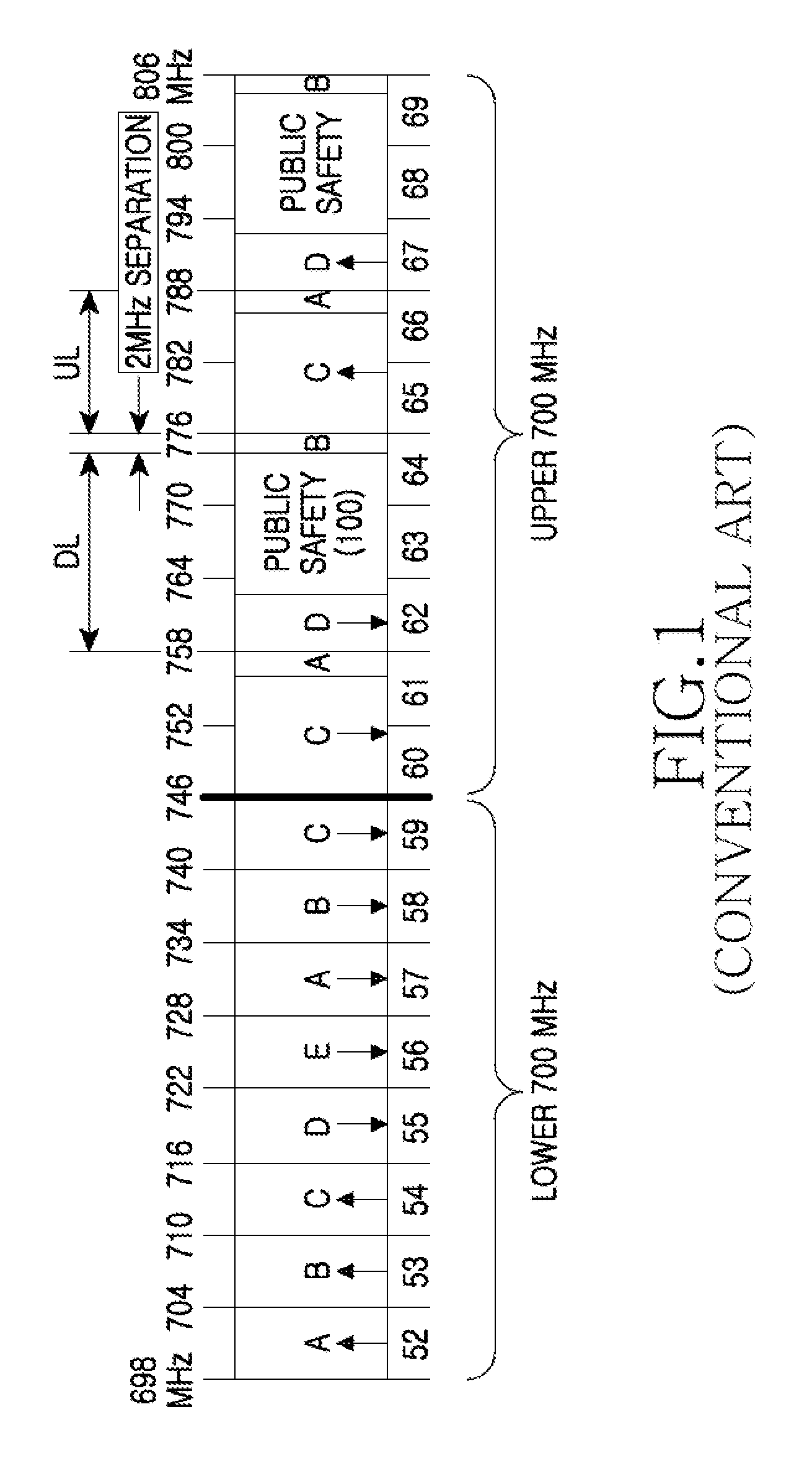
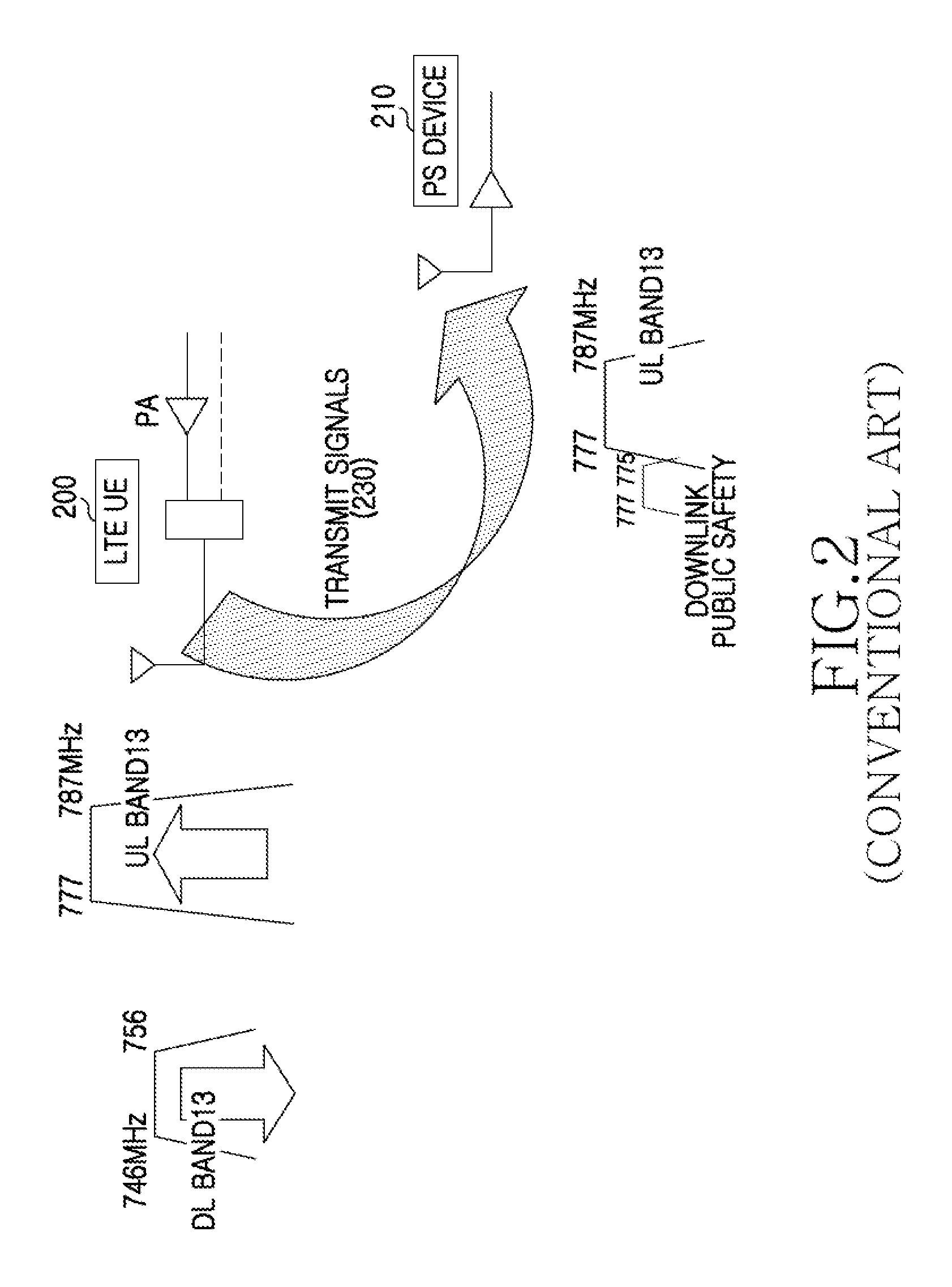
Apparatus and method for controlling interference in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20100128689A1Control interferenceCanceling DL interferenceTransmission monitoringOrthogonal multiplexCommunications systemReceived signal strength indication
An apparatus and a method for controlling interference in a wireless communication system are provided. The method includes receiving a signal of a DownLink (DL) frequency band that is adjacent to an UpLink (UL) frequency band supported by a User Equipment (UE), measuring a Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) of the DL frequency band signal, comparing the measured RSSI with a threshold value, and, if the measured RSSI is less than the threshold value, limiting UL transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
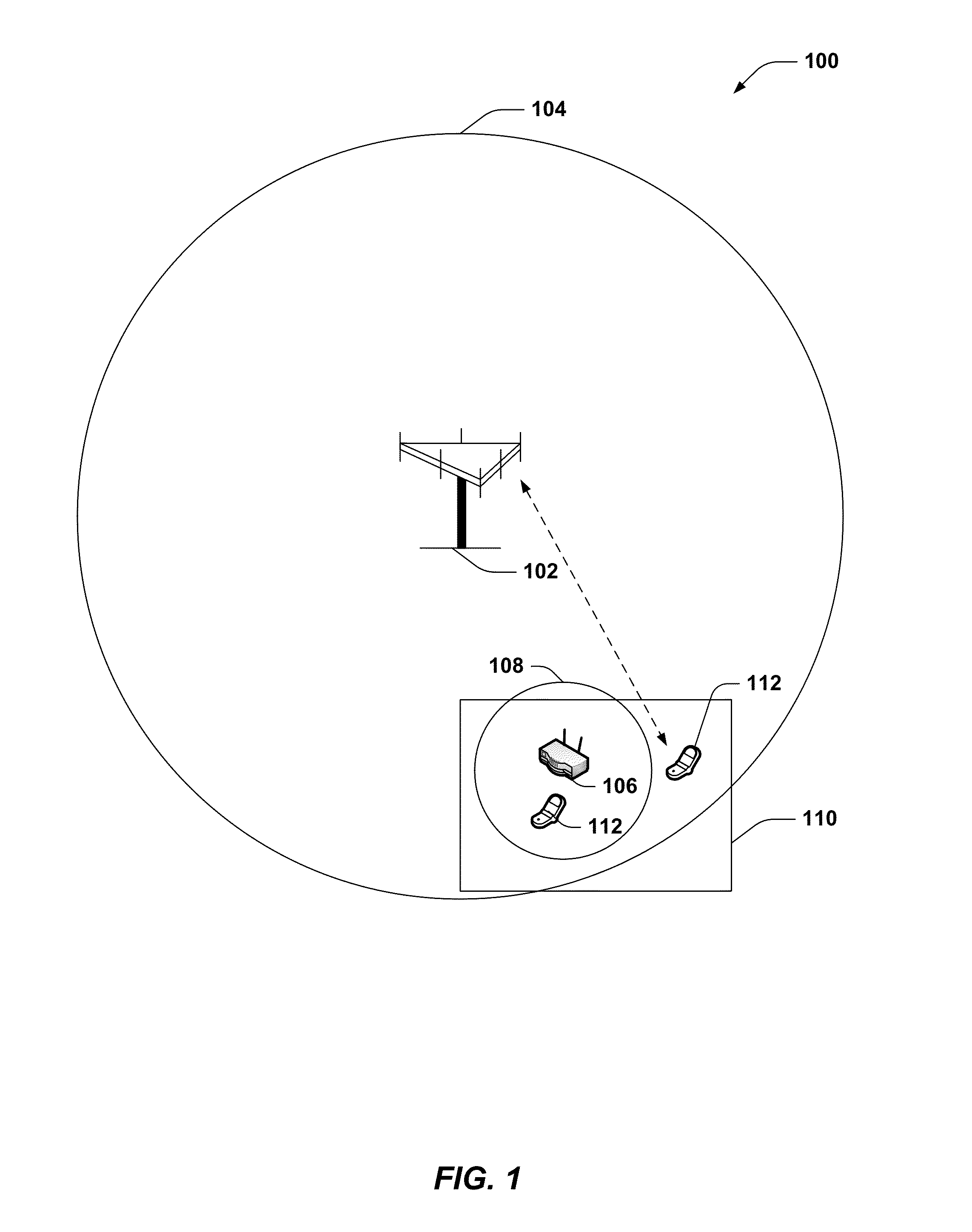
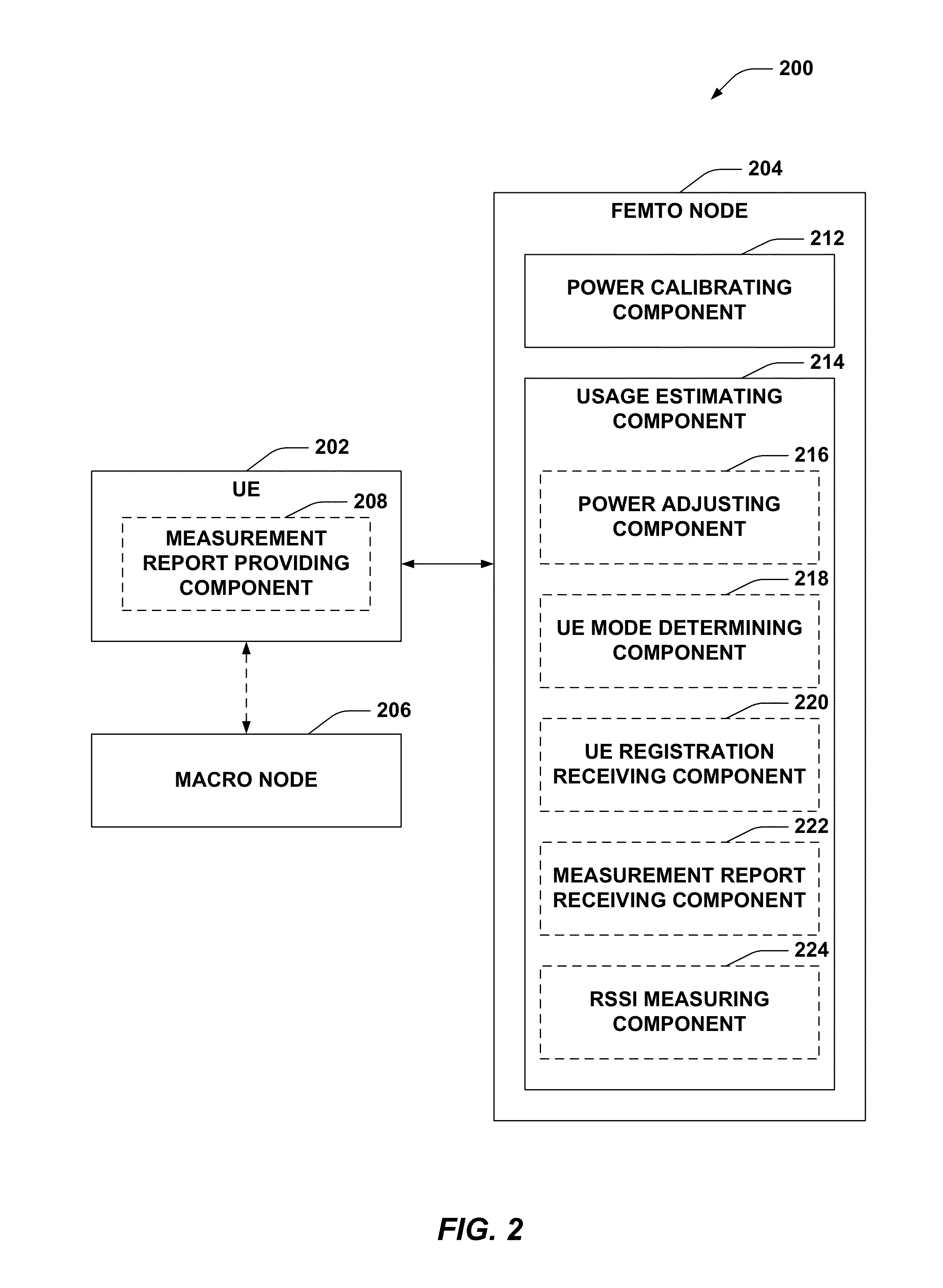
Method and apparatus for calibrating transmit power of a femto node
ActiveUS20130102309A1Increase coverageInterference minimizationTransmitters monitoringPower managementTransmitted powerReceived signal strength indication
Methods and apparatuses are provided that include calibrating transmit power of a femto node based on measuring one or more parameters related to usage of the femto node. The femto node can temporarily increase transmit power and analyze received measurement reports to determine a transmit power calibration. The femto node can additionally measure uplink received signal strength indicators over multiple time periods following handover of a user equipment (UE) to determine whether to increase transmit power to cover the UE.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
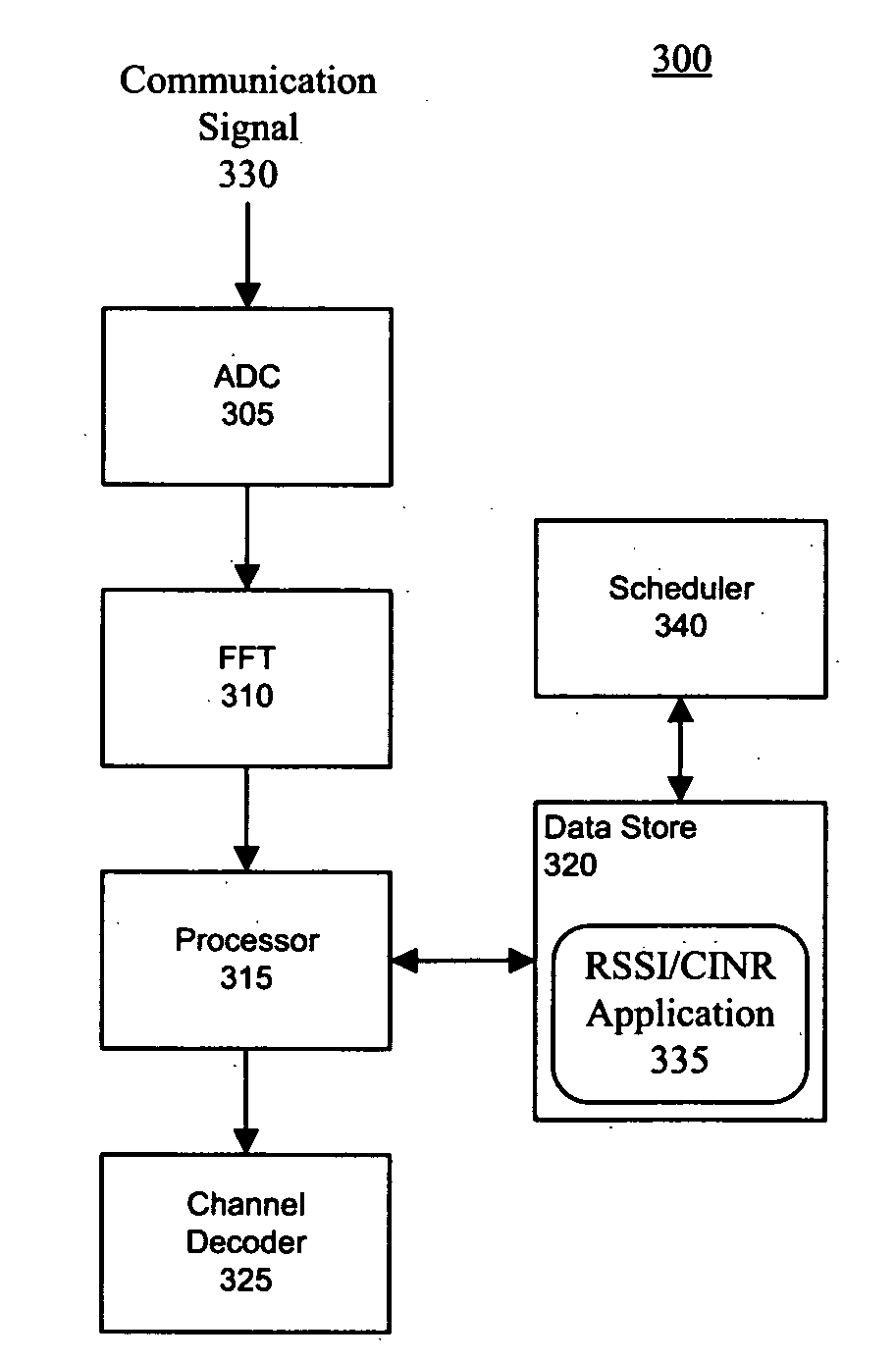
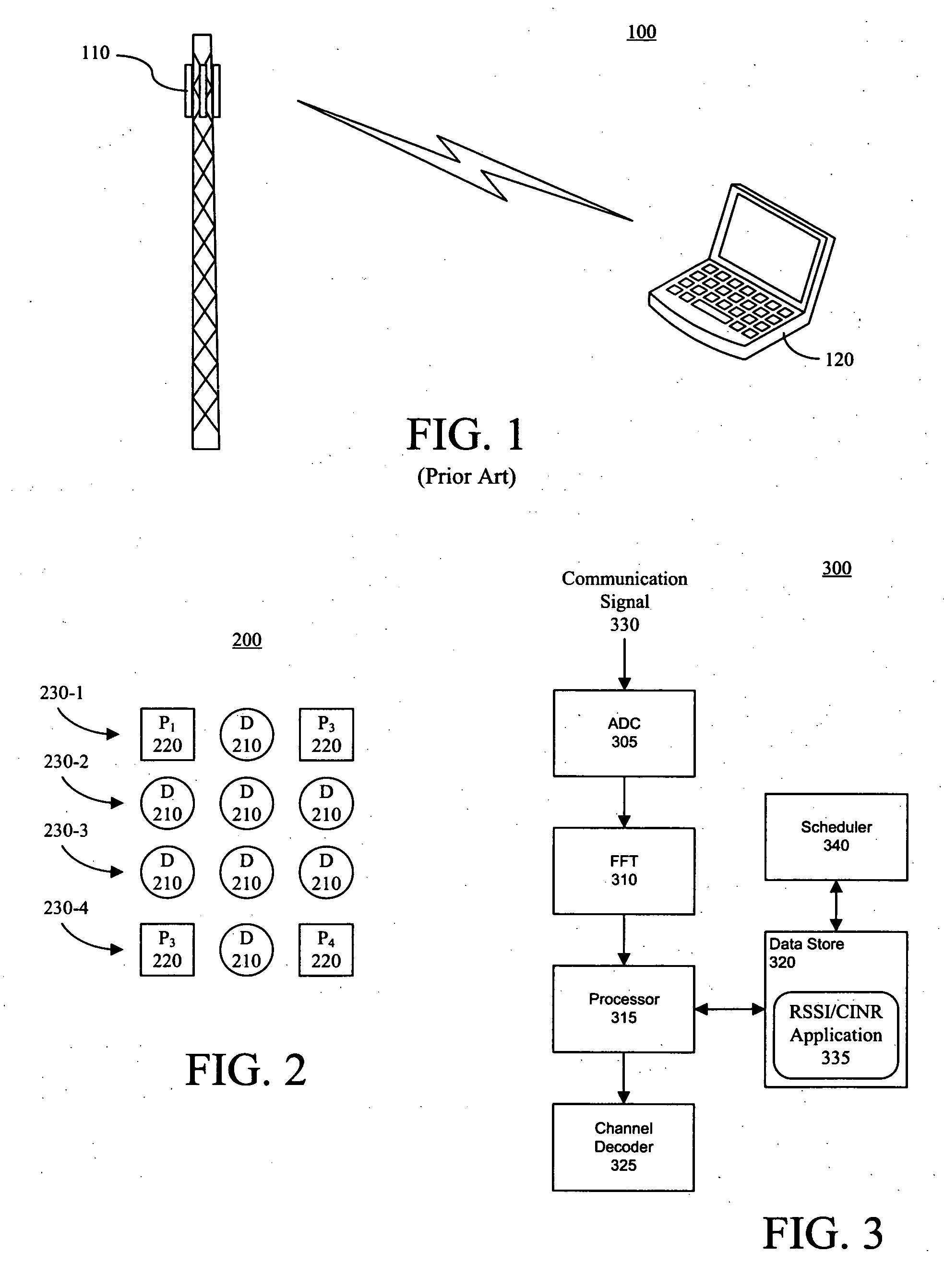
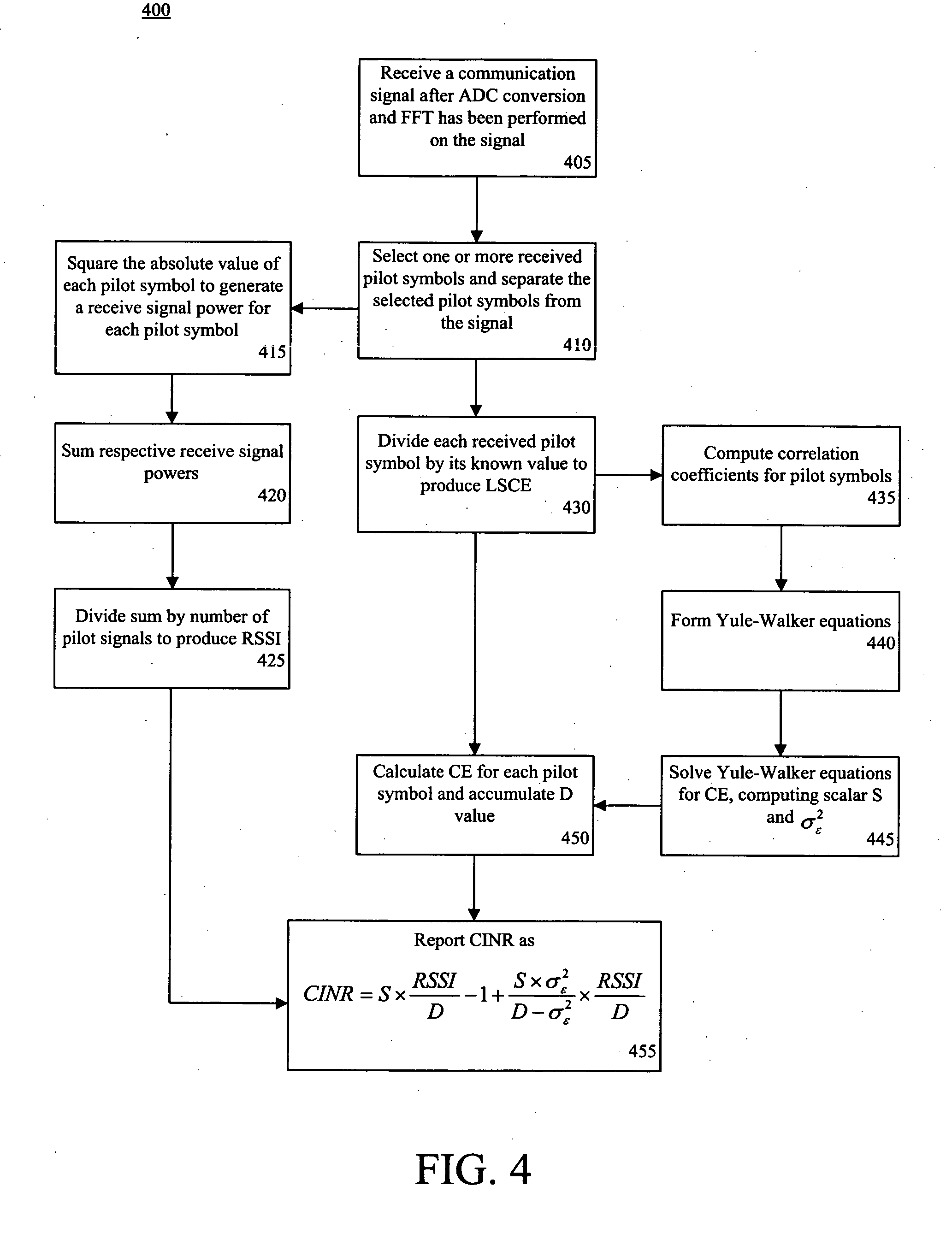
Estimation of CINR and RSSI in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20070293176A1Modulated-carrier systemsCriteria allocationCommunications systemReceived signal strength indication
A method for selecting at least one operating parameter of a communication system (100). The method can include determining a receive signal strength indicator (RSSI) for a communication signal (330). An intermediate value (D) for the communication signal can be determined based on, at least in part, a received value (ri) of at least one known datum, a predetermined value (pi) of the known datum and a channel estimate ({tilde over (h)}i). Further, a carrier to interference and noise ratio (CINR) can be estimated based on, at least in part, the RSSI and the intermediate value. The operating parameter can be selected based on, at least in part, the estimated CINR.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
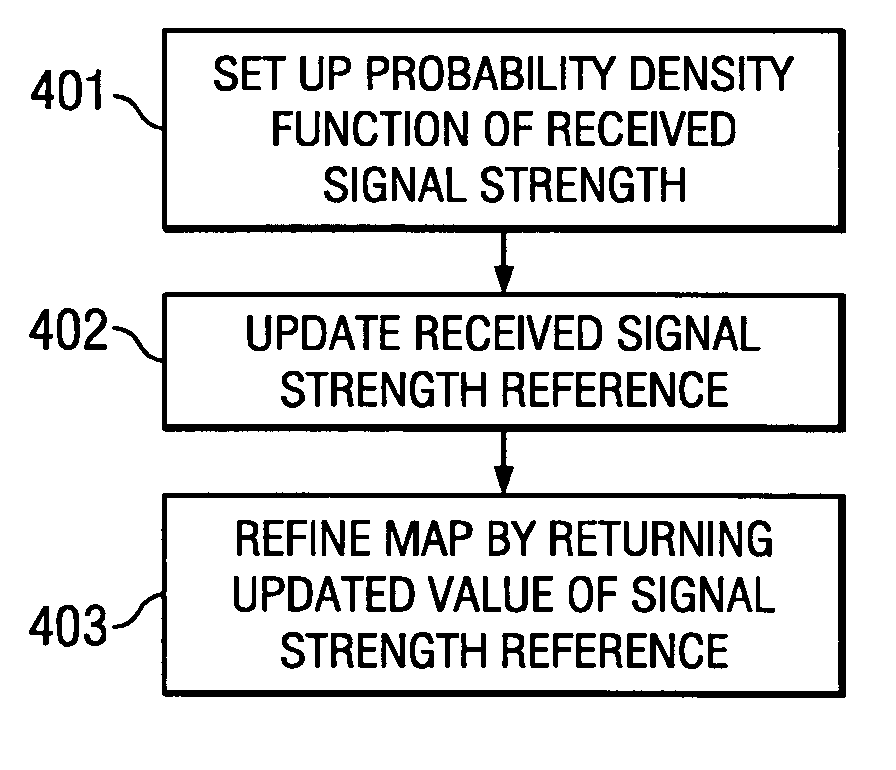
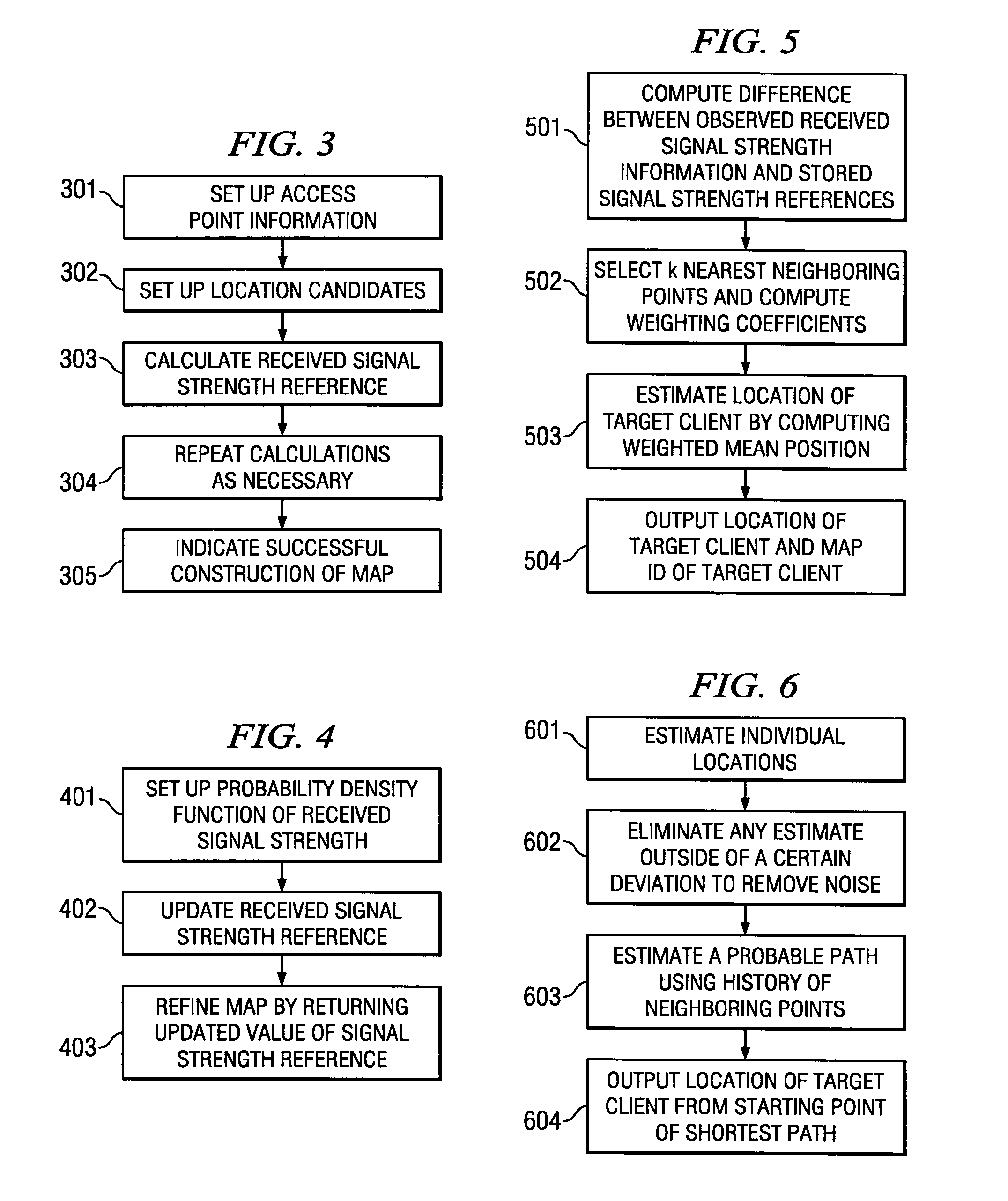
Location determination and location tracking in wireless networks
ActiveUS7359718B2Improve accuracyReduce eliminateDigital data processing detailsSpecial service for subscribersWireless mesh networkLocation tracking
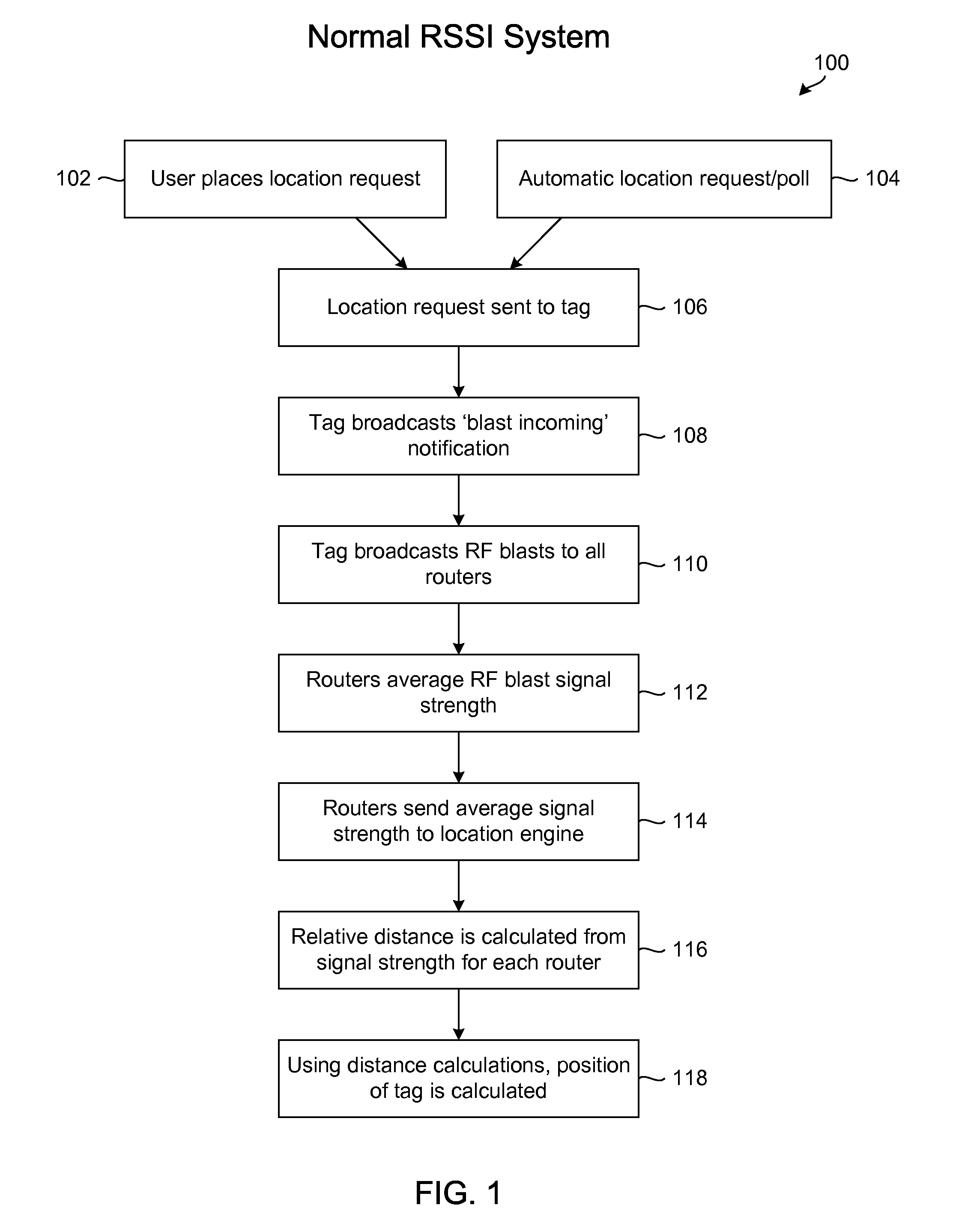
The present invention is directed to systems and methods which monitor a network environment, collect client information available online, and refine location determinations of individual clients based on observed information as well as online information. More particularly, the present invention is directed to systems and methods which monitor the wireless network, collect online receive signal strength indicator (RSSI) information observations from client users, without requiring knowledge of those clients' locations. The present invention is additionally directed to systems and methods to enhance the accuracy of the location determinations in a network, based on observed client information such as, for example, signal strength references.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
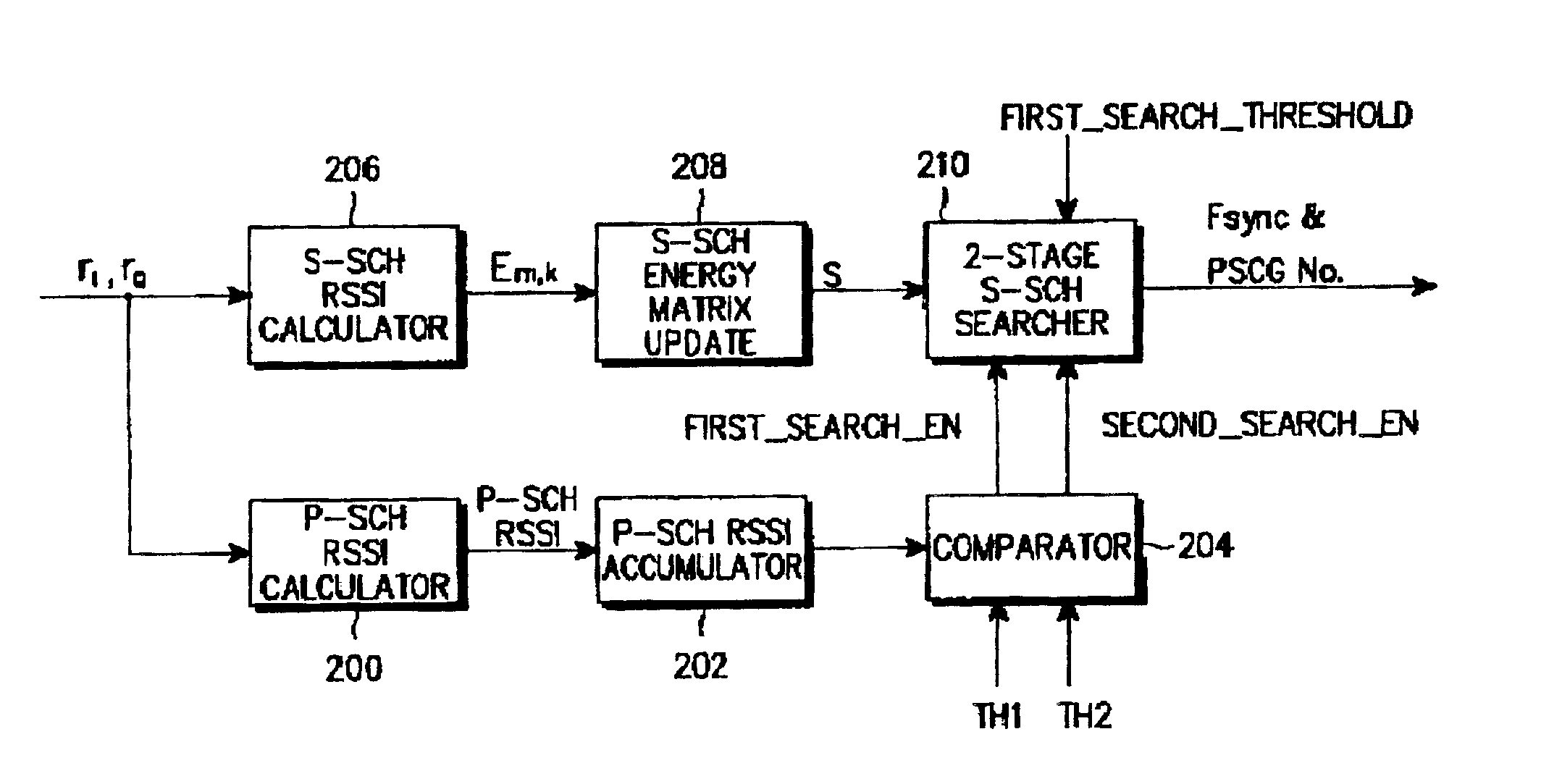
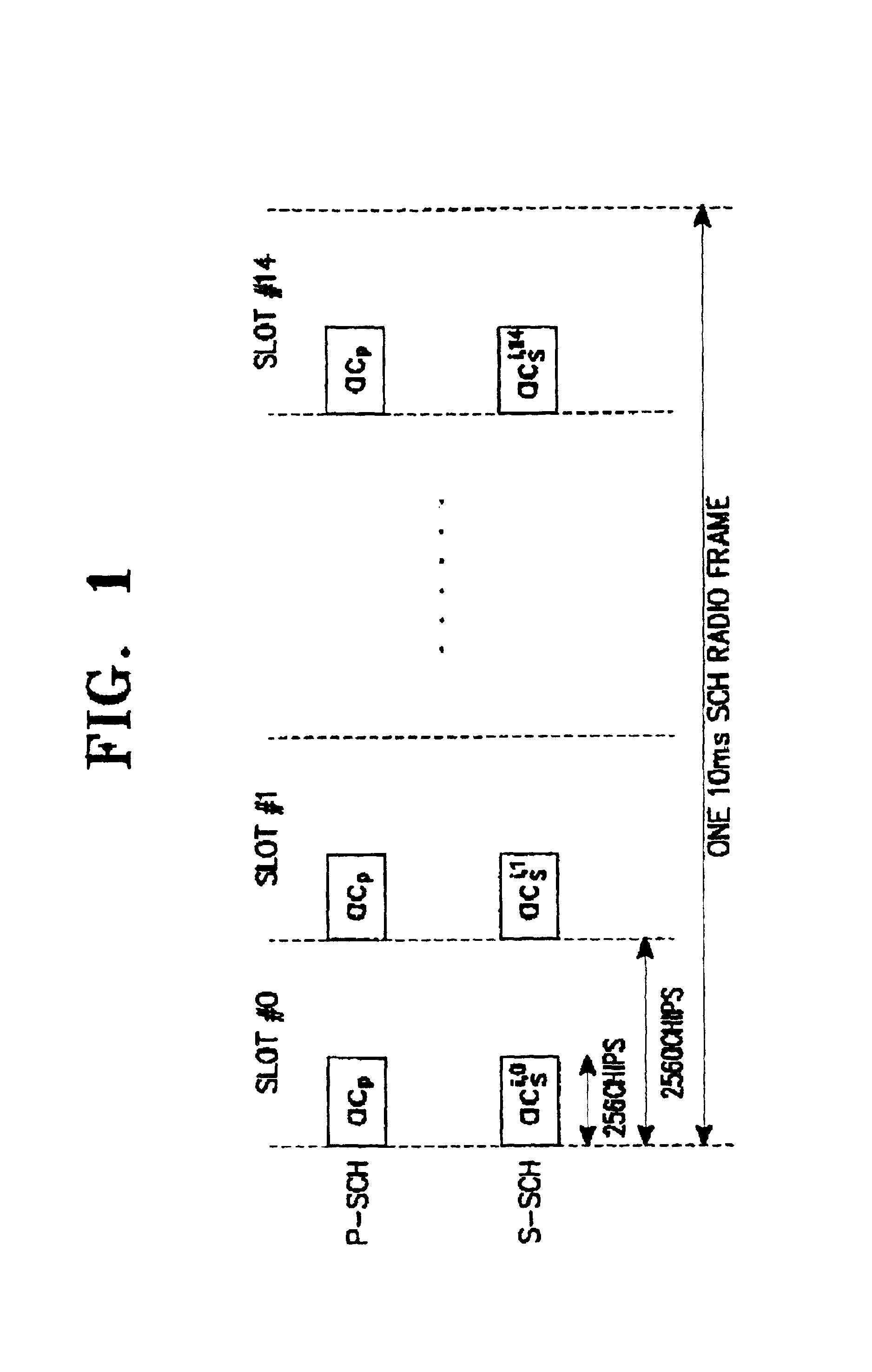
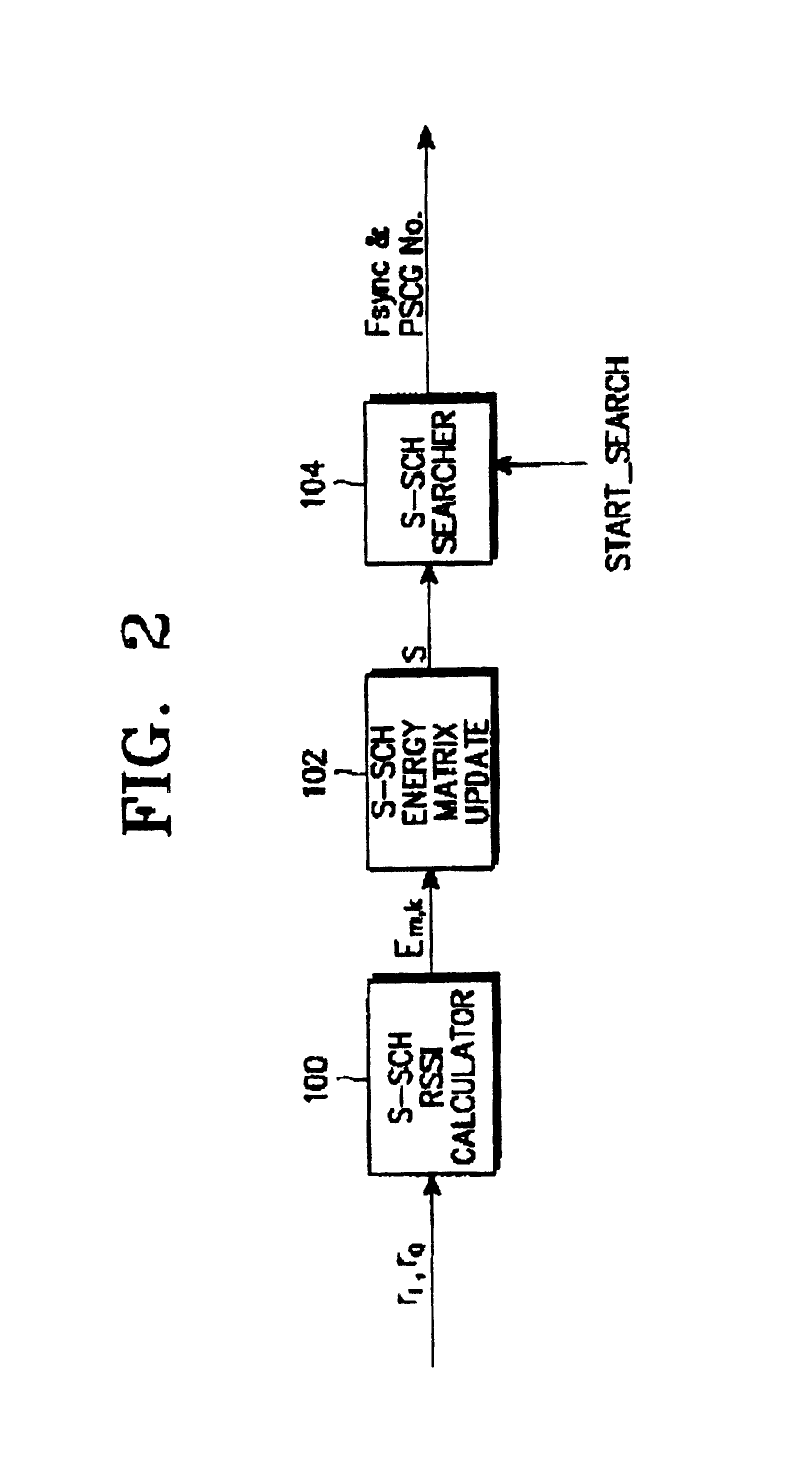
Apparatus and method for searching a base station in an asynchronous mobile communications system
InactiveUS6894996B2Improve search speedReduce search timeAssess restrictionTime-division multiplexCommunications systemSignal on
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for searching a base station in a mobile communications system, in which a mobile station acquires slot timing synchronization from a first signal on a primary sync channel (P-SCH) out of the P-SCH and a secondary sync channel (S-SCH) used for base station search, acquires frame timing synchronization (Fsync) from a second signal on the S-SCH, and determines a primary scrambling code group (PSCG) corresponding to the scrambling codes used by the respective base stations. The method comprises calculating and accumulating P-SCH RSSI values from the first signal at every slot and comparing the accumulated P-SCH RSSI values with first and second accumulation thresholds and providing the first and second search commands; and calculating S-SCH channel received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values from the second signal at every slot in one frame, and updating S-SCH RSSI values corresponding to the one frame as energy matrix values; calculating energy hypotheses corresponding to the energy matrix values using the energy matrix values and a predetermined secondary sync code (SSC) table in response to a first search command, and determining energy hypotheses having a value higher than a predetermined threshold as passed hypotheses; and calculating energy values for the passed hypotheses using the determined passed hypotheses and the SSC table in response to a second search command, and determining an energy hypothesis having a maximum energy as the Fsync and the PSCG.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
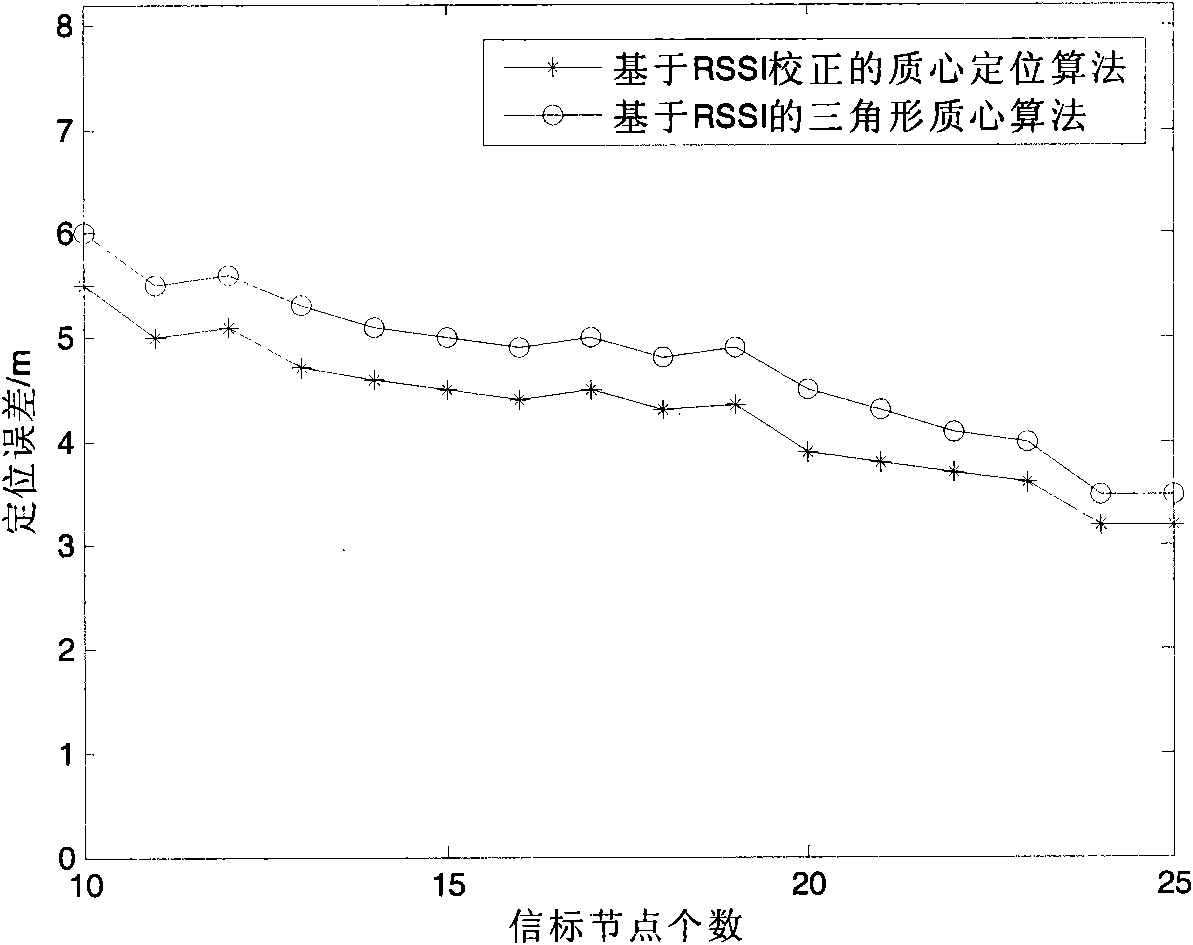
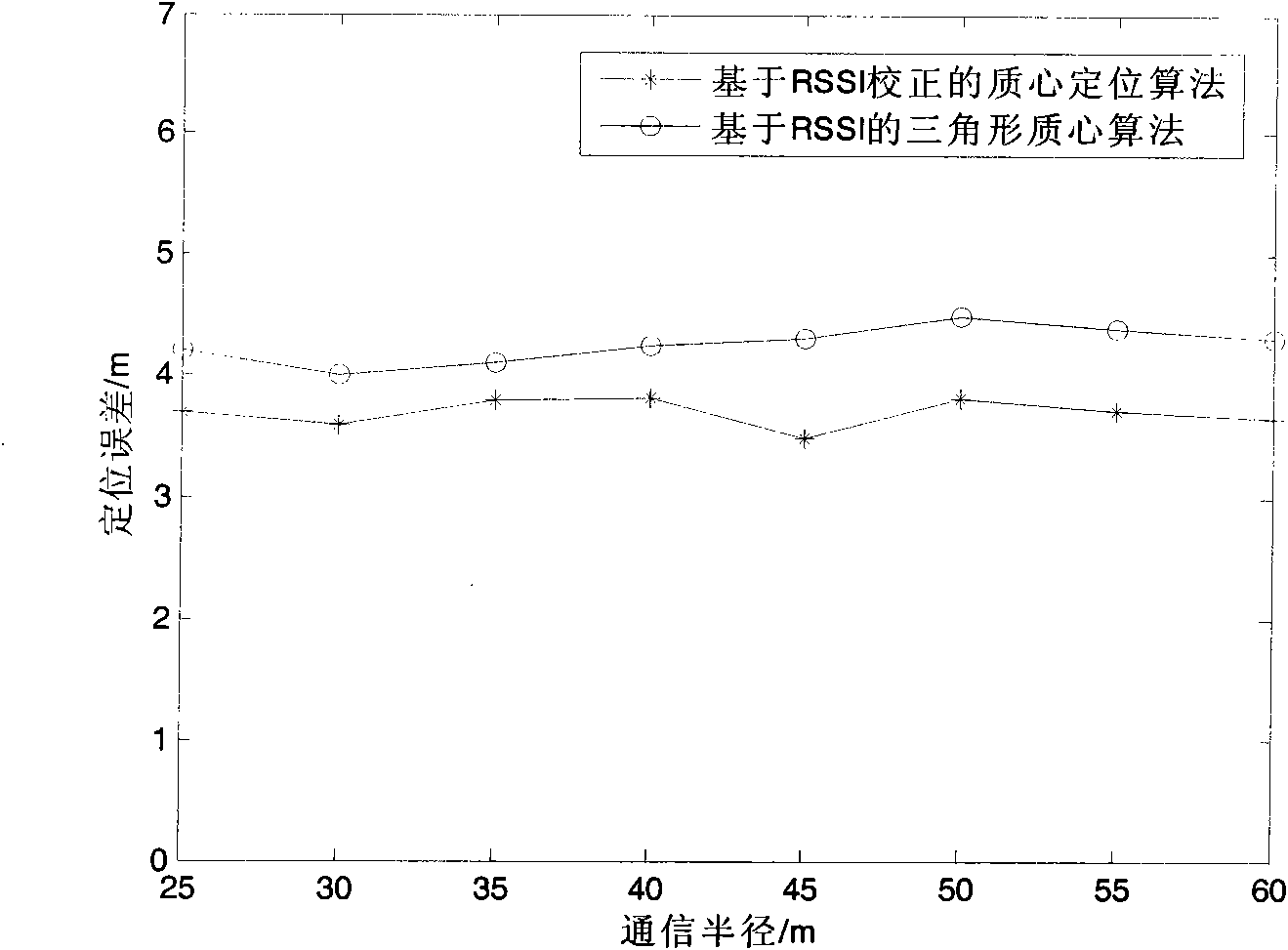
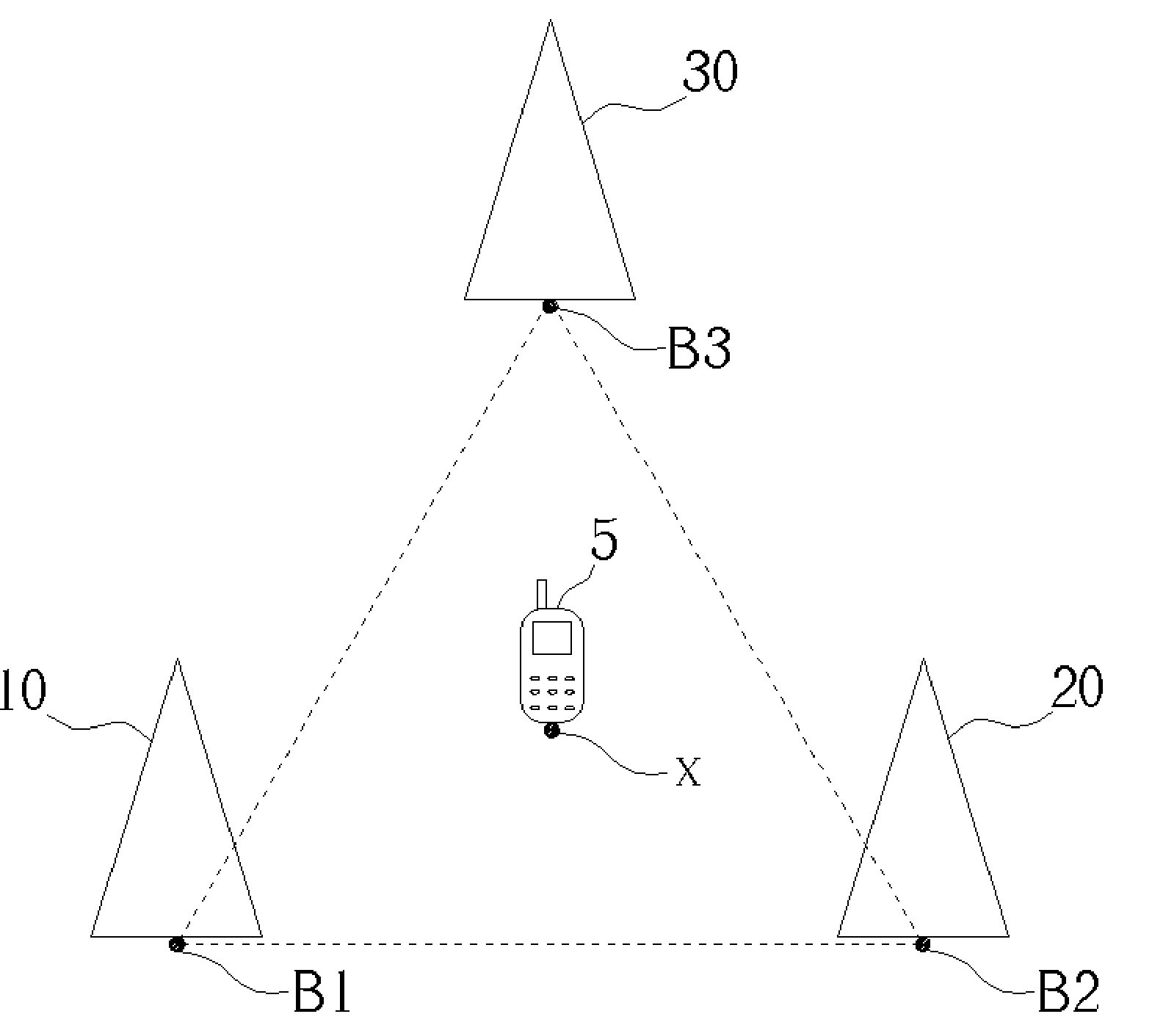
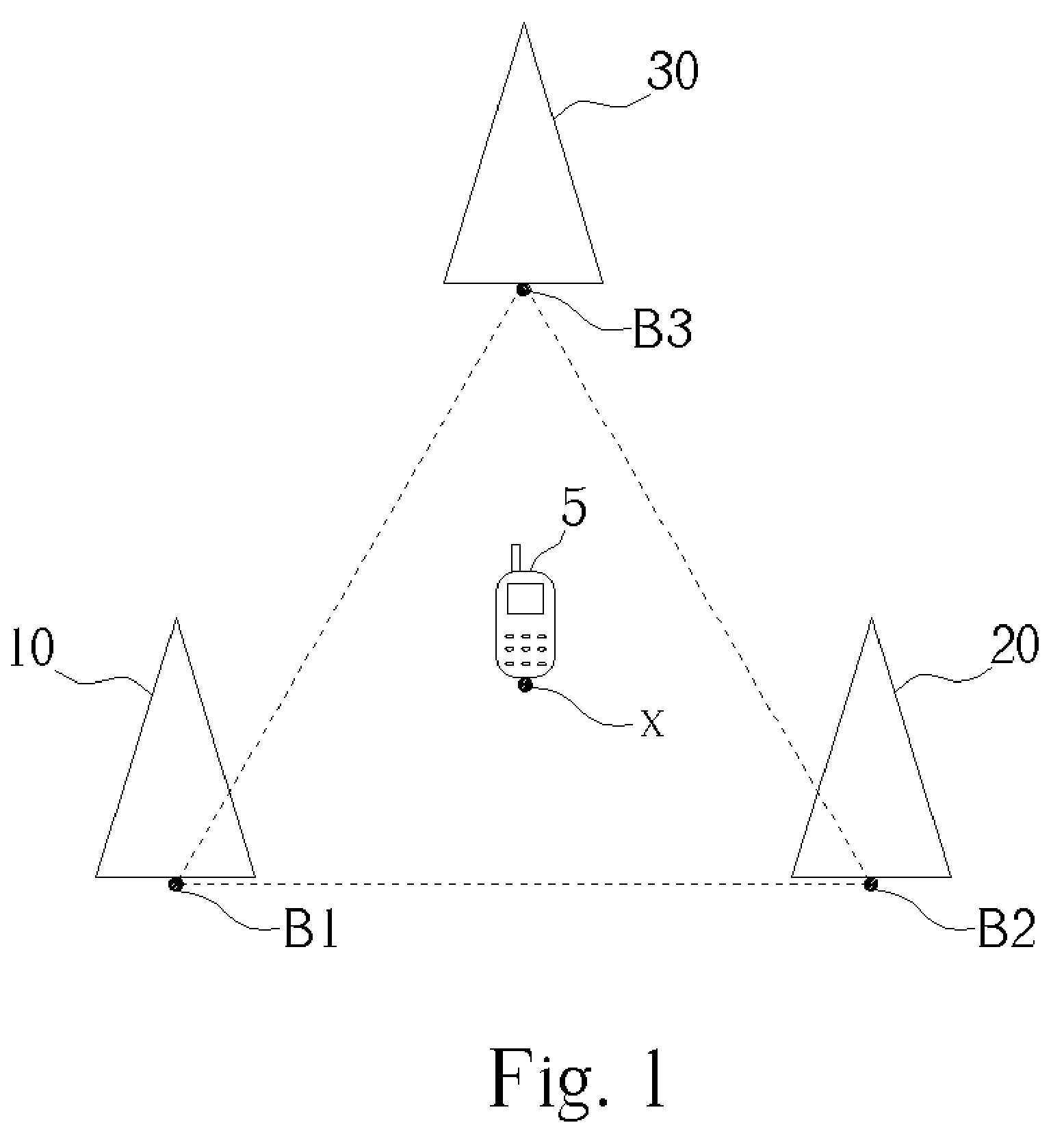
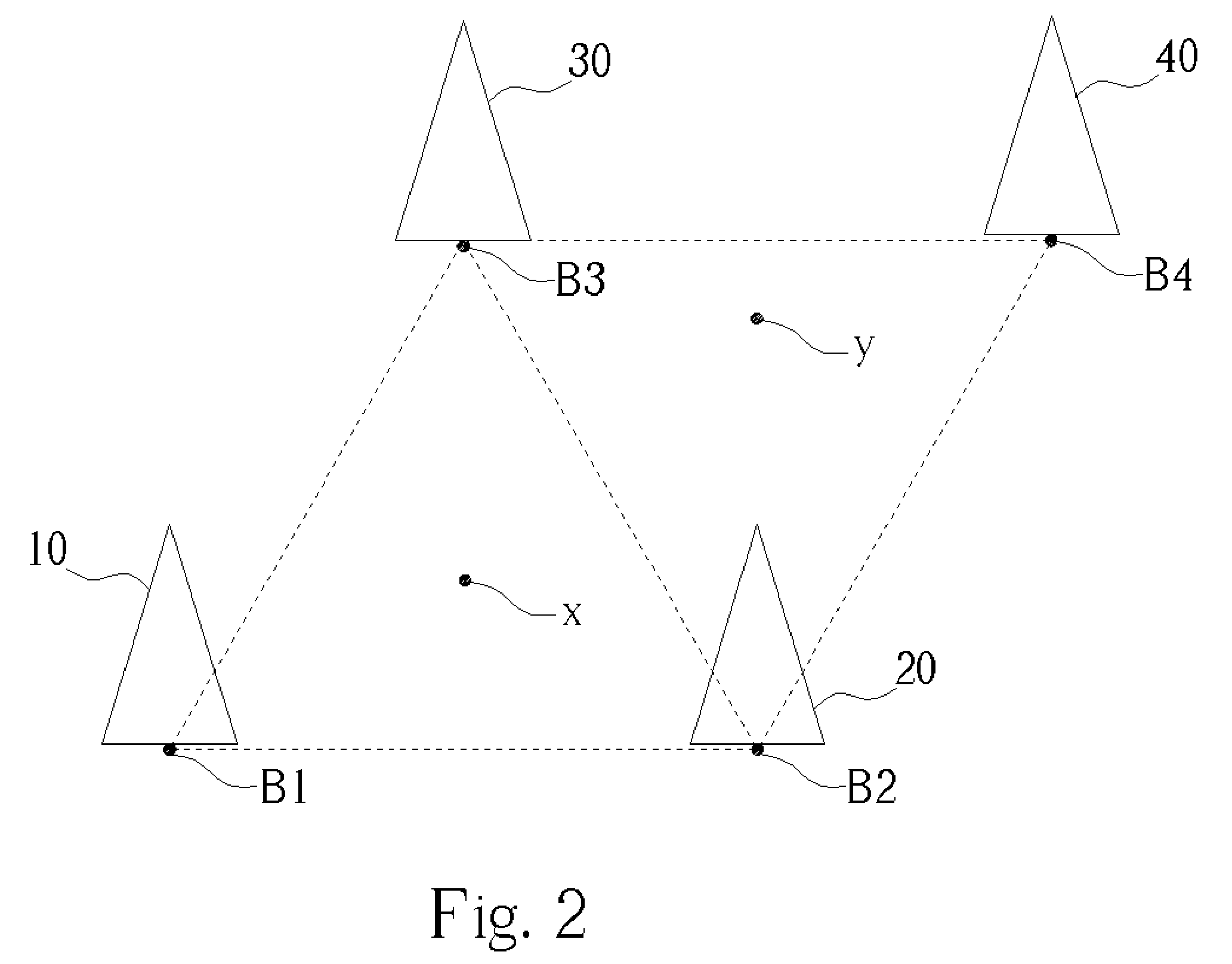
Centroid location algorithm based on RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indication) correction for wireless sensor network
InactiveCN102123495AReduce measurement errorHigh positioning accuracyTransmission monitoringWireless communicationObservational errorWireless mesh network
The invention discloses a centroid location algorithm based on RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indication) correction for a wireless sensor network, and the centroid location algorithm comprises: (1) anchor nodes periodically broadcast information around, wherein the information contains respective node ID (identity) and coordinates; and ordinary nodes average the RSSI of the same anchor node after receiving the information; (2) the ordinary nodes do not receive new information any more after collecting the information of n anchor nodes, wherein n is greater than 3 and less than or equal to 100; the ordinary nodes sort the anchor nodes according to the RSSI from strong to weak and establish mapping of the RSSI value and the distance from the nodes to the anchor nodes; (3) the anchor nodes with the RSSI value greater than or equal to minus 93dbm and less than or equal to minus 113dbm is selected for self-location calculation; and (4) the calculated unknown node coordinate set is aggregated and averaged to obtain the unknown node coordinates. In the invention, the point-to-point distance between the nodes is measured by correcting an RSSI ranging technology, and a triangle centroid location algorithm is adopted for location, thus the measurement error of the RSSI is reduced. Compared with the triangle centroid location algorithm based on the RSSI, the centroid location algorithm provided by the invention has the advantage that the location accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
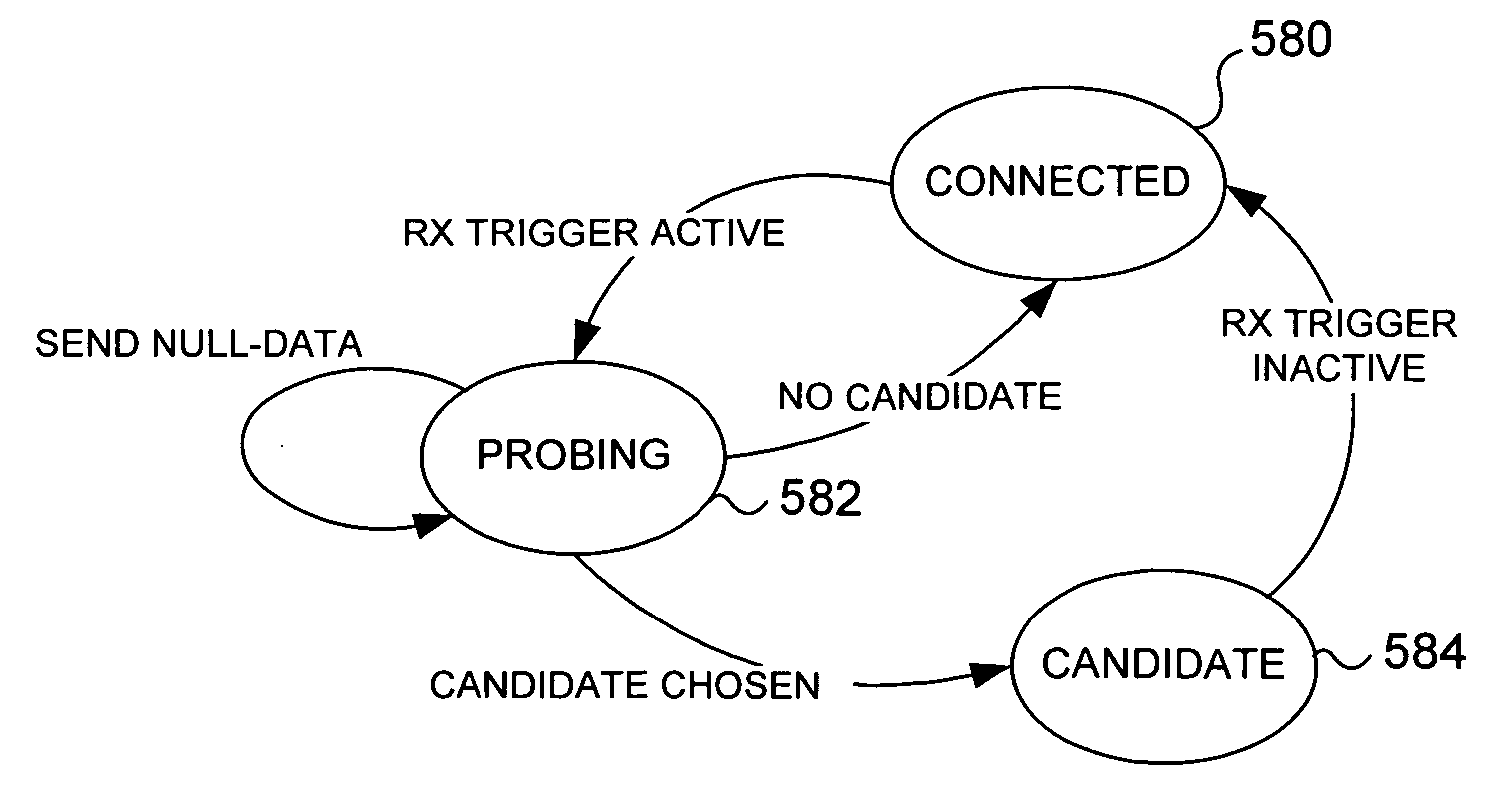
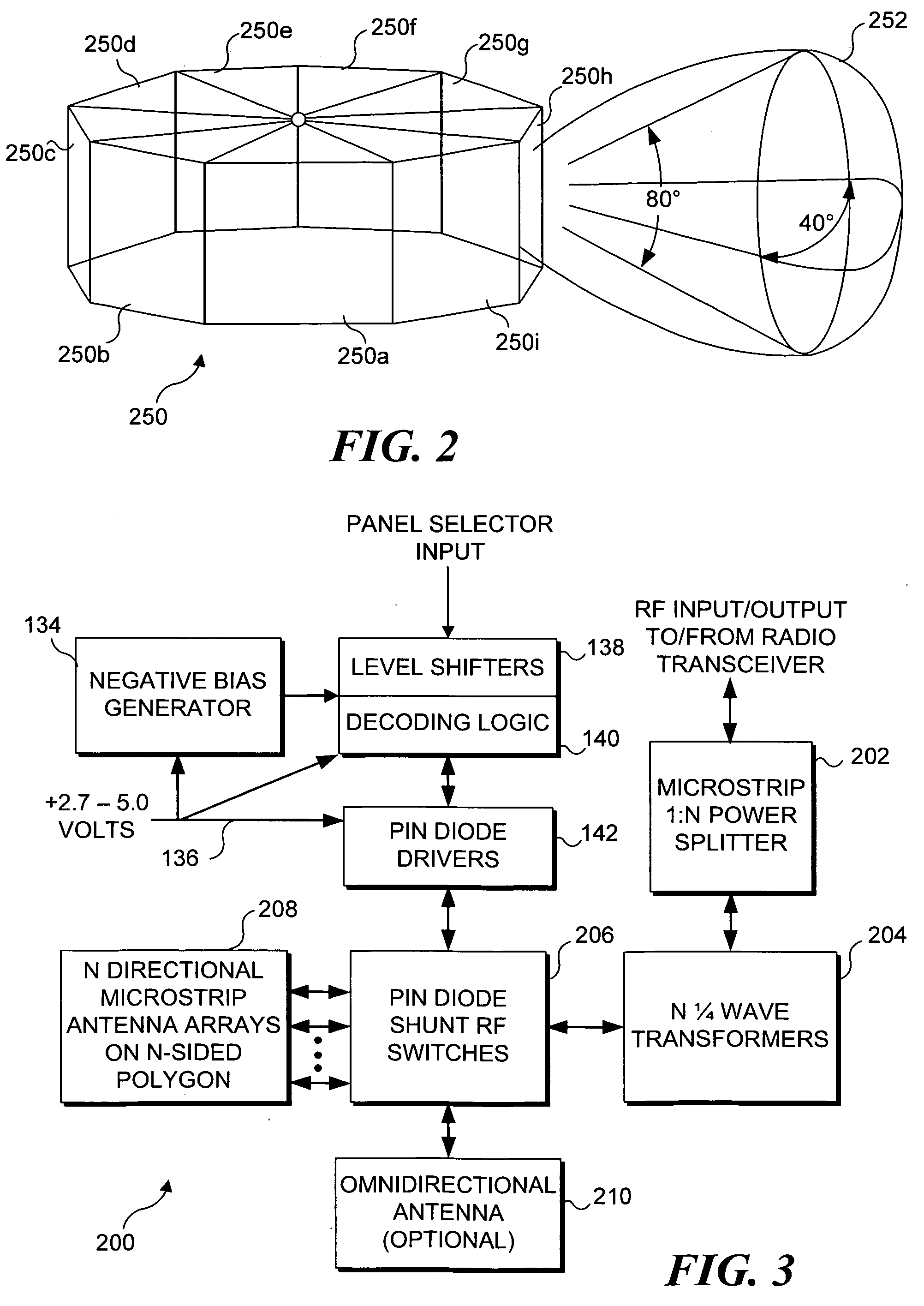
Control of a multi-sectored antenna system to improve channel efficiency
InactiveUS20060171357A1Increase data rateAchieve benefitsAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentOmnidirectional antennaSignal quality
A wireless device is coupled to a multi-sector antenna that includes a plurality of different sectors, any of which can be activated to transmit and receive in a desired direction specific to that sector. Optionally, an omnidirectional antenna is included for initially establishing a wireless connection with another wireless device, such as an access point. A parameter indicative of signal quality, such as throughput or received signal strength indication (RSSI) is determined by polling with each antenna sector to establish a prioritized candidate list. If a receive Trigger becomes active in response to a parameter falling below a threshold level, a new candidate sector is selected from the current list based upon a next-best signal quality. The directionality of the multi-sector antenna provides a substantially higher data rate compared to that of the conventional omnidirectional antenna.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
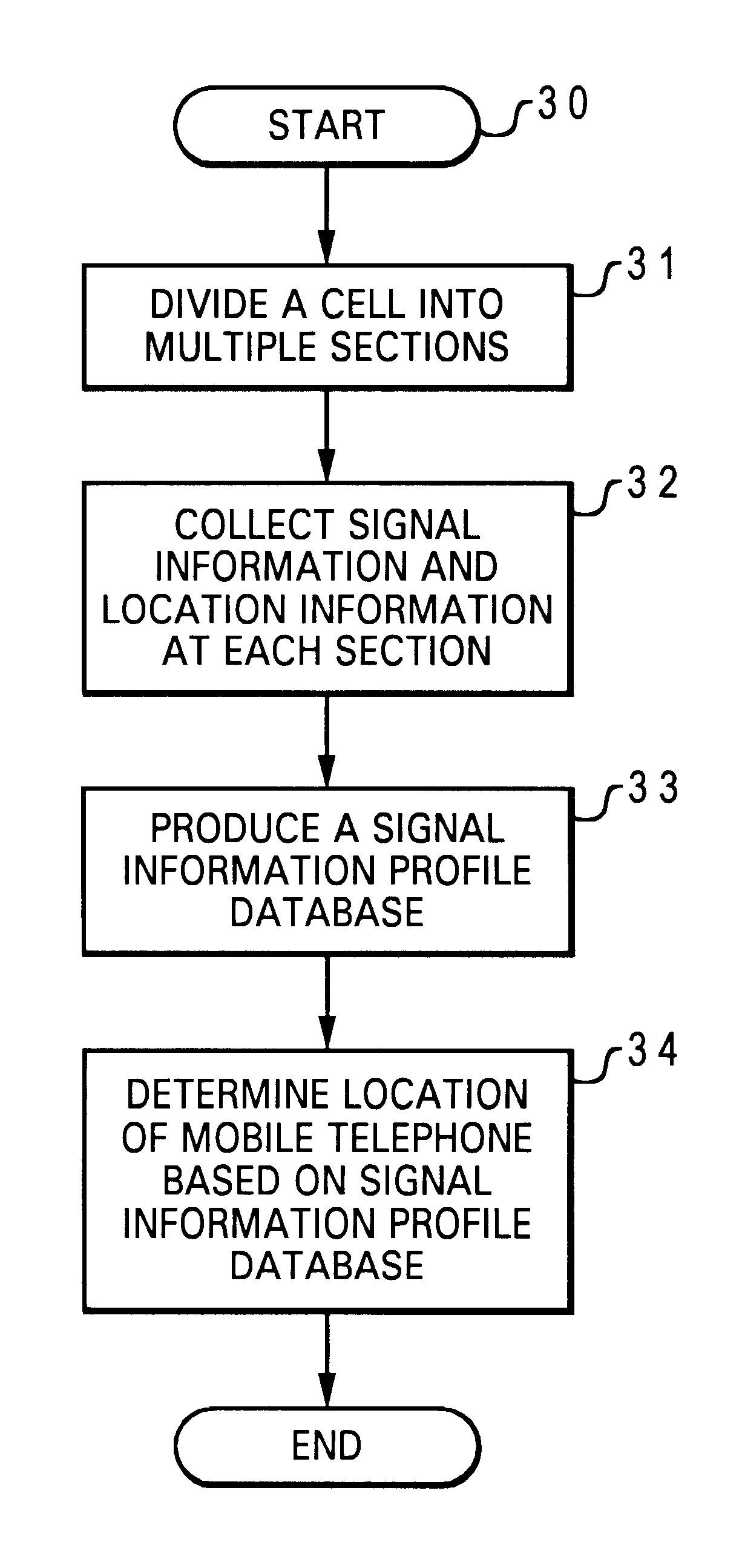
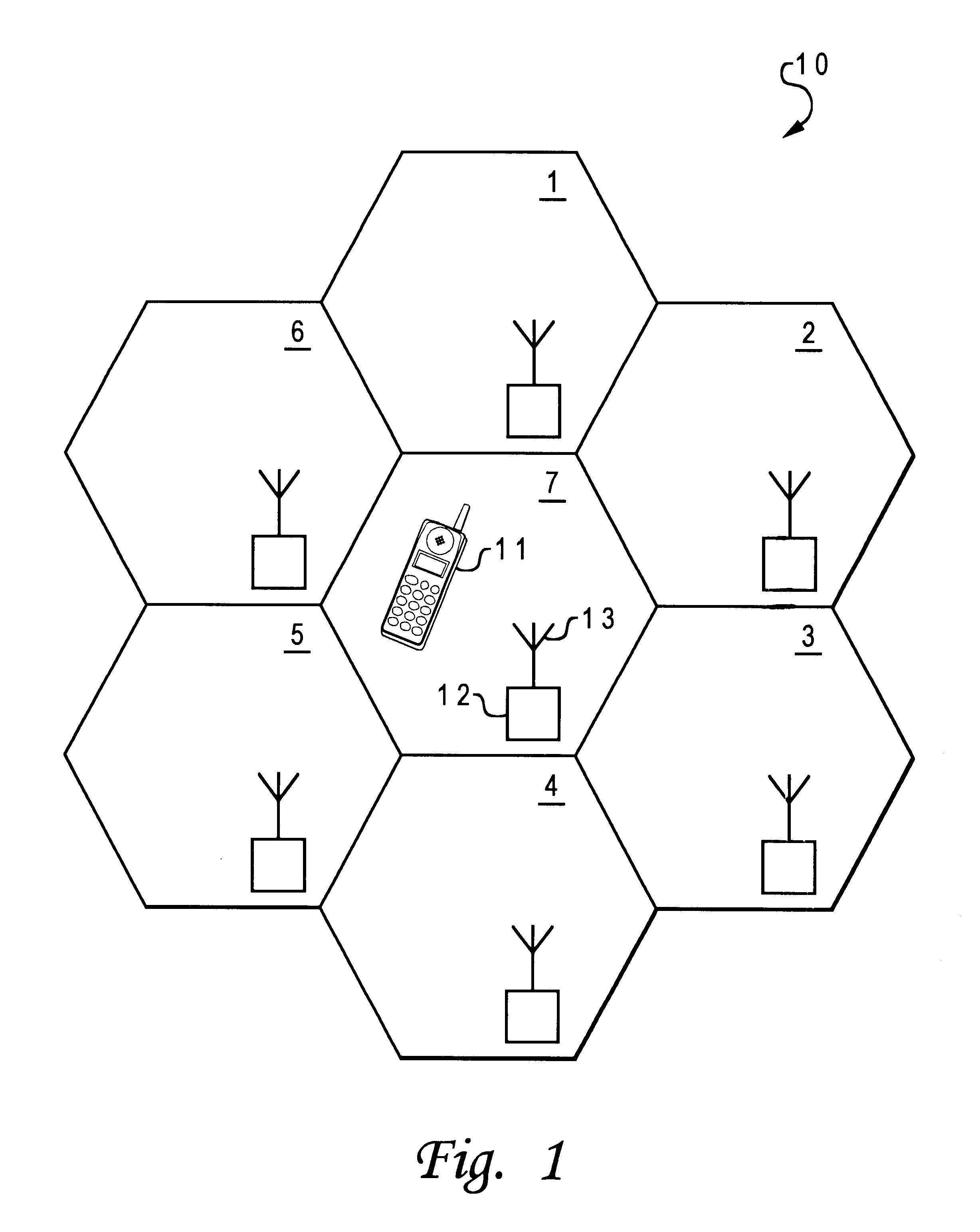
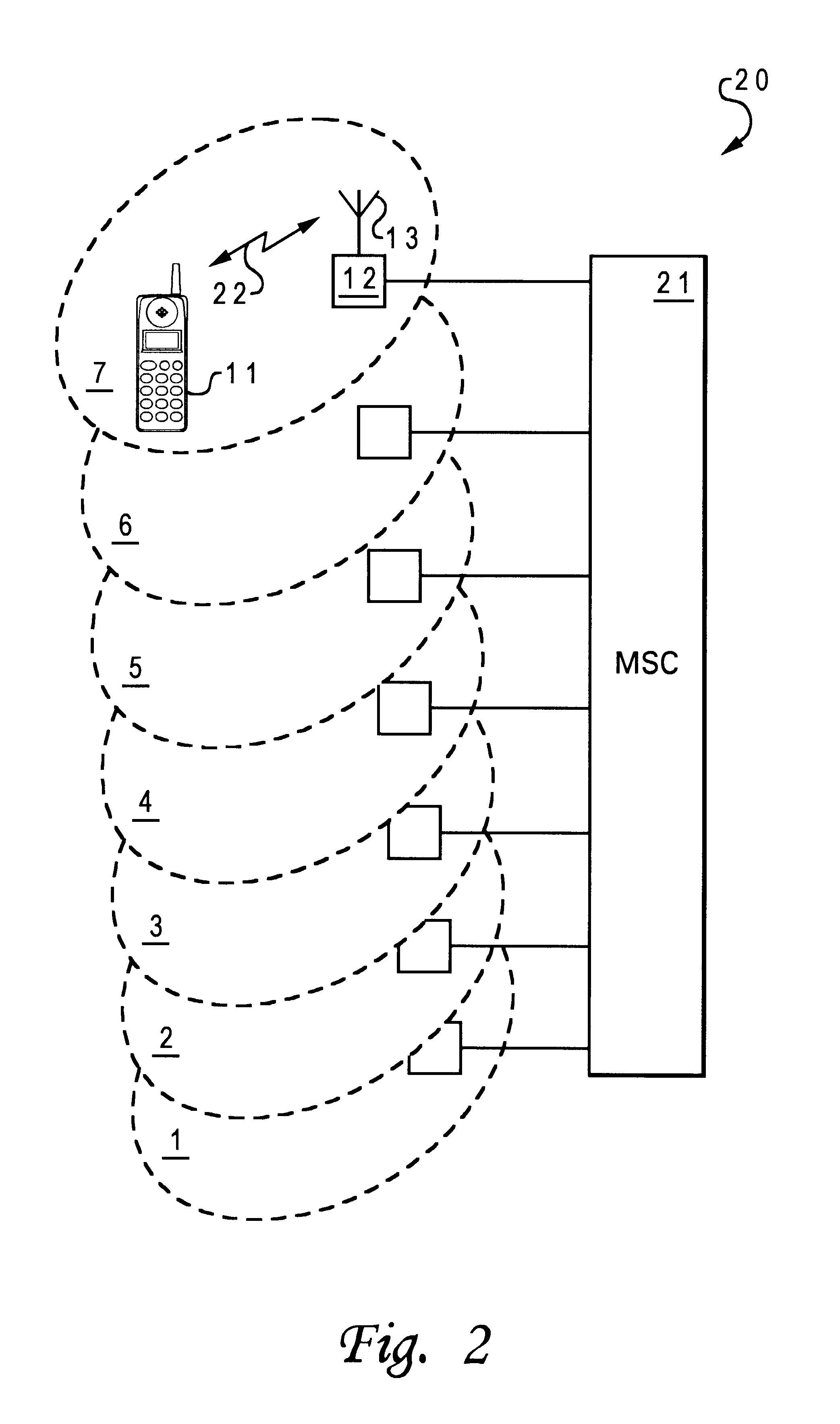
Method and system for locating a mobile telephone within a mobile telephone communication network
InactiveUS6799046B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationReceived signal strength indicationImproved method
An improved method for locating a mobile telephone within a cellular telephone communication network is disclosed. The mobile telephone communication network has multiple cells, with each of the cells having a base station coupled to at least one antenna. A cell is initially divided into a number of sections. A location information and a signal information, such as a received signal strength indication, is then collected at each of the sections within the cell. The collected location information and signal information are subsequently processed into a signal information profile database. Utilizing the signal information profile database, the section within the cell at which a mobile telephone is located can be determined.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
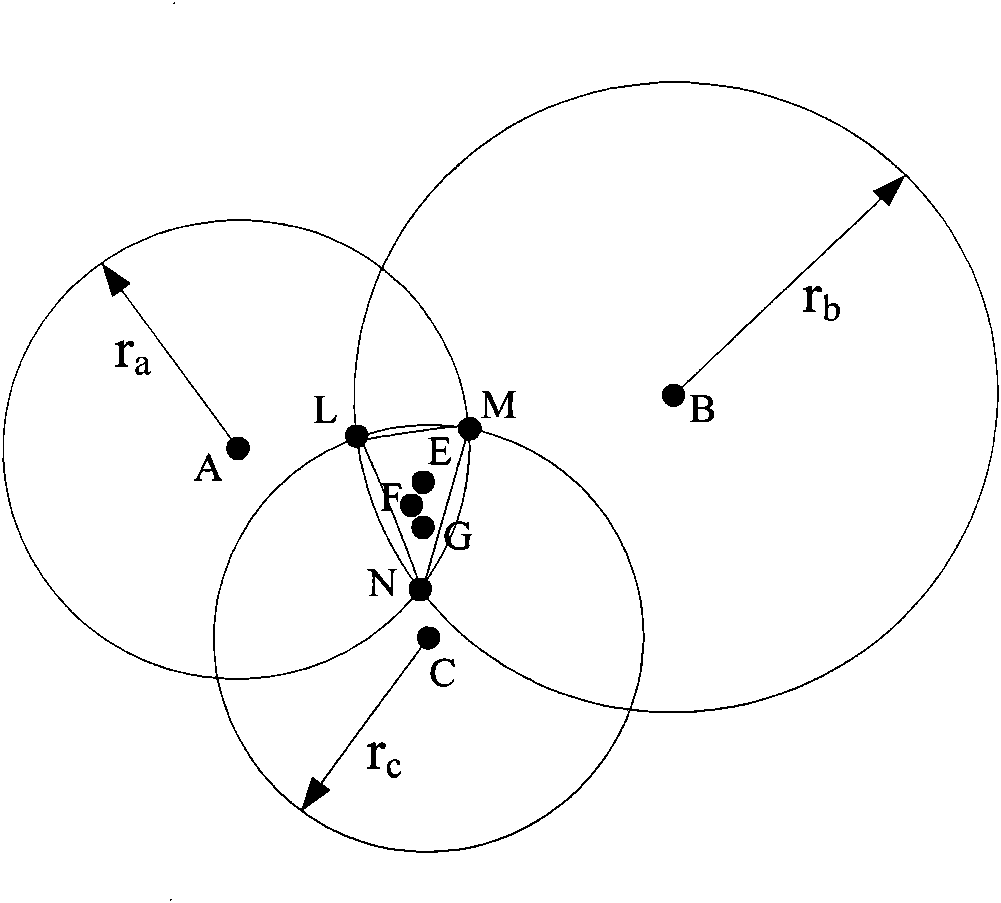
Method for using base station power measurements to detect position of mobile stations
InactiveUS20050227703A1Satellite radio beaconingTransmissionReceived signal strength indicationMobile station
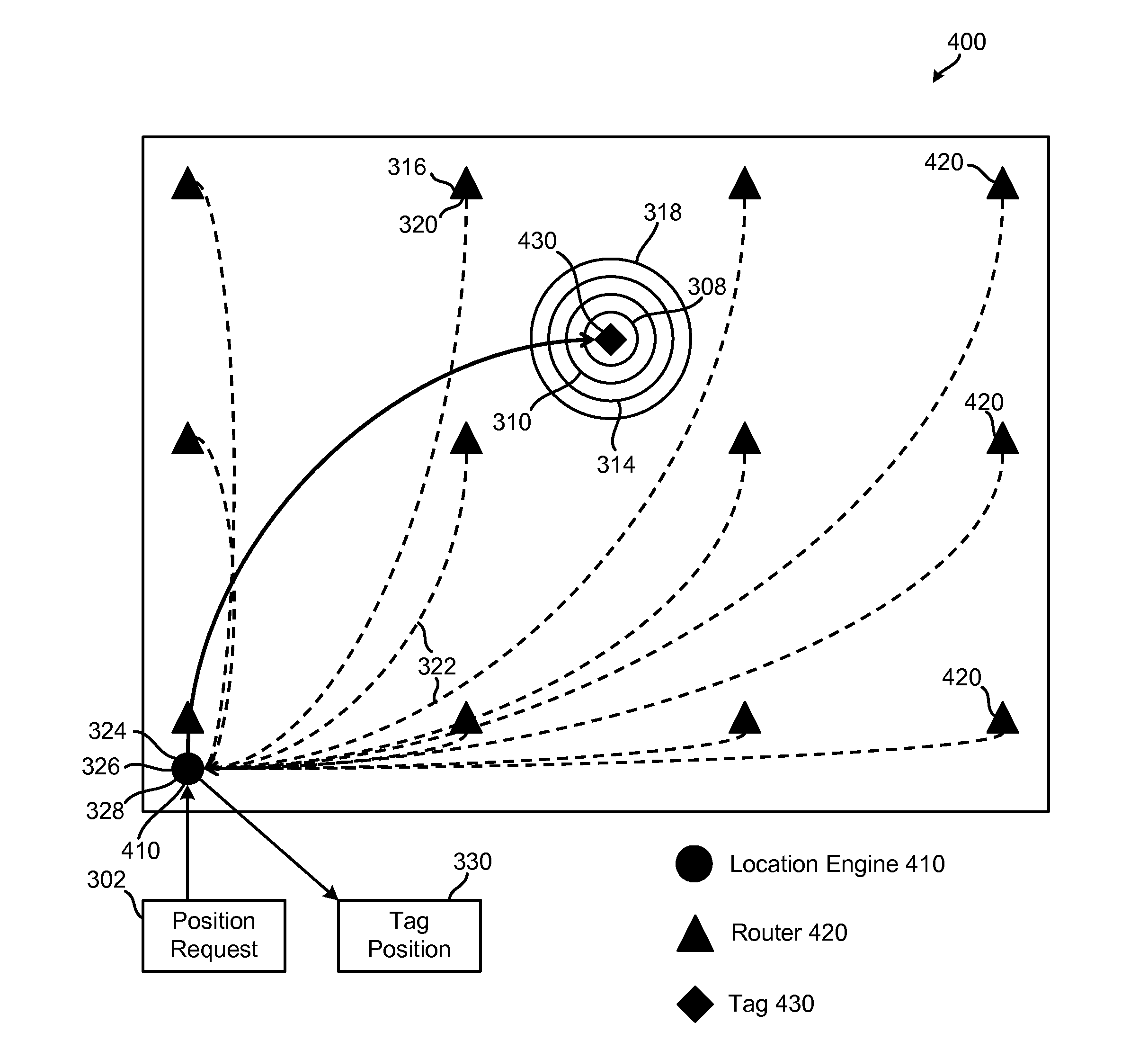
A method of using power measurements from base stations to calculate position of a mobile station. The method includes providing position coordinates for a plurality of base stations in a mobile phone network, measuring Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) levels of nearby base stations with a mobile station, identifying three base stations for which the mobile station measures strongest RSSI levels, the mobile station receiving the position coordinates of the three identified base stations, calculating a curved path of possible positions of the mobile station for each of the three identified base stations according to the measured RSSI levels of each of the three identified base stations, and calculating the position of the mobile station based on the position coordinates of the three identified base stations and the three curved paths of possible positions of the mobile station.
Owner:BENQ CORP
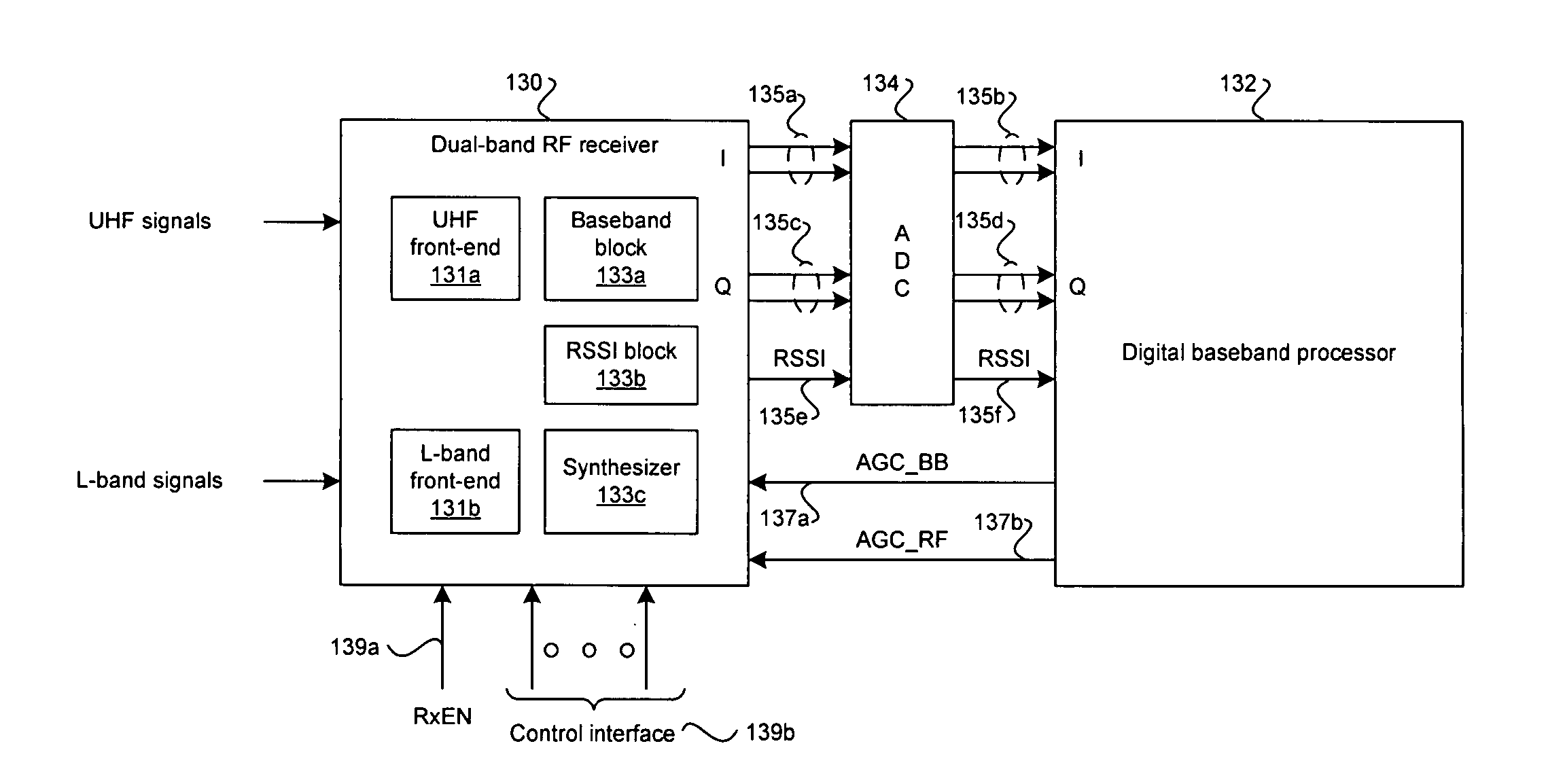
Method and system for multi-band direct conversion CMOS mobile television tuner
Aspects of a method and system for a multi-band direct conversion CMOS mobile television tuner are provided. A single-chip multi-band RF receiver in a mobile terminal comprising UHF and L-band front-ends receives and amplifies an RF signal utilizing an LNA integrated into the front-end that corresponds to the type of signal received. A received signal strength indicator (RSSI) value may be determined for the amplified signal within the single-chip receiver and may be utilized to adjust a gain of the LNA. The adjustment may be made via on-chip or off-chip processing of the RSSI value. The single-chip receiver may directly convert the amplified signal to a baseband frequency signal and generate in-phase and quadrature components. The components of the baseband frequency signal may be filtered and / or amplified via programmable devices within the single-chip receiver. Circuitry within the single-chip receiver may be controller via an on-chip digital interface.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Reducing power consumption in a mobile communication device in response to motion detection
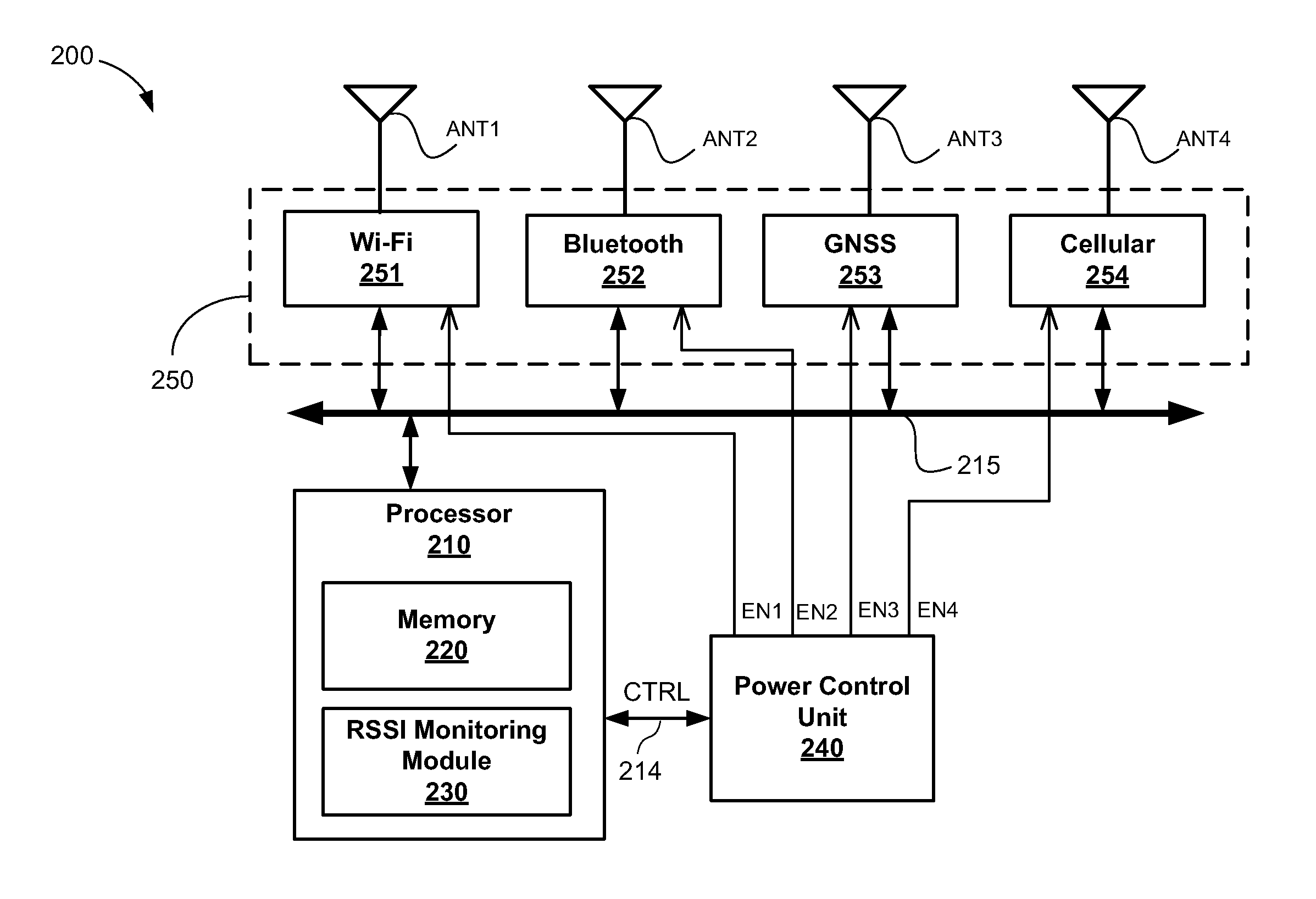
InactiveUS20130176869A1Power managementEnergy efficient ICTReceived signal strength indicationEngineering
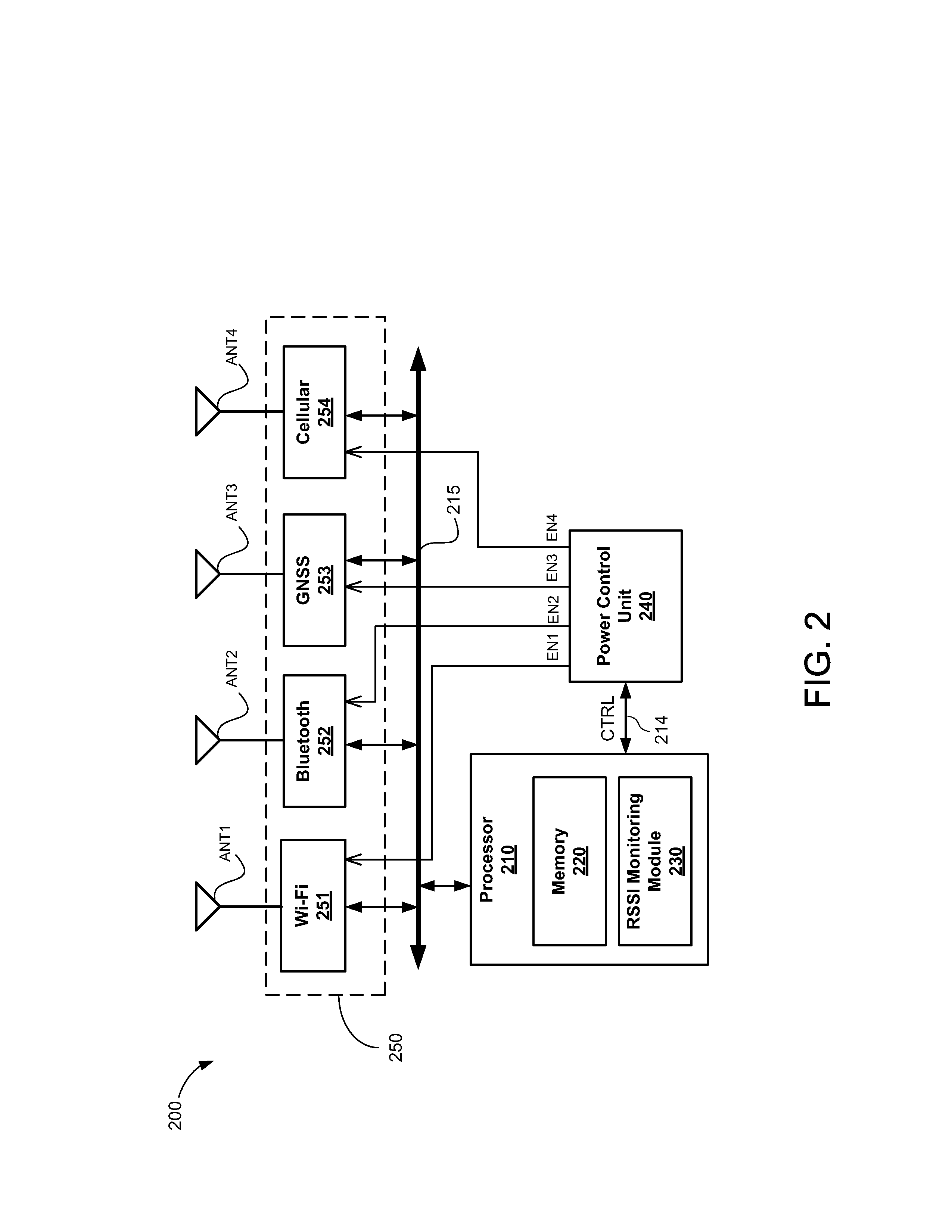
A method and apparatus to selectively enable and disable one or more modules in a mobile communication device based on a variation in received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values to reduce power consumption while the mobile device is relatively stationary.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Real-time network node location system and method
InactiveUS20100238862A1Position fixationWireless commuication servicesReceived signal strength indicationDirectional antenna
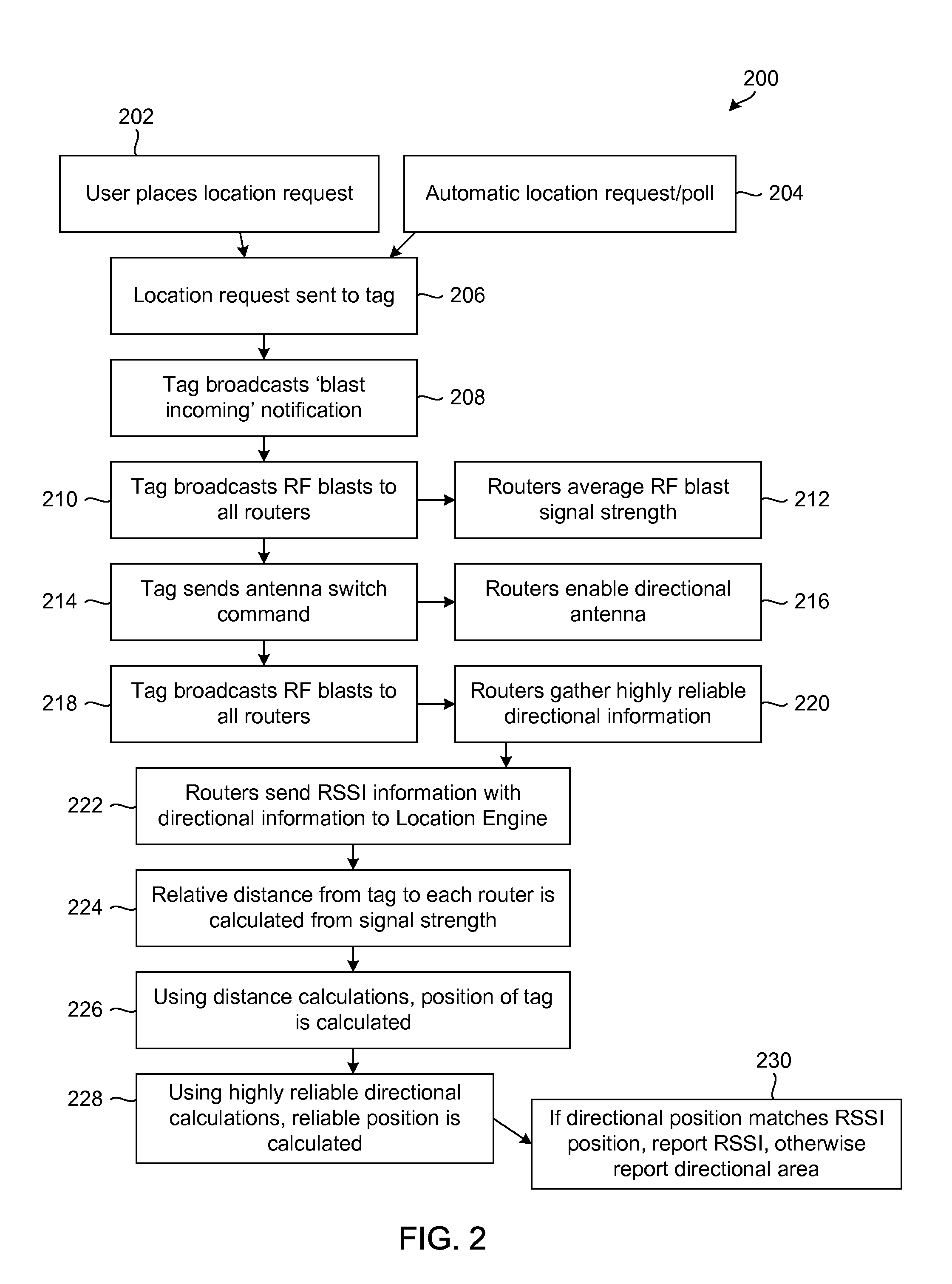
A real-time location system and method for a wireless network includes, in one embodiment: (a) obtaining received signal-strength indicator measurements between stationary routers and mobile devices; (b) determining the relative angles of mobile devices from stationary routers using directional antenna systems; and (c) using signal strength and angle information to calculate the location of mobile devices.
Owner:BUZBY NETWORKS
Radio frequency fingerprint positioning method and system as well as access controller (AC) and positioning server
ActiveCN102056293AAchieve positioningGuaranteed minimum requirementsWireless communicationFeature vectorWireless control
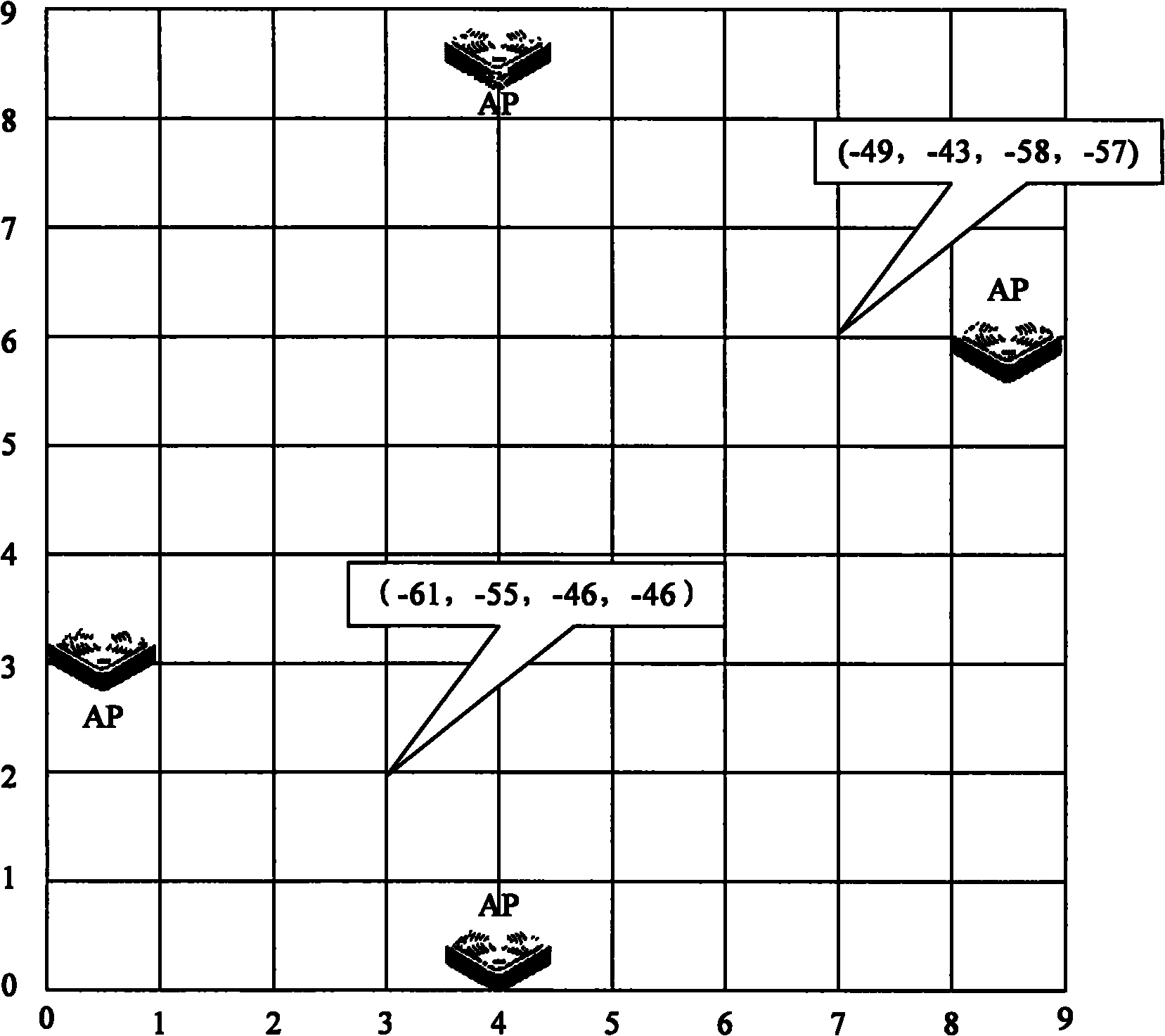
The invention provides a radio frequency fingerprint positioning method and system as well as an access controller (AC) and a positioning server. The method comprises the following steps: the positioning server sends a first positioning indication message which contains an identifier of the appointed equipment to an access point (AP) through the AC, so the AP can collect the received signal strength indication (RSSI) of the appointed equipment; the AC receives the RSSI of the appointed equipment fed back from the AP, filters the RSSI of the appointed equipment according to a preset dimensional threshold value and an RSSI threshold value to generate a fingerprint feature vector at least containing the preset dimensional threshold value number of the RSSI, and sends the fingerprint feature vector to the positioning server; and the positioning server positions the appointed equipment according to the fingerprint feature vector and a preserved standard fingerprint feature vector containing at least the preset dimensional threshold value number of the RSSI and position coordinates. By utilizing the technical scheme of the invention, the complexity of positioning by using a radio frequency fingerprint technique can be decreased, and the positioning precision can be increased.
Owner:BEIJING XINWANG RUIJIE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Indoor positioning method for goal nodes of mobile social network
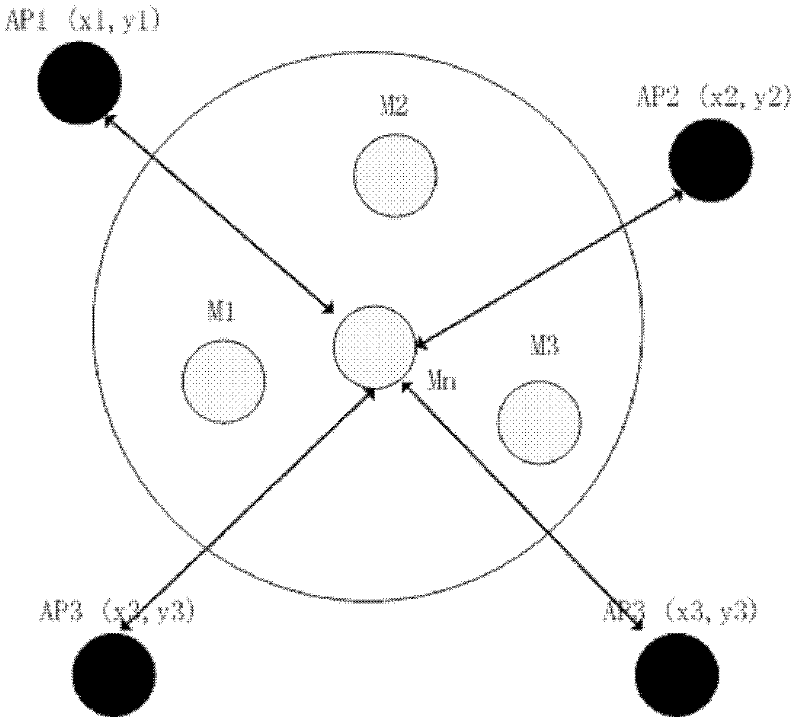
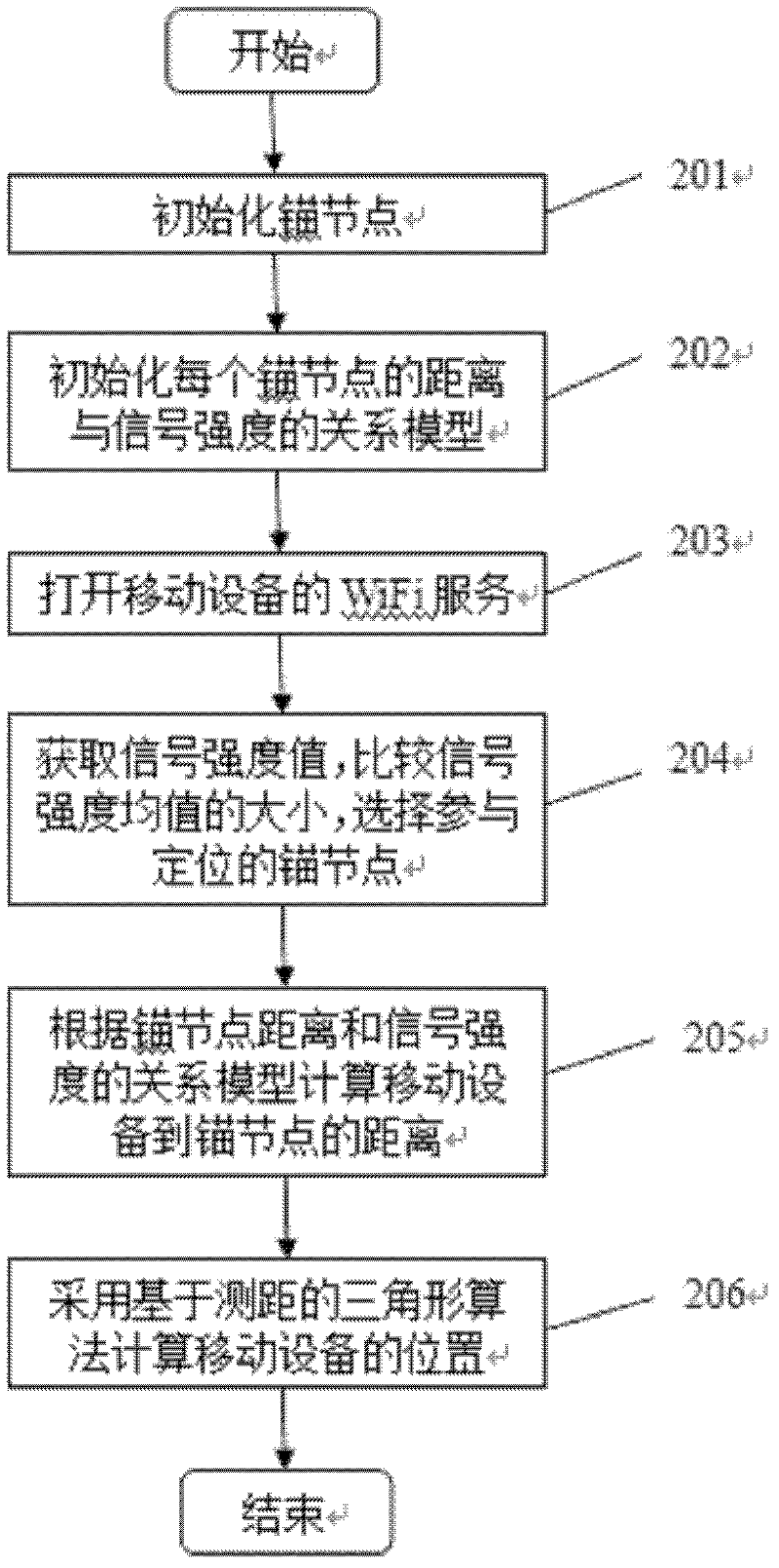
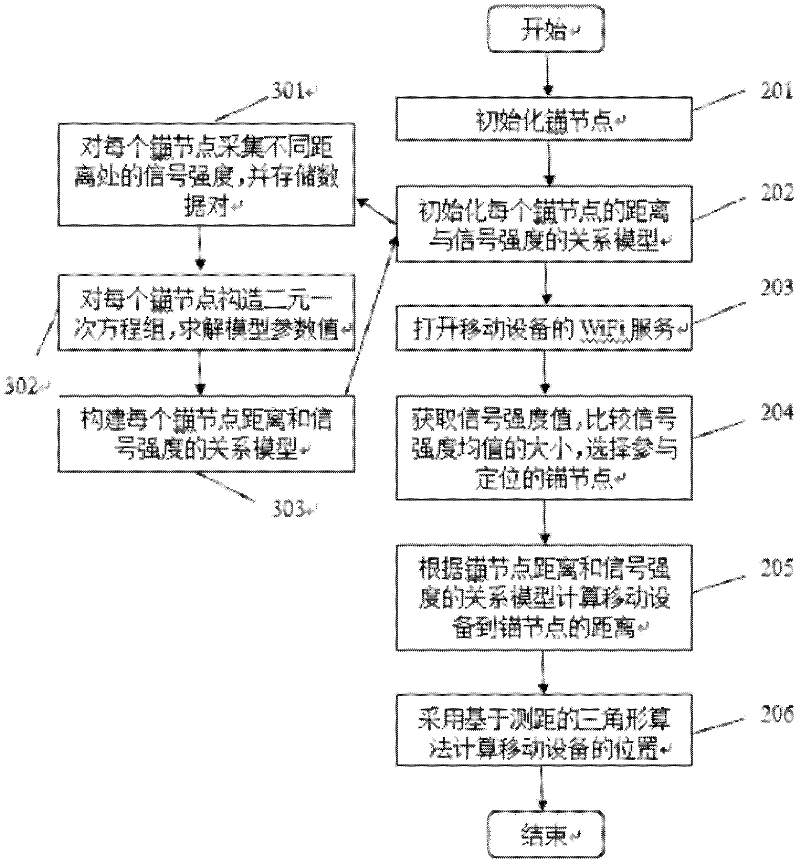
InactiveCN102595592AOvercome the influence of positioningAchieve positioningWireless communicationRelational modelReceived signal strength indication
The invention discloses an indoor positioning method for goal nodes of a mobile social network. The indoor positioning method comprises the following steps of: respectively placing at least three access points AP in different positions, using known coordinate points as anchor nodes, obtaining a relational model between signal strengths and distances of all the anchor points, obtaining the signal strength value of each signal by using a mobile smart terminal, selecting the anchor nodes with the strongest signal strengths as the nodes needing to particle in positioning, respectively putting the three anchor nodes into the relational model between the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indication) and the distances of the corresponding anchor nodes, and working out the distances from the mobile smart terminal to the corresponding anchor nodes; and working out the position coordinates of the mobile smart terminal by using an angular positioning algorithm. According to the indoor positioning method, the positioning of mobile nodes can be realized in a mobile social network environment, the impact of the environment on positioning is overcome to a certain extend, thereby the positioning accuracy is improved, and the positioning requirement can be basically satisfied in the mobile social network environment.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com