Patents
Literature
1541 results about "Propagation time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
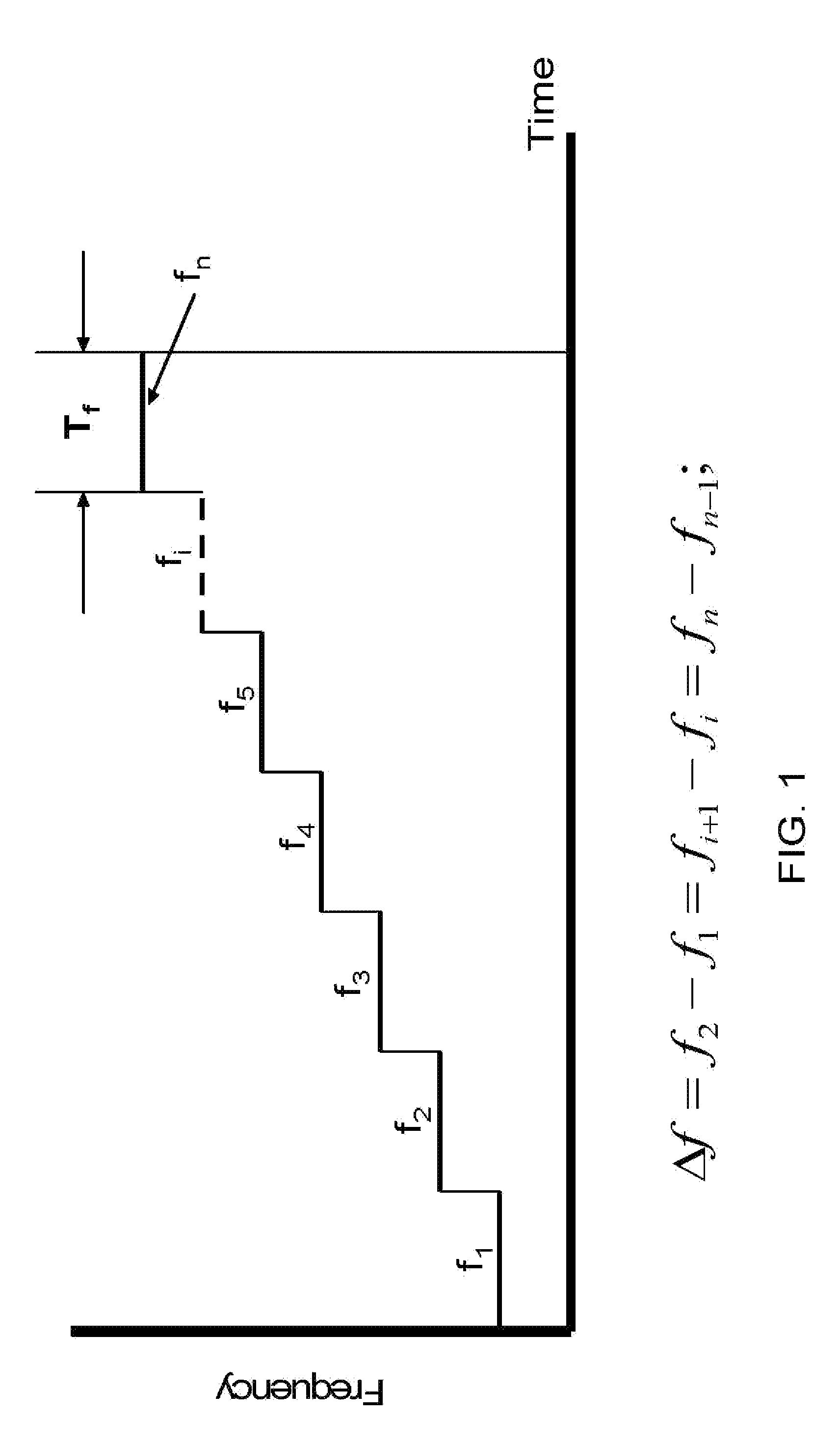
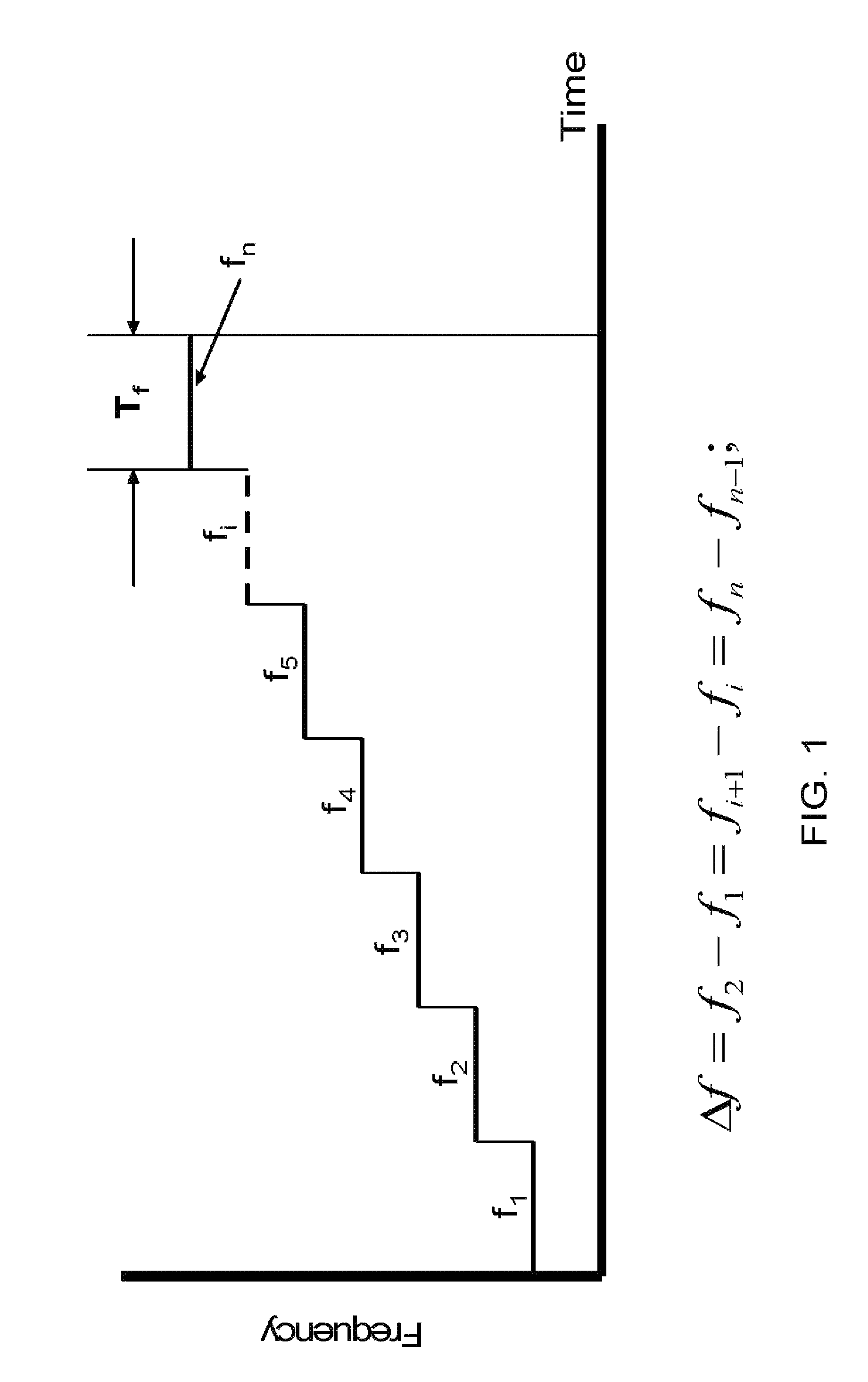
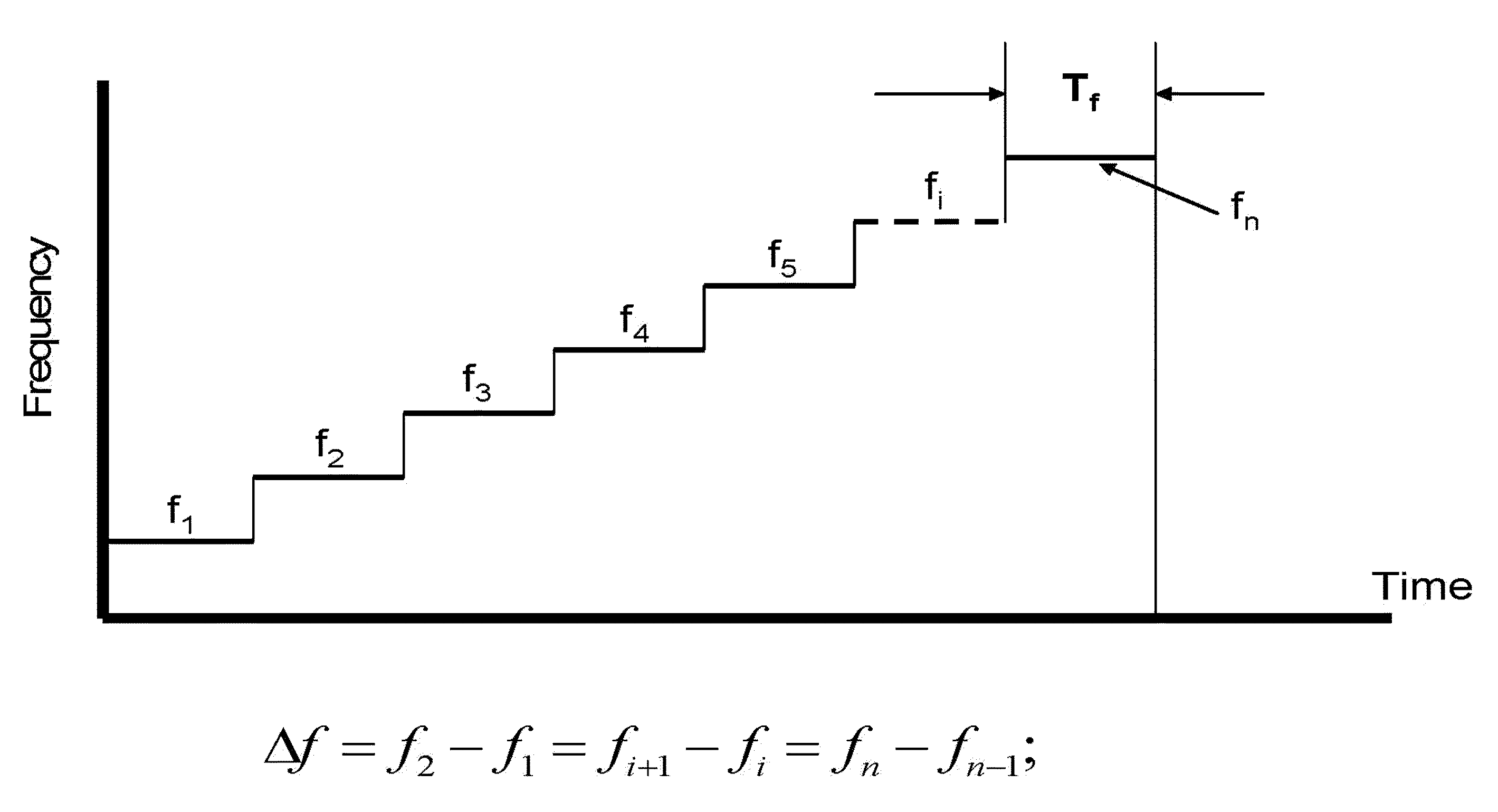
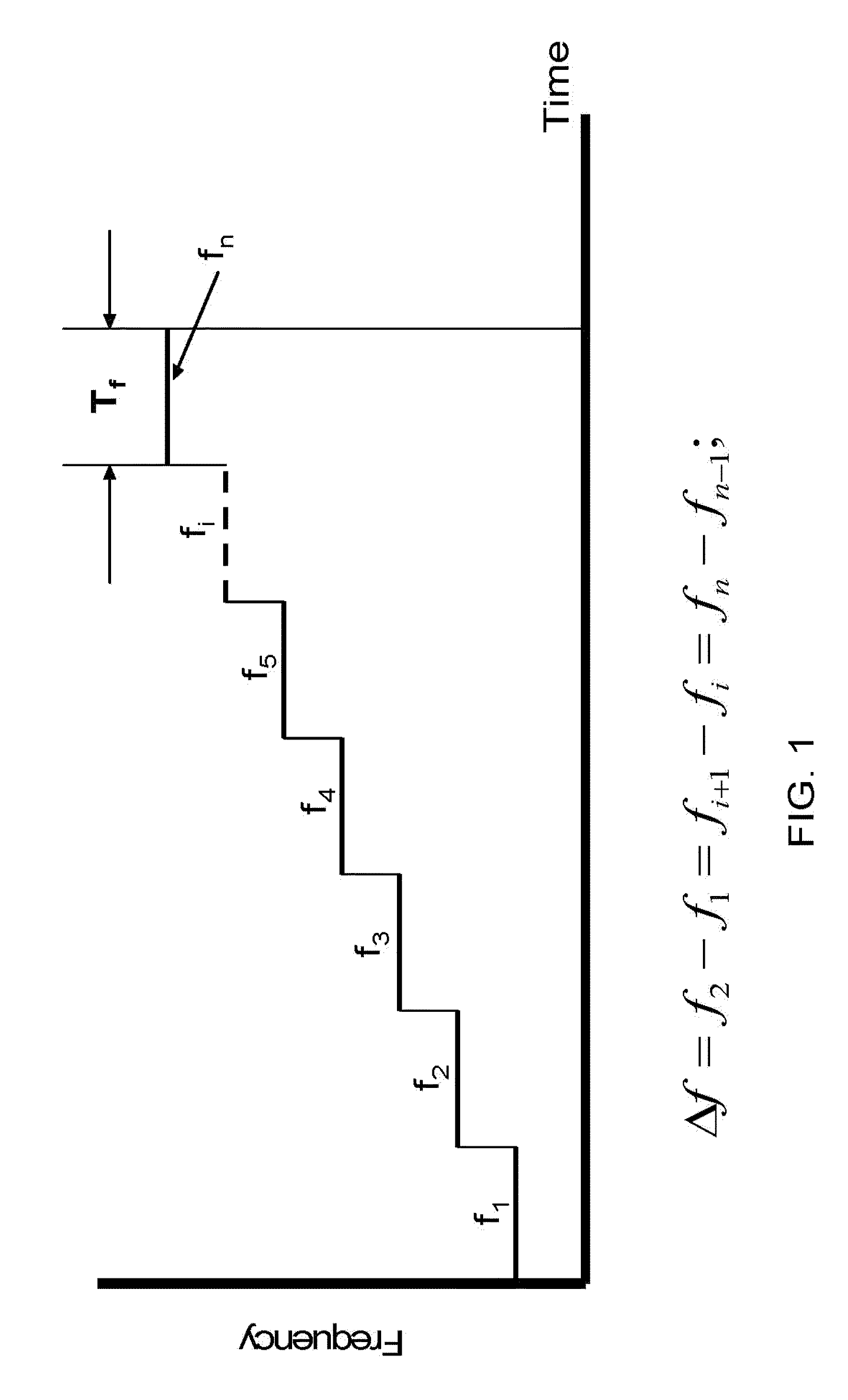
In digital circuits, propagation time is the delay of the basic inverter of a given family. Thus, it measures the speed at which such family can operate.
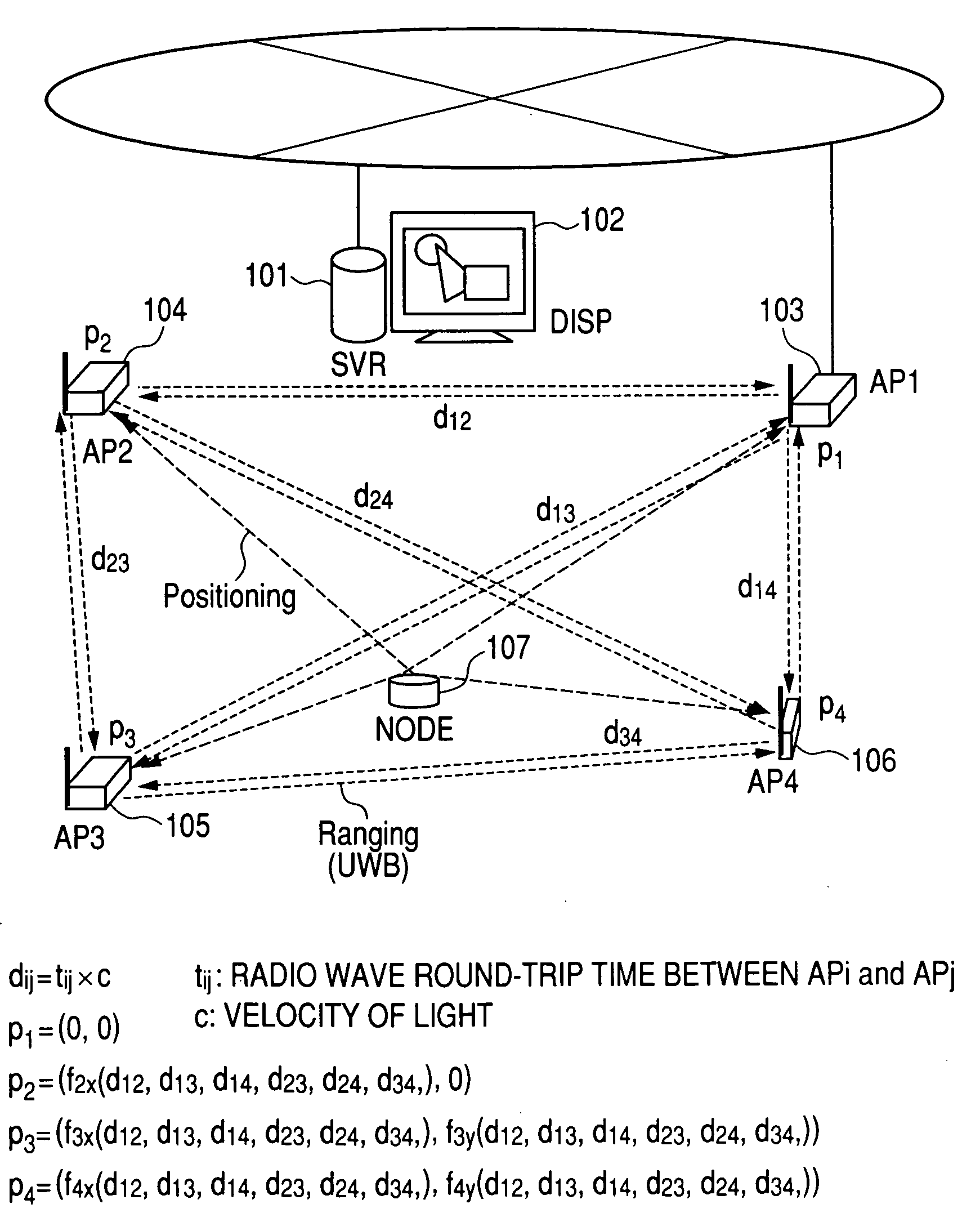
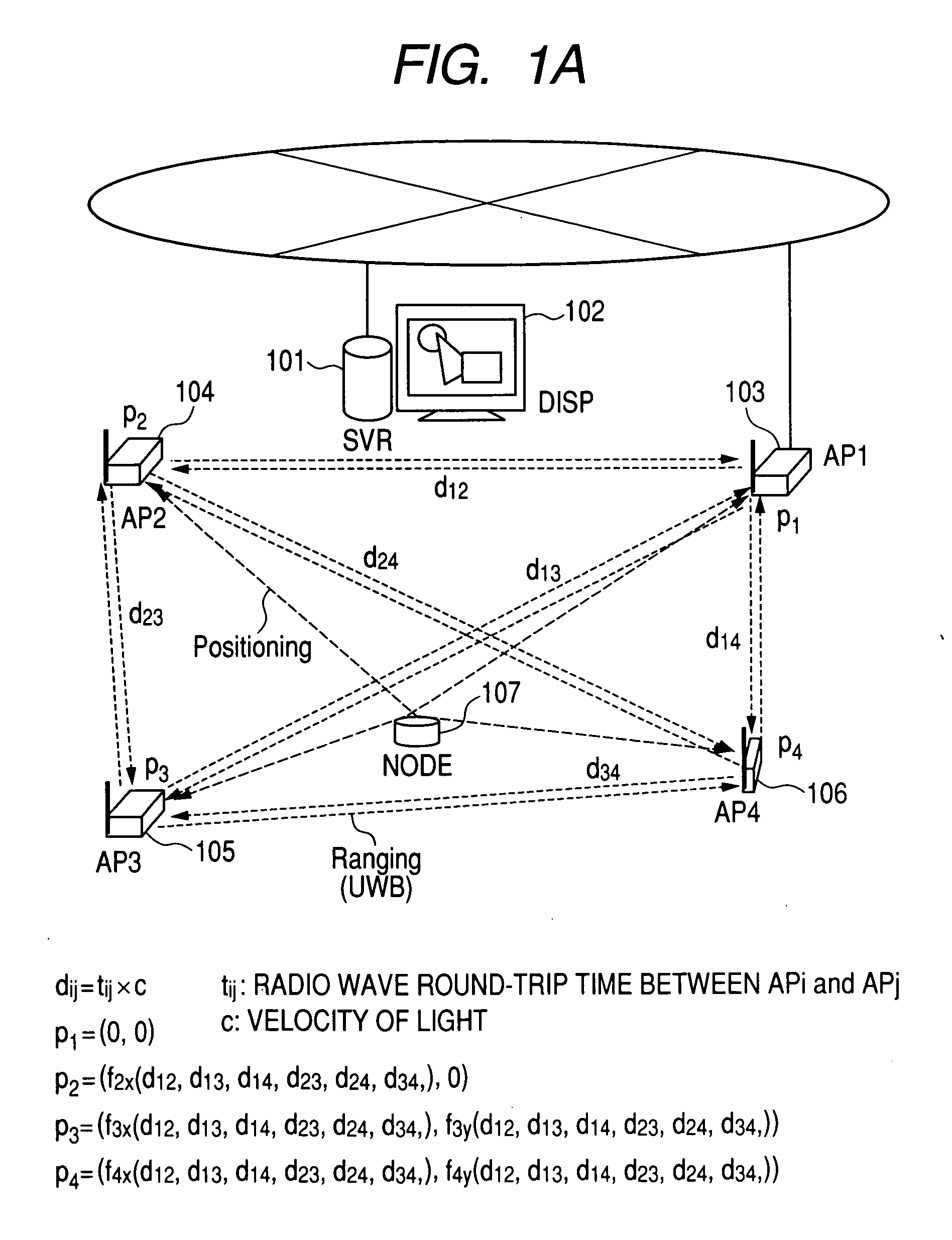
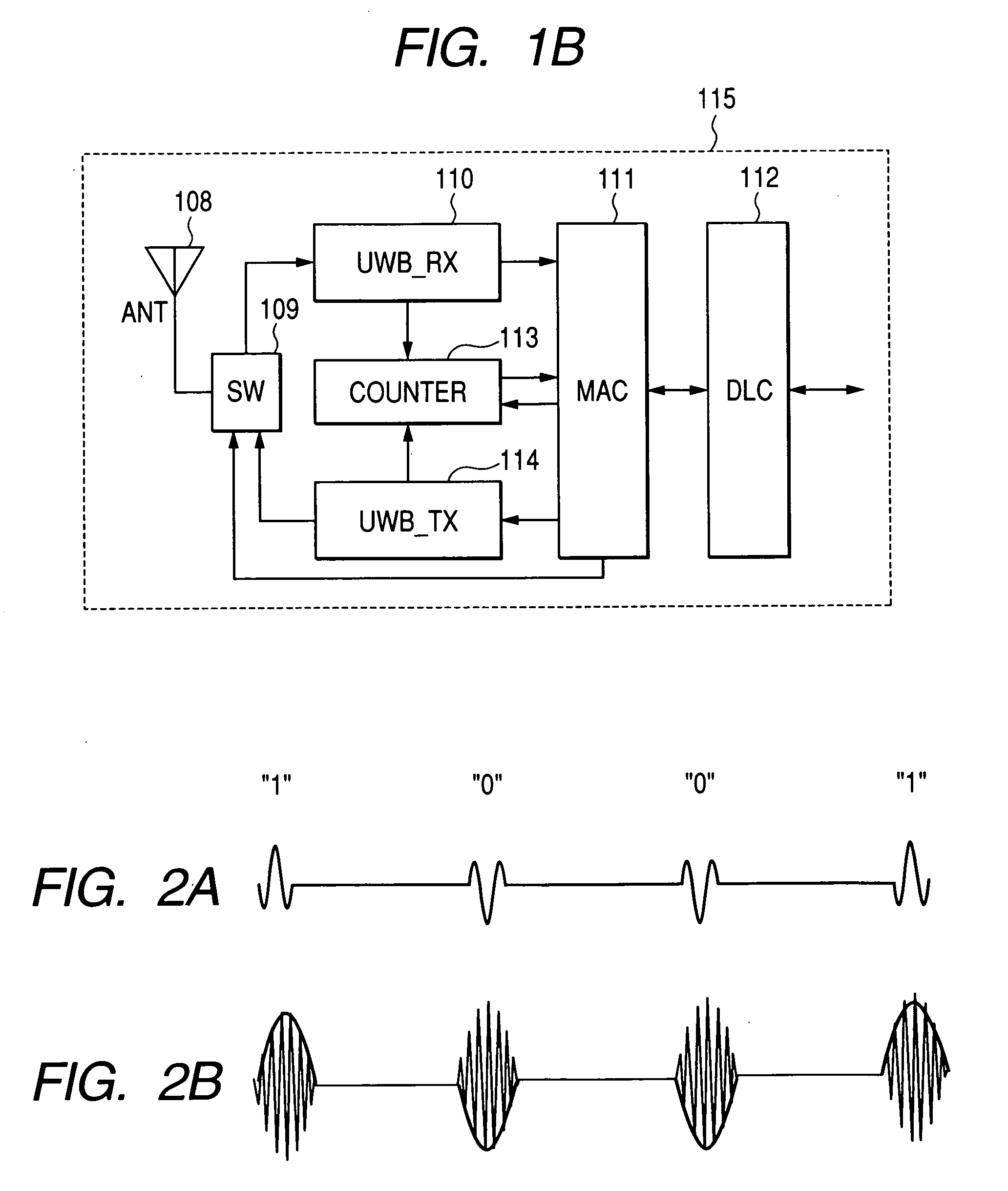
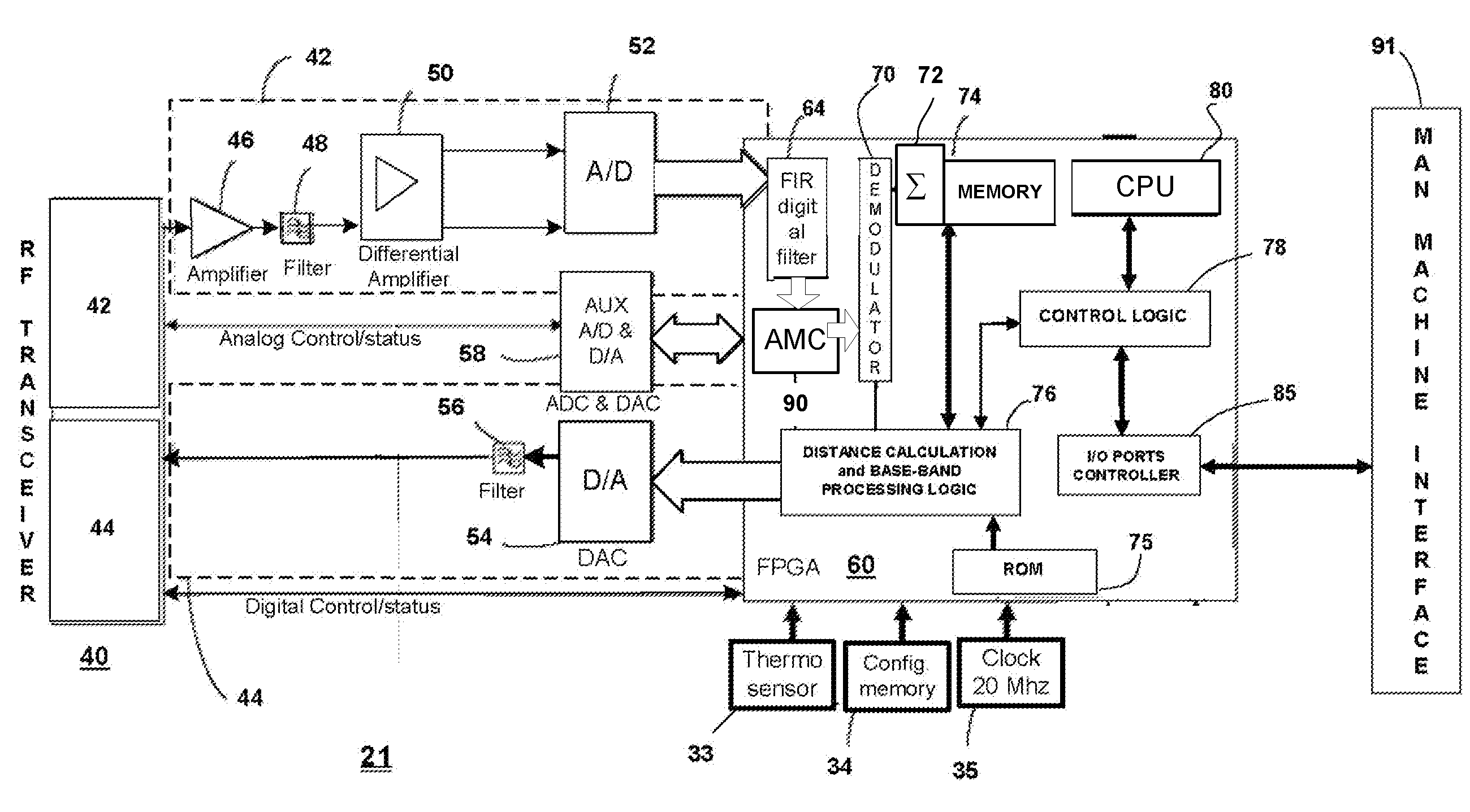
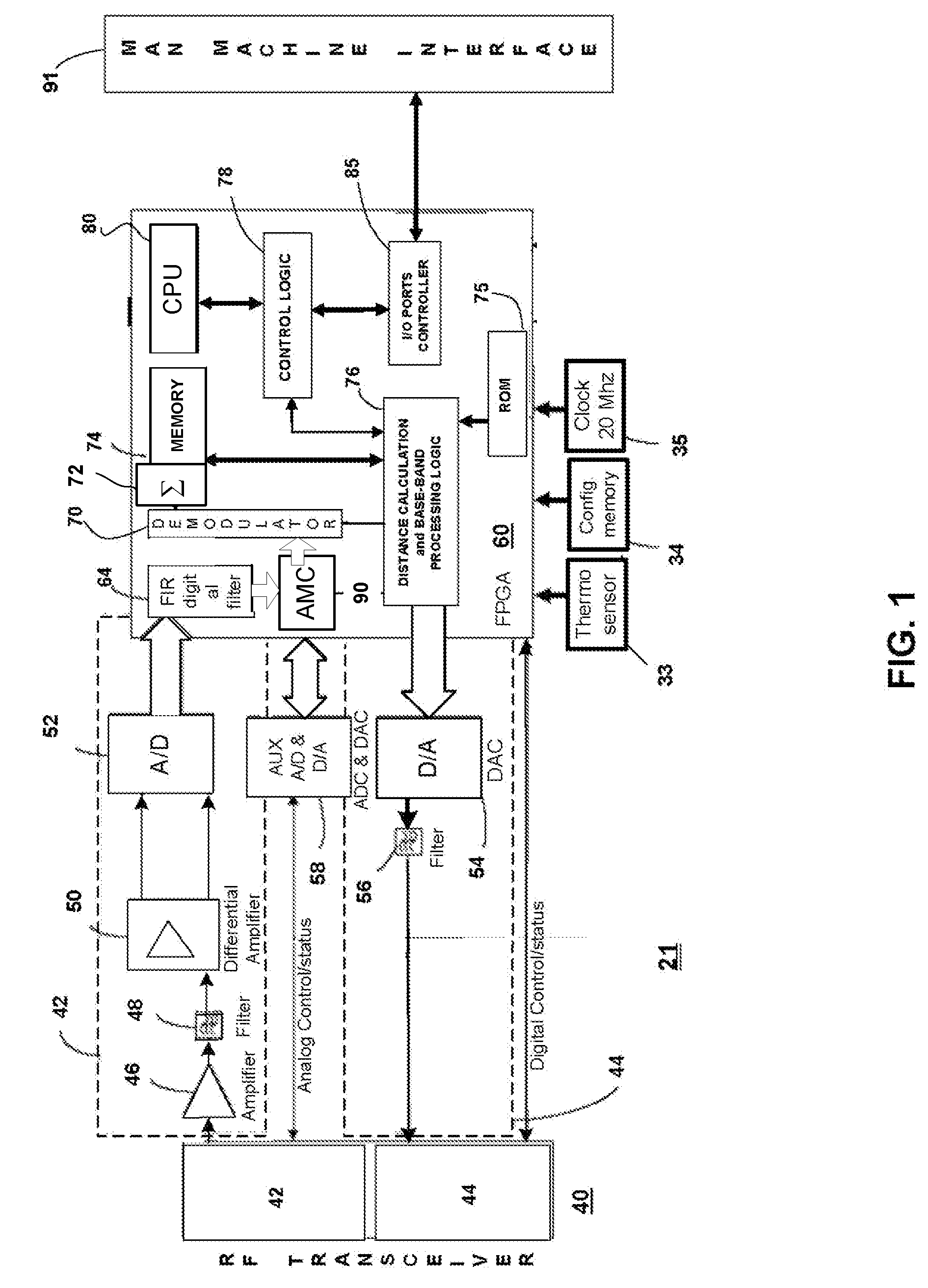
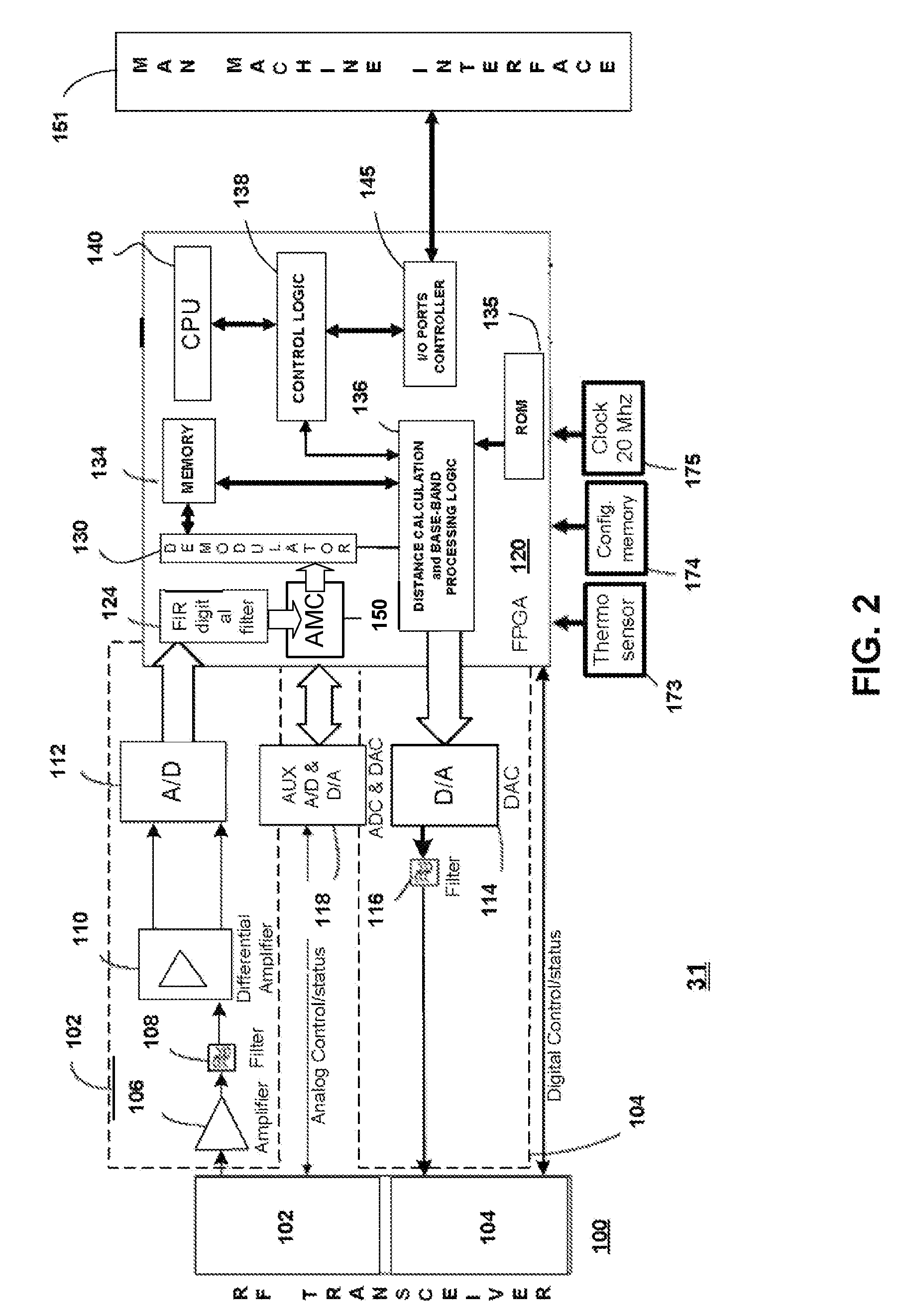
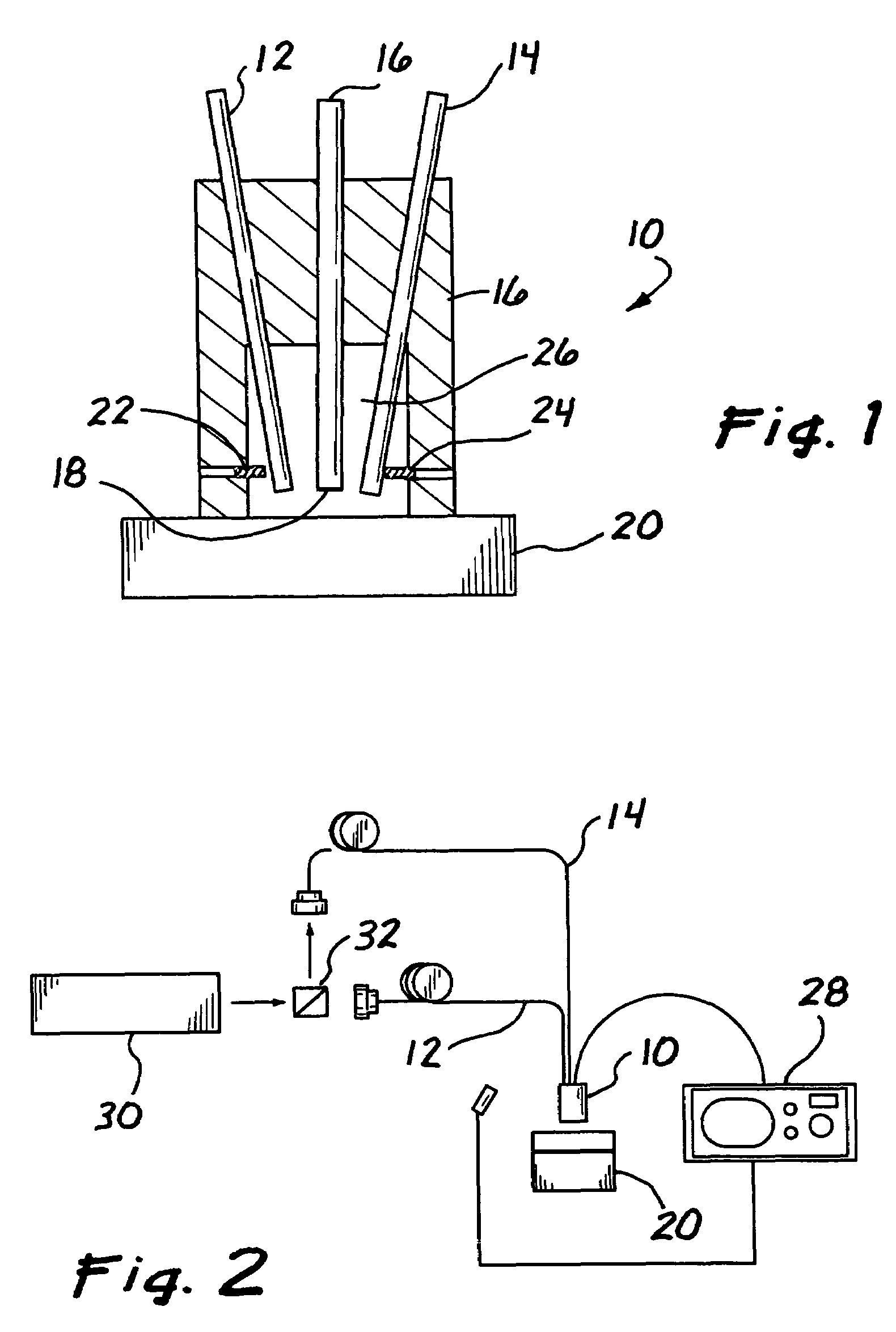
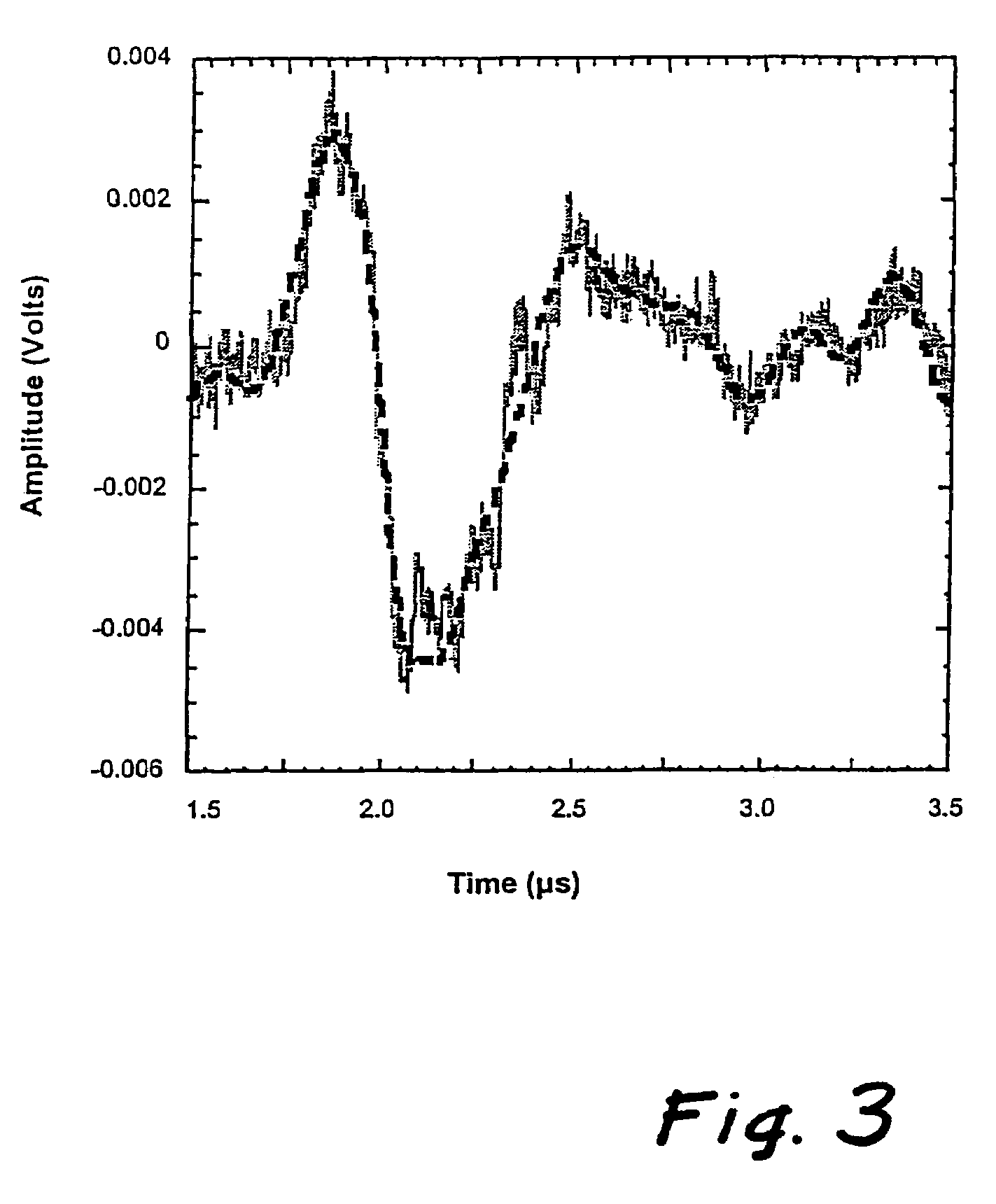
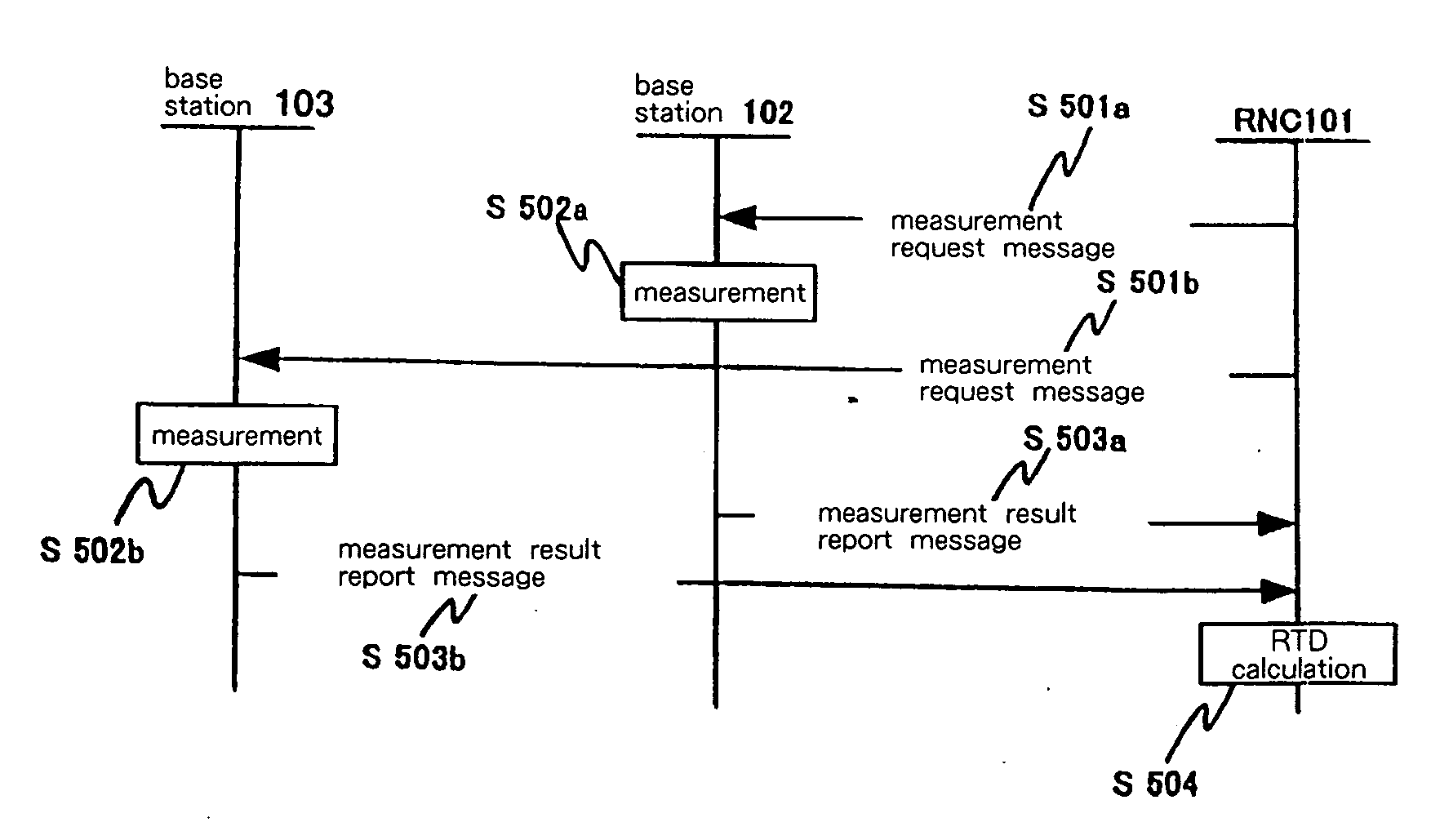
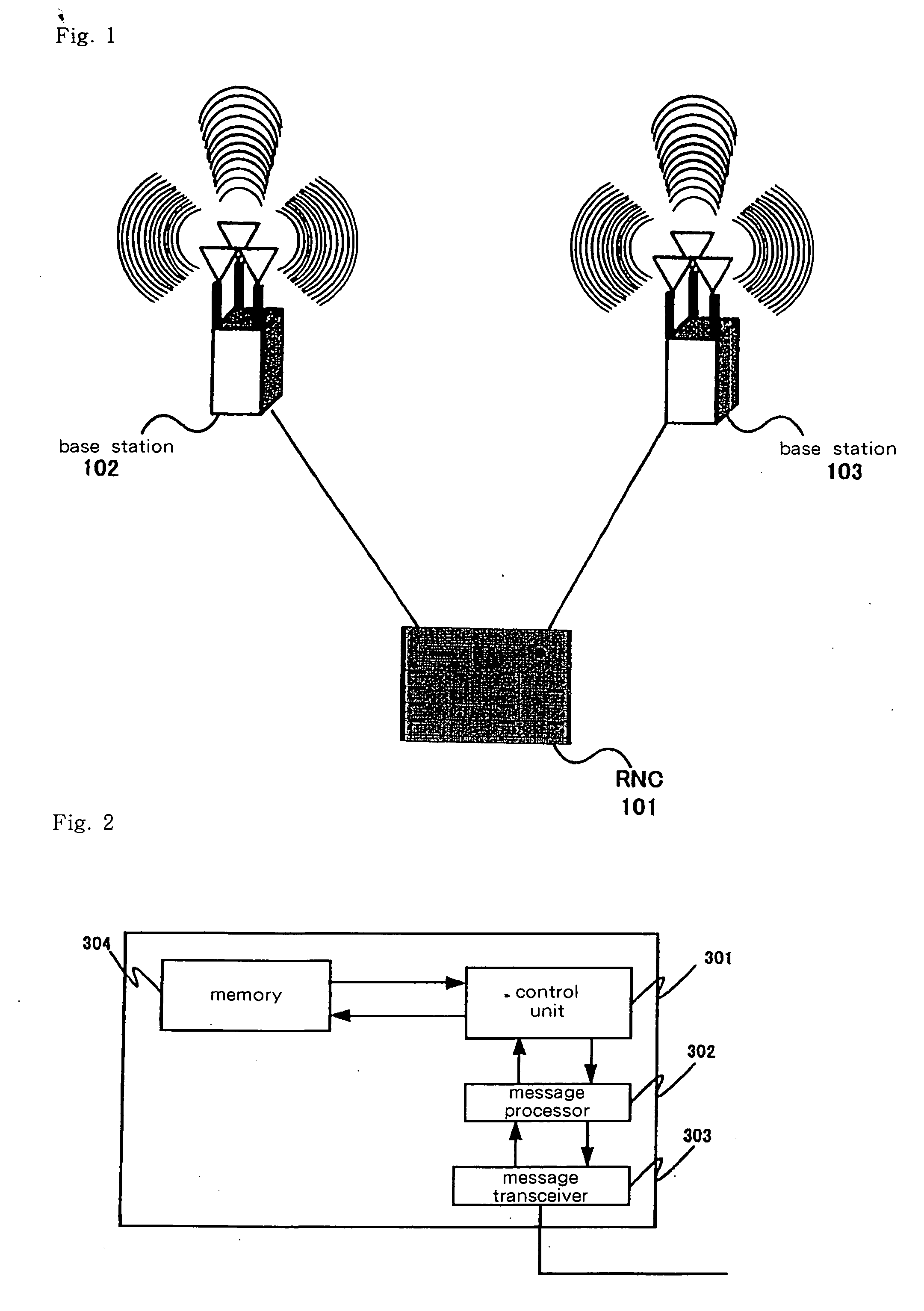
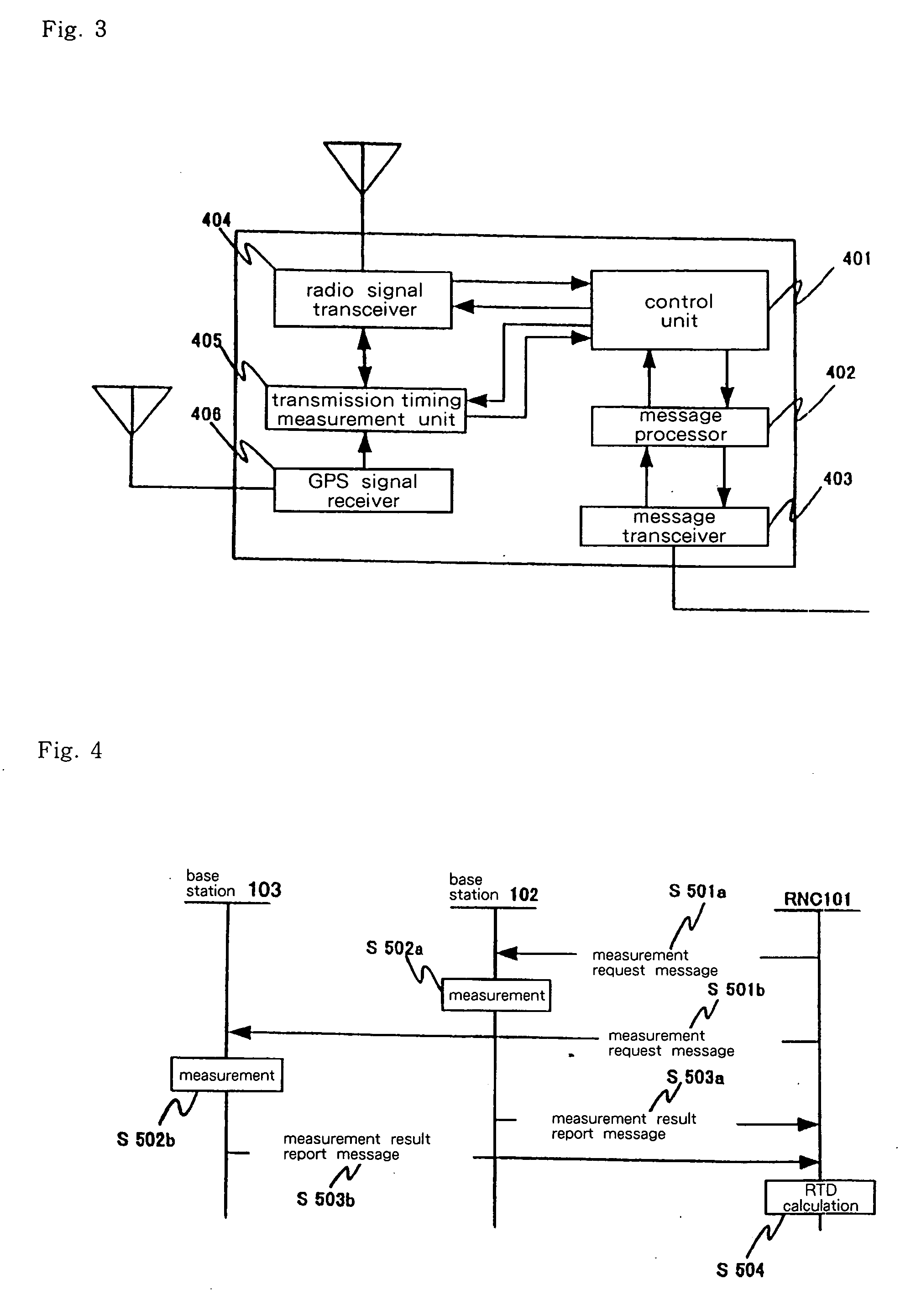
Object location monitoring system
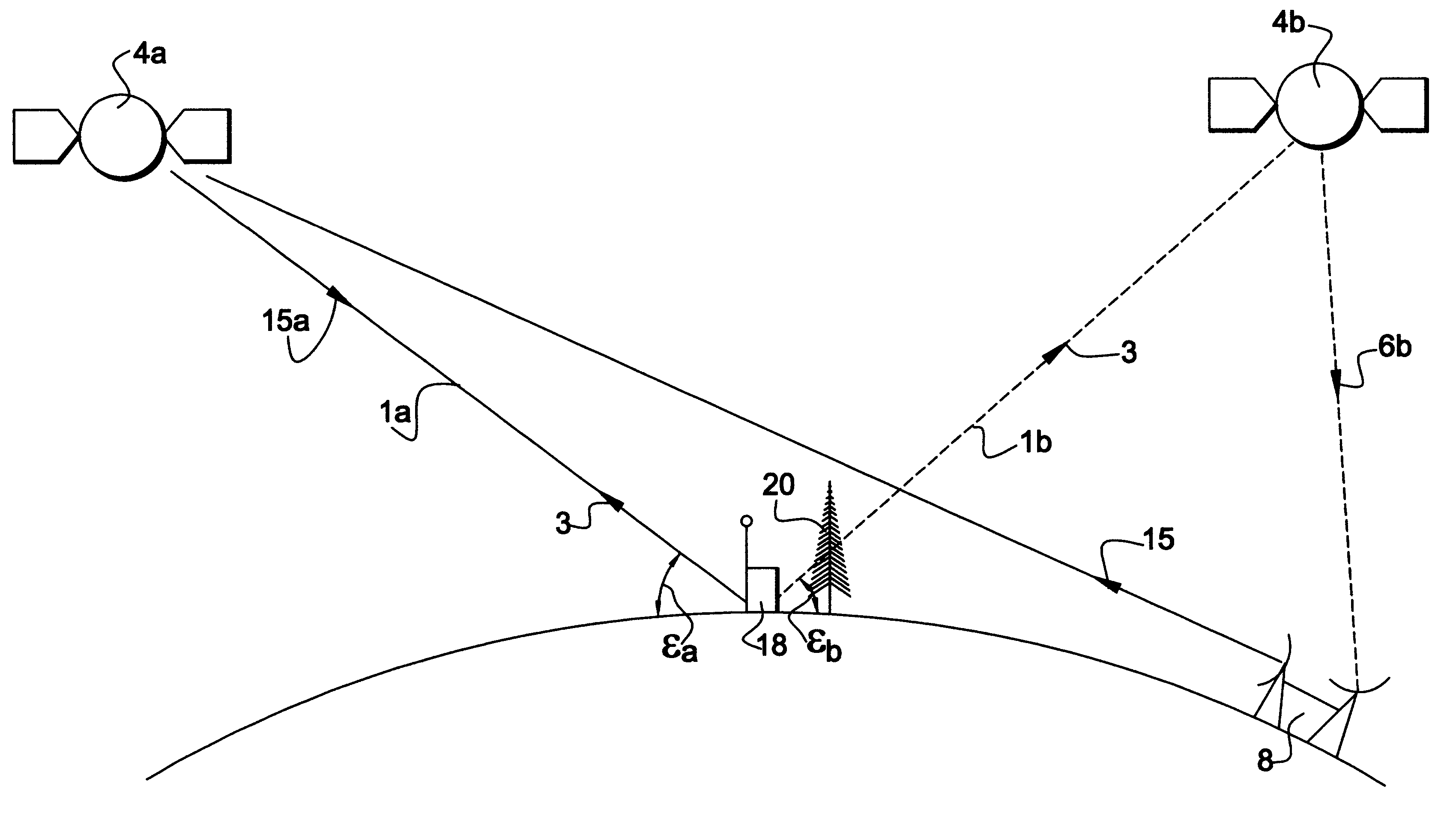
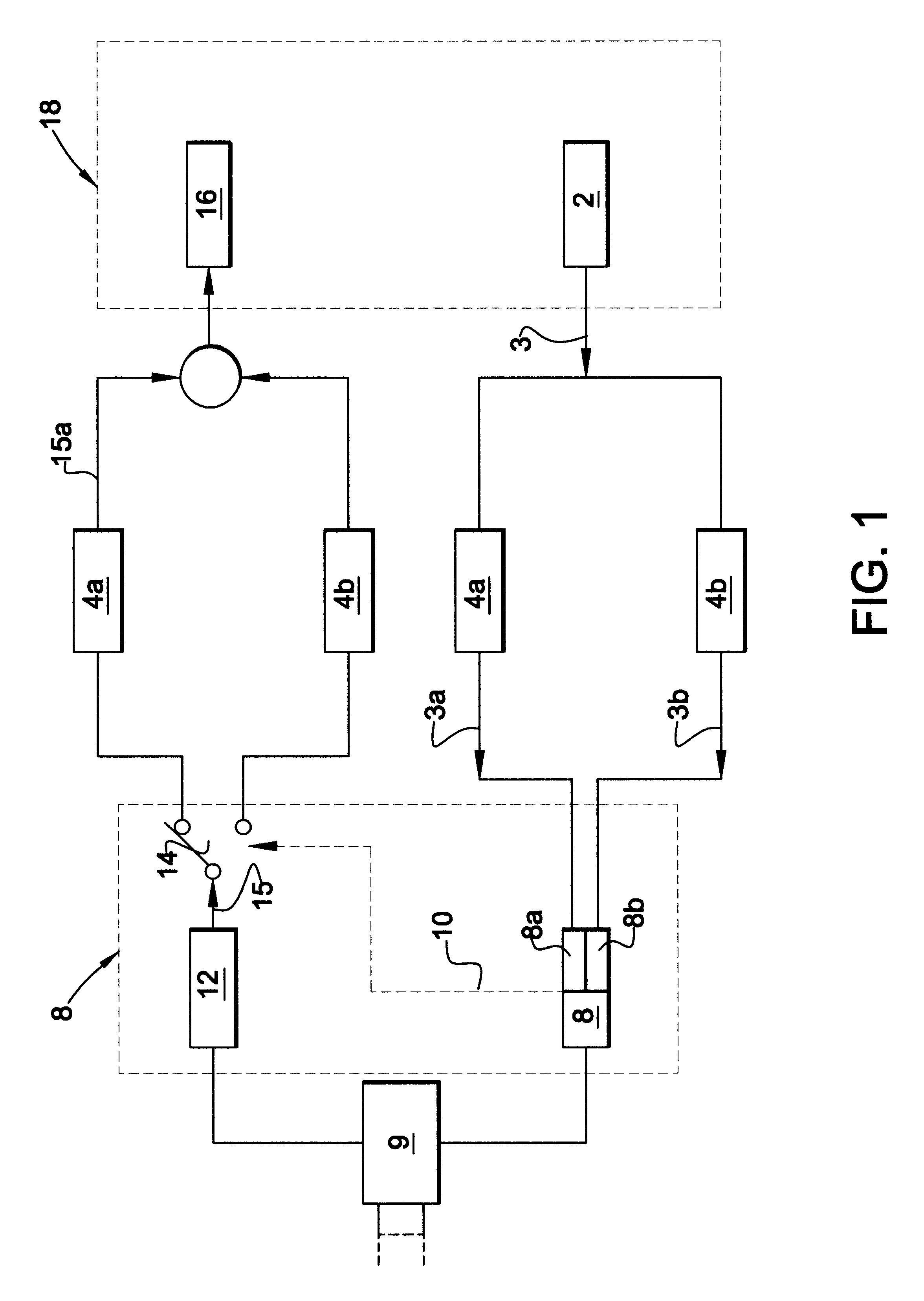
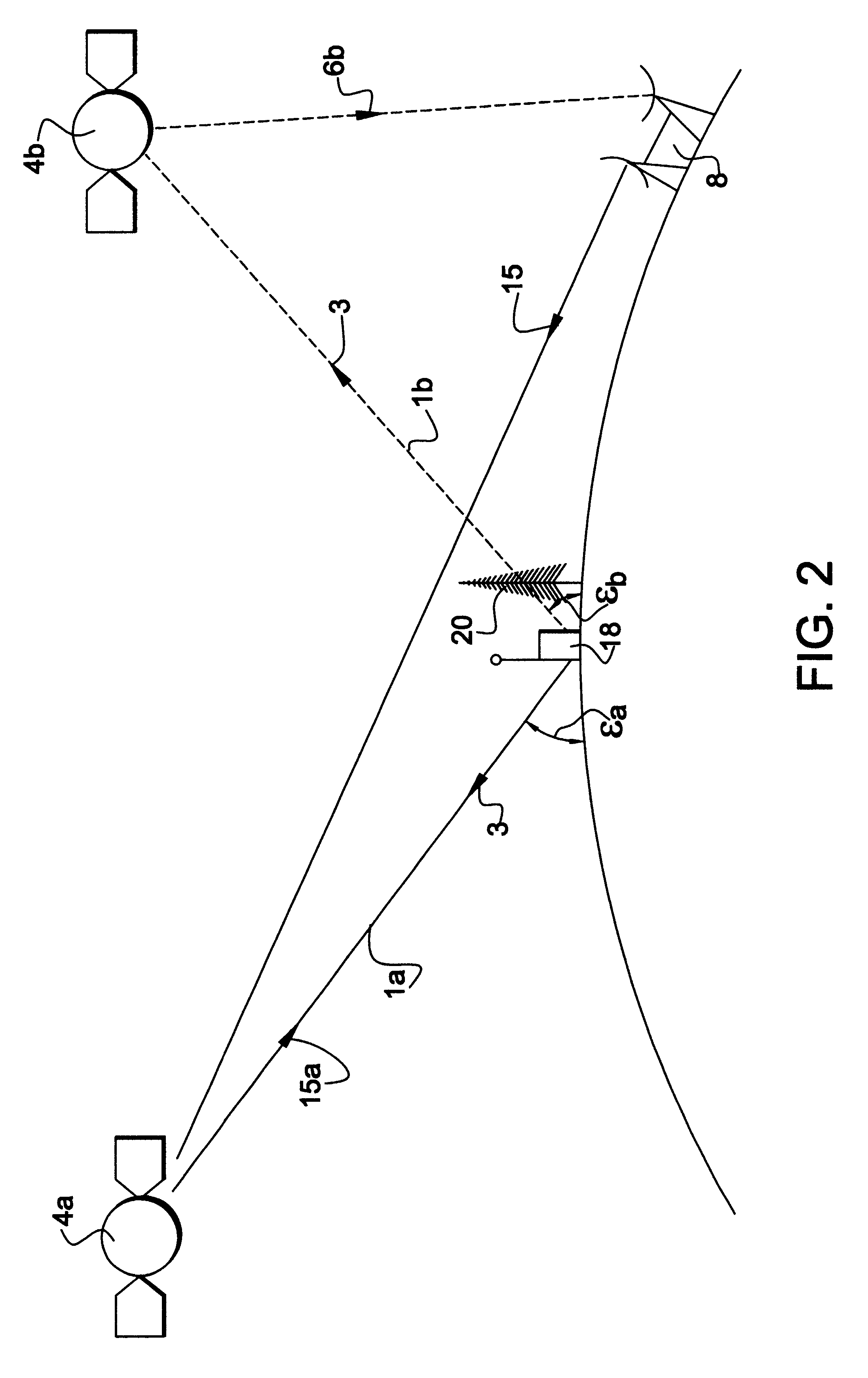
InactiveUS6958677B1Direction finders using radio wavesElectric testing/monitoringTriangulationPropagation time
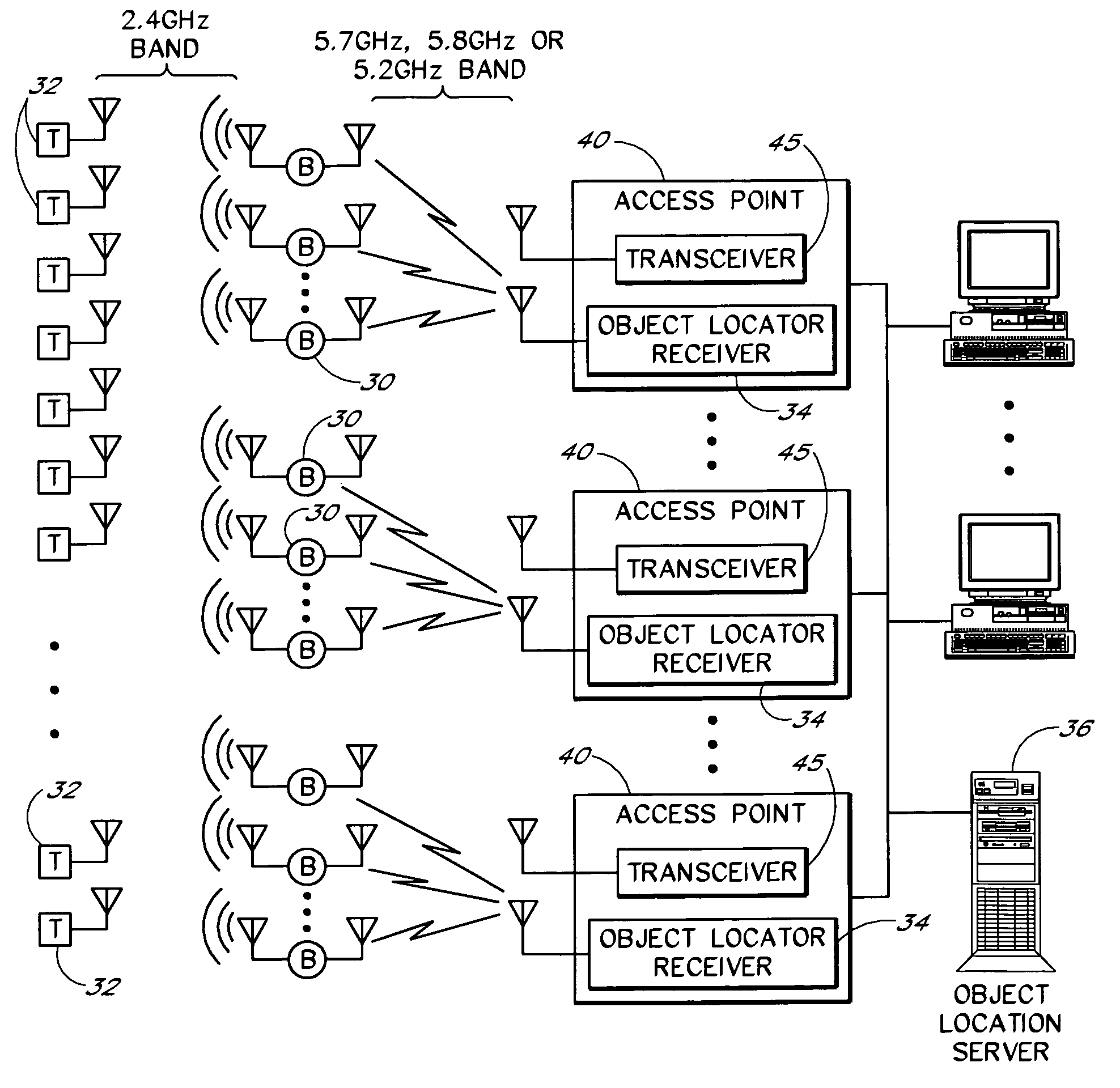
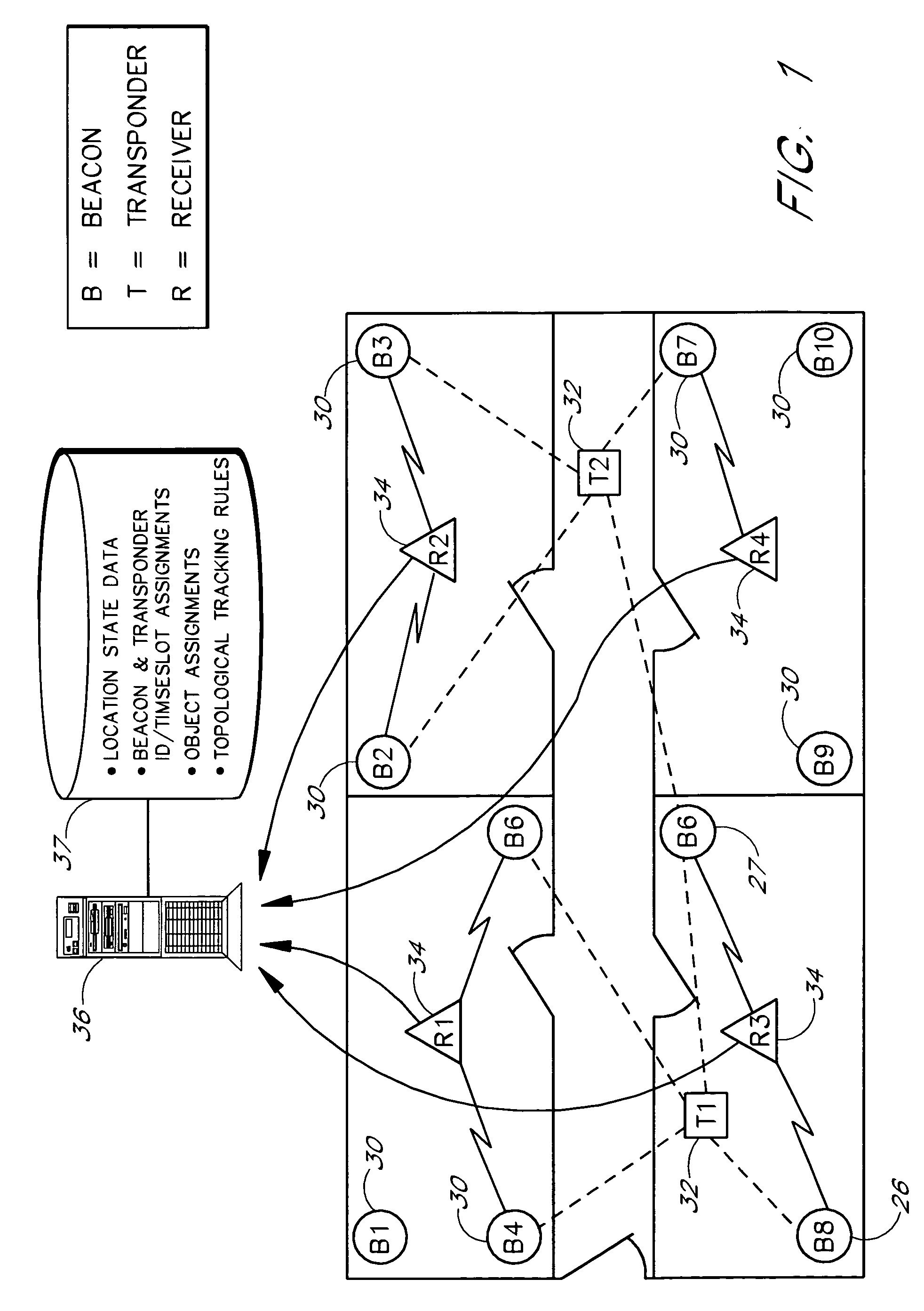
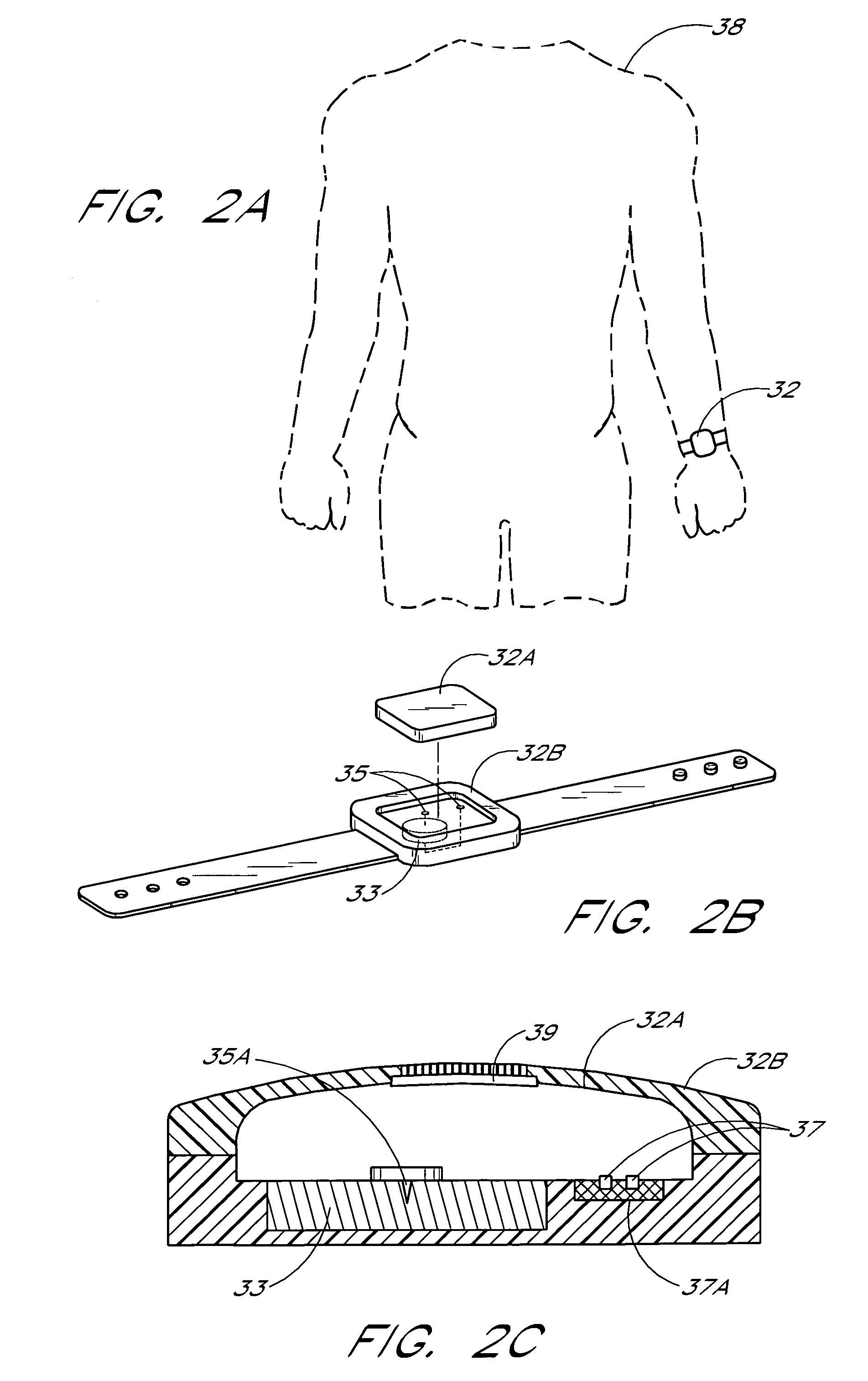
An object location monitoring system includes beacons that are spatially distributed throughout an area to be monitored. The beacons transmit interrogation signals that are received and echoed by transponders that attach to moveable objects. Each beacon retransmits its interrogation signal, and any transponder response thereto, to a receiver that measures a time difference between the two signals. This time difference reflects the signal propagation time, and thus the distance, between the beacon and the transponder. One such receiver preferably analyzes the retransmitted signals of multiple (e.g., 50 to 100) beacons. A triangulation method is used to determine the location of each transponder based on the transponder's distances from a set of beacons. In one embodiment, the transponders are provided as or within disposable ID bracelets worn by patients, and are used to track the locations of the patients within a hospital.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
Multi-path mitigation in rangefinding and tracking objects using reduced attenuation RF technology
ActiveUS20110111751A1Small incremental costImprove accuracyMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingSignal element
A method and system for identification, tracking and locating in wireless communications and wireless networks. The method and system use reference and / or pilot signals that are present in wireless communications and wireless networks. The method and system might also use RTT, TOA and time-stamping measurements / techniques to determine one or more reference signals traveling time between the Base Station (eNB) or its functional equivalent and mobile device (UE) and or network device. Other wireless networks that do not use reference and / or pilot signals may employ one or more of the following types of alternate embodiments of present invention: 1) where a portion of frame is dedicated to the ranging signal / ranging signal elements; 2) where the ranging signal elements are embedded into (spread across) transmit / receive signals frame(s); and 3) where the ranging signal elements are embedded with the data. The method and system includes multi-path mitigations processor and multi-path mitigations techniques and algorithms which improve the track-locate accuracy. The method and system allow achieving increased accuracy by using multi-path mitigations processor and multi-path mitigations techniques and algorithms. The techniques of Digital Signal Processing and Software-Defined Radio are used.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECHNOLOGIES INC
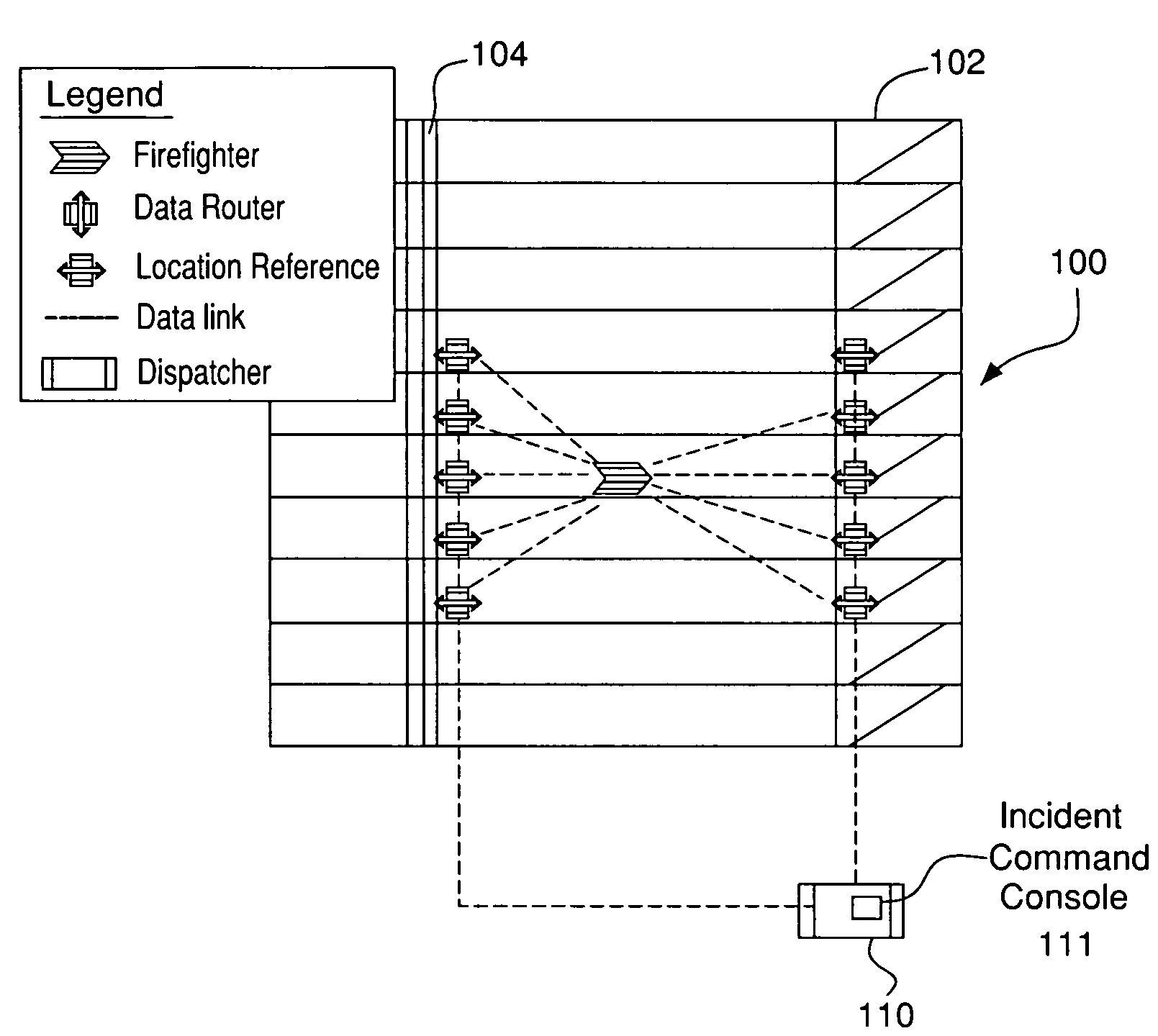
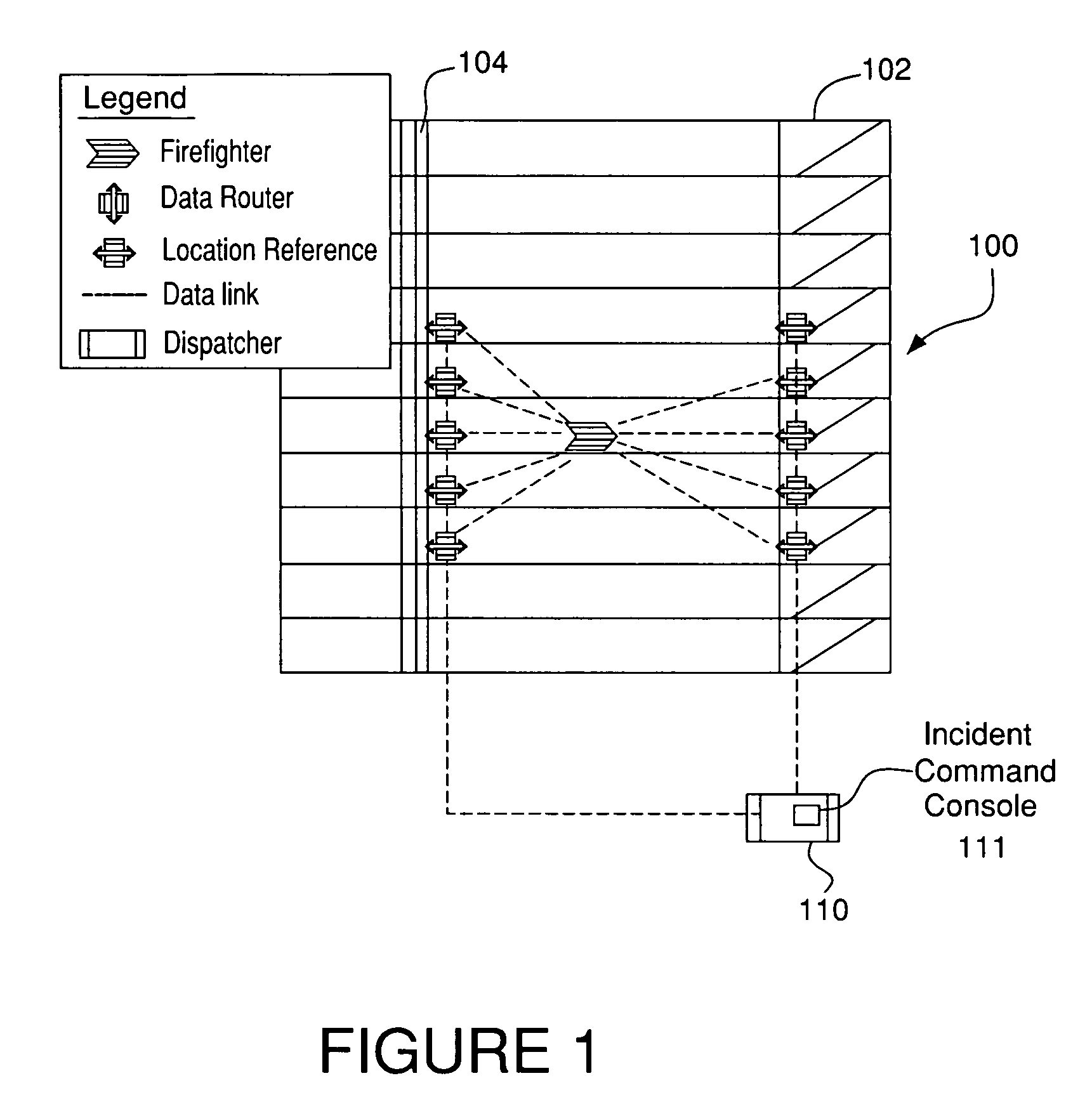
System and method for identifying the floor number where a firefighter in need of help is located using received signal strength indicator and signal propagation time
ActiveUS7126951B2Quickly and accurately identifyPower managementTransmission control/equalisingWireless routerPropagation time
A system and method for deploying a network of wireless devices, including mobile terminals, wireless routers and a least one control console, within a three dimensional deployment area such as a building, so that communication, identification and position calculations of personnel, such as firefighters, using the mobile terminals can be achieved regardless of building structure. The wireless routers are deployed in a substantial vertical manner in staircases and elevator shafts of a building of interest, either in advance as part of a safety program or immediately upon arrival of firefighters or other team at the building during an emergency. The system and method according to the embodiment of the present invention described herein uses both TOF and RSSI between the mobile terminals and wireless routers to identify the floor numbers where firefighters are located and to track firefighter movements.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
System for determining position of an emitter
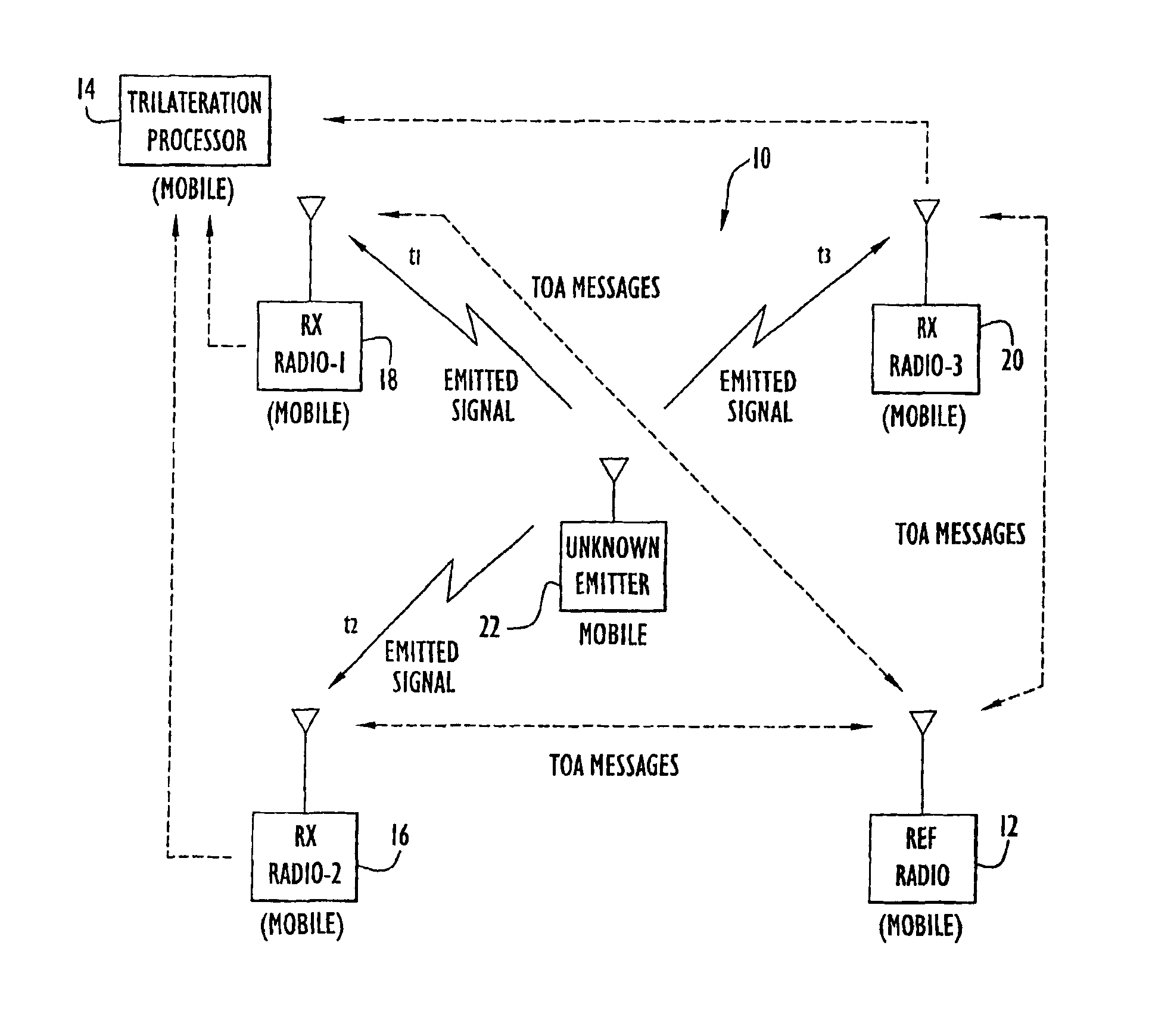
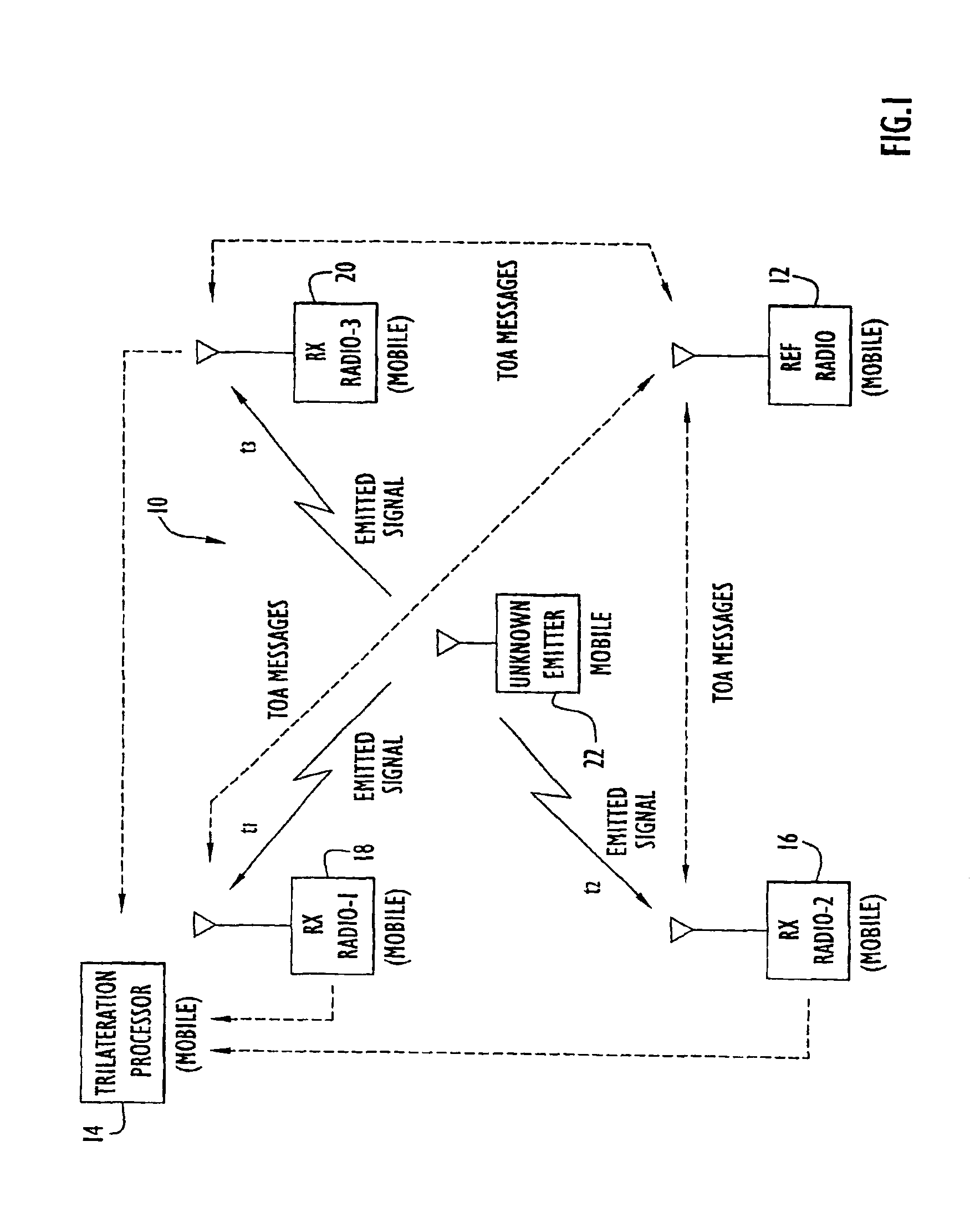
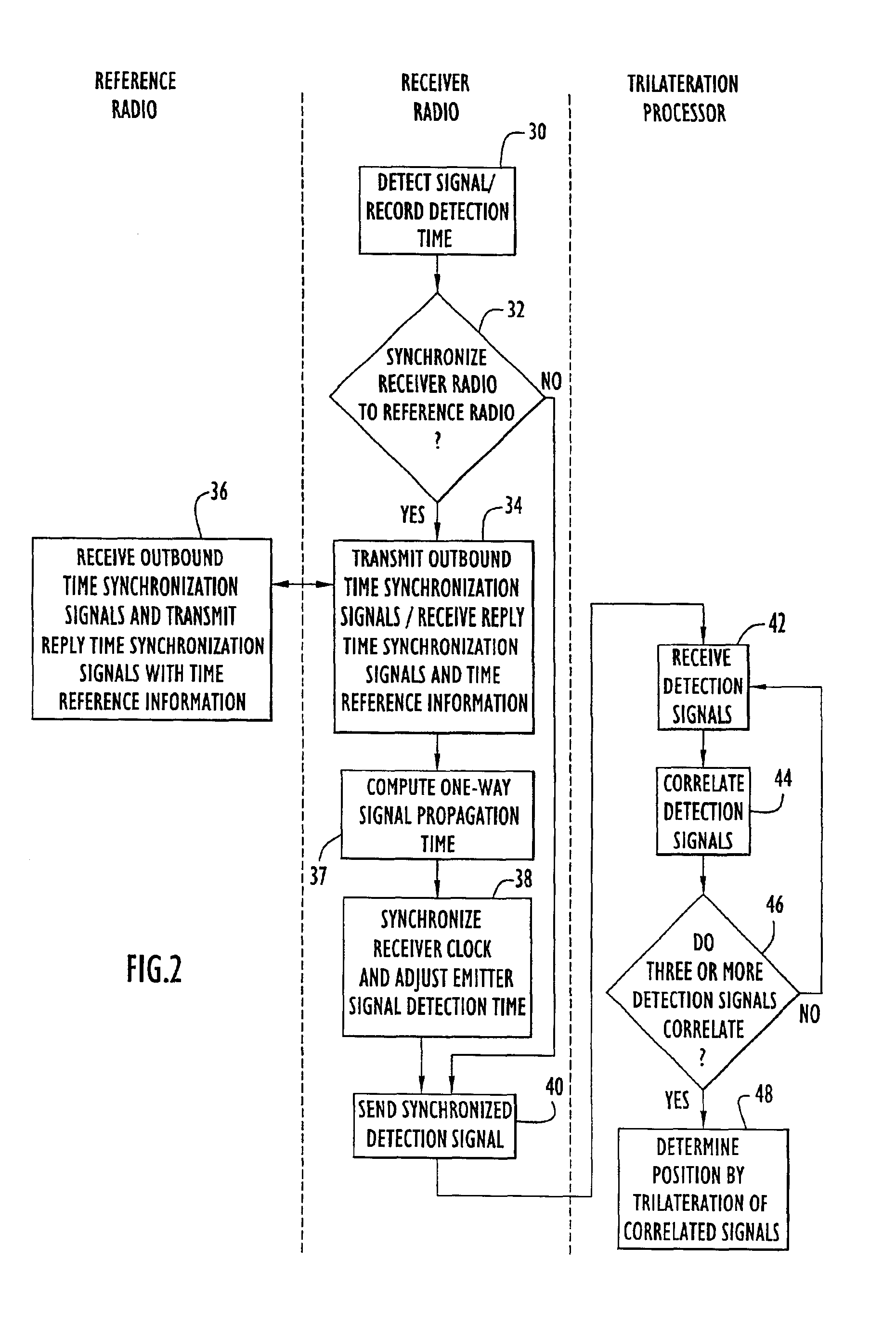
InactiveUS6861982B2Improve accuracyMinimizes designDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationPropagation timeExchange time
The position of a non-cooperating emitter is determined by detecting a signal from the emitter at three or more receiver communication devices positioned at different locations. The receiver communication devices determine respective detection times of the emitted signal in respective local time reference frames. To establish a common time reference frame for the emitted signal detections, each receiver communication device exchanges time synchronization signals with a reference communication device. Since any of the receiver communication devices and the reference communication device may be mobile, the signal exchange allows each receiver communication device to accurately determine the signal propagation time between itself and the reference communication device and factor the signal propagation time into an accurate adjustment of the local time reference frame. Using trilateration, the position of the emitter is determined from known positions of the receiver communication devices and the emitted signal detection times from the receiver communication devices.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
Terminal location system and positioning method
InactiveUS20070217379A1Simple introductionFacilitates initial introduction and maintenance and expansionPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPropagation timeEngineering
A location system of a configuration that facilitates initial introduction, maintenance, and system expansion. A terminal location system basically has at least (N+1) base station (here, N=1 to 3) and a location server and finds a position of a terminal performing wireless communication in N-dimensional coordinates. Further, the terminal location system calculates distances among the at least (N+1) base stations, finds relative coordinates of the base stations, evaluates the obtained relative coordinates, determines switching to terminal location processing of finding the position of the terminal, and finds the position of the terminal using propagation times of radio signals transmitted / received among the terminal and the base stations and the obtained relative coordinates of the base stations.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
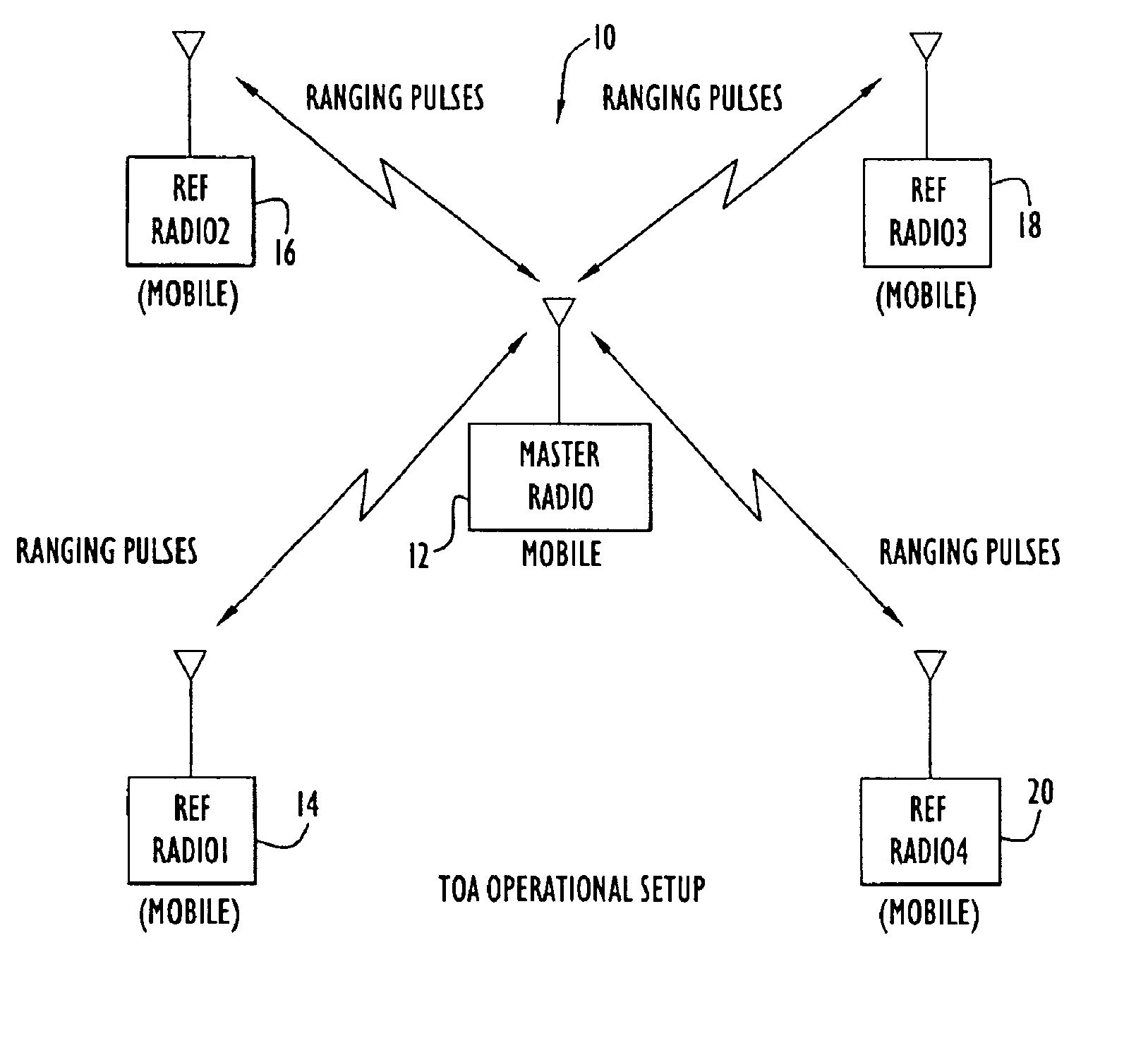
Method and apparatus for high-accuracy position location using search mode ranging techniques
InactiveUS6876326B2Improve abilitiesReduce impactDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesRadio equipmentCommunications system
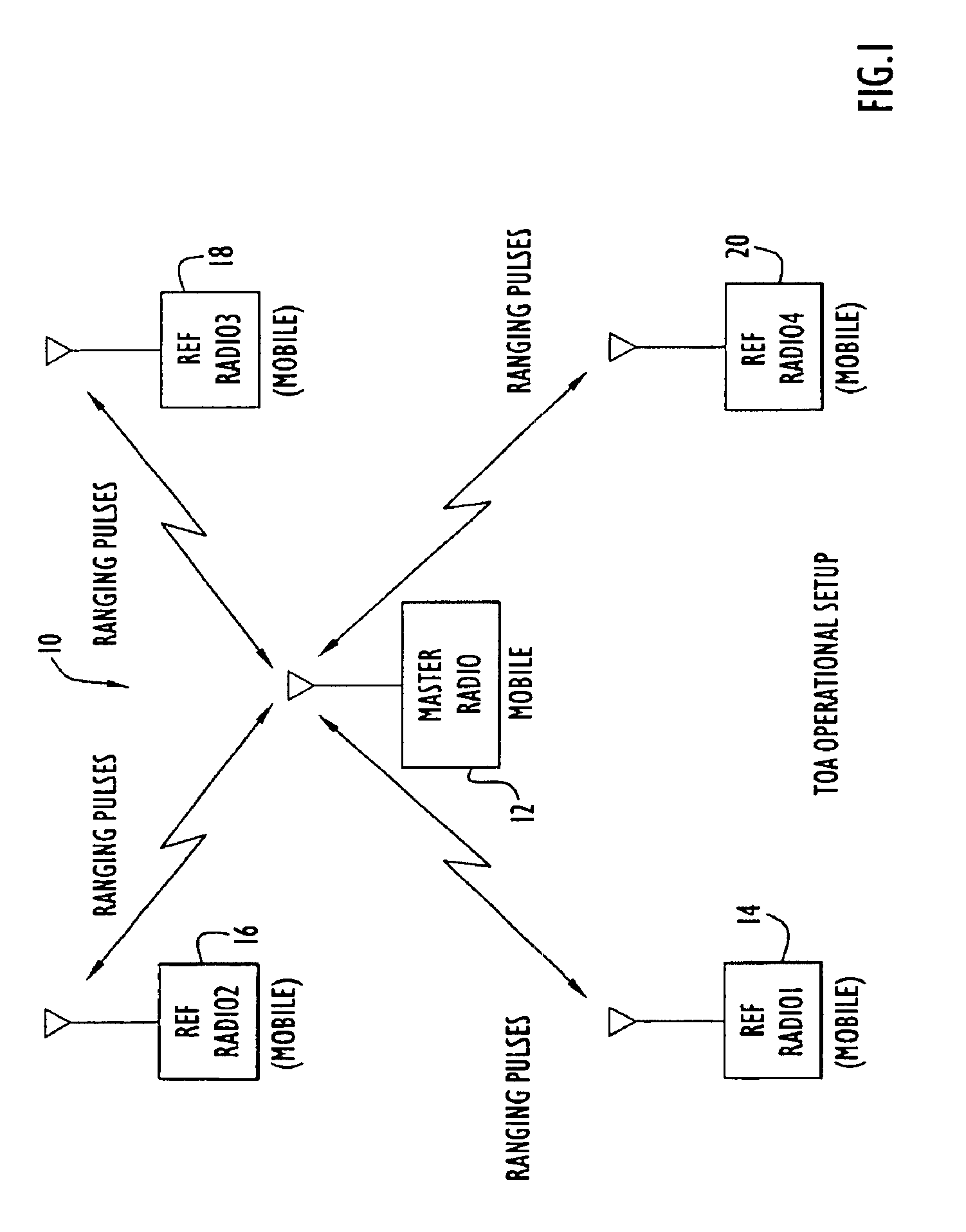
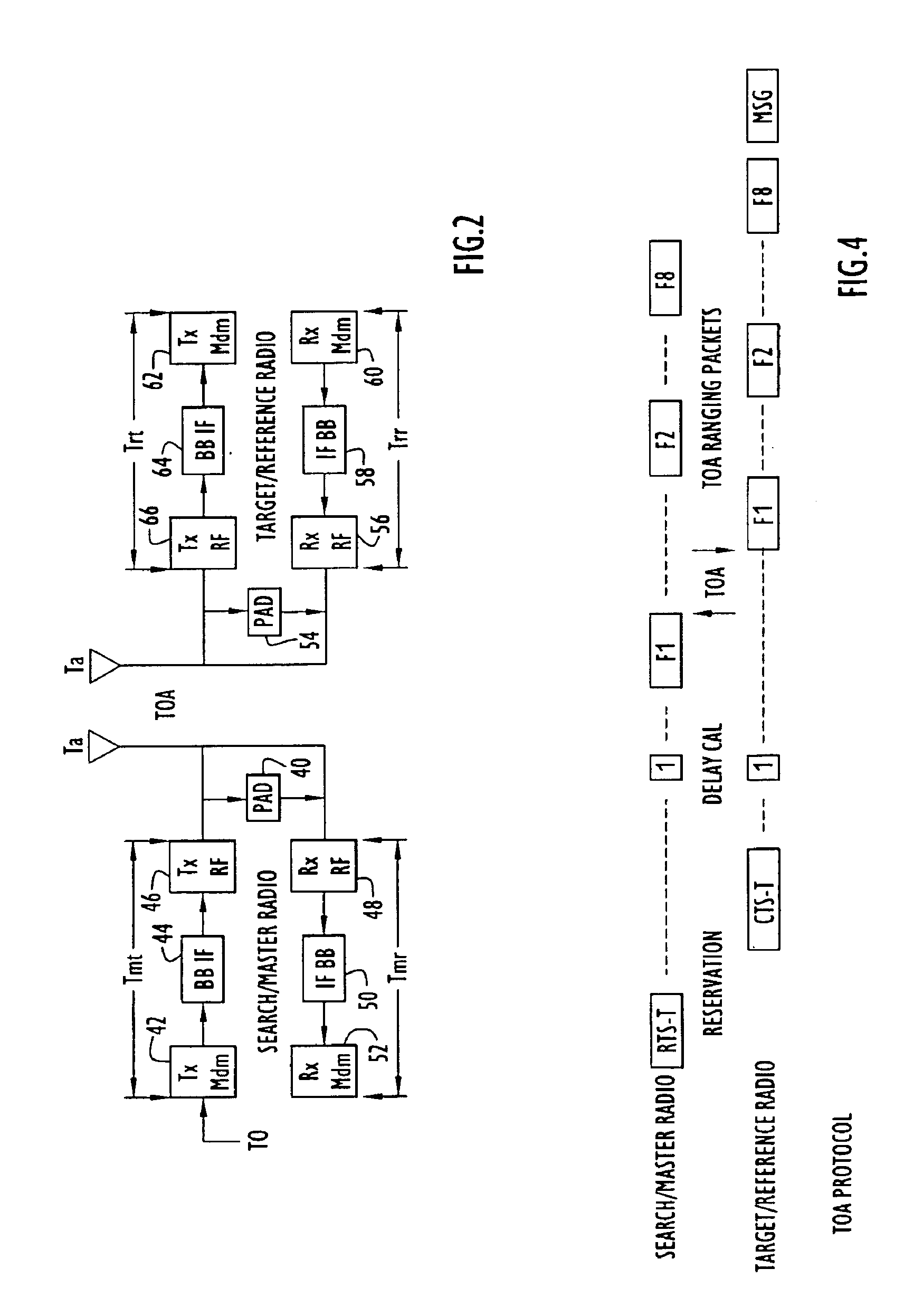
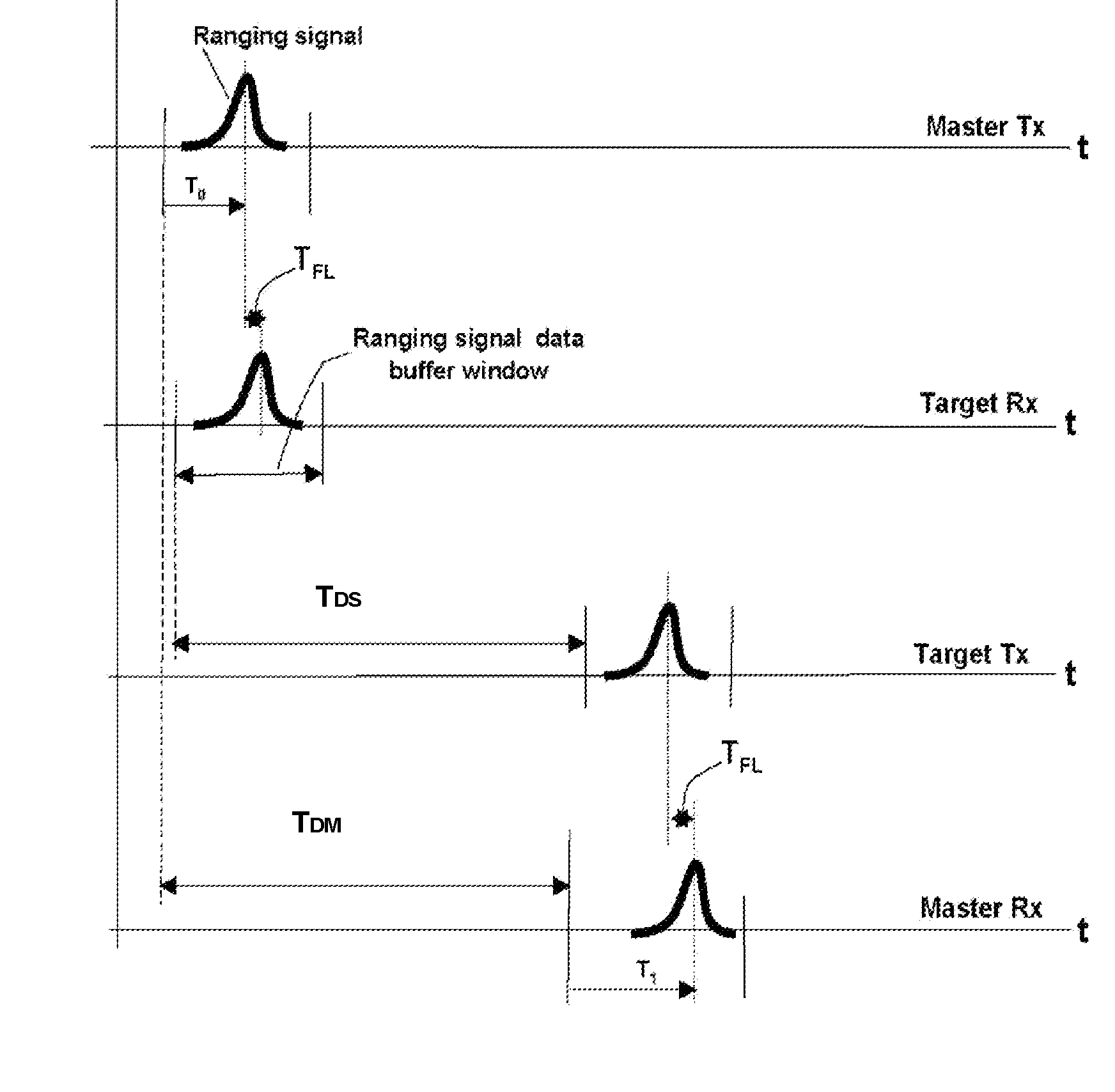
A high accuracy search and tracking system that uses a round-trip messaging scheme in which the time of arrive (TOA) of ranging signals is accurately determined to yield the range estimates between a target communications device and one or more search communications devices. Successive ranging estimates are used by a search device to home in upon the target device. The physical location pinpoint communications system can be used alone, or in combination with other location estimation systems that can be used initially, or throughout the search and tracking process to pinpoint the physical location of the target device. The search radio(s) transmits ranging signals to the target radio which responds by transmitting reply ranging signals. Upon reception of the reply ranging signal, the search radio determines the range to the reference radio from the signal propagation time. Errors in TOA estimates can be minimized using advanced processing techniques, if required.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
Methods and system for reduced attenuation in tracking objects using RF technology
ActiveUS20070139200A1Minimizes loss loss of accuracyMinimizes propagation loss lossPosition fixationRadio transmission for post communicationDigital signal processingUltrasound attenuation
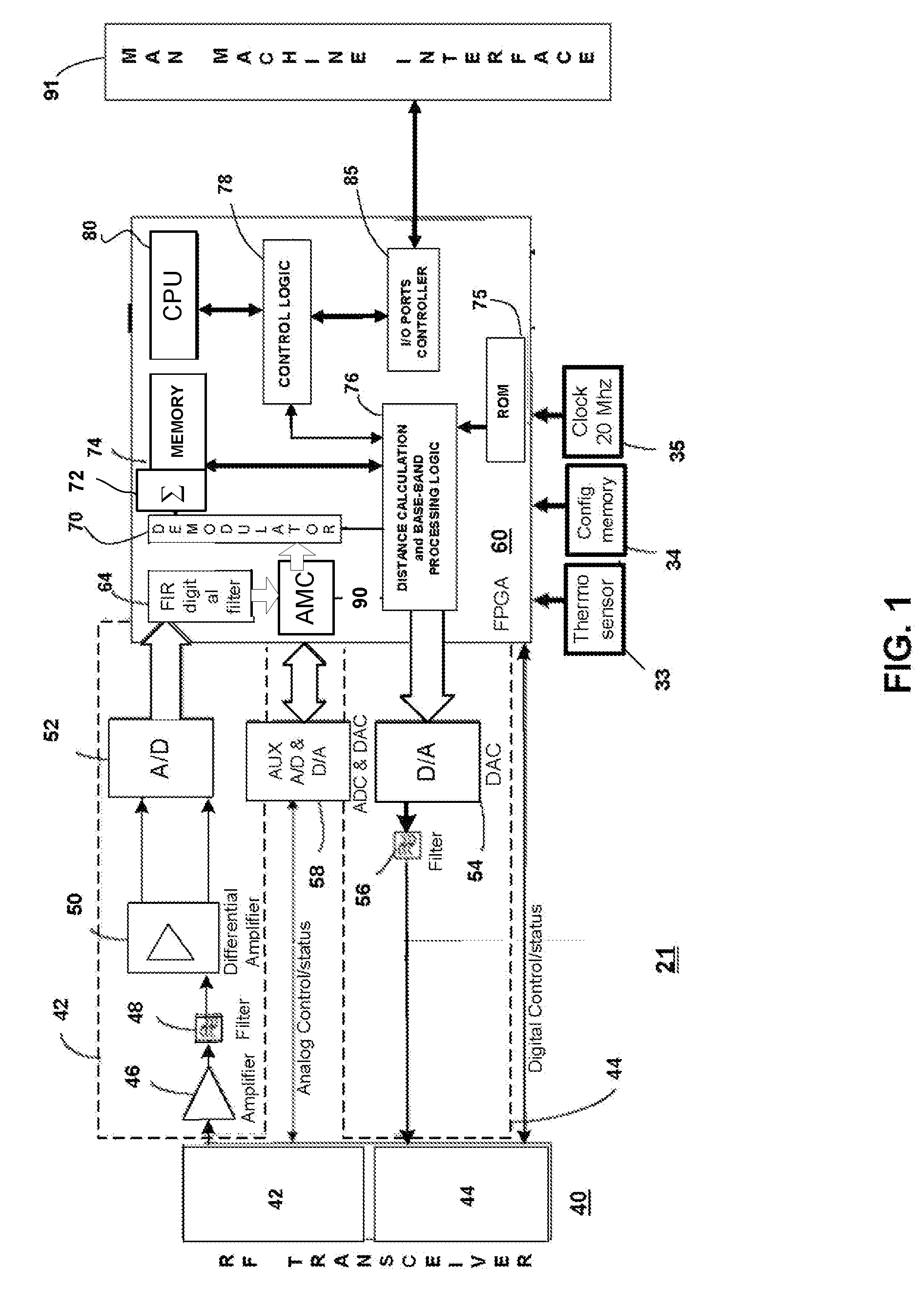
A method and system for a Radio Frequency (RF)-based identification, tracking and locating of objects. The method and system use a narrow bandwidth signal in VHF of lower frequency range, which minimizes propagation loss and loss of accuracy of the RF locating signals. The signal is sent from a Master Unit(s) to a Tag. The signal traveling time is recorded and the distance between the Master(s) and the Tag is calculated. The method and system allow achieving a longer distance of the RF signal penetration and an increased accuracy by using VHF bands. The techniques of Digital Signal Processing and Software-Defined Radio are used. The actual waveforms transmitted and received by the radios are defined by the software. The roles of the Master Unit(s) and the Tag can be reversed.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECHNOLOGIES INC
Ultrasonic tracking and locating system
ActiveUS20060013070A1Improve data transfer performanceDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationUltrasonic sensorSonification
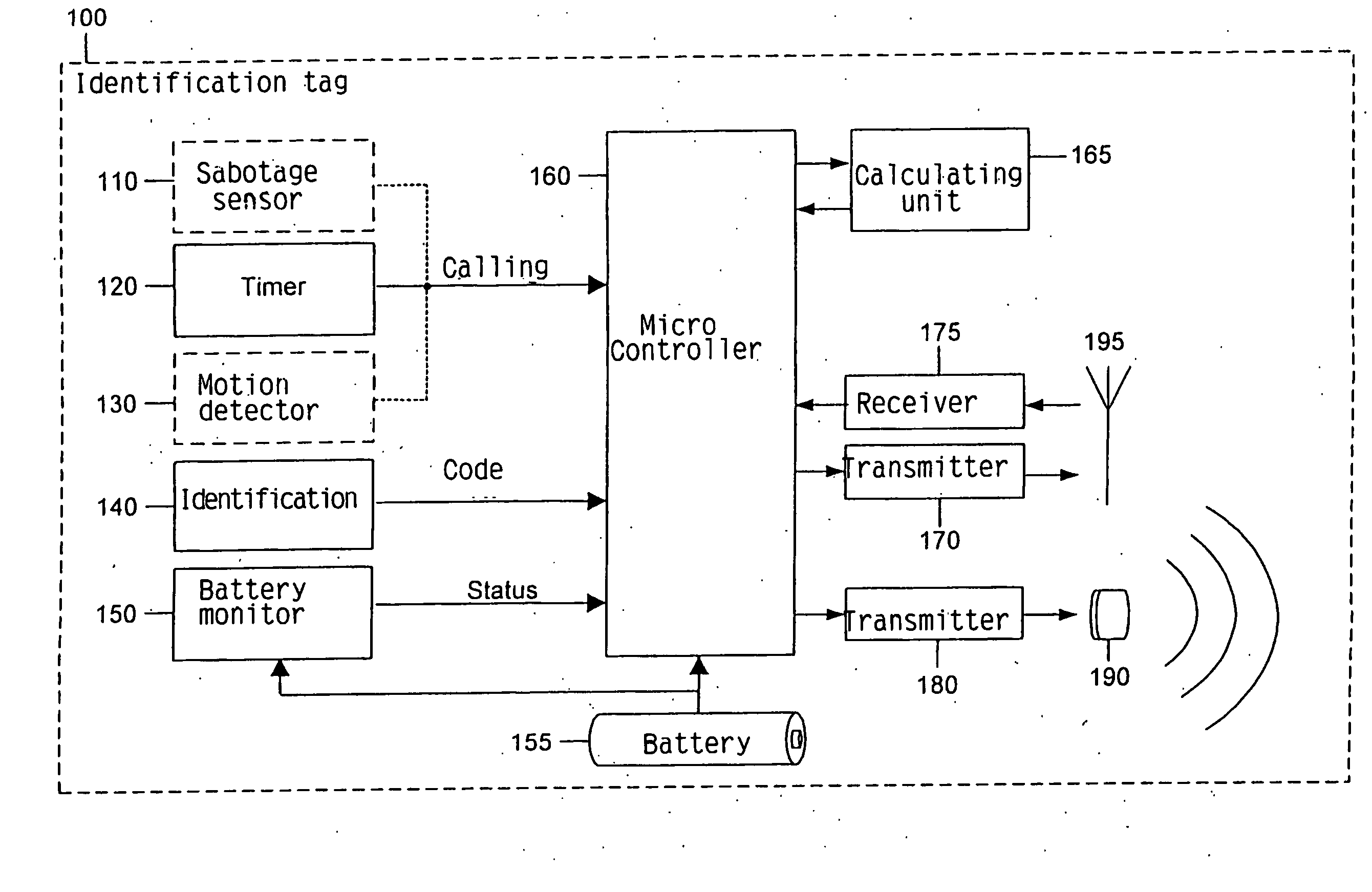
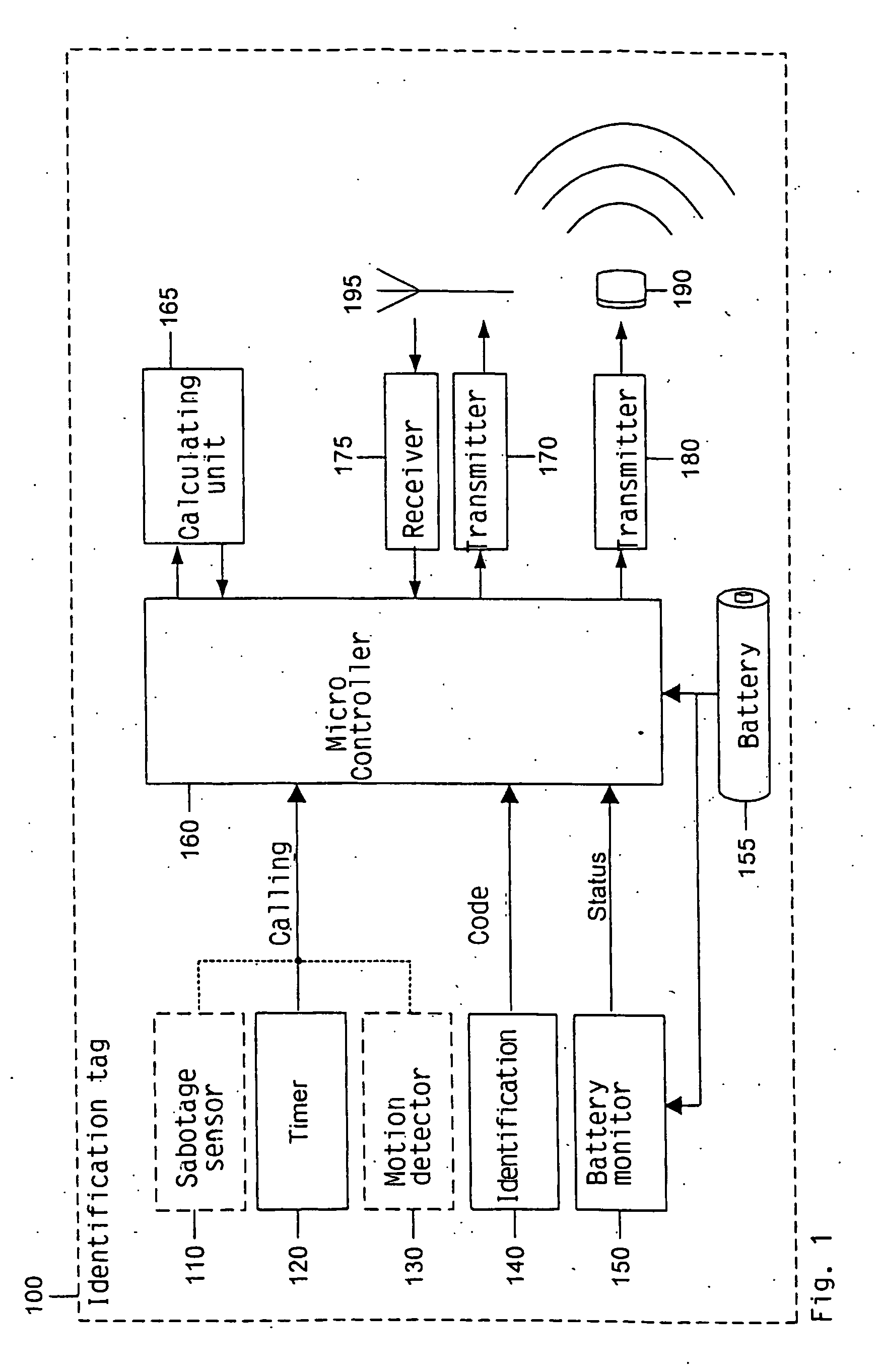
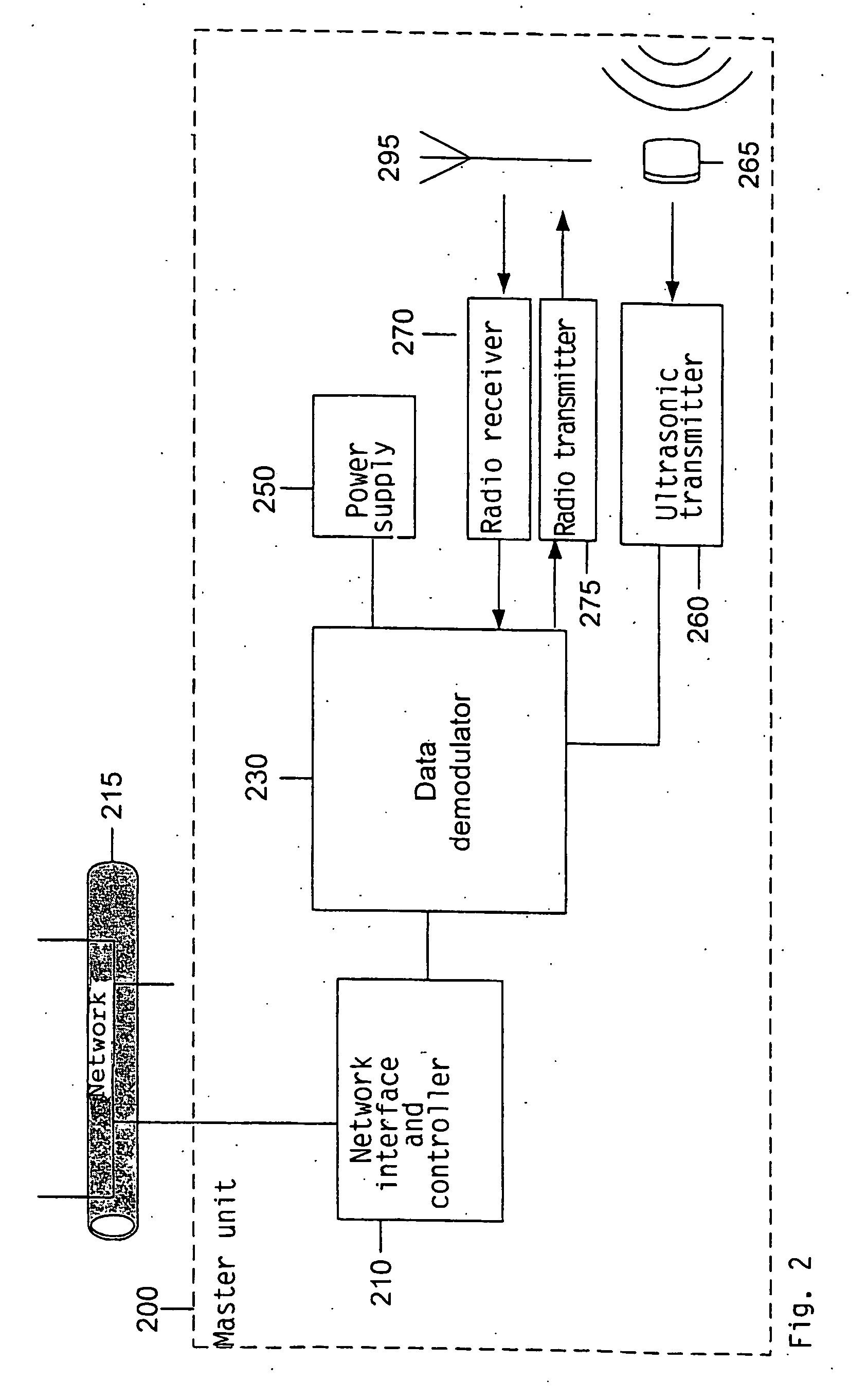
The invention relates to a method and a system for monitoring and position determination of objects and / or living beings within an area, such as, e.g. a room in a building. The system comprises a plurality of electronic units, called identification tags, which are attached to the objects that have to be monitored. Each identification tag has its own identification code (ID code) and is equipped with an ultrasonic transmitter, radio transmitter and radio receiver. The ultrasonic signals are recieved by one or more master and slave units which calculate transit time differences of ultrasonic pulses. This information together with the identification tags' ID code, identification of the room in which it is located, and any additional information are transmitted to a central processing unit which calculates the identification tag's position and presents it to a user of the system.
Owner:SONITOR TECH
Methods and system for reduced attenuation in tracking objects using RF technology
ActiveUS7561048B2Minimizes of accuracyMinimizes propagationPosition fixationRadio transmission for post communicationDigital signal processingUltrasound attenuation
A method and system for a Radio Frequency (RF)-based identification, tracking and locating of objects. The method and system use a narrow bandwidth signal in VHF of lower frequency range, which minimizes propagation loss and loss of accuracy of the RF locating signals. The signal is sent from a Master Unit(s) to a Tag. The signal traveling time is recorded and the distance between the Master(s) and the Tag is calculated. The method and system allow achieving a longer distance of the RF signal penetration and an increased accuracy by using VHF bands. The techniques of Digital Signal Processing and Software-Defined Radio are used. The actual waveforms transmitted and received by the radios are defined by the software. The roles of the Master Unit(s) and the Tag can be reversed.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECHNOLOGIES INC
Multi-path mitigation in rangefinding and tracking objects using reduced attenuation RF technology
ActiveUS7969311B2Small incremental costImprove accuracyMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesPosition fixationDigital signal processingSignal element
A method and system for identification, tracking and locating in wireless communications and wireless networks. The method and system use reference and / or pilot signals that are present in wireless communications and wireless networks. The method and system might also use RTT, TOA and time-stamping measurements / techniques to determine one or more reference signals traveling time between the Base Station (eNB) or its functional equivalent and mobile device (UE) and or network device. Other wireless networks that do not use reference and / or pilot signals may employ one or more of the following types of alternate embodiments of present invention: 1) where a portion of frame is dedicated to the ranging signal / ranging signal elements; 2) where the ranging signal elements are embedded into (spread across) transmit / receive signals frame(s); and 3) where the ranging signal elements are embedded with the data. The method and system includes multi-path mitigations processor and multi-path mitigations techniques and algorithms which improve the track-locate accuracy. The method and system allow achieving increased accuracy by using multi-path mitigations processor and multi-path mitigations techniques and algorithms. The techniques of Digital Signal Processing and Software-Defined Radio are used.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECHNOLOGIES INC
Methods and system for multi-path mitigation in tracking objects using reduced attenuation RF technology
ActiveUS7872583B1Small incremental costImprove accuracyPosition fixationDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingUltrasound attenuation
A method and system for a long range Radio Frequency (RF)-based identification, tracking and locating of objects. The method and system use a narrow bandwidth ranging signal(s), including VHF of lower frequency bands, which minimizes propagation loss and loss of accuracy of the RF locating signals. The method and system includes narrow bandwidth ranging signal multi-path mitigations processor, which further improves the track-locate accuracy. The signal is sent from a Master Unit(s) to a Tag. The signal traveling time is recorded and the distance between the Master(s) and the Tag is calculated. The method and system allow achieving a longer distance of the RF narrow bandwidth ranging signal penetration and an increased accuracy by using VHF bands in conjunction with the narrow bandwidth ranging signal multi-path mitigations processor. The techniques of Digital Signal Processing and Software-Defined Radio are used. The actual waveforms transmitted and received by the radios are defined by the software. The roles of the Master Unit(s) and the Tag can be reversed.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECHNOLOGIES INC
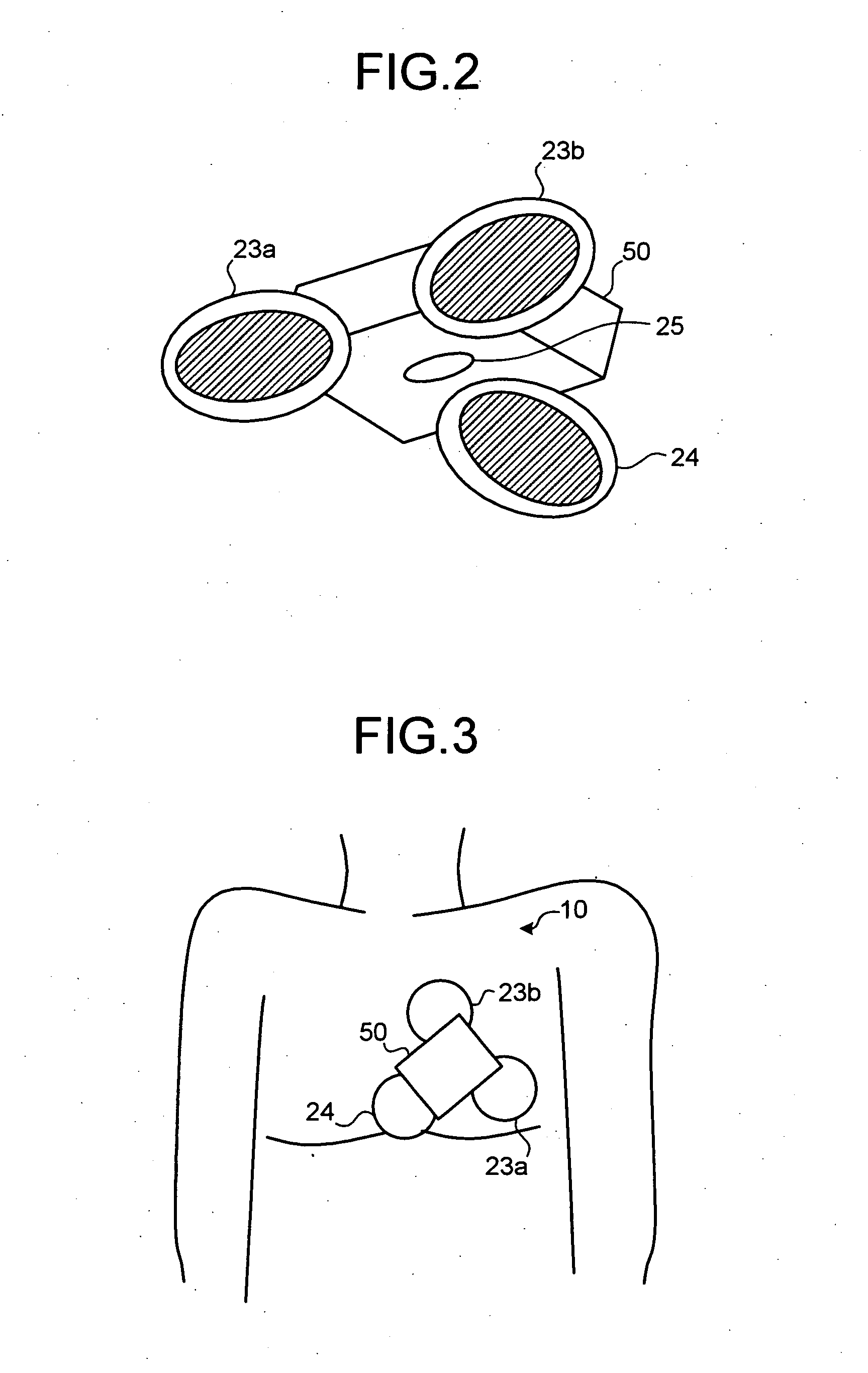
System and methods for detecting ischemia with a limited extracardiac lead set
Disclosed is a system for detecting pathophysiological cardiac conditions from a reduced number of extracardiac leads. A right side lead measures the electrical signal between the middle superior chest region over the heart and inferior right torso position. A left side lead measures the electrical signal between the left precordial chest region and an inferior left lateral or posterior torso position. The lead montage is preferably chosen so that, regardless of patient position (e.g. supine, upright), negative ST segments and / or T waves are used to detect right coronary or left circumflex ischemia. Also, in these positions, reduced slope of the final deflection in the QRS can be used to detect these types of ischemia. To detect transmural ischemia, the system examines changes in QRS slopes, ST segment, T wave and the difference between the J point and the PQ potentials. In addition, for transmural ischemia associated with the left anterior descending artery, a proxy for the propagation time across the front of the heart is examined by comparing QRS features of the right side lead with QRS features of the left side lead. Histogram profiles, trends, and statistical summaries, especially running averages, of all of the above mentioned features, corrected for heart rate, are maintained.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
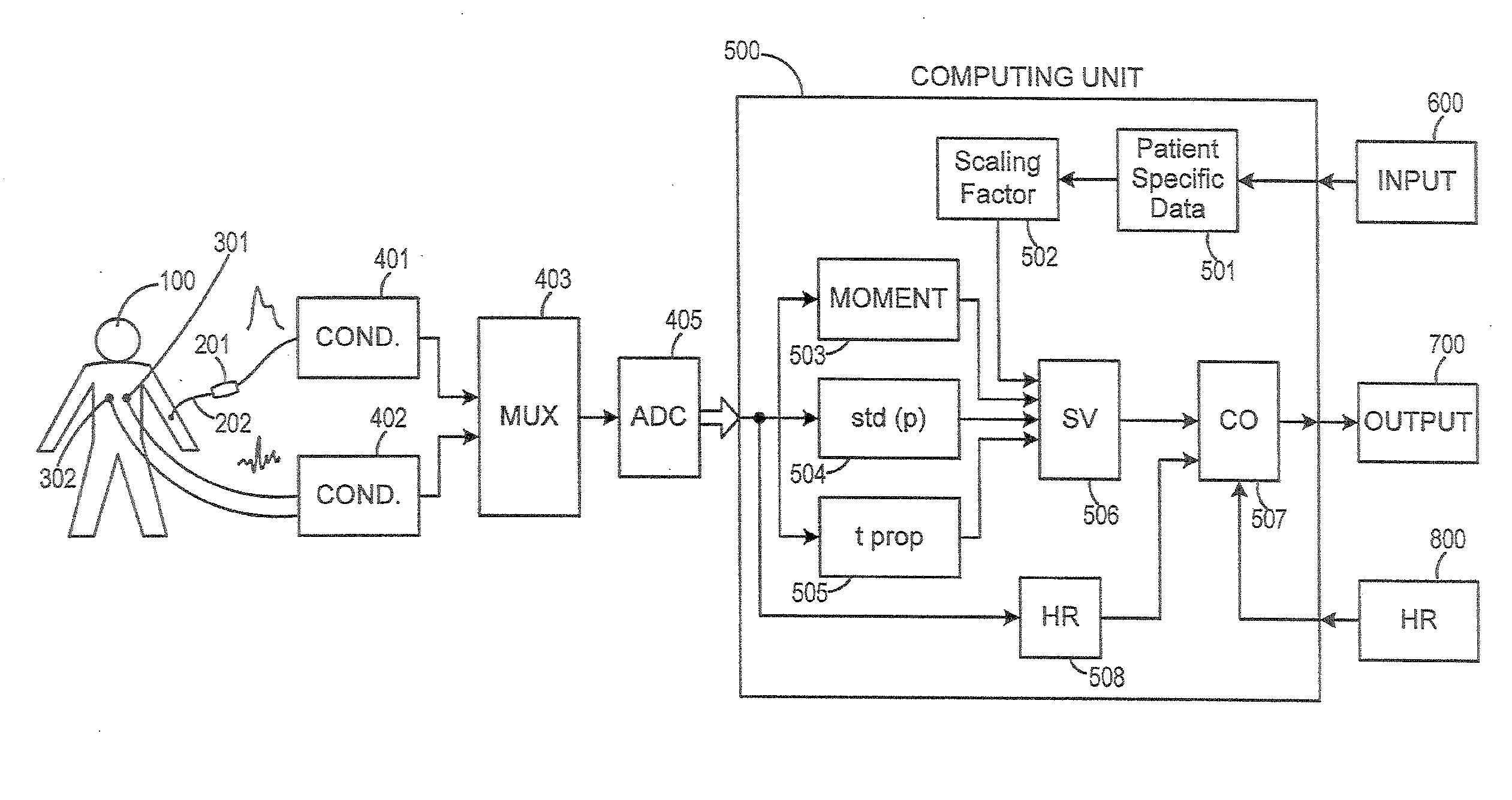
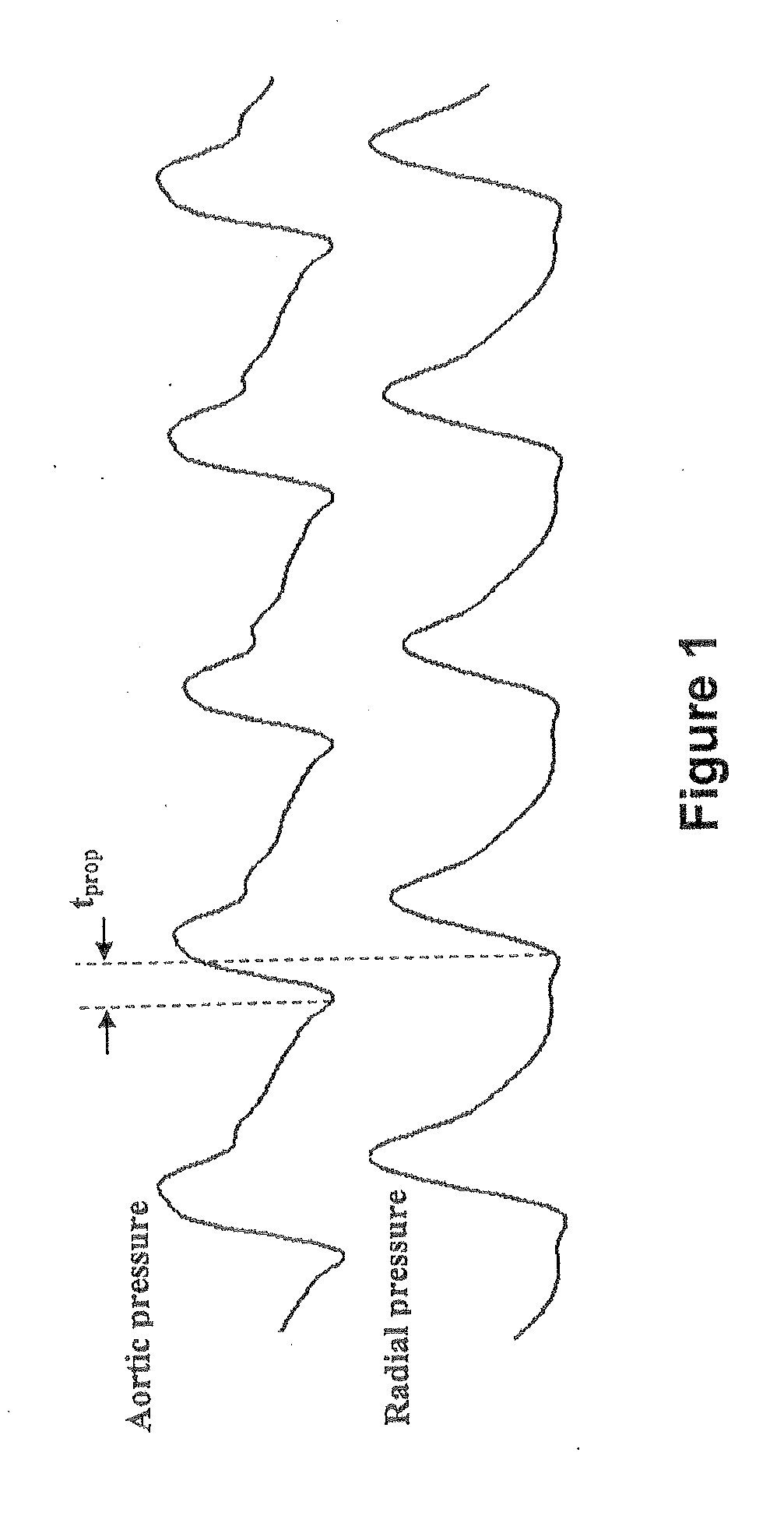
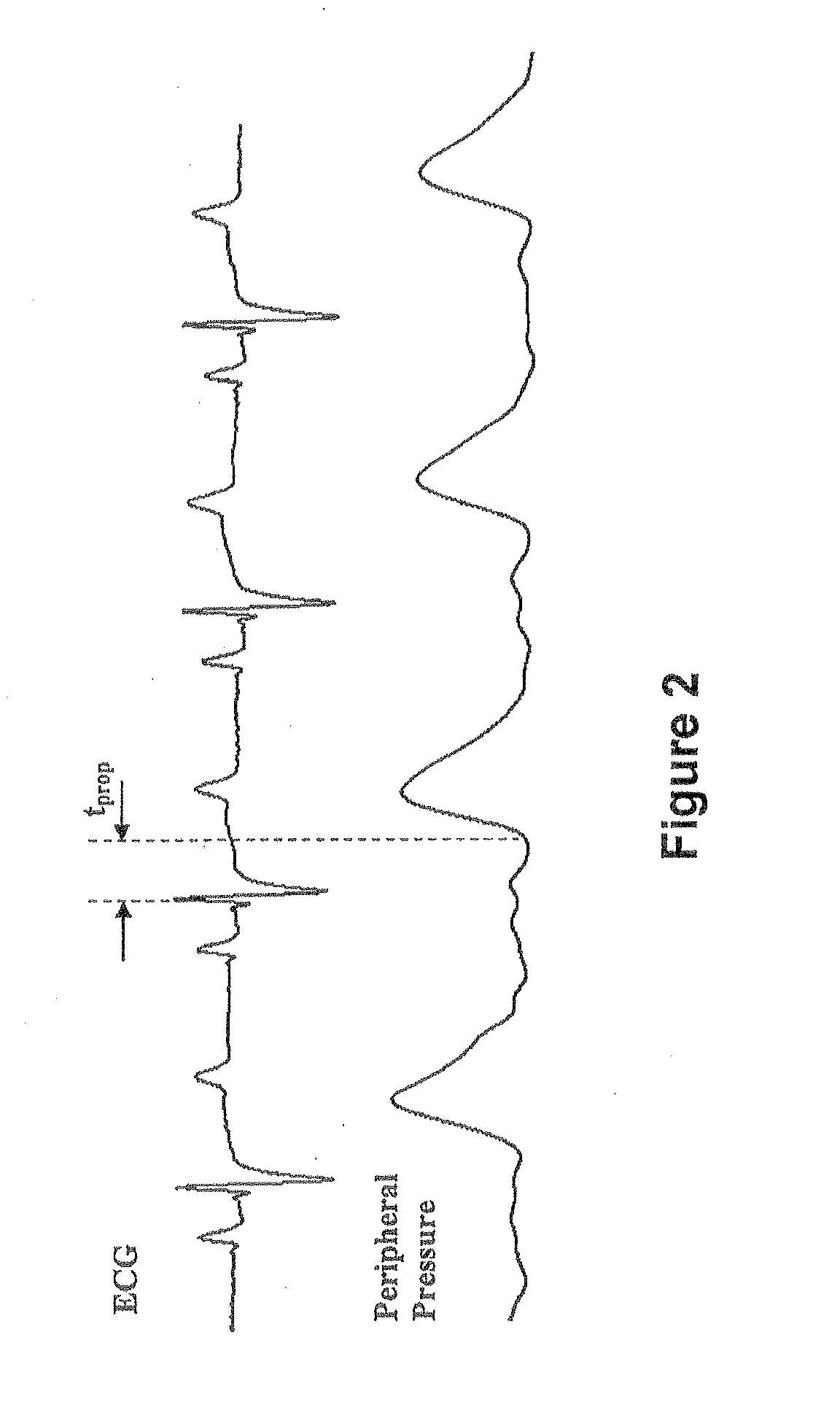
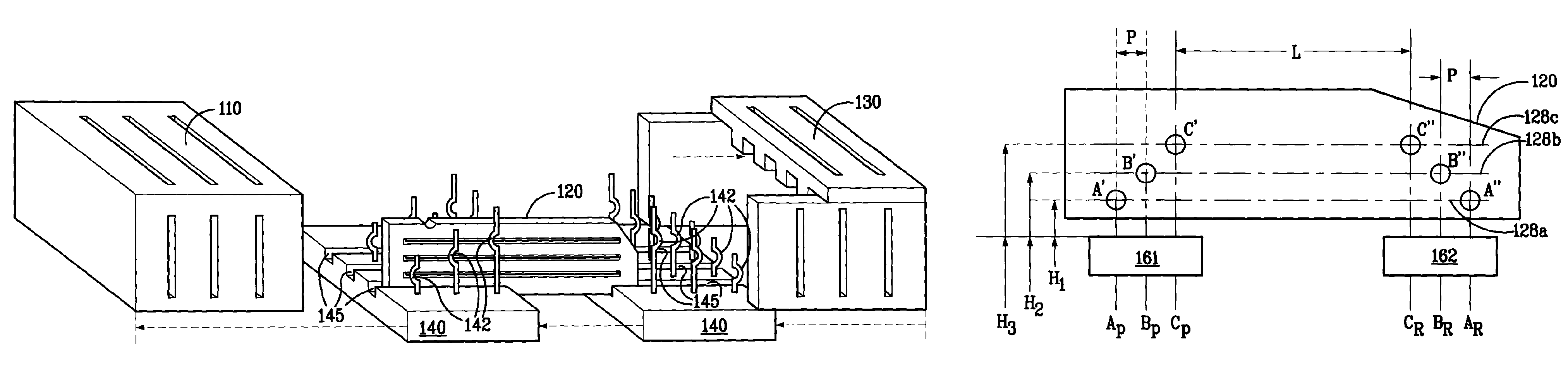
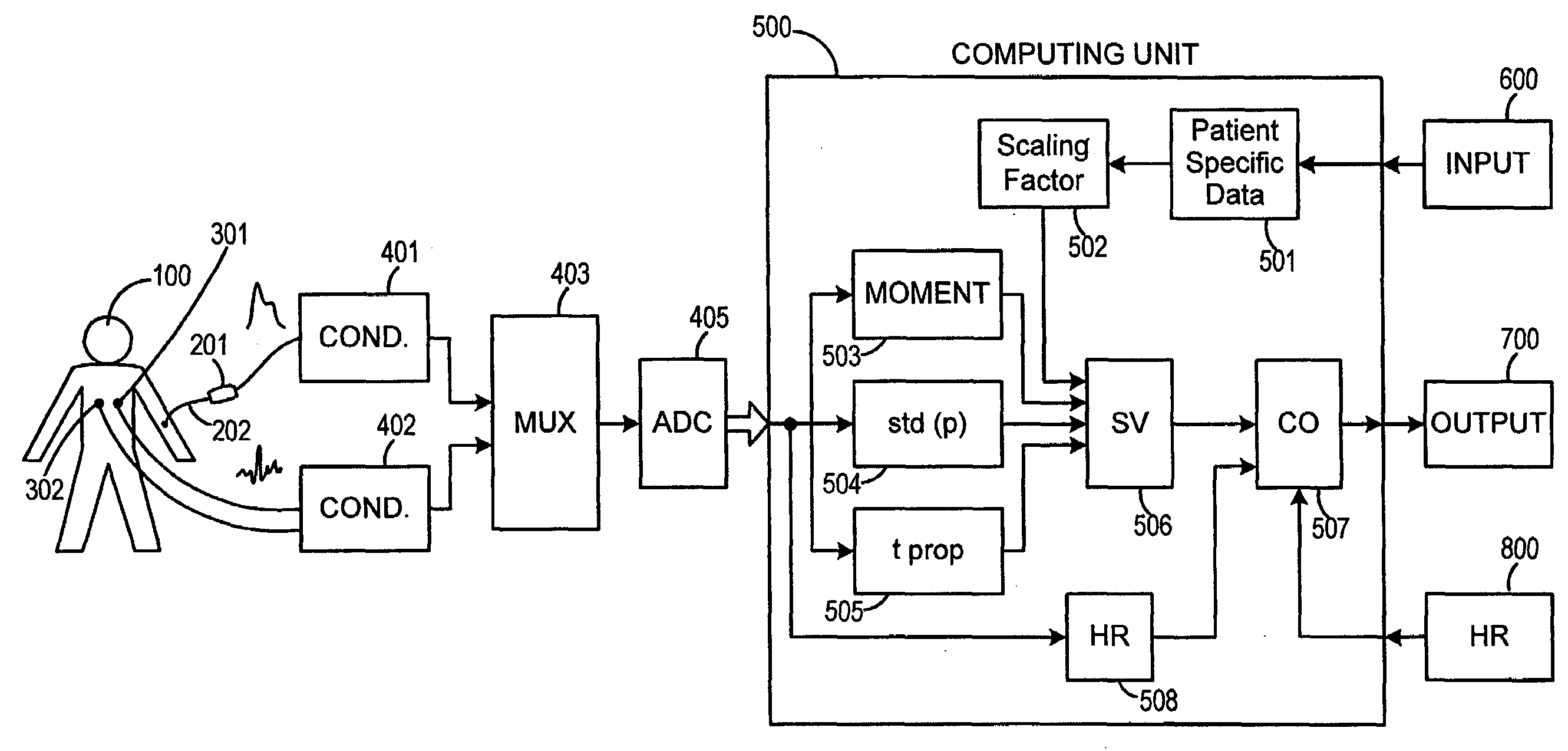
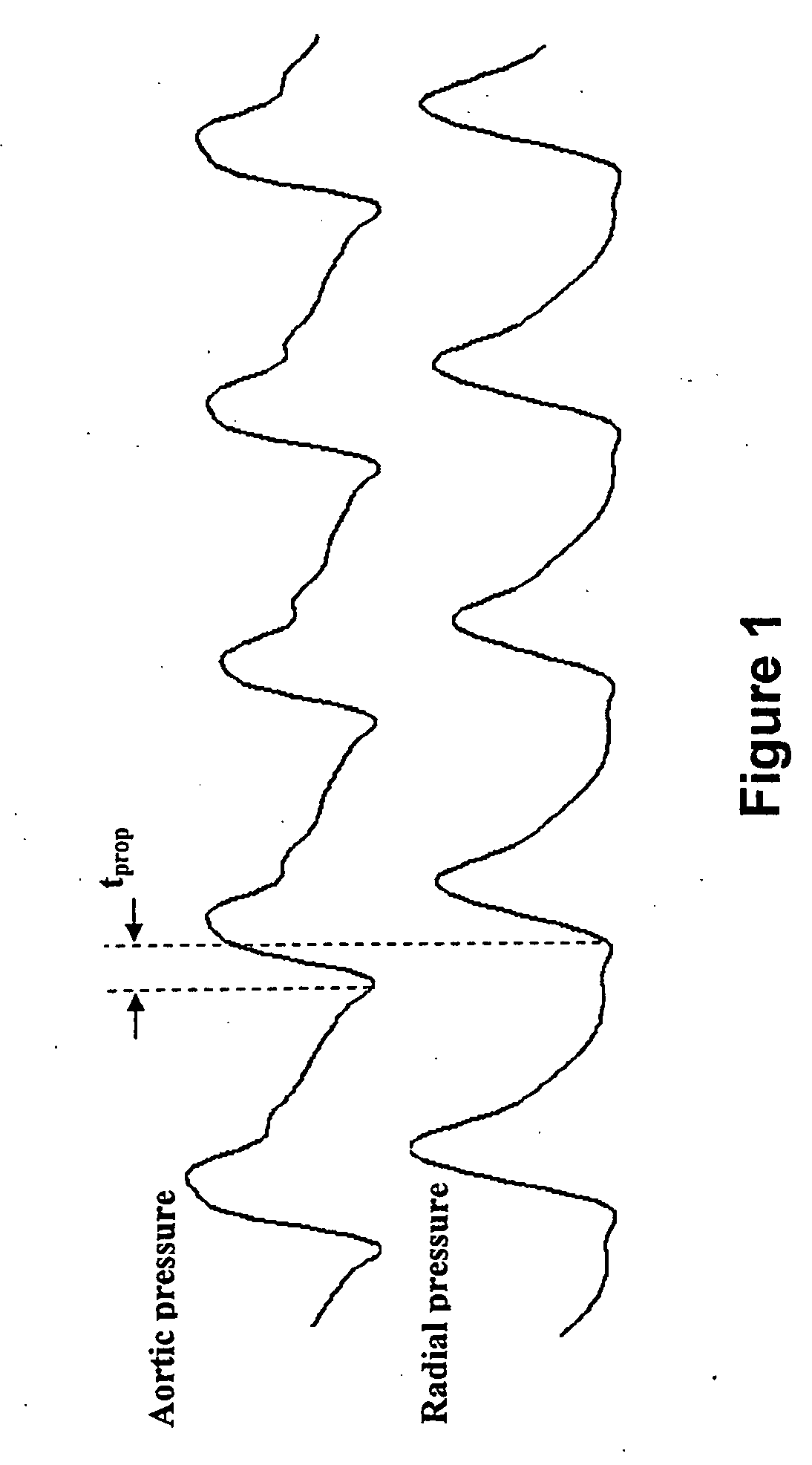
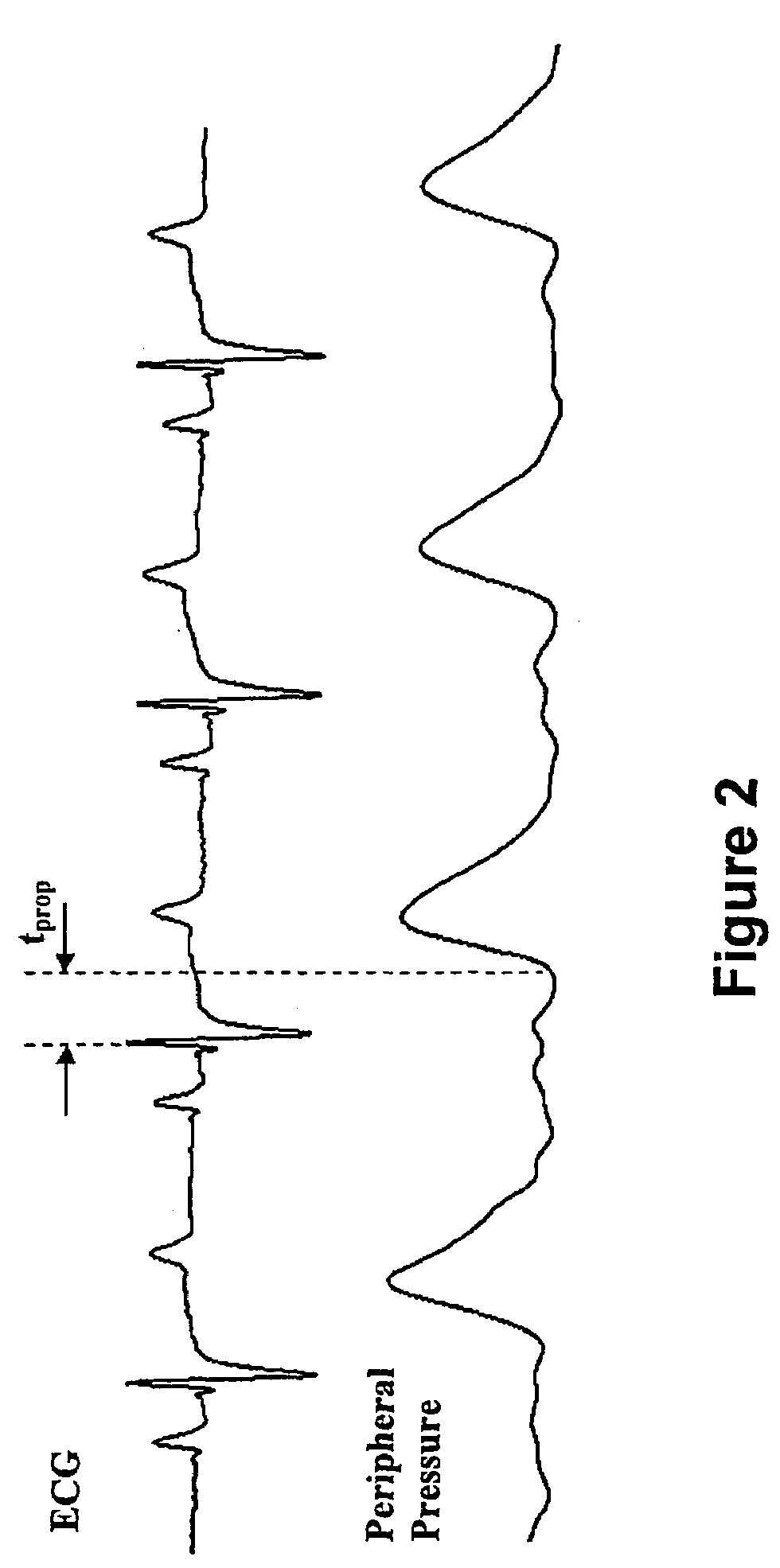
Method and Apparatus for Continuous Assessment of a Cardiovascular Parameter Using the Arterial Pulse Pressure Propagation Time and Waveform
InactiveUS20080015451A1ElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesCardiac cycleArterial pulse pressure
A method and apparatus for determining a cardiovascular parameter including receiving an input signal corresponding to an arterial blood pressure measurement over an interval that covers at least one cardiac cycle, determining a propagation time of the input signal, determining at least one statistical moment of the input signal, and determining an estimate of the cardiovascular parameter using the propagation time and the at least one statistical moment.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
In vivo port wine stain, burn and melanin depth determination using a photoacoustic probe
ActiveUS7322972B2Avoid introducingSurgical instrument detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringBurning tissueBurn tissue
A photoacoustic probe for port wine stain (PWS), burn and melanin depth measurements is comprised of optical fibers for laser light delivery and a piezoelectric element for acoustic detection. The probe induced and measured photoacoustic waves in acryl amide tissue phantoms and PWS skin in vivo. Acoustic waves were denoised using spline wavelet transforms, then deconvolved with the impulse response of the probe to yield initial subsurface pressure distributions in phantoms and skin. The waves were then analyzed for epidermal melanin concentration, using a photoacoustic melanin index (PAMI) related to the amount of laser energy absorbed by melanin. Propagation time of the photoacoustic wave was used to determine the depth of blood perfusion underlying necrotic, burned tissue. Thus, the photoacoustic probe can be used for determining PWS, burn and melanin depth for most patients receiving laser therapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
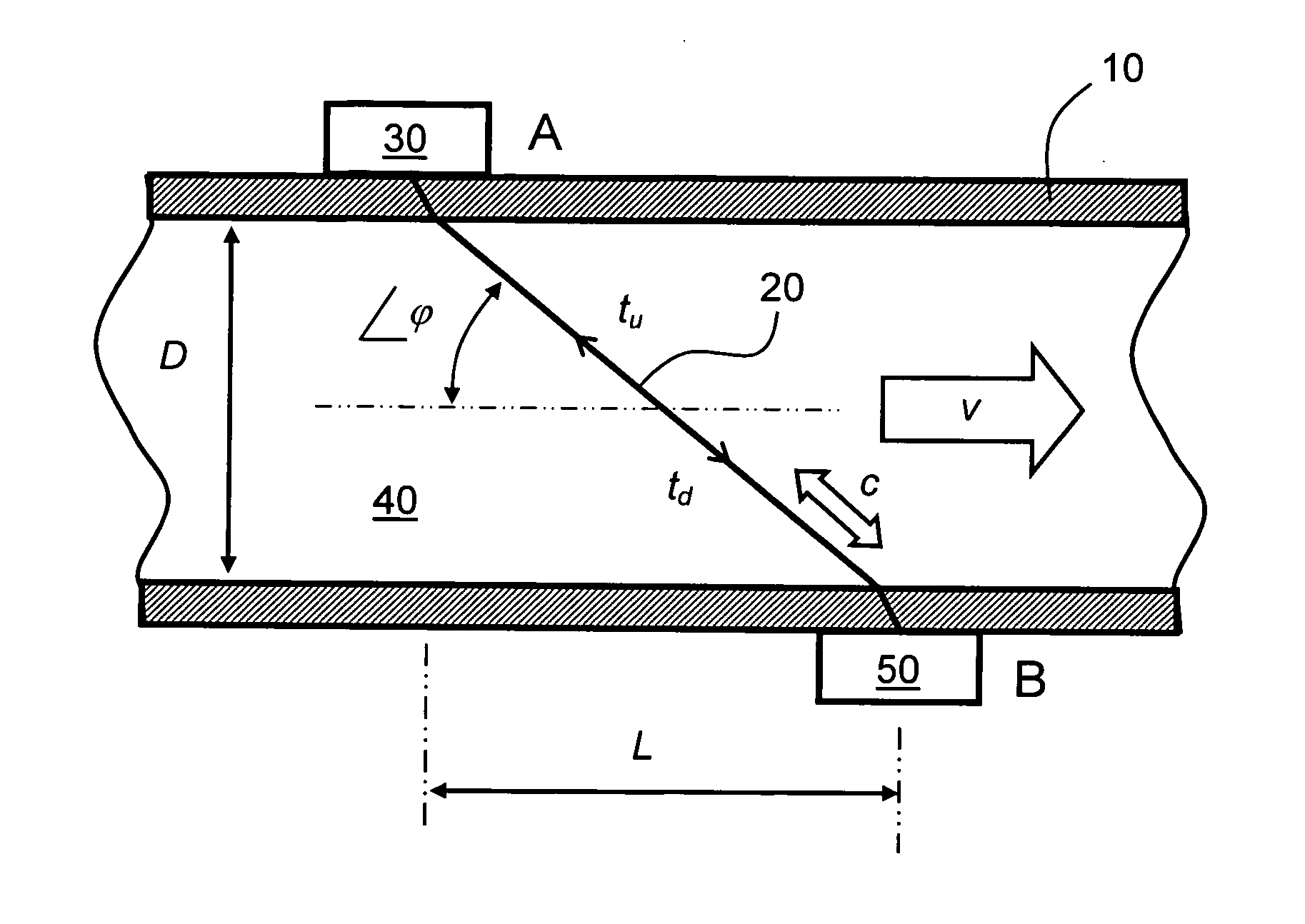
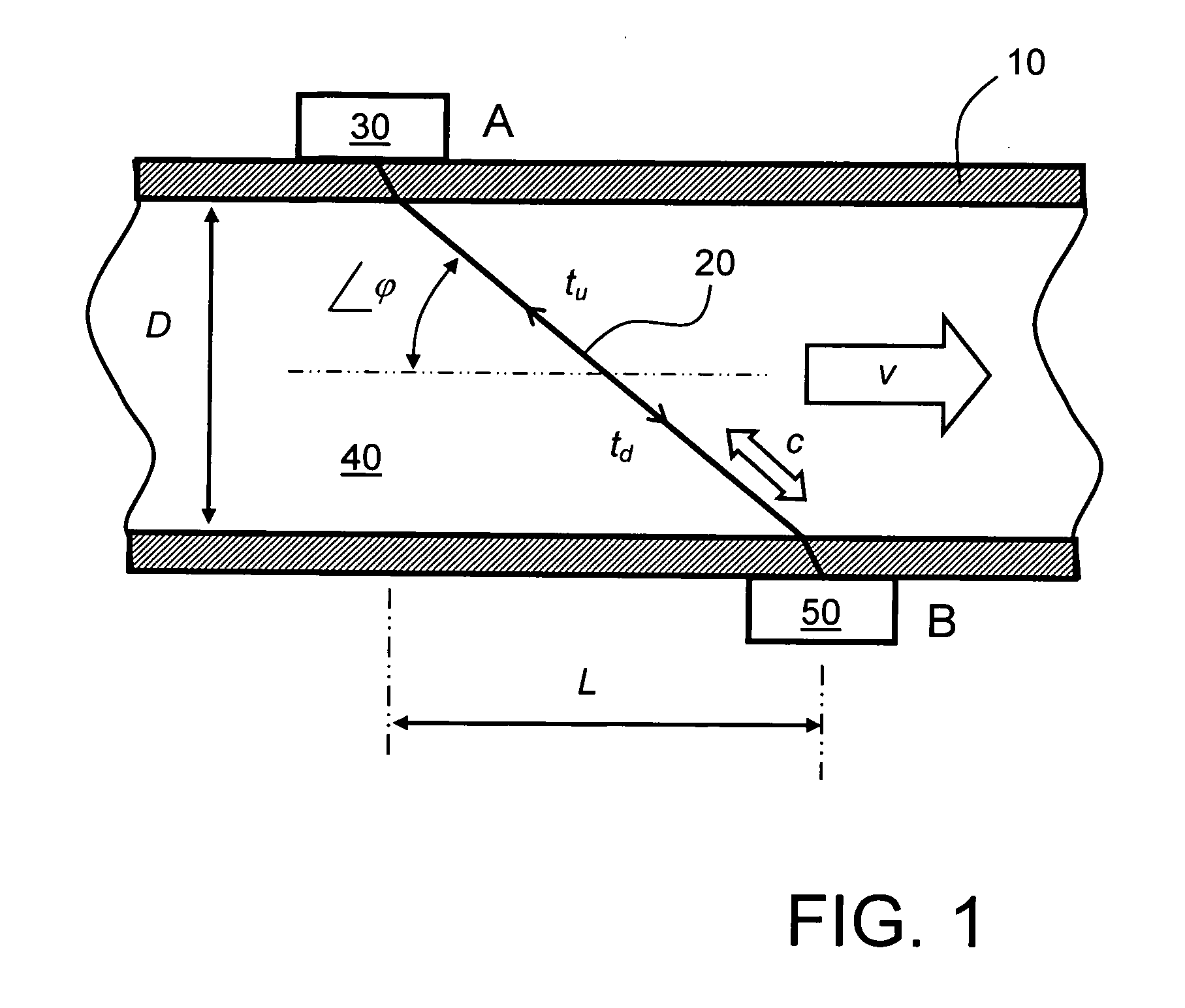
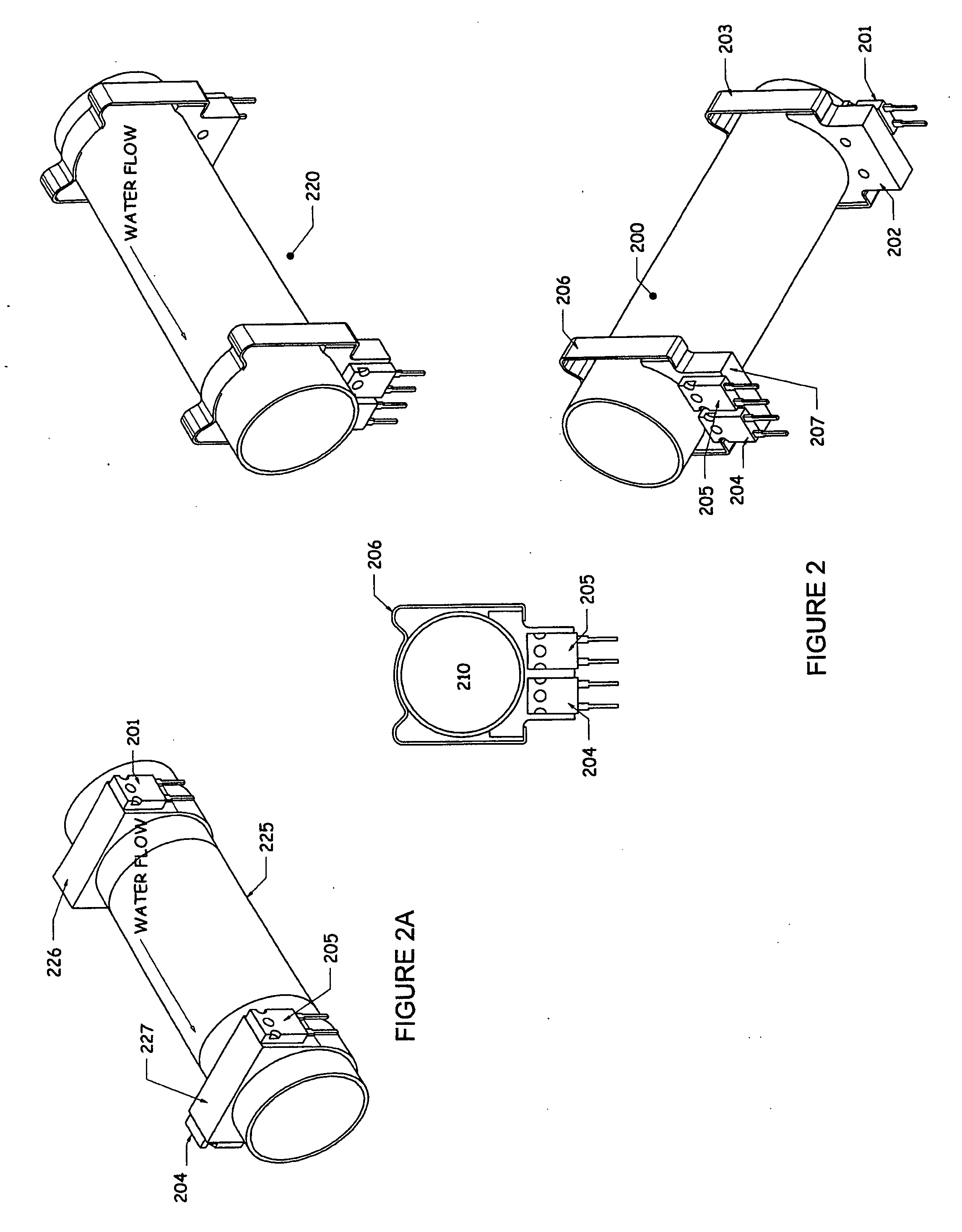
Flow measuring apparatus
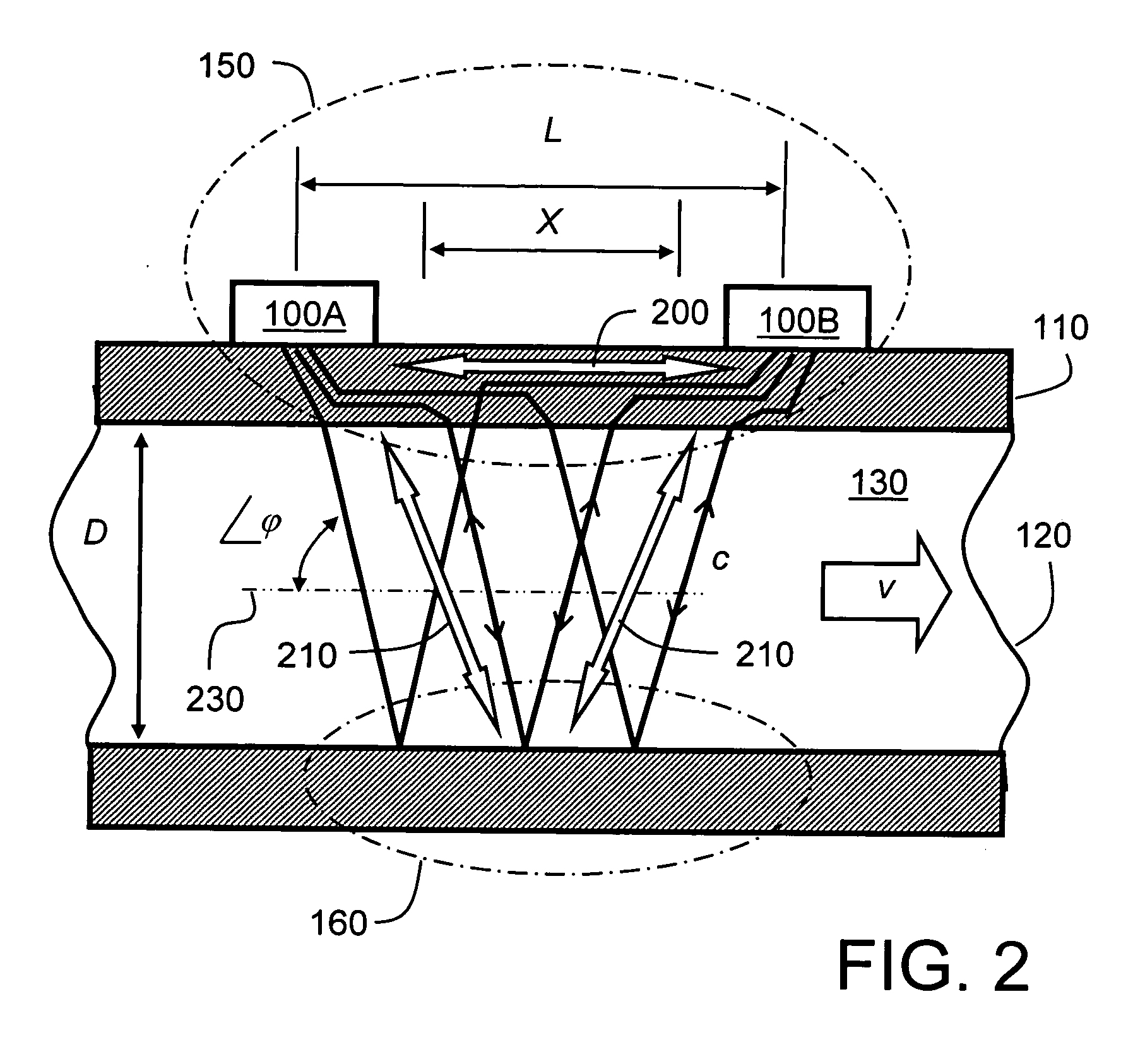
ActiveUS20110271769A1Reliable and accurate measurementImprove energy transferFlow propertiesVolume flow measuring devicesPropagation timeUltrasonic radiation
A flow measuring apparatus (300, 500) measures a fluid flow (130) within a conduit (120) including a wall (110). The apparatus (300, 500) includes a transducer arrangement including at least two transducers (100A, 100B) for alternately emitting and receiving ultrasonic radiation through the conduit wall (110) and the flow (130). The apparatus (300, 500) also includes a signal processing arrangement (310) for generating signals to excite the transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) and for processing received signals provided by the transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) for generating output signals from the signal processing arrangement (310) indicative of properties of the flow. The transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) in cooperation with the conduit (120) provides a first path (200) for Lamb-wave ultrasonic radiation coupling directly from a first of the at least two transducers (100A, 100B), to a second of said at least two transducers to generate a first received signal. The transducer arrangement (100A, 100B) in cooperation with the conduit (120) provides at least one second path (210) for ultrasonic propagation along the wall (100) via Lamb waves coupling to at least a portion of the flow (130) from a first of the at least two transducers (100A, 100B) to a second of the at least two transducers (100A, 100B) to generate a second received signal. The signal processing arrangement (310) determines from said first and second received signals ultrasonic radiation propagation time periods through the first path (200) and through the at least one second path (210), and to perform computational operations on the propagation time periods to determine properties of the flow including, but not limited to, at least one of: fluid flow velocity (v) in the conduit (120), a sound velocity (c) through the fluid (130).
Owner:XSENS
Apparatus and Method to Identify Targets Through Opaque Barriers
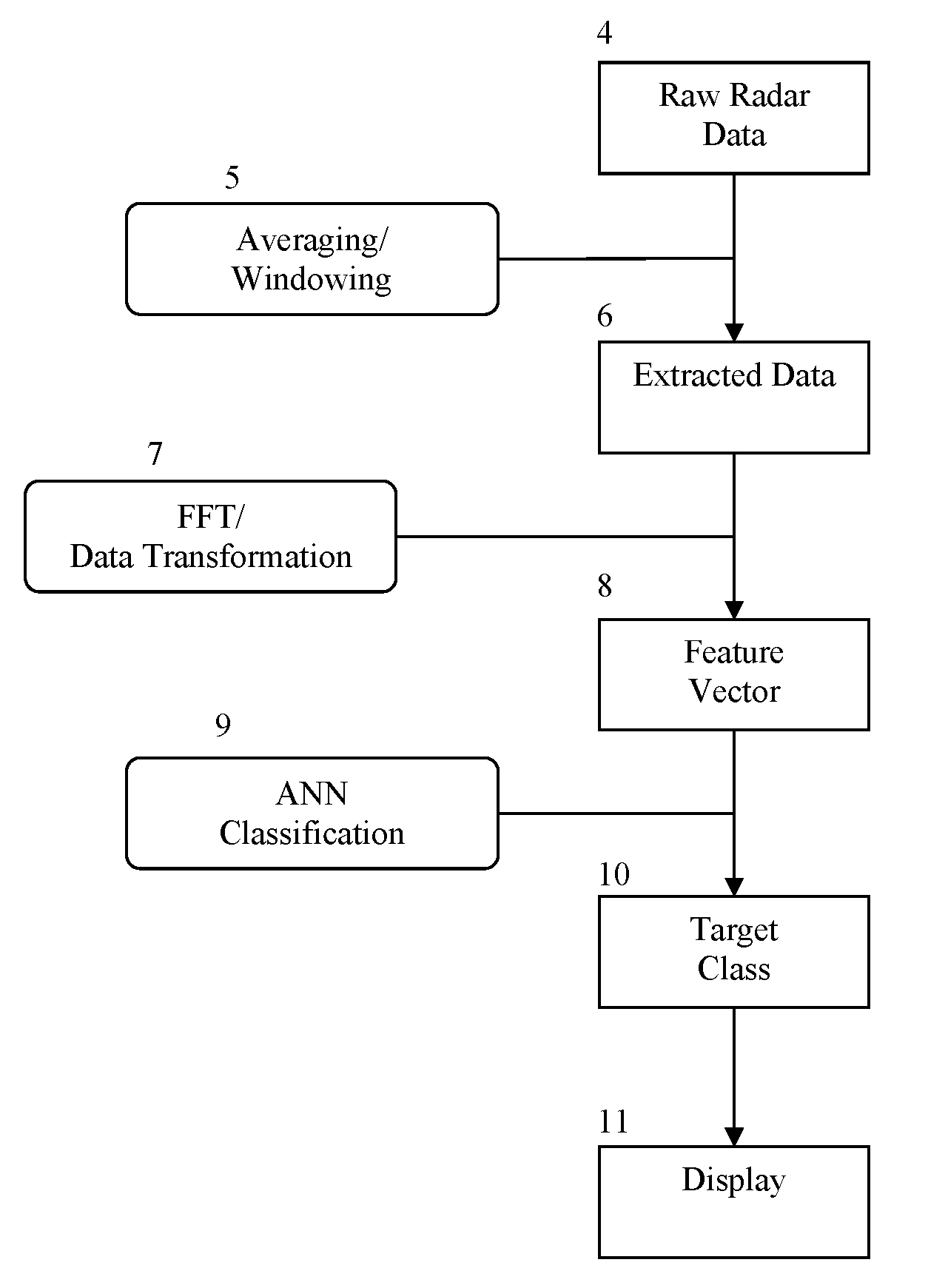
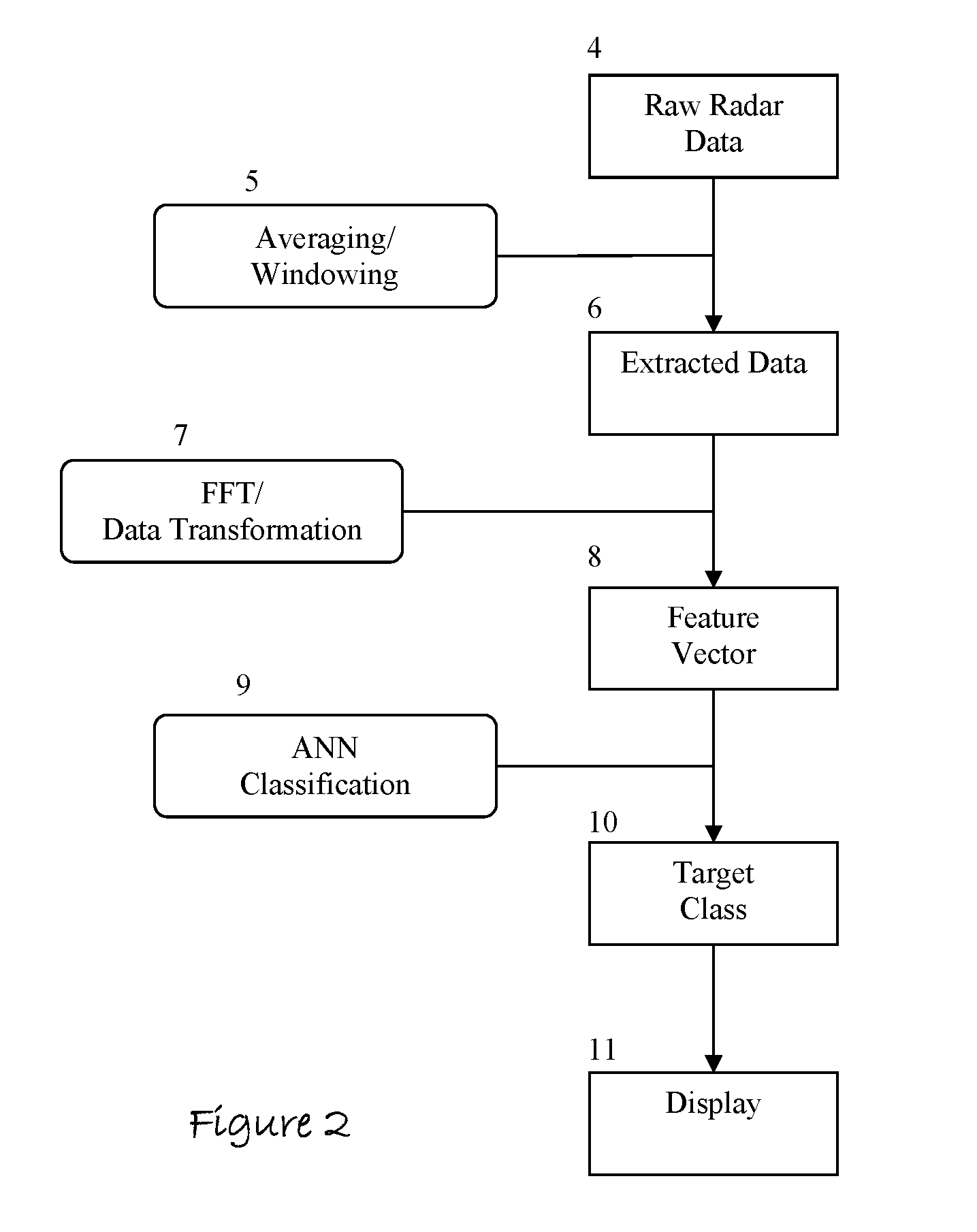
InactiveUS20070205937A1Well representedMitigation extensionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra-widebandFrequency spectrum
The present invention is a method and apparatus that provides detection, characterization, and intuitive dissemination of targets. This disclosure combines improvements to ultra-wideband (UWB) sensing and machine target characterization with a means to convey data in a format that is quickly and readily understood by practitioners of the technology. The invention is well suited for Situational Awareness (SA) support in areas that are occluded by rain, fog, dust, darkness, distance, foliage, building walls, and any material that can be penetrated by ultra-wideband RF signals. Sense Through The Wall (STTW) performance parameters including target range, stand-off distance, and probability of detection are improved herein by combining a dynamically positioned sliding windowing function with orthogonal feature vectors that include but are not limited to time amplitude decay, spectral composition, and propagation time position in the return signal data. This invention is particularly useful for STTW and SA applications including urban combat, law enforcement, fire protection, transportation security, and homeland security. The invention can also be used to detect objects that are concealed by clothing, debris, and other non-metallic materials.
Owner:REALTRONICS CORP
Multi-beam TDMA satellite mobile communications system
InactiveUS6314269B1Reduce congestionReduce errorsRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesNadirSignal quality
An earth station receives a return signal via more than one satellite link from a mobile terminal using TDMA. The earth station selects one or more of the satellite links for transmitting a forward signal on the basis of the quality of signal received via each link. The earth section allocates frequency channels to the mobile terminals according to their location on the surface of the earth, so that the propagation time to and from those mobile terminals which share the same frequency channel is approximately the same. The satellite includes an antenna which generates an array of beams which are individually pointed to fixed regions of the earth, until the elevation of the satellite relative to a fixed region falls below a minimum value, in which case the corresponding beam is redirected to a new area, while the other beams remain pointed at the corresponding fixed areas. In this way, beam-to-beam handover is reduced, while maintaining the boresight of the antenna pointing at the nadir.
Owner:INMARSAT GLOBAL
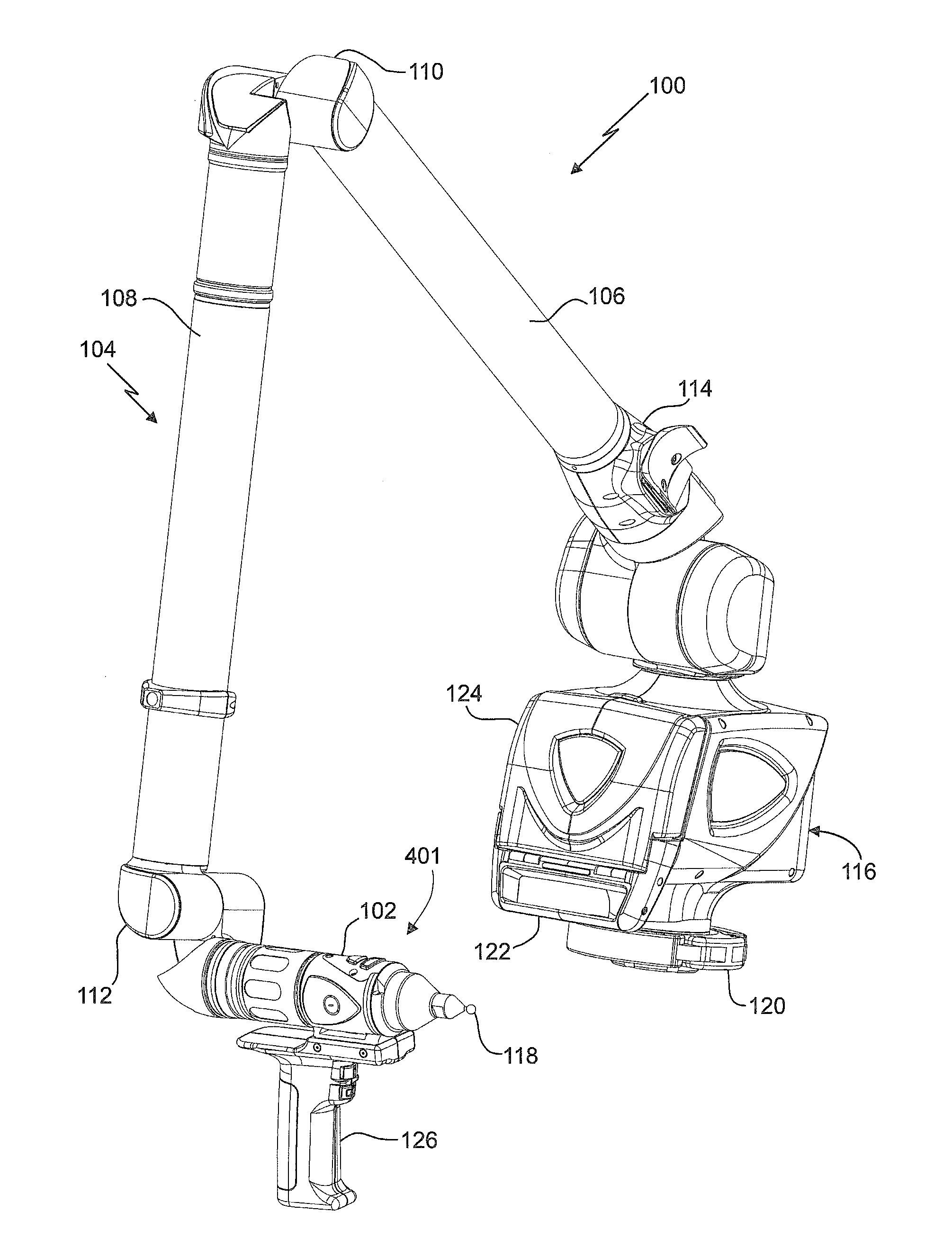
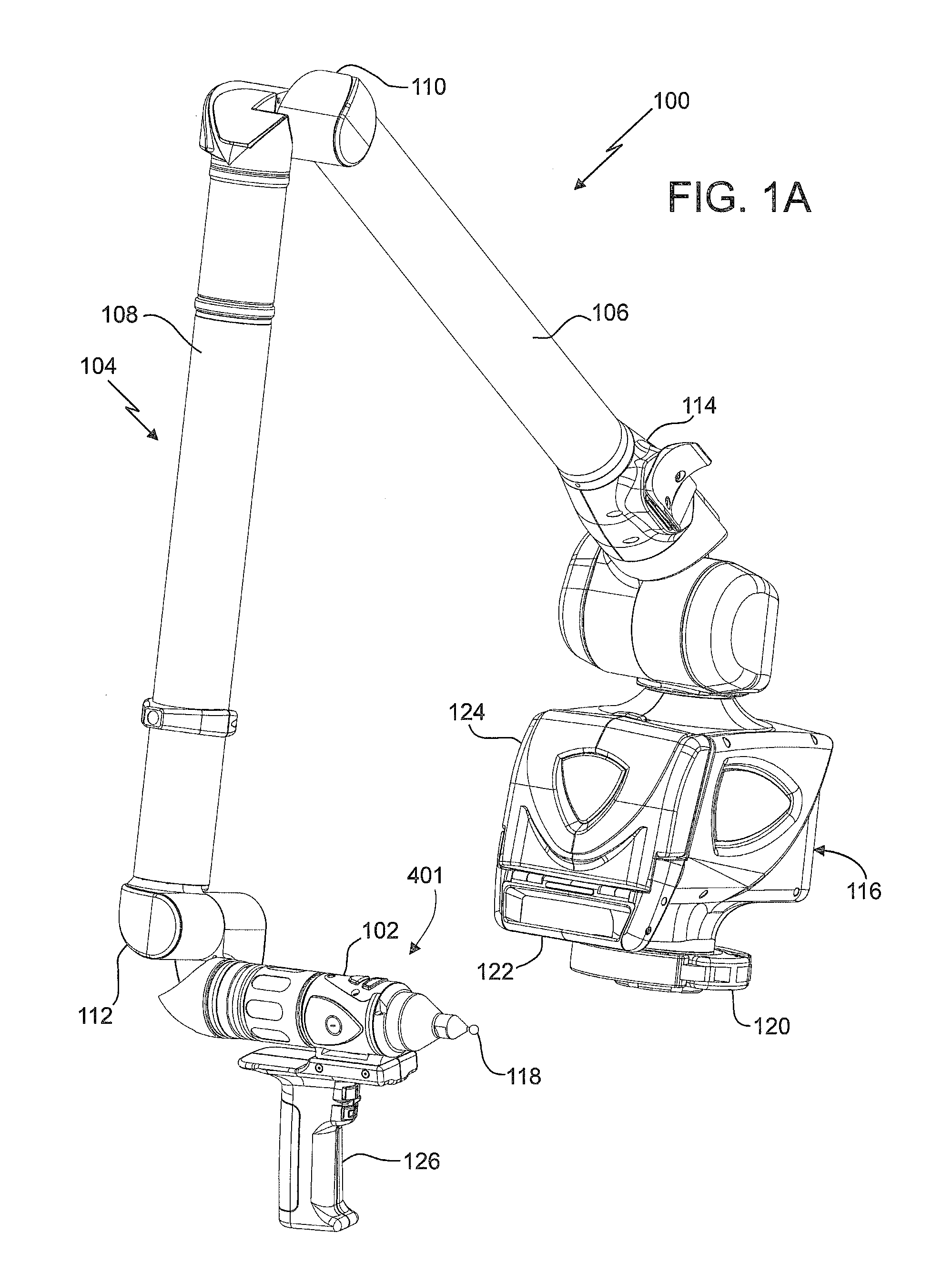
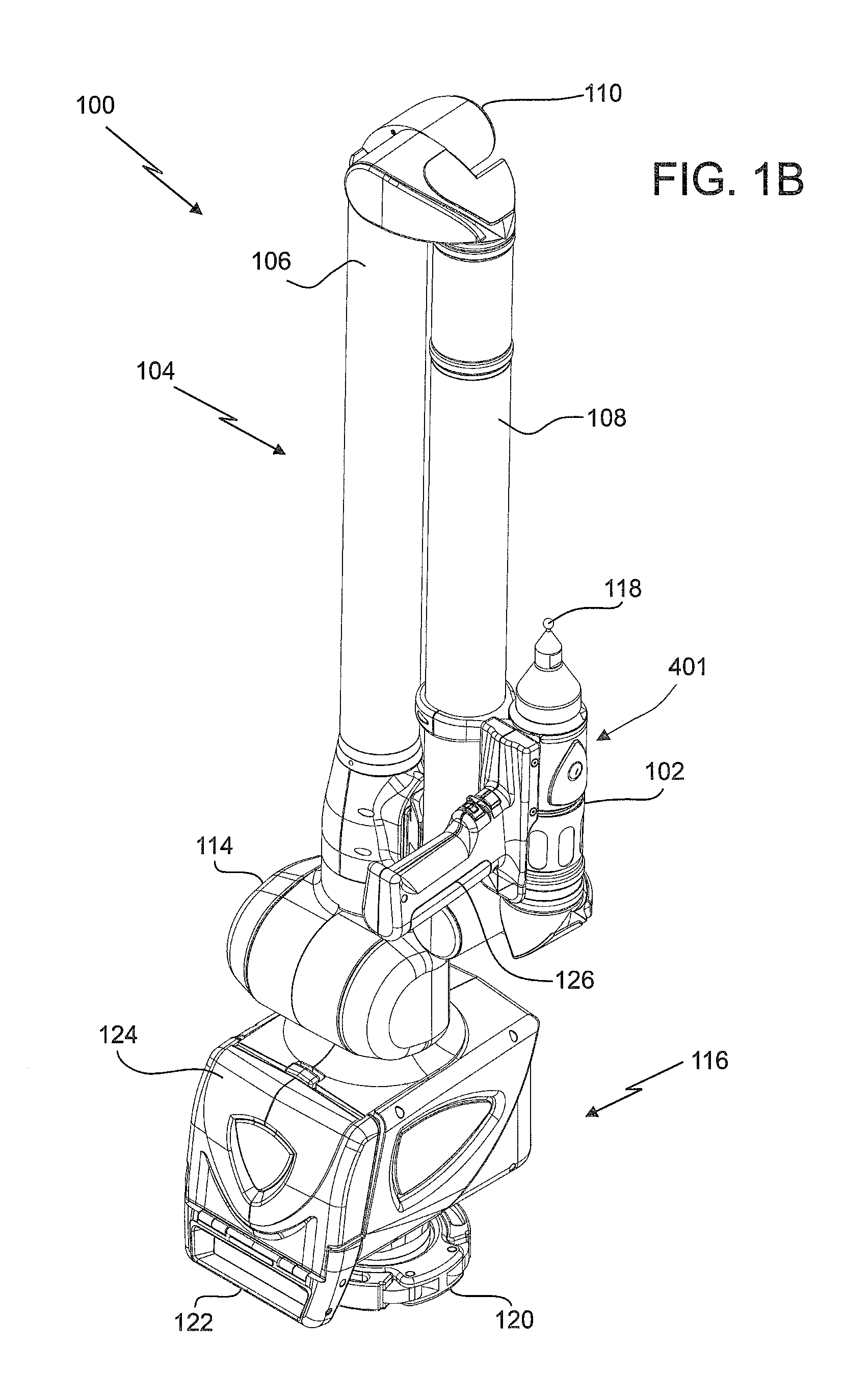
Coordinate measurement machines with removable accessories
A portable articulated arm coordinate measuring machine for measuring the coordinates of an object in space is provided. The AACMM includes a base and a arm portion having an opposed first end and second end. The arm portion includes a plurality of connected arm segments, each arm segment including at least one position transducer for producing a position signal. An electronic circuit is provided that receives the position signal from the at least one position transducer. A probe member is disposed is coupled to the first end. A noncontact three-dimensional measuring device is coupled to the probe member, the device having an electromagnetic radiation transmitter and is configured to determine a distance to an object based at least in part on the propagation time of the emitted and reflected light beams.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Distance measuring device
ActiveUS9103669B2High measurement accuracyReduces maximum possible measurement distanceOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationElectricityMeasurement device
An optoelectronic distance measuring device is disclosed. The device has a transmitting unit with a driver stage for emitting optical pulses, a receiving unit for receiving a portion of the optical pulses, said portion being reflected from a target object, and converting it into an electrical reception signal, via a photosensitive electrical component. It also has an analog-digital converter for digitizing the reception signal, and an electronic evaluation unit to ascertain a distance from the target object on the basis of a signal propagation time using the digitized reception signal. The driver stage can be designed so that at least two pulse durations of different length for the optical pulses can be set.
Owner:VECTRONIX AG
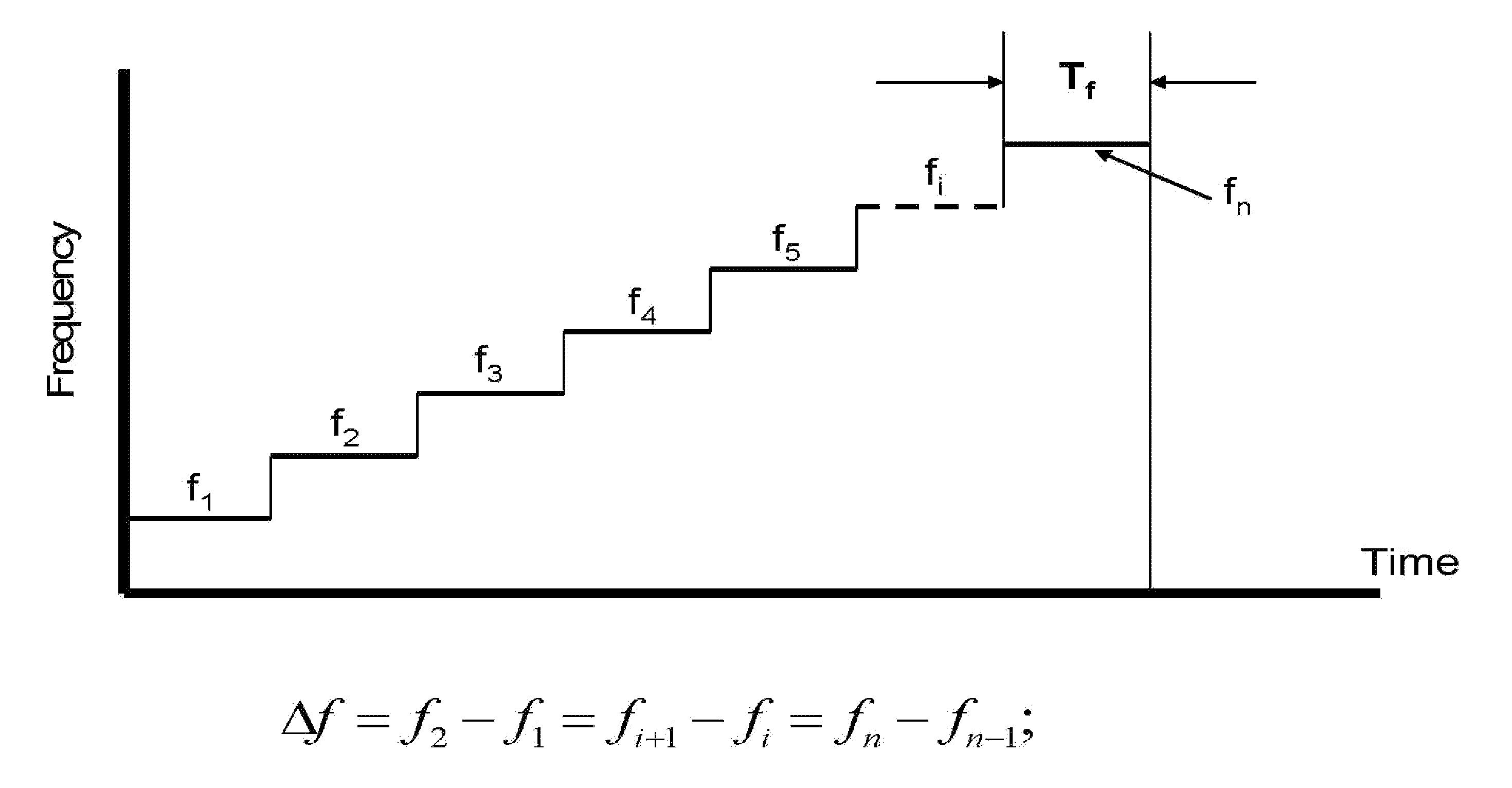
Transmission time difference measurement method and system
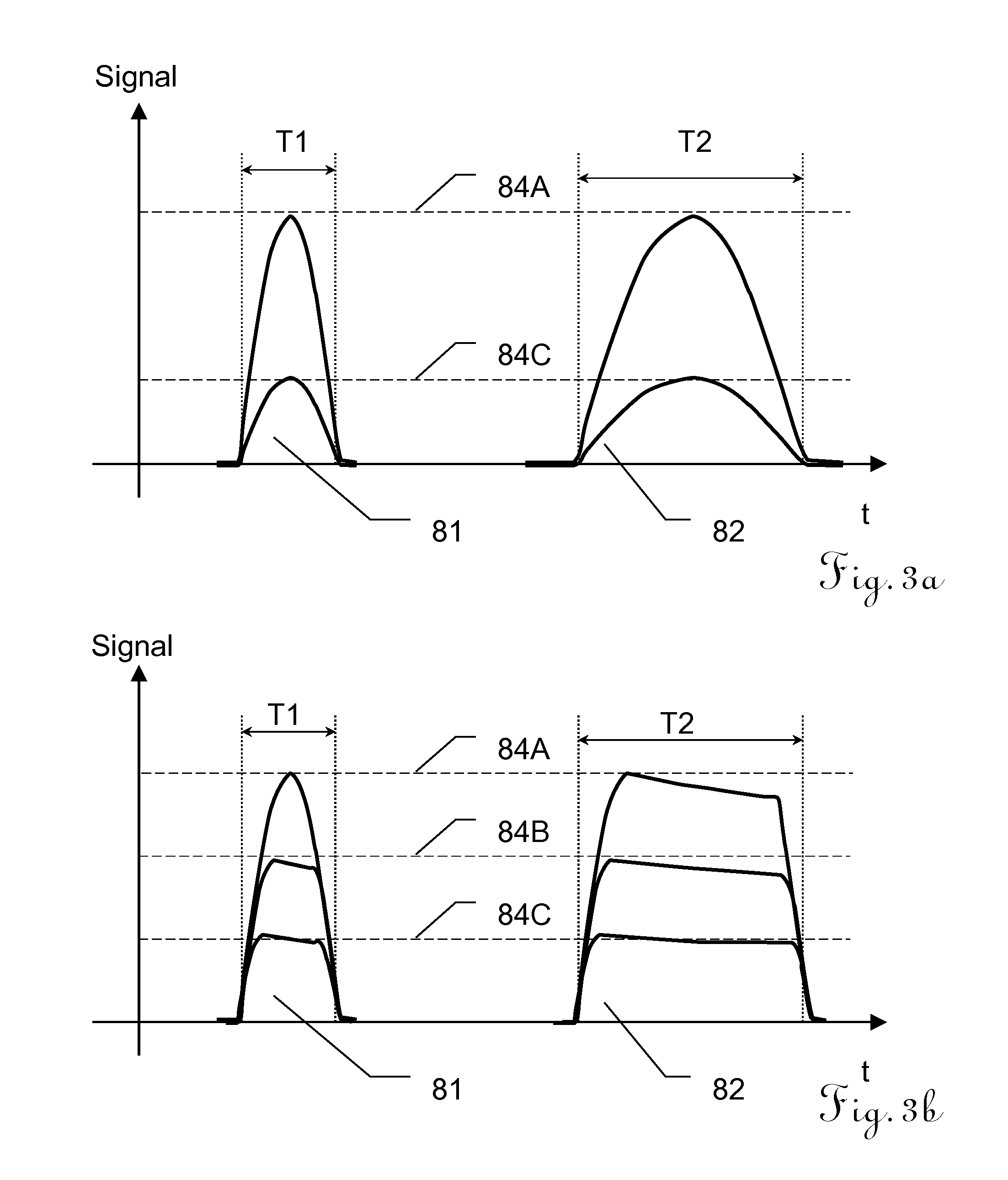
The propagation time (1605) of signals between a terminal (1304) and a base station (1302) is calculated from the round-trip time (1601) of signals between the terminal (1304) and the base station (1302) and the turn-around time (1603) from the reception by terminal (1304) of a signal from base station (1302) until the transmission of the signal to the base station (1302). The propagation time (1606) of signals between the terminal (1304) and another base station (1303) is similarly calculated. The difference between the propagation times (1605 and 1606) and the arrival time difference (1607) that is calculated in the terminal (1304) are then compared to calculate the transmission time difference (1608) between the base stations (1302 and 1303).
Owner:NEC CORP
Acoustic propagation velocity modeling methods, apparatus and systems
InactiveUS20080008037A1Easy assessment processSimple structureSeismology for water-covered areasVelocity propogationMathematical modelPropagation time
Methods, apparatus, and systems for accurately estimating acoustic propagation velocity are described. One method comprises deploying in a marine environment a towed seismic spread comprising a plurality of acoustic positioning transmitters and a plurality of positioning point receivers, and using travel times for signals between at least some of the transmitters and point receivers to derive a mathematical model describing acoustic propagation velocity for the marine environment as a function of at least one spread spatial dimension, distances between transmitters and receivers, and any combination thereof. This abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract, and allows a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
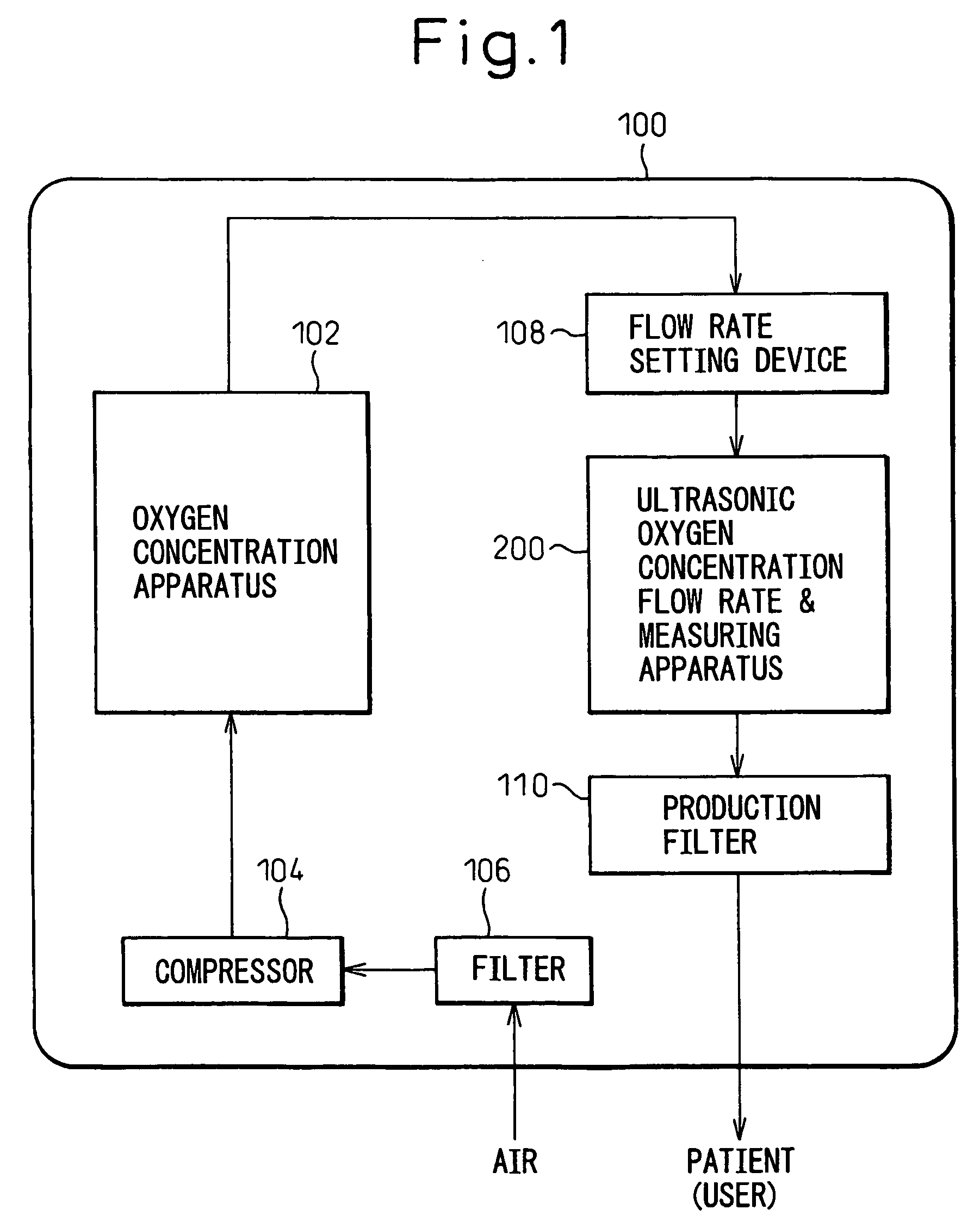
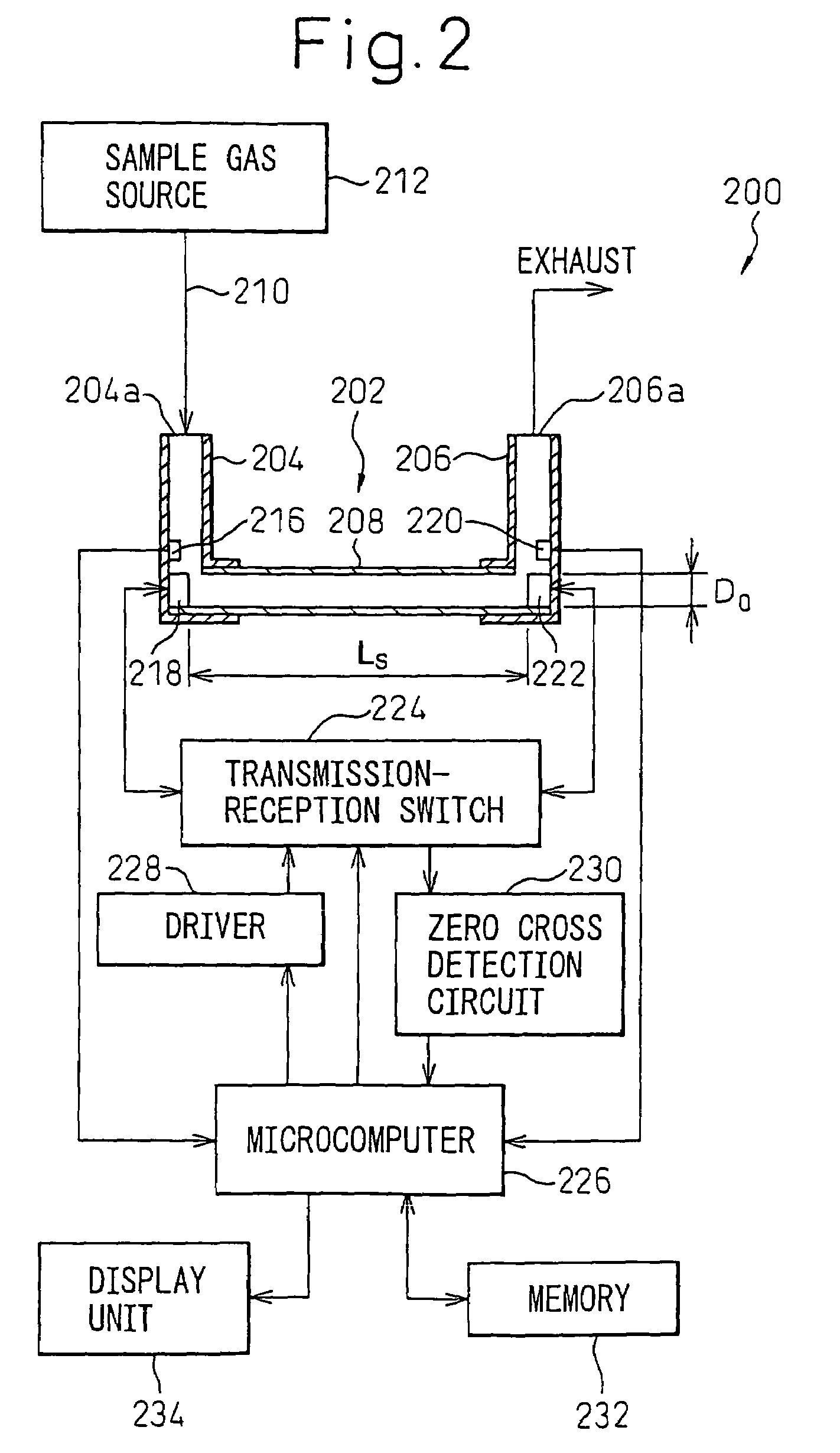
Ultrasonic apparatus and method for measuring the concentration and flow rate of gas
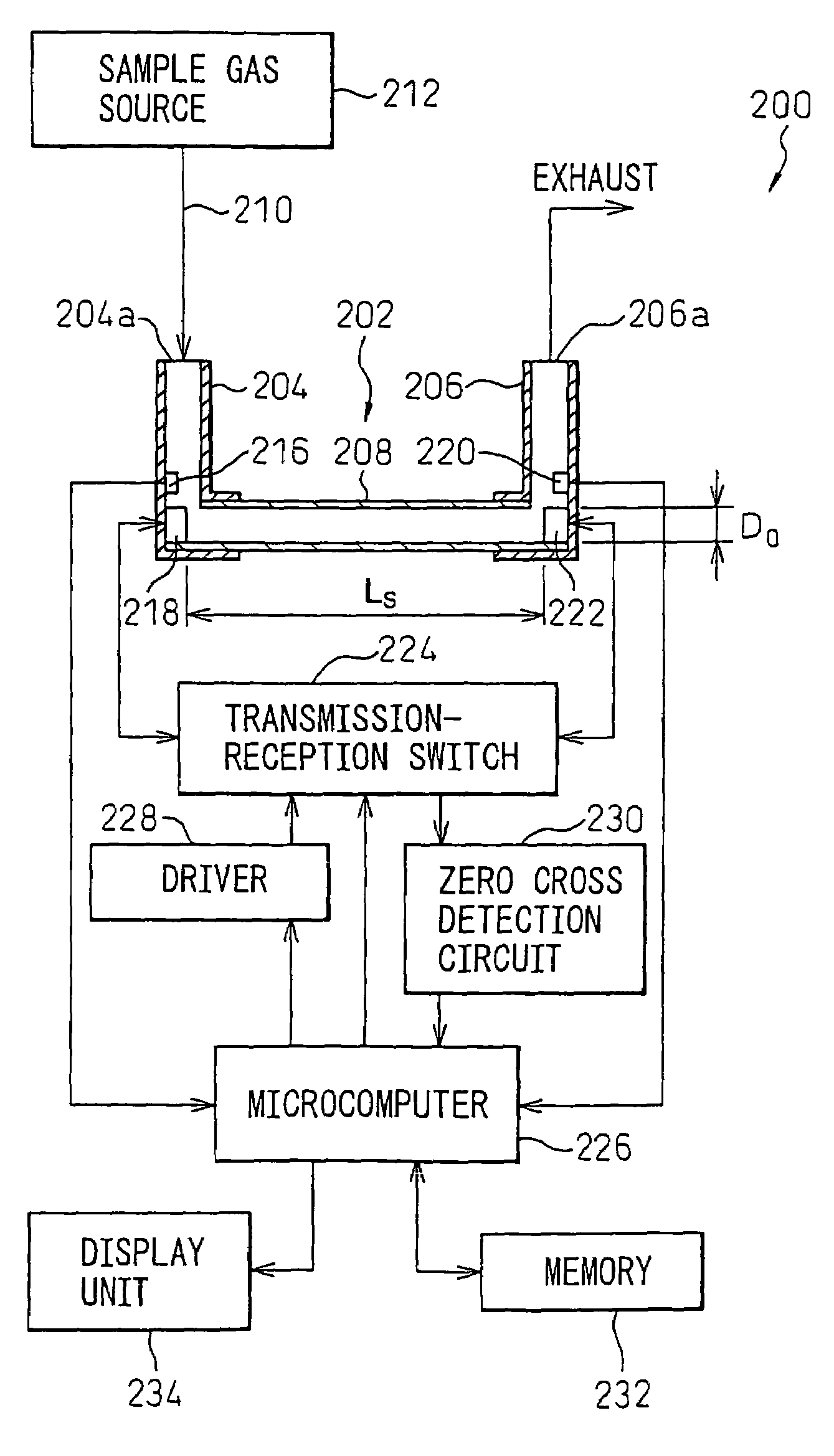
ActiveUS7213468B2Accurate measurementAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume/mass flow measurementUltrasound devicePropagation time
An ultrasonic apparatus measures the concentration and flow rate of a sample gas by calculating a possible propagation time range on the basis of the gas temperature, determining whether or not the phases at which two first trigger signals, respectively generated on the basis of forward and backward waveforms of the ultrasonic waves, coincide with each other, processing the zero-cross signals so that the phases coincide with each other, obtaining reference zero-cross time instant by calculating mean value of the forward and backward zero-cross time instants, obtaining an ultrasonic reception point by subtracting an integral multiple of the cycle of the ultrasonic waves so that the results of the subtraction falls into a possible propagation time range and estimating the ultrasonic propagation time on the basis of the ultrasonic reception point.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
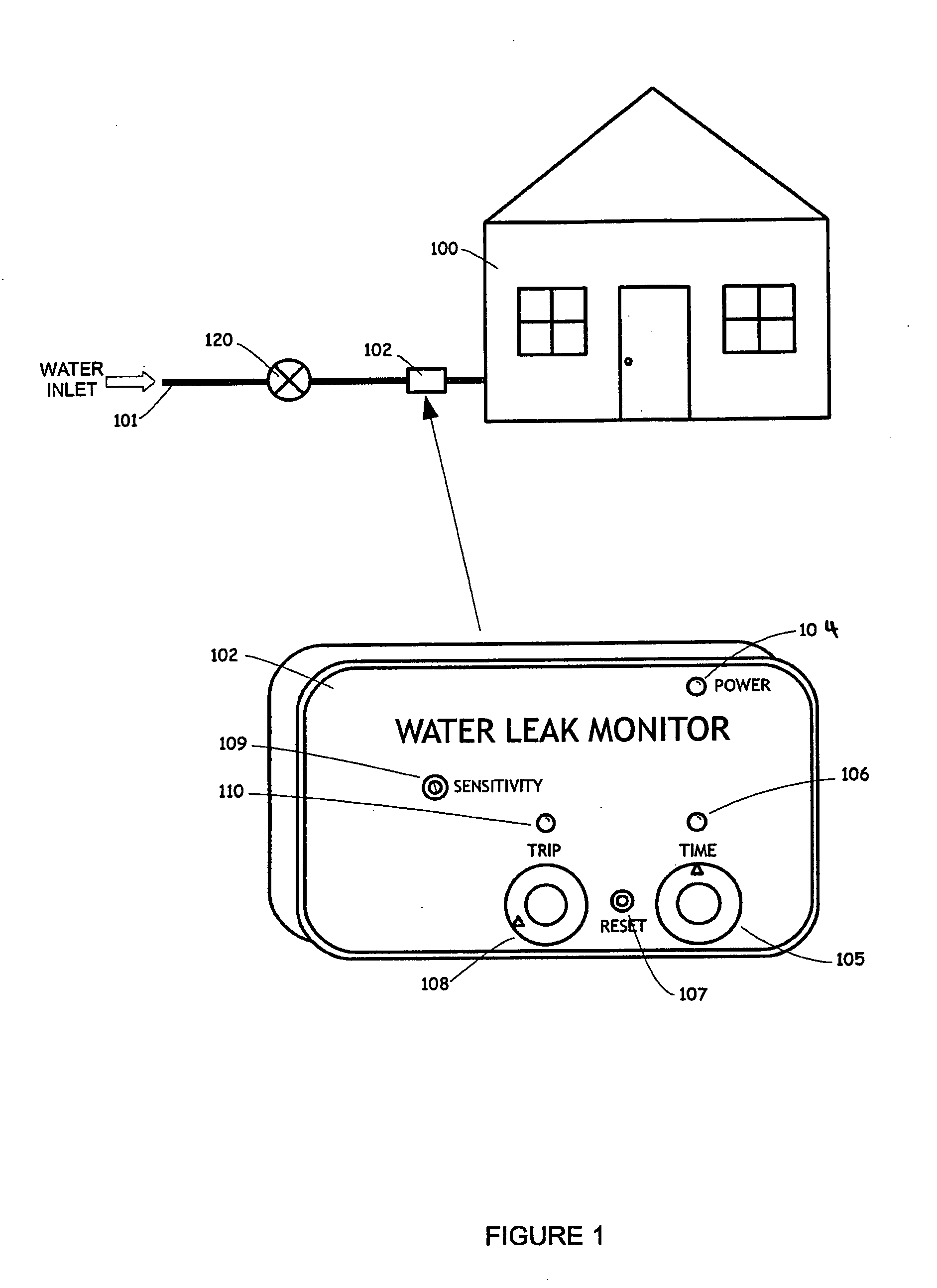
Non-invasive Thermal Dispersion Flow Meter with Chronometric Monitor for Fluid Leak Detection
ActiveUS20120180877A1Conservation promotedCost promotedDetection of fluid at leakage pointOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPropagation timeEngineering
A non-invasive thermal dispersion flow meter with chronometric monitor for fluid leak detection includes a heater, an ambient temperature sensor and a flow rate sensor which are configured to sense the temperature of a fluid in a conduit, and then monitor the flow of that fluid through the conduit. The fluid flow sensor is incorporated into a Wheatstone bridge circuit which is used to provide increased sensitivity to the outputs of the sensors. Based upon the ambient temperature sensor readings, the flow rate sensor and heater may be adjusted to optimize the operation of the system to detect leaks. An alternative embodiment utilizes a single sensor and separate heater which work together to determine heat propagation times which in turn is used to calculate flow rate.
Owner:SENTINEL HYDROSOLUTIONS
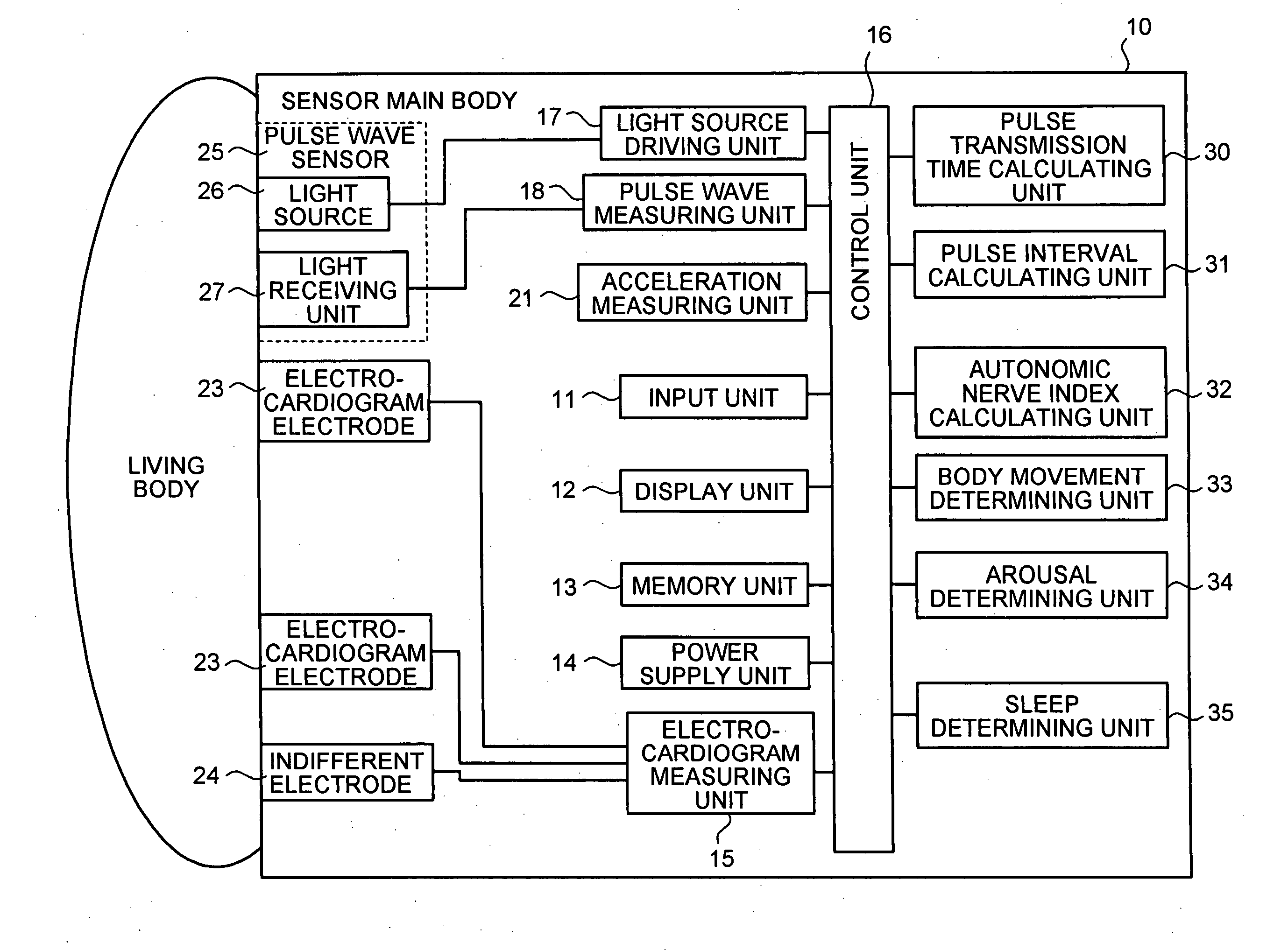
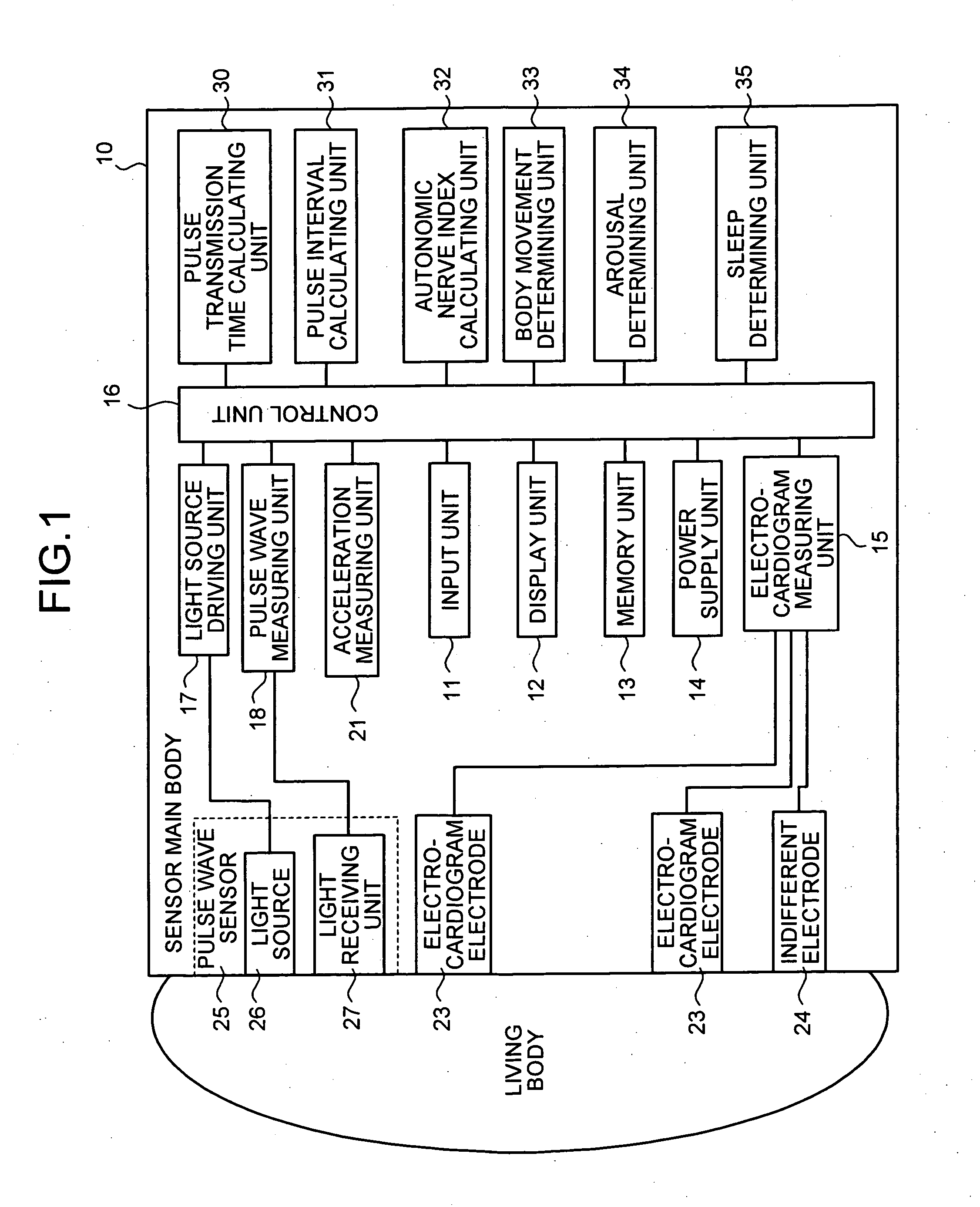
Health management apparatus, health management system, health management method and computer program product
A health management apparatus includes a first pulse wave measuring unit that measures a first pulse wave of a subject during sleep; and a second pulse wave measuring unit that measures a second pulse wave of the subject during sleep. The second pulse wave is different from the first pulse wave in propagation time from the heart of the subject. The apparatus also includes a pulse transmission time calculating unit that calculates a pulse transmission time indicating a time difference between the first and second pulse waves; a pulse interval calculating unit that calculates a pulse interval based on at least one of the first and second pulse waves; an autonomic nerve index calculating unit that calculates an autonomic nerve index based on the pulse transmission time and the pulse interval; and a health determining unit that determines the condition of health of the subject based on the autonomic nerve index.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Electronic circuitry protected against transient disturbances and method for simulating disturbances
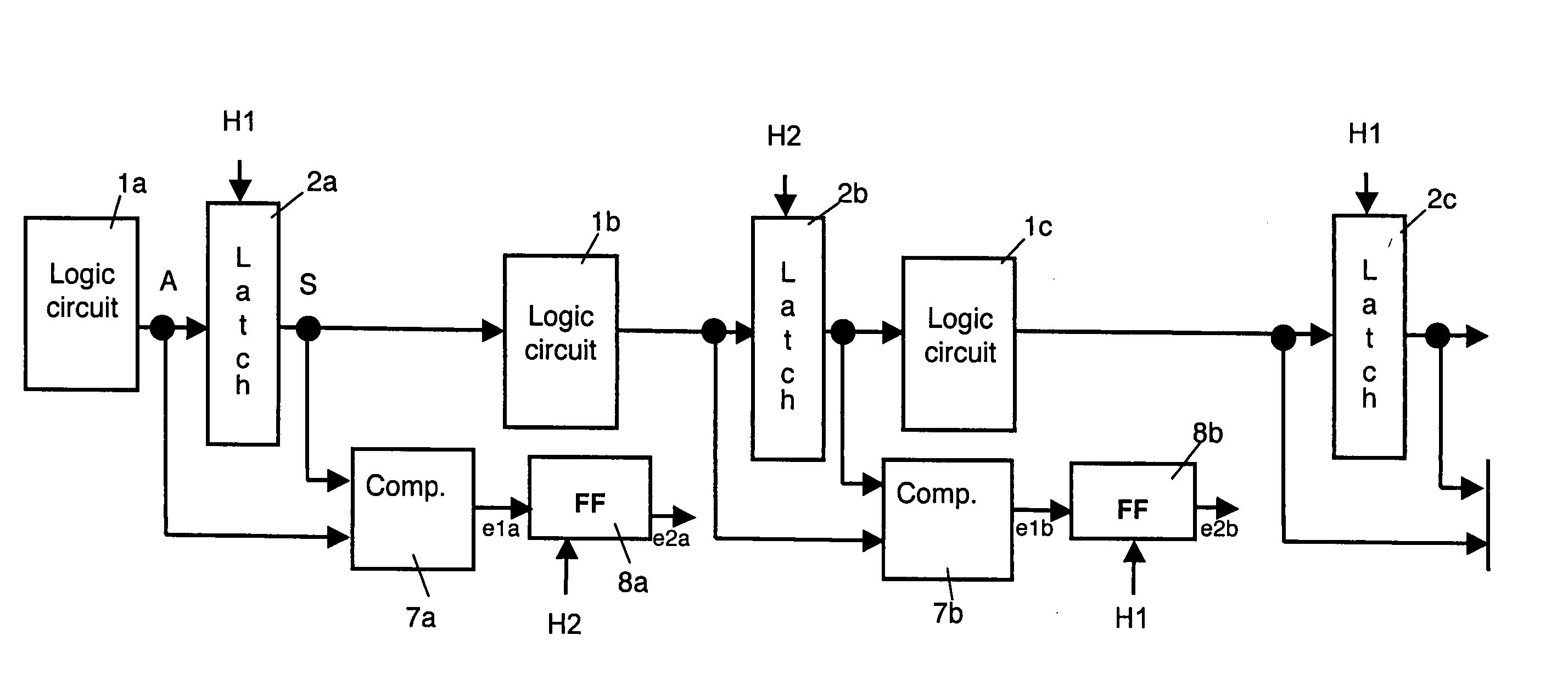
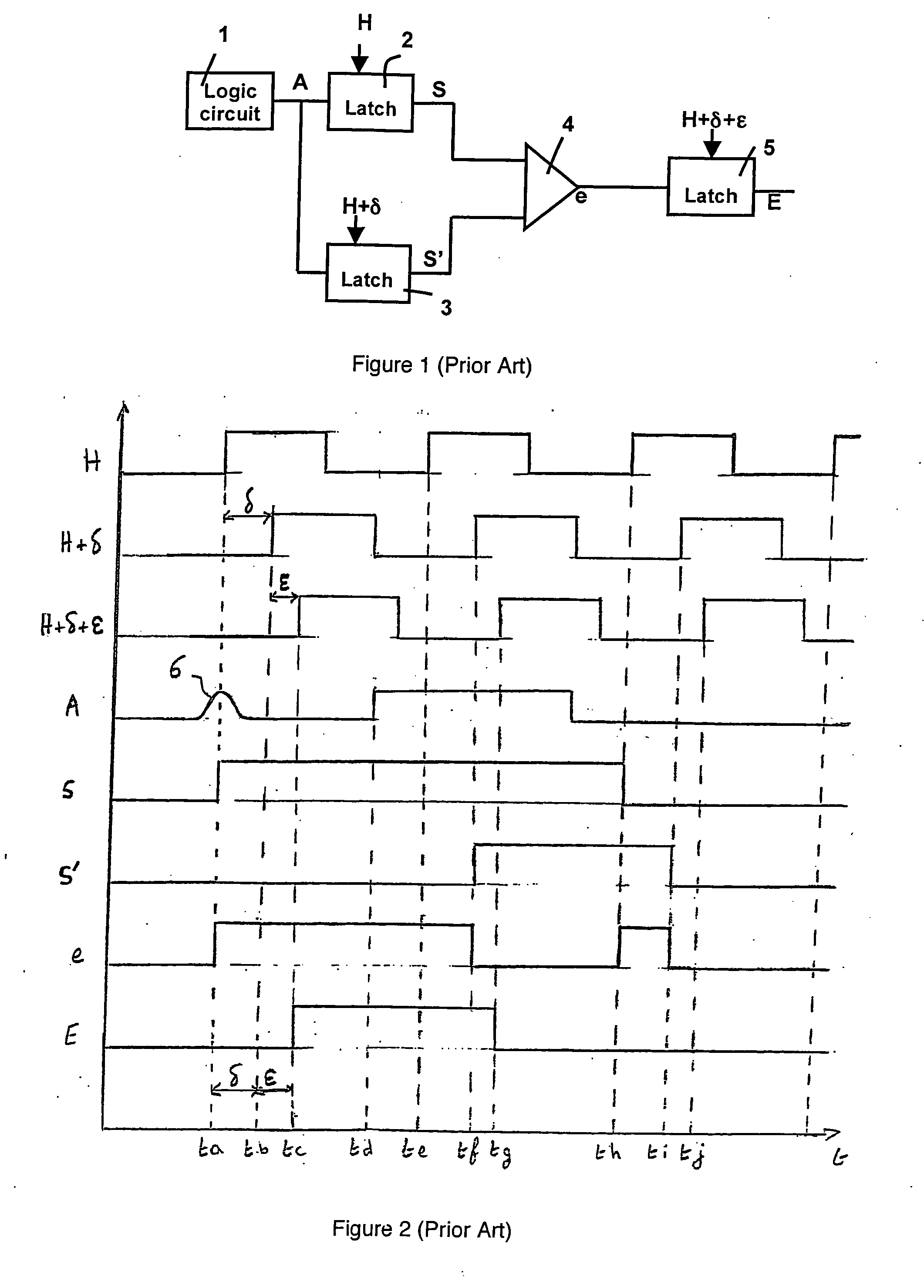
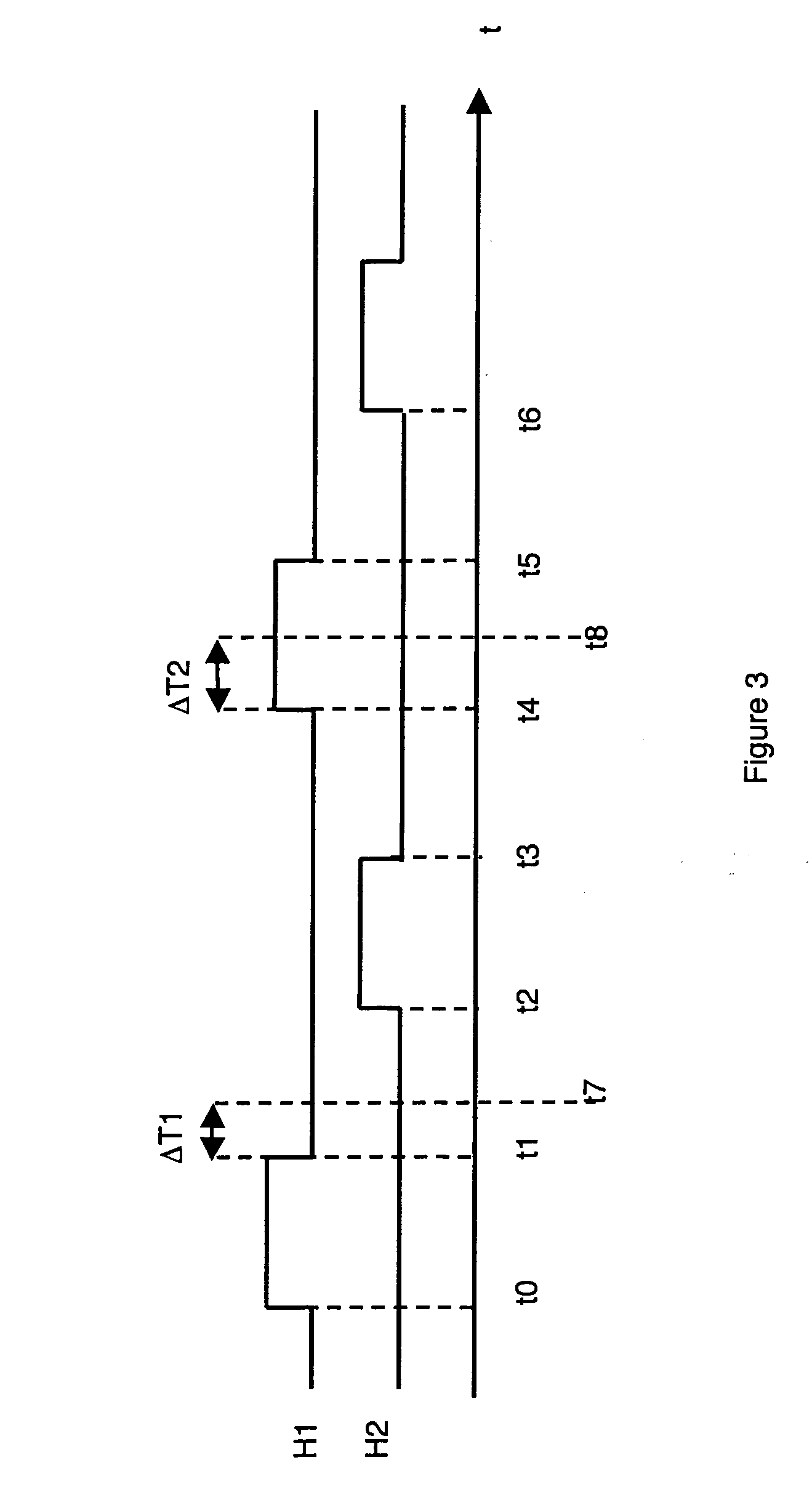
ActiveUS20060220716A1Improve protectionElectrical testingElectric pulse generatorPropagation timeEngineering
The circuitry comprises successive stages, each comprising a combinatory logic circuit connected to the input of a first latch. Staggered clock signals are respectively associated with the first latches of the odd and even stages. Means for detecting a transient disturbance affecting the first latch of a stage and liable to propagate downstream, compare, in each stage, a value present on the output of the first latch of the stage considered at an observation time with a value present on the input of said first latch at a predetermined observation time taking account of the various propagation times.
Owner:IROC TECH
Localization system, robot, localization method, and sound source localization program
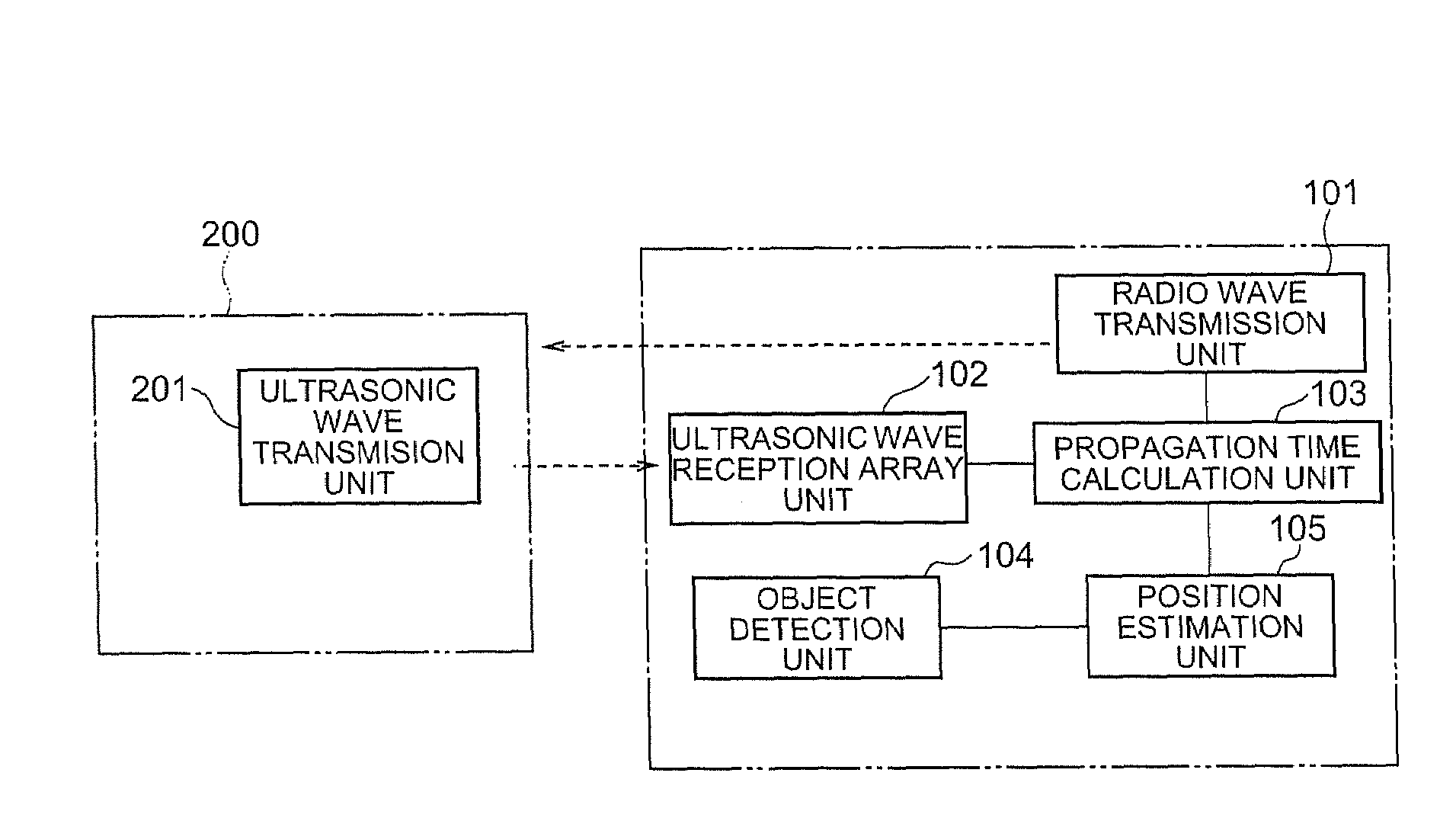
InactiveUS20090262604A1Accurate measurementDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationSound source locationSound sources
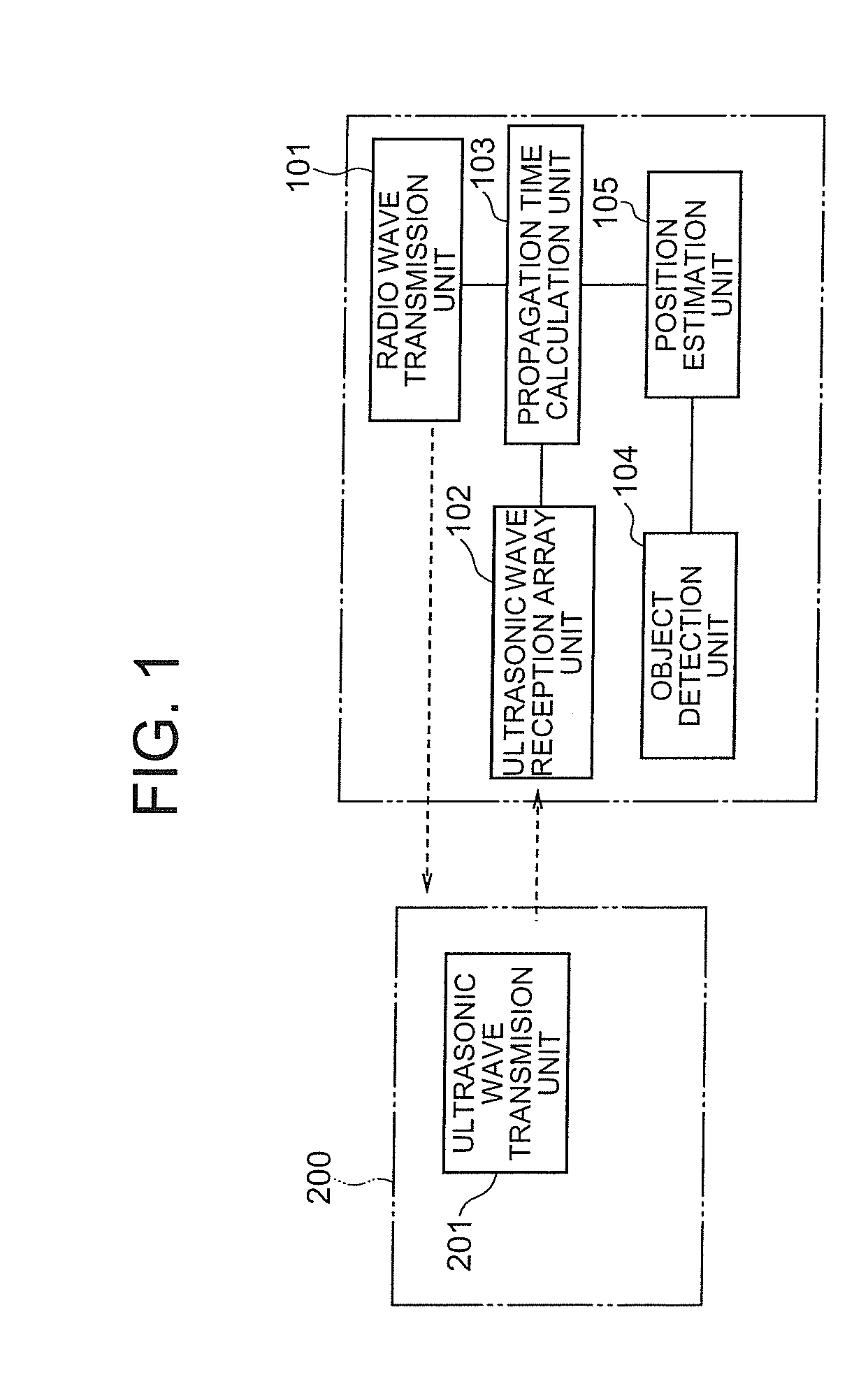
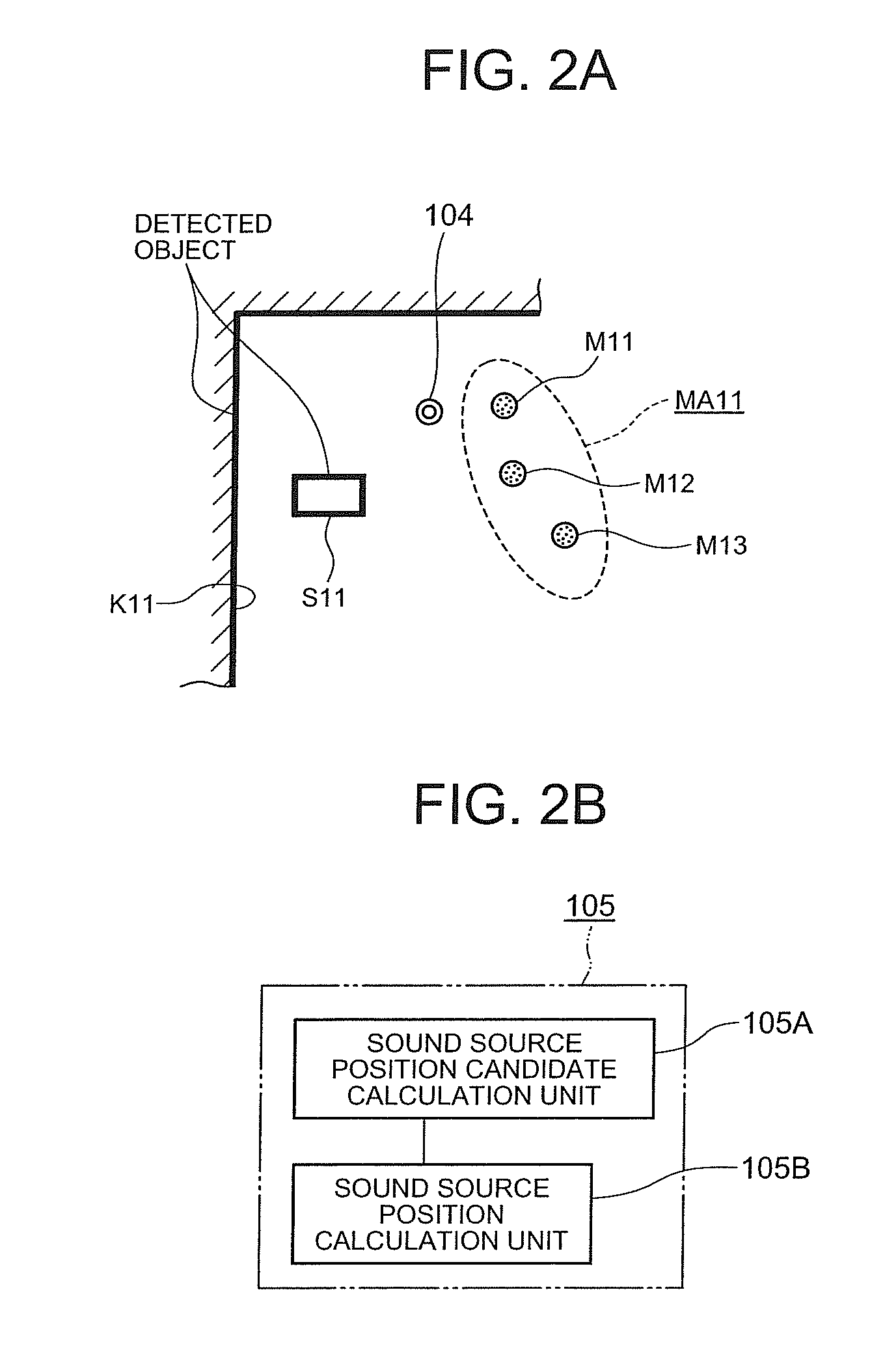
To measure an accurate positional relationship between an ultrasonic tag and a microphone and identify a sound source position, even if an object is present between the ultrasonic tag and the microphone. When a radio transmission unit transmits a radio wave, an ultrasonic wave transmission unit of an ultrasonic tag receives it and transmits an ultrasonic wave. Then, a plurality of microphones in an ultrasonic wave reception array unit receive the ultrasonic wave. A propagation time calculation unit calculates a time from when the radio wave is transmitted by the radio transmission unit till when an ultrasonic wave reaches each of the microphones in the ultrasonic wave reception array unit. A position estimation unit calculates the position (sound source) of the ultrasonic tag according to the arrival time at each of the microphones and the result of object detection while considering reflection of the ultrasonic wave.
Owner:NEC CORP
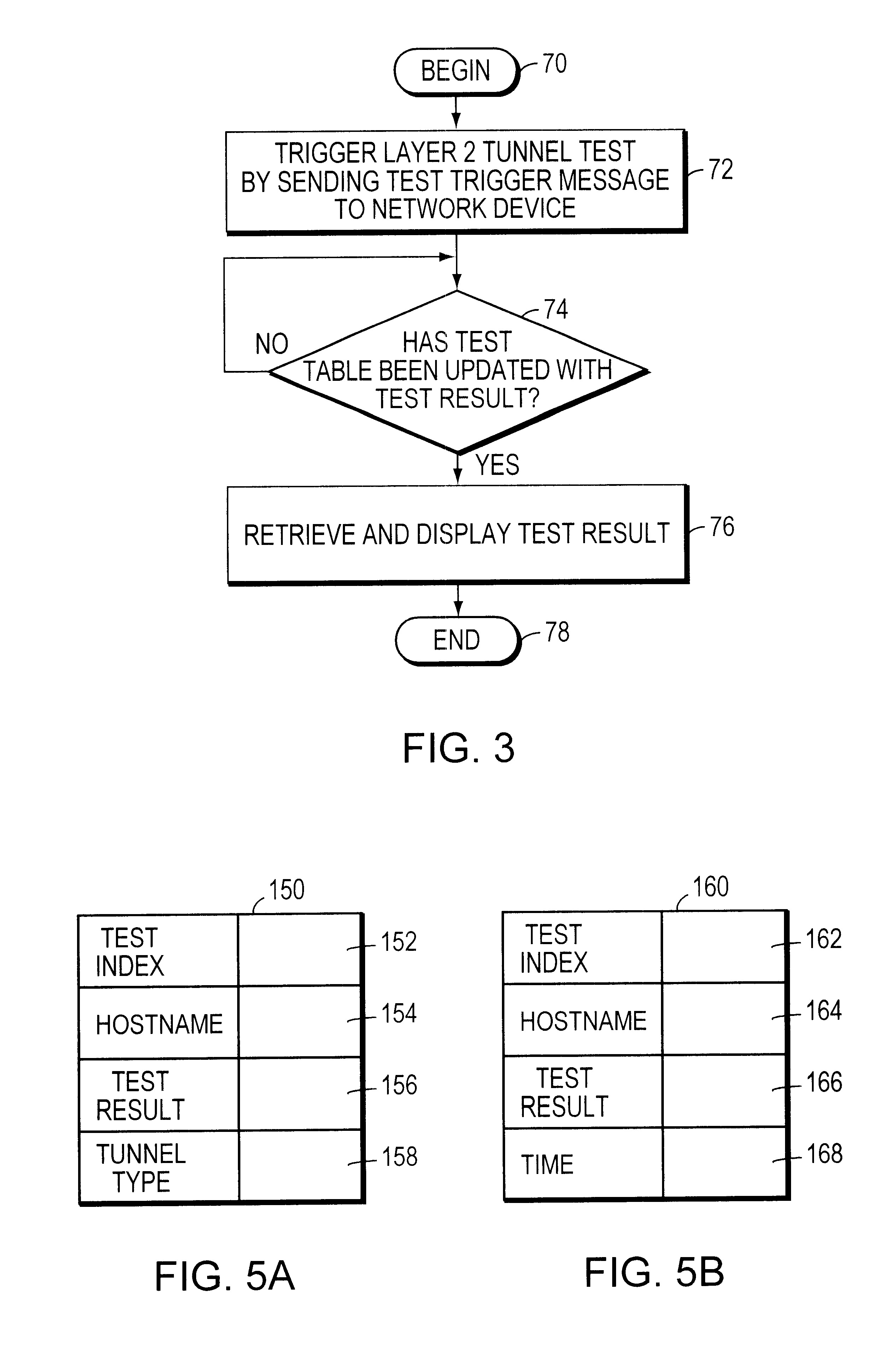
Method and system for testing a layer-2 tunnel in a data communication network
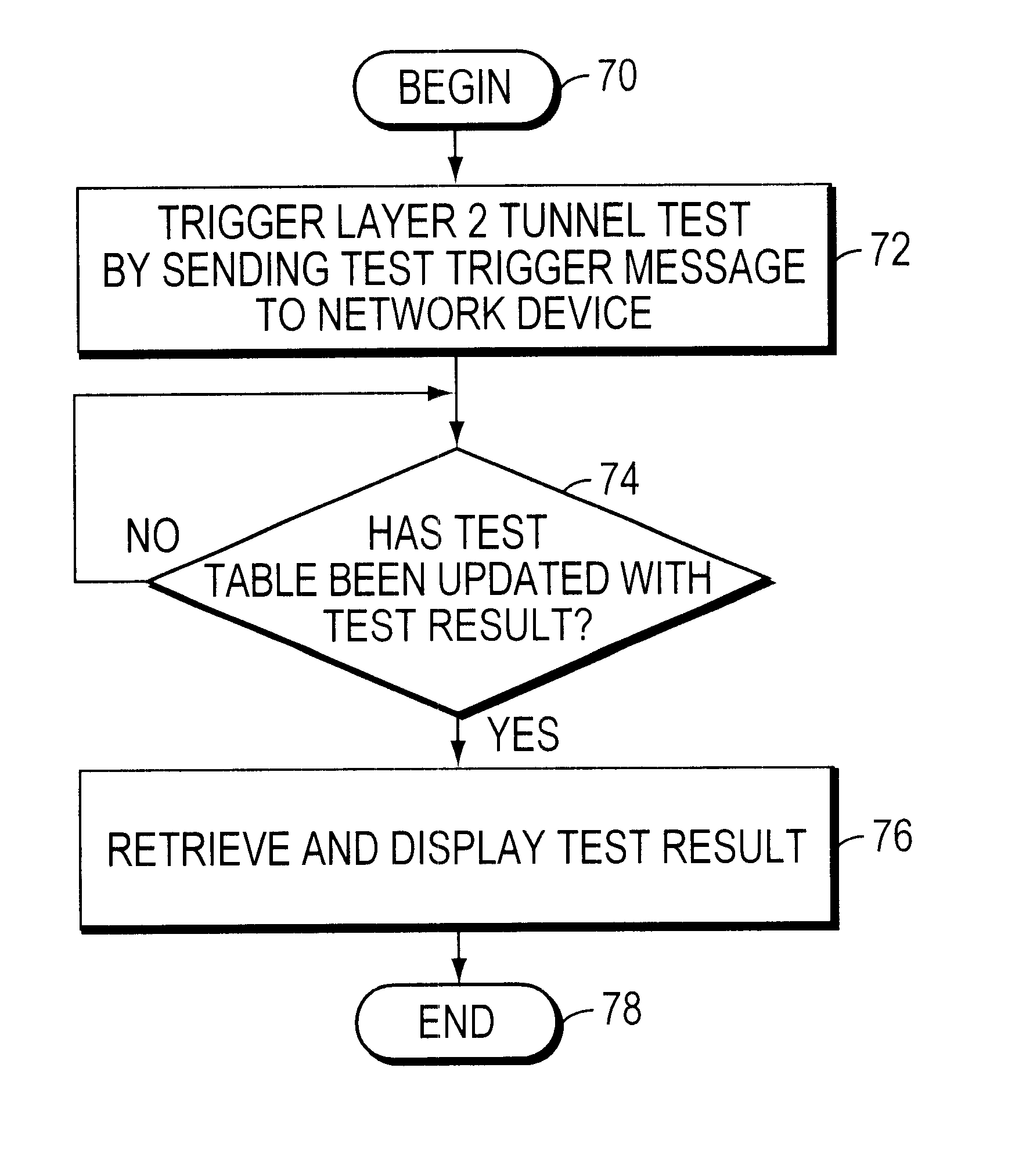
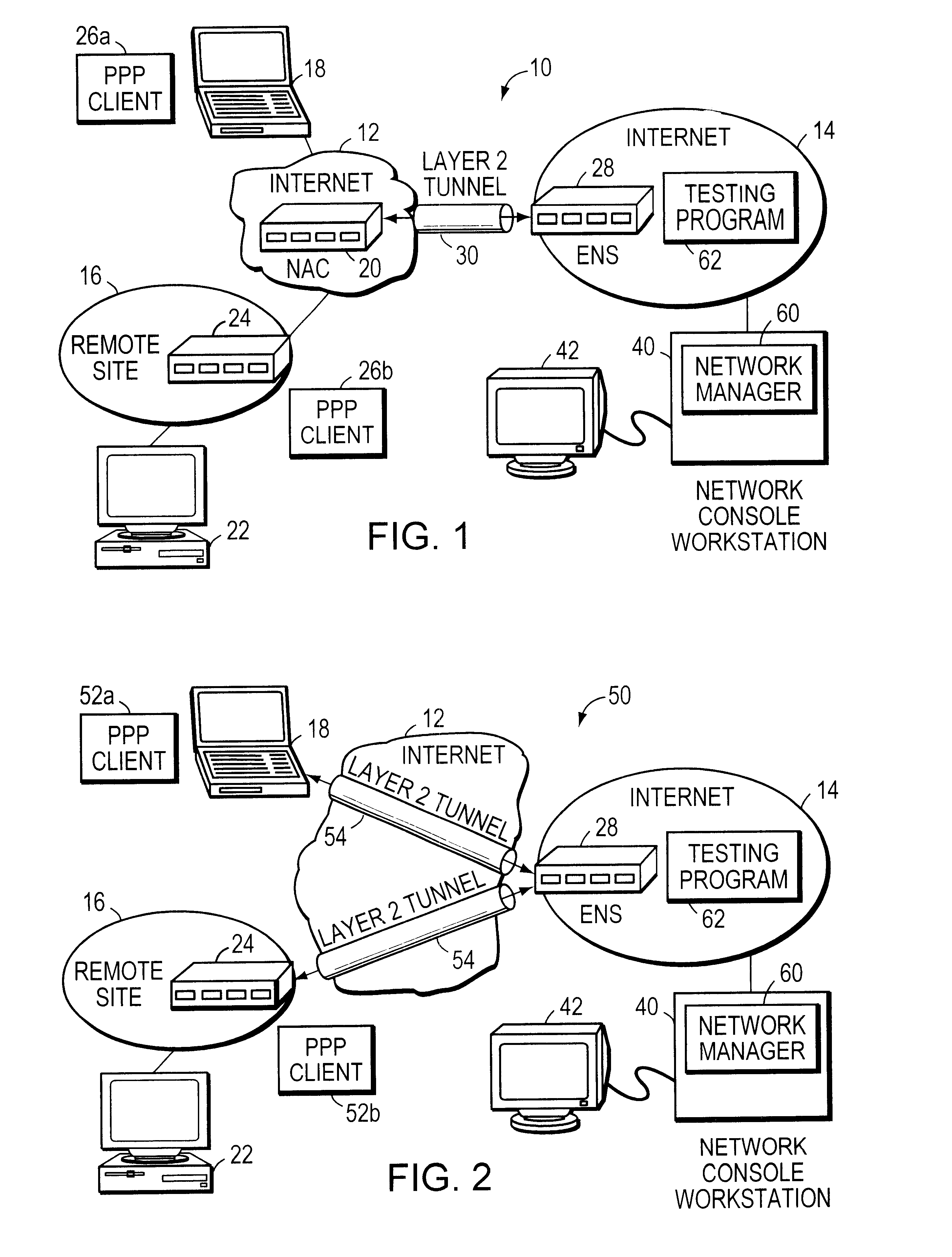
InactiveUS6473798B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksPropagation timeNetwork management
A method and system for testing a Layer 2 tunnel in a data communication network including a network device and a network manager are described. According to the method, a test invocation is received from the network manager at the network device. In response to receipt of the test invocation at the network device, a Layer 2 tunnel within the data communication network is tested, and a result of the test is reported to the network manager. The tests that may be conducted include a connectivity test to determine if a Layer 2 tunnel can be established and a responsiveness test to determine the propagation time of a Layer 2 tunnel. Advantageously, both compulsory and voluntary Layer-2 tunnels can be tested, thereby enabling all Layer 2 protocols (e.g., L2TP, L2F, and PPTP) to be supported.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
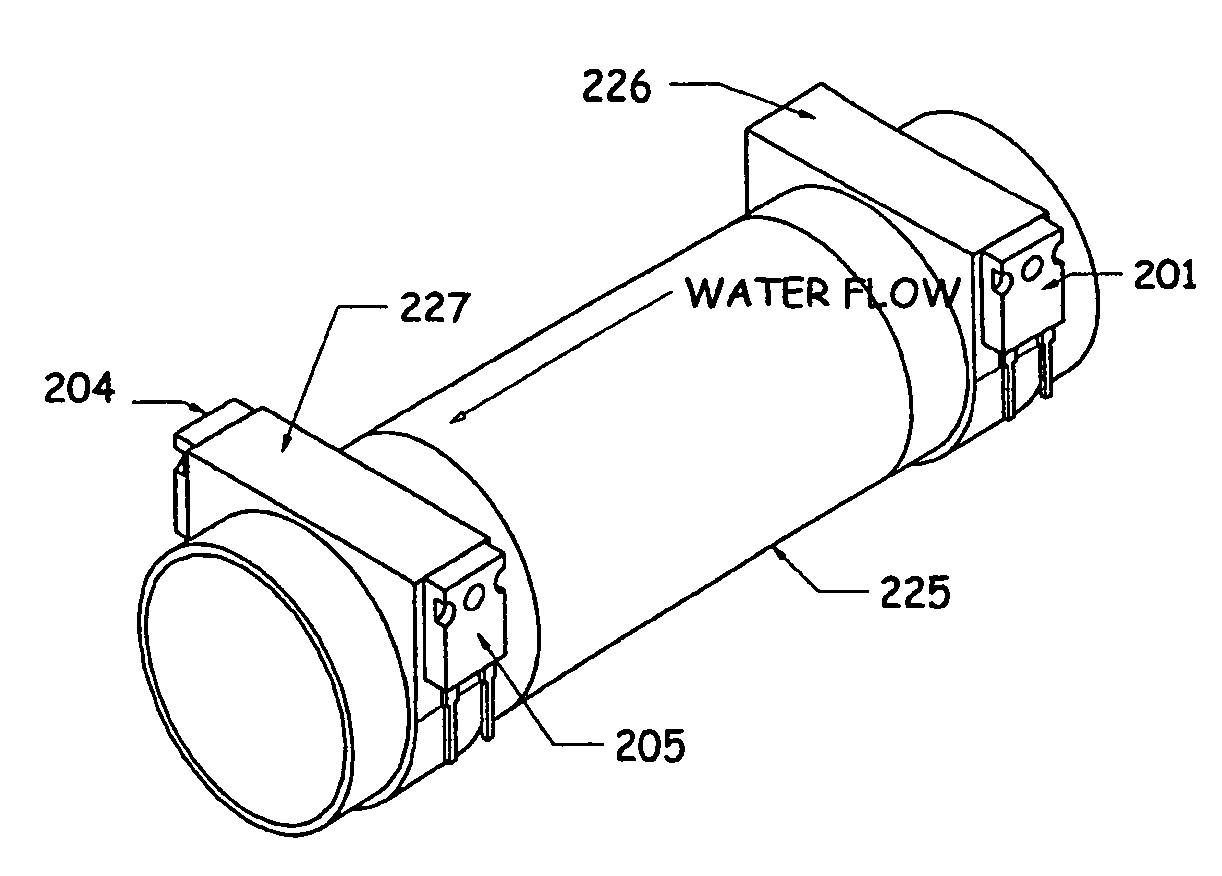
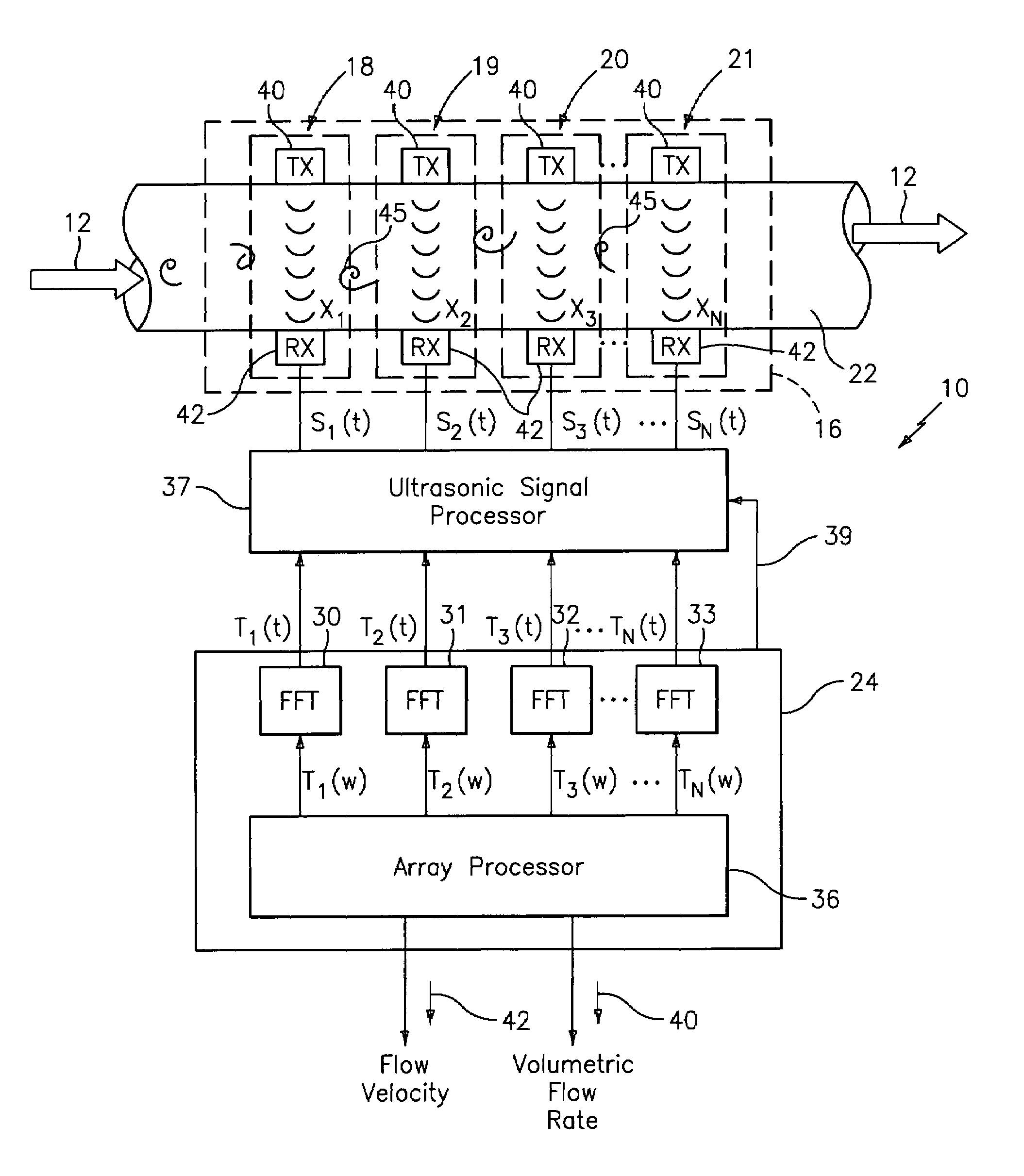
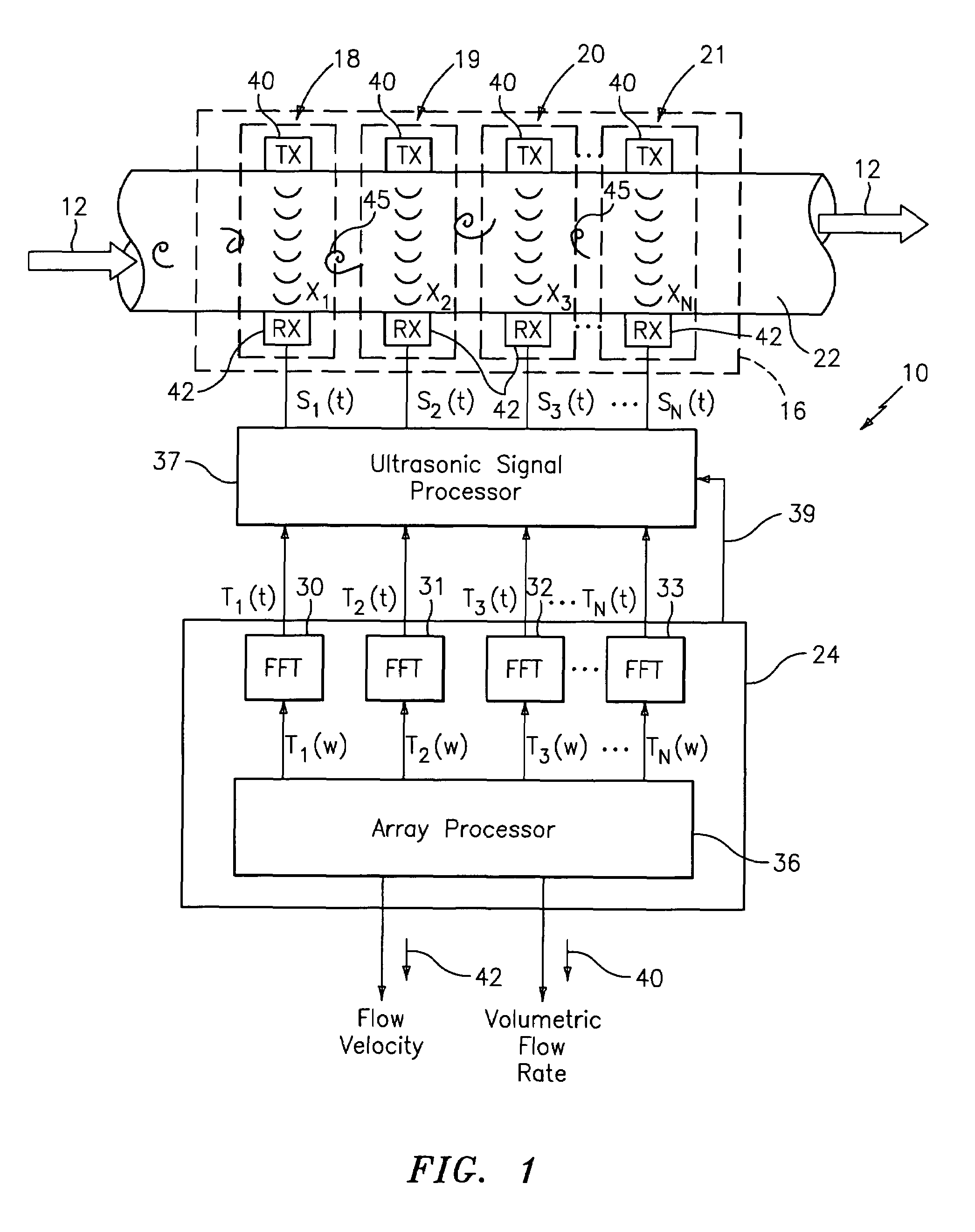
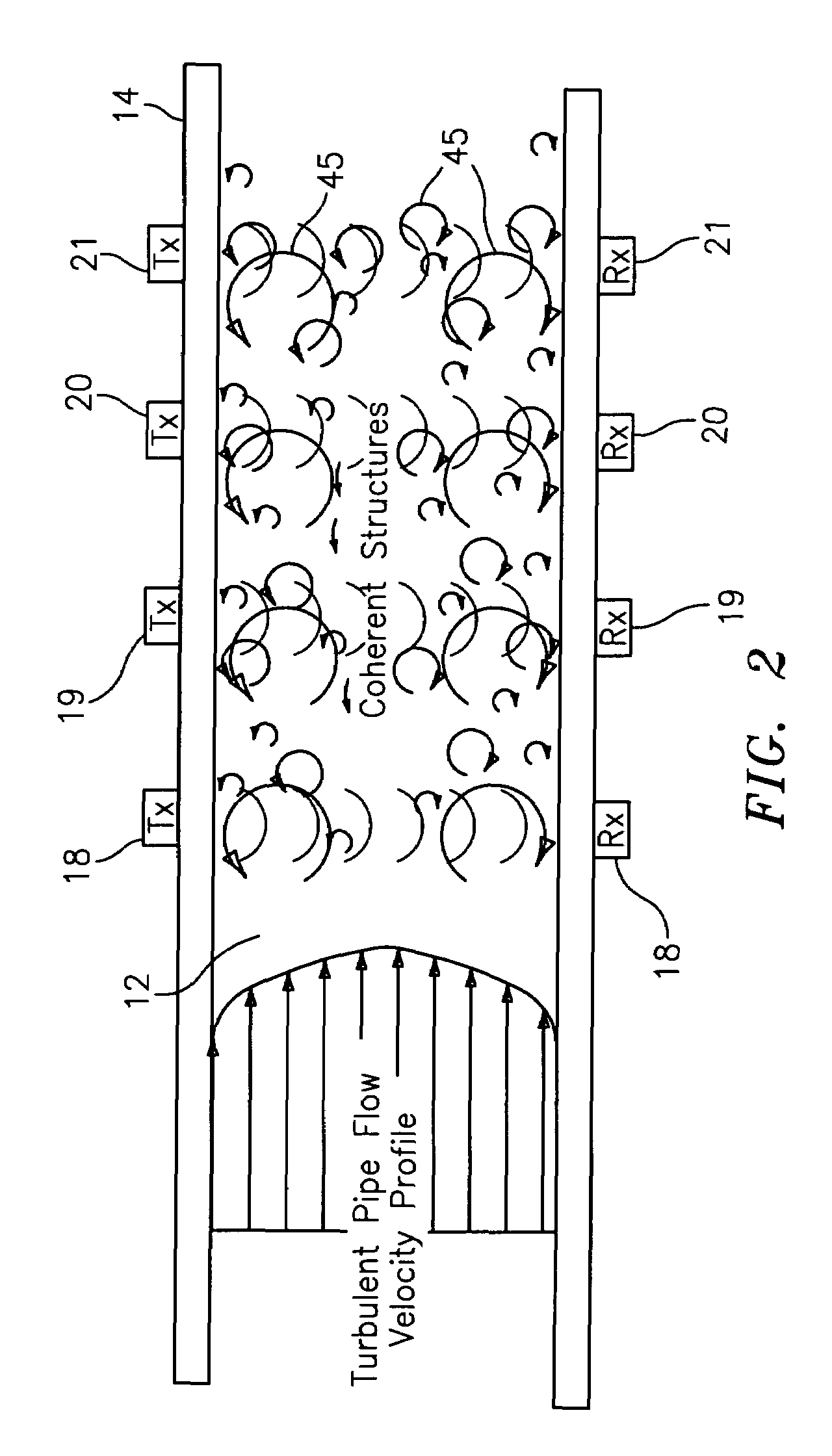
Apparatus and method using an array of ultrasonic sensors for determining the velocity of a fluid within a pipe
ActiveUS7389187B2LiquidityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationVolume/mass flow measurementSonificationPropagation time
An apparatus and method for measuring the flow velocity of a fluid flowing through a pipe that includes an array of at least two ultrasonic sensor units (with as many as 16 sensor units) disposed at predetermined locations along the pipe. Each sensor unit includes an ultrasonic transmitter and an ultrasonic receiver. Each sensor unit provides a respective signal indicative of a parameter of the transit time or amplitude of the ultrasonic signal propagating between each respective ultrasonic transmitter and ultrasonic receiver. A signal processor defines a convective ridge in the k-ω plane in response to the ultrasonic signals using an adaptive beamforming algorithm, such as Capon and Music. The signal processor further determines the slope of at least a portion of the convective ridge to determine the flow velocity of the fluid.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
High speed connectors that minimize signal skew and crosstalk
ActiveUS7281950B2Maximize signal densityMinimize intermingling electrical fieldsElectrically conductive connectionsPrinted circuitsPropagation timeElectrical connector
Owner:FCI AMERICAS TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for continuous assessment of a cardiovascular parameter using the arterial pulse pressure propagation time and waveform
ActiveUS20080033305A1ElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesCardiac cycleArterial pulse pressure
A method and apparatus for determining a cardiovascular parameter including receiving an input signal corresponding to an arterial blood pressure measurement over an interval that covers at least one cardiac cycle, determining a propagation time of the input signal, determining at least one statistical moment of the input signal, and determining an estimate of the cardiovascular parameter using the propagation time and the at least one statistical moment.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com